Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- 1 Product Introduction
- 2 Hardware Installation
- 3 Getting Started
- 4 Web-based Switch Configuration
- Web-based Management
- Tool Bar > Save Menu
- Tool Bar > Tools Menu
- Tool Bar > Online Help
- Function Tree
- Device Information
- System > System Settings
- System > DHCP Auto Configuration
- System > Port Settings
- System > Port Description
- System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
- System > IP Interface
- System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 System Settings
- System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings
- System > User Accounts
- System > MAC Address Aging Time
- System > ARP Aging Time Settings
- System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings
- System > Web Settings
- System > Telnet Settings
- System > SSH Settings
- System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings
- System > Ping Test
- System > Trace Route
- System > MAC Notification Settings
- System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
- System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server
- System > Time Profile
- System > Power Saving
- System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings
- Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
- Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN PVID
- Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global Settings
- Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port Settings
- Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice Device List
- Configuration > Voice VLAN > LLDE-MED Voice Device List
- Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto Surveillance Properties
- Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC Settings and Surveillance Device
- Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF IPC Information
- Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF NVR Information
- Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings
- Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation Settings
- Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings
- Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
- Configuration > ISM VLAN Settings
- Configuration > Jumbo Frame
- Configuration > Port Mirroring
- Configuration > Loopback Detection
- Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
- Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings
- Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global Settings
- Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Interface Settings
- Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
- Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information
- Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings
- Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Vendor Info
- Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Forwarding
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filter Mode
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > IP Multicast Profile Settings
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Limited Multicast Range Settings
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > MAX Multicast Group Settings
- QoS > Traffic Control
- QoS > Bandwidth Control
- QoS > QoS Settings
- RMON > RMON Basic Settings
- RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
- RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
- RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration
- RMON > RMON Event Configuration
- Security > Trusted Host
- Security > Safeguard Engine
- Security > Port Security
- Security > Port Security FDB Entry
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
- Security > 802.1X > Radius Accounting Settings
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS Server
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN
- Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC
- Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Policy Settings
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Application Authentication Settings
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Login Method Lists
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Enable Method Lists
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Local Enable Password Settings
- Security > Traffic Segmentation
- Security > DoS Prevention Settings
- Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
- Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
- Security > Smart Binding > White List
- Security > Smart Binding > Black List
- Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
- Monitoring > Statistics
- Monitoring > Session Table
- Monitoring > CPU Utilization
- Monitoring > Memory Utilization
- Monitoring > Port Utilization
- Monitoring > Packet Size
- Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX)
- Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX)
- Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX)
- Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX)
- Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX)
- Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
- Monitoring > System Log
- Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
- Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
- Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
- Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
- Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
- Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
- Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
- Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
- ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
- ACL > Access Profile List
- ACL > ACL Finder
- ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
- ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
- ACL > CPU Filter Finder
- PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only)
- PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only)
- LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
- LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
- LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
- LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
- LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
- LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
- LLDP > LLDP-MED Settings
- L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
- L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder
- L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
- L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder
- Appendix A - Ethernet Technology
- Appendix B - Technical Specifications
- Appendix C – Rack mount Instructions
D-Link DGS-2000-52 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for DGS-2000-52 by D-Link which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.

Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
i
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ............................................................................................................................................. i
About This Guide ............................................................................................................................................. 1
Terms/Usage .................................................................................................................................................. 1
Copyright and Trademarks ............................................................................................................................ 1
1 Product Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 2
DGS-2000-10 ................................................................................................................................................. 3
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 3
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 3
DGS-2000-10P ............................................................................................................................................... 4
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 4
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 5
DGS-2000-10MP ............................................................................................................................................ 5
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 5
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 6
DGS-2000-20 ................................................................................................................................................. 6
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 6
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 7
DGS-2000-26 ................................................................................................................................................. 7
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 7
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 8
DGS-2000-28 ................................................................................................................................................. 8
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 8
Rear Panel .................................................................................................................................................. 9
DGS-2000-28P ............................................................................................................................................... 9
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 9
Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................................ 10
DGS-2000-28MP .......................................................................................................................................... 10
Front Panel ............................................................................................................................................... 10
Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................................ 11
DGS-2000-52 ............................................................................................................................................... 11
Front Panel ............................................................................................................................................... 12
Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................................ 12
DGS-2000-52MP .......................................................................................................................................... 12
Front Panel ............................................................................................................................................... 12
Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................................ 14
LED Indicators .............................................................................................................................................. 14
2 Hardware Installation ................................................................................................................................ 16
Safety Cautions ............................................................................................................................................ 16
Step 1: Unpacking ........................................................................................................................................ 17
Step 2: Switch Installation ............................................................................................................................ 17
Desktop or Shelf Installation ..................................................................................................................... 17
Rack Installation ....................................................................................................................................... 17
Step 3: Plugging in the AC Power Cord with Power Cord Clip .................................................................... 18
Power Failure ........................................................................................................................................... 21
Grounding the Switch ............................................................................................................................... 21
3 Getting Started ........................................................................................................................................... 23
Management Options ................................................................................................................................... 23
Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
ii
Using Web-based Management .................................................................................................................. 23
Supported Web Browsers ........................................................................................................................ 23
Connecting to the Switch .......................................................................................................................... 23
Login Web-based Management ............................................................................................................... 23
Smart Wizard ............................................................................................................................................... 24
Web-based Management ............................................................................................................................. 24
D-Link Network Assistant ............................................................................................................................. 24
4 Web-based Switch Configuration ............................................................................................................ 25
Web-based Management ............................................................................................................................. 25
Tool Bar > Save Menu ................................................................................................................................. 26
Save Configuration ................................................................................................................................... 26
Save Log .................................................................................................................................................. 26
Tool Bar > Tools Menu ................................................................................................................................. 26
Reset System ........................................................................................................................................... 26
Reboot Device .......................................................................................................................................... 26
Configuration Backup and Restore .......................................................................................................... 27
System Log Backup.................................................................................................................................. 27
Firmware Backup and Upgrade ................................................................................................................ 28
Firmware Information................................................................................................................................ 28
Configuration Information ......................................................................................................................... 28
Tool Bar > Online Help ................................................................................................................................. 29
Function Tree ............................................................................................................................................... 29
Device Information.................................................................................................................................... 29
System > System Settings ....................................................................................................................... 30
System > DHCP Auto Configuration ........................................................................................................ 30
System > Port Settings ............................................................................................................................. 31
System > Port Description ........................................................................................................................ 32
System > IP Interface ............................................................................................................................... 32
System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 System Settings ....................................................................................... 33
System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 Neighbor Settings ..................................................................................... 33
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State ..................................................................................... 34
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table ........................................................................................ 34
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table ..................................................................................... 35
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table ....................................................................................... 35
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table ............................................................................. 36
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table ........................................................................................ 36
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID ......................................................................................... 36
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings .................................................................................... 37
System > User Accounts .......................................................................................................................... 37
System > MAC Address Aging Time ........................................................................................................ 38
System > ARP Aging Time Settings ......................................................................................................... 38
System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings ......................................................................................... 38
System > Web Settings ............................................................................................................................ 39
System > Telnet Settings ......................................................................................................................... 39
System > SSH Settings ............................................................................................................................ 40
System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings ............................................................................................ 40
System > Ping Test .................................................................................................................................. 40
System > Trace Route .............................................................................................................................. 41
System > MAC Notification Settings ........................................................................................................ 41

Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
iii
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings .................................................................. 42
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server ..................................................................... 42
System > Time Profile .............................................................................................................................. 43
System > Power Saving ........................................................................................................................... 43
System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings ...................................................................................................... 44
Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN .................................................................................................................. 44
Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN PVID ........................................................................................................ 46
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global Settings ................................................................... 46
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port Settings ....................................................................... 48
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice Device List ..................................................................................... 49
Configuration > Voice VLAN > LLDE-MED Voice Device List ................................................................. 49
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto Surveillance Properties................................................ 49
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC Settings and Surveillance Device ............................... 50
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF IPC Information ........................................................ 50
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF NVR Information ...................................................... 51
Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings ..................................................................................................... 51
Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation Settings ................................................................................. 52
Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings ................................................................................. 53
Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings.......................................................................... 53
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping ................................................................................. 54
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings .......................................................... 57
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table ......................................................................................... 57
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings .............................................. 57
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings ...................................................................... 58
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table .................................................................................. 58
Configuration > ISM VLAN Settings ......................................................................................................... 58
Configuration > Jumbo Frame .................................................................................................................. 59
Configuration > Port Mirroring .................................................................................................................. 60
Configuration > Loopback Detection ........................................................................................................ 60
Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings ...................................................................................... 61
Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings .............................................................................. 62
Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global Settings ................................................................. 63
Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Interface Settings .............................................................. 65
Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings ............................................................................................ 65
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings .................................................................................................. 66
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings ................................................................ 66
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings ............................................................................... 68
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification ......................................................... 69
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings ........................................................................ 70
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information ....................................................................... 70
Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings............................................ 71
Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration ................................ 71
Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings ..................................................................................................... 72
Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Settings ................................................................................ 73
Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings ......................................................... 73
Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings ............................................................... 74
Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings ................................................................... 74
Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings ................................................................... 75
Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table .............................................................................................. 75

Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
iv
Configuration > DDM > DDM Vendor Info ................................................................................................ 76
Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings .......................................................................................... 76
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Forwarding ................................................ 76
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filter Mode ................................................ 77
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > IP Multicast Profile Settings ..................................... 77
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Limited Multicast Range Settings ............................ 78
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > MAX Multicast Group Settings ................................. 78
QoS > Traffic Control ................................................................................................................................ 79
QoS > Bandwidth Control ......................................................................................................................... 80
QoS > QoS Settings ................................................................................................................................. 81
RMON > RMON Basic Settings................................................................................................................ 82
RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration ................................................................................... 82
RMON > RMON History Control Configuration ........................................................................................ 82
RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration ...................................................................................................... 83
RMON > RMON Event Configuration ....................................................................................................... 83
Security > Trusted Host ............................................................................................................................ 84
Security > Safeguard Engine.................................................................................................................... 84
Security > Port Security ............................................................................................................................ 84
Security > Port Security FDB Entry .......................................................................................................... 85
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings ....................................................................................................... 85
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User ............................................................................................................. 87
Security > 802.1X > Radius Accounting Settings ..................................................................................... 87
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS Server ................................................................... 87
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN ................................................................................................ 88
Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC .......................................................................................... 89
Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table ................................................................. 89
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Policy Settings ............................................ 89
Security > Access Authentication Control > Application Authentication Settings .................................... 90
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group .............................................. 90
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server ......................................................... 91
Security > Access Authentication Control > Login Method Lists .............................................................. 92
Security > Access Authentication Control > Enable Method Lists ........................................................... 92
Security > Access Authentication Control > Local Enable Password Settings ........................................ 93
Security > Traffic Segmentation ............................................................................................................... 93
Security > DoS Prevention Settings ......................................................................................................... 94
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings ................................................................................. 94
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding ............................................................................................... 95
Security > Smart Binding > White List ...................................................................................................... 96
Security > Smart Binding > Black List ...................................................................................................... 96
Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List .................................................................................... 97
Monitoring > Statistics .............................................................................................................................. 97
Monitoring > Session Table ...................................................................................................................... 98
Monitoring > CPU Utilization .................................................................................................................... 98
Monitoring > Memory Utilization ............................................................................................................... 99
Monitoring > Port Utilization ..................................................................................................................... 99
Monitoring > Packet Size ........................................................................................................................ 100
Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX) .............................................................................................. 101
Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX) .................................................................................................. 102
Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) ................................................................................................. 103

Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
v
Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX) ..................................................................................................... 104
Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX).................................................................................................. 105
Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics ............................................................................................................. 106
Monitoring > System Log ........................................................................................................................ 107
Monitoring > Browse ARP Table ............................................................................................................ 107
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log .......................................................... 107
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics ............................................................ 108
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group ........................................................................ 108
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host ........................................................................... 109
Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group ............................................................................ 109
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication ................................................................. 110
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client ................................................................ 110
ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard ........................................................................................................... 111
ACL > Access Profile List ....................................................................................................................... 113
ACL > ACL Finder .................................................................................................................................. 114
ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard ................................................................................................. 114
ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List ..................................................................................................... 115
ACL > CPU Filter Finder ......................................................................................................................... 116
PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only) ............................................. 116
PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only) ........................................ 118
LLDP > LLDP Global Settings ................................................................................................................ 118
LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings .......................................................................................................... 119
LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings ......................................................................................... 120
LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings ......................................................................................... 120
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings ....................................................................................... 121
LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table ................................................................................................................ 122
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table ........................................................................................... 122
LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table .............................................................................................................. 123
LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table .......................................................................................................... 124
LLDP > LLDP-MED Settings .................................................................................................................. 125
L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route ........................................................................................................... 126
L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder ............................................................................................. 127
L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route ........................................................................................................... 127
L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder ............................................................................................. 127
Appendix A - Ethernet Technology ............................................................................................................ 129
Gigabit Ethernet Technology ..................................................................................................................... 129
Fast Ethernet Technology .......................................................................................................................... 129
Switching Technology ................................................................................................................................ 129
Appendix B - Technical Specifications ..................................................................................................... 130
Hardware Specifications ............................................................................................................................ 130
Features ..................................................................................................................................................... 134
L2 Features ............................................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
L3 Features ............................................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
VLAN ......................................................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
QoS (Quality of Service) ............................................................................................ 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
Security ...................................................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
OAM .......................................................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
Management .............................................................................................................. 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。

Table of Contents D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
vi
D-Link Green Technology ......................................................................................... 錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
Appendix C – Rack mount Instructions .................................................................................................... 136
About This Guide D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
About This Guide
This guide provides instructions to install the D-Link DGS-2000 series Ethernet Switch, and to configure
Web-based Management step-by-step.
Note: T
he model you have purchased may
appear slightly different from the illustrations
shown in the document. Refer to the Product
Instruction and Technical Specification sections
for
detailed information about your switch, its
components, network connections, and technical
specifications.
This guide is mainly divided into four parts:
1. Hardware Installation: Step-by-step hardware installation procedures.
2. Getting Started: A startup guide for basic switch installation and settings.
3. Web Configuration: Information about the function descriptions and configuration settings via Web.
4. Command Line Interface: Information about the function descriptions and configuration settings via
Telnet.
Terms/Usage
In this guide, the term “Switch” (first letter capitalized) refers to the Smart Switch, and “switch” (first letter
lower case) refers to other Ethernet switches. Some technologies refer to terms “switch”, “bridge” and
“switching hubs” interchangeably, and both are commonly accepted for Ethernet switches.
A NOTE indicates important
information that
helps a better use of the device.
A CAUTION indicates potential property damage
or personal injury.
Copyright and Trademarks
Information in this document is subjected to change without notice.
© 2020 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of D-Link Corporation is strictly
forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-LINK logo are trademarks of D-Link Corporation; Microsoft
and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the
marks and names or their products. D-Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
2
1 Product Introduction
Thank you and congratulations on your purchase of D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch Products.
D-Link's next generation DGS-2000 Series Ethernet switch series blends plug-and-play simplicity with
exceptional value and reliability for small and medium-sized business (SMB) networking. All models are
housed in a new style rack-mount metal case with easy-to-view front panel diagnostic LEDs, and provides
advanced features including network security, traffic segmentation, QoS and versatile management.
Flexible Port Configurations. The DGS-2000 series is the new generation of DGS-2000 Ethernet Switch
series. DGS-2000 series including 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ-45 ports, 100/1000 Mbps combo ports, and
100/1000 Mbps SFP ports. The DGS-2000-10, DGS-2000-26, DGS-2000-10P, and DGS-2000-10MP models
feature 2 100/1000 Mbps SFP ports, while all other DGS-2000 Series models feature 4 GbE/SFP combo
ports, allowing you to choose the most suitable media type for your requirements.
D-Link Green Technology. D-Link Green devices are about providing eco-friendly alternatives without
compromising performance. D-Link Green Technology includes a number of innovations to reduce energy
consumption on DGS-2000 series such as shutting down a port, or turning off some LED indicators, or
adjusting the power usage according to the Ethernet cable connected to it.
Extensive Layer 2 Features. Implemented as complete L2 devices, these switches include functions such
as IGMP snooping, port mirroring, Spanning Tree, 802.3ad LACP and Loopback Detection to enhance
performance and network resiliency.
Traffic Segmentation, QoS and Auto Surveillance VLAN. The switches support 802.1Q VLAN standard
tagging to enhance network security and performance. The switches also support 802.1p priority queues,
enabling users to run bandwidth-sensitive applications such as streaming multimedia by prioritizing that
traffic in network. These functions allow switches to work seamlessly with VLAN and 802.1p traffic in the
network. Auto Surveillance VLAN will automatically place the vedio traffic from pre-defined IP surveillance
devices to an assigned VLAN with higher priority, so it can be separated from normal data traffic. Asymmetric
VLAN is implemented in these switches for a more efficient use of shared resources, such as server or
gateway devices.
Network Security. D-Link’s innovative Safeguard Engine function protects the switches against traffic
flooding caused by virus attacks. Additional features like 802.1X port-based authentication provide access
control of the network with external RADIUS servers. ACL is a powerful tool to screen unwanted IP or MAC
traffic. Storm Control can help to keep the network from being overwhelmed by abnormal traffic. Port
Security is another simple but useful authentication method to maintain the network device integrity.
Versatile Management. The new generation of D-Link DGS-2000 Ethernet Switches provides growing
businesses simple and easy management of their network. The Web-Based management interface allows
administrators to remotely control their network down to the port level. The intuitive easily allows customers
to discover multiple D-Link DGS-2000 Ethernet Switches in the same L2 network segment.
With this utility, users do not need to change the IP address of PC and provides easy initial setting of smart
switches. The switches within the same L2 network segment connected to user’s local PC are displayed on
the screen for instant access. It allows extensive switch configuration setting, and basic configuration of
discovered devices such as a password change or firmware upgrade.
Users can also access the Switch via Telnet. Basic tasks such as changing the Switch IP address, resetting
the settings to factory defaults, setting the administrator password, rebooting the Switch, or upgrading the
Switch firmware can be performed using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
In addition, users can utilize the SNMP MIB (Management Information Base) to poll the switches for
information about the status, or send out traps of abnormal events. SNMP support allows users to integrate

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
3
the switches with other third-party devices for management in an SNMP-enabled environment. D-Link DGS-
2000 Series Ethernet Switches provides easy-to-use graphic interface and facilitates the operation efficiency.
DGS-2000-10
8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps, plus 2 SFP Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.1 – DGS-2000-10 Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-10 switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-8): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (9F, 10F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.2 – DGS-2000-10 Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
4
DGS-2000-10P
8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps, plus 2 SFP Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet PoE switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.3 – DGS-2000-10P Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-10P switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• PoE Max: The solid amber of PoE Max LED indicates the Switch reaches the maximum power budget
defined by the administrator via PoE System Settings page of Web GUI or the default power budget of
65 Watts. The blinking amber of PoE Max LED represents the switch is in guradband mode (available
power left is less 7 watts).
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-8): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (9F-10F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: The port 1 ~ port 8 are PoE ports. When user press the
Mode button to PoE mode, only port 1 ~ port 8 will light up.
CAUTION: This equipment can
be connected only to PoE
networks without routing to the outside plant.
L’équipement est conçu pour une installation dans un bâtiment et
ne doit pas être connecté à des réseaux exposés (installations
extérieures), notamment des environnements de campus, et l’ITE
doit être connecté uniquement à des réseaux PoE sans
acheminement vers une installation extérieure." ou équivalent.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
5
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.4 – DGS-2000-10P Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
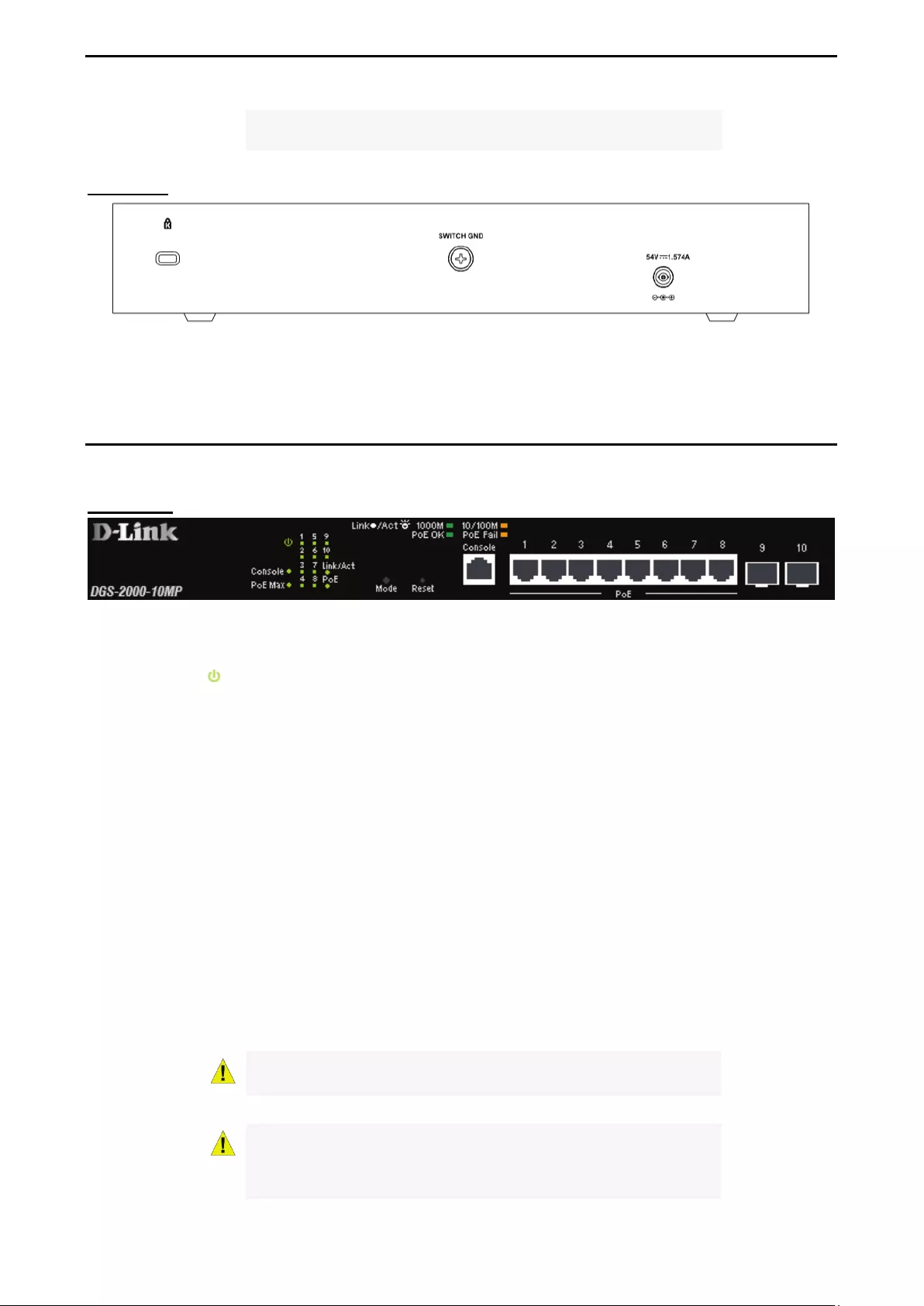
DGS-2000-10MP
8-Port 10/100/1000Mbps, plus 2 SFP Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet PoE switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.5 – DGS-2000-10MP Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-10MP switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Fan Error: The FAN LED shows the status of the fans, light off indicates all fans work fine and the red
light indicates that one or multiple fans are working abnormally.
• PoE Max: The solid amber of PoE Max LED indicates the Switch reaches the maximum power budget
defined by the administrator via PoE System Settings page of Web GUI or the default power budget of
130 Watts. The blinking amber of PoE Max LED represents the switch is in guradband mode (available
power left is less 7 watts).
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-8): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (9F-10F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
6
I.
NOTE: The port 1 ~ port 8 are PoE ports. When user press the
Mode button to PoE mode, only port 1 ~ port 8 will light up.
CAUTION: This equipment can
be connected only to PoE
networks without routing to the outside plant.
L’équipement est conçu pour une installation dans un bâtiment et
ne doit pas être connecté à des réseaux exposés (installations
extérieures), notamment des environnements de campus, et l’ITE
doit être connecté uniquement à des réseaux PoE sans
acheminement vers une installation extérieure." ou équivalent.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standal
one version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.6 – DGS-2000-10MP Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
DGS-2000-20
20-Port 10/100/1000Mbps, includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.7 – DGS-2000-20 Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-20 switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-20): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (16F-20F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
7
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.8 – DGS-2000-20 Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port.
DGS-2000-26
24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps plus 2 SFP Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.9 – DGS-2000-26 Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-26 switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-24): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (25F-26F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
8
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.10 – DGS-2000-26 Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
DGS-2000-28
28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.11 – DGS-2000-28 Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-28 switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-28): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (25F-28F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL li
sted Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-dessous ou son
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
9
équivalent :« Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.12 – DGS-2000-28 Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
DGS-2000-28P
28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet PoE Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.13 – DGS-2000-28P Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-28P switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Fan Error: The FAN LED shows the status of the fans, light off indicates all fans work fine and the red
light indicates that one or multiple fans are working abnormally.
• PoE Max: The solid amber of PoE Max LED indicates the Switch reaches the maximum power budget
defined by the administrator via PoE System Settings page of Web GUI or the default power budget of
193 Watts. The blinking amber of PoE Max LED represents the switch is in guradband mode (available
power left is less 7 watts).
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-28): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (25F-28F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
0
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: The port 1 ~ port 24 are PoE ports. When user press the
Mode button to PoE mode, only port 1 ~ port 24 will light up.
CAUTION: This equipment can
be connected only to PoE
networks without routing to the outside plant.
L’équipement est conçu pour une installation dans un bâtiment et
ne doit pas
être connecté à des réseaux exposés (installations
extérieures), notamment des environnements de campus, et l’ITE
doit être connecté uniquement à des réseaux PoE sans
acheminement vers une installation extérieure." ou équivalent.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.14 – DGS-2000-28P Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
DGS-2000-28MP
28-Port 10/100/1000Mbps includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet PoE Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.15 – DGS-2000-28MP Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-28MP switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Fan Error: The FAN LED shows the status of the fans, light off indicates all fans work fine and the red
light indicates that one or multiple fans are working abnormally.
• PoE Max: The solid amber of PoE Max LED indicates the Switch reaches the maximum power budget
defined by the administrator via PoE System Settings page of Web GUI or the default power budget of
370 Watts. The blinking amber of PoE Max LED represents the switch is in guradband mode (available
power left is less 7 watts).
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
1
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-28): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: The port 1 ~ port 24 are PoE ports. When user press the
Mode button to PoE mode, only port 1 ~ port 24 will light up.
CAUTION: This equipment can
be connected only to PoE
networks without routing to the outside plant.
L’équipement est conçu pour une installation dans un bâtiment et
ne doit pas être connecté à des réseaux exposés (installations
extérieures), notamment des environnements de campus, et l’ITE
doit être connecté uniquement à des réseaux PoE sans
acheminement vers une installation extérieure." ou équivalent.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.16 – DGS-2000-28MP Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
DGS-2000-52
52-Port 10/100/1000Mbps includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet Switch.
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
2
Front Panel
Figure 1.17 – DGS-2000-52 Front Panel
The front panel of the DGS-2000-52 switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-52): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (49F-52F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :« Ce produit est
destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
Rear Panel
Figure 1.18 – DGS-2000-52 Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
DGS-2000-52MP
52-Port 10/100/1000Mbps includes 4 SFP Combo Ports (100/1000Mbps) Ethernet PoE Switch.
Front Panel
Figure 1.19 – DGS-2000-52MP Front Panel

1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
3
The front panel of the DGS-2000-52MP switch consists out of the following:
• Power LED : The Power LED lights up when the Switch is connected to a power source.
• Fan Error: The FAN LED shows the status of the fans, light off indicates all fans work fine and the red
light indicates that one or multiple fans are working abnormally.
• PoE Max: The solid amber of PoE Max LED indicates the Switch reaches the maximum power budget
defined by the administrator via PoE System Settings page of Web GUI or the default power budget of
370 Watts. The blinking amber of PoE Max LED represents the switch is in guradband mode (available
power left is less 7 watts).
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (1-52): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When a port has an amber light, this indicates that the port is running on 10M or 100M. When
it has a green light it is running on 1000M.
• Port Link/Act/Speed LED (49F-52F): The Link/Act/Speed LED flashes, which indicates a network link
through the corresponding port. Blinking indicates that the Switch is either sending or receiving data to
the port. When the port LED glows in amber, it indicates the port is running on 100M. When the port
LED glows in green, it is running on 1000Mbps.
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
• Reset: Press the Reset button for 1~5 seconds to reset the Switch back to the default settings and led
will be solid light with amber for 1 second.
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
Si le transceiveur optique n'est pas livré avec l'appareil, le manuel
d'utilisation doit comporter la description ci-
dessous ou son
équivalent :«
Ce produit est destiné à être utilisé avec un
transceiveur optique homologué UL,tension DC3.3V, classe laser
I.
NOTE: The port 1 ~ port 48 are PoE ports. When user press the
Mode button to PoE mode, only port 1 ~ port 48 will light up.
CAUTION: This equipment can
be connected only to PoE
networks without routing to the outside plant.
L’équipement est conçu pour une installation dans un bâtiment et
ne doit pas être connecté à des réseaux exposés (installations
extérieures), notamment des environnements de campus, et l’ITE
doit être connecté uniquement à des réseaux PoE sans
acheminement vers une installation extérieure." ou équivalent.
NOTE: Once user enter in loader mode, you can use DNA tool
(standalone version 2.0.2.4 only (No support by Chrome
DNA3.x.x.x)) to download the image or call D-
Link Technical
Support for further help.
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
14
4
Rear Panel
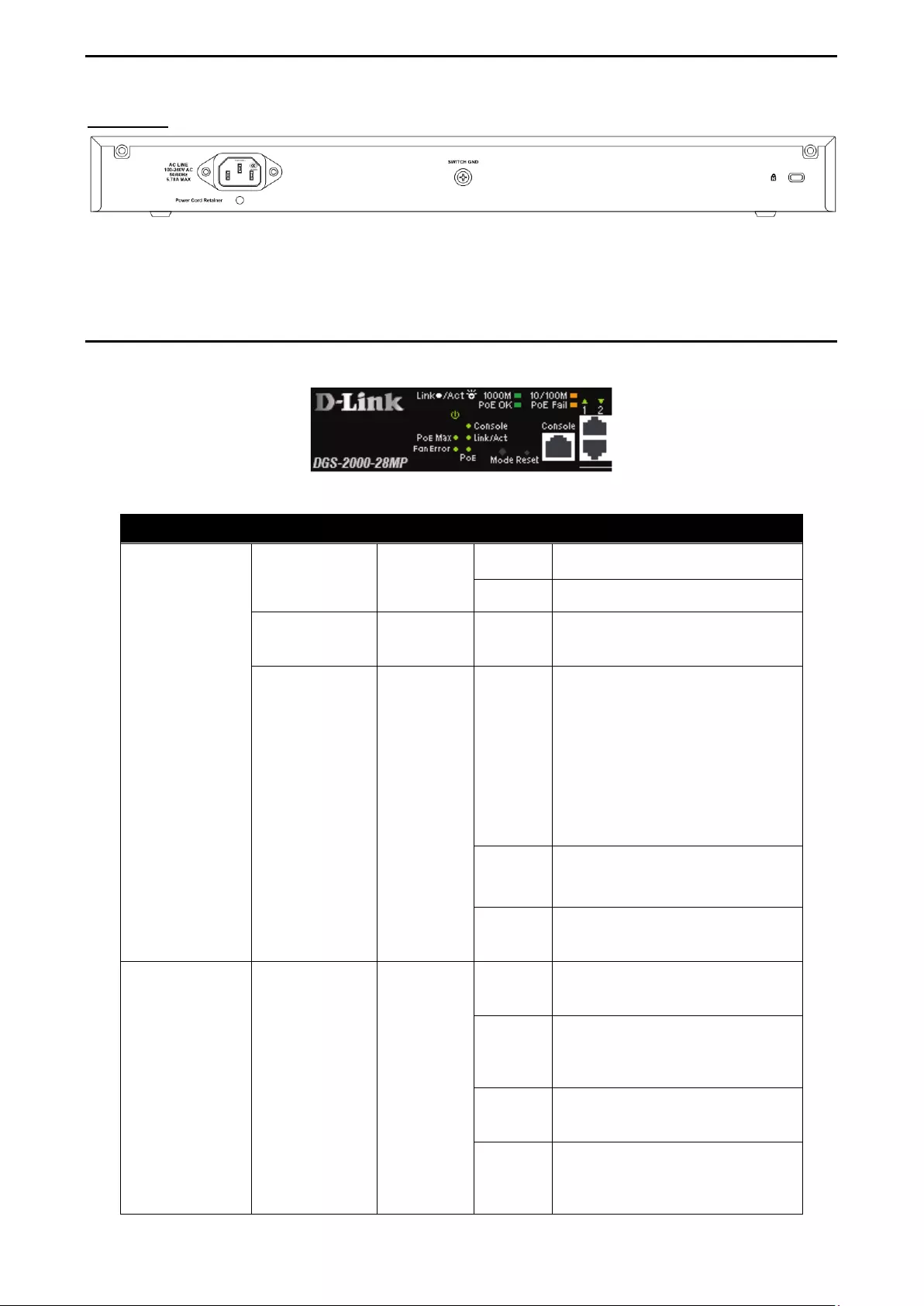
Figure 1.20 – DGS-2000-52MP Rear Panel
Power: Connect the supplied AC power cable to this port
LED Indicators
The Switch supports LED indicators for Power, Fan, and Link/Act for each port. The following shows the LED
indicators for the DGS-2000 series Ethernet Switch along with an explanation of each indicator.
Figure 1.21 –LED Indicators on DGS-2000 series
Location LED Indicative Color Status Description
Per Device
Power Green
Solid Light
Power on
Light off Power off
Fan Error Red Solid light The fan has runtime failure and is
brought offline.
PoE Max. Amber
Solid light
The PoE Max LED lights up when
the total PoE output of Switch
reached or exceeded:
DGS-2000-10P: 65 Watts
DGS-2000-10MP: 130 Watts
DGS-2000-28P: 193 Watts
DGS-2000-28MP and DGS-2000-
52MP: 370 Watts
In the meantime, no additional PoE
device can be supported.
Blinking
Amber
Total PoE output of Switch reached
guard band mode. (Max. PoE
budget < 7 Watts )
Light off
When the system power usage
does not reach the guard band
range.
LED Per
10/100/1000
Mbps
Copper Port
Link/Act Green/Amber
Solid
Green
When there is a secure 1000Mbps
Ethernet connection (or link) at any
of the ports.
Blinking
Green
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act) of
data occurring at a 1000Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
Solid
Amber
When there is a secure
10/100Mbps Ethernet connection
(or link) at any of the ports.
Blinking
Amber
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act) of
data occurring at a 10/100Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
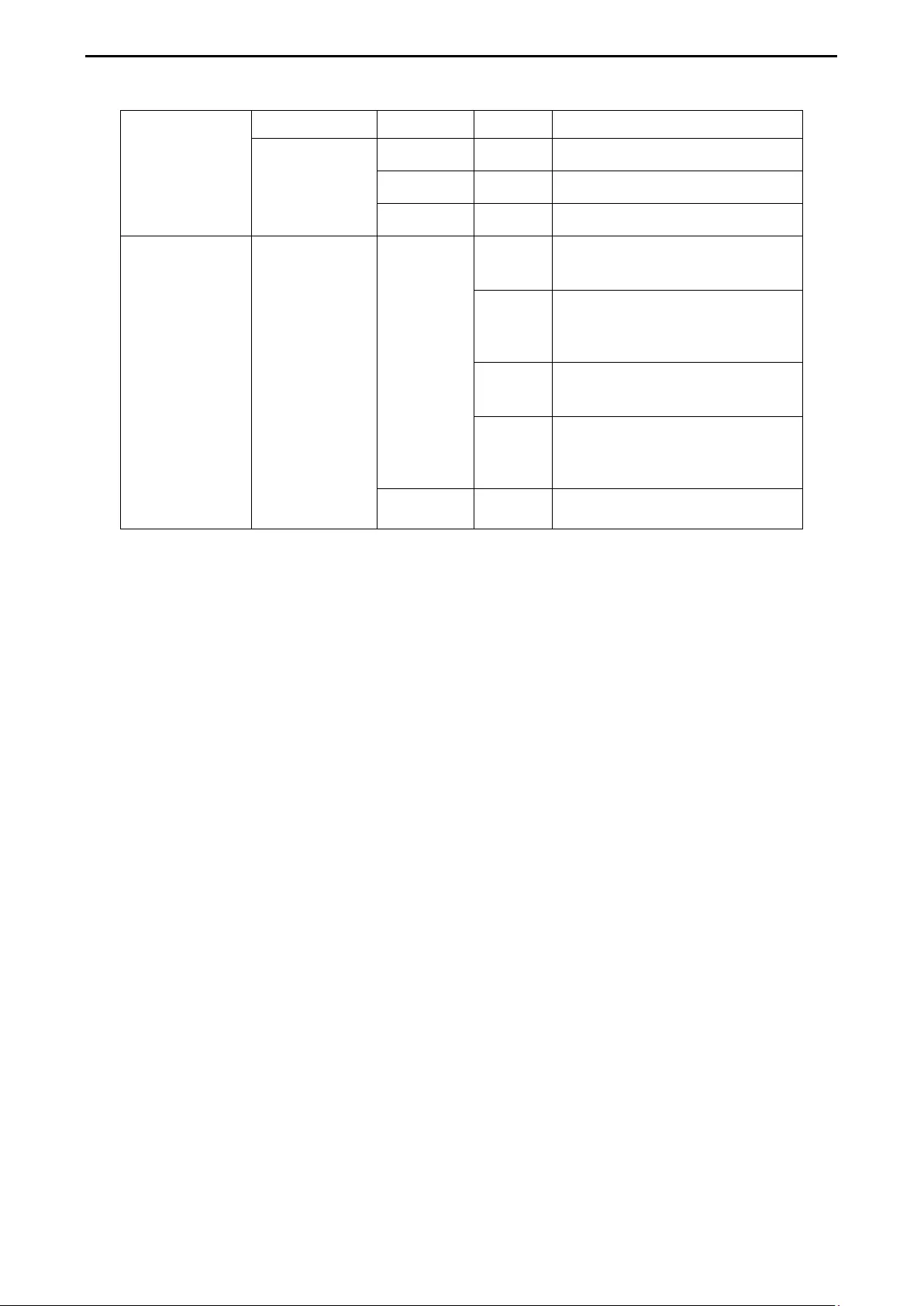
1 Product Introduction D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
15
5
Light off No link.
PoE Mode
Green Solid Light
Power feeding.
Amber Solid Light
Error Condition.
Off Solid Off No Power feeding.
LED Per
100/1000Mbps
SFP Port
Link/Act
Green/Amber
Solid
Green
When there is a secure 1000Mbps
Ethernet connection (or link) at any
of the ports.
Blinking
Green
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act) of
data occurring at a 1000Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
Solid
Amber
When there is a secure 100Mbps
Ethernet connection (or link) at any
of the ports.
Blinking
Amber
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act) of
data occurring at a 100Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
Off Solid off No link.

2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
16
6
2 Hardware Installation
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet
Switch.
Safety Cautions
To reduce the risk of bodily injury, electrical shock, fire and damage to the equipment, observe the following
precautions:
• Observe and follow service markings
Do not service any product except as explained in your system documentation.
Opening or removing covers that are marked with the triangular symbol with a lightning bolt may
expose you to electrical shock.
• Only a trained service technician should service components inside these compartments.
• If any of the following conditions occur, unplug the product from the electrical outlet and replace the
part or contact your trained service provider:
The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged.
An object has fallen into the product.
The product has been exposed to water.
The product has been dropped or damaged.
The product does not operate correctly when you follow the operating instructions.
• Keep your system away from radiators and heat sources. Also, do not block cooling vents.
• Do not spill food or liquids on your system components, and never operate the product in a wet
environment. If the system gets wet, contact your trained service provider.
• Do not push any objects into the openings of your system. Doing so can cause fire or electric shock by
shorting out interior components.
• Use the product only with approved equipment.
• Allow the product to cool before removing covers or touching internal components.
• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated on the electrical ratings label.
If you are not sure of the type of power source required, consult your service provider or local power
company.
• Also, be sure that attached devices are electrically rated to operate with the power available in your
location.
• Use only approved power cable(s). If you have not been provided with a power cable for your system or
for any AC powered option intended for your system, purchase a power cable that is approved for use
in your country. The power cable must be rated for the product and for the voltage and current marked
on the product’s electrical ratings label. The voltage and current rating of the cable should be greater
than the ratings marked on the product.
• To help prevent electric shock, plug the system and peripheral power cables into properly grounded
electrical outlets.
• These cables are equipped with three-prong plugs to help ensure proper grounding. Do not use
adapter plugs or remove the grounding prong from a cable. If you must use an extension cable, use a
3-wire cable with properly grounded plugs.
• Observe extension cable and power strip ratings. Make sure that the total ampere rating of all products
plugged into the extension cable or power strip does not exceed 80 percent of the ampere ratings limit
for the extension cable or power strip.
• To help protect your system from sudden, transient increases and decreases in electrical power, use a
surge suppressor, line conditioner, or uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
• Position system cables and power cables carefully; route cables so that they cannot be stepped on or
tripped over. Be sure that nothing rests on any cables.
• Do not modify power cables or plugs. Consult a licensed electrician or your power company for site
modifications.
• Always follow your local/national wiring rules.
2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
17
7
• When connecting or disconnecting power to hot-pluggable power supplies, if offered with your system,
observe the following guidelines:
Install the power supply before connecting the power cable to the power supply.
Unplug the power cable before removing the power supply.
If the system has multiple sources of power, disconnect power from the system by unplugging all
power cables from the power supplies.
• Move products with care; ensure that all casters and/or stabilizers are firmly connected to the system.
Avoid sudden stops and uneven surfaces.
Step 1: Unpacking
Open the shipping carton and carefully unpack its contents. Please consult the packing list located in the
User Manual to make sure all items are present and undamaged. If any item is missing or damaged, please
contact your local D-Link reseller for replacement.
One D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch
One Multilingual Getting Started Guide
User Guide CD
Power cord and Power Cord Retainer
Rack-mount kit and rubber feet
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact the local reseller for replacement.
Step 2: Switch Installation
For safe switch installation and operation, it is recommended that you:
Visually inspect the power cord to see that it is secured fully to the AC power connector.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation around the switch.
Do not place heavy objects on the switch.
Desktop or Shelf Installation
When installing the switch on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet included with the device must be attached
on the bottom at each corner of the device’s base. Allow enough ventilation space between the device and
the objects around it.
Figure 2.1 – Attach the adhesive rubber pads to the bottom
Rack Installation
The switch can be mounted in an EIA standard size 19-inch rack, which can be placed in a wiring closet with
other equipment. To install, attach the mounting brackets to the switch’s side panels (one on each side) and
secure them with the screws provided (please note that these brackets are not designed for palm size
switches).
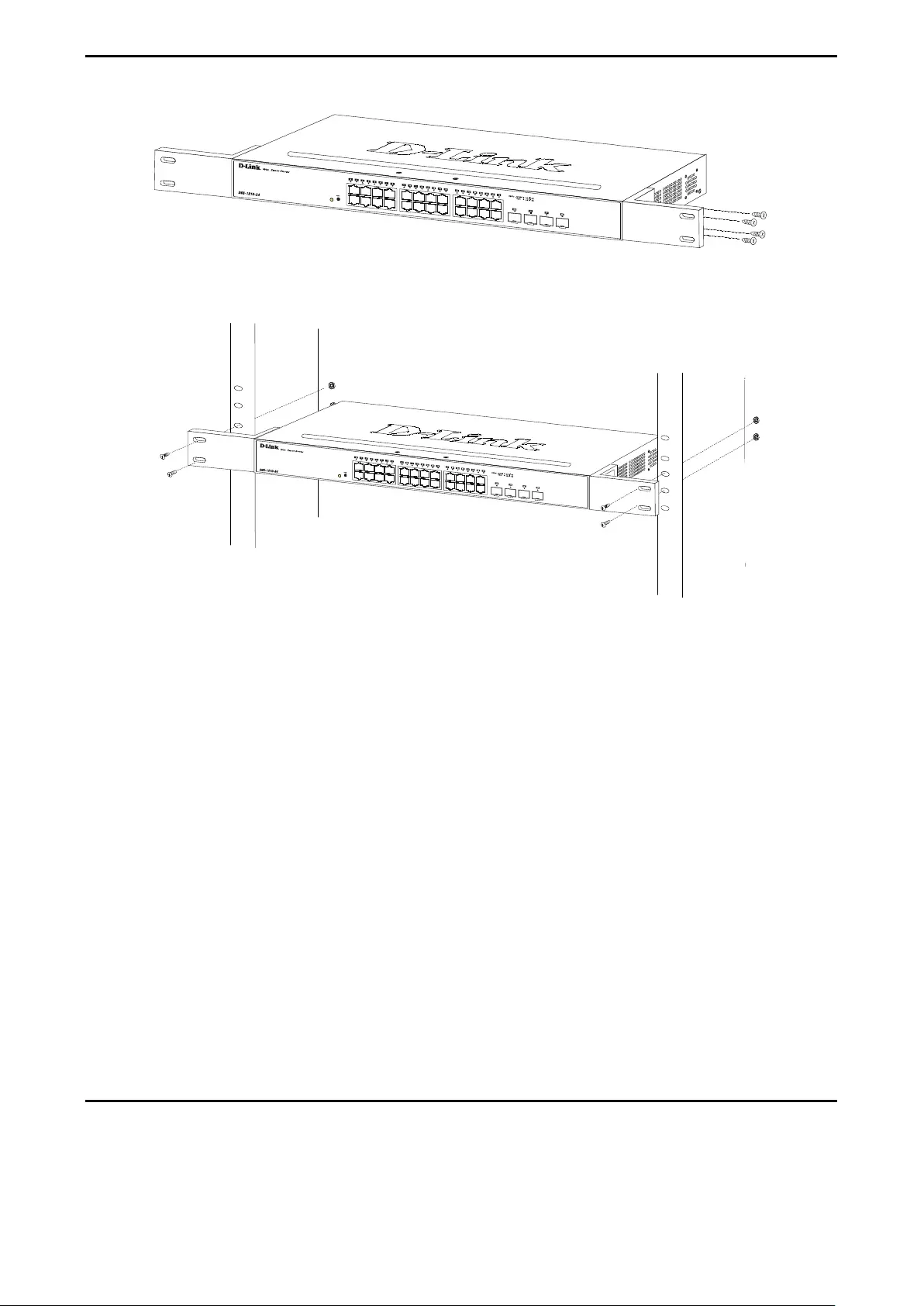
2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
18
8
Figure 2.2 – Attach the mounting brackets to the Switch
Then, use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the switch in the rack.
Figure 2.3 – Mount the Switch in the rack or chassis
Please be aware of following safety Instructions when installing:
A) Elevated Operating Ambient - If installed in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating ambient
temperature of the rack environment may be greater than room ambient. Therefore, consideration should be
given to installing the equipment in an environment compatible with the maximum ambient temperature (Tma)
specified by the manufacturer.
B) Reduced Air Flow - Installation of the equipment in a rack should be such that the amount of air flow
required for safe operation of the equipment is not compromised.
C) Mechanical Loading - Mounting of the equipment in the rack should be such that a hazardous condition is
not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
D) Circuit Overloading - Consideration should be given to the connection of the equipment to the supply
circuit, and the effect that overloading of the circuits might have on overcurrent protection and supply wiring.
Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate ratings should be used when addressing this concern.
E) Reliable Earthing - Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained. Particular
attention should be given to supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. use
of power strips)."
Step 3: Plugging in the AC Power Cord with Power Cord Clip
To prevent accidental removal of the AC power cord, it is recommended to install the power cord clip
together with the power cord.
A) With the rough side facing down, insert the Tie Wrap into the hole below the power socket.
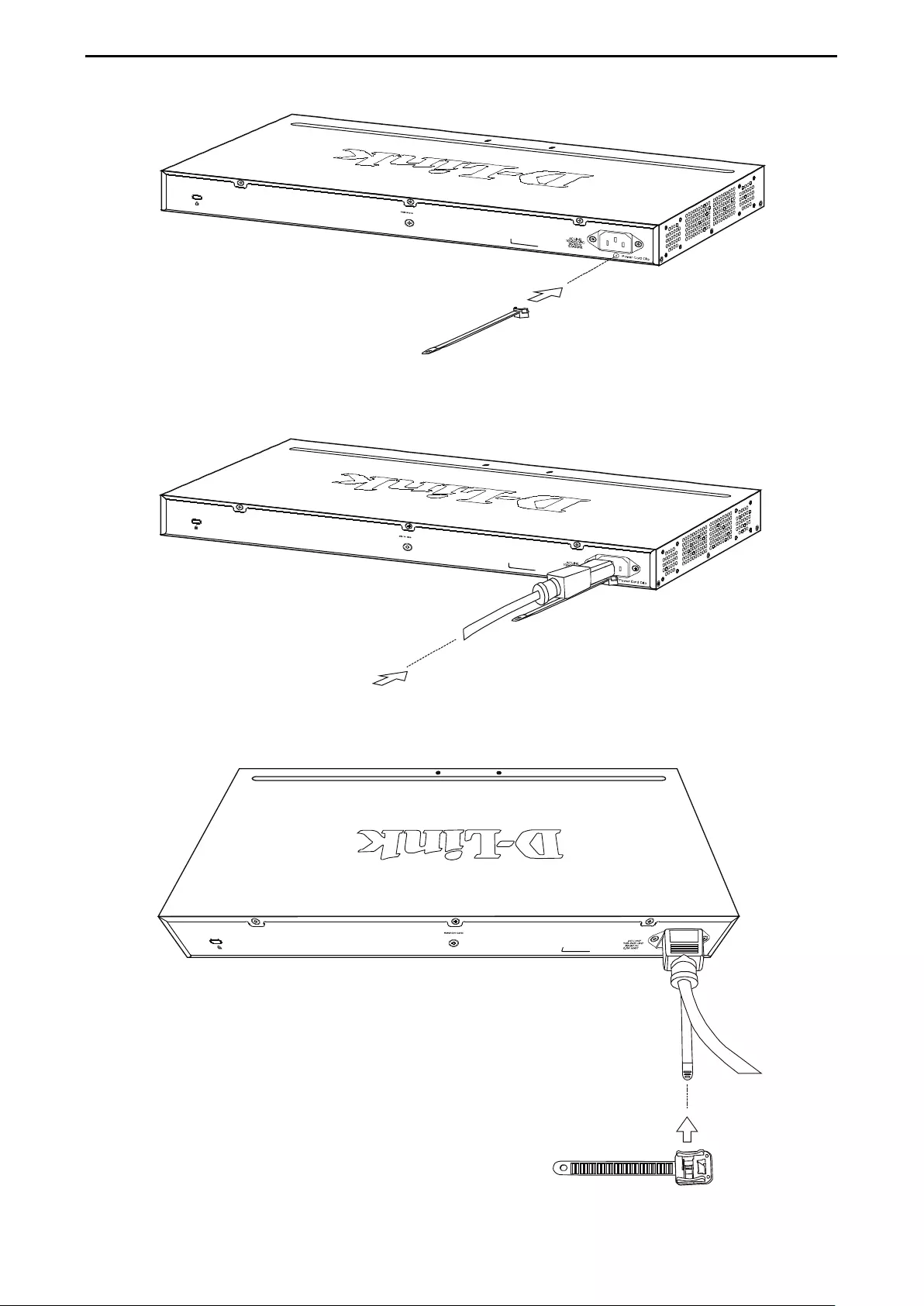
2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
19
9
Figure 2.4 – Insert Tie Wrap to the Switch
B) Plug the AC power cord into the power socket of the Switch.
Figure 2.5 – Connect the power cord to the Switch
C) Slide the Retainer through the Tie Wrap until the end of the cord.
Figure 2.6 – Slide the Retainer through the Tie Wrap
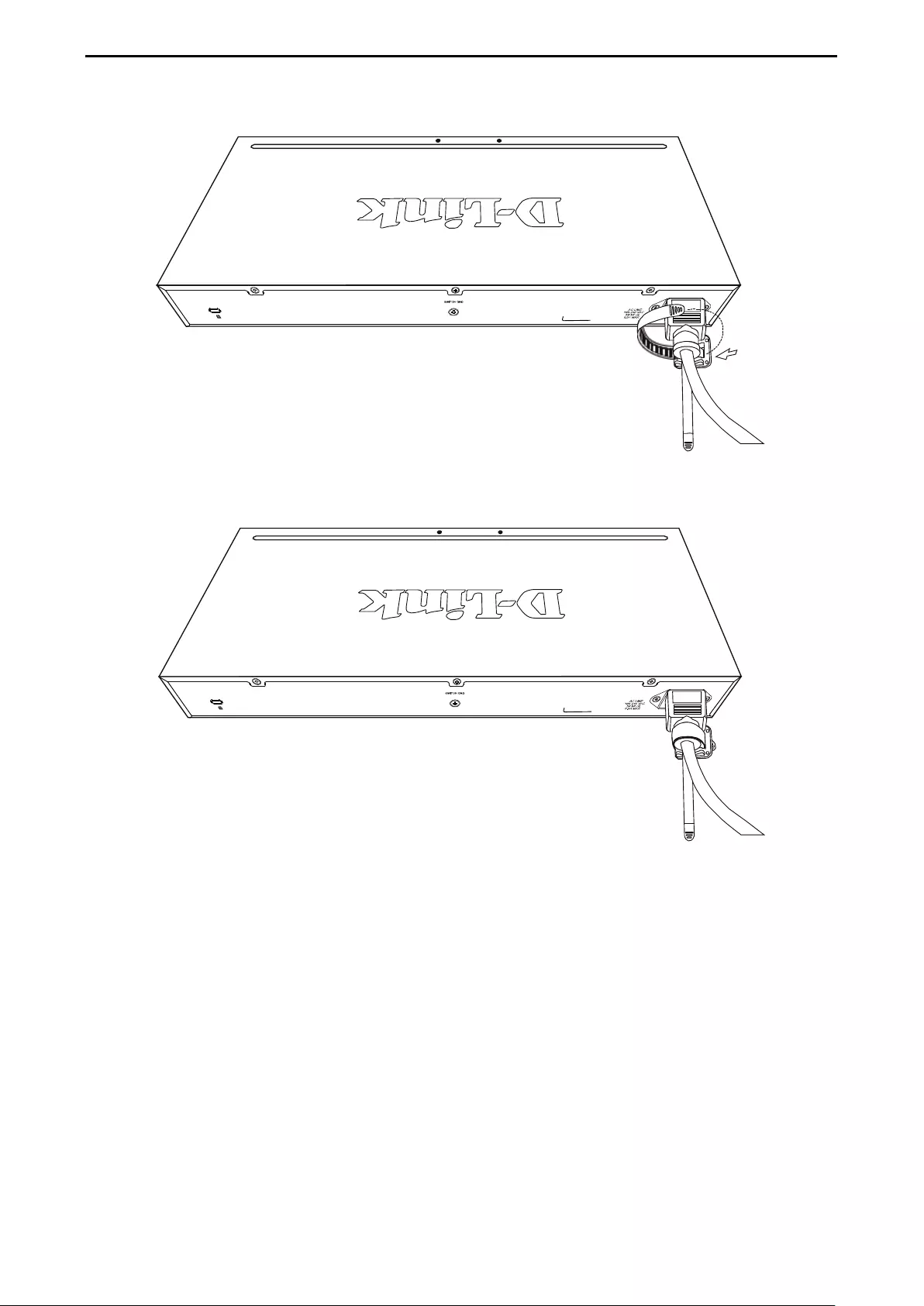
2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
20
0
D) Circle the tie of the Retainer around the power cord and into the locker of the Retainer.
Figure 2.7 – Circle around the power cord
E) Fasten the tie of the Retainer until the power cord is secured.
Figure 2.8 – Secure the power cord
F) Users may now connect the AC power cord to an electrical outlet (preferably one that is grounded and
surge protected).
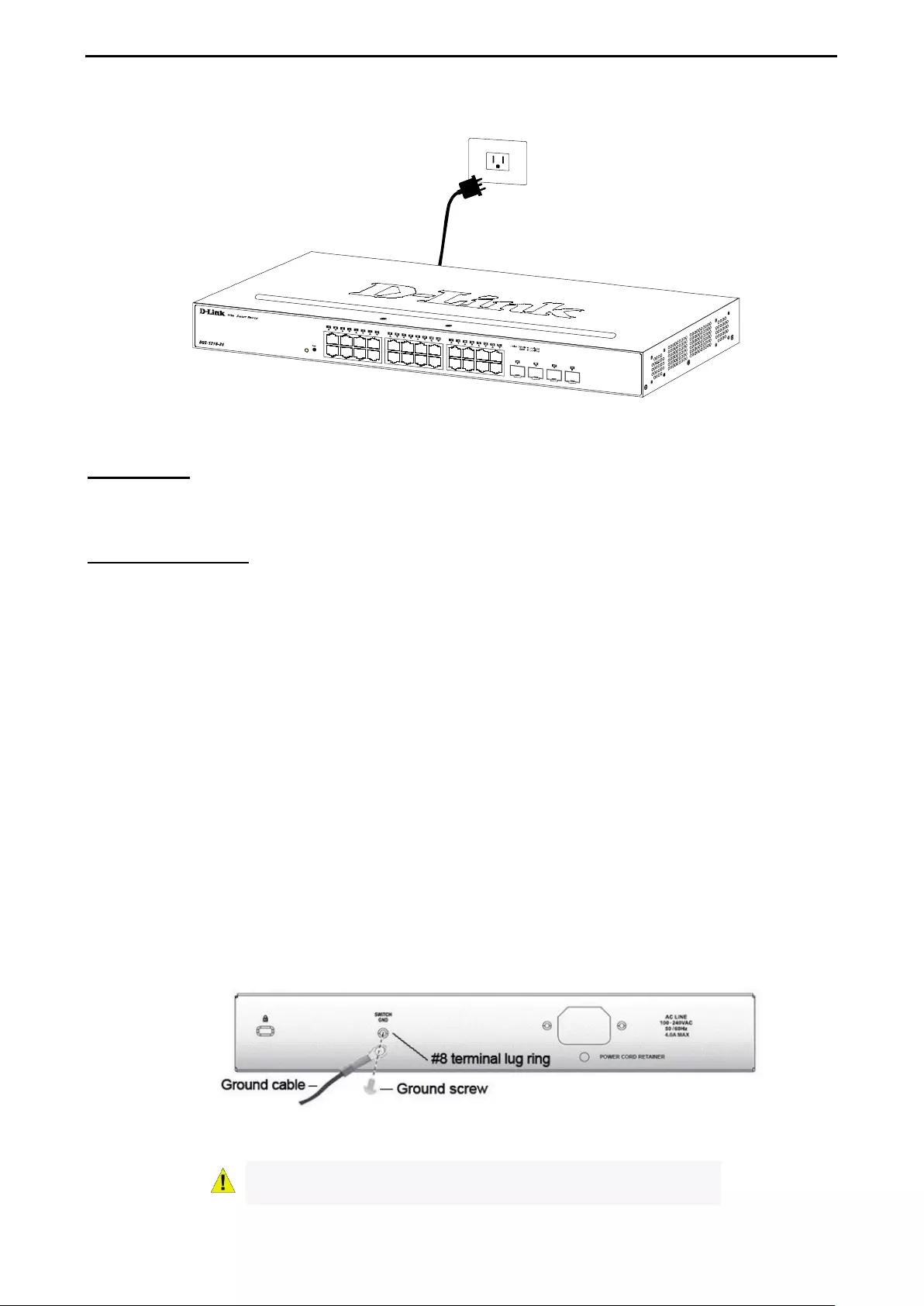
2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
21
1
Figure 2.9 – Plugging the switch into an outlet
Power Failure
As a precaution, the switch should be unplugged in case of power failure. When power is resumed, plug the
switch back in.
Grounding the Switch
This section describes how to connect the DGS-2000 Series Switch to ground. You must complete this
procedure before powering your switch.
Required Tools and Equipment
• Ground screws (included in the accessory kit): One M4 x 6 mm (metric) pan-head screw.
• Ground cable (not included in the accessory kit): The grounding cable should be sized according to
local and national installation requirements. Depending on the power supply and system, a 12 to 6
AWG copper conductor is required for U.S installation. Commercially available 6 AWG wire is
recommended. The length of the cable depends on the proximity of the switch to proper grounding
facilities.
• A screwdriver (not included in the accessory kit)
The following steps let you connect the switch to a protective ground:
Step 1: Verify if the system power is off.
Step 2: Use the ground cable to place the #8 terminal lug ring on top of the ground-screw opening, as
seen in the figure below.
Step 3: Insert the ground screw into the ground-screw opening.
Step 4: Using a screwdriver, tighten the ground screw to secure the ground cable to the switch.
Step 5: Attach the terminal lug ring at the other end of the grounding cable to an appropriate grounding
stud or bolt on rack where the switch is installed.
Step 6: Verify if the connections at the ground connector on the switch and the rack are securely
attached.
Figure 2.10 – Connect a Grounding Cable
CAUTION: The equipment power supply cord shall be connected
to a socket-outlet with earthing connection.

2 Hardware Installation D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
22
2
Le cordon d'alimentation de l'équipement doit être branché sur une
prise de courant dotée d'une connexion à la terre.
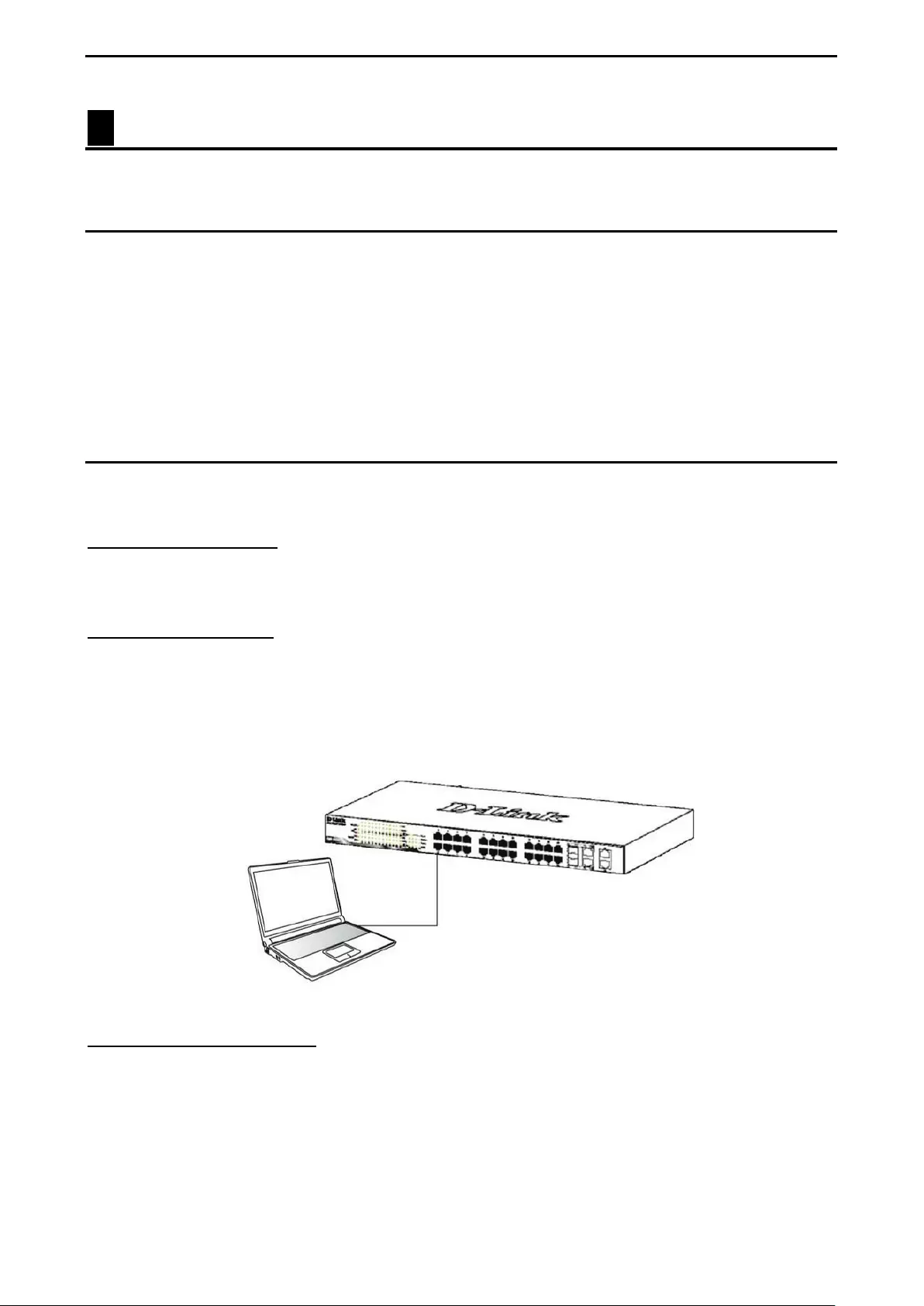
3 Getting Started D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
23
3
3 Getting Started
This chapter introduces the management interface of D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch.
Management Options
The D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch can be managed through any port on the device by using the
Web-based
Management.
Each switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with Web-Based
Management or a SNMP network manager. The PC should have an IP address in the same range as the
switch. Each switch can allow up to four users to access to the Web-Based Management concurrently.
Please refer to the following installation instructions for the Web-based Management.
Using Web-based Management
After a successful physical installation, you can configure the Switch, monitor the network status, and display
statistics using a web browser.
Supported Web Browsers
The embedded Web-based Management currently supports the following web browsers:
Web Browser via IE8(or later version), Firefox, Chrome and Safari.
Connecting to the Switch
You will need the following equipment to begin the web configuration of your device:
1. A PC with a RJ-45 Ethernet connection
2. A standard Ethernet cable
Connect the Ethernet cable to any of the ports on the front panel of the switch and to the Ethernet port on the
PC.
Figure 3.1 – Connected Ethernet cable
Login Web-based Management
In order to login and configure the switch via an Ethernet connection, the PC must have an IP address in the
same subnet as the switch. For example, if the switch has an IP address of 10.90.90.90, the PC should have
an IP address of 10.x.y.z (where x/y is a number between 0 ~ 254 and z is a number between 1 ~ 254), and
a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0. There are two ways to launch the Web-based Management, you may either click
the Web Access button at the top of the SmartConsole Utility or open the web browser and enter 10.90.90.90
(the factory-default IP address) in the address bar. Then press <Enter>.
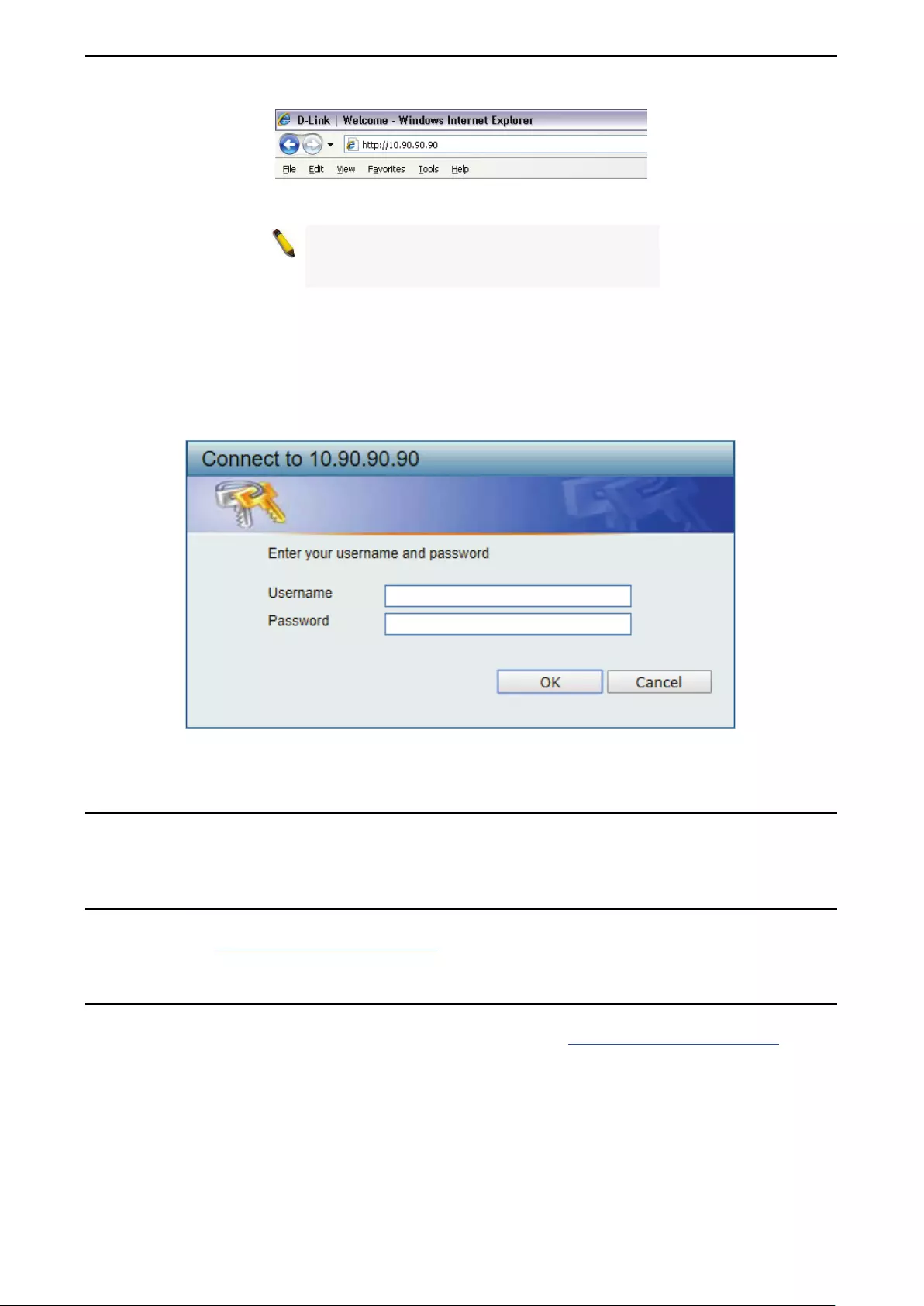
3 Getting Started D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
24
4
Figure 3.2 –Enter the IP address 10.90.90.90 in the web browser
NOTE: The switch's factory default IP address is
10.90.90.90 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 and
a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
The web configuration can also be accessed through the SmartConsole Utility. Open the SmartConsole
Utility and double-click the switch as it appears in the Monitor List. This will automatically load the web
configuration in your web browser.
When the following logon dialog box appears, enter the password of the Web-based Management interface
then click OK.
By default, the username and password are null.
Figure 3.3 – Logon Dialog Box
Smart Wizard
After a successful login, the Smart Wizard will guide you through essential settings of the D-Link DGS-2000
Series Ethernet Switch. Please refer to the Smart Wizard Configuration section for details.
Web-based Management
By clicking the Exit button in the Smart Wizard, you will enter the Web-based Management interface. Please
refer to Chapter 4 Web-based Switch Configuration for detailed instructions.
D-Link Network Assistant
D-Link Network Assistant (DNA) is a program that is used to discover switches which are in the same layer 2
network segment as your PC. You can download the DNA utility from http://tools.dlink.com/intro/dna/. Please
go to above link for details.
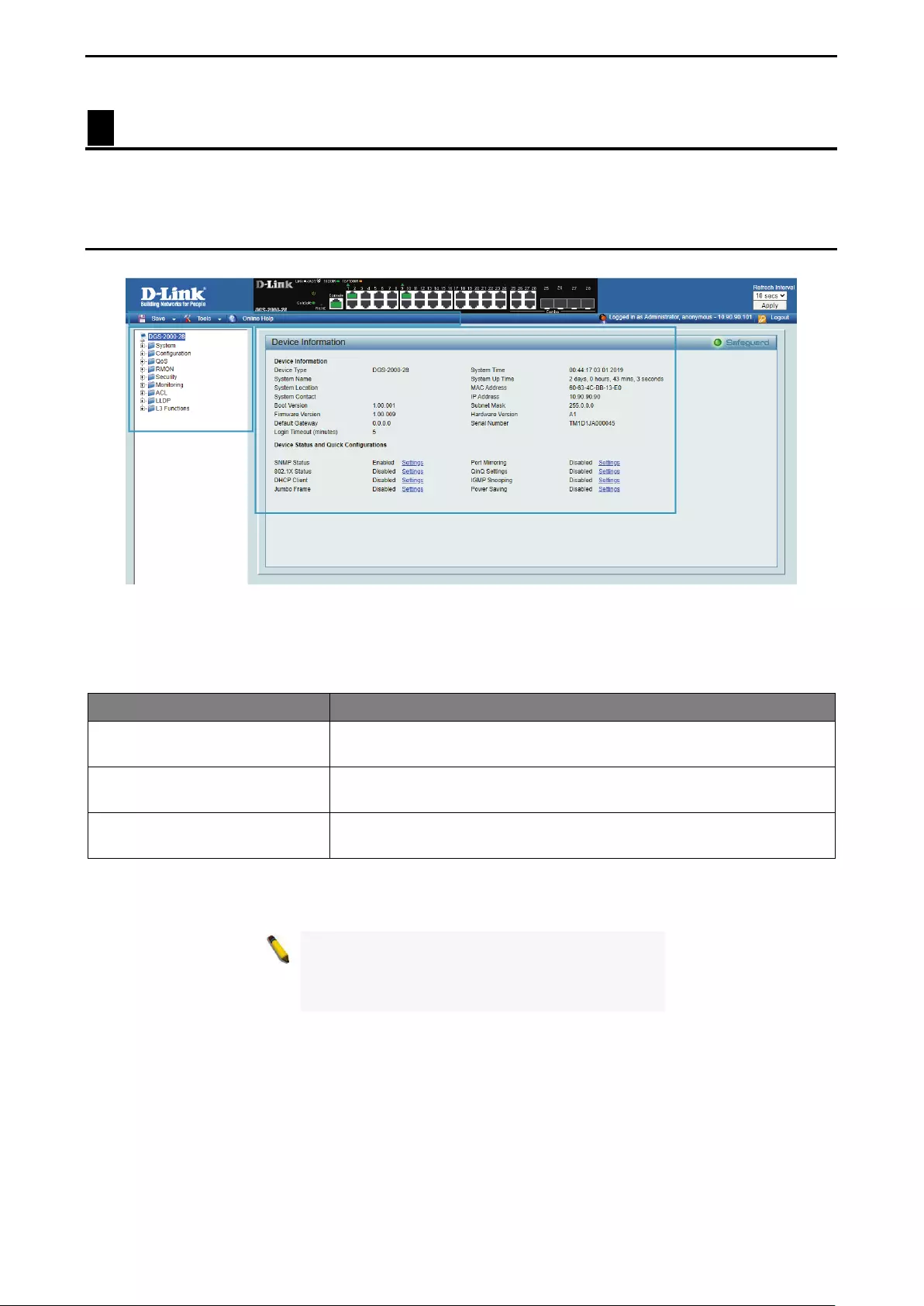
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
25
5
4 Web-based Switch Configuration
The features and functions of the D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch can be configured for optimum
use through the Web-based Management Utility.
Web-based Management
After clicking the Exit button in Smart Wizard you will see the screen below:
Figure 4.1 – Web-based Management
The above image is the Web-based Management screen. The three main areas are the Tool Bar on top, the
Function Tree, and the Main Configuration Screen.
Item Area Description
Tool Bar To provide a quick and convenient way for essential utility functions
like firmware and configuration management.
Function Tree By choosing different functions in the Function Tree, you can change
all the settings in the Main Configuration Screen.
Main Configuration Screen To display the current status of your Switch by clicking the model name
on top of the function tree.
At the upper right corner of the screen the username and current IP address will be displayed.
Under the username is the Logout button. Click this to end this session.
NOTE:
If you close the web browser without
clicking the Logout button first, then it will be seen
as an abnormal exit and the login session will still
be occupied.
Finally, by clicking on the D-Link logo at the upper-left corner of the screen you will be redirected to the local
D-Link website.
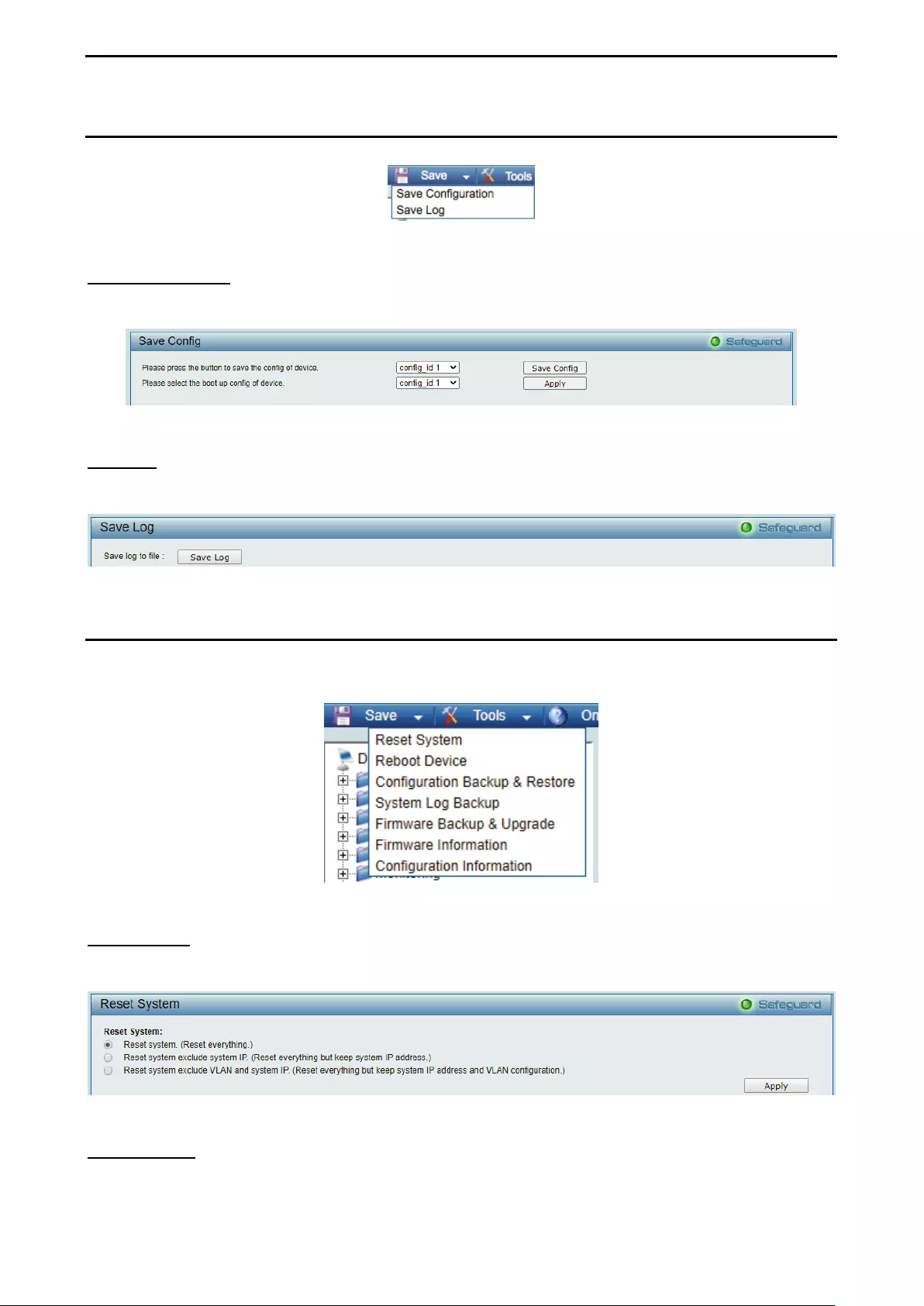
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
26
6
Tool Bar > Save Menu
The Save Menu provides Save Configuration and Save Log functions.
Figure 4.2 – Save Menu
Save Configuration
Select to save the entire configuration changes to configuration ID 1 or 2 you have made to the device to
switch’s non-volatile RAM.
Figure 4.3 – Save Configuration
Save Log
Save the log entries to your local drive and a pop-up message will prompt you for the file path. You can view
or edit the log file by using text editor (e.g. Notepad).
Figure 4.4 – Save Log
Tool Bar > Tools Menu
The Tools Menu offers global function controls such as Reset System, Reboot Device, Configuration Backup
& Restore, System Log Backup, Firmware Backup & Upgrade, Firmware Information and Configuration
Information.
Figure 4.5 – Tool Menu
Reset System
Provide variable safe reset options for the Switch. User may chose any one of these options to perform
system reset.
Figure 4.6 – Tool Menu > Reset System
Reboot Device
Provide a safe way to reboot the system. Select YES or NO to save the current settings before action. And
click Reboot to restart the switch.
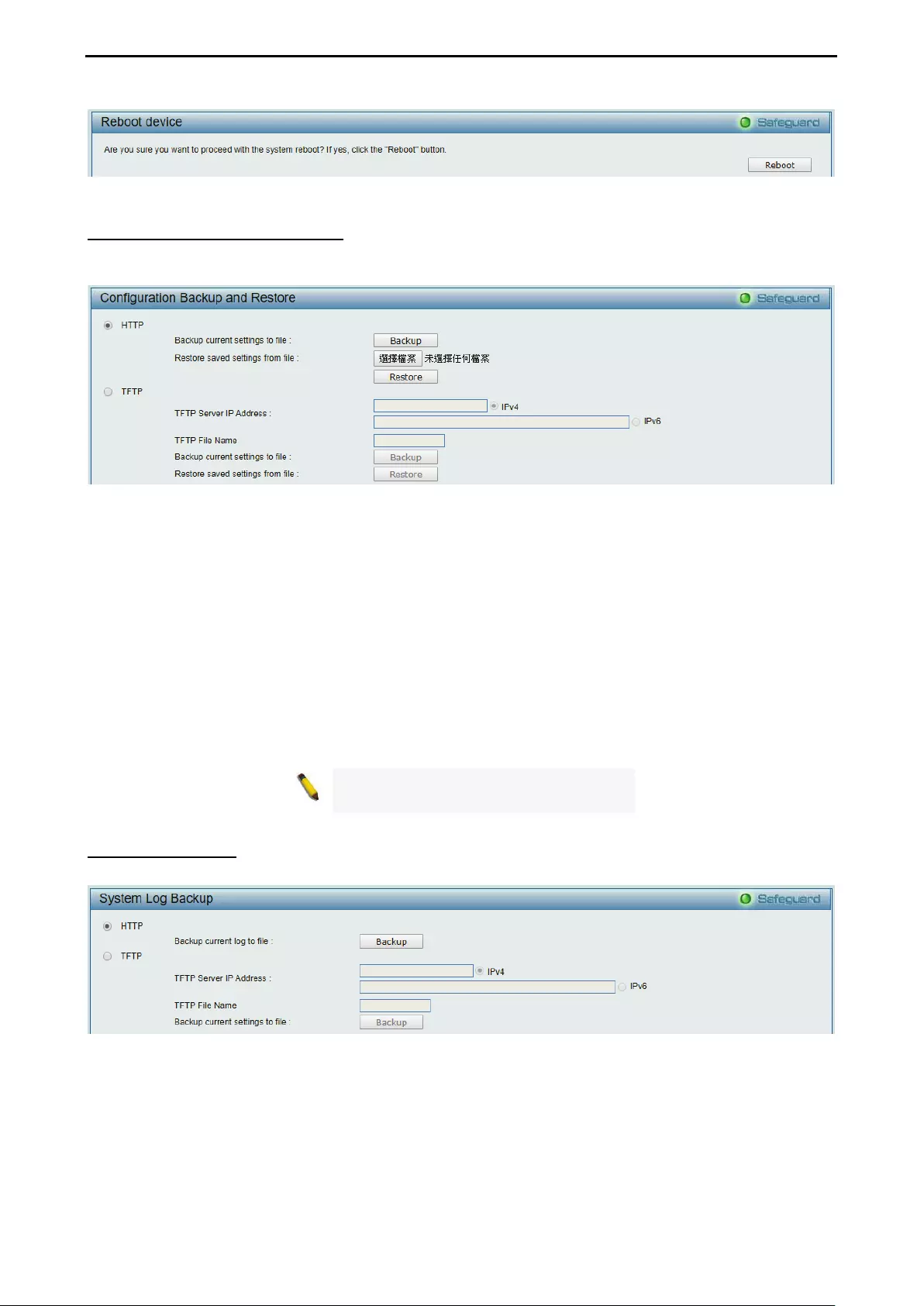
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
27
7
Figure 4.7 – Tool Menu > Reboot Device
Configuration Backup and Restore
Allow the current configuration settings to be saved to a file (not including the password), and if necessary,
you can restore configuration settings from this file. Two methods can be selected: HTTP or TFTP.
Figure 4.8 – Tool Menu > Configure Backup and Restore
HTTP: Backup or restore the configuration file to or from your local drive.
Click Backup to save the current settings to your disk.
Click Choose File to browse your inventories for a saved backup settings file.
Click Restore after selecting the backup settings file you want to restore.
TFTP: TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a file transfer protocol that allows you to transfer files to a
remote TFTP server. TFTP Server IP Address with IPv4 or IPv6 address and TFTP File Name for the
configuration file you want to save to / restore from.
Click Backup to save the current settings to the TFTP server.
Click Restore after selecting the backup settings file you want to restore.
Note: Switch will reboot after restore, and
all current configurations will be lost.
System Log Backup
Backup system logs via HTTP or TFTP.
Figure 4.9 – Tool Menu > System Log Backup
HTTP: Backup log to your local drive directly from HTTP.
TFTP: Specify IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) and file name. Click Backup to start process.
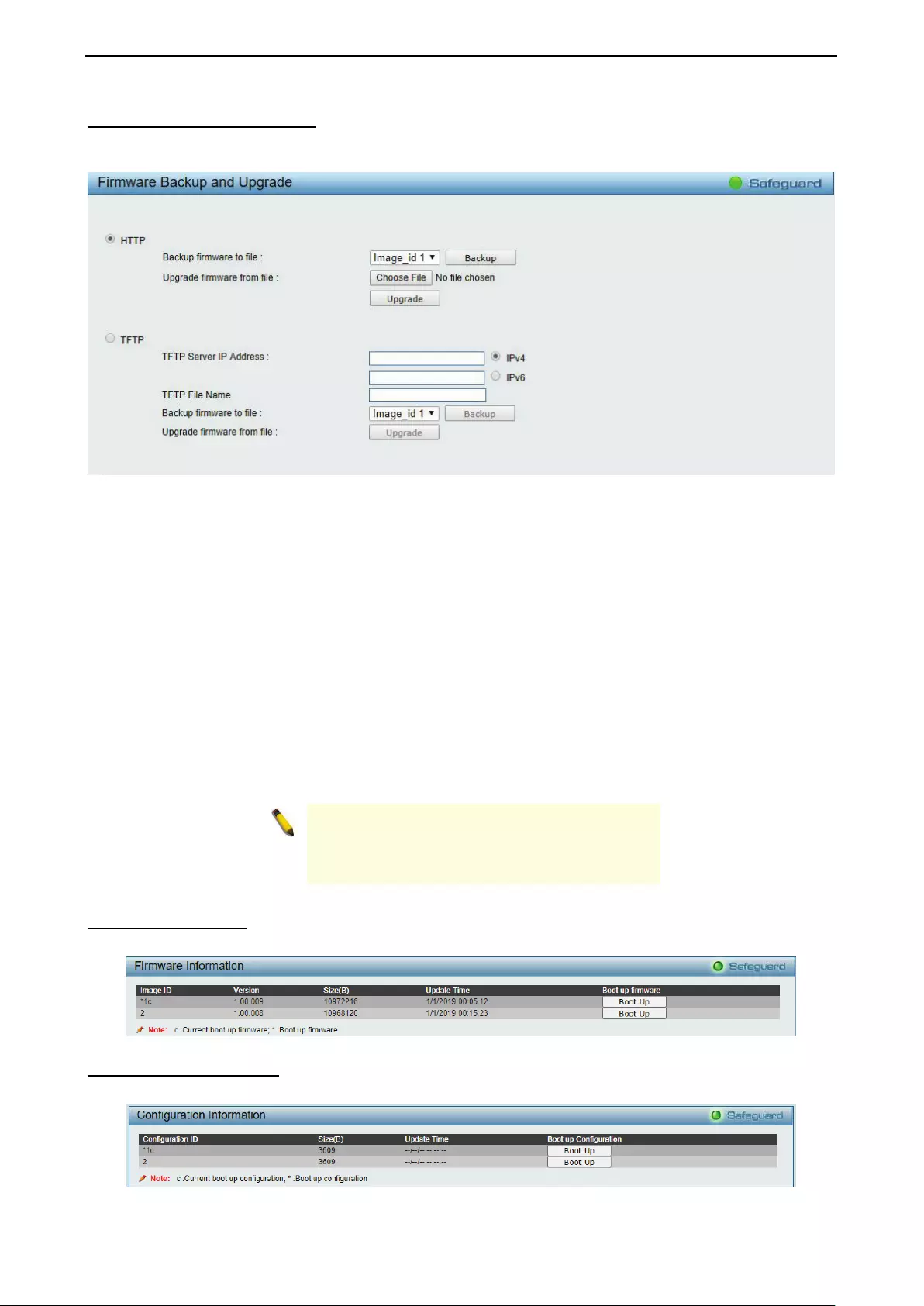
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
28
8
Firmware Backup and Upgrade
Allow for the firmware to be saved, or for an existing firmware file to be uploaded to the Switch. Two methods
can be selected: HTTP or TFTP.
Figure 4.10 – Tool Menu > Firmware Backup and Upload
HTTP: Backup or upgrade the firmware to or from your local PC drive.
Backup firmware to file: Select image_id 1 or image_id 2.
Click Backup to save the firmware to your disk.
Click Choose File to browse your inventories for a saved firmware file.
Click Upgrade after selecting the firmware file you want to restore.
TFTP: Specifies the Image_id 1 or Image_id 2 to backup or upgrade the firmware to or from a remote TFTP
server. Specifies TFTP Server IP Address with IPv4 or IPv6 address and TFTP File Name for the
configuration file you want to save to / restore from.
Backup firmware to file: Select Image_id1 or Image_id 2.
Click Backup to save the firmware to the TFTP server.
Click Upgrade after selecting the firmware file you want to restore.
NOTE: Do not disconnect the PC or remove the
power cord from device until the upgrade
completes. The Switch may crash if the
Firmware upgrade is incomplete.
Firmware Information
This page displays the firmware information and allow user to identify the image used for system boot.
Figure 4.11 – Tool Menu > Firmware Information
Configuration Information
This page displays the configuration information and allow user to identify the config used for system boot.
Figure 4.12 – Tool Menu > Configuration Information
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
2
29
9
Tool Bar > Online Help
The Online Help provides two ways of online support: D-Link Support Site will lead you to the D-Link
website where you can find online resources such as updated firmware images; User Guide can offer an
immediate reference for the feature definition or configuration guide.
Figure 4.13 – Online Help
Function Tree
All configuration options on the switch are accessed through the Setup menu on the left side of the screen.
Click on the setup item that you want to configure. The following sections provide more detailed description
of each feature and function.
Figure 4.14 –Function Tree
Device Information
The Device Information provides an overview of the switch, including essential information such as firmware
& hardware information, and IP address.
Figure 4.15 – Device Information
It also offers an overall status of common software features:
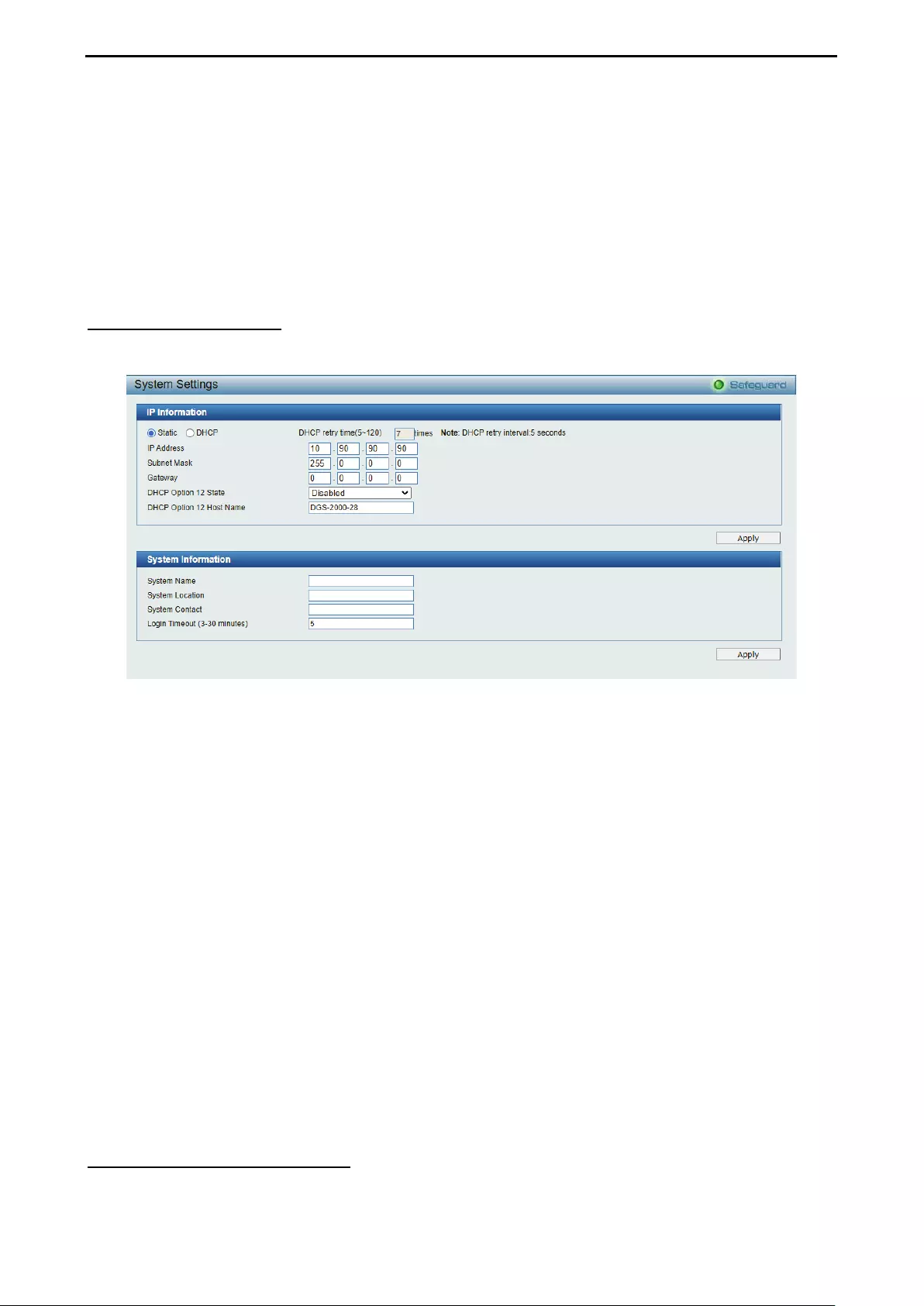
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
30
0
SNMP Status: Click Settings to link to SNMP > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings. Default is disabled.
802.1X Status: Click Settings to link to AAA > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings. Default is disabled.
DHCP Client: Click Settings to link to System > System Settings. Default is disabled.
Jumbo Frame: Click Settings to link to L2 Functions > Jumbo Frame. Default is disabled.
Port Mirroring: Click Settings to link to L2 Functions > Port Mirroring. Default is disabled.
QinQ Setting: Click Settings to link to Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings. Default is disabled.
IGMP Snooping: Click Settings to link to L2 Functions > Multicast > IGMP Snooping. Default is disabled.
Power Saving: Click Settings to link to System > Power Saving. Default is disabled
System > System Settings
The System Setting allows the user to configure the IP address and the basic system information of the
Switch.
Figure 4.16 – System > System Settings
IPv4 Information: There are three ways for the switch to obtain an IP address: Static, DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol) and BOOTP.
When using static mode, the Interface Name, VLAN Name, Interface Admin State, IPv4 Address,
NetMask and Gateway can be manually configured. When using DHCP mode, the Switch will first look for a
DHCP server to provide it with an IP address (including network mask and default gateway) before using the
default or previously entered settings. By default the IP setting is static mode with IP address is 10.90.90.90
and subnet mask is 255.0.0.0.
DHCP Option 12 State: Specifies the DHCP option 12 state is enabled or disabled.
DHCP Option 12 Host Name: Specifies the host name for DHCP.
DHCP Retry Times: Specifies the retry time of DHCP.
System Information: The fields for System Name and System Location which provide network
administrator unique identification information for different switches. Also, system information can be read
and printed on SmartConsole utility.
Login Timeout: The Login Timeout controls the idle time-out period for security purposes, and when there is
no action for a specific time span in the Web-based Management. If the current session times out (expires),
the user is required a re-login before using the Web-based Management again. Selective range is from 3 to
30 minutes, and the default setting is 5 minutes.
System > DHCP Auto Configuration
The DHCP Auto Configuration page allows user to enable the DHCP Auto Configuration feature on the
Switch. When enabled, the Switch becomes a DHCP client and gets the configuration file from a TFTP
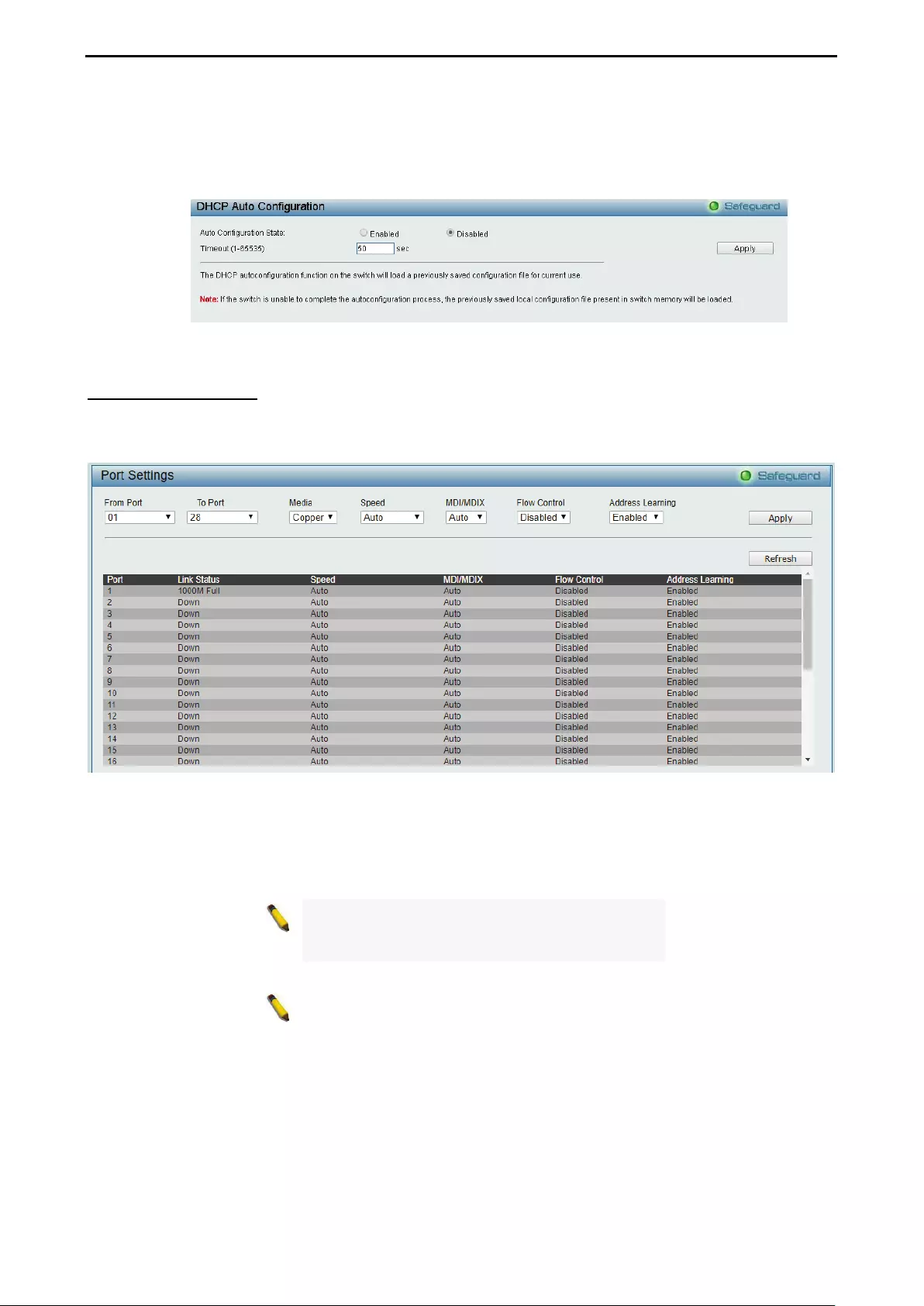
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
31
1
server automatically on next boot up. To accomplish this, the DHCP server must deliver the TFTP server IP
address and configuration file name information in the DHCP reply packet. The TFTP server must be up and
running and store the necessary configuration file in its base directory when the request is received from the
Switch.
Figure 4.17 – System > DHCP Auto Configuration
System > Port Settings
In the Port Setting page, the status of all ports can be monitored and adjusted for optimum configuration. By
selecting a range of ports (From Port and To Port), the Speed can be set for all selected ports by clicking
Apply. Press the Refresh button to view the latest information.
Figure 4.18 – System > Port Settings
Speed: Gigabit Fiber connections can operate in 1000M Auto or Disabled. Copper connections can operate
in Forced Mode settings (2500M Full, 1000M Full, 100M Full, 100M Half, 10M Full, 10M Half), Auto, or
Disabled. The default setting for all ports is Auto.
NOTE:
Be sure to adjust port speed settings
appropriately after changing the connected cable
media types.
NOTE: All ports do not support MDI/MDI-X
function when the speed links to 1000M force
mode.
MDI/MDIX:
A medium dependent interface (MDI) port is an Ethernet port connection typically used on the Network
Interface Card (NIC) or Integrated NIC port on a PC. Switches and hubs usually use Medium dependent
interface crossover (MDIX) interface. When connecting the Switch to end stations, user have to use
straight through Ethernet cables to make sure the Tx/Rx pairs match up properly. When connecting the
Switch to other networking devices, a crossover cable must be used.
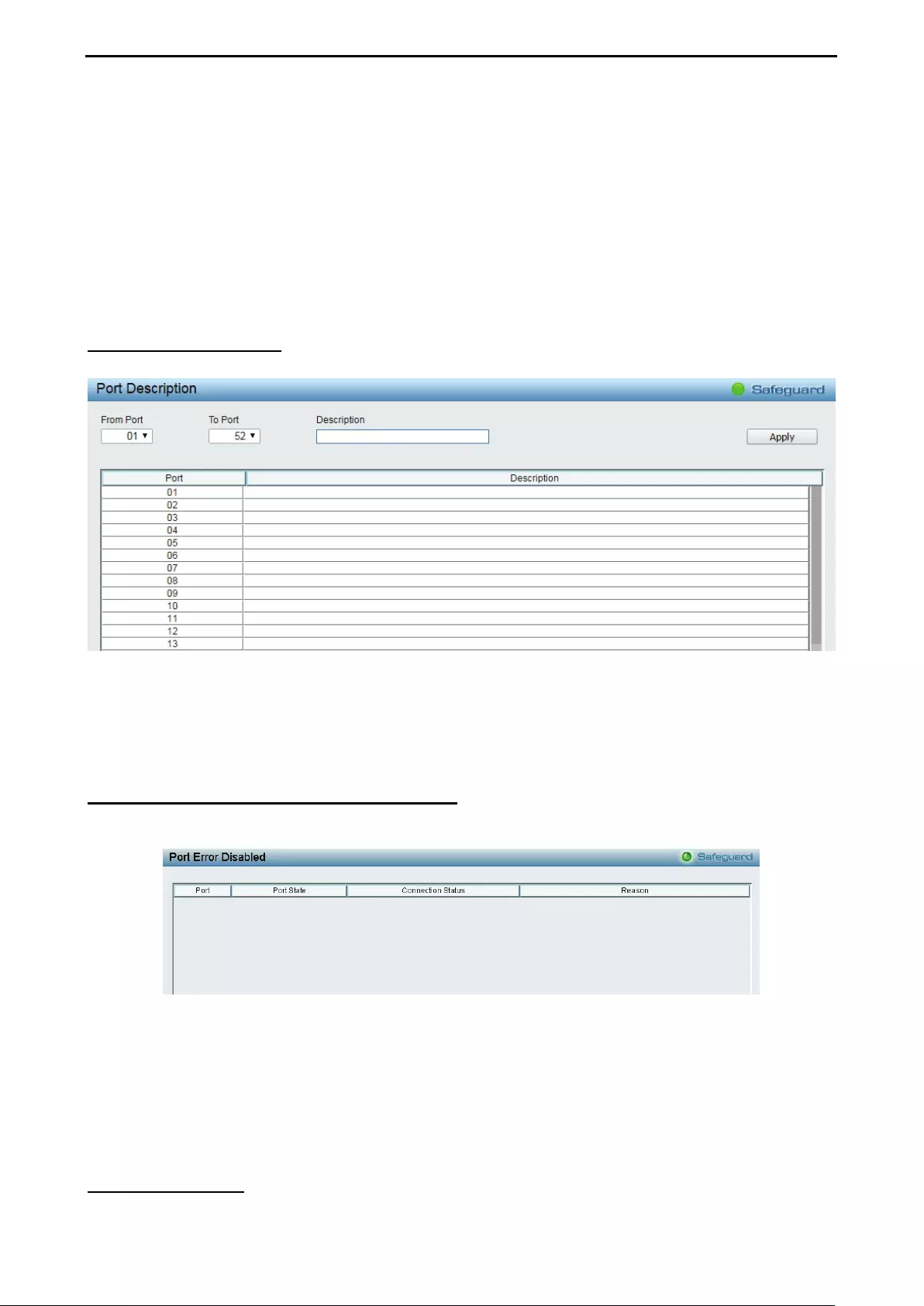
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
32
2
This switch provides a configurable MDI/MDIX function for users. The switches can be set as an MDI port in
order to connect to other hubs or switches without an Ethernet crossover cable.
Auto MDI/MDIX is designed on the switch to detect if the connection is backwards, and automatically
chooses MDI or MDIX to properly match the connection. The default setting is “Auto” MDI/MDIX.
Flow Control: You can enable this function to mitigate the traffic congestion. Ports configured for full-duplex
use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex ports use backpressure flow control. The default setting is Disabled.
Auto Downgrade: Enable or disable automatically downgrading advertised speed. This function only takes
effect, when Speed is configured as Auto.
Capability Advertised: When the Speed is set to Auto, these capabilities are advertised during auto-
negotitation.
System > Port Description
Port description can be given on this page.
Figure 4.19 – System > Port Description
From Port / To Port: Specifies the range of ports to describe.
Description: Specifies the description for the chosen ports.
Click Apply to set the description in the table.
System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
The Port Error Disabled page displays the information about ports that have had their connection status
disabled, for reasons such as STP loopback detection or link down status.
Figure 4.20 – System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
Port: Displays the port that has been error disabled.
Port State: Describes the current running state of the port, whether Enabled or Disabled.
Connection Status: This field will read the uplink status of the individual ports, whether Enabled or Disabled.
Reason: Describes the reason why the port has been error-disabled, such as a STP loopback occurrence.
System > IP Interface
Used to configure IP Interface parameters for system interface.
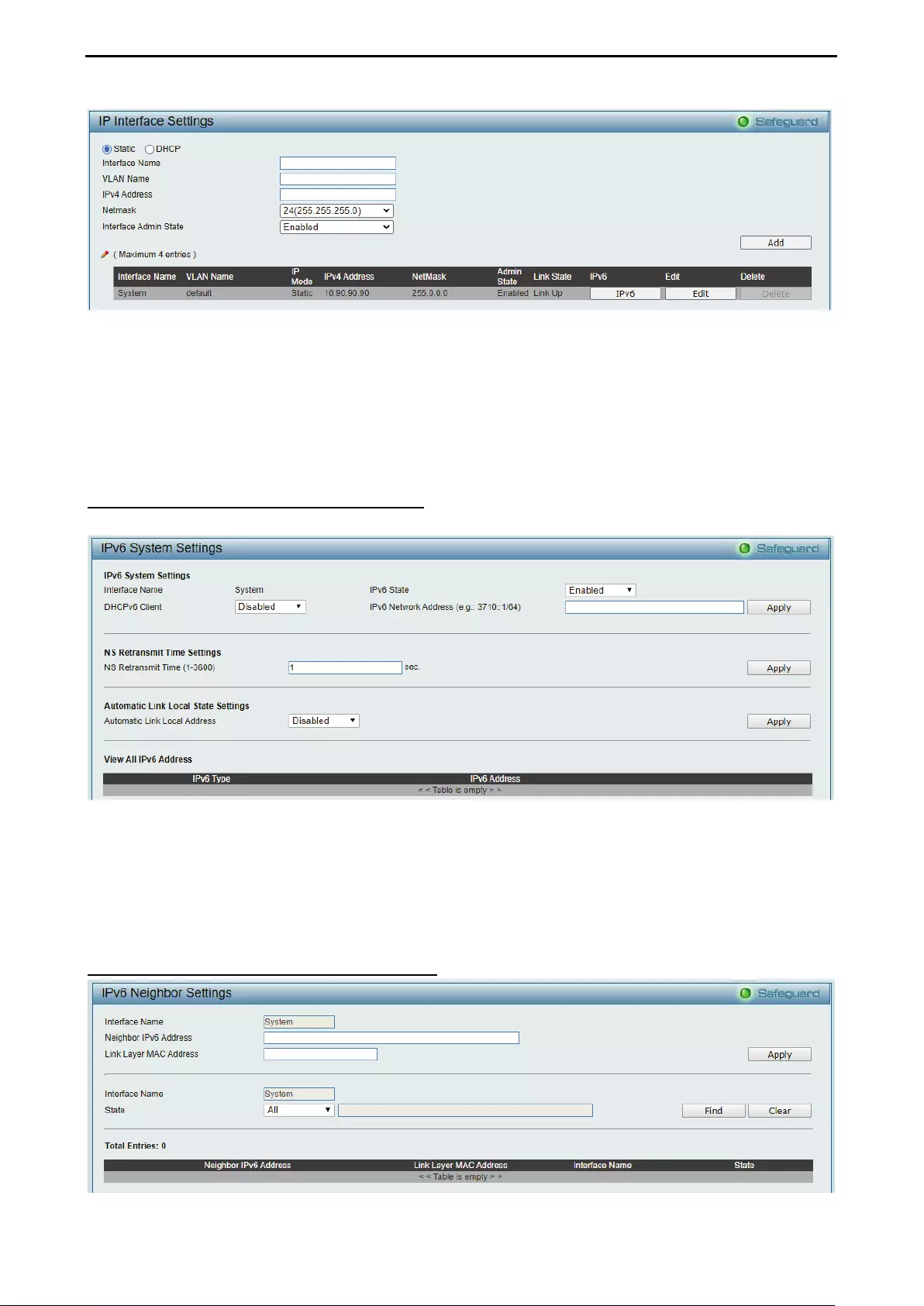
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
33
3
Figure 4.21 – System > IP Interface Settings
Interface Name: Specifies the name of IP interface.
VLAN Name: Specifies the VLAN name of IP interface.
IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address for the interface.
Netmask: Select the netmask of IP address.
Interface Admin State: Enables or disables the interface administration state.
System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 System Settings
Used to configure IPv6 parameters for system interface.
Figure 4.22 – System > IPv6 Interface Settings
IPv6: Options to enable/disable IPv6 address of system interface.
DHCPv6 Client: Options to enable/disable DHCPv6 client mode on system interface.
NS Retransmit Time Settings: Specify the time period for sending NS.
Automatic Link Local State Setting: Options to enable/disable Link Local address of system interface.
System > IPv6 Setting > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
Figure 4.23 – System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
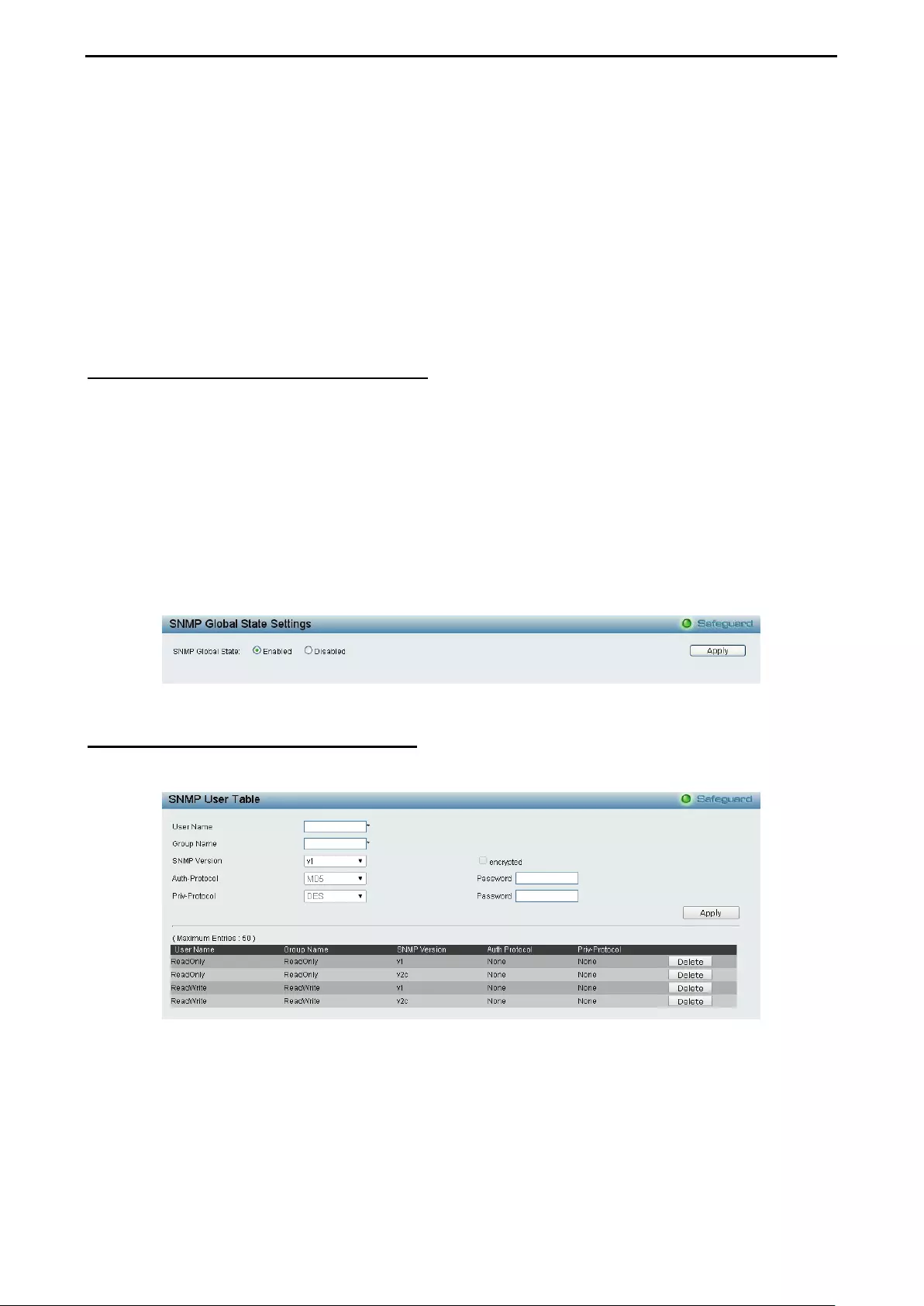
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
34
4
Neighbor IPv6 Address: Specifies the neighbor IPv6 address.
Link Layer MAC Address: Specifies the link layer MAC address.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
To search for all the current interfaces on the Switch, go to the second Interface Name field in the middle
part of the window, tick the All check box. Tick the Hardware option to display all the neighbor cache entries
which were written into the hardware table.
State: Use the drop-down menu to select All, Address, Static or Dynamic. When the user selects address
from the drop-down menu, the user will be able to enter an IP address in the space provided next to the state
option.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) protocol designed
specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to
read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to
configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the
Switch or LAN.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the
device. A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage
the device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard
presentation of the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of the
MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network.
The default SNMP global state is disabled. Select Enable and click Apply to enable the SNMP function.
Figure 4.24 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
This page is used to maintain the SNMP user table for the use of SNMPv3. SNMPv3 allows or restricts users
using the MIB OID, and also encrypts the SNMP messages sent out between users and Switch.
Figure 4.25 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
User Name: Enter a SNMP user name of up to 32 characters.
Group Name: Specify the SNMP group of the SNMP user.
SNMP Version: Specify the SNMP version of the user. Only SNMPv3 encrypts the messages.
Encrypt: Specifies the Encrypt is enabled or disabled when the SNMP Version is V3.
Auth-Protocol/Password: Specify either HMAC-MD5-96 or HMAC-SHA to be the authentication protocol.
Enter a password for SNMPv3 encryption in the right column.
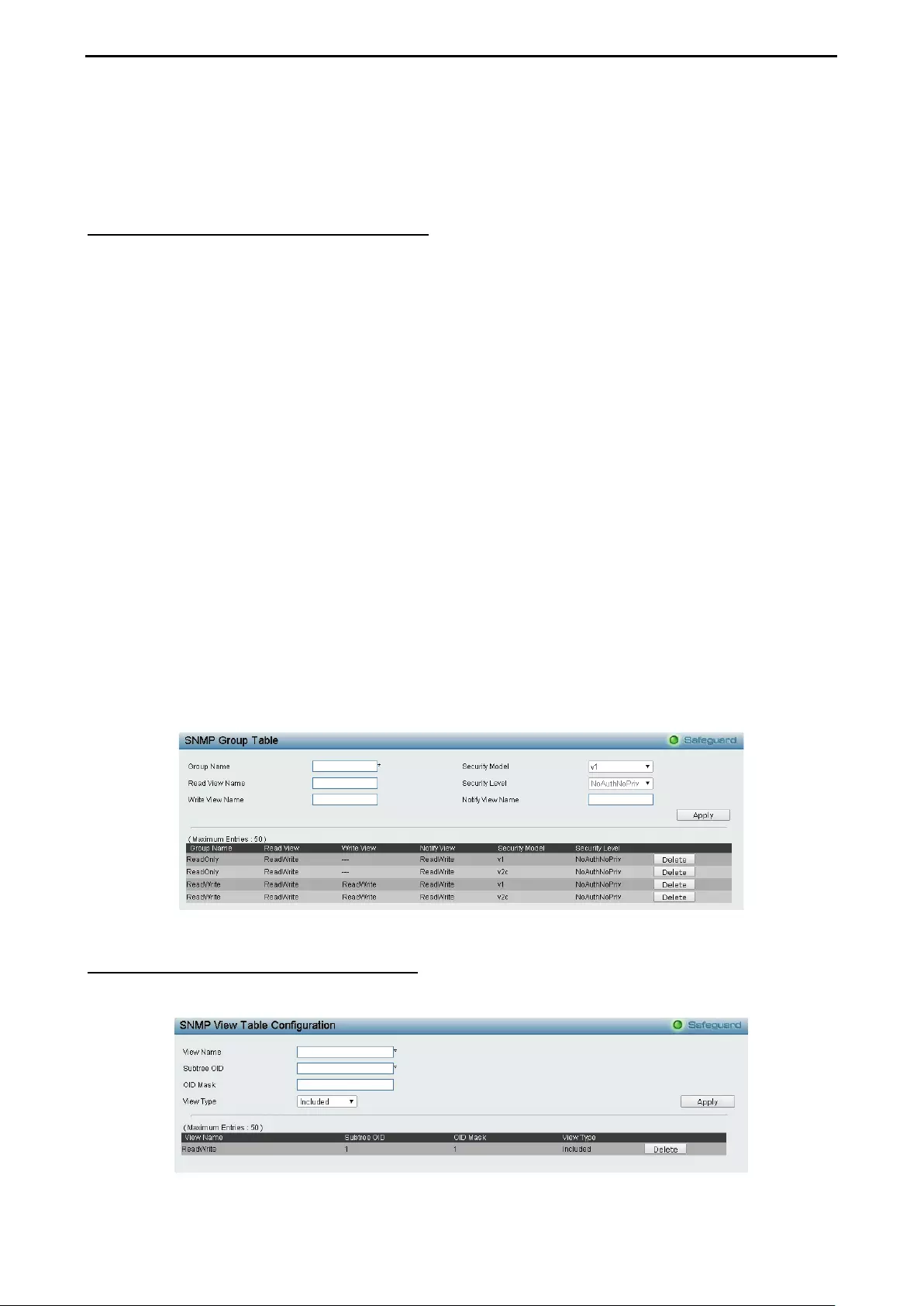
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
35
5
Priv-Protocol/Password: Specify either no authorization or DES 56-bit encryption and then enter a
password for SNMPv3 encryption in the right column.
Click Apply to create a new SNMP user account, and click Delete to remove any existing data.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
This page is used to maintain the SNMP Group Table associating to the users in SNMP User Table.
SNMPv3 can control MIB access policy, security policy for a user group directly.
Group Name: Specify the SNMP user group of up to 32 characters.
Read View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that are allowed SNMP read privileges to the
Switch's SNMP agent.
Write View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that are allowed SNMP write privileges to the
Switch's SNMP agent.
Security Model: Select the SNMP security model.
SNMPv1 - SNMPv1 does not support the security features.
SNMPv2 - SNMPv2 supports both centralized and distributed network management strategies. It
includes improvements in the Structure of Management Information (SMI) and adds some security
features.
SNMPv3 - SNMPv3 provides secure access to devices through a combination of authentication and
encrypting packets over the network.
Security Level: This function is only available when user select SNMPv3 security level.
NoAuthNoPriv - No authorization and no encryption for packets sent between the Switch and SNMP
manager.
AuthNoPriv - Authorization is required, but no encryption for packets sent between the Switch and
SNMP manager.
AuthPriv – Both authorization and encryption are required for packets sent between the Switch and
SNMP manger.
Notify View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that can receive SNMP trap messages generated
by the Switch's SNMP agent.
Figure 4.26– System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
This page allows user to maintain SNMP views to community strings that define the MIB objects which can
be accessed by a remote SNMP manager.
Figure 4.27 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
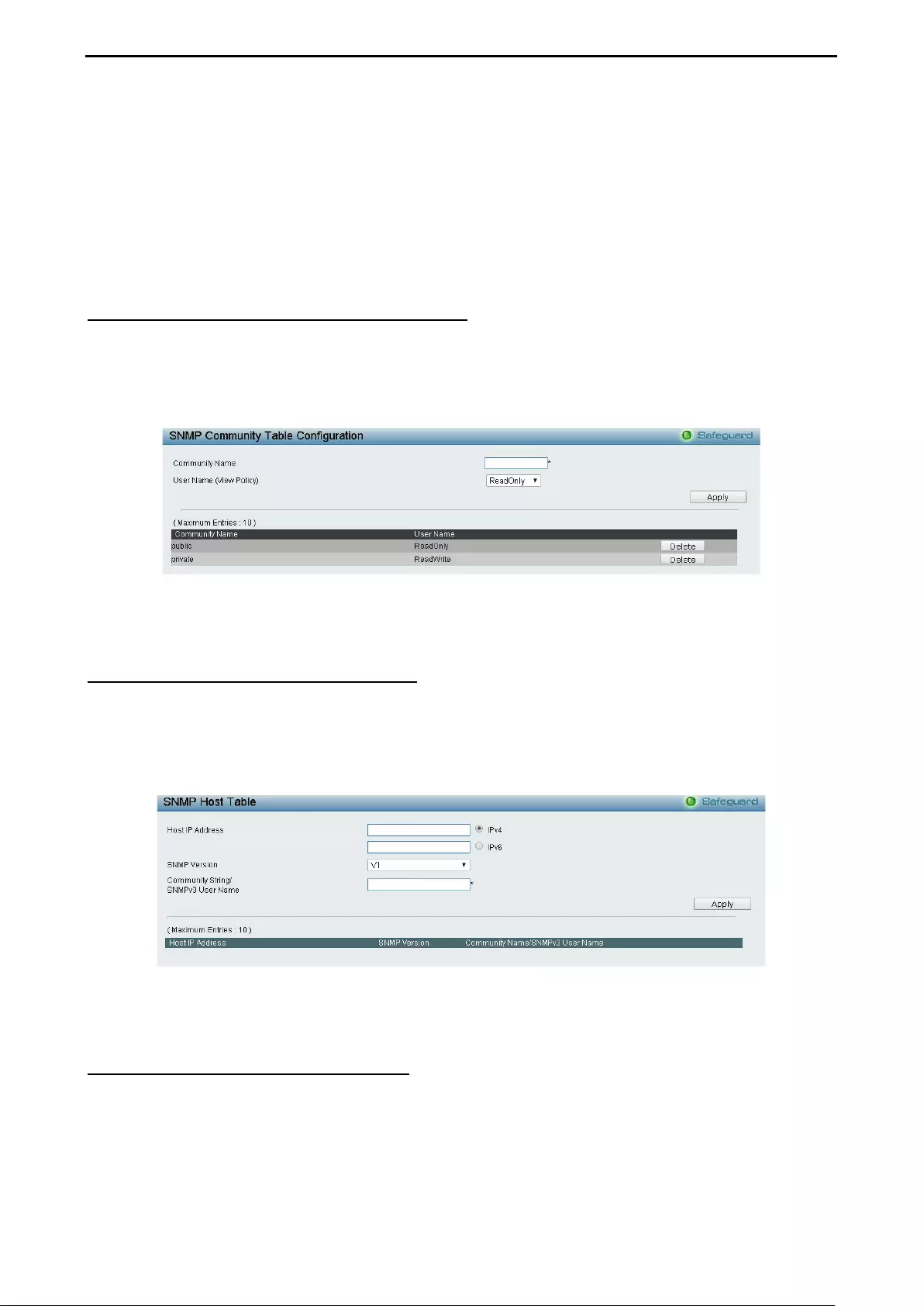
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
36
6
View Name: Name of the view, up to 32 characters.
Subtree OID: The Object Identifier (OID) Subtree for the view. The OID identifies an object tree (MIB tree)
that will be included or excluded from access by an SNMP manager.
OID Mask: The mask of the Subtree OID. 1 means this object number is concerned, 0 means do not
concerned. For example 1.3.6.1.2.1.1 with mask 1.1.1.1.1.1.0 means 1.3.6.1.2.1.X.
View Type: Specify the configured OID is Included or Excluded that a SNMP manager can access.
Click Apply to create a new view, Delete to remove an existing view.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
This page is used to maintain the SNMP community string of the SNMP managers using the same
community string are permitted to gain access to the Switch's SNMP agent.
Community Name: Name of the community string
User Name (View Policy): Specify the read/write or read-only level permission for the MIB objects
accessible to the SNMP community.
Figure 4.28 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
Click Apply to create a new SNMP community, Delete to remove an existing community.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table
This page is to configure the SNMP trap recipients.
Host IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and specify the IP address of SNMP management host.
SNMP Version: Specify the SNMP version to be used to the management host.
Community String/SNMPv3 User Name: Specify the community string or SNMPv3 user name for the
management host.
Figure 4.29– System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table
Click Apply to create a new SNMP host, Delete to remove an existing host.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID
The Engine ID is a unique identifier used to identify the SNMPv3 engine on the Switch.
Input the Engine ID then click Apply to apply the changes and click Default resets to default value.
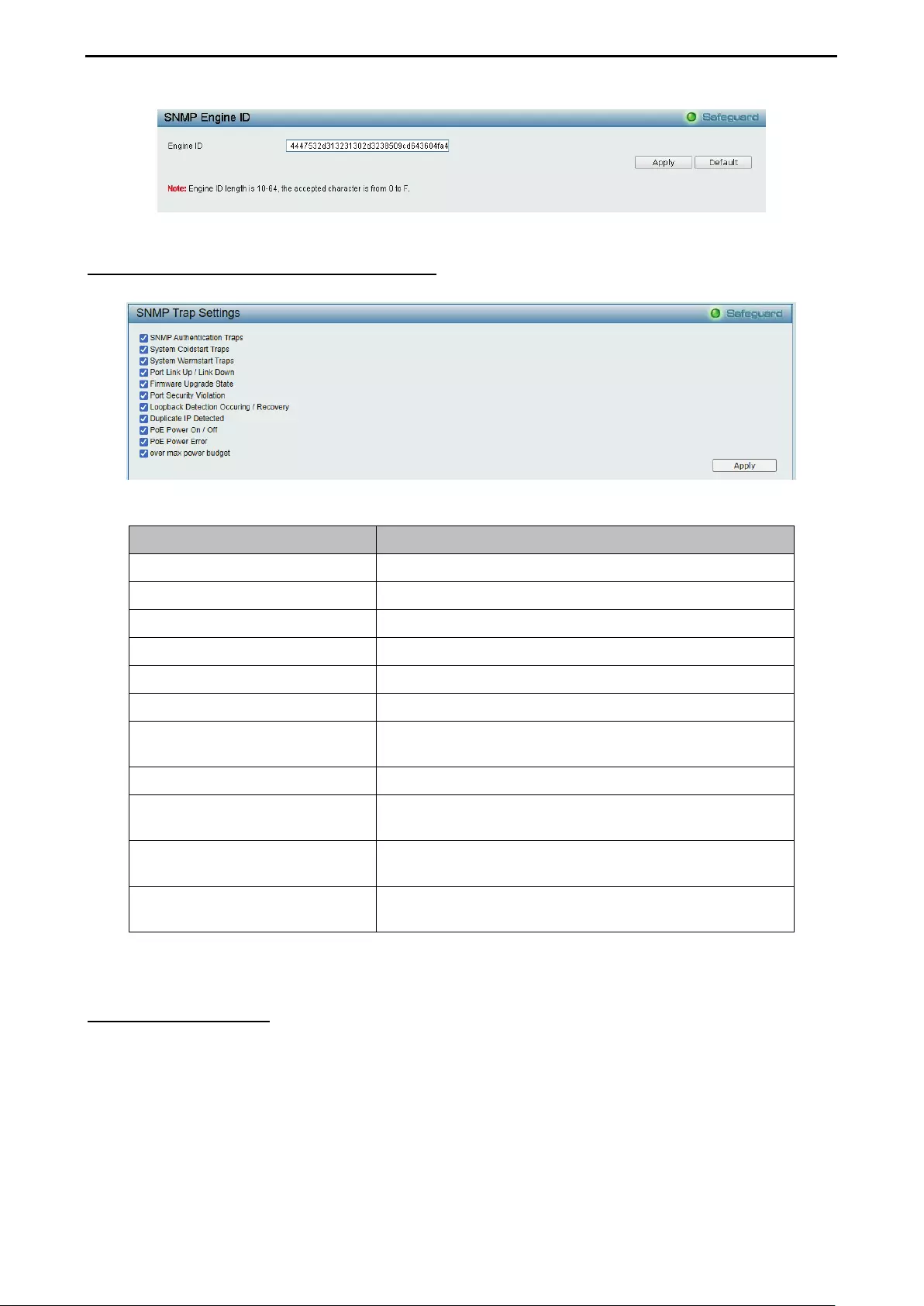
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
37
7
Figure 4.30 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings
The SNMP Trap Settings page provide user to Specify whether the device can send SNMP notifications.
Figure 4.31 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings
Type Description
SNMP Authentication Traps Trap event of authentication failure.
System Coldstart Traps Trap event of device cold boot up.
System Warmstart Traps Trap event of device warn boot up.
Port Link Up / Link Down Trap event of link state changes (link down/link up).
Firmware Upgrade State Trap event of firmware upgrade status (success/failure).
Port Security Violation Trap event of violations for port security.
Loopback Detection occuring /
recovery
Trap events of state changes (detected/recovery) for
loopback detection.
Duplicate IP Detected Trap event when duplicate IP address detected.
Trap notification if PoE Power
On / Off
Trap event of PoE powering state in port basis.
Trap notification if PoE Power
Error
Trap event of PoE error.
Trap notification if over max
power budget
Trap event when device supplies power over
the max
power budget.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > User Accounts
The User Accounts page provides user to control user privileges. To add a new user by typing in a User
Name, Password and retype the same password in the Confirm Password and choose the level of
privilege (Admin, Operator, or User) from the Access Right drop-down menu, then click the Apply button.
User can modify existing user account in the User Account Table. To change the password, type in the Old
Password, New Password and retype it in the Confirm New Password entry field and select the Encrypt,
then click the Edit button. To delete the user account, click on the Delete button.
Also, the Password Encryption mechanism offer encryption of account password in config file.
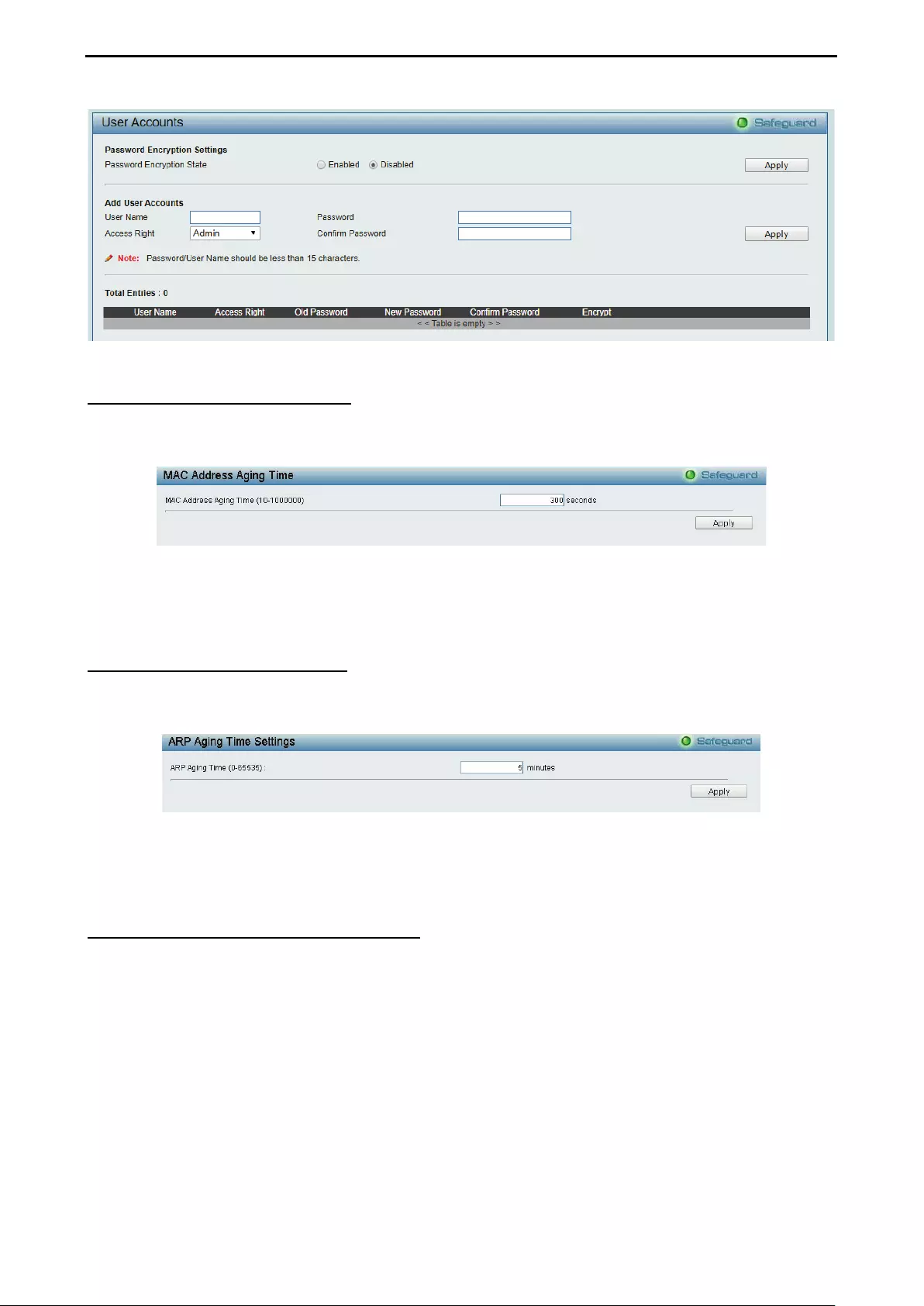
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
38
8
Figure 4.32– System > User Accounts
System > MAC Address Aging Time
The MAC Address Aging Time page specifies the length of time a learned MAC Address will remain in the
forwarding table without being accessed (that is, how long a learned MAC address is allowed to remain idle).
To change this, type in a different value representing the MAC address age-out time in seconds.
Figure 4.33 – System > MAC Address Aging Time
MAC Address Aging Time (10-1000000): Specifies the aging time of MAC address on the Switch. The
range is from 10 to 1000000, and the default is 300 seconds.
System > ARP Aging Time Settings
The ARP Aging Time Settings page provides user to globally set the maximum amount of time, in minutes,
and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entry can remain in the Switch’s ARP table, without being accessed,
before it is dropped from the table.
Figure 4.34 – System > ARP Aging Time Settings
ARP Aging Time (0-65535): Specifies the ARP aging time on the Switch. The range is from 0 to 65535 with
a default setting of 5 minutes.
System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings
The PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings page specifies the configuration of settings. When enabled, the
system will insert the circuit tag to the received PPPoE discover request and the request packet if the tag is
absent. It will remove the circuit ID tag from the received PPPoE offer and session confirmation packet.
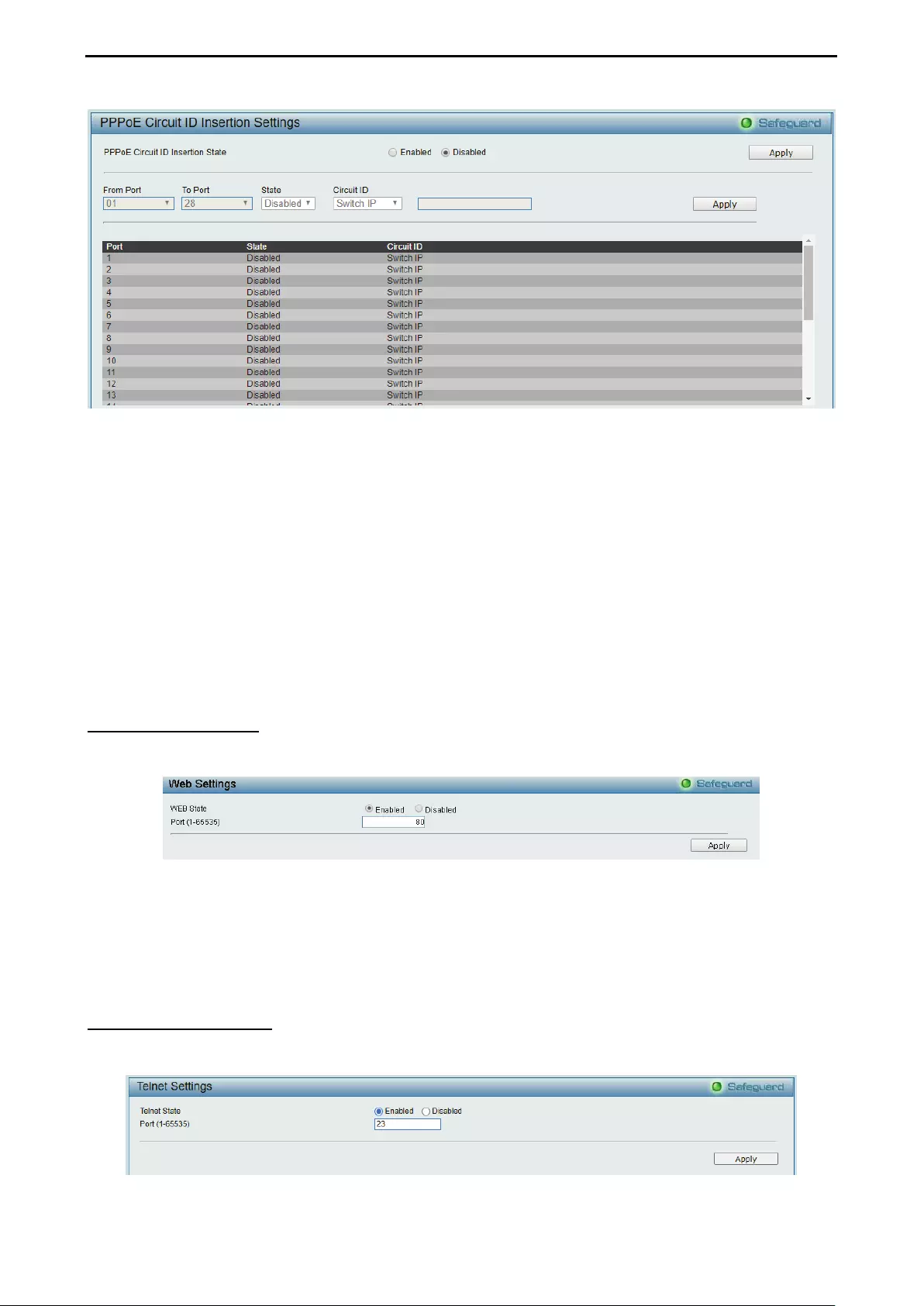
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
3
39
9
Figure 4.35 – System > PPPoE Circult ID Insertion Settings
PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion State: Enable or disable the PPPoE circuit insertion state, and Click Apply to
make the configurations take effect.
From Port/ To Port: Specifies the ports to be configured.
State: Enable or disable the state of specified ports.
Circuit ID: Specifies the Circuit ID is Switch IP, Switch MAC, UDF String, Vendor2 and Vendor3.
Switch IP – The Switch’s IP address will be used to encode the circuit ID option. This is the default.
Switch MAC – The MAC address of the Switch will be used to encode the circuit ID option.
UDF String – A user specified string to be used to encode the circuit ID option. Enter a string with
the maximum length of 32.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > Web Settings
The WEB State is Enabled by default. If user chooses to disable this by selecting Disabled, user will lose the
ability to configure the system through the web interface as soon as these settings are applied.
Figure 4.36 – System > Web Settings
Port (1-65535): Specifies the Port number. The range is between 1 and 65535 with the well-known default is
80.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > Telnet Settings
Telnet configuration is Enabled by default. If user does not want to allow the Telnet configuration, they only
need to disable the Telnet State.
Figure 4.37 – System > Telnet Settings
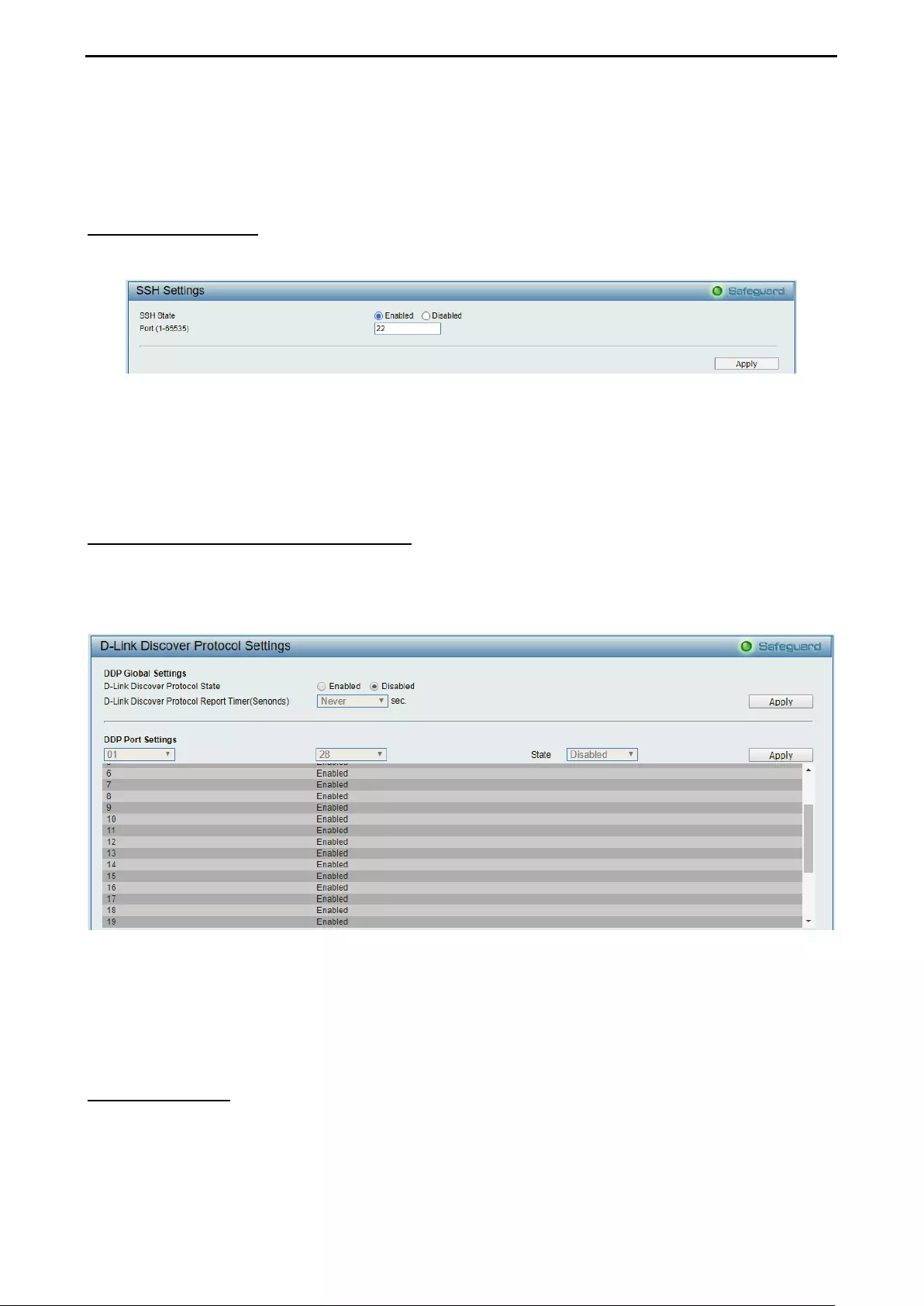
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
40
0
Port (1-65535): The TCP port number. TCP ports are numbered between 1 and 65535. The well-known TCP
port for the Telnet protocol is 23.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > SSH Settings
SSH configuration is Enabled by default. If user does not want to allow the SSH configuration, they only
need to disable the SSH State.
Figure 4.38 – System > SSH Settings
Port (1-65535): The TCP port number. TCP ports are numbered between 1 and 65535. The well-known TCP
port for the SSH protocol is 22.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings
For the D-Link Discovery Protocol (DDP) supported device, this page is an option for user to disable DDP or
configure the DDP packet report timer.
D-Link Discover Protocol State: The default setting is Disabled.
Figure 4.39 – System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings
D-Link Discover Protocol Report Timer (Seconds): Configure the report timer of D-Link Discover Protocol
in seconds. The values are 30, 60, 90, 120 or Never. The default is 30 seconds.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > Ping Test
The Ping Test is a small program that sends ICMP Echo packets to the IP address user specified. The
destination node then responds to or “echoes” the packets sent the Switch. This is very useful to verify
connectivity between the Switch and other nodes on the network.
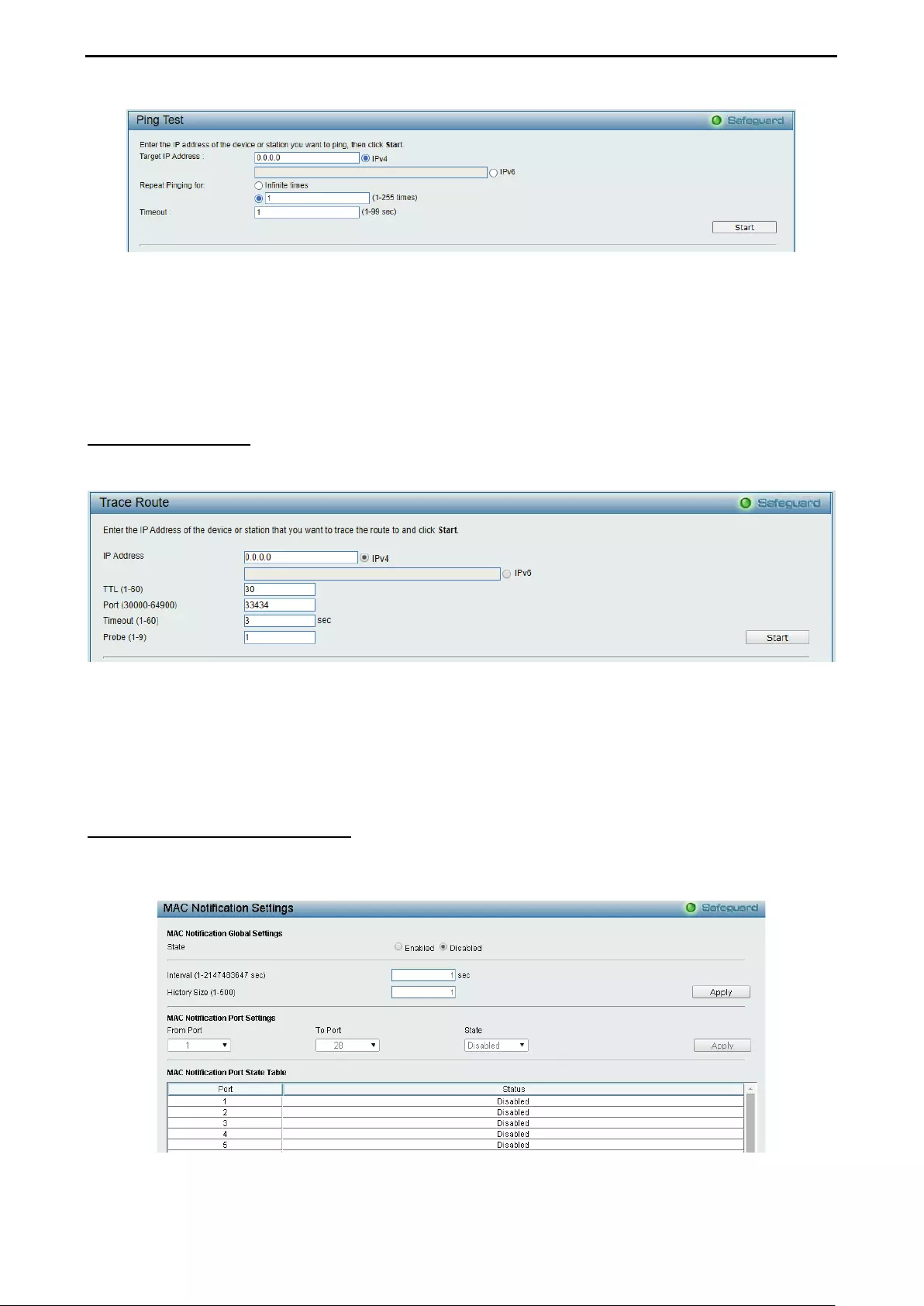
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
41
1
Figure 4.40 – System > Ping Test
Target IP address allows both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses format.
The time of ping can be configured in Repeat Pinging filed; Infinite and range of 1-255 are available options
to use.
Timeout filed specifies the timeout value of every single ping packet. The timeout range from 1- 99 seconds.
Click Start to initiate the Ping Program
System > Trace Route
Perform trace route command direct on system interface. This command used to probe path to the specific
destination address.
Figure 4.41 – System > Trace Route
IP address: Specify the destination IP address
TTL: Specify the maximum Time-to-Live
Timeout: Specify the maximum time for response in a hop.
Probe: Specify the time to probe the destination.
System > MAC Notification Settings
MAC Notification page is used to monitor MAC addresses learned and entered into the forwarding database.
To globally set MAC notification on the Switch, user should enabled or disabled state, input the Time Interval
between notification and History Size then click the Apply button.
Figure 4.42 – System > MAC Notification Settings
State: Enabled or Disabled MAC notification globally on the Switch.
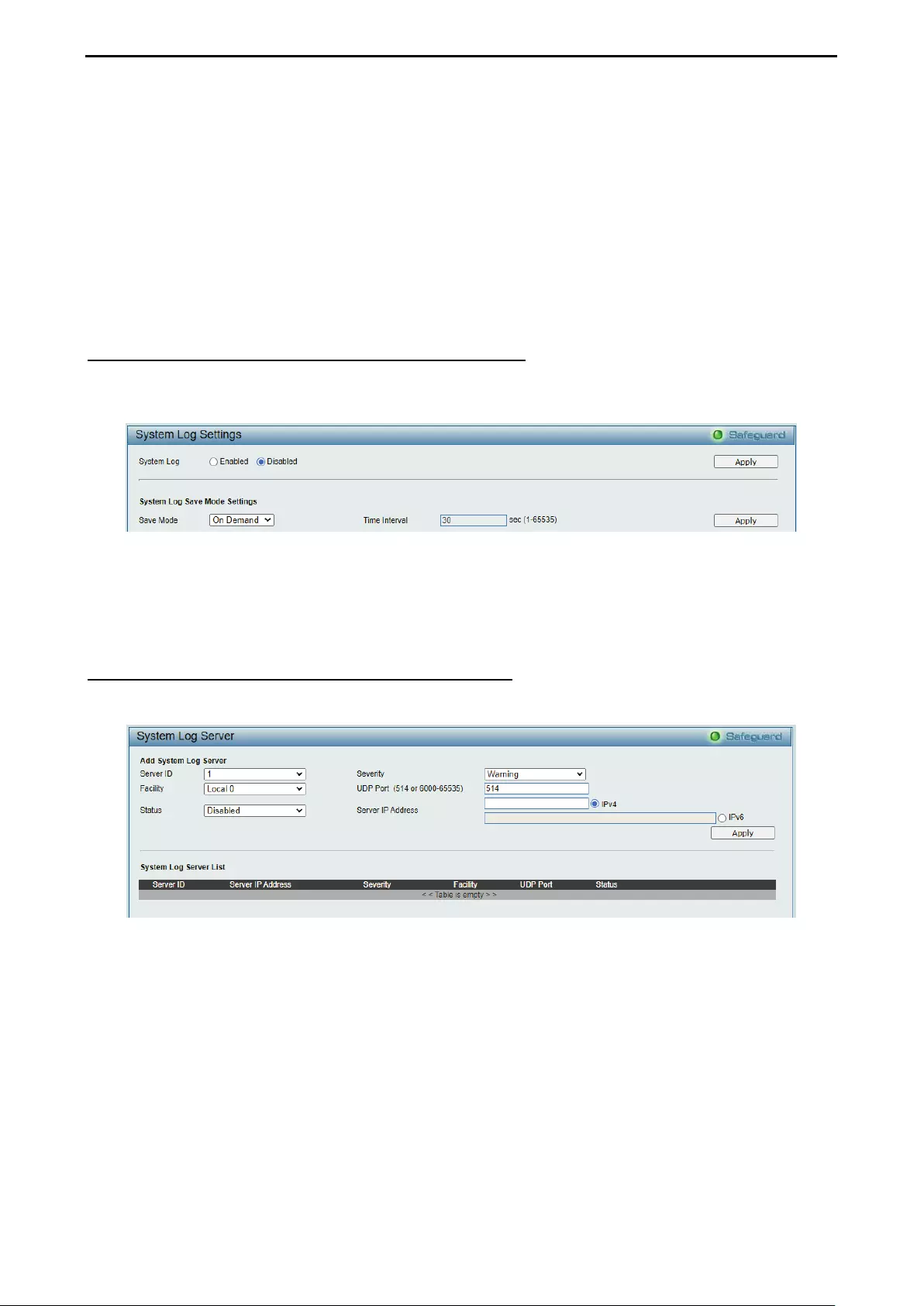
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
42
2
Interval (1-2147483647 sec): The time in seconds between notifications.
History Size (1-500): The maximum number of entries listed in the history log used for notification. Up to
500 entries can be specified.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
To change MAC notification settings for a port or group of ports on the Switch, configure the following
parameters. , then click the Apply button.
From Port / To Port: Select a port or group of ports to enable for MAC notification using the pull-down
menus.
State: Enable MAC Notification for the ports selected using the pull-down menu.
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
System Logs record and manage events, as well as report errors and informational messages. Message
severity determines a set of event message will be sent. Click Enable so user can start to configure the
related settings of remote system log server, then press Apply for the changes to take effect.
Figure 4.43 – System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
Save Mode: Use this drop-down menu to choose the method that will trigger a log entry. User can choose
between On Demand, Time Interaval and Log Trigger.
Time Interval: Enter a time interval, in seconds, for which user would like a log entry to be made.
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server
The user can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers using the System Log Server. It
supports maximum 500 system log entries. To set the System Log Server configuration, click Apply.
Figure 4.44 - System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server
Server ID: Specifies the Server ID. The field range is 1-4.
Severity: Specifies the minimum severity from which warning messages are sent to the server. There are
three levels. When a severity level is selected, all severity level choices above the selection are selected
automatically. The possible levels are:
Warning - The lowest level of a device warning. The device is functioning, but an operational
problem has occurred.
Informational - Provides device information.
All - Displays all levels of system logs.
Server IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address of the system log server.
Server IPv6 Address: Specifies the IPv6 address of the system log server.
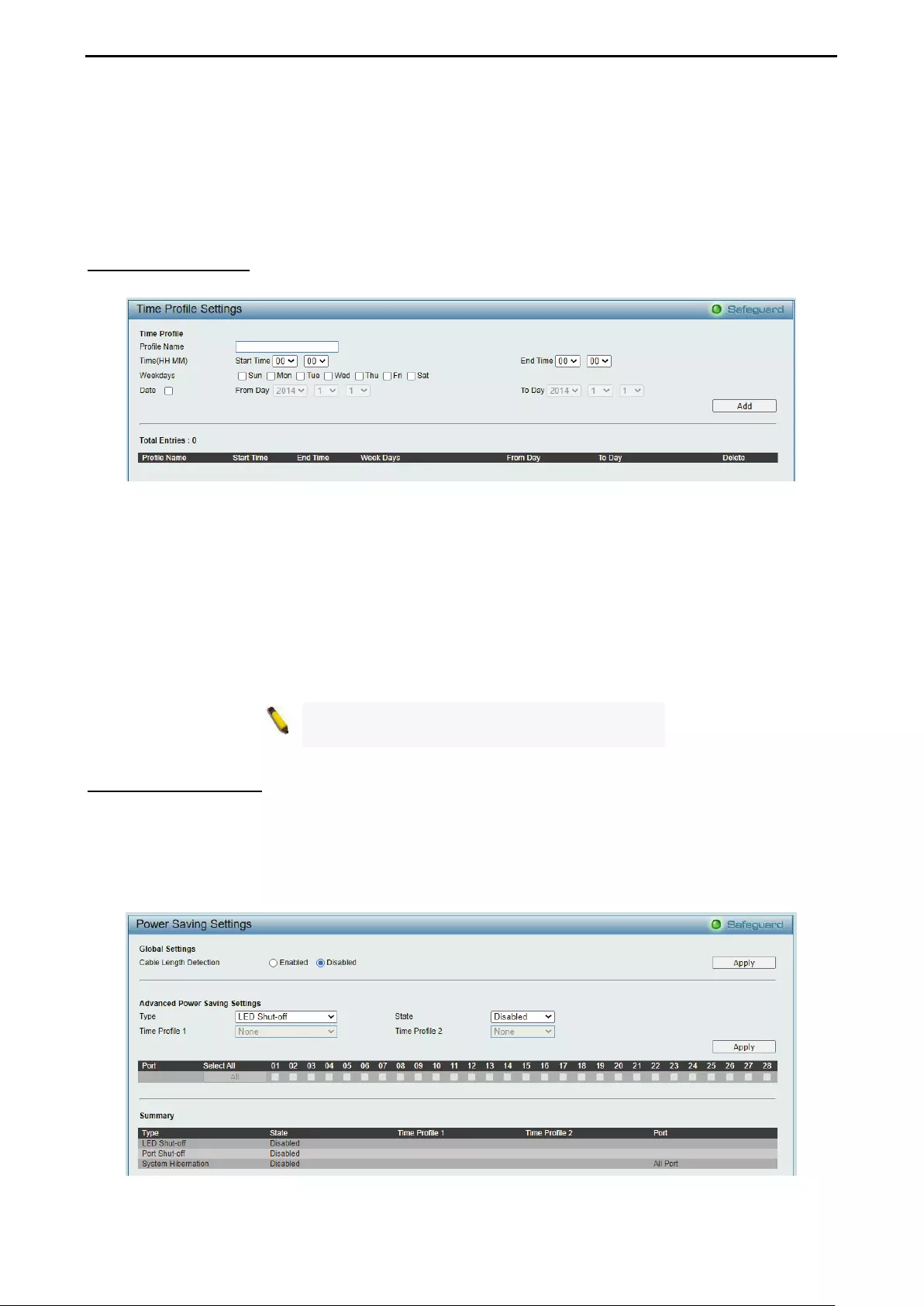
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
43
3
Facility: Specifies an application from which system logs are sent to the remote server. Only one facility can
be assigned to a single server. If a second facility level is assigned, the first facility is overwritten. There are
up to eight facilities can be assigned (Local 0 ~ Local 7).
UDP Port: Specifies the UDP port to which the server logs are sent. The possible range is 6000 – 65535,
and the default value is 514.
Status: Specifies the status is enable or disable
System > Time Profile
The Time Profile page allows users to configure the time profile settings of the device.
Figure 4.45 – System > Time Profile Settings
Range Name: Specifies the profile name for the time profile to be configured.
Date: Select Date and specifies the From Day and To Day of the time profile.
Hours (HH MM): Specifies the Start Time and End Time.
Weekdays: Specifies the work day for the time profile. Or tick Select All Days to select all days for the time
profile.
Click Apply to create a new time profile or click Delete to delete a time profile from the table.
NOTE: The time must be set after current time,
otherwise it will take effect on the next cycle time.
System > Power Saving
The Power Saving mode feature reduces power consumption automatically when the RJ-45 port is link down
or the connected devices are turned off. Less power will be consumed also when the short cable is used
(less than 20 meters).
By reducing power consumption, less heat is produced, resulting in extended product life and lower
operating costs. By default, the Cable Length Detection and Link Status Detection are enabled. Click Apply
to make the change effective.
Figure 4.46 – System > Power Saving
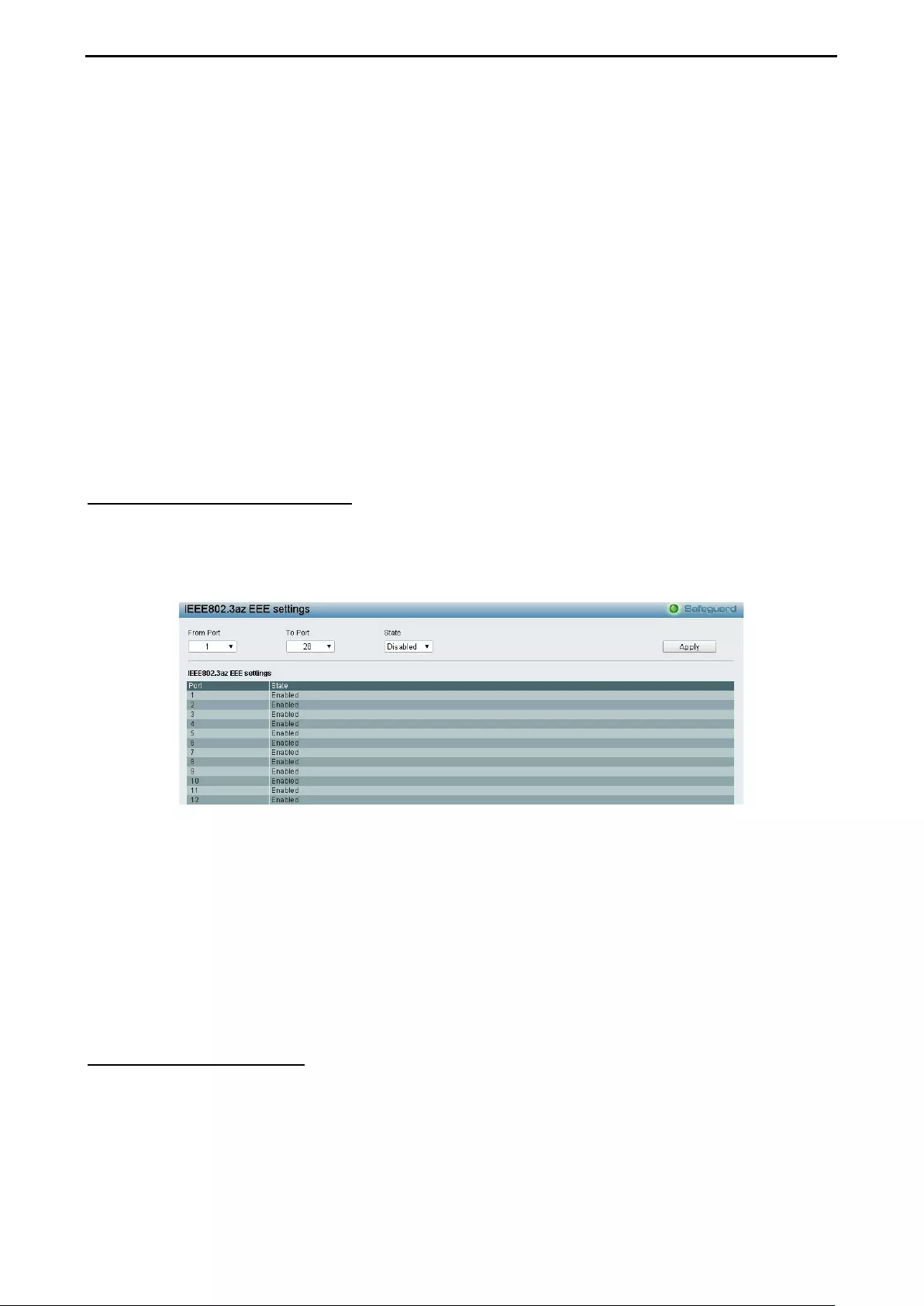
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
44
4
Advanced Power Saving Settings:
Type: Specifies the Power Saving type to be LED Shut-off, Port Shut-off, Port Standby or System
Hibernation.
LED Shut-off - The LED Shut-off gets high priority. If the user select LED Shut-off, the profile
function will not take effect. It means the LED cannot be turned on after Time Profile time’s up when
the state is disabled. On the contrary, if the LED is enabled, the Time Profile function will work.
Port Shut-off - The Port Shut-off state has high priority (the priority rule is the same as LED.)
Therefore, if the Port Shut-off sate is already disabled the Time Profile function will not take effect.
System Hibernation - In this mode, switches get most power-saving figures since main chipsets
(both MAC and PHY) are disabled for all ports, and energy required to power the CPU is minimal.
State: Specifies the power saving state to be Enabled or Disabled.
Time Profile 1: Specifies the time profile or None.
Time Profile 2: Specifies the time profile or None.
Port: Specifies the ports to be configure of the Power Saving.
Click Select All configure all ports, or click Clear to uncheck all port. Then Click Apply to make the
configurations take effect.
System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings
The IEEE 802.3 EEE standard defines mechanisms and protocols intended to reduce the energy
consumption of network links during periods of low utilization, by transitioning interfaces into a low-power
state without interrupting the network connection. The transmitted and received sides should be
IEEE802.3az EEE compliance. By default, the switch enabled the 802.3az EEE function. Users can disable
this feature by individual port via the IEEE802.3az EEE setting page.
Figure 4.47 – System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
State: Enabled or Disabled the IEEE802.3az EEE for the specified ports. By default, all ports are disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
If the connection speed drops down from 1000M to 100M, or the first link up takes longer time, please follow
below steps and check again:
1. Upgrade driver of Ethernet adapter or LAN controller for the host PC.
2. Disable EEE function on the switch port
Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they were in
the same area.
VLANs can be easily organized to reflect department groups (such as R&D, Marketing), usage groups (such
as e-mail), or multicast groups (multimedia applications such as video conferencing), and therefore help to
simplify network management by allowing users to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change
any physical connections.
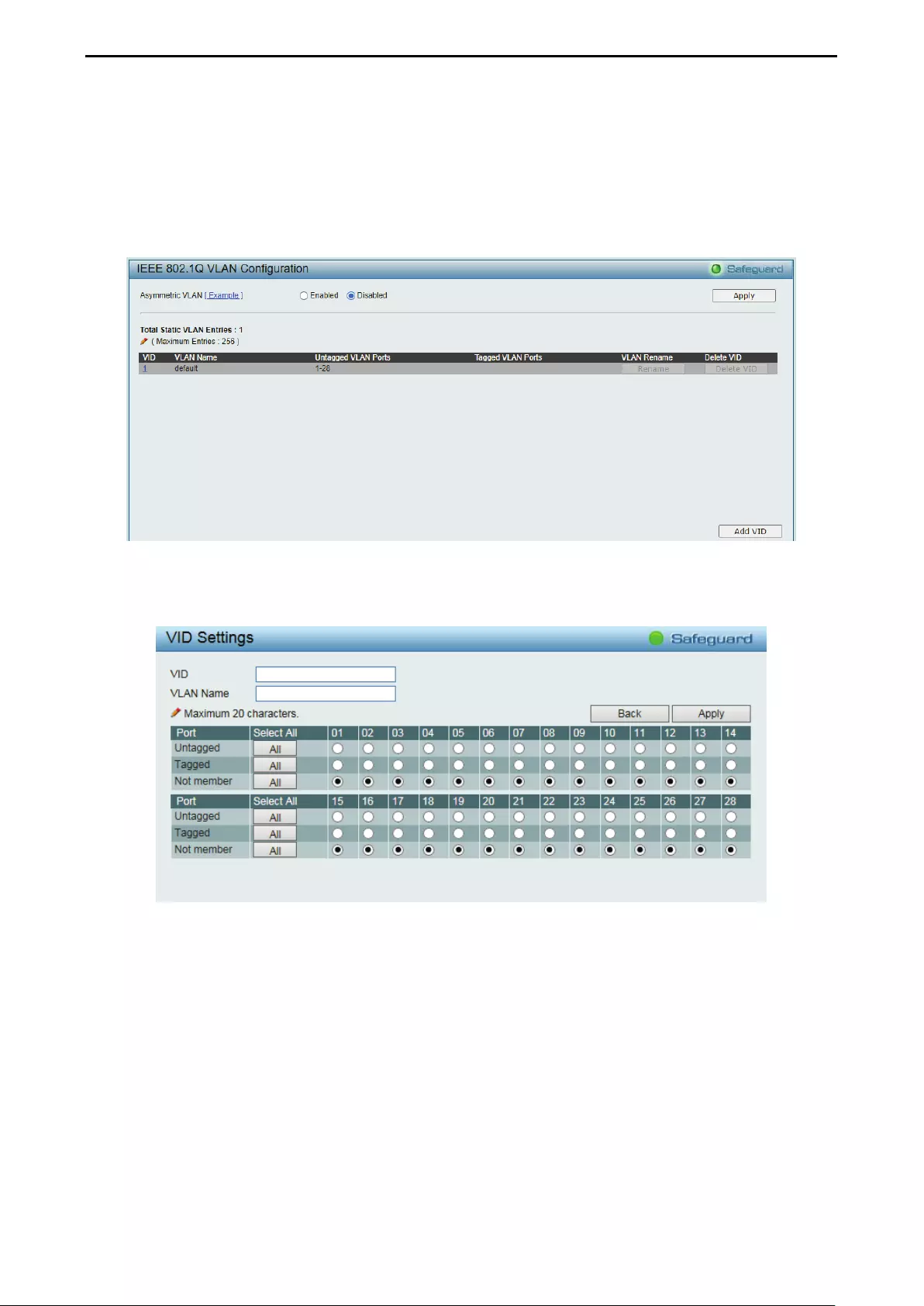
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
45
5
The IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Configuration page provides powerful VID management functions. The original
settings have the VID as 1, no default name, and all ports as “Untagged”
Rename: Click to rename the VLAN group.
Delete VID: Click to delete the VLAN group.
Add New VID: Click to create a new VID group, assigning ports from 01 to 28 as Untag, Tag, or Not
Member. A port can be untagged in only one VID. To save the VID group, click Apply.
You may change the name accordingly to the desired groups, such as R&D, Marketing, email, etc.
Figure 4.48 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
Click Add to create a new VID group, entering the VID and VLAN name, assigning ports role as Untag, Tag
or Not Member. To save the VID group, click Apply.
Figure 4.49 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Add VID
After click Apply, the 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Table will displayed with updates.
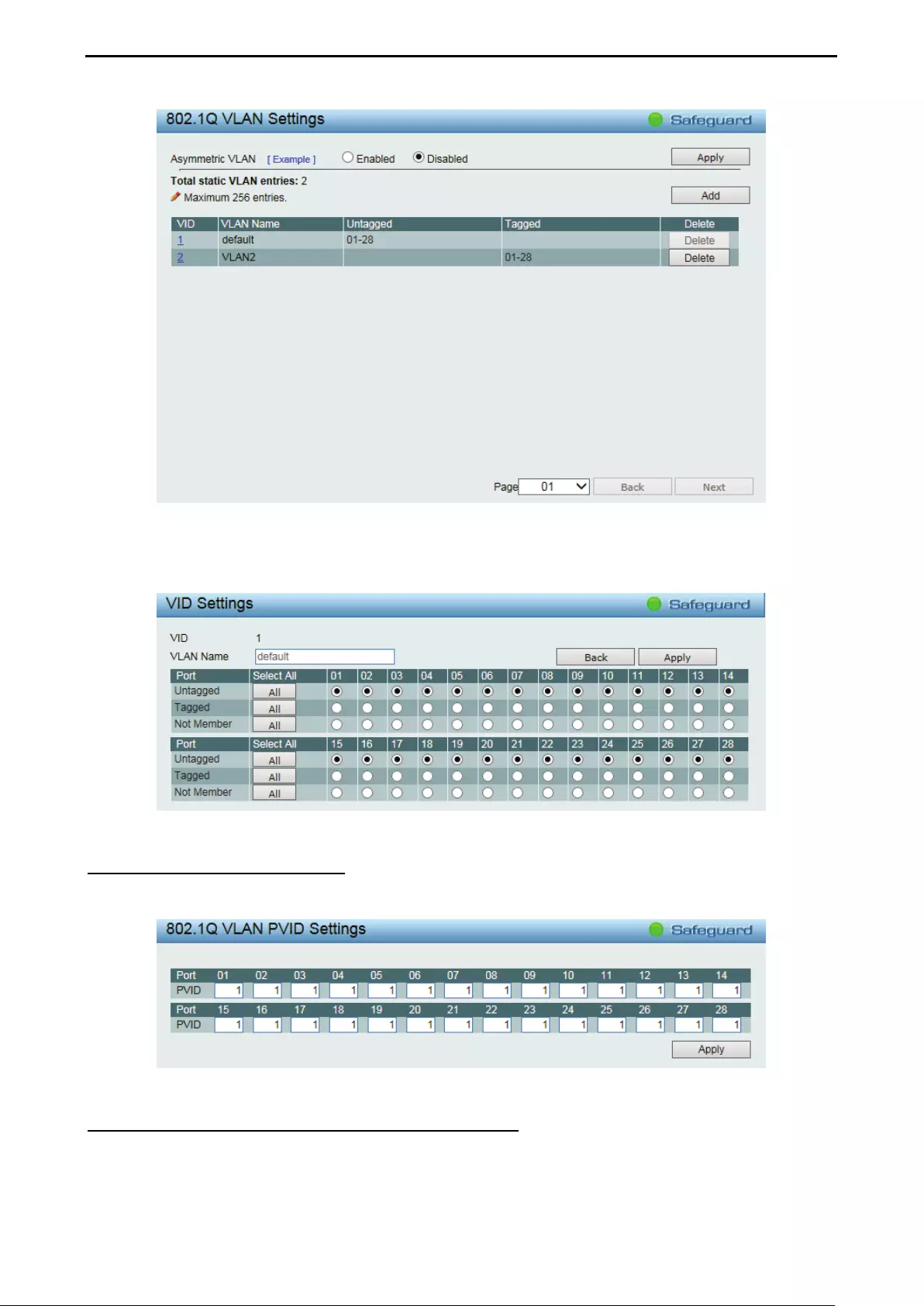
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
46
6
Figure 4.50 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Add VLAN
Click the VID number, the configuration of VLAN group which selected by user will displayed.
Change the port assignment then click Apply to implement changes made.
Figure 4.51 - Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > VID Assignments
Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN PVID
The 802.1Q VLAN PVID setting allows user to configure the PVID for each ports. Click Apply to implement
changes made.
Figure 4.52 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN PVID
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global Settings
Voice VLAN is a feature that allows you to automatically place the voice traffic from IP phone to an assigned
VLAN to enhance the VoIP service. With a higher priority and individual VLAN, the quality and the security of
VoIP traffic are guaranteed. If a VoIP packet comes with a VLAN tag, the Voice VLAN function won’t replace
the original VLAN tag.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
47
7
Figure 4.53 – VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global Settings
Voice VLAN: Select to enable or disable Voice VLAN. The default is Disabled. After you enabled Voice
VLAN, you can configure the Voice VLAN Global Settings.
VLAN ID: The ID of VLAN that user wants to assign voice traffic to. 802.1Q VLAN group must be created
before assigned it into Voice VLAN. The member port that configured in 802.1Q VLAN setting page will be
the static member port of voice VLAN. To dynamically add ports into the voice VLAN, please enable the
Auto Detection function
Priority: The 802.1p priority levels of the traffic in the Voice VLAN.
Aging Time (1-120): Enter a period of time (in hours) to remove a port from the voice VLAN if the port is an
automatic VLAN member. When the last voice device stops sending traffic and the MAC address of this
voice device is aged out, the voice VLAN aging timer will start. The port will be removed from the voice VLAN
after the expiration of the voice VLAN aging timer. Selectable range is from 1 to 120 hours, and default is 1.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Voice VLAN OUI Settings: This allows the user to configure the user-defined voice traffic’s OUI. An
Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) is the first three bytes of the MAC address. This identifier uniquely
identifies a vendor, manufacturer, or other organization.
There are some pre-defined OUIs and when the user configures personal OUI, these pre-defined OUIs must
be avoided. Below are the pre-defined voice traffic’s OUI:
OUI Vendor Mnemonic Name
00:E0:BB 3Com 3com
00:03:6B Cisco cisco
00:E0:75 Veritel veritel
00:D0:1E Pingtel pingtel
00:01:E3 Siemens siemens
00:60:B9 NEC/ Philips nec&philips
00:0F:E2 Huawei-3COM huawei&3com
00:09:6E Avaya avaya
Default OUI: Pre-defined OUI values, including brand names of 3COM, Cisco, Veritel, Pingtel, Siemens,
NEC/Philips, Huawei3COM, and Avaya.
User defined OUI: It is able to manually create a Telephony OUI with a description. The maximum number
of user defined OUIs is 10.
Select the OUI and press Add to the lower table to complete the Auto Voice VLAN setting.
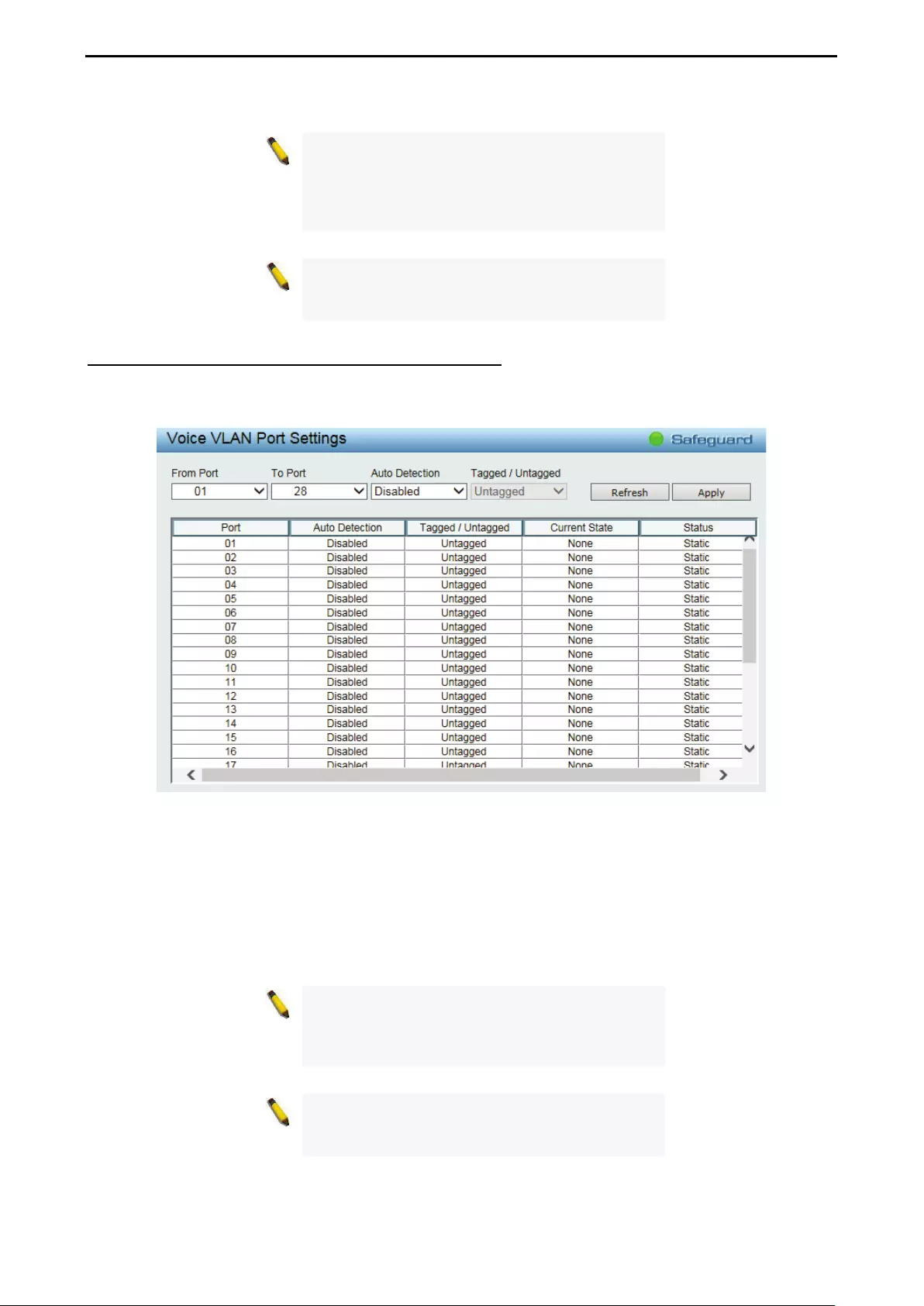
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
48
8
Note: Voice VLAN has higher priority than any
other features (including QoS). Therefore the
voice traffic will be operated according to the
Voice VLAN setting and not impacted by the QoS
feature.
Note: It is recommended
setting the highest
priority for Voice VLAN to guarantee the quality of
VoIP traffic.
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port Settings
The Voice VLAN Port Settings page allows users to automatically place the voice traffic from IP phone to an
assigned VLAN to enhance the VoIP service. With a higher priority and individual VLAN, the quality and the
security of VoIP traffic are guaranteed.
Figure 4.54 – VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port Settings
From Port / To Port: A consecutive ports may be selected by From Port and To Port dropdown lists.
Auto Detection: Switch will add ports to the voice VLAN automatically if it detects the device OUI matches
the Telephony OUI configured in Voice VLAN OUI Setting page. Use the drop-down menu to enable or
disable the OUI auto detection function. The default is Disabled
Tagged / Untagged: Tagged or untagged the ports.
Click Apply to implement changes made and Refresh to refresh the voice vlan table.
Note:
Voice VLAN has higher priority than any
other features even QoS. Therefore the voice
traffic will be operated according to Voice VLAN
setting and not impacted by QoS feature.
Note:
It is recommended setting the highest
priority for Voice VLAN to guarantee the quality of
VoIP traffic.
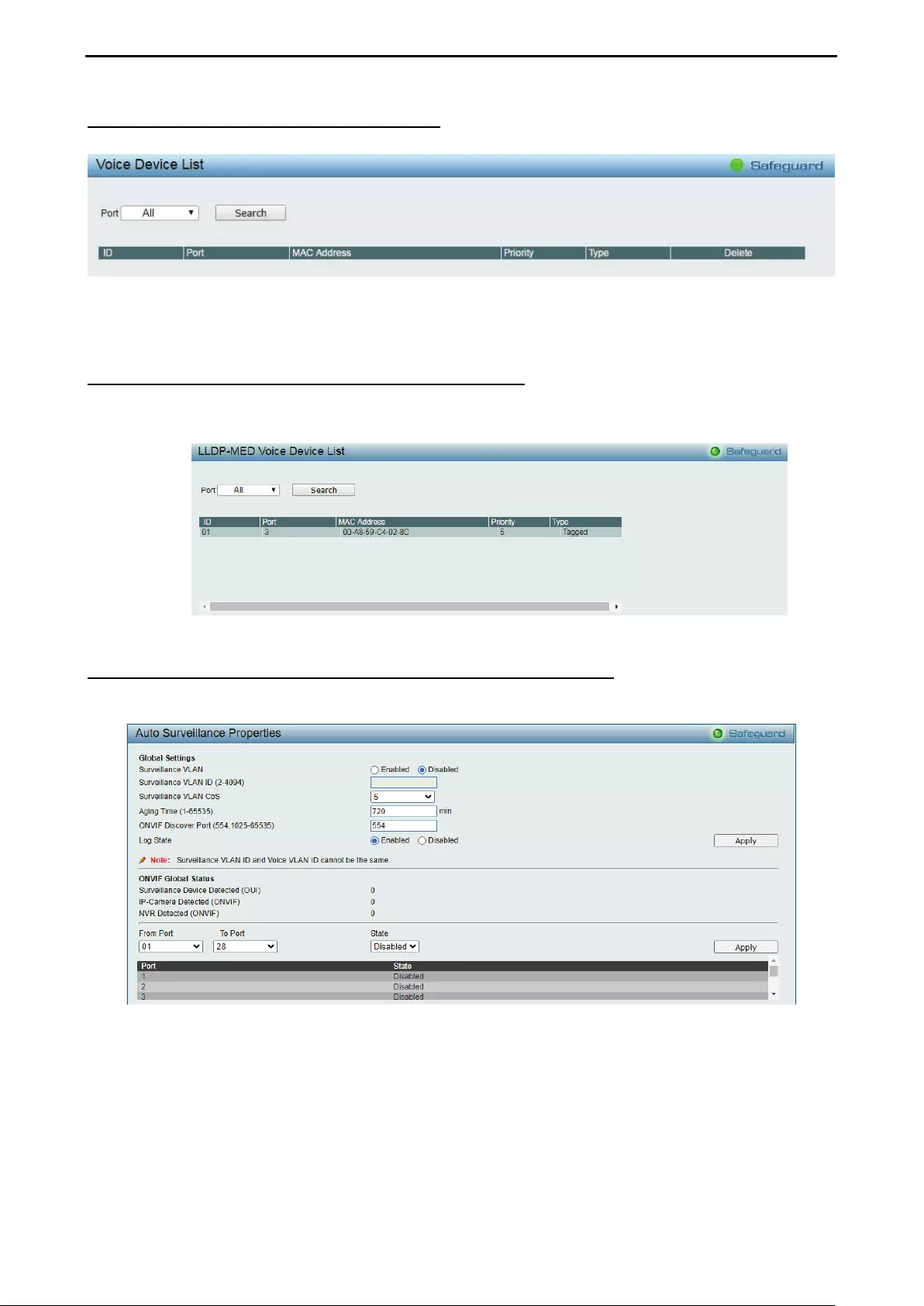
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
4
49
9
Configuration > Voice VLAN > Voice Device List
The Voice Device List page displays the information of Voice VLAN.
Figure 4.55 – VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice Device List
Select a port or all ports and click Search to display the Voice Device information in the table.
Configuration > Voice VLAN > LLDE-MED Voice Device List
The Voice Device List page displays the information of voice device learned from LLDP-MED protocol. The
device information is retrieved from Network Policy contained in LLDP-MED packets.
Figure 4.56 - Configuration > Voice VLAN > LLDP-MED Voice Device List
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto Surveillance Properties
The Auto Surveillance Properties page allows user to configure and display the ports surveillance VLAN
settings and information.
Figure 4.57 – VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > Auto Surveillance Properties
Global Settings: To configure the related auto surveillance VLAN global settings.
Auto Surveillance VLAN: To enable or disable the auto surveillance VLAN state.
Surveillance VLAN ID: Specifies the surveillance VLAN ID. The range is from 2 to 4094.
Surveillance VLAN CoS: Specifies the priority of the surveillance VLAN. The range is from 0 to 7.
Tagged Uplink/Downlink Port: Specifies the port or ports to be tagged uplink port or downlink port for the
Auto Surveillance VLAN.
Aging Time (1-65535): Specifies the aging time of surveillance VLAN. The range is from 1 to 65535 minutes.
The default value is 720 minutes. The aging time is used to remove a port from surveillance VLAN if the port
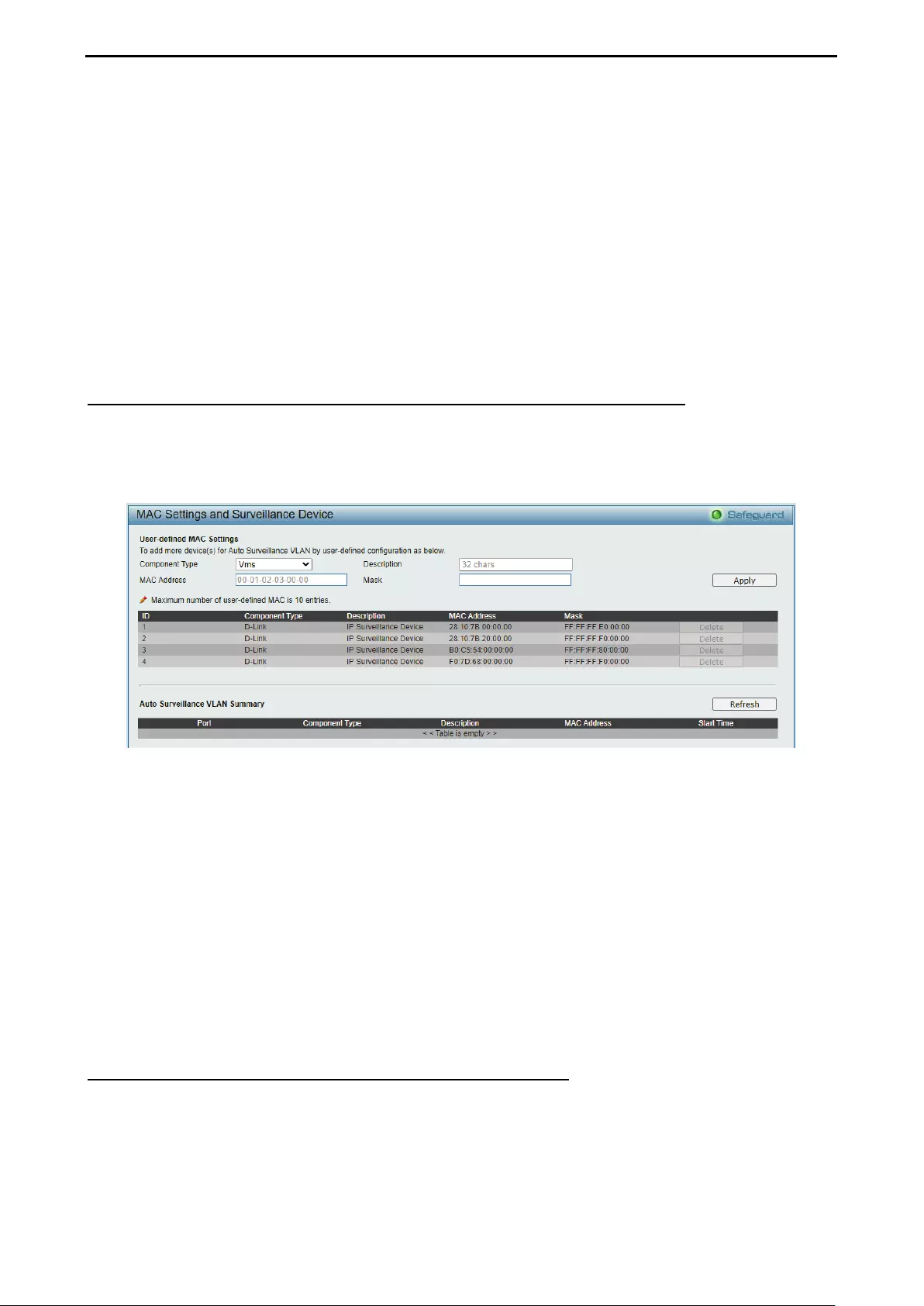
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
50
0
is an automatic surveillance VLAN member. When the last surveillance device stops sending traffic and the
MAC address of this surveillance device is aged out, the surveillance VLAN aging timer will be started. The
port will be removed from the surveillance VLAN after expiration of surveillance VLAN aging timer. If the
surveillance traffic resumes during the aging time, the aging timer will be reset and stop.
Discover Port (554, 1024-65535): Specifies the TCP/UDP port number for surveillance VLAN. The range is
either 554, or between 1024 and 65535. This is used to configure the TCP/UDP port number for RTSP
stream snooping. ONVIF-capable IPC and ONVIF-capable NVR utilize WS-Discovery to find other devices.
Once IPCs are discovered, the Switch can further discover NVRs by snooping RTSP, HTTP, and HTTPS
packets between NVRs and IPCs. These packets cannot be snooped if the TCP/UDP port is not equal to the
RTSP port number.
Log State: To enable or disable the log state of surveillance VLAN.
Click the Apply button to implement changes made.
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC Settings and Surveillance Device
Similar as Voice VLAN, Auto Surveillance VLAN is a feature that allows you to automatically place the video
traffic from D-Link IP cameras to an assigned VLAN to enhance the IP surveillance service. With a higher
priority and individual VLAN, the quality and the security of surveillance traffic are guaranteed. The Auto
Surveillance VLAN function will check the source MAC address / VLAN ID on the incoming packets. If it
matches specified MAC address / VLAN ID, the packets will pass through switch with desired priority.
Figure 4.58 – VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > MAC Settings and Surveillance Device
User-defined MAC Settings:
Component Type: Auto Surveillance VLAN will automatically detect D-Link Surveillance Devices by default.
There are another five surveillance components that could be configured to be auto-detected by the Auto
Surveillance VLAN. These five components are Video Management Server (VMS), VMS Client/Remote
viewer, Video Encoder, Network Storage and Other IP Surveillance Devices.
Description: Here to input the description for the component type.
MAC Address: User can manually create an MAC or OUI address for the surveillance component. The
maximum number of user defined MAC address is 5.
Mask: Specifies the mask address for the MAC or OUI.
Click Add to create a new surveillance component and Refresh to refresh the Auto Surveillance VLAN
summary table.
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF IPC Information
The ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) IPC Information page displays the information on each IP
camera connected to the switch. Information includes the port number, IP address, MAC address, throughput
and other information such as port description and model name.
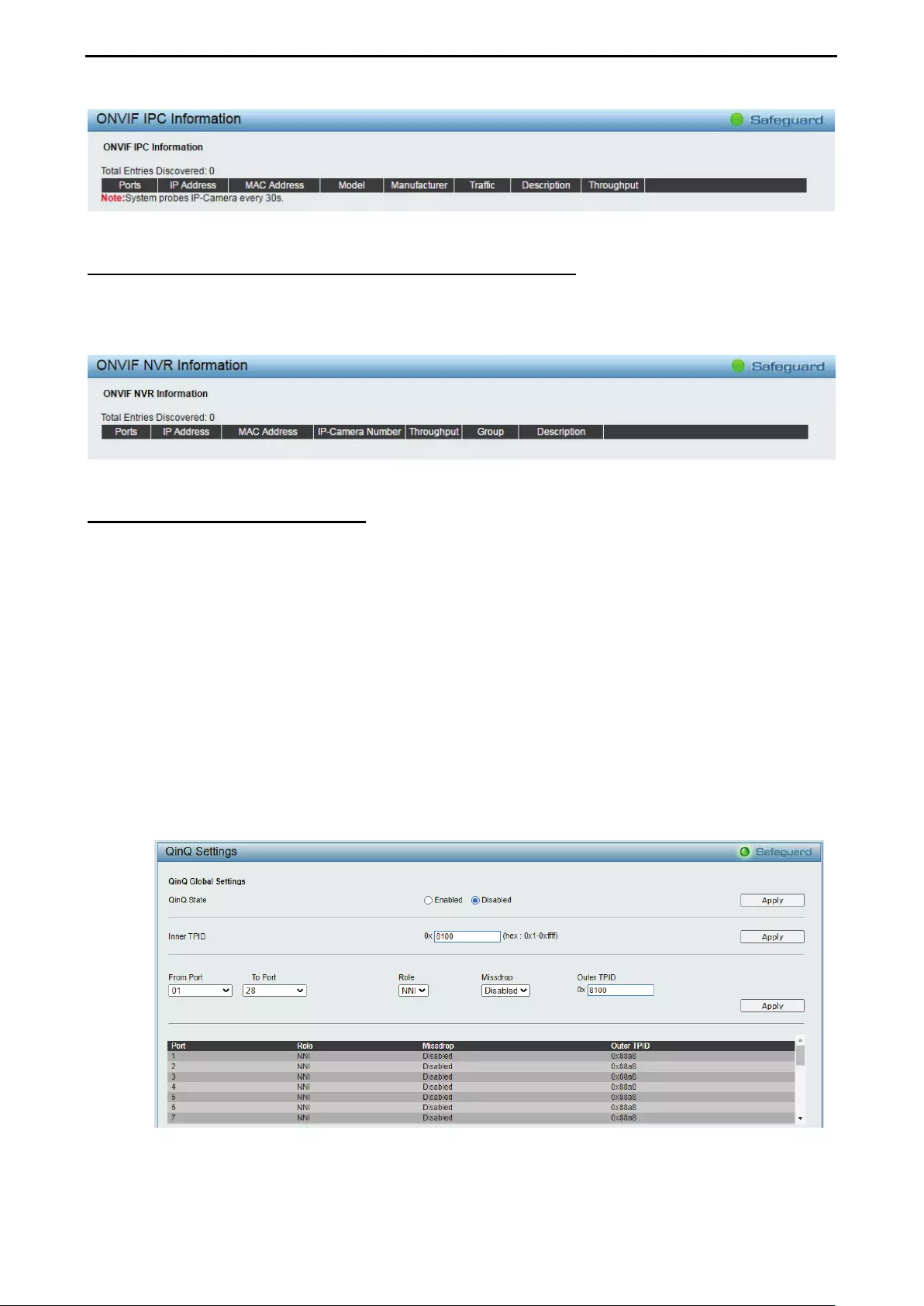
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
51
1
Figure 4.59 – VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF IPC Information
Configuration > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF NVR Information
The ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) NVR Information page displays the information on each
NVR connected to the switch. Including the port number, IP address, MAC address, IP-Camera number,
throughput and description relating to the cameras connected to the NVR, such as the group name, total
number of cameras and the port and IP address of each camera.
Figure 4.60 – VLAN > Auto Surveillance VLAN > ONVIF NVR Information
Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings
The QinQ Settings page allows user to enable or disable the Q-in-Q function. Q-in-Q is designed for service
providers to carry traffic from multiple users across a network.
Q-in-Q is used to maintain customer specific VLAN and Layer 2 protocol configurations even when the same
VLAN ID is being used by different customers. This is achieved by inserting SPVLAN tags into the
customer’s frames when they enter the service provider’s network, and then removing the tags when the
frames leave the network.
Customers of a service provider may have different or specific requirements regarding their internal VLAN
IDs and the number of VLANs that can be supported. Therefore customers in the same service provider
network may have VLAN ranges that overlap, which might cause traffic to become mixed up. So assigning a
unique range of VLAN IDs to each customer might cause restrictions on some of their configurations
requiring intense processing of VLAN mapping tables which may exceed the VLAN mapping limit. Q-in-Q
uses a single service provider VLAN (SPVLAN) for customers who have multiple VLANs. Customer’s VLAN
IDs are segregated within the service provider’s network even when they use the same customer specific
VLAN ID. Q-in-Q expands the VLAN space available while preserving the customer’s original tagged packets
and adding SPVLAN tags to each new frame. Select Enabled or Disabled then click Apply to enable or
disable the Q-in-Q Global Settings.
Figure 4.61 - Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports that are part of the VLAN configuration starting with the
selected port.
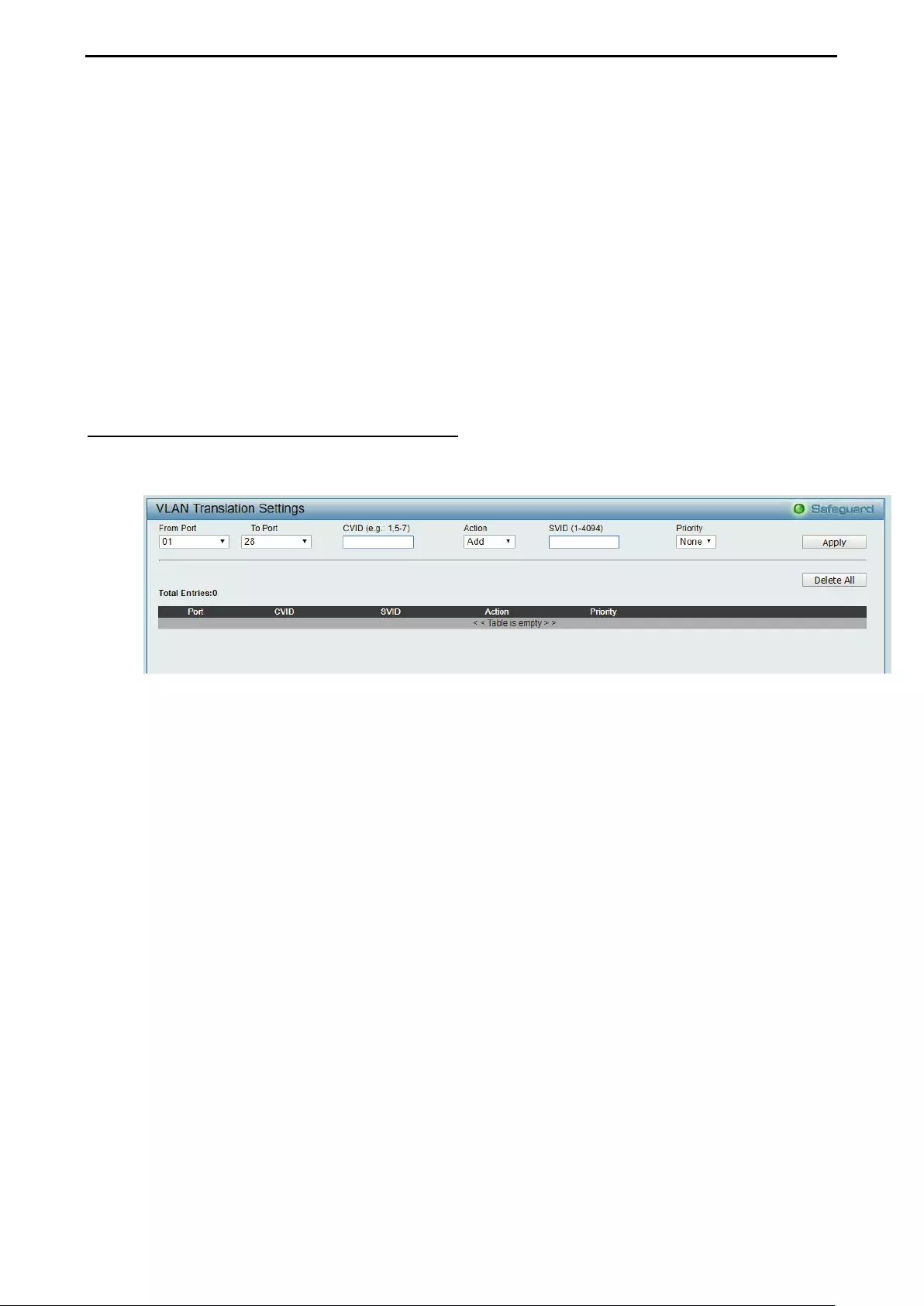
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
52
2
Role: The user can choose between UNI or NNI role.
UNI – To select a user-network interface which specifies that communication between the specified
user and a specified network will occur.
NNI – To select a network-to-network interface specifies that communication between two specified
networks will occur.
Outer TPID (hex: 0x1-0xffff): The Outer TPID is used for learning and switching packets. The Outer TPID
constructs and inserts the outer tag into the packet based on the VLAN ID and Inner Priority.
Miss Drop: Specifies to enable or disable the Miss Drop. If Miss Drop is enabled, the packet does not match
any assignment rule in the VLAN translation and Q-in-Q profile will be dropped. If disabled, the packet will be
forwarded and will be assigned to the PVID of the received port.
Add Inner Tag: Unselect the Disable check box and enter an entry that an Inner Tag will be added to the
entry.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation Settings
The VLAN Translation translates the VLAN ID carried in the data packets it receives from private networks
into those used in the Service Providers network.
Figure 4.62 - Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation Settings
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports that are part of the VLAN configuration starting with the
selected port.
Action: Specify for SPVID packets to be added or replaced.
CVID List (1-4094): The customer VLAN ID List to which the tagged packets will be added.
SVID (1-4094): This configures the VLAN to join the Service Providers VLAN as a tagged member.
Priority: Specifies the CVID entry priority.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. Click Delete All to remove all the CVID entries.
Q-in-Q and VLAN Translation Rules:
For Ingress untagged packets at UNI ports:
1. The Switch does not reference the VLAN translation table.
2. Check the Switch VLAN tables. The Sequence is MAC-based VLAN -> subnet-based VLAN ->
protocol-based VLAN -> port-based VLAN. If matched, the matched VLAN will become this packet’s
SPVLAN.
For Ingress tagged packets at UNI ports:
1. The Switch looks up the VLAN translation table. If matched, the VLAN tag will be translated
(replace CEVLAN with SPVLAN, or add SPVLAN).
2. Or, check the Switch VLAN tables. The sequence is the same as above. The matched VLAN
becomes this packet’s SPVLAN.
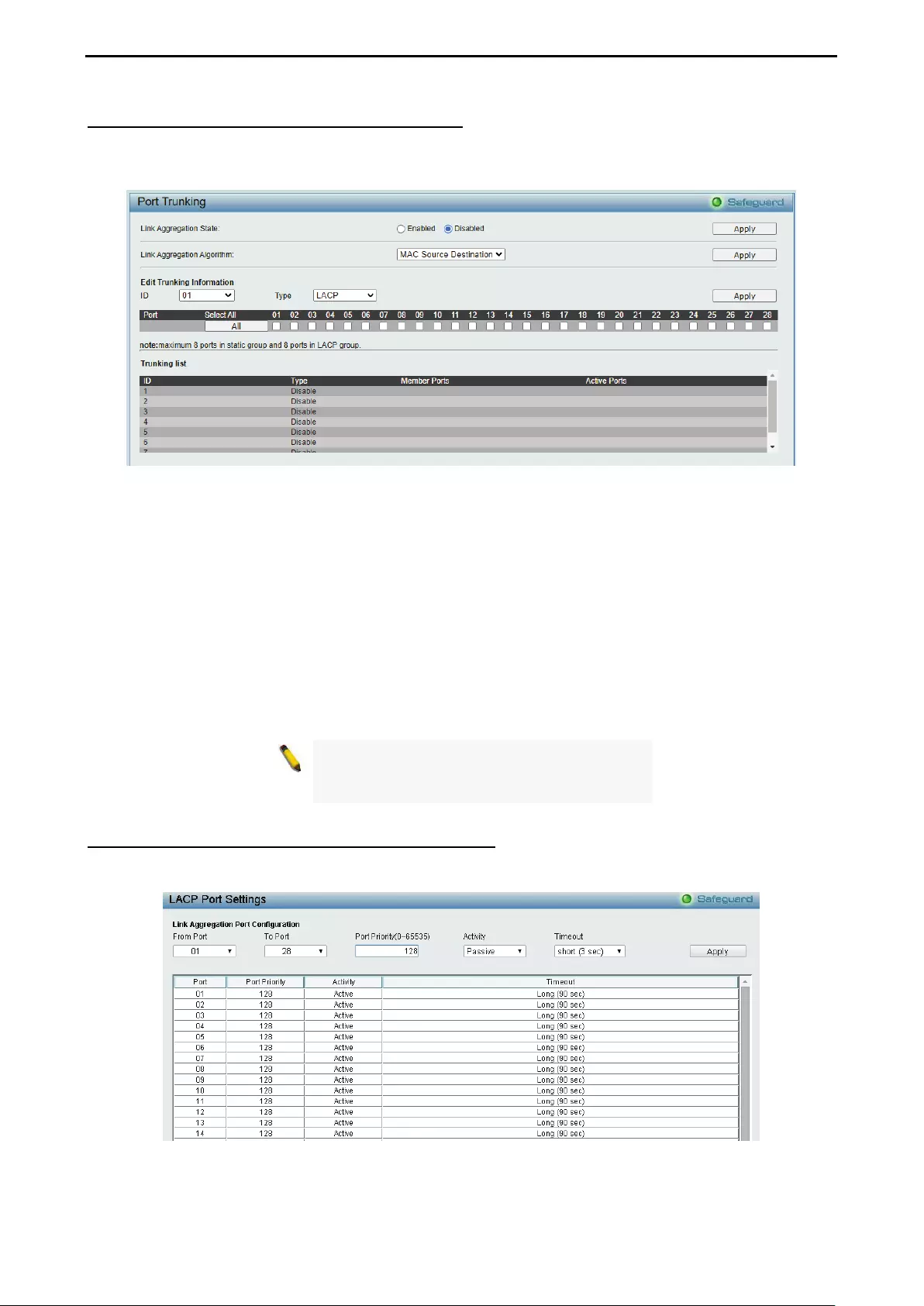
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
53
3
Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings
The Port Trunkings function enables the combining of two or more ports together to increase bandwidth. Up
to eight Trunk groups may be created, and each group consists up to eight ports. Select Enabled and click
Apply to active the Link Aggregation State.
Figure 4.63 – Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings
Link Aggregation Algorithm: Specify the algorithm to be MAC Source, MAC Destination, MAC Source
Destination, IP Source, IP Destination or IP Source Destination, and then Click Apply to make the
configurations take effect.
Edit Trunking Information:
Specify the ID, Type and Master Port then select the ports to be grouped together, and then click Apply to
activate the selected Trunking groups. Two types of link aggregation can be selected:
Static - Static link aggregation.
LACP - LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is enabled on the device. LACP allows for the
automatic detection of links in a Port Trunking Group.
Disable - Remove all members in this trunk group.
NOTE:
Each combined trunk port must be
connected to devices within the same VLAN
group.
Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
The LACP Port Settings is used to create port trunking groups on the Switch. The user may set which ports
will be active and passive in processing and sending LACP control frames.
Figure 4.64 – Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
From Port: The beginning of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
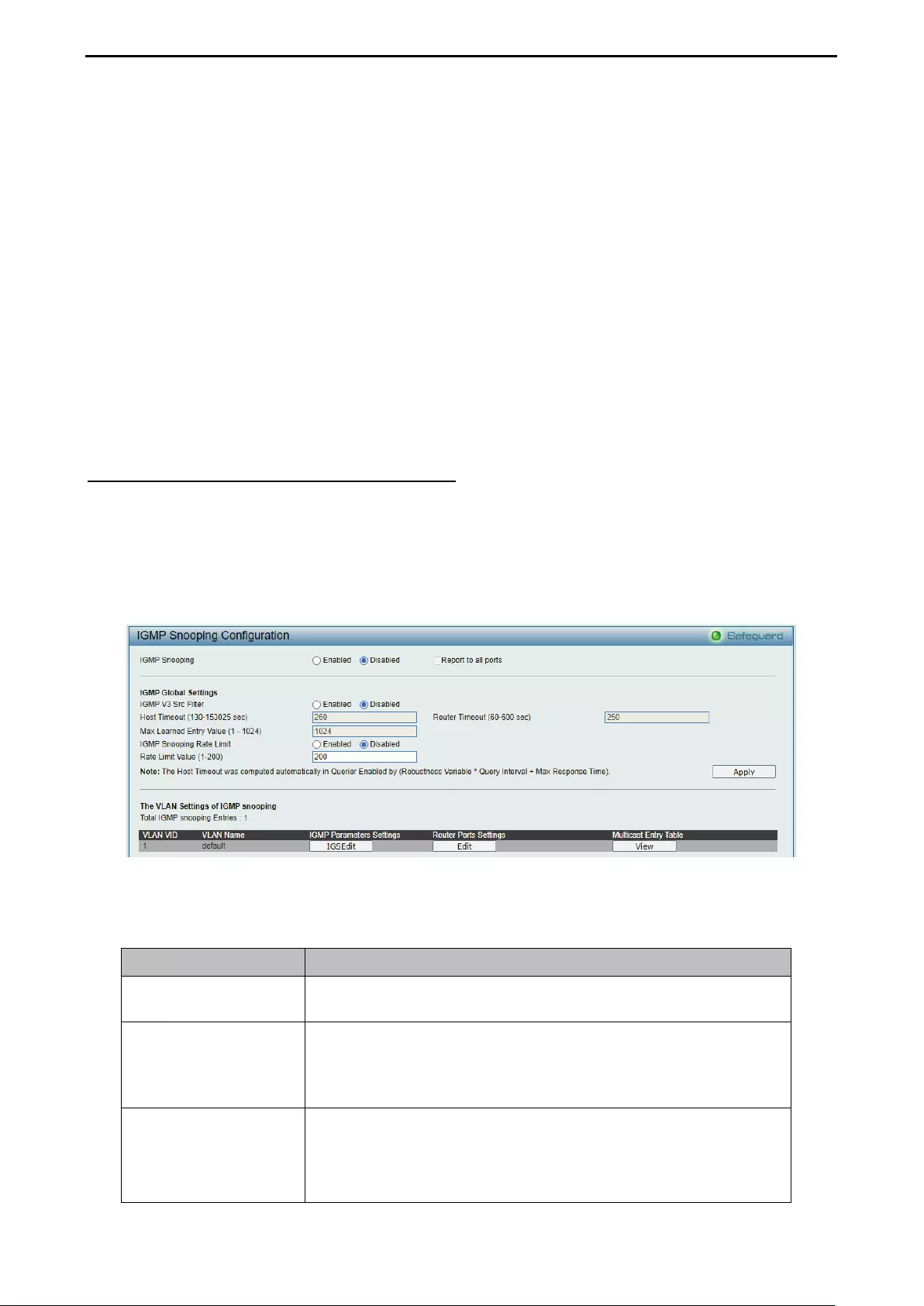
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
54
4
To Port: The ending of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Port Priority (0-65535): Displays the LACP priority value for the port. Default is 128.
Activity: There are two different roles of LACP ports:
Active - Active LACP ports are capable of processing and sending LACP control frames. This allows
LACP compliant devices to negotiate the aggregated link so the group may be changed dynamically
as needs require. In order to utilize the ability to change an aggregated port group, that is, to add or
subtract ports from the group, at least one of the participating devices must designate LACP ports as
active. Both devices must support LACP.
Passive - LACP ports that are designated as passive cannot initially send LACP control frames. In
order to allow the linked port group to negotiate adjustments and make changes dynamically, one
end of the connection must have "active" LACP ports.
Timeout: Specify the administrative LACP timeout. The possible field values are:
Short (3 Sec) - Defines the LACP timeout as 3 seconds.
Long (90 Sec) - Defines the LACP timeout as 90 seconds. This is the default value.
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
With Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping, the DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch can
make intelligent multicast forwarding decisions by examining the contents of each frame’s Layer 2 MAC
header.
IGMP snooping can help reduce cluttered traffic on the LAN. With IGMP snooping enabled globally, the
DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch will forward multicast traffic only to connections that have group members
attached.
The settings of IGMP snooping is set by each VLAN individually.
Figure 4.65 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
By default, IGMP is disabled. If enabled, the IGMP Global Settings will need to be entered:
Parameters Description
IGMP Snooping Used to control IGMP snooping global state; the radi
os buttons
enable/disable to change the state.
IGMP V3 Src Filter Enable: Specifies that the multicast group will be based on the host
mode.
Disable: Specifies that the multicast forwarding lookup will be based
on the port mode.
Host Timeout
(130-153025 sec)
This is the interval after which a learned host port entry will be
purged. For each host port learned, a 'Port Purge Timer' runs for
'Host Port Purge Interval'. This timer will be restarted whenever a
report message from host is received over that port. If no report
messages are received for 'Host Port Purge Interval' time, the
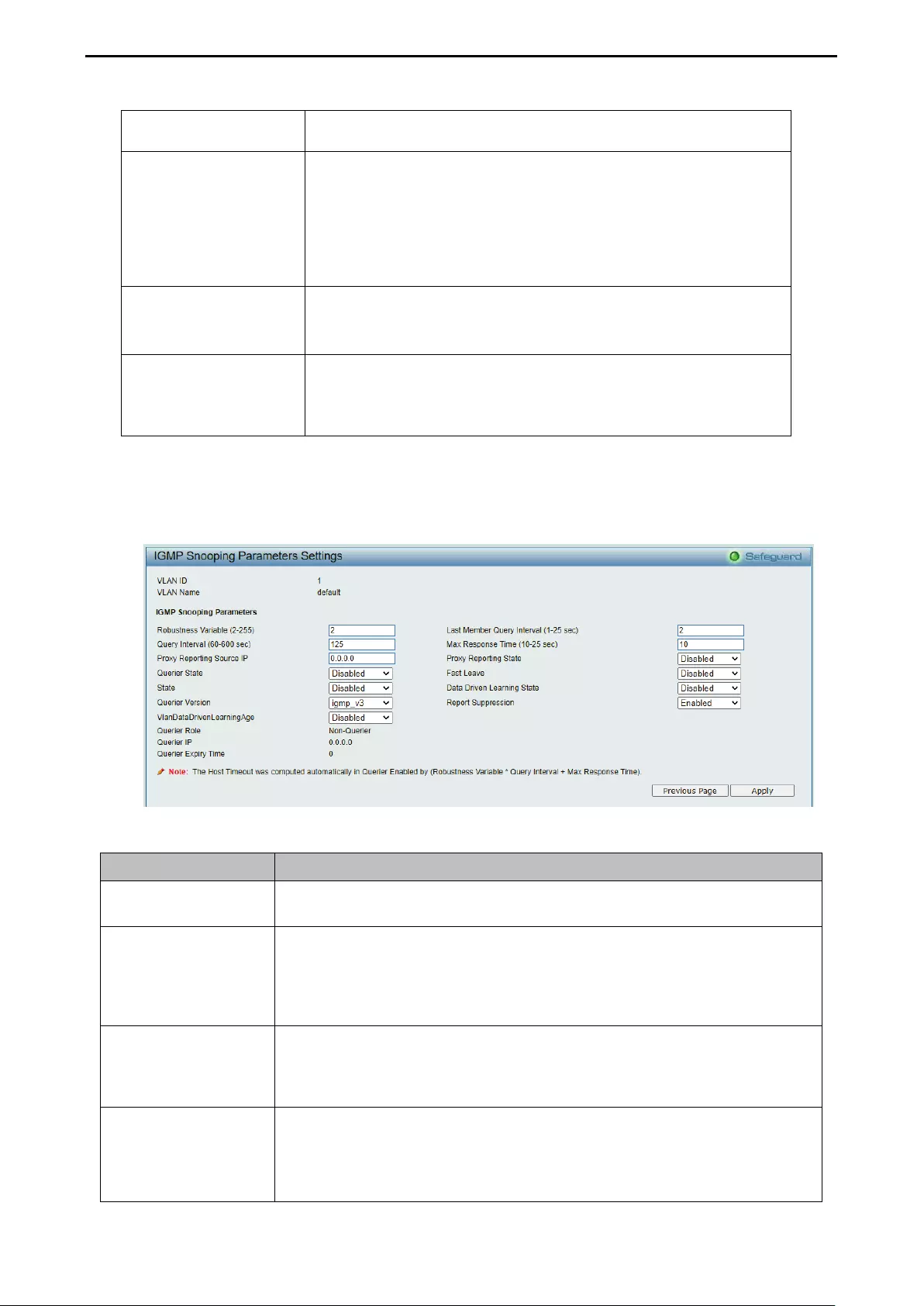
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
55
5
learned host entry will be purged from the multicast group. The
default value is 260 seconds.
Router Timeout
(60-600 sec)
This is the interval after which a learned router port entry will be
purged. For each router port learned, a 'Router Port Purge Timer'
runs for 'Router Port Purge Interval'. This timer will be restarted
whenever a Query control message is received over that port. If
there were no Query control messages received for 'Router Port
Purge Interval' time, the learned router port entry will be purged.
Default is 260 seconds.
Max Learned Entry
Value
(1-1024)
The maximum IGMP group(s) allowed to be learned for entire
system. The range from 1 to 1024 groups. The default value is 1024
groups.
IGMP Snooping Rate
Limit
Used to control if system has the maximum process limit especially
for IGMP packet (IGMP report, IGMP leave and IGMP query). Lower
rate helps to lower the CPU loading. Rate Limit Value is a range
from 1-200 in PPS.
Clicking Apply button for apply the changes.
Click IGSEdit button to enter the IGMP Parameters Settings page.
Figure 4.66 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Parameters Settings
Parameters Description
State Used to control IGMP snooping state for this particular VLAN group. The
state Enabled/Disabled can be selected in drop-down list.
Robustness Variable
(2-255 sec)
The Robustness Variable allows adjustment for the expected packet loss on
network. The larger robustness variable help to prevent packet lost occurred
in network; the key types of packet for IGMP: report, leave and query. The
Robustness Variable cannot be set to zero, and it SHOULD NOT be. Default
is 2 seconds
Query Interval
(60-600 sec)
The Query Interval is th
e interval between General Queries sent. By
adjusting the Query Interval, the number of IGMP messages can be
increased or decreased; larger values will cause IGMP Queries to be sent
less often. Default value is 125 seconds.
Last Member Query
Interval
(1-25 sec)
The Last Member Query Interval is the Max Response Time inserted into
Group-Specific Queries sent in response to Leave Group messages, and is
also the amount of time between Group-
Specific Query messages. This
value may be adjusted to modify the "l
eave latency" of the network. A
reduced value results in reduced time to detect the loss of the last member of
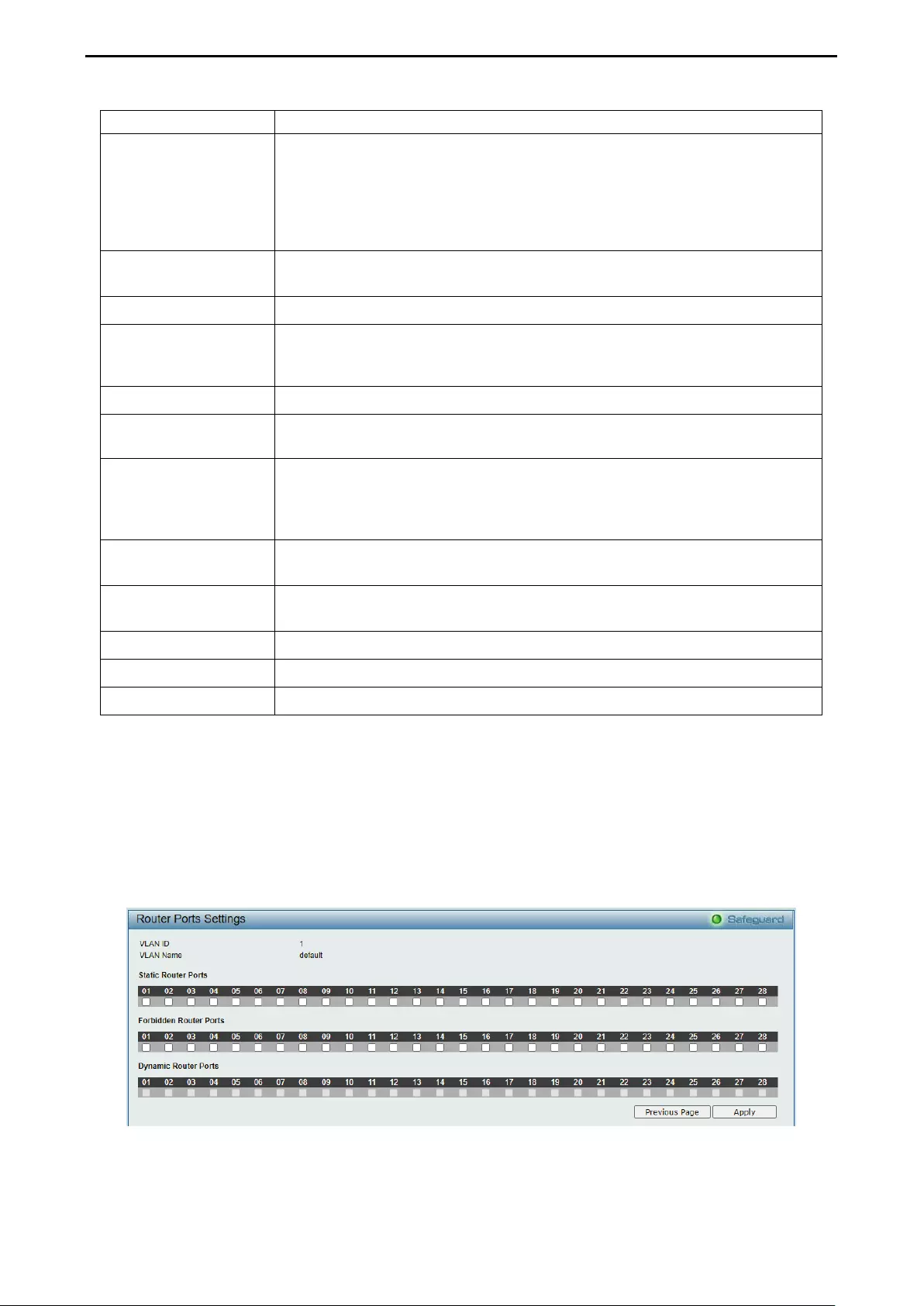
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
56
6
a group. Default is 1 second.
Max Response Time
(10-25 sec)
The Max Response Time specifies the maximum allowed time before
sending a respondin
g report message. Adjusting this setting effects the
"leave latency", or the time between the moment the last host leaves a group
and when the multicast server is notified that there are no more members. It
also allows adjustments for controlling the frequency of IGMP traffic on a
subnet. Default is 10 seconds.
Proxy Reporting
Source IP
Enter the proxy reporting source IP address.
Proxy Reporting Use the drop-down menu to enable and disable the proxy report state.
Querier State
Device starts sending general query packets by Query Interval when state
configured to Enabled. Device stop sending general query packet when state
configured to
Disabled
.
Querier Version Specify the general query packet version; v1, v2 and v3 are available to use.
Fast Leave If enabled, the membership is immediately removed when the system receive
the IGMP leave message.
Data Driven Learning
State
Data Driven learning is a mechanism that helps to register the IGMP group
via multicast traffic packet. The feature helps to solve some special network
application that end host does not support IGMP function but only sending
multicast traffic; for example, IP camera.
VLANDateDrivenLear
ningAge
Specifies that the aging out of the entry will be enabled or disabled.
Report Suppression By Enabled Report Suppression, the device forward 1 IGMP report that
registered the same IGMP group in 10 seconds period.
Querier Role Display the current information for Querier Role.
Querier IP Display the current information of Querier IP address.
Querier Expiry Time Display the current information for Querier Expiry Time.
Clicking Apply button for apply the changes.
Clicking Previous Page returned to IGMP Snooping Configuration page.
Click Edit button to enter the Router Port Settings page, and the ports to be assigned as router ports for
IGMP snooping for the VLAN.
A router port configured manually is a Static Router Port, a Forbidden Router Port and a Dynamic Router
Port is dynamically configured by the Switch when a query control message is received. Press Apply for
changes to take effect.
Figure 4.67 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping-Router Port Settings
To view the Multicast Entry Table for a given VLAN, press the View button.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
57
7
Figure 4.68– Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping-Multicast Entry Table
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
The IGMP Access Control Settings page is used to enable or disable the IGMP access control of selected
ports.
Figure 4.69 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
From Port/To Port: Select the port ranges to be configured.
Status: Enable or disable the IGMP Access Control of specified ports.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table
The Host Table page displays the information of Host Table. Including VLAN ID, Group, Port Number and
Host IP.
Figure 4.70 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
The IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings page allows the Switch to read the Multicast Group IP address
and the corresponding MAC address from IGMP packets that pass through the Switch.
Figure 4.71- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
VLAN Name: Specifies the VLAN name of the multicast group.
VID List: Specifies the VID list or of the multicast group.
IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
58
8
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
The MLD Snooping Settings page allows user to configure the max multicast group for IGMP Snooping.
Figure 4.72- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
MLD Snooping: Enable or disable the MLD Snooping.
MLD Global Settings:
Host Timeout (130-153025 sec): Specifies the time interval in seconds after which a port is removed from a
Multicast Group. Ports are removed if a Multicast group MLD report was not received from a Multicast port
within the defined Host Timeout period. The possible field range is 130 - 153025 seconds. The default
timeout is 260 seconds.
Router Timeout (60-600): Specifies the time interval in seconds the Multicast router waits to receive a
message before it times out. The possible field range is 60 - 600 seconds. The default timeout is 125
seconds.
Max Learned Entry Value (1-1024): Specifies the max learned entry value for MLD Snooping. The field
range is 1-1024. The default is 256.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. Press the Edit button under Router Port Setting, and
select the ports to be assigned for MLD snooping for the VLAN, and press Apply for changes to take effect.
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
The MLD Host Table page displays the MLD Snooping information.
Figure 4.73- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
Configuration > ISM VLAN Settings
In a switching environment, multiple VLANs may exist. Every time a multicast query passes through the
Switch, the switch must forward separate different copies of the data to each VLAN on the system, which, in
turn, increases data traffic and may clog up the traffic path. To lighten the traffic load, multicast VLANs may
be incorporated. These multicast VLANs will allow the Switch to forward this multicast traffic as one copy to
recipients of the multicast VLAN, instead of multiple copies.
Regardless of other normal VLANs that are incorporated on the Switch, users may add any ports to the
multicast VLAN where they wish multicast traffic to be sent. Users are to set up a source port, where the
multicast traffic is entering the switch, and then set the ports where the incoming multicast traffic is to be sent.
The source port cannot be a recipient port and if configured to do so, will cause error messages to be
produced by the switch. Once properly configured, the stream of multicast data will be relayed to the receiver
ports in a much more timely and reliable fashion.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
5
59
9
The ISM VLAN Settings page allows the user to configure the ISM VLAN.
Figure 4.74 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > ISM VLAN Settings
ISM VLAN Global State: Enable or disable the IGMP Snooping Multicast (ISM) VLAN Global State.
Click Apply button to confirm the ISM VLAN Global State.
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the selected Multicast VLAN.
VID: Add the corresponding VLAN ID of the Multicast VLAN. Users may enter a value between 2 and 4094.
VLAN Name: Enter the name of the new Multicast VLAN to be created. This name can be up to 32
characters in length.
Member Ports: Enter a port or list of ports to be added to the Multicast VLAN. Member ports shall be the
untagged members of the multicast VLAN.
Tagged Member Ports: Enter a port or list of ports that will become tagged members of the Multicast VLAN.
Source Ports: Enter a port or list of ports to be added to the Multicast VLAN. Source ports shall be the
tagged members of the multicast VLAN.
IPv4 Replace Source: This field is used to replace the source IPv4 address of incoming packets sent by the
host before being forwarded to the source port.
IPv6 Replace Source IP: This field is used to replace the source IPv6 address of incoming packets sent by
the host before being forwarded to the source port.
Click Add to add the ISM VLAN which will appear in the table, or click Clear All to clear all fields.
Click Edit button to modify the parameters and update the ISM VLAN Setting or click Delete to delete the
ISM VLAN.
Click View to display the detail information of ISM VLAN.
Figure 4.75 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > ISM VLAN Settings
Configuration > Jumbo Frame
D-Link Gigabit Ethernet Switches support jumbo frames (frames larger than the Ethernet frame size of 1536
bytes) of up to 10000 bytes (tagged). Default is disabled, Select Enabled then click Apply to turn on the
jumbo frame support.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
60
0
Figure 4.76 – L2 Functions > Jumbo Frame
Configuration > Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming and/or
outgoing packet from one port of the Switch to another port, where the packet can be studied. This enables
network managers to better monitor network performances.
Figure 4.77 – L2 Functions > Port Mirroring
Selection options for the Source Ports are as follows:
TX (transmit) mode: Duplicates the data transmitted from the source port and forwards it to the Target Port.
Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
RX (receive) mode: Duplicates the data that is received from the source port and forwards it to the Target
Port. Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
TX/RX (transmit and receive) mode: Duplicate both the data transmitted from and data sent to the source
port, and forwards all the data to the assigned Target Port. Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
None: Turns off the mirroring of the port. Click “all” to remove all ports from mirroring.
Configuration > Loopback Detection
The Loopback Detection function is used to detect the loop created by ports which other prevention
mechanism is not available, for example: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). It usually happens when link
partner is hub or un-management switch. Loopback Detection feature can automatically shutdown the port
and sends a log to the administrator when loop occurred. Also, Loopback Detection function offers recovery
mechanism when loop condition removed.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
61
1
Figure 4.78 – L2 Functions > Loopback Detection
Loopback Detection: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable loopback detection. The default is
Disabled.
Mode: Specifies Port-based or VLAN-based mode. If port-based mode is selected, the loop happening port
will be shut down and affect all member VLANs. If VLAN-based mode is selected, only the member port in
the loop happening VLAN will be shut down.
VID List: Specifies the VID.
Interval (1-32767): Set a Loop detection Interval between 1 and 32767 seconds. The default is 2 seconds.
Recover Time (0 or 60-1000000): Time allowed (in seconds) for recovery when a Loopback is detected.
The Loop Detection Recover Time can be set at 0 seconds, or 60 to 1000000 seconds. Entering 0 will
disable the Loop Detection Recover Time. The default is 60 seconds.
From Port: The beginning of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
To Port: The ending of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
State: Use the drop-down menu to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Default is Disabled.
Click the Apply button to implement changes made or click Refresh to refresh the Loopback Detection table.
Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
SNTP or Simple Network Time Protocol is used by the Switch to synchronize the clock of the computer. The
SNTP settings folders contain two windows: Time Settings and TimeZone Settings. Users can configure the
time settings for the switch, and the following parameters can be set or are displayed in the Time Settings
page.
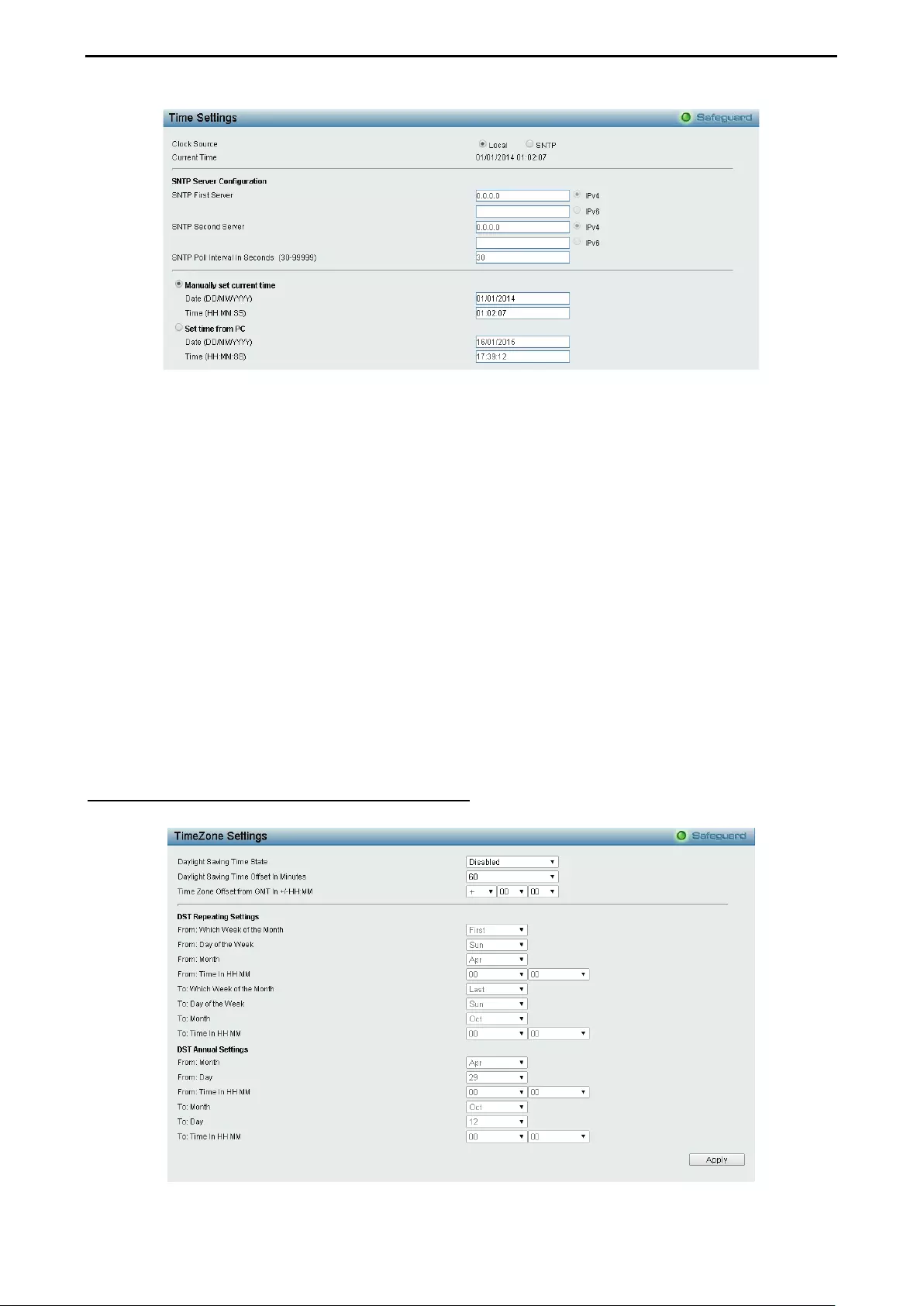
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
62
2
Figure 4.79 – Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
Clock Source: Specify the clock source by which the system time is set. The possible options are:
Local - Indicates that the system time is set locally by the device.
SNTP - Indicates that the system time is retrieved from a SNTP server.
Current Time: Displays the current date and time for the switch.
If choosing SNTP for the clock source, then the following parameters will be available:
SNTP First Server: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and specify the IP address of the primary SNTP server from which
the system time is retrieved.
SNTP Second Server: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and specify the IP address of the secondary SNTP server from
which the system time is retrieved.
SNTP Poll Interval in Seconds (30-99999): Defines the interval (in seconds) at which the SNTP server is
polled for Unicast information. The Poll Interval default is 30 seconds.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
When selecting Local for the clock source, users can select from one of two options:
Manually set current time: Users input the system time manually.
Set time from PC: The system time will be synchronized from the local computer.
Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings
The TimeZone Setting Page is used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings time settings for SNTP.
Figure 4.80 – Configuration > SNTP > TimeZone Settings
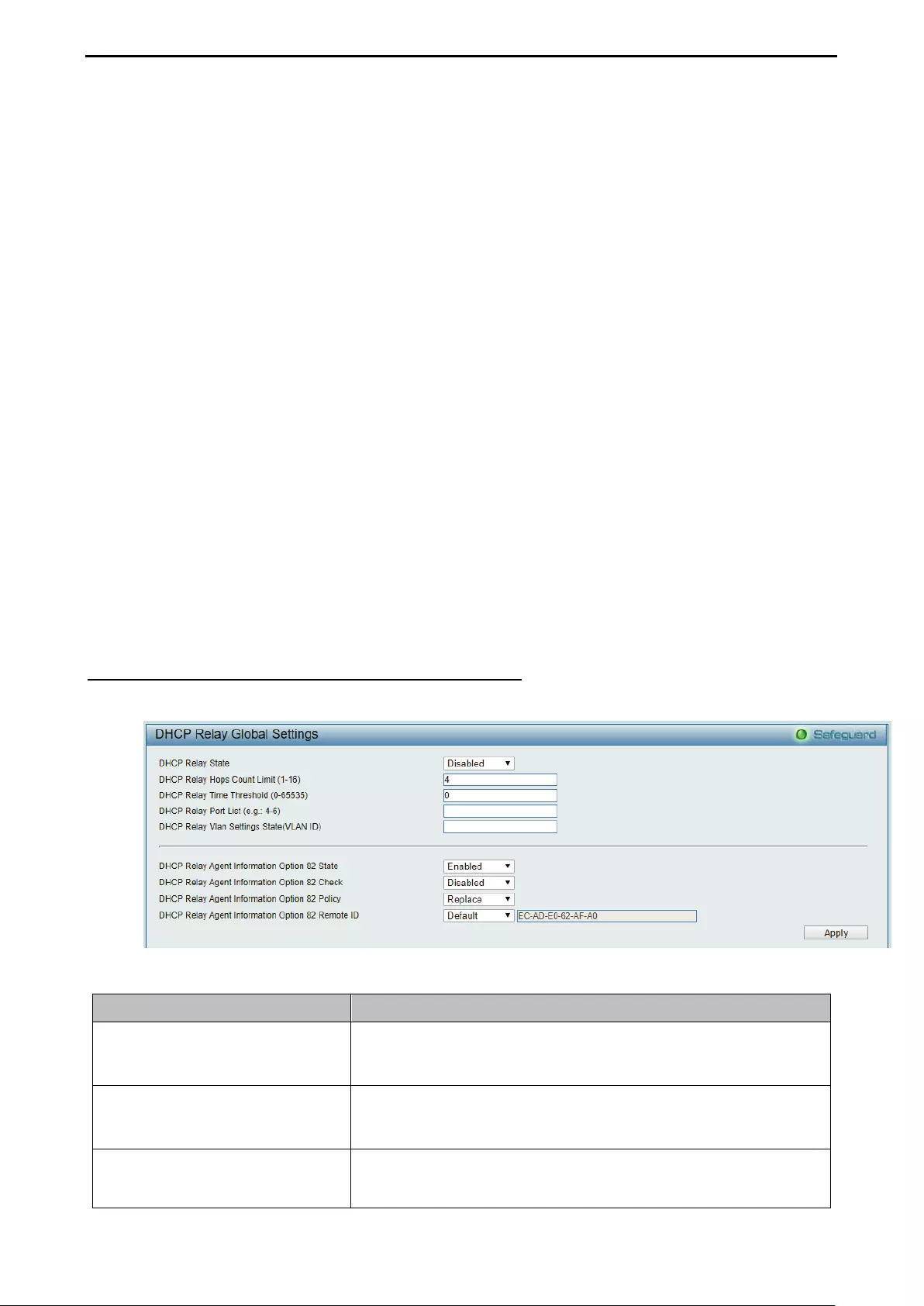
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
63
3
Daylight Saving Time State: Enable or disable the DST Settings.
Daylight Saving Time Offset: Use this drop-down menu to specify the amount of time that will constitute the
local DST offset - 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes.
Time Zone Offset GMT +/- HH:MM: Use these drop-down menus to specify the local time zone's offset from
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT.)
DST Repeating Settings:
From: Which Week of the Month: Enter the Week of Month will start on, each year.
From: Day of the Week: Enter the Day DST will start on, each year.
From: Month: Enter the month DST will start on, each year.
From: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will start on, each year.
To: Which Week of the Month: Enter the Week of Month will end on, each year.
To: Day of the Week: Enter the day of week that DST will end on, each year.
To: Month: Enter the month DST and date DST will end on, each year.
To: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
DST Annual Settings:
From: Month / Day: Enter the month DST and date DST will start on, each year.
From: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will start on, each year.
To: Month / Day: Enter the month DST and date DST will end on, each year.
To: Time HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global Settings
User can enable and configure DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings on the Switch.
Figure 4.81 - Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Global Settings
Parameters Descriptions
DHCP Relay State This field can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled using the
pull-down menu. It is used to enable or disable the DHCP/BOOTP
Relay service on the Switch. The default is Disabled.
DHCP Relay Hops Count Limit
(1-16)
This field allows an entry between 1 and 16 to define the maximum
number of router hops DHCP/BOOTP messages can be forwarded
across. The default hop count is 4.
DHCP Relay Time Threshold
(0-65535)
Allows an entry between 0 and 65535 seconds, and defines the
maximum time limit for routing a DHCP/BOOTP packet. If a value
of 0 is entered, the Switch will not process the value in the
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
64
4
seconds field of the BOOTP or DHCP packet. If a non-zero value
is entered, the Switch will use that value, along with the hop count
to determine whether to forward a given BOOTP or DHCP packet.
DHCP Relay Port List Specify the ports for BOOTP relay.
DHCP Relay VLAN Setting State Specify the VLAN ID to monitor DHCP client activity. The range is
from 1 – 4094.
DHCP Relay Agent Information
Option 82 State
It is used to enable or disable the DHCP Agent Information Option
82 on the Switch. The default is Disabled.
Enabled – When this field is toggled to Enabled the relay agent will
insert and remove DHCP relay information (option 82 field) in
mess
ages between DHCP servers and clients. When the relay
agent receives the DHCP request, it adds the option 82
information, and the IP address of the relay agent (if the relay
agent is configured), to the packet. Once the option 82 information
has been added to the packet it is sent on to the DHCP server.
When the DHCP server receives the packet, if the server is
capable of option 82, it can implement policies like restricting the
number of IP addresses that can be assigned to a single remote ID
or circuit ID. Then the DHCP server echoes the option 82 field in
the DHCP reply. The DHCP server unicasts reply to the back to the
relay agent if the request was relayed to the server by the relay
agent. The switch verifies that it originally inserted the option 82
da
ta. Finally, the relay agent removes the option 82 field and
forwards the packet to the switch port that connects to the DHCP
client that sent the DHCP request.
Disabled - If the field is toggled to Disabled the relay agent will not
insert and remove DHCP
relay information (option 82 field) in
messages between DHCP servers and clients, and the check and
policy settings will have no effect.
DHCP Relay Agent Information
Option 82 Check
It filed is used to enable or disable the ability to check DHCP option
82 information in DHCP packets:
Enabled – When the field is configured to Enabled, the relay agent
checks if DHCP packets carries option 82 information. If option 82
does not carried, the DHCP packet would be dropped.
Disabled – No check would be executed
when check state
configured to Disabled.
DHCP Relay Agent Information
Option 82 Policy
This filed is used to configure the policy for each port. It is used to
set the Switches policy for handling packets when the DHCP
Agent Information Option 82 Check is set to Disabled. There are
3 policies available to use:
Replace - The option 82 field will be replaced if the option 82 field
already exists in the packet received from the DHCP client.
Drop - The packet will be dropped if the option 82 field already
exists in the packet received from the DHCP client.
Keep -
The option 82 field will be retained if the option 82 field
already exists in the packet received from the DHCP client.
DHCP Relay Agent Information
Option 82 Remote ID
This filed is used to configure the contents of Remote ID used in
option 82. Options: Default, User Define are available to use.
Click Apply to apply the configurations.
NOTE: If the Switch receives a packet that contains the
option-82 field from a DHCP client and the information-
checking feature is enabled, the switch drops the packet
because it is invalid. However, in some instances, user
might configure a client with the option-82 field. In this
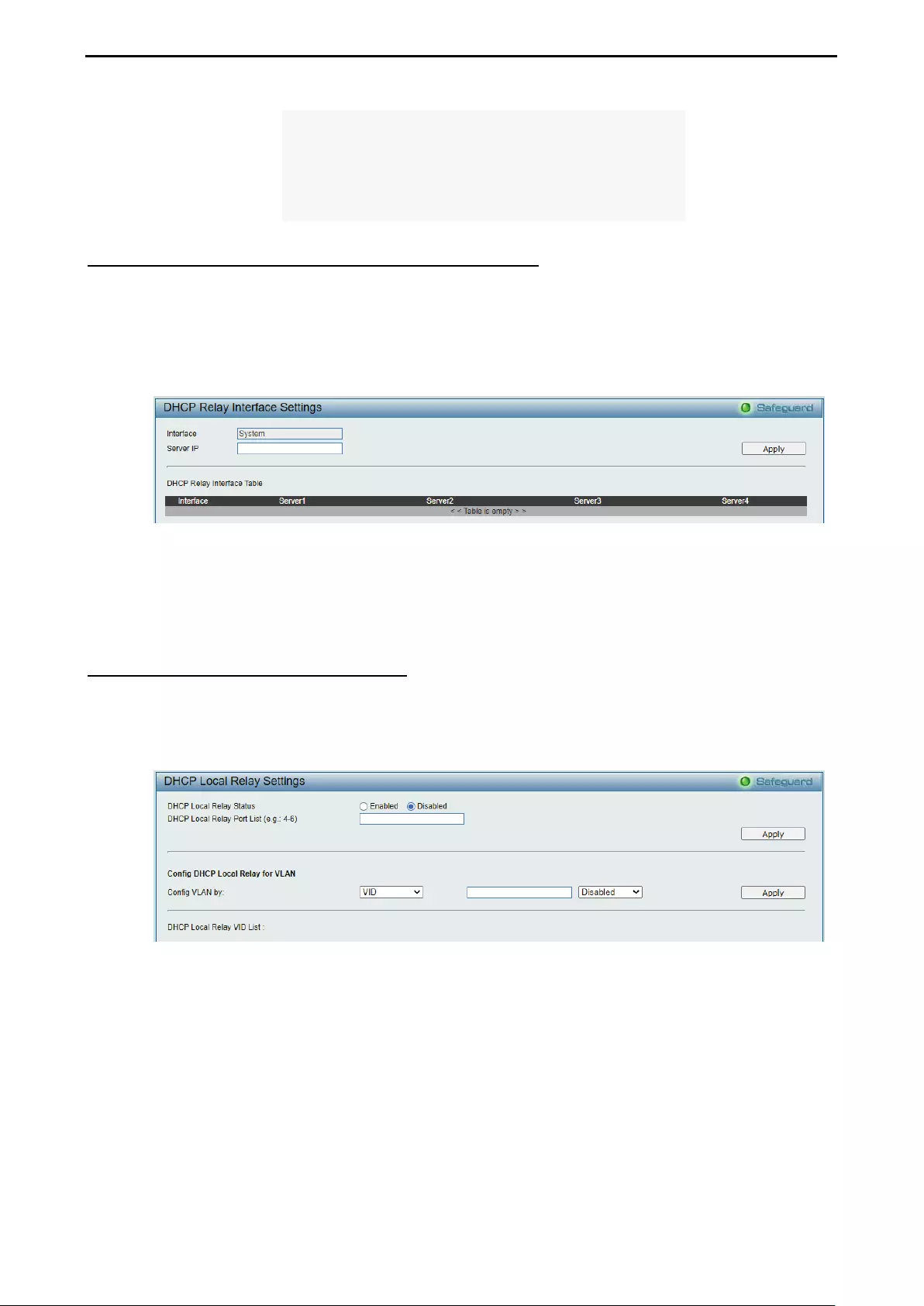
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
65
5
situation, user should disable the information-check
feature so that the switch does not remove the option-82
field from the packet. User can configure the action that
the switch takes when it receives a packet with existing
option-82 information by configuring the DHCP Agent
Information Option 82 Policy.
Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Interface Settings
This page allows the user to set up a server, by IP address, for relaying DHCP information the switch. The
user may enter a previously configured IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to the DHCP
server using the following window. Properly configured settings will be displayed in the DHCP Relay Table at
the bottom of the following window, once the user clicks the Add button under the Apply heading. The user
may add up to four server IPs per IP interface on the Switch. Entries may be deleted by clicking Delete
button.
Figure 4.82 - Configuration > DHCP Relay > DHCP Relay Interface Settings
Interface: The IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to the Server.
Server IP: Enter the IP address of the DHCP server. Up to four server IPs can be configured per IP Interface.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
The DHCP Local Relay Settings page allows the user to configure DHCP Local Relay. DHCP broadcasts are
trapped by the switch CPU, and replacement broadcasts are forwarded with Option 82. Replies from the
DHCP servers are trapped by the switch CPU, the Option 82 is removed and the reply is sent to the DHCP
Client.
Figure 4.83 - Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
DHCP Local Relay Status: Specifies whether DHCP Local Relay is enabled on the device.
Enabled – Enables DHCP Local Relay on the device.
Disabled – Disables DHCP Local Relay on the device. This is the default value.
DHCP Local Relay Port List: Specifies the port or ports for DHCP local relay port.
Config VLAN by: Configure the VLAN by VID or VLAN Name of drop-down menu.
State: Specifies whether DHCP Local Relay is enabled on the VLAN.
Enabled – Enables DHCP Local Relay on the VLAN.
Disabled – Disables DHCP Local Relay on the VLAN.
DHCP Local Relay VID List: Displays the list of VLANs on which DHCP Local Relay has been defined.
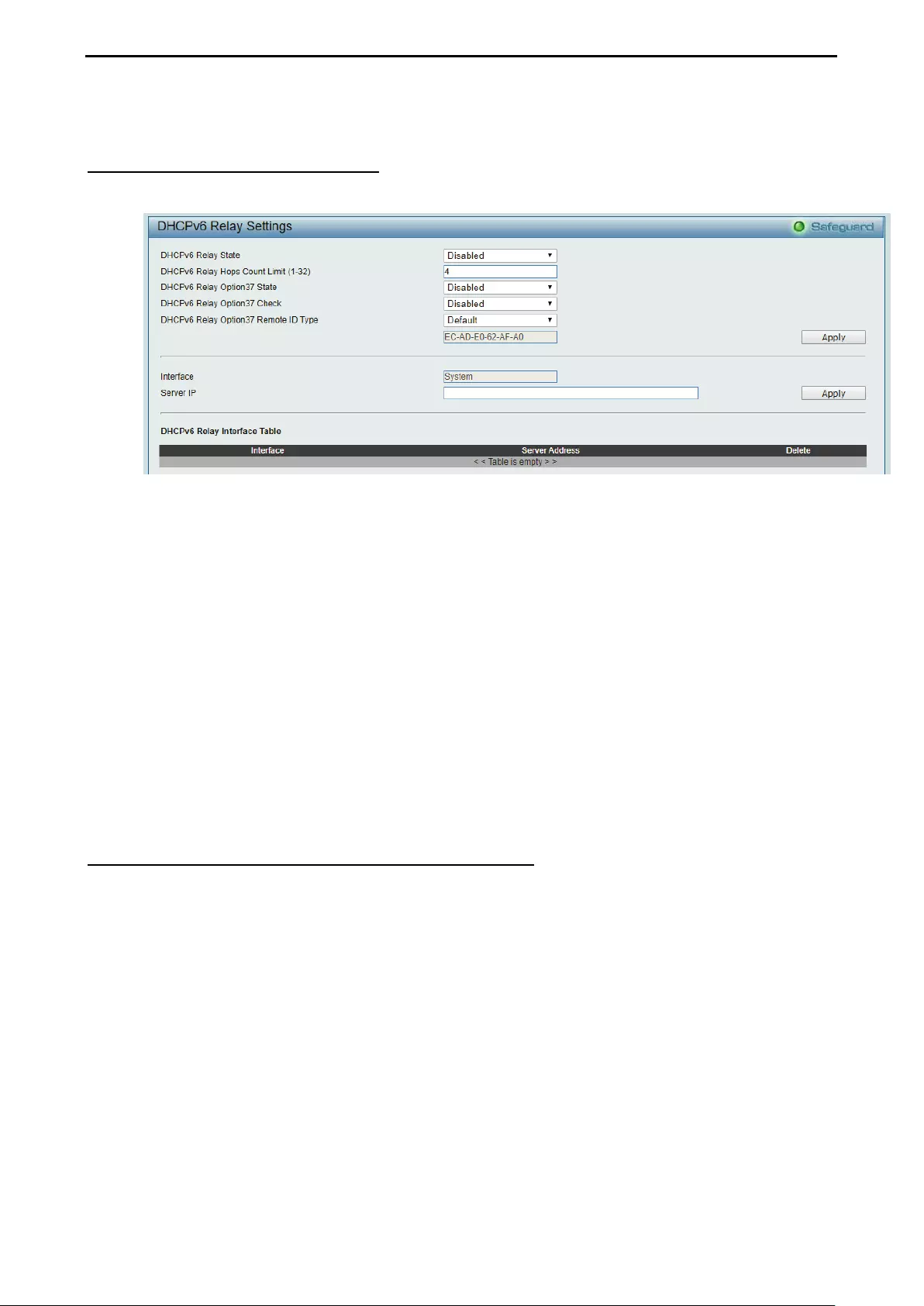
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
66
6
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings
The DHCPv6 Relay Settings page allows user to configure the DHCPv6 settings.
Figure 4.84 - Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings
DHCPv6 Relay Status: Specifies whether DHCPv6 Relay is enabled on the device.
Enabled – Enables DHCPv6 Relay on the device.
Disabled – Disables DHCPv6 Relay on the device. This is the default value.
DHCPv6 Relay Hops Count Limit (1-32): The field allows and entry between 1 and 32 to define the
maximum number of router hops DHCPv6 messages can be forwarded. The default hop count is 4.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 State: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option37 State to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Check: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Check to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Remote ID Type: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Remote ID type is CID
with User Defined, User Defined or Default.
Interface: Enter a name of the interface.
Server IP: Enter the server IP address.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
The Switch implements three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol, the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
(RSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1w specification and a version compatible with the IEEE 802.1D STP
and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) as defined by the IEEE802.1 specification. RSTP can operate
with legacy equipment implementing IEEE 802.1D, however the advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) evolved from the 802.1D STP standard. RSTP was
developed in order to overcome some limitations of STP that impede the function of some recent switching
innovations. The basic function and much of the terminology is the same as STP. Most of the settings
configured for STP are also used for RSTP. This section introduces some new Spanning Tree concepts and
illustrates the main differences between the two protocols.
The IEEE 802.1 Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) provides various load balancing scenarios by allowing
multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance, providing multiple pathways across the
network. For example, while port A is blocked in one STP instance, the same port can be placed in the
Forwarding state in another STP instance.
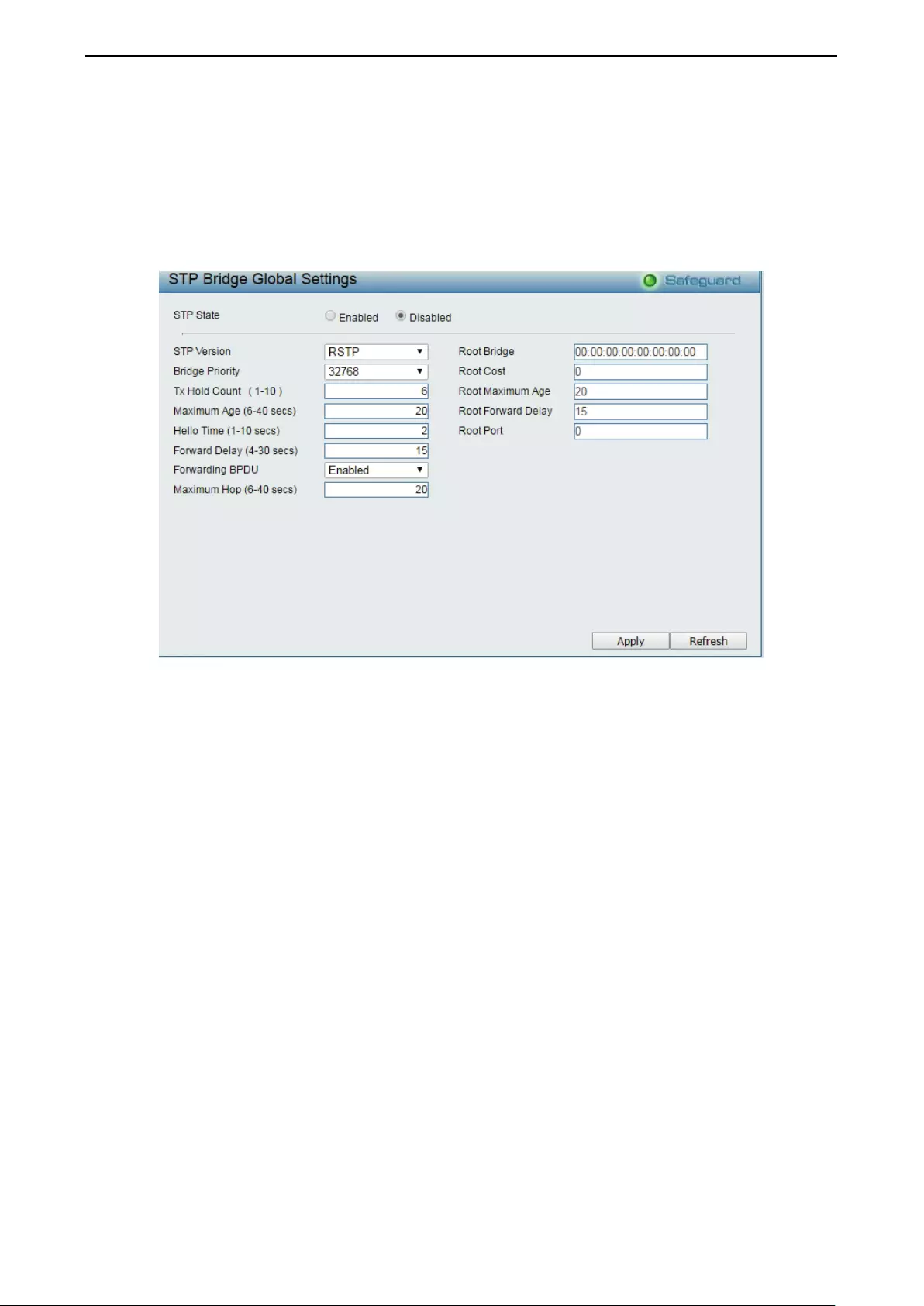
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
67
7
By default, Rapid Spanning Tree is disabled. If enabled, the Switch will listen for BPDU packets and its
accompanying Hello packet. BPDU packets are sent even if a BPDU packet was not received. Therefore,
each link between bridges is sensitive to the status of the link. Ultimately this difference results in faster
detection of failed links, and thus faster topology adjustment.
By default Multiple Spanning Tree is enabled. It will tag BPDU packets to receiving devices and distinguish
spanning tree instances, spanning tree regions and the VLANs associated with them.
After enabling STP, setting the STP Global Setting includes the following options:
Figure 4.85 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
STP State: Specify the Spanning Tree Protocol to be Enabled or Disabled.
STP Version: Choose MSTP, RSTP or STP Compatible. The default setting is MSTP.
Bridge Priority: This value between 0 and 61410 specifies the priority for forwarding packets: the lower the
value, the higher the priority. The default is 32768.
TX Hold Count (1-10): Used to set the maximum number of Hello packets transmitted per interval. The
count can be specified from 1 to 10. The default is 6.
Maximum Age (6-40 sec): This value may be set to ensure that old information does not endlessly circulate
through redundant paths in the network, preventing the effective propagation of the new information. Set by
the Root Bridge, this value will aid in determining that the Switch has spanning tree configuration values
consistent with other devices on the bridged LAN. If the value ages out and a BPDU has still not been
received from the Root Bridge, the Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other switches for permission
to become the Root Bridge. If it turns out that the Switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the
Root Bridge. A time interval may be chosen between 6 and 40 seconds. The default value is 20. (Max Age
has to have a value bigger than Hello Time)
Hello Time (1-10 sec): The user may set the time interval between transmissions of configuration messages
by the root device, thus stating that the Switch is still functioning. The default is 2 seconds.
Forward Delay (4-30 sec): This sets the maximum amount of time that the root device will wait before
changing states. The default is 15 seconds.
Forwarding BPDU: Bridges use Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) to provide spanning tree information.
STP BPDUs filtering is useful when a bridge interconnects two regions; each region needing a separate
spanning tree. BPDU filtering functions only when STP is disabled either globally or on a single interface.
Enabled - BPDU filtering is enabled on the port.
Disabled - BPDU forwarding is enabled on the port (if STP is disabled).
Maximum Hop (6-40 secs): Specifies the number of hops between devices in a spanning tree region before
the BPDU (bridge protocol data unit) packet sent by the Switch will be discarded. Each switch on the hop
count will reduce the hop count by one until the value reaches zero. The Switch will then discard the BPDU
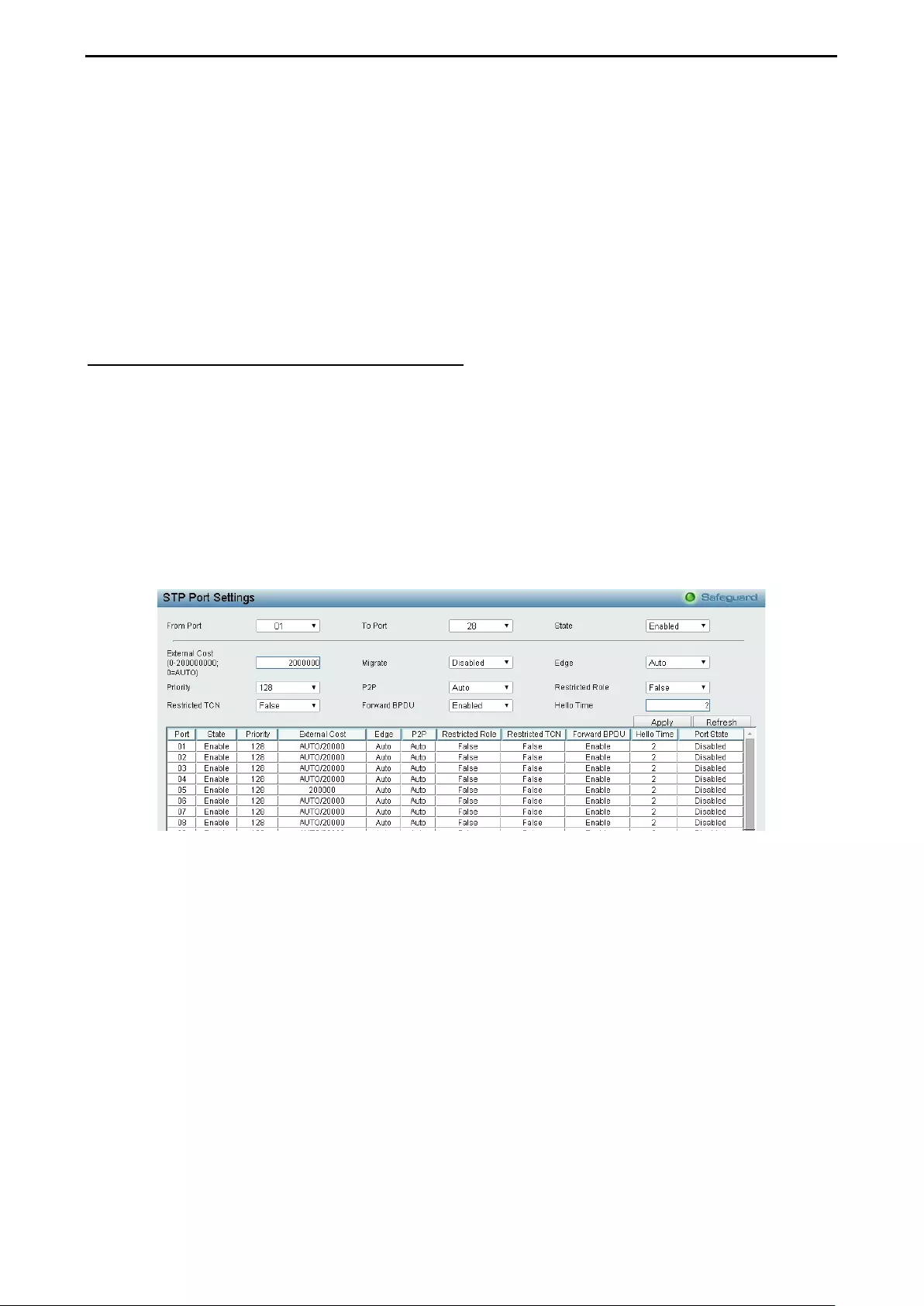
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
68
8
packet and the information held for the port will age out. The user may set a hop count from 6 to 40. The
default is 20.
Root Bridge: Displays the MAC address of the Root Bridge.
Root Cost: Defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list.
Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto).
Root Maximum Age: Displays the Maximum Age of the Root Bridge. The default is 20.
Root Forward Delay: Displays the Forward Delay of the Root Bridge. The default is 15.
Root port: Displays the root port.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect. Click Refresh to renew the page.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
STP can be set up on a port per port basis. In addition to setting Spanning Tree parameters for use on the
switch level, the Switch allows for the configuration of the groups of ports, each port-group of which will have
its own spanning tree, and will require some of its own configuration settings.
An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge
concept is replaced with a root port concept. A root port is a port of the group that is elected based on port
priority and port cost, to be the connection to the network for the group. Redundant links will be blocked, just
as redundant links are blocked on the switch level.
The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices). The
port level STP will block redundant links within an STP Group.
It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports.
Figure 4.86 – Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable STP by per-port based. It will be selectable after the
global STP is enabled.
External Cost: This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified
port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. Thedefault value is 0 (auto).
0 (auto) - Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the
specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency. Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit
port = 20000.
Value 1-200000000 - Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine the external cost. The
lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
Migrate: Setting this parameter as Yes will set the ports to send out BPDU packets to other bridges,
requesting information on their STP setting. If the Switch is configured for RSTP, the port will be capable to
migrate from 802.1d STP to 802.1w RSTP. Migration should be set as yes on ports connected to network
stations or segments that are capable of being upgraded to 802.1w RSTP on all or some portion of the
segment.
Edge: Selecting the True parameter designates the port as an edge port. Edge ports cannot create loops,
however an edge port can lose edge port status if a topology change creates a potential for a loop. An edge
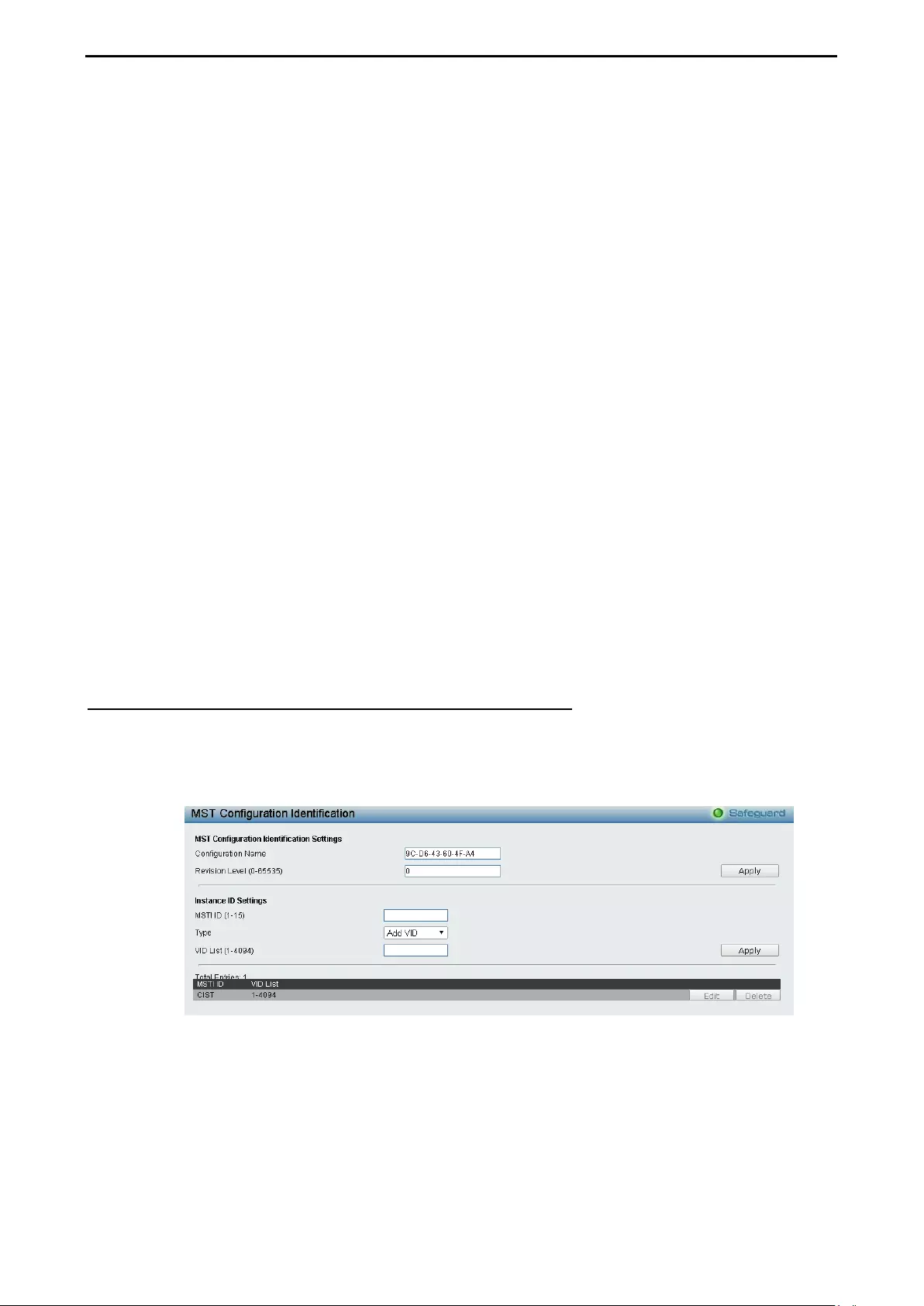
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
6
69
9
port normally should not receive BPDU packets. If a BPDU packet is received, it automatically loses edge
port status. Selecting the False parameter indicates that the port does not have edge port status. Selecting
the Auto parameter indicates that the port have edge port status or not have edge port status automatically.
Priority: Specify the priority of each port. Selectable range is from 0 to 240, and the default setting is 128.
The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen as a root port.
P2P: Choosing the True parameter indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shared link. P2P ports are similar to edge
ports, however they are restricted in that a P2P port must operate in full-duplex.
Like edge ports, P2P ports transition to a forwarding state rapidly thus benefiting from RSTP. A p2p value of
false indicates that the port cannot have p2p status. Auto allows the port to have p2p status whenever
possible and operate as if the p2p status were true. If the port cannot maintain this status, (for example if the
port is forced to half-duplex operation) the p2p status changes to operate as if the p2p value were False. The
default setting for this parameter is Auto.
Restricted Role: Toggle between True and False to set the restricted role state of the packet. If set to True,
the port will never be selected to be the Root port. The default value is False.
Restricted TCN: Toggle between True and False to set the restricted TCN of the packet. Topology Change
Notification (TCN) is a BPDU that a bridge sends out to its root port to signal a topology change. If set to
True, it stops the port from propagating received TCN and to other ports. The default value is False.
Forwarding BPDU: Bridges use Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) to provide spanning tree information.
STP BPDUs filtering is useful when a bridge interconnects two regions; each region needing a separate
spanning tree. BPDU filtering functions only when STP is disabled either globally or on a single interface.
The possible field values are:
Disabled – BPDU filtering is enabled on the port.
Enabled – BPDU forwarding is enabled on the port (if STP is disabled).
Hello Time: The interval between two transmissions of BPDU packets sent by the Root Bridge to indicate to
all other switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge. The default value is 2.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Click Refresh to renew the page.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification
The MST Configuration Identification page allows user to configure a MSTI instance on the switch. These
settings will uniquely identify a multiple spanning tree instance set on the switch. The Switch initially
possesses one CI ST or Common Internal Spanning Tree of which the user may modify the parameters for but
cannot change the MSTI ID for, and cannot be deleted.
Figure 4.87 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification
MST Configuration Identification Settings:
Configuration Name: A previously configured name set on the Switch to uniquely identify the MSTI (Multiple
Spanning Tree Instance). If a configuration name is not set, this field will show the MAC address to the
device running MSTP. This field can be set in the STP Bridge Global Set-tings window.
Revision Level: This value, along with the Configuration Name will identify the MSTP region configured on
the Switch. The user may choose a value between 0 and 65535 with a default setting of
0
.
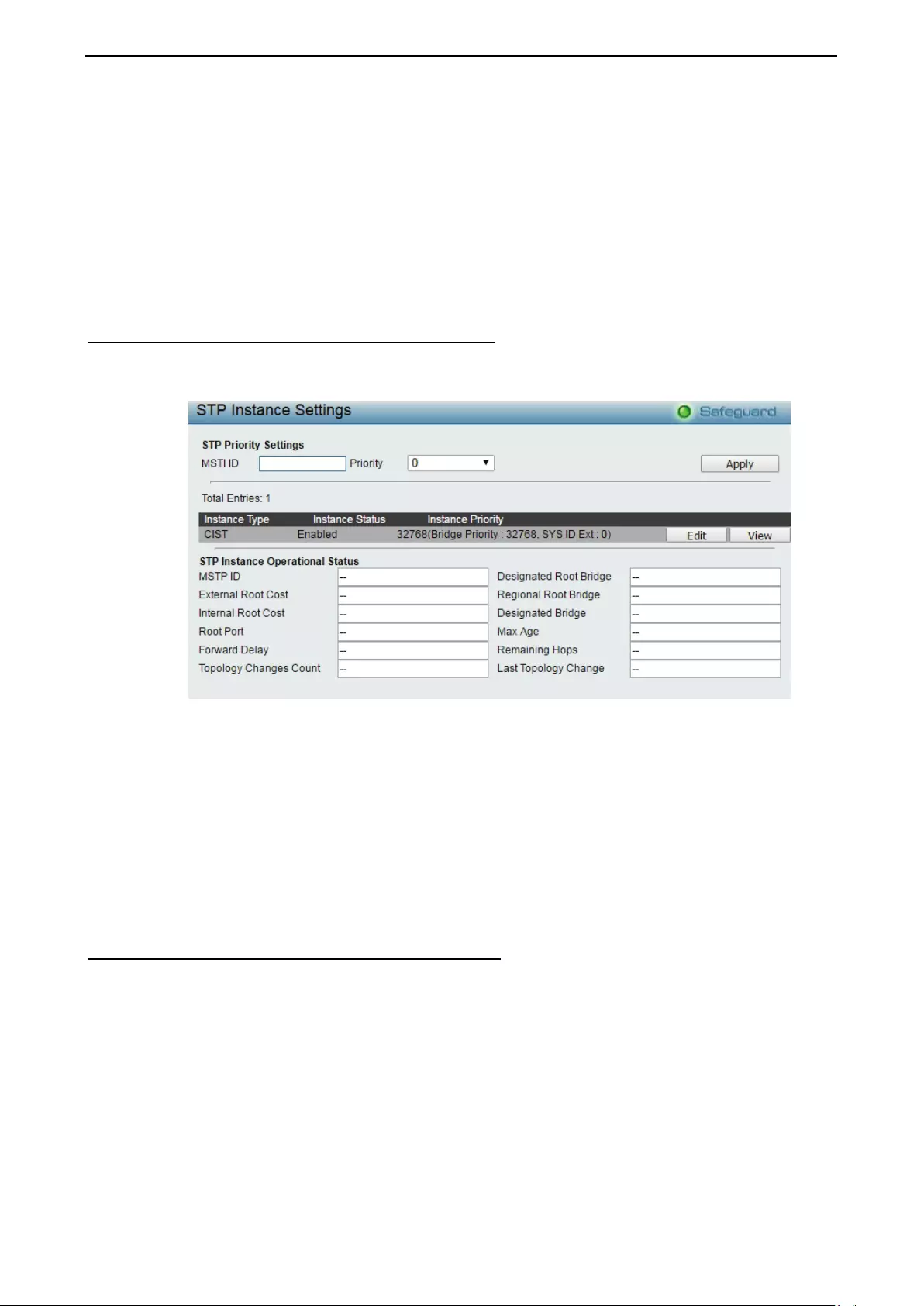
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
70
0
MSTI ID (1-15): Enter a number between 1 and 15 to set a new MSTI on the Switch.
Type: This field allows the user to choose a desired method for altering the MSTI settings.
Add VID - Select this parameter to add VIDs to the MSTI ID, in conjunction with the VID List
parameter.
Remote VID – Select this parameter to remove VIDs from the MSTI ID, in con-junction with the VID
List parameter.
VID List (1-4094): This field displays the VLAN IDs associated with the specific MSTI.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings
The STP Instance Settings page display MSTIs currently set on the Switch and allows users to change the
Priority of the MSTPs.
Figure 4.88 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings
To modify an entry on the table, click the Edit button. To view more information about and entry on the table
at the top of the window, click the view button.
The window above contains the following information:
MSTI ID: Enter the MSTI ID in this field. An entry of 0 denotes the CIST (default MSTI).
Priority: Enter the new priority in the Priority field. The user may set a priority value between 0-61440.
Click Apply to implement the new priority setting.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information
The MSTP Port Information page can be used to update the port configuration for an MSTI ID. If a loop
occurs, the MSTP function will use the port priority to select an interface to put into the forwarding state. Set
a higher priority value for interfaces to be selected for forwarding first. In instances where the priority value is
identical, the MSTP function will implement the lowest MAC address into the forwarding state and other
interfaces will be blocked.
To View the MSTI settings for a particular port, select the Port number and click Find button. To modify the
settings for a particular MSTI Instance, click Edit button, then modify the MSTP Port Setting and click Apply.
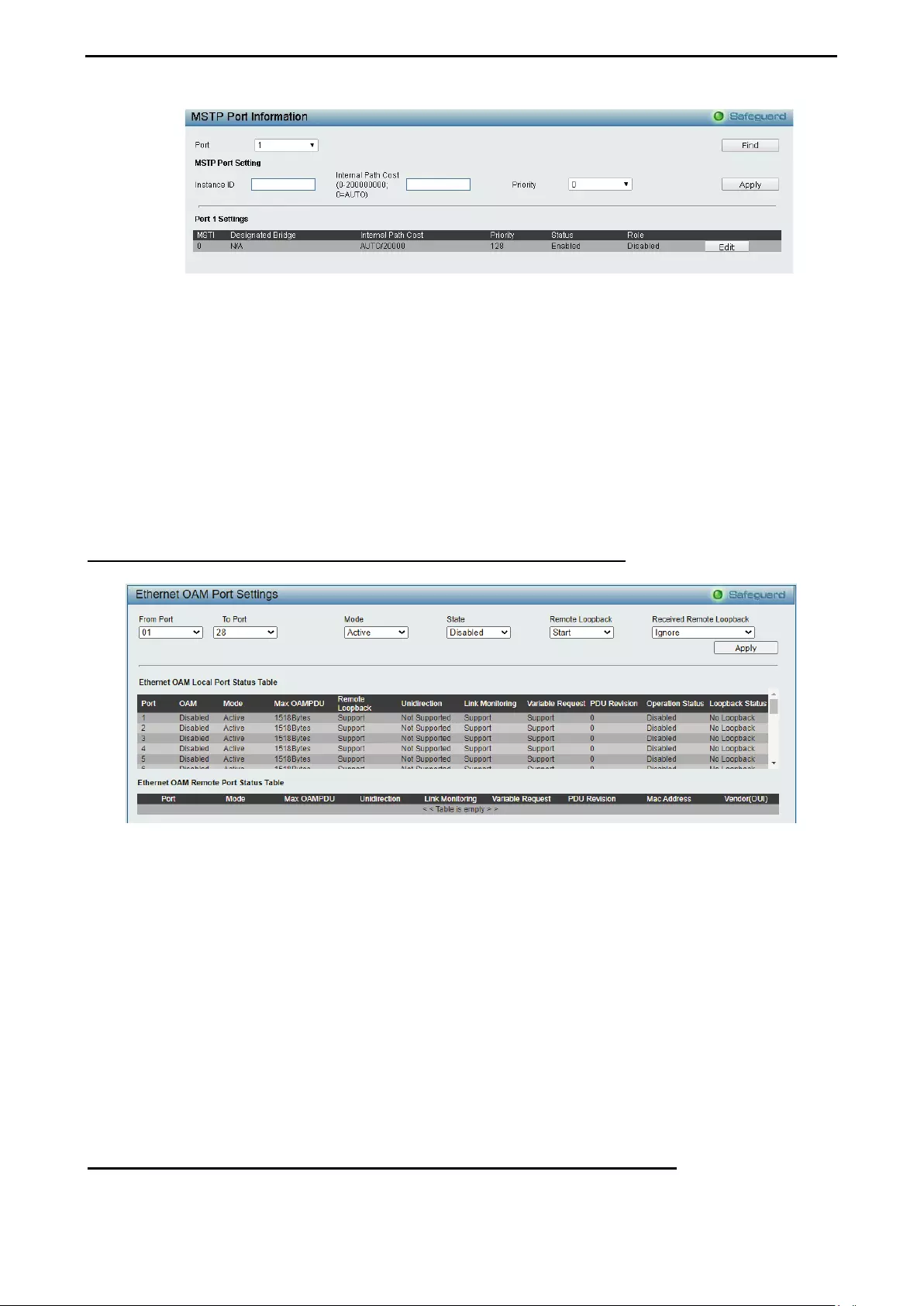
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
71
1
Figure 4.89 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port Information
Instance ID: Displays the MSTI ID of the instance being configured. An entry of 0 in this field denotes the
CIST (default MSTI).
Internal Path Cost (0=Auto): This parameter is set to represent the relative cost of forwarding packets to
specified ports when an interface is selected within a STP instance. The default setting is 0 (auto).
0 (Auto) - Selecting this parameter for the internal Cost will set quickest route automatically and
optimally for an interface. The default value is derived from the media speed of the interface.
Value 0-2000000 - Selecting this parameter with a value in the range of 0 to 2000000 will set the
quickest route then a loop occurs. A lower internal cost represents a quicker transmission.
Priority: Enter a value between 0 and 240 to set the priority for the port interface. A higher priority will
designate the interface to forward packets first. A lower number denotes a higher priority.
Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings
The Ethernet OAM Port Settings page allows user to configure the Ethernet OAM settings.
Figure 4.90 - Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings
From Port/To Port: Select a range of ports to be configured.
Mode: Use the drop-down menu to select to operate in either Active or Passive. The default mode is Active.
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the OAM function.
Remote Loopback: Specifies the Ethernet OAM remote loopback is None or Start.
None – Select to disable the remote loopback.
Start – Select to request the peer to change to the remote loopback mode.
Received Remote Loopback: To configure the client to process or to ignore the received Ethernet OAM
remote loopback command.
Process – Select to process the received Ethernet OAM remote loopback command.
Ignore – Select to ignore the received Ethernet OAM remote loopback command.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > 802.3ah EthernetLink OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
The Ethernet OAM Event Configuration page allows user to configure the Ethernet OAM configuration
settings.
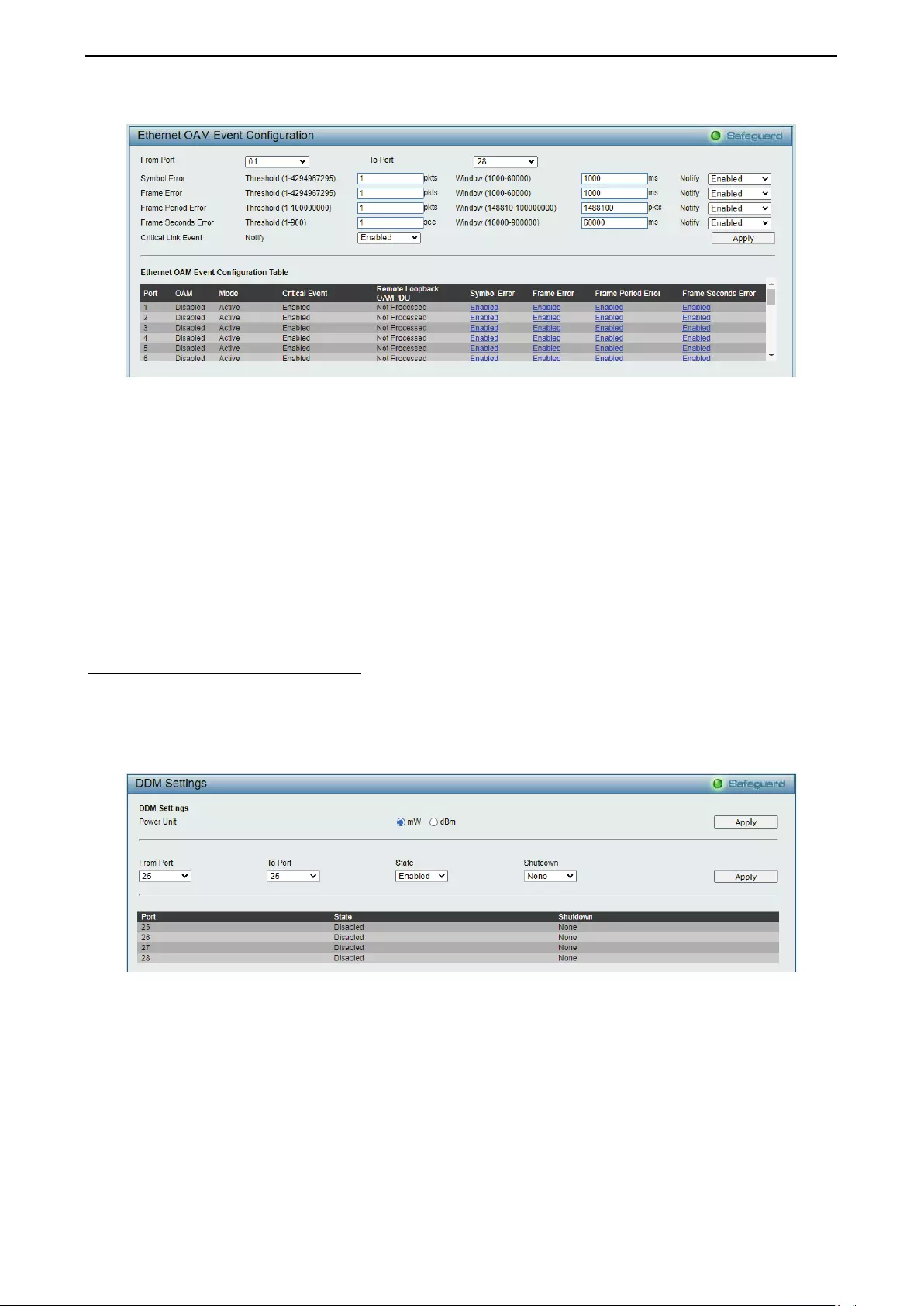
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
72
2
Figure 4.91 - Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
From Port / To Port: Select a range of ports to be configured.
Link Event: Select the link event, Link Monitor or Critical Link Event.
Link Monitor: Select the link monitor. Avaliable options are Symbol Error, Frame Error, Frame Period
Error, and Frame Seconds Error.
Threshold (0-4294967295): Enter the number of error frame or symbol in the period is required to be equal
to or greater than in order for the event to be generated.
Window (1000-60000): Enter the period of error frame or symbol in milliseconds summary event.
Notify: Select the notification to be enabled or disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
The Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) functions allow the user to view the digital diagnostic monitoring
status of SFP modules inserting to the Switch and to configure related settings.
The DDM Settings page allows user to configure the action that will occur for specific ports when an
exceeding alarm threshold or warning threshold event is encountered.
Figure 4.92 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
Power Unit: Specifies the power unit for DDM. The options are mW (milliwatts) and dBm (decibel-milliwatts).
From Port / To Port: Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
State: Specifies to enable or disable the DDM settings state.
Shutdown: Specifies whether or not to shutdown the port, when the operating parameter exceeds the Alarm
or Warning threshold.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
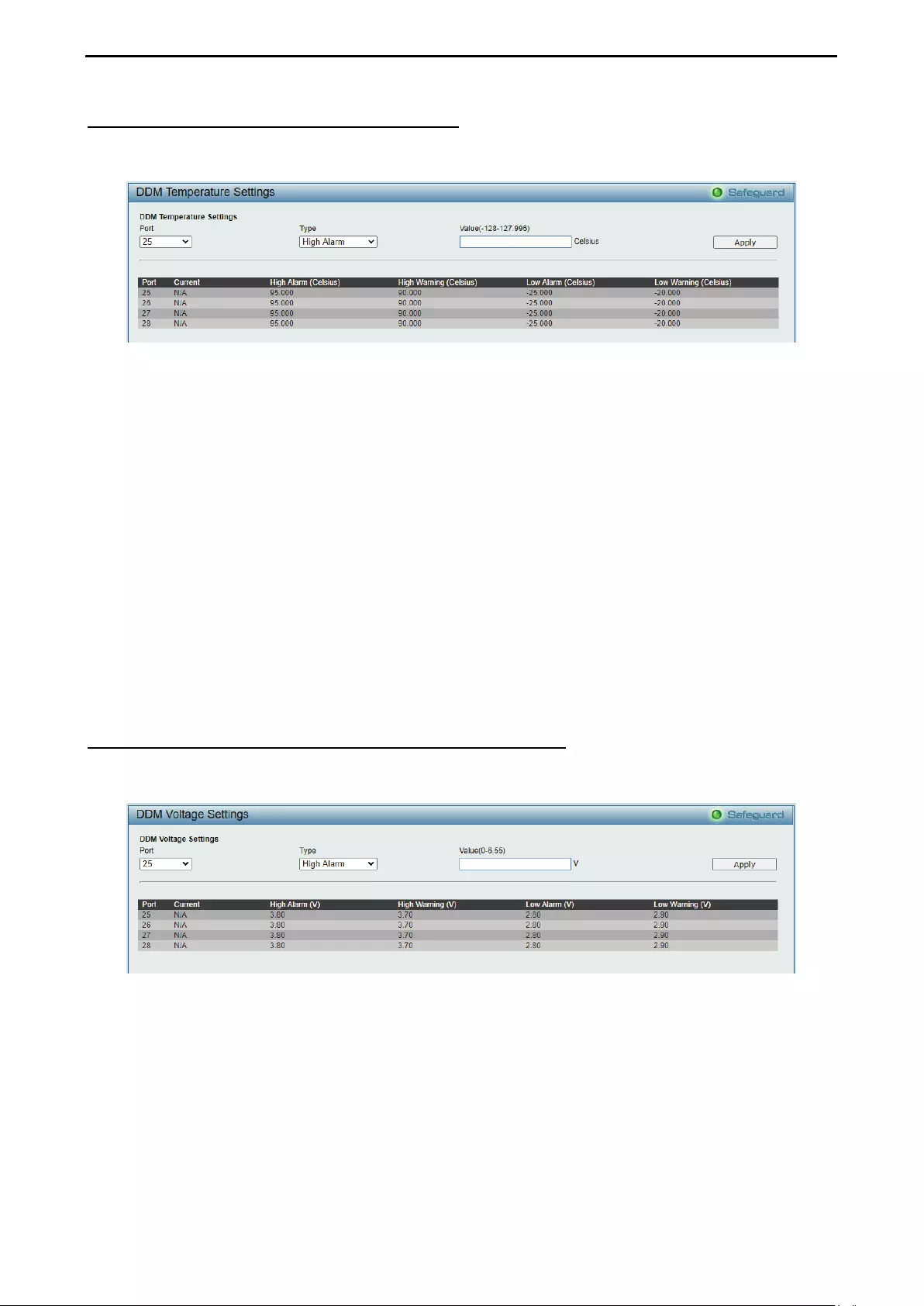
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
73
3
Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Settings
The DDM Temperature Threshold Settings page allows user to configure the DDM temperature threshold for
specific ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.93 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the type for the operating parameter, the options are High Alarm, Low Alarm, High Warning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the operating temperature rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the operating temperature falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the operating temperature rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the operating temperature falls
below the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (-128 – 127.996): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings
The DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings page is used to configure the DDM voltage threshold for
specific ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.94 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the type for the operating parameter, the options are High Alarm, Low Alarm, High Warning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the operating Voltage rises above the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the operating Voltage falls below the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the operating Voltage rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
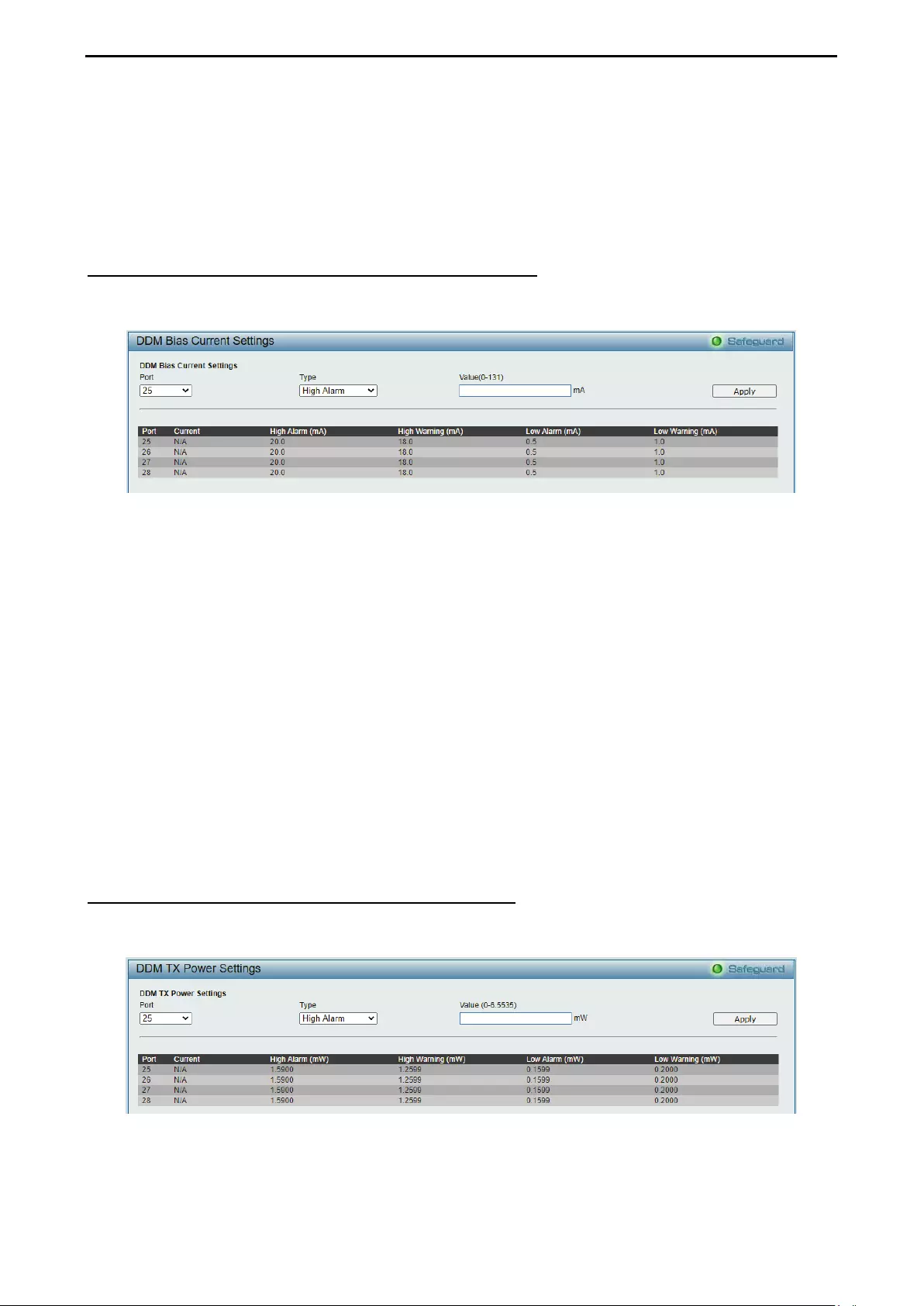
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
74
4
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the operating Voltage falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.55): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
The DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings page is used to configure the DDM Bias current threshold for
specific ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.95 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the type for the operating parameter, the options are High Alarm, Low Alarm, High Warning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the Bias current threshold rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the Bias current threshold falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the Bias current threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the Bias current threshold falls
below the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 131): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
The DDM TX Power Threshold Settings page is used to configure the threshold of TX power for specific
ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.96 - Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the type for the operating parameter, the options are High Alarm, Low Alarm, High Warning
and Low Warning.
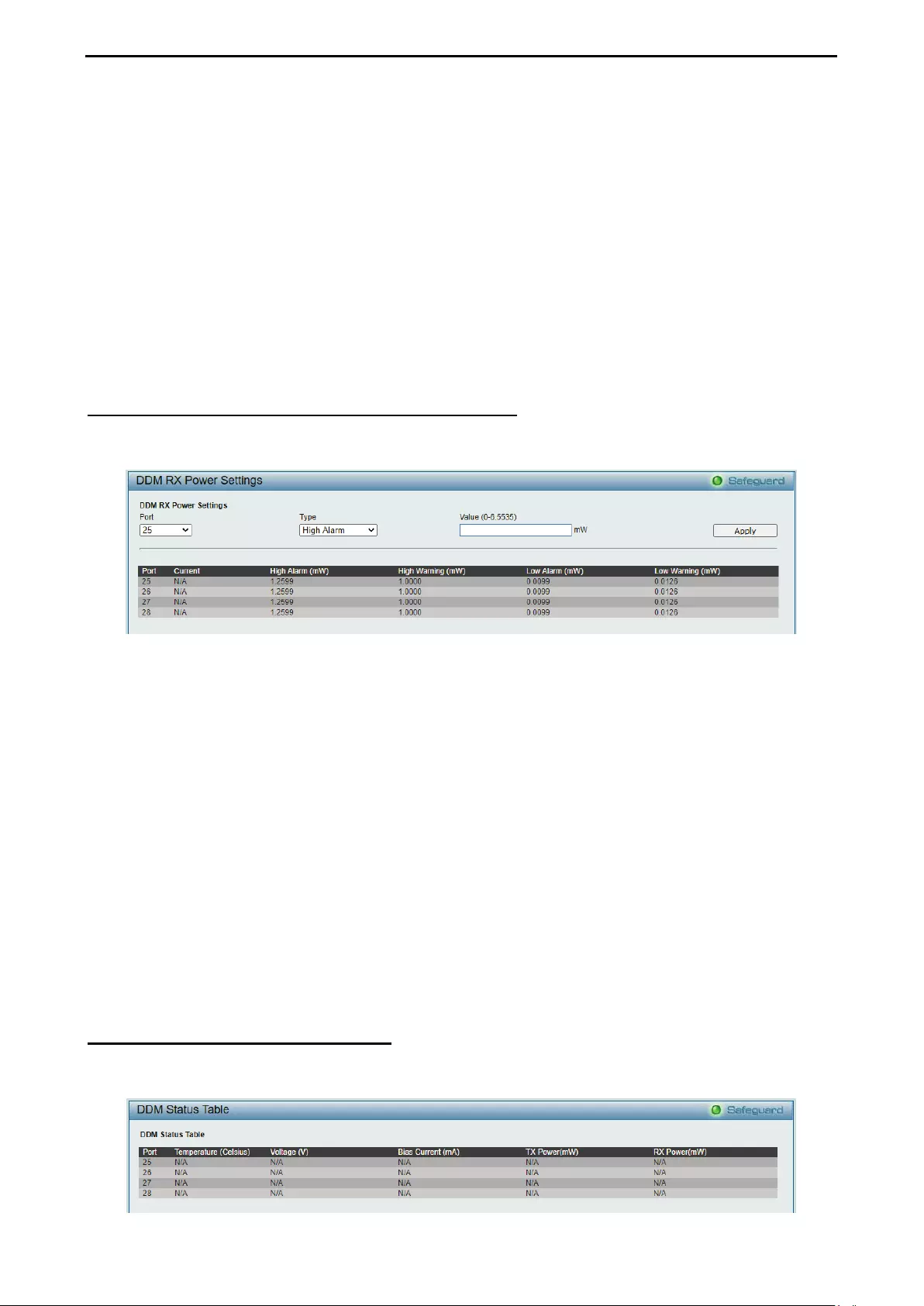
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
75
5
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the TX power threshold rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the TX power threshold falls below the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the TX power threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the TX power threshold falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.5535): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
The DDM RX Power Threshold Settings page is used to configure the threshold of RX power for specific
ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.97 - Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the type for the operating parameter, the options are High Alarm, Low Alarm, High Warning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the RX power threshold rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the RX power threshold falls below the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the RX power threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the RX power threshold falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.5535): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
The DDM Status Table page displays the current operating digital diagnostic monitoring parameters and their
values on the SFP module for specified ports.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
76
6
Figure 4.98 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
Configuration > DDM > DDM Vendor Info
The DDM Vendor Info page displays the current vendor’s operating digital diagnostic monitoring parameters
and their values on the SFP module for specified ports.
Figure 4.99 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Vendor Info
Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
The DULD Port Settings page allows user to configure the unidirectional link detection on ports.
Unidirectional link detection provides discovery mechanism based on 802.3ah to discovery its neighbor. If
the OAM discovery can complete in configured discovery time, it concludes the link is bidirectional.
Otherwise, it starts detecting task to detect the link status.
Figure 4.100 - Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
From Port / To Port: Specifies a range of ports to be configured.
Admin State: Enable or disable the port unidirectional link detection status. The default is disabled.
Mode: Specifies the mode of DULD.
Normal – Only log and event when a unidirectional link is detected.
Shutdown – If any unidirectional link is detected, disable the port and log an event.
Discovery Time (5-65535): Specifies these ports neighbor discovery time. If the discovery is timeout, the
unidirectional link detection will start. The default discovery time is 5 seconds.
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Forwarding
Allow user to create static multicast entry.
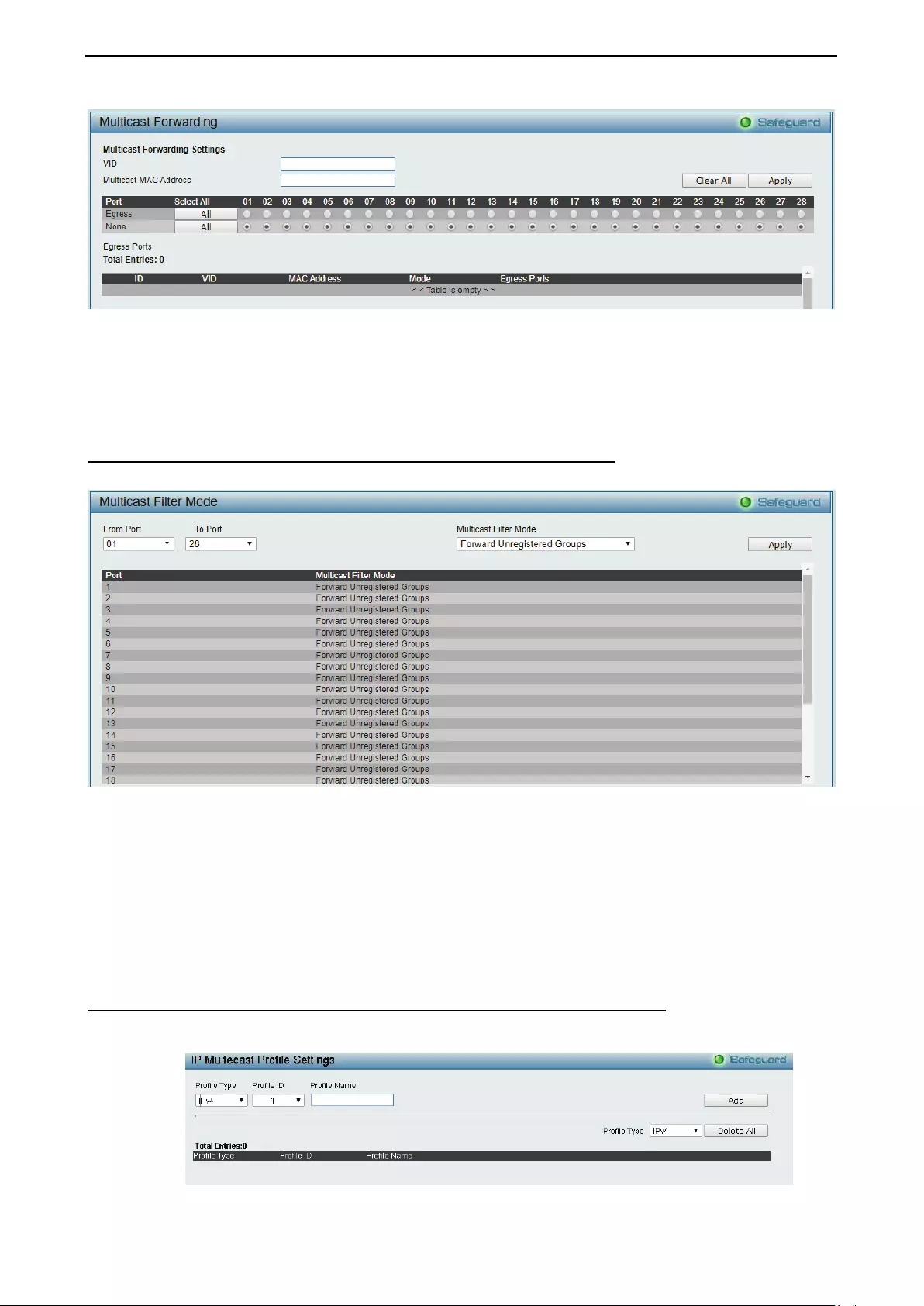
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
77
7
Figure 4.101 - Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filter > Multicast Forwarding
VID: Specify the VID
Multicast MAC Address: Specify the multicast address.
Egress: Click the Port Number for multicast traffic.
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filter Mode
The Multicast Filtering Mode page allows user to set up the filtering mode.
Figure 4.102 - Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filtering
From Port / To Port: Specify the ports of the VLAN on which the corresponding MAC address belongs to.
Multicast Filtering Mode: This drop-down menu allows user to select the action the Switch will take when it
receives a multicast packet that is to be forwarded to one of the ports in the range specified above.
Forward Unregistered Groups - This will instruct the Switch to forward a multicast packet whose
destination is an unregistered multicast group residing within the range of ports specified above.
Filter Unregistered Groups - This will instruct the Switch to filter any multicast packets whose
destination is an unregistered multicast group residing within the range of ports specified above.
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > IP Multicast Profile Settings
The IP Multicast Profile Settings page allows user to configure the IP Multicast Profile.
Figure 4.103 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IP Multicast Profile Settings
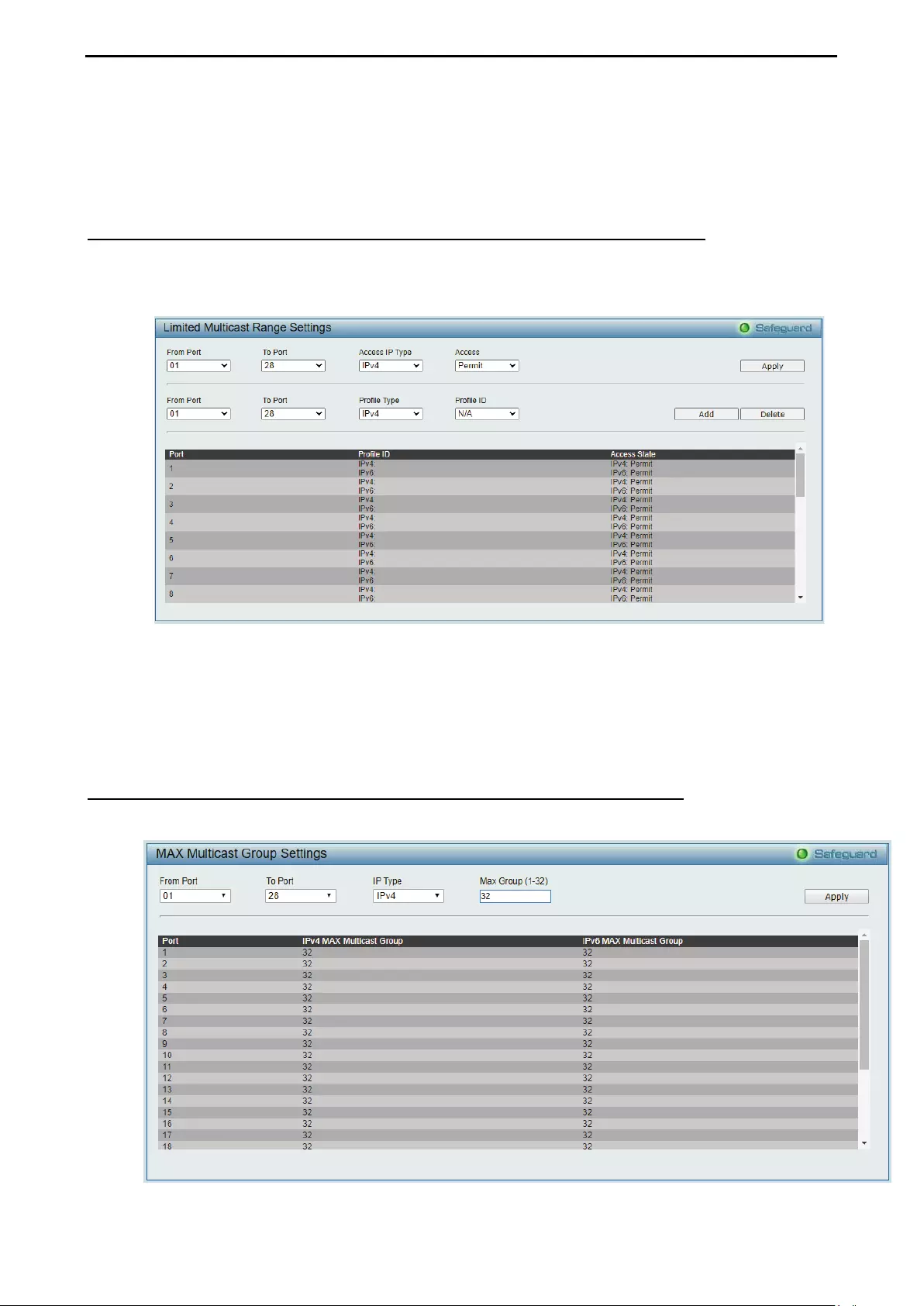
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
78
8
Profile ID: Specify the Profile ID.
Profile Name: Specify the Profile Name.
Click Add to create a new IP Multicast Profile or click Delete All to clear all the entries.
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Limited Multicast Range Settings
The Limited Multicast Range Settings page allows user to configure the Limited Multicast. Specify the port
range, select Access IP Type is IPv4 or IPv6 and select the Access is Deny or Permit then Click Apply to
make the configurations take effect.
Figure 4.104- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Limited Multicast Range Settings
From Port / To Port: Specify the port ranges to be configured.
Profile Type: Specify the profile type is IPv4 or IPv6.
Profile ID: Specify the Profile ID.
Click Add to create the Profile ID with specified ports or click Delete to remove the ports
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > MAX Multicast Group Settings
The Max Multicast Group Settings page allows user to configure the max multicast group for IGMP Snooping.
Figure 4.105- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Max Multicast Group Settings
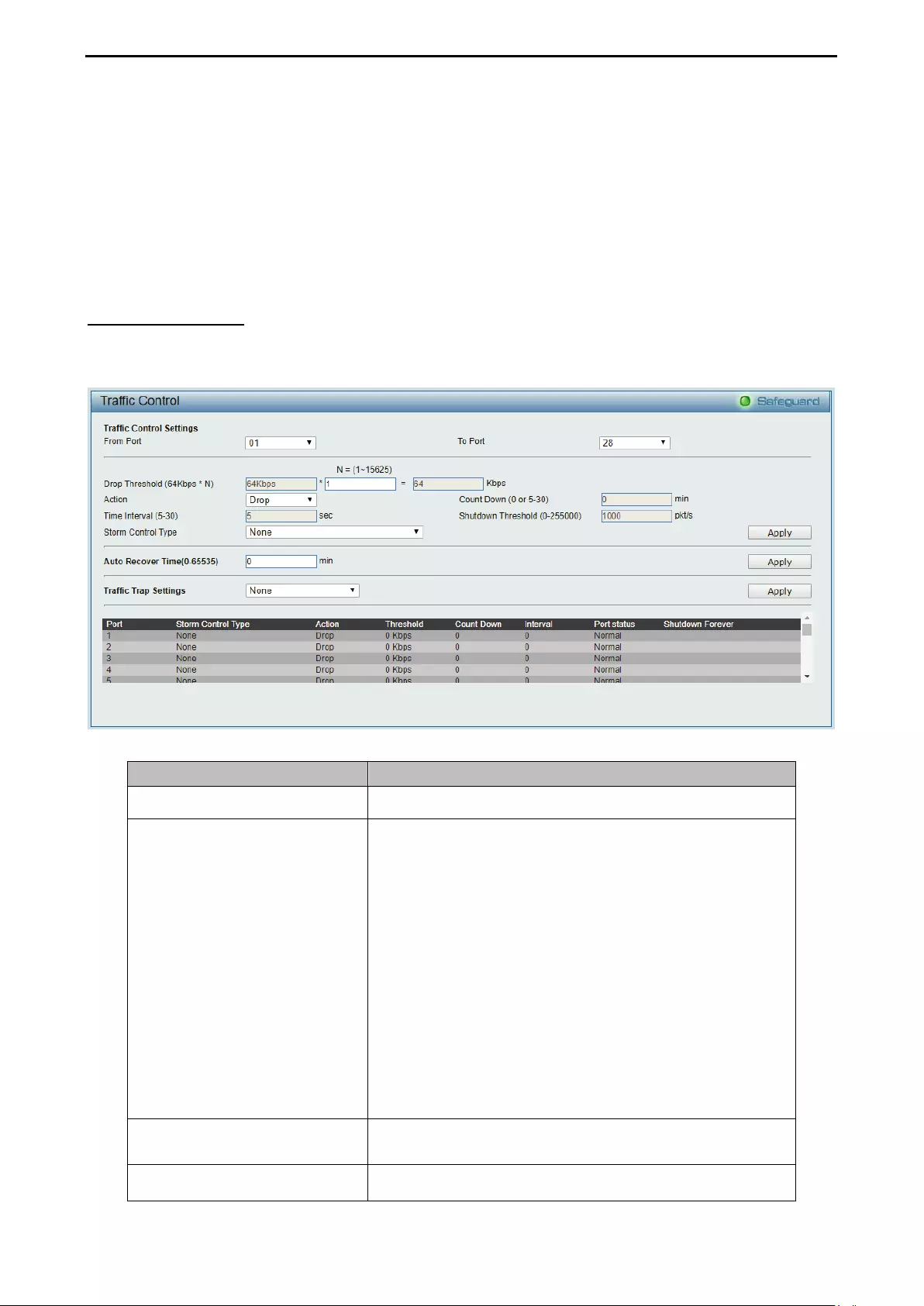
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
7
79
9
From Port / To Port: Specify the port ranges to be configured.
IP Type: Specify the IP type is IPv4 or IPv6.
Max Group (1-32): Specify the Max Group to be configured.
Action: Use the drop-down menu to select the appropriate action for this rule. The user can select Drop to
initiate the drop action or the user can select Replace to initiate the replace action.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > Traffic Control
The Traffic Control feature provides the ability to control the receive rate of broadcast, multicast, and
unknown unicast packets. Once a packet storm has been detected, the Switch will drop packets coming into
the Switch until the storm has subsided.
Figure 4.106 – QoS > Traffic Control
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port Specify the From and To port(s) to be configured.
Action
Drop
: Utilizes the hardware Traffic Control mechanism,
which means the Switch’s hardware will determine the
Packet Storm based on the Threshold value stated and
drop packets until the issue is resolved.
Shutdown: Utilizes the Switch’s software
Traffic Control
mechanism to determine the Packet Storm occurring. Once
detected, the port will deny all incoming traffic to the port
except STP BPDU packets, which are essential in keeping
the Spanning Tree operational on the Switch. If the
countdown time
r has expired and yet the Packet Storm
continues, the port will be placed in rest mode and if no
action is taken will enter auto-
recovery mode after a five
minute period. Choosing this option obligates the user to
configure the interval setting as well, wh
ich will provide
packet count samplings from the Switch’s chip to determine
if a Packet Storm is occurring.
Drop Threshold
(64Kbps * N) Specify the threshold from 64 ~ 1,024,000 Kbit per second,
with steps (N) of 64Kbps. N can be from 1 to 16000.
Count Down
(0 or 5-30)
The countdown timer is set to determine the amount of
time, in minutes, that the Switch will wait before shutting

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
80
0
down the port that is experiencing a traffic storm. This
parameter is only useful for ports configured as Shutdown
in their Action field and therefore will not operate for
Hardware based Traffic Control implementations. The
possible time settings for this field are 0, 5-30 minutes. 0
denotes that the port will never shutdown.
Time Interval (5-30)
The interval will set the time between Multicast and
Broadcast packet counts sent from the Switch’s chip to the
Traffic Control function. These packet counts are the
determining factor in deciding when incoming packets
exceed the Threshold value. The interval may be set
between 5 and 30 seconds with the default setting of 5
seconds.
Shutdown Threshold
(0-255000)
Specify the shutdown threshold for traffic threshold.
Storm Control Type
User can select the
different Storm type from Broadcast,
Multicast, Broadcast + Multicast, Unknown Unicast,
Broadcast + Unknown Unicast, Multicast + Unknown
Unicast, and Broadcast + Multicast + Unknown Unicast.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
Auto Recover Time (0-65535): Specify the auto recover time. The value is from 0 to 65535.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
Traffic Trap Settings: Specify the traffic trap is None, Storm Occurred, Storm Cleared or Both.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
NOTE: Traffic Control cannot be implemented on
ports that are set for Link Aggregation.
NOTE: Ports that are in the rest mode will be
seen as Discarding in Spanning Tree windows
and implementations though these ports will still
be forwarding BPDUs to the Switch’s CPU.
NOTE: Ports that are in rest mode will be seen as
lin
k down in all windows and screens until it
enters the auto-
recovery mode or the user
recovers these ports by configuring the port state.
QoS > Bandwidth Control
The Bandwidth Control page allows network managers to define the bandwidth settings for a specified port’s
transmitting and receiving data rates.
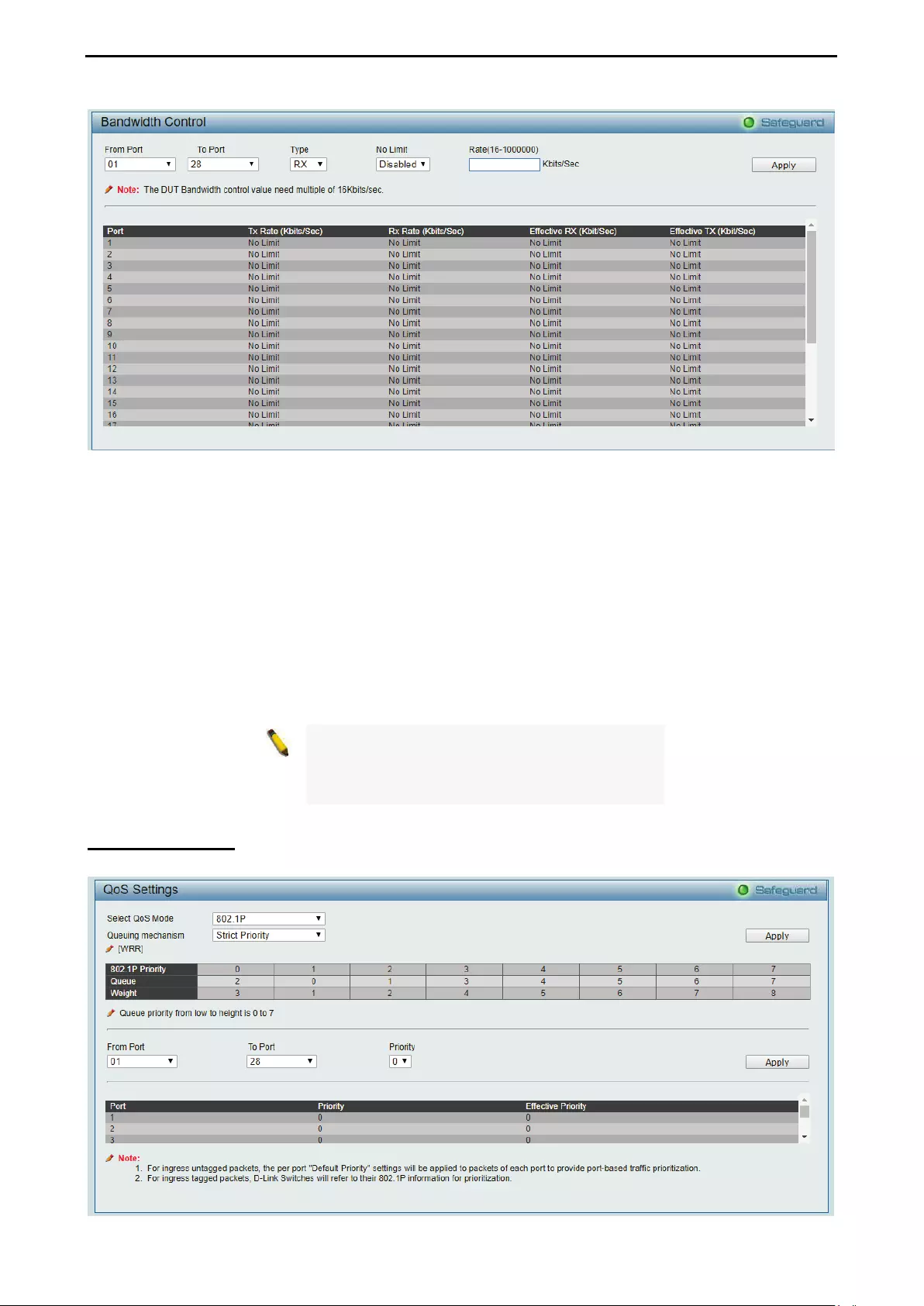
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
81
1
Figure 4.107 – QoS > Bandwidth Control
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Type: This drop-down menu allows user to select between RX (receive), TX (transmit), and Both. This
setting will determine whether the bandwidth ceiling is applied to receiving, transmitting, or both receiving
and transmitting packets.
No Limit: This drop-down menu allows user to specify that the selected port will have no bandwidth limit.
Enabled disables the limit.
Rate 16-1000000): This field allows user to enter the data rate, in Kbits per second, will be the limit for the
selected port. The value is between 63 and 1024000.
Click Apply to set the bandwidth control for the selected ports.
NOTE: The TX rate for Gigabit ports can only be
configured in multiples of 1850kbps. If any other
value is used, the system automatically rounds it
down to the lower multiple of 1850.
QoS > QoS Settings
This page allows user to configure Qos port priority and queue mechanism.
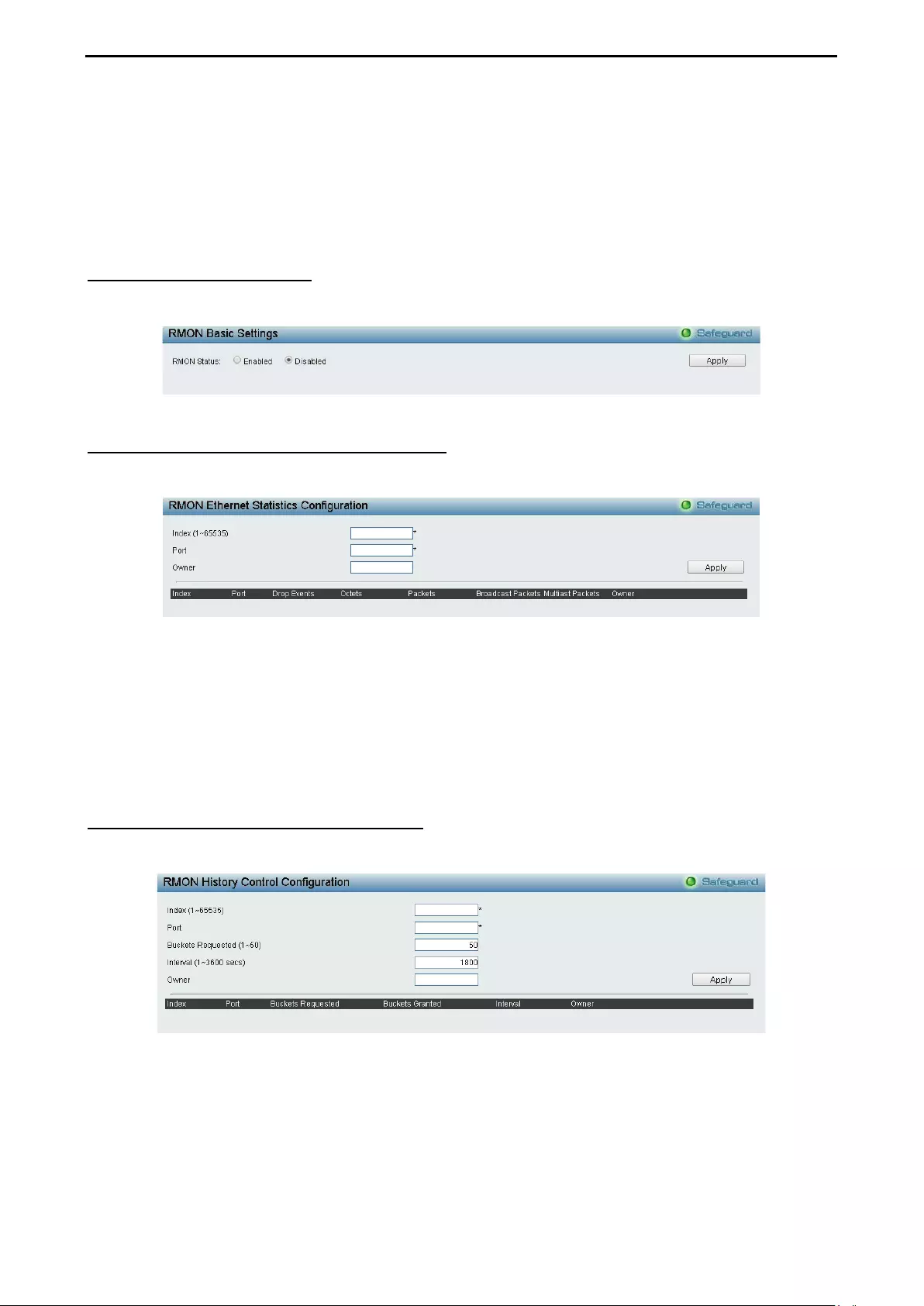
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
82
2
Figure 4.108 – QoS > QoS Setting
Select QoS Mode: Select QoS mode from options “Port Base”, “802.1P” and “DSCP”
Queuing mechanism: Select options from “Strict Priority” and “WRR”
From Port / To Port: Select the port that will port priority would applied
Priority: Priority from 0-7
RMON > RMON Basic Settings
Users can enable and disable remote monitoring (RMON) status for the SNMP function on the Switch. In
addition, RMON Rising and Falling Alarm Traps can be enabled and disabled. Click Apply to make effects.
Figure 4.109 - RMON > RMON Basic Settings
RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
The RMON Statistics Configuration page displays the information of RMON Ethernet Statistics and allows
the user to configure the settings.
Figure 4.110 - RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
The RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates the RMON Ethernet Statistics entry number.
Port: Specifies the port from which the RMON information was taken.
Owner: Displays the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
The RMON History Control Configuration page contains information about samples of data taken from ports.
For example, the samples may include interface definitions or polling periods.
Figure 4.111 - RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
The History Control Configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates the history control entry number.
Port: Specifies the port from which the RMON information was taken.
Buckets Requested (1 ~ 50): Specifies the number of buckets that the device saves.
Interval (1 ~ 3600): Indicates in seconds the time period that samplings are taken from the ports. The field
range is 1-3600. The default is 1800 seconds (equal to 30 minutes).

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
83
3
Owner: Displays the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration
The RMON Alarm Configuration page allows the user to configure the network alarms. Network alarms occur
when a network problem, or event, is detected.
Figure 4.112 - RMON > RMON Alarm Settings
The configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates a specific alarm.
Variable: Specify the selected MIB variable value.
Rising Threshold (0 ~ 2^31-1): Displays the rising counter value that triggers the rising threshold alarm.
Rising Event Index (1 ~ 65535): Displays the event that triggers the specific alarm. The possible field values are
user defined RMON events.
Owner: Displays the device or user that defined the alarm.
Interval (1 ~ 2^31-1): Defines the alarm interval time in seconds.
Sample type: Defines the sampling method for the selected variable and comparing the value against the
thresholds. The possible field values are:
Delta value – Subtracts the last sampled value from the current value. The difference in the values
is compared to the threshold.
Absolute value – Compares the values directly with the thresholds at the end of the sampling
interval.
Falling Threshold (0 ~ 2^31-1): Displays the falling counter value that triggers the falling threshold alarm.
Falling Event Index (1 ~ 65535): Displays the event that triggers the specific alarm. The possible field values are
user defined RMON events.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON Event Configuration
The RMON Event page contains fields for defining, modifying and viewing RMON events statistics.
Figure 4.113 - RMON > RMON Event Configuration
The RMON Events Page contains the following fields:
Index (1~ 65535): Displays the event.
Description: Specifies the user-defined event description.
Type: Specifies the event type. The possible values are:
None – Indicates that no event occurred.
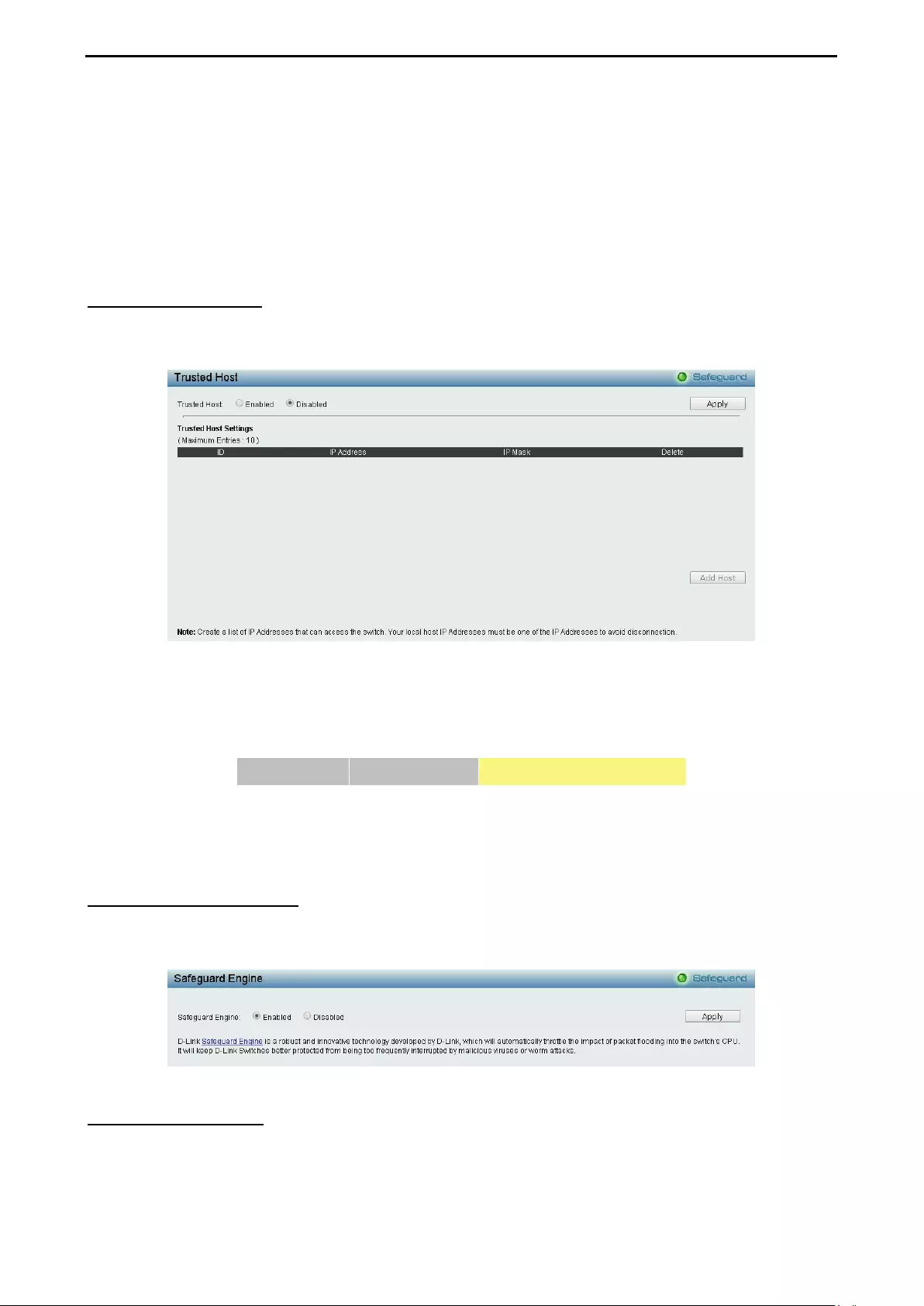
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
84
4
Log – Indicates that the event is a log entry.
SNMP Trap – Indicates that the event is a trap.
Log and Trap – Indicates that the event is both a log entry and a trap.
Community: Specifies the community to which the event belongs.
Owner: Specifies the time that the event occurred.
Click Apply to add a new RMON event.
Security > Trusted Host
Use Trusted Host function to manage the switch from a remote station. User can specify up to ten
designated management stations networks by defining the IP address/Subnet Mask as seen in the figure
below.
Figure 4.114 - Security > Trusted Host
To define a management station IP setting, click the Add Host button and type in the IP address and Subnet
mask. Click the Apply button to save the settings. User may permit only single or a range of IP addresses by
different IP mask settings, the format can either be 192.168.1.1/255.255.255.0 or 192.168.0.1/24. Please
see the example below for permitting the IP range
IP Address Subnet Mask Permitted IP
192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1~192.168.0.255
172.17.5.215 255.0.0.0 172.0.0.1~172.255.255.255
To delete the IP address, simply click the Delete button. Check the unwanted address, and then click Apply.
Security > Safeguard Engine
D-Link’s Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology that automatically throttles the impact of
packet flooding into the switch's CPU. This function helps protect the Switch from being interrupted by
malicious viruses or worm attacks. This option is enabled by default.
Figure 4.115 – Security > Safeguard Engine
Security > Port Security
Port Security is a security feature that prevents unauthorized computers (with source MAC addresses)
unknown to the Switch prior to stopping auto-learning processing from gaining access to the network.
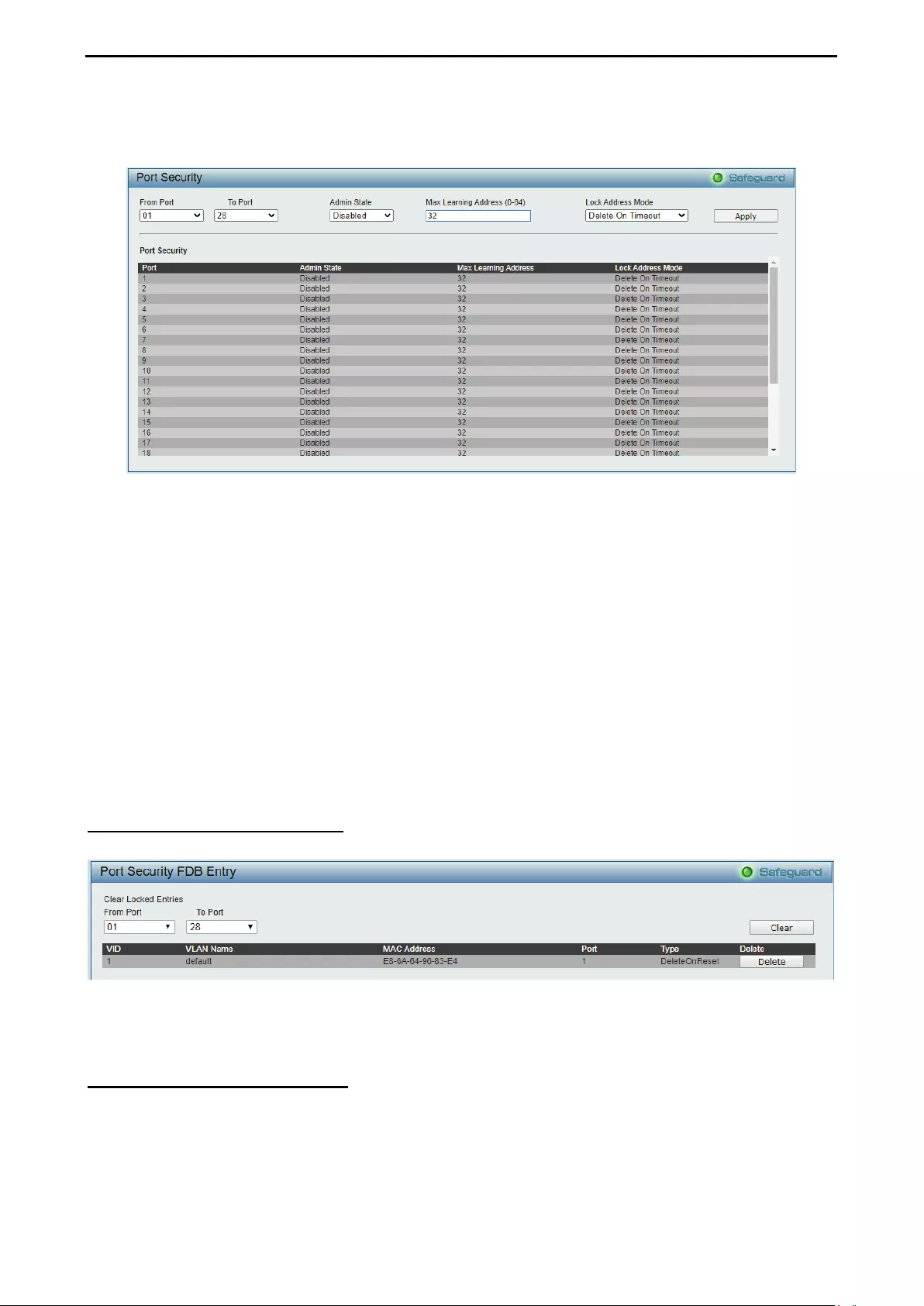
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
85
5
A given ports’ (or a range of ports') dynamic MAC address learning can be stopped such that the current
source MAC addresses entered into the MAC address forwarding table cannot be changed once the port is
enabled.
Figure 4.116 - Security > Port Security
The Port Security page contains the following fields:
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Admin State: This pull-down menu allows users to enable or disable Port Security (locked MAC address
table for the selected ports).
Max. Learning Address (0-64): The number of MAC addresses that will be in the MAC address-forwarding
table for the selected switch and group of ports.
Lock Address Mode: This pull-down menu allows user to select how the MAC address table locking will be
implemented on the Switch, for the selected group of ports. The options are:
Delete On Reset – The locked addresses will not age out until the Switch has been reset.
Delete On Timeout – The locked addresses will age out after the aging timer expires.
Permanent – The locked addresses will not age out after the aging timer expires.
Click Apply to make configurations make effects.
Security > Port Security FDB Entry
The page displays the MAC entries that trigger port security reaction.
Figure 4.117 - Configuration > Port Security FDB Entry
By click Delete, the MAC entry will be released for Port Security FDB.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
Network switches provide easy and open access to resources by simply attaching a client PC. Unfortunately
this automatic configuration also allows unauthorized personnel to easily intrude and possibly gain access to
sensitive data.
IEEE-802.1X provides a security standard for network access control, especially in Wi-Fi wireless networks.
802.1X holds a network port disconnected until authentication is completed. The switch uses Extensible
Authentication Protocol over LANs (EAPOL) to exchange authentication protocol client identity (such as a
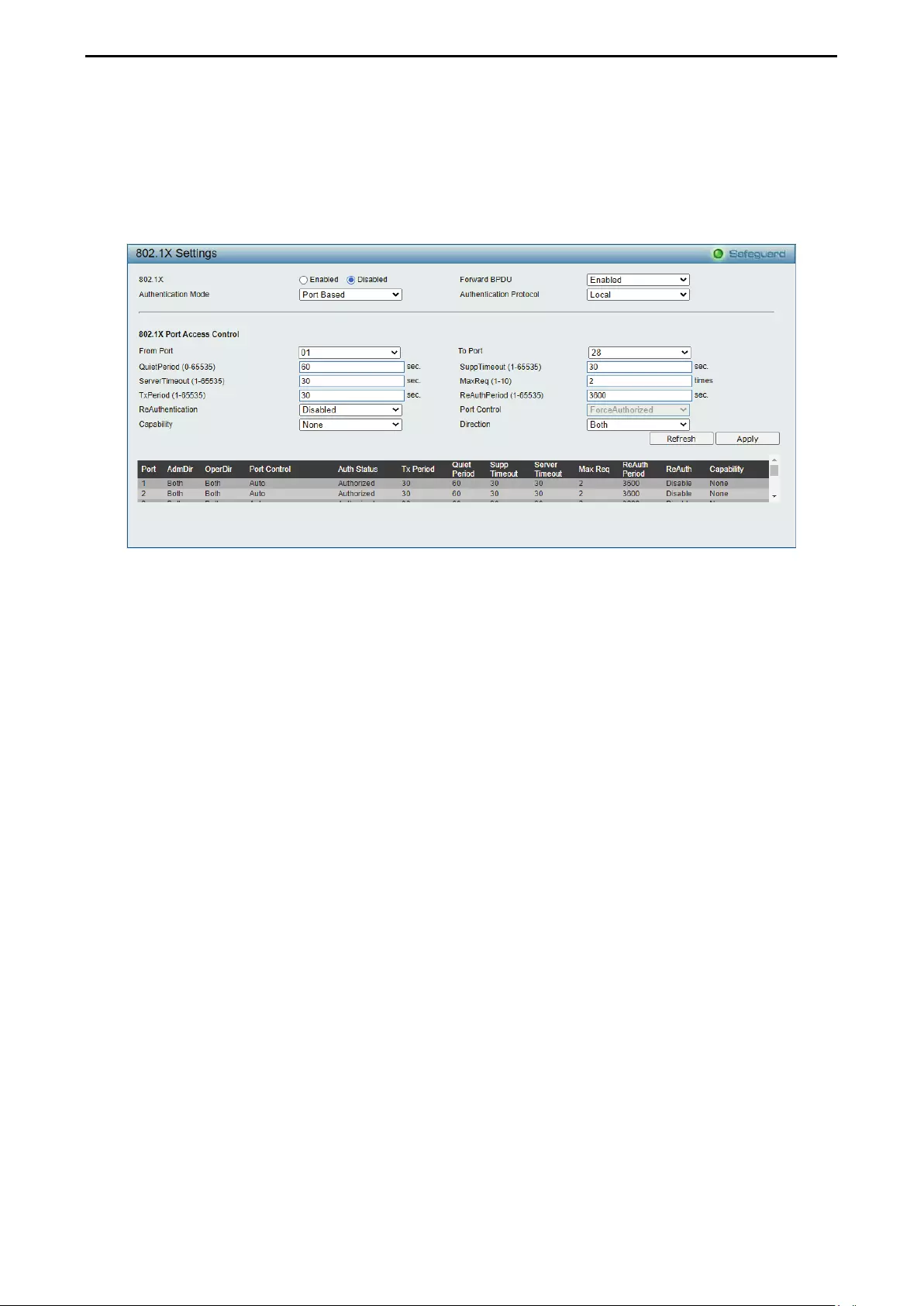
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
86
6
user name) with the client, and forward it to another remote RADIUS authentication server to verify access
rights. The EAP packet from the RADIUS server also contains the authentication method to be used. The
client can reject the authentication method and request another, depending on the configuration of the client
software and the RADIUS server. Depending on the authenticated results, the port is either made available
to the user, or the user is denied access to the network.
The RADIUS servers make the network a lot easier to manage for the administrator by gathering and storing
the user lists.
Figure 4.118 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
By default, 802.1X is disabled. To use EAP for security, select enabled and set the Authentication Mode
and Authentication Protocol then click Apply.
Authentication Mode: Indicates the 802.1X mode enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
Port Based – Enables 802.1X on ports. This is the default value.
MAC Based – Enables 802.1X on MAC addresses.
Authentication Protocol: Indicates the 802.1X Protocol on the device. The possible field values are Local
and RADIUS EAP.
From Port/To Port: Enter the port or ports to be set.
QuietPeriod (0 – 65535 sec): Sets the number of seconds that the switch remains in the quiet state
following a failed authentication exchange with the client. Default is 60 seconds.
ServerTimeout (1 – 65535 sec): Sets the amount of time the switch waits for a response from the client
before resending the response to the authentication server. Default is 30 seconds.
TxPeriod (1 – 65535 sec): This sets the TxPeriod of time for the authenticator PAE state machine. This
value determines the period of an EAP Request/Identity packet transmitted to the client. Default is 30
seconds.
ReAuthentication: Determines whether regular reauthentication will take place on this port. The default
setting is Disabled.
Capability: Indicates the capability of the 802.1X. The possible field values are:
Authenticator – Specify the Authenticator settings to be applied on a per-port basis.
None – Disable 802.1X functions on the port.
SuppTimeout (1 – 65535 sec): This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the
Authenticator and the client. Default is 30 seconds.
MaxReq (1 – 10): This parameter specifies the maximum number of times that the switch retransmits an
EAP request (md-5challnege) to the client before it times out the authentication session. Default is 2 times.
ReAuthPeriod (1 – 65535 sec): A constant that defines a nonzero number of seconds between periodic
reauthentication of the client. The default setting is 3600 seconds.
Port Control: This allows user to control the port authorization state.
Select ForceAuthorized to disable 802.1X and cause the port to transition to the authorized state
without any authentication exchange required. This means the port transmits and receives normal
traffic without 802.1X-based authentication of the client.
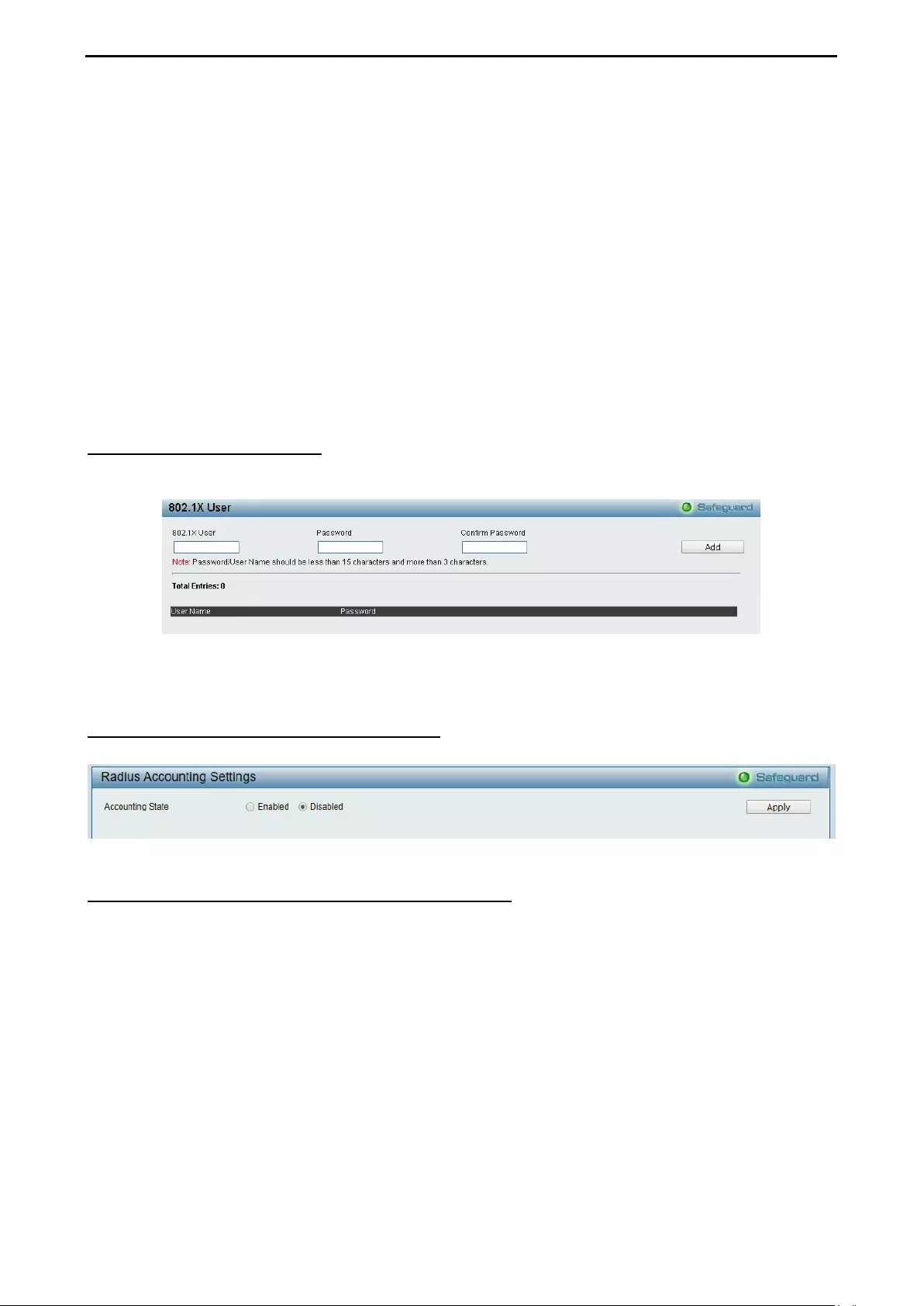
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
87
7
If ForceUnauthorized is selected, the port will remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all
attempts by the client to authenticate. The Switch cannot provide authentication services to the client
through the interface.
If Auto is selected, it will enable 802.1X and cause the port to begin in the unauthorized state,
allowing only EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port. The authentication process
begins when the link state of the port transitions from down to up, or when an EAPOL-start frame is
received. The Switch then requests the identity of the client and begins relaying authentication
messages between the client and the authentication server.
The default setting is Auto.
Direction: Sets the administrative-controlled direction on the port. The possible field values are:
Both – Specify the control is exerted over both incoming and outgoing traffic through the controlled
port selected in the first field.
In – Disables the support in the present firmware release.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
The 802.1X User page allows user to set different local users on the Switch. Enter a 802.1X User name,
Password and Confirm Password. Properly configured local users will be displayed in the table.
Figure 4.119 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
Click Add to add a new 802.1X user.
Security > 802.1X > Radius Accounting Settings
The page allows user to turn of accounting state in 802.1x.
Figure 4.120 - Security > 802.1X > Radius Accounting Settings
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS Server
The 802.1X Authentication RUAIUS of the Switch allows user to facilitate centralized user administration as
well as providing protection against a sniffing, active hacker.
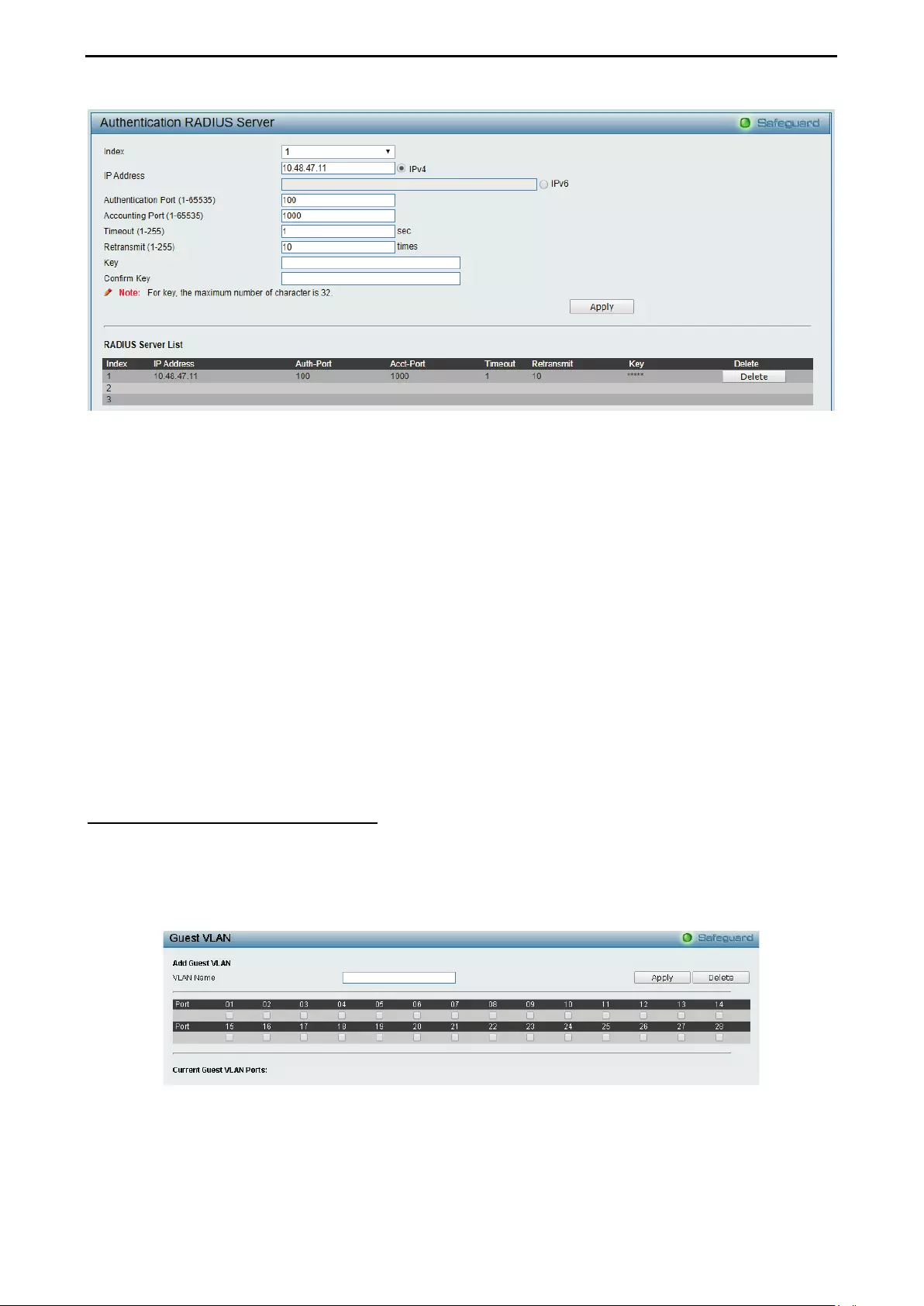
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
88
8
Figure 4.121 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RUDIUS
Index: Choose the desired RADIUS server to configure: 1, 2 or 3.
IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP address.
Authentication Port (1 - 65535): Set the RADIUS authentic server(s) UDP port. The default port is 1812.
Accounting Port (1 - 65535): Set the RADIUS account server(s) UDP port. The default port is 1813.
Timeout (1 – 255 sec): This field will set the time the Switch will wait for a response of authentication from
the user. The user may set a time between 1 and 255 seconds. The default setting is 5 seconds.
Retransmit (1 – 255 times): This command will configure the maximum number of times the Switch will
accept authentication attempts. Users failing to be authenticated after the set amount of attempts will be
denied access to the Switch and will be locked out of further authentication attempts. Command line
interface users will have to wait 60 seconds before another authentication attempt. Telnet and web users will
be disconnected from the Switch. The user may set the number of attempts from 1 to 255. The default
setting is 2.
Key: Set the key the same as that of the RADIUS server.
Confirm Key: Confirm the shared key is the same as that of the RADIUS server.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN
The 802.1X Guest VLAN page allows user to set a Guest VLAN, and the user must first configure a normal
VLAN which can be enabled here for Guest VLAN status.
Enter the pre-configured VLAN name to create as a Guest 802.1X VLAN and select the port or ports. Click
Apply to implement the settings.
Figure 4.122 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN
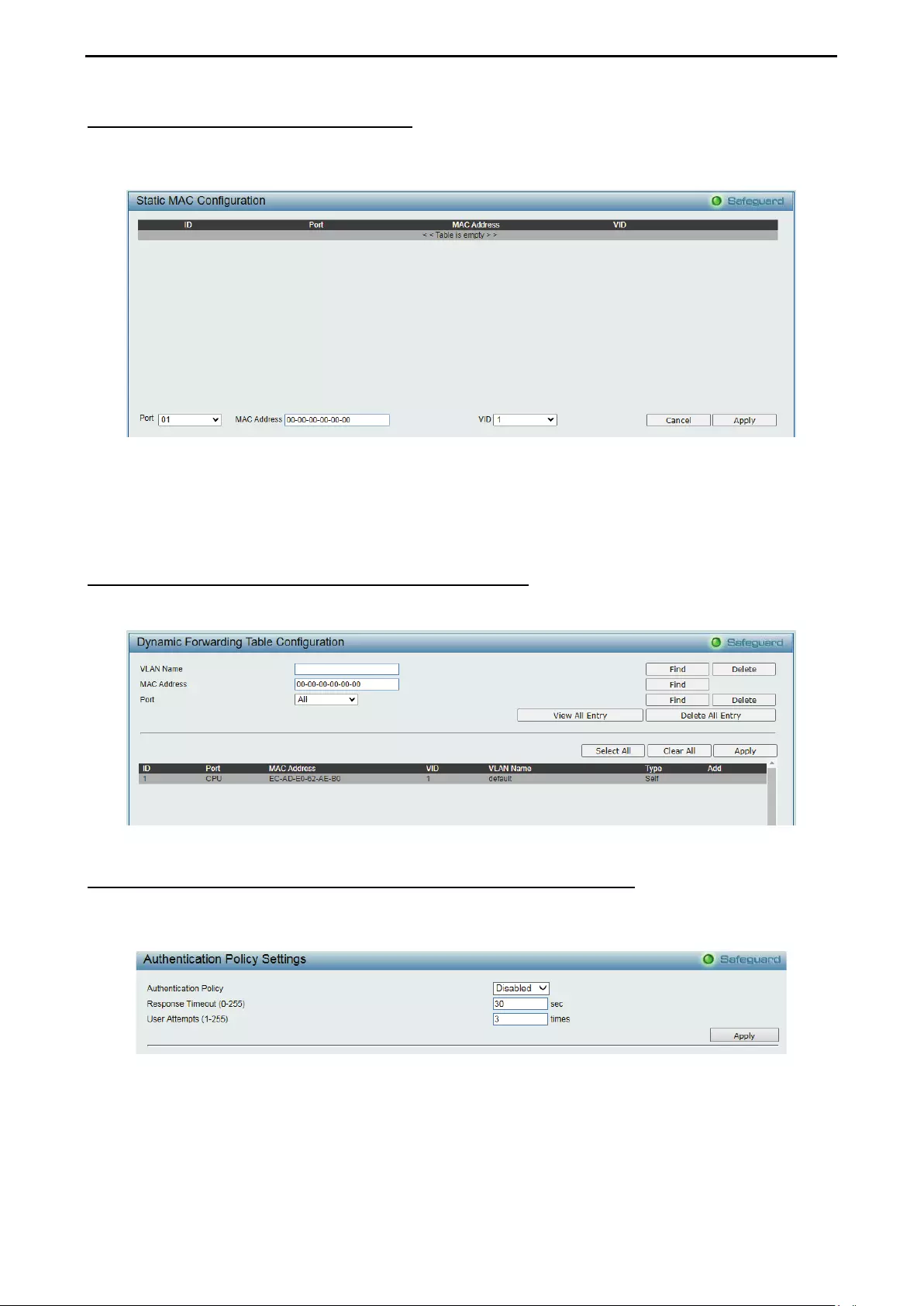
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
8
89
9
Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC
Allow user to create static MAC address entry into forwarding table. This feature usually used in the port
connected to certain devices that are permanent used in network, for example: DHCP servers, syslog server,
network gateway location, etc.
Figure 4.123 – Security > MAC Address Table > Static Mac Address
The Static MAC Address Lists table displays the static MAC addresses connected, as well as the VID.
Add Static MAC Address: you need to select the assigned Port number. Enter both the Mac Address and
VID, and then Click Add. Click Delete to remove one entry or click Delete all to clear the list.
Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table
For each port, this table displays the MAC address learned by the Switch. To add a MAC address to the
Static Mac Address List, click the Add checkbox, and then click Apply associated with the identified address.
Figure 4.124 – Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Policy Settings
This feature will enable an administrator-defined authentication policy for users trying to access the Switch.
When enabled, the device will check the Login Method List and choose a technique for user authentication
upon login.
Figure 4.125 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Policy Settings
Authentication Policy: Use the pull-down menu to enable or disable the Authentication Policy on the Switch.
Response Timeout (0 - 255): This field will set the time the Switch will wait for a response of authentication
from the user. The user may set a time between 0 and 255 seconds. The default setting is 30 seconds.
User attempts (1 - 255): This command will configure the maximum number of times the Switch will accept
authentication attempts. Users failing to be authenticated after the set amount of attempts will be denied
access to the Switch and will be locked out of further authentication attempts. Command line interface users
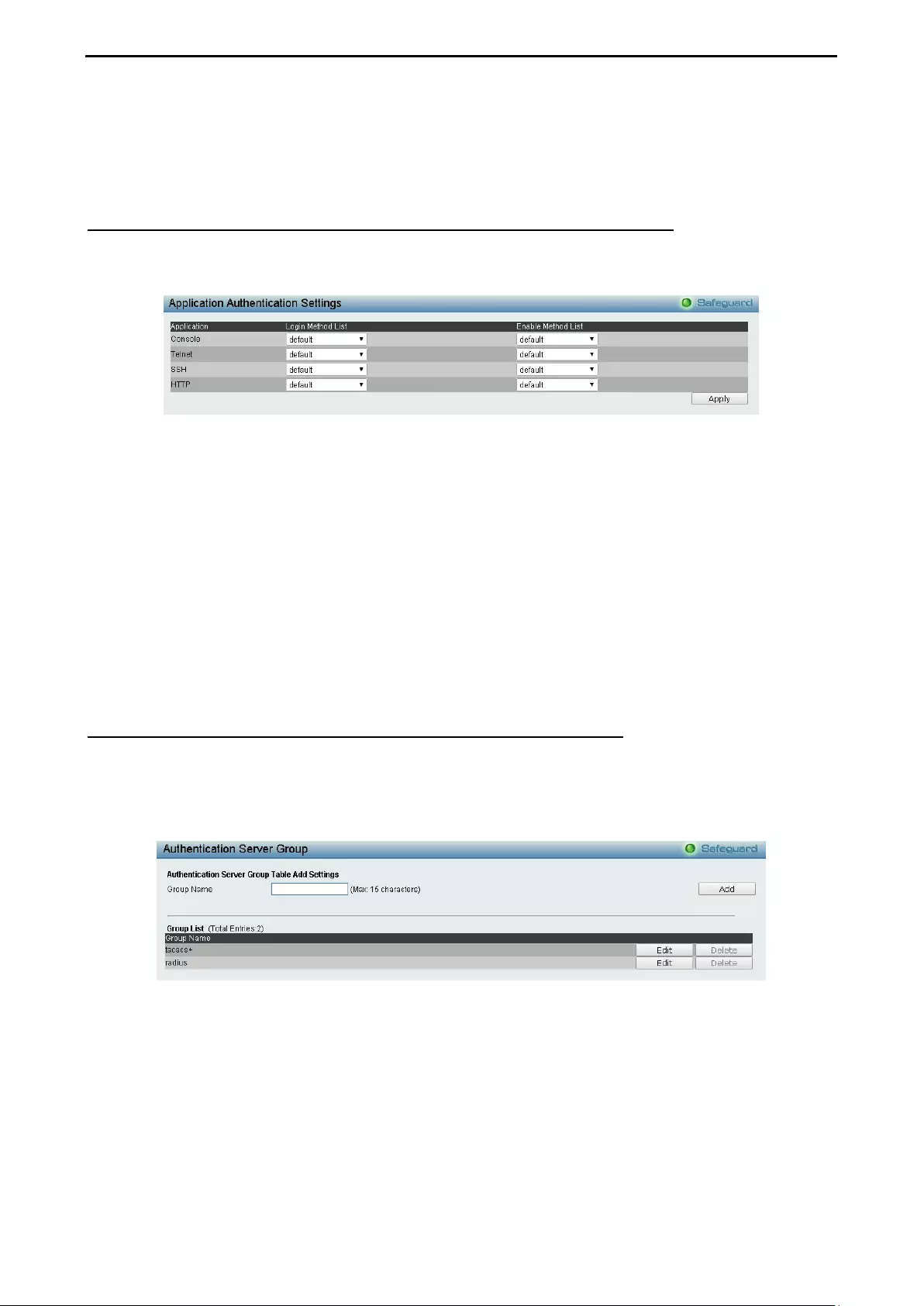
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
90
0
will have to wait 60 seconds before another authentication attempt. Telnet and web users will be
disconnected from the Switch. The user may set the number of attempts from 1 to 255. The default setting is
3.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Application Authentication Settings
The Application Authentication Settings page allows user to configure switch configuration applications
(Console, Telnet, SSH, HTTP) for login at the user level and at the administration level (Enable Admin)
utilizing a previously configured method list.
Figure 4.126 – Security > Access Authentication control > Application Authentication Settings
Application: Lists the configuration applications on the Switch. The user may configure the Login Method
List and Enable Method List for authentication for Console, Telnet application, SSH and the WEB (HTTP)
application.
Login Method List: Using the pull-down menu, configure an application for normal login on the user level,
utilizing a previously configured method list. The user may use the default Method List or other Method List
configured by the user.
Enable Method List: Using the pull-down menu, configure an application for normal login on the user level,
utilizing a previously configured method list. The user may use the default Method List or other Method List
configured by the user.
Click Apply to implement configuration changes.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group
A server group is a technique used to group TACACS+ and RADIUS server hosts into user-defined
categories for authentication using method lists. The user may define the type of server group by protocol or
by previously defined server group. The Switch has three built-in Authentication Server Groups that cannot
be removed but can be modified.
To add a user-defined group to the list, click the Add button in the Authentication Server Group page.
Figure 4.127 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server Group
Simply enter a group name of no more than 15 alphanumeric characters to define the user group to add.
After clicking Apply, the new user-defined group will be displayed in the Server Group table. Here, it can be
configured as the user desires.
F
The Switch has two built-in Authentication Server Groups that cannot be removed but can be modified. To
modify a particular group, click Edit button, which will then display the following window.
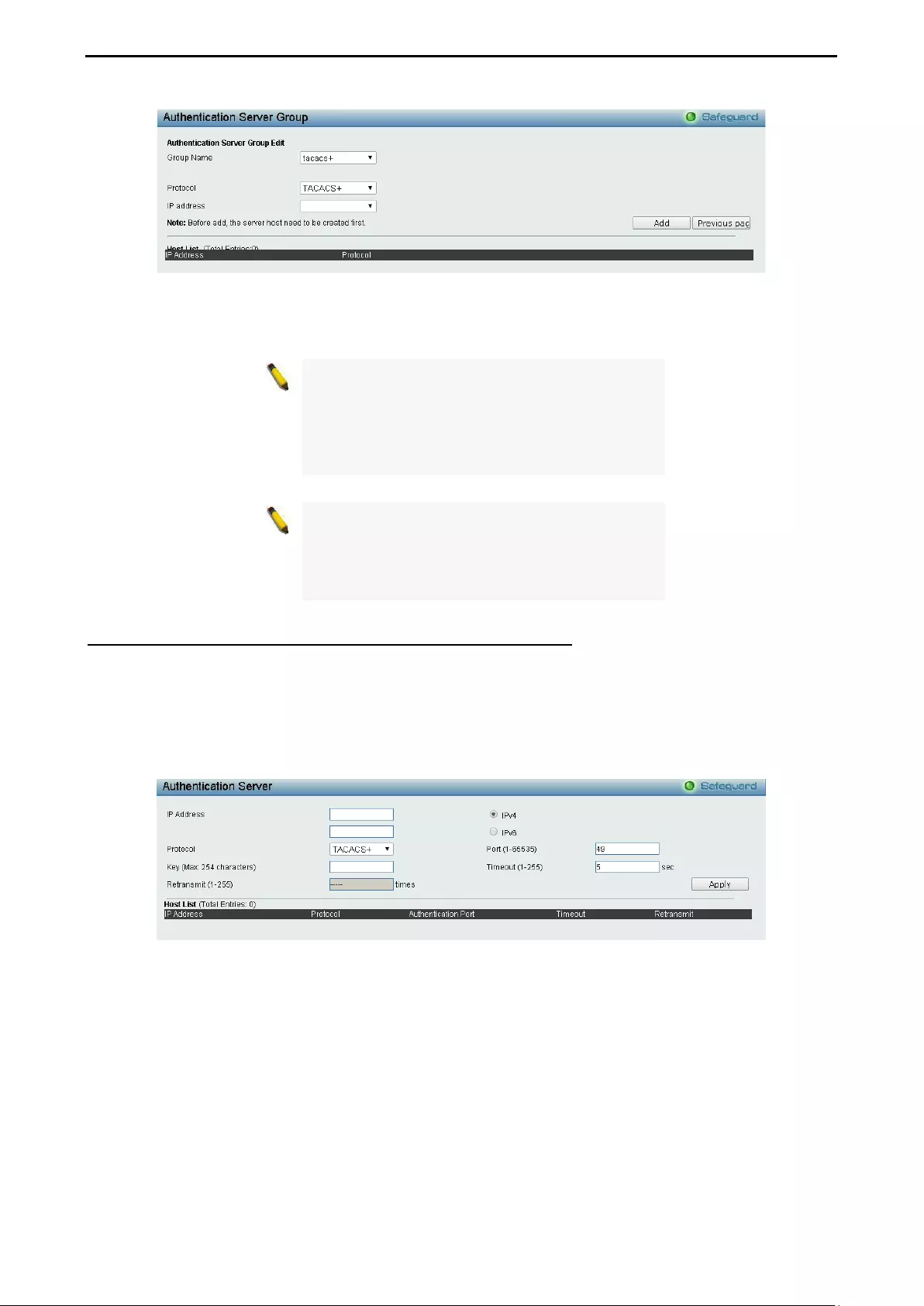
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
91
1
Figure 4.128 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server Group-Edit
Select Group Name, Protocol and IP address then click Add to implement the changes.
NOTE: The user mu
st configure Authentication
Server Hosts using the Authentication Server
Hosts page before adding hosts to the list.
Authentication Server Hosts must be configured
for their specific protocol on a remote centralized
server before this function can work properly.
NOTE: The two built in server groups can only
have server hosts running the same TACACS
daemon. The TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols
are separate entities and are not compatible with
each other.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server
This Authentication Server page will set user-defined Authentication Server Hosts for the TACACS+ and
RADIUS security protocols on the Switch. When a user attempts to access the Switch with Authentication
Policy enabled, the Switch will send authentication packets to a remote TACACS+ or RADIUS server host on
a remote host. The TACACS+ or RADIUS server host will then verify or deny the request and return the
appropriate message to the Switch. More than one authentication protocol can be run on the same physical
server host but, remember that TACACS+ and RADIUS are separate entities and are not compatible with
each other. The maximum supported number of server hosts is 16.
Figure 4.129 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server
To add an Authentication Server Host:
IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP address.
Protocol: The protocol used by the server host. The user may choose one of the following:
TACACS+ – Enter this parameter if the server host utilizes the TACACS+ protocol.
RADIUS – Enter this parameter if the server host utilizes the RADIUS protocol.
Key: Authentication key to be shared with a configured TACACS+ or RADIUS servers only. Specify an
alphanumeric string up to 254 characters.
Port (1 - 65535): Enter a number between 1 and 65535 to define the virtual port number of the
authentication protocol on a server host. The default port number is 49 for TACACS+ server and 1813 for
RADIUS servers but the user may set a unique port number for higher security.
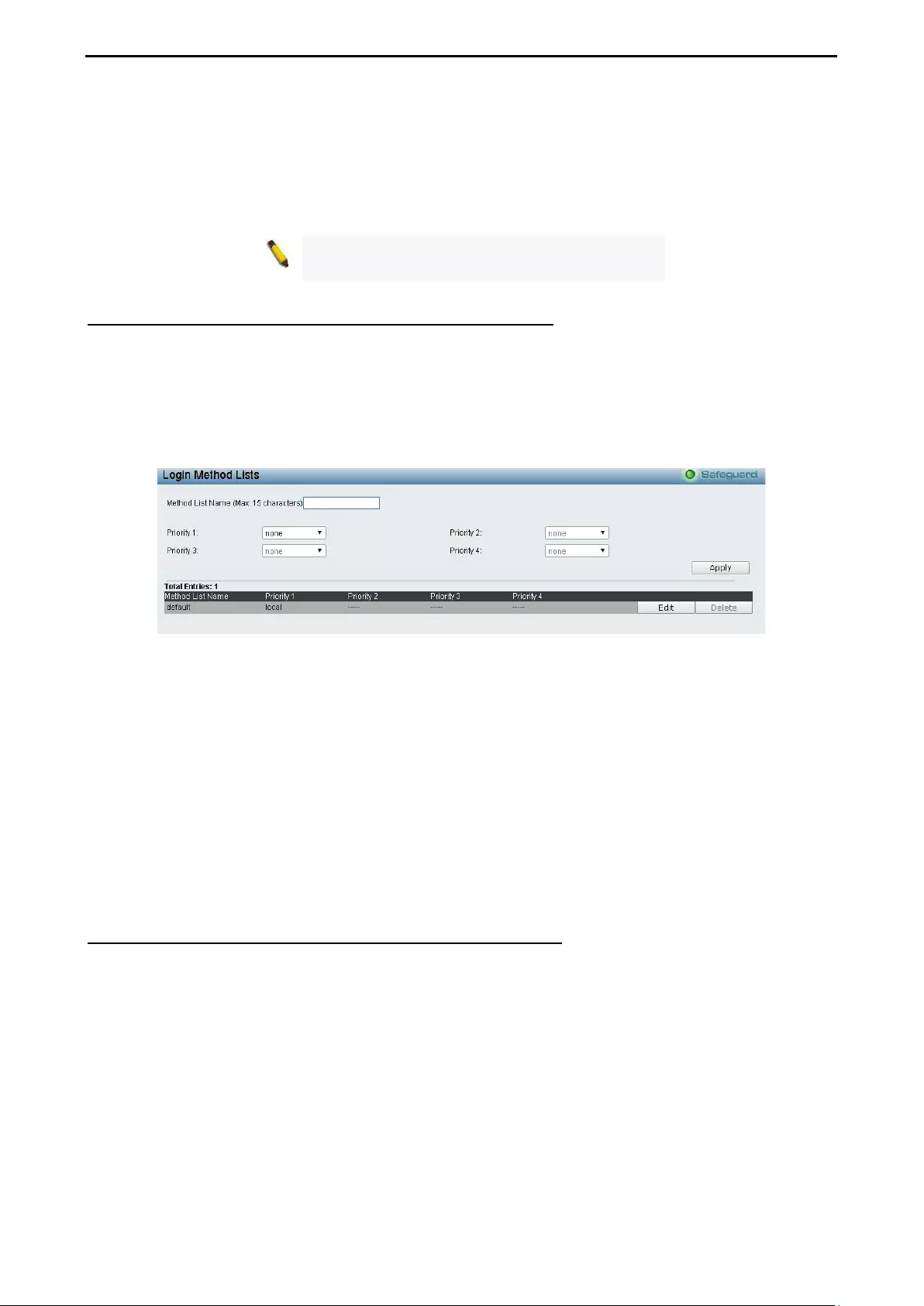
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
92
2
Timeout (1 - 255): Enter the time in seconds the Switch will wait for the server host to reply to an
authentication request. The default value is 5 seconds.
Retransmit (1 - 255): Enter the value in the retransmit field to change how many times the device will resend
an authentication request when the TACACS server does not respond.
Click Apply to add a new Authentication Server Host.
NOTE: More than one authentication protocol can
be run on the same physical server host.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Login Method Lists
This feature will configure a user-defined or default Login Method List of authentication techniques for users
logging on to the Switch. Successful login using any of these techniques will give the user a "User" privilege
only. To upgrade his or her status to the administrator level, the user must use the Enable Admin window, in
which the user must enter a previously configured password, set by the administrator.
The Switch contains one Method List that is set and cannot be removed, yet can be modified. To delete a
Login Method List defined by the user, click Delete button. To modify the Login Method List, click Edit button.
Figure 4.130 – Security > Access Authentication control > Login Method Lists
To define a Login Method List, set the following parameters and click Apply:
Method List Name: Enter a method list name defined by the user of up to 15 characters.
Priority 1, 2, 3, 4: The user may add one, or a combination of up to four of the following authentication
methods to this method list:
none – Adding this parameter will require an authentication to access the Switch.
local – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the local user account
database on the Switch.
tacacs+ – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the TACACS+
protocol from a remote TACACS+ server.
radius – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the RADIUS protocol from a
remote RADIUS server.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Enable Method Lists
The Enable Method Lists page is used to set up Method Lists to promote users with user level privileges to
Administrator (Admin) level privileges using authentication methods on the Switch. Once a user acquires
normal user level privileges on the Switch, he or she must be authenticated by a method on the Switch to
gain administrator privileges on the Switch, which is defined by the Administrator. A maximum of eight
Enable Method Lists can be implemented on the Switch, one of which is a default Enable Method List. This
default Enable Method List cannot be deleted but can be configured.
To delete an Enable Method List defined by the use, click Delete button to the entry desired to be deleted.
To modify and Enable Method List, click Edit button to make the changes and click Apply.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
93
3
Figure 4.131 – Security > Access Authentication control > Enable Method Lists
To define an Enable Login Method List, set the following parameter and click Apply:
Method List Name: Enter a method list name defined by the user of up to 15 characters.
Priority 1, 2, 3, 4: The user may add one, or a combination of up to four of the following authentication
methods to this method list:
none – Adding this parameter will require an authentication to access the Switch.
local – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the local user account
database on the Switch.
tacacs+ – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the TACACS+
protocol from a remote TACACS+ server.
radius – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the RADIUS protocol
from a remote RADIUS server.
Security > Access Authentication Control > Local Enable Password Settings
The Local Enable Password Settings page allows user to configure the locally enabled password. When a
user chooses the "local_enable" method to promote user level privileges to administrator privileges, he or
she will be prompted to enter the password configured here that is locally set on the Switch.
Figure 4.132 – Security > Access Authentication control > Local Enable Password Settings
To set the Local Enable Password, set the following parameters and click Apply:
Old Local Enable Password: If a password was previously configured for this entry, enter it here in order to
change it to a new password.
New Local Enable Password: Enter the new password that user specified for the Switch to authenticate
users attempting to access Administrator Level privileges on the Switch. The user may set a password of up
to 15 characters.
Confirm Local Enable Password: Confirm the new password entered above. Entering a different password
here from the one set in the New Local Enabled field will result in a fail message.
Security > Traffic Segmentation
This feature provides administrators to limit traffic flow from a single port to a group of ports on a single
Switch. This method of segmenting the flow of traffic is similar to using VLANs to limit traffic, but is more
restrictive.
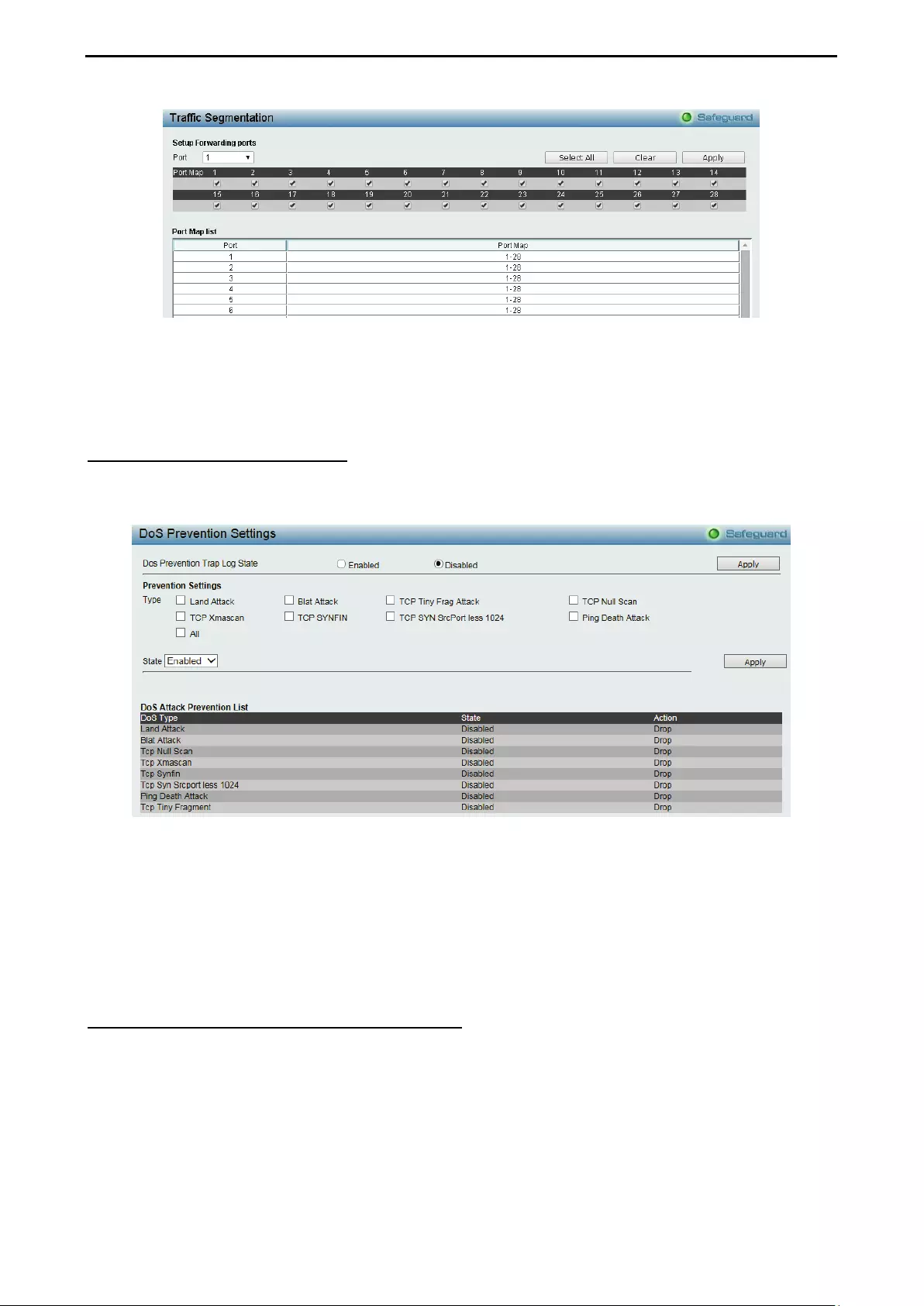
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
94
4
Figure 4.133 – Security > Traffic Segmentation
To configure traffic segmentation specify a port or All ports from the switch, using the Port pull-down menu
and select Port Map then click Apply to enter the settings into the Switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
Click Select All to select all port maps or click Clear button to uncheck port maps.
Security > DoS Prevention Settings
The DoS is a malicious attack against a network. This attack is designed to stop a network from functioning
by flooding it with useless traffic. Symptoms of a malicious attack include the inability to access any web site
or a particular web site being unavailable and network performance slowing down.
Figure 4.134 – Security > DoS Prevention Settings
Prevention Settings:
Type: Select the attack types to be prevented. The types are Land Attack, TCP Tine Frag Attack, TCP Null
Scan, TCP Xmascan, TCP SYNFIN, TCP SYN SrcPortless 1024, Ping Death Attack or All.
State: Specify the state to be enabled or disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
The primary purpose of Smart Binding is to restrict client access to a switch by enabling administrators to
configure pairs of client MAC and IP addresses that are allowed to access networks through a switch.
The Smart Binding function is port-based, meaning that a user can enable or disable the function on any
individual port. Once Smart Binding is enabled on a switch port, the switch will restrict or allow client access
by checking the pair of IP-MAC addresses with the pre-configured database, also known as the “IMPB white
list”.
Users can enable or disable the Packet Inspection and DHCP Snooping on the Switch.
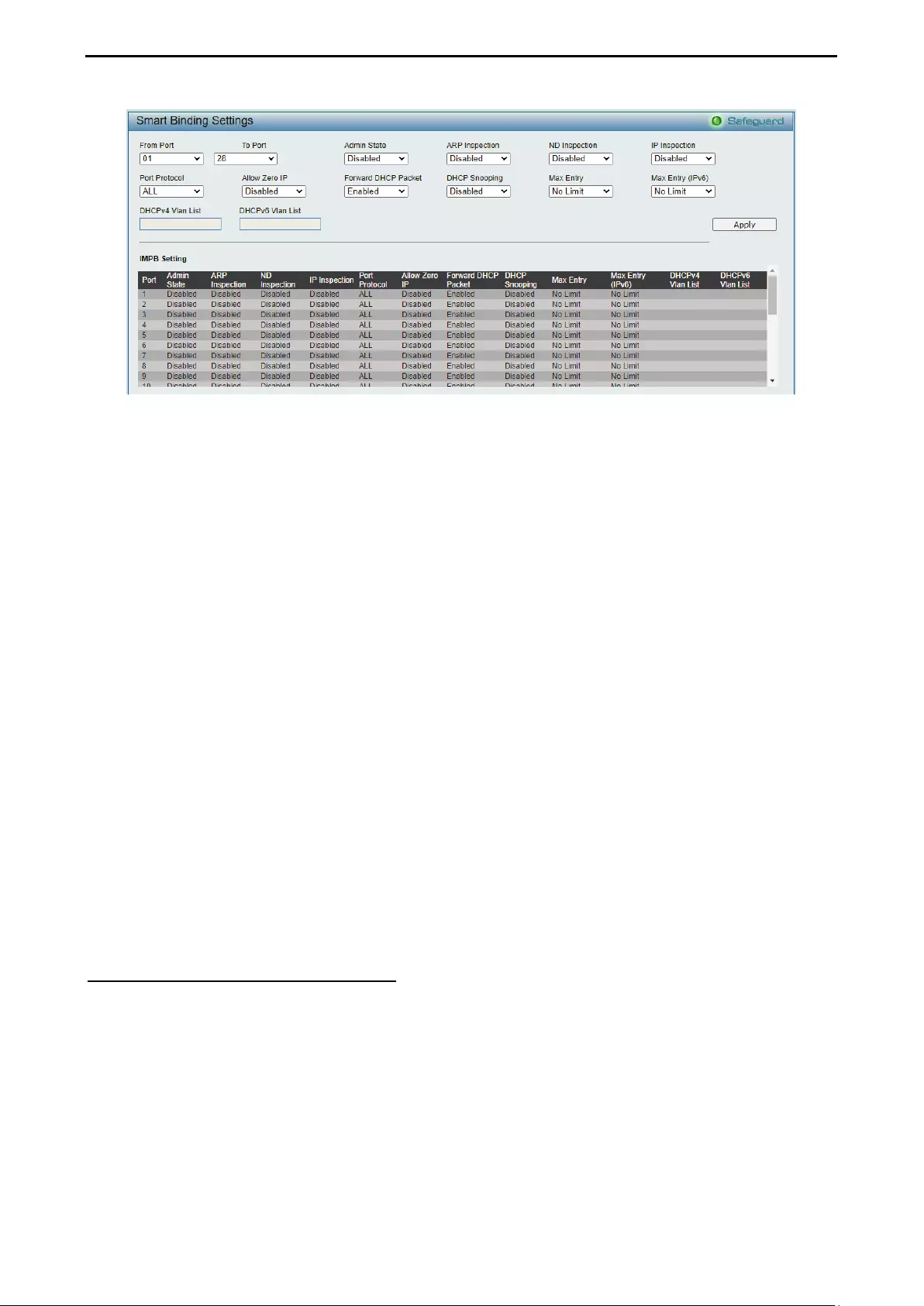
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
95
5
Figure 4.135 – Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
The Smart Binding Settings page contains the following fields:
From Port/ To Port: Select a range of ports to set for IP-MAC-port binding.
Admin State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable these ports for Smart Binding.
Enabled –Enable Smart Binding with related configurations to the ports
Disabled –Disable Smart Binding.
ARP Inspection: If ARP inspection is enabled, the Switch will inspect incoming ARP packets and compare
them with the Switch’s Smart Binding white list entries. If the IP-MAC pair of an ARP packet is not found in
the white list, the Switch will block the MAC address. A major benefit of Loose state is that it uses less CPU
resources. However, it cannot block malicious users who send only unicast IP packets. An example of this is
that a malicious user can perform DoS attacks by statically configuring the ARP table on their PC. In this
case, the Switch cannot block such attacks because the PC will not send out ARP packets.
IP Inspection: When IP Inspection is enabled, and ARP Inspection is disabled, all non-IP packets are
forwarded by default. If ARP Inspection and IP Inspection mode are enabled, the Switch will inspect all
incoming ARP and IP packets and compare them to the IMPB white list. If the IP-MAC pair find a match in
the white list, the packets from that MAC address are unblocked. If not, the MAC address will stay blocked.
While the mode examines every ingress ARP and IP packet, it enforces better security.
Allow Zero IP: Enable or disable to allow zero IP to configure the state which allows ARP packets with
0.0.0.0 source IP to bypass.
Forward DHCP Packet: Enable or disable to forward DHCP packet.
DHCP Snooping: By enable DHCP Snooping, the switch will snoop the packets sent from DHCP Server and
clients, and update information to the White List.
Max Entry: Specifies the max entries of Smart Binding. The range is between 1 and 10, or No Limit.
Max Entry (IPv6): Specifies the IPv6 max entries of Smart Binding. The range is between 1 and 10, or No
Limit.
Click Apply to make configurations make effects.
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
The Smart Binding page allows the user to create Static IP-MAC-Port Binding entries on the Switch.
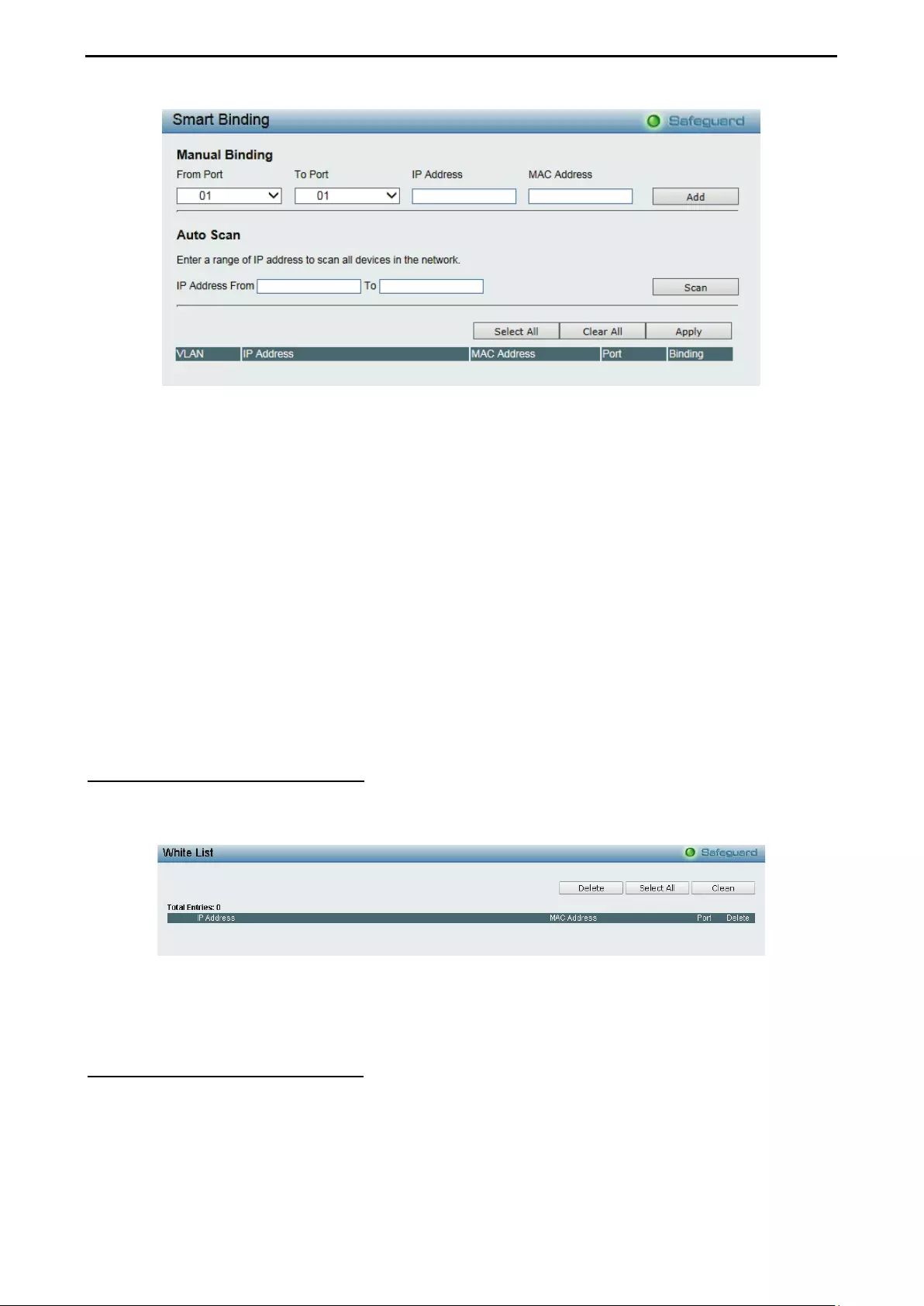
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
96
6
Figure 4.136 – Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
The Manual Binding Settings contains the following fields:
From Port / To Port: Specifies the port ranges for MAC address to bind to the IP address of Binding list.
IP Address: Specifies the IP address to bind to the MAC address set below.
MAC Address: Specifies the MAC address to bind to the IP address set above.
Click Add to add a new entry.
Auto Scan: Specifies to scan connected devices in a range of IP address.
IP Address From/To: Specifies the range of IP Address to scan all devices in the network.
Click Scan and the search results will be listed in below table.
Binding: check the box to select desired binding devices.
Apply: click Apply to set IP-MAC-Port Binding entries.”
Select All: to check the boxes of Binding for all found devices.
Clear All: to cancel the box of Binding.
Security > Smart Binding > White List
When IP+ARP Inspection Mode were selected, the White List page displays finished IP-MAC-Port Binding
entries from page Smart Binding. Only IP packets or ARP packets carrying matched IP-MAC-Port
information can access to the switch. User can cancel a device’s authorization by deleting it from the table.
Figure 4.137 – Security > Smart Binding > White List
Click Select All to select all entries of the table or click Clean to select none entries. Please keep at least
one management host in the White List.
Security > Smart Binding > Black List
The Black List page shows unauthorized accesses. When ARP Inspection is selected and a device sends
out an ARP packet containing unmatched IP-MAC-Port information, the device will be forbidden and listed
here.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
97
7
Figure 4.138 – Security > Smart Binding > Black List
By giving conditions, desired devices information can be screened out below then click Find to search for a
list of the entry:
VID: Enter the VLAN ID number of the device.
IP Address: Enter the IP Address of the device.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC Address of the device.
Port: Enter the port number which the device connects.
Check a box of Delete column to release an entry from the forbidden list then click Apply to delete an entry
from the list.
Click Select All to select all entries, or click Clean to select none of the entries.
Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
The DHCP Snooping List page shows the DHCP Snooping list.
Figure 4.139 – Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
Monitoring > Statistics
The Statistics screen displays the status of each port packet count.
Figure 4.140 – Monitoring > Statistics
Refresh All: Renews the details collected and displayed.
Clear All: To reset the details displayed.
TxOK: Number of packets transmitted successfully.
RxOK: Number of packets received successfully.
TxError: Number of transmitted packets resulting in error.
RxError: Number of received packets resulting in error.
To view the statistics of individual ports, click one of the linked port numbers for details.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
98
8
Figure 4.141 – Monitoring > Port Statistics
Previous Page: Go back to the Statistics main page.
Refresh: To renew the details collected and displayed.
Clear Counter: To reset the details displayed.
Monitoring > Session Table
The Session Table allows the user to view detailed information on the current configuration session of the
Switch. Information such as the Session ID of the user, initial Login Time, Live Time, configuration
connection From the Switch, Level and Name of the user are displayed. Click Reload to refresh this window.
Figure 4.142 – Monitoring > Session Table
Monitoring > CPU Utilization
The CPU Utilization displays the percentage of the CPU being used, expressed as an integer percentage
and calculated as a simple average by time interval. The window will automatically refresh with new updated
statistics.
Figure 4.143 – Monitoring > CPU Utilization
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
9
99
9
Monitoring > Memory Utilization
The Memory Utilization displays the percentage of the memory being used, expressed as an integer
percentage and calculated as a simple average by time interval. Click Apply to implement the configured
settings. The window will automatically refresh with new updated statistics.
Figure 4.144 – Monitoring > Memory Utilization
The information is described as follows:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where "s" stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
Show/Hide: Check whether to display Five Secs, One Min, and/or Five Mins.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
Monitoring > Port Utilization
The Port Utilization page displays the percentage of the total available bandwidth being used on the port.
Figure 4.145 – Monitoring > Port Utilization
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
00
0
The user may use the real-time graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page to view utilization statistics
per port by clicking on a port. Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. The following field can be
set:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where "s" stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
Show/Hide: Check whether to display Utilization.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
Monitoring > Packet Size
The Web Manager allows packets received by the Switch, arranged in six groups and classed by size, to be
viewed as either a line graph or a table. Two windows are offered. To select a port to view these statistics for,
select the port by using the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time graphic of the Switch
at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.146 – Monitoring > Packet Size
To view the Packet Size Analysis Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.147 – Monitoring > Packet Size Table
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
64: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were 64 octets in length (excluding
framing bits but including FCS octets).
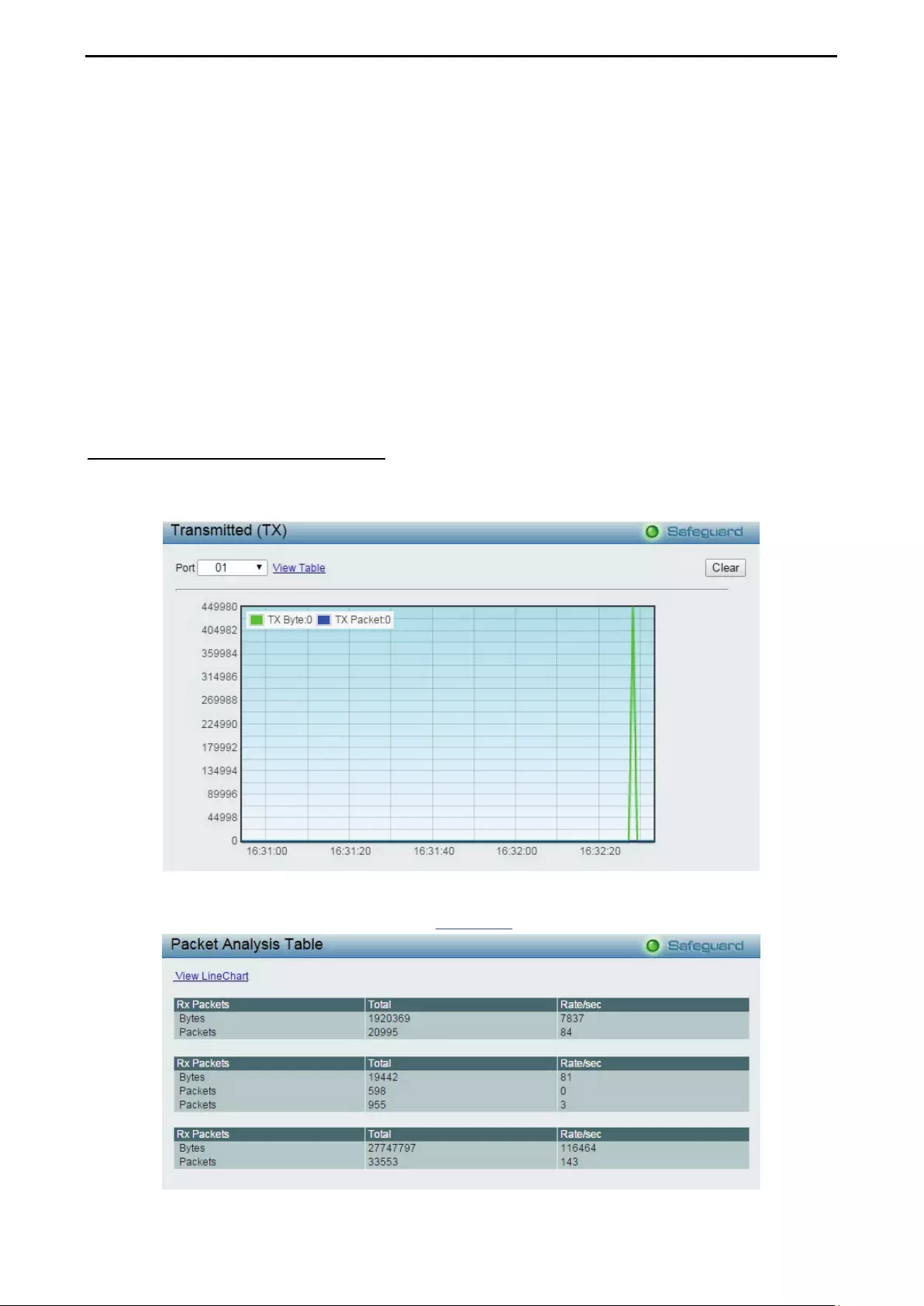
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
01
1
65-127: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 65 and 127 octets
in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
128-255: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 128 and 255
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
256-511: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 256 and 511
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
512-1023: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 512 and 1023
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
1024-1518: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 1024 and 1518
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display 64, 65-127, 128-255, 256-511, 512-1023, and 1024-1518
packets received.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX)
The Transmitted (TX) page displays the following graph of packets transmitted from the Switch. To select a
port to view these statistics for, use the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time graphic of
the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.148 - Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX) (line graph for Bytes and Packets)
To view the Transmitted (TX) Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.149 - Monitoring > Packet s > Transmitted (TX) (table for Bytes and Packets)
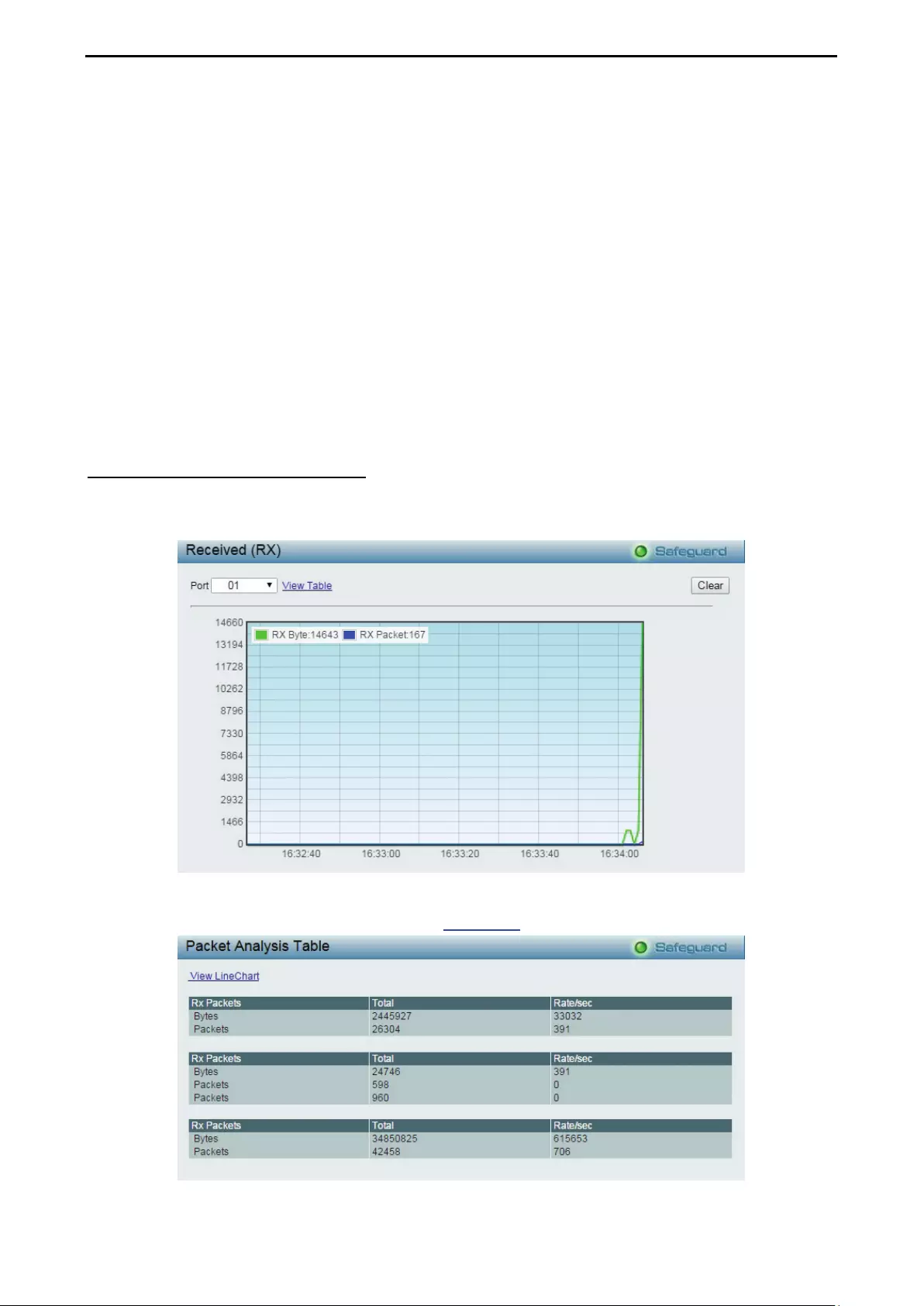
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
02
2
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
Bytes: Counts the number of bytes successfully sent from the port.
Packets: Counts the number of packets successfully sent on the port.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Bytes and Packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX)
The Received (RX) page displays the following graph of packets received on the Switch. To select a port to
view these statistics for, use the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time graphic of the
Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.150 - Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX) (line graph for Bytes and Packets)
To view the Received Packets Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.151 - Monitoring > Packet s > Received (RX) (table for Bytes and Packets)
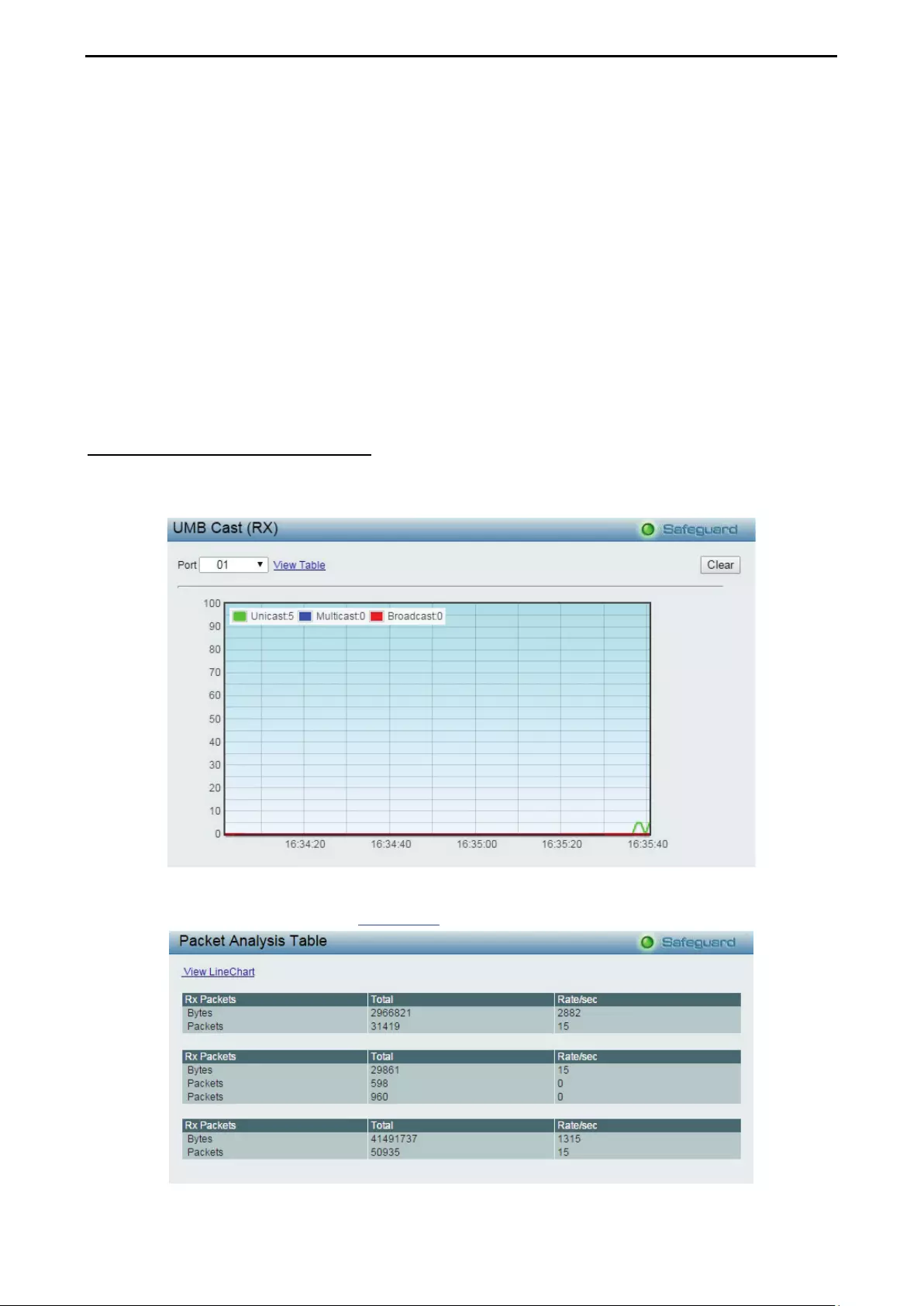
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
03
3
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
Bytes: Counts the number of bytes received on the port.
Packets: Counts the number of packets received on the port.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Bytes and Packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX)
The UMB Cast (RX) page displays the following graph of UMB cast packets received on the Switch. To
select a port to view these statistics for, use the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time
graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.152 - Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) (line graph for Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast Packets)
To view the UMB Cast Table, click the View Table link, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.153 - Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) (table for Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast Packets)
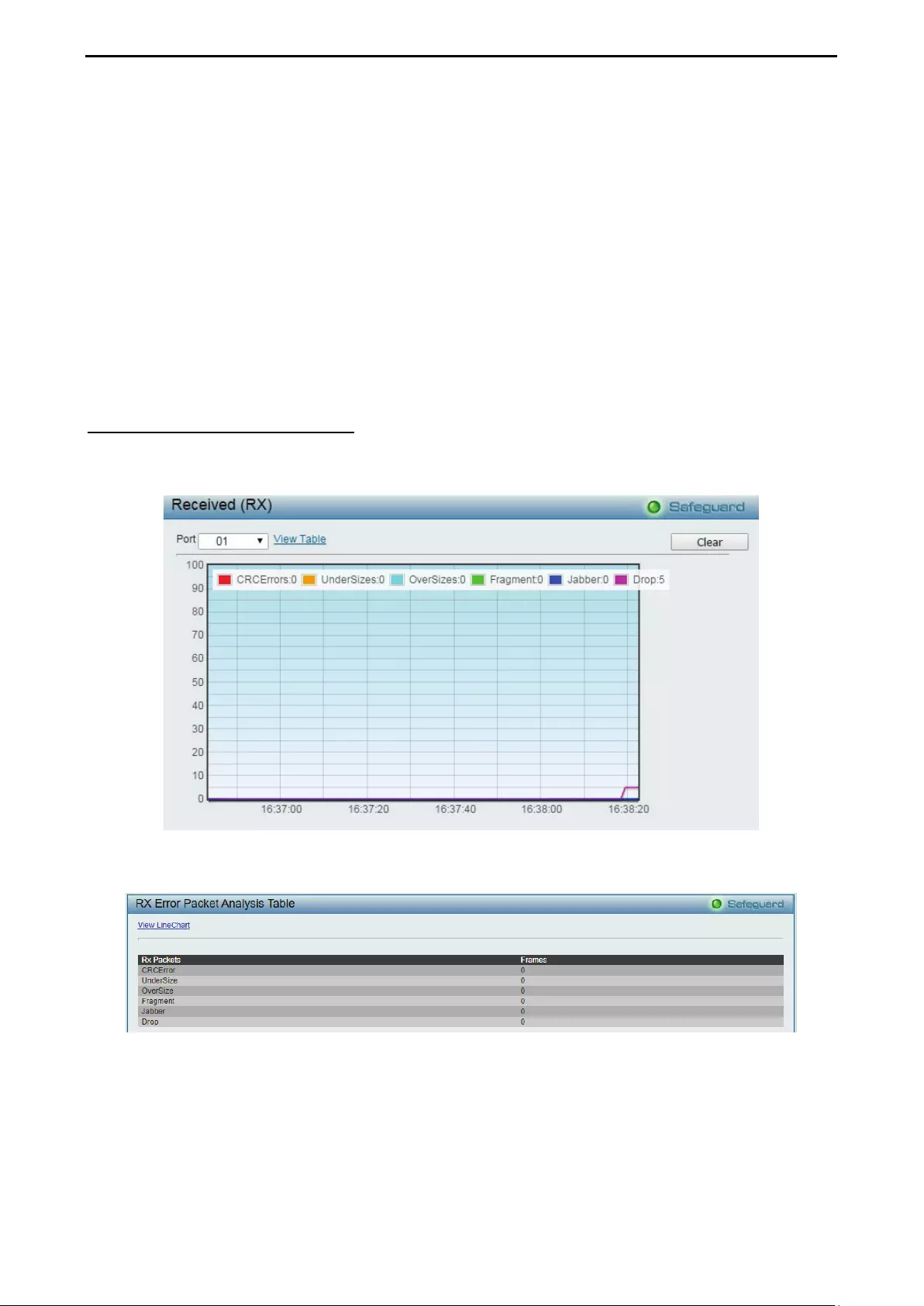
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
04
4
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Multicast, Broadcast and Unicast packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX)
This page displays the following graph of error packets received on the Switch. To select a port to view these
statistics for, select the port by using the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time graphic
of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.154 - Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX) (line graph)
To view the Received Error Packets Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.155 - Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX) (table)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.
CRC Error: Counts otherwise valid packets that did not end on a byte (octet) boundary.
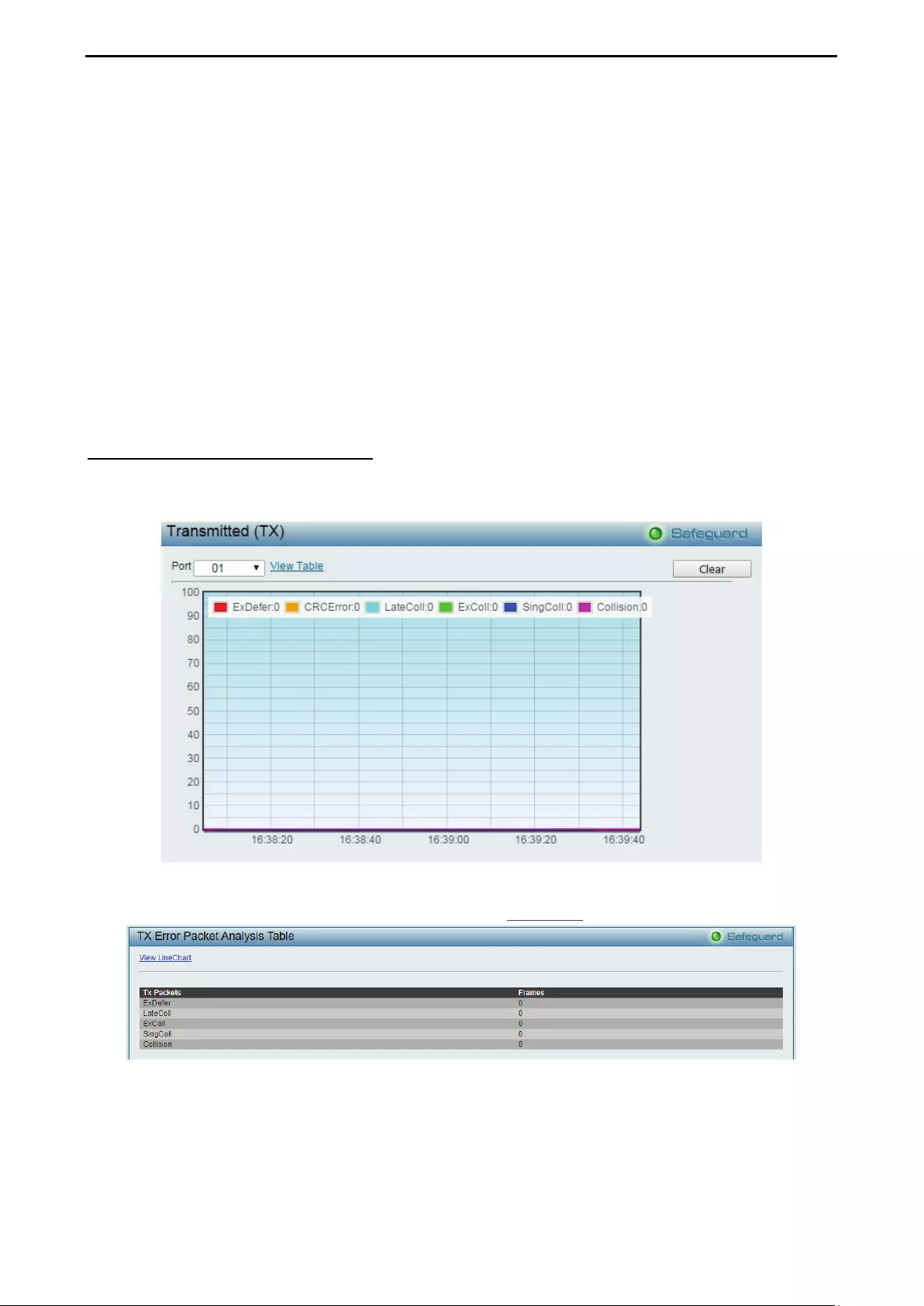
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
05
5
UnderSize: The number of packets detected that are less that the minimum permitted packets size of 64
bytes and have a good CRC. Undersize packets usually indicate collision fragments, a normal network
occurrence.
OverSize: Counts packets received that were longer that 1518 octets, or if a VLAN frame is 1522 octets, and
less that the MAX_PKT_LEN. Internally, MAX_PKT_LEN is equal to 1522.
Fragment: The number of packets less than 64 bytes with either bad framing or an invalid CRC. These are
normally the result of collisions.
Jabber: The number of packets with lengths more than the MAX_PKT_LEN bytes. Internally,
MAX_PKT_LEN is equal to 1522.
Drop: The number of packets that are dropped by this port since the last Switch reboot.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display CRC Error, Under Size, Over Size, Fragment, Jabber, and
Drop errors.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX)
This page displays the following graph of error packets transmitted on the Switch. To select a port to view
these statistics for, select the port by using the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time
graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.156 - Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX) (line graph)
To view the Transmitted Error Packets Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.157 - Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX) (table)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select number of times the Switch will be polled between 20 and 200. The default value is
200.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
06
6
ExDefet: Counts the number of packets for which the first transmission attempt on a particular interface was
delayed because the medium was busy.
CRC Error: Counts otherwise valid packets that did not end on a byte (octet) boundary.
LateColl: Counts the number of times that a collision is detected later than 512 bit-times into the
transmission of a packet.
ExColl: Excessive Collisions. The number of packets for which transmission failed due to excessive
collisions.
SingColl: Single Collision Frames. The number of successfully transmitted packets for which transmission is
inhibited by more than one collision.
Coll: An estimate of the total number of collisions on this network segment.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display ExDefer, LateColl, ExColl, SingColl, and Coll errors.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
The Cable Diagnostics is designed primarily for administrators and customer service representatives to
examine of the copper cable quality. It rapidly determines the type of cable errors occurred in the cable.
Select a port and then click the Test Now button to start the diagnosis.
Figure 4.158 - Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
Test Result: The description of the cable diagnostic results.
•OK means the cable is good for the connection.
•Short in Cable means the wires of the RJ45 cable may be in contact somewhere.
•Open in Cable means the wires of RJ45 cable may be broken or the other end of the cable is simply
disconnected.
•Test Failed means some other errors occurred during cable diagnostics. Please select the same port and
test again.
Cable Fault Distance (meters): Indicates the distance of the cable fault from the Switch port, if the cable is
less than 2 meters, it will show “No Cable”, whether the fiber is connected to the port or not.
Cable Length (meter): If the test result shows OK, then cable length will be indicated for the total length of
the cable. The cable lengths are categorized into four types: <50 meters, 50~80 meters, 80~100 meters and
>100 meters. Deviation is +/-2 meters, therefore "No Cable" may be displayed under "Test Result," when the
cable used is less than 2 m in length. This test can only be performed when the port is up and operating at 1
Gbps.
NOTE:
Cable length detection is effective on Gigabit

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
07
7
ports only.
The definition of cable pair is listed below:
Pair1: PIN4, PIN5
Pair2: PIN1, PIN2
Pair3: PIN3, PIN6
Pair4: PIN7, PIN8
Monitoring > System Log
The System Log page provides information about system logs, including information when the device was
booted, how the ports are operating, when users logged in, when sessions timed out, as well as other
system information.
Figure 4.159 - Monitoring > System Log
ID: Displays an incremented counter of the System Log entry. The Maximum entries are 500.
Time: Displays the time in days, hours, and minutes the log was entered.
Log Description: Displays the description of event recorded.
Severity: Displays a severity level of the event recorded.
Click Refresh to renew the page, and click Clear to clean out all log entries.
Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
The Browse ARP Table page provides information regarding ARP VLANs, including which IP address was
mapped to what MAC address. To clear the ARP Table, click Clear All.
Figure 4.160 - Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
Click Find, The table updates and displays the values required.
Interface Name: Defines the name of ARP mappings.
IP Address: Defines the station IP address, which is associated with the MAC address.
MAC Address: Displays the MAC address associated with the IP address.
Type: Indicates how the MAC was assigned. The possible values are:
Dynamic – Indicates that the MAC address is dynamically created.
Static – Indicates the MAC address is a static IP address.
Port: Defines the ARP mapping ports.
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
The Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log page displays the ports Ethernet OAM event log information.
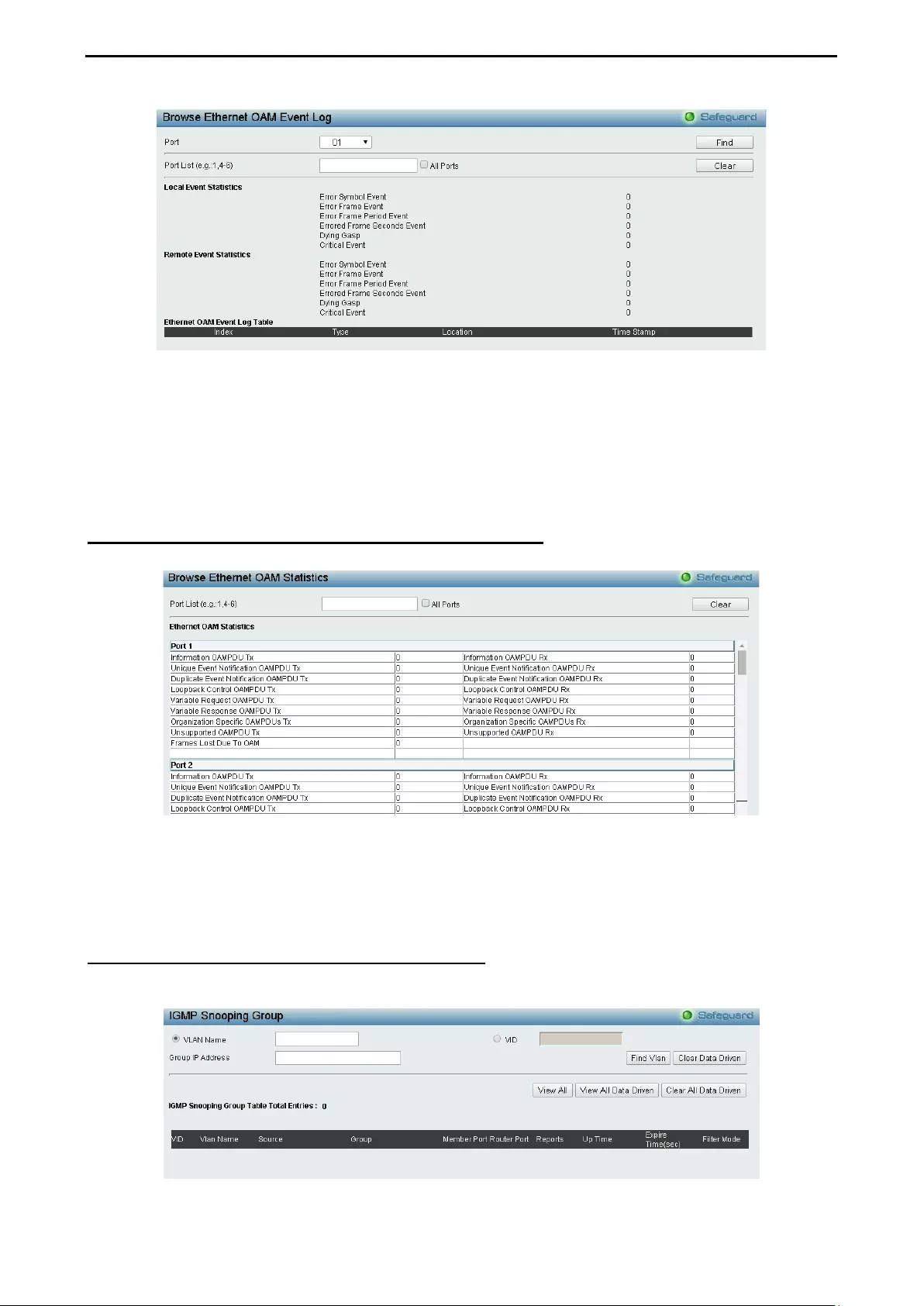
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
08
8
Figure 4.161 - Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
Port: Select the port to be viewed.
Port List: Enter a list of ports. Tick the All Ports check box to select all ports.
Click Find to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click Clear to clear all the information entered in the fields.
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
The Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics page displays the ports Ethernet OAM statistics information.
Figure 4.162 - Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
Port List: Enter a list of ports. Tick the All Ports check box to select all ports.
Click Clear to clear all the information entered in the fields.
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
The IGMP Snooping Group page is used to display the current IGMP snooping static group information on
the Switch.
Figure 4.163 - Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
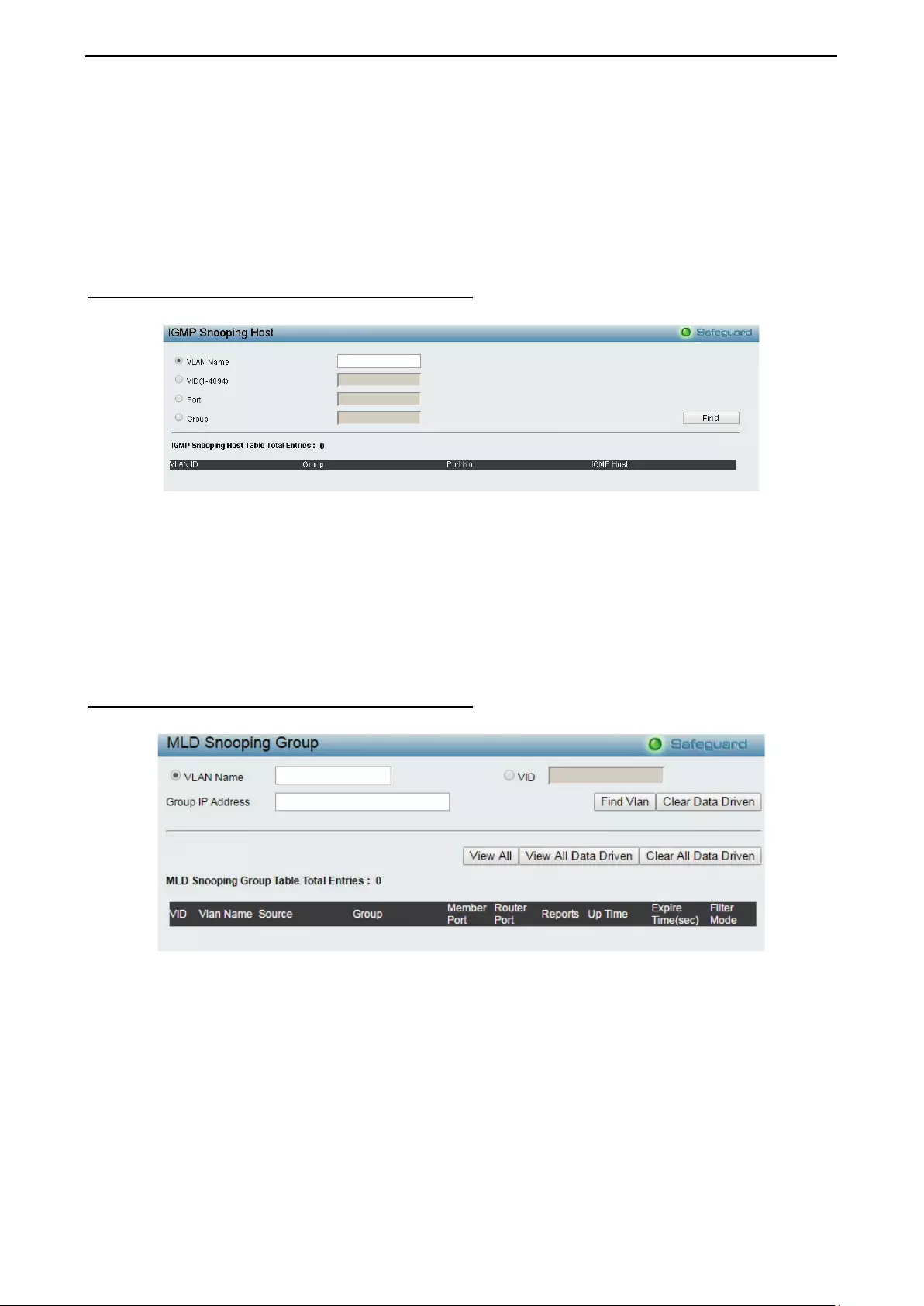
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
10
09
9
VLAN Name: Specify the name of the VLAN for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Group nformation.
VID: Specify the list of the VLAN IDs for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Group information.
Group IP Address: Specify the static group address for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping static
group information.
Click Find VLAN to display the IGMP group information or click Clear Data Driven to clear the IGMP group
information.
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
The IGMP Snooping Host page allows user to display the information of IGMP Snooping Host.
Figure 4.164 - Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
VLAN Name: Specify the name of the VLAN for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Host information.
VID (1-4094): Specify the list of the VLAN IDs for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Host information.
Port: Specify the ports of IGMP Snooping Host information to be displayed.
Group: Specify the group of IGMP Snooping Host information to be displayed.
Click Find to display the information.
Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
The MLD Snooping Group page allows user to configure the MLD Snooping group settings.
Figure 4.165 - Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
VLAN Name: Specify the VLAN name for MLD Snooping group.
VID: Specify the VID for MLD Snooping group.
Group IP Address: Specify the IP address for the specified VLAN.
Click Find Vlan to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click View All to display all the existing entries.
Click View All Data Driven to display all existing entire entries.
Click Clear All Data Driven to clear data driven information for all entries.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
10
0
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
This table contains information concerning the activity of the RADIUS authentication client on the client side
of the RADIUS authentication protocol. It has one row for each RADIUS authentication server that the client
shares a secret with.
Figure 4.166 - Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
The user may also select the desired time interval to update the statistics, between 1s and 60s, where “s”
stands for seconds. The default value is one second. To clear the current statistics shown, click the Clear
button in the top left hand corner.
The following fields can be viewed:
Server Index: The identification number assigned to each RADIUS Authentication server that the client
shares a secret with.
UDP Port: The UDP port the client is using to send requests to this server.
Timeouts: The number of authentication timeouts to this server. After a timeout the client may retry to the
same server, send to a different server, or give up. A retry to the same server is counted as a retransmit as
well as a timeout. A send to a different server is counted as a Request as well as a timeout.
Requests: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets sent to this server. This does not include
retransmissions.
Challenges: The number of RADIUS Access-Challenge packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
Accepts: The number of RADIUS Access-Accept packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
Rejects: The number of RADIUS Access-Reject packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
RoundTripTime: The time interval (in hundredths of a second) between the most recent Access-
Reply/Access-Challenge and the Access-Request that matched it from this RADIUS authentication server.
AccessRetrans: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets retransmitted to this RADIUS
authentication server.
PendingRequests: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets destined for this server that have not
yet timed out or received a response. This variable is incremented when an Access-Request is sent and
decremented due to receipt of an Access-Accept, Access-Reject or Access-Challenge, a timeout or
retransmission.
AccessResponses: The number of malformed RADIUS Access-Response packets received from this
server. Malformed packets include packets with an invalid length. Bad authenticators or Signature attributes
or known types are not included as malformed access responses.
BadAuthenticators: The number of RADIUS Access-Response packets containing invalid authenticators or
Signature attributes received from this server.
UnknownTypes: The number of RADIUS packets of unknown type which were received from this server on
the authentication port.
PacketsDropped: The number of RADIUS packets of which were received from this server on the
authentication port and dropped for some other reason.
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
This RADIUS Account Client page shows managed objects used for managing RADIUS accounting clients,
and the current statistics associated with them. It has one row for each RADIUS authentication server that
the client shares a secret with.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
11
1
Figure 4.167 - Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
The user may also select the desired time interval to update the statistics, between 1s and 60s, where “s”
stands for seconds. The default value is one second. To clear the current statistics shown, click the Clear
button in the top left hand corner.
The following fields can be viewed:
Server IP Addr: The IP address assigned to each RADIUS Accounting server that the client shares a secret
with.
Server Port Number: The UDP port the client is using to send requests to this server.
Timeouts: The number of accounting timeouts to this server. After a timeout the client may retry to the same
server, send to a different server, or give up. A retry to the same server is counted as a retransmit as well as
a timeout. A send to a different server is counted as an Accounting-Request as well as a timeout.
Requests: The number of RADIUS Accounting-Request packets sent. This does not include retransmissions.
Responses: The number of RADIUS packets received on the accounting port from this server.
RoundTripTime: The time interval between the most recent Accounting-Response and the Accounting-
Request that matched it from this RADIUS accounting server.
AccessRetrans: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets retransmitted to this RADIUS
authentication server.
PendindRequests: The number of RADIUS Accounting-Request packets sent to this server that have not
yet timed out or received a response. This variable is incremented when an Accounting-Request is sent and
decremented due to receipt of an Accounting-Response, a timeout or a retransmission.
MalformedResponses: The number of malformed RADIUS Accounting-Response packets received from
this server. Malformed packets include packets with an invalid length. Bad authenticators and unknown types
are not included as malformed accounting responses.
BadAuthenticators: The number of RADIUS Accounting-Response packets, which contained invalid
authenticators, received from this server.
UnknownTypes: The number of RADIUS packets of unknown type which were received from this server on
the accounting port.
PacketsDropped: The number of RADIUS packets, which were received from this server on the accounting
port and dropped for some other reason.
ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
Access Control List (ACL) allows user to establish criteria to determine whether or not the Switch will forward
packets based on the information contained in each packet's header. These criteria can be specified on a
basis of MAC address, or IP address.
The ACL Configuration Wizard will aid with the creation of access profiles and ACL Rules. The ACL Wizard
will create the access rule and profile automatically. The maximum usable profiles are 50 and with 240 Rules
in total for the switch.
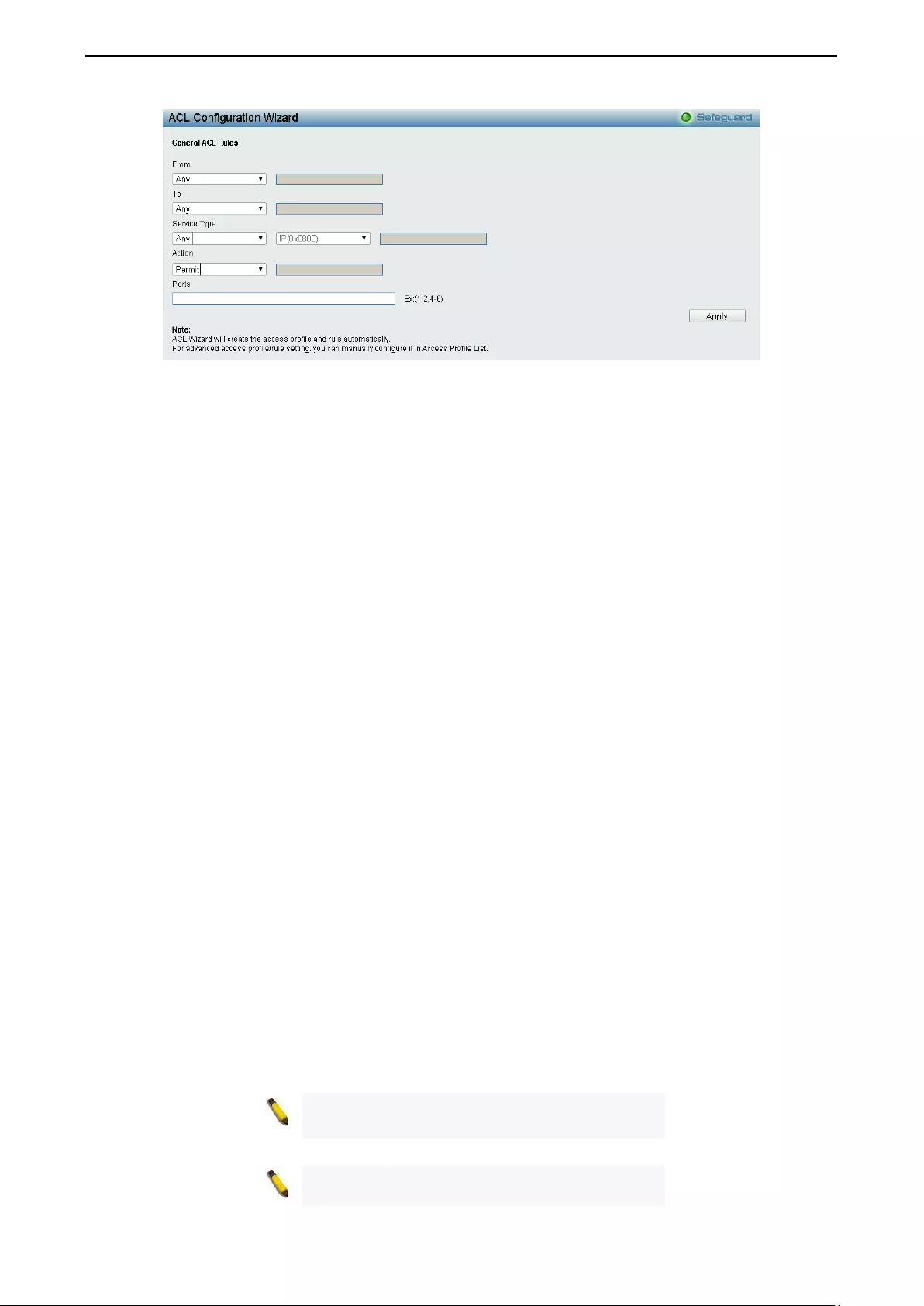
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
12
2
Figure 4.168 - ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
From: Specify the origin of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any source.
MAC Address - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this MAC address.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv6 source address
To: Specify the destination of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any source.
MAC Address - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this MAC address. The field of format
is xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv6 source address.
Service Type: Specify the type of service. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any service type.
Ether type - Specifies an Ethernet type for filtering packets.
ICMP All - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from ICMP packets.
IGMP - IGMP packets can be filtered by IGMP message type.
TCP All - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from TCP Packets.
TCP Source Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Source Port.
TCP Destination Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Destination Port.
UDP All - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from UDP Packets.
UDP Source Port - Matches the packet to the UDP Source Port.
UDP Destination Port - Matches the packet to the UDP Destination Port.
Action: Specify the ACL forwarding action matching the rule criteria.
Permit - Forwards packets if all other ACL criteria are met.
Deny - Drops packets if all other ACL criteria is met.
Mirror - Mirrors packets if all other ACL criteria is met.
Rate Limit - Rate limiting is activated if all other ACL criteria is met.
Replace DSCP - Reassigns a new DSCP value to the packet if all other ACL criteria are met.
Ports: Enter a range of ports to be configured.
Press Apply for the settings to take effect.
NOTE:
Once the ACL rules conflict, rules with
smaller rule ID will take higher priority.
NOTE: Be careful when configuring ACL rules, an
inappropriate may cause management access
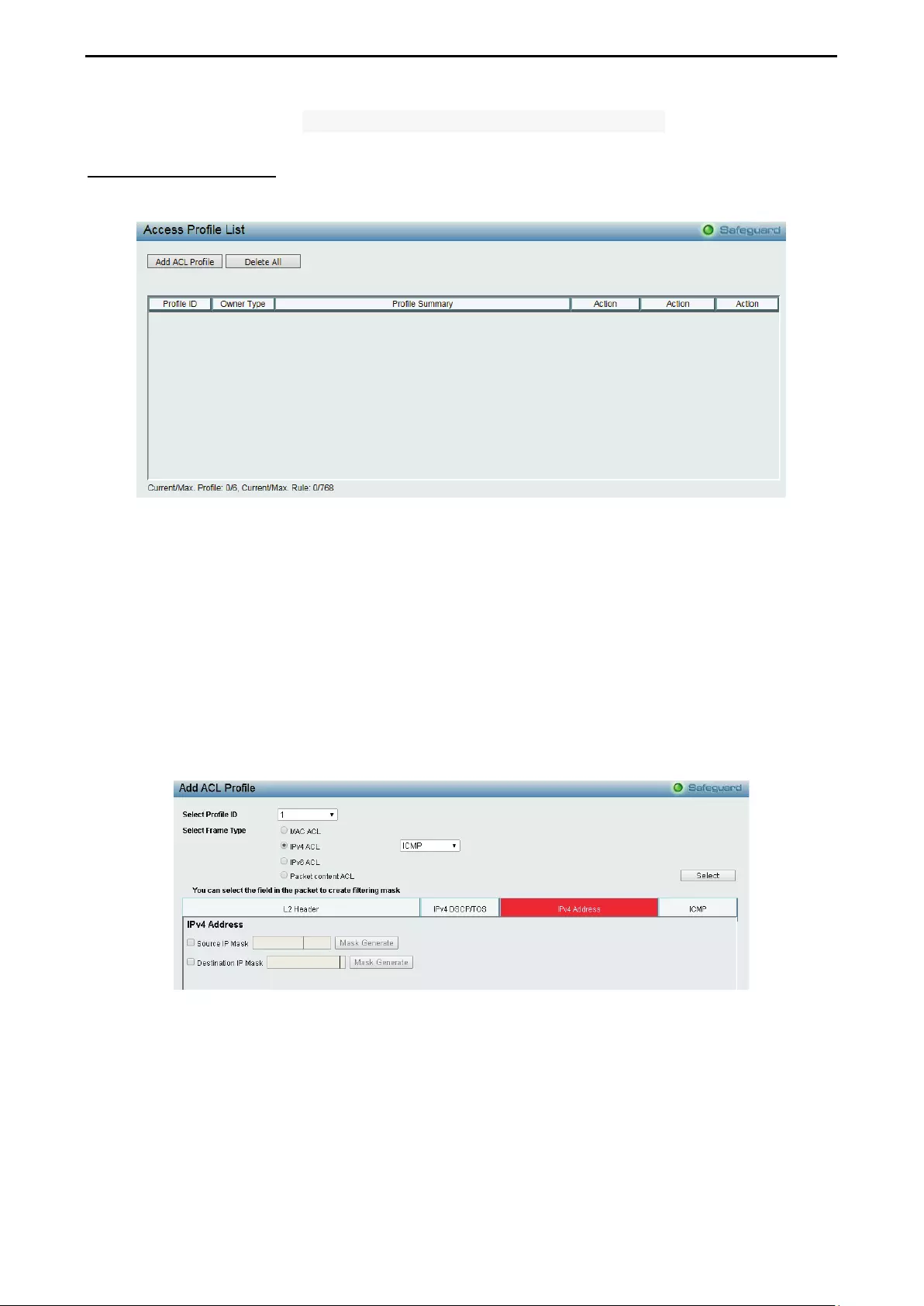
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
13
3
failed.
ACL > Access Profile List
The Access Profile List provides information for configuring ACL Profiles manually. ACL profiles are attached
to interfaces, and define how packets are forwarded if they match the ACL criteria.
Figure 4.169 - ACL > Access Profile List
The contents of Access Profile List table include:
Profile ID: Indicates the profile Identification number. The possible configured profile IDs are 1~50, and
profile ID 51~55 are reserved for the pre-defined features.
Owner Type: The owner type of ACL profile; it can be normal ACL, Voice VLAN or Surveillance VLAN.
Profile Summary: Displays the profile summary.
Show Details: To display an ACL’s profile details. The ACL profile details are displayed below the ACL table.
Show Rules: To show the access rule in this profile.
To add a new rule, please see Access Rule List in the next section.
Delete: To delete an access profile.
To manually add a profile, click Add ACL Profile:
Figure 4.170 - Add ACL Profile
The steps of adding an access profile is like below:
1) After selecting the Profile ID and Frame Type (MAC, IPv4, IPv6 or Packet content ACL), specify
attributes like Untagged/Tagged (for MAC), ICMP/IGMP/TCP/UDP/Protocol ID (for IPv4), or
ICMPv6/TCP/UDP (for IPv6), then click Select and a simplified frame diagram will be displayed.
2) Select the field of interest and related columns will be displayed in lower part of the page. Enter the
filtering mask and click Create when done. A filtering mask is to specify the digit that user wants to check.
For example, if user wants to check a network of 192.168.1.0/24, then it should enter the IP mask as
255.255.255.0.
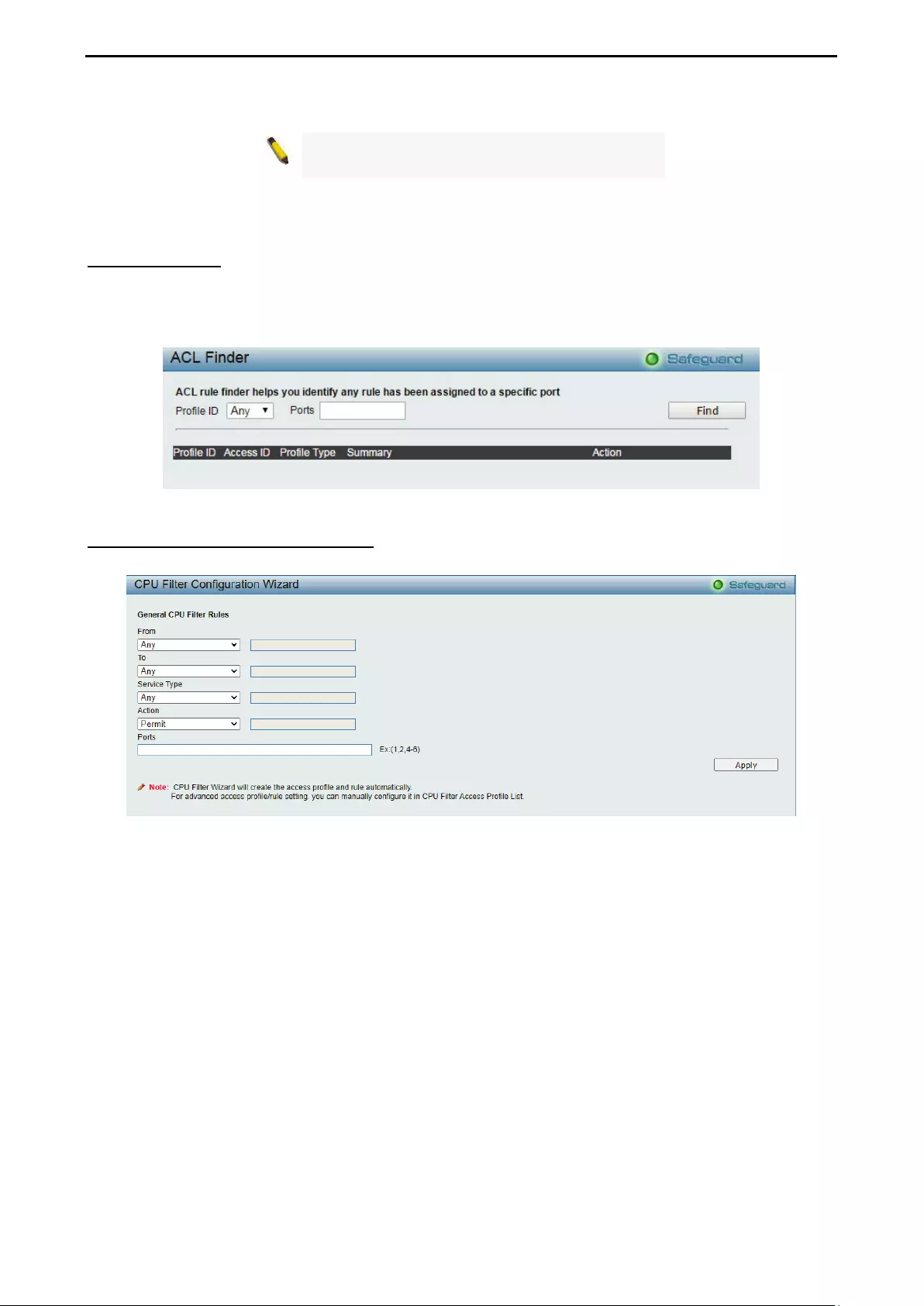
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
14
4
NOTE: Unable to select Payload in a MAC ACL,
or L2 Header in IP ACL.
3) After the Profile ID has been created, it will go back to the main Access Profile List page.
ACL > ACL Finder
The ACL Finder page is used to help user to find a previously configured ACL entry. To search for an entry,
enter the Profile ID from the drop-down menu, select a port that user would like to view and click Find. The
table on the lower half of the screen will display the entries. To delete an entry click the corresponding
Delete button.
Figure 4.171 - ACL > ACL Finder
ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
The CPU Filter Configuration Wizard will aid with the creation of CPU Filter Rules.
Figure 4.172 - ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
From: Specify the origin of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from any source.
MAC Address - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from this MAC address.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from this IPv6 source address.
To: Specify the destination of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to any source.
MAC Address - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to this MAC address. The field of
format is xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to this IPv6 source address.
Service Type: Specify the type of service. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets of any service type.
Ether type - Specifies an Ethernet type for filtering packets.
ICMP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all ICMP packets.
IGMP - IGMP packets can be filtered by IGMP message type.
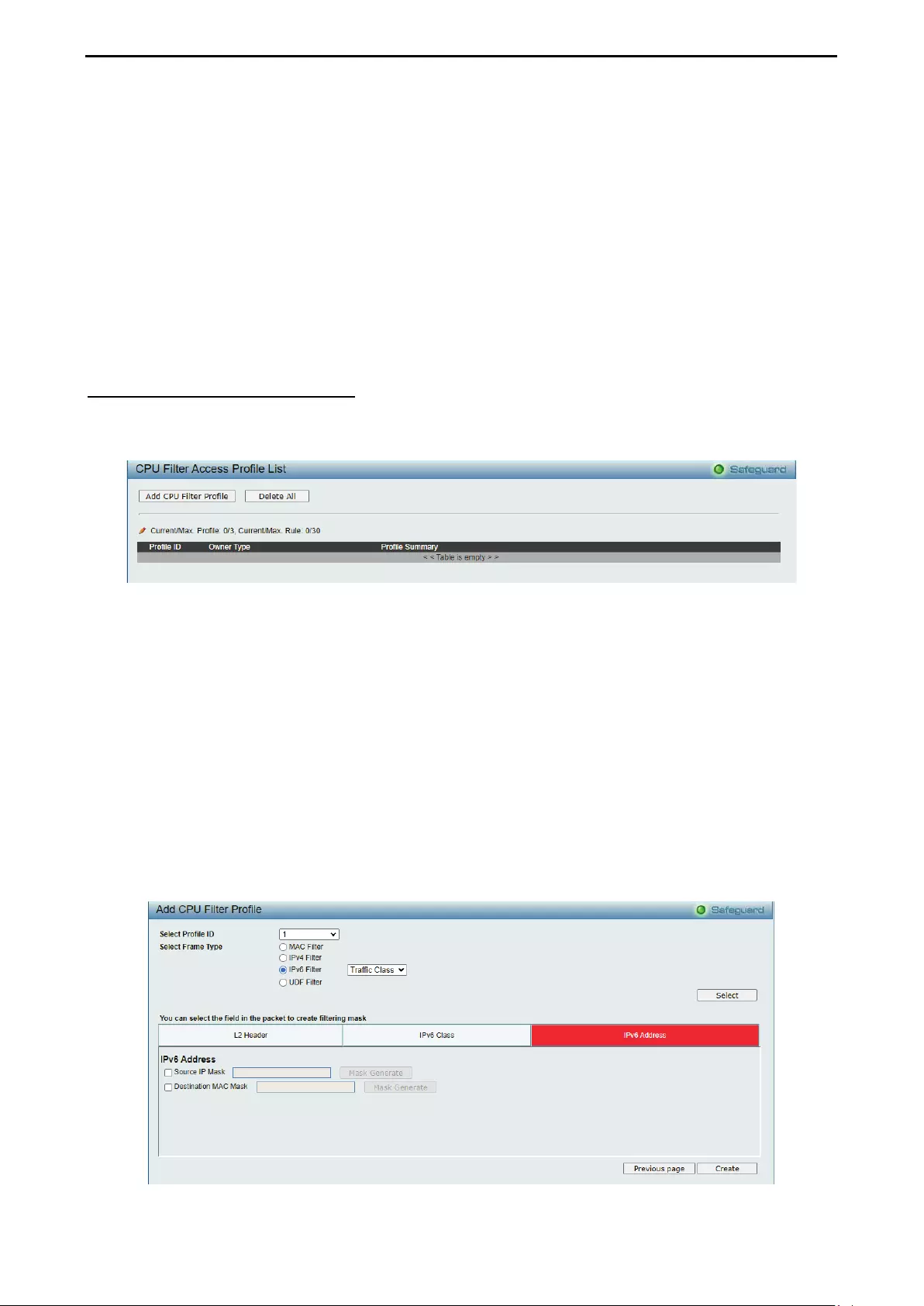
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
15
5
TCP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all TCP Packets.
TCP Source Port - Take effect if TCP Source Port matches.
TCP Destination Port - Take effect if TCP Destination Port matches.
UDP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all UDP Packets.
UDP Source Port - Take effect if UDP Source Port matches.
UDP Destination Port - Take effect if UDP Destination Port matches.
Action: Specify the CPU Filter forwarding action matching the rule criteria.
Permit - Forwards packets if all other CPU Filter criteria are met.
Deny - Drops packets if all other CPU Filter criteria is met.
Press Apply for the settings to take effect.
ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
The CPU Filter Access Profile List provides information for configuring CPU Profiles manually. CPU Filter
Access profiles are attached to interfaces, and define how packets are forwarded if they match the CPU
Filter criteria.
Figure 4.173 - ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
The contents of CPU Filter Access Profile List table include:
Profile ID: Indicates the profile Identification number. The possible configured profile IDs are 1~50, and
profile ID 51 is reserved for Voice VLAN.
Owner Type: The owner type of CPU Filter profile, it can be normal CPU Filter, Voice VLAN or Surveillance
VLAN.
Profile Summary: Displays the profile summary.
Show Details: To display a CPU Filter’s profile details. The CPU Filter profile details are displayed below the
CPU Filter table.
Edit/New Rules: To configure or add the CPU access rule in this profile.
To add a new rule, please see Add CPU Filter Profile in the next section.
Delete All: To delete all access profile.
To manually add a profile, click Add CPU Filter Profile.
Figure 4.174 - ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List -Add CPU Filter Profile

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
16
6
The steps of adding a CPU Filter profile is like below:
1) After selecting the Profile ID and Frame Type (MAC, IPv4, IPv6 or UDF), specify attributes like
Untagged/Tagged (for MAC), or ICMP/IGMP/TCP/UDP/Protocol ID (for IPv4), or Traffic Class (for IPv6), then
click Select and a simplified frame diagram will be displayed.
2) Select the field of interest and related columns will be displayed in lower part of the page. Enter the
filtering mask and click Create when done. A filtering mask is to specify the digit that user wants to check.
For example, if user wants to check a network of 192.168.1.0/24, then it should enter the IP mask as
255.255.255.0.
3) After the Profile ID has been created, it will go back to the main CPU Filter Access Profile List page.
ACL > CPU Filter Finder
The CPU Filter Finder page is used to help user to find a previously configured CPU entry. To search for an
entry, enter the Profile ID from the drop-down menu, select a port that user would like to view and click Find.
The table on the lower half of the screen will display the entries. To delete an entry click the corresponding
Delete button.
Figure 4.175 - ACL > CPU Filter Finder
PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only)
DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) as defined by the IEEE
specification.
DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP works with all D-Link 802.3af or 802.3at capable devices. The
Switch also works in PoE mode with all non-802.3af capable D-Link AP, IP Cam and IP phone equipment via
the PoE splitter DWL-P50.
IEEE 802.3at defined that the PSE provides power according to the following classification:
Class Usage Output power limit by PSE
0 Default 15.4W
1 Optional 4.0W
2 Optional 7.0W
3 Optional 15.4W
4 Reserved 30W
The PoE port table will display the PoE status including, Port Enable, Power Limit, Power (W), Voltage (V),
Current (mA), Classification, Port Status. User can select From Port / To Port to control the PoE functions of
a port. DGS-2000-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME will auto disable the ports if port current is over
375mA in 802.3af mode or 625mA in pre-802.3at mode.
Note:
The PoE Status information of Power
current, Power Voltage, and Current is the power
usage information of the connected PD; please
"Refresh" to renew the information.
Note: The following table listed PoE hardware specificati
ons for each
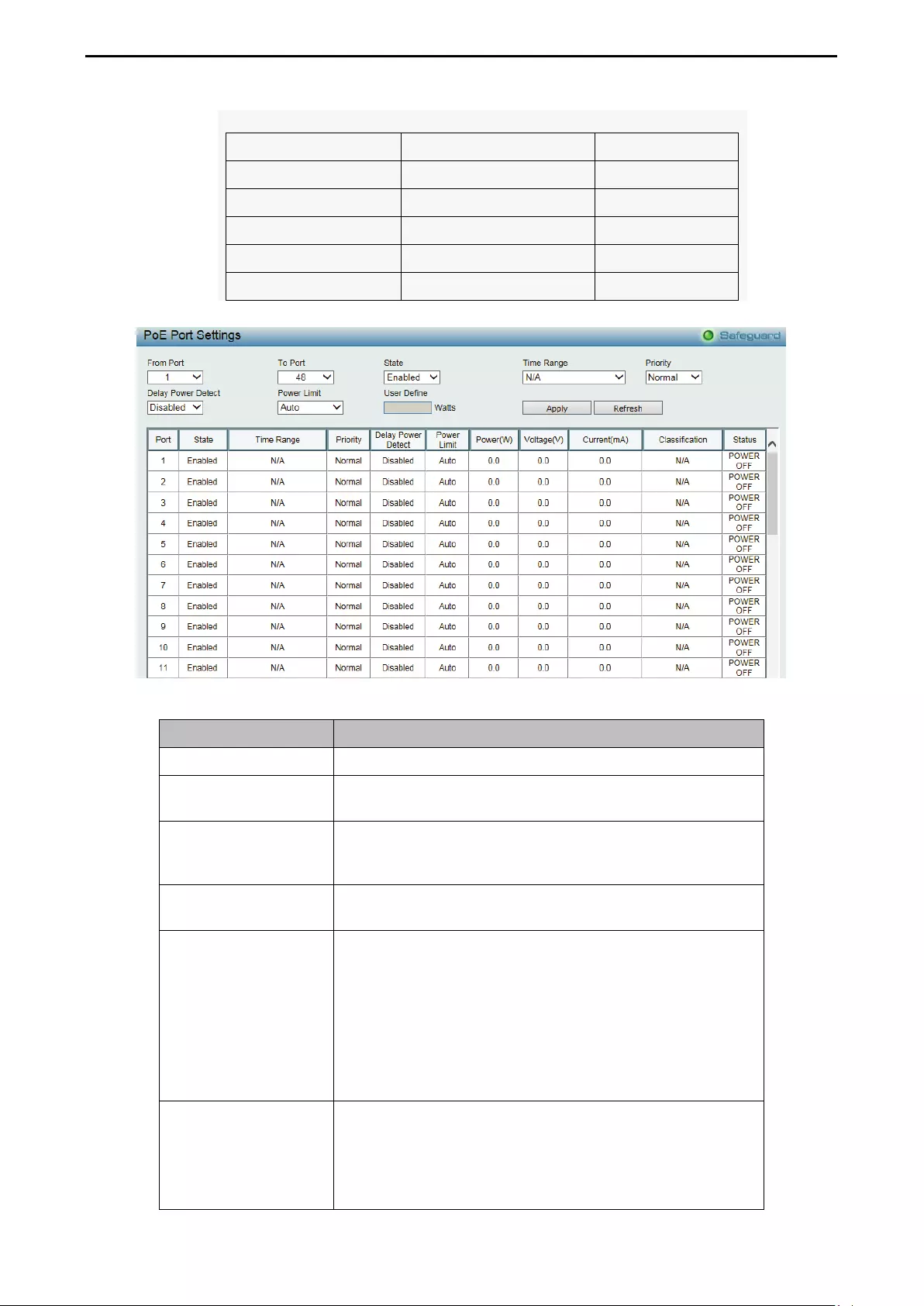
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
17
7
model of DGS-2000/ME series:
Model 802.3at compliance port System Budget
DGS-2000-10P 1-8 65 Watts
DGS-2000-10MP 1-8 130 Watts
DGS-2000-28P 1-24 193 Watts
DGS-2000-28MP 1-24 370 Watts
DGS-2000-52MP 1-8 370 Watts
Figure 4.176 – PoE > PoE Port Settings
Parameter Description
From Port/To Port Specifies the PoE function of a port or ports
State Select “Enabled” or “Disabled” to configure PoE function for
designated port(s). Default is Enabled
Time Range Select the PoE time profile configured from Time-Based
PoE > Time Range Settings to enable the time-based PoE
function on designated port(s). Default setting is N/A
Priority Configure the power supply priority as “Low”, “Normal”, or
“High” on designated port(s). Default is Normal.
Delay Power Detect
Configure the delay power detection. Default is Disabled.
This switch conforms to IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at
standards. The IEEE PoE standard requires a switch to
shut off power to a port if the power draw is less than 10mA
within a 400ms time interval. To support some non-
standard devices that may take longer, user may enable
this feature to extend the time interval to 500ms. If the PD
is still not powering on, please contact the vendor of the
device for support.
Power Limit This feature allows user to specify the power limit for each
ports. If a port requested the power exceeds its power limit,
it will shut down. There are options as the following list:
Auto: Automatic classification the PD’s power consumption.
Class 1: Specifies that the power limit will be set to 4W
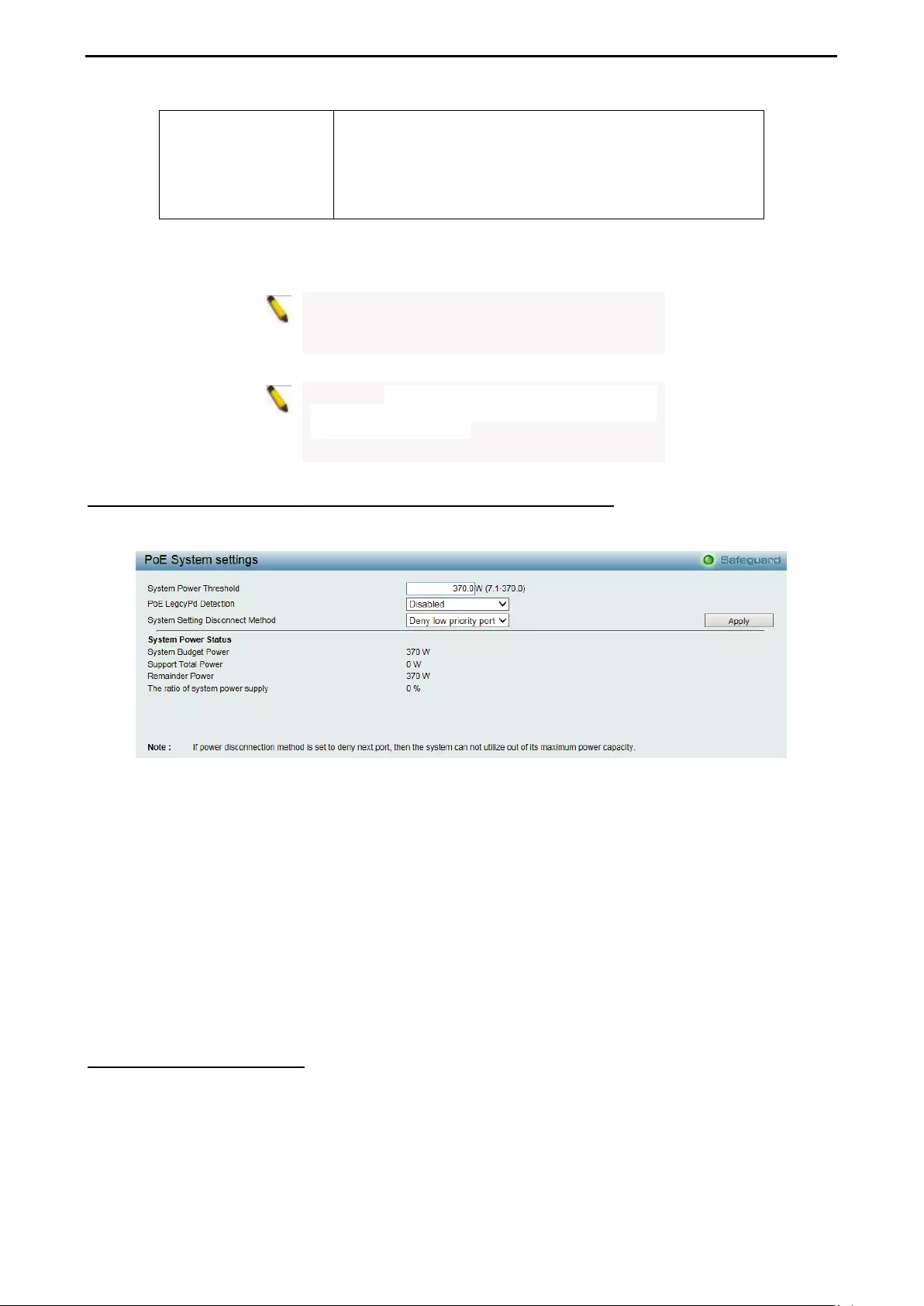
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
18
8
Class 2: Specifies that the power limit will be set to 7W
Class 3: Specifies that the power limit will be set to 15.4W
Class 4: For 802.3at compliance PD devices. Supports up
to 30W in this class.
User Define: Maximum supports to 30W
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect or click Refresh to redisplay the table.
Note: For the PoE Port Settings table, if the
classification was shown as “Legacy PD”, it will be
classified to non-AF PD or Legacy PD.
Note: The ports 1-4 are capable of feeding power
up to 30 watts to devices with the LLDP-Med
function is enabled of the connected PD. Or the
ports can only feeding power up to 15.4 watts.
PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-2000-10P/10MP/28P/28MP/52MP only)
This PoE System Settings page will display the PoE status including System Budget Power, Support Total
Power, Remainder Power, and The ratio of system power supply.
Figure 4.177 – PoE > PoE System Settings
System Power Threshold: Manually configure the system power budget 7.1 ~ 193.0 watts for DGS-2000-
28P/ME.
PoE LeacyPD Detection: Specifies the legacy PDs detection status.
System Setting Disconnect Method: Defines the method used to deny power to a port once the threshold
is reached. The possible fields are:
Deny next port: When the power budget is exceeded, the next port attempting to power up is
denied, regardless of the port priority.
Deny low priority port: The port with the lower priority will be shut down to allow the higher priority
port to power up.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) provides IEEE 802.1AB standards-based method for switches to
advertise themselves to neighbor devices, as well as to learn about neighbor LLDP devices. The switch will
keep the information in the Management Information Base (MIB). SNMP utilities can learn the network
topology by obtaining the MIB information in each LLDP device. The LLDP function is enabled by default.
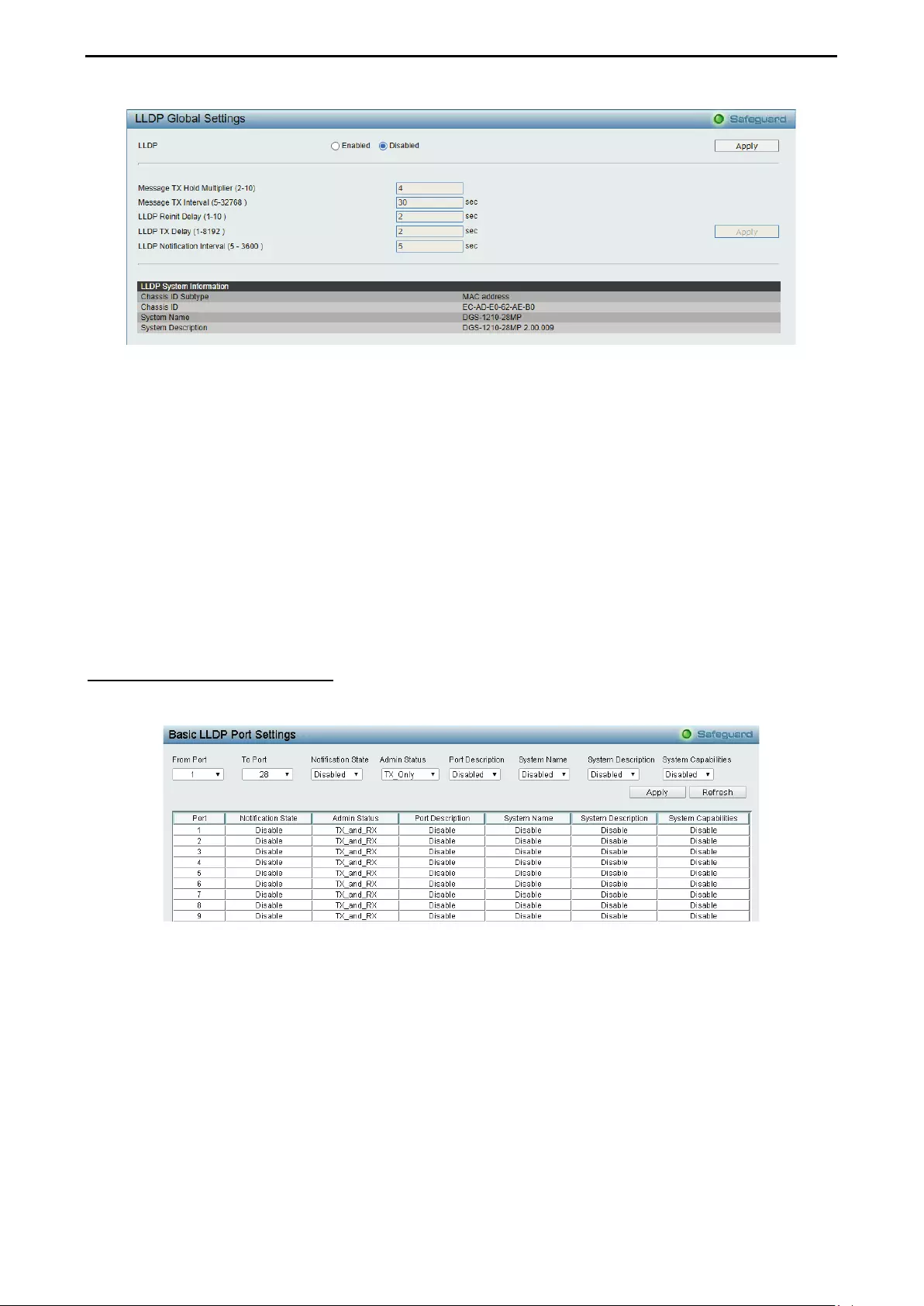
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
11
19
9
Figure 4.178 – LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
LLDP: When this function is Enabled, the switch can start to transmit, receive and process the LLDP packets.
For the advertisement of LLDP packets, the switch announces the information to its neighbor through ports.
For the receiving of LLDP packets, the switch will learn the information from the LLDP packets advertised
from the neighbor in the neighbor table. Click Apply to make the change effective.
Message TX Hold Multiplier (2-10): This parameter is a multiplier that determines the actual TTL value
used in an LLDPDU. The default value is 4.
Message TX Interval (5-32768): This parameter indicates the interval at which LLDP frames are transmitted
on behalf of this LLDP agent. The default value is 30 seconds.
LLDP Reinit Delay (1-10): This parameter indicates the amount of delay from the time adminStatus
becomes "disabled" until re-initialization is attempted. The default value is 2 seconds.
LLDP TX Delay (1-8192): This parameter indicates the delay between successive LLDP frame
transmissions initiated by value or status changes in the LLDP local systems MIB. The value for txDelay is
set by the following range formula: 1 < txDelay < (0.25 °— msgTxInterval). The default value is 2 seconds.
LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
The Basic LLDP Port Settings page displays LLDP port information and contains parameters for configuring
LLDP port settings.
Figure 4.179– LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
From Port/ To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Notification State: Specifies whether notification is sent when an LLDP topology change occurs on the port.
The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables LLDP notification on the port.
Disabled – Disables LLDP notification on the port. This is the default value.
Admin Status: Specifies the LLDP transmission mode on the port. The possible field values are:
TX_Only – Enables transmitting LLDP packets only.
RX_Only – Enables receiving LLDP packets only.
TX_and_RX – Enables transmitting and receiving LLDP packets. This is the default.
Disabled – Disables LLDP on the port.
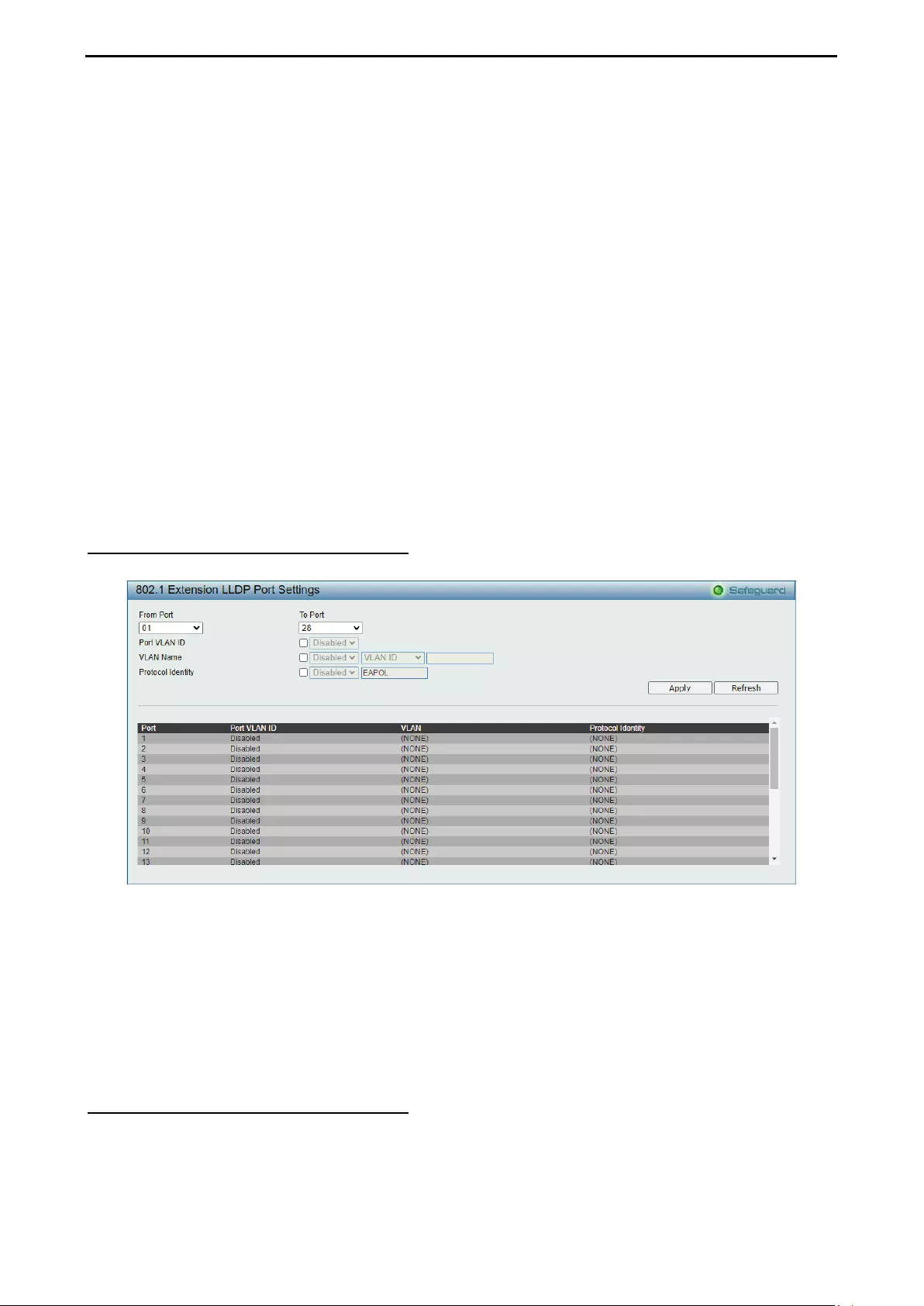
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
20
0
Port Description: Specifies whether the Port Description TLV is enabled on the port. The possible field
values are:
Enabled – Enables the Port Description TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the Port Description TLV on the port.
System Name: Specifies whether the System Name TLV is enabled on the port. The possible field values
are:
Enabled – Enables the System Name TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Name TLV on the port.
System Description: Specifies whether the System Description TLV is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the System Description TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Description TLV on the port.
System Capabilities: Specifies whether the System Capabilities TLV is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the System Capabilities TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Capabilities TLV on the port.
Define these parameter fields. Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the
table information.
LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings
This 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings page is used to configure the LLDP Port settings.
Figure 4.180 – LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings
From Port / To Port : A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Port VLAN ID : Specifies the Port VLAN ID to be enabled or disabled.
VLAN Name : Specifies the VLAN name to be enabled or disabled in the LLDP port. If select Enabled, users
can specifies the content of VLAN Name.
Protocol Identity : Specifies the Protocol Identity to be enabled or disabled in the LLDP port. If select
Enabled, users can specifies the EAPOL, LACP, GVRP, STP or ALL.
Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the table information.
LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings
The 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings page displays 802.3 Extension LLDP port information and contains
parameters for configuring 802.3 Extension LLDP port settings.
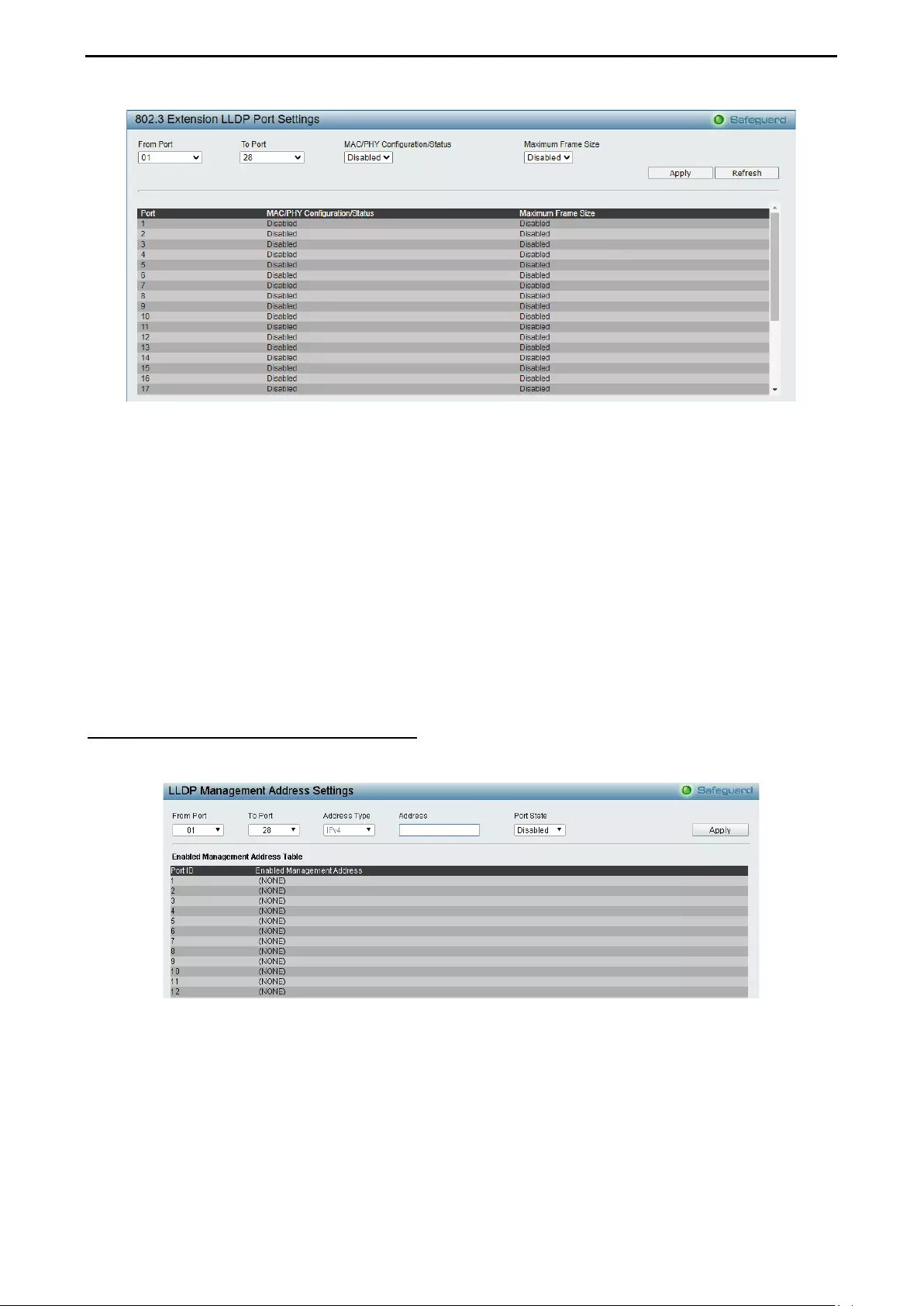
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
21
1
Figure 4.181 – LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
MAC/PHY Configuration/Status: Specifies whether the MAC/PHY Configuration Status is enabled on the
port. The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables the MAC/PHY Configuration Status on the port.
Disabled – Disables the MAC/PHY Configuration Status on the port.
Maximum Frame Size: Specifies whether the Maximum Frame Size is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the Maximum Frame Size configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the Maximum Frame Size configured on the port.
Define these parameter fields. Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the
table information.
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
The LLDP Management Address Settings allows the user to set management address which is included in
LLDP information transmitted.
Figure 4.182 – LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Address Type: Specify the LLDP address type on the port. The value is always IPv4.
Address: Specify the address.
Port State: Specify whether the Port State is enabled n the port. The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables the port state configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the port state configured on the port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
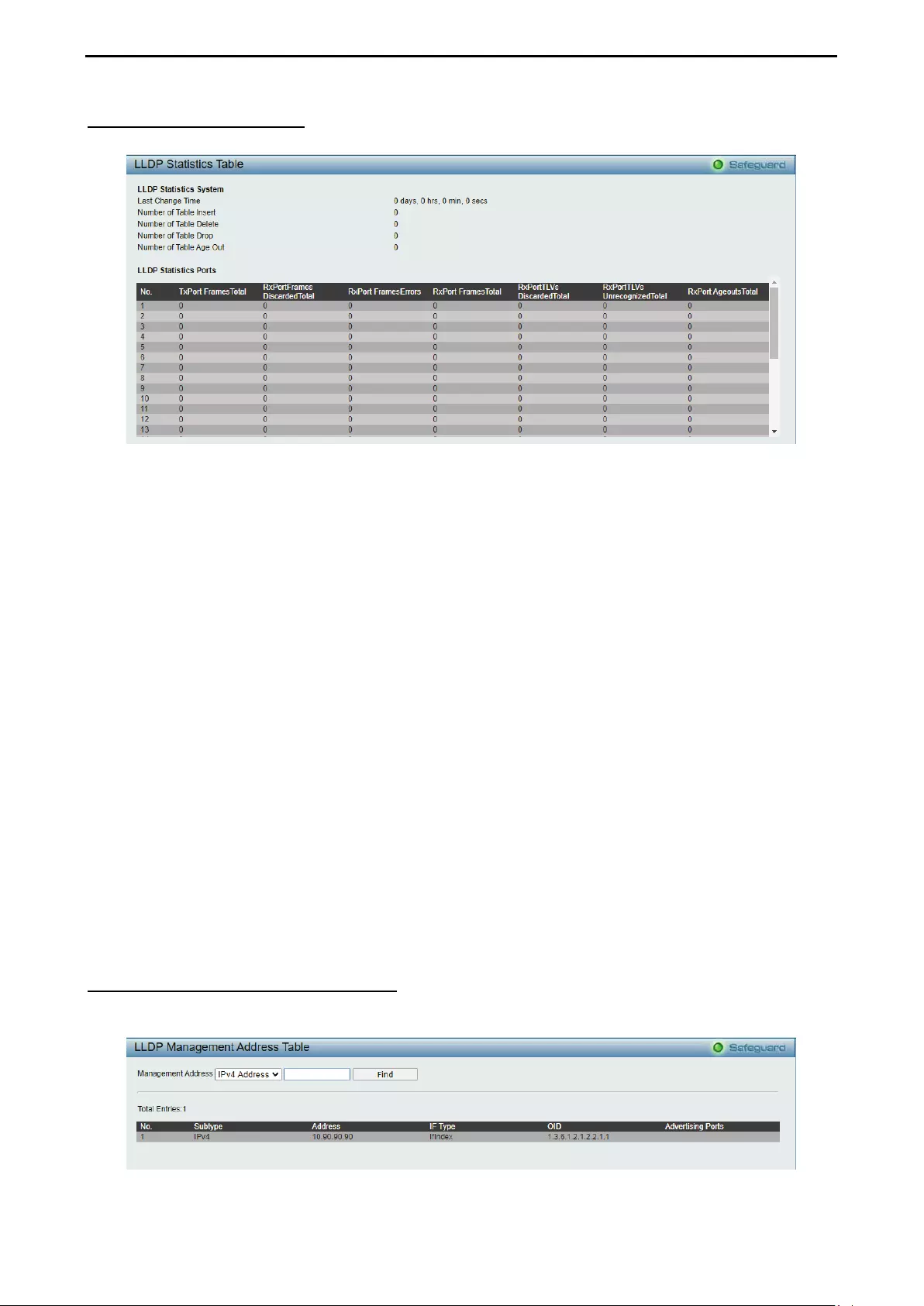
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
22
2
LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
The LLDP Statistics page displays an overview of all LLDP traffic.
Figure 4.183 – LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
The following information can be viewed:
LLDP Statistics System: Displays the counters that refer to the whole switch.
Last Change Time – Displays the time for when the last change entry was last deleted or added. It
is also displays the time elapsed since last change was detected.
Number of Table Insert – Displays the number of new entries inserted since switch reboot.
Number of Table Delete – Displays the number of new entries deleted since switch reboot.
Number of Table Drop – Displays the number of LLDP frames dropped due to that the table was
full.
Number of Table Age Out – Displays the number of entries deleted due to Time-To-Live expiring.
LLDP Port Statistics: Displays the counters that refer to the ports.
TxPort FramesTotal – Displays the total number of LLDP frames transmitted on the port.
RxPort FramesDiscarded – Displays the total discarded frame number of LLDP frames received on
the port.
RxPort FramesErrors – Displays the Error frame number of LLDP frames received on the port.
RxPort Frames – Displays the total number of LLDP frames received on the port.
RxPortTLVsDiscarded – Each LLDP frame can contain multiple pieces of information, known as
TLVs. If a TLV is malformed, it is counted and discarded.
RxPortTLVsUnrecognized – Displays the number of well-formed TLVs, but with a known type value.
RxPort Ageouts – Each LLDP frame contains information about how long time the LLDP information is valid.
If no new LLDP frame is received within the age out time, the LLDP information is removed, and the Age-Out
counter is incremented.
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
The LLDP Management Address Table page displays the detailed management address information for the
entry.
Figure 4.184 – LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
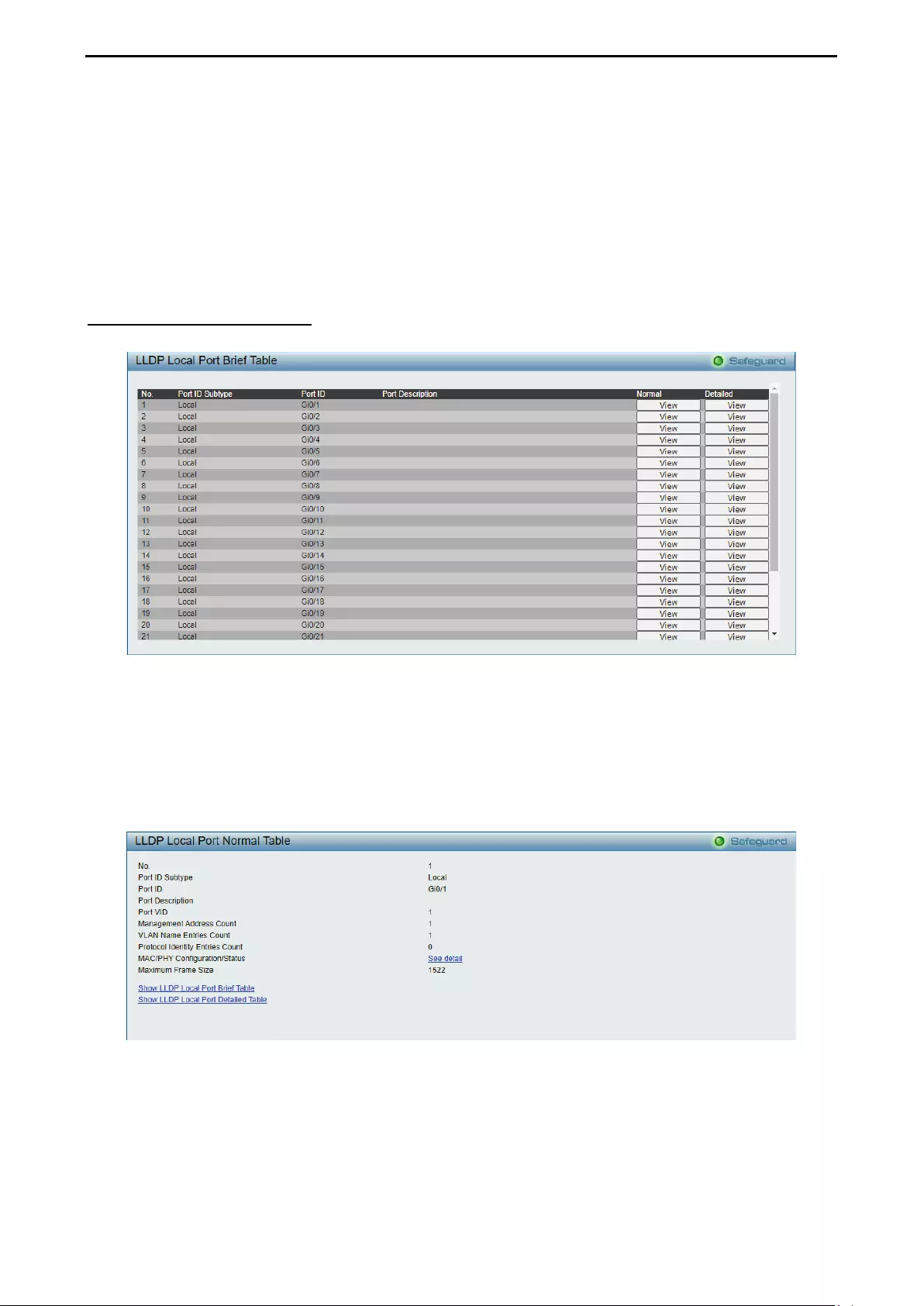
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
23
3
Management Address: Specifies IPv4 or IPv6 address then enter the address. Click Search and the table
will update and display the values required.
Subtype: Displays the managed address subtype. For example, MAC or IPv4.
Management Address: Displays the IP address.
IF Type: Displays the IF Type.
OID: Displays the SNMP OID.
Advertising Ports: Displays the advertising ports.
LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
The LLDP Local Port Table page displays LLDP local port information.
Figure 4.185 –LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
No: Displays the port number.
Port ID Subtype: Displays the port ID subtype.
Port ID: Displays the port ID (Unit number/Port number).
Port Description: Displays the port description.
Click View of Normal column to display more information.
Figure 4.186 – LLDP > LLDP Local Port Normal Table
Click View of Detailed column to display detail information.
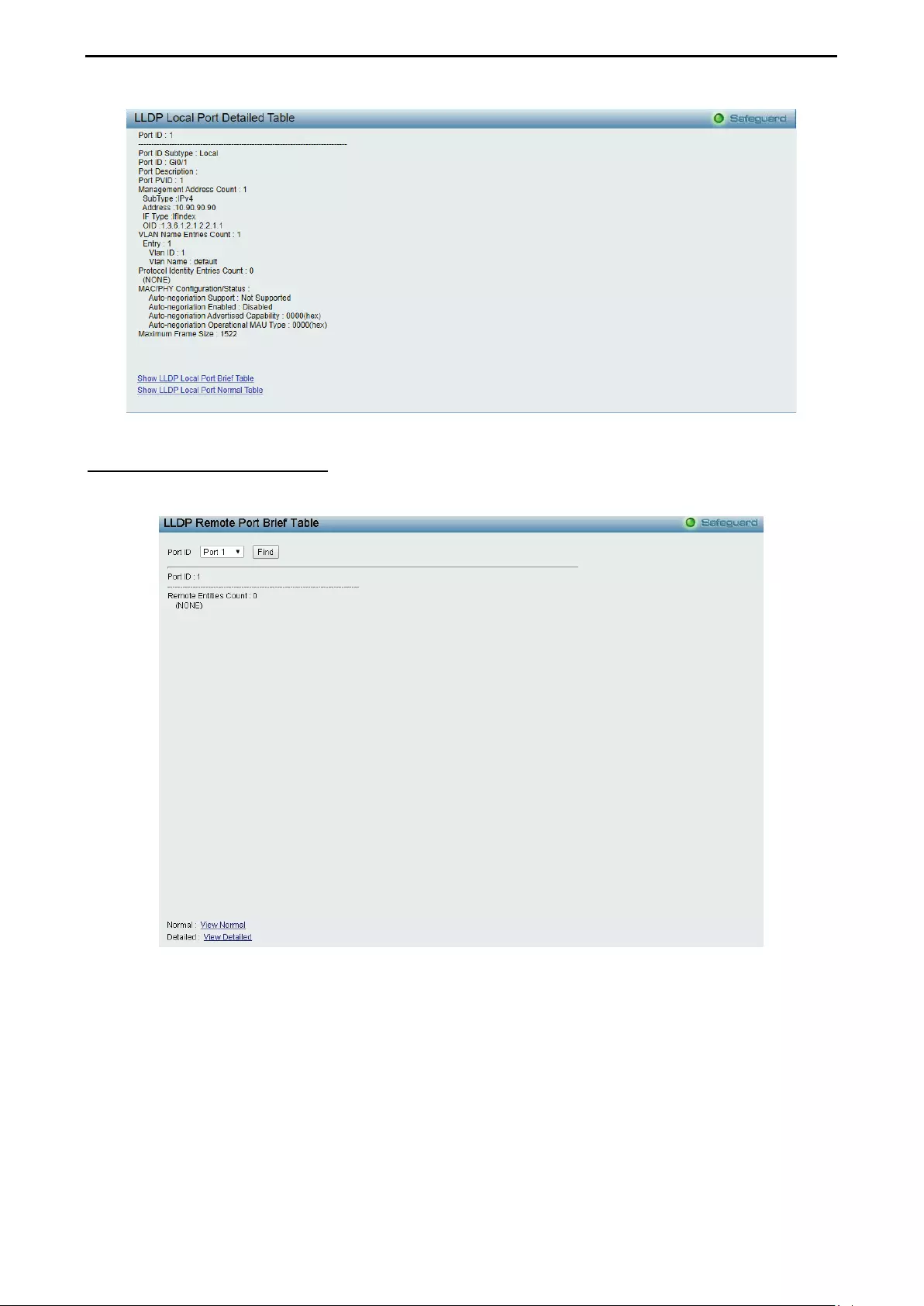
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
24
4
Figure 4.187 – LLDP > LLDP Local Port Detailed Table
LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
This LLDP Remote Port Table page is used to display the LLDP Remote Port Brief Table. Select port
number and click Search to display additional information.
Figure 4.188 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
To view the settings for a remote port, click View Normal and the following page displays.

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
25
5
Figure 4.189 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Normal Table
To view the detail settings for a remote port, click View Detailed and the following page displays.
Figure 4.190 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Detailed Table
LLDP > LLDP-MED Settings
By selecting a range of ports (From Port and To Port), the power PSE TLV type can be enabled for all
selected ports to indicate the power source equipment (PSE) switch to transmit high power (15.4 to 30 Watts)
to the pre-standard of 802.3at power devices via LLDP MDI TLV. Through this feature, the PSE can provide
precise output power to the pre-standard of 802.3at power devices and achieve optimal power management.
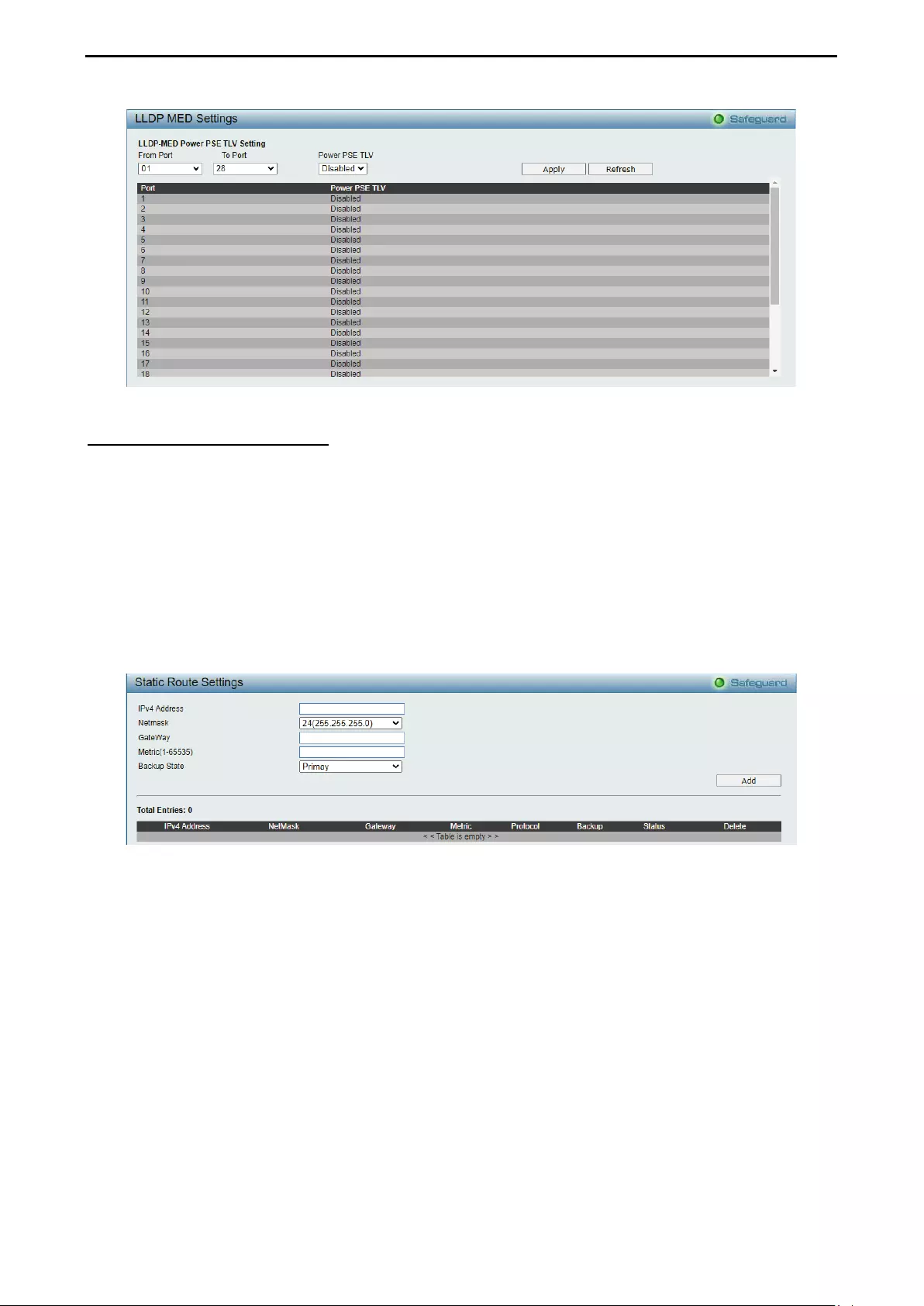
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
26
6
Figure 4.191 – LLDP > LLDP –MED Settings
L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
By The Switch supports static routing for IPv4 formatted addressing. User can create up to 256 static route
entries for IPv4. For IPv4 static routes, once a static route has been set, the Switch will send an ARP request
packet to the next hop router that has been set by the user. Once an ARP response has been retrieved by
the Switch from that next hop, the route becomes enabled. However, if the ARP entry already exists, an ARP
request will not be sent.
The Switch also supports a floating static route, which means that the user may create an alternative static
route to a different next hop. This secondary next hop device route is considered as a backup static route for
when the primary static route is down. If the primary route is lost, the backup route will uplink and its status
will become active. Entries into the Switch’s forwarding table can be made using both an IP address subnet
mask and a gateway.
Figure 4.192 – L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
IPv4 Address: Specifies an IPv4 address to be assigned to the static route.
Netmask: Specifies a subnet mask to be applied to the corresponding subnet mask of the IPv4 address.
Gateway: Specifies the entry of a Gateway IP address to be applied to the corresponding gateway of the
IPv4 address.
Metric (1-65535): Represents the metric value of the IP interface entered into the table. The value ranges
between 1 and 65535.
Backup State: Each IP address can only have one primary route, while other routes should be assigned to
the backup state. When the primary route failed, Switch will try the backup routes according to the order
learnt by the routing table until route success. The field represents the Backup state that the Static and
Default Route is configured for.
Click Add to create a new IPv4 static route entry.
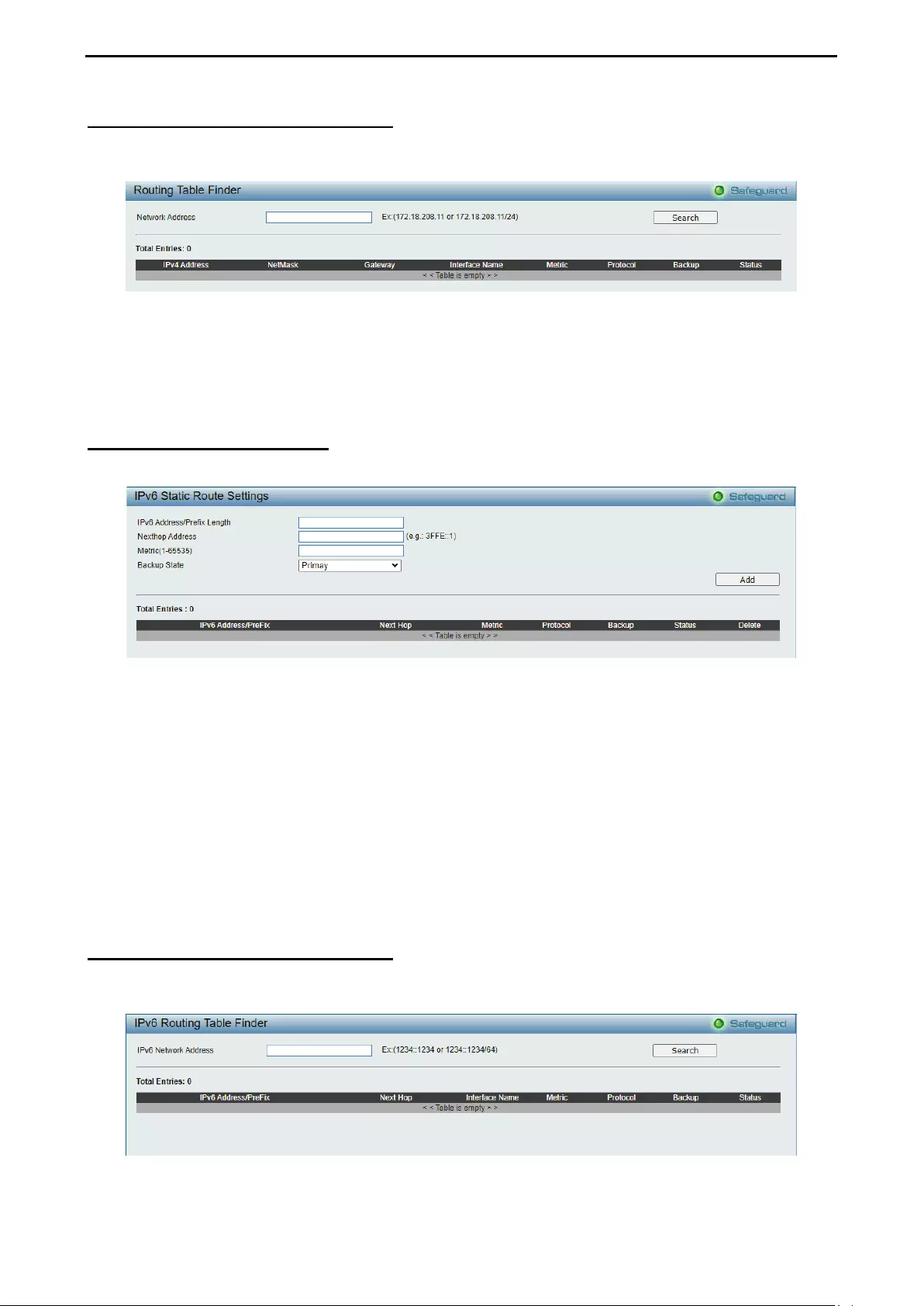
4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
27
7
L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder
The IPv4 routing table stores all the external routes information of the Switch. The IPv4 Routing Table
Finder page displays all the routing information on the Switch.
Figure 4.193 – L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder
Network Address; Specifies the destination network address of the route to be displayed.
Click Search to display the information of specified route entry.
L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
A static entry of an IPv6 address can be entered into the Switch’s routing table for IPv6 formatted addresses.
Figure 4.194 – L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
IPv6 Address / Prefix Length: Specifies an IPv6 address to be assigned to the static route.
Nexthop Address: Specifies the corresponding IPv6 address for the next hop gateway address in IPv6
format.
Metric (1-65535): Specifies a metric of the IPv6 interface into the table representing the number of routers
between the Switch and the IPv6 address above. The value ranges between 1 and 65535.
Backup State: Each IPv6 address can only have one primary route, while other routes should be assigned
to the backup state. When the primary route failed, the Switch will try the backup routes according to the
order learnt by the routing table until route success. This field represents the backup state for the IPv6
configured. This field may be Primary or Backup.
Click Add to create a new IPv6 static route entry.
L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder
The IPv6 routing table stores all the external routes information of the Switch. The IPv6 Routing Table
Finder page displays all the routing information on the Switch.
Figure 4.195 – L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder

4 Web-based Switch Configuration D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
28
8
Network Address; Specifies the destination network address of the route to be displayed.
Click Search to display the information of specified route entry.

Appendix A - Ethernet Technology D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
12
29
9
Appendix A - Ethernet Technology
This chapter will describe the features of the D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch and provide some
background information about Ethernet/Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet switching technology.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format, and
support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex, and management objects, but with a tenfold increase in
theoretical throughput of over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps Ethernet.
Since it is compatible with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit Ethernet provides a
straightforward upgrade without wasting existing investments in hardware, software, or trained personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet is essential in solving network
bottlenecks, which frequently develops as more advanced computer users and newer applications continue
to demand greater network resources. Upgrading key components, such as backbone connections and
servers to Gigabit Ethernet technology, can greatly improve network response times as well as significantly
speed up the traffic between subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fiber connections to support video conferencing, complex imaging, and
similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet,
servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to perform 10 times the number of operations in the
same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet is the most cost-effective method to
take advantage of today and tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technologies. With expected advances in the coming years in silicon technology and digital signal processing,
which will enable Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling, a flexible
foundation for the next generation of network technology products will be created. This will outfit your
network with a powerful 1000-Mbps-capable backbone/server connection.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs, and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications are
fueling the need for high performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies have been
proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve client/server response times. Among them, 100BASE-T
(Fast Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the current 10BASE-T technology. The
non-disruptive and smooth evolution nature, and the dominating potential market base, virtually guarantees
cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3 LAN committee. It is an extension of the
10Mbps Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while maintaining the
CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps Fast Ethernet is compatible with all other 10Mbps Ethernet
environments, it provides a straightforward upgrade and utilizes existing investments in hardware, software,
and personnel training.
Switching Technology
Another approach to push beyond the limits of Ethernet technology is the development of switching
technology. A switch bridges Ethernet packets at the MAC address level of the Ethernet protocol transmitting
among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network capacity available to users on a local area
network. A switch increases capacity and decreases network loading by dividing a local area network into
different segments, which won’t compete with each other for network transmission capacity.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual segments. The switch, without
interfering with any other segments, automatically forwards traffic that needs to go from one segment to
another. By doing this the total network capacity is multiplied, while still maintaining the same network
cabling and adapter cards.
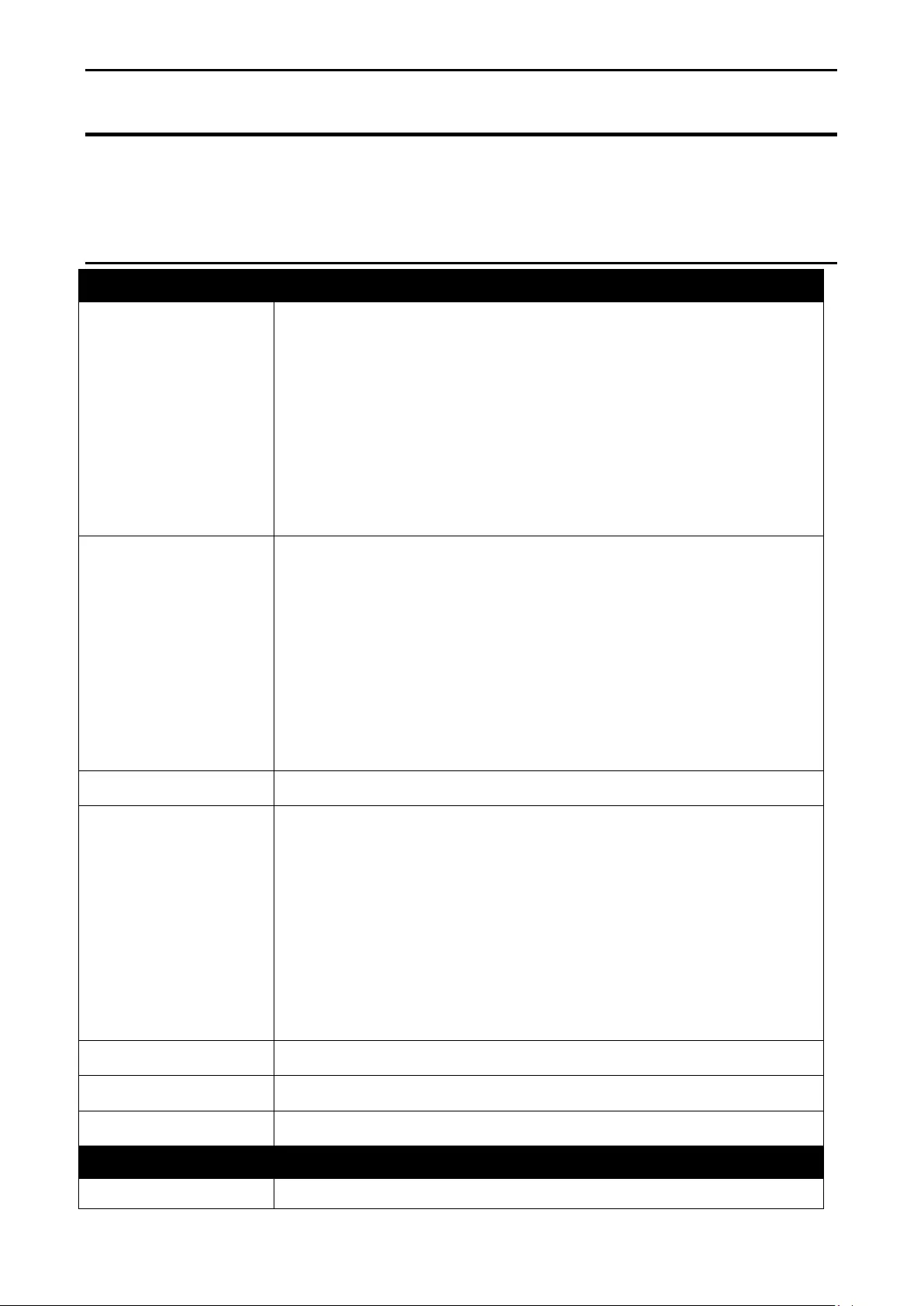
Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
130
Appendix B - Technical Specifications
This appendix contains the device specifications, and contains the topics:
• Hardware Specifications
• Features
Hardware Specifications
Key Components / Performance
Switching Capacity
DGS-2000-10: 20Gbps
DGS-2000-10P: 20Gbps
DGS-2000-10MP: 20Gbps
DGS-2000-20: 40Gbps
DGS-2000-26: 52Gbps
DGS-2000-28: 56Gbps
DGS-2000-28P: 56Gbps
DGS-2000-28MP: 56Gbps
DGS-2000-52: 104Gbps
DGS-2000-52MP: 104Gbps
Max. Forwarding Rate
DGS-2000-10: 14.88 Mpps
DGS-2000-10P: 14.88 Mpps
DGS-2000-10MP: 14.88 Mpps
DGS-2000-20: 29.8 Mpps
DGS-2000-26: 38.7 Mpps
DGS-2000-28: 41.7 Mpps
DGS-2000-28P: 41.7 Mpps
DGS-2000-28MP: 41.7 Mpps
DGS-2000-52: 77.4 Mpps
DGS-2000-52MP: 77.4 Mpps
Forwarding Mode Store and Forward
Packet Buffer memory
DGS-2000-10: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-10P: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-10MP: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-20: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-26: 4.1 Mbitss
DGS-2000-28: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-28P: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-28MP: 4.1 Mbits
DGS-2000-52: 12 Mbits
DGS-2000-52MP: 12 Mbits
DDRIII for CPU 256M bytes
Flash Memory 32M bytes
Priority Queues 8
Port Functions
10/100/1000BASE-TX
8 x 10/100/1000BaseT ports for DGS-2000-10, DGS-2000-10P and DGS-
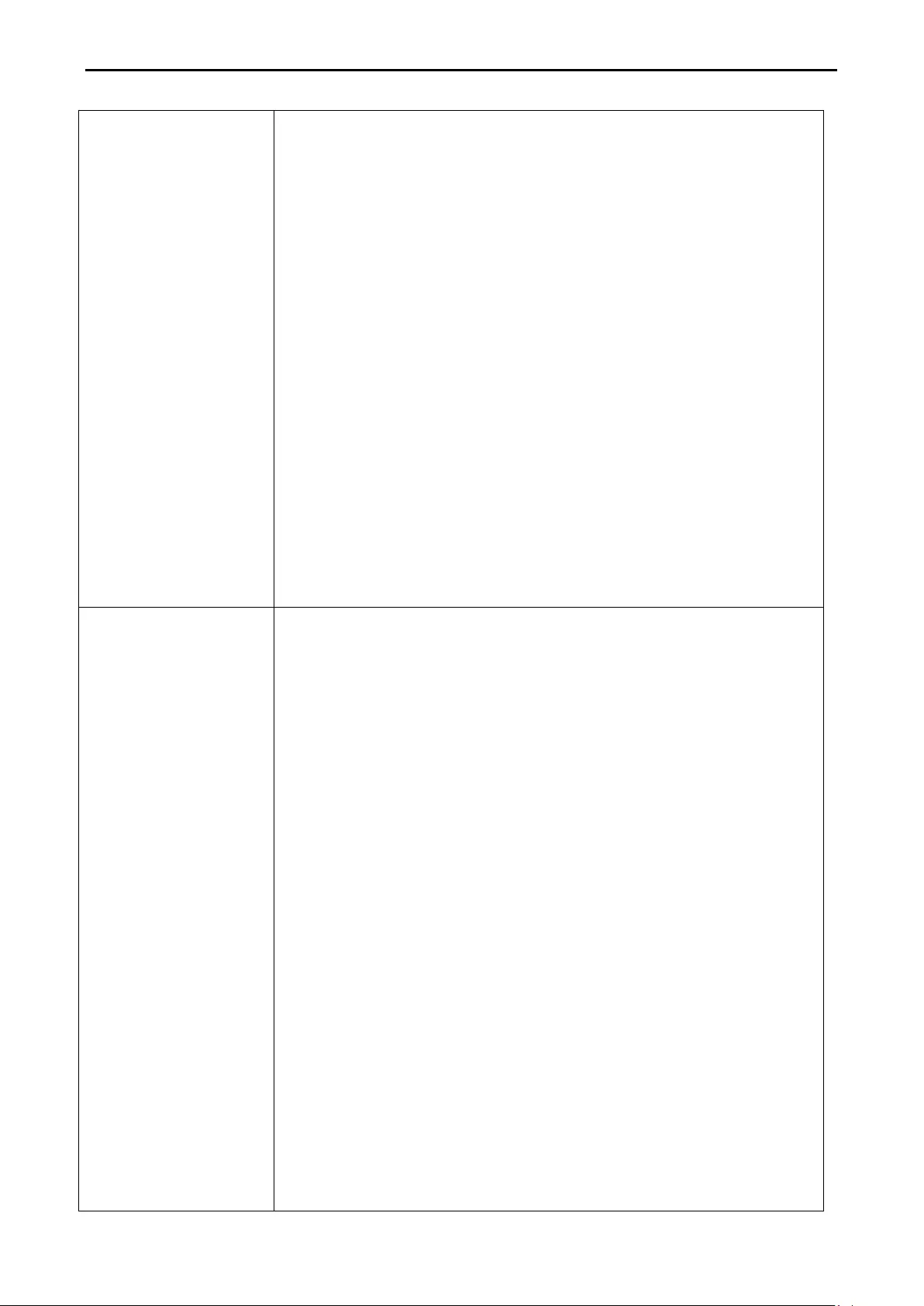
Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
31
1
Ethernet ports
2000-10MP
20 x 10/100/1000BaseT ports for DGS-2000-20
24 x 10/100/1000BaseT ports for DGS-2000-26
28 x 10/100/1000BaseT ports for DGS-2000-28, DGS-2000-28P, DGS-2000-
28MP
52 x 10/100/1000BaseT ports for DGS-2000-52, DGS-2000-52MP
1000Base-T ports compliant to following standards:
- IEEE 802.3 compliance
- IEEE 802.3u compliance
- IEEE 802.3ab compliance
Support Half/Full-Duplex operations
- IEEE 802.3x Flow Control support for Full-Duplex mode
- Back Pressure for Half-Duplex mode
- Head-of-line blocking prevention
Support manual/auto MDI/MDIX configuration
Support Auto-Negotiation for each port
SFP ports
Port 9 ~ 10 for DGS-2000-10, DGS-2000-10P and DGS-2000-10MP
Port 17 ~ 20 for DGS-2000-20
Port 25 ~ 26 for DGS-2000-26
Port 25 ~ 28 for DGS-2000-28, DGS-2000-28P, DGS-2000-28MP
Port 49 ~ 52 for DGS-2000-52 and DGS-2000-52MP
SFP ports comply with following standards:
- IEEE 802.3u compliance (Support 100M transceivers)
- IEEE 802.3z compliance
- IEEE 802.3ah compliance
Support Transceivers:
- 100M/1000M SFP Transceivers
- WDM SFP Transceivers
- 1000BASE-T Transceivers
SFP Transceivers Supported:
- DGS-712 (1000Base-T)
- DEM-210 (100BASE-FX, 15km)
- DEM-211 (100BASE-FX, 2km)
- DEM-310GT (1000BASE-LX, 10km)
- DEM-311GT (1000BASE-SX, 550m)
- DEM-314GT (1000BASE-LH, 50km)
- DEM-315GT (1000BASE-ZX, 80km)
- DEM-312GT2 (1000BASE-SX, 2km)
Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
32
2
WDM Transceivers Supported:
- DEM-220T (100Base-BX,TX-1550/RX-1310nm, 20km)
- DEM-220R (100Base-BX,TX-1310/RX-1550nm, 20km)
- DEM-330T (1000Base-BX,TX-1550/RX-1310nm, 10km)
- DEM-330R (1000Base-BX,TX-1310/RX-1550nm, 10km)
- DEM-331T (1000Base-BX,TX-1550/RX-1310nm, 40km)
- DEM-331R (1000Base-BX,TX-1310/RX-1550nm, 40km)
Physical & Environment
Power Consumption
DGS-2000-10:
Standby power consumption: 2.03 Watts
DGS-2000-10P:
Maximum power consumption: 81.9 Watts (PoE On),7.6 Watts (PoE Off)
Standby power consumption: 2.5 Watts
DGS-2000-10MP:
Maximum power consumption: 152.3 Watts (PoE On), 9.4 Watts (PoE Off)
Standby power consumption: 5.2 Watts
DGS-2000-20:
Standby power consumption: 5.47 Watts
DGS-2000-26:
Standby power consumption: 5.01 Watts
DGS-2000-28:
Standby power consumption: 6.49 Watts
DGS-2000-28P:
Maximum power consumption: 263.9 Watts (PoE On), 30.6 Watts (PoE Off)
Standby power consumption: 19.6 Watts
DGS-2000-28MP:
Maximum power consumption: 446.1 Watts (PoE On), 29.8 Watts (PoE Off)
Standby power consumption: 18.5 Watts
DGS-2000-52:
Standby power consumption: 13.7 Watts
DGS-2000-52MP:
Maximum power consumption: 478.9 Watts (PoE On), 54.4 Watts (PoE Off)
Standby power consumption: 32 Watts
Power Supply DGS-2000-10P: DC:54V / 1.574A
DGS-2000-10/10MP/20/26/28/28P/28MP/52/52MP: AC:100~240V, 50/60Hz
Fans
DGS-2000-28P: 2pcs Smart Fan
DGS-2000-28MP: 2pcs Smart Fan
DGS-2000-52: 2pcs Smart Fan
DGS-2000-52MP: 2pcs Smart Fan
Operating Temperature -5~50°C
Storage Temperature -20~70°C
Humidity Storage: 0%~90% non-condensing
Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
33
3
Dimensions
DGS-2000-10: 280 x 126 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-10P: 280 x 126 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-10MP: 330 x 180 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-20: 280 x 180 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-26: 440 x 140 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-28: 440 x 140 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-28P: 440 x 250 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-28MP: 440 x 250 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-52:440 x 210 x 44 mm
DGS-2000-52MP: 440 x 430 x 44 mm
Weight
DGS-2000-10: 0.98 kg
DGS-2000-10P: 0.95 kg
DGS-2000-10MP: 1.77 kg
DGS-2000-20: 1.75 kg
DGS-2000-26: 2.06 kg
DGS-2000-28: 2.15 kg
DGS-2000-28P: 3.75 kg
DGS-2000-28MP: 3.94 kg
DGS-2000-52: 3.46 kg
DGS-2000-52MP: 6.26 kg
EMI CE, FCC/IC, VCCI, BSMI, C-Tick
Safety UL, CB, BSMI

Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
34
4
Features
L2 Features
Supports up to 8K MAC address
Supports 256 static MAC
Jumbo frame: Supports up to 10,000
bytes.
IGMP Snooping v1/v2/v3 awareness:
- Supports 256 multicast groups
- Supports at least 32 static multicast groups
MLD Snooping:
- Supports max. 32 MLD Snooping groups
802.1D Spanning Tree
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
802.1s MSTP
Loopback Detection
802.3ad Link Aggregation:
Port mirroring
SNTP
LLDP/LLDP-MED
IPv6 neighbor Discovery (ND): Supports
256 dynamic + static ND entries
L2 Multicast Filtering
L3 Features
ARP:
Max 128 ARP entries
- Support 128 static ARP entries
Support 4 IPv4 and 4 IPv6 interfaces
Support IPv6 Neighbor Discovery:
- Max 256 ND entries
- Support up to 256 static ND
entries
Max. 128 IPv4 and 128 IPv6 static route
entries
Supports default route backup entry
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN standard (VLAN Tagging)
Up to 256 static VLAN groups
Asymmetric VLAN
Management VLAN
Auto Voice VLAN
Auto Surveillance VLAN 2.0
QoS (Quality of Service)
Priority queue mapping by :
- 802.1p
- DSCP
- Port Base
Up to 8 queues per port
Supports Strict in queue handling
Bandwidth Control
AAA
802.1X port-based access control
Support RADIUS server
ACL
Max 150 ingress ACL access-list
Ingress ACL rules: 200 rules (each rule
can be associated to a single port or
multiple ports)
Support different ACL policy packet
contents:
- 802.1p priority
- VLAN
- MAC address
- Ethernet Type
- IPv4/IPv6 address
- DSCP
- Protocol type
- TCP/UDP port number
- IPv6 Traffic class
Security
Trusted Host
Port Security: Support 64 MAC addresses
per port
Traffic Segmentation
D-Link Safeguard Engine
Broadcast Storm Control
Smart Binding
- Support manual configuration and
scanning for binding.
- Supports ARP and IP packet inspection
as an option.
- Supports DHCP Snooping
OAM
Cable Diagnostics
Reset button (reset to factory default)
Management
Web-based GUI or D-Link Network
Assistant (DNA)
D-Link CLI style
SNMP support
DHCP client
Trap setting for destination IP, system
events, fiber port events,
Password access control
Web-based configuration backup /
restoration
Web-based firmware backup/restore
Firmware upgrade using D-Link Network
Assistant (DNA) & Web-based
management
Reset, Reboot

Appendix B - Technical Specifications D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
1
13
35
5
D-Link Green Technology
Power Saving: Enabled by default to save
power:
- By Link Status: Drastically save power
when the switch port link is down. For
example, no PC connection or the
connected PC is powered off.
- By LED Shut-Off: LEDs can be turned
on/off by port or system through schedule.
- By Port Shut-Off: Each port on the system
can be turned on/off by schedule.
- By System Hibernation: System enters
hibernation by schedule. In this mode,
switches save most power since main
chipsets (both MAC and PHY) are disabled
for all ports, and energy required to power
the CPU is minimal.

Appendix C – Rack mount Instructions D-Link DGS-2000 Series Ethernet Switch User Manual
136
Appendix C – Rack mount Instructions
Safety Instructions - Rack Mount Instructions - The following or similar rack-mount instructions are included
with the installation instructions:
A) Elevated Operating Ambient - If installed in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating ambient
temperature of the rack environment may be greater than room ambient. Therefore, consideration should be
given to installing the equipment in an environment compatible with the maximum ambient temperature (Tma)
specified by the manufacturer.
B) Reduced Air Flow - Installation of the equipment in a rack should be such that the amount of air flow
required for safe operation of the equipment is not compromised.
C) Mechanical Loading - Mounting of the equipment in the rack should be such that a hazardous condition is
not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
D) Circuit Overloading - Consideration should be given to the connection of the equipment to the supply
circuit and the effect that overloading of the circuits might have on overcurrent protection and supply wiring.
Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate ratings should be used when addressing this concern.
E) Reliable Earthing - Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained. Particular
attention should be given to supply connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. use
of power strips).
