Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Web-based Switch Configuration
- 3. System
- 4. Management
- 5. Layer 2 Features
- 6. Layer 3 Features
- 7. Quality of Service (QoS)
- 8. Access Control List (ACL)
- 9. Security
- Port Security
- 802.1X
- AAA
- RADIUS
- TACACS
- IMPB
- DHCP Server Screening
- ARP Spoofing Prevention
- BPDU Attack Protection
- MAC Authentication
- Web-based Access Control
- Japanese Web-based Access Control
- Network Access Authentication
- Safeguard Engine
- Trusted Host
- Traffic Segmentation Settings
- Storm Control
- DoS Attack Prevention Settings
- SSH
- SSL
- 10. OAM
- 11. Monitoring
- 12. Green
- 13. Save and Tools
- Appendix A - System Log Entries
- 802.1X
- AAA
- Auto Save Configuration
- Auto Surveillance VLAN
- BPDU Attack Protection
- Configuration/Firmware
- DAI
- DDM
- DHCPv6 Client
- DHCPv6 Relay
- DNS Resolver
- DoS Prevention
- Interface
- JWAC
- LACP
- LBD
- LLDP-MED
- Login/Logout CLI
- MAC-based Access Control
- MSTP Debug Enhancement
- Peripheral
- PoE
- Port Security
- Safeguard
- SNMP
- SSH
- Stacking
- Storm Control
- Telnet
- Voice-VLAN
- Web
- Web-Authentication
- Appendix B - Trap Entries
- 802.1X
- Authentication Fail
- BPDU Attack Protection
- DDM
- DHCP Server Screen Prevention
- DoS Prevention
- ErrDisable
- General Management
- Gratuitous ARP Function
- IMPB
- LACP
- LBD
- LLDP
- MAC-based Access Control
- MAC-notification
- MSTP
- Peripheral
- PoE
- Port
- Port Security
- RMON
- Safeguard
- Stack
- SIM
- Start
- Storm Control
- System File
- Web-Authentication
- Appendix C - RADIUS Attributes Assignment
- Appendix D - IETF RADIUS Attributes Support
- Appendix E - ERPS Information
D-Link DGS-1510-20 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for DGS-1510-20 by D-Link which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.

1

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
ii
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Reproduction of this document in any manner,
without the written permission of the D-Link Corporation, is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-Link logo are trademarks of the D-Link Corporation; Microsoft and
Windows are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either as the entities claiming the
marks and the names or their products. D-Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
© 2015 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
October 2015

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
iii
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................. 1
Audience ...................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Other Documentation ................................................................................................................................................... 1
Conventions ................................................................................................................................................................. 1
Notes, Notices, and Cautions ...................................................................................................................................... 1
2. Web-based Switch Configuration .......................................................................................................................... 3
Management Options ................................................................................................................................................... 3
Connecting using the Web User Interface ................................................................................................................... 3
Logging onto the Web Manager .................................................................................................................................. 3
Smart Wizard ............................................................................................................................................................... 4
Web User Interface (Web UI) ....................................................................................................................................... 7
Areas of the User Interface ..................................................................................................................................... 7
3. System ...................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Device Information ....................................................................................................................................................... 9
System Information Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 9
Peripheral Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 10
Port Configuration ...................................................................................................................................................... 11
Port Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 11
Port Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 12
Port Auto Negotiation ............................................................................................................................................ 13
Error Disable Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 14
Jumbo Frame ........................................................................................................................................................ 15
PoE (DGS-1510-28P and DGS-1510-28XMP Only) ................................................................................................. 15
PoE System .......................................................................................................................................................... 16
PoE Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 16
PoE Configuration ................................................................................................................................................. 17
PoE Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................ 18
PoE Measurement ................................................................................................................................................ 19
PoE LLDP Classification ....................................................................................................................................... 20
System Log ................................................................................................................................................................ 21
System Log Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 21
System Log Discriminator Settings ....................................................................................................................... 22
System Log Server Settings ................................................................................................................................. 23
System Log ........................................................................................................................................................... 24
System Attack Log ................................................................................................................................................ 24
Time and SNTP ......................................................................................................................................................... 25
Clock Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 25
Time Zone Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 25
SNTP Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
Time Range................................................................................................................................................................ 28
4. Management .......................................................................................................................................................... 29
User Account Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 29
Password Encryption ................................................................................................................................................. 30
Login Method ............................................................................................................................................................. 31
SNMP ......................................................................................................................................................................... 32
SNMP Global Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 33
SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings ......................................................................................................................... 34
SNMP View Table Settings ................................................................................................................................... 35

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
iv
SNMP Community Table Settings ........................................................................................................................ 36
SNMP Group Table Settings .............................................................................................................................. 37
SNMP Engine ID Local Settings ........................................................................................................................... 38
SNMP User Table Settings ................................................................................................................................... 39
SNMP Host Table Settings ................................................................................................................................... 40
RMON ........................................................................................................................................................................ 41
RMON Global Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 41
RMON Statistics Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 41
RMON History Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 42
RMON Alarm Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 43
RMON Event Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 44
Telnet/Web ................................................................................................................................................................. 45
Session Timeout ........................................................................................................................................................ 46
DHCP ......................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Service DHCP ....................................................................................................................................................... 47
DHCP Class Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 47
DHCP Relay ......................................................................................................................................................... 48
DHCPv6 Relay ...................................................................................................................................................... 54
DHCP Auto Configuration ..................................................................................................................................... 55
DNS ............................................................................................................................................................................ 55
DNS Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 56
DNS Name Server Settings .................................................................................................................................. 57
DNS Host Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 57
NTP ............................................................................................................................................................................ 58
NTP Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 58
NTP Server Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 59
NTP Peer Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 59
NTP Access Group Settings ................................................................................................................................. 60
NTP Key Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 61
NTP Interface Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 62
NTP Associations ................................................................................................................................................. 62
NTP Status............................................................................................................................................................ 63
IP Source Interface .................................................................................................................................................... 64
File System ................................................................................................................................................................ 64
Physical Stacking ....................................................................................................................................................... 66
Virtual Stacking (SIM) ................................................................................................................................................ 70
Single IP Settings ................................................................................................................................................. 72
Topology ............................................................................................................................................................... 73
Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................................................ 80
Configuration File Backup/Restore ....................................................................................................................... 80
Upload Log File ..................................................................................................................................................... 81
D-Link Discovery Protocol .......................................................................................................................................... 81
5. Layer 2 Features .................................................................................................................................................... 83
FDB ............................................................................................................................................................................ 83
Static FDB ............................................................................................................................................................. 83
MAC Address Table Settings................................................................................................................................ 84
MAC Address Table .............................................................................................................................................. 85
MAC Notification ................................................................................................................................................... 86
VLAN .......................................................................................................................................................................... 87
802.1Q VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................ 87
802.1v Protocol VLAN .......................................................................................................................................... 88
GVRP .................................................................................................................................................................... 89

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
v
Asymmetric VLAN ................................................................................................................................................. 93
MAC VLAN............................................................................................................................................................ 94
VLAN Interface ..................................................................................................................................................... 94
Auto Surveillance VLAN ....................................................................................................................................... 97
Voice VLAN .......................................................................................................................................................... 99
Spanning Tree ......................................................................................................................................................... 102
STP Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 105
STP Port Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 106
MST Configuration Identification ........................................................................................................................ 108
STP Instance ...................................................................................................................................................... 109
MSTP Port Information ....................................................................................................................................... 109
ERPS (G.8032) ........................................................................................................................................................ 110
ERPS .................................................................................................................................................................. 110
ERPS Profile ....................................................................................................................................................... 113
Loopback Detection ................................................................................................................................................. 114
Link Aggregation ...................................................................................................................................................... 115
L2 Multicast Control ................................................................................................................................................. 118
IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................................................. 118
MLD Snooping .................................................................................................................................................... 123
Multicast Filtering ................................................................................................................................................ 129
LLDP ........................................................................................................................................................................ 130
LLDP Global Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 130
LLDP Port Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 132
LLDP Management Address List ........................................................................................................................ 133
LLDP Basic TLVs Settings .................................................................................................................................. 133
LLDP Dot1 TLVs Settings ................................................................................................................................... 134
LLDP Dot3 TLVs Settings ................................................................................................................................... 135
LLDP-MED Port Settings .................................................................................................................................... 136
LLDP Statistics Information ................................................................................................................................ 137
LLDP Local Port Information............................................................................................................................... 138
LLDP Neighbor Port Information ........................................................................................................................ 140
6. Layer 3 Features .................................................................................................................................................. 141
ARP .......................................................................................................................................................................... 142
ARP Aging Time ................................................................................................................................................. 142
Static ARP........................................................................................................................................................... 143
Proxy ARP .......................................................................................................................................................... 143
ARP Table........................................................................................................................................................... 144
Gratuitous ARP ........................................................................................................................................................ 144
UDP Helper .............................................................................................................................................................. 145
IP Forward Protocol ............................................................................................................................................ 145
IP Helper Address ............................................................................................................................................... 146
IPv4 Interface ........................................................................................................................................................... 147
IPv4 Static/Default Route ......................................................................................................................................... 149
IPv4 Route Table ..................................................................................................................................................... 149
IPv6 Interface ........................................................................................................................................................... 150
IPv6 Neighbor .......................................................................................................................................................... 152
IPv6 Static/Default Route ......................................................................................................................................... 153
IPv6 Route Table ..................................................................................................................................................... 153
7. Quality of Service (QoS) ..................................................................................................................................... 155
Basic Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 155
Port Default CoS ................................................................................................................................................. 155

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
vi
Port Scheduler Method ....................................................................................................................................... 155
Queue Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 157
CoS to Queue Mapping ...................................................................................................................................... 157
Port Rate Limiting ............................................................................................................................................... 158
Queue Rate Limiting ........................................................................................................................................... 159
Advanced Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 160
DSCP Mutation Map ........................................................................................................................................... 160
Port Trust State and Mutation Binding ................................................................................................................ 161
DSCP CoS Mapping ........................................................................................................................................... 162
CoS Color Mapping ............................................................................................................................................ 163
DSCP Color Mapping ......................................................................................................................................... 163
Class Map ........................................................................................................................................................... 164
Aggregate Policer ............................................................................................................................................... 166
Policy Map .......................................................................................................................................................... 169
Policy Binding ..................................................................................................................................................... 171
8. Access Control List (ACL) .................................................................................................................................. 173
ACL Configuration Wizard ....................................................................................................................................... 173
ACL Access List ....................................................................................................................................................... 203
Standard IP ACL ................................................................................................................................................. 204
Extended IP ACL ................................................................................................................................................ 207
Standard IPv6 ACL ............................................................................................................................................. 224
Extended IPv6 ACL ............................................................................................................................................ 228
Extended MAC ACL ............................................................................................................................................ 240
Extended Expert ACL ......................................................................................................................................... 243
ACL Interface Access Group ................................................................................................................................... 269
ACL VLAN Access Map ........................................................................................................................................... 269
ACL VLAN Filter ....................................................................................................................................................... 271
9. Security ................................................................................................................................................................ 272
Port Security............................................................................................................................................................. 272
Port Security Global Settings .............................................................................................................................. 272
Port Security Port Settings .................................................................................................................................. 273
Port Security Address Entries ............................................................................................................................. 274
802.1X ...................................................................................................................................................................... 275
802.1X Global Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 279
802.1X Port Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 279
Authentication Session Information .................................................................................................................... 281
Authenticator Statistics ....................................................................................................................................... 281
Authenticator Session Statistics ......................................................................................................................... 282
Authenticator Diagnostics ................................................................................................................................... 282
AAA .......................................................................................................................................................................... 283
AAA Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 283
Application Authentication Settings .................................................................................................................... 283
Application Accounting Settings ......................................................................................................................... 284
Authentication Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 284
Accounting Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 286
RADIUS .................................................................................................................................................................... 288
RADIUS Global Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 288
RADIUS Server Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 289
RADIUS Group Server Settings ......................................................................................................................... 289
RADIUS Statistic ................................................................................................................................................. 290
TACACS ................................................................................................................................................................... 291

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
vii
TACACS Server Settings .................................................................................................................................... 291
TACACS Group Server Settings ........................................................................................................................ 292
TACACS Statistic ................................................................................................................................................ 293
IMPB ........................................................................................................................................................................ 293
IPv4 ..................................................................................................................................................................... 293
IPv6 ..................................................................................................................................................................... 306
DHCP Server Screening .......................................................................................................................................... 311
DHCP Server Screening Global Settings ........................................................................................................... 312
DHCP Server Screening Port Settings ............................................................................................................... 313
ARP Spoofing Prevention ........................................................................................................................................ 313
BPDU Attack Protection ........................................................................................................................................... 314
MAC Authentication ................................................................................................................................................. 315
Web-based Access Control ..................................................................................................................................... 317
Web Authentication ............................................................................................................................................. 319
WAC Port Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 319
WAC Customize Page ........................................................................................................................................ 320
Japanese Web-based Access Control ..................................................................................................................... 321
JWAC Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 321
JWAC Port Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 324
JWAC Customize Page Language ..................................................................................................................... 324
JWAC Customize Page ...................................................................................................................................... 325
Network Access Authentication ............................................................................................................................... 326
Guest VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................ 326
Network Access Authentication Global Settings................................................................................................. 327
Network Access Authentication Port Settings .................................................................................................... 328
Network Access Authentication Sessions Information ....................................................................................... 330
Safeguard Engine .................................................................................................................................................... 331
Safeguard Engine Settings ................................................................................................................................. 332
CPU Protect Counters ........................................................................................................................................ 333
CPU Protect Sub-Interface ................................................................................................................................. 333
CPU Protect Type ............................................................................................................................................... 334
Trusted Host............................................................................................................................................................. 334
Traffic Segmentation Settings .................................................................................................................................. 335
Storm Control ........................................................................................................................................................... 336
DoS Attack Prevention Settings ............................................................................................................................... 338
SSH .......................................................................................................................................................................... 339
SSH Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 340
Host Key ............................................................................................................................................................. 340
SSH Server Connection ...................................................................................................................................... 341
SSH User Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 341
SSL .......................................................................................................................................................................... 342
SSL Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 343
Crypto PKI Trustpoint ......................................................................................................................................... 343
SSL Service Policy ............................................................................................................................................. 344
10. OAM ...................................................................................................................................................................... 346
Cable Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................................... 346
DDM ......................................................................................................................................................................... 346
DDM Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 346
DDM Temperature Threshold Settings ............................................................................................................... 347
DDM Voltage Threshold Settings ....................................................................................................................... 348
DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings ............................................................................................................... 348
DDM TX Power Threshold Settings .................................................................................................................... 349

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
viii
DDM RX Power Threshold Settings ................................................................................................................... 350
DDM Status Table .............................................................................................................................................. 351
11. Monitoring ............................................................................................................................................................ 352
Utilization .................................................................................................................................................................. 352
Port Utilization ..................................................................................................................................................... 352
Statistics ................................................................................................................................................................... 353
Port ..................................................................................................................................................................... 353
Port Counters ...................................................................................................................................................... 354
Counters ............................................................................................................................................................. 356
Mirror Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 357
sFlow ........................................................................................................................................................................ 359
sFlow Agent Information ..................................................................................................................................... 359
sFlow Receiver Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 359
sFlow Sampler Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 360
sFlow Poller Settings .......................................................................................................................................... 361
Device Environment ................................................................................................................................................. 362
12. Green .................................................................................................................................................................... 363
Power Saving ........................................................................................................................................................... 363
EEE .......................................................................................................................................................................... 364
13. Save and Tools .................................................................................................................................................... 366
Save Configuration .................................................................................................................................................. 366
Firmware Upgrade & Backup ................................................................................................................................... 366
Firmware Upgrade from HTTP ........................................................................................................................... 366
Firmware Upgrade from TFTP ............................................................................................................................ 367
Firmware Backup to HTTP ................................................................................................................................. 367
Firmware Backup to TFTP .................................................................................................................................. 368
Configuration Restore & Backup ............................................................................................................................. 368
Configuration Restore from HTTP ...................................................................................................................... 368
Configuration Restore from TFTP ...................................................................................................................... 369
Configuration Backup to HTTP ........................................................................................................................... 370
Configuration Backup to TFTP ........................................................................................................................... 370
Log Backup .............................................................................................................................................................. 371
Log Backup to HTTP .......................................................................................................................................... 371
Log Backup to TFTP ........................................................................................................................................... 371
Ping .......................................................................................................................................................................... 372
Trace Route ............................................................................................................................................................. 374
Language Management ........................................................................................................................................... 375
Reset ........................................................................................................................................................................ 376
Reboot System ........................................................................................................................................................ 376
Appendix A - System Log Entries ............................................................................................................................. 378
Appendix B - Trap Entries .......................................................................................................................................... 403
Appendix C - RADIUS Attributes Assignment ......................................................................................................... 413
Appendix D - IETF RADIUS Attributes Support ....................................................................................................... 416
Appendix E - ERPS Information................................................................................................................................. 418

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
1
1. Introduction
This manual’s command descriptions are based on the software release 1.30. The commands listed
here are the subset of commands that are supported by the DGS-1510 Series SmartPro switch.
Audience
This reference manual is intended for network administrators and other IT networking professionals
responsible for managing the switch by using the Web User Interface (Web UI). The Web UI is the
secondary management interface to the DGS-1510 Series switch, which will be generally be referred
to simply as “the Switch” within this manual. This manual is written in a way that assumes that you
already have the experience and knowledge of Ethernet and modern networking principles for Local
Area Networks.
Other Documentation
The documents below are a further source of information in regards to configuring and
troubleshooting the switch. All the documents are available either from the CD, bundled with this
switch, or from the D-Link website. Other documents related to this switch are:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Hardware Installation Guide
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch CLI Reference Guide
Conventions
Convention
Description
Boldface Font
Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu, or menu item. For
example: Open the File menu and choose Cancel. Used for
emphasis. May also indicate system messages or prompts
appearing on screen. For example: You have mail. Bold font is
also used to represent filenames, program names and commands.
For example: use the copy command.
Initial capital letter
Indicates a window name. Names of keys on the keyboard have
initial capitals. For example: Click Enter.
Menu Name > Menu Option
Indicates the menu structure. Device > Port > Port Properties
means the Port Properties menu option under the Port menu
option that is located under the Device menu.
Blue Courier Font
This convention is used to represent an example of a screen
console display including example entries of CLI command input
with the corresponding output.
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
Below are examples of the three types of indicators used in this manual. When administering your
switch using the information in this document, you should pay special attention to these indicators.
Each example below provides an explanatory remark regarding each type of indicator.
NOTE: A note indicates important information that helps you make better use of your
device.
NOTICE: A notice indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells
you how to avoid the problem.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
2
CAUTION: A caution indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
3
2. Web-based Switch Configuration
Management Options
Connecting using the Web User Interface
Logging onto the Web Manager
Smart Wizard
Web User Interface (Web UI)
Management Options
The Switch provides multiple access platforms that can be used to configure, manage and monitor
networking features available on the Switch. Currently there are three management platforms
available and they are described below.
The Command Line Interface (CLI) through the RJ45 Console port or remote Telnet
The Switch can be managed, out-of-band, by using the console port on the front panel of the Switch.
Alternatively, the Switch can also be managed, in-band, by using a Telnet connection to any of the
LAN ports on the Switch. The command line interface provides complete access to all switch
management features.
SNMP-based Management
The Switch can be managed with an SNMP-compatible console program. The Switch supports SNMP
version 1.0, version 2.0 and version 3.0. The SNMP agent decodes the incoming SNMP messages
and responds to requests with MIB objects stored in the database. The SNMP agent updates the MIB
objects to generate statistics and counters.
Web-based Management Interface
After successfully installing the Switch, the user can configure the Switch, monitor the LED panel, and
display statistics graphically using a Web browser, such as Microsoft® Internet Explorer, Mozilla
Firefox, Safari, or Google Chrome.
Connecting using the Web User Interface
Most software functions of the DGS-1510 Series switches can be managed, configured and monitored
via the embedded web-based (HTML) interface. Manage the Switch from remote stations anywhere
on the network through a standard web browser. The web browser acts as a universal access tool
and can communicate directly with the Switch using the HTTP or HTTPS protocol.
NOTE: The Command Line Interface (CLI) provides the functionality of managing,
configuring, and monitoring all of the software features that are available on the Switch.
Logging onto the Web Manager
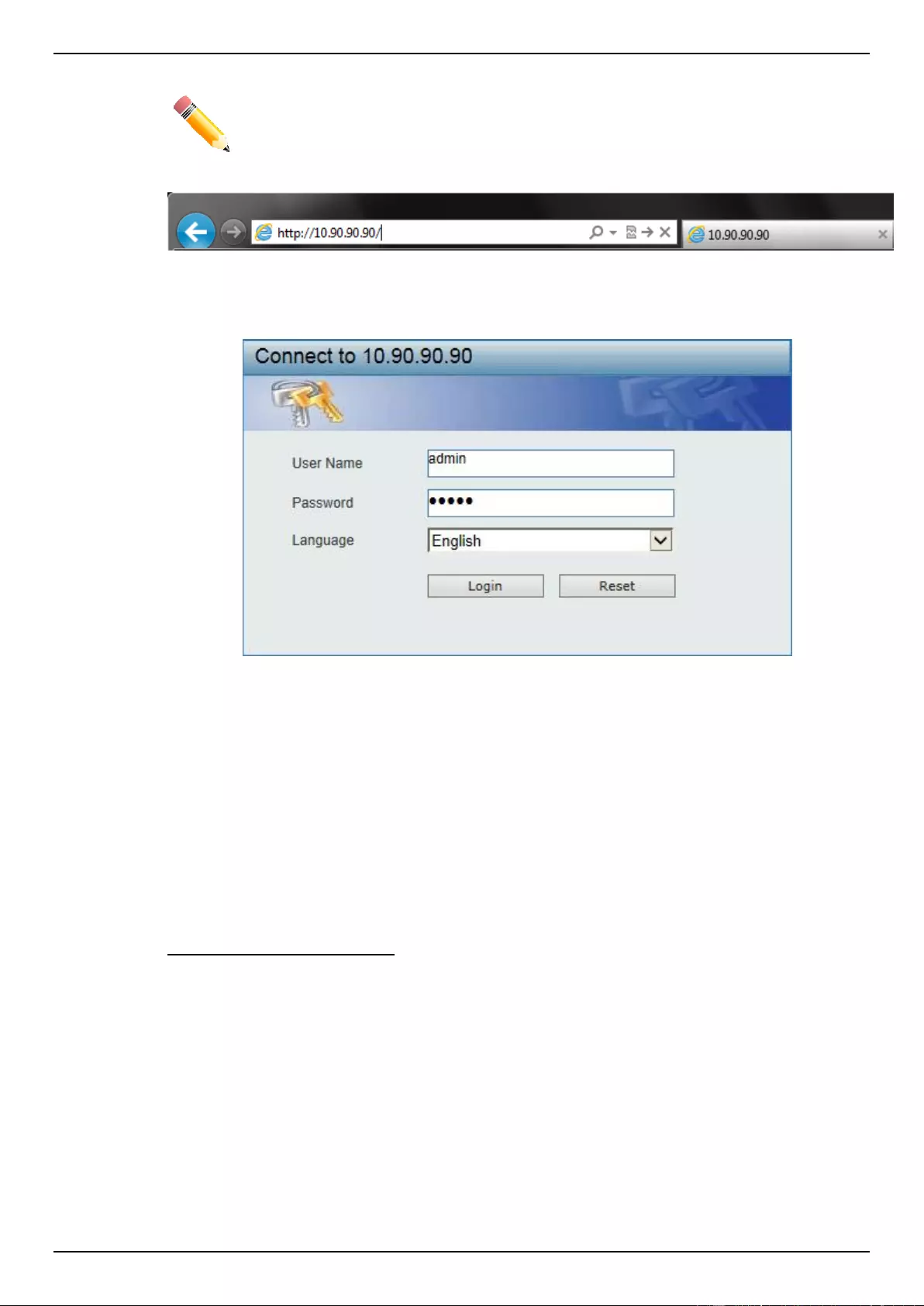
To access the Web User Interface, simply open a standard web browser on the management PC and
enter the Switch’s default IP address into the address bar of the browser and press the Enter key.
NOTE: The default IP address of this switch is 10.90.90.90, with a subnet mask of
255.0.0.0.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
4
NOTE: The default username and password is admin.
Figure 2-1 Displays entering the IP address in Internet Explorer
This will open the user authentication window, as seen below.
Figure 2-2 User Authentication window
Enter the User Name and Password in the corresponding fields and click Login. The default
username is admin and the default password is admin. This will open the Web-based user interface.
The Switch’s management features available in the web-based manager are explained below.
Smart Wizard
After a successfully connecting to the Web User Interface for the first time, the Smart Wizard
embedded Web utility will be launched. This wizard will guide the user through basic configuration
steps that is essential for first time connection to the Switch.
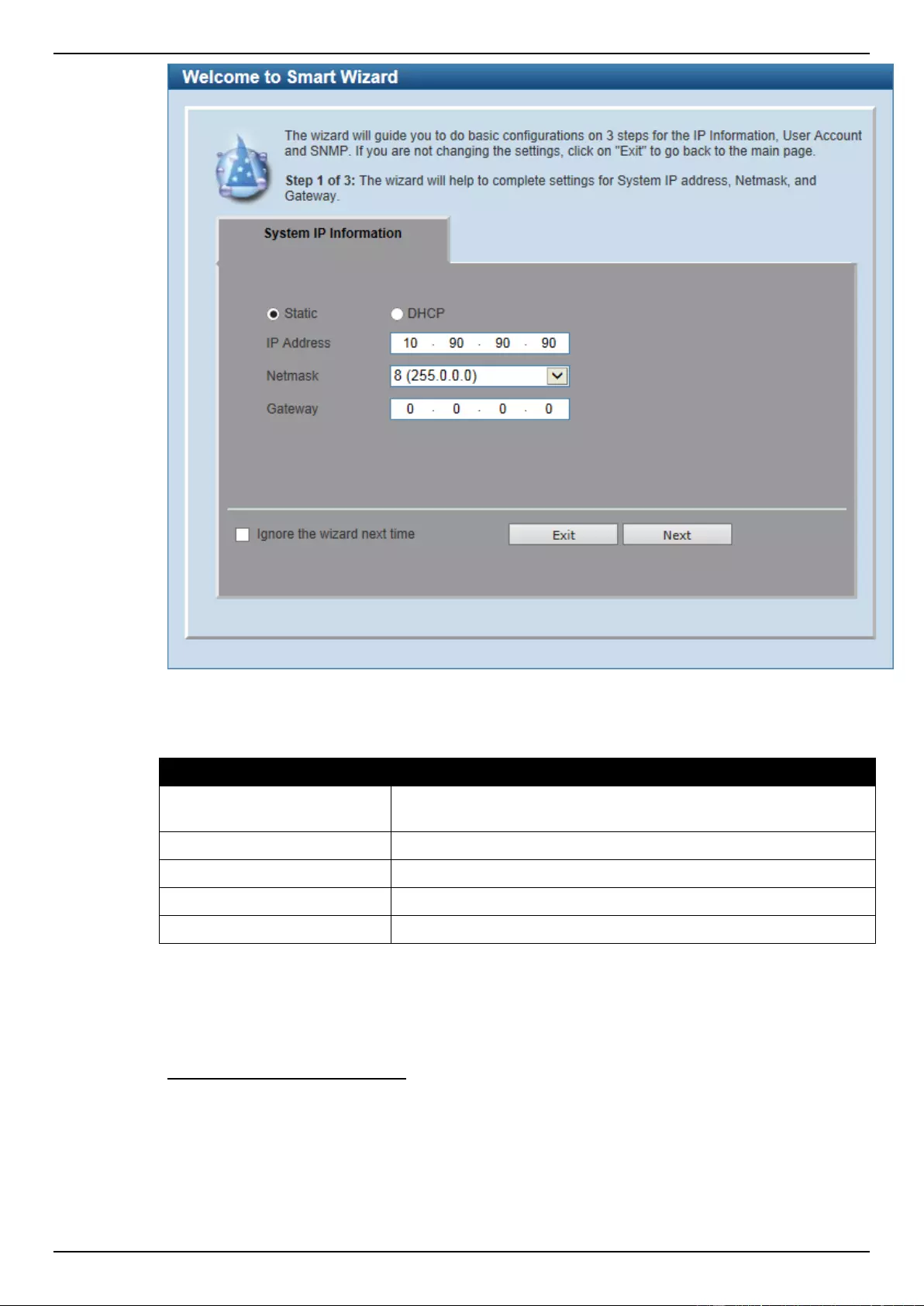
Step 1 – System IP Information
In this window, the user can configure the IP address assignment method, the static IP address,
Netmask and Gateway address.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
5
Figure 2-3 System IP Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Static
Select this option to manually configure and use IP address settings
on this switch.
DHCP
Select this option to obtain IP address settings from a DHCP server.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the Switch here.
Netmask
Select the Netmask option here.
Gateway
Enter the default gateway IP address here.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web UI.
Click the Next button to accept the changes made and continue to the next step.
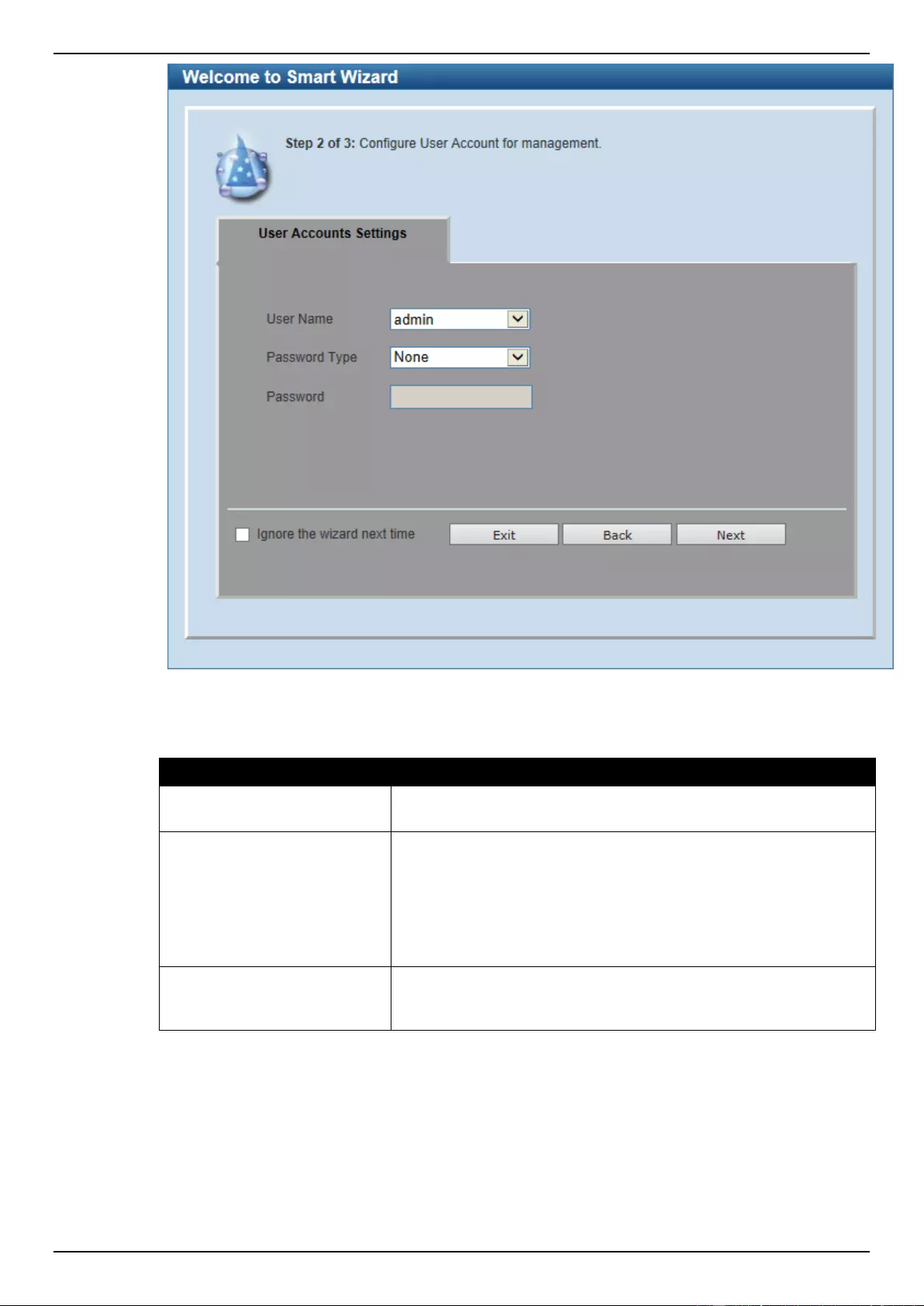
Step 2 – User Accounts Settings
In this window, the user can configure the user account settings. This step can only be modified by a
user account with the privilege level of 15.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
6
Figure 2-4 SNMP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
User Name
Select the user name of the administrator level account with the
privilege level of 15.
Password Type
Select the password type here. Options to choose from are None,
Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 and Encrypted-MD5. When selecting
Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-MD5, the password will not be
encrypted from the plain-text format to the encrypted format.
Instead, the encrypted password must be entered. To encrypt the
password from the plain-text format to the encrypted format, refer to
the Password Encryption window.
Password
After selecting Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-MD5 as
the Password Type, this field will be available. Enter the password
for the user account here.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web UI.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous step.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made and continue to the Web UI.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
7
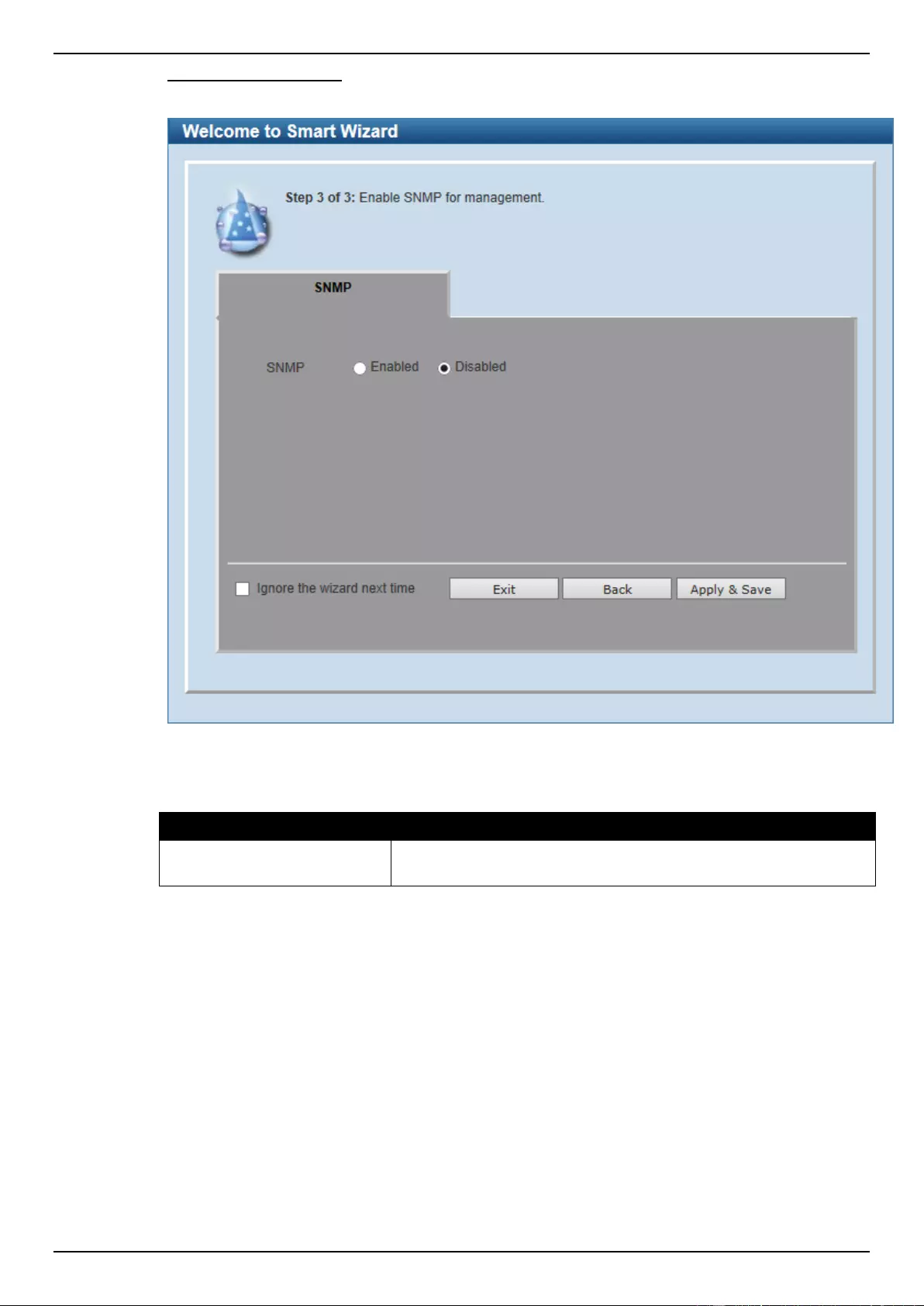
Step 3 – SNMP Settings
In this window, the user can enable or disable the SNMP function.
Figure 2-5 SNMP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
SNMP
Select the Enabled option to enable the SNMP function. Select the
Disabled option to disable the SNMP function.
Tick the Ignore the wizard next time option to skip the Smart Wizard on the next login.
Click the Exit button to discard the changes made, exit the Smart Wizard, and continue to the Web UI.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous step.
Click the Apply & Save button to accept the changes made and continue to the Web UI.
Web User Interface (Web UI)
By clicking the Exit button in the Smart Wizard, you will enter the Web-based Management interface.
Areas of the User Interface
The figure below shows the user interface. Three distinct areas that divide the user interface, as
described in the table.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
8
Figure 2-6 Main Web UI window
Area Number
Description
AREA 1
Select the folder or window to display. Open folders and click the
hyperlinked window buttons and subfolders contained within them to
display windows.
AREA 2
Presents a graphical near real-time image of the front panel of the
Switch. This area displays the Switch's ports and expansion
modules and shows port activity, depending on the specified mode.
Some management functions, including port monitoring are
accessible here. Click the D-Link logo to go to the D-Link Website.
AREA 3
Presents Switch status based on user selection and the entry of
configuration data. In addition, hyperlinks are offered for many
Switch features to enable quick configuration.
AREA 4
Presents a toolbar used to access function like Save, Tools, the
Wizard, Online Help, and Language preference.
AREA 1
AREA 2
AREA 3
AREA 4
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
9
3. System
Device Information
System Information Settings
Peripheral Settings
Port Configuration
PoE (DGS-1510-28P and DGS-1510-28XMP Only)
System Log
Time and SNTP
Time Range
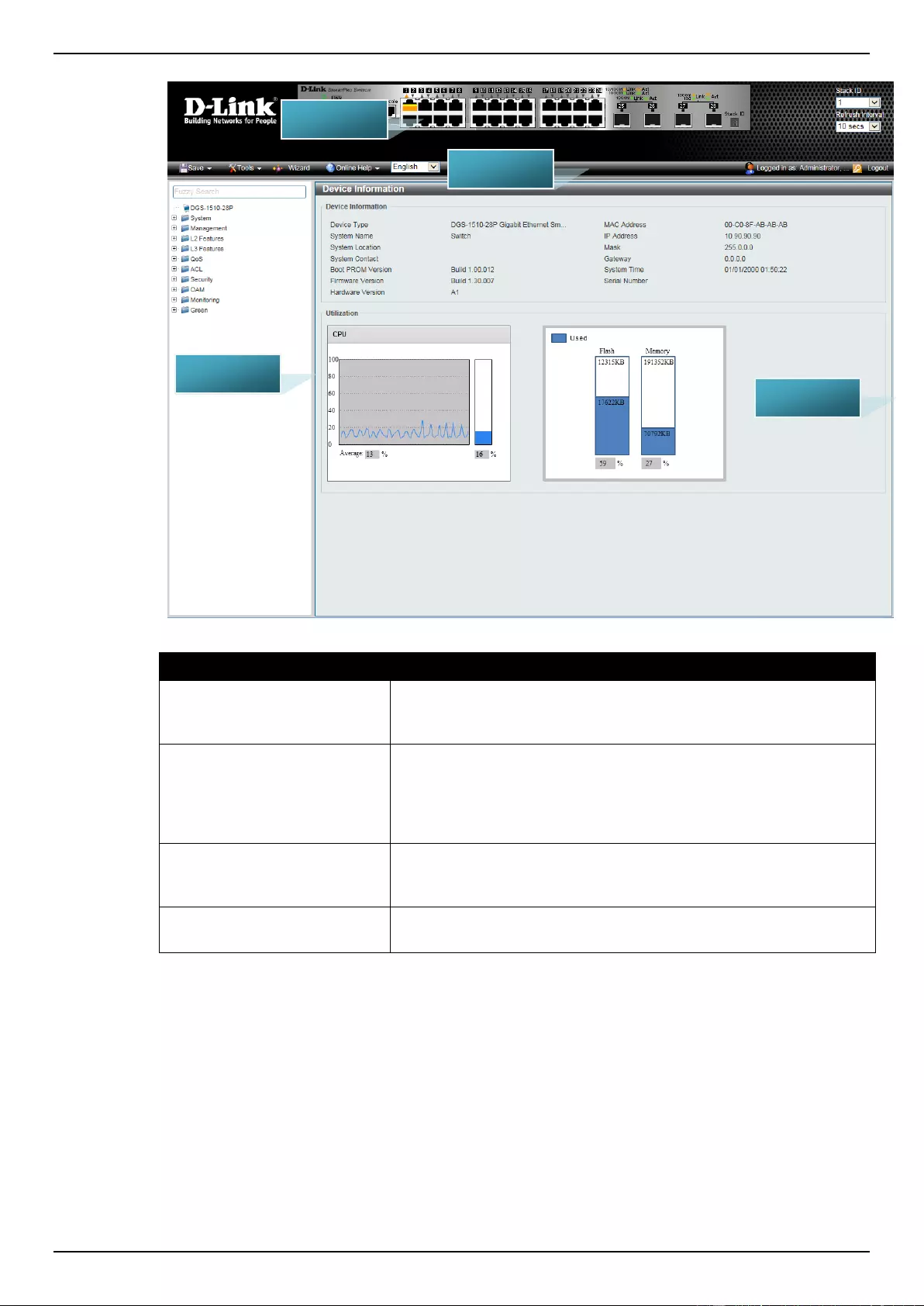
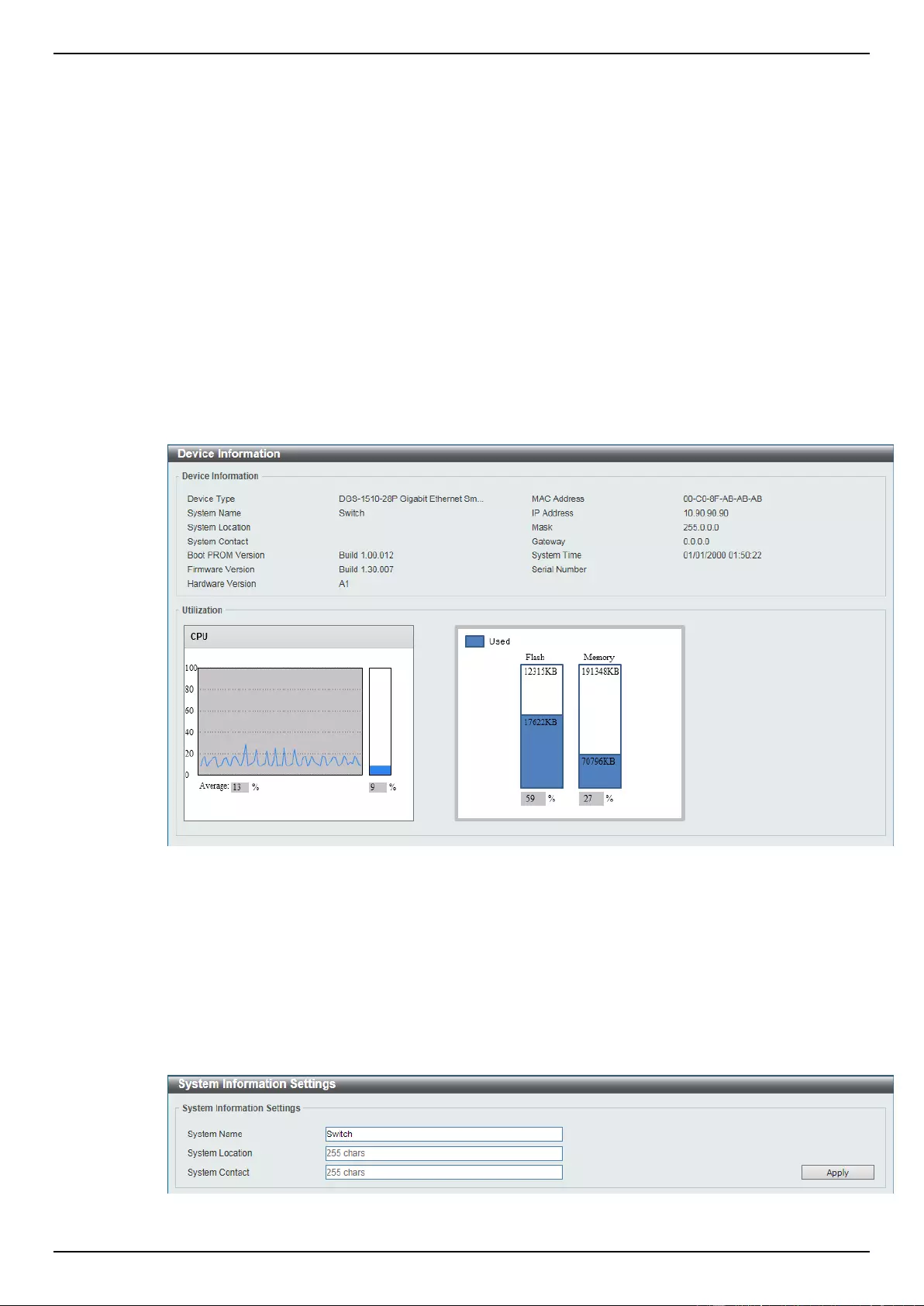
Device Information
In this window, the Device Information, CPU, and Used status are displayed. It appears automatically
when you log in the Switch. To return to the Device Information window after viewing other windows,
click the DGS-1510-28P link.
Figure 3-1 Device Information window
System Information Settings
The user can enter a System Name, System Location, and System Contact to aid in defining the
Switch.
To view the following window, click System > System Information Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-2 System Information Settings window
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
10
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
System Name
Enter a system name for the Switch, if so desired. This name will
identify it in the Switch network.
System Location
Enter the location of the Switch, if so desired. This string can be up
to 255 characters long.
System Contact
Enter a contact name for the Switch, if so desired. This string can
be up to 255 characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
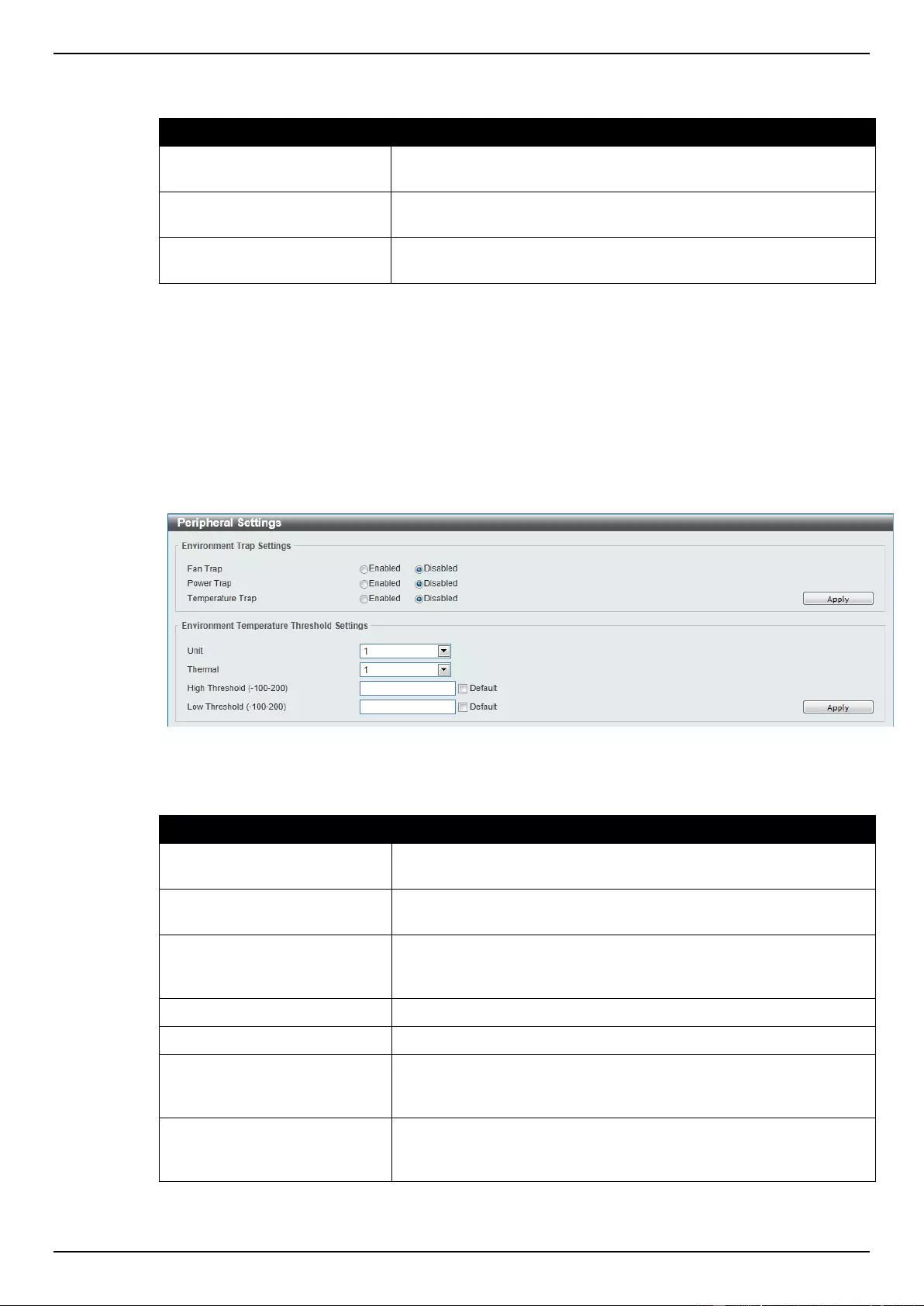
Peripheral Settings
This window is used to configure the environment trap settings and environment temperature
threshold settings.
To view the following window, click System > Peripheral Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-3 Peripheral Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fan Trap
Click to enable or disable the fan trap state for waning fan event
(fan failed or fan recover).
Power Trap
Click to enable or disable the power trap state for waning power
event (power failed or power recover).
Temperature Trap
Click to enable or disable the temperature trap state for waning
temperature event (temperature exceeds the thresholds or
temperature recover).
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Thermal
Select the thermal sensor ID.
High Threshold
Enter the high threshold value of the warning temperature setting.
The range is from -100 to 200 Celsius degree. Tick the Default
check box to return to the default value.
Low Threshold
Enter the low threshold value of the warning temperature setting.
The range is from -100 to 200 Celsius degree. Tick the Default
check box to return to the default value.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
11
Port Configuration
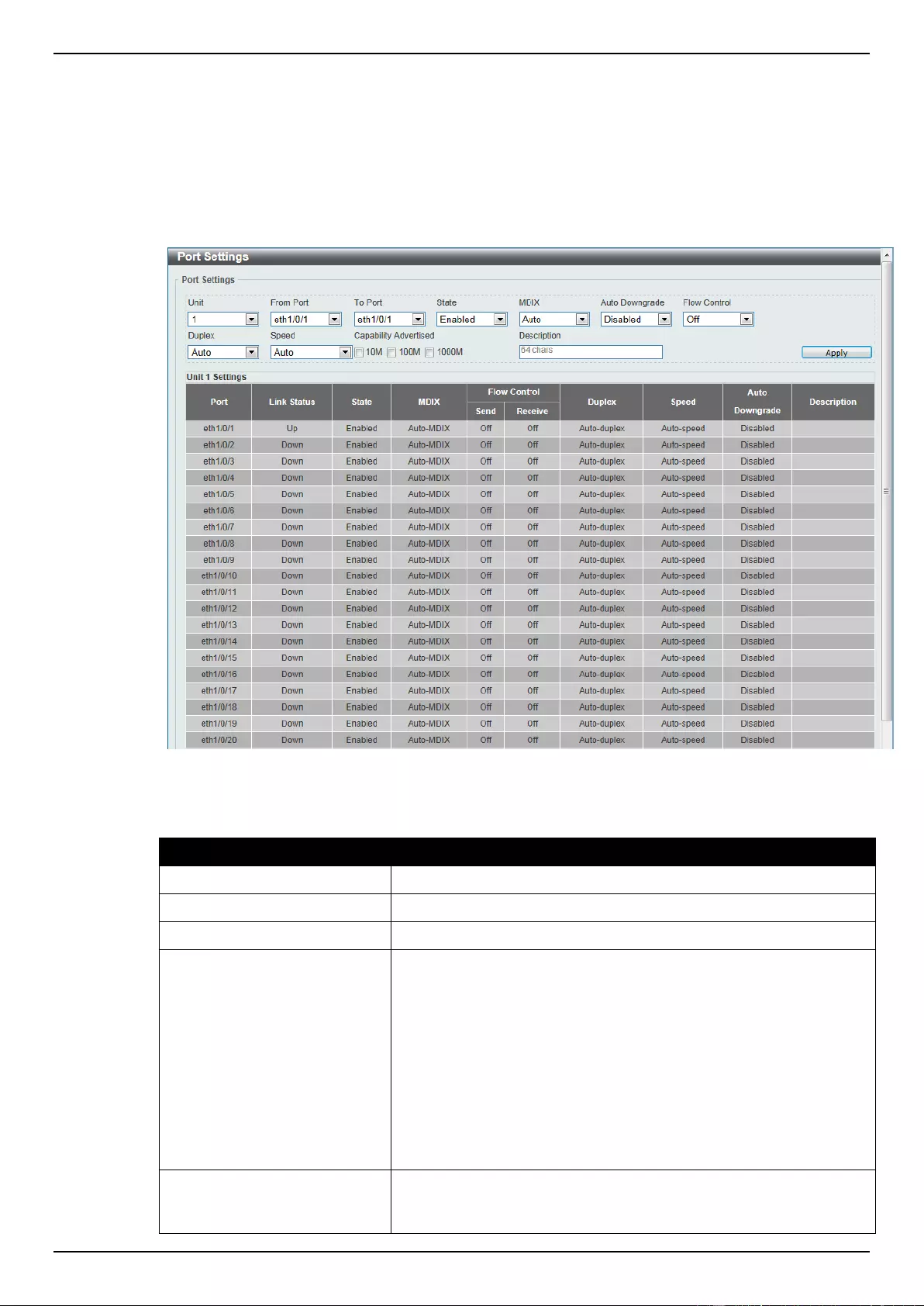
Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Switch’s port settings.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Port Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-4 Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the physical port here.
MDIX
Select the Medium Dependent Interface Crossover (MDIX) option
here. Options to choose from are Auto, Normal, and Cross.
Auto - Select this option for auto-sensing of the optimal type of
cabling.
Normal - Select this option for normal cabling. If this option is
selected, the port is in the MDIX mode and can be connected to a
PC’s NIC using a straight-through cable or a port (in the MDIX
mode) on another switch through a cross-over cable.
Cross - Select this option for cross cabling. If this option is selected,
the port is in the MDI mode and can be connected to a port (in the
MDIX mode) on another switch through a straight cable.
Auto Downgrade
Select this option to enable or disable automatically downgrading
advertised speed in case a link cannot be established at the
available speed.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
12
Flow Control
Select to either turn flow control On or Off here. Ports configured for
full-duplex use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex ports use back-
pressure flow control, and Auto ports use an automatic selection of
the two.
Duplex
Select the duplex mode used here. Options to choose from are
Auto, Half, and Full.
Speed
Select the port speed option here. This option will manually force
the connected on the selected port to only connect at the speed
specified here. Options to choose from are Auto, 10M, 100M,
1000M, 1000M Master, 1000M Slave, and 10G. The Switch allows
users to configure two types of gigabit connections; 1000M Master
and 1000M Slave which refer to connections running a 1000BASE-
T cable for connection between the Switch port and another device
capable of a gigabit connection. The master setting (1000M Master)
will allow the port to advertise capabilities related to duplex, speed
and physical layer type. The master setting will also determine the
master and slave relationship between the two connected physical
layers. This relationship is necessary for establishing the timing
control between the two physical layers. The timing control is set on
a master physical layer by a local source. The slave setting (1000M
Slave) uses loop timing, where the timing comes from a data stream
received from the master. If one connection is set for 1000M
Master, the other side of the connection must be set for 1000M
Slave. Any other configuration will result in a link down status for
both ports.
Capability Advertised
When the Speed is set to Auto, these capabilities are advertised
during auto-negotiation.
Description
Enter a 64 characters description for the corresponding port here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
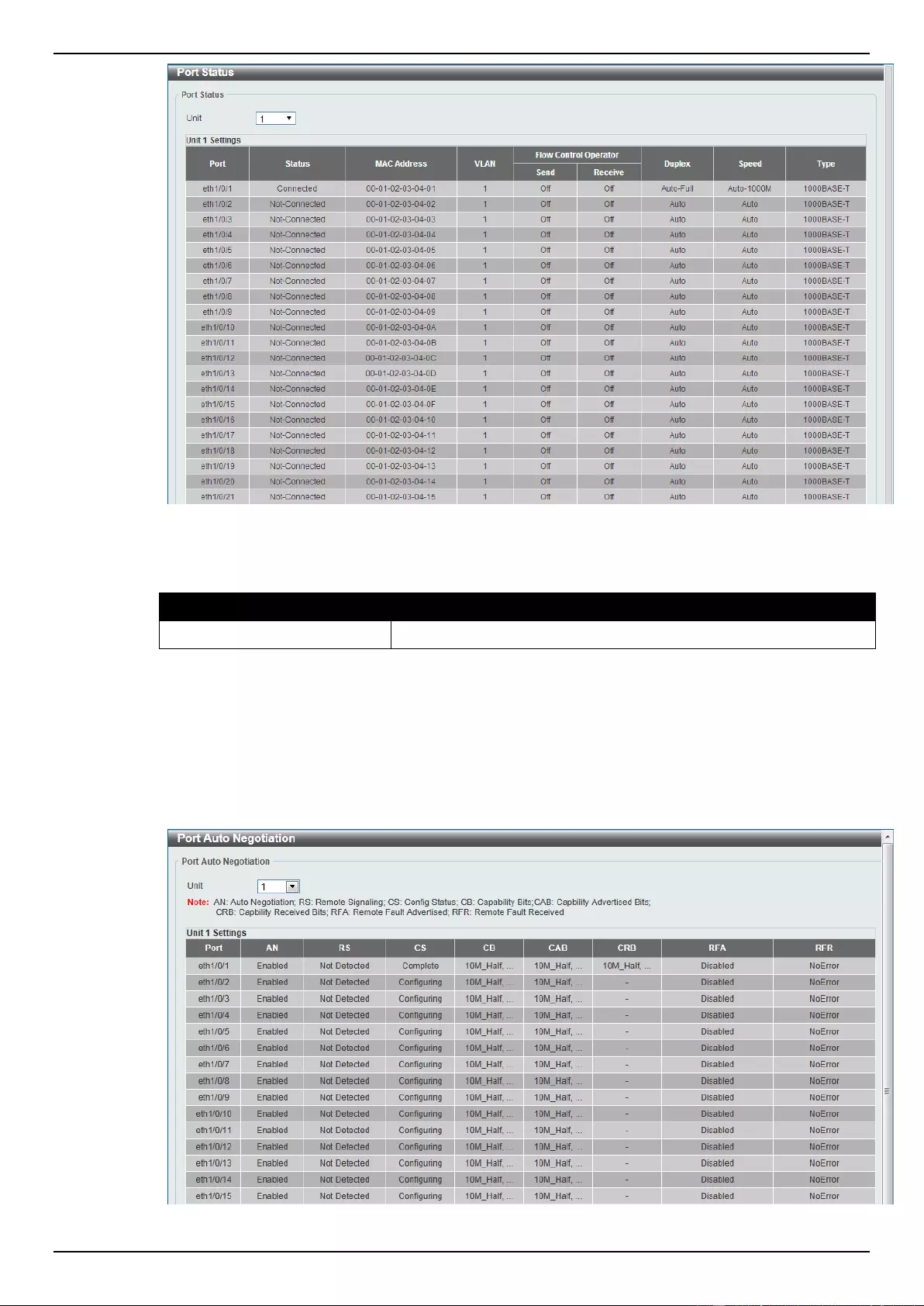
Port Status
This window is used to view the Switch’s physical port status and settings.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Port Status, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
13
Figure 3-5 Port Status window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
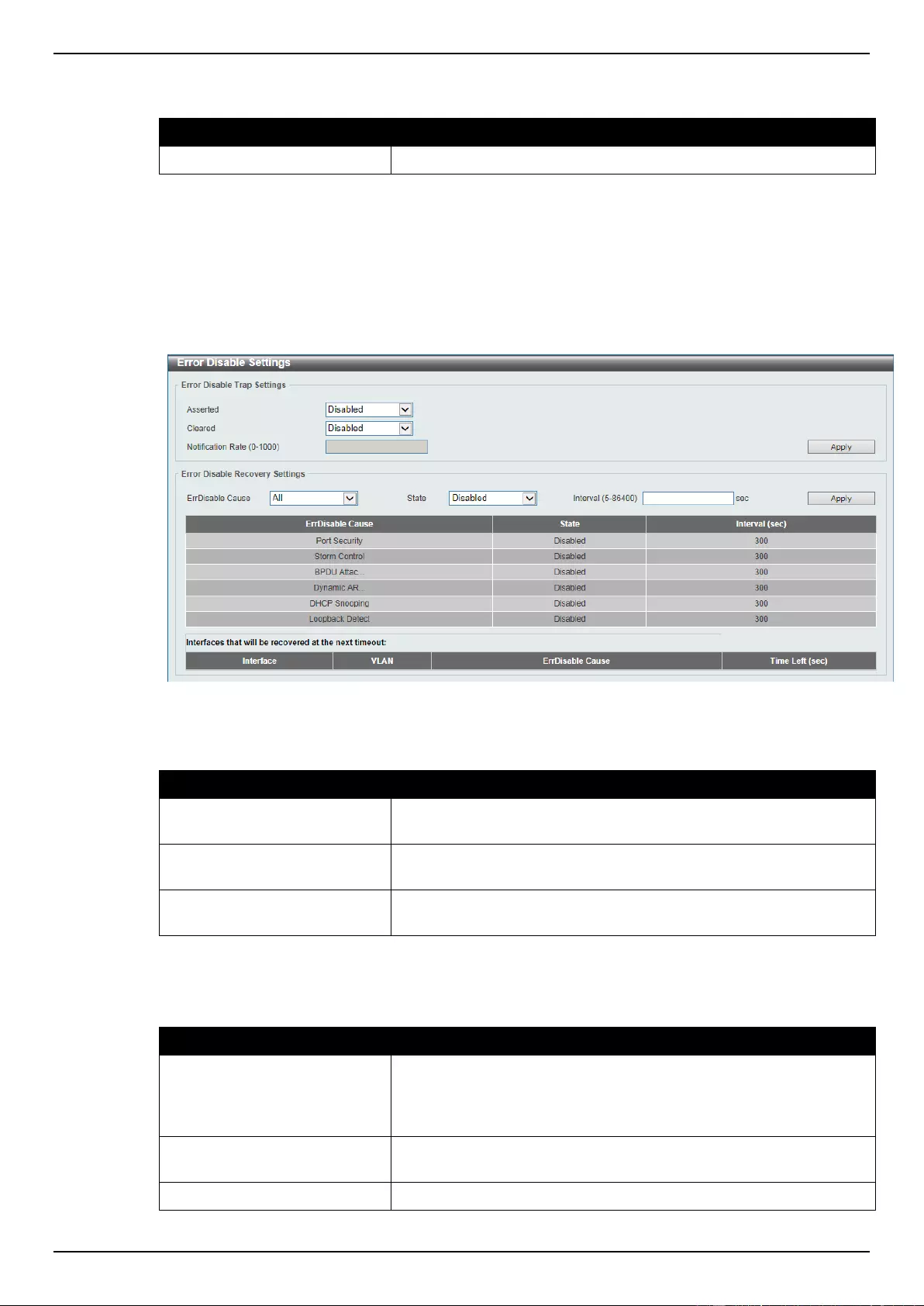
Port Auto Negotiation
This window is used to view detailed port auto-negotiation information.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Port Auto Negotiation, as
shown below:
Figure 3-6 Port Auto Negotiation window
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
14
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
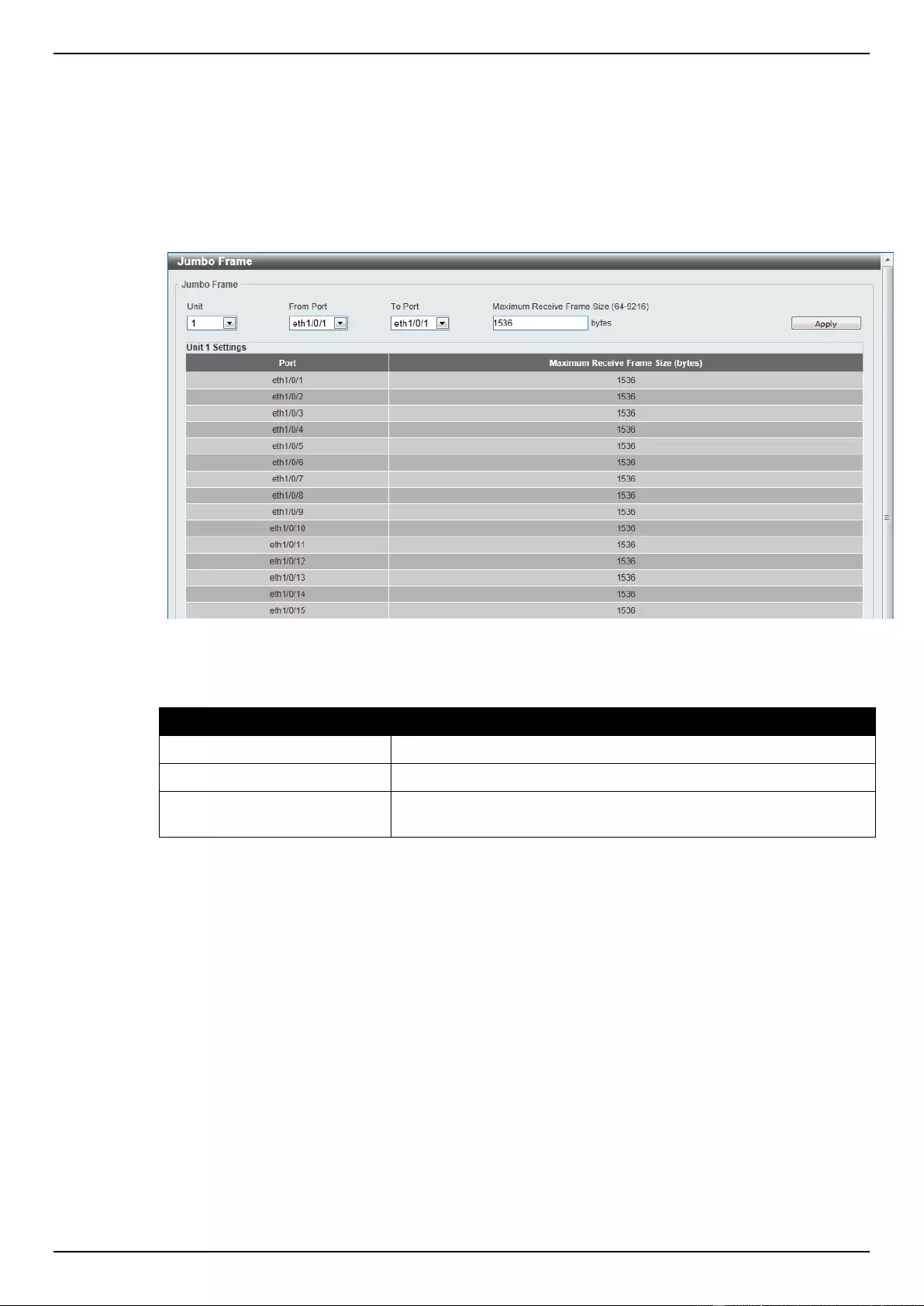
Error Disable Settings
This window is used to configure the sending of SNMP notifications for error disable state.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Error Disable Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 3-7 Error Disable Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Error Disable Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Asserted
Select this option to enable or disable the notifications when
entering into the error disabled state.
Cleared
Select this option to enable or disable the notifications when exiting
from the error disabled state.
Notification Rate
Enter the number of traps per minute. The packets that exceed the
rate will be dropped. The value is between 0 and 1000.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Error Disable Recovery Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
ErrDisable Cause
Select the error disable causes here. Options to choose from are
All, Port Security, Storm Control, BPDU Attack Protection,
Dynamic ARP Inspection, DHCP Snooping, and Loopback
Detect.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the auto-recovery for an error
port caused by the specified cause.
Interval
Enter the time between 5 and 86400 seconds to recover the port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
15
Jumbo Frame
This window is used to view and configure the Jumbo Frame size and settings. The Switch supports
jumbo frames. Jumbo frames are Ethernet frames with more than 1,518 bytes of payload. The Switch
supports jumbo frames with a maximum frame size of up to 9216 bytes.
To view the following window, click System > Port Configuration > Jumbo Frame, as shown below:
Figure 3-8 Jumbo Frame window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Maximum Receive Frame
Size
Enter the maximum receive frame size value here. This value must
be between 64 and 9216 bytes. By default, this value is 1536 bytes.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
PoE (DGS-1510-28P and DGS-1510-28XMP Only)
The DGS-1510-28P and DGS-1510-28XMP switches support Power over Ethernet (PoE) as defined
by the IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at. All ports can support PoE up to 30W. Ports 1-24 can supply about
48 VDC power to Powered Devices (PDs) over Category 5 or Category 3 UTP Ethernet cables. The
Switch follows the standard PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) pin-out Alternative A, whereby power is
sent out over pins 1, 2, 3 and 6. The Switches work with all D-Link 802.3af capable devices.
The Switch includes the following PoE features:
Auto-discovery recognizes the connection of a PD (Powered Device) and automatically sends
power to it.
The Auto-disable feature occurs under two conditions: firstly, if the total power consumption
exceeds the system power limit; and secondly, if the per port power consumption exceeds the
per port power limit.
Active circuit protection automatically disables the port if there is a short. Other ports will remain
active.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
16
Based on 802.3af/at PDs receive power according to
the following classification:
PSE provides power according to the following classification:
Class
Maximum power used by PD
Class
Max power supplied by PSE
0
12.95W
0
16.2W
1
3.84W
1
4.2W
2
6.49W
2
7.4W
3
12.95W
3
16.2W
4
25.5W
4
31.6W
PoE System
This window is used to configure the PoE system, and display the detailed power information and PoE
chip parameters for PoE modules.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE System, as shown below:
Figure 3-9 PoE System window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Usage Threshold
Enter the usage threshold to generate a log and send the
corresponding standard notification. The range is from 1 to 99
percent.
Policy Preempt
Select this option to enable or disable the disconnection of PD
which in power-provisioned with lower priority in order to release the
power to the new connected PD with higher priority under power
shortage conditions.
Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the sending of PoE
notifications.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Show Detail button to see the PoE system Parameters table at the bottom of the window.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following table will appear.
PoE Status
This window is used to configure the description, and display the PoE status of each port.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
17
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Status, as shown below:
Figure 3-10 PoE Status window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Description
Enter the text that describes the PD connected to a PoE interface.
The maximum length is 32 characters.
Click the Delete Description button to clear the setting in the corresponding Description field.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
PoE Configuration
This window is used to configure the PoE port.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Configuration, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
18
Figure 3-11 PoE Configuration window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Priority
Select the priority for provisioning power to the port. Options to
choose from are Critical, High and Low.
Legacy Support
Select this option to enable or disable the support of legacy PD.
Mode
Select the power management mode for the PoE ports. Options to
choose from are Auto and Never.
Max Wattage
When selecting Auto in the Mode drop-down list, this option
appears. Tick the check box and enter the maximum wattage of
power that can be provisioned to the auto-detected PD. If the value
is not entered, the class of the PD automatically determines the
maximum wattage which can be provisioned. The valid range for
maximum wattage is between 1000 mW and 30000 mW.
Time Range
When selecting Auto in the Mode drop-down list, this option
appears. Tick the check box and enter the name of the time range
to determine the activation period.
Click the Delete Time Range button to clear the setting in the corresponding Time Range field.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
PoE Statistics
This window is used to display the PoE statistics.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Statistics, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
19
Figure 3-12 PoE Statistics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Click the Clear All button to clear PoE statistics for all ports.
Click the Clear button to clear the PoE statistics for the corresponding port.
PoE Measurement
This window is used to display the PoE measurement.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE Measurement, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
20
Figure 3-13 PoE Measurement window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
PoE LLDP Classification
This window is used to display the PoE LLDP Classification.
To view the following window, click System > PoE > PoE LLDP Classification, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
21
Figure 3-14 PoE LLDP Classification window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
System Log
System Log Settings
This window is used to view and configure the system’s log settings.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-15 System Log Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Global State are described below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
22
Parameter
Description
Source Interface State
Select this option to enable or disable the source interface’s global
state.
Type
Select the type of interface that will be used. Option to choose from
is VLAN.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used here. The value is between 1 and 4094.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Buffer Log Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Buffer Log State
Select whether the enable or disable the buffer log’s global state
here. Options to choose from are Enable, Disabled, and Default.
When selecting the Default option, the buffer log’s global state will
follow the default behavior.
Severity
Select the severity value of the type of information that will be
logged. Options to choose from are 0 (Emergencies), 1 (Alerts), 2
(Critical), 3 (Errors), 4 (Warnings), 5 (Notifications), 6
(Informational), and 7 (Debugging).
Discriminator Name
Enter the discriminator name used here. This name can be up to 15
characters long.
Write Delay
Enter the interval for periodic writing of the logging buffer to FLASH.
This value must be between 0 and 65535 seconds. By default, this
value is 300 seconds. Tick the Infinite option, to disable the write
delay feature.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Console Log Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Console Log State
Select whether the enable or disable the console log’s global state
here.
Severity
Select the severity value of the type of information that will be
logged. Options to choose from are 0 (Emergencies), 1 (Alerts), 2
(Critical), 3 (Errors), 4 (Warnings), 5 (Notifications), 6
(Informational), and 7 (Debugging).
Discriminator Name
Enter the discriminator name used here. This name can be up to 15
characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
System Log Discriminator Settings
This window is used to view and configure the system log’s discriminator settings.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log Discriminator Settings,
as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
23
Figure 3-16 System Log Discriminator Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Discriminator Name
Enter the discriminator name here. This name can be up to 15
characters long.
Action
Select the facility’s behavior option and the type of facility that will
be associated with the selected behavior here. Behavior options to
choose from are Drops and Includes.
Severity
Select the severity behavior option and the value of the type of
information that will be logged. Behavior options to choose from are
Drops and Includes. Severity value options to choose from are 0
(Emergencies), 1 (Alerts), 2 (Critical), 3 (Errors), 4 (Warnings), 5
(Notifications), 6 (Informational), and 7 (Debugging).
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
System Log Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure system log’s server settings.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log Server Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 3-17 System Log Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
24
Parameter
Description
Host IPv4 Address
Enter the system log server’s IPv4 address here.
Host IPv6 Address
Enter the system log server’s IPv6 address here.
UDP Port
Enter the system log server’s UDP port number here. This value
must be 514 or between 1024 and 65535. By default, this value is
514.
Severity
Select the severity value of the type of information that will be
logged. Options to choose from are 0 (Emergencies), 1 (Alerts), 2
(Critical), 3 (Errors), 4 (Warnings), 5 (Notifications), 6
(Informational), and 7 (Debugging).
Facility
Select the facility value here. Options to choose from are 0 to 23.
Discriminator Name
Enter the discriminator name here. This name can be up to 15
characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
System Log
This window is used to view and clear the system log.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Log, as shown below:
Figure 3-18 System Log window
Click the Clear Log button to clear the system log entries displayed in the table.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
System Attack Log
This window is used to view and clear the system attack log.
To view the following window, click System > System Log > System Attack Log, as shown below:
Figure 3-19 System Attack Log window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
25
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Click the Clear Attack Log button to clear the system attack log entries displayed in the table.
Time and SNTP
The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) is a protocol for synchronizing computer clocks through
the Internet. It provides comprehensive mechanisms to access national time and frequency
dissemination services, organize the SNTP subnet of servers and clients, and adjust the system clock
in each participant.
Clock Settings
This window is used to configure the time settings for the Switch.
To view the following window, click System > Time and SNTP > Clock Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-20 Clock Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Time (HH:MM:SS)
Enter the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds.
Date (DD / MM / YYYY)
Enter the current day, month, and year to update the system clock.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Time Zone Settings
This window is used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings Time settings for SNTP.
To view the following window, click System > Time and SNTP > Time Zone Settings, as shown
below:
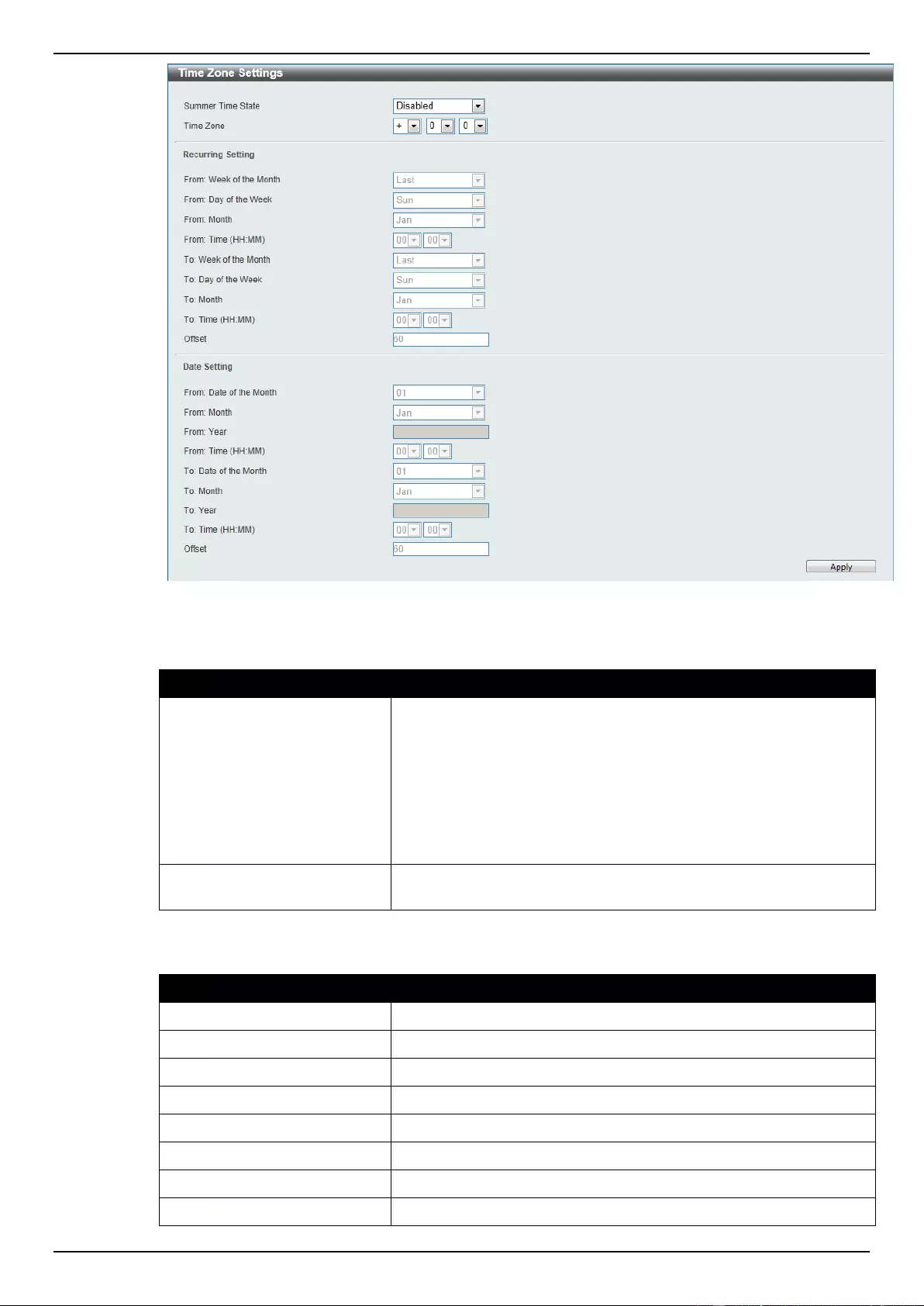
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
26
Figure 3-21 Time Zone Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Summer Time State
Select the summer time setting. Options to choose from are
Disabled, Recurring Setting, and Date Setting.
Disabled - Select to disable the summer time setting.
Recurring Setting - Select to configure the summer time that
should start and end on the specified week day of the specified
month.
Date Setting - Select to configure the summer time that should start
and end on the specified date of the specified month.
Time Zone
Select to specify your local time zone’s offset from Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC).
The fields that can be configured for Recurring Setting are described below:
Parameter
Description
From: Week of the Month
Select week of the month that summer time will start.
From: Day of the Week
Select the day of the week that summer time will start.
From: Month
Select the month that summer time will start.
From: Time (HH:MM)
Select the time of the day that summer time will start.
To: Week of the Month
Select week of the month that summer time will end.
To: Day of the Week
Select the day of the week that summer time will end.
To: Month
Select the month that summer time will end.
To: Time (HH:MM)
Select the time of the day that summer time will end.
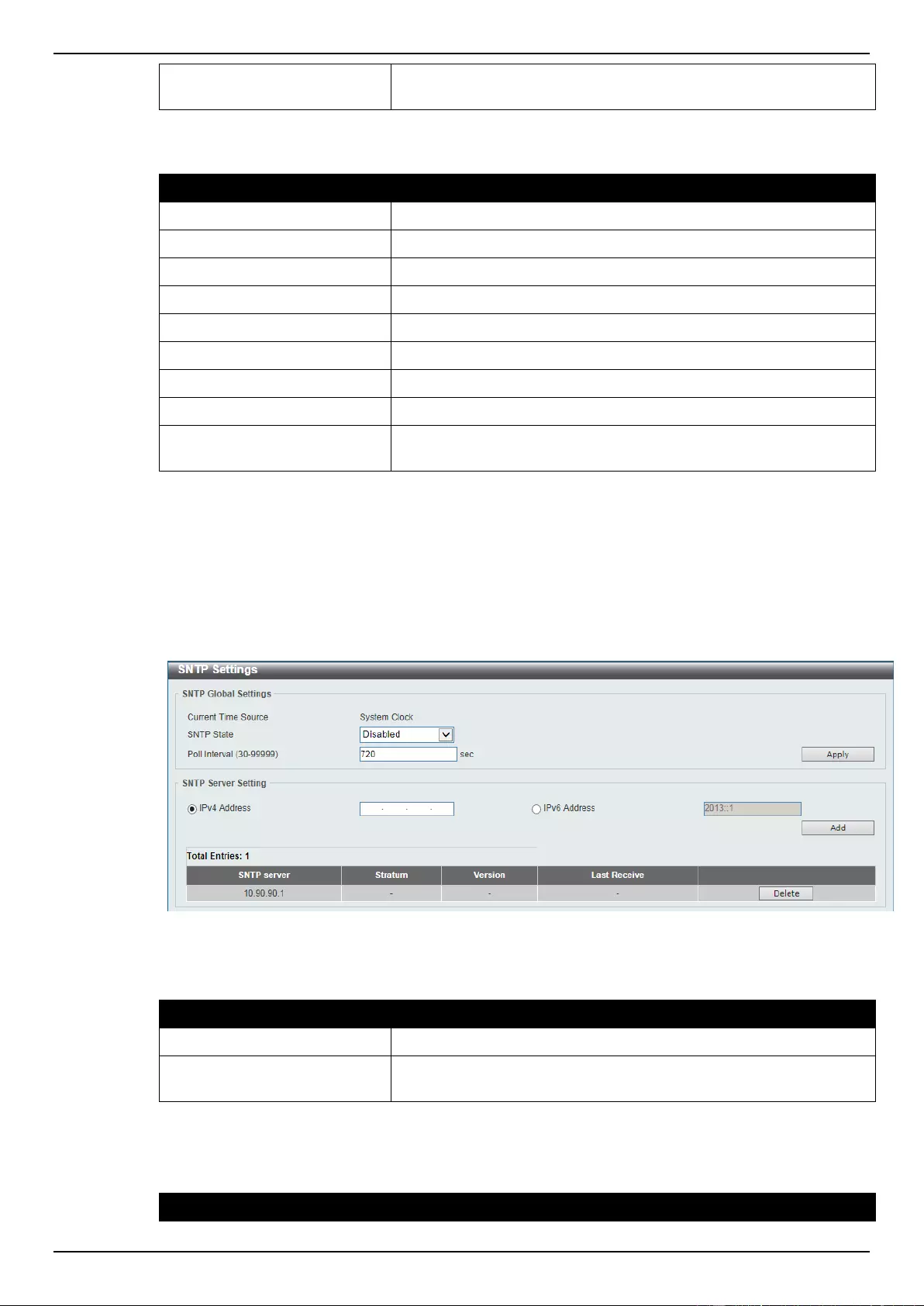
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
27
Offset
Enter the number of minutes to add during summer time. The
default value is 60. The range of this offset is 30, 60, 90 and 120.
The fields that can be configured for Date Setting are described below:
Parameter
Description
From: Date of the Month
Select date of the month that summer time will start.
From: Month
Select the month that summer time will start.
From: Year
Enter the year that the summer time will start.
From: Time (HH:MM)
Select the time of the day that summer time will start.
To: Date of the Month
Select date of the month that summer time will end.
To: Month
Select the month that summer time will end.
To: Year
Enter the year that the summer time will end.
To: Time (HH:MM)
Select the time of the day that summer time will end.
Offset
Enter the number of minutes to add during summer time. The
default value is 60. The range of this offset is 30, 60, 90 and 120.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SNTP Settings
This window is used to configure the time settings for the Switch.
To view the following window, click System > Time and SNTP > SNTP Settings, as shown below:
Figure 3-22 SNTP Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SNTP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
SNTP State
Select this option to enable or disable SNTP.
Poll Interval
Enter the synchronizing interval in seconds. The value is from 30 to
99999 seconds. The default interval is 720 seconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for SNTP Server Setting are described below:
Parameter
Description
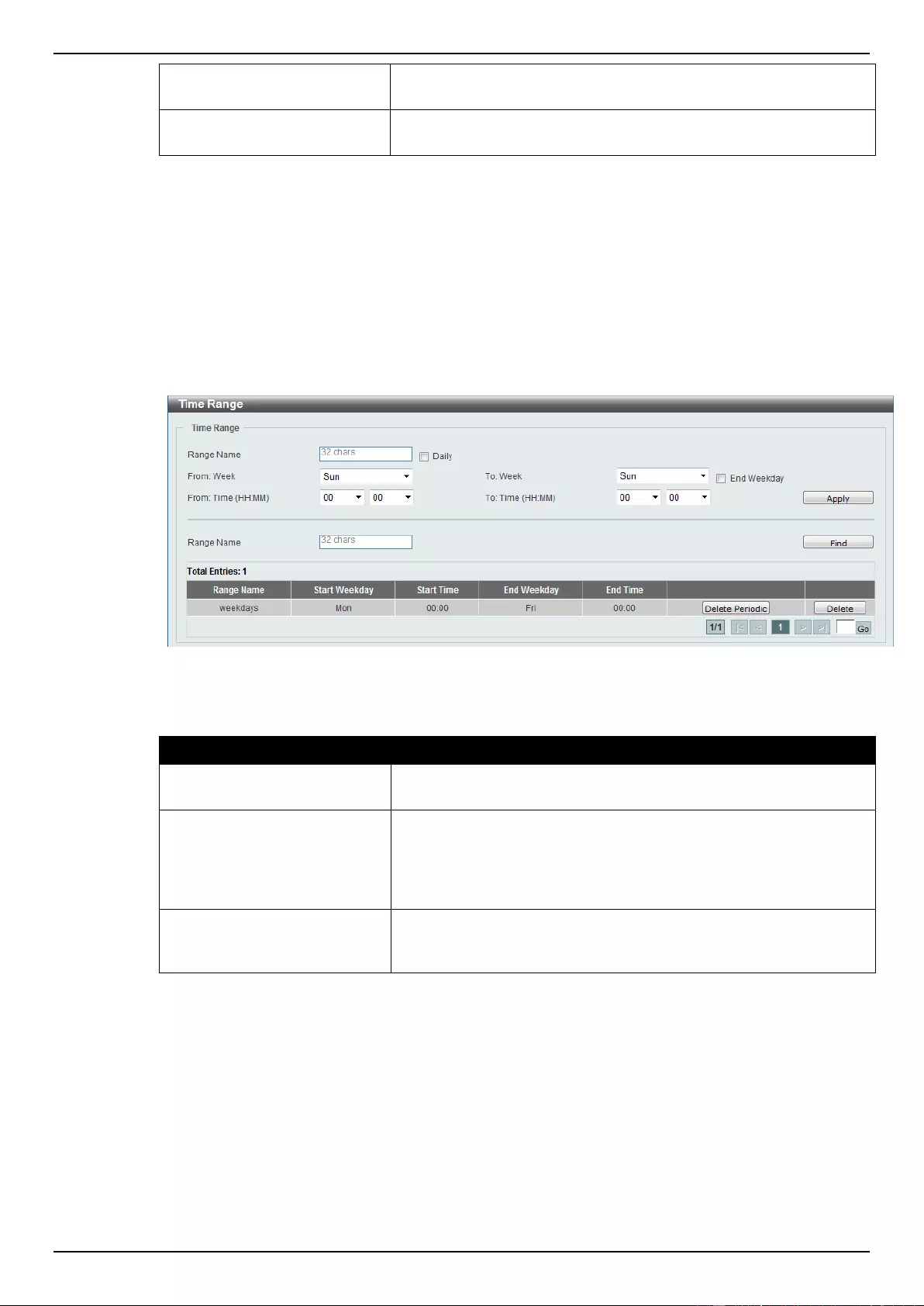
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
28
IPv4 Address
Enter the IP address of the SNTP server which provides the clock
synchronization.
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address of the SNTP server which provides the clock
synchronization.
Click the Add button to add the SNTP server.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Time Range
This window is used to view and configure the time range settings.
To view the following window, click System > Time Range, as shown below:
Figure 3-23 Time Range window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Range Name
Enter the name of the time range. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
From Week / To Week
Select the starting and ending days of the week that will be used for
this time range. Tick the Daily option to use this time range for
every day of the week. Tick the End Week Day option to use this
time range from the starting day of the week until the end of the
week, which is Sunday.
From Time / To Time
Select the starting and ending time of the day that will be used for
this time range. The first drop-down menu selects the hour and the
second drop-down menu selects the minute.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete Periodic button to delete the periodic entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
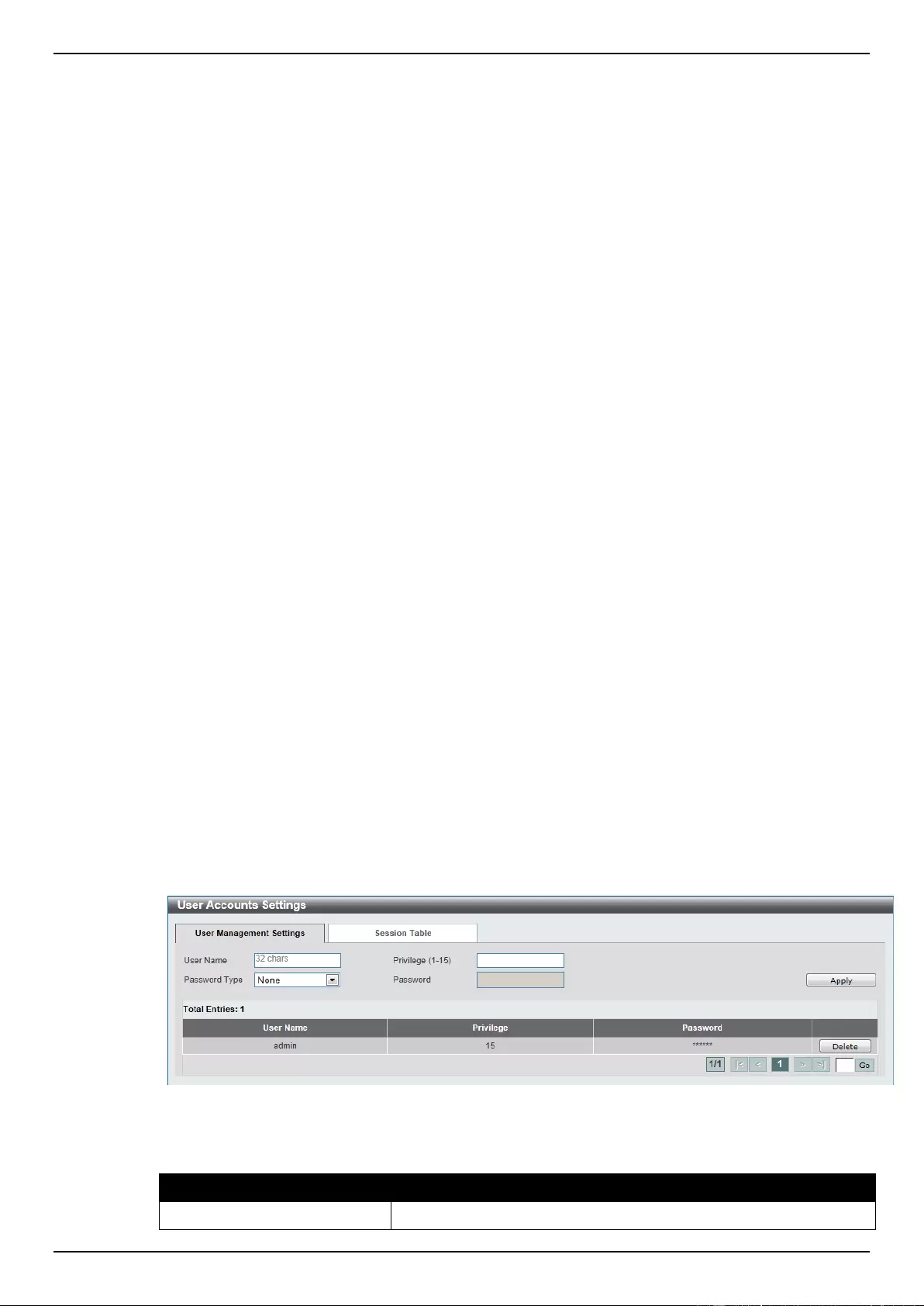
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
29
4. Management
User Account Settings
Password Encryption
Login Method
SNMP
RMON
Telnet/Web
Session Timeout
DHCP
DNS
NTP
IP Source Interface
File System
Physical Stacking
Virtual Stacking (SIM)
D-Link Discovery Protocol
User Account Settings
This window is used to create and configure the user accounts. The active user account sessions can
be viewed.
There are several configuration options available in the Web User Interface (Web UI). The set of
configuration options available to the user depends on the account’s Privilege Level. A user account
created with a higher privilege level will be given access to configure more features than a user
account created with a lower privilege level.
The pre-defined user account privilege levels supported by this switch are:
Basic User - Privilege Level 1. This user account level has the lowest priority of the user
accounts. The purpose of this type of user account level is for basic system checking.
Operator - Privilege Level 12. This user account level is used to grant system configuration
rights for users who need to change or monitor system configuration, except for security
related information such as user accounts and SNMP account settings.
Administrator - Privilege Level 15. This administrator user account level can monitor all
system information and change any of the system configuration settings expressed in this
guide.
To view the following window, click Management > User Account Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-1 User Management Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
User Name
Enter the user account name here. This name can be up to 32
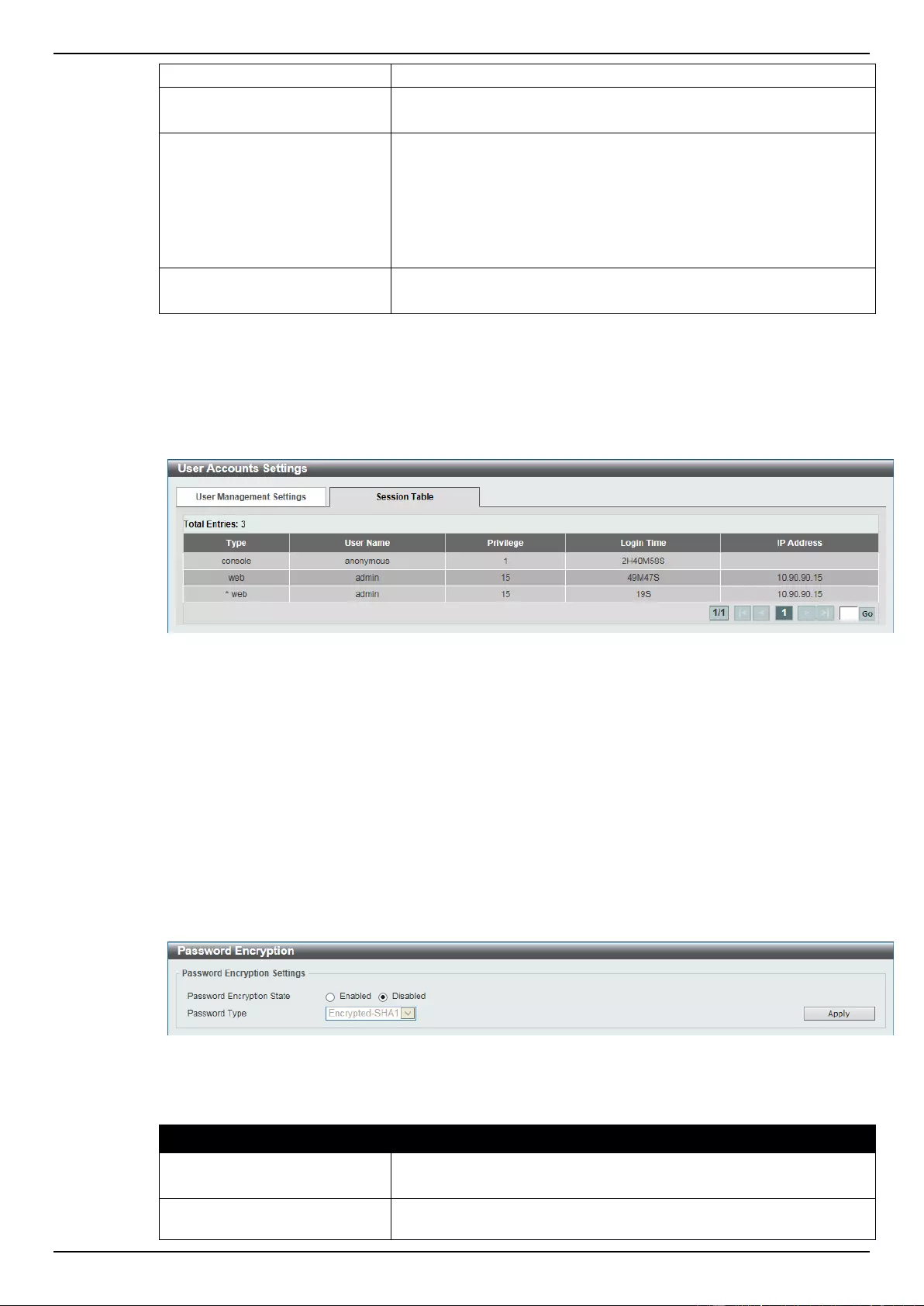
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
30
characters long.
Privilege
Enter the privilege level for this account here. This value must be
between 1 and 15.
Password Type
Select the password type for this user account here. Options to
choose from are None, Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 and
Encrypted-MD5. When selecting Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-
MD5, the password will not be encrypted from the plain-text format
to the encrypted format. Instead, the encrypted password must be
entered. To encrypt the password from the plain-text format to the
encrypted format, refer to the Password Encryption window.
Password
After selecting Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-MD5 as
the Password Type, enter the password for this user account here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified user account entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Session Table tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 4-2 Session Table window
A list of active user account session will be displayed.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Password Encryption
This window is used to configure whether to save the encryption of the password in the configuration
file.
To view the following window, click Management > Password Encryption, as shown below:
Figure 4-3 Password Encryption window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Password Encryption State
Select this option to enable or disable the encryption of the
password before stored in the configuration file.
Password Type
After the Password Encryption State is Enabled, this filed will be
available. Options to choose from are Encrypted-SHA1 and
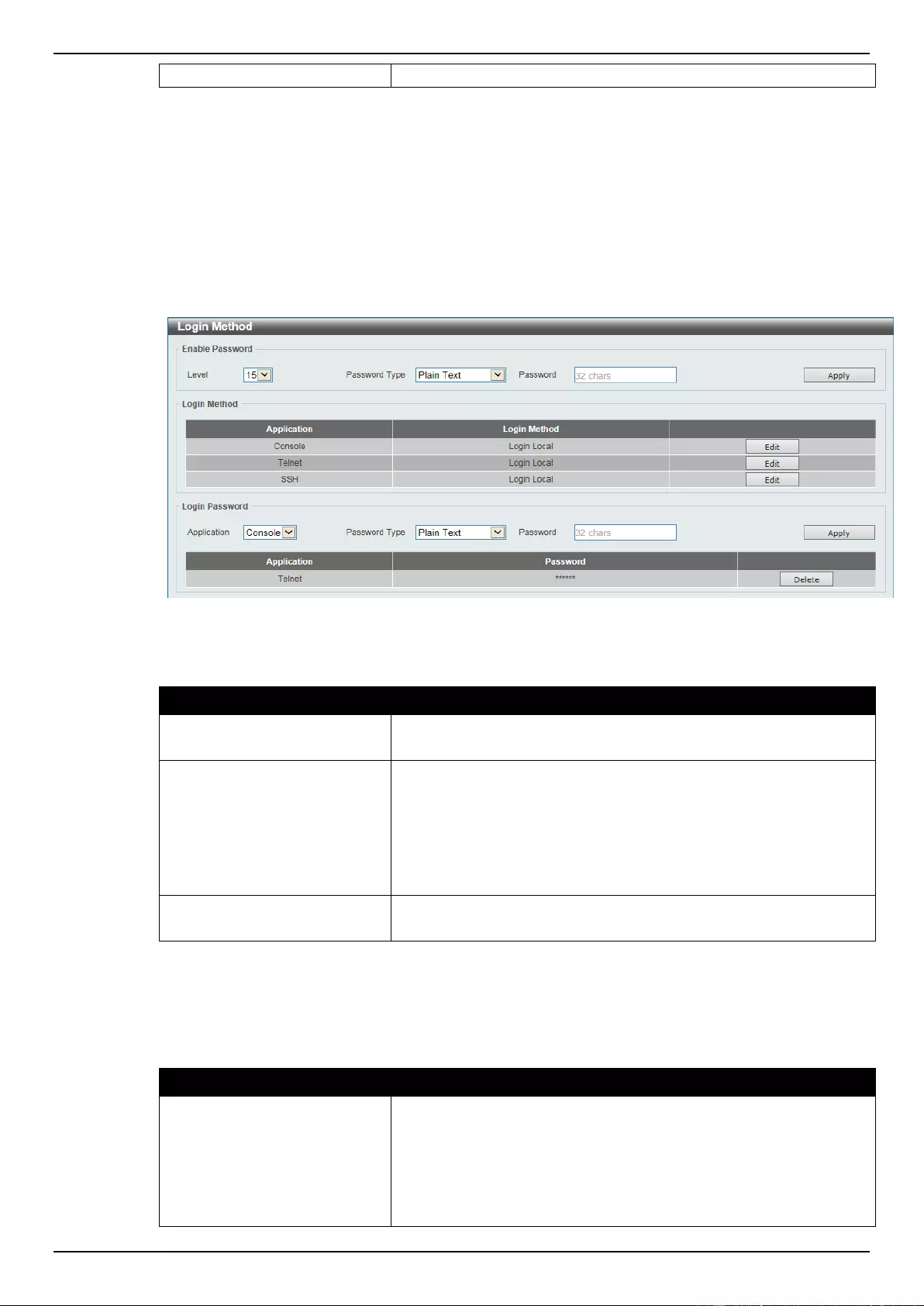
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
31
Encrypted-MD5.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Login Method
This window is used to configure the login method for each management interface that this Switch
supports.
To view the following window, click Management > Login Method, as shown below:
Figure 4-4 Login Method window
The fields that can be configured for Enable Password settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Level
Select the password level here. This value must be between 1 and
15.
Password Type
Select the password type here. Options to choose from are Plain
Text, Encrypted-SHA1 and Encrypted-MD5. When selecting
Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-MD5, the password will not be
encrypted from the plain-text format to the encrypted format.
Instead, the encrypted password must be entered. To encrypt the
password from the plain-text format to the encrypted format, refer to
the Password Encryption window.
Password
After selecting Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 or Encrypted-MD5 as
the Password Type, enter the password for this user account here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The Login Method section will only be available when Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
(AAA) feature is disabled. The fields that can be configured for Login Method settings are described
below:
Parameter
Description
Login Method
After clicking the Edit button this parameter can be configured.
Select the login method for the specified application here. Options
to choose from are No Login, Login and Login Local. No Login,
as the name implies, requires no login authentication to access the
specified application. Login will require the user to at least enter a
password when trying to access the application specified. Login
Local requires the user to enter a username and a password to

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
32
access the specified application.
Click the Edit button to modify the corresponding login method.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Login Password settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Application
Select the application that will be configured here. Options to
choose from are Console, Telnet and SSH.
Password Type
Select the password encryption type that will be used here. Options
to choose from are Plain Text, Encrypted-SHA1 and Encrypted-
MD5..
Password
Enter the password for the selected application here. This password
will be used when the Login Method for the specified application is
set as Login.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the password from the specified application.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed
specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management
stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices.
Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect
potential problems in the Switch, switch group or network.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on
the device. A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used
to manage the device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which
provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP
defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over
the network.
The Switch supports the SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of
security provided between the management station and the network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v.2, user authentication is accomplished using ‘community strings’, which function
like passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the Switch SNMP must use the same
community string. SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored
(dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are:
public – Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
private – Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects.
SNMPv3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts. The first
part is to maintain a list of users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SNMP managers. The
second part describes what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager.
The Switch allows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges. The
SNMP version may also be set for a listed group of SNMP managers. Thus, you may create a group
of SNMP managers that are allowed to view read-only information or receive traps using SNMPv1

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
33
while assigning a higher level of security to another group, granting read/write privileges using
SNMPv3.
Using SNMPv3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be
restricted from performing specific SNMP management functions. The functions allowed or restricted
are defined using the Object Identifier (OID) associated with a specific MIB. An additional layer of
security is available for SNMPv3 in that SNMP messages may be encrypted. To read more about how
to configure SNMPv3 settings for the Switch read the next section.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the Switch. The events can
be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port
status change. The Switch generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network manager).
Typical traps include trap messages for Authentication Failure, Topology Change and
Broadcast\Multicast Storm.
MIBs
The Switch in the Management Information Base (MIB) stores management and counter information.
The Switch uses the standard MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values
for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network management software. In addition to
the standard MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended
Management Information Base. Specifying the MIB Object Identifier may also retrieve the proprietary
MIB. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
The Switch incorporates a flexible SNMP management for the switching environment. SNMP
management can be customized to suit the needs of the networks and the preferences of the network
administrator. Use the SNMP V3 menus to select the SNMP version used for specific tasks.
The Switch supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. The
administrator can specify the SNMP version used to monitor and control the Switch. The three
versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided between the management station and the
network device.
SNMP settings are configured using the menus located on the SNMP V3 folder of the Web manager.
Workstations on the network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the Switch can be restricted
with the Management Station IP Address menu.
SNMP Global Settings
This window is used to configure the SNMP global settings and trap settings.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
34
Figure 4-5 SNMP Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SNMP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
SNMP Global State
Select this option to enable or disable the SNMP feature.
SNMP Response Broadcast
Request
Select this option to enable or disable the server to response to
broadcast SNMP GetRequest packets.
SNMP UDP Port
Enter the SNMP UDP port number.
Trap Source Interface
Enter the interface whose IP address will be used as the source
address for sending the SNMP trap packet.
The fields that can be configured for Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap Global State
Select this option to enable or disable the sending of all or specific
SNMP notifications.
SNMP Authentication Trap
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP authentication
failure notifications. An authenticationFailuretrap is generated when
the device receives an SNMP message that is not properly
authenticated. The authentication method depends on the version of
SNMP being used. For SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, authentication failure
occurs if packets are formed with an incorrect community string. For
SNMPv3, authentication failure occurs if packets are formed with an
incorrect SHA/MD5 authentication key.
Port Link Up
Tick this option to control the sending of port link up notifications. A
linkup trap is generated when the device recognizes that one of the
communication links has come up.
Port Link Down
Tick this option to control the sending of port link down notifications.
A linkDown trap is generated when the device recognizes a failure
in one of the communication links.
Coldstart
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP coldStart
notifications.
Warmstart
Tick this option to control the sending of SNMP warmStart
notifications.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings
This window is used to configure the SNMP link change trap settings.
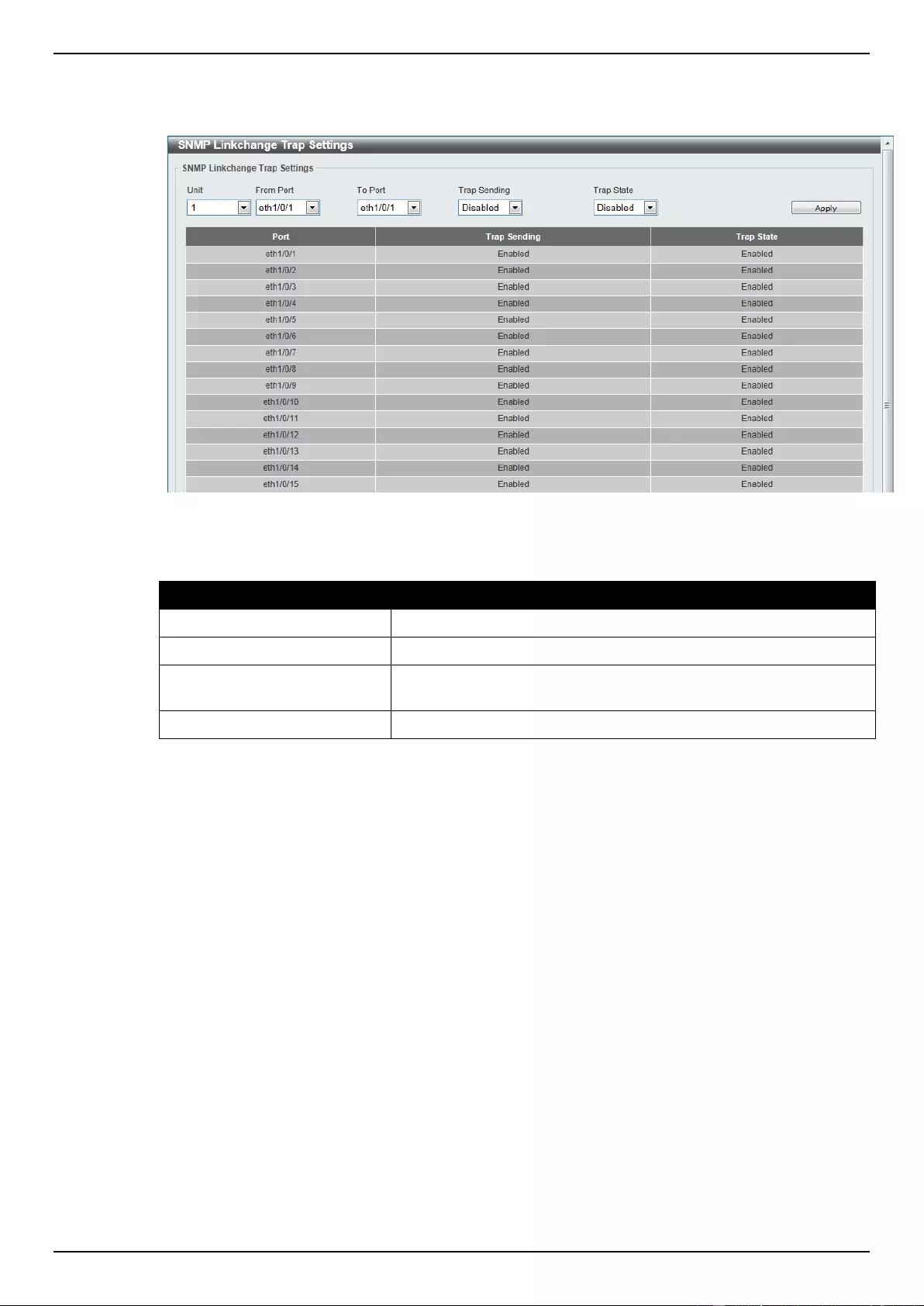
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
35
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 4-6 SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Trap Sending
Select this option to enable or disable the sending of the SNMP
notification traps that is generated by the system.
Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the SNMP link change trap.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SNMP View Table Settings
This window is used to assign views to community strings that define which MIB objects can be
accessed by a remote SNMP manager. The SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users
(identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views created in the previous window.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP View Table Settings, as shown
below:
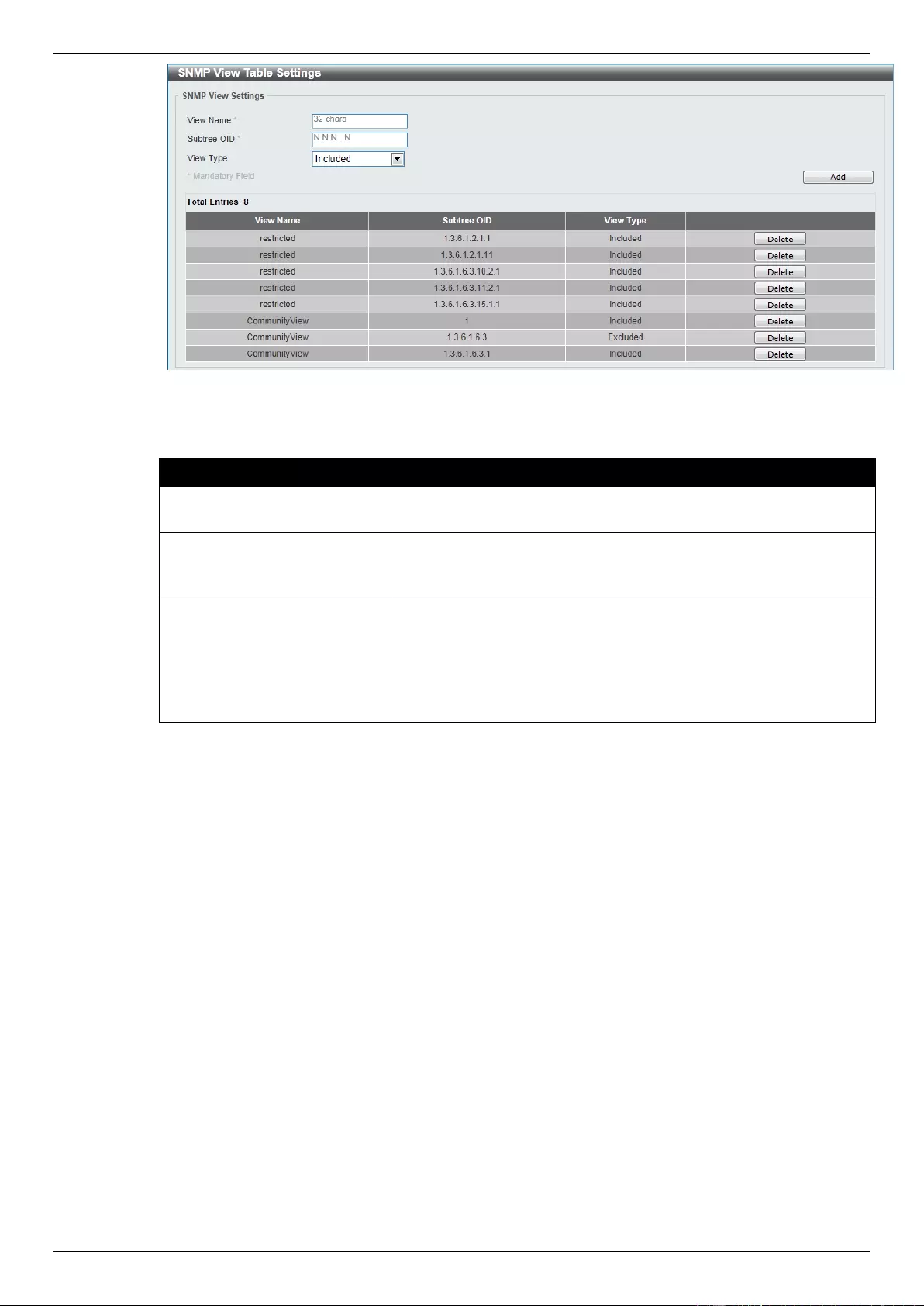
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
36
Figure 4-7 SNMP View Table Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
View Name
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to
identify the new SNMP view being created.
Subtree OID
Type the Object Identifier (OID) Subtree for the view. The OID
identifies an object tree (MIB tree) that will be included or excluded
from access by an SNMP manager.
View Type
Select the view type here. Options to choose from are Included,
and Excluded.
Included - Select to include this object in the list of objects that an
SNMP manager can access.
Excluded - Select to exclude this object from the list of objects that
an SNMP manager can access.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
SNMP Community Table Settings
This window is used to create an SNMP community string to define the relationship between the
SNMP manager and an agent. The community string acts like a password to permit access to the
agent on the Switch. One or more of the following characteristics can be associated with the
community string:
An Access List of IP addresses of SNMP managers that are permitted to use the community
string to gain access to the Switch’s SNMP agent.
Any MIB view that defines the subset of all MIB objects will be accessible to the SNMP
community.
Read/write or read-only level permission for the MIB objects accessible to the SNMP community.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Community Table Settings, as
shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
37
Figure 4-8 SNMP Community Table Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Key Type
Select the key type for the SNMP community. Options to choose
from are Plain Text, and Encrypted.
Community Name
Enter an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that is used to
identify members of an SNMP community. This string is used like a
password to give remote SNMP managers access to MIB objects in
the Switch’s SNMP agent.
View Name
Enter an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that is used to
identify the group of MIB objects that a remote SNMP manager is
allowed to access on the Switch. The view name must exist in the
SNMP View Table.
Access Right
Select the access right here. Options to choose from are Read
Only, and Read Write.
Read Only - SNMP community members using the community
string created can only read the contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
Read Write - SNMP community members using the community
string created can read from, and write to the contents of the MIBs
on the Switch.
IP Access-List Name
Enter the name of the standard access list to control the user to use
this community string to access to the SNMP agent.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
SNMP Group Table Settings
An SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the
views created in the previous window.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Group Table Settings, as shown
below:
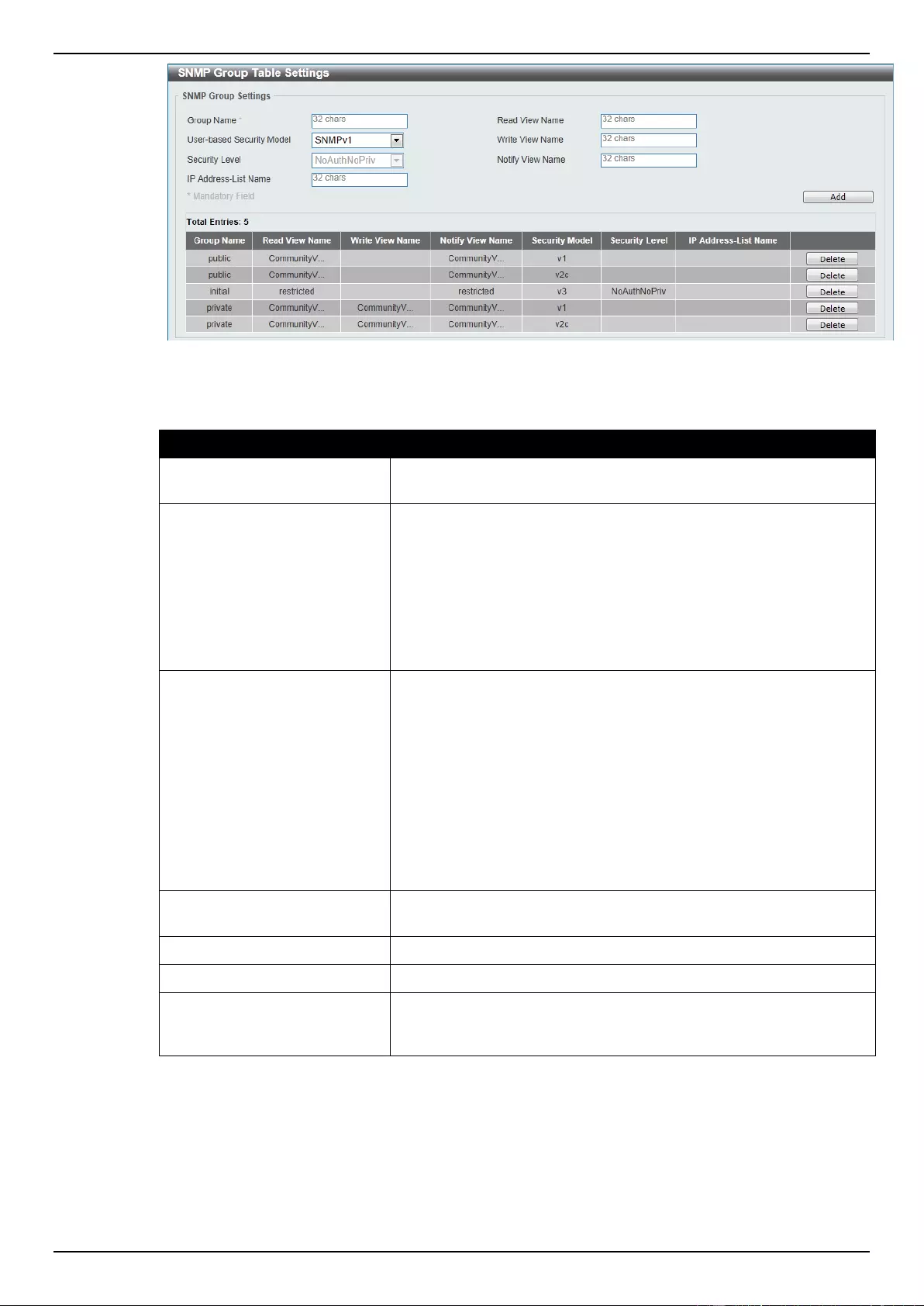
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
38
Figure 4-9 SNMP Group Table Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Group Name
Enter the group name of a maximum of 32 characters. The syntax is
general string that does not allow space.
User-based Security Model
Select the security model here. Options to choose from are
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
SNMPv1 - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv1
security model.
SNMPv2c - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv2c
security model.
SNMPv3 - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv3
security model.
Security Level
When selecting SNMPv3 in the User-based Security Model drop-
down list, this option is available.
NoAuthNoPriv - Specify that there will be no authorization and no
encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP
manager.
AuthNoPriv - Specify that authorization will be required, but there
will be no encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a
remote SNMP manager.
AuthPriv - Specify that authorization will be required, and that
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manger will
be encrypted.
IP Address-List Name
Enter the standard IP access control list (ACL) to associate with the
group.
Read View Name
Enter the read view name that the group user can access.
Write View Name
Enter the write view name that the group user can access.
Notify View Name
Enter a write view name that the group user can access. The notify
view describes the object that can be reported its status via trap
packets to the group user.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
SNMP Engine ID Local Settings
The Engine ID is a unique identifier used for SNMP V3 implementations on the Switch.
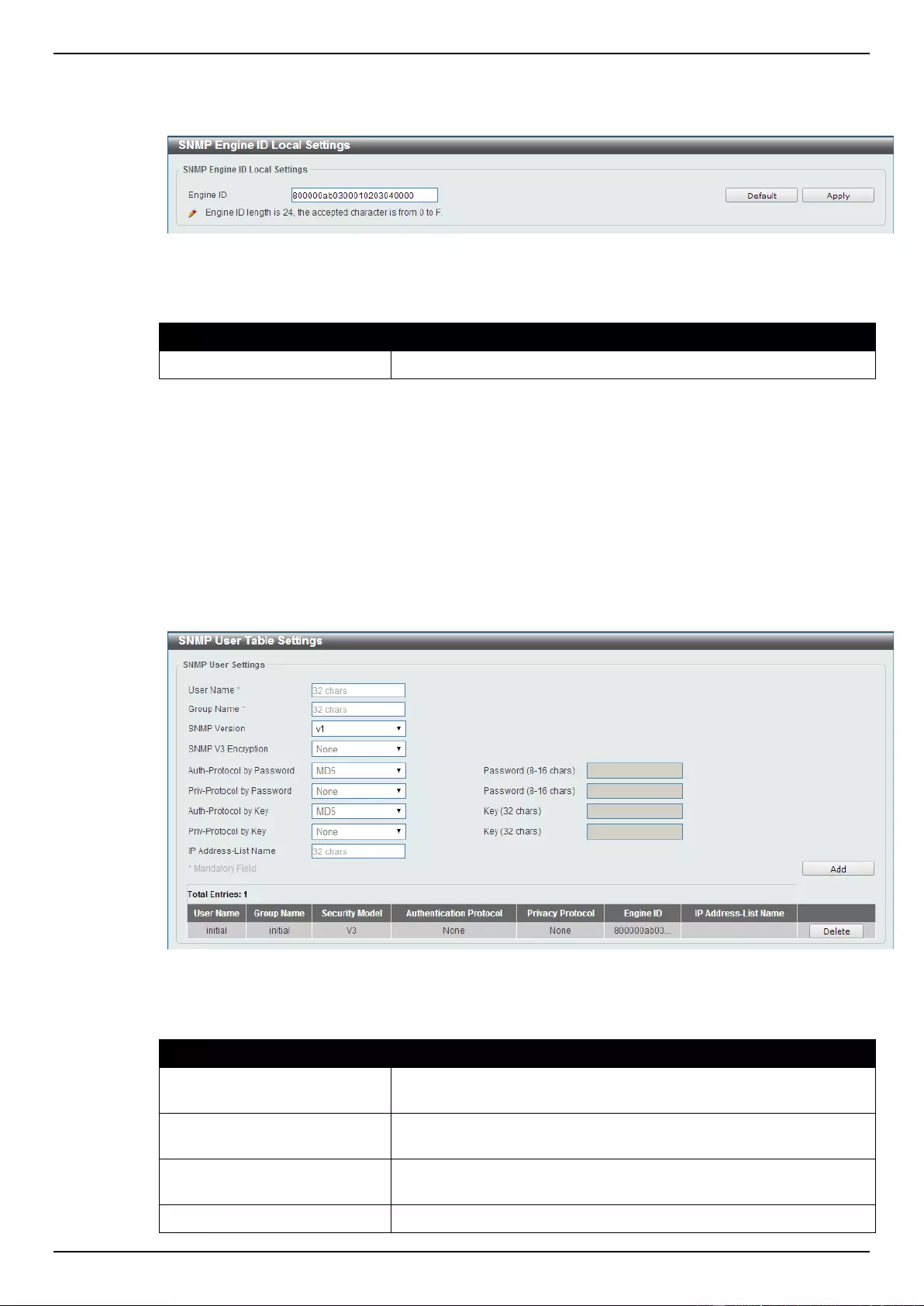
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
39
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Engine ID Local Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 4-10 SNMP Engine ID Local Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Engine ID
Enter the engine ID string with the maximum of 24 characters.
Click the Default button to revert the engine ID to the default.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SNMP User Table Settings
This window is used to configure and display the SNMP users that are currently configured on the
Switch.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP User Table Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-11 SNMP User Table Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
User Name
Enter an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to
identify the SNMP users.
Group Name
Enter the SNMP group name to which the user belongs. The syntax
is general string that does not allow spaces.
SNMP Version
Select the SNMP version. Options to choose from are v1, v2c, and
v3.
SNMP V3 Encryption
When selecting v3 in the SNMP Version drop-down list, this option
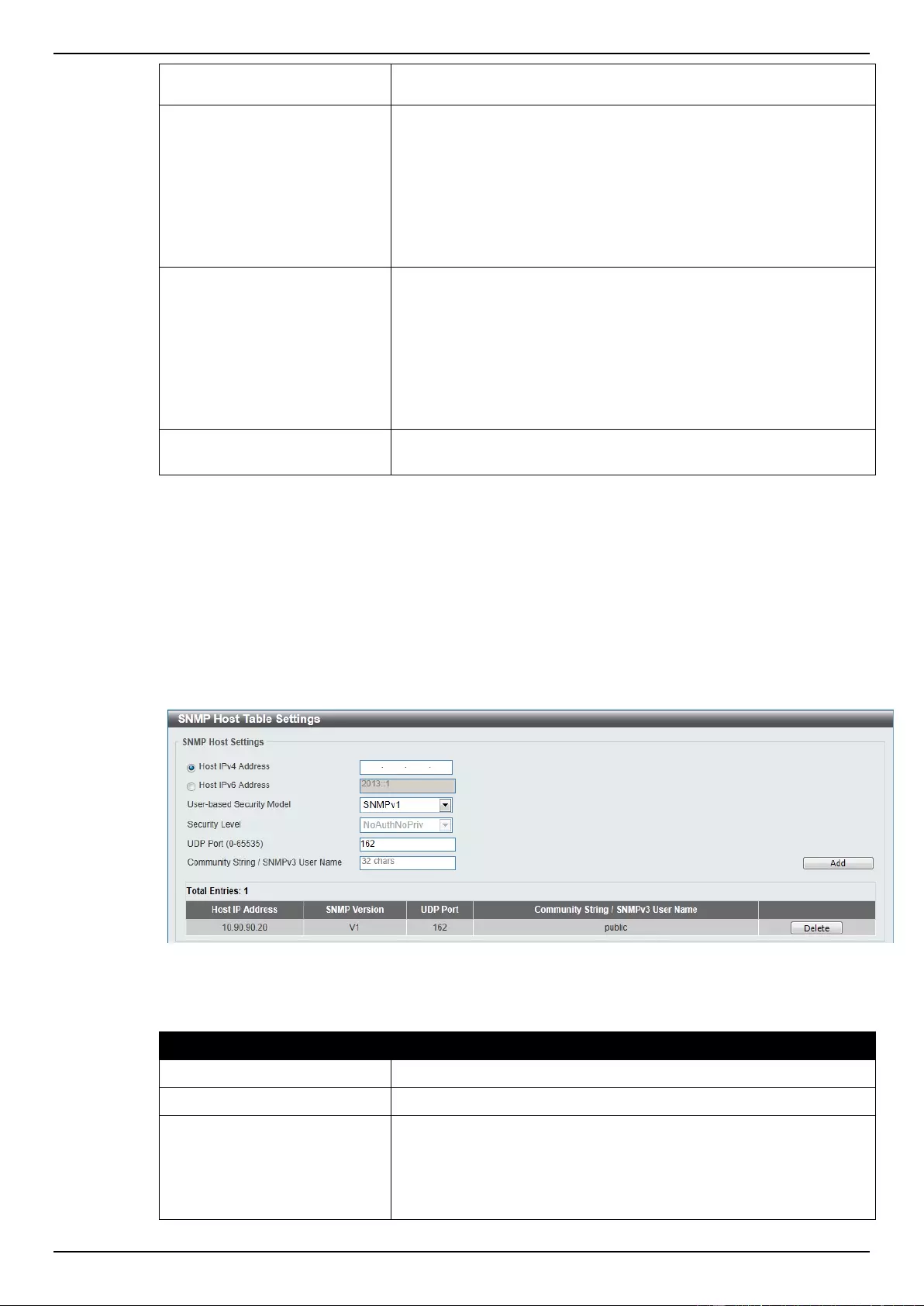
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
40
is available. Options to choose from are None, Password, and
Key.
Auth-Protocol
When selecting v3 in the SNMP Version drop-down list, and
selecting either Password or Key in the SNMP V3 Encryption drop-
down list, this option is available. Select the authentication level.
Options to choose from are MD5, and SHA.
MD5 - Select to use the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level. This
field will require the user to enter a password or a key.
SHA - Specify that the HMAC-SHA authentication protocol will be
used. This field will require the user to enter a password or a key.
Priv-Protocol
When selecting v3 in the SNMP Version drop-down list, and
selecting either Password or Key in the SNMP V3 Encryption drop-
down list, this option is available. Select the private protocol.
Options to choose from are None, and DES56.
None - Specify that no authorization protocol is in use.
DES56 - Specify that DES 56-bit encryption is in use, based on the
CBC-DES (DES-56) standard. This field will require the user to
enter a password or a key.
IP Address-List Name
Enter the standard IP access control list (ACL) to associate with the
user.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
SNMP Host Table Settings
This window is used to configure and display the recipient of the SNMP notification.
To view the following window, click Management > SNMP > SNMP Host Table Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-12 SNMP Host Table Settings
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Host IPv4 Address
Enter the IPv4 address of the SNMP notification host.
Host IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address of the SNMP notification host.
User-based Security Model
Select the security model here. Options to choose from are
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
SNMPv1 - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv1
security model.
SNMPv2c - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv2c

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
41
security model.
SNMPv3 - Select to allow the group user to use the SNMPv3
security model.
Security Level
When selecting SNMPv3 in the User-based Security Model drop-
down list, this option is available.
NoAuthNoPriv - Specify that there will be no authorization and no
encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP
manager.
AuthNoPriv - Specify that authorization will be required, but there
will be no encryption of packets sent between the Switch and a
remote SNMP manager.
AuthPriv - Specify that authorization will be required, and that
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manger will
be encrypted.
UDP Port
Enter the UDP port number. The default trap UDP port number is
162. The range of UDP port numbers is from 0 to 65535. Some port
numbers may conflict with other protocols.
Community String / SNMPv3
User Name
Enter the community string to be sent with the notification packet.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
RMON
RMON Global Settings
This window is used to enable or disable remote monitoring (RMON) for the rising and falling alarm
trap feature for the SNMP function on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Management > RMON > RMON Global Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-13 RMON Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
RMON Rising Alarm Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the RMON Rising Alarm Trap
Feature.
RMON Falling Alarm Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the RMON Falling Alarm Trap
Feature.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
RMON Statistics Settings
This window is used to configure and display the RMON statistics on the specified port.
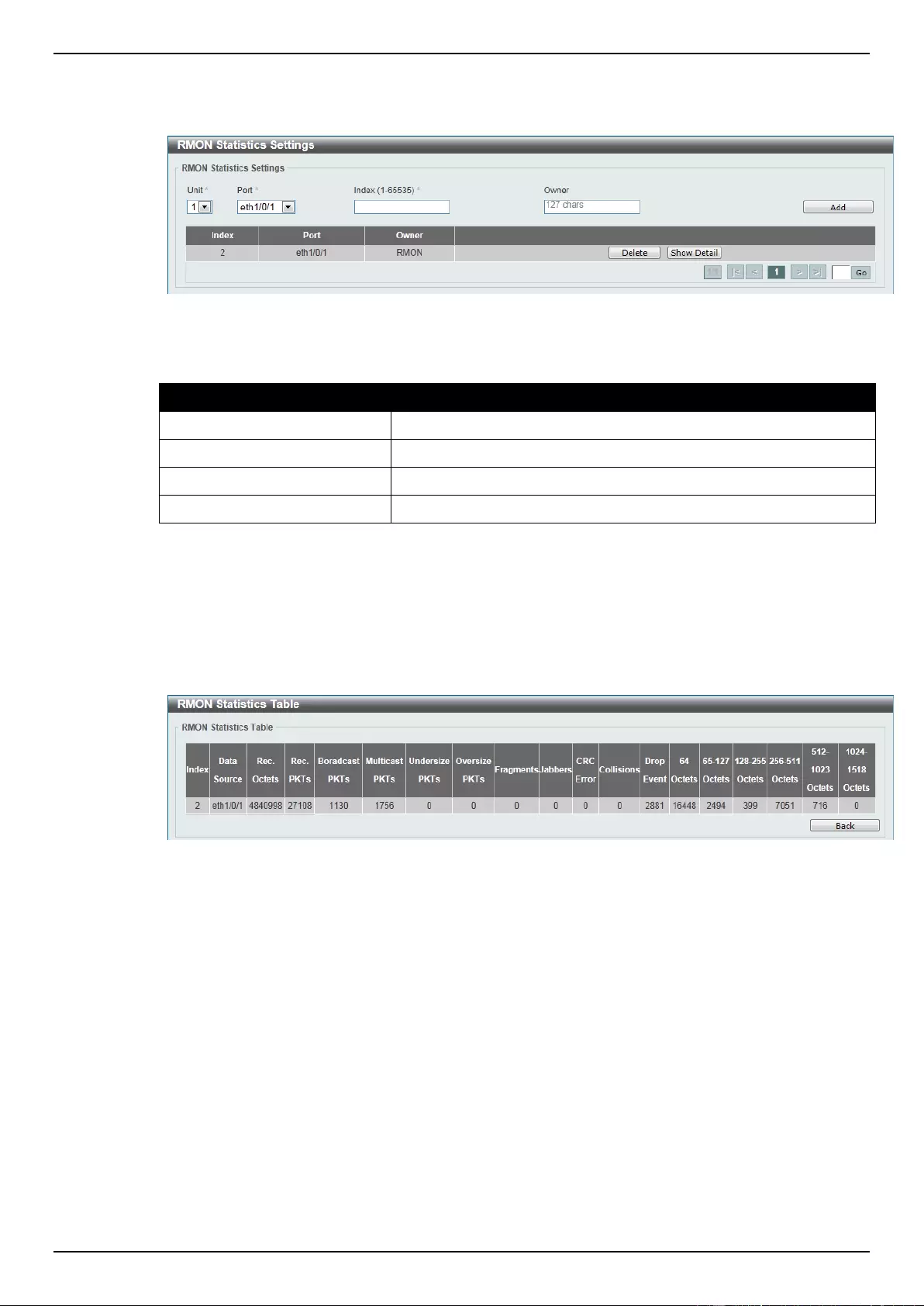
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
42
To view the following window, click Management > RMON > RMON Statistics Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-14 RMON Statistics Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select to choose the port.
Index
Enter the RMON table index. The value is from 1 to 65535
Owner
Enter the owner string. The string can be up to 127 characters.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific port.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-15 RMON Statistics Table window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
RMON History Settings
This window is used to configure and display RMON MIB history statistics gathering on the specified
port.
To view the following window, click Management > RMON > RMON History Settings, as shown
below:
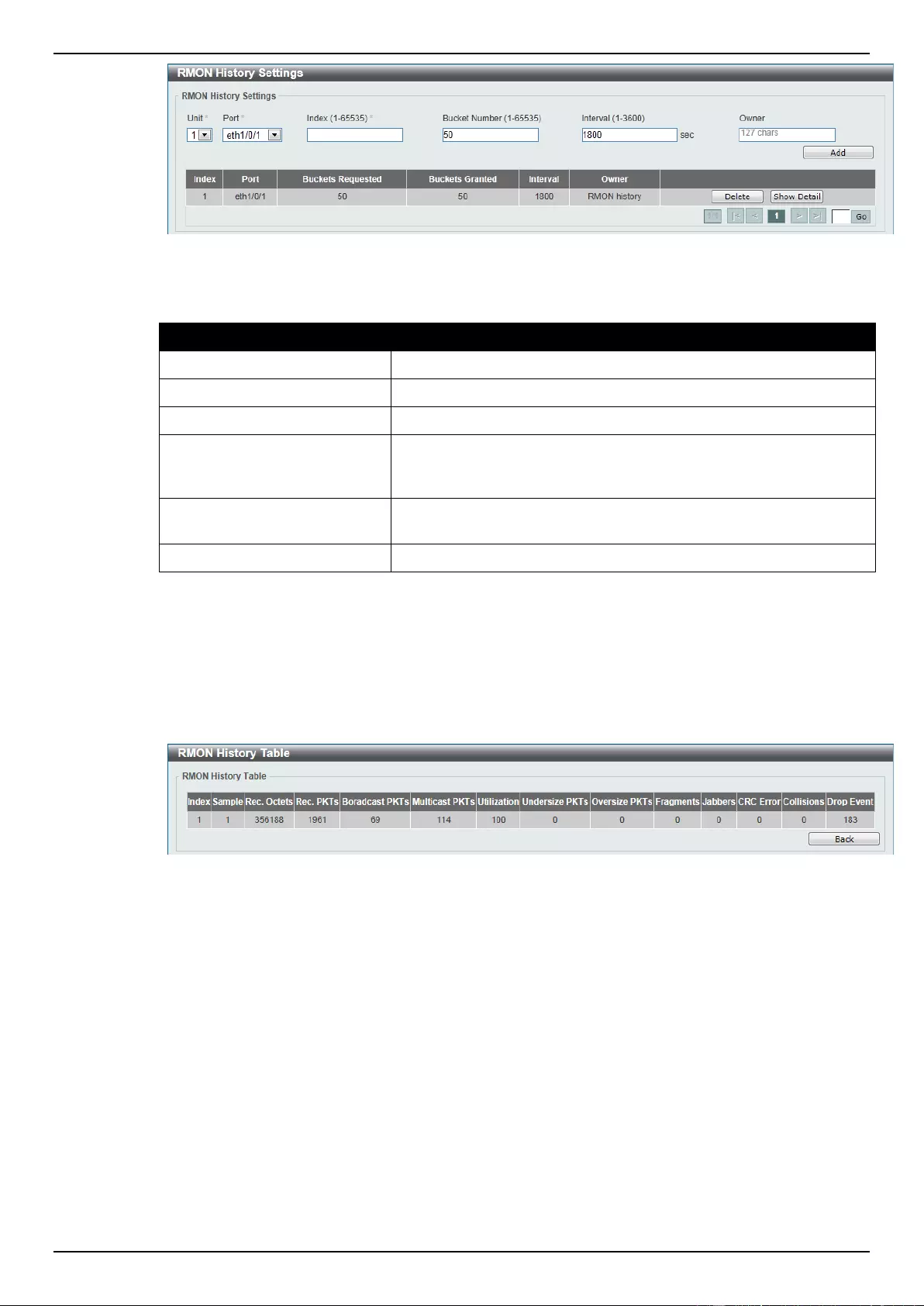
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
43
Figure 4-16 RMON History Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select to choose the port.
Index
Enter the history group table index. The value is from 1 to 65535.
Bucket Number
Enter Specifies the number of buckets specified for the RMON
collection history group of statistics. The range is from 1 to 65535.
The default value is 50.
Interval
Enter the time in seconds in each polling cycle. The range is from 1
to 3600.
Owner
Enter the owner string. The string can be up to 127 characters.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific port.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-17 RMON History Table window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
RMON Alarm Settings
This window is used to configure and display alarm entries to monitor an interface.
To view the following window, click Management > RMON > RMON Alarm Settings, as shown
below:
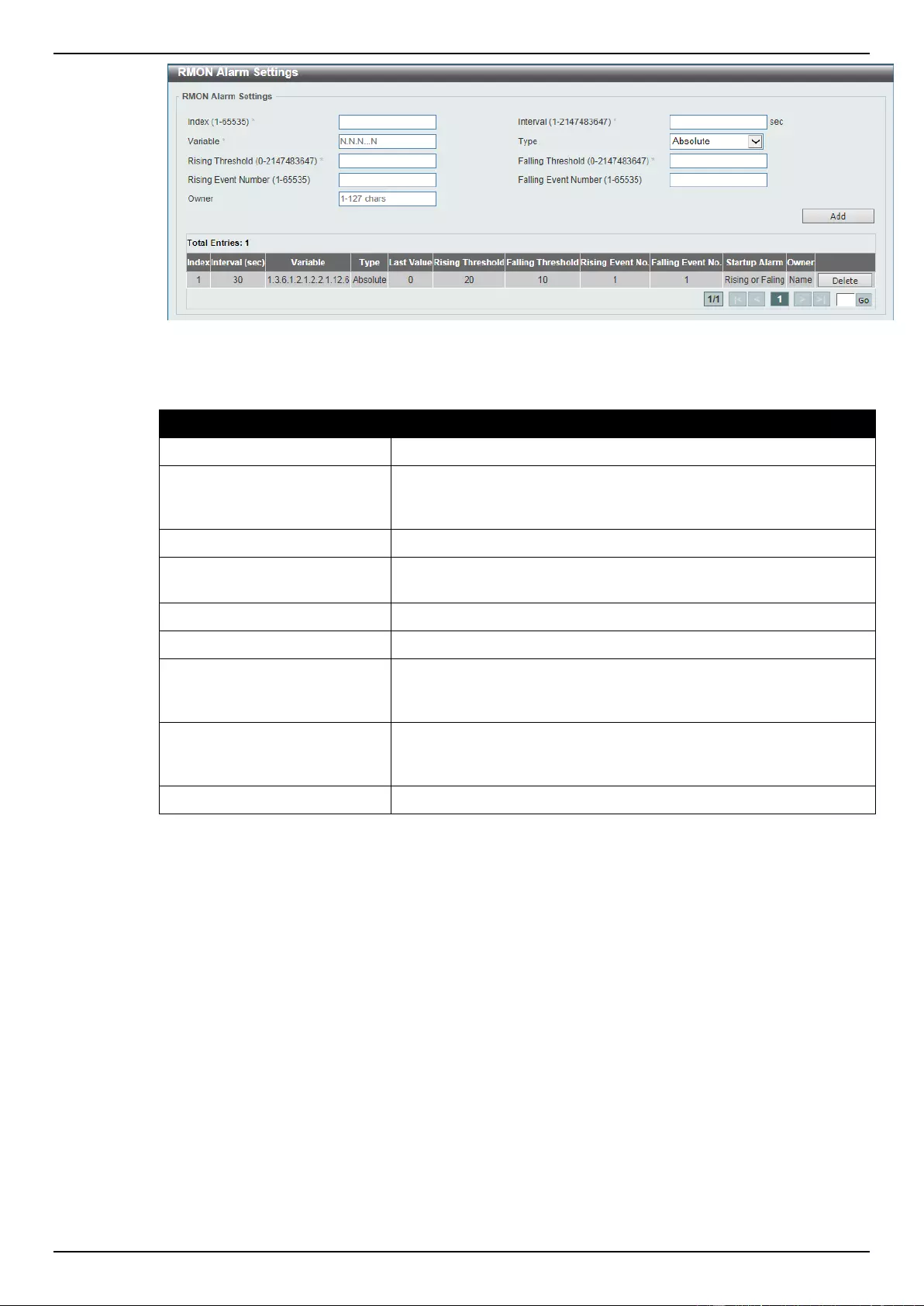
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
44
Figure 4-18 RMON Alarm Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Index
Enter the alarm index. The range is from 1 to 65535.
Interval
Enter the interval in seconds for the sampling of the variable and
checking against the threshold. The valid range is from 1 to
2147483647 seconds.
Variable
Enter the object identifier of the variable to be sampled.
Type
Select the monitoring type. Options to choose from are Absolute
and Delta.
Rising Threshold
Enter the rising threshold value between 0 and 2147483647.
Falling Threshold
Enter the falling threshold value between 0 and 2147483647.
Rising Event Number
Enter the index of the event entry that is used to notify the rising
threshold crossing event. The valid range is from 1 to 65535. If not
specified, no action is taken while crossing the ringing threshold.
Falling Event Number
Enter the index of the event entry that is used to notify the falling
threshold crossing event. The valid range is from 1 to 65535. If not
specified, no action is taken while crossing the falling threshold.
Owner
Enter the owner string up to 127 characters.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
RMON Event Settings
This window is used to configure and display event entries.
To view the following window, click Management > RMON > RMON Event Settings, as shown below:
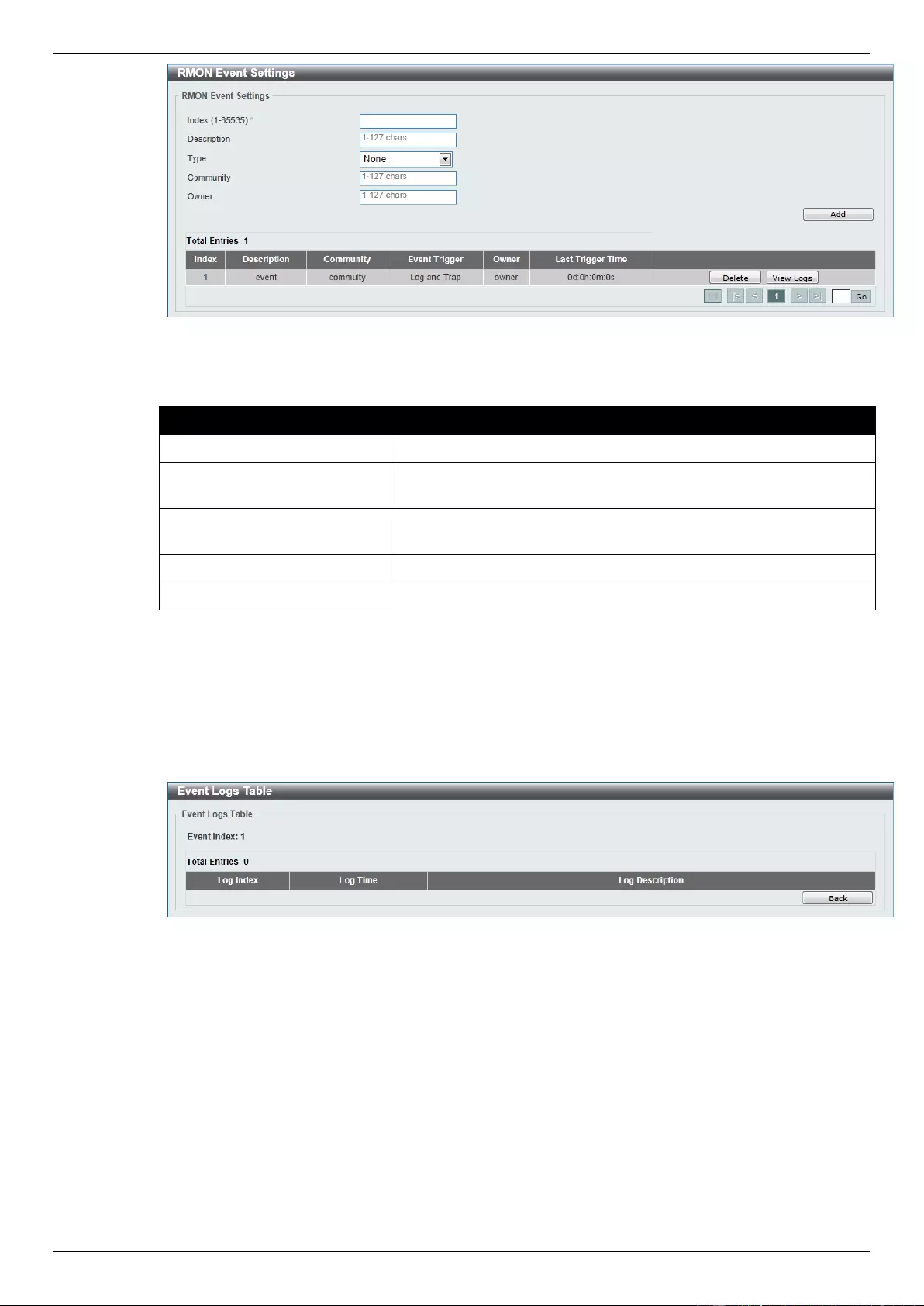
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
45
Figure 4-19 RMON Event Settings
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Index
Enter the index of the alarm entry between 1 and 65535.
Description
Enter a description for the RMON event entry. The string is up to
127 characters long.
Type
Select the RMON event entry type. Options to choose from are
None, Log, Trap, and Log and Trap.
Community
Enter the community string. The string can be up to 127 characters.
Owner
Enter the owner string. The string can be up to 127 characters.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the View Logs button to see the detail information of the specific port.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the View Logs button, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-20 Event Logs Table window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Telnet/Web
This window is used to configure Telnet and Web settings on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Management > Telnet/Web, as shown below:
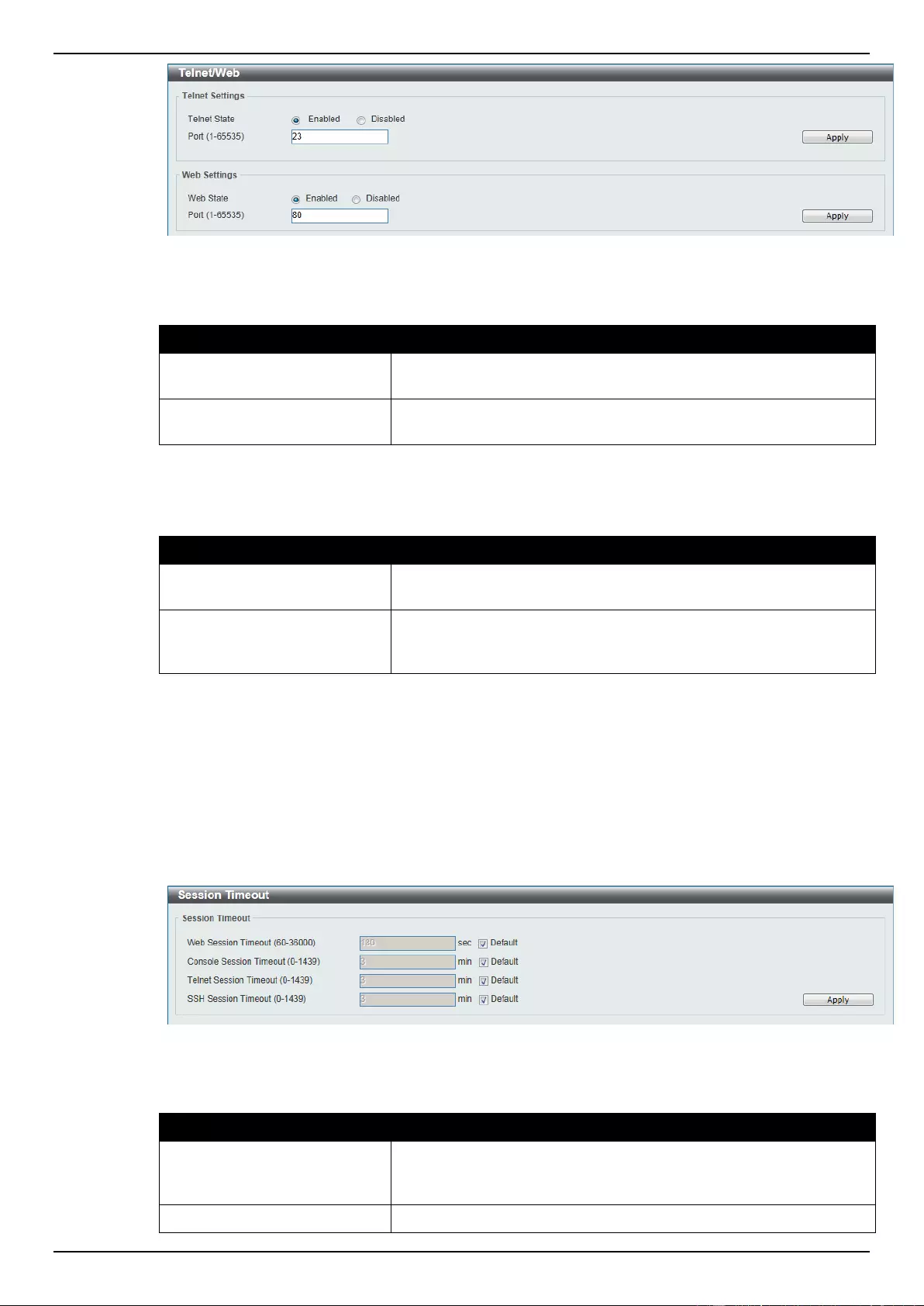
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
46
Figure 4-21 Telnet/Web window
The fields that can be configured for Telnet Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Telnet State
Select this option to enable or disable the configuration through
Telnet.
Port
Enter the TCP port number used for Telnet management of the
Switch. The “well-known” TCP port for the Telnet protocol is 23.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Web Setting are described below:
Parameter
Description
Web State
Select this option to enable or disable the configuration through the
web.
Port
Enter the TCP port number used for Web-based management of the
Switch. The “well-known” TCP port for the Web-based protocol is
80.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Session Timeout
This window is used to configure the session timeout.
To view the following window, click Management > Session Timeout, as shown below:
Figure 4-22 Session Timeout window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Web Session Timeout
Enter the time in seconds of the web session timeout. Tick the
Default check box to return to the default setting. The value is from
60 to 36000 seconds. The default value is 180 seconds.
Console Session Timeout
Enter the time in minutes of the web session timeout. Tick the
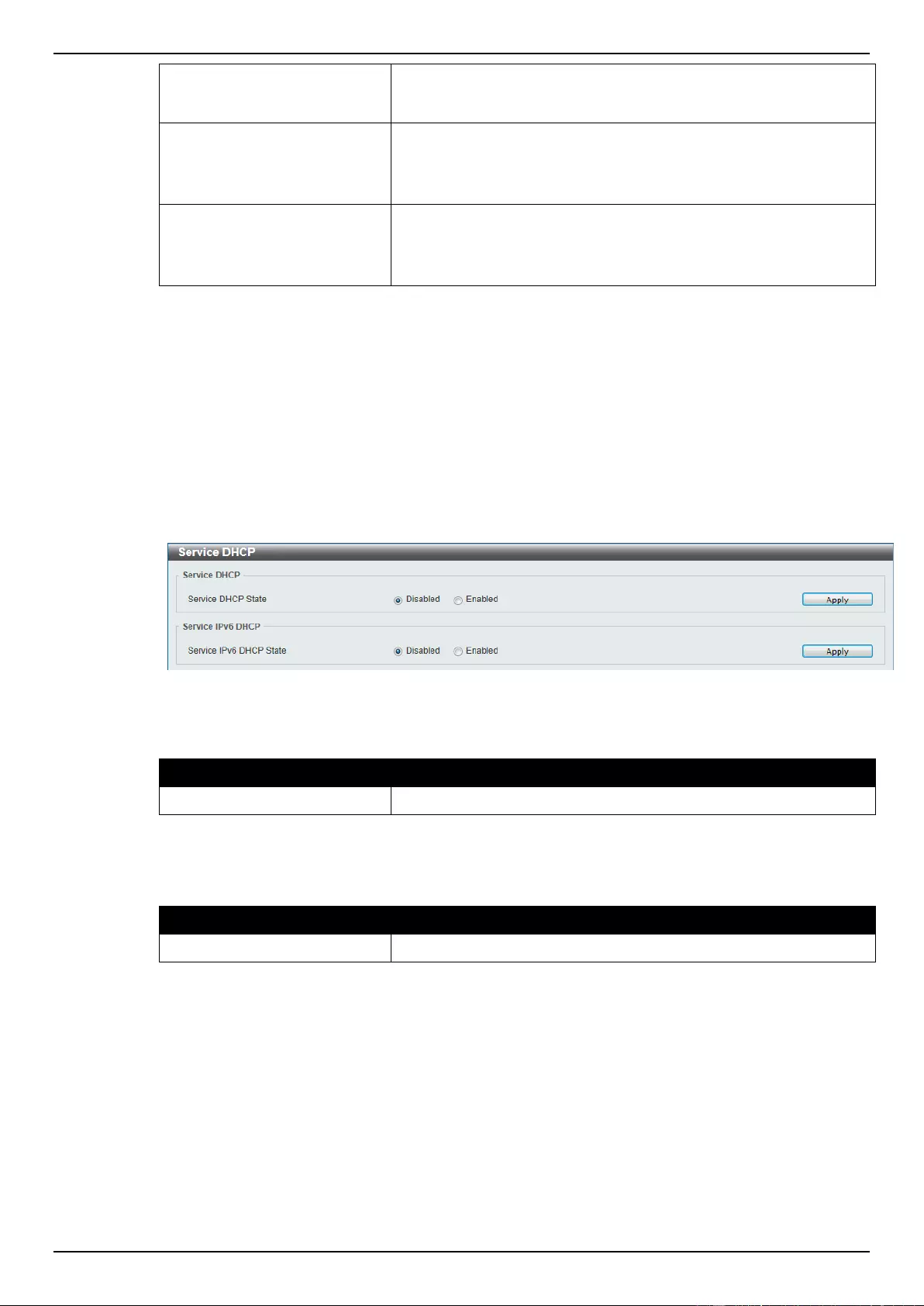
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
47
Default check box to return to the default setting. The value is from
0 to 1439 minutes. 0 means never timeout. The default value is 3
minutes.
Telnet Session Timeout
Enter the time in minutes of the Telnet session timeout. Tick the
Default check box to return to the default setting. The value is from
0 to 1439 minutes. 0 means never timeout. The default value is 3
minutes.
SSH Session Timeout
Enter the time in minutes of the SSH session timeout. Tick the
Default check box to return to the default setting. The value is from
0 to 1439 minutes. 0 means never timeout. The default value is 3
minutes.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP
Service DHCP
This window is used to configure the DHCP relay service on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > Service DHCP, as shown below:
Figure 4-23 Service DHCP window
The fields that can be configured for Service DHCP are described below:
Parameter
Description
Service DHCP State
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCP relay service.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Service IPv6 DHCP are described below:
Parameter
Description
Service IPv6 DHCP State
Select this option to enable or disable the IPv6 DHCP relay service.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Class Settings
This window is used to configure and display the DHCP class and the DHCP option matching pattern
for the DCHP class.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > Service DHCP, as shown below:
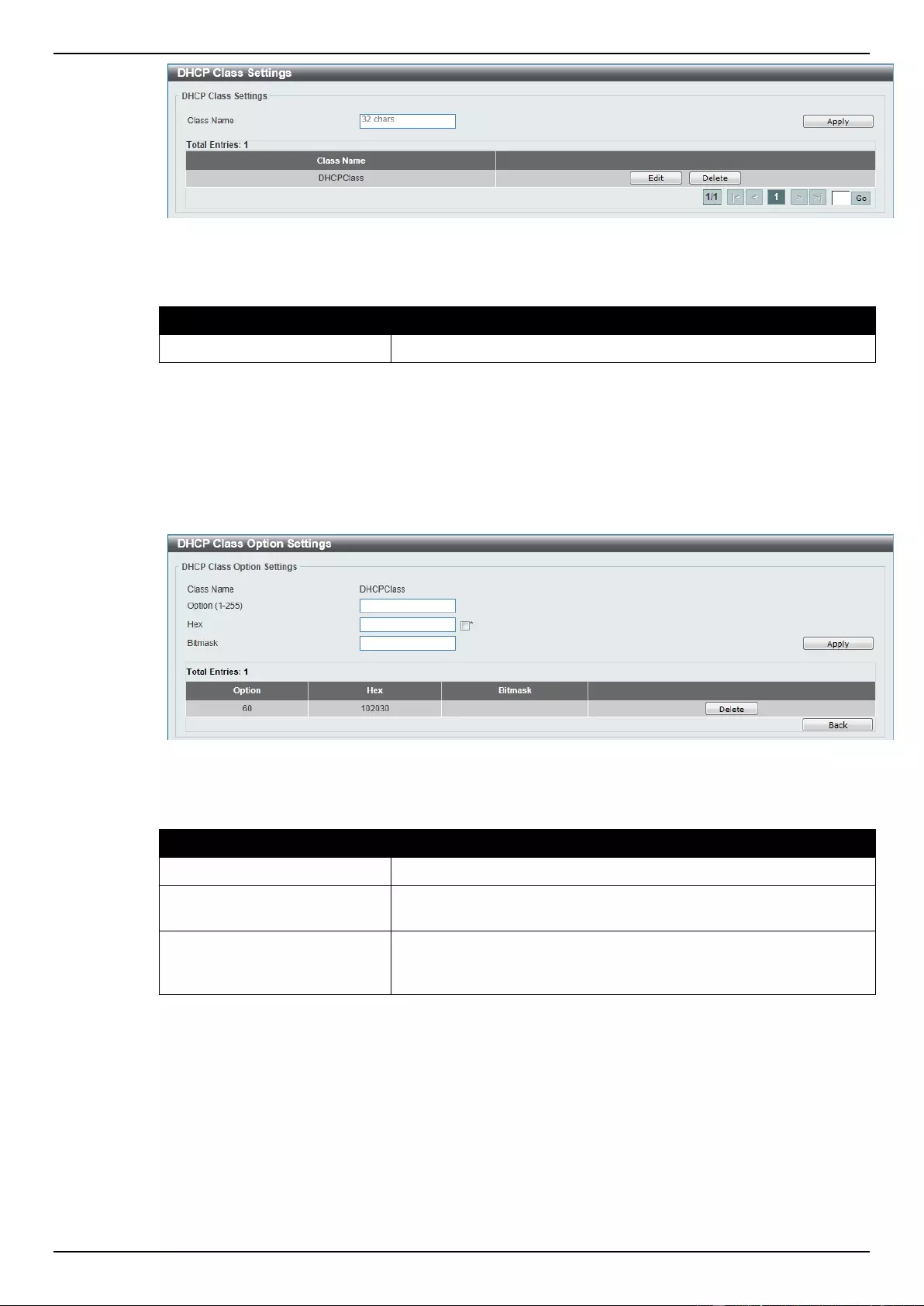
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
48
Figure 4-24 DHCP Class Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Class Name
Enter the DHCP class name with a maximum of 32 characters.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to modify the DHCP option matching pattern for the corresponding DCHP class.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Edit button, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-25 DHCP Class Option Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Option
Enter the DHCP option number. The range is from 1 to 255.
Hex
Enter the hex pattern of the specified DHCP option. Tick the * check
box not to match the remaining bits of the option.
Bitmask
Enter the hex bit mask for masking of the pattern. The masked
pattern bits will be matched. If not specified, all bits entered in Hex
will be checked.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
DHCP Relay
DHCP Relay Global Settings
This window is used to configure the smart relay feature of the DHCP relay agent.
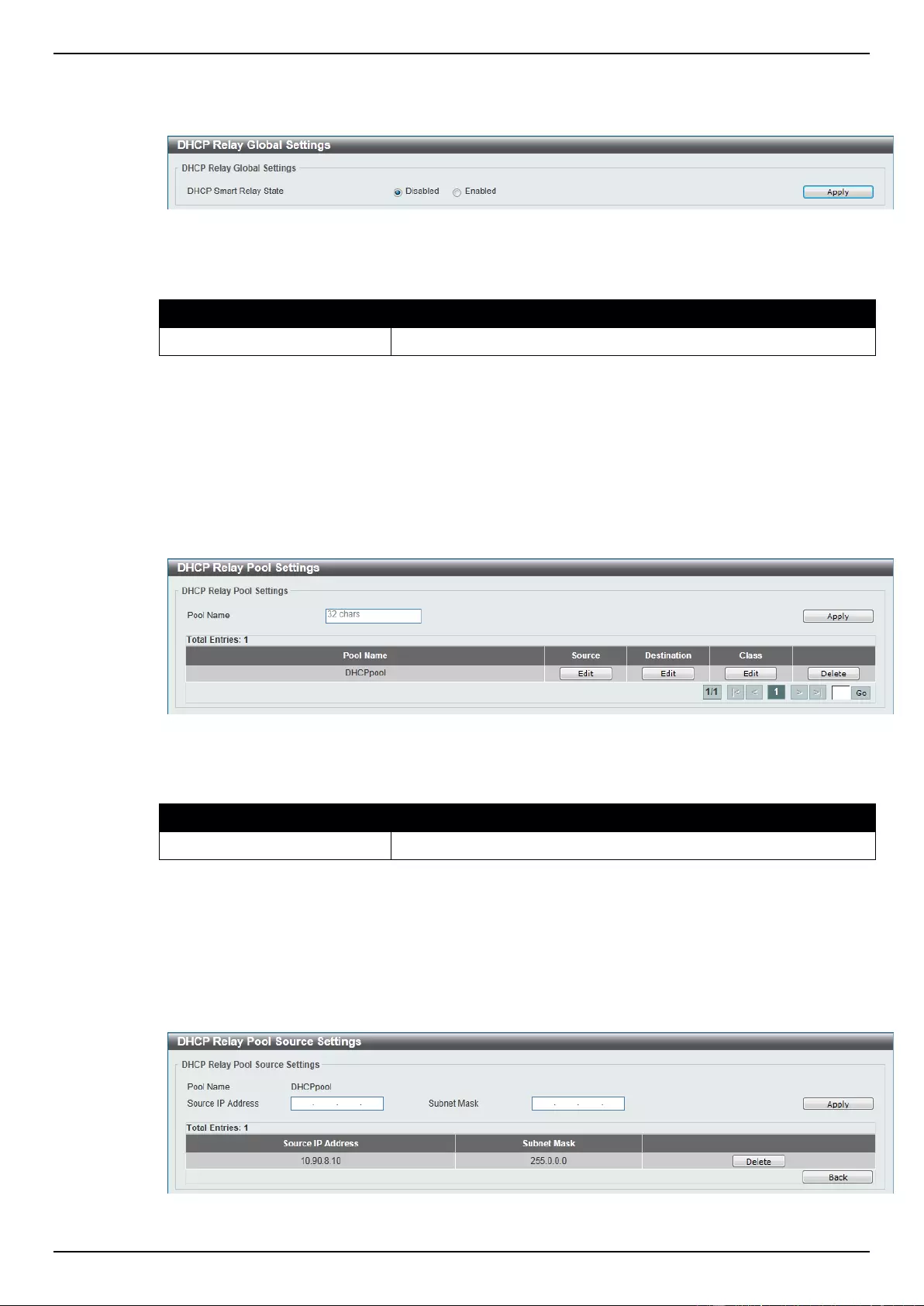
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
49
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global
Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-26 DHCP Relay Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DCHP Smart Relay State
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCP smart relay.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Relay Pool Settings
This window is used to configure and display the DHCP relay pool on a DHCP relay agent.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Pool
Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-27 DHCP Relay Pool Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Pool Name
Enter the address pool name with a maximum of 32 characters.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to modify the corresponding information of the specific DHCP pool.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Edit button under Source, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-28 DHCP Relay Pool Source Settings window
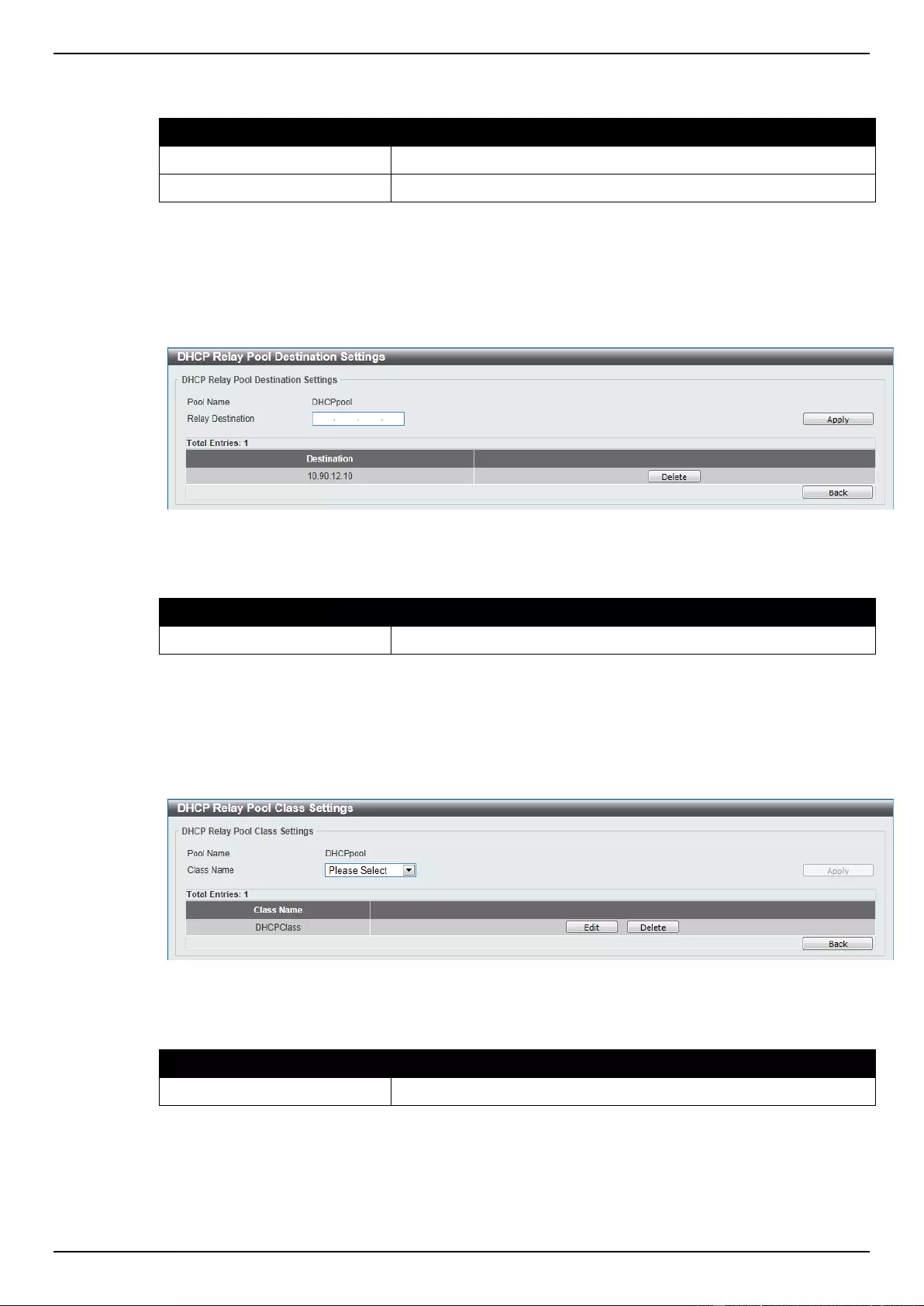
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
50
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source IP Address
Enter the source subnet of client packets.
Subnet Mask
Enter the network mask of the source subnet.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After clicking the Edit button under Destination, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-29 DHCP Relay Pool Destination Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Relay Destination
Enter the relay destination DHCP server IP address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After clicking the Edit button under Class, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-30 DHCP Relay Pool Class Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Class Name
Select the DHCP class name.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to edit more information.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
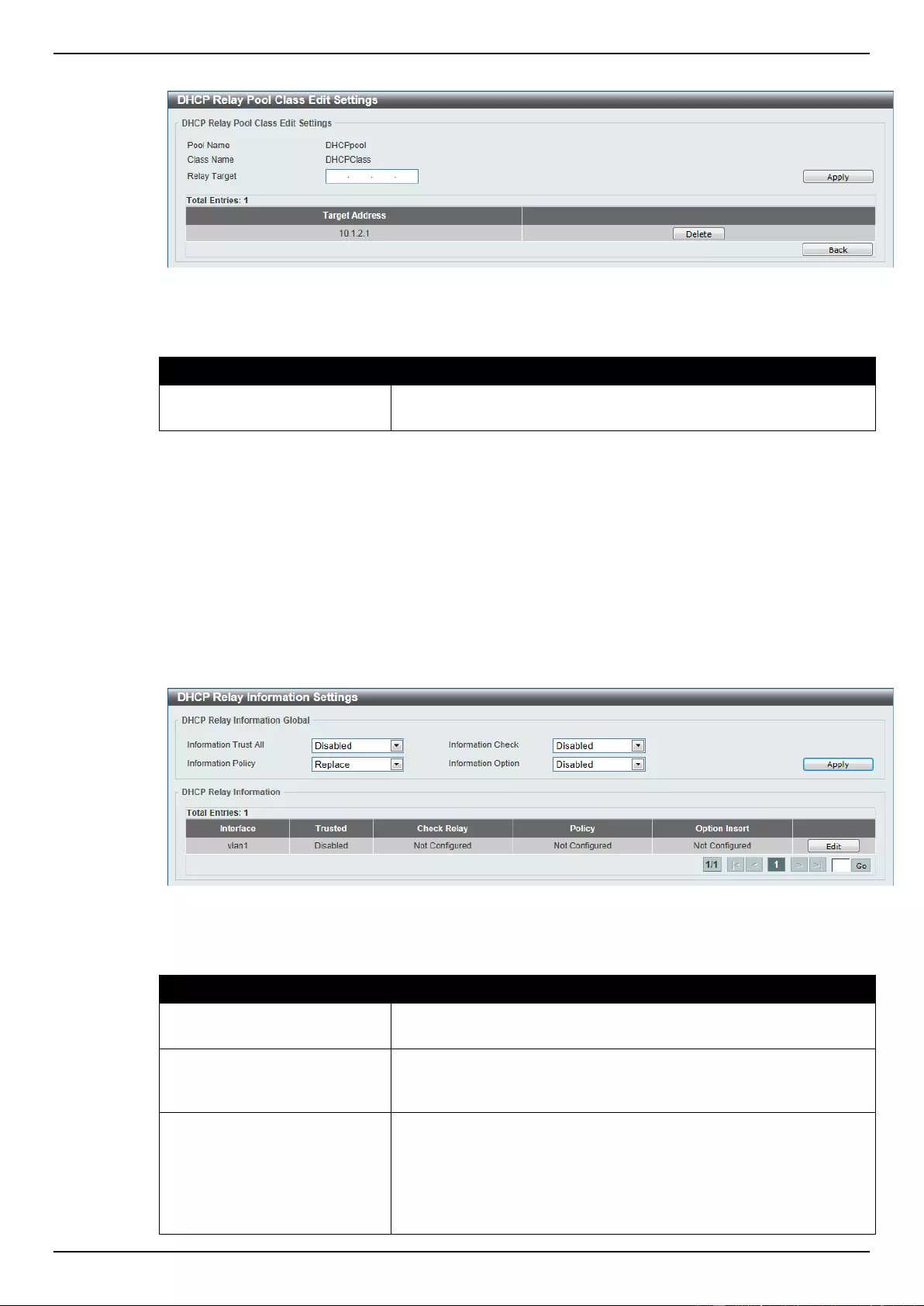
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
51
After clicking the Edit button, the following window will appear.
Figure 4-31 DHCP Relay Pool Class Edit Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Relay Target
Enter the DHCP relay target for relaying packets that matches the
value pattern of the option defined in the DHCP class.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
DHCP Relay Information Settings
This window is used to configure and display the DHCP relay information.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay
Information Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-32 DHCP Relay Information Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Information Trust All
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCP relay agent to trust
the IP DHCP relay information for all interfaces.
Information Check
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCP relay agent to
validate and remove the relay agent information option in the
received DHCP reply packet.
Information Policy
Select the Option 82 re-forwarding policy for the DHCP relay agent.
Options to choose from are Keep, Drop, and Replace.
Keep - Select to discard the packet that already has the relay
option.
Drop - Select that the DHCP request packet that already has the
relay option is left unchanged and directly relayed to the DHCP
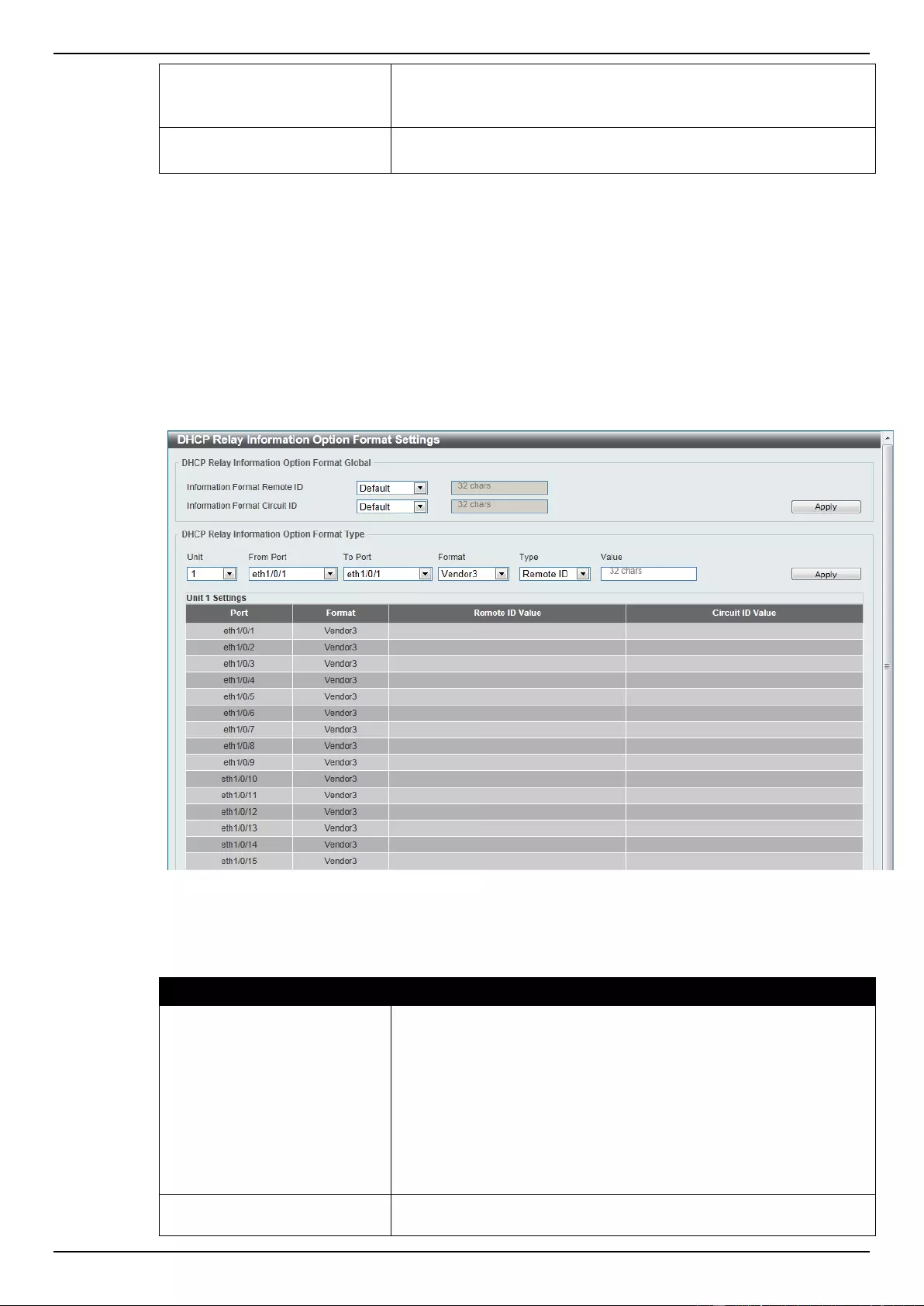
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
52
server.
Replace - Select that the DHCP request packet that already has the
relay option will be replaced by a new option.
Information Option
Select this option to enable or disable the insertion of relay agent
information (Option 82) during the relay of DHCP request packets.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to modify the corresponding interface.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
DHCP Relay Information Option Format Settings
This window is used to configure and display the DHCP information format.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay
Information Option Format Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-33 DHCP Relay Information Option Format Settings window
The fields that can be configured for DHCP Relay Information Option Format Global are described
below:
Parameter
Description
Information Format Remote
ID
Select the DHCP information remote ID sub-option. Options to
choose from are Default, User Define, Vendor2, and Vendor3.
Default - Select to use the Switch's system MAC address as the
remote ID.
User Define - Select to use a user-defined remote ID. Enter the
user-defined string with the maximum of 32 characters in the text
box.
Vendor2 - Select to use vender 2 as the remote ID.
Vendor3 - Select to use vender 3 as the remote ID.
Information Format Circuit ID
Select the DHCP information circuit ID sub-option. Options to
choose from are Default, User Define, Vendor1, Vendor2,

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
53
Vendor3, Vendor4, Vendor5, and Vendor6.
Default - Select to use the default circuit ID sub-option.
User Define - Select to use a user-defined circuit ID. Enter the
user-defined string with the maximum of 32 characters in the text
box.
Vendor1 - Select to use vender 1 as the circuit ID.
Vendor2 - Select to use vender 2 as the circuit ID.
Vendor3 - Select to use vender 3 as the circuit ID.
Vendor4 - Select to use vender 4 as the circuit ID.
Vendor5 - Select to use vender 5 as the circuit ID.
Vendor6 - Select to use vender 6 as the circuit ID.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for DHCP Relay Information Option Format Type are described
below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Format
Select the DHCP information circuit ID format. Option to choose
from is Vendor3.
Type
Select the DHCP information circuit ID format typ. Options to
choose from are Remote ID, and Circuit ID.
Value
Enter the vendor-defined string.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Local Relay VLAN
This window is used to configure local relay on a VLAN or a group of VLANs.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Relay > DHCP Local Relay
VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 4-34 DHCP Local Relay VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DHCP Local Relay VID List
Enter the VLAN ID for DHCP local relay. Tick the All VLANs check
box to select all VLANs.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCP local relay on the
specific VLAN(s).
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
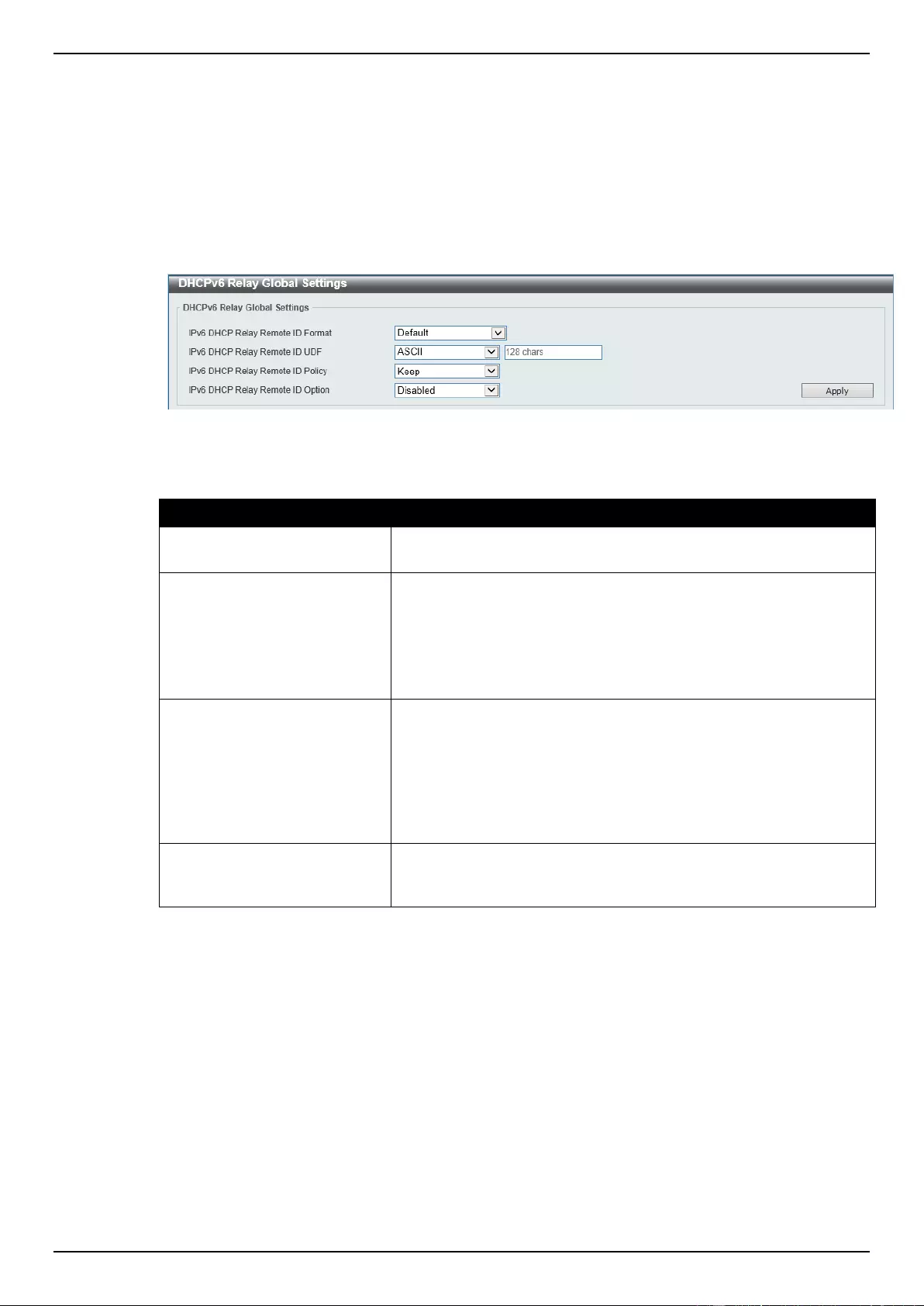
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
54
DHCPv6 Relay
DHCPv6 Relay Global Settings
This window is used to configure the DHCPv6 relay remote ID.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCPv6 Relay > DHCPv6 Relay
Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-35 DHCPv6 Relay Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv6 DHCP Relay Remote ID
Format
Select to choose the sub-type of the remote ID. Options to choose
from are Default, CID with User Define, and User Define.
IPv6 DHCP Relay Remote ID
UDF
Select to choose the User Define Field (UDF) for remote ID. Options
to choose from are ASCII, and Hex.
ASCII - Select to enter the ASCII string with a maximum of 128
characters in the text box.
HEX - Select to enter the hexadecimal string with a maximum of
256 characters in the text box.
IPv6 DHCP Relay Remote ID
Policy
Select to choose Option 37 forwarding policy for the DHCPv6 relay
agent. Options to choose from are Keep, and Drop.
Keep - Select to discard the packet that already has the relay agent
Remote-ID Option 37.
Drop - Select that the DHCPv6 request packet that already has the
relay agent Remote-ID option is left unchanged and directly relayed
to the DHCPv6 server.
IPv6 DHCP Relay Remote ID
Option
Select this option to enable or disable the insertion of the relay
agent remote ID Option 37 during the relay of DHCP for IPv6
request packets.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCPv6 Relay Interface Settings
This window is used to configure and display the DHCPv6 relay interface settings.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCPv6 Relay > DHCPv6 Relay
Interface Settings, as shown below:
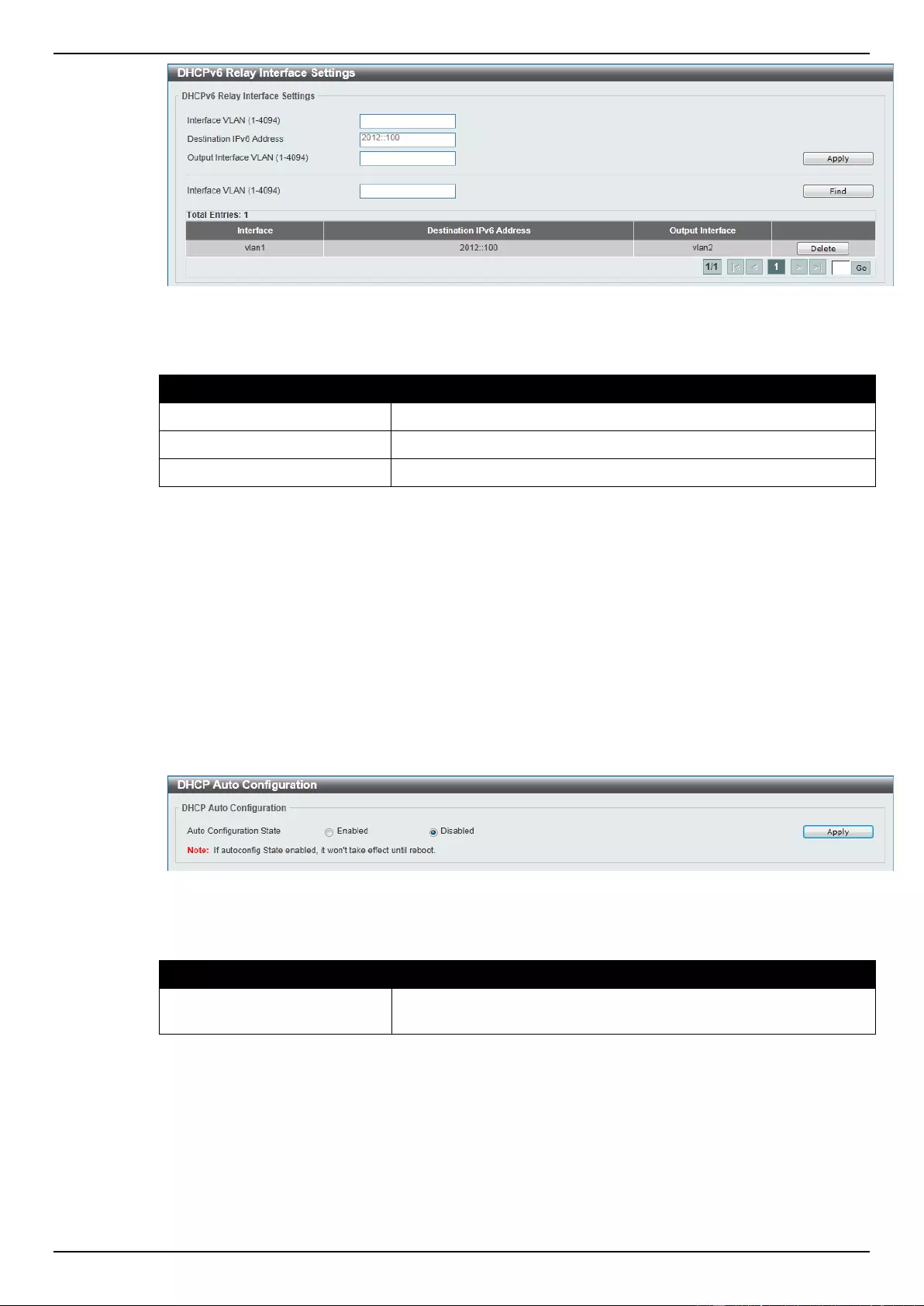
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
55
Figure 4-36 DHCPv6 Relay Interface Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter the VLAN from 1 to 4094 for DHCPv6 relay.
Destination IPv6 Address
Enter the DHCPv6 relay destination address.
Output Interface VLAN
Enter the output interface for the relay destination.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
DHCP Auto Configuration
This window is used to configure the DHCP auto-configuration function.
To view the following window, click Management > DHCP > DHCP Auto Configuration, as shown
below:
Figure 4-37 DHCP Auto Configuration window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Auto Configuration State
Select this option to enable or disable the auto-configuration
function.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DNS
Computer users usually prefer to use text names for computers for which they may want to open a
connection. Computers themselves, require 32 bit IP addresses. Somewhere, a database of network
devices’ text names and their corresponding IP addresses must be maintained.
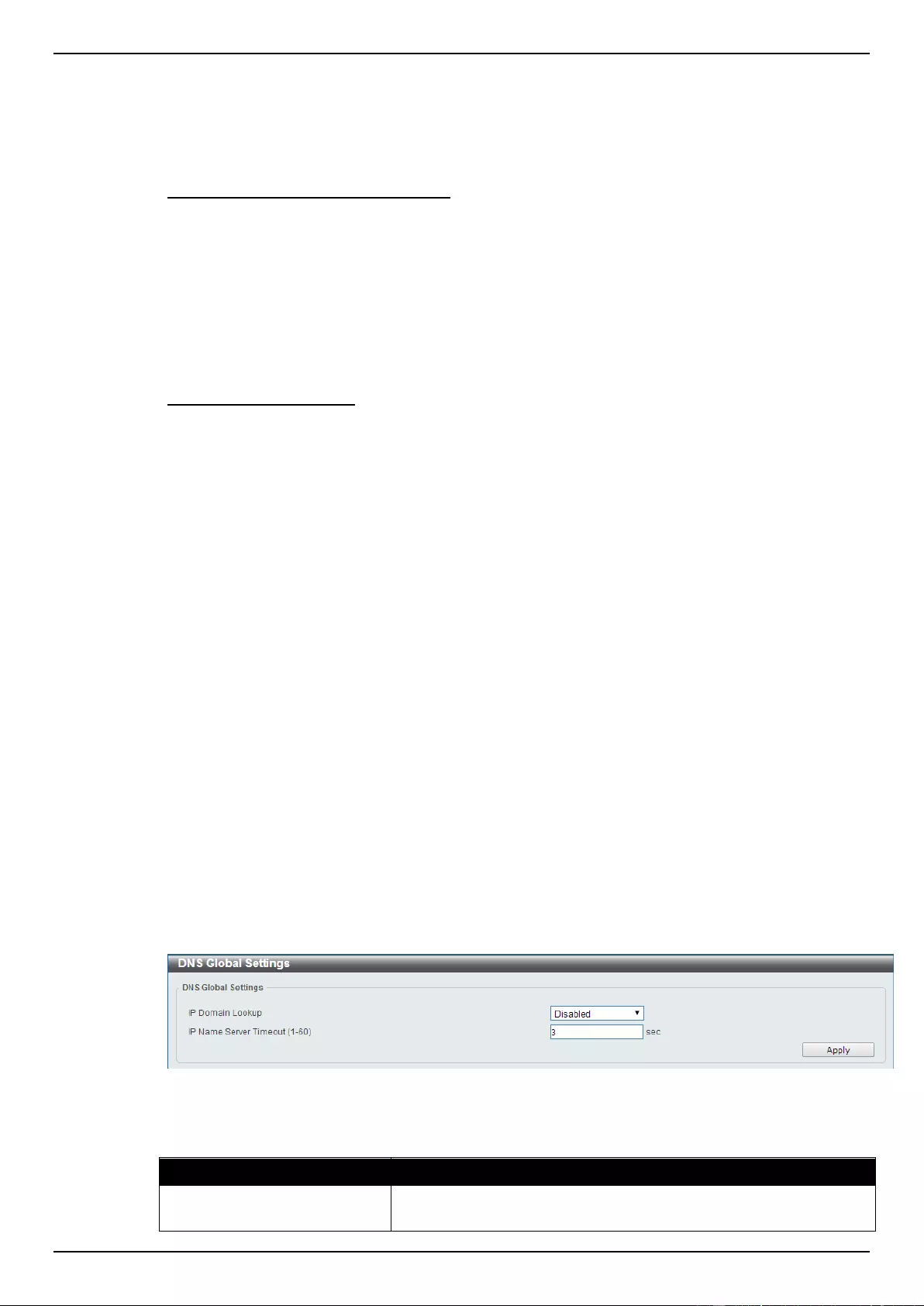
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
56
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to map names to IP addresses throughout the Internet and
has been adapted for use within intranets. For two DNS servers to communicate across different
subnets, the DNS Relay of the Switch must be used. The DNS servers are identified by IP addresses.
Mapping Domain Names to Addresses
Name-to-address translation is performed by a program called a Name server. The client program is
called a Name resolver. A Name resolver may need to contact several Name servers to translate a
name to an address.
The Domain Name System (DNS) servers are organized in a somewhat hierarchical fashion. A single
server often holds names for a single network, which is connected to a root DNS server - usually
maintained by an ISP.
Domain Name Resolution
The domain name system can be used by contacting the name servers one at a time, or by asking the
domain name system to do the complete name translation. The client makes a query containing the
name, the type of answer required, and a code specifying whether the domain name system should
do the entire name translation, or simply return the address of the next DNS server if the server
receiving the query cannot resolve the name.
When a DNS server receives a query, it checks to see if the name is in its sub domain. If it is, the
server translates the name and appends the answer to the query, and sends it back to the client. If the
DNS server cannot translate the name, it determines what type of name resolution the client
requested. A complete translation is called recursive resolution and requires the server to contact
other DNS servers until the name is resolved. Iterative resolution specifies that if the DNS server
cannot supply an answer, it returns the address of the next DNS server the client should contact.
Each client must be able to contact at least one DNS server, and each DNS server must be able to
contact at least one root server.
The address of the machine that supplies domain name service is often supplied by a DHCP or
BOOTP server, or can be entered manually and configured into the operating system at startup.
DNS Global Settings
This window is used to configure the DNS global settings.
To view the following window, click Management > DNS > DNS Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-38 DNS Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Domain Lookup
Select this option to enable or disable the DNS to carry out the
domain name resolution.
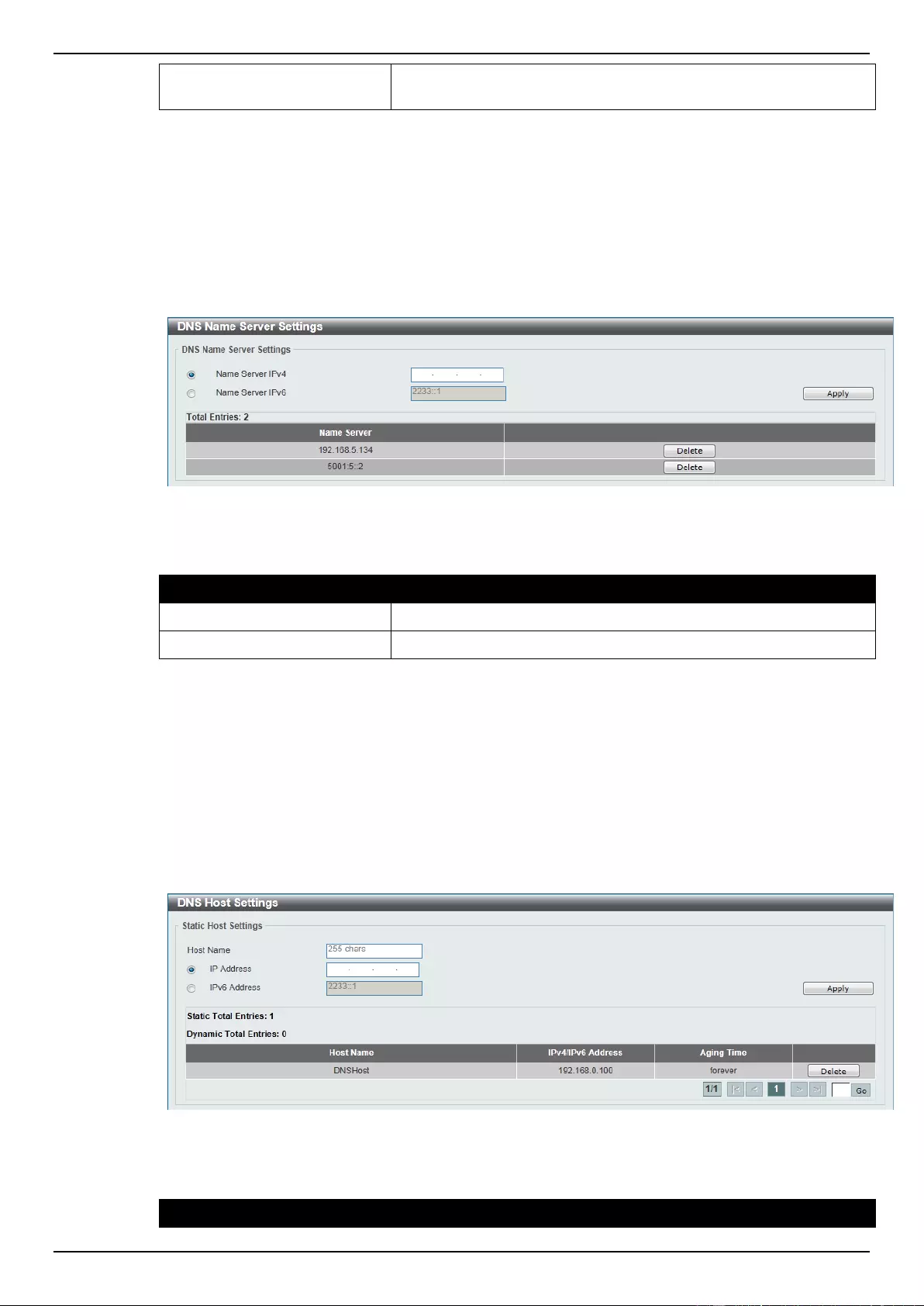
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
57
IP Name Server Timeout
Enter the maximum time to wait for a response from a specified
name server. This value is between 1 and 60 seconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DNS Name Server Settings
This window is used to configure and display the IP address of a domain name server.
To view the following window, click Management > DNS > DNS Name Server Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-39 DNS Name Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Name Server IPv4
Select and enter the IPv4 address of the DNS server.
Name Server IPv6
Select and enter the IPv6 address of the DNS server.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
DNS Host Settings
This window is used to configure the static mapping entry for the host name and the IP address in the
host table.
To view the following window, click Management > DNS > DNS Host Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-40 DNS Host Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
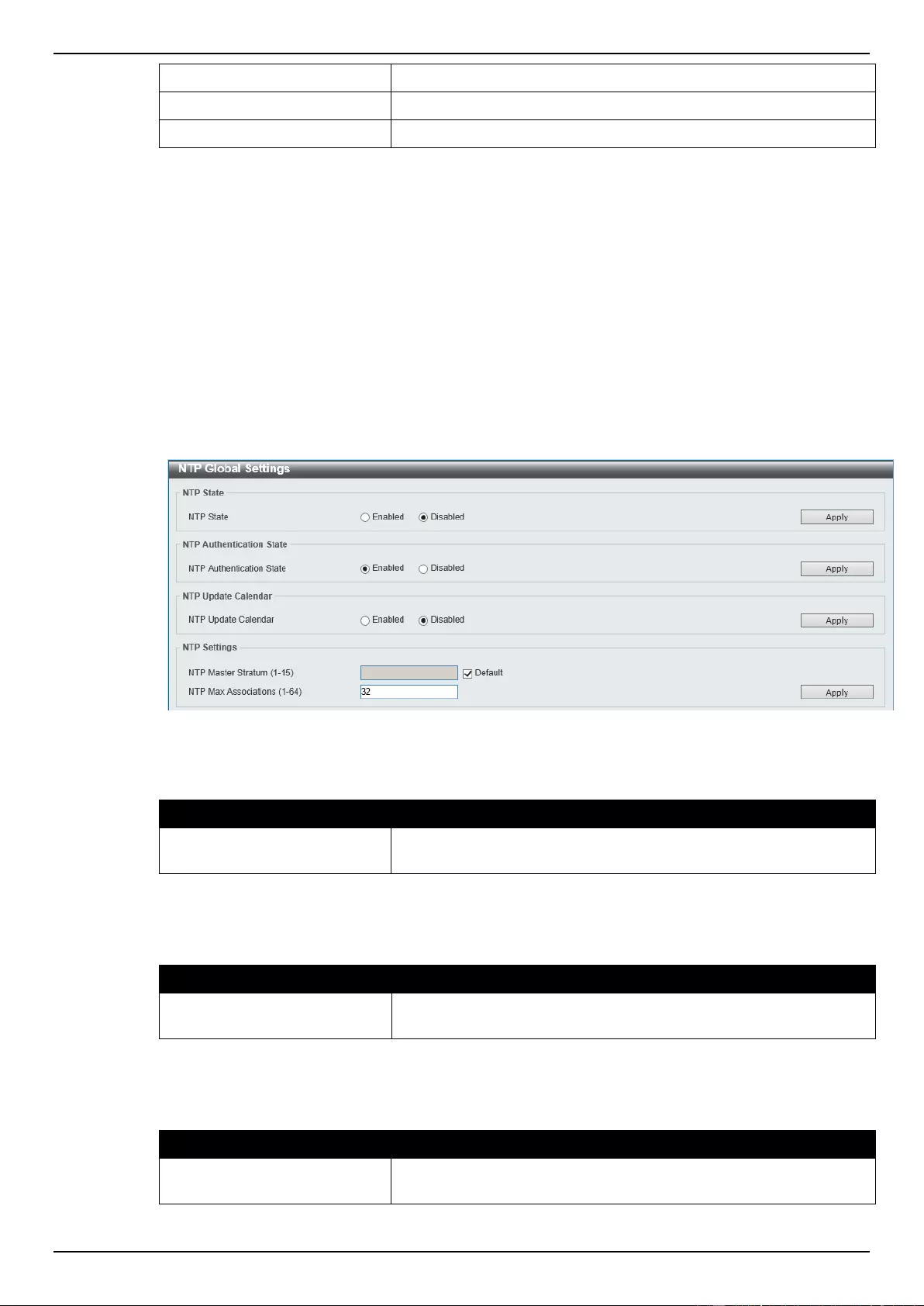
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
58
Host Name
Enter the host name of the equipment.
IP Address
Select and enter the IPv4 address of the equipment.
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the IPv6 address of the equipment.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NTP
NTP Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Network Time Protocol (NTP) global settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-41 NTP Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for NTP State are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP State
Select the NTP feature’s global state here. Options to choose from
are Enabled and Disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for NTP Authentication State are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP Authentication State
Select the NTP feature’s authentication state here. Options to
choose from are Enabled and Disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for NTP Update Calendar are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP Update Calendar
Select the NTP feature’s update calendar state here. Options to
choose from are Enabled and Disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
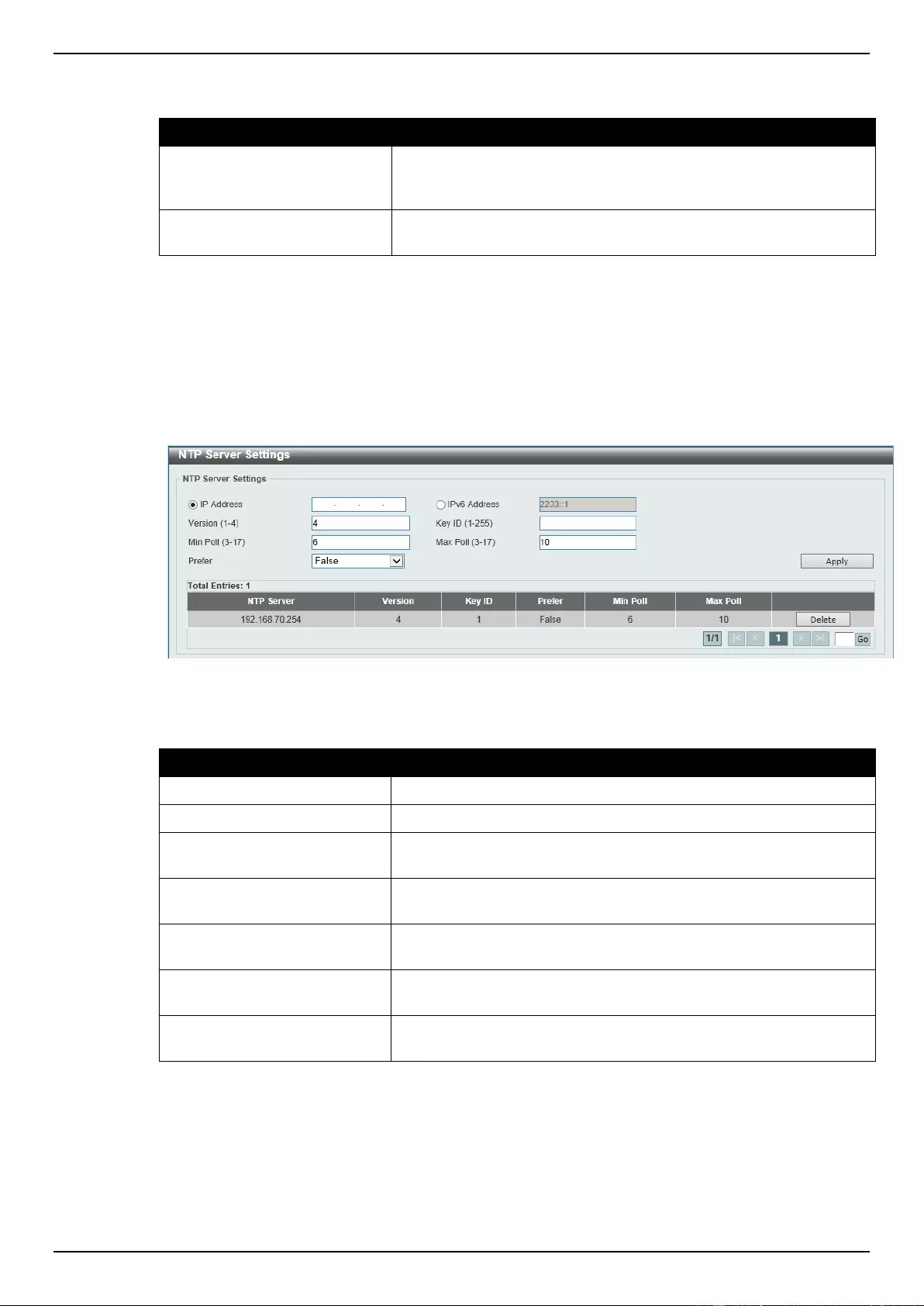
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
59
The fields that can be configured for NTP Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP Master Stratum
Enter the NTP master stratum value here. This value must be
between 1 and 15. Select the Default option to use the default
value.
NTP Max Associations
Enter the NTP maximum amount of associations here. This value
must be between 1 and 64.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
NTP Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure the NTP server’s settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Server Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-42 NTP Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Select and enter the NTP server’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the NTP server’s IPv6 address here.
Version
Enter the NTP server’s version number here. This value must be
between 1 and 4.
Key ID
Enter the authentication key ID here. This ID must be between 1
and 255.
Min Poll
Enter the minimum poll intervals for NTP messages here. This value
must be between 3 and 17 seconds.
Max Poll
Enter the maximum poll intervals for NTP messages here. This
value must be between 3 and 17 seconds.
Prefer
Select whether this server is the preferred server in the list or not.
Options to choose from are True and False.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NTP Peer Settings
This window is used to view and configure the NTP peer settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Peer Settings, as shown below:
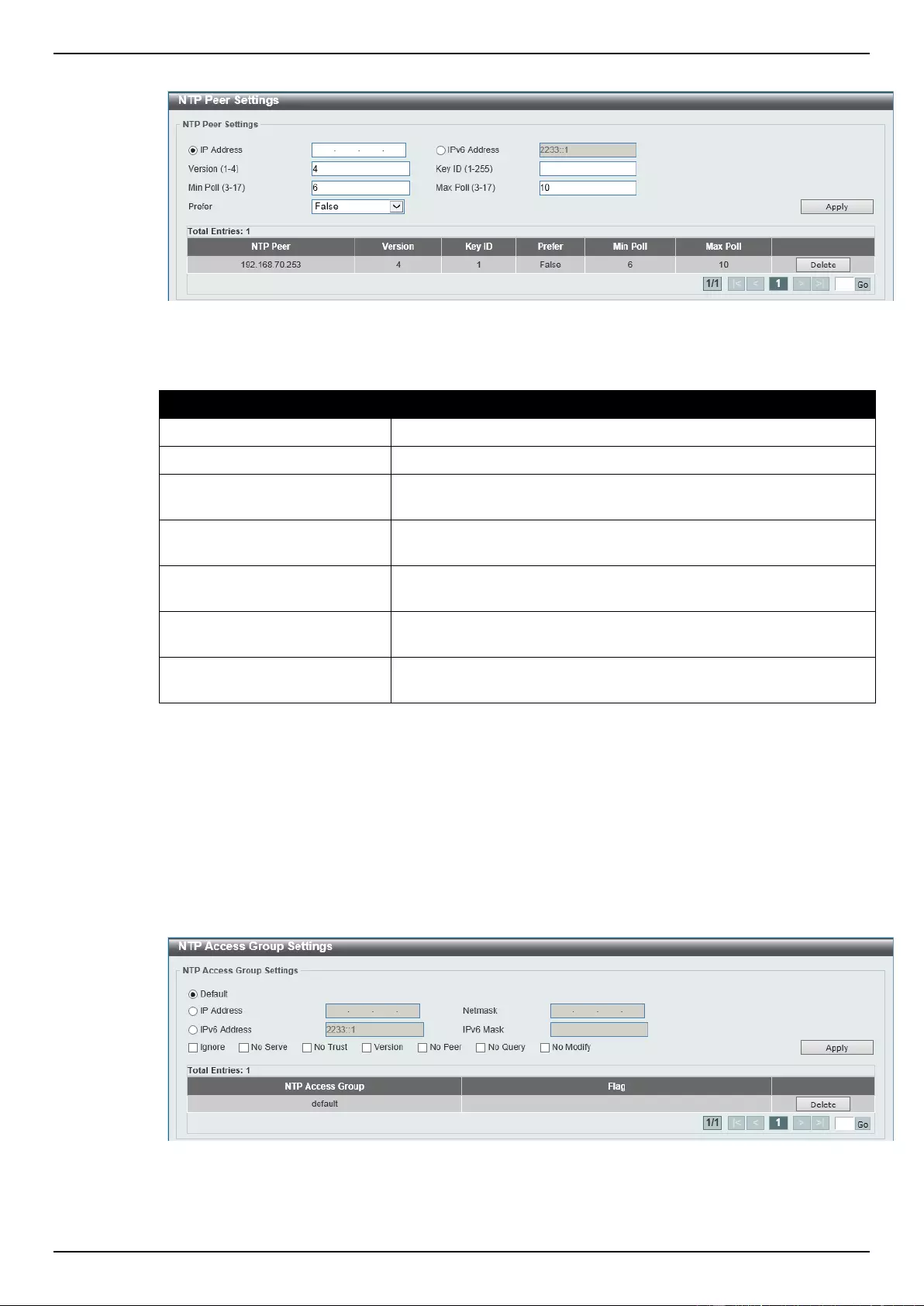
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
60
Figure 4-43 NTP Peer Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Select and enter the NTP peer’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the NTP peer’s IPv6 address here.
Version
Enter the NTP peer’s version number here. This value must be
between 1 and 4.
Key ID
Enter the authentication key ID here. This ID must be between 1
and 255.
Min Poll
Enter the minimum poll intervals for NTP messages here. This value
must be between 3 and 17 seconds.
Max Poll
Enter the maximum poll intervals for NTP messages here. This
value must be between 3 and 17 seconds.
Prefer
Select whether this peer is the preferred peer in the list or not.
Options to choose from are True and False.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NTP Access Group Settings
This window is used to view and configure the NTP access group settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Access Group Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 4-44 NTP Access Group Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
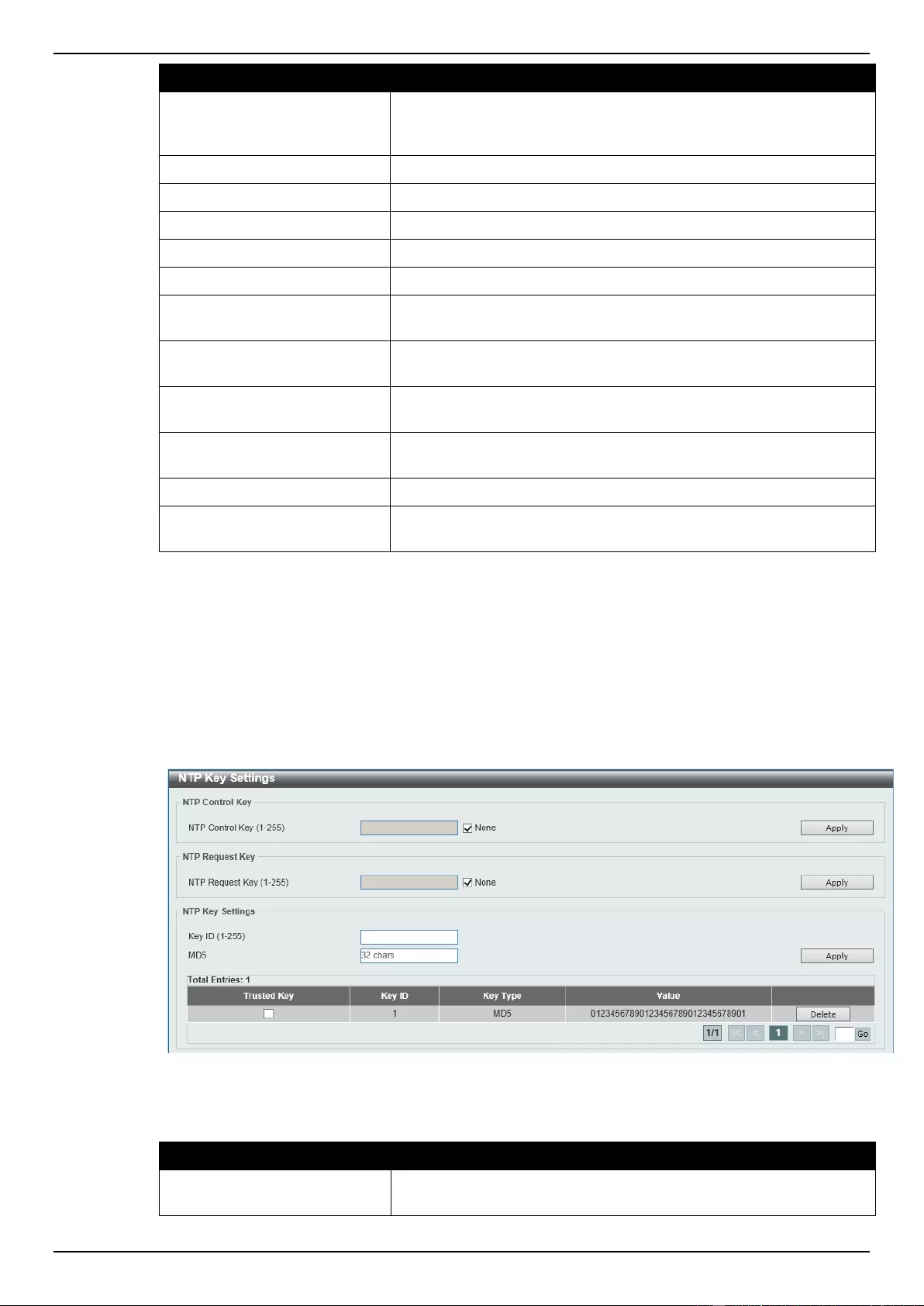
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
61
Parameter
Description
Default
Select this option to specify that a default entry (address 0.0.0.0,
mask 0.0.0.0) will always be included and is the lowest priority in the
list.
IP Address
Select and enter the IPv4 address of the host or network here.
Netmask
Select and enter the IPv4 network mask of the host or network here.
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the IPv6 address of the host or network here.
IPv6 Mask
Select and enter the IPv6 network mask of the host or network here.
Ignore
Select this option to ignore all NTP related packets.
No Serve
Select this option to deny all NTP related packets, except for NTP
control queries.
No Trust
Select this option to deny all NTP related packets that are not
cryptographically authenticated.
Version
Select this option to deny all NTP related packets that don’t match
the current NTP version.
No Peer
Select this option to deny all NTP related packets that might
mobilize an association unless authenticated.
No Query
Select this option to deny all NTP control queries.
No Modify
Select this option to deny NTP control queries that attempted to
modify the state of the server.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NTP Key Settings
This window is used to view and configure the NTP key settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Key Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-45 NTP Key Settings window
The fields that can be configured for NTP Control Key are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP Control Key
Enter the NTP control key here. This key must be between 1 and
255. Select the None option to not use an NTP control key.
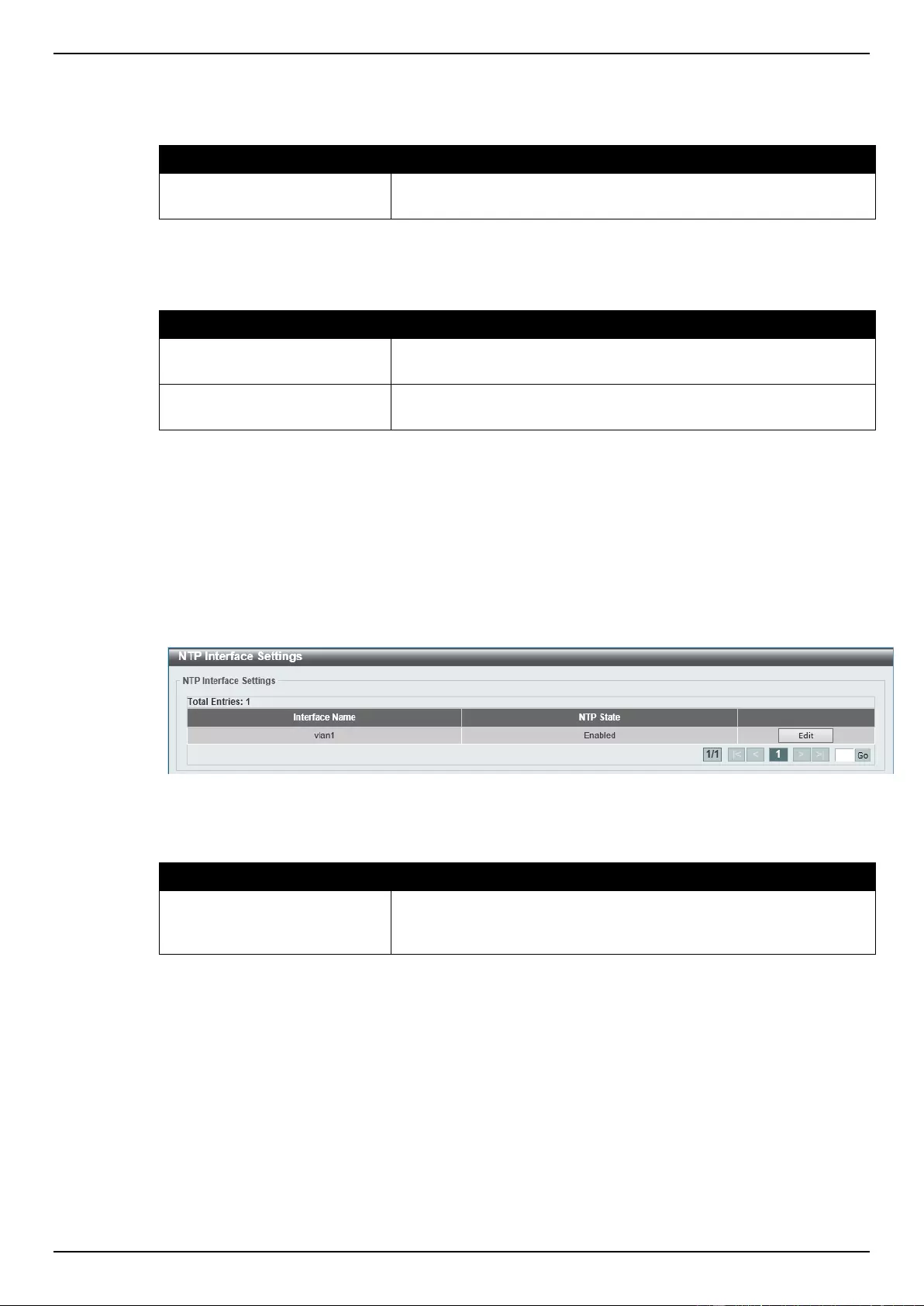
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
62
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for NTP Request Key are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP Request Key
Enter the NTP request key here. This key must be between 1 and
255. Select the None option to not use an NTP request key.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for NTP Key Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Key ID
Enter the NTP key number here. This authentication key number
must be between 1 and 255.
MD5
Enter the MD5 NTP key here. This key can be up to 32 characters
long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NTP Interface Settings
This window is used to view and configure the NTP interface settings.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Interface Settings, as shown below:
Figure 4-46 NTP Interface Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
NTP State
After click the Edit button, select the NTP feature’s state on the
interface specified. Options to choose from are Enabled and
Disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
NTP Associations
This window is used to view a list of NTP associations.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Associations, as shown below:
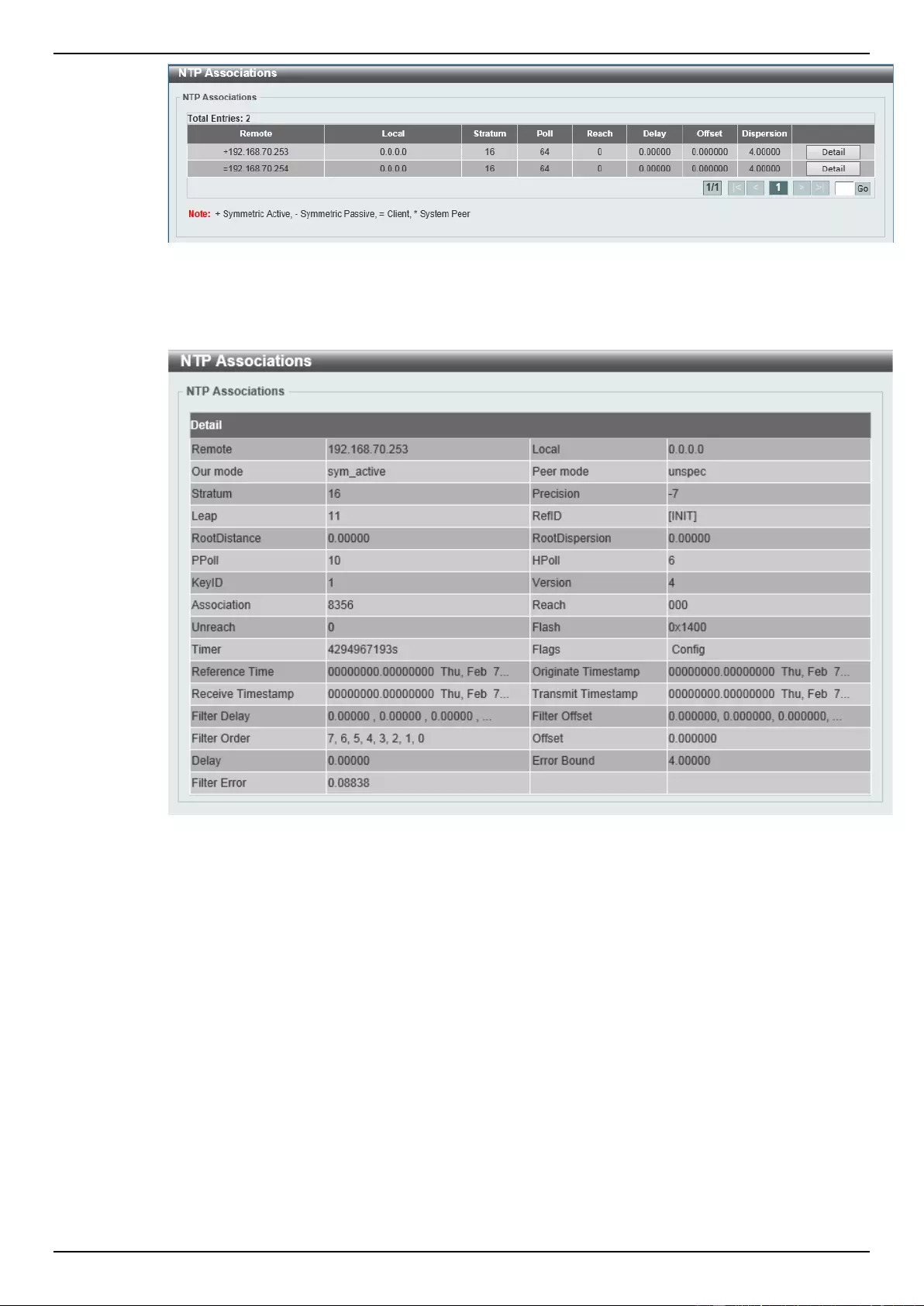
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
63
Figure 4-47 NTP Associations window
Click the Detail button, next to the specified entry, to view more information about the NTP
association, as shown below:
Figure 4-48 NTP Associations (Detail) window
NTP Status
This window is used to view NTP status information.
To view the following window, click Management > NTP > NTP Status, as shown below:
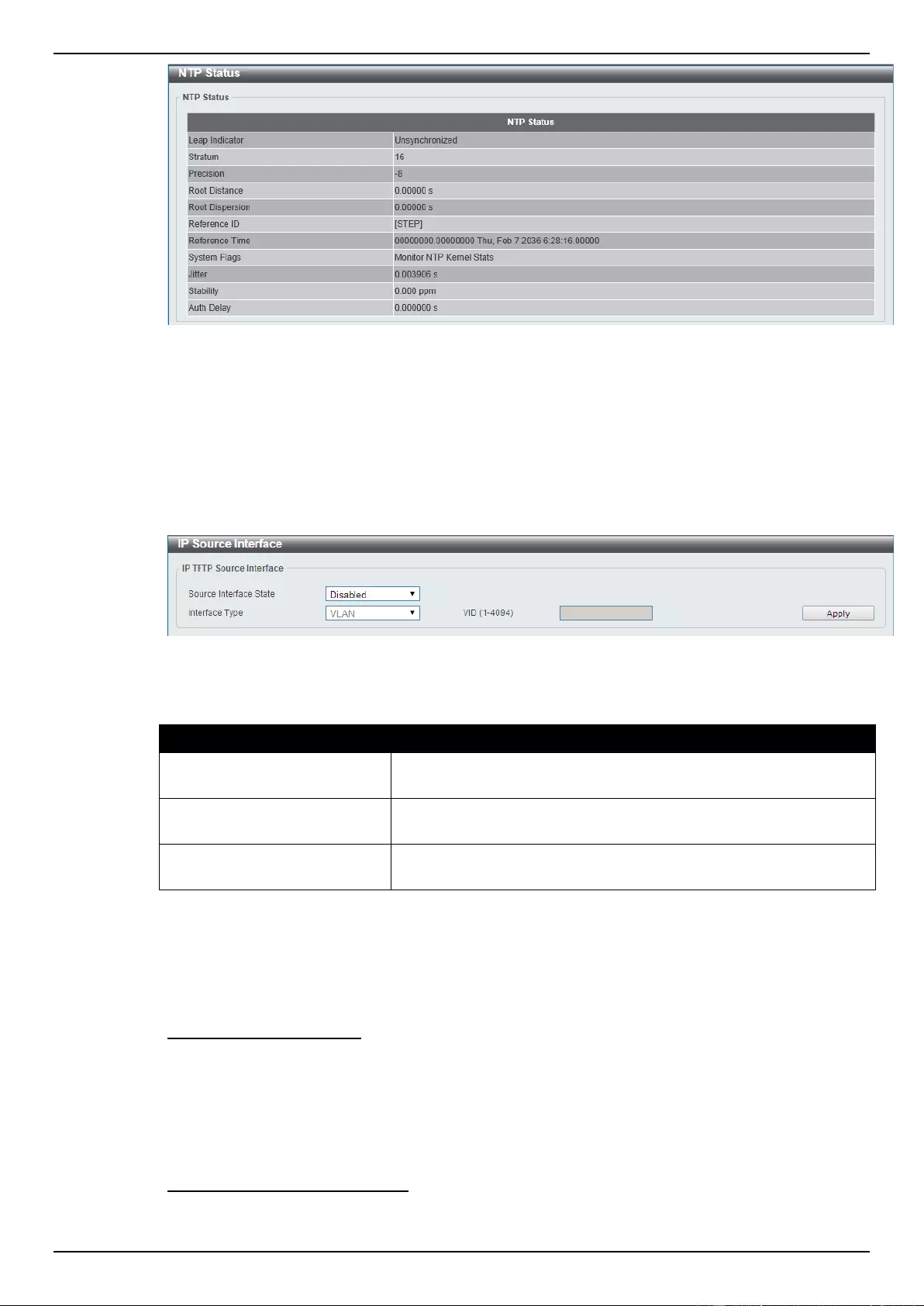
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
64
Figure 4-49 NTP Status window
IP Source Interface
This window is used to configure the IP source interface settings.
To view the following window, click Management > IP Source Interface, as shown below:
Figure 4-50 IP Source Interface window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source Interface State
Select to Enable or Disable the source interface feature’s global
state here.
Interface Type
After enabling the Source Interface State option, select the
interface type here. The only option available is VLAN.
VID (1-4094)
After selecting the VLAN as the Interface Type, enter the VLAN ID
used here. This value must be between 1 and 4094.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
File System
Why use flash file system:
In old switch system, the firmware, configuration and log information are saved in a flash with fixed
addresses and size. This means that the maximum configuration file can only be 2Mb, and even if the
current configuration is only 40Kb, it will still take up 2Mb of flash storage space. The configuration file
number and firmware numbers are also fixed. A compatible issue will occur in the event that the
configuration file or firmware size exceeds the originally designed size.
Flash File System in our system:
The Flash File System is used to provide the user with flexible file operation on the Flash. All the
firmware, configuration information and system log information are stored in the Flash as files. This
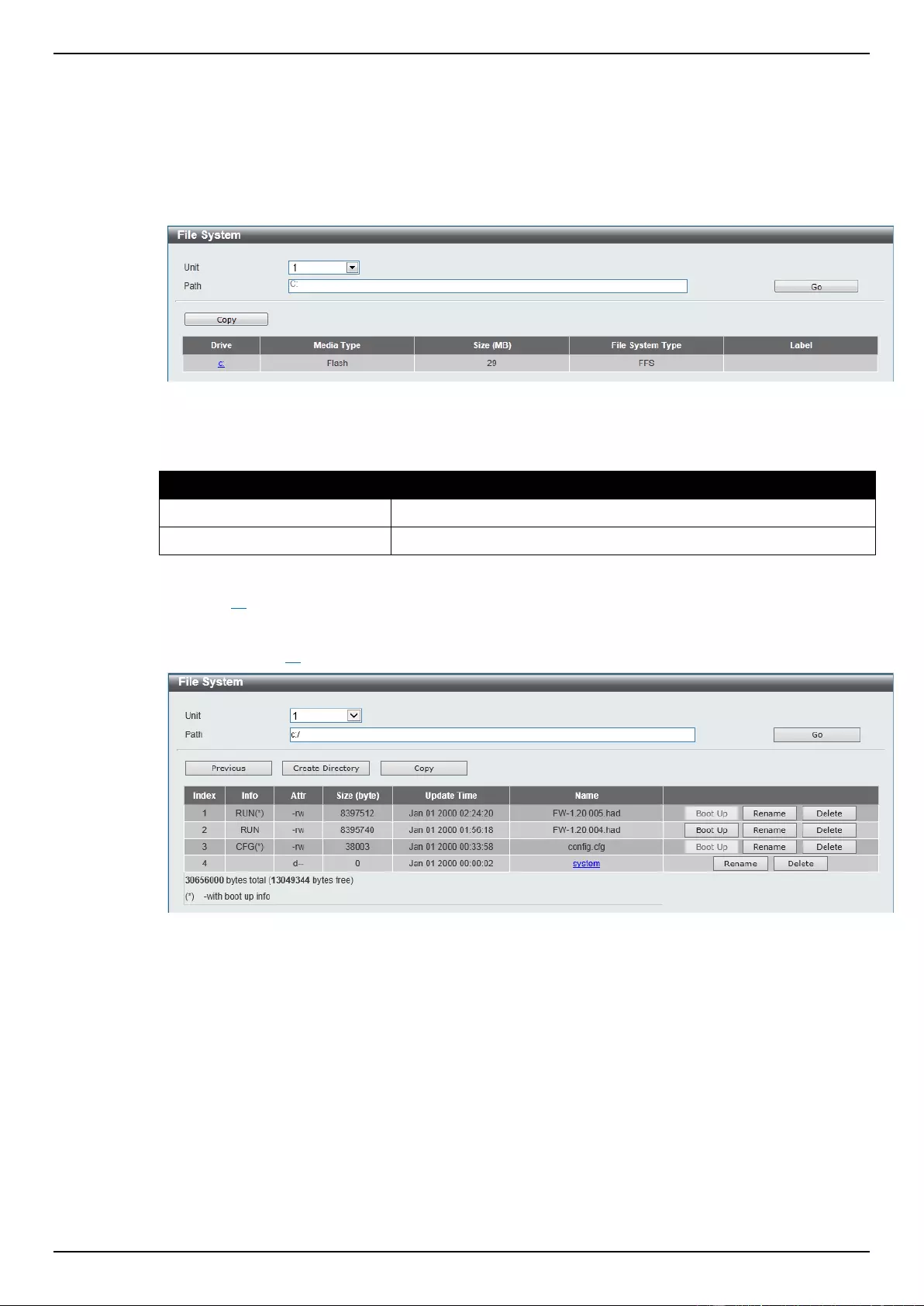
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
65
means that the Flash space taken up by all the files are not fixed, it is the real file size. If the Flash
space is enough, the user could download more configuration files or firmware files and use
commands to display Flash file information, rename file names, and delete it. Furthermore, the user
can also configure the boot up runtime image or the running configuration file if needed.
To view this window, click Management > File System as shown below:
Figure 4-51 File System window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Path
Enter the path string
Click the Go button to navigate to the path entered.
Click the C: hyperlink to navigate the C: drive.
After clicking the C: hyperlink, the following window will appear:
Figure 4-52 File System - Search for Drive window
Click the Previous button to return to the previous window.
Click the Create Directory button to create a new directory within the file system of the Switch.
Click the Copy button to copy a specific file to the Switch.
Click the Boot Up button to set a specific runtime image as the boot up image.
Click the Rename button to rename a specific file’s name.
Click the Delete button to remove a specific file from the file system.
Click the Copy button to see the following window.
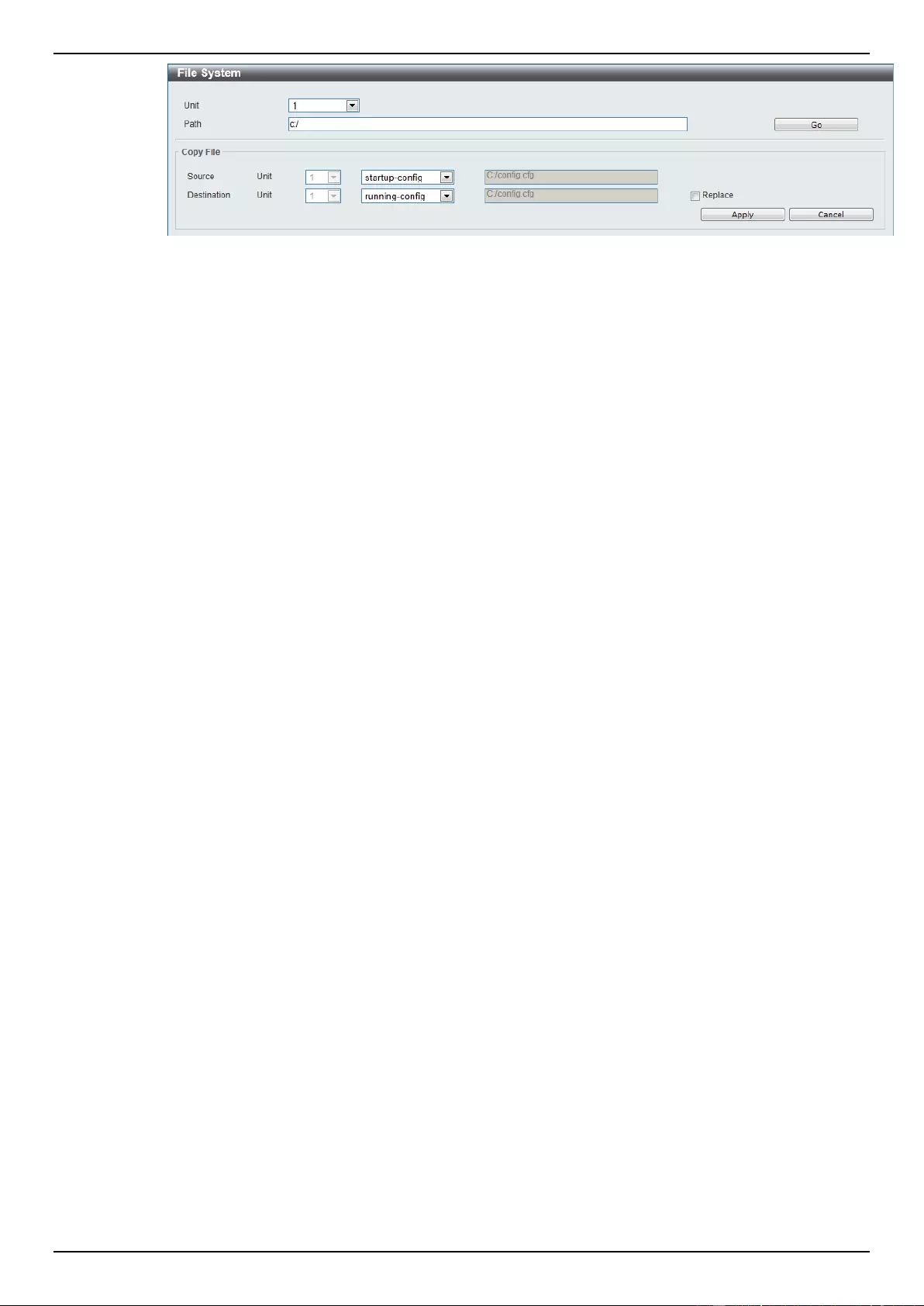
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
66
Figure 4-53 File System - Copy window
When copying a file to the file system of this switch, the user must enter the Source and Destination
path. Tick the Replace check box to replace the current running configuration with the indicated
configuration file.
Click the Apply button to initiate the copy.
Click the Cancel button the discard the process.
Physical Stacking
The Switch supports switch stacking, where a set of 6 switches can be combined to be managed by
one IP address through Telnet, the Web User Interface, the RJ45 console port, or through SNMP.
Each switch of this series has two stacking ports located at the front of the device, which can be used
to connect other devices and make them stack together. After adding these stacking ports, the user
may connect these ports together using fiber cables or Direct Attach Cables (DAC) in one of two
possible topologies.
Duplex Chain – As shown in Figure 4-54, The Duplex Chain topology stacks switches together in a
chain-link format. Using this method, data transfer is only possible in one direction and if there is a
break in the chain, then data transfer will obviously be affected.
Duplex Ring – As shown in Error! Reference source not found., the Duplex Ring stacks switches
n a ring or circle format where data can be transferred in two directions. This topology is very resilient
due to the fact that if there is a break in the ring, data can still be transferred through the stacking
cables between switches in the stack.
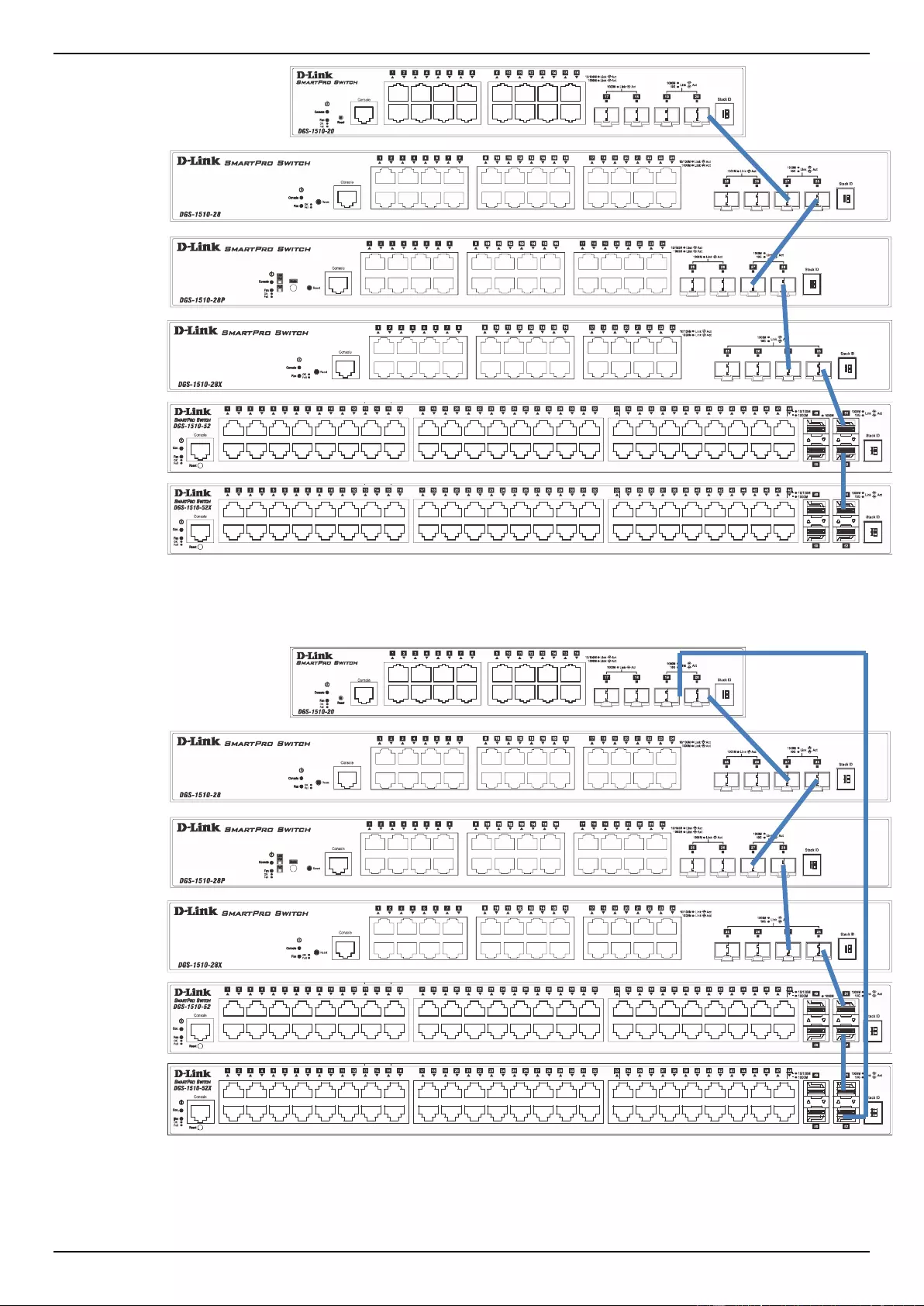
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
67
Figure 4-54 Switches stacked in a Duplex Chain
Figure 4-55 Switches stacked in a Duplex Ring

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
68
Within each of these topologies, each switch plays a role in the Switch stack. These roles can be set
by the user per individual Switch, or if desired, can be automatically determined by the Switch stack.
Three possible roles exist when stacking with the Switch.
Primary Master – The Primary Master is the leader of the stack. It will maintain normal operations,
monitor operations and the running topology of the Stack. This switch will also assign Stack Unit IDs,
synchronize configurations and transmit commands to remaining switches in the switch stack. The
Primary Master can be manually set by assigning this Switch the highest priority (a lower number
denotes a higher priority) before physically assembling the stack, or it can be determined
automatically by the stack through an election process which determines the lowest MAC address and
then will assign that switch as the Primary Master, if all priorities are the same. The Primary master
are physically displayed by the seven segment LED to the far right on the front panel of the switch
where this LED will flash between its given Box ID and ‘H’.
Backup Master – The Backup Master is the backup to the Primary Master, and will take over the
functions of the Primary Master if the Primary Master fails or is removed from the Stack. It also
monitors the status of neighboring switches in the stack, will perform commands assigned to it by the
Primary Master and will monitor the running status of the Primary Master. The Backup Master can be
set by the user by assigning this Switch the second highest priority before physically assembling the
stack, or it can be determined automatically by the stack through an election process which
determines the second lowest MAC address and then will assign that switch as the Backup Master, if
all priorities are the same. The Backup master are physically displayed by the seven segment LED to
the far right on the front panel of the switch where this LED will flash between its given Box ID and ‘h’.
Slave – Slave switches constitute the rest of the switch stack and although not Primary or Backup
Masters, they can be placed into these roles when these other two roles fail or are removed from the
stack. Slave switches perform operations requested by the master, monitor the status of neighbor
switches in the stack and the stack topology and adhere to the Backup Master’s commands once it
becomes a Primary Master. Slave switches will do a self-check to determine if it is to become the
Backup Master if the Backup Master is promoted to the Primary Master, or if the Backup Master fails
or is removed from the switch stack. If both Primary and Backup masters fail, or are removed from the
Switch stack, it will determine if it is to become the Primary Master. These roles will be determined,
first by priority and if the priority is the same, the lowest MAC address.
Once switches have been assembled in the topology desired by the user and powered on, the stack
will undergo three processes until it reaches a functioning state.
Initialization State – This is the first state of the stack, where the runtime codes are set and initialized
and the system conducts a peripheral diagnosis to determine each individual switch is functioning
properly.
Master Election State – Once the codes are loaded and initialized, the stack will undergo the Master
Election State where it will discover the type of topology used, elect a Primary Master and then a
Backup Master.
Synchronization State – Once the Primary Master and the Backup Master have been established,
the Primary Master will assign Stacking Unit IDs to switches in the stack, synchronize configurations
for all switches and then transmit commands to the rest of the switches based on the users
configurations of the Primary Master.
Once these steps have been completed, the switch stack will enter a normal operating mode.
Stack Switch Swapping
The stacking feature of the Switch supports “hot swapping” of switches in and out of the running stack.
Users may remove or add switches to the stack without powering down or largely affecting the
transfer of data between switches in the stack, with a few minor provisions.
When switches are “hot inserted” into the running stack, the new switch may take on the Primary
Master, Backup Master or Slave role, depending on configurations set on the newly added switch,
such as configured priority or MAC address. Yet, if adding two stacks together that have both
previously undergone the election process, and therefore both have a Primary Master and a Backup
master, a new Primary Master will be elected from one of the already existing Primary Masters, based
on priority or MAC address. This Primary Master will take over all of the Primary Master’s roles for all
new switches that were hot inserted. This process is done using discovery packets that circulate
through the switch stack every 1.5 seconds until the discovery process has been completed.
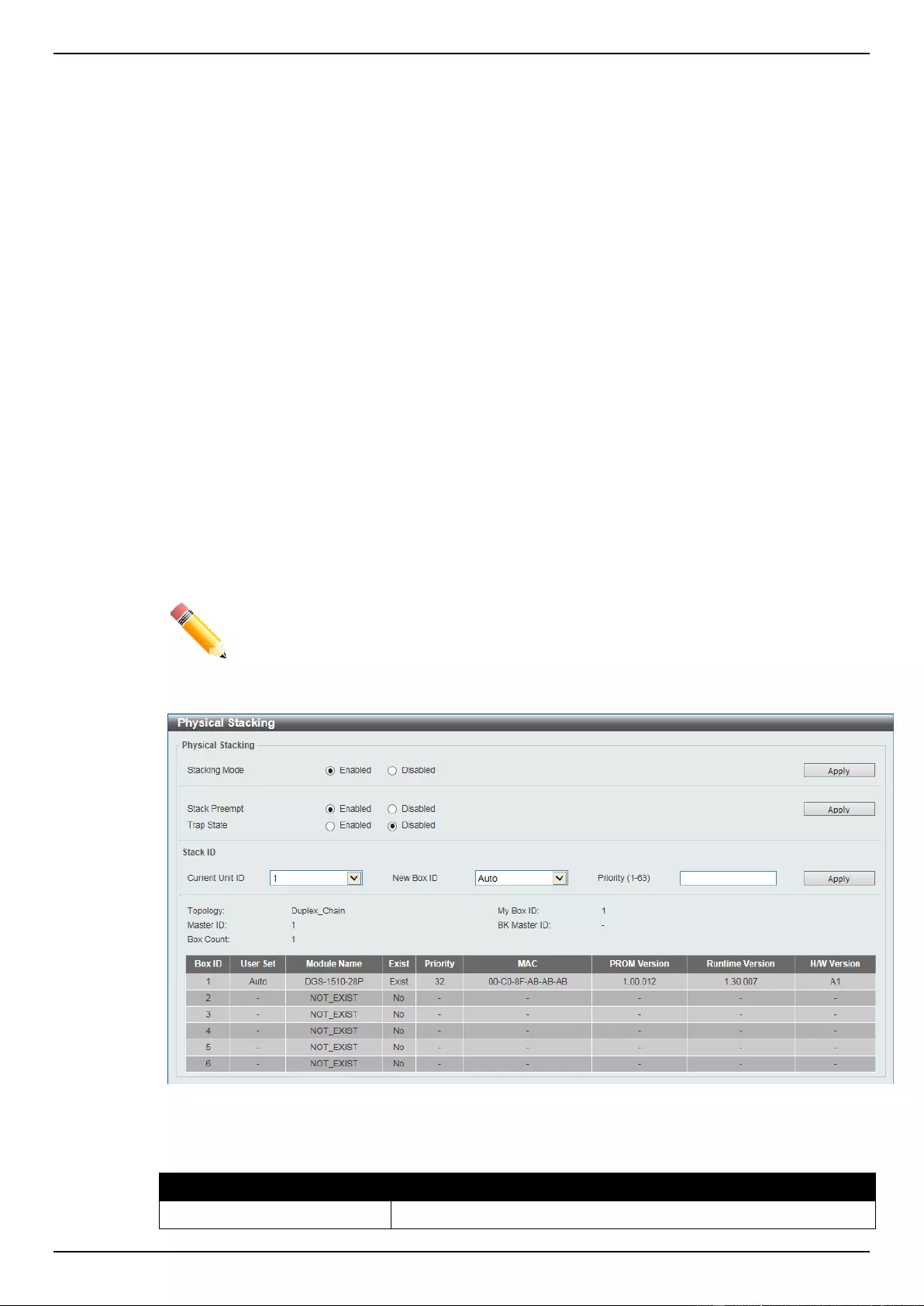
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
69
The “hot remove” action means removing a device from the stack while the stack is still running. The
hot removal is detected by the stack when it fails to receive heartbeat packets during its specified
interval from a device, or when one of the stacking ports links is down. Once the device has been
removed, the remaining switches will update their stacking topology database to reflect the change.
Any one of the three roles, Primary Master, Backup Master or Slave, may be removed from the stack,
yet different processes occur for each specific device removal.
If a Slave device has been removed, the Primary Master will inform other switches of the hot remove
of this device through the use of unit leave messages. Switches in the stack will clear the
configurations of the unit removed, and dynamically learned databases, such as ARP, will be cleared
as well.
If the Backup Master has been hot removed, a new Backup Master will be chosen through the
election process previously described. Switches in the stack will clear the configurations of the unit
removed, and dynamically learned databases, such as ARP, will be cleared as well. Then the Backup
Master will begin backing up the Primary Master when the database synchronization has been
completed by the stack.
If the Primary Master is removed, the Backup Master will assume the Primary Master’s role and a new
Backup Master will be chosen using the election process. Switches in the stack will clear the
configurations of the unit removed, and dynamically learned databases, such as ARP, will be cleared
as well. The new Primary Master will inherit the MAC and IP address of the previous Primary Master
to avoid conflict within the stack and the network itself.
If both the Primary Master and the Backup Master are removed, the election process is immediately
processed, and a new Primary Master and Backup Master are determined. Switches in the stack will
clear the configurations of the units removed, and dynamically learned databases, such as ARP, will
be cleared as well. Static switch configurations still remain in the database of the remaining switches
in the stack and those functions will not be affected.
NOTE: If there is a Box ID conflict when the stack is in the discovery phase, the device will
enter a special standalone topology mode. Users can only get device information,
configure Box IDs, save and reboot. All stacking ports will be disabled and an error
message will be produced on the local console port of each device in the stack.
Users must reconfigure Box IDs and reboot the stack.
Figure 4-56 Physical Stacking window
The fields that can be configured for Physical Stacking are described below:
Parameter
Description
Stacking Mode
Select this option to enable or disable the stacking mode.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
70
Stack Preempt
Select this option to enable or disable preemption of the master role
to come into play when a unit with a better priority is added to the
Switch later.
Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable sending of stacking related
traps.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Stack ID are described below:
Parameter
Description
Current Unit ID
Select the unit ID of the switch in the stack.
New Box ID
Select the new box ID for the switch that is selected in the Current
Unit ID. The user may choose any number between 1 and 6 to
identify the switch in the switch stack. Auto will automatically assign
a box number to the switch in the switch stack.
Priority
Enter the priority of the switch stacking unit. The range is from 1 to
63.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Virtual Stacking (SIM)
D-Link Single IP Management (SIM) is a concept that will stack switches together over Ethernet
instead of using stacking ports or modules. There are some advantages in implementing the Single IP
Management feature:
1. SIM can simplify management of small workgroups or wiring closets while scaling the network to
handle increased bandwidth demand.
2. SIM can reduce the number of IP address needed in your network.
3. SIM can eliminate any specialized cables for stacking connectivity and remove the distance
barriers that typically limit your topology options when using other stacking technology.
Switches using D-Link Single IP Management (labeled here as SIM) must conform to the following
rules:
SIM is an optional feature on the Switch and can easily be enabled or disabled through the
Command Line Interface or Web Interface. SIM grouping has no effect on the normal operation of
the Switch in the user’s network.
There are three classifications for switches using SIM. The Commander Switch (CS), which is
the master switch of the group, Member Switch (MS), which is a switch that is recognized by the
CS a member of a SIM group, and a Candidate Switch (CaS), which is a Switch that has a
physical link to the SIM group but has not been recognized by the CS as a member of the SIM
group.
A SIM group can only have one Commander Switch (CS).
A SIM group accepts up to 32 switches (numbered 1-32), not including the Commander Switch
(numbered 0).
Members of a SIM group cannot cross a router.
There is no limit to the number of SIM groups in the same IP subnet (broadcast domain);
however a single switch can only belong to one group.
If multiple VLANs are configured, the SIM group will only utilize the management VLAN on any
switch.
SIM allows intermediate devices that do not support SIM. This enables the user to manage
switches that are more than one hop away from the CS.
The SIM group is a group of switches that are managed as a single entity. The Switch may take on
three different roles:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
71
1. Commander Switch (CS) – This is a switch that has been manually configured as the controlling
device for a group, and takes on the following characteristics:
a. It has an IP Address.
b. It is not a command switch or member switch of another Single IP group.
c. It is connected to the member switches through its management VLAN.
2. Member Switch (MS) – This is a switch that has joined a single IP group and is accessible from
the CS, and it takes on the following characteristics:
a. It is not a CS or MS of another IP group.
b. It is connected to the CS through the CS management VLAN.
3. Candidate Switch (CaS) – This is a switch that is ready to join a SIM group but is not yet a
member of the SIM group. The Candidate Switch may join the SIM group of the Switch by
manually configuring it to be a MS of a SIM group. A switch configured as a CaS is not a member
of a SIM group and will take on the following characteristics:
a. It is not a CS or MS of another Single IP group.
b. It is connected to the CS through the CS management VLAN
The following rules also apply to the above roles:
Each device begins in a Candidate state.
A CS must change its role to CaS and then to MS, to become a MS of a SIM group. Thus, the CS
cannot directly be converted to a MS.
The user can manually configure a CS to become a CaS.
A MS can become a CaS by:
o Being configured as a CaS through the CS.
o If report packets from the CS to the MS time out.
The user can manually configure a CaS to become a CS
The CaS can be configured through the CS to become a MS.
After configuring one switch to operate as the CS of a SIM group, additional DGS-1510 Series
switches may join the group by manually configuring the Switch to be a MS. The CS will then serve as
the in band entry point for access to the MS. The CS’s IP address will become the path to all MS’s of
the group and the CS’s Administrator’s password, and/or authentication will control access to all MS’s
of the SIM group.
With SIM enabled, the applications in the CS will redirect the packet instead of executing the packets.
The applications will decode the packet from the administrator, modify some data, and then send it to
the MS. After execution, the CS may receive a response packet from the MS, which it will encode and
send it back to the administrator.
When a CaS becomes a MS, it automatically becomes a member of the first SNMP community
(includes read/write and read only) to which the CS belongs. However, if a MS has its own IP address,
it can belong to SNMP communities to which other switches in the group, including the CS, do not
belong.
Upgrade to v1.61
To better improve SIM management, the DGS-1510 Series switches have been upgraded to version
1.61 in this release. Many improvements have been made, including:
1. The Commander Switch (CS) now has the capability to automatically rediscover member
switches that have left the SIM group, either through a reboot or web malfunction. This feature is
accomplished through the use of Discover packets and Maintenance packets that previously set
SIM members will emit after a reboot. Once a MS has had its MAC address and password saved
to the CS’s database, if a reboot occurs in the MS, the CS will keep this MS information in its
database and when a MS has been rediscovered, it will add the MS back into the SIM tree
automatically. No configuration will be necessary to rediscover these switches.
There are some instances where pre-saved MS switches cannot be rediscovered. For example, if the
Switch is still powered down, if it has become the member of another group, or if it has been
configured to be a Commander Switch, the rediscovery process cannot occur.
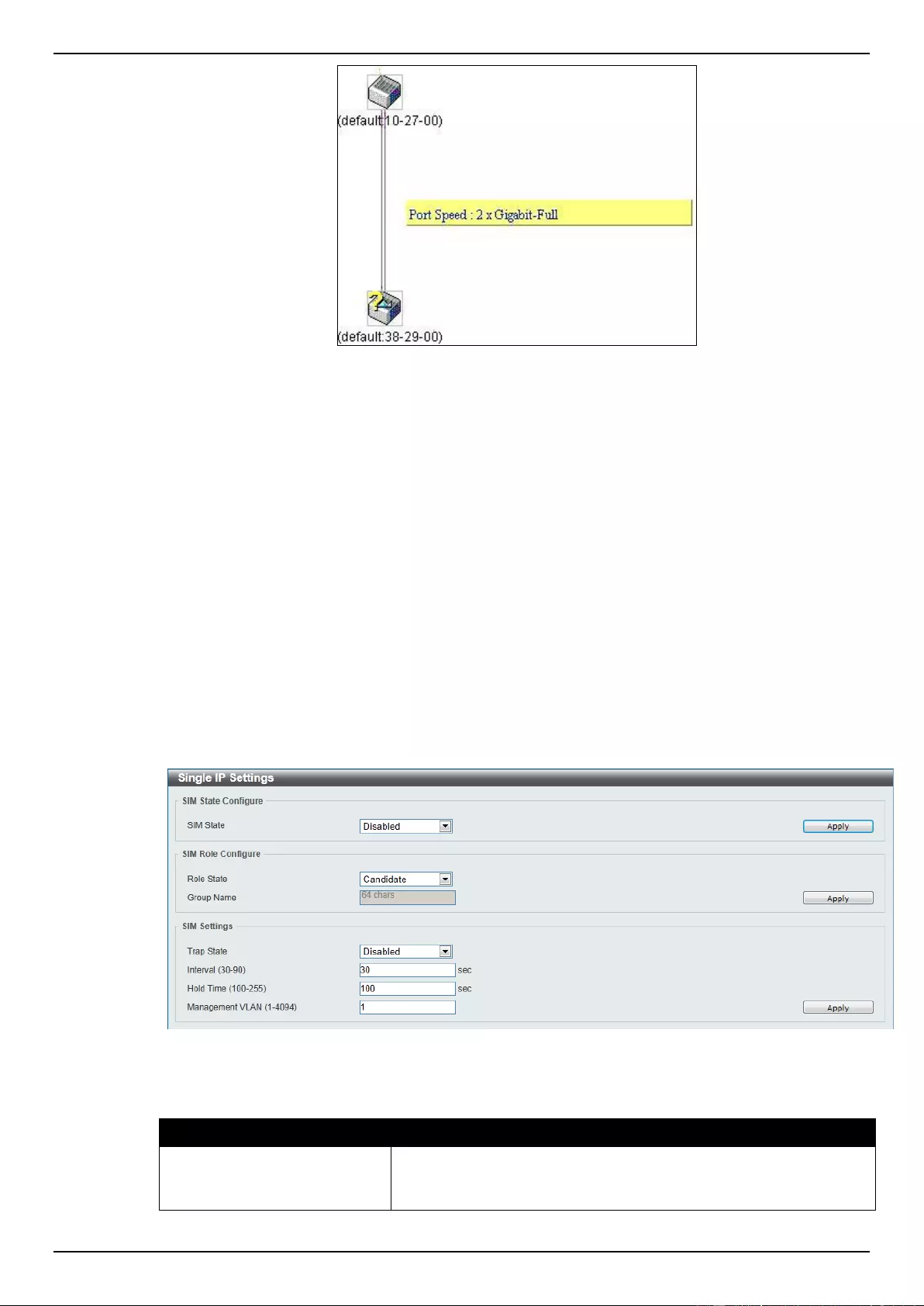
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
72
2. The topology map now includes new features for connections that are a member of a port
trunking group. It will display the speed and number of Ethernet connections creating this port
trunk group, as shown in the adjacent picture.
3. This version will support switch upload and downloads for firmware, configuration files and log
files, as follows:
a. Firmware – The switch now supports MS firmware downloads from a TFTP server.
b. Configuration Files – This switch now supports downloading and uploading of configuration
files both to (for configuration restoration) and from (for configuration backup) MS’s, using a
TFTP server.
c. Log – The Switch now supports uploading MS log files to a TFTP server.
4. The user may zoom in and zoom out when utilizing the topology window to get a better, more
defined view of the configurations.
Single IP Settings
This window is used to configure the SIM settings. The Switch is set as a Candidate (CaS) as the
factory default configuration and Single IP Management is disabled.
To view the following window, click Management > Virtual Stacking (SIM) > Single IP Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 4-57 Single IP Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SIM State Configure are described below:
Parameter
Description
SIM State
Select this option to enable or disable the SIM state on the Switch.
Select Disabled to render all SIM functions on the Switch
inoperable.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
73
The fields that can be configured for SIM Role Configure are described below:
Parameter
Description
Role State
Select to change the SIM role of the Switch. Options to choose from
are Candidate, and Commander.
Candidate - A Candidate Switch (CaS) is not the member of a SIM
group but is connected to a Commander Switch. This is the default
setting for the SIM role of the Switch.
Commander – Select to make the Switch a Commander Switch
(CS). The user may join other switches to this Switch, over
Ethernet, to be part of its SIM group. Choosing this option will also
enable the Switch to be configured for SIM.
Group Name
Enter a group name. This is optional. This name is used to segment
switches into different SIM groups.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for SIM Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Traps State
Select to enable or disable the SIM trap state.
Interval
Enter the interval in seconds. The range is from 30 to 90.
Hold Time
Enter the hold-time in seconds. The range is from 100 to255.
Management VLAN
Enter the single IP management message VLAN ID.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After enabling the Switch to be a Commander Switch (CS), the Single IP Management folder will
then contain four added links to aid the user in configuring SIM through the web, including Topology,
Firmware Upgrade, Configuration Backup/Restore and Upload Log File.
Topology
This window is used to configure and manage the Switch within the SIM group and requires Java
script to function properly on your computer.
To view the following window, click Management > Virtual Stacking (SIM) > Topology, as shown
below:
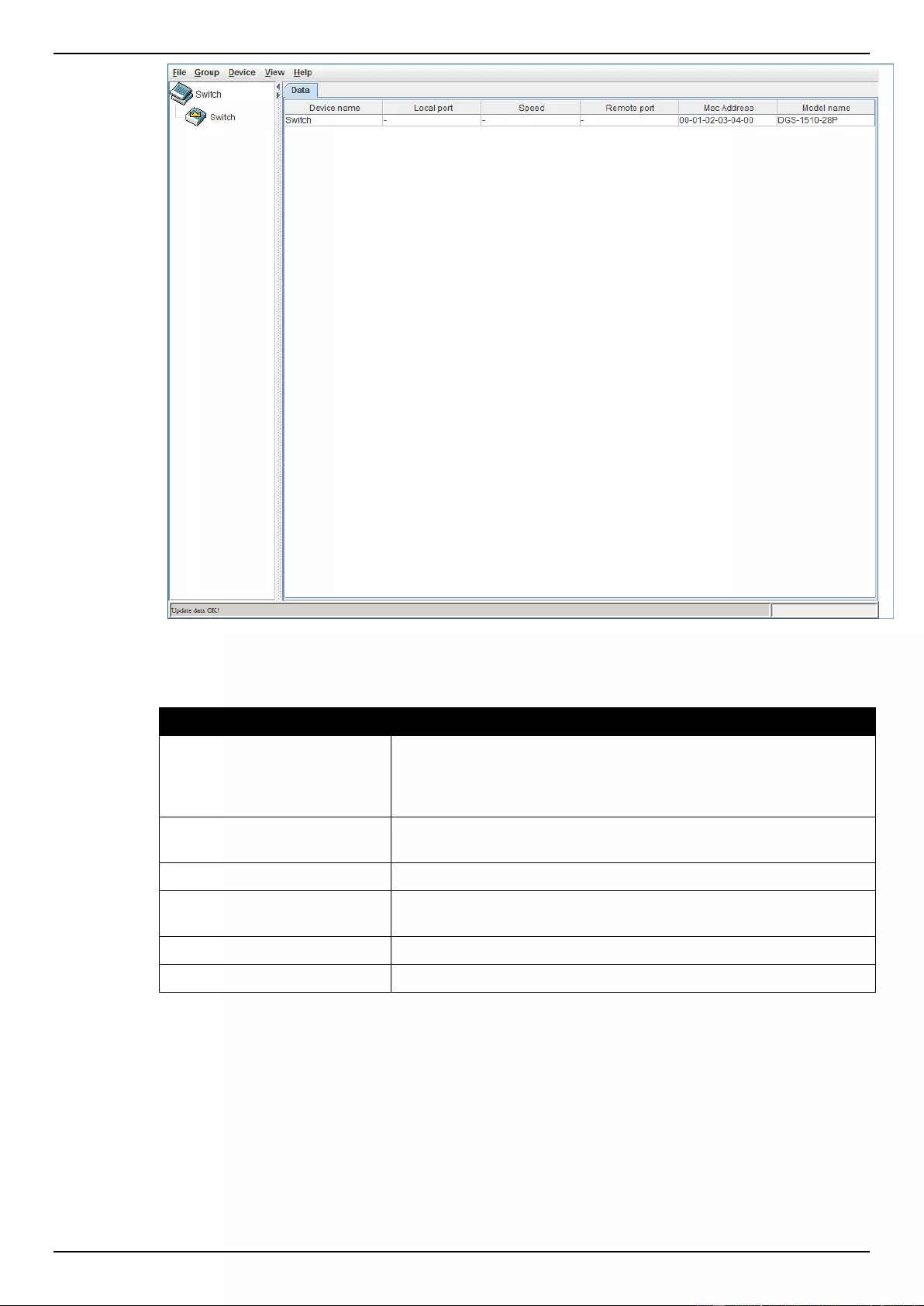
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
74
Figure 4-58 Single IP Management window - Tree View
The fields that can be displayed are described below:
Parameter
Description
Device Name
Display the Device Name of the switches in the SIM group
configured by the user. If no device is configured by the name, it will
be given the name default and tagged with the last six digits of the
MAC Address to identify it.
Local Port
Display the number of the physical port on the CS that the MS or
CaS is connected to. The CS will have no entry in this field.
Speed
Display the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS.
Remote Port
Display the number of the physical port on the MS or CaS to which
the CS is connected. The CS will have no entry in this field.
MAC Address
Display the MAC Address of the corresponding Switch.
Model Name
Display the full Model Name of the corresponding Switch.
To view the Topology View window, open the View drop-down menu in the toolbar and then click
Topology, which will open the following Topology Map. This window will refresh itself periodically (20
seconds by default).
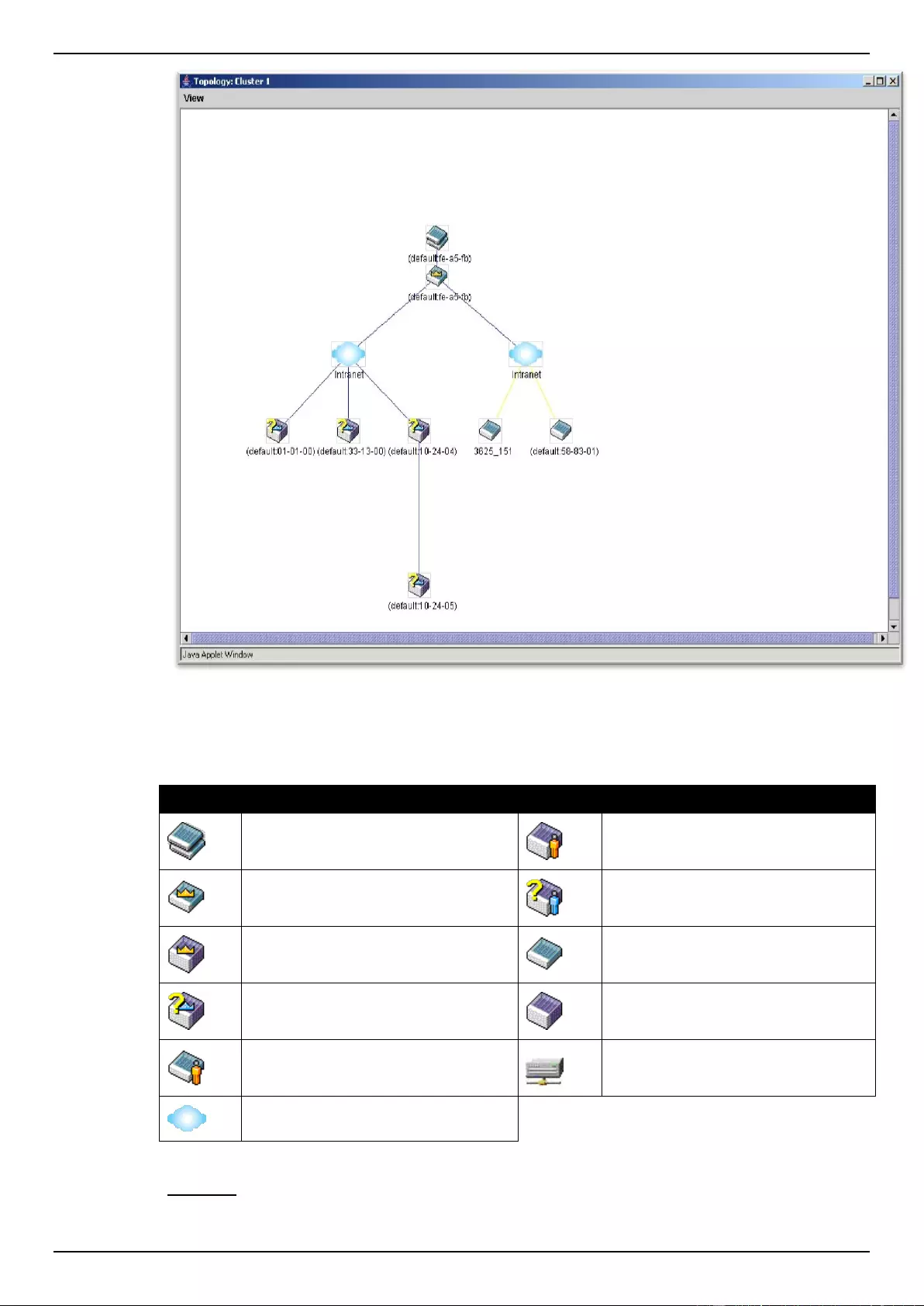
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
75
Figure 4-59 Topology view
This window will display how the devices within the Single IP Management Group connect to other
groups and devices. Possible icons on this window are as follows:
Icon
Description
Icon
Description
Group
Layer 3 member switch
Layer 2 commander switch
Member switch of other group
Layer 3 commander switch
Layer 2 candidate switch
Commander switch of other group
Layer 3 candidate switch
Layer 2 member switch
Unknown device
Non-SIM devices
Tool Tips
In the Topology view window, the mouse plays an important role in configuration and in viewing
device information. Setting the mouse cursor over a specific device in the topology window (tool tip)
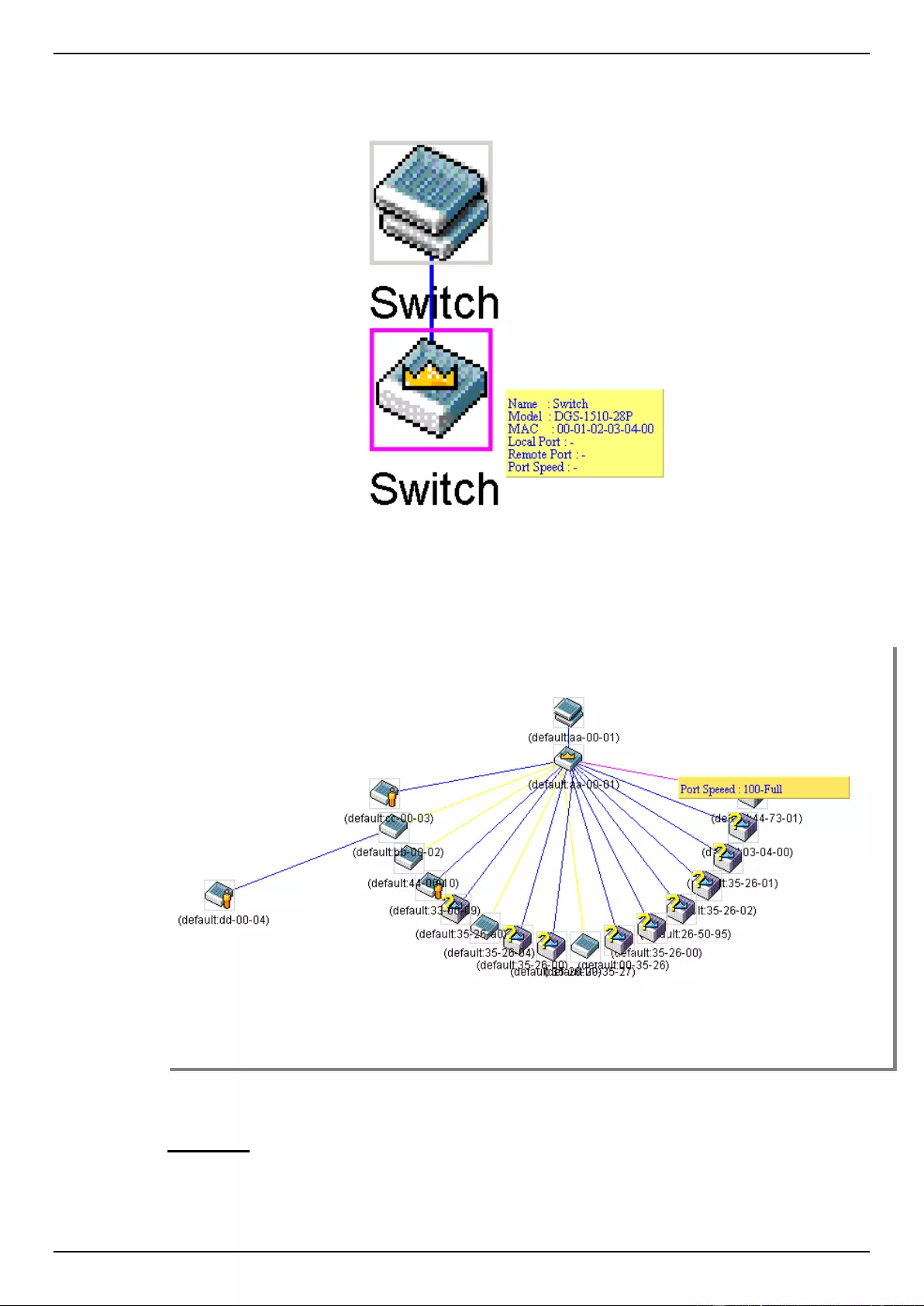
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
76
will display the same information about a specific device as the Tree view does. See the window
below for an example.
Figure 4-60 Device Information Utilizing the Tool Tip
Setting the mouse cursor over a line between two devices will display the connection speed between
the two devices, as shown below.
Figure 4-61 Port Speed Utilizing the Tool Tip
Right-Click
Right-clicking on a device will allow the user to perform various functions, depending on the role of the
Switch in the SIM group and the icon associated with it.
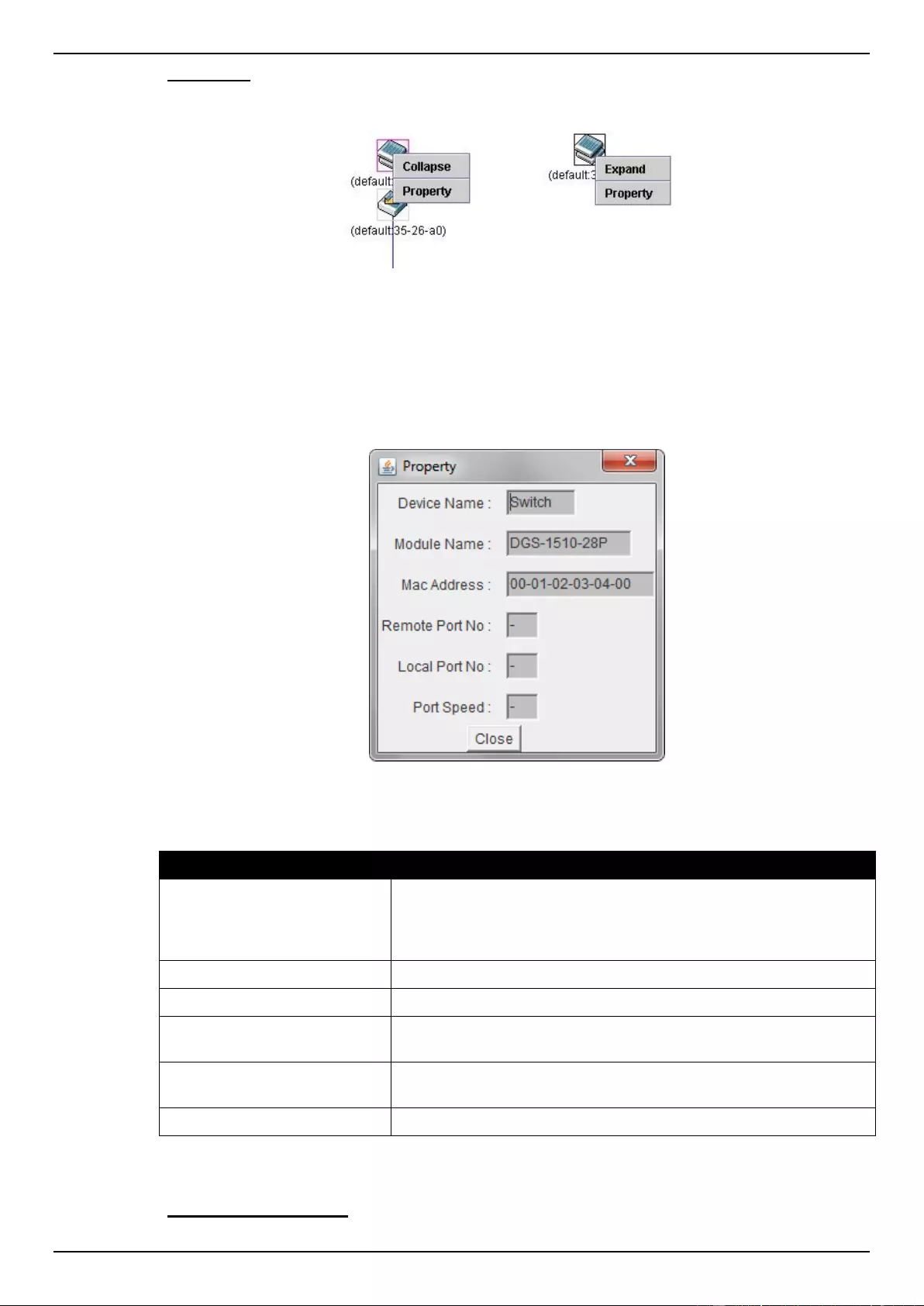
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
77
Group Icon
Figure 4-62 Right-Clicking a Group Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse - To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
Expand - To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Property - To pop up a window to display the group information.
Figure 4-63 Property window
The fields that can be displayed are described below:
Parameter
Description
Device Name
Display the Device Name of the switches in the SIM group
configured by the user. If no Device Name is configured by the
name, it will be given the name default and tagged with the last six
digits of the MAC Address to identify it.
Module Name
Display the full module name of the switch that was right-clicked.
MAC Address
Display the MAC Address of the corresponding Switch.
Remote Port No
Display the number of the physical port on the MS or CaS that the
CS is connected to. The CS will have no entry in this field.
Local Port No
Display the number of the physical port on the CS that the MS or
CaS is connected to. The CS will have no entry in this field.
Port Speed
Display the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS.
Click the Close button to close the property window.
Commander Switch Icon
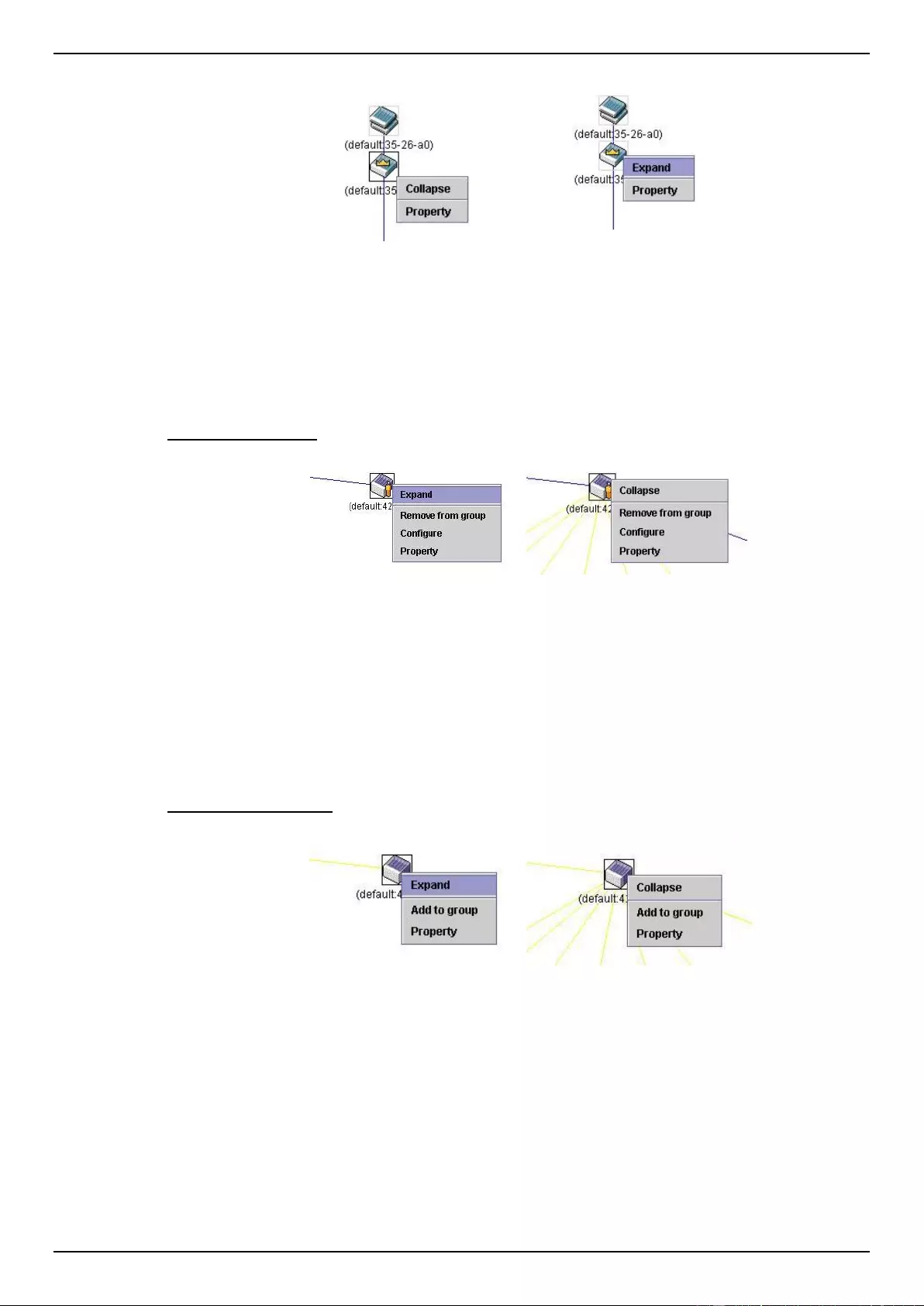
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
78
Figure 4-64 Right-clicking a Commander Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse - To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
Expand - To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Property - To pop up a window to display the group information.
Member Switch Icon
Figure 4-65 Right-clicking a Member icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse - To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
Expand - To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Remove from group - Remove a member from a group.
Configure - Launch the web management to configure the Switch.
Property - To pop up a window to display the device information.
Candidate Switch Icon
Figure 4-66 Right-clicking a Candidate icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
Collapse - To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
Expand - To expand the SIM group, in detail.
Add to group - Add a candidate to a group. Clicking this option will reveal the following dialog
box for the user to enter a password for authentication from the Candidate Switch before
being added to the SIM group. Click OK to enter the password or Cancel to exit the dialog
box.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
79
Figure 4-67 Input password window
Property - To pop up a window to display the device information.
Menu Bar
The Single IP Management window contains a menu bar for device configurations, as seen below.
Figure 4-68 Menu Bar of the Topology View
File
Print Setup - Will view the image to be printed.
Print Topology - Will print the topology map.
Preference - Will set display properties, such as polling interval, and the views to open at SIM
startup.
Group
Add to group - Add a candidate to a group. Clicking this option will reveal the following dialog
box for the user to enter a password for authentication from the Candidate Switch before
being added to the SIM group. Click OK to enter the password or Cancel to exit the dialog
box.
Figure 4-69 Input password window
Remove from group - Remove an MS from the group.
Device
Configure - Will open the Web manager for the specific device.
View
Refresh - Update the views with the latest status.
Topology - Display the Topology view.
Help
About - Will display the SIM information, including the current SIM version.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
80
Figure 4-70 About window
Firmware Upgrade
This window is used to upgrade firmware from the Commander Switch to the Member Switch.
Member Switches will be listed in the table
To view the following window, click Management > Virtual Stacking (SIM) > Firmware Upgrade, as
shown below:
Figure 4-71 Firmware Upgrade window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server IP address.
Path\Filename
Enter the path and file name.
Click the Download button to update the firmware.
To specify a certain Switch for firmware download, tick its corresponding check box.
Configuration File Backup/Restore
This window is used to upgrade configuration files from the Commander Switch to the Member Switch
using a TFTP server. Member Switches will be listed in the table.
To view the following window, click Management > Virtual Stacking (SIM) > Configuration File
Backup/Restore, as shown below:
Figure 4-72 Configuration File Backup/Restore window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
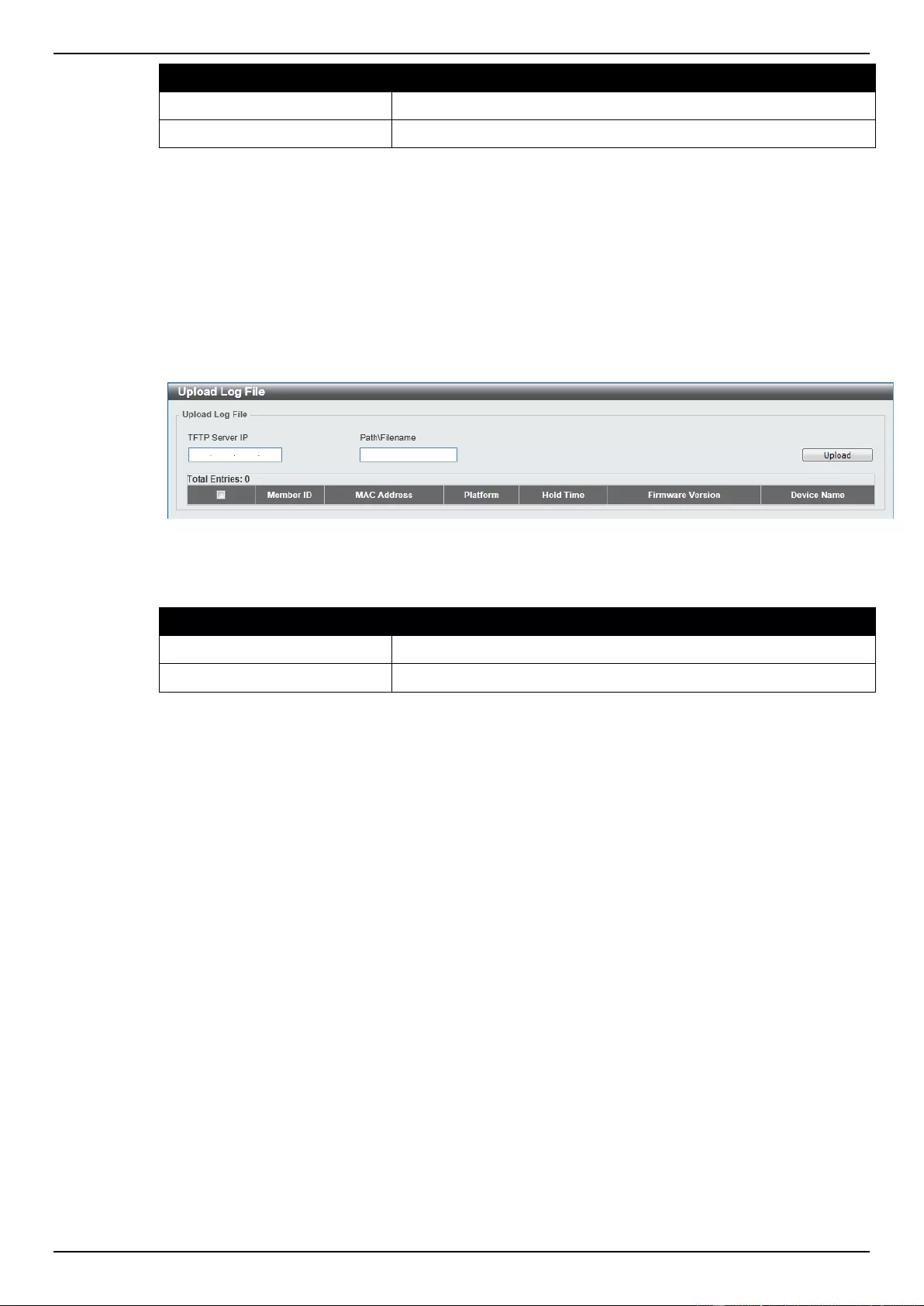
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
81
Parameter
Description
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server IP address.
Path\Filename
Enter the path and file name.
Click the Restore button to update the configuration from a TFTP server to the member switch.
Click the Backup button to back up the configuration file to a TFTP server.
Upload Log File
This window is used to upload log files from SIM member switches to a specified PC.
To view the following window, click Management > Virtual Stacking (SIM) > Upload Log File, as
shown below:
Figure 4-73 Upload Log File window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server IP address.
Path\Filename
Enter the path and file name.
Click the Upload button to initiate the file transfer.
D-Link Discovery Protocol
This window is used to configure and display D-Link Discovery Protocol (DDP).
To view the following window, click Management > D-Link Discovery Protocol, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
82
Figure 4-74 D-Link Discovery Protocol window
The fields that can be configured for D-Link Discovery Protocol are described below:
Parameter
Description
D-Link Discovery Protocol
State
Select this option to enable or disable DDP global state.
Report Timer
Select the interval in seconds between two consecutive DDP report
messages. Options to choose from are 30, 60, 90,120, and Never.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for DDP Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable DDP port state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
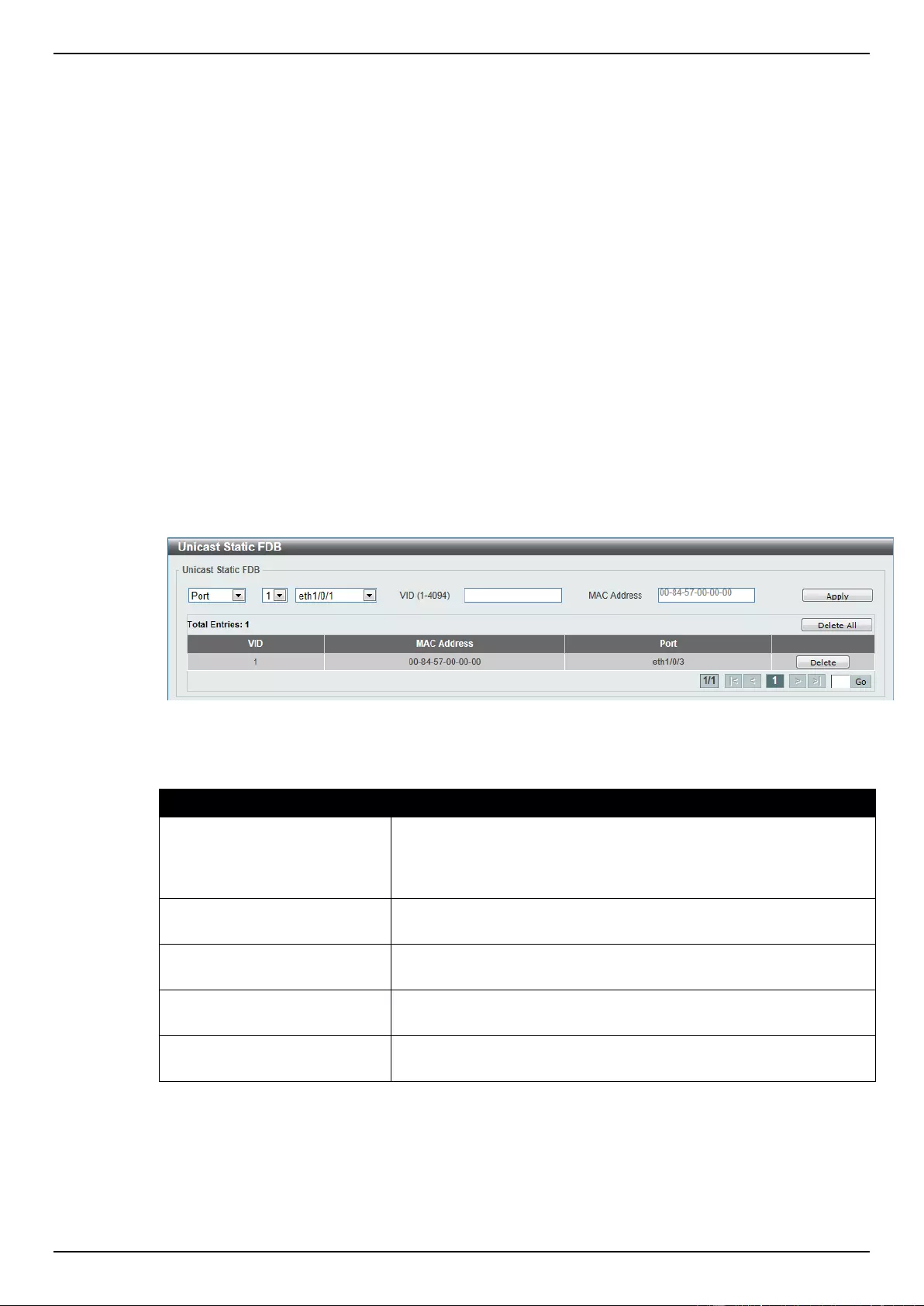
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
83
5. Layer 2 Features
FDB
VLAN
Spanning Tree
ERPS (G.8032)
Loopback Detection
Link Aggregation
L2 Multicast Control
LLDP
FDB
Static FDB
Unicast Static FDB
This window is used to view and configure the static unicast forwarding settings on the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > Static FDB > Unicast Static FDB, as
shown below:
Figure 5-1 Unicast Static FDB window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Port / Drop
Allows the selection of the port number on which the MAC address
entered resides. This option could also drop the MAC address from
the unicast static FDB. When selecting Port, select the switch unit
and port number.
Unit Number
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here,
when Port is selected in the previous drop-down list.
Port Number
Select the port number used here, when Port is selected in the
previous drop-down list.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID on which the associated unicast MAC address
resides.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address to which packets will be statically forwarded
or dropped. This must be a unicast MAC address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete All button to delete all the entries found in the display table.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
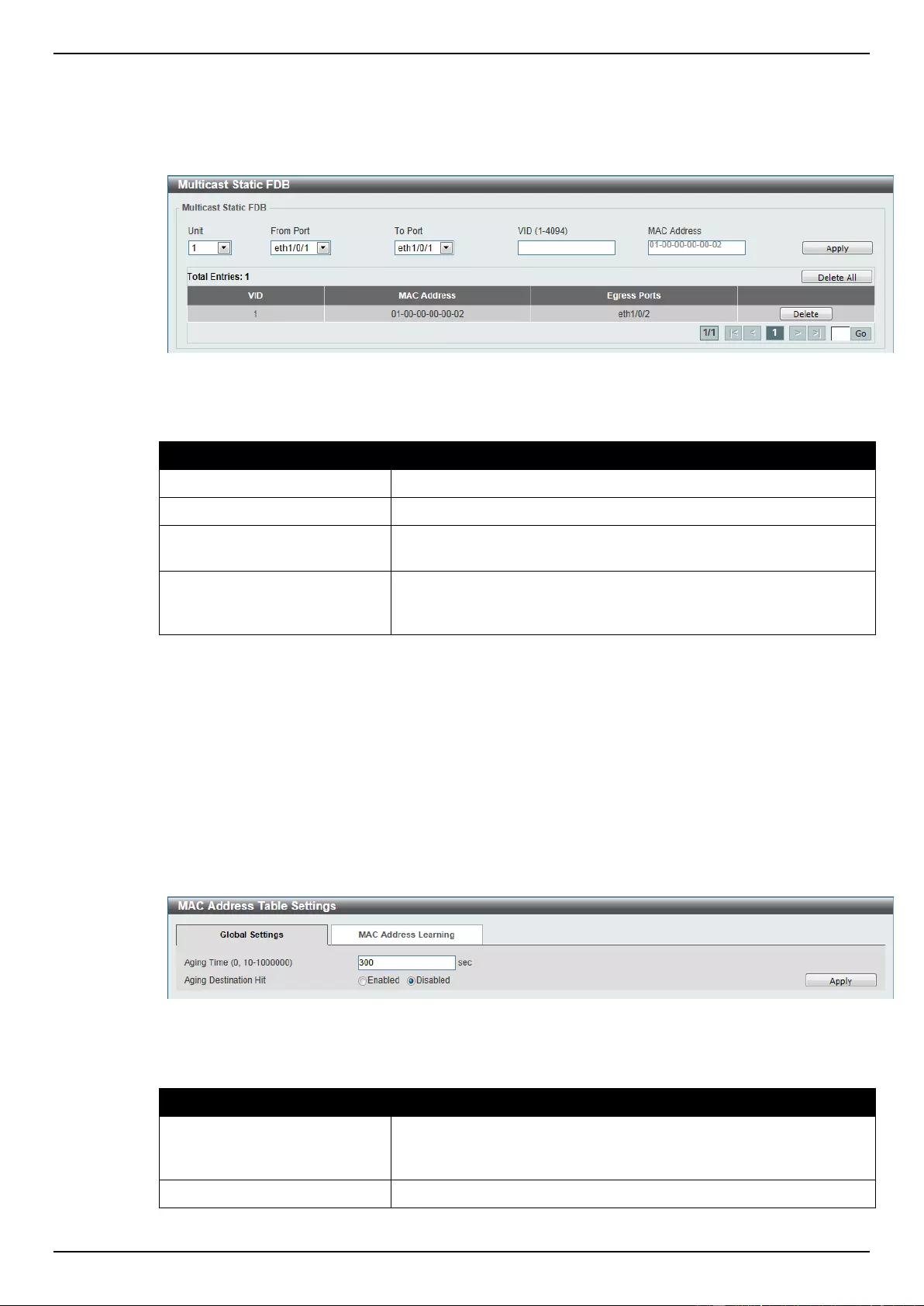
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
84
Multicast Static FDB
This window is used to view and configure the multicast static FDB settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > Static FDB > Multicast Static FDB, as
shown below:
Figure 5-2 Multicast Static FDB window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID of the VLAN the corresponding MAC address
belongs to.
MAC Address
Enter the static destination MAC address of the multicast packets.
This must be a multicast MAC address. The format of the
destination MAC address is 01-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete All button to remove all the entries.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
MAC Address Table Settings
This window is used to view and configure the MAC address table’s global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > MAC Address Table Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 5-3 MAC Address Table Settings (Global Settings) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Aging Time
Enter the MAC address table’s aging time value here. This value
must be between 10 and 1000000 seconds. Entering 0 will disable
MAC address aging. By default, this value is 300 seconds.
Aging Destination Hit
Select to enable or disable the aging destination hit function.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
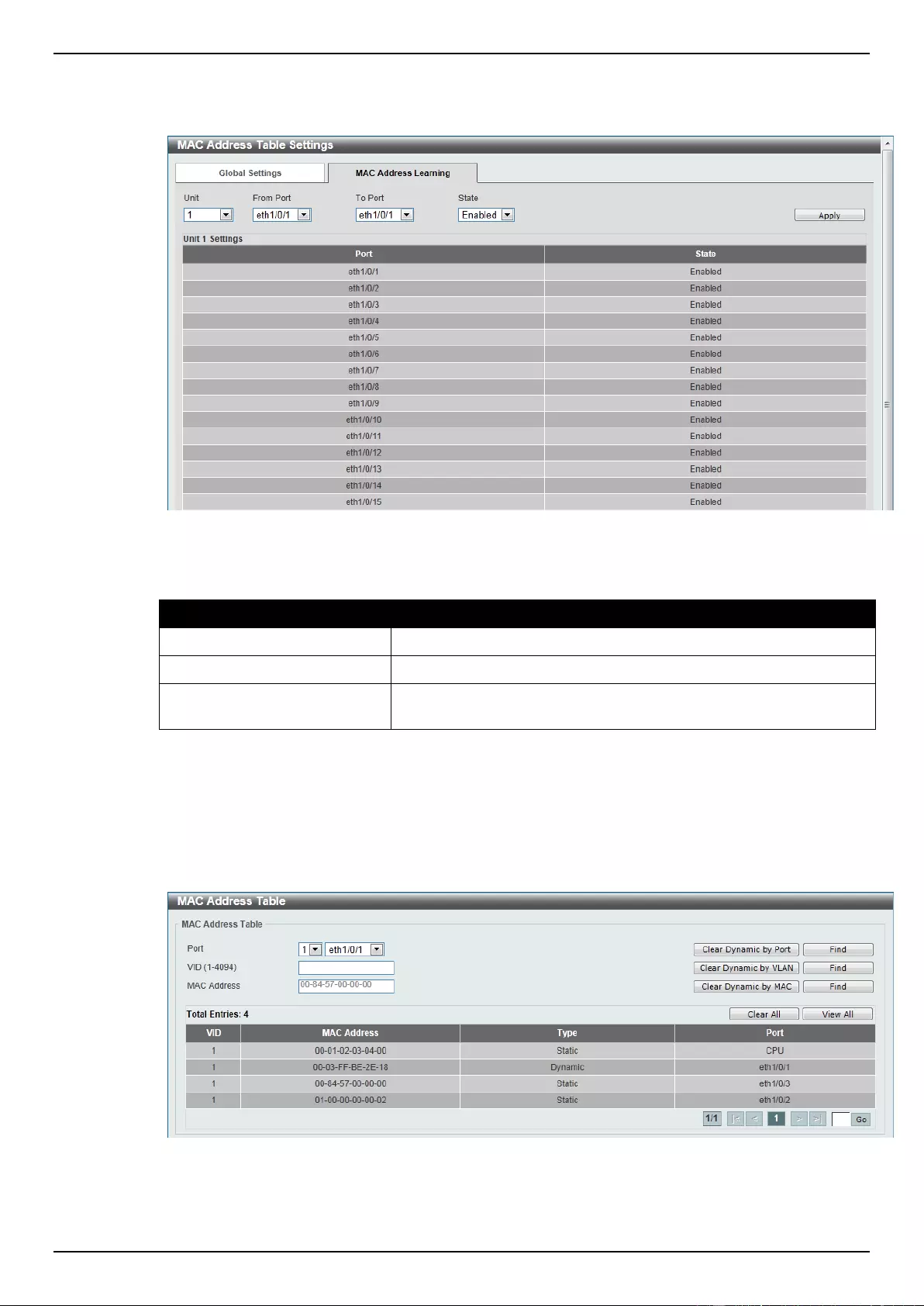
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
85
After clicking the MAC Address Learning tab, at the top of the page, the following page will be
available.
Figure 5-4 MAC Address Table Settings (MAC Address Learning) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the range of ports that will be used for this configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the MAC address learning function on
the ports specified here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
MAC Address Table
This window is used to view the entries listed in the MAC address table.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > MAC Address Table, as shown below:
Figure 5-5 MAC Address Table window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
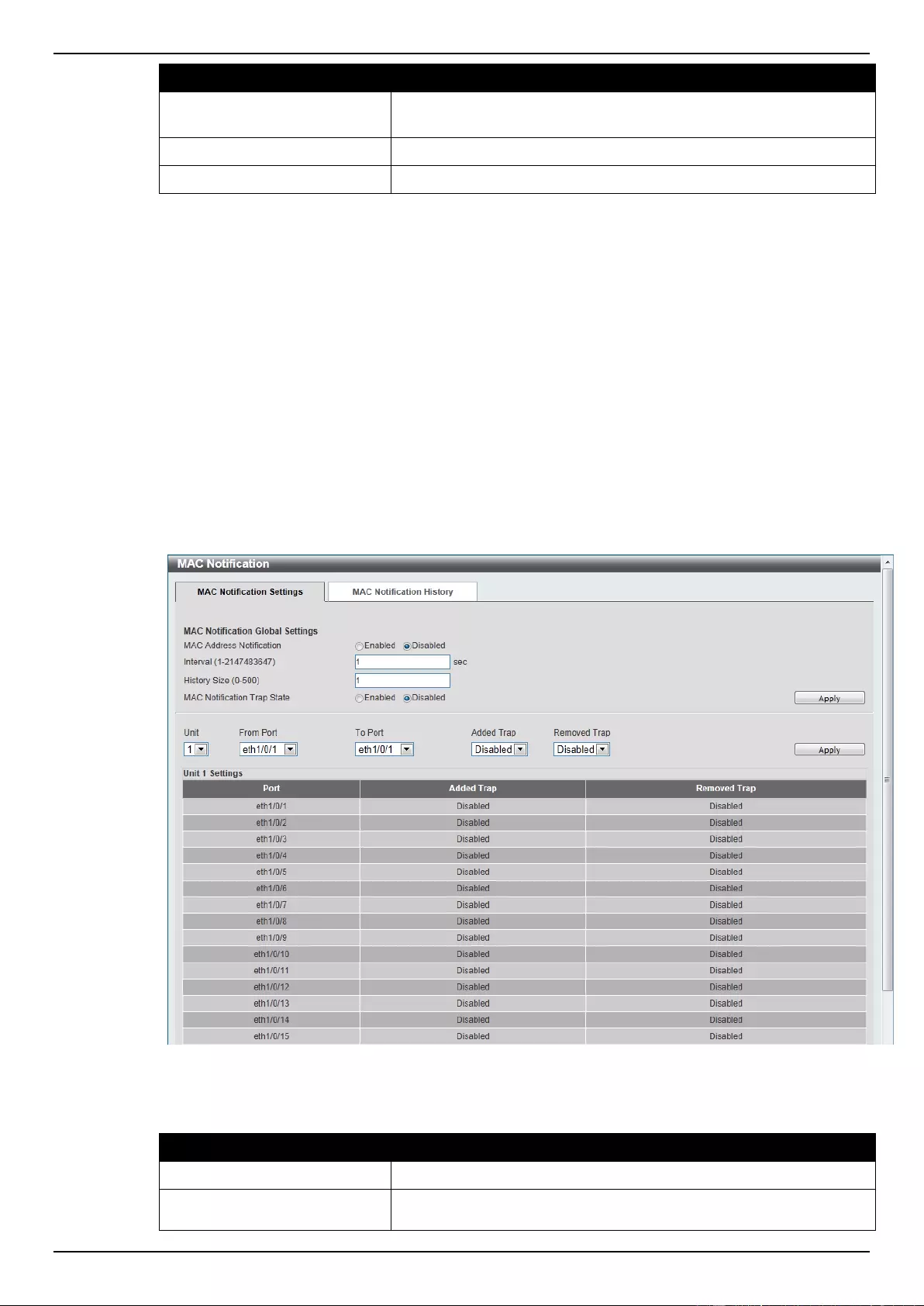
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
86
Parameter
Description
Port
Select the switch unit and the port that will be used for this
configuration here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be used for this configuration here.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address that will be used for this configuration here.
Click the Clear Dynamic by Port button to clear the dynamic MAC address listed on the
corresponding port.
Click the Clear Dynamic by VLAN button to clear the dynamic MAC address listed on the
corresponding VLAN.
Click the Clear Dynamic by MAC button to clear the dynamic MAC address entered.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear All button to clear all dynamic MAC addresses.
Click the View All button to display all the MAC addresses recorded in the MAC address table.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
MAC Notification
This window is used to view and configure MAC notification.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > FDB > MAC Notification, as shown below:
Figure 5-6 MAC Notification (MAC Notification Settings) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Address Notification
Select to enable or disable MAC notification globally on the Switch.
Interval
Enter the time value between notifications. This value must be
between 1 and 2147483647 seconds. By default, this value is 1
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
87
second.
History Size
Enter the maximum number of entries listed in the history log used
for notification. This value must be between 0 and 500. By default,
this value is 1.
MAC Notification Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the MAC notification trap
state.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the range of ports that will be used for this configuration
here.
Added Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the added trap for the port(s)
selected.
Removed Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the removed trap for the
port(s) selected.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
After clicking the MAC Notification History tab, the following page will be available.
Figure 5-7 MAC Notification (MAC Notification History) window
A list of MAC notification messages will be displayed.
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the VLAN settings on this switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1Q VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 5-8 802.1Q VLAN window
The fields that can be configured for 802.1Q VLAN are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list that will be created here.
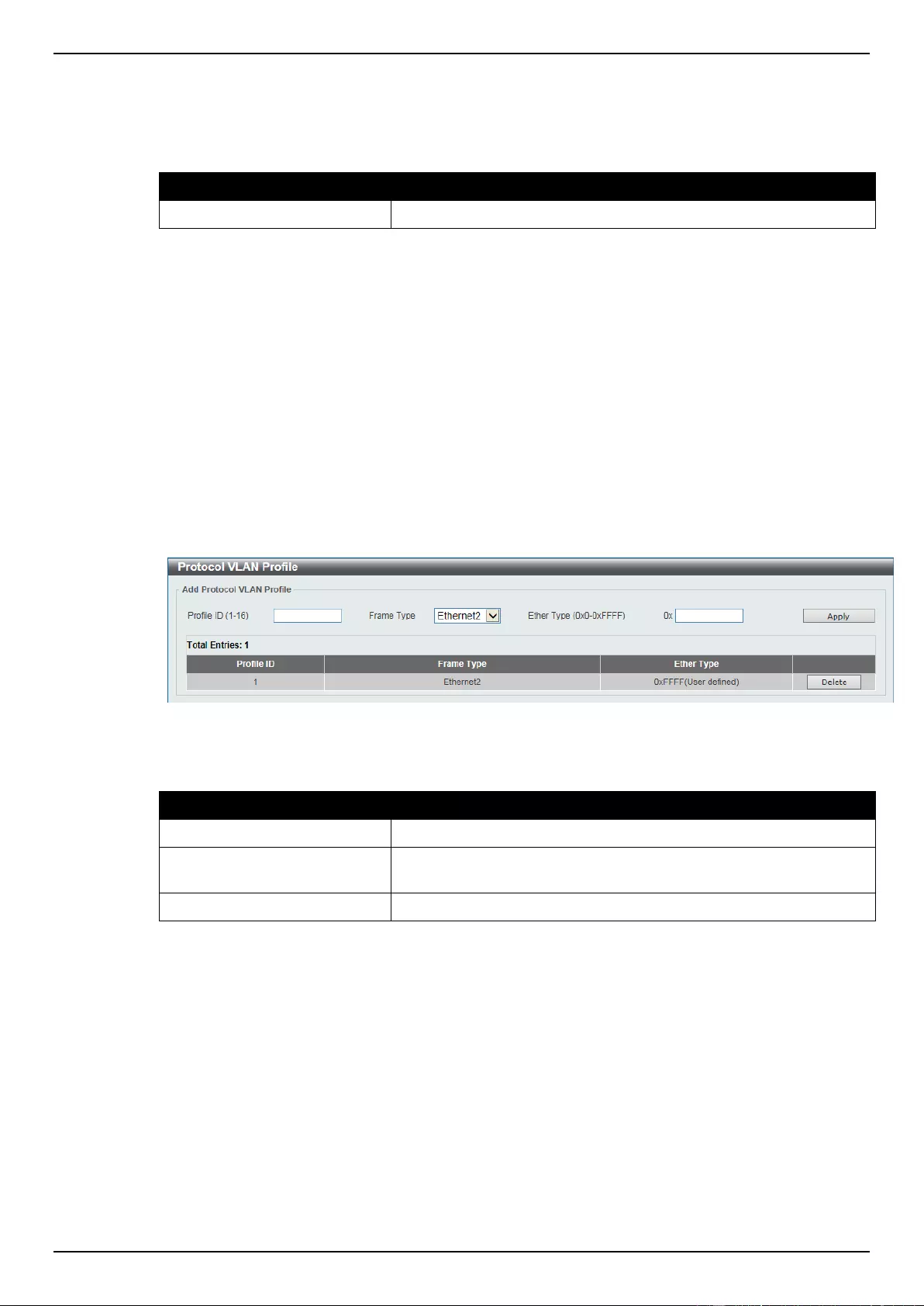
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
88
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
The fields that can be configured for Find VLAN are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be displayed here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the View All button to locate all the entries.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
802.1v Protocol VLAN
Protocol VLAN Profile
This window is used to view and configure the Protocol VLAN profile.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > Protocol VLAN
Profile, as shown below:
Figure 5-9 9 Protocol VLAN Profile window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Profile ID
Enter the profile ID that will be created here.
Frame Type
Select the frame type here. Options to choose from are Ethernet2,
SNAP and LLC.
Ether Type
Enter the Ethernet type in hexadecimal form.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Protocol VLAN Profile Interface
This window is used to view and configure the Protocol VLAN profile interface.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > Protocol VLAN
Profile Interface, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
89
Figure 5-10 Protocol VLAN Profile Interface window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Port
Select the switch unit and the port that will be used for this
configuration here.
Profile ID
Select the ID of the protocol group.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID of the Protocol VLAN.
Priority
Select the priority of the Protocol VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
GVRP
GVRP Global
This window is used to view and configure the GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) global
settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP > GVRP Global, as shown below:
Figure 5-11 GVRP Global window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Global GVRP State
Select this option to enable or disable the global GVRP state here.
Dynamic VLAN Creation
Select this option to enable or disable the dynamic VLAN creation
function here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
GVRP Port
This window is used to view and configure the GVRP port settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP > GVRP Port, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
90
Figure 5-12 GVRP Port window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
GVRP Status
Select this option to enable or disable the GVRP port status. This
enables the port to dynamically become a member of a VLAN. By
default, this option is disabled.
Join Time
Enter the Join Time value in centiseconds. This value must be
between 10 and 10000 centiseconds. By default, this value is 20
centiseconds.
Leave Time
Enter the Leave Time value in centiseconds. This value must be
between 10 and 10000 centiseconds. By default, this value is 60
centiseconds.
Leave All Time
Enter the Leave All Time value in centiseconds. This value must be
between 10 and 10000 centiseconds. By default, this value is 1000
centiseconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
GVRP Advertise VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the GVRP advertised VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP > GVRP Advertise VLAN, as
shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
91
Figure 5-13 GVRP Advertise VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the advertised VLAN to port mapping action that will be taken
here. Options to choose from are All, Add, Remove and Replace.
When selecting All, all the advertised VLANs will be used.
Advertise VID List
Enter the advertised VLAN ID list here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
GVRP Forbidden VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the GVRP forbidden VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP > GVRP Forbidden VLAN, as
shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
92
Figure 5-14 GVRP Forbidden VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the forbidden VLAN to port mapping action that will be taken
here. Options to choose from are All, Add, Remove and Replace.
When selecting All, all the forbidden VLANs will be used.
Forbidden VID List
Enter the forbidden VLAN ID list here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
GVRP Statistics Table
This window is used to display GVRP statistics information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP > GVRP Statistics Table, as
shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
93
Figure 5-15 GVRP Statistics Table window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port number of which GVRP statistic information will be
displayed.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
Click the View All button to view all GVRP statistic information.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Asymmetric VLAN
This window is used to configure the asymmetric VLAN function.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Asymmetric VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 5-16 Asymmetric VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Asymmetric VLAN State
Select this option to enable or disable the asymmetric VLAN
function
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
94
MAC VLAN
This window is used to view and configure MAC-based VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > MAC VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 5-17 MAC VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address that will be used for this configuration here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID for the MAC-based VLAN.
Priority
Select the priority of the MAC-based VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
VLAN Interface
This window is used to view and configure VLAN interface settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > VLAN Interface, as shown below:
Figure 5-18 VLAN Interface window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
95
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Click the View Detail button to view more detailed information about the VLAN on the specific
interface.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
After clicking the VLAN Detail button, the following page will appear.
Figure 5-19 VLAN Interface Information window
More detailed information about the VLAN of the specific interface is displayed.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After click the Edit button, the following window will appear. This is a dynamic window that will change
when a different VLAN Mode was selected. When Access was selected as the VLAN Mode, the
following page will appear.
Figure 5-20 Configure VLAN Interface - Access window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VLAN Mode
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from are
Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Acceptable Frame
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit All.
Ingress Checking
Select this option to enable or disable the ingress checking function.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used for this configuration here. This value must
be between 1 and 4094.
Clone
Tick this option to apply the configuration to the specified ports.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
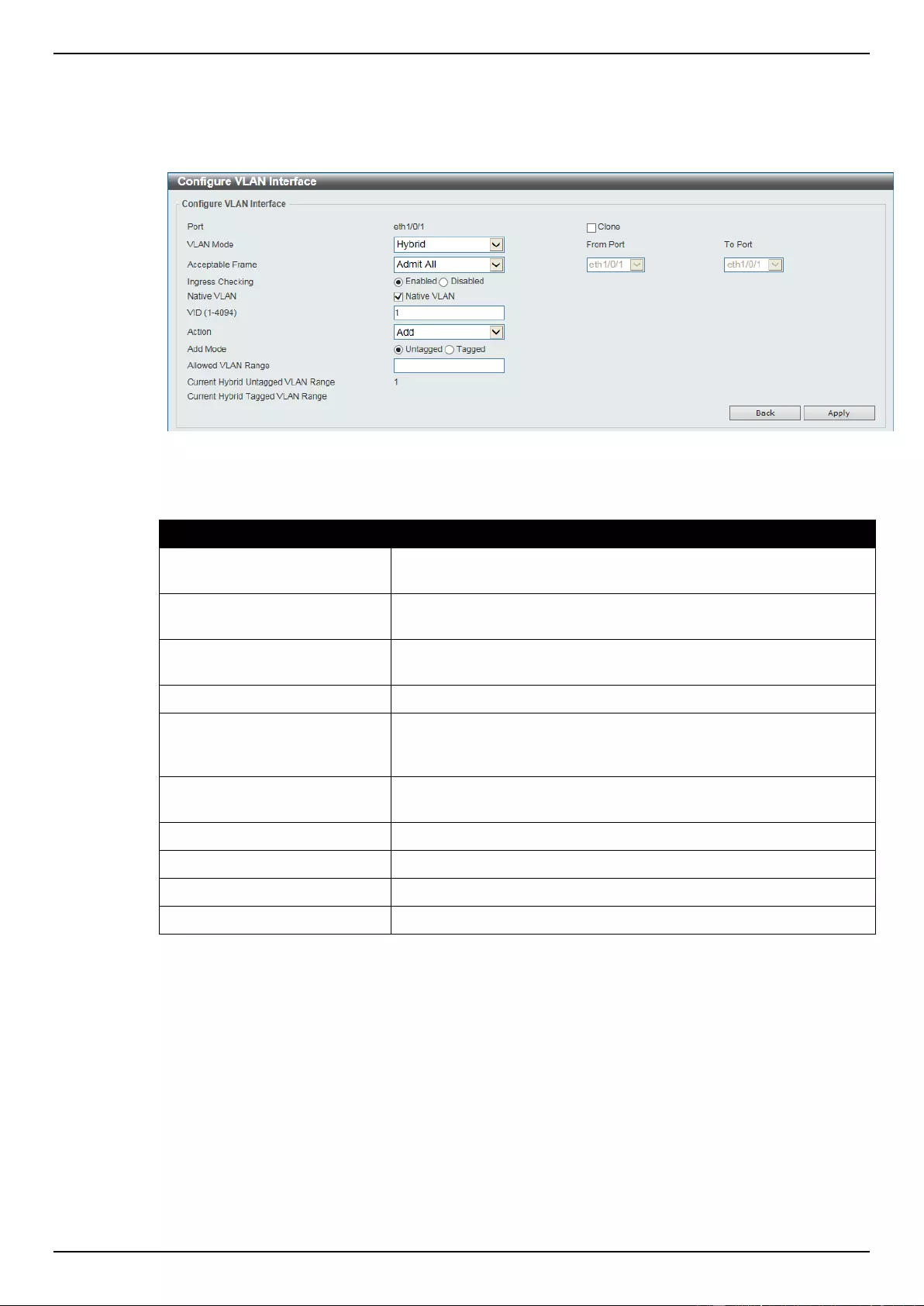
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
96
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
When Hybrid was selected as the VLAN Mode, the following page will appear.
Figure 5-21 Configure VLAN Interface - Hybrid window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VLAN Mode
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from are
Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Acceptable Frame
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit All.
Ingress Checking
Select the check box to enable or disable the ingress checking
function.
Native VLAN
Tick this option to enable the native VLAN function.
VID
After ticking the Native VLAN check box, this option will be
available. Enter the VLAN ID used for this configuration here. This
value must be between 1 and 4094.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add, Remove, Tagged, and Untagged.
Add Mode
Select whether to add an Untagged or Tagged parameters.
Allowed VLAN Range
Enter the allowed VLAN range information here.
Clone
Tick this option to apply the configuration to the specified ports.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
When Trunk was selected as the VLAN Mode, the following page will appear.
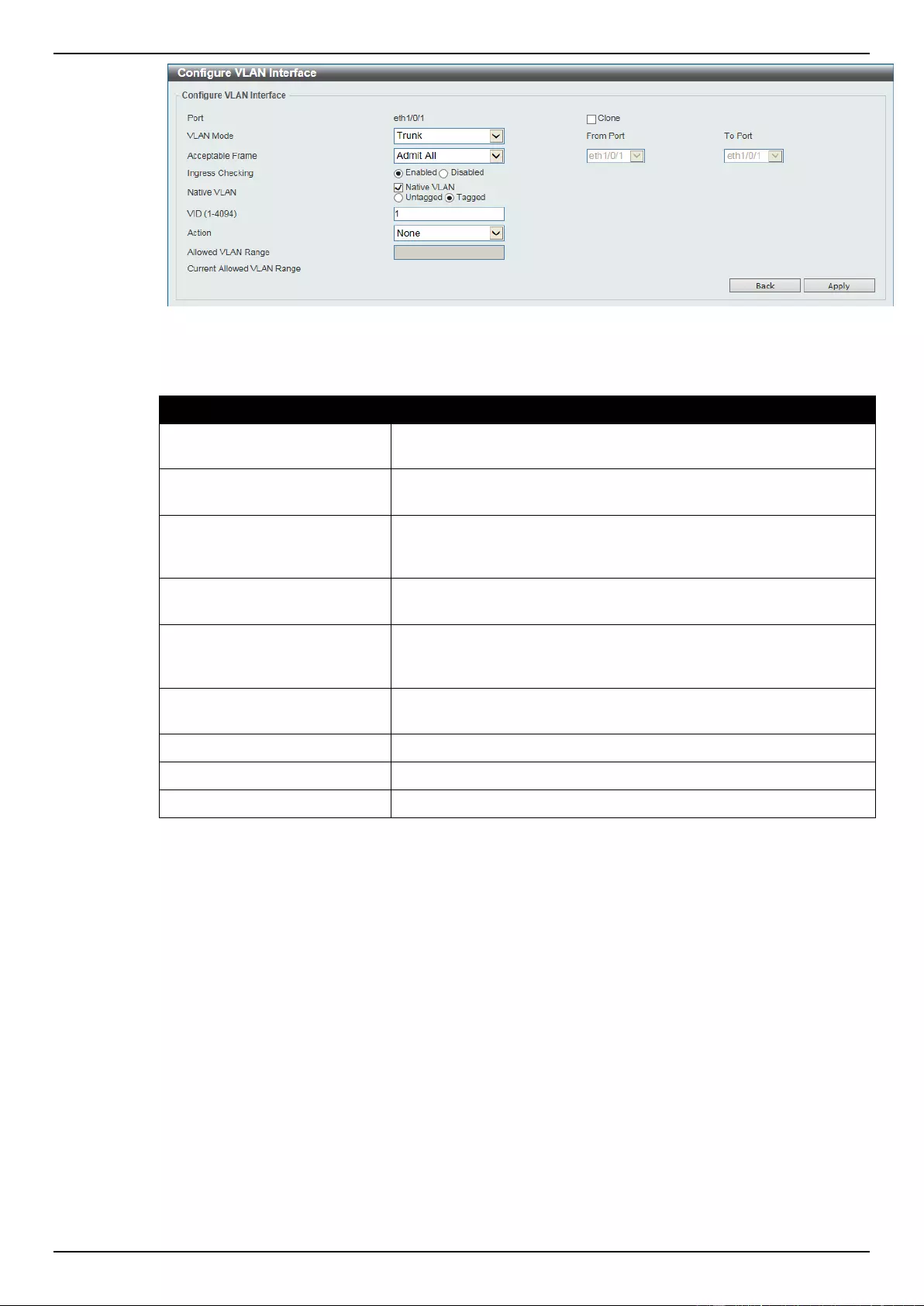
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
97
Figure 5-22 Configure VLAN Interface - Trunk window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VLAN Mode
Select the VLAN mode option here. Options to choose from are
Access, Hybrid, and Trunk.
Acceptable Frame
Select the acceptable frame behavior option here. Options to
choose from are Tagged Only, Untagged Only, and Admit All.
Ingress Checking
After selecting Trunk as the VLAN Mode the following parameter
will be available. Select to enable or disable the ingress checking
function.
Native VLAN
Tick the check box to enable the native VLAN function. Also select if
this VLAN supports Untagged or Tagged frames.
VID
After ticking the Native VLAN check box, this option will be
available. Enter the VLAN ID used for this configuration here. This
value must be between 1 and 4094.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
All, Add, Remove, Except, and Replace.
Allowed VLAN Range
Enter the allowed VLAN range information here.
Clone
Tick this option to apply the configuration to the specified ports.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Auto Surveillance VLAN
Auto Surveillance Properties
This window is used to configure the auto surveillance VLAN global settings and display the ports
surveillance VLAN information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto
Surveillance Properties, as shown below:
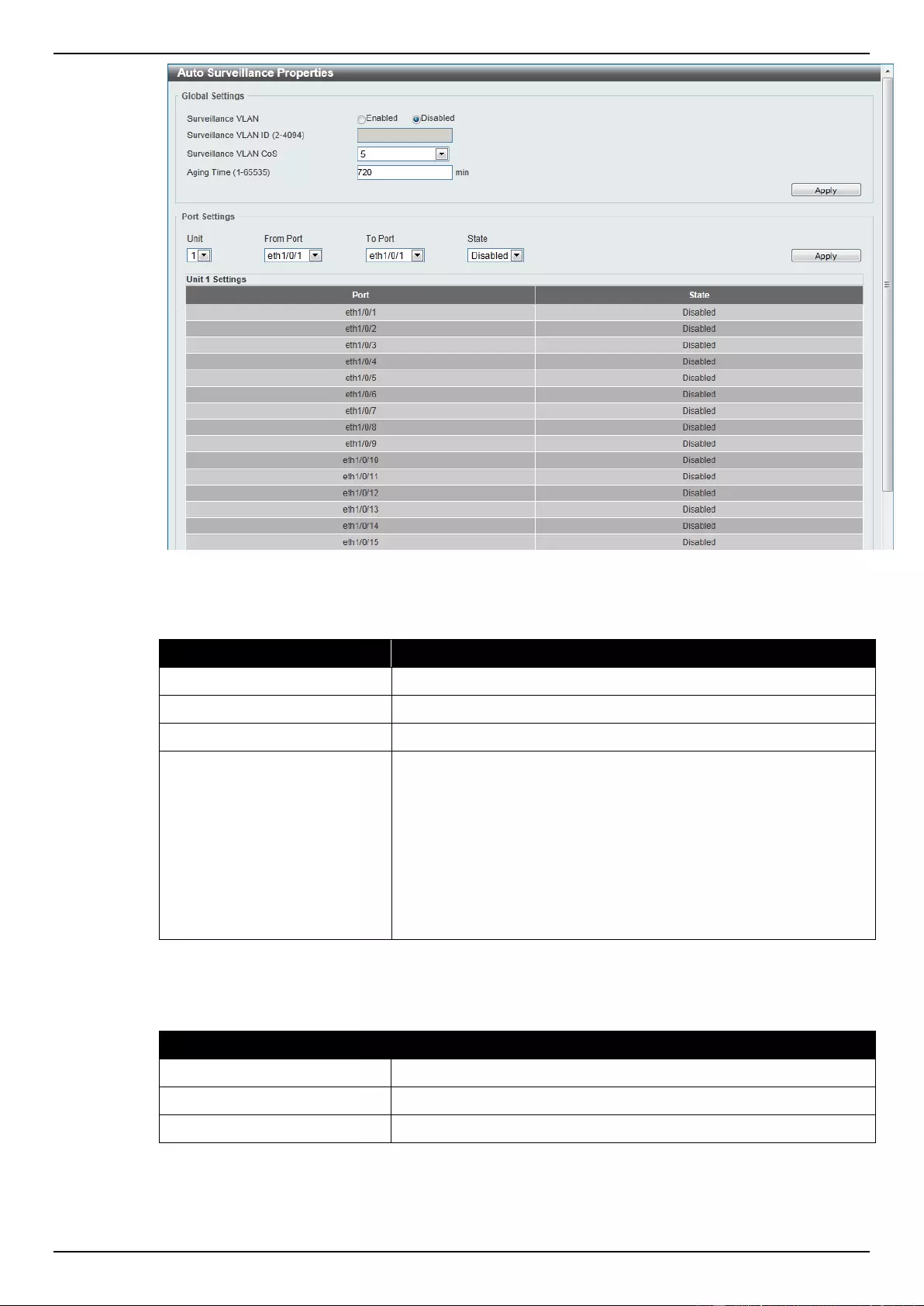
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
98
Figure 5-23 Auto Surveillance Properties window
The fields that can be configured for Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Surveillance VLAN
Select this option to enable or disable the surveillance VLAN state
Surveillance VLAN ID
Enter the surveillance VLAN ID. The range is from 2 to 4094.
Surveillance VLAN CoS
Select the priority of the surveillance VLAN from 0 to 7.
Aging Time
Enter the aging time of surveillance VLAN. The range is from 1 to
65535 minutes. The default value is 720 minutes. The aging time is
used to remove a port from surveillance VLAN if the port is an
automatic surveillance VLAN member. When the last surveillance
device stops sending traffic and the MAC address of this
surveillance device is aged out, the surveillance VLAN aging timer
will be started. The port will be removed from the surveillance VLAN
after expiration of surveillance VLAN aging timer. If the surveillance
traffic resumes during the aging time, the aging timer will be reset
and stop.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the state of the port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
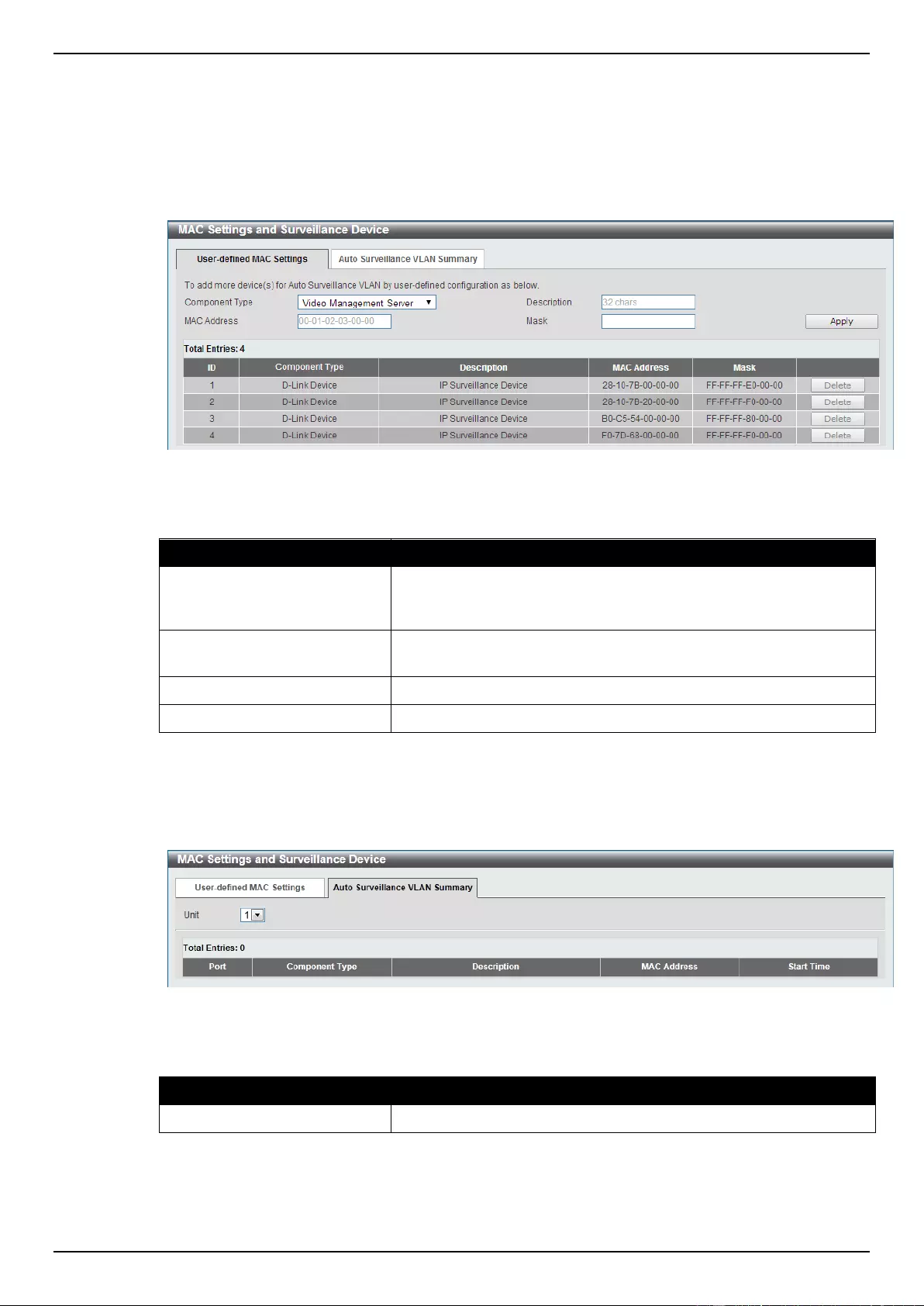
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
99
MAC Settings and Surveillance Device
This window is used to configure the user-defined surveillance device OUI and display the
surveillance VLAN information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC
Settings and Surveillance Device, as shown below:
Figure 5-24 User -defined MAC Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Component Type
Select the surveillance component type. Options to choose from are
Video Management Server, VMS Client/Remote Viewer, Video
Encoder, Network Storage, and Other IP Surveillance Device.
Description
Enter the description for the user-defined OUI with a maximum of 32
characters.
MAC Address
Enter the OUI MAC address.
Mask
Enter the OUI MAC address matching bitmask.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
After clicking the Auto Surveillance VLAN Summary tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 5-25 Auto Surveillance VLAN Summary window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Voice VLAN
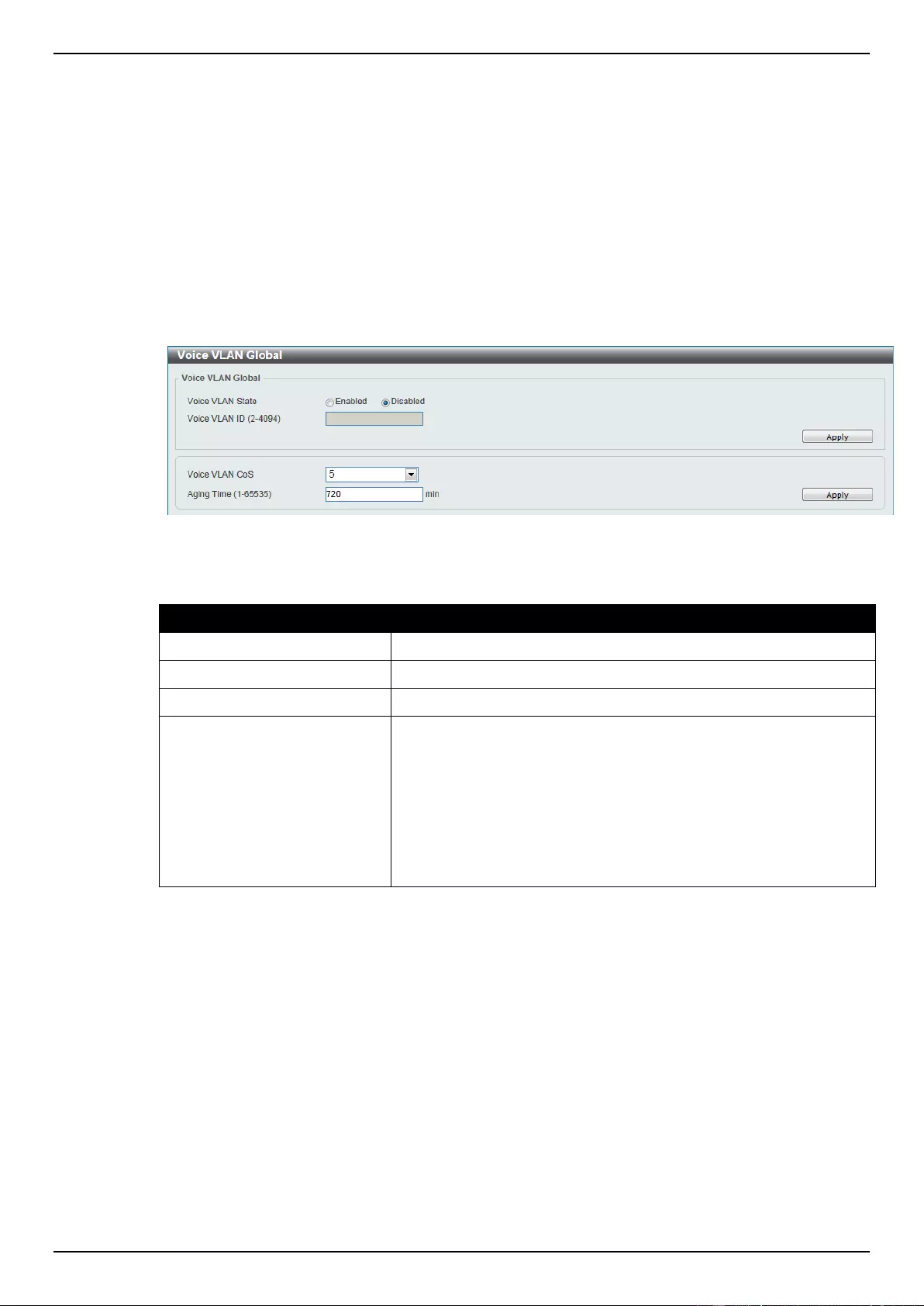
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
100
Voice VLAN Global
Voice VLAN is a VLAN used to carry voice traffic from IP phone. Because the sound quality of an IP
phone call will be deteriorated if the data is unevenly sent, the quality of service (QoS) for voice traffic
shall be configured to ensure the transmission priority of voice packet is higher than normal traffic.
The switches determine whether a received packet is a voice packet by checking its source MAC
address. If the source MAC addresses of packets comply with the organizationally unique identifier
(OUI) addresses configured by the system, the packets are determined as voice packets and
transmitted in voice VLAN.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global, as
show below:
Figure 5-26 Voice VLAN Global window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Voice VLAN State
Select this option to enable or disable the voice VLAN.
Voice VLAN ID
Enter the voice VLAN ID. The value is range from 2 to 4094.
Voice VLAN CoS
Select the priority of the voice VLAN from 0 to 7.
Aging Time
Enter the aging time of surveillance VLAN. The range is from 1 to
65535 minutes. The default value is 720 minutes. The aging time is
used to remove a port from voice VLAN if the port is an automatic
VLAN member. When the last voice device stops sending traffic and
the MAC address of this voice device is aged out, the voice VLAN
aging timer will be started. The port will be removed from the voice
VLAN after expiration of voice VLAN aging timer. If the voice traffic
resumes during the aging time, the aging timer will be reset and
stop.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Voice VLAN Port
This window is used to show the ports voice VLAN information.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port, as
show below:
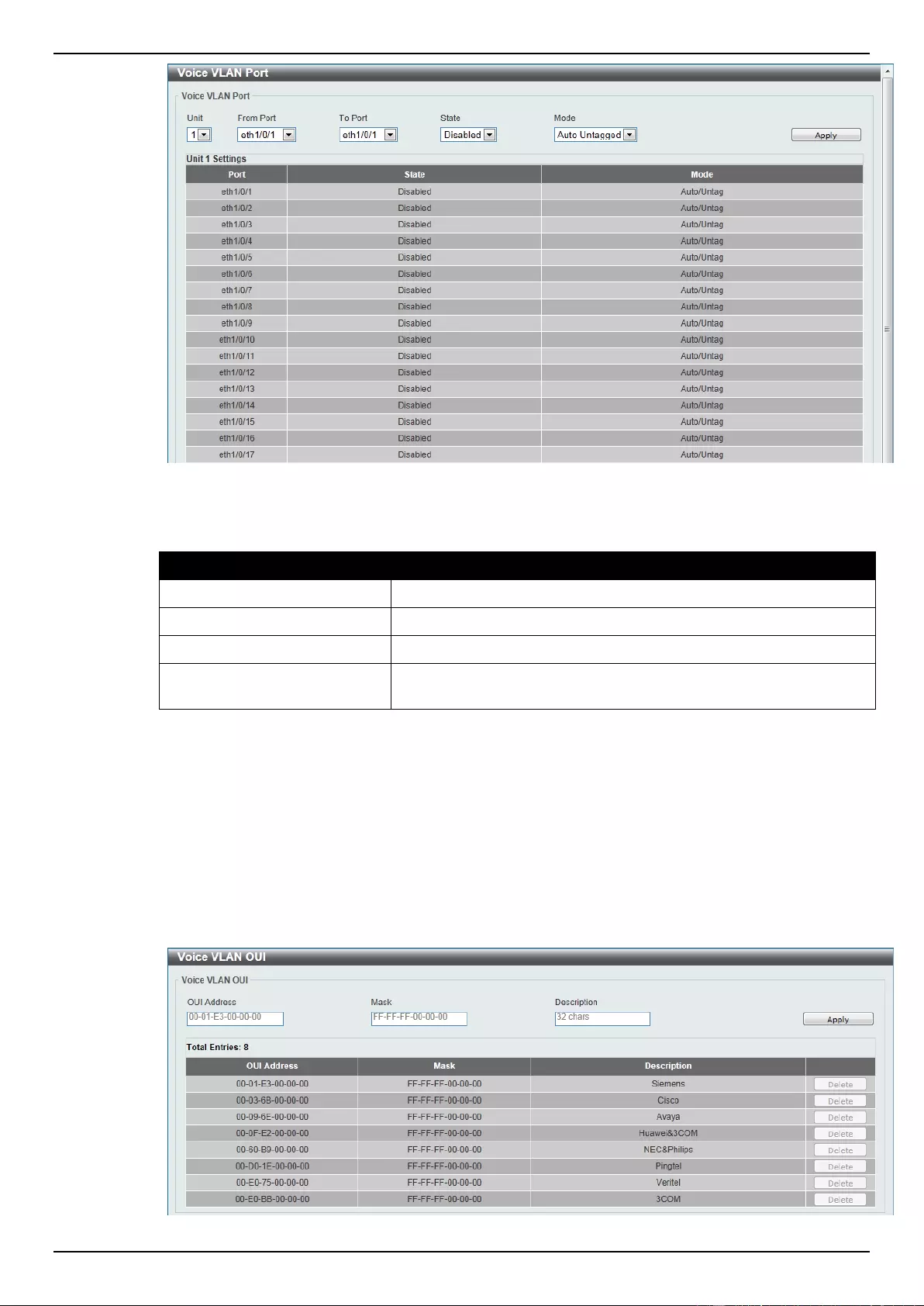
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
101
Figure 5-27 Voice VLAN Port window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the state of the port.
Mode
Select the mode of the port. Options to choose from are Auto
Untagged, Auto Tagged, and Manual.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Voice VLAN OUI
This window is used to configure the user-defined voice traffic’s OUI. The OUI is used to identify the
voice traffic. There are a number of pre-defined OUIs. The user can further define the user-defined
OUIs if needed. The user-defined OUI cannot be the same as the pre-defined OUI.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN OUI, as show
below:
Figure 5-28 Voice VLAN OUI window
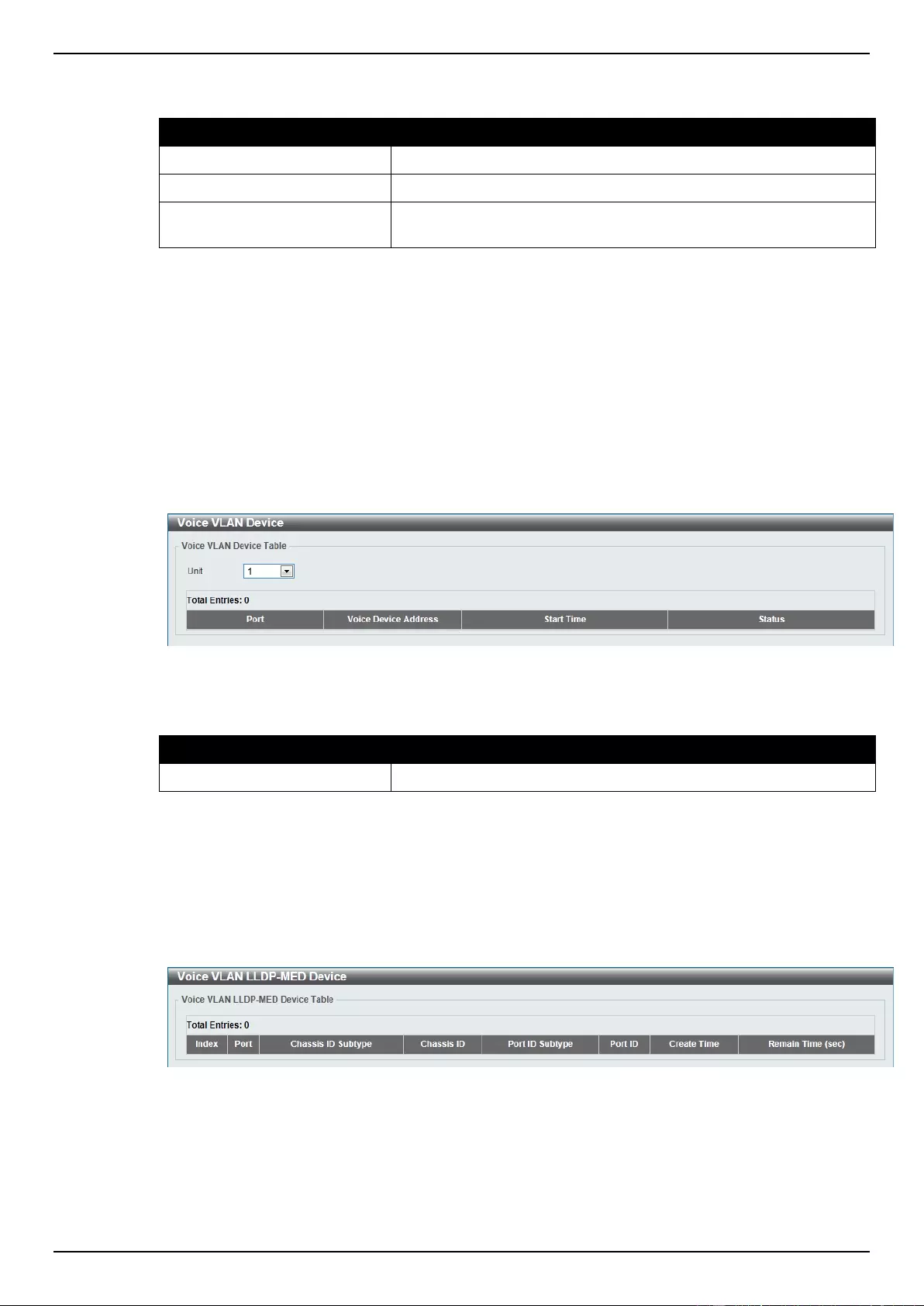
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
102
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
OUI Address
Enter the OUI MAC address.
Mask
Enter the OUI MAC address matching bitmask.
Description
Enter the description for the user-defined OUI with a maximum of
32 characters.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Voice VLAN Device
This window is used to show voice devices that are connected to the ports. The start time is the time
when the device is detected on this port, the activate time is the latest time saw the device sending
the traffic.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Device, as
show below:
Figure 5-29 Voice VLAN Device window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Device
This window displays the voice VLAN LLDP-MED voice devices connected to the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN LLDP-MED
Device, as show below:
Figure 5-30 Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Device window
Spanning Tree
This Switch supports three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol: 802.1D-1998 STP, 802.1D-2004
Rapid STP, and 802.1Q-2005 MSTP. 802.1D-1998 STP will be familiar to most networking

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
103
professionals. However, since 802.1D-2004 RSTP and 802.1Q-2005 MSTP have been recently
introduced to D-Link managed Ethernet switches, a brief introduction to the technology is provided
below followed by a description of how to set up 802.1D-1998 STP, 802.1D-2004 RSTP, and 802.1Q-
2005 MSTP.
802.1Q-2005 MSTP
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol, or MSTP, is a standard defined by the IEEE community that allows
multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance, which will provide multiple pathways
across the network. Therefore, these MSTP configurations will balance the traffic load, preventing
wide scale disruptions when a single spanning tree instance fails. This will allow for faster
convergences of new topologies for the failed instance. Frames designated for these VLANs will be
processed quickly and completely throughout interconnected bridges utilizing any of the three
spanning tree protocols (STP, RSTP or MSTP).
This protocol will also tag BPDU packets so receiving devices can distinguish spanning tree instances,
spanning tree regions and the VLANs associated with them. An MSTI ID will classify these instances.
MSTP will connect multiple spanning trees with a Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The
CIST will automatically determine each MSTP region, its maximum possible extent and will appear as
one virtual bridge that runs a single spanning tree. Consequentially, frames assigned to different
VLANs will follow different data routes within administratively established regions on the network,
continuing to allow simple and full processing of frames, regardless of administrative errors in defining
VLANs and their respective spanning trees.
Each switch utilizing the MSTP on a network will have a single MSTP configuration that will have the
following three attributes:
1. A configuration name defined by an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters (defined in the
MST Configuration Identification window in the Configuration Name field).
2. A configuration revision number (named here as a Revision Level and found in the MST
Configuration Identification window) and;
3. A 4094-element table (defined here as a VID List in the MST Configuration Identification
window), which will associate each of the possible 4094 VLANs supported by the Switch for a
given instance.
To utilize the MSTP function on the Switch, three steps need to be taken:
1. The Switch must be set to the MSTP setting (found in the STP Bridge Global Settings window
in the STP Version field)
2. The correct spanning tree priority for the MSTP instance must be entered (defined here as a Pri-
ority in the MSTI Config Information window when configuring MSTI ID settings).
3. VLANs that will be shared must be added to the MSTP Instance ID (defined here as a VID List in
the MST Configuration Identification window when configuring an MSTI ID settings).
802.1D-2004 Rapid Spanning Tree
The Switch implements three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol, the Multiple Spanning Tree
Protocol (MSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1Q-2005, the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) as
defined by the IEEE 802.1D-2004 specification and a version compatible with the IEEE 802.1D-1998
STP. RSTP can operate with legacy equipment implementing IEEE 802.1D-1998; however the
advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802.1D-2004 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) evolved from the 802.1D-1998 STP
standard. RSTP was developed in order to overcome some limitations of STP that impede the
function of some recent switching innovations, in particular, certain Layer 3 functions that are
increasingly handled by Ethernet switches. The basic function and much of the terminology is the
same as STP. Most of the settings configured for STP are also used for RSTP. This section
introduces some new Spanning Tree concepts and illustrates the main differences between the two
protocols.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
104
Port Transition States
An essential difference between the three protocols is in the way ports transition to a forwarding state
and in the way this transition relates to the role of the port (forwarding or not forwarding) in the
topology. MSTP and RSTP combine the transition states disabled, blocking and listening used in
802.1D-1998 and creates a single state Discarding. In either case, ports do not forward packets. In
the STP port transition states disabled, blocking or listening or in the RSTP/MSTP port state discard-
ing, there is no functional difference, the port is not active in the network topology. Table 7-3 below
compares how the three protocols differ regarding the port state transition.
All three protocols calculate a stable topology in the same way. Every segment will have a single path
to the root bridge. All bridges listen for BPDU packets. However, BPDU packets are sent more
frequently - with every Hello packet. BPDU packets are sent even if a BPDU packet was not received.
Therefore, each link between bridges is sensitive to the status of the link. Ultimately this difference
results in faster detection of failed links, and thus faster topology adjustment. A drawback of 802.1D-
1998 is this absence of immediate feedback from adjacent bridges.
802.1Q-2005
MSTP
802.1D-2004
RSTP
802.1D-1998 STP
Forwarding
Learning
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
No
No
Discarding
Discarding
Blocking
No
No
Discarding
Discarding
Listening
No
No
Learning
Learning
Learning
No
Yes
Forwarding
Forwarding
Forwarding
Yes
Yes
RSTP is capable of a more rapid transition to a forwarding state - it no longer relies on timer
configurations - RSTP compliant bridges are sensitive to feedback from other RSTP compliant bridge
links. Ports do not need to wait for the topology to stabilize before transitioning to a forwarding state.
In order to allow this rapid transition, the protocol introduces two new variables: the edge port and the
point-to-point (P2P) port.
Edge Port
The edge port is a configurable designation used for a port that is directly connected to a segment
where a loop cannot be created. An example would be a port connected directly to a single work-
station. Ports that are designated as edge ports transition to a forwarding state immediately without
going through the listening and learning states. An edge port loses its status if it receives a BPDU
packet, immediately becoming a normal spanning tree port.
P2P Port
A P2P port is also capable of rapid transition. P2P ports may be used to connect to other bridges.
Under RSTP/MSTP, all ports operating in full-duplex mode are considered to be P2P ports, unless
manually overridden through configuration.
802.1D-1998/802.1D-2004/802.1Q-2005 Compatibility
MSTP or RSTP can interoperate with legacy equipment and is capable of automatically adjusting
BPDU packets to 802.1D-1998 format when necessary. However, any segment using 802.1D-1998
STP will not benefit from the rapid transition and rapid topology change detection of MSTP or RSTP.
The protocol also provides for a variable used for migration in the event that legacy equipment on a
segment is updated to use RSTP or MSTP.
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) operates on two levels:
1. On the switch level, the settings are globally implemented.
2. On the port level, the settings are implemented on a per-user-defined group of ports basis.
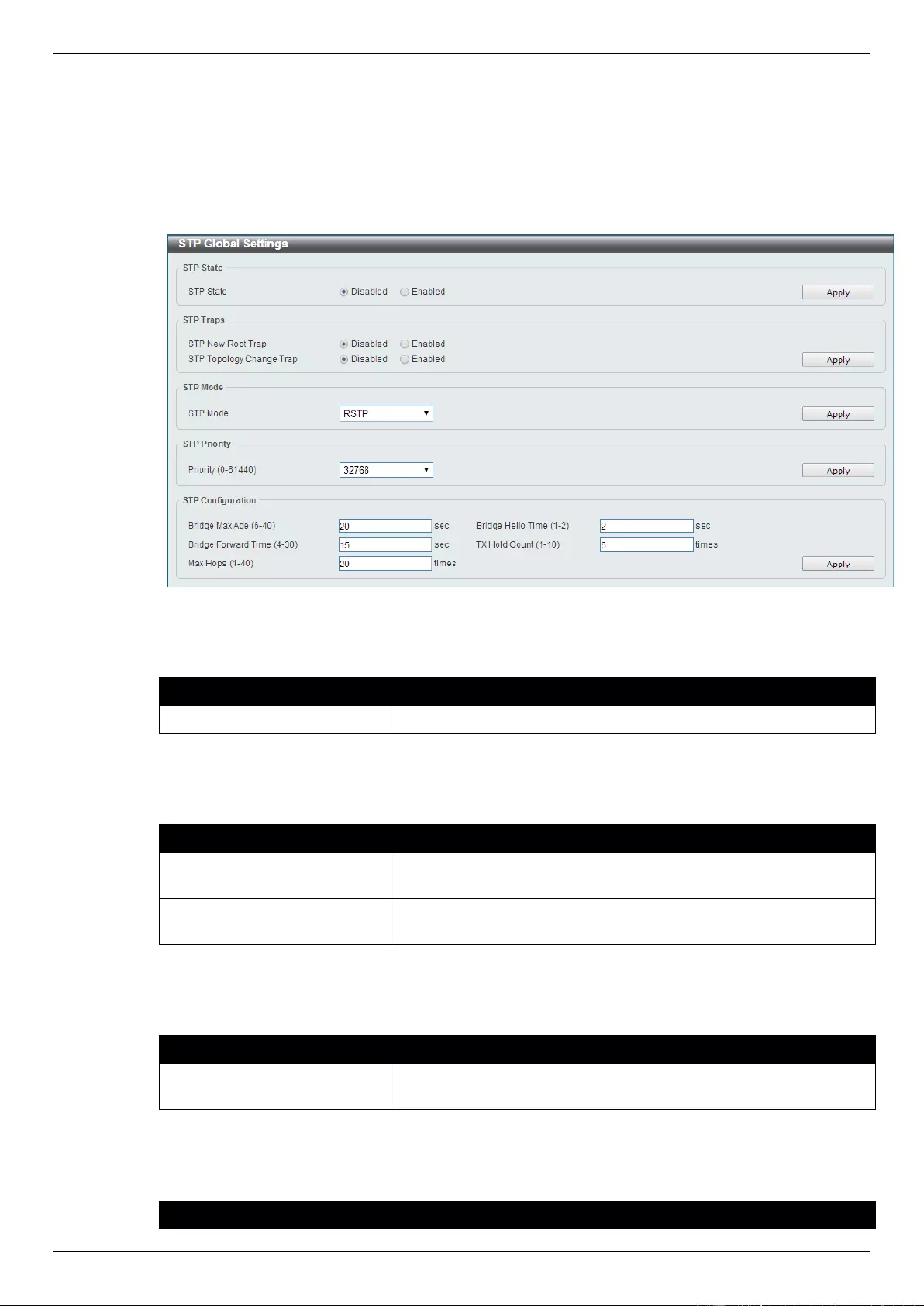
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
105
STP Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the STP global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > STP Global Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 5-31 STP Global Settings window
The field that can be configured for Spanning Tree State is described below:
Parameter
Description
Spanning Tree State
Select this option to enable or disable the STP global state here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for STP Traps are described below:
Parameter
Description
STP New Root Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the STP new root trap option
here.
STP Topology Change Trap
Select this option to enable or disable the STP topology change trap
option here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for STP Mode are described below:
Parameter
Description
STP Mode
Select the STP mode used here. Options to choose from are MSTP,
RSTP, and STP.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Spanning Tree Priority are described below:
Parameter
Description
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
106
Priority
Select the STP priority value here. This value is between 0 and
61440. By default, this value is 32768. The lower the value, the
higher the priority.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Spanning Tree Configuration are described below:
Parameter
Description
Bridge Max Age
Enter the bridge’s maximum age value here. This value must be
between 6 and 40 seconds. By default, this value is 20 seconds.
The maximum age value may be set to ensure that old information
does not endlessly circulate through redundant paths in the
network, preventing the effective propagation of the new
information. Set by the Root Bridge, this value will aid in determining
that the Switch has spanning tree configuration values consistent
with other devices on the bridged LAN.
Bridge Hello Time
After selecting RSTP/STP as the STP Mode, this parameter will be
available. Enter the bridge’s hello time value here. This value must
be between 1 and 2 seconds. By default, this value is 2 seconds.
This is the interval between two transmissions of BPDU packets
sent by the Root Bridge to tell all other switches that it is indeed the
Root Bridge. This field will only appear here when STP or RSTP is
selected for the STP Version. For MSTP, the Hello Time must be
set on a port per port basis.
Bridge Forward Time
Enter the bridge’s forwarding time value here. This value must be
between 4 and 30 seconds. By default, this value is 15 seconds.
Any port on the Switch spends this time in the listening state while
moving from the blocking state to the forwarding state.
TX Hold Count
Enter the transmit hold count value here. This value must be
between 1 and 10 times. By default, this value is 6 times. This value
is used to set the maximum number of Hello packets transmitted per
interval.
Max Hops
Enter the maximum number of hops that are allowed. This value
must be between 1 and 40 hops. By default, this value is 20 hops.
This value is used to set the number of hops between devices in a
spanning tree region before the BPDU (bridge protocol data unit)
packet sent by the Switch will be discarded. Each switch on the hop
count will reduce the hop count by one until the value reaches zero.
The Switch will then discard the BDPU packet and the information
held for the port will age out.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
STP Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the STP port settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings, as shown
below:
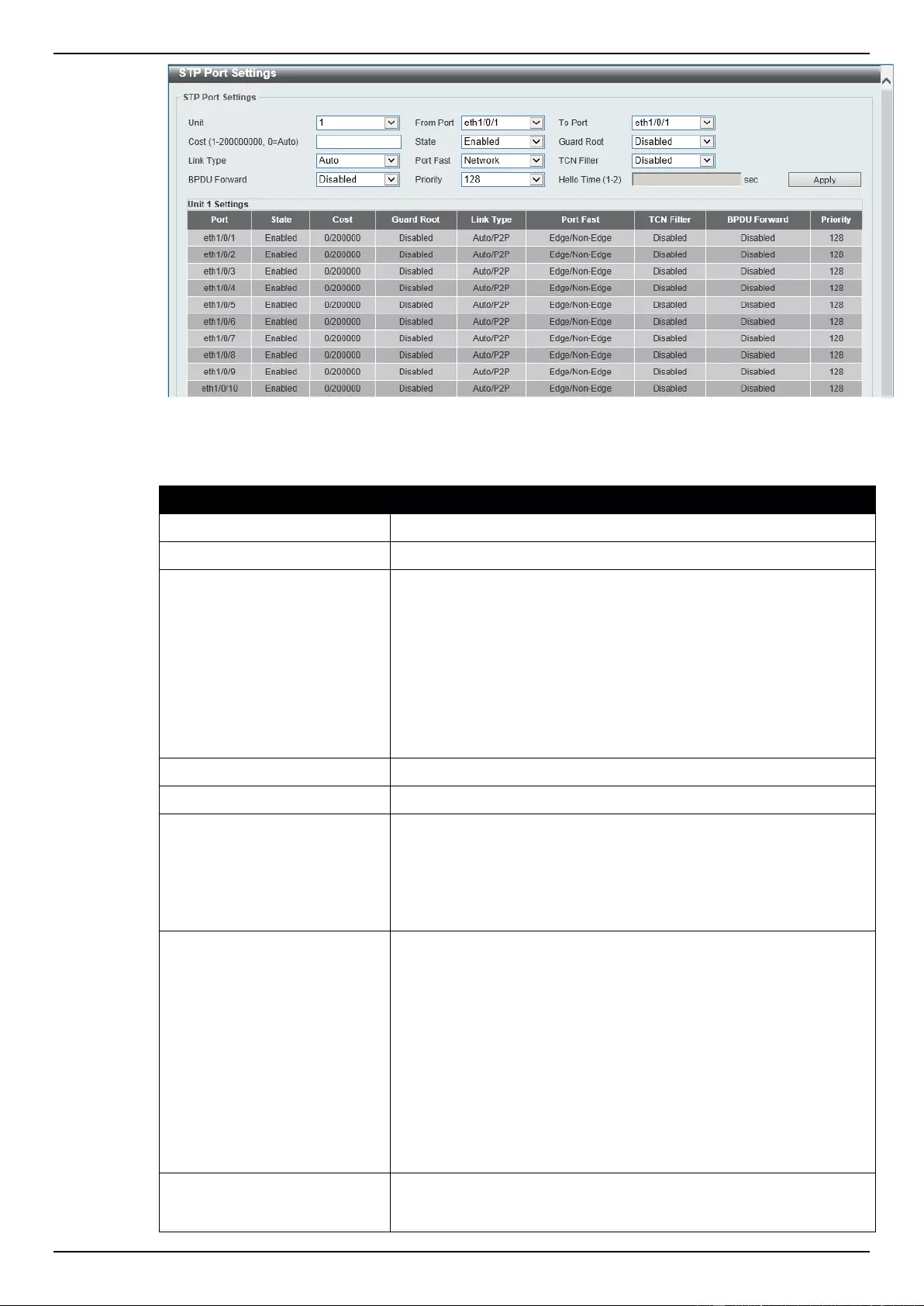
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
107
Figure 5-32 STP Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Cost
Enter the cost value here. This value must be between 1 and
200000000. This value defines a metric that indicates the relative
cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list. Port cost can be
set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto).
Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for
forwarding packets to the specified port(s) in the list for optimal
efficiency. The default port cost for a 100Mbps port is 200000 and
the default port cost for a Gigabit port is 20000. The lower the
number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to
forward packets.
State
Select to enable or disable the STP port state.
Guard Root
Select to enable or disable the guard root function.
Link Type
Select the link type option here. Options to choose from are Auto,
P2P, and Shared. A full-duplex port is considered to have a point-
to-point (P2P) connection. On the opposite, a half-duplex port is
considered to have a Shared connection .The port cannot transit
into the forwarding state rapidly by setting the link type to Shared.
By default this option is Auto.
Port Fast
Select the port fast option here. Options to choose from are
Network, Disabled, and Edge. In the Network mode, the port will
remain in the non-port-fast state for three seconds. The port will
change to the port-fast state if no BPDU is received and changes to
the forwarding state. If the port received the BPDU later, it will
change to the non-port-fast state. In the Disabled mode, the port
will always be in the non-port-fast state. It will always wait for the
forward-time delay to change to the forwarding state. In the Edge
mode, the port will directly change to the spanning-tree forwarding
state when a link-up occurs without waiting for the forward-time
delay. If the interface receives a BPDU later, its operation state
changes to the non-port-fast state. By default, this option is
Network.
TCN Filter
Select to enable or disable the TCN filter option. Enabling TC
filtering on a port is useful for an ISP to prevent the external bridge
to a core region of the network, causing address flushing in that
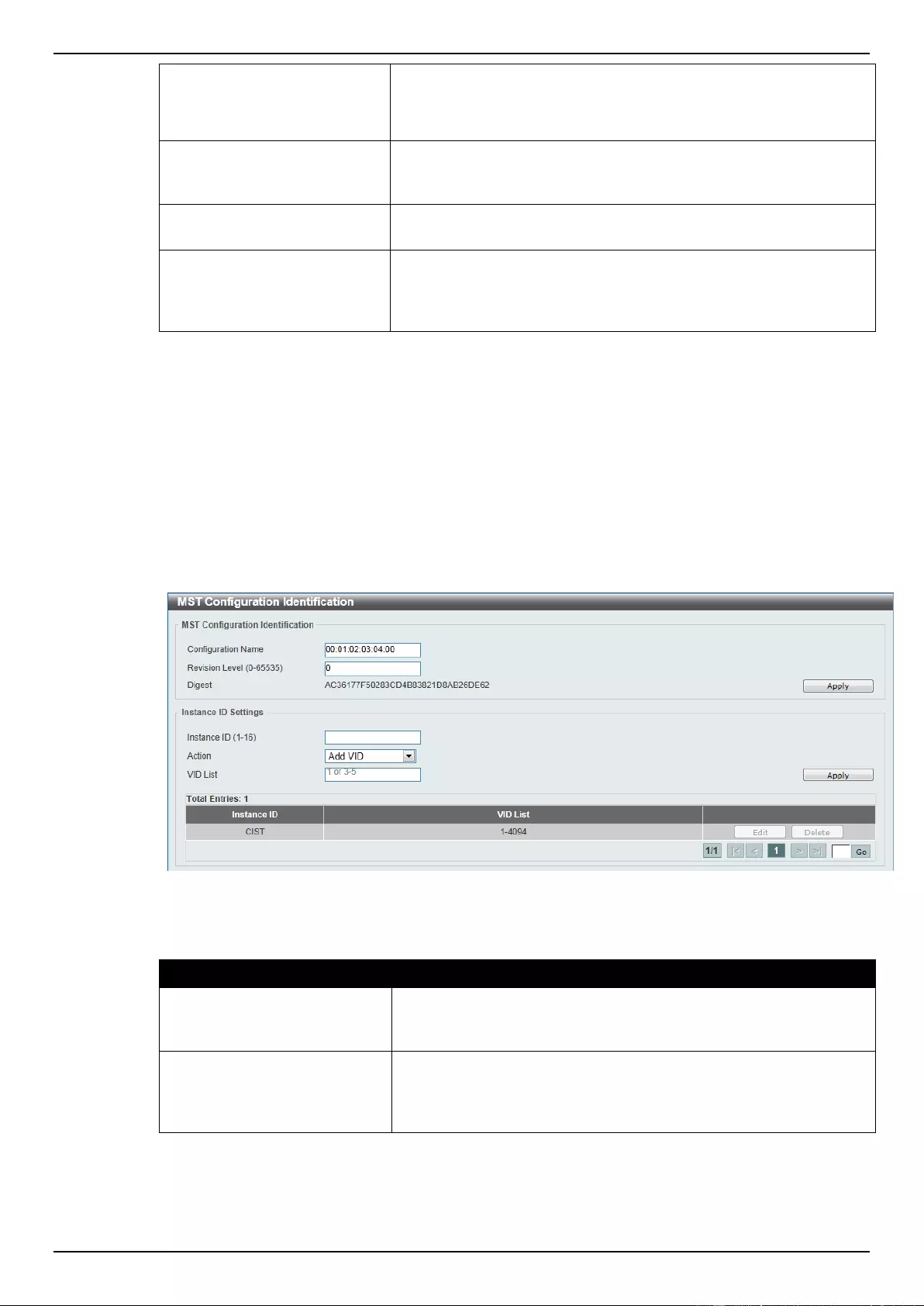
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
108
region, possibly because those bridges are not under the full control
of the administrator. When a port is set to the TCN filter mode, the
TC event received by the port will be ignored. By default, this option
is Disabled.
BPDU Forward
Select to enable or disable BPDU forwarding. If enabled, the
received STP BPDU will be forwarded to all VLAN member ports in
the untagged form. By default, this option is Disabled.
Priority
Select the priority value here. Options to choose from are 0 to 240.
By default this option is 128. A lower value has higher priority.
Hello Time
Enter the hello time value here. This value must be between 1 and 2
seconds. This value specifies the interval that a designated port will
wait between the periodic transmissions of each configuration
message.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
MST Configuration Identification
This window is used to view and configure the MST configuration identification settings. These
settings will uniquely identify a multiple spanning tree instance set on the Switch. The Switch initially
possesses one CIST, or Common Internal Spanning Tree, of which the user may modify the
parameters for but cannot change the MSTI ID for, and cannot be deleted.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration
Identification, as shown below:
Figure 5-33 MST Configuration Identification window
The fields that can be configured for MST Configuration Identification are described below:
Parameter
Description
Configuration Name
Enter the MST This name uniquely identifies the MSTI (Multiple
Spanning Tree Instance). If a Configuration Name is not set, this
field will show the MAC address to the device running MSTP.
Revision Level
Enter the revision level value here. This value must be between 0
and 65535. By default, this value is 0. This value, along with the
Configuration Name, identifies the MSTP region configured on the
Switch.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Instance ID Settings are described below:
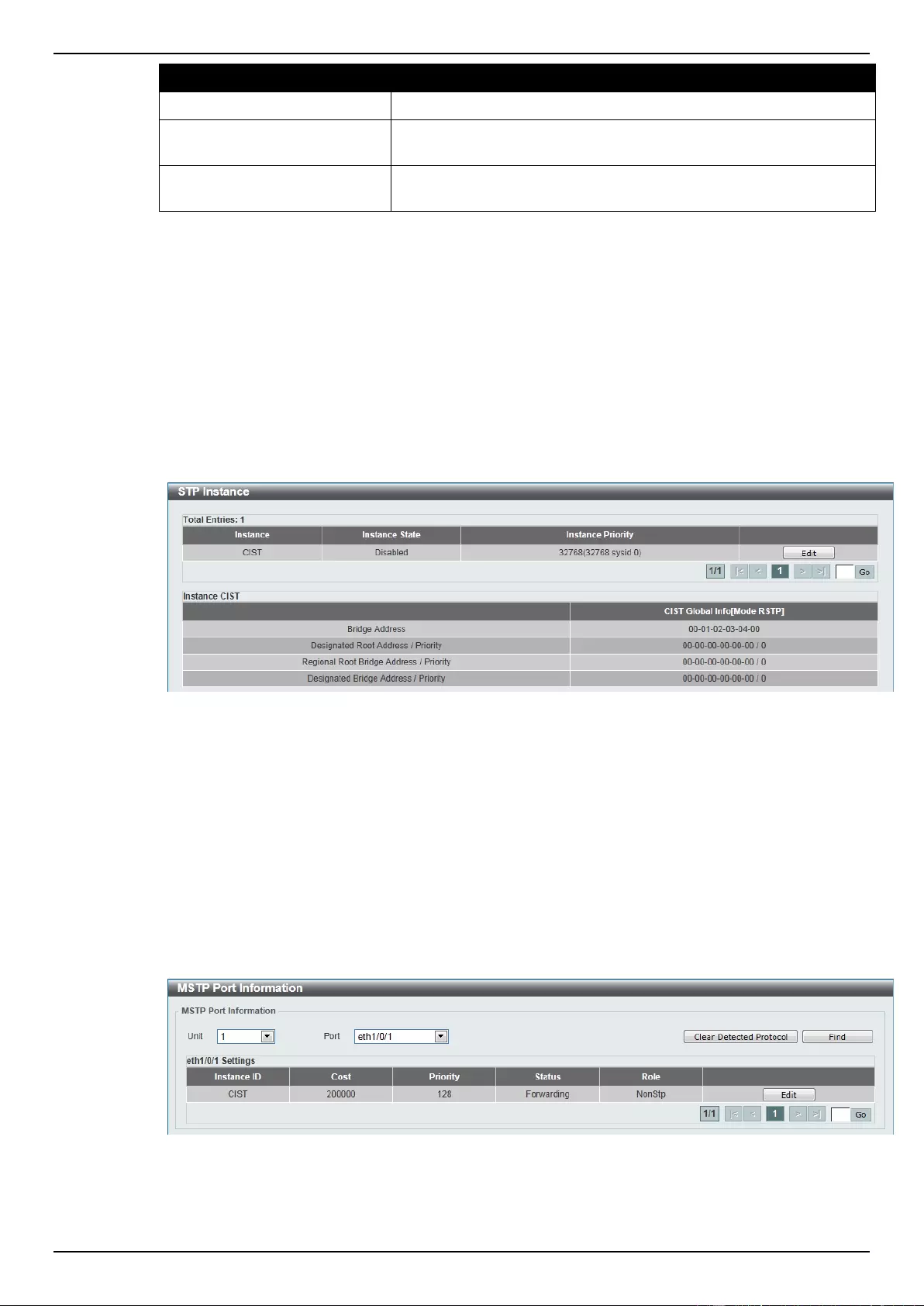
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
109
Parameter
Description
Instance ID
Enter the instance ID here. This value must be between 1 and 16.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add VID and Remove VID.
VID List
Enter the VID list value here. This field is used to specify the VID
range from configured VLANs set on the Switch.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
STP Instance
This window is used to view and configure the STP instance settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > STP Instance, as shown below:
Figure 5-34 STP Instance window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
MSTP Port Information
This window is used to view and configure the MSTP port information settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information, as
shown below:
Figure 5-35 MSTP Port Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
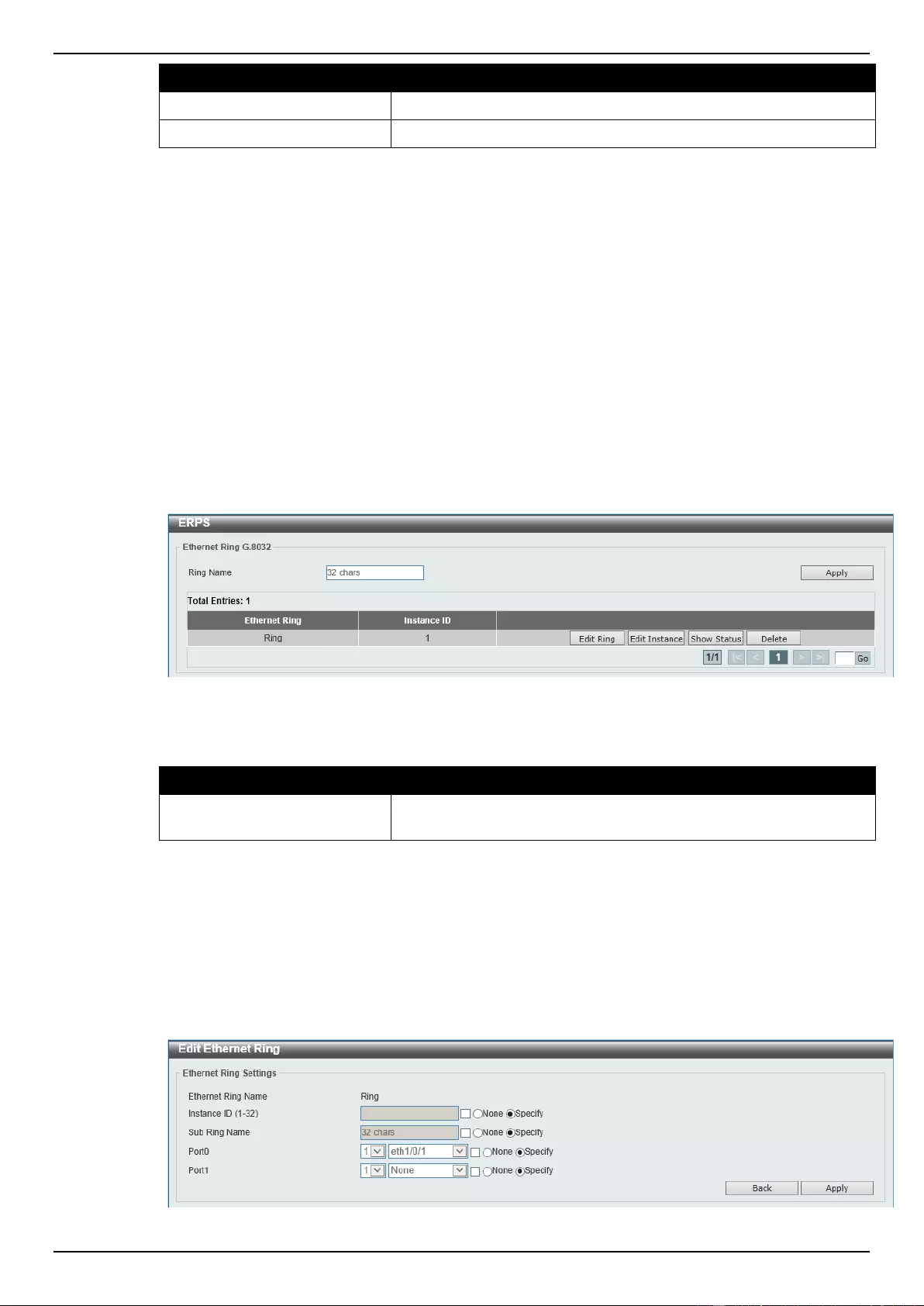
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
110
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port number that will be cleared here.
Click the Clear Detected Protocol button to clear the detected protocol settings for the port selected.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
ERPS (G.8032)
For more information, refer to Appendix E - ERPS Information.
ERPS
This window is used to view and configure Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > ERPS (G.8032) > ERPS, as shown below:
Figure 5-36 ERPS window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Ring Name
Enter the Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance’s name here.
This name can be up to 32 characters long.
Click the Apply button to create an ITU-T G.8032 ERP physical ring.
Click the Edit Ring button to modify an ITU-T G.8032 ERP physical ring.
Click the Edit Instance button to configure the ERP instance.
Click the Show Status button to view the ITU-T G.8032 ERP physical ring’s status information.
Click the Delete button to delete the specified ITU-T G.8032 ERP physical ring.
After click the Edit Ring button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-37 ERPS (Edit Ring) window
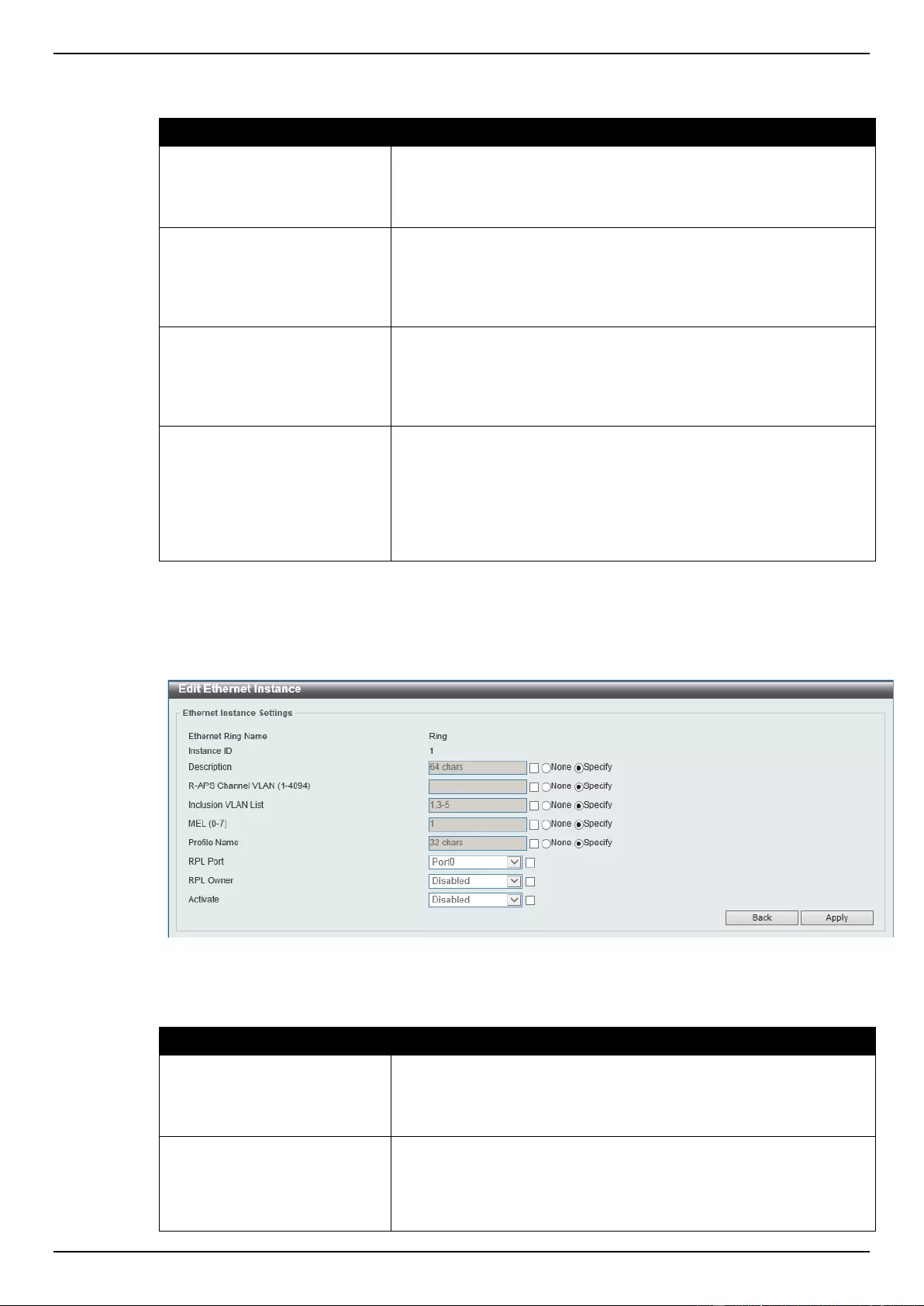
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
111
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Instance ID
Select the checkbox and enter the ERP instance number here. This
value must be between 1 and 32. Select the Specify radio button to
configure this parameter as per normal. Select the None radio
button to revert this parameter to the default setting.
Sub Ring Name
Select the checkbox and enter the physical ring’s sub-ring name
here. This name can be up to 32 characters long. Select the
Specify radio button to configure this parameter as per normal.
Select the None radio button to revert this parameter to the default
setting.
Port0
Select the checkbox and then select the switch’s unit ID and the
port number that will be the first ring port of the physical ring. Select
the Specify radio button to configure this parameter as per normal.
Select the None radio button to revert this parameter to the default
setting.
Port1
Select the checkbox and then select the switch’s unit ID and the
port number that will be the second ring port of the physical ring.
Select the None option, from the drop-down menu, specifies that
the inter-connected node is a local node endpoint of an open ring.
Select the Specify radio button to configure this parameter as per
normal. Select the None radio button to revert this parameter to the
default setting.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous window.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After click the Edit Instance button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-38 ERPS (Edit Instance) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Description
Select the checkbox and enter the ERP instance’s description here.
This description can be up to 64 characters long. Select the Specify
radio button to configure this parameter as per normal. Select the
None radio button to revert this parameter to the default setting.
R-APS Channel VLAN
Select the checkbox and enter the R-APS channel VLAN’s ID for
the ERP instance here. The APS channel VLAN of a sub-ring
instance is also the virtual channel of the sub-ring. This value must
be between 1 and 4094. Select the Specify radio button to
configure this parameter as per normal. Select the None radio
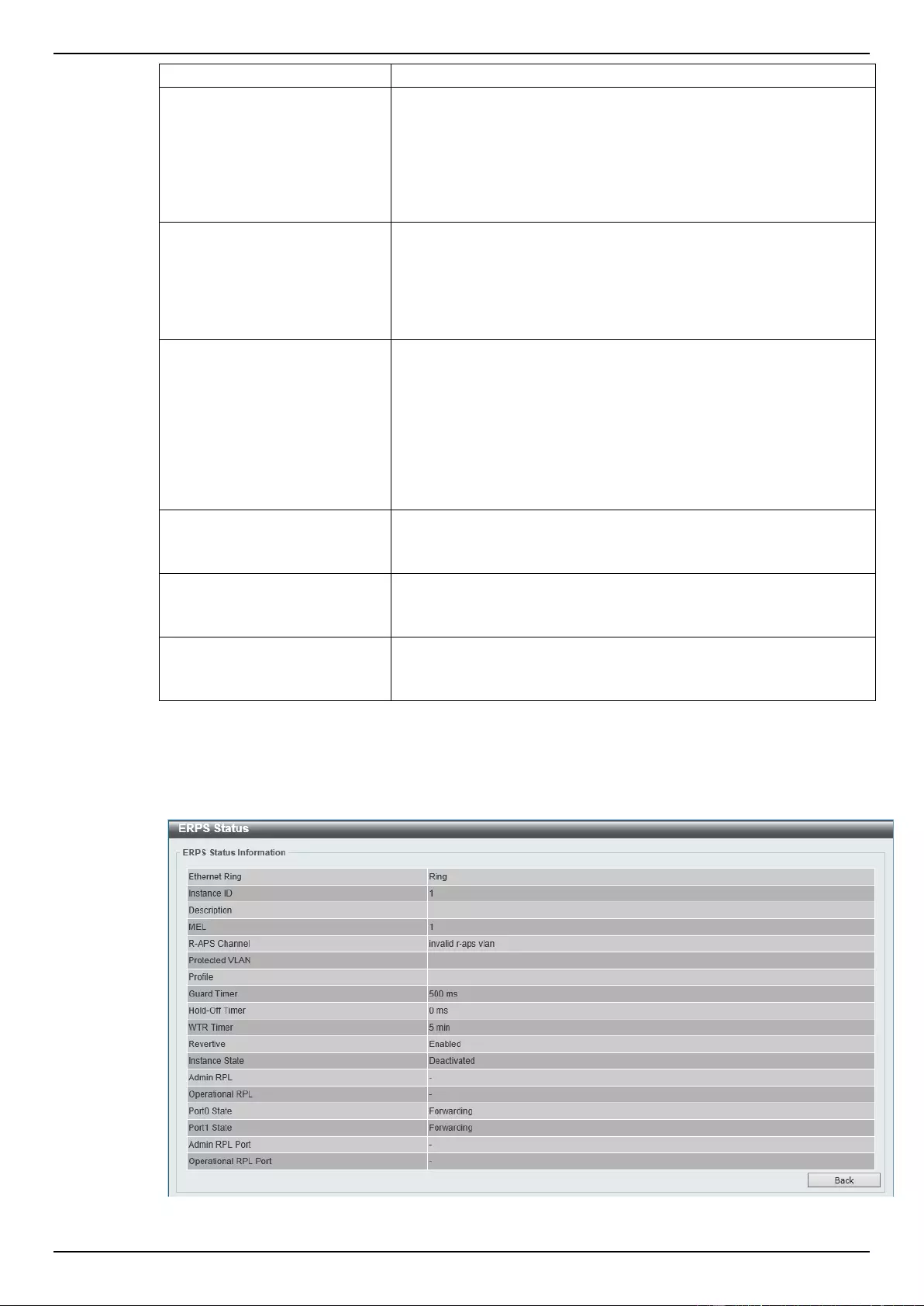
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
112
button to revert this parameter to the default setting.
Inclusion VLAN List
Select the checkbox and enter the inclusion VLAN list here. A range
is identified when a hyphen (-) is used. For example VLANs 1 to 5
can be entered as 1-5. A list is identified when commas (,) are used.
For example, use VLANs 1,3,5. The VLANs specified here will be
protected by the ERP mechanism. Select the Specify radio button
to configure this parameter as per normal. Select the None radio
button to revert this parameter to the default setting.
MEL
Select the checkbox and enter the ring MEL value of the ERP
instance here. This value must be between 0 and 7. The configured
MEL value of all ring nodes that participate in the same ERP
instance should be identical. Select the Specify radio button to
configure this parameter as per normal. Select the None radio
button to revert this parameter to the default setting.
Profile Name
Select the checkbox and enter the G.8032 profile’s name here that
will be associated with this ERP instance. Multiple ERP instances
can be associated with the same G.8032 profile. The instances
associated with the same profile protect the same set of VLANs, or
the VLANs protected by one instance are a subset of LANs
protected by another instance. This name can be up to 32
characters long. Select the Specify radio button to configure this
parameter as per normal. Select the None radio button to revert this
parameter to the default setting.
RPL Port
Select the checkbox and then select the RPL port option here.
Options to choose from are Port0 and Port1. The option selected
will be configured as the RPL port.
RPL Owner
Select the checkbox and then select whether this node is the RPL
owner or neighbor. Options to choose from are Enabled and
Disabled. Enabling this option will specify this RPL as an owner.
Activate
Select the checkbox and then select whether or not to active this
ERP instance. Options to choose from are Enabled and Disabled.
Enabling this option will active this ERP instance.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous window.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After click the Show Status button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-39 ERPS (View Status) window

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
113
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
ERPS Profile
This window is used to view and configure the Ethernet Ring G.8032 profile settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > ERPS (G.8032) > ERPS Profile, as shown below:
Figure 5-40 ERPS Profile window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Profile Name
Enter the G.8032 profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long. Multiple ERP instances can be associated with the
same G.8032 profile. The instances associated with the same
profile protect the same set of VLANs, or the VLANs protected by
one instance are a subset of LANs protected by another instance.
Click the Apply button to associate the G.8032 profile with the ERP instance created.
Click the Delete button to disassociate the G.8032 profile based on the Profile Name entered.
Click the Edit button to modify the specified G.8032 profile.
After click the Edit button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-41 ERPS Profile (Edit) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
TCN Propagation
Select the checkbox and then select the TCN propagation state.
Options to choose from are Enable and Disabled. This function is
used to enable the propagation of the topology change notifications
from the sub-ERP instance to the major instance.
Revertive
Select the checkbox and then select the revertive state. Options to
choose from are Enable and Disabled. This function is used to
revert back to the working transport entity, for example, when the
RPL was blocked.
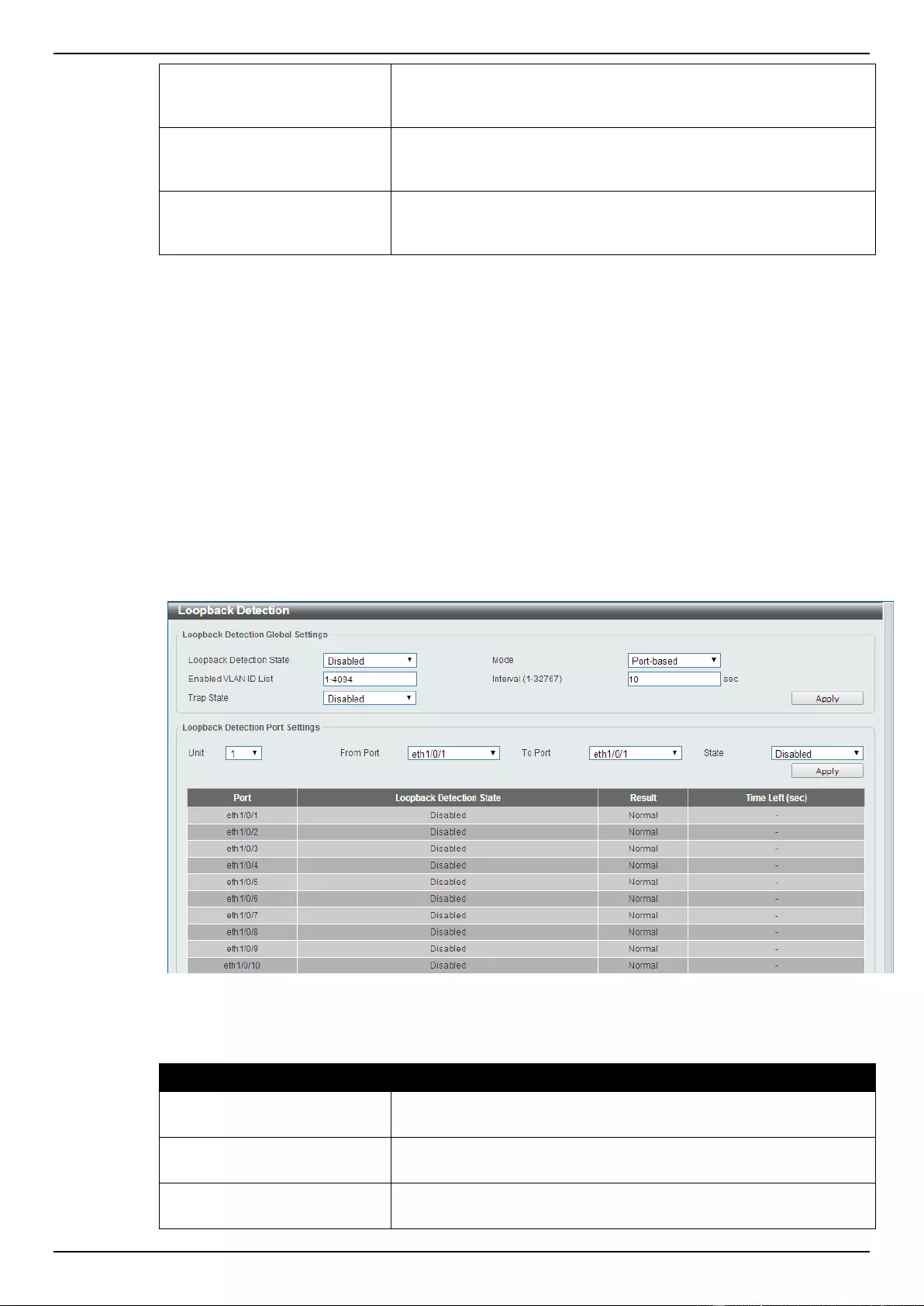
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
114
Guard Timer
Select the checkbox and enter the guard timer value here. This
value must be between 10 and 2000 milliseconds. By default, this
value is 500 milliseconds.
Hold-Off Timer
Select the checkbox and enter hold-off timer value here. This value
must be between 0 and 10000 milliseconds. By default, this value is
0 milliseconds.
WTR Timer
Select the checkbox and enter the WTR timer value here. This
value must be between 1 and 12 minutes. By default, this value is 5
minutes.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous window.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Loopback Detection
The Loopback Detection (LBD) function is used to detect the loop created by a specific port. This
feature is used to temporarily shut down a port on the Switch when a CTP (Configuration Testing
Protocol) packet has been looped back to the Switch. When the Switch detects CTP packets received
from a port or a VLAN, this signifies a loop on the network. The Switch will automatically block the port
or the VLAN and send an alert to the administrator. The Loopback Detection function can be
implemented on a range of ports at a time. The user may enable or disable this function using the
drop-down menu.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Loopback Detection, as shown below:
Figure 5-42 Loopback Detection window
The fields that can be configured for Loopback Detection Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Loopback Detection State
Select to enable or disable loopback detection. The default is
Disabled.
Mode
Select the loopback detection mode. Options to choose from are
Port-based and VLAN-based.
Enable VLAN ID List
Enter the VLAN ID for loop detection. This only takes effect when
the VLAN-based is selected in the Mode drop-down list.
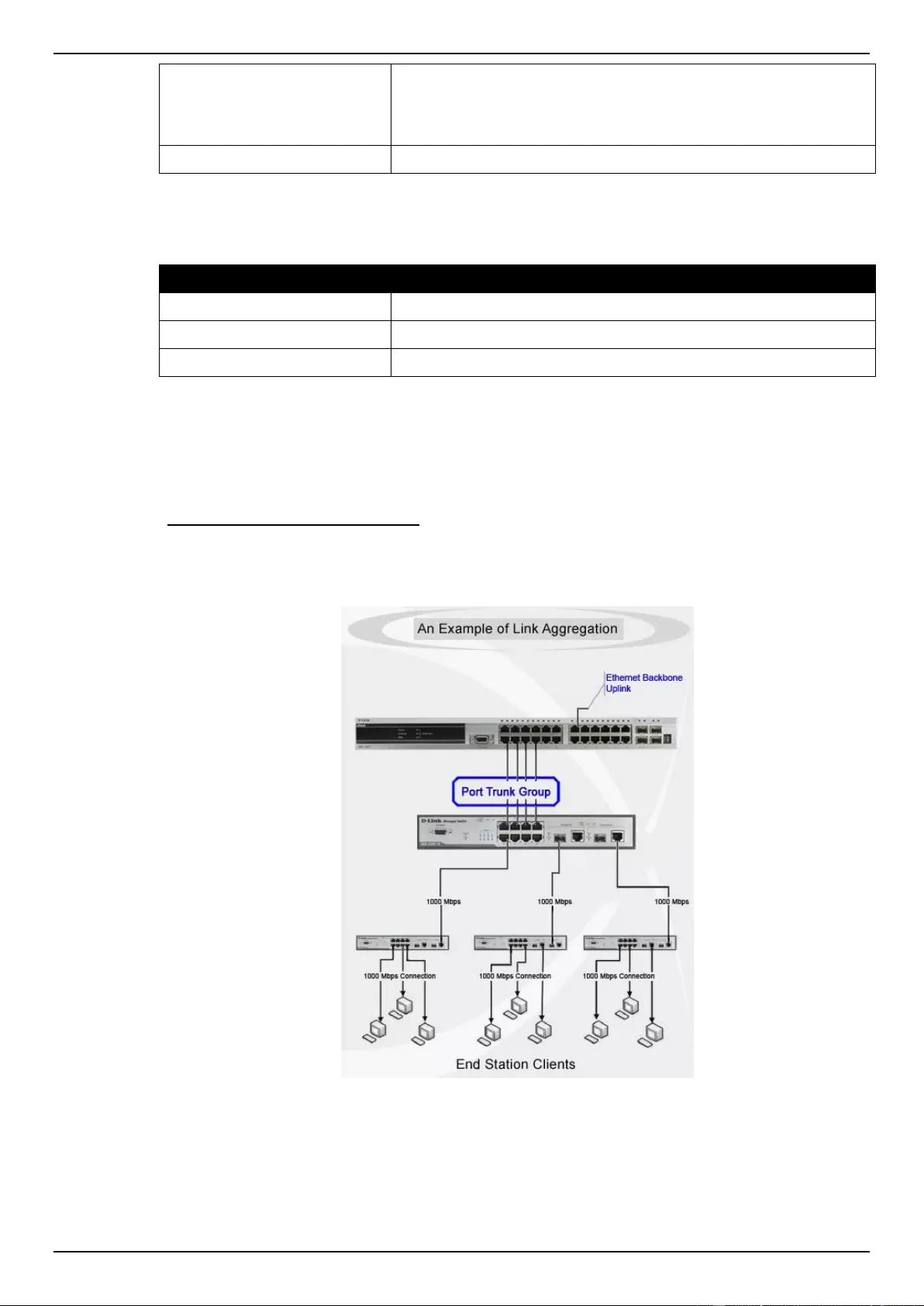
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
115
Interval
Enter the interval in seconds that the device will transmit all the CTP
(Configuration Test Protocol) packets to detect a loop-back event.
The valid range is from 1 to 32767 seconds. The default setting is
10 seconds.
Traps State
Select to enable or disable the loopback detection trap state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Loopback Detection Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the state of the port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Link Aggregation
Understanding Port Trunk Groups
Port trunk groups are used to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth
data pipeline. The Switch supports up to 32 port trunk groups with 1 to 8 ports in each group.
Figure 5-43 Example of Port Trunk Group
The Switch treats all ports in a trunk group as a single port. Data transmitted to a specific host
(destination address) will always be transmitted over the same port in a trunk group. This allows
packets in a data stream to arrive in the same order they were sent.
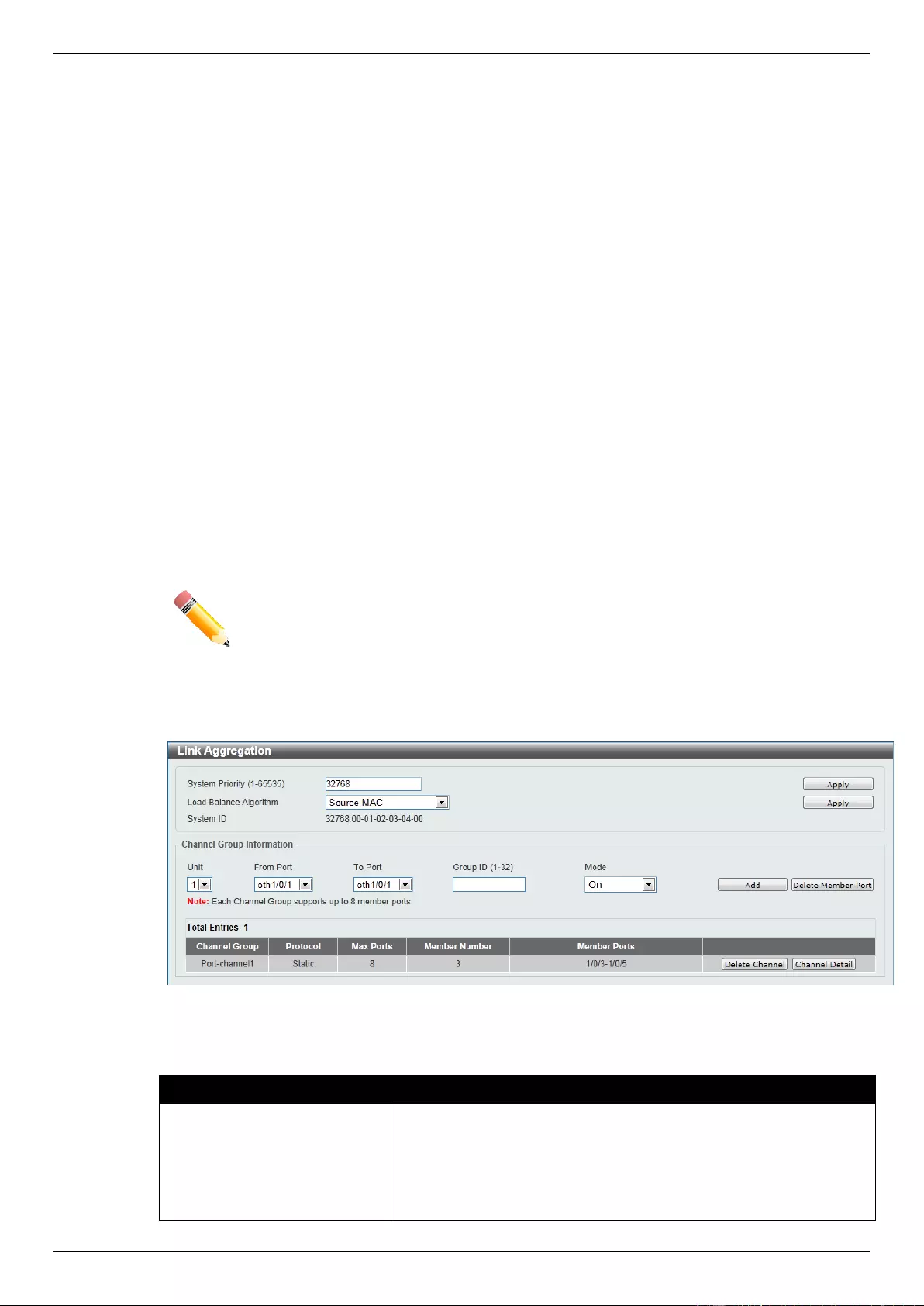
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
116
Link aggregation allows several ports to be grouped together and to act as a single link. This gives a
bandwidth that is a multiple of a single link's bandwidth.
Link aggregation is most commonly used to link a bandwidth intensive network device or devices,
such as a server, to the backbone of a network.
The Switch allows the creation of up to 32 link aggregation groups, each group consisting of 1 to 8
links (ports). Each port can only belong to a single link aggregation group.
All of the ports in the group must be members of the same VLAN, and their STP status, static
multicast, traffic control; traffic segmentation and 802.1p default priority configurations must be
identical. Port locking and 802.1X must not be enabled on the trunk group. Further, the LACP
aggregated links must all be of the same speed and should be configured as full duplex.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the ports in the aggregated group, and a link failure within
the group causes the network traffic to be directed to the remaining links in the group.
The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat a link aggregation group as a single link, on the switch level. On
the port level, the STP will use the port parameters of the Master Port in the calculation of port cost
and in determining the state of the link aggregation group. If two redundant link aggregation groups
are configured on the Switch, STP will block one entire group; in the same way STP will block a single
port that has a redundant link.
NOTE: If any ports within the trunk group become disconnected, packets intended for the
disconnected port will be load shared among the other linked ports of the link aggregation
group.
This window is used to view and configure the link aggregation settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Link Aggregation, as shown below:
Figure 5-44 Link Aggregation window
The fields that can be configured for Link Aggregation are described below:
Parameter
Description
System Priority
Enter the system’s priority value used here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535. By default, this value is 32768. The system
priority determines which ports can join a port-channel and which
ports are put in the stand-alone mode. The lower value has a higher
priority. If two or more ports have the same priority, the port number
determines the priority.
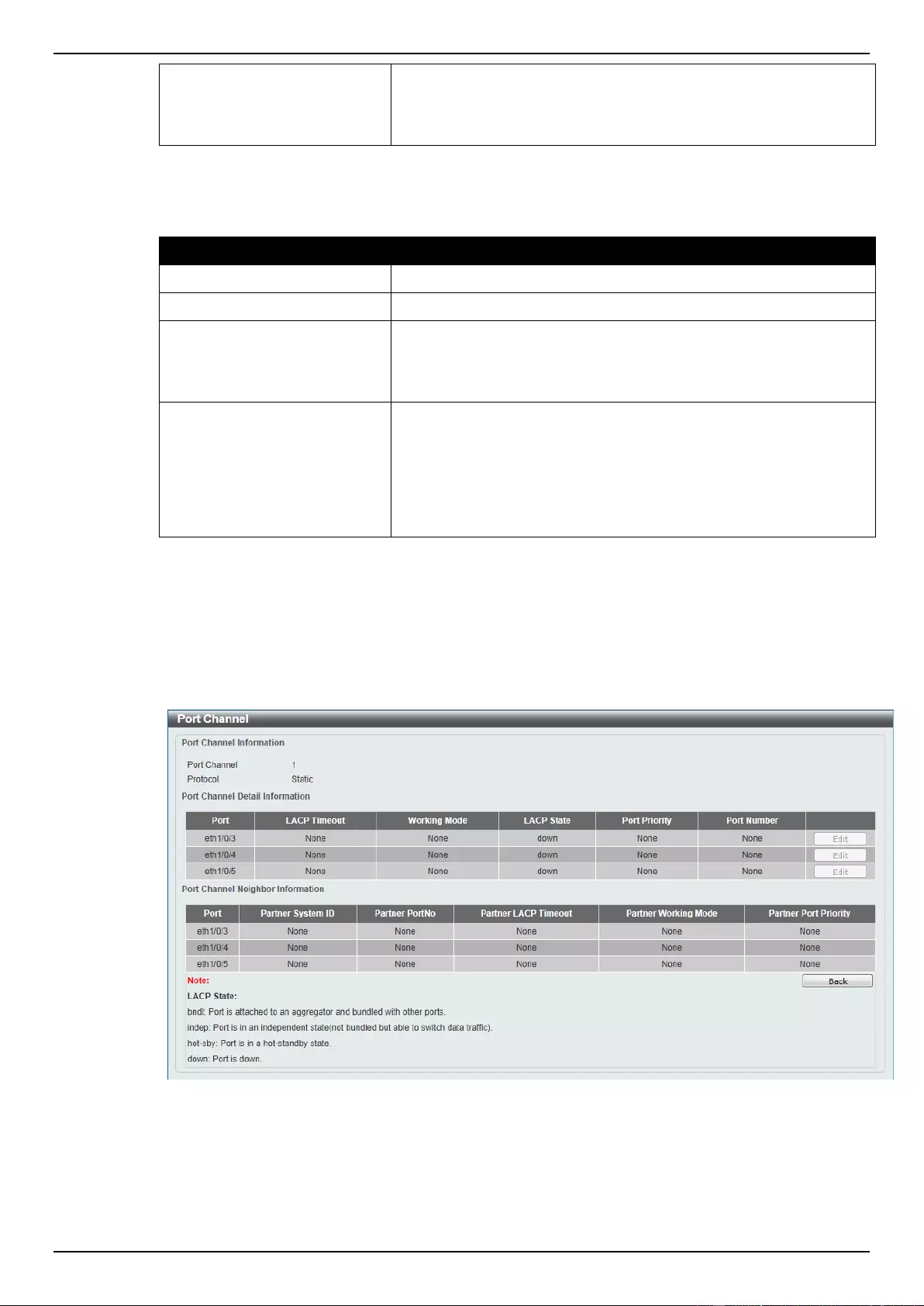
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
117
Load Balance Algorithm
Select the load balancing algorithm that will be used here. Options
to choose from are Source MAC, Destination MAC, Source
Destination MAC, Source IP, Destination IP, and Source
Destination IP. By default, this option is Source MAC.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Channel Group Information are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Group ID
Enter the channel group number here. This value must be between
1 and 32. The system will automatically create the port-channel
when a physical port first joins a channel group. An interface can
only join one channel-group.
Mode
Select the mode option here. Options to choose from are On,
Active, and Passive. If the mode On is specified, the channel
group type is static. If the mode Active or Passive is specified, the
channel group type is LACP. A channel group can only consist of
either static members or LACP members. Once the type of channel
group has been determined, other types of interfaces cannot join
the channel group.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete Member Port button to remove the specific member port.
Click the Delete Channel button to remove the specific entry.
Click the Channel Detail button to view more detailed information about the channel.
After clicking the Channel Detail button, the following page will be available.
Figure 5-45 Port Channel window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
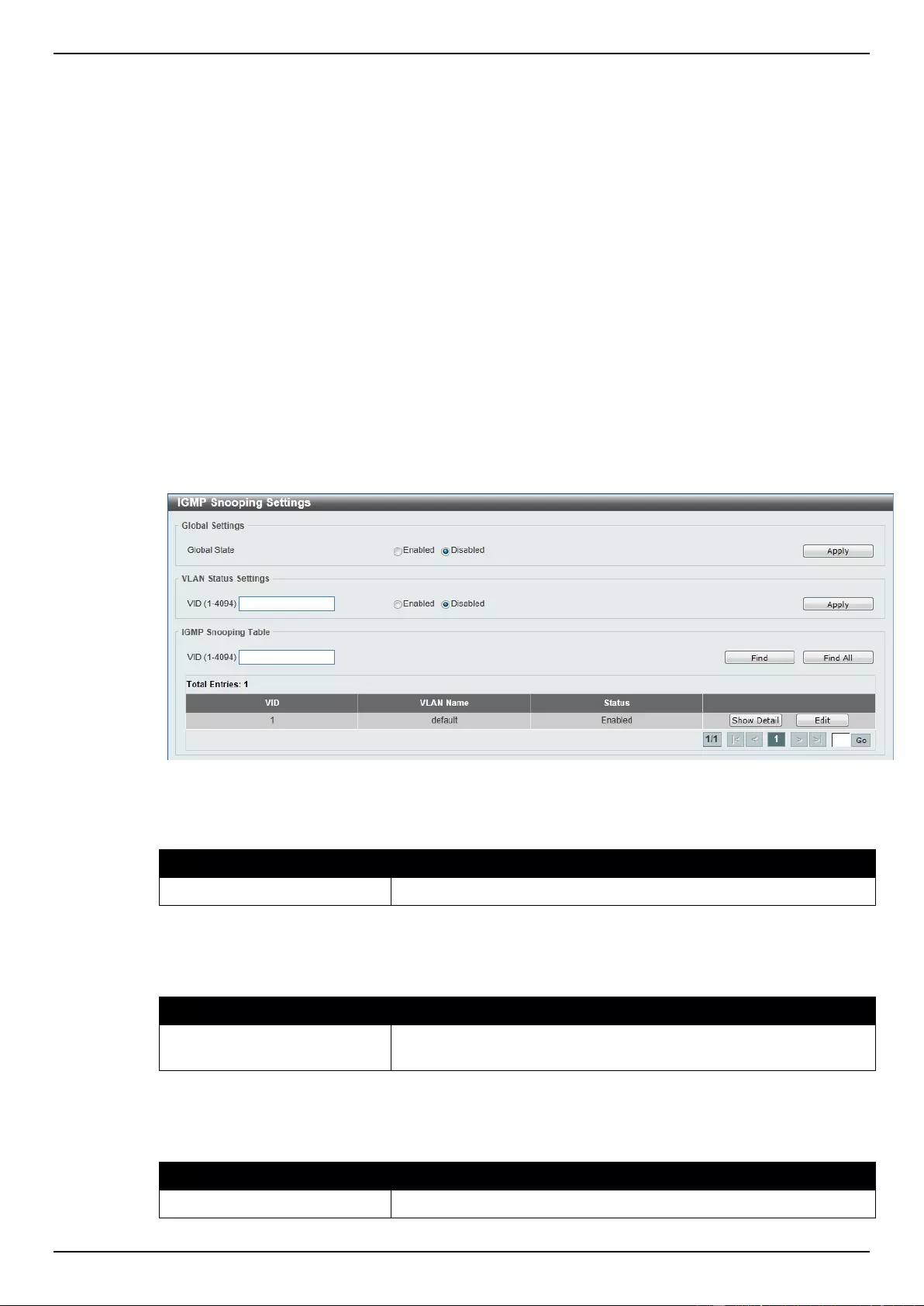
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
118
L2 Multicast Control
IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping allows the Switch to recognize IGMP queries
and reports sent between network stations or devices and an IGMP host.
IGMP Snooping Settings
In order to use IGMP Snooping it must first be enabled for the entire Switch under IGMP Global
Settings at the top of the window. You may then fine-tune the settings for each VLAN by clicking the
corresponding Edit button. When enabled for IGMP snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to
a specific multicast group member based on IGMP messages sent from the device to the IGMP host
or vice versa. The Switch monitors IGMP messages and discontinues forwarding multicast packets
when there are no longer hosts requesting that they continue.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-46 IGMP Snooping Settings window
The field that can be configured for Global Settings is described below:
Parameter
Description
Global State
Select this option to enable or disable IGMP snooping global state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Status Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to enable or disable
IGMP snooping on the VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094.
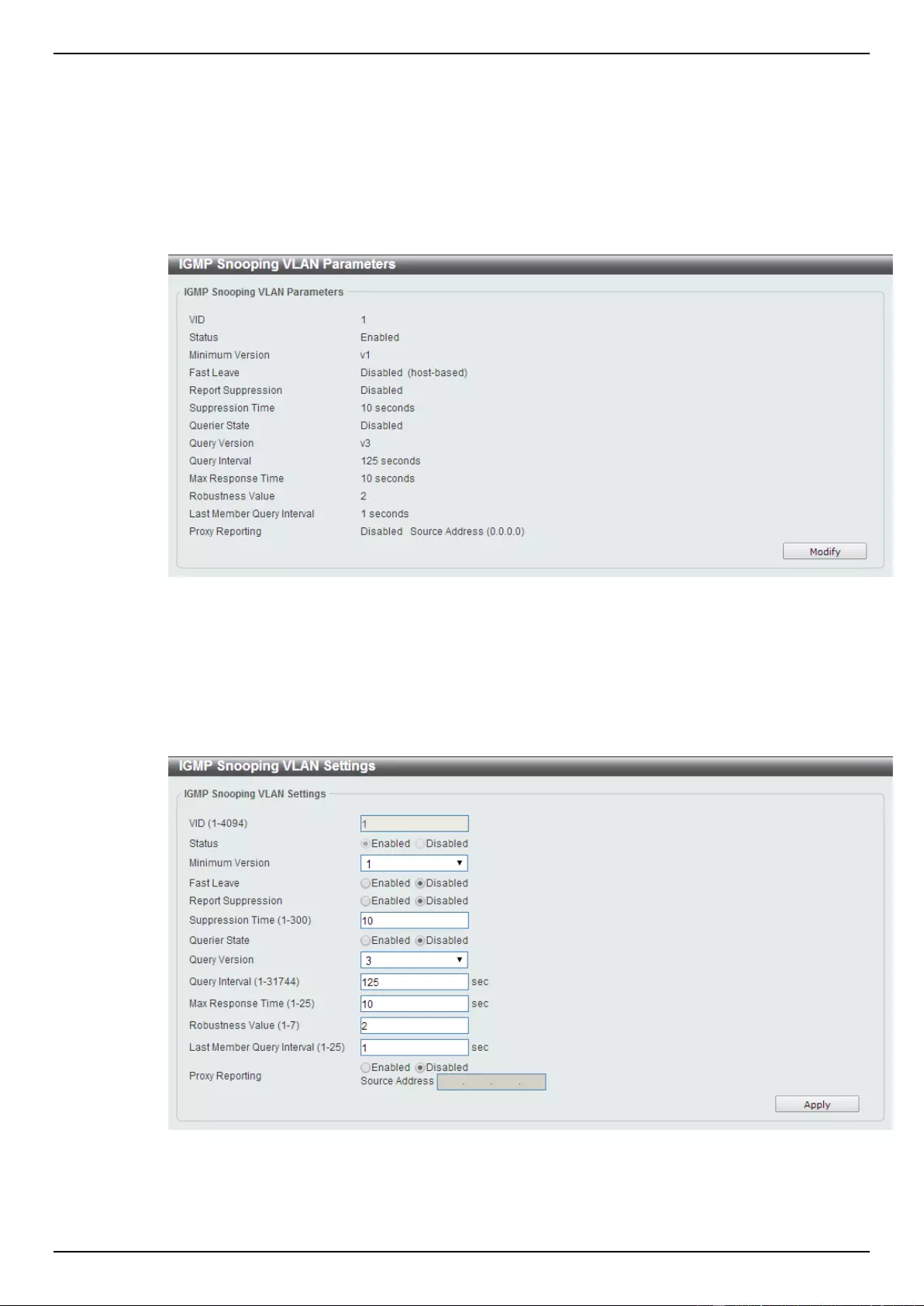
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
119
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific VLAN.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-47 IGMP Snooping VLAN Parameters window
The window displays the detail information about IGMP snooping VLAN. Click the Modify button to
edit the information in the following window.
After clicking the Modify or Edit button in IGMP Snooping Settings window, the following window will
appear.
Figure 5-48 IGMP Snooping VLAN Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
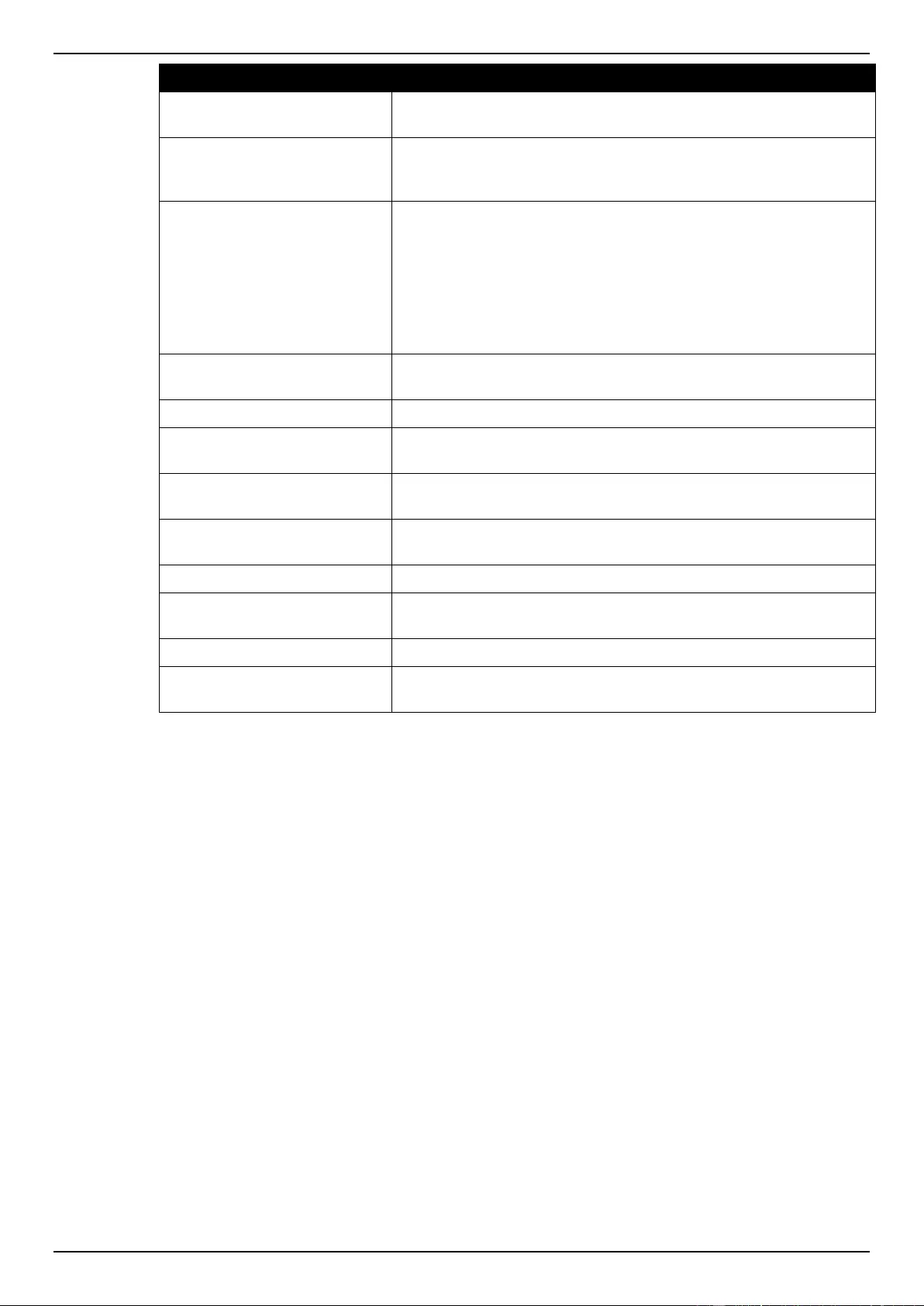
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
120
Parameter
Description
Minimum Version
Select the minimum version of IGMP hosts that is allowed on the
VLAN.
Fast Leave
Select this option to enable or disable the IGMP snooping fast leave
function. If enabled, the membership is immediately removed when
the system receive the IGMP leave message.
Report Suppression
Select this option to enable or disable the report suppression. The
report suppression function only works for IGMPv1 and IGMPv2
traffic. When report suppression is enabled, the Switch suppresses
the duplicate reports sent by hosts. The suppression for the same
group report or leave will continue until the suppression time
expired. For report or leave messages to the same group, only one
report or leave message is forwarded. The remaining report and
leave messages are suppressed.
Suppression Time
Enter the interval of suppressing duplicate IGMP reports or leaves.
The range is from 1 to 300.
Querier State
Select this option to enable or disable the querier state.
Query Version
Select the general query packet version sent by the IGMP snooping
querier. Options to choose from are 1, 2, and 3.
Query Interval
Enter the interval at which the IGMP snooping querier sends IGMP
general query messages periodically.
Max Response Time
Enter the maximum response time, in seconds, advertised in IGMP
snooping queries. The range is 1 to 25.
Robustness Value
Enter the robustness variable used in IGMP snooping.
Last Member Query Interval
Enter the interval at which the IGMP snooping querier sends IGMP
group-specific or group-source-specific (channel) query messages.
Proxy Reporting
Select this option to enable or disable the proxy-reporting function.
Source Address
Enter the source IP of proxy reporting. This is available when
Enabled is selected in Proxy Reporting.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IGMP Snooping Groups Settings
This window is used to configure and view the IGMP snooping static group, and view IGMP snooping
group.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Groups Settings, as shown below:
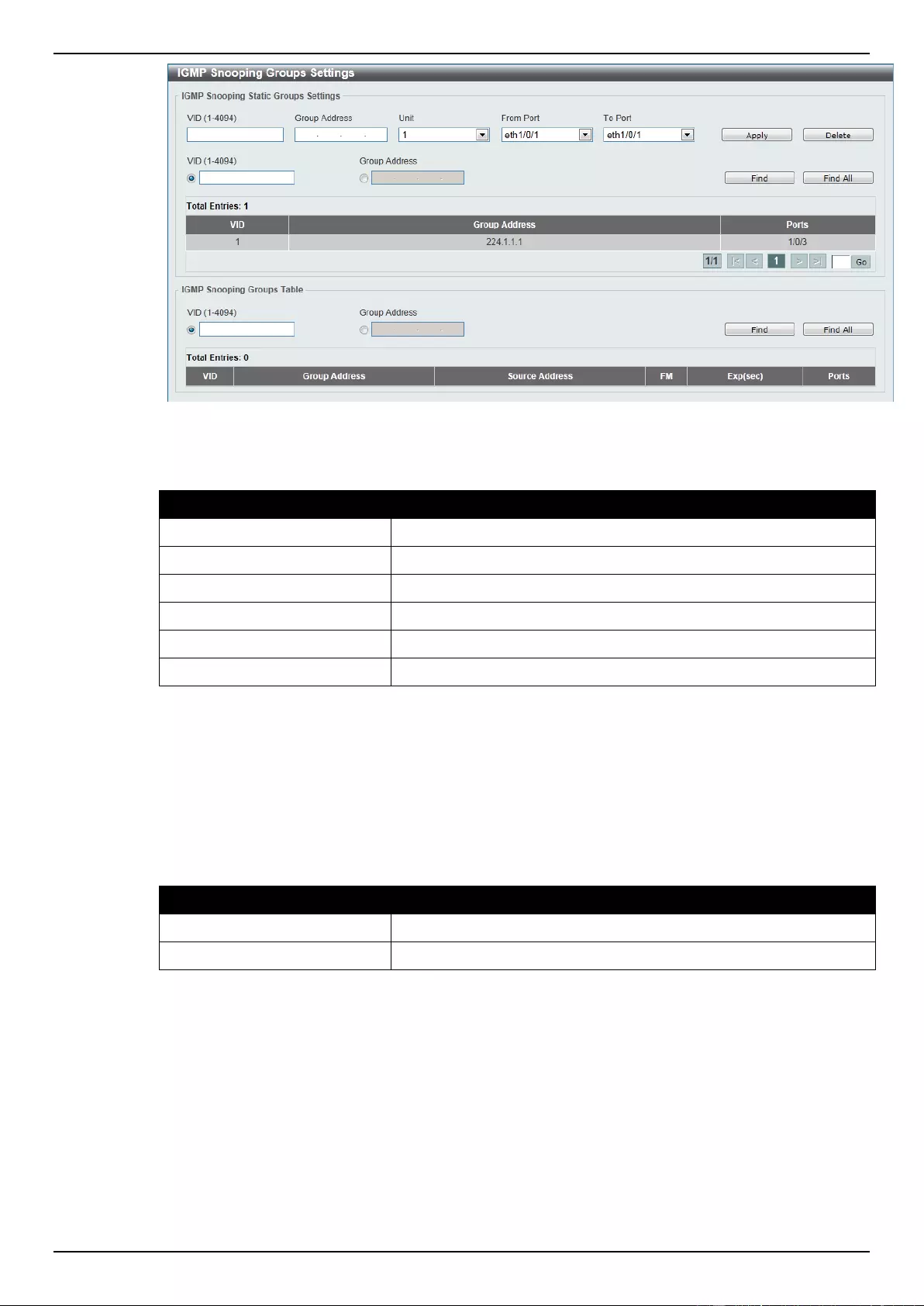
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
121
Figure 5-49 IGMP Snooping Groups Settings
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Static Groups Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Enter an IP multicast group address.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
VID
Click the radio button and enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Click the radio button and enter an IP multicast group address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Groups Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Click the radio button and enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Click the radio button and enter an IP multicast group address.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
IGMP Snooping Mrouter Settings
This window is used to configure the specified interface(s) as the multicast router ports or as
forbidden to be multicast router ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Mrouter Settings, as shown below:
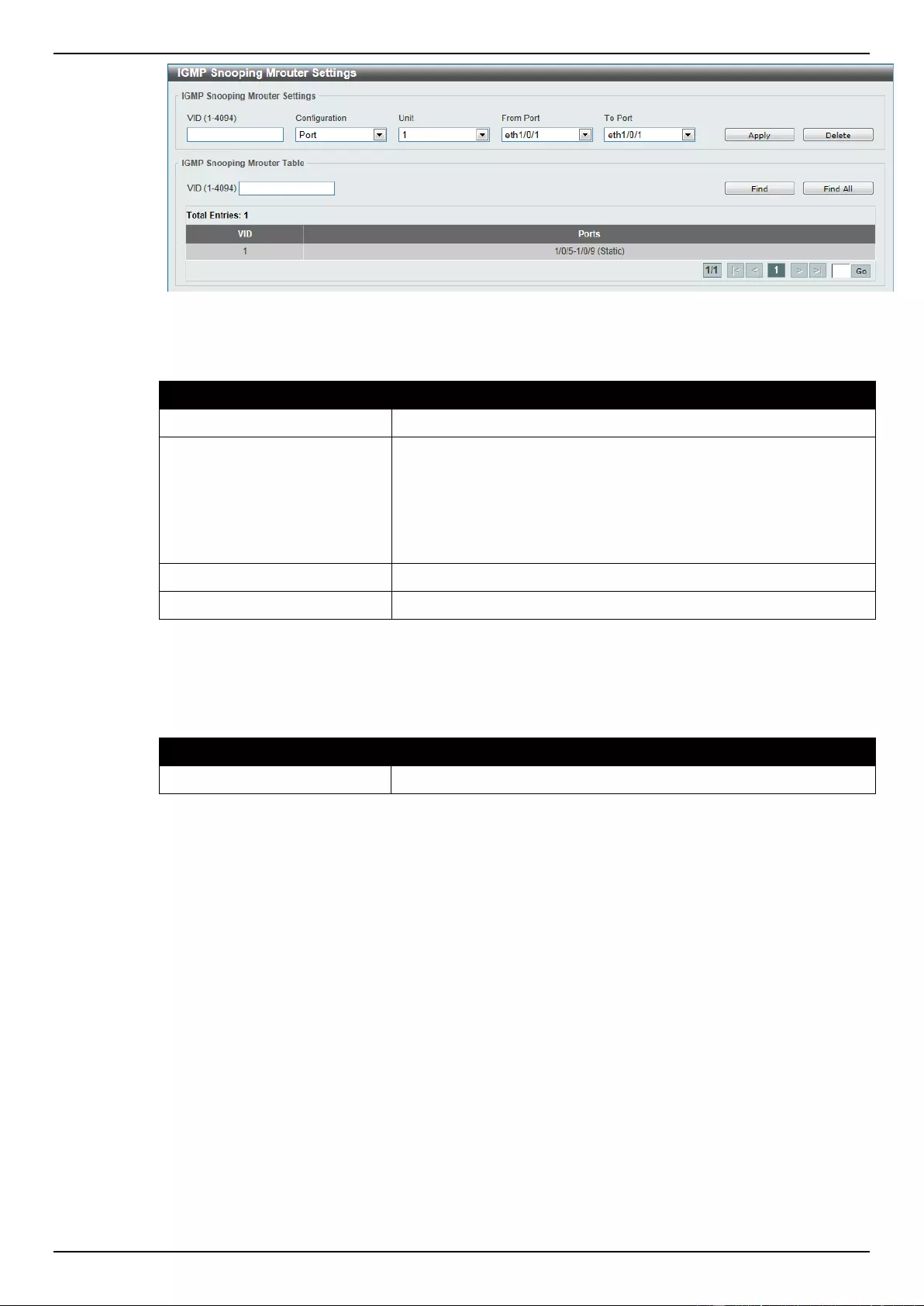
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
122
Figure 5-50 IGMP Snooping Mrouter Settings window
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Mrouter Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
Configuration
Select the port configuration. Options to choose from are Port, and
Forbidden Port.
Port - Select to have the configured ports to be static multicast
router ports.
Forbidden Port – Select to have the configured ports not to be
multicast router ports.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Mrouter Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IGMP Snooping Statistics Settings
This window is used to clear and display the IGMP snooping related statistics.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP
Snooping Statistics Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
123
Figure 5-51 IGMP Snooping Statistics Settings window
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Statistics Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Statistics
Select the interface here. Options to choose from are All, VLAN,
and Port.
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094. This is available when VLAN
is selected in the Statistics drop-down list.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Statistics drop-down
list.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Statistics drop-down
list.
Click the Clear button to clear the IGMP snooping related statistics.
The fields that can be configured for IGMP Snooping Statistics Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
Find Type
Select the interface type. Options to choose from are VLAN, and
Port.
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094. This is available when VLAN
is selected in the Find Type drop-down list.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Find Type drop-down
list.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Find Type drop-down
list.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping is an IPv6 function used similarly to IGMP snooping in
IPv4. It is used to discover ports on a VLAN that are requesting multicast data. Instead of flooding all
ports on a selected VLAN with multicast traffic, MLD snooping will only forward multicast data to ports
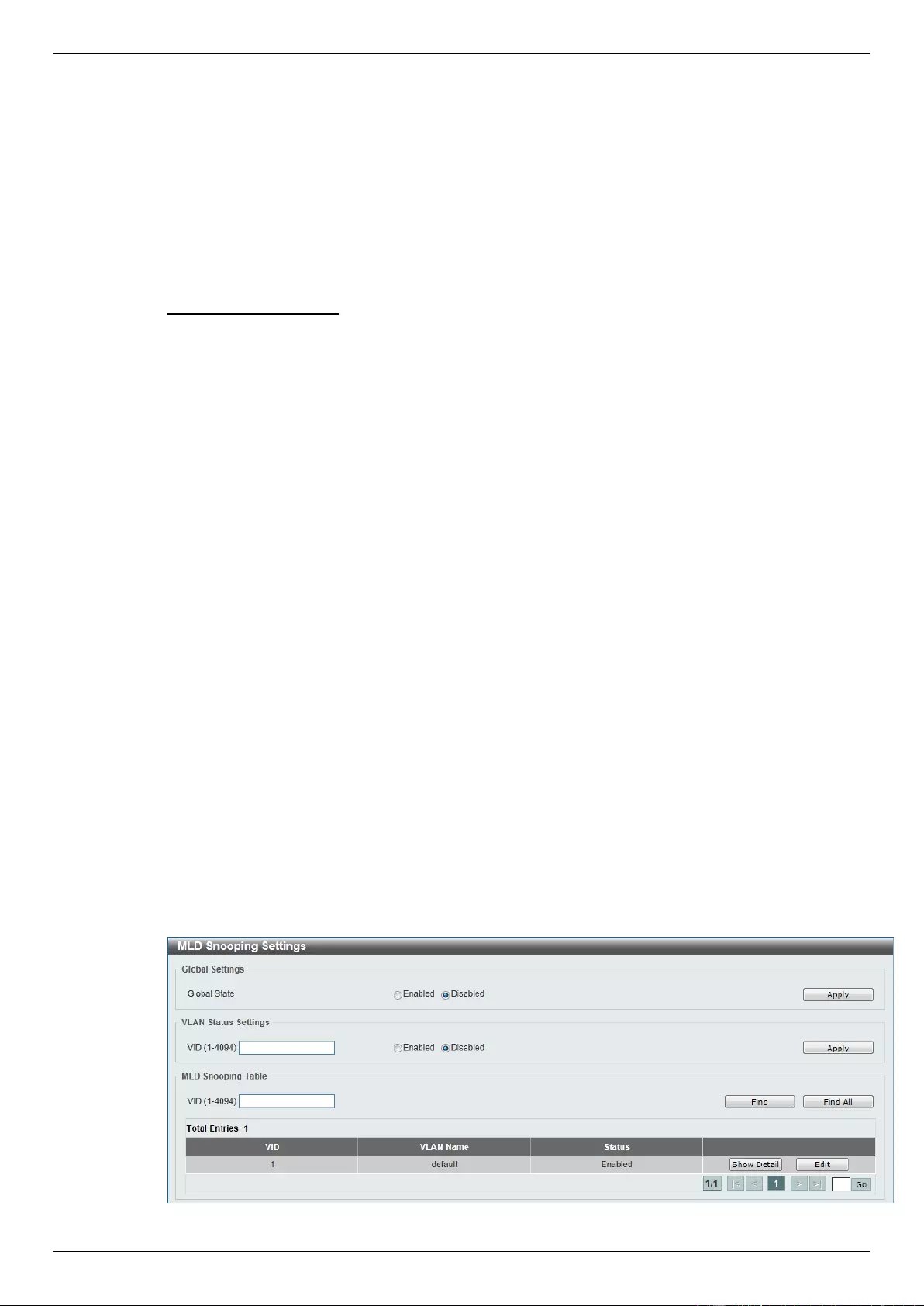
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
124
that wish to receive this data through the use of queries and reports produced by the requesting ports
and the source of the multicast traffic.
MLD snooping is accomplished through the examination of the layer 3 part of an MLD control packet
transferred between end nodes and a MLD router. When the Switch discovers that this route is
requesting multicast traffic, it adds the port directly attached to it into the correct IPv6 multicast table,
and begins the process of forwarding multicast traffic to that port. This entry in the multicast routing
table records the port, the VLAN ID, and the associated multicast IPv6 multicast group address, and
then considers this port to be an active listening port. The active listening ports are the only ones to
receive multicast group data.
MLD Control Messages
Three types of messages are transferred between devices using MLD snooping. These three
messages are all defined by four ICMPv6 packet headers, labeled 130, 131, 132, and 143.
1. Multicast Listener Query – Similar to the IGMPv2 Host Membership Query for IPv4, and labeled
as 130 in the ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the router to ask if any link is
requesting multicast data. There are two types of MLD query messages emitted by the router.
The General Query is used to advertise all multicast addresses that are ready to send multicast
data to all listening ports, and the Multicast Specific query, which advertises a specific multicast
address that is also ready. These two types of messages are distinguished by a multicast
destination address located in the IPv6 header and a multicast address in the Multicast Listener
Query Message.
2. Multicast Listener Report, Version 1 – Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv2,
and labeled as 131 in the ICMP packet header, this message is sent by the listening port to the
Switch stating that it is interested in receiving multicast data from a multicast address in response
to the Multicast Listener Query message.
3. Multicast Listener Done – Akin to the Leave Group Message in IGMPv2, and labeled as 132 in
the ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the multicast listening port stating that it is no
longer interested in receiving multicast data from a specific multicast group address, therefore
stating that it is “done” with the multicast data from this address. Once this message is received
by the Switch, it will no longer forward multicast traffic from a specific multicast group address to
this listening port.
4. Multicast Listener Report, Version 2 - Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv3,
and labeled as 143 in the ICMP packet header, this message is sent by the listening port to the
Switch stating that it is interested in receiving multicast data from a multicast address in response
to the Multicast Listener Query message.
MLD Snooping Settings
This window is used to configure the MLD snooping settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-52 MLD Snooping Settings window
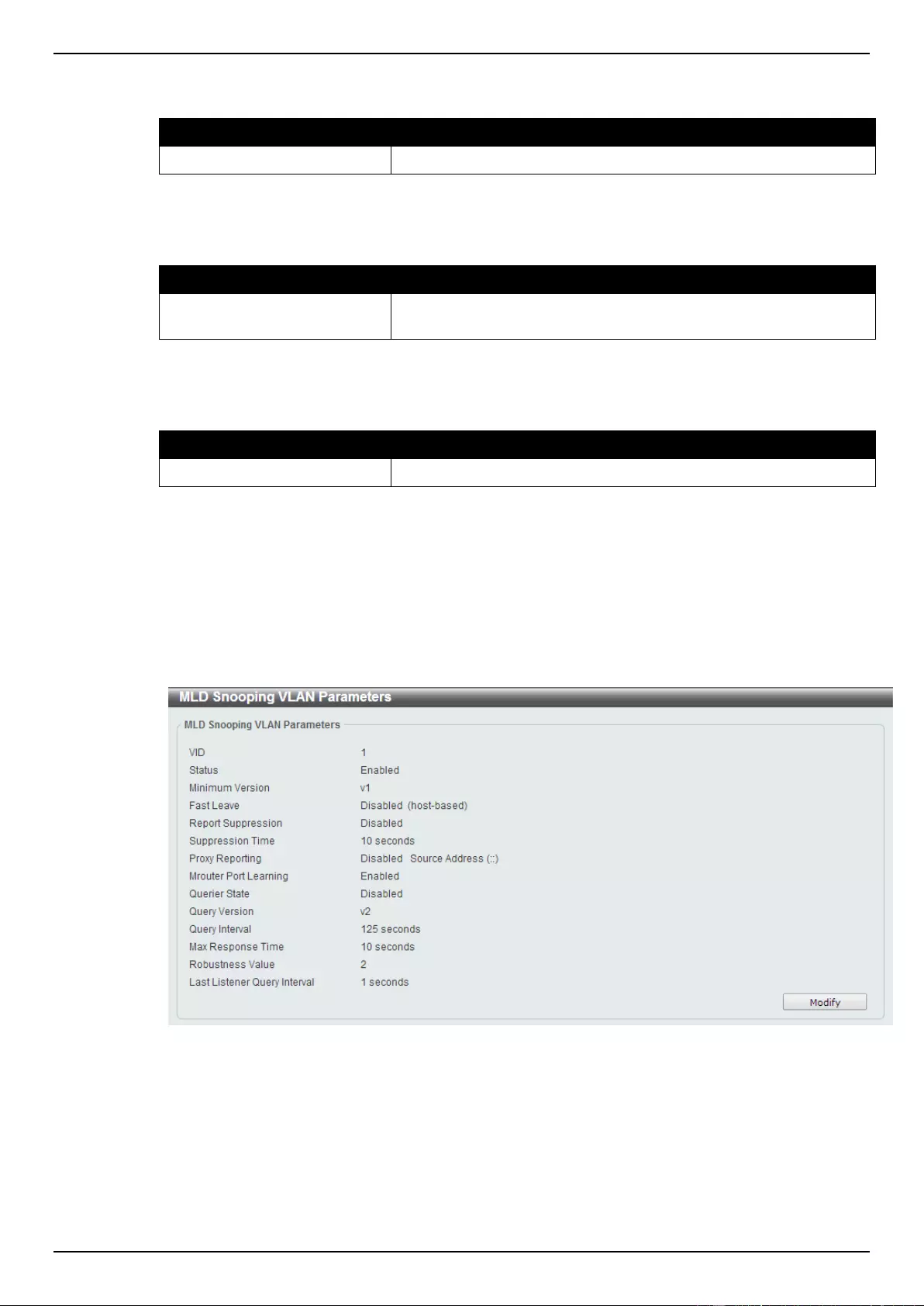
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
125
The field that can be configured for Global Settings is described below:
Parameter
Description
Global State
Select this option to enable or disable MLD snooping global state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for VLAN Status Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094, and select to enable or disable
MLD snooping on the VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID from 1 to 4094.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific VLAN.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-53 MLD Snooping VLAN Parameters window
The window displays the detail information about MLD snooping VLAN. Click the Modify button to edit
the information in the following window.
After clicking the Modify or Edit button in MLD Snooping Settings window, the following window will
appear.
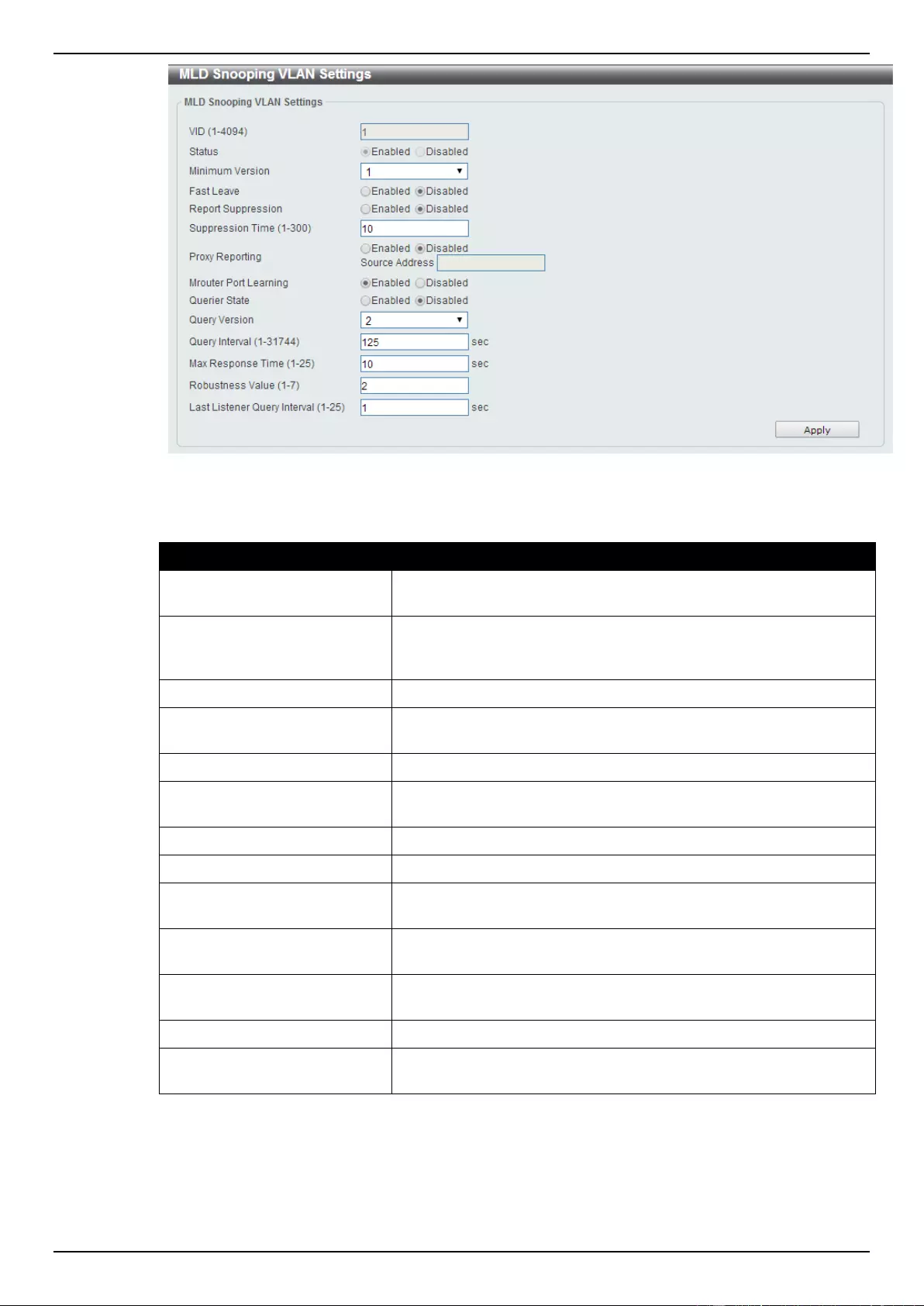
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
126
Figure 5-54 MLD Snooping VLAN Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Minimum Version
Select the minimum version of MLD hosts that is allowed on the
VLAN.
Fast Leave
Select this option to enable or disable the MLD snooping fast leave
function. If enabled, the membership is immediately removed when
the system receive the MLD leave message.
Report Suppression
Select this option to enable or disable the report suppression.
Suppression Time
Enter the interval of suppressing duplicate MLD reports or leaves.
The range is from 1 to 300.
Proxy Reporting
Select this option to enable or disable the proxy-reporting function.
Source Address
Enter the source IP of proxy reporting. This is available when
Enabled is selected in Proxy Reporting.
Mrouter Port Learning
Select this option to enable or disable Mrouter port learning.
Querier State
Select this option to enable or disable the querier state.
Query Version
Select the general query packet version sent by the MLD snooping
querier. Options to choose from are 1, and 2.
Query Interval
Enter the interval at which the MLD snooping querier sends MLD
general query messages periodically.
Max Response Time
Enter the maximum response time, in seconds, advertised in MLD
snooping queries. The range is 1 to 25.
Robustness Value
Enter the robustness variable used in MLD snooping.
Last Listener Query Interval
Enter the interval at which the MLD snooping querier sends MLD
group-specific or group-source-specific (channel) query messages.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
MLD Snooping Groups Settings
This window is used to configure and view the MLD snooping static group, and view MLD snooping
group.
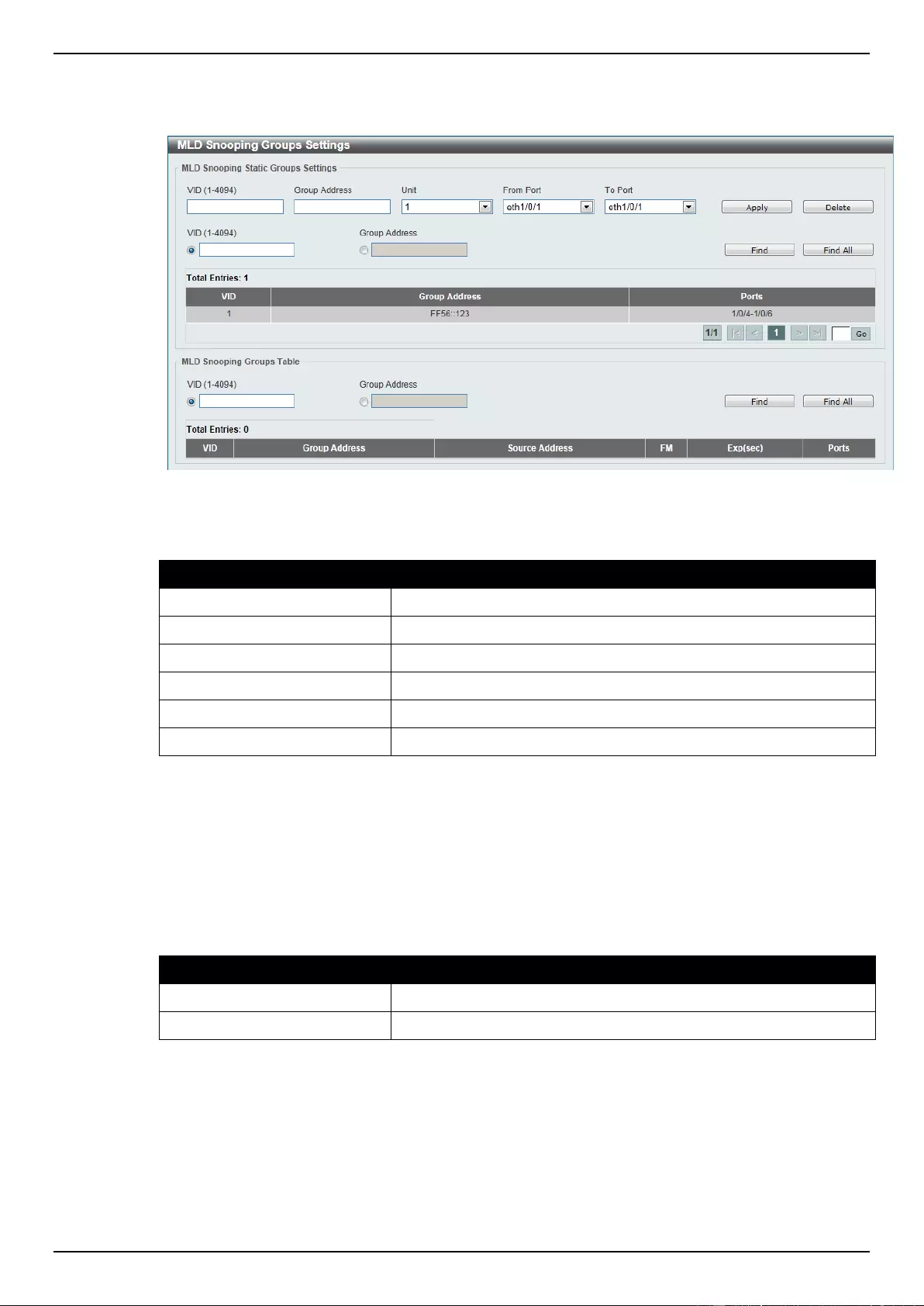
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
127
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Groups Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-55 MLD Snooping Group Settings window
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Static Groups Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Enter an IPv6 multicast group address.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
VID
Click the radio button and enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Click the radio button and enter an IP multicast group address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Groups Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Click the radio button and enter a VLAN ID of the multicast group.
Group Address
Click the radio button and enter an IP multicast group address.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
MLD Snooping Mrouter Settings
This window is used to configure the specified interface(s) as the router ports or forbidden to be IPv6
multicast router ports on the VLAN interface on the Switch.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
128
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Mrouter Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-56 MLD Snooping Mrouter Settings window
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Mrouter Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
Configuration
Select the port configuration. Options to choose from are Port,
Forbidden Port, and Learn pimv6.
Port - Select to have the configured ports as being connected to
multicast-enabled routers.
Forbidden Port - Select to have the configured ports as being not
connected to multicast-enabled routers.
Learn pimv6 - Select to enable dynamic learning of multicast router
port.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Mrouter Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
MLD Snooping Statistics Settings
This window is used to clear and display the MLD snooping related statistics.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD
Snooping Statistics Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
129
Figure 5-57 MLD Snooping Statistics Settings window
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Statistics Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Statistics
Select the interface here. Options to choose from are All, VLAN,
and Port.
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094. This is available when VLAN
is selected in the Statistics drop-down list.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Statistics drop-down
list.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Statistics drop-down
list.
Click the Clear button to clear the MLD snooping related statistics.
The fields that can be configured for MLD Snooping Statistics Table are described below:
Parameter
Description
Find Type
Select the interface type. Options to choose from are VLAN, and
Port.
VID
Enter a VLAN ID between 1 and 4094. This is available when VLAN
is selected in the Find Type drop-down list.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Find Type drop-down
list.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
This is available when Port is selected in the Find Type drop-down
list.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Find All button to view all the entries.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Multicast Filtering
This window is used to view and configure the Layer 2 multicast filtering settings.
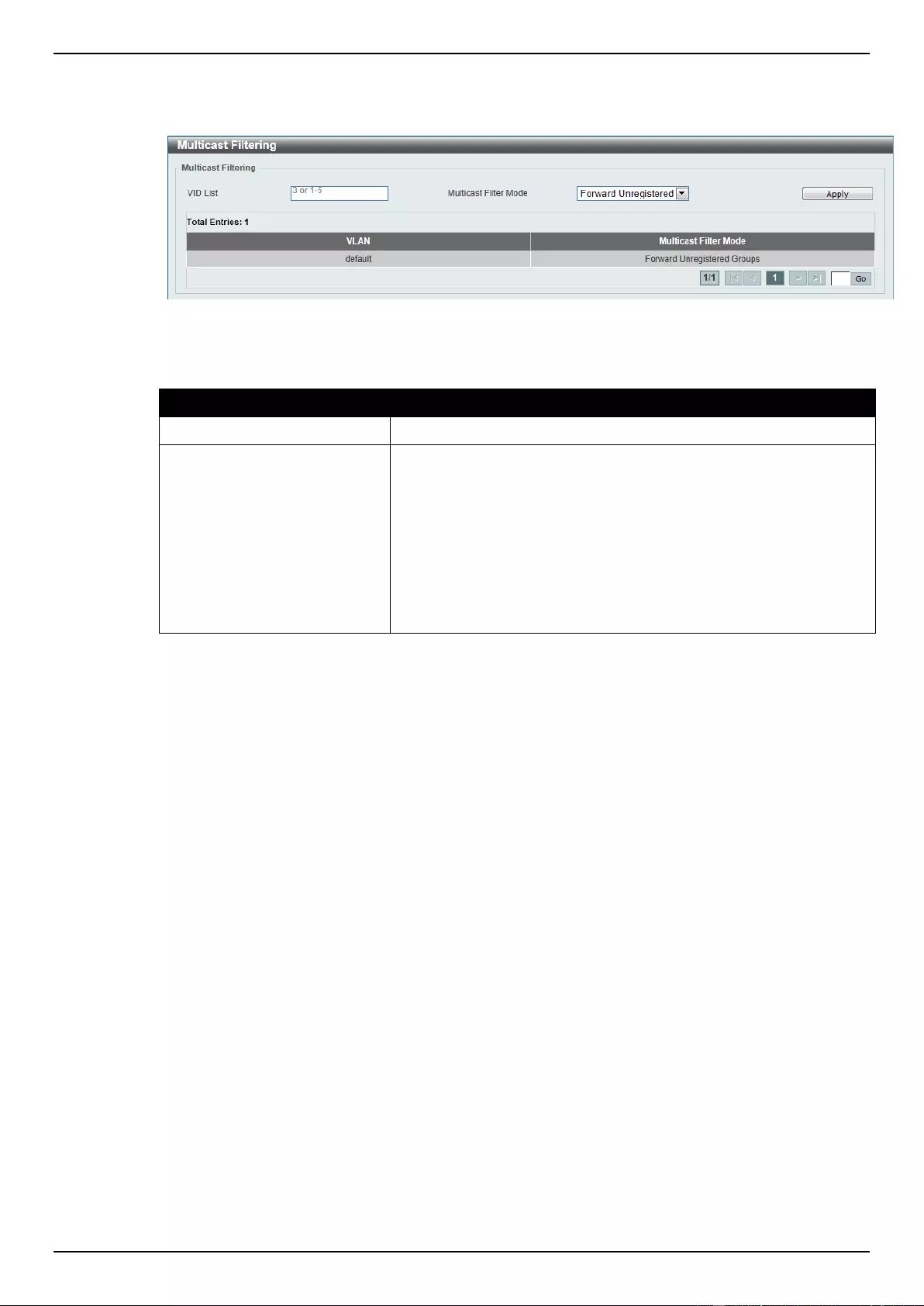
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
130
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > Multicast Filtering, as
shown below:
Figure 5-58 Multicast Filtering window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list that will be used for this configuration here.
Multicast Filter Mode
Select the multicast filter mode here. Options to choose from are
Forward Unregistered, Forward All, and Filter Unregistered.
When selecting the Forward Unregistered option, registered
multicast packets will be forwarded based on the forwarding table
and all unregistered multicast packets will be flooded based on the
VLAN domain. When selecting the Forward All option, all multicast
packets will be flooded based on the VLAN domain. When selecting
the Filter Unregistered option, registered packets will be forwarded
based on the forwarding table and all unregistered multicast packets
will be filtered.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
LLDP
LLDP Global Settings
This window is used to configure the LLDP global settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Global Settings, as shown below:
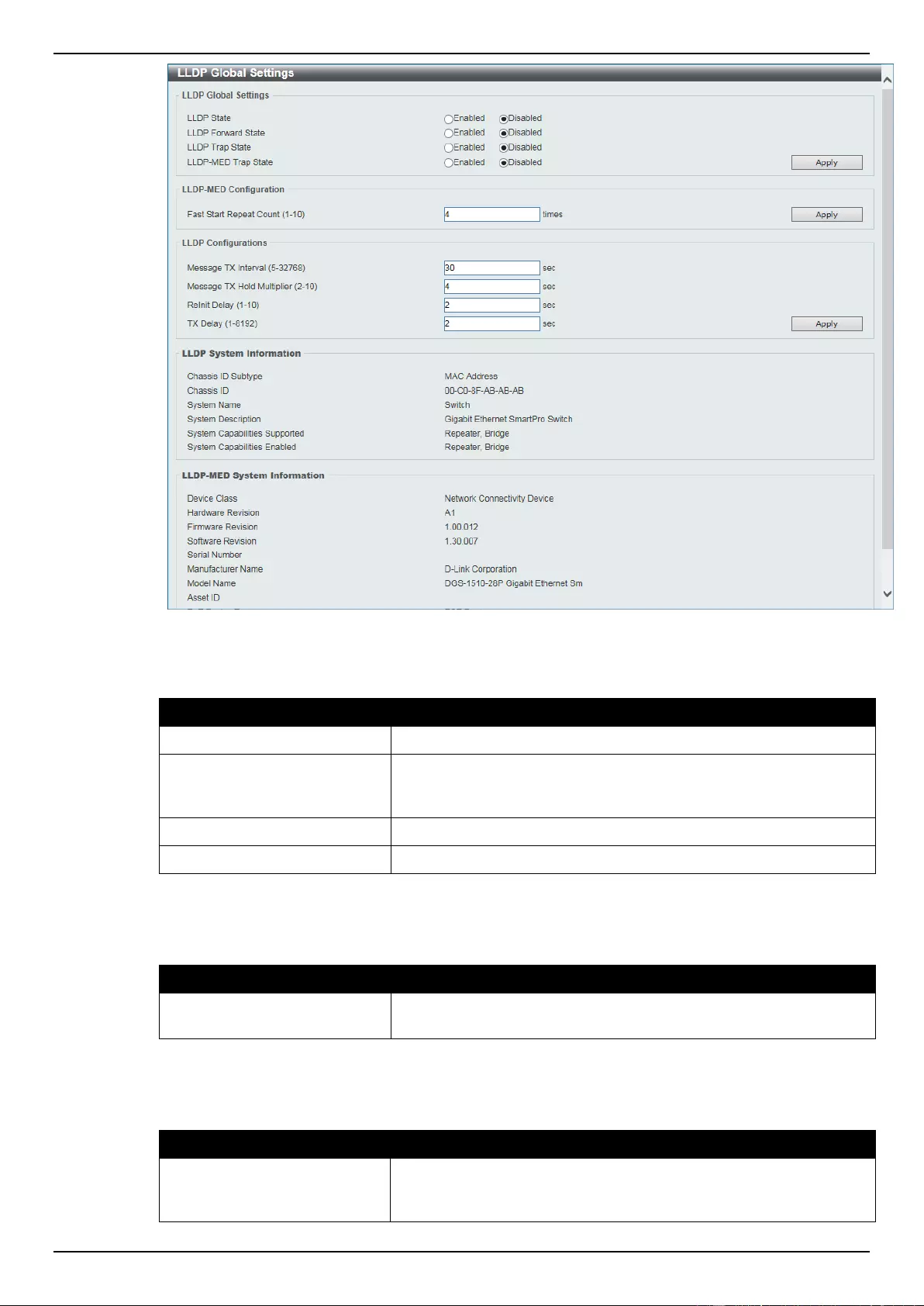
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
131
Figure 5-59 LLDP Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for LLDP Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
LLDP State
Select this option to enable or disable the LLDP feature
LLDP Forward State
Select this option to enable or disable LLDP forward state. When
the LLDP State is disabled and LLDP Forward Sate is enabled,
the received LLDPDU packet will be forwarded.
LLDP Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the LLDP trap state.
LLDP-MED Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the LLDP-MED trap state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for LLDP-MED Configuration are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fast Start Repeat Count
Enter the LLDP-MED fast start repeat count value. This value must
be between 1 and 10.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for LLDP Configurations are described below:
Parameter
Description
Message TX Interval
Enter the interval between consecutive transmissions of LLDP
advertisements on each physical interface. The range is from 5 to
32768 seconds.
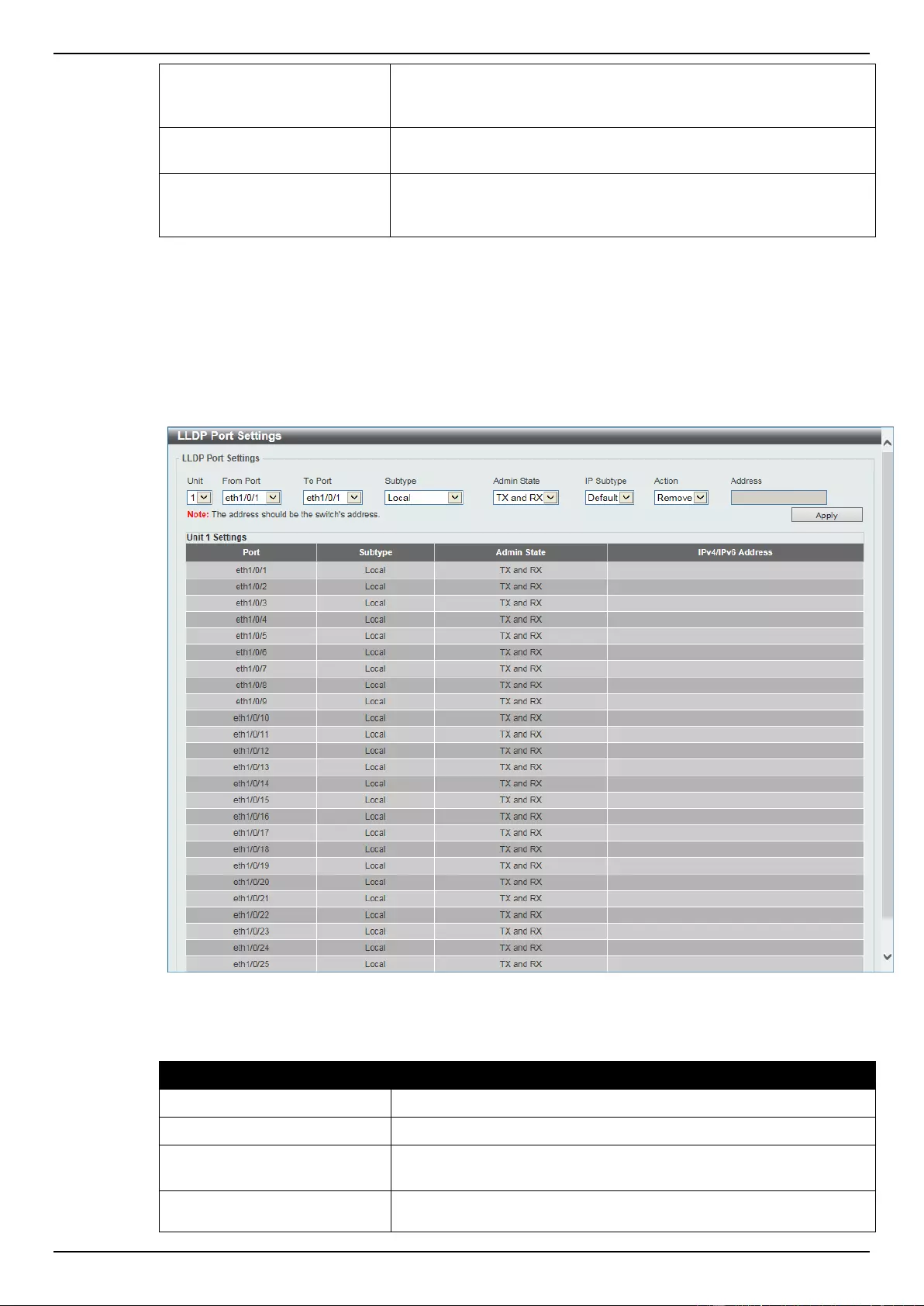
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
132
Message TX Hold Multiplier
Enter the multiplier on the LLDPDUs transmission interval that used
to compute the TTL value of an LLDPDU. This value must be
between 2 and 10.
Relnit Delay
Enter the delay value for LLDP initialization on an interface. This
value must be between 1 and 10 seconds.
TX Delay
Enter the delay value for sending successive LLDPDUs on an
interface. The valid values are from 1 to 8192 seconds and should
not be greater than one-fourth of the transmission interval timer.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
LLDP Port Settings
This window is used to configure the LLDP port settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Port Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-60 LLDP Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Subtype
Select the subtype of LLDP TLV(s). Options to choose from are
MAC Address, and Local.
Admin State
Select the local LLDP agent and allow it to send and receive LLDP
frames on the port. Options to choose from are TX, RX, TX and RX,

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
133
and Disabled.
TX - The local LLDP agent can only transmit LLDP frames.
RX - The local LLDP agent can only receive LLDP frames.
TX and RX - The local LLDP agent can both transmit and receive
LLDP frames.
Disabled - The local LLDP agent can neither transmit nor receive
LLDP frames.
The default value is TX and RX.
IP Subtype
Select the type of the IP address information to be sent. Options to
choose from are Default, IPv4 and IPv6.
Action
Select this option to enable or disable the action field.
Address
Enter the IP address that will be sent.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
NOTE: The IPv4 or IPv6 address entered here should be an existing LLDP management
IP address.
LLDP Management Address List
This window is used to view the LLDP management address list.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Management Address List, as
shown below:
Figure 5-61 LLDP Management Address List window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
All/IPv4/IPv6
Select the subtype. Options to choose from are All, IPv4 and IPv6.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
LLDP Basic TLVs Settings
Type-length-value (TLV) allows the specific sending information as a TLV element within LLDP
packets. This window is used to enable the settings for the Basic TLVs Settings. An active LLDP port
on the Switch always included mandatory data in its outbound advertisements. There are four optional
data types that can be configured for an individual port or group of ports to exclude one or more of
these data types from outbound LLDP advertisements. The mandatory data type includes four basic
types of information (end of LLDPDU TLV, chassis ID TLV, port ID TLV, and Time to Live TLV). The
mandatory data types cannot be disabled. There are also four data types which can be optionally
selected. These include Port Description, System Name, System Description and System Capability.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Basic TLVs Settings, as shown
below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
134
Figure 5-62 LLDP Basic TLVs Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Port Description
Select this option to enable or disable the Port Description option.
System Name
Select this option to enable or disable the System Name option.
System Description
Select this option to enable or disable the System Description
option.
System Capabilities
Select this option to enable or disable the System Capabilities
option.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
LLDP Dot1 TLVs Settings
LLDP Dot1 TLVs are organizationally specific TLVs which are defined in IEEE 802.1 and used to
configure an individual port or group of ports to exclude one or more of the IEEE 802.1 organizational
port VLAN ID TLV data types from outbound LLDP advertisements.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Dot1 TLVs Settings, as show
below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
135
Figure 5-63 LLDP Dot1 TLVs Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Port VLAN
Select this option to enable or disable the port VLAN ID TLV to
send. The Port VLAN ID TLV is an optional fixed length TLV that
allows a VLAN bridge port to advertise the port’s VLAN identifier
(PVID) that will be associated with untagged or priority tagged
frames.
Protocol VLAN
Select this option to enable or disable Port and Protocol VLAN ID
(PPVID) TLV to send, and enter the VLAN ID in PPVID TLV.
VLAN Name
Select this option to enable or disable the VLAN name TLV to send,
and enter the ID of the VLAN in the VLAN name TLV.
Protocol Identity
Select this option to enable or disable the Protocol Identity TLV to
send, and the protocol name. Options for protocol name to choose
from are None, EAPOL, LACP, GVRP, STP, and All.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
LLDP Dot3 TLVs Settings
This window is used to configure an individual port or group of ports to exclude one or more IEEE
802.3 organizational specific TLV data type from outbound LLDP advertisements.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Dot3 TLVs Settings, as show
below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
136
Figure 5-64 LLDP Dot3 TLVs Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
MAC/PHY
Configuration/Status
Select this option to enable or disable the MAC/PHY
Configuration/Status TLV to send. The MAC/PHY
Configuration/Status TLV is an optional TLV that identifies (1) the
duplex and bit-rate capability of the sending IEEE 802.3 LAN node,
and (2) the current duplex and bit-rate settings of the sending IEEE
802.3 LAN node.
Link Aggregation
Select this option to enable or disable the Link Aggregation TLV to
send. The Link Aggregation TLV indicates contains the following
information. Whether the link is capable of being aggregated,
whether the link is currently in an aggregation, and the aggregated
port channel ID of the port. If the port is not aggregated, then the ID
is 0.
Maximum Frame Size
Select this option to enable or disable the Maximum Frame Size
TLV to send. The Maximum Frame Size TLV indicates the
maximum frame size capability of the implemented MAC and PHY.
Power Via MDI
Select this option to enable or disable the power via MDI TLV to
send. Three IEEE 802.3 PMD implementations (10BASE-T,
100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T) allow power to be supplied over
the link for connected non-powered systems. The Power Via MDI
TLV allows network management to advertise and discover the MDI
power support capabilities of the sending IEEE 802.3 LAN station.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
LLDP-MED Port Settings
This window is used to enable or disable transmitting LLDP-MED TLVs.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP-MED Port Settings, as show below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
137
Figure 5-65 LLDP-MED Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Capabilities
Select this option to enable or disable transmitting the LLDP-MED
capabilities TLV.
Network Policy
Select this option to enable or disable transmitting the LLDP-MED
network policy TLV.
PSE
Select this option to enable or disable transmitting the LLDP-MED
extended power via MDI TLV, if the local device is PSE device or
PD device.
Inventory
Select this option to enable or disable transmitting the LLDP-MED
inventory management TLV.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
LLDP Statistics Information
This window is used to view the neighbor detection activity, LLDP Statistics and the settings for
individual ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Statistics Information, as show
below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
138
Figure 5-66 LLDP Statistics Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be displayed.
Port
Select the port number that will be displayed.
Click the Clear Counter button to clear the counter information for the statistics displayed.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the counter information displayed.
LLDP Local Port Information
This window is used to display the information on a per port basis currently available for populating
outbound LLDP advertisements in the local port brief table shown below.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Local Port Information, as show
below:
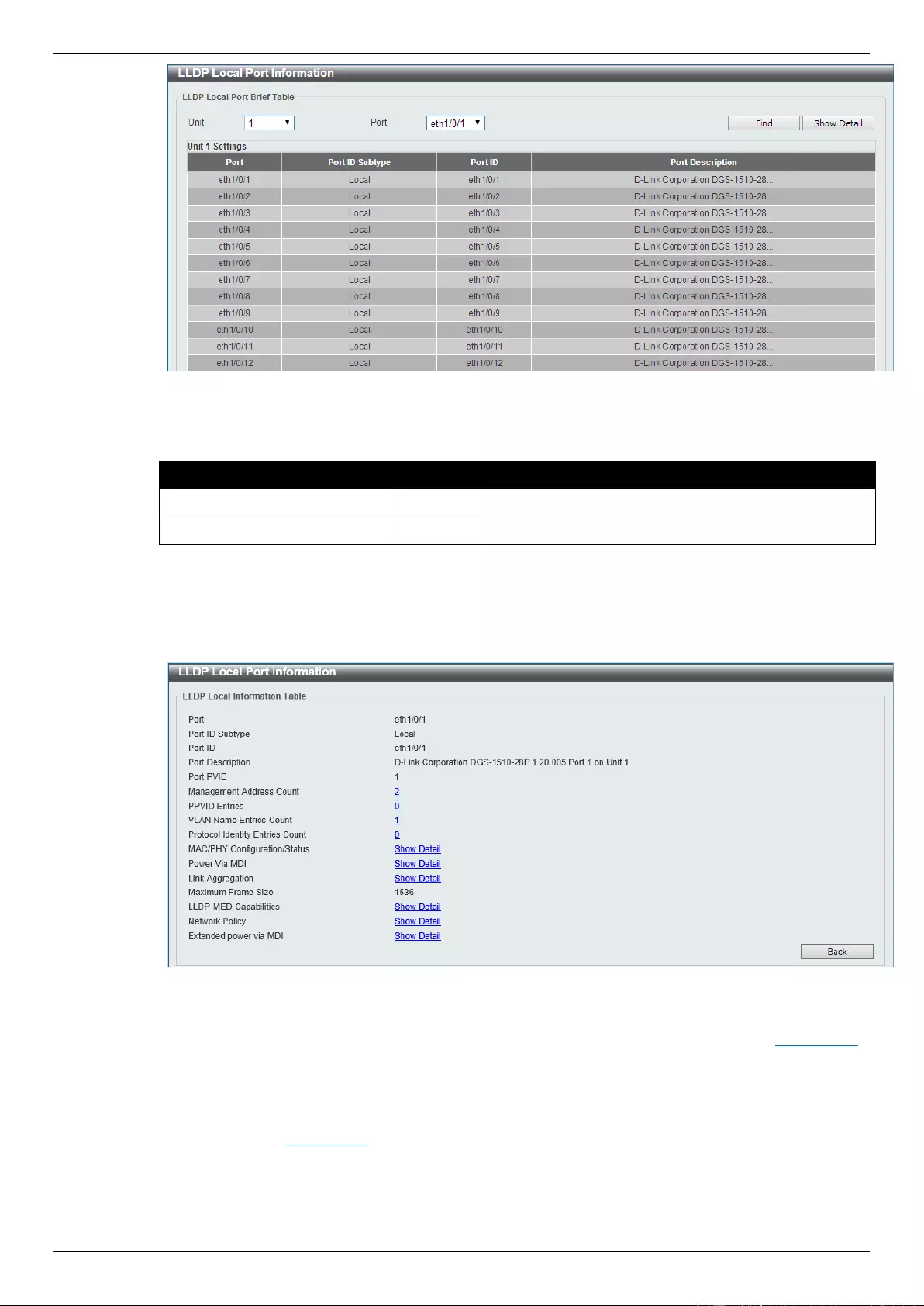
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
139
Figure 5-67 LLDP Local Port Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be displayed.
Port
Select the port number that will be displayed.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Show Detail button to view detailed information of the specific port.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 5-68 LLDP Local Port Information - Show Detail window
To view more details about, for example, the MAC/PHY Configuration/Status, click the Show Detail
hyperlink.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After clicking the Show Detail hyperlink, a new section will appear at the bottom of the window.
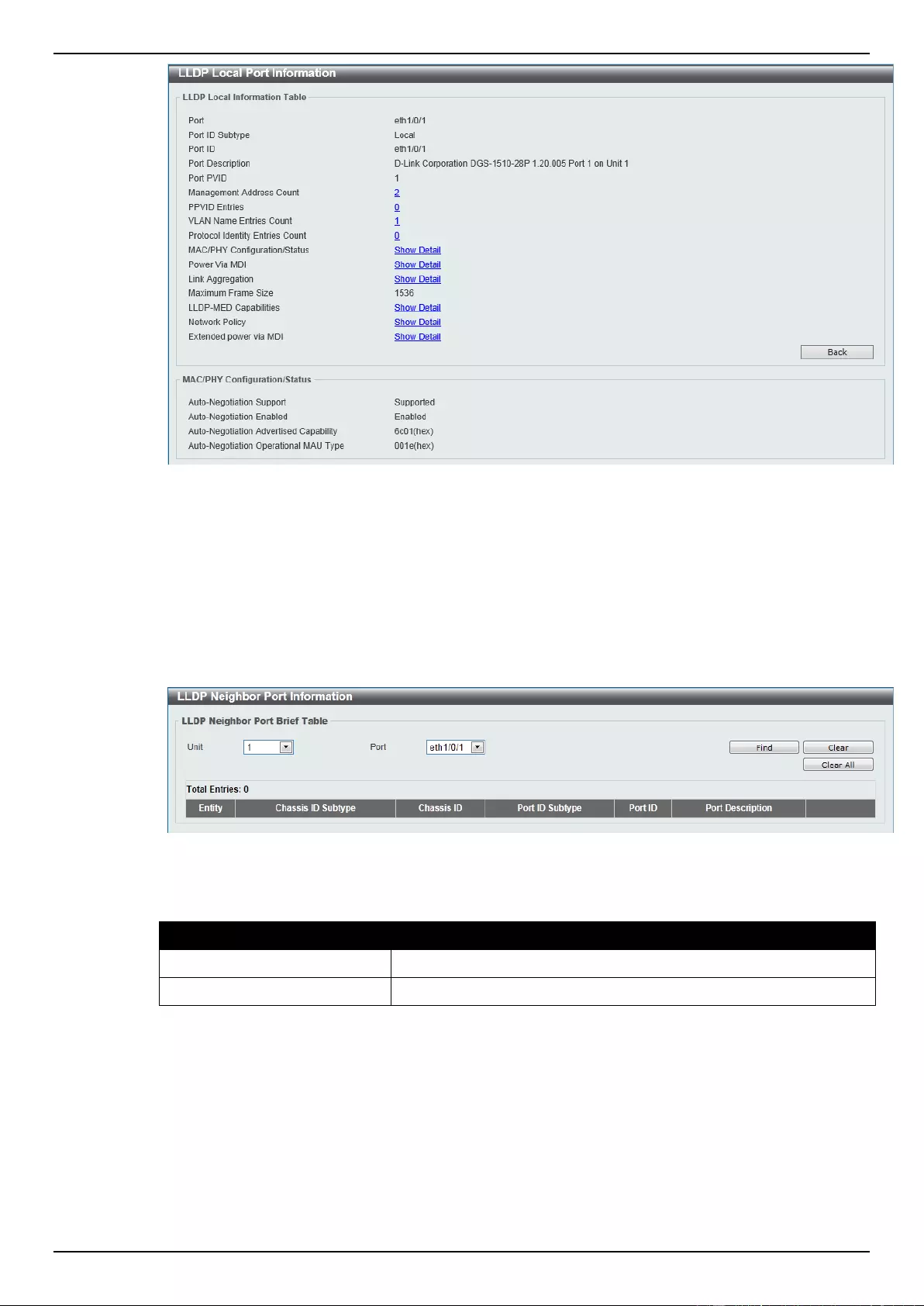
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
140
Figure 5-69 LLDP Local Port Information - Show Detail window
LLDP Neighbor Port Information
This window is used to display the information learned from the neighbors. The switch receives
packets from a remote station but is able to store the information as local.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > LLDP > LLDP Neighbor Port Information, as
show below:
Figure 5-70 LLDP Neighbor Port Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be displayed.
Port
Select the port number that will be displayed.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear button to clear the specific port information.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the port information displayed.
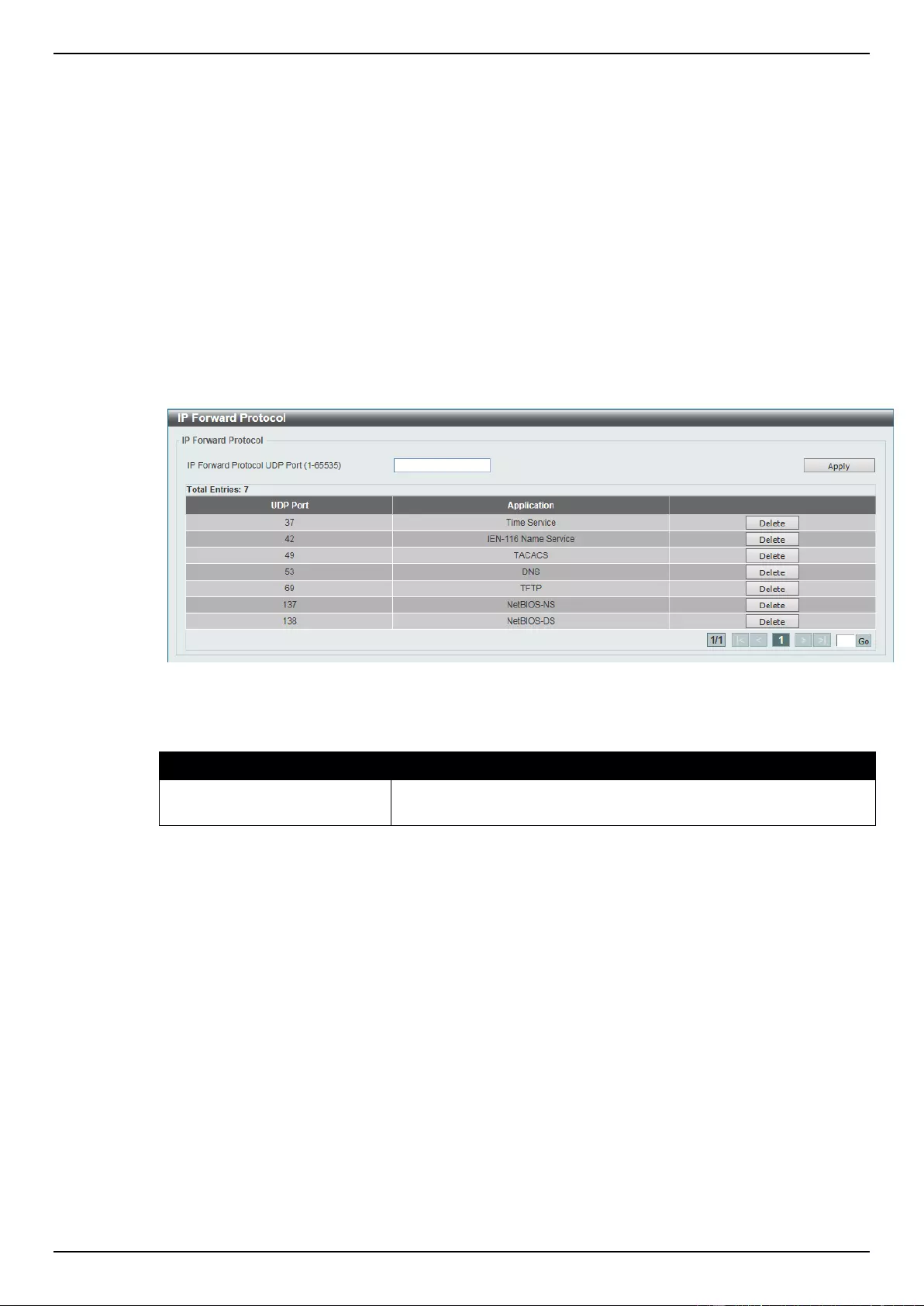
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
141
6. Layer 3 Features
ARP
Gratuitous ARP
UDP Helper
UDP Helper
IP Forward Protocol
This window is used to view and configure the IP helper forwarding on ports.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > UDP Helper > IP Forward Protocol, as shown
below:
Figure 6-6 IP Forward Protocol window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Forward Protocol UDP
Port
Enter the destination port of the UDP service to be forwarded.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IP Helper Address
This window is used to view and configure the IP helper forwarding on VLAN.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > UDP Helper > IP Helper Address, as shown
below:
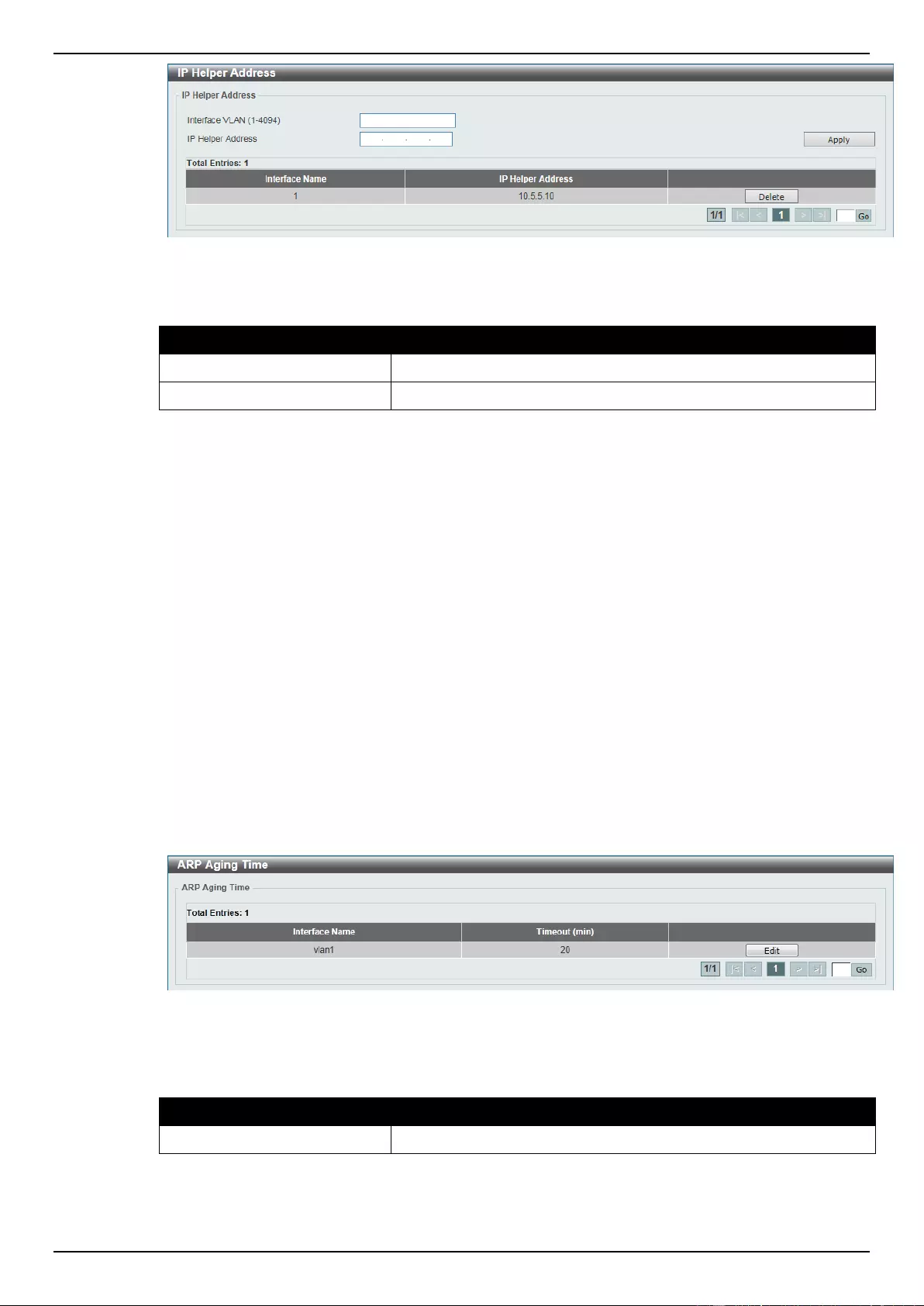
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
142
Figure 6-7 IP Helper Address window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter the ID of VLAN interface.
IP Helper Address
Enter the IP helper address for the specified VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IPv4 Interface
IPv4 Static/Default Route
IPv4 Route Table
IPv6 Interface
IPv6 Neighbor
IPv6 Static/Default Route
IPv6 Route Table
ARP
ARP Aging Time
This window is used to view and configure the ARP aging time settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > ARP > ARP Aging Time, as shown below:
Figure 6-1 ARP Aging Time window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Timeout
Enter the ARP aging timeout value here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
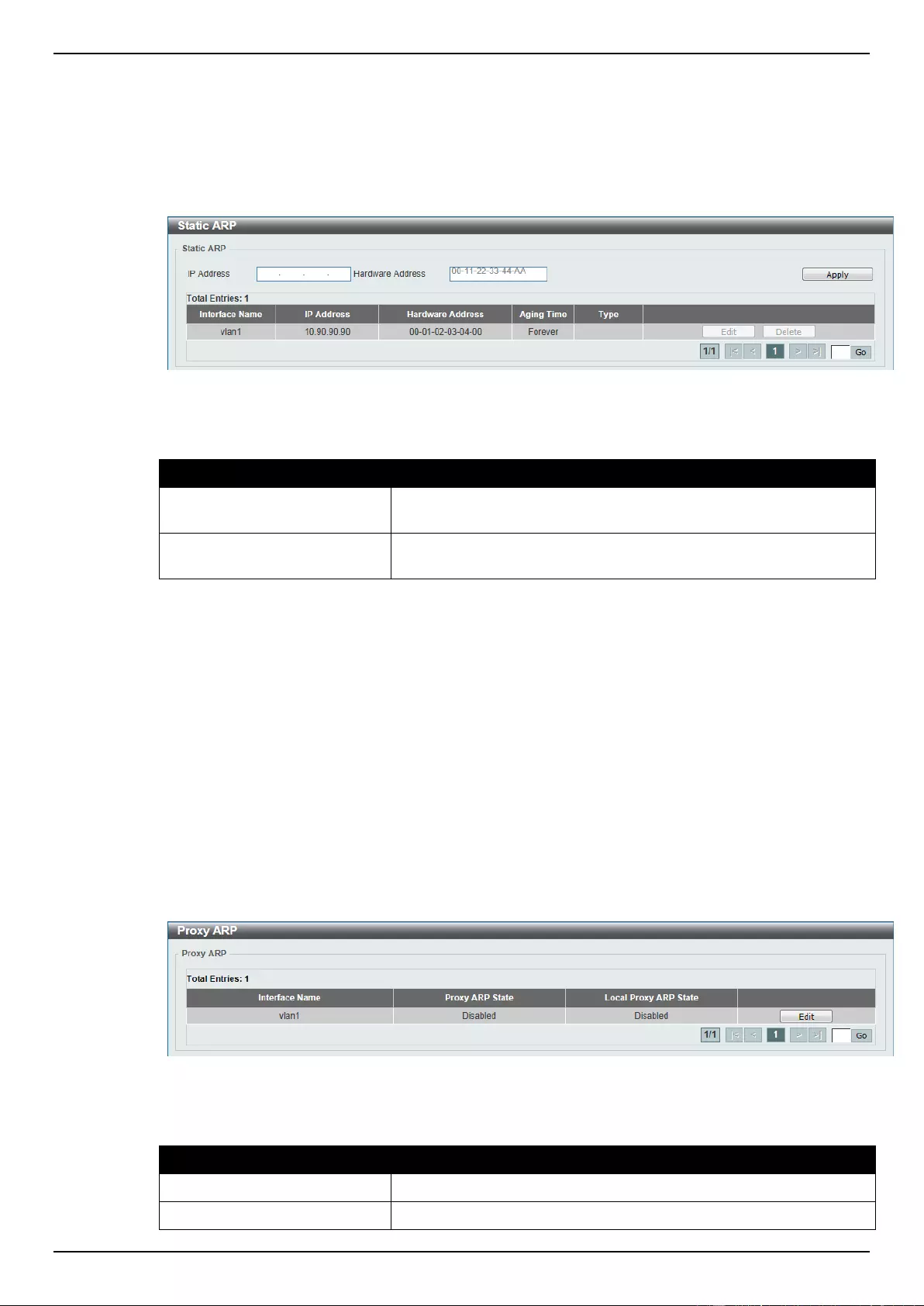
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
143
Static ARP
This window is used to view and configure the static ARP settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > ARP > Static ARP, as shown below:
Figure 6-2 Static ARP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Enter the IP address that will be associated with the MAC address
here.
Hardware Address
Enter the MAC address that will be associated with the IP address
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Proxy ARP
This window is used to view and configure the proxy ARP settings. The Proxy ARP feature of the
Switch will allow the Switch to reply to ARP requests destined for another device by faking its identity
(IP and MAC Address) as the original ARP responder. Therefore, the Switch can then route packets
to the intended destination without configuring static routing or a default gateway. The host, usually a
Layer 3 switch, will respond to packets destined for another device.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > ARP > Proxy ARP, as shown below:
Figure 6-3 Proxy ARP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Proxy ARP State
Select to enable or disable the proxy ARP state here.
Local Proxy ARP State
Select to enable or disable the local proxy ARP state here. This
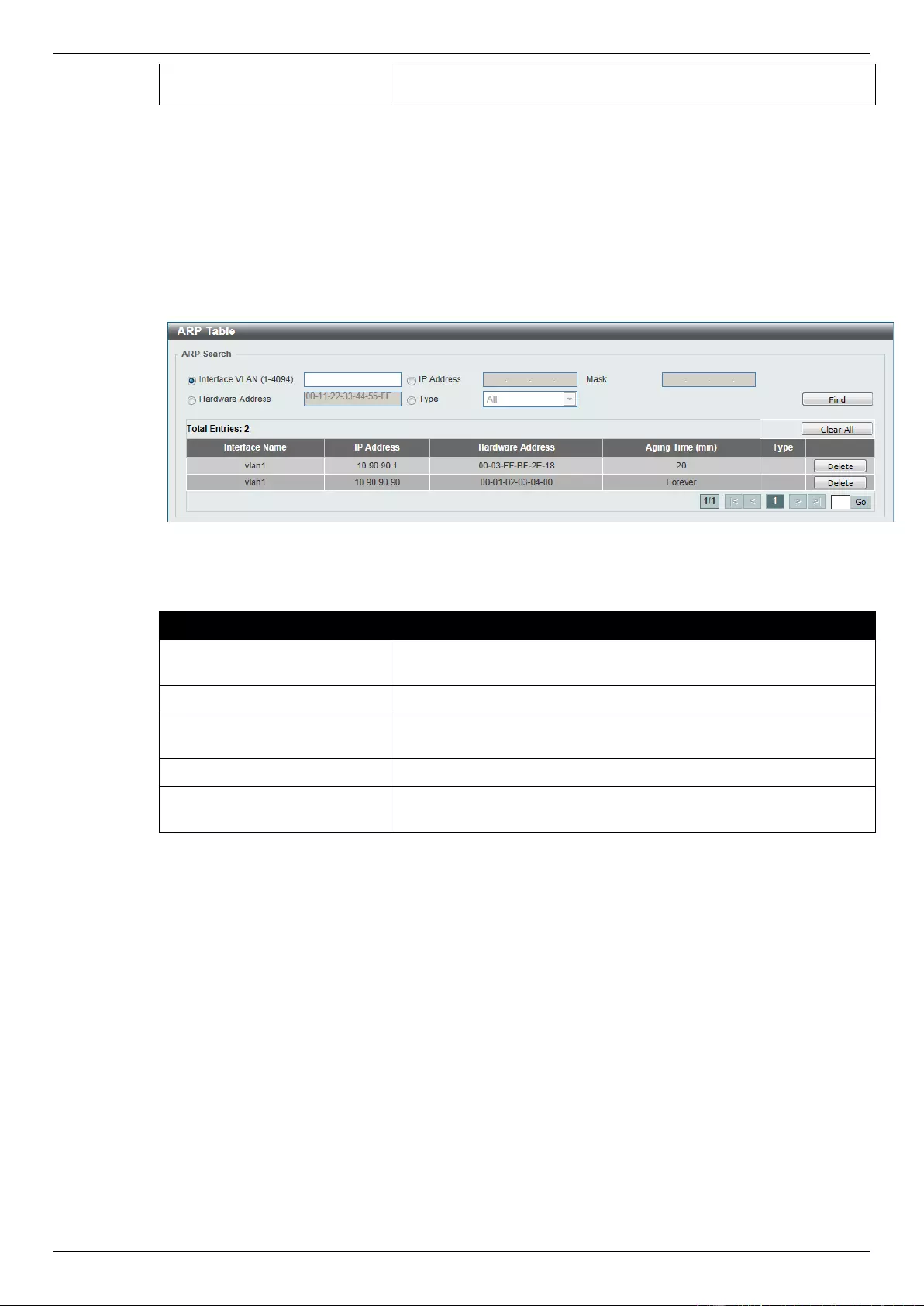
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
144
local proxy ARP function allows the Switch to respond to the proxy
ARP, if the source IP and destination IP are in the same interface.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
ARP Table
This window is used to view and configure the ARP table settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > ARP > ARP Table, as shown below:
Figure 6-4 ARP Table window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Select and enter the interface’s VLAN ID used here. This value
must be between 1 and 4094.
IP Address
Select and enter the IP address to display here.
Mask
After the IP Address option was selected, enter the mask address
for the IP address here.
Hardware Address
Select and enter the MAC address to display here.
Type
Select the type option here. Options to choose from are All and
Dynamic.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Gratuitous ARP
This window is used to view and configure the gratuitous ARP settings. A gratuitous ARP request
packet is an ARP request packet where the source and the destination IP address are both set to the
IP address of the sending device and the destination MAC address is the broadcast address.
Generally, a device use the gratuitous ARP request packet to discover whether the IP address is
duplicated by other hosts or to preload or reconfigure the ARP cache entry of hosts connected to the
interface.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > Gratuitous ARP, as shown below:
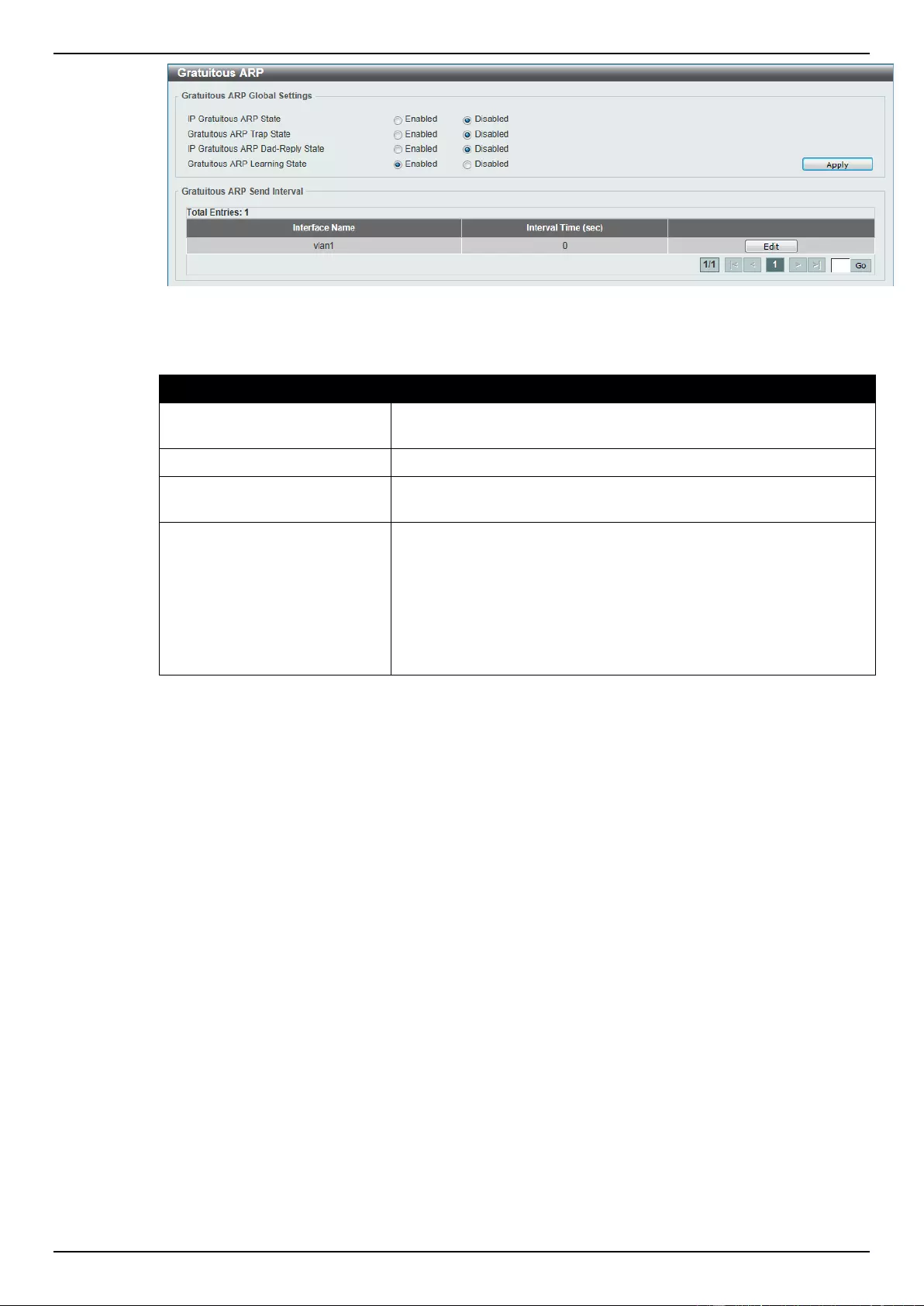
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
145
Figure 6-5 Gratuitous ARP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Gratuitous ARP State
Select this option to enable or disable the learning of gratuitous
ARP packets in the ARP cache table.
Gratuitous ARP Trap State
Select this option to enable or disable the ARP trap state.
IP Gratuitous ARP Dad-
Reply State
Select this option to enable or disable the IP gratuitous ARP Dad-
reply state.
Gratuitous ARP Learning
State
Select this option to enable or disable the gratuitous ARP learning
state. Normally, the system will only learn the ARP reply packet or a
normal ARP request packet that asks for the MAC address that
corresponds to the system’s IP address. This option used to enable
or disable the learning of ARP entries in the ARP cache based on
the received gratuitous ARP packet. The gratuitous ARP packet is
sent by a source IP address that is identical to the IP that the packet
is queries for.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
UDP Helper
IP Forward Protocol
This window is used to view and configure the IP helper forwarding on ports.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > UDP Helper > IP Forward Protocol, as shown
below:
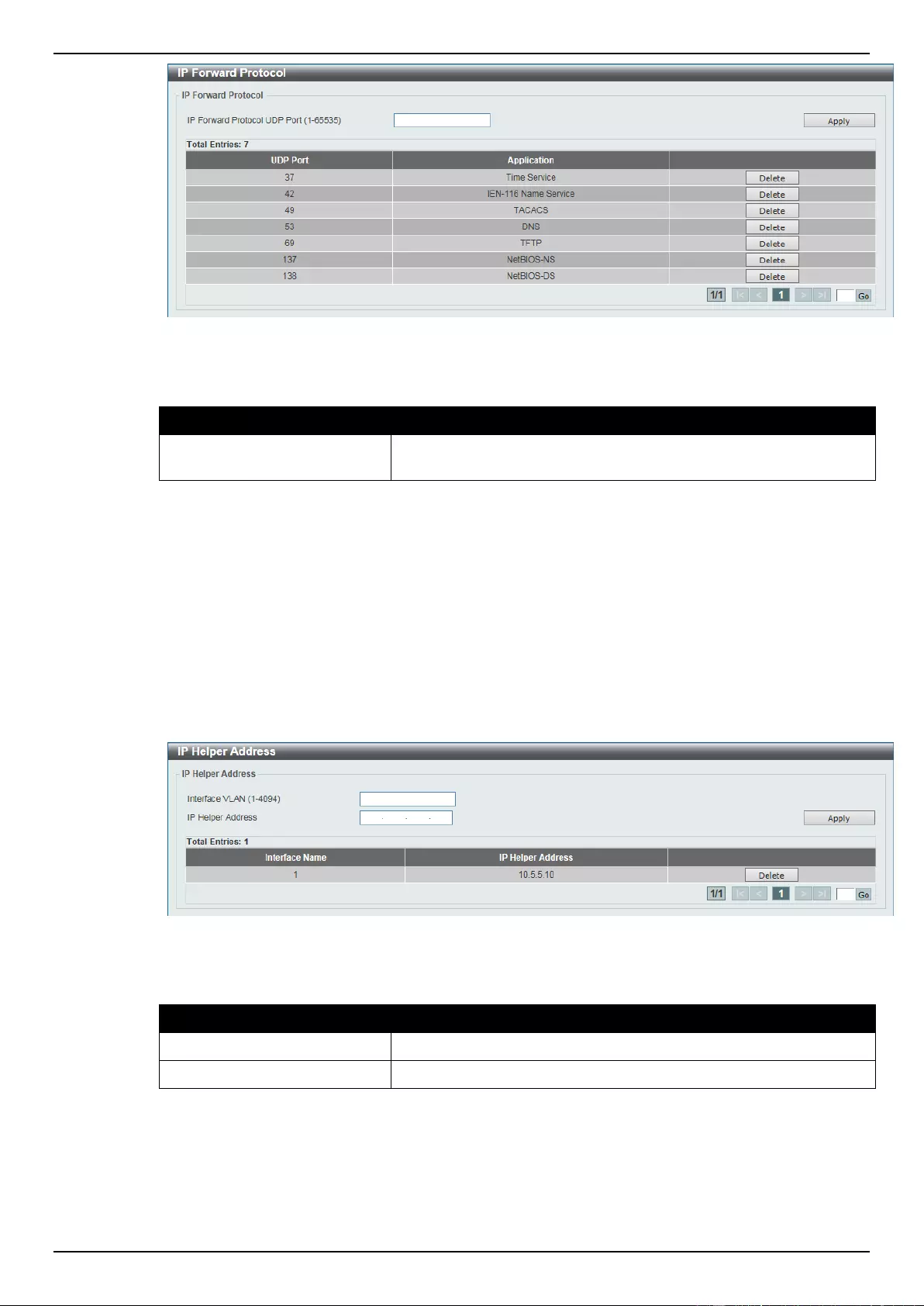
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
146
Figure 6-6 IP Forward Protocol window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Forward Protocol UDP
Port
Enter the destination port of the UDP service to be forwarded.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IP Helper Address
This window is used to view and configure the IP helper forwarding on VLAN.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > UDP Helper > IP Helper Address, as shown
below:
Figure 6-7 IP Helper Address window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter the ID of VLAN interface.
IP Helper Address
Enter the IP helper address for the specified VLAN.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
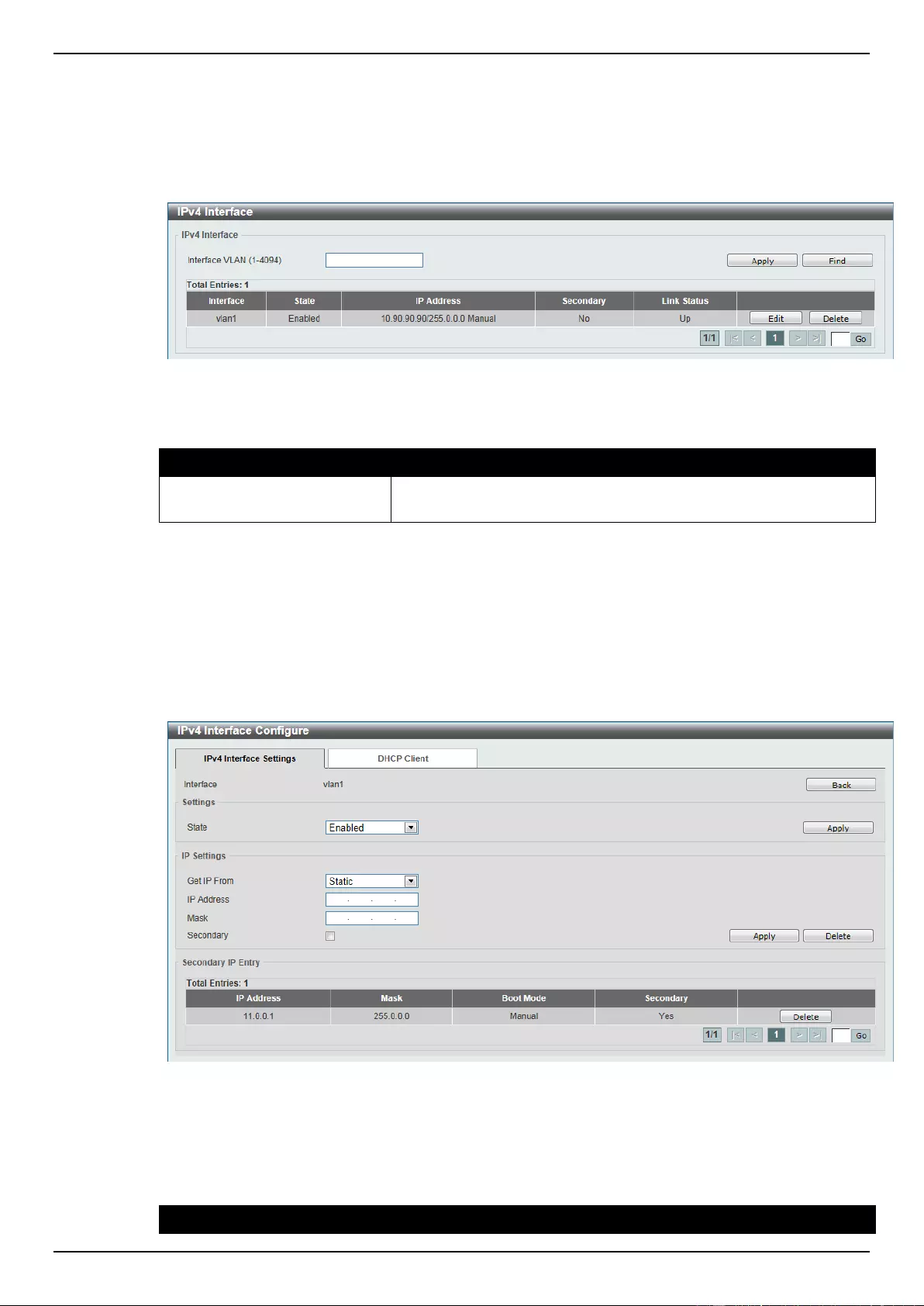
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
147
IPv4 Interface
This window is used to view and configure the IPv4 interface settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv4 Interface, as shown below:
Figure 6-8 IPv4 Interface window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter the interface’s VLAN ID here. This value must be between 1
and 4094.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Edit button, the following window will be available.
Figure 6-9 IPv4 Interface Configure window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
The field that can be configured for Settings is described below:
Parameter
Description
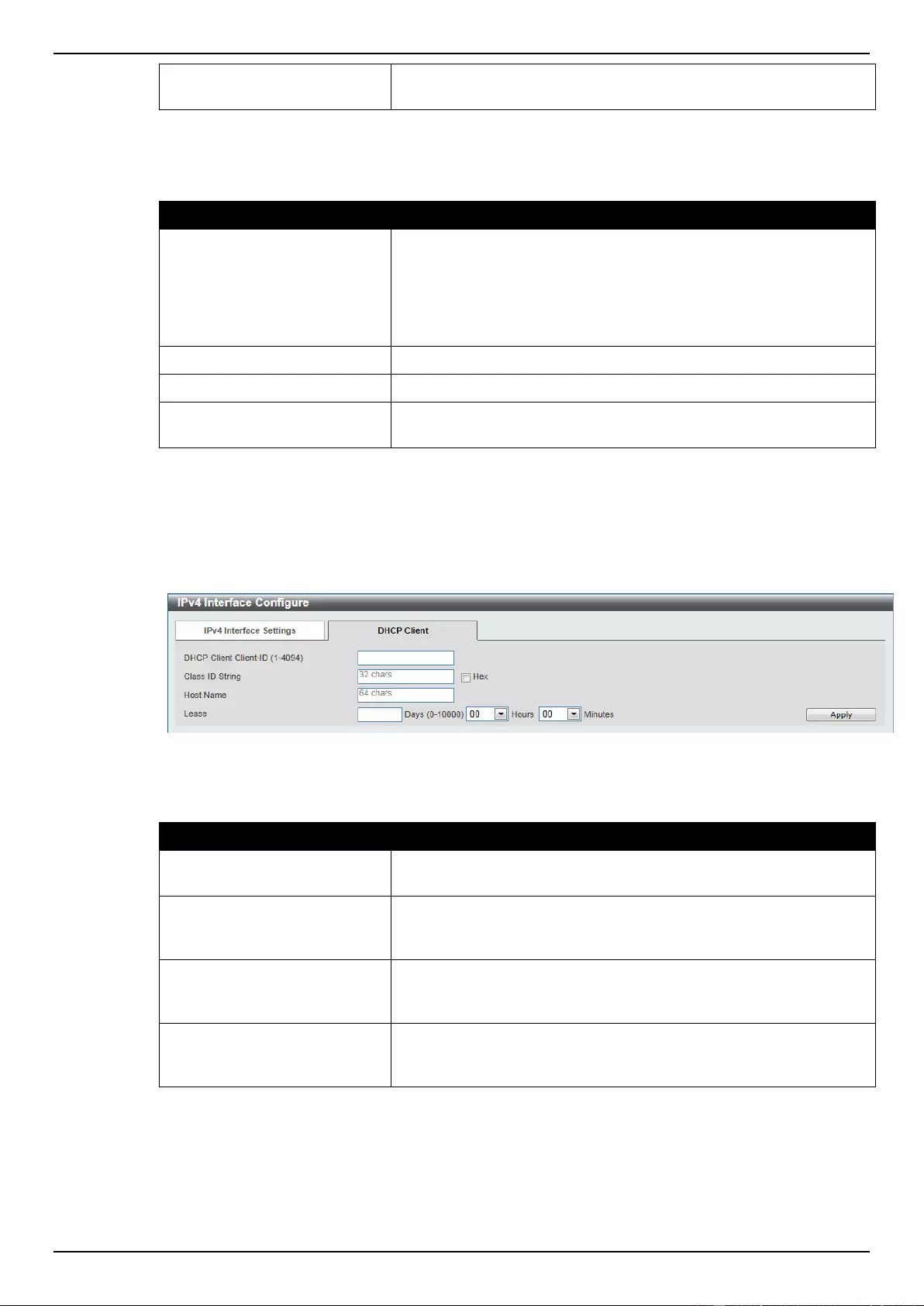
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
148
State
Select this option to enable or disable the IPv4 interface’s global
state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IP Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Get IP From
Select the get IP from option here. Options to choose from are
Static and DHCP. When the Static option is selected, users can
enter the IPv4 address of this interface manually in the fields
provided. When the DHCP option is selected, this interface will
obtain IPv4 information automatically from the DHCP server located
on the local network.
IP Address
Enter the IPv4 address for this interface here.
Mask
Enter the IPv6 subnet mask for this interface here.
Secondary
Tick the check box to use the IPv4 address and mask as the
secondary interface configuration.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the DHCP Client tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 6-10 DHCP Client window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DHCP Client Client-ID
Enter the VLAN interface, whose hexadecimal MAC address will be
used as the client ID to be sent with the discover message.
Class ID String
Enter the vendor class identifier with the maximum of 32 characters.
Tick the Hex check box to have the class identifier in the
hexadecimal form.
Host Name
Enter the host name. The maximum length is 64 characters. The
host name must start with a letter, end with a letter or digit, and only
with interior characters letters, digits, and hyphens.
Lease
Specify the preferred lease time for the IP address to request from
the DHCP server. Enter the day duration of the lease, or select the
hour and minute duration of the lease.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
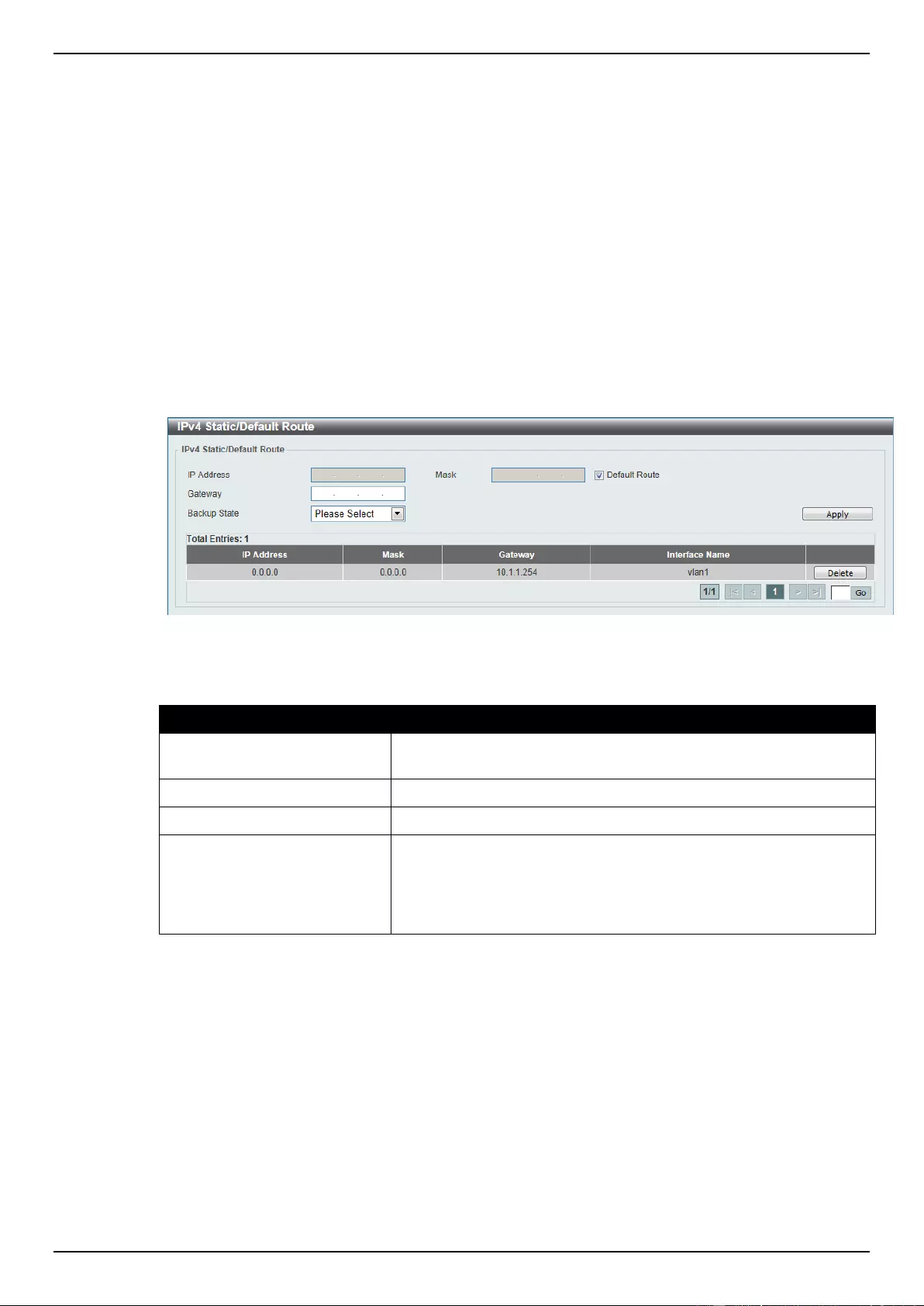
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
149
IPv4 Static/Default Route
This window is used to view and configure the IPv4 static and default route settings. The Switch
supports static routing for IPv4 formatted addressing. Users can create up to 64 static route entries for
IPv4. For IPv4 static routes, once a static route has been set, the Switch will send an ARP request
packet to the next hop router that has been set by the user. Once an ARP response has been
retrieved by the Switch from that next hop, the route becomes enabled. However, if the ARP entry
already exists, an ARP request will not be sent.
The Switch also supports a floating static route, which means that the user may create an alternative
static route to a different next hop. This secondary next hop device route is considered as a backup
static route for when the primary static route is down. If the primary route is lost, the backup route will
uplink and its status will become active.
Entries into the Switch’s forwarding table can be made using both an IP address subnet mask and a
gateway.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv4 Static/Default Route, as shown below:
Figure 6-11 IPv4 Static/Default Route window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Enter the IPv4 address for this route here. Tick the Default Route
check box to use the default route as the IPv4 address.
Mask
Enter the IPv4 network mask for this route here.
Gateway
Enter the gateway address for this route here.
Backup State
Select the backup state option here. Options to choose from are
Primary, and Backup. When the Primary option is selected, the
route will be used as the primary route to the destination. When the
Backup option is selected, the route will be used as the backup
route to the destination.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IPv4 Route Table
This window is used to view and configure the IPv4 route table settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv4 Route Table, as shown below:
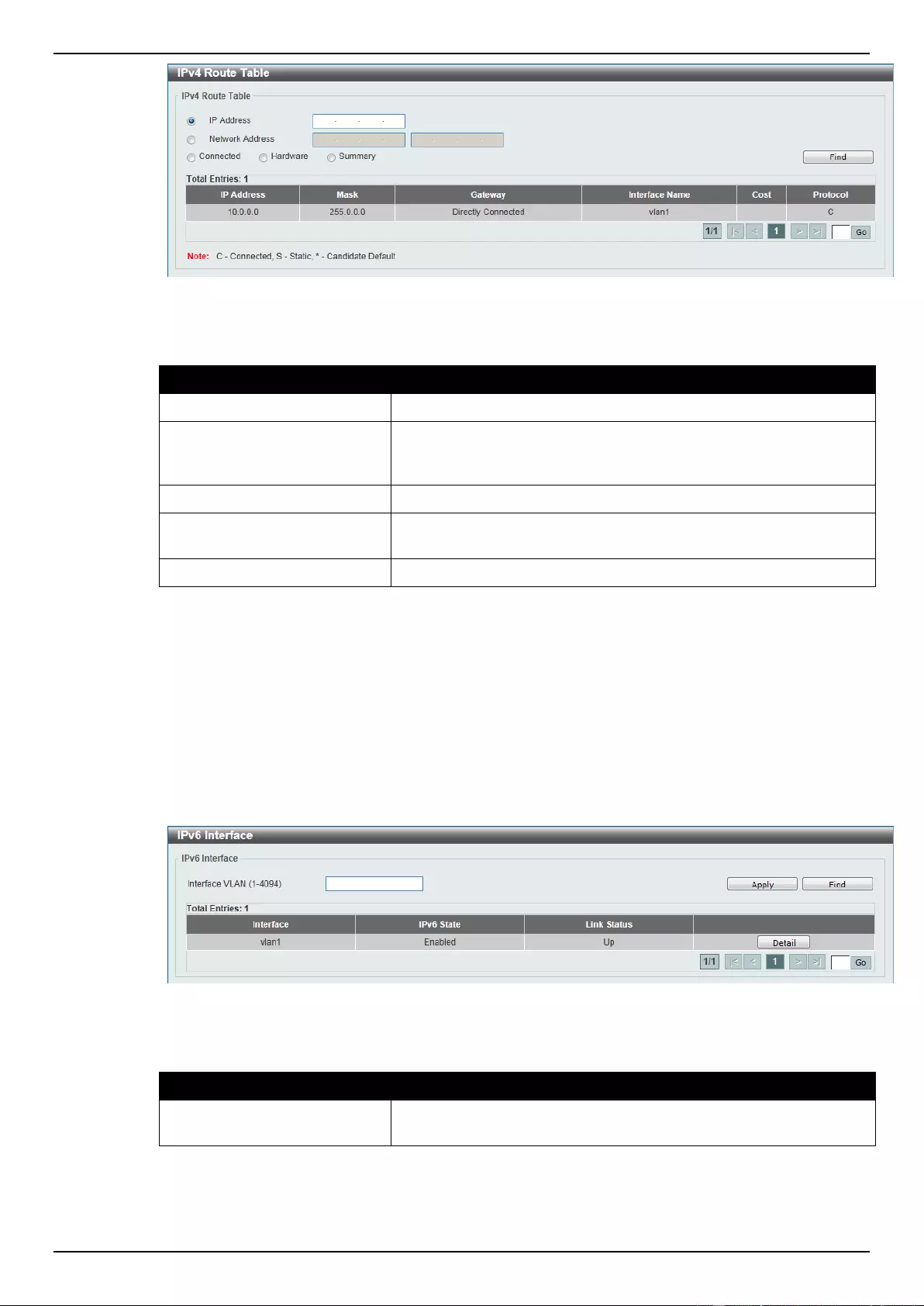
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
150
Figure 6-12 IPv4 Route Table window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Select and enter the single IPv4 address here.
Network Address
Select and enter the IPv4 network address here. In the first space
enter the network prefix and in the second space enter the network
mask.
Connected
Select this option to display only connected routes.
Hardware
Select this option to display only hardware routes. Hardware routes
are routes that have been written into the hardware chip.
Summary
Display the brief information of the active routing entries.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IPv6 Interface
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 interface’s settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv6 Interface, as shown below:
Figure 6-13 IPv6 Interface window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter the VLAN interface’s ID that will be associated with the IPv6
entry.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Detail button to view and configure more detailed settings for the IPv6 interface entry.
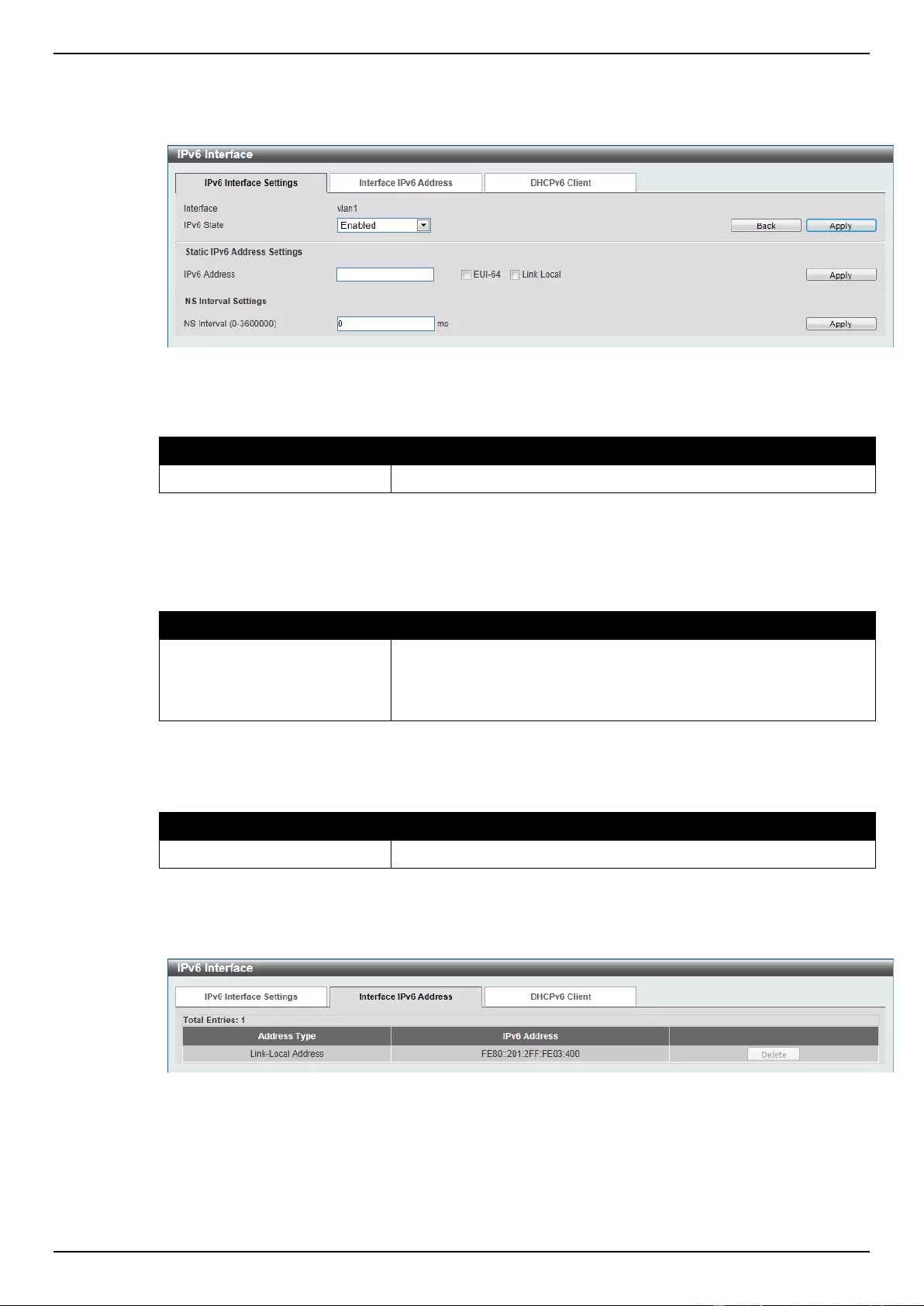
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
151
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Detail button, the following page will be available.
Figure 6-14 IPv6 Interface - Detail, IPv6 Interface Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Interface are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv6 State
Select to enable or disable the IPv6 interface’s global state here.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Static IPv6 Address Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address for this IPv6 interface here. Select the EUI-
64 option to configure an IPv6 address on the interface using the
EUI-64 interface ID. Select the Link Local option to configure a link-
local address for the IPv6 interface.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for NS Interval Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
NS Interval
Enter the NS interval between 0 and 3600000 milliseconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After clicking the Interface Address tab, at the top of the page, the following page will be available.
Figure 6-15 IPv6 Interface - Detail, Interface IPv6 Address window
Click the Delete button to delete the specified entry.
After clicking the DHCPv6 Client tab, at the top of the page, the following page will be available.
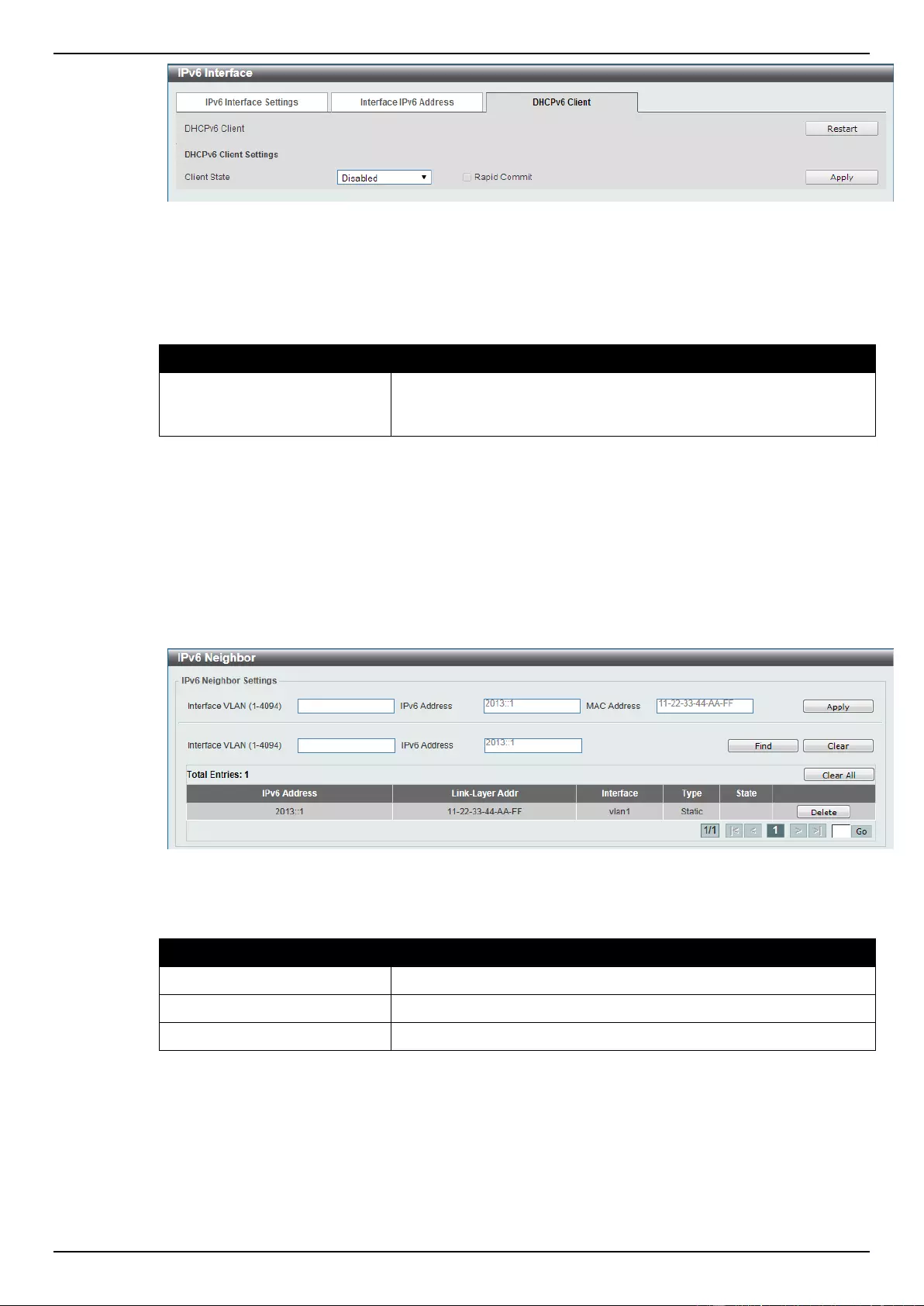
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
152
Figure 6-16 IPv6 Interface - Detail, Interface IPv6 Address window
Click the Restart button to restart DHCPv6 client on an interface.
The fields that can be configured for DHCPv6 Client Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Client State
Select this option to enable or disable the DHCPv6 client state. Tick
the Rapid Commit check box to proceed with two-message
exchange for prefix delegation.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IPv6 Neighbor
This window is used to configure and view the IPv6 neighbor settings.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv6 Neighbor, as shown below:
Figure 6-17 IPv6 Neighbor window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interface VLAN
Enter an interface VLAN ID.
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
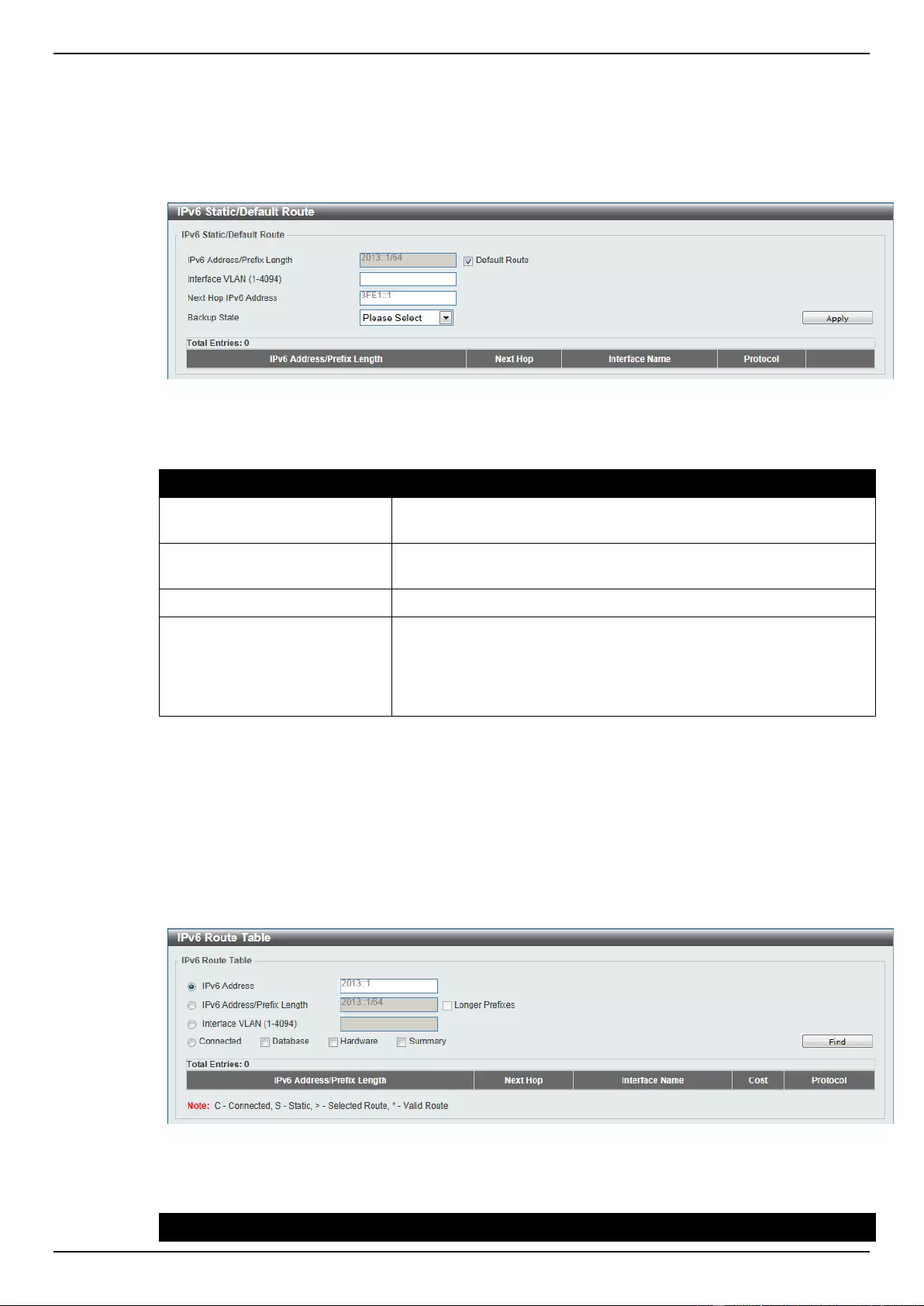
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
153
IPv6 Static/Default Route
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 static or default routes.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv6 Static/Default Route, as shown below:
Figure 6-18 IPv6 Static/Default Route window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv6 Address/Prefix Length
Enter the IPv6 address and prefix length for this route here. Tick the
Default Route option to use the default route as the IPv6 address.
Interface VLAN
Enter the interface’s VLAN ID that will be associated with this route
here.
Next Hop IPv6 Address
Enter the next hop IPv6 address here.
Backup State
Select the backup state option here. Options to choose from are
Primary, and Backup. When the Primary option is selected, the
route is specified as the primary route to the destination. When the
Backup option is selected, the route is specified as the backup
route to the destination.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IPv6 Route Table
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 route table.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IPv6 Route Table, as shown below:
Figure 6-19 IPv6 Route Table window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
154
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the IPv6 address to display here.
IPv6 Address/Prefix Length
Select and enter the IPv6 address and prefix length to display here.
Select the Longer Prefixes option to display the route and all of the
more specific routes.
Interface VLAN
Select and enter the interface’s VLAN ID to display here.
Connected
Select this option to display only connected routes.
Database
Select to view all the related entries in the routing database instead
of just the best route.
Hardware
Select this option to display only hardware routes. Hardware routes
are routes that have been written into the hardware chip.
Summary
Display the brief information of the active routing entries.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
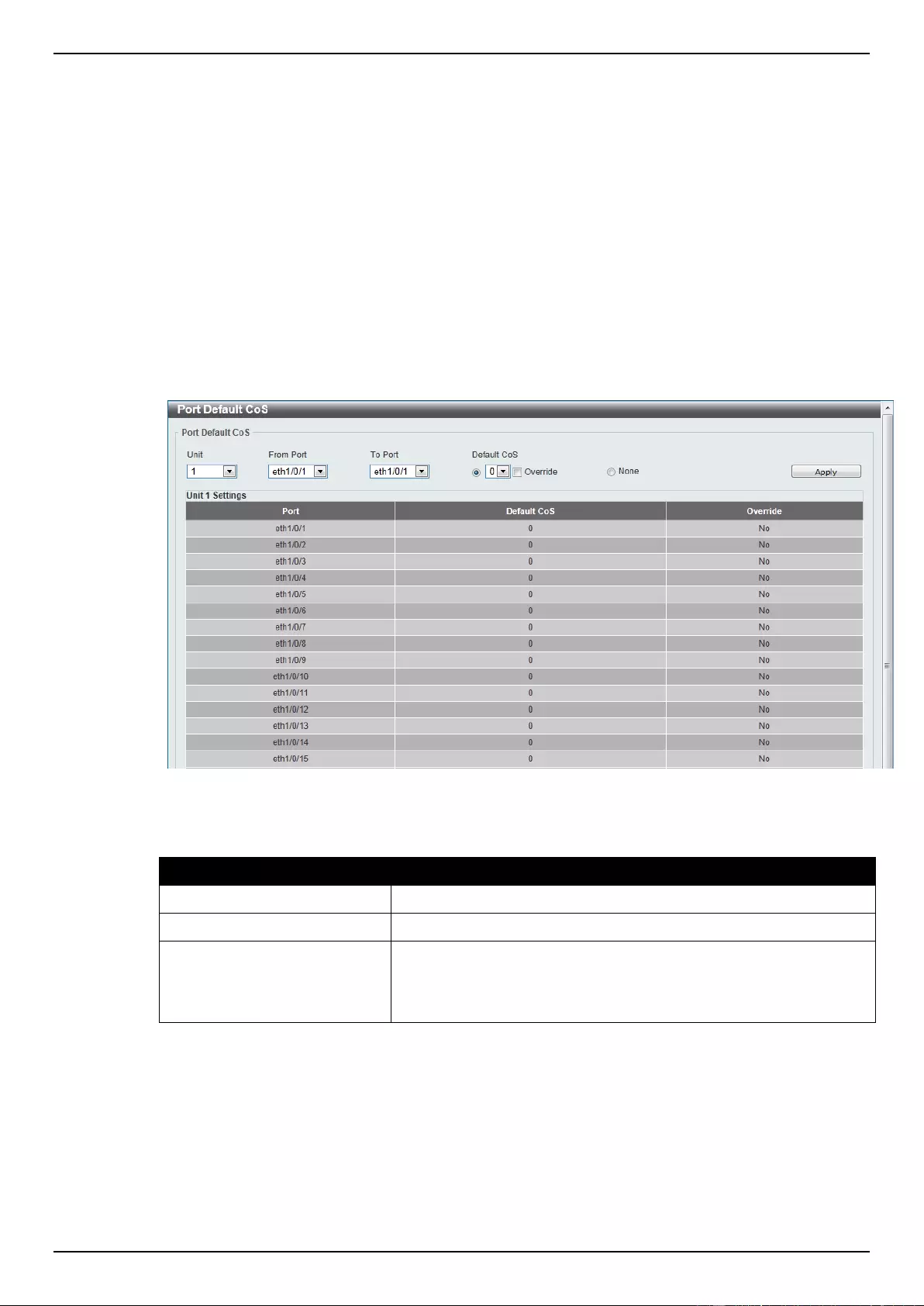
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
155
7. Quality of Service (QoS)
Basic Settings
Advanced Settings
Basic Settings
Port Default CoS
This window is used to view and configure the port’s default CoS settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > Port Default CoS, as shown below:
Figure 7-1 Port Default CoS window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Default CoS
Select the default CoS option for the port(s) specified here. Options
to choose from are 0 to 7. Click the Override check box to apply the
port's default CoS to all packets (tagged or untagged) received by
the port. Select the None option to use the default settings.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Port Scheduler Method
This window is used to view and configure the port scheduler method settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > Port Scheduler Method, as shown
below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
156
Figure 7-2 Port Scheduler Method window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Scheduler Method
Select the scheduler method that will be applied to the specified
port(s). Options to choose from are Strict Priority (SP), Round-Robin
(RR), Weighted Round-Robin (WRR), and Weighted Deficit Round-
Robin (WDRR). By default, the output queue scheduling algorithm is
WRR.
WDRR operates by serving an accumulated set of backlogged
credits in the transmit queue in a round robin order. Initially, each
queue sets its credit counter to a configurable quantum value. Every
time a packet from a CoS queue is sent, the size of the packet is
subtracted from the corresponding credit counter and the service
right is turned over to the next lower CoS queue. When the credit
counter drops below 0, the queue is no longer serviced until its
credits are replenished. When the credit counters of all CoS queues
reaches 0, the credit counters will be replenished at that time. All
packets are serviced until their credit counter is zero or negative
and the last packet is transmitted completely. When this condition
happens, the credits are replenished. When the credits are
replenished, a quantum of credits are added to each CoS queue
credit counter. The quantum for each CoS queue may be different
based on the user configuration.
To set a CoS queue in the SP mode, any higher priority CoS queue
must also be in the strict priority mode.
WRR operates by transmitting permitted packets into the transmit
queue in a round robin order. Initially, each queue sets its weight to
a configurable weighting. Every time a packet from a higher priority
CoS queue is sent, the corresponding weight is subtracted by 1 and
the packet in the next lower CoS queue will be serviced. When the
weight of a CoS queue reaches zero, the queue will not be serviced
until its weight is replenished. When weights of all CoS queues
reach 0, the weights get replenished at a time.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
157
Queue Settings
This window is used to view and configure the queue settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > Queue Settings, as shown below:
Figure 7-3 Queue Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Queue ID
Enter the queue ID value here. This value must be between 0 and
7.
WRR Weight
Enter the WRR weight value here. This value must be between 0
and 127. To satisfy the behavior requirements of Expedited
Forwarding (EF), the highest queue is always selected by the Per-
hop Behavior (PHB) EF and the schedule mode of this queue
should be strict priority scheduling. So the weight of the last queue
should be zero while the Differentiate Service is supported.
WDRR Quantum
Enter the WDRR quantum value here. This value must be between
0 and 127.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
CoS to Queue Mapping
This window is used to view and configure the CoS-to-Queue mapping settings.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
158
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > CoS to Queue Mapping, as shown
below:
Figure 7-4 CoS to Queue Mapping window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Queue ID
Select the queue ID that will be mapped to the corresponding CoS
value. Options to choose from are 0 to 7.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Port Rate Limiting
This window is used to view and configure the port rate limiting settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > Port Rate Limiting, as shown below:
Figure 7-5 Port Rate Limiting window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
159
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Direction
Select the direction option here. Options to choose from are Input
and Output. When Input is selected, the rate limit for ingress
packets is configured. When Output is selected, the rate limit for
egress packets is configured.
Rate Limit
Select and enter the rate limit value here.
When Bandwidth is selected, enter the input/output bandwidth
value used in the space provided. This value must be between 64
and 10000000 kbps. Also, enter the Burst Size value in the space
provided. This value must be between 0 and 128000 kilobytes.
When Percent is selected, enter the input/output bandwidth
percentage value used in the space provided. This value must be
between 1 and 100 percent (%). Also, enter the Burst Size value in
the space provided. This value must be between 0 and 128000
kilobytes.
Select the None option to remove the rate limit on the specified
port(s). The specified limitation cannot exceed the maximum speed
of the specified interface. For the ingress bandwidth limitation, the
ingress can trigger a pause frame or a flow control frame when the
received traffic exceeds the limitation.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Queue Rate Limiting
This window is used to view and configure the queue rate limiting settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Basic Settings > Queue Rate Limiting, as shown below:
Figure 7-6 Queue Rate Limiting window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
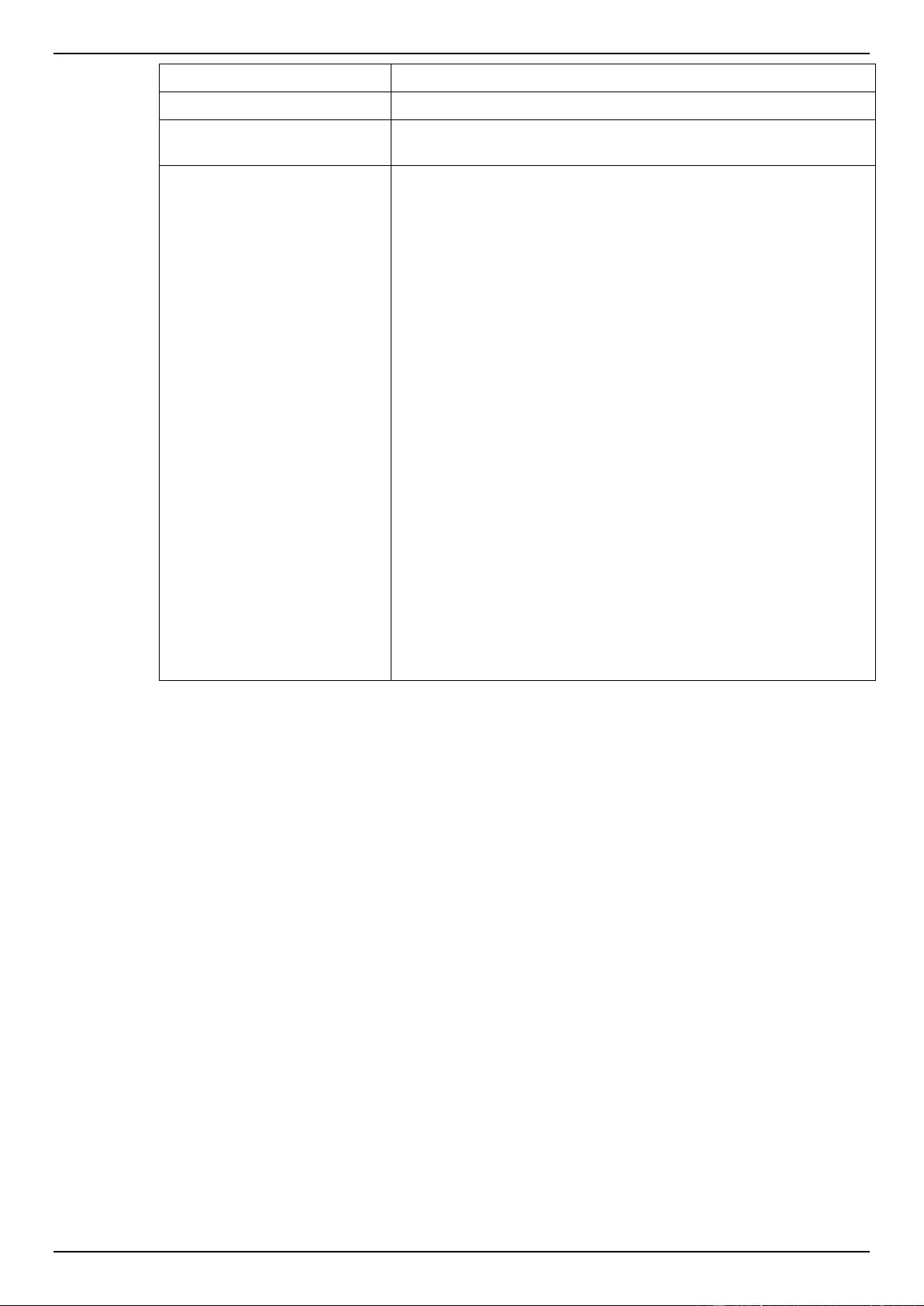
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
160
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Queue ID
Select the queue ID that will be configured here. Options to choose
from are 0 to 7.
Rate Limit
Select and enter the queue rate limit settings here.
When the Min Bandwidth option is selected, enter the minimum
bandwidth rate limit value in the space provided. This value must be
between 64 and 10000000 kbps. Also enter the maximum
bandwidth (Max Bandwidth) rate limit in the space provided. This
value must be between 64 and 10000000 kbps. The granularity is
64.
When the minimal bandwidth is configured, the packet transmitted
from the queue can be guaranteed. When the maximum bandwidth
is configured, packets transmitted from the queue cannot exceed
the maximum bandwidth even if the bandwidth is available.
When configuring the minimal bandwidth, the aggregate of the
configured minimum bandwidth must be less than 75 percent of the
interface bandwidth to make sure the configured minimal bandwidth
can be guaranteed. It is not necessary to set the minimum
guaranteed bandwidth for the highest strict priority queue. This is
because the traffic in this queue will be serviced first if the minimal
bandwidth of all queues is satisfied.
The configuration of this command can only be attached to a
physical port but not a port-channel. That is the minimum
guaranteed bandwidth of one CoS cannot be used across physical
ports.
When the Min Percent option is selected, enter the minimum
bandwidth percentage value in the space provided. This value must
be between 1 and 100 percent (%). Also enter the maximum
percentage value (Max Percent) in the space provided. This value
must be between 1 and 100 percent (%).
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Advanced Settings
DSCP Mutation Map
This window is used to view and configure the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) mutation
map settings. When a packet is received by an interface, based on a DSCP mutation map, the
incoming DSCP can be mutated to another DSCP immediately before any QoS operations. The
DSCP mutation is helpful to integrate domains with different DSCP assignments. The DSCP-CoS
map and DSCP-color map will still be based on the packet’s original DSCP. All the subsequent
operations will base on the mutated DSCP.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > DSCP Mutation Map, as shown
below:
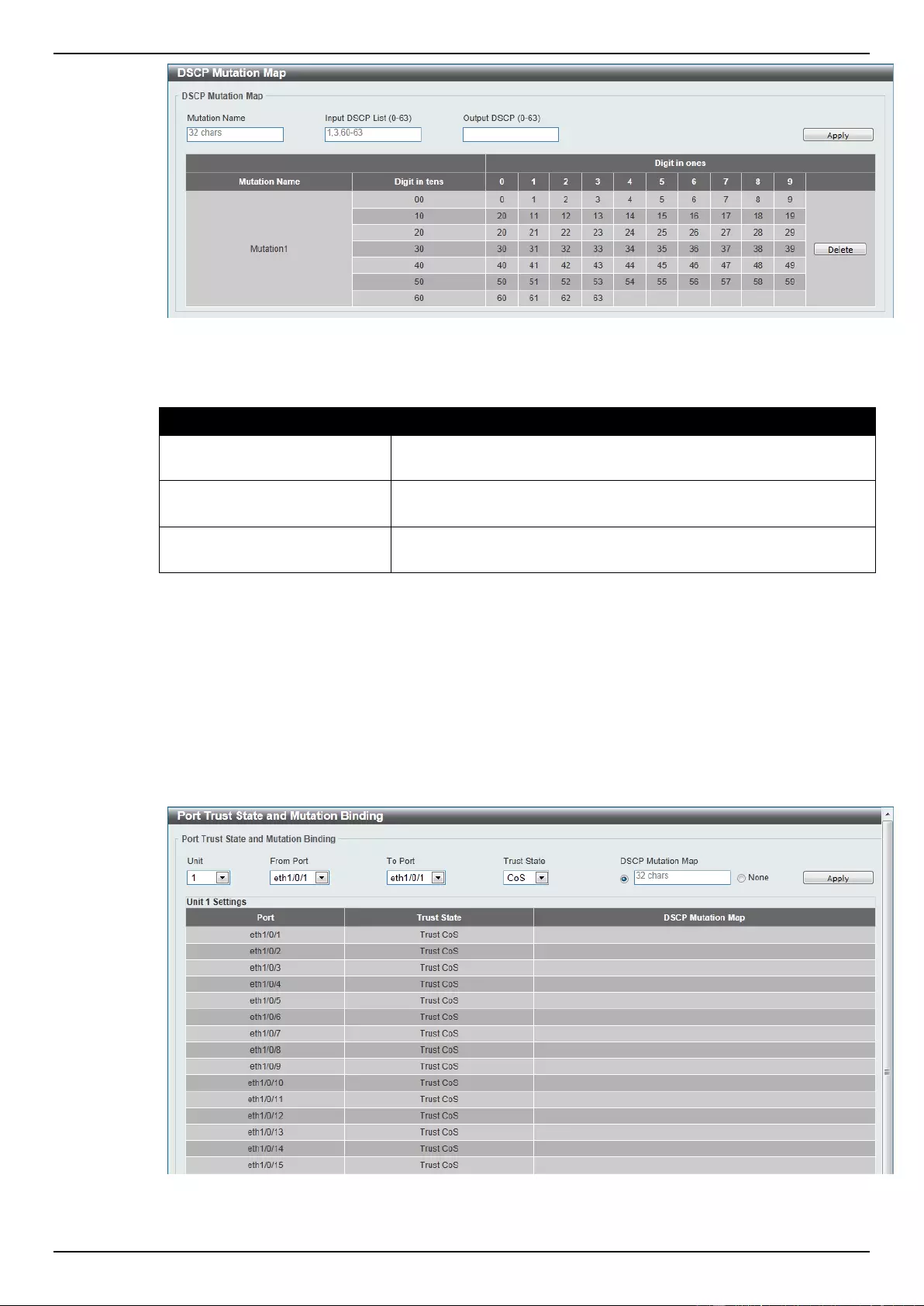
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
161
Figure 7-7 DSCP Mutation Map window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Mutation Name
Enter the DSCP mutation map name here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
Input DSCP List
Enter the input DSCP list value here. This value must be between 0
and 63.
Output DSCP
Enter the output DSCP value here. This value must be between 0
and 63.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Port Trust State and Mutation Binding
This window is used to view and configure port trust state and mutation binding settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > Port Trust State and Mutation
Binding, as shown below:
Figure 7-8 Port Trust State and Mutation Binding window
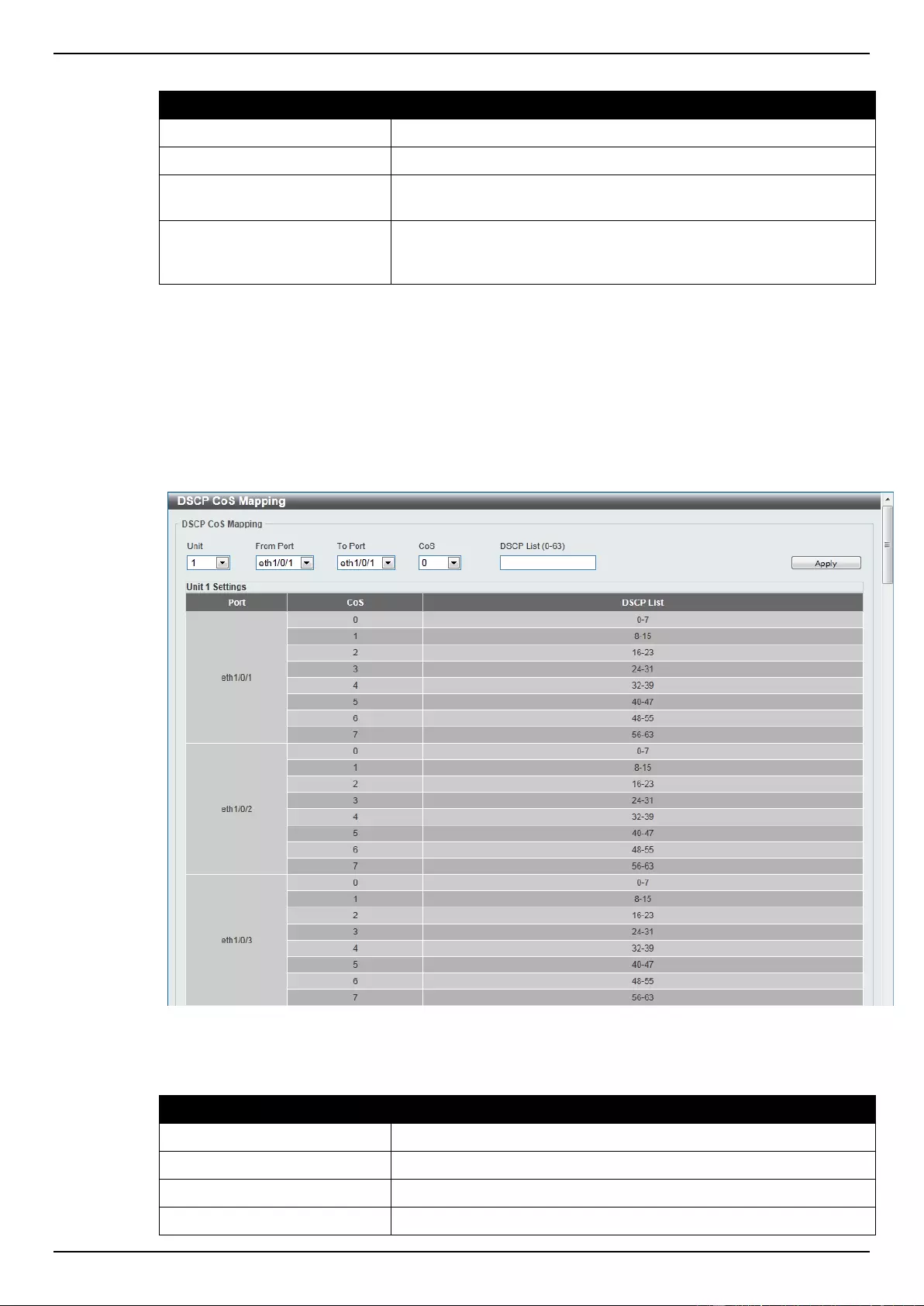
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
162
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Trust State
Select the port trust state option here. Options to choose from are
CoS and DSCP.
DSCP Mutation Map
Select and enter the DSCP mutation map name used here. This
name can be up to 32 characters long. Select the None option to
not allocate a DSCP mutation map to the port(s).
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DSCP CoS Mapping
This window is used to view and configure the DSCP CoS mapping settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > DSCP CoS Mapping, as shown
below:
Figure 7-9 DSCP CoS Mapping window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
CoS
Select the CoS value. Options to choose from are 0 to 7.
DSCP List
Enter the DSCP list value to map to the CoS value here. This value
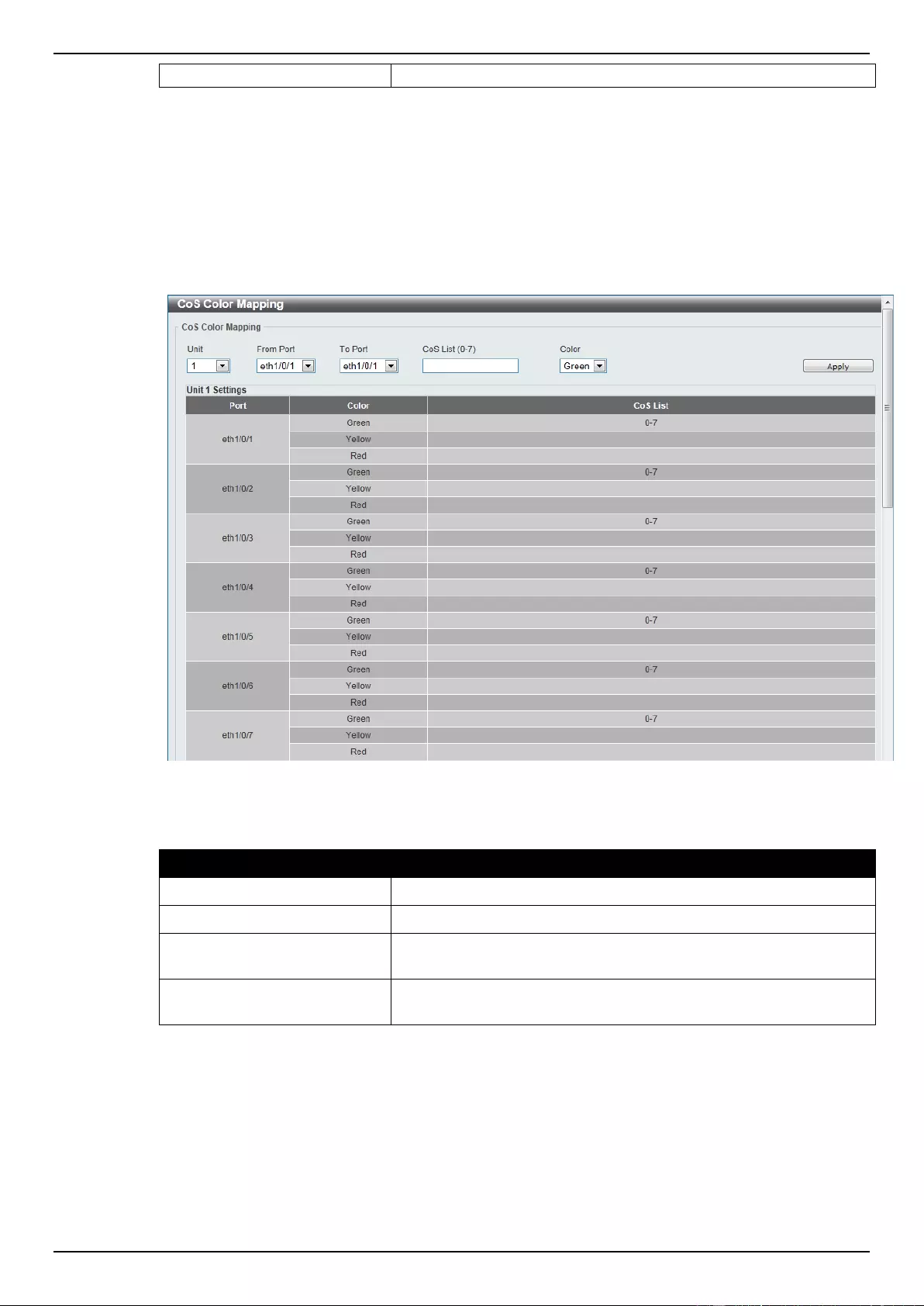
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
163
must be between 0 and 63.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
CoS Color Mapping
This window is used to view and configure the CoS color mapping settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > CoS Color Mapping, as shown
below:
Figure 7-10 CoS Color Mapping window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
CoS List
Enter the CoS value that will be mapped to the color. This value
must be between 0 and 7.
Color
Select the color option. Options to choose from are Green, Yellow,
and Red.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DSCP Color Mapping
This window is used to view and configure the DSCP color mapping settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > DSCP Color Mapping, as shown
below:
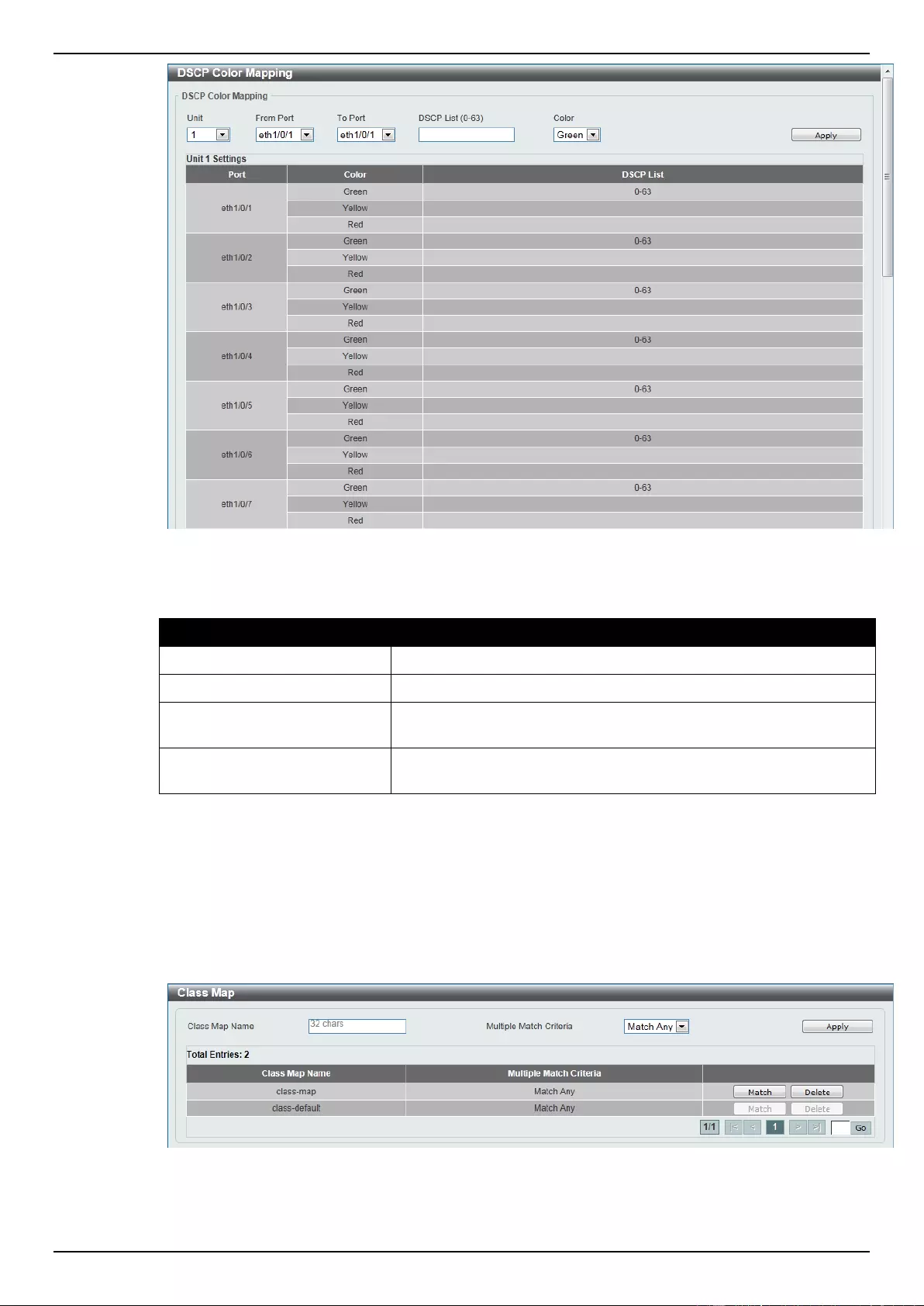
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
164
Figure 7-11 DSCP Color Mapping window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
DSCP List
Enter the DSCP list value here that will be mapped to a color. This
value must be between 0 and 63.
Color
Select the color option that will be mapped to the DSCP value.
Options to choose from are Green, Yellow, and Red.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Class Map
This window is used to view and configure the class map settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > Class Map, as shown below:
Figure 7-12 Class Map window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
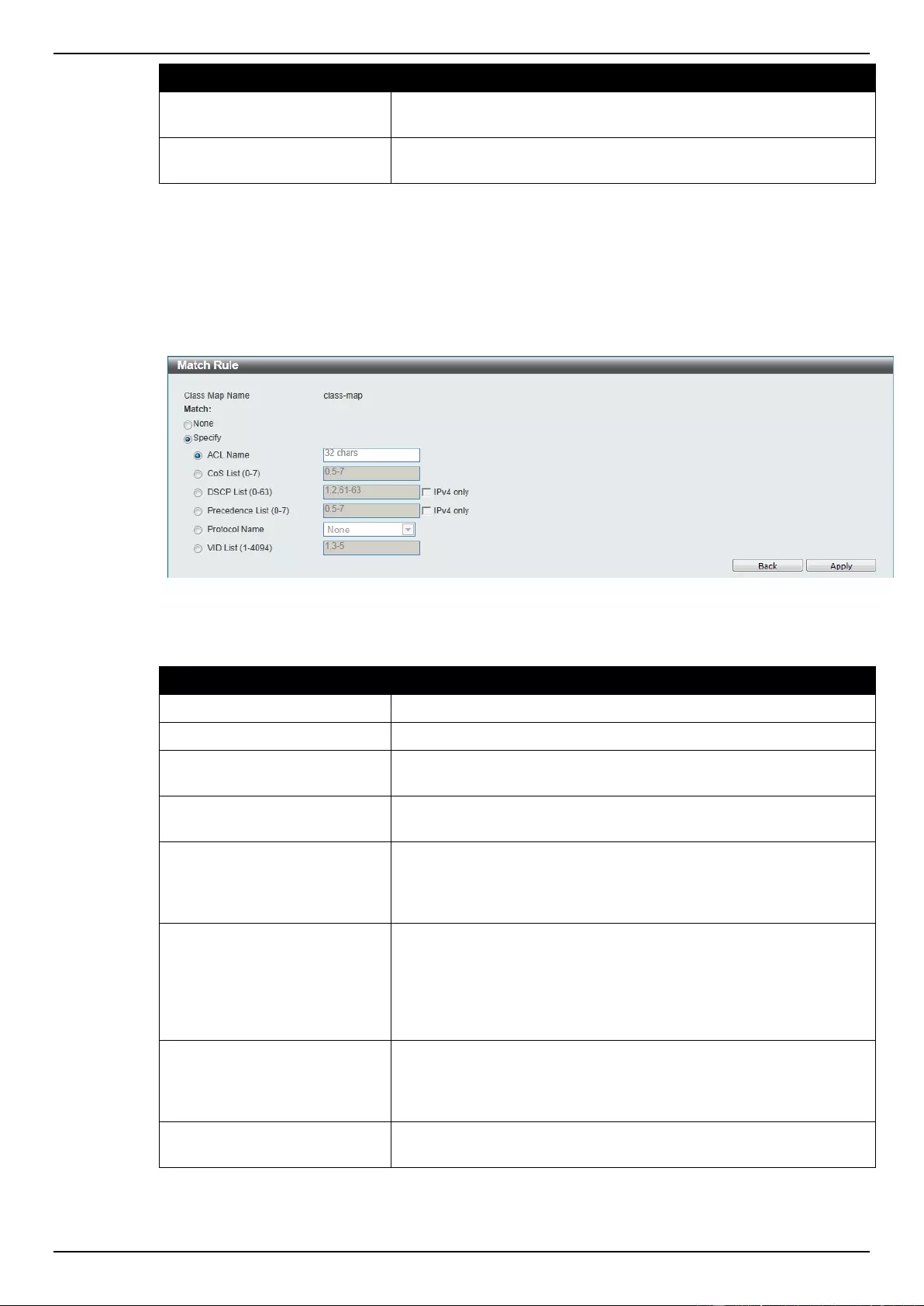
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
165
Parameter
Description
Class Map Name
Enter the class map name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Multiple Match Criteria
Select the multiple match criteria option here. Options to choose
from are Match All and Match Any.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Match button to configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Match button, the following window will appear.
Figure 7-13 Match Rule window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
None
Select this option to match nothing to this class map.
Specify
Select the option to match something to this class map.
ACL Name
Select and enter the access list name that will be matched with this
class map here. This name can be up to 32 characters long.
CoS List
Select and enter the CoS list value that will be matched with this
class map here. This value must be between 0 and 7.
DSCP List
Select and enter the DSCP list value that will be matched with this
class map here. This value must be between 0 and 63. Tick the
IPv4 only check box to match IPv4 packets only. If not specified,
the match is for both IPv4 and IPv6 packets.
Precedence List
Select and enter the precedence list value that will be matched with
this class map here. This value must be between 0 and 7. Tick the
IPv4 only check box to match IPv4 packets only. If not specified,
the match is for both IPv4 and IPv6 packets. For IPv6 packets, the
precedence is most three significant bits of traffic class of IPv6
header.
Protocol Name
Select the protocol name that will be matched with the class map
here. Options to choose from are None, ARP, BGP, DHCP, DNS,
EGP, FTP, IPv4, IPv6, NetBIOS, NFS, NTP, OSPF, PPPOE, RIP,
RTSP, SSH, Telnet, and TFTP.
VID List
Select and enter the VLAN list value that will be matched with the
class map here. This value must be between 1 and 4094.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
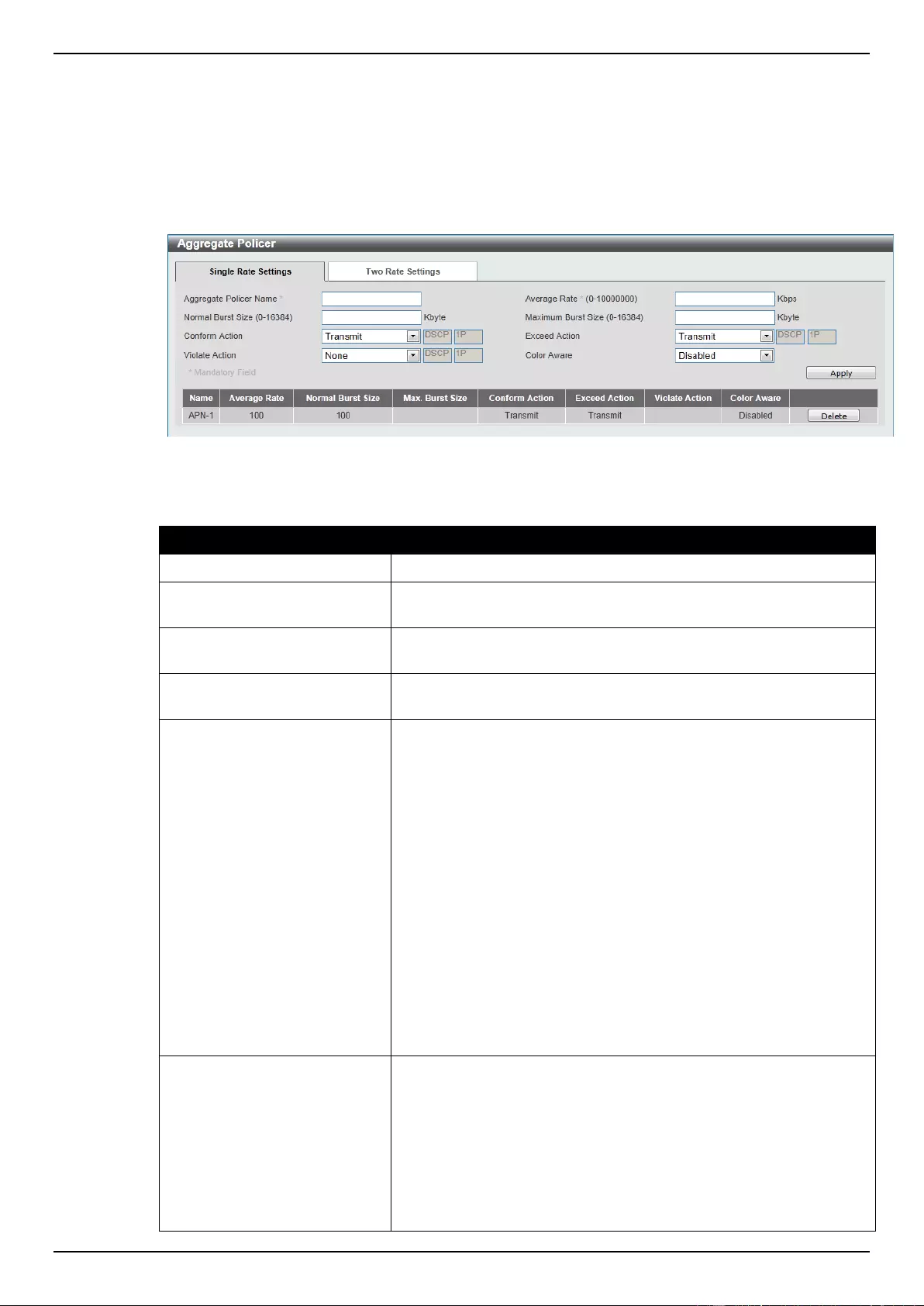
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
166
Aggregate Policer
This window is used to view and configure the aggregate policer settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > Aggregate Policer, as shown
below:
Figure 7-14 Aggregate Policer window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Aggregate Policer Name
Enter the aggregate policer’s name here.
Average Rate
Enter the average rate value here. This value must be between 0
and 10000000 kbps.
Normal Burst Size
Enter the normal burst size value here. This value must be between
0 and 16384 Kbytes.
Maximum Burst Size
Enter the maximum burst size value here. This value must be
between 0 and 16384 Kbytes.
Confirm Action
Select the confirm action here. The confirm action specifies the
action to take on green color packets. If the confirm action is not
specified, the default action is to Transmit. Options to choose from
are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-Transmit, Transmit, and
Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Exceed Action
Select the exceed action here. The exceed action specifies the
action to take on packets that exceed the rate limit. For a two rate
policer, if the exceed action is not specified, the default action is
Drop. Options to choose from are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-
1P-Transmit, Transmit, and Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
167
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Violate Action
Select the violate action here. The violate action specifies the action
to take on packets that violate the normal and maximum burst sizes
for singe rate policing. It specifies the action to take for those
packets that did not conform to both CIR and PIR. For a single rate
policer, if the violate action is not specified, it will create a single-
rate two-color policer. For a two-rate policer, if the violation action is
not specified, the default action is equal to the exceed action.
Options to choose from are None, Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-
1P-Transmit, Transmit, and Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Color Aware
Select this option to enable or disable color aware option here.
When color aware is not specified, the policer works in the color
blind mode. When color aware is enabled, the policer works in the
color aware mode.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
After clicking the Two Rate Setting tab, at the top of the page, the following page will be available.
Figure 7-15 Two Rate Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Aggregate Policer Name
Enter the aggregate policer’s name here.
CIR
Enter the Committed Information Rate (CIR) value here. This value
must be between 0 and 10000000 kbps. The committed packet rate
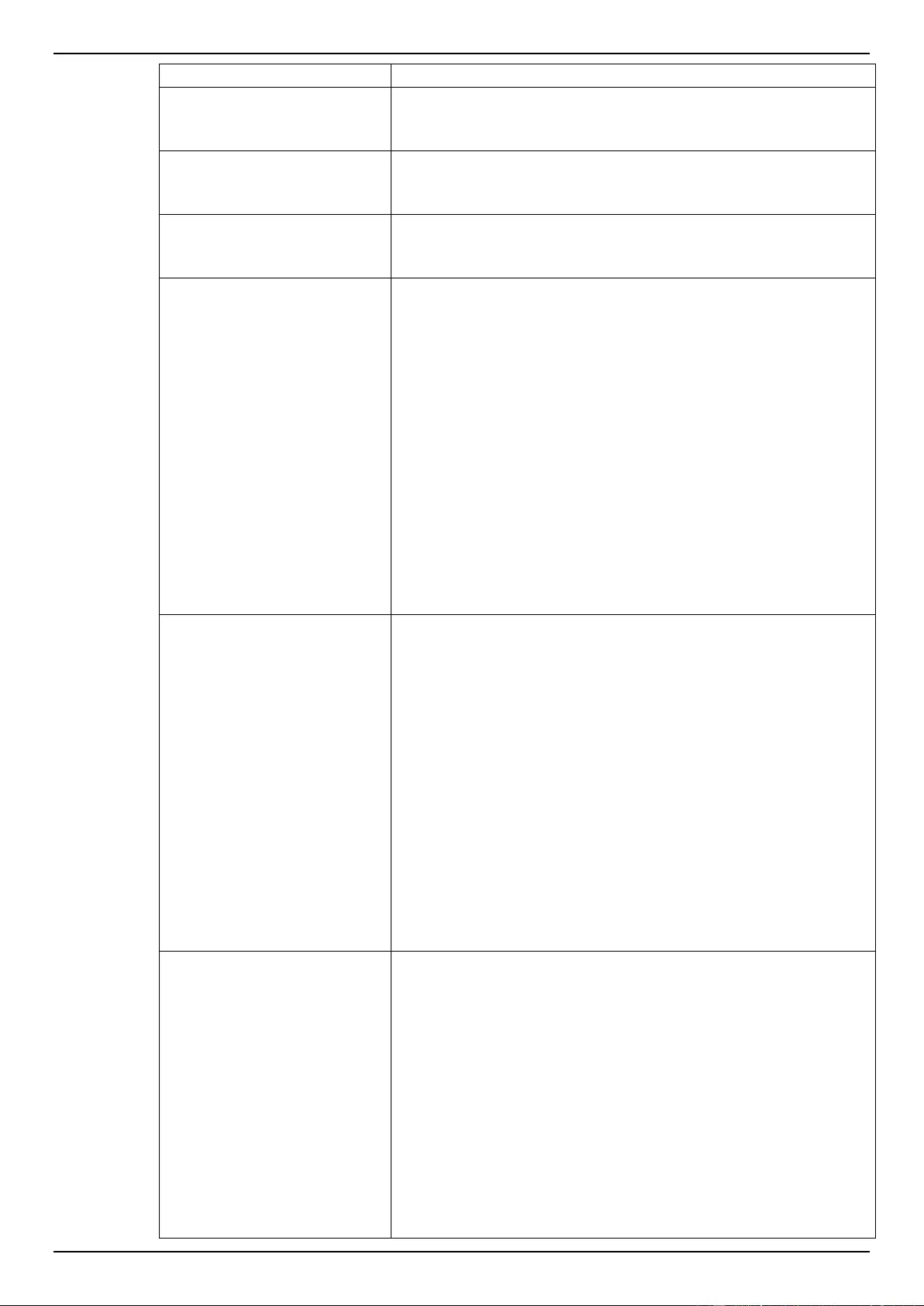
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
168
is the first token bucket for the two-rate metering.
Confirm Burst
Enter the confirm burst value here. This value must be between 0
and 16384 Kbytes. The confirm burst value specifies the burst size
for the first token bucket in kbps.
PIR
Enter the Peak information Rate (PIR) value here. This value must
be between 0 and 10000000 kbps. The peak information rate is the
second token bucket for the two-rate metering.
Peak Burst
Enter the peak burst value here. This value must be between 0 and
16384 Kbytes. The peak burst value is the burst size for the second
token bucket in kilobytes.
Confirm Action
Select the confirm action here. The confirm action specifies the
action to take on green color packets. If the confirm action is not
specified, the default action is to Transmit. Options to choose from
are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-Transmit, Transmit, and
Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Exceed Action
Select the exceed action here. The exceed action specifies the
action to take on packets that exceed the rate limit. For a two rate
policer, if the exceed action is not specified, the default action is
Drop. Options to choose from are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-
1P-Transmit, Transmit, and Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Violate Action
Select the violate action here. The violate action specifies the action
to take on packets that violate the normal and maximum burst sizes
for singe rate policing. It specifies the action to take for those
packets that did not conform to both CIR and PIR. For a single rate
policer, if the violate action is not specified, it will create a single-
rate two-color policer. For a two-rate policer, if the violation action is
not specified, the default action is equal to the exceed action.
Options to choose from are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-
Transmit, Transmit, and Set-DSCP-1P.
When selecting the Drop option, the packet will be dropped.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-Transmit option, enter the IP DSCP
value in the space provided. This value sets the IP differentiated
services code point (DSCP) value and transmits the packet with the
new IP DSCP value.
When selecting the Set-1P-Transmit option, enter the 1P transmit
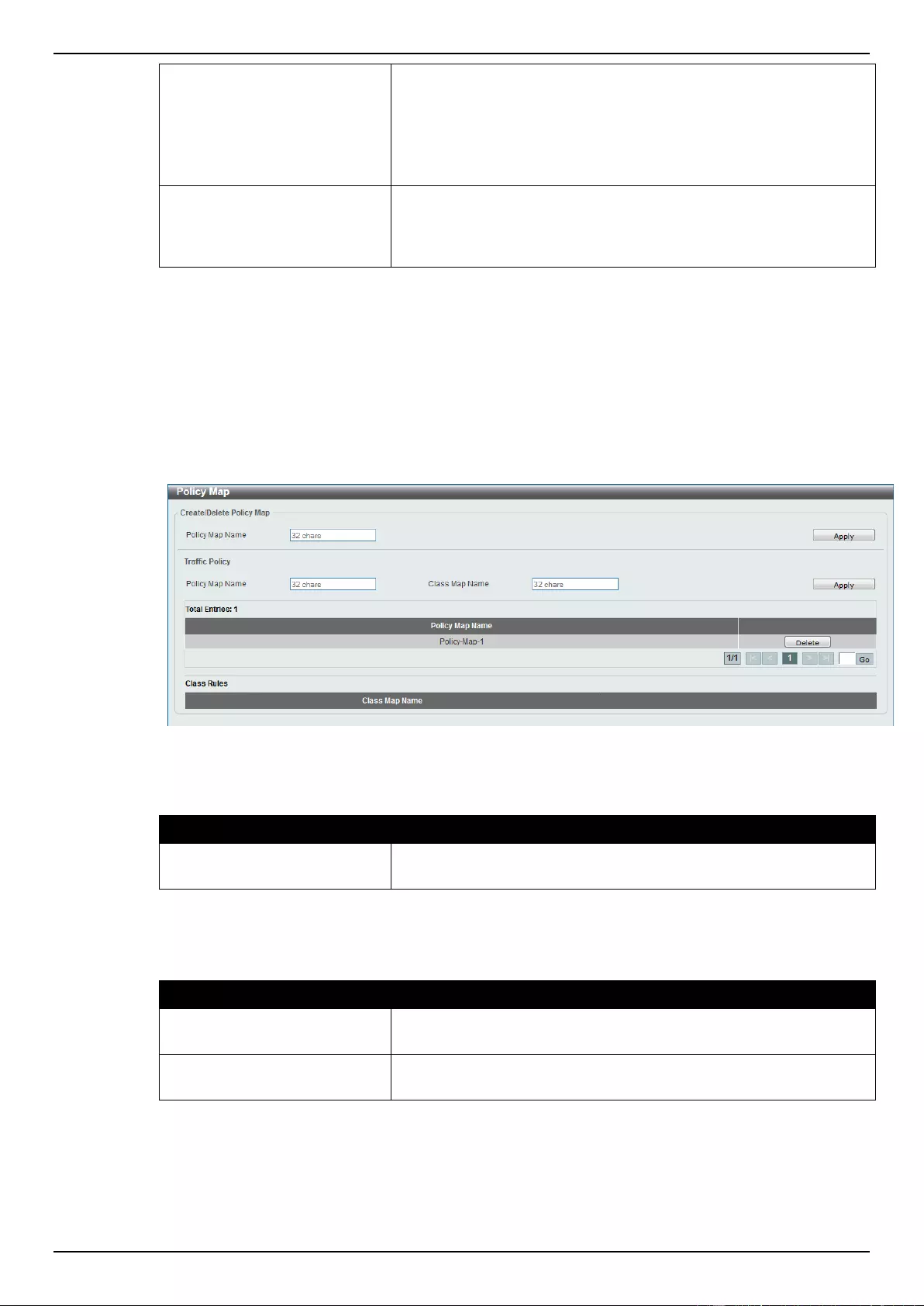
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
169
value in the space provided. This value sets the 802.1p value and
transmits the packet with the new value.
When selecting the Set-DSCP-1P option, enter the IP DSCP and
1P transmit values in the spaces provided.
When selecting the Transmit option, packets will be transmitted
unaltered.
Color Aware
Select this option to enable or disable color aware option here.
When color aware is not specified, the policer works in the color
blind mode. When color aware is enabled, the policer works in the
color aware mode.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Policy Map
This window is used to view and configure the policy map settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > Policy Map, as shown below:
Figure 7-16 Policy Map window
The fields that can be configured for Create/Delete Policy Map are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Map Name
Enter the policy map’s name here that will be created or deleted.
This name can be up to 32 characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Traffic Policy are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Map Name
Enter the policy map’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Class Map Name
Enter the class map’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
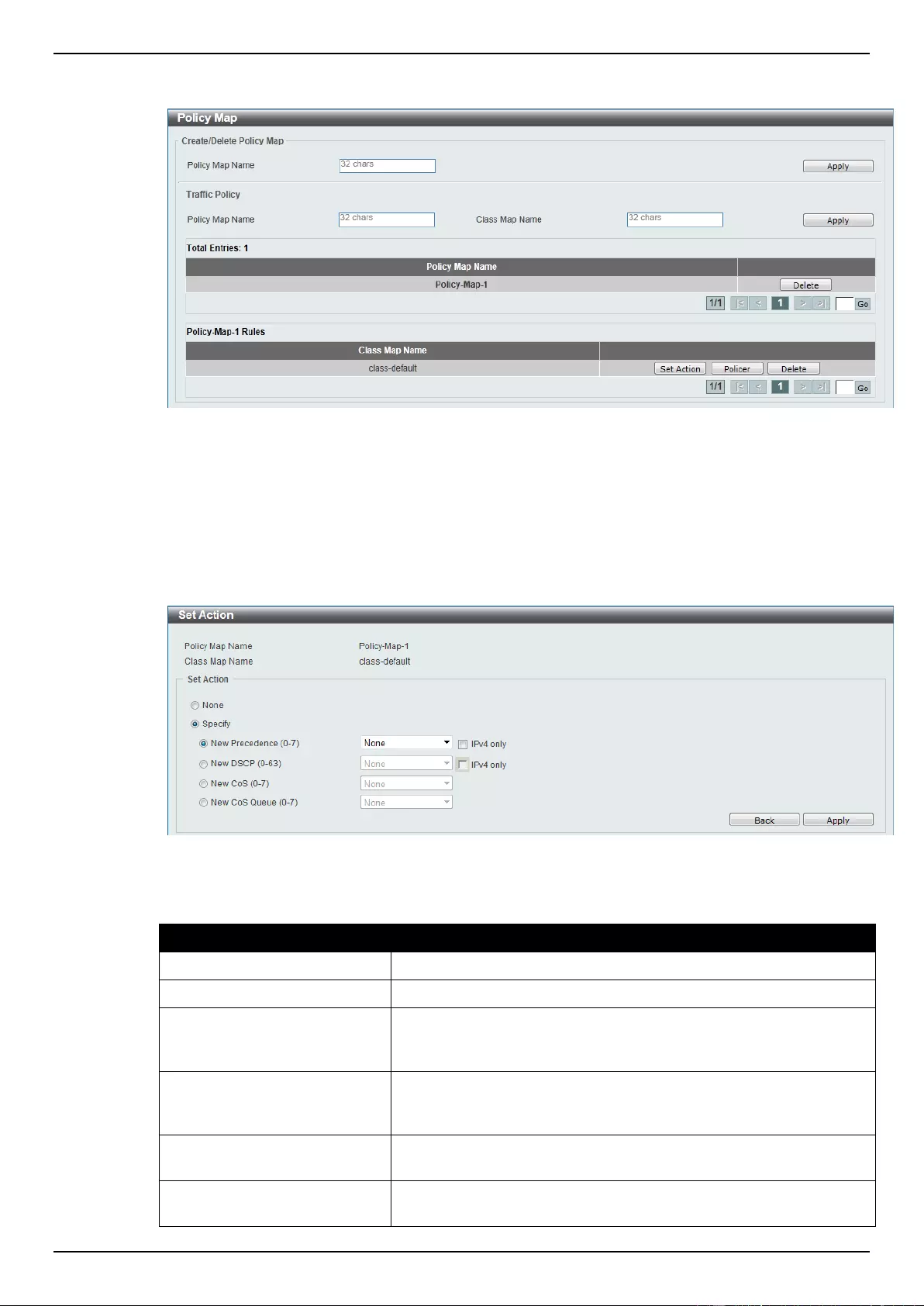
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
170
To view the rules of a specific policy map, click the policy map name in the table (the Policy Map
Name will toggle to the bold font).
Figure 7-17 Policy Map (View Rules) window
Click the Set Action button to configure the action for the policy map.
Click the Policer button to configure the policer action for the policy map.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
After clicking the Set Action button, the following window will appear.
Figure 7-18 Set Action window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
None
Select this option to match nothing to this policy map.
Specify
Select the option to match something to this policy map.
New Precedence
Select a new precedence for the packet. This value must be
between 0 and 7. Tick the IPv4 only to only mark IPv4 precedence.
Setting the precedence will not affect the CoS queue selection.
New DSCP
Select a new DSCP for the packet. This value must be between 0
and 63. Tick the IPv4 only to only mark IPv4 precedence. Setting
DSCP will not affect the CoS queue selection.
New CoS
Select a new CoS value for the packet. This value must be between
0 and 7. Setting CoS will not affect the CoS queue selection.
New CoS Queue
Select a new CoS queue for the packet. This value must be
between 0 and 7. This overwrites the original CoS queue selection.
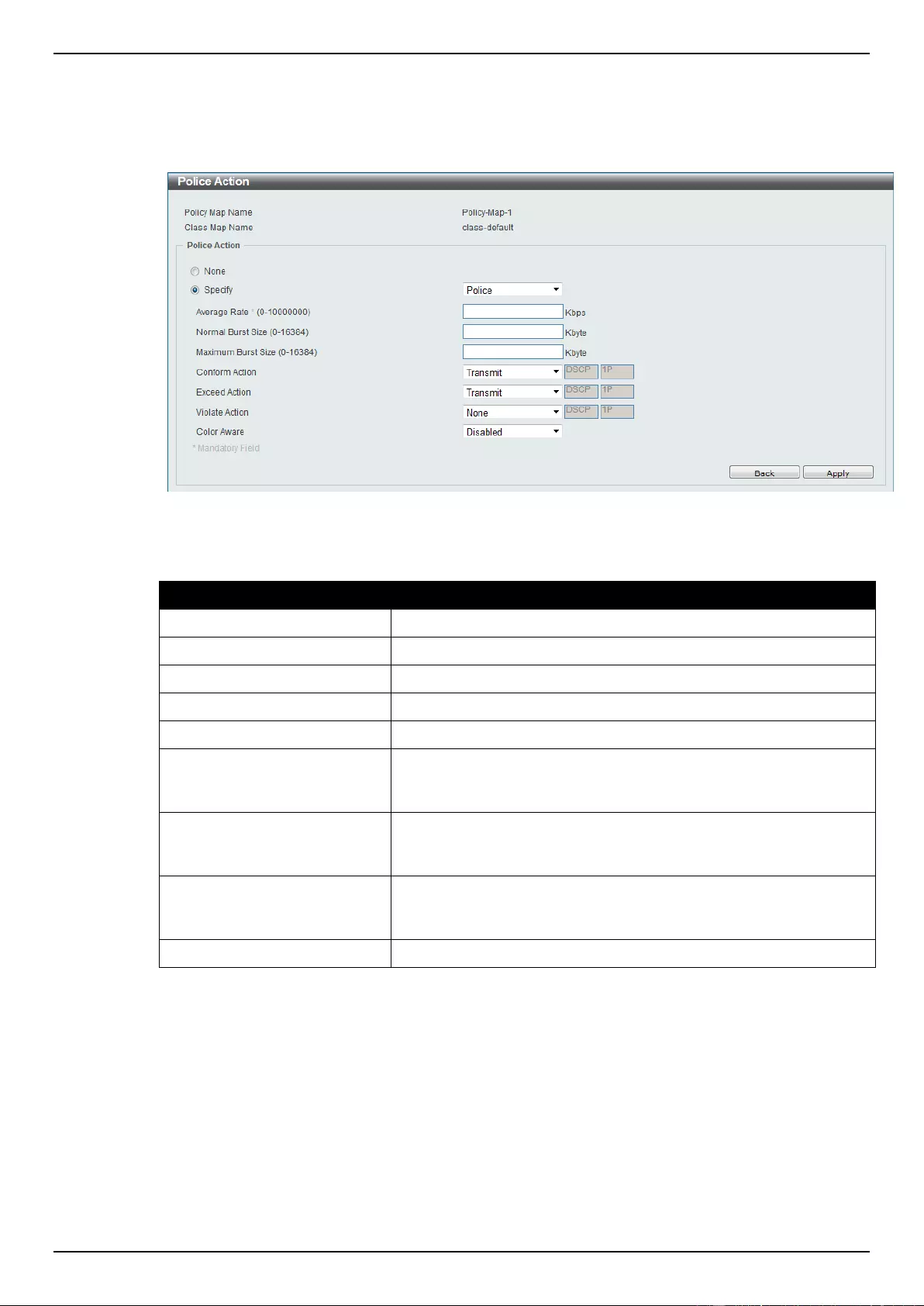
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
171
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
After clicking the Policer button, the following window will appear.
Figure 7-19 Police Action window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
None
Select this option to match nothing to this policy map.
Specify
Select the option to match something to this policy map.
Average Rate
Enter the average rate in kilobits per second.
Normal Burst Size
Enter the normal burst size in kilobytes.
Maximum Burst Size
Enter the maximum burst in kilobytes.
Conform Action
Select the action to take on green color packets. Options to choose
from are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-Transmit, Transmit,
and Set-DSCP-1P.
Exceed Action
Select the action to take on yellow color packets. Options to choose
from are Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-Transmit, Transmit,
and Set-DSCP-1P.
Violate Action
Select the action to take on red color packets. Options to choose
from are None, Drop, Set-DSCP-Transmit, Set-1P-Transmit,
Transmit, and Set-DSCP-1P.
Color Aware
Select this option to enable or disable color aware mode.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Policy Binding
This window is used to view and configure the policy binding settings.
To view the following window, click QoS > Advanced Settings > Policy Binding, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
172
Figure 7-20 Policy Binding window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Direction
Select the direction option here. Option to choose from is Input.
Input represents Input specified ingress traffic.
Policy Map Name
Enter the policy map name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long. Select the None option to not tie a policy map to
this entry.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
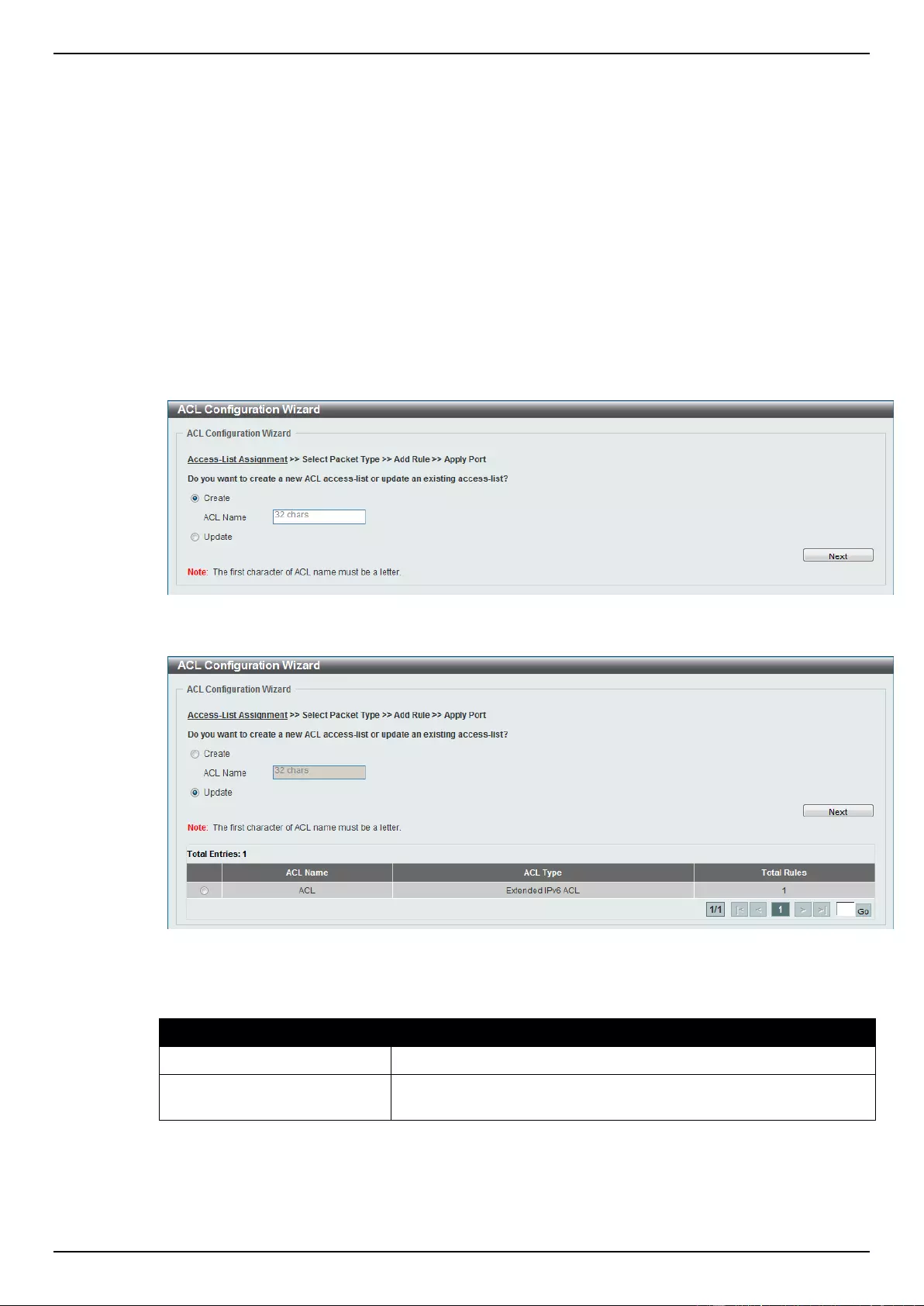
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
173
8. Access Control List (ACL)
ACL Configuration Wizard
ACL Access List
ACL Interface Access Group
ACL VLAN Access Map
ACL VLAN Filter
ACL Configuration Wizard
This window is used to guide the user to create a new ACL access list or configure an existing ACL
access list.
To view the following window, click ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard, as shown below:
Figure 8-1 ACL Configuration Wizard (Access-List Assignment) - Create window
Figure 8-2 ACL Configuration Wizard (Access-List Assignment) - Update window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Create
Select and enter the ACL name with a maximum of 32 characters.
Update
Select to see a table below with the existing ACL access lists.
Select the specific re-configure the entry.
Click the Next button to continue.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Next button, the following window will appear.
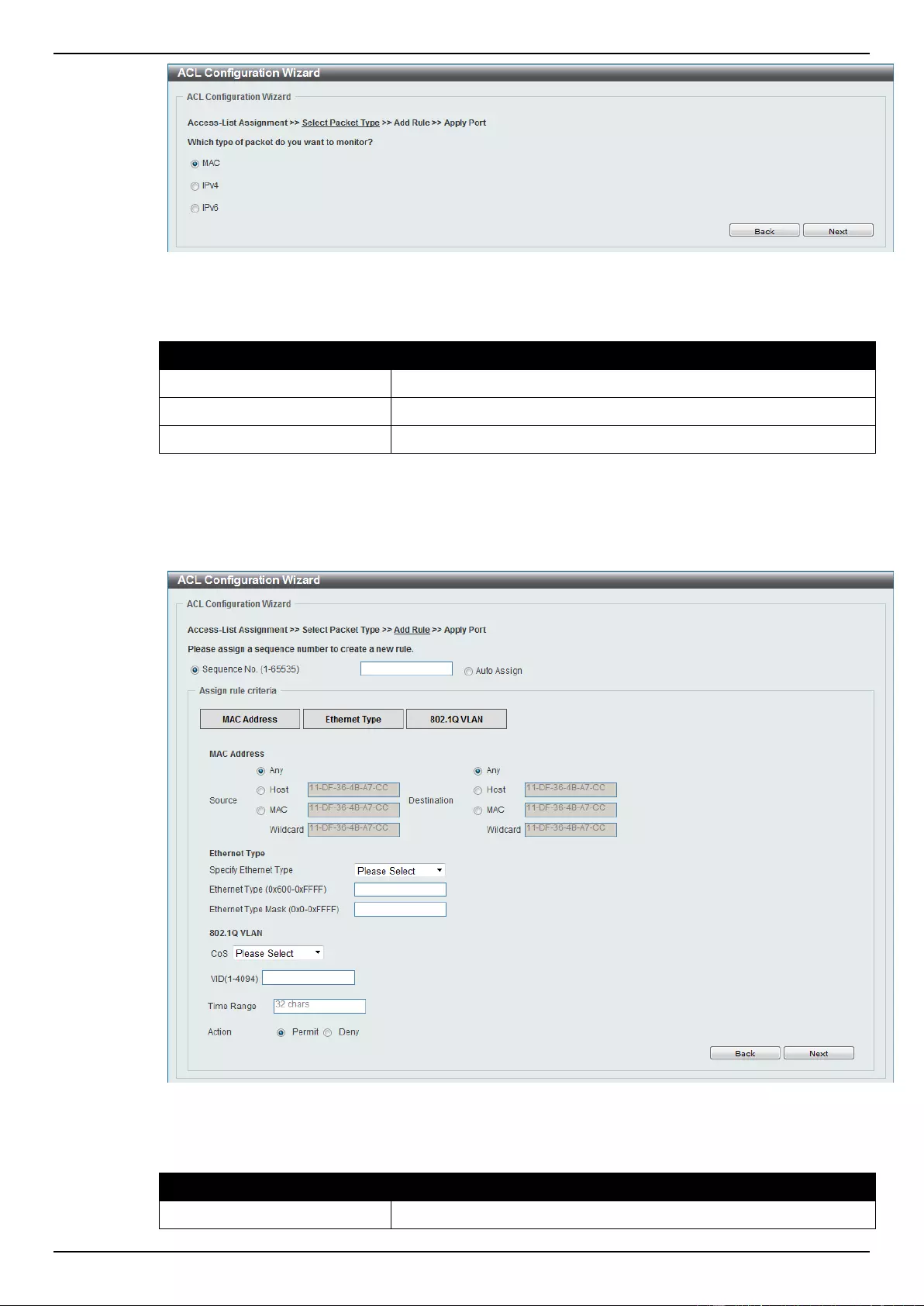
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
174
Figure 8-3 ACL Configuration Wizard (Select Packet Type) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC
Select to be MAC ACL.
IPv4
Select to be IPv4 ACL.
IPv6
Select to be IPv6 ACL.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Next button to continue.
After clicking the MAC radio button and the Next button, the following window will appear.
Figure 8-4 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for MAC ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
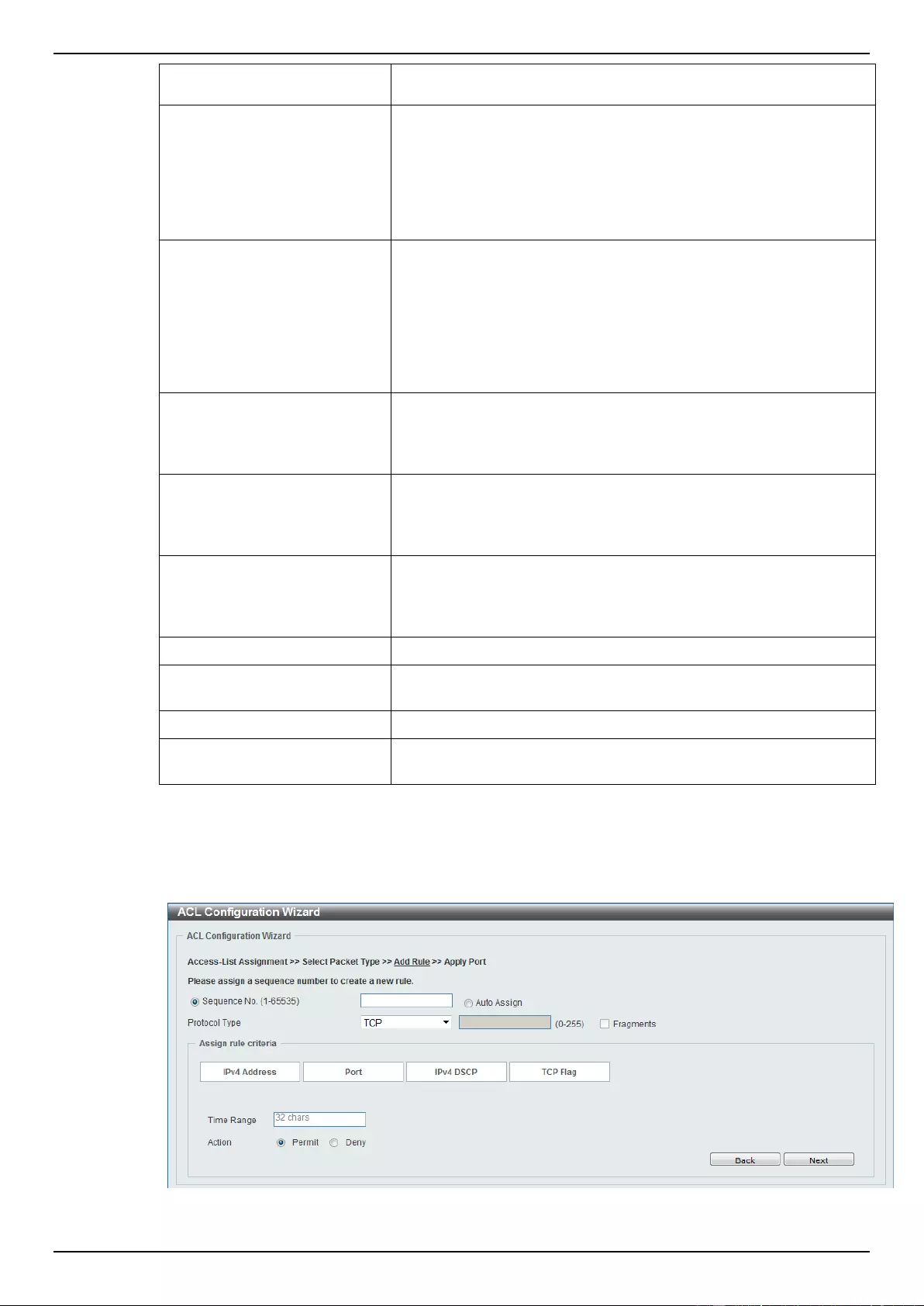
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
175
65535. Select Auto Assign to automatically generate an ACL rule
number for this entry.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
Specify Ethernet Type
Select the Ethernet type option here. Options to choose from are
aarp, appletalk, decent-iv, etype-6000, etype-8042, lat, lavc-sca,
mop-console, mop-dump, vines-echo, vines-ip, xns-idp, and
arp.
Ethernet Type
Enter the Ethernet type hexadecimal value here. This value must be
between 0x600 and 0xFFFF. When any Ethernet type profile is
selected in the Specify Ethernet Type drop-down list, the
appropriate hexadecimal value will automatically be entered.
Ethernet Type Mask
Enter the Ethernet type mask hexadecimal value here. This value
must be between 0x0 and 0xFFFF. When any Ethernet type profile
is selected in the Specify Ethernet Type drop-down list, the
appropriate hexadecimal value will automatically be entered.
CoS
Select the CoS value used here. This value is between 0 and 7.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Next button to continue.
After clicking the IPv4 radio button and the Next button, the following window will appear.
Figure 8-5 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) window
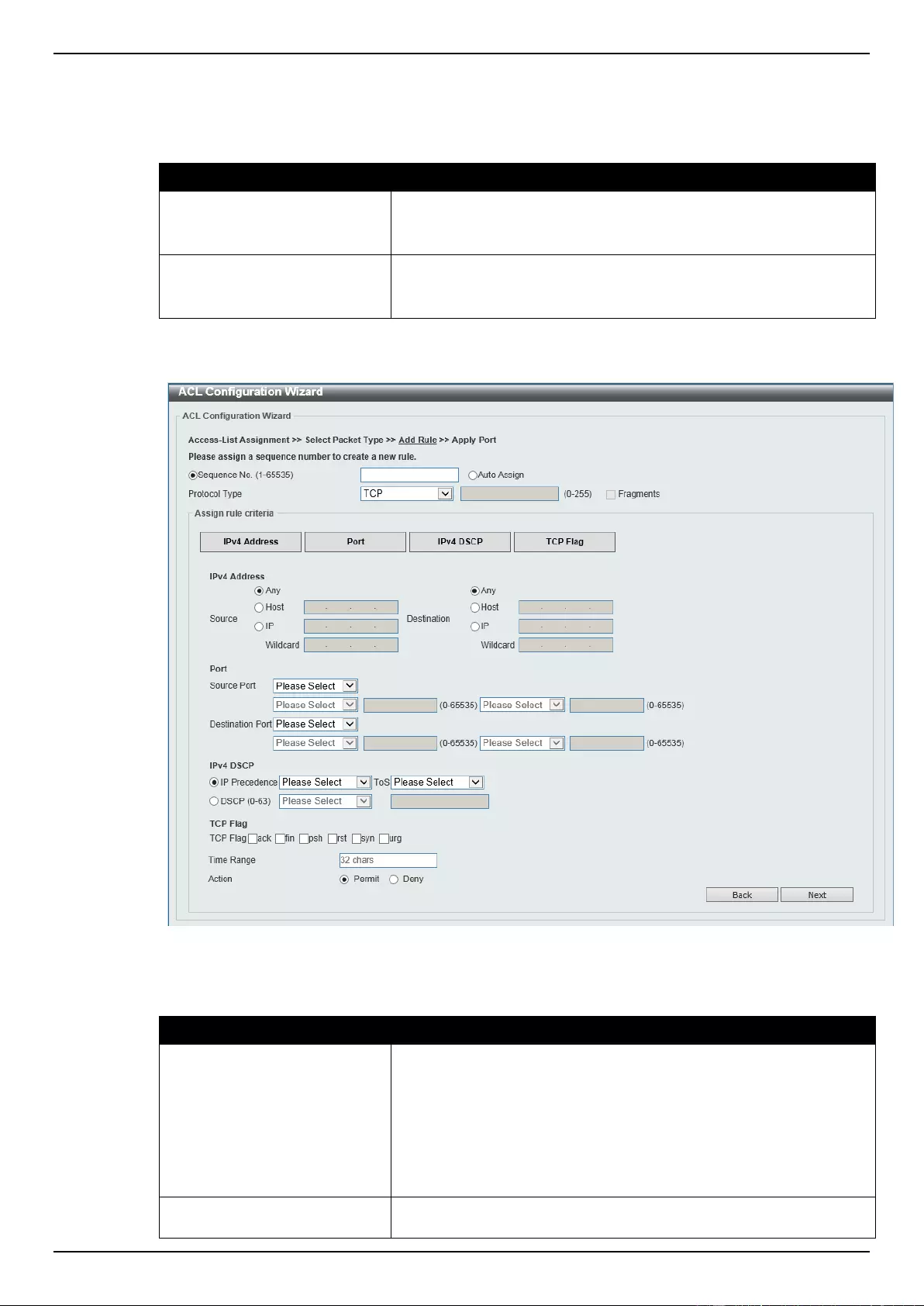
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
176
This window has a dynamic section. Every selection made in the Protocol Type drop-down list will
change the bottom part of this window.
The fixed fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. Select Auto Assign to automatically generate an ACL rule
number for this entry.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol type option here. Options to choose from are
TCP, UDP, ICMP, EIGRP, ESP, GRE, IGMP, OSPF, PIM, VRRP,
IP-in-IP, PCP, Protocol ID, and None.
After selecting the TCP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-6 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) TCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
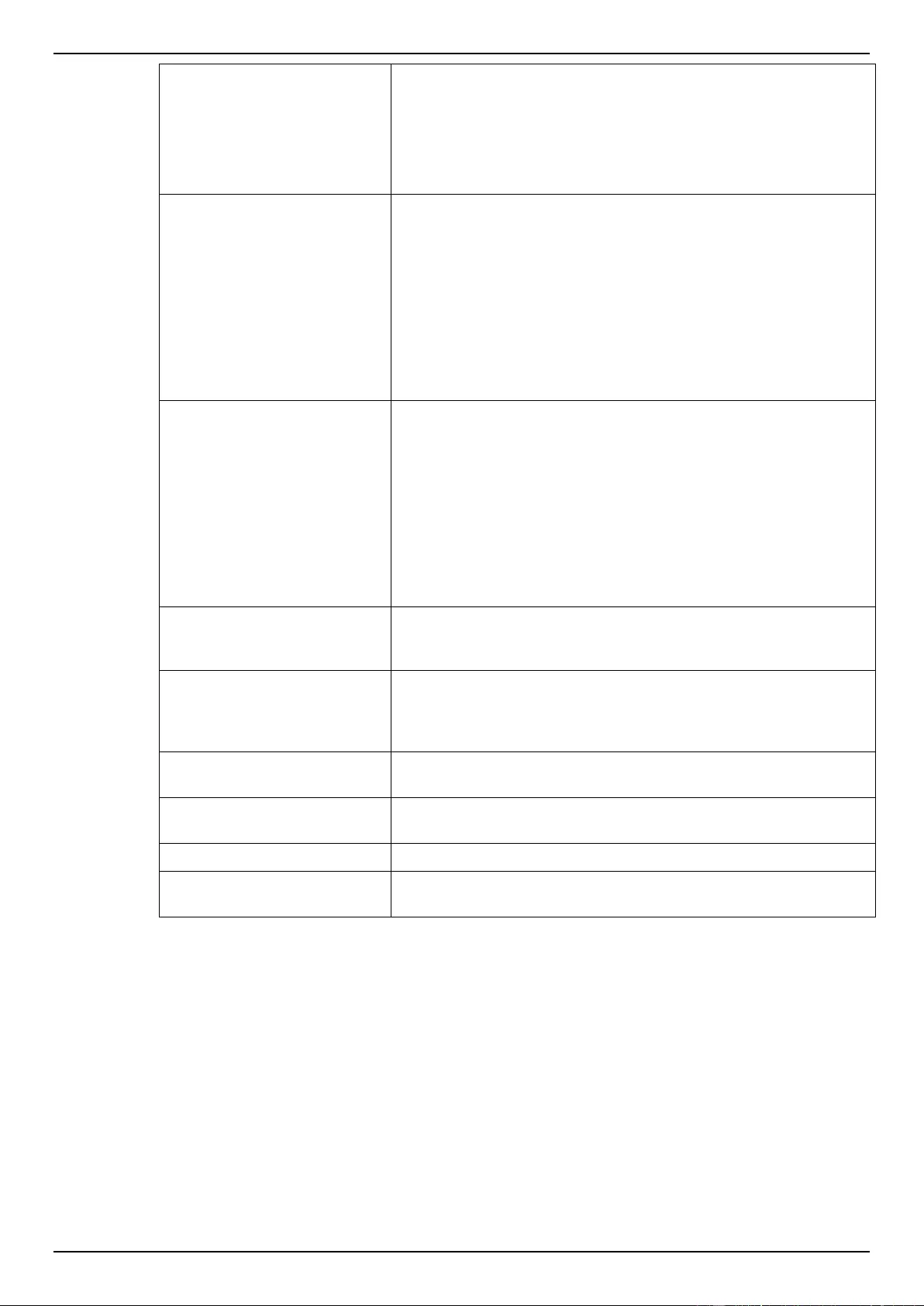
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
177
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
TCP Flag
Tick the appropriate TCP flag option to include the flag in this rule.
Options to choose from are ack, fin, psh, rst, syn, and urg.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
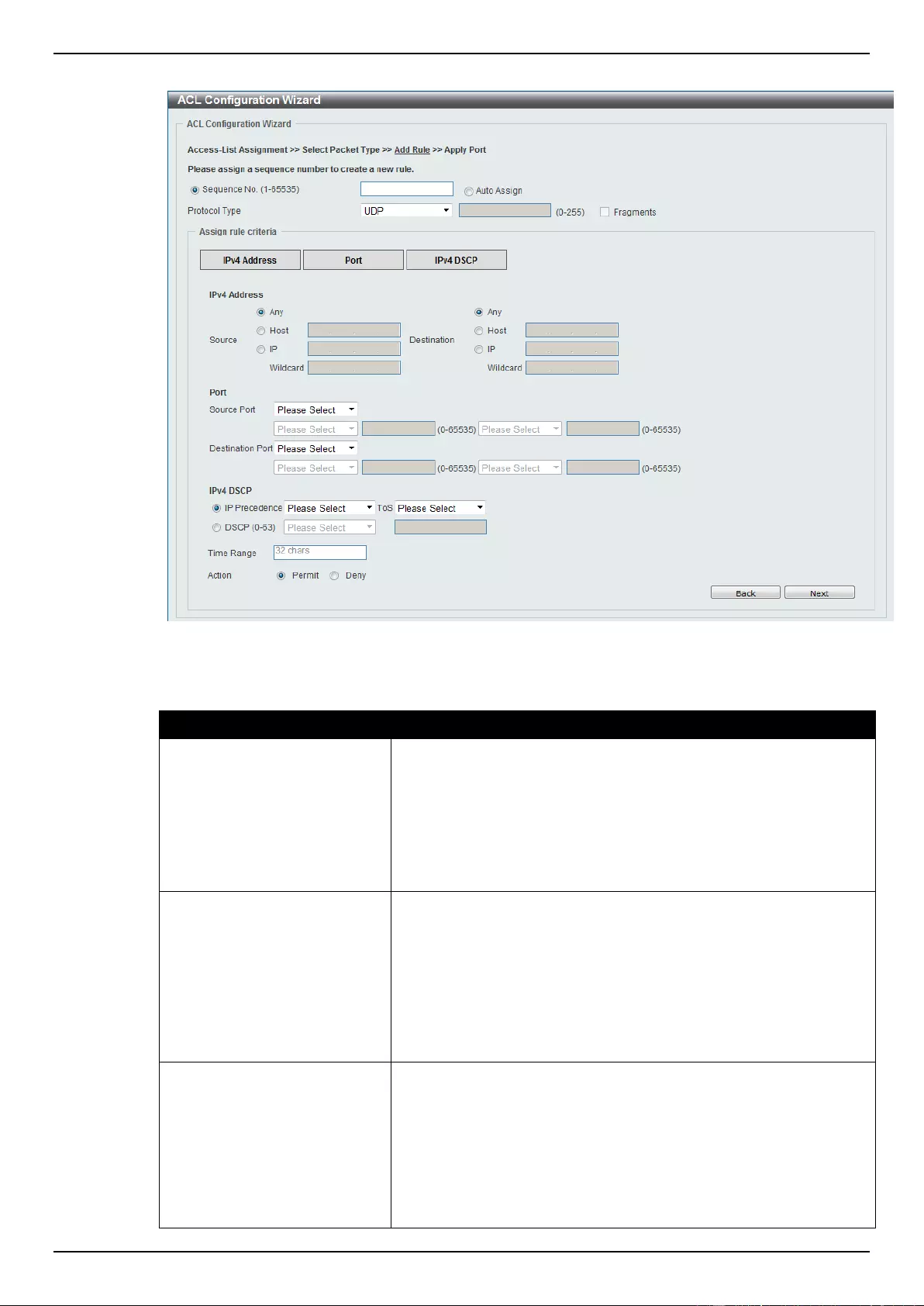
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
178
After selecting the UDP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-7 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) UDP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
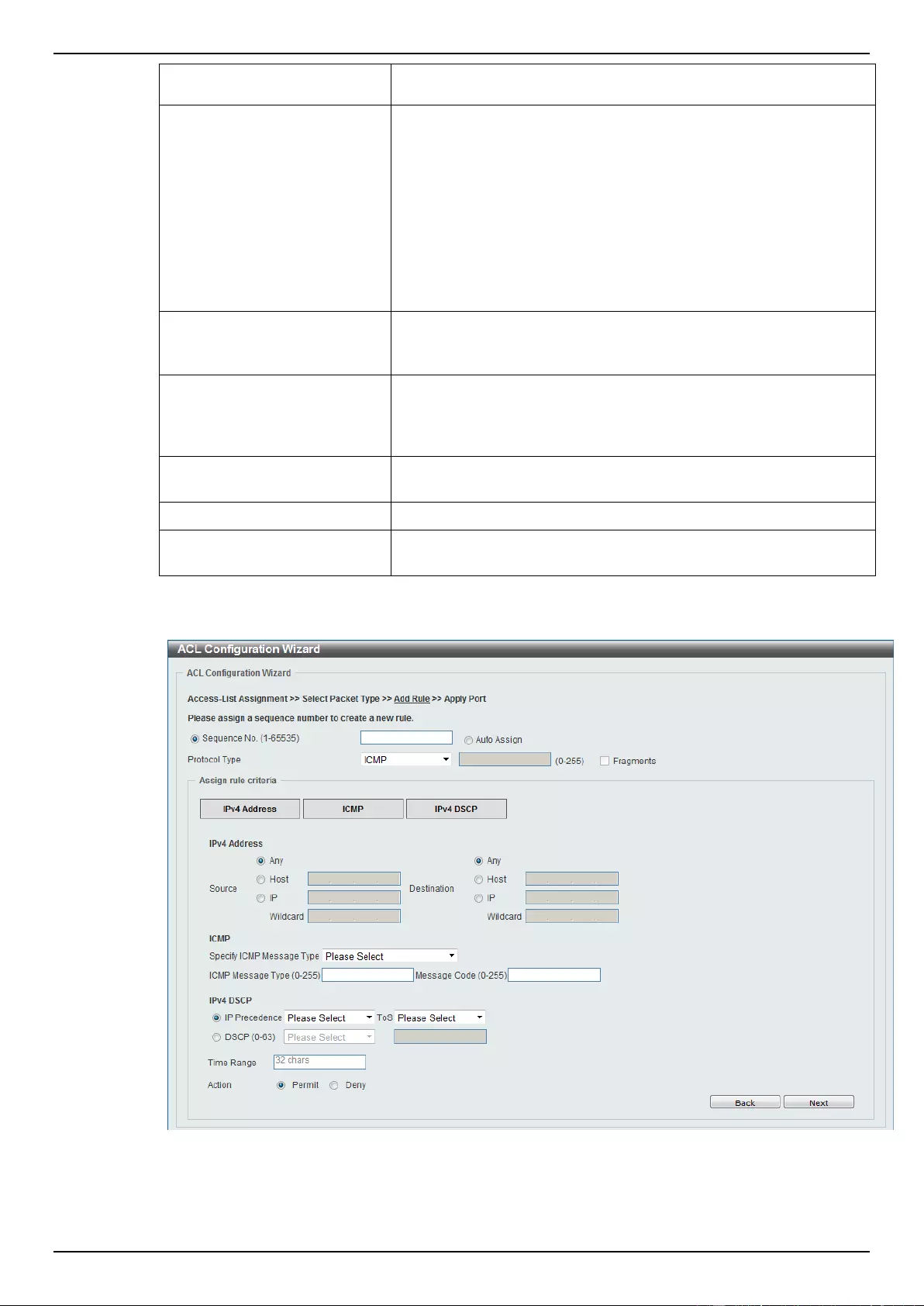
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
179
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the ICMP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-8 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) ICMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
180
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Specify ICMP Message Type
Select the ICMP message type used here.
ICMP Message Type
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected, enter the ICMP
Message Type numerical value used here. When the ICMP
Message Type is selected, this numerical value will automatically
be entered.
Message Code
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected, enter the Message
Code numerical value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is
selected, this numerical value will automatically be entered.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
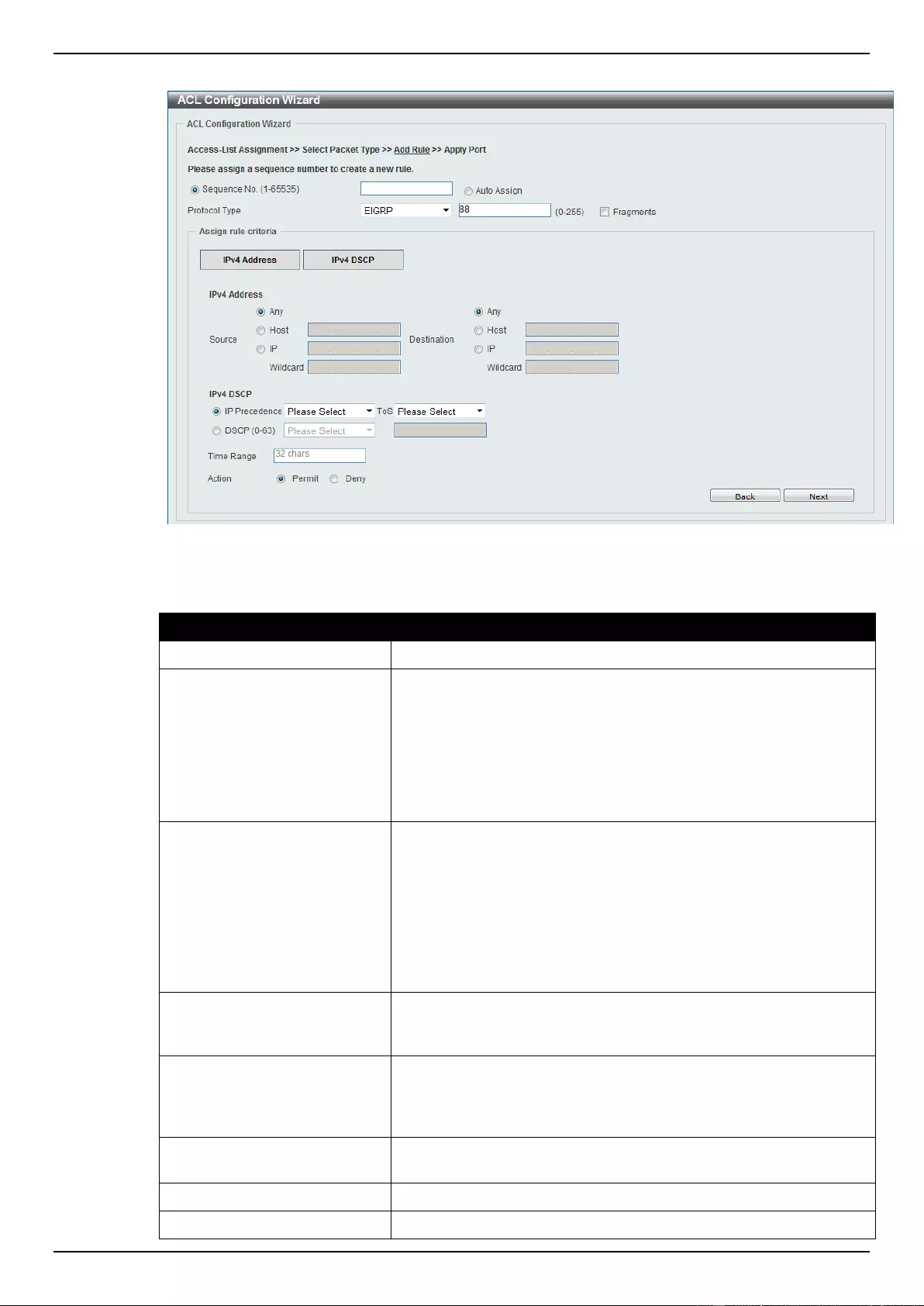
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
181
After selecting the EIGRP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-9 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) EIGRP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
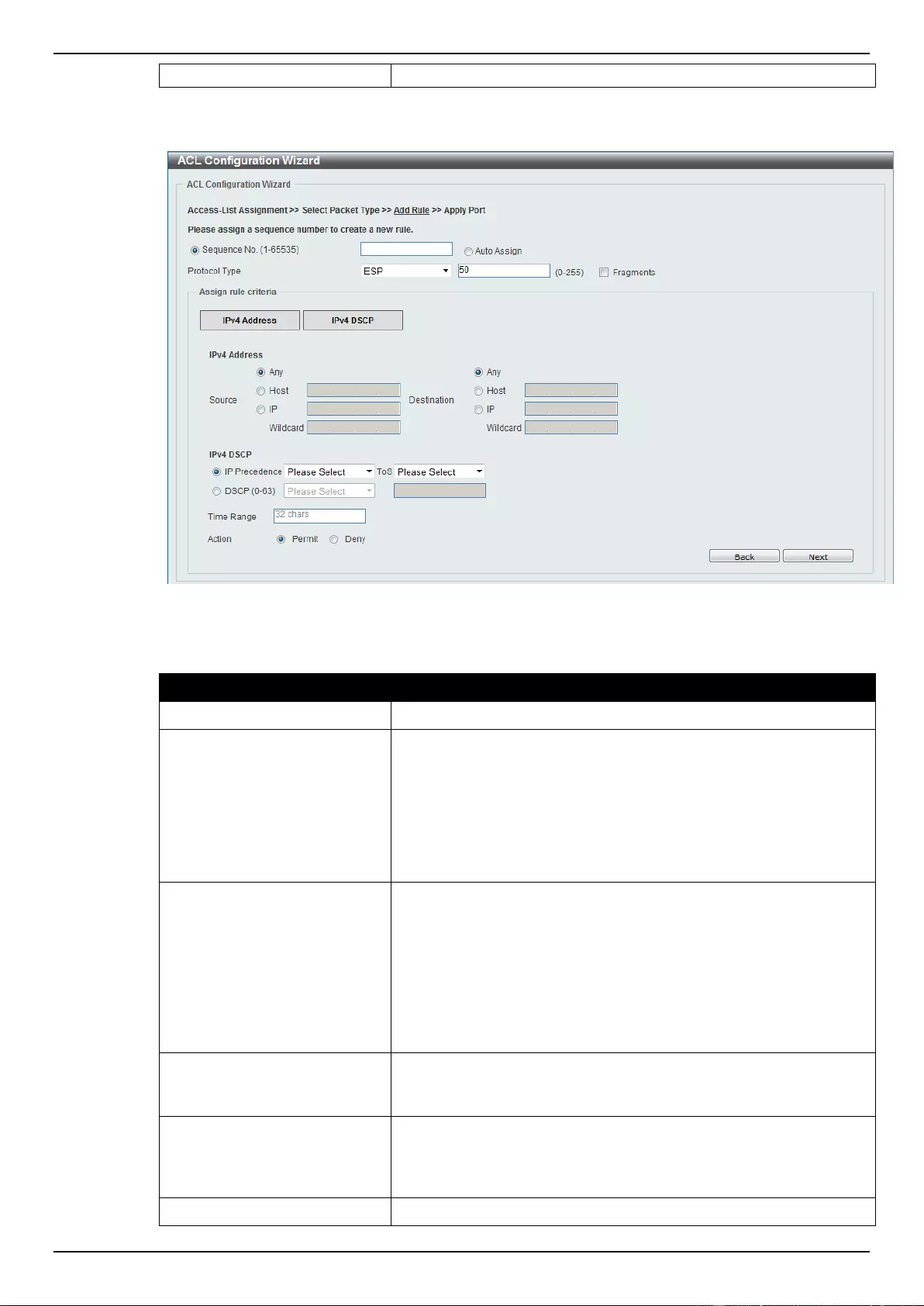
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
182
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the ESP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-10 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) ESP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
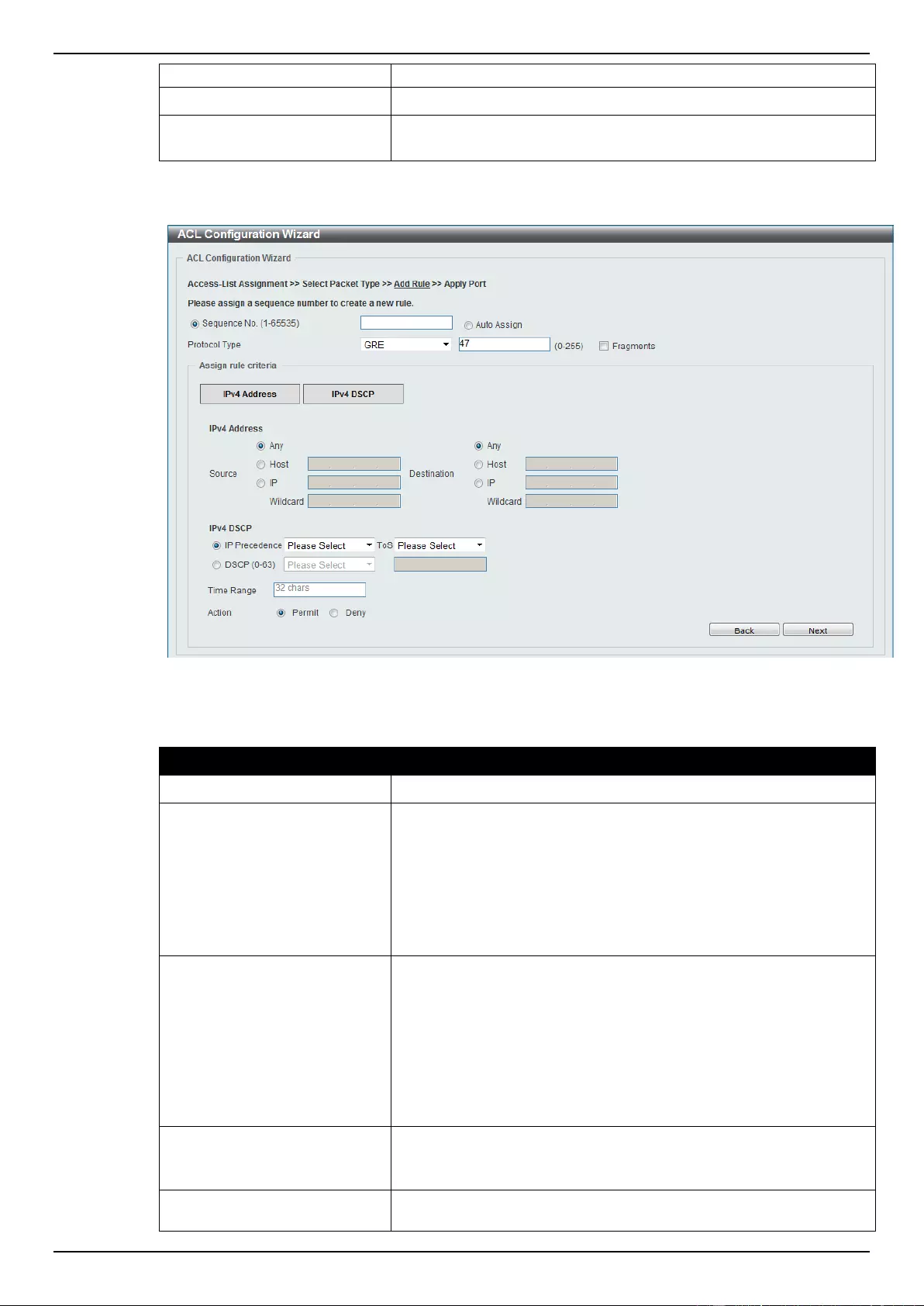
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
183
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the GRE option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-11 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) GRE window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
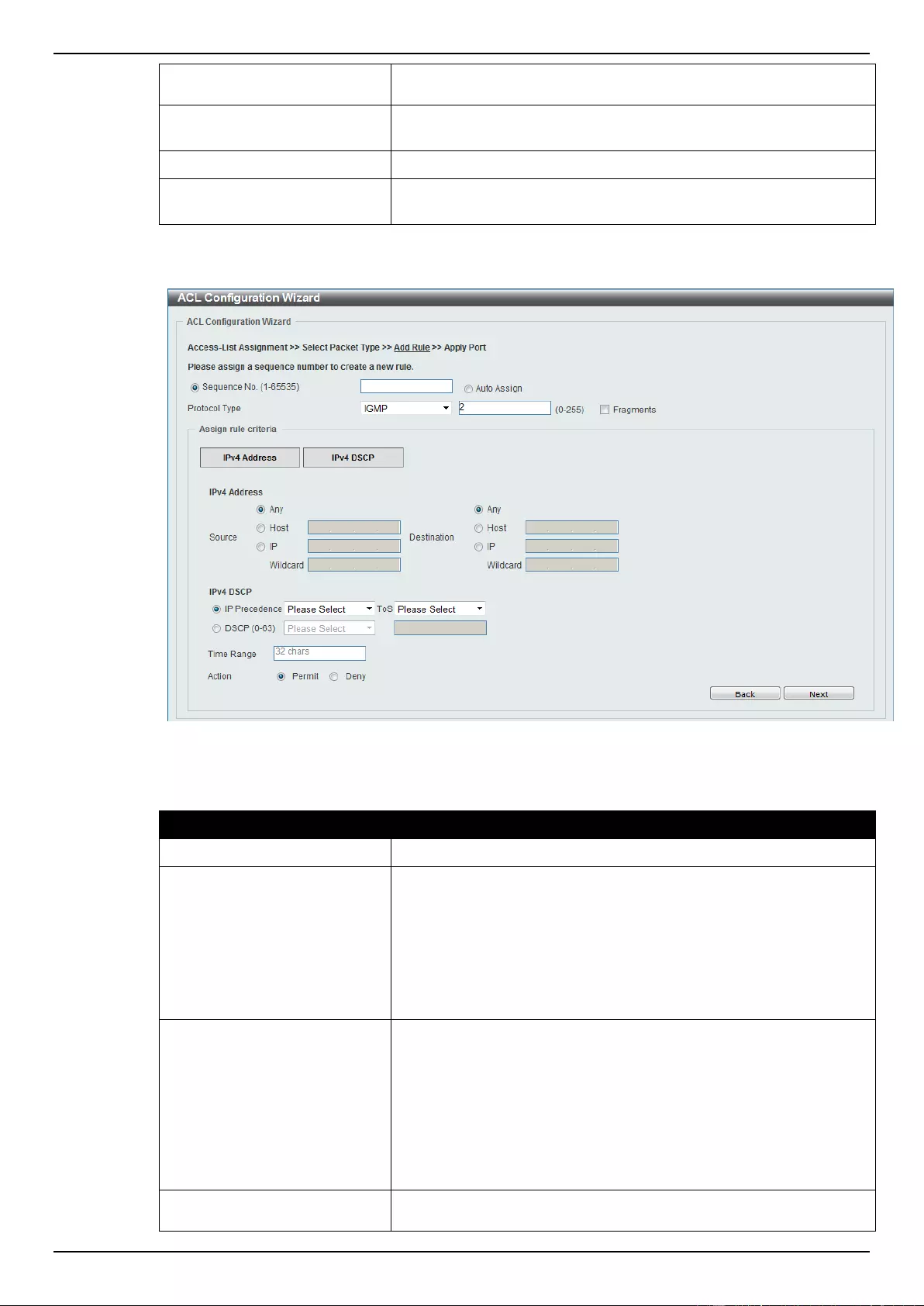
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
184
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the IGMP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-12 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) IGMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
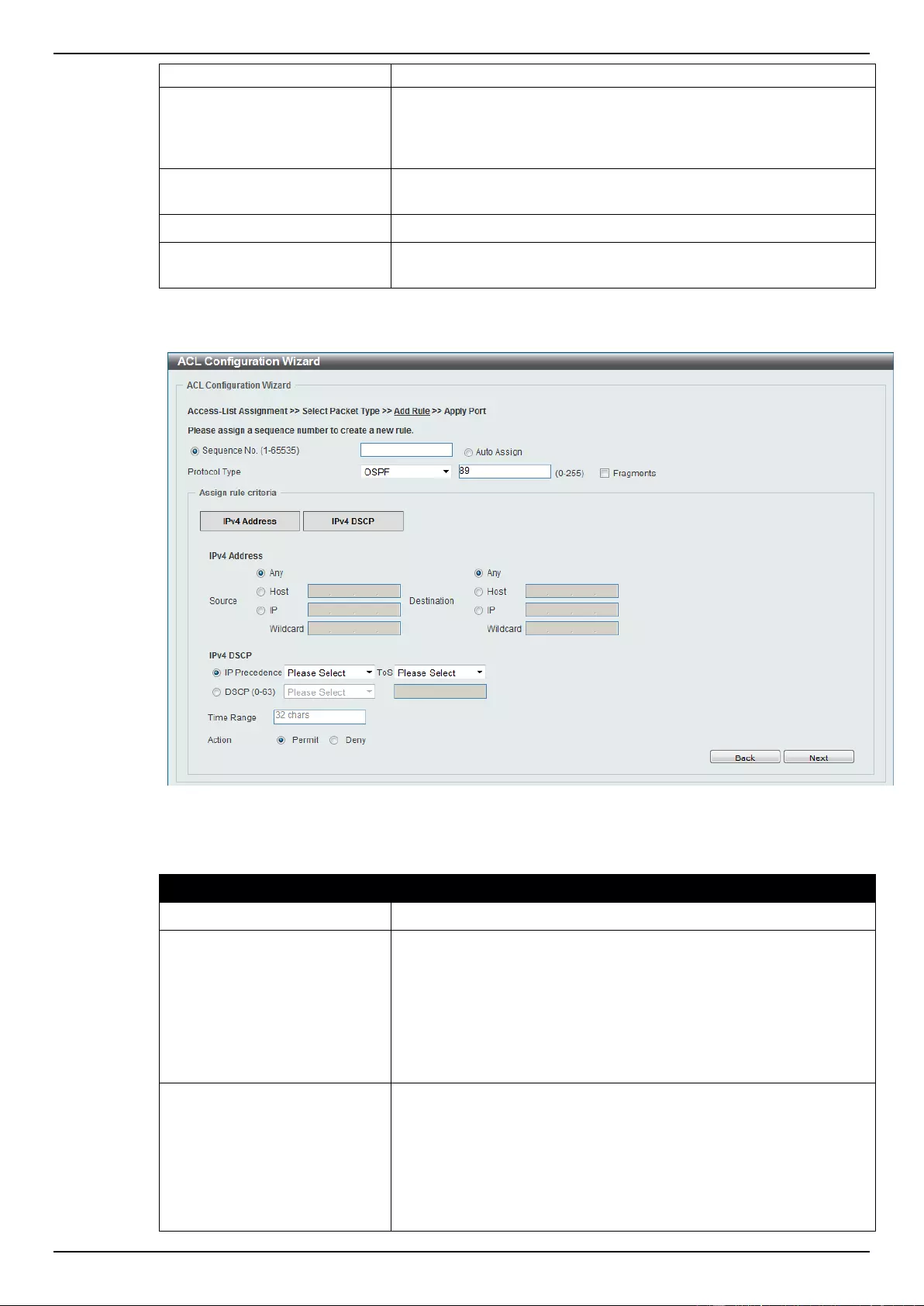
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
185
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the OSPF option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-13 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) OSPF window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
186
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the PIM option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-14 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) PIM window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
187
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the VRRP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-15 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) VRRP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
188
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the IP-in-IP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-16 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) IP-in-IP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
189
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the PCP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-17 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) PCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
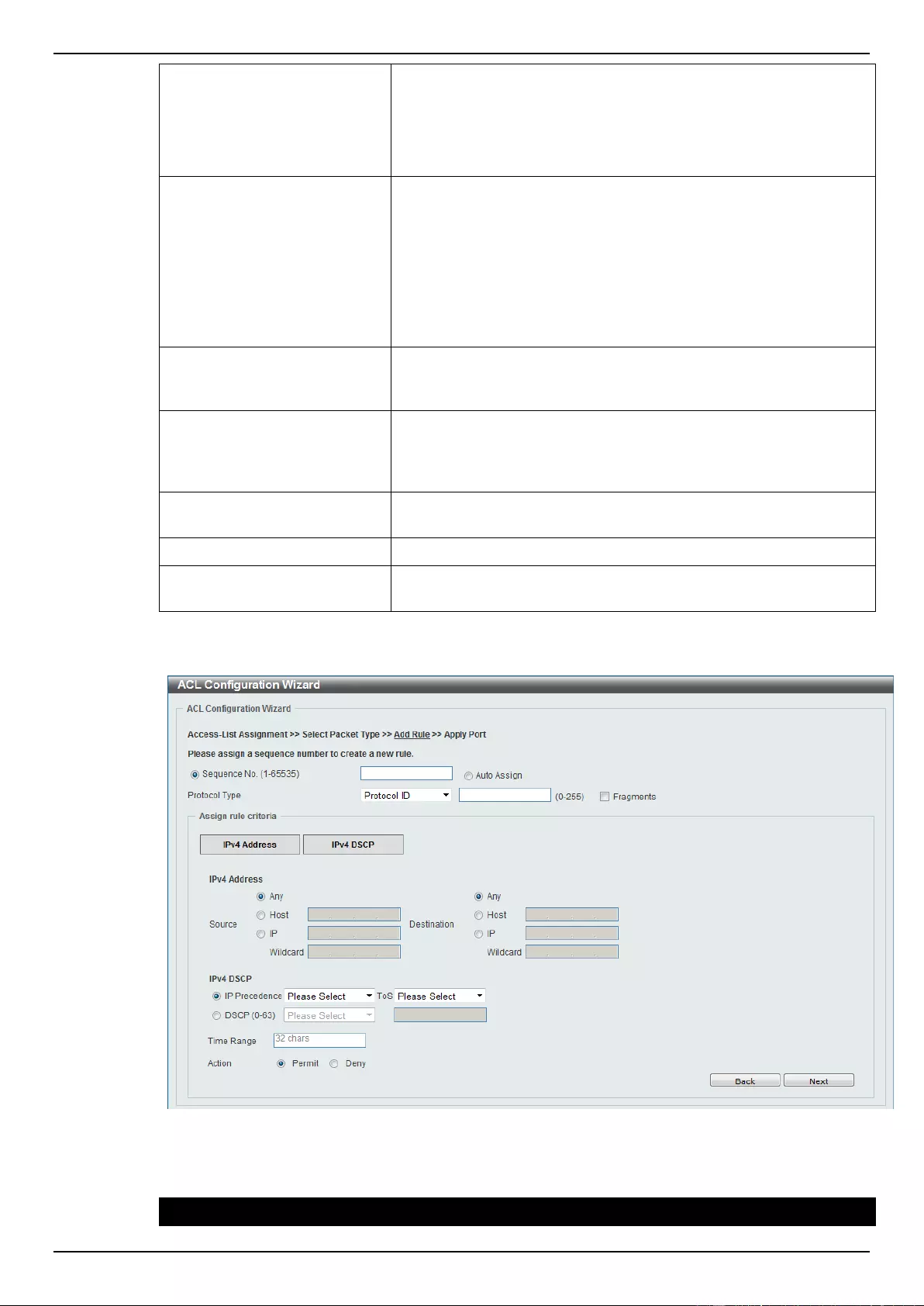
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
190
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the Protocol ID option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-18 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) Protocol ID window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
191
Protocol
Enter the Protocol ID value in the space provided. This value must
be between 0 and 255.
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the None option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
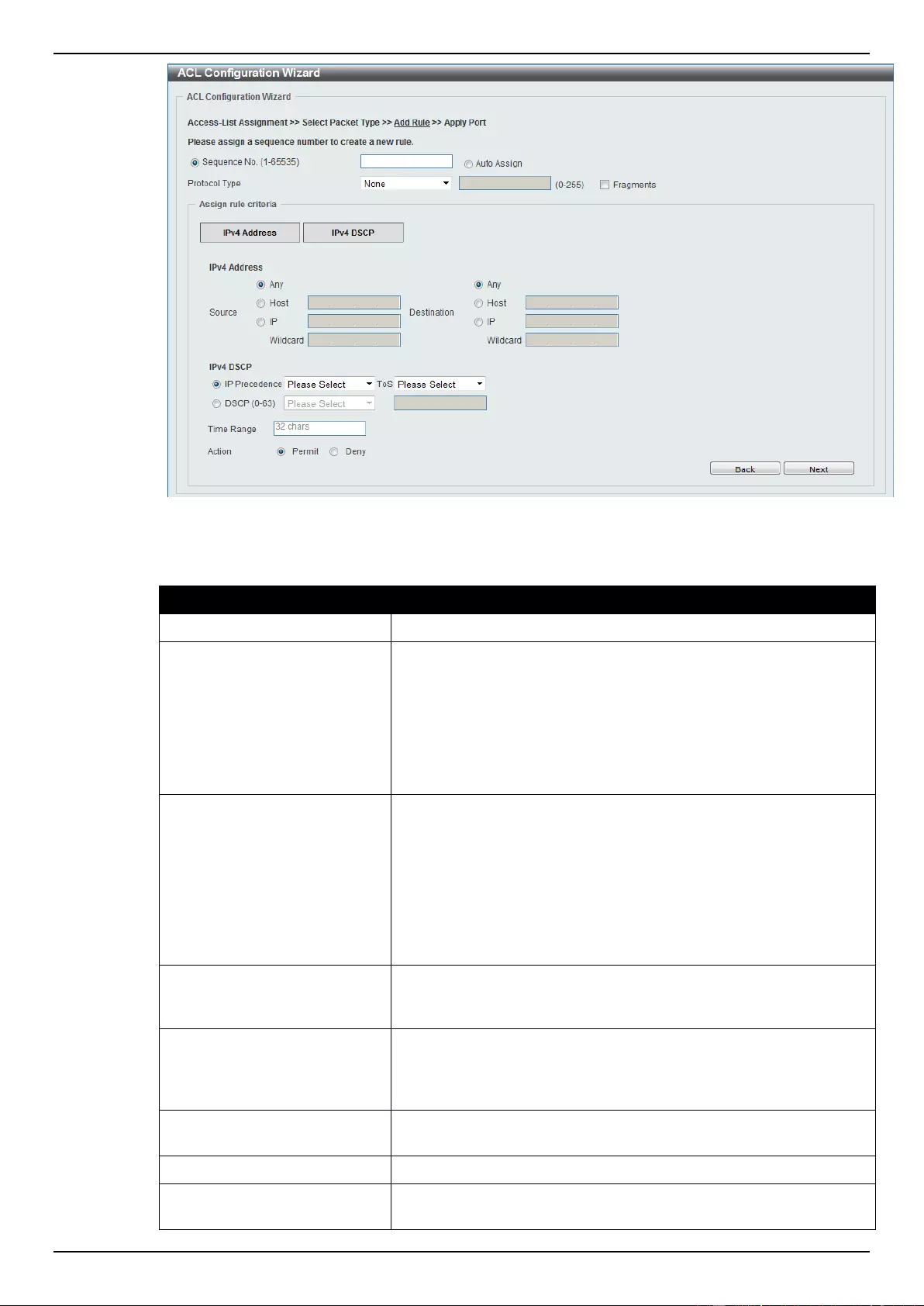
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
192
Figure 8-19 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv4 ACL) None window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
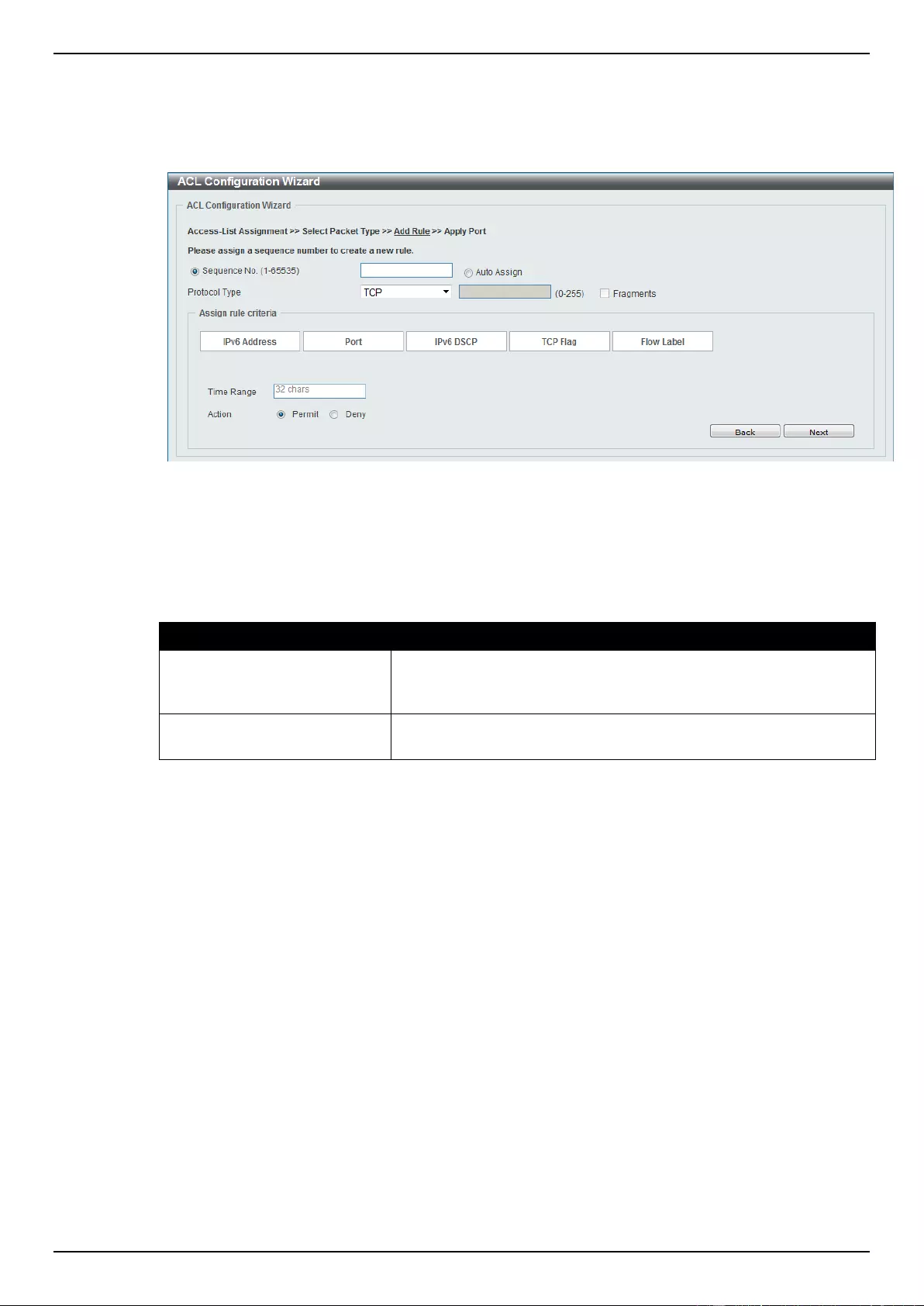
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
193
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Next button to continue.
After clicking the IPv6 radio button and the Next button, the following window will appear.
Figure 8-20 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) window
This window has a dynamic section. Every selection made in the Protocol Type drop-down list will
change the bottom part of this window.
The fixed fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. Select Auto Assign to automatically generate an ACL rule
number for this entry.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol type option here. Options to choose from are
TCP, UDP, ICMP, Protocol ID, ESP, PCP, SCTP, and None.
After selecting the TCP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
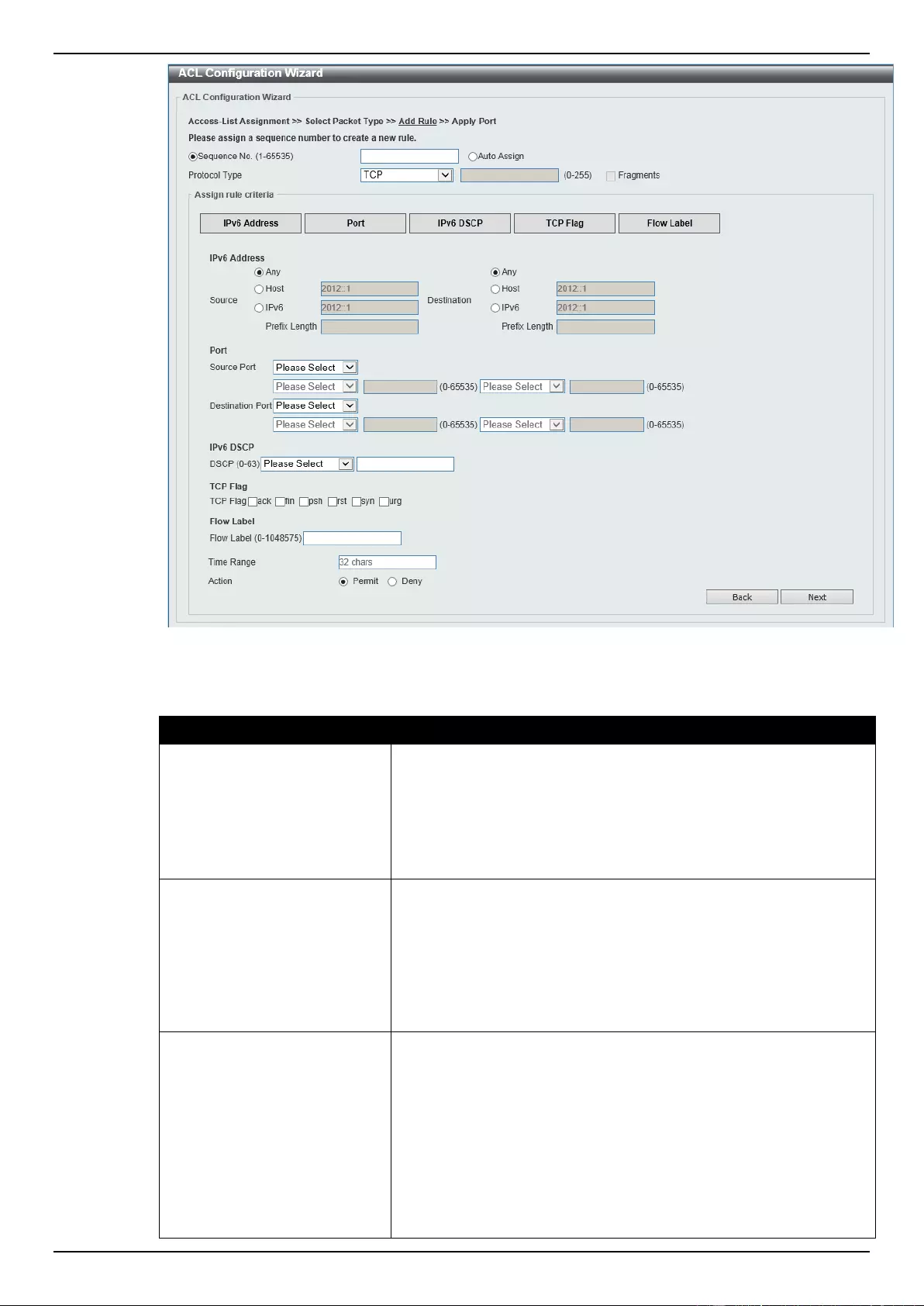
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
194
Figure 8-21 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) TCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
195
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
TCP Flag
Tick the appropriate TCP flag option to include the flag in this rule.
Options to choose from are ack, fin, psh, rst, syn, and urg.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the UDP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-22 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) UDP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
196
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the ICMP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
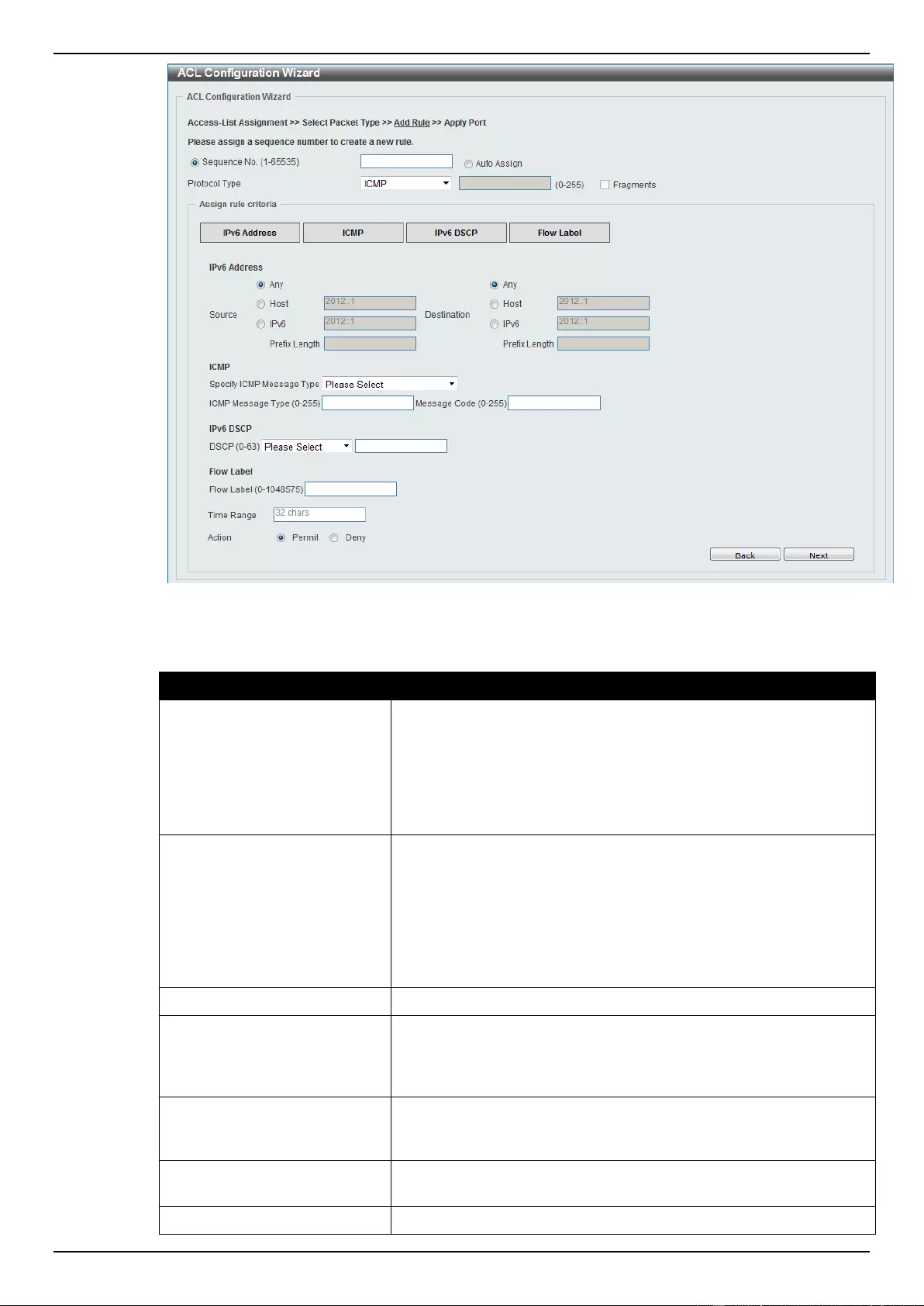
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
197
Figure 8-23 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) ICMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Specify ICMP Message Type
Select the ICMP message type used here.
ICMP Message Type
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected, enter the ICMP
Message Type numerical value used here. When the ICMP
Message Type is selected, this numerical value will automatically
be entered.
Message Code
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected, enter the Message
Code numerical value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is
selected, this numerical value will automatically be entered.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
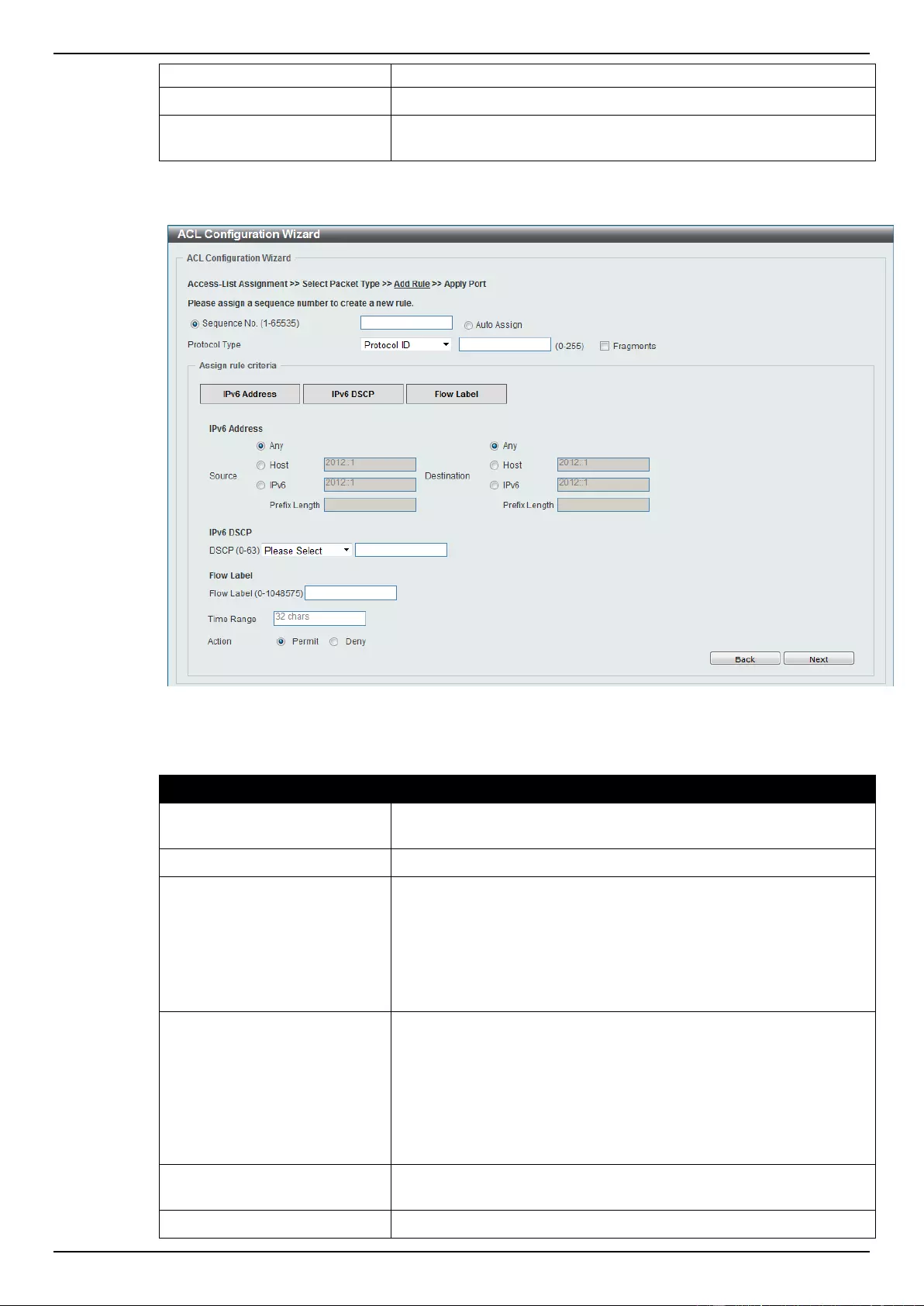
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
198
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the Protocol ID option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-24 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) Protocol ID window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Enter the Protocol ID value used here. This value must be between
0 and 255.
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
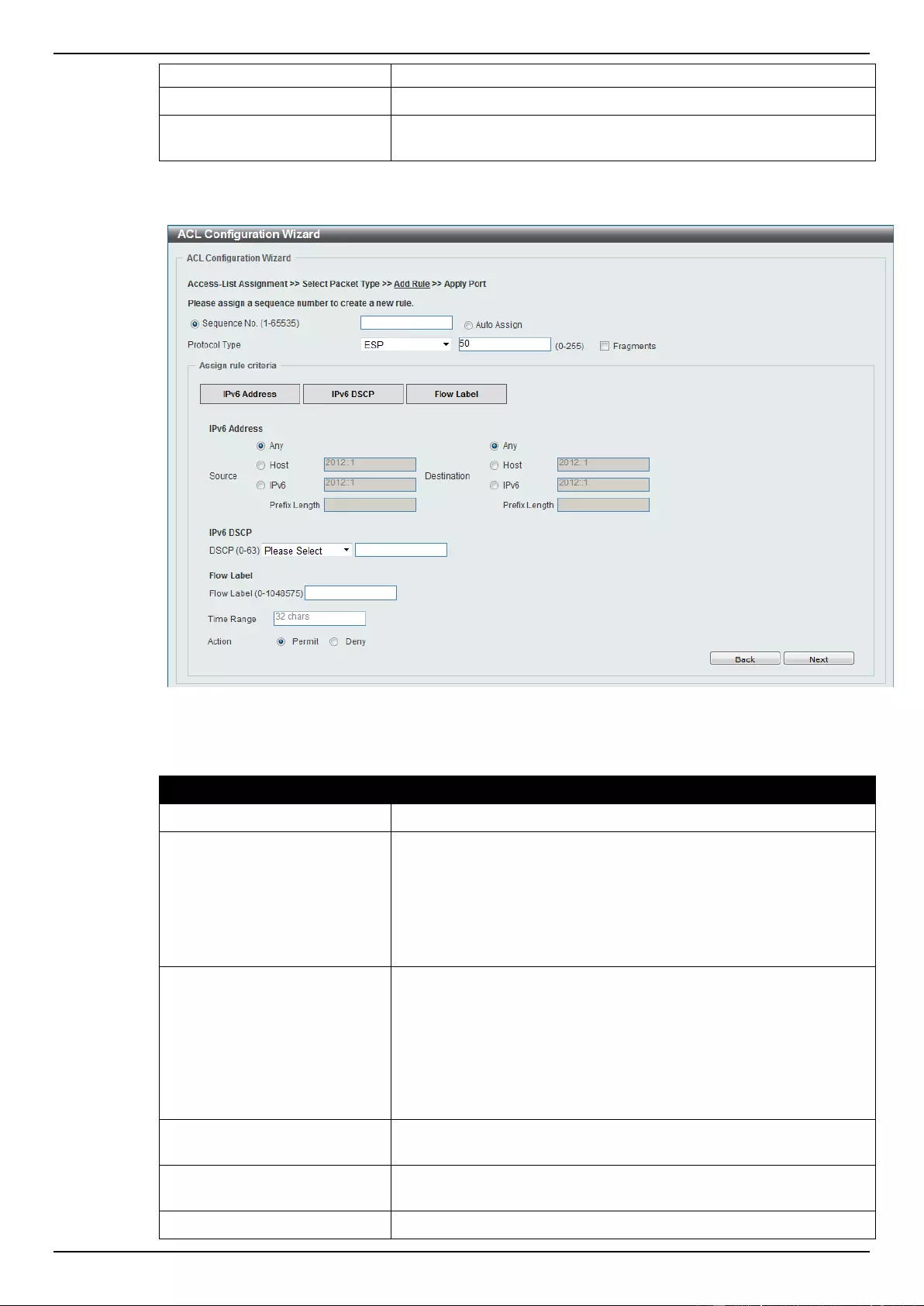
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
199
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the ESP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-25 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) ESP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
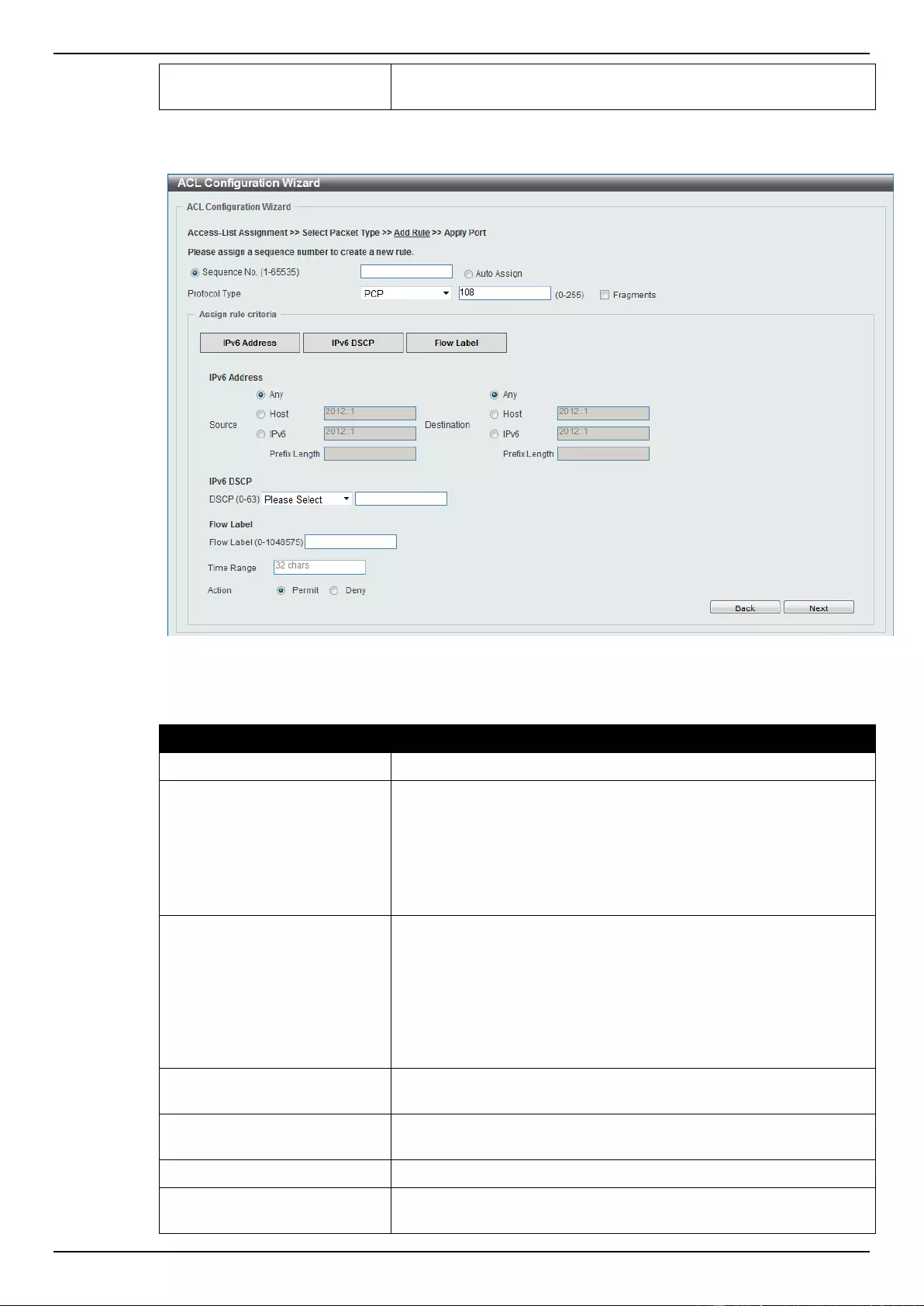
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
200
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the PCP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-26 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) PCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
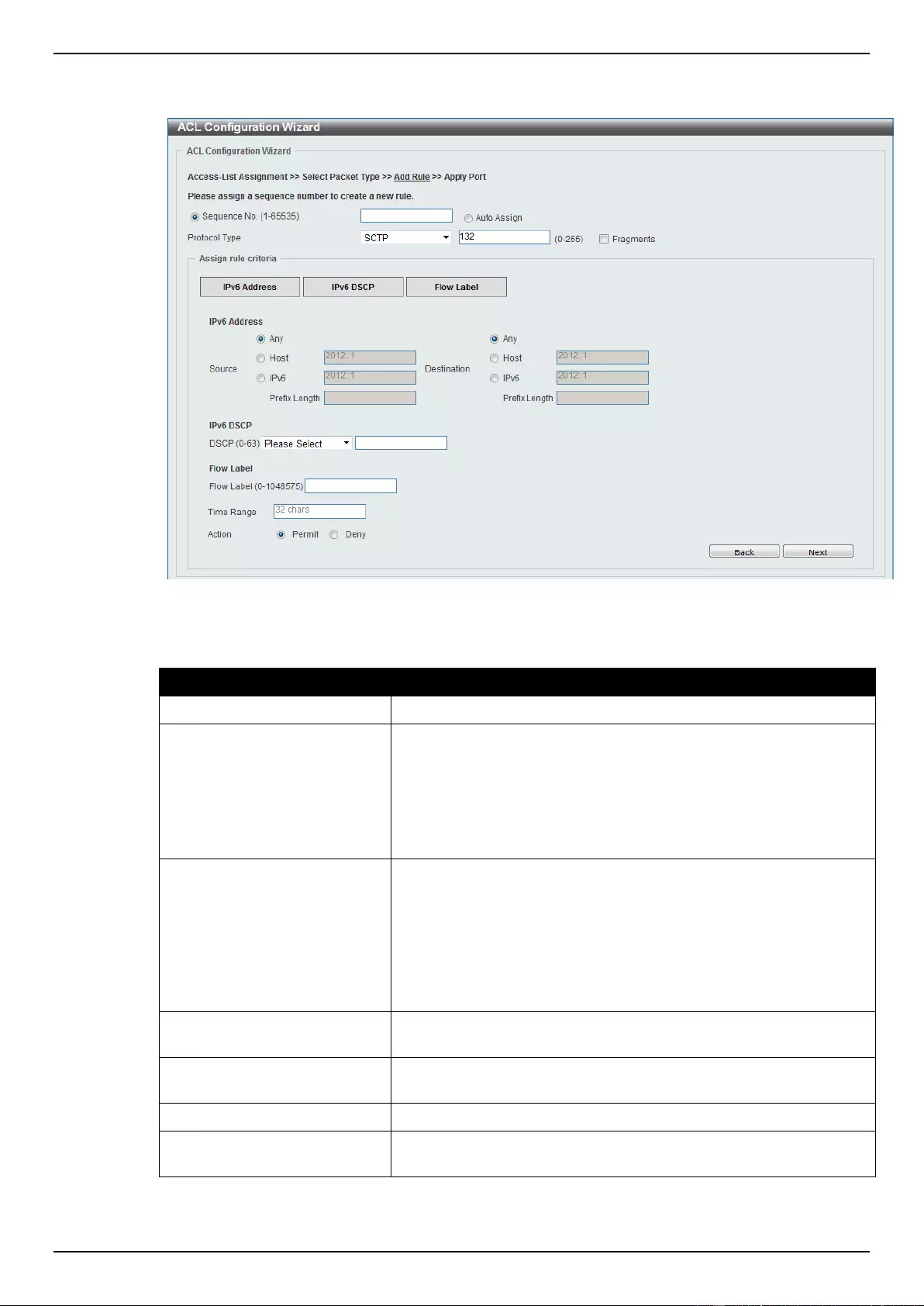
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
201
After selecting the SCTP option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
Figure 8-27 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) SCTP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
After selecting the None option as the Protocol Type, the following section will appear.
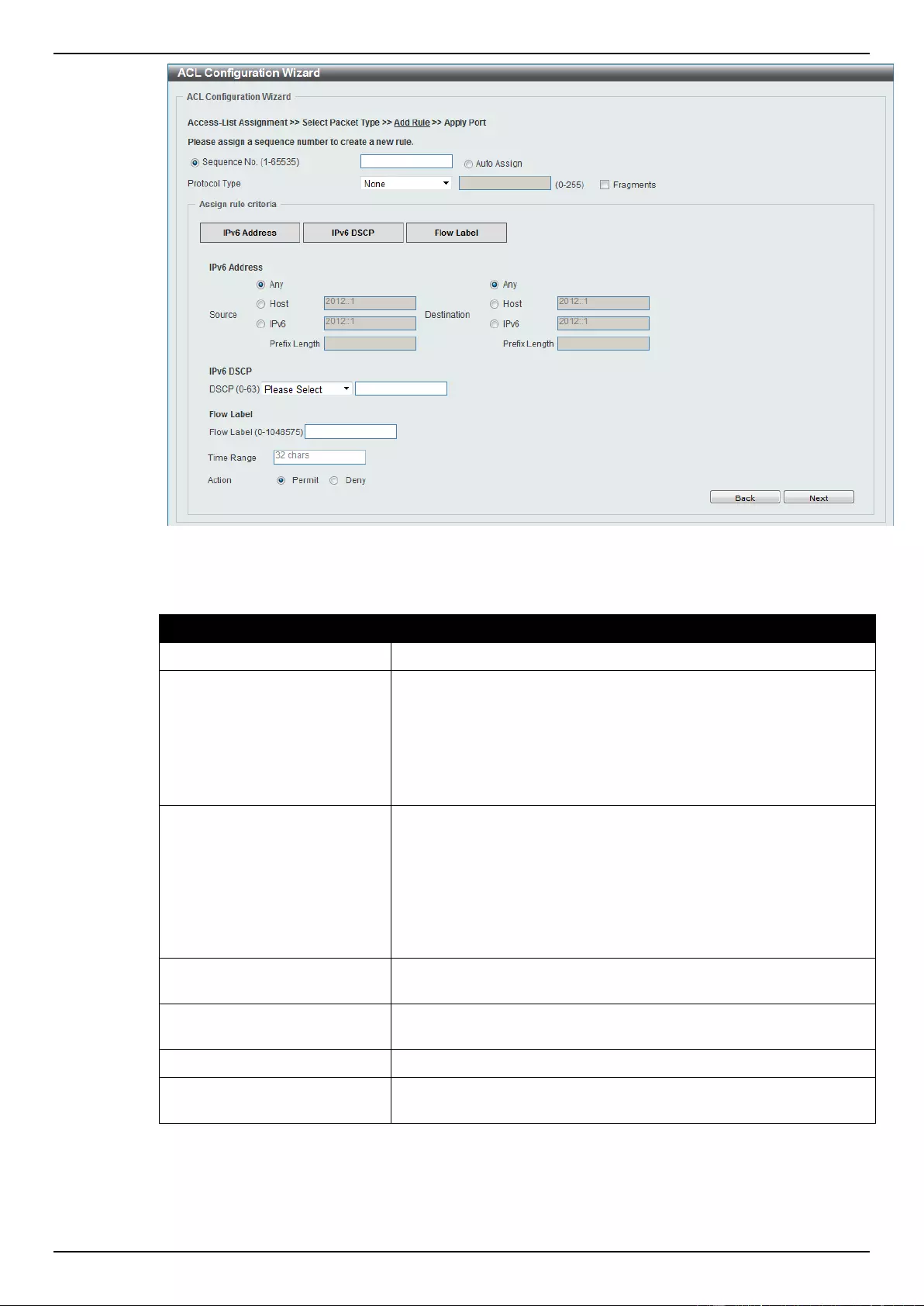
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
202
Figure 8-28 ACL Configuration Wizard (Add Rule for IPv6 ACL) None window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Next button to continue.
After clicking the Next button, the following window will appear.
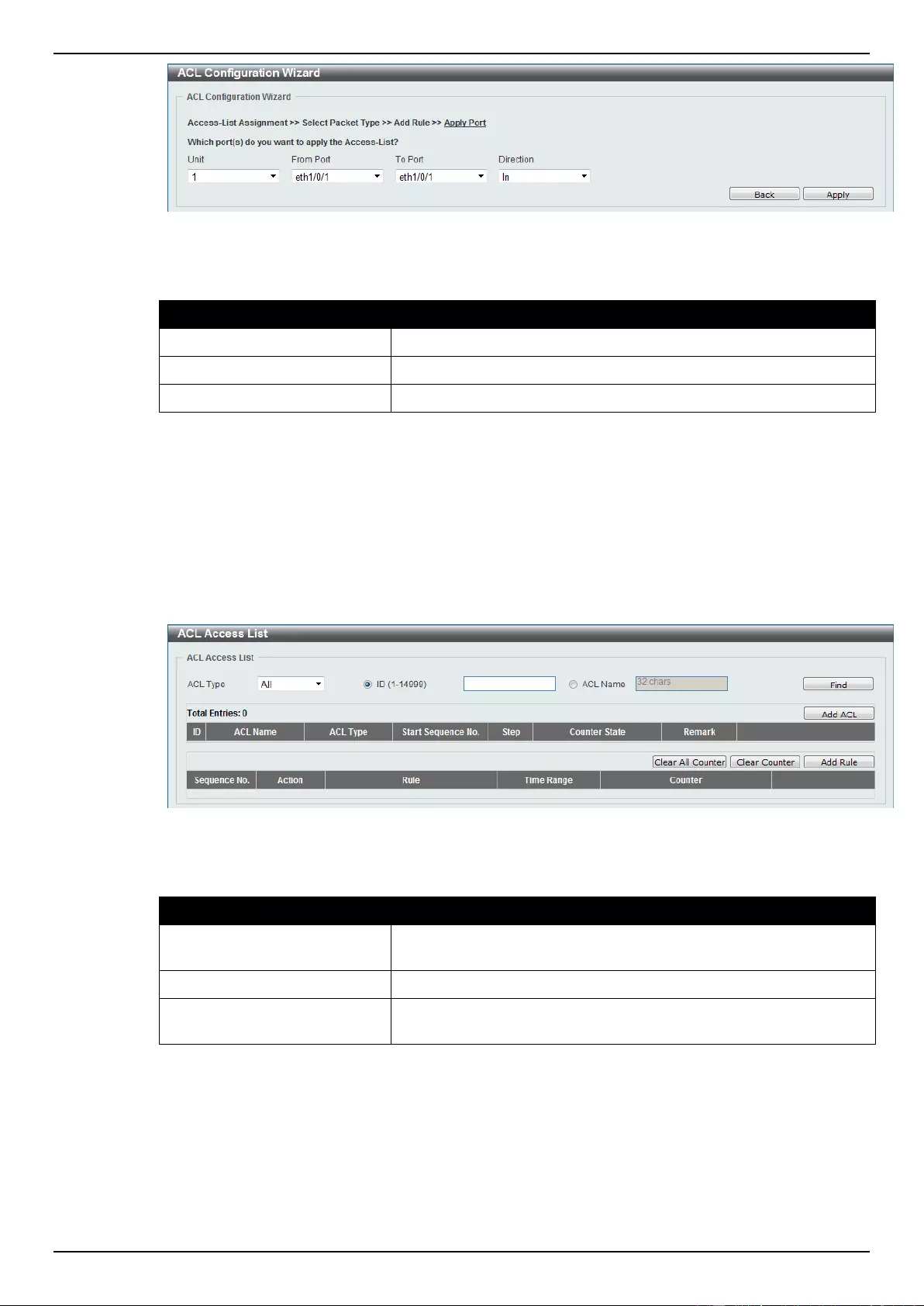
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
203
Figure 8-29 ACL Configuration Wizard (Apply Port) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Direction
Select the direction here. Option to choose from is In.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
ACL Access List
This window is used to view and configure the ACL access list settings.
To view the following window, click ACL > ACL Access List, as shown below:
Figure 8-30 ACL Access List window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type to find here. Options to choose from are
All, IP ACL, IPv6 ACL, MAC ACL, and Expert ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID here. The range is from 1 to 14999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL name here. This name can be up to 32 characters
long.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Add ACL button to create a new ACL profile.
Click the Clear All Counter button to clear all the counter information displayed.
Click the Clear Counter button to clear the counter information for the rule displayed.
Click the Add Rule button to create an ACL rule for the ACL profile selected.
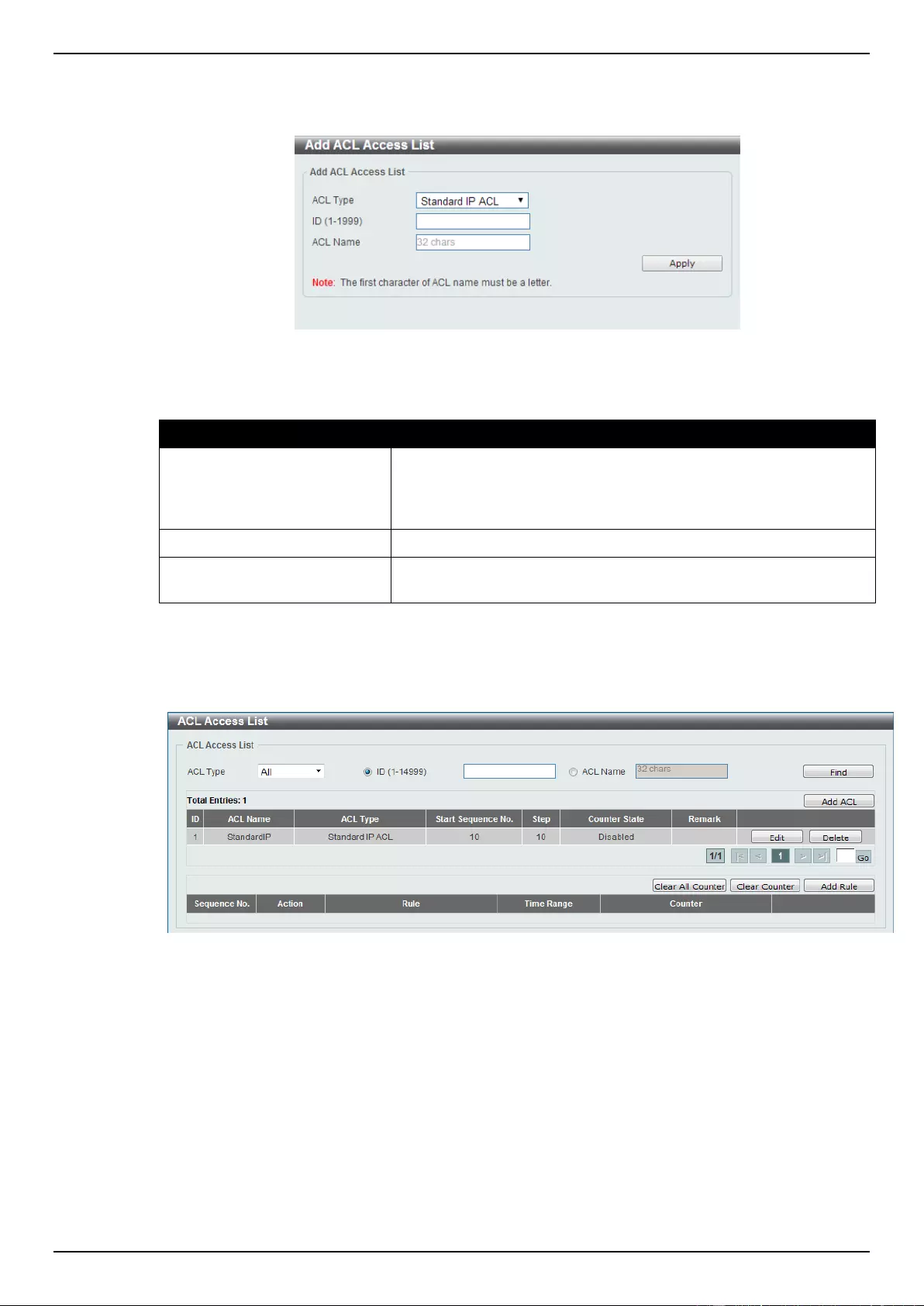
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
204
Standard IP ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-31 Standard IP ACL (Add ACL Access List) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 1 to 1999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating a Standard IP ACL profile, the newly created Standard IP ACL profile will be displayed
in the ACL profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-32 Standard IP ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
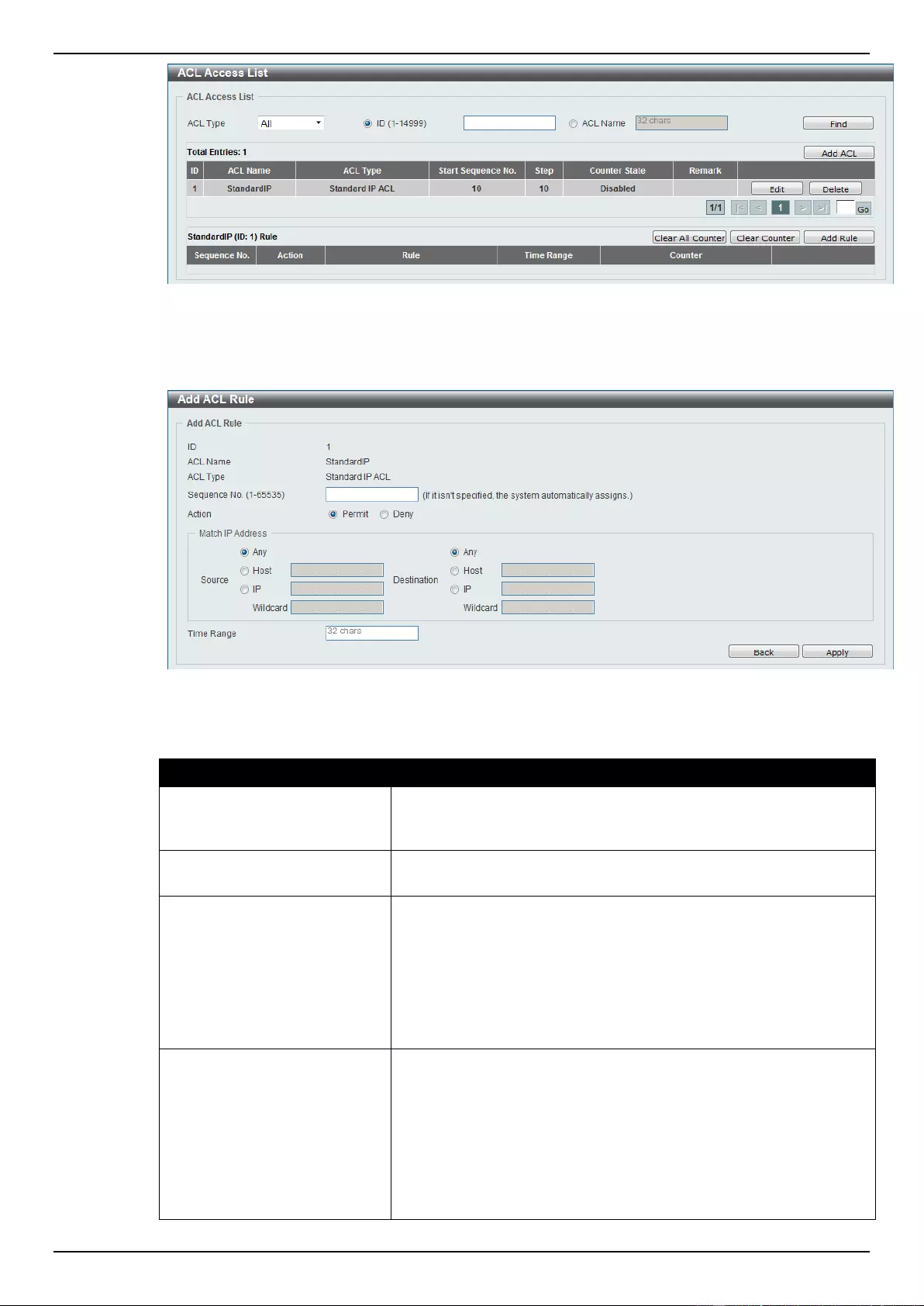
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
205
Figure 8-33 Standard IP ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-34 Standard IP ACL (Add Rule) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
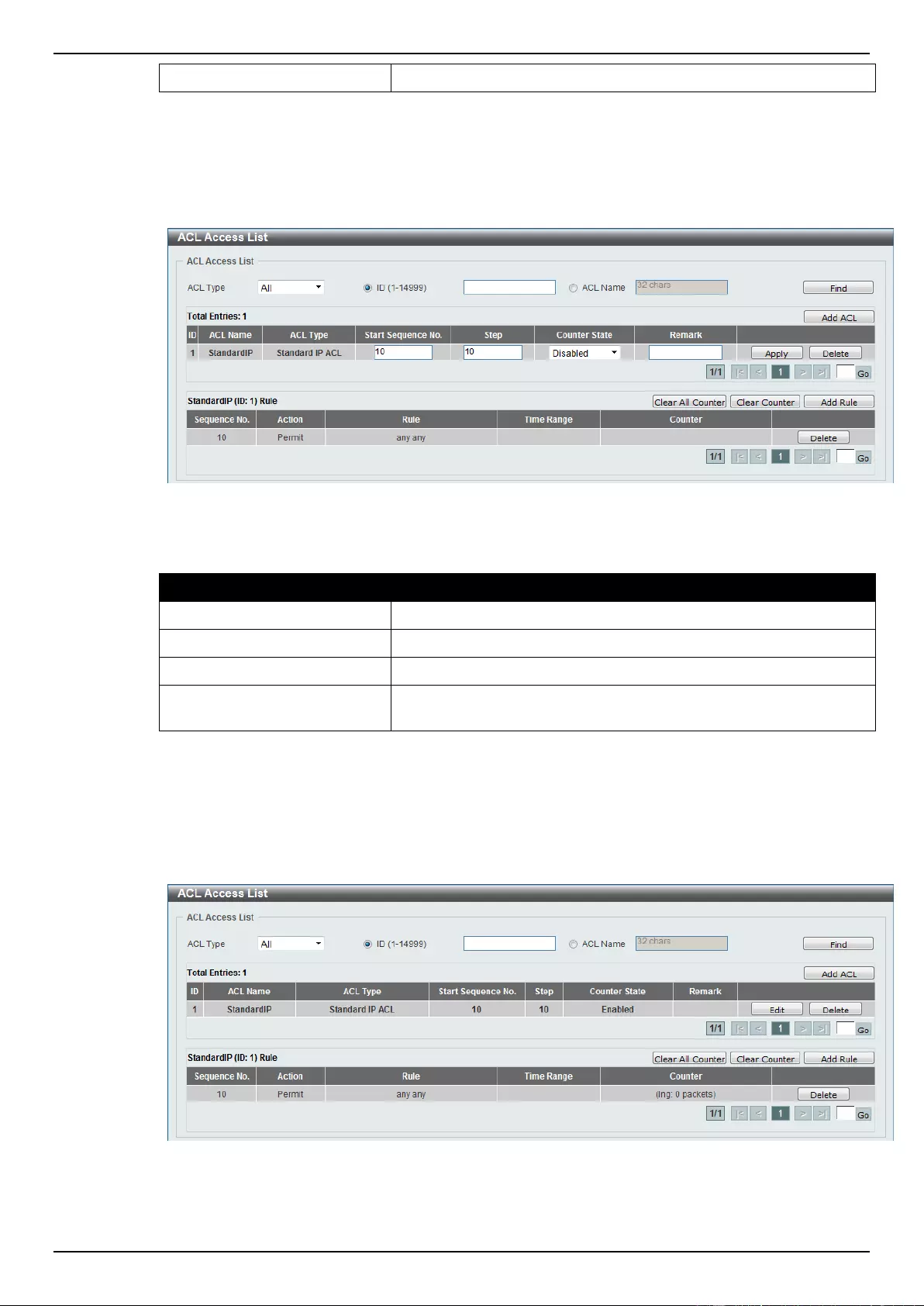
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
206
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).
Figure 8-35 Standard IP ACL (Edit ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Step
Enter the sequence number increment here.
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-36 Standard IP ACL (Rule Display) window
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
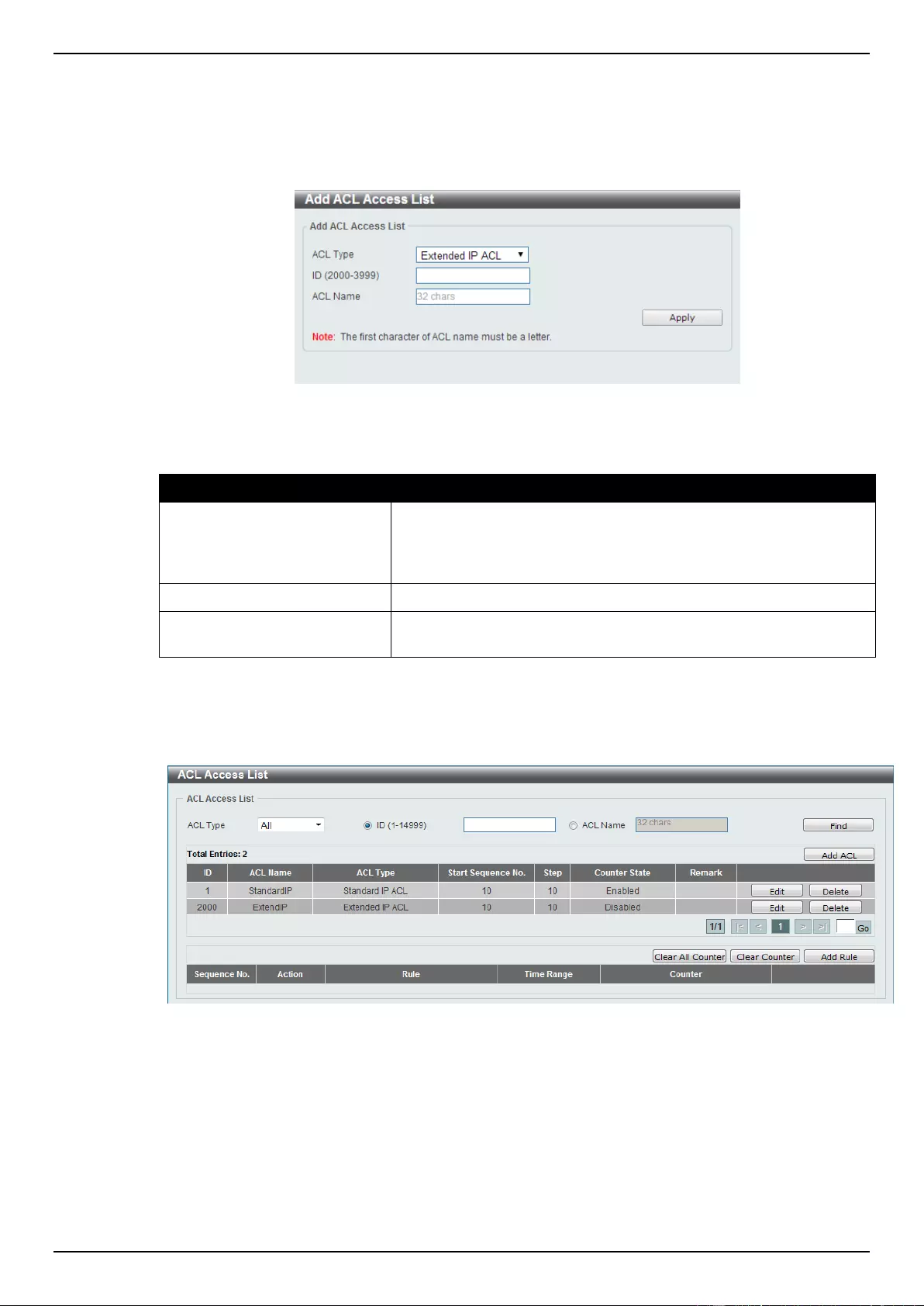
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
207
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Extended IP ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-37 Extended IP ACL (Add Profile) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 2000 to 3999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating an Extend IP ACL profile, the newly created Extend IP ACL profile will be displayed in
the ACL profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-38 Extended IP ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
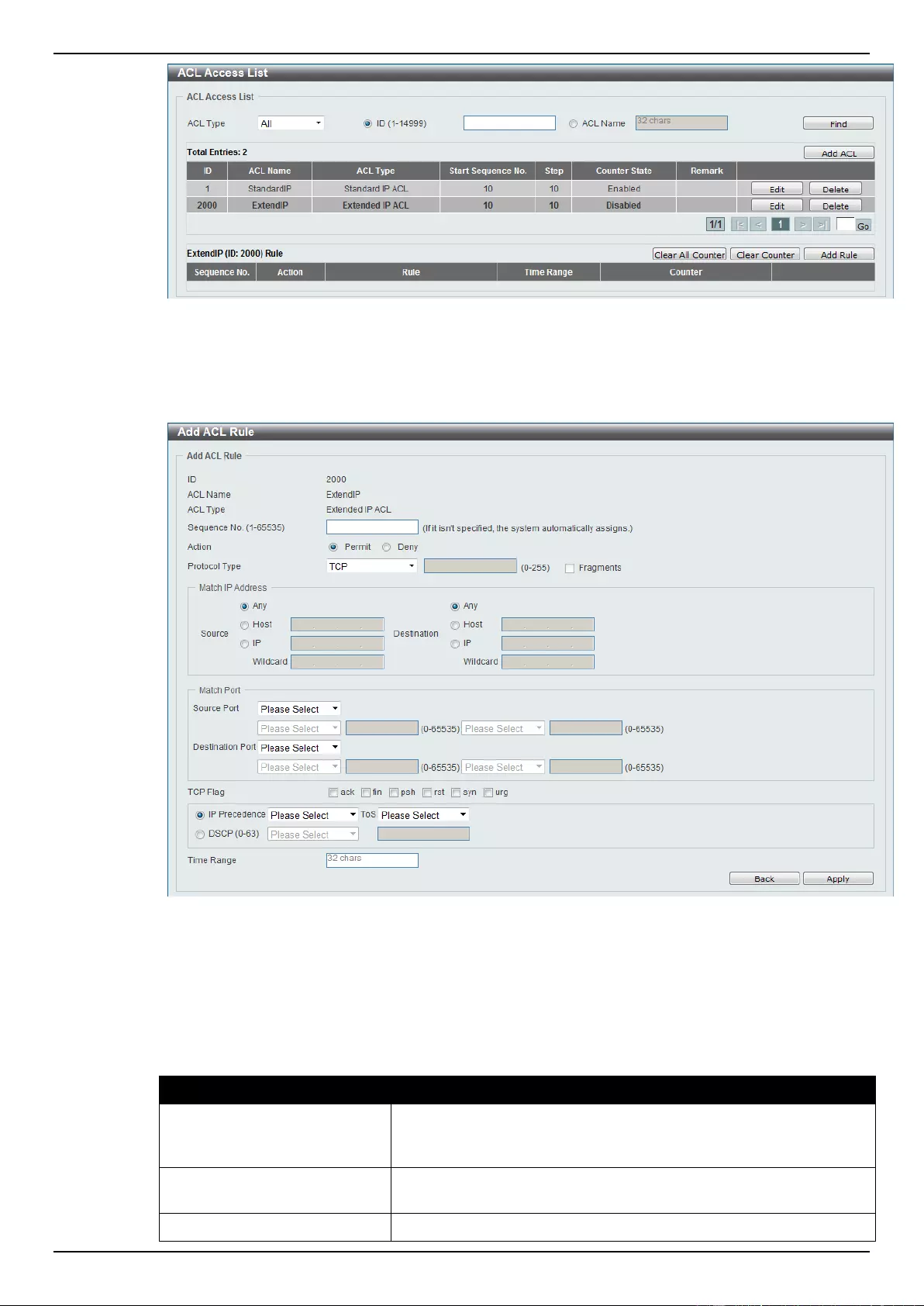
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
208
Figure 8-39 Extended IP ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-40 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) window
This is a dynamic page. Every selection made in the Protocol Type drop-down list will change the
bottom part of this window.
The fixed fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol type option here. Options to choose from are
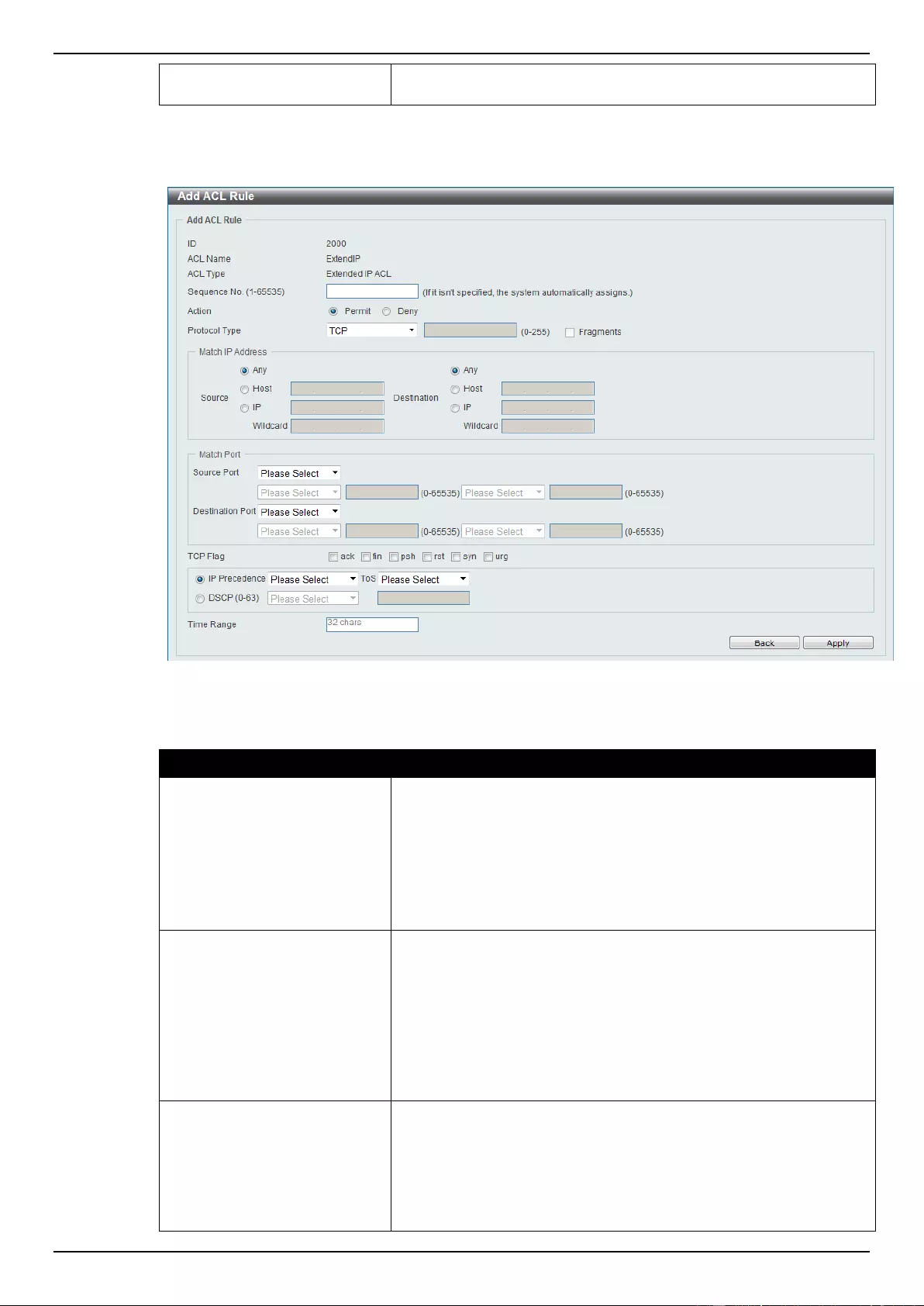
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
209
TCP, UDP, ICMP, EIGRP, ESP, GRE, IGMP, OSPF, PIM, VRRP,
IP-in-IP, PCP, Protocol ID, and None.
After selecting the TCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-41 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) TCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
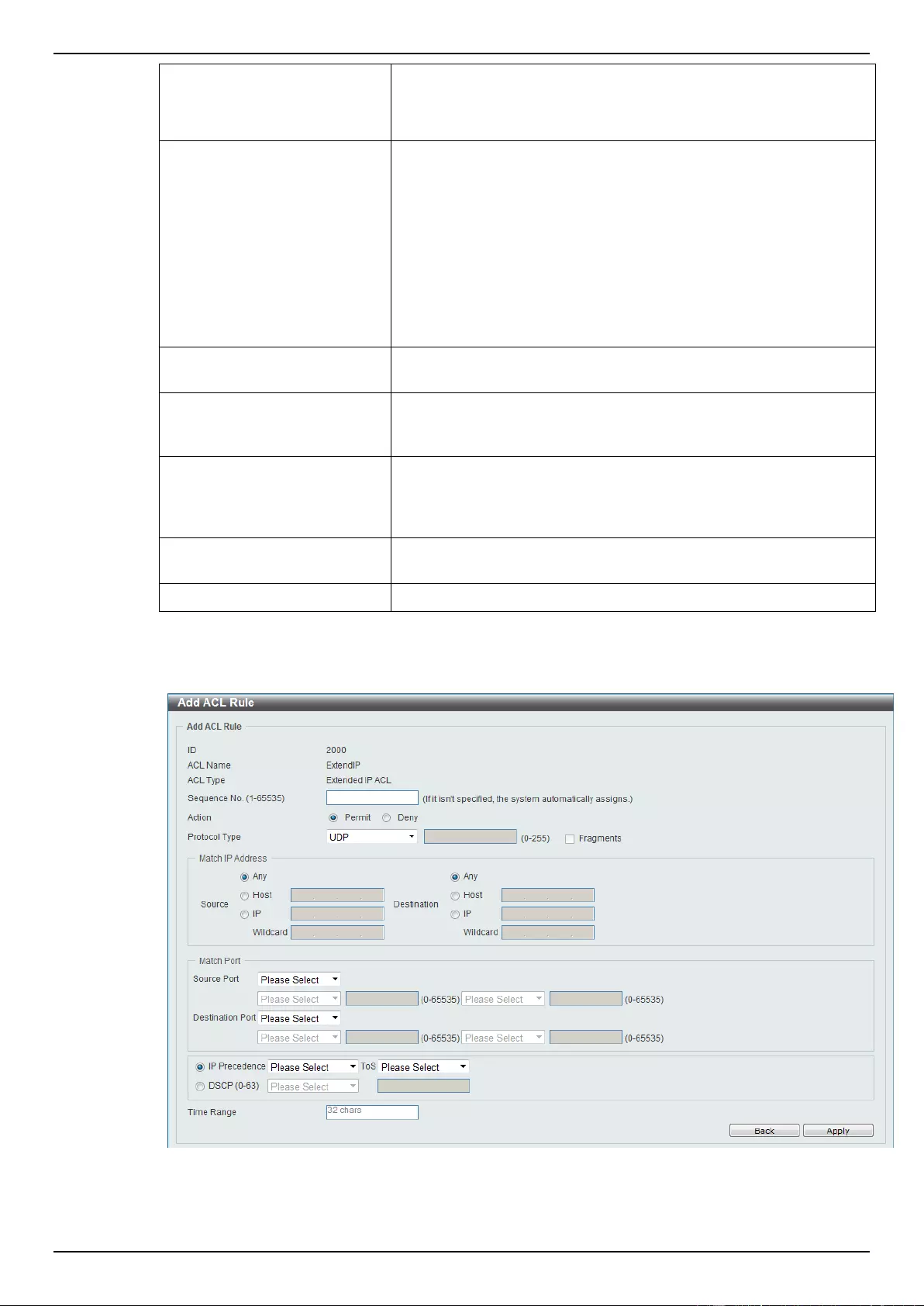
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
210
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
TCP Flag
Tick the appropriate TCP flag option to include the flag in this rule.
Options to choose from are ack, fin, psh, rst, syn, and urg.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the UDP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-42 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) UDP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
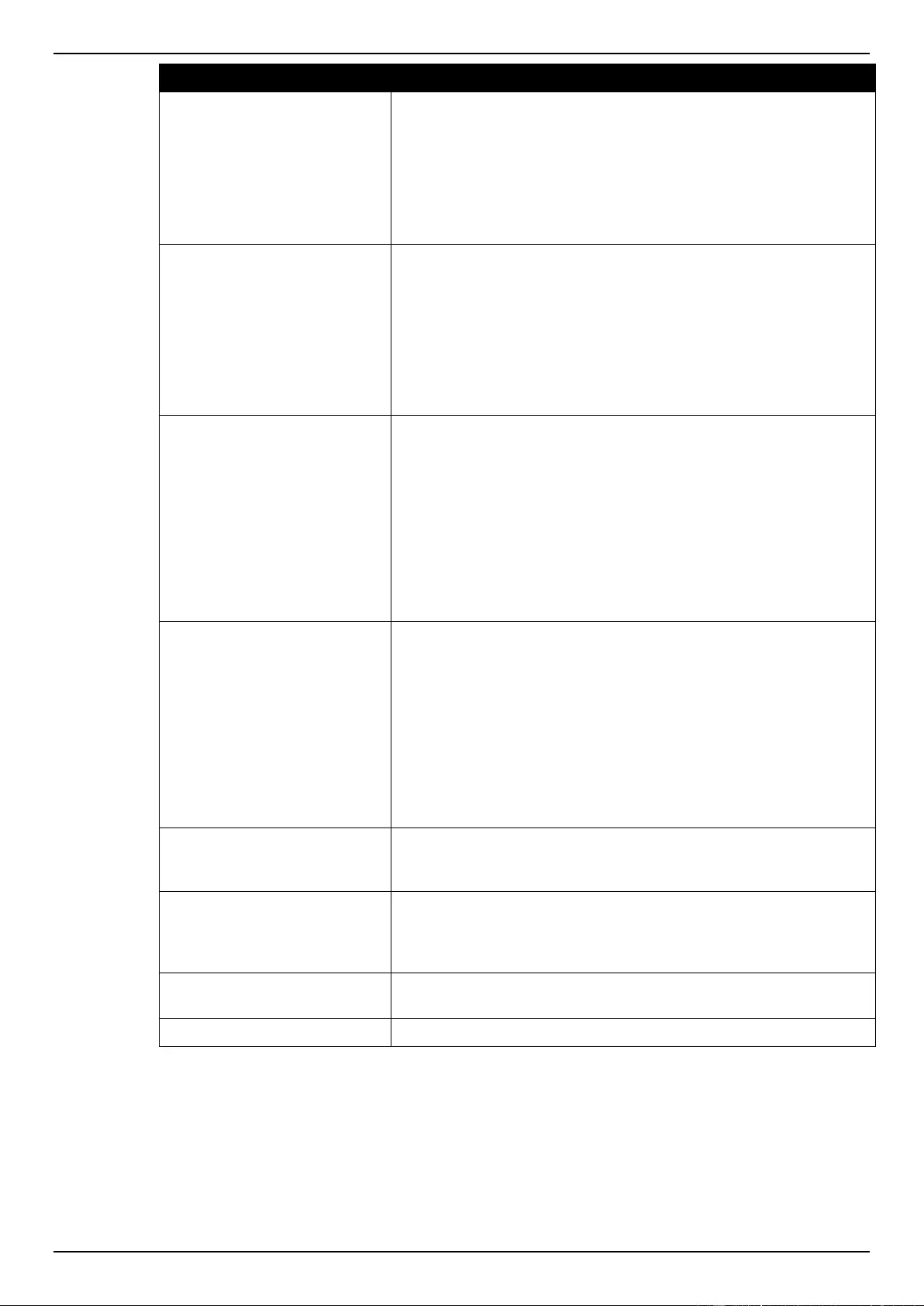
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
211
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
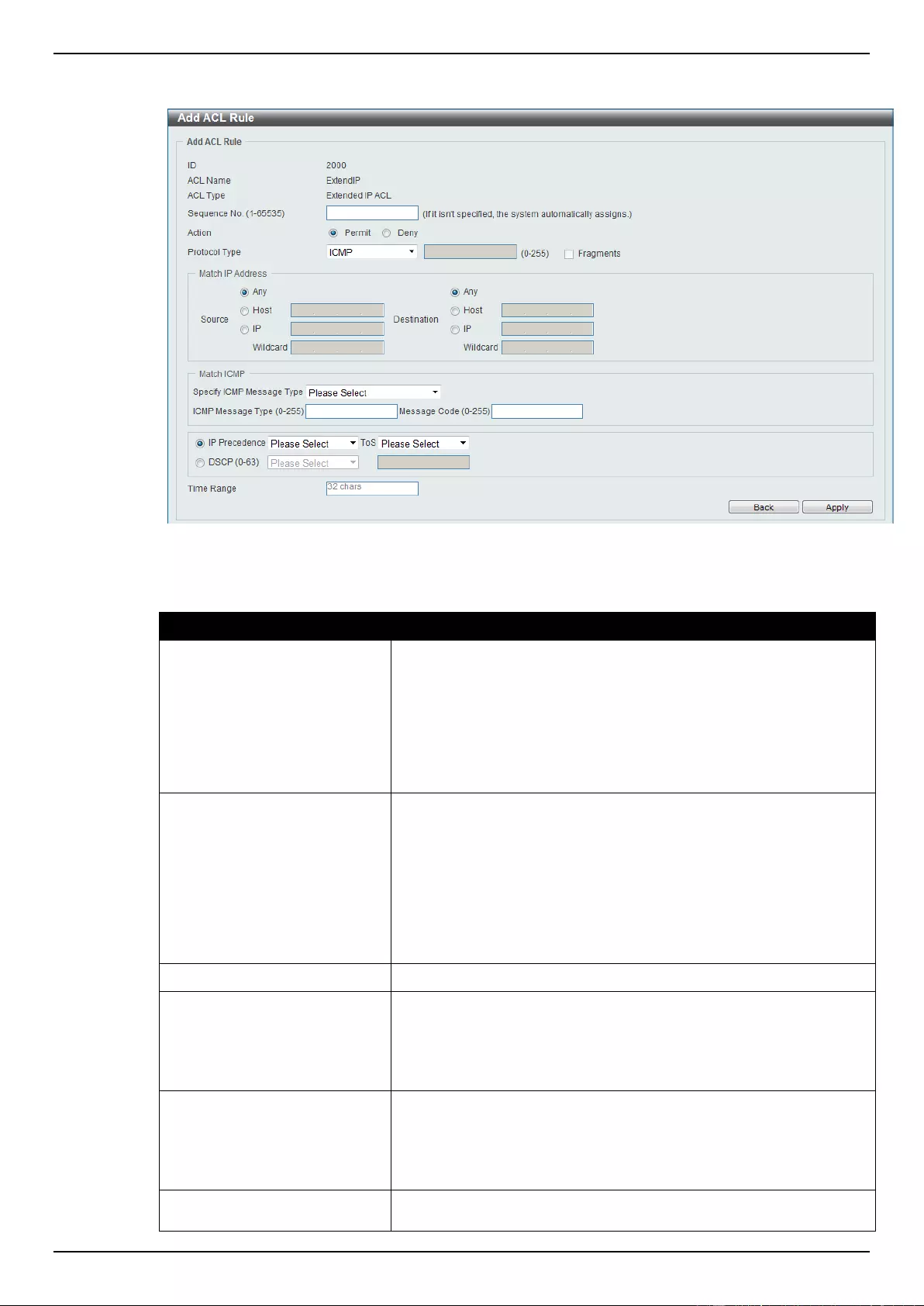
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
212
After selecting the ICMP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-43 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) ICMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Specify ICMP Message Type
Select the ICMP message type used here.
ICMP Message Type
When the ICMP message type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the ICMP Message Type
numerical value used here. When the ICMP message type is
selected in the Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this
numerical value will automatically be entered.
Message Code
When the ICMP message type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the Message Code numerical
value used here. When the ICMP message type is not selected in
the Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this numerical
value will automatically be entered.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
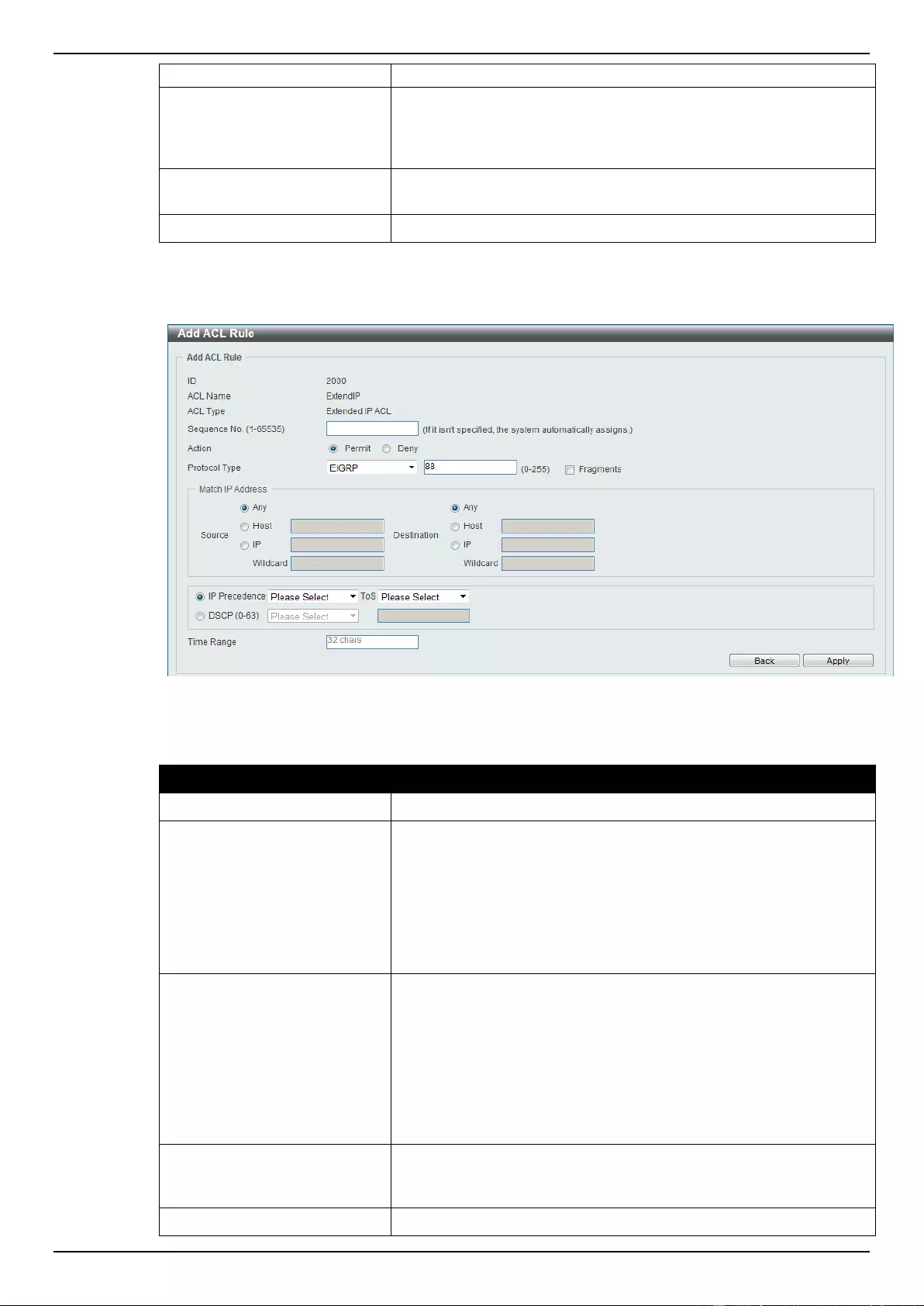
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
213
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the EIGRP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-44 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) EIGRP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
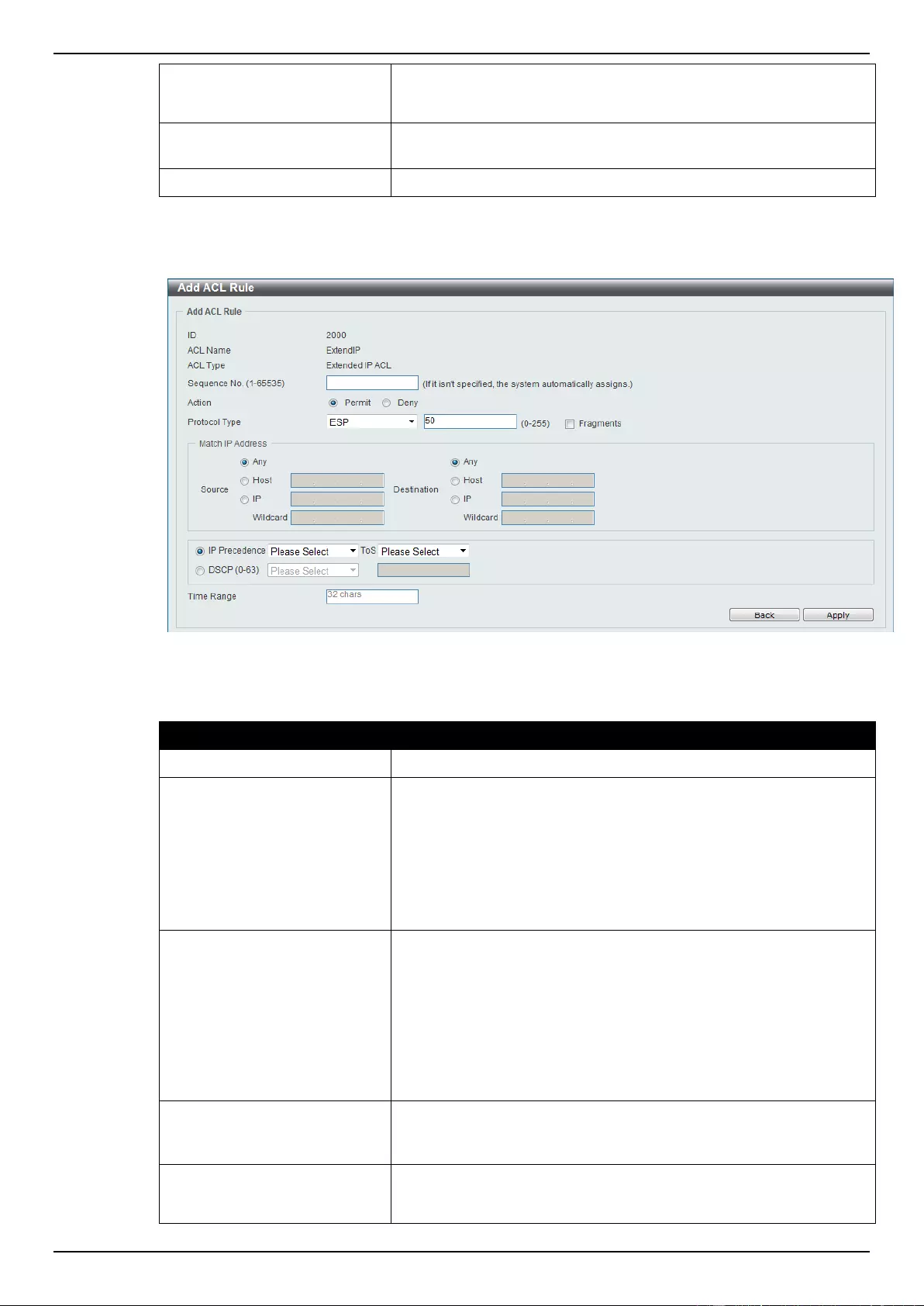
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
214
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the ESP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-45 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) ESP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
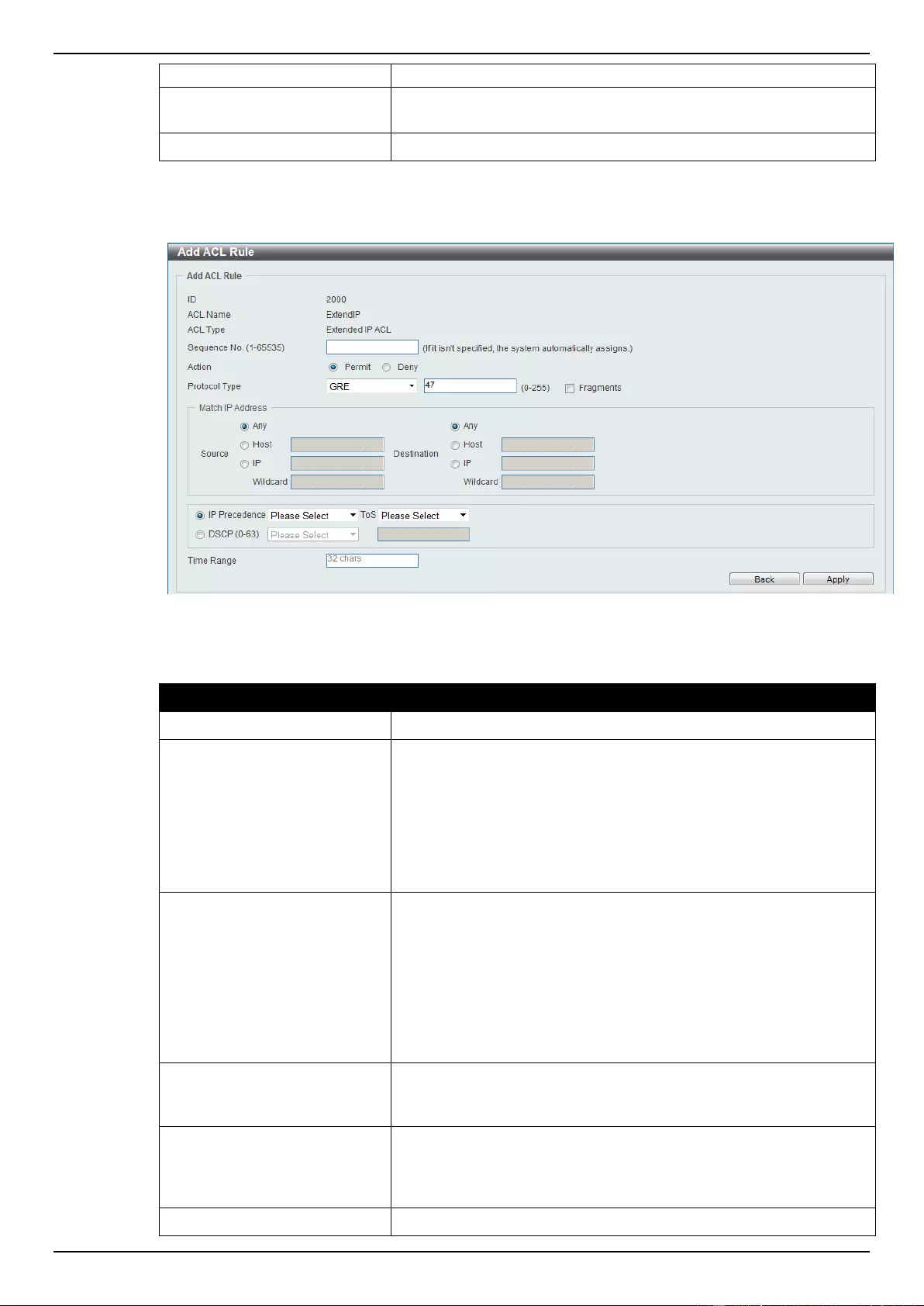
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
215
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the GRE option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-46 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) GRE window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
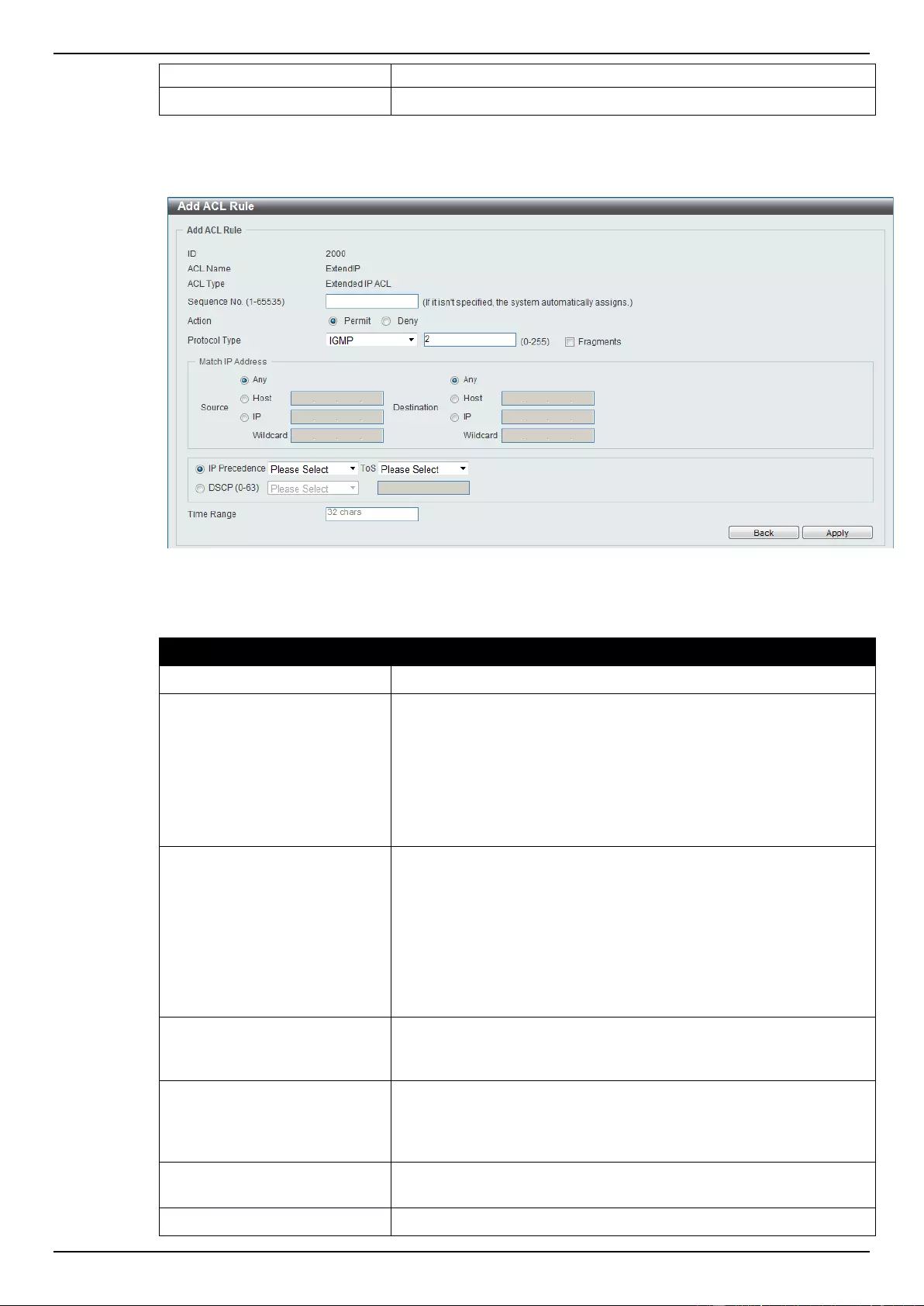
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
216
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the IGMP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-47 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) IGMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
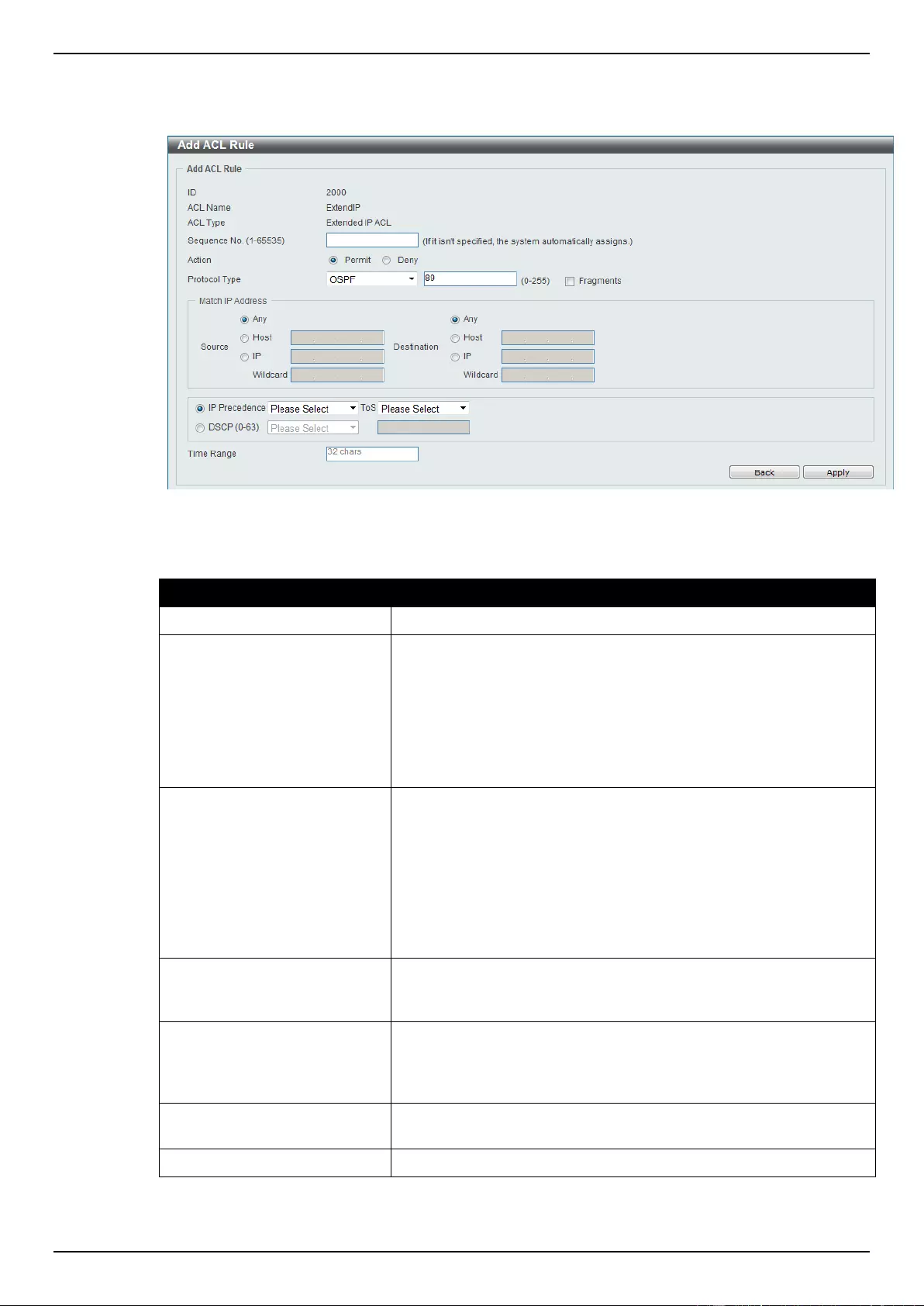
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
217
After selecting the OSPF option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-48 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) OSPF window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
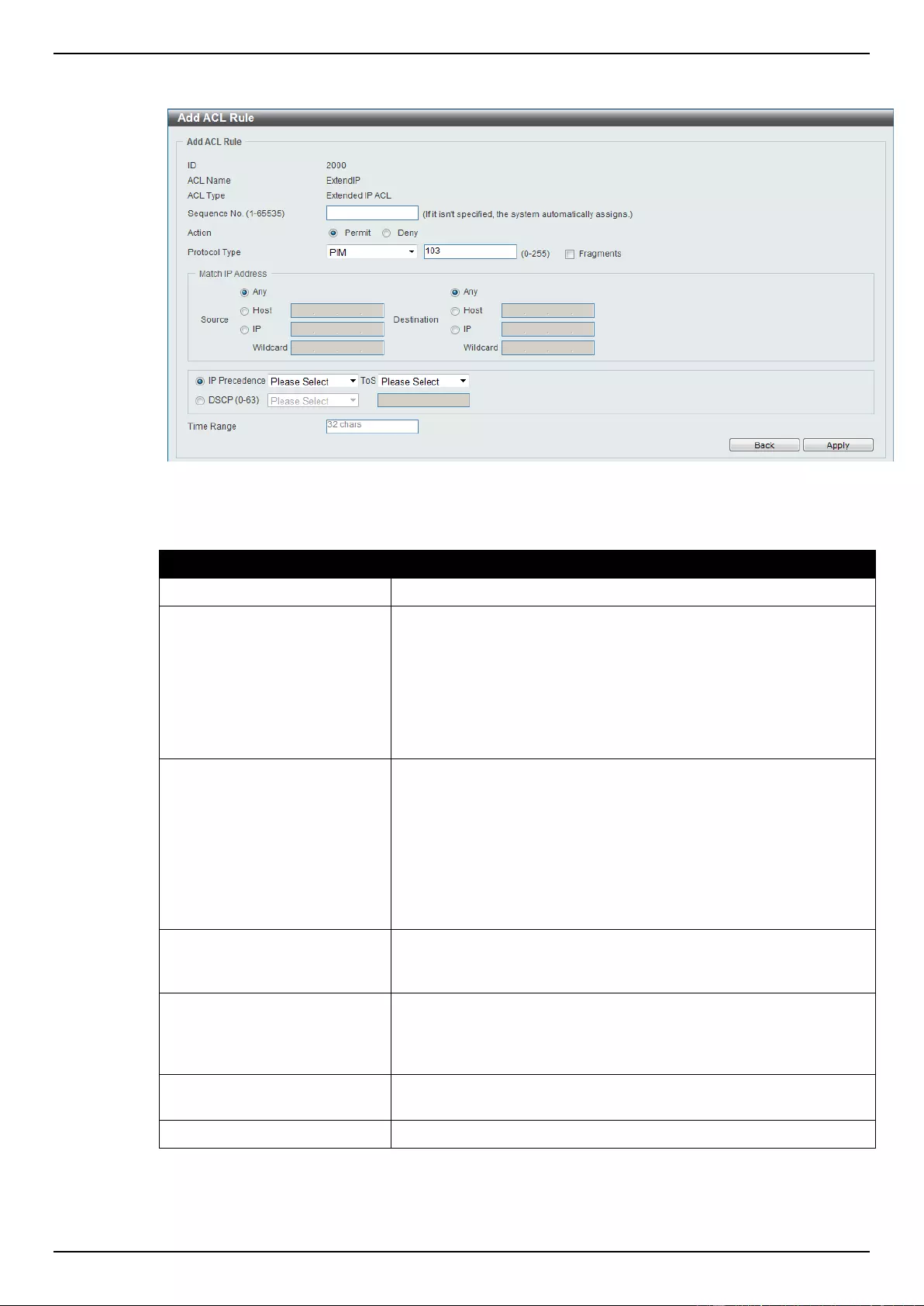
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
218
After selecting the PIM option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-49 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) PIM window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the VRRP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
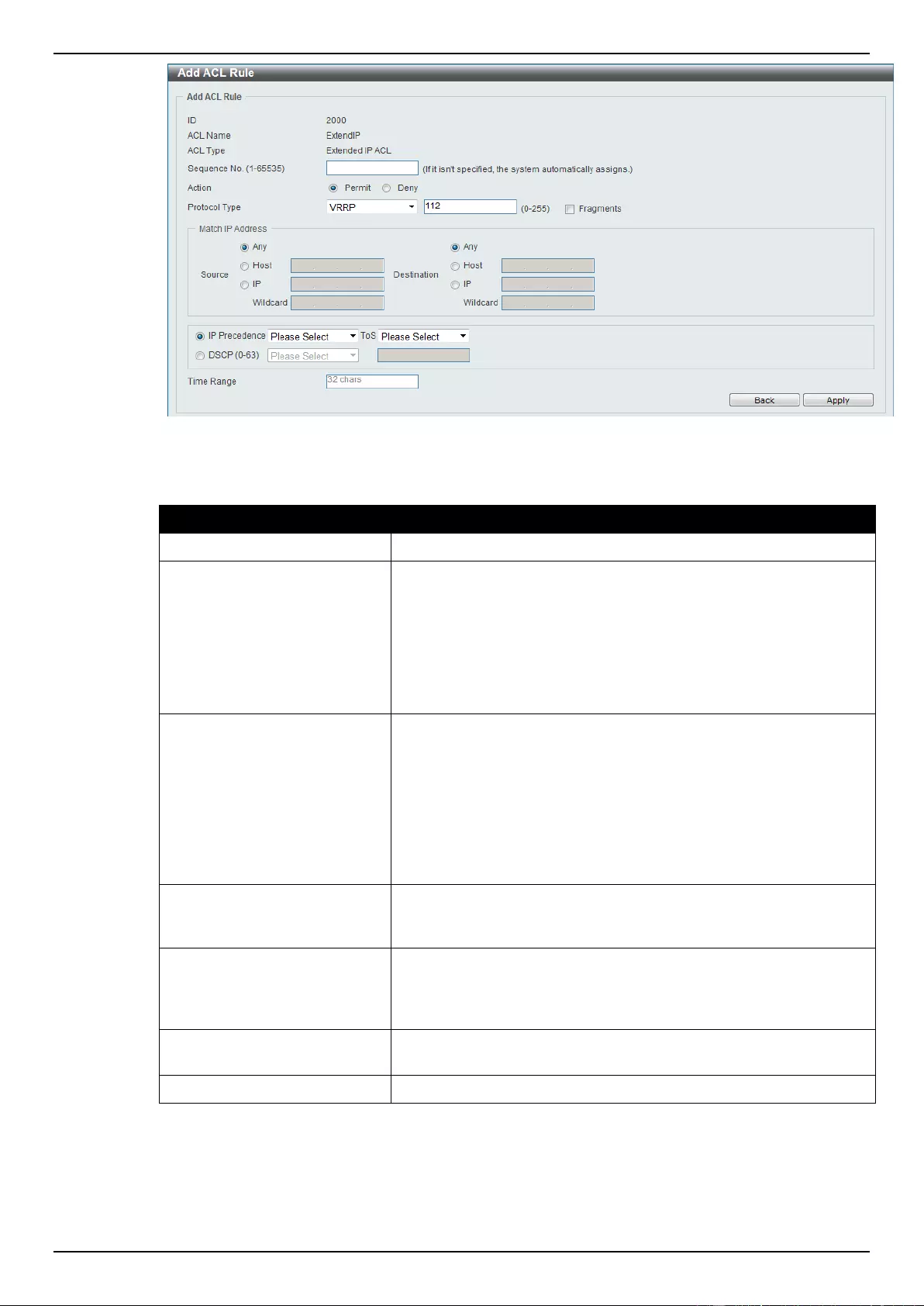
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
219
Figure 8-50 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) VRRP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the IP-in-IP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
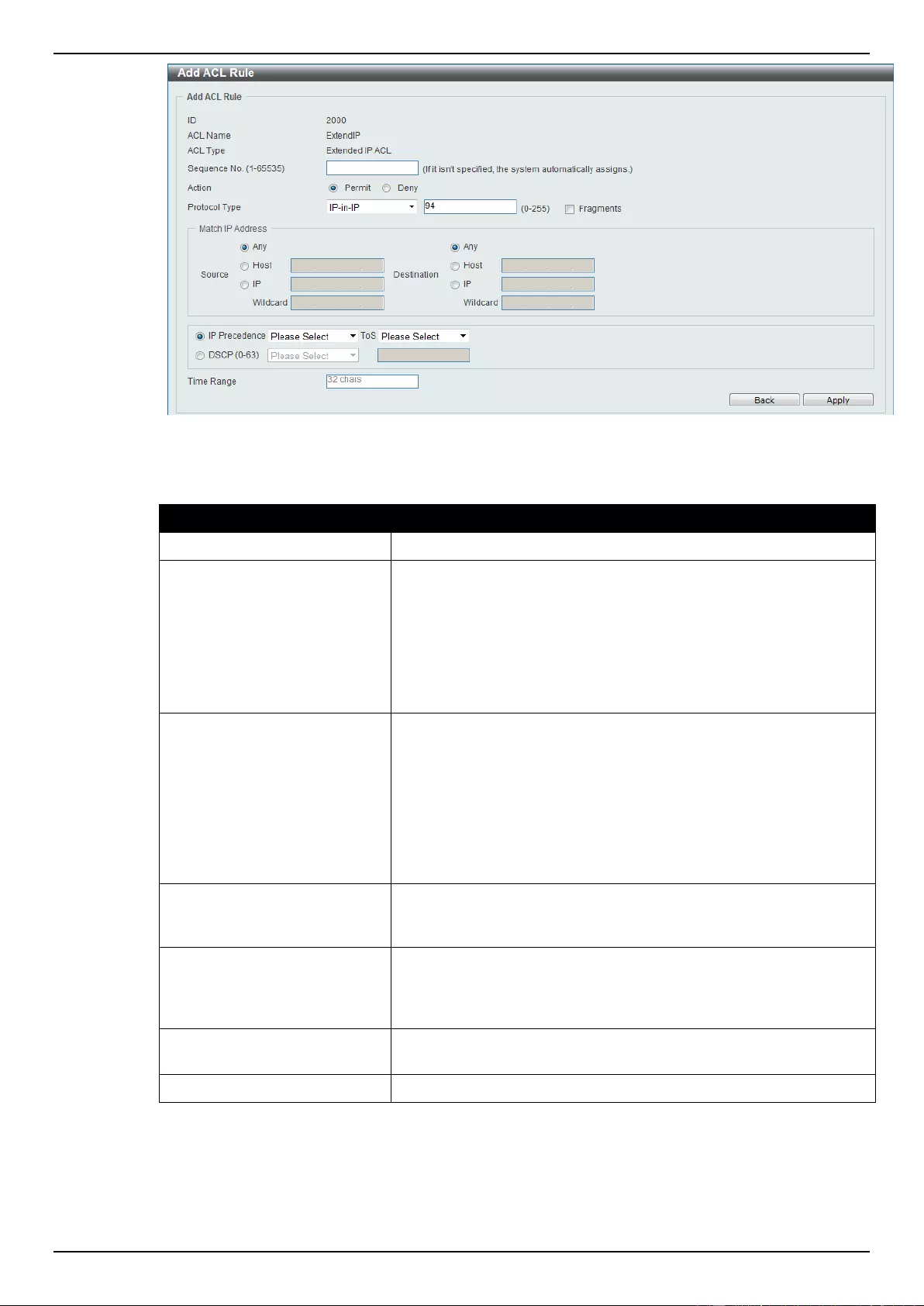
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
220
Figure 8-51 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) IP-in-IP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the PCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
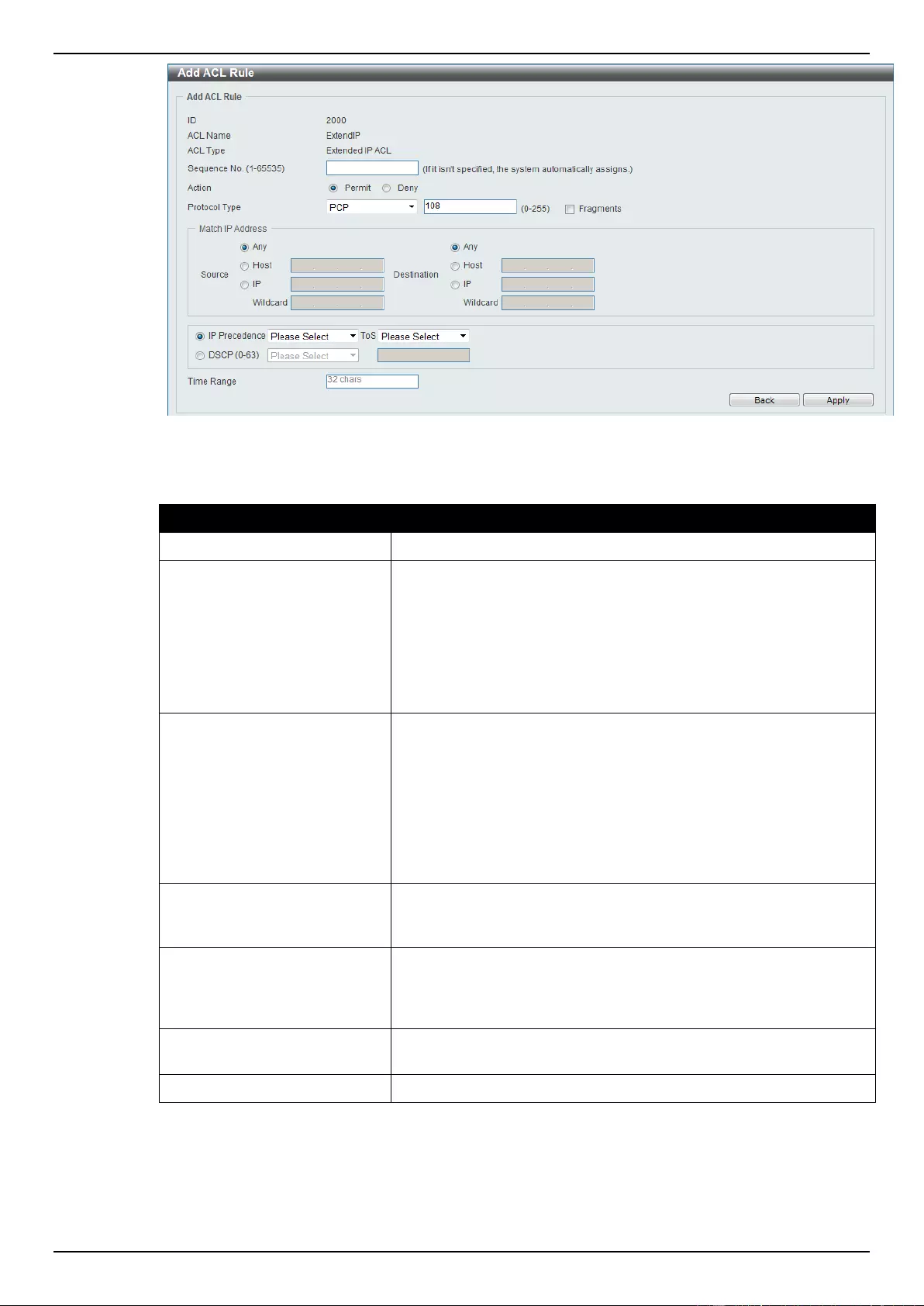
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
221
Figure 8-52 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) PCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the Protocol ID option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will
be available, as shown below:
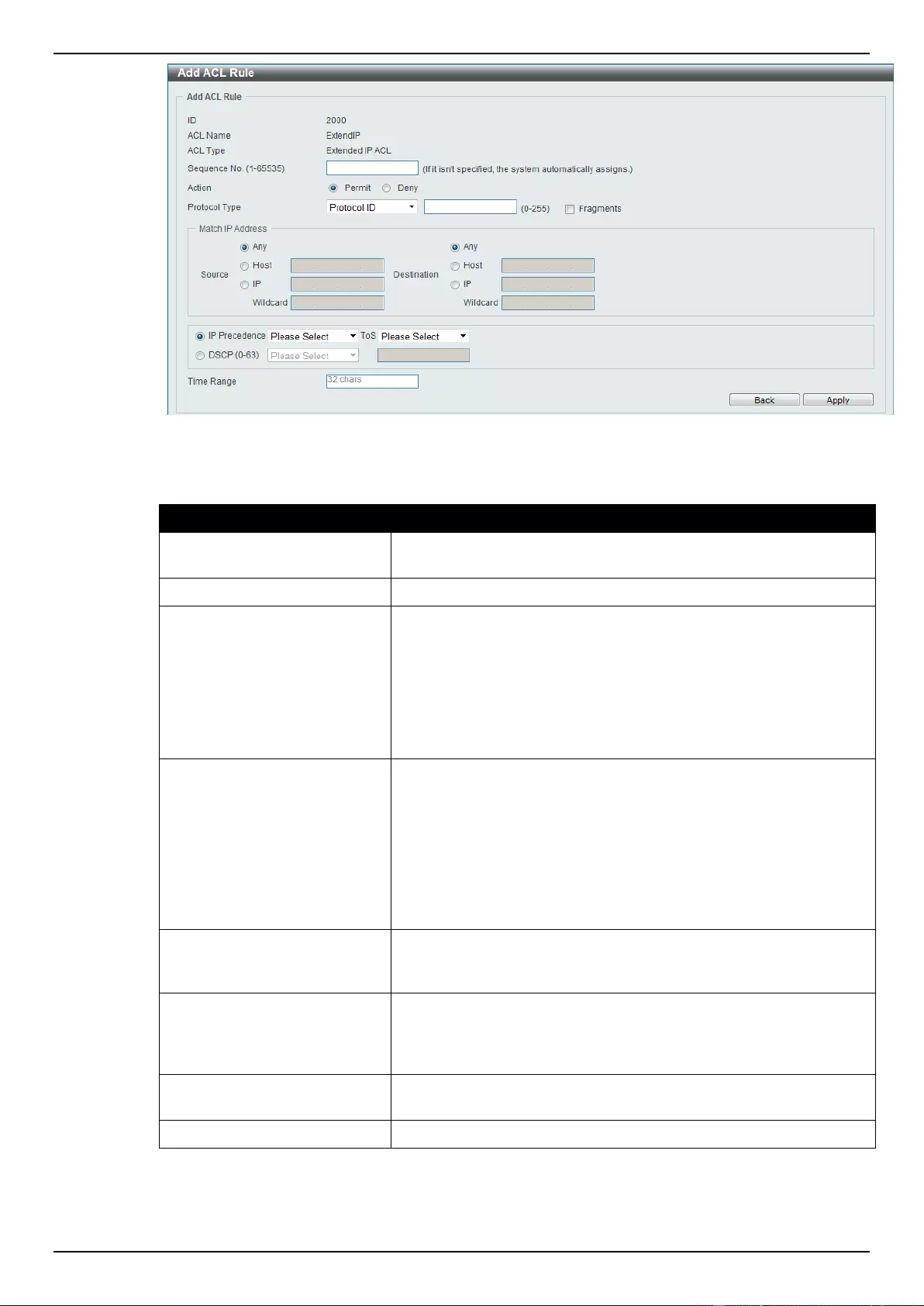
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
222
Figure 8-53 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) Protocol ID window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Enter the Protocol ID value in the space provided. This value must
be between 0 and 255.
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the None option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
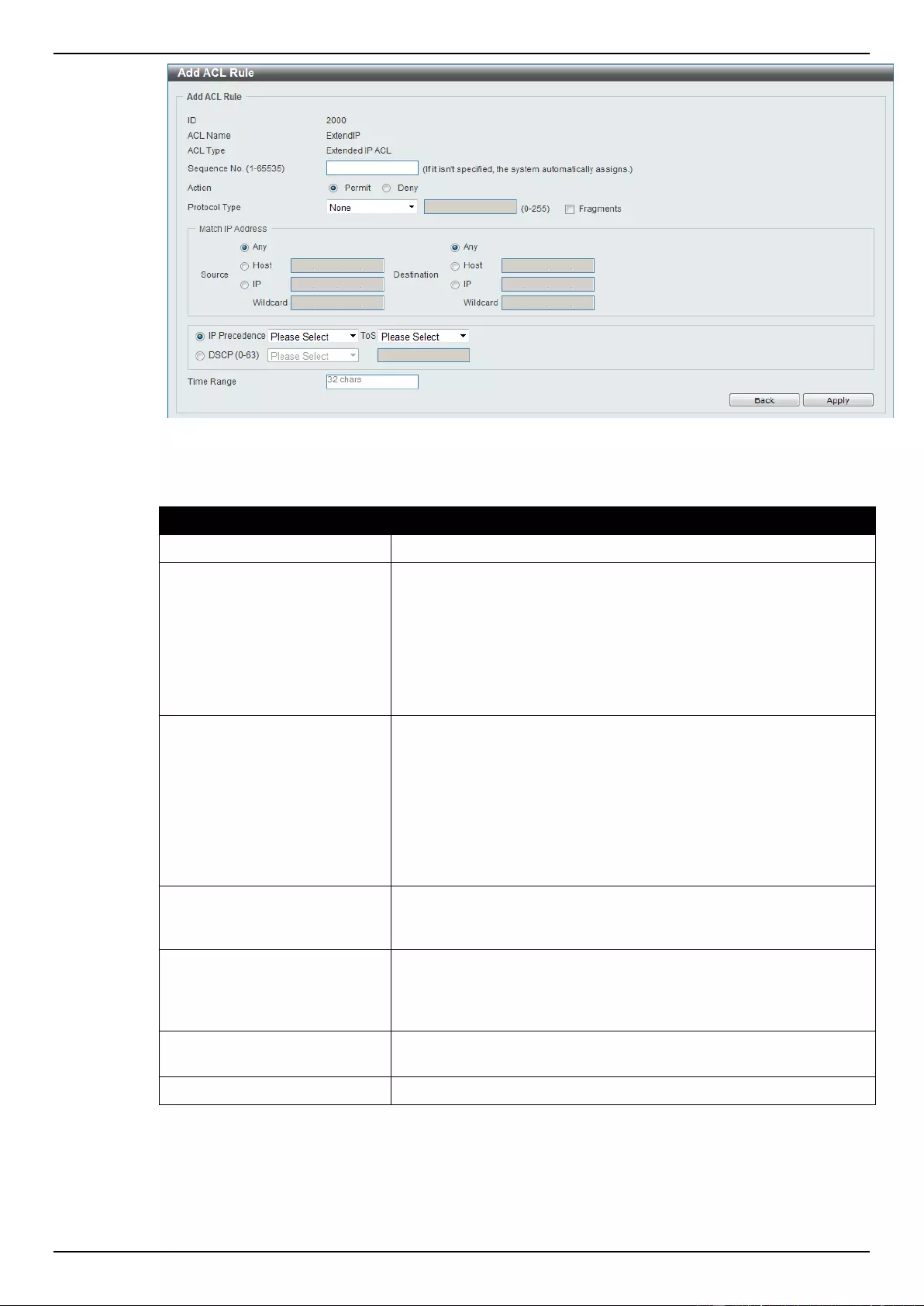
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
223
Figure 8-54 Extended IP ACL (Add Rule) None window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
224
Figure 8-55 Extended IP ACL (Edit ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Step
Enter the sequence number increment here.
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-56 Extended IP ACL (Rule Display) window
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Standard IPv6 ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
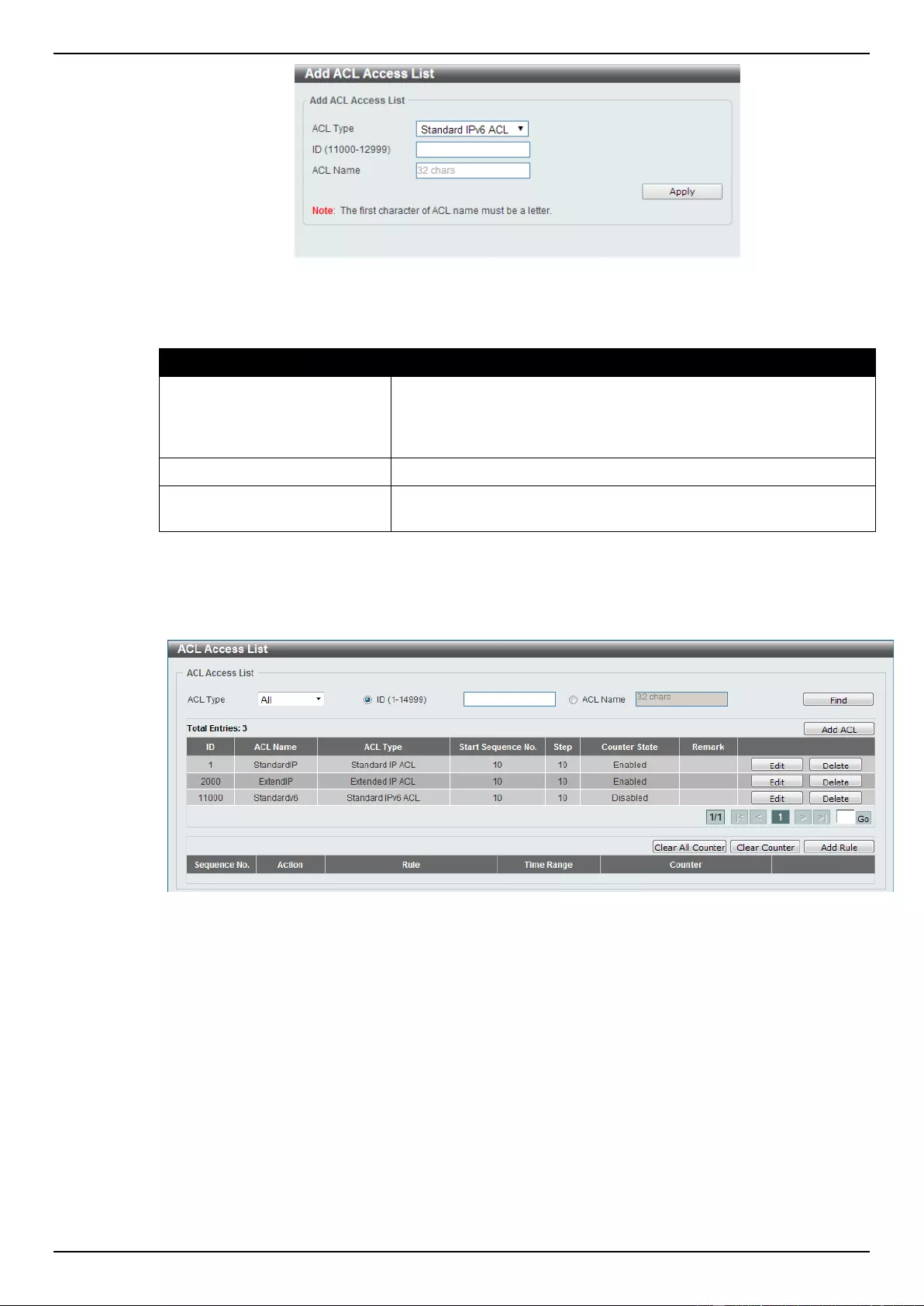
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
225
Figure 8-57 Standard IPv6 ACL (Add Profile) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 11000 to 12999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating a Standard IPv6 ACL profile, the newly created Standard IPv6 ACL profile will be
displayed in the ACL profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-58 Standard IPv6 ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
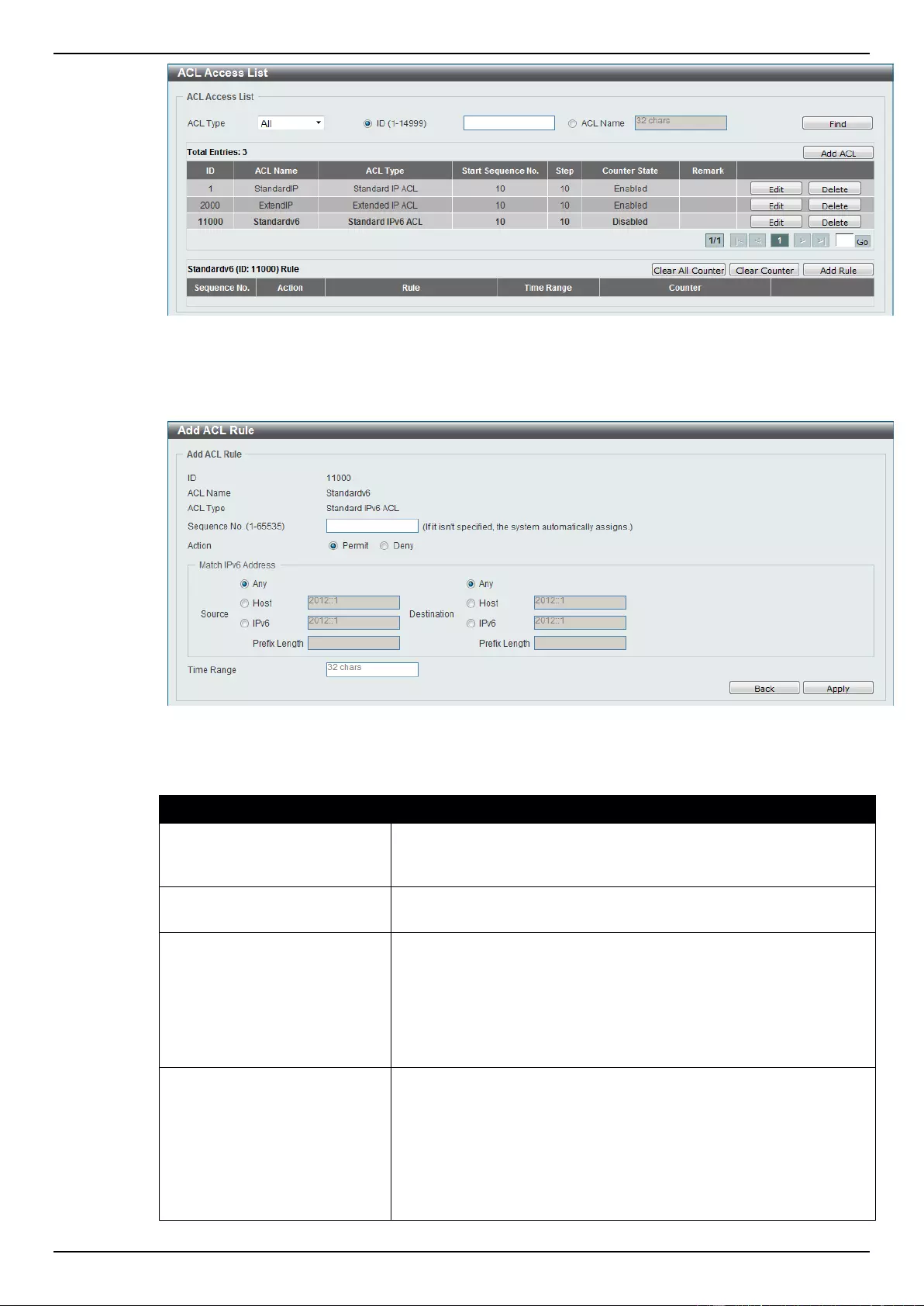
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
226
Figure 8-59 Standard IPv6 ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-60 Standard IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Rule Number
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
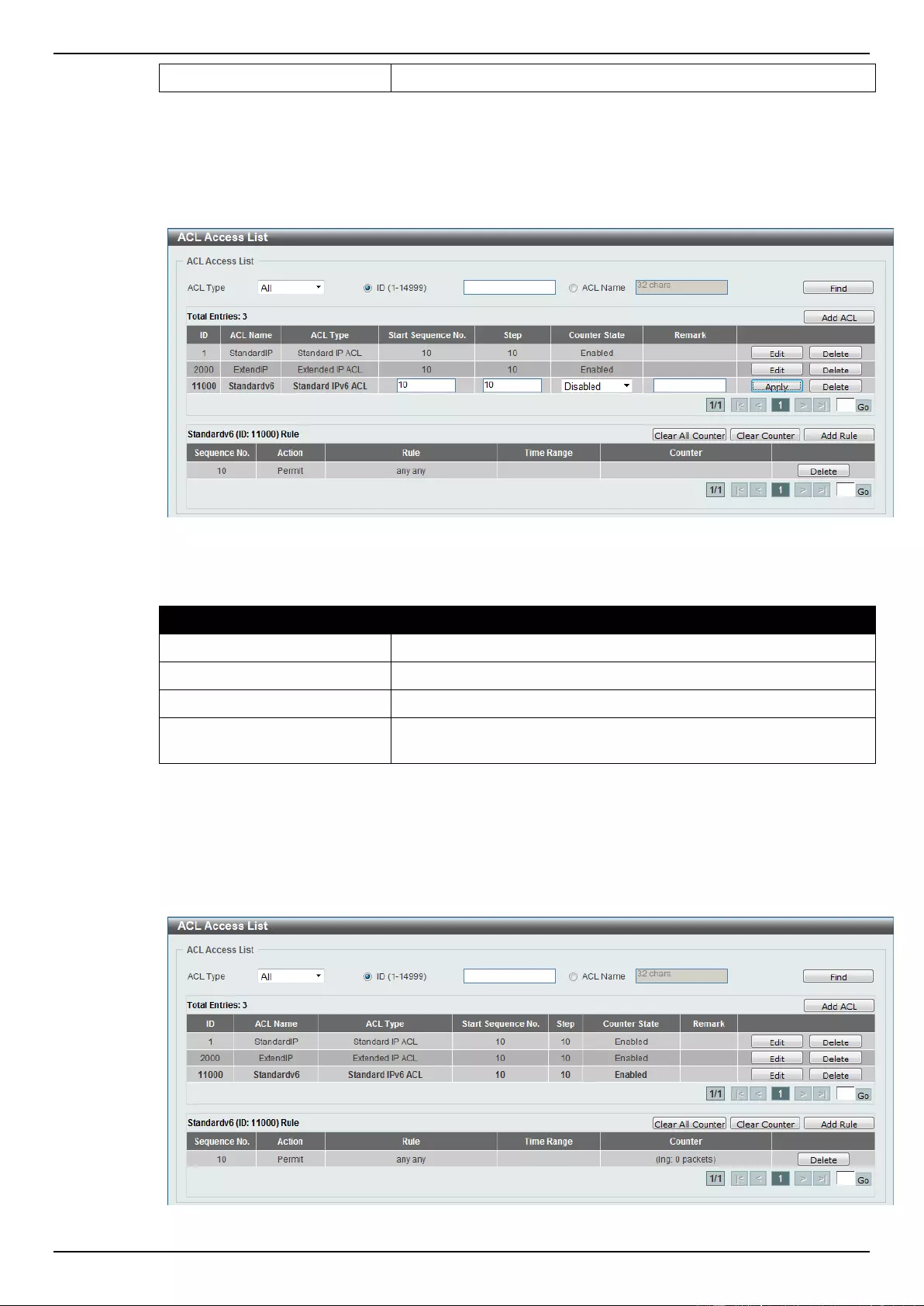
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
227
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).
Figure 8-61 Standard IPv6 ACL (Edit ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Step
Enter the sequence number increment here.
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-62 Standard IPv6 ACL (Rule Display) window
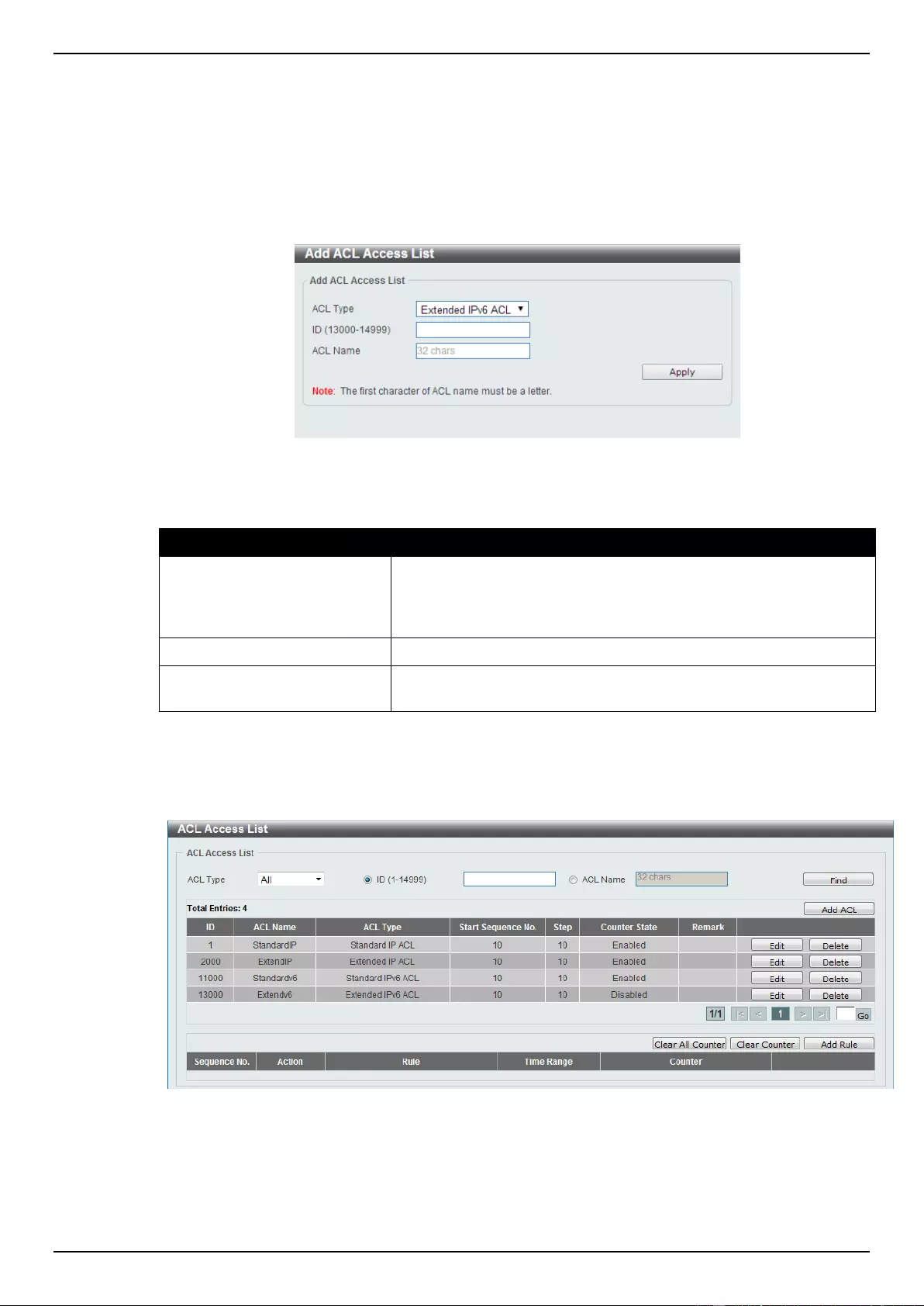
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
228
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Extended IPv6 ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-63 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Profile) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 13000 to 14999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating an Extend IPv6 ACL profile, the newly created Extend IPv6 ACL profile will be displayed
in the ACL profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-64 Extended IPv6 ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
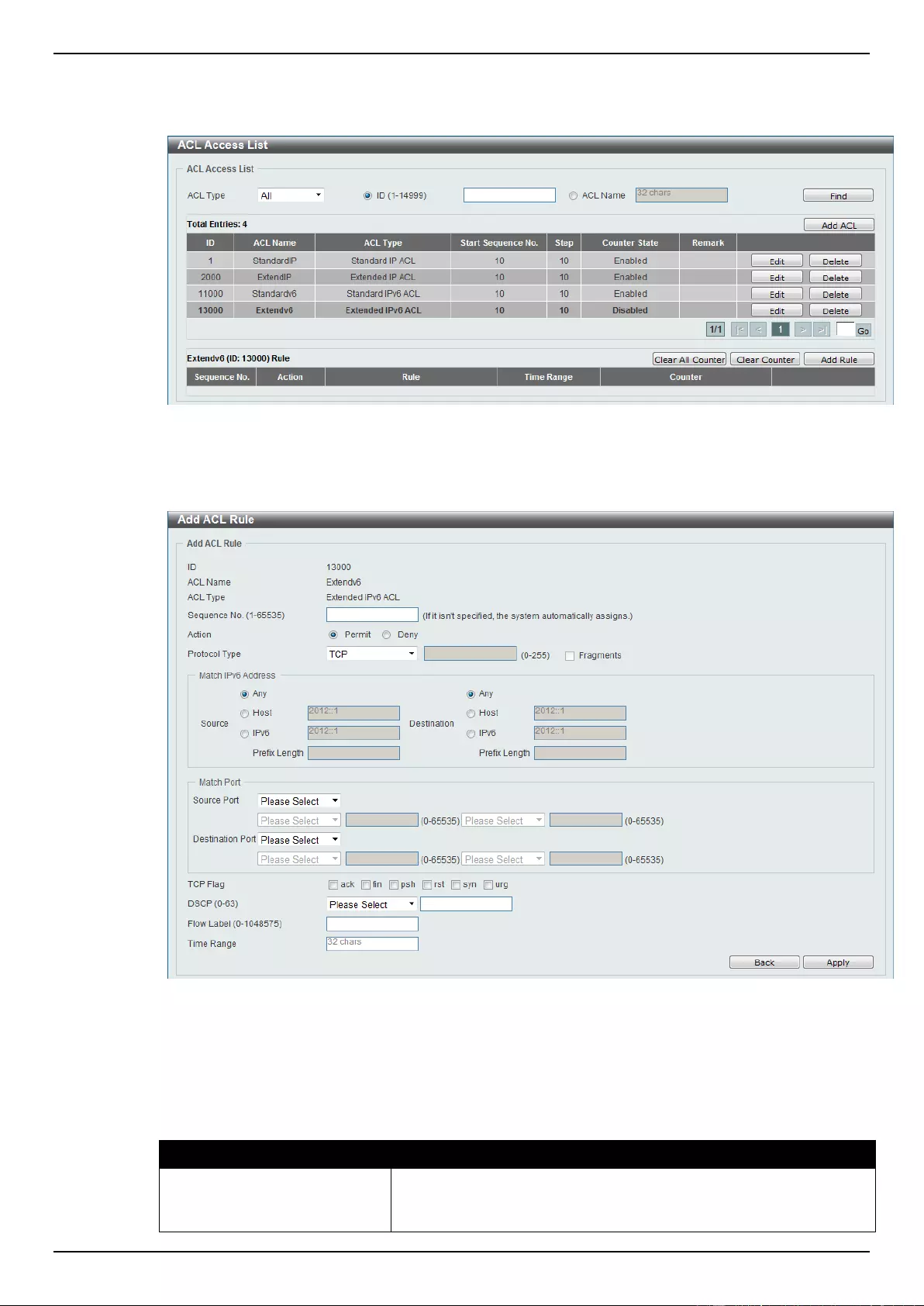
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
229
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
Figure 8-65 Extended IPv6 ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-66 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) window
This is a dynamic page. Every selection made in the Protocol Type option will change the bottom
part of this window.
The fixed fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
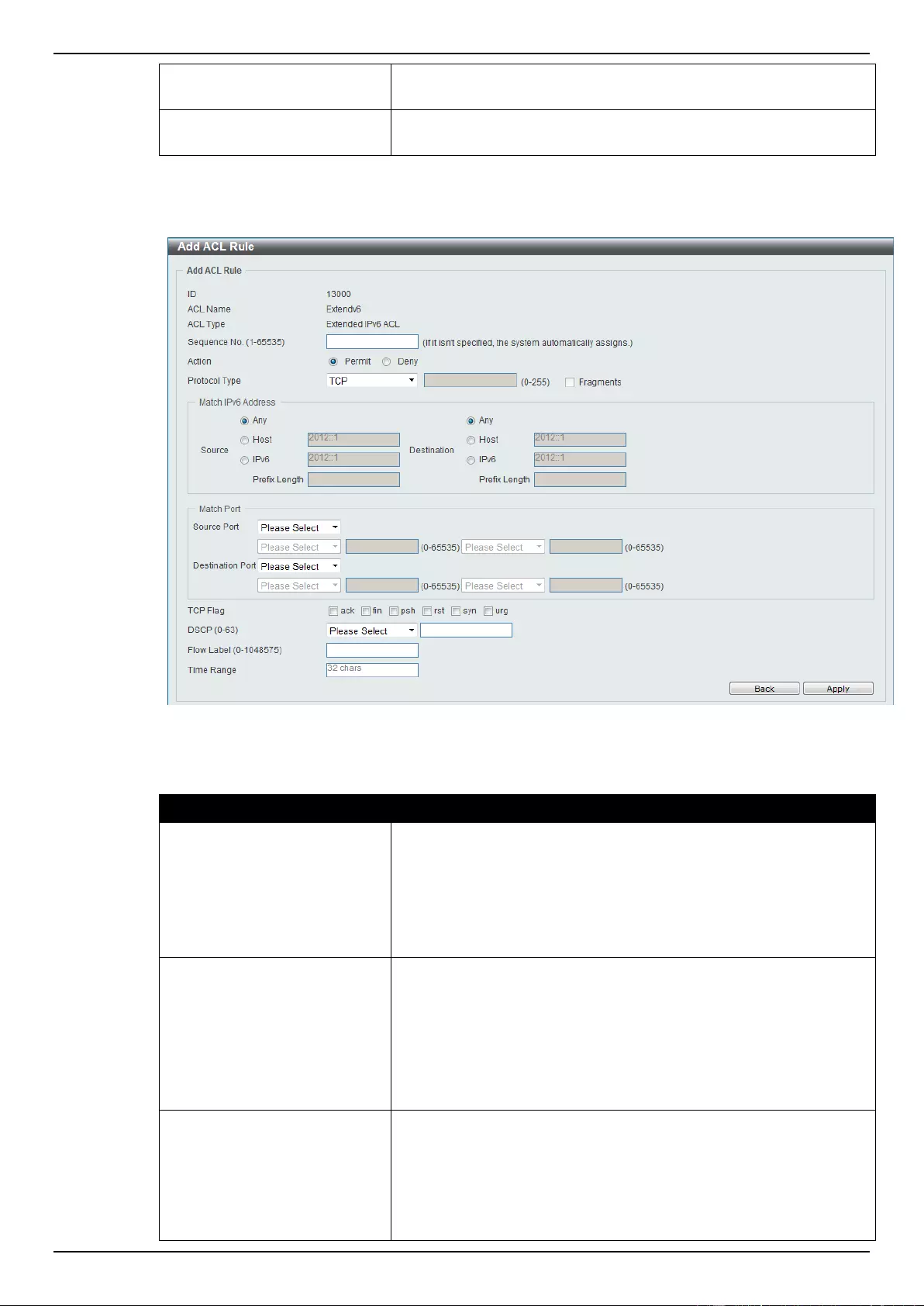
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
230
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol type option here. Options to choose from are
TCP, UDP, ICMP, Protocol ID, ESP, PCP, SCTP, and None.
After selecting the TCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-67 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) TCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
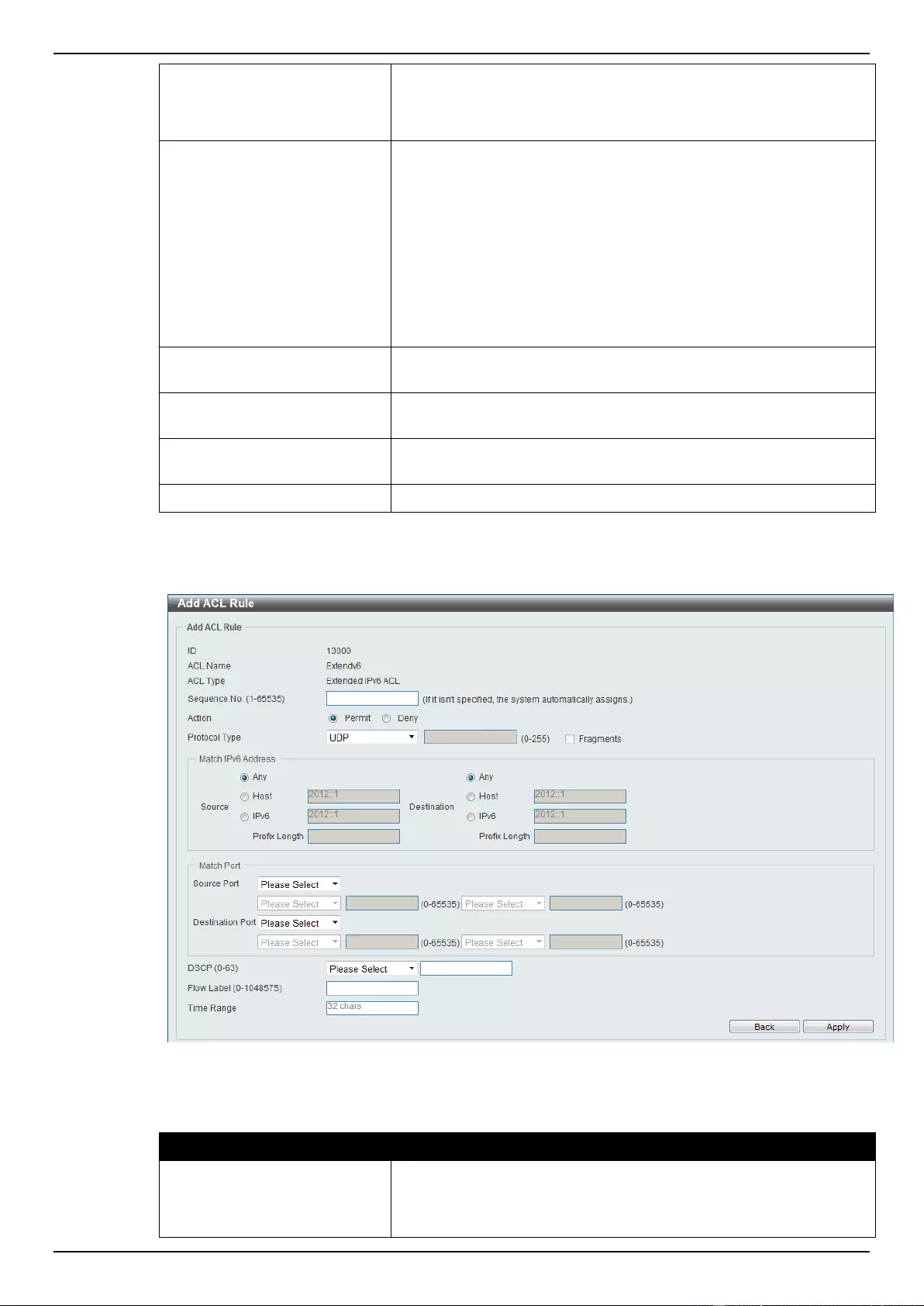
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
231
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
TCP Flag
Tick the appropriate TCP flag option to include the flag in this rule.
Options to choose from are ack, fin, psh, rst, syn, and urg.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the UDP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-68 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) UDP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
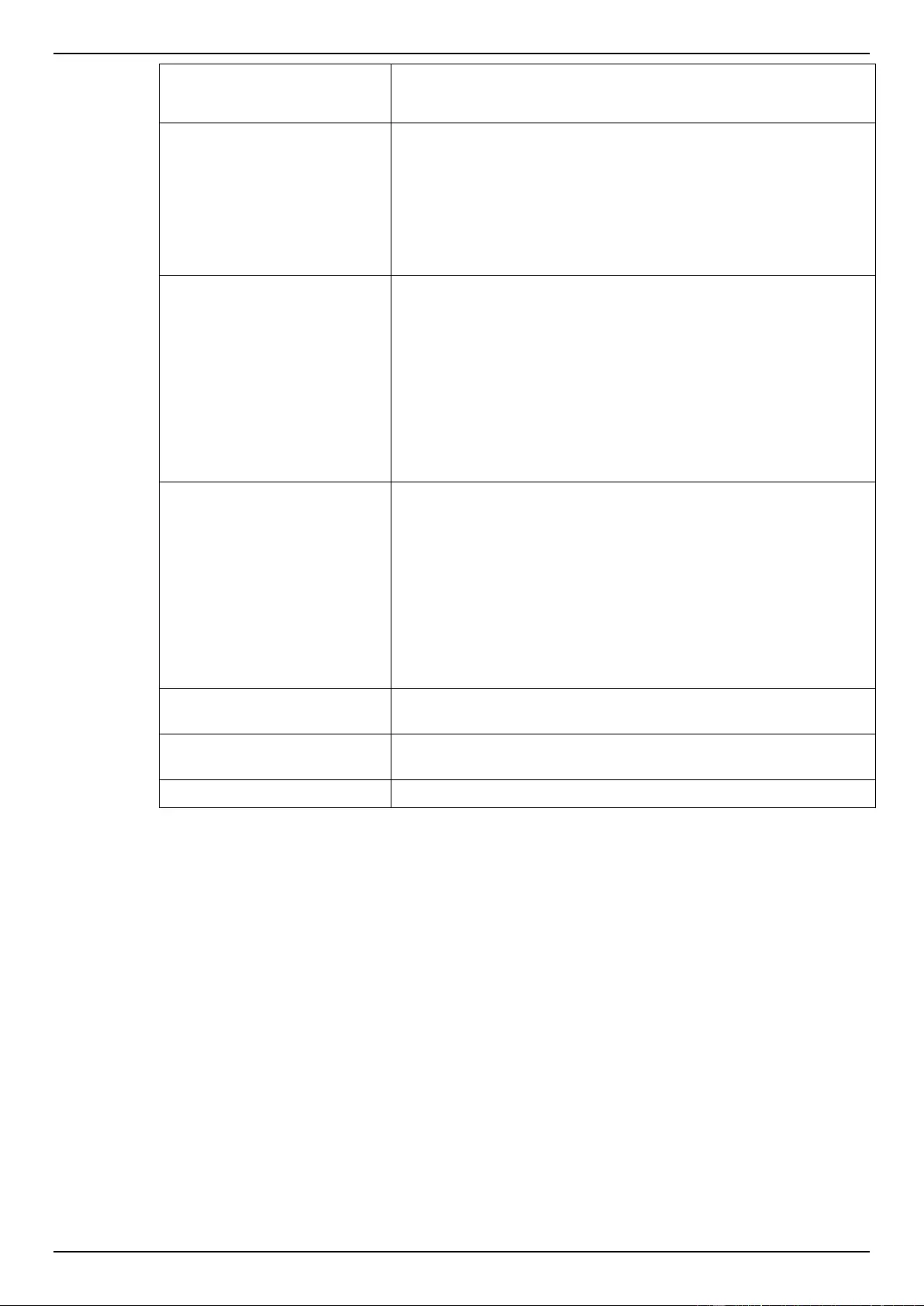
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
232
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the ICMP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
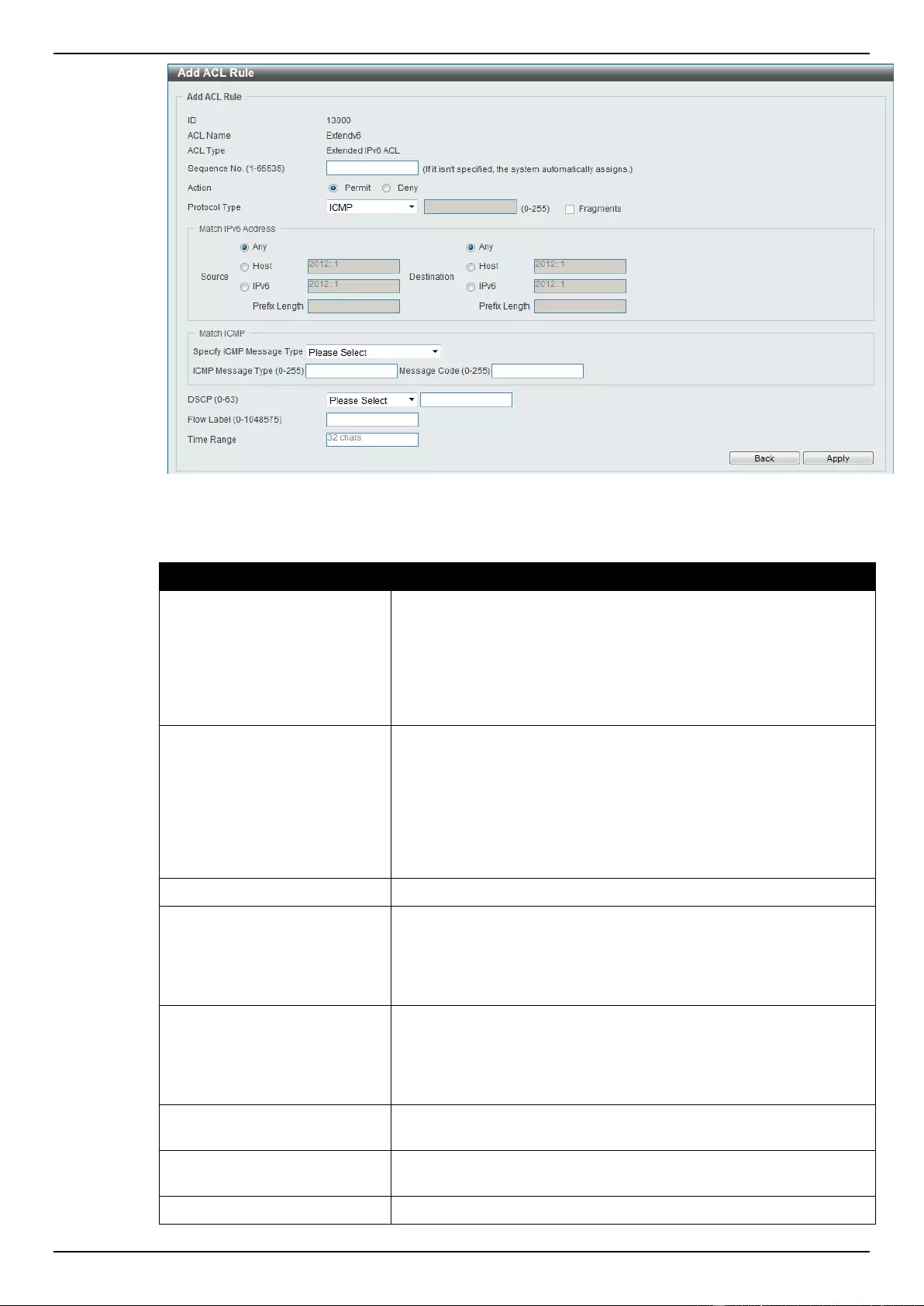
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
233
Figure 8-69 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) ICMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
Specify ICMP Message Type
Select the ICMP message type used here.
ICMP Message Type
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the ICMP Message Type
numerical value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is
selected in the Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this
numerical value will automatically be entered.
Message Code
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the Message Code numerical
value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is selected in the
Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this numerical value
will automatically be entered.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
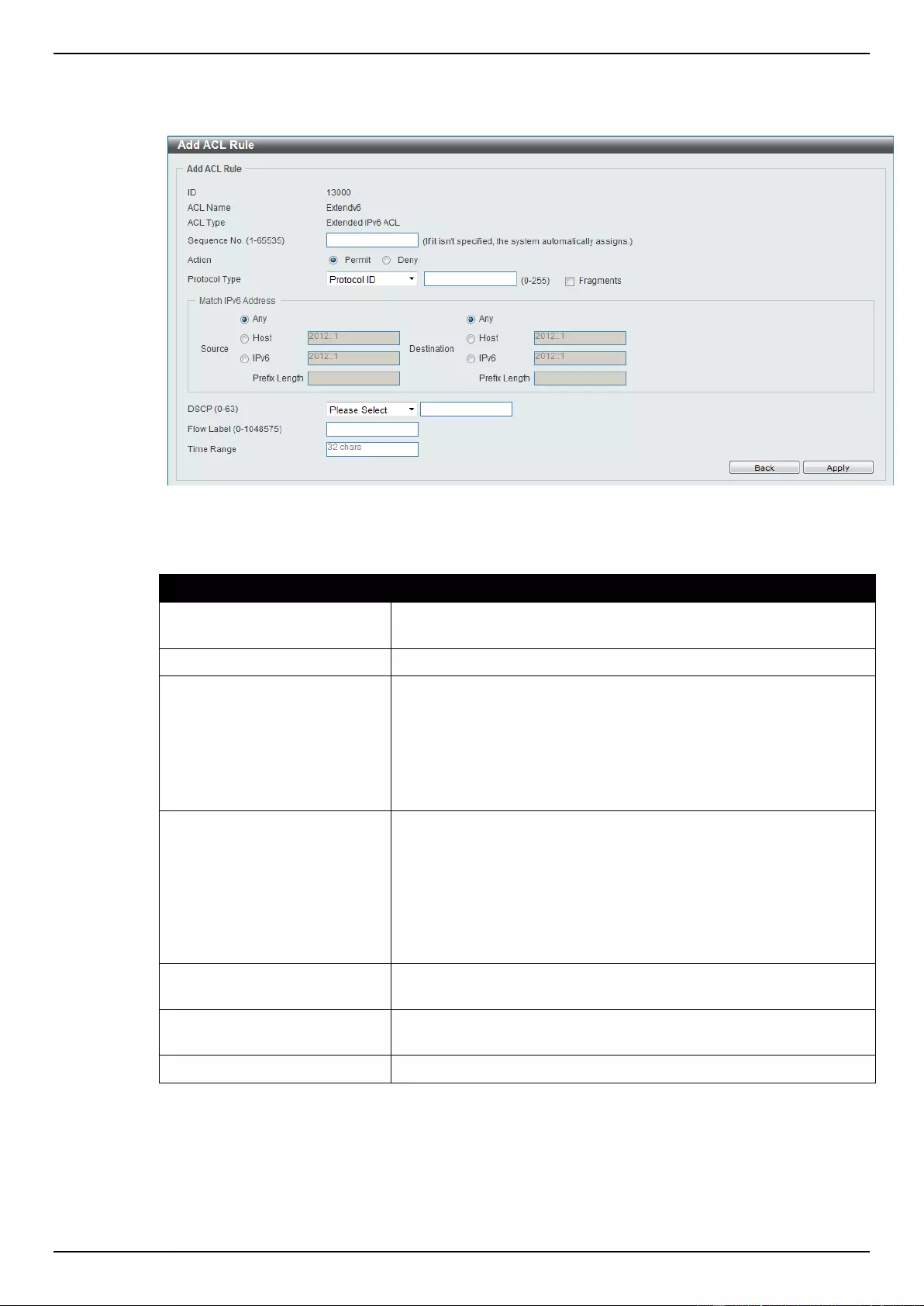
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
234
After selecting the Protocol ID option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will
be available, as shown below:
Figure 8-70 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) Protocol ID window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Enter the Protocol ID value used here. This value must be between
0 and 255.
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the ESP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
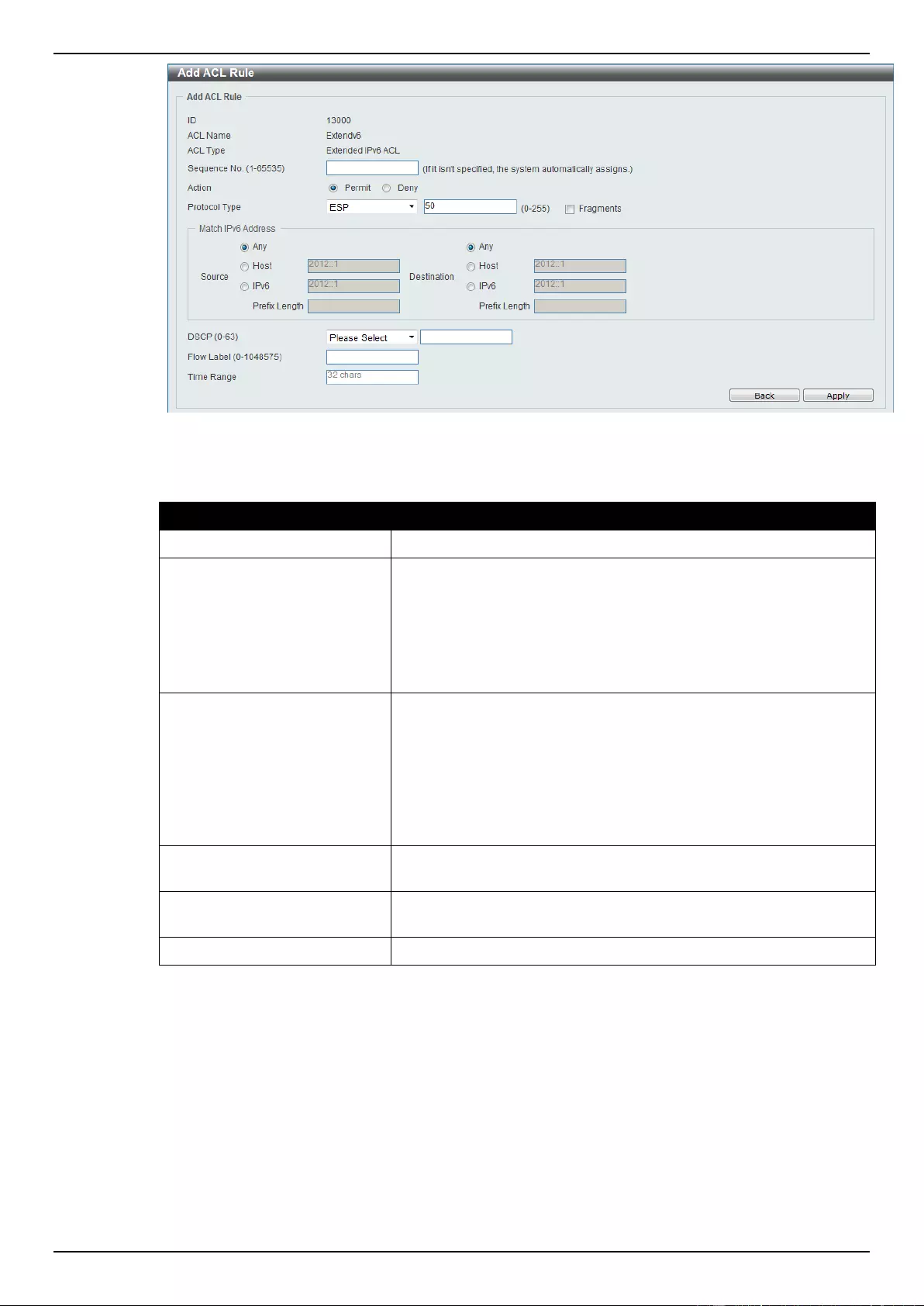
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
235
Figure 8-71 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) ESP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6th. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the PCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
236
Figure 8-72 Extend IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) PCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the SCTP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
237
Figure 8-73 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) SCTP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the None option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
238
Figure 8-74 Extended IPv6 ACL (Add Rule) None window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is selected, the Prefix
Length option will also be available. Enter the source IPv6 address
and prefix length value in the spaces provided.
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IPv6. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IPv6 address here. When the IPv6 option is
selected, the Prefix Length option will also be available. Enter the
destination IPv6 address and prefix length value in the spaces
provided.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
Flow Label
Enter the flow label value here. This value must be between 0 and
1048575.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).
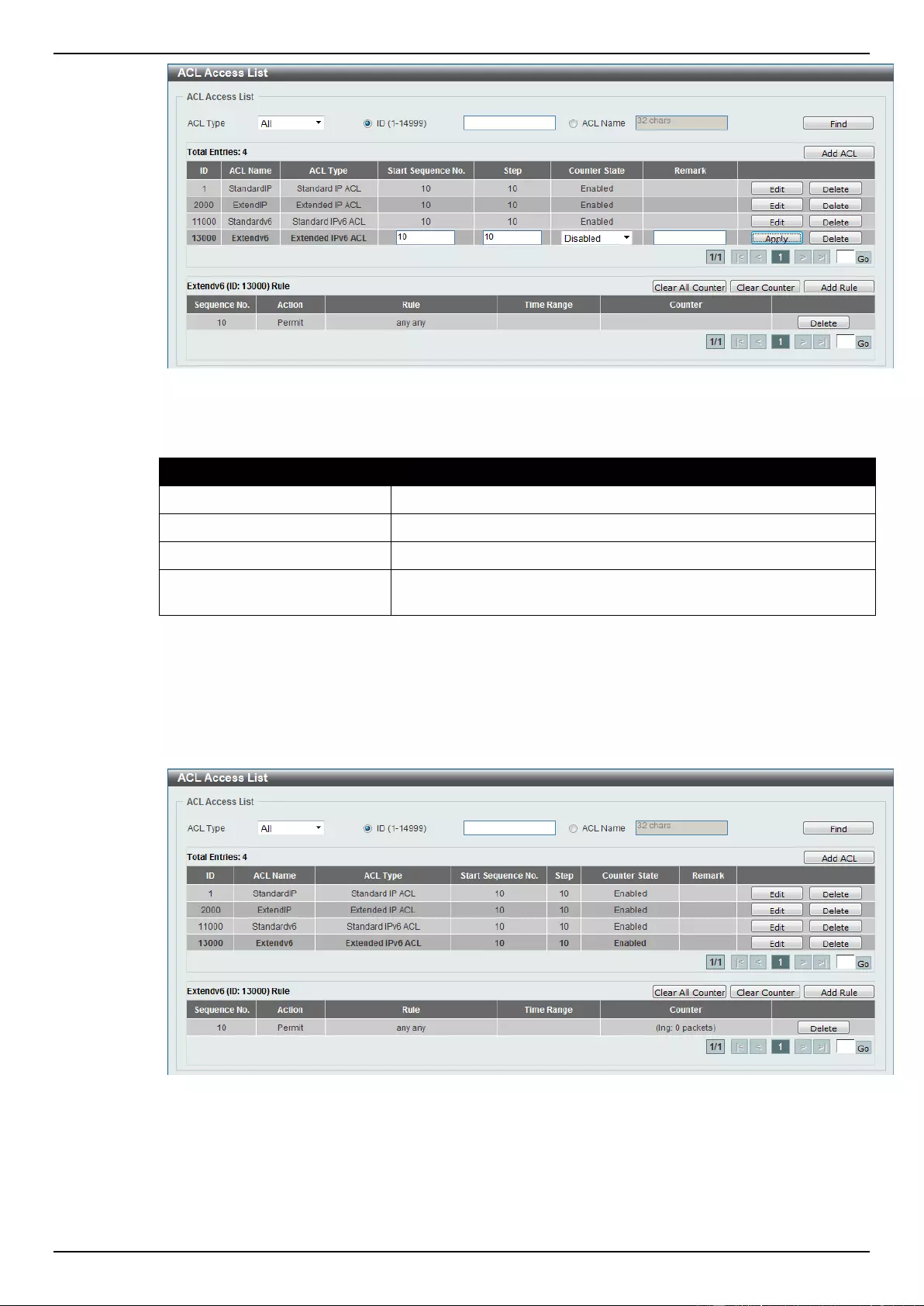
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
239
Figure 8-75 Extended IPv6 ACL (Counter State Enabled) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Stop
Enter the stop sequence number here.
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-76 Extended IPv6 ACL (Rule Display) window
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
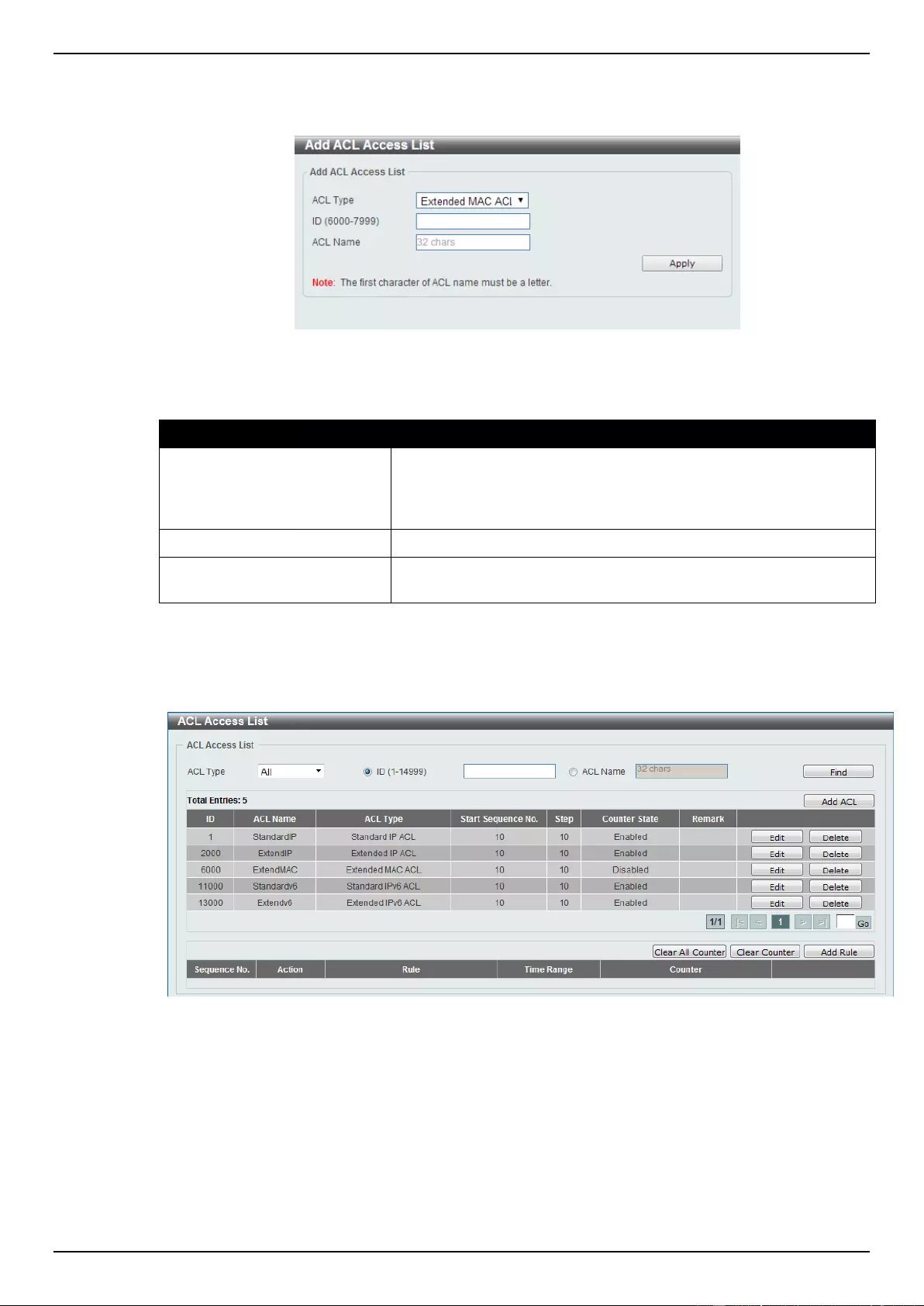
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
240
Extended MAC ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-77 Extended MAC ACL (Add Profile) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 6000 to 7999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating an Extend MAC ACL profile, the newly created Extend MAC ACL profile will be
displayed in the ACL profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-78 Extended MAC ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
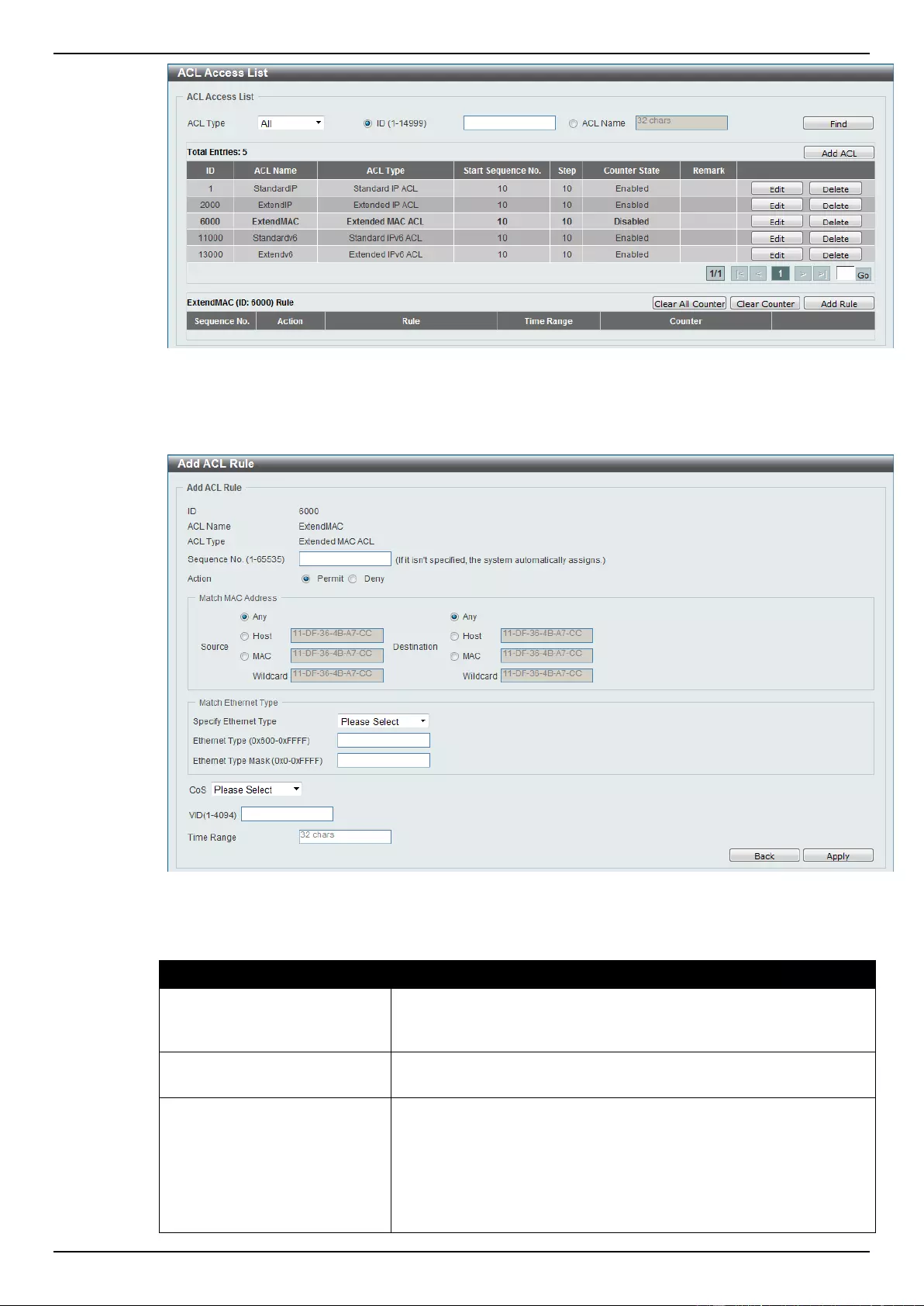
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
241
Figure 8-79 Extended MAC ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-80 Extended MAC ACL (Add Rule) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Rule Number
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Source
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
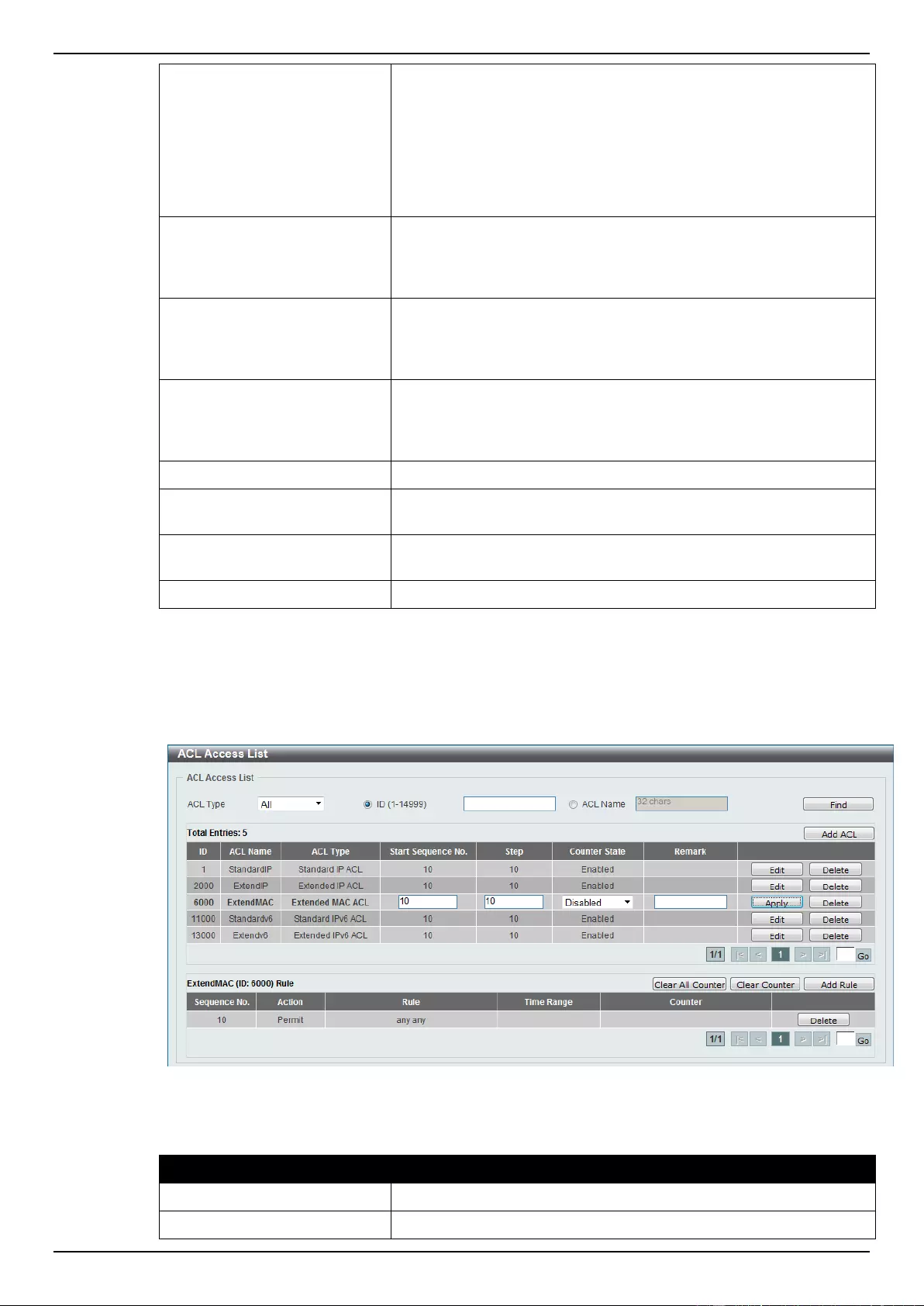
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
242
Destination
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
Specify Ethernet Type
Select the Ethernet type option here. Options to choose from are
aarp, appletalk, decent-iv, etype-6000, etype-8042, lat, lavc-sca,
mop-console, mop-dump, vines-echo, vines-ip, xns-idp, and
arp.
Ethernet Type
Enter the Ethernet type hexadecimal value here. This value must be
between 0x600 and 0xFFFF. When any Ethernet type profile is
selected in the Specify Ethernet Type drop-down list, the
appropriate hexadecimal value will automatically be entered.
Ethernet Type Mask
Enter the Ethernet type mask hexadecimal value here. This value
must be between 0x0 and 0xFFFF. When any Ethernet type profile
is selected in the Specify Ethernet Type drop-down list, the
appropriate hexadecimal value will automatically be entered.
CoS
Select the CoS value used here. This value is between 0 and 7.
Inner CoS
Select the inner CoS value used here. This value is between 0 and
7.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).
Figure 8-81 Extended MAC ACL (Edit ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Stop
Enter the stop sequence number here.
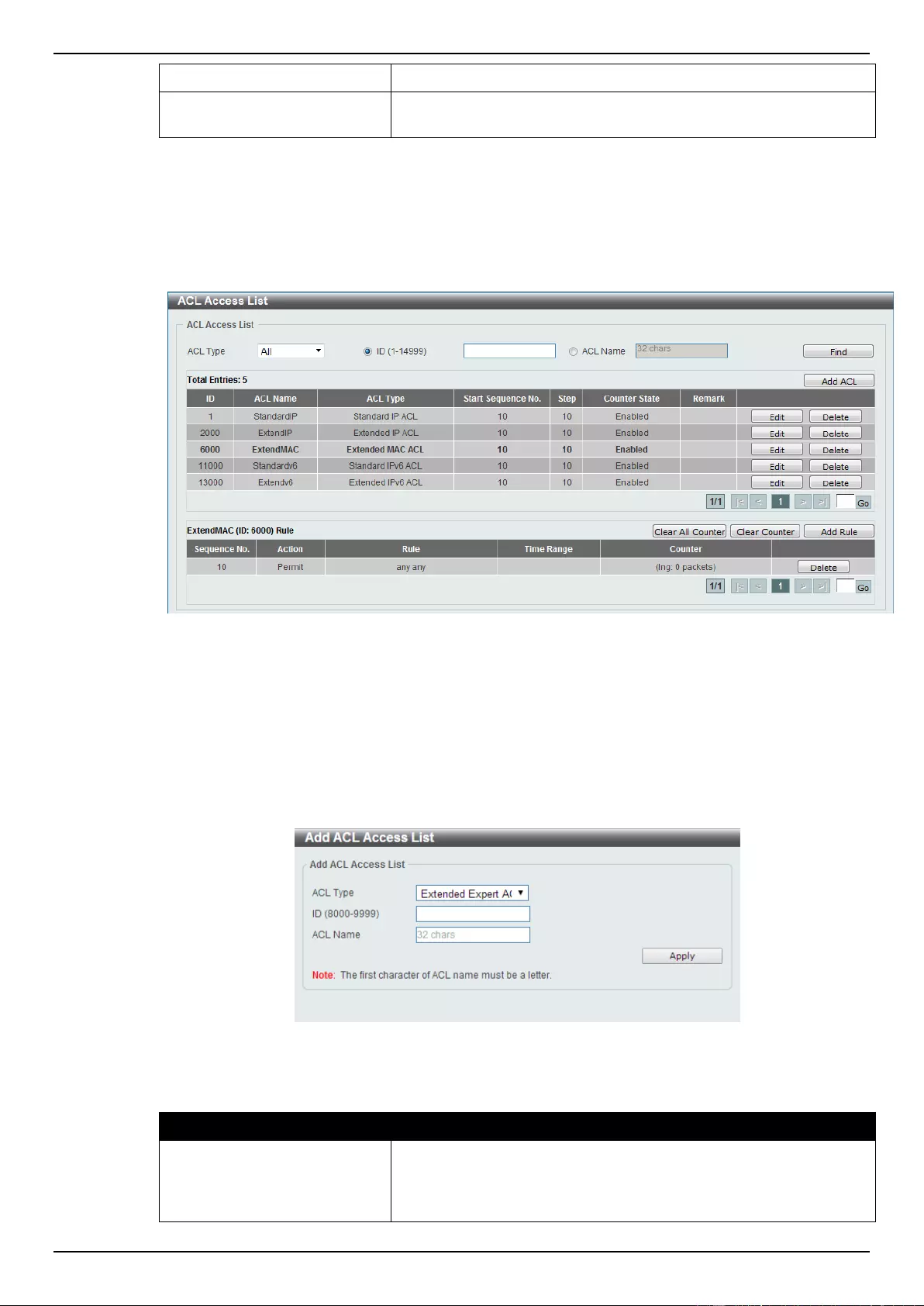
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
243
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-82 Extended MAC ACL (Rule Display) window
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Extended Expert ACL
After clicking the Add ACL button, users can create a new ACL profile, as shown below:
Figure 8-83 Extended Expert ACL (Add Profile) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Type
Select the ACL profile type here. Options to choose from are
Standard IP ACL, Extended IP ACL, Standard IPv6 ACL,
Extended IPv6 ACL, Extended MAC ACL, and Extended Expert
ACL.
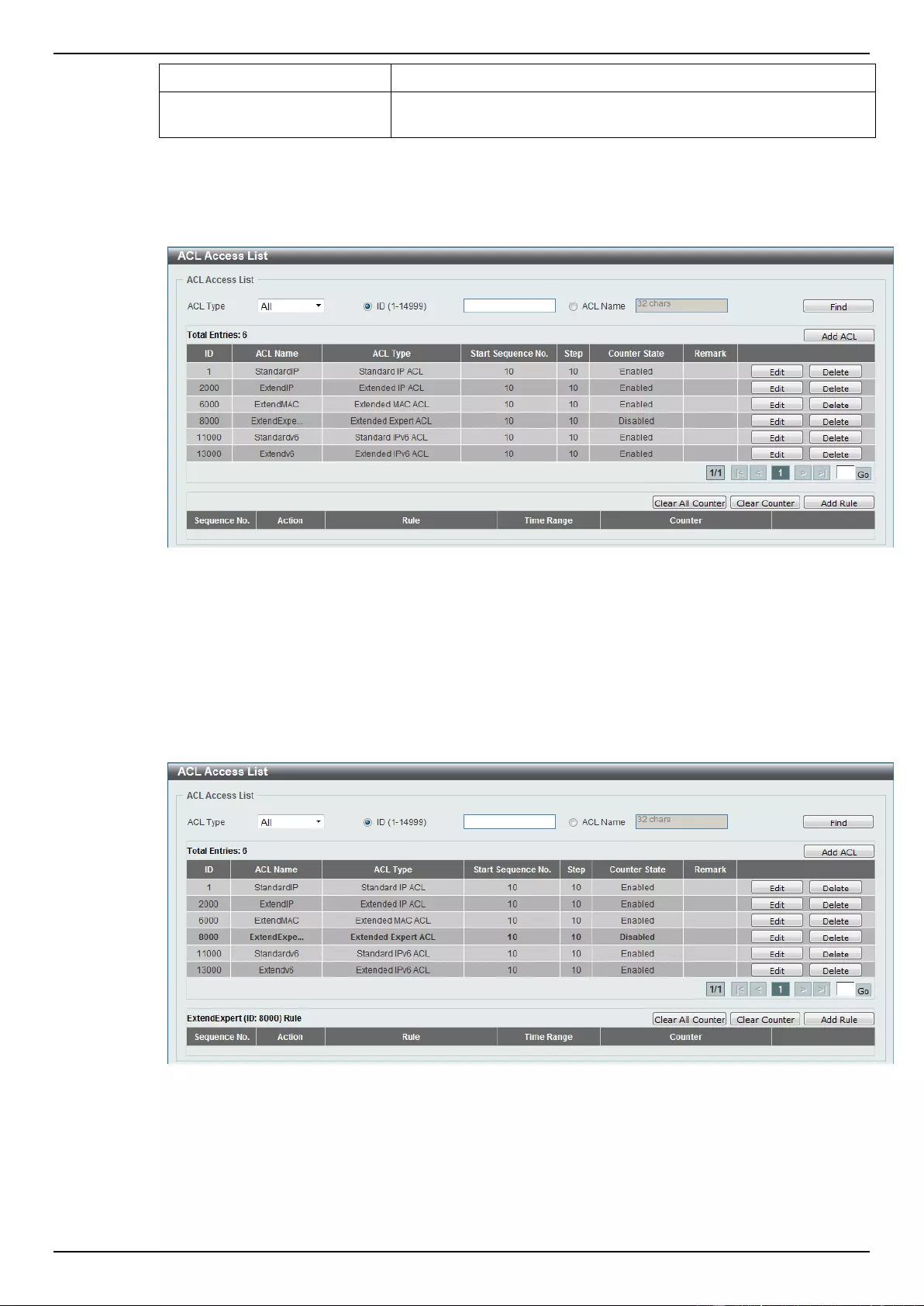
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
244
ID
Enter the ACL ID from 8000 to 9999.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to create the new ACL profile.
After creating an Expert ACL profile, the newly created Expert ACL profile will be displayed in the ACL
profile display table, as shown below:
Figure 8-84 Extended Expert ACL (Main) window
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific ACL profile.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL profile.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
To add an ACL rule in the ACL profile, select it (the ACL profile will toggle to the bold font), and click
the Add Rule button.
Figure 8-85 Extended Expert ACL (Selected) window
After selecting the ACL profile and clicking the Add Rule button, users can configure the new ACL
rule, in the selected ACL profile, as shown below:
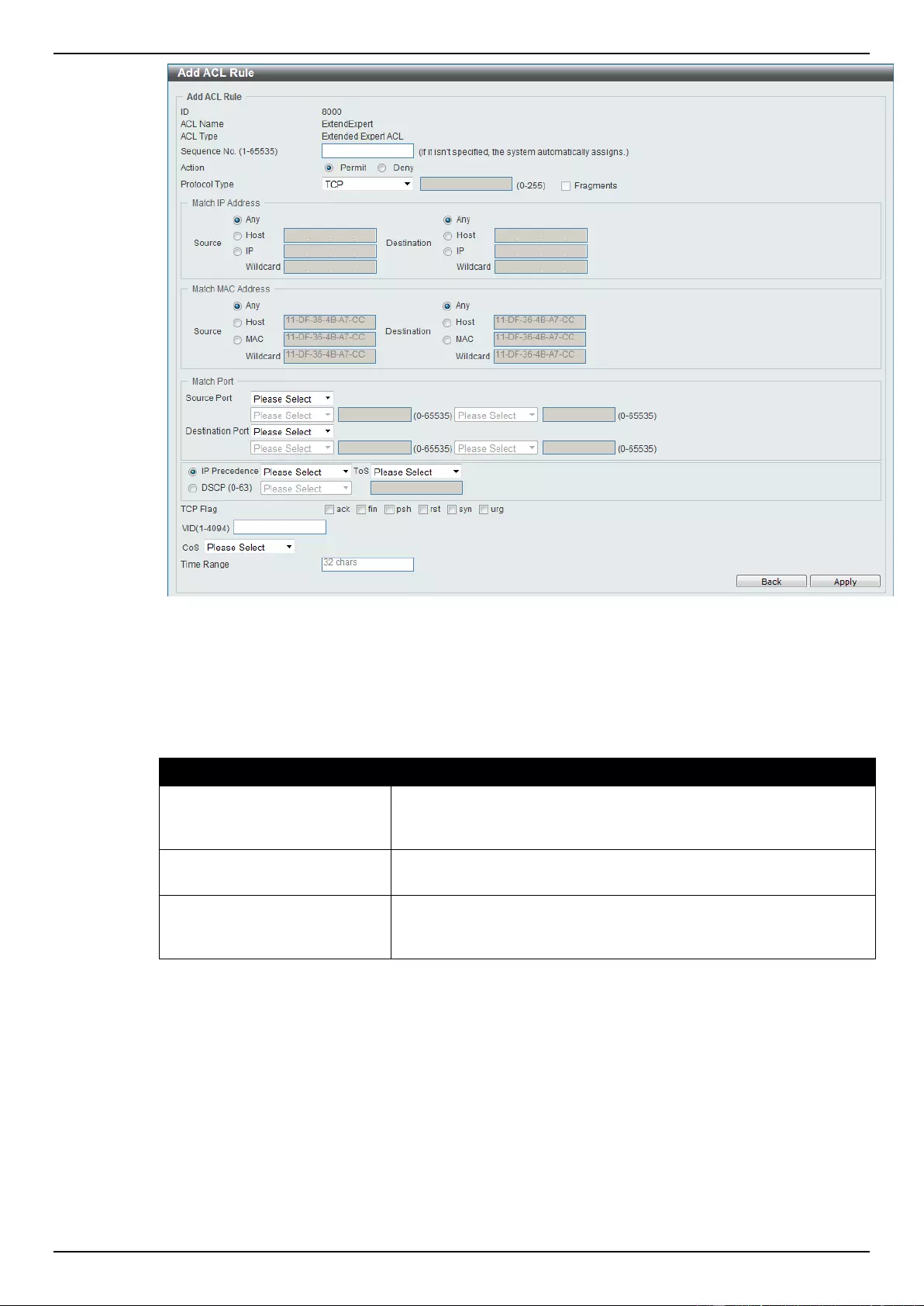
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
245
Figure 8-86 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) window
This is a dynamic page. Every selection made in the Protocol Type option will change the bottom
part of this window.
The fixed fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sequence No.
Enter the ACL rule number here. This value must be between 1 and
65535. If this value is not specified, the system will automatically
generate an ACL rule number for this entry.
Action
Select the action that this rule will take here. Options to choose from
are Permit and Deny.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol type option here. Options to choose from are
TCP, UDP, ICMP, EIGRP, ESP, GRE, IGMP, OSPF, PIM, VRRP,
IP-in-IP, PCP, Protocol ID, and None.
After selecting the TCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
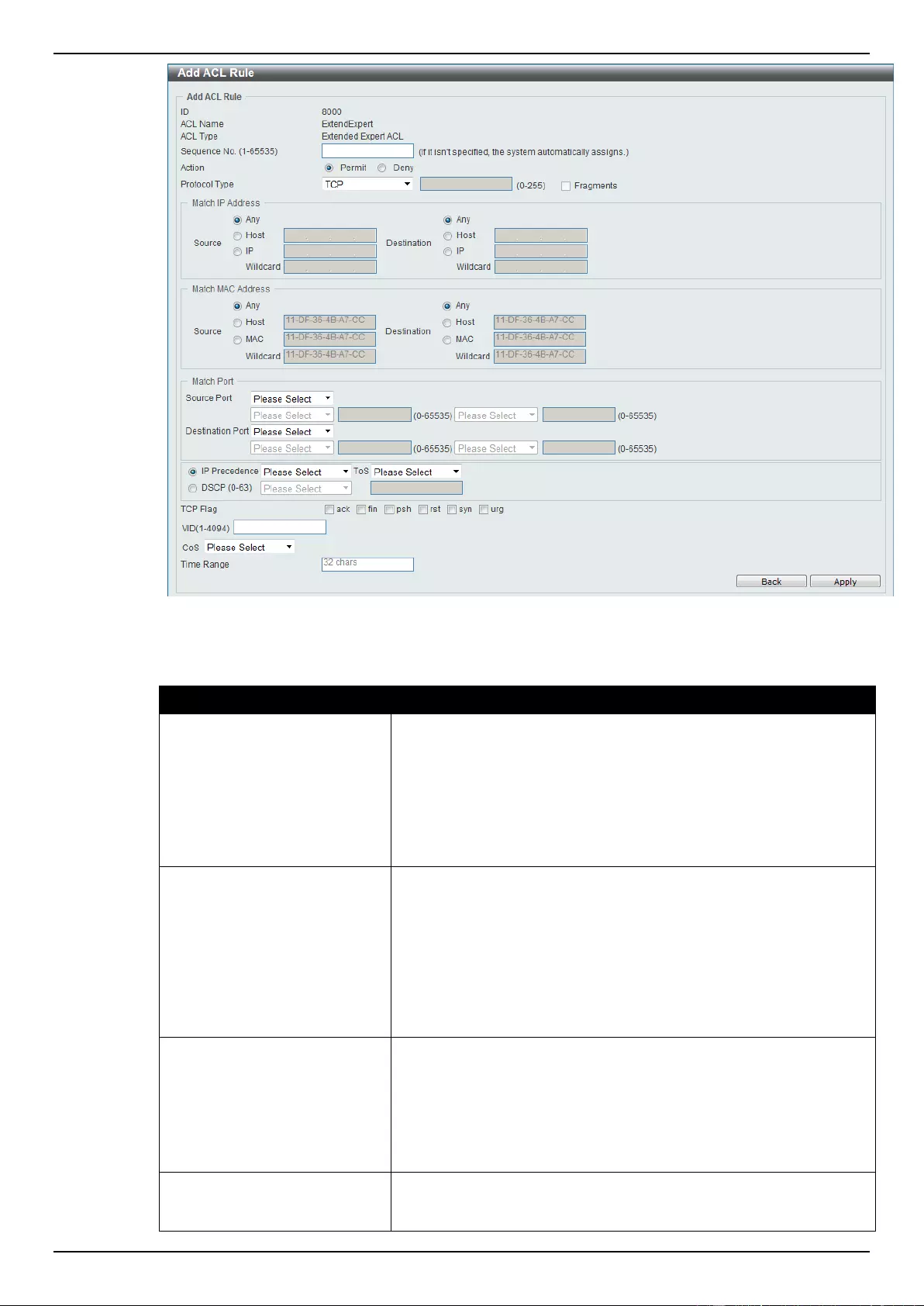
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
246
Figure 8-87 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) TCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
247
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
TCP Flag
Tick the appropriate TCP flag option to include the flag in this rule.
Options to choose from are ack, fin, psh, rst, syn, and urg.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
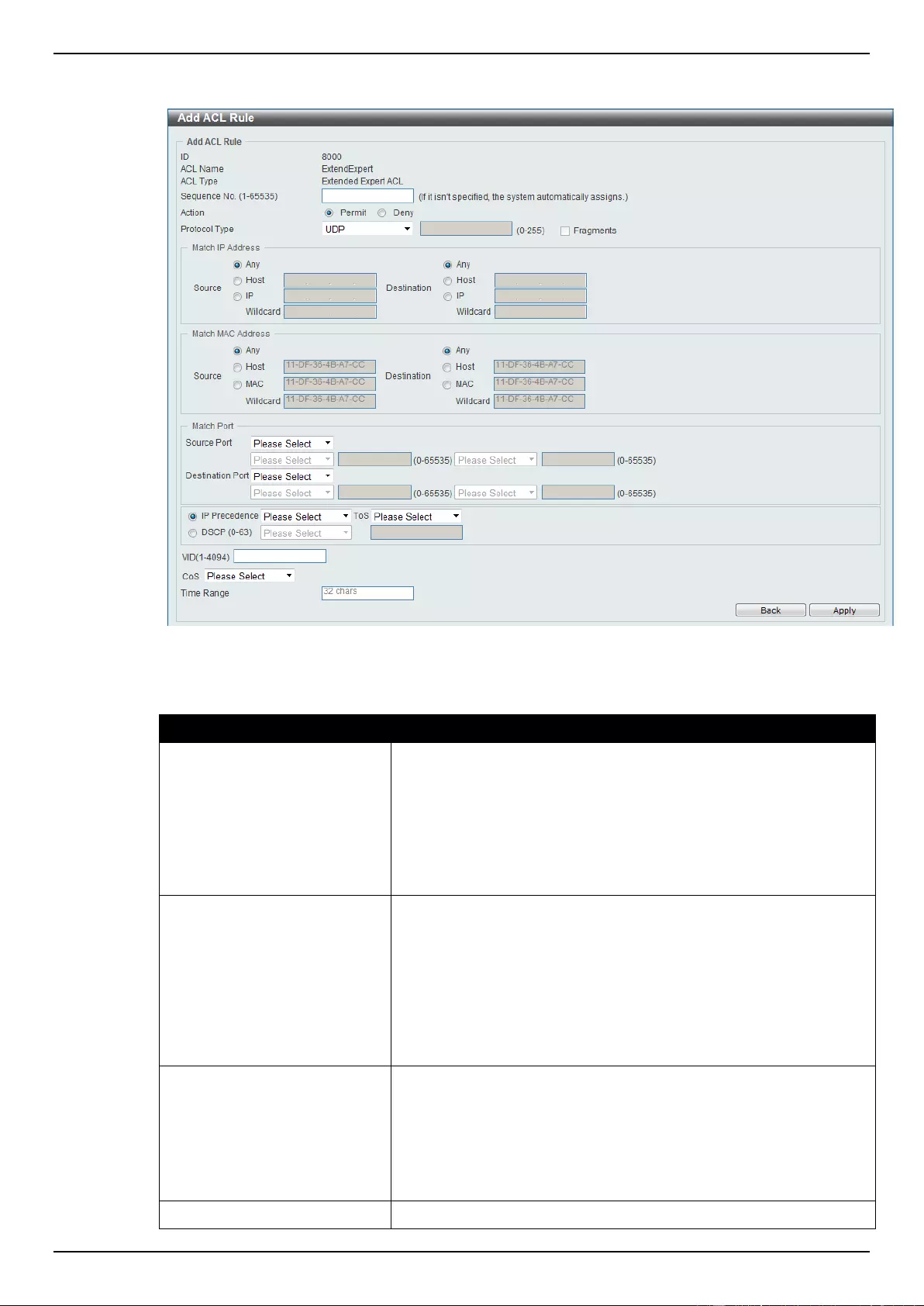
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
248
After selecting the UDP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-88 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) UDP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
249
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
Source Port
Select and enter the source port value here. Options to choose from
are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the specific
selected port number will be used. When selecting the > option, all
ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When selecting
the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will be used.
When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the selected port,
will be used. When selecting the Range option, the start port
number and end port number selected, of the range, will be used.
Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered in the
space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in the
drop-down list.
Destination Port
Select and enter the destination port value here. Options to choose
from are =, >, <, ≠, and Range. When selecting the = option, the
specific selected port number will be used. When selecting the >
option, all ports greater than the selected port, will be used. When
selecting the < option, all ports smaller than the selected port, will
be used. When selecting the ≠ option, all ports, excluding the
selected port, will be used. When selecting the Range option, the
start port number and end port number selected, of the range, will
be used. Alternatively, the port number(s) can manually be entered
in the space(s) provided, if the port number(s) is/are not available in
the drop-down list.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
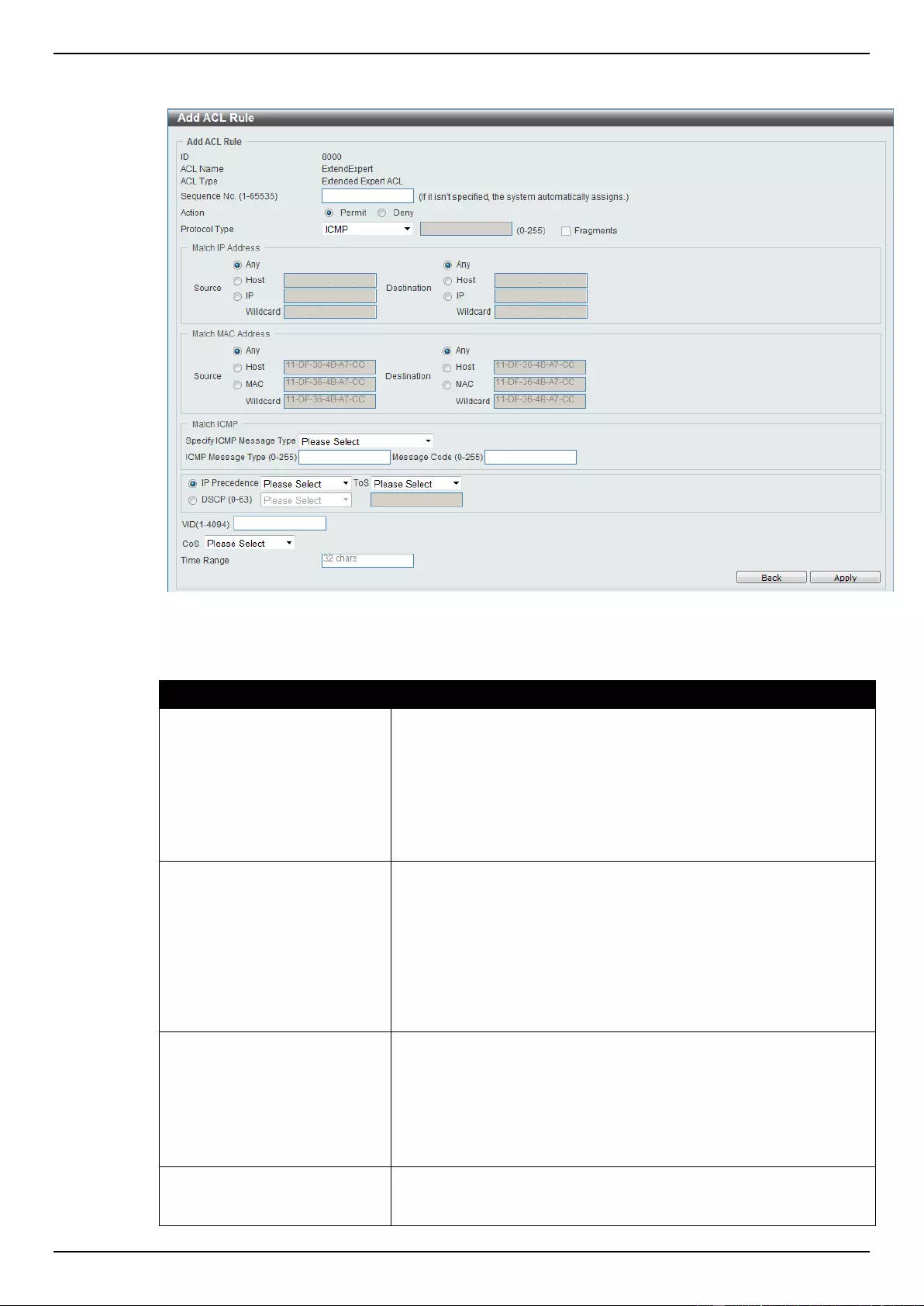
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
250
After selecting the ICMP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-89 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) ICMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
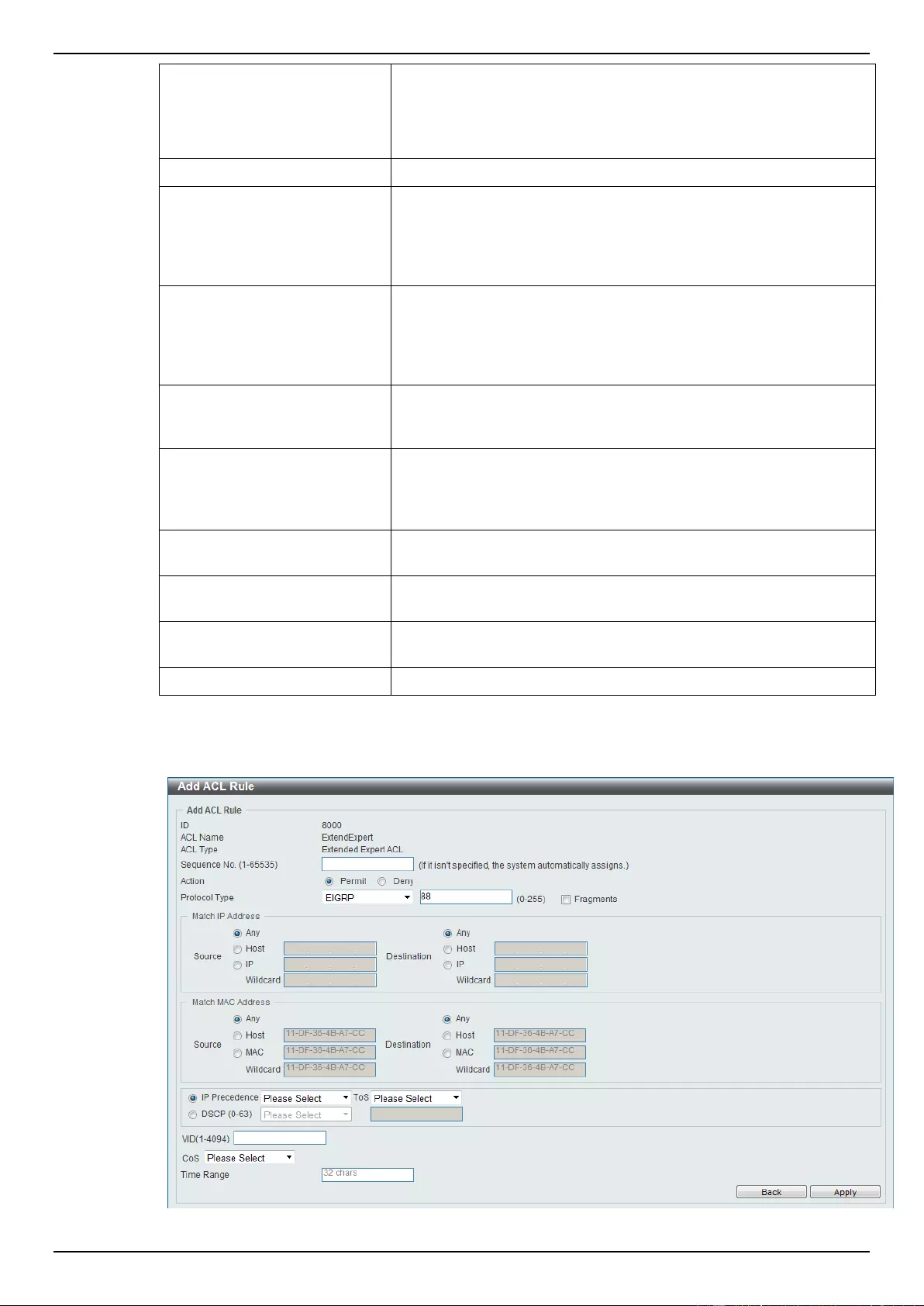
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
251
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
Specify ICMP Message Type
Select the ICMP message type used here.
ICMP Message Type
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the ICMP Message Type
numerical value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is
selected in the Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this
numerical value will automatically be entered.
Message Code
When the ICMP Message Type is not selected in the Specify ICMP
Message Type drop-down list, enter the Message Code numerical
value used here. When the ICMP Message Type is selected in the
Specify ICMP Message Type drop-down list, this numerical value
will automatically be entered.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the EIGRP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-90 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) EIGRP window
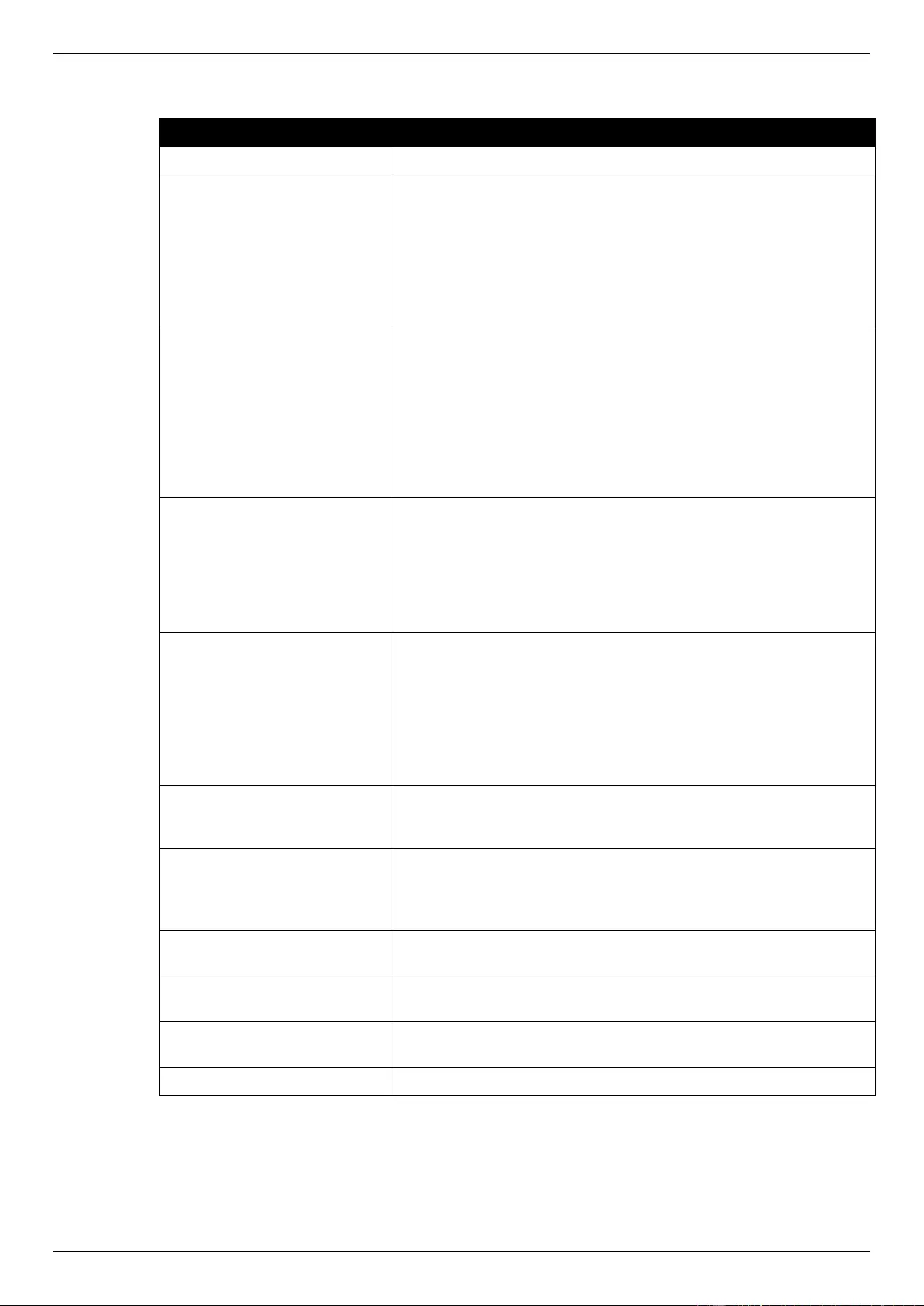
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
252
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the ESP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
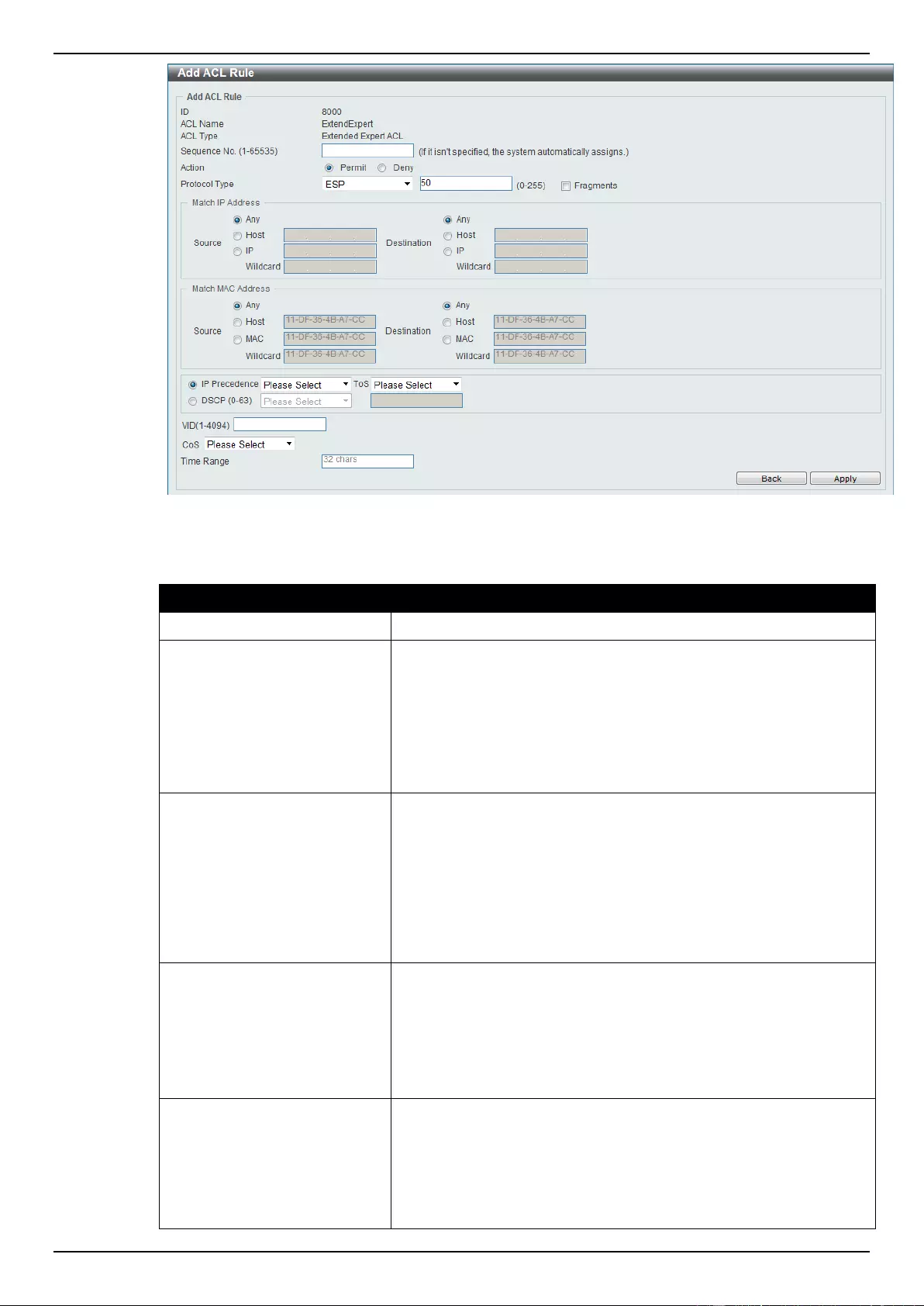
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
253
Figure 8-91 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) ESP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
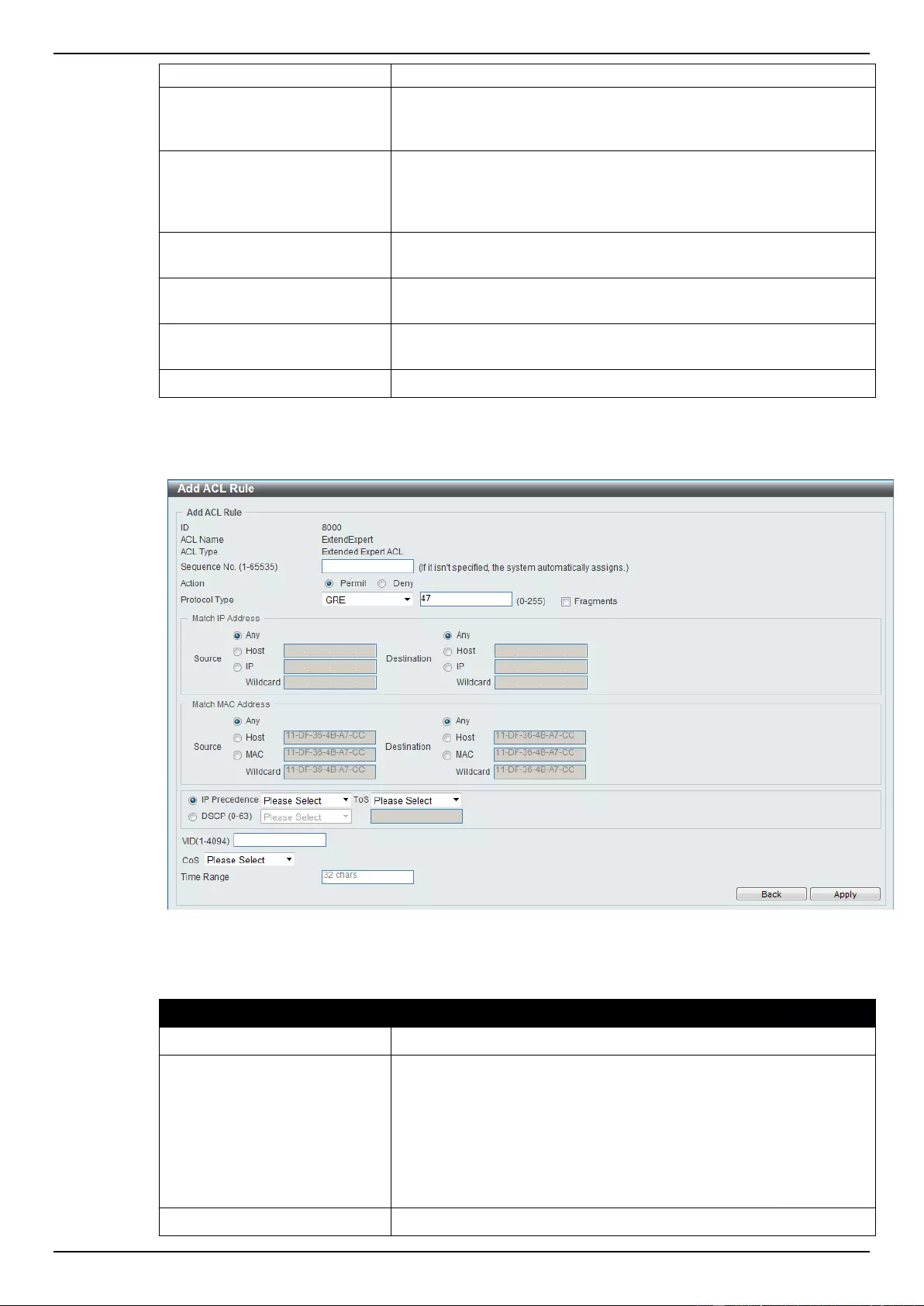
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
254
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the GRE option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-92 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) GRE window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
255
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the IGMP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
256
Figure 8-93 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) IGMP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
257
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the OSPF option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-94 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) OSPF window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
258
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the PIM option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
259
Figure 8-95 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) PIM window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
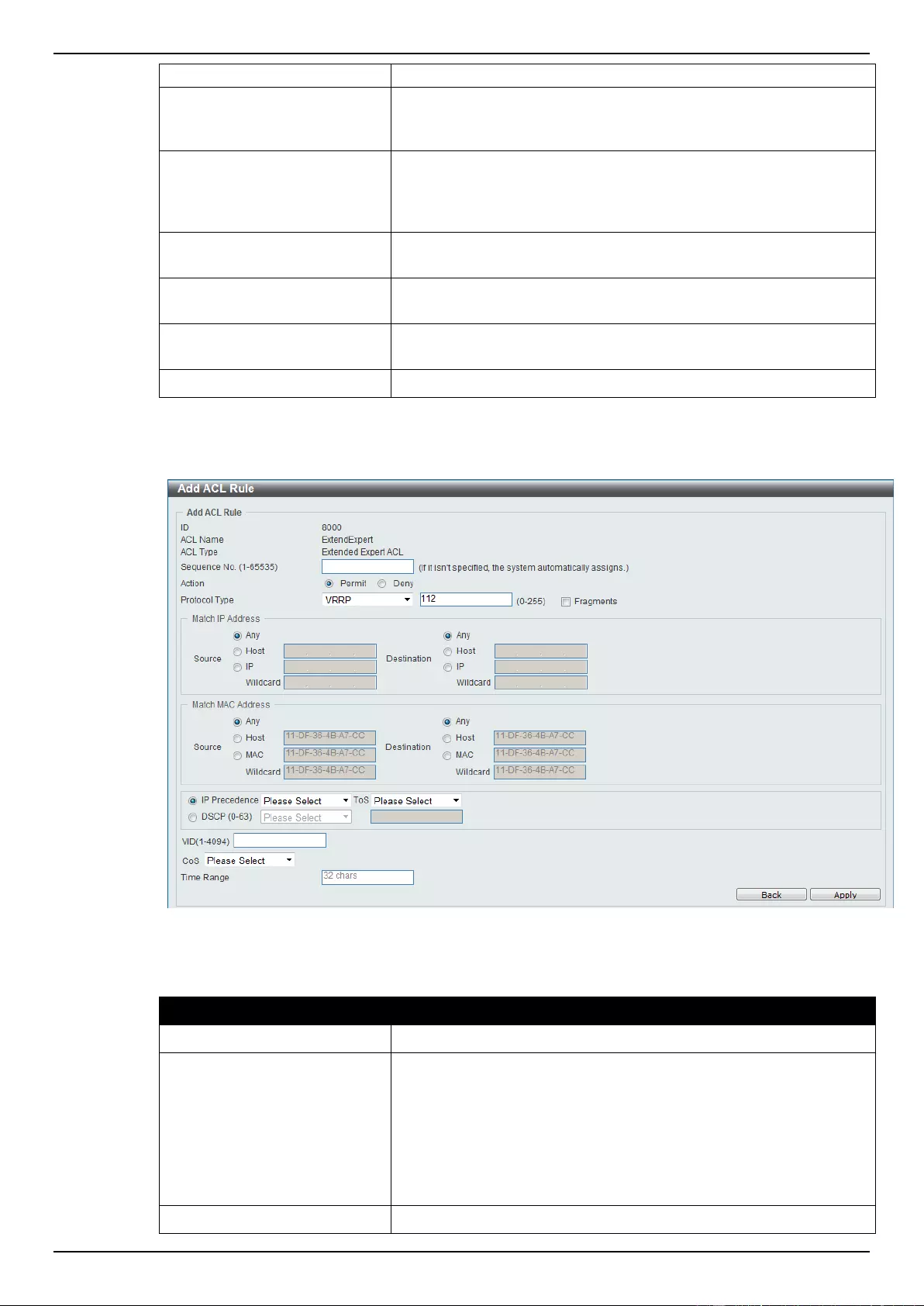
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
260
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the VRRP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-96 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) VRRP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
261
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the IP-in-IP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
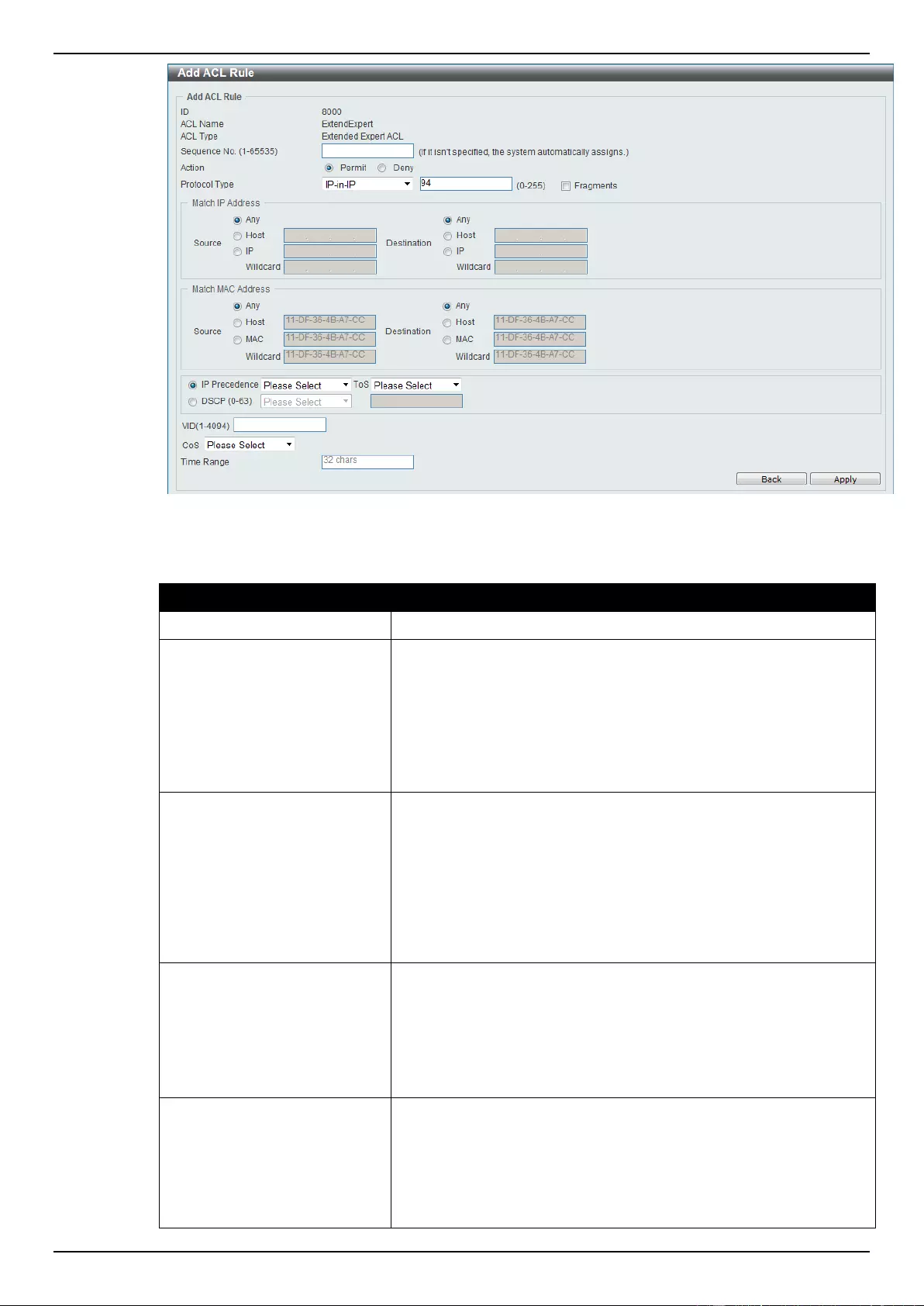
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
262
Figure 8-97 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) IP-in-IP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
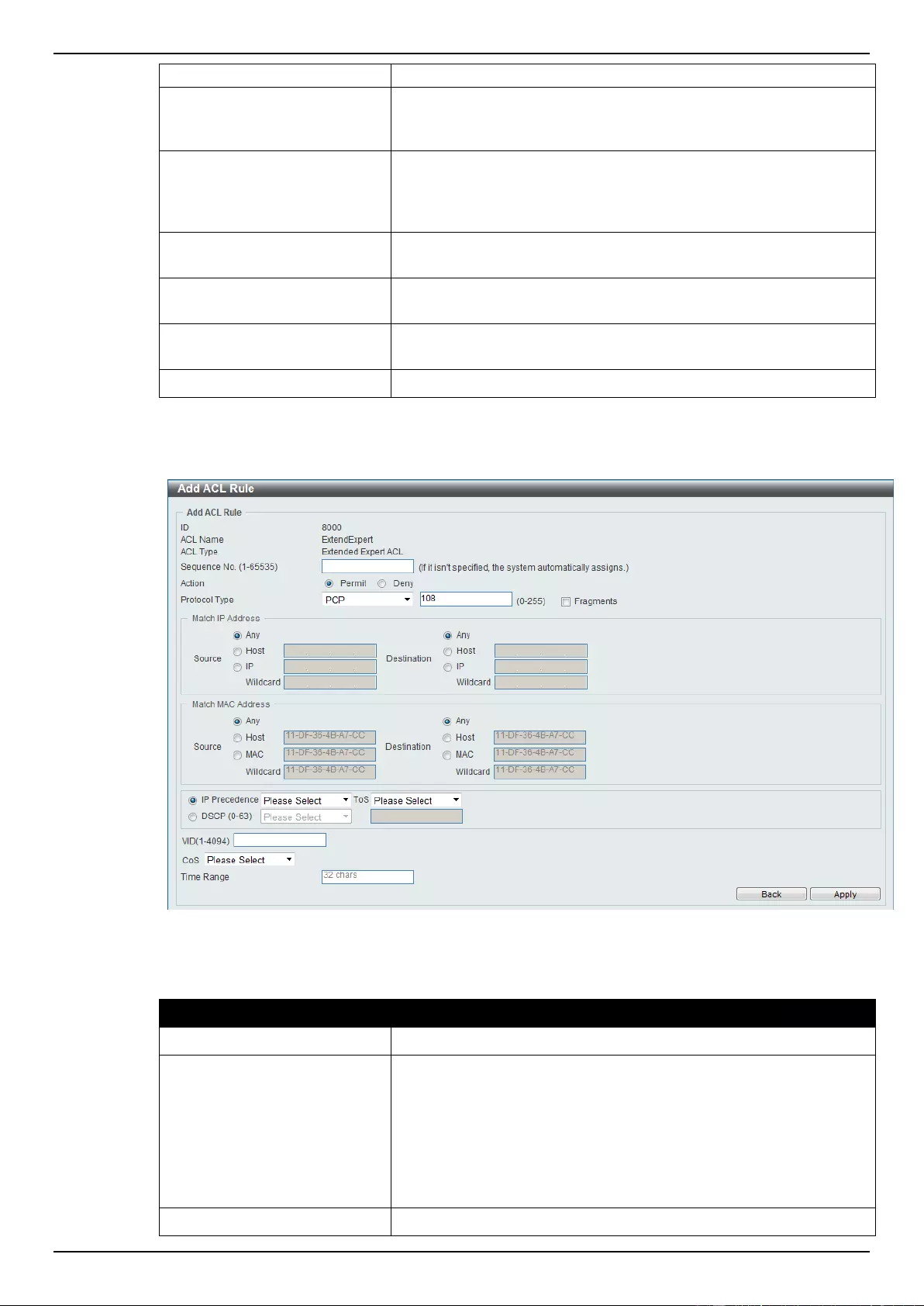
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
263
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the PCP option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-98 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) PCP window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
264
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the Protocol ID option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will
be available, as shown below:
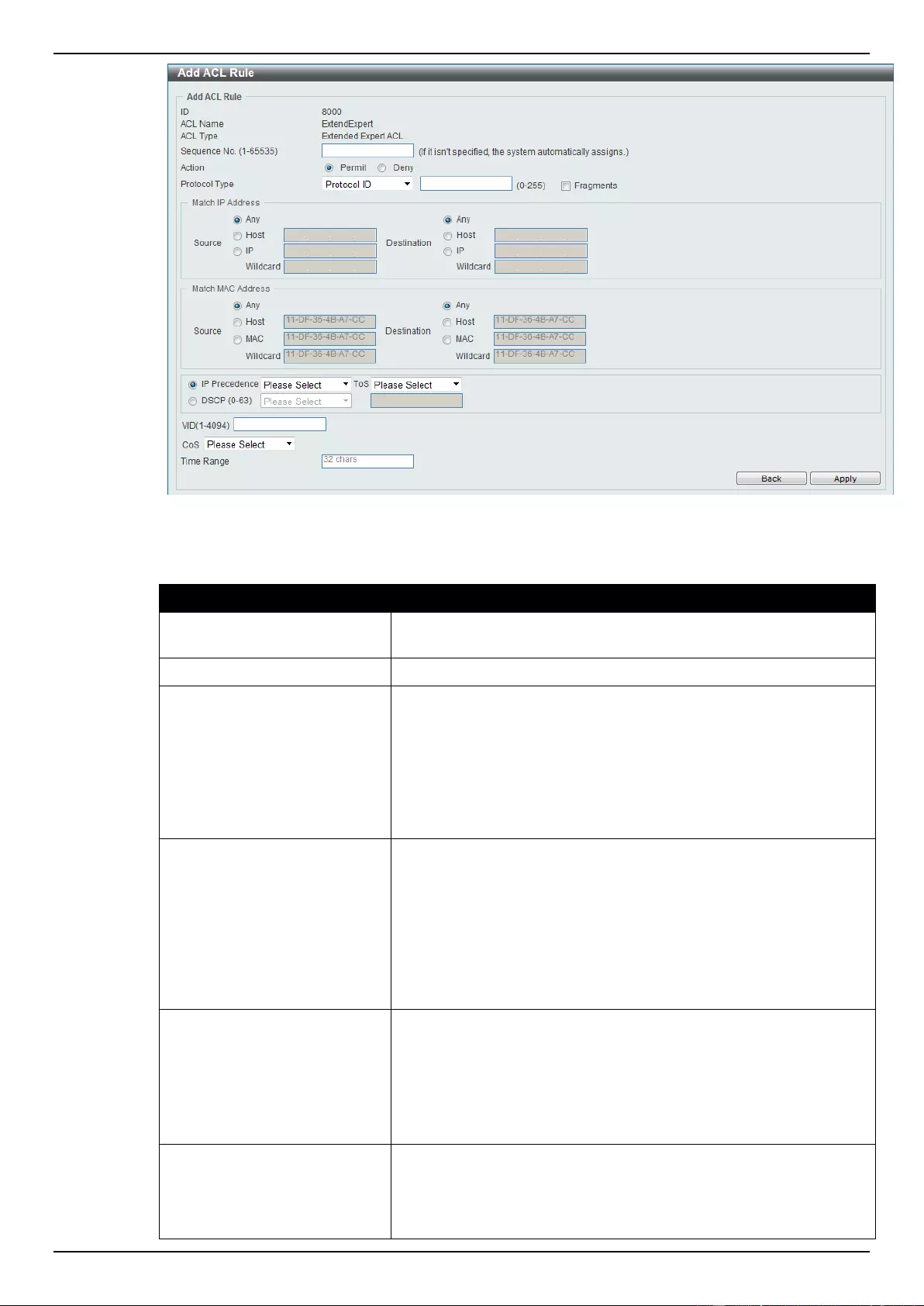
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
265
Figure 8-99 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) Protocol ID window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Enter the Protocol ID value used here. This value must be between
0 and 255.
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
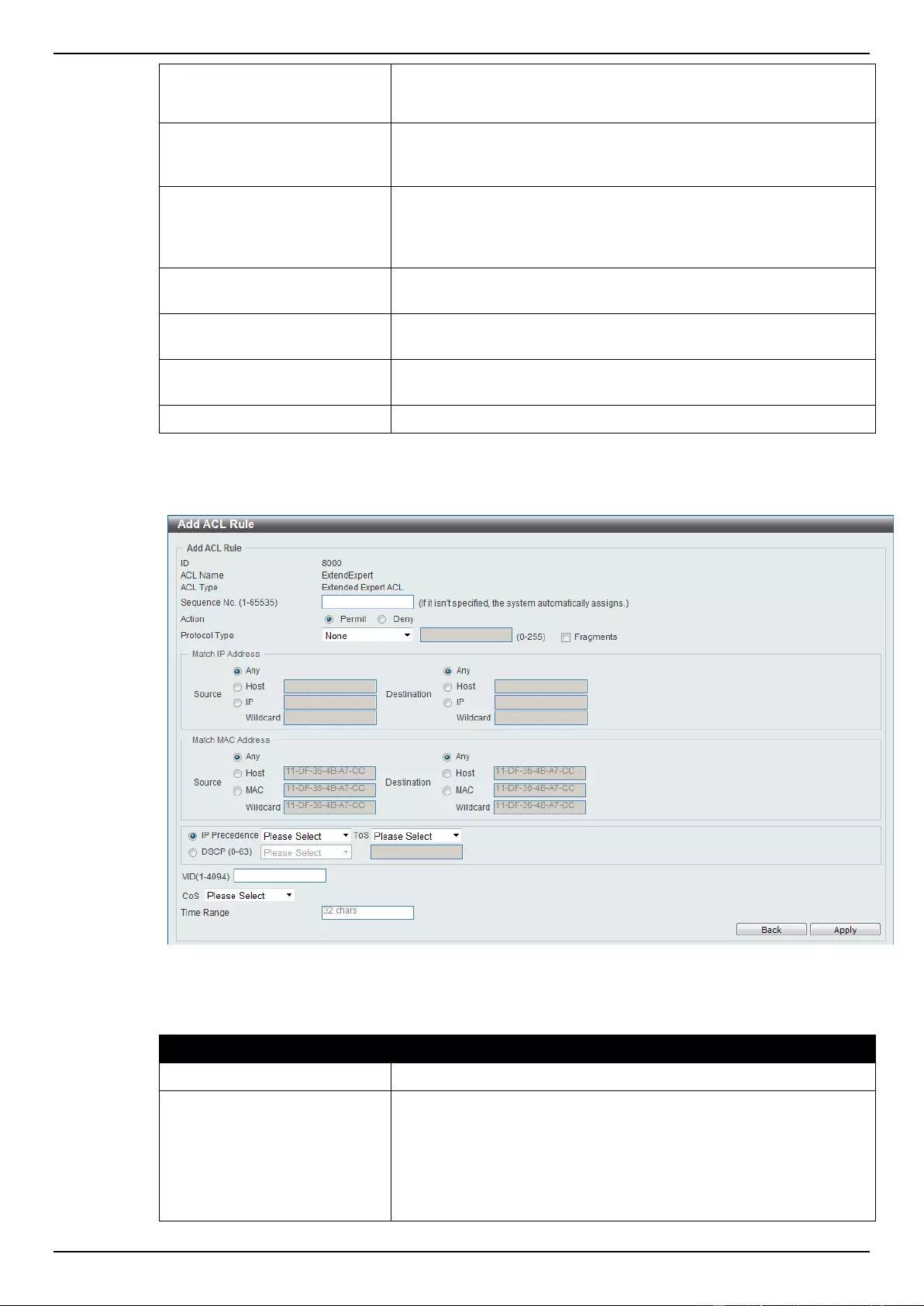
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
266
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
After selecting the None option as the Protocol Type, the following page and parameters will be
available, as shown below:
Figure 8-100 Extended Expert ACL (Add Rule) None window
The dynamic fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Fragments
Select the Fragments option to include packet fragment filtering.
Source IP Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is selected, any
source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of this
rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s IP
address here. When the IP option is selected, the Wildcard option
will also be available. Enter the group of source IP addresses by
using a wildcard bitmap. The bit corresponding to the bit value 1 will
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
267
be ignored. The bit corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Destination IP Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and IP. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s IP address here. When the IP option is selected,
the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the group of
destination IP addresses by using a wildcard bitmap. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 1 will be ignored. The bit
corresponding to the bit value 0 will be checked.
Source MAC Address
Select and enter the source information here. Options to choose
from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is selected,
any source traffic will be evaluated according to the conditions of
this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the source host’s
MAC address here. When the MAC option is selected, the Wildcard
option will also be available. Enter the source MAC address and
wildcard value in the spaces provided.
Destination MAC Address
Select and enter the destination information here. Options to
choose from are Any, Host, and MAC. When the Any option is
selected, any destination traffic will be evaluated according to the
conditions of this rule. When the Host option is selected, enter the
destination host’s MAC address here. When the MAC option is
selected, the Wildcard option will also be available. Enter the
destination MAC address and wildcard value in the spaces
provided.
IP Precedence
Select the IP precedence value used here. Options to choose from
are 0 (routine), 1 (priority), 2, (immediate), 3 (flash), 4 (flash-
override), 5 (critical), 6 (internet), and 7 (network).
ToS
After selecting the IP precedence value, select the Type-of-Service
(ToS) value that will be used here. Options to choose from are 0
(normal), 1 (min-monetary-cost), 2 (max-reliability), 3, 4 (max-
throughput), 5, 6, 7, 8 (min-delay), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15.
DSCP
Select or enter the DSCP value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 63.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID that will be associated with this ACL rule here.
This value must be between 1 and 4094.
CoS
Select the Class of Service (CoS) value here. Options to choose
from are from 0 to 7.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with this ACL rule.
Click the Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
To enable the Counter State option or to enter a Remark for the profile, click the Edit button, next to
the specific ACL profile (found in the ACL profile table).
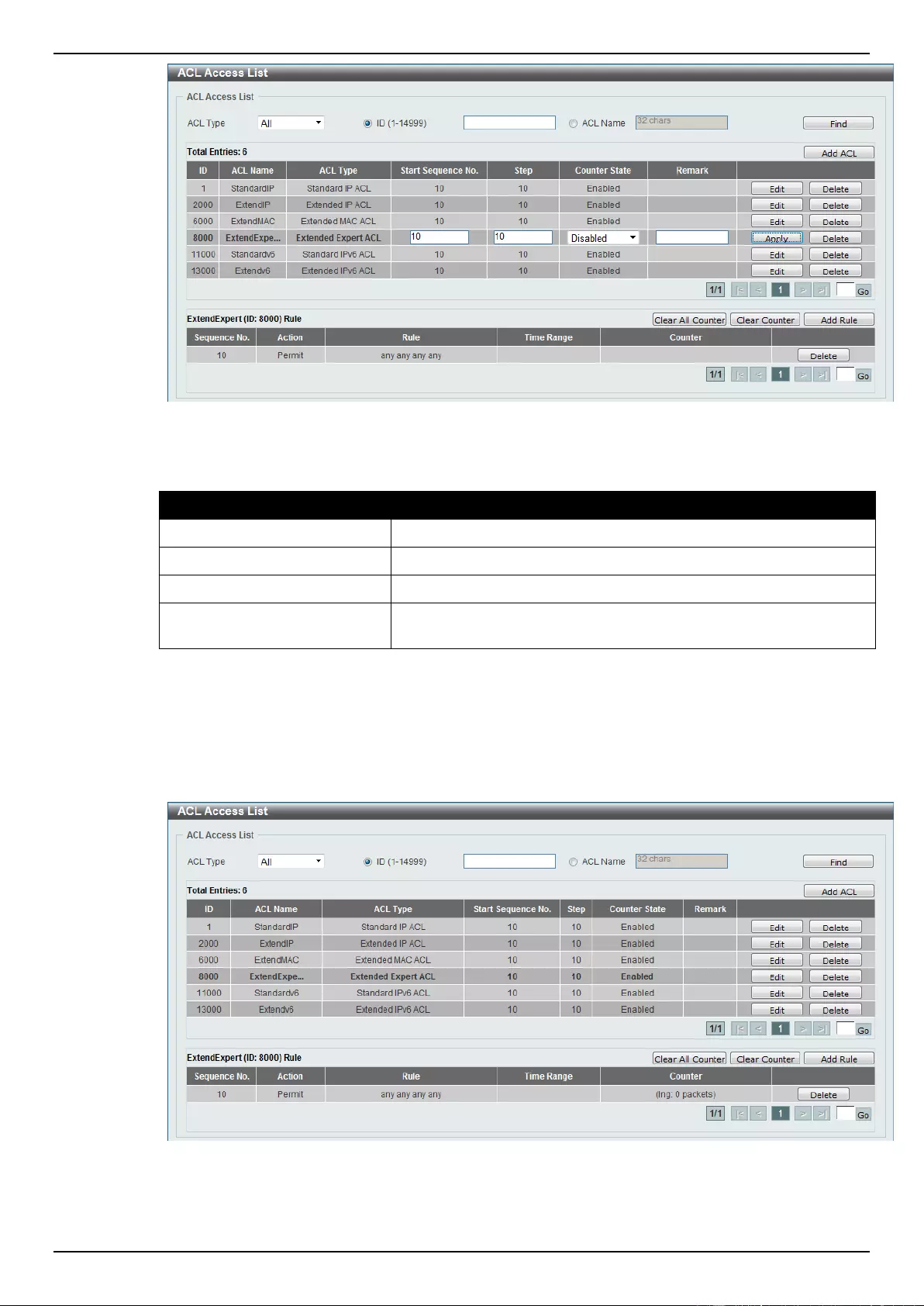
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
268
Figure 8-101 Extended Expert ACL (Edit ACL) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Start Sequence No.
Enter the start sequence number here.
Stop
Enter the stop sequence number here.
Counter State
Select to enable or disable the counter state option here.
Remark
Enter an optional remark that will be associated with this profile
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
To view the list of rules, that are associated with an ACL profile, select the ACL profile (found in the
ACL profile table). The rule of ACL rules, connected to the selected ACL profile, will be displayed in
the ACL rule table, as shown below:
Figure 8-102 Extended Expert ACL (Rule Display) window
Click the Delete button to remove the specific ACL rule.
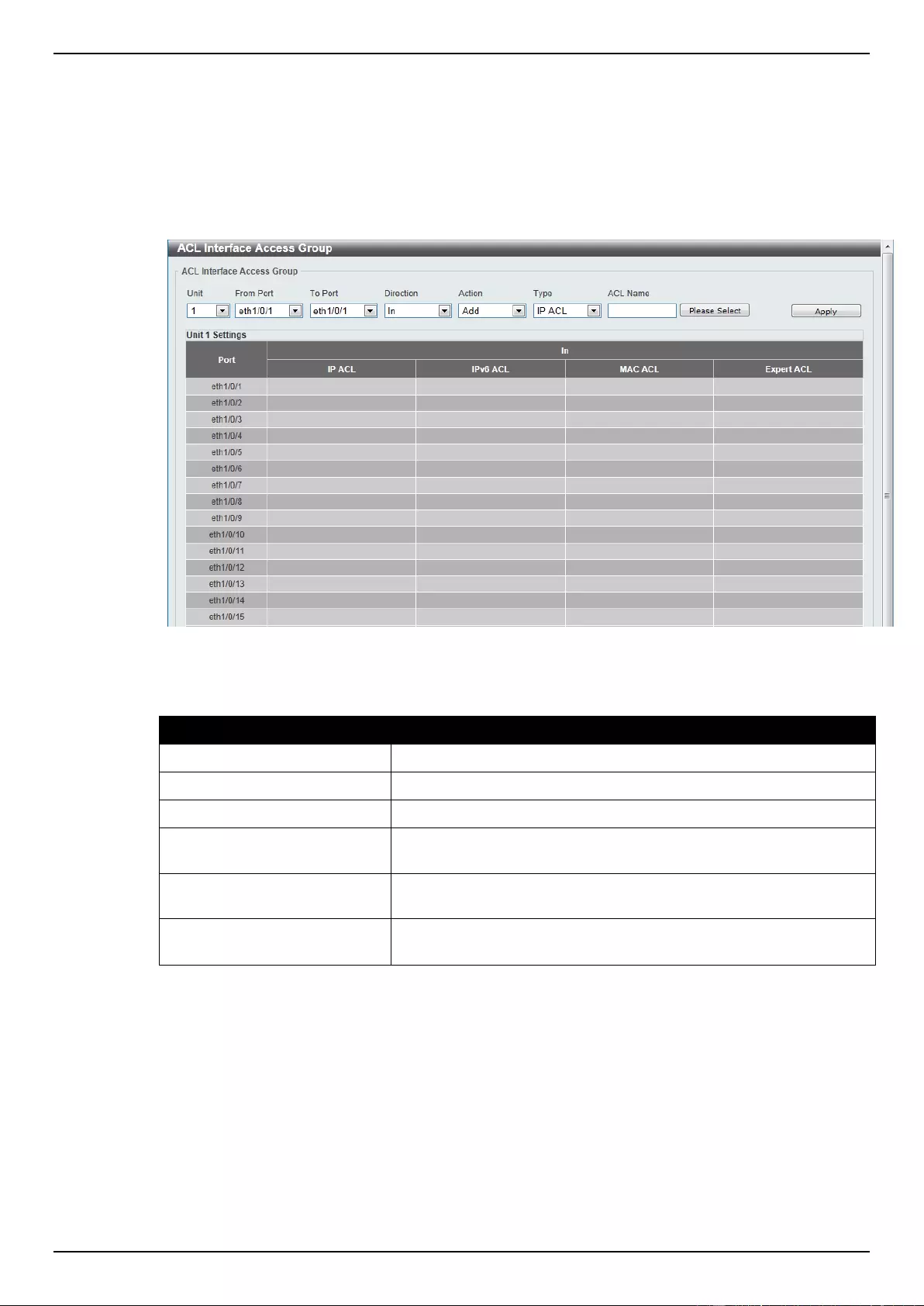
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
269
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
ACL Interface Access Group
This window is used to view and configure the ACL interface access group settings.
To view the following window, click ACL > ACL Interface Access Group, as shown below:
Figure 8-103 ACL Interface Access Group window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Direction
Select the direction here. Option to choose from is In.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the ACL type here. Options to choose from are IP ACL, IPv6
ACL, MAC ACL, and Expert ACL.
ACL Name
Enter the ACL profile’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Please Select button to choose the ACL profile that has been created.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
ACL VLAN Access Map
This window is used to view and configure the ACL VLAN access map settings.
To view the following window, click ACL > ACL VLAN Access Map, as shown below:
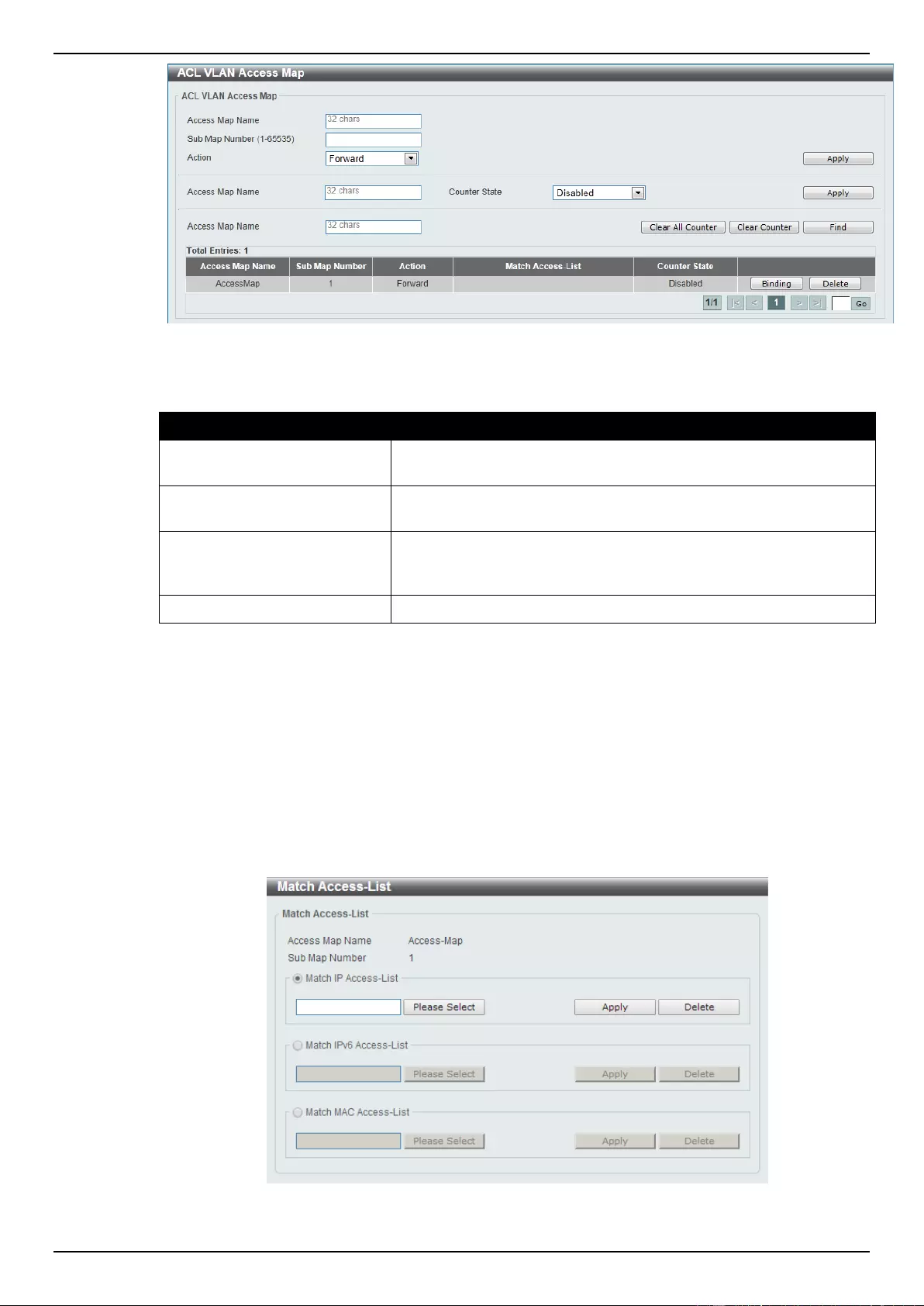
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
270
Figure 8-104 ACL VLAN Access Map window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Access Map Name
Enter the access map’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Sub Map Number
Enter the sub-map’s number here. This value must be between 1
and 65535.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Forward, Drop, and Redirect. When the Redirect option is
selected, select the redirected interface from the drop-down list.
Counter State
Select whether to enable or disable the counter state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Click the Clear All Counter button to clear the counter information for all the access maps.
Click the Clear Counter button to the clear the counter information for the specified access map.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Binding button to configure a new match access list.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
After clicking the Binding button, the following page will appear.
Figure 8-105 Match Access-List window
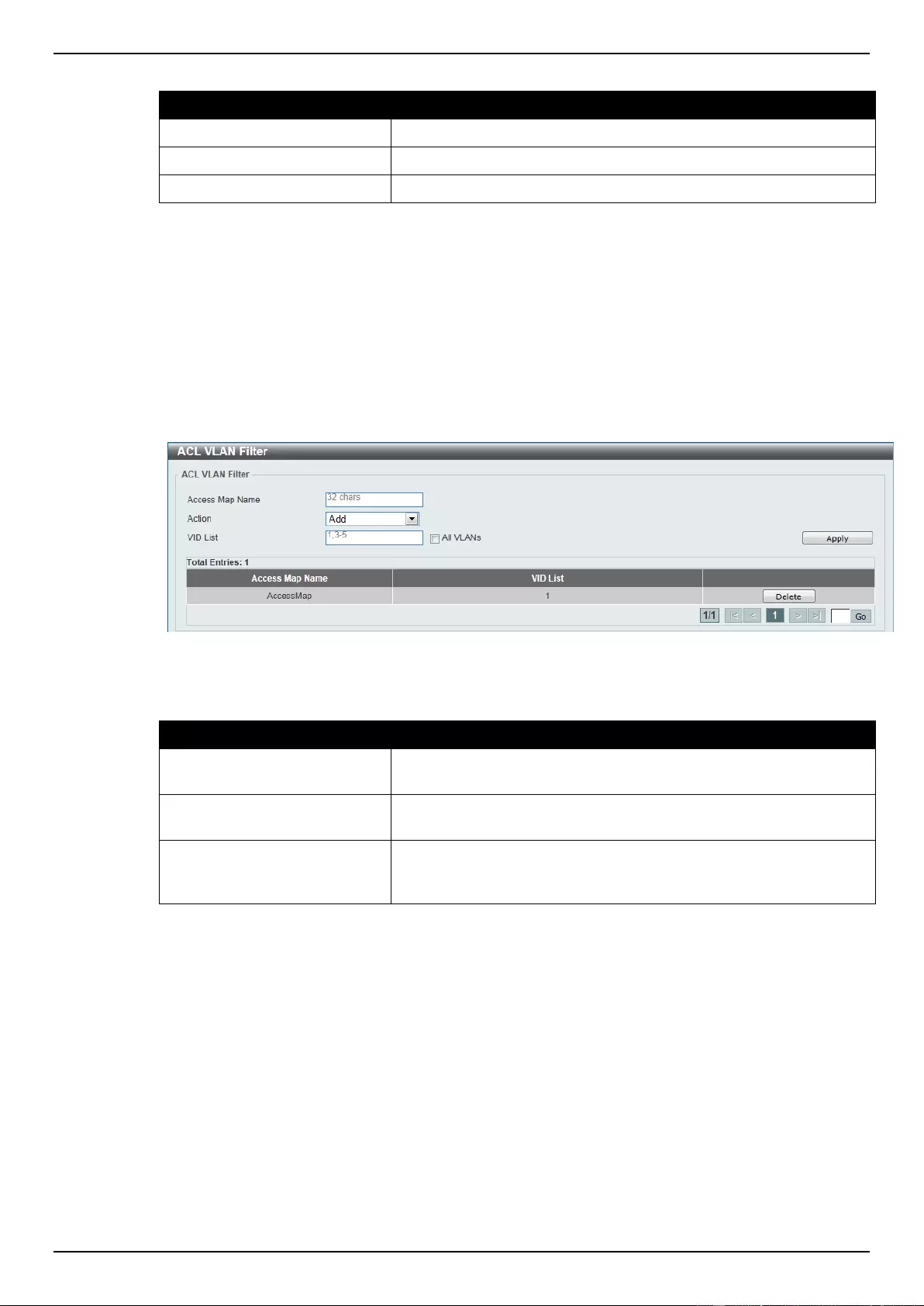
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
271
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Match IP Access-List
Select the standard or extended IP ACL.
Match IPv6 Access-List
Select the standard or extended IPv6 ACL.
Match MAC Access-List
Select the standard or extended MAC ACL.
Click the Please Select button to choose the ACL profile that has been created.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
ACL VLAN Filter
This window is used to view and configure the ACL VLAN filter settings.
To view the following window, click ACL > ACL VLAN Filter, as shown below:
Figure 8-106 ACL VLAN Filter window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Access Map Name
Enter the access map’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list that will be used here. Select the All VLANs
option to apply this configuration to all the VLANs configured on this
switch.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
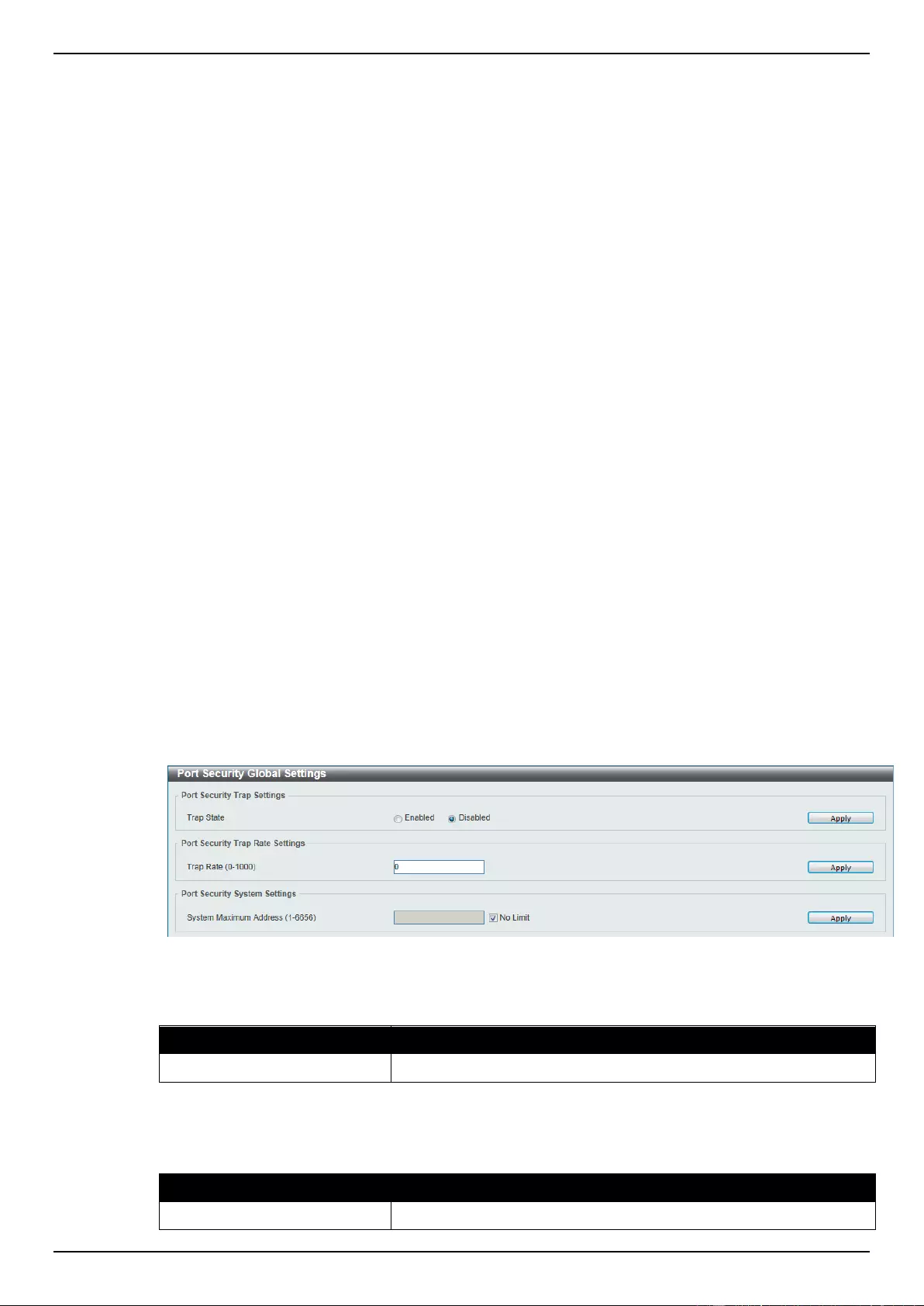
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
272
9. Security
Port Security
802.1X
AAA
RADIUS
TACACS
IMPB
DHCP Server Screening
ARP Spoofing Prevention
BPDU Attack Protection
MAC Authentication
Web-based Access Control
Japanese Web-based Access Control
Network Access Authentication
Safeguard Engine
Trusted Host
Traffic Segmentation Settings
Storm Control
DoS Attack Prevention Settings
SSH
SSL
Port Security
Port Security Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the port security global settings. Port Security is a security
feature that prevents unauthorized computers (with source MAC addresses) unknown to the Switch
prior to locking the port (or ports) from connecting to the Switch's locked ports and gaining access to
the network.
To view the following window, click Security > Port Security > Port Security Global Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 9-1 Port Security Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Port Security Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap State
Click to enable or disable port security traps on the Switch.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Port Security Trap Rate Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap Rate
Enter the number of traps per second. The range is from 0 to 1000.
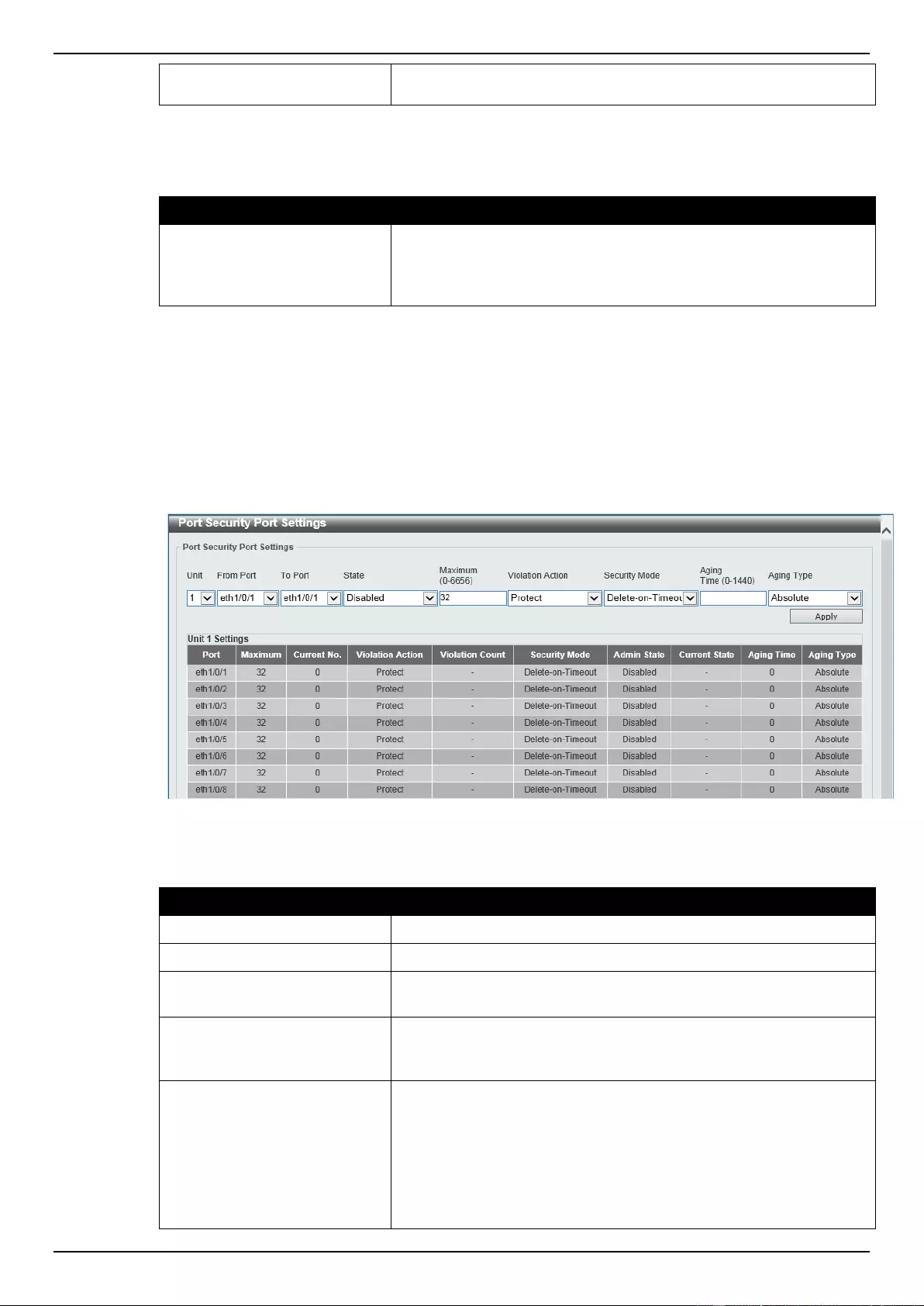
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
273
The default value 0 indicates an SNMP trap to be generated for
every security violation.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Port Security System Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
System Maximum Address
Enter the maximum number of secure MAC addresses allowed. If
not specified, the default value is No Limit. The valid range is from 1
to 6656. Tick the No Limit checkbox to allow the maximum number
of secure MAC address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Port Security Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the port security port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Port Security > Port Security Port Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 9-2 Port Security Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the port security feature on the port(s)
specified.
Maximum
Enter the maximum number of secure MAC addresses that will be
allowed on the port(s) specified. This value must be between 0 and
6656. By default, this value is 32.
Violation Action
Select the violation action that will be taken here. Options to choose
from are Protect, Restrict, and Shutdown. Selecting Protect
specifies to drop all packets from the insecure hosts at the port-
security process level, but does not increment the security-violation
count. Selecting Restrict specifies to drop all packets from the
insecure hosts at the port-security process level and increments the
security-violation count and record the system log. Selecting
Shutdown specifies to shut down the port if there is a security
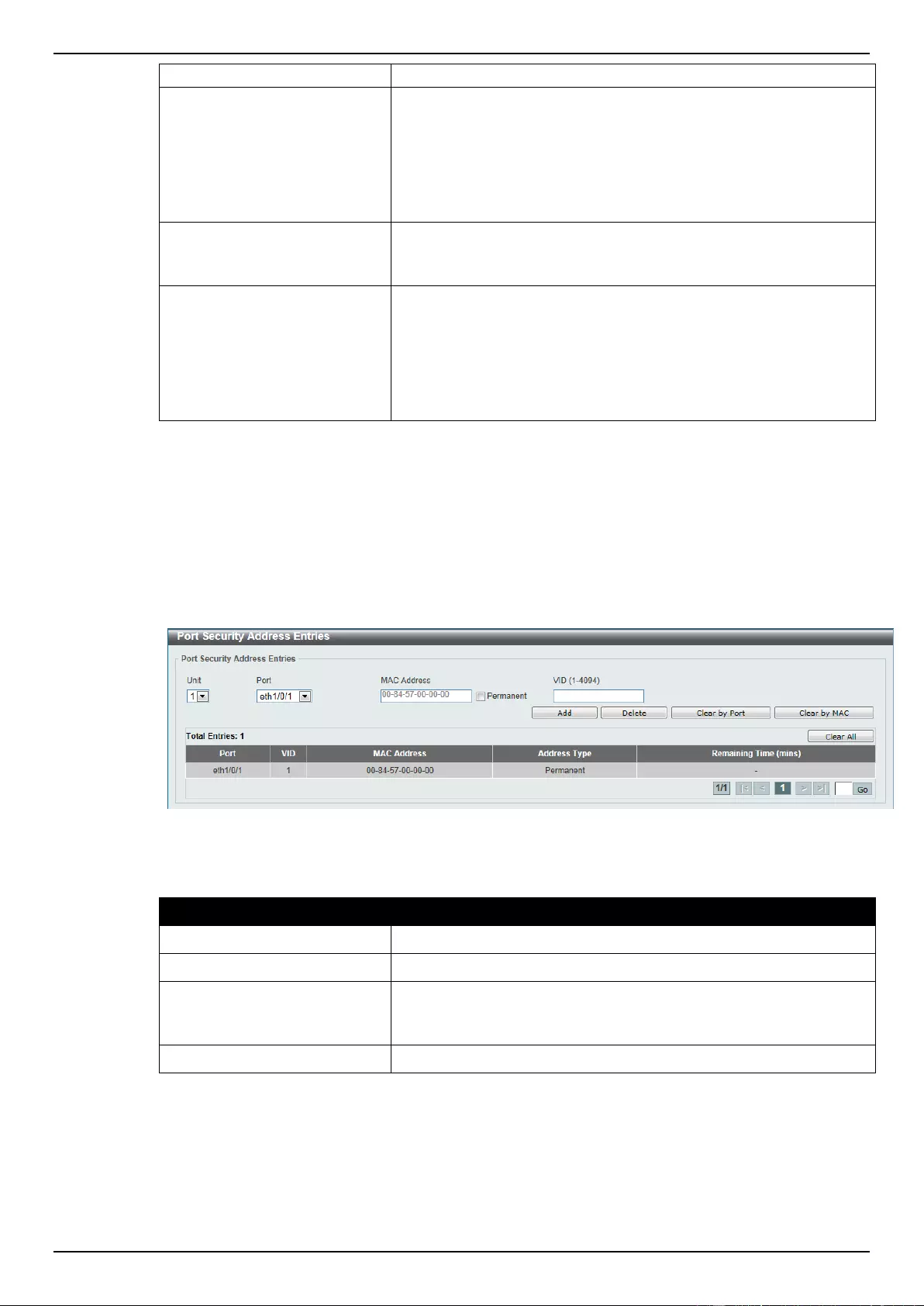
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
274
violation and record the system log.
Security Mode
Select the security mode option here. Options to choose from are
Permanent and Delete-on-Timeout. Selecting Permanent
specifies that under this mode, all learned MAC addresses will not
be purged out unless the user manually deletes those entries.
Selecting Delete-on-Timeout specifies that under this mode, all
learned MAC addresses will be purged out when an entry is aged
out or when the user manually deletes these entries.
Aging Time
Enter the aging time value used for auto-learned dynamic secured
addresses on the specified port here. This value must be between 0
and 1440 minutes.
Aging Type
Select the aging type here. Options to choose from are Absolute
and Inactivity. Selecting Absolute specifies that all the secure
addresses on this port age out exactly after the time specified and is
removed from the secure address list. This is the default type.
Selecting Inactivity specifies that the secure addresses on this port
age out only if there is no data traffic from the secure source
address for the specified time period.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Port Security Address Entries
This window is used to view, clear and configure the port security address entries.
To view the following window, click Security > Port Security > Port Security Address Entries, as
shown below:
Figure 9-3 Port Security Address Entries window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address here. Tick the Permanent check box so
that all learned MAC addresses will not be purged out unless the
user manually deletes those entries.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID here. This value must be between 1 and 4094.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear by Port button to clear the information based on the port selected.
Click the Clear by MAC button to clear the information based on the MAC address entered.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
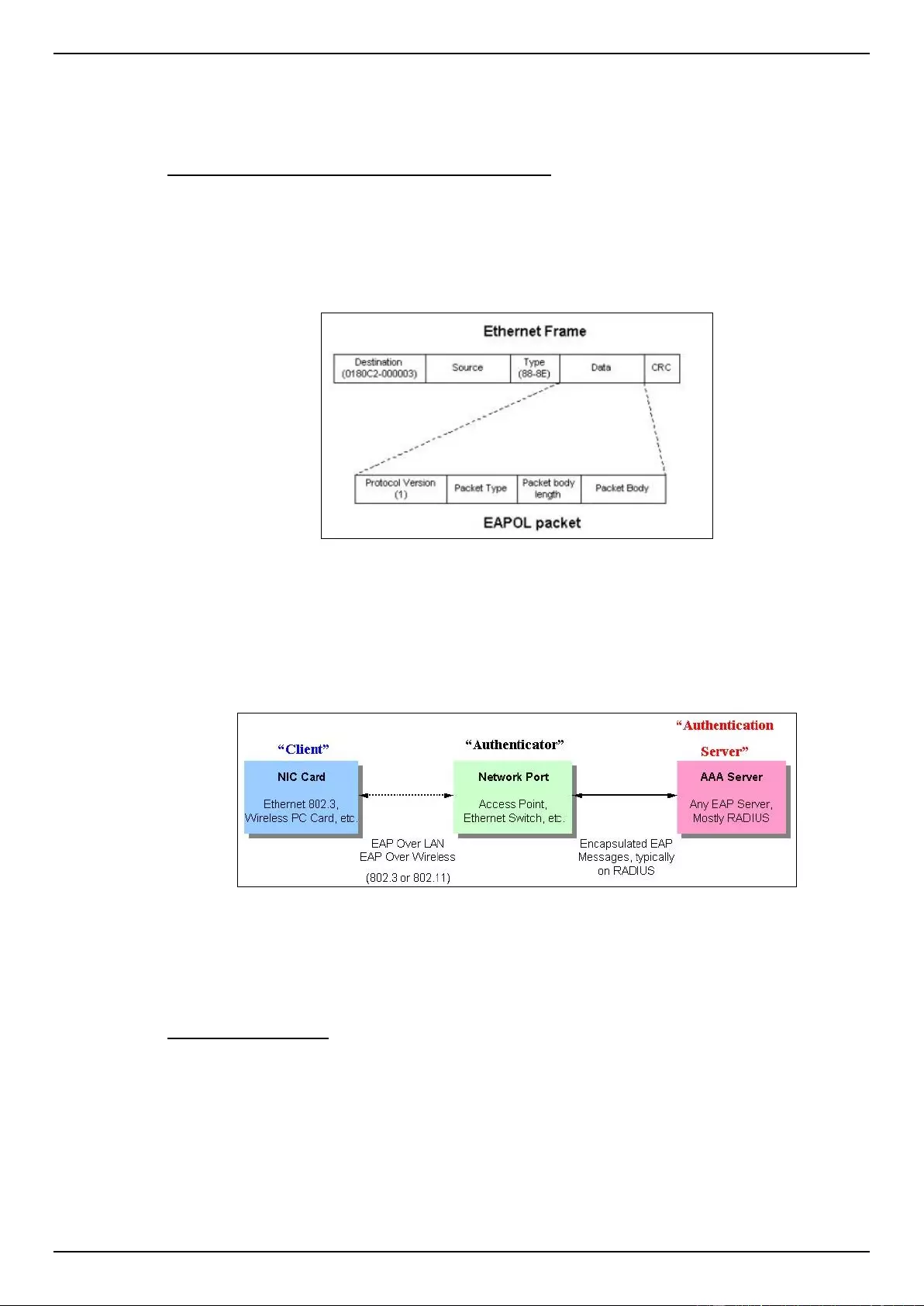
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
275
802.1X
802.1X (Port-based and Host-based Access Control)
The IEEE 802.1X standard is a security measure for authorizing and authenticating users to gain
access to various wired or wireless devices on a specified Local Area Network by using a Client and
Server based access control model. This is accomplished by using a RADIUS server to authenticate
users trying to access a network by relaying Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPOL)
packets between the Client and the Server.
The following figure represents a basic EAPOL packet:
Figure 9-4 The EAPOL Packet
Utilizing this method, unauthorized devices are restricted from connecting to a LAN through a port to
which the user is connected. EAPOL packets are the only traffic that can be transmitted through the
specific port until authorization is granted. The 802.1X access control method has three roles, each of
which are vital to creating and up keeping a stable and working Access Control security method.
Figure 9-5 The three roles of 802.1X
The following section will explain the three roles of Client, Authenticator and Authentication Server in
greater detail.
Authentication Server
The Authentication Server is a remote device that is connected to the same network as the Client and
Authenticator, must be running a RADIUS Server program and must be configured properly on the
Authenticator (Switch). Clients connected to a port on the Switch must be authenticated by the
Authentication Server (RADIUS) before attaining any services offered by the Switch on the LAN. The
role of the Authentication Server is to certify the identity of the Client attempting to access the network
by exchanging secure information between the RADIUS server and the Client through EAPOL
packets and, in turn, informs the Switch whether or not the Client is granted access to the LAN and/or
switches services.
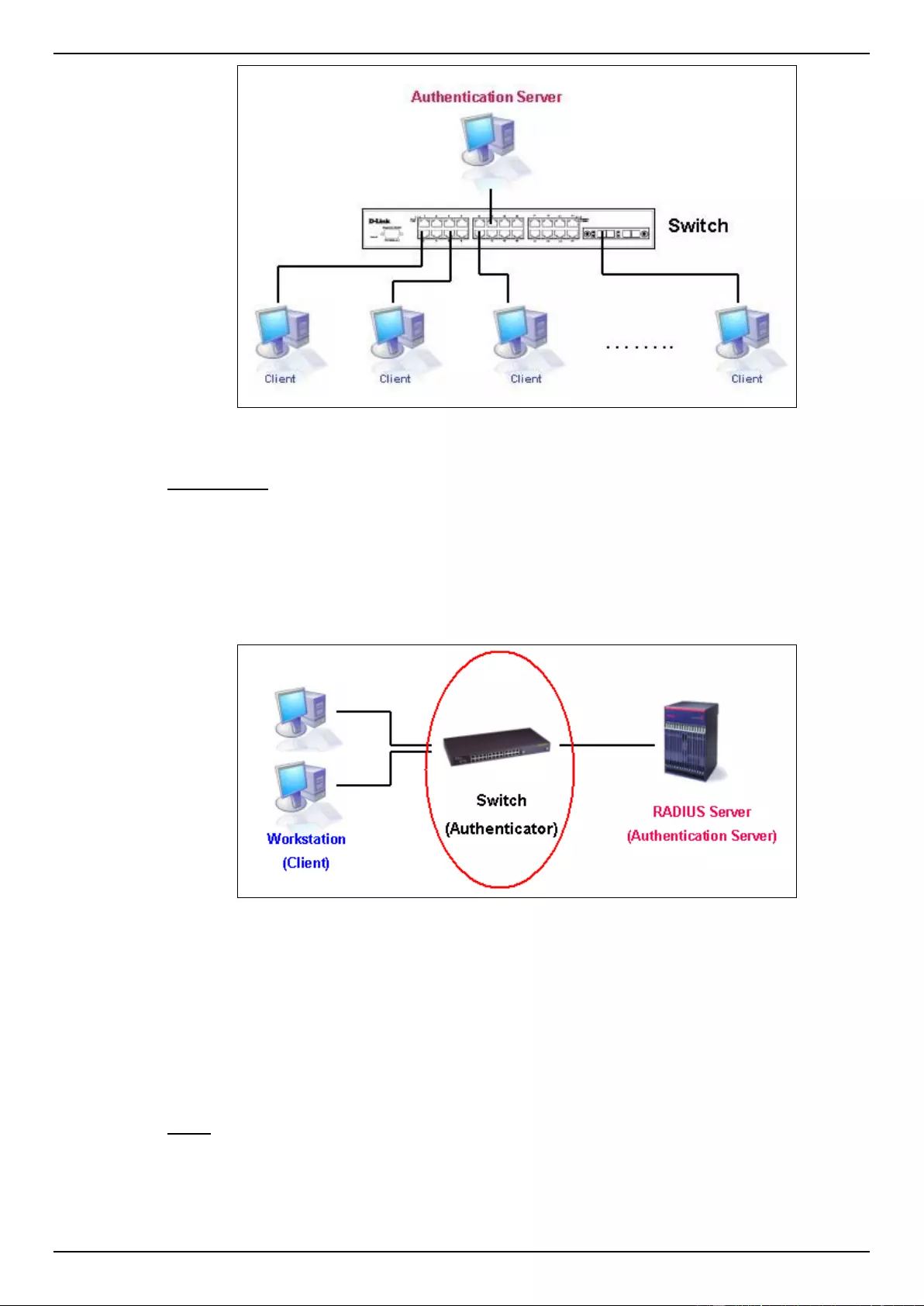
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
276
Figure 9-6 The Authentication Server
Authenticator
The Authenticator (the Switch) is an intermediary between the Authentication Server and the Client.
The Authenticator serves two purposes when utilizing the 802.1X function. The first purpose is to
request certification information from the Client through EAPOL packets, which is the only information
allowed to pass through the Authenticator before access is granted to the Client. The second purpose
of the Authenticator is to verify the information gathered from the Client with the Authentication Server,
and to then relay that information back to the Client.
Figure 9-7 The Authenticator
Three steps must be implemented on the Switch to properly configure the Authenticator.
The 802.1X State must be Enabled. (Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Global Settings)
The 802.1X settings must be implemented by port (Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Port
Settings)
A RADIUS server must be configured on the Switch. (Security > RADIUS > RADIUS Server
Settings)
Client
The Client is simply the end station that wishes to gain access to the LAN or switch services. All end
stations must be running software that is compliant with the 802.1X protocol. For users running
windows XP and windows Vista, that software is included within the operating system. All other users
are required to attain 802.1X client software from an outside source. The Client will request access to
the LAN and or Switch through EAPOL packets and, in turn will respond to requests from the Switch.
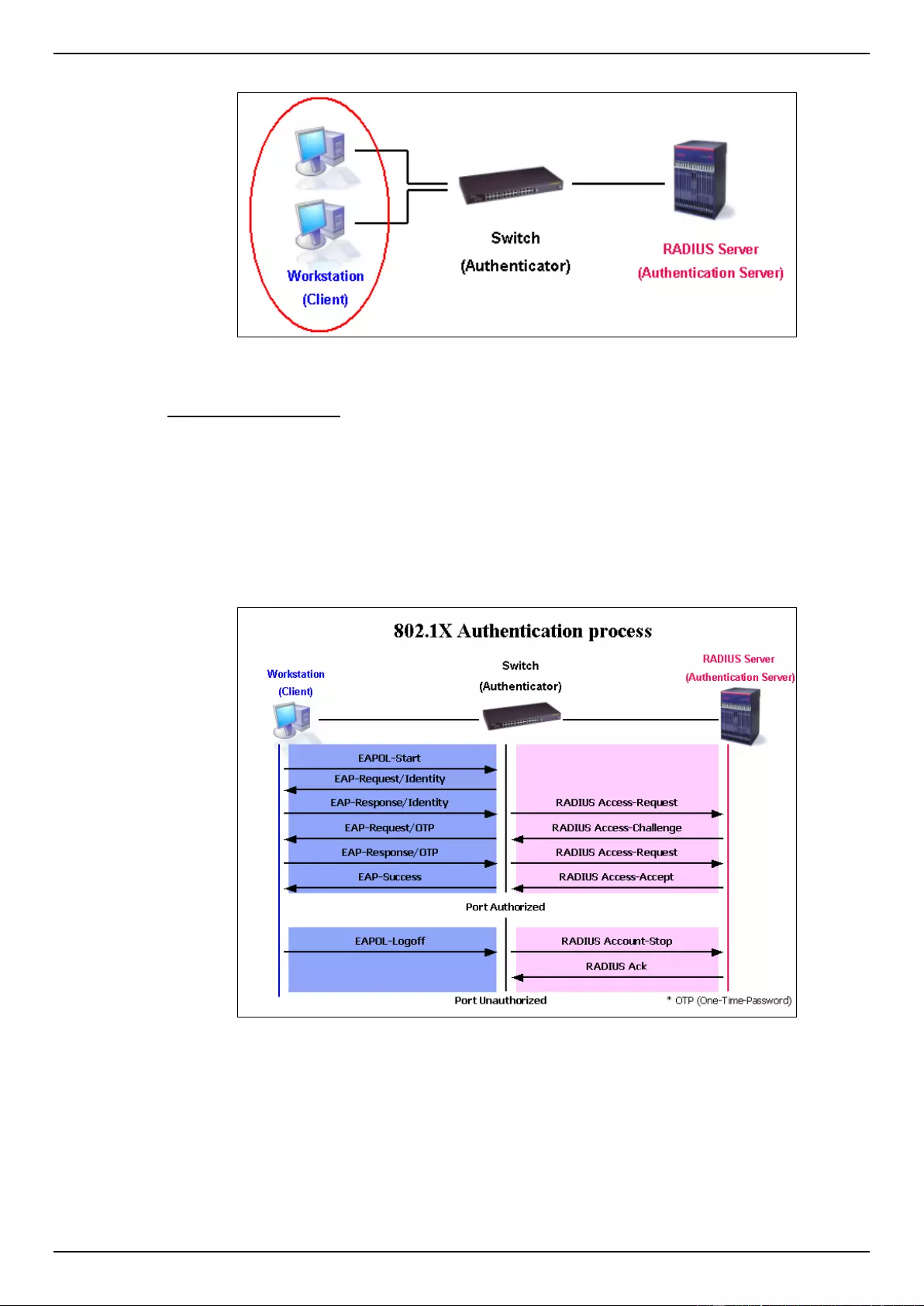
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
277
Figure 9-8 The Client
Authentication Process
Utilizing the three roles stated above, the 802.1X protocol provides a stable and secure way of
authorizing and authenticating users attempting to access the network. Only EAPOL traffic is allowed
to pass through the specified port before a successful authentication is made. This port is “locked”
until the point when a Client with the correct username and password (and MAC address if 802.1X is
enabled by MAC address) is granted access and therefore successfully “unlocks” the port. Once the
port is unlocked, normal traffic is allowed to pass through the port. The following figure displays a
more detailed explanation of how the authentication process is completed between the three roles
stated above.
Figure 9-9 The 802.1X Authentication Process
The D-Link implementation of 802.1X allows network administrators to choose between two types of
Access Control used on the Switch, which are:
Port-based Access Control – This method requires only one user to be authenticated per
port by a remote RADIUS server to allow the remaining users on the same port access to the
network.
Host-based Access Control – Using this method, the Switch will automatically learn up to a
maximum of 448 MAC addresses by port and set them in a list. Each MAC address must be
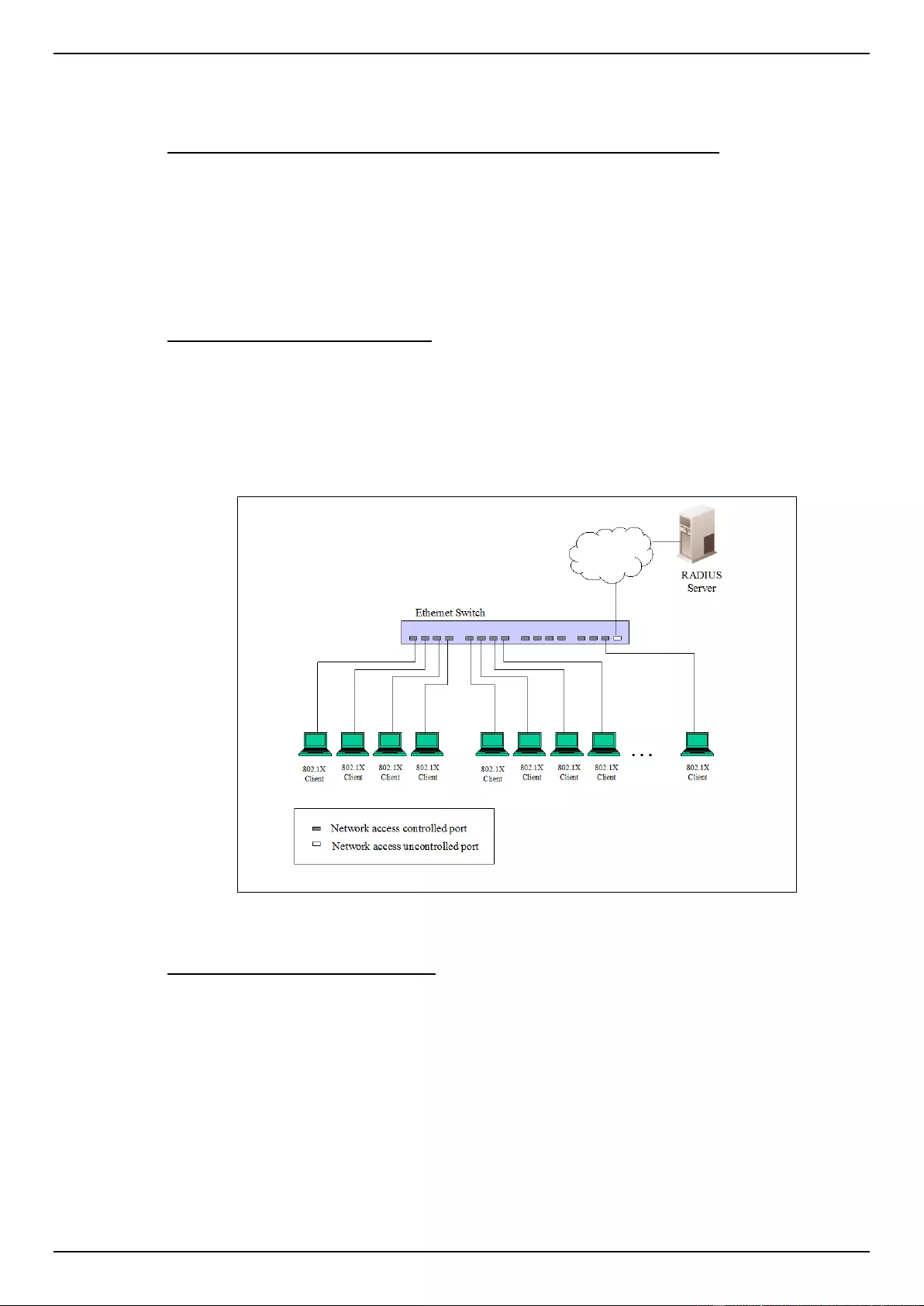
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
278
authenticated by the Switch using a remote RADIUS server before being allowed access to
the Network.
Understanding 802.1X Port-based and Host-based Network Access Control
The original intent behind the development of 802.1X was to leverage the characteristics of point-to-
point in LANs. As any single LAN segment in such infrastructures has no more than two devices
attached to it, one of which is a Bridge Port. The Bridge Port detects events that indicate the
attachment of an active device at the remote end of the link, or an active device becoming inactive.
These events can be used to control the authorization state of the Port and initiate the process of
authenticating the attached device if the Port is unauthorized. This is the Port-based Network Access
Control.
Port-based Network Access Control
Once the connected device has successfully been authenticated, the Port then becomes Authorized,
and all subsequent traffic on the Port is not subject to access control restriction until an event occurs
that causes the Port to become Unauthorized. Hence, if the Port is actually connected to a shared
media LAN segment with more than one attached device, successfully authenticating one of the
attached devices effectively provides access to the LAN for all devices on the shared segment.
Clearly, the security offered in this situation is open to attack.
Figure 9-10 Example of Typical Port-based Configuration
Host-based Network Access Control
In order to successfully make use of 802.1X in a shared media LAN segment, it would be necessary
to create “logical” Ports, one for each attached device that required access to the LAN. The Switch
would regard the single physical Port connecting it to the shared media segment as consisting of a
number of distinct logical Ports, each logical Port being independently controlled from the point of
view of EAPOL exchanges and authorization state. The Switch learns each attached devices’
individual MAC addresses, and effectively creates a logical Port that the attached device can then use
to communicate with the LAN via the Switch.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
279
Figure 9-11 Example of Typical Host-based Configuration
802.1X Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the 802.1X global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-12 802.1X Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
802.1X State
Select to enable or disable the 802.1X global state here.
802.1X Trap State
Select to enable or disable the 802.1X trap state here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
802.1X Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the 802.1X port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Port Settings, as shown below:
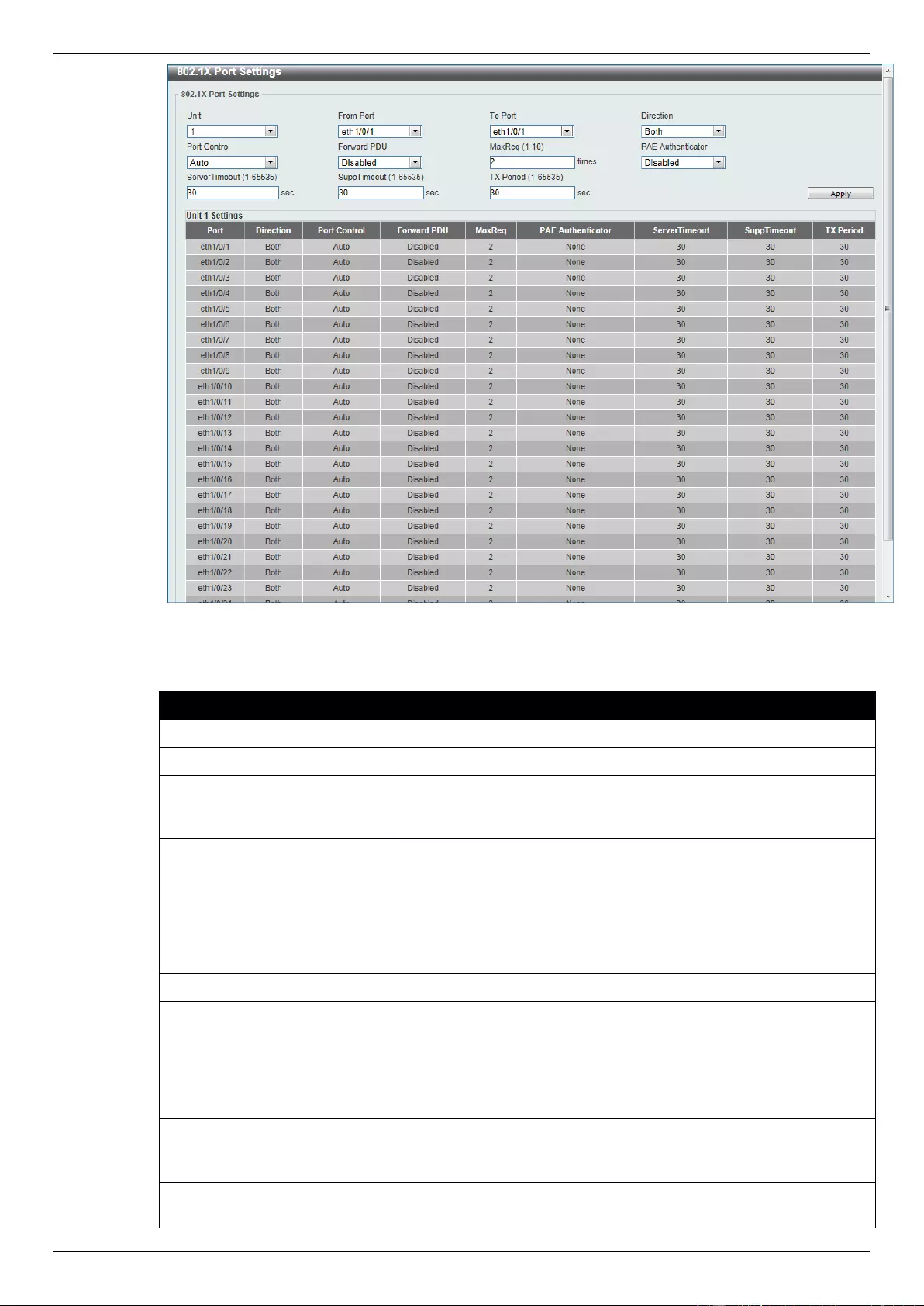
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
280
Figure 9-13 802.1X Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Direction
Select the direction here. Options to choose from are Both and In.
This option configures the direction of the traffic on a controlled port
as unidirectional (In) or bidirectional (Both).
Port Control
Select the port control option here. Options to choose from are
ForceAuthorized, Auto, and ForceUnauthorized. If the port
control is set to force-authorized, then the port is not controlled in
both directions. If the port control is set to automatic, then the
access to the port for the controlled direction needs to be
authenticated. If the port control is set to force-unauthorized, then
the access to the port for the controlled direction is blocked.
Forward PDU
Select to enable or disable the forward PDU option here.
MaxReq
Enter the maximum required times value here. This value must be
between 1 and 10. By default, this option is 2. This option
configures the maximum number of times that the backend
authentication state machine will retransmit an Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) request frame to the supplicant
before restarting the authentication process.
PAE Authenticator
Select to enable or disable the PAE authenticator option here. This
option configures a specific port as an IEEE 802.1X port access
entity (PAE) authenticator.
Server Timeout
Enter the server timeout value here. This value must be between 1
and 65535 seconds. By default, this value is 30 seconds.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
281
Supp Timeout
Enter the supplicant timeout value here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535 seconds. By default, this value is 30 seconds.
TX Period
Enter the transmission period value here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535 seconds. By default, this value is 30 seconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Authentication Session Information
This window is used to view and configure the authentication session information.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > Authentication Session Information, as
shown below:
Figure 9-14 Authentication Session Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Init by Port button to initiate the session information based on the selections made.
Click the ReAuth by Port button to re-authenticate the session information based on the selections
made.
Authenticator Statistics
This window is used to view and clear the authenticator statistics.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > Authenticator Statistics, as shown below:
Figure 9-15 Authenticator Statistics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this query here.
Port
Select the appropriate port used for the query here.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
282
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear Counters button to clear the counter information based on the selections made.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Authenticator Session Statistics
This window is used to view and clear the authenticator session statistics.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > Authenticator Session Statistics, as
shown below:
Figure 9-16 Authenticator Session Statistics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this query here.
Port
Select the appropriate port used for the query here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Clear Counters button to clear the counter information based on the selections made.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Authenticator Diagnostics
This window is used to view and clear the authenticator diagnostics information.
To view the following window, click Security > 802.1X > Authenticator Diagnostics, as shown
below:
Figure 9-17 Authenticator Diagnostics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this query here.
Port
Select the appropriate port used for the query here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
283
Click the Clear Counters button to clear the counter information based on the selections made.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
AAA
AAA Global Settings
This window is used to enable or disable the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
global state.
To view the following window, click Security > AAA > AAA Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-18 AAA Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
AAA State
Select to enable or disable the Authentication, Authorization, and
Accounting (AAA) global state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Application Authentication Settings
This window is used to view and configure the application authentication settings.
To view the following window, click Security > AAA > Application Authentication Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 9-19 Application Authentication Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Login Method List
After clicking the Edit button for the specific entry, enter the login
method list name used here.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
284
Application Accounting Settings
This window is used to view and configure the application accounting settings.
To view the following window, click Security > AAA > Application Accounting Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 9-20 Application Accounting Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Exec Method List
After clicking the Edit button for the specific entry, enter the EXEC
method list name used here.
Application
Select the application used here. Options to choose from are
Console, Telnet, and SSH.
Level
Select the privilege level used here. Options to choose from are
levels 1 to 15.
Commands Method List
Enter the commands method list name used here.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Authentication Settings
This window is used to view and configure the AAA network and EXEC authentication settings.
To view the following window, click Security > AAA > Authentication Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
285
Figure 9-21 Authentication Settings window
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication 802.1X are described below:
Parameter
Description
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA 802.1X authentication state
here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, local, group and radius.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication JWAC are described below:
Parameter
Description
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA JWAC authentication state
here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, local, group and radius.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication MAC-Auth are described below:
Parameter
Description
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA MAC authentication state here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, local, group and radius.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication WEB-Auth are described below:
Parameter
Description
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA Web authentication state here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, local, group and radius.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
286
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After clicking the AAA Authentication Exec tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 9-22 AAA Authentication Exec window
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication Enable are described below:
Parameter
Description
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA authentication enable state
here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, enable, group, radius, and
tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for AAA Authentication Login are described below:
Parameter
Description
List Name
Enter the method list name that will be used with the AAA
authentication login option here.
Status
Select to enable or disable the AAA authentication login state here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, enable, group, radius, and
tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Accounting Settings
This window is used to view and configure the AAA accounting settings.
To view the following window, click Security > AAA > Accounting Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-23 Accounting Settings window

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
287
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Default
Select to enable or disable the use of the default method list here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, group, radius, and tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After clicking the AAA Accounting System tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 9-24 AAA Accounting System window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Default
Select to enable or disable the use of the default method list here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, group, radius, and tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After clicking the AAA Accounting Exec tab, the following page will appear.
Figure 9-25 AAA Accounting Exec window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
List Name
Enter the method list name that will be used with the AAA
accounting EXEC option here.
Method 1 to 4
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, group, radius, and tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
After clicking the AAA Accounting Commands tab, the following page will appear.
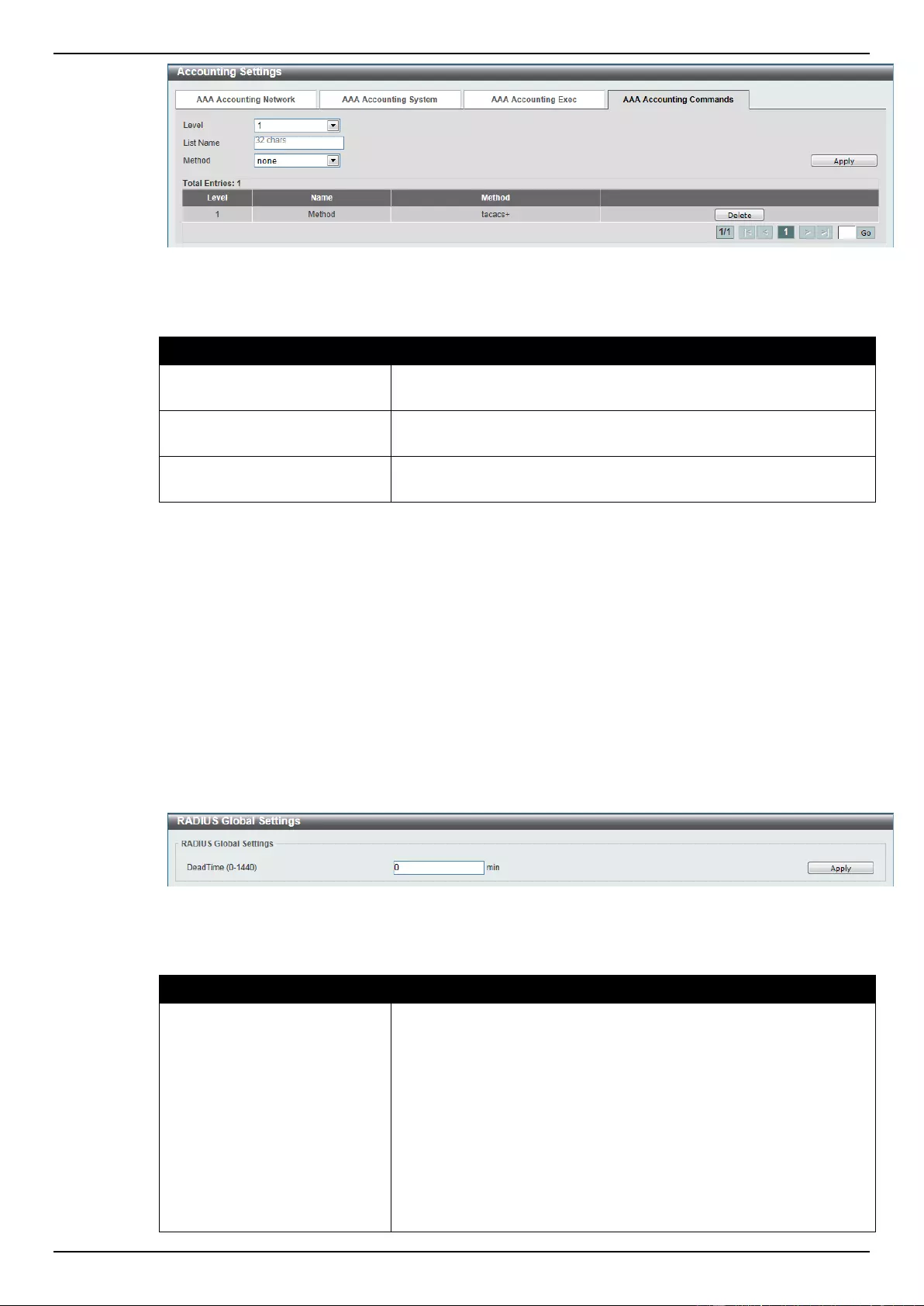
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
288
Figure 9-26 AAA Accounting Commands window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Level
Select the privilege level used here. Options to choose from are
levels 1 to 15.
List Name
Enter the method list name that will be used with the AAA
accounting commands option here.
Method
Select the method lists that will be used for this configuration here.
Options to choose from are none, group, and tacacs+.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
RADIUS
RADIUS Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the RADIUS global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > RADIUS > RADIUS Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-27 RADIUS Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Dead Time
Enter the dead time value here. This value must be between 1 and
1440 minutes. By default, this value is 0 minutes. When this option
is 0, the unresponsive server will not be marked as dead. This
setting can be used to improve the authentication processing time
by setting the dead time to skip the unresponsive server host
entries.
When the system performs authentication with the authentication
server, it attempts one server at a time. If the attempted server does
not respond, the system will attempt the next server. When the
system finds a server does not respond, it will mark the server as
down, start a dead time timer, and skip them in authentication of the
following requests until expiration of the dead time.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
289
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
RADIUS Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure the RADIUS server settings.
To view the following window, click Security > RADIUS > RADIUS Server Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-28 RADIUS Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP Address
Enter the RADIUS server’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
Enter the RADIUS server’s IPv6 address here.
Authentication Port
Enter the authentication port number used here. This value must be
between 0 and 65535. By default, this value is 1812. If no
authentication is used, use the value 0.
Accounting Port
Enter the accounting port number used here. This value must be
between 0 and 65535. By default, this value is 1813. If no
accounting is used, use the value 0.
Retransmit
Enter the retransmit value used here. This value must be between 0
and 20. By default, this value is 3. To disable this option, enter the
value 0.
Timeout
Enter the timeout value used here. This value must be between 1
and 255 seconds. By default, this value is 5 seconds.
Key Type
Select the key type that will be used here. Options to choose from
are Plain Text and Encrypted.
Key
Enter the key, used to communicate with the RADIUS server, here.
This key can be up to 32 characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
RADIUS Group Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure the RADIUS group server settings.
To view the following window, click Security > RADIUS > RADIUS Group Server Settings, as
shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
290
Figure 9-29 RADIUS Group Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Group Server Name
Enter the RADIUS group server’s name here. This name can be up
to 15 characters long.
IP Address
Enter the group server’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
Enter the group server’s IPv6 address here.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Detail button to view and configure more detailed settings for the RADIUS group server.
After clicking the Detail button, the following page will be available.
Figure 9-30 RADIUS Group Server Settings - Detail window
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
RADIUS Statistic
This window is used to view and clear the RADIUS statistics information.
To view the following window, click Security > RADIUS > RADIUS Statistic, as shown below:
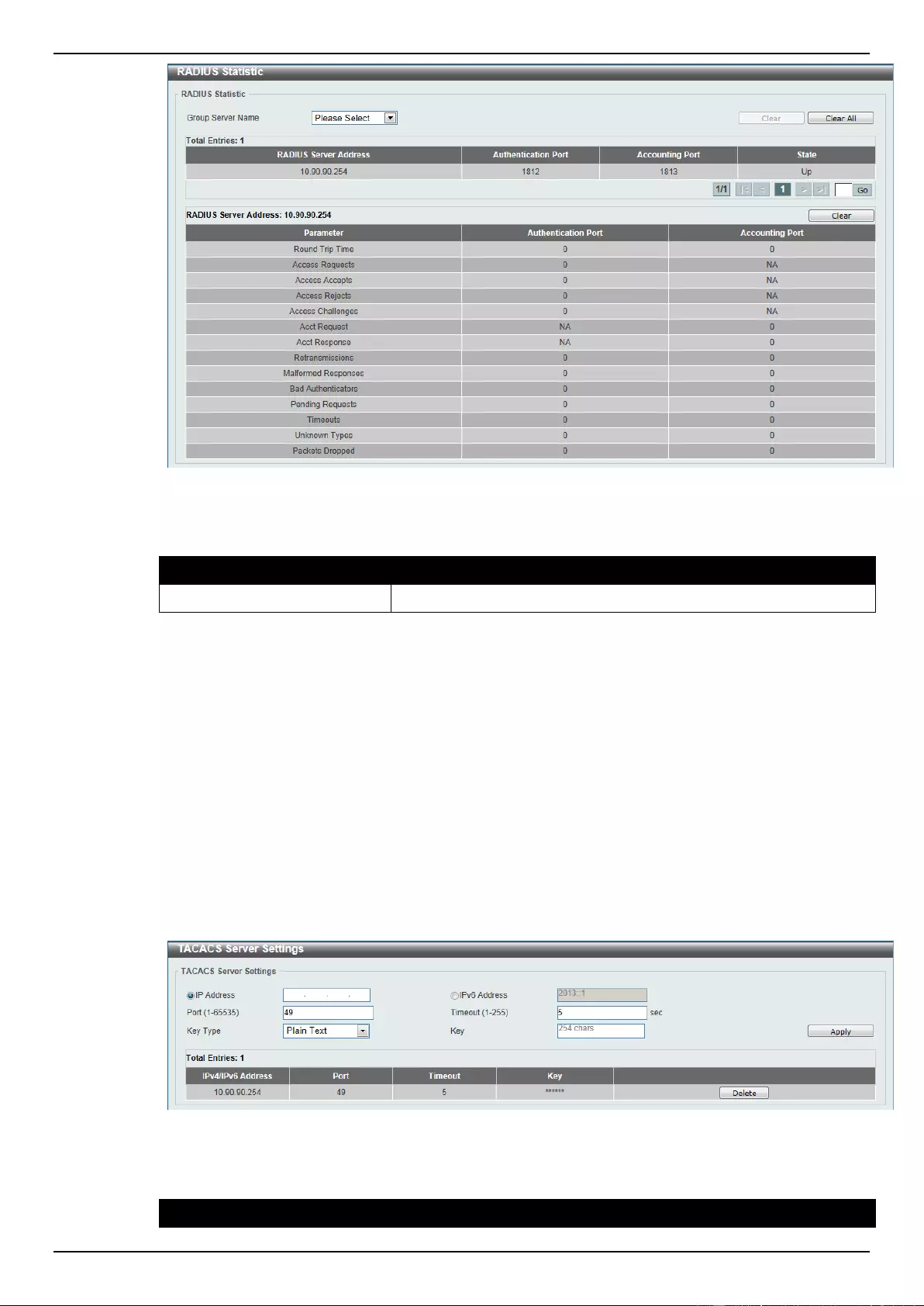
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
291
Figure 9-31 RADIUS Statistic window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Group Server Name
Select the RADIUS group server name from this list here.
Click the Clear button to clear the information based on the selections made.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
TACACS
TACACS Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure the TACACS server settings.
To view the following window, click Security > TACACS > TACACS Server Settings, as shown
below:
Figure 9-32 TACACS Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
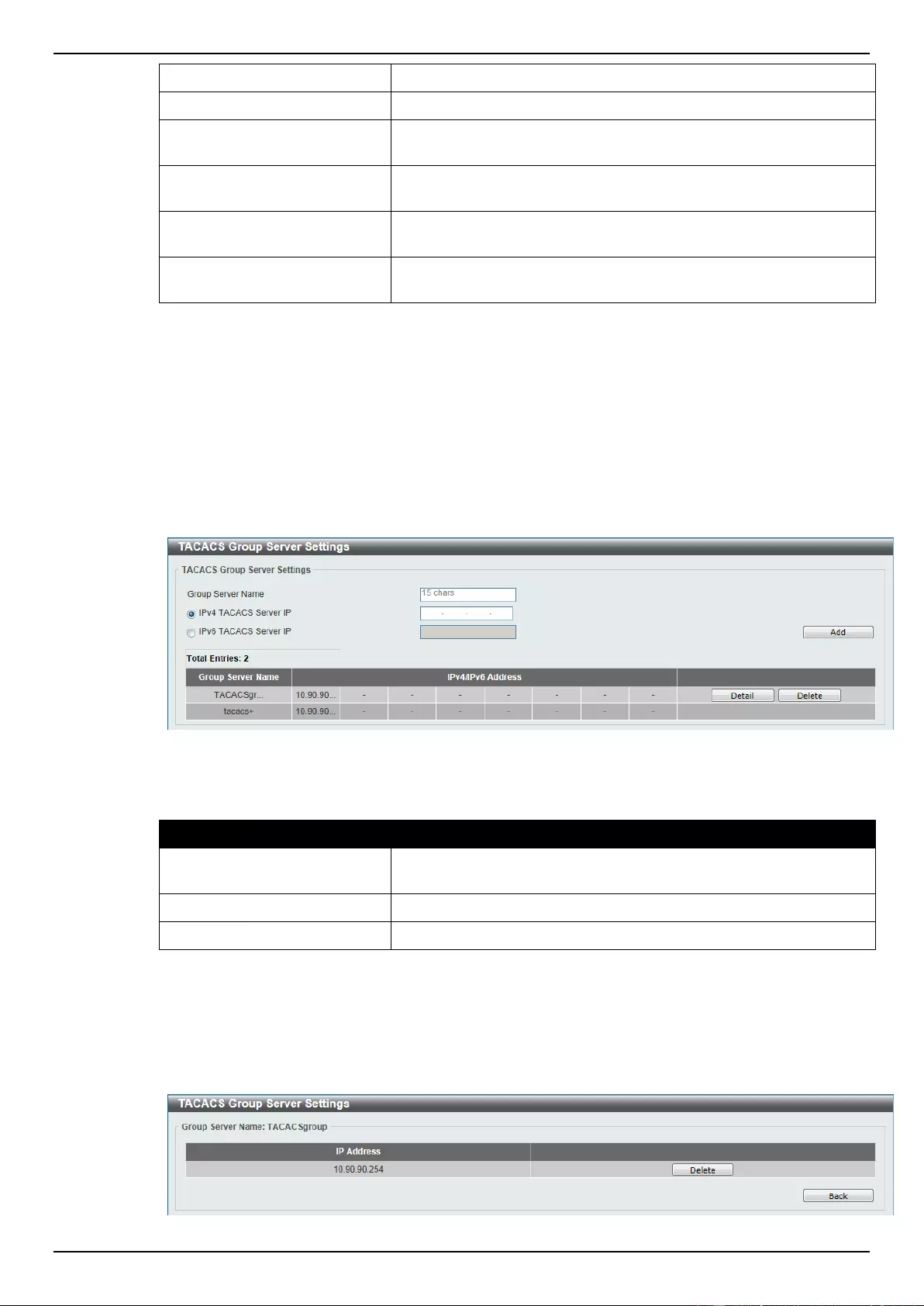
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
292
IP Address
Enter the TACACS server’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
Enter the TACACS server’s IPv6 address here.
Port
Enter the port number used here. This value must be between 1
and 65535. By default, this value is 49.
Timeout
Enter the timeout value here. This value must be between 1 and
255 seconds. By default, this value is 5 seconds.
Key Type
Select the key type that will be used here. Options to choose from
are Plain Text and Encrypted.
Key
Enter the key, used to communicate with the TACACS server, here.
This key can be up to 254 characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
TACACS Group Server Settings
This window is used to view and configure the TACACS group server settings.
To view the following window, click Security > TACACS > TACACS Group Server Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 9-33 TACACS Group Server Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Group Server Name
Enter the TACACS group server’s name here. This name can be up
to 15 characters long.
IPv4 TACACS Server IP
Enter the group server’s IPv4 address here.
IPv6 TACACS Server IP
Enter the group server’s IPv6 address here.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Detail button to view and configure more detailed settings for the TACACS group server.
After clicking the Detail button, the following page will be available.
Figure 9-34 TACACS Group Server Settings - Detail window
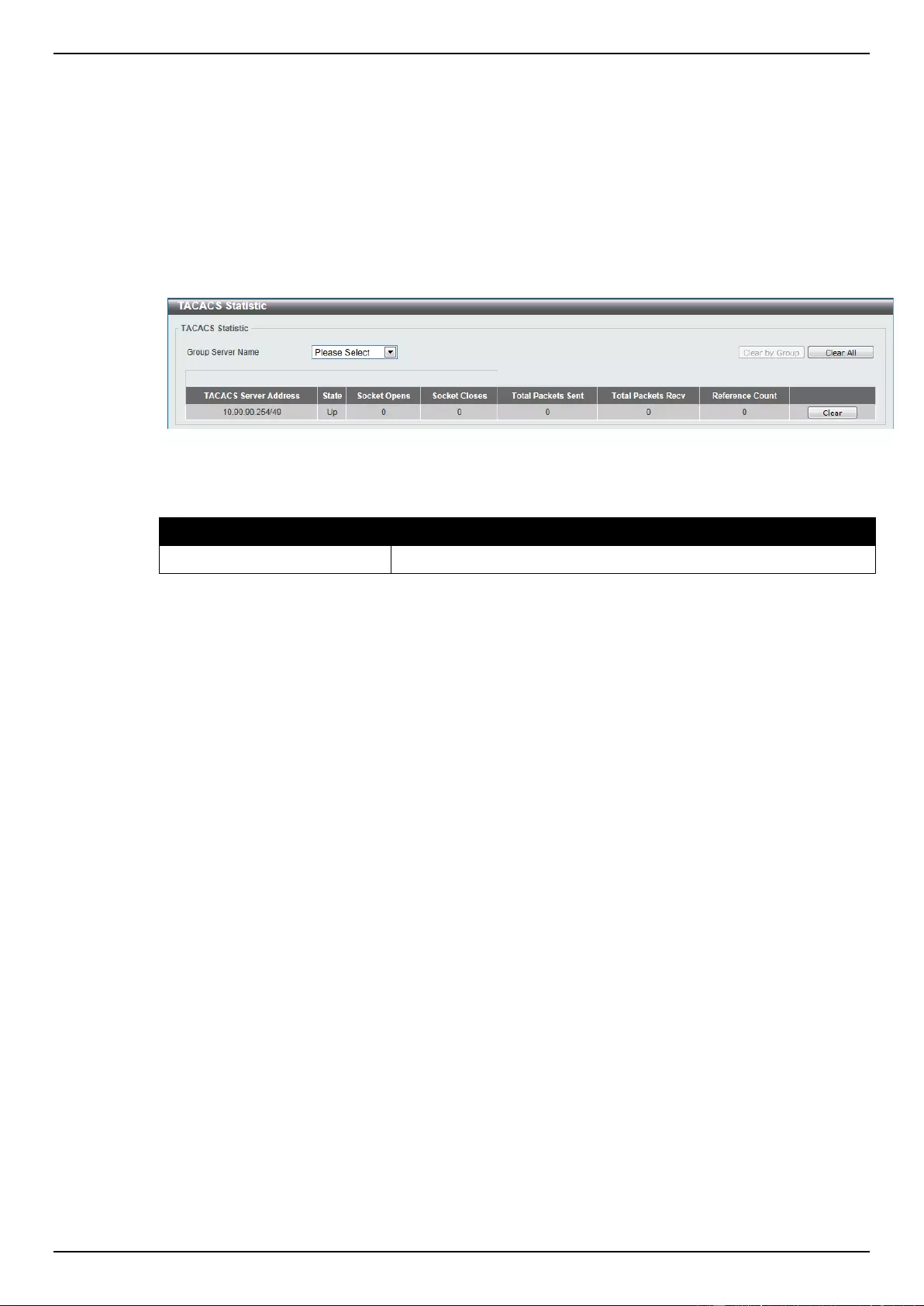
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
293
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
TACACS Statistic
This window is used to view and clear the TACACS statistic information.
To view the following window, click Security > TACACS > TACACS Statistic, as shown below:
Figure 9-35 TACACS Statistic window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Group Server Name
Select the TACACS group server name from this list here.
Click the Clear by Group button to clear the information based on the group selected.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
IMPB
The IP network layer uses a four-byte address. The Ethernet link-layer uses a six-byte MAC address.
Binding these two address types together allows the transmission of data between the layers. The
primary purpose of IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB) is to restrict the access to a switch to a number of
authorized users. Authorized clients can access a switch’s port by either checking the pair of IP-MAC
addresses with the pre-configured database or if DHCP snooping has been enabled in which case the
switch will automatically learn the IP/MAC pairs by snooping DHCP packets and saving them to the
IMPB white list. If an unauthorized user tries to access an IP-MAC binding enabled port, the system
will block the access by dropping its packet. Active and inactive entries use the same database. The
function is port-based, meaning a user can enable or disable the function on the individual port.
IPv4
DHCPv4 Snooping
DHCP Snooping Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP snooping global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > DHCPv4 Snooping > DHCP
Snooping Global Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
294
Figure 9-36 DHCP Snooping Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
DHCP Snooping
Select to enable or disable the DHCP snooping global status.
Information Option Allow
Untrusted
Select to enable or disable the option to globally allow DHCP
packets with the relay Option 82 on the untrusted interface.
Source MAC Verification
Select to enable or disable the verification that the source MAC
address in a DHCP packet matches the client hardware address.
Station Move Deny
Select to enable or disable the DHCP snooping station move state.
When DHCP snooping station move is enabled, the dynamic DHCP
snooping binding entry with the same VLAN ID and MAC address
on the specific port can move to another port if it detects that a new
DHCP process belong to the same VLAN ID and MAC address.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Snooping Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP snooping port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > DHCPv4 Snooping > DHCP
Snooping Port Settings, as shown below:
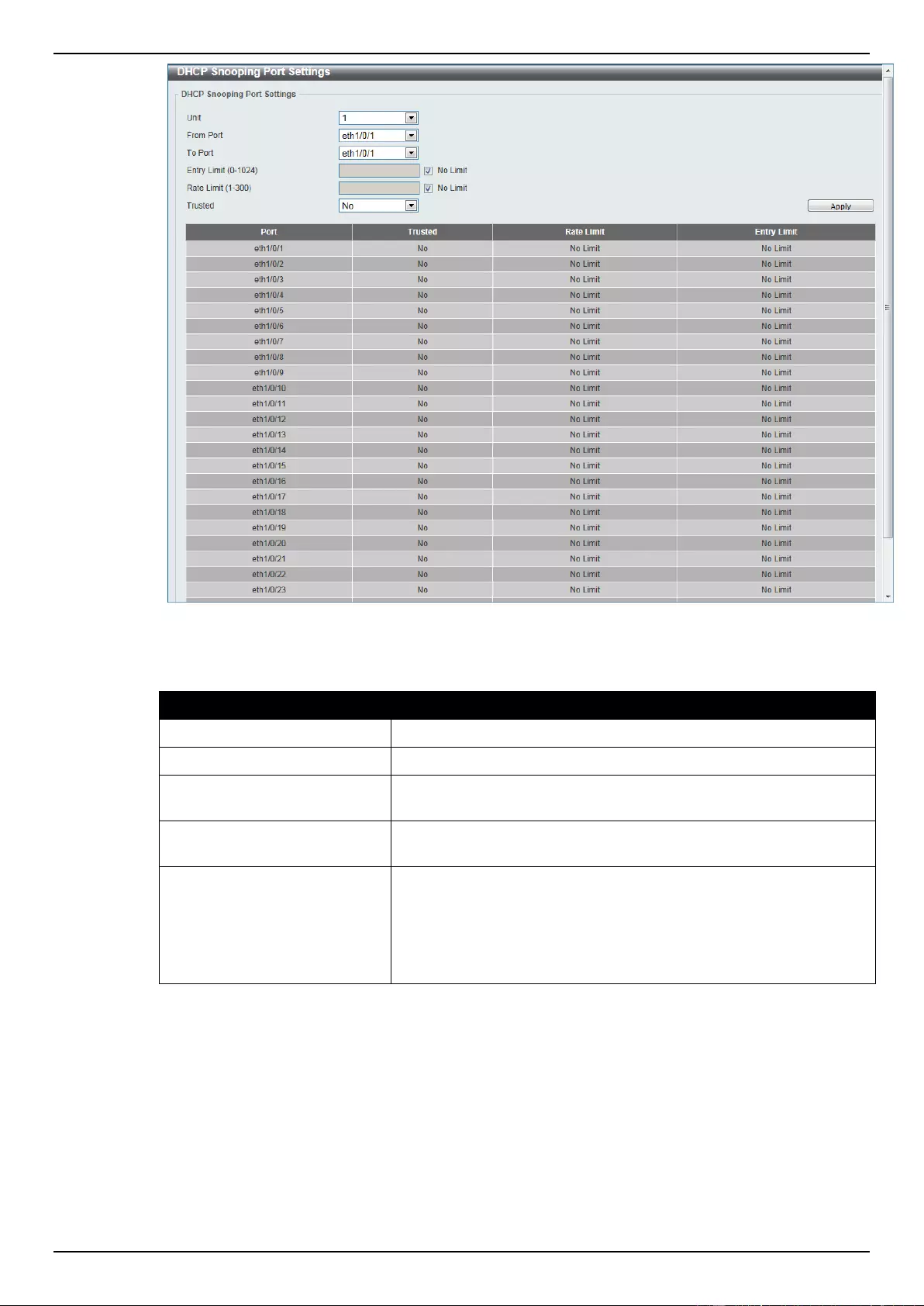
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
295
Figure 9-37 DHCP Snooping Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Entry Limit
Enter the entry limit value here. This value must be between 0 and
1024. Tick the No Limit option to disable the function.
Rate Limit
Enter the rate limit value here. This value must be between 1 and
300. Tick the No Limit option to disable the function.
Trusted
Select the trusted option here. Options to choose from are No and
Yes. Ports connected to the DHCP server or to other switches
should be configured as trusted interfaces. The ports connected to
DHCP clients should be configured as untrusted interfaces. DHCP
snooping acts as a firewall between untrusted interfaces and DHCP
servers.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Snooping VLAN Settings
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP snooping VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > DHCPv4 Snooping > DHCP
Snooping VLAN Settings, as shown below:
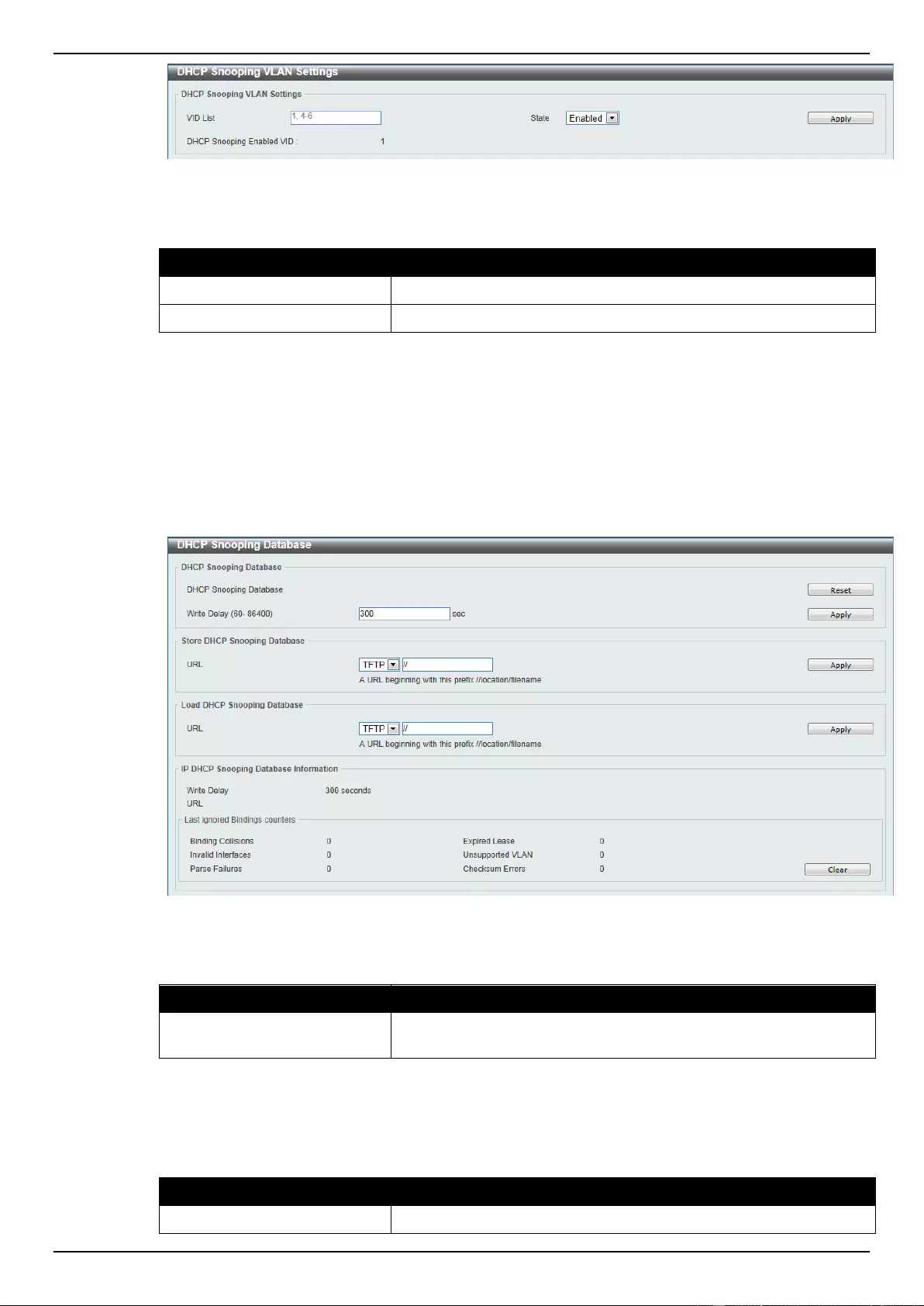
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
296
Figure 9-38 DHCP Snooping VLAN Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list used here.
State
Select to enable or disable the DHCP snooping VLAN setting here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DHCP Snooping Database
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP snooping database settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > DHCPv4 Snooping > DHCP
Snooping Database, as shown below:
Figure 9-39 DHCP Snooping Database window
The fields that can be configured for DHCP Snooping Database are described below:
Parameter
Description
Write Delay
Enter the write delay time value here. This value must be between
60 and 86400 seconds. By default, this value is 300 seconds.
Click the Reset button to reset the information entered.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Store DHCP Snooping Database are described below:
Parameter
Description
URL
Select the location from the drop-down list and enter the URL where
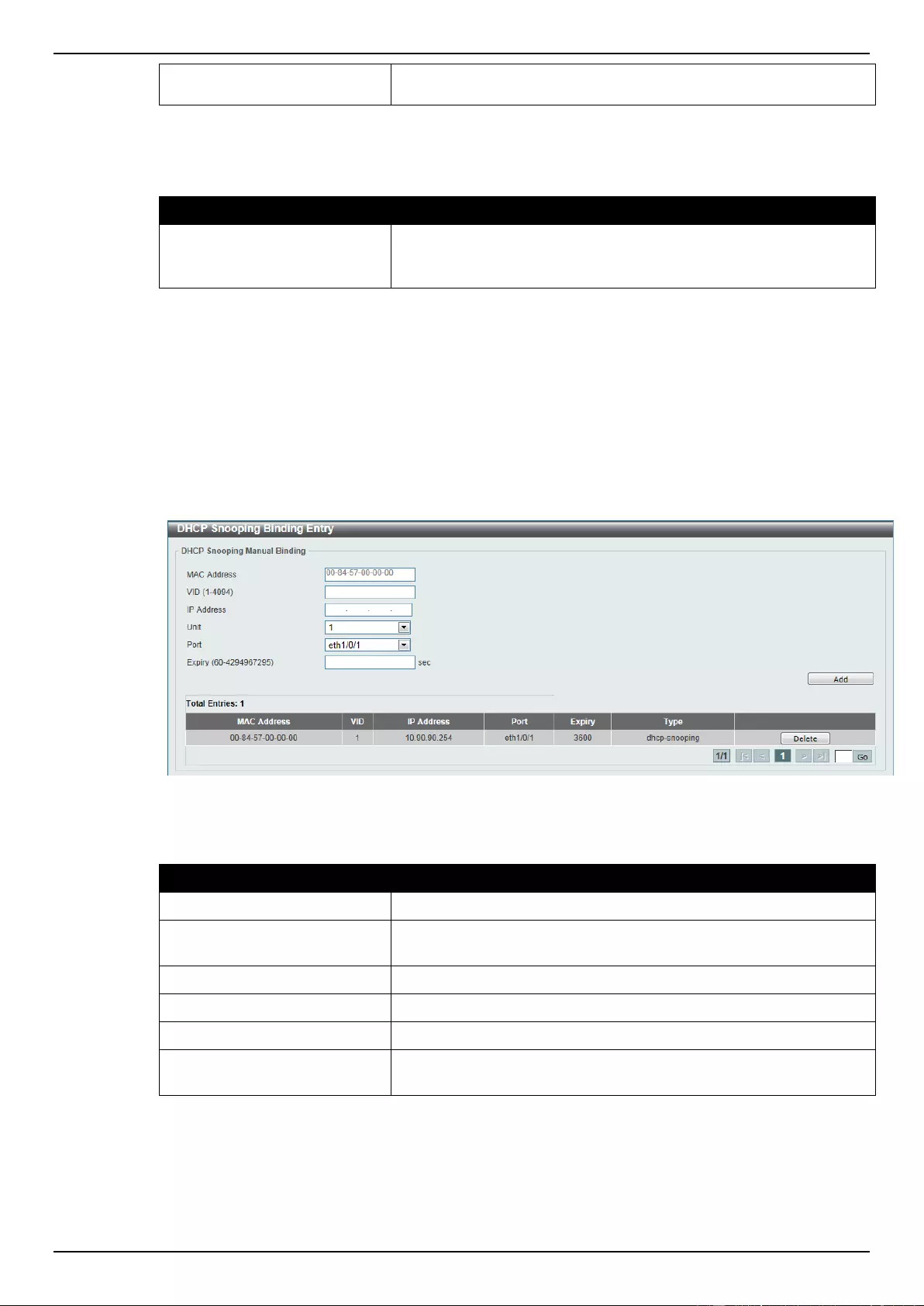
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
297
the DHCP snooping database will be stored to here. Location to
choose from is TFTP.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Load DHCP Snooping Database are described below:
Parameter
Description
URL
Select the location from the drop-down list and enter the URL where
the DHCP snooping database will be loaded from here. Location to
choose from is TFTP.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Clear button to clear all the counter information.
DHCP Snooping Binding Entry
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP snooping binding entries.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > DHCPv4 Snooping > DHCP
Snooping Binding Entry, as shown below:
Figure 9-40 DHCP Snooping Binding Entry window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address of the DHCP snooping binding entry here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID of the DHCP snooping binding entry here. This
value must be between 1 and 4094.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the DHCP snooping binding entry here.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the appropriate port used for the configuration here.
Expiry
Enter the expiry time value used here. This value must be between
60 and 4294967295 seconds.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
298
Dynamic ARP Inspection
ARP Access List
This window is used to view and configure the dynamic ARP inspection settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Access List, as shown below:
Figure 9-41 ARP Access List window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ARP Access List Name
Enter the ARP access list name used here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
After clicking the Edit button, the following window will appear.
Figure 9-42 ARP Access List - Edit window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Permit and Deny.
IP
Select the type of sender IP address that will be used here. Options
to choose from are Any, Host, and IP with Mask.
Sender IP
After selecting the Host or IP with Mask options as the type of IP,
enter the sender IP address used here.
Sender IP Mask
After selecting the IP with Mask option as the type of IP, enter the
sender IP mask used here.
MAC
Select the type of sender MAC address that will be used here.
Options to choose from are Any, Host, and MAC with Mask.
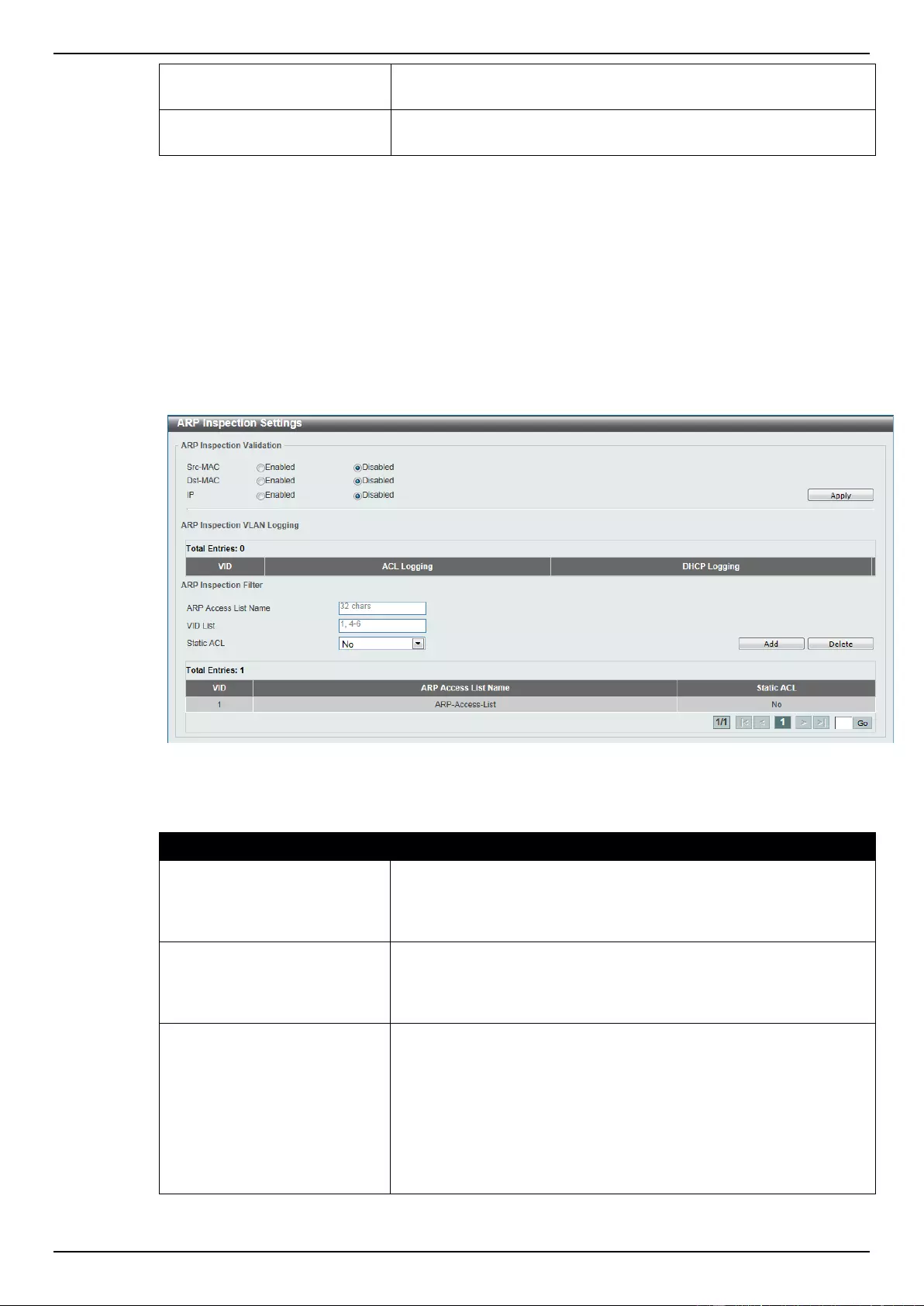
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
299
Sender MAC
After selecting the Host or MAC with Mask options as the type of
MAC, enter the sender MAC address used here.
Sender MAC Mask
After selecting the MAC with Mask option as the type of MAC,
enter the sender MAC mask used here.
Click the Back button to return to the previous page.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
ARP Inspection Settings
This window is used to view and configure the ARP inspection settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Inspection Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-43 ARP Inspection Settings window
The fields that can be configured for ARP Inspection Validation are described below:
Parameter
Description
Src-MAC
Select to enable of disable the source MAC option here. This option
specifies to check for ARP requests and response packets and the
consistency of the source MAC address in the Ethernet header
against the sender MAC address in the ARP payload.
Dst-MAC
Select to enable of disable the destination MAC option here. This
option specifies to check for ARP response packets and the
consistency of the destination MAC address in the Ethernet header
against the target MAC address in the ARP payload.
IP
Select to enable of disable the IP option here. This option specifies
to check the ARP body for invalid and unexpected IP addresses. It
also specifies to check the validity of IP address in the ARP
payload. The sender IP in both the ARP request and response and
target IP in the ARP response are validated. Packets destined for
the IP addresses 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.255, and all IP multicast
addresses are dropped. Sender IP addresses are checked in all
ARP requests and responses, and target IP addresses are checked
only in ARP responses.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
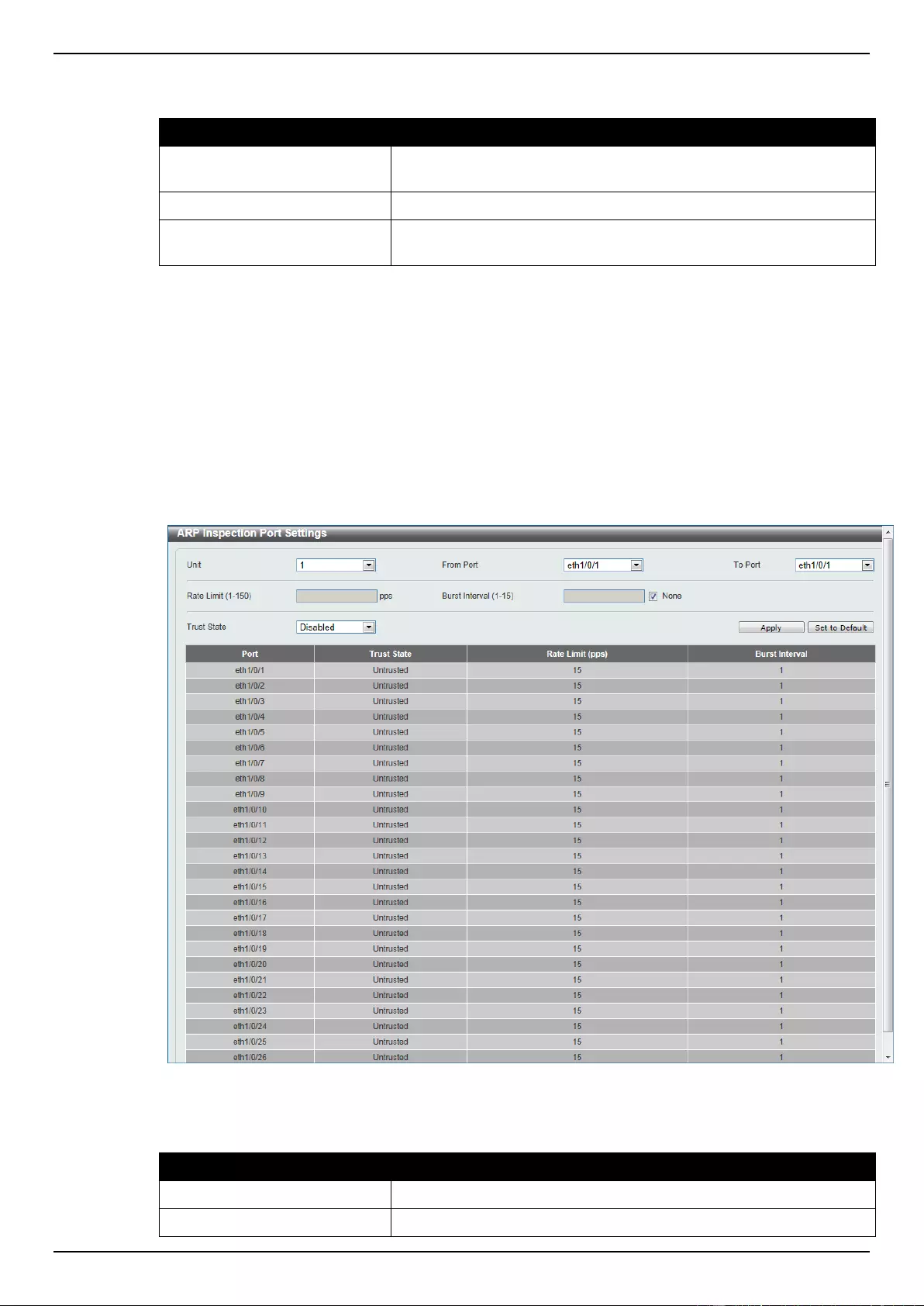
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
300
The fields that can be configured for ARP Inspection Filter are described below:
Parameter
Description
ARP Access List Name
Enter the ARP access list name used here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list used here.
Static ACL
Select whether to use a static ACL or not here by either selecting
Yes or No.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove an entry based on the information entered.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
ARP Inspection Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the ARP inspection port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Inspection Port Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-44 ARP Inspection Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
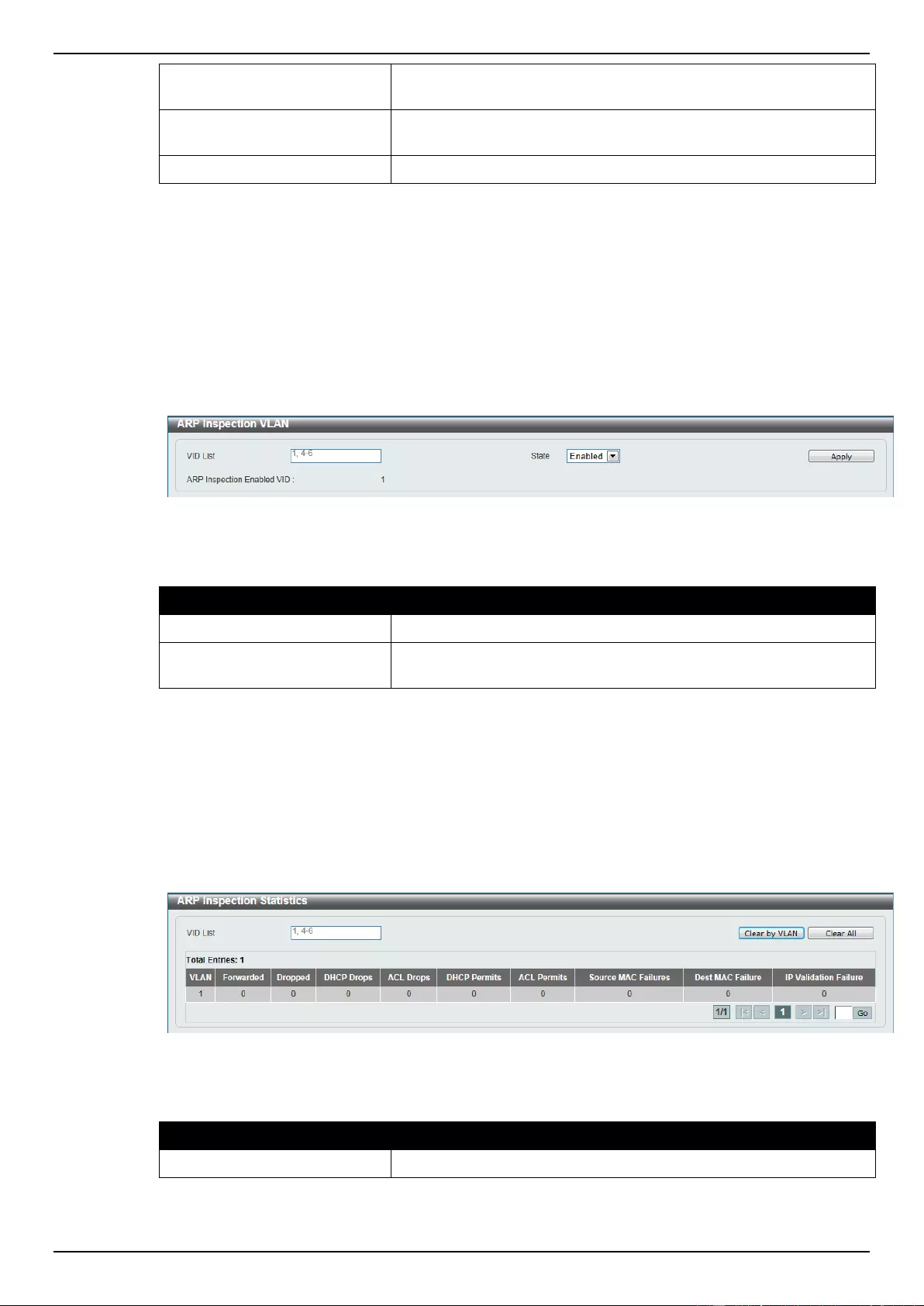
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
301
Rate Limit
Enter the rate limit value here. This value must be between 1 and
150 packets per seconds.
Burst Interval
Enter the burst interval value here. This value must be between 1
and 15. Tick the None option to disable the option.
Trust State
Select to enable or disable the trust state here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Set to Default button to change the information to the default values.
ARP Inspection VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the ARP inspection VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Inspection VLAN, as shown below:
Figure 9-45 ARP Inspection VLAN window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list used here.
State
Select to enable or disable the ARP inspection option’s state for the
specified VLAN here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
ARP Inspection Statistics
This window is used to view and clear the ARP inspection statistics information.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Inspection Statistics, as shown below:
Figure 9-46 ARP Inspection Statistics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list used here.
Click the Clear by VLAN button to clear the information based on the VLAN ID(s) entered.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
302
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
ARP Inspection Log
This window is used to view, configure and clear the ARP inspection log information.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Dynamic ARP Inspection > ARP
Inspection Log, as shown below:
Figure 9-47 ARP Inspection Log window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Log Buffer
Enter the log’s buffer value used here. This value must be between
1 and 1024. By default, this value is 32.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Clear Log button to clear the log.
IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the IP source guard port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > IP Source Guard > IP Source Guard
Port Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-48 IP Source Guard Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the IP source guard’s state for the
specified port(s) here.
Validation
Select the validation method used here. Options to choose from are
IP and IP-MAC. Selecting IP means that the IP address of the
received packets will be checked. Selecting IP-MAC means that the
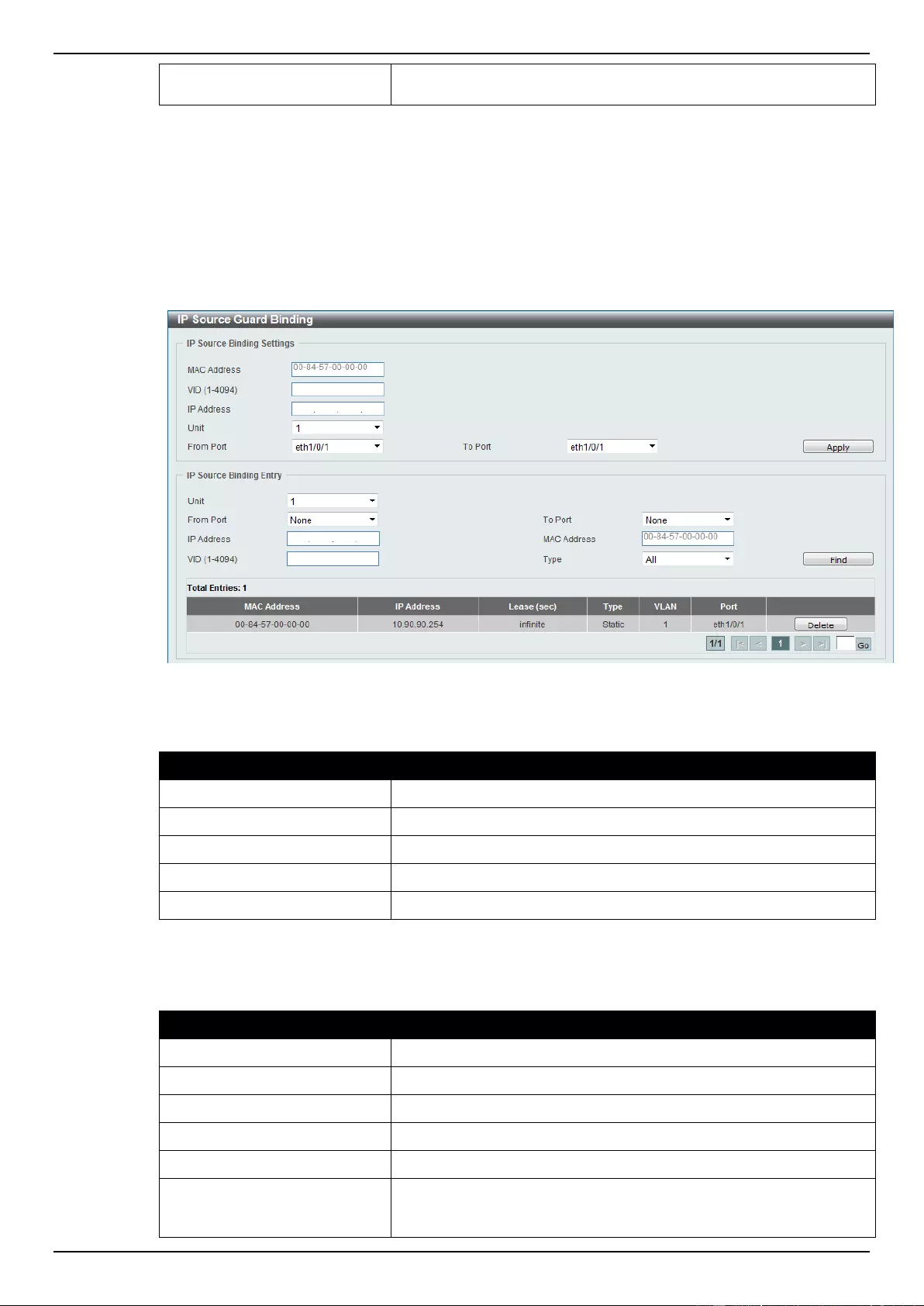
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
303
IP address and the MAC address of the received packets will be
checked.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IP Source Guard Binding
This window is used to view and configure the IP source guard binding settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > IP Source Guard > IP Source Guard
Binding, as shown below:
Figure 9-49 IP Source Guard Binding window
The fields that can be configured for IP Source Binding Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address of the binding entry here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID of the binding entry here.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the binding entry here.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IP Source Binding Entry are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this query here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the query here.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the binding entry here.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address of the binding entry here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID of the binding entry here.
Type
Select the type of binding entry to find here. Options to choose from
are All, DHCP Snooping, and Static. Selecting All specifies that all
the DHCP binding entries will be displayed. Selecting DHCP
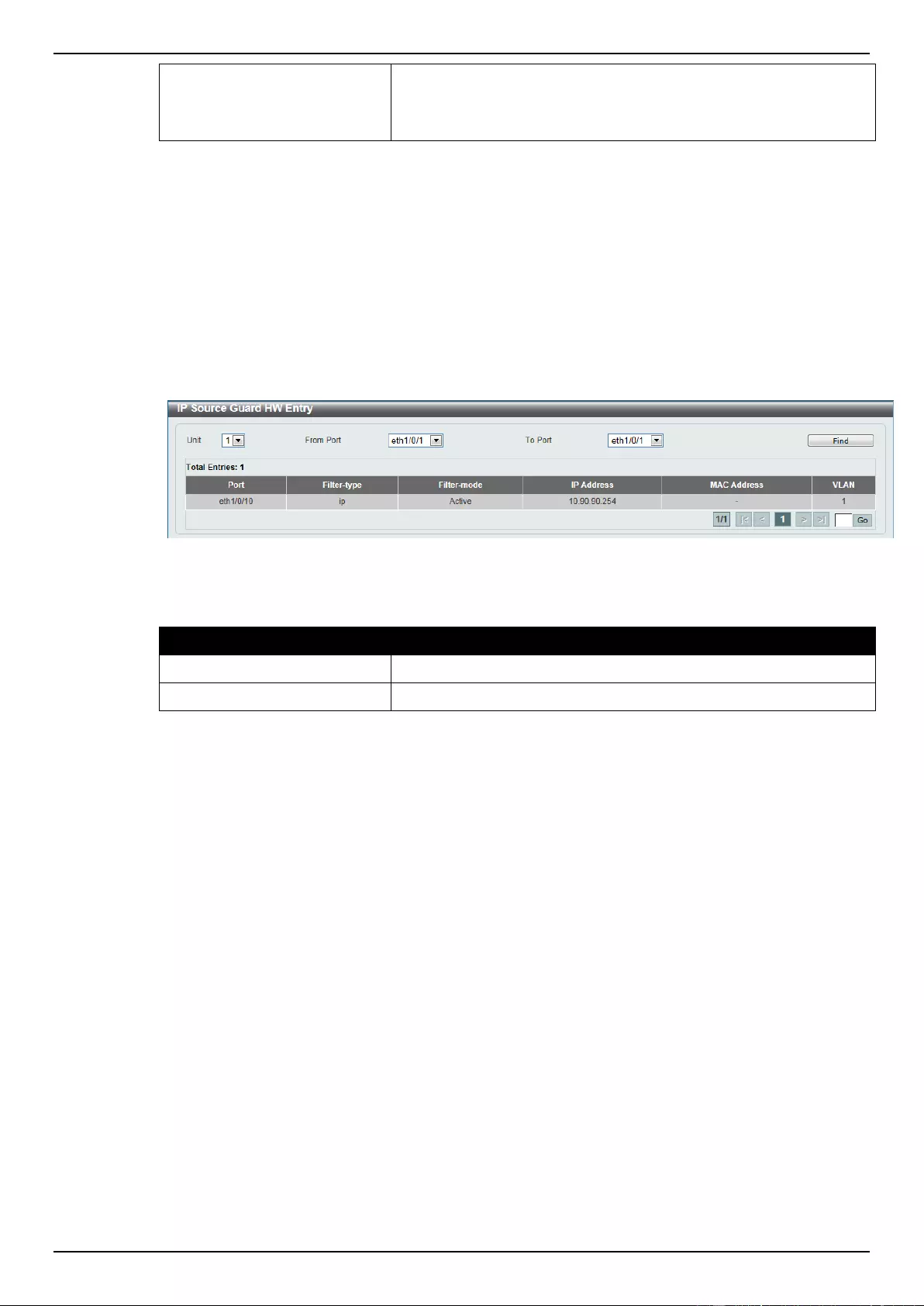
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
304
Snooping specifies to display the IP-source guard binding entry
learned by DHCP binding snooping. Selecting Static specifies to
display the IP-source guard binding entry that is manually
configured.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IP Source Guard HW Entry
This window is used to view the IP source guard hardware entries.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > IP Source Guard > IP Source Guard
HW Entry, as shown below:
Figure 9-50 IP Source Guard HW Entry window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this query here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the query here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Advanced Settings
IP-MAC-Port Binding Settings
This window is used to view and configure the IP-MAC-Port binding settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Advanced Settings > IP-MAC-Port
Binding Settings, as shown below:
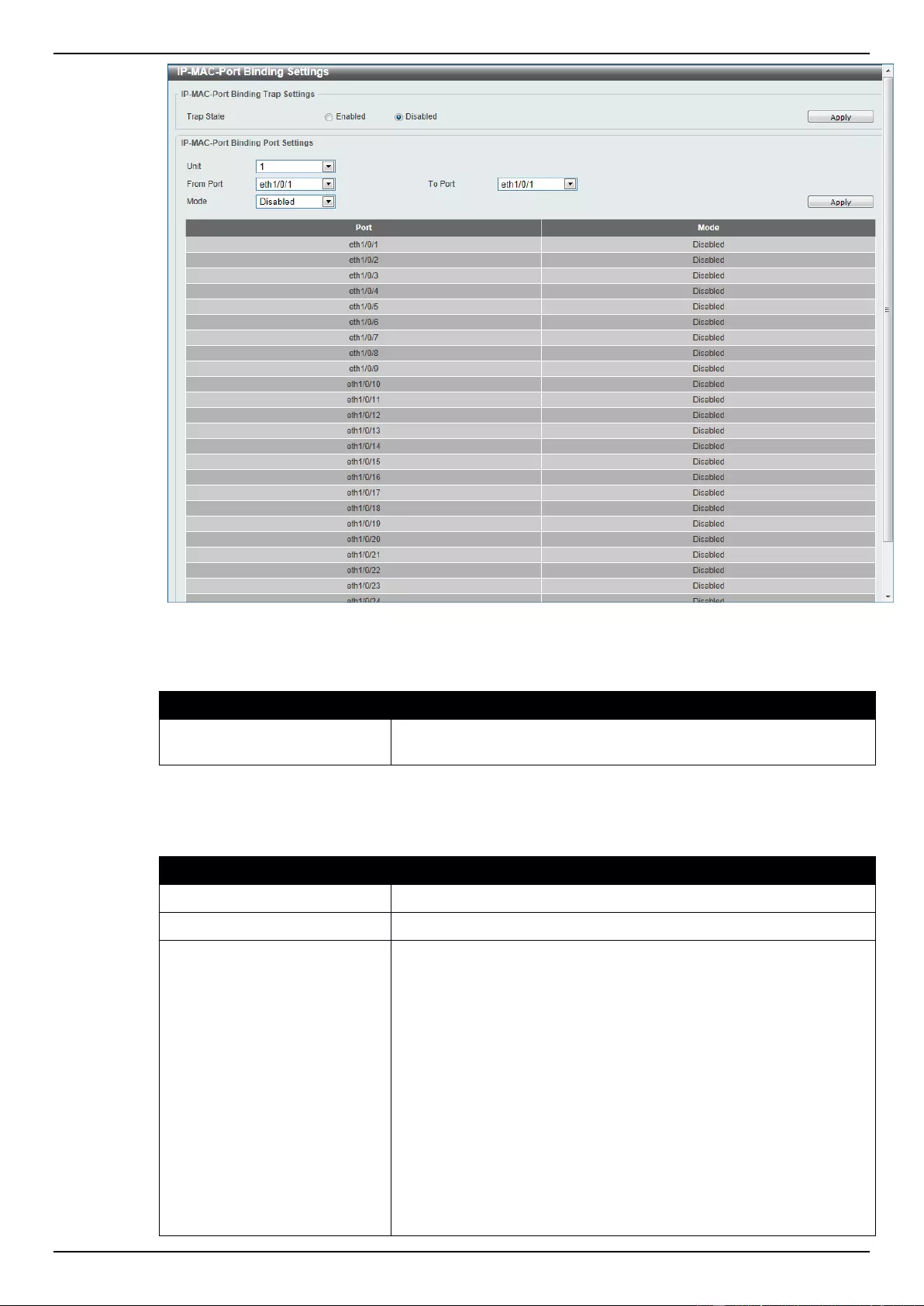
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
305
Figure 9-51 IP-MAC-Port Binding Settings window
The fields that can be configured for IP-MAC-Port Binding Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap State
Select the enable or disable the IP-MAC-Port binding option’s trap
state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IP-MAC-Port Binding Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Mode
Select the mode of access control that will be used here. Options to
choose from are Disabled, Strict, and Loose. When a port is
enabled for IMPB strict-mode access control, a host can only
access the port after the host sends ARP or IP packets and the
ARP packet or IP packet sent by the host passes the binding check.
To pass the binding check, the source IP address, source MAC
address, VLAN ID, and arrival port number must match any of the
entries defined by either the IP source guard static binding entry or
the DHCP snooping learned dynamic binding entry. When a port is
enabled for IMPB loose-mode access control, a host will be denied
to access the port after the host sends ARP or IP packets and the
ARP packet or IP packet sent by the host does not pass the binding
check. To pass the binding check, the source IP address, source
MAC address, VLAN ID, and arrival port must match any of the
entries defined by either the IP source guard static binding entry or
the DHCP snooping learned dynamic binding entry.
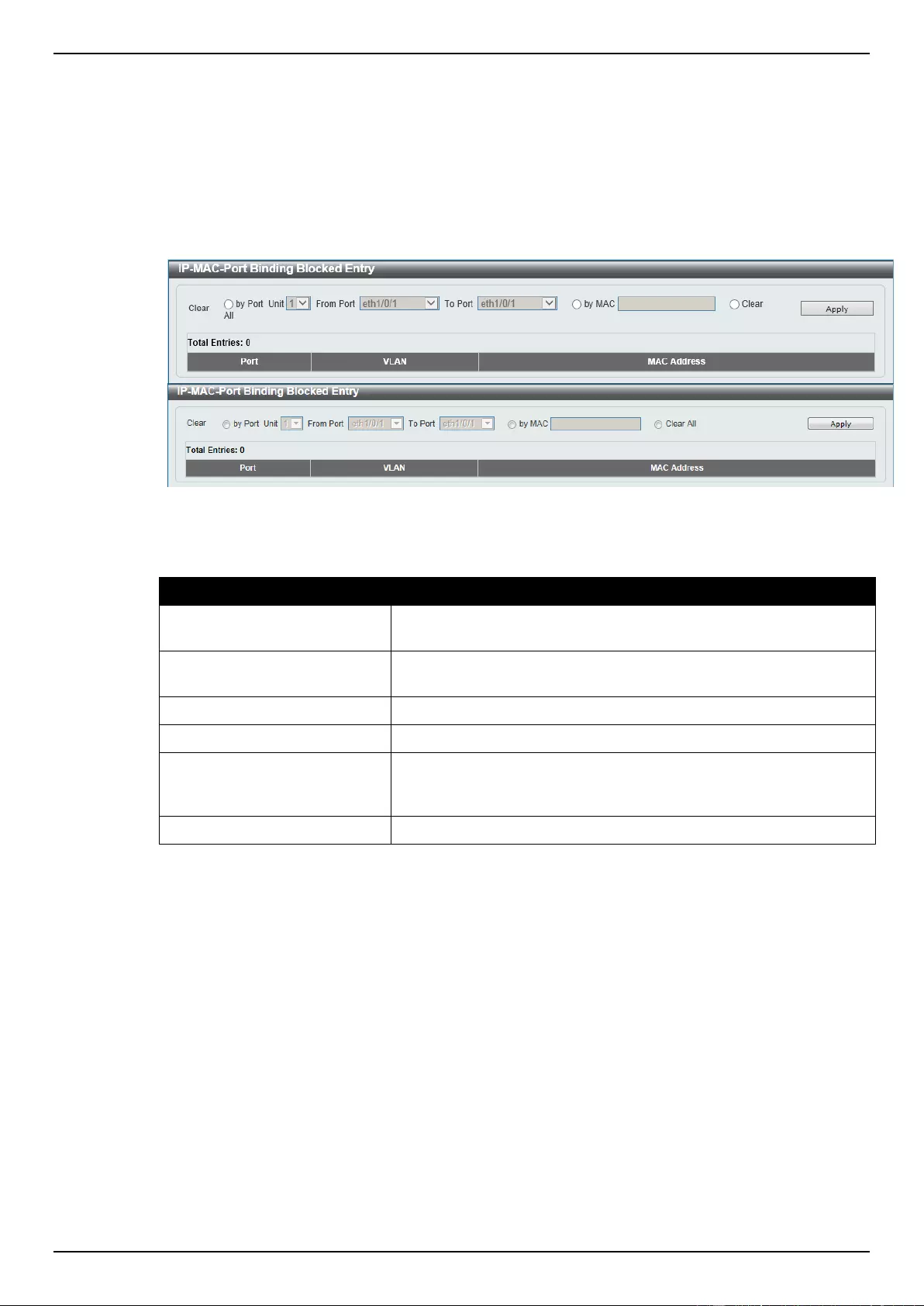
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
306
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IP-MAC-Port Binding Blocked Entry
This window is used to view and clear the IP-MAC-Port binding blocked entry table.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv4 > Advanced Settings > IP-MAC-Port
Binding Blocked Entry, as shown below:
Figure 9-52 IP-MAC-Port Binding Blocked Entry window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Clear All
Leave all fields unselected and click the Apply button to clear all
IMPB blocked entry information.
Clear by Port
Select this option to clear the entry table based on the port(s)
selected.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be clear here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range that will be cleared here.
Clear by MAC
Select this option to clear the entry table based on the MAC address
entered. Enter the MAC address that will be cleared in the space
provided.
Clear All
Select this option to clear all entries that contain MAC addresses.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
IPv6
IPv6 Snooping
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 snooping settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 Snooping, as shown below:
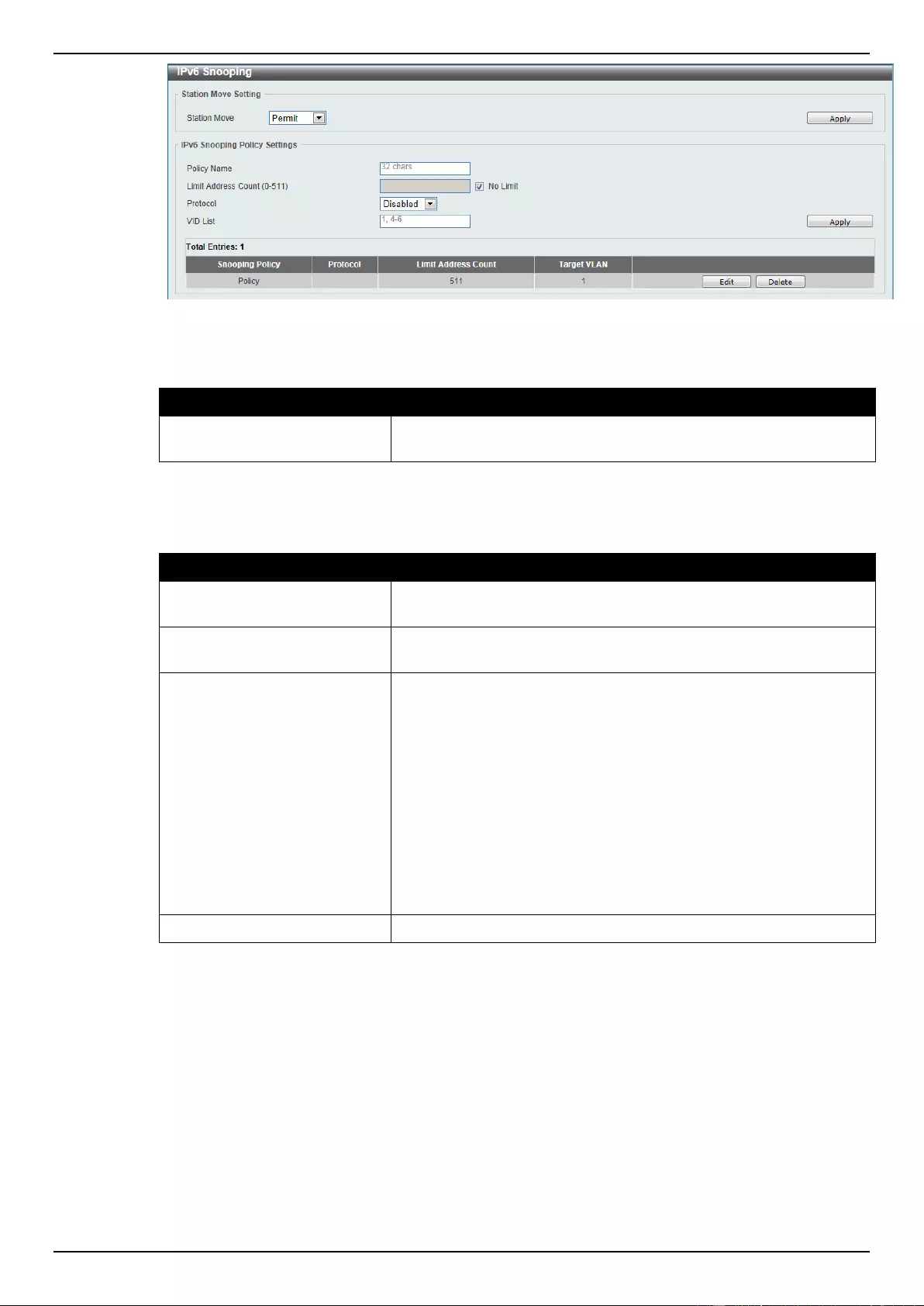
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
307
Figure 9-53 IPv6 Snooping window
The fields that can be configured for Station Move Setting are described below:
Parameter
Description
Station Move
Select the station move options here. Options to choose from are
Permit and Deny.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IPv6 Snooping Policy Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the IPv6 snooping policy name used here. This name can be
up to 32 characters long.
Limit Address Count
Enter the address count limit value used here. This value must be
between 0 and 511. Tick the No Limit option to disable this option.
Protocol
Select the protocol that will be associated with this policy here.
Options to choose from are Disabled, DHCP, NDP, and All.
DHCPv6 Snooping sniffs the DHCPv6 packets sent between the
DHCPv6 client and server in the address assigning procedure.
When a DHCPv6 client successfully got a valid IPv6 address,
DHCPv6 snooping creates its binding database. ND Snooping is
designed for a stateless auto-configuration assigned IPv6 address
and manually configured IPv6 address. Before assigning an IPv6
address, the host must perform Duplicate Address Detection first.
ND snooping detects DAD messages (DAD NS and DAD NA) to
build its binding database. The NDP packet (NS and NA) is also
used to detect whether a host is still reachable and determine
whether to delete a binding or not.
VID List
Enter the VLAN ID list used here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
IPv6 ND Inspection
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 ND inspection settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 ND Inspection, as shown below:
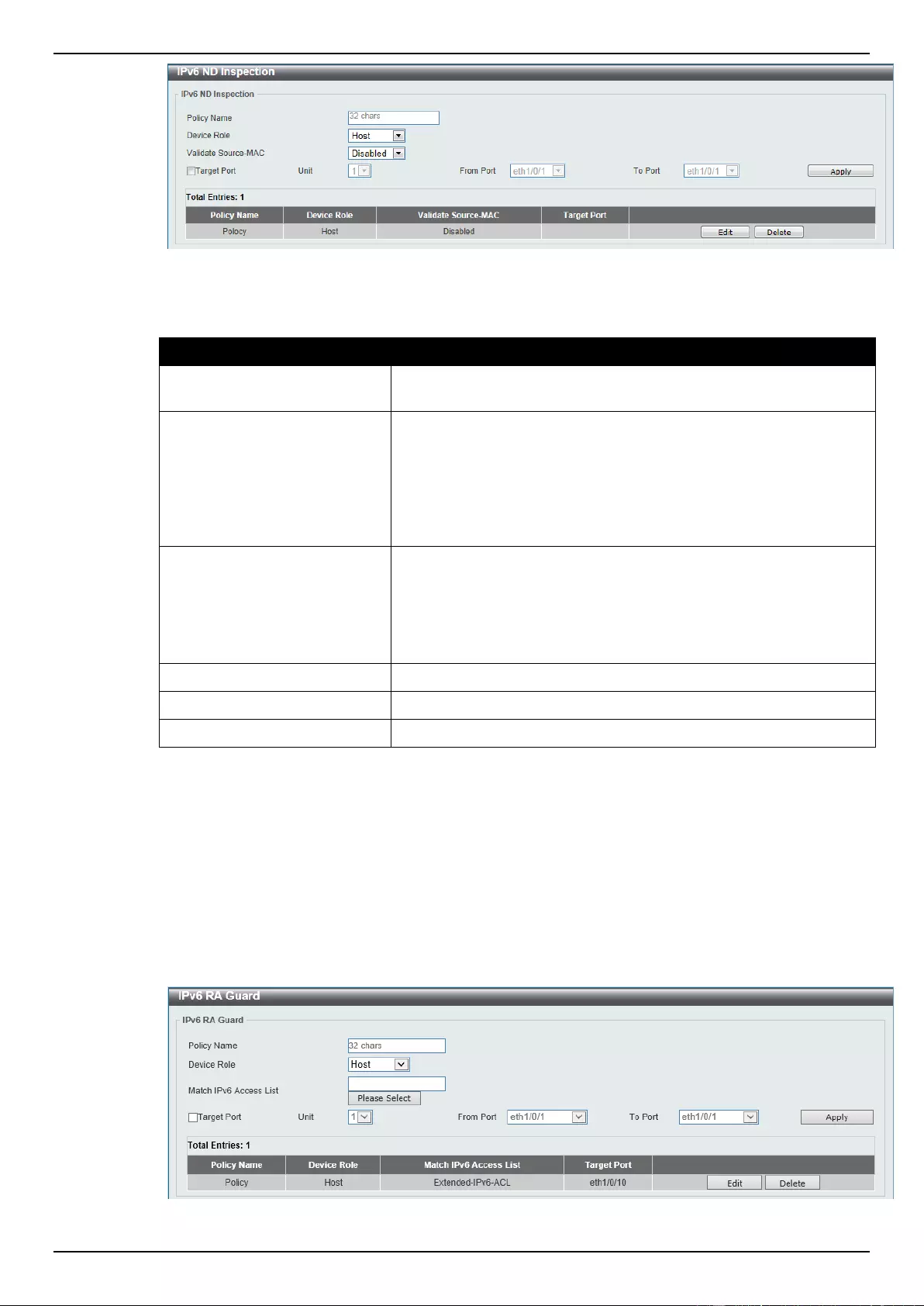
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
308
Figure 9-54 IPv6 ND Inspection window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the policy name used here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Device Role
Select the device role here. Options to choose from are Host and
Router. By default, the device’s role is set as host and inspection
for NS and NA messages are performed. If the device role is set as
router, the NS and NA inspection is not performed. When
performing NS/NA inspection, the message will be verified against
the dynamic binding table learned from the ND protocol or from the
DHCP.
Validate Source-MAC
Select to enable or disable the validation of the source MAC
address option here. When the Switch receives an ND message
that contains a link-layer address, the source MAC address is
checked against the link-layer address. The packet will be dropped
if the link-layer address and the MAC addresses are different from
each other.
Target Port
Tick this option to specify the target port.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
IPv6 RA Guard
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) guard settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 RA Guard, as shown below:
Figure 9-55 IPv6 RA Guard window
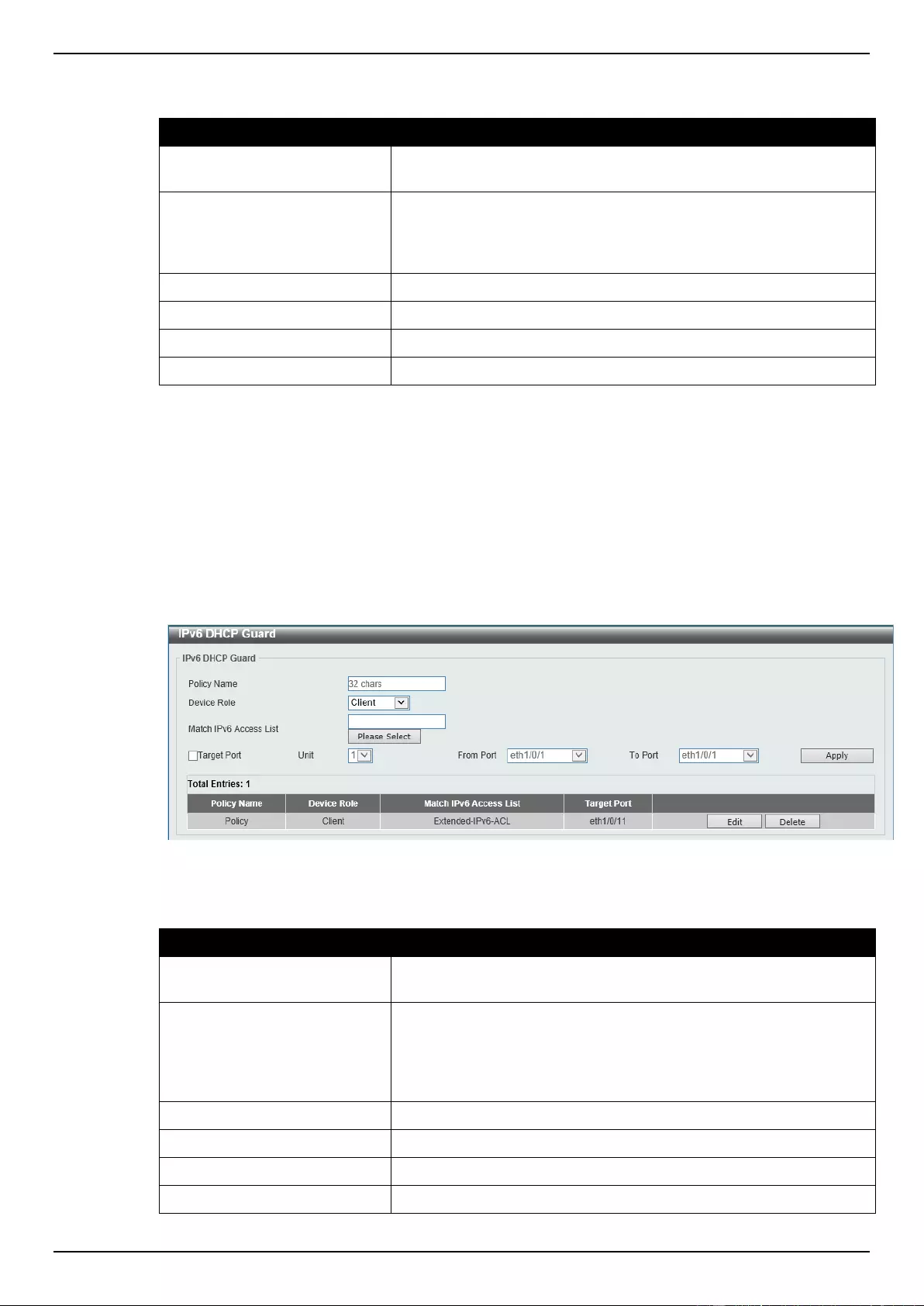
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
309
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the policy name here. This name can be up to 32 characters
long.
Device Role
Select the device role here. Options to choose from are Host and
Router. By default, the device's role is Host, which will block all the
RA packets. If the device's role is Router, RA packets will be
forwarded according to the port's bound ACL.
Match IPv6 Access List
Enter or select the IPv6 access list to match here.
Target Port
Tick this option to specify the target port.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
IPv6 DHCP Guard
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 DHCP guard settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 DHCP Guard, as shown below:
Figure 9-56 IPv6 DHCP Guard window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the policy name here. This name can be up to 32 characters
long.
Device Role
Select the device role here. Options to choose from are Client and
Server. By default, the device's role is set as Client, which will
block all the DHCPv6 packets from the DHCPv6 Server. If the
device's role is set as Server, DHCPv6 Server packets will be
forwarded according to the port's bound ACL.
Match IPv6 Access List
Enter or select the IPv6 access list to match here.
Target Port
Tick this option to specify the target port.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
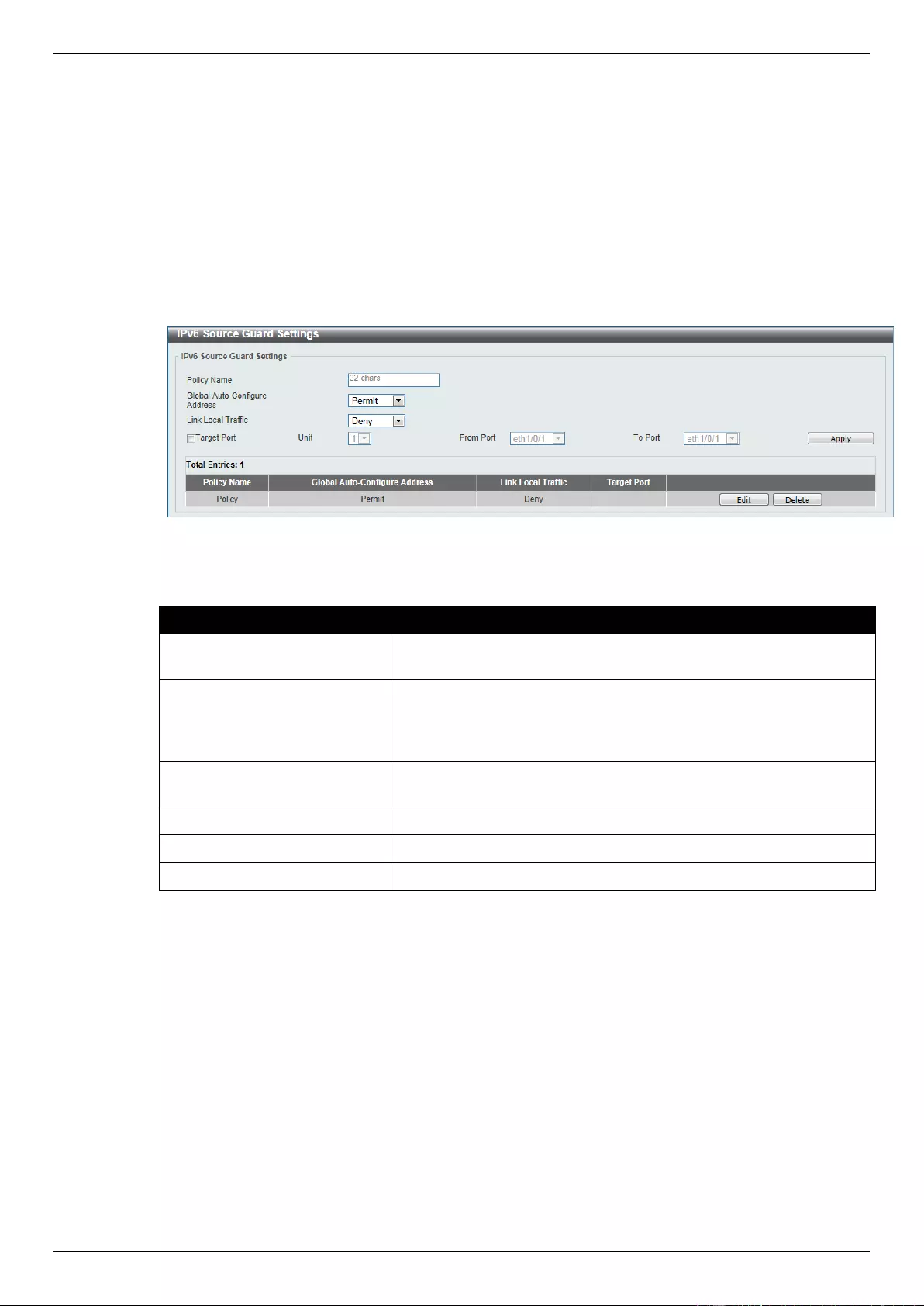
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
310
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
IPv6 Source Guard
IPv6 Source Guard Settings
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 source guard settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 Source Guard > IPv6 Source
Guard Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-57 IPv6 Source Guard Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the policy name here. This name can be up to 32 characters
long.
Global Auto-Configure
Address
Select to permit of deny data traffic from the auto-configured global
address. It is useful when all global addresses on a link are
assigned by DHCP and the administrator that wants to block hosts
with self-configured addresses from sending traffic.
Link Local Traffic
Select to permit of deny hardware permitted data traffic send by the
link-local address.
Target Port
Tick this option to specify the target port.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
IPv6 Neighbor Binding
This window is used to view and configure the IPv6 neighbor binding settings.
To view the following window, click Security > IMPB > IPv6 > IPv6 Source Guard > IPv6 Neighbor
Binding, as shown below:
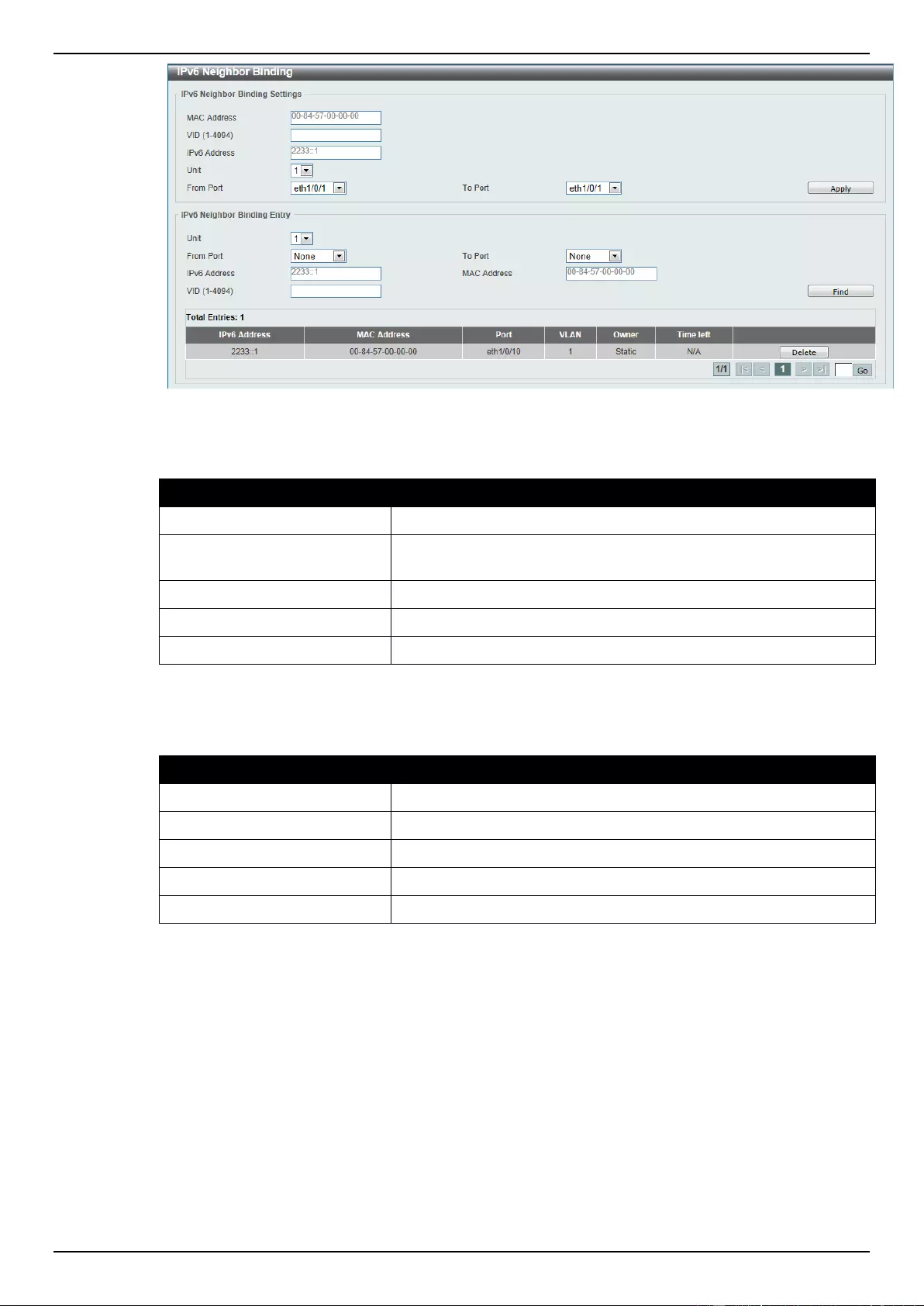
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
311
Figure 9-58 IPv6 Neighbor Binding window
The fields that can be configured for IPv6 Neighbor Binding Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address used here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used here. This value must be between 1 and
4094.
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address used here.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for IPv6 Neighbor Binding Entry are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this search here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the search here.
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address to find here.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address to find here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID to find here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
DHCP Server Screening
This function allows users to not only to restrict all DHCP server packets but also to receive any
specified DHCP server packet by any specified DHCP client. It is useful when one or more DHCP
servers are present on the network and both provide DHCP services to different distinct groups of
clients.
The first time the DHCP filter is enabled it will create both an access profile entry and an access rule
per port entry, it will also create other access rules. These rules are used to block all DHCP server
packets. In addition to a permit DHCP entry it will also create one access profile and one access rule
entry the first time the DHCP client MAC address is used as the client MAC address. The Source IP
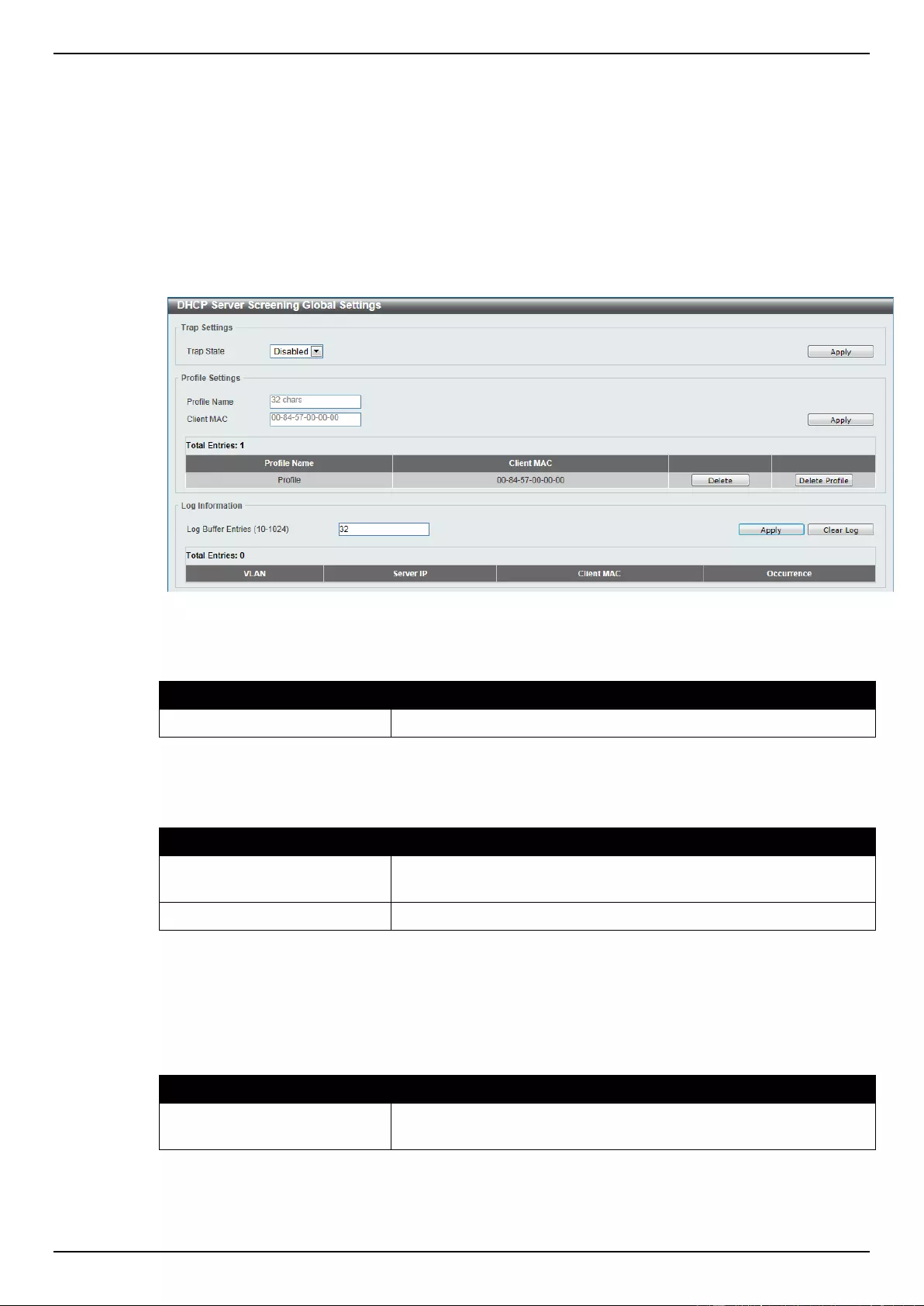
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
312
address is the same as the DHCP server’s IP address (UDP port number 67). These rules are used to
permit the DHCP server packets with specific fields, which the user has configured.
When DHCP Server filter function is enabled all DHCP Server packets will be filtered from a specific
port.
DHCP Server Screening Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP server screening global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening
Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-59 DHCP Server Screening Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap State
Select to enable or disable the DHCP server screening trap here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Profile Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Profile Name
Enter the DHCP server screening profile name here. This name can
be up to 32 characters long.
Client MAC
Enter the MAC address used here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Click the Delete Profile button to remove the specified profile.
The fields that can be configured for Log Information are described below:
Parameter
Description
Log Buffer Entries
Enter the logged buffer entries value here. This value must be
between 10 and 1024. By default, this value is 32.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Clear Log button to clear the log.
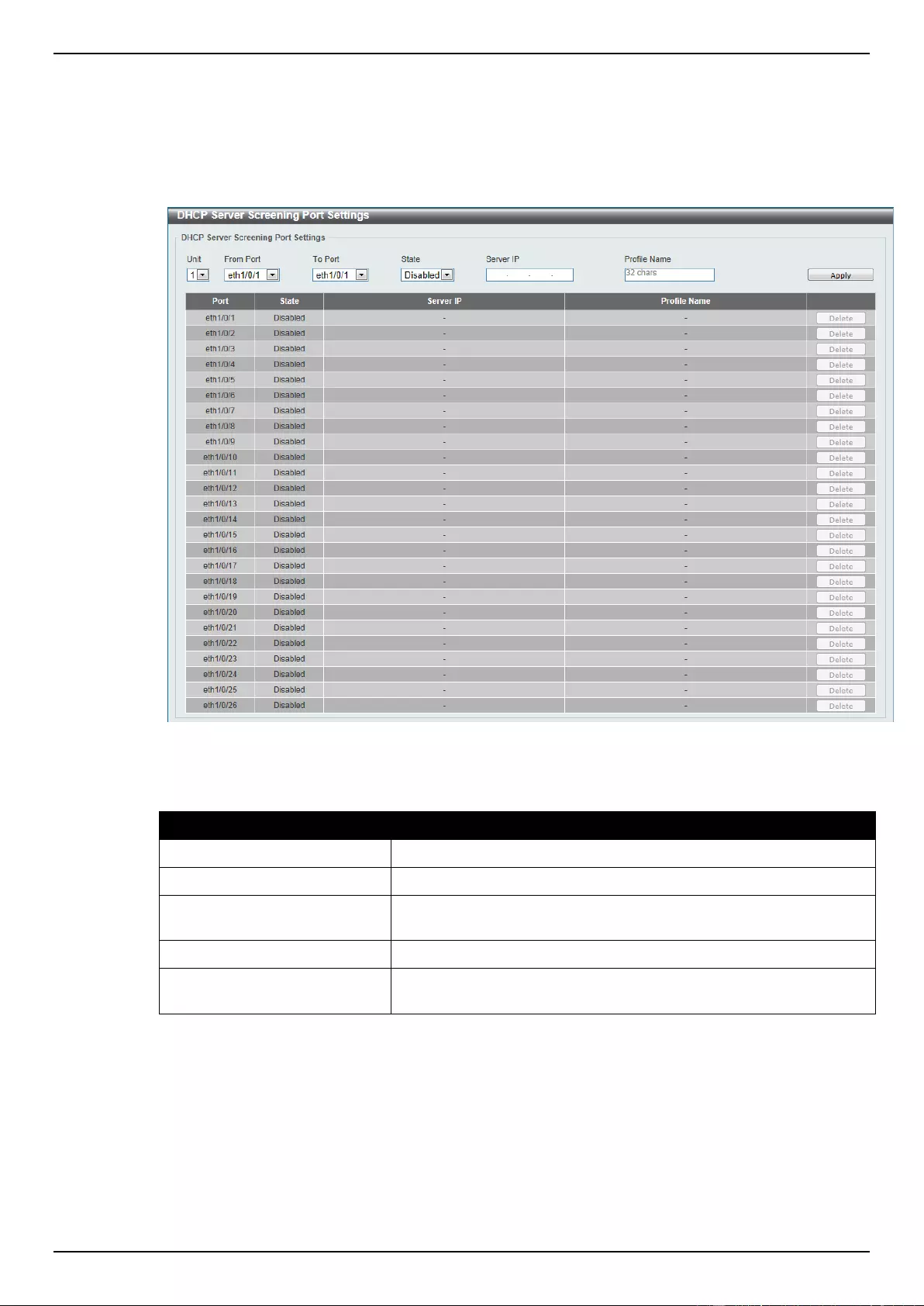
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
313
DHCP Server Screening Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the DHCP server screening port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening
Port Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-60 DHCP Server Screening Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the DHCP server screening function on
the port(s) specified.
Server IP
Enter the DHCP server’s IP address here.
Profile Name
Enter the DHCP server screening profile that will be used for the
port(s) specified here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
ARP Spoofing Prevention
This window is used to view and configure the ARP spoofing prevention settings. When an entry is
created, ARP packets whose sender IP address matches the gateway IP address, of an entry, but its
sender MAC address field does not match the gateway MAC address, of the entry, will be dropped by
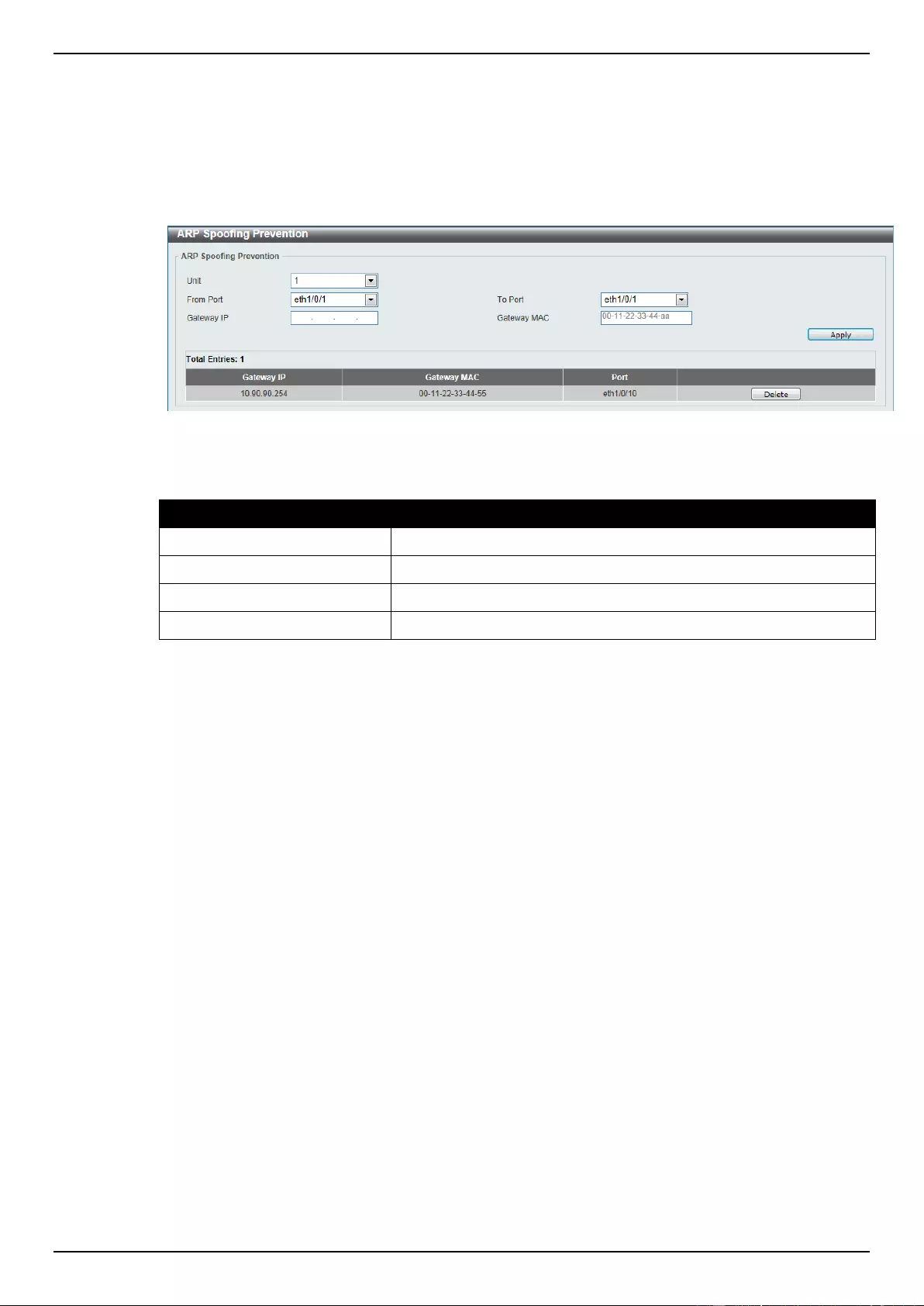
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
314
the system. The ASP will bypass the ARP packets whose sender IP address doesn’t match the
configured gateway IP address.
If an ARP address matches a configured gateway’s IP address, MAC address, and port list, then
bypass the Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) check no matter if the receiving port is ARP trusted or
untrusted.
To view the following window, click Security > ARP Spoofing Prevention, as shown below:
Figure 9-61 ARP Spoofing Prevention window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Gateway IP
Enter the gateway’s IP address used here.
Gateway MAC
Enter the gateway’s MAC address used here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
BPDU Attack Protection
This window is used to view and configure the BPDU attack protection settings. In generally, there are
two states in the BPDU attack protection function. One is normal state, and another is under attack
state. The under attack state have three modes: drop, block, and shutdown. A BPDU protection
enabled port will enter an under attack state when it receives one STP BPDU packet and it will take
action based on the configuration. Thus, BPDU protection can only be enabled on the STP-disabled
port.
BPDU protection has a higher priority than the FBPDU setting configured by configure STP command
in the determination of BPDU handling. That is, when FBPDU is configured to forward STP BPDU but
BPDU protection is enabled, then the port will not forward STP BPDU.
BPDU protection also has a higher priority than the BPDU tunnel port setting in determination of
BPDU handling. That is, when a port is configured as BPDU tunnel port for STP, it will forward STP
BPDU. But if the port is BPDU protection enabled. Then the port will not forward STP BPDU.
To view the following window, click Security > BPDU Attack Protection, as shown below:
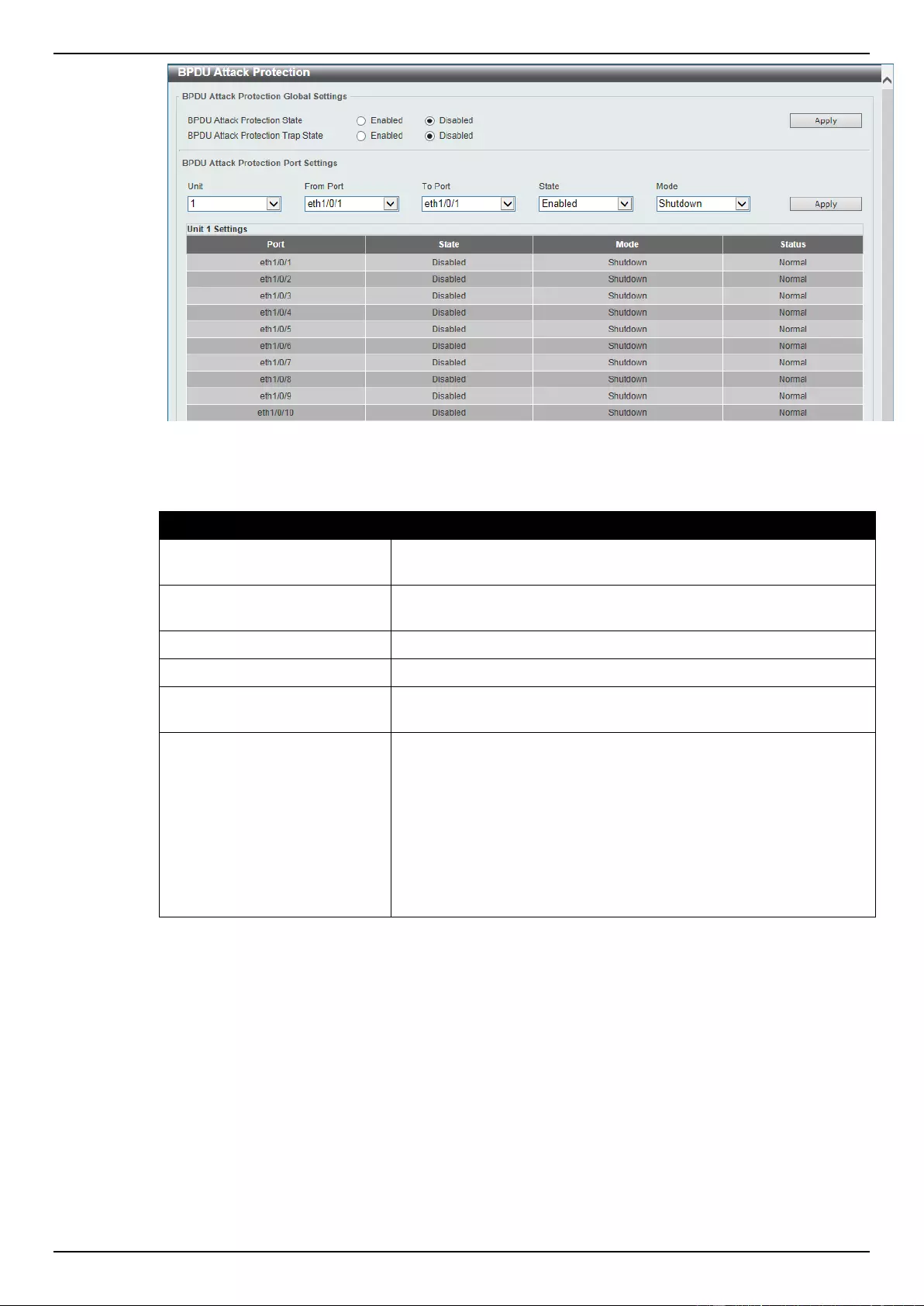
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
315
Figure 9-62 BPDU Attack Protection window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
BPDU Attack Protection
State
Select to enable or disable the BPDU attack protection feature’s
global state here.
BPDU Attack Protection Trap
State
Select to enable or disable the BPDU attack protection feature’s
trap state here.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the BPDU attack protection feature’s
state on the port(s) specified.
Mode
Select the BPDU attack protection feature’s mode that will be
applied to the port(s) specified. Options to choose from are Drop,
Block and Shutdown.
Drop – Drop all received BPDU packets when the port enters under
attack state.
Block – Drop all packets (include BPDU and normal packets) when
the port enters under attack state.
Shutdown – Shut down the port when the port enters under attack
state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
MAC Authentication
This window is used to view and configure the MAC authentication settings. MAC authentication is a
feature designed to authenticate a user by MAC address when the user is trying to access the
network via the Switch. The Switch itself can perform the authentication based on a local database or
be a RADIUS client and perform the authentication process via the RADIUS protocol with a remote
RADIUS server.
To view the following window, click Security > MAC Authentication, as shown below:
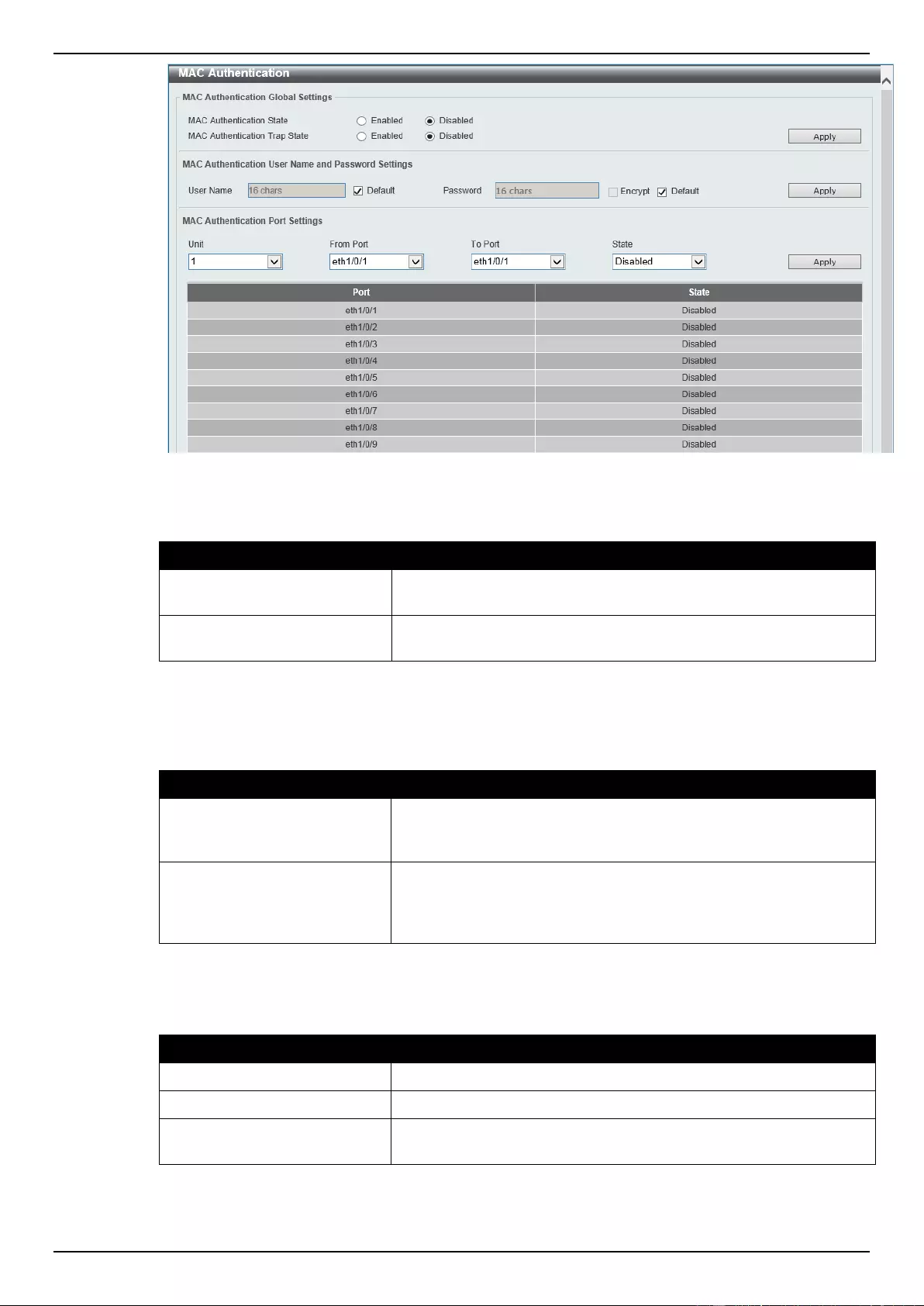
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
316
Figure 9-63 Port Security Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for MAC Authentication Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
MAC Authentication State
Select to enable or disable the MAC authentication feature’s global
state.
MAC Authentication Trap
State
Select to enable or disable the MAC authentication feature’s trap
state.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for MAC Authentication User Name and Password Settings are
described below:
Parameter
Description
User Name
Enter the username used for MAC authentication here. This name
can be up to 16 characters long. Tick the Default option to restore
the username to the client’s MAC address here.
Password
Enter the password used for MAC authentication here. Tick the
Encrypt option save this password in the encrypted form. Tick the
Default option to restore the password to the client’s MAC address
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for MAC Authentication Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable MAC authentication for the port(s)
specified here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
317
Web-based Access Control
Web-based Access Control (WAC) is a feature designed to authenticate a user when the user is trying
to access the Internet via the Switch. The authentication process uses the HTTP or HTTPS protocol.
The Switch enters the authenticating stage when users attempt to browse Web pages (e.g.,
http://www.dlink.com) through a Web browser. When the Switch detects HTTP or HTTPS packets and
this port is unauthenticated, the Switch will launch a pop-up user name and password window to
query users. Users are not able to access the Internet until the authentication process is passed.
The Switch can be the authentication server itself and do the authentication based on a local
database, or be a RADIUS client and perform the authentication process via the RADIUS protocol
with a remote RADIUS server. The client user initiates the authentication process of WAC by
attempting to gain Web access.
D-Link’s implementation of WAC uses a virtual IP that is exclusively used by the WAC function and is
not known by any other modules of the Switch. In fact, to avoid affecting a Switch’s other features,
WAC will only use a virtual IP address to communicate with hosts. Thus, all authentication requests
must be sent to a virtual IP address but not to the IP address of the Switch’s physical interface.
Virtual IP works like this, when a host PC communicates with the WAC Switch through a virtual IP, the
virtual IP is transformed into the physical IPIF (IP interface) address of the Switch to make the
communication possible. The host PC and other servers’ IP configurations do not depend on the
virtual IP of WAC. The virtual IP does not respond to any ICMP packets or ARP requests, which
means it is not allowed to configure a virtual IP on the same subnet as the Switch’s IPIF (IP interface)
or the same subnet as the host PCs’ subnet.
As all packets to a virtual IP from authenticated and authenticating hosts will be trapped to the
Switch’s CPU, if the virtual IP is the same as other servers or PCs, the hosts on the WAC-enabled
ports cannot communicate with the server or PC which really own the IP address. If the hosts need to
access the server or PC, the virtual IP cannot be the same as the one of the server or PC. If a host
PC uses a proxy to access the Web, to make the authentication work properly the user of the PC
should add the virtual IP to the exception of the proxy configuration. Whether or not a virtual IP is
specified, users can access the WAC pages through the Switch’s system IP. When a virtual IP is not
specified, the authenticating Web request will be redirected to the Switch’s system IP.
The Switch’s implementation of WAC features a user-defined port number that allows the
configuration of the TCP port for either the HTTP or HTTPS protocols. This TCP port for HTTP or
HTTPs is used to identify the HTTP or HTTPs packets that will be trapped to the CPU for
authentication processing, or to access the login page. If not specified, the default port number for
HTTP is 80 and the default port number for HTTPS is 443. If no protocol is specified, the default
protocol is HTTP.
The following diagram illustrates the basic six steps all parties go through in a successful Web
Authentication process:
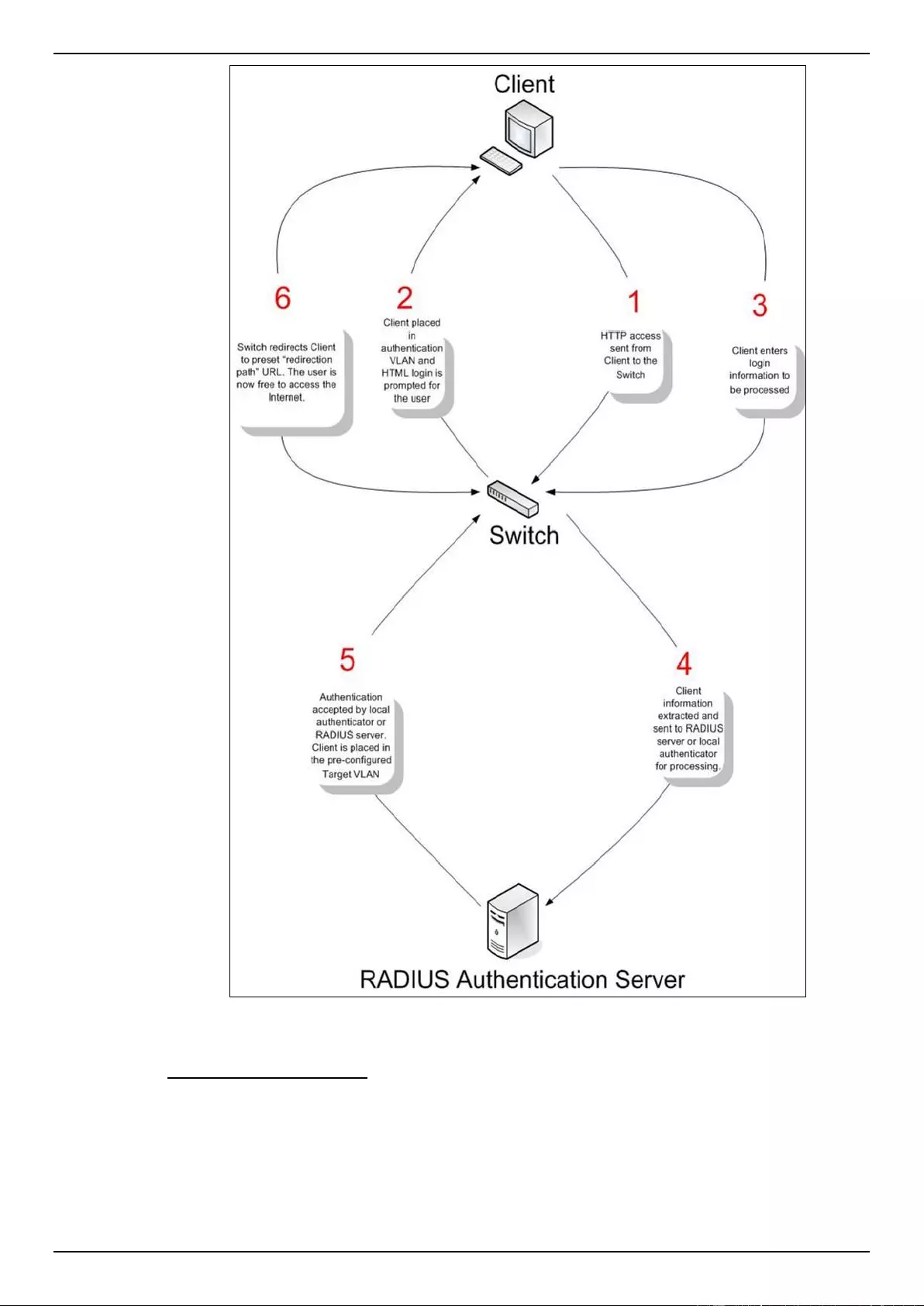
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
318
Figure 9-64 RADIUS Authentication Server
Conditions and Limitations
If the client is utilizing DHCP to attain an IP address, the authenticating VLAN must provide a
DHCP server or a DHCP relay function so that client may obtain an IP address.
Certain functions exist on the Switch that will filter HTTP packets, such as the Access Profile
function. The user needs to be very careful when setting filter functions for the target VLAN,
so that these HTTP packets are not denied by the Switch.
If a RADIUS server is to be used for authentication, the user must first establish a RADIUS
Server with the appropriate parameters, including the target VLAN, before enabling Web
Authentication on the Switch.
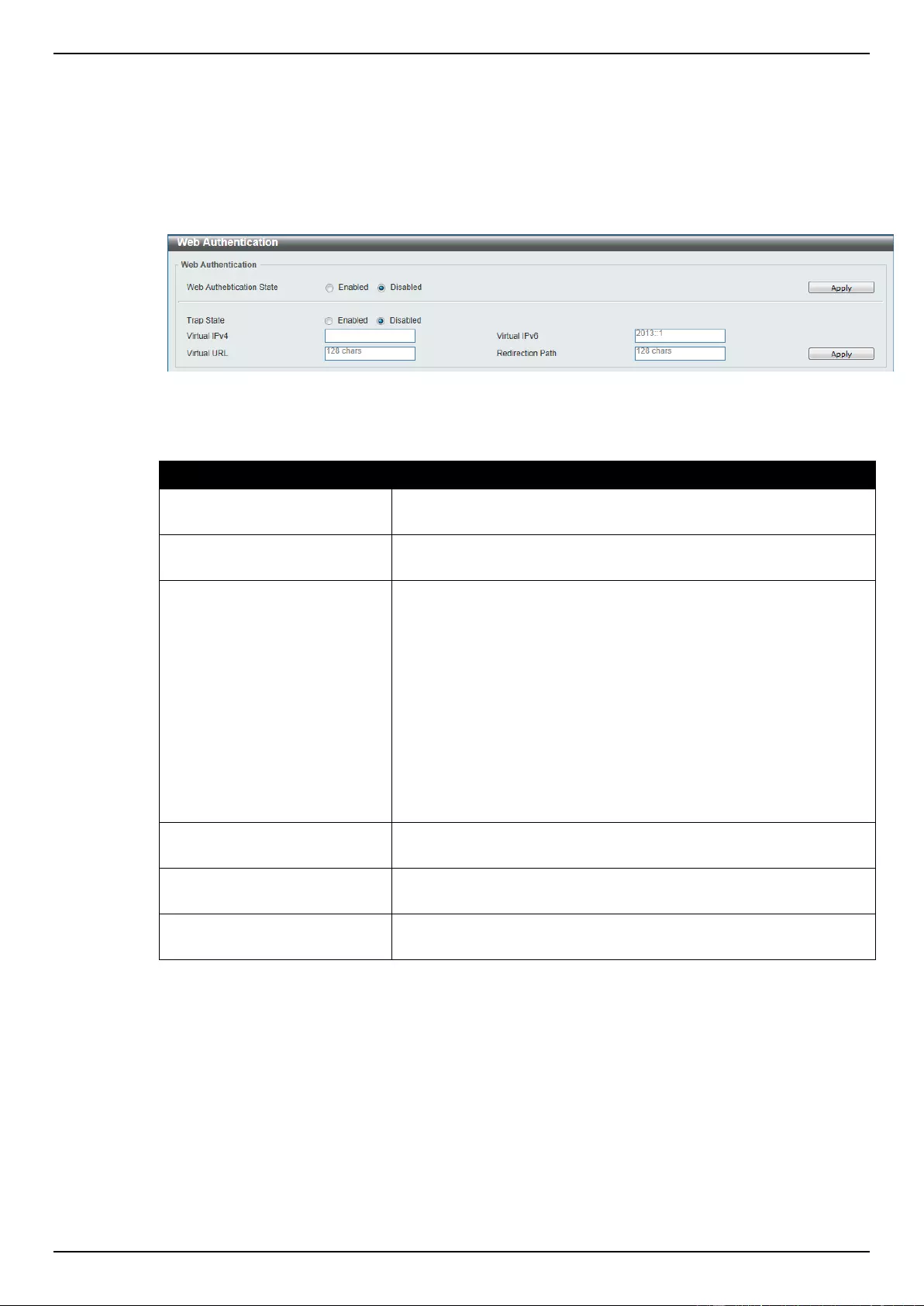
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
319
Web Authentication
This window is used to view and configure the Web authentication settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Web-based Access Control > Web Authentication,
as shown below:
Figure 9-65 Port Security Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Web Authentication State
Select to enable or disable the Web authentication feature’s global
state.
Trap State
Select to enable or disable the Web authentication feature’s trap
state.
Virtual IPv4
Enter the virtual IPv4 address used here. The virtual IP of Web
authentication is just the characterization of the Web authentication
function on the Switch. All Web authentication processes
communicate with this IP address, however, the virtual IP does not
respond to any ICMP packet or ARP request. So it’s not allowed to
configure virtual IP in the same subnet as the Switch’s IP interface
or the same subnet as the host PCs’ subnet, otherwise the Web
authentication cannot operate correctly. The defined URL only takes
effect when the virtual IP address is configured. The users get the
FQDN URL stored on the DNS server to get the virtual IP address.
The obtained IP address must match the virtual IP address
configured by the command. If the IPv4 virtual IP is not configured,
the IPv4 access cannot start a Web authentication.
Virtual IPv6
Enter the virtual IPv6 address used here. If the IPv6 virtual IP is not
configured, the IPv6 access cannot start a Web authentication.
Virtual URL
Enter the virtual URL used here. This URL can be up to 128
characters long.
Redirection Path
Enter the redirection path here. This path can be up to 128
characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
WAC Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the WAC port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Web-based Access Control > WAC Port Settings,
as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
320
Figure 9-66 WAC Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select to enable or disable the WAC feature on the port(s) specified.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
WAC Customize Page
This window is used to view and configure the WAC customized login page.
To view the following window, click Security > Web-based Access Control > WAC Customize
Page, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
321
Figure 9-67 WAC Customize Page window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Page Title
Enter a custom page title message here. This message can be up
to 128 characters long.
Login window Title
Enter a custom login window title here. This title can be up to 64
characters long.
User Name Title
Enter a custom username title here. This title can be up to 32
characters long.
Password Title
Enter a custom password title here. This title can be up to 32
characters long.
Logout window Title
Enter a custom logout window title here. This title can be up to 64
characters long.
Notification
Enter additional information to display in the notification area here.
This information can be up to 128 characters long for each line.
There a 5 lines available for additional information.
Click the Set to Default button to replace the information with the default information.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Japanese Web-based Access Control
JWAC Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Japanese Web-based Access Control (JWAC) global
settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Japanese Web-based Access Control > JWAC
Global Settings, as shown below:
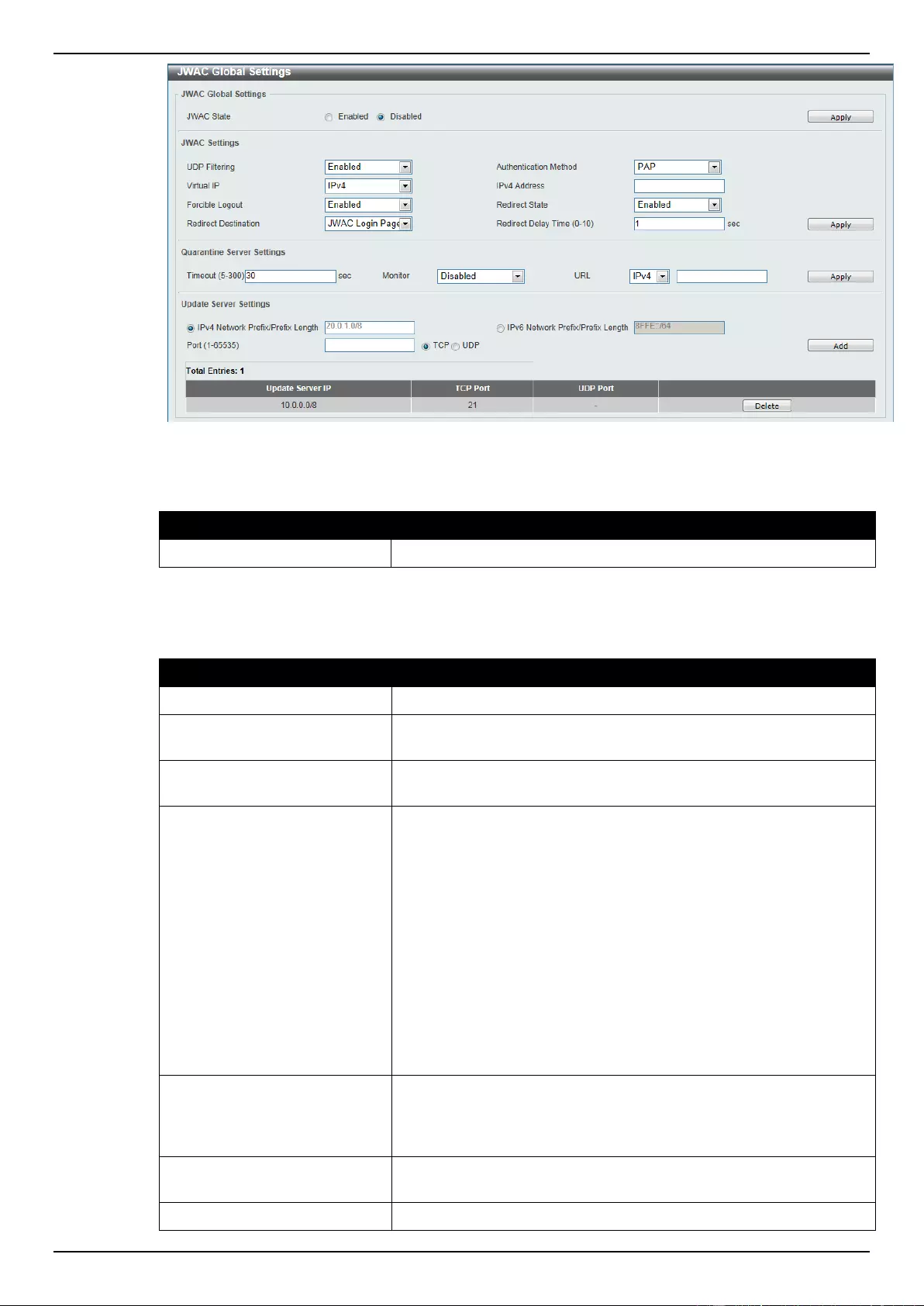
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
322
Figure 9-68 JWAC Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for JWAC Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
JWAC State
Select to enable or disable the JWAC feature’s global state here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for JWAC Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
UDP Filtering
Select to enable or disable UDP filtering here.
Authentication Method
Select the authentication method used here. Options to choose
from are MD5, CHAP, PAP, MS-CHAP, and MS-CHAP-v2.
Virtual IP
Select the virtual IP option used here. Options to choose from are
IPv4, IPv6, and URL.
IPv4 Address
After selecting IPv4 as the Virtual IP, the following field will be
available. Enter the virtual IPv4 address used here. All JWAC
authentication processes communicate with this IP address,
however, the virtual IP does not respond to any ICMP packets or
ARP requests. So it’s not allowed to configure virtual IP in the same
subnet as the switch’s IP interface or the same subnet as the host
PCs’ subnet, otherwise JWAC authentication cannot operate
correctly.
The defined URL only takes effect when the virtual IP address is
configured. The users get the FQDN URL stored on the DNS server
to get the virtual IP address. The obtained IP address must match
the virtual IP address configured by the command.
If the IPv4 virtual IP is not configured, the IPv4 access cannot start
JWAC authentication.
IPv6 Address
After selecting IPv6 as the Virtual IP, the following field will be
available. Enter the virtual IPv6 address used here. If the IPv6
virtual IP is not configured, the IPv6 access cannot start a JWAC
authentication.
Virtual URL
After selecting URL as the Virtual IP, the following field will be
available. Enter the virtual URL used here.
Forcible Logout
Select to enable or disable the forcible logout option here. When the

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
323
forcible logout feature is enabled, a ping packet from an
authenticated host to the JWAC switch with a TTL of 1 will be
regarded as a logout request and the host will be moved back to
unauthenticated state.
Redirect State
Select to enable or disable the redirection state here. When redirect
is enabled, all Web access is redirected to the quarantine server or
JWAC login page.
Redirect Destination
Select the redirect destination here. Options to choose from are
Quarantine Server and JWAC Login Page. When redirecting to
the quarantine server, the unauthenticated host will be redirected to
the quarantine server when it tries to access a random URL. When
redirecting to the JWAC login page, the unauthenticated host will be
redirected to the JWAC login page in the switch to finish
authentication. When redirecting to the quarantine server is
specified, a quarantine server must be configured first before
enabling the JWAC function globally. When redirect is disabled, all
Web access is denied except for access to the quarantine server or
JWAC login page.
Redirect Delay Time
Enter the redirect delay time value here. This value must be
between 0 and 10 seconds. By default, this value 1 second.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Quarantine Server Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Timeout
Enter the quarantine server’s timeout value here. This value must
be between 5 and 300 seconds. By default, this value is 30
seconds.
Monitor
Select to enable or disable the monitor option here. When the
JWAC quarantine server monitor feature is enabled, the JWAC
switch will monitor the quarantine server to ensure the server is
okay. If the switch detects no quarantine server, it will redirect all
unauthenticated HTTP accesses to the JWAC Login Page if the
redirect option is enabled and the redirect destination is configured
to be quarantine server.
URL
Select the whether the quarantine server uses an IPv4 or IPv6
address and enter the respective IP address in the space provided.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Update Server Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv4 Network Prefix/Prefix
Length
Enter the update server’s IPv4 address and prefix length here. Any
servers (like update.microsoft.com or some sites of Antivirus
software companies, which ActiveX needs to access to accomplish
the authentication before the client passes the authentication)
should be added with its IP address or with the network address. By
adding the network address, an entry can serve multiple update
servers on the same network. Multiple update server addresses or
network addresses can be configured.
IPv6 Network Prefix/Prefix
Length
Enter the update server’s IPv6 address and prefix length here.
Port
Enter the update server’s port used here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535. Also select whether this port is a TCP or
UDP port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
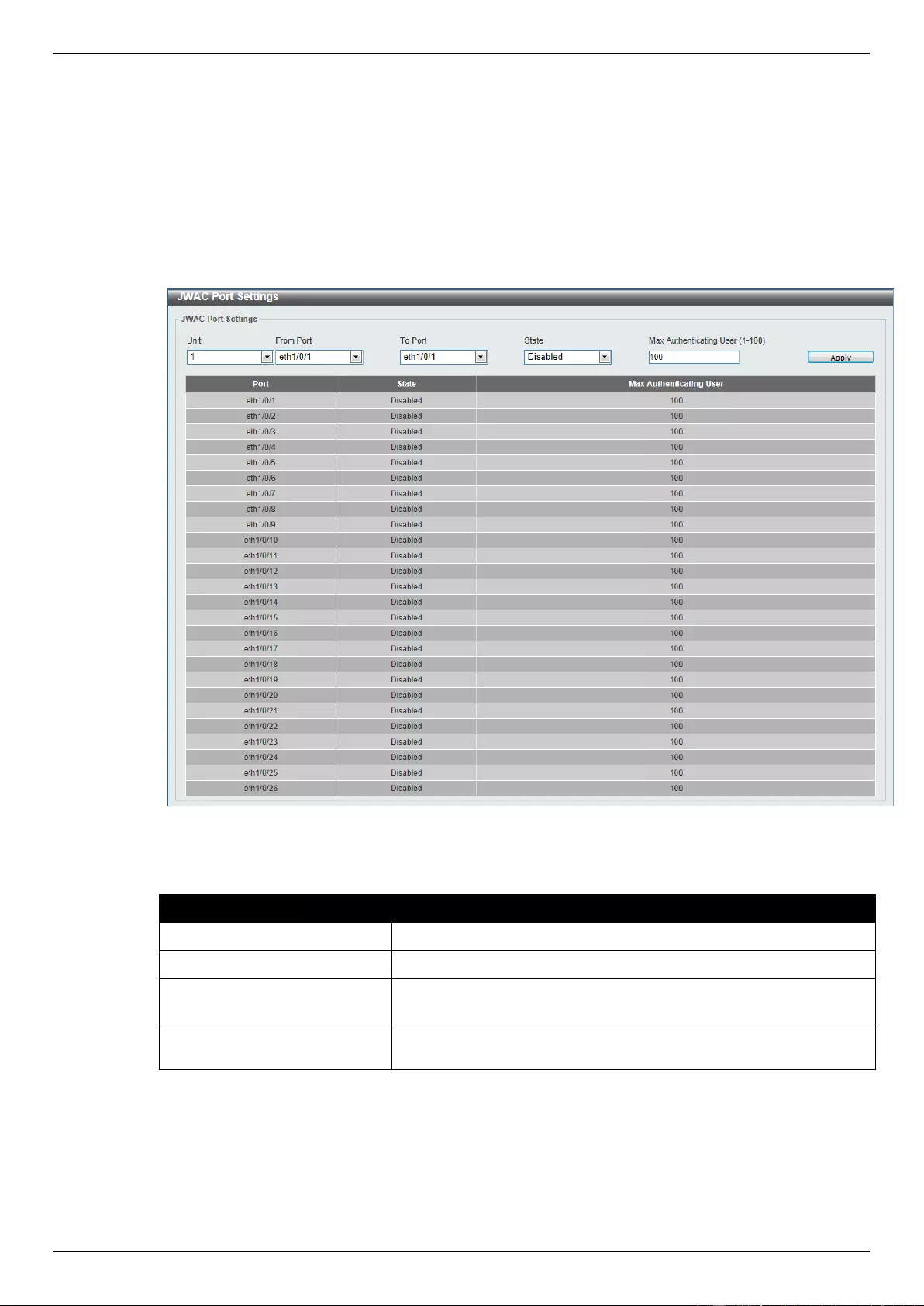
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
324
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
JWAC Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the JWAC port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Japanese Web-based Access Control > JWAC Port
Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-69 JWAC Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select whether JWAC is enabled or disabled on the port(s)
specified.
Max Authenticating User
Enter the maximum number of authentication users allowed here.
This value must be between 1 and 100.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
JWAC Customize Page Language
This window is used to view and configure the JWAC customize page’s language.
To view the following window, click Security > Japanese Web-based Access Control > JWAC
Customize Page Language, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
325
Figure 9-70 JWAC Customize Page Language window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Customize Page Language
Select the language option that will be used when the JWAC login
page is displayed.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
JWAC Customize Page
This window is used to view and configure the JWAC customize page settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Japanese Web-based Access Control > JWAC
Customize Page, as shown below:
Figure 9-71 JWAC Customize Page (English) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Page Title
Enter a custom page title message here. This message can be up
to 128 characters long.
Login window Title
Enter a custom login window title here. This title can be up to 64
characters long.
User Name Title
Enter a custom username title here. This title can be up to 32
characters long.
Password Title
Enter a custom password title here. This title can be up to 32
characters long.
Logout window Title
Enter a custom logout window title here. This title can be up to 64
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
326
characters long.
Notification
Enter additional information to display in the notification area here.
This information can be up to 128 characters long for each line.
There a 5 lines available for additional information.
Click the Set to Default button to replace the information with the default information.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After changing the language to Japanese the JWAC customize page will look like this.
Figure 9-72 JWAC Customize Page (Japanese) window
Click the Set to Default button to replace the information with the default information.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Network Access Authentication
Guest VLAN
This window is used to view and configure the network access authentication guest VLAN settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Network Access Authentication > Guest VLAN, as
shown below:
Figure 9-73 Guest VLAN window

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
327
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used here. This value must be between 1 and
4094.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Network Access Authentication Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the network access authentication global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Network Access Authentication > Network Access
Authentication Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-74 Network Access Authentication Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Network Access Authentication MAC Format Settings are
described below:
Parameter
Description
Case
Select the case format that will be used for the network access
authentication MAC address here. Options to choose from are
Lowercase and Uppercase.
Delimiter
Select the delimiter that will be used for the network access
authentication MAC address here. Options to choose from are
Hyphen, Colon, Dot, and None.
Delimiter Number
Select the delimiter number option here. Options to choose from are
1, 2, and 5.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for General Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
328
Max Users
Enter the maximum amount of users allowed here. This value must
be between 1 and 1000. By default, this option is 1000.
Deny MAC-Move
Select to enable or disable the deny MAC-move feature here. This
option controls whether to allow authenticated hosts to do roaming
across different switch ports and only controls whether a host which
is authenticated at a port set to the multi-authenticate mode is
allowed to move to another port.
If a station is allowed to move, there are two situations. It may either
need to be re-authenticated or directly moved to the new port
without re-authentication based on the following rule. If the new port
has the same authentication configuration as the original port, then
re-authentication is not needed. The host will inherit the same
authorization attributes with new port. The authenticated host can
do roaming from port 1 to port 2, and inherit the authorization
attributes without re-authentication. If the new port has the different
authentication configuration as the original port, then re-
authentication is needed. The authenticated host on port 1 can
move and re-authenticated by port 2. If the new port has no
authentication method enabled, then the station is directly moved to
the new port. The session with the original port is removed. The
authenticated host on port 1 can be moved to port 2.
If this feature is disabled and an authenticated host moves to
another port, then this is treated as a violation error.
Authorization State
Select to enable or disable the authorized state here. The option is
used to enable or disable the acceptance of an authorized
configuration. When authorization is enabled for authentication, the
authorized attributes (for example VLAN, 802.1p default priority,
bandwidth, and ACL) assigned by the RADIUS server will be
accepted if the authorization status is enabled. Bandwidth and ACL
are assigned on a per-port basis. If in the multi-authenticated mode,
VLAN and 802.1p are assigned on a per-host basis. Otherwise,
Bandwidth and ACL are assigned on a per-port basis.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for User Information are described below:
Parameter
Description
User Name
Enter the user name used here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
VID
Enter the VLAN ID used here.
Password Type
Select the password type option here. Options to choose from are
Plain Text and Encrypted.
Password
Enter the password used here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Network Access Authentication Port Settings
This window is used to view and configure the network access authentication port settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Network Access Authentication > Network Access
Authentication Port Settings, as shown below:
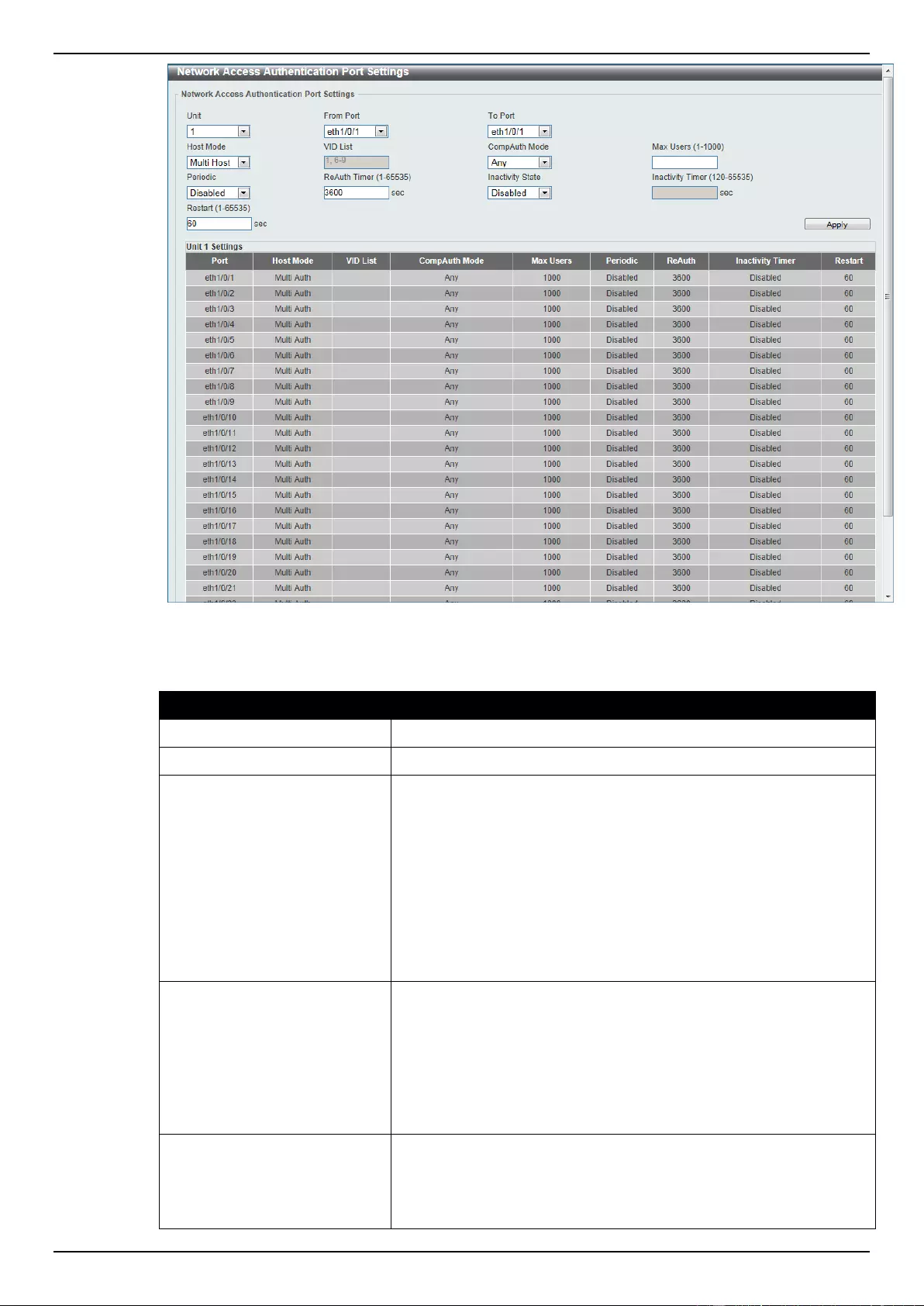
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
329
Figure 9-75 Network Access Authentication Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Host Mode
Select the host mode option that will be associated with the selected
port(s) here. Options to choose from are Multi Host and Multi
Auth. If the port is operated in the multi-host mode, and if one of the
hosts is authenticated, then all other hosts are allowed to access
the port. According to 802.1X authentication, if the re-authentication
fails or the authenticated user logs off, the port will be blocked for a
quiet period. The port restores the processing of EAPOL packets
after the quiet period. If the port is operated in the multi-
authenticated mode, then each host needs to be authenticated
individually to access the port. A host is represented by its MAC
address. Only the authorized host is allowed to access.
VID List
After selecting the Multi Auth option as the Host Mode, the
following parameter is available. Enter the VLAN ID used here. This
is useful when different VLANs on the Switch have different
authentication requirements. After the client is authenticated, the
client will not be re-authenticated when received from other VLANs.
This option is useful for trunk ports to do per-VLAN authentication
control. When a port’s authentication mode is changed to multi-host,
the previous authentication VLAN(s) on this port will be cleared.
CompAuth Mode
Select the compound authentication mode option here. Options to
choose from are Any, MAC-JWAC, and MAC-WAC. Selecting Any
specifies that if any of the authentication method (802.1X, MAC-
based Access Control, WAC, or JWAC) to passes, then pass.
Selecting MAC-JWAC specifies to verify MAC-based authentication
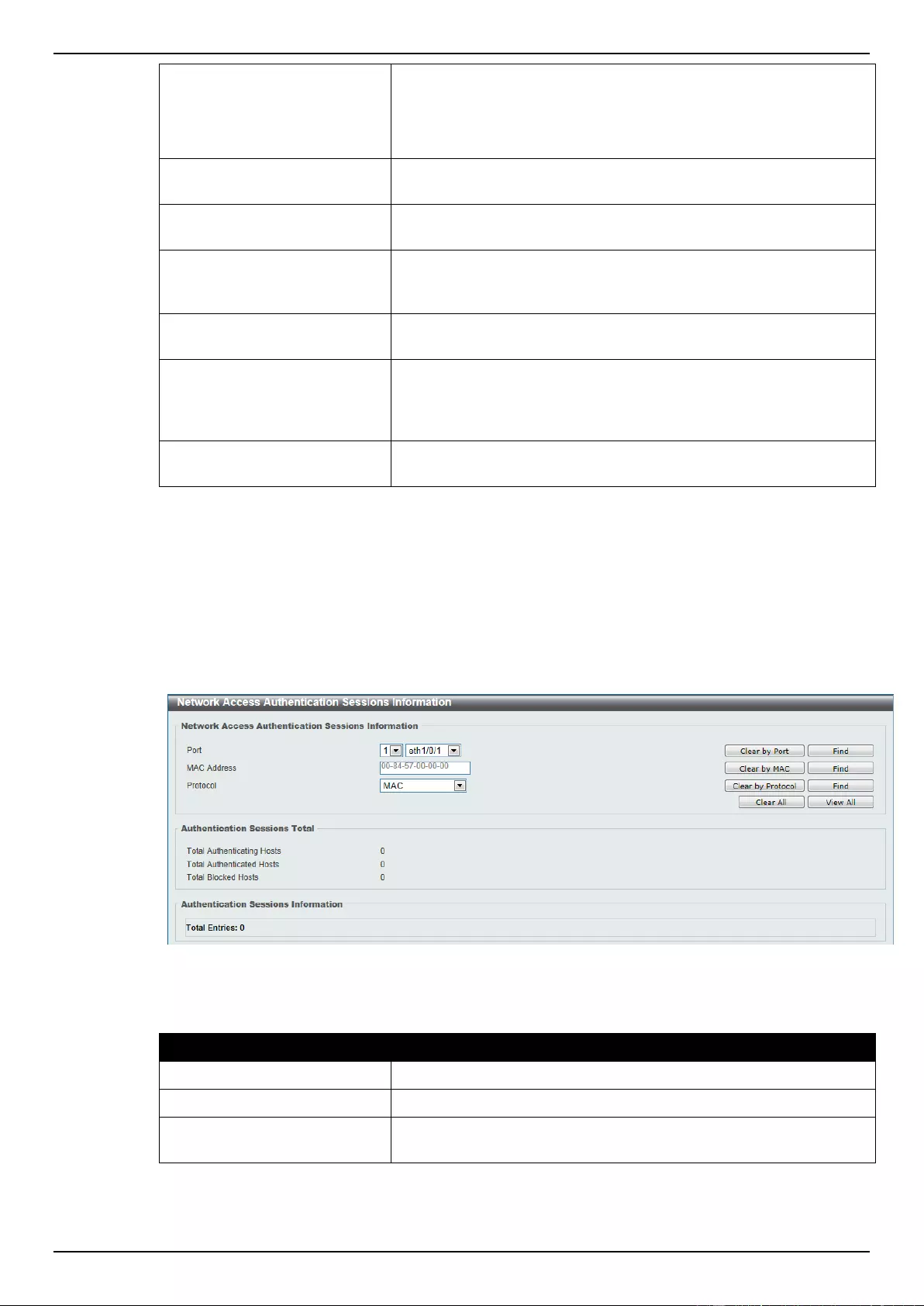
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
330
first. If the client passes, JWAC will be verified next. Both
authentication methods need to be passed. Selecting MAC-WAC
specifies to verify MAC-based authentication first. If the client
passes, WAC will be verified next. Both authentication methods
need to be passed.
Max Users
Enter the maximum users value used here. This value must be
between 1 and 1000.
Periodic
Select to enable or disable periodic re-authentication for the
selected port here. This parameter only affects the 802.1X protocol.
ReAuth Timer
Enter the re-authentication timer value here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535 seconds. By default, this value is 3600
seconds.
Inactivity State
Select to enable or disable the inactivity state here. Select the Time
option to enable this feature.
Inactivity Timer
When the Inactivity State is enabled, enter the inactivity timer
value here. This value must be between 120 and 65535 seconds.
This parameter only affects the WAC and JWAC authentication
protocols.
Restart
Enter the restart time value used here. This value must be between
1 and 65535 seconds.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Network Access Authentication Sessions Information
This window is used to view and clear the network access authentication session information.
To view the following window, click Security > Network Access Authentication > Network Access
Authentication Sessions Information, as shown below:
Figure 9-76 Network Access Authentication Sessions Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Port
Select the appropriate switch unit and port used for the query here.
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address used here.
Protocol
Select the protocol option used here. Options to choose from are
MAC, WAC, JWAC, and DOT1X.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Clear by Port button to the clear the information based on the port selected.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
331
Click the Clear by MAC button to the clear the information based on the MAC address entered.
Click the Clear by Protocol button to the clear the information based on the protocol selected.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the View All button to locate and display all the entries.
Safeguard Engine
Periodically, malicious hosts on the network will attack the Switch by utilizing packet flooding (ARP
Storm) or other methods. These attacks may increase the switch’s CPU load beyond its capability. To
alleviate this problem, the Safeguard Engine function was added to the Switch’s software.
The Safeguard Engine can help the overall operability of the Switch by minimizing the workload of the
Switch while the attack is ongoing, thus making it capable to forward essential packets over its
network in a limited bandwidth.
If the CPU load rises above the rising threshold value, the Safeguard Engine function will be activated
and the Switch will enter the exhausted mode. In the exhausted mode, the Switch will limit the
bandwidth available for ARP and broadcast IP packets. If the CPU load falls below the falling
threshold value, the Safeguard Engine will be deactivated and the Switch will exit the exhausted mode
and enter the normal mode.
Packets that are destined to the CPU can be classified into three groups. These groups, otherwise
known as sub-interfaces, are logical interfaces that the CPU will use to identify certain types of traffic.
The three groups are Protocol, Manage, and Route. Generally, the Protocol group should receive
the highest priority when the Switch’s CPU processes received packets and the Route group should
receive the lowest priority as the Switch’s CPU usually does get involved in the processing of routing
packets. In the Protocol group, packets are protocol control packets identified by the router. In the
Manage group, packets are destined to any router or system network management interface by
means of interactive access protocols, like Telnet and SSH. In the Route group, packets are identified
as traversing routing packets that is generally processed by the router CPU.
In the following table a list of supported protocols are displayed with their respective sub-interfaces
(groups):
Protocol Name
Sub-interface (Group)
Description
802.1X
Protocol
Port-based Network Access Control
ARP
Protocol
Address resolution Protocol (ARP)
DHCP
Protocol
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DNS
Protocol
Domain Name System
GVRP
Protocol
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
ICMPv4
Protocol
Internet Control Message Protocol
ICMPv6-Neighbor
Protocol
IPv6 Internet Control Message Protocol Neighbor
Discovery Protocol (NS/NA/RS/RA)
ICMPv6-Other
Protocol
IPv6 Internet Control Message Protocol except
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NS/NA/RS/RA)
IGMP
Protocol
Internet Group Management Protocol
LACP
Protocol
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
SNMP
Manage
Simple Network Management Protocol
SSH
Manage
Secure Shell
STP
Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol
Telnet
Manage
Telnet
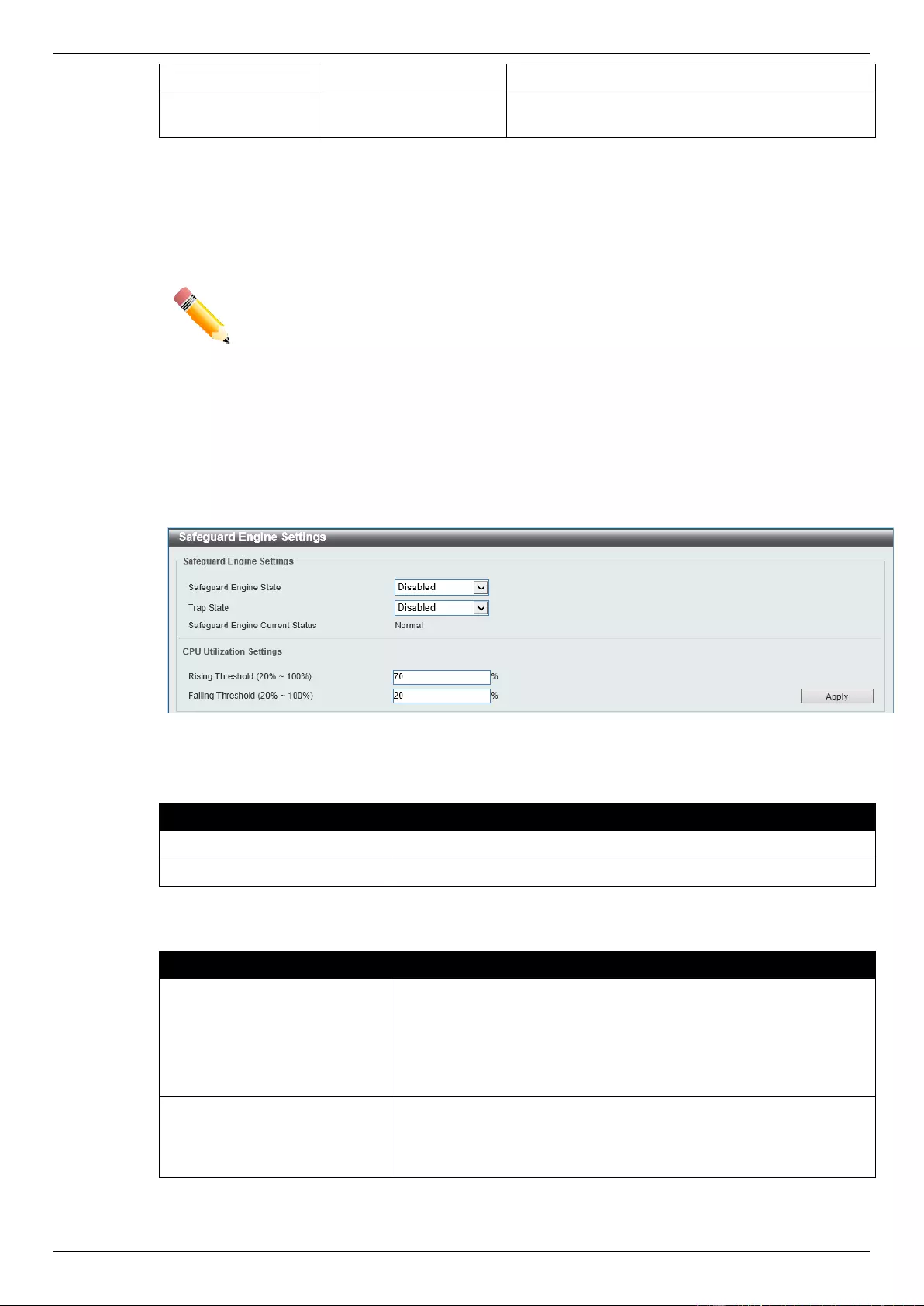
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
332
TFTP
Manage
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
Web
Manage
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Hypertext
Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
A customized rate limit (in packets per second) can be assigned to the Safeguard Engine’s sub-
interfaces as a whole or to individual protocols specified by the user in the management interface. Be
careful when customizing the rate limit for individual protocols, using this function, as improper rate
limits can cause the Switch to process packets abnormally.
NOTE: When Safeguard Engine is enabled, the Switch will allot bandwidth to various
traffic flows (ARP, IP) using the FFP (Fast Filter Processor) metering table to control the
CPU utilization and limit traffic. This may limit the speed of routing traffic over the network.
Safeguard Engine Settings
This window is used to view and configure the safeguard engine settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Safeguard Engine > Safeguard Engine Settings, as
shown below:
Figure 9-77 Safeguard Engine Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Safeguard Engine Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Safeguard Engine State
Select to enable or disable the safeguard engine feature here.
Trap State
Select to enable or disable the safeguard engine trap state here.
The fields that can be configured for CPU Utilization Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Rising Threshold
Enter the rising threshold value here. This value must be between
20% and 100%. This value is used to configure the acceptable level
of CPU utilization before the Safeguard Engine mechanism is
enabled. Once the CPU utilization reaches this percentage level,
the Switch will move into Exhausted mode, based on the
parameters provided in this window.
Falling Threshold
Enter the falling threshold value here. This value must be between
20% and 100%. This value is used to configure the acceptable level
of CPU utilization as a percentage, where the Switch leaves the
Safeguard Engine state and returns to normal mode.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
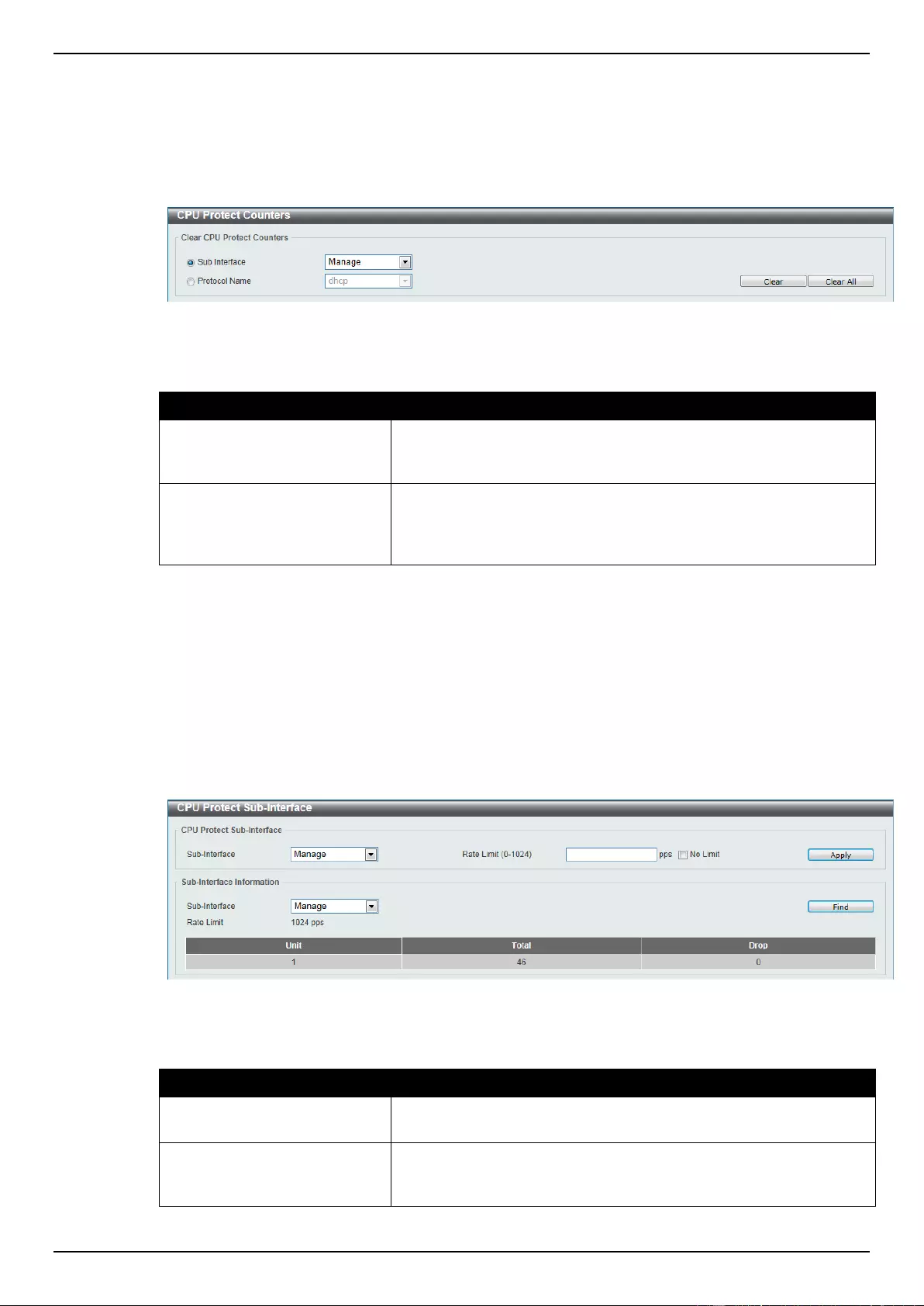
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
333
CPU Protect Counters
This window is used to view and clear the CPU protection counter information.
To view the following window, click Security > Safeguard Engine > CPU Protect Counters, as
shown below:
Figure 9-78 CPU Protect Counters window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sub Interface
Select the sub-interface option here. Options to choose from are
Manage, Protocol, Route, and All. This option specifies to clear
the CPU protect related counters of sub-interfaces.
Protocol Name
Select the protocol name option here. Options to choose from are
DHCP, ARP, DNS, GVRP, ICMPv4, ICMPv6-Neighbor, ICMPv6-
Other, IGMP, LACP, SNMP, SSH, STP, Telnet, TFTP, Web,
802.1X, and All.
Click the Clear button to clear the information based on the selections made.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
CPU Protect Sub-Interface
This window is used to view and configure the CPU protection sub-interface settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Safeguard Engine > CPU Protect Sub-Interface, as
shown below:
Figure 9-79 CPU Protect Sub-Interface window
The fields that can be configured for CPU Protect Sub-Interface are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sub-Interface
Select the sub-interface option here. Options to choose from are
Manage, Protocol, and Route.
Rate Limit
Enter the rate limit value used here. This value must be between 0
and 1024 packets per second. Tick the No Limit option to disable
the rate limit.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
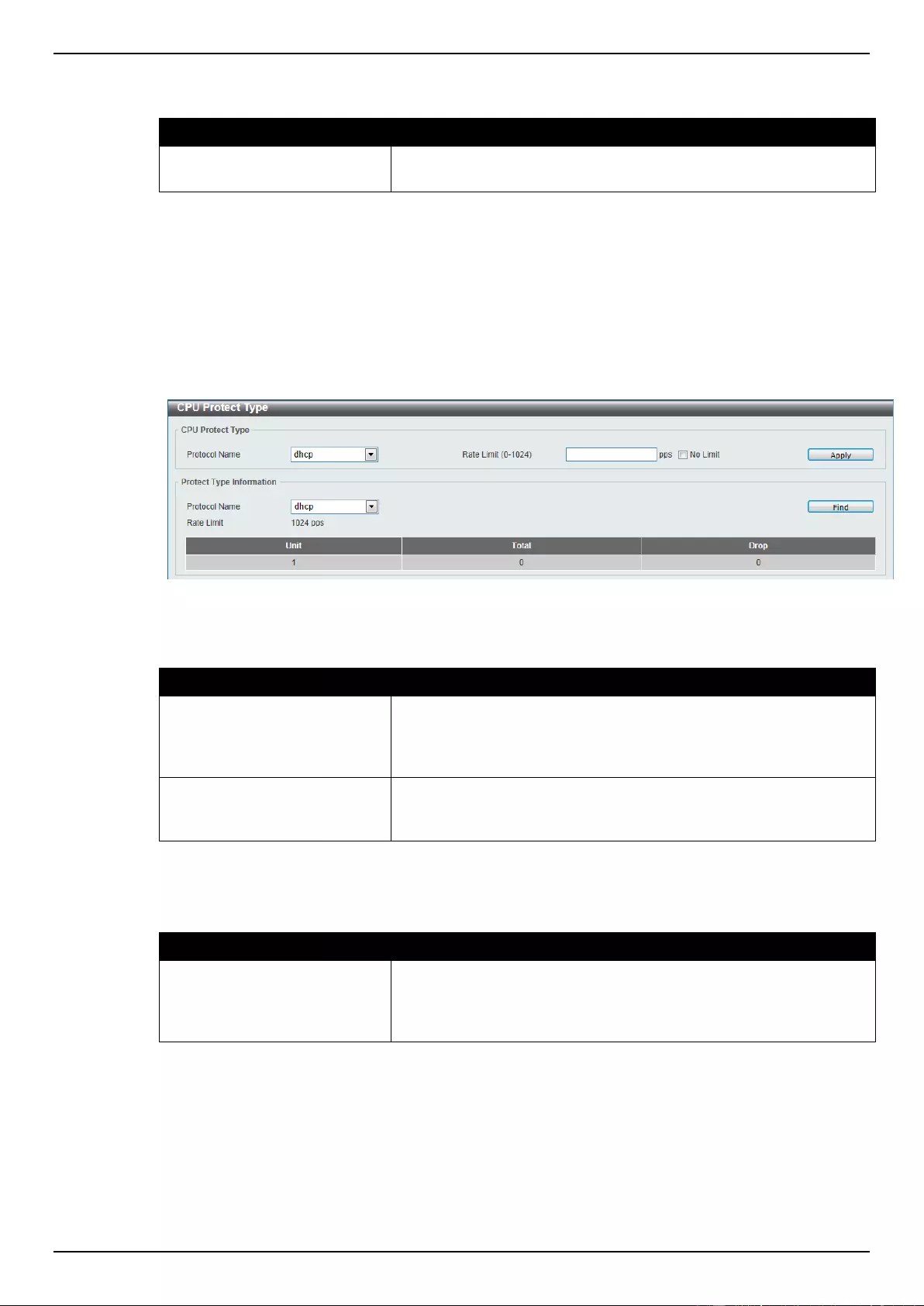
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
334
The fields that can be configured for Sub-Interface Information are described below:
Parameter
Description
Sub-Interface
Select the sub-interface option here. Options to choose from are
Manage, Protocol, and Route.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
CPU Protect Type
This window is used to view and configure the CPU protection type settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Safeguard Engine > CPU Protect Type, as shown
below:
Figure 9-80 CPU Protect Type window
The fields that can be configured for CPU Protect Type are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol Name
Select the protocol name option here. Options to choose from are
DHCP, ARP, DNS, GVRP, ICMPv4, ICMPv6-Neighbor, ICMPv6-
Other, IGMP, LACP, SNMP, SSH, STP, Telnet, TFTP, Web, and
802.1X.
Rate Limit
Enter the rate limit value used here. This value must be between 0
and 1024 packets per second. Tick the No Limit option to disable
the rate limit.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Protect Type Information are described below:
Parameter
Description
Protocol Name
Select the protocol name option here. Options to choose from are
DHCP, ARP, DNS, GVRP, ICMPv4, ICMPv6-Neighbor, ICMPv6-
Other, IGMP, LACP, SNMP, SSH, STP, Telnet, TFTP, Web, and
802.1X.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Trusted Host
This window is used to view and configure the trusted host settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Trusted Host, as shown below:
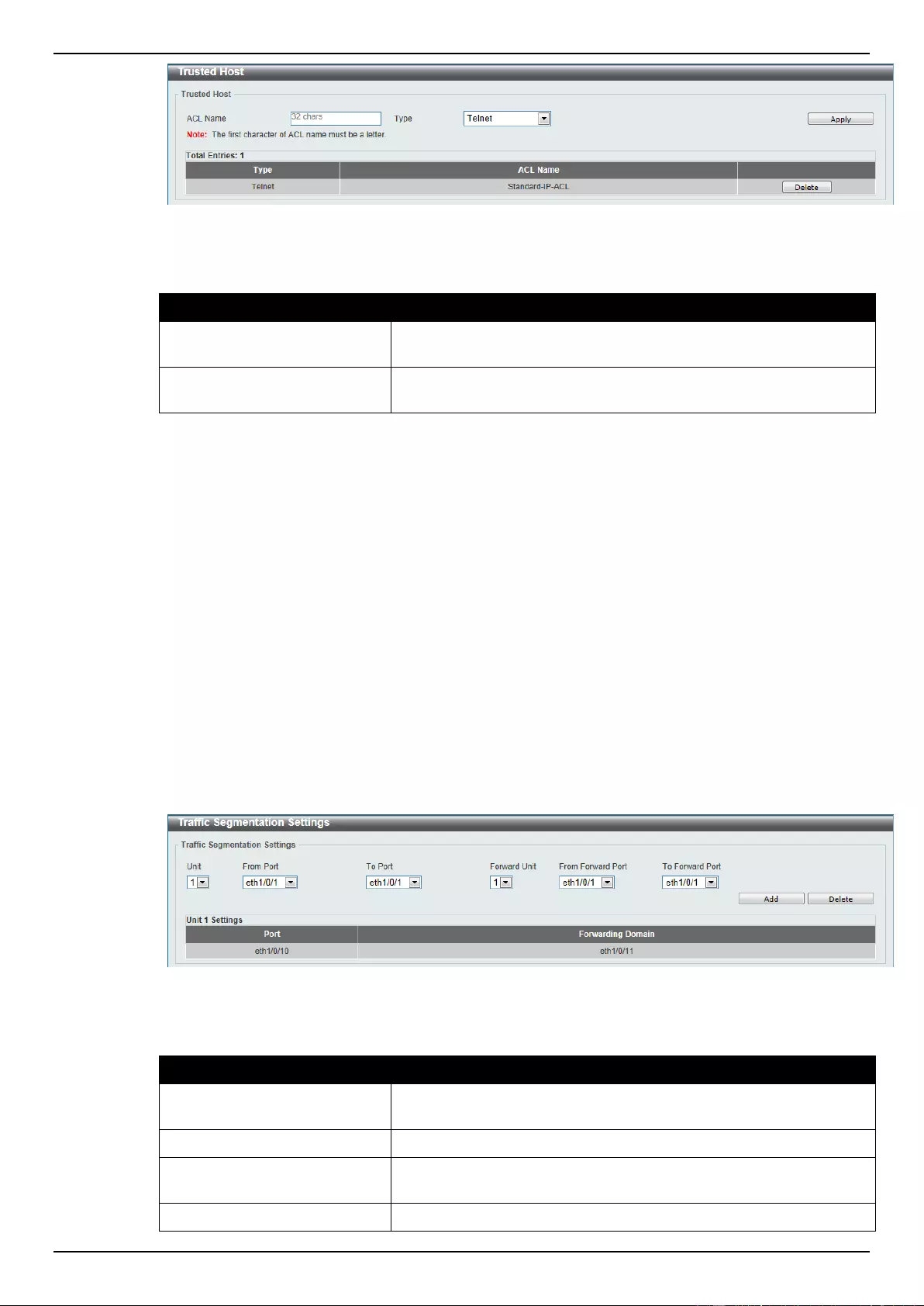
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
335
Figure 9-81 Trusted Host window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
ACL Name
Enter the ACL name used here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Type
Select the trusted host type here. Options to choose from are
Telnet, SSH, Ping, HTTP, and HTTPS.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Traffic Segmentation Settings
This window is used to view and configure the traffic segmentation settings. When the traffic
segmentation forwarding domain is specified, packets received by the port will be restricted in Layer 2
packet forwarding to interfaces within the domain. When the forwarding domain of a port is empty,
Layer 2 forwarding for packets received by the port is not restricted.
The traffic segmentation member list can be comprised of different interface types, for example port
and port-channel in the same forwarding domain. If the interfaces specified by the command include a
port-channel, all the member ports of this port-channel will be included in the forwarding domain.
If the forwarding domain of an interface is empty, then there is no restriction on Layer 2 forwarding of
packets received by the port.
To view the following window, click Security > Traffic Segmentation Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-82 Traffic Segmentation Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the receiving switch unit that will be used for this
configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the receiving port range used for the configuration here.
Forward Unit
Select the forward switch unit that will be used for this configuration
here.
From Forward Port / To
Select the forward port range used for the configuration here.
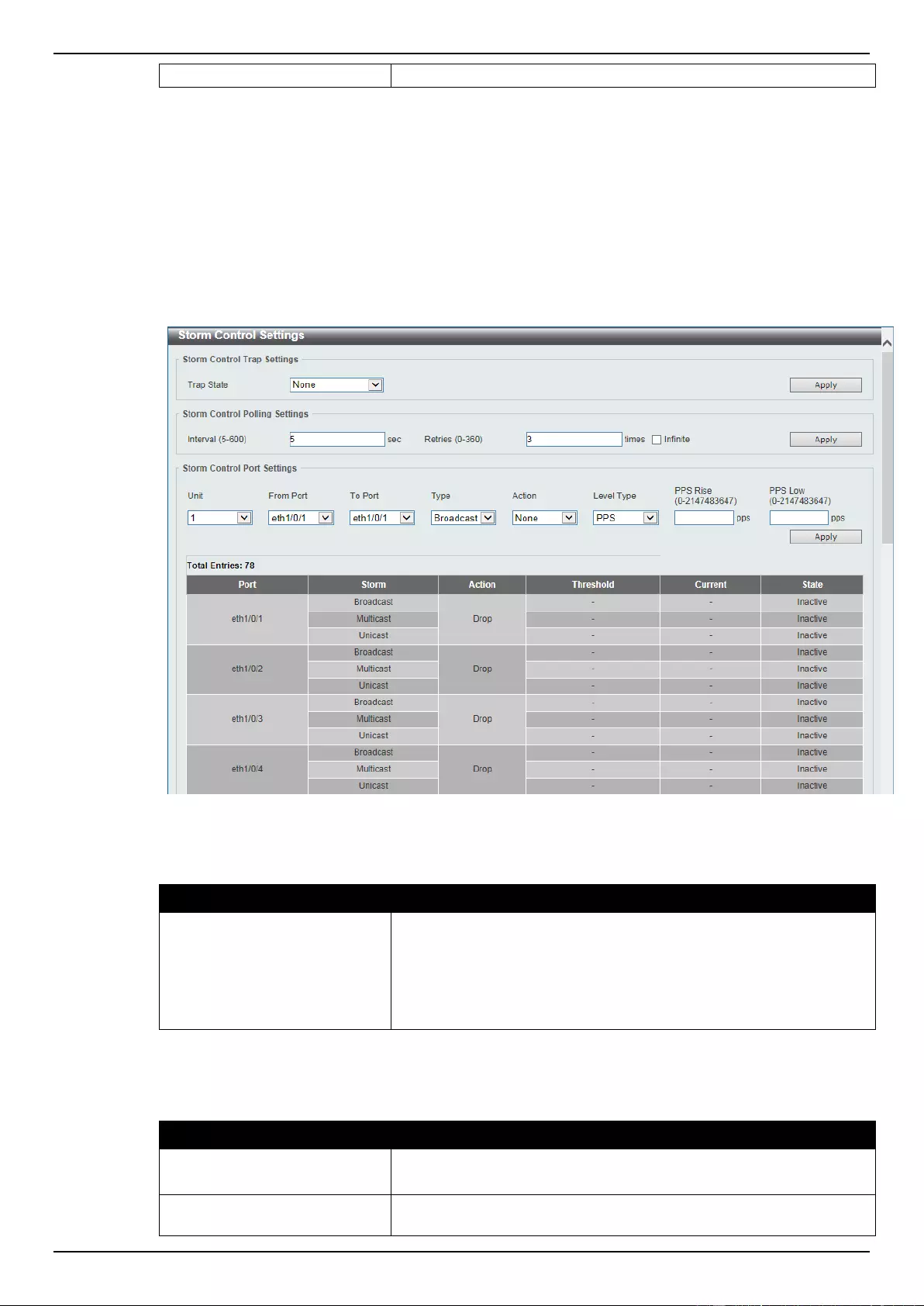
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
336
Forward Port
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove an entry based on the information entered.
Storm Control
This window is used to view and configure the storm control settings.
To view the following window, click Security > Storm Control, as shown below:
Figure 9-83 Storm Control window
The fields that can be configured for Storm Control Trap Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap State
Select the storm control trap option here. Options to choose from
are None, Storm Occur, Storm Clear, and Both. When None is
selected, no traps will be sent. When Storm Occur is selected, a
trap notification will be sent when a storm event is detected. When
Storm Clear is selected, a trap notification will be sent when a
storm event is cleared.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Storm Control Polling Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Interval
Enter the interval value used here. This value must be between 5
and 600 seconds. By default, this value is 5 seconds.
Retries
Enter the retries value used here. This value must be between 0
and 360. By default, this value is 3. Tick the Infinite option to

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
337
disable this feature.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Storm Control Port Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Type
Select the type of storm attack that will be controlled here. Options
to choose from are Broadcast, Multicast, and Unicast. When the
action is configured as the shutdown mode, the unicast refers to
both known and unknown unicast packets; that is, if the known and
unknown unicast packets hit the specified threshold, the port will be
shutdown. Otherwise, unicast refers to unknown unicast packets.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
None, Shutdown, and Drop. Selecting None specifies not to filter
the storm packets. Selecting Shutdown specifies to shut down the
port when the value specified for rise threshold is reached.
Selecting Drop specifies to discard packets that exceed the risen
threshold.
Level Type
Select the level type option here. Options to choose from are PPS,
Kbps, and Level.
PPS Rise
Enter the rise packets per second value here. This option specifies
the rise threshold value in packets count per second. This value
must be between 0 and 2147483647 packets per second. If the low
PPS value is not specified, the default value is 80% of the specified
risen PPS.
PPS Low
Enter the low packets per second value here. This option specifies
the low threshold value in packets count per second. This value
must be between 0 and 2147483647 packets per second. If the low
PPS value is not specified, the default value is 80% of the specified
risen PPS.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After selecting the Kbps option as the Level Type, the following parameters are available.
Figure 9-84 Storm Control (Kbps) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
KBPS Rise
Enter the rise KBPS value used here. This option specifies the rise
threshold value as a rate of kilobits per second at which traffic is
received on the port. This value must be between 0 and
2147483647 Kbps.
KBPS Low
Enter the low KBPS value used here. This option specifies the low
threshold value as a rate of kilobits per second at which traffic is
received on the port. This value must be between 0 and
2147483647 Kbps. If the low KBPS is not specified, the default
value is 80% of the specified risen KBPS.
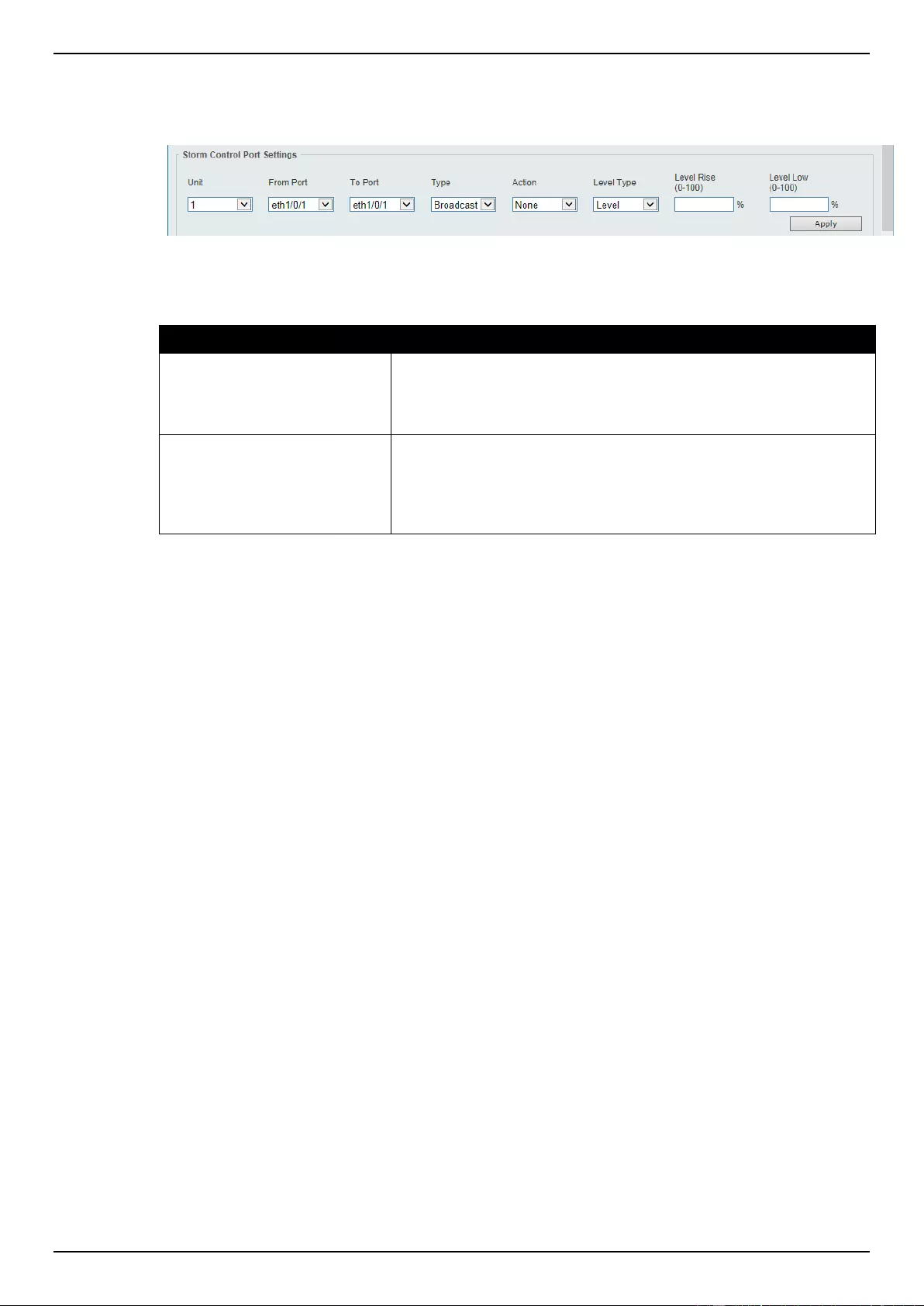
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
338
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
After selecting the Level option as the Level Type, the following parameters are available.
Figure 9-85 Storm Control (Level) window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Level Rise
Enter the rise level value used here. This option specifies the rise
threshold value as a percentage of the total bandwidth per port at
which traffic is received on the port. This value must be between 0%
and 100%.
Level Low
Enter the low level value used here. This option specifies the low
threshold value as a percentage of the total bandwidth per port at
which traffic is received on the port. This value must be between 0%
and 100%. If the low level is not specified, the default value is 80%
of the specified risen level.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DoS Attack Prevention Settings
This window is used to view and configure the Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack prevention settings. The
following well-known DoS types which can be detected by most switches:
Land Attack: This type of attack involves IP packets where the source and destination
address are set to the address of the target device. It may cause the target device to reply to
itself continuously.
Blat Attack: This type of attack will send packets with the TCP/UDP source port equal to the
destination port of the target device. It may cause the target device to respond to itself.
TCP-Null: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which contain
a sequence number of 0 and no flags.
TCP-Xmas: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which
contain a sequence number of 0 and the Urgent (URG), Push (PSH), and FIN flags.
TCP SYN-FIN: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific packets which
contain SYN and FIN flags.
TCP SYN SrcPort Less 1024: This type of attack involves port scanning by using specific
packets which contain source port 0 to 1023 and SYN flag.
Ping of Death Attack: A ping of death is a type of attack on a computer that involves sending
a malformed or otherwise a malicious ping to a computer. A ping is normally 64 bytes in size
(many computers cannot handle a ping larger than the maximum IP packet size) which is
65535 bytes. The sending of a ping of this size can crash the target computer. Traditionally,
this bug has been relatively easy to exploit. Generally, sending a 65536 byte ping packet is
illegal according to networking protocol, but a packet of such a size can be sent if it is
fragmented; when the target computer reassembles the packet, a buffer overflow can occur,
which often causes a system crash.
TCP Tiny Fragment Attack: The Tiny TCP Fragment attacker uses IP fragmentation to
create extremely small fragments and force the TCP header information into a separate
packet fragment to pass through the check function of the router and issue an attack.
All Types: All of above types.
To view the following window, click Security > DoS Attack Prevention Settings, as shown below:
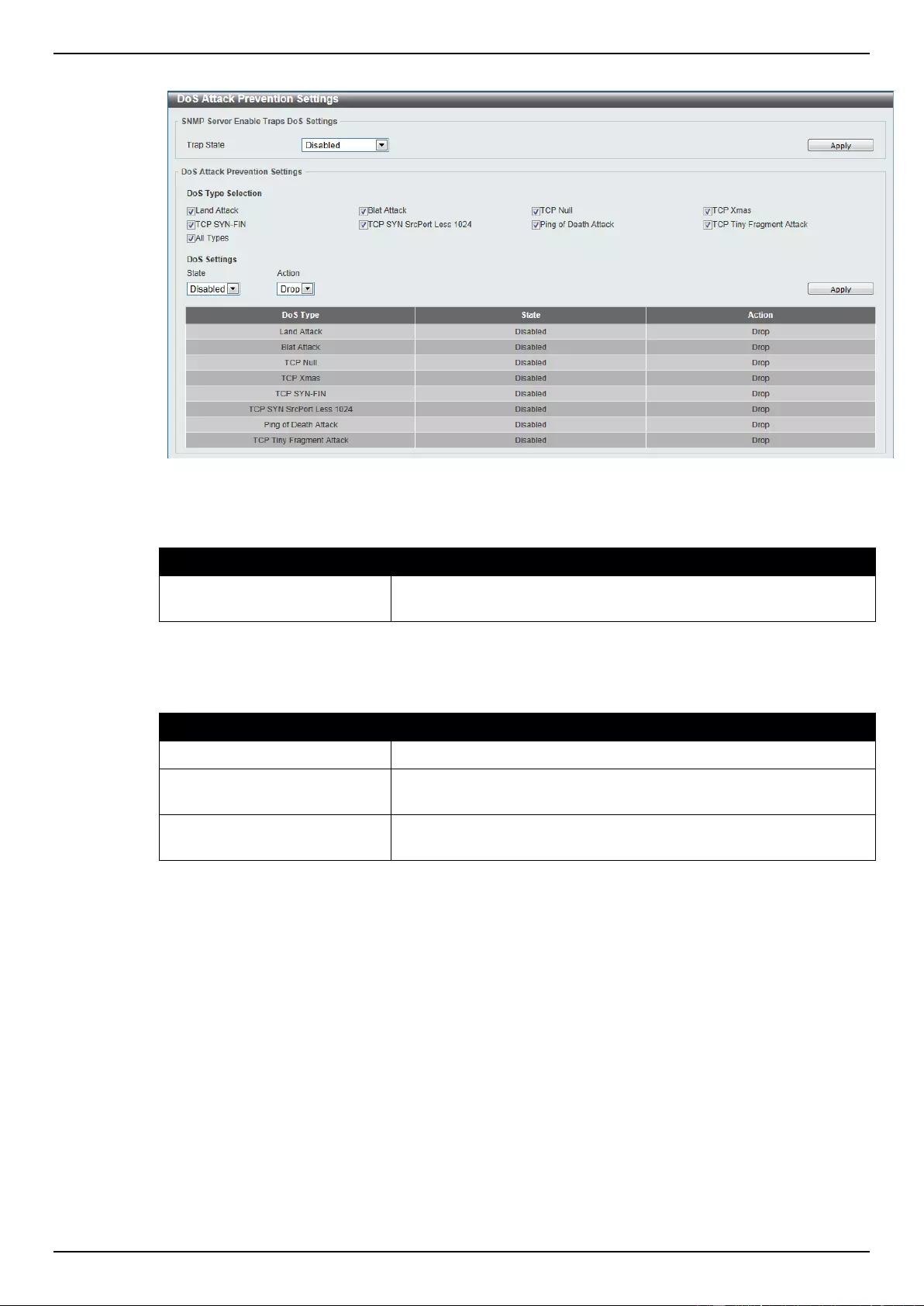
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
339
Figure 9-86 DoS Attack Prevention Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SNMP Server Enable Traps DoS Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trap State
Select to enable or disable the DoS attack prevention trap state
here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for DoS Attack Prevention Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
DoS Type Selection
Tick the DoS type option that will be prevented here.
State
Select to enable or disable the DoS attack prevention feature’s
global state here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken when the DoS attack was
detected here. The only option to select here is Drop.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) is a program allowing secure remote login and secure network services over an
insecure network. It allows a secure login to remote host computers, a safe method of executing
commands on a remote end node, and will provide secure encrypted and authenticated
communication between two non-trusted hosts. SSH, with its array of unmatched security features is
an essential tool in today’s networking environment. It is a powerful guardian against numerous
existing security hazards that now threaten network communications.
The steps required to use the SSH protocol for secure communication between a remote PC (the
SSH client) and the Switch (the SSH server) are as follows:
Create a user account with admin-level access using the User Accounts window. This is
identical to creating any other admin-level User Account on the Switch, including specifying a
password. This password is used to logon to the Switch, once a secure communication path
has been established using the SSH protocol.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
340
Configure the User Account to use a specified authorization method to identify users that are
allowed to establish SSH connections with the Switch using the SSH User Authentication
Mode window. There are three choices as to the method SSH will use to authorize the user,
which are Host Based, Password, and Public Key.
Configure the encryption algorithm that SSH will use to encrypt and decrypt messages sent
between the SSH client and the SSH server, using the SSH Authentication Method and
Algorithm Settings window.
Finally, enable SSH on the Switch using the SSH Configuration window.
After completing the preceding steps, a SSH Client on a remote PC can be configured to manage the
Switch using a secure, in band connection.
SSH Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the SSH global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSH > SSH Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-87 SSH Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
IP SSH Server State
Select to enable or disable the SSH server’s global state.
IP SSH Service Port
Enter the SSH service port number used here. This value must be
between 1 and 65535. By default, this number is 22.
Authentication Timeout
Enter the authentication timeout value here. This value must be
between 30 and 600 seconds. By default, this value is 120 seconds.
Authentication Retries
Enter the authentication retries value here. This value must be
between 1 and 32. By default, this value is 3.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Host Key
This window is used to view and generate the SSH host key.
To view the following window, click Security > SSH > Host Key, as shown below:
Figure 9-88 Host Key window
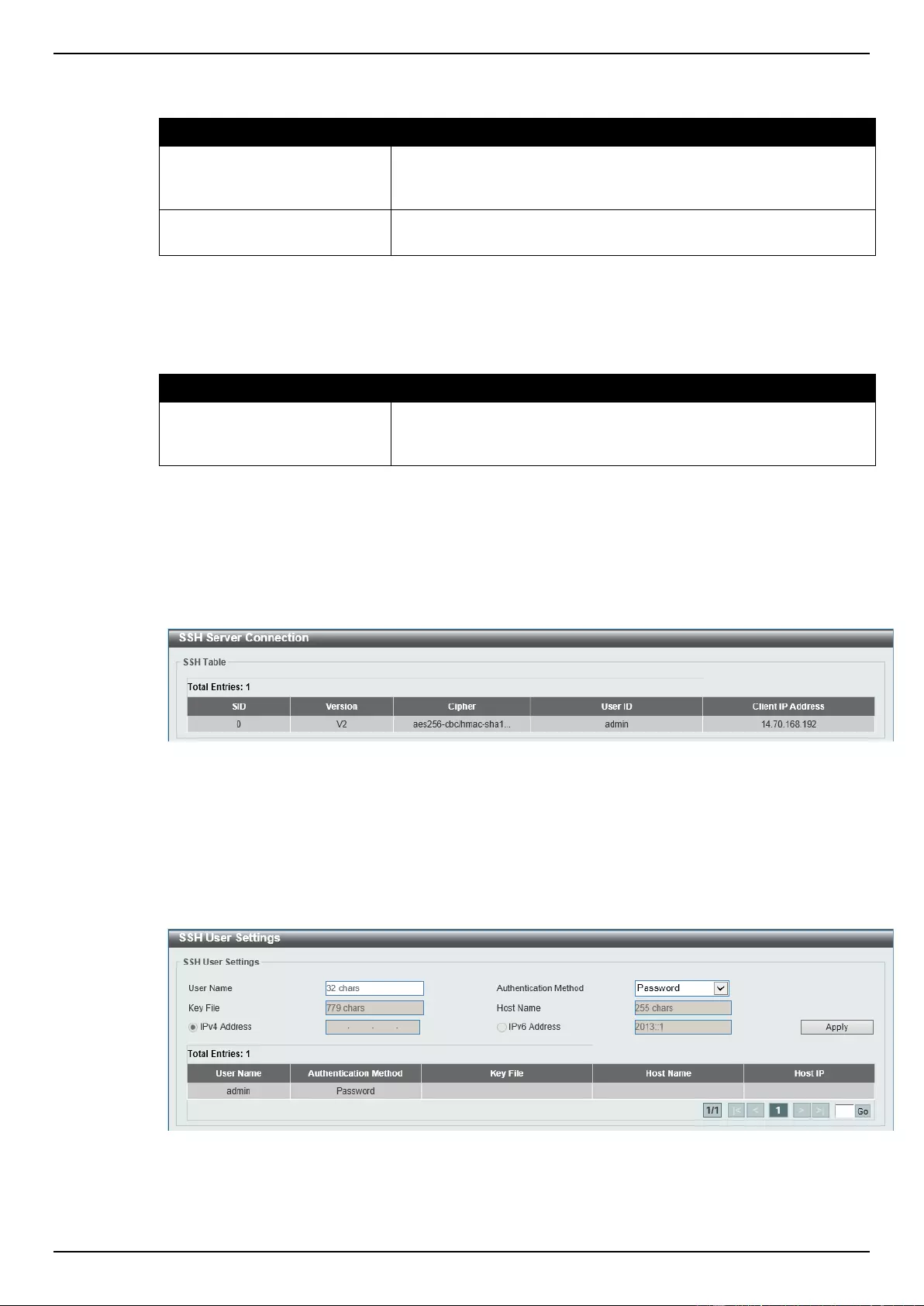
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
341
The fields that can be configured for Host Key Management are described below:
Parameter
Description
Crypto Key Type
Select the crypto key type used here. Options to choose from are
the Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA) key type and the Digital
Signature Algorithm (DSA) key type.
Key Modulus
Select the key modulus value here. Options to choose from are 360,
512, 768, 1024, and 2048 bit.
Click the Generate button to generate a host key based on the selections made.
Click the Delete button to remove a host key based on the selections made.
The fields that can be configured for Host Key are described below:
Parameter
Description
Crypto Key Type
Select the crypto key type used here. Options to choose from are
the Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA) key type and the Digital
Signature Algorithm (DSA) key type.
SSH Server Connection
This window is used to view the SSH server connections table.
To view the following window, click Security > SSH > SSH Server Connection, as shown below:
Figure 9-89 SSH Server Connection window
SSH User Settings
This window is used to view and configure the SSH user settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSH > SSH User Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-90 SSH User Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
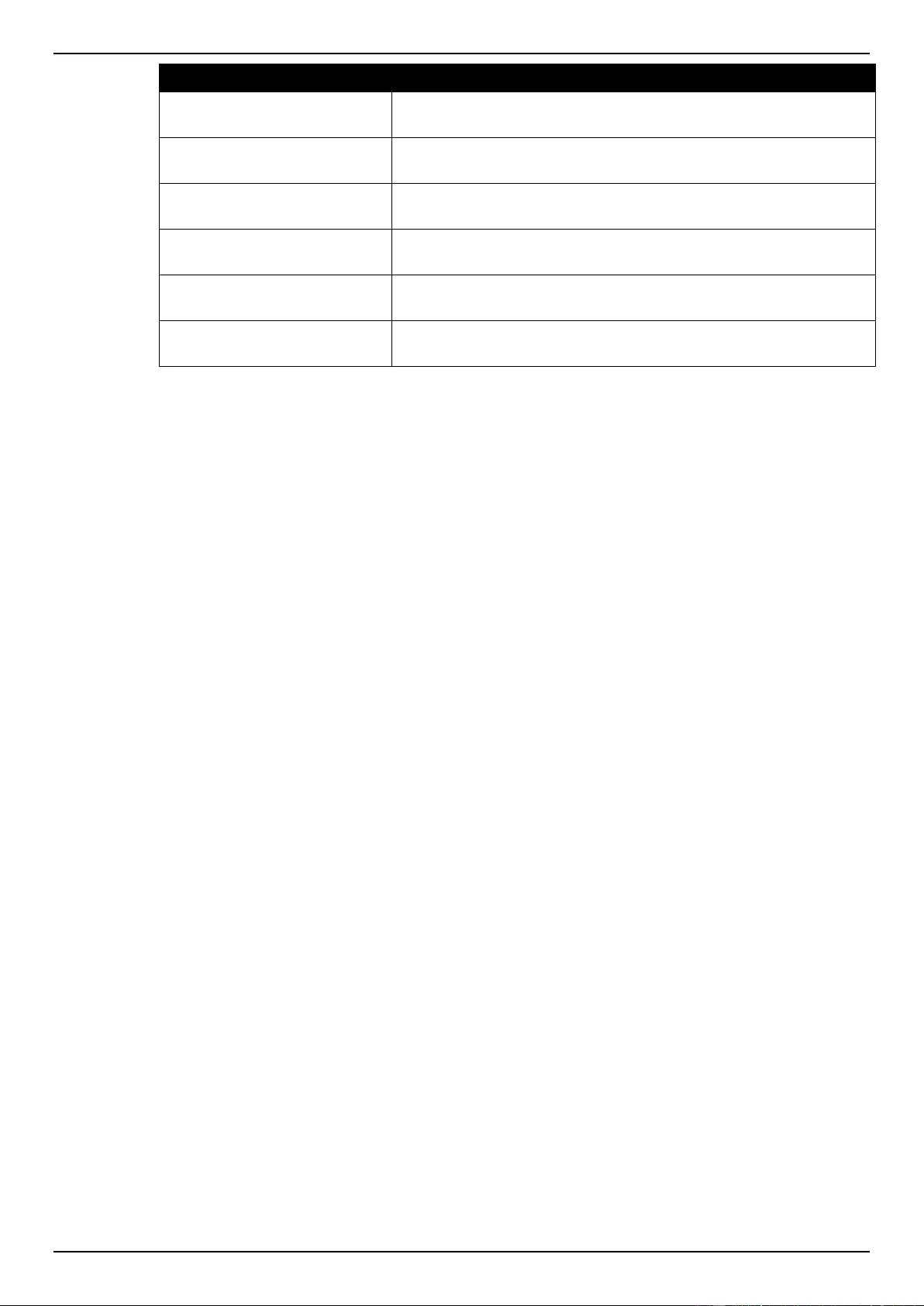
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
342
Parameter
Description
User Name
Enter the SSH user’s username used here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
Authentication Method
Select the authentication methods used here. Options to choose
from are Password, Public Key, and Host-based.
Key File
After selecting the Public Key or Host-based option as the
Authentication Method, enter the public key here.
Host Name
After selecting the Host-based option as the Authentication
Method, enter the host name here.
IPv4 Address
After selecting the Host-based option as the Authentication
Method, select and enter the IPv4 address here.
IPv6 Address
After selecting the Host-based option as the Authentication
Method, select and enter the IPv6 address here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security feature that will provide a secure communication path
between a host and client through the use of authentication, digital signatures and encryption. These
security functions are implemented through the use of a cipher suite, which is a security string that
determines the exact cryptographic parameters, specific encryption algorithms and key sizes to be
used for an authentication session and consists of three levels:
Key Exchange: The first part of the Cipher suite string specifies the public key algorithm to
be used. This switch utilizes the Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA) public key algorithm and the
Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA), specified here as the DHE DSS Diffie-Hellman (DHE)
public key algorithm. This is the first authentication process between client and host as they
“exchange keys” in looking for a match and therefore authentication to be accepted to
negotiate encryptions on the following level.
Encryption: The second part of the cipher suite that includes the encryption used for
encrypting the messages sent between client and host. The Switch supports two types of
cryptology algorithms:
o Stream Ciphers – There are two types of stream ciphers on the Switch, RC4 with 40-
bit keys and RC4 with 128-bit keys. These keys are used to encrypt messages and
need to be consistent between client and host for optimal use.
o CBC Block Ciphers – CBC refers to Cipher Block Chaining, which means that a
portion of the previously encrypted block of encrypted text is used in the encryption of
the current block. The Switch supports the 3DES EDE encryption code defined by the
Data Encryption Standard (DES) to create the encrypted text.
Hash Algorithm: This part of the cipher suite allows the user to choose a message digest
function which will determine a Message Authentication Code. This Message Authentication
Code will be encrypted with a sent message to provide integrity and prevent against replay
attacks. The Switch supports two hash algorithms, MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA
(Secure Hash Algorithm).
These three parameters are uniquely assembled in four choices on the Switch to create a three-
layered encryption code for secure communication between the server and the host. The user may
implement any one or combination of the cipher suites available, yet different cipher suites will affect
the security level and the performance of the secured connection. The information included in the
cipher suites is not included with the Switch and requires downloading from a third source in a file
form called a certificate. This function of the Switch cannot be executed without the presence and
implementation of the certificate file and can be downloaded to the Switch by utilizing a TFTP server.
The Switch supports SSLv3. Other versions of SSL may not be compatible with this Switch and may
cause problems upon authentication and transfer of messages from client to host.
When the SSL function has been enabled, the web will become disabled. To manage the Switch
through the web based management while utilizing the SSL function, the web browser must support

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
343
SSL encryption and the header of the URL must begin with https://. (Ex. https://xx.xx.xx.xx) Any other
method will result in an error and no access can be authorized for the web-based management.
Users can download a certificate file for the SSL function on the Switch from a TFTP server. The
certificate file is a data record used for authenticating devices on the network. It contains information
on the owner, keys for authentication and digital signatures. Both the server and the client must have
consistent certificate files for optimal use of the SSL function. Currently, the Switch comes with a
certificate pre-loaded though the user may need to download more, depending on user circumstances.
SSL Global Settings
This window is used to view and configure the SSL feature’s global settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSL > SSL Global Settings, as shown below:
Figure 9-91 SSL Global Settings window
The fields that can be configured for SSL Global Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
SSL Status
Select to enable or disable the SSL feature’s global status here.
Service Policy
Enter the service policy name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The fields that can be configured for Import File are described below:
Parameter
Description
File Select
Select the file type that will be loaded here. Options to choose from
are Certificate and Private Key. After selecting the file type,
browse to the appropriate file, located on the local computer, by
pressing the Browse button.
Destination File Name
Enter the destination file name used here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Crypto PKI Trustpoint
This window is used to view and configure the crypto PKI trust point settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSL > Crypto PKI Trustpoint, as shown below:
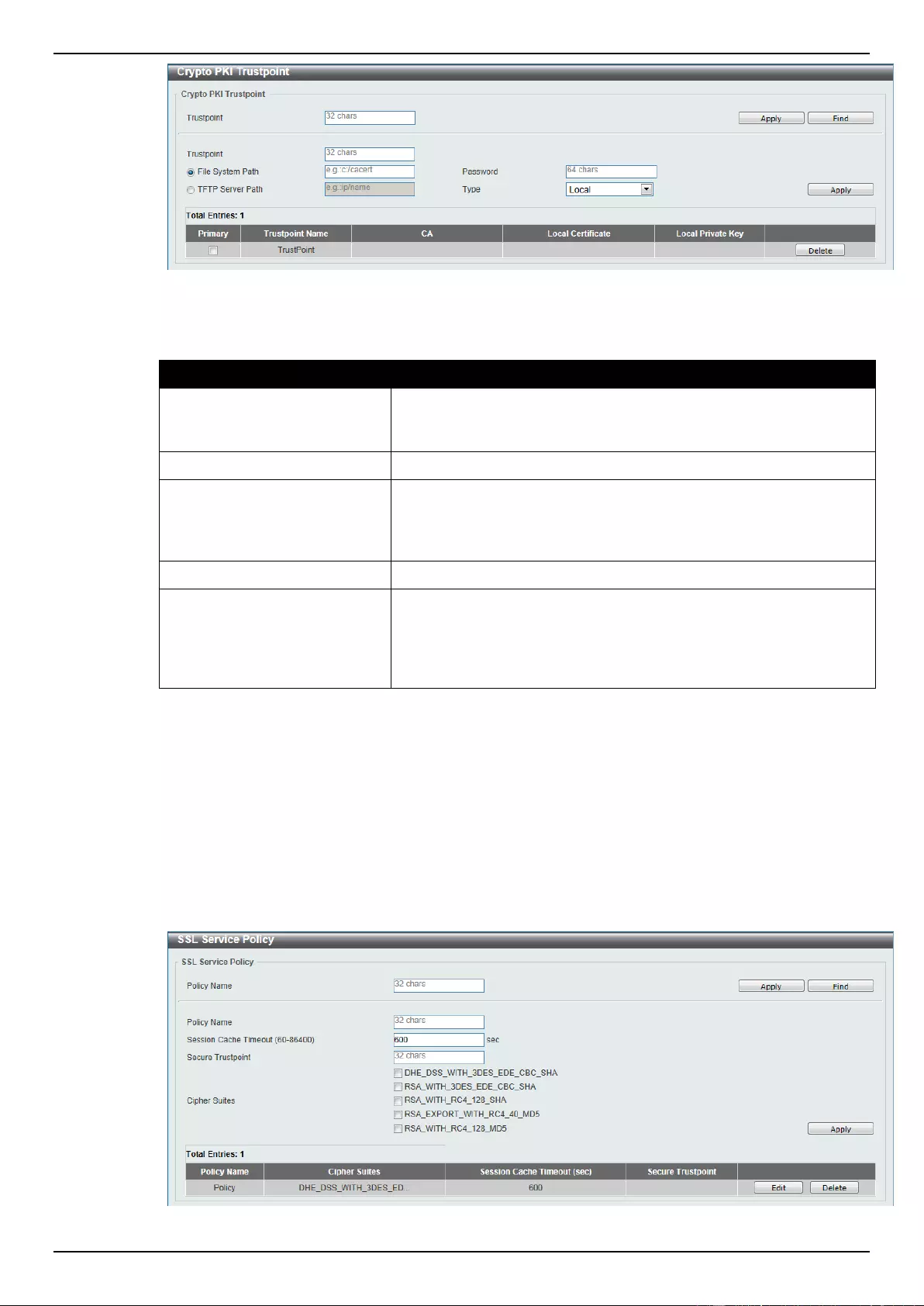
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
344
Figure 9-92 Crypto PKI Trustpoint window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Trustpoint
Enter the name of the trust-point that is associated with the
imported certificates and key pairs here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
File System Path
Enter the file system path for certificates and key pairs here.
Password
Enter the encrypted password phrase that is used to undo
encryption when the private keys are imported here. The password
phrase is a string of up to 64 characters. If the password phrase is
not specified, the NULL string will be used.
TFTP Server Path
Enter the TFTP server’s path here.
Type
Select the type of certificate that will be imported here. Options to
choose from are Both, CA, and Local. Selecting Both specifies to
import the CA certificate, local certificate and key pairs. Selecting
CA specifies to import the CA certificate only. Selecting Local
specifies to import local certificate and key pairs only.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
SSL Service Policy
This window is used to view and configure the SSL service policy settings.
To view the following window, click Security > SSL > SSL Service Policy, as shown below:
Figure 9-93 SSL Service Policy window

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
345
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Policy Name
Enter the SSL service policy name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Session Cache Timeout
Enter the session cache timeout value used here. This value must
be between 60 and 86400 seconds. By default, this value is 600
seconds.
Secure Trustpoint
Enter the secure trust point’s name here. This name can be up to 32
characters long.
Cipher Suites
Select the cipher suites that will be associated with this profile here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
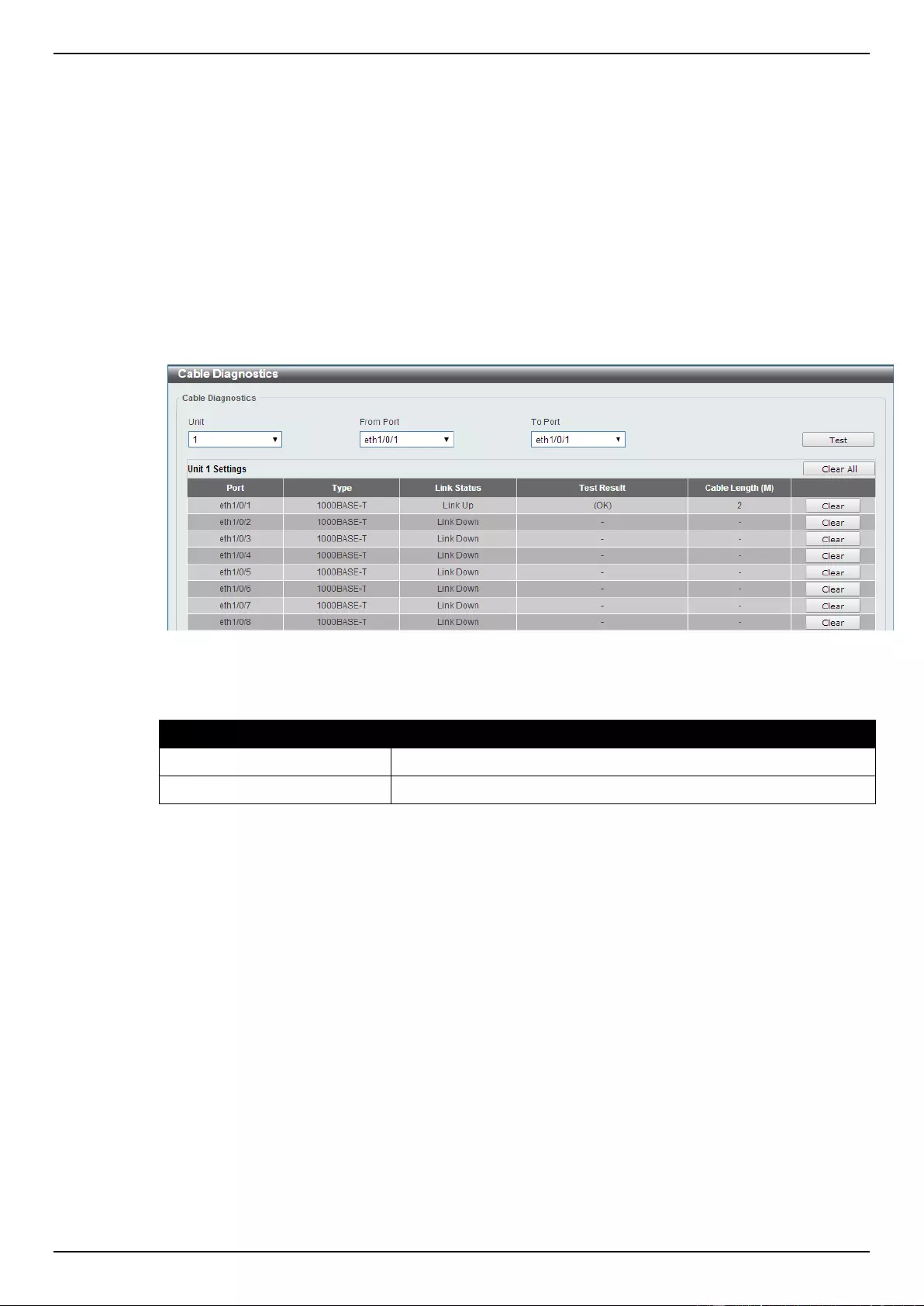
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
346
10. OAM
Cable Diagnostics
DDM
Cable Diagnostics
The cable diagnostics feature is designed primarily for administrators or customer service
representatives to verify and test copper cables; it can rapidly determine the quality of the cables and
the types of error.
To view the following window, click OAM > Cable Diagnostics, as shown below:
Figure 10-1 Cable Diagnostics window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Test button to test the specific port.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific port.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
DDM
This folder contains windows that perform Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) functions on the
Switch. There are windows that allow the user to view the digital diagnostic monitoring status of SFP
modules inserting to the Switch and to configure alarm settings, warning settings, temperature
threshold settings, voltage threshold settings, bias current threshold settings, Tx power threshold
settings, and Rx power threshold settings.
DDM Settings
The window is used to configure the action that will occur for specific ports when an exceeding alarm
threshold or warning threshold event is encountered.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM Settings, as show below:
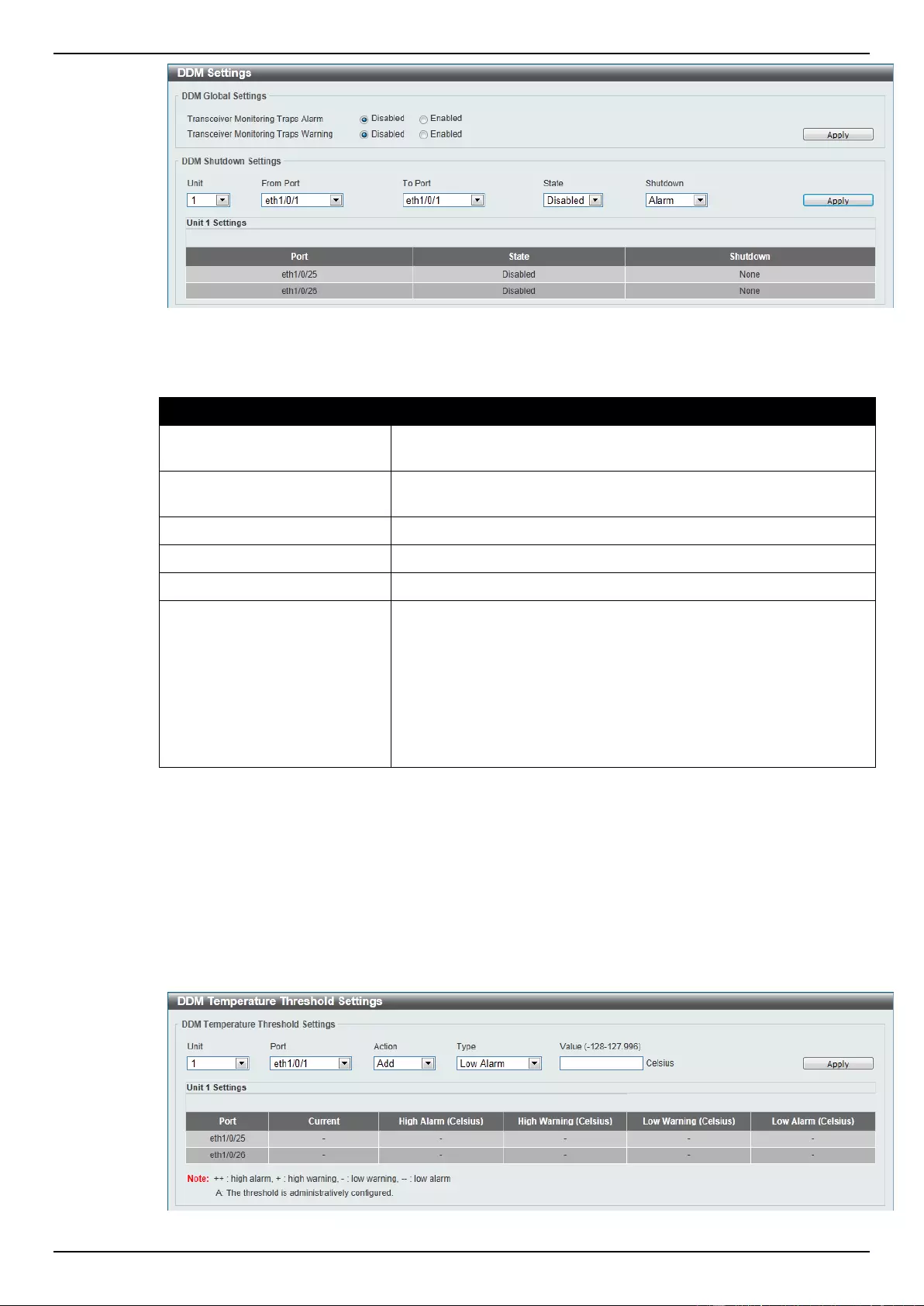
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
347
Figure 10-2 DDM Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Transceiver Monitoring
Traps Alarm
Select this option to enable or disable sending alarm level trap.
Transceiver Monitoring
Traps Warning
Select this option to enable or disable sending warning level trap.
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the DDM state.
Shutdown
Specify whether to shut down the port, when the operating
parameter exceeds the Alarm or Warning threshold.
Alarm - Shutdown the port when the configured alarm threshold
range is exceeded.
Warning - Shutdown the port when the configured warning
threshold range is exceeded.
None - The port will never shutdown regardless if the threshold
ranges are exceeded or not. This is the default.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
DDM Temperature Threshold Settings
This window is used to configure the DDM Temperature Threshold Settings for specific ports on the
Switch.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM Temperature Threshold Settings, as show
below:
Figure 10-3 DDM Temperature Threshold Settings window
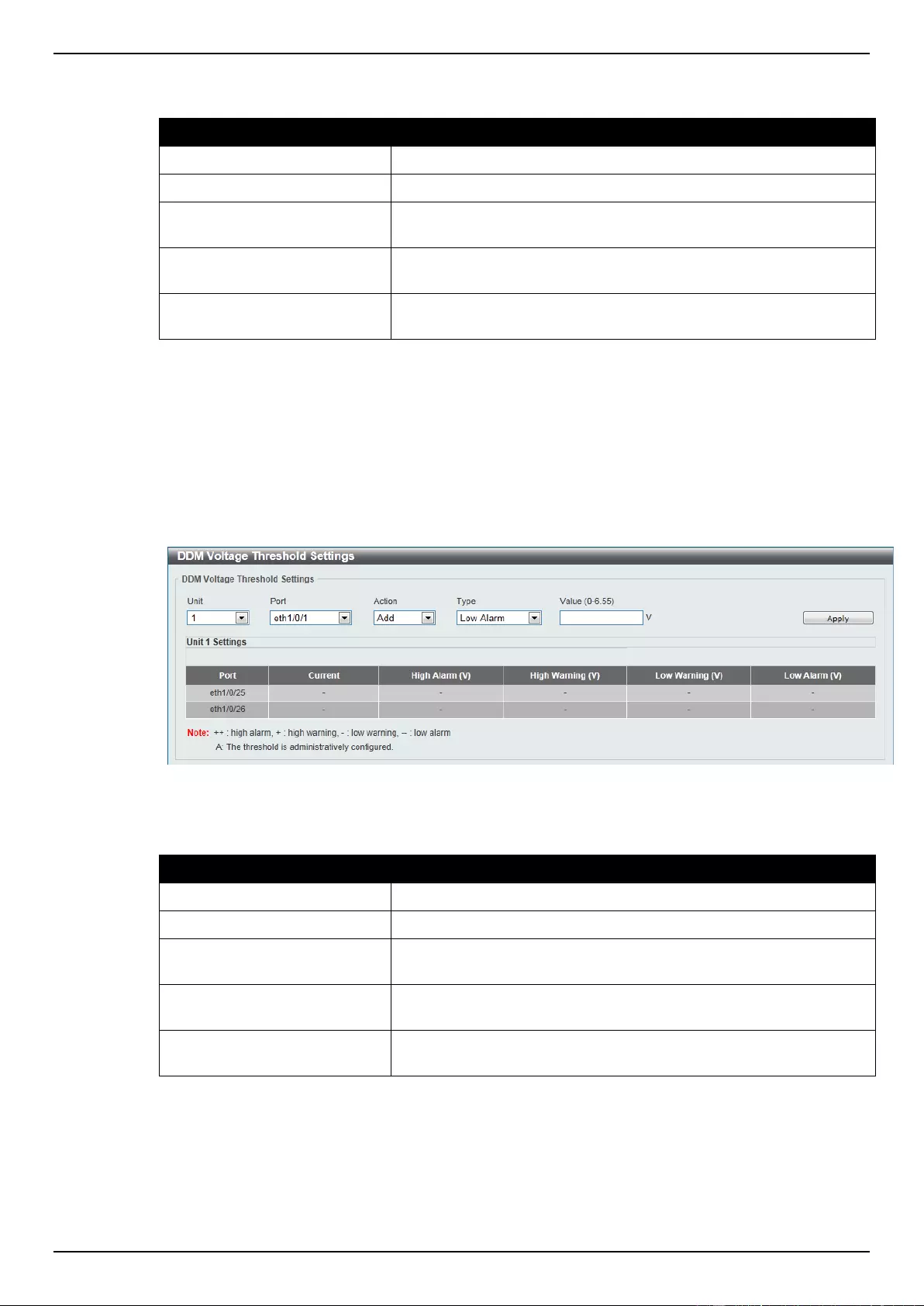
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
348
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the type of temperature threshold. Options to choose from
are Low Alarm, Low Warning, High Alarm, and High Warning.
Value
Enter the threshold value. This value must be between -128 and
127.996 °C.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DDM Voltage Threshold Settings
This window is used to configure the DDM Voltage Threshold Settings for specific ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM Voltage Threshold Settings, as show
below:
Figure 10-4 DDM Voltage Threshold Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the type of voltage threshold. Options to choose from are
Low Alarm, Low Warning, High Alarm, and High Warning.
Value
Enter the threshold value. This value must be between 0 and 6.55
Volt.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
This window is used to configure the threshold of the bias current for specific ports on the Switch.
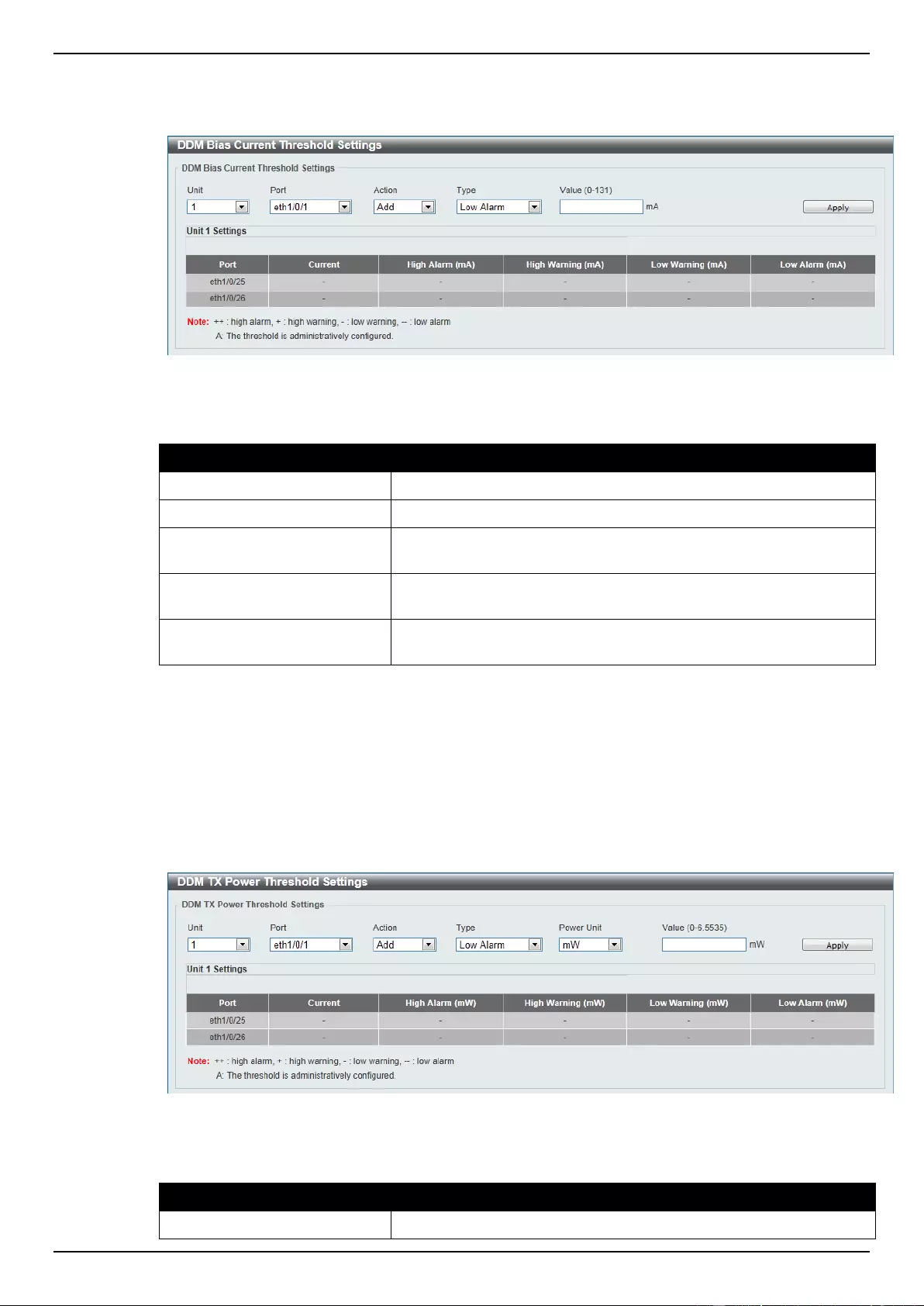
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
349
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings, as show
below:
Figure 10-5 DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the type of bias current threshold. Options to choose from
are Low Alarm, Low Warning, High Alarm, and High Warning.
Value
Enter the threshold value. This value must be between 0 and 131
mA.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
This window is used to configure the threshold of TX power for specific ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings, as show
below:
Figure 10-6 DDM TX Power Threshold Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
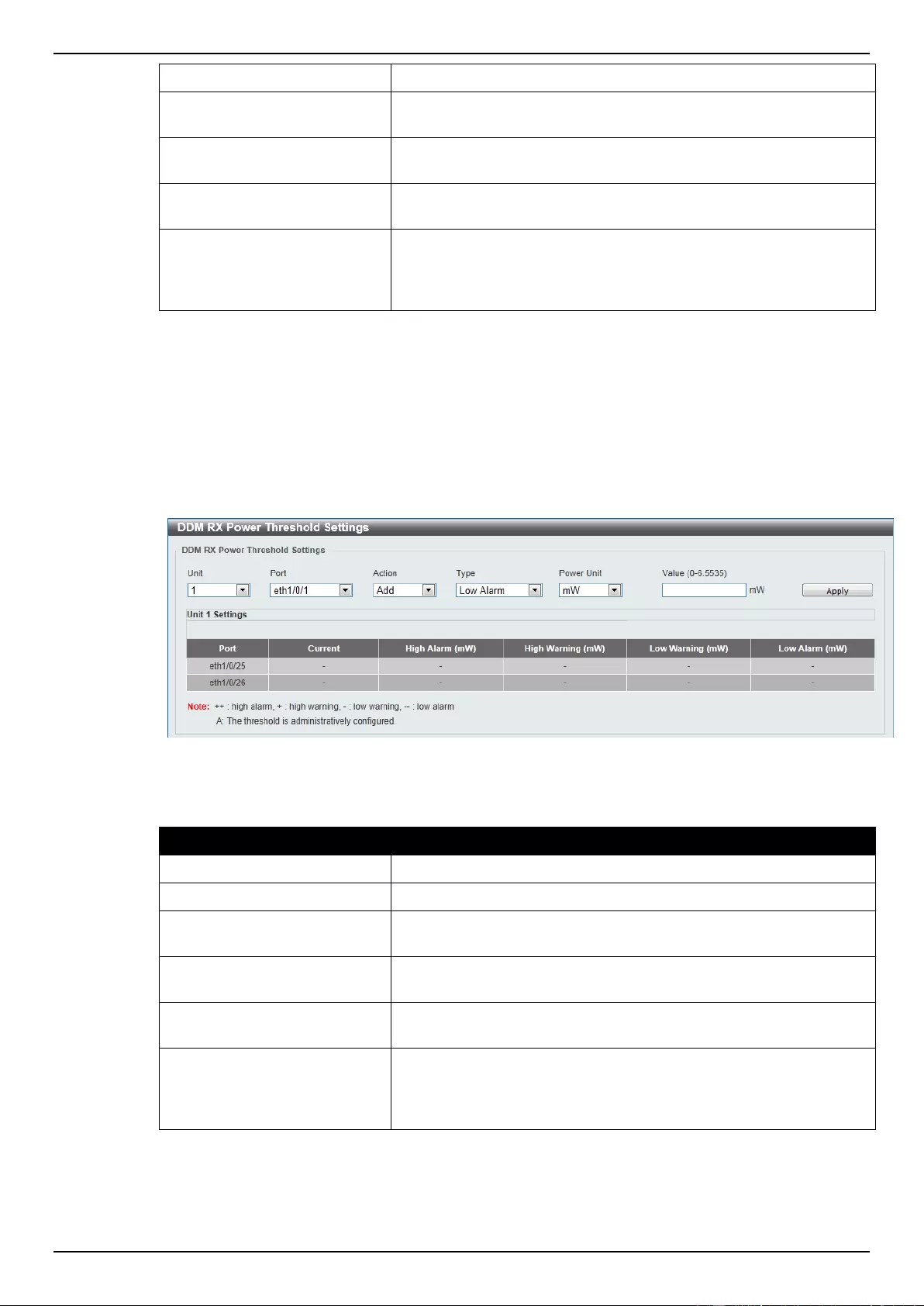
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
350
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the type of TX power threshold. Options to choose from are
Low Alarm, Low Warning, High Alarm, and High Warning.
Power Unit
Select the power unit here. Options to choose from are mW and
dBm.
Value
Enter the threshold value. When selecting mW in the Power Unit
drop-down list, this value must be between 0 and 6.5535. When
selecting dBm in the Power Unit drop-down list, this value must be
between -40 and 8.1647.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
This window is used to configure the threshold of RX power for specific ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings, as show
below:
Figure 10-7 DDM RX Power Threshold Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Port
Select the port used for the configuration here.
Action
Select the action that will be taken here. Options to choose from are
Add and Delete.
Type
Select the type of RX power threshold. Options to choose from are
Low Alarm, Low Warning, High Alarm, and High Warning.
Power Unit
Select the power unit here. Options to choose from are mW and
dBm.
Value
Enter the threshold value. When selecting mW in the Power Unit
drop-down list, this value must be between 0 and 6.5535. When
selecting dBm in the Power Unit drop-down list, this value must be
between -40 and 8.1647.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
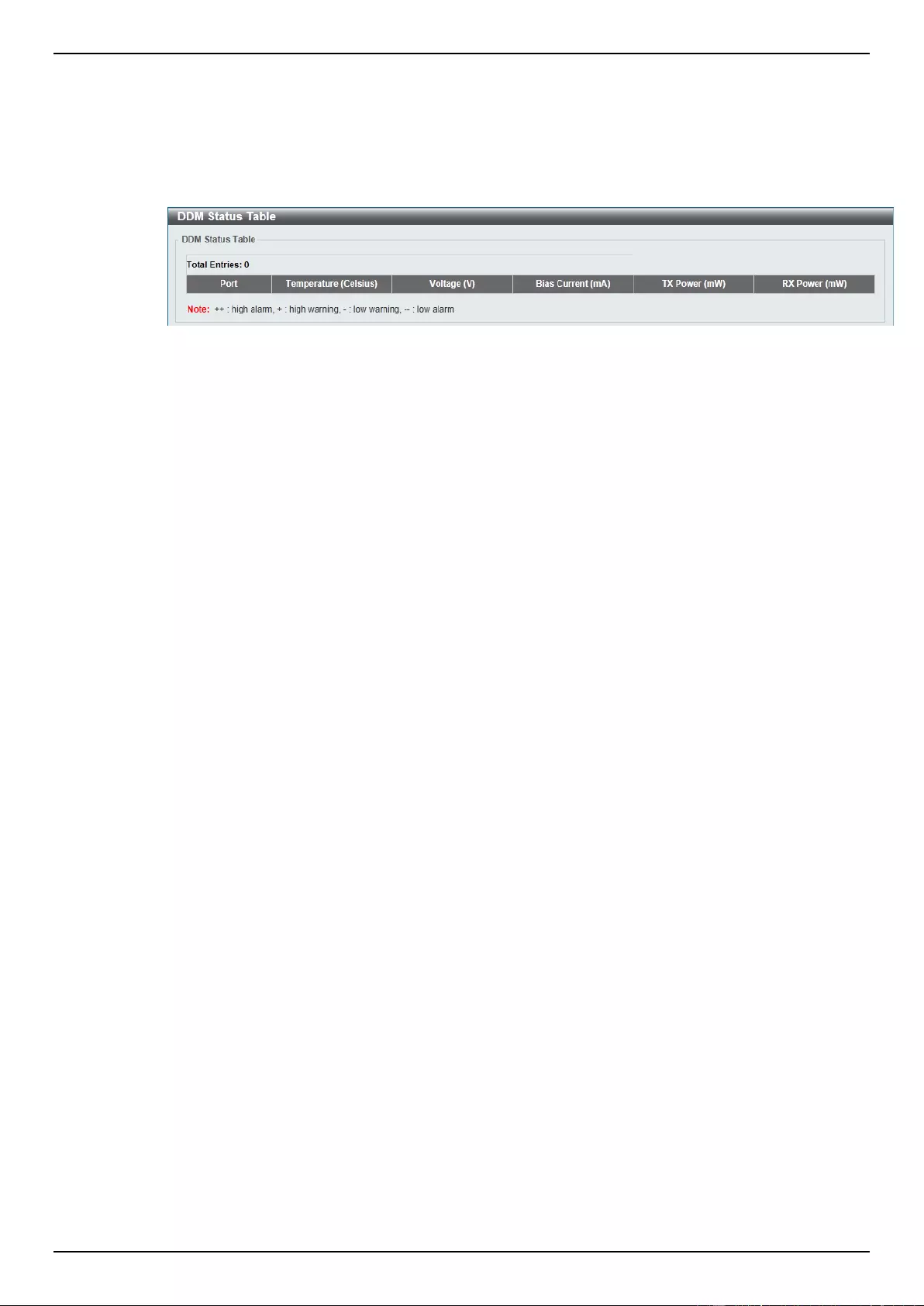
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
351
DDM Status Table
This window is used to display the current operating digital diagnostic monitoring parameters and their
values on the SFP module for specified ports.
To view the following window, click OAM > DDM > DDM Status Table, as show below:
Figure 10-8 DDM Status Table window
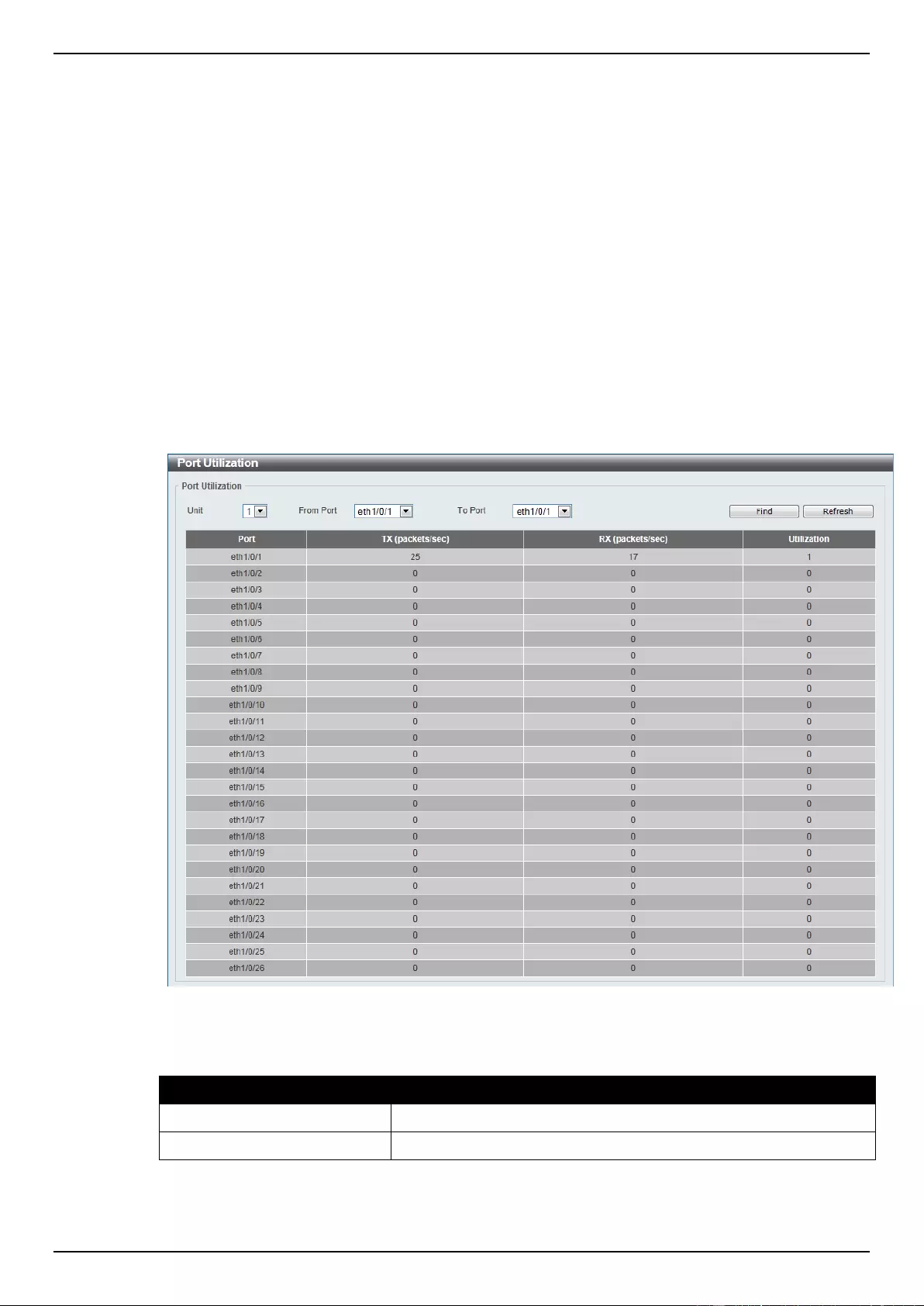
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
352
11. Monitoring
Utilization
Statistics
Mirror Settings
sFlow
Device Environment
Utilization
Port Utilization
This window is used to display the percentage of the total available bandwidth being used on the port.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Utilization > Port Utilization, as show below:
Figure 11-1 Port Utilization window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
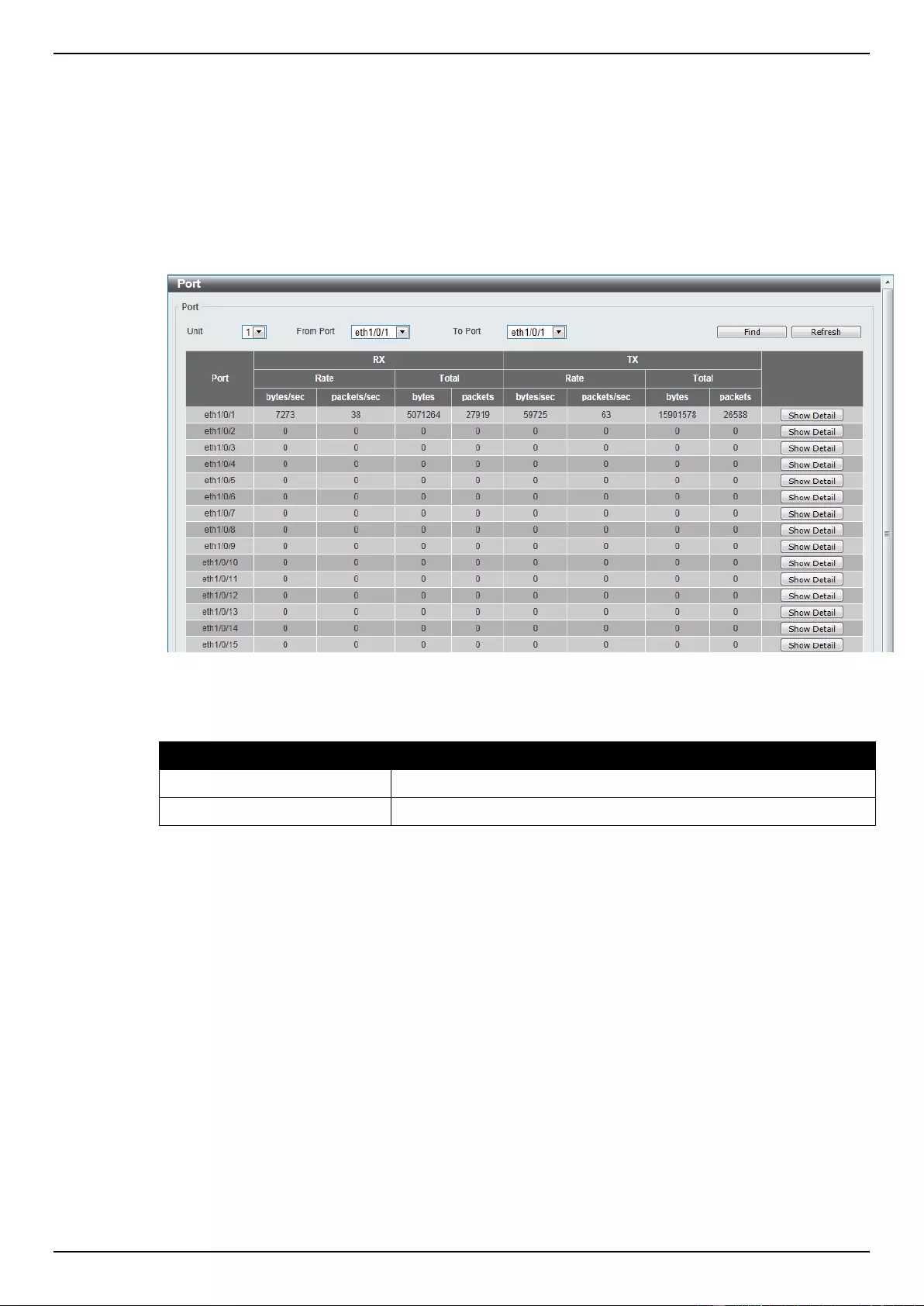
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
353
Statistics
Port
This window is used to display the packet statistics of ports.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Statistics > Port, as show below:
Figure 11-2 Port window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific port.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following page will appear.
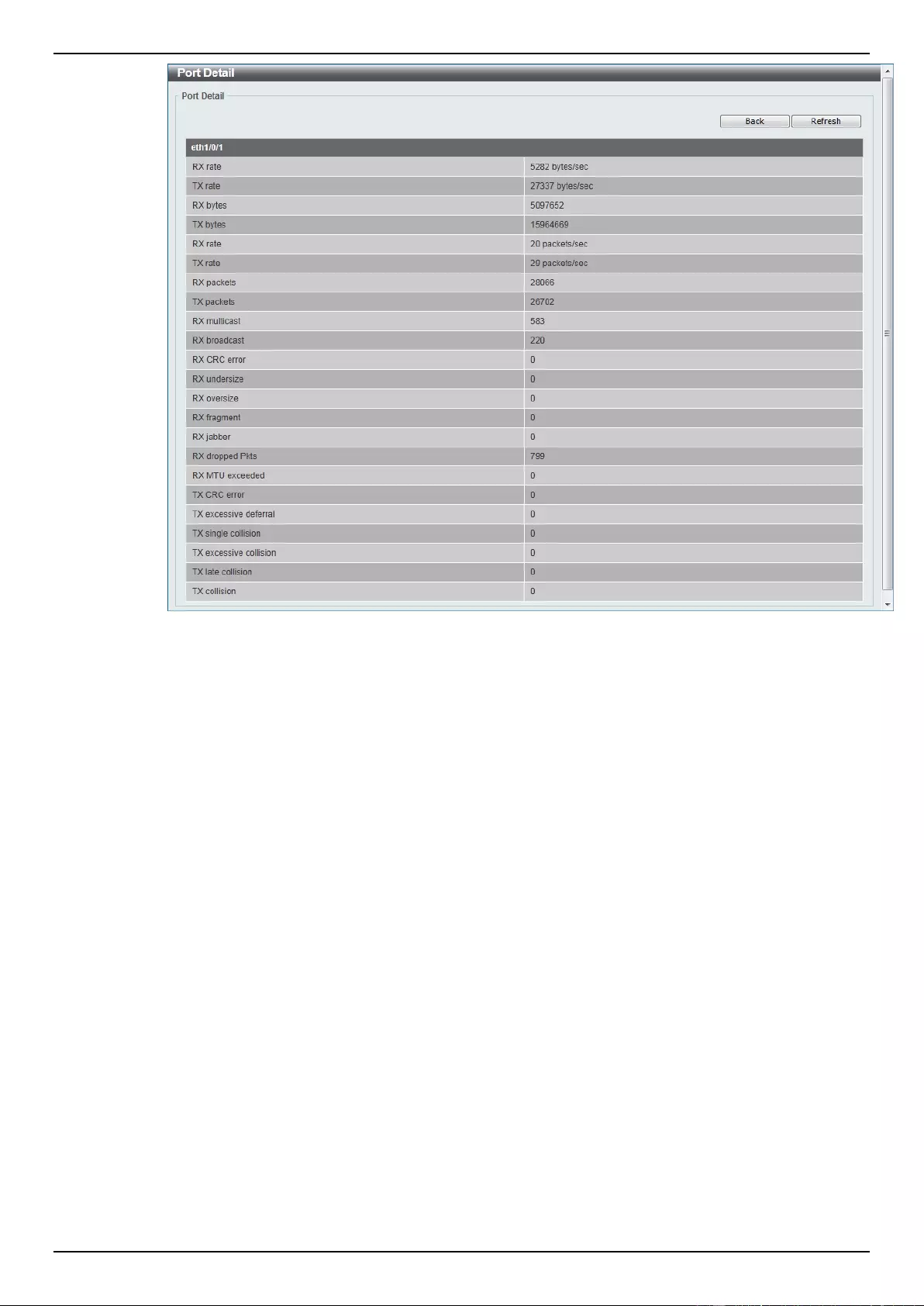
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
354
Figure 11-3 Port Detail window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Port Counters
This window is used to display port counter statistics.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Statistics > Port Counters, as show below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
355
Figure 11-4 Port Counters window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Click the Show Errors button to see all error counters of the specific port.
After clicking the Show Errors button, the following page will appear.
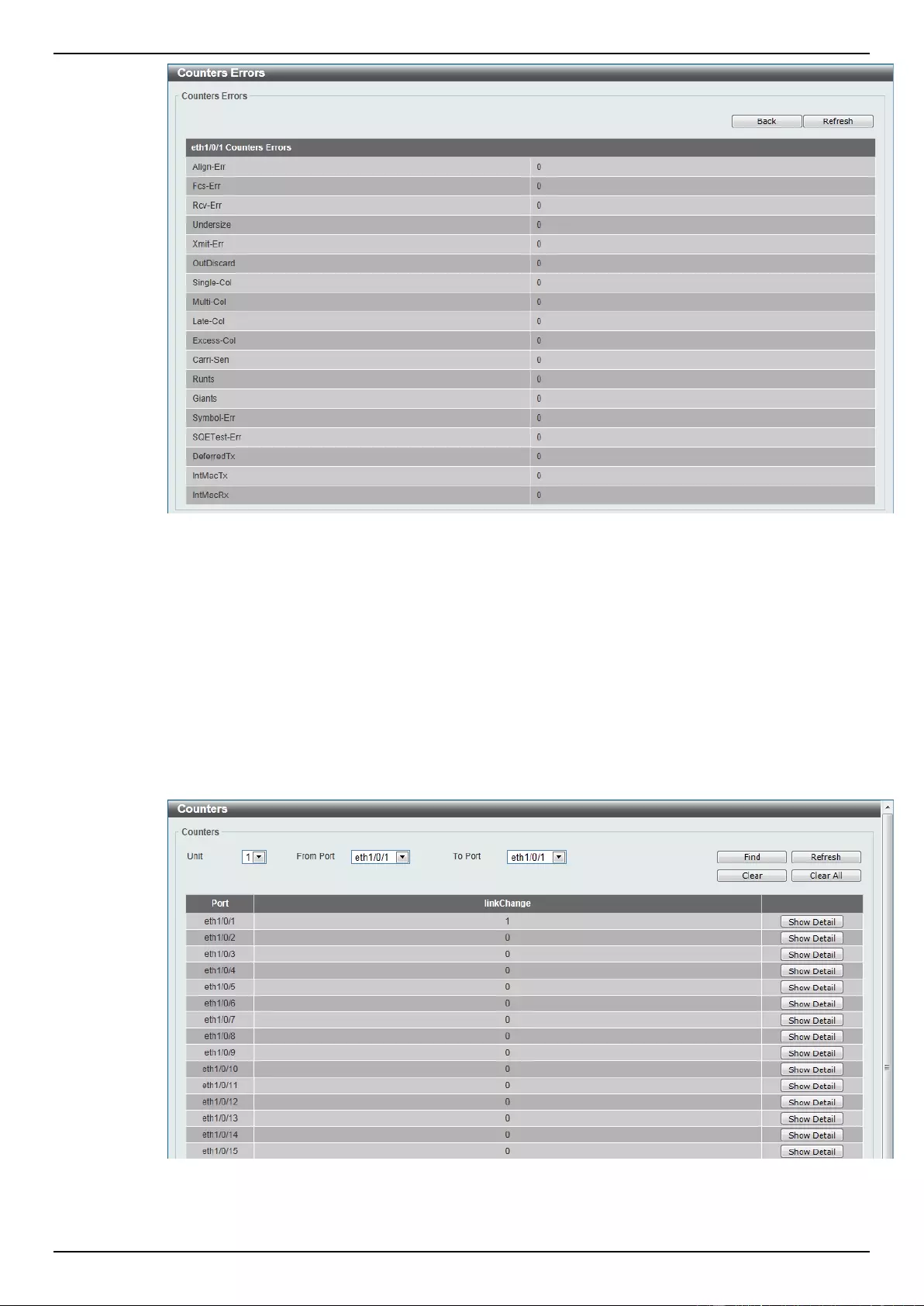
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
356
Figure 11-5 Counters Errors window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Counters
This window is used to display all port counters, and clear the port counters of the specified or all
ports.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Statistics > Counters, as show below:
Figure 11-6 Counters window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
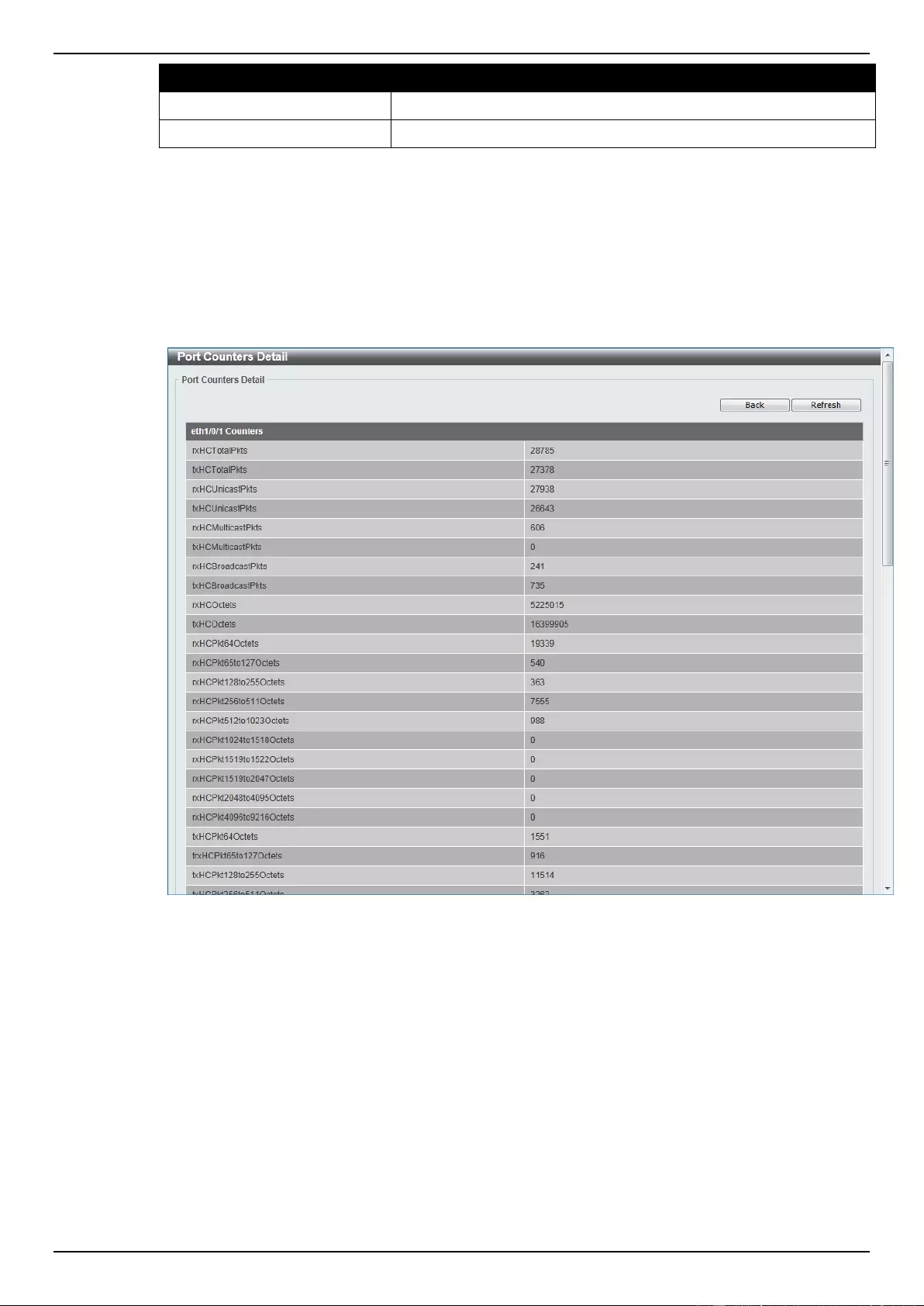
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
357
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Click the Clear button to clear all the information for the specific ports.
Click the Clear All button to clear all the information in this table.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific port.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following page will appear.
Figure 11-7 Port Counters Detail window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display table.
Mirror Settings
This window is used to view and configure the mirror feature’s settings. The Switch allows users to
copy frames transmitted and received on a port and redirect the copies to another port. Attach a
monitoring device to the mirroring port, such as a sniffer or an RMON probe, to view details about the
packets passing through the first port. This is useful for network monitoring and troubleshooting
purposes.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Mirror Settings, as shown below:

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
358
Figure 11-8 Mirror Settings window
The fields that can be configured for Mirror Settings are described below:
Parameter
Description
Session Number
Select the mirror session number for this entry here. This number is
between 1 and 4.
Destination
Tick the checkbox, next to the Destination option, to configure the
destination for this port mirror entry.
In the first drop-down menu select the Port option.
In the second drop-down menu select the destination switch’s Unit
ID.
In the third drop-down menu select the destination switch’s port
number.
Source
Tick the checkbox, next to the Source option, to configure the
source for this port mirror entry.
In the first drop-down menu we can select the source type. Options
to choose from are Port and ACL.
After selecting the Port option, in the first drop-down menu, select
the source switch’s Unit ID. From the From Port drop-down menu,
select the starting port number and from the To Port drop-down
menu, select the ending port number. Lastly select the Frame Type
option from the fifth drop-down menu. Options to choose from as
the Frame Type are Both, RX, TX, and TX Forwarding. When
selecting Both, traffic in both the incoming and outgoing directions
will be mirrored. When selecting RX, traffic in only the incoming
direction will be mirrored. When selecting TX, traffic in only the
outgoing direction will be mirrored. When selecting TX Forwarding,
traffic in the outgoing direction will be mirrored only when the port(s)
is/are in the STG forwarding state.
After selecting the ACL option, enter the ACL profile name in the
space provided.
Click the Add button to add the newly configured mirror entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete button to delete an existing mirror entry based on the information entered.
The fields that can be configured for Mirror Session Table are described below:
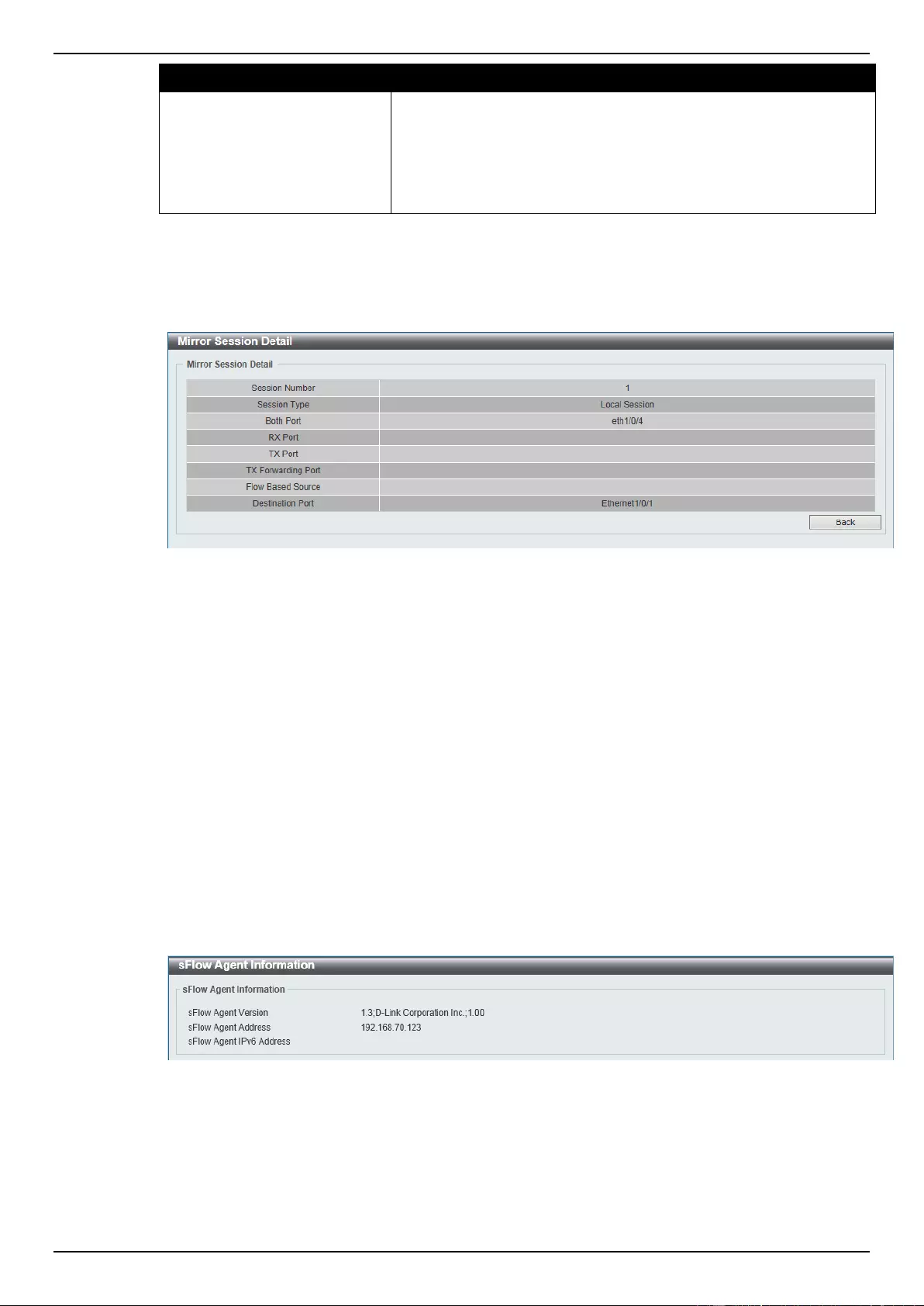
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
359
Parameter
Description
Mirror Session Type
Select the mirror session type of information that will be displayed
from the drop-down menu. Options to choose from are All Session,
and Session Number.
After selecting the Session Number option, select the session
number from the second drop-down menu. This number is from 1 to
4.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Show Detail button to see the detail information of the specific session.
After clicking the Show Detail button, the following window will appear.
Figure 11-9 Mirror Session Detail window
Click the Back button to return to the previous window.
sFlow
sFlow (RFC3176) is a technology for monitoring traffic in data networks containing switches and
routers. The sFlow monitoring system consists of an sFlow Agent (embedded in a switch or router or
in a standalone probe) and a central sFlow Collector. The architecture and sampling techniques used
in the sFlow monitoring system were designed for providing continuous site-wide (and enterprise-wide)
traffic monitoring of high speed switched and routed networks.
sFlow Agent Information
This window is used to view the sFlow agent information.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Agent Information, as show below:
Figure 11-10 sFlow Agent Information window
sFlow Receiver Settings
This window is used to view and configure receivers for the sFlow agents. Receivers cannot be added
to or removed from the sFlow agent.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Receiver Settings, as show below:
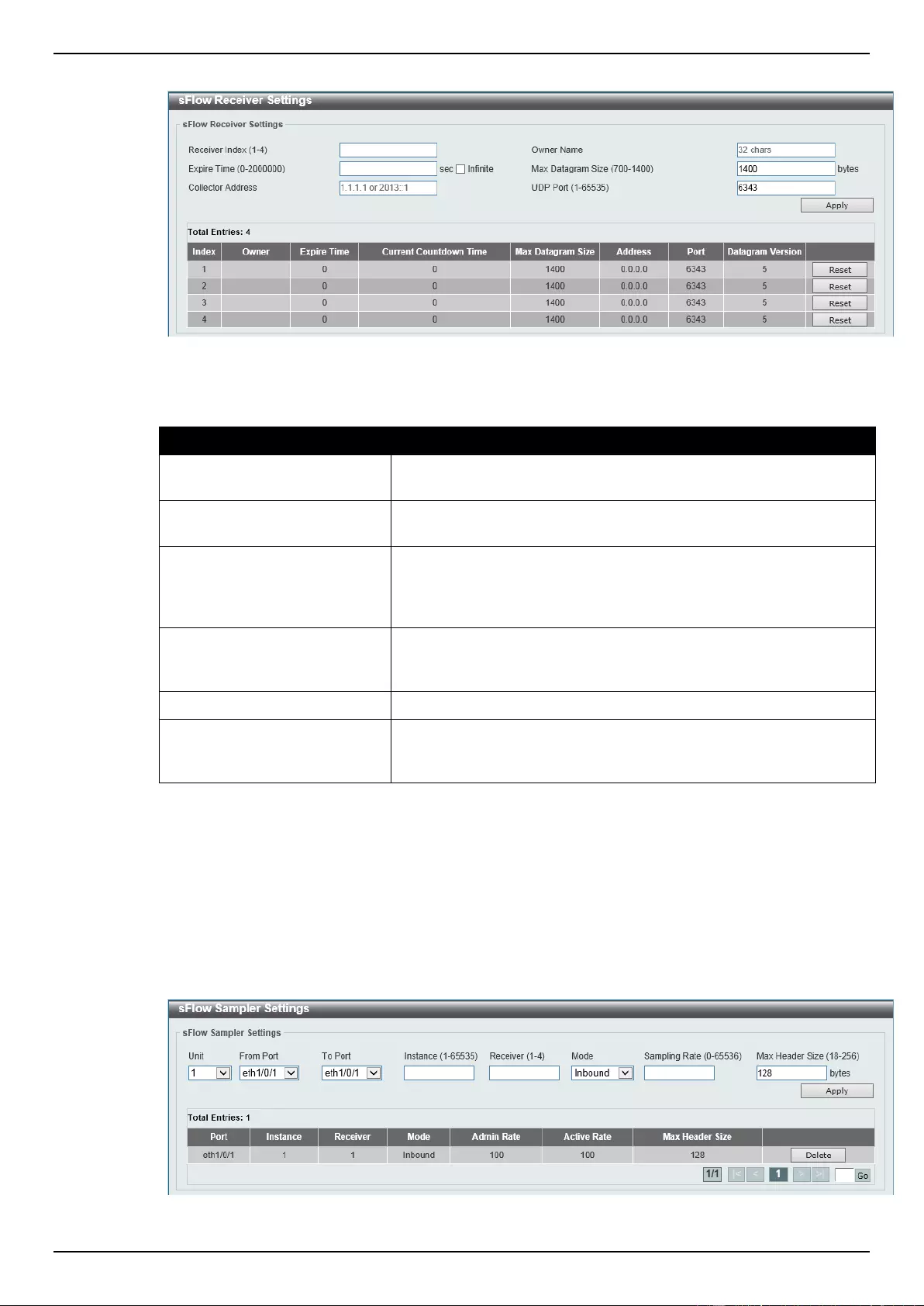
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
360
Figure 11-11 sFlow Receiver Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Receiver Index
Enter the index number of the receiver here. This number must be
between 1 and 4.
Owner Name
Enter the owner name of the receiver here. This name can be up to
32 characters long.
Expire Time
Enter the expiration time for the entry here. The parameters of the
entry will reset when the timer expired. The range is from 0 to
2000000 seconds. Selecting Infinite specifies that the entry will not
expire.
Max Datagram Size
Enter the maximum number of data bytes of a single sFlow
datagram here. The range is from 700 to 1400 bytes. By default,
this value is 1400 bytes.
Collector Address
Enter the remote sFlow collector’s IPv4 or IPv6 address here.
UDP Port
Enter the remote sFlow collector’s UDP port number here. This
number must be between 1 and 65535. By default, this value is
6343.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Reset button to reset the specified entry’s settings to the default settings.
sFlow Sampler Settings
This window is used to view and configure
To view the following window, click Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Sampler Settings, as show below:
Figure 11-12 sFlow Sampler Settings window
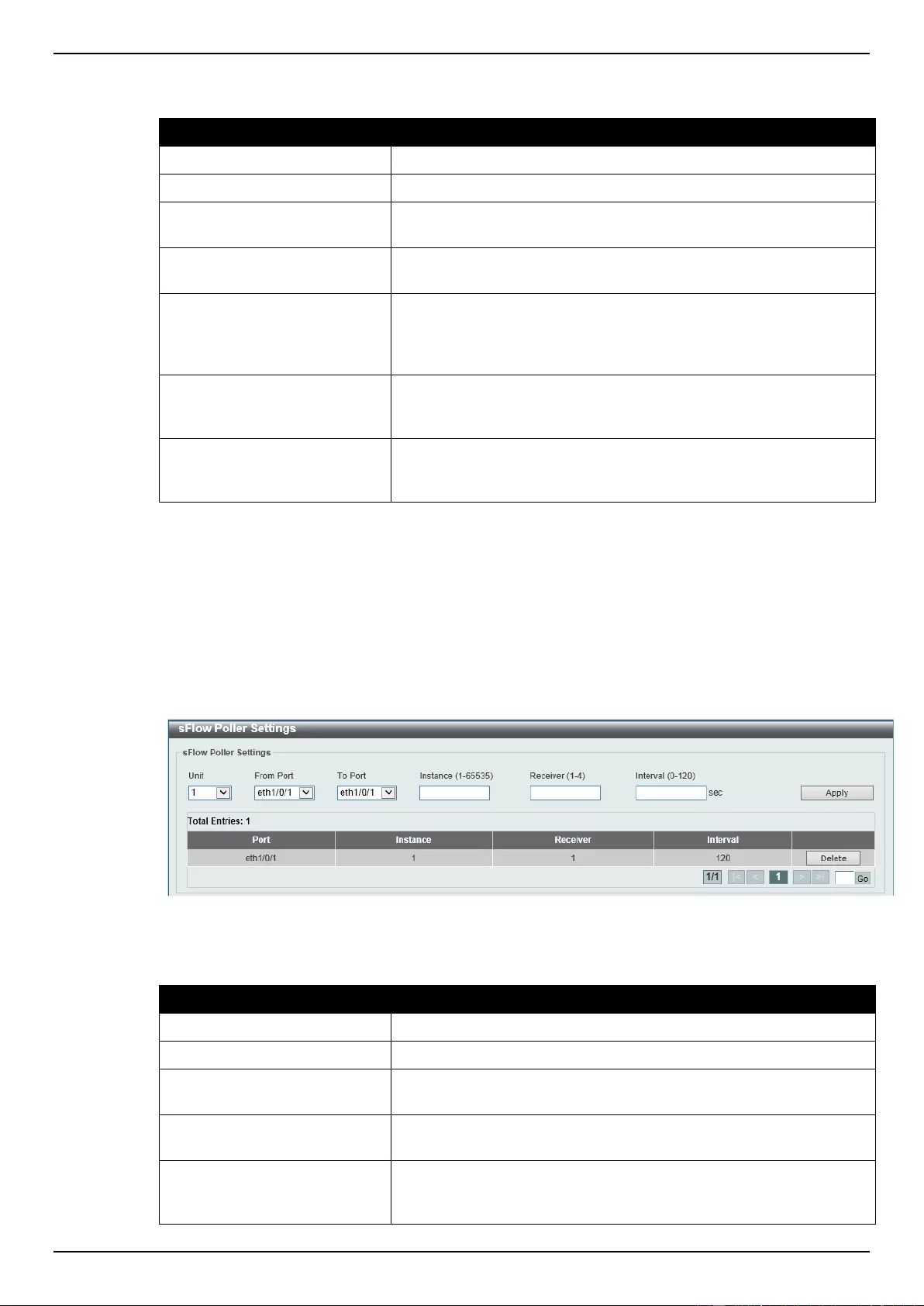
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
361
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Instance
Enter the instance’s index number if multiple samplers are
associated with one interface. The valid range is from 1 to 65535.
Receiver
Enter the receiver’s index for this sampler. If not specified, the value
is 0. This value must be between 1 and 4.
Mode
Select the mode here. Options to choose from are Inbound and
Outbound. Selecting Inbound specifies to sample ingress packets.
This is the default direction of a sampler. Selecting Outbound
specifies to sample egress packets.
Sampling Rate
Enter packet sampling rate here. This value must be between 0 and
65536. Entering 0 will disable this function. If not specified, the
default value is 0.
Max Header Size
Enter the maximum number of bytes that should be copied from
sampled packets. This value must be between 18 and 256 bytes. By
default, this value is 128 bytes.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
sFlow Poller Settings
This window is used to view and configure
To view the following window, click Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Poller Settings, as show below:
Figure 11-13 sFlow Poller Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Instance
Enter the instance’s index number if multiple samplers are
associated with one interface. The valid range is from 1 to 65535.
Receiver
Enter the receiver’s index value for this poller here. This value must
be between 1 and 4.
Interval
Enter the maximum number of seconds between successive polling
samples. This value must be between 0 and 120 seconds. Entering
0 will disable this feature. By default this value is 0.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
362
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
Device Environment
The device environment feature displays the Switch internal temperature status.
To view the following window, click Monitoring > Device Environment, as shown below:
Figure 11-14 Device Environment window
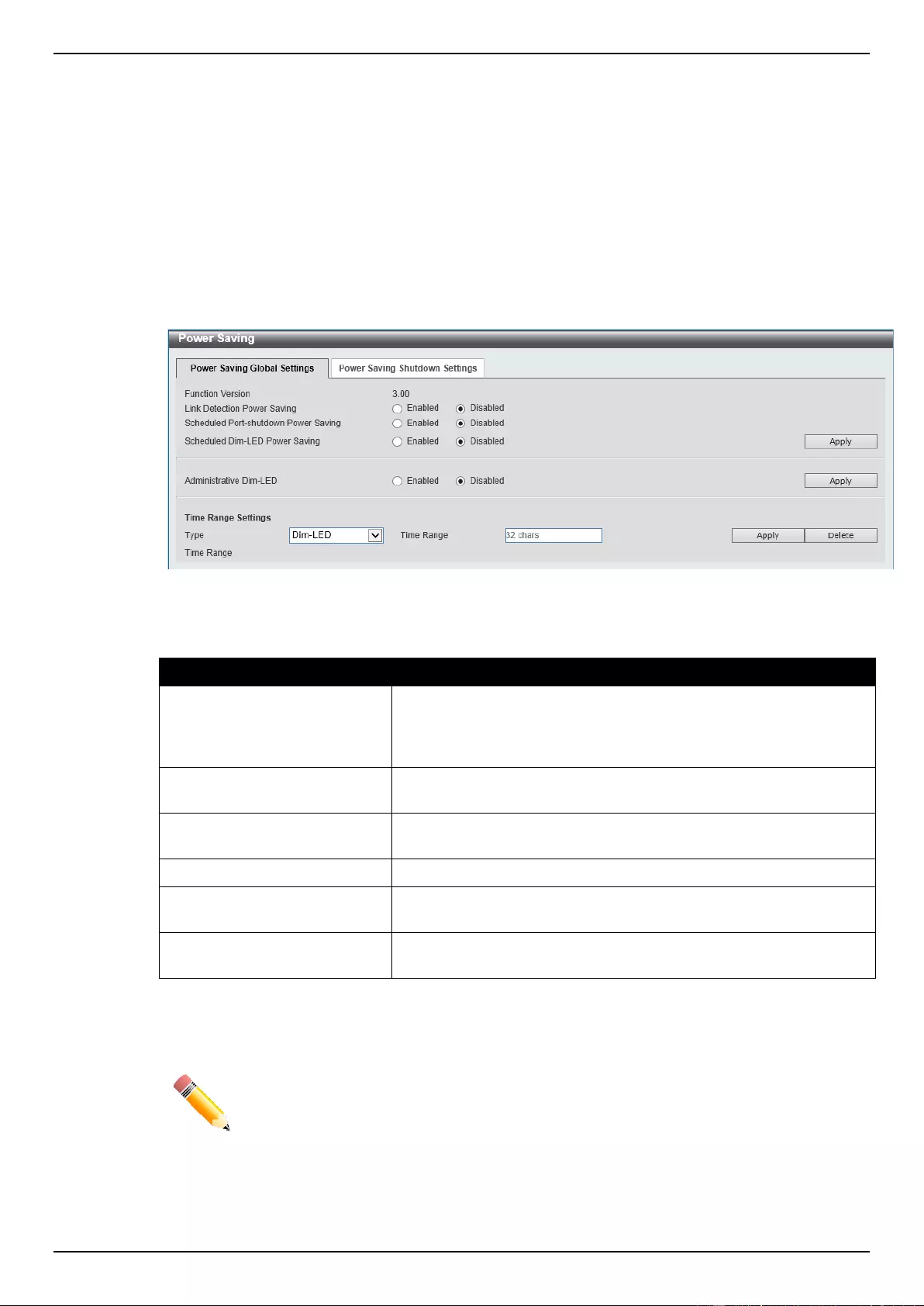
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
363
12. Green
Power Saving
EEE
Power Saving
This window is used to configure the power saving settings of the Switch.
To view the following window, click Green > Power Saving, as shown below:
Figure 12-1 Power Saving window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Link Detection Power Saving
Select this option to enable or disable the link detection state. When
enabled, a port which has a link down status will be turned off to
save power to the Switch. This will not affect the port’s capabilities
when the port status is link up.
Scheduled Port-shutdown
Power Saving
Select this option to enable or disable applying the power saving by
scheduled port shutdown.
Scheduled Dim-LED Power
Saving
Select this option to enable or disable applying the power saving by
scheduled dimming LEDs.
Administrative Dim-LED
Select this option to enable or disable the port LED function.
Type
Select the type of power saving. Options to choose from are Dim-
LED and Hibernation.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associate with the power
saving type.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for each individual section.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
NOTE: The hibernation feature can only be configured when physical stacking is
disabled on this switch.
After clicking the Power Saving Shutdown Settings tab, the following page will appear.
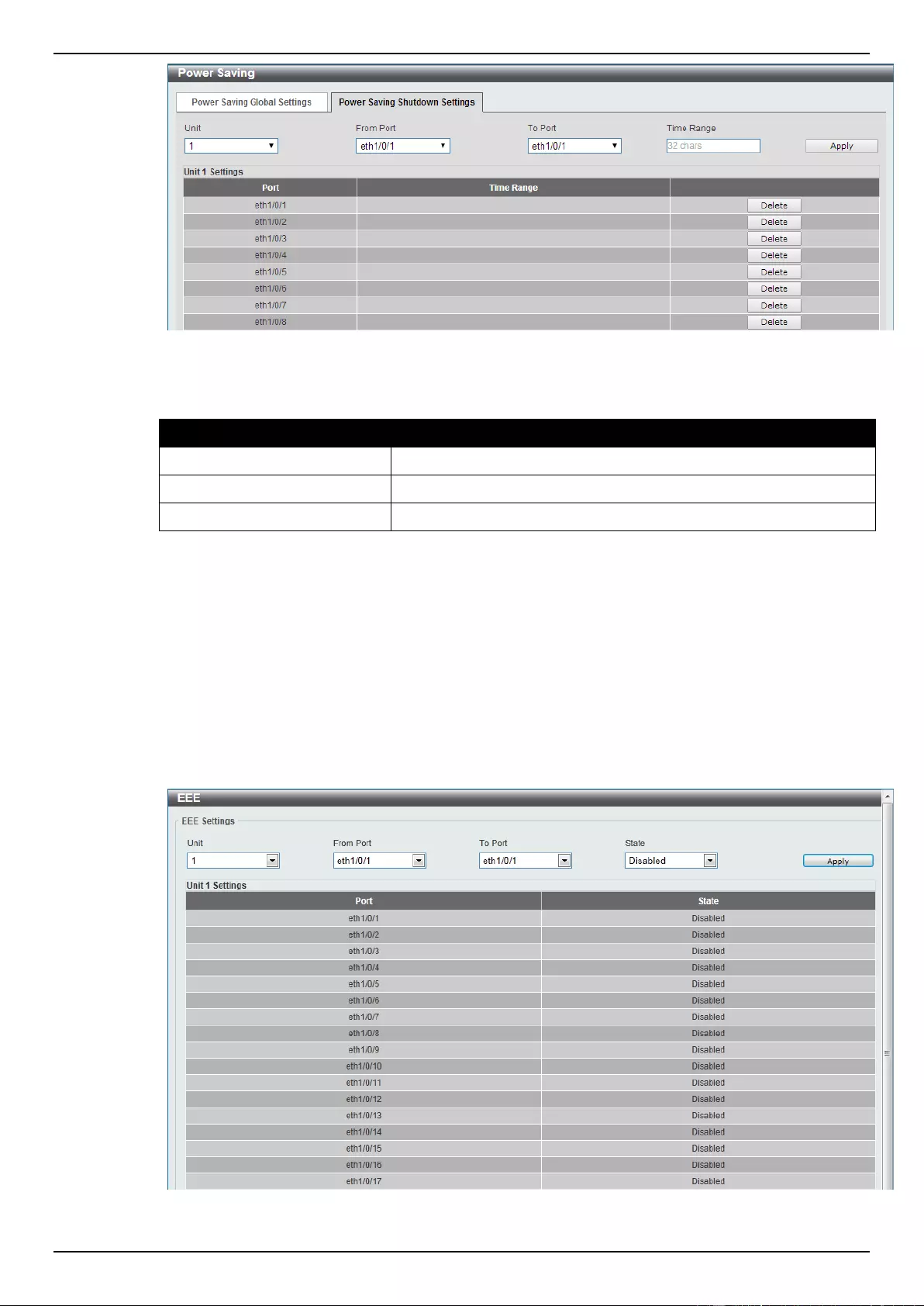
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
364
Figure 12-2 Power Saving Shutdown Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
Time Range
Enter the name of the time range to associated with the ports.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specified entry.
EEE
Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) is defined in IEEE 802.3az. It is designed to reduce the energy
consumption of a link when no packets are being sent.
To view the following window, click Green > EEE, as shown below:
Figure 12-3 EEE window
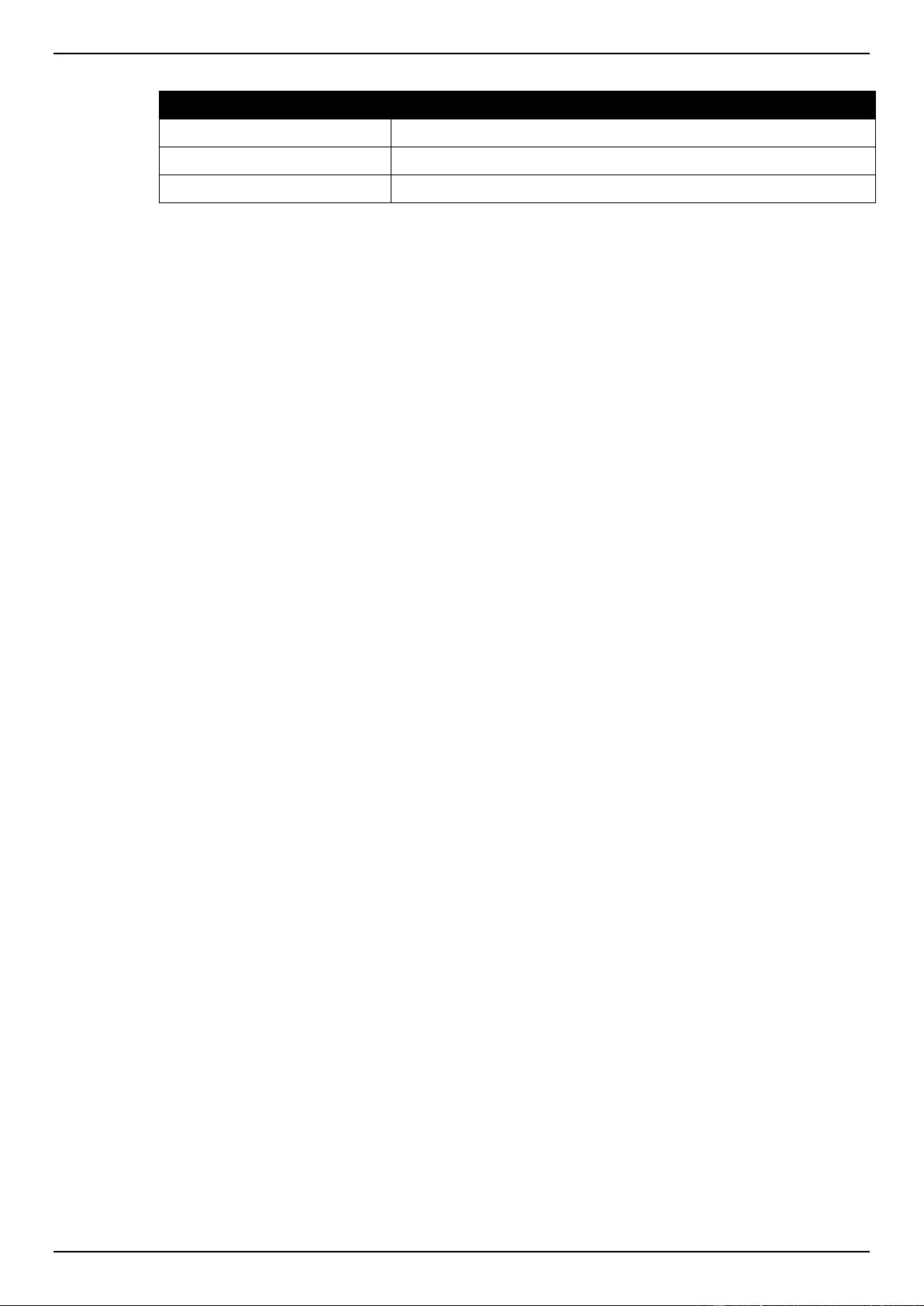
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
365
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
From Port / To Port
Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here.
State
Select this option to enable or disable the state of this feature here.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
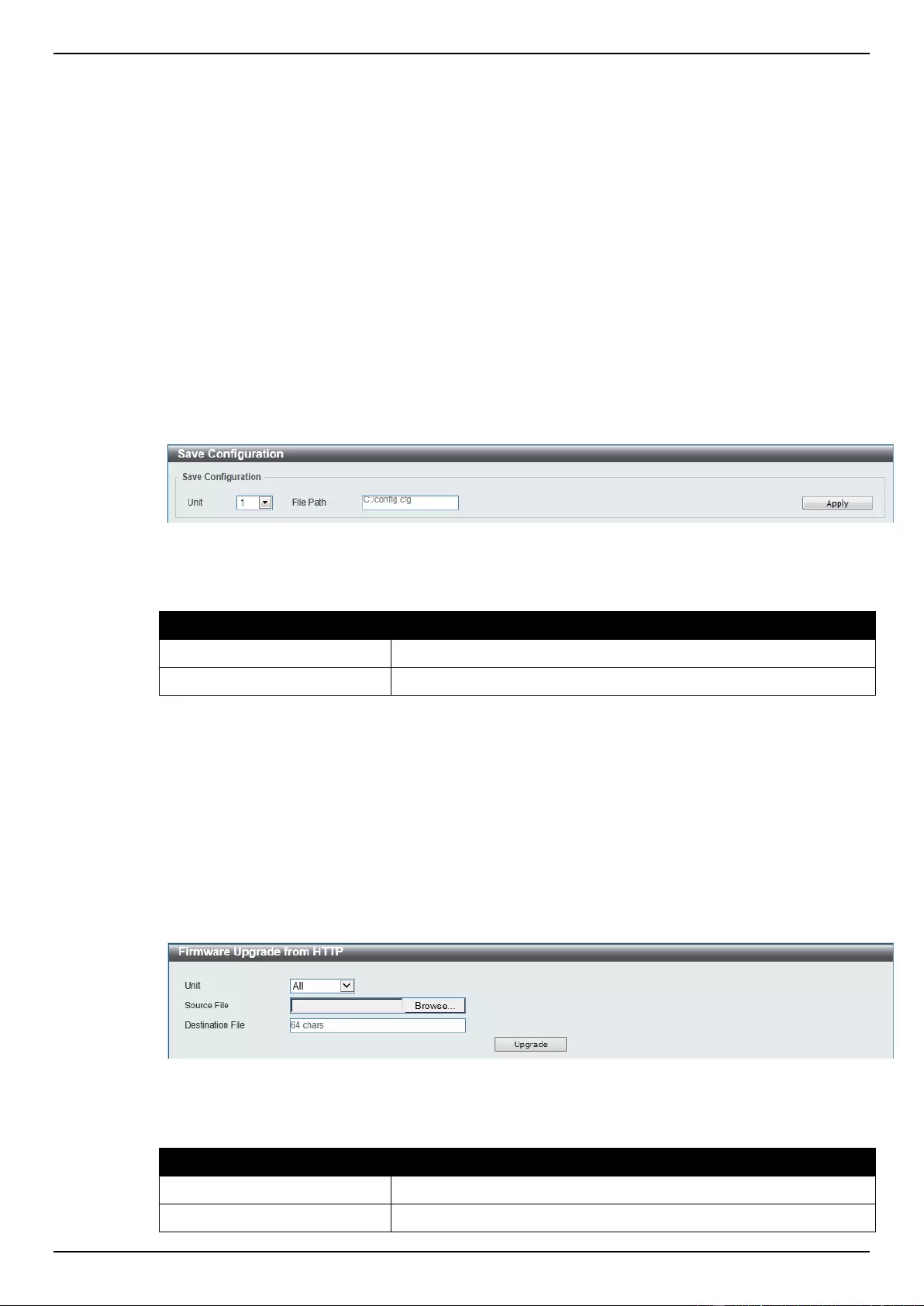
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
366
13. Save and Tools
Save Configuration
Firmware Upgrade & Backup
Configuration Restore & Backup
Log Backup
Ping
Trace Route
Language Management
Reset
Reboot System
Save Configuration
This window is used to save the running configuration to the start-up configuration or the file system of
the Switch. This is to prevent the loss of configuration in the event of a power failure.
To view the following window, click Save > Save Configuration, as shown below:
Figure 13-1 Save Configuration window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
File Path
Enter the filename and path in the space provided.
Click the Apply button to save the configuration.
Firmware Upgrade & Backup
Firmware Upgrade from HTTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware upgrade from a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Upgrade
from HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-2 Firmware Upgrade from HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file located on
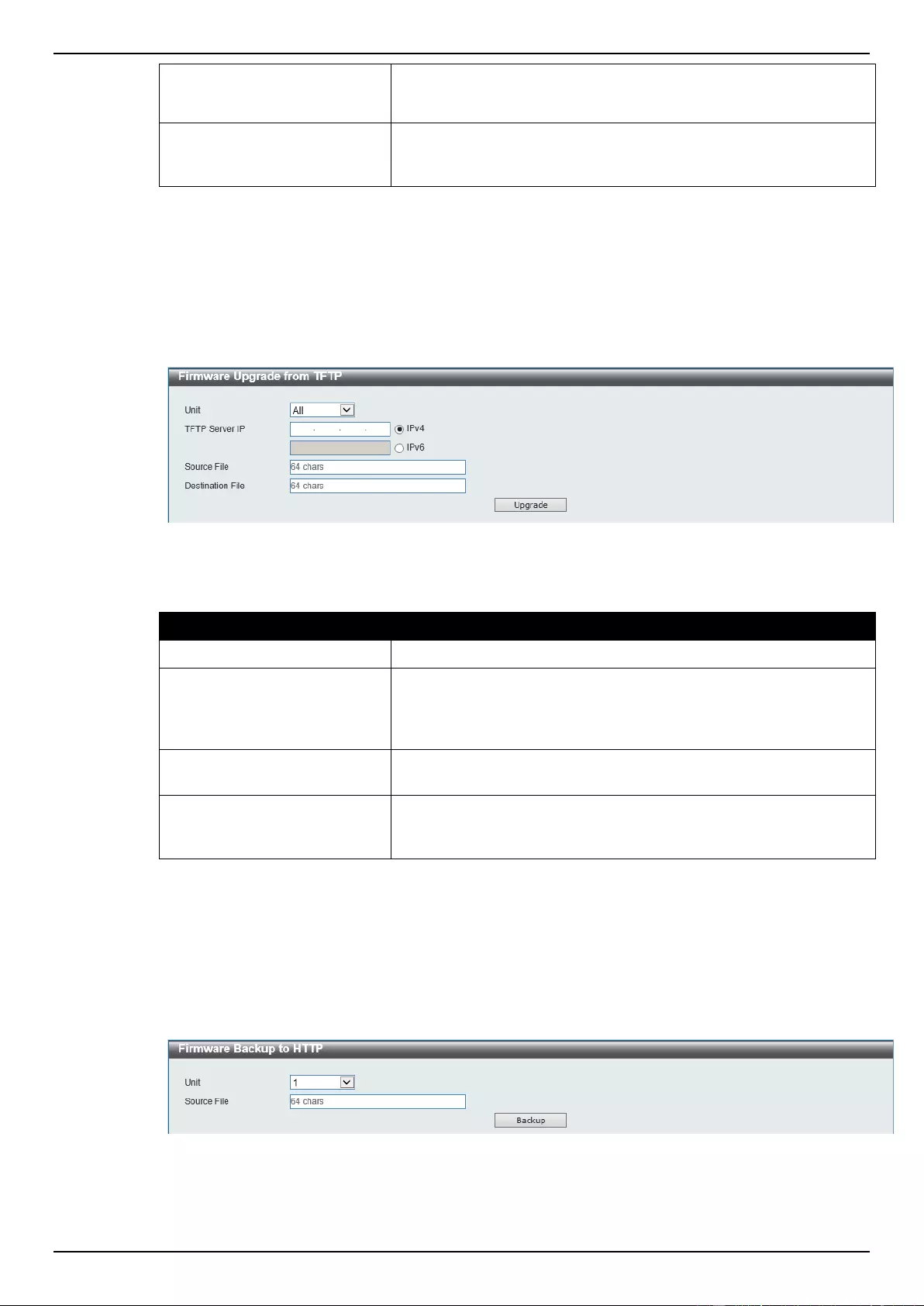
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
367
the local PC. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Alternatively click the Browse button to navigate to the location of
the firmware file located on the local PC.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the new firmware
should be stored on the Switch. This field can be up to 64
characters long.
Click the Upgrade button to initiate the firmware upgrade.
Firmware Upgrade from TFTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware upgrade from a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > firmware Upgrade
from TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-3 Firmware Upgrade from TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server’s IP address here. When select the IPv4
option, enter the IPv4 address of the TFTP server in the space
provided. When the IPv6 option is selected, enter the IPv6 address
of the TFTP server in the space provided.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file located on
the TFTP server here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the new firmware
should be stored on the Switch. This field can be up to 64
characters long.
Click the Upgrade button to initiate the firmware upgrade.
Firmware Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware backup to a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Backup to
HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-4 Firmware Backup to HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
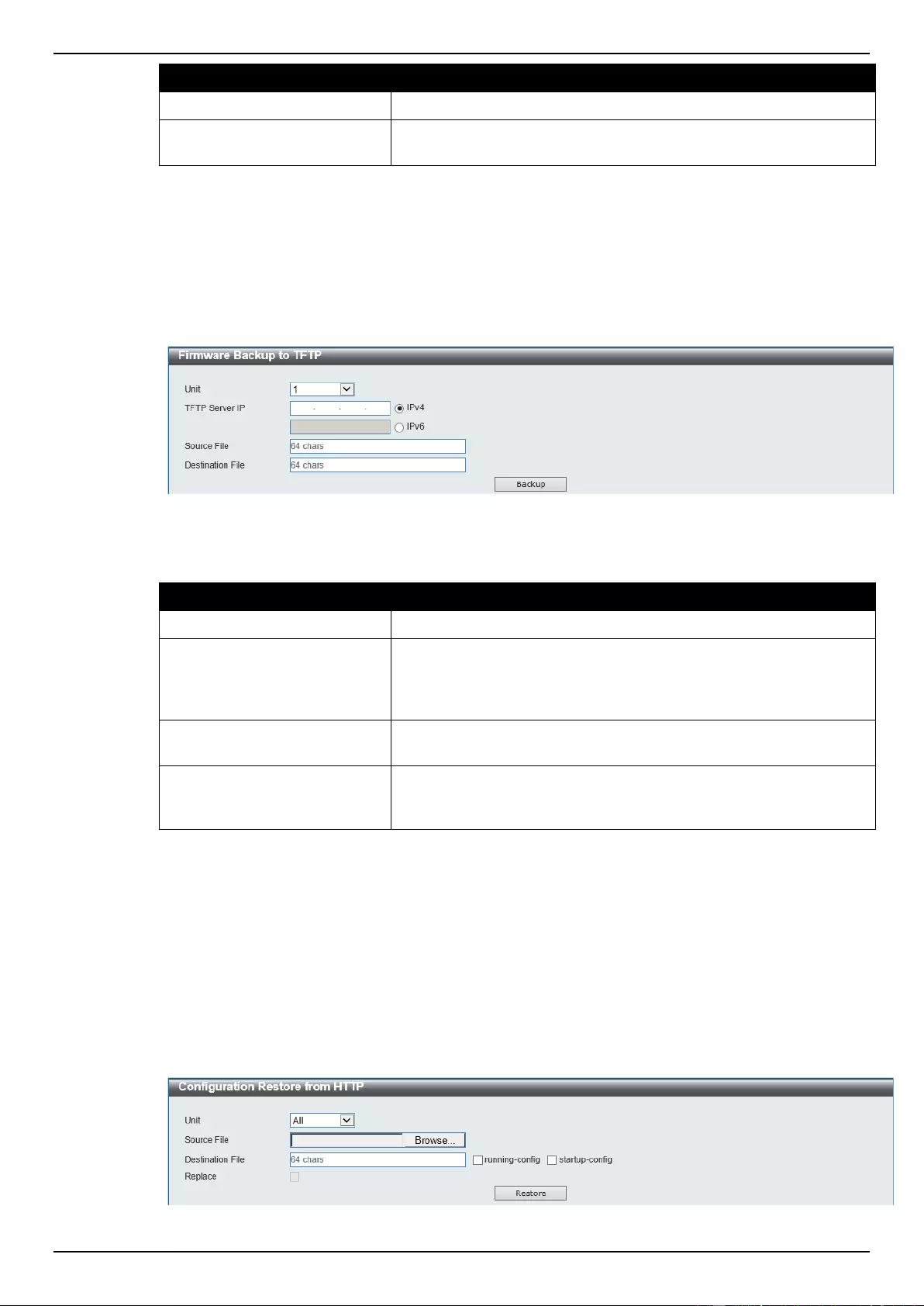
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
368
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file located on
the Switch here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Click the Backup button to initiate the firmware backup.
Firmware Backup to TFTP
This window is used to initiate a firmware backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Firmware Upgrade & Backup > Firmware Backup to
TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-5 Firmware Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server’s IP address here. When select the IPv4
option, enter the IPv4 address of the TFTP server in the space
provided. When the IPv6 option is selected, enter the IPv6 address
of the TFTP server in the space provided.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the firmware file located on
the Switch here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the firmware should
be stored on the TFTP server. This field can be up to 64 characters
long.
Click the Backup button to initiate the firmware backup.
Configuration Restore & Backup
Configuration Restore from HTTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration restore from a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Restore from HTTP, as shown below:
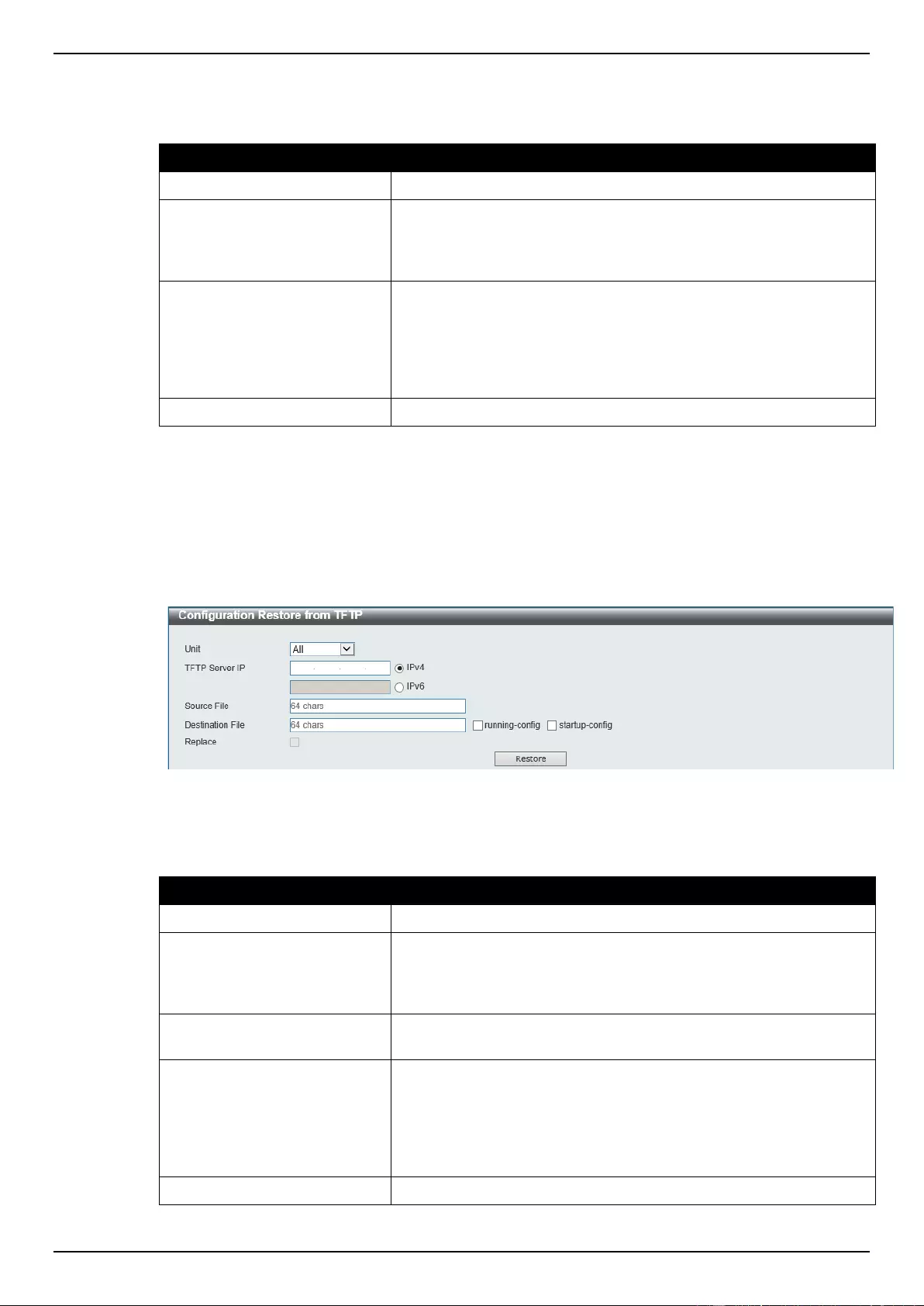
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
369
Figure 13-6 Configuration Restore from HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file located
on the local PC. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Alternatively click the Browse button to navigate to the location of
the configuration file located on the local PC.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the configuration file
should be stored on the Switch. This field can be up to 64
characters long. Select the running-config option to restore and
overwrite the running configuration file on the Switch. Select the
startup-config option to restore and overwrite the start-up
configuration file on the Switch.
Replace
Select this option to replace the current running configuration.
Click the Restore button to initiate the configuration restore.
Configuration Restore from TFTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration restore from a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Restore from TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-7 Configuration Restore from TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server’s IP address here. When select the IPv4
option, enter the IPv4 address of the TFTP server in the space
provided. When the IPv6 option is selected, enter the IPv6 address
of the TFTP server in the space provided.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file located
on the TFTP server here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the configuration file
should be stored on the Switch. This field can be up to 64
characters long. Select the running-config option to restore and
overwrite the running configuration file on the Switch. Select the
startup-config option to restore and overwrite the start-up
configuration file on the Switch.
Replace
Select this option to replace the current running configuration.
Click the Restore button to initiate the configuration restore.
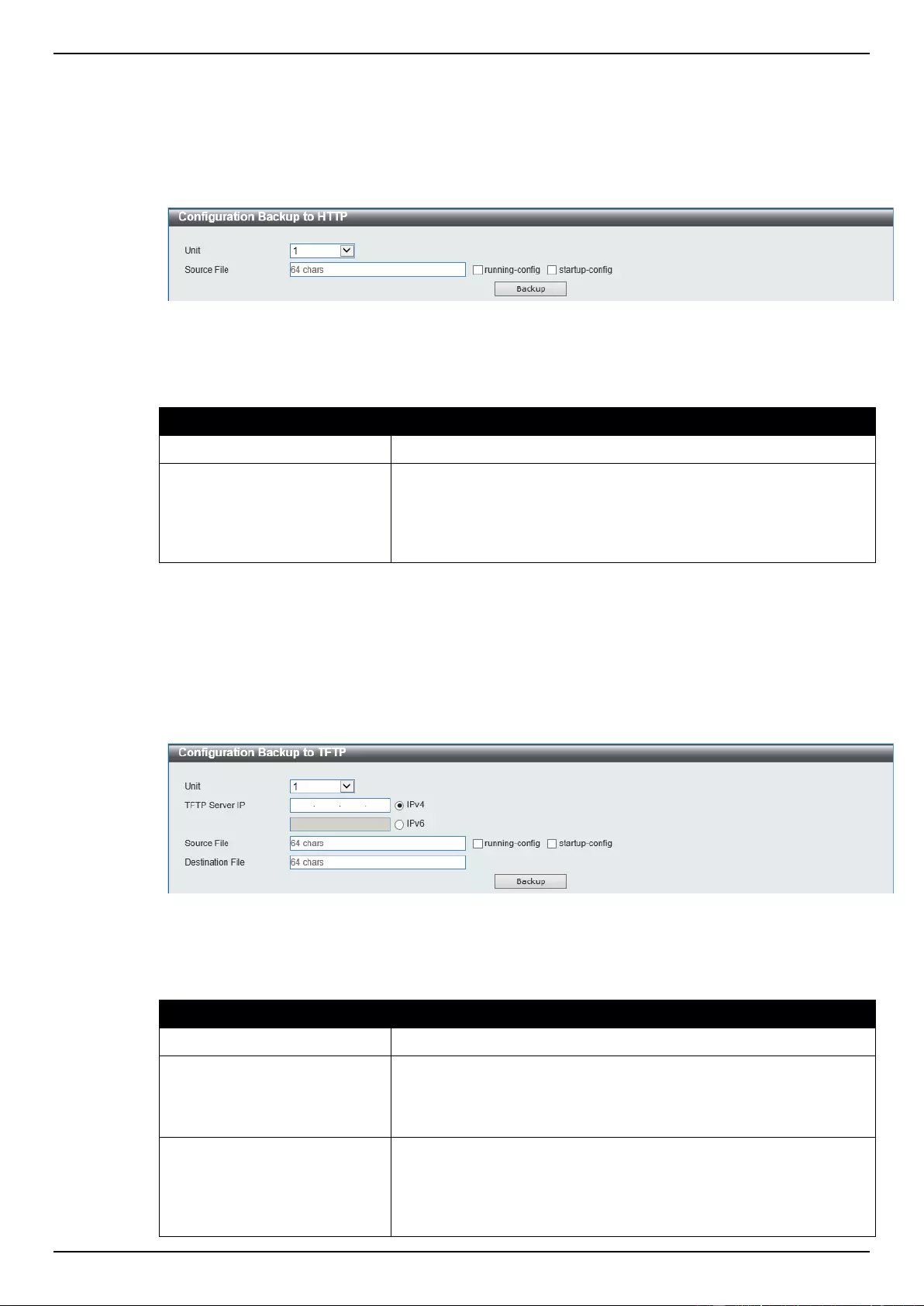
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
370
Configuration Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration file backup to a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Backup to HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-8 Configuration Backup to HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file located
on the Switch here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Select the running-config option to back up the running
configuration file from the Switch. Select the startup-config option
to back up the start-up configuration file from the Switch.
Click the Backup button to initiate the configuration file backup.
Configuration Backup to TFTP
This window is used to initiate a configuration file backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Configuration Restore & Backup > Configuration
Backup to TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-9 Configuration Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Unit
Select the switch unit that will be used for this configuration here.
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server’s IP address here. When select the IPv4
option, enter the IPv4 address of the TFTP server in the space
provided. When the IPv6 option is selected, enter the IPv6 address
of the TFTP server in the space provided.
Source File
Enter the source filename and path of the configuration file located
on the switch here. This field can be up to 64 characters long.
Select the running-config option to back up the running
configuration file from the Switch. Select the startup-config option
to back up the start-up configuration file from the Switch.
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
371
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the configuration file
should be stored on the TFTP server. This field can be up to 64
characters long.
Click the Backup button to initiate the configuration file backup.
Log Backup
Log Backup to HTTP
This window is used to initiate a system log backup to a local PC using HTTP.
To view the following window, click Tools > Log Backup > Log Backup to HTTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-10 Log Backup to HTTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Log Type
Select the log type that will be backed up to the local PC using
HTTP. When the System Log option is selected, the system log will
be backed up. When the Attack Log is selected, the attack log will
be backed up.
Click the Backup button to initiate the system log backup.
Log Backup to TFTP
This window is used to initiate a system log backup to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Tools > Log Backup > Log Backup to TFTP, as shown below:
Figure 13-11 Log Backup to TFTP window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
TFTP Server IP
Enter the TFTP server’s IP address here. When select the IPv4
option, enter the IPv4 address of the TFTP server in the space
provided. When the IPv6 option is selected, enter the IPv6 address
of the TFTP server in the space provided.
Destination File
Enter the destination filename and path where the log file should be
stored on the TFTP server. This field can be up to 64 characters
long.
Log Type
Select the log type that will be backed up to the TFTP server. When
the System Log option is selected, the system log will be backed
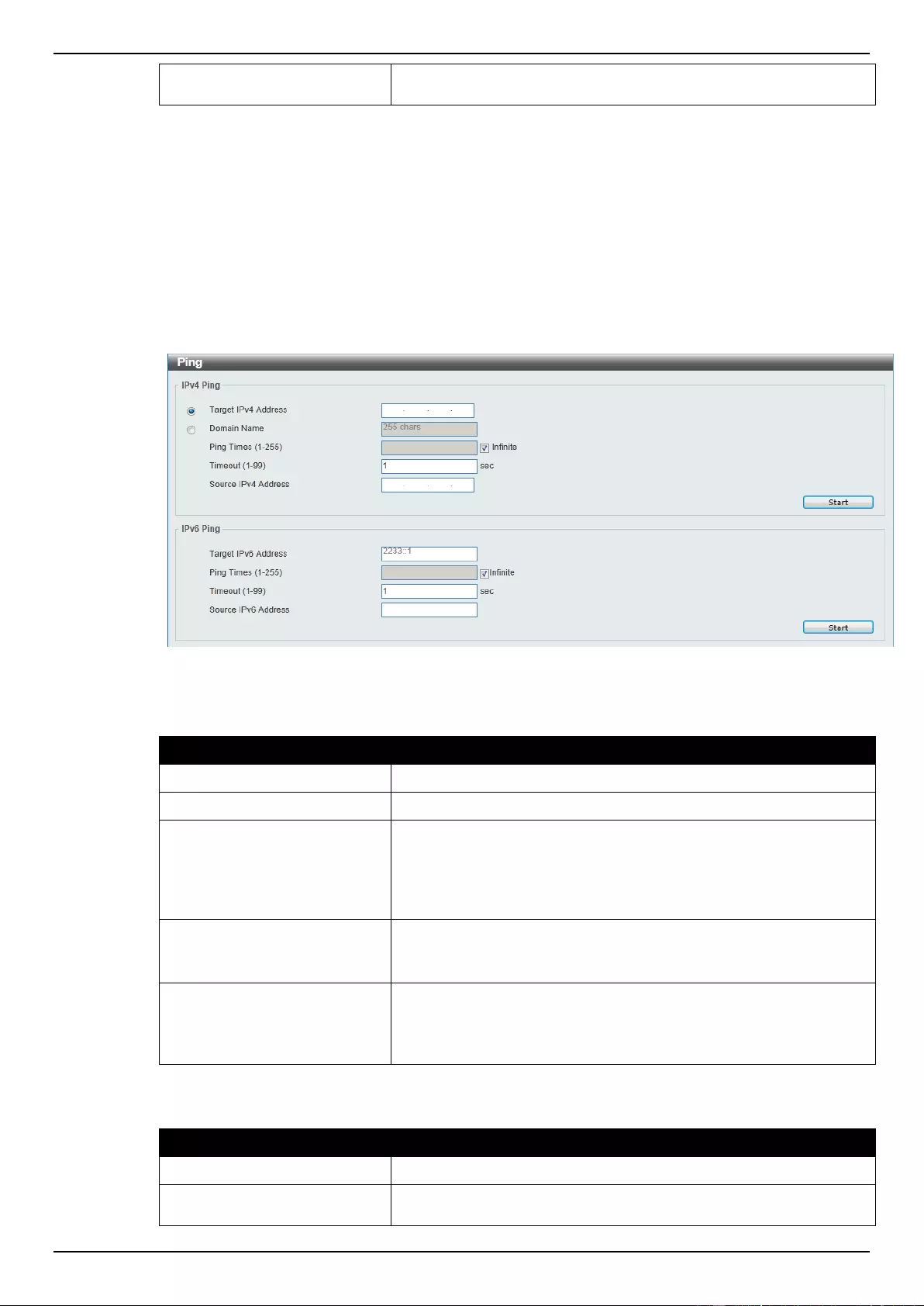
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
372
up. When the Attack Log is selected, the attack log will be backed
up.
Click the Backup button to initiate the system log backup.
Ping
Ping is a small program that sends ICMP Echo packets to the IP address you specify. The destination
node then responds to or “echoes” the packets sent from the Switch. This is very useful to verify
connectivity between the Switch and other nodes on the network.
To view the following window, click Tools > Ping, as shown below:
Figure 13-12 Ping window
The fields that can be configured for IPv4 Ping are described below:
Parameter
Description
Target IPv4 Address
Select and enter an IP address to be pinged.
Domain Name
Select and enter the domain name of the system to discover.
Ping Times
Enter the number of times desired to attempt to Ping the IPv4
address configured in this window. Users may enter a number of
times between 1 and 255. Tick the Infinite check box to keep
sending ICMP Echo packets to the specified IP address until the
program is stopped.
Timeout
Select a timeout period between 1 and 99 seconds for this Ping
message to reach its destination. If the packet fails to find the IP
address in this specified time, the Ping packet will be dropped.
Source IPv4 Address
Enter the source IPv4 address. If the current switch has more than
one IP address, you can enter one of them to this field. When
entered, this IPv4 address will be used as the packets’ source IP
address sent to the remote host, or as primary IP address.
The fields that can be configured for IPv6 Ping are described below:
Parameter
Description
Target IPv6 Address
Enter an IPv6 address to be pinged.
Ping Times
Enter the number of times desired to attempt to Ping the IPv6
address configured in this window. Users may enter a number of

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
373
times between 1 and 255. Tick the Infinite check box to keep
sending ICMP Echo packets to the specified IPv6 address until the
program is stopped.
Timeout
Select a timeout period between 1 and 99 seconds for this Ping
message to reach its destination. If the packet fails to find the IP
address in this specified time, the Ping packet will be dropped.
Source IPv6 Address
Enter the source IPv6 address. If the current switch has more than
one IPv6 address, you can enter one of them to this field. When
entered, this IPv6 address will be used as the packets’ source IP
address sent to the remote host, or as primary IP address.
Click the Start button to initiate the Ping Test for each individual section.
After clicking the Start button in IPv4 Ping section, the following IPv4 Ping Result section will appear:
Figure 13-13 Ping - IPv4 Ping Result window
Click the Stop button to halt the Ping Test.
Click the Back button to return to the IPv4 Ping section.
After clicking the Start button in IPv6 Ping section, the following IPv6 Ping Result section will appear:
Figure 13-14 Ping – IPv6 Ping Result window
Click the Stop button to halt the Ping Test.
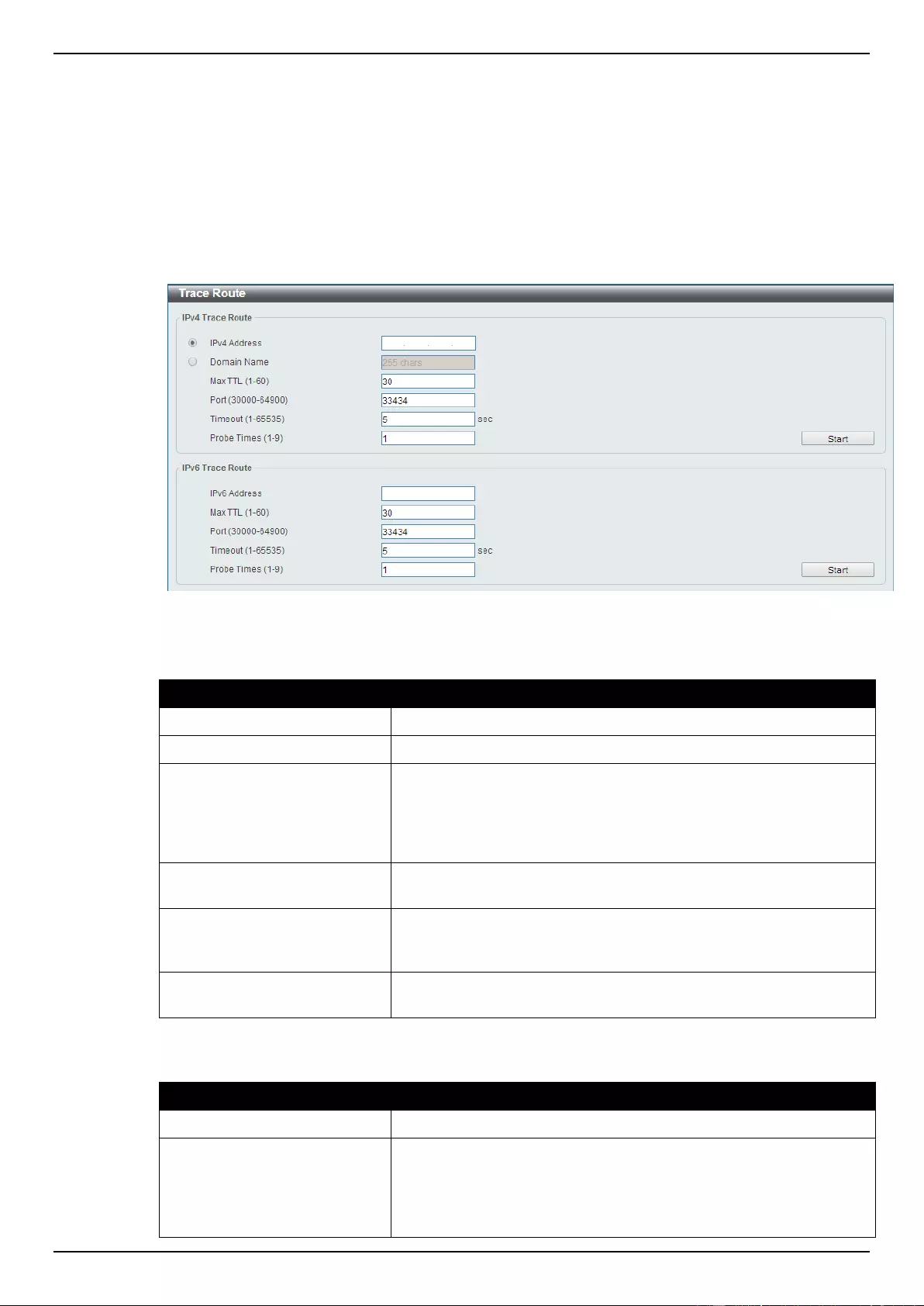
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
374
Click the Back button to return to the IPv4 Ping section.
Trace Route
The trace route page allows the user to trace a route between the Switch and a given host on the
network.
To view the following window, click Tools > Trace Route, as shown below:
Figure 13-15 Trace Route window
The fields that can be configured for IPv4 Trace Route are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv4 Address
Select and enter the IPv4 address of the destination here.
Domain Name
Select and enter the domain name of the destination here.
Max TTL
Enter the Time-To-Live (TTL) value of the trace route request here.
This is the maximum number of routers that a trace route packet
can pass. The trace route option will cross while seeking the
network path between two devices. The range for the TTL is 1 to 60
hops.
Port
Enter the port number here. The value range is from 30000 to
64900.
Timeout
Enter the timeout period while waiting for a response from the
remote device here. A value of 1 to 65535 seconds can be
specified. The default is 5 seconds.
Probe Times
Enter the probe time number here. The range is from 1 to 9. If
unspecified, the default value is 1.
The fields that can be configured for IPv6 Trace Route are described below:
Parameter
Description
IPv6 Address
Select and enter the IPv6 address of the destination here.
Max TTL
Enter the Time-To-Live (TTL) value of the trace route request here.
This is the maximum number of routers that a trace route packet
can pass. The trace route option will cross while seeking the
network path between two devices. The range for the TTL is 1 to 60
hops.
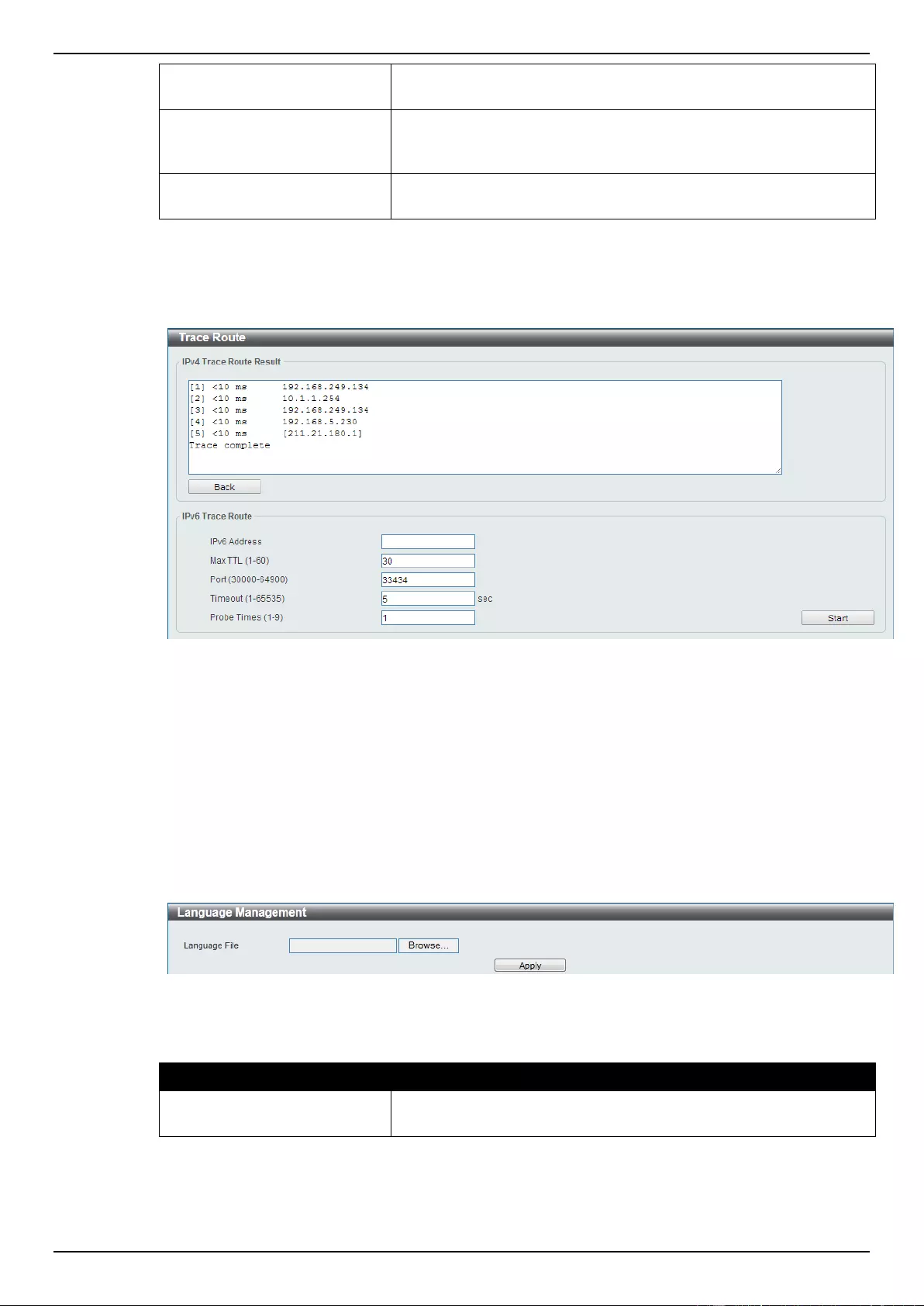
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
375
Port
Enter the port number here. The value range is from 30000 to
64900.
Timeout
Enter the timeout period while waiting for a response from the
remote device here. A value of 1 to 65535 seconds can be
specified. The default is 5 seconds.
Probe Times
Enter the probe time number here. The range is from 1 to 9. If
unspecified, the default value is 1.
Click the Start button to initiate the route trace for each individual section.
After clicking the Start button in IPv4 Trace Route section, the following IPv4 Trace Route Result
section will appear:
Figure 13-16 Trace Route - IPv4 Trace Route Result window
Click the Back button to stop the trace route and return to the IPv4 Trace Route section.
Language Management
This window is used to install the language file to the Switch.
To view the following window, click Tools > Language Management, as shown below:
Figure 13-17 Language Management window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter
Description
Language File
Click the Browse button to navigate to the location of the firmware
file located on the local PC.
Click the Apply button to initiate the language pack installation.
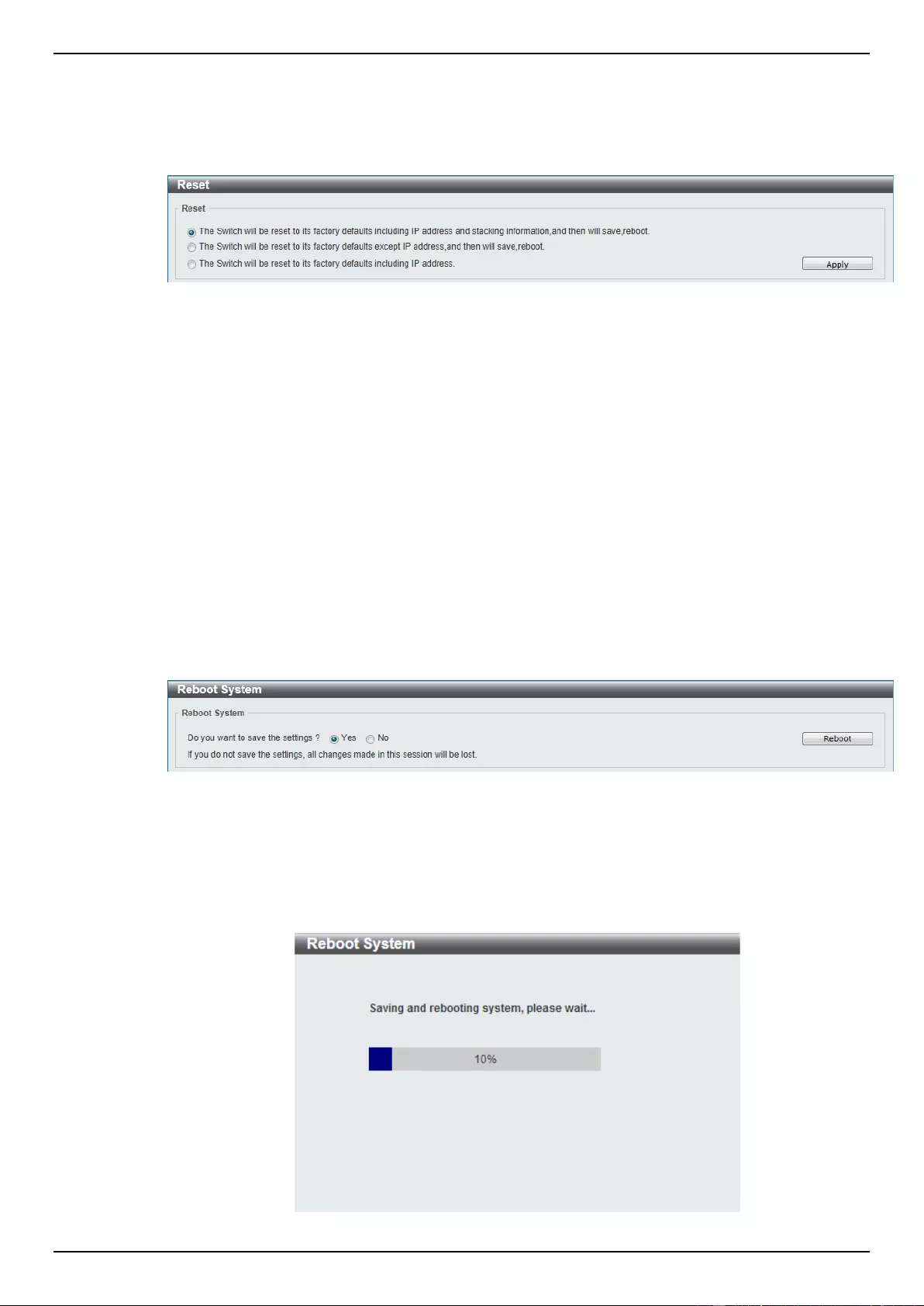
DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
376
Reset
This window is used to reset the Switch’s configuration to the factory default settings.
To view the following window, click Tools > Reset, as shown below:
Figure 13-18 Reset window
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory defaults including IP address and stacking
information, and the will save, reboot option to reset the Switch’s configuration to its factory default
settings.
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory default except IP address, and then will save,
reboot option to reset the Switch’s configuration to its factory default settings. This option will exclude
the IP address from being changed.
Select the The Switch will be reset to its factory defaults including IP address option to reset the
Switch’s configuration to its factory default settings.
Click the Apply button to initiate the factory default reset and reboot the Switch.
Reboot System
This window is used to reboot the Switch and alternatively save the configuration before doing so. To
view the following window, click Tools > Reboot System, as shown below:
Figure 13-19 Reboot System window
When rebooting the Switch, any configuration changes that was made during this session, will be lost
unless the Yes option is selected when asked to save the settings.
Click the Reboot button to alternatively save the settings and reboot the Switch.
Figure 13-20 Reboot System - Rebooting window

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
377

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
378
Appendix A - System Log Entries
The following table lists all possible entries and their corresponding meanings that will appear in the
System Log of this switch.
802.1X
Log Description
Severity
Event description: 802.1X Authentication failure.
Log Message: 802.1X authentication fail [due to <reason>] from (Username:
<username>, <interface-id>, MAC: <mac-address>)
Parameters description:
reason: The reason for the failed authentication. The possible reason
may be:
(1) user authentication failure.
(2) no server(s) responding.
(3) no servers configured.
(4) no resources.
(5) user timeout expired.
username: The user that is being authenticated..
interface-id: The switch interface number.
mac-address: The MAC address of the authenticated device.
Critical
Event description: 802.1X Authentication successful.
Log Message: 802.1X authentication success (Username: <username>,
<interface-id>, MAC: <mac-address>)
Parameters description:
username: The user that is being authenticated.
interface-id: The interface name.
mac-address: The MAC address of the authenticated device.
Informational
AAA
Log Description
Severity
Event description: This log will be generated when AAA global state is enabled
or disabled.
Log Message: AAA is <status>.
Parameters description:
status: The status indicates the AAA enabled or disabled.
Informational
Event description: This log will be generated when login successfully.
Log Message: Successful login through <exec-type> <from client-ip>
authenticated by AAA <aaa-method> <server-ip> (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
aaa-method: It indicates the authentication method, e.g.: none, local,
server.
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address if authentication
method is remote server.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
379
Username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Event description: This log will be generated when login failure.
Log Message: Login failed through <exec-type> <from client-ip> authenticated
by AAA <aaa-method> <server-ip> (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
aaa-method: It indicates the authentication method, e.g.: local, server.
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address if authentication
method is remote server.
username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Warning
Event description: This log will be generated when the remote server does not
respond to the login authentication request.
Log Message: Login failed through <exec-type> <from client-ip> due to AAA
server <server-ip> timeout (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address.
username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Warning
Event description: This log will be generated when enable privilege
successfully.
Log Message: Successful enable privilege through <exec-type> <from client-ip>
authenticated by AAA <aaa-method> <server-ip> (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
aaa-method: It indicates the authentication method, e.g.: none, local,
server.
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address if authentication
method is remote server.
Username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Informational
Event description: This log will be generated when enable privilege failure.
Log Message: Enable privilege failed through <exec-type> <from client-ip>
authenticated by AAA <aaa-method> <server-ip> (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
aaa-method: It indicates the authentication method, e.g.: local, server.
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address if authentication
method is remote server.
username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Warning
Event description: This log will be generated when the remote server does not
respond to the enable password authentication request.
Log Message: Enable privilege failed through <exec-type> <from client-ip> due
to AAA server <server-ip> timeout (Username: <username>).
Parameters description:
exec-type: It indicates the EXEC types, e.g.: Console, Telnet, SSH,
Web, Web(SSL).
client-ip: It indicates the client’s IP address if valid through IP protocol.
Warning

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
380
server-ip: It indicates the AAA server IP address.
username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Event description: This log will be generated when RADIUS assigned a valid
VLAN ID attributes.
Log Message: RADIUS server <server-ip> assigned VID: <vid> to port
<interface-id> (Username: <username>)
Parameters description:
server-ip: It indicates the RADIUS server IP address.
vid: The assign VLAN ID that authorized by from RADIUS server.
interface–id: It indicates the port number of the client authenticated.
Username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Informational
Event description: This log will be generated when RADIUS assigned a valid
bandwidth attributes.
Log Message: RADIUS server <server-ip> assigned <direction> bandwidth:
<threshold> to port < interface -id> (Username: <username>)
Parameters description:
server-ip: It indicates the RADIUS server IP address.
Direction: It indicates the direction for bandwidth control, e.g.: ingress
or egress.
Threshold: The assign threshold of bandwidth that authorized by from
RADIUS server.
interface–id: It indicates the port number of the client authenticated.
Username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Informational
Event description: This log will be generated when RADIUS assigned a valid
priority attributes.
Log Message: RADIUS server <server-ip> assigned 802.1p default priority:
<priority> to port < interface -id> (Username: <username>)
Parameters description:
server-ip: It indicates the RADIUS server IP address.
priority: The assign priority that authorized by from RADIUS server.
interface–id: It indicates the port number of the client authenticated.
Username: It indicates the username for authentication.
Informational
Event description: This log will be generated when RADIUS assigned ACL
script but fails to apply to the system due to insufficient resource.
Log Message: RADIUS server <server-ip> assigns <username> ACL failure at
port < interface -id> (<acl-script>)
Parameters description:
server-ip: It indicates the RADIUS server IP address.
username: It indicates the username for authentication.
interface-id: It indicates the port number of the client authenticated.
acl-script: The assign ACL script that authorized by from RADIUS
server.
Warning
Auto Save Configuration
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Record the event when the configure information of ddp is
saved automatically.
Log Message:CONFIG-6-DDPSAVECONFIG: [Unit <unitID>, ]Configuration
automatically saved to flash due to configuring from DDP(Username:
<username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
Unit: Box ID
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
381
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address
Auto Surveillance VLAN
Log Description
Severity
Event description: When a new surveillance device is detected on an interface.
Log Message: New surveillance device detected (<interface-id>, MAC: < mac-
address >)
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
mac-address: Surveillance device MAC address.
Informational
Event description: When an interface which is enabled surveillance VLAN joins
the surveillance VLAN automatically.
Log Message: <interface-id> add into surveillance VLAN <vid >
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
vid:VLAN ID
Informational
Event description: When an interface leaves the surveillance VLAN and at the
same time, no surveillance device is detected in the aging interval for that
interface, the log message will be sent.
Log Message: <interface-id> remove from surveillance VLAN <vid >
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
vid:VLAN ID
Informational
BPDU Attack Protection
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Record the event when the BPDU attack happened.
Log Message: <interface-id> enter STP BPDU under protection state (mode:
<mode>)
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which detected STP BPDU attack.
mode: BPDU Protection mode of the interface. Mode can be drop,
block, or shutdown
Informational
Event description: Record the event when the STP BPDU attack recovered.
Log Message: <interface-id> recover from BPDU under protection state.
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which detected STP BPDU attack.
Informational
Configuration/Firmware
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Firmware upgraded successfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Firmware upgraded by <session> successfully
(Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>], Server IP:
<serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
382
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Event description: Firmware upgraded unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Firmware upgraded by <session> unsuccessfully
(Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>], Server IP:
<serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Warning
Event description: Firmware uploaded successfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Firmware uploaded by <session> successfully
(Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>], Server IP:
<serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Informational
Event description: Firmware uploaded unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Firmware uploaded by <session> unsuccessfully
(Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>], Server IP:
<serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Warning

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
383
Event description: Configuration downloaded successfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Configuration downloaded by <session>
successfully. (Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>],
Server IP: <serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Informational
Event description: Configuration downloaded unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Configuration downloaded by <session>
unsuccessfully. (Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>],
Server IP: <serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Warning
Event description: Configuration uploaded successfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Configuration uploaded by <session>
successfully. (Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>],
Server IP: <serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Informational
Event description: Configuration uploaded unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Configuration uploaded by <session>
unsuccessfully. (Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>],
Server IP: <serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
Warning

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
384
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Event description: Unknown type files downloaded unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Downloaded by <session> unsuccessfully.
(Username: <username>[, IP: <ipaddr>, MAC: <macaddr>], Server IP:
<serverIP>, File Name: <pathFile>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
session: The user’s session.
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
macaddr : Represent client MAC address.
serverIP: Server IP address.
pathFile: Path and file name on server.
Warning
DAI
Log Description
Severity
Event description: This log will be generated when DAI detect invalid ARP
packet.
Log Message: Illegal ARP <type> packets (IP: <ip-address>, MAC: <mac-
address>, VLAN <vlan-id>, on <interface-id>).
Parameters description:
type: The type of ARP packet, it indicates that ARP packet is request or
ARP response.
Warning
Event description: This log will be generated when DAI detect valid ARP packet.
Log Message: Legal ARP <type> packets (IP: <ip-address>, MAC: <mac-
address>, VLAN <vlan-id>, on <interface-id>).
Parameters description:
type: The type of ARP packet, it indicates that ARP packet is request or
ARP response.
Informational
DDM
Log Description
Severity
Event description: when the any of SFP parameters exceeds from the warning
threshold.
Log Message: Optical transceiver <interface-id> <component> <high-low>
warning threshold exceeded.
Parameters description:
interface-id: port interface ID.
component: DDM threshold type. It can be one of the following types:
temperature
supply voltage
bias current
TX power
Warning

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
385
RX power
high-low: High or low threshold.
Event description: when the any of SFP parameters exceeds from the alarm
threshold.
Log Message: Optical transceiver <interface-id> <component> <high-low>
alarm threshold exceeded.
Parameters description:
interface-id: port interface ID.
component: DDM threshold type. It can be one of the following types:
temperature
supply voltage
bias current
TX power
RX power
high-low: High or low threshold.
Critical
Event description: when the any of SFP parameters recovers from the warning
threshold.
Log Message: Optical transceiver <interface-id> <component> back to normal.
Parameters description:
interface-id: port interface ID.
component: DDM threshold type. It can be one of the following types:
temperature
supply voltage
bias current
TX power
RX power
Warning
DHCPv6 Client
Log Description
Severity
Event description: DHCPv6 client interface administrator state changed.
Log Message: DHCPv6 client on interface <ipif-name> changed state to
[enabled | disabled].
Parameters description:
<ipif-name>: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: DHCPv6 client obtains an ipv6 address from a DHCPv6
server.
Log Message: DHCPv6 client obtains an ipv6 address < ipv6address > on
interface <ipif-name>.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: The ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server starts
renewing.
Log Message: The IPv6 address < ipv6address > on interface <ipif-name>
starts renewing.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: The ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server renews
success.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
386
Log Message: The IPv6 address < ipv6address > on interface <ipif-name>
renews success.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Event description: The ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server starts
rebinding
Log Message: The IPv6 address < ipv6address > on interface <ipif-name>
starts rebinding.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: The ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server rebinds
success
Log Message: The IPv6 address < ipv6address > on interface <ipif-name>
rebinds success.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: The ipv6 address from a DHCPv6 server was deleted.
Log Message: The IPv6 address < ipv6address > on interface <ipif-name> was
deleted.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: ipv6 address obtained from a DHCPv6 server.
ipif-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client interface.
Informational
Event description: DHCPv6 client PD interface administrator state changed.
Log Message: DHCPv6 client PD on interface <intf-name> changed state to
<enabled | disabled>
Parameters description:
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
Event description: DHCPv6 client PD obtains an IPv6 prefix from a delegation
router.
Log Message: DHCPv6 client PD obtains an ipv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr> on
interface <intf-name>
Parameters description:
ipv6networkaddr: ipv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
Event description: The IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router starts
renewing.
Log Message: The IPv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr > on interface <intf-name>
starts renewing.
Parameters description:
ipv6networkaddr: IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
Event description: The IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router renews
success.
Log Message: The IPv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr > on interface <intf-name>
renews success.
Parameters description:
ipv6anetworkaddr: IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
Event description: The IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router starts
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
387
rebinding.
Log Message: The IPv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr > on interface <intf-name>
starts rebinding.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Event description: The IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router rebinds
success.
Log Message: The IPv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr > on interface <intf-name>
rebinds success.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
Event description: The IPv6 prefix from a delegation router was deleted.
Log Message: The IPv6 prefix < ipv6networkaddr > on interface <intf-name>
was deleted.
Parameters description:
ipv6address: IPv6 prefix obtained from a delegation router.
intf-name: Name of the DHCPv6 client PD interface.
Informational
DHCPv6 Relay
Log Description
Severity
Event description: DHCPv6 relay on a specify interface’s administrator state
changed
Log Message: DHCPv6 relay on interface <ipif-name> changed state to
[enabled | disabled]
Parameters description:
<ipif-name>: Name of the DHCPv6 relay agent interface.
Informational
DNS Resolver
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Duplicate Domain name cache added, leads a dynamic
domain name cache be deleted
Log Message: [DNS_RESOLVER(1):]Duplicate Domain name case name:
<domainname>, static IP: <ipaddr>, dynamic IP:<ipaddr>
Parameters description:
domainame: the domain name string.
ipaddr: IP address.
Informational
DoS Prevention
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Detect DOS attack.
Log Message: <dos-type> is dropped from (IP: <ip-address> Port <interface-
id>).
Parameters description:
dos-type: DOS attack type
Notice

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
388
ip-address: IP address.
interface-id: Interface name
Interface
Log Description
Severity
Event description: When port is down
Log Message: Port <port-type>< interface-id> link down
Parameters description:
port-type: port type
interface-id: Interface name
Informational
Event description: When port is up
Log Message: Port <port-type>< interface-id> link up, <link-speed>
Parameters description:
port-type: port type
interface-id: Interface name
link-speed: port link speed.
Informational
JWAC
Log Description
Severity
Event description: when a host has passed the authentication.
Log Message: JWAC host login success (Username: <string>, IP: <ipaddr |
ipv6address>, MAC: <mac-address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>).
Parameters description:
Username: The host username.
IP: The host IP address
mac-address: The host MAC addresses.
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated.
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists.
Informational
Event description: When a host fail to pass the authentication.
Log Message: JWAC host login fail (Username: <string>, IP: <ipaddr |
ipv6address>, MAC: <mac-address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>)
Parameters description:
Username: The host username.
IP: The host IP address
mac-address: The host MAC addresses..
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated.
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists.
Critical
Event description: when the authorized user number on the whole device has
reached the maximum user limit.
Log Message: JWAC enters stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: when the authorized user number on the whole device is
below the maximum user limit in a time interval.
Log Message: JWAC recovers from stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: when the ACL hardware resource is exhausted..
Log Message: JWAC cannot work correctly because ACL rule resource is not
available.
Alert

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
389
LACP
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Link Aggregation Group link up.
Log Message: Link Aggregation Group < group_id > link up.
Parameters description:
group_id: The group id of the link down aggregation group.
Informational
Event description: Link Aggregation Group link down.
Log Message: Link Aggregation Group < group_id > link down.
Parameters description:
group_id: The group id of the link down aggregation group.
Informational
Event description: Member port attach to Link Aggregation Group.
Log Message: <ifname> attach to Link Aggregation Group <group_id>.
Parameters description:
ifname: The interface name of the port that attach to aggregation group.
group_id: The group id of the aggregation group that port attach to.
Informational
Event description: Member port detach from Link Aggregation Group.
Log Message: <ifname> detach from Link Aggregation Group <group_id>.
Parameters description:
ifname: The interface name of the port that detach from aggregation
group.
group_id: The group id of the aggregation group that port detach from.
Informational
LBD
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Record the event when an interface detect loop.
Log Message: <interface-id> LBD loop occurred.
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which loop is detected.
Critical
Event description: Record the event when an interface detect loop.
Log Message: <interface-id > VLAN <vlan-id> LBD loop occurred.
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which loop is detected.
vlan-id: VLAN on which loop is detected.
Critical
Event description: Record the event when an interface loop recovered
Log Message: <interface-id> LBD loop recovered.
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which loop is detected.
Critical
Event description: Record the event when an interface loop recovered.
Log Message: <interface-id> VLAN <vlan-id> LBD loop recovered.
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface on which loop is detected.
vlan-id: VLAN on which loop is detected.
Critical
Event description: Record the event when the number of VLANs that loop back
has occurred exceeds a reserved number.
Log Message: Loop VLAN numbers overflow.
Critical
LLDP-MED

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
390
Log Description
Severity
Event description: LLDP-MED topology change detected
Log Message: LLDP-MED topology change detected (on port <portNum>.
chassis id: <chassisType>, <chassisID>, port id: <portType>, <portID>, device
class: <deviceClass>)
Parameters description:
portNum: The port number.
chassisType: chassis ID subtype.
Value list:
1. chassisComponent(1)
2. interfaceAlias(2)
3. portComponent(3)
4. macAddress(4)
5. networkAddress(5)
6. interfaceName(6)
7. local(7)
chassisID: chassis ID.
portType: port ID subtype.
Value list:
1. interfaceAlias(1)
2. portComponent(2)
3. macAddress(3)
4. networkAddress(4)
5. interfaceName(5)
6. agentCircuitId(6)
7. local(7)
portID: port ID.
deviceClass: LLDP-MED device type.
Notice
Event description: Conflict LLDP-MED device type detected
Log Message: Conflict LLDP-MED device type detected ( on port < portNum >,
chassis id: < chassisType>, <chassisID>, port id: < portType>, <portID>, device
class: <deviceClass>)
Parameters description:
portNum: The port number.
chassisType: chassis ID subtype.
Value list:
1. chassisComponent(1)
2. interfaceAlias(2)
3. portComponent(3)
4. macAddress(4)
5. networkAddress(5)
6. interfaceName(6)
7. local(7)
chassisID: chassis ID.
portType: port ID subtype.
Value list:
1. interfaceAlias(1)
2. portComponent(2)
3. macAddress(3)
4. networkAddress(4)
5. interfaceName(5)
6. agentCircuitId(6)
Notice

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
391
7. local(7)
portID: port ID.
deviceClass: LLDP-MED device type.
Event description: Incompatible LLDP-MED TLV set detected
Log Message: Incompatible LLDP-MED TLV set detected ( on port < portNum
>, chassis id: < chassisType>, <chassisID>, port id: < portType>, <portID>,
device class: <deviceClass>)
Parameters description:
portNum: The port number.
chassisType: chassis ID subtype.
Value list:
1. chassisComponent(1)
2. interfaceAlias(2)
3. portComponent(3)
4. macAddress(4)
5. networkAddress(5)
6. interfaceName(6)
7. local(7)
chassisID: chassis ID.
portType: port ID subtype.
Value list:
1. interfaceAlias(1)
2. portComponent(2)
3. macAddress(3)
4. networkAddress(4)
5. interfaceName(5)
6. agentCircuitId(6)
7. local(7)
portID: port ID.
deviceClass: LLDP-MED device type.
Notice
Login/Logout CLI
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Login through console successfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ]Successful login through Console (Username:
<username>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
username: Represent current login user.
Informational
Event description: Login through console unsuccessfully.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ] Login failed through Console (Username:
<username>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
username: Represent current login user.
Warning
Event description: Console session timed out.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ] Console session timed out (Username:
<username>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
392
username: Represent current login user.
Event description: Logout through console.
Log Message: [Unit <unitID>, ] Logout through Console (Username:
<username>)
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
username: Represent current login user.
Informational
Event description: Login through telnet successfully.
Log Message: Successful login through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Informational
Event description: Login through telnet unsuccessfully.
Log Message: Login failed through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Warning
Event description: Telnet session timed out.
Log Message: Telnet session timed out (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Informational
Event description: Logout through telnet.
Log Message: Logout through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Informational
Event description: Login through SSH successfully.
Log Message: Successful login through SSH (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Informational
Event description: Login through SSH unsuccessfully.
Log Message: Login failed through SSH (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Critical
Event description: SSH session timed out.
Log Message: SSH session timed out (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
Informational
Event description: Logout through SSH.
Log Message: Logout through SSH (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
username: Represent current login user.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
393
ipaddr: Represent client IP address.
MAC-based Access Control
Log Description
Severity
Event description: A host has passed the authentication.
Log Message: MAC-based Access Control host login success (MAC: <mac-
address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>).
Parameters description:
mac-address: The host MAC address
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists
Informational
Event description: A host has aged out.
Log Message: MAC-based Access Control host aged out (MAC: <mac-
address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>).
Parameters description:
mac-address: The host MAC address
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists
Informational
Event description: A host failed to pass the authentication.
Log Message: MAC-based Access Control host login fail (MAC: <mac-
address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>).
Parameters description:
mac-address: The host MAC address
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists
Critical
Event description: The authorized user number on the whole device has
reached the maximum user limit.
Log Message: MAC-based Access Control enters stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: The authorized user number on the whole device is below
the maximum user limit in a time interval.
Log Message: MAC-based Access Control recovers from stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: The authorized user number on an interface has reached the
maximum user limit.
Log Message: <interface-id> enters MAC-based Access Control stop learning
state.
Parameters description:
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated
Warning
Event description: The authorized user number on an interface is below the
maximum user limit in a time interval.
Log Message: <interface-id> recovers from MAC-based Access Control stop
learning state.
Parameters description:
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated
Warning
MSTP Debug Enhancement
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Used to record the event that Spanning Tree Protocol is
enabled.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
394
Log Message: Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled.
Event description: Used to record the event that Spanning Tree Protocol is
disabled
Log Message: Spanning Tree Protocol is disabled.
Informational
Event description: Used to record MSTP instance topology change event.
Log Message: Topology changed (Instance : < Instance-id >,<interface_id>,
MAC:<macaddr> )
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
interface_id: The port number which detect or receive topochange
information.
macaddr: The system of bridge mac address.
Notice
Event description: Used to record MSTP instance new root bridge selected.
Log Message: [CIST | CIST Regional | MSTI Regional] New Root bridge
selected ([Instance: <Instance-id>] MAC: <macaddr> Priority :< priority>)
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
macaddr: The system of bridge mac address.
priority: The bridge priority value must be divisible by 4096.
Informational
Event description: Used to record MSTP instance new root port selected.
Log Message: New root port selected (Instance:<Instance-id >, <interface_id >)
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
interface_id: The port number which detect or receive topochange
information.
Notice
Event description: Used to record MSTP instance port state change event.
Log Message: Spanning Tree port status change (Instance :< Instance-id >,
<interface_id>) <old_status> -> <new_status>
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
interface_id: The port number which detect or receive topochange
information.
old status:
new status:
The port of STP state. The value may be Disable, Discarding, Learning,
Forwarding
Notice
Event description: Used to record MSTP instance port role change event.
Log Message: Spanning Tree port role change (Instance :< Instance-id >,
<interface_id>) <old_role> -> <new_role>
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
Interface_id: The port number which detect or receive topochange
information.
old role:
new role :
The port role of stp. The value may be Disable, Alternate, Backup,
Root, Designated
Informational
Event description: Use to record action to create an MST instance.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
395
Log Message: Spanning Tree instance created (Instance :< Instance-id >)
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
Event description: Use to record action to delete an MST instance.
Log Message: Spanning Tree instance deleted (Instance :< Instance-id >)
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
Informational
Event description: Use to record action to change the STP version.
Log Message: Spanning Tree version change (new version :< new_version>)
Parameters description:
new_version: Running under which version of STP.
Informational
Event description: Spanning Tree MST configuration ID name and revision level
change (name :< name>, revision level <revision_level>).
Log Message: Used to record the configuration name and revision level
changed in the MST Configuration Identification.
Parameters description:
name: The name given for a specified MST region.
revision_level: Switches using the same given name but with a different
revision level are considered members of different MST regions.
Informational
Event description: Use to record action to maps a VLAN(s) to an MST instance.
Log Message: Spanning Tree MST configuration ID VLAN mapping table
change (instance: <Instance-id> add vlan <startvlanid> [- <endvlanid>])
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
startvlanid: The start vid of add vlan range.
endvlanid: The end vid of add vlan range.
Informational
Event description: Use to record action to delete a VLAN(s) from an MST
instance.
Log Message: Spanning Tree MST configuration ID VLAN mapping table
change (instance: <Instance-id> delete vlan <startvlanid> [- <endvlanid>])
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
startvlanid: The start vid of add vlan range.
endvlanid: The end vid of add vlan range.
Informational
Event description: Used to record the event that port role change to alternate
due to guard root.
Log Message: Spanning Tree port role change (Instance :< instance-id >,
<interface-id>) to alternate port due to the guard root
Parameters description:
Instance-id: MST instance id. Instance 0 represents for default
instance, CIST.
Interface_id: The port number which detect the event.
Peripheral
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Fan Recovered.
Log Message: Unit <id>, <fan-descr> back to normal.
Critical

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
396
Parameters description:
Unit <id>: The unit ID.
fan-descr: The FAN ID and position.
Event description: Fan Fail
Log Message: Unit <id> <fan-descr> failed
Parameters description:
Unit <id>: The unit ID.
fan-descr: The FAN ID and position.
Critical
Event description: Temperature sensor enters alarm state.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> <thermal-sensor-descr> detects abnormal
temperature <degree>
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
thermal-sensor-descr: The sensor ID and position.
degree: The current temperature.
Critical
Event description: Temperature recovers to normal.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> <thermal-sensor-descr> temperature back to
normal
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
thermal-sensor-descr: The sensor ID and position.
Critical
Event description: Power failed.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> <power-descr> failed
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
power-descr: The power position and ID.
Critical
Event description: Power is recovered.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> <power-descr> back to normal
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
power-descr: The power position and ID.
Critical
Event description: Press the factory reset button.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> factory reset button pressed.
Parameters description:
unitID: The unit ID.
Critical
PoE
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Total power usage threshold is exceeded
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> usage threshold <percentage> is exceeded
Parameters description:
unit-id : box id
percentage : usage threshold
Warning
Event description: Total power usage threshold is recovered.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id> usage threshold <percentage> is recovered
Parameters description:
unit-id : box id
percentage : usage threshold
Warning

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
397
Port Security
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Address full on a port
Log Message: MAC address <macaddr> causes port security violation on
<interface-id>.
Parameters description:
macaddr: The violation MAC address.
interface-id: The interface name.
Warning
Event description: Address full on system
Log Message: Limit on system entry number has been exceeded.
Warning
Safeguard
Log Description
Severity
Event description: the host enters the mode of exhausted.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id>, Safeguard Engine enters EXHAUSTED mode.
Parameters description:
unit-id: The Unit ID
Warning
Event description: the host enters the mode of normal.
Log Message: Unit <unit-id>, Safeguard Engine enters NORMAL mode.
Parameters description:
unit-id: The Unit ID
Informational
SNMP
Log Description
Severity
Event Description: SNMP request received with invalid community string
Log Message: SNMP request received from <ipaddr> with invalid community
string.
Parameters Description:
ipaddr: The IP address.
Informational
SSH
Log Description
Severity
Event description: SSH server is enabled.
Log Message: SSH server is enabled
Informational
Event description: SSH server is disabled.
Log Message: SSH server is disabled
Informational
Stacking
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Hot insertion.
Log Message: Unit: <unitID>, MAC: <macaddr> Hot insertion.
Parameters description:
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
398
unitID: Box ID.
Macaddr: MAC address.
Event description: Hot removal.
Log Message: Unit: <unitID>, MAC: <macaddr> Hot removal.
Parameters description:
unitID: Box ID.
Macaddr: MAC address.
Informational
Event description: Stacking topology change.
Log Message: Stacking topology is <Stack_TP_TYPE>. Master(Unit <unitID>,
MAC:<macaddr>).
Parameters description:
Stack_TP_TYPE: The stacking topology type is one of the following:
1. Ring,
2. Chain.
unitID: Box ID.
Macaddr: MAC address.
Informational
Event description: Backup master changed to master.
Log Message: Backup master changed to master. Master (Unit: <unitID>).
Parameters description:
unitID: Box ID.
Informational
Event description: Slave changed to master
Log Message: Slave changed to master. Master (Unit: <unitID>).
Parameters description:
unitID: Box ID.
Informational
Event description: Box ID conflict.
Log Message: Hot insert failed, box ID conflict: Unit <unitID> conflict (MAC:
<macaddr> and MAC: <macaddr>).
Parameters description:
unitID: Box ID.
macaddr: The MAC addresses of the conflicting boxes.
Critical
Storm Control
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Storm occurrence.
Log Message: <Broadcast | Multicast | Unicast> storm is occurring on
<interface-id>.
Parameters description:
Broadcast: Storm is resulted by broadcast packets(DA =
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF).
Multicast: Storm is resulted by multicast packets, including unknown L2
multicast, known L2 multicast, unknown IP multicast and known IP
multicast.
Unicast: Storm is resulted by unicast packets, including both known and
unknown unicast packets
interface-id: The interface ID on which a storm is occurring.
Warning
Event description: Storm cleared.
Log Message: <Broadcast | Multicast | Unicast> storm is cleared on <interface-
id>.
Parameters description:
Broadcast: Broadcast storm is cleared.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
399
Multicast: Multicast storm is cleared.
Unicast: Unicast storm (including both known and unknown unicast
packets) is cleared.
interface-id: The interface ID on which a storm is cleared.
Event description: Port shut down due to a packet storm
Log Message: <interface-id> is currently shut down due to the <Broadcast |
Multicast | Unicast> storm.
Parameters description:
interface-id: The interface ID on which is error-disabled by storm.
Broadcast: The interface is disabled by broadcast storm.
Multicast: The interface is disabled by multicast storm.
Unicast: The interface is disabled by unicast storm (including both
known and unknown unicast packets).
Warning
Telnet
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Successful login through Telnet.
Log Message: Successful login through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
ipaddr: The IP address of telnet client.
username: the user name that used to login telnet server.
Informational
Event description: Login failed through Telnet.
Log Message: Login failed through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
ipaddr: The IP address of telnet client.
username: the user name that used to login telnet server.
Warning
Event description: Logout through Telnet.
Log Message: Logout through Telnet (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>)
Parameters description:
ipaddr: The IP address of telnet client.
username: the user name that used to login telnet server.
Informational
Event description: Telnet session timed out.
Log Message: Telnet session timed out (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
ipaddr: The IP address of telnet client.
username: the user name that used to login telnet server.
Informational
Voice-VLAN
Log Description
Severity
Event description: When a new voice device is detected on an interface.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
400
Log Message: New voice device detected (<interface-id>, MAC: < mac-address
>)
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
mac-address: Voice device MAC address
Event description: When an interface which is in auto voice VLAN mode joins
the voice VLAN
Log Message: < interface-id > add into voice VLAN <vid >
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
vid:VLAN ID
Informational
Event description: When an interface leaves the voice VLAN and at the same
time, no voice device is detected in the aging interval for that interface, the log
message will be sent.
Log Message: < interface-id > remove from voice VLAN <vid >
Parameters description:
interface-id: Interface name.
vid:VLAN ID
Informational
Web
Log Description
Severity
Event description: Successful login through Web.
Log Message: Successful login through Web (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login HTTP server.
ipaddr: The IP address of HTTP client.
Informational
Event description: Login failed through Web.
Log Message: Login failed through Web (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login HTTP server.
ipaddr: The IP address of HTTP client.
Warning
Event description: Web session timed out.
Log Message: Web session timed out (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login HTTP server.
ipaddr: The IP address of HTTP client.
Informational
Event description: Logout through Web.
Log Message: Logout through Web (Username: <username>, IP: <ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login HTTP server.
ipaddr: The IP address of HTTP client.
Informational
Event description: Successful login through Web (SSL).
Log Message: Successful login through Web (SSL) (Username: <username>,
IP: <ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login SSL server.
ipaddr: The IP address of SSL client.
Informational

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
401
Event description: Login failed through Web (SSL).
Log Message: Login failed through Web (SSL) (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login SSL server.
ipaddr: The IP address of SSL client.
Warning
Event description: Web (SSL) session timed out.
Log Message: Web (SSL) session timed out (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login SSL server.
ipaddr: The IP address of SSL client.
Informational
Event description: Logout through Web(SSL).
Log Message: Logout through Web(SSL) (Username: <username>, IP:
<ipaddr>).
Parameters description:
username: The use name that used to login SSL server.
ipaddr: The IP address of SSL client.
Informational
Web-Authentication
Log Description
Severity
Event description: When a host has passed the authentication.
Log Message: Web-Authentication host login success (Username: <string>, IP:
<ipaddr | ipv6address>, MAC: <mac-address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>)
Parameters description:
Username: The host username.
IP: The host IP address
mac-address: The host MAC addresses.
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated.
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists.
Informational
Event description: When a host fail to pass the authentication.
Log Message: Web-Authentication host login fail (Username: <string>, IP:
<ipaddr | ipv6address>, MAC: <mac-address>, <interface-id>, VID: <vlan-id>).
Parameters description:
Username: The host username.
IP: The host IP address
mac-address: The host MAC addresses..
interface-id: The interface on which the host is authenticated.
vlan-id: The VLAN ID on which the host exists.
Critical
Event description: when the authorized user number on the whole device has
reached the maximum user limit.
Log Message: Web-Authentication enters stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: when the authorized user number on the whole device is
below the maximum user limit in a time interval.
Log Message: Web-Authentication recovers from stop learning state.
Warning
Event description: when the ACL hardware resource is exhausted..
Log Message: Web-Authentication cannot work correctly because ACL rule
resource is not available.
Alert

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
402

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
403
Appendix B - Trap Entries
The following table lists all possible trap log entries and their corresponding meanings that will appear
in the switch.
802.1X
Trap Name
Description
OID
dDot1xExtLoggedSuccess
The trap is sent when a host has successfully logged
in (passed 802.1X authentication).
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(3) dnaSessionAuthVlan
(4) dnaSessionAuthUserName
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.30.0.1
dDot1xExtLoggedFail
The trap is sent when a host failed to pass 802.1X
authentication (login failed).
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(3) dnaSessionAuthVlan
(4) dnaSessionAuthUserName
(5) dDot1xExtNotifyFailReason
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.30.0.2
Authentication Fail
Trap Name
Description
OID
authenticationFailure
An authenticationFailure trap signifies that the
SNMPv2 entity, acting in an agent role, has received
a protocol message that is not properly
authenticated. While all implementations of the
SNMPv2 must be capable of generating this trap, the
snmpEnableAuthenTraps object indicates whether
this trap will be generated.
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.5
BPDU Attack Protection
Trap Name
Description
OID
dBpduProtectionAttackOccur
This trap is sent when the BPDU attack happened on
an interface.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dBpduProtectionIfCfgMode
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.47.0.1
dBpduProtectionAttackRecover
This trap is sent when the BPDU attack recovered on
an interface.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.47.0.2
DDM

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
404
Trap Name
Description
OID
dDdmAlarmTrap
A notification is generated when an abnormal alarm
situation occurs or recovers from an abnormal alarm
situation to normal status. Only when the current
value > low warning or current value < high warning
will send recover trap.
Binding objects:
(1) dDdmNotifyInfoIfIndex,
(2) dDdmNotifyInfoComponent
(3) dDdmNotifyInfoAbnormalLevel
(4) dDdmNotifyInfoThresholdExceedOrRecover
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.72.0.1
dDdmWarningTrap
A notification is generated when an abnormal
warning situation occurs, or recovers from an
abnormal warning situation to normal status.
Binding objects:
(1) dDdmNotifyInfoIfIndex,
(2) dDdmNotifyInfoComponent
(3) dDdmNotifyInfoAbnormalLevel
(4) dDdmNotifyInfoThresholdExceedOrRecover
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.72.0.2
DHCP Server Screen Prevention
Trap Name
Description
OID
dDhcpFilterAttackDetected
When DHCP Server Screen is enabled, if the switch
received the forge DHCP Server packet, the switch
will trap the event if any attacking packet is received.
Binding objects:
(1) dDhcpFilterLogBufServerIpAddr
(2) dDhcpFilterLogBufClientMacAddr
(3) dDhcpFilterLogBufferVlanId
(4) dDhcpFilterLogBufferOccurTime
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.133.0.1
DoS Prevention
Trap Name
Description
OID
dDosPreveAttackDetectedPacke
t
The trap is sent when detect DoS attack.
Binding objects:
(1) dDoSPrevCtrlAttackType
(2) dDosPrevNotiInfoDropIpAddr
(3) dDosPrevNotiInfoDropPortNumber
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.59.0.2
ErrDisable
Trap Name
Description
OID
dErrDisNotifyPortDisabledAssert
The trap is sent when a port enters into error
disabled state.
Binding objects:
(1) dErrDisNotifyInfoPortIfIndex
(2) dErrDisNotifyInfoReasonID
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.45.0.1
dErrDisNotifyPortDisabledClear
The trap is sent when a port loop restarts after the
1.3.6.1.4.1.17

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
405
interval time.
Binding objects:
(1) dErrDisNotifyInfoPortIfIndex
(2) dErrDisNotifyInfoReasonID
1.14.45.0.2
General Management
Trap Name
Description
OID
dGenMgmtLoginFail
This trap is sent when the user login failed to the
switch.
Binding objects:
(1) dGenMgmtNotifyInfoLoginType
(2) dGenMgmtNotifyInfoUserName
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.165.0.1
Gratuitous ARP Function
Trap Name
Description
OID
agentGratuitousARPTrap
The trap is sent when IP address conflicted.
Binding objects:
(1) ipaddr
(2) macaddr
(3) portNumber
(4) agentGratuitousARPInterfaceName
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.75.0.1
IMPB
Trap Name
Description
OID
dImpbViolationTrap
The address violation notification is generated when
IP-MAC-Port Bindingaddress violation is detected.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dImpbViolationIpAddrType
(3) dImpbViolationIpAddress
(4) dImpbViolationMacAddress
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.22.0.1
LACP
Trap Name
Description
OID
linkUp
A linkUp trap signifies that the SNMP entity, acting in
an agent role, has detected that the ifOperStatus
object for one of its communication links left the
down state and transitioned into some other state
(but not into the notPresent state). This other state is
indicated by the included value of ifOperStatus.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) if AdminStatus
(3) ifOperStatu
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.4
linkDown
A linkDown trap signifies that the SNMP entity, acting
in an agent role, has detected that the ifOperStatus
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
406
object for one of its communication links is about to
enter the down state from some other state (but not
from the notPresent state). This other state is
indicated by the included value of ifOperStatus.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) if AdminStatus
(3) ifOperStatu
1.5.3
LBD
Trap Name
Description
OID
dLbdLoopOccurred
his trap is sent when an interface loop occurs.
Binding objects:
(1) dLbdNotifyInfoIfIndex
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.46.0.1
dLbdLoopRestart
This trap is sent when an interface loop restarts after
the interval time.
Binding objects:
(1) dLbdNotifyInfoIfIndex
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.46.0.2
dLbdVlanLoopOccurred
This trap is sent when an interface with a VID loop
occurs.
Binding objects:
(1) dLbdNotifyInfoIfIndex
(2) dLbdNotifyInfoVlanId
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.46.0.3
dLbdVlanLoopRestart
This trap is sent when an interface loop with a VID
restarts after the interval time.
Binding objects:
(1) dLbdNotifyInfoIfIndex
(2) dLbdNotifyInfoVlanId
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.46.0.4
LLDP
Trap Name
Description
OID
lldpRemTablesChange
A lldpRemTablesChange notification is sent when
the value of lldpStatsRemTableLastChangeTime
changes. It can be utilized by an NMS to trigger
LLDP remote systems table maintenance polls.
Binding objects:
(1) lldpStatsRemTablesInserts
(2) lldpStatsRemTablesDeletes
(3) lldpStatsRemTablesDrops
(4) lldpStatsRemTablesAgeouts
1.0.8802.1.1.
2.0.0.1
lldpXMedTopologyChangeDetect
ed
A notification generated by the local device sensing a
change in the topology that indicates that a new
remote device attached to a local port, or a remote
device disconnected or moved from one port to
another.
Binding objects:
(1) lldpRemChassisIdSubtype
(2) lldpRemChassisId
(3) lldpXMedRemDeviceClass
1.0.8802.1.1.
2.1.5.4795.0.
1

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
407
MAC-based Access Control
Trap Name
Description
OID
dMacAuthLoggedSuccess
The trap is sent when a MAC-based Access Control
host is successfully logged in.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(3) dnaSessionAuthVlan
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.153.0.1
dMacAuthLoggedFail
The trap is sent when a MAC-based Access Control
host login fails.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(3) dnaSessionAuthVlan
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.153.0.2
dMacAuthLoggedAgesOut
The trap is sent when a MAC-based Access Control
host ages out.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(3) dnaSessionAuthVlan
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.153.0.3
MAC-notification
Trap Name
Description
OID
dL2FdbMacNotificatio
This trap indicate the MAC addresses variation in the
address table.
Binding objects:
(1) dL2FdbMacChangeNotifyInfo
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.3.0.1
MSTP
Trap Name
Description
OID
newRoot
The newRoot trap indicates that the sending agent
has become the new root of the Spanning Tree; the
trap is sent by a bridge soon after its election as the
new root, e.g., upon expiration of the Topology
Change Timer, immediately subsequent to its
election. Implementation of this trap is optional.
1.3.6.1.2.1.17
.0.1
topologyChange
A topologyChange trap is sent by a bridge when any
of its configured ports transitions from the Learning
state to the Forwarding state, or from the Forwarding
state to the Blocking state. The trap is not sent if a
newRoot trap is sent for the same transition.
Implementation of this trap is optional
1.3.6.1.2.1.17
.0.2
Peripheral
Trap Name
Description
OID
dEntityExtPowerStatusChg
Power Status change notification.
Binding objects:
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.5.0.3

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
408
(1) dEntityExtEnvPowerUnitId
(2) dEntityExtEnvPowerIndex
(3) dEntityExtEnvPowerStatus
dEntityExtFanStatusChg
Fan status change notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dEntityExtEnvFanUnitId
(2) dEntityExtEnvFanIndex
(3) dEntityExtEnvFanStatus
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.5.0.1
dEntityExtThermalStatusChg
Temperature status change notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dEntityExtEnvTempUnitId
(2) dEntityExtEnvTempIndex
(3) dEntityExtEnvTempStatus
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.5.0.2
dEntityExtFactoryResetButton
Press factory reset button notification
Binding objects:
(1) dEntityExtUnitIndex
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.5.0.5
PoE
Trap Name
Description
OID
pethMainPowerUsageOnNotifica
tion
This trap indicates PSE Threshold usage indication is
on, the usage power is above the threshold. At least
500 msec must elapse between notifications being
emitted by the same object instance.
Binding objects:
(1) pethMainPseConsumptionPower
1.3.6.1.2.1.10
5.0.2
pethMainPowerUsageOffNotifica
tion
This trap indicates PSE Threshold usage indication is
off, the usage power is below the threshold. At least
500 msec must elapse between notifications being
emitted by the same object instance.
Binding objects:
(1) pethMainPseConsumptionPower
1.3.6.1.2.1.10
5.0.3
dPoeIfPowerDeniedNotification
This Notification indicates if PSE state diagram
enters the state POWER_DENIED. At least 500
msec must elapse between notifications being
emitted by the same object instance.
Binding objects:
(1) pethPsePortPowerDeniedCounter
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.24.0.1
dPoeIfPowerOverLoadNotificatio
n
This trap indicates if PSE state diagram enters the
state ERROR_DELAY_OVER. At least 500 msec
must elapse between notifications being emitted by
the same object instance.
Binding objects:
(1) pethPsePortOverLoadCounter
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.24.0.2
dPoeIfPowerShortCircuitNotificat
ion
This trap indicates if PSE state diagram enters the
state ERROR_DELAY_SHORT. At least 500 msec
must elapse between notifications being emitted by
the same object instance.
Binding objects:
(1) pethPsePortShortCounter
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.24.0.3

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
409
Port
Trap Name
Description
OID
linkUp
A notification is generated when port linkup.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) if AdminStatus
(3) ifOperStatu
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.4
linkDown
A notification is generated when port linkdown.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) if AdminStatus
(3) ifOperStatu
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.3
Port Security
Trap Name
Description
OID
dPortSecMacAddrViolation
When the port security trap is enabled, new MAC
addresses that violate the pre-defined port security
configuration will trigger trap messages to be sent
out.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dPortSecIfCurrentStatus
(3) dPortSecIfViolationMacAddress
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.8.0.1
RMON
Trap Name
Description
OID
risingAlarm
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm
entry crosses its rising threshold and generates an
event that is configured for sending SNMP traps.
Binding objects:
(1) alarmIndex
(2) alarmVariable
(3) alarmSampleType
(4) alarmValue
(5) alarmRisingThreshold
1.3.6.1.2.1.16
.0.1
fallingAlarm
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm
entry crosses its falling threshold and generates an
event that is configured for sending SNMP traps.
Binding objects:
(1) alarmIndex
(2) alarmVariable
(3) alarmSampleType
(4) alarmValue
(5) alarmFallingThreshold
1.3.6.1.2.1.16
.0.2
Safeguard

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
410
Trap Name
Description
OID
dSafeguardChgToExhausted
This trap indicates System change operation mode
from normal to exhaust.
Binding objects:
(1) dSafeguardEngineCurrentMode
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.19.1.1.0.
1
dSafeguardChgToNormal
This trap indicates system change operation mode
from exhausted to normal.
Binding objects:
(1) dSafeguardEngineCurrentMode
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.19.1.1.0.
2
Stack
Trap Name
Description
OID
dStackInsertNotification
Unit Hot Insert notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dStackNotifyInfoBoxId
(2) dStackInfoMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.9.0.1
dStackRemoveNotification
Unit Hot Remove notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dStackNotifyInfoBoxId
(2) dStackInfoMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.9.0.2
dStackFailureNotification
Unit Failure notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dStackNotifyInfoBoxId
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.9.0.3
dStackTPChangeNotification
The stacking topology change notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dStackNotifyInfoTopologyType
(2) dStackNotifyInfoBoxId
(3) dStackInfoMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.9.0.4
dStackRoleChangeNotification
The stacking unit role change notification.
Binding objects:
(1) dStackNotifyInfoRoleChangeType
(2) dStackNotifyInfoBoxId
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.9.0.5
SIM
Trap Name
Description
OID
swSingleIPMSColdStart
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a cold start notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.11
swSingleIPMSWarmStart
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a warm start notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.12
swSingleIPMSLinkDown
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a link down notification.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.13

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
411
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
(3) ifIndex
swSingleIPMSLinkUp
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a link up notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
(3) ifIndex
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.14
swSingleIPMSAuthFail
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates an authentation failure
notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.15
swSingleIPMSnewRoot
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a new root notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.16
swSingleIPMSTopologyChange
The commander switch will send this notification
when its member generates a topology change
notification.
Binding objects:
(1) swSingleIPMSID
(2) swSingleIPMSMacAddr
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.12.8.6.0.17
Start
Trap Name
Description
OID
coldStart
A coldStart trap signifies that the SNMPv2 entity,
acting in an agent role, is reinitializing itself and that
its configuration may have been altered.
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.1
warmStart
A warmStart trap signifies that the SNMPv2 entity,
acting in an agent role, is reinitializing itself such that
its configuration is unaltered.
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.
1.5.2
Storm Control
Trap Name
Description
OID
dStormCtrlOccurred
This trap is sent when dStormCtrlNotifyEnable is
'stormOccurred' or 'both' and a storm is detected.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) dStormCtrlNotifyTrafficType
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.25.0.1
dStormCtrlStormCleared
This trap is sent when dStormCtrlNotifyEnable is
'stormCleared' or 'both' and a storm is cleared.
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex,
(2) dStormCtrlNotifyTrafficType
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.25.0.2

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
412
System File
Trap Name
Description
OID
dsfUploadImage
The notification is sent when the user uploads image
file successfully.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.14.0.1
dsfDownloadImage
The notification is sent when the user downloads
image file successfully.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.14.0.2
dsfUploadCfg
The notification is sent when the user uploads
configuration file successfully.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.14.0.3
dsfDownloadCfg
The notification is sent when the user downloads
configuration file successfully.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.14.0.4
dsfSaveCfg
The notification is sent when the user saves
configuration file successfully.
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.14.0.5
Web-Authentication
Trap Name
Description
OID
dWebAuthLoggedSuccess
The trap is sent when a host has successfully logged
in (passed Web-Authentication).
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dnaSessionAuthVlan
(3) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(4) dnaSessionClientAddrType
(5) dnaSessionClientAddress
(6) dnaSessionAuthUserName
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.154.0.1
dWebAuthLoggedFail
The trap is sent when a host has failed to pass Web-
Authentication (login failed).
Binding objects:
(1) ifIndex
(2) dnaSessionAuthVlan
(3) dnaSessionClientMacAddress
(4) dnaSessionClientAddrType
(5) dnaSessionClientAddress
(6) dnaSessionAuthUserName
1.3.6.1.4.1.17
1.14.154.0.2

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
413
Appendix C - RADIUS Attributes Assignment
The RADIUS Attributes Assignment on the DGS-1510 is used in the following modules: Console,
Telnet, SSH, Web, 802.1X, MAC-based Access Control, JWAC, and WAC.
The description that follows explains the following RADIUS Attributes Assignment types:
Privilege Level
Ingress/Egress Bandwidth
802.1p Default Priority
VLAN
ACL
To assign the Privilege Level by the RADIUS server, the proper parameters should be configured on
the RADIUS server. The table below shows the parameters for the bandwidth.
The parameters of the Vendor-Specific attributes are:
Vendor-Specific
Attribute
Description
Value
Usage
Vendor-ID
Defines the vendor.
171 (DLINK)
Required
Vendor-Type
Defines the attribute.
1
Required
Attribute-Specific Field
Used to assign the privilege
level of the user to operate
the switch.
Range (1-15)
Required
If the user has configured the privilege level attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, level 15)
and the Console, Telnet, SSH, and Web authentication is successful, the device will assign the
privilege level (according to the RADIUS server) to this access user. However, if the user does not
configure the privilege level attribute and authenticates successfully, the device will not assign any
privilege level to the access user. If the privilege level is configured less than the minimum supported
value or greater than the maximum supported value, the privilege level will be ignored.
To assign the Ingress/Egress Bandwidth by the RADIUS server, the proper parameters should be
configured on the RADIUS Server. The table below shows the parameters for bandwidth.
The parameters of the Vendor-Specific attributes are:
Vendor-Specific
Attribute
Description
Value
Usage
Vendor-ID
Defines the vendor.
171 (DLINK)
Required
Vendor-Type
Defines the attribute.
2 (for ingress bandwidth)
3 (for egress bandwidth)
Required
Attribute-Specific Field
Used to assign the
bandwidth of a port.
Unit (Kbits)
Required
If the user has configured the bandwidth attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, ingress
bandwidth 1000Kbps), and 802.1X, MAC-based Access Control, JWAC or WAC authentication is
successful, the device will assign the bandwidth (according to the RADIUS server) to the port.
However, if the user does not configure the bandwidth attribute and authenticates successfully, the
device will not assign any bandwidth to the port. If the bandwidth attribute is configured on the
RADIUS server with a value of “0”, the effective bandwidth will be set “no_limited”, and if the

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
414
bandwidth is configured less than “0” or greater than maximum supported value, the bandwidth will be
ignored.
To assign the 802.1p Default Priority by the RADIUS server, the proper parameters should be
configured on the RADIUS server. The table below shows the parameters for 802.1p default priority.
The parameters of the Vendor-Specific attributes are:
Vendor-Specific
Attribute
Description
Value
Usage
Vendor-ID
Defines the vendor.
171 (DLINK)
Required
Vendor-Type
Defines the attribute.
4
Required
Attribute-Specific Field
Used to assign the 802.1p
default priority of the port.
0 to 7
Required
If the user has configured the 802.1p priority attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, priority 7)
and 802.1X, MAC-based Access Control, JWAC or WAC authentication is successful, the device will
assign the 802.1p default priority (according to the RADIUS server) to the port. However, if the user
does not configure the priority attribute and authenticates successfully, the device will not assign a
priority to this port. If the priority attribute is configured on the RADIUS server is a value out of range
(>7), it will not be set to the device.
To assign the VLAN by the RADIUS server, the proper parameters should be configured on the
RADIUS server. To use VLAN assignment, RFC 3580 defines the following tunnel attributes in
RADIUS packets.
The table below shows the parameters for a VLAN:
RADIUS Tunnel Attribute
Description
Value
Usage
Tunnel-Type
This attribute indicates the
tunneling protocol(s) to be
used (in the case of a
tunnel initiator) or the
tunneling protocol in use (in
the case of a tunnel
terminator).
13 (VLAN)
Required
Tunnel-Medium-Type
This attribute indicates the
transport medium being
used.
6 (802)
Required
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID
This attribute indicates
group ID for a particular
tunneled session.
A string (VID)
Required
A summary of the Tunnel-Private-Group-ID Attribute format is shown below.
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Type | Length | Tag | String...
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
The table below shows the definition of Tag field (different with RFC 2868):

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
415
Tag field value
String field format
0x01
VLAN name (ASCII)
0x02
VLAN ID (ASCII)
Others
(0x00, 0x03 ~ 0x1F, >0x1F)
When the switch receives the VLAN setting string, it will think it is
the VLAN ID first. In other words, the switch will check all existing
VLAN IDs and check if there is one matched. If the switch can find
one matched, it will move to that VLAN. If the switch cannot find the
matched VLAN ID, it will think the VLAN setting string as a “VLAN
Name”. Then it will check that it can find out a matched VLAN
Name.
NOTE: A tag field of greater than 0x1F is interpreted as the first octet of the following field.
If the user has configured the VLAN attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, VID 3), and the
802.1X, MAC-based Access Control, JWAC or WAC authentication is successful, the port will be
assigned to VLAN 3. However if the user does not configure the VLAN attributes, when the port is not
guest VLAN member, it will be kept in its current authentication VLAN, and when the port is guest
VLAN member, it will be assigned to its original VLAN.
To assign the ACL by the RADIUS server, the proper parameters should be configured on the
RADIUS server. The table below shows the parameters for an ACL.
The parameters of the Vendor-Specific Attribute are:
RADIUS Tunnel Attribute
Description
Value
Usage
Vendor-ID
Defines the vendor.
171 (DLINK)
Required
Vendor-Type
Defines the attribute.
14 (for ACL script)
Required
Attribute-Specific Field
Used to assign the ACL
script. The format is based
on Access Control List
(ACL) Commands.
ACL Script
For example:
ip access-list a1;permit
host 10.90.90.100;exit;
mac access-list
extended m1;permit
host 00-00-00-01-90-10
any; exit;
Required
If the user has configured the ACL attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, ACL script: ip access-
list a1;permit host 10.90.90.100;exit; mac access-list extended m1;permit host 00-00-00-01-90-10 any;
exit;), and the 802.1X, MAC-based Access Control, JWAC or WAC authentication is successful, the
device will assign the ACL script according to the RADIUS server. The enter Access-List
Configuration Mode and exit Access-List Configuration Mode must be a pair, otherwise the ACP
script will be reject. For more information about the ACL module, please refer to Access Control List
(ACL) Commands chapter.

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
416
Appendix D - IETF RADIUS Attributes Support
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) attributes carry specific authentication,
authorization, information and configuration details for the request and reply. This appendix lists the
RADIUS attributes currently supported by the switch.
RADIUS attributes are supported by the IETF standard and Vendor-Specific Attribute (VSA). VSA
allows the vendor to create an additionally owned RADIUS attribute. For more information about D-
Link VSA, refer to the RADIUS Attributes Assignment Appendix.
IETF standard RADIUS attributes are defined in the RFC 2865 Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service (RADIUS), RFC 2866 RADIUS Accounting, RFC 2868 RADIUS Attributes for Tunnel Protocol
Support, and RFC 2869 RADIUS Extensions.
The following table lists the IETF RADIUS attributes supported by the D-Link switch.
RADIUS Authentication Attributes:
Number
IETF Attribute
1
User-Name
2
User-Password
3
CHAP-Password
4
NAS-IP-Address
5
NAS-Port
6
Service-Type
7
Framed-Protocol
8
Framed-IP-Address
12
Framed-MTU
18
Reply-Message
24
State
26
Vendor-Specific
27
Session-Timeout
29
Termination-Action
30
Called-Station-ID
31
Calling-Station-ID
32
NAS-Identifier
60
CHAP-Challenge
61
NAS-Port-Type
64
Tunnel-Type
65
Tunnel-Medium-Type
77
Connect-Info
79
EAP-Message
80
Message-Authenticator
81
Tunnel-Private-Group-ID
85
Acct-Interim-Interval

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
417
87
NAS-Port-ID
95
NAS-IPv6-Address
RADIUS Accounting Attributes:
Number
IETF Attribute
1
User-Name
4
NAS-IP-Address
5
NAS-Port
6
Service-Type
8
Framed-IP-Address
31
Calling-Station-ID
32
NAS-Identifier
40
Acct-Status-Type
41
Acct-Delay-Time
42
Acct-Input-Octets
43
Acct-Output-Octets
44
Acct-Session-ID
45
Acct-Authentic
46
Acct-Session-Time
47
Acct-Input-Packets
48
Acct-Output-Packets
49
Acct-Terminate-Cause
52
Acct-Input-Gigawords
53
Acct-Output-Gigawords
61
NAS-Port-Type
95
NAS-IPv6-Address

DGS-1510 Series Gigabit Ethernet SmartPro Switch Web UI Reference Guide
418
Appendix E - ERPS Information
Only hardware-based ERPS (external PHY) supports the fast link drop interrupt feature with a
recovery time of 50ms.
Model Name
ERPS
Port 1 to 8
Port 9 to 16
Port 17 to 20
DGS-1510-20
Hardware-based
Software-based
V
V
V
Model Name
ERPS
Port 1 to 8
Port 9 to 24
Port 25 to 28
DGS-1510-28
DGS-1510-28P
DGS-1510-28X
DGS-1510-
28XMP
Hardware-based
V
Software-based
V
V
Model Name
ERPS
Port 1 to 8
Port 9 to 24
Port 25 to
32
Port 33 to
52
DGS-1510-52
Hardware-based
V
V
Software-based
V
V
Model Name
ERPS
Port 1
to 8
Port 9
to 24
Port 25
to 32
Port 33
to 48
Port 49
and 50
Port 51
and 52
DGS-1510-52X
Hardware-based
V
V
V
Software-based
V
V
V