Table of Contents
- Working on your computer
- Removing and installing components
- Technology and components
- System specifications
- System setup
- Boot menu
- Navigation keys
- System setup options
- General screen options
- System Configuration screen options
- Video screen options
- Secure Boot screen options
- Intel software guard extensions screen options
- Performance screen options
- Power management screen options
- POST behavior screen options
- Manageability
- Virtualization support screen options
- Wireless screen options
- Maintenance screen options
- System logs screen options
- Updating the BIOS in Windows
- System and setup password
- Software
- Troubleshooting
- Contacting Dell
DELL 7390 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 7390 by DELL which is a product in the Notebooks category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Latitude 7390 2-in-1
Owner's Manual
Regulatory Model: P29S
Regulatory Type: P29S002

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
Copyright © 2018 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other
trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.
2018 - 01
Rev. A01

Working on your computer
Topics:
• Safety precautions
• Before working inside your computer
• After working inside your computer
Safety precautions
The safety precautions chapter details the primary steps to be taken before performing any disassembly instructions.
Observe the following safety precautions before you perform any installation or break/x procedures involving disassembly or reassembly:
• Turn o the system and all attached peripherals.
• Disconnect the system and all attached peripherals from AC power.
• Disconnect all network cables, telephone, and telecommunications lines from the system.
• Use an ESD eld service kit when working inside any notebook to avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
• After removing any system component, carefully place the removed component on an anti-static mat.
• Wear shoes with non-conductive rubber soles to reduce the chance of getting electrocuted.
Standby power
Dell products with standby power must be unplugged before you open the case. Systems that incorporate standby power are essentially
powered while turned o. The internal power enables the system to be remotely turned on (wake on LAN) and suspended into a sleep
mode and has other advanced power management features.
Unplugging, pressing and holding the power button for 15 seconds should discharge residual power in the system board, notebooks
Bonding
Bonding is a method for connecting two or more grounding conductors to the same electrical potential. This is done through the use of a
eld service electrostatic discharge (ESD) kit. When connecting a bonding wire, ensure that it is connected to bare metal and never to a
painted or non-metal surface. The wrist strap should be secure and in full contact with your skin, and ensure that you remove all jewelry
such as watches, bracelets, or rings prior to bonding yourself and the equipment.
Electrostatic discharge — ESD protection
ESD is a major concern when you handle electronic components, especially sensitive components such as expansion cards, processors,
memory DIMMs, and system boards. Very slight charges can damage circuits in ways that may not be obvious, such as intermittent
problems or a shortened product life span. As the industry pushes for lower power requirements and increased density, ESD protection is an
increasing concern.
Due to the increased density of semiconductors used in recent Dell products, the sensitivity to static damage is now higher than in previous
Dell products. For this reason, some previously approved methods of handling parts are no longer applicable.
1
Working on your computer 3

Two recognized types of ESD damage are catastrophic and intermittent failures.
•Catastrophic – Catastrophic failures represent approximately 20 percent of ESD-related failures. The damage causes an immediate and
complete loss of device functionality. An example of catastrophic failure is a memory DIMM that has received a static shock and
immediately generates a "No POST/No Video" symptom with a beep code emitted for missing or nonfunctional memory.
•Intermittent – Intermittent failures represent approximately 80 percent of ESD-related failures. The high rate of intermittent failures
means that most of the time when damage occurs, it is not immediately recognizable. The DIMM receives a static shock, but the
tracing is merely weakened and does not immediately produce outward symptoms related to the damage. The weakened trace may
take weeks or months to melt, and in the meantime may cause degradation of memory integrity, intermittent memory errors, etc.
The more dicult type of damage to recognize and troubleshoot is the intermittent (also called latent or "walking wounded") failure.
Perform the following steps to prevent ESD damage:
• Use a wired ESD wrist strap that is properly grounded. The use of wireless anti-static straps is no longer allowed; they do not provide
adequate protection. Touching the chassis before handling parts does not ensure adequate ESD protection on parts with increased
sensitivity to ESD damage.
• Handle all static-sensitive components in a static-safe area. If possible, use anti-static oor pads and workbench pads.
• When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the component from the anti-static packing
material until you are ready to install the component. Before unwrapping the anti-static packaging, ensure that you discharge static
electricity from your body.
• Before transporting a static-sensitive component, place it in an anti-static container or packaging.
ESD eld service kit
The unmonitored Field Service kit is the most commonly used service kit. Each Field Service kit includes three main components: anti-static
mat, wrist strap, and bonding wire.
Components of an ESD eld service kit
The components of an ESD eld service kit are:
•Anti-Static Mat – The anti-static mat is dissipative and parts can be placed on it during service procedures. When using an anti-static
mat, your wrist strap should be snug and the bonding wire should be connected to the mat and to any bare metal on the system being
worked on. Once deployed properly, service parts can be removed from the ESD bag and placed directly on the mat. ESD-sensitive
items are safe in your hand, on the ESD mat, in the system, or inside a bag.
•Wrist Strap and Bonding Wire – The wrist strap and bonding wire can be either directly connected between your wrist and bare metal
on the hardware if the ESD mat is not required, or connected to the anti-static mat to protect hardware that is temporarily placed on
the mat. The physical connection of the wrist strap and bonding wire between your skin, the ESD mat, and the hardware is known as
bonding. Use only Field Service kits with a wrist strap, mat, and bonding wire. Never use wireless wrist straps. Always be aware that the
internal wires of a wrist strap are prone to damage from normal wear and tear, and must be checked regularly with a wrist strap tester
in order to avoid accidental ESD hardware damage. It is recommended to test the wrist strap and bonding wire at least once per week.
•ESD Wrist Strap Tester – The wires inside of an ESD strap are prone to damage over time. When using an unmonitored kit, it is a best
practice to regularly test the strap prior to each service call, and at a minimum, test once per week. A wrist strap tester is the best
method for doing this test. If you do not have your own wrist strap tester, check with your regional oce to nd out if they have one.
To perform the test, plug the wrist-strap's bonding-wire into the tester while it is strapped to your wrist and push the button to test. A
green LED is lit if the test is successful; a red LED is lit and an alarm sounds if the test fails.
•Insulator Elements – It is critical to keep ESD sensitive devices, such as plastic heat sink casings, away from internal parts that are
insulators and often highly charged.
•Working Environment – Before deploying the ESD Field Service kit, assess the situation at the customer location. For example,
deploying the kit for a server environment is dierent than for a desktop or portable environment. Servers are typically installed in a rack
within a data center; desktops or portables are typically placed on oce desks or cubicles. Always look for a large open at work area
that is free of clutter and large enough to deploy the ESD kit with additional space to accommodate the type of system that is being
repaired. The workspace should also be free of insulators that can cause an ESD event. On the work area, insulators such as Styrofoam
and other plastics should always be moved at least 12 inches or 30 centimeters away from sensitive parts before physically handling any
hardware components
•ESD Packaging – All ESD-sensitive devices must be shipped and received in static-safe packaging. Metal, static-shielded bags are
preferred. However, you should always return the damaged part using the same ESD bag and packaging that the new part arrived in.
The ESD bag should be folded over and taped shut and all the same foam packing material should be used in the original box that the
new part arrived in. ESD-sensitive devices should be removed from packaging only at an ESD-protected work surface, and parts should
4Working on your computer

never be placed on top of the ESD bag because only the inside of the bag is shielded. Always place parts in your hand, on the ESD mat,
in the system, or inside an anti-static bag.
•Transporting Sensitive Components – When transporting ESD sensitive components such as replacement parts or parts to be
returned to Dell, it is critical to place these parts in anti-static bags for safe transport.
ESD protection summary
It is recommended that all eld service technicians use the traditional wired ESD grounding wrist strap and protective anti-static mat at all
times when servicing Dell products. In addition, it is critical that technicians keep sensitive parts separate from all insulator parts while
performing service and that they use anti-static bags for transporting sensitive components.
Transporting sensitive components
When transporting ESD sensitive components such as replacement parts or parts to be returned to Dell, it is critical to place these parts in
anti-static bags for safe transport.
Before working inside your computer
1 Ensure that your work surface is at and clean to prevent the computer cover from being scratched.
2 Turn o your computer.
3 If the computer is connected to a docking device (docked), undock it.
4 Disconnect all network cables from the computer (if available).
CAUTION: If your computer has an RJ45 port, disconnect the network cable by rst unplugging the cable from your
computer.
5 Disconnect your computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
6 Open the display.
7 Press and hold the power button for few seconds, to ground the system board.
CAUTION: To guard against electrical shock unplug your computer from the electrical outlet before performing Step # 8.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching an
unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
8 Remove any installed ExpressCards or Smart Cards from the appropriate slots.
After working inside your computer
After you complete any replacement procedure, ensure that you connect external devices, cards, and cables before turning on your
computer.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the computer, use only the battery designed for this particular Dell computer. Do not use batteries
designed for other Dell computers.
1 Connect any external devices, such as a port replicator or media base, and replace any cards, such as an ExpressCard.
2 Connect any telephone or network cables to your computer.
CAUTION: To connect a network cable, rst plug the cable into the network device and then plug it into the
computer.
3 Connect your computer and all attached devices to their electrical outlets.
4 Turn on your computer.
Working on your computer 5

Removing and installing components
Topics:
• Recommended tools
• Screw size list
• Micro Secure Digital Card
• Subscriber Identity Module SIM Card
• Base cover
• Battery
• PCIe Solid State Drive (SSD)
• WLAN card
• WWAN card
• Power board
• Speaker
• Smart Card Cage
• Fingerprint Board
• LED Board
• Heat Sink
• Display Assembly
• System Board
• Real time clock
• Keyboard
• Touchpad Buttons
• Palm rest
Recommended tools
The procedures in this document require the following tools:
• Phillips #0 screwdriver
• Phillips #1 screwdriver
• Plastic scribe
NOTE: The #0 screw driver is for screws 0-1 and the #1 screw driver is for screws 2-4
2
6 Removing and installing components

Screw size list
Table 1. Latitude 7390- Screw size list
Component M 2.5 x 2.5L M 2.5 x 4.0L M 2.0 x 3.0L M 2 x 2L
K3.6D
M 2.0 x 2L
K7D
M 2 x 1.7L M 1.98 x 4L M 2.5 x 5
Hinge
bracket to
Cover
6
G-sensor to
Cover 1
Lcm frame
down to
Cover
2
Hinge
bracket to
Low
4
Power Board 2
LED Board 2
Fingerprint
bracket 1
Touchpad
button 2
Smart Card 2
K/B to K/B
plate 6
K/B plate 13
Bottom Door
Assy 8
System
board 6
Fan 1 1
Thermal 4
Battery 4
WLAN 1
WWAN 1
EDP Bracket 2
USB Type C 2
Micro Secure Digital Card
Removing and installing components 7

Removing the Micro Secure Digital Card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Push the Micro Secure Digital (SD) card to release it from the computer.
3 Slide the Micro Secure Digital (SD) card out of the computer.
Installing the Micro Secure Digital Card
1 Slide the Micro SD into the slot until it clicks into place.
2 Follow the procedures in After working inside your computer.
Subscriber Identity Module SIM Card
Removing the micro SIM card or the micro SIM card tray
CAUTION: Removing the micro SIM card when the computer is on may cause data loss or damage the card.
NOTE: Micro SIM card tray is available only for systems that are shipped with WWAN card.
1 Insert a pin or a micro SIM card removal tool into the pinhole on the micro SIM card tray.
2 Use a scribe to pull the micro SIM card tray.
3 If a micro SIM card is available, remove the micro SIM card from the micro SIM card tray.
Replacing SIM card
1 Insert a paperclip or a SIM card removal tool into the pinhole on the SIM card tray.
2 Use a scribe to pull the SIM card tray
3 Place on the SIM card on the tray.
4 Insert the SIM card tray into the slot.
Base cover
Removing the base cover
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Loosen the 8 (M2.5 x 5.0) captive screws that secure the base cover to the computer.
8Removing and installing components

3 Use a plastic scribe to pry the base cover starting from the hinges at the top edge of the base cover and lift it from the computer.
NOTE: The recesses are located near the hinges at the rear side of the computer.
4 Remove the base cover
Removing and installing components 9

Installing the base cover
1 Align the base cover tabs to the slots on the edges of the computer.
2 Press the edges of the cover until it clicks into place.
3 Tighten the 8 (M2.5 x 5.0) captive screws to secure the base cover to the computer.
4 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Battery
Removing the battery
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
3 To remove the battery:
a Lift the ribbon, disconnect and remove the battery cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Remove the 4 (M1.98 x 4 L) screws that secure the battery to the computer [2].
c Lift the battery from the computer [3].
10 Removing and installing components

Installing battery
1 Insert the battery into the slot on the computer.
2 Connect the battery cable to the connector on the system board.
3 Replace the 4 (M1.98 x 4L) screws to secure the battery to the computer.
4 Install the:
aBase cover
bSIM card tray
cMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
PCIe Solid State Drive (SSD)
Removing the NVMe SSD card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the NVMe SSD card:
a Loosen the 2 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure SSD thermal plate in place [1].
Removing and installing components 11

b Lift the thermal plate from the SSD card [2].
c Remove the SSD card from the slot [3].
Installing the NVMe SSD
1 Insert the NVMe SSD card into the connector.
2 Install the thermal plate over the SSD card.
3 Tighten the 2 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws to secure the SSD thermal plate.
4 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WLAN card
Removing the WLAN card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
12 Removing and installing components

dBattery
3 To remove the WLAN card:
a Remove 1 (M2.0 x 3.0) screw that secures the wireless card bracket in place [1].
b Lift the wireless card bracket [2].
c Disconnect the WLAN cables from the connectors on the WLAN card [3].
d Remove the WLAN card [4].
Installing the WLAN card
1 Insert the WLAN card into the connector on the system board.
2 Connect the WLAN cables to the connectors on the WLAN card.
3 Place the wireless card bracket and replace 1 (M2.0 x 3.0) screw to secure WLAN card to the computer.
4 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WWAN card
Removing the WWAN card
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
Removing and installing components 13

aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the WWAN card:
a Remove 1 (M2.0 x 3.0) screw that secures the WWAN card bracket in place [1].
b Lift the WWAN card bracket that secures the WWAN card [2].
c Disconnect the WWAN cables from the connectors on the WWAN card [3].
d Lift the WWAN card from the computer [4].
Installing the WWAN card
1 Insert the WWAN card into the connector on the system board.
2 Connect the WWAN cables to the connectors on the WWAN card.
3 Place the metal bracket and replace the M2.0 x 3.0 screw to secure the WLAN card to the computer.
4 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
NOTE: The IMEI number can also be found on the WWAN card.
14 Removing and installing components

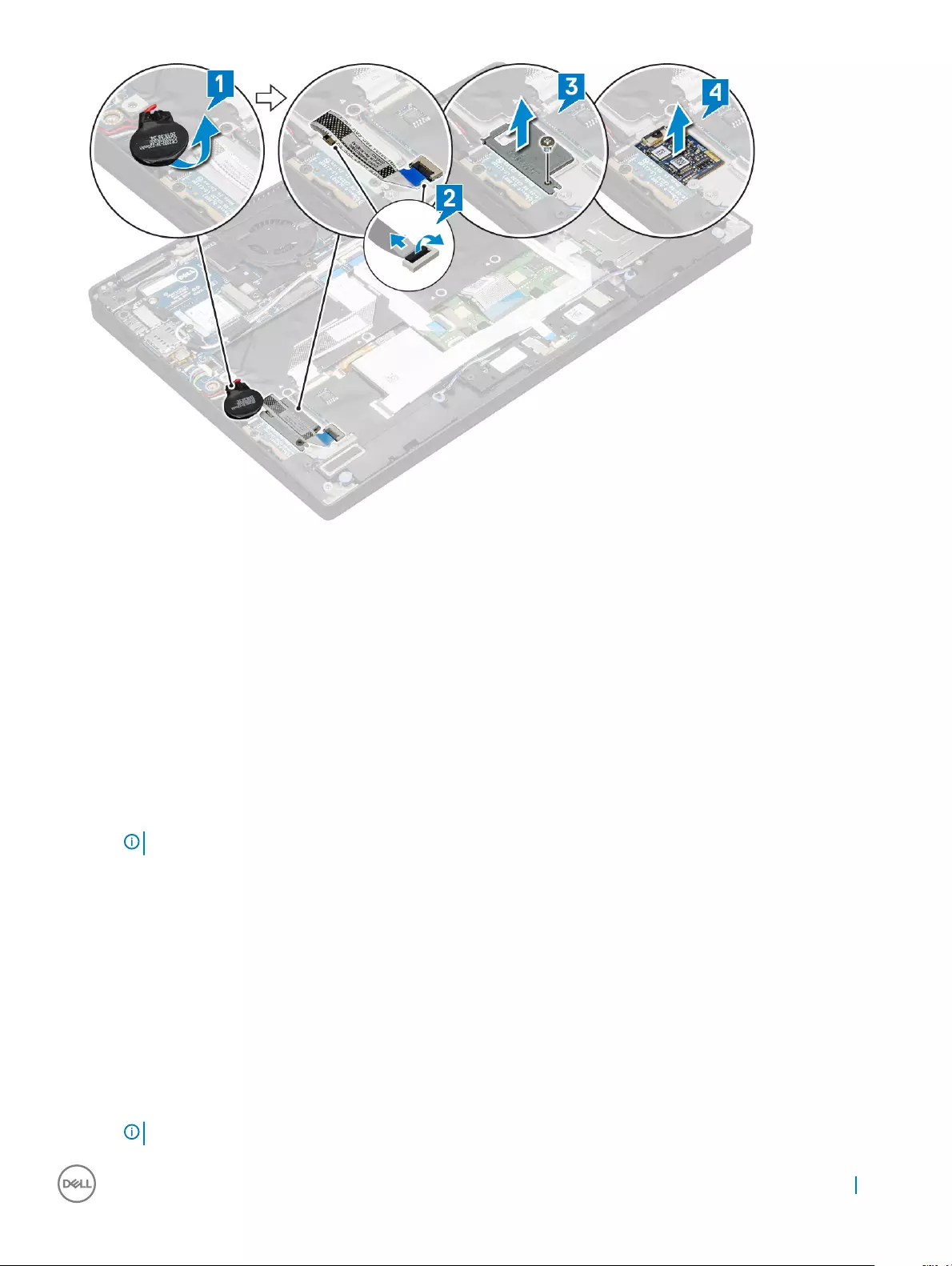
Power board
Removing the power board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the power board:
a Peel and ip over the coin cell battery [1].
b Disconnect the power daughter board cable from the system board [2].
c Remove the 2 (M2X3) screws securing the power board in place [3].
d Lift the power board from the computer [4].
Installing the power board
1 Place the power board by aligning it to the screw holes.
2 Replace the 2 (M2.0x3.0) screws to secure the power board to the computer.
3 Connect the power board cable to the connector on the system board.
4 Ax the coin cell battery on the computer.
5 Install the:
Removing and installing components 15

aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Speaker
Removing the speaker module
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicroSD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
ePower board
3 To disconnect the cables:
a Disconnect and fold back the smart card cable from the USH board [1].
b Disconnect and fold back the LED daughter board FFC from the LED daughter board for easy access in removing the speaker
module [2].
4 To release the speaker module:
a Disconnect the speaker cable from the connector on the system board [1].
b Un route the speaker cable from the retention clips and remove the tapes that secure the speaker cable [2].
16 Removing and installing components
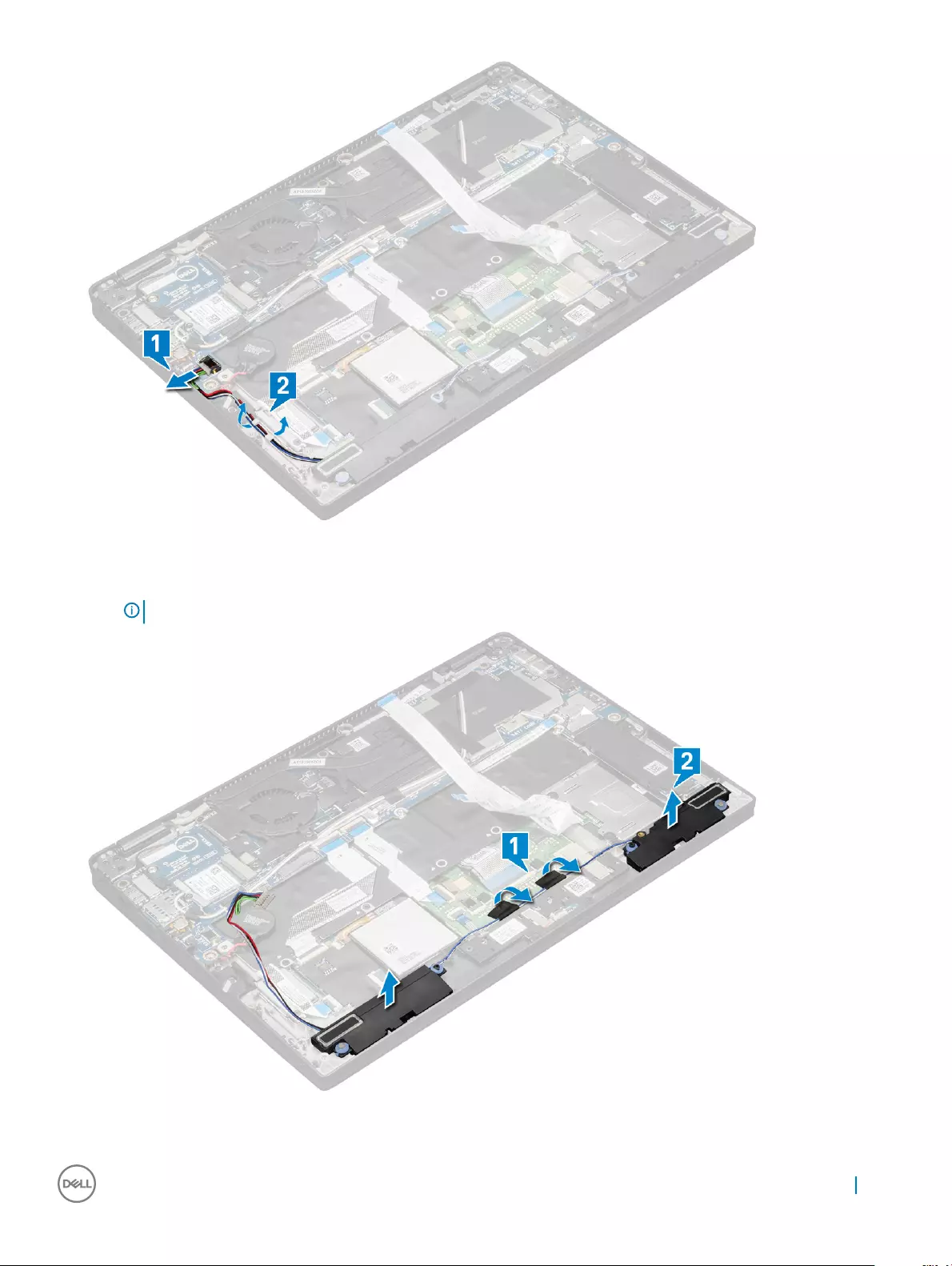

5 To remove the speaker module:
a Un route the speaker cable by removing the tapes near the palm rest [1].
b Lift the speaker module from the computer.
NOTE: You can use a plastic scribe to lift the speaker module from the computer.
Removing and installing components 17

Installing the speaker module
1 Place the speaker module into the slots on the computer.
2 Route the speaker cable through the routing channel and secure it with the tapes.
3 Connect the speaker cable to the connector on the system board.
4 Connect the smart cable to the connector on the palm rest.
5 Install the:
aPower board
bBattery
cBase cover
dSIM card tray
eMicro SD
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Smart Card Cage
Removing the smart card cage
NOTE: Always remove the smart card from the smart card reader.
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
eSSD card
3 To disconnect the cables:
a Disconnect the smart card cable [1].
b Disconnect the LED board cable [2].
c Peel the SSD thermal pad from the SSD slot [3].
NOTE: You may need to apply force to peel o the SSD thermal
pad.
18 Removing and installing components

4 To remove the smart card cage:
a Remove the 2 (M2 x 2.0) screws that secure the smart card cage to the computer [1].
b Slide it out and lift the smart card cage from the computer [2].
Removing and installing components 19

Installing the smart card cage
1 Slide the smart card cage into the slot to align with the screw holders on the computer.
2 Replace the 2 (M2 x 2.0) screws to secure the smart card cage to the computer.
3 Ax the thermal pad on the SSD module.
4 Ax the LED board cable and connect it to the LED board on the computer.
5 Ax the smart card cable and connect it to the USH board on the computer .
6 Install the:
aSSD card
bbattery
cbase cover
dSIM card tray
eMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
7 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Fingerprint Board
Removing the ngerprint reader board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the ngerprint reader board:
a Lift the coin cell battery axed to the speaker cables [1].
b Disconnect the nger print reader cables from the ngerprint reader board and the USH board [2].
NOTE: The cable should be released so that it does not tear.
c Remove 1(M2 x 3) screw that secures the ngerprint reader bracket to the computer [3].
d Lift the ngerprint reader bracket from the ngerprint reader board [4].
e Lift the ngerprint reader board from the slot on the computer.
NOTE: Fingerprint reader board is axed to the palm rest and you may need a plastic scribe to lift the ngerprint
reader board.
20 Removing and installing components

Installing the ngerprint reader board
1 Install the ngerprint reader board into the slot.
2 Place the ngerprint reader bracket on the board.
3 Replace 1(M2 x 3) screw to secure the bracket to the board.
4 Connect the ngerprint reader cable to the ngerprint reader board and the USH board.
5 Ax the coin cell battery on the speaker cable
6 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
7 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
LED Board
Removing the LED board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
Removing and installing components 21

cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the LED board:
a Disconnect the LED board cable from the LED board [1].
b Remove the tape that secures the LED board to the touchpad panel [2].
c Remove the 2 (M2 x 3) screws that secure the LED board on the computer [3].
d Lift the LED board from the computer [4].
Installing the LED board
1 Install the LED board into the slot.
2 Replace the 2 (M2 x 3) screws to secure the LED board.
3 Ax the tape to secure the LED board.
4 Connect the LED board cable to the LED board.
5 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Heat Sink
22 Removing and installing components

Removing heat sink assembly
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
3 To remove the heat sink assembly:
a Disconnect the fan cable from the system board [1].
b Remove the 2 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure the fan to the system board [2].
c Remove the 4 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure the heat sink to the system board [3].
d Lift the heat sink assembly from the system board.
Installing heat sink assembly
1 Align the heat sink assembly with screw holders on the system board.
2 Replace the 4 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws to secure the heat sink to the system board.
NOTE: Tighten the screws on the system board in the order of the callout numbers [1, 2, 3, 4] as indicated on the heat sink.
3 Replace the 2 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws to secure the fan to the system board.
4 Connect the fan cable to the connector on the system board.
5 Install the:
aBattery
bBase cover
Removing and installing components 23

cSIM card tray
dMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
6 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display Assembly
Removing the display assembly
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
eWLAN card
fWWAN card
3 Peel the tapes that secure the antenna cables to the system board and remove the cables from the routing clips.
4 Disconnect the :
a IR camera and touchscreen cable [1].
b Remove the 2 (M 2 x 1.7L) screws that secure the eDP bracket and lift it away from the computer [2].
c Disconnect the eDP cable from the system board [3].
d Disconnect the G-sensor and eDP cables [4].
24 Removing and installing components

5 Lift the base of the computer away from the display assembly.
6 To remove the display assembly:
a Place the base of the computer with the display assembly.
NOTE: To open as shown in the illustration.
b Remove the 4 (M2.5 x 4.0) screws that secure the display hinge brackets [1].
c Lift the display assembly away from the computer [2].
Removing and installing components 25

Installing the display assembly
1 Place the base of the computer on a at surface.
2 Align the display assembly with the display hinge screw holders.
3 Replace the 4 (M2.5 x 4.0) screws to secure the display assembly.
4 Close the display assembly and ip the computer.
5 Connect the cables:
a G-sensor and eDP cable
b Place the eDP bracket on the eDP cable and replace the 2 (M2 x 2) screw on the bracket.
c IR camera and touch screen cables
6 Route the antenna cables through the routing clips
7 Ax the tapes to secure the antenna cables to the system board.
8 Install the:
aWWAN card
bWLAN card
cBattery
dBase cover
eSIM card tray
fMicroSD card
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
9 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
System Board
26 Removing and installing components

Removing system board
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
NOTE: To remove both cards if equipped and no need to remove the blank ller
cBase cover
dBattery
eSSD card
fWLAN card
gWWAN card
hHeatsink assembly
3 Disconnect the :
a IR camera and touchscreen cable [1].
b Remove the 2 (M 2 x 1.7L) screws that secure the eDP bracket and lift it away from the computer [2].
c Disconnect the eDP cable from the system board [3].
d Disconnect th G-sensor and eDP cables [4].
4 Disconnect the following cables from the system board .
a Touchpad cable
b USH cable
c LED board cable
Removing and installing components 27

5 To release the cables:
a Flip the coin cell battery to reveal the speaker cable [1].
b Disconnect the speaker cable from the system board [2].
c Disconnect the power board cable from the system board [3].
6 Peel the tapes that secure antenna cables and remove the cables from the routing clips.
28 Removing and installing components

7 To remove the system board:
a Remove the 2 (M 1.98 x 4) screws securing the USB Type-C bracket [1].
b Lift the USB Type-C bracket from the Type-C module [2].
c Remove the 6 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure the system board to the computer [3].
d Lift the system board away from the computer[4].
Removing and installing components 29

Installing system board
1 Align the system board with the screw holders on the computer.
2 Replace the 6 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws to secure the system board to the computer.
3 Place the USB Type-C bracket on the Type-C module.
4 Replace the 2 (M 1.98 x 4L) screws to secure the USB Type-C bracket to the Type-C module.
5 Route the antenna cable through the routing clips and ax the tapes to secure the antenna cables.
6 Connect the power board and the speaker cable to the system board.
7 Ax the coin cell battery on the speaker cable.
8 Connect the USH board, Touchpad board and LED board cables to the system board.
1NOTE: If your computer has a WWAN card, then SIM card tray installation is a requirement.
9 Install the:
aHeatsink module
Connect the following cables from the system board
1 LED board cable
2 USH cable
3 Touchpad cable
b Connect the G-sensor and eDP cable
c Place the eDP bracket on the eDP cable and replace the 2 (M2 x 1.7L) screw on the bracket.
d Connect the IR camera and touch screen cables
eWWAN card
fWLAN card
gSSD card
hBattery
iBase cover
jSIM card tray
kMicro SD
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
10 Connect the cables:
11 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Real time clock
Removing the Coin cell battery
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aMircro SD card
bSIM card tray
NOTE: SIM Card tray is available only if your computer is shipped with a WWAN card.
cBase cover
dBattery
eSSD card
fWLAN card
gWWAN card
hHeat sink assembly
30 Removing and installing components

iSystem board
3 Disconnect and remove the coin-cell battery cable from the system board.
Installing real time clock
1 Connect the coin cell battery cable to the system board.
2 Install:
aSystem board
bHeat sink module
cWWAN card
dWLAN card
eSSD card
fBattery
gBase cover
hSIM card tray
iMicro SD
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
3 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
RTC is located on the system board and hence system board must be installed after the installation of the RTC.
Keyboard
Removing keyboard assembly
NOTE: The keyboard and the keyboard tray together are called the keyboard assembly.
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aMicro SD
bSIM card tray
Removing and installing components 31

NOTE: SIM Card tray is available only if your computer is shipped with a WWAN card.
cBase cover
dBattery
eSSD card
fWLAN card
gWWAN card
hHeatsink assembly
iSystem board
3 disconnect and peel back the cables and SSD thermal pad:
a Touchpad and USH board cable [1]
b LED board cable [2]
c SSD thermal pad [3]
d Keyboard and keyboard backlit cable [4]
4 To remove the keyboard:
a Remove the 13 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure the keyboard to the chassis [1].
b Lift the keyboard from the chassis [2].
32 Removing and installing components

Removing keyboard from the keyboard tray
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the Keyboard
3 Remove the keyboard from the keyboard support tray:
a Remove the 6 (M2.0 x 2.0) screws that secure the keyboard to the keyboard assembly [1].
b Lift the keyboard away from the keyboard support tray [2].
Removing and installing components 33

Installing keyboard to the keyboard tray
1 Align the keyboard with the screw holders on the keyboard tray.
2 Tighten the 6 (M2.0 x 2.0) screws to secure the keyboard to the keyboard tray.
3 Install the Keyboard.
Installing keyboard assembly
NOTE: The keyboard and the keyboard tray together are called the keyboard assembly.
1 Align the keyboard assembly with the screw holders on the chassis.
2 Replace the 13 (M2.0 x 3.0) screws that secure the keyboard to the chassis.
3 Ax and connect the keyboard and the backlit keyboard cables to the keyboard.
4 Ax the LED board cable on the keyboard.
5 Ax the SSD thermal pad on the SSD module.
NOTE: If your computer has a WWAN card, then SIM card tray installation is a requirement.
6 Install the:
aSystem baord
bHeatsink module
cWWAN card
dWLAN card
eSSD card
fBattery
gBase cover
hSIM card tray
iMicro SD
NOTE: To install both cards if equipped.
7 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
34 Removing and installing components

Touchpad Buttons
Removing the touchpad
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aBase cover
bBattery
cSSD module
dWLAN card
eWWAN card
fHeat sink assembly
gSpeaker
hDisplay assembly
iSystem board
jKeyboard
3 Removing the touchpad buttons.
a Disconnect the touchpad cable [1].
b Remove the tape that secures the touch buttons to the system board [2].
c Remove the 2 (M2 x 3) screws that secure the touchpad buttons [3].
d Lift the touchpad buttons from the computer [4].
Installing the touchpad
1 Place the touchpad buttons into the slot.
2 Replace the 2 (M2xL3) screws that secure touchpad buttons.
Removing and installing components 35

3 Insert the touchpad cable.
4 Install the:
aKeyboard
bSystem board
cDisplay assembly
dSpeaker
eHeat sink assembly
fWWAN card
gWLAN card
hSSD module
iBattery
jBase cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Palm rest
Replacing palm rest
1 Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2 Remove the:
aBase cover
bBattery
cSSD module
dWLAN card
eWWAN card
fHeat sink assembly
gSpeaker
hLED board
iDisplay assembly
jSystem board
kKeyboard
lTouchpad buttons
36 Removing and installing components

The component you are left with is the palm rest.
3 Replace the palm rest.
4 Install the:
aTouchpad buttons
bKeyboard assembly
cSystem board
dDisplay assembly
eLED board
fSpeaker
gHeat sink
hWLAN card
iWWAN card
jPCIe SSD
kBattery
lBase cover
5 Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Removing and installing components 37

Technology and components
This chapter details the technology and components available in the system.
Topics:
• HDMI 1.4
• USB features
• USB Type-C
• Thunderbolt over USB Type-C
HDMI 1.4
This topic explains the HDMI 1.4 and its features along with the advantages.
HDMI (High-Denition Multimedia Interface) is an industry-supported, uncompressed, all-digital audio/video interface. HDMI provides an
interface between any compatible digital audio/video source, such as a DVD player, or A/V receiver and a compatible digital audio and/or
video monitor, such as a digital TV (DTV). The intended applications for HDMI TVs, and DVD players. The primary advantage is cable
reduction and content protection provisions. HDMI supports standard, enhanced, or high-denition video, plus multichannel digital audio on
a single cable.
NOTE: The HDMI 1.4 will provide 5.1 channel audio support.
HDMI 1.4 Features
•HDMI Ethernet Channel - Adds high-speed networking to an HDMI link, allowing users to take full advantage of their IP-enabled
devices without a separate Ethernet cable
•Audio Return Channel - Allows an HDMI-connected TV with a built-in tuner to send audio data "upstream" to a surround audio system,
eliminating the need for a separate audio cable
•3D - Denes input/output protocols for major 3D video formats, paving the way for true 3D gaming and 3D home theater applications
•Content Type - Real-time signaling of content types between display and source devices, enabling a TV to optimize picture settings
based on content type
•Additional Color Spaces - Adds support for additional color models used in digital photography and computer graphics
•4K Support - Enables video resolutions far beyond 1080p, supporting next-generation displays that will rival the Digital Cinema systems
used in many commercial movie theaters
•HDMI Micro Connector - A new, smaller connector for phones and other portable devices, supporting video resolutions up to 1080p
•Automotive Connection System - New cables and connectors for automotive video systems, designed to meet the unique demands of
the motoring environment while delivering true HD quality
Advantages of HDMI
• Quality HDMI transfers uncompressed digital audio and video for the highest, crispest image quality.
• Low -cost HDMI provides the quality and functionality of a digital interface while also supporting uncompressed video formats in a
simple, cost-eective manner
• Audio HDMI supports multiple audio formats from standard stereo to multichannel surround sound
• HDMI combines video and multichannel audio into a single cable, eliminating the cost, complexity, and confusion of multiple cables
currently used in A/V systems
3
38 Technology and components

• HDMI supports communication between the video source (such as a DVD player) and the DTV, enabling new functionality
USB features
Universal Serial Bus, or USB, was introduced in 1996. It dramatically simplied the connection between host computers and peripheral
devices like mice, keyboards, external drivers, and printers.
Let's take a quick look on the USB evolution referencing to the table below.
Table 2. USB evolution
Type Data Transfer Rate Category Introduction Year
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 5 Gbps Super Speed 2010
USB 2.0 480 Mbps High Speed 2000
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB)
For years, the USB 2.0 has been rmly entrenched as the de facto interface standard in the PC world with about 6 billion devices sold, and
yet the need for more speed grows by ever faster computing hardware and ever greater bandwidth demands. The USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1
nally has the answer to the consumers' demands with a theoretically 10 times faster than its predecessor. In a nutshell, USB 3.1 Gen 1
features are as follows:
• Higher transfer rates (up to 5 Gbps)
• Increased maximum bus power and increased device current draw to better accommodate power-hungry devices
• New power management features
• Full-duplex data transfers and support for new transfer types
• Backward USB 2.0 compatibility
• New connectors and cable
The topics below cover some of the most commonly asked questions regarding USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
Speed
Currently, there are 3 speed modes dened by the latest USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 specication. They are Super-Speed, Hi-Speed and Full-
Speed. The new SuperSpeed mode has a transfer rate of 4.8Gbps. While the specication retains Hi-Speed, and Full-Speed USB mode,
commonly known as USB 2.0 and 1.1 respectively, the slower modes still operate at 480Mbps and 12Mbps respectively and are kept to
maintain backward compatibility.
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 achieves the much higher performance by the technical changes below:
• An additional physical bus that is added in parallel with the existing USB 2.0 bus (refer to the picture below).
• USB 2.0 previously had four wires (power, ground, and a pair for dierential data); USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 adds four more for two pairs
of dierential signals (receive and transmit) for a combined total of eight connections in the connectors and cabling.
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 utilizes the bidirectional data interface, rather than USB 2.0's half-duplex arrangement. This gives a 10-fold
increase in theoretical bandwidth.
Technology and components 39

With today's ever increasing demands placed on data transfers with high-denition video content, terabyte storage devices, high megapixel
count digital cameras etc., USB 2.0 may not be fast enough. Furthermore, no USB 2.0 connection could ever come close to the 480Mbps
theoretical maximum throughput, making data transfer at around 320Mbps (40MB/s) — the actual real-world maximum. Similarly, USB
3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 connections will never achieve 4.8Gbps. We will likely see a real-world maximum rate of 400MB/s with overheads. At this
speed, USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 is a 10x improvement over USB 2.0.
Applications
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 opens up the laneways and provides more headroom for devices to deliver a better overall experience. Where USB
video was barely tolerable previously (both from a maximum resolution, latency, and video compression perspective), it's easy to imagine
that with 5-10 times the bandwidth available, USB video solutions should work that much better. Single-link DVI requires almost 2Gbps
throughput. Where 480Mbps was limiting, 5Gbps is more than promising. With its promised 4.8Gbps speed, the standard will nd its way
into some products that previously weren't USB territory, like external RAID storage systems.
Listed below are some of the available SuperSpeed USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 products:
• External Desktop USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• Portable USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Drive Docks & Adapters
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Flash Drives & Readers
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Solid-state Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 RAIDs
• Optical Media Drives
• Multimedia Devices
• Networking
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Adapter Cards & Hubs
Compatibility
The good news is that USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 has been carefully planned from the start to peacefully co-exist with USB 2.0. First of all,
while USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 species new physical connections and thus new cables to take advantage of the higher speed capability of
the new protocol, the connector itself remains the same rectangular shape with the four USB 2.0 contacts in the exact same location as
before. Five new connections to carry receive and transmitted data independently are present on USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 cables and only
come into contact when connected to a proper SuperSpeed USB connection.
Windows 8/10 will be bringing native support for USB 3.1 Gen 1 controllers. This is in contrast to previous versions of Windows, which
continue to require separate drivers for USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 controllers.
40 Technology and components

Microsoft announced that Windows 7 would have USB 3.1 Gen 1 support, perhaps not on its immediate release, but in a subsequent Service
Pack or update. It is not out of the question to think that following a successful release of USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 support in Windows 7,
SuperSpeed support would trickle down to Vista. Microsoft has conrmed this by stating that most of their partners share the opinion that
Vista should also support USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
Super-Speed support for Windows XP is unknown at this point. Given that XP is a seven-year-old operating system, the likelihood of this
happening is remote.
USB Type-C
USB Type-C is a new, tiny physical connector. The connector itself can support various exciting new USB standard like USB 3.1 and USB
power delivery (USB PD).
Alternate Mode
USB Type-C is a new connector standard that's very small. It's about a third the size of an old USB Type-A plug. This is a single connector
standard that every device should be able to use. USB Type-C ports can support a variety of dierent protocols using “alternate modes,”
which allows you to have adapters that can output HDMI, VGA, DisplayPort, or other types of connections from that single USB port
USB Power Delivery
The USB PD specication is also closely intertwined with USB Type-C. Currently, smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices often use
a USB connection to charge. A USB 2.0 connection provides up to 2.5 watts of power — that'll charge your phone, but that's about it. A
laptop might require up to 60 watts, for example. The USB Power Delivery specication ups this power delivery to 100 watts. It's bi-
directional, so a device can either send or receive power. And this power can be transferred at the same time the device is transmitting
data across the connection.
This could spell the end of all those proprietary laptop charging cables, with everything charging via a standard USB connection. You could
charge your laptop from one of those portable battery packs you charge your smartphones and other portable devices from today. You
could plug your laptop into an external display connected to a power cable, and that external display would charge your laptop as you used
it as an external display — all via the one little USB Type-C connection. To use this, the device and the cable have to support USB Power
Delivery. Just having a USB Type-C connection doesn't necessarily mean they do.
USB Type-C and USB 3.1
USB 3.1 is a new USB standard. USB 3's theoretical bandwidth is 5 Gbps, while USB 3.1 Gen2 is10Gbps . That's double the bandwidth, as
fast as a rst-generation Thunderbolt connector. USB Type-C isn't the same thing as USB 3.1. USB Type-C is just a connector shape, and
the underlying technology could just be USB 2 or USB 3.0. In fact, Nokia's N1 Android tablet uses a USB Type-C connector, but underneath
it's all USB 2.0 — not even USB 3.0. However, these technologies are closely related.
Thunderbolt over USB Type-C
Thunderbolt is a hardware interface that combines data, video, audio, and power in a single connection. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express
(PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into one serial signal, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Thunderbolt 1 and Thunderbolt 2 use
the same connector [1] as miniDP (DisplayPort) to connect to peripherals, while Thunderbolt 3 uses a USB Type-C connector [2].
Technology and components 41

Figure 1. Thunderbolt 1 and Thunderbolt 3
1 Thunderbolt 1 and Thunderbolt 2 (using a miniDP connector)
2 Thunderbolt 3 (using a USB Type-C connector)
Thunderbolt 3 over USB Type-C
Thunderbolt 3 brings Thunderbolt to USB Type-C at speeds up to 40 Gbps, creating one compact port that does it all - delivering the
fastest, most versatile connection to any dock, display or data device like an external hard drive. Thunderbolt 3 uses a USB Type-C
connector/port to connect to supported peripherals.
1 Thunderbolt 3 uses USB Type-C connector and cables - It is compact and reversible
2 Thunderbolt 3 supports speed up to 40 Gbps
3 DisplayPort 1.2 – compatible with existing DisplayPort monitors, devices and cables
4 USB Power Delivery - Up to 130W on supported computers
Key Features of Thunderbolt 3 over USB Type-C
1 Thunderbolt, USB, DisplayPort and power on USB Type-C on a single cable (features vary between dierent products)
2 USB Type-C connector and cables which are compact and reversible
3 Supports Thunderbolt Networking (*varies between dierent products)
4 Supports up to 4K displays
5 Up to 40 Gbps
NOTE: Data transfer speed may vary between dierent devices.
42 Technology and components

System specications
Topics:
• Technical specications
• Keyboards Hot Key Denitions
Technical specications
This topic lists out the technical specications.
Table 3. Specications
Type Feature
Model Number Latitude 7390 2-in-1
Processor family Intel Kaby Lake U and R (7th and 8th generation i3/i5/i7)
Operating System • Microsoft Windows 10 Pro 64 bit
• Microsoft Windows 10 Home 64 bit
Memory • LPDDR3 SDRAM 1866 MHz; Up to 8 GB (on board)
• LPDDR3 SDRAM 2133 MHz; 16 GB (on board)
Chipset Intel Kaby Lake U and R (integrated with processor)
Graphics • Intel Integrated HD Graphics 620 (7th generation Intel core)
• Intel Integrated UHD Graphics 620 (8th generation Intel core)
Display 13.3 inches FHD 16:9 (1920 x 1080) WVA Touch with Corning Gorilla Glass 4,
Active Pen Support, Anti-Reective and Anti-Smudge, 255 nits
Storage options Primary Storage:
• 128 GB M.2 2280 SATA SSD
• 256 GB M.2 2280 SATA SSD
• 256 GB M.2 2280 PCIeSSD
• 512 GB M.2 2280 PCIeSSD
• 1 TB M.2 2280 PCIeSSD
• 256 GB M.2 2280 SED PCIeSSD
• 512 GB M.2 2280 SED PCIeSSD
Secondary Storage:
• 128 GB M.2 2230 PCIeSSD
• 256 GB M.2 2230 PCIeSSD
Multimedia • Microsoft Skype for Business Certied
4
System specications 43

• Optional HD or IR Camera (User-Facing xed focus) with LED
• Stereo Speaker with Maxx Audio Pro
• 4 x Noise reducing integrated array microphones
• Headset/Mic combo jack
Battery options • 45 Whr (3 Cell) Polymer Battery, with ExpressCharge
• 60 Whr (4 Cell) Polymer Battery, with ExpressCharge
• 60 Whr (4Cell) Long Life Cycle Polymer Battery
Power adapter • 45 W adapter, USB Type-C
• 65 W adapter, USB Type-C
• 90 W adapter, USB Type-C
Connectivity Microsoft Modern Standby compliant
WiFi Display (Miracast) 14
Wireless LAN Options:
• Qualcomm QCA61x4A 802.11ac Dual Band (2x2) Wireless Adapter +
Bluetooth 4.1 (non vPro)
• Qualcomm QCA6174A Extended Range 802.11 ac MU-MIMO Dual Band
(2x2) Wi-Fi + Bluetooth 4.1
• Intel Dual-Band Wireless-AC 8265 Wi-Fi + BT 4.2 Wireless Card (2x2).
Bluetooth Optional
Optional Mobile Broadband Options:
• Dell Wireless Qualcomm Snapdragon X7 LTE-A (DW5811e) for AT&T,
Verzion&Sprint (US)
• Dell Wireless Qualcomm Snapdragon X7 LTE-A (DW5811e) (EMEA/APJ/
ROW)
• Dell Wireless Qualcomm Snapdragon X7 LTE-A (DW5816e for Japan/ANZ/
China
• Dell Wireless Qualcomm Snapdragon X7 HSPA+ (DW5811e) (Indonesia)
Ports, Slots and Chassis • 1x USB 3.1 Gen 1
• 1x USB 3.1 Gen 1 with PowerShare
• 2 x DisplayPorts over USB Type-C with optional Thunderbolt 3
• HDMI 1.4
• microSIM card slot (WWAN only)
• microSD 4.0 Memory card reader
• Noble Wedge Lock slot
Security TPM 2.0 FIPS 140-2 certied, TCG Certied*
Optional Hardware Authentication Bundle 1:
• Contacted Smart Card with Control Vault 2.0 Advanced authentication with
FIPS 140-2 level 3 certication
Optional Hardware Authentication Bundle 2:
• Touch Fingerprint Reader, FIPS 201 Contacted Smart Card, Contactless
Smart Card/NFC5, Control Vault 2.0 Advanced authentication with FIPS
140-2 level 3 certication
• Optional face IR camera (Windows Hello compliant)
• Dell Client Command Suite
• Optional Dell Data Security and Management Software:
44 System specications

• Dell Data Protection | Endpoint Security Suite Enterprise
• Dell Data Protection | Encryption (Enterprise or Personal Edition)
• MozyPro, MozyEnterprise
• Dell Data Protection | Threat Defense
• Dell Protected Workspace
• Dell Data Guardian
• RSA NetWitness Endpoint
• VMware Airwatch
• Absolute Data & Device Security
• RSA SecurID Access
Input device • 10-Finger Touch Display
• 4 microphones available with standard bezel
• Headset/Mic combo jack
• Integrated ISO Keyboard
• Active Pen (Optional, sold separately)
Docking option • Dell Business Dock
• Dell Business Dock with Monitor stand
• Dell Business Thunderbolt Dock
* TCG certication (February 2018)
Keyboards Hot Key Denitions
Table 4. Hot key combinations
Fn Key Combination Function
Fn+ESC Fn Toggle
Fn+ F1 Speaker Mute
Fn + F2 Volume Down
Fn + F3 Volume Up
Fn + F4 Mic Mute
Fn + F5 Num Lock
Fn + F6 Scroll Lock
Fn + F8 Display Toggle (Win + P)
Fn + F9 Search
Fn + F10 Increase Keyboard Backlight Brightness
(Pressing this function cycle keyboard backlight to the next level in
the sequence: 50%, 100%, o)
Fn + F11 Print Screen
Fn + F12 Insert
Fn + Home Toggle Radio On/O
System specications 45

Fn + End Sleep
Fn + Up arrow Brightness up
Fn + down arrow Brightness down
Fn Key Mode:
Standard = The F1-F12 keys behave as function keys. Holding <Fn> is required to access their secondary functions.
Secondary~14~= The F1-F12 keys control the secondary functions. <Fn> is required to access the standard functions
46 System specications

System setup
System setup enables you to manage your notebook hardware and specify BIOS level options. From the System setup, you can:
• Change the NVRAM settings after you add or remove hardware
• View the system hardware conguration
• Enable or disable integrated devices
• Set performance and power management thresholds
• Manage your computer security
Topics:
• Boot menu
• Navigation keys
• System setup options
• General screen options
• System Conguration screen options
• Video screen options
• Secure Boot screen options
• Intel software guard extensions screen options
• Performance screen options
• Power management screen options
• POST behavior screen options
• Manageability
• Virtualization support screen options
• Wireless screen options
• Maintenance screen options
• System logs screen options
• Updating the BIOS in Windows
• System and setup password
Boot menu
Press <F12> when the Dell logo appears to initiate a one-time boot menu with a list of the valid boot devices for the system. Diagnostics
and BIOS Setup options are also included in this menu. The devices listed on the boot menu depend on the bootable devices in the system.
This menu is useful when you are attempting to boot to a particular device or to bring up the diagnostics for the system. Using the boot
menu does not make any changes to the boot order stored in the BIOS.
The options are:
• UEFI Boot:
• Windows Boot Manager
•
• Other Options:
5
System setup 47

• BIOS Setup
• BIOS Flash Update
• Diagnostics
• Change Boot Mode Settings
Navigation keys
NOTE: For most of the System Setup options, changes that you make are recorded but do not take eect until you restart the
system.
Keys Navigation
Up arrow Moves to the previous eld.
Down arrow Moves to the next eld.
Enter Selects a value in the selected eld (if applicable) or follow the link in the eld.
Spacebar Expands or collapses a drop‐down list, if applicable.
Tab Moves to the next focus area.
NOTE: For the standard graphics browser only.
Esc Moves to the previous page until you view the main screen. Pressing Esc in the main screen displays a message
that prompts you to save any unsaved changes and restarts the system.
System setup options
NOTE: Depending on the notebook and its installed devices, the items listed in this section may or may not appear.
General screen options
This section lists the primary hardware features of your computer.
Option Description
System Information This section lists the primary hardware features of your computer.
• System Information: Displays BIOS Version, Service Tag, Asset Tag, Ownership Tag, Manufacture Date,
Ownership Date, Express Service Code, the Signed Firmware update—enabled by default
• Memory Information: Displays Memory Installed, Memory Available, Memory Speed, Memory Channels Mode,
Memory Technology
• Processor Information: Displays Processor Type, Core Count, Processor ID, Current Clock Speed, Minimum
Clock Speed, Maximum Clock Speed, Processor L2 Cache, Processor L3 Cache, HT Capable, and 64-Bit
Technology
• Device Information: Displays M.2 SATA, M.2 PCIe SSD-0, M.2 PCIe SSD-1, Passthrough MAC address, Video
Controller, Video BIOS Version, Video Memory, Panel Type, Native Resolution, Audio Controller, Wi-Fi Device,
Cellular Device, Bluetooth Device
Battery Information Displays the battery status health and whether the AC adapter is installed.
Boot Sequence Allows you to change the order in which the computer attempts to nd an operating system.
• Diskette Drive
• USB Storage Device
• CD/DVD/CD-RW Drive
• Onboard NIC
48 System setup

Option Description
Boot sequence
options • Windows boot manager
• WindowsIns
Boot list options • Legacy
• UEFI—selected by default
Advanced Boot
Options
This option allows you the legacy option ROMs to load. By default, the Enable Legacy Option ROMs is disabled.
Enable Attempt Legacy Boot is disabled by default.
UEFI boot path
security • Always, except internal HDD
• Always
• Never
Date/Time Allows you to change the date and time.
System Conguration screen options
Option Description
SATA Operation Allows you to congure the internal SATA hard-drive controller. The options are:
• Disabled
• AHCI
• RAID On: This option is enabled by default.
Drives Allows you to congure the SATA drives on board. All drives are enabled by default. The options are:
• SATA-2 — enabled by default
• M.2 PCIe SSD-0 — enabled by default
• M.2 PCIe SSD-1 — enabled by default
SMART Reporting This eld controls whether hard drive errors for integrated drives are reported during system startup. This
technology is part of the SMART (Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology) specication. This option is
disabled by default.
• Enable SMART Reporting
USB Conguration This is an optional feature.
This eld congures the integrated USB controller. If Boot Support is enabled, the system is allowed to boot any
type of USB Mass Storage Devices—HDD, memory key, oppy.
If USB port is enabled, device attached to this port is enabled and available for OS.
If USB port is disabled, the OS cannot see any device attached to this port.
The options are:
• Enable USB Boot Support—enabled by default
• Enable External USB Port—enabled by default
System setup 49

Option Description
NOTE: If the Fastboot option is set to "Minimal", the "Enable USB Boot support " setting is ignored and
the system will not boot from any Pre-boot USB devices.
NOTE: A USB Keyboard and/or mouse connected to the platform's USB ports will continue to function
within BIOS Setup if the "Enable External USB Port" option is disabled.
Dell Type-C Dock
Conguration
This section allows connection to the Dell WD and TB family of docks (Typr-C docks) independent of USB and
Thunderbolt Adapter conguration settings.
• Always Allow Dell Docks is disabled
Thunderbolt Adapter
Conguration
This section allows Thunderbolt Adapter Conguration.
• Enable Thunderbolt Technology Support—is enabled by default
• Enable Thunderbolt Adapter Boot Support—is disabled
• Enable Thunderbolt Adapter Pre-boot Modules—is disabled
• Enable Thunderbolt (and PCIE behind TBT) Preboot
• Security level-No security—is disabled
• Security level-User conguration—enabled by default
• Security level-Secure connect—is disabled
• Security level- Display port only—is disabled
USB PowerShare This eld congures the USB PowerShare feature behavior. This option allows you to charge external devices using
the stored system battery power through the USB PowerShare port. This option is disabled by default
Audio This eld enables or disables the integrated audio controller. By default, the Enable Audio option is selected. The
options are:
• Enable Microphone—enabled by default
• Enable Internal Speaker—enabled by default
Keyboard
Illumination
This eld lets you choose the operating mode of the keyboard illumination feature. The keyboard brightness level
can be set from 0% to 100%. The options are:
• Disabled
• Dim
• Bright—enabled by default
Keyboard Backlight
Timeout on AC
The Keyboard Backlight Timeout dims out with AC option. The main keyboard illumination feature is not aected.
Keyboard Illumination will continue to support the various illumination levels. This eld has an eect when the
backlight is enabled. The options are:
• 5 sec
• 10 sec—enabled by default
• 15 sec
• 30 sec
• 1 min
• 5 min
• 15 min
• Never
50 System setup

Option Description
Keyboard Backlight
Timeout on Battery
The Keyboard Backlight Timeout dims out with the Battery option. The main keyboard illumination feature is not
aected. Keyboard Illumination will continue to support the various illumination levels. This eld has an eect when
the backlight is enabled. The options are:
• 5 sec
• 10 sec—enabled by default
• 15 sec
• 30 sec
• 1 min
• 5 min
• 15 min
• Never
Touchscreen It controls whether the screen is enabled or disabled. This option is enabled by default.
Unobtrusive Mode This option, when enabled, pressing Fn+F7 turns o all light and sound emissions in the system. To resume normal
operation, press Fn+F7 again. This option is disabled by default.
Miscellaneous
Devices
Allows you to enable or disable the following devices:
• Enable Camera—enabled by default
• Enable Secure Digital (SD) Card—enabled by default
• Secure Digital (SD) Card Boot—disabled by default
• Secure Digital (SD) Card Read-Only-Mode—disabled by default
Video screen options
Option Description
LCD Brightness Allows you to set the display brightness depending up on the power source—On Battery and On AC. The LCD
brightness is independent for battery and AC adapter. It can be set using the slider.
NOTE: The video setting is visible only when a video card is installed into the system.
Secure Boot screen options
Option Description
Secure Boot Enable This option enables or disables the Secure Boot Enable
• Disabled - by default
• Enabled
Default setting: disabled.
Expert Key
management
This option enables or disables the Expert Key management
• PK—enabled by default
• KEK
• db
• dbx
System setup 51

Intel software guard extensions screen options
Option Description
Intel SGX Enable This eld species you to provide a secured environment for running code/storing sensitive information in the
context of the main OS. The options are:
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Software controlled
Default setting: Software controlled
Enclave Memory
Size
This option allows you to set the SGX Enclave Reserve Memory Size. The options are:
• 32 MB
• 64 MB
• 128 MB—enabled by default
Performance screen options
Option Description
Multi-Core Support This eld species whether the process has one or all cores enabled. The performance of some applications
improves with the additional cores. This option is enabled by default. Allows you to enable or disable multi-core
support for the processor. The installed processor supports two cores. If you enable Multi-Core Support, two cores
are enabled. If you disable Multi-Core Support, one core is enabled.
• Enable Multi-Core Support
Default setting: The option is enabled.
Intel SpeedStep Allows you to enable or disable the Intel SpeedStep feature.
• Enable Intel SpeedStep
Default setting: The option is enabled.
C-States Control Allows you to enable or disable the additional processor sleep states.
• C states
Default setting: The option is enabled.
Intel TurboBoost Allows you to enable or disable the Intel TurboBoost mode of the processor.
• Enable Intel TurboBoost
Default setting: The option is enabled.
HyperThread
Control
Allows you to enable or disable the Hyper-Threading in the processor.
• Disabled
• Enabled
52 System setup

Option Description
Default setting: Enabled is selected.
Power management screen options
Option Description
AC Behavior Allows you to enable or disable the computer from turning on automatically when an AC adapter is connected.
Default setting: Wake on AC is not selected.
Enable Intel Speed
Shift Technology • Enable Intel Speed Shift Technology
Default setting: Enabled
Auto On Time Allows you to set the time at which the computer must turn on automatically. The options are:
• Disabled
• Every Day
• Weekdays
• Select Days
Default setting: Disabled
USB Wake Support Allows you to enable USB devices to wake the system from Standby.
NOTE: This feature is only functional when the AC power adapter is connected. If the AC power adapter
is removed during Standby, the system setup removes power from all the USB ports to conserve battery
power.
• Enable USB Wake Support
• Wake on Dell USB-C dock
Default setting: The option is disabled.
Wake on WLAN Allows you to enable or disable the feature that powers on the computer from the O state when triggered by a
LAN signal.
• Disabled
• WLAN
Default setting: Disabled
Block Sleep This option lets you block entering to sleep (S3 state) in operating system environment.
Block Sleep (S3 state)
Default setting: This option is disabled
Peak Shift This option enables you to minimize the AC power consumption during the peak power times of day. After you
enable this option, your system runs only in battery even if the AC is attached.
• Enable peak shift—is disabled
• Set battery threshold (15% to 100%) - 15 % (enabled by default)
System setup 53
Option Description
Advanced Battery
Charge
Conguration
This option enables you to maximize the battery health. By enabling this option, your system uses the standard
charging algorithm and other techniques, during the non work hours to improve the battery health.
Disabled
Default setting: Disabled
Primary Battery
Charge
Conguration
Allows you to select the charging mode for the battery. The options are:
• Adaptive—enabled by default
• Standard—Fully charges your battery at a standard rate.
• ExpressCharge—The battery charges over a shorter time using Dell’s fast charging technology.
• Primarily AC use
• Custom
If Custom Charge is selected, you can also congure Custom Charge Start and Custom Charge Stop.
NOTE: All charging mode may not be available for all the batteries. To enable this option, disable the
Advanced Battery Charge Conguration option.
Type-C connector
power • 7.5 Watts
• 15 Watts—enabled by default
POST behavior screen options
Option Description
Adapter Warnings Allows you to enable or disable the system setup (BIOS) warning messages when you use certain power adapters.
Default setting: Enable Adapter Warnings
Keypad
(Embedded)
Allows you to choose one of two methods to enable the keypad that is embedded in the internal keyboard.
• Fn Key Only—default.
• By Numlock
NOTE: When setup is running, this option has no eect. Setup works in Fn Key Only mode.
Numlock Enable Allows you to enable the Numlock option when the computer boots.
Enable Network. This option is enabled by default.
Fn Key Emulation Allows you to set the option where the Scroll Lock key is used to simulate the Fn key feature.
Enable Fn Key Emulation (default)
Fn Lock Options Allows you to let hot key combinations Fn + Esc toggle the primary behavior of F1–F12, between their standard
and secondary functions. If you disable this option, you cannot toggle dynamically the primary behavior of these
keys. The available options are:
• Fn Lock—enabled by default
• Lock Mode Disable/Standard—enabled by default
• Lock Mode Enable/Secondary
Fastboot Allows you to speed up the boot process by bypassing some of the compatibility steps. The options are:
54 System setup

Option Description
• Minimal—enabled by default
• Thorough
• Auto
Extended BIOS
POST Time
Allows you to create an extra preboot delay. The options are:
• 0 seconds—enabled by default.
• 5 seconds
• 10 seconds
Full Screen Log • Enable Full Screen Logo—not enabled
Warnings and errors • Prompt on warnings and errors—enabled by default
• Continue on warnings
• Continue on warnings and errors
Sign of Life
Indication • Enable Sign of Life Keyboard Backlight Indication—enabled by default
Manageability
Option Description
USB provision Enable USB provision is not selected by default
MEBX Hotkey —
enabled by default
Allows you to specify whether the MEBx Hotkey function should enable, during the system boot.
• Disabled
• Enabled
Default setting: Disabled
Virtualization support screen options
Option Description
Virtualization This eld species whether a virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) can utilize the conditional hardware capabilities
provided by Intel Virtualization Technology.
Enable Intel Virtualization Technology—enabled by default.
VT for Direct I/O Enables or disables the Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) from utilizing the additional hardware capabilities provided
by Intel® Virtualization technology for direct I/O.
Enable VT for Direct I/O - enabled by default.
Trusted Execution This option species whether a Measured Virtual Machine Monitor (MVMM) can utilize the additional hardware
capabilities provided by Intel Trusted Execution Technology. The TPM Virtualization Technology, and the
Virtualization technology for direct I/O must be enabled to use this feature.
Trusted Execution - disabled by default.
System setup 55

Wireless screen options
Option
Description
Wireless Switch Allows to set the wireless devices that can be controlled by the wireless switch. The options are:
• WWAN
• GPS (on WWAN Module)
• WLAN
• Bluetooth
All the options are enabled by default.
NOTE: For WLAN enable or disable controls are tied together and they cannot be enabled or disabled
independently.
Wireless Device
Enable
Allows you to enable or disable the internal wireless devices.
• WWAN/GPS
• WLAN
• Bluetooth
All the options are enabled by default.
NOTE: IMEI number for WWAN can be found ont the outer box or the WWAN card.
Maintenance screen options
Option Description
Service Tag Displays the Service Tag of your computer.
Asset Tag Allows you to create a system asset tag if an asset tag is not already set. This option is not set by default.
BIOS Downgrade This controls ashing of the system rmware to previous revisions. Option 'Allow BIOS downgrade' is enabled by
default.
Data Wipe This eld allows users to erase the data securely from all internal storage devices. Option 'Wipe on Next boot' is not
enabled by default. The following is list of devices aected:
• Internal SATA HDD/SSD
• Internal M.2 SATA SDD
• Internal M.2 PCIe SSD
• Internal eMMC
BIOS Recovery This eld allows you to recover from certain corrupted BIOS conditions from a recover le on the user primary hard
drive or an external USB key.
• BIOS Recovery from Hard Drive—enabled by default
• Always perform integrity check—disabled by default
56 System setup

System logs screen options
Option Description
BIOS Events Allows you to view and clear the System Setup (BIOS) POST events.
Thermal Events Allows you to view and clear the System Setup (Thermal) events.
Power Events Allows you to view and clear the System Setup (Power) events.
Updating the BIOS in Windows
It is recommended to update your BIOS (System Setup), when you replace the system board or if an update is available. For laptops, ensure
that your computer battery is fully charged and connected to a power outlet
NOTE: If BitLocker is enabled, it must be suspended prior to updating the system BIOS, and then re-enabled after the BIOS
update is completed.
NOTE: AC adapter must be plugged in before attempting to update BIOS.
1 Restart the computer.
2 Go to Dell.com/support.
• Enter the Service Tag or Express Service Code and click Submit.
• Click Detect Product and follow the instructions on screen.
3 If you are unable to detect or nd the Service Tag, click Choose from all products.
4 Choose the Products category from the list.
NOTE: Choose the appropriate category to reach the product page
5 Select your computer model and the Product Support page of your computer appears.
6 Click Get drivers and click Drivers and Downloads.
The Drivers and Downloads section opens.
7 Click Find it myself.
8 Click BIOS to view the BIOS versions.
9 Identify the latest BIOS le and click Download.
10 Select your preferred download method in the Please select your download method below window, click Download File.
The File Download window appears.
11 Click Save to save the le on your computer.
12 Click Run to install the updated BIOS settings on your computer.
Follow the instructions on the screen.
NOTE: It is recommended not to update the BIOS version for more than three revisions. For example: If you want to update the
BIOS from 1.0 to 7.0, then install version 4.0 rst and then install version 7.0.
Updating BIOS on systems with bitlocker enabled
CAUTION: If BitLocker is not suspended before updating the BIOS, the next time you reboot the system it will not recognize the
BitLocker key. You will then be prompted to enter the recovery key to progress and the system will ask for this on each reboot. If
the recovery key is not known this can result in data loss or an unnecessary operating system re-install. For more information on
this subject, see Knowledge Article: http://www.dell.com/support/article/us/en/19/SLN153694/updating-bios-on-systems-
with-bitlocker-enabled
System setup 57

Updating your system BIOS using a USB ash drive
If the system cannot load into Windows but there is still a need to update the BIOS, download the BIOS le using another system and save
it to a bootable USB Flash Drive.
NOTE: You will need to use a bootable USB Flash drive. Please refer to the following article for further details: http://
www.dell.com/support/article/us/en/19/SLN143196/how-to-create-a-bootable-usb-ash-drive-using-dell-diagnostic-
deployment-package--dddp-
1 Download the BIOS update .EXE le to another system.
2 Copy the le e.g. O9010A12.EXE onto the bootable USB Flash drive.
3 Insert the USB Flash drive into the system that requires the BIOS update.
4 Restart the system and press F12 when the Dell Splash logo appears to display the One Time Boot Menu.
5 Using arrow keys, select USB Storage Device and click Return.
6 The system will boot to a Diag C:\> prompt.
7 Run the le by typing the full lename e.g. O9010A12.exe and press Return.
8 The BIOS Update Utility will load, follow the instructions on screen.
Figure 2. DOS BIOS Update Screen
Updating the Dell BIOS in Linux and Ubuntu environments
If you want to update the system BIOS in a Linux environment such as Ubuntu, see http://www.dell.com/support/article/us/en/19/
SLN171755/updating-the-dell-bios-in-linux-and-ubuntu-environments.
Flashing the BIOS from the F12 One-Time boot menu
Updating your system BIOS using a BIOS update .exe le copied to a FAT32 USB key and booting from the F12 one time boot menu.
BIOS Update
You can run the BIOS update le from Windows using a bootable USB key or you can also update the BIOS from the F12 One-Time boot
menu on the system.
58 System setup

Most Dell systems built after 2012 have this capability and you can conrm by booting your system to the F12 One-Time Boot Menu to see
if BIOS FLASH UPDATE is listed as a boot option for your system. If the option is listed, then the BIOS supports this BIOS update option.
NOTE: Only systems with BIOS Flash Update option in the F12 One-Time Boot Menu can use this function.
Updating from the One-Time Boot Menu
To update your BIOS from the F12 One-Time boot menu, you will need:
• USB key formatted to the FAT32 le system (key does not have to be bootable)
• BIOS executable le that you downloaded from the Dell Support website and copied to the root of the USB key
• AC power adapter connected to the system
• Functional system battery to ash the BIOS
Perform the following steps to execute the BIOS update ash process from the F12 menu:
CAUTION: Do not power o the system during the BIOS update process. Powering o the system could make the system fail to
boot.
1 From a power o state, insert the USB key where you copied the ash into a USB port of the system .
2 Power on the system and press the F12 key to access the One-Time Boot Menu, Highlight BIOS Flash Update using the arrow keys
then press Enter.
3 The Bios ash menu will open then click the browse button.
System setup 59

4 The E5450A14.exe le is shown as an example in the following screenshot. The actual le name may vary.
5 Once the le is selected, it will show in the le selection box and you can click the OK button to continue.
60 System setup

6 Click the Begin Flash Update button.
7 A warning box is displayed asking you if you want to proceed. Click the Yes button to begin the ash.
System setup 61

8 At this point the BIOS ash will execute, the system will reboot and then the BIOS ash will start and a progress bar will show the
progress of the ash. Depending on the changes included in the update, the progress bar may go from zero to 100 multiple times and
the ash process could take as long as 10 minutes. Generally this process takes two to three minutes.
9 Once complete, the system will reboot and the BIOS update process is completed.
System and setup password
You can create a system password and a setup password to secure your computer.
Password type Description
System password Password that you must enter to log on to your system.
Setup password Password that you must enter to access and make changes to the BIOS settings of your computer.
62 System setup

CAUTION: The password features provide a basic level of security for the data on your computer.
CAUTION: Anyone can access the data stored on your computer if it is not locked and left unattended.
NOTE: System and setup password feature is disabled.
Assigning a system password and setup password
You can assign a new System Password only when the status is in Not Set.
To enter the system setup, press F2 immediately after a power-on or re-boot.
1 In the System BIOS or System Setup screen, select Security and press Enter.
The Security screen is displayed.
2 Select System Password and create a password in the Enter the new password eld.
Use the following guidelines to assign the system password:
• A password can have up to 32 characters.
• The password can contain the numbers 0 through 9.
• Only lower case letters are valid, upper case letters are not allowed.
• Only the following special characters are allowed: space, (”), (+), (,), (-), (.), (/), (;), ([), (\), (]), (`).
3 Type the system password that you entered earlier in the Conrm new password eld and click OK.
4 Press Esc and a message prompts you to save the changes.
5 Press Y to save the changes.
The computer reboots.
Deleting or changing an existing system and or setup password
Ensure that the Password Status is Unlocked (in the System Setup) before attempting to delete or change the existing System and/or
Setup password. You cannot delete or change an existing System or Setup password, if the Password Status is Locked.
To enter the System Setup, press F2 immediately after a power-on or reboot.
1 In the System BIOS or System Setup screen, select System Security and press Enter.
The System Security screen is displayed.
2 In the System Security screen, verify that Password Status is Unlocked.
3 Select System Password, alter or delete the existing system password and press Enter or Tab.
4 Select Setup Password, alter or delete the existing setup password and press Enter or Tab.
NOTE: If you change the System and/or Setup password, re-enter the new password when promoted. If you delete the
System and/or Setup password, conrm the deletion when promoted.
5 Press Esc and a message prompts you to save the changes.
6 Press Y to save the changes and exit from System Setup.
The computer reboots.
System setup 63

Software
This chapter details the supported operating systems along with instructions on how to install the drivers.
Topics:
• Supported operating systems
• Downloading drivers
• Intel chipset drivers
• Video driver
• Audio driver
• Network drivers
• USB driver
• Storage drivers
• Battery drivers
• Intel HID Event Filter
• Intel Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework
• Intel Management engine
• Disk drivers
• Bluetooth drivers
• Security drivers
Supported operating systems
The topic lists the operating systems supported for .
Table 5. Supported operating systems
Supported operating systems Description
Windows 10 • Microsoft Windows 10 Pro 64-bit
• Microsoft Windows 10 Home 64-bit
Other • Ubuntu 16.04 LTS SP1 64-bit
• NeoKylin v6.0 64-bit
Downloading drivers
1 Turn on the notebook.
2 Go to Dell.com/support.
3 Click Product Support, enter the Service Tag of your notebook, and then click Submit.
NOTE: If you do not have the Service Tag, use the auto detect feature or manually browse for your notebook model.
4 Click Drivers and Downloads.
5 Select the operating system installed on your notebook.
6
64 Software

6 Scroll down the page and select the driver to install.
7 Click Download File to download the driver for your notebook.
8 After the download is complete, navigate to the folder where you saved the driver le.
9 Double-click the driver le icon and follow the instructions on the screen.
Intel chipset drivers
Verify if the Intel chipset drivers are already installed in the system.
Table 6. Intel chipset drivers
Before Installation After Installation
Video driver
Verify if the video driver is already installed in the system.
Software 65

Audio driver
Verify if audio drivers are already installed in the system.
Table 7. Audio driver
Before Installation After Installation
Network drivers
Install the WLAN and Bluetooth drivers from the Dell support site.
Table 8. Network drivers
Before installation After installation
USB driver
Verify if the USB drivers are already installed in the system.
Table 9. USB driver
Before Installation After Installation
Storage drivers
Verify if the storage controller drivers are installed in the system.
66 Software

Table 10. Storage drivers
Before Installation After Installation
None
Battery drivers
The latest battery drivers are installed in the computer.
Table 11. Battery drivers
Before Installation After Installation
Intel HID Event Filter
Verify if the Intel HID event lter is already installed in the computer.
Software 67

Table 12. Intel HID Event Filter
Before Installation After Installation
Intel Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework
Verify if the Intel dynamic platform and thermal framework is already installed in the computer.
Table 13. Intel Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework
After Installation
68 Software

Intel Management engine
Verify if the Intel dynamic platform and thermal framework is already installed in the computer.
Table 14. Intel management engine interface
Before Installation After Installation
Disk drivers
Disk drivers installed in the system
Bluetooth drivers
This platform supports a variety of Bluetooth drivers. The following is an example
Table 15. Bluetooth drivers
Before Installation After Installation
Software 69

Security drivers
This section lists the security devices in the Device Manager.
Security device drivers
Verify if the security device drivers are installed in the computer.
Fingerprint sensor drivers
Verify if the Fingerprint sensor drivers are installed in the computer.
70 Software

Troubleshooting
Dell Enhanced Pre-Boot System Assessment — ePSA
diagnostic 3.0
You can invoke the ePSA diagnostics by performing either of the following steps:
• Press the F12 key when the system boots and choosing Diagnostics option.
• Press Fn+PWR when the system boots.
For more details, see Dell EPSA Diagnostic 3.0.
Real Time Clock reset
The Real Time Clock (RTC) reset function allows you or the service technician to recover the recently launched model Dell Latitude and
Precision systems from select No POST/No Boot/No Power situations. You can initiate the RTC reset on the system from a power o
state only if it is connected to AC power. Press and hold the power button for 25 seconds. The system RTC reset occurs after you release
the power button.
NOTE: If AC power is disconnected from the system during the process or the power button is held longer than 40 seconds, the
RTC reset process is aborted.
The RTC reset will reset the BIOS to Defaults, un-provision Intel vPro and reset the system date and time. The following items are
unaected by the RTC reset:
• Service Tag
• Asset Tag
• Ownership Tag
• Admin Password
• System Password
• HDD Password
• Key Databases
• System Logs
The following items may or may not reset based on your custom BIOS setting selections:
• The Boot List
• Enable Legacy OROMs
• Secure Boot Enable
• Allow BIOS Downgrade
7
Troubleshooting 71

Contacting Dell
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can nd contact information on your purchase invoice, packing slip,
bill, or Dell product catalog.
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. Availability varies by country and product, and some services
may not be available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer service issues:
1 Go to Dell.com/support.
2 Select your support category.
3 Verify your country or region in the Choose a Country/Region drop-down list at the bottom of the page.
4 Select the appropriate service or support link based on your need.
8
72 Contacting Dell