Table of Contents
- Welcome to Dell Wyse 5060 thin client
- Installation and setup
- Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client
- Displays
- Networks
- Peripherals
- Power state
- Software
- Management interface of Wyse 5060 thin client
- System specifications
- Troubleshooting your system
Dell Wyse 5060 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 5060 by Dell Wyse which is a product in the Thin Clients category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals
Dell Wyse 5060 Thin Client
User Guide
Regulatory Model: N07D
Regulatory Type: N07D001

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2016 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property
laws. Dell and the Dell logo are trademarks of Dell Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All other marks and names mentioned herein
may be trademarks of their respective companies.
2016 - 10
Rev. A00

1
Welcome to Dell Wyse 5060 thin client
Dell Wyse 5060 thin client is a mid-range thin client. These thin clients have a x86 processor, which allows you to run Wyse ThinOS,
Wyse ThinLinux, and Windows Embedded Standard 7P. The platform is used as a thin client by connecting to any monitor and
allows you to use a remote access client for VDI or cloud-based computing.
About this guide
This guide is intended for Wyse 5060 thin clients which run Wyse ThinOS, Wyse ThinLinux, and Windows Embedded Standard 7P. It
provides hardware specifications and OS specific configurations to help you work with Wyse 5060 thin clients.
Dell Wyse external references
This section provides links to technology related support and self-service sites for Dell Wyse thin clients.
•Dell reference guides
•Dell Wyse Technology End User License Agreement
•Dell Service and Support — Latest software images
•Dell Wyse Device Manager — Information about Dell remote management software
•Dell and the Environment — Information about Dell compliance with RoHS and with the Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment (WEEE)
•Dell and e-Recycling — Information about recycling and reuse of Dell products
•Dell Warranty Registration* — Register your product
3

2
Installation and setup
This section describes about the following topics:
• Dell Wyse 5060 thin client hardware setup.
• Accessing thin client BIOS settings.
Wyse 5060 thin client hardware installation
For more information on the hardware installation, see
Dell Wyse 5060 thin client Quick Start Guide
.
Accessing thin client BIOS settings on WES7P
While starting a thin client, a Dell logo is displayed for a short period.
1. During the start-up, press the Del key.
The BIOS Settings dialog box is displayed.
2. When prompted, enter Fireport as the password.
3. Change the BIOS Settings as required.
Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinOS
After starting your thin client you will see a Dell logo for a short period of time. During this period you can press and hold the Delete
key to enter the BIOS with Fireport as the password to make necessary modifications. For example, you can use the F7 key to use
Optimized Defaults (load optimal default values for all the items in the BIOS setup utility).
Accessing thin client BIOS settings on Wyse ThinLinux
This section describes about the Wyse 5060 thin client BIOS settings.
How to invoke BIOS settings and select boot source
The standard BIOS features and boot options are common to all platforms with the following boot options:
• Boot from HardDisk –Boots from the internal SSD storage.
• Boot from USB – Boots the USB storage from any of the USB ports (this option is disabled by default).
• Boot from PXE – Boots from the network through PXE.
• Boot from CLOUD – Not supported by ThinLinux.
The following are the BIOS Hot Key functions while booting:
•P-Key – The key invokes to the boot selection menu. It is used to select or alter the temporary boot order.
•Del-key – The key invokes to the BIOS settings. The BIOS settings is protected by a password and the default password is
Fireport.
4

3
Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client
This section includes the following topics:
•Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running WES7P.
•Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running ThinOS.
•Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running ThinLinux
Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running WES7P
For security reasons, automatic logon to a User desktop is enabled on the thin client by default.
To log in as a different user or administrator:
1. Click Start Menu → Log off, to log off the current desktop and hold the Shift key until the logon window is displayed.
2. Log in using one of the following options:
•Administrators — The default name is Administrator which is displayed automatically and default password is DellCCCvdi.
•Users — The default name is User which is displayed automatically and default password is DellCCCvdi.
Important: Passwords are case-sensitive.
NOTE: As an administrator, you can use Auto Logon to configure your thin client to start with the Logon window so
that you can simply log in as an administrator.
3. If automatic logon is not enabled, the logon window is displayed when you boot the thin client. You can log in using the options
mentioned in step 2.
We recommend you change the default passwords of your thin client. To change a password:
1. Disable the File Based Write Filter before you change a password, and then enable it after your change.
2. Log in as an Administrator, and then open Windows Security window by holding CTRL+ALT+DEL key combination.
3. Click Change a Password, and then use the Change a Password dialog box to specify your old password and new password.
Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running Wyse ThinOS
What you see after logging on to the server depends on the administrator configurations.
•Users with a Classic Desktop - will see the classic ThinOS desktop with full taskbar, desktop, and Connect Manager familiar to
ThinOS users. This option is the default out-of-the-box experience and is recommended for terminal server environments with
published applications and for backward compatibility with ThinOS 6.x versions.
•Users with a Zero Desktop - will see the Zero Desktop with the Zero Toolbar showing the assigned list of connections from
which to select. This option is recommended for VDI and any full-screen only connections.
In any desktop case, you can select the desktop option you want (Classic Desktop or Zero Desktop) and create the connections you
need using the Visual Experience tab on the Remote Connections dialog box.
To open the Remote Connections dialog box, perform one of the following tasks:
5

•Classic Desktop — Click User Name , and then select System Setup → Remote Connections.
NOTE: User Name is the user who is logged-on and is located at the lower-left pane of the taskbar
•Zero Desktop — Click the System Settings icon on the Zero Toolbar, and then select Remote Connections.
Logging on to the Wyse 5060 thin client running ThinLinux
On your initial configuration, Dell recommends that you connect by using a wired connection by plugging in the network connected
Ethernet cable to your thin client.
After you turn on your thin client, you are automatically logged in to the local thinuser account. By default, the password of the
thinuser account is set to thinuser.
NOTE: In cases where a GDM login is needed (for example, AD/Domain login, PNAgent login and so on), the auto-login
option can be turned off through the GUI or by using the INI.
Admin mode enables you to perform system administration tasks such as adding or removing connections and setting up specific
device settings. To enter into the Admin mode, click the Switch to Admin button from Setting application screen to admin mode
and then enter the default root password in the Password Needed window. The default root password is admin.
6
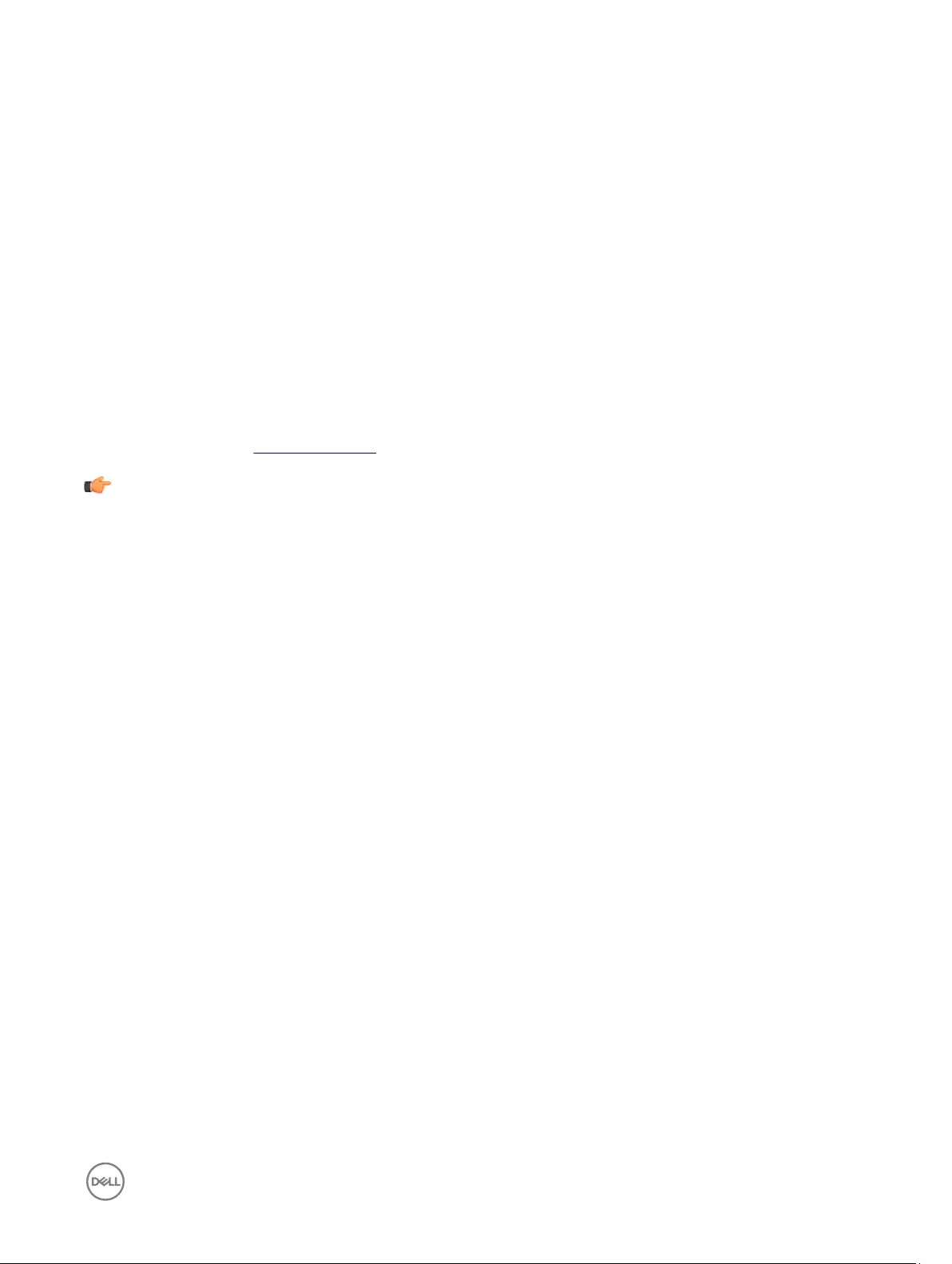
4
Displays
This section provides information about the multiple monitor configurations.
Display: Dual Monitor Display on WES7P
This section describes about the dual monitor display of Wyse 5060 thin client running WES7P.
To configure the dual monitor settings, go to Start → Control Panel → Display → Change Display Settings. The configurations
are made in the Screen Resolution window and it is applicable for Dual-Monitor capable thin clients only.
For more information, refer www.microsoft.com.
Tip: While configuring Dual-Monitor settings, set the same screen resolution for both the monitors.
Configuring the dual head display settings on Wyse ThinOS
To configure the Dual head display settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Display.
The Display dialog box is displayed.
2. Click Dual Head tab, and use the following guidelines:
7
This feature is applicable for supported Dual Monitor Capable thin clients Only.
a. Dual Head—Select Mirror Mode to have the two monitors work in a matching state, or Span Mode to have the two
monitors work separately second is extended from first.
b. Main Screen—Select which of the two monitors you want to be the main screen (Screen1 or Screen2). The other screen
is extended from the main screen.
c. Layout—Select how you want the two monitors to be oriented to each other.
Horizontal — where you move between the monitors from the left and right of the screens.
Vertical— where you move between the monitors from the top and bottom of the screens.
d. Alignment— Select how you want the monitors to be aligned Bottom, Center, or Top.
Bottom means screens are bottom-aligned in a horizontal orientation; Center means screens are center-aligned; Top means
screens are top-aligned in a horizontal orientation.
e. Taskbar (Classic Desktop Only)—Select under which screen you want the Taskbar to appear Whole Screen or Main
Screen
Gamma Supported Monitors Only— Use the Gamma Setup tab to adjust the saturation values for Red, Green and Blue on
VGA connected monitors supporting gamma settings, if you feel the default settings are too light. Be aware that the
Gamma Setup tab will be disabled once you click Save+Exit. You can enable it again by setting rgamma={1-100}
ggamma={1-100} bgamma={1-100} in the Resolution INI parameter. For more information, see Dell Wyse ThinOS INI Guide.
8
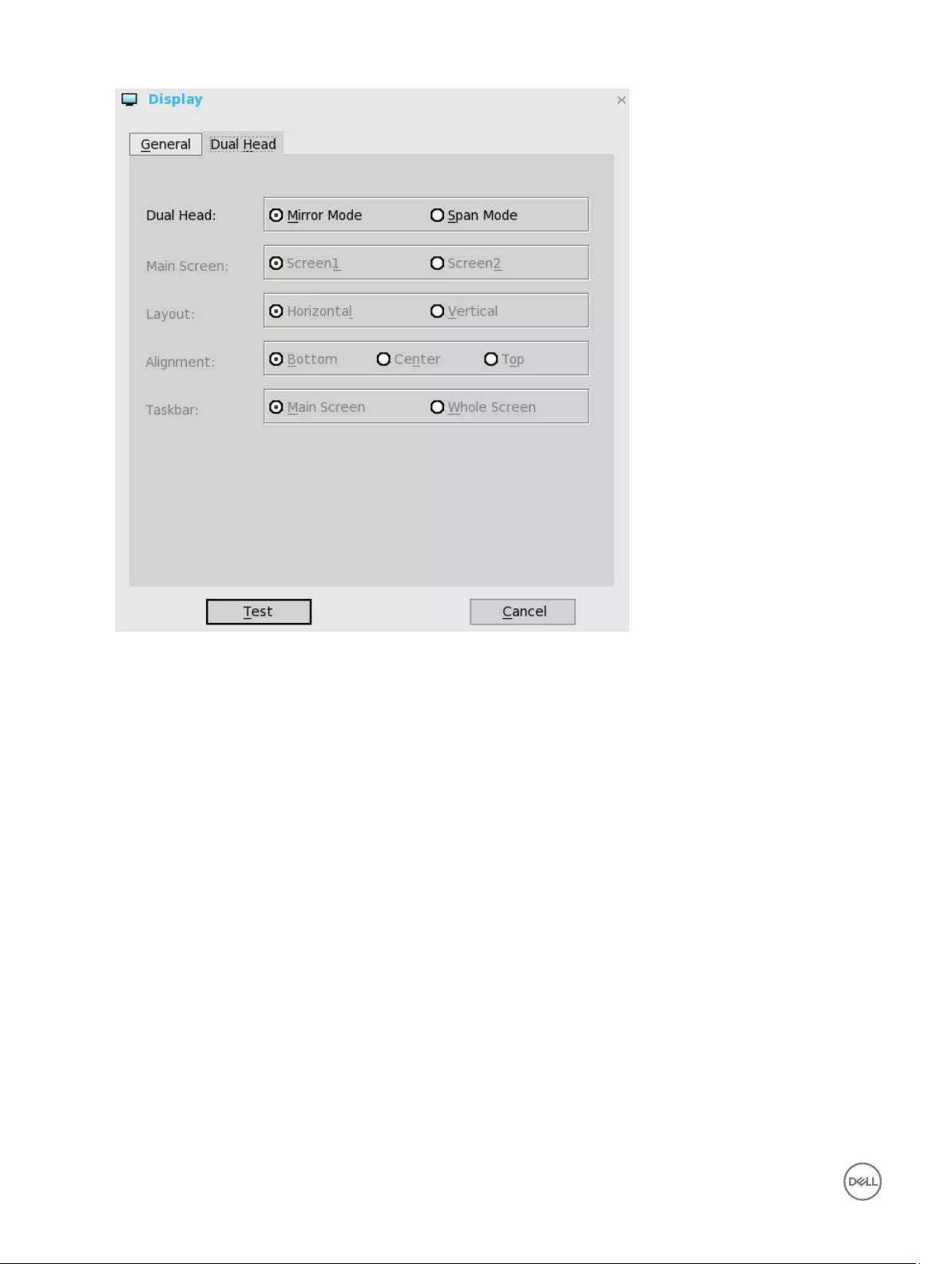
For Swap dual screens, when you set Main Screen to Screen2, an additional check box is displayed at the bottom of the tab
that allows you to swap dual screens. If you clear the check box, the Screen1 is usually the left one or the top one in dual
display. When you set Main Screen to Screen2, the main screen is changed to the right screen or bottom screen. If you
select the swap dual screens check box, you are able to set Main Screen to Screen2, but still have it at the left side or the
top side, which is considered more user friendly.
Configuring your display on Wyse ThinLinux
By default, the Customize your display screen is available in both User mode and Admin mode. Any changes to display preferences
made through this screen is saved and available for the built-in thinuser. In a Dual-monitor configuration, if both monitors are
connected, then by default, the monitors are in extended mode. The primary monitor is on the left (monitor 1) and the secondary
monitor is on the right (monitor 2). The resolutions of the monitors are auto detected by the system by analyzing the monitor’s
capabilities.
1. Click the Display tab.
The Customize Your Display page is displayed.
9
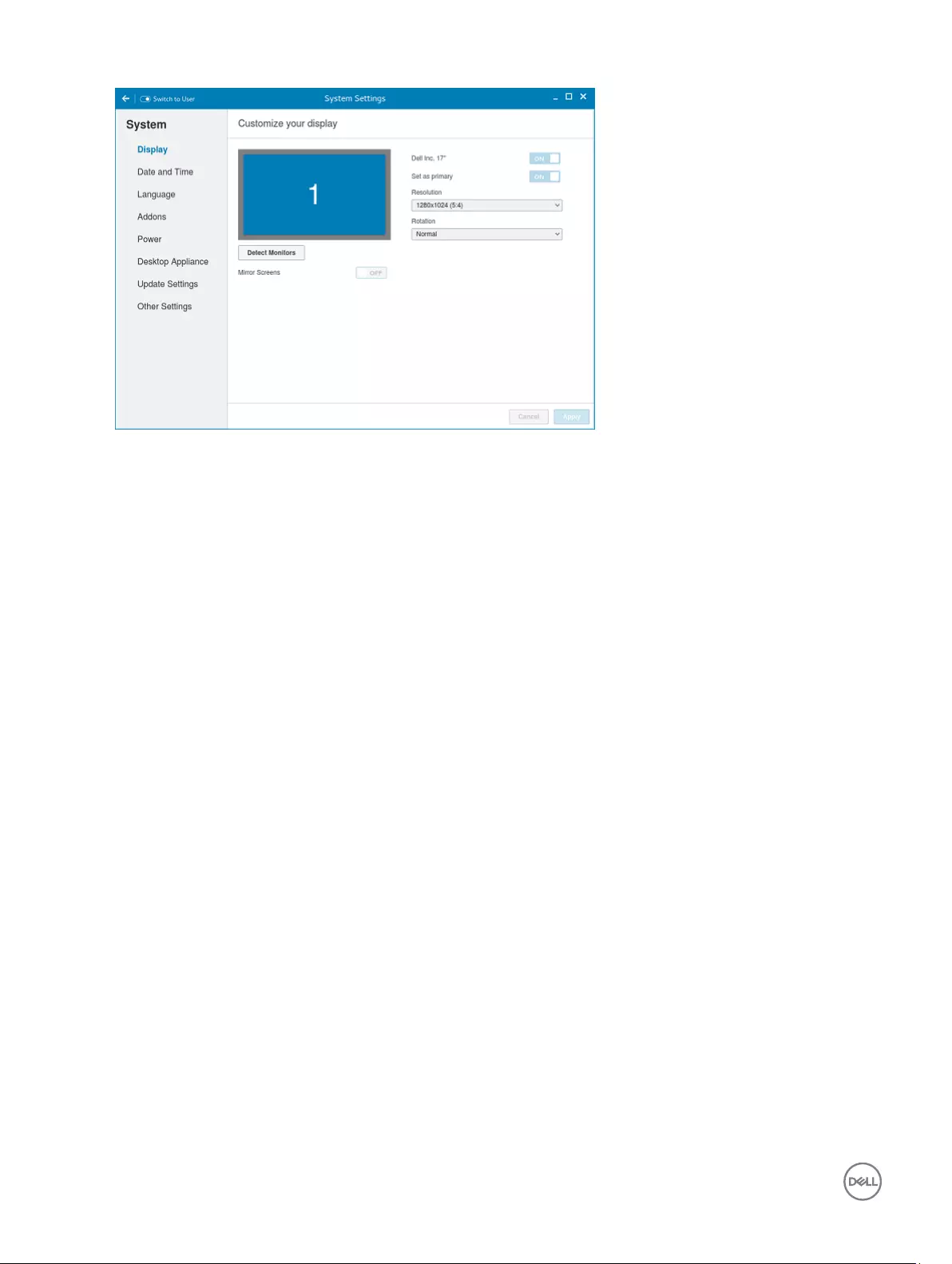
Figure 1. Display Settings
2. Select the preferred Resolution from the drop-down list.
3. Select the Rotation type from the drop-down list.
• Normal
• Right
• Left
• Upside-down
4. Click the ON/OFF button to switch between dual display and mirror mode in a dual monitor configuration.
5. Click the ON/OFF button to enable the Set as primary option. This option allows you to set the selected monitor as primary.
6. Click the ON/OFF button to enable the Monitor On/Off option. This option allows you to switch off and switch on the
preferred monitor in a dual monitor configuration.
10

5
Networks
This section describes about the network configurations of Wyse 5060 thin client.
• For network configurations on WES7P, see Configuring the neetwork settings on WES7P
• For network configurations on Wyse ThinOS, see Configuring the network settings on ThinOS.
• For network configurations on Wyse ThinLinux, see Configuring the network settings on ThinLinux
Configuring network settings on WES7P
If Dell Wyse supported WLAN hardware modules are installed on the thin client, clicking the Network and Sharing Center icon in
the Control Panel allows you to:
1. Manage Wireless Networks (click the Manage Wireless Networks link):
• Add —Click Add to open and use the wizard to add a wireless network to edit an existing wireless network, right-click it,
and then select Properties to open and use the Network Properties dialog box.
• Adapter Properties —Click Adapter Properties to open and use the properties dialog box for the wireless adapter.
• Profile Types —Click Profile Types to open and use a dialog box to the enable or disable the ability to create Per User
Profiles.
• Network and Sharing Center - Click Network Sharing Center to return to the Network and Sharing Center dialog box
provides network settings, and gives access to network settings.
2. Change Adapter Settings click the Change Adapter Settings link:
• Click Organize to open the list of options you can use to organize your network connections.
• Select a connection to display the list of command buttons you can use to view the status, connect to, enable, disable,
diagnose, rename, and change the settings of the connection.
3. Change Advanced Sharing Settings (click the Change Advanced Sharing Settings link): Select the network profile settings
you want for each of your networks.
Configuring the network settings on Wyse ThinOS
To configure the network settings use the following options:
•Configuring the general settings.
•Configuring the DHCP options settings.
•Configuring the ENET settings.
•Configuring the WLAN settings.
Configuring the General Settings
To configure the general network settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
11
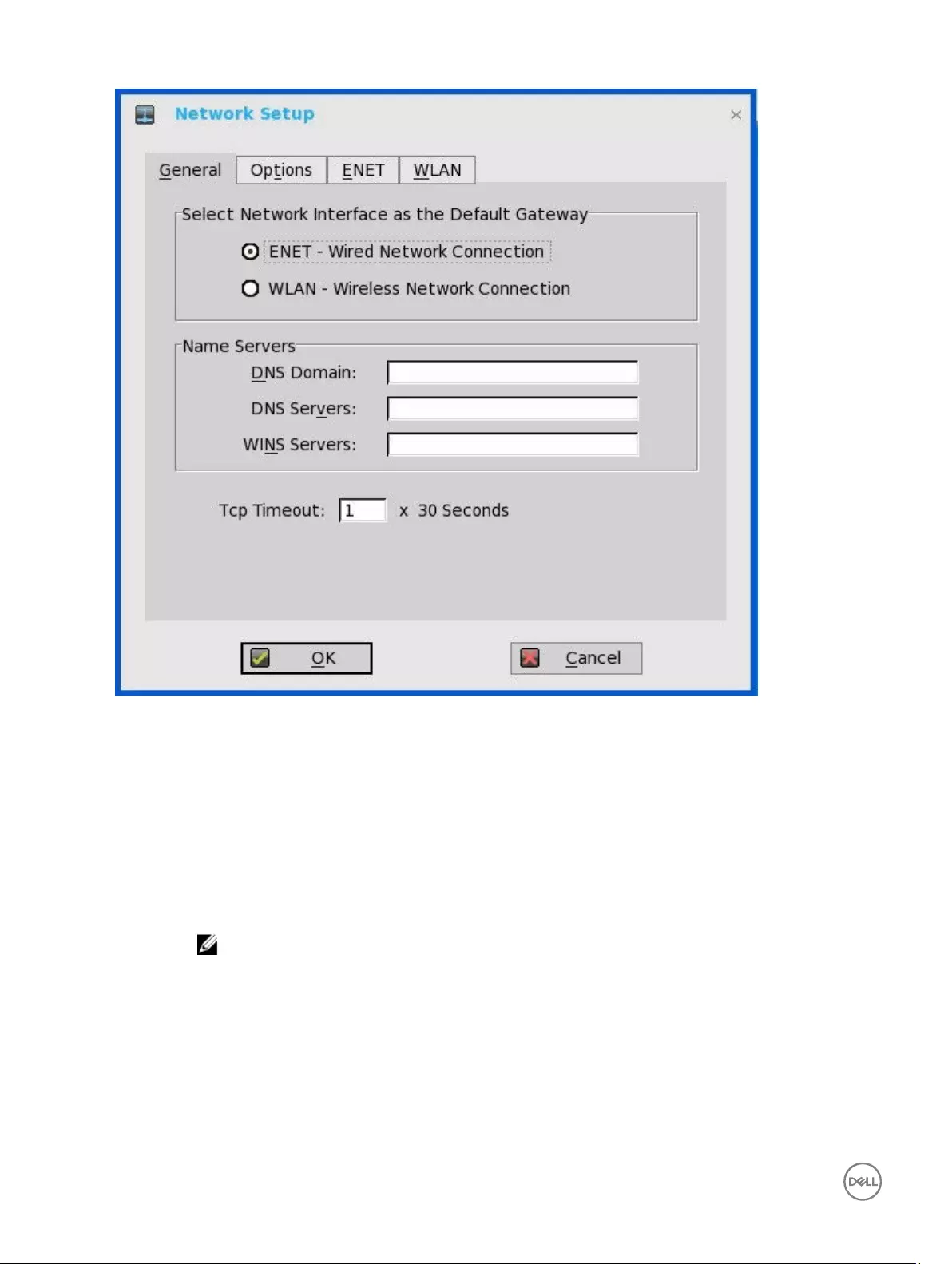
2. Click the General tab, and use the following guidelines:
a. To set the default gateway, select the type of network interface from the available options.
1. Single Network support — Either wireless or wired network is connected.
•ENET — Click this option, if you want set up the Ethernet Wired Network Connection.
•WLAN — Click this option, if you want set up the Wireless Network Connection.
• If the user use wireless network after selecting ENET connection or wired network after selecting WLAN
connection, then the system log "WLAN: set default gate way xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx" for first case and "ENET: set
default gate way xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx" for second case are printed to ensure that the UI setting reflects the actual
usage.
NOTE: The User Interface (UI) will not be changed automatically.
2. Dual Network support — Both wireless and wired networks are connected. The default gateway is determined by
the UI settings.
b. Enter the URL address of the DNS Domain in the DNS Domain box.
c. Enter the IP address of the DNS Server in the DNS Server box.
Use of DNS is optional. DNS allows you to specify remote systems by their host names rather than IP addresses. If a
specific IP address (instead of a name) is entered for a connection, it is used to make the connection. Enter the DNS
Domain and the network address of an available DNS Server. The function of the DNS Domain entry is to provide a default
suffix to be used in name resolution. The values for these two boxes may be supplied by a DHCP server. If the DHCP server
12
supplies these values, they replace any locally configured values. If the DHCP server does not supply these values, the
locally configured values will be used.
NOTE: You can enter up to 16 DNS Server addresses, separated by a semicolon, comma, or space. The first
address is for the primary DNS server and the rest are secondary DNS servers or backup DNS servers .
d. Enter the IP address of the WINS Server in the WINS Server box.
Use of WINS is optional. Enter the network address of an available WINS name server. WINS allows you to specify remote
systems by their host names rather than IP addresses. If a specific IP address (instead of a name) is entered for a
connection, it is used to make the connection. These entries can be supplied through DHCP, if DHCP is used. DNS and
WINS provide essentially the same function, name resolution. If both DNS and WINS are available, the thin client attempts
to resolve the name using DNS first and then WINS.
You can enter two WINS Server addresses (primary and secondary), separated by a semicolon, comma, or space.
e. Enter the digit multiplier of 30 seconds in the TCP Timeout box to set the time-out value of a TCP connection. The value
must be 1 or 2 which means the connection time-out value is from 1x30= 30 seconds to 2x30= 60 seconds. If the data for
connecting to the server is not acknowledged and the connection is time out, setting the time-out period retransmits the
sent data and again tries to connect to the server till the connection is established.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring the DHCP Options Settings
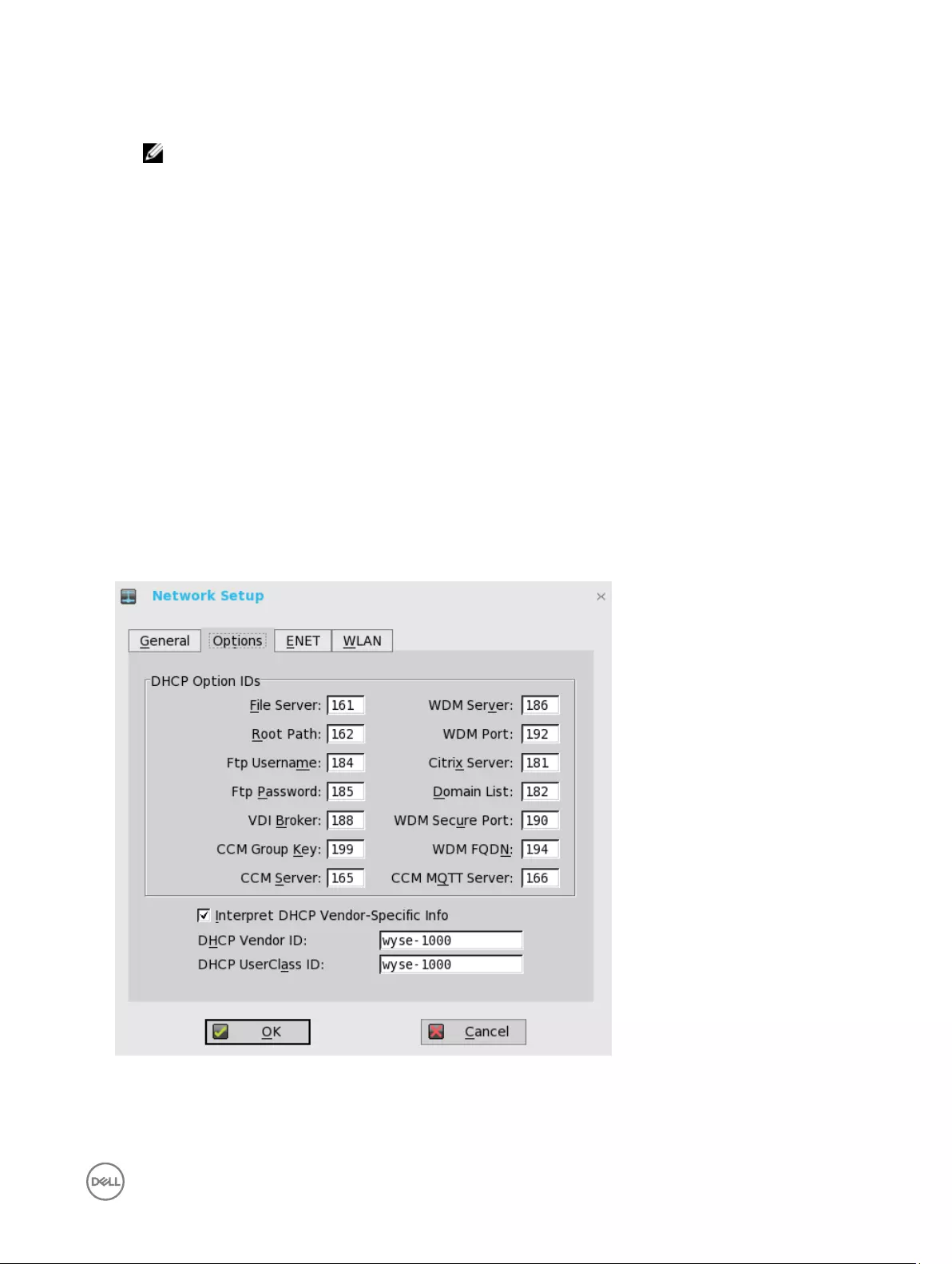
To configure the options settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
2. Click the Options tab, and use the following guidelines:
a. DHCP Option IDs — Enter the supported DHCP options. Each value can only be used once and must be between 128 and
254.
b. Interpret DHCP Vendor-Specific Info — Select this check box for automatic interpretation of the vendor information.
13
c. DHCP Vendor ID — Shows the DHCP Vendor ID when the dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP option is selected.
d. DHCP UserClass ID — Shows the DHCP UserClass ID when the dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP option is
selected.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring the ENET Settings
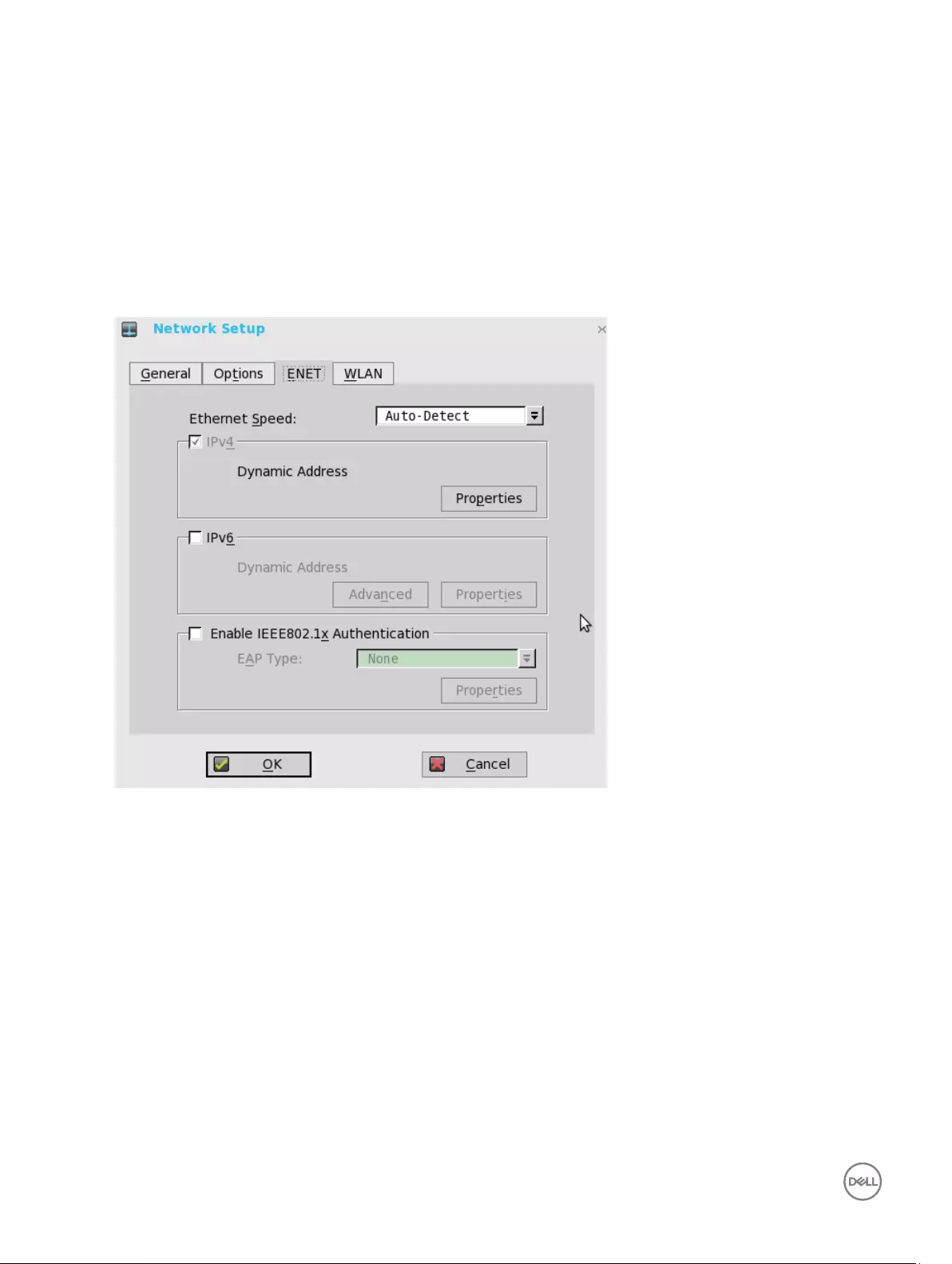
To configure the ENET settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
2. Click the ENET tab, and use the following guidelines:
a. Ethernet Speed — Normally the default (Auto-Detect) should be selected, but another selection can be made if
automatic negotiation is not supported by your network equipment. Selections include Auto-Detect, 10 MB Half-Duplex,
10 MB Full-Duplex, 100 MB Half-Duplex, 100 MB Full-Duplex, and 1 GB Full-Duplex.
The 10 MB Full-Duplex option can be selected locally at the device, however, this mode may need to be negotiated
through AutoDetect.
b. The IPV4 check box is selected by default. Click Properties to set various options supported by IPV4.
•Dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP — Selecting this option enables your thin client to automatically receive
information from the DHCP server. The network administrator must configure the DHCP server using DHCP options to
provide information. Any value provided by the DHCP server replaces any value entered locally on the Options tab,
however, locally entered values are used if the DHCP server fails to provide replacement values.
•Statically specified IP Address — Select this option to manual enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default
Gateway:
–IP Address — Must be a valid network address in the server environment. The network administrator must provide
this information.
14

–Subnet Mask — Enter the value of the subnet mask. A subnet mask is used to gain access to machines on other
subnets. The subnet mask is used to differentiate the location of other IP addresses with two choices: same subnet
or other subnet. If the location is other subnet, messages sent to that address must be sent through the Default
Gateway, whether specified through local configuration or through DHCP. The network administrator must provide
this value.
–Default Gateway — Use of gateways is optional. Gateways are used to interconnect multiple networks (routing or
delivering IP packets between them). The default gateway is used for accessing the internet or an intranet with
multiple subnets. If no gateway is specified, the thin client can only address other systems on the same subnet.
Enter the address of the router that connects the thin client to the internet. The address must exist on the same
subnet as the thin client as defined by the IP address and the subnet mask. If DHCP is used, the address can be
supplied through DHCP.
c. Select the IPV6 check box, and then click Advanced to select various IPV6 supported setting options from the available
check boxes.
d. Click properties and use the following guidelines:
•Wait DHCP — Selecting this option enables your thin client to wait for IPV6 DHCP before the sign-in, if not selected
the system will only wait for IPV4 DHCP if enabled.
•Dynamically allocated over DHCP/BOOTP — Selecting this option enables your thin client to automatically receive
information from the DHCP server. The network administrator must configure the DHCP server (using DHCP options)
to provide information. Any value provided by the DHCP server replaces any value entered locally on the Options tab,
however, locally entered values are used if the DHCP server fails to provide replacement values.
•Statically specified IP Address — Select this option to manually enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default
Gateway.
–IP Address — Must be a valid network address in the server environment. The network administrator must provide
this information.
–Subnet Mask — Enter the value of the subnet mask. For more information, see various options supported by IPV4
in this section.
–Default Gateway — Use of gateways is optional. For more information, see various options supported by IPV4 in
this section.
•DNS Servers — Use of DNS is optional. DNS allows you to specify remote systems by their host names rather than IP
addresses. If a specific IP address (instead of a name) is entered for a connection, it rather than DNS is used to make
the connection. Enter the network address of an available DNS Server. The value for this box may be supplied by a
DHCP server. If the DHCP server supplies this value, it replaces any locally configured value. If the DHCP server does
not supply this value, the locally configured value is used.
e. Select the check box to enable IEEE802.1x Authentication.
•EAP Type — If you have enabled the Enable IEEEE 802.1x authentication check box, select the EAP Type option you
want (TLS, LEAP or PEAP).
•TLS — If you select the TLS option, click Properties to open and configure the Authentication Properties dialog box.
– Select the Validate Server Certificate check box because it is mandatory to validate your server certificate.
NOTE:
The CA certificate must be installed on the thin client. Also note that the server certificate text field supports
a maximum of approximately 127 characters, and supports multiple server names.
– If you select the Connect to these servers check box, the box is enabled where you can enter the IP address of
server.
– Click Browse to find and select the Client Certificate file and Private Key file you want.
The following kinds of server names are supported — all examples are based on Cert Common name company.dell.com
15
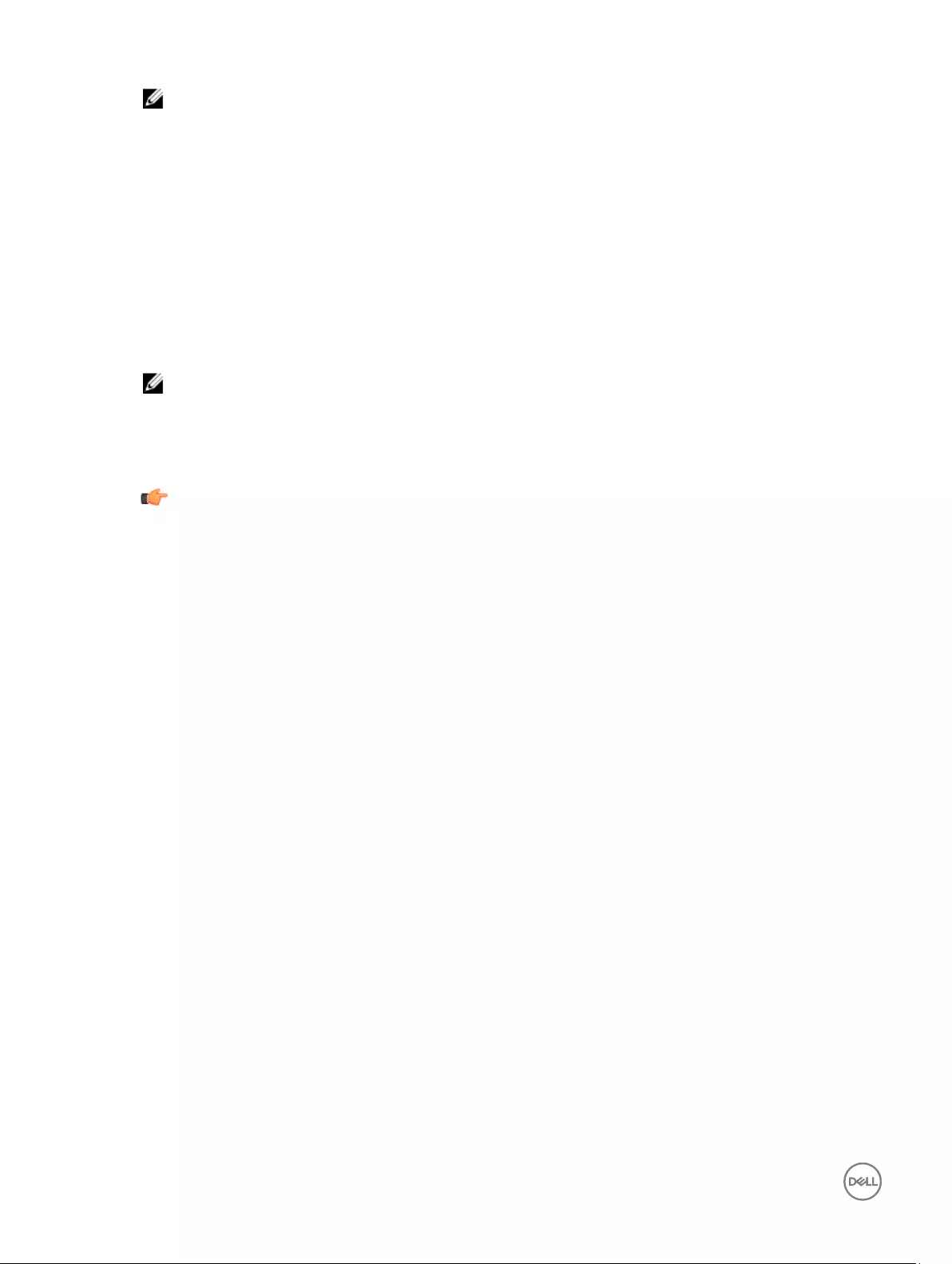
NOTE:
Using only the FQDN, that is company.wyse.com does not work. You must use one of the options (note that
*.dell.com is the most common option as multiple authentication servers may exist): servername.dell.com
*.dell.com
*dell.com
*.com
f. LEAP — If you select the LEAP option, click Properties to open and configure the Authentication Properties dialog box.
Be sure to use the correct Username and Password for authentication. The maximum length for the username or the
password is 64 characters.
g. PEAP — If you select the PEAP option, click Properties to open and configure the Authentication Properties dialog box.
Be sure to select either EAP_GTC or EAP_MSCHAPv2, and then use the correct Username, Password and Domain.
Validate Server Certificate is optional.
NOTE:
The server certificate text box for LEAP and PEAP supports a maximum of approximately 127 characters, and
supports multiple server names.
h. To configure EAP-GTC, enter the username only. The password or PIN is required when authenticating.
To configure EAP-MSCHAPv2, enter the username, password and domain.
Important: The domain/username in the username box is supported, but you must leave the domain box blank.
The CA certificate must be installed on the thin client and the server certificate is forced to be validated. When EAP-
MSCCHAPV2 is selected in EAP type in the Authentication Properties dialog box (for PEEP IEEE802.1x authentication),
an option to hide the domain is available for selection. Username and Password boxes are available for use, but the Domain
text box is disabled.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring the WLAN Settings
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Network Setup.
The Network Setup dialog box is displayed.
2. Click the WLAN tab, and use the following guidelines:
16
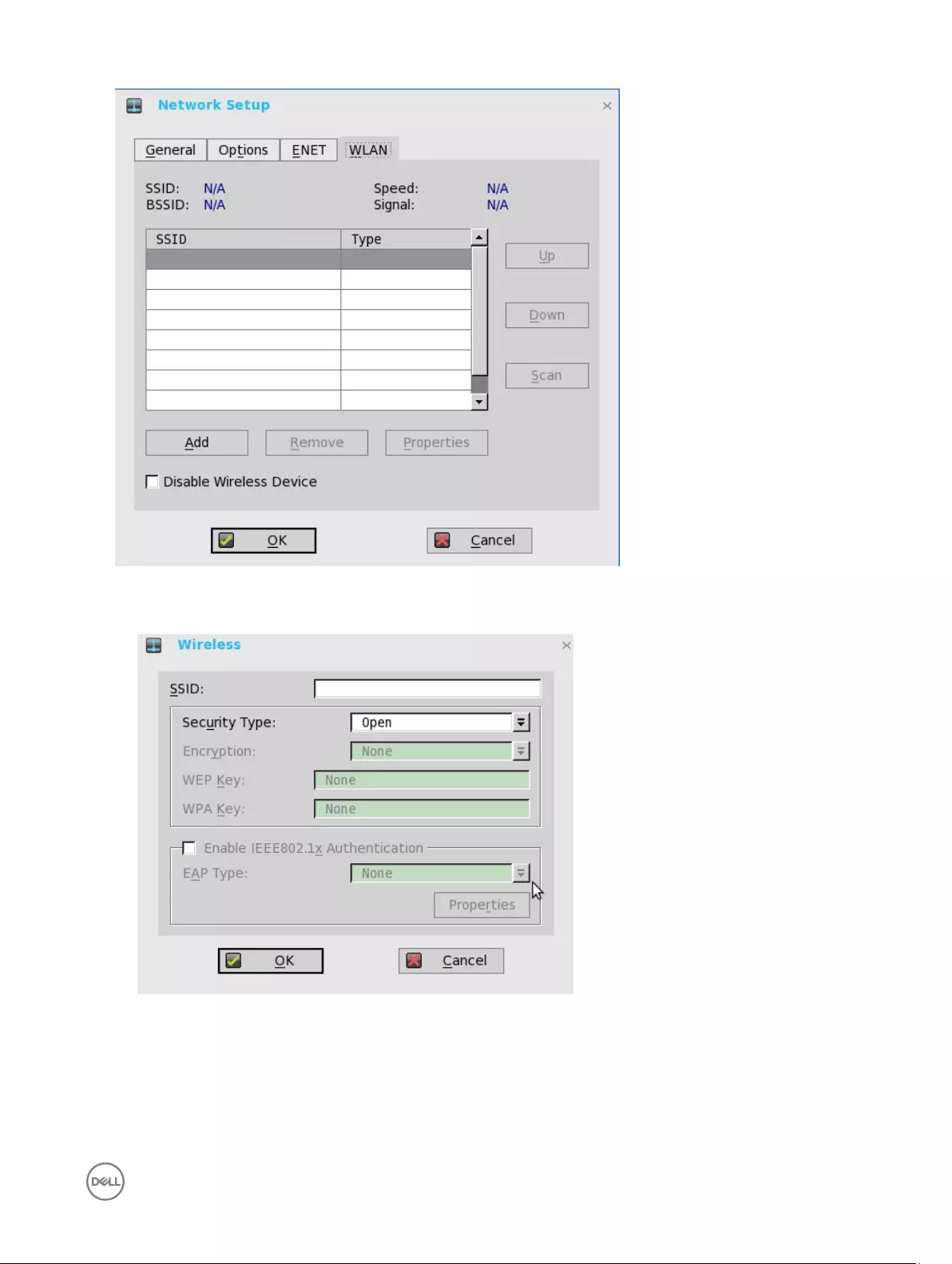
a. Add— Use this option to add and configure a new SSID connection.
You can configure the SSID connection from the available security type options.
b. After you configure the SSID connection, the added SSID connection is listed on the page of the WLAN tab.
c. Remove — Use this option, if you want to remove a SSID connection by selecting the SSID connection from the list.
d. Properties — Use this option to view and configure the authentication properties of a SSID connection that is displayed in
the list.
e. Select the Disable Wireless Device check box, if you want to disable a wireless device.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
17
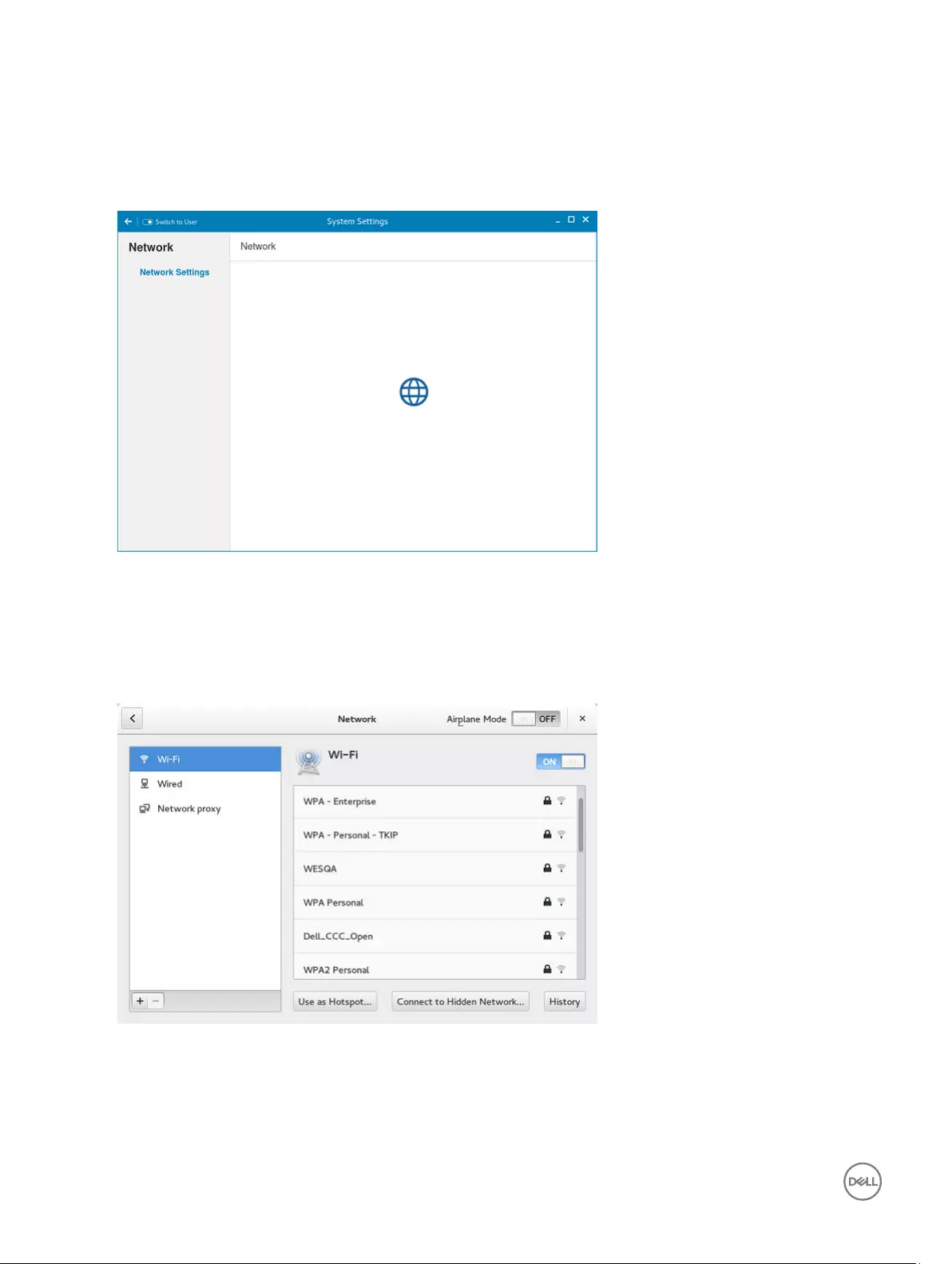
Configuring the network settings on ThinLinux
On the System Settings page, click the Network tab to view the Network Settings page.
1. Click the Network icon.
Figure 2. Network Settings
2. The Network settings page is displayed. In the left-pane, the following tabs are available for you to configure.
• Wi-Fi
• Wired
• Network proxy
Figure 3. Network Settings page
Configuring the wi-fi settings
To configure the Wi-Fi settings, perform the following steps:
18
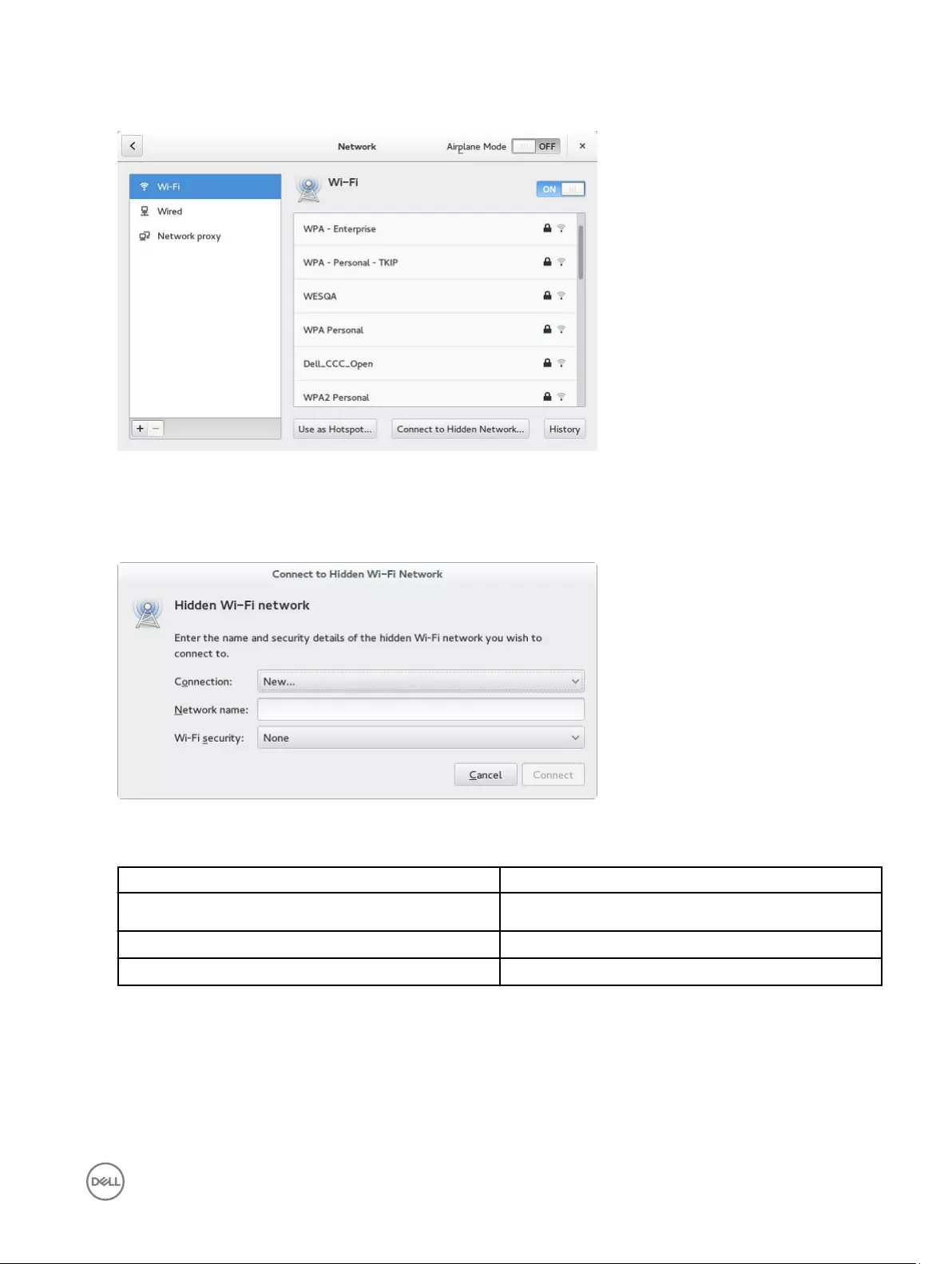
1. In the left-pane, click Wi-Fi tab.
2. Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable the Wi-Fi option. The list of wireless SSID is displayed if broadcast is enabled.
Figure 4. Wi-Fi Settings
3. To connect to Wi-Fi connection, select the preferred wireless SSID from the list displayed.
4. Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable the Airplane Mode option after you log in to the session.
5. Click the Connect to Hidden Wi-Fi Network button. The Connect to Hidden Wi-Fi Network window is displayed.
Figure 5. Hidden Wi-Fi Network
6. Enter the name and security details of the hidden network that you want to connect to.
Parameter Description
Connection From the drop-down list, select the type of connection.
Network name Enter the preferred network name.
Wi-Fi security From the drop-down list, select the security type.
7. On the Network page, click the History button to view the previous Wi-Fi connections and details.
Configuring wired network connection settings
To configure the wired connection settings, perform the following steps:
1. Click the Wired tab. The following attributes are displayed if the network cable is connected to your thin client and wired
connection is established.
19
• IP Address
• Hardware Address
• Default Route
• DNS
NOTE: After the network is disconnected, only hardware address and last used information are displayed.
2. On the lower-right corner of the page, click the Settings icon to configure the Wired Network connections.
a. In the Details tab, the following attributes are displayed.
• IP Address
• Link Speed
• Hardware Address
• Default Route
• DNS
3. Click the Security tab to configure the 802.1x security settings.
a. Click the ON button to enable the 802.1x Security for your network connection.
b. From the Authentication drop-down list, select the type of authentication you want to set for your network connection.
The available options are:
• MDS
• TLS
• FAST
• Tunneled TLS
• Protected EAP (PEAP)
c. If the authentication type is selected as MD5, you must configure the following options.
Parameter Description
Username Enter the Username for the network connection.
Password Enter the password you want to set for the connection.
Ask for this password every time If this check box is selected, you will be prompted to enter
the password every time when you connect to the network.
Show Password Select this check box if you want to allow the user
to view the hidden password.
d. If the authentication type is selected as TLS, you must configure the following options.
Parameter Description
Identity Enter your Identity.
User certificate Select the User certificate from the list or upload your
personal certificate stored locally.
To upload your personal certificate, click the Folder icon,
and then browse to the location where you have stored the
certificate.
CA Certificate Select the CA certificate from the list or upload your CA
certificate stored locally.
To upload your CA certificate, click the Folder icon, and
then browse to the location where you have stored the
certificate.
20
Parameter Description
Private key Select the private key from the list or upload your private
key stored locally.
To upload your private key, click the Folder icon, and then
browse to the location where you have stored the
certificate.
Private key password Enter the password that you want to set for the private
key.
Show Password Select this check box if you want to allow the user
to view the hidden password.
e. If the authentication type is selected as FAST, you must configure the following options.
Parameter Description
Anonymous identity Enter the username you want to set for Anonymous
Authentication Identity.
PAC provisioning Select this check box to enable the PAC provisioning
authentication. From the drop-down list, select any of the
following PAC provisioning options:
Anonymous – Select this option to establish a secure
anonymous TLS communication with the client and provide
it with a PAC.
Authenticated – Select this option to enable a secure
server-side authentication and provide the client with a
proxy auto-config (PAC) file.
Both – Select this option if you want to allow both
Anonymous and Authenticated PAC provisioning.
PAC file Select the PAC file from the list or upload your CA
certificate stored locally.
To upload your PAC file, click the Folder icon, and then
choose the certificate from the location where you have
stored the certificate.
Inner authentication From the drop-down list, select the inner authentication
method you want to set. The available options are GTC and
MSCHAPv2.
Username Enter the Username for the network connection.
Password Enter the password you want to set for the connection.
Ask for this password every time If this check box is selected, you will be prompted to enter
the password every time when you connect to the network.
Show Password Select this check box if you want to allow the user
to view the hidden password.
f. If the authentication type is selected as Tunneled TLS, you must configure the following options.
21
Parameter Description
Anonymous identity Enter the username that you want to set for Anonymous
Authentication Identity.
CA certificate Select the CA certificate from the list or upload your CA
certificate stored locally.
To upload your CA certificate, click the Folder icon, and
then browse to the location where you have stored the
certificate.
Inner authentication From the drop-down list, select the inner authentication
method that you want to set. The available options are GTC
and MSCHAPv2.
Username Enter the Username for the network connection.
Password Enter the password that you want to set for the
connection.
Ask for this password every time If this check box is selected, you will be prompted to enter
the password every time when you connect to the network.
Show Password Select this check box if you want to allow the user
to view the hidden password.
g. If the Authentication type is selected as Protected EAP (PEAP), you must configure the following options.
Parameter Description
Anonymous identity Enter the username you want to set for Anonymous
Authentication Identity.
CA certificate Select the CA certificate from the list or upload your CA
certificate stored locally.
To upload your CA certificate, click the Folder icon, and
then browse to the location where you have stored the
certificate.
PEAP version Select the PEAP version type you want to use for EAP
authentication. The available options are:
• Automatic
• Version 0
• Version 1
Inner authentication From the drop-down list, select the inner authentication
method that you want to set. The available options are GTC
and MSCHAPv2.
Username Enter the Username for the network connection.
Password Enter the password that you want to set for the
connection.
Ask for this password every time If this check box is selected, you will be prompted to enter
the password every time when you connect to the network.
22
Parameter Description
Show Password Select this check box if you want to allow the user
to view the hidden password.
4. Click the Identity tab and configure the following settings:
NOTE: Only Administrators are allowed to authenticate these settings by entering the admin password in the root
privilege authentication dialog box after a particular setting is changed or configured.
a. Name— Specifies the default name of the wired connection. If you want to set your preferred name for the connection,
enter the name and then click Apply.
b. MAC Address— Specifies the MAC address of the network connection.
c. Cloned Address— Specifies the IP address that is cloned by the router.
d. Maximum transmission unit (MTU)— Specifies the size (in bytes) of the largest protocol data unit that the protocol layer
can pass onwards.
e. Connect automatically— Select this check box to automatically connect to the network after you plug-in the network
wire.
f. Make available to other users— Select this check box if you want to allow other users to configure these settings.
5. Click the IPv4 tab and do the following:
a. Enable the IPv4 button to configure the IPv4 settings.
b. From the Addresses drop-down menu, select the type of IPv4 configuration. The available options are:
• Automatic (DHCP)
• Manual
• Link-Local Only
c. If Automatic (DHCP) option is selected, you must configure the following options.
Parameter Description
DNS Enable the Automatic button, if you want the thin client to
automatically fetch the DNS Server.
Server Specifies the IP address of the DNS Server.
Click the + icon to add a new DNS server to the list.
Routes Enable the Automatic button to turn on the automatic IPv4
routing.
Address Specifies the Router IP address.
Netmask Specifies the Netmask. Netmask is used to divide an IP
address into subnets and specify the network's available
hosts.
Gateway Specifies the IP address of the default Gateway.
Metric Specifies the Metric value for the network connection.
Use this connection only for resources on its network Select this check box, if you want to allow the wired
connection only for resources on its network.
d. If Manual option is selected, you must specify the IP address, Netmask IP and Gateway IP along with the parameters
mentioned in Table 1: Automatic (DHCP).
e. If Link-Local Only option is selected, the DNS and Routes options are disabled. This is applicable only for communications
within the host link or the host domain.
6. Click the IPv6 tab and do the following:
a. Enable the IPv6 button to configure the IPv6 settings.
23

b. From the Addresses drop-down menu, select the type of IPv6 configuration. The available options are:
• Automatic
• Automatic, DHCP only
• Manual
• Link-Local Only
The IPv6 configuration is similar to configuring the IPv4 Settings. For IPv4 configuration, see the IPv4 settings in this
section.
7. Click the Reset tab and do the following:
a. Click Reset to reset the settings for your network connection, including passwords. However, the previous network is
displayed as a preferred network.
b. Click Forget to remove all details relating to this network that you do not want to automatically connect to.
8. Click Apply to save your configured settings.
NOTE: Click the Add Profile tab to add a new network profile. On the right pane, you must configure the following
options:
• Security
• Identity
• IPv4
• IPv6
The configuration of all these tabs are similar to Wired Network connections configurations described in this section.
Configuring the network proxy settings
To configure the Network proxy settings, complete the following task:
1. Click the Network proxy tab.
2. From the Proxy drop-down menu, select the type of Proxy method you want to deploy. The available Proxy methods are:
• None
• Manual
• Automatic
3. If Manual proxy method is selected, you must configure the following options:
a. Enter the HTTP Proxy port details for your network connection.
b. Enter the HTTPS Proxy port details for your network connection.
c. Enter the FTP Proxy port details for your network connection.
d. Enter the SOCKS host port details for your network connection.
e. Use the Ignore Hosts option to set up proxy to ignore all local addresses.
4. If Automatic proxy method is selected, you must type the configuration URL address in the field.
NOTE: Web Proxy Autodiscovery is used when a Configuration URL is not provided. Dell does not recommend this
option for untrusted public networks.
Adding a network connection
NOTE: Adding additional wired Ethernet connections is allowed but the added interface is not used in any of the
ThinLinux features.
To add a new network connection, complete the following tasks:
1. On the lower-left corner of the page, click the + icon.
The Add Network Connection dialog box is displayed. The following options are listed for you to configure.
• VPN
• Bond
24

• Bridge
• VLAN
2. Click VPN to add a VPN network connection. You must import a file from the stored location to configure the VPN settings.
3. Click Bond to add and configure the Bond network connection for your thin client.
a. Click the General tab to select or deselect the following check boxes.
• Automatically connect to this network when it is available.
• All users may connect to this network.
• Automatically connect to VPN when using this connection.
b. Click the Bond tab, and configure the following options:
1. Type a name for your network interface.
2. The number of bonded connections that are set up are listed here. To add a new bond connection, click the Add
button and select the type of connection you want to create. The available options are Ethernet and InfiniBand.
3. Select the type of Network Mode from the drop-down list. The available options are:
• Round-robin
• Active Backup
• XOR
• Broadcast
• 802.3ad
• Adaptive transmit load balancing
• Adaptive load balancing
4. Link Monitoring — Select the type of link monitoring from the drop-down list. The available options are:
• MII (recommended)
• ARP
5. Enter the time in ms for the link up delay duration.
6. Enter the time in ms for the link down delay duration.
c. Click the IPv4 Settings tab, and do the following:
1. From the drop-down list select the following method for IPv4 authentication.
• If Automatic (DHCP) method is selected, you must configure the following options:
1. Additional DNS Servers — Type the IP addresses of domain name users that are used to resolve host names.
Use commas to separate multiple domain name server addresses.
2. Additional Search Domains — Type the IP addresses of domains used when resolving host names. Use
commas to separate multiple domains.
3. DHCP client ID — Enter the ID for the DHCP client. This client identifier allows the network administrator to
customize your computer’s configuration.
4. Require IPv4 addressing for this connection to complete — The IPv4 address is required to complete the
connection. If the IPv4 address is not available, then the connection is not configured.
5. Click the Routes button to edit IPv4 routes for Bond connection.
a. Click Add to add an IP address. After an IP is added, Netmask, Gateway and Metric specific to that IP
are displayed.
b. Select the check box if you want to ignore the automatically obtained routes.
c. Select this check box if you want to use your connection only for resources on that particular network.
• If Automatic (DHCP) addresses only method is selected, you must configure the following options:
1. DNS Servers — Type the IP addresses of domain name users that are used to resolve host names. Use
commas to separate multiple domain name server addresses.
25

2. Search domains — Type the IP addresses of domains that are used when resolving host names. Use
commas to separate multiple domains.
3. DHCP client ID — Enter the ID for the DHCP client. This client identifier allows you to customize your
computer’s configuration.
NOTE: The other settings remain same as described in automatic (DHCP) method for IPv4
authentication.
• If Manual method is selected, you must configure the following options:
1. Click Add to add an IP address. After an IP is added, Netmask, Gateway specific to that IP are displayed.
2. DNS Servers — Type the IP addresses of domain name users that are used to resolve host names. Use
commas to separate multiple domain name server addresses.
3. Search domains — Type the IP addresses of domains used when resolving host names. Use commas to
separate multiple domains.
NOTE: The DHCP client ID option and Ignore automatically obtained routes check boxes are disabled.
The other settings remains the same as described in automatic (DHCP) method for IPv4 authentication.
• If Link-Local Only method is selected, the DNS Servers, Search domains, DHCP client ID, and Routes options are
disabled. You can select the Require IPv4 addressing for this connection to complete check box to allow the
connection to complete. The IPv4 address is required to complete the connection. If the IPv4 address is not
available, then the connection is not configured.
• If Shared to other computers method is selected, the DNS Servers, Search domains, DHCP client ID, and Routes
options are disabled. You can select the Require IPv4 addressing for this connection to complete check box to
allow the connection to complete. The IPv4 address is required to complete the connection. If the IPv4 address is
not available, then the connection is not configured.
d. Click the IPv6 Settings tab. From the drop-down list, select the following method type for IPv4 authentication. The
available options are:
• Ignore
• Automatic
• Automatic, addresses only
• Manual
• Link-Local Only
NOTE: The settings are same as configuring the IPv4 settings tab described in this section.
4. Add and configure the Bridge network connection for your thin client.
a. Click the Bridge tab, and configure the following options:
1. Interface name — Type the name for your network interface.
2. Bridged connections — The number of bonded connections that are set up are listed here. To add a new bond
connection, click the Add button and select the type of connection you want to create. The available options are
Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and VLAN.
3. Aging time — Enter the Aging time duration in seconds.
4. Enable STP — Select this check box to enable the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) for your connection.
5. Priority — Enter the priority value.
6. Forward delay — Enter the forward delay duration in seconds.
7. Hello time — Enter the hello time duration in seconds.
8. Max age — Enter the value for the maximum age.
b. To configure the General tab, IPv4 Settings tab, and IPv6 Settings tab for Bridge connection, see the configuration details
for Bond connection in this section.
5. Configure the VLAN network connection for your thin client.
26

a. Click the VLAN tab, and configure the following options:
1. Parent interface — Type the name for your parent interface.
2. VLAN id — Enter the value for the VLAN id.
3. VLAN interface name — Type the name for your VLAN interface.
4. Cloned MAC address — Type the cloned MAC address.
5. MTU —Specifies the size (in bytes) of the largest protocol data unit that the protocol layer can pass onwards.
b. To configure the General tab, IPv4 Settings tab, and IPv6 Settings tab for VLAN connection, see the configuration details
for Bond connection in this section.
6. Click Save to save your settings.
27

6
Peripherals
This section provides the information about using and configuring the peripherals on Wyse 5060 thin client.
Configuring and Using Peripherals on WES7P
The thin client has USB ports available on it.
To provide the services through the ports, install the appropriate software for the thin client.
NOTE:
• You can install other services and add-ins that are available from the Dell website for free or for a licensing fee.
For more information, see the Dell Wyse Support Site.
• You can configure the thin client device to use Bluetooth- enabled Peripherals. For more information, see Bluetooth
connections on WES7P.
Device Manger: Bluetooth Connections
You can access Bluetooth- enabled devices in your thin-client device, if your thin-client has optional Wireless Bluetooth capability.
1. To manage an existing Bluetooth device :
a. Go to Start → Control Panel → Device Manager
b. Click Bluetooth Radios.
c. To manage an existing Bluetooth device, double-click on the Bluetooth icon
You can update drivers using the Driver tab
2. To add Bluetooth- enabled device:
a. Go to Start → Control Panel → Devices and Printers
Devices and Printers window is displayed
b. Click Add a Device.
c. Turn on the Bluetooth — enabled devcie and ensure that the device is discoverable.
d. When the device is discoverable by the thin-client device, click Next and follow the wizard.
Configuring peripherals settings on Wyse ThinOS
The Peripherals dialog box enables you to configure the settings for the keyboard, mouse, camera, and printer.
•Configuring keyboard settings
•Configuring mouse settings
•Configuring camera settings
•Configuring printer setup
28
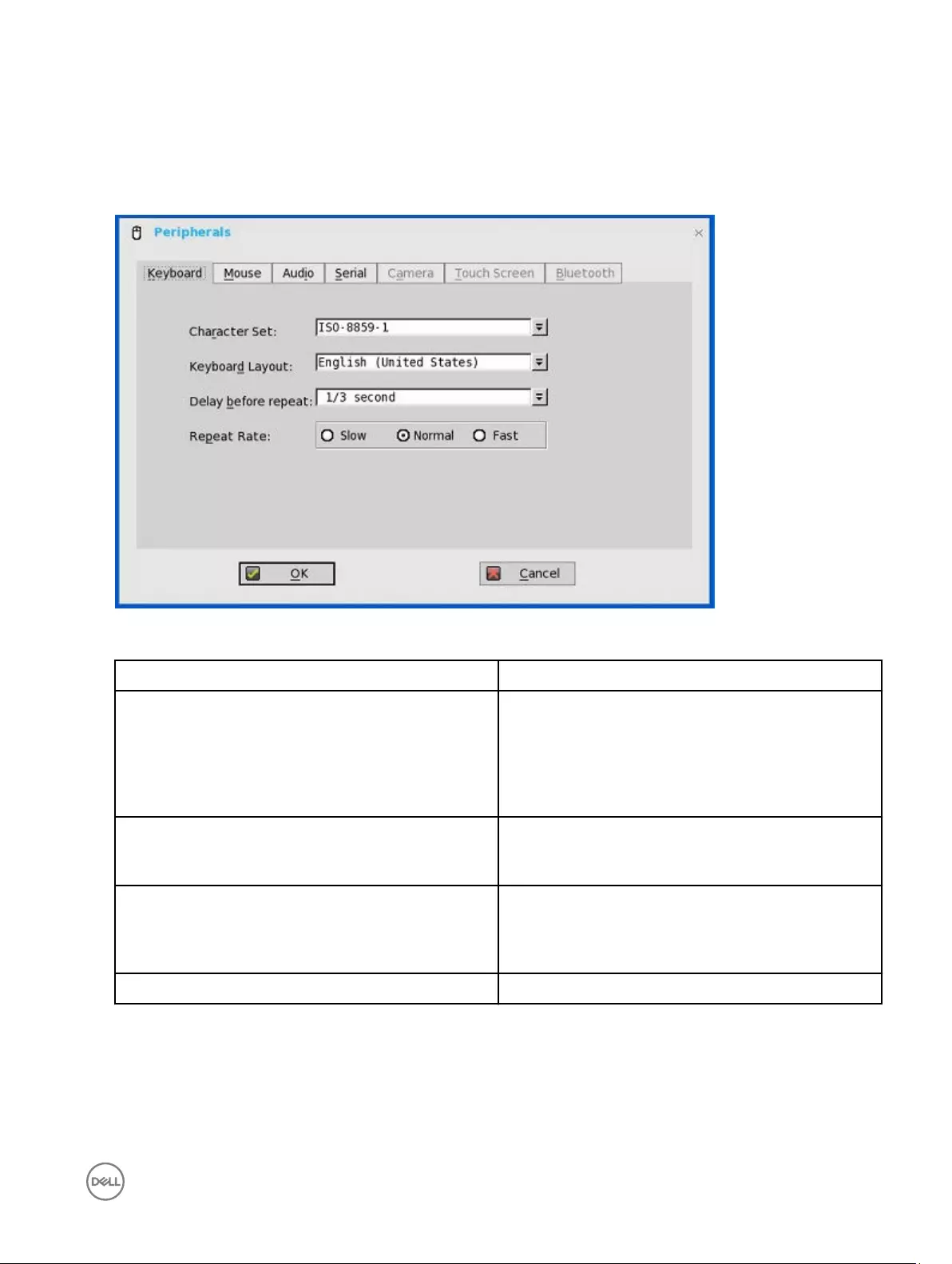
Configuring keyboard settings
To configure the Keyboard settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Peripherals.
The Peripherals dialog box is displayed.
2. Click the Keyboard tab and set the Character Set, Keyboard Layout, Delay Before Repeat and Repeat Rate parameters. The
following table explains the parameters present on the Peripherals dialog box.
Parameter Description
Character Set Specifies the character set. Each character is represented by
a number. The ASCII character set, for example, uses the
numbers 0 through 127 to represent all English characters
and special control characters. European ISO character sets
are similar to ASCII, but they contain additional characters for
European languages.
Keyboard Layout Presently the keyboard languages listed in the Keyboard
layout drop-down list are supported. The default value is
English (United States).
Delay Before Repeat Specifies the repeat parameters for held-down key. Select
the Delay before repeat value as either 1/5 second, 1/4
second, 1/3 second, 1/2 second, 3/4 second, 1 second, 2
seconds, or No Repeat. The default is 1/3 second.
Repeat Rate Select Slow, Medium, or Fast. The default value is Medium.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring mouse settings
To configure the Mouse settings:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Peripherals.
29
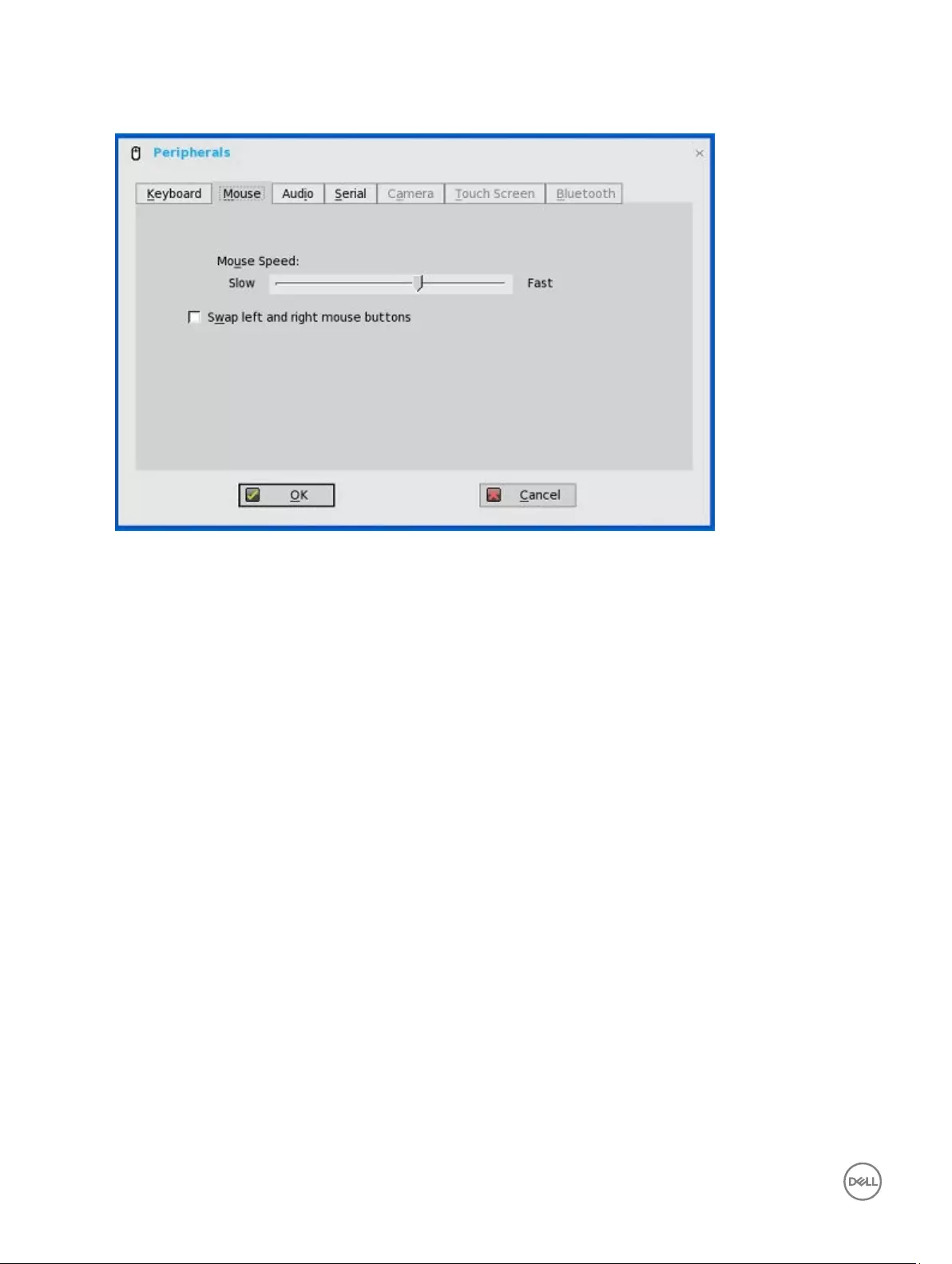
The Peripherals dialog box is displayed.
2. Click the Mouse tab to select the mouse speed and mouse orientation.
3. Select the Swap left and right mouse buttons check box to swap mouse buttons for left-handed operations.
4. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring camera settings
Use the Camera tab to interface with cameras that are locally connected to the thin client (USB) and supported by a UVC driver.
When using the HDX RealTime webcam feature of XenDesktop 5 or XenApp 6, you can control options such as maximum resolution
and frames per second (10 FPS is recommended).
By default, the format of USB camera is set to RAW.
30
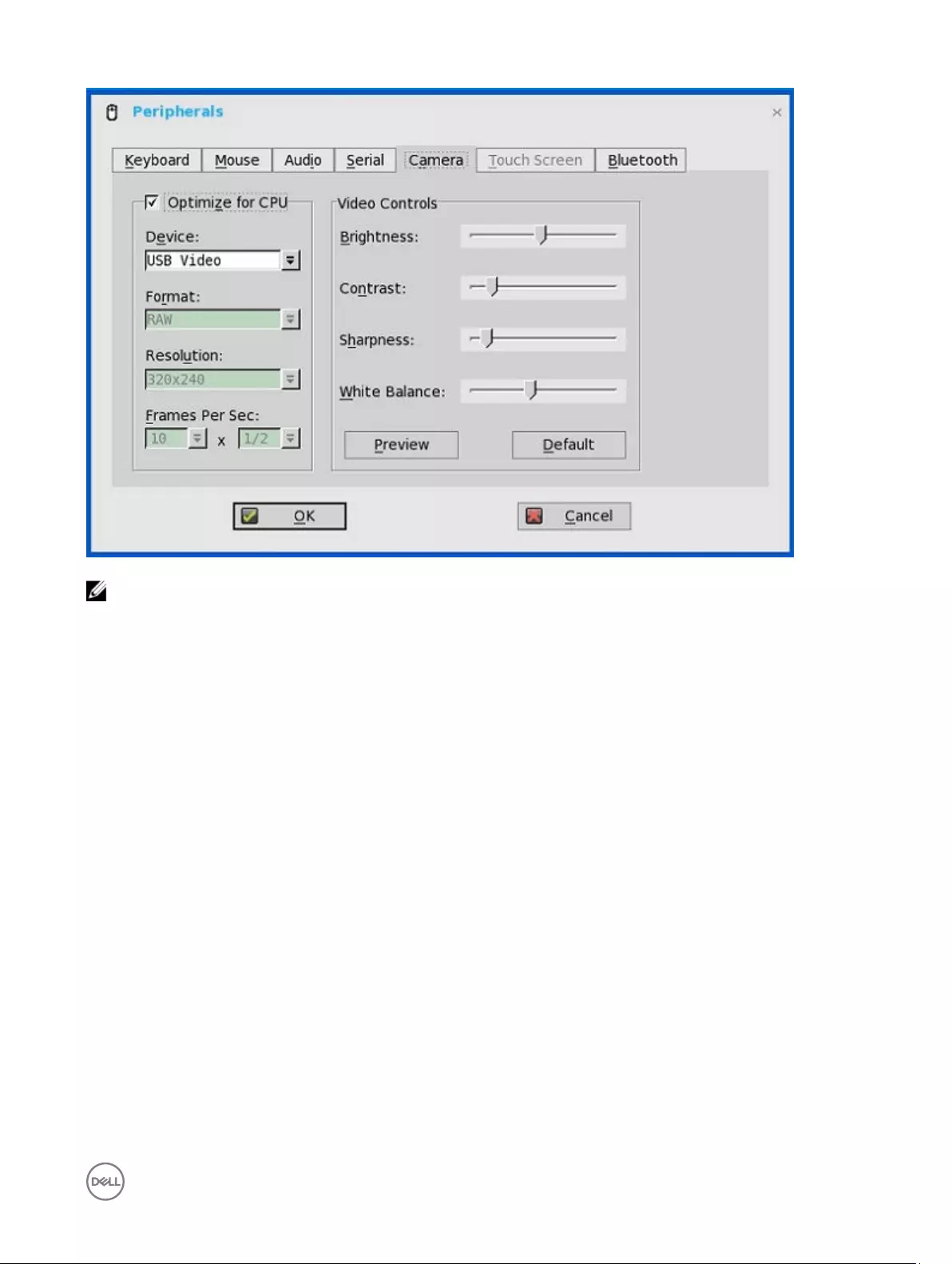
NOTE:
You can optimize performance and modify the frame rate per second, if the Optimize for CPU check box is selected—
supported values include 1/1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, and 1/6– directly from the thin client (if the webcam supports Universal Video
Driver).
This feature is experimental and does not currently support central configuration (INI parameters). Also, this feature is CPU
intensive and is recommended for high performance products such as the Wyse 5010 thin client with ThinOS (D10D), Wyse
3030 LT thin client with ThinOS and Wyse 3030 LT thin client with PCoIP.
Configuring printer settings
Use the Printer Setup dialog box to configure network printers and local printers that are connected to the thin client. Through its
USB ports, a thin client can support multiple printers. If more than one printer is to be used and another port is not available on your
thin client and the port that is to be used must be shared with a USB modem converter, connect a USB hub to the port.
Configuring peripherals settings on Wyse ThinLinux
On the System Settings page, click the Peripherals icon. The following tabs are displayed on the left pane of the System Settings
page.
• Keyboard
• Mouse
• Printers
• Sound
Setting the keyboard preferences
The Keyboard setting page enables you to set the Keyboard preferences and make the Keyboard layout.
31
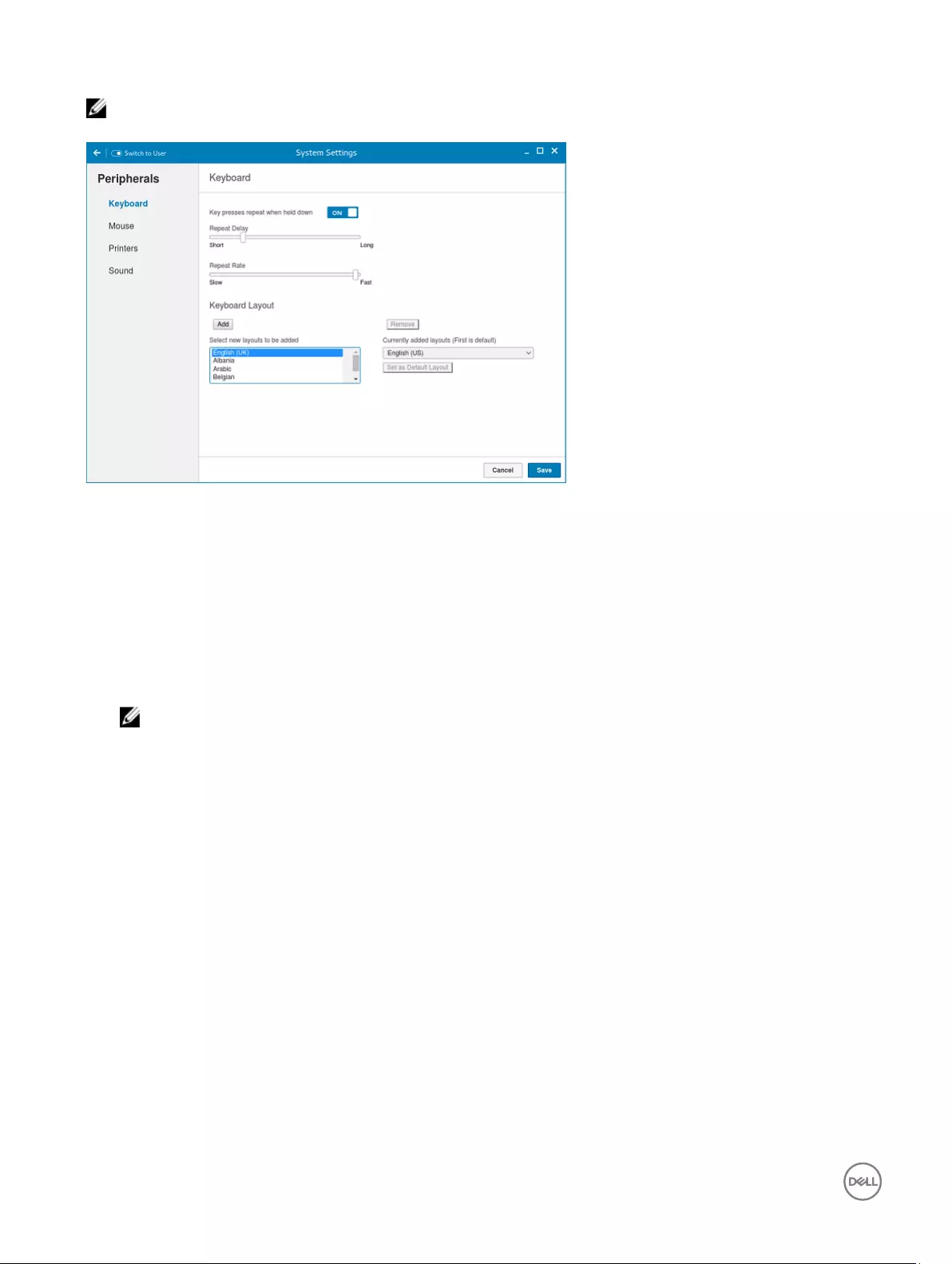
NOTE: By default, the Keyboard screen is available in both User mode and Admin mode. Any changes made through
Keyboard preferences screen is saved and continued for the built-in thinuser
Figure 6. Keyboard Preferences
1. Click the ON/OFF button to disable or enable the Key presses repeat when held down option after you log in to the session.
2. Move the slider to the left to decrease the repeated delay time of the pointer or move the slider to the right to increase the
repeated delay time of the pointer.
3. Move the slider to the left to decrease the repeat rate of the pointer or move the slider to the right to increase the repeat rate
of the pointer.
4. In the keyboard layout box, select the layout you want to use and click Add to include the preferred layout in the currently
added layouts list.
5. Select the preferred keyboard layout from the currently added layouts list, and click Set as Default Layout button to set the
default layout.
NOTE: The default keyboard layout is listed on the top of the currently added layout list.
6. Click Save to save your changes.
Setting the mouse preferences
By default, the Mouse screen is available in both User mode and Admin mode. Any changes made through the Mouse preferences
screen is saved and continued for the built-in thinuser.
32
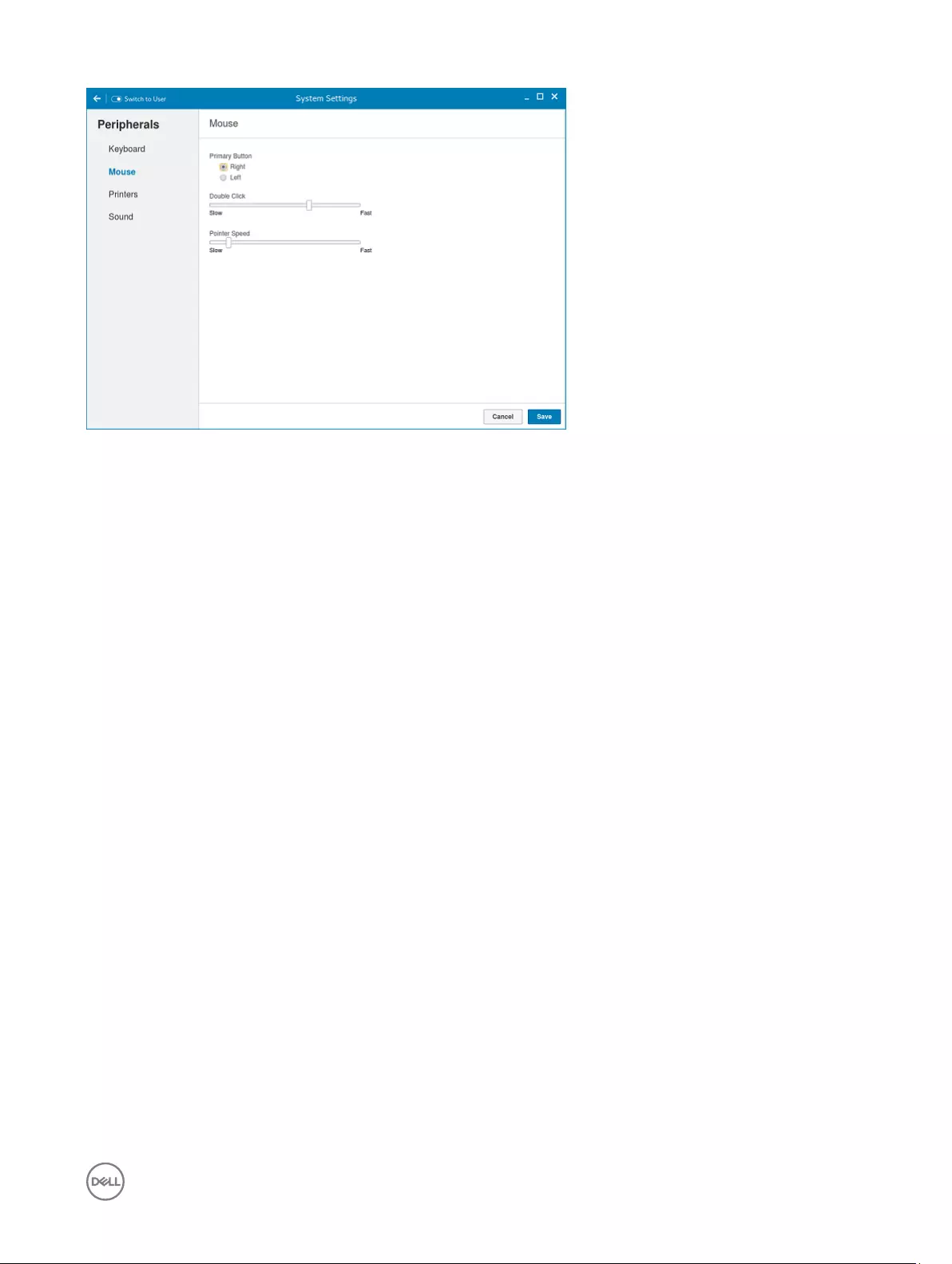
Figure 7. Mouse Preferences
The Mouse setting page enables you to set the Mouse preferences.
1. Click Right or Left to set the primary button of the mouse.
2. Move the slider to the left to increase the speed of the pointer when double-clicked or move the slider to the right to decrease
the length of double-clicked.
3. Move the slider to the left to increase the speed of the mouse pointer or move the slider to the right to decrease the speed of
the mouse pointer.
4. Click Save to save your changes.
Configuring the printer settings
By default, the Printers screen is available only in Admin mode. On the Printer setting page, click the printer icon to start the
gnome-control-center printer.
33
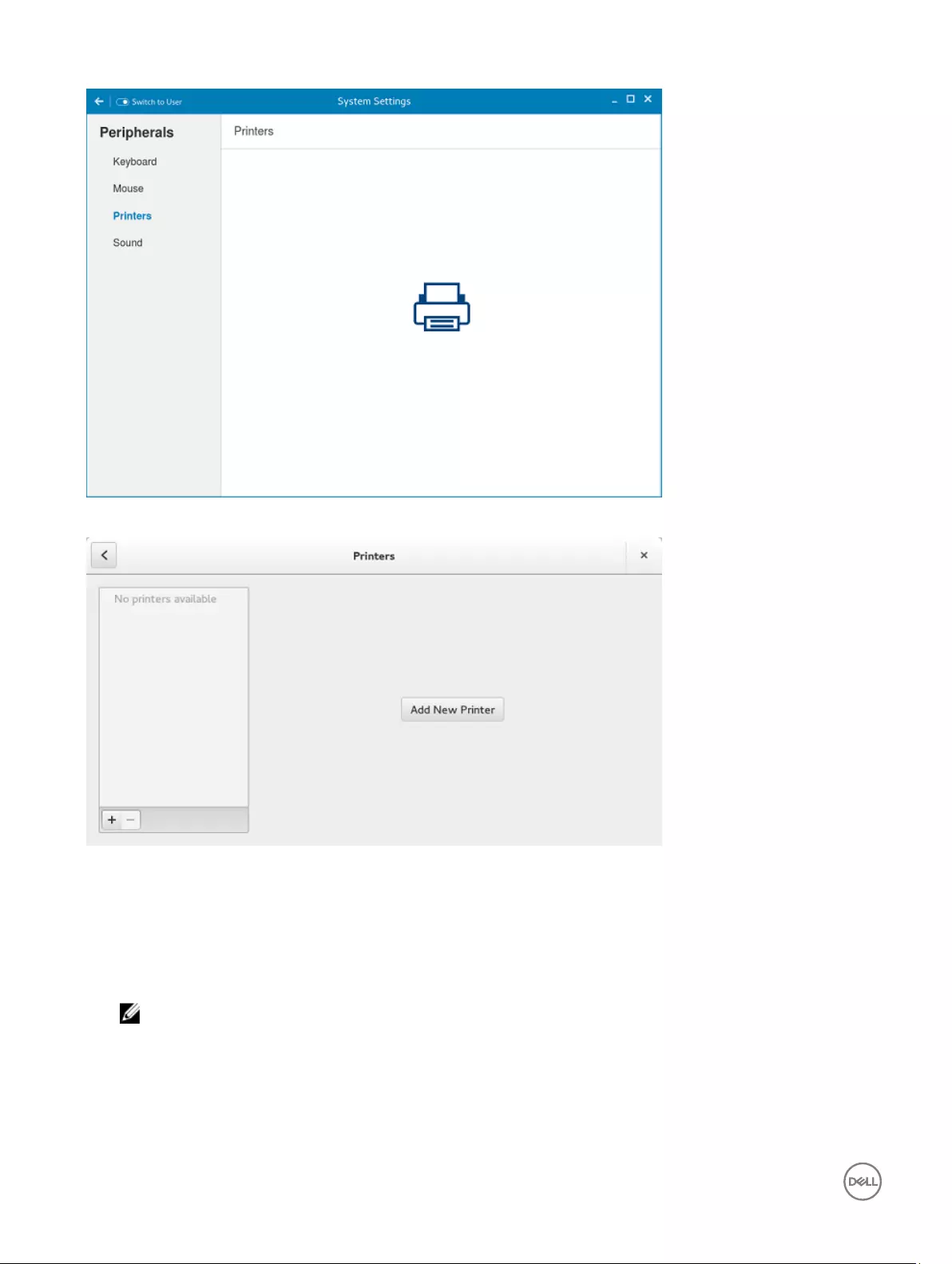
Figure 8. Printer Settings
Figure 9. Add New Printer
1. Click the printer icon.
The gnome-control-center printer dialog box is displayed.
2. Click Add New Printer button to include the new printer in the printers list available on the left pane.
The Add a new printer window is displayed.
3. Enter the address of the printer or the text to filter results.
NOTE: If a USB printer is connected, then it is displayed by default. The printer is not found if wrong address is
provided or the USB is not attached.
4. Click the Add option. Click Print Test Page to test the printer and click (- )icon to remove the printer.
34
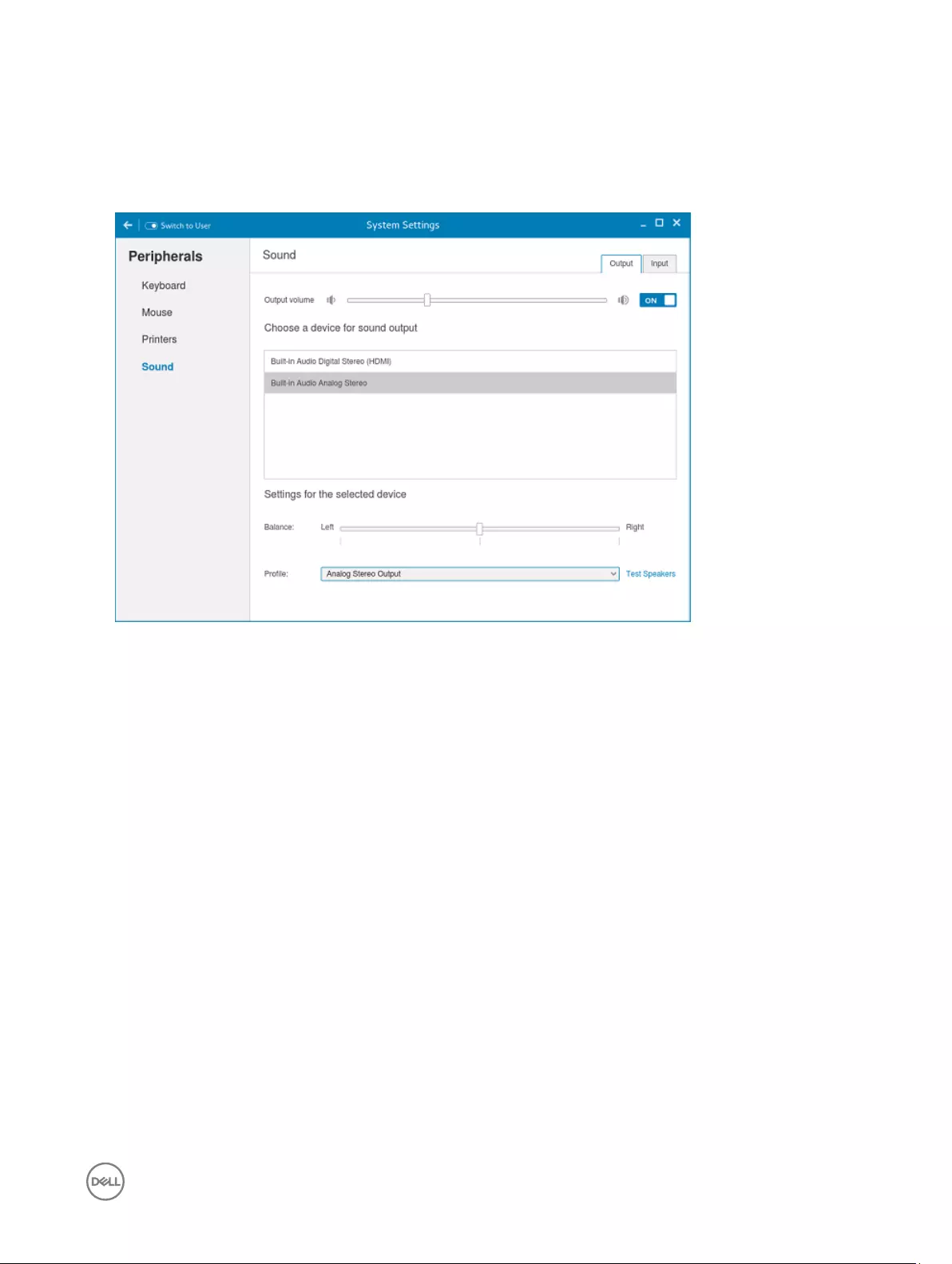
Configuring the sound settings
By default, the Sound screen is available in both User mode and Admin mode. Any changes made through Sound screen is saved
and retained for the built-in thinuser.
1. Click the Output tab to configure the audio output settings.
Figure 10. Sound Settings
a. Move the Output volume slider to adjust the output or speaker volume. Click the Output volume button to enable or
disable the output volume.
b. Select the device for sound output from the listed output devices. The default audio output is the Analog Output.
c. Based on the channels available for the selected output device and profile, you can adjust the Balance and Fade values by
moving Balance and Fade sliders respectively.
d. Select the audio profile from the drop-down list.
e. Click the Test Speakers option. A dialog box is displayed. You can perform the speaker testing by playing sample wave files.
2. Click the Input tab to configure the audio input settings.
35
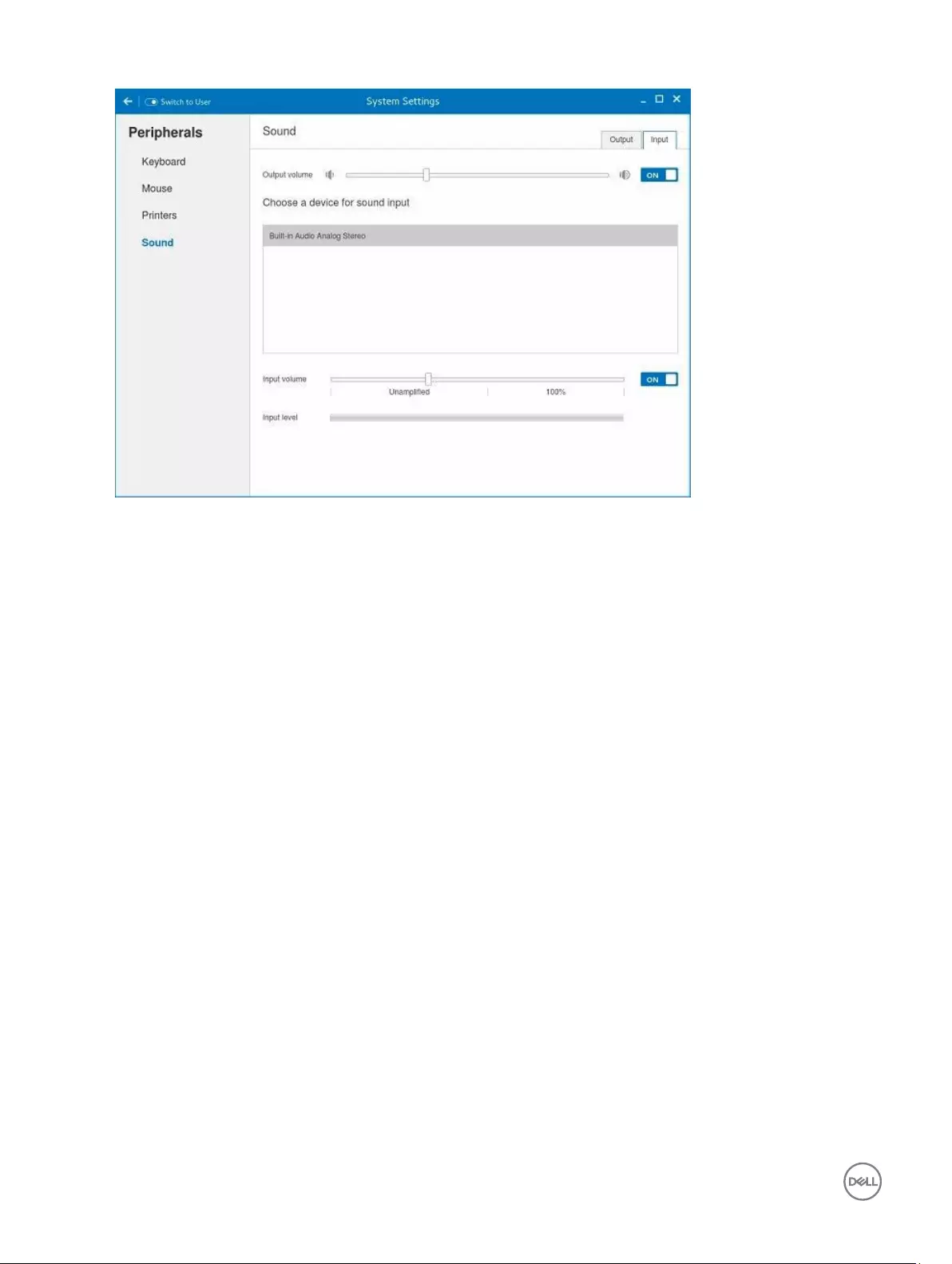
Figure 11. Sound Settings
a. Move the Output volume slider to adjust the output or speaker volume. Click the Output volume option to enable or disable
the output volume.
b. Select the device for sound input from the listed input devices. The default audio input is the Analog input.
c. Move the Input Volume slider to adjust the input or Mic volume. Click the Input volume option to enable or disable the
input volume.
d. The Input level meter bar shows the input volume peak level.
36

7
Power state
Wyse 5060 thin client running WES7P.
You can change the power state options of the thin client device by following the steps mentioned here:
1. On the task bar, click the Start button.
2. From the Start menu, point to the arrow next to the log off button, and then click any one of the following:
•Restart— To restart your thin client.
•Sleep— This mode enables the power-saving state and allows the thin client to quickly resume full power operations when
you want to start working again.
•Shut down– Preferred for orderly closing of the operating system.
3. You can also log off the thin client by any of the following ways:
• From the Start menu, click log off if you want to log off your thin client.
• Press CTRL+ALT+DEL and then click log off.
• Press ALT+F4 to log off from the session.
NOTE: If automatic logon is enabled, the thin client will immediately logs on to the default user desktop. We
recommend you use Shut down button to turn off your thin client.
Wyse 5060 LT thin client running Wyse ThinOS.
Use the Shutdown dialog box to select the available option you want:
• Classic Desktop — Click Shutdown in the Connect Manager or Desktop Menu.
• Zero Desktop — Click the Shutdown icon on the Zero Toolbar.
Wyse 5060 LT thin client running Wyse ThinLinux
On your initial configuration, Dell recommends that you connect by using a wired connection by plugging in the network connected
Ethernet cable to your thin client.
After you turn on your thin client, you are automatically logged in to the thinuser account. By default, the password of the thinuser
account is set to thinuser.
NOTE: In cases where a GDM login is needed (for example, AD/Domain login, PNAgent login and so on), the auto-login
option can be turned off through the GUI or by using the INI.
Admin mode enables you to perform system administration tasks such as adding or removing connections and setting up specific
device settings. To enter into the Admin mode, click the Switch to Admin button from Setting application screen to admin mode
and then enter the default root password in the Password Needed window. The default root password is admin.
37

8
Software
This section describes about establishing and configuring the virtual broker connections for Wyse 5060 thin client.
• For configuring the virtual broker connection on WES7P, see configuring connections locally on WES7P.
• For configuring the virtual broker connection on ThinOS, see configuring the broker setup on Wyse ThinOS.
• For configuring the virtual broker connection on ThinLinux, see Configuring connections locally on Wyse ThinLinux
Configuring Connections locally on WES7P
When you log in to your thin client as a User, the Windows desktop displays certain notable features.
You can perform the following activities:
• Configure Citrix Receiver session services, see Using the Citrix Receiver on WES7P
• Remote Desktop Connections, see Configuring a remote desktop connection session services on WES7P
• To configure vWorkspace connections, see Configuring a vWorkspace Connection on WES7P
Using the Citrix Receiver on WES7P
Citrix Receiver is a server-based computing technology that separates the logic of an application from its user interface. The Citrix
Receiver client software installed on the thin client device allows the user to interact with the application GUI, while all of the
application processes are executed on the server.
Citrix Receiver session services can be made available on the network using either Windows 2008/2012 Server with Terminal
Services and one of the following installed:
• XenDesktop 7.5
• XenDesktop 7.6
• XenDesktop 7.8
• XenDesktop 7.9
NOTE: If you use a Windows 2003/2008 Server or Citrix XenApp 5.0 with Windows Server 2008, a Terminal Services
Client Access License (TSCAL) server must also be accessible on the network. The server grants a temporary license,
which expires after 120 days. After the temporary license expires, purchase and install the TSCALs on the server. You
cannot make a connection without a temporary or permanent license.
To access the Citrix Receiver session:
• On the thin client Administrator desktop, double-click the Citrix Receiver icon.
• Click the Start button on the taskbar, click All Programs, and then click Citrix Receiver on the Programs Menu.
For information about configuring the Citrix receiver, go to www.citrix.com, and then refer to Citrix Documentation.
Configuring a remote desktop connection session services on WES7P
Remote Desktop Connection is a network protocol that provides a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a
network connection.
Use the Remote Desktop Connection dialog box to establish and manage connections to remote applications.
38

To configure a Remote Desktop Connection:
1. Log in as user or administrator.
2. On the taskbar, click the start button, and then click All Programs.
3. Click Remote Desktop Connection on the Programs menu, and then click Remote Desktop Connection.
The Remote Desktop Connection dialog box is displayed.
You can also double-click the Remote Desktop Connection icon on the desktop to open the Remote Desktop Connection
dialog box.
4. In the Computer box, enter the computer or the domain name. For advanced configuration options, click Show Options.
a. In the General tab, you can enter the logon credentials, open an existing RDP connection, or save a new RDP connection
file.
b. In the Display tab, manage the display and the color quality of your remote desktop.
• Move the slider to increase or decrease the size of your remote desktop. To use full screen, move the slider all the way
to the right.
• Select the color quality of your preference for your remote desktop from the drop-down list.
• Select or clear the Display the connection bar when I use the full screen check box to display or hide the connection
bar in full screen mode.
c. In the Local Resources tab configure audio, keyboard, or local devices and resources for your remote desktop.
• In the Remote audio section, click Settings for advanced audio settings options.
• In the Keyboard section, from the drop-down list select the desired environment you want to apply the keyboard
combinations.
• In the Local devices and resources section, select devices and resources that you want to use in your remote session.
Click More for more options.
d. In the Programs tab, to start a default program with the remote session, select the Start the following program on
connection check box and specify the details.
e. In the Experience tab optimize the performance of your remote session based on the connection quality.
NOTE: If you find that the File Based Write Filter cache is filling up, you can disable Bitmap caching in the
Experience tab after clicking Show Options in the window.
f. In the Advanced tab, in the Server Authentication section, from the drop-down list, select the action you want the thin
client to perform when the server authentication fails.
In the Connect from anywhere section, click Settings to configure the connection settings such as Remote Desktop
Gateway server settings and logon settings when you are working remotely.
5. Click Connect.
6. Enter the login credentials for connecting to the remote session in the Security dialog box.
NOTE: The standard version (default) is used for a single monitor display, while the Span version can be used when
extending a single session to two monitors for dual-monitor capable thin clients. The Span version can be used when
extending a single session to two monitors for dual-monitor.
Configuring a vWorkspace Connection on WES7P
vWorkspace is a concept in which the desktop environment of a computer is separated from the physical computer and hosted as a
virtual workspace on multiple environments, such as a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), terminal servers, and/or blade PCs
running in a data center.
Workspace virtualization helps group and deliver a list of applications or desktops together as a single complete virtual workspace. It
isolates and centralizes an entire computing workspace. vWorkspace provides flexible, location and platform independent access by
delivering virtual workspace from multiple virtualization platforms.
To configure a vWorkspace connection:
1. Log in as a user or administrator.
2. On the taskbar, click Start → All Programs → Dell Wyse vWorkspace, or double-click the vWorkspace icon on the desktop.
39

The vWorkspace window is displayed.
3. In the vWorkspace window, enter the vWorkspace Server IP, or your registered email address or website address, and then
press Enter.
4. To retrieve your connector configuration from vWorkspace server, provide the Username, Password, and Domain credentials.
Select the Save Credentials (encrypted) check box if you want to save your login credentials.
5. Select your preferred vWorkspace Farm location from the following options:
• Inside Office
• Outside Office
6. Click Connect.
7. In the Login Credentials dialog box, enter the following credentials to connect to the vWorkspace Farm:
• Username
• Password
• Domain
The vWorkspace Farm screen is displayed.
For more information about managing your vWorkspace connection, go to documents.software.dell.com/vworkspace.
Configuring the broker setup on Wyse ThinOS
To configure the Broker setup:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Remote Connections.
The Remote Connections dialog box is displayed.
40
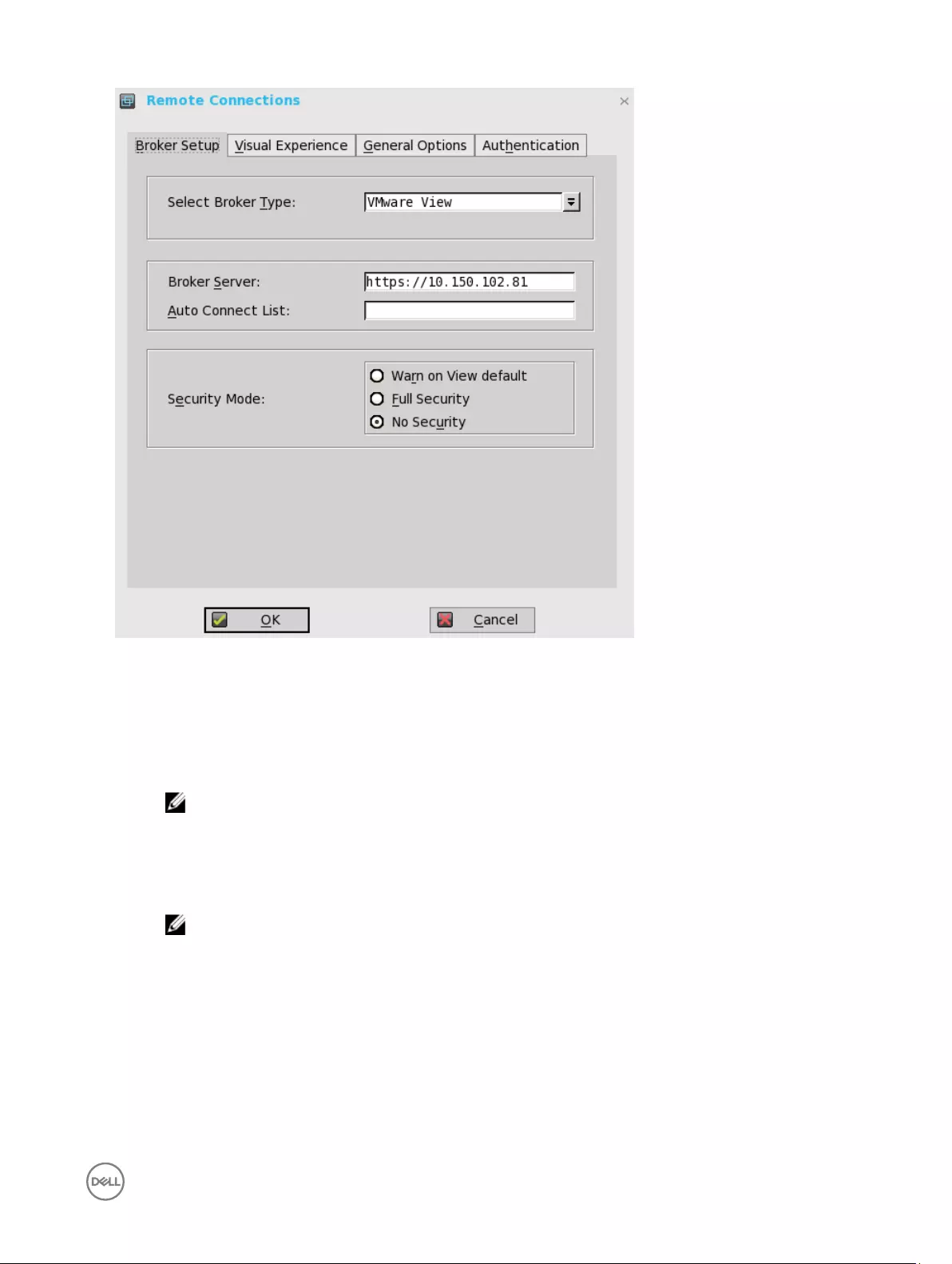
2. Select Broker type from the drop-down list.
a. If you select None from the list, click either of the following connection protocols:
b. If you select the Citrix Xen, use the following guidelines:
• Select the check box to enable the StoreFront style.
•Broker Server— Enter the IP address of the Broker Server.
• Select the check box to enable automatic reconnection at logon.
NOTE:
If you enable the automatic reconnection, you are able to select from the reconnection options. Click either of the
options where you can connect to the disconnected sessions only or connect to both active and disconnected
sessions.
• Select the check box to enable automatic reconnection from the button menu.
NOTE: If you enable the automatic reconnection, you are able to select from the reconnection options. Click
either of the options where you can connect to the disconnected sessions only or connect to both active and
disconnected sessions.
•Account Self-service Server— Enter the IP address of the Account self-service server.
•XenApp — Use this option, if you want to set default settings to XenApp.
•XenDesktop— Use this option, if you want to set default settings to XenDesktop.
c. If you select the VMware View, use the following guidelines:
•Broker Server— Enter the IP address of the Broker server.
•Security Mode
41
— Use this option to select the Security Mode. The available options are Warn on View default, Full security, and No
security.
d. If you select the Microsoft, enter the IP address of the Broker Server in the Broker Server box, and then click OK to save
the settings.
e. If you select Dell vWorkspace, use the following guidelines:
•Broker Server— Enter the IP address of the Broker Server.
• Select the check box to enable vWorkspace Gateway.
•vWorkspace Gateway— Enter the IP Address of the vWorkspace Gateway.
f. If you select Other, you must enter the IP address of the Broker server in the Broker Server box.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring connections locally on Wyse ThinLinux
On the System Settings page, click the Connections icon. The Connections page contains the following tabs:
• Citrix
• VMware
NOTE: The description names for all the connections can not be edited once you create the connection.
Configuring and managing Citrix connections
The Citrix Connections page enables you to create and manage the Citrix connections both locally and globally.
Figure 12. Citrix connection settings
To configure the local Citrix settings:
1. Click the + icon to add a new Citrix Connection.
The Citrix Connections page is displayed.
2. Enter the name of the Citrix connection for which you specify the Server URL address.
3. From the Connection Type drop-down list, select any of the following connection types:
• Server
• Published Application
42
• Storefront
4. Click Save to save the changes.
Configuring and managing VMware connections
The VMware connections page enables you to create and manage the View client 3.5 connections.
To configure the VMware Settings, complete the following task:
1. Click the + icon to add a new VMware Connection.
The VMware Connections page is displayed.
Figure 13. VMware connections settings
2. Enter the name of the VMware connection.
3. Configure the following options in the Login tab:
43
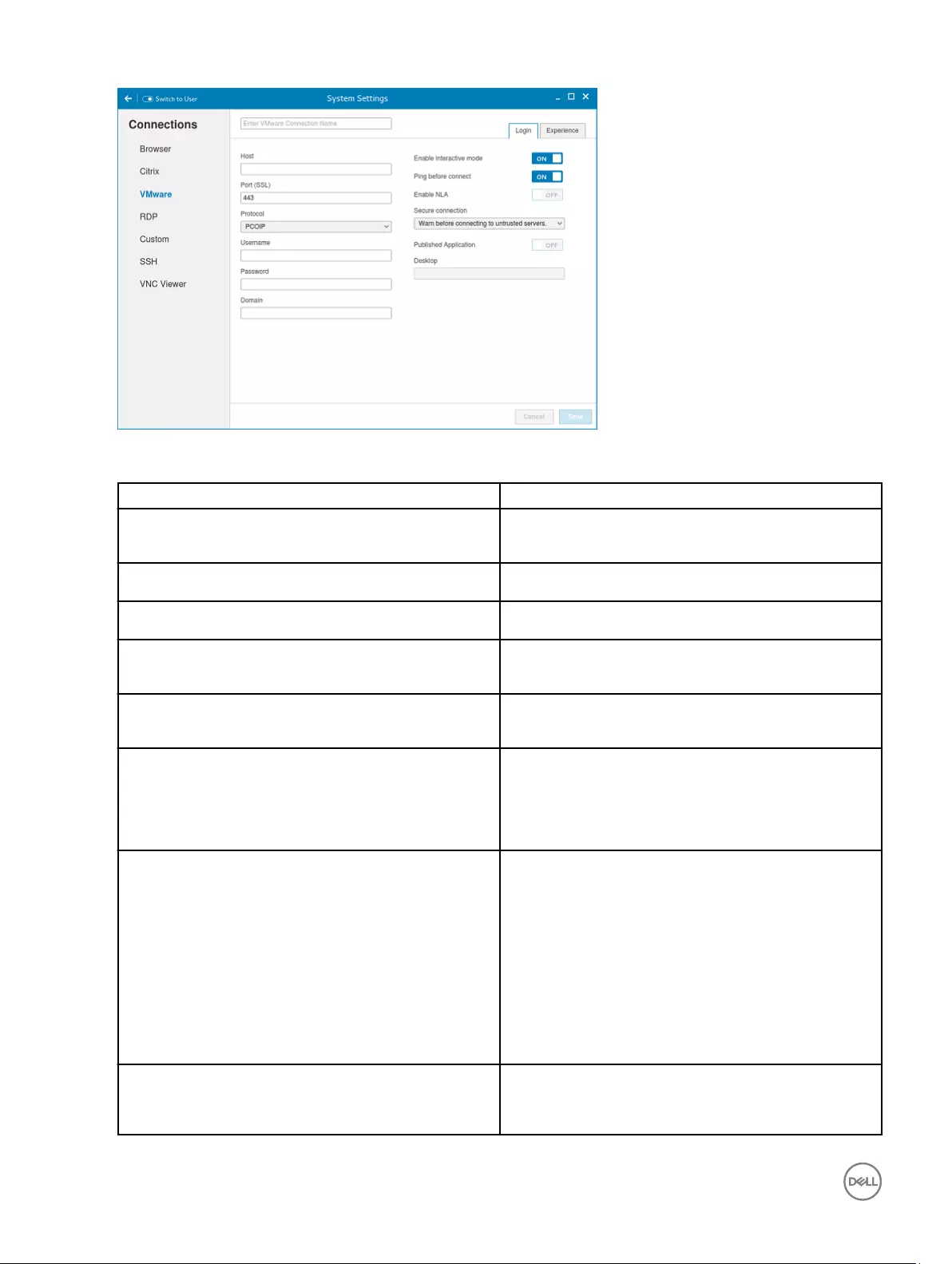
Figure 14. VMware login settings
Parameter Description
Host Enter the host name or IP address or FQDN of the Horizon
of the VMware View Server.
Port Enter the port number of the host.
Protocol From the drop-down list, select the specific protocol.
Username Enter the User ID that is used to log in to the remote Horizon
server.
Password Enter the password that is used to log in to the remote
Horizon server.
Published Application Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
If enabled, specify the Published Application name.
If disabled, specify the Published desktop name.
Enable interactive mode Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
If enabled, then after a successful connection to the server, it
displays all the published application and desktop icons. You
can start the applications or desktop sessions based on your
choice.
If disabled, then the Published Applications option is enabled
in the Login tab.
Selecting that option enables you to directly start the
application or desktop that you specify.
Ping before connect Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option. If
enabled, it pings the connection is checked in server IP/
FQDN before connecting to a session.
44
Parameter Description
Enable NLA Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
Enable the Network Level Authentication (NLA), if NLA is
enabled on your remote computer. Your remote computer
requires NLA user authentication before you establish a full
Remote Desktop connection and the login screen is
displayed.
Secure connection Click the Secure Preferences tab and select any of the
options that determine how the client should proceed when it
cannot verify that your connection to the server is secure.
Domain Enter the Domain name. It is used to log in the remote
Horizon server.
Desktop If interactive mode is disabled, you can specify Published
desktop name.
Application If interactive mode is disabled, you can specify the Published
application name.
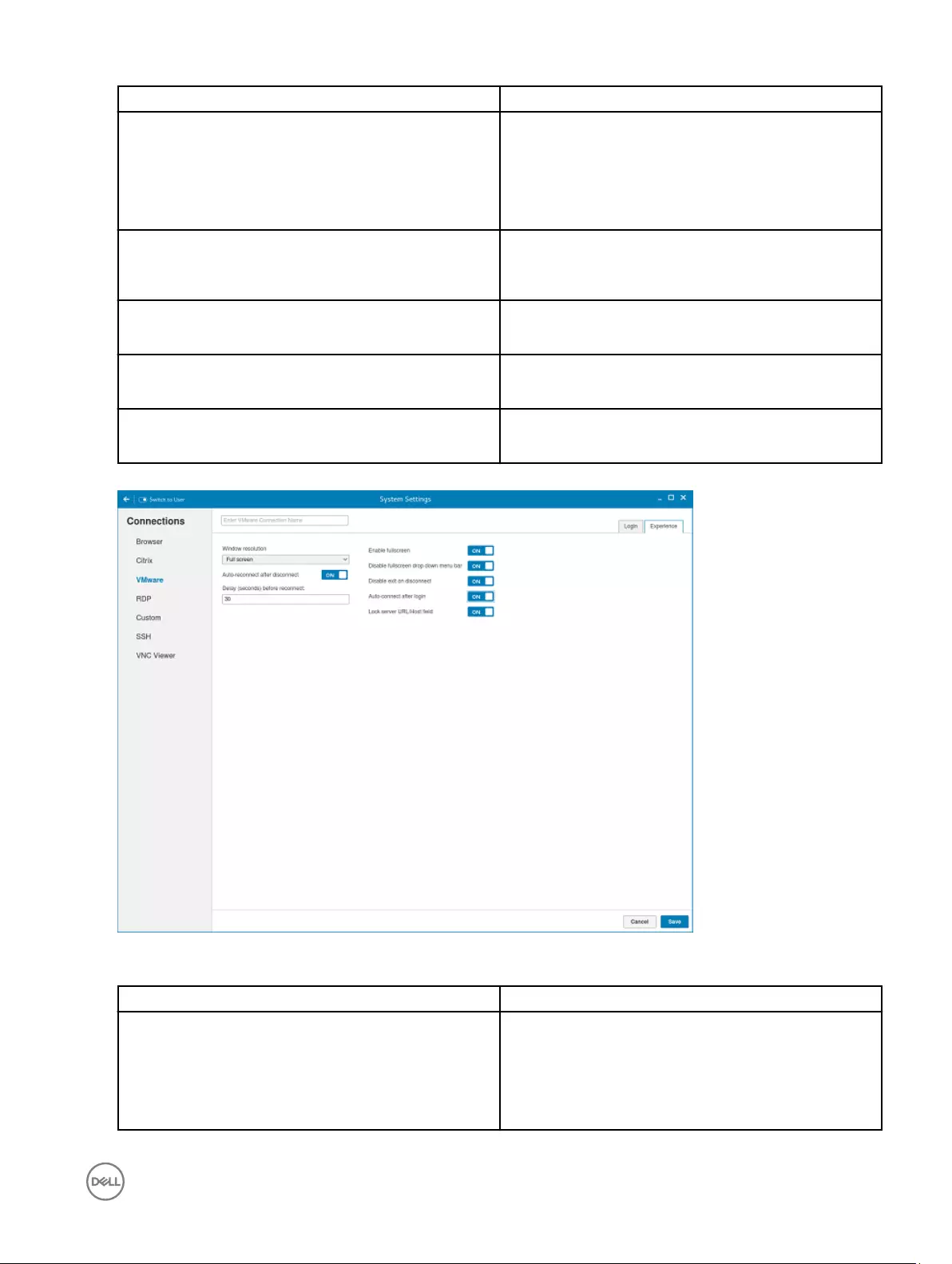
4. The following options must be configured in the Experience tab:
Figure 15. VMware experience settings
Parameter Description
Windows resolution Select the Windows resolution that you want to get the best
display on your monitor. The available resolutions are:
Use All Monitors
Full Screen
45
Parameter Description
Large Screen
Small Screen
1024X768
800X600
640X480
Auto-Reconnect after disconnect. Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option. If
enabled, the connection is automatically re-established after
you disconnect from the session.
Delay (seconds) before reconnect. Select the amount of time in seconds to delay the
reconnection attempt after a disconnection occurs.
Enable fullscreen Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
Select this option to view the remote session in full screen
mode in all the monitors.
Disable fullscreen drop-down menu bar Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
Select this option to disable the drop-down menu bar in the
full screen mode.
Disable exit on the disconnect Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
Select this option if you do not want the Horizon server to
retry connecting if there is a connection error. You can
typically select this option if you use kiosk mode.
Auto-connect after login. Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
Select this option to reconnect automatically after a
disconnection occurs.
Lock server URL/Host field Click the ON/OFF button to enable or disable this option.
5. Click Save to save the settings.
46

9
Management interface of Wyse 5060 thin client
This section describes about the management interface of Wyse 5060 thin client.
• For WDM software for remote administration on WES7P, see WDM software for remote administration on WES7P.
• For WDA settings on ThinOS, see Configuring the WDA settings on Wyse ThinOS.
• For WDA settings on ThinLinux, see Configuring the WDA settings on Wyse ThinLinux.
Wyse Device Manager (WDM) software for remote administration on
WES7P
WDM servers provide network management services to the thin client complete user-desktop control—with features such as
remote shadow, reboot, shutdown, boot, rename, automatic device check-in support, Wake-On-LAN, change device properties, and
so on. With WDM you can manage all of your network devices from one simple-to-use console.
Configuring the WDA settings on Wyse ThinOS
Use this tab to configure the WDM and CCM settings.
To configure the WDA settings, do the following:
1. From the desktop menu, click System Setup, and then click Central Configuration.
The Central Configuration dialog box is displayed.
2. Click WDA, and use the following guidelines.
WDM is selected by default. WDA service automatically runs after the client boot up.
47
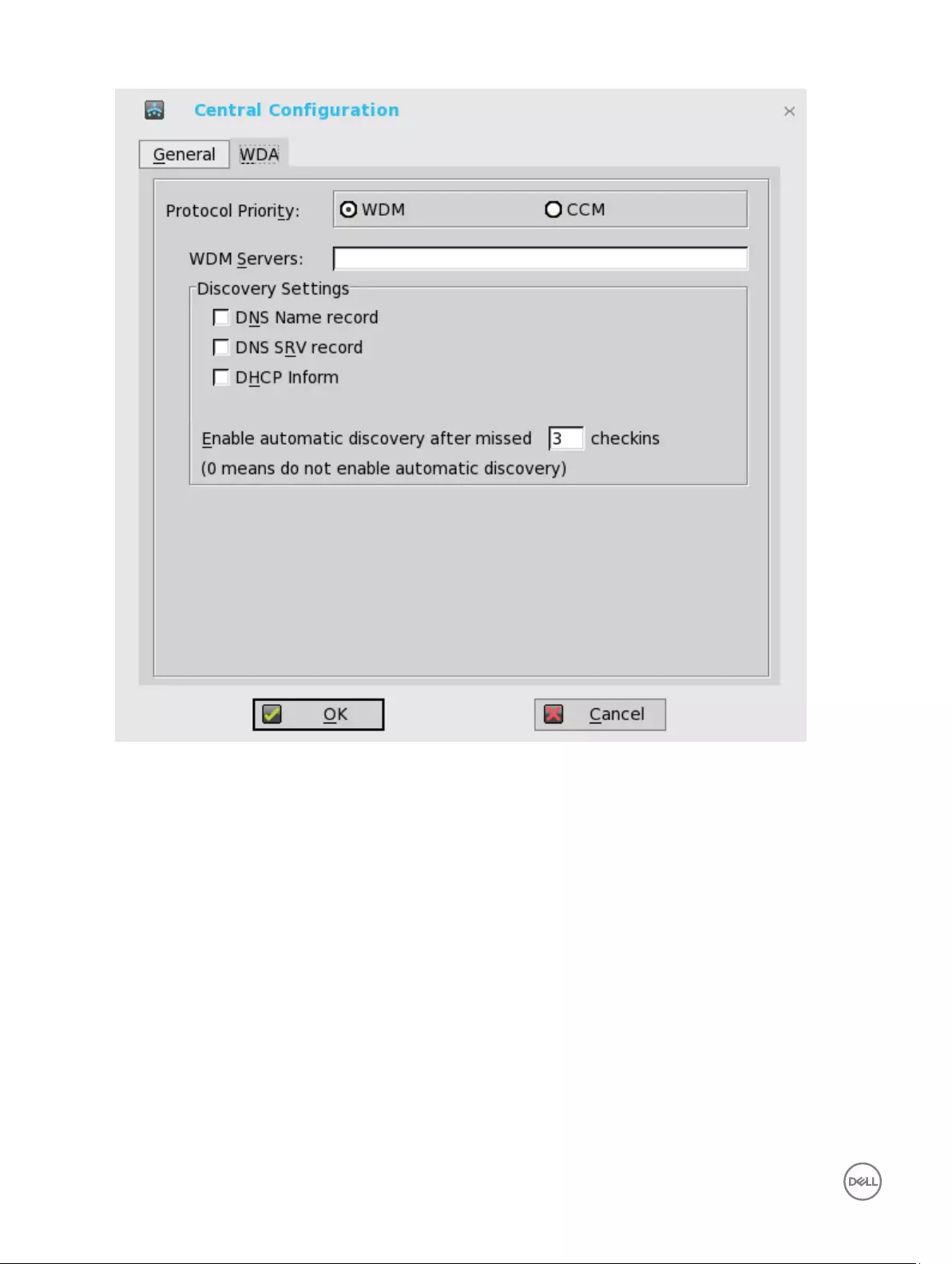
If the first discovery, for example, the WDM service is not successful, then it seeks for the next priority, for example, CCM
service. This continues till a discovery is successful. If all discoveries fail, then it is started again automatically after a fixed time
(24 hours).
a. WDM Servers — Enter the IP addresses or host names, if WDM is used. Locations can also be supplied through user
profiles, if user INI profiles are used.
b. DNS Name Record — (Dynamic Discovery) Allows devices to use the DNS host name lookup method to discover a WDM
Server.
c. DHCP Inform — (Dynamic Discovery) Allows devices to use DHCP Inform to discover a WDM Server.
d. Enable Automatic Discovery After Missed Check-ins — Select the number of missed check-ins after which you want the
auto discovery options enabled.
3. Click OK to save the settings.
Service checked in status is displayed in System Information.
48
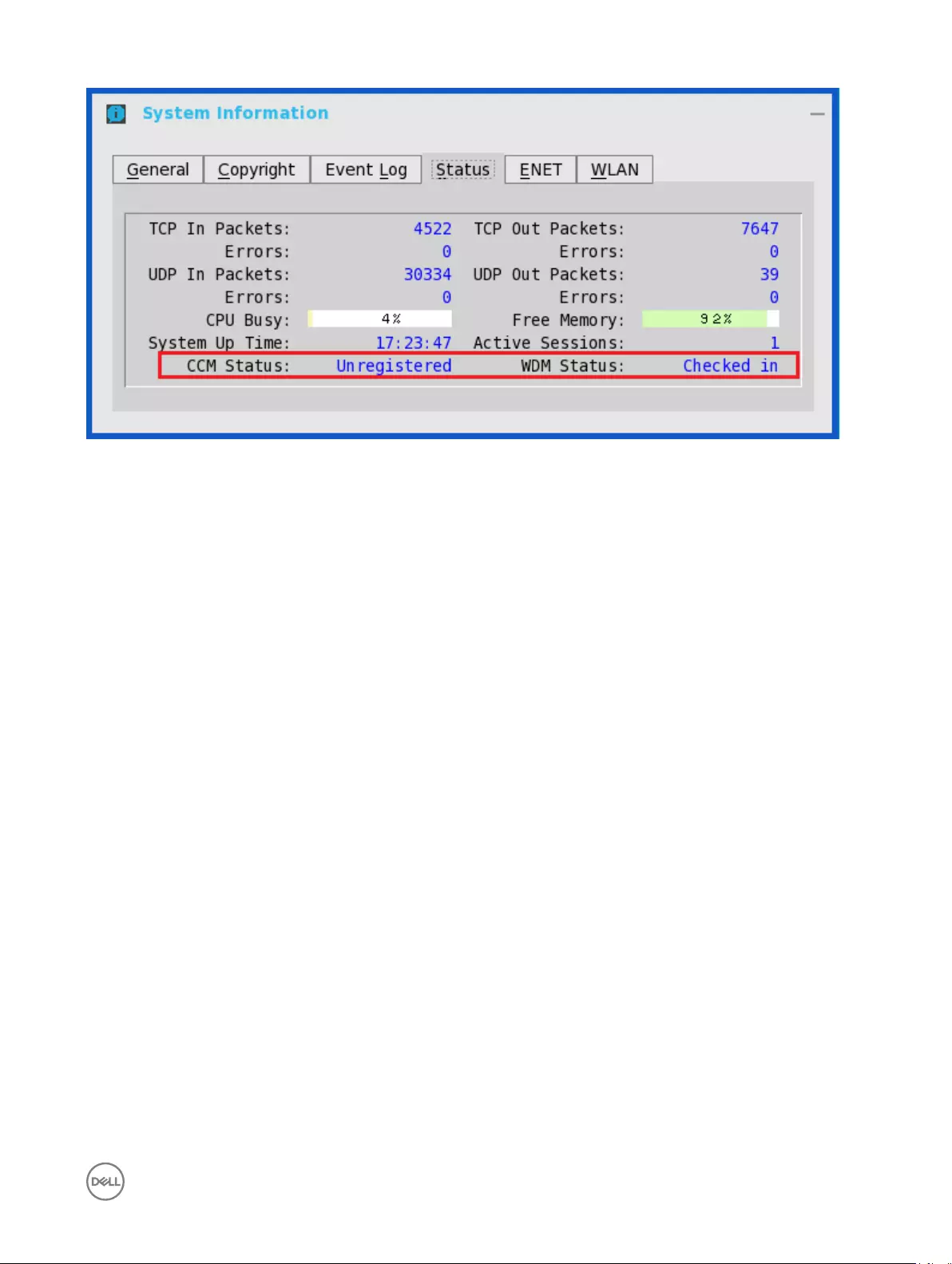
The following is the INI parameter for this feature:
WDAService={yes(default),no}Priority ={WDM(default),CCM,“WDM;CCM”,“CCM;WDM”}
To configure the CCM settings, do the following:
1. Click CCM, and use the following guidelines.
a. Enable Cloud Client Manager (CCM) — Select the check box to enable the Cloud Client Manager(CCM).
49
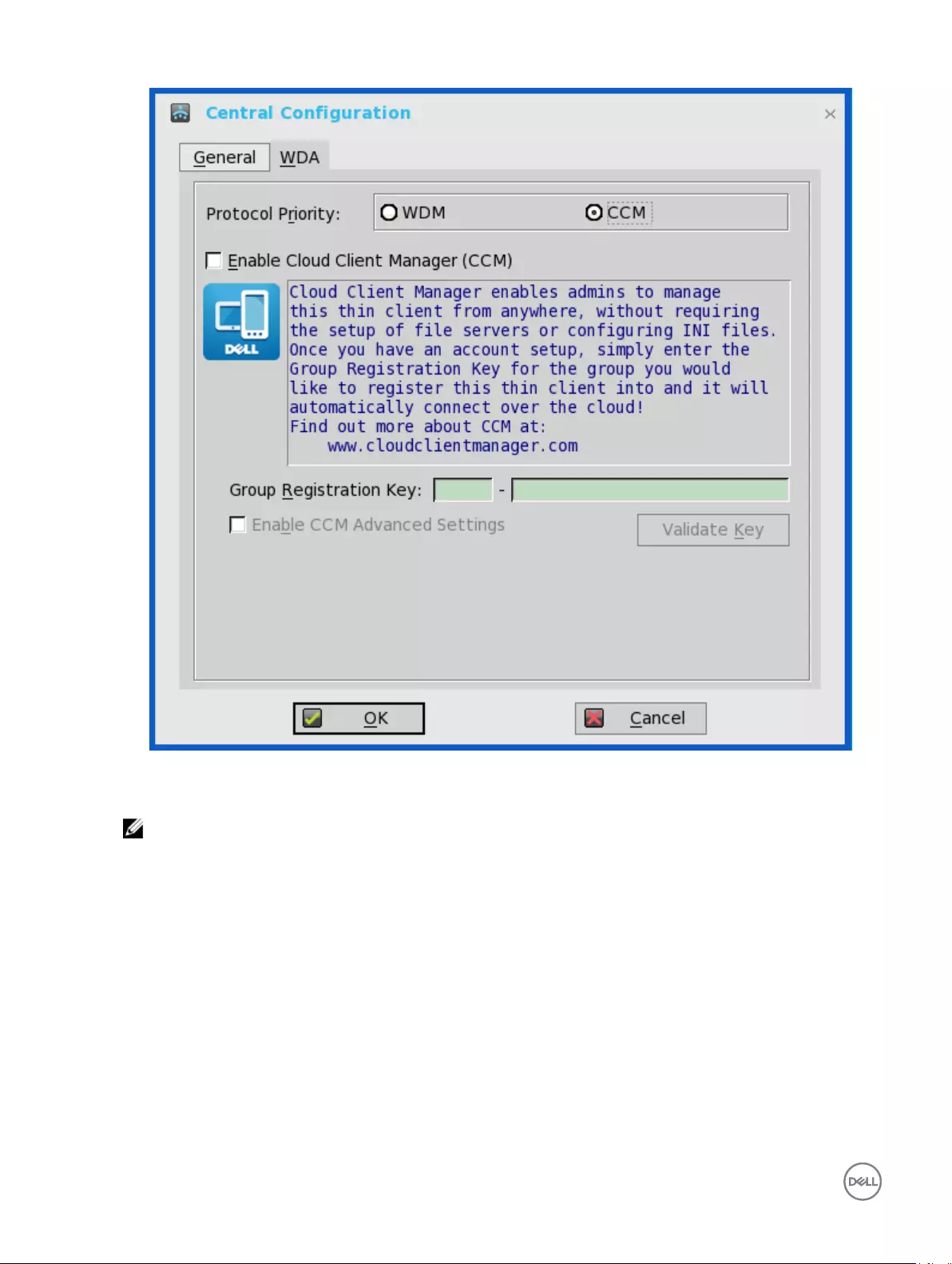
b. Group Registration Key — Enter the Group Registration Key as configured by your cloud Client Manager administrator
for the desired group.
NOTE: If you enable the Cloud Client Manager (CCM ), make sure that you have entered the Group Registration
Key and enabled the CCM Advanced Settings.
2. Click OK to save the settings.
Configuring the WDA settings on Wyse ThinLinux
The Wyse Device Agent (WDA) on the ThinLinux device supports only the features of Cloud Client Manager (CCM) device
management solution. Wyse Device Agent is for configuring the CCM (Cloud Client Manager) client settings and registering a
ThinLinux device into CCM and it is available only for admin user.
50
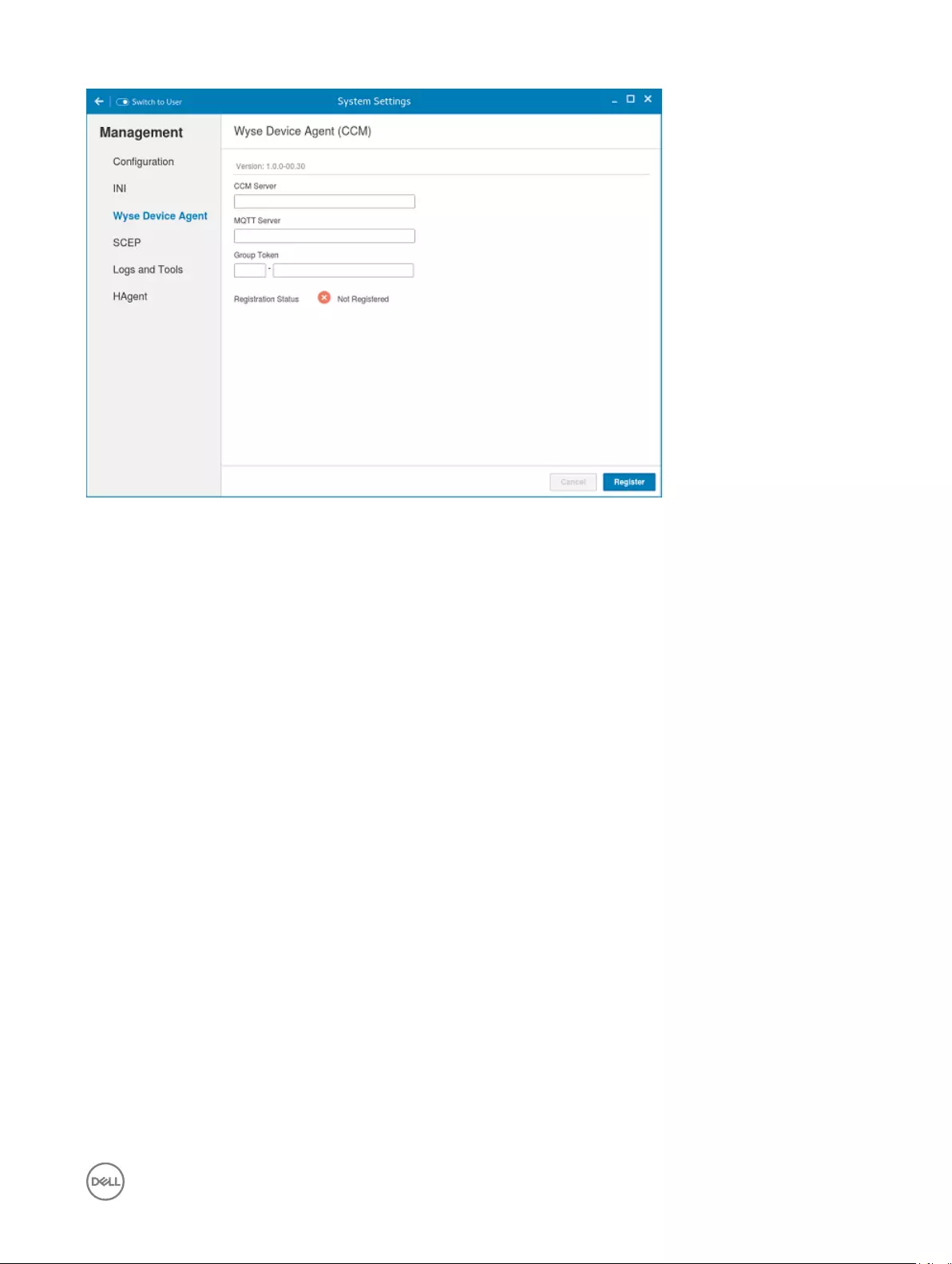
Figure 16. Wyse Device Agent (CCM)
If the device is not registered to a CCM server, the Wyse Device Agent screen shows the registration status as Not Registered.
1. In the CCM Server input box, enter the URL of CCM server you want to connect to.
2. In the MQTT Server input box, enter the IP address or hostname of Message Queue Telemetry Transport (MQTT) server.
3. In the Group Token input boxes, enter your group registration key to manage your ThinLinux device. This is a unique key for
registering your thin client device. Thin clients can be directly registered to Groups directly and must have a Group Registration
Key enabled to perform this action.
4. Do one of the following options:
• Click Register to register your thin client on CCM server. When your thin client is successfully registered, the status is
shown as Registered with green color icon next to the Registration Status label, and caption of Register button changes to
Unregister.
• Click Unregister, if you want to remove your thin client from the CCM management system. If Unregister fails, a dialog box
for Force Unregister confirmation is displayed. Click Yes to forcefully unregister your device which is managed by CCM.
When you perform Register or Unregister or Force Unregister from Agent screen, the applet should not be closed until
Registration Status. After successful registration, you can access the CCM management server screen where you can view
and manage Device Asset Details, Real-Time commands, and Troubleshooting information of your registered thin client.
Directing the Thin Client to CCM Server:
• To direct your thin client to CCM server, you must provide CCM/MQTT server details and Group registration Key. These
details is discovered by Wyse Device Agent using any of the following ways:
– DHCP Scope options
– Using INI parameter
– Using the Wyse Device Agent screen
• Directing the thin client to CCM Server using DHCP Scope options. The CCM/MQTT server details and Group Registration
Key that are required for CCM registration can be obtained by querying the DHCP server with following option tags:
– 199 – Scope option for Group Token (type = String, value = CCM-group-key).
– 165 – Scope option for CCM server.
– 166 – Scope option for MQTT server.
51

• Directing the thin client to CCM Server using INI parameters, INI syntax for CCM configuration:
– CCMEnable={yes,no} CCMServer=<CCM Server URL> GroupRegistrationKey=<tenant code-group code>
MQTTServer=<MQTT server>[:<MQTT port>]
NOTE:
When INI discovery method is used for registering the device, if you want to unregister the device, you must delete the INI
parameters and restart the device first and then unregister the device. Else you have to perform the unregister process
twice. For more information, see ThinLinux INI Guide .
52
10
System specifications
Table 1. Brand/Sub-brand/Model Number/Chassis description/Series Level/Category Type
Features Specification
Ambient operation 0 to 35 degree Celsius (32 to 95 degree F)
Non-operation temperature -40 to 65 degree Celsius (-40 to 149 degree Fahrenheit)
Humidity 20% to 80% (non condensing)
Max Altitude -15.2 to 3048m (-50 to 10,000 ft)
OEM Ready Yes
Table 2. Processor/chipset
Features Specification
SOC-AMD Steppe Eagle
CPU core AMD steppe Eagle GX-424 (2.4 GHz Quad Core) (TDP @ 15W
adjusted by BIOS)
Graphics AMD integrated graphics Radeon R5E
TPM Version 1.2 0r 2.0 (option; FW configurable).
NOTE: ThinOS does not support TPM.
Table 3. Memory
Features Description
System memory 4GB/8GB DDR3 1600MHz(2*SO-DIMM)
storage 8GB/64GB SATA3 flash module only.
Network WLAN+BT Combo Module: Intel 7265 M.22230(PCIe/USB
interface)
Table 4. I/O (front)
Features Specification
LEDs • 1*Power button (blue color)
• 1*Power button (bi-color)
USB 2.0 2*USB 2.0
Audio 1*Audio combo jack
53
Table 5. I/O (rear)
Features Specification
Antenna 2*Antenna (2T2R) option
USB 2.0 2*USB 2.0 (stacked)
USB 3.0 2*USB 3.0 (stacked)
Display Port 2*DP
Physical security 1*Kensington Lock Slot
RJ 45 Ethernet 1 * RJ-45 (10/100 /1000 Base-T Ethernet)
Table 6. Form factor
Features Specification
Chassis leveraged Dell Wyse 5020 (Oberon)
Chassis access Sealed chassis, accessible with tools
Optional mounting Wall mount / vesa mount
Height(Z)mm 40
Width(x)mm 185
Depth(Y)mm 170
Weight (pounds / kilograms) 0.93kg (2.05 lb)
Total no of HDDs/SDDs supported 0
Table 7. Power requirement
Features Specification
AC input voltage range (comply with L.P.S) 19V 65W
Table 8. BIOS
Features Specification
Standard BIOS, UEFI as implemented using Phoenix UEFI Y
Support Wake-On-LAN Y
Table 9. Operating system
Features Specification
OS and system software Launch at RTS
• ThinLinux (post RTS)
• ThinOS
• WES7P
• Windows 10 IoT Enterprise(downgraded to WES7P) (post
RTS)
54
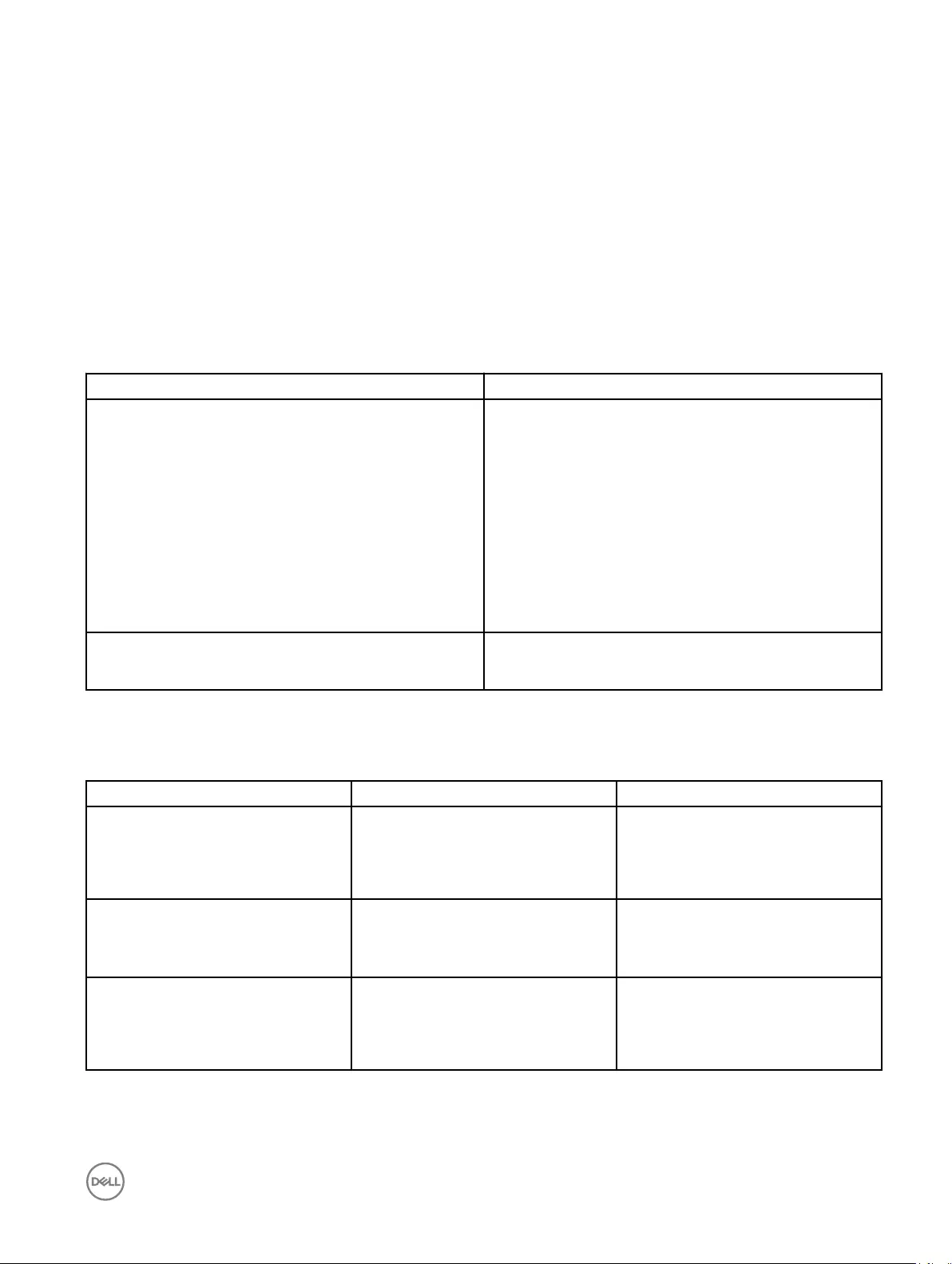
11
Troubleshooting your system
You can troubleshoot your system using indicators like diagnostic lights, and error messages during the operation of the device.
Power states and LED behavior
Table 10. Power states and LED behavior
States Behavior
Indicators • Power LED: Blue
• Activity LED: Bi-color, Green/Amber
• Power state:
– S0–On: Power LED Blue, Activity LED green
– S3 – Standby/Sleep: Power LED off, Activity LED
blinking.
– S5 – Off: All LED off
• Operation State:
– Boot: Power LED on, Activity LED.
– In O/S: Power LED on, Activity LED green
Power button control • On/Off-state detection: Push power button is < 4s
• Force Off-state: Push and hold power button is >= 4s
Diagnostic power LED codes
Table 11. Diagnostic power LED codes
Power LED light status Possible cause Troubleshooting steps
At first power apply :No LED light up
briefly
Both power LED and activity LED come
up briefly and then turn off. • Check AC power, call your utility
company
• Check AC power cord is plug-in
• Check DC plug is plug into the unit
At first power apply : Both LED stay ON Both power LED and activity LED come
up briefly and then turn off • Logic board defect
• BIOS malfunctioning
• Abnormal power source
Push power button the LED does not turn • Power LED should come up in steady
BLUE
• Activity LED should turn on in steady
AMBER
• Logic board defect
• Power button defect
• Mechanical assembly misalign cause
miss actuation
55