Table of Contents
- Me and My Dell For Inspiron, G-Series, XPS, and Alienware computers
- Contents
- Setting up your computer
- About your computer
- Using your computer
- Ports and connectors
- Software and Applications
- Restoring your operating system
- Troubleshooting
- BIOS
- Getting help and contacting Dell
- References
DELL 5620 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 5620 by DELL which is a product in the Notebooks category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Me and My Dell
For Inspiron, G-Series, XPS, and Alienware computers
January 2021
Rev. A08

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid
the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2016-2022 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Other trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.

Chapter 1: Setting up your computer............................................................................................. 7
Connecting to the internet................................................................................................................................................ 7
Connecting to the internet using LAN......................................................................................................................7
Connecting to the internet using WLAN.................................................................................................................. 7
Connecting to the internet using WWAN................................................................................................................ 8
Setting up audio................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Configuring 5.1 and 7.1 audio...................................................................................................................................... 9
Connecting 5.1 speakers.............................................................................................................................................10
Connecting 7.1 speakers.............................................................................................................................................10
Setting up your printer...................................................................................................................................................... 11
Windows 10 and 8.1...................................................................................................................................................... 11
Windows 7...................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Setting up your webcam................................................................................................................................................... 11
Integrated webcam.......................................................................................................................................................11
External webcam...........................................................................................................................................................11
Setting up Bluetooth......................................................................................................................................................... 12
Connecting multiple monitors......................................................................................................................................... 12
Windows 10....................................................................................................................................................................12
Windows 8......................................................................................................................................................................12
Windows 7......................................................................................................................................................................13
Chapter 2: About your computer.................................................................................................. 14
Power adapter.................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Battery.................................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Coin-cell battery.................................................................................................................................................................15
Touchpad............................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Display...................................................................................................................................................................................15
Touch screen.................................................................................................................................................................15
3D.....................................................................................................................................................................................15
Wireless display.............................................................................................................................................................16
Camera................................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Webcam..........................................................................................................................................................................16
3D camera...................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Intel RealSense 3D camera........................................................................................................................................ 16
Wireless display.............................................................................................................................................................16
Keyboard.............................................................................................................................................................................. 16
Physical keyboard.........................................................................................................................................................16
On-screen keyboard.................................................................................................................................................... 17
Keyboard connection types....................................................................................................................................... 18
Service Tag and Express Service code.........................................................................................................................18
Locating the label on your computer.......................................................................................................................18
Storage device....................................................................................................................................................................19
Internal storage devices............................................................................................................................................. 19
Removable storage devices....................................................................................................................................... 19
Contents
Contents 3

Memory module.................................................................................................................................................................. 21
System board...................................................................................................................................................................... 21
Chipset................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Processor............................................................................................................................................................................ 22
Computer fan..................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Heat sink..............................................................................................................................................................................22
Thermal grease.................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Video card........................................................................................................................................................................... 23
TV tuners.............................................................................................................................................................................23
Speakers.............................................................................................................................................................................. 24
2.1 Audio.........................................................................................................................................................................24
5.1 Audio........................................................................................................................................................................ 24
7.1 Audio.........................................................................................................................................................................25
Webcam...............................................................................................................................................................................25
Network............................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Local Area Network.................................................................................................................................................... 25
Wireless Local Area Network....................................................................................................................................25
Wireless Wide Area Network.................................................................................................................................... 25
Wireless Personal Area Network............................................................................................................................. 25
Modem........................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Router............................................................................................................................................................................ 26
Network‑Interface Controller...................................................................................................................................26
Wireless Local‑Area Network adapter................................................................................................................... 26
Wireless Wide Area Network adapter.....................................................................................................................26
Bluetooth....................................................................................................................................................................... 26
Near-Field Communication........................................................................................................................................26
Chapter 3: Using your computer.................................................................................................. 27
Charging the battery........................................................................................................................................................ 27
Using your keyboard......................................................................................................................................................... 27
Keyboard shortcuts.....................................................................................................................................................27
Keyboard shortcuts for Windows 8.1 and Windows RT..................................................................................... 28
Customizing your keyboard.......................................................................................................................................29
Using numeric keypad on a laptop.......................................................................................................................... 30
Using your touchpad........................................................................................................................................................ 30
Touchpad gestures..................................................................................................................................................... 30
Using your touch screen..................................................................................................................................................32
Touch screen gestures...............................................................................................................................................32
Using Bluetooth................................................................................................................................................................. 34
Pairing a Bluetooth device with your computer or tablet..................................................................................34
Using the webcam............................................................................................................................................................ 35
Chapter 4: Ports and connectors................................................................................................. 36
Audio.....................................................................................................................................................................................36
Types of audio ports................................................................................................................................................... 36
USB....................................................................................................................................................................................... 37
USB ports...................................................................................................................................................................... 37
USB standards..............................................................................................................................................................37
eSATA.................................................................................................................................................................................. 38
4Contents

Visual Graphics Array....................................................................................................................................................... 38
Digital Visual Interface..................................................................................................................................................... 38
DisplayPort..........................................................................................................................................................................38
HDMI.................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
SPDIF................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Chapter 5: Software and Applications......................................................................................... 40
Absolute...............................................................................................................................................................................40
Dell SupportAssist............................................................................................................................................................. 40
PC Check............................................................................................................................................................................ 40
Quickset................................................................................................................................................................................41
NVIDIA 3D Applications.................................................................................................................................................... 41
Chapter 6: Restoring your operating system............................................................................... 43
System recovery options.................................................................................................................................................43
Dell Backup and Recovery...............................................................................................................................................43
Dell Backup and Recovery Basic..............................................................................................................................44
Dell Backup and Recovery premium........................................................................................................................44
Dell Factory Image Restore.............................................................................................................................................45
System Restore................................................................................................................................................................. 46
Windows 10................................................................................................................................................................... 46
Windows 8.1.................................................................................................................................................................. 47
Windows 7..................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Operating System disc..................................................................................................................................................... 47
System reinstall media................................................................................................................................................48
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting......................................................................................................... 49
Basic troubleshooting steps............................................................................................................................................49
Diagnostics..........................................................................................................................................................................49
Pre-Boot System Assessment..................................................................................................................................49
Enhanced PSA..............................................................................................................................................................50
LCD BIST....................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Beep codes.................................................................................................................................................................... 51
Chapter 8: BIOS.......................................................................................................................... 52
Changing BIOS settings...................................................................................................................................................52
Entering BIOS setup program........................................................................................................................................ 52
Resetting BIOS password............................................................................................................................................... 52
Boot Sequence...................................................................................................................................................................53
Chapter 9: Getting help and contacting Dell................................................................................ 54
Chapter 10: References............................................................................................................... 55
Computer maintenance................................................................................................................................................... 55
Power management..........................................................................................................................................................55
Configuring power settings.......................................................................................................................................55
Configuring the power button behavior................................................................................................................ 56
Dell Power Manager................................................................................................................................................... 56
Improving battery life....................................................................................................................................................... 56
Contents 5

Migration tips..................................................................................................................................................................... 57
Ergonomic instructions.................................................................................................................................................... 58
Dell and the environment................................................................................................................................................ 59
Regulatory compliance policy......................................................................................................................................... 60
6 Contents

Setting up your computer
The setup procedure varies according to your computer. For setup instructions specific to your computer or tablet, see the
Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Connecting to the internet
You can connect your computer to the internet using cable, DSL, dial‑up, or a WWAN connection. You may also install a wired
or wireless router to share your cable or DSL internet connection with multiple devices. Some cable and DSL modems also have
built-in wireless routers.
NOTE: Before connecting your computer to the internet using a cable or DSL modem, ensure your broadband modem and
router are configured. For information on setting up your modem and router, contact your internet service provider.
Connecting to the internet using LAN
1. Connect the Ethernet cable to the modem or router and to your computer.
2. Check for activity lights on the modem or router, and your computer.
NOTE: Some computers may not have activity lights.
3. Open your web browser to verify internet connection.
Connecting to the internet using WLAN
NOTE: Ensure WiFi is enabled on your computer. For more information on enabling wireless on your computer, see the
Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Windows 10
1. Click or tap the wireless icon in the notification menu.
2. Click or tap the network you want to connect to.
3. Click or tap Connect.
NOTE: Enter the network password, if prompted. You may have configured the network password while setting up the
router or the router may have a default network password. For details, contact the router manufacturer.
4. Turn on or off file sharing (optional).
Windows 8.1
1. Click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar.
2. Click or tap the wireless icon.
3. Click or tap the network you want to connect to.
4. Click or tap Connect.
NOTE: Enter the network password, if prompted. You may have configured the network key while setting up the router
or the router may have a default network key. For details, contact the router manufacturer.
5. Turn on or off file sharing (optional).
1
Setting up your computer 7
Windows 7
1. Click or tap the wireless icon in the notification menu.
2. Click the network you want to connect to.
3. Click Connect.
NOTE: Enter the network password, if prompted. You may have configured the network key while setting up the router
or the router may have a default network key. For details, contact the router manufacturer.
4. Turn on or off file sharing (optional).
Connecting to the internet using WWAN
WWAN connection does not require a modem or a router to allow your laptop or tablet to connect to the internet. The WWAN
card on your computer connects directly to the service provider’s network, like your mobile phone.
If you purchased a tablet with a network service contract, the internet may already be activated.
NOTE: Ensure Wi-Fi is enabled on your computer. For more information on enabling wireless on your computer, see the
Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Windows 10
1. Click or tap the wireless icon in the notification menu.
2. Click or tap the name of your mobile broadband network.
3. Click or tap Connect.
4. If prompted, type the access point name (APN) or PIN, the user name, and the password.
Windows 8.1
1. Click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar.
2. Click or tap the wireless icon in the notification menu.
3. Click or tap the network you want to connect to.
4. Click or tap Connect.
5. If prompted, type the access point name (APN) or PIN, the user name, and the password.
Windows 7
1. Click the Start icon, type Mobile Broadband Utility in the search box and press Enter.
2. In the Mobile Broadband Utility window, click Connect.
3. If prompted, type the access point name (APN) or PIN, the user name, and the password.
Setting up audio
Dell computers and tablets have built-in speakers that support 2‑channel audio. To use the built-in speakers, play the media and
set the volume to your desired level.
Dell computers and tablets also support a 3.5 mm audio port allowing you to connect external speakers. If you are setting up
2‑channel audio, connect the speakers to the 3.5 mm headphone port or the audio port.
Dell desktops may support 5.1 or 7.1 audio. If you are setting up 5.1 or 7.1 audio, you must connect the speakers to the
appropriate ports for best audio output.
NOTE: For more information on the ports available on your computer or tablet, see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your
computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
NOTE: For best results, place the speakers as specified in the documents shipped with your speakers.
8 Setting up your computer

NOTE: On computers with a discrete sound card, connect the speakers to the connectors on the card.
Configuring 5.1 and 7.1 audio
Configure your computer to provide multi-channel audio output.
Windows 10 and 8.1
1. Type Audio in the search box.
NOTE: In Windows 10, click or tap the search icon to access the search box. In Windows 8.1, access the search charm
to access the search box.
2. Click or tap Manage audio devices.
3. Under the Playback tab, click or tap Speakers or Headphones.
4. Click or tap Configure and click or tap Test.
You should hear a tone from each speaker.
5. Click or tap Next, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Windows 7
1. Click the Start icon, type Sound in the search box and press Enter.
In the results list, click Sound. Or, click Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Sound.
2. Select Speakers, and click Configure.
The Speaker Setup window appears.
3. Under the Playback tab, click or tap Speakers or Headphones.
4. Select a speaker configuration under Audio channels: and click Test.
You should hear a tone from each speaker.
5. Click Next, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Setting up your computer 9
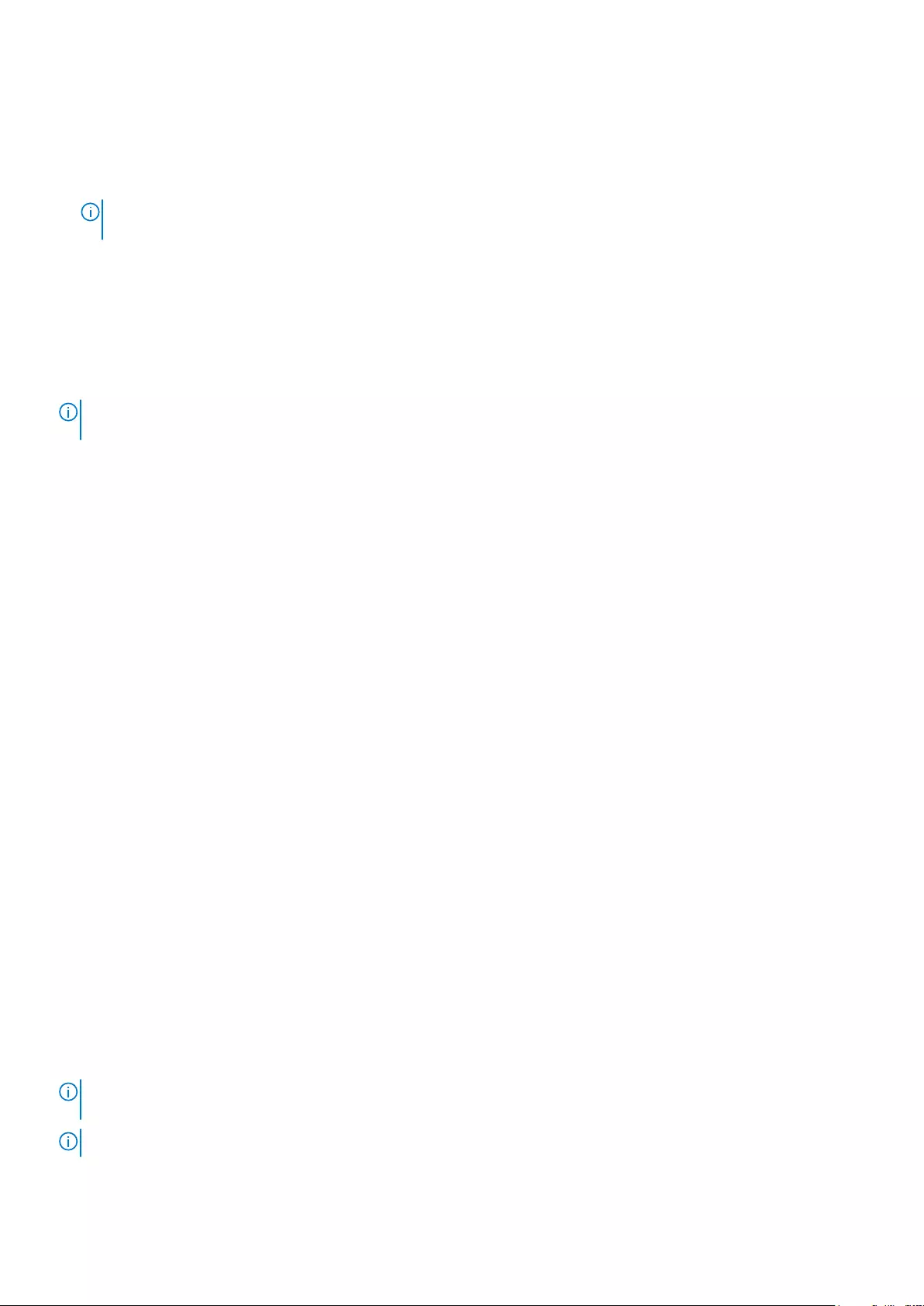
Connecting 5.1 speakers
Figure 1. Connecting 5.1 speakers
1. Rear audio connector on the computer 2. Center/LFE surround out on the computer
3. Front audio connector on the computer 4. 5.1 channel audio cable
5. Center/LFE surround out on the speaker 6. Front audio connector on the speaker
7. Rear audio connector on the speaker
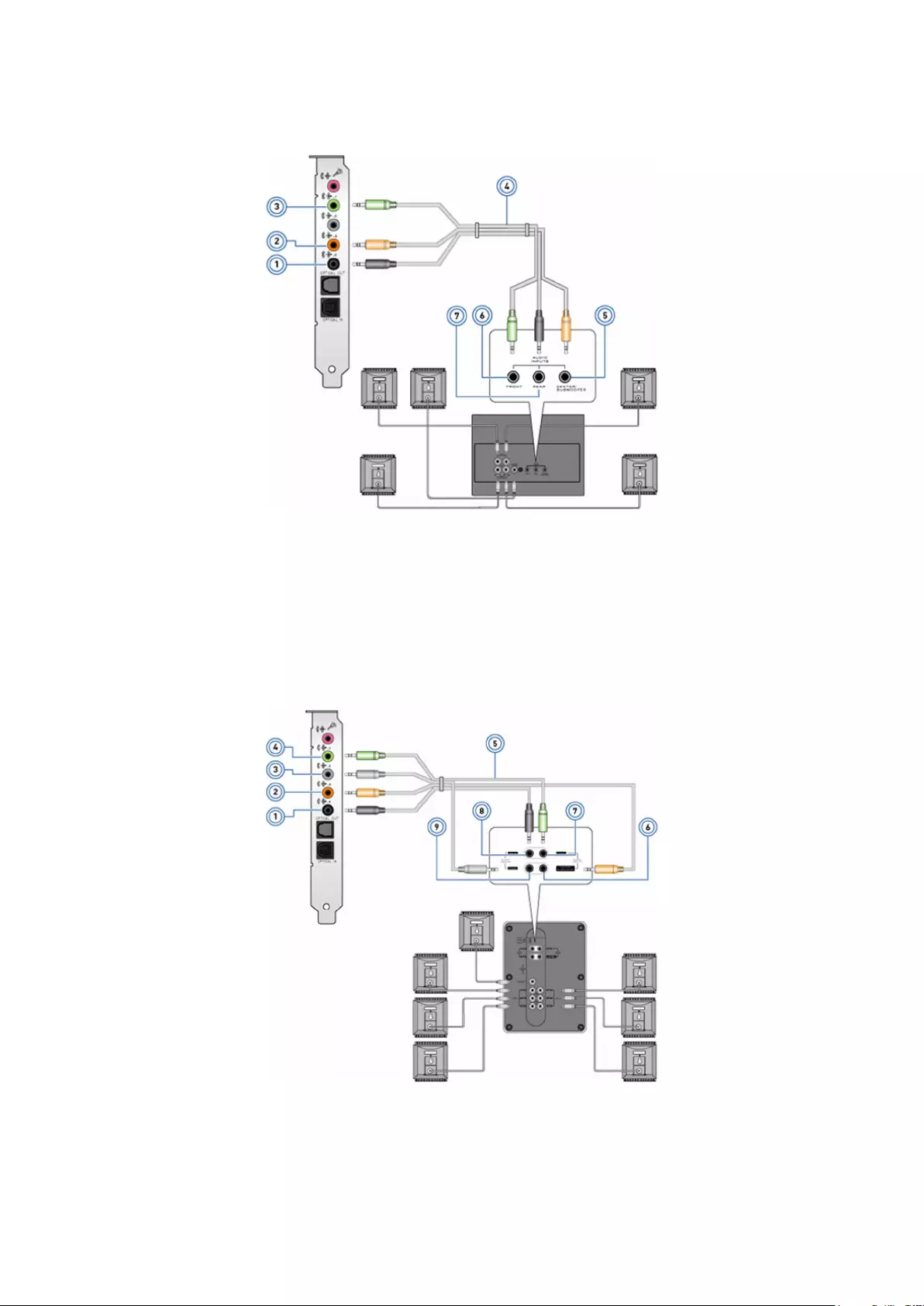
Connecting 7.1 speakers
Figure 2. Connecting 7.1 speakers
1. Rear audio connector on the computer 2. Center/LFE surround out on the computer
3. Side audio connector on the computer 4. Front audio connector on the computer
5. 7.1 channel audio cable 6. Center/LFE surround out on the speaker
10 Setting up your computer

7. Front audio connector on the speaker 8. Rear audio connector on the speaker
9. Side audio connector on the speaker
Setting up your printer
You can connect a printer to the USB port on your computer. Some printers may also support Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connections.
NOTE: The features of the printer and the steps to install may vary depending on the printer model. For more information
on setting up the printer, see the documentation shipped with your printer.
●If you are installing a wired printer, connect the printer to your computer using the USB cable before performing these
steps.
●If you are installing a wireless printer, follow the instructions in the documentation of your printer.
Windows 10 and 8.1
1. Type Devices in the search box.
NOTE: In Windows 10, click or tap the search icon to access the search box. In Windows 8.1, access the search charm
to access the search box.
2. Click or tap Devices and Printers.
3. Click or tap Add a printer.
The Add a device window appears.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions.
NOTE: If your printer is installed, it should appear in the list on the right side. If your printer is not in this list, click or tap
Add a device at the top of the device list. Select your printer from this list to install it. For more information on setting
up the printer, see the documentation shipped with your printer.
Windows 7
1. Click Start > Devices and Printers.
2. Click Add a Printer.
The Add Printer window appears.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions.
NOTE: You may be prompted to install the printer driver while adding your printer. Use the printer-driver media, or
download the drivers from the printer manufacturer’s website. For more information on setting up the printer, see the
documentation shipped with your printer.
Setting up your webcam
Integrated webcam
The integrated webcam is present on the laptop display or external display. If you order the webcam along with your computer,
the drivers and software are installed when you receive your computer. Use the media shipped with the computer only to
reinstall them. For more information, see Using the webcam.
External webcam
Use the media that is shipped with your webcam to install the drivers and other required software to use all the features of your
webcam. For more information, see the documentation shipped with your webcam.
Setting up your computer 11

Setting up Bluetooth
You can enable Bluetooth on your computer by turning on the wireless. Most computers and tablets are shipped with a built-in
Bluetooth card. For more information about pairing your device with your computer, see Using Bluetooth.
NOTE: To find out if your computer or tablet has an internal Bluetooth card, see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your
computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Connecting multiple monitors
Most desktop PC graphics or video cards can support two or more monitors, depending on the graphics card and PC
specifications. Typically, laptop PCs can support up to two monitors depending on the PC specifications. Identify the type
of video connectors available on your computer or laptop. The number of video connectors depends on the type of graphics
card that is installed in the computer or laptop.
1. Connect the power cord to the monitor and the wall outlet.
2. Connect a video cable from the monitor to the video connector on your computer or laptop.
3. Turn on the power on the monitor and your computer or your laptop.
Windows 10
Once the cables are connected securely, your computer should automatically detect and display the desktop screen on the
connected monitors. You can now select the display style that best suits your needs.
Microsoft Windows provides multiple display style options on how the desktop screen is displayed across multiple monitors that
are connected to your PC.
●PC Screen only—Use only display 1 and show nothing on display 2. The second monitor is ignored and only the primary
monitor is used.
●Duplicate (also called Clone mode)—Show the entire desktop on both displays. The second or other monitors mirror the
primary monitor.
●Extend—Stretch the desktop across the two displays. The desktop screen of your PC is extended across all the detected
monitors and enables you to have a desktop screen that spans across all monitors.
●Second Screen only—Use only display 2 and show nothing on display 1. The primary monitor will be disabled and only the
second monitor will be used.
Windows 8
Windows mode
1. Invoke Windows Charms by swiping in from the right or moving the mouse cursor to one of the right-hand side corners.
2. Choose Devices.
3. Select Second Screen.
4. Select any of the following options:
●PC Screen only—Use only display 1 and show nothing on display 2. The second monitor is ignored and only the primary
monitor is used.
●Duplicate (also called Clone mode)—Show the entire desktop on both displays. The second or other monitors mirror the
primary monitor.
●Extend—Stretch the desktop across the two displays. The desktop screen of your PC is extended across all the
detected monitors and enables you to have a desktop screen that spans across all monitors.
●Second Screen only—Use only display 2 and show nothing on display 1. The primary monitor will be disabled and only
the second monitor will be used.
Traditional desktop mode
1. Go to the Control Panel and choose Display.
12 Setting up your computer

2. Choose Change Display Settings on the left.
3. In the Change Display Settings window, click and drag the virtual monitors to mimic your physical setup.
4. Click OK to finish.
Windows 7
1. Close all open programs.
2. Hold down the Windows logo key and press the P key on your keyboard.
3. Select one of the following options:
●Computer only—Show the screen image only on your laptop monitor.
●Duplicate—Duplicate your laptop screen image on both monitors based on the monitor with the lower resolution.
●Extend—Move a window from one monitor to the other by clicking the Title Bar of the window and dragging the window
to a new location.
●Projector only—Typically chosen when your laptop is used as a desktop computer, so you can enjoy the higher
resolution of a large external monitor.
Setting up your computer 13

About your computer
This section provides more information on the components which can be found in your computer.
Power adapter
Power adapters are used to supply power to portable computers, tablets, and certain desktop computers. The Dell power-
adapter kit consists of the power adapter and the power cable. The power‑adapter rating (90 W, 65 W, and so on) depends on
the device it is designed for, and the power cable varies based on the country where the power adapter is shipped.
CAUTION: To avoid damaging your computer, it is recommended to use only the power adapter shipped with
your device or a Dell‑approved replacement power adapter.
Battery
Batteries are classified by their power ratings, such as 45 WHr, 65 WHr, and so on. The battery allows you to use your device
when it is not connected to a power outlet. The life cycle of the battery is the number of times it can be discharged and
recharged without affecting the operating time significantly. After the battery life-cycle reaches its end of life, you must replace
the battery. Depending on the computer model, the battery on your computer may be user-replaceable or may require a Dell
service technician to replace.
NOTE: High-capacity batteries generally have a longer life-cycle, since you need to charge high-capacity batteries less
often compared to low capacity batteries.
NOTE: For tips on improving the battery life, see Improving battery life.
NOTE: Dell Power Manager feature is not supported in Alienware systems.
2
14 About your computer

Coin-cell battery
Coin-cell battery provides power to the Complementary Metal‑Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) chip while the computer is turned
off. The CMOS chip contains the time, date, and other configuration information about your computer. Under normal usage
conditions, the coin-cell battery can last for several years. Factors affecting the coin‑cell battery life are the type of system
board, temperature, the time for which the computer is powered off, and so on.
Touchpad
A touchpad is available on most laptops and provides the functionality of a mouse. It has a touch-sensitive surface that senses
the motion and position of your fingers. You can use the touchpad to move the cursor, drag or move selected items, and click
by tapping the surface. Gesture‑enabled touchpads support gestures such as zoom, pinch, rotate, scroll, and so on. You can also
purchase external touchpads. A precision touchpad is a new class of input device that provides high precision pointer input and
gesture functionality. Precision touchpads interact with the operating system directly without the need for a driver.
NOTE: For more information, see Using your touchpad.
Display
Displays are classified according to their screen size, resolution, color gamut, and so on. Generally, a screen with higher
resolution and better color support provides better image quality. Some external displays also have USB ports, media-card
readers, and so on. Displays may also support features such as, touch screen, 3D, and wireless connection.
Touch screen
Touch screen is a display device that lets you interact with the objects on the screen by touching the display instead of using
a mouse, touch pad, or a keyboard. You can operate a touch screen with a finger, or another passive object, such as a stylus.
Touch screens are commonly used in phones, tablets, computers, and so on. Commonly used touch screen technologies are
capacitive touch and resistive touch.
NOTE: Touch screen may not be supported on all computers.
NOTE: For more information, see Using your touch screen.
3D
3D-capable displays can display 3D images and videos. 3D works by presenting separate 2D images to the left and right eye.
These images are combined and interpreted by the brain as one image with depth.
NOTE: You may need specially designed 3D glasses to view 3D images.
About your computer 15

Wireless display
The wireless display feature enables you to share your computer display with a compatible TV without the use of cables. To
check if your TV supports this feature, see the documentation of the TV.
NOTE: Wireless display may not be supported on all computers. For more information, see www.intel.com.
Camera
Webcam
The webcam enables you to video chat, capture photos, and record videos.
3D camera
You can use a 3D camera to capture and stream 3-dimensional images, making it possible to perceive distance, size, dimensions
of objects through the built-in sensors. This feature enables enhanced interactivity during video conferencing, online gaming,
and so on.
Intel RealSense 3D camera
RealSense cameras feature three lenses, a standard 2D camera for regular photo and video, along with an infrared camera and
an infrared laser projector. The infrared parts allow RealSense to see the distance between objects, separating objects from the
background layers behind them and allowing for much better object, facial, and gesture recognition than a traditional camera.
The devices are available in three options: front-facing, rear‑facing, and snapshot.
Wireless display
The wireless display feature enables you to share your computer display with a compatible TV without the use of cables. To
check if your TV supports this feature, see the documentation of the TV.
NOTE: Wireless display may not be supported on all computers. For more information, see www.intel.com.
Keyboard
Keyboards allow you to type characters and perform special functions using shortcut keys. The number of keys and the
characters available may differ based on the country where the keyboard is shipped. Laptops have built-in keyboards. Tablets
generally have on-screen keyboards and some tablets also support external keyboards. Dell desktops have an external keyboard
connected using USB or wireless signals.
The common keys available on the keyboard are:
●Alphanumeric keys for typing letters, numbers, punctuation, and symbols
●Multimedia and application shortcut keys
●Control keys such as Ctrl, Alt, Esc, and the Windows key
●Shortcut keys to perform specific tasks or to launch specific features
●Function keys, F1 through F1
●Navigation keys for moving the cursor around in documents or windows
Physical keyboard
Physical keyboards are used with laptop and desktop computers. Laptops generally have a built-in keyboard. External keyboards
are generally used with desktop computers. Some keyboards may have features such as keys for volume adjustment, application
shortcuts, built-in touch pad, programmable shortcut keys, back-light, and so on.
16 About your computer

Keyboard backlight
The backlight present on some physical keyboards illuminate the symbols on the keys for using the keyboard in dark
environments. You can turn on the backlight manually or configure the backlight to turn on automatically when your computer is
placed in a dark environment.
The backlit keyboards on Dell laptops have different lighting states. Press the Fn and the right-arrow key to switch between the
various lighting states. RGB backlit keyboards are lighted by RGB light per key on the keyboard. You can configure the settings
of the backlight to suit your in-game actions.
NOTE: Backlit keyboard may not be available on all computers. To check if backlit keyboard is available on your computer,
see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
On-screen keyboard
On-screen keyboards are available on almost all computers and tablets. However, they are used in touch screen devices such as
tablets and all-in-one computers. You can select the keys using a mouse or by touching the keys on a touch screen.
About your computer 17

Keyboard connection types
Keyboards can be connected to your computer with a cable (wired) or using wireless signals (wireless).
Wired
Wired keyboards are connected to the computer using a cable (generally USB) and do not require additional power source, such
as batteries.
Wireless
Wireless keyboards use Radio Frequency (RF) or Bluetooth (BT) to connect to your computer. Cable clutter is reduced and
gives you the flexibility to use the keyboard from a more comfortable position within a few meters from the computer. Such
keyboards require batteries to operate.
A keyboard that uses RF technology usually ships with a receiver that you must connect to your computer. Bluetooth keyboards
can pair with your computer’s built-in Bluetooth card or an external Bluetooth adapter.
Service Tag and Express Service code
You can find the Service Tag and the Express Service Code of your computer using one of the following:
●Label on the computer or tablet
●SupportAssist tile on your computer. For more information, see Dell SupportAssist.
●Dell support website at www.dell.com/support.
●BIOS setup program
Locating the label on your computer
Laptops—Bottom of the laptop under system badge, or in battery bay
Desktops—Back or top of the computer chassis
Tablets—Back or bottom of the tablet
NOTE: For the specific location of the label on your device, see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see
the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Dell support website
1. Go to www.dell.com/support.
2. Click or tap Detect Product, and follow the on-screen instructions.
BIOS setup program
1. Turn on or restart your computer.
2. When the DELL logo is displayed, watch for the F2 prompt to appear and then press F2 immediately to enter BIOS setup
program.
NOTE: The F2 prompt stays active only for a short time. If you miss the prompt, wait for your computer to boot up to
the desktop, then turn off your computer and try again.
3. Navigate to the Main tab and look for Service Tag. For more information about BIOS setup program, see the Service
Manual of your computer at www.dell.com/support.
18 About your computer

Storage device
Storage devices allow you to store data for later use. Storage devices can be internal or external. Most storage devices store
data until you manually delete the data. Examples of storage devices are hard‑disk drives (HDD), solid‑state drives (SSD),
optical-disc drives, flash drives, and so on.
Internal storage devices
Internal storage devices are installed on your computer and generally cannot be removed while the computer is turned on.
The most common internal storage devices are hard-disk drives—HDDs and solid-state drives—SSDs. HDDs and SSDs use
SATA interface to transfer information. SSDs are also physically similar to HDDs, which makes them compatible with existing
computers. HDDs contain disk platters. SSDs use flash memory which makes SSDs faster, quieter, energy-efficient, and shock
resistant.
Removable storage devices
Storage devices that can be removed from your computer without turning off your computer are called removable storage
devices. Commonly used removable storage devices include:
●Optical discs
●Memory cards
●Flash drives
●External hard drives
Optical drives and discs
Your computer may support a DVD RW or a DVD RW and Blu-ray combo drive. Optical discs can be read-only, write-once, or
re-writeable. Some of the common types of drives are:
●Blu-ray writer—Reads and writes to Blu-ray Discs, DVDs, and CDs.
●Blu-ray reader + DVD RW combo—Reads Blu-ray Discs. Reads and writes to DVDs and CDs.
●DVD RW—Reads and writes to DVDs and CDs.
Memory cards
Memory cards, also referred to as media or flash cards, use flash memory to store data. They are re-writable, fast, and retain
data even when power supply is cut off. They are commonly used in devices such as digital cameras, mobile phones, media
players, gaming consoles, and so on. Your computer may have a media-card reader to read and write to these cards.
Some common types of memory cards are:
Table 1. Examples of common types of memory cards
Secure Digital (SD)/Secure Digital High Capacity (SDHC)
About your computer 19

Table 1. Examples of common types of memory cards (continued)
Secure Digital Extended Capacity (SDXC) [card with Ultra
High Speed (UHS)]
Secure Digital miniSD
Multimedia Card (MMC)
MultiMedia Card plus (MMC+)
MultiMedia Card (MMC) Mobile
RS MMC
Extreme Digital (xD)
Memory Stick XC (MSXC)
Compact Flash I, II/Compact Flash MD
20 About your computer

Table 1. Examples of common types of memory cards (continued)
Memory Stick Duo
Memory Stick Pro Duo
Memory Stick Pro-HG Duo
Memory Stick (MS)/Memory Stick Pro (MS Pro)
Smart Media/Smart Media XD
Memory module
A memory module stores temporary data that your computer needs to perform tasks. Any file or application loads in the memory
modules before you can open or use them. Memory modules are categorized based on their capacity (in GB) and speed (in
MHz). Faster and higher amount of memory generally provides better performance. Common memory‑module types are:
●Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM)—Used in desktop computers.
●Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module (SODIMM)—Smaller in size than DIMMs. Generally used in laptop
computers. However SODIMM may also be used in some compact desktops and all-in-one computers.
System board
A system board forms the central part of computers. All other devices connect to the system board to be able to interact
with each other. The system board holds various controllers and connectors that help in exchange of data among various
components of the computer. A system board may also have integrated graphics, sound, and network capabilities. Some
important components of a system board are:
●Processor socket
●Memory-module connectors
●Expansion‑card slots
●CMOS to store the BIOS
About your computer 21

Chipset
The chipset controls the components on the system board and enables communication between various components. Generally,
the chipset is part of the system board. However, with some new generation processors, the chipset may be integrated in the
processor.
Processor
Processors receive data and instructions from applications and process the data as requested by the software. Processors are
designed specifically for desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and so on. Generally, the processor designed for one type of device
cannot be used on another type of device. Processors designed for laptops and mobile devices consume less power compared
to the processors designed for desktops or servers.
Processors are mainly classified based on:
●Number of processing cores
●Speed or frequency measured in GigaHertz (GHz) or MegaHertz (MHz)
●On-board memory, also referred to as cache
These aspects also determine the performance of the processor. Higher values generally mean better performance. Some
processors may be integrated on the system board. Some of the processor manufacturers are Intel, AMD, Qualcomm, and so on.
Computer fan
A computer fan cools the internal components of a computer by expelling hot air from the computer. Computer fans are
commonly used to cool components that have high power consumption and thus generate a high amount of heat. Keeping the
components cool helps in protecting them from overheating, malfunctioning, and damage.
Heat sink
Heat sinks are used to dissipate heat generated by the processor, some high-end graphics cards, and on-board chipsets. Heat
sinks generally have a fan mounted above or beside them to increase airflow. A heat sink is made up of fins or blades instead of
a single block of metal. This helps increase the surface area for increased heat dissipation. A layer of thermal grease is applied
between the processor or graphics card and the heat sink for easy exchange of heat.
22 About your computer

Thermal grease
Thermal grease, also called thermal gel or thermal compound, is used to create a heat-inductive layer between a processor and
heat sink. Applying thermal grease between the processor and heat sink increases the heat transfer from the processor to the
heat sink, as the thermal grease has better conductivity than air.
Video card
Video cards process graphics data and send video output to a display device such as a monitor or projector. Video cards can be
of two types:
●Integrated–Often referred to as on-board video card, it is integrated on the system board. In some computers, the video
card is integrated on the processor. Integrated video cards generally share the system memory (RAM) and the may also
utilize the processor to perform video processing.
An Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) is integrated on the same die as the processor and provides higher data transfer rates
while reducing the power consumption.
●Discrete– Discrete video cards are installed separately on the systemboard. Discrete video cards have dedicated memory
on the cardsand generally provide higher performance than integrated videocards. These cards are best suited for graphic
intensive applications,high‑definition video games, and so on.
NOTE: When a discrete video card is installed on a computer that also has an integrated video card, the integrated
video card is disabled by default. Use the BIOS setup program to select which card to use.
Switchable graphics allow computers equipped with both a low‑power integrated graphics chip, and a high‑power discrete
graphics card to switch between either cards, depending on the load and requirements.
TV tuners
You can use TV tuners to watch television on your computer. TV tuners are available for desktop and laptop computers as
internal or external devices.
NOTE: TV tuners are not supported in all computers.
Internal
●PCI-E
●PCI
External
●USB
●PC Card
●ExpressCard
About your computer 23

TV tuners are mostly standalone, however some video cards also have built-in TV tuners. For more information on using TV
tuners, see the documentation for the TV tuner.
Speakers
Laptops and tablets have built-in speakers for audio output. Desktops also have a built-in speaker. However, they are used only
to produce beeps to indicate errors or failures.
You can also connect external speakers to your computer or tablet. Speakers may support 3.5 mm audio connector, USB, or
wireless connection to your computer.
Speakers are generally categorized by the number of audio channels they support such as; 2, 2.1, 5.1, 7.1, and so on. The digit
before the decimal point indicates the number of channels and the digit after the decimal indicates the sub-woofer.
NOTE: Your sound card and speakers must support 5.1/7.1 channels for producing 5.1/7.1 channel audio.
2.1 Audio
2.1 refers to a system with two speakers (left and right channel) and one subwoofer.
5.1 Audio
5.1 refers to the number of audio channels in most surround-sound configurations. A 5.1 audio system uses five main audio
channels (front left, front right, center, left surround, and right surround) and one low-frequency audio channel.
24 About your computer

7.1 Audio
7.1 refers to the number of audio channels in high-end surround-sound configurations. A 7.1 audio system uses two additional
speakers (rear left and rear right) in combination with the 5.1 audio system. For more information on setting up audio, see
Setting up audio.
Webcam
A webcam enables you to capture videos and photos, and can also be used for video calls. Your display may have a built-in
webcam or you can connect external webcam to your computer. Camera quality is mainly defined by the number of pixels it can
capture.
To use the webcam, you must install webcam drivers and software. If you ordered the webcam along with your computer, the
drivers and software are generally installed when you receive your computer. For more information on setting up the webcam,
see Setting up your webcam.
Network
A network allows you to connect your devices with each other and to the internet. These devices include computers, tablets,
phones, printers, and other peripherals. You can set up your network using cables (LAN) or using wireless devices (WLAN).
Networks can be set up using Ethernet, Wi-Fi, WWAN, Bluetooth, and so on.
Local Area Network
Replace this text with your content. Devices are connected using Ethernet cables and cover a relatively small area, generally
within a house or a building.
Wireless Local Area Network
Devices are connected wirelessly and cover a relatively small area, generally within a house or a building. The wireless
connection used for setting up WLAN is generally Wi-Fi (802.11x where x refers to the different 802.11 protocols).
Wireless Wide Area Network
Also known as Mobile Broadband, this service is generally provided by the phone companies for use on mobile devices. A mobile
device or laptop must support WWAN technology to connect to this network.
Wireless Personal Area Network
Devices are generally connected wirelessly using Bluetooth, RF, Near-Field Communication (NFC), and so on. This type of
network generally operates within a few feet of the devices. To connect your computer or tablet to the internet, see Connecting
to the internet.
Modem
Modems allow you to connect your computer or router to the internet. Modems can be analog (dial-up) or digital (DSL or cable).
DSL or cable modems are generally provided by your internet service provider.
●Dial-up modem—Electronic devices that convert analog phone signals into digital signals that the computer can process
and digital computer signals into analog signals that can be transmitted over the telephone lines. Dial-up modems can be
internal or external.
●Digital modem—Used to send and receive data to and from a digital telephone line, like Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) or
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN).
About your computer 25

Router
A router is a device that forwards data between computer networks. The most familiar type of routers are home and small office
routers that allow you to share your internet connection between multiple devices at the same time.
Routers can be wired or wireless. A wired router allows you to connect your computer using a Ethernet (RJ45) cable. Most
wired home routers have four ports allowing you to connect up to four computers to the internet at the same time. A wireless
router uses Wi‑Fi technology allows you to wirelessly connect your phones, tablets, computers, and other devices to the
network.
Wireless routers can connect to several devices at the same time. For more information, see the documentation for your router.
Network‑Interface Controller
Network‑Interface Controllers (NIC), also referred to as network adapters or Local‑Area Network (LAN) adapters, connect to a
network using an Ethernet cable. NICs can be internal (integrated to the system board) or external (expansion cards). Most new
computers have integrated network adapters.
Wireless Local‑Area Network adapter
WLAN adapters use Wi‑Fi technology and allow your devices to connect to a wireless router. Your computer may have an
internal (expansion cards or integrated to the system board) or an external WLAN adapter.
Wireless Wide Area Network adapter
Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) controllers allow wireless connectivity through cellular tower technology. This technology
is mainly available on phones, tablets, and business-class laptops. A SIM card and a service contract may be required for WWAN
connectivity.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth allows you to connect other Bluetooth-enabled devices to your computer or tablet, over a short distance. Bluetooth
devices may include phones, headsets, keyboard, mice, printers, and so on. Bluetooth adapters can be internal (expansion cards
or integrated to the system board) or external.
More sophisticated routers, such as enterprise routers, connect large business or ISP networks up to the powerful core routers
that forward data at high speed along the optical fiber lines of the internet backbone.
Near-Field Communication
Near-Field Communication (NFC) allows you to exchange data between two devices by touching the devices with each other or
by bringing them to close proximity. You can use NFC-enabled devices to read NFC-tags, make payments, share files between
compatible devices, and so on.
On Dell laptops and tablets that support NFC, it is enabled by default when wireless in turned on.
NOTE: For connecting your NFC-enabled device to your computer or tablet, see the documentation for your device.
NOTE: File sharing works only between devices using Windows operating system.
26 About your computer

Using your computer
Charging the battery
Connect the power adapter to your computer or tablet to charge the battery.
The battery gets charged when the computer or tablet is in use or turned off. The internal circuitry of the battery prevents it
from overcharging.
NOTE: If the battery becomes too hot due to being in a hot environment, it may not charge when you connect the power
adapter.
Allow the battery to cool down for it to resume charging.
NOTE: For steps on improving the battery life of your computer, see Improving battery life.
Using your keyboard
Press the keys on your physical keyboard or tap the characters on the on‑screen keyboard to type text and to perform other
functions.
Keyboard shortcuts
Some keys on the laptop keyboard, and some external keyboards, may perform two or more functions when pressed along with
other special keys, such as Fn. Some computers allow you to select the default behavior of the key using BIOS setup program or
using keyboard shortcuts
Table 2. List of keyboard shortcuts
Ctrl, Shift and Esc Open the Task Manager window.
Fn and F8 Toggle between display devices — main display only,
duplicate, extend to both displays, and second display only.
Highlight the desired icon to switch the display to that option.
Fn and up-arrow key Increase brightness on an integrated display only (not on an
external display).
Fn and down-arrow key Decrease brightness on the integrated display only (not on an
external display).
Windows and L key Lock the system.
Fn and Esc Activate a power management mode. You can reprogram this
keyboard shortcut to activate a different power management
mode using the Advanced tab in the Power Options
Properties window.
F2 Rename the selected item.
F3 Search for a file or folder.
F4 Display the address bar drop-down in Windows Explorer.
F5 Refresh the active window.
F6 Cycle through screen elements in a window or on the desktop.
3
Using your computer 27
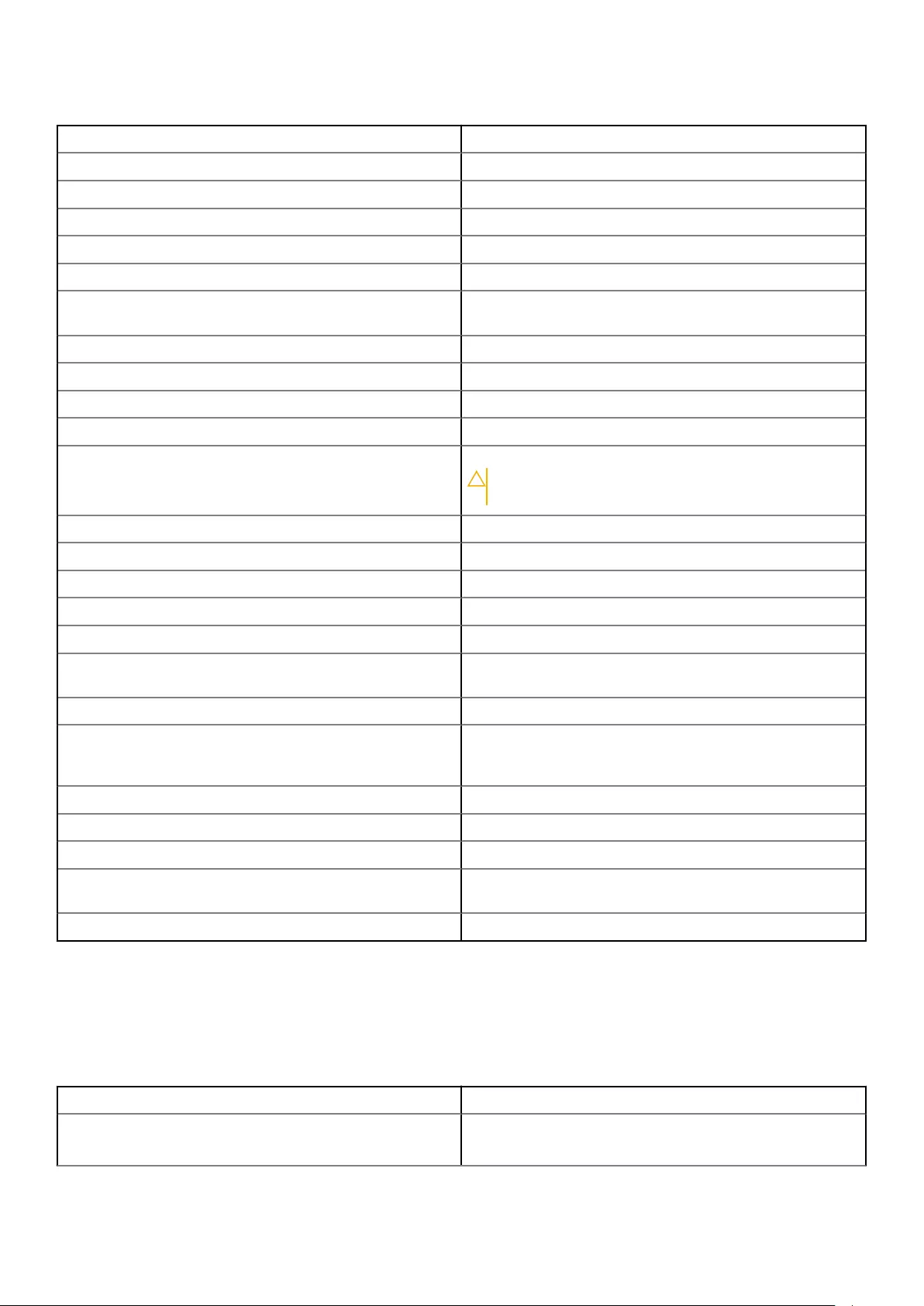
Table 2. List of keyboard shortcuts (continued)
F10 Activate the menu bar in the active program.
Ctrl and c Copy a selected item.
Ctrl and x Cut a selected item.
Ctrl and v Paste a selected item.
Ctrl and z Undo an action.
Ctrl and a Select all items in a document or window.
Ctrl and F4 Close the active window (in programs that allow you to have
multiple documents open simultaneously).
Ctrl, Alt and Tab Use the arrow keys to switch between open items.
Alt and Tab Switch between open applications.
Alt and Esc Cycle through items in the order in which they were opened.
Delete Delete a selected item and move it to the Recycle Bin.
Shift and Delete Delete the selected item without moving it to the Recycle Bin.
CAUTION: Files deleted using this method cannot be
recovered from the Recycle Bin.
Ctrl and right-arrow key Move the cursor to the beginning of the next word.
Ctrl and left-arrow key Move the cursor to the beginning of the previous word.
Ctrl and down-arrow key Move the cursor to the beginning of the next paragraph.
Ctrl and up-arrow key Move the cursor to the beginning of the previous paragraph.
Ctrl, Shift with an arrow key Select a block of text.
Shift with any arrow key Select more than one item in a window or on the desktop, or
select text within a document.
Windows key and m Minimize all open windows.
Windows key, Shift and m Restore all minimized windows. This key combination
functions as a toggle to restore minimized windows following
the use of the Windows key and m combination.
Windows key and e Start Windows Explorer.
Windows key and r Open the Run dialog box.
Windows key and f Open the Search Results dialog box
Windows key and Ctrl and f Open the Search Results-Computer dialog box (if the
computer is connected to a network).
Windows key and Pause Open the System Properties dialog box.
Keyboard shortcuts for Windows 8.1 and Windows RT
This table provides some keyboard shortcuts specific to Windows 8.1 and Windows RT. These keyboard shortcuts are in addition
to the keyboard shortcuts that are already available in earlier versions of the Windows.
Table 3. List of keyboard shortcuts
Windows key and start typing Search your computer.
Ctrl and + Zoom in to a large number of items on the screen such as
apps pinned on the Start screen.
28 Using your computer

Table 3. List of keyboard shortcuts (continued)
Ctrl and - Zoom out of a large number of items on the screen such as
apps pinned on the Start screen.
Windows key and c Open the charms sidebar.
Windows key and f Open the Search charm to search files on your computer.
Windows key and h Open the Search charm.
Windows key and i Open the Settings charm.
Windows key and j Switch between the main app and snapped app.
Windows key and k Open the Devices charm.
Windows key and o Lock the screen orientation (portrait or landscape).
Windows key and q Open the Search charm to search apps on your computer.
Windows key and w Open the Search charm to search computer settings controls
on your computer.
Windows key and z Displays the options available in the app.
Windows key and spectacular Switch input language and keyboard layout.
Windows key, Ctrl, and spacebar Switch to a previously selected input language and keyboard
layout.
Windows key and Tab Cycles through open apps while displaying them in a vertical
sidebar at the left side of the screen.
Windows key, Ctrl, and Tab Displays the sidebar of open apps and keeps the sidebar on
screen even after you release the keys. You can then navigate
through open apps using the up/down arrow keys.
Windows key, Shift, and . Snap an app to the left.
Windows key and . Cycle through open apps.
NOTE: For special shortcut keys available on your computer, see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see
the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/support.
Customizing your keyboard
You can customize your keyboard as follows:
●Change the time before keyboard characters repeat when you press and hold a key
●Change the speed at which keyboard characters repeat
●Change the cursor blink rate
●Customize key sequences for input languages
To customize your keyboard:
Windows 10 and 8.1
1. Type Control Panel in the search box.
NOTE: In Windows 10, click or tap the search icon to access the search box. In Windows 8.1, access the Search charm
to access the search box.
2. Click Control Panel.
Using your computer 29

3. If your Control Panel is displayed by Category, click or tap on the View by: drop-down menu and select Small icons or
Large icons.
4. Click or tap Keyboard.
5. Adjust the keyboard settings you want to change and click or tap OK to save the settings and close the window.
Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel.
2. If your Control Panel is displayed by Category, click the View by: drop-down menu and select Small icons or Large icons.
3. Click Keyboard.
4. Adjust the keyboard settings you want to change and click OK to save the settings and close the window.
Using numeric keypad on a laptop
1. Numeric keypad
Your laptop may have a numeric keypad integrated into the keyboard. The keypad corresponds to the keypad on an extended
keyboard.
●To type a number or symbol, press and hold Fn and press the desired key.
●To enable the numeric keypad, press Num Lock. The Num Lock light indicates that the keypad is active.
●To disable the numeric keypad, press Num Lock again.
NOTE: Some laptops may have a dedicated numeric keypad.
Using your touchpad
Use the touchpad to move the cursor or select objects on the screen.
●To move the cursor, gently slide your finger over the touchpad.
●To left-click or select an object, press the left touchpad button or tap the touchpad once.
●To right-click an object, tap the right touchpad button once.
●To double-click an object, press the left touchpad button twice or tap twice on the touchpad.
●To select and move (or drag) an object, position the cursor on the object and tap twice quickly on the touchpad without
removing your finger from the touchpad after the second tap, then move the selected object by sliding your finger over the
surface.
Touchpad gestures
NOTE: Some touchpad gestures may not be supported on your computer.
30 Using your computer
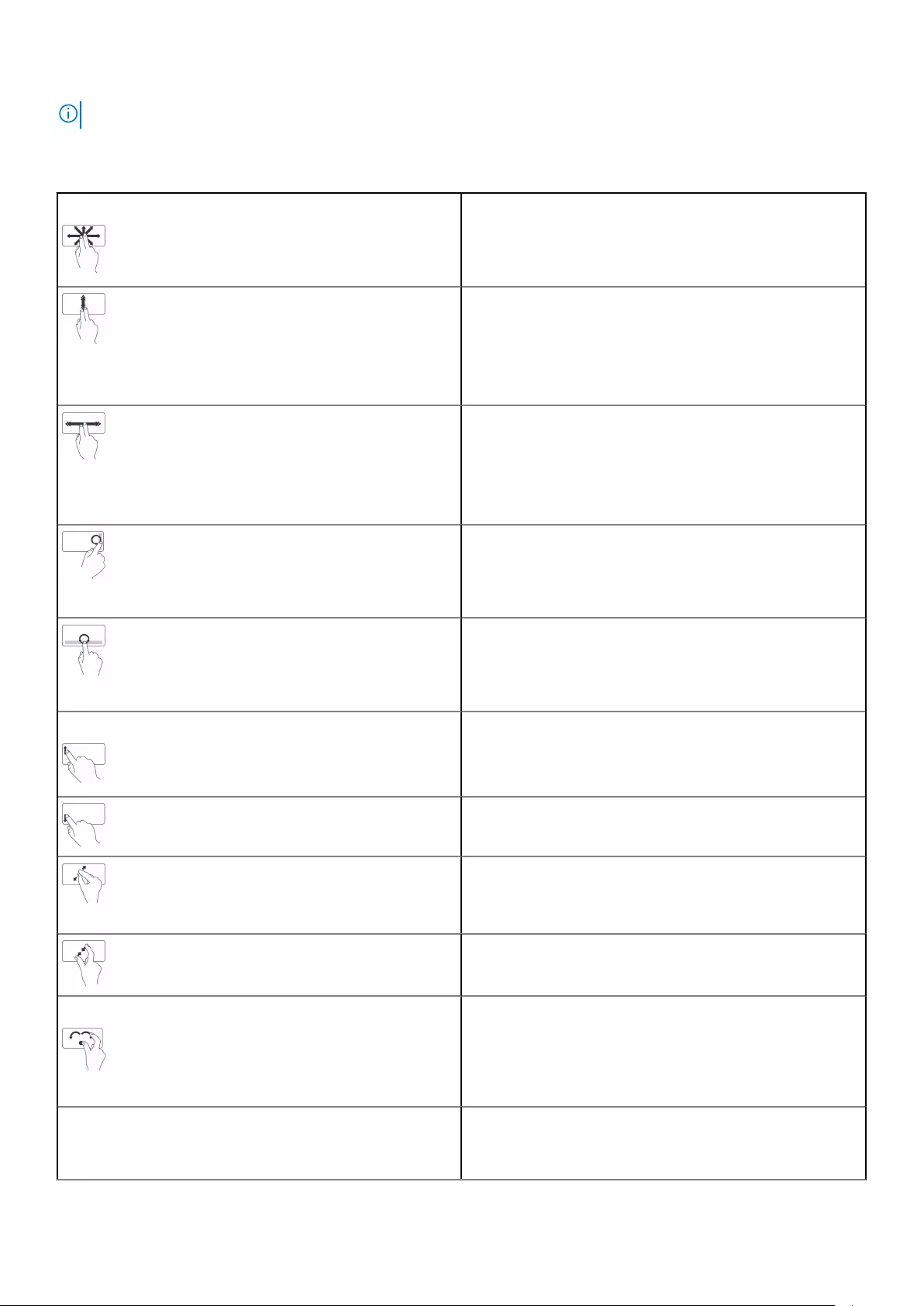
NOTE: You can change the touchpad gestures settings by double‑clicking the touchpad icon in the notification area.
Your computer may support Scroll, Zoom, Rotate, Flick, and Quick Launch gestures.
Table 4. List of touchpad gestures
Scroll Pan—Move the focus on the selected object when the entire
object is not visible. Move two fingers in the desired direction
to pan scroll the selected object.
Vertical Auto‑Scroll—Scroll up or down on the active
window.
Move two fingers up or down at a fast pace to start vertical
auto‑scroll.
Tap on the touchpad to stop auto‑scroll.
Horizontal Auto‑Scroll—Scroll left or right on the active
window.
Move two fingers left or right at a fast pace to start
horizontal auto‑scroll.
Tap on the touchpad to stop auto scrolling.
Circular Scroll Up/Down—Scroll up or down.
In the vertical‑scroll zone at the right edge of the touchpad,
move your finger clockwise to scroll up and counterclockwise
to scroll down.
Circular Scroll Left/Right—Scroll left or right.
In the horizontal‑scroll zone at the bottom edge of the
touchpad, move your finger clockwise to scroll right and
counterclockwise to scroll left.
Zoom One‑finger zoom—Zoom-in or zoom-out by moving one
finger in the zoom zone (at the left edge of the touchpad).
Move a finger up in the zoom zone to zoom‑in.
Move a finger down in the zoom zone to zoom‑out.
Two‑finger zoom—Zoom-in or zoom-out using two fingers.
Place two fingers on the touchpad and then move them apart
to zoom‑in.
Place two fingers on the touchpad and then bring them closer
to zoom‑out.
Rotate Twist—Rotate active content, in 90‑degree increments,
using two fingers.
Keeping the thumb in place, move the index finger in an
arched direction right or left to rotate the selected item
90‑degree clockwise or counterclockwise.
Flick Flip content forward or backward.
Move three fingers quickly to the left or right to flip content
backwards or forward.
Using your computer 31

Table 4. List of touchpad gestures (continued)
Quick Launch Open your favorite applications.
Tap three fingers on the touchpad to launch the pre-
configured application.
NOTE: Use the touchpad configuration tool to choose the
application to be launched.
Using your touch screen
NOTE: Avoid using the touch screen in dusty, hot, or humid environments.
NOTE: Sudden change in temperature may cause condensation on the inner surface of the screen. This does not affect
normal usage and disappears after the computer is kept on for at least 48 hours.
If your computer or tablet has a touch screen display, you can touch the screen to interact with the items instead of using
a mouse or a keyboard. Some of the basic tasks that you can perform using a touch screen are open files, folder, and apps,
zoom‑in, zoom‑out, scroll, rotate images, and so on.
You can perform the tasks that you would normally perform using a mouse, such as open files, folders, and applications, scroll
using the scroll bar, close and minimize windows using the buttons on the window, and so on.
You can also use the on‑screen keyboard using the touch screen.
Touch screen gestures
Touch screen gestures enhance the usability of a touch screen by allowing you to perform tasks like zoom, scroll, rotate, and so
on, by sliding or flicking your finger on the display.
NOTE: Some of these gestures are application-specific and may not work in all applications.
Table 5. List of touch screen gestures
Zoom Place two fingers on the touch screen and then move them
apart to zoom‑in.
Place two fingers on the touch screen and then bring them
closer to zoom‑out.
32 Using your computer

Table 5. List of touch screen gestures (continued)
Dwell Touch and hold the item on the screen to open the context
menu.
Flick Move a finger quickly in the desired direction to flip through
content in the active window like pages in a book.
Flick also works vertically when navigating content such as
images or songs in a playlist
Rotate Rotate clockwise—Keeping a finger or thumb in place, move
the other finger in an arched direction to the right.
Rotate counter-clockwise—Keeping a finger or thumb in
place, move the other finger in an arched direction to the left.
You can also rotate the active content by moving both the
fingers in a circular motion.
Scroll Pan–Move the focus on the selected object when the entire
object is not visible.
Move two fingers in the desired direction to pan the selected
object.
Using your computer 33

Table 5. List of touch screen gestures (continued)
Scroll Vertical–Scroll up or scroll down on the active
window.
Move a finger up or down to start vertical scrolling.
Scroll Horizontal–Scroll right or left on the active window.
Move a finger to the right or left to start horizontal scrolling.
Using Bluetooth
You can connect (pair) Bluetooth devices such as mice, keyboard, headsets, phones, TV, and so on. For details on pairing the
device with your computer, see the documentation of the device.
NOTE: Ensure that you have Bluetooth drivers installed on your computer.
Pairing a Bluetooth device with your computer or tablet
Windows 10
1. Enable Bluetooth on your computer or tablet and the device you are pairing. On a Dell laptop, turn on wireless to enable
Bluetooth.
NOTE: For information to turn on Bluetooth on your device, see the documentation shipped with your device.
2. Swipe in from the right edge of the display to open Action Center.
3. Press and hold Bluetooth and then tap Go to settings.
4. From the list of devices, tap the device you want to pair with and tap.
NOTE: If your device is not listed, ensure that your device is discoverable.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the pairing process.
NOTE: A passcode may be displayed on your computer or tablet and the device. A message confirming the pairing of
the device appears once the pairing is complete.
Windows 8.1
1. Enable Bluetooth on your computer or tablet and the device you are pairing.
On a Dell laptop, turn on wireless to enable Bluetooth.
NOTE: For information to turn on Bluetooth on your device, see the documentation shipped with your device.
2. Right-click the Bluetooth icon in the notification area of your taskbar and click or tap Add a Device.
NOTE: If you are unable to locate the Bluetooth icon, click or tap the arrow next to the notification area.
34 Using your computer

3. In the Add a device window, select the device and click or tap Next.
NOTE: If your device is not listed, ensure that your device is discoverable.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the pairing process.
NOTE: A passcode may be displayed on your computer or tablet and the device.
A message confirming the pairing of the device appears, indicating the pairing is complete.
Windows 7
1. Enable Bluetooth on your computer or tablet and the device you are pairing. On a Dell laptop, turn on wireless to enable
Bluetooth.
NOTE: For information to turn on Bluetooth on your device, see the documentation shipped with your device.
2. Click Start > Control Panel.
3. In the Control Panel search box, type Bluetooth, and then click Change Bluetooth settings.
4. To make your computer discoverable to Bluetooth enabled devices, select the check box for Allow Bluetooth devicesto
find this computer.
Using the webcam
If your computer or display has a built-in webcam, the drivers are installed and configured at the factory. The webcam gets
activated automatically when you start a video chat or video capture application.
You can also use Dell Webcam Central (Windows 7 only) to capture still images and videos using the webcam.
Capturing a still image
1. Open Dell Webcam Central.
2. Click or tap the Snap Photos tab.
3. Click or tap the camera icon to capture a still image.
NOTE: To configure options such as image size, self-timer, burst‑capture, image format, and so on, click or tap the
drop‑down arrow next to the camera icon.
Recording a video
1. Open Dell Webcam Central.
2. Click or tap the Record Videos tab.
3. Click or tap the recording icon to start recording a video.
4. Once you have completed recording the video, click or tap the recording icon again to stop recording.
NOTE: To configure options such as video size, self-timer, time‑lapse recording, video quality and so on, click or tap the
drop‑down arrow next to the recording icon.
Selecting the camera and microphone
If your computer has multiple webcams or microphones (integrated or external), you can select the webcam and microphone
you want to use with Dell Webcam Central.
1. Open Dell Webcam Central.
2. Click or tap the drop‑down arrow next to the camera icon at the bottom‑left corner of the window.
3. Click or tap the camera you want to use.
4. Click or tap the Record Videos tab.
5. Click or tap the drop‑down arrow next to the microphone icon below the preview area.
6. Click or tap the microphone you want to use.
Using your computer 35
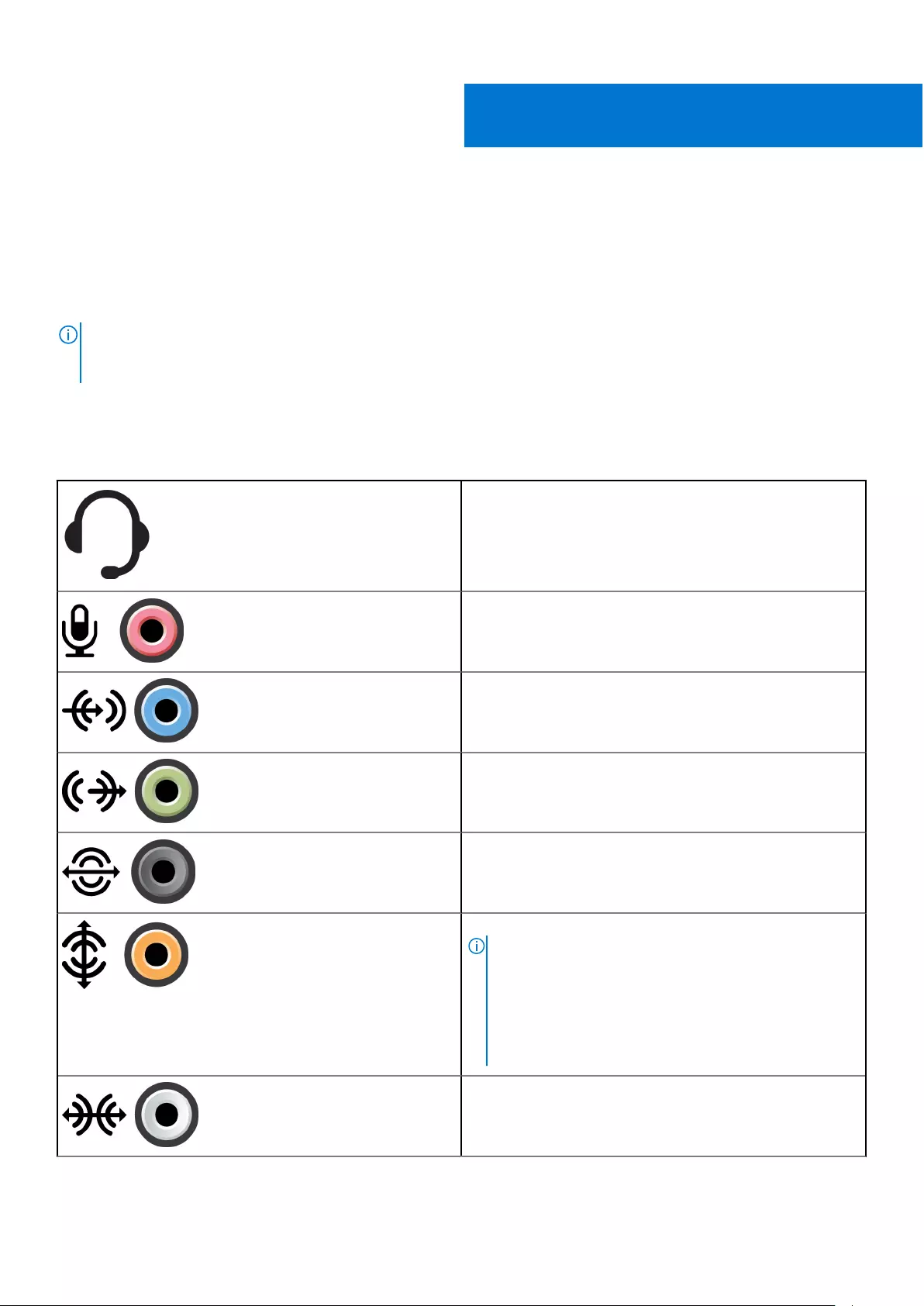
Ports and connectors
Audio
Audio connectors allow you to connect speakers, headphones, microphones, sound systems, amplifiers, or TVs audio output.
NOTE: Your computer may not support all the audio ports. For information on the ports available on your computer
or tablet, see the Quick Start Guide shipped with your computer or see the Setup and Specifications at www.dell.com/
support.
Types of audio ports
Table 6. Types of audio ports
Headphone port—Connect headphones, powered speaker,
or sound system.
Microphone port—Connect external microphone for voice or
sound input.
Line-in port—Connect a recording/playback device such as
a cassette player, CD player, or VCR.
Line-out port—Connect headphones or speakers that have
an integrated amplifier.
Rear‑surround out port—Connect multi‑channel capable
speakers.
Center/LFE surround out —Connect a single subwoofer.
NOTE: The Low Frequency Effects (LFE) audio channel,
found in digital surround sound audio schemes, carries
only frequency information (80 Hz and below). The LFE
channel drives a subwoofer to provide extremely low bass
extension. Systems not using subwoofers can shunt the
LFE information to the main speakers in the surround
sound setup.
Side-surround sound port—Connect left/right speakers.
4
36 Ports and connectors

Table 6. Types of audio ports (continued)
RCA S/PDIF port—Transmits digital audio without the need
of analog audio conversion.
Optical S/PDIF port—Transmits digital audio, using optical
signals, without the need of analog audio conversion.
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) enables you to connect peripherals to a computer or a tablet. These peripherals include the mouse,
keyboard, printer, external drives, cameras, phones, and so on.
USB port may be used to transfer data between your computer and the device and also to charge supported devices. For more
information, see the documentation for your device.
Some computers also have USB ports with integrated PowerShare feature that enables you to charge your USB devices even
when the computer in turned off.
USB also supports Plug-and-Play and hot swapping.
●Plug‑and‑Play—Enables your computer to recognize and configure a device automatically.
●Hot swapping—Enables you to remove and connect USB devices without restarting your computer.
USB ports
Table 7. Types of USB ports
Standard USB The standard USB port is present on most laptops and desktops. Most USB devices connect to
the computer using this port.
Mini‑USB A mini‑USB port is used in small electronic devices such as cameras, external storage drives,
tablets, and so on.
Micro‑USB A micro-USB port is smaller than mini-USB port and is used in phones, tablets, wireless
headphones, and other small electronic devices.
Powered USB A powered USB port uses a more complex connector than a standard USB. It essentially has two
connectors in a single cable, one for standard USB plug and the other for power, thus allowing
higher-power devices to be connected without the use of an independent power supply. It is used
in retail equipment such as barcode reader and receipt printers.
USB standards
Table 8. USB standards
USB 3.1 Gen 2 This is also referred to as SuperSpeed USB+. This port supports peripherals such as storage
devices, printers, and so on. Provides data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps. It can be found with
USB Type-C connections and has capabilities of Gen 1 in addition to DisplayPort over USB video
capability.
USB 3.1 Gen 1 This is also referred to as SuperSpeed USB. This port supports peripherals such as storage
devices, printers, and so on. Provides data transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps. Systems with Legacy
USB 3.0 ports are now USB 3.1 Gen 1.
USB 2.0 This is referred to as Hi-Speed USB. It provides additional bandwidth for multimedia and storage
applications. USB 2.0 supports data transmission speed up to 480 Mbps.
USB 1.x Legacy USB standard supporting data transfer speeds up to 11 Mbps.
Ports and connectors 37

Table 8. USB standards (continued)
USB PowerShare The USB PowerShare feature enables you to charge USB devices when the computer is powered
off or is in sleep state. The icon indicates that the USB port supports PowerShare
feature.
NOTE: Certain USB devices may not charge when the computer is powered off or in sleep
state. In such cases, turn on the computer to charge the device.
NOTE: If you turn off your computer while charging a USB device, the device may stop
charging. To continue charging, disconnect the device and connect it again.
NOTE: On laptops, PowerShare feature stops charging the device when the laptop battery
charge reaches 10%. You can configure this limit using BIOS setup program.
USB-C Depending on your device, this port may support USB 3.1, Display over USB-C, and Thunderbolt 3
devices. For more information, see the documentation that shipped with your device.
Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C)
port
You can connect USB 3.1 Gen 2, USB 3.1 Gen 1, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt devices to this port.
It enables you to connect to external display using dongles. Provides data transfer rates up to 40
Gbps.
Debug port The debug port enables a user to run the USB 3.0 ports in USB 2.0 mode temporarily for
troubleshooting purposes and also when operating system is reinstalled using a USB optical drive
or a flash drive.
eSATA
eSATA enables you to connect external storage devices, such as hard drives and optical drives, to your computer. It provides
the same bandwidth as internal SATA ports.
Your computer may have a standalone eSATA port or an eSATA/USB combo port.
Visual Graphics Array
Visual Graphics Array (VGA) enables you to connect to monitors, projectors, and so on.
You can connect to a HDMI or DVI port using the VGA to HDMI or VGA to DVI adapters respectively.
Digital Visual Interface
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) enables you to connect your computer to displays such as flat-panel monitors, projectors, and so
on.
There are three types of DVI connections:
●DVI-D (DVI-Digital)—DVI-D transmits digital video‑signals between the video card and the digital display. This provides
fast and high-quality video output.
●DVI-A (DVI-Analog)—DVI‑A transmits analog video‑signals to an analog display such as a CRT monitor or an analog LCD
monitor.
●DVI- I (DVI-Integrated)—DVI-I is an integrated connector that can transmit a digital or an analog signal. This port is more
versatile as it can be used in both digital and analog connections.
DisplayPort
DisplayPort provides digital connection between your computer and display devices such as monitors, projectors, and so on. It
supports both video and audio signals. DisplayPort was designed specifically to be used with computer displays.
38 Ports and connectors

Mini DisplayPort
Mini DisplayPort is a smaller version of the DisplayPort.
NOTE: DisplayPort and Mini DisplayPort are compatible with each other but the ports and connectors vary in size. If the
port sizes are different, use a converter.
Advantages of DisplayPort
●Supports high resolutions and high refresh‑rates
●Supports 3D transmission
●Supports multiple display‑devices simultaneously
●Supports High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP)
●Supports plug-and-play adapters that allow you to connect displays using older connection standards such as DVI, HDMI,
and VGA
●DisplayPort cables can extend up to 15 m (49.21 ft) without requiring signal boosters.
HDMI
High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) provides digital connection between your computer, display devices, and other
multi-media devices. It supports both video and audio signals.
HDMI ports are commonly available on computers, TVs, set-top boxes, DVD and Blu-ray players, gaming consoles, and so on.
Advantages of HDMI
●Supports high resolutions and high refresh‑rates
●Supports 3D transmission
●Supports HDCP
●Commonly available in most computers and consumer multi‑media devices
●Can be used to set up audio‑only, video‑only, or an audio and video connection
●Compatible with fixed-pixel displays such as LCDs, plasma displays, and projectors
Mini HDMI
Mini High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) provides digital connection between your computer and portable devices such
as smartphones, laptops, and so on.
Micro HDMI
Micro High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) provides digital connection between your computer and portable devices
such as smart phones, laptops, and so on. This connector resembles the micro-USB connector found on most smartphones.
SPDIF
S/PDIF is a standard for transferring audio in digital format. You can use S/PDIF to audio devices such as sound cards,
speakers, home theater systems, TVs, and so on. It provides 5.1 audio support.
There are two kinds of S/PDIF connections:
●Optical—Uses optical fiber with TOSLINK connectors
●Coaxial—Uses coaxial cable with RCA connector
Ports and connectors 39

Software and Applications
Absolute
Absolute provides persistent endpoint security and data risk management solutions for computers, tablets, and smartphones.
Persistence technology enables you to consistently assess risk, secure the lifecycle of each device, and preemptively respond to
security incidents.
NOTE: Persistence technology may not be supported on all computers.
Getting Help on Absolute
Dell provides help on persistence technology through Absolute Software. You can contact Absolute Software for help on
installation, configuration, usage, and troubleshooting.
To contact Absolute Software see the Absolute Software website at www.absolute.com or send an email to
techsupport@absolute.com.
Dell SupportAssist
SupportAssist provides information about the Product, Model, Risk Notification, Service Tag, Express Service Code and
Warranty details. Some features include:
●Notifications—provide messages about the overall health of the system and offers self-help options to resolve issues.
●Checkup status—provides diagnostics information, tools and utilities to detect and fix system issues.
●System Info—provides complete information about the system software and hardware configuration.
●Support—provides Product Support information's such as: contact options, manuals, forums and more. The following links
and Dell Resources are available in the Support section
Downloading Dell SupportAssist
SupportAssist is already installed on all new Dell computers and tablets. To reinstall SupportAssist, download the application and
run the installation program.
Accessing SupportAssist
●Windows 10—Click or tap the Dell Help & Support icon on the Start screen.
●Windows 8.1— Click or tap the My Dell icon on the Start screen.
●Windows 7—Click Start > All Programs > Dell > My Dell > My Dell.
PC Check
NOTE: PC checkup is available only on selected models.
Use PC Checkup to check your hard‑drive usage, run hardware diagnostics, and track the changes made to your computer.
●Drive Space Manager—Manage your hard drive using a visual representation of the space consumed by each type of file.
●Performance and Configuration History—Monitor system events and changes over time. This utility displays all hardware
scans, tests, system changes, critical events, and restoration points of the system.
○Detailed System Information—View detailed information about your hardware and operating system configurations;
access copies of your service contracts, warranty information, and warranty renewal options.
○Get Help—View Dell Technical Support options, Customer Support, Tours and Training, Online Tools, Service Manual,
Warranty Information, FAQs, and so on.
○Backup and Recovery—Access system recovery tools that allow you to:
5
40 Software and Applications

■Create a Dell Factory Image Restore file on your computer to restore your computer at a later point.
■Create a Backup and Recovery media.
○System Performance Improvement Offers—Acquire software and hardware solutions that help improve your system
performance.
Quickset
Quickset is a suite of software applications that provide enhanced functionality to your Dell computer. It provides easy access
to various functions that would normally require several steps. Some of the features that you can access using Dell Quickset
include:
●Configure a wireless shortcut key.
●Disable or enable battery charging.
●Change the Fn key behavior.
NOTE: Quickset may not be supported on all computers.
Installing Quickset
Quickset is preinstalled on a new Dell computer. If you need to reinstall Quickset, download it from the Dell support website at
www.dell.com/support .
NOTE: If you restore your computer using PC Restore or a similar application, Quickset is restored as well.
NVIDIA 3D Applications
The NVIDIA 3DTV Play application installed on your computer enables you to play 3D games, watch Blu-ray 3D videos, and
browse 3D photos. It supports the same games as NVIDIA 3D Vision. For a list of supported 3D games, see www.nvidia.com.
NOTE: Refer to NVIDIA support for more details on this application.
NOTE: NVIDIA 3D application is not available on all computers.
Playing games in 3D
1. Launch the game in full-screen mode.
2. If you see a message stating that the current mode is not HDMI v1.4 compatible, set the in-game resolution to 1280 x 720
(720p) in HD 3D mode.
Keyboard shortcuts
The following are some of the keyboard shortcuts available for 3D gaming:
Table 9. Keyboard shortcuts for 3D gaming
Keys Description Function
<Ctrl><t> Shows/hides stereoscopic 3D
effects
Turns 3DTV Play on or off.
NOTE: The gaming performance may reduce
when using HD 3D mode even if 3DTV Play is
disabled. To maximize performance, select HD or
SD mode when 3DTV Play is disabled.
<Ctrl><F4> Increases 3D depth Increases the 3D depth in the current game.
<Ctrl><F3> Decreases 3D depth Decreases the 3D depth in the current game.
Software and Applications 41
Table 9. Keyboard shortcuts for 3D gaming (continued)
Keys Description Function
<Ctrl><F11> Captures a 3D screen shot of the current game, and
saves the file in a folder in the Documents folder. To
view the file, use the NVIDIA 3D Photo Viewer.
<Ctrl><Alt><Insert> Shows/hides in-game compatibility
message
Displays the NVIDIA recommended settings for the
current game.
<Ctrl><F6> Increases convergence Move objects towards you; maximum convergence
places all objects in front of the scene in your space;
also used to place the laser sight.
<Ctrl><F5> Decreases convergence Moves objects away from you; minimum
convergence places all objects behind the scene in
your space; also used to place the laser sight.
NOTE: For more information, see the NVIDIA application help file.
42 Software and Applications

Restoring your operating system
System recovery options
CAUTION: Using Dell Factory Image Restore or the operating system disc permanently deletes all files on your
computer. If possible, back up your data files before using these options.
You can restore the operating system on your computer using one of the following options:
Table 10. System recovery options
Option Description
Dell Backup and Recovery Use this option as the first solution to recover your operating
system.
System reinstall discs Use this option when operating system failure prevents the
use of Dell Backup and Recovery or when installing Windows
on a new or replacement hard drive.
System Restore Use this option to restore your operating system configuration
to an earlier point in time without affecting your files.
Dell Factory Image Restore Use this as the last option to restore your operating system.
This method deletes all files and applications that you might
have saved or installed on your computer.
Dell Backup and Recovery
Dell Backup and Recovery has two versions:
●Dell Backup and Recovery Basic
●Dell Backup and Recovery Premium
Table 11. Dell Backup and Recovery features
Features Basic Premium
Restore your system back to factory state
Backup files manually
Restore files from backup
Continuously backup files to minimize data loss
Create a full system backup including applications and settings
6
Restoring your operating system 43

Table 11. Dell Backup and Recovery features (continued)
Features Basic Premium
Merge multiple backups and archive old backups
Backup and restore files based on type
Dell Backup and Recovery Basic
Accessing Dell Backup and Recovery
Windows 10
1. Click Start, type Backup in the search box.
2. Click the Dell Backup and Recovery icon and follow the on-screen instructions.
Windows 8
1. Access the search charm.
2. Click or tap Apps and type Dell Backup and Recovery in the search box.
3. Click or tap Dell Backup and Recovery in the search result list and follow the on-screen instructions.
Creating system reinstall discs
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap Factory Recovery Media tile.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Restoring your computer
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap the Recovery tile.
3. Click or tap System Recovery.
4. Click or tap Yes, Continue.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Dell Backup and Recovery premium
CAUTION: Although you are provided with an option to preserve your personal files during the recovery process,
it is recommended that you backup your personal files on a separate drive or disk before using the recovery
option.
NOTE: If you ordered Dell Backup and Recovery Premium with your computer through Digital Delivery application, you need
to download the Dell Backup and Recovery Basic first to get the Dell Backup and Recovery Premium option.
Upgrading to Dell Backup and Recovery premium
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
44 Restoring your operating system

2. Click or tap the Backup tile and select Data Backup.
3. Click or tap Upgrade to Dell Backup and Recovery Premium.
Restoring data from a system backup
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap the Backup tile and select System Backup.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Restoring specific files or folders from a Full System Backup
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap the Recovery tile, and then select Data Recovery.
3. Click or tap Yes, Continue.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Restoring specific files or folders from a file and folder backup
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap the Recovery tile, and then select Recover your Data.
3. Click or tap Browse, choose your files and folders, then select OK.
4. Click or tap Restore Now.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Creating a full system backup
1. Launch Dell Backup and Recovery.
2. Click or tap the Backup tile, and then select System Recovery.
3. Click or tap Backup Now.
4. Follow the instructions on the screen.
Dell Factory Image Restore
CAUTION: Using the Dell Factory Image Restore option permanently removes any programs or drivers installed
after you received your computer. Prepare backup media of applications you need to reinstall before using Dell
Factory Image Restore.
NOTE: Dell Factory Image Restore may not be available in certain countries or on certain computers.
Use Dell Factory Image Restore only as the last method to restore your operating system. This option restores the software on
your hard drive to the state is was initially shipped. Any programs or files added after you received your computer—including
data files such as pictures, music, and videos—are permanently deleted.
Accessing Dell Factory Image Restore
CAUTION: Using Dell Factory Image Restore permanently deletes all data on the hard drive and removes any
programs or drivers installed after you received your computer. If possible, back up the data before performing
Dell Factory Image Restore. Use Dell Factory Image Restore only if other recovery methods fail.
After two failed attempts to boot the operating system, the boot sequence automatically attempts to perform system recovery
options and perform an automatic repair.
Restoring your operating system 45

Starting Dell Factory Image Restore
NOTE: Using Dell Factory Image Restore permanently deletes all data on the hard drive and removes any programs or
drivers installed after you received your computer. If possible, back up the data before performing Dell Factory Image
Restore. Use Dell Factory Image Restore only if System Restore did not resolve your operating system problem.
1. Turn on or restart the computer.
2. When the DELL logo appears, press F8 a few times to access the Advanced Boot Options window.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft
Windows desktop; then, reboot your computer and try again.
3. Select Repair Your Computer.
The System Recovery Options window appears.
4. Select a keyboard layout and click or tap Next.
5. Log on to a local computer.
6. Select Dell Factory Image Restore or Dell Factory Tools > Dell Factory Image Restore (depending on the
configuration of your computer).
7. Click or tap Next.
The Confirm Data Deletion screen appears.
NOTE: If you do not want to proceed with Dell Factory Image Restore, click or tap Cancel.
8. Select the check box to confirm that you want to continue reformatting the hard drive and restoring the system software to
the factory condition, then click or tap Next. The restore process begins and may take 20 or more minutes to complete.
9. When the restore operation is complete, click or tap Finish to restart the computer.
System Restore
CAUTION: Backup data files regularly. System Restore does not monitor or recover your data files.
System Restore is a Microsoft Windows tool that helps you undo software changes to your computer without affecting your
personal files like documents, photos, emails, and so on.
Every time you install a software or device driver, your computer updates Windows system files to support the new software or
device. Sometimes, this may cause some unexpected errors. System Restore helps you restore the Windows system files to the
state prior to the installation of the software or device driver.
System Restore creates and saves restore points at regular intervals. You use these restore points (or create your own restore
points) to restore your computer’s system files to an earlier state.
Use system restore if changes to software, drivers or other system settings have left your computer in an undesirable operating
state.
NOTE: If newly installed hardware may be a cause, remove or disconnect the hardware and try a system restore.
NOTE: System restore does not backup your personal files and hence it cannot recover your personal files that are deleted
or damaged
Windows 10
Using system restore
1. Right-click (or press and hold) the Start button, and then select Control Panel.
2. Type Recovery in the search box.
3. Click or tap Recovery.
4. Click or tap Open System Restore.
5. Click or tap Next and follow the on-screen instructions.
46 Restoring your operating system

Undoing the last system restore
1. Right-click (or press and hold) the Start button, and then select Control Panel.
2. Click or tap Security and Maintenance.
3. Click or tap Recovery.
4. Click or tap Open System Restore and follow the on-screen instructions to undo the last system restore.
Windows 8.1
Using system restore
1. Click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar.
2. Click or tap Control Panel.
3. Type Recovery in the search box.
4. Click or tap Recovery and click or tap Open System Restore.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Undoing the last system restore
1. Click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar.
2. Click or tap Control Panel.
3. In the System window, click or tap Action Center.
4. At the lower-right corner of Action Center window, click or tap Recovery.
5. Click or tap Open System Restore and follow the on-screen instructions to undo the last system restore.
Windows 7
Using system restore
1. Click Start.
2. In the search box, type System Restore and press Enter.
NOTE: The User Account Control window may appear. If you are an administrator on the computer, click or tap
Continue; otherwise, contact the administrator of the computer.
3. Click Next and follow the on-screen instructions.
Undoing the last system restore
In the event that System Restore did not resolve the issue, you may undo the last system restore.
NOTE: Before you undo the last system restore, save and close all open files and exit any open programs. Do not alter,
open, or delete any files or programs until the system restoration is complete.
1. Click or tap Start.
2. In the search box, type System Restore and press Enter.
3. Click or tap Undo my last restoration, click or tap Next and follow the on-screen instructions.
Operating System disc
CAUTION: Reinstalling the operating system using the Operating System disc permanently deletes all data and
software from your computer.
NOTE: The Operating System disc is optional and may not ship with your computer.
Restoring your operating system 47
You can use the operating system disc to install or reinstall the operating system on your computer. You must reinstall all drivers
and software after reinstalling the operating system using the operating system disc.
Reinstalling the operating system using the Operating System disc
To reinstall the operating system:
1. Insert the Operating System disc and restart the computer.
2. When the DELL logo appears, press F12 immediately to access the boot menu.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until your computer loads the
operating system; then, restart your computer and try again.
3. Select the CD/DVD drive from the list and press Enter.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions.
System reinstall media
The system reinstall media created using Dell Backup and Recovery enables you to return your hard drive to the operating state
it was in when you purchased the computer while preserving the data files on your computer. Use Dell Backup and Recovery to
create the system reinstall media.
Restoring your computer using system reinstall media
To restore your computer using the system reinstall media:
1. Turn off your computer.
2. Insert the system recovery disc into the optical drive or connect the USB key and turn on the computer.
3. When the DELL logo appears, press F12 immediately to access the boot menu.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until your computer loads the
operating system; then, restart your computer and try again.
4. Highlight the media you are using to restore, and press Enter.
5. If prompted, quickly press any key to boot from the boot device.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the recovery process.
48 Restoring your operating system

Troubleshooting
Basic troubleshooting steps
This section lists some basic troubleshooting steps you can use to resolve common issues with your computer.
●Ensure your computer is turned on and all the components are receiving power.
●Ensure all the cables are firmly connected to the respective ports.
●Ensure that the cables are not damaged or frayed.
●Ensure that there are no bent or broken pins on the connectors.
●Restart your computer and check whether the problem persists.
●For internet connection issues, unplug your modem and router from the electrical outlet, wait for about 30 seconds, plug in
the power cables, and try connecting again.
●For audio issues, ensure that the volume button is not on mute or connect an external speaker and check for sound.
NOTE: For more information on troubleshooting, solutions to common problems, and FAQs, see www.dell.com/support. To
contact Dell for technical support, see Contact Dell.
Diagnostics
Your computer has built-in diagnostic tools to help you determine the issue with you computer. These tools may notify you of a
problem using error messages, light codes, or beep codes.
Pre-Boot System Assessment
You can use the Pre-Boot System Assessment (PSA) to diagnose various hardware problems. The ePSA tests devices such as
the system board, keyboard, display, memory, hard drive, and so on.
NOTE: PSA may not be supported on all computers.
Invoking PSA
1. Turn on or restart your computer.
2. Press F12 at the Dell logo to access the BIOS setup program.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows desktop,
then restart your computer and try again.
3. Select Diagnostics and press Enter.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the test.
If a component fails the test, the test stops, the computer beeps, and an error code is displayed. Note the error code(s) and
search for solutions at www.dell.com/support or Contact Dell.
Follow the on-screen instructions to continue to the next test, retest the component that failed, or stop the test and restart the
computer. If the PSA completes successfully, the following message appears on your screen: No problems have been found
with this system so far. Do you want to run the remaining memory tests? This will take about 30 minutes or more.
Do you want to continue? (Recommended).
Press <y> to continue if you are experiencing memory issue, otherwise press <n> to finish the test.
NOTE: Press Esc anytime during the test to abort testing and restart your computer.
7
Troubleshooting 49

Enhanced PSA
You can use the Enhanced Pre-Boot System Assessment (ePSA) to diagnose various hardware problems. The ePSA tests
devices such as the system board, keyboard, display, memory, hard drive, and so on.
NOTE: ePSA may not be supported on all computers.
The ePSA home screen is divided into three areas:
●Devices window—Appears on the left of the ePSA home screen. It displays all the devices in your computer and can be
used to select devices.
●Control window—Appears at the bottom-right of the ePSA home screen.
○Selecting the Thorough Test Mode check-box in the control window maximizes the extent and duration of the tests.
○Status bar appears at the bottom left side of the control window and indicates the overall completion of the tests.
○To test selected devices, click or tap Run Tests.
○To exit the ePSA and restart your computer, click or tap Exit.
●Status window—Appears on the right of the ePSA home screen.
The status area has four tabs:
●Configuration—Displays detailed configuration and status information about all devices that can be tested using ePSA.
●Results— Displays all tests that are executed, their activity, and results for each test.
●System Health—Displays the status of the battery, power adapter, fans, and so on.
●Event Log—Provides detailed information about all tests.
The Stat column displays the status of the tests.
LCD BIST
LCD BIST (Built‑In Self Test) helps you determine if a display problem is caused by the LCD or some other part. The test may
displays different colors and text on the screen and if you do not notice the problem during the test then the issue lies outside
of the LCD.
NOTE: Peripherals may have diagnostics specific to them. For more information, see the documentation shipped along with
your peripheral.
Starting LCD BIST
1. Turn on or restart your computer.
2. Press F12 at the Dell logo to access the BIOS setup program.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows desktop,
then restart your computer and try again.
3. Select Diagnostics and press Enter.
4. If you do not see colored lines on the screen, press N to enter the LCD BIST.
Invoking ePSA
To invoke ePSA:
1. Restart the computer.
2. Press F12 at the Dell logo to access the BIOS setup program.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows desktop,
then restart your computer and try again
3. Select Diagnostics and press Enter.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the test and note any error messages that appear.
If a component fails the test, the test stops, the computer beeps, and an error code is displayed. Note the error code(s) and
search for solutions at www.dell.com/support or Contact Dell.
Follow the instructions on the screen to continue to the next test, retest the component that failed, or stop the test and restart
the computer.
50 Troubleshooting

If the PSA completes successfully, the following message appears on your screen: No problems have been found with this
system so far. Do you want to run the remaining memory tests? This will take about 30 minutes or more. Do you
want to continue? (Recommended).
Press <y> to continue if you are experiencing memory issue, otherwise press <n> to finish the test.
If the ePSA completes with errors, the following message appears on your screen: Testing completed. One or more errors
were detected.
The Event Log tab in the Status window displays the errors that occurred during the ePSA tests.
Beep codes
Your computer may emit a series of beeps during start-up if there are errors or problems. This series of beeps, called a beep
code, identifies a problem. If this occurs, note the beep code and contact Dell for assistance.
NOTE: Some of the beep codes mentioned in the table below may not apply to your computer.
Table 12. Beep codes and possible problems
Beep codes Possible problems
One Possible system board failure—BIOS ROM checksum failure.
Two No RAM detected
NOTE: If you installed or replaced the memory module, ensure that the memory module is
seated properly.
Three Possible system board failure—Chipset error
Four RAM read/write failure
Five Real‑time Clock failure
Six Video card or video controller failure
Seven Processor failure
NOTE: This beep code is supported for computers with Intel processor only.
Eight Display failure
Troubleshooting 51
BIOS
BIOS stores hardware information about your computer and passes on the information to the operating system when the
computer boots up. You can make changes to the basic hardware settings stored in the BIOS using BIOS setup program.
You can use BIOS setup program to:
●Set or change a user-selectable option such as the user password.
●Determine the devices installed on your computer, such as amount of memory, type of hard drive, and so on.
●Change the system configuration information after you add, change, or remove any hardware in your computer.
Changing BIOS settings
NOTE: Incorrect settings in BIOS setup program may cause your computer to not boot, work incorrectly, or damage your
computer.
You may need to change settings such as date and time, boot devices and boot sequence, enable or disable PowerShare, and
so on. To change the settings, enter BIOS setup program, locate the setting that you want to change, and follow the on-screen
instructions.
Entering BIOS setup program
1. Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2. During POST, when the DELL logo is displayed, watch for the F2 prompt to appear, and then press F2 immediately.
NOTE: The F2 prompt indicates that the keyboard is initialized. This prompt can appear very quickly, so you must watch
for it, and then press F2. If you press F2 before the F2 prompt, this keystroke is lost. If you wait too long and the
operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the desktop. Then, turn off your computer and try again.
Resetting BIOS password
BIOS passwords are used to add extra security to computers. You can configure your computer to prompt for a password when
booting or when entering BIOS setup program.
Use one of the following methods, depending on your computer type, to reset lost or forgotten BIOS passwords.
CAUTION: Resetting the BIOS password involves clearing all data from the CMOS. If you have changed any BIOS
settings, you must make those changes again after resetting the password.
Remove the CMOS battery
CAUTION: Read the safety instructions before working inside your computer.
Almost all system boards use a coin‑cell battery that helps retain BIOS settings, including the password. To reset the password,
remove the coin‑cell battery, wait for 15 to 30 seconds and replace the coin‑cell battery.
NOTE: For more information on the location of the coin‑cell battery and instruction on removing and replacing it, see the
Service Manual at www.dell.com/support.
8
52 BIOS

Use system‑board jumper
NOTE: System-board jumper is available only on desktop computers.
Almost all system boards on desktop computers contain a jumper to clear CMOS settings along with the BIOS password. The
location of this jumper varies depending upon the system board. Look for the jumpers near the CMOS battery, usually labeled as
CLR, CLEAR, CLEAR CMOS, and so on.
For procedure on clearing passwords and clearing CMOS settings, see your computer Service Manual at www.dell.com/support.
Boot Sequence
Boot Sequence allows you to bypass the System Setup–defined boot device order and boot directly to a specific device (for
example: optical drive or hard drive). During the Power-on Self Test (POST), when the Dell logo appears, you can:
●Access System Setup by pressing F2 key
●Bring up the one-time boot menu by pressing F12 key
The one-time boot menu displays the devices that you can boot from including the diagnostic option. The boot menu options
are:
●Removable Drive (if available)
●STXXXX Drive
NOTE: XXX denotes the SATA drive number.
●Optical Drive (if available)
●SATA Hard Drive (if available)
●Diagnostics
NOTE: Choosing Diagnostics, will display the ePSA diagnostics screen.
The boot sequence screen also displays the option to access the System Setup screen.
BIOS 53

Getting help and contacting Dell
Self-help resources
You can get information and help on Dell products and services using these self-help resources:
Table 13. Self-help resources
Self-help resources Resource location
Information about Dell products and services www.dell.com
My Dell app
Tips
Contact Support In Windows search, type Contact Support, and press
Enter.
Online help for operating system www.dell.com/support/windows
www.dell.com/support/linux
Access top solutions, diagnostics, drivers and downloads, and
learn more about your computer through videos, manuals and
documents.
Your Dell computer is uniquely identified by a Service Tag or
Express Service Code. To view relevant support resources for
your Dell computer, enter the Service Tag or Express Service
Code at www.dell.com/support.
For more information on how to find the Service Tag for your
computer, see Locate the Service Tag on your computer.
Dell knowledge base articles for a variety of computer
concerns
1. Go to www.dell.com/support.
2. On the menu bar at the top of the Support page, select
Support > Knowledge Base.
3. In the Search field on the Knowledge Base page, type the
keyword, topic, or model number, and then click or tap the
search icon to view the related articles.
Contacting Dell
To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer service issues, see www.dell.com/contactdell.
NOTE: Availability varies by country/region and product, and some services may not be available in your country/region.
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can find contact information about your purchase invoice,
packing slip, bill, or Dell product catalog.
9
54 Getting help and contacting Dell

References
Computer maintenance
It is recommended that you perform the following tasks to avoid general computer problems:
●Provide direct access to a power source, adequate ventilation, and a level surface to place your computer.
●Do not block, push objects into, or allow dust to accumulate in the air vents.
●Back up your data regularly.
●Perform a virus scan regularly.
●Check your computer for errors using SupportAssist and other tools available on your computer.
●Clean your computer regularly using a soft, dry cloth.
CAUTION: Using water or other solvents to clean your computer may damage your computer.
●Ensure that there is enough free space on your device storage. Not having enough free space may result in degraded
performance.
●Enable automatic Microsoft Windows and other software updates to address software issues and improve computer
security.
Power management
Power management helps you reduce the electricity consumption of yourcomputer by regulating power supply to the various
components. The BIOS setup program and the operating system allow you to configure when the power supply to certain
components should be reduced or cut off.
Some common power-saving states in Microsoft Windows are:
●Sleep—Sleep is a power-saving state that enables a computer to quickly resume full-power operation (typically within a few
seconds) when you want to start working again.
●Hibernation—Hibernation puts your open documents and programs on your computer storage, and then turns off your
computer.
●Hybrid sleep—Hybrid sleep is a combination of sleep and hibernation. It puts any open documents and programs in memory
and on your computer storage, and then puts your computer into a low-power state so that you can quickly resume your
work. When hybrid sleep is turned on, putting your computer into sleep automatically puts your computer into hybrid sleep.
●Shut down—Shutting down your computer helps when you are not planning to use the computer for a considerable period
of time. It helpskeep the computer secure and also saves more energy. Shut down your computer before adding or removing
hardware inside the computer.
Shutting down is not a recommended when you need to resume work quickly.
Configuring power settings
Windows 10 and 8.1
1. Click or tap Start > All apps.
2. Under Windows System, click or tap Control Panel.
NOTE: For Windows 8.1/Windows RT click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar and click or tap Control panel.
3. If your Control Panel is displayed by category, click or tap the View by: drop down and select Small icons or Large icons.
4. Click or tap Power Options.
5. You can choose a plan from the list of options available depending on your computer usage.
6. To modify the power settings, click or tap Change plan settings.
10
References 55

Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Power Options.
2. You can choose from a plan from the list of options available depending on your computer usage.
3. To modify the power settings, click Change plan settings.
Configuring the power button behavior
To configure the power button behavior:
Windows 10 and 8.1
1. Click or tap Start > All apps.
2. Under Windows System, click or tap Control Panel.
NOTE: For Windows 8.1/Windows RT click or tap Settings in the charms sidebar and click or tap Control panel.
3. If your Control Panel is displayed by Category, click or tap the View by: drop‑down and select Small icons or Large icons.
4. Click or tap Power Options.
5. Click or tap Choose what the power buttons do.
You may choose different option when your computer is running on battery and when it is connected to a power adapter.
6. Click or tap Save changes.
Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Power Options.
2. Click Choose what the power buttons do.
3. From the drop-down menu next to When I press the power button, select the preferred response from your computer
when you press the power button. You may select a different option when your computer is running on battery or when it is
connected to a power adapter.
4. Click Save changes.
Dell Power Manager
NOTE: This software is only supported on computers running on Windows 10 operating systems.
Dell Power Manager is a software that enables you to efficiently manage the power settings for Dell notebooks and tablets. The
software offers these key features:
●Battery Information–Display health information for up to six installed batteries, depending on system capabilities, and edit
battery settings or create a custom battery setting.
●Advanced Charge–Control battery charging to prolong battery life.
●Peak Shift–Reduce power consumption by automatically switching the system to battery power during certain times of the
day, even when the system is plugged into a direct power source.
●Thermal Management–Control processor and cooling fan settings to manage performance, system surface temperature,
and fan noise.
●Battery Extender–Conserve battery charge by adjusting CPU power level, screen brightness and keyboard illumination
levels, and by muting audio.
●Alert Settings–Restore to default alert settings.
For more information on Dell Power Manager, see the Dell Power Manager User Guide at www.dell.com/support.
Improving battery life
The operating time of a battery, which is the time the battery can hold a charge, varies depending on how you use your laptop
computer.
56 References

The operating time of your battery significantly reduces if you use:
●Optical drives
●Wireless communication devices, ExpressCards, media cards, or USB devices.
●High-brightness display settings, 3D screen savers, or other power‑intensive programs like complex 3D graphics applications
and games.
You can improve the battery performance by:
●Operating the computer on AC power when possible. Battery life reduces with the number of times the battery is discharged
and recharged.
●Configuring the power management settings using Microsoft Windows Power Options to optimize your computer’s power
usage (see Power management).
●Enabling the sleep/standby and hibernation features of your computer.
NOTE: The life of the battery decreases over time depending on how often the battery is used and the conditions under
which it is used. You can configure the battery‑charging behavior to increase the battery life.
Dell longevity mode
Frequently connecting and disconnecting your computer from a power source without allowing the battery to fully discharge
may reduce battery life. The longevity mode feature protects the battery health by moderating the extent to which your battery
charges, and prevents your battery from frequent charge and discharge cycles.
Your Dell laptop automatically monitors the charging and discharging behavior of your battery, and if applicable, displays a
message to enable longevity mode.
NOTE: Dell longevity mode may not be supported on all laptops. To configure Dell longevity mode:
1. Right-click the battery icon on the Windows notification area and click or tap Dell Extended Battery Life Options.
The Battery Meter dialog box appears.
2. Click or tap the Longevity mode tab.
3. Click or tap Enable to turn on, or Disable to turn off Dell longevity mode.
4. Click or tap OK.
NOTE: When longevity mode is enabled, the battery charges only between 88% to 100% of its capacity.
Dell desktop mode
If you primarily use your computer with the power adapter connected, you can enable the desktop mode to moderate the extent
to which your battery is charged. This reduces the number of charge/discharge cycles and improves battery life.
Your Dell laptop automatically monitors the charging and discharging behavior of your battery, and if applicable, displays a
message to enable desktop mode.
NOTE: Dell desktop mode may not be supported on all computers.
To enable or disable desktop mode:
1. Right-click the battery icon on the Windows notification area, and then click or tap Dell Extended Battery Life Options.
The Battery Meter dialog box is displayed.
2. Click or tap the Desktop mode tab.
3. Click or tap Enable or Disable based on your preference.
4. Click or tap OK.
NOTE: When desktop mode is enabled, the battery charges only between 50% to 100% percent of its capacity.
Migration tips
Computer migration is the moving of data and applications between two different computers. The most common reasons
requiring a computer migration are when you purchase a new computer or when you upgrade to a new operating systems.
References 57

CAUTION: While there are several utilities that simplify migration, it is recommended that you backup your files
like pictures, music, documents, and so on.
Migrating from one Windows operating system to a newer Windows
operating system
While migrating to a newer operating system, refer to the Microsoft guidelines provided for migration from one operating
system to another.
For more information, see www.microsoft.com.
Ergonomic instructions
CAUTION: Improper or prolonged keyboard use may result in injury.
CAUTION: Viewing the monitor screen for extended periods of time may result in eye strain.
For comfort and efficiency, use the ergonomic guidelines when setting up and using your computer.
Laptops are not necessarily designed for continuous operation as office equipment. If you intend to use you laptop continuously,
it is recommended that you connect an external keyboard.
●Position your computer so that the monitor and keyboard are directly in front of you as you work. Special shelves are
available (from Dell and other sources) to help you correctly position your keyboard.
●Place the external monitor at a comfortable viewing distance. The recommended distance is 510 mm to 610 mm (20 in to 24
in) from your eyes.
●Ensure the monitor is at eye level or slightly lower when you are sitting in front of the monitor.
●Adjust the tilt of the monitor, its contrast and brightness settings, and the lighting around you (such as overhead lights, desk
lamps, and the curtains or blinds on nearby windows) to minimize reflections and glare on the monitor screen.
●Use a chair that provides good back support.
●Keep your forearms horizontal with your wrists in a neutral, comfortable position while using the keyboard or mouse.
●Always leave space to rest your hands while using the keyboard or mouse.
●Let your upper arms hang naturally at your sides.
●Sit erect, with your feet resting on the floor and your thighs level.
●When sitting, ensure the weight of your legs is on your feet and not on the front of your chair seat. Adjust your chair’s height
or use a footrest, if necessary, to maintain proper posture.
●Vary your work activities. Try to organize your work so that you do not have to type for extended periods of time. When you
stop typing, try to do things that use both hands.
●Keep the area under the desk clear of obstruction and cables or power cords that may interfere with comfortable seating or
present a potential trip hazard.
58 References

1. Monitor at or below eye level 2. Monitor and keyboard positioned directly in front of the user
3. Monitor stand 4. Feet flat on the floor
5. Arms at desk level 6. Wrists relaxed and flat
NOTE: For the latest ergonomic instructions, see www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Dell and the environment
Green is not about limitation, it is about possibility. It is about finding a better way.
Every day, you have the opportunity to make greener choices, but when choosing technology, you do not want to compromise
on cost, performance, or reliability. At Dell, we believe you should not have to, which is why we strive to ensure that people and
companies do not have to make trade-offs to be green.
We make this a reality by delivering practical products and services that make an impact on real environmental issues, because
at the heart of green is the powerful idea that better ways are possible. Better ways to use time, money, and resources. Better
ways to live, work, and succeed in our world.
Table 14. Dell and the environment
Bamboo—Nature’s eco-friendly packaging solution
To help achieve the shared goal of finding new ways to
help preserve our planet’s natural resources, Dell provides
practical, but innovative packaging solutions that help
minimize environmental effects. Less packaging means less
hassle for customers. Recyclable packaging makes it easy to
dispose. And sustainable materials are good for our planet.
Bamboo packaging is used to ship several Dell products. For
easy disposal, our bamboo packaging is biodegradable and
certified ‘compostable’ by the Soil Control Lab. We know
that responsible sourcing is important to you, so the bamboo
References 59

Table 14. Dell and the environment (continued)
used in our packaging is sourced from a forest far away from
pandas’ known habitats.
Join the Plant a Tree program
Dell created the Plant a Tree program to make it easy for you
to offset the greenhouse gas emissions from your computer
equipment and to help build a healthier planet—one tree and
forest at a time. For more information, see www.dell.com/
plantatree.
Recycle with Dell
As you upgrade computers and electronics, please join our
efforts to keep technology out of the world’s landfills.
Recycling your home and business computers with us is fast,
convenient, and secure.
Do yourself and your planet a favor. Dispose of your
technology responsibly with Dell.
Regulatory compliance policy
For complete details, visit www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Contact details for regulatory compliance web site
For any questions related to Product Safety, EMC or Ergonomics, send an e-mail to Regulatory_Compliance@dell.com.
Additional compliance information
The World Wide Trade Compliance Organization (WWTC) is responsible for managing Dell’s compliance to import and export
regulations, including product classification. Classification data for Dell manufactured systems is provided within the product-
specific, system Product Safety, EMC and Environmental Datasheet.
For any questions related to import or export classification of Dell products, send an e-mail to
US_Export_Classification@dell.com.
60 References