LevelOne GEP-2650 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for GEP-2650 by LevelOne which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Introduction
Reader object
This book is suitable for the following personnel to read
Network Engineer
Technology promotion personnel
Network administrator
Relevant information
Manual name
Description
Product installation
manual
This manual describes some characteristics of the products in the functional and
physical, provides procedures, hardware installation troubleshooting, module
specifications of equipment, as well as the cable and connector specifications and
standards.
Product manual
commands
This manual does a detailed description of the product support configuration command.
Including a description of the command mode, parameters and using the guidelines,
and equipped with specific examples.
The product WEB
management manual
This manual supports various functional products‘ WEB interface and describiation, and
a detailed configuration example.

The book agreed…
the command line format conventions
By using the Arial command line font,The following specific correlation scheme:
Bold:Command keywords (unchanged must according to lose part of command) is represented by bold font.
Italic:The command line parameters (the actual value for replacement parts must be ordered in the italicized)
[ ] :Represented by [] the enclosed part, in command configuration is optional.
{ x | y | ... }:Select one of the two or more options.
[ x | y | ... ]:Said to choose a or not selected from two or more options.
//:Started by the double slash line expressed as comments..
1) general format conventions
2) Terminal information display format:英文用 Courier New ,Chinese with Song typeface, font size 5,
representing the output information screen. The user with information from the terminal input information,
represented by the bold font.
3) various types of marks
The book also expressed in the operating process should pay special attention to place the various eye-catching
signs, these signs meaning:
s, tricks, the operation content descriptions are necessary supplement.
Statement:
It illustrates the port type part with the actual might be inconsistent, needs to be configured according to the
port types supported by the product of the actual operation.
This manual section for example display may contain other products information content (such as product
type, description), specific display information please refer to the actual use of the equipment information shall
prevail.
router and router icon mentioned in this manual, on behalf of the general meaning of the router, and run a
three layer switch routing protocol.

Table of contens
This section introduces the configuration guide related content, including the following:
1. Configuration command line interface
2. Configuration management
3. Configuration interface
4. Configure access/trunk port
5. Configure Link-aggregation Port
6. Configure VLAN
7. Configure MAC address
8. Configuration of POE
9. configuration IGMP Snooping
10. Configure SNMP
11. Configure SPAN
12. Configure the flow control based port
13. Anti-illegal DHCP Server
14. Anti-ARP-Spoofing
15. Port Rate Limit
16. Loopback Detection
17. Access Control
18. File system Configuration

1. Configuration command line interface
This section describes methods to use the command line interface, you can manage the network
equipment by using the command line interface
1.1. Command mode
Device management interface is divided into a number of different models, the user the command
mode determines the commands that you can use.
Enter a question mark button at the command prompt (?) can list every command mode to support the
use of command. When a user and network equipment management interface, a new session is
connected, the user first in the user model (User EXEC model),You can use the user mode command.
In user mode, can only use a small amount of commands, and command functions also have some
limitations, such as the show command. User mode command operating results will not be saved.
To use all of the commands, you must first enter privilege mode (Privileged EXEC).Usually, enter
privilege mode password must enter privilege mode. In privileged mode, the user can use all the
privileges of command, and can enter global configuration mode.
Use the configuration mode (global configuration mode, interface configuration mode) command, will
have an impact on the current running configuration. If the user to save the configuration information,
these commands will be preserved, and perform again at system restart. To enter configuration mode,
you must first enter global configuration mode. Starting from the global configuration mode, can enter
interface configuration mode and other configuration sub model.
The following table lists the command mode, how to access each mode, mode of prompt, how to leave
mode. The assumption here network device name for the default "Switch”
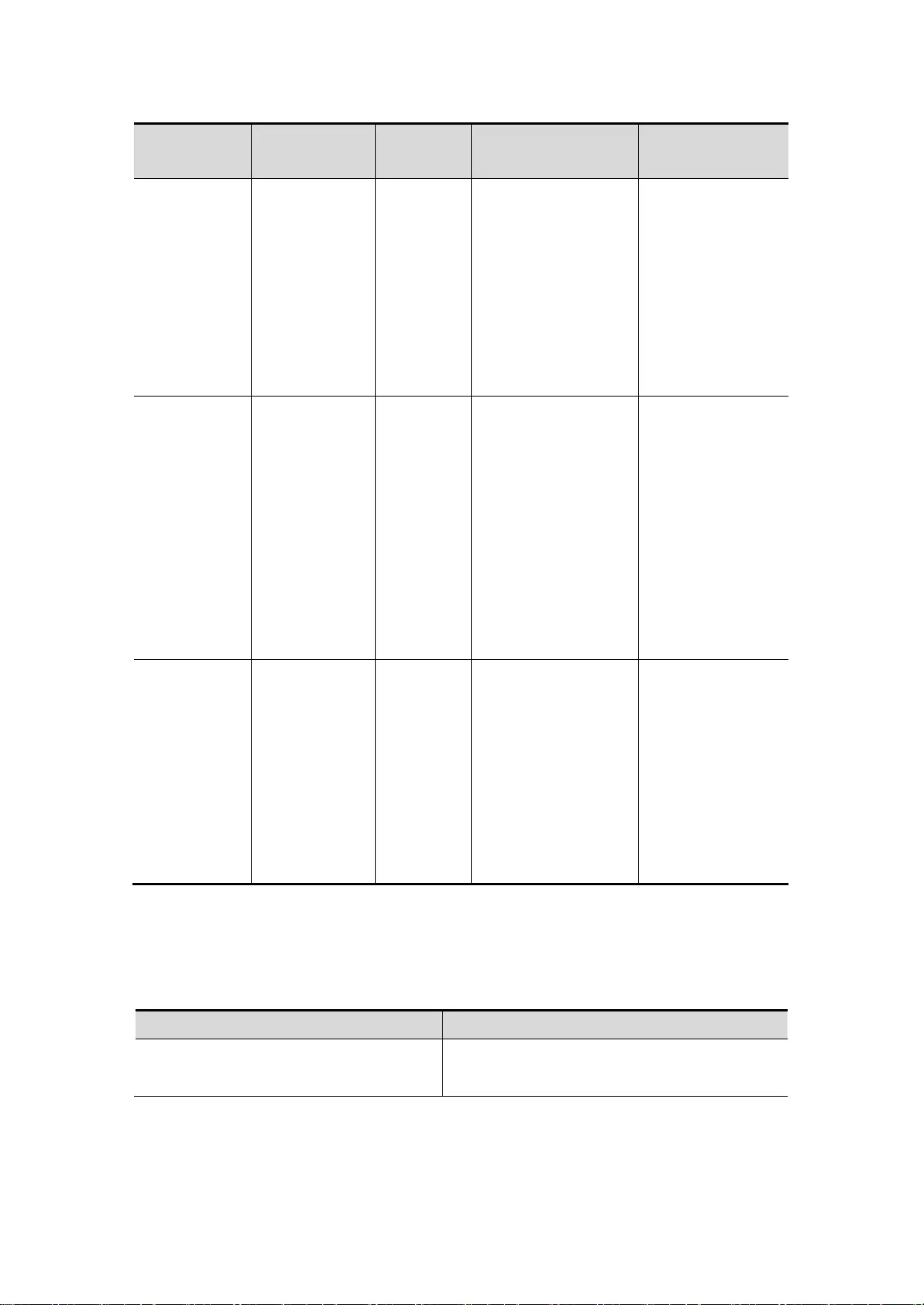
Command mode.:
Command
mode
Access method
Prompt
To leave or access
mode
About the model
User
EXEC(user
mode)
First entered
the access
network
equipment.
Switch>
Enter the exit
command to leave
the mode.
To enter privilege
mode, enter the
enable command.
To carry out the
test, this model is
used to display
system
information
Privileged
EXEC(privile
ged mode)
In user mode,
use the enable
command to
enter this
mode.
Switch#
To return to user
mode, enter the
disable command.
To verify the
results of using
the set command
mode. This mode
is protected with a
password.
Command
mode
Access method
Prompt
To leave or access
mode
About the model
Global
configuration(
global
configuration
mode)
In privileged
mode, use the
configure
command to
enter this
mode
Switch(co
nfig)#
To enter global
configuration mode,
enter the configure
command.
To return to the
privileged mode,
enter the exit
command or the end
command, or type
Ctrl+Z
Using the mode
command to
configure the
network to set
global parameters.
Interface
configuration
(The
interface
configuration
mode)
In global
configuration
mode, use the
interface
gigabitEtherne
t_id command
to enter this
mode
Switch(co
nfig-if-Gig
abitEthern
et-0/1)#
To enter the
interface
configuration mode,
enter the interface
gigabitEthernet_id
command.
To return to the
privileged mode,
enter the end
command, or type
the Ctrl+Z key
combination.
Various interfaces
using the mode
configuration of
network devices.
Config-vlan
(The VLAN
configuration
mode)
In global
configuration
mode, use the
VLAN vlan_id
command to
enter this
mode
Switch( co
nfig-
vlan)#
To enter the VLAN
configuration mode,
enter the VLAN
vlan_id command.
To return to the
privileged mode,
enter the end
command, or type
the Ctrl+Z key
combination.
This model is used
to configure VLAN
Parameters.
1.2. get help
The user can enter a question mark button at the command prompt (?) lists the support each
command mode command. The user can also list the parameter information of the same command
keywords or each command. See the table below:
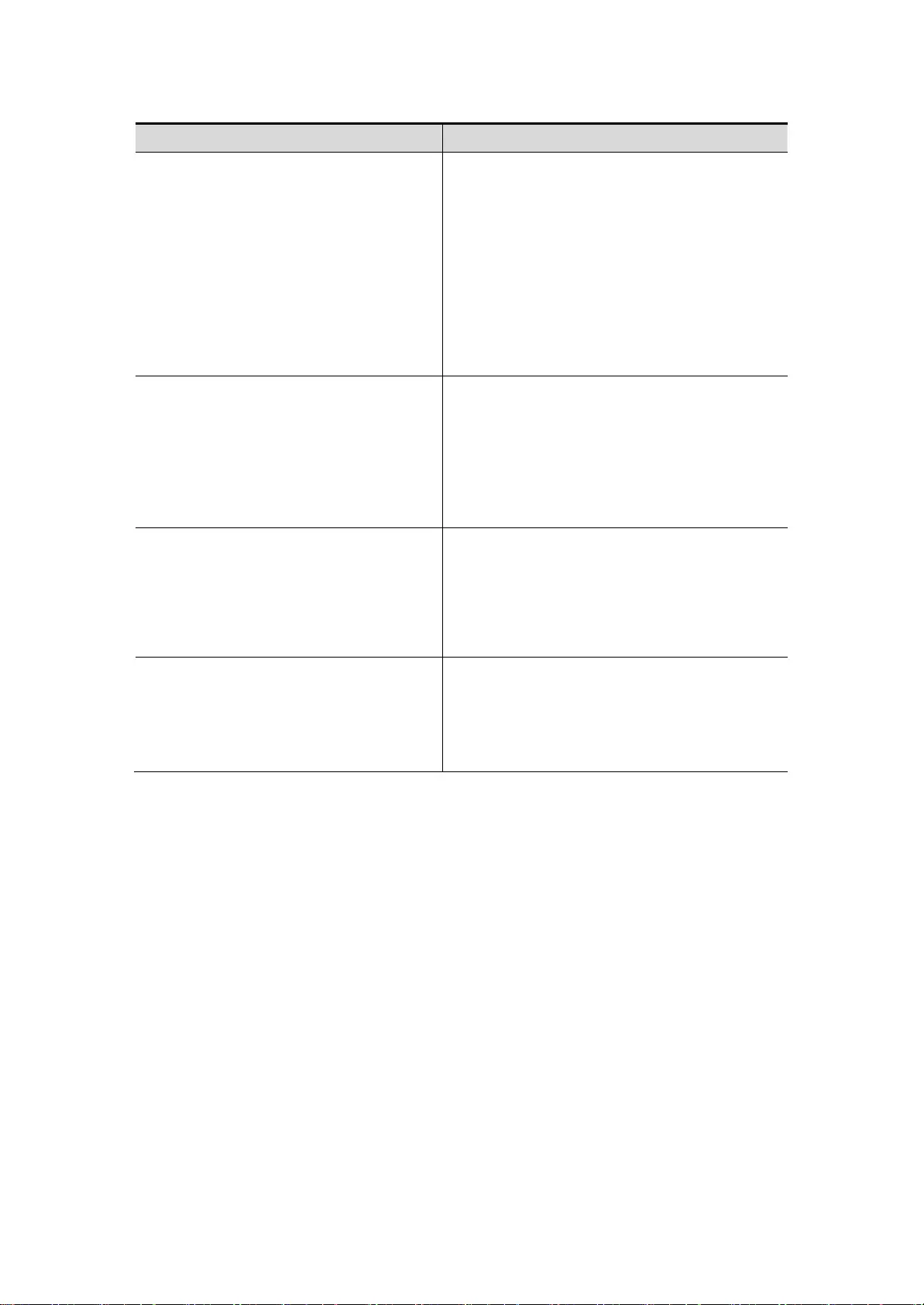
Command
Function
Help
Get the help system description information in
any Command mode.
Command
Function
abbreviated-command-entry?
To obtain the command key string the same
beginning.
Example:
Switch# di?
disable Turn off privileged commands
display Show something for debug
purpose
abbreviated-command-entry<Tab>
The command key integrity
Example:
Switch# show star<Tab>
Switch# show startup-config ?
?
Listed under the command of an associated
keywords.
Example:
Switch# show?
command keyword ?
The command key integrity.
Example:
Switch(config)# snmp-server community ?
<WORD> Community name
1.3. command
If you want to abbreviate command, only need to enter the command key part of a character, as long
as this part of the character recognition only enough command keyword.
For example show running-config The command can be written as:
Switch# show runn
1.4. The command can be written as
Almost all commands are no options. Usually, use the no option to disable certain features or
functions, or the executive and the command itself opposite operation. For example, interface
configuration command no shutdown performs the inverse operation interface off shutdown
commands, namely open interface. Used without no option keyword open characteristics are closed or
opened by default is closed.
Prompt information to understand CLI
The following table lists the user may be encountered in the use of CLI network management device
error messages.
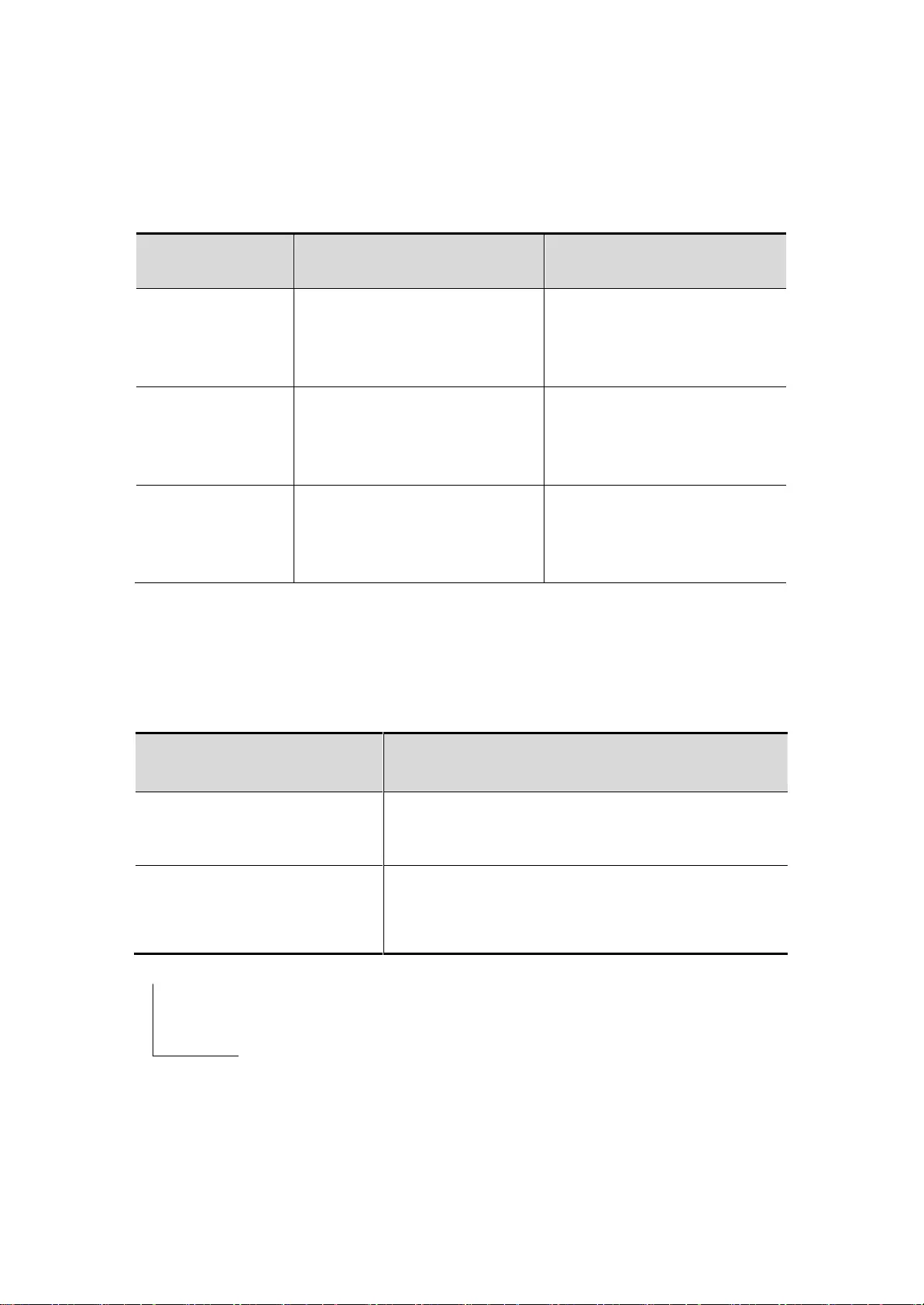
CLI error information common:
Error message
Meaning
How to get help
% Ambiguous
command: "show
c"
The user does not have enough
input character, network
equipment cannot recognize the
unique command.
Re enter the command, followed
by a ambiguous words enter a
question mark. May the entered
keyword will be displayed.
Type "speed ?" for
a list of
subcommands
The user does not enter the
command must be the key
word or variable parameters.
Re enter the command, input
space and then enter a question
mark. May be variable
parameter input keyword or will
be displayed.
% Invalid input
detected at '^'
marker
The user input command error,
symbol (^) indicates the error
word position.
Command mode prompt on the
seat under the input of a
question mark, this mode allows
the command key will be
displayed.
1.5. Use the history command
The system provides the user input command records. The characteristics in the input again long and
complex command will be very useful. From the command history records re call input commands,
perform actions in the following table::
Operation
Result
Ctrl-P Or up arrow
Browse before a command in the command history table.
From the beginning of last record, repeated use of the
operation can query the earlier records.
Ctrl-N Or down arrow key
After using Ctrl-P or the key operational direction, using
the operation back to a command closer in history
command table. Use again the operation can query the
more recent record.
Tip : the terminal supports standard keys.
1.6. Use the edit properties
The possibility of using this section describes the command line editing editing functions.
1.6.1. Edit shortcuts
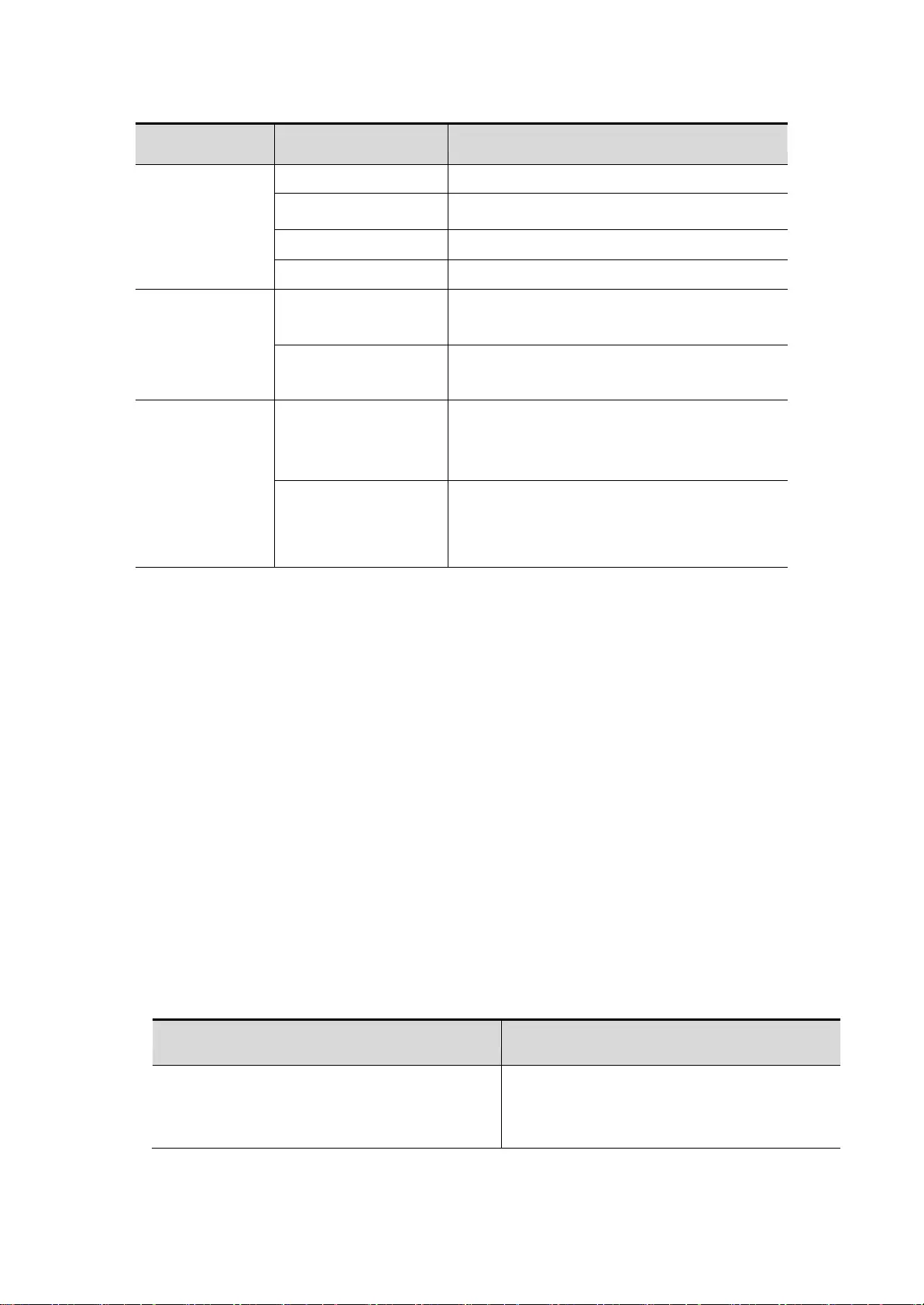
Listed in the following table editing shortcuts:
Function
Operation
Result
Move the cursor in
the edit line.
Left arrow or Ctrl-B
Move the cursor to a character to the left.
Left arrow or Ctrl-B
Move the cursor to a character on the right.
Ctrl-A
Move the cursor to the first command line.
Ctrl-E
Move the cursor to the first command line
Delete the input
character.
Backspace
A character to delete from the cursor to the left
of the
Delete key
A character to delete from the cursor to the left
of the
©
Return key
When the contents are displayed by enter key
will output the contents to the rolling line,
showing a line of content, using only the output
is not the end.
Space key
When the contents are displayed using the
space bar will output the contents to scrolling a
page, the next page content, only in the output
content does not end use.
1.7. Visit CLI
Before using CLI, users need to use a terminal or PC and network equipment connection. To start the
network equipment, network software and hardware initialization can be used after CLI. in network
equipment used for the first time only when using the serial port (Console) connected network device,
called out of band (Outband) management.
2. Configuration management
2.1. Login authentication control
2.1.1. Summary
Through the authentication control can prevent illegal user access switch.
2.1.2. To configure the local user
To establish a user identity authentication, please in global configuration mode, according to specific
needs, execute the following command:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# user name [password
password | password encryption-type
encrypted password]
Use encrypted password based user
authentication
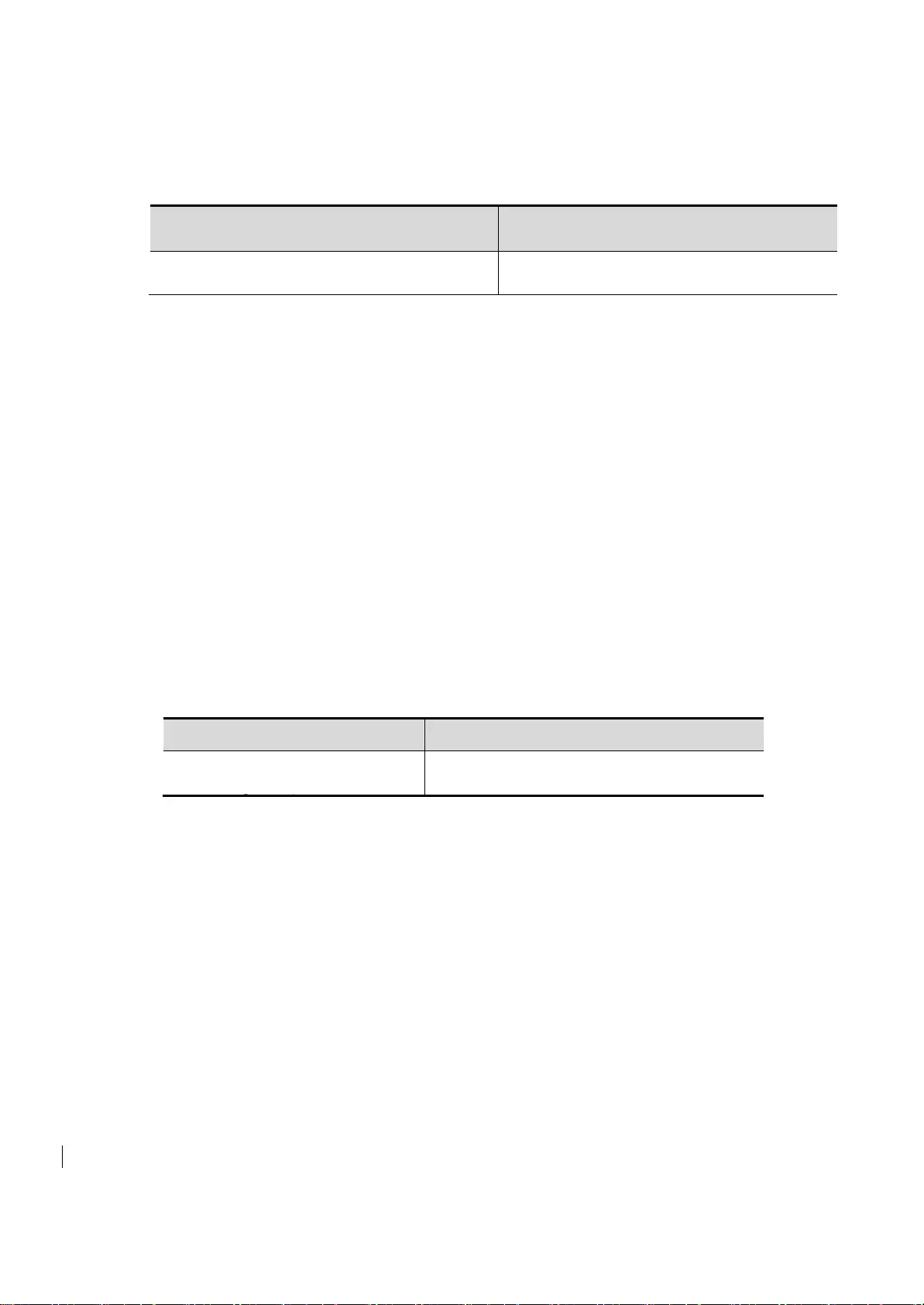
Command
Function
Switch(config-line)# login local
Set line login authentication local
2.1.3. Configuration line login authentication
To build the line login authentication, please in line configuration mode, according to specific needs,
execute the following command:
Step 1
2.2. System configuration
2.2.1. Summary
Each network device has its own system clock, the clock to provide specific date (year, month, day)
and time (time, minutes, seconds) and other information. For a network device, when the first time you
first need to manually configure the network equipment system clock for the current date and time. Of
course you can also, according to the need, the system clock correction at any time. The system clock
network equipment is mainly used for system log to record events.
2.2.2. Set the system time
You can set the network equipment on time by manual way. When you set the clock network
equipment, network equipment clock will you set the time is running down, even if the network
equipment, network equipment clock continues to run. So the network equipment clock settings once
in principle, do not need to be provided, unless you need to fix network equipment on time.
But for the network equipment do not provide the hardware clock, manually set the network equipment
on time is actually set the software clock, it only on the effective operation, when the network
equipment of electric, manual setting time to failure.
command
Function
Switch# clock Year
Month Day Hour Minute
Second
Date and set the clock system.
Such as the system time into 2003-6-20,10:10:12
Switch# clock 2003 6 20 10 10 12
Switch# show clock
FRI JUN 20 10:10:15 2003
2.2.3. View the system time
You can use the show clock in privileged mode command to display the system time information,
display format as follows: Switch# show clock // Display the current system time
FRI JUN 20 10:10:15 2003

command
Function
Switch(Config)# hostname name
Set system name, name must be
composed of printable characters, not
longer than 63 bytes.
command
Function
Switch(config)#ntp server ip-address
version [1-3]
Open the clock synchronization, the clock
server configuration and version of IP.
Switch(config)#ntp synchronize
Clock synchronization.
Switch(config)#ntp update-calendar
The hardware clock.
Switch#show ntp status
Check the NTP clock.
2.2.4. Set the clock synchronization
In setting the clock synchronization, can be better to view the system of log time, web operating time,
convenient track record.
2.3. The system name and a command prompt
2.3.1. summary
In Command to facilitate the management of, you can for a network device configuration system name
(System Name) to identify it. At the same time if you are not configured for the CLI command prompt,
then the system name (if the system name exceeds 32 characters, interception
The first 32 characters) will be the default command prompt, prompt will change with the name of the
default system.
2.3.2. Set system name
products provide global configuration mode command to configure the system name::
Step 1
The following example will name network equipment into Switch1:
Switch# configure terminal // Enter global configuration mode Switch(config)# hostname
Switch1 // Set the network device name Switch1 Switch1(config)# // The name has
changed
2.4. Check the information system
2.4.1. Summary
You can check some information in the command line to display, including the version information
system, equipment information system and so on..
2.4.2. View the system, version information
Including the system describes the system information, system power on time, system hardware,
system software version, Ctrl version of the software system layer, Boot layer software version of the

command
Function
Switch# show version
Display system, version information
Command
Function
Switch(config-line)# speed speed
The transmission rate set console, in
units of bps. for serial interface, you
can only the transmission rate is set to
9600,
A 19200, 38400, 115200, 4800, 2400,
9600 is the default rate
system. You can know the general situation of the network system through the information. You can in
privileged mode using the following table command display the system information:
Step 1
2.5. Console rate allocation
2.5.1. Summary
Network equipment have a console interface (Console), through the console interface, can be on the
network equipment management. When the network equipment used for the first time, must use the
configure it through the console port. You may need to change according to the rate of network
equipment serial. Note, used for network management equipment terminal rate setting must and
network equipment console rate.
2.5.2. Set console rate
On line configuration mode, rate, you can use the following command to set the console::
Step 1
2.6. Connection timeout
2.6.1. Summary
Through the connection timeout configuration of equipment, connection control the equipment has
been established (including has accepted the connection, and the device to a remote terminal
session), when the idle time exceeds the set value, without any input and output information, interrupt
this connection.
2.6.2. Connection timeout
The connection is currently accepted, within the specified time, without any input information, the
server will interrupt this connection. Ruijie products provide LINE configuration mode command to
configure the connection timeout:
Command
Function
Switch(config-line)# exec-timeout minutes
[seconds]
The configuration of LINE, has accepted the
connection timeout, when over allocation of
time, do not have any input, will break the
connection. Minutes: the number of minutes the
timeout specified; seconds: the specified
number of seconds timeout;

You can use the no exec-timeout command in the LINE configuration mode, cancel the timeout
connected LINE.
Switch# configure terminal // Enter global configuration mode Switch#
line vty 0 // Enter the LINE configuration mode Switch(config-line)#
exec-timeout 20 // Set the timeout period for the 20min
2.7. The configuration of LINE model
2.7.1. Summary
This chapter describes some of the operation of LINE:
Enter the LINE configuration mode
Increase / decrease in the number of LINE VTY
2.7.2. To enter LINE mode
Through access to the specified LINE mode, can be in LINE mode, the configuration of the specific
LINE. To enter to the specified LINE mode, execute the following command:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# line [console | vty ]
first-line [last-line]
Access to the specified LINE model
2.7.3. Configure user authentication local
By default, the user can directly through the console port or telnet directly connected to the switch, can
be connected to the switch by allowing the user to enter the username and password
Command
Function
Switch(config)# user Switch password 0 Switch
Configure user name and password :Switch
Switch(config)# line vty 0 12
Enter the VTY configuration mode
Switch(config)# login local
Start the local authentication configuration
2.7.4. Configure the WEB user login timeout
The default user five minutes without operation switch, system automatically disconnect the related
connected this time can be modified according to the needs of users
Command
Function
Switch(config)# line vty 0 12
Enter the VTY configuration mode
Switch(config-line)# exec-timeout 10
The configuration is not the action timeout
time is 10 minutes, 0 never timeout

3. Configuration interface
3.1. Interface type Summary
This chapter mainly to Ruijie equipment interface types are divided, and a detailed definition of each
interface type interface type Ruijie equipment can be divided into the following two categories:
(L2 interface)
(L3 interface) (Layer three device support)
3.1.1. This section describes the type two layer interface and the related
definition, can be divided into the following types (L2 interface)
This section describes the type two layer interface and the related definition, can be divided into the
following types
Switch Port
Link-aggregation Port
3.1.2. Switch Port
Switch Port consists of a single physical port on the device, only the two layer switching function. The
port can be a Access Port, Hybrid Port or a Trunk Port, you can use the Switch Port interface
configuration command, a port configured as a Access Port, Hybrid Port or Trunk Port.Switch Port is
used to manage the physical interface and the second related protocols, and does not handle routing
and bridging.
3.1.3. Access Port
Each Access Port can only belong to one VLAN, it only belongs to the VLAN transmission frame is
generally used to connect computers..
The default VLAN:
Each Access Port belongs to only one VLAN, so the default VLAN it is the VLAN, can not use the
settings.
Computer
Receiving and sending frames
Access Port sends out the data frame is not with the TAG, and it can only receive the following three
forms of frame:
Untagged Frame
VID IS Access Port VLAN Tagged Frame
Untagged Frame
The Access Port to receive frames without the TAG ,And for the without TAG frame add default
VLAN TAG, Before sending to remove add TAG, send again.
Tagged Frame
The received data frame to the Access port with TAG, will be in accordance with the following
conditions for processing:

When the TAG VID (VLAN ID) the same with the default VLAN ID, receiving the data frame, and
removed when it is sent
The TAG sign and send.
When the TAG VID (VLAN ID) as the default VLAN ID, receiving the data frame. In TAG, VID =
default VLAN ID for the identification of priority.
3.1.4. Trunk Port
Trunk port can belong to multiple VLAN, capable of receiving and transmitting belong to more than
one VLAN frame, generally used for connection between devices, can also be used to connect the
user's computer.
The default VLAN
Because Trunk Port can belong to more than one VLAN, so we need to set up a Native VLAN as the
default VLAN. when switching Trunk port received no VLAN tag with the frame to the frame, it
increases the Native VLAN label, the frame belongs to Native VLAN; when Trunk port sends frame, if
the frame of VLAN and Native same as VLAN, will remove the VLAN label.
Tip
Recommend the end device Trunk port of the native VLAN and the end
Trunk port of the native VLAN configuration is consistent, otherwise may
not be the correct port forwarding packets.

Receiving and sending frames
Trunk port can receive Untagged frame and tagged frame.Trunk port allows Port to send VLAN range
of non Native VLAN frame are TAG, sending Native VLAN frame without TAG.
Untagged Frame
If the received Trunk port frame without IEEE802.1Q TAG, then the frame in the interface of the Native
VLAN transmission.
Tagged Frame
If the received frame is Trunk port TAG, will be in accordance with the following conditions for
processing:
receiving the data frame; in sending the frame, remove and send TAG.
AN, but
VID
Tip The Untagged message is ordinary Ethernet message, the PC card can
identify this message communication; change of the TAG message
structure is in the source MAC address and a destination MAC address,
plus the 4bytes VLAN information, namely VLAN TAG head.

3.1.5. Hybrid port
Hybrid type of port can belong to multiple VLAN, can message receiving and transmitting a plurality of
VLAN, can be used for the connection between devices, can also be used for different user
computer.Hybrid port and the Trunk port is sending Hybrid port allows multiple VLAN message without
a label, and only allowed to send the default Trunk port VLAN message without a label, the need to pay
attention to is: Hybrid port with VLAN must already exist.
3.1.6. Link-aggregation Port
Link-aggregation Port is formed by multiple physical member port aggregation. We can take multiple
physical links tied together to form a simple logical link, link, the logic we call a Link-aggregation Port.
For the two layer switch AP is like a high bandwidth Switch port, it allows multiple port bandwidth
stacking up,,,,,,,,, expanding the bandwidth. In addition, through the Link-aggregation, Port frames
transmitted will be in the Link-aggregation Port member port on flow balance, if a member link in AP
failure, Link-aggregation Port will automatically transfer the link traffic to other effective members of the
link, improve the reliability of the connection.
3.1.7. (L3 interface)
This section describes the type three layer interface and the related definition, can be divided into the
following types
SVI (Switch virtual interface)
The SVI is switched virtual interface, to achieve the three layer switch interface to.SVI logic can be
used as a management interface of the machine, through the management interface, administrators
can manage the equipment.
You can through the interface VLAN interface configuration command to create a SVI, and then to the
SVI IP address assigned to the establishment of VLAN
Routing between.
3.2. Configuration interface
This section describes the default configuration, interface configuration guide, configuration steps,
configuration example
3.2.1. Interface ID rules
For Switch Port, the numbers start at 1.
For Link-aggregation Port, the number of the number of AP support the 116 equipment. For SVI, its
number is the SVI corresponding VLAN VID.
3.2.2. Using the interface configuration command
You can be in the global configuration mode. Use the Interface command to enter interface
configuration mode..
command
Function
Switch(config)# Interface
gigabitEthernet port- ID
Enter the Interface gigabitEthernet _ID
command in global configuration mode, enter
interface configuration mode.
Under the given into the Gigabitethernet 0/1 interface example:
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#
In interface configuration mode you can attribute configuration interface.
You can use interface in global configuration mode command into the SVI interface configuration
mode.
Command
Function
Switch(config)# interface vlan
vlan
ID
Enter the interface command in global configuration
mode, enter the SVI interface configuration mode.
Under the given into the interface vlan1 interface example:
Switch(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch(config-if-vlan1)#
In the SVI interface configuration mode you can configure the IP address of the interface.
3.2.3. Select the interface media type
Some of these interfaces, can have a variety of media types for the user to choose. You can choose
one kind of medium. Once you have selected the medium type, connection status, speed, duplex,
fluidic attribute interface all refer to the properties of the medium type, if you change the media type, the
new media types of these properties will use the default values, you can according to need to set these
properties.
This configuration command only to the physical port.Link-aggregation Port and the SVI interface is not
supported media type setting. This configuration command only for media port.
Configuration for the Link-aggregation Port member export port, the medium type must be consistent,
otherwise cannot be added to the AP.
The Link-aggregation port type Port members and can not be changed.
3.2.4. Configuration interface description and management state
In Command to help you remember an interface function for each interface, you can come up with a
name that identifies this interface, also is the description of the interface (Description). You can set the
interface according to the specific name, to express the meaning of such as: you want to put the
Gigabitethernet 0/1 assigned to the user A special use, you can use this interface description is set to
"User A”.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/2)#
description string
Set interface description, up to a maximum of
240 characters.
The following example shows how to set the interface Gigabitethernet 0/1 description:
Switch# config terminal
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#description User A

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#
speed {10 | 100 | 1000 |auto }
The rate parameter setting interface, or set to
auto:
1000 only to Gigabit mouth;
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#
duplex {auto | full | half }
Duplex mode interface.
Be careful.
Gigabit ports can only be set to Full mode;
In some cases, may need to disable an interface. By setting the interface management state to close
the corresponding interface. If you close an interface, the interface will not receive and transmit any
frames, all functions will lose the interface corresponding to. Also by setting up the management state
to re open the closed interface interface management state has two types: Up and Down, when the
interface is closed, interface management state is down, otherwise up
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-
0/1)# {shutdown|no
shutdown}
Close an interface or open an interface
The following example describes how to close the interface 0/1:
Switch# config terminal
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# shutdown
The following example describes how to enable the interface 0/1:
Switch# config terminal
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#no shutdown
3.2.5. This section describes how to configure the interface speed, duplex mode.
This section describes how to configure the interface speed, duplex mode..
Step 1
Step 2
3.2.6. The configuration interface MTU
When a port for high throughput data exchange, may encounter greater than Ethernet frame length
frame, this frame is called
Jumbo frame. The user can set the port MTU to control the maximum frame the port allows the
transceiver. MTU is the effective data frame length, not including Ethernet encapsulation overhead.
Port received or forwarding of frames, if the length is more than the MTU, will be discarded.
MTU allows setting for 64~10240 bytes, 1518 bytes by default.
This configuration command only to the physical port.SVI interface does not support the MTU setting.
Command
Function
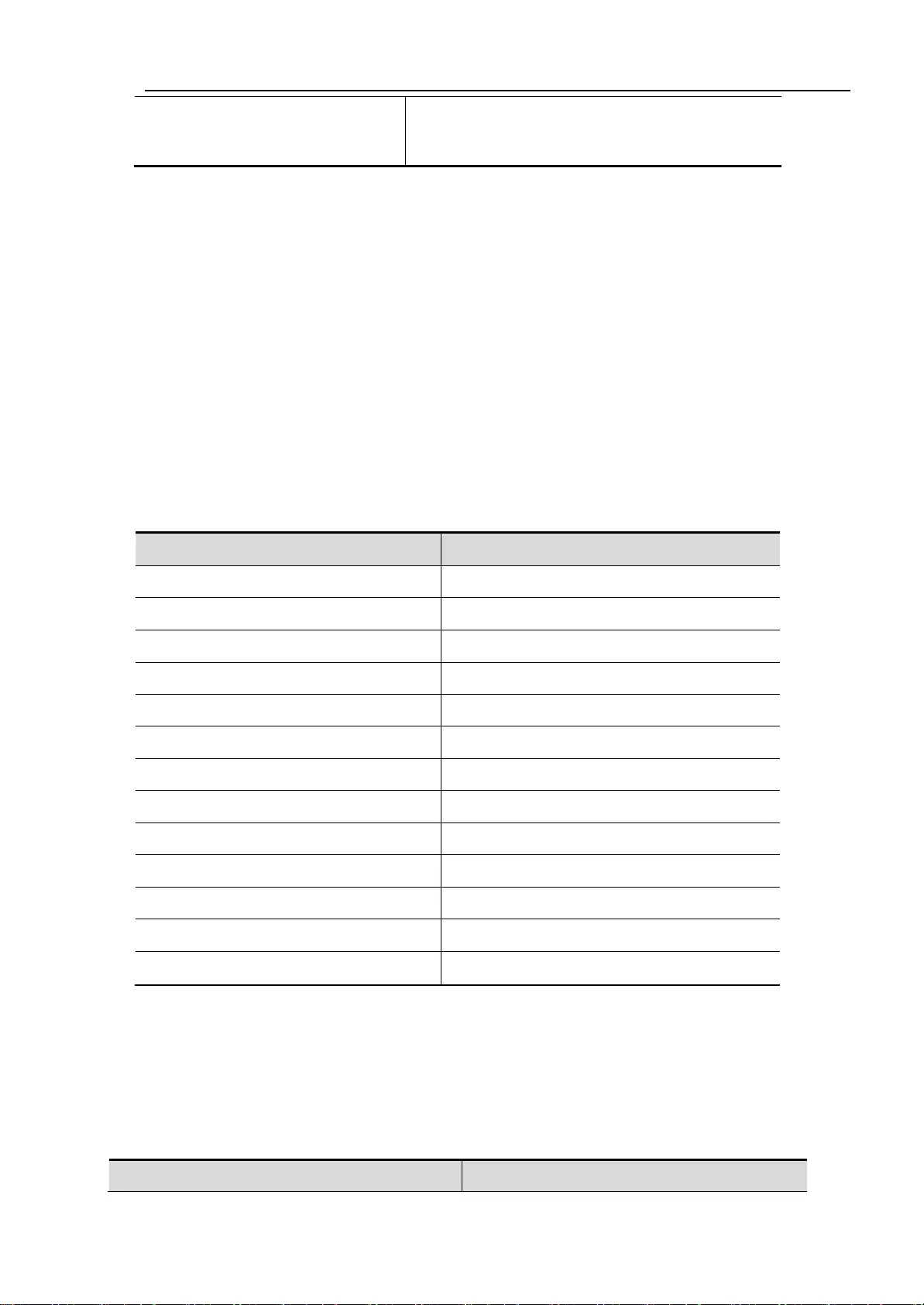
Switch(config-if-gigabitEther
net-0/1)# Mtu num
Set port MTU Num:<64-10240>
The following example shows how to set the interface Gigabitethernet 0/1 MTU:
Switch# config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)# interface
gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# Mtu 64
3.2.7. Two layer interface configuration
The following table shows the default configuration of two layer interface, please refer to the "VLAN"
and "VLAN and port configuration
The port based on flow control ".
The default configuration of two layer interface are given in the following table:
Attribute
The default settings
Working mode
L2 swith
Switch port mode
access port
Allow VLAN range
VLAN 1~4094
The default VLAN (for access
port)
VLAN 1
Native VLAN(TO trunk port )
VLAN 1
Interface management state
Enable
Interface description
Empty
Speed
Auto negotiation
Duplex mode
Auto negotiation
Link-aggregation Port
None
Storm control
closed
To protect the port
closed
Port security
closed
4. Configure access/trunk port
This section mainly shows how to configure the Switch Operation mode (access/trunk port) and
relevant configuration in each mode. You can configure the relevant attributes of Switch port by
switch under port configuration mode or other Commands.
Commands
Function
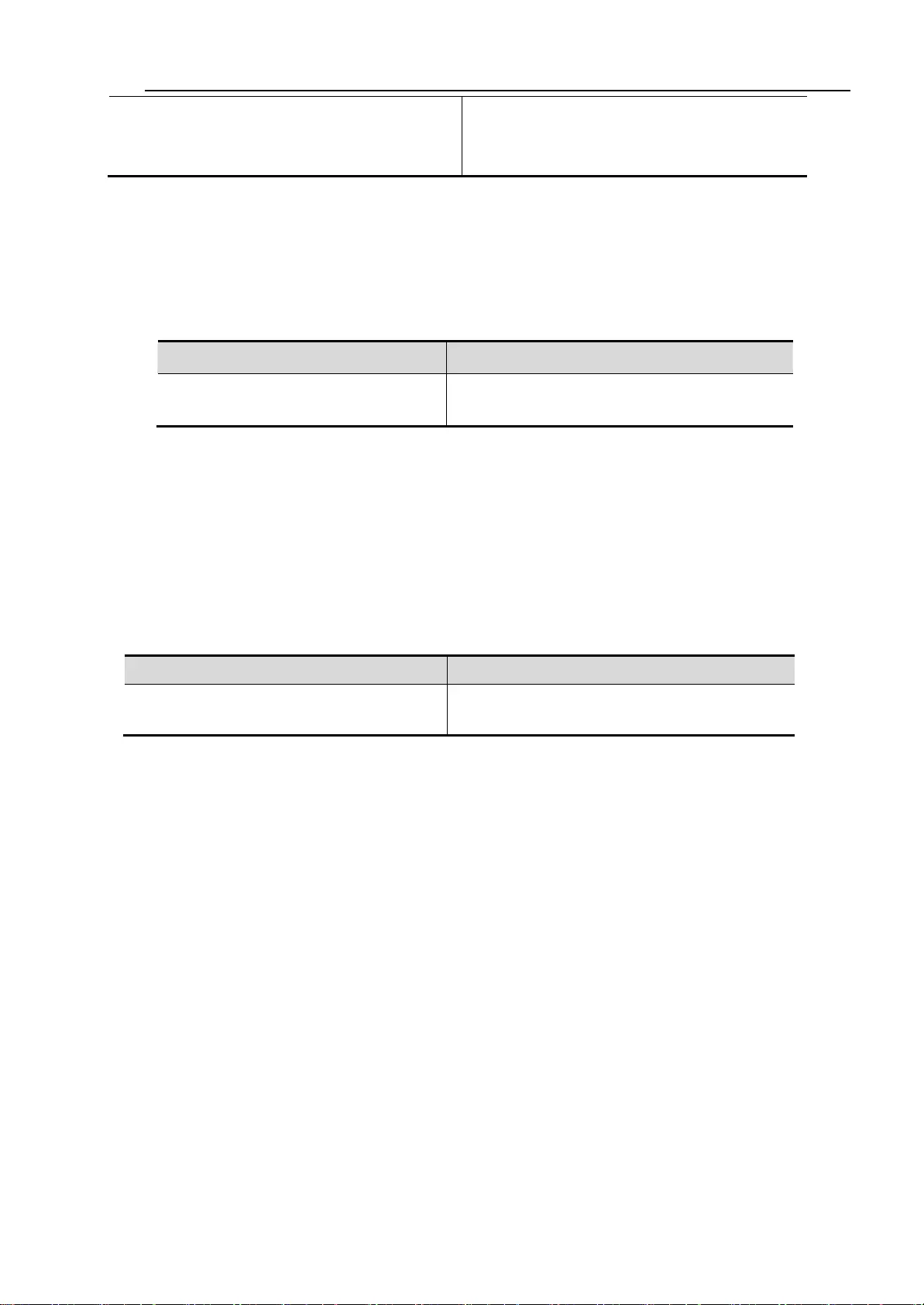
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch mode {access |trunk |
hybrid}
Configuration port operation mode.
Below is the example how to configure gigabitethernet 0/2 into access port operation mode.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch mode access
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)#
switch access vlan vlan-id
Configuration port operation mode.
Below is the example how to configure the belonged VLAN of access port gigabit ethernet 0/2 to be
100。
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch access vlan 100
Configure the trunk port’s native VLAN
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)#
switch trunk native vlan vlan-id
Configure the trunk port’s NATIVE VLAN。
Below is the example to configure Trunk Port Gigabitethernet 0/2’s Native vlan to be10。
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch mode trunk
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch trunk native vlan 10
Please refer to “Configure port rate,Duplex, fluid control” to configure the port rate ,duplex, fluid control.
Below is the example to configure Gigabitethernet 0/2 to be access port , belonged VlAN to be 100,
Rate,Duplex,fluid control to be self-negotiation model,port safe to be open:
Switch# configure terminal
:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)# interface
gigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# onfigure the Hybrid port.

switch access vlan 100
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# speed auto
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# duplex auto
4.1.1. port
You can confirgure the Hy bid port by below steps:
S
t
e
p
1
S
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch mode hybrid
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch hybrid native vlan 3
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/2)# switch hybrid vlan 20 untagged
4.1.2. Configure the Link-aggregation port
This section mainly shows how to create Link-aggregation Port and some configurations of
Link-aggregation Port。 You can creat Link-aggregation Port in the port configuration pattern by using
Link-aggregation Port,Specific configuration process ,please refer to “Configure Link-aggregation
Port”。
4.1.3. Clear the port statistics .
Clear the port statistics by “Clear” Command in the privileged mode
Command
Function
Switch# clear counters [all | gigabitEthernet] [id]
Clear the port statistics。
You can check the port statistics by Command: show interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 statistics in
the privileged mode .You can clear the statistics by Command: clear counters GigabitEthernet
0/1 in the privileged mode。
Command
Function
configure terminal
Enter the configuration pattern
Interface gigabitEthernet <portnumber>
Enter the port configuration pattern
100M,1000M,10000M
switchport mode hybrid
Configure port to be hybrid port
switchport hybrid native vlan id
Configure the default port to be VLAN
switchport hybrid vlan id [[tagged | untaged]]
Congfigure the port output rule.
Below is the example to show how to clear the Gigabitethernet 0/1 counters:
Switch# clear counters GigabitEthernet 0/1
4.1.4. Configure SVI
This section mainly show how to describle SVI and some configurations of SVI .
Create a SVI or revise an exsited SVI by interface vlan.
SVI configuration:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# interface vlan vlan-id
Enter SVI port configuration mode.
Below example will show how to enter the port configuration mode and assign IP address to SVI1.:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch(config-if-vlan1)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
4.2. Show the port configuration and Status
This section describles the port’s display content and display examples.You can chec the port status by
“Show” Command in the privileged mode.You can also check the port status by using below
Commands in the privileged mode.:
Command
Function
Switch# show interface GigabitEthernet [id]
Show the specficed interface’s all status and
configuration information
Switch# show interface GigabitEthernet [id]
configuration
Show the configuration information of the port.
Switch# show interface GigabitEthernet [id] media
Show the specificed port’s physical attribute。
Switch# show interface GigabitEthernet [id]
statistics
Show the specificed port’s statistics information may
contain the rate . Random error 0.5%。

Below is the example how to show the port status of Gigabitethernet 0/3:
Switch#show interface GigabitEthernet 0/3
interface gigabitEthernet 0/3 configuration information
Description :
Status : Enabled
Link : Down
Set Speed : Auto
Act Speed : Unkown
Set Duplex : Auto
Act Duplex : Unkown
Set Flow Control : Off
Act Flow Control : Off
Mdix : Auto
Mtu : 1518
Link Delay : 1
Storm Control : Unicast Disabled
Storm Control : Broadcast Disabled
Storm Control : Multicast Disabled
Storm Action : None
native vlan : 40
Below is the example to show the port physical attribute.:
Switch#show interface gigabitEthernet 0/9 media
Gi 0/9: media: fiber(optical interface)
Switch#show interface gigabitEthernet 0/3 media
Gi 0/3: media: copper(electrical port)
Below example shows the port’s statistics.
Switch#show interface gigabitEthernet 0/9 statistics
interface gigabitEthernet 0/9 statistics information:
5 minutes input rate : 1656 bits/sec ,19 packets/sec
5 minutes output rate : 190 bits/sec ,2 packets/sec
RxOctets : 1327408
RxUcastPkts : 2406
RxMulticastPkts : 2172
RxBroadcastPkts : 6843
TxOctets : 2705325
TxUcastPkts : 3023
TxMulticastPkts : 35638
TxBroadcastPkts : 410
CRCErrors : 0
DropPacketEvents : 0
TotalOctets : 4032733

TotalPkts : 50492
TotalUcastPkts : 5429
TotalBroadcastPkts : 7253
TotalMulticastPkts : 37810
TotalSymbolErrors : 0
TotalAlignmetErrors : 0
TotalUndersizePkts : 0
TotalOversizePkts : 0
TotalFragments : 0
TotalJabbers : 0
TotalCollisions : 0
TotalPkts64Octets : 43300
TotalPkts65to127Octets : 5005
TotalPkts128to255Octets : 1125
TotalPkts256to511Octets : 695
TotalPkts512to1023Octets : 244
TotalPkts1024to1518Octets: 123

5. Configure Link-aggregation Port
This section will descirbls how to configure Link-aggregation Port based on the Ruijie equipment。
5.1. Summarize
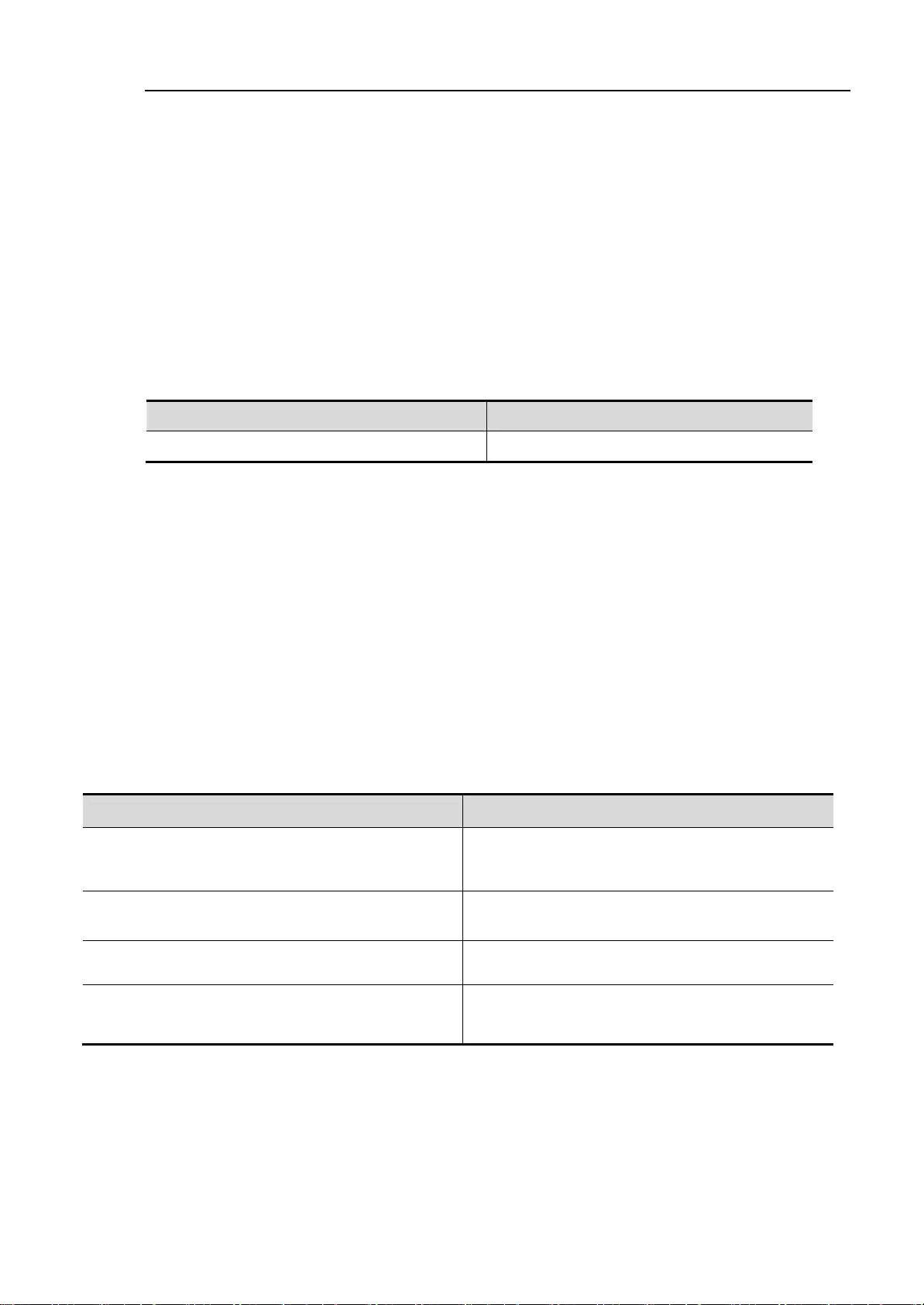
5.1.1. Understand Link-aggregation Port
We can bind many physical links into a logistical links,We call this logistical links Link-aggregation
Port(AP)。AP offered by Ruijie compliant with IEEE802.3,It can be used to enlarge the link
barndwidth to provide higher connection reliability。
AP supports flow balance, it can assign flow to each link evenly. AP realize the linke backup.When
one of the link in the AP disconnected,syestem will assign this link’s flow to the other effective links
automaticly。One broadcast or more broadcasts received by one link in the AP will not be transmitted
to other links.
Typical AP configuration.
Tip
When Flow balance mode is configured as source IP,destination IP,
Source IP+destination IP, it should balance the flow by using the
equipment’s default mode to 2 layer packets. Default model can be
gotten by Command “show link-aggregation group AP_id” when
the equipment has not been configured link-aggregation
load-balance.
AP flow balance diagram
5.2. Configure Link-aggregation Port instructor
5.2.1. Default Link-aggregation Port configuration
AP default configurations as follow :
Feature
Default
Two layer AP port
N/A
Flow Balance
Assign the flow according the input packets
source MAC address.
5.2.2. Link-aggregation Port configuration Instructor
AP members ports’ rate, status,duplex, transmission media must be the same. 成
Two layer port can only join two layer AP,the port contains the member is forbidden to change the two
layer attribute.
A port join the AP, the port attribute will be replaced by the AP’s attribute.
A port removed from the AP, its attribute can recover to the attribute before it joined.

Tip Once a port join an AP, any configuration can be set on the port until the port
exit the AP.
5.2.3. Creat Link-aggregation Port
First creat the Link aggregation group, then let the port join the AP as follow stepsinthe port
configuration mode.:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# link-aggregation [ap-id]
mode {lacp | manual}
Creat an AP group (AP group has lacp and manual
two modes,the AP mode should be the same
between two switches.
Switch(config-port-range)#
link-aggregation [ap-id] {active | passive |
manual}
Join this port into the created AP group. (If the
AP group is lacp mode, the port should be confired
to active or passive mode.If the AP group is manual
mode the port needs to be configured to be manual
mode.
Using the Command no link-aggregation [ap-id] to exit a physical port in the port configuration
mode.
Below is the example to configure two layer Ethernet port 0/1 and 0/3 to be one memberoftow layer
AP.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#link-aggregation 1 mode manual
Switch(config)#port 0/1,0/3
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-range)# link-aggregation 1 manual
You can use the Command “Switch(config)# link-aggregationn” (n means AP number) to enter the
AP Congiguration mode in the global configuration mode.(if AP n is not exsit ,using
link-aggregation [ap-id] mode {lacp | manual} to create.)
Tip
When two switches AP group configured to LACP mode,related AP group
physical port attribute need to be active mode at least a section. If both
ports are passive mode, it can not communicate.
5.2.4. Configure Link-aggregation Port
flow balance.
In the congiguration mode, plase configure AP flow balance as follow steps:
Command
function
Switch(config)# link-aggregation
[ap-id] load-balance {mac | ip-mac | ip}
Configure AP flow balance,choose the way of
algorithm.:
mac:According to the input packets’ source MAC
address to assign.
ip-mac:According to input packtes’ resource
packets’ MAC address to assign flow.
ip:According input packets resource IP address
to assign flow.
5.3. show Link-aggregation Port
In the privileged mode, please show the AP configuration as follow steps.
Command
Function
Switch# show link-aggregation
group [ap-id]
Show AP configuration。
Switch#show link-aggregation group 1
Link Aggregation 1
Mode: Manual Description:
Load balance method: mac
Number of ports in total: 1
Number of ports attached: 1
Gi 0/1: DETACHED
Gi 0/3: ATTACHED
6. Configure VLAN
This section describles how to configure IEEE802.1Q VLAN
6.1. Summarize
VLAN is the abbreviation of Virtual Local Area Network,it is a logical net divided from a physical
network.This network corresponds to the second layer of the ISO mode. How to divide the VLAN is
not limited by the actual physical position of the network port.的 划分不受网。VLAN has the same
attribute with the common physical network. It is the same as the common LAN except that it
doesn’t have the limitation of physical position. The unicasting and broadcasting and multicasting in
the second layer transimit and spread in a VLAN,will not enter other VLAN.So if a host wants to

Command
Function
Access
An Access port can only belong to a VLAN,and assign VLAN by Manual
Setup.
Trunk
A Trunk port can configure more than on VLAN but only native VLAN can
without VLAN mark.
Hybrid
A Hybrid port can figure to be belonged to more than one VLAN ,It also
can configure if VLAN has VLAN MARK or not accord ing to customer’s
requirements。
communicate with other host which is not in the same VLAN. It needs a 3 layers equipment.see
figure below。
A port can be defined as a member of a VLAN. All of the terminals connected to this port are a part of
virtual network, The entire network can support more than one VLAN.There is no need to adjust the
network configuration from the physical when add, remove and revise the user.
Normally like the same as a phosical network, VLAN is connected with a subnet IP。A typical
example, All the hosts in a same IP subnet belong to the same VLAN, VLANs must communicate
with each other by 3 layers equipment.The Ruijie equipment can configure the SVI of the IP
router between the VLAN by using the SVI interfaces.About the configuration of the SVI, please
refer to the port management and IP unicast router configuration.
6.1.1. Supported VLAN
Products supported VLAN abides to IEEE802.1Q,most support 4094 VLAN(VLAN ID 1-4094),
VLAN 1 can not be removed default VLAN。
Tip
License configuration VLAN ID in the range of 1-4094
When the hardware lacks of resources, system will return the failed to
create a VLAN information
6.1.2. VLAN member type
By configuring a port’s VLAN member type to make sure this port will pas which kind of frame and how
many VLAN can this port belong to. Please refer to the follow table to see the VLAN member type’s
detailed type.
Command
Function
Switch(config)# vlan vlan-id
Input a VLAN ID。If you input a new one the
queipment will create a VLAN.if you input an
exsited one,it will amend specific VLAN,
Switch(config-vlan888)# description
vlan-name
(Optional)Name for a VLAN,If you do not do
this step,it will name for it as VLAN xxxx
automaic,xxxx is started with 0 which has
four numbers of VLAN ID number。For
example,VLAN 0004 is VLAN 4’s default
name。
6.2. VLAN Configuration
A VLAN is identified by VLAN ID。In the equipment ,you can add ,remove, revise VLAN 2-4094,
but VLAN 1 is created by the device automatic and can not be removed.
You can configure a port’s VLAN member type or add ,rmove a VLAN in port configurationmode.
6.2.1. Save VLAN configuration information
When you type the Command “Write”in the privileged mode,the configuration informationofthe VLAN
will be saved in configuration file.You can use Command “Show vlan” to check VLAN configuration
information.
6.2.2. Default VLAN configuration
Parameter
Default
Range
VLAN ID
1
1-4094
description
VLAN xxxx
6.2.3. Create, amend a VLAN
In the global configuration mode, you can create or amend a VLAN
Step 1
Step 2
If you want to change the name of VLAN back to its default name, just type “no description”.
Below is an example to create VLAN888 and name it as VLAN888:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# vlan 888
Switch(config-vlan 888)# description test888
Command
Function
Switch(config)# no vlan vlan-id
Input a VLAN ID and delete it。
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# switch
mode access
Identiy the member type of the VLAN 2
layers ACCESs)
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# switch
access vlan vlan-id
Assign this port to a VLAN.
6.2.4. Remove a VLAN
Default VLAN(VLAN 1)is not allowed to delete。 Delete an existed VLAN in the global
configuration mode:
6.2.5. Assign access port to VLAN
Assign a port to a VLAN in the interface configuration mode.:
Below is the example to take GigabitEthernet 0/1 as Access port to join VLAN20:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# switch mode access
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# switch access vlan 20
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# end
Below is the example to show how to check if the configuration information is right or not .:
Switch#show vlan 20
1 20 VLAN0020
----[Untag Port]----
Gi 0/1
----[Tag Port]----
6.3. Configure Trunk VlAN
6.3.1. Trunking Summarize.
A Trunk is a point-to-point link which connect one or more ethernet exchange port with other network
equipment (Router or Switch),A Trunk link can transmit more than one VLAN flow.
Ruijie’s Trunk take 802.1Q standard to seal。Below picture shows a network uses Trunk
connection。

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch mode trunk
Identify the port type to be 2 layers
Trunk port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch trunk native vlan vlan-id
Specify a Native VLAN for this interface
Native VLAN
You can set a common Ethernet port or a link-aggregation port as a Trunk port.(Please refer to
link-aggregation port for link-aggregation port deatils.
Use switch mode Command to switch a port between access mode and truck mode.
Command
Function
S
t
e
p
1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch mode access
Set a port to be Access mode.
S
t
e
p
2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1#
switch mode trunk
Set a port to be Trunk mode.
Must assigned a Native VLAN for Trunk port. So called Native VLAN is received and sent by this port.
UNTAG packets are belonged to this VLAN.。Obvious,the default VLAN ID of this port 这个( PVID
of IEEE
802.1Q is Native VLAN’s VLAN ID ,transmit frame belonged to Native VLAN on the trunk must take
UNTAG method. Each Trunk’s default Native VLAN is VLAN1.,When configure the Trunk link, please
confirm the ports on the link two sides are using the same native vlan.
6.3.2. Configure a Trunkport
In the interface configuration mode,you can configure a port to be a Trunk port.
Step 1
Step 2

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch trunk native vlan vlan-id
Configure Native VLAN
If you want to recovery a Trunk port’s all trunk attributes to default, please use the Command switch
mode access 。
6.3.3. Identiy Trunk’s permission VLAN list.
You can limit some flow of VLAN can pass this Trunk port or not by configuring Truck port’s
permission VLAN list.
At the interface configuration mode, you can amend a Trunk port’s permission WLAN list.
Below is an example to remove a VLAN 2 from GigabitEthernet 0/1 permission list.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no switch trunk allowed vlan 2
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# end
6.3.4. Configure Native VLAN
A Trunk can receive and send TAG or UNTAG 802.1Q frame.。UNTAG frame used to transmit
Native.
VLAN flow。 Default Native VLAN is VLAN 1。
In the port configuration mode, can configure Native VLAN fro a Trunk port.
Step 1
If you want to change Trunk’s Native VLAN list back to the default VLAN 1, please use no switch
trunk native vlan Command .
6.4. Configure Hybrid Vlan
6.4.1. Hybrid OverView
Hybrid Vlan’s usage scenario is similar with Trunk Vlan,The only difference is that Hybrid Vlani is
assigned the packets sent from related ports whether print the specificed VLAN mark or not by user
manual.
Command
Function
Switch( config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch trunk allowed vlan {all |
vlan-list }
Can choose to configure this Trunk’s
permission VLAN list.
Parameter can be a VLAn,, “all “ means
permission VLAN list contains all supported
VLAN.

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch mode hybrid
Define the port type to be a 2 layer
hybrid port.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch hybrid native vlan vlan-id
Assign a Native VLAN for this port.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
switch hybrid native vlan vlan-id
Configure Native VLAN
6.4.2. Configure a Hyhrid port
In the port configuration mode can configure a port to be a hybrid port.
Step 1
Step 2
6.4.3. Define Hybrid permission VLAN list.
In port configuration mode can amend a HYBRID port’s permission VLAN list.
Below is an example to remove a VLAN 2 from GigabitEthernet 0/1 port’s permission list.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no switch hybrid vlan 2 untagged
6.4.4. Configure Native VLAN
Native vlan in the hybrid port confirm to recive without vlan marked packet and confirmitis transmitted
in that vlan.
In the port configuration can configure Native VLAN for a Hybrid.。
Step 1
If you want to change Trunk’s Native VLAN list back to default VLAN1, please use Command no
switch hybrid native vlan to configure.。
6.5. Show VLAN
Only In the privilege mode can check the VLAN information.The information includes VLAN VID、
VLAN status、VLAN member port and VLAN configuration information.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)
# switch hybrid vlan vlan-list
{tagged | untagged }
Choose to configure this Hybrid port’s
permission VLAN lsit.
Parameter “tagged” means the packets
transmitted from this VLAN with “VLAN”
Mark. Parameter “untagged” means the
packets transmitted from tthis VLAN
without”VLAN” mark.

Command
Function
show vlan [vlan-id]
Show all or specificed VLAN parameters.
Related show Commands are as follow:
Below is the example to show the VLAN.
Switch#show vlan
vlan total num --------------- 4------------------------------- --------------------
NO. VID VLAN-Name Interface-Name
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
1 1 DEFAULT
----[Untag Port]----
Gi 0/5 Gi 0/9 link-aggregation 1
----[Tag Port]----
2 40 VLAN0040
----[Untag Port]----
Gi 0/4 Gi 0/7 Gi 0/8
----[Tag Port]----
3 60 VLAN0060
----[Untag Port]----
Gi 0/2
----[Tag Port]----
4 90 VLAN0090
----[Untag Port]----
Gi 0/6
----[Tag Port]----
Gi 0/5
7. Configure MAC address
Ethernet switches through the MAC address table in the data link layer to forward packets,
this article is description of configuration method of MAC address.
7.1. Understand MAC address table
7.1.1. Overview
By identifying the data link layer information to forward packet is main functions of the
Ethernet switch(Referred to as forward capability on the second floor) through purpose of the
MAC address carried by the message, Ethernet switches forward the message to the
corresponding ports, and purpose of the MAC address and port information when using MAC
address table to storage and forward packet.

All MAC address in MAC address table of Ethernet switch is associated with the VLAN.Each
VLAN will maintain its own logic address table. A MAC address that has been learned by
VLAN, still be unknown by other VLANs.
The MAC address of the Ethernet switch consists of the following information:
User MAC
Port
Port Method
VLAN
MAC address table
User MAC :MAC address information in table
Port:MAC address corresponding to the port information
Port Method:It marks dynamic address, static address or filtering address.
VLAN:VLAN belonging to MAC address
Ethernet switch MAC address table update and maintain by following two ways:
Dynamic address learning
Manual configuration address
Ethernet switches in the forwarded message through the message MAC address, and
message belonging to a VLAN ID information in the MAC address table to find the
corresponding forward output port, according to the search results to forward packets in
unicast, multicast or broadcast.
Unicast forwarding: Ethernet switch can check it MAC address and corresponding tables of
VLAN ID,and table output port is only one, and message output directly from a table item of
the corresponding port
Multicast forwarding: Ethernet switch can check message’s purpose MAC address and
tables that is correspond to VLAN ID, then forward message from multicast ports.
Broadcasting forwards: Ethernet switches received message of destination address to FFFF.
FFFF. FFFF or in the MAC address table, you can't find the corresponding item, the
message from under their VLAN all ports (in addition to receiving port) will be forwarded.
7.1.2. Dynamic address learning
MAC address produced by automatic address learning process of Ethernet switch is called
dynamic address, only dynamic address will be deleted by aging mechanism of address
table.
Normally the MAC address table maintenance is conducted by means of dynamic address
learning, its working principle is as following:
In condition of MAC address of Ethernet switch is empty, UserA will communicate with UserB, UserA
first send message to Gigabit port of switch. Then Ethernet switch will learn MAC address of UserA to
MAC address table. As there is no source MAC address of UserB in the address table, then Ethernet
switch will send message in broadcasting method all ports except for UserA, and UserC can receive
message from UserA, that does not belong to it.

Step one of learning dynamic address
User MAC
Port
Port Method
VLAN
00d0.f8a6.5af7
2
Dynamic
1
Table one of Ethernet switch MAC address
UserB after receiving the message will reply message through Ethernet switch Gigabit port Ethernet
0/3 send UserA, at this point in the Ethernet switch MAC address table has been in existence UserA's
MAC address, so the message is in the form of unicast forwarding to Gigabit Ethernet 0/2 ports,
Ethernet switches at the same time will learn UserB MAC address, and the difference from the step 1is
that UserC don’t receive message that UserB sent to UserA.
Dynamic address learning step two
User MAC
Port
Port Method
VLAN
00d0.f8a6.5af7
2
Dynamic
1
00d0.f864.e9b6
3
Dynamic
1
Ethernet switch MAC address table 2
3. Through UserA and UserB after an interactive process, Ethernet switches learn to UserA and UserB
source MAC address, after UserA and UserB message interaction forward in unicast way, then UserC
will no longer receive the interaction between the UserA and UserB message.
7.1.3. Address aging
Ethernet switch MAC address table has a capacity limitation, Ethernet switch address table aging
mechanism will eliminate inactive item address table.
Ethernet switches at the same time of learning to a new address to launch the address of the aging
time, before reaching the aging time, if the Ethernet switches does not receive the address as the
source MAC address of the message, that the address will be deleted from the MAC address table
when reaching to aging time.
7.1.4. Filter addresses
Manual configuration of the MAC address table entries for discarded in the Ethernet switch to the
configured MAC address for the source or destination address of the packet, such address only by
manual configuration to add and delete, restart after saving the configuration equipment , filtering to
address will not be lost.
Through manual configuring illegal users access to the source MAC address for the filtering ways of
implementation method of filtering the illegal user access.
7.2. Default Configuration
Function Performance
Default Value
Dynamic address aging time
300 seconds
Port MAC address learning ability
Open
MAC Address change notifications
Close
7.3. Dynamic address configuration
7.3.1.
Check configuration
The
following example illustrates how to view the equipment on the physical interface Gigabi t Ethernet 0/9
of all dynamic VLAN
Switch#show mac-address all
VLAN MAC TYPE interface STATE index
---- -------------- ------- -------------------- -------- ------
1 0000.0000.0000 DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 4
1 0009.E8F3.F817 DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 216
1 0287.4500.000D DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 444
1 C860.00E0.2BCC DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 1184
1 3883.45EE.7332 DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 1576
1 C860.00E0.2B80 DYNAMIC Gi 0/1 FWD 2080
The following example illustrates how to view on the device address table statistics
Switch#show mac-address count
Static Mac Address Count : 0
Drop Mac Address Count : 0
Dynamic Mac Address Count : 20
Total Mac Addresses : 20
7.4. Dynamic Address Aging Time Configuration
7.4.1. Aging Time Configuration
Command
Function
Switch(config)# mac-address
agint-time [10 | 893]
set the time span of an address kept in
dynamic address table after being learned.
The unit is second.
Command
Function
Switch#show mac-address all
Check all address information on device
Switch#show mac-address
dynamic
Check all dynamic address information
on device
Switch#show mac-address
interface gigabitEthernet port-id
{all | dynamic | static}
Check address information for ports
Switch#show mac-address
link-aggregation ap-id {all |
dynamic | static}
check the address information of link
together group
Switch#show mac-address vlan
vlan-id {all | dynamic | static}
Check address information for Vlan
Switch#show mac-address
aging-time
Check MAC address aging time
Switch# show mac-address count
Check the address table statistics
Switch(config)#on mac-address
agint-time
Resume address aging time to default value.
The following example illustrates how to set the aging time of the equipment to be 180 seconds:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)#mac-address
aging-time 180
The following example illustrates how to view the time configuration of address in the equipment:
Switch#show mac-address aging-time
Aging time : 180 s
7.5. Static Address Configuration
7.5.1. Static Address Management
Command
Function
Switch(config)# mac-address static
mac-address vlan vlan-id {interface
gigabitEthernet port-id|link-aggregation ap-id |
drop }
mac-address: the destination MAC address
corresponding to specified table item.
vlan-id:specify VLAN the address belongs
to.
port-id:the interface that package forwards to.
ap-id:the link aggregation interface that
package forwards to.
drop:discarded data package
Switch(config)# no mac-address static
mac-address vlan vlan-id {interface
gigabitEthernet port-id | link-aggregation
ap-id | drop }
Delete static address list item, the parameter
is the same with the added command.
The following example illustrates how to add a static IP address 00d0.f800.073c. when the received
destination address in VLAN 4 is the message of the address, the message will be forwarded to the
specified interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/3.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)# mac-address static
00d0.f800.073c vlan 4 interface GigabitEthernet 0/3
The following example illustrates how to delete the added static address 00d0.f800.073c in the
previous example:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)#no mac-address
static 00d0.f800.073c vlan 4 interface GigabitEthernet 0/3

7.5.2. View Configuration
Command
Function
Switch#show mac-address static
View all the information of static
address.
The following example illustrates how to view all the information of static address:
Switch#show mac-address static
VLAN MAC TYPE interface STATE index
---- -------------- ------- -------------------- -------- ------
1 1212.1212.1202 STATIC Gi 0/9 FWD -----
7.6. Filtering Address Configuration
7.6.1. Filtering Address Management
Command
Function
Switch(config)# mac-address
static mac-address vlan vlan-id
drop
mac-address:the corresponding MAC
address of the specified table item.
vlan-id:specified the VLAN that the
address belonged to.
when the equipment receives the message
with address specified by mac-address as
source address or destination address from
the specified VLAN of vlan-id of the
equipment, the message will be discarded.
Switch(config)# no
mac-address static
mac-address vlan vlan-id drop
Delete filtering address list item, the
parameter is the same with the added
command.
The following example illustrates how to add a filtering address 00d0.f800.073c, when the received
source address or destination address in VLAN 1 is the message of the address, the message will be
discarded.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)# mac-address static
00d0.f800.073c vlan 1 drop
The following example illustrates how to delete the static address 00d0.f800.073c in the previous
example:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z. Switch(config)#no mac-address
static 00d0.f800.073c vlan 1 drop
7.6.2. View Configuration
Command
Function
Switch#show mac-address drop
View all filtering address information.
The following example illustrates how to view all the information of static address:
Switch#show mac-address drop
VLAN MAC TYPE interface STATE index
---- -------------- ------- -------------------- -------- ------
VLAN MAC TYPE interface STATE index
------ -------------- ------- ----------- -------- -------
40 0012.2131.1211 DROP ----- ---
7.7. Example of the Typical Configuration of MAC Address
Table Management
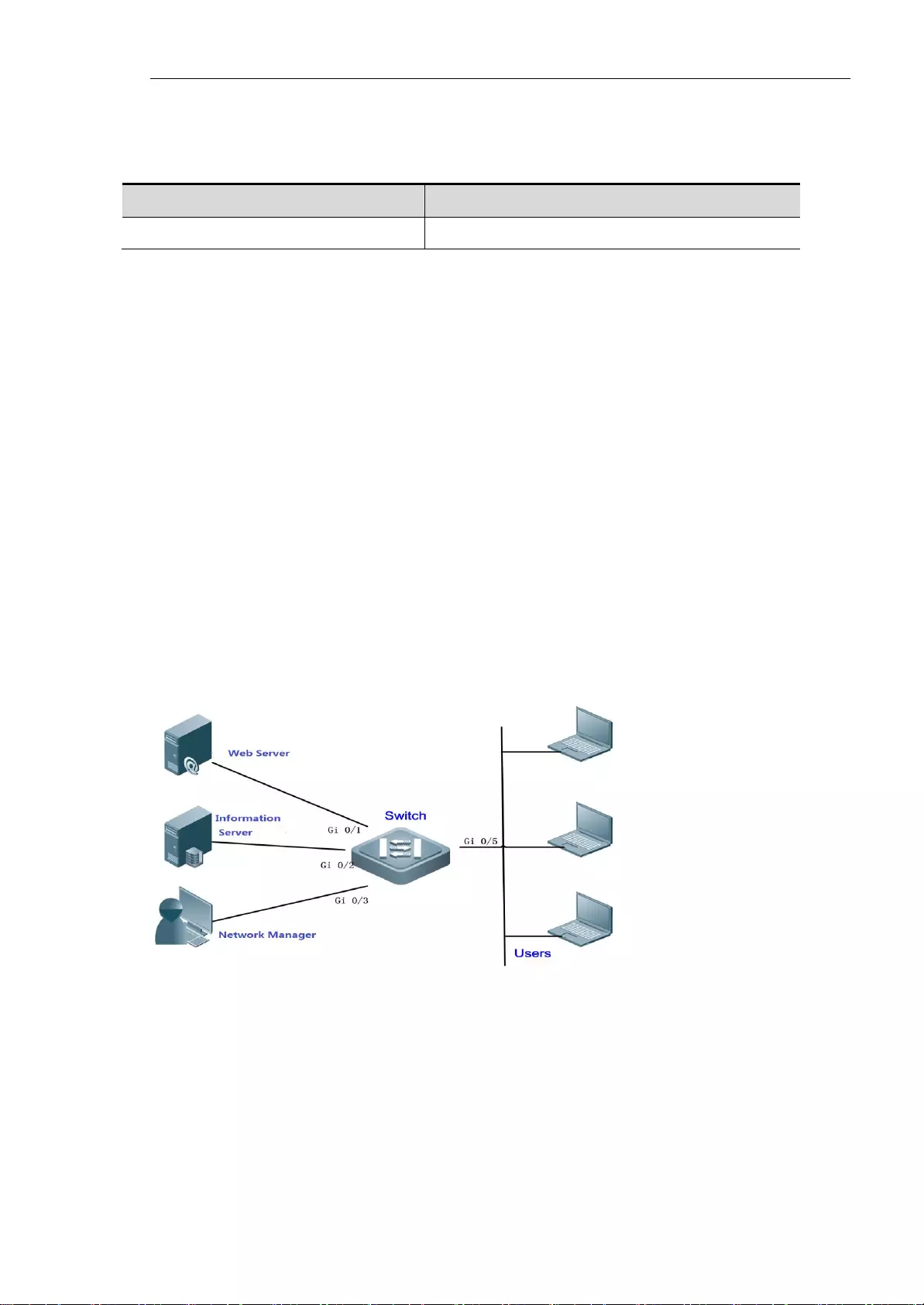
7.7.1. Topological Diagram
Below is a network diagram for an information system. Web server, database server is connected to
the Ethernet switch respectively through Gi0/1 and Gi0/2 , server administrators connected to the
Ethernet switch through Gi0/3 , other normal users access to the Web server through the Ethernet
switch Gi0/5 port . All the data are forwarded in the VLAN 10.
Static MAC address use network topology
7.7.2. Application Requirements
For the information security of interaction between a WEB server and database information and
interaction between server administrator and server, assuring the data forwarding between WEB
server and database server, between administrator and each server is adopted unicast way by
configuring static address. This can effectively avoid the data is forwarded to the general users to in
the form of broadcast.
7.7.3. Point of Configuration
Configure static MAC address table entries, make sure the following three elements:
1, destination MAC address the specified table item corresponding to.
2, specify the VLAN that the address belonging to(VLAN id)
3, interface ID (port - ID)
When the switch receives the message with Mac-address as its destination address from the Vlan-id
specified VLAN of the switch, the message will be forwarded to the interface specified by port-id.
The corresponding relationship of MAC address between VLAN, interface in the example is shown in
the table below:
Role
MAC Address
VLAN ID
Interface ID
Web Server
00d0.3232.0001
VLAN10
Gi 0/1
Information Server
00d0.3232.0002
VLAN10
Gi 0/2
Network Administrator
00d0.3232.1000
VLAN10
Gi 0/3
7.7.4. Configuration Steps
!enter the global configuration mode of the switch:
Switch>en
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
!Add static MAC address (indicates the belonging VLAN, interface)
Switch(config)#mac-address static 00d0.3232.0001 vlan 10 interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config)#mac-address static 00d0.3232.0002 vlan 10 interface GigabitEthernet 0/2
Switch(config)#mac-address static 00d0.3232.1000 vlan 10 interface GigabitEthernet 0/3
7.7.5. Configuration Verification
Add static MAC address (indicates the belonging VLAN, interface):
Switch#show mac-address static
VLAN MAC TYPE interface STATE index
------ -------------- ------- ----------- -------- -------
10 00D0.3232.0002 STATIC Gi 0/2 FWD ----
10 00D0.3232.0001 STATIC Gi 0/1 FWD ----
10 00D0.3232.1000 STATIC Gi 0/3 FWD ----

8. Configuration of POE
8.1. Overview
Power over Ethernet,Referred to as PoE,Is a technology that it can through in the Ethernet
twisted-pair cable to transmit power and data to the device. With the technology including network
telephone, WIFI AP, network camera, hubs, computer and other devices can get power directly from
the twisted-pair cable.
8.1.1. Basic concepts
In the use of PoE switches build PoE system, PoE switches play PoE power supply and the
combination of PSE. Users of electrical equipment, such as WLAN wireless AP, VoIP phone, etc., can
be called the PD. PoE switch power supply in accordance with the standards for the longest distance
of 100 m. Support PoE switches can statistical each port and the whole equipment power supply, and
is displayed by a query command.
PoE system consists of three parts:
PoE power supply
PoE power for the whole of PoE power supply system ,the PoE system is divided into two types, that is,
external power supply and Internal power supply. In our products, Cassette PoE switches generally
have internal power supply, some products also supports external power supply, external power
supply is called the RPS.
PSE
PSE(Power Sourcing Equipment)。PSE on PoE interface circuit to find and detect PD, PD for grading,
and to the power supply.When detected PD uproot, PSE stop power supply.
PD
PD is accept PSE power supply equipment. Divided into standard PD and non-standard PD, Standard
PD refers to comply with the IEEE 802.3 af and 802.3 at standard of PD equipment. PD equipment in
PoE power supply at the same time, allowed to connect other power supply, power supply redundancy
backup.
8.1.2. The related protocol specification
At present there are IEEE 802.3 af and IEEE 802.3 at PoE tandard, the main features and the
difference between these two standard shown in the table below:
Parameters
802.3af
802.3at
PD Available power
12.95W
25.50W
PSE provide maximum power
15.4W
30W
PSE Voltage range
44.0-57.0V
50.0-57.0V
PD Voltage range
37.0-57.0V
42.5-57.0V
The largest cable impedance
20 Ω
12.5 Ω
Power management ways
To divide the power
level when the line is
initialized
When line initialization is divided into
four levels or using 0.1W as a unit to
Dynamic adjustment.
Support Cable
CAT3 or CAT5
CAT5

According to the standard of the IEEE 802.3 af, PoE switches
can use twisted-pair idle line to supply power , can also use
the twisted pair Signal line to supply power , PD equipment
shall supply power at the same time support the free line of
power supply and signal lines in two ways.
IEEE 802.3 at switches provide backward compatibility ability,
support at 802.3 PoE switches can use only support on the
IEEE 802.3 af of PD equipment.
8.2. POE Configuration
8.2.1. Set port POE function
The user can enable or close port PoE function. By default, the access layer switch port of PoE
function is enable, the core switches PoE function is closed.Please configure the following at the
interface mode.
If you use interface range command batch configuration port PoE
function,Due to the range command is configuration interfaces
one by one, a port PoE function were switched on or off, will affect
the equipment global supply management. So maybe can appear
in the process of configuration interface to electricity up and down
phenomenon, which belongs to the normal phenomenon.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet
port-id
Enter interface configuration mode,
specified to configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe
enable
Enable remote power supply of the port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no
poe enable
Close port of the remote power supply
Switch(config)# end
Back in privileged mode
Switch# write
Save Settings to parameter file
8.2.2. Set the power management mode
Power supply management mode is refers to the equipment connection of PD for power distribution.
PoE switches support power management model includes Auto mode、Energy-saving mode and Static
mode.
Auto mode, according to detect the type of port PD grading to allocate power. About PD of class0 ~
3 the equipment allocate the power in the following relations: Class0 - 15.4 W, Class1 - 4W,Class2 -
7W,Class3 - 15.4W,Class4 - 30W。In this mode, such as there is a distribution to Class3 equipment,
even if the consumption of only 11 W, PoE power supply equipment will be in accordance with the
power for port distribution power of 15.4 W.Auto mode for PoE switch power supply management
mode by default.
Energy-saving mode, the actual consumption of equipment in accordance with the PD adjustment of
dynamic power allocation. Set to this mode, PoE power supply equipment for more PD equipment
power supply, but also may be due to partial PD power fluctuations affect other PD equipment of
power supply. Optional modes of energy saving mode for PoE switches, if the switch does not support
the pattern, will output the corresponding message in the configuration.
Static mode, the distribution of power, according to the user's configuration each port must be
assigned to power supply. When switch to static mode, if all the port is not set up distribution power
(through POE alloc - power configuration), the system will automatically for port power distribution. If
the power distribution of power is not enough to all ports, so part of the port from small allocation in
Command to supply power allocation is finished.
PoE switch power supply management mode of comparison
B
y
default, the equipment of the power supply management mode to auto mode.
For example, set up the equipment of power supply management mode of energy - saving mode:
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)# poe mode energy-saving
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# poe mode { auto |
energy-saving | static }
Set the PoE system of power supply
management mode to automatic mode,
energy-saving mode or static mode.
Mode\Features
Auto Mode
Energy-saving Mode
Static Mode
Power calculation basis
PD equipment
classification power
PD current consumed power
of the equipment
User's configuration
Whether the default mode
Default mode
Optional mode
Optional mode

Switching power supply management mode, all PoE port under
electricity, ports in accordance with the new management model of
power supply to electricity.
When switch to static mode, if there is no port assignments power set,
the system automatically port configuration for power distribution,
support only 802.3 af equipment distribution of each port 15.4 W,
support at 802.3 equipment, distribution of each port 30 W.
8.2.3. The POE port power priority
The user can configure the PoE switch port power supply priority.Priority from high to low in turn
is:Critical、High 、Intermediate and Low。In automatic mode and energy-saving mode, high priority as
well as power supply port.At the time of PoE switch machine power shortage, low priority port first off
electricity, under the condition of the same priority, actual consumption power will be out of
electricity.The default priority of the interface are all low.
Same priority port, the new insert port, will not affect the already in the state of the power supply of PD
equipment power supply.Different priority of ports is not affected by this feature, high-priority ports can
preempt the low
priority.
For example, Set port 1 remote power supply for Critical priority, and close the POE priority, restore
the port priority as the default mode.
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#poe priority critical
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#no poe priority
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#end
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet
interface-id
Enter interface configuration mode, specified
to configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe
priority { low | high | critical }
Set port power supply priority
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no poe
priority
Restore power to port as the default priority

This command at the time of power supply management model for the
static model is meaningless, because in the static mode of port power
according to the user configuration force distribution, the switch can't be
selected automatically, so the command is not effective in the static mode.If
before the switch to static mode ports have configured the priority, then the
command will be displayed, but do not take effect.
8.2.4. Set port maximum power
Users can configure port maximum power, to limit the maximum output power
In automatic mode and energy-saving mode, set the maximum power can limit the maximum output
power of the port, when the port's power more than setting the maximum power of a certain time, port
power supply stopped, electrical port on the device. After 10 seconds, the port will once again be on
the electricity, the power still exceed the maximum power, if the port port will once again be the electric
cycle and the process.
If the user doesn't configure port maximum power, then the port on the examination of the maximum
power.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#poe max-power 17
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#poe enable
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#end
The command is in effect only in automatic mode and energy-saving mode.
If in automatic mode and energy-saving mode, the Max - power is set to 0, port off
electricity, and no longer on the electricity.
Support only 802.3 af PoE switches, Max - power configuration in the range of <
0-15.4 >
If the power supply management mode in automatic mode, and configured with Max -
power command, so the power supply according to user's Max - power management
algorithm configuration commands to calculate the distribution of the port power.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet port-id
Enter interface configuration mode, specified to
configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe
max-power int
Sets the maximum power at the port, the range of 0 to
30, the unit is watt, support setting up to three decimal
places.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no poe
max-power
Close port maximum power Settings

8.2.5. Set port’s distribution power
Users can configure the porti's distribution power, to setting output value of the port in the static
mode.
When the power supply management model for the static mode, the command is used to power the
distribution of the specified port.When switch to static mode for the first time, if the user has no port
configuration for power distribution, on the support only 802.3 af POE switches, the distribution of the
system will configuration for each port 15.4 W power, on the support 802.3at POE switches, the
distribution of the system configuration for each port 30 W power.If the system power is not enough to
assigned to all ports, the port number assigned small port
For example, in the static mode setting port of the maximum power of 20 w, then can make port PoE
function.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe alloc-power 20
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#poe enable
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#end
When the power supply management model for static mode,
you must configure port‘s distribution power, Port to the power
supply.
This command takes effect only in the static mode.
If in the static mode, will alloc - power is set to 0, port off
electricity, and no longer on the electricity.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet
port-id
Enter interface configuration mode, specified
to configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe
alloc-power int
Sets the maximum power at the port, the
range of 0 to 30, the unit is watt, support
setting up to three decimal places.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# no
poe alloc-power
Cancel the port assignments power set, if in
the static mode, the ports of the power supply
will stop.
8.2.6. Set system’s Reserve power
When using energy-saving mode, PoE switches according to the actual consumption of PD equipment
power to calculate the power consumption of the system.If there is a PD device in this mode
consumed power fluctuation is very big, will lead to damage of PoE switches under the heavy load
PoE equipment.
PoE switches provide Settings PoE system reserved power command to protect PoE switch power
has always been "surplus", the current consumption of power will not exceed the limit of PoE switch
itself.
System’s preserving power default is 0%.
For example, set up the system for the power of retention of 20%.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)# poe reserve-power 20
Switch(config)# no poe reserve-power
Set up command system to retain power, only in the current PoE switch power
supply management mode to save energy when.
In energy-saving mode to retain power, it may lead to port under electric has
access to electricity.
8.2.7. Use hot start uninterrupted power supply function
If you need to restart the switch in practical applications, such as restart the PoE switches after
upgrade PoE switche's management software,But this time there are many PD equipment is in the
normal power supply on the PoE switch,If restart directly, may cause the working PD equipment off
the electricityand then to electricity,PD equipment work there will be a period of time interrupt.
The switch provides the hot start uninterrupted power supply,At the time of system restart, has been in
a state of power supply of PD equipment in the process of hot start PoE switches will not off
electricity.Hot start is completed, the system back to save the configuration file in the state.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# poe reserve-power int
Set to retain power of the percentage of the total
power of system, the range of 0% to 50%.
Switch(config)# no poe reserve-power
Restore the reserved power as the default
value, the default is 0%

For example, Enable and disenable the hot start uninterrupted power supply function
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)# poe uninterruptible-power
Switch(config)# no poe uninterruptible-power
Switch(config)#end
After enable and disenable this function must to save the configuration to ensure
effective in the reduction of the next. If the user forgot to save the configuration,
or to save the configuration and then change the POE configuration, system will
prompt the user to save the configuration.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)#poe uninterruptible-power
Enable the hot start uninterrupted power supply
function
Switch(config)# end
Return to the global model
Switch#write
Save the configuration, to ensure effective at the
time of the next start
Switch(config)# no poe uninterruptible-power
Closed hot start uninterrupted power supply
function

8.2.8. Set the power recovery mode
If power supply equipment off electricity in actual application, can be set up port recovery mode to
restore power,there are auto and manual in two ways,In auto mode,Power supply equipment to
restore power, connection of PD equipment automatically restore power,in manual mode, through the
user manual to restore power, the default configuration for manual. Also can sets the recovery interval
time by recover - time, the default is 60 seconds, can be installed range 5-3600 seconds.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)#poe recover-time
{Time range(s)}
Sets the restore clearance time
Switch(config)# no poe recover-time
Restore clearance for the default 60 s
Switch(config)# interface
gigabitEthernet port-id
Enter interface configuration mode, specified to
configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)
#poe recover [auto|manual]
Set the recovery mode
Auto,Power supply equipment to restore power, PD
device automatically restore power
Manual, Power supply equipment to restore power,
through the user Settings to restore power
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)
#no poe recover
Close the auto mode, revert to the default manual
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)
#end
Return to the privileged mode
For example,Set power supply recovery clearance time is 30 s and revert to the default interval of
time.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#poe recover-time 30
Switch(config)#no poe recover-time
For example,Enter interface configuration mode, set the power supply recovery mode for auto and
revert to the default manual.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#poe recover auto
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#no poe recover
8.2.9. Set port's PD descriptor
In practice it is often necessary to record specified PoE port access PD name,In RFC3621 provides
pethPsePortType item to set port of PD.
Switches also provides the CLI Settings to set this value.
Command
Function
Switch# configure terminal
Enter global configuration mode
Switch(config)# interface
gigabitEthernet port-id
Enter interface configuration mode, specified to
configure the physical port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-
0/1)#poe pd-description
pd-name
PD descriptor configuration interface, parameter as
a string, the maximum support
32 characters
Switch(config)# end
Return to the global model
Switch#write
Save the configuration, to ensure effective at the
time of the next start
For example, set gigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of PD descriptors.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# poe pd-description test
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#end
8.3. Display POE Status
8.3.1. POE port status display
The user can in privileged mode through the show command to view the interface state.
F
o
r
e
x
a
m
p
l
e
,
display the single port fastEthernet 0/1 state of power supply:
Switch#show poe interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Interface : Gi0/1
Pd Description : test
Command
Function
Switch# show poe interface
gigabitEthernet [port-id]
Display power supply state about designated
port
Switch# show poe interfaces status
Show all PoE port state of power supply (8
ports can rely on PoE power supply system)
Switch# show poe interfaces
configuration
Show all PoE port configuration information(8
ports can rely on PoE power supply system)

Power control : Normal
Power status : Detecting
Max power : 29.123 W
Allocate power : 19.124 W
Current power : 0 W
Average power : 0 W
Peak power : 0 W
Voltage : 0 V
Current : 0 mA
PD class : NO PD Devices
Trouble cause : None
Priority : Low
Trouble Recover Mode : manual
Power management : Auto

The meaning of the information displayed is:
Trouble cause Said the electricity
Display Item
Instructions
Interface
The interface number.
Power control
Whether have enable the PoE function.
Power status
Whether the PoE has already started to power supply. 。
Max power
Port to support maximum power.
Allocate power
Port’s distribution power
Current power
Port’s consumed power.
Average power
Port’s current average power After power on port "port
current consumed power" of the sample average.
Peak Power
Port’s peak power
Voltage
The current voltage of the port.
Current
The current electricity of the port.
PD class
Port's level, according to the regulations of the
802.3af/802.3at, PD equipment is divided into four levels.
Trouble cause
The cause of the problem of none said there is no system
failure.
Priority
The port priority:
low,Low priority, the default priority for port;
high,High priority, requires the user to configure;
critical,The highest priority, the user configuration is
required.
Trouble Recover Mode
Power recovery mode:
Auto,Automatically restore power
Manual,Requires the user to manually restore power
Power management
Power supply management mode:
auto,Automatic mode;
energy-saving,Energy-saving mode;
static,The static model.

Users can not enter the port number,through the show poe interfaces status command to display all
port state of POE power supply,can show poe interface configuration command to display all the ports
of POE configuration information.
Show all PoE port state of power supply:
Switch#show poe interfaces status
Interface Power Power Curr Avg Peak Curr Trouble PD
Control Status Power Power Power Current Cause Class
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Gi0/1 Normal Powering 2.138W 2.217W 2.296W 40mA 0 3
* Gi0/2 Normal Powering 17.106W 17.186W 17.267W 320mA 0 4
Gi0/3 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Gi0/4 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Gi0/5 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Gi0/6 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Gi0/7 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Gi0/8 Normal Detecting 0W 0W 0W 0mA 0 N/A
Display all POE port configuration information:
Switch#show poe interfaces configuration
Interface Power Power Max Alloc Port Port
Control Status Power Power Priority Legacy
-----------------------------------------------------------------
* Gi0/1 Normal Powering 30W 20W High N/A
* Gi0/2 Normal Powering 30W 30W High N/A
Gi0/3 Normal Detecting 15.123W 30W Critical N/A
Gi0/4 Normal Detecting 30W 30W Critical N/A
Gi0/5 Normal Detecting 30W 0W Low N/A
Gi0/6 Normal Detecting 30W 0W Low N/A
Gi0/7 Normal Detecting 30W 0W Low N/A
Gi0/8 Normal Detecting 30W 0W Low N/A
I
D
Port trouble cause
Instructions
0
None
Normal power supply
1
Overload During Startup
Detection stage, found that the current is too big and
disconnect
2
Power Overload due to Icut
PD equipment overload and disconnect the power
3
Short Circuit Detected
PD equipment short circuit and broken
4
Thermal Powerdown
High temperature protection and shut down
5
Power Management
Shut down power management
6
VEE UVLO
Hardware fault and shut down
8.3.2. Display POE status
The user can in privileged mode by the show command to view the system state of PoE.
The following example to show the PoE system state of power supply:
Switch#show poe powersupply
Power-Over-Ethernet System power status:
Powerring Port List : Gi0/1, Gi0/2,
Power Management Method : Auto
Poe uninterruptible power : Disable
Error Recover Interval : 60s
System Total Power : 400 W
Power Consumption : 15.4 W
Available power : 384.6 W [96%]
PSE reserve power : 0%
The meaning of the information displayed is:
Command
Function
Switch#show poe powersupply
Display POE power supply state of the whole
system
Display Item
Instructions
Powerring Port List
Currently in power supply port
Power management
Power supply management mode:
auto,Automatic mode;
energy-saving,Energy-saving mode;
static,The static model.
Poe uninterruptible power
Whether to enable hot start not power down mode, the
default for the disable
Error Recover Interval
Recovery time, the default 60 s, range: 5-3600 - s
System Total Power
This system can support the maximum power.
power consumption
The current system power consumption.
Available power
The current system of power distribution, in different power
supply management mode, the system of distribution of
power is different.
PSE reserve power
The percentage of the system to retain power.
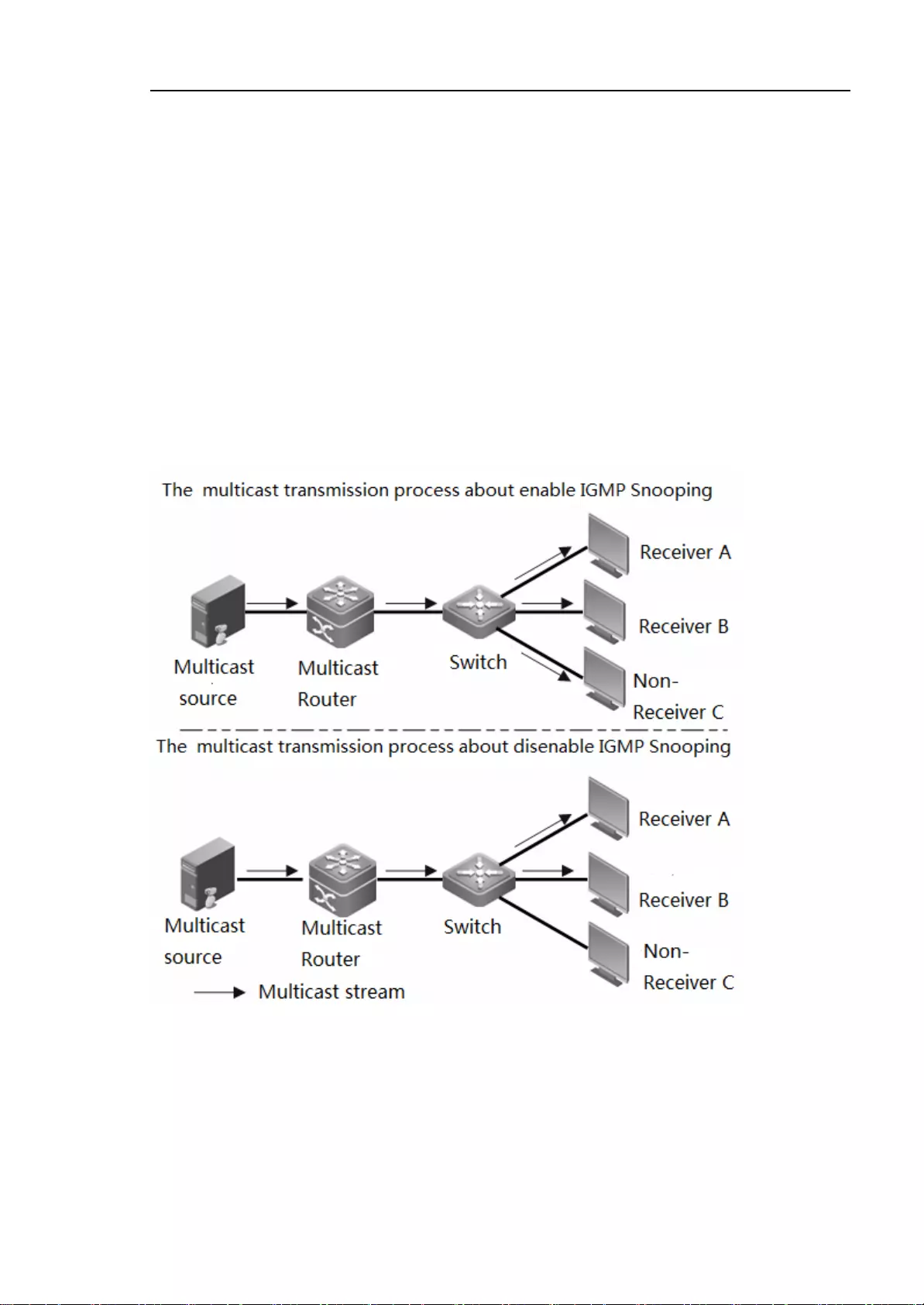
9. configuration IGMP Snooping
9.1. Overview
9.1.1. Understand the working principle of IGMP Snooping
IGMP Snooping is short for Internet Group Management Protocol.It is to run on the VLAN IP multicast
constraint mechanism,Used to manage and control the IP multicast flow within the VLAN
forwarding,Belong to the second layer of multicast functionality.IGMP Snooping function described
below,Is carried out within the VLAN, related port is refers to the internal members of the VLAN.
Run the IGMP Snooping devices through analyze the IGMP packets received,For port and multicast
address set up mapping relationship,and according to the mapping relationship of such forwarding IP
multicast data packets.As shown in the figure below,When the switch is not running IGMP Snooping,
IP multicast data packets within a VLAN is broadcast;After the switch to run the IGMP Snooping,
known IP multicast group's multicast data packets not within a VLAN is broadcast, but sent to the
designated recipient.
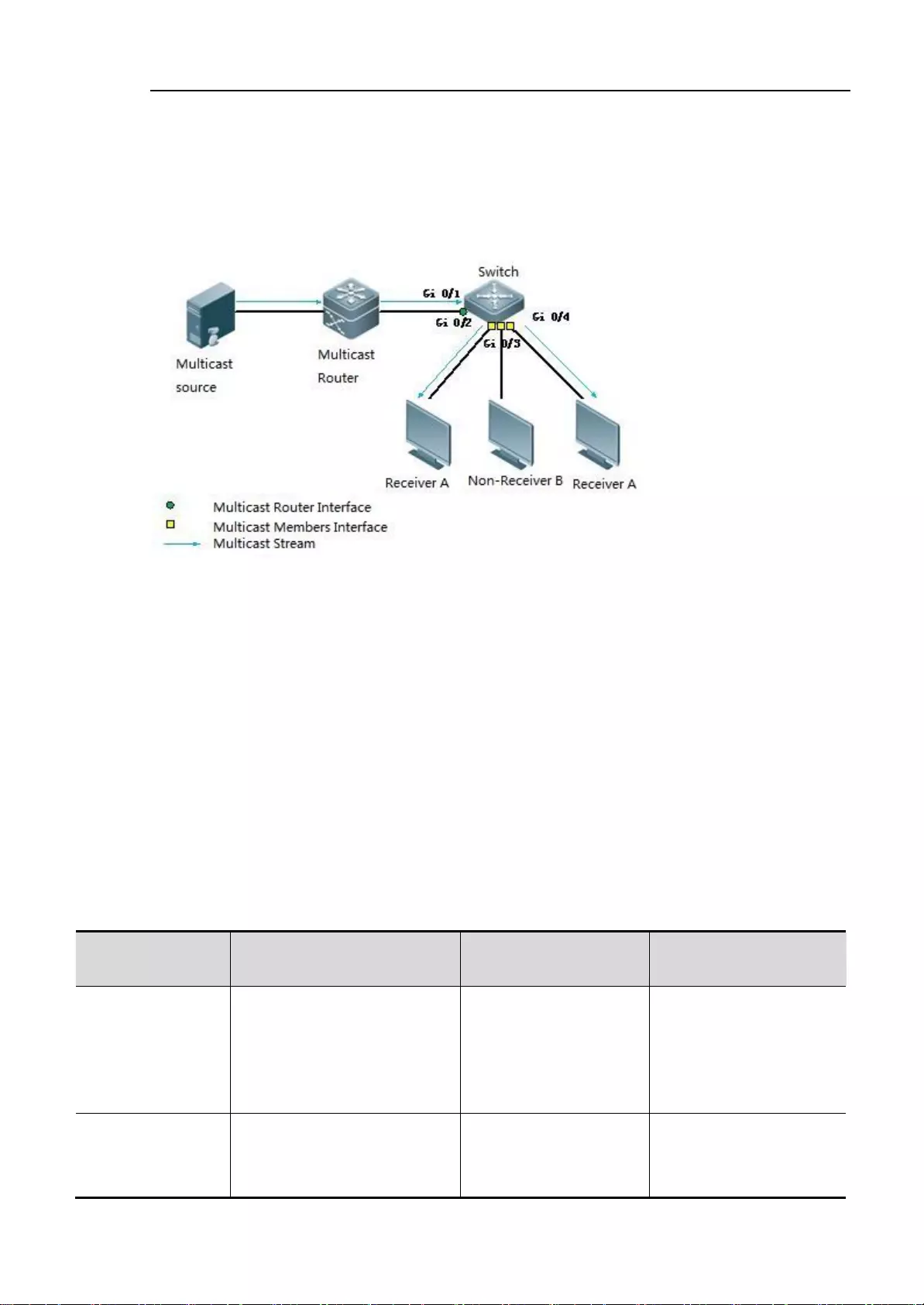
9.1.2. Understand the two types of IGMP Snooping port
As shown in the figure below, the Router connection multicast source, run in the Switch A IGMP
Snooping, Host A and Host C for receiver Host (i.e., IP multicast group members).
Two types of IGMP Snooping port
Multicast Router Port:Switches connected multicast router(three layer multicast equipment),Such as
the Switch of A Gi 0/1 port.Switches connect all routing of this device ports (including dynamic and
static ports) are recorded in the routing connection list.Router connection by default is corresponding
to the receiver of multicast data within a VLAN can be added to the IGMP Snooping in turn.
Member Port:Short for IP multicast group members port,Also known as the Listener Port,Said switch
connection port of the IP multicast group side,Such as the SwitchA of Gi 0/2、Gi 0/3 and Gi 0/4 port。
Switch to all members of the ports on the device (including dynamic and static port) is recorded in the
IGMP Snooping in turn.
9.1.3. Understanding the dynamic aging timer of the port
IGMP Snooping Dynamic port of aging timer
Type
Description
Start the event triggered
a timer
Timeout after the switch
Aging timer
dynamic routing
connection port
Switch for each dynamic
routing connections
are starting a timer aging
time, thetimeout is the
dynamic routing connection
port
IGMP group received
query message or PIM
Hello message
The port is removed from
the routing connections
list
Aging timer dyna
mic member port
Switch to the port starts a
timer, the timeout is dynamic
state members port aging
time
IGMP queries received
message
The port is removed from
the IGMP Snooping
multicast group

9.1.4. Understand the working mechanism of IGMP Snooping
Conventional query and specific queries
IGMP will send all the hosts and routers in the network common set of query message,In Command to
query the network segment what IP multicast address is 224.0.0.1 multicast groups.After receiving the
IGMP universal set is the query message, switch the query message to the all port forwarding out
within a VLAN, and receiving port of the newspaper article to do the following:
If the port is already in routing connection port list, timer is reset to its aging.
If the port is not in routing connections list, then add it to the list of routing connectors, and start the
aging time.
After receive IGMP‘s common set of query message, multicast equipment will be switched to all
members of the port their aging timer,timer for configuration of IGMP query message to the longest
response time,When the timer timeout, argues that the port no more members to receive multicast
stream,multicast equipment will turn the port from the IGMP Snooping published.
Report the membership
The following case,The host will report to the IGMP inquirers IGMP membership to send a message:
When IP multicast group members of the host after receiving the IGMP query message,IGMP
membership report will reply message.
If the host IP to join a multicast group,It will take the initiative to send IGMP inquirers IGMP
membership report message to declare to join the IP multicast group.
IGMP membership after receiving the report message,Switch it to all routing within a VLAN connection
port forwarding to go out,
From the analysis of the message in the host IP multicast group address to join,and receiving port of
the newspaper article to do the following:
If there is no corresponding turned this IP multicast group published items,create the forwarding table
entries,add the port as members of the dynamic port to a port in the list,and start the aging timer;
If there are corresponding to the IP multicast forwarding table entries,but the output port does not
contain the list of ports,then the port as a dynamic member port is added to the list of ports,and start
the aging timer;
If there are corresponding to the IP multicast forwarding table entries,And the dynamic member port
already contains the list of ports,then aging timer is reset.
9.1.5. Leave the multicast group
For the IGMP V2,when the host left the IP multicast group, IGMP leave group by sending a
message,in Command to inform the multicast router left an IP multicast group.When the switch from
one port on dynamic members receive IGMP leave group message,Switches will deal with it according
to whether launched immediately leave accordingly.If the switch opens the leave immediately, the port
is removed from the multicast table,If does not start to leave immediately, send a specific set of query
message,If have not received the report within the timeout message, will be the port is removed from
the multicast table.If you remove the port after the multicast group members have no port, switch to
routing port forwarding to leave a message.
9.1.6. Understand IGMP Profiles

Command
Function
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping
Enable and set the IGMP Snooping, lack of
provincial situation, IGMP Snooping in the
closed state.
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping
version {1| 2 | 3}
Configuration IGMP version 1, 2, 3;The
default configuration version 2.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping
IGMP Snooping global shutdown function.
IGMP Profiles is actually a set of filters,It can be defined as a series of multicast address range,and
the definition of the multicast address access permit or deny action,For later "routing connection
filtering of multicast data range", "IGMP Filtering" using the features.
9.2. Configure IGMP Snooping
We will from the following sections describe how to configure the IGMP Snooping:
9.2.1. Enable IGMP Snooping
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
The following example is Enable and set up IGMP Snooping and configure IGMPv2
Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping
Switch(config)#end
Switch# show ip igmp snooping
Global IGMP Snooping configuration:
-----------------------------
IGMP Snooping : Enabled
Report Suppression : Enabled
TCN solicit query : Disabled
TCN flood query count : 2
Last Member Query Interval : 1000
IGMP version : 2
ProtoStatus : Enabled
Router-port aging time : 255
Report-port aging time : 260
Vlan ID:1
-----------
IGMP Snooping : Enabled
IGMPv2 immediate leave : Disabled
Last Member Query Interval : 1000
Router-port aging time : 255
Report-port aging time : 260
Vlan ID:2
-----------
IGMP Snooping : Enabled
IGMPv2 immediate leave :Disabled
Last Member Query Interval : 1000
Router-port aging time : 255
Report-port aging time : 260
9.2.2. Close the IGMP Snooping
In the global mode, follow these steps to close the IGMP Snooping:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping
Close the IGMP Snooping, by default, the IGMP
Snooping in the closed state.
Switch(config)# show ip igmp snooping
If confirm the configuration take effect.
9.2.3. Based on the VLAN start IGMP Snooping
By default, when the global open IGMP Snooping, all VLAN will automatically open the IGMP
Snooping function.If you need to specific VLAN off the IGMP Snooping function, can use the following
command.
In the global mode, follow these steps to close the IGMP Snooping:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping vlan
num
Close the VLAN num IGMP Snooping, by default,
VLAN num of IGMP Snooping in the open state.
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan num
Open the VLAN num IGMP Snooping function.
The following example is close the vlan 3 IGMP Snooping:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping vlan 3
9.2.4. Aging timer configuration of router’s connection port
For dynamic routing connection port,,before the aging time timeout not received the IGMP query
message,switch will turn the port is removed from the list of router port.
In the global mode, press the following steps to configure the dynamic port aging timer:
Command
Function

Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping timer
router-port expiry time
Configure dynamic routing connection port aging
time, time:<60-300> the default value is 255s.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping timer
router-port expiry
The aging time to recover dynamic routing
connection port as the default, the default value is
255s.
The following is a dynamic routing configuration joint aging time of 100 s instance:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping timer router-port expiry 100
9.2.5. Configure the aging timer of member port
For member port, if the aging time timeout did not receive IGMP join message,the switch will remove
the port from the list of member port.
In the global mode, follow these steps to configure the aging timer of member port
Command
Function
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping timer
report-port expiry time
Member connecting port aging time,
time:60-300, the default value is 260s.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping timer
report-port expiry
The aging time recovery member interface as
the default, the default value is 260s.
The following is a member of the aging time of 100s interface configuration example:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping timer report-port expiry 100
9.2.6. Configure IGMP Profiles
IGMP Profiles is actually a set of filters,For the following "routing connection filtering multicast data
range", "IGMP Filtering" using the features.
In the global mode, follow these steps to set up a Profile:

Command
Function
Switch(config)# ip igmp profile
profile-number
Enter the IGMP Profile model, assign a number
for logos, the number range of 1-1024, by default,
did not match any Profile.
Switch (config-igmp-profile)# permit
| deny
(optional) configured to permit or deny that a
batch of multicast address range, the default
value is deny.This behavior: enable / disable the
following range within the multicast address,
multicast address and ban / allow other.
Switch(config-igmp-profile)# range
low-address high_address
Adding the multicast address range, the value
can be a single IP group address can also be a
group address interval (in front of the low IP
group address, behind the high IP group
address), also can configure multiple
rangerange.
Switch(config)# end
Return to the privileged mode.
Command
Function
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id
mrouter {interface gig port-id | link-aggregation ap-id}
Set the interface to the static
routing joint.
Switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id
mrouter {interface gig port-id | link-aggregation ap-id}
Cancel the interface for static
routing connections.
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
If you want to delete one of the IGMP profile, you can use the no IP IGMP profile profile number to
execute.
Which of the following is an example says the Profile of the configuration process:
Switch(config)# ip igmp profile 1
Switch(config-profile)# permit
Switch(config-profile)# range 224.0.1.0 239.255.255.255
Switch(config-profile)# end
Switch# show ip igmp profile 1
IGMP profile 1:
----------------
Permit
range 224.0.1.0, 239.255.255.255
According to the above configuration,The rules of the IGMP Profile is a multicast address to permit
224.0.1.0 -239.255.255.255 , other multicast address is deny.
9.2.7. Configure the routing connections
By default, VLAN will be undertaken within the dynamic routing link learning,
You can configure the closed dynamic multicast routing connection of the function of learning,With
the corresponding no option ordered closed dynamic learning,And empty all dynamically learned
routing connectors.
Also can through the command connect the switch port configuration as the static routing.
In the global mode, press the following steps to configure the router connection:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# interface
GigabitEthernet id
Enter the configuration interface.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
ip igmp filter
profile-number
(optional) Profile is applied to the port, the
Profile number range 1-1024.By default, a
port is not associated with any profile.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
no ip igmp filter
(optional) delete associated profile on
interface, the interface will be allowed by all
groups.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
ip igmp max-groups number
(optional) allows for up to a few dynamic
group of the port, and the number range of
0-500.By default, 500.
The following example is set Ethernet interface 0/1 to VLAN1 static routing connection
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 mrouter interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config)# end
Switch#show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Vlan SourceAddr Interface
---- --------- --------
1 0.0.0.0 Gi 0/1(static)
9.2.8. Configure port IGMP Filtering
In some cases, you may need to control a certain ports can only receive a number of specific multicast
data flow, under the control of the port allows dynamic most how many groups to join.IGMP Filtering to
meet the demand.
You can put a IGMP Profile application in a port,if the port receives a IGMP Report message, the two
layer multicast device will find this port to join the multicast address is in the allowable range of IGMP
Profile.If yes, are allowed to join, only after the subsequent processing.
You can also count on a port configuration allows up to j oin the group,Over the range, two layer
multicast equipment is no longer receiving, processing the IGMP Report message.
In the global mode,According to the following steps to configure the IGMP Filtering:
Step 1
Step 2
The following is the example of IGMP Filtering configuration:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#link-aggregation 1
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#ip igmp snooping filter 1

9.3. Check the IGMP Snooping information
We offer to view the IGMP snooping related information is as follows:
9.3.1. View the current mode
IGMP Snooping in privileged mode using the following command to view the current working mode
and global configuration:
Command
Function
Switch# show ip igmp snooping
Check the IGMP Snooping current work mode
and global configuration.
The following example uses the show ip igmp snooping to view IGMP Snooping configuration
information:
Switch# show ip igmp snooping
Global IGMP Snooping configuration:
-----------------------------
IGMP Snooping : Enabled
Report Suppression : Enabled
TCN solicit query : Disabled
TCN flood query count : 2
Last Member Query Interval : 1000
IGMP version : 2
ProtoStatus : Enabled
Router-port aging time : 255
Report-port aging time : 260
Vlan ID:1
-----------
IGMP Snooping : Enabled
IGMPv2 immediate leave : Disabled
Last Member Query Interval : 1000
Router-port aging time : 255
Report-port aging time : 260
9.3.2. Check the IGMP Snooping statistics
In privileged mode using the following command to view IGMP Snooping statistics information:
Command
Function
Switch# show ip igmp snooping interface
GigabitEthernetstatistics
Check the IGMP Snooping statistics.

The following example uses show ip igmp snooping interface statistics command to view IGMP
Snooping routing connection information:
Switch#show ip igmp snooping interface GigabitEthernet statistics
interface GrpNum
----- -------
Gi 0/1 0
Gi 0/2 0
Gi 0/3 0
Gi 0/4 0
Gi 0/5 0
Gi 0/6 0
Gi 0/7 0
Gi 0/8 0
Gi 0/9 0
link-aggregation 1 0
9.3.3. View the routing connection information
In privileged mode using the following command to check the IGMP Snooping routing connection
mouth information:
Command
Function
Switch# show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Check the IGMP Snooping routing connection
information.
The following example uses the show ip igmp snooping command to view IGMP Snooping routing
connection mouth information:
Switch#show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Vlan SourceAddr Interface
---- --------- --------
1 0.0.0.0 Gi 0/1(static)
1 0.0.0.0 link-aggregation 1(static)
9.3.4. View the forwarding table
In privileged mode using the following command to view the port forwarding rules in the multicast
Group, namely view Group Destination Address GDA (Group Destination Address) table:
command
Function
Switch# show ip igmp snooping
groups
Check the port in the multicast
forwarding rule table.

The following example is to check the GDA table of each group multicast group information, and all the
members of a multicast group port information:
Switch#show ip igmp snooping groups
Vlan Group Version Interface Status
---- --------------- ------- ------------------- --------------
1 239.255.255.250 3 Gi 0/3 V2 members
9.3.5. View the IGMP Profile
In privileged mode using the following command to check the IGMP Profile information:
Command
Function
Switch# show ip igmp profile
profile-number
View the IGMP Profile information
The following to view the IGMP Profile information:
Switch#show ip igmp profile
IGMP profile 11:
----------------
permit
range 224.1.1.1 224.1.1.100
10. Configure SNMP
10.1. SNMP relevant knowledge
10.1.1. Overview
SNMP s the abbreviation of Simple Network Management Protocol,In August 1988, it became the
network management standards RFC1157 .Up to now, because of many manufacturers support for
the deal,SNMP has become the de facto standard of network management,Network equipment by
using SNMP protocol,The network administrator can for hosts on the network information
query,network configuration, fault location, capacity planning, network monitoring and management is
the basic function of SNMP.
SNMP is an application layer protocol for the client/server mode, including three parts:
SNMP Network Manager
SNMP Agent
MIB Management Informatio Bbase
SNMP Network Manager, is using SNMP to control and monitor network system, also known as NMS
(Network Management System).
SNMP Agent is running on the managed devices software, data acquisition board is responsible for
accepting and processing and response from NMS monitor and control the message, also can take
the initiative to send some to trap the alarm information to the NMS.
NMS and Agent relationship can be represented in the following figure:

Fig. 1-1 NMS and Agent relationship
MIB(Management Information Base)Is a virtual network management information base.Managed
network device contains a large amount of information,in order to be able to in the SNMP message
uniquely identifies a particular management unit,MIB with tree like hierarchical structure to describe
the management unit in the network equipment.The tree node represents a specific management
unit.The diagram below MIB object named tree,For a management unit System uniquely identifies the
network equipment in the,A list of Numbers can be used to represent such as {1.3.6.1.2.1.1},this string
of Numbers is the management unit of the Object Identifier,MIB is a collection of network equipment
unit identifier.
Figure 1-2 MIB tree hierarchy
10.1.2. SNMP Protocol Version
The SNMP version supports the following:
SNMPv1 :The first official version of the simple network management protocol, defined in RFC1157.
SNMPv2C:SNMPv2 management structure of Community-Based, defined in RFC1901 an
experimental protocol.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2C are the security architecture of Community-based.By the definition of the
host address and authentication name (CommunityString) is defined to proxy MIB operation manager.

SNMPv2C increased the Get-bulk operating mechanism and it can return an error message type more
detailed of the management workstation.Get-bulk operation can obtain all information in the form or
access to large amounts of data,to reduce the number of the request response.SNMPv2C error
handling ability improvement including expansion of error code to distinguish between different types
of errors,in SNMPv1 these errors only an error code.Now through the error code can distinguish wrong
type.Because the Internet may exist support SNMPv1 and SNMPv2C management workstation,so the
SNMP agent must be able to identify SNMPv1 and SNMPv2C message, and can return the
corresponding version of the message.
10.1.3. SNMP Management Operations
The interactive information between SNMP protocol NMS and Agent, defines 6 types of operations:
Get-request operation:NMS extracted one or more parameter values from the Agent.
Get-next-request operation:NMS extracted from one or more parameters from Agent under a
parameter value.Get-bulk Operation: NMS extracted from Agent batch parameter values;
Set-request Operation: NMS set one or more of the parameters of the Agent.
Get-response Operation: the Agent returns one or more parameter values, is the Agent of NMS front
three response operation of the operation.
Trap Operation: the Agent unsolicited message, notify the NMS is what will happen.
In front of the four message are sent from the NMS to Agent,Behind the two is the Agent to NMS(note:
SNMPv1 version does not support the Get - bulk operations).
Below describes the kinds of operations.
NMS to Agent in the front of the three kinds of operation and the response Agent operation using UDP
port 161.Agent of the Trap operation using UDP port 162.
10.1.4. SNMP Security
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 version use certification name used to identify whether has the right to use the
MIB object.In order to be able to manage equipment, network management system (NMS) certification
name must be in accordance with defined in an equipment name.
A certification name can have the following properties:
Read-only:Provide authorized management workstation to all read access to the MIB variables.

Read-write:For the authorized management workstation provides read and write access to all MIB
variables.
Currently available security model there are two categories:SNMPv1、SNMPv2C。
The table below for the currently available security model and security level
10.2. Configure SNMP
Configuration of SNMP is completed in the global configuration mode of network equipment, in the
SNMP configuration, please enter global configuration mode.
10.2.1. Set authentication name and access permissions
The security scheme of Community-based SNMPv1/SNMPv2C.The SNMP agent only accept from the
same authentication name (Community-String) management operations,SNMP packets and network
equipment certification name does not match will not be response, discarded directly.Certification
name equivalent to between NMS and Agent password.
Can set the access list, only the specified IP address NMS can manage;
Can set permissions of operation of the community, it is ReadOnly or ReadWrite.
Specify the name for the view, view based management.The default does not specify a view, which
allows access to all MIB objects;
You can specify to use the certification of management IP. If not specified, were not limiting the use of
the certification of management of IP address.The default is not to limit the use of the certification of
management of IP address;
To configure SNMP authentication, execute the following command in the global configuration mode:
can configure one or more specified, to specify a number of different community name,Allows network
devices to NMS for different permissions management,To delete the community name and
permissions, in global configuration mode,execute no snmp-server community Community name
command.
Command
Function
Switch#configure terminal
Enter the global model
Switch(config)#snmp-server start
Enable SNMP
Switch(config)#
snmp-server community
Community name
[ro | r w|] IP access list number [1-1000]
Set authentication and authority.
Security
model
Security level
Identify
Encryption
Instructions
SNMPv1
noAuthNoPriv
Certificat
e name
none
Through the certification confirmed data
validity
SNMPv2c
noAuthNoPriv
Certificat
e name
none
Through the certification confirmed data
validity
10.2.2. Configure SNMP host address
The Agent in certain cases,also will send a message to the NMS,to configure the Agent actively send
messages NMS host address,In global configuration mode, perform the following command:
10.2.3. Set the SNMP agent parameters
The basic parameters of SNMP Agent configuration,Set equipment contact network elements,
equipment of coded information, equipment, location information, serial number,NMS through access
device of these parameters,can be told of the contact device, device information such as the physical
location.
To configure SNMP agent parameters in global configuration mode, perform the following command:
10.2.4. Close the SNMP agent
To close the SNMP agent services in global configuration mode, perform the following command:
10.2.5. Configuration agent take the initiative to send NMS sends the Trap
message
The Trap is Agent without request to take the initiative to send messages to the NMS,Used to report
some urgent and important event.The default is not to allow Agent to send Trap messages,If you want
to permit, in global configuration mode, perform the following command:
Command
Function
Switch(config)# snmp-server enable traps [type]
[option]
Permit active Agent sends
the Trap message
Command
Function
Switch#configure terminal
Enter the global model
Switch(config)#snmp-server start
Enable SNMP
Switch(config)# snmp-server host { host-addr
[ traps ] community name [ version { 1 | 2}
Set the SNMP host address
Switch(config)# no snmp-server host community
name
Delete the existing host, the use of
the community name removed
Command
Function
Switch(config)# snmp-server contact text
Set up the system's contact information
Switch(config)# snmp-server location text
Sets the position of system
Command
Function
Switch(config)# no snmp-server start
Close the SNMP agent

Switch(config)# no snmp-server enable traps [type]
[option]
Deny active Agent sends
the Trap message
10.2.6. Configure the link the trap strategy
In the equipment can be based on the interface configuration LinkTrap whether to send the
interface,When the function is enabled, if the interface changes state of the Link, the SNMP will send
LinkTrap,don't send conversely.By default, this function enable. Need to come into force in the open
Trap alarm function.
10.3. The SNMP monitoring and maintenance
10.3.1. View the current SNMP Open state
In privileged user mode, execute show snmp-status to view the current SNMP open state
Switch#show snmp-status
SNMP ON
SNMP Trap OFF
10.3.2. View the current state of SNMP
In privileged user mode, execute show snmp-server to view the current state of SNMP.
Switch#show snmp-server
0 SNMP packets input:
0 Bad SNMP version errors
0 Unknown community name
0 Illegal operation for community name supplied
0 Encoding errors
0 Number of requested variables
0 Number of altered variables
0 Get-request PDUs
0 Get-next PDUs
0 Set-request PDUs
18 SNMP packets output:
0 Too big errors
0 No such name errors
Command
Function
Switch#configure terminal
Enter the global model
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet port id
Enter interface mode
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#snmp-trap
-link-status
Enable send the interface link trap
function
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)#no
snmp-trap-link-status
Close send the interface link trap
function

0 Bad values errors
0 General errors
0 Response PDUs
18 Trap PDUs
10.3.3. View the current state of SNMP community
In privileged user mode, execute show community to view the current state of the SNMP community.
Switch#show community
----------------------------------------------------
| Community | Read/Write |
----------------------------------------------------
private RW
publice RW
----------------------------------------------------
10.3.4. View user configuration information of host
In privileged user mode, execute show snmp-server Host to view the current proxy user configuration
information of host.
Switch#show snmp-server Host
Trap destination Community Trap-Switch Informs-Switch Version
==========================================================================
192.168.100.72 public ON OFF Ver 2
10.4. RMON
10.4.1. Overview
RMON(Remote Monitoring)is IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)standard monitoring
specification,The specification can make between various network monitors and console systems
network monitoring data.Place the RMON detector in the network nodes,network management
platform decided what information these detectors,Such as statistical information is monitored,
collecting historical information to use time etc..For example, switches and routers and other network
equipment, at the network is a network node, through the RMON function, can monitor the node
location information.
The development of RMON has experienced three stages, the first stage is the Ethernet Remote
Monitoring; second stage has been added to the token ring function, called token ring remote monitor
module; the third stage is known as RMON2, so that the higher level of RMON function to monitor the
development agreement.
The first phase of the RMON (hereinafter referred to as RMON1) contains ninegroup, all groups
are optional (but not mandatory), but some groups must have other group support.
Switch to achieve one of the 1, 2, 3, 9 groups of content: statistics group, history group, Alarm group,
event group.

10.4.1.1. Statistics group
Statistics group was first in group RMON, each sub network basic statistical information statistics
statistical monitoring.At present, only the network equipment’s interface interface can be monitoring,
statistics. The group contains an Ethernet statistics, statistical content including discarded packets,
broadcast packets, CRC error, size block, conflicts, etc.
10.4.1.2. History group
The history group is the second group in the RMON, historical groups regularly collecting network
statistics, and recorded for later processing. It contains two group:
HistoryControl Group:Used to set the sampling interval, sampling the data source control
information.
EthernetHistory Group:Provides network traffic, packet error, broadcast packets, utilization and the
number of collisions and other statistical information of historical data for the administrator.
10.4.1.3. Alarm group
The alarm group is the third groups in the RMON,At specified time intervals to monitor a specific
MIB(Management Information Base)object,When the MIB object value exceeds the upper limit of a
set or below the lower limit value of a set, will trigger the alarm.Alerts are treated as events to handle,
the handling of events to log or sending SNMP Trap.
10.4.1.4. Event group
The event group is the ninth groups in the RMON,determine the result of the alarm events, processing
behavior is to produce a log record or an SNMP Trap.
10.4.2. Configure RMON
10.4.2.1. Configure event group
You can use the following command to add a table statistics.
Statistics of the series of products the current version only
supports Ethernet interface.
The index value should be an integer between 1-65535.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if)# rmon collection stats index
[owner ownername]
Add a covariance item
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# no rmon
collection stats index
Delete a covariance item

10.4.2.2. Configuration history control group
You can use the following command to add a history control table:
Statistics of the series of products the current version only
supports Ethernet interface.
The index value should be an integer between 1-65535.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# rmon
collection history index
[owner ownername] [buckets bucket-number]
[interval seconds]
Add a history control table
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/1)# no rmon
collection history index
To delete a history control table
Bucket-number:Control specifies the data source, time interval.Each sampling interval, are a
sampling.Sampling results preserved,Bucket-number A specifies the maximum number of sampling
save, when sampling record peak, covering the earliest records.Bucket-number value range is
1-65535, the default value is 10.
Interval:Sampling interval.The default value is 1800 seconds, value between 1-3600.
10.4.2.3. Configure alarm and event groups
You can use the following command to configure warning table:
number:Alarm table index (event), range 1-65535.
variable:The alarm table monitoring variables.Variables must be an integer type.
interval:Sampling interval.Range of <1-4294967295>
Keyword Absolute said with each sampled value and upper, lower comparison,Keywords Delta
utilization and last sampling and upper limit, lower limit of difference comparison.
Value defines the upper limit, lower limit value.
Event-number:When more than the upper limit or lower limit, the triggering event group index for
Event-number events.
Keyword Log said event trigger action is: the record of events
Keywords Trap represents the event triggered action is: send Trap message to the management
station.
Community:When sending Trap certification name.
Description-string:The description of the event.
Ownername:Alarm or event group owner.
Command
Function
Switch(config)# rmon alarm number variable
interval {absolute | delta} rising-threshold value
[event-number] falling-threshold value
[event-number] [owner ownername]
Add an alarm table
Switch(config)# rmon event number [log] [trap
community] [description description-string] [owner
ownername]
Add an event group table
Switch(config)# no rmon alarm number
Delete an alarm group
Switch(config)# no rmon event number
Delete an event group
10.4.2.4. Display RMON status
10.4.3. RMON configuration instance
10.4.3.1. Statistical group instance configuration
If you want to statistics Ethernet port 3, using the following commands:
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/3
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/13)# rmon collection stats 1 owner zhangsan
10.4.3.2. History group instance configuration
If you want the 500 historical information every 10 minutes and statistics third Ethernet ports, use the
following command:
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/3
Switch(config-if-gigabitEthernet-0/3)#rmon collection history control 1 500 interval 600 owner
zhangsan
10.4.3.3. Alarm and Event groups instance configuration
If you want to configure for a statistical MIB variables alarm function.In the following example
illustrates thMIB-II IfEntry Table instance ifInNUcastPkts. 6 (port 6 received on the number of unicast
frame, for instance identifier 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12.6)set alarm function.Specific functions as follows:
Switches every 30 seconds to check port 6 received on the change of the number of unicast frame,If
received a unicast frame number than the last time check (30 seconds ago) increased by 20 or more
than 20,or more than the last time only 10 or 10 below, the alarm is triggered,at the same time, the
alarm will trigger event 1 for the corresponding operation(logged in, and send the certification called
rmon "Trap", the description of the event as "ifInNUcastPkts is too much").Alarm and event owners are
zhangsan item table.
Switch(config)# rmon alarm 10 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.12.6 30 delta risingthreshold 20 1
fallingthreshold 10 1 owner zhangsan
Switch(config)#rmon event 1 log 200 trap rmon description "ifInNUcastPktsistoomuch" owner
zhangsan
10.4.3.4. Rmon status display instance
Show rmon alarm
Switch#show rmon alarm
Alarm 10 is active, owned by zhangsan
Monitoring variable: ifInNUcastPkts.6, Sample interval: 30 second(s)
Taking samples type: delta, last value was 0
Rising threshold : 20, assigned to event: 1
Command
Function
Switch#show rmon alarm
Display alarm group
Switch#show rmon event
Display event group
Switch#show rmon
history[control|ethernet]
Display history group
Switch#show rmon statistics ethernet
Display statistics group

Falling threshold : 10, assigned to event: 1
show rmon event
Switch#show rmon event
Event 1 is active, owned by zhangsan
Description : "ifInNUcastPktsistoomuch"
Event firing causes: log, last fired at 00:20:35
Current log entries:
logIndex logTime Description
----------------------------------------------------------------
1 00:19:35 "ifInNUcastPktsistoomuch"
2 00:20:05 "ifInNUcastPktsistoomuch"
3 00:20:35 "ifInNUcastPktsistoomuch"
show rmon history control
Switch#show rmon history control
----------------------------------
RMON history control entry index: 1
Data source: IfIndex.3
Buckets request: 500
Buckets granted: 1
Interval: 600
Owner: zhangsan
Entry status: Valid
show rmon statistics ethernet
Switch#show rmon statistics ethernet
-------------------------------
Ethernet statistics table information:
Index: 1
Data Source: ifIndex.3
Owner: zhangsan
Status: Valid
------------------------------
ifIndex.3 statistics information:
------------------------------
DropEvents:0
Octets: 8257011
Pkts:100635
BroadcastPkts:377
MulticastPkts:288
CRCAlignErrors:0
UndersizePkts:0
OversizePkts:0
Fragments:0
Jabbers:0
Collisions:0
Pkts64Octets:218
Pkts65to127Octets:100334
Pkts128to255Octets:76
Pkts256to511Octets:7
Pkts512to1023Octets:0
Pkts1024to1518Octets:0
11. Configure SPAN
11.1. Overview
11.1.1. Learning SPAN
The user can use the port mirroring (SPAN) provides the function, the Design-Port packet is copied to
the switch on another connected with network monitoring equipment port, for network monitoring and
troubleshooting.
Through the SPAN can monitor all incoming and output message from the source port.For example,
in the following figure,Port 5 on all the packets are mapped to the port 10,Connected on port 10 of
the network analyzer although not direct connected with port 5, but can be received by all the packets
on port 5.
SPAN configuration instance
SPAN does not affect the message source and destination ports exchange,just from the source port
all input and output message copying a to the port of destination.When the image flow of source
port more than the destination port's bandwidth,For example, the 100Mbps destination port
monitoring 1000Mbps source port traffic, may cause packet is discarded.
11.2. SPAN concepts and terminology
11.2.1. SPAN Session
SPAN session is to mirror the flow of data between source port and destination port,can monitor a
single or multiple ports of input, output, two-way message.Interface and AP type of port can be
configured to SPAN session source port and destination port..Port after joining SPAN session does
not affect the normal operation of the switch.
The user can in the shutdown port configuration SPAN session,But the SPAN session is inactive,
only the relevant port is opened, the SPAN session will become active.In addition, the SPAN session
on the switch power does not take effect immediately,until the destination port in an operational state,

the SPAN session is only active.Operation users can view the SPAN session through the
command show monitor session .
11.2.2. Image data flow
11.2.2.1. Data flow direction
The SPAN session consists of the following three direction of data flow:
The input data stream:All of the source port receives the message will be copied to the port of
destination.In a SPAN session, users can monitor one or more source port input message.For
some reason (e.g., port security), from the source port input message may be discarded,but
this does not affect the function of SPAN, the newspaper article will still be the mirror to the
port of destination.
The output data stream:All messages sent from the source port will be a copy to the
destination port.In a SPAN session, users can monitor one or more source port output message.If
for some reason, a message sent to the source port from other port may be
discarded,similarly, the packet will not send to the port of destination.For some reason from
the source port output message format may change,for example, the source port output
after routing message,the message of the source MAC, destination MAC, VLAN ID and TTL
changes,as well, the format of the message copy to the destination port will also change.
Bidirectional data flow:Including the above two kinds of data flow.In a SPAN session, the user
can monitor one or more of the source port of the direction of the input and output data stream.
11.2.2.2. SPAN Traffic
Using SPAN can monitor all communications, including multicast frames, BPDU frame, etc.
11.2.3. Source port
Source port, also known as being monitored, the SPAN session, the data flow on the source port be
monitored,for network analysis and troubleshooting.In a single SPAN session, the user can
monitor the input, output, and bidirectional data flow, and the source port there is no limit to the
number of the big。
Source port has the following features:
The source port is not AP.
The source port cannot at the same time as the destination port.
Source and destination ports can belong to the same VLAN, can also belong to different VLAN.
11.2.4. Destination port
SPAN session has a destination port (also known as a monitoring port), for message receiving source
port copy. The destination port has the following features:
The destination port is not AP port.
The destination port cannot at the same time as the source port.
11.3. Configure SPAN
11.3.1. SPAN default state
Features
Default value
SPAN status
close
11.3.2. Create the SPAN session and specify the destination port and port
Users can create the SPAN session according to the following steps and specify the destination port
(monitor port) and port (by monitoring port):
If you want to remove the SPAN session, you can use the no monitor session session_num global
configuration command.
Use the no monitor session session_num source interface Gigabitethernet port-id
command can delete the source port.
Use no monitor session session_num destination interface Gigabitethernet port-id can delete the
destination port.
The following example shows how to create a SPAN session:Session 1, first of all, will be clear of the
current session 1 configuration,then set the port gigabitEthernet 0/1 message to the mirror port
gigabitEthernet 0/8. Show monitor session privilege commands are used to confirm the configuration
was successful.
Switch(config)# no monitor session 1
Switch(config)# monitor session 1 source interface Gigabitethernet 0/1 both
Switch(config)# monitor session 1 destination interface Gigabitethernet 0/8
Switch(config)# end
Switch#show monitor session
--------------
Session :1
Type : Local Session
Source interface: Gi 0/1
BOTH :Gi 0/1
Destination interface: Gi 0/8
Command
Function
Switch(config)# monitor session session_num
source iUsers can create the SPAN session
according to the following steps and specify the
destination port (monitor port) and port (by
monitoring port):nterface Gigabitethernet id {both |
rx | tx}
Specified Source port.For
Gigabitethernet id, please specify
the corresponding slogans.
Switch(config)# monitor session session_num
destination interface Gigabitethernet id
Specified destination port.For
Gigabitethernet id, please specify
the corresponding slogans.

Command
Function
Switch(config)# no monitor session
session_num
Delete the specified SPAN session.
11.3.3.
Delete the SPAN session
Users can follow the steps below to remove from a SPAN session.
Step 1
Use the no monitor session session_num global configuration command to delete from the specified
SPAN group.The following example shows how to delete SPAN 1 and confirm the configuration was
successful.
Switch(config)# no monitor session 1
Switch(config)# end
Switch#show monitor session
11.4. Display SPAN status
The use of show monitor privilege command can display the current SPAN configuration state,The
following example illustrates how to command displays the current state of SPAN session by show
monitor privileges.
Switch#show monitor session
--------------
Session :1
Type : Local Session
Source interface: Gi 0/1
BOTH :Gi 0/1
Destination interface: Gi 0/8
12. Configure the flow control based port
12.1. Storm Control
12.1.1. Overview
When there is an excess of broadcast, multicast or unknown unicast data flows in LAN,lead to the
decline of the network performance, and even network paralysis,in this case we call the LAN storm.
We can respectively for broadcast and multicast storm and unknown unicast data flow
executive storm control.When the switch port receives the broadcast and multicast or unicast
unknown data flow rate is more than the bandwidth of the set,equipment will only be allowed
through set with wide data flow,beyond the bandwidth of data flow will be discarded, until the
data flow back to normal,to avoid excessive flood data flow into the LAN formed in the storm.
12.1.2. Configure Storm Control
Command
Function
Switch# show storm-control
Show storm control information.
In interface configuration mode, please use the following command to configure the storm control:
S
t
e
p
1
Interface configuration mode by the command no storm-control to close the storm interface and
corresponding control function.
The following example opens the broadcast storm on port GigabitEthernet 0/1 control function,
and is set to 64K.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# storm-control multicast bps 64
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# end
12.1.3. Show storm control enable state
Show storm control enable state
Step 1
The following example to show the state of storm control function enable state
Switch#show storm-control
interface unicast broadcast multicast action
Gi 0/1 enable enable disable none
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthern
et-0/1)# storm-control
{broadcast | multicast |
unicast| brd_multi | uni_brd |
uni_brd_multi | uni_multi }
[kbps rate-kbps]
broadcast Enable to the control function of the
broadcast storm.
multicast Enable Open to the unknown multicast
storm control functions.
unicast Enable to the unknown unicast storm control
function.
brd_multi:Enable the control function of broadcast and
multicast storm.
uni_brd:Enable to the unknown unicast and broadcast
storm control function.
uni_brd_multi:Enable to the unknown unicast, broadcast
and multicast storm control functions.
uni_multi:Enable to the unknown unicast and multicast
storm control function.
Rate-bps
is an unit with bit set, namely Kbits per second, allow by kilobits per second.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#isolate-p
ort {link-aggregation ap-id| interface port-id}
The interface and related interface
segregation
Command
Function
Switch# show isolate-port
Show the separation configuration
Gi 0/2 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/3 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/4 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/5 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/6 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/7 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/8 disable disable disable none
Gi 0/9 disable disable disable none
12.2. Isolate Port
12.2.1. Overview
Some application environment, require the part between ports on a switch can't communicate,Can set
some Port to Isolate port to achieve a goal.
After the port is set as the isolated port, isolation between ports cannot communicate each other,The
isolate port between the non isolated port can be normal communication.When the two protection port
to a SPAN port, SPAN port to send or receive a frame can still image into the SPAN destination port.
Equipment support link-aggregation Port is set to the isolation port,When a link-aggregation
Port is set to the isolation port, all members of the link-aggregation Port is set to isolation port..
12.2.2. Configuration Isolate Port
Set interface for the protection of port:
Through the no switch isolate-port {link-aggregation ap-id| interface port-id} interface
configuration command to a port reset to protect the mouth.
The following example illustrates how the Gigabitethernet 0/1 and Gigabitethernet 0/2 set to isolate
Port.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#isolate-port interface GigabitEthernet 0/2
12.2.3. Display Isolate Port configuration
Step 1
Through the show isolate-port command to view the protection port settings

Switch#show isolate-port
Gi 0/1 : Gi 0/2
Gi 0/2 : Gi 0/1
Gi 0/3 :
Gi 0/4 :
Gi 0/5 :
Gi 0/6 :
Gi 0/7 :
Gi 0/8 :
Gi 0/9 :
link-aggregation 1 :
12.3. Port Security
12.3.1. Overview
Port security function through the source MAC address message to define whether packet can enter
the switch port,You can set a specific static MAC addresses or learn to limit the number of dynamic
MAC address to control the message whether can enter the port.Enable port security port called port
security.Only the source MAC address is the port security address table configuration or has to learn
the MAC address message,before they can enter the exchange communication,other packets will be
dropped.You can also set the port security address bind IP+MAC+PORT to port security address used
to limit must be consistent with the binding for the source MAC address of the packet to switch the
communication;In accordance with ARP message IP+MAC+PORT can enter the switch,Does not
conform to the IP+MAC+PORT message binding will be dropped.
Port security also supports the function of the Sticky MAC address,by enable the function,Can be
dynamically learned to address the safety of the conversion for static configurationIn show
running-config, can be seen in the configuration,Save the configuration after the restart, without
having to learn these dynamic security address,And if this feature is not enabled, then the dynamic
learning into the safety of the MAC address on the switch after the restart to learn again.You can
secure address for each security port configured maximum security address number,maximum
security address number refers to the total number of static configuration and dynamic learning
security address,when the security port security address does not reach the maximum number of
safety,security port can dynamically learn new dynamic security address,when security address
number reaches maximum number,Safe port will no longer study dynamic security address,If there
are new user access security port, will produce a security violation.You can handle security violation
according to the following three ways:
protect:When the number of address is full, safe port will discard all new user data access
flow.The processing mode as the default for violation processing mode.
12.3.2. The default configuration of port security
The following table shows the default configuration of port security:
Features
Default value
Port safety switch
All ports are closed port security function
Security address
None
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/3)#port-secu
rity enable default [deny|permit]
Enable the port security functions of the
interface:Deny:Unbound port refused
Permit:Unbound port permit
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/3)#
port-security disable
Close the port security functions of the
interface.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
port-security add ip-address X.X.X.X
mac-address XXXX.XXXX.XXXX Description
xxxx
In configuration mode, the port to allow
access to the host's IP address and MAC and
port.
Safe way of address binding
None
Dynamic MAC addresses learning
Enable
12.3.3. Configure port security
In interface configuration mode, please configure port security and exception processing mode uses
the following commands:
The following example illustrates the enable port security function interface on
gigabitethernet0/3.Binding method for IPMAC
Switch# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/3)#port-security add ip-address 1.1.1.1 mac-address
0000.0000.0001 Description xxxx
12.3.4. configure Security address of security port .
In the port mode, please use the following command added security for safe port address:
In the port mode, use the command port-security move ip-address X.X.X.X mac-address
XXXX.XXXX.XXXX to delete the address table configuration.
The following example shows how to configure port security binding and access mode
Switch# configure terminal

Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#port-security add ip-address 1.1.1.1 mac-address
0000.0000.0001
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#port-security visitor ip-address 1.1.1.3 mac-address
0000.0000.0002 times 5 Description xxx
Tip
When the host match permit rule, which is to permit the host biggest
quantity is full can also access the network;
When refused to host matching rules, which is to allow the host
biggest quantity under cannot access the network.

Command
Function
Switch#show port-security active-table
View the current port security is not binding
information
Switch#show port-security all
View the current port security all information
Switch#show port-security default
View the current port security unbounded port is
granted or denied
Switch#show port-security rule
View the current port security binding information
Switch#show port-security visitor
View the current port security visitor information
12.3.5. View port security information
In privileged mode, through the following command to check port security information:
The following example shows the port security of all address table information:
Switch#show port-security all
IP address MAC address interface-name bind-code age-t(m) out-t(m)
description
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
192.168.10.11 0012.1102.1133 Gi 0/1 IPMACPORT 0
----
The following example shows the port security not binding IP and MAC:
Switch#show port-security active-table
IP address MAC address interface-name bind-code age-t(m) out-t(m)
description
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
192.168.100.7 0086.302A.05E1 link-aggregation 1 ACTIVE(UNBIND) 10 9
192.168.100.24 0800.27A1.3A4C link-aggregation 1 ACTIVE(UNBIND) 10 9
192.168.100.61 80C1.6EDF.AF7F Gi 0/5 ACTIVE(UNBIND) 10 9
The following example shows the port security unbounded port is granted or denied:

Switch#show port-security default
IP address MAC address interface-name bind-code age-t(m) out-t(m)
description
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
----- ---- ---- PERMIT(DEFAULT) 0 ---- ----
The following example shows the current port security binding information:
Switch#show port-security rule
IP address MAC address interface-name bind-code age-t(m) out-t(m)
description
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
192.168.10.11 0012.1102.1133 Gi 0/1 IPMACPORT 0
----
The following example shows the current port security visitor information:
Switch#show port-security visitor
IP address MAC address interface-name bind-code age-t(m) out-t(m)
description
---- ---- -------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
192.164.1.2 0012.0001.0002 Gi 0/5 VISITOR 50 49
13. Anti-illegal DHCP Server
13.1. Summary
DHCP is a dynamic protocol to assign IP addresses to the PC client dynamically. It can be used for
users or internal network administrator as central management to all the computers.
DHCP Snooping technique is DHCP security features, its main effect is filtering untrusted DHCP
information through configuring untrusted port. The information refers to the DHCP information from
untrusted port. The following are some of the explanation of the concept of DHCP Snooping:
DHCP Snooping TRUST port: DHCP Snooping divided the ports into two types, TRUST port and
UNTRUST port, equipment only forwards the DHCP Offer message TRUST port received,

But discards all the DHCP Offer message from UNTRUST port, then we set legal DHCP Server
connected port as TRUST port, and the other port set as UNTRUST port, this can realize the shielding
of illegal DHCP Server.
1-1
As shown in diagram 1-1 network environment. The Client obtain IP address and surf the Internet
through legal DHCP Server. Set the switch port connected by client as untrust port according to the
requirement, set the switch port connected by DHCP Server as trust port. So we can put an end to the
affect to other user that private set up illegal DHCP Server user caused.
13.2. DHCP Snooping Configuration
13.2.1. Enabling DHCP Snooping
Only after enabling the DHCP Snooping, DHCP Snooping function will take effect, the configured
trusted port and untrusted port can work properly.
Command
Function
Switch(config)# dhcp-snooping
Enable DHCP Snooping, DHCP Snooping
is disabled by default.
Enabling DHCP Snooping in global configuration mode:
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#dhcp-snooping
Global DHCP mode: enable
13.2.2. Trusted Port Configuration
Use the following command to configure DHCP Snooping trusted port in interface configuration mode:

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
dhcp-snooping trust
set the port as DHCP Snooping trusted
port.
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
no dhcp-snooping trust
delete the port from trusted port, that is, to
set it as untrusted port.
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#dhc
p-snooping trust
set the link aggregation group as DHCP
Snooping trusted link aggregation
group(the link aggregation group must has
been established)
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#no
dhcp-snooping trust
delete the link aggregation group from
trusted link aggregation group, that is, to
set it as untrusted port.
The following example is to configure DHCP Snooping trusted port:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#dhcp-snooping trust
The following example is to configure DHCP Snooping untrusted port:
:
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no dhcp-snooping trust
The following example is to configure DHCP Snooping trusted AP port:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#link-aggregation 1
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#dhcp-snooping trust
The following example is to configure DHCP Snooping untrusted AP port:
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#no dhcp-snooping trust
13.2.3. Disable DHCP Snooping
Command
Function
Switch(config)#no dhcp-snooping
Disable DHCP Snooping
The following example is to disable global DHCP Snooping.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)#no dhcp-snooping
Global DHCP mode: disable
13.3. View DHCP Snooping Information
Use the following command to view DHCP Snooping information in privileged mode:
Command
Function
Switch#show dhcp-snooping
Display DHCP Snooping information.
The following example is to display DHCP Snooping information:
Switch#show dhcp-snooping
dhcp-snooping configuration information:
dhcp-snooping status:enable
dhcp-snooping port information :
--------------------------------------------------
interface trust-status
Gi 0/1 trust
Gi 0/2 untrust
Gi 0/3 untrust
Gi 0/4 untrust
Gi 0/5 untrust
Gi 0/6 untrust
Gi 0/7 untrust
Gi 0/8 untrust
Gi 0/9 untrust
link-agg 1 trust

14. Anti-ARP-Spoofing
14.1. Summary
According to the design of the ARP protocol, in order to reduce the excessive ARP data
communication in the network, a host, even if received ARP reply is not requested itself, it also can
insert it into the ARP cache table, but the ARP protocol itself does not check the validity of ARP
message it received. It will cause attackers using leaky agreement and forged IP address and MAC
address for ARP spoofing attacks.
In addition to cause the user privacy disclosure, ARP spoofing can also cause a network failure,
network impassability,etc.
Anti-ARP spoofing function will filter the possible ARP spoofing attacks by the establishment of anti
spoofing sheet, record suspicious attack source.
14.2. Anti-ARP-Spoofing Configuration
14.2.1. Enable Anti-ARP-Spoofing
Please use the following command to configure Anti-ARP-Spoofing in interface configuration mode:
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)
#arp-inspection
Enable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function of the
port
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#arp
-inspection
Enable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function of the
link aggregation group.
The following example is to enable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)# arp-inspection
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#link-aggregation 1
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)# arp-inspection
14.2.2. Disable Anti-ARP-Spoofing
Please use the following command to configure Anti-ARP-Spoofing in interface configuration mode:

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#
no arp-inspection
Disable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function of the
port
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#no
arp-inspection
Disable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function of the
link aggregation group.
The following example is to disable Anti-ARP-Spoofing function:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no arp-inspection
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#link-aggregation 1
Switch(config-link-aggregation1)#no arp-inspection
14.3. View information of Anti-ARP-Spoofing
Use the following command to view Anti-ARP-Spoofing information in Privileged mode:
Command
Function
Switch#show arp-inspection config
Display the configuration information of
Anti-ARP-Spoofing function
Switch#show arp-inspection status
Display the list item information of
Anti-ARP-Spoofing function.
The following example is to view the configuration information of Anti-ARP-Spoofing function:
Switch#show arp-inspection config
interface-name status
---- ---- --------------------------------
Gi 0/1 arp-inspection: disable
Gi 0/2 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/3 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/4 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/5 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/6 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/7 arp-inspection: enable

Gi 0/8 arp-inspection: enable
Gi 0/9 arp-inspection: enable
link-aggregation 1 arp-inspection: enable
Notes: enable:enable Anti-ARP-Spoofing disable:disable Anti-ARP-Spoofing
The following example is to view the list item information of Anti-ARP-Spoofing function:
Switch#show arp-inspection status
VID MAC address IP address interface-name tbl-status ---- ----
-------------------------------- -----------------------------------------
40 0001.7AD2.4D8C 192.168.100.1 Gi 0/4 AFFIRM 40
DDCC.BBAA.4B79 0.0.0.1 Gi 0/4 ATTACK 40
0087.2380.9EA7 192.168.1.137 Gi 0/4 AFFIRM 40
C860.00E0.2B80 192.168.100.51 Gi 0/4 ATTACK
40 7427.EA36.DD67 192.168.0.145 Gi 0/4 AFFIRM
40 7427.EA36.DE14 10.10.10.5 Gi 0/4 AFFIRM
Notes:
Vid:the vlan where the port is; MAC address:MAC Address
IP address:IP address interface-name:port name
tbl-status:the status of Anti-ARP-Spoofing table, AFFIRM refers to normal,
ATTACK refers to the member is attacking.

15. Port Rate Limit
15.1. Overview
With the rapid development of the Internet, there are more and more needs to transmit
multimedia stream on the Internet. Generally speaking, Users ask different service quality for
different multimedia application. It needs the network can allocate and schedule the resource
according to the users’ needs. Therefore, the network administrator need to limit the rate of
corresponding ports.
15.2. Configure port rate limit
Enter the interface pattern to configure the Upstream Rate limitation.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-
0/1)#rate-limit {Rate}
{ Committed Burst size} { Excess
Burst size}
Configure the port rate limitation
rate:
Committed Burst size:
Excess Burst size:
Below is the example to configure the Upstream Rate limitation:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#rate-limit 10000 100000 100000
Enter the interface pattern to configure the Downstream Rate limitation.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#traffi
c-shape {Rate} { Committed Burst size}
{ Excess Burst size}
Configure the port rate limitation
rate:
Excess Burst size:
Below is the example to configure the port Rate limitation Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#traffic-shape 64 1
15.3. Close the port rate limitation
Enter the interface pattern to close the Rate limitation.
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-
0/1)#no rate-limit
Close the port Upstream Rate Limitation
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/
1)#no traffic-shape
Close the port Downstream Rate Limitation
Below is the example to close the port upstream Rate limitation:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no rate-limit
Below is the example to close the port Downstream Rate limitation:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no traffic-shap
15.4 Check the port upstream rate limitation information
Enter the privileged pattern, check the port upstream limitation information by below
Commands.
Command
Function
Switch#show rate-limit [interface]
Show the upstream rate limitation information.
Below is the example to show the port upstream Rate limitation information
:
Switch#show rate-limit
Gi 0/1
rate-limit 64 12000 120000
64:Rate
12000:Excess Burst size
120000:Excess Burst size

15.4. Check the port Downstream rate limitation
information
In the privileged pattern, check the port Downstream limitation information by below
Commands.
Command
Function
Switch#show traffic-shape
[interface]
Show the downstream rate limitation
information.
Below is the example to show the port Downstream Rate limitation information:
Switch#show traffic-shape
Gi 0/1
traffic-shape 128 1000
Gi 0/2
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/3
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/4
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/5
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/6
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/7
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/8
The traffic shape is not configured
Gi 0/9
The traffic shape is not configured
16. Loopback Detection
16.1. Overview
Loopback-detection bases on the port configuration, it monitors if the Ethernet frame
transmitted from the port comes back to the equipment through the same port. Judge if the
port TX-RX self-loop or the network exists loop.

16.2. Configure loop detection.
Enter global patterns to configure loop detection.
Command
Function
Switch(config)#loopback-detection
[enable|interval|errdisable]
Configure loop detection,enable: Open
detection (default on)
Interval:Set loop detection time.(2-15secs,
Default3s)
Errdisable:Port recovery time(30-86400S
Default 60s)
Below is the example that configuration port open loop detection and set the detection time
slot:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#loopback-detection enable
Switch(config)#loopback-detection interval 2
Switch(config)#loopback-detection errdisable recover 30
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#loopback-detection enable
Switch(config)#loopback-detection interval 2
Switch(config)#loopback-detection errdisable recover 30
16.3. loop detection processing mechanism
Processing mechanism when Enter the port patterns to revise the loop
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#loopback-
detection control
processing mechanism:
Close the port
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#noloopba
ck-detection control
processing
mechanism :Warning
Below is the example to revise the port loop processing mechanism function.
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#loopback-detection control
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no loopback-detection control.
Notes: Revise the link aggregation loop processing mechanism, Similarly
16.4. Check loopback detection
Enter the privileged pattern to check the loopback-detection.
Command
Function
Switch#show loopback-detection
Check loopback detection and
configuration:
Below is the example to check loopback detection.
Switch#show loopback-detection
Loopback detection is Runing on!
Detection interval time is 2 seconds
Error Disable recover time is 60 seconds
Interface Action State
-------------------- ---------- -----------
Gi 0/5 WARNING LINK_DOWN
Gi 0/6 CONTROL LINK_DOWN
Gi 0/7 CONTROL LINK_DOWN
Gi 0/8 CONTROL LINK_DOWN
link-aggregation 1 CONTROL NORMAL
link-aggregation 2 CONTROL LINK_DOWN
16.5. close loopback detection.
Enter the global patterns to close loopback detection.
Command
Function
Switch(config)#no loopback-detection
Close loopback detection.
Below is the example to close loopback detection:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.

Switch(config)#no loopback-detection enable
17. Access Control
17.1. Overview
Information between port and port and communication inside and outside is essential
business requirements of enterprise internet. To ensure security of the network, it
needs safety strategy to ensure unauthorized users can only access specific
network resources to reach and control visits.
In brief, ACL can filter network traffic and is a type of internet technology of access
control.
17.2. configure access control
Enter into global mode and configure access control:
Step 1
Command
Function
Switch(config)#ip access-list
[standard|extended](0-9|10-19)
Configuration list of access control:
Standard:it can configure table 0-9
Extended:it can configure table 10-19
Switch(config)#mac access-list
extended (20-25)
Access-list extended:extended mac
access control list can configure table
20-25
Step 2
Enter into standard IPSwitch(config)#ip access-list standard 9 and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-std-ip-nacl)#0
[permit|deny][any|host|sip]
Rule of configuration:
Permit:Allow matching rules of IP data flow
Deny:Refuse matching rules of IP data flow

Enter into extended IP Switch(config)#ip access-list extended 10and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-ext-ip-nacl)#0
[permit|deny] [any|host|sip]
Rule of configuration:
Permit: Allow matching rules of IP data flow
Deny: Refuse matching rules of IP data flow
Enter into extended MAC Switch(config)#mac access-list extended 20 and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-ext-mac-nacl)# 0
[permit|deny] [any|host]
Rule of configuration:
Permit: Allow matching rules of MAC data flow
Deny:Refuse matching rules of MAC data flow
Step 3
Enter into standard IP rule table Switch(config)#ip access-list standard 9 and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-std-ip-nacl)#0
permit [any|host|sip]
Rule of configuration access list:
Any: Any source IP address
Host: specified source IP
Sip: specified source IP and mask
Enter into extended IP rule table Switch(config)#ip access-list extended 10and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-std-ip-nacl)#0
permit ip [any|host|sip]
Rule of configuration access list:
specified protocol type:igmp、ip、tcp、udp
Any:Any source IP address,parameter (any|host|dip)
host:specified source IP(any|host|dip)
sip: specified source IP, mask and parameter
(any|host|dip)

Enter into extended MAC Switch(config)#mac access-list extended 20and configure
Command
Function
Switch(config-ext-mac-
nacl)# 0 deny
[any|host]
Rule of configuration access list:
Any:Any source mac address, objective MAC
parameters (any|host)
host:specified source mac, objective MAC
parameters (any|host)
Protocol: <0x0000-0xffff> optional
After the success of the configuration rules into port under application configuration
Command
Function
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#mac
access-list 20 commit
Application of list rule in ports
Following example for configure standard IP, extended IP, extended MAC:
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#ip access-list standard 0
Switch(config-std-ip-nacl)#0 deny host 1.1.1.1
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#ip access-list extended 10
Switch(config-ext-ip-nacl)#0 permit ip sip 1.1.1.3 255.255.255.0 host 1.1.2.1
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#mac access-list extended 20
Switch(config-ext-mac-nacl)# 0 deny host 0000.0000.0001 host 0000.1111.1111
17.3. Configure access control of closing the
command
Enter port cancel the configuration access control:

Command
Function
Switch(config-if-Gigabit
Ethernet-0/3)#no ip
access-list
(0-9|10-19)
Cancel configuration access control list:
0-9:cancel standard IP access control list on ports from
0-9 table
10-19:cancel extended IP access control list on ports
from 10-19 table
Switch(config-if-Gigabit
Ethernet-0/3)#no mac
access-list (20-25)
Configure access control list: cancel port extended mac
access control list from 20-25
Enter into global mode and delete access control list:
Command
Function
Switch(config)#no
access-list
(0-9|10-19|20-25)
Cancel configuration access control list:
0-9: cancel standard IP access control list from table0-9
10-19: cancel extended IP access control list from table10-19
20-25: cancel extended mac access control list from table 20-25
Enter rule table Switch(config)#ip access-list extended 10 and delete access control table:
Command
Function
Switch(config-ext-ip-nacl)#no [0-9]
Cancel configure access control list:
0-9:delete extended IP access control list rule
to configure table 0-9(standard IP, extended
MAC, same command)
Following example is to close access control from ports, delete rule tables, and rules:
Close access control from ports
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if-GigabitEthernet-0/1)#no ip access-list 10
Delete rule tables
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#no access-list 9
Delete rules
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL+Z.
Switch(config)#ip access-list extended 10
Switch(config-ext-ip-nacl)#no 9
17.4. Check access control list
Enter into privilege mode and check access-list:
Command
Function
Switch#show access-list
Check access-list all information
Following is to check access control function:
Switch#show access-list
ip access-list standard 9
0 permit host 192.168.1.23
ip access-list extended 10
1 deny tcp any any
mac access-list extended 20
mac access-list extended 21
3 deny host 0012.0012.0012 any
18. File system Configuration
18.1. Overview
Switch files containing several types, The main file types for the IOS image file and the
configuration file. The configuration file is divided into:
1.Startup-config:Boot for the first time, will read and parse the file, and perform the
configuration file.
2.Running-config:This file is a copy of the current state of the use of the command, the file
is dynamic, and will be updated after each configuration commands.
18.2. Filesystem operation
Enter file configuration mode, the implementation of file system basic operation command:

Command
Function
Switch#configure filesystem
Enter the file configuration mode
Switch(config-fs)#dir
Dir command to display the directory file, the
default directory is usually Flash file systems.
Switch(config-fs)#dir {word}
Display files in the specified directory, word:
directory name
Switch(config-fs)#copy tftp
{Server IP} {The file name on the
server }{Save the file name on
switch }
Switches through the TFTP download file
Switch(config-fs)#mkdir {word}
Create adirectory, word: directory name
Switch(config-fs)#cd {word}
Enter directory, word: directory name
The following example for input dir the default display:
Switch#configure filesystem
Switch(config-fs)#dir
size date time name
-------- ------ ------ --------
0 JAN-01-1980 00:00:04 config <DIR>
0 JAN-01-1980 00:00:04 script <DIR>
0 JAN-01-1980 00:00:28 more <DIR>
0 JAN-01-1980 00:00:00 log <DIR>
0 JAN-01-1980 00:00:04 flash <DIR>
The following example for download files via TFTP Server:
Switch#configure filesystem
Switch(config-fs)#copy tftp 192.168.100.83 1.txt 192.168.100.93
The following example for creating and into the err directory, then delete the err directory:
Switch(config-fs)#mkdir test
Switch(config-fs)#cd test
Switch(config-fs)#rmdir test
WARNING:

The Data of this dir will be lost! if OS is deleted,the system will hangup!
Please confirm to continue?(Yes/No)y
Switch(config-fs)#
