LevelOne GTP-5271 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for GTP-5271 by LevelOne which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Web Management Guide
(GTP-5271)
V1.0
Digital Data Communications GmbH.
http://www.level1.com
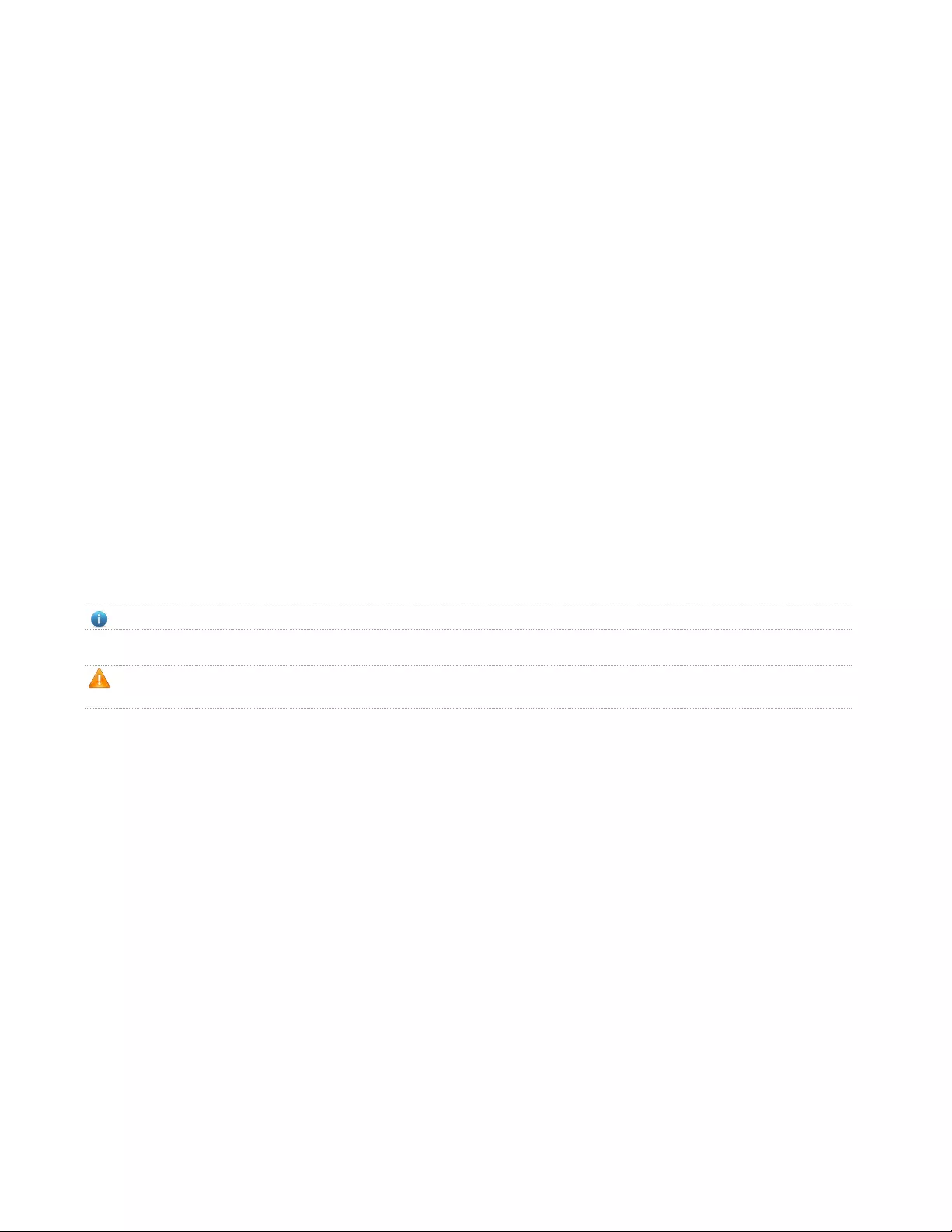
Copyright Statement
Our company reserves all copyrights of this document. Any reproduction, excerption, backup,
modification, transmission, translation or commercial use of this document or any portion of this
document, in any form or by any means, without the prior written consent of our company is prohibited.
Exemption Statement
This document is provided "as is". The contents of this document are subject to change without any
notice. Please obtain the latest information through our company website. Our company endeavors to
ensure content accuracy and will not shoulder any responsibility for losses and damages caused due to
content omissions, inaccuracies or errors.
Preface
Thank you for using our products. This manual will guide you through the installation of the device.
This manual describes the functional and physical features and provides the device installation steps,
hardware troubleshooting, WEB configuration, module technical specifications, and specifications and
usage guidelines for cables and connectors.
Audience
It is intended for the users who have some experience in installing and maintaining network At the same
time, it is assumed that the users are already familiar with the related terms and concepts.
Symbol Conventions
It means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references.
It means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.

Table of Contents
1. Product Introduction ......................................................................................................... 1
1.1. Product Overview ........................................................................................................................... 1
1.2. Features ......................................................................................................................................... 1
1.3. External Component Description ................................................................................................... 1
1.3.1. Front Panel .......................................................................................................................... 1
1.3.2. Rear Panel ........................................................................................................................... 3
1.4. Package Contents .......................................................................................................................... 4
2. Installing and Connecting the Switch ............................................................................. 5
2.1. Installation ...................................................................................................................................... 5
2.1.1. Desktop Installation ............................................................................................................. 5
2.1.2. Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet .................................................................. 5
2.1.3. Power on the Switch ............................................................................................................ 6
2.2. Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch .......................................................................................... 6
2.3. Switch connection to the PD .......................................................................................................... 7
3. How to Login the Switch .................................................................................................. 8
3.1. Switch to End Node ....................................................................................................................... 8
3.2. How to Login the Switch ................................................................................................................ 8
4. WEB Configuration Guide .............................................................................................. 10
4.1. Basic Setting ................................................................................................................................ 10
4.1.1. System Info ........................................................................................................................ 10
4.1.2. General Setup .................................................................................................................... 11
4.1.3. IP Setup ............................................................................................................................. 12
4.1.3.1. Vlan interface ........................................................................................................... 12
4.1.3.2. Vlan interface Config ............................................................................................... 13
4.1.3.3. StaticRoute .............................................................................................................. 15
4.1.4. Port Setup .......................................................................................................................... 16
4.1.5. Dhcp Server ....................................................................................................................... 17
4.1.6. Dhcp-Relay ........................................................................................................................ 18
4.1.7. Stacking ............................................................................................................................. 18
4.1.7.1. Stacking Status ........................................................................................................ 19
4.1.7.2. Stacking Configuration ............................................................................................ 20
4.2. Advanced Application .................................................................................................................. 21
4.2.1. VLAN ................................................................................................................................. 22
4.2.1.1. VLAN Status ............................................................................................................ 23
4.2.1.2. VLAN Port Settings .................................................................................................. 23
4.2.1.3. Static VLAN ............................................................................................................. 25
4.2.2. MAC Address Forwarding .................................................................................................. 26
4.2.3. Spanning Tree Protocol ..................................................................................................... 27
4.2.3.1. Spanning Tree Protocol Status ................................................................................ 28
4.2.3.2. Spanning Tree Configuration ................................................................................... 29
4.2.3.3. Compatible/Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ............................................................. 30
4.2.3.4. Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol ............................................................................. 32
4.2.4. ERPS Protocol ................................................................................................................... 34
4.2.5. EAPS Protocol ................................................................................................................... 35
4.2.5.1. Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching ................................................................ 35
4.2.5.2. EAPS Domain .......................................................................................................... 37
4.2.6. Layer 2 Protocol Tunnel ..................................................................................................... 38
4.2.7. PPPOE IA .......................................................................................................................... 39

4.2.7.1. Intermediate Agent .................................................................................................. 39
4.2.7.2. Port .......................................................................................................................... 39
4.2.8. Bandwidth Control ............................................................................................................. 40
4.2.9. Broadcast Storm Control ................................................................................................... 41
4.2.10. Mirroring ........................................................................................................................... 43
4.2.11. Link Aggregation .............................................................................................................. 44
4.2.11.1. Link Aggregation status ......................................................................................... 45
4.2.11.2. Link Aggregation Setting ....................................................................................... 45
4.2.11.3. Link Aggregation Control Protocol ......................................................................... 46
4.2.12. Port Sercurity ................................................................................................................... 47
4.2.13. POE Settings ................................................................................................................... 47
4.2.13.1. POE Settings ......................................................................................................... 48
4.2.13.2. POE Port Settings ................................................................................................. 49
4.2.14. Classifier .......................................................................................................................... 49
4.2.15. Policy Rule ....................................................................................................................... 50
4.2.16. Queuing Method .............................................................................................................. 51
4.2.17. Multicast ........................................................................................................................... 51
4.2.17.1. Multicast Status ..................................................................................................... 52
4.2.17.2. Multicast Settings .................................................................................................. 52
4.2.17.3. IGMPSnooping Dney VLAN .................................................................................. 54
4.2.17.4. IGMP Filtering Profile ............................................................................................ 54
4.2.18. IPv6 Multicast .................................................................................................................. 55
4.2.18.1. IPv6 Multicast Status ............................................................................................. 56
4.2.18.2. IPv6 Multicast Setting ............................................................................................ 56
4.2.18.3. MLD Snooping Dney VLAN ................................................................................... 58
4.2.19. Dos attack protect ............................................................................................................ 59
4.2.20. DHCP Snooping Setting .................................................................................................. 59
4.2.20.1. DHCP Snooping Setting ........................................................................................ 60
4.2.20.2. IP Source Guard .................................................................................................... 62
4.2.21. SNTP Setting ................................................................................................................... 63
4.2.22. LLDP Protocol .................................................................................................................. 64
4.2.22.1. LLDP Status .......................................................................................................... 64
4.2.22.2. LLDP Setting ......................................................................................................... 65
4.2.23. AAA .................................................................................................................................. 66
4.2.23.1. 802.1x .................................................................................................................... 66
4.2.23.2. Radius Domain ...................................................................................................... 68
4.2.23.3. Remote Authentication .......................................................................................... 68
4.2.23.4. TACACS+ Server Setup ........................................................................................ 69
4.2.23.5. Radius Server Setup ............................................................................................. 70
4.3. Management ................................................................................................................................ 71
4.3.1. Management &Maintenance .............................................................................................. 71
4.3.2. Access Control ................................................................................................................... 72
4.3.2.1. SNMP ...................................................................................................................... 72
4.3.2.2. User Information ...................................................................................................... 73
4.3.2.3. Logins ...................................................................................................................... 75
4.3.3. Diagnostic .......................................................................................................................... 76
4.3.4. Syslog ................................................................................................................................ 77
4.3.4.1. Syslog Setup ........................................................................................................... 78
4.3.4.2. Syslog Server Setup ................................................................................................ 79

1
1. Product Introduction
Congratulations on your purchasing of the 48-Port Gigabit + 4-Port 10G SFP+ L2 Managed PoE Switch.
Before you install and use this product, please read this manual carefully for full exploiting the functions of
this product.
1.1. Product Overview
This is a new generation designed for high security and high performance network the L2 switch.
Provides forty-eight 10/100/1000Mbps self-adaption RJ45 port, plus four 10G SFP+ optical port, it can be
used to link bandwidth higher upstream equipment. Support VLAN ACL based on port, easily implement
network monitori-ng, traffic regulation, priority tag and traffic control. Support traditional STP/RSTP/MSTP
2 link protection technology; greatly improve the ability of fault tolerance, redundancy backup to ens-ure
the stable operation of the network. Support ACL control based on the time, easy control the access time
accurately. Support 802.1x authentication based on the port and MAC, easily set user access. Perfect
QOS strategy and plenty of VLAN function, easy to maintenance and management, meet the networking
and access requirements of enterprises, intelligent village, hotel, office network and
campus network.Built-in high reliability, de-sign for wide voltage input application power supply, even if
the voltage is not stable of power grid, also can guarantee the equipment can work normally.
48 ports have PoE power supply function, support IEEE802.3at standard, 802.3af downward compatibility,
power supply equipment for Ethernet, can automatically detect identification standard of electrical
equipment, and through the cable for the power supply.
1.2. Features
l Supports IEEE 802.3i,IEEE 802.3u,IEEE802.3ab,IEEE802.3z,IEEE802.3ae,IEEE802.3x,
IEEE802.3at,IEEE802.3af,IEEE802.3az.
l Supports PoE power up to 30W for each PoE port, all power up to 400W.
l Integrated High-Performance Cortex-A9 processor.
l Supports MAC address auto-learning and auto-aging.
l Forty-eight 10/100/1000Mbps self-adaption RJ45 port, plus four 10g SFP+ port, it can be used to link
bandwidth higher upstream equipment.
l Store and forward mode operates.
l LED indicators for monitoring power, link/activity,Speed,PoE.
l Support QoS, port mirroring, link aggregation protocol.
l 19 inches full metal iron shell and internal 450W high performance power supply design, suitable for
rack installation
1.3. External Component Description
1.3.1. Front Panel
The front panel of the Switch consists of a series of LED indicators, 48 x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports,
1x Console port, four gigabit SFP+ ports and 1 x Reset button as shown as below.

2
Figure 1 - Front Panel
10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports (1~48):
Designed to connect to the device with a bandwidth of 10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps. Each has a
corresponding Link/Act/Speed and PoE indicator.
Figure 2 - RJ45 Connection
Console port (Console):
Designed to connect with the serial port of a computer or terminal for monitoring and configuring the
Switch.
Figure 3 - Console Port Connection
SFP+ ports (48~52):
Designed to install the SFP module and connect to the device with bandwidth 1000/10000Mbps .Each
has two corresponding LED indicators.
Figure 4 - SFP+ Connection
Reset button (Reset):
Keep the device powered on and push a paper clip into the hole. Press down the button for 5 seconds to
restore the Switch to its original factory default settings.

3
LED indicators:
The LED Indicators will allow you to monitor, diagnose and troubleshoot any potential problem with the
Switch, connection or attached devices.
The following chart shows the LED indicators of the Switch along with explanation of each indicator.
LED Indicator
Faceplate
Marker
Status
Indication
Power Indicator
PWR
Off
Power Off
Solid green
Power On
10/100/1000 BASE-
T adaptive Ethernet
port indicators
(1-48)
Link/Act
/Speed
Off
The port is NOT connected.
Solid green
The port is connected at
1000Mbps.
Solid orange
The port is connected at
100/10Mbps
Blinking
The port is transmitting or
receiving data.
SFP port indicators
(49-52)
Link/Act
/Speed
Off
The port is NOT connected.
Solid green
The port is connected at 10Gbps.
Solid orange
The port is connected at 1Gbps
Blinking
The port is transmitting or
receiving data.
SYS indicator
SYS
Off
System is abnormal or not
running
Blinking
green
System is normal
1.3.2. Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch contains Heat vent shown as below.
Figure 5 - Rear Panel

4
Grounding Terminal:
Located on the left side of the power supply connector, use wire grounding to lightning protection.
AC Power Connector:
Power is supplied through an external AC power adapter. It supports AC 100~240V, 50/60Hz.
1.4. Package Contents
Before installing the Switch, make sure that the following the "packing list" listed OK. If any part is lost
and damaged, please contact your local agent immediately. In addition, make sure that you have the
tools install switches and cables by your hands.
l One PoE Web Smart Ethernet Switch.
l One Installation Component
l One AC power cord.
l One User Manual.

5
2. Installing and Connecting the Switch
This part describes how to install your PoE Ethernet Switch and make connections to it. Please read the
following topics and perform the procedures in the order being presented.
2.1. Installation
Please follow the following instructions in avoid of incorrect installation causing device damage and
security threat.
l Put the Switch on stable place or desktop in case of falling damage.
l Make sure the Switch works in the proper AC input range and matches the voltage labeled on the
Switch.
l To keep the Switch free from lightning, do not open the Switch's shell even in power failure.
l Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around the Switch.
l Make sure the cabinet to enough back up the weight of the Switch and its accessories.
2.1.1. Desktop Installation
Sometimes users are not equipped with the 19-inch standard cabinet. So when installing the Switch on a
desktop, please attach these cushioning rubber feet provided on the bottom at each corner of the Switch
in case of the external vibration. Allow adequate space for ventilation between the device and the objects
around it.
Figure 6 - Desktop Installation
1. Please keep the switch in a dry and well ventilated environment.
2. Keep the workbench stable and well-earthed.
3. Do not restrict airflow by covering or obstructing air inlets of the switch. Keep more than 10
centimeters free on all sides for cooling. Be sure there is adequate airflow in the room or wiring
closet where the switch is installed.
4. Don’t put heavy articles on the Switch.
5. Make sure there is more than 1.5 centimeters vertical distance free between devices that stack
each other.
2.1.2. Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet
The Switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-sized, 19-inch rack, which can be placed in a wiring
closet with other equipment. To install the Switch, please follow these steps:
A. attach the mounting brackets on the Switch's side panels (one on each side) and secure them with
the screws provided.
6
Figure 7 - Bracket Installation
B. Use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the Switch on the rack and tighten it.
Figure 8 - Rack Installation
2.1.3. Power on the Switch
The Switch is powered on by the AC 100-240V 50/60Hz internal high-performance power supply. Please
follow the next tips to connect:
AC Electrical Outlet:
It is recommended to use single-phase three-wire receptacle with neutral outlet or multifunctional
computer professional receptacle. Please make sure to connect the metal ground connector to the
grounding source on the outlet.
AC Power Cord Connection:
Connect the AC power connector in the back panel of the Switch to external receptacle with the included
power cord, and check the power indicator is ON or not. When it is ON, it indicates the power connection
is OK.
2.2. Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch
Please insert the NIC into the computer, after installing network card driver, please connect one end of
the twisted pair to RJ-45 jack of your computer, the other end will be connected to any RJ-45 port of the
7
Switch, the distance between Switch and computer is around 100 meters. Once the connection is OK and
the devices are power on normally, the LINK/ACT/Speed status indicator lights corresponding ports of the
Switch.
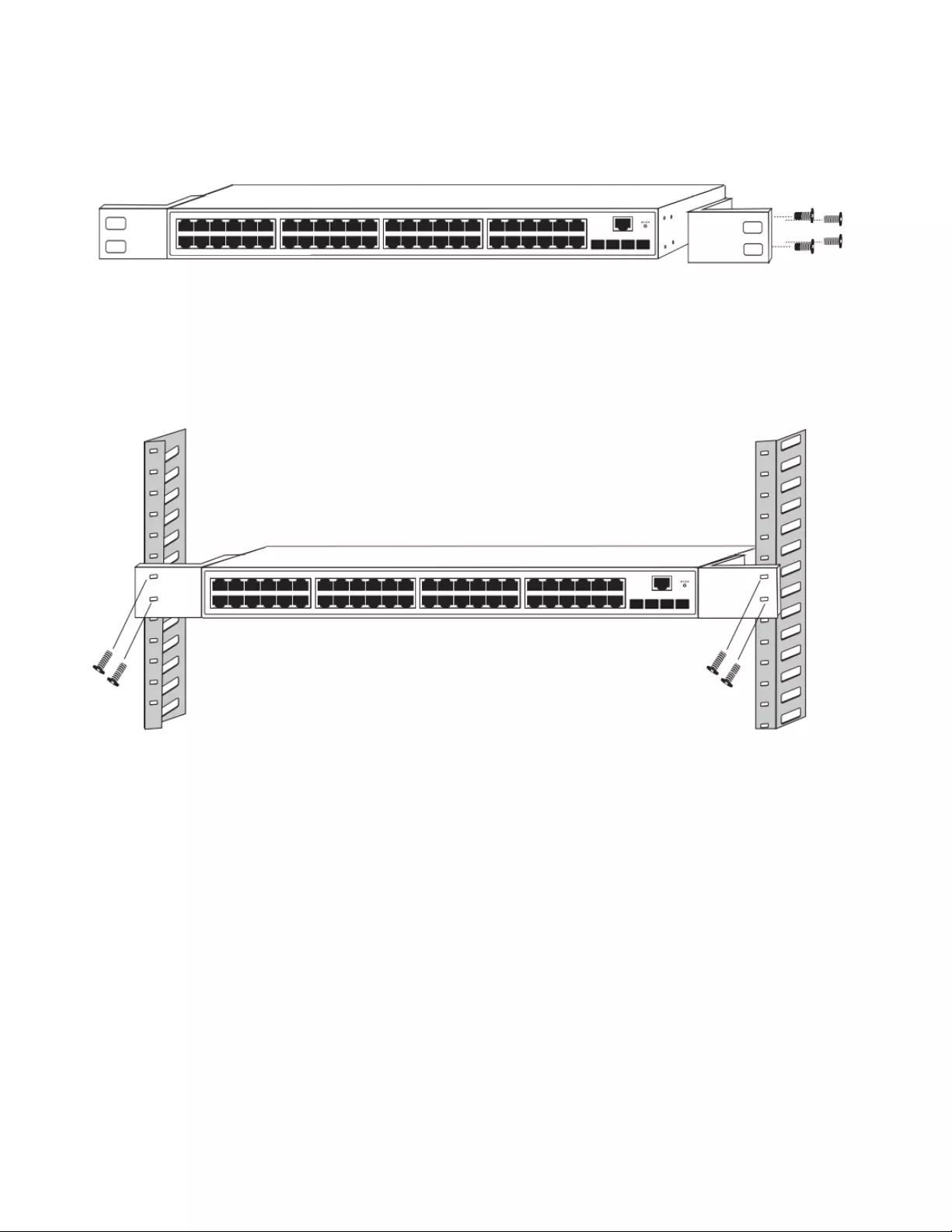
2.3. Switch connection to the PD
1-48 ports of the Switch have PoE power supply function, the maximum output power up to 30W each
port, it can make PD devices, such as internet phone, network camera, wireless access point work. You
only need to connect the Switch PoE port directly connected to the PD port by network cable.
Figure 9 - PD devices connection

8
3. How to Login the Switch
3.1. Switch to End Node
Use standard Cat.5/5e Ethernet cable (UTP/STP) to connect the Switch to end nodes as described below.
Switch ports will automatically adjust to the characteristics (MDI/MDI-X, speed, duplex) of the device to
which is connected.
Figure 10 - Connect PC to Switch
Please refer to the LED Indicators. The LINK/ACT/Speed LEDs for each port lights on when the link is
available.
3.2. How to Login the Switch
As the Switch provides Web-based management login, you can configure your computer’s IP address
manually to log on to the Switch. The default settings of the Switch are shown below.
Parameter
Default Value
Default IP address
192.168.1.1
Default user name
admin
Default password
admin
You can log on to the configuration window of the Switch through following steps:
1.Connect the Switch with the computer NIC interface.
2.Power on the Switch.
3.Check whether the IP address of the computer is within this network segment: 192.168.1.xxx ("xxx"
ranges 2~254), for example, 192.168.1.100.
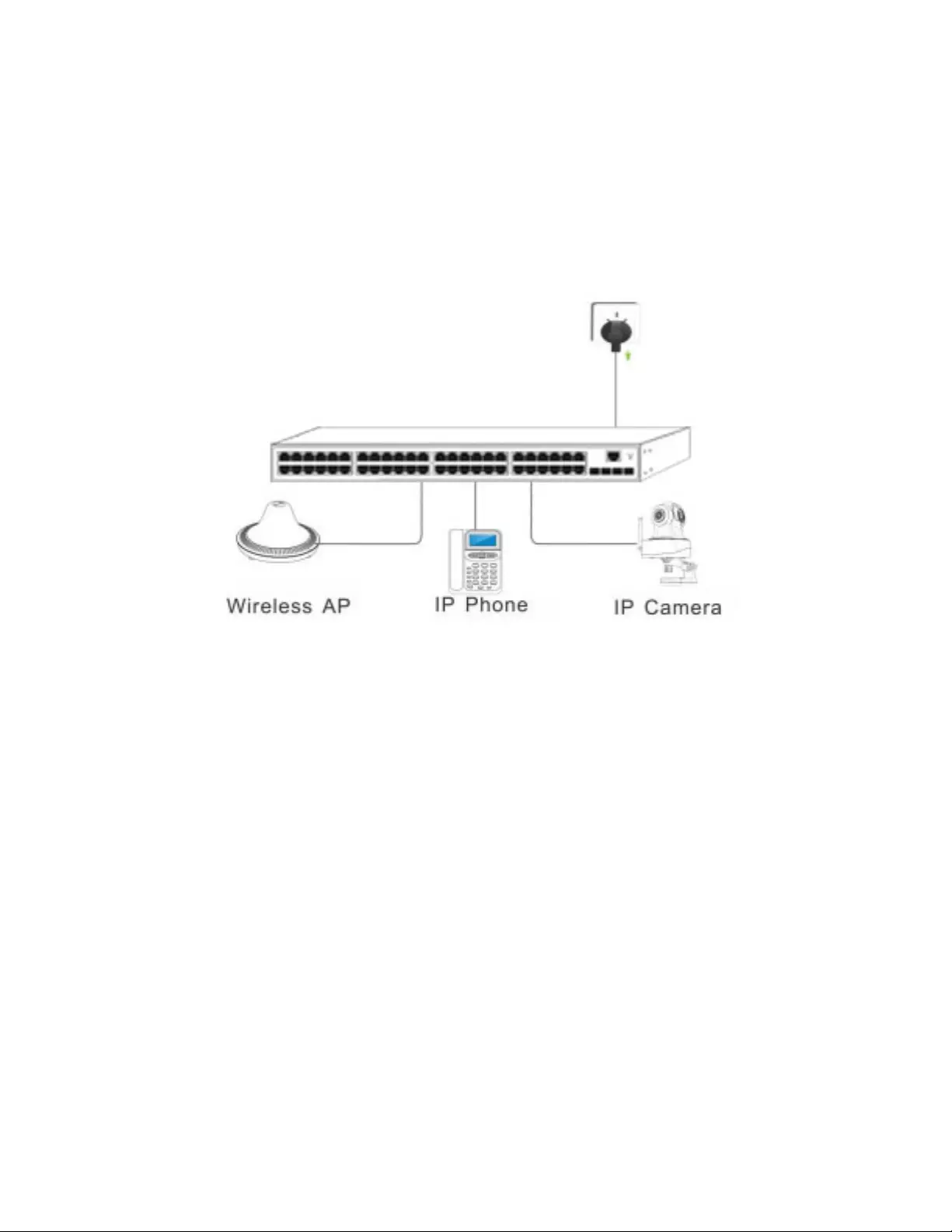
4.Open the browser, and enter http://192.168.1.1 and then press "Enter". The Switch login window
appears, as shown below.
9
Figure 7- Login Windows
5. Switching language to English .Enter the Username and Password (The factory default Username is
admin and Password is admin), and then click "LOGIN" to log in to the Switch configuration window
10
4. WEB Configuration Guide
Switch configuration interface consists of 3 main areas, areas for the status bar at the top, the area on the
left menu bar, right the main configuration window. Select the different functions in the function menu bar,
you can modify all settings in the main configuration window.
4.1. Basic Setting
Choose Basic Setting, and the following page appears. There are "System Info", "General Setup ", "IP
Setup", "Port Setup", “Dhcp server”, “DHCP-Relay” and “Stacking” configuration web pages.
4.1.1. System Info
Selecting “Basic Setting>System Information settings" in the navigation bar, you can view the basic
information of System and configure the IP address and System name.

11
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Product description
Brief description of device type.
Software version
Show switch's current Software version.
MAC address
Show switch’s physical addres
IP Address
The management IP of Switch
Subnet Mask
Config the corresponding subnet mask of the
IP address specified above. The default is
255.255.255.0.
Gateway
Specify a gateway address for the switch.
System name
System name
System Location
Specify the system location
【Instructions】
You can view and configure Running System status.
4.1.2. General Setup
Selecting “Basic Setting>General Setup" in the navigation bar, you can view the basic information of
Switch, Such as System description and so on. You can also modify System name, System contact and
System location.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
System name
System name
System Location
Specify the system location
System contact
Including company or related URL
Product description
Brief description of device type.

12
【Configuration example】
To configure general system information:
1. Click Basic Setting > General Setup.
2. Specify the system name as Switch, location as office, and contact information as admin for the system
administrator.
3. Click Apply
4.1.3. IP Setup
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup" in the navigation bar, you can configure IP.
4.1.3.1. Vlan interface
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup>Vlan interface" in the navigation bar, you can configure Vlan
interface.

13
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Interface
Selecting the interface:
vlan-interface
Supervlan-interface
Vlan ID
You can specify the vlan ID
Name
The name of interface
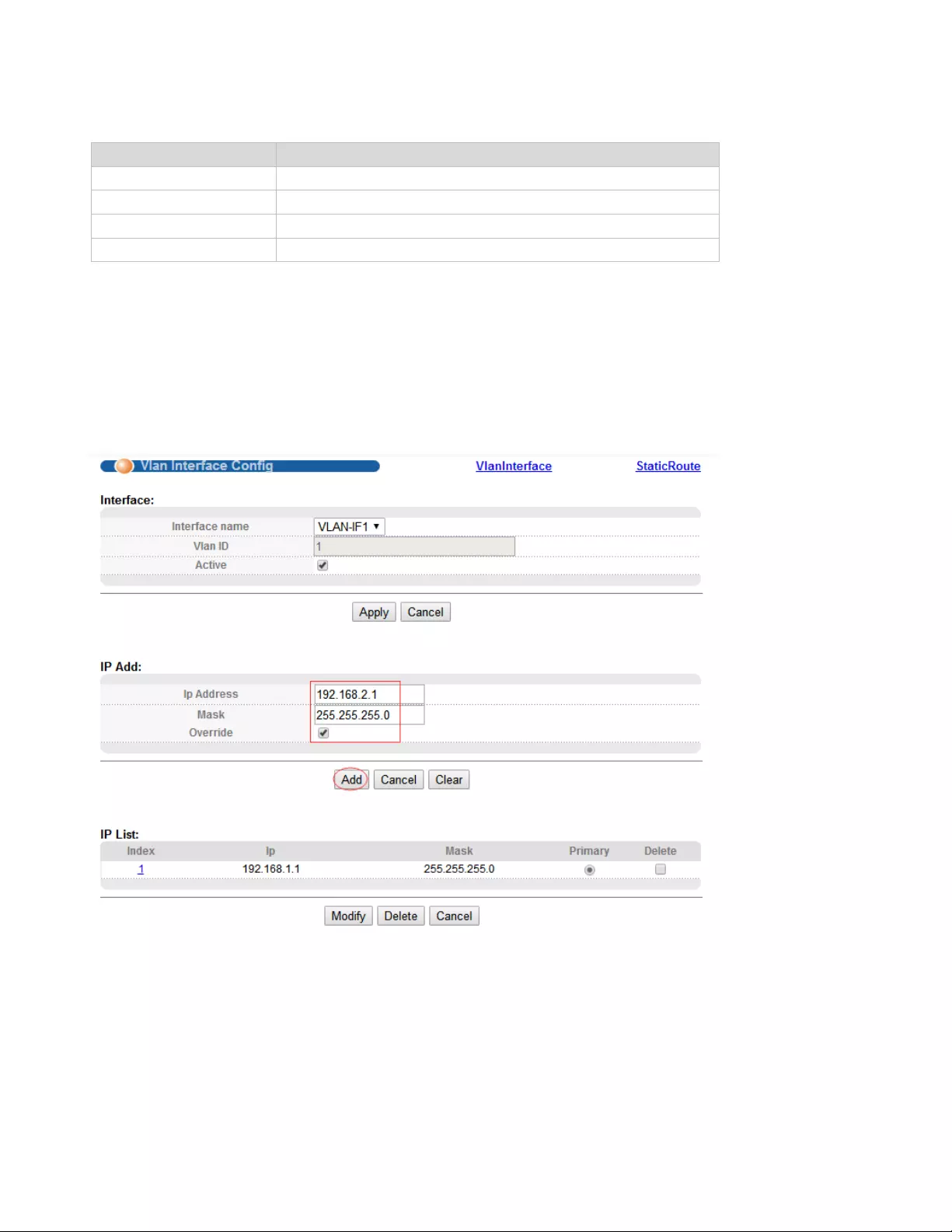
4.1.3.2. Vlan interface Config
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup>Vlan interface" in the navigation bar, you can configure Vlan
interface.
14
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Interface name
Name of interface
Vlan ID
You can specify the vlan ID
IP Address
User login in Switch using the IP Address
Override
You can override former original primary IP or not
【Configuration example】
To configure general system information:
1. Click Basic Setting > IP Setup >Vlan interface Config .
2. Specify the IP Address as 192.168.2.1.
3. Click Add.
15
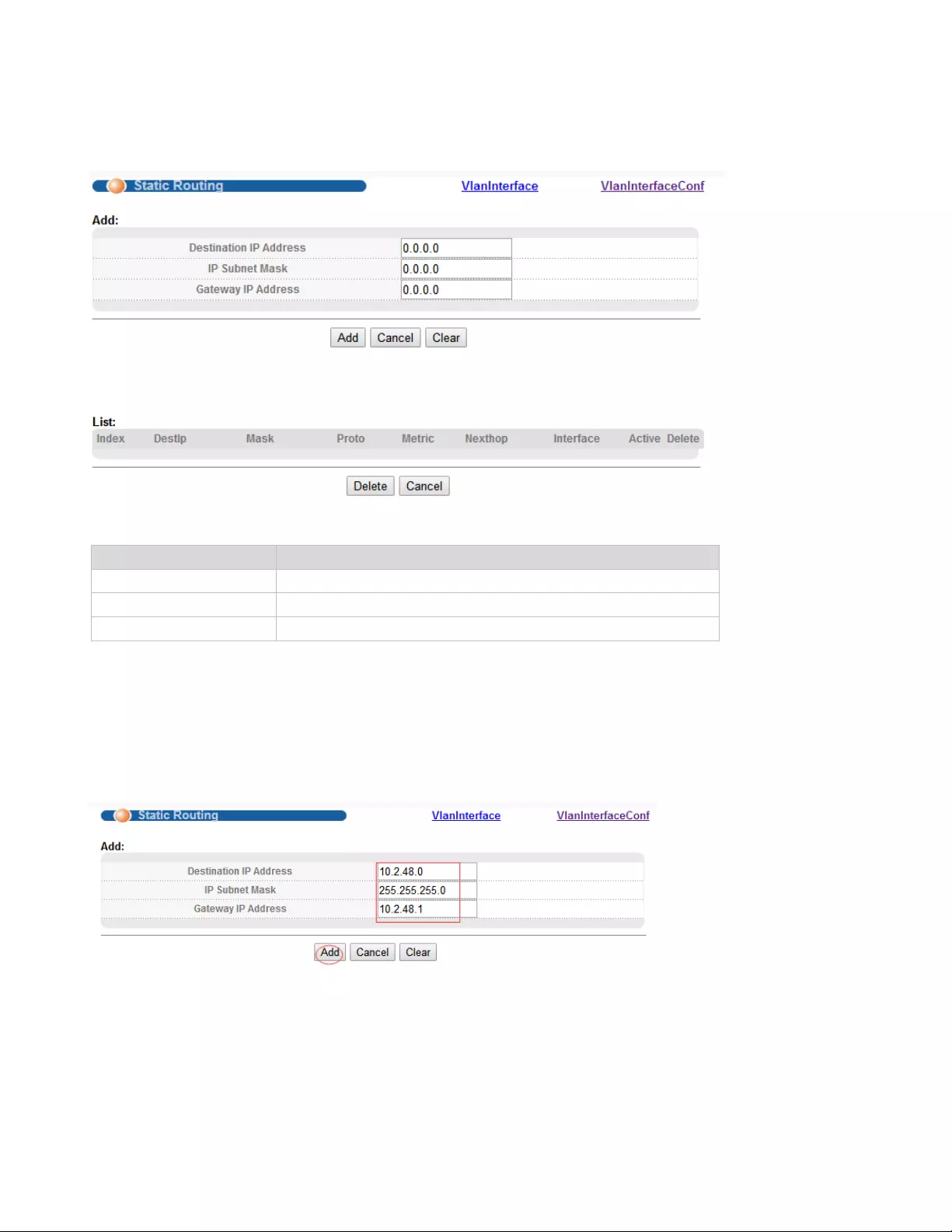
4.1.3.3. StaticRoute
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup>StaticRoute" in the navigation bar, you can configure StaticRoute.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Destination IP Address
Setting destination IP Address of Static Routing.
IP Subnet Mask
Setting IP Subnet Mask.
Gateway IP Address
Setting Gateway IP Address.
【Configuration example】
To configure static routes:
1. Click Basic Setting > IP Setup >Static Route .
2. Enter the destination IP address, IP Subnet Mask and gateway IP address.
3. Click Add.
To display static routes:
1. Click Basic Setting > IP Setup >Static Route.
2. Select Show from the Action List.

16
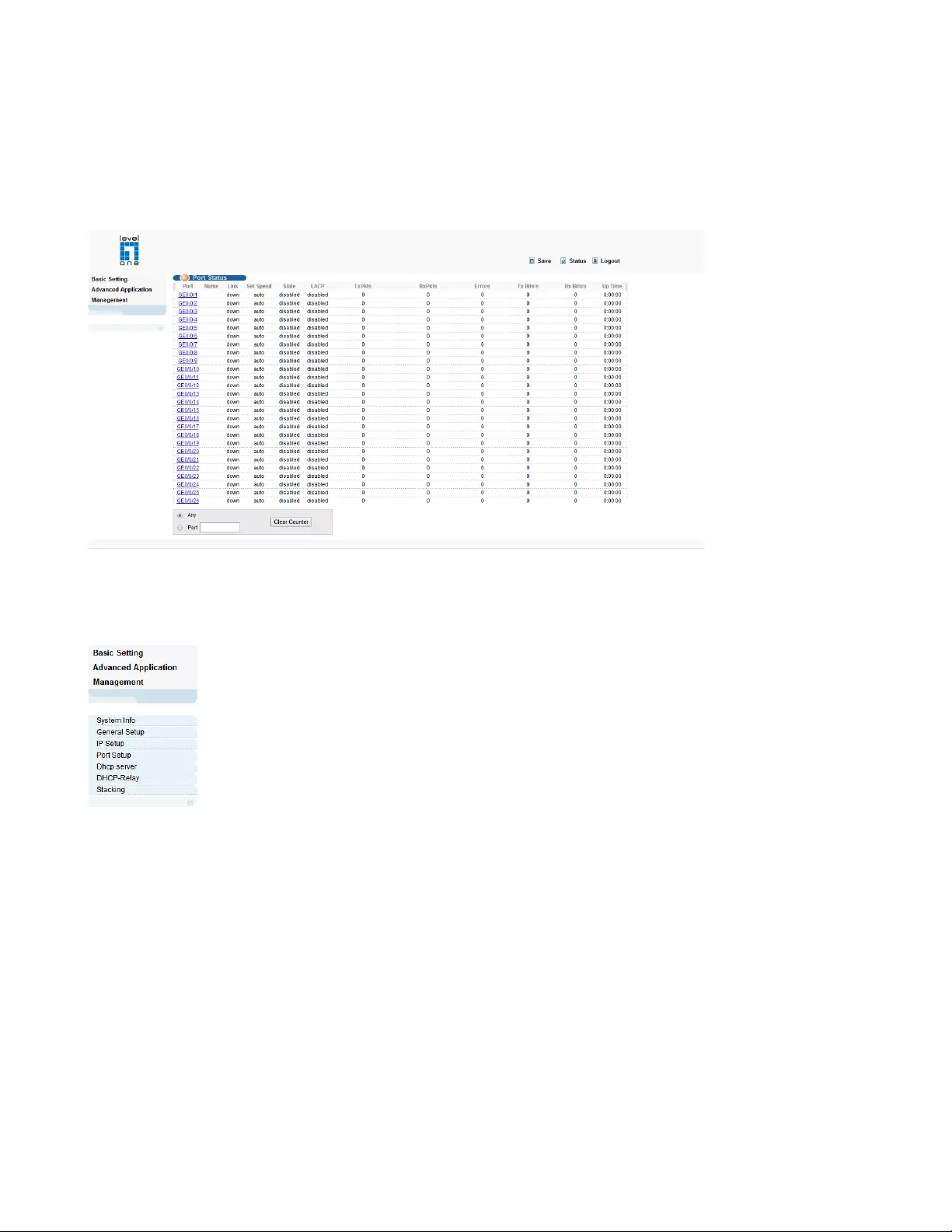
4.1.4. Port Setup
Selecting “Basic Setting>Port Setup" in the navigation bar, you can configure the related parameter of
port.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Port
Port number
status
Choose whether to close link port
link
Status:
Down
up
priority
Set port priority, the range of 0-7
Set speed
Choose the following modes:
auto
full-1000
auto-100
auto-1000
Full-duplex: Ports operating in Full-duplex mode can send
and receive packets concurrently.
Half-duplex: Ports operating in Half-duplex mode can either
send or receive packets at a given time.
Auto: Auto-negotiation, ports operating in
Auto-negotiation mode determine their duplex mode
through auto-negotiation with peer ports. By default, Auto
(Auto-negotiation) is enabled for the Speed/Duplex option.
Mode
Choose the following kinds:
auto
slave
master
Actual speed
The actual speed of the port

17
Parameter
Description
Port description
The port is described
【Configuration example】
To configure static routes:
1.Click Basic Setting > Port Setup
2.Configure the related parameters for port 1, Status is “enable", Priority is “1", Set speed is “auto", Mode
is “auto", Port description is “port 1".
3.Click Modify.
4.1.5. Dhcp Server
Selecting “Basic Setting>Dhcp Server" in the navigation bar, you can configure the related parameter of
port.This page allows you to enable the DHCP Server function, configure the included IP Address.
【Configuration example】
To configure IP addresses excluded for DHCP clients:
1. Click Basic Setting > Dhcp Server.
2. Select Configure Excluded Addresses from the Step list.
3. Enter an address range.
4. Click Add.

18
4.1.6. Dhcp-Relay
Selecting “Basic Setting>Dhcp-Relay" in the navigation bar, you can You can turn on the DHCP relay
function, Hidden DHCP Server. Set the source IP used. If L3 DHCP relay is enabled, and this switch sees
a DHCP request broadcast, it inserts its own IP address into the request so that the DHCP server will
know the subnet where the client is located. Then, the switch forwards the packet to the DHCP server.
When the server receives the DHCP request, it allocates a free IP address for the DHCP client from its
defined scope for the DHCP client’s subnet, and sends
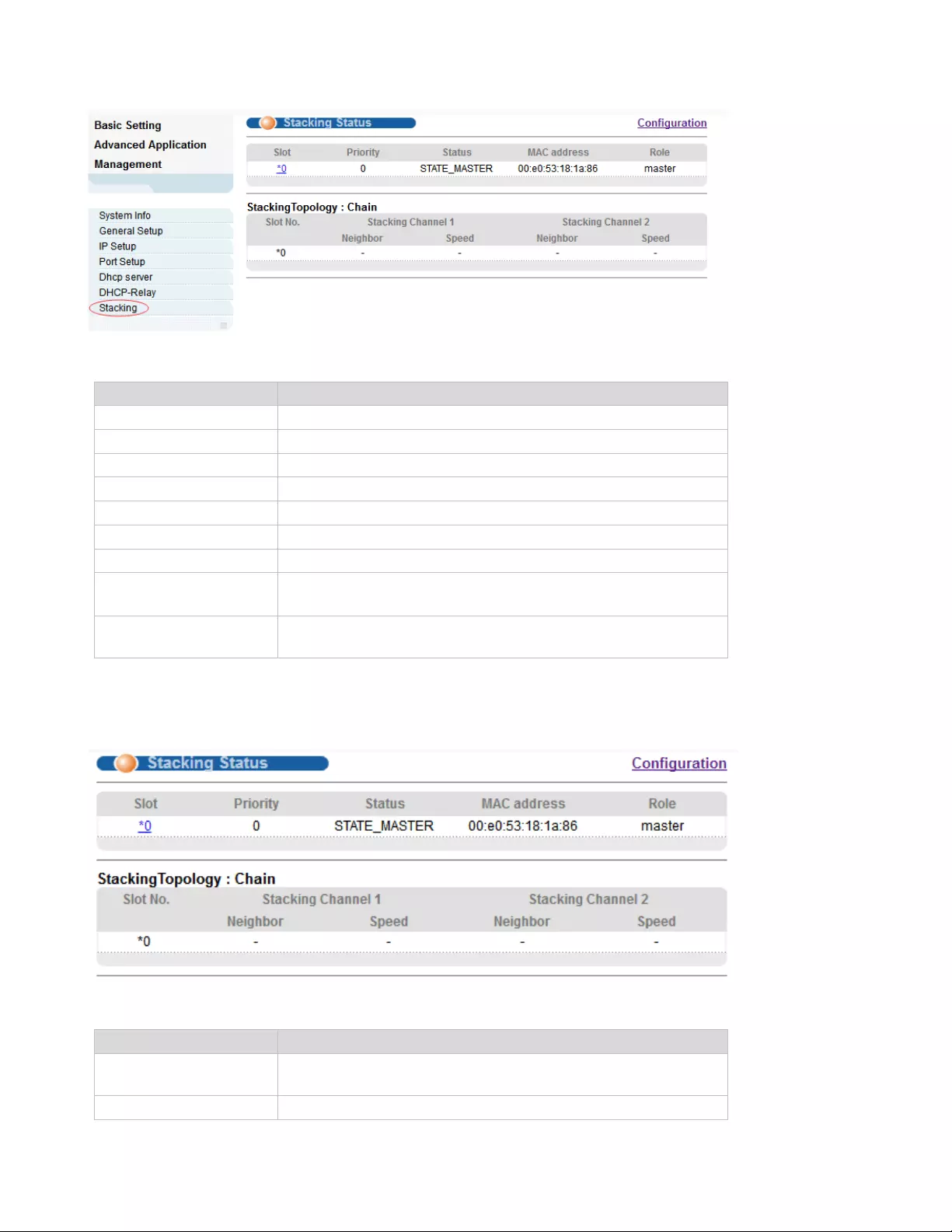
4.1.7. Stacking
Selecting “Basic Setting>Stacking" in the navigation bar, you can view the stack interface information,
neighbor interface information, start the stack function and set system priority. Before configuring the
stack, we highly recommend you to prepare the configuration planning with a clear set of the role and
function of each member device. Some configuration needs device reboot to take effect, so you are kindly
recommended to configure the stack at first, next connect the devices physically after powering off them,
then you can power them on and the devices will join the stack automatically. After stack is established,
users can log in the stack system through any member devices to configure and manage it.
19
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
ip pool
ip pool ID
name
Set the name of ip pool
hire time
Set hire time
Gate Address
Set Gate Address
Ip Mask
Set Ip Mask
First DNS
Set First DNS
Secondary DNS
Set Secondary DNS
start address
The first one of the IP addresses that should not be
assigned.
End Address
The last one of the IP addresses that should not be
assigned.
4.1.7.1. Stacking Status
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup>Stacking Status" in the navigation bar, you can view the stack
interface information, neighbor interface information.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Slot
Each device in the system must manually specify an
unrepeatable ID number to unique identify
Status
Two different working modes:

20
Parameter
Description
Single-machine mode: this mode is the same as the
general switch, not to provide the stack function.
Stack mode: this mode opens the stack function, can make
up a stack system with other devices.
Priority
Each device in the system can be assigned a priority,
devices with higher-priority more likely to be elected as
main device.
4.1.7.2. Stacking Configuration
Selecting “Basic Setting>IP Setup>Stacking Configuration" in the navigation bar, you can open stack
and set System Priority.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Active
Select open or close stack
System Priority
Set system priority, the default is 0
Slot id Freeze
Freeze slot ID

21
【Configuration example】
As shown in the figure, configure SW1 as Master and SW2 as Slave.
SW1
1.Enable Stack function.
2.Configure device-id as 0.
3.Configure left port of SW1.
4.Configure System priority as 200.
SW2:
1.Enable Stack function.
2.Configure device-id as 0.
3.Configure left port of SW2.
4.Configure System priority as 100.
After restarting the two devices, connect two devices according to Figure.
4.2. Advanced Application
Choose Advanced Application, and the following page appears. There are "VLAN", "MAC Address
Forwarding","Spanning Tree Protocol",“ERPS Protocol",”EAPS Protocol", “Layer 2 Tunneling
Protocol”, “PPPOE IA", “Bandwidth Control", “Broadcast Storm Control", “Mirroring", “Link
Aggregation", “Port Security", “PoE Settings", “Classifier", “Policy Rule", “Queuing Method",
“Multicast", “IPv6 Multicast", “Dos attack protect”, DHCP Snooping Setting" , “SNTP Setting",
“QinQ", “LLDP Protocol" and “AAA"configuration web pages.

22
4.2.1. VLAN
Selecting “Advanced Application>VLAN" in the navigation bar, you can configure VLAN.
【Instructions】
The traditional Ethernet is a data network communication technology basing on CSMA/CD
(Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect) via shared communication medium. Through
the traditional Ethernet, the overfull hosts in LAN will result in serious collision, flooding
broadcasts, poor performance or even breakdown of the Internet. Though connecting the
LANs through switches can avoid the serious collision, the flooding broadcasts cannot be
prevented, which will occupy plenty of bandwidth resources, causing potential serious security
problems.
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical
scheme rather than the physical layout. The VLAN technology is developed for switches to
control broadcast in LANs. By creating VLANs in a physical LAN, you can divide the LAN into
multiple logical LANs, each of which has a broadcast domain of its own. Hosts in the same

23
VLAN communicate with one another as if they are in a LAN. However, hosts in different VLANs
cannot communicate with one another directly. Therefore, broadcast packets are limited in a
VLAN. Hosts in the same VLAN communicate with one another via Ethernet whereas hosts in
different VLANs communicate with one another through the Internet devices such as Router,
the Layer3 switch, etc. The following figure illustrates a VLAN implementation.
4.2.1.1. VLAN Status
Selecting “Advanced Application>VLAN>VLAN Status", in the navigation bar, you can view VLAN
status.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
VLAN Status
View all vlans configured in the device
VLAN Search by VID
Enter VID to view the specified VLAN
【Configuration example】
Such as: View the VLAN of VID as “1".
4.2.1.2. VLAN Port Settings
Selecting “Advanced Application>VLAN>VLAN Port Settings", in the navigation bar, you can set
VLAN port.
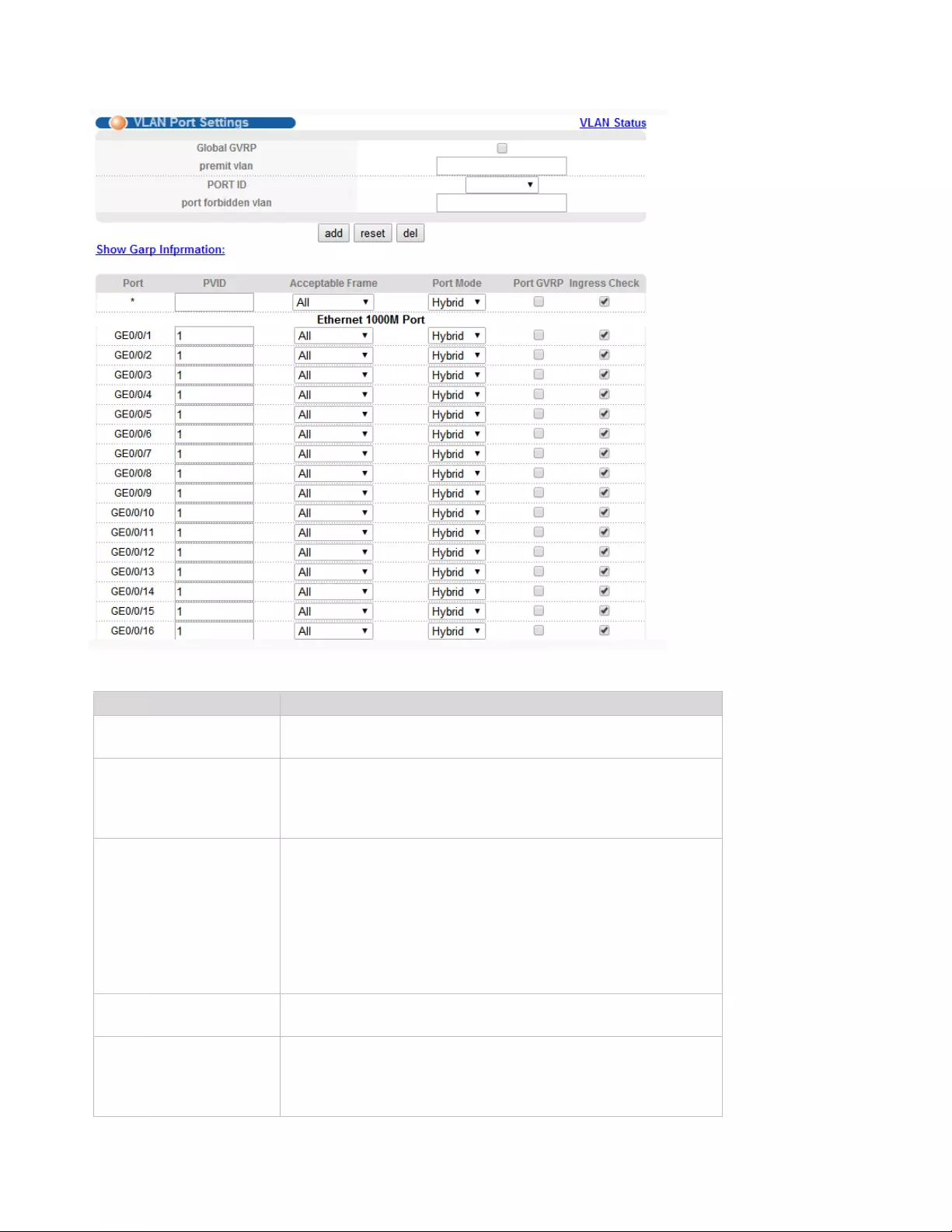
24
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
PVID
The PVID of the port can be modified, the default port
PVID is "1"
Acceptable Frame
Choose the following kinds:
All
Tagged only
Untagged only
Port Mode
Choose the following modes:
Hybrid: The port can be either a tag member or untag
member in a VLAN and can be a member port for multiple
vlans.
Trunk: The port can only be an tag member in a VLAN and
can be a member port for multiple vlans
Access: The port can only be a member of untag in VLAN
and the port can only be in a VLAN.
Port GVRP
Select open or close GVRP, dynamic VLAN learning
function, port mode must be Trunk mode
Ingress Check
Open port filtering function. If the port settings only receive
the Tagged type of message, if the Ingress Check function
is opened, the Untagged type of message will be
discarded when the port receives the message of the
25
Parameter
Description
untagged type of message, otherwise it can be forwarded.
The default port filtering function opens.
【Instructions】
Hybrid port to packet:
Receives a packet, judge whether there is a VLAN information: if there is no play in port PVID,
exchanged and forwarding, if have, whether the Hybrid port allows the VLAN data into: if can be
forwarded, or discarded (untag on port configuration is not considered, untag configuration only work
when to send it a message).
Hybrid port to send packet:
1. Determine the VLAN in this port attributes (disp interface can see the port to which VLAN untag, which
VLAN tag).
2. If it is untag stripping VLAN information, send again, if the tag is sent directly.
【Configuration example】
1. Click Advanced Application > VLAN> VLAN Port Settings.
2. The PVID of port 1 is set to “1", the frame type is set to “All", the port mode is set to “Hybrid", and the
port GVRP is not turned on and the entry inspection function is opened.
3.Click Apply.
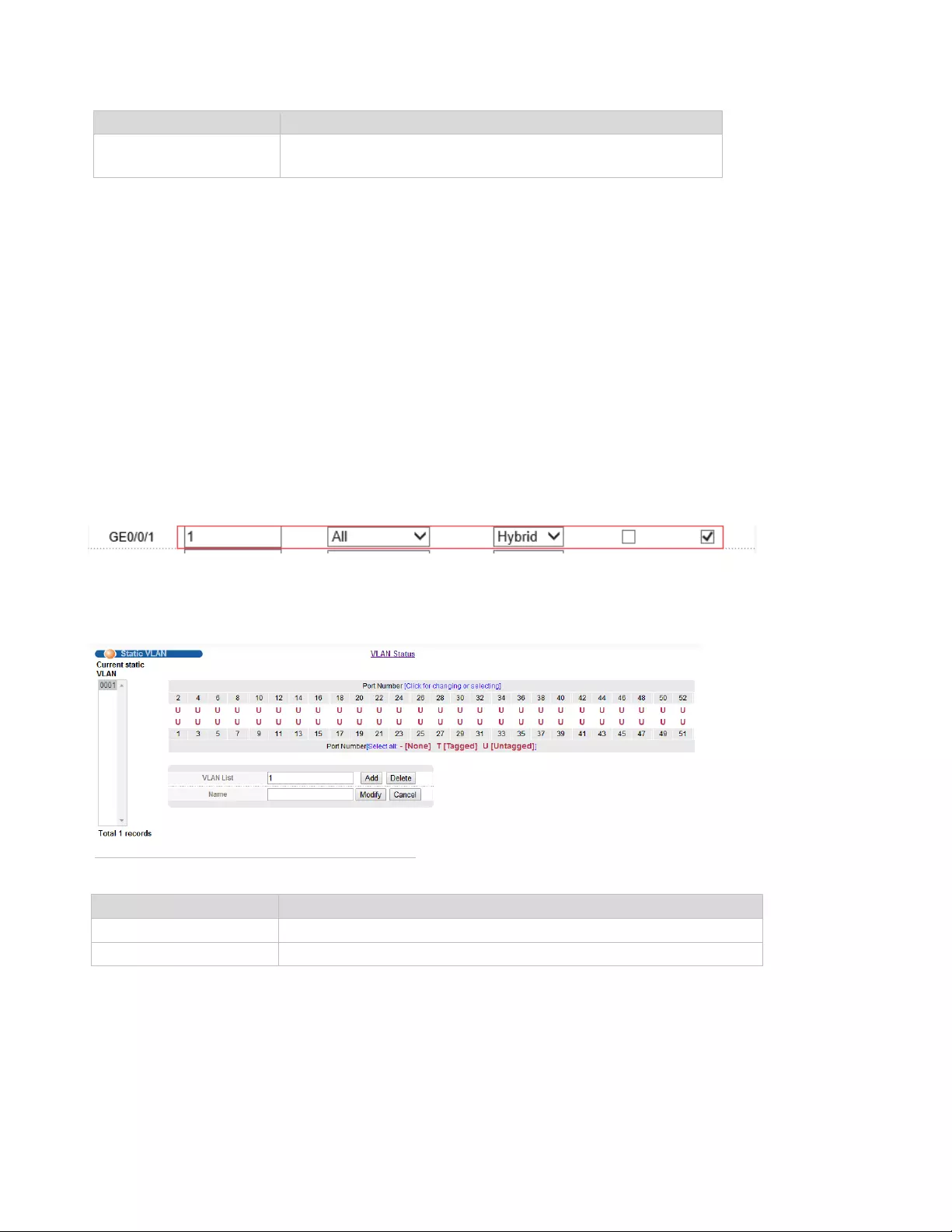
4.2.1.3. Static VLAN
Selecting “Advanced Application>Static VLAN" in the navigation bar, you can configure Static VLAN.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
VLAN List
VLAN Group ID
Name
VLAN Group name
【Configuration example】
To Add and delete VLAN members
1.Click Advanced Application > VLAN> Static VLAN.
2.Adding a new VLAN, VLAN Group ID 120 contains non-untag member port 1-4. Tag member port 5-8.
The user can modify the port member by clicking on the white area below the port number.
3.Click Apply.
26
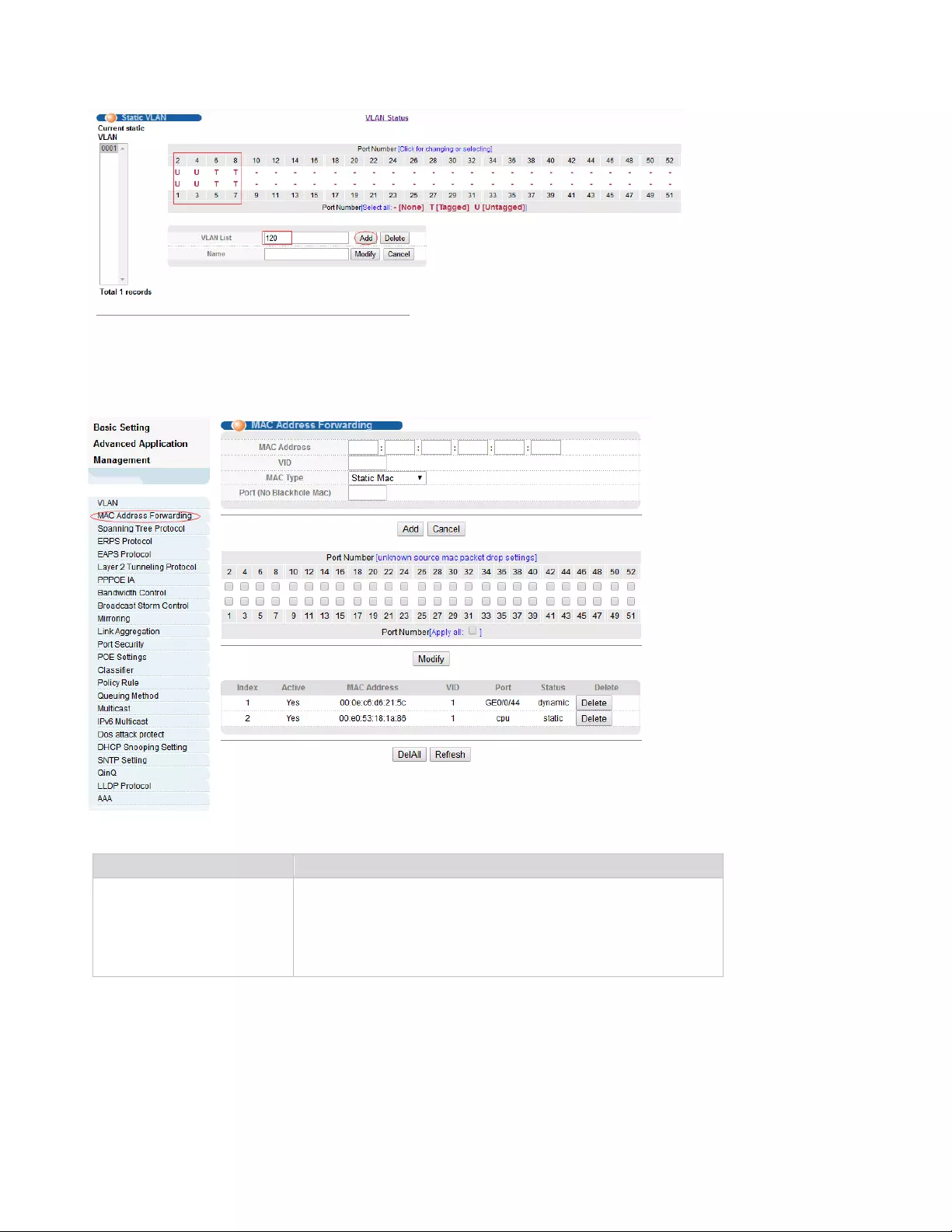
4.2.2. MAC Address Forwarding
Selecting “Advanced Application>MAC Address Forwarding" in the navigation bar, you can configure
MAC Address Forwarding.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
MAC Type
MAC Type:
Static MAC
Dynamic MAC
Blackhole MAC
Permanent MAC
【Instructions】
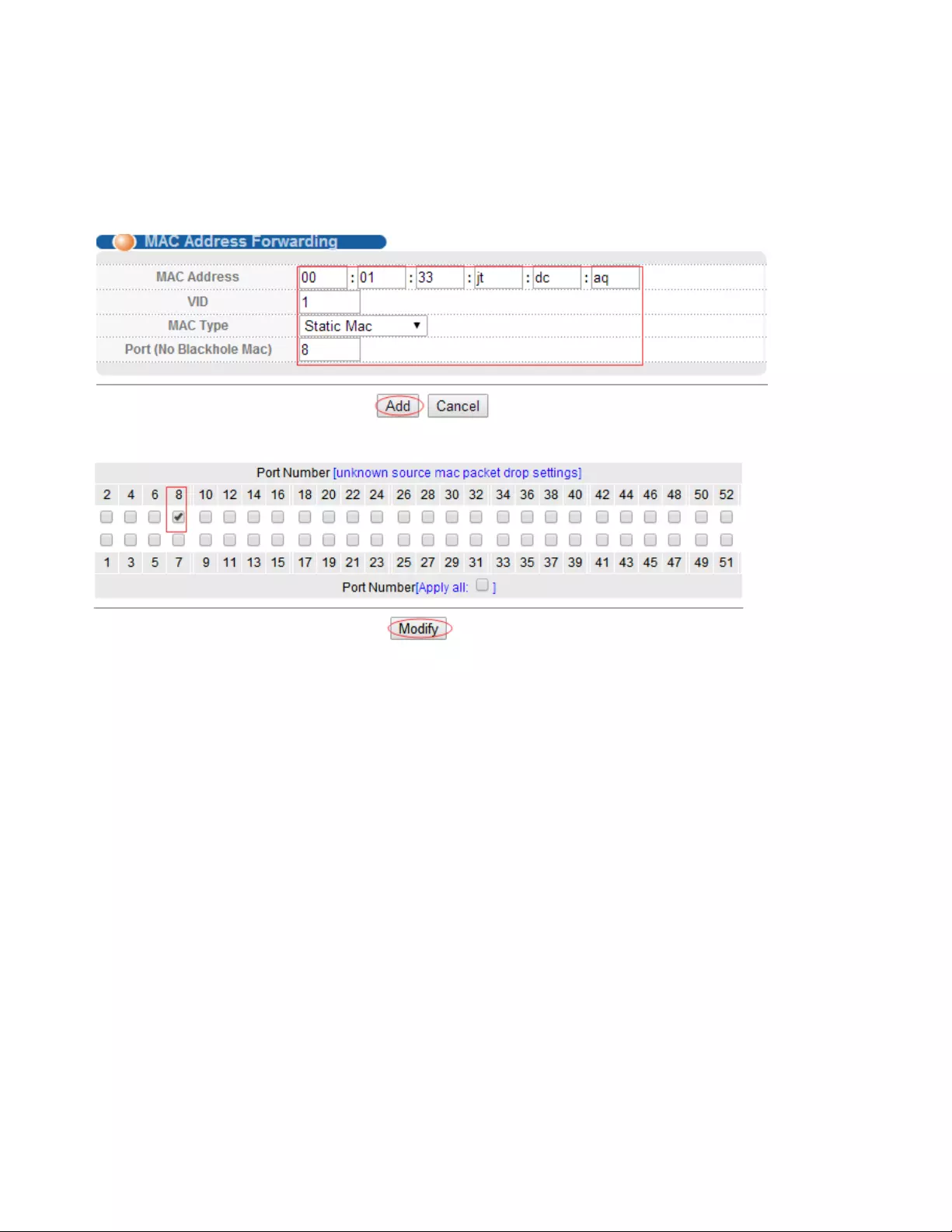
27
Blackhole MAC: If a PC's MAC address is configured on a switch to be a blackhole MAC, then the PC's
package will be discarded by the switch and not forwarded to the network.
【Configuration example】
1. Click Advanced Application > MAC Address Forwarding.
2. MAC Address Forwarding
3. Unknown source mac packet drop settings.
4.Click Modify.
4.2.3. Spanning Tree Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>Spanning Tree Protocol", in the navigation bar, you can configure
spanning tree protocol.STP (Spanning Tree Protocol), subject to IEEE 802.1D standard, is to disbranch a
ring network in the Data Link layer in a local network. Devices running STP discover loops in the network
and block ports by exchanging information, in that way, a ring network can be disbranched to form a tree-
topological ring-free network to prevent packets from being duplicated and forwarded endlessly in the
network.
28
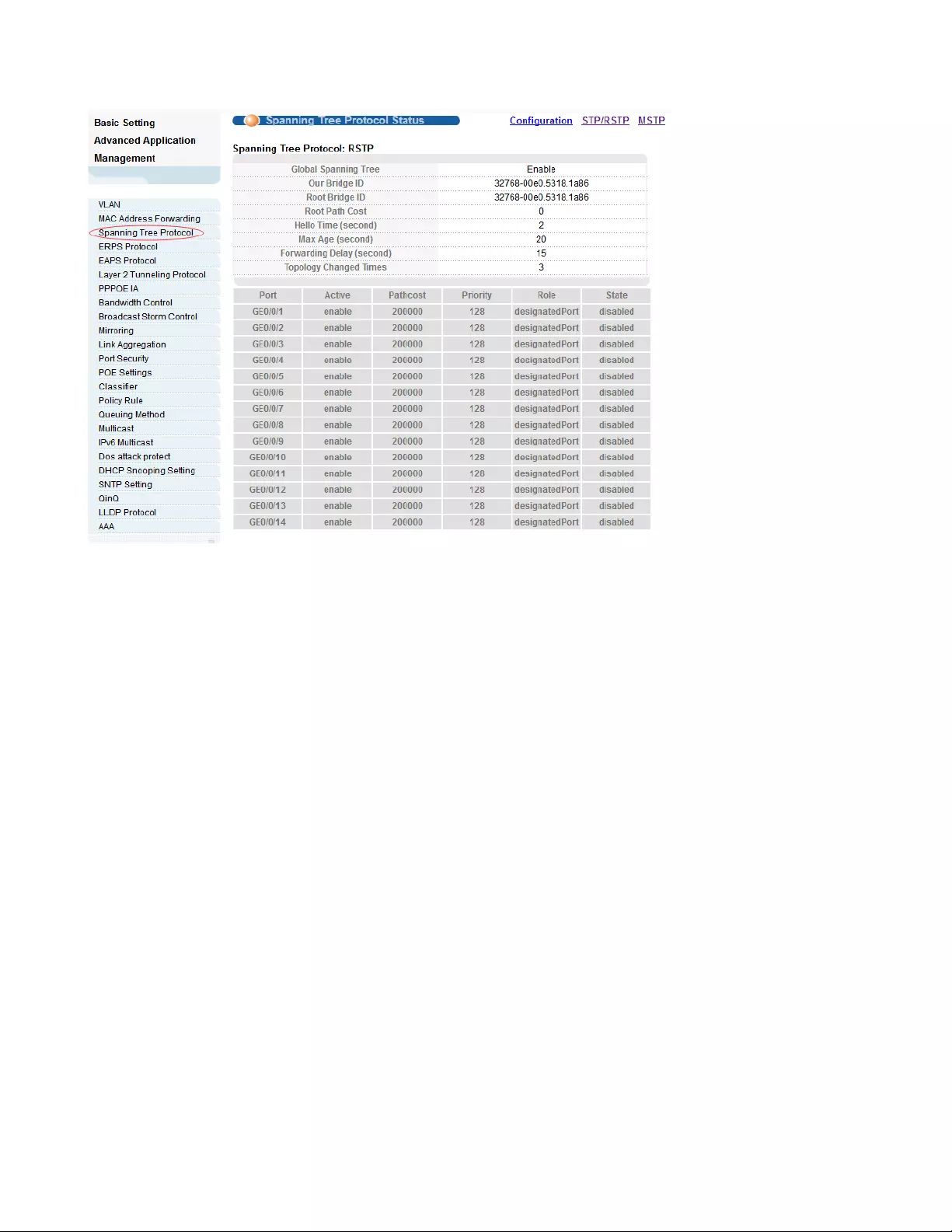
4.2.3.1. Spanning Tree Protocol Status
Selecting “Advanced Application>Spanning Tree Protocol>Spanning Tree Protocol status"; in the
navigation bar, you can view spanning tree protocol status.

29
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Root Path Cost
Configure Root Path Cost
Hello time(second)
Switches sends bpdu in packet interval
Max age(second)
Ports are not yet received a message in the time, will
initiate topology changes
Forwarding
delay(second)
The state of the port switch time
Topology changed
times
The number of topology changes
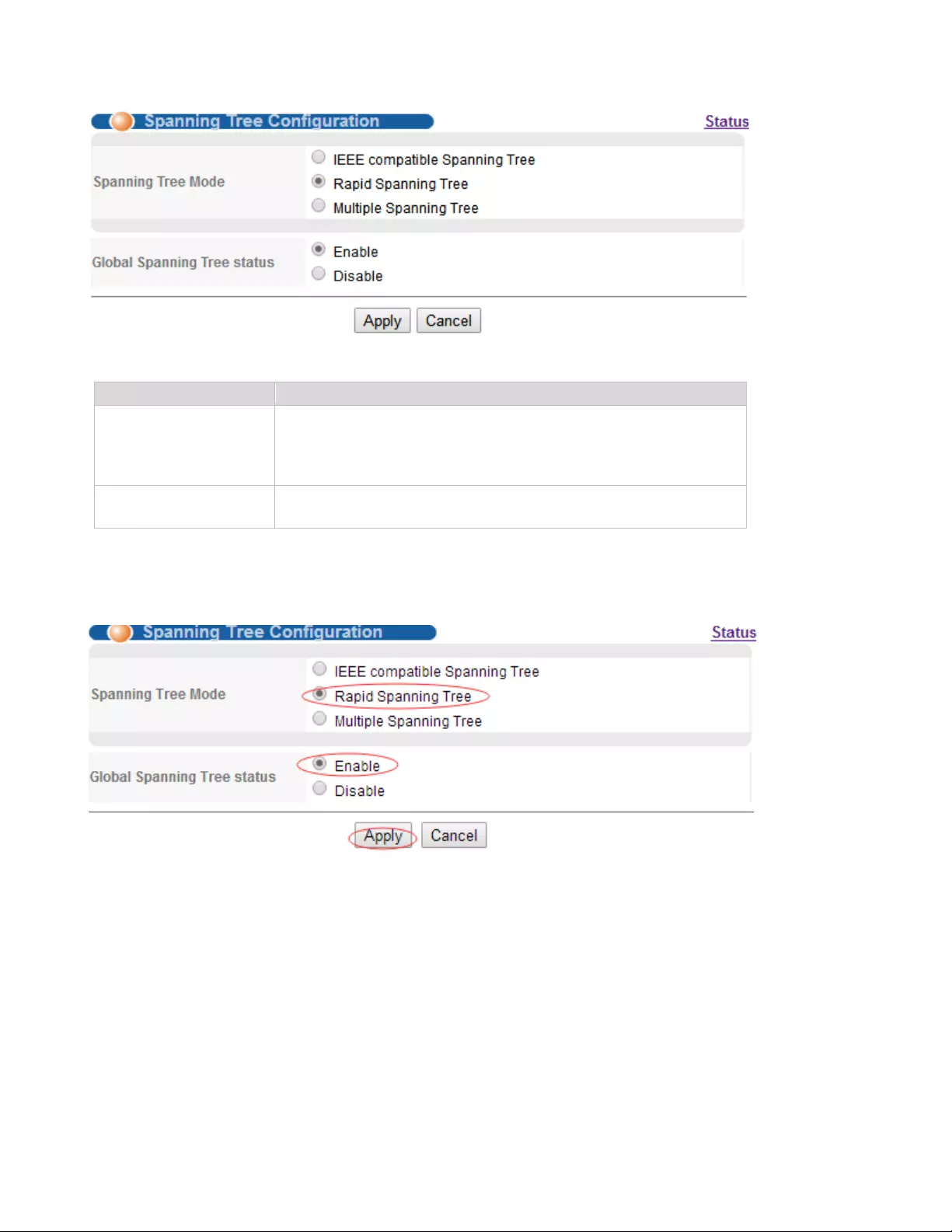
4.2.3.2. Spanning Tree Configuration
Selecting “Advanced Application>Spanning Tree Protocol>Spanning Tree configuration", in the
navigation bar, you can configure spanning tree.
30
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Spanning Tree Mode
Spanning tree mode:
IEEE Compatible Spanning Tree
Rapid Spanning Tree
Multiple Spanning Tree
Global Spanning Tree
Status
Select open or close Global Spanning
【Configuration example】
Such as: Spanning Tree Mode as “Rapid Spanning Tree", open Global Spanning.
4.2.3.3. Compatible/Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>Spanning Tree Protocol>Compatible/Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol", in the navigation bar, you can configure Compatible/Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol.

31
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Bridge Priority
Set bridge priority, the default instance bridge priority for 32768
Hello Time
Switches sends bpdu in packet interval
Max Age
Ports are not yet received a message in the time, will initiate
topology changes
Forwarding Delay
The state of the port switch time
Port Priority
Set port instance priority, defaults to 128
Path Cost
Configure port costs
【Configuration example】
Such as:
1. Configure the bridge priority as 32768, the Hello Time is 2 seconds, the MAX Age is 20 seconds, and
the Forwarding Delay is 15 seconds.
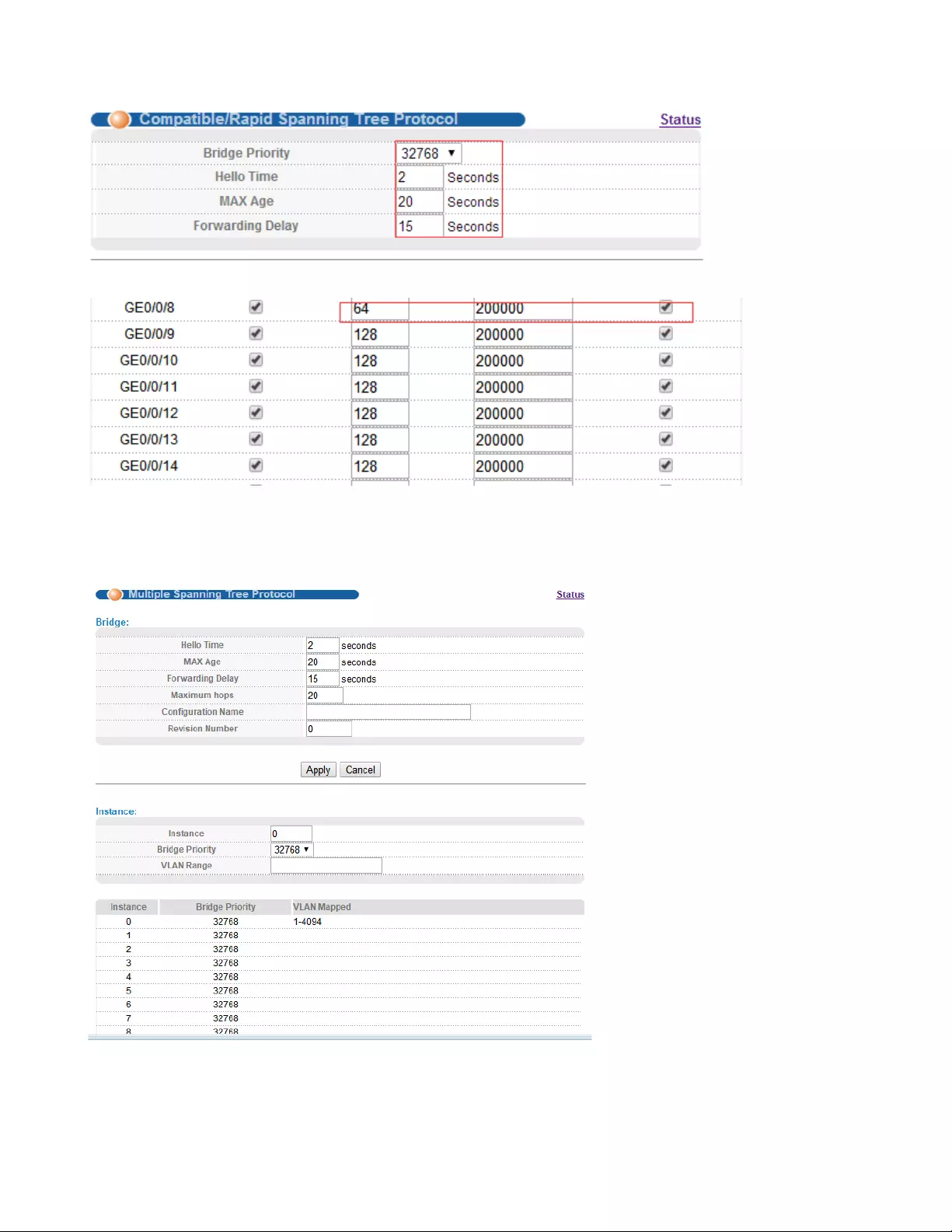
32
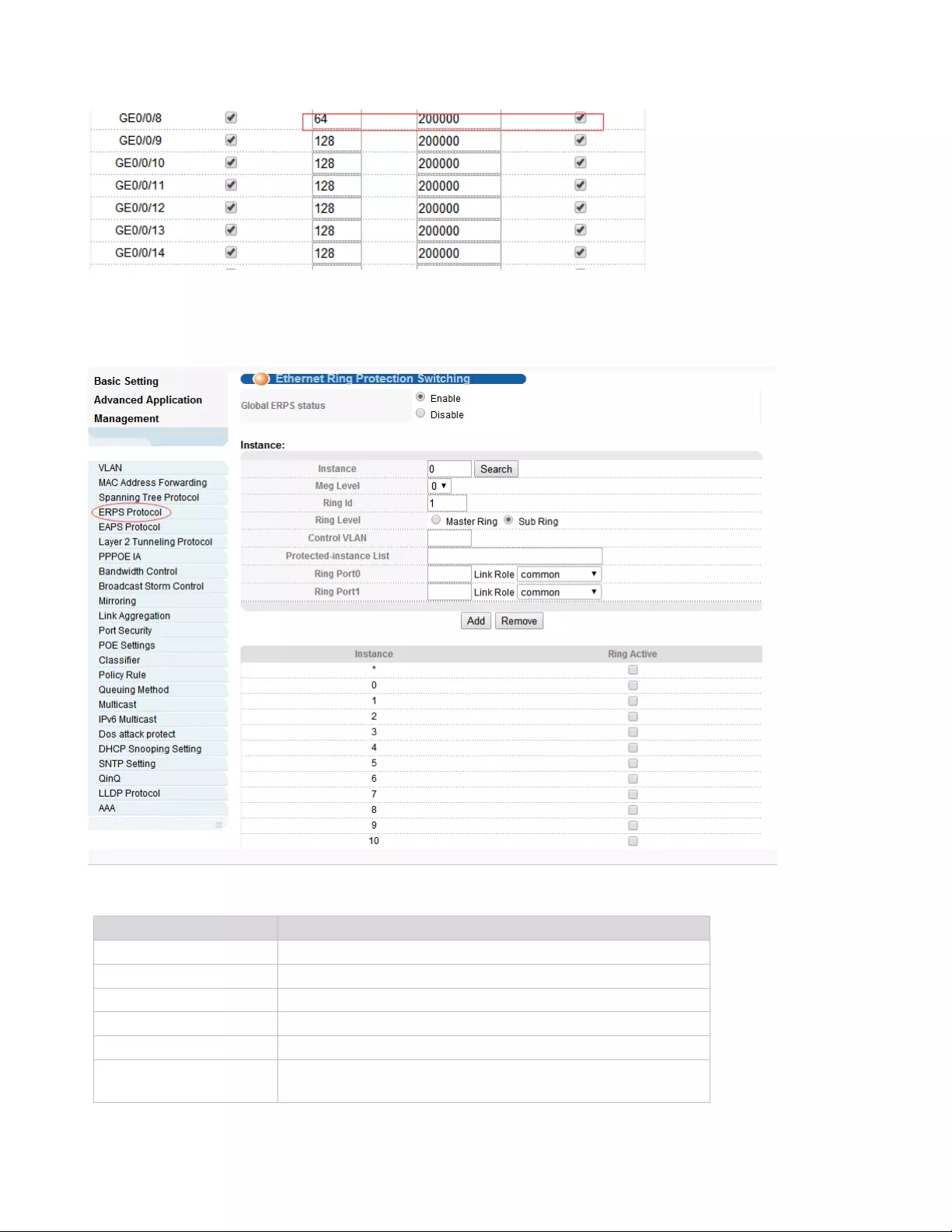
2. The priority of port 8 is 64, and the path cost is 200000.
4.2.3.4. Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>Spanning Tree Protocol>Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol", in the
navigation bar, you can configure Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol.
33
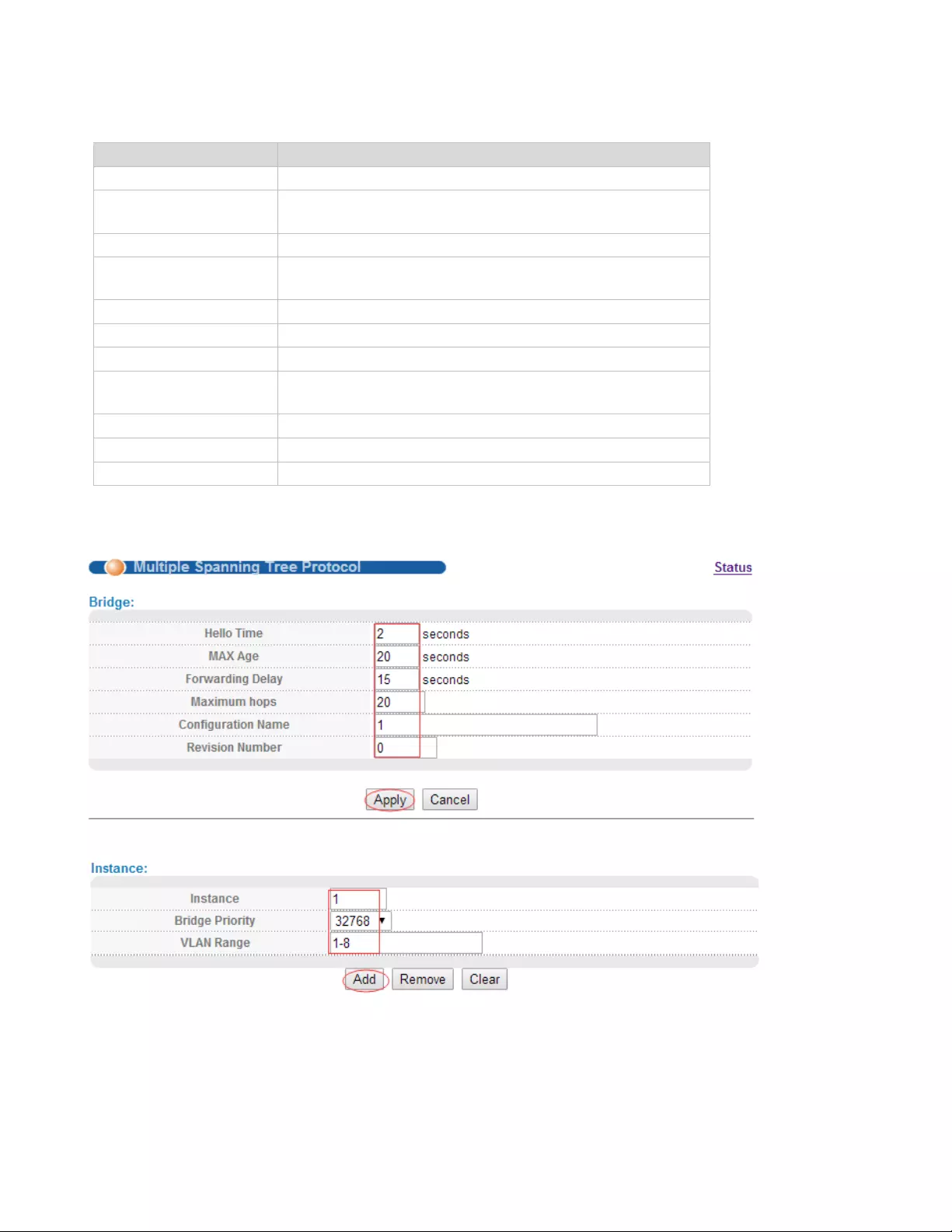
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Hello Time
Switches sends bpdu in packet interval
Max age
Ports are not yet received a message in the time, will
initiate topology changes
Forwarding Delay
The state of the port switch time
Maximum Hops
Set the maximum number of hops that BPDUs can
support in the spanning tree
Configuration Name
Fill in configuration name
Revision Number
Set revision number
Instance
Instance number
Bridge Priority
Priority setting bridge example, the default instance
bridge priority for 32768
VLAN Range
Set VLAN range
Port Priority
Set port instance priority, defaults to 128
Path Cost
Configure port costs
【Configuration example】
1. Bridge
2. Instance
3. The priority of port 8 is 64, and the path cost is 200000.
34
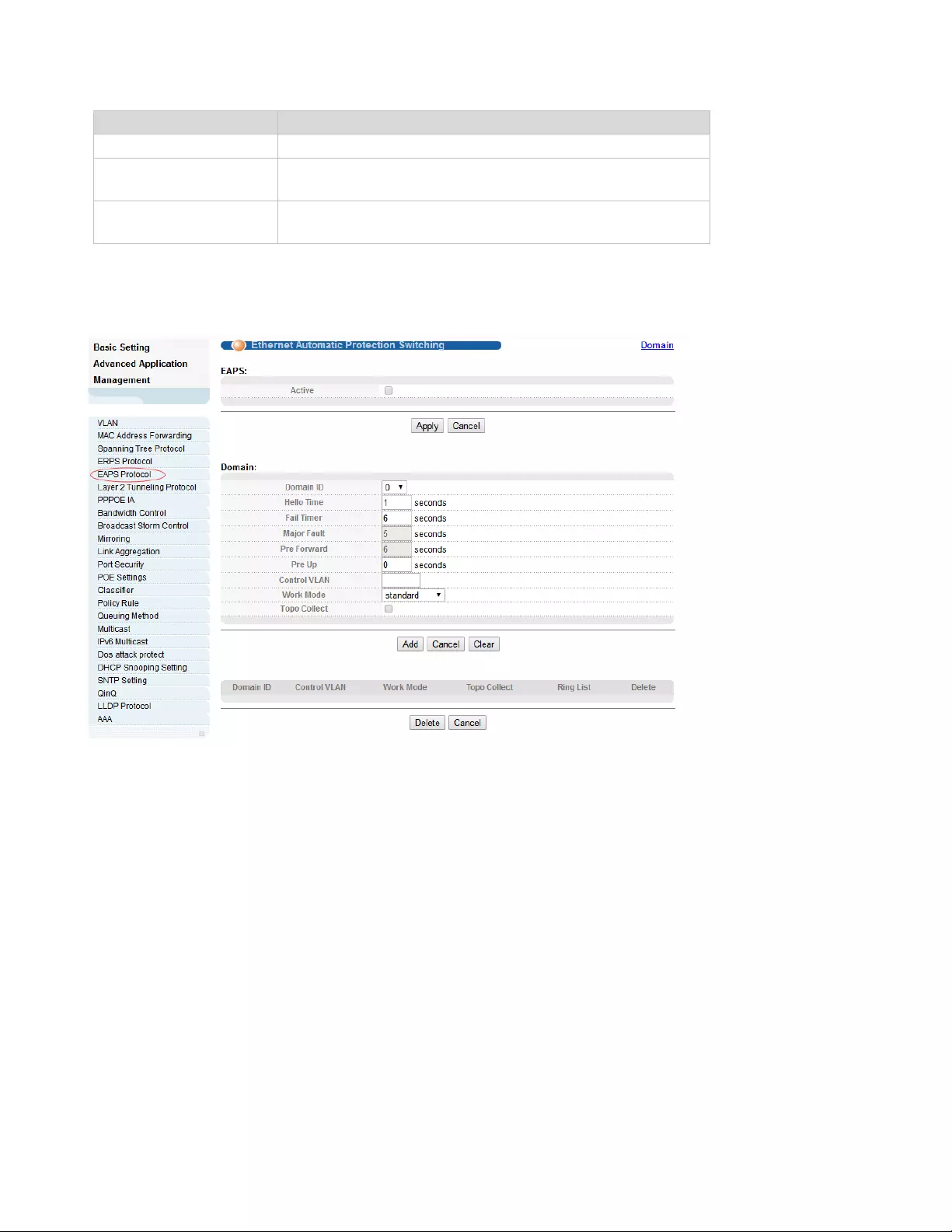
4.2.4. ERPS Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>ERPS Protocol", in the navigation bar, you can configure ERPS
protocol.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Global ERPS status
Select open or close ERPS
Instance
The range of 0-15, active instance.
Meg level
The range of 0-7
Ring Id
The range of 1-239
Ring Level
Master Ring and Sub Ring
Control VLAN
You must configure the VLAN before configuring the
ERRP ring
35
Parameter
Description
Protected-instance List
Application of MST instance
Ring port1
Configurable ports are common, owner, neighbor, next-
neighbor
Ring port2
Configurable ports are common, owner, neighbor, next-
neighbor
4.2.5. EAPS Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>EAPS Protocol", in the navigation bar, you can configure EAPS
protocol.
4.2.5.1. Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching
Selecting “Advanced Application>EAPS Protocol>Ethernet automatic protection switching", in the
navigation bar, you can configure Ethernet automatic protection switching.
36
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Active
Select open or close EAPS
Hello time
Switches sends bpdu in packet interval
Fail Timer
Configure the information timeout
Major Fault
The Major Fault timer will be automatically updated by
the system
Pre Forward
The Pre forward timer will be automatically updated by
the system
Pre Up
Loop recovery wait time
Domain ID
You need to specify the Domain ID when creating the
EAPS Domain
Control VLAN
You must configure the VLAN before configuring the
EAPS Ring
Work mode
Work mode:
standard
huawei
eips-subring
Topo Collect
Select open or close Topo Collect
【Configuration example】
1.EAPS
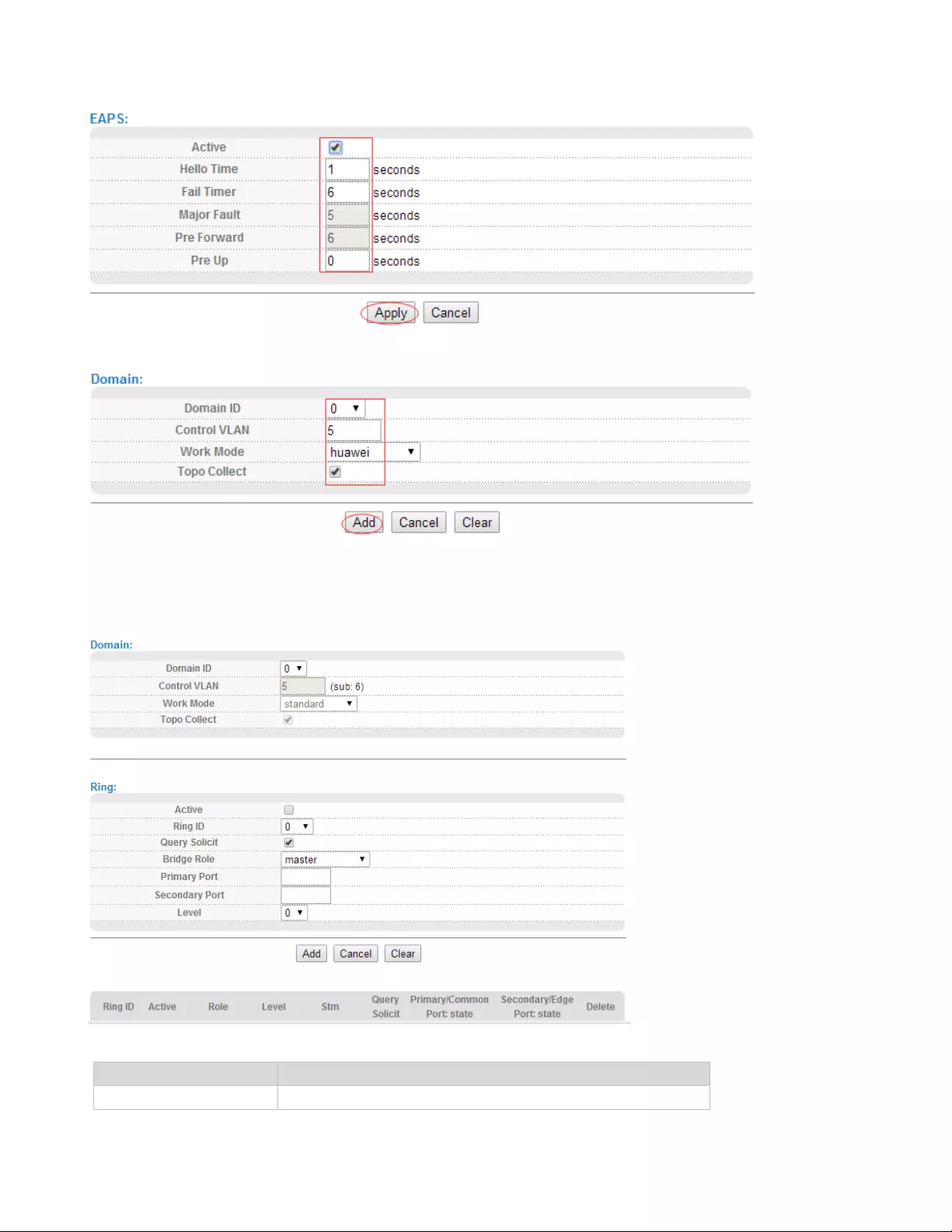
37
2.Domain
4.2.5.2. EAPS Domain
Selecting“Advanced Application>EAPS Protocol>EAPS Domain", in the navigation bar, you can
configure EAPS Domain.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Domain ID
Select Domain ID
38
Parameter
Description
Control VLAN
You must configure the VLAN before configuring the
EAPS Ring
Work mode
Work mode:
standard
huawei
eips-subring
Topo Collect
Select open or close Topo Collect
Active
Select open or close Ring
Ring ID
Select ring ID
Query Solicit
Select open or close Query Solicit
Bridge Role
Bridge Role:
mastesr
transit
edge
assistant-edge
Level
Level:
0, 1
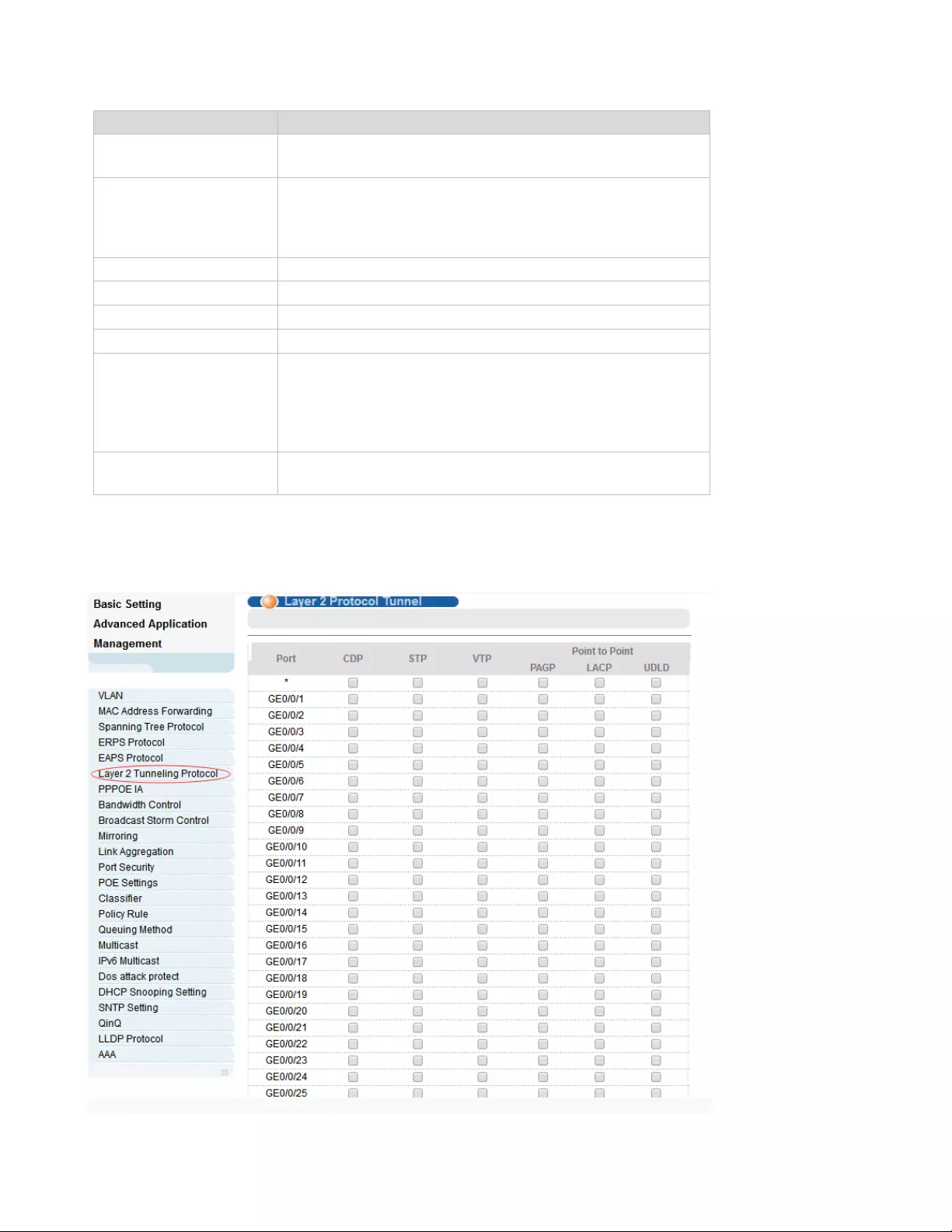
4.2.6. Layer 2 Protocol Tunnel
Selecting “Advanced Application>Layer 2 Protocol Tunnel", in the navigation bar, you can configure
the specified protocol message that enters the port to perform a tunnel operation.
39
4.2.7. PPPOE IA
Selecting “Advanced Application>PPPOE IA", in the navigation bar, you can configure PPPoE IA.
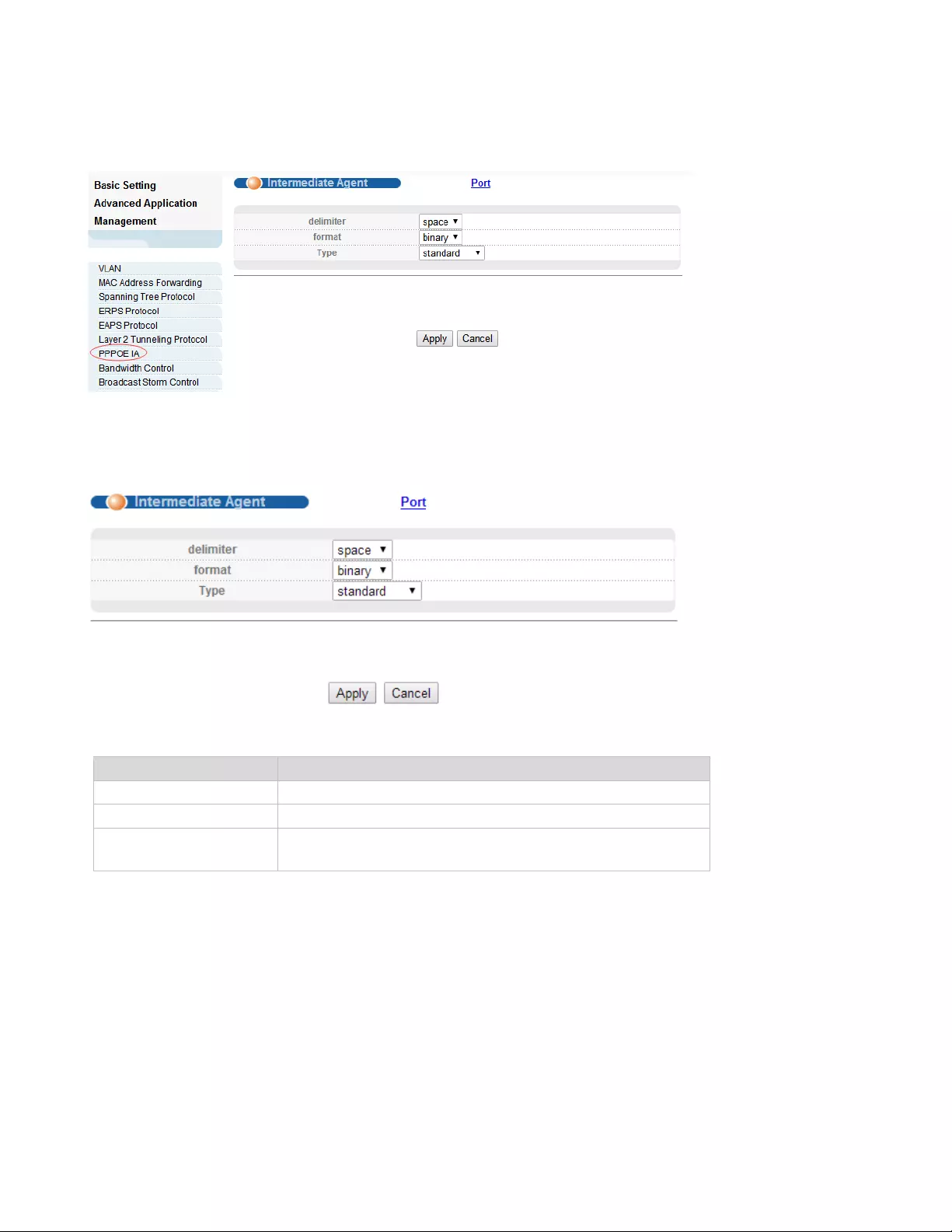
4.2.7.1. Intermediate Agent
Selecting “Advanced Application>PPPoE IA>Intermediate Agent", in the navigation bar, you can
configure Intermediate Agent.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
delimiter
Configure delimiter, choose “space", “:", “.", “#", “/"
format
Configure format, choose binary, ascii
type
Configure the message type, choose standard, Huawei,
self-defined
4.2.7.2. Port
Selecting “Advanced Application>PPPoE IA>Port", in the navigation bar, you can configure port.

40
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
active
Select open or close port PPPOE IA
Server Trusted State
Configure the upstream port to be Trusted or Untrusted
Drop
Configure the pppoe padi/pado packets received by the
port
Strategy
Configuration options to handle policies, choose Drop,
Keep, Replace
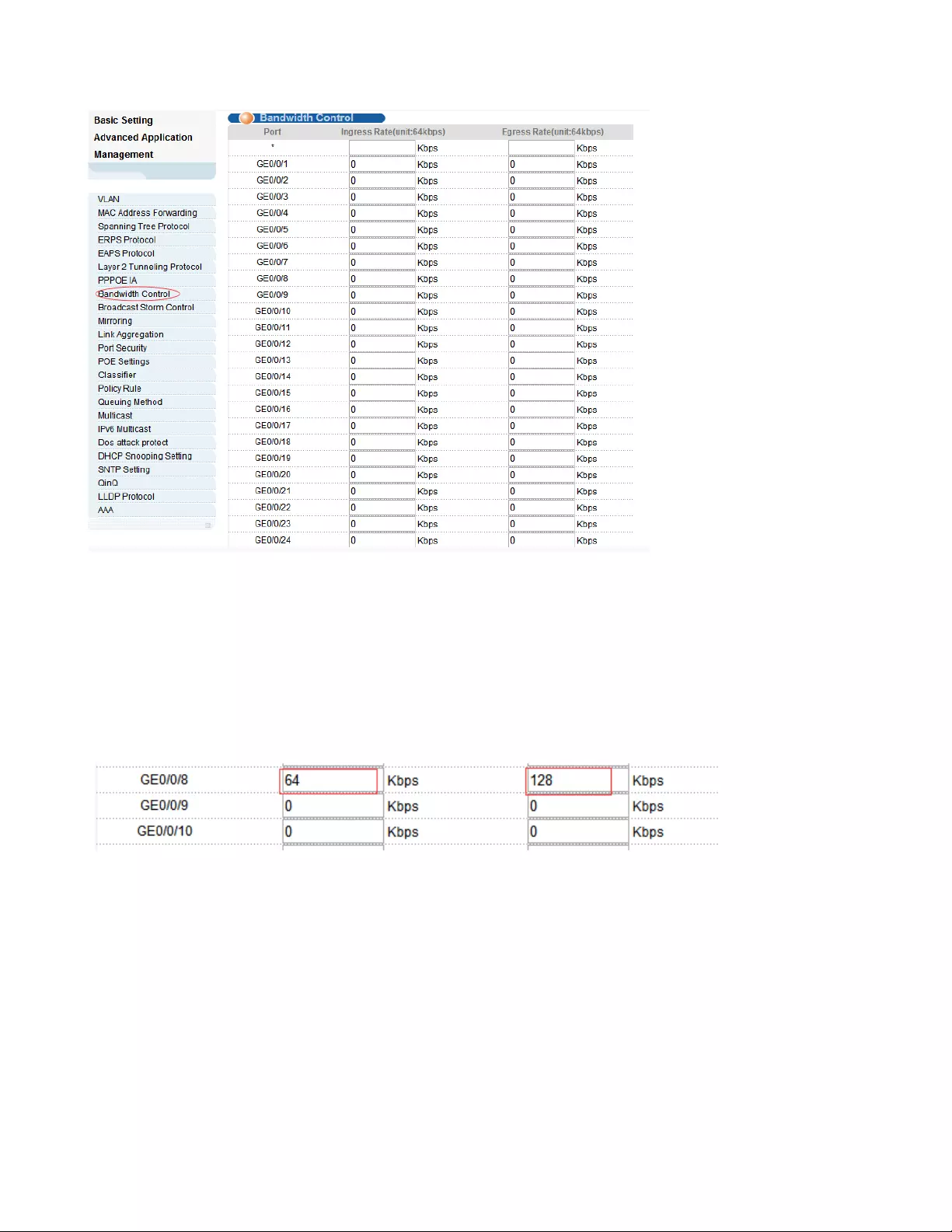
4.2.8. Bandwidth Control
Selecting “Advanced Application>Bandwidth Control", in the navigation bar, you can configure
Bandwidth Control.
41
【Instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s. That is, the theoretical rate of 1M bandwidth is 125
KB/s.
【Configuration example】
To configure bandwidth control of port8.
1.Click Basic Setting > Bandwidth Control.
2.Configure port-8 Ingress Rate is 64kbps, Egress Rate is 128kbps.
3. Click Apply.
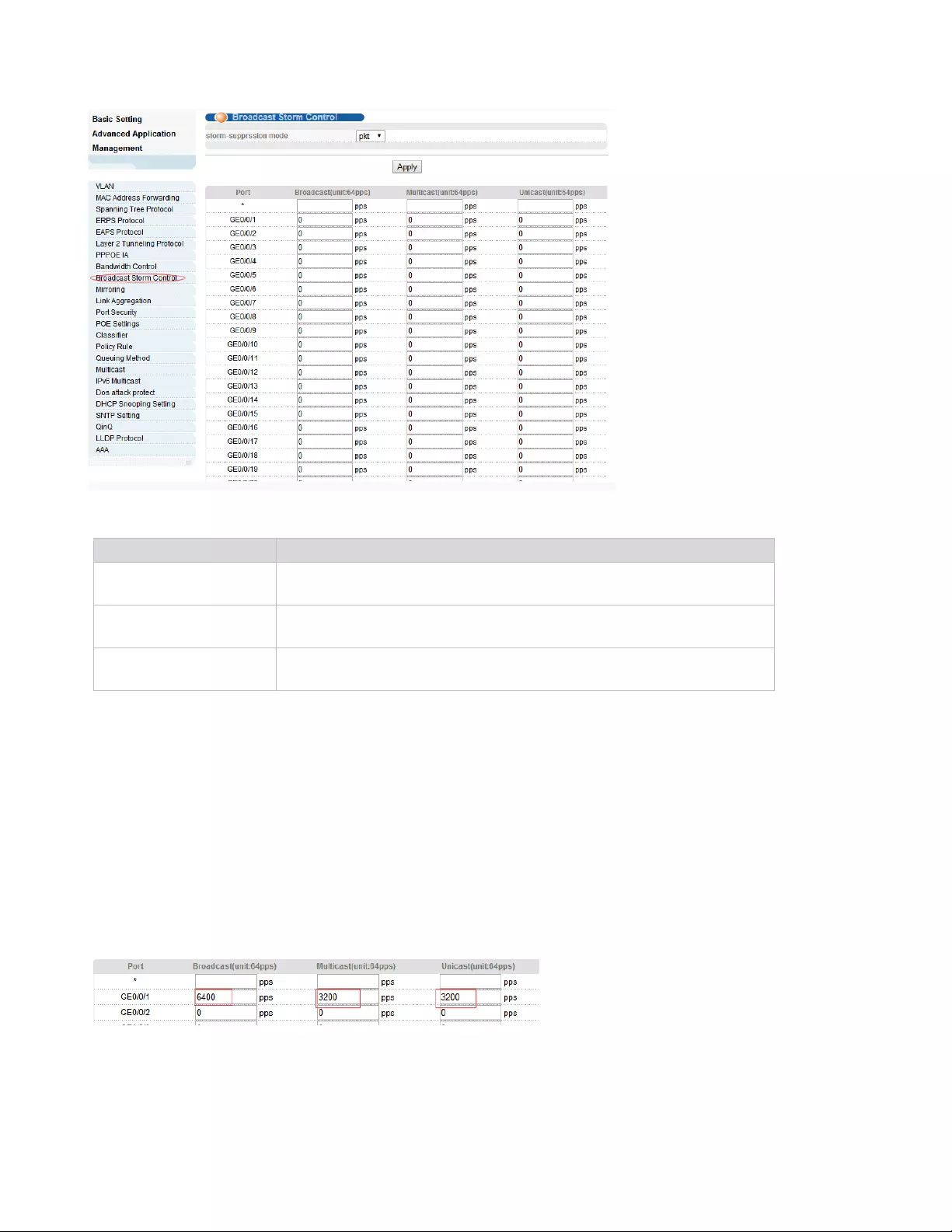
4.2.9. Broadcast Storm Control
Selecting “Advanced Application>Broadcast Storm Control"; in the navigation bar, you can configure
Broadcast Storm Control.
42
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s. That is, the theoretical rate of 1M bandwidth is 125
KB/s.
【Configuration example】
To configure broadcast storm control of port1.
1.Click Basic Setting > Broadcast Storm Control.
2.Set Port1 broadcast as 6400 pps, multicast as 3200 pps, unicast as 3200 pps.
3.Click Apply.
Parameter
Description
Broadcast
Broadcast rate limitation(the range of: 64-32000000, unit: pps, you
must enter multiple of 64, default to 49984)
Multicast
Multicast rate limitation(the range of: 64-32000000, unit: pps, you
must enter multiple of 64, default to 49984)
Unicast
Unicast rate limitation(the range of: 64-32000000, unit: pps, you
must enter multiple of 64, default to 49984)
43
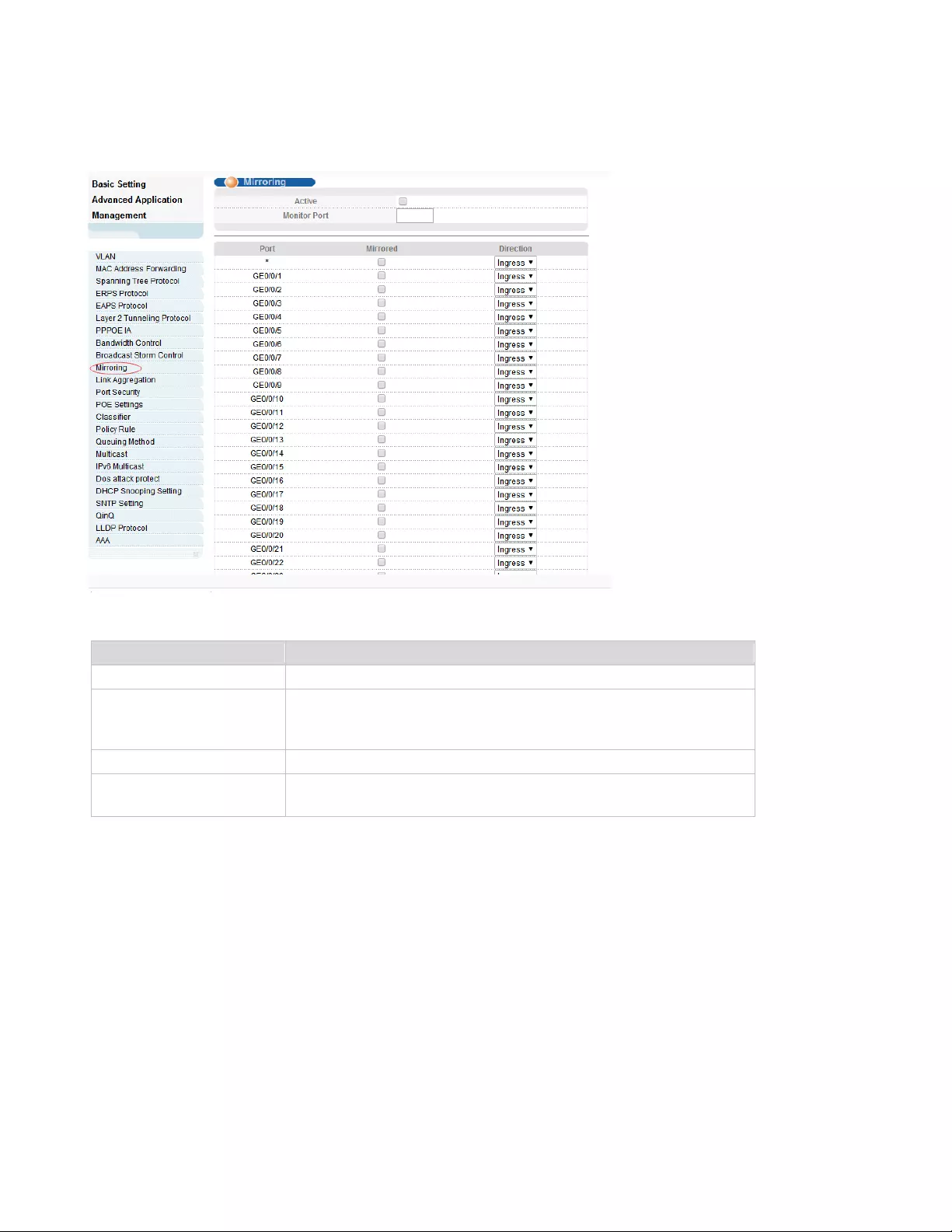
4.2.10. Mirroring
Selecting “Advanced Application>Mirroring", in the navigation bar, you can configure mirroring.
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration example】
1. Click Advanced Application > Mirroring.
2. Open mirroring, configure monitoring port is port 8, the source port is port 7, and the mirror message is
in both direction.
3. Click Apply.
Parameter
Description
Active
Select open or close Mirroring
Monitor Port
Set up the monitoring port and forward the flow data of the
source port to the message analyzer to analyze the message
and then forward to the monitoring port
Mirrored
Check the box to configure the mirror source port
Direction
Configure the direction of the mirror message, choose:
Ingress, Egress, Both

44
4.2.11. Link Aggregation
Selecting “Advanced Application>Link Aggregation", in the navigation bar, you can configure link
aggregation.With the LAG (Link Aggregation Group) function, you can aggregate multiple physical ports
into a logical interface to increase link bandwidth and configure the backup ports to enhance the
connection reliability. You can configure LAG in two ways:
• Static LAG: The member ports are manually added to the LAG.
• LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol): The switch uses LACP to implement dynamic
link aggregation and disaggregation by exchanging LACP packets with its partner. LACP
extends the flexibility of the LAG configuration.

45
4.2.11.1. Link Aggregation status
Selecting “Advanced Application>Link Aggregation>Link Aggregation Status", in the navigation bar,
you can view link aggregation status, you can view Group ID, Enabled Ports, Synchronized Ports,
Aggregator ID, Criteria, Status.
4.2.11.2. Link Aggregation Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>Link Aggregation>Link Aggregation Setting", in the navigation bar,
you can set Link Aggregation.
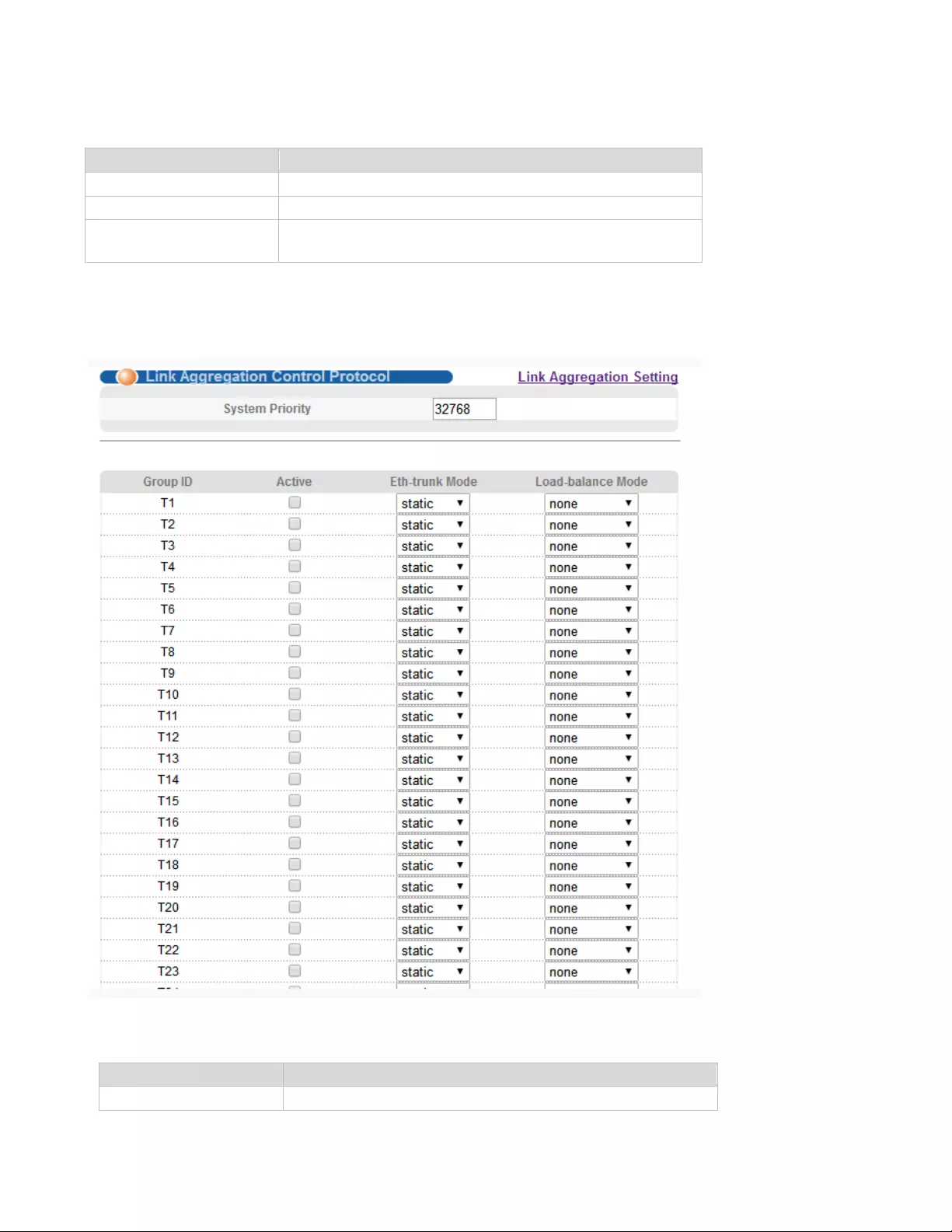
46
【Parameter Description】
4.2.11.3. Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>Link Aggregation>Link Aggregation Control Protocol", in the
navigation bar, you can configure Link Aggregation Control Protocol.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Group ID
Add the port to the specified Aggregation Group ID
Port LACP mode
Configure port aggregation(static/active/passive)
Criteria
Configure the Aggregation Group load balancing
(src-mac/dst-mac/src-dst-mac/src-ip/dst-ip/src-dst-ip)
Parameter
Description
System priority
Aggregation group system priority, the default is
47
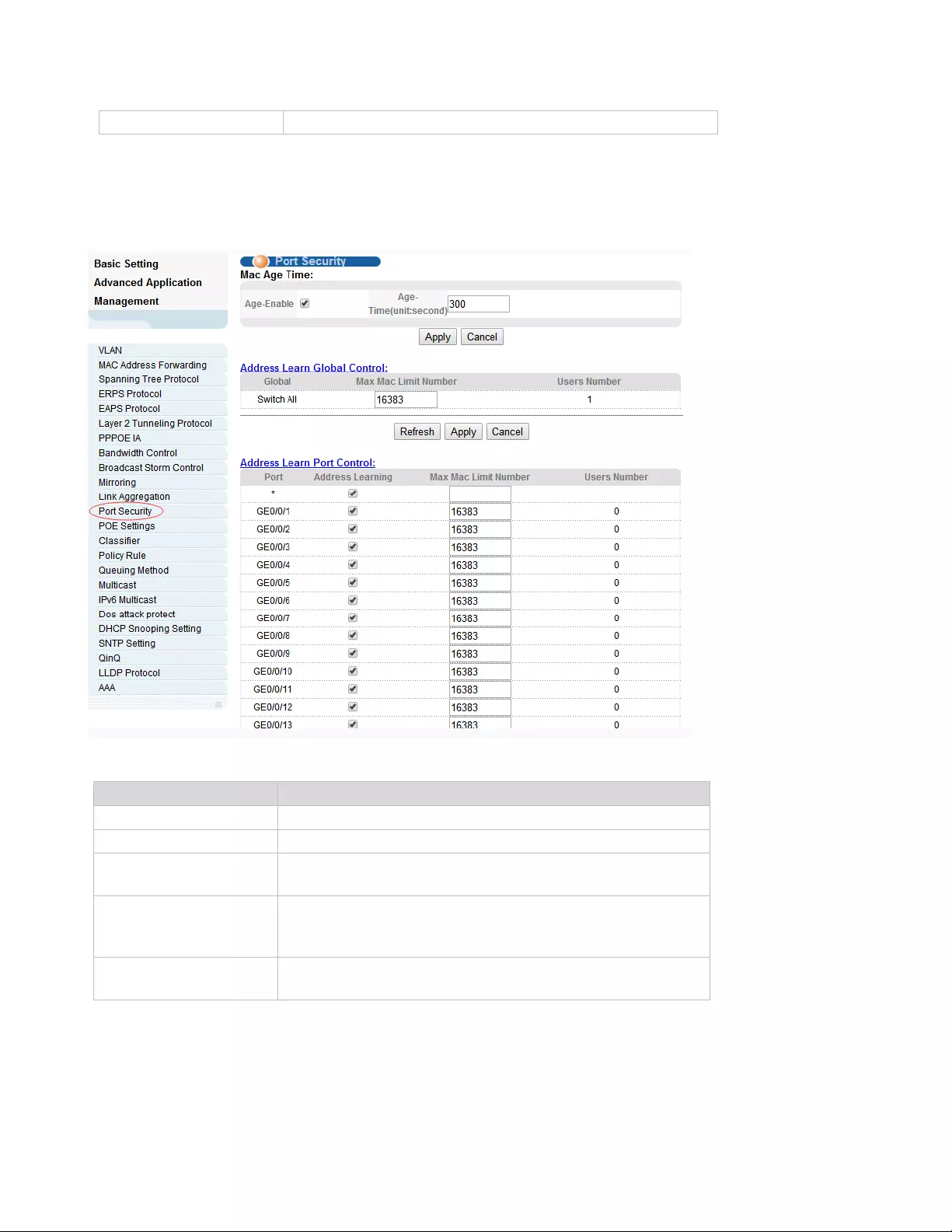
4.2.12. Port Sercurity
Selecting “Advanced Application>Port Sercurity", , you can configure port address learn control.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Age-Enable
Open age-enable
Age-Time
Set Age Time(the range of 10-1000000, unit: second)
Max Mac Limit
Number (Global)
Set the global Max MAC Limit Number(0-16384)
Address Learning
The MAC address learning function of port enables the
power switch (the default port MAC learning function
opens)
Max Mac Limit
Number (Port)
Set the port Max MAC Limit Number( 0-16384)
4.2.13. POE Settings
Selecting “Advanced Application>POE Settings", you can configure POE.
32768( the range of 1-65535)
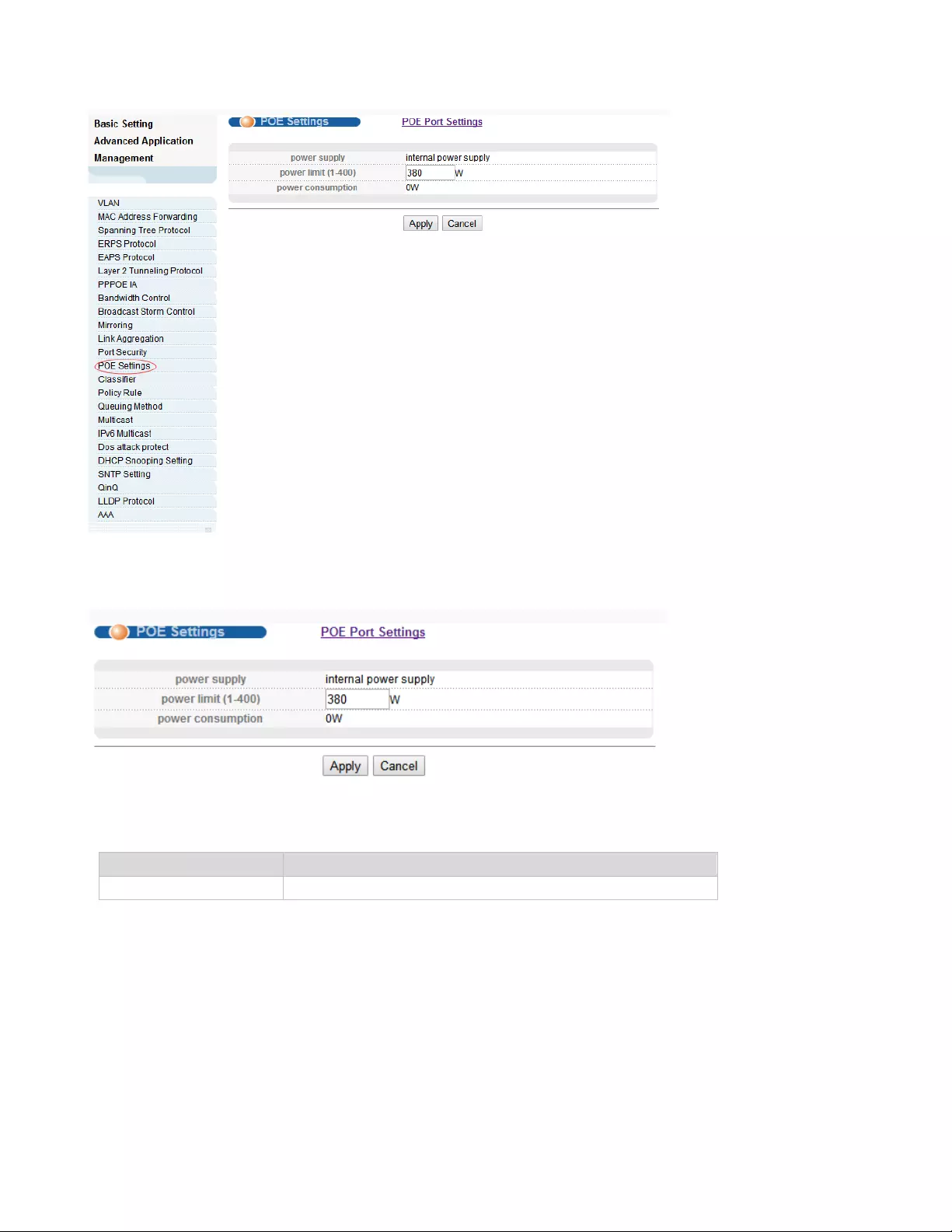
48
4.2.13.1. POE Settings
Selecting “Advanced Application>POE Settings", you can configure POE.
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration example】
Such as: set power limit is 360 W.
Parameter
Description
power limit
The power of switch POE can be limited

49
4.2.13.2. POE Port Settings
Selecting “Advanced Application>POE Port Settings", in the navigation bar, you can configure POE
Port.
【Parameter Description】
4.2.14. lassifier
Selecting “Advanced Application>Classifier", in the navigation bar, you can configure Classifier.
Parameter
Description
Enable
Turn the port POE power on and off and the default is
open
Standard
Configure ieee802.3af, ieee802.3at mode, default to
ieee802.3at
Priority
Configure port Priority low, critical, high, the default
priority is low
Power limit
The power of switch POE can be limited

50
【Parameter Description】
4.2.15. Policy Rule
Selecting “Advanced Application>Policy Rule", in the navigation bar, you can configure Policy Rule.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Active
Active Classifier
Parameter
Description
Active
Active Classifier
51
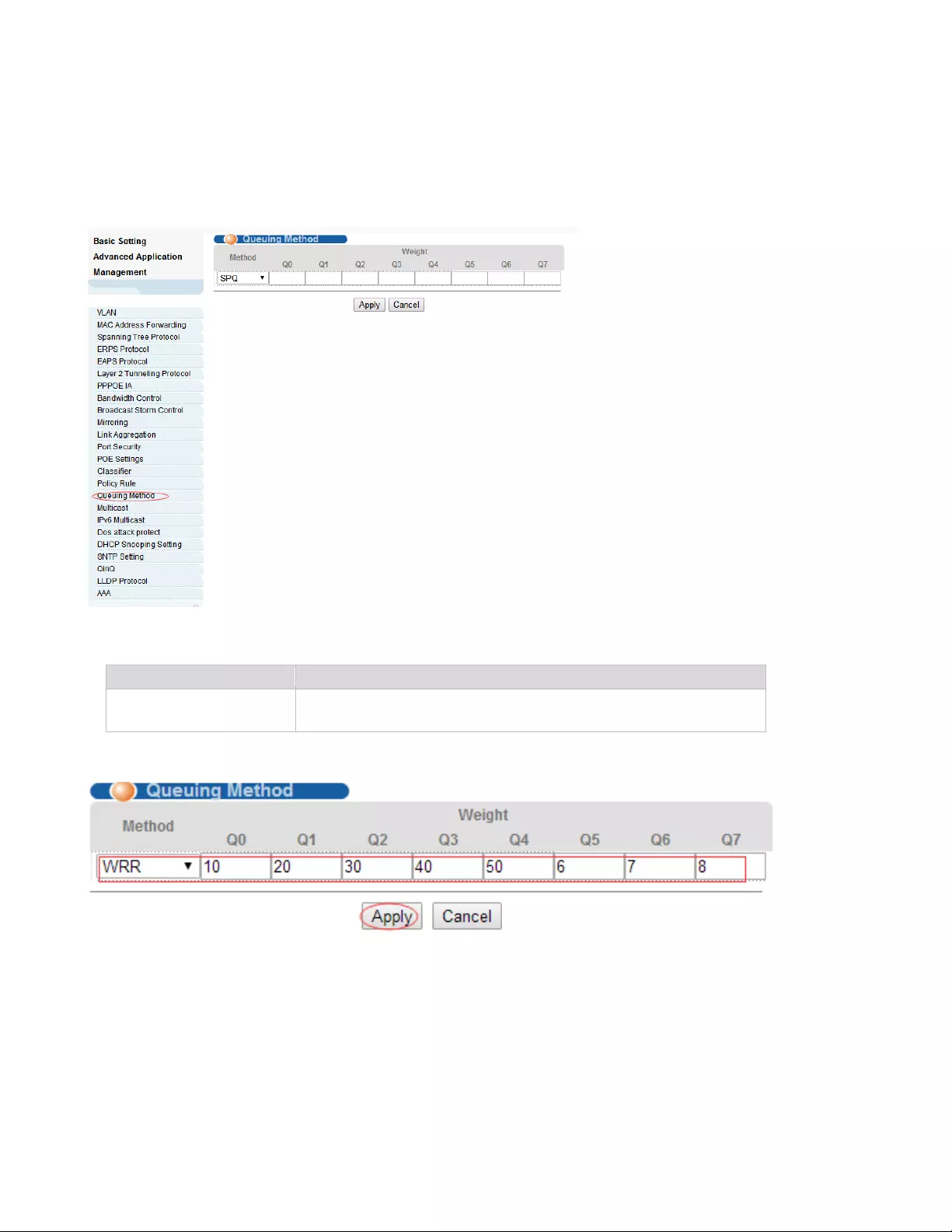
4.2.16. Queuing Method
Selecting “Advanced Application>Queuing Method", in the navigation bar, you can configure queuing
method.
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
4.2.17. Multicast
Selecting “Advanced Application>Multicast", in the navigation bar, you can configure Multicast.
Parameter
Description
Method
Five method:
SPQ,WRR,SP+WRR,WFQ,SP+WFQ
52
4.2.17.1. Multicast Status
Selecting “Advanced Application>Multicast>Multicast Status", in the navigation bar, you can view all
multicast. This includes the static configuration and the multicast that is learned through the IGMP-
Snooping protocol.
4.2.17.2. Multicast Settings
Selecting “Advanced Application>Multicast>Multicast Settings", in the navigation bar, you can set
multicast.

53
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
Active
Open IGMP-snooping
Querier
Open IGMP-snooping timed query function
Host Timeout
Configure the dynamic group sowing time (default 300s)
IGMP Route Port
Forward
Open IGMP Route Port Forward
Max Group Limit
Max learning group of configuration port ( default 1020)
Fast Leave
Open port quick exit function (i.e., when the port receives the
IGMP and leaves the message, immediately remove the port
from the reshuffle group)
Multicast Vlan
The configuration group multicast the default VLAN
IGMP Filtering Profile
The configuration port refers to the multicast preview, which
can only be learned to the group broadcast group that is
allowed in the group broadcast preview, and cannot be
learned to the multicast group which is forbidden by the group
broadcast preview
54
4.2.17.3. IGMPSnooping Dney VLAN
Selecting “Advanced Application>Multicast>IGMP Snooping Dney VLAN", in the navigation bar, you
can preview the banned group broadcast group, unable to learn the multicast group that is prohibited by
the group preview.
【Parameter Description】
4.2.17.4. IGMP Filtering Profile
Selecting “Advanced Application>Multicast>IGMP Filtering Profile", in the navigation bar, you can
add and remove the preview feature of the modified group.
Parameter
Description
Vid
Vlan’s ID

55
【Parameter Description】
4.2.18. IPv6 Multicast
Selecting “Advanced Application>IPv6 Multicast", in the navigation bar, you can configure IPv6
Multicast.
Parameter
Description
Profile ID
The range of 1-128
Profile Limit
Profile rules can be permit or deny
Input Format
The preview address can be configured to be either IP or MAC

56
4.2.18.1. IPv6 Multicast Status
Selecting “Advanced Application>IPv6 Multicast>IPv6 Multicast Status", in the navigation bar, you can
view all IPv6 Multicast groups.
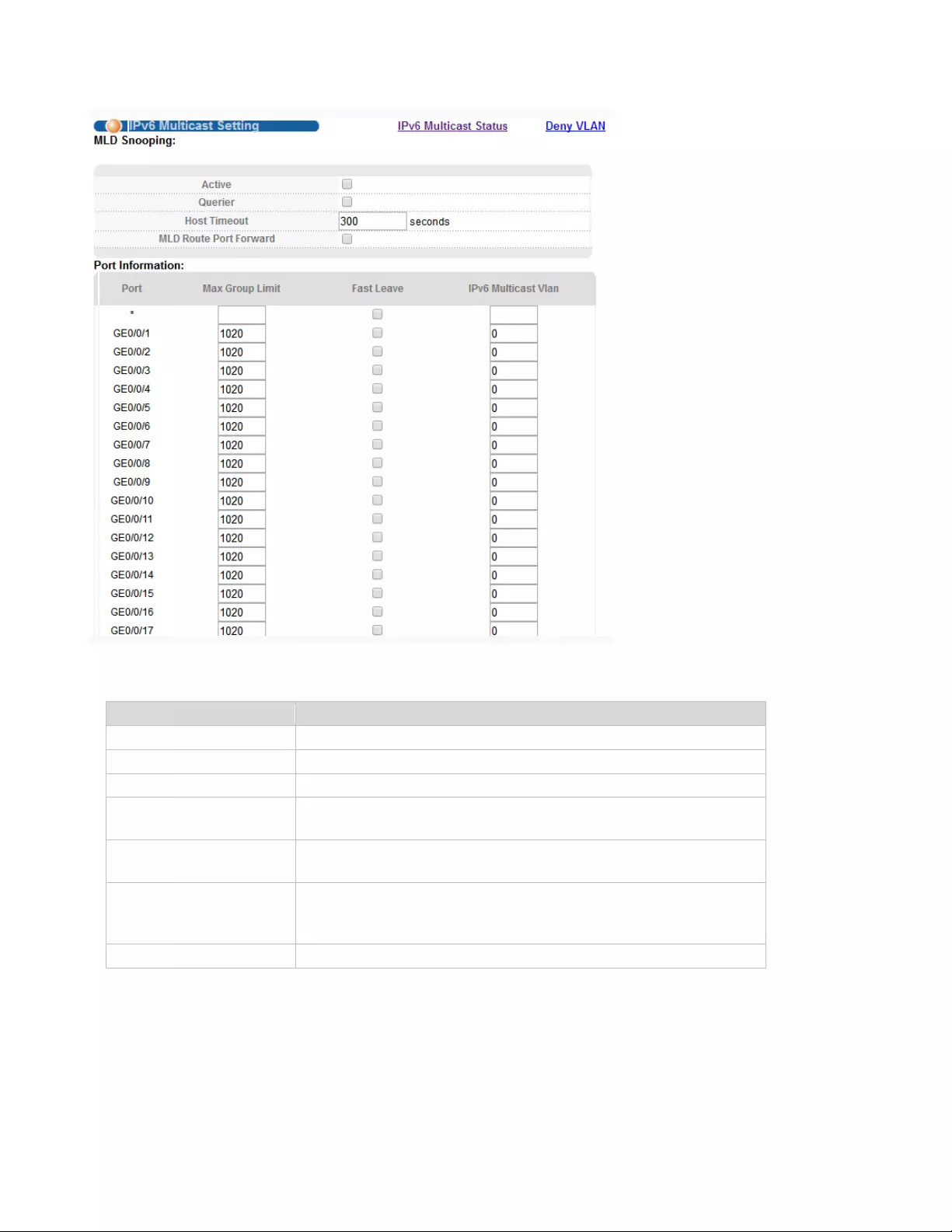
4.2.18.2. IPv6 Multicast Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>IPv6 Multicast>IPv6 Multicast Setting", in the navigation bar, you
can configure IPv6 Multicast.
57
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
Active
Enable or disable MLD snooping
Querier
Enable or disable MLD snooping timed Querier
Host Timeout
Configure Dynamic IPv6 multicast aging time (default 300s)
MLD Route Port
Forward
Enable or disable MLD Route Port Forward
Max Group Limit
Configure maximum learning IPv6 Multicast message
of port(default 1020)
Fast Leave
Enable or disable Fast Leave (That is, when the port receives
IGMP leave message, the port is deleted immediately from the
IPv6 multicast group)
IPv6 Multicast VLAN
Configure IPv6 multicast default VLAN

58
4.2.18.3. MLD Snooping Dney VLAN
Selecting “Advanced Application>IPv6 Multicast>MLD Snooping Dney VLAN", in the navigation bar,
you can configure MLD Snooping Dney VLAN.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Vid
Vlan ID
59
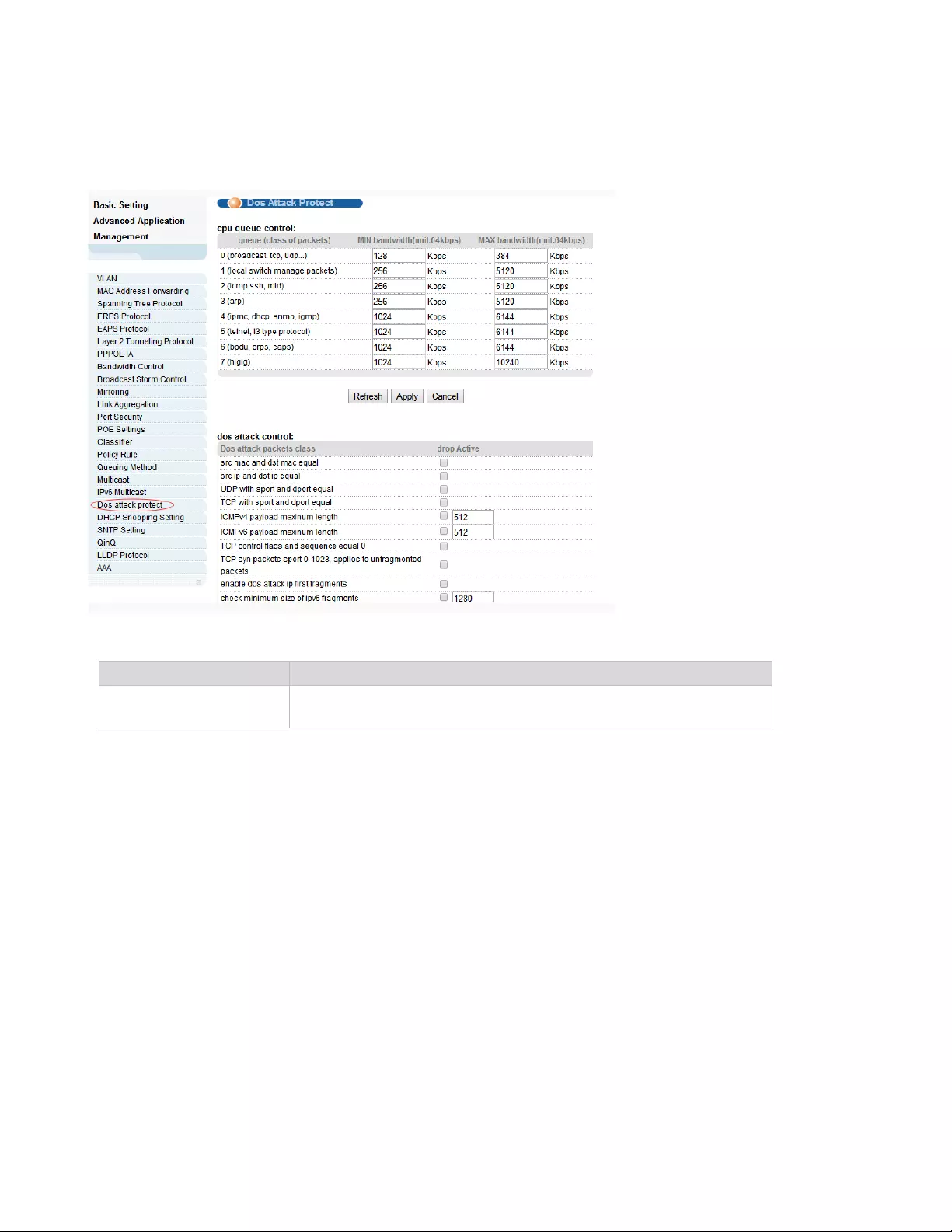
4.2.19. Dos attack protect
Selecting “Advanced Application>Dos attack protect", in the navigation bar, you can configure dos
attack protect.
【Parameter Description】
4.2.20. DHCP Snooping Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>DHCP Snooping Setting", in the navigation bar, you can configure
DHCP Snooping.
Parameter
Description
dos attack control
The DOS attack is controlled by the discarding behavior of the
corresponding message
60
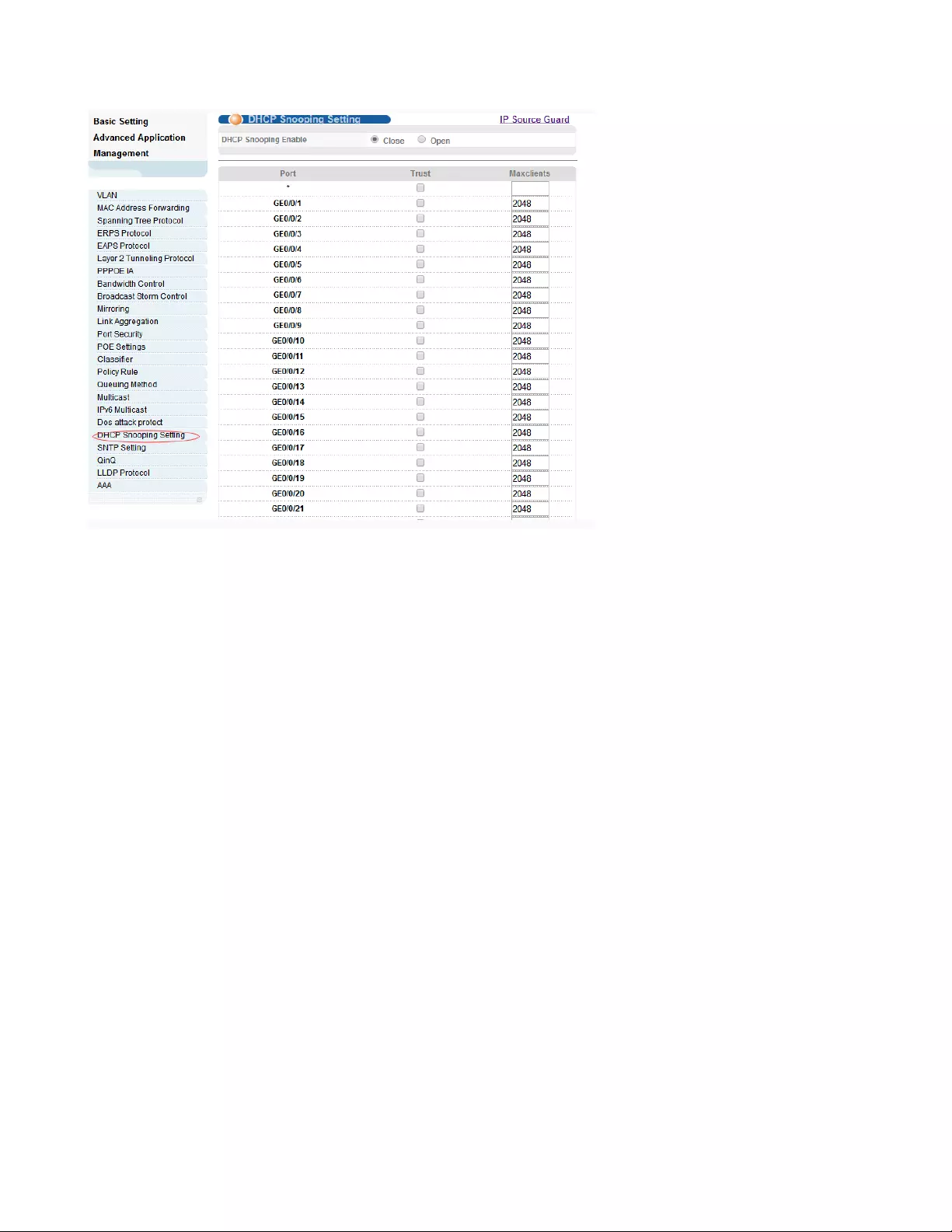
4.2.20.1. DHCP Snooping Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>DHCP Snooping Setting>DHCP Snooping Setting", in the
navigation bar, you can configure DHCP Snooping.Nowadays, the network is getting larger and more
complicated. The amount of the PCs always exceeds that of the assigned IP addresses. The wireless
network and the laptops are widely used and the locations of the PCs are always changed. Therefore, the
corresponding IP address of the PC should be updated with a few configurations. DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol, the network configuration protocol optimized and developed basing on the
BOOTP, functions to solve the above mentioned problems.

61
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
DHCP Snooping
Enable
Enable or disable DHCP Snooping serve
Trust
Enable or disable the DHCP Snooping port trust property state
Maxclients
Set Maxclients

62
4.2.20.2. IP Source Guard
Selecting “Advanced Application>DHCP Snooping Setting>IP Source Guard", in the navigation bar,
you can configure IP Source Guard.
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
If you want to access shall be binding and switch the IP address of the same network segment.
Parameter
Description
Disable unbinding entry
to access network
Enable or Disable unbinding entry to access network

63
4.2.21. SNTP Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>SNTP Setting", in the navigation bar, you can configure SNTP.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
SNTP Client Enable
Enable or disable SNTP Client
SNTP Client Mode
SNTP Client Mode:
broadcast,
anycast
multicast
unicast
SNTP Client Poll
Interval
It’s interval that SNTP Client sends requests to SNTP Server
SNTP Client
Retransmit Times
If SNTP Client does not receive a response within a certain
period of time after sending a request,it will resend the
request until the number of retransmissions exceeds the set
value
SNTP Client
Retransmit Interval
It’s interval that SNTP Client resends requests to SNTP Server
SNTP Server IP
Address
Set SNTP Server IP Address
Valid Server List Server
IP
SNTP only receives the messages from
Valid Server List Server IP configured
SNTP Client Enable
Enable or disable SNTP Client
SNTP Client Mode
SNTP Client Mode:
broadcast,
anycast
multicast

64
【Instructions】
SNTP Client receives and transmits messages from any SNTP Server when work mode of SNTP Client is
broadcast or multicast.Local time cannot be synchronized to standard time if there is a malicious attack
server (which provides incorrect time)
4.2.22. LLDP Protocol
Selecting “Advanced Application>LLDP Protocol", in the navigation bar, you can configure LLDP.
4.2.22.1. LLDP Status
Selecting “Advanced Application>LLDP Protocol>LLDP Status", in the navigation bar, you can view
LLDP staus.
unicast
SNTP Client Poll
Interval
It’s interval that SNTP Client sends requests to SNTP Server
SNTP Client
Retransmit Times
If SNTP Client does not receive a response within a certain
period of time after sending a request,it will resend the
request until the number of retransmissions exceeds the set
value
Valid Server List Server
IP
SNTP only receives the messages from Valid Server List
Server IP configured

65
4.2.22.2. LLDP Setting
Selecting “Advanced Application>LLDP Protocol>LLDP Setting", in the navigation bar, you can
configure LLDP.

66
4.2.23. AAA
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA", in the navigation bar, you can configure AAA.
4.2.23.1. 802.1x
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA>802.1x", in the navigation bar, you can configure 802.1x.
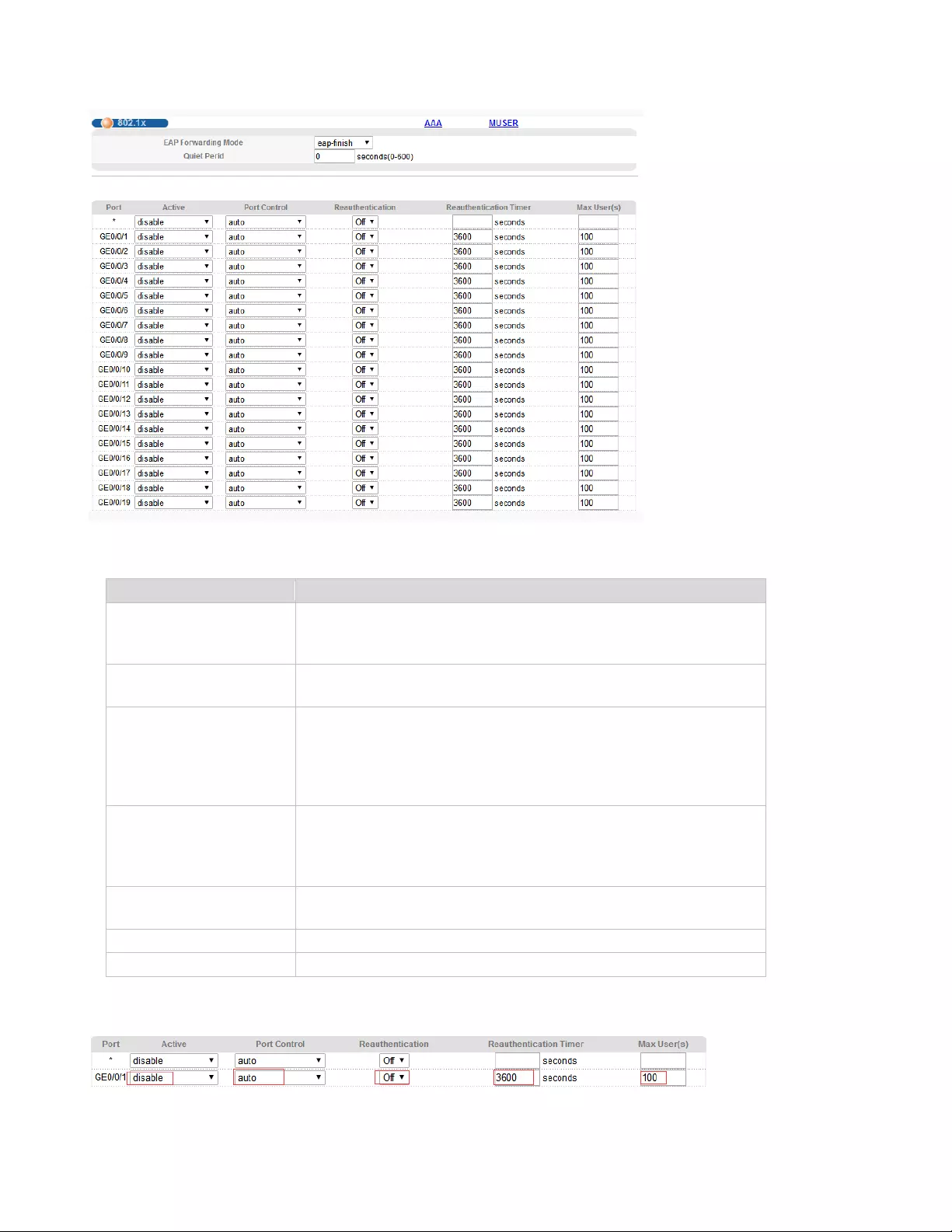
67
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
EAP Forwarding Mode
EAP Forwarding Mode :
eap-finish,
Eap-tansfer
Quiet Period
If the same user fails to log in more than the allowed value, he
or she will not be allowed to try to log in at a certain time
Active
Active:
disable
portbased(multi)
portbased(single)
macbased
Port Control
Port Control:
auto
forceauthorized
forceunauthorized
Reauthentication
After user authentication is passed, the port can be configured
to reauthenticate or periodically re-authenticate
Reauthentication Timer
Time range of Reauthentication Timer: 10-3600 seconds
Max user(s)
The maximum number of users: 1-100

68
4.2.23.2. Radius Domain
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA>Radius Domain", in the navigation bar, you can configure
Radius Domain.
【Parameter Description】
【Instructions】
It needs to provide user name and password when the client is authenticated. The user name information
generally includes the ISP information of user, domain and the ISP one-to-one correspondence, the main
information domain is the domain of the user is authenticated and accounted by which RADIUS server.
4.2.23.3. Remote Authentication
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA>Remote Authentication", in the navigation bar, you can
configure Remote Authentication.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Active
Enable or disable radius domain
Domain Name
Set domain name
Radius Server Name
Set Radius Server name
Force Max Number
Maximum number of user connections range: 1-640
69
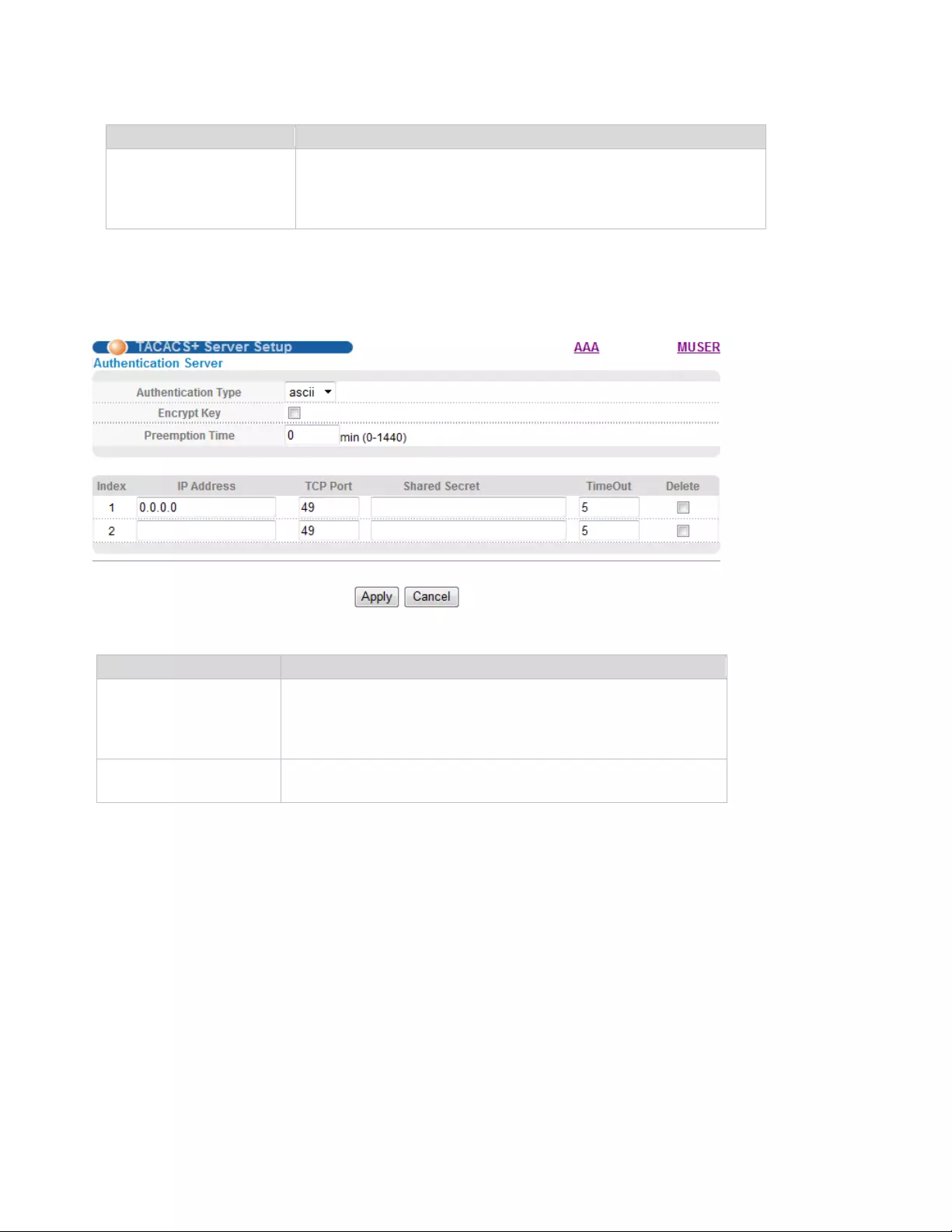
4.2.23.4. TACACS+ Server Setup
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA>TACACS+ Server Setup", in the navigation bar, you can
configure TACACS+ Server Setup.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Authenication Mode
Authenication Mode:
Local,
Radius,
Tacacs+
Parameter
Description
Authenication Type
Authenication Mode:
ascii,
Chap,
pap
Preemption Time
The time range of Preemption Time:
0-1440 minutes

70
4.2.23.5. Radius Server Setup
Selecting “Advanced Application>AAA>Radius Server Setup", in the navigation bar, you can configure
Radius Server Setup.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
8021P Priority
After this function is turned on, if the user authentication is
pass, it will modify the PVID of the user's port.
H3C Cams
In this feature, you can configure the version information of
transmitting clients to the radius server through the radius
attribute client-version.
Bandwidth limit
After this function is turned on, if the user authentication is
pass, it will modify the Bandwidth of the user's port.

71
4.3. Management
Choose Management, and the following page appears. There are "Management & Maintenance",
"Access Control ", "Diagnostic", "Syslog", configuration web pages.
4.3.1. Management &Maintenance
Selecting “Management> Management & Maintenance", in the navigation bar, you can Upgrade
Firmware , Restart System and Maintenance switch.
【Configuration Example】
1.Firmware Upgrade
2.Restart system. Restart type: Restart, Restart with Factory Defaults.
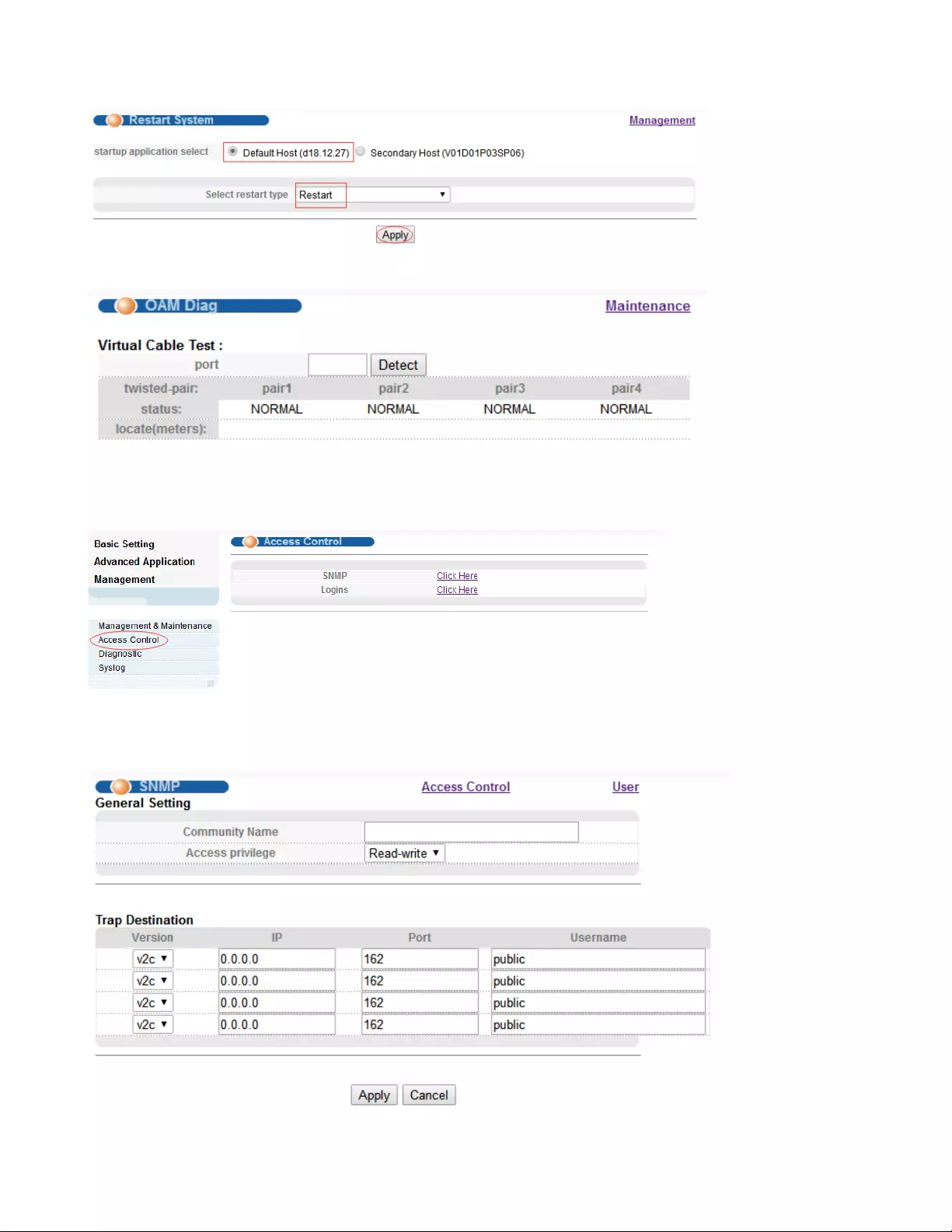
72
3.OAM Diag, Virtual cable can be tested.
4.3.2. Access Control
Selecting “Management> Access Control", in the navigation bar, you can set SNMP and Logins.
4.3.2.1. SNMP
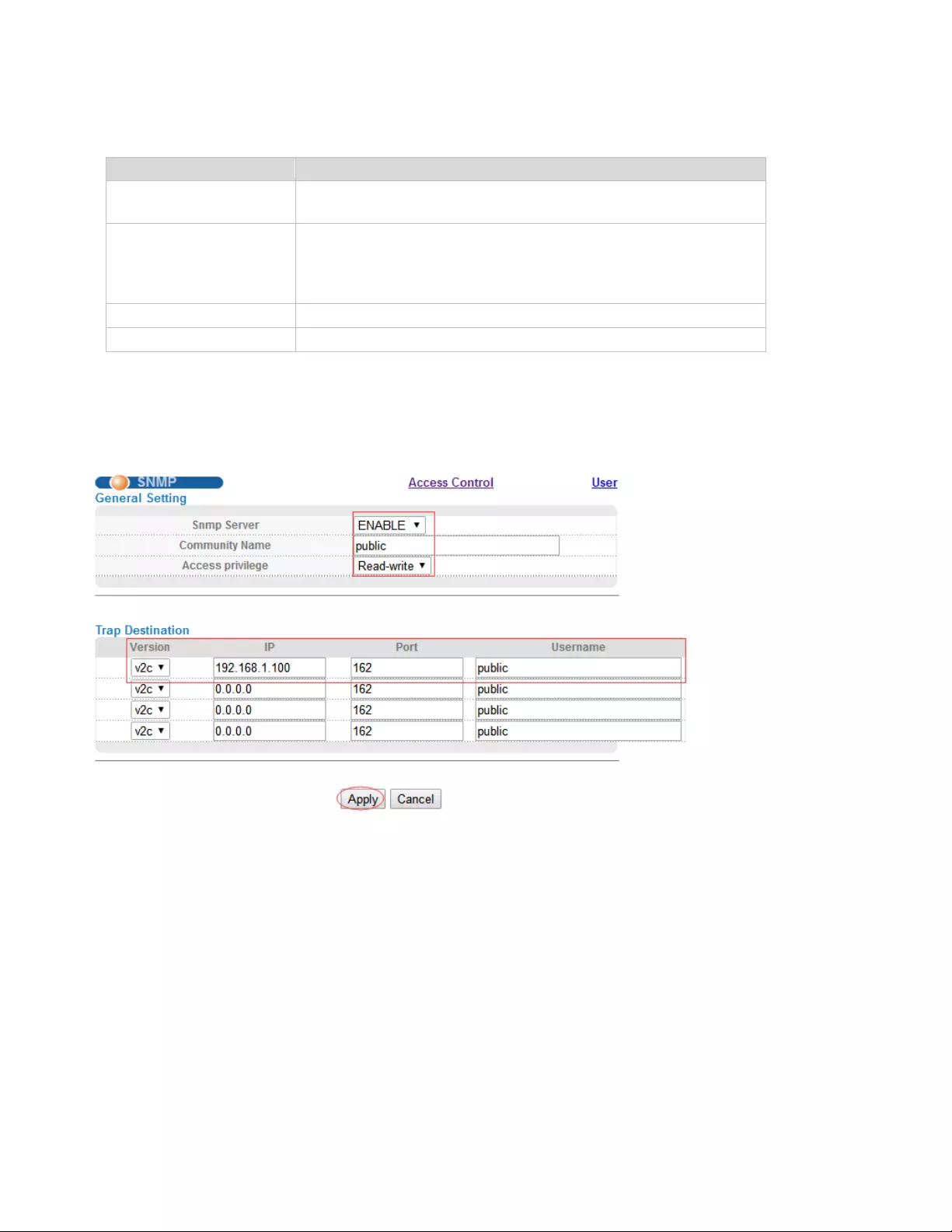
Selecting “Management> Access Control>SNMP", in the navigation bar, you can configure SNMP.
73
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Add a group name public community, access to Read-Write. Set host 192.168.1.100 to receive
trap messages. The specified version is v2c.
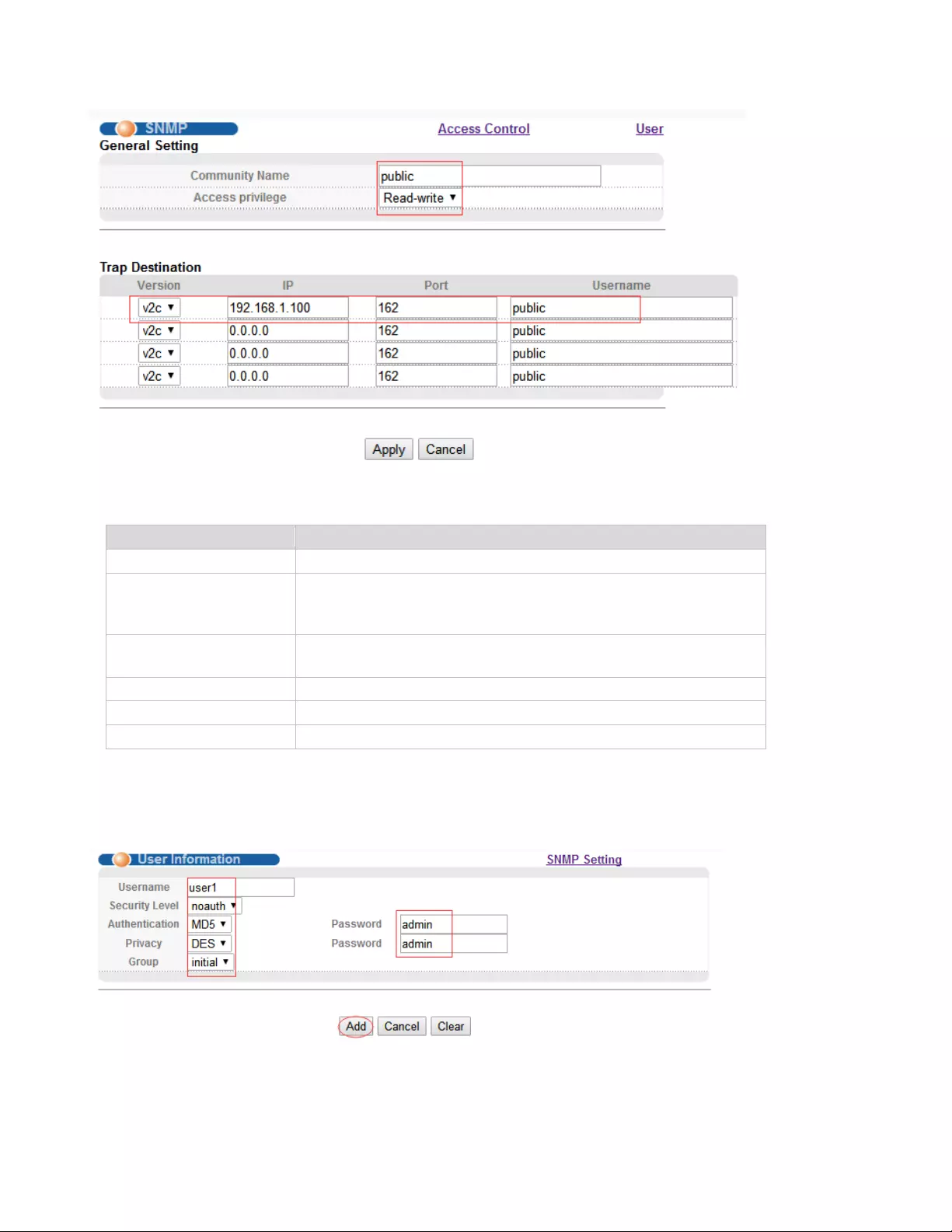
4.3.2.2. User Information
Selecting “Management> Access Control>User Information", in the navigation bar, you can add user,
set Security Level, Authentication, Privacy, Group, Password.
Parameter
Description
Community Name
Community string, is equal to the NMS and Snmp agent
communication between the password
Access privilege
Read-only: specify the NMS (Snmp host) of MIB variables can
only be read, cannot be modified
Read- write: specify the NMS (Snmp host) of MIB variables
can only read, can also be modified
Version
Set version: v1, v2c, v3
IP
Set the IP address of the trap host
74
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Add group initial, add username user1.
Parameter
Description
Username
Snmp username
Security Level
noauth
auth
pri
Authentication
MD5
SHA
Privacy
DES Privacy
Group
User group name
Password
Encrypted password
75
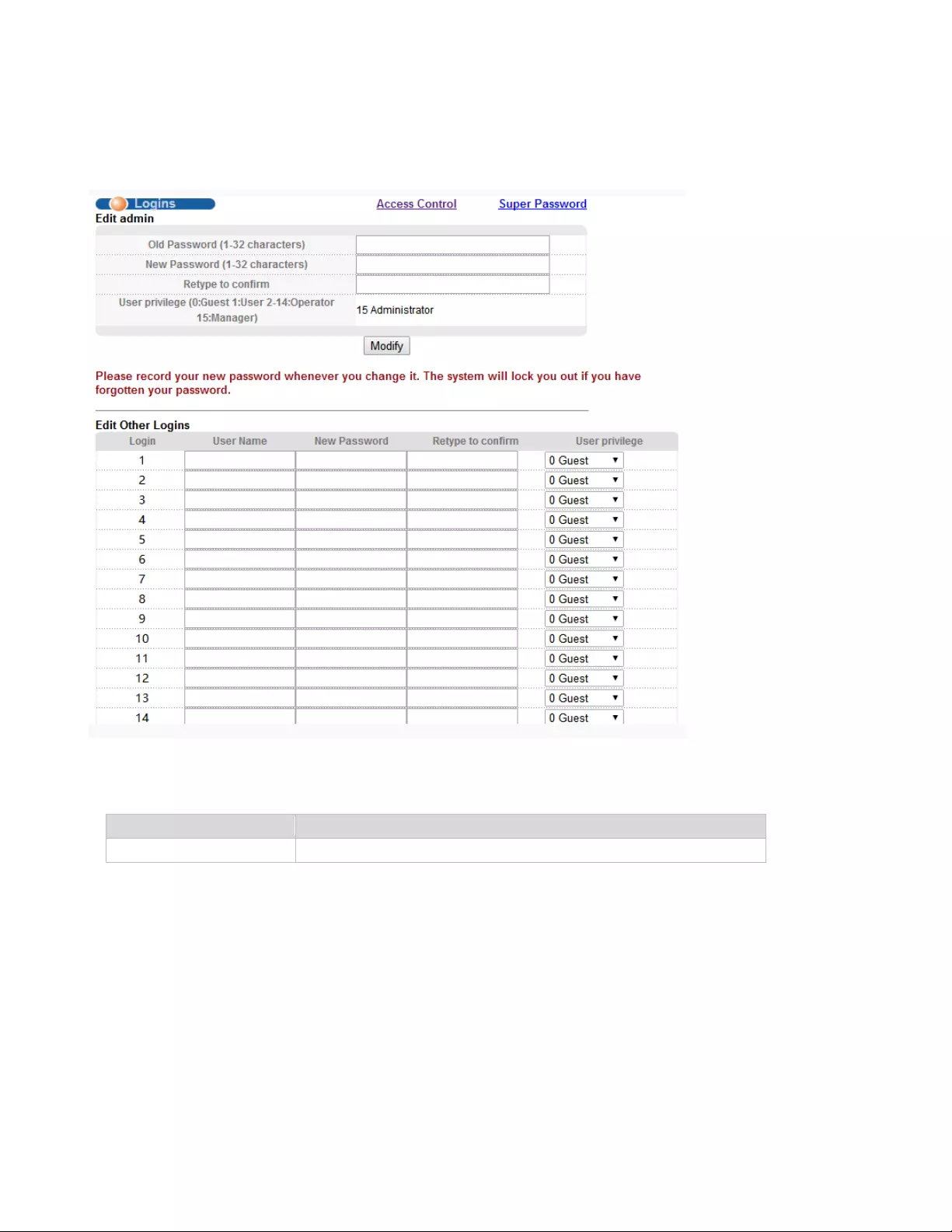
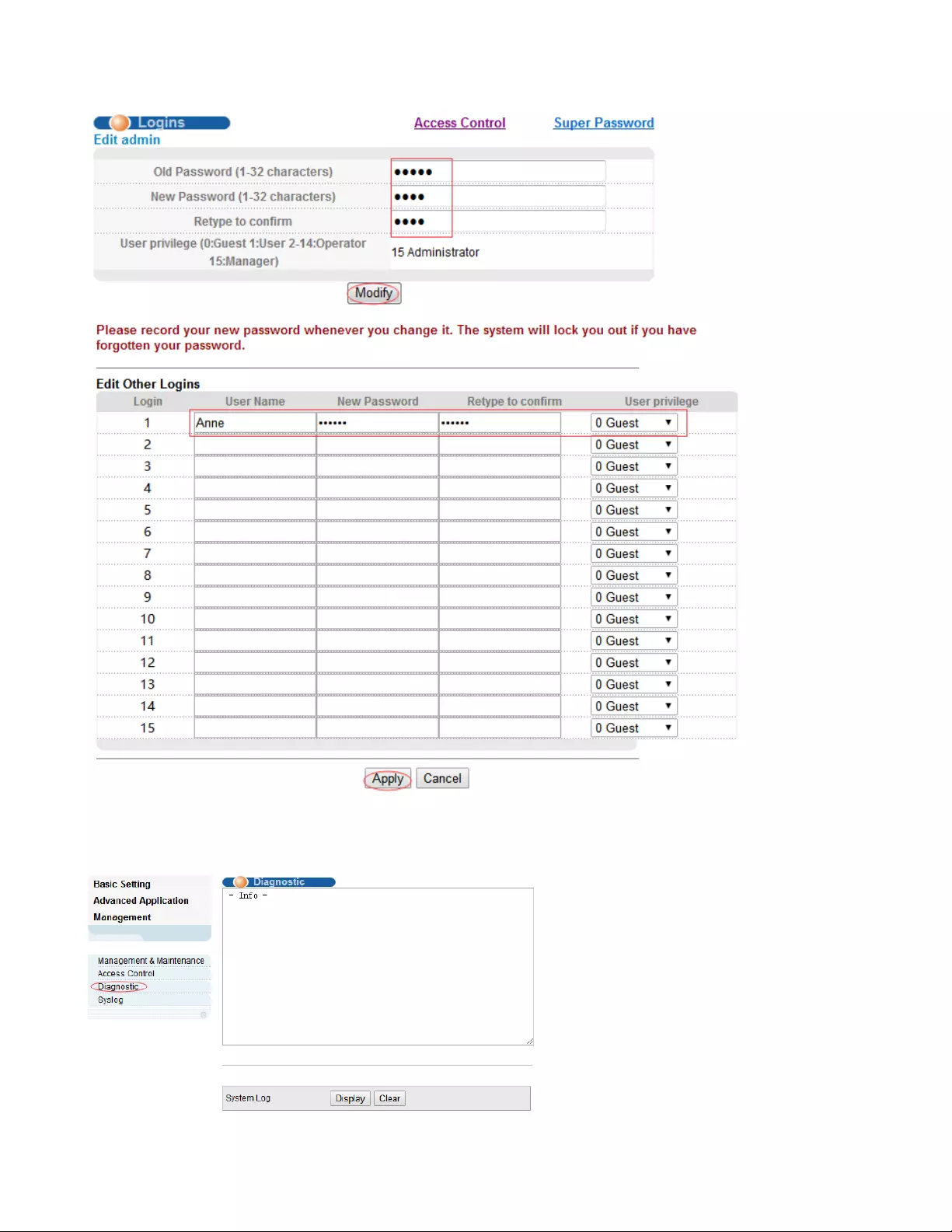
4.3.2.3. Logins
Selecting “Management>Access Control>Logins", in the navigation bar, you can modify admin
password, configurable ordinary users.
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Parameter
Description
User privilege
0-1: Normal 2-15: administrator
76
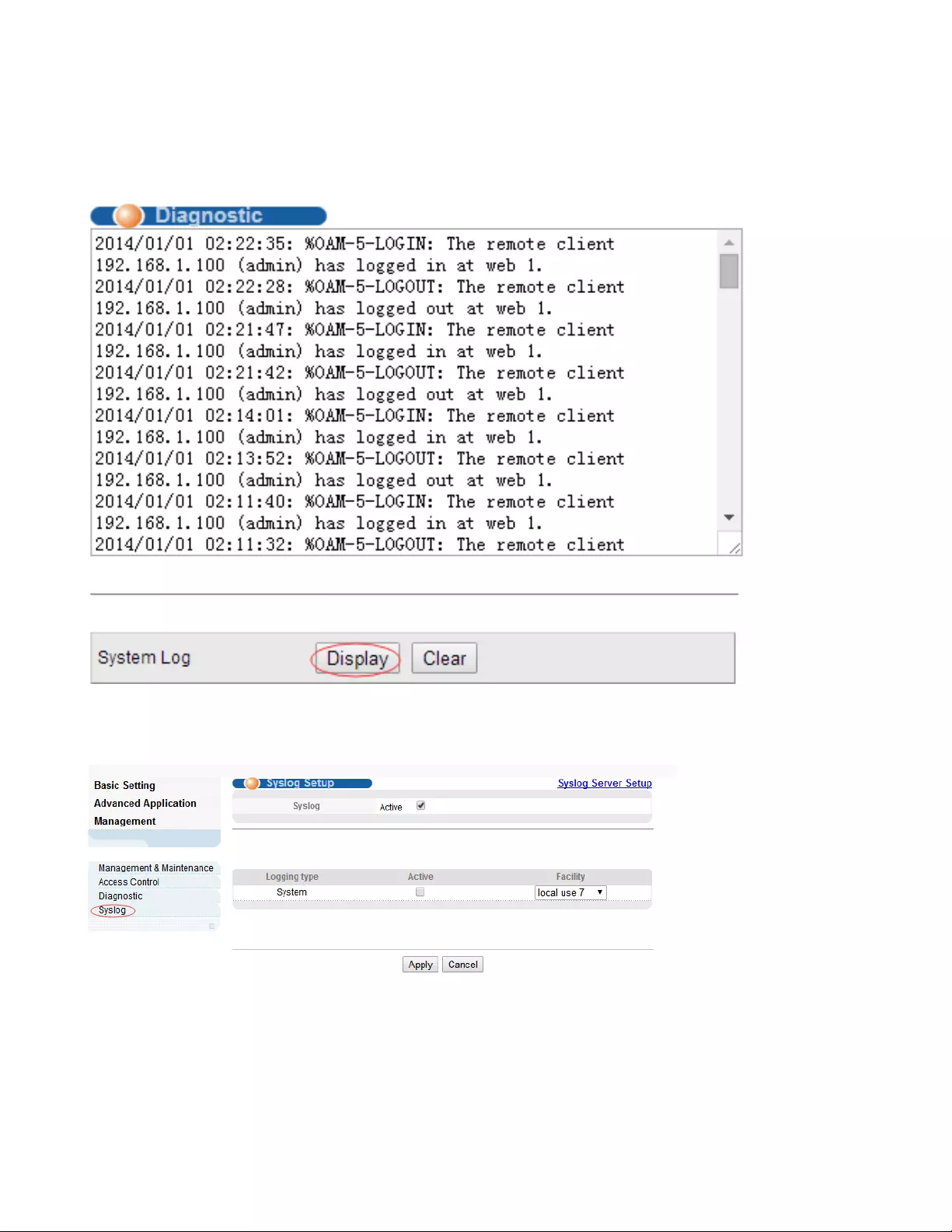
4.3.3. Diagnostic
Selecting “Management> Diagnostic", in the navigation bar, you can Display or Clear System Log.
77
【Configuration Example】
Such as: Display System Log.
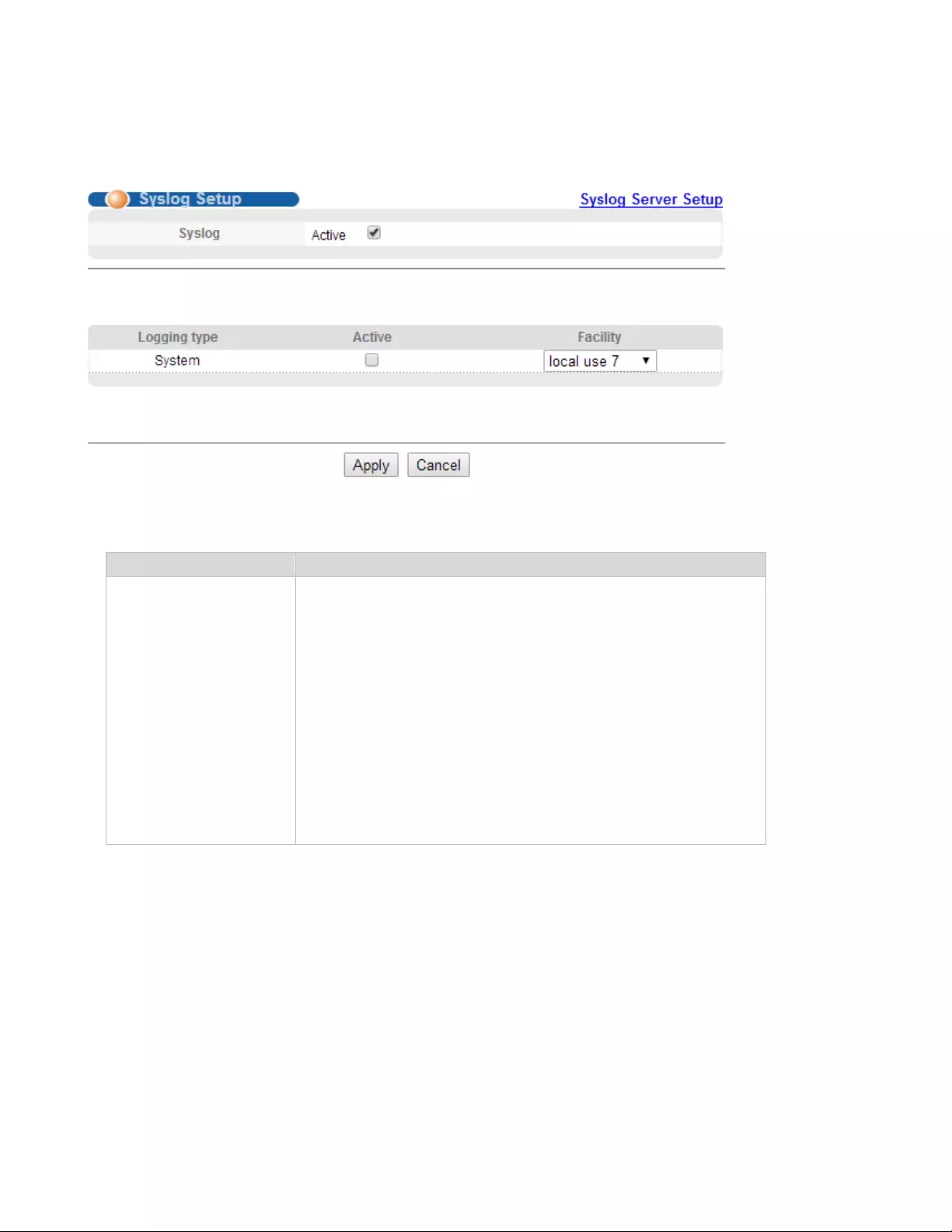
4.3.4. Syslog
Selecting “Management> Syslog", in the navigation bar, you can configure syslog.
78
4.3.4.1. Syslog Setup
Selecting “Management>Syslog>Syslog Setup", in the navigation bar, you can start the logging
function globally and the logging function of the corresponding module.
【Parameter Description】
【Configuration Example】
Such as:
Parameter
Description
Facility
local use 0-7
kernel
userlevel
mail
system
sercurity_1-2
sysogd
lineprinter
Networknews
uucp
clock_1-2
ftp
logaudit
logalert
79
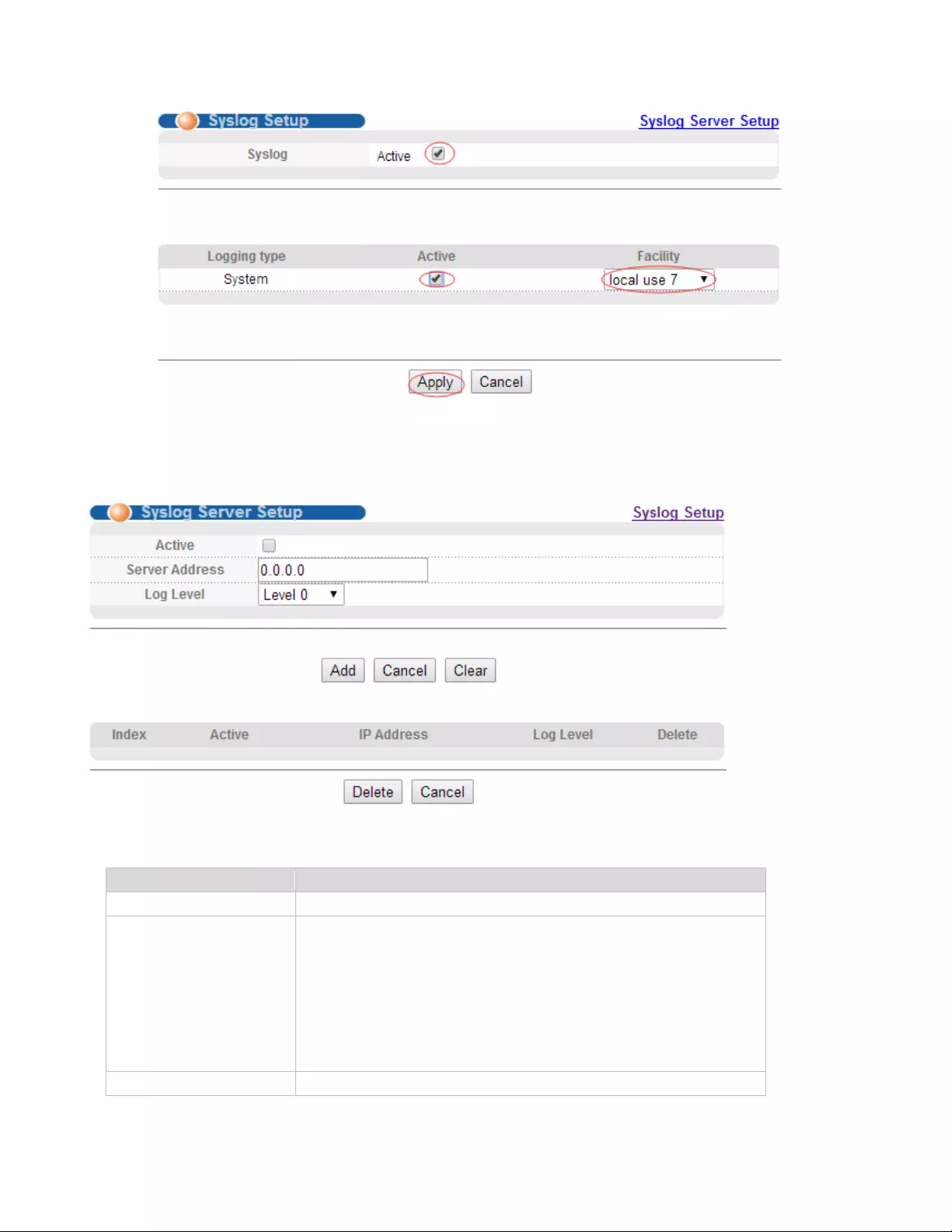
4.3.4.2. Syslog Server Setup
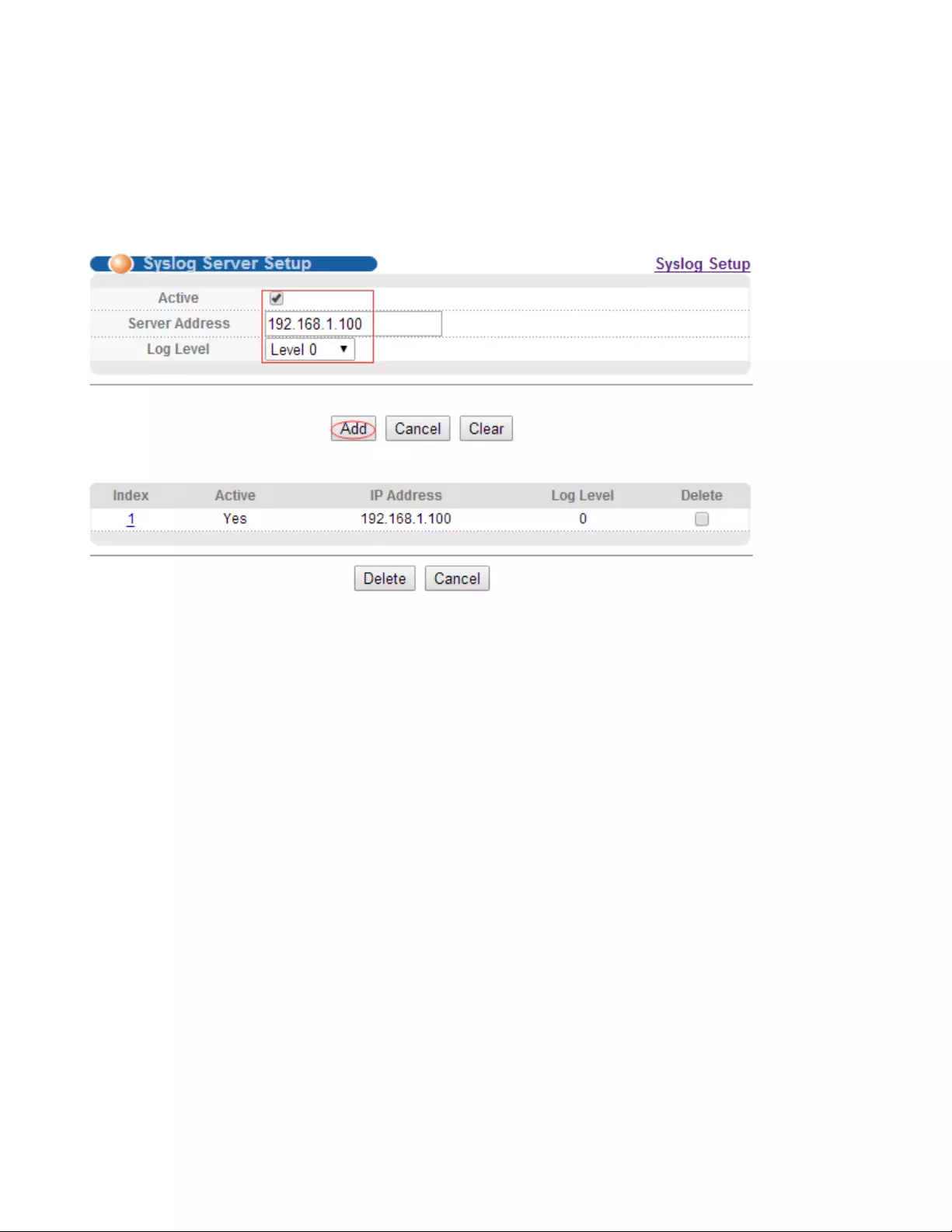
Selecting “Management>Syslog>Syslog Server Setup", in the navigation bar, you can set syslog
server.
【Parameter Description】
Parameter
Description
Server Address
Syslog Server Address
Log Level
Level 0
Level 0-1
Level 0-2
Level 0-3
Level 0-4
Level 0-5
Level 0-6
Level 0-7
Server Address
Syslog Server Address
80
【Instructions】
Open the log switch, set up the syslog server, and the system log will be automatically pushed to the
server.
【Configuration Example】
Such as: 1)set server address is 192.168.1.100.