Canon F-605 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for F-605 by Canon which is a product in the Calculators category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals
Scientific Calculator
F-605
EN
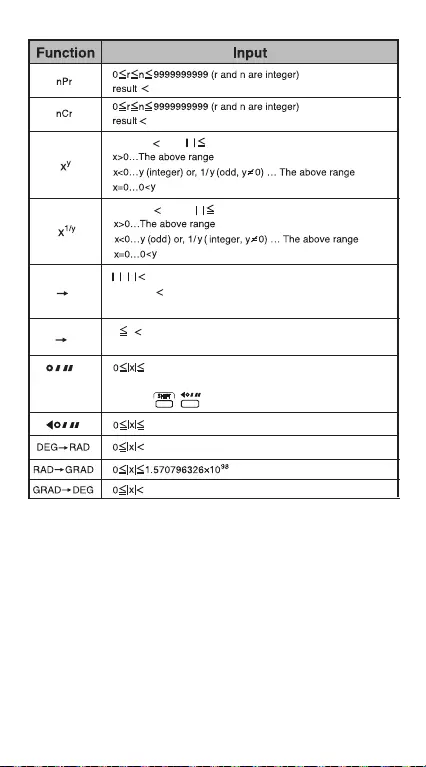
CALCULATION
EXAMPLES

CONTENTS
2
HOW TO OPEN / CLOSE THE COVER ........................P.3
DISPLAY........................................................................P.4
GETTING STARTED......................................................P.5
1. Check the current calculation mode ........................P.5
2. Key symbols ............................................................P.5
3. Order of operations ...............................................P.18
4. Calculation range ..................................................P.19
5. Statistical calculations ...........................................P.21
6. Errors.....................................................................P.25
CALCULATION EXAMPLES .......................................P.26
1. Decimal calculations .............................................P.26
2. Binary / Octal / Hexadecimal calculations .............P.30
3. Basic function calculations ....................................P.32
4. Applied calculations ...............................................P.37
5. Operation range and accuracy.............................. P.39
BATTERY REPLACEMENT.........................................P.42
ADVICE AND PRECAUTIONS .................................... P.43
SPECIFICATIONS........................................................ P.44
IMPORTANT: READ BEFORE USE
Please read the following instructions and safety
precautions before using the Scientific Calculator.
Keep this manual on hand for future reference.
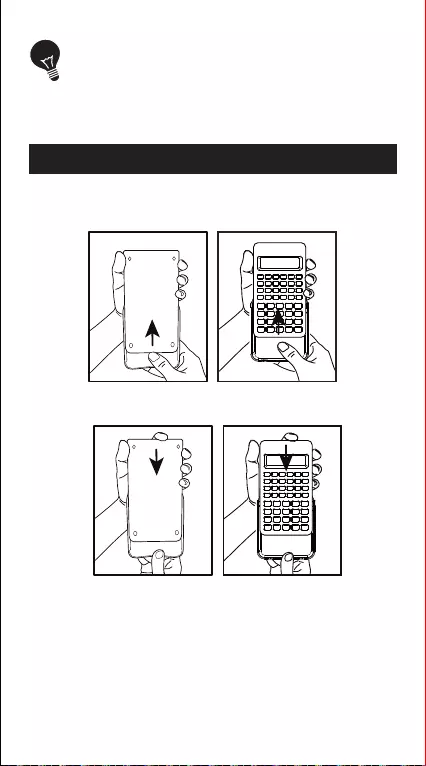
Open or close the cover by sliding as shown in
the figures.
HOW TO OPEN / CLOSE THE COVER
OPEN
CLOSE
3
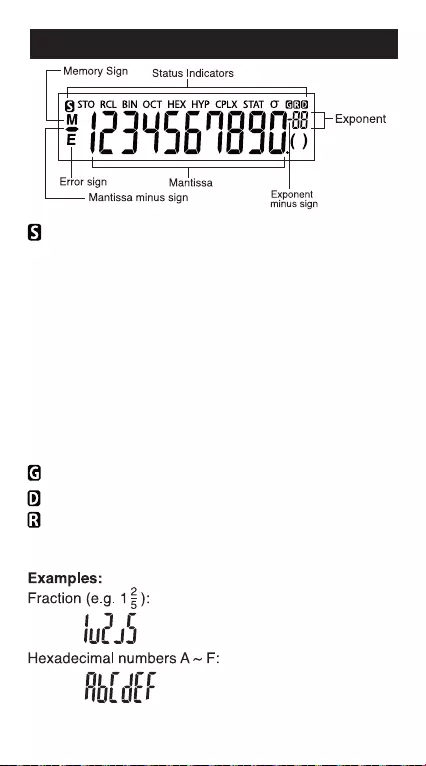
: Shift Key
STO : Store Memory
RCL : Recall Memory
BIN : Binary Mode
OCT : Octal Mode
HEX : Hexadecimal Mode
HYP : Hyperbolic
CPLX : Complex Mode
STAT : Statistics Mode
σ : Standard Deviation of Population
: Gradient Mode
: Degree Mode
: Radian Mode
DISPLAY
Note: For possible errors, see page 25 "Errors".
4
GETTING STARTED
1. Check the Current Calculation Mode
Be sure to check the status indicators that indicate the
current calculation mode (DEG, BIN, STAT and CPLX)
and display formats setting (Floating mode).
Note! If you get into trouble, hold + to reset
the calculator.
2. Key Symbols
The "D" key is colored in gray.
To use a function printed above a key in gray,
press the key while in Hexadecimal mode.
Note:
The blue keys are active in Statistic mode only. In
Statistic mode ("STAT" indicator lights up), they
work as follows.
Calculate the number of data samples when it is
pressed.
2nd function key: Calculate the summation of
" " data were input when it is pressed
immediately after .
Example
Example
5
To use a function printed on a key, press the key.
To use a function printed above a key, press the
key while in decimal mode.

Power ON, OFF
Auto Power Off Function
When the calculator is not used for about 7 minutes,
the calculator will automatically power off.
Reset Key: Reset the calculator when
these keys are pressed. The memory is
cleared, and the calculation mode is reset
to Decimal Calculation (Floating mode).
Hold + to reset the calculator.
Turns the calculator off.
6
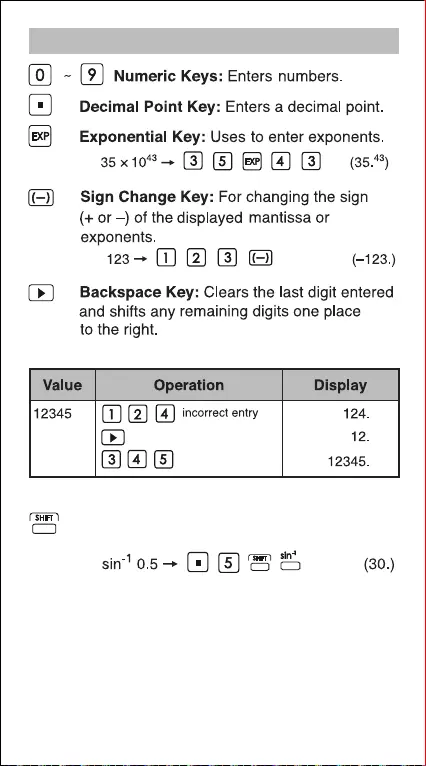
Numeric Entry and Mode Selection Keys
Shift Key: For performing second functions
indicated above the keys.
Example:
Example:
Example:
Example:
7
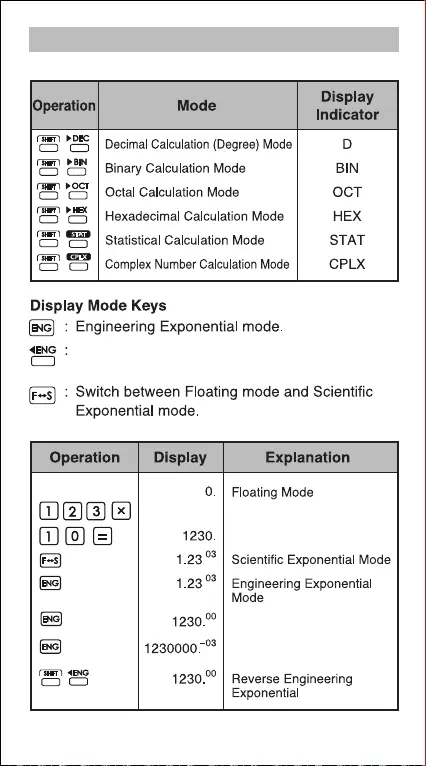
Mode Selection
To specify the calculation mode:
Return to previous mode from Engineering
Exponential mode.
Example:
STAT
CPLX
8
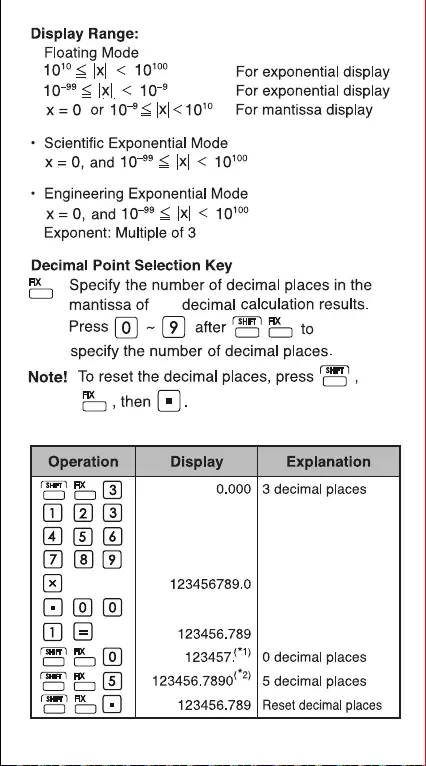
the
Example:
9
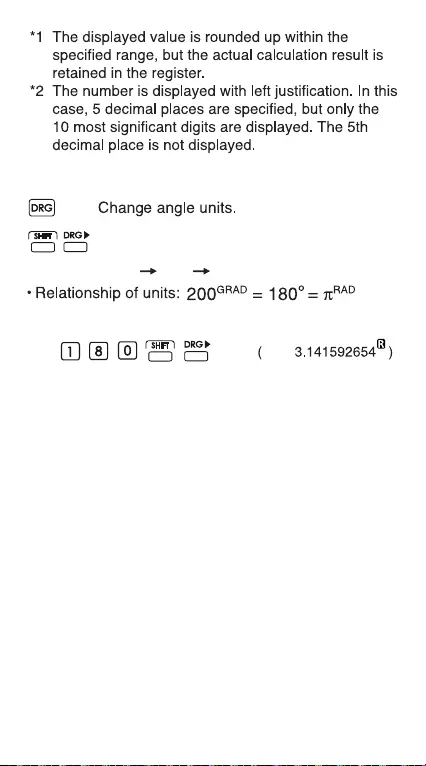
Angle Unit Conversion Mode: For
converting angle values to different units.
(DEG RAD GRAD)
Degree / Radian / Gradient Mode Key
Example (in Degree mode):
10
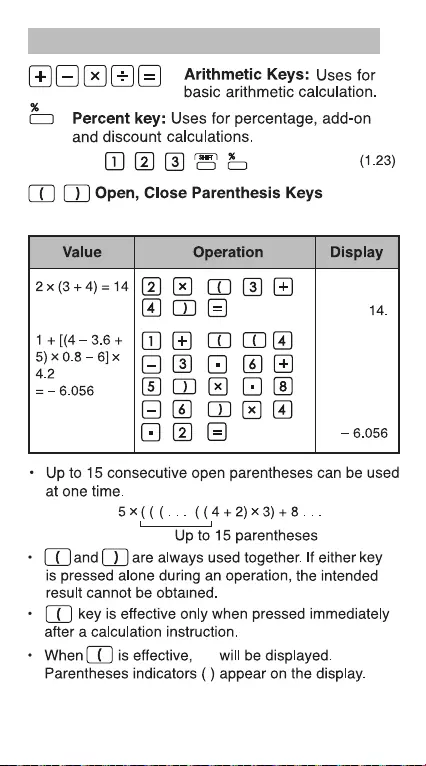
Basic Calculation Keys
"0"
Example:
Example:
Example:
11
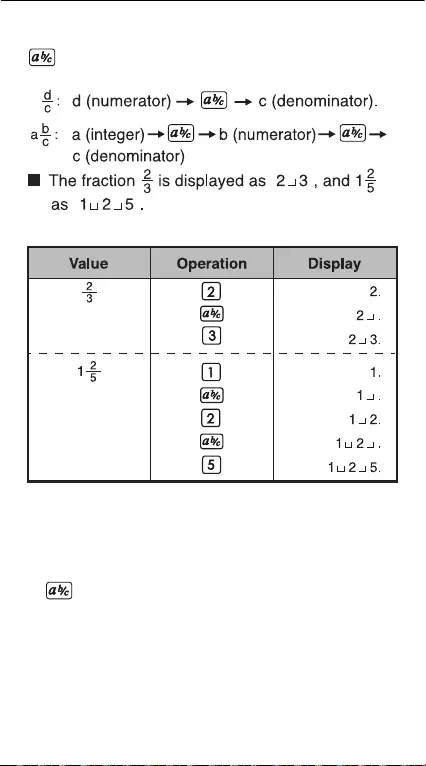
Fraction Key: Use this key to enter both mixed
and improper fractions.
""
""
Example:
Note!
• Fraction calculation results will be displayed in
decimal format
automatically whenever the total digits
of a fractional value (integer +
numerator +
denominator + separator marks) exceeds 10.
• can convert the results of fractional calculations
to decimal notation, and vice versa.
Fraction Calculation Keys
12
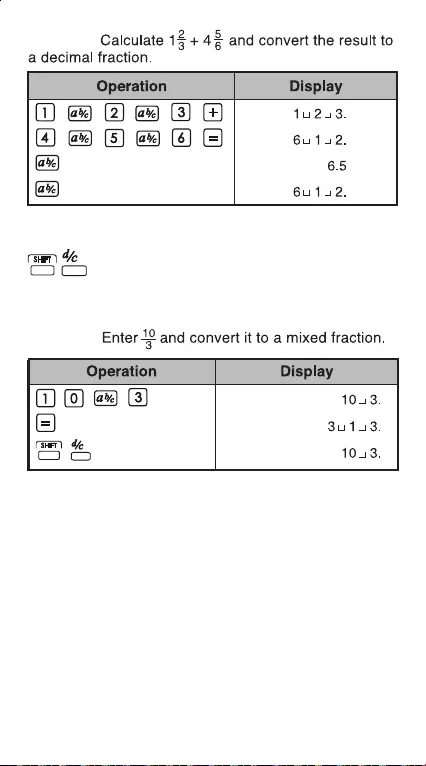
Example:
Mixed / Improper Fraction Conversion Key:
It converts
mixed fractions to improper
fractions and vice versa. It changes
alternatively each time the key is pressed.
Example:
13
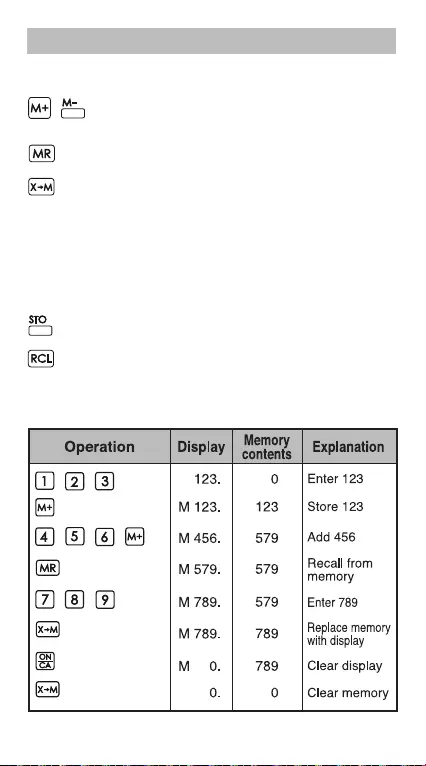
Memory Keys
Independent Memory: The data in the independent
memory is retained even when the calculator is turned off.
Memory Plus and Minus Key: Add or
Substract numbers to the independent
memory.
Memory Recall Key: Retrieve the value
of the independent memory.
Exchange Memory By Display Value:
Replaces the displayed number with the
contents of the independent memory.
Memory Variables: You can assign a specific value
or a calculation result to a variable. There are 6 memory
variables (A, B, C, D, E and F) to store data, results, or
dedicated values.
Store Values Key: To store variable into
memory.
Recall Values Key: To recall the memory
variable.
Example: Using the independent memory:
14
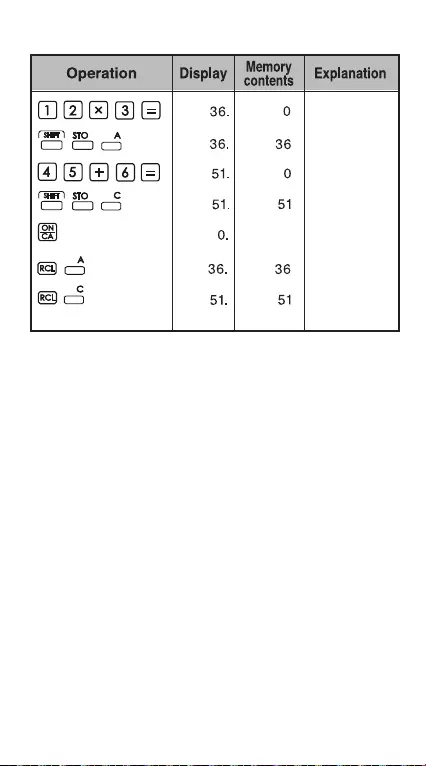
Example: Using the memory variable
Store value
to variable A
Clear display
Recall the contents
of variable A
Enter value
Enter value
Store value
to variable C
A= 36
C= 51
Recall the contents
of variable C
15
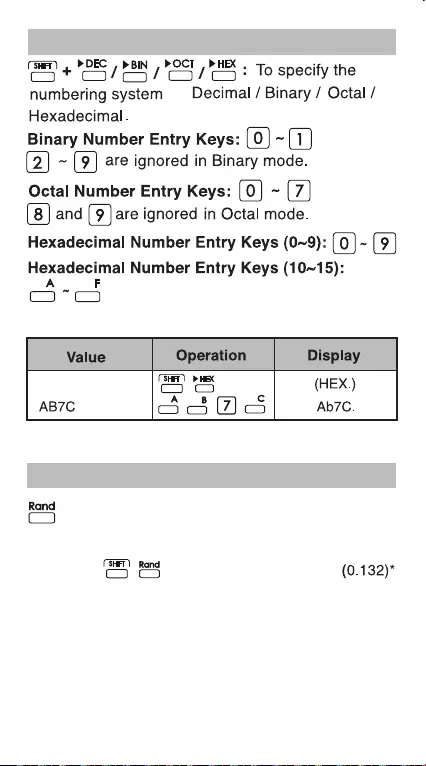
Binary / Octal / Hexadecimal Number Keys
as
Example:
Random Number Generation
Random Key: To generate a random number
* The value being generated will differ each time
between 0.000 and 0.999.
Example:
16
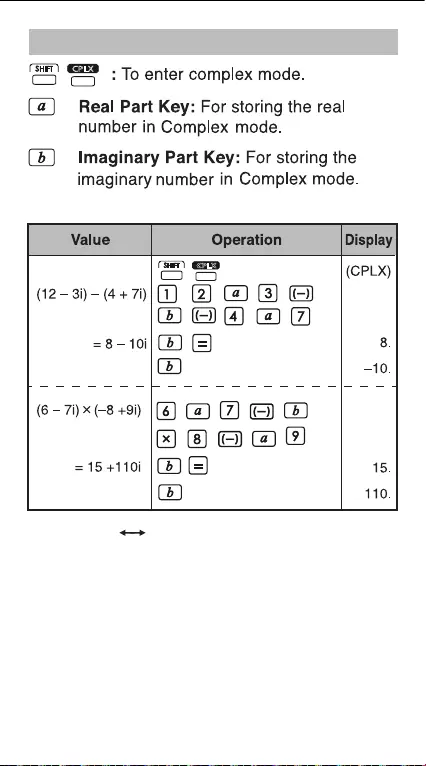
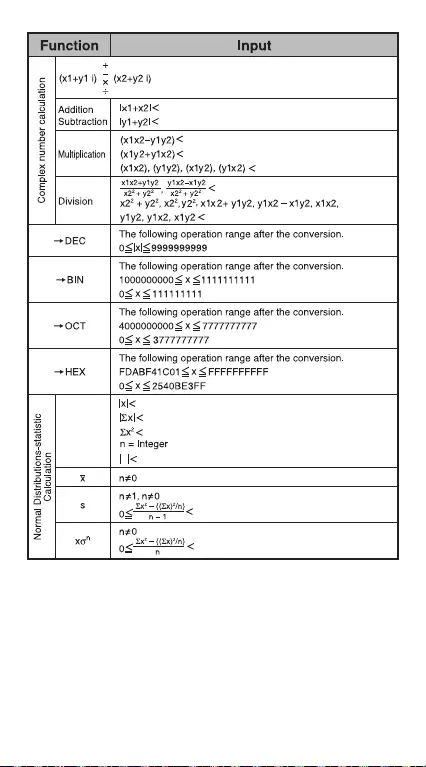
Complex Number Calculation
CPLX
Example:
Rectangular Polar Conversion
See P.36 "Basic Function Calculations".
CPLX
17
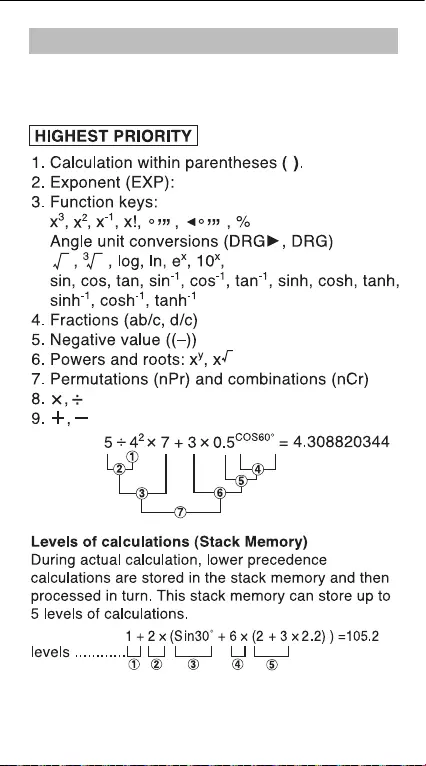
3. Order Of Operations
Example:
Example:
18
The calculator will automatically determine the
operation priority of each individual command as
follows:
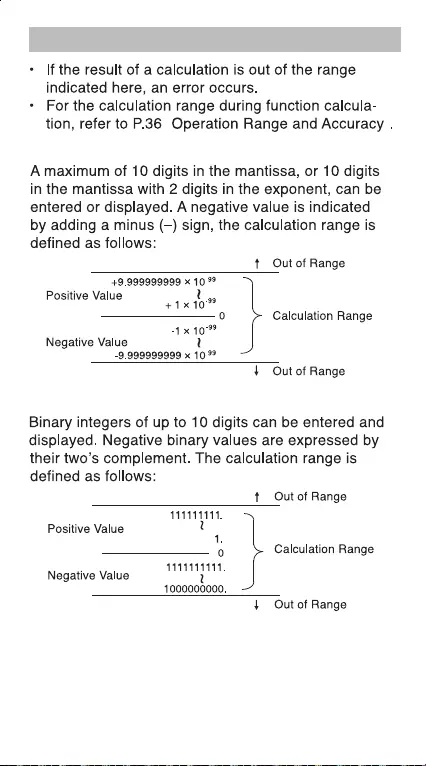
4. Calculation Range
""
Decimal Numbers
Binary Numbers
19
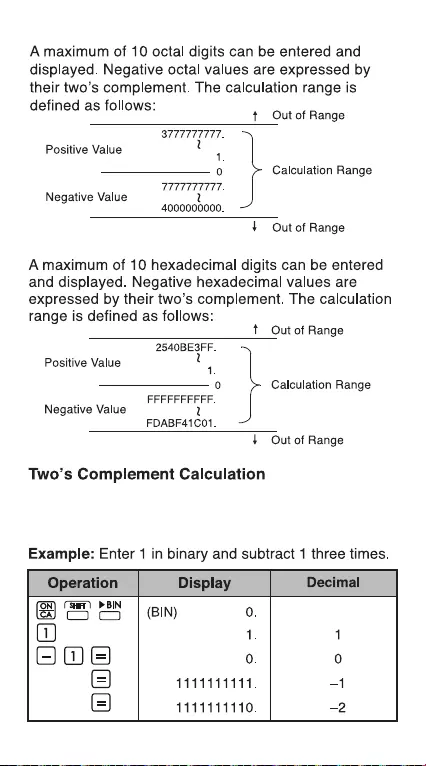
In computer calculations the complement is used to
express negative values without using + and – signs.
Subtraction is performed by adding the complement.
Octal Number
Hexadecimal Numbers
20
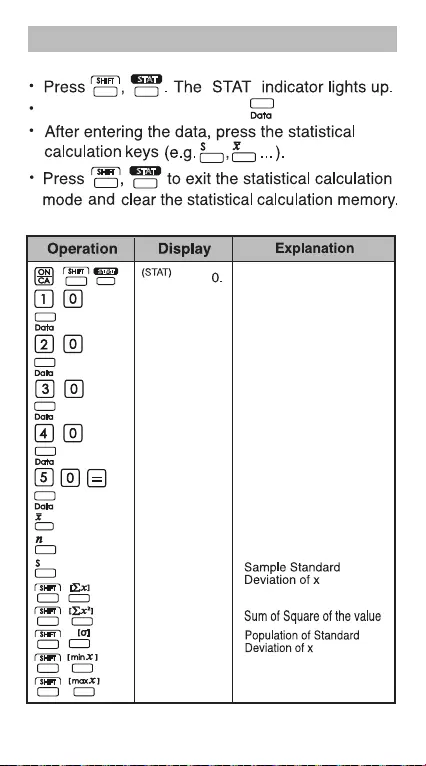
Enter the first data and press .
5. Statistical Calculations
STAT
STAT
""
Basic procedure
Example:
STAT
Statistic mode
Enter 10
Data 1 entry
Enter 20
Data 2 entry
Enter 30
Data 3 entry
Enter 40
Data 4 entry
Enter 50
Data 5 entry
Mean of x
30.
5.
15.8113883.
150.
5500.
14.14213562.
10.
50.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
10.
20.
30.
40.
50.
21
The max data
The min data
Total number of data
sample
Summation of x
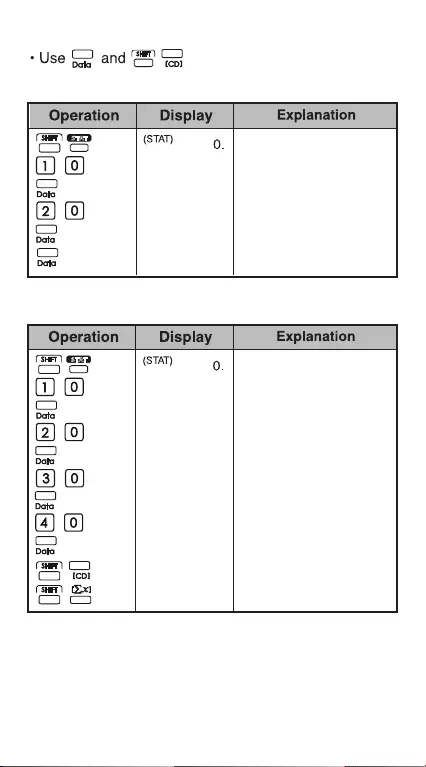
22
Add / Delete Statistical Data
Example: Add LCD current display
STAT
Statistic mode
Enter 10
Data 1 entry
Enter 20
Data 2 entry
3.
1.
2.
10.
20.
3.
Example: Delete LCD display
STAT
Statistic mode
Enter 10
Data 1 entry
Enter 20
Data 2 entry
1.
2.
10.
20.
Enter 30
Data 3 entry
Enter 40
Data 4 entry
3.
4.
30.
40.
96.
Delete data
Data 3 entry
23
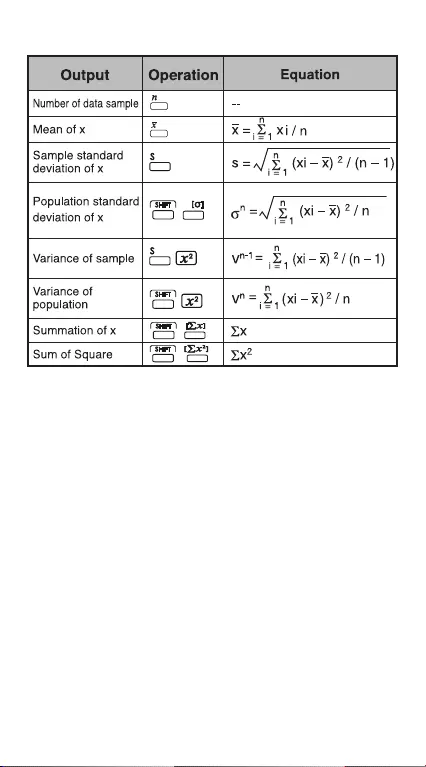
Output of Statistical Calculation Results
24
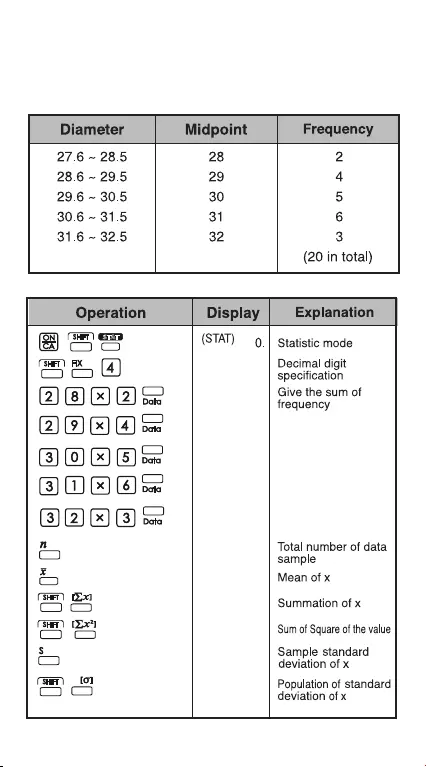
Statistical Calculation Examples
STAT
0.0000
2.0000
6.0000
11.0000
17.0000
20.0000
20.0000
30.2000
604.0000
18270.0000
1.2397
1.2083
You bought 20 pieces of pizza. However, the diameter
of each pizza is varied as shown in the following table.
Please calculate the statistic based on this information.

25
6. Errors
(1) If S is calculated with only one data input
(2) To find , and S when n = 0
(3) When any input is outside the allowable calculation
range:
1 x 10100
1 x 10100
1 x 10100
1 x 10100
(4) When any input is outside the allowable calculation
range:
When the number of operators stored in the calculator
during parentheses and arithmetic calculation exceeds
5 levels.
When more than 15 open paretheses are used at one
time.
x: calculation result
1 x 10100
26
CALCULATION EXAMPLES
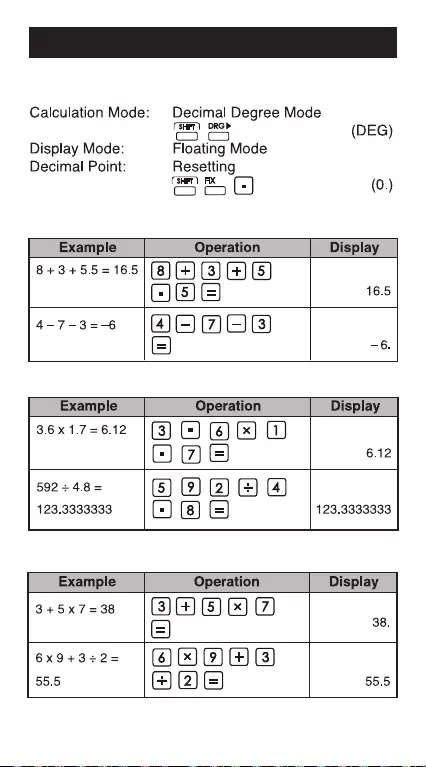
1. Decimal Calculations (Degree Mode)
Initial mode setting:
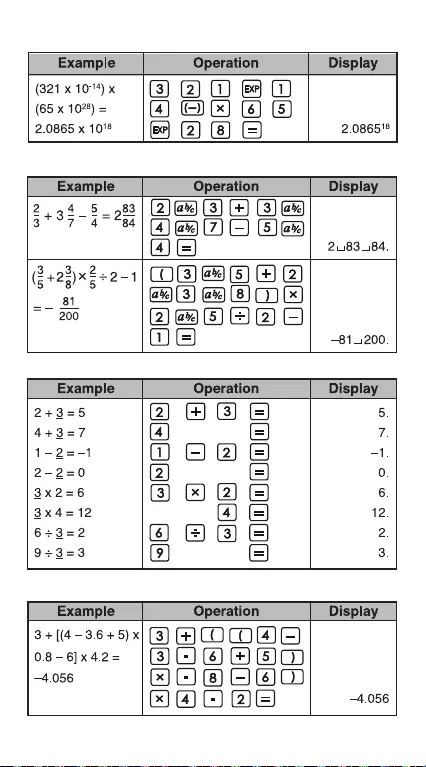
Addition and Subtraction
Multiplication and Division
Mixed Calculations
27
Fractional Calculations
Constant Calculations
Parentheses Calculations
Exponential Calculations
28
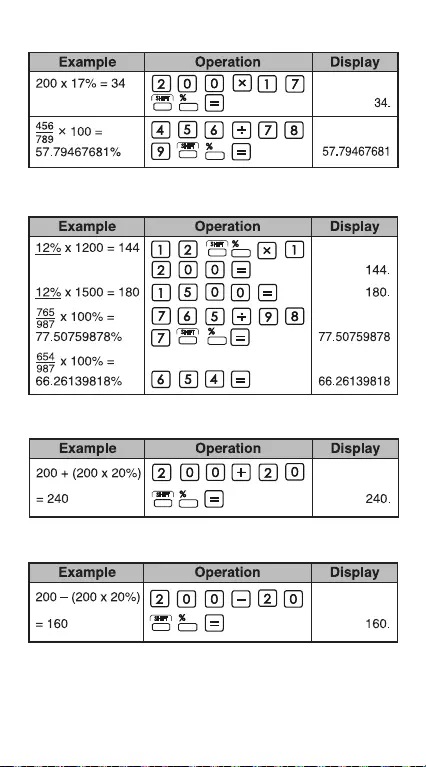
Percentage Calculations
Constant Percentage Calculations
Add-On (Mark Up) Calculation
Discount Calculation
29
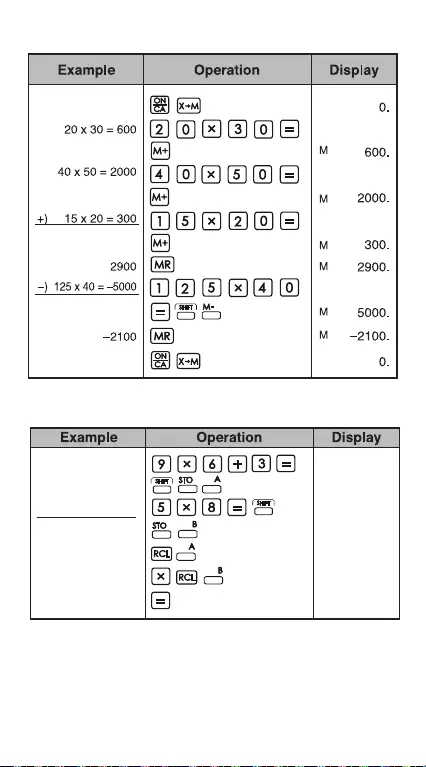
Memory Variable Calculation
Independent Memory Calculation
9 x 6 + 3 = 57
x) 5 x 8 = 40
2,280
57.
40.
57.
40.
2280.
30
2. Binary / Octal / Hexadecimal Calculations
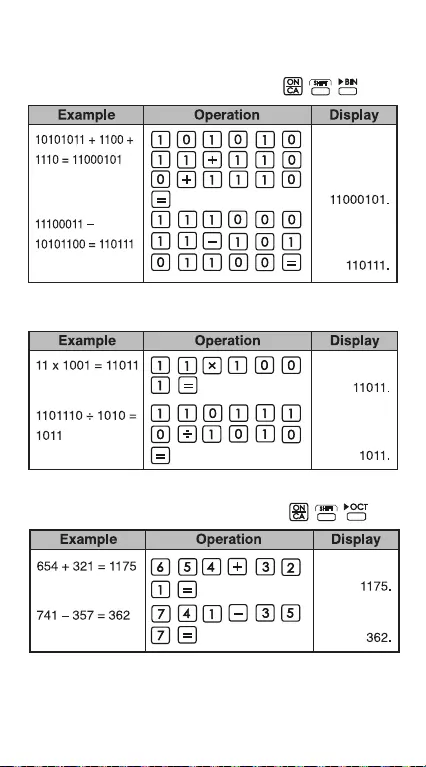
Binary Calculations
• Addition and Subtraction (BIN):
• Multiplication and Division (BIN)
Octal Calculations
• Addition and Subtraction (OCT):
31
• Multiplication and Division (OCT)
• Mixed Calculations (OCT)
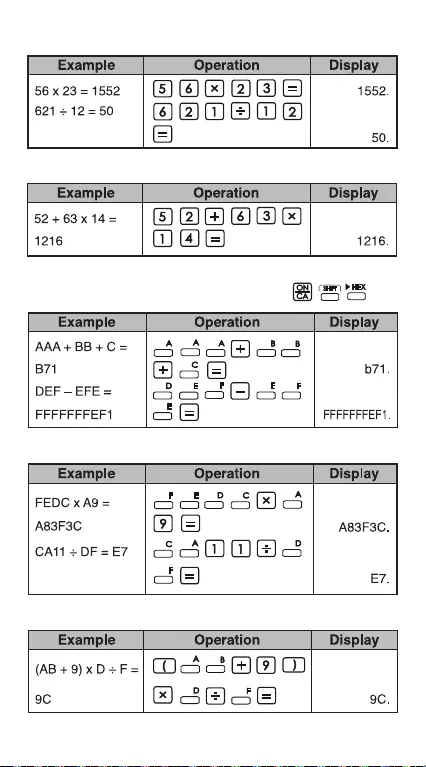
Hexadecimal Calculations
• Addition and Subtraction (HEX):
• Multiplication and Division (HEX)
• Mixed Calculations (HEX)
32
3. Basic Function Calculations
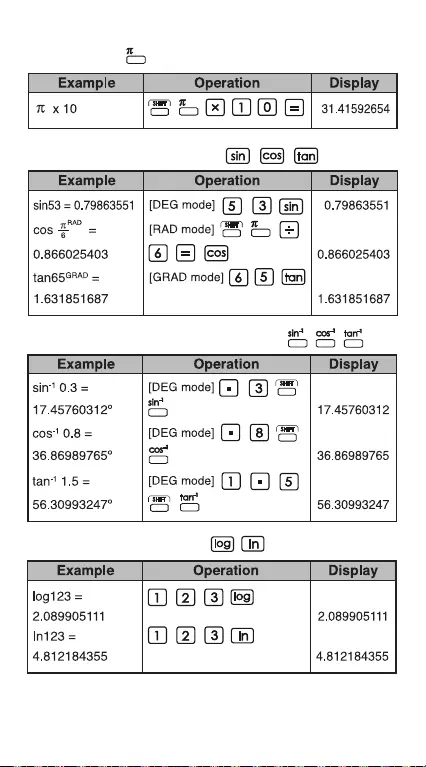
Pi Function:
Trigonometric Functions:
Inverse Trigonometric Functions:
Logarithmic Functions:
33
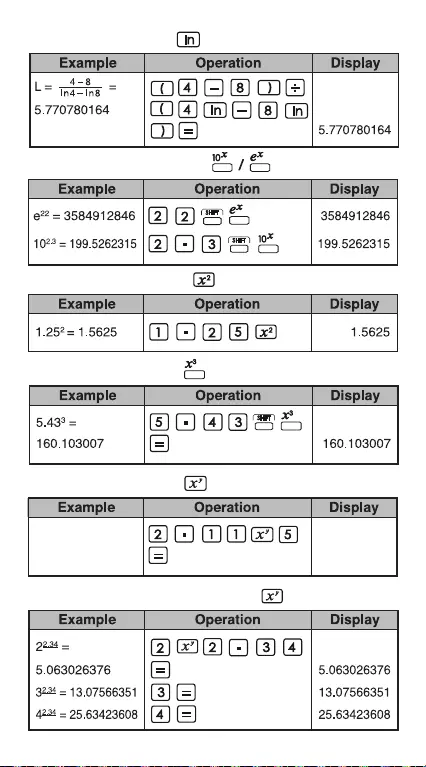
Logarithmic Mean:
Exponential Functions:
Square Calculations:
Power Calculations:
Cubic Calculations:
Constant Power Calculations:
2.11
5
=
41.82272021 41.82272021
34
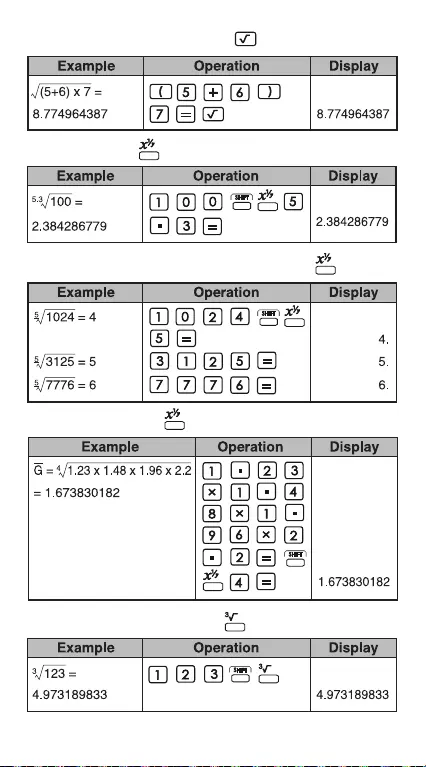
Extraction of Square Root:
Multiple Root:
Constant Multiple Root Calculations:
Geometric Mean:
Extraction of Cubic Root:
35
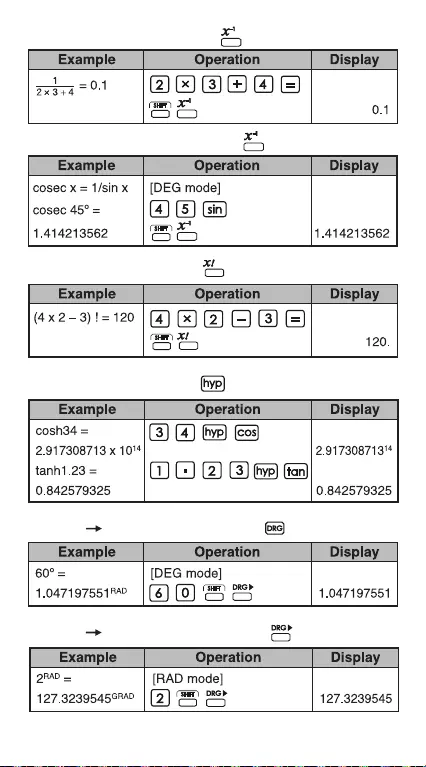
Reciprocal Calculations:
Trigonometric Calculations:
Factorial Calculations:
Hyperbolic Functions:
Degree Radian Conversion:
Radian Gradient Conversion:
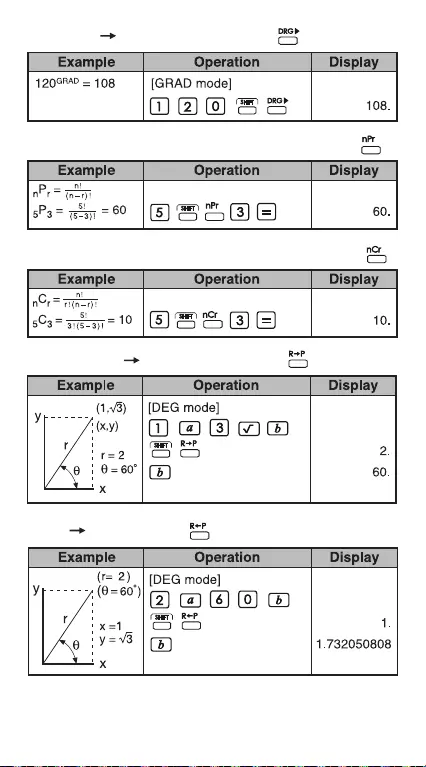
36
Polar Rectangular:
Gradient Degree Conversion:
Permutations (of n things taken r at a time):
Combinations (of n things taken r at a time):
Rectangular Polar Conversion:
37
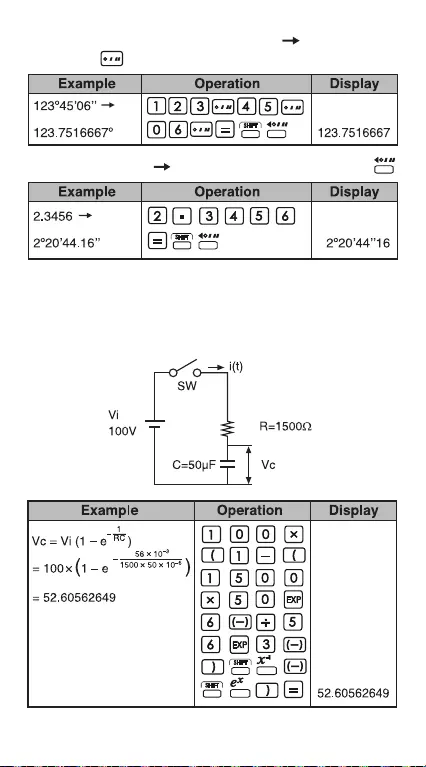
Decimal Degrees Degrees-Minutes-Seconds:
Degrees-Minutes-Seconds (DMS) Decimal
Degrees:
4. Applied Calculations
Electricity - Integrating Circuit Problem
Obtain the voltage Vc across the capacitor at t=56ms
after the switch is turned on.
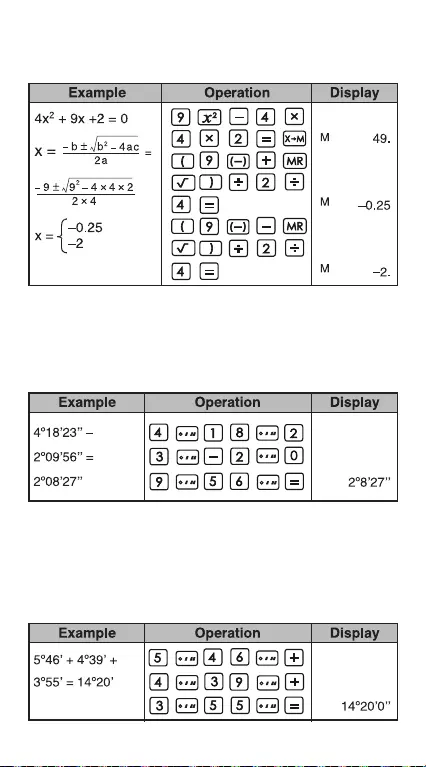
38
Algebra
The Root of a Quadratic Equation (only for problems
having a real root)
Calculation of time
Example 1:
The air flight departs at 2 o'clock 9 minutes
and 56 seconds (2o09'56"), and arrives at 4 o'clock
18 minutes and 23 seconds (4o18'23").
What is the travel time
Example 2:
The following shows the amount of time worked in
three days. What was the total time?
1st day : 5 hours 46 minutes (5o46')
2nd day : 4 hours 39 minutes (4o39')
3rd day : 3 hours 55 minutes (3o55')
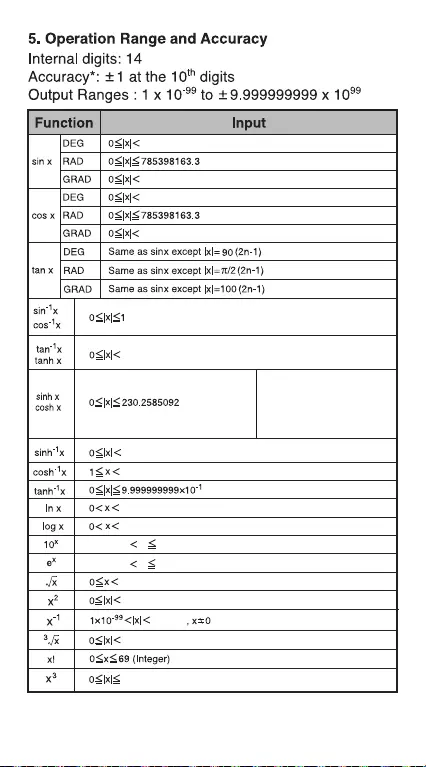
39
4.5x1010
5x1010
4.5x1010
5x1010
1x10100
When x=0, sinh and tanh,
being in some condition,
will have more possibility of
error, and influence
accurancy.
5x1099
5x1099
1x10100
1x10100
–1x10100 x 99.99999999
–1x10100 x 230.2585092
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
2.154434689x1033
40
–1x10100 y • In x 230.2585092
1x10100
–1x10100 1/y • In x 230.2585092
R P
x , y 1x10100
(x2+y2)1/2 1x10100
y/x same as tan–1x
P R θ : same as sinx, cosx
0 r 1x10100
999999.9999
When input 999999.9999 the result can not converted to
DMS by
999999”59’
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
>
41
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
n 1x10100
1x10100
1x10100
* In the case of consecutive calculations, errors are
cumulative. This is also true when internal consecutive
calculations are performed; for example, (xy) , x1/y, x!,
nPr, nCr, etc. In this case, the cumulative data may
become large.
DATA
INPUT
42
BATTERY REPLACEMENT
When the display characters are dim, turn it off, and
replace the alkaline battery immediately.
Please replace the alkaline battery using the following
procedure:
1. Press to power off the calculator.
2. Remove the screw that secrues the battery cover in
place.
3. Slide the battery cover slightly and lift it.
4. Remove the old battery with a ball point pen or
similar sharp object.
5.
Load the new battery with positive "+" side facing up.
6. Replace the battery cover, tighten the screw, and
press , + to initialize the calculator.
CAUTION: There is risk of explosion if the
battery is replaced by an incorrect type.
Dispose of used battery according to the below
instructions.
Electromagnetic interference or electrostatic
discharge may cause the display to malfunction
or the contents of the memory to be lost or
altered. Should this occur, press to restart
the calculator.
++
43
ADVICE AND PRECAUTIONS
• This calculator contains precision components such as LSI
chips and should not be used in a place subject to rapid
variations in temperature, excessive humidity dirt or dust, or
exposed to direct sunlight.
• The liquid crystal display panel is made of glass and should
not be subjected to excessive pressure.
• When cleaning the device do not use a damp cloth or volatile
liquid such as paint thinner. Instead, use only a soft, dry
cloth.
• Do not under any circumstances, disassemble this device.
If you believe that the calculator is not functioning properly,
either bring or mail the device together with proof of purchase
to a Canon Business office service representative.
• Never dispose the calculator improperly such as burning; it
can create risks of personal injury or harm. You are suggested
to dispose this product according to your national law.
• Replace the battery once every two years even it is not
used frequently.
Battery Caution!
• Keep the Battery out of reach of children. If the battery is
swallowed, contact a doctor immediately.
• Misuse of battery may cause leakage, explosion, damages
or personal injury.
• Don’t recharge or disassemble the battery, it could cause a
short circuit.
• Never expose the battery to high temperatures, direct heat,
or dispose by incineration.
• Never leave a dead battery in the calculator as the dead
battery may leak and cause damage to the calculator.
•
Continue using the calculator in the low battery condition may
cause improper calculations or the stored memory may get
corrupted or lost completely. Keep written records of
important data all the time; and replace the battery as soon
as possible.
When you are not sure of the current calculations and
setting mode, you are recommended to initialize the
calculator to default value by pressing + .

44
SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply : Alkaline battery (LR54 x 1)
Power Consumption : DC1.5V / 0.038mW
Battery Life : Approximately 2.5 years
(Based on 1 hour operation per day)
Auto power off : Approx. 7 minutes
Usable Temperature : 0O ~ 40O C (32O F ~ 104O F)
Size: 122 (L) x 73 (W) x 12 (H) mm (with cover)
4-51/64" x 2-7/8" x 15/32" (with cover)
Weight : 70 g (2.4 oz) with cover
* Specifications are subject to change without notice