LevelOne WAP-6112 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for WAP-6112 by LevelOne which is a product in the Wireless Access Points category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

LevelOne
Managed Wireless Access Point,
User’s Manual
V1. 0_20160106

1
Table of Contents
About This Guide ..................................................................................................................... 3
Purpose and Scope .................................................................................................................... 3
Web UI Style ........................................................................................................................... 3
Factory Default Settings ............................................................................................................ 4
Chapter 1 Product Overview ............................................................................................. 5
1.1 Key Features ........................................................................................................ 5
1.2 Specification ........................................................................................................ 6
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation ....................................................................................... 7
2.1 In-Wall Access Point ........................................................................................... 7
2.1.1 Panel Descriptions .............................................................................................. 7
2.1.2 Preparing for Installation ..................................................................................... 8
2.1.3 Items Required for Installation ............................................................................ 8
2.2 In-Ceiling Access Point ....................................................................................... 9
2.2.1 Panel Descriptions .............................................................................................. 9
2.2.2 Preparing for Installation ..................................................................................... 9
2.2.3 Items Required for Installation .......................................................................... 10
2.3 Desktop Access Point ....................................................................................... 10
2.3.1 Panel Descriptions ............................................................................................ 10
2.3.2 Preparing for Installatio ..................................................................................... 12
2.3.3 Installing the Device .......................................................................................... 12
2.4 Typical Deployment Scenarios ......................................................................... 13
Chapter 3 Logging in to the Device ................................................................................ 14
3.1 Configuring Your Computer .............................................................................. 14
3.2 Logging to the Device ....................................................................................... 15
Chapter 4 Fit AP ................................................................................................................ 17
AP Centralized Management Overview .................................................................................... 17
4.1 Terminology ....................................................................................................... 17
4.2 Communication Process ................................................................................... 17
4.3 Layer 2 Roaming............................................................................................... 19
4.4 System mode: ................................................................................................... 20
4.5 Configuration of LAN port ................................................................................. 20
4.6 Fixed IP access ................................................................................................. 21
4.7 Dynamic IP access ........................................................................................... 21
4.8 Status of wireless host ...................................................................................... 22
4.9 System information ........................................................................................... 23
Chapter 5 Start menu ....................................................................................................... 24
5.1 Configuration Wizard ........................................................................................ 24
5.2 Running status .................................................................................................. 26
5.3 Port flow ............................................................................................................ 26
5.4 System mode: ................................................................................................... 27
5.5 Restarting device .............................................................................................. 28
Chapter 6 Network parameters ....................................................................................... 29

2
Configuration of LAN port ...................................................................................................... 29
DHCP server .......................................................................................................................... 29
6.1 DHCP server settings ....................................................................................... 29
6.2 Static DHCP ...................................................................................................... 30
6.3 DHCP client list ................................................................................................. 32
6.4 Case of DHCP configuration ............................................................................. 32
Chapter 7 Wireless configuration ................................................................................... 34
System mode: ........................................................................................................................ 34
Wireless basic configuration .................................................................................................... 34
7.1 AP Mode ........................................................................................................... 35
7.2 Repeater Mode ................................................................................................. 36
7.3 Bridge Mode ...................................................................................................... 38
7.4 Lazy Mode ........................................................................................................ 38
7.5 Wireless configuration instance ........................................................................ 39
Wireless security configuration ................................................................................................ 43
7.6 No security mechanism .................................................................................... 43
7.7 WEP .................................................................................................................. 44
7.8 WPA/WPA2 ....................................................................................................... 45
7.9 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK ...................................................................................... 46
Filtering of wireless MAC address ........................................................................................... 46
Wireless Advanced Configuration ............................................................................................ 48
Status of wireless host ............................................................................................................. 49
Chapter 8 System management ...................................................................................... 51
8.1 Administrator configuration ............................................................................... 51
8.2 Clock management ........................................................................................... 52
8.3 Configuration management .............................................................................. 53
8.4 Software upgrade.............................................................................................. 54
8.5 Scheduled task ................................................................................................. 55
Chapter 9 System status .................................................................................................. 57
9.1 Running status .................................................................................................. 57
9.2 System information ........................................................................................... 57
Appendix A FAQ ..................................................................................................................... 59
Q1. How to connect a Windows XP PC to the Device wirelessly?.......................................... 59
Q2. A-2 How to connect a Windows 7 PC to the Device wirelessly? ...................................... 60
Q3. How to reset the Device to factory default settings? ....................................................... 60
Appendix B Hex ASCII Codes............................................................................................... 62
Appendix C LICENSE STATEMENT / GPL CODE STATEMENT ......................................... 63
3
About This Guide
Note: For best use of our product, it is recommended that you upgrade your Internet
Explorer to version 10 or higher.
Purpose and Scope
This guide describes the features and functions of the WAP-6111/H、WAP-6112/H、WAP-6201、
WAP-6202 Wireless Access Points. It provides an overview of the access points, as well as the
information you need to install and configure your access point through the Web interface.
This guide will be updated as new information becomes available.
Web UI Style
The Device’s Web User Interface (Web UI) follows the web standards. A typical Web UI page
includes the following elements:
:Radio Button: Allows you to choose only one of a predefined set of options.
:Check Box: Allows you to choose one or more options.
:Button: Allows you to click to perform an action.
:Text Box: Allows you to enter text information.
:List Box: Allows you to select one or more items from a list
contained within a static, multiple line text box.
:Drop-down List: Allows you to choose one item from a list.
When a drop-down list is inactive, it displays a single item. When activated, it drops down a list of
items, from which you may select one.
4
Factory Default Settings
The following table lists the factory default settings of the Device.
Parameter
Default Value
Description
Administrator User Name
admin
Both the User Name and
Password are case sensitive.
Administrator Password
admin
LAN IP Address
192.168.1.253/255.255.255.0
You can use this IP address to
access the Device through a
Web browser.
SSID
LEVELONE_ABCDEF
To connect to the Device,
wireless clients must use the
same SSID as the Device.
XXXXXX is the Device’s
serial number in hexadecimal
format.
Table 0-1 Factory Default Settings

5
Chapter 1 Product Overview
This chapter describes the features and functions of the WA Series Wireless Access Points in brief.
1.1 Key Features
Support Fit AP and Fat AP modes, which can be switched easily
Support automatic firmware and configuration update
Support static IP and DHCP connection types
Support DHCP server
Support static DHCP
Support multiple wireless modes
Support multiple wireless security modes
Support wireless MAC address filtering
Support hidden SSID
Support WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)
Support firmware upgrade via the Web UI
Support configuration backup and restore
Note:
The WA Series Wireless Access Points include multiple models. Features and specifications may
vary depending on the specific model. For information on the feature and specification differences
among them, please visit our website or contact our customer service department.。

6
1.2 Specification
Conform to IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g standards
Conform to IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet standards
Support TCP/IP, DHCP, etc.
Each physical port supports auto-negotiation for the port speed and duplex mode
Each physical port supports auto MDI/MDI-X
Provide system and port LEDs
Operating Environment:
Temperature: 32° to 104° F (0° to 40° C)
Relative Humidity: 10% to 90%, Non-condensing
Height: 0m to 4000m

7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
This chapter describes the physical characteristics of the WA Series Wireless Access Points, and
explains how to install them.
2.1 In-Wall Access Point
2.1.1 Panel Descriptions
The in-wall wireless access point supports IEEE 802.3af PoE. The dimension is 86 x 86 x 36 mm,
It can be directly installed on standard 86 base box. Figure 2 1 shows the front panel.。
Figure 2-1 Front Panel – In-wall AP
1) Ports
Ports
Type
Description
PHONE
RJ11 Phone Port
Used to connect a telephone.
USB
USB Charging Port
Used to charge USB devices like a cell phone or MP3
player.
LAN
RJ45 Ethernet Port
The two LAN ports (10/100M, auto MDI/MDI-X) are
used to connect computers or other Ethernet devices to
the wired LAN.
Table 2-1 Description of Ports – In-wall AP

8
2.1.2 Preparing for Installation
1) Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation around the Device.
2) Position the Device out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat and ignition.
3) Position the Device away from sources of electrical noise, such as high power radio
transmitters, radar stations, and so on.
2.1.3 Items Required for Installation
1) Preparation of related devices:
(1) Broadband Internet connection
(2) PoE PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) device like PoE switch
(3) PC with an Ethernet card and TCP/IP installed
2)Phillips screwdriver, crimping tool like crimping plier, etc.
2.1.4 Installing the Device
Before you install the Device, make sure your Internet connection and PSE device are working
properly.
Follow these steps to install the Device:
1) Use your crimping tool to crimp a network cable and a telephone line to the corresponding
wiring port on the Device. Make sure crimp the wires in the right order.
2) Mount the Device on a wall.
3) Connect the other end of the cable that you just crimped to a PoE PSE device (like PoE
switch). As a PD (Powered Device), the Device will communicate with and receive power
from the PSE via the cable.
4) Configure the Device: Connect your computer to the Device either via an Ethernet cable or
wirelessly), and then configure the Device through its own Web interface. The Device in Fit
AP mode can also be managed by a WAC-1000/ WAC-1001
5) Connect client devices: Connect each computer or other device in your network to the
Device, via an Ethernet cable or wirelessly.
9
2.2 In-Ceiling Access Point
2.2.1 Panel Descriptions
The in-ceiling wireless access point supports IEEE 802.3af PoE. A system status LED is located at
the front panel, a LAN port is located at the bottom panel, and a reset button is located at the side
panel.
1)LED
LED
Description
System Status LED
The LED flashes twice per second when the system is operating
properly, and it will flash slower if the system is under heavy
load.
Table 2-2 Description of LED – In-ceiling AP
2) Port
Port
Description
LAN
Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 port, auto MDI/MDI-X
Table 2-3 Description of Ports – In-ceiling AP
3) Reset Button
If you forget the administrator password, you can use the Reset button to reset the Device to
factory default settings. The operation is as follows: With the Device powered on, press and hold
the Reset button for more than 5 seconds, and then release the button. The Device will restart with
factory default settings.
Note:The reset operation will clear all custom settings on the Device, so do it with caution.
2.2.2 Preparing for Installation
1) Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation around the Device.
2) Position the Device out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat and ignition.
3) Position the Device away from sources of electrical noise, such as high power
radiotransmitters, radar stations, and so on.

10
2.2.3 Items Required for Installation
The following items are required for installation:
1. Broadband Internet connection
2. Tools and equipment
• Wireless LAN controller or normal router
• PC with an Ethernet card and TCP/IP installed
• Power outlet
• (Optional) PoE PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) device like PoE switch
• Ethernet cables
• Phillips screwdriver.。
Installing the Device
Before you install the Device, make sure your Internet connection is working properly. In
addition, it is recommended that you configure the Device before you deploy it in the network.
Follow these steps to install the Device:
1. Use the supplied power adapter to connect the Device to a power outlet.
2. Connect your computer to the Device either via an Ethernet cable or wirelessly, and then
login to the Web UI to configure the Device.
3. After you configure the Device, unplug the power adapter, and the Ethernet cable, if
used.
4. Mount the Device on a ceiling or wall.
5. If needed, use an Ethernet cable to connect other network device (like PoE switch,
WLAN controller) to the LAN port of the Device.
6. Power the Device by using the supplied power adapter, a PoE adapter, or a PoE switch.
7. Connect client devices: Connect each computer or other device in your network to the
Device wirelessly.
2.3 Desktop Access Point
2.3.1 Panel Descriptions
Depending on the model, the desktop wireless access points may have either one or two antennas.
Here we take the WAP-6015 as an example. The WAP-6015 is a desktop wireless AP with two
antennas, and the dimension is 200mm×124mm×28.4mm. Figure 2-2 shows the front panel of the
WAP-6015.
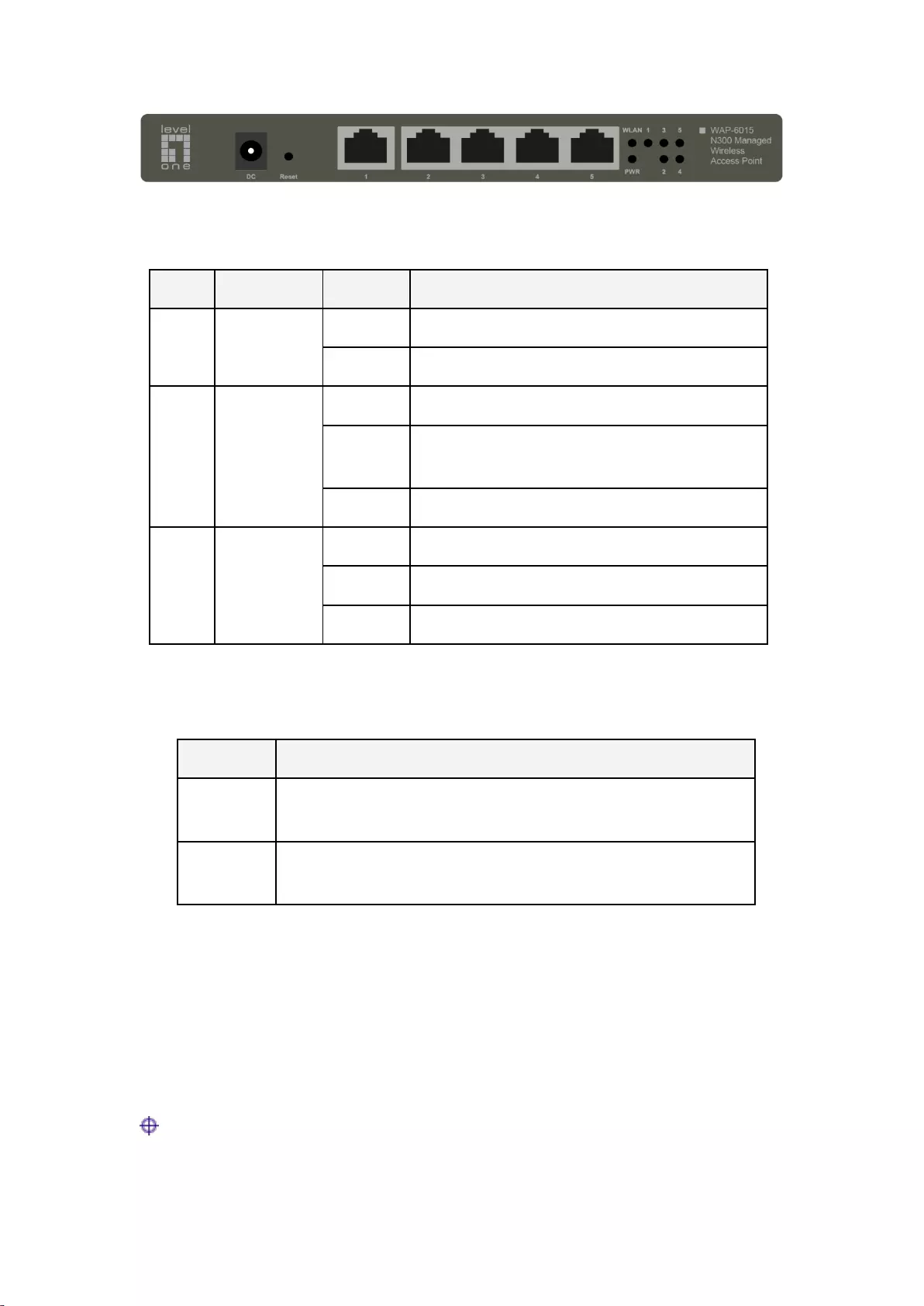
11
Figure 2-2 Front Panel – Desktop AP
1) LED
LED
Full Name
State
Description
PWR
Power LED
On
The Device is powered on.
Off
The Device is powered off.
WLAN
Wireless
Status LED
On
The wireless function is enabled.
Flashing
The Device is sending or receiving data over the
wireless network.
Off
The wireless function is disabled.
1, 2,
3,4,5
LAN Port
Status LED
On
A valid link is established on the corresponding port.
Flashing
The corresponding port is sending or receiving data.
Off
No link is established on the corresponding port.
Table 2-4 Description of LED –Desktop AP
2) Port
Port
Description
LAN
The five LAN ports (10/100M, auto MDI/MDI-X) are used to connect
computers or other Ethernet devices to the wired LAN.
Antenna
Located at the real panel of the Device.
Antennas are used to transmit and receive wireless signals.
Table 2-5 Description of Ports – Desktop AP
3) Reset Button
If you forget the administrator password, you can use the Reset button to reset the Device to
factory default settings. The operation is as follows: With the Device powered on, press and hold
the Reset button for more than 5 seconds, and then release the button. The Device will restart with
factory default settings.
Note
:
The reset operation will clear all custom settings on the Device, so do it with caution.

12
2.3.2 Preparing for Installation
Installation Guidelines
When determining where to place the Device, observe these guidelines:
Make sure that the bench is level and stable.
Do not place heavy objects on the Device.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation
around the Device.
Position the Device out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat
and ignition.
Position the Device away from sources of electrical noise, such as high
power radio transmitters, radar stations, and so on.
Please use the supplied power Adapter.
Items Required for Installation
The following items are required for installation:
1. Broadband Internet connection
2. Tools and equipment
Wireless LAN controller or normal router
PC with an Ethernet card and TCP/IP installed
Ethernet cables
Power outlet
2.3.3 Installing the Device
Before you install the Device, make sure your Internet connection is working properly.
Follow these steps to install the Device:
1. Make sure the Device is powered off.
2. Place the Device upside down on a sturdy, flat bench.
3. Remove the adhesive backing from the supplied rubber feet. Attach the four
rubber feet to the recessed areas on the bottom of the Device.
4. Turn the Device over to make it right side up on the bench.

13
2.4 Typical Deployment Scenarios
Here we take the WAP-6112/H as an example. The WAP-6112/H can operate in either
Fit AP or Fat AP mode. Figure 2-2 depicts a typical Fit access point deployment, and
Figure 2- depicts a typical Fat access point deployment.
As shown in Figure 2-, two access points act as Fit APs, a WAC-1000 / WAC-1001
controller acts as the gateway. The access points are managed by the WAC-1000 /
WAC-1001, and clients access the network through the access points.
Figure 2-3 Fit Access Point Deployment
As shown in Figure 2-, an access point acts as a Fat AP. The access point is directly connected to
the default gateway, and clients access the network through the access point.
Figure 2-4 Fat Access Point Deployment
14
Chapter 3 Logging in to the Device
This chapter describes how to configure TCP/IP settings on your computer, and how to login to
the Device. In addition, it briefly describes the layout of the Device’s Web interface.
3.1 Configuring Your Computer
To configure the Device via Web UI, you need to properly configure TCP/IP settings on the
computer that you use to manage the Device. To do this, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect the computer to a LAN port of the Device, or connect the computer
to the Device wirelessly.
Step 2 Install TCP/IP protocol on your computer. If it is already installed, please
skip this step.
Step 3 Configure TCP/IP settings on your computer: set the IP address to an
unused one in the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet, set the subnet mask to
255.255.255.0, and set the default gateway to the IP address of your
gateway. Note: the Device’s default LAN IP address is 192.168.1.253
with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
Step 4 Use the Ping command to verify network connectivity between the
computer and the Device. Open the command prompt on the computer, type
ping 192.168.1.253, and then press Enter. The following uses Windows XP
as an example.
A successful ping will look like this:
A n unsuccessful ping will look like this:
Pinging 192.168.1.253 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.253: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.253: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.253: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Reply from 192.168.1.253: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.253:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms

15
If the Ping command is successful, the connection between the computer and the Device is
working properly. If the Ping command fails, please do the following:
1) Check physical connection: Verify that the LAN LED on the Device and the LED on your
computer’s network card are lit.
2)Check TCP/IP settings: Verify that your computer is on the same subnet as the Device’s LAN
interface. E.g., if the Device’s LAN IP address is 192.168.1.253 (default), the computer’s IP
address must be an unused IP address in the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet.
3.2 Logging to the Device
No matter what operating system is installed on your computer, such as, MS Windows, Macintosh,
UNIX, or Linux, and so on, you can configure the Device through the Web browser (e.g., Internet
Explorer, Firefox).
To login to the Device, do the following: Launch a Web browser, enter the Device’s LAN IP
address (default is 192.168.1.253) in the address bar, and then press Enter, as shown in Figure
3-1.。
Figure 3-1 Entering IP address in the Address Bar
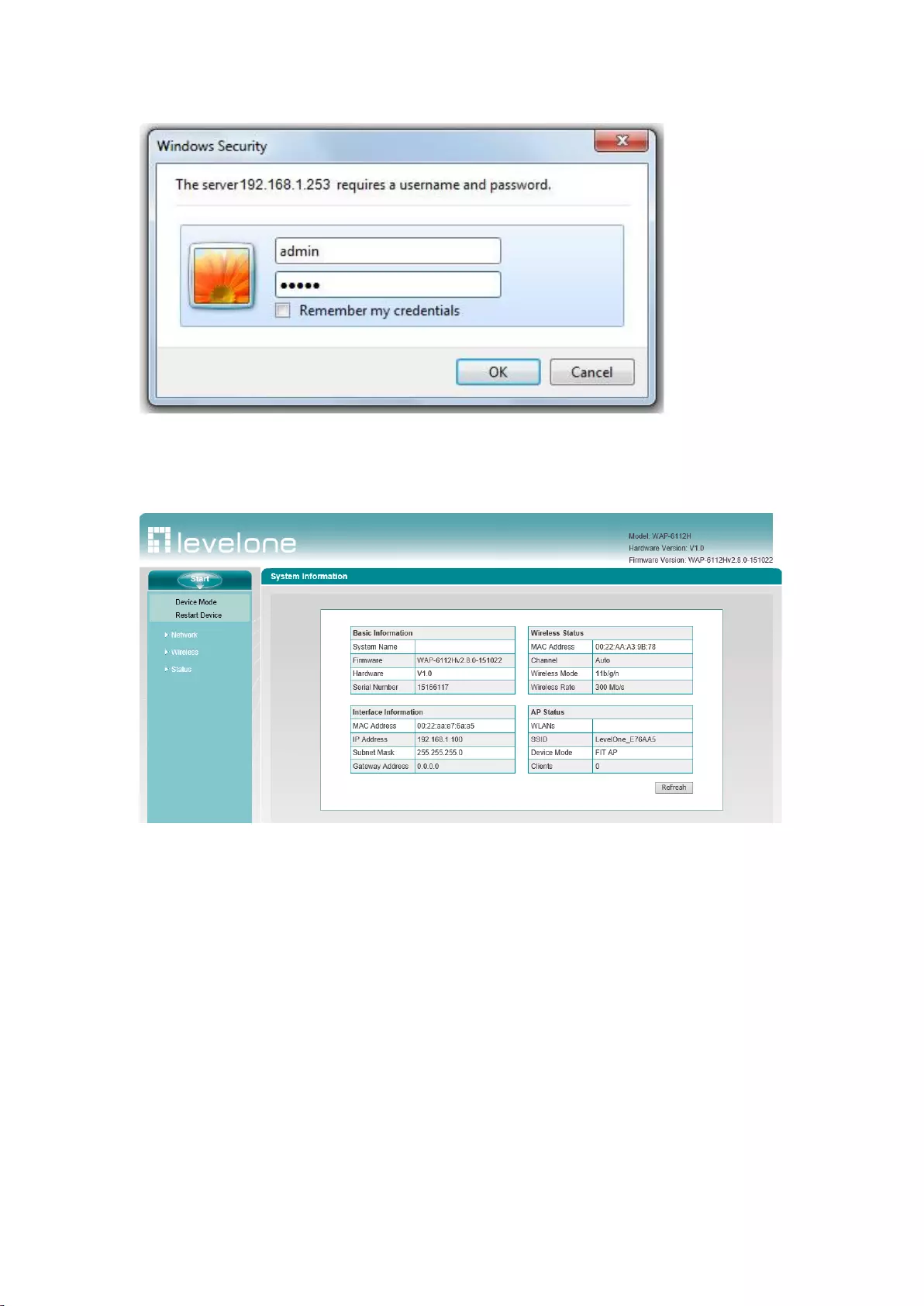
The login window appears, as shown in Figure 3-2. The first time you login to the Device, you
should enter the default login information (default user name and password both are admin), and
then click OK.
Pinging 192.168.1.253 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.253:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
16
Figure 3-2 Web UI Login Window
If the login is successful, the home page appears, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Web UI Home Page
Home Description:
1) The top-right corner of the page displays device model, software version, hardware version.
2) This page displays the main menu bar on the left.
3) The main operating page is located on the right of the page, in which you can configure
various functions of the device, view the related configuration information and status
information, etc.

17
Chapter 4 Fit AP
In this chapter, we first provide an overview of AP centralized management. Then we describe the
features and parameters supported in Fit AP mode.。
AP Centralized Management Overview
4.1 Terminology
Client: A PC, laptop, or other terminals with a wireless Network Interface Card.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network): A WLAN is a type of local area network that uses high
frequency radio waves rather than wires to transmit data.
WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 (Wireless LAn Controller): An WAC-1000 / WAC-1001, also known as
WLAN controller, is a network device that is used to control and manage access points in the
network.
AP (Access Point): An AP is a network device that acts as a base station for the wireless LAN, and
acts as a bridge between wired and wireless networks.
Fat AP: A standalone AP that independently controls and manages wireless clients.
Fit AP: A simple AP that relies on WLAN controller to control and manage wireless clients. The
Device in Fit AP mode can retrieve firmware and configuration file from the WLAN controller.
Intra-Controller Roaming: Intra-controller roaming occurs when a wireless client roams between
APs managed by the same WLAN controller.
Layer 2 Roaming: Layer 2 roaming occurs when a wireless client roams between APs on the
same subnet and VLAN.
4.2 Communication Process
The figure below shows the communication process between a fit AP and WAC-1000 /
WAC-1001.
For the implementation of Fit AP + WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 solution, the first and crucial step is
the issue of Fit AP's registration on the three-layer switch, and the WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 can
manage Fit AP only after Fit AP is successful in registration. In the practical applications, it is
common for WAC-1000 / WAC-1001+Fit AP to register by crossing three-layer network. Our

18
device has three ways of implementation: the first is the DNS mode, which requires the support
from DNS, DHCP Server, and is relatively complex; the second is the DHCP Option43 attribute
mode, that is, using the Option43 attribute of the DHCP Server; the third is to configure the
WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 address on AP, and this method is relatively simple.
When the wireless controller WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 is connected with the Fit AP by crossing
three-layer network, the Option 43 mode is used; when Fit AP is connected to the wireless
controller by crossing three-layer network, Fit AP can directly obtain the IP address of the wireless
controller through the Option 43 attribute of DHCP, thus completing the registration on the
wireless controller. The specific process is shown in the figure below:
Figure 4-1 WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 and AP centralized manager communicate on the second floor
When the Fit AP and the wireless controller cross three layers of network connection, the
registration procedure of the Fit AP in the wireless controller through the Option 43 attribute of
DHCP server is as follows:
1) Fit AP obtains IP address, option 43 attribute (the attribute carries the IP address of the
three-layer switches) through the DHCP server.
2) Fit AP will obtain the IP address of three-layer switch from the option 43 attribute, and then
sends the unicast discovery request to the wireless controller.
3) The wireless controller of the wireless switch that receives the discovery request packet will
check if the Fit AP has the access to this machine, and answers that it discovers a response if any.
4) Fit AP downloads the latest version of software from wireless controller of the wireless switch.
5) Fit AP downloads the latest configuration from the wireless controller.

19
6) Fit AP begins to work normally to exchange of user data packets with the wireless controller.
Tip:
(1) In the process of device operation, while the configuration file is modified on the AP,
for instance, it joins in a service area, WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 will save the
modified configuration file locally and send it to AP, and the configuration file will
be deleted after WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 powers off.
(2) WAC-1000 / WAC-1001 will delete the configuration file saved before after
recovering the AP to its factory configuration remotely.
(3) The AP uploaded configuration file will not be displayed in the configuration file list.
(4) AP can start transmitting user data immediately after successfully obtaining the
software, configuration file.
4.3 Layer 2 Roaming
Mobility, or roaming, is a wireless client’s ability to move from one AP coverage area to another
without interruption in service or loss in connectivity.
The Device supports layer 2 roaming, which allows wireless clients to roam across access points
on the same subnet and VLAN. To implement layer 2 roaming, you need to assign the same
WLAN profile to the access points, so that they have the same SSID, on the same subnet and the
same VLAN. Figure 4-2 shows intra-controller layer 2 roaming, which occurs when the two APs
are joined.
Figure 4-2 Intra-Controller Layer 2 Roaming
As shown in the above figure, AP1, AP2 are associated with WAC-1000 / WAC-1001.

20
1) A terminal is wirelessly associated with AP1, and AP1 is connected to WAC-1000 /
WAC-1001.
2) The terminal disconnects its association with AP1, and roams into the AP2 connecting the
wireless controller WAC-1000 / WAC-1001.
The process that the terminal is connected to AP2 is referred to as two-layer wireless roaming.
Way of implementation: Configure a service area on the device and enable the two-layer roaming
function by adding AP1, AP2 into the same service area.
4.4 System mode:
The device supports fat AP mode and thin AP mode, and the device's factory default mode of
operation is thin AP mode. If you need to change the working mode of the device, please go to
Start-> System mode Page, or Wireless configuration -> System mode page for modification,
while modifying via AC remotely.
Note: The AP will automatically restarted during switching of modes.
Figure 4-3 Working mode
4.5 Configuration of LAN port
The default IP address of the device LAN port is 192.168.1.253, and the IP address of the device's
LAN port needs to be changed to adapt to the existing network, which can be modified by either
of the following methods.
Method I: Local modification
Enter Network parameters ->LAN port configuration page to configure the LAN port IP
address of the device. The access mode supported by the device LAN port: fixed IP access,
dynamic IP access. These two access modes will be introduced respectively in the subsequent
sections.
Method II: Remotely modification
When the device is connected to AC as a thin AP, the administrator can modify the device's LAN
port IP address on AC through remote management. For configuration details, refer to Item 2.8

21
Advanced Configuration of Wireless Controller.
4.6 Fixed IP access
The default of LAN port access is fixed IP access. The following describes the meaning of the
parameters for configuration of fixed IP access.
Figure 4-4 Fixed IP access
Access mode: Selects fixed IP access here;
IP address: The IP address of device LAN port, through which the administrator can manage
this device;
Subnet mask: It is the subnet mask of device LAN port, which should be consistent with the
subnet mask of the network computer;
Gateway address: The IP address of the device LAN port with the intranet as a gateway;
AC address: Sets the IP address of AC.
Primary/Secondary DNS server: Sets the IP address of the primary/secondary DNS server.
MAC address: It is the MAC address of device LAN port, which needs no change if there are
no special requirements.
4.7 Dynamic IP access
If the IP address of device LAN port is acquired from the DHCP server dynamically, select the
access way of dynamic IP.

22
Figure 4-5 Dynamic IP access
Tip:
1) After the address of the LAN port is modified, please log in the device using the new IP
address of LAN port.
2) When the LAN access mode is dynamic IP access, please confirm the LAN port IP address at
the DHCP server.
4.8 Status of wireless host
Enter System status-> Wireless host status page, to view the status of the host through a wireless
access device.
Figure 4-6 Wireless host status list

23
4.9 System information
EnterSystem State -> System informationpage, and the administrators can view the information
about the device.
Figure 4-7 System information
Basic Information
Basic information bar displays device name, software version, hardware version and serial number
of devices.
Wireless status
MAC address: Shows the MAC address of the device broadcasting SSID;
Channel: Displays the channel used by the device;
Wireless mode: Displays the wireless mode selected for the device;
Wireless rate: Displays the wireless rate of the device.
Interfacing information
Interface information bar shows device LAN port IP address, MAC address, subnet mask, and
gateway address.
AP status
Service area: Displays the service area to which the device is a member, and the device can
be a member of up to 4 service areas at maximum;
SSID: Displays the SSID of the service area where the device resides;
Work mode: Displays the work mode of the device, FIT AP means thin AP;
Number of clients: Shows the number of hosts for the access device.

24
Chapter 5 Start menu
Starting from this chapter, the function parameters of the device that operates in fat AP mode are
described. The parameters already introduced in Chapter 4 Thin AP Configuration will not be
detailed again subsequently.
Start menu is located on the top of the Level 1 menu bar of the WEB interface, providing the
interface for 5 common pages, including: configuration wizard, running status, port flow, system
modes, device reboot. With the Start menu, you can quickly configure the basic parameters
required by the device in working properly, view the information about device LAN port, and
view the statistics data of wired/wireless devices' real-time traffic.
5.1 Configuration Wizard
When the work mode of the device is configured as fat AP, the page will go directly to the page
the Configuration Wizard page, as shown in Figure 5-1:
Figure 5-1 Home page of configuration wizard
In logging next time, the wizard will no longer automatically pop up: When checked, you can
go directly to theSystem Informationpage in logging next time;
Exit the wizard: Exits the Configuration Wizard and returns to the system information page;
Next: Enters into theConfiguration Wizard ->LAN port configurationpage.
LAN access mode consists of: fixed IP access, dynamic IP access. As Figure 5-2 shown in the
page, choose the access mode of the device depending upon your real situation.
1) Fixed IP access
The default of LAN port access is fixed IP access. Please enter the relevant parameters depending

25
upon your situation, and then click
< Complete >, to save the configuration to the LAN port.
Figure 5-2 LAN port configuration - Fixed IP access
2) Dynamic IP access
If you acquire the IP address for configuring LAN port in a dynamic manner, please click
<Complete> directly in the interface as shown in the figure below, and save the configuration to
the LAN port.
Figure 5-3 Configuration Wizard - Dynamic IP access
Tip:
1) Configuration Wizard's operation can take effect only by clicking <Complete >.
2) After the address of the LAN port is modified, please log in the device using the new IP
address of LAN port.
3) When the LAN access mode is dynamic IP access, please confirm the LAN port IP address at
the DHCP server.

26
5.2 Running status
This section describes the Start-> Running status page, in which you can view the information
about the device's LAN port. As Figure 5-4 shown in the interface, the connection type,
connection status, IP address and other information about LAN port can be viewed.
Figure 5-4 Information about running status
5.3 Port flow
This section describes the Start-> Port flow page, as shown in Figure 5-5. You can view the
average, maximum, sum and current realtime rate for wired ports to receive and send data,
wireless ports, and provide different units (kbit/s and KB/s) for them.
Tip:
If this page fails to display properly, please click the hyperlink "if it does not display properly,
please install svgviewer" to have the svgviewer plug-in installed.

27
Figure 5-5 Port flow
Wired: Click this tab to view the dynamic diagram of a device in receiving and sending
dynamic data;
Wireless: Click this tab to view the dynamic diagram of a device in receiving and sending
wireless data;
Timeline: The x-coordinate in the flow chart. You can click on the timeline options (1x, 2x,
4x, 6x in the figure) in the figure to determine the display effect;
Flowline: The y-ordinate in the flow chart. You can choose the display results as needed
(standardization, maximization as shown in the figure);
Display: Provides two display options, solid effect and hollow effect;
Color: It can be selected for display according to needs and preferences, such as red, blue,
black etc;
Reverse: Click the Reverse button, and the colors can swap to receive and send data.
5.4 System mode:
In the Start -> System mode page, you can configure the work mode of the device, please refer to
the section: System mode.

28
5.5 Restarting device
If you need to restart the device, just enter into the Start-> Restart device page to click
<Restart>.
Figure 5-6 Restart device
Tip: Upon restarting, all users will be disconnected from the device.
29
Chapter 6 Network parameters
In the network parameters menu, you can configure the basic network parameters for the device,
including LAN configuration, DHCP server.
This chapter mainly introduces the Network parameters -> DHCP server page, including DHCP
server settings, static DHCP and DHCP client list.
Configuration of LAN port
In the Network parameters ->LAN configuration page, you can configure the LAN port of the
device, please refer to the section: LAN port configuration for details.
DHCP server
6.1 DHCP server settings
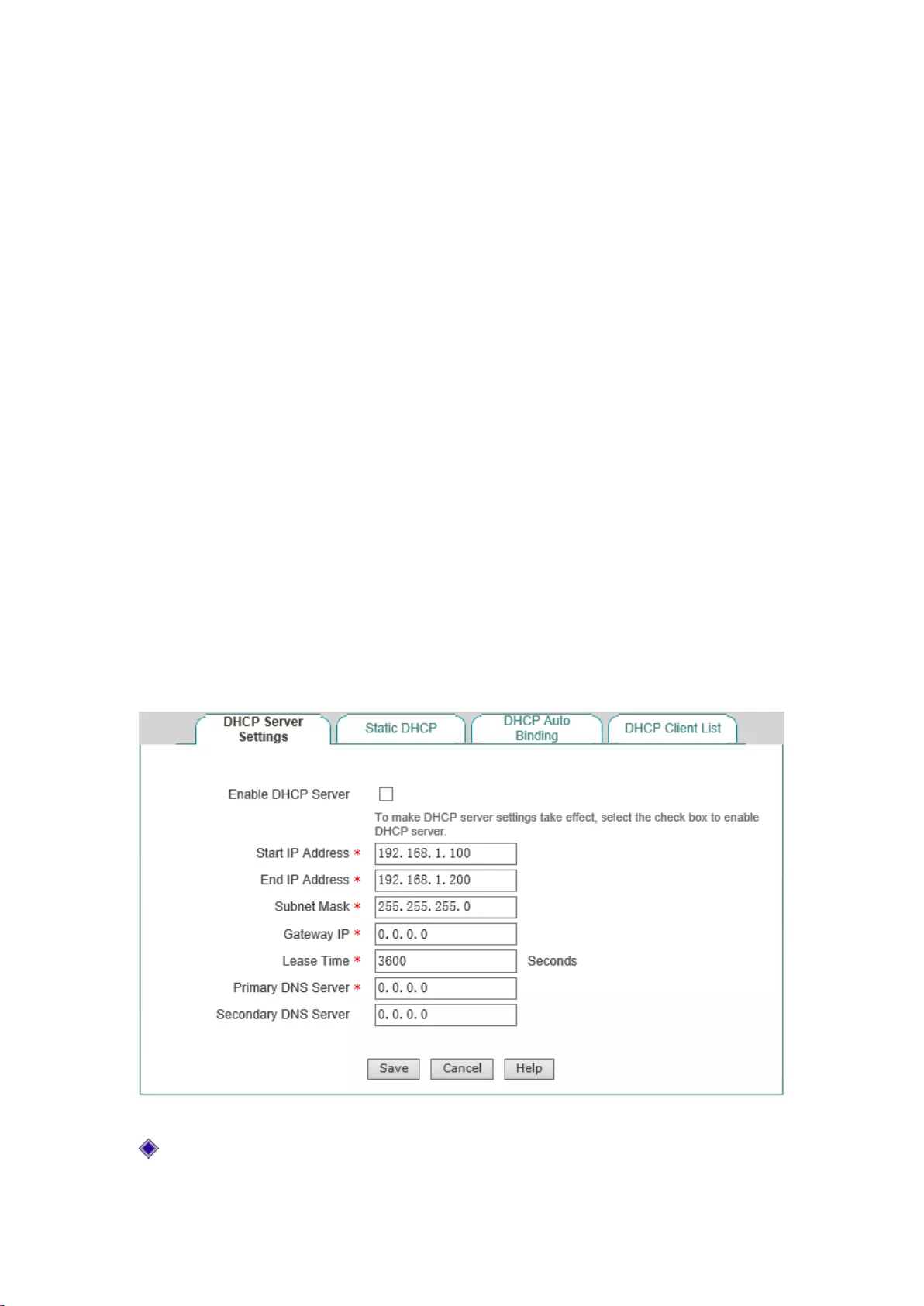
The the DHCP server functions on the device are disabled by default.
Figure 6-1 Configuring the DHCP service
Enable DHCP server: Select to enable the device's DHCP server function;

30
Origin and destination address: The IP address fields the DHCP server assigns to the network
computer automatically (which should be on the same network segment as the IP address of
the device LAN port);
Subnet mask: The subnet mask automatically assigned by the DHCP server to the network
computer (which should be consistent with that of the LAN port of the device);
Gateway address: The gateway IP address the DHCP server automatically assigns to the
network computer (which is set to the LAN IP address of the device with Intranet as a
gateway);
Leasing time: The leasing time for the network computers to obtain the IP address assigned
by the device(Unit: Seconds).
Primary DHCP server: The IP address of the primary DNS server assigned by the DHCP
server to the network computers automatically.
Secondary DNS server: The IP address of the secondary DNS server assigned by the DHCP
server to the network computers automatically.
Tip:
1. If the device's DHCP server function is to be used, network computer's TCP/IP protocol can
be set to "obtain an IP address automatically".
2. In the case where the Intranet already has a DHCP server, it is not recommended to enable the
DHCP server function of the device.
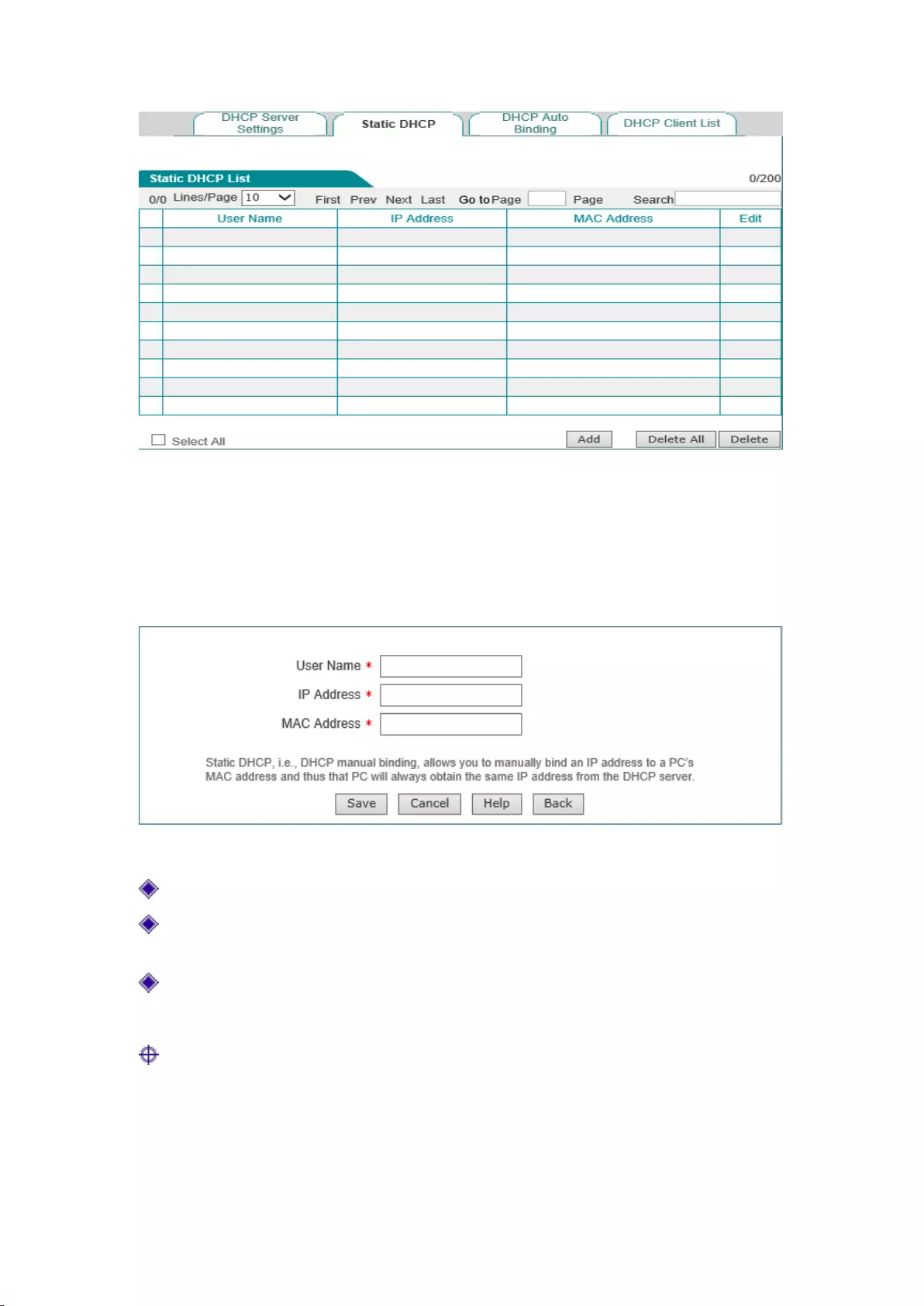
6.2 Static DHCP
This section describes the static DHCP list and the way to configure a static DHCP.
Using the DHCP service to automatically configure TCP/IP properties for the network computers
is very convenient, but it can cause a computer to be assigned with different IP address at different
times. And some Intranet computers may need a fixed IP address, in this case, the static DHCP
function is required, to bind the computer's MAC address with an IP address, as shown in Figure
6-2. When a computer having this MAC address requests the address from the DHCP server
(device) , the device will find a corresponding fixed IP address based on its MAC address and
assign it to the computer.
1) Static DHCP list
31
Figure 6-2 Static DHCP list
2) Static DHCP configuration
Click <Add new entry> in the page as shown in Figure 6-2, to enter into the Static DHCP
configuration page as shown below. Below shows the meaning of the parameters for configuring
static DHCP.
Figure 6-3 Static DHCP configuration
User name: Configure the user name of the computer bound by this DHCP;
IP address: The reserved IP address, which must be the valid IP address within the address
range specified by the DHCP server;
MAC address: The MAC address of the computer to use this reserved IP address in a fixed
way;
Tip:
1) After the setting is successful, the device will assign the preset IP address for the specified
computer in a fixed way;
2) The assigned IP addresses must be within the range provided by the DHCP server.

32
6.3 DHCP client list
For the IP address already assigned to the network computer, its information can be viewed in the
DHCP client list. Information as shown in the figure below: The DHCP server assigns the IP
address of 192.168.1.100 in the address pool to the network computers whose MAC address is
6C:62:6D:E9:6D:13, and the rest of the time for the computer to lease this IP address is 85,954
seconds.
Figure 6-4 DHCP client list
6.4 Case of DHCP configuration
Application requirements
In this case, the DHCP function must be enabled on the device, with the origin address as
192.168.1.10, and a total of 50 addresses can be assigned; here, the host with the MAC address
of00:21:85:9B:45:46 assigns the fixed IP address of 192.168.1.15, and the host with the MAC
address of00:1F:3C:0f:07:F4assigns the fixed IP address of192.168.1.10.
Configuration steps
The first step is to enter into the Network parameters -> DHCP server -> DHCP service
settings page;
The third step is to enable the DHCP function, configure the related DHCP service parameters (as
shown in Figure 6-5), and click <Save> after the end of configuration.

33
Figure 6-5 DHCP service settings - Instance
The third step is to enter theNetwork parameters -> DHCP server-> Static DHCP page, and
click <Add new entry>, to configure the two static DHCP instances in the request (such as Figure
6-6, Figure 6-7);
Figure 6-6 Static DHCP configuration - Instance A
Figure 6-7 Static DHCP configuration - Instance B
At this point, the configuration is complete, and you can view the information about 2 static
DHCP entries in the "static DHCP information list", as shown in Figure 6-8.
Figure 6-8 Static DHCP information list - Instance

34
Chapter 7 Wireless configuration
In the wireless configuration, the relevant wireless functions and parameters are set in the device,
including: system mode, wireless basic configuration, wireless security configuration, wireless
MAC address filtering, and wireless advanced configuration. In addition, you can also view the
status information about the wireless host.
System mode:
In the Start-> System mode page, the work mode of the device can be configured, please refer to
the section: System mode.
Wireless basic configuration
This section describes the Wireless Configuration -> Wireless basic configuration page and the
configuration methods. In this page, you can configure the AP work mode, SSID, wireless mode,
channel, channel bandwidth, enabling or disabling the SSID broadcast and other functions of the
device. IN This section, the AP working mode is used: The wireless basic configuration is
introduced in the order of AP Mode and WDS.
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) wireless distributed system, is a protocol for two access
points (AP) in wireless connection. Throughout the WDS wireless network, multiple APs are
connected by the way of bridging or repeater, make the entire LAN be dominated by wireless
mode.
The WDS configuration provided by the device consists of three modes: Bridge Mode, Repeater
Mode and Lazy Mode, which only plays a bridging function only in the practical application, and
in configuration, the LAN IP of the device must be in the same network segment, while the
parameters for security mode and channel bandwidth for connecting with each other must be
consistent.
35
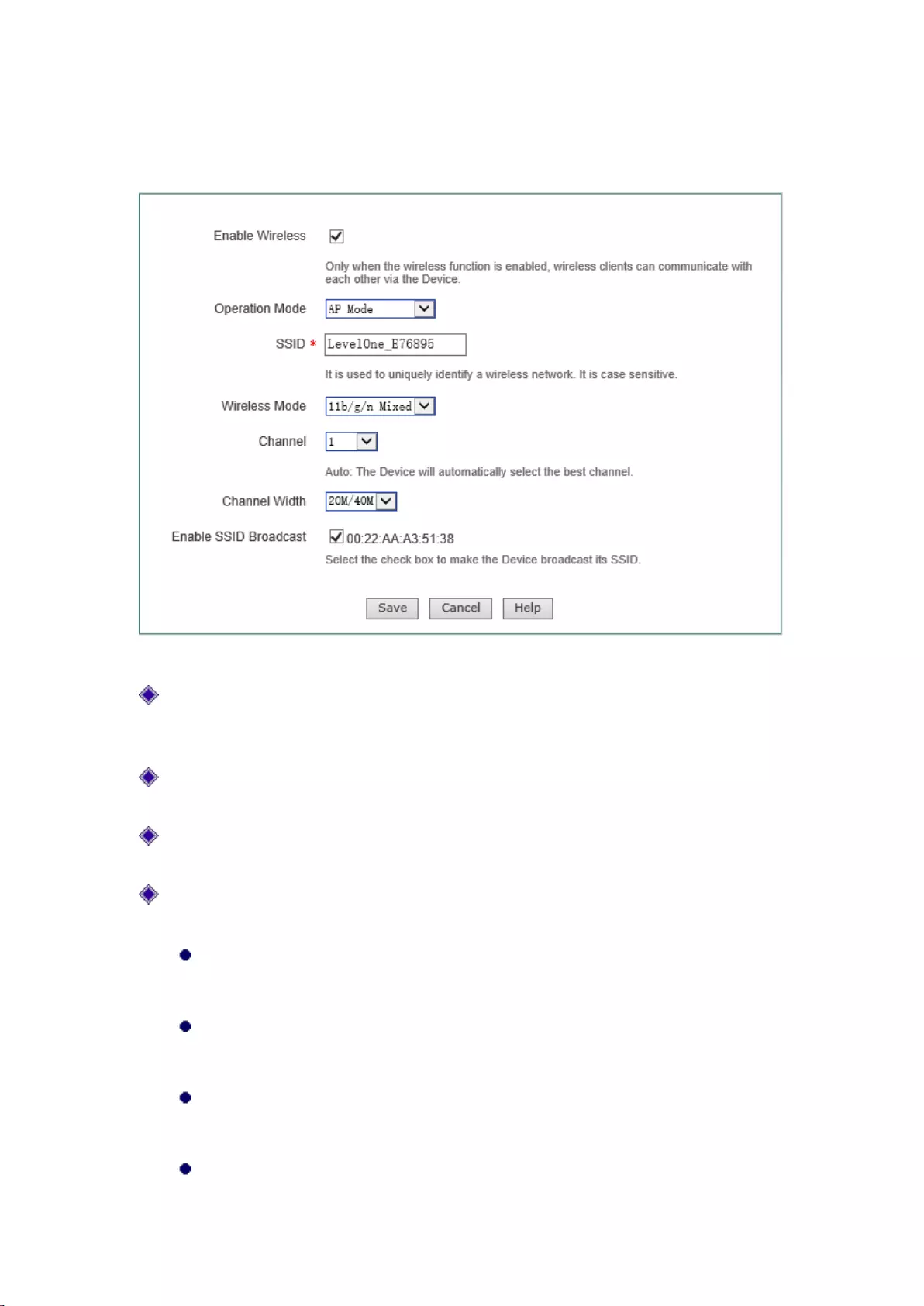
7.1 AP Mode
Figure 7-1 AP Mode
Enable wireless function: Only after the wireless function is enabled can the wireless clients
be connected to the device, to have wireless communications through the device, connect and
access the cable network to which the device is connected;
AP work mode: Selecting the AP Mode, namely the pure AP mode, in which the peer device
can be a single cli ent;
SSID (Service Set Identification) is used to uniquely identify a character string of wireless
network, and is case sensitive.
Wireless mode: This parameter is used to set the modes of the wireless device, to providing
four options: only 11g, only 11n, 11b/g/n hybrid and 11g/n hybrid:
Only 11g: pure 802.11g mode, in which the maximum rate is up to 54M bps. The
wireless sites compatible with the IEEE 802.11g standard can be connected to the
device;
Only 11n: pure 802.11n mode, in which the maximum rate is up to 300M bps. The
wireless sites compatible with the IEEE 802.11n standard can be connected to the
device;
11b/g/n hybrid: The wireless sites in compliance with IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g or
802.11n standard will be connected according to their modes, with the maximum rates
of 11M bps, 54M bps and 300M bps respectively;
11g/n hybrid: The wireless sites in compliance with IEEE 802.11g or 802.11n standard

36
will be connected according to their modes, with the maximum rates of 54M bps and
300M bps respectively;
Channel: This parameter is used to select the frequency bands in which the wireless network
works, with the available range from 1 to 13, and it provides automatic options, which means
that the device can automatically select the optimal frequency band. If there is more than one
wireless device, the settings of frequency band of the devices cannot affect each other;
Channel bandwidth: The channel bandwidth occupied by the wireless data transmission, with
the options: 20M/40M 和20M. Note that this parameter works only with the wireless site
accessed using the 802.11n standard; for those using the 802.11b or 802.11g standard, only
the channel bandwidth of 20M can be used:
20M/40M: When 20M/40M is selected, it means the wireless sites accessed using
the 802.11n standard will use the channel bandwidths of 20M or 40M according to
the results of the negotiation with the accessed peer end;
20M: When 20M is selected, it means the wireless sites accessed by using the
802.11g standard will use the channel bandwidth of 20M.
SSID broadcast: Enables or disables the SSID broadcast function. If this function is enabled,
the device will broadcast its own SSID to all the wireless sites so that the wireless sites
without SSID (null) will get the correct SSID, to be able to connect to the device, and join
into the wireless network with this SSID identifier. This function is enabled at risk (illegal
sites are very easy to get the SSID information), so it is generally recommended to disable
this function.
Tip:
1) The device enables the wireless function by default and its work mode is AP Mode;
2) After the wireless parameters are modified, the device's wireless module will reboot, and
rebooting of the wireless module will disconnect all wireless connections;
3) The AP work modes function differently, and should be selected according to the specific
occasions, uses in configuration.
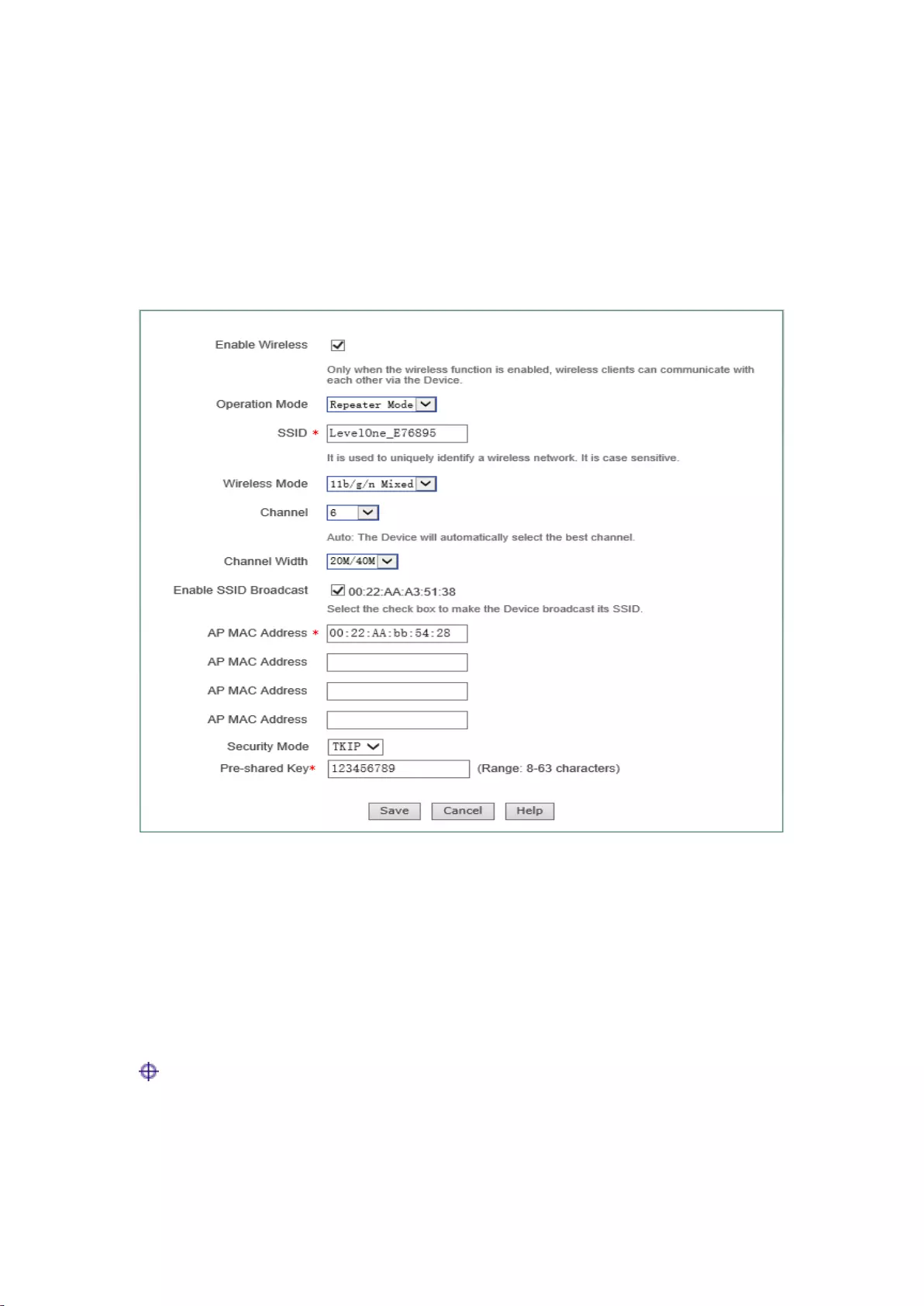
7.2 Repeater Mode
The device can exchange data with the network devices and single clients in Bridge Mode,
Repeater Mode, Lazy Mode when its work mode is set to Repeater Mode, to realize network
connectivity.

37
Figure 7-2 Repeater Mode
For the meaning of enabling wireless function, AP work mode, SSID, wireless mode, channel,
channel bandwidth, enabling SSID broadcast, see the section: AP Mode for relevant explanations,
and these terms will no longer be detailed if any in the subsequent configuration;
MAC address of AP: MAC address of the peer device.
Security mode: The encryption mode used in the establishment of connection through the
WDS function, including four options, "No security mechanism", "WEP", "TKIP" and
"AES".
No security mechanism: It means that no encryption algorithms will not be used to
protect communication data in the data exchange process;
WEP: It means that the WEP encryption algorithm is used to protect data during the data
exchange process. For details, please refer to the section: WEP;
TKIP: It means that the TKIP encryption algorithm is used to protect data during the
data exchange process. For details, please refer to the section: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK;
AES: It means that the AES encryption algorithm is used to protect data during the data
exchange process. For details, please refer to the section: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
38
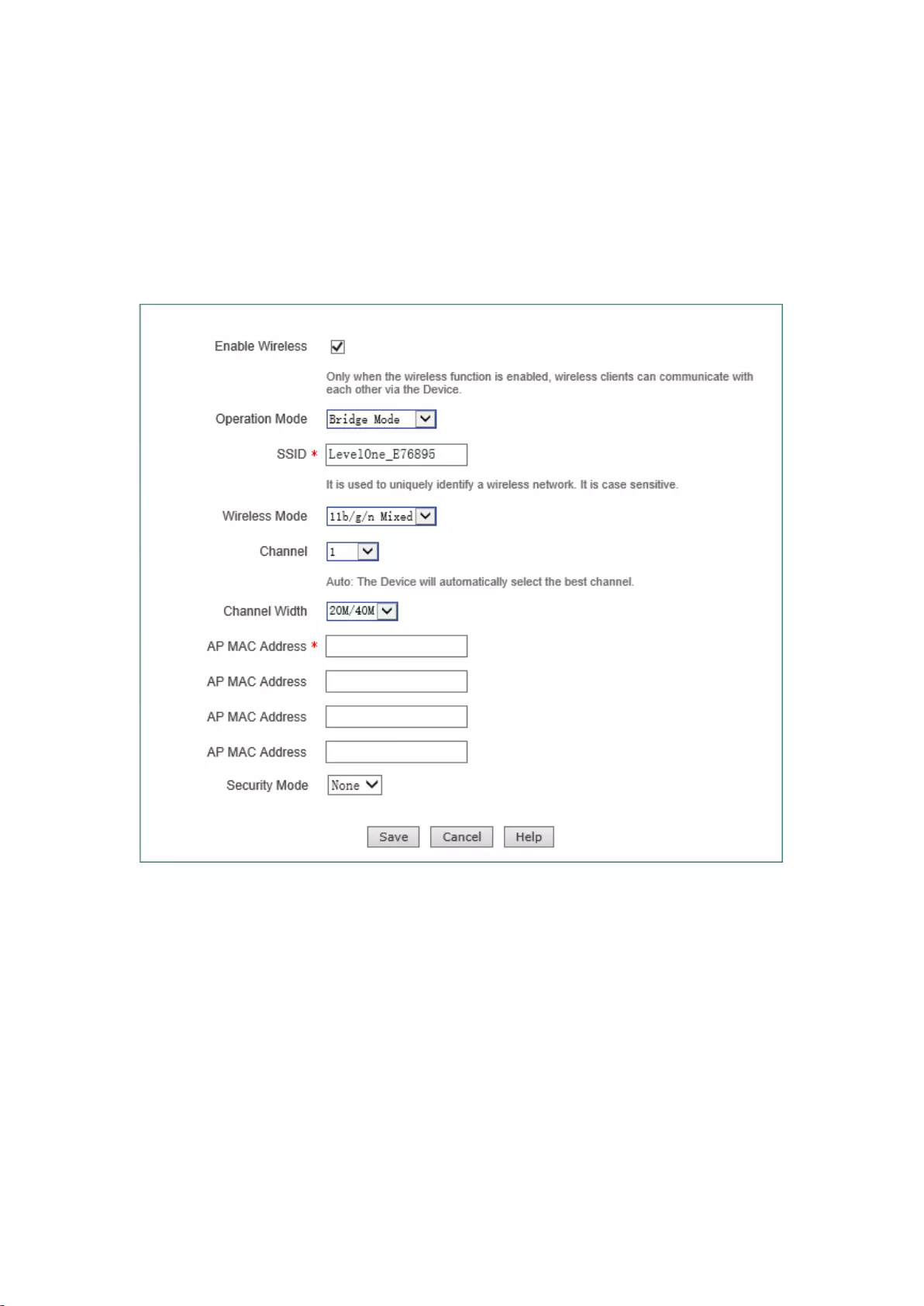
7.3 Bridge Mode
Bridge Mode, in which the device is connected to two or more wired networks, and the device will
no longer send wireless signals to other clients, to exchange data with the network devices in
Bridge Mode, Repeater Mode, Lazy Mode. The meaning of related configuration parameters is the
same as the Repeater Mode .
Figure 7-3 Bridge Mode
7.4 Lazy Mode
The device can exchanges data with network devices and single clients in the Repeater Mode,
Bridge Mode mode when its work mode is Lazy Mode, to realize network connectivity. The
meaning of related configuration parameters is the same as AP Mode and Repeater Mode.
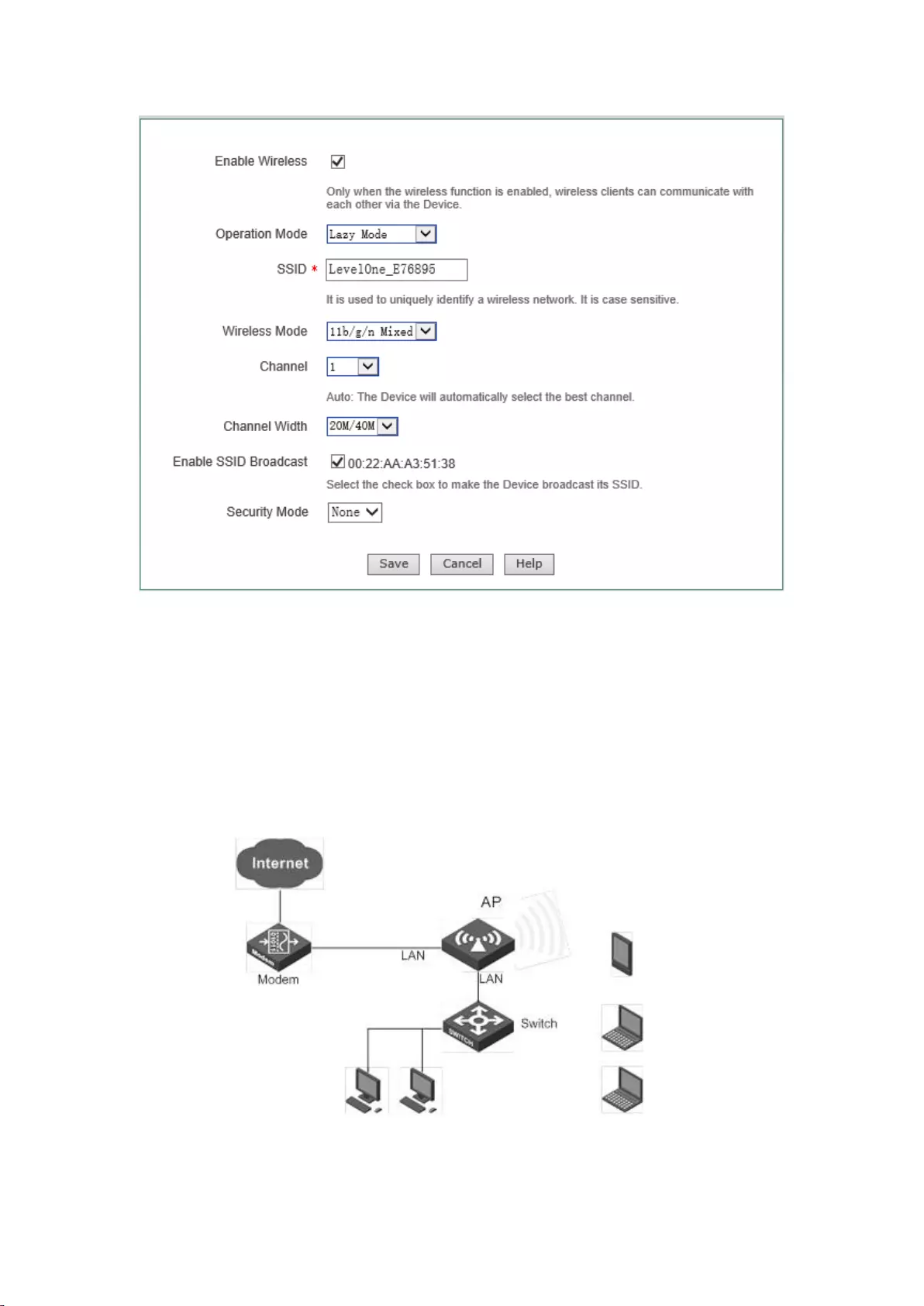
39
Figure 7-4 Lazy Mode
7.5 Wireless configuration instance
This section lists configuration instances where the device works in the AP Mode, Repeater Mode
and other AP work modes according to the four AP work modes of the device.
I. AP Mode configuration instance
Figure 7-5 AP Mode networking environment
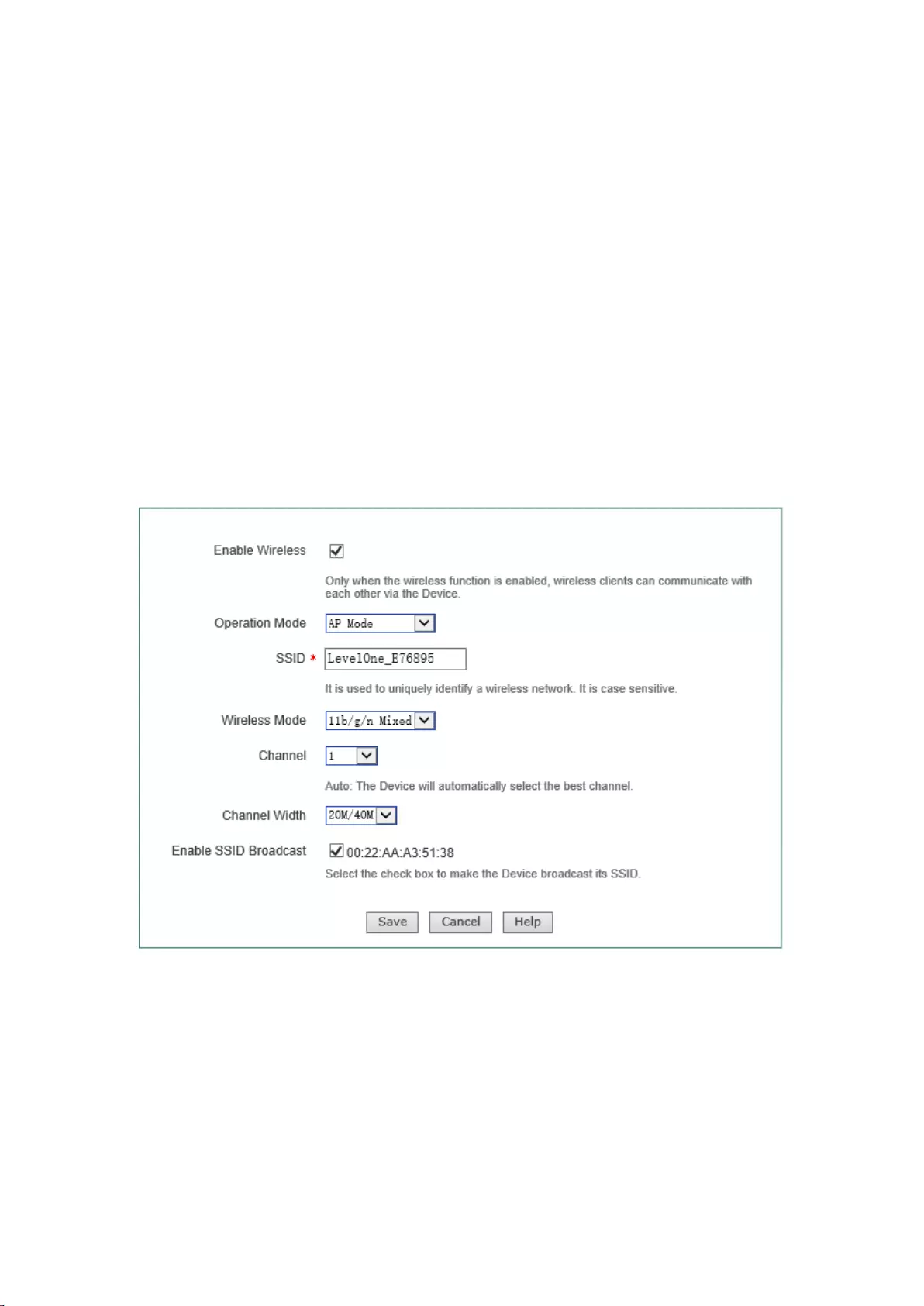
40
1. Requirements:Some home users want to put desktop computer, laptop, Tablet PC,
smartphones on the Internet via wireless devices, and prevent users other than their home
from accessing to wireless devices. Here, the gateway address is 192.168.1.1.
2. Analysis:Desktop computers are connected via a network cable to the LAN port of the
wireless device; laptop, Tablet PC, etc. are wirelessly connected to a wireless device and need
to be authenticated.
3. Configuration steps:
1) Configure the TCP/IP properties for network computer;
2) Upon logging in the device, change the work mode of the device to fat AP; then
configure the LAN port of the device, here, the gateway address is set as 192.168.1.1;
3) Enter into the Wireless Configuration -> Wireless basic configuration page, configure
the device's wireless basic parameters, as shown in the figure below, the AP work mode
is set to: AP Mode.
Figure 7-6 AP Mode configuration
4) Enter into the Wireless configuration -> Wireless security configuration page, to
configure the authentication methods and key for wireless communication.
Through the above configuration, wireless users can connect to the wireless devices so long
as they pass the authentication, and access to the Internet through it.
41
II. WDS configuration instance
Figure 7-7 Repeater Mode networking environment
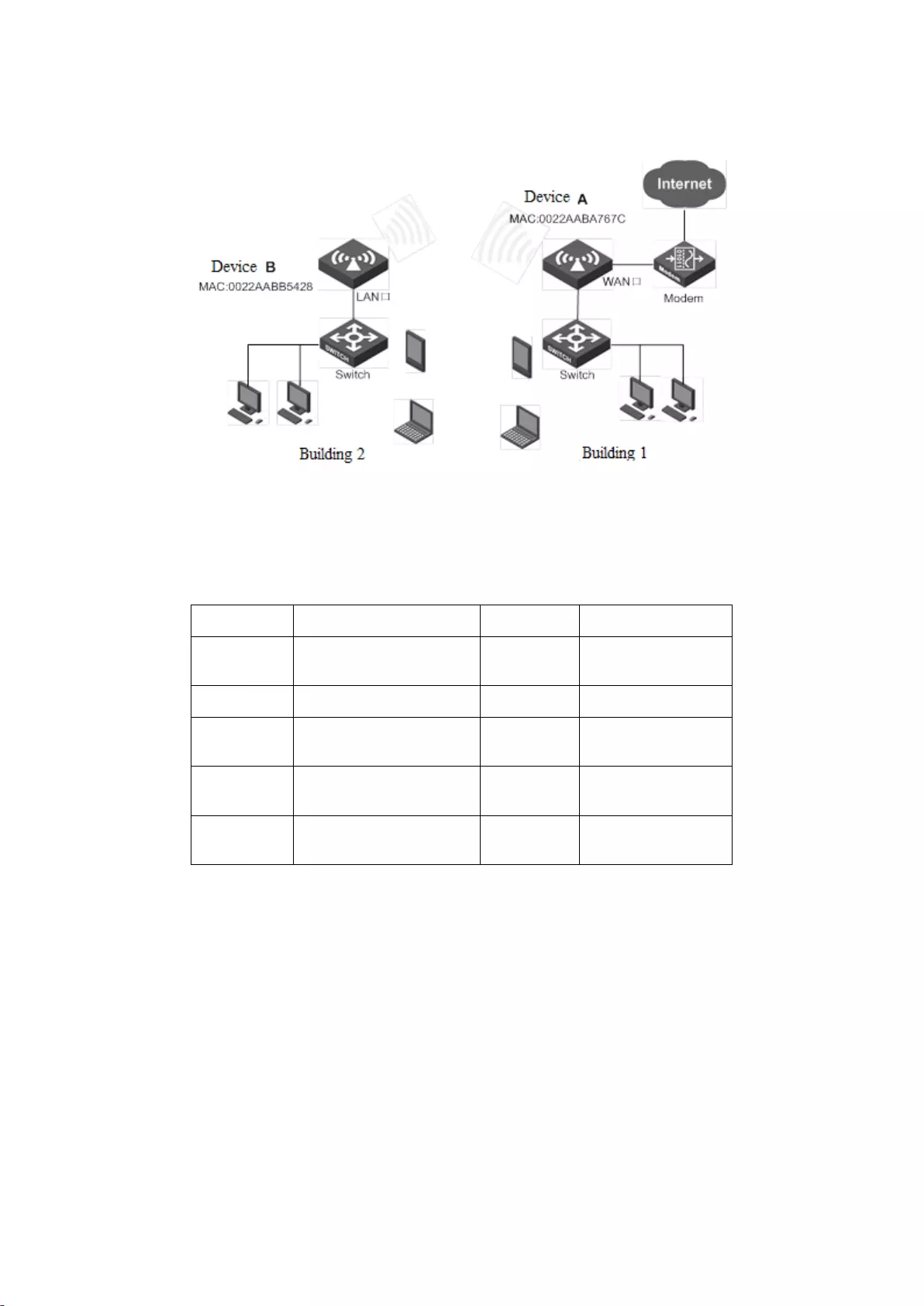
1. Requirements:The office personnel in Building 2 need to be wirelessly connected to Device
A, and access to the Internet through the gateway. The related parameters of Device A are as
follows:
Item
Parameters
Item
Parameters
Address of
LAN port
192.168.1.253/24
Gateway
address
192.168.1.1
SSID
UTT-HIPER-b87a9a
MAC
0022AABA767C
Wireless
mode
11b/g/n hybrid
Channel
6
Security
mode
WPA-PSK/WAP2-PSK
Pre-shared
key
123456789
Encryption
algorithm
Automatic
WPA
version
Automatic
2. Analysis:The following solutions can be used to achieve the goal
Solution I: Devices A and B are set to Repeater Mode mode.
Solution II: Devices A and B are set to Bridge Mode mode.
Solution III: Devices A and B are set to Repeater Mode, Bridge Mode respectively.
Solution IV: Devices A and B are set to Repeater Mode, Lazy Mode mode respectively.
Solution V: Devices A and B are set to Bridge Mode, Lazy Mode mode respectively.
3. Configuration steps:
Solution I: Both are Repeater Mode
42
1) To configure the LAN port of Devices A, B, enter Network parameters -> LAN
configuration to configure the IP address (on the same network segment) of the LAN
port IP address of Devices A and B, with the gateway address directed to the export
gateway;
2) Configure the AP mode of Device A as Repeater Mode, with the MAC address of AP as
the MAC address of Device B, and the configuration content is shown in the figure
below:
Figure 7-8 Repeater Mode instance
3) Configure the AP mode of Device B as Repeater Mode, and the SSID, wireless mode,
channel, channel bandwidth, security mode, pre-shared key are configured in the same
way as Device A, and the AP MAC address is: 0022AABA767C (the MAC address of
Device A);
Through the above configurations, the office personnel in Building 2 can connect to Device A
through Device B in Building 1, and access to the Internet through a gateway.
Tip:
1) The gateway of the computer in Building 2 is directed to the LAN port of Device A;
2) The IP address of LAN port of Device B is in the same network segment as the LAN
port address of Device A.

43
4. Connectivity verification:
Ping the LAN IP address of Device A on a computer in Building 2. If it can be pinged
successfully, then it means that the connection between the two wireless devices has been
established.
Solutions II, III, IV, V can follow Solution I.
Tip:
1) The device in Bridge Mode cannot be connected to the wireless single clients, such as laptops,
smart phones, etc;
2) The devices in Lazy Mode can be connected to the wireless single clients;
3) In configuration, the SSID and key of Devices A, B must be kept consistent,and the MAC
address of AP is that of the peer device (It is not required to configure the MAC address of the
peer device when the AP mode is Lazy Mode);
4) Device A and B must be in the same network segment.
Wireless security configuration
This section describes the Wireless configuration -> Wireless security configuration interface
and configuration methods, this device provides three wireless security mechanisms, WEP,
WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK, while users are allowed not to use the security mechanism.
In the following sections, the meaning of their configuration parameters are described separately.
7.6 No security mechanism
Figure 7-9 WEP
No security mechanism: Means that the client can access to the network without using any
security mechanism for authentication.

44
7.7 WEP
Figure 7-10 WEP
Security mechanism: Selecting "WEP" here means that the device will use the most basic
WEP security mechanism provided by the 802.11 Protocol;
Authentication type: When using the WEP encryption mechanism, three options, automatic,
open systems, Shared keys are available:
Auto: Means that the device can automatically choose Open System or Pre-shared key
mode according to the requests of wireless clients.
Open system: At this point, the wireless client host can pass the authentication and be
associate with the wireless devices on the premise of providing no authentication key;
but a correct key must be provided if data transmission is to be made.
Shared key: At this point, the wireless client host must provide the correct key to pass
the authentication; otherwise, it cannot be associated with the wireless devices, and
cannot perform data transmission.
Key format: Two formats hexadecimal code and ASCII code are provided:
When the hexadecimal code is used, the key characters can be 0 ~ 9, A, B, C, D, E, F.
When the ASCII code is used, the key characters can be all ASCII codes.
Key selection: The user can enter 1 ~ 4 keys according to needs, and these 4 keys can be in
different types.
WEP key: Sets the key value, and the length of the key is affected by key types:
When choosing a 64 - bit key, you can input 10 hexadecimal characters or 5 ASCII
characters.
When choosing a 128 - bit key, you can input 26 hexadecimal characters or 13 ASCII
characters.

45
Key types: Selects key types, and provides three options, Disable, 64 bits, 128 bits. Among
them, Disable means not to use the current key, but 64 bits, 128 bits, and used to specify the
length of the WEP key.
7.8 WPA/WPA2
Figure 7-11 WPA/WPA2
Security mechanism: Selecting "WPA/WPA2" here means that the device will use WPA or
WPA2 security mechanism. Under the security mechanism, the device will make
authentication and obtain the key using the Radius server;
WPA version: Sets the security mode this device will use:
Auto: Means that the device can automatically choose WPA or WPA2 security mode
according to the requests of wireless clients.
WPA: Means that the device will use the security mode of WPA.
WPA2: Means that the device will use the security mode of WPA2.
Encryption algorithm: It is the security algorithm used to encrypt wireless data, with the
options like Auto, TKIP and AES.
Auto: Means that the device will automatically choose encryption algorithms according
to needs.
TKIP: Means that all wireless data will use TKIP as the encryption algorithm.
AES: Means that all wireless data will use AES as the encryption algorithm.
Radius Server IP: It is the IP address of the Radius server used to the authenticate wireless
hosts.
Radius port: The service port number used by the Radius server for authenticating wireless
hosts.
Radius password: Sets the password for accessing to the Radius service.
Key update cycle: It is the timed update cycle used to specify the key. Value range is 60 ~
86400, in the unit of seconds. The default value is 3600, which means no update when the
value is 0.

46
7.9 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Figure 7-12 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Security mechanism: Here, you can select "WPA-PSK /WPA2-PSK", which means that the
device will use WPA-PSK /WPA2-PSK security mechanism. Under this security mechanism,
this device will use the WPA mode based on the Pre-Shared key.
WPA version: Sets the security mode this device will use:
Auto: Means that the device can automatically choose WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK
security mode according to the requests of wireless clients.
WPA: Means that the device will use the security mode of WPA-PSK.
WPA2: Means that the device will use the security mode of WPA2-PSK.
Encryption algorithm: It is the security algorithm used to encrypt wireless data, with the
options like Auto, TKIP and AES.
Auto: Means that the device will automatically choose encryption algorithms
according to needs.
TKIP: Means that all wireless data will use TKIP as the encryption algorithm.
AES: Means that all wireless data will use AES as the encryption algorithm.
Pre-shared key: The preset initialization key, with the value of 8 ~ 63 characters.
Key update cycle: It is the timed update cycle used to specify the key. Value range is 60 ~
86400, in the unit of seconds. The default value is 3600, which means no update when the
value is 0.
Filtering of wireless MAC address
This section describes the Wireless configuration-> Wireless MAC address filtering page and
the configuration of wireless MAC address filtering. By setting the MAC address filtering
function, you can enable or disable wireless hosts to or from access to the device and the wireless
network.

47
Figure 7-13 Filtering of wireless MAC address
Enable MAC address filtering: enable or disable the MAC address filtering function,
checking it means to enable it;
Filtering rules: Sets the rules for MAC address filtering;
Permission: It indicates that only the wireless clients that correspond to the MAC
addresses in the MAC address filtering information list are allowed to access to the
device and it is prohibited to connect the wireless clients out of the filtering table;
Prohibition: It indicates that only the wireless clients that correspond to the MAC
addresses in the MAC address filtering information list are prohibited to access to the
device, and the wireless clients out of the filtering table are allowed to access;
Add new entry: Click this button to enter intoWireless MAC address filteringpage to
configure the MAC addresses to be filtered, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 7-14 Configuration of MAC address filtering

48
Wireless Advanced Configuration
This section describes the meaning of the wireless advanced parameters in the Wireless
Configuration-> Wireless advanced configuration.
In this page, you can set wireless advanced parameters, and under normal circumstances, keep the
default values of these parameters. If you have special needs, you can configure in this page.
Figure 7-15 Wireless Advanced Configuration
RTS threshold: When a packet exceeds this threshold, it will activate the RTS mechanism.
Before transmitting data frames, the device will send RTS (Request to Send) packet to the
destination site for negotiation; after receiving an RTS frame, the wireless site will respond to
the device by sending a CTS (Clear to Send) frame, which means wireless communication
can be made between both of them. Value range is generally 1~2347 bytes, and the default is
2347 bytes;
The RTS mechanism is used to avoid data transmission conflicts in the wireless LAN. The
transmission frequency of the RTS packet needs to be set reasonably, and setting of the RTS
threshold requires weighing. If this parameter is set to low, the transmission rate of RTS
packets is increased, consuming more bandwidths, which may significantly affect the
throughput of other network packets. But the more frequently the RTS packet is sent, the
more quickly the system can recover from disruption or conflict;
Segmentation threshold: It is used to define the maximum transmission length of the wireless
data packets allowed by the wireless MAC layer to be transmitted, when the length of Data
frames exceeds this value, they will automatically be segmented into multiple data frames,
and then transmitted again. If the segmented transmission is interrupted, only the parts that
are not sent successfully need to be sent, and the throughput of segmented packets is
generally low. Value range is generally 256~2346 bytes, and the default is 2346 bytes.

49
The transmission efficiency for large segments is high, but if there is a clear conflict in the
wireless network, or if the network is used at a high frequency, the reduction of segments can
improve the reliability of data transfer. In most cases, keep the default value as 2346;
Beacon interval: The device synchronizes the wireless network connection through regular
Radio Beacon frames. This parameter is used to define the transmission interval of beacon
frames which are transmitted periodically at the specified time interval. Value range is
generally 20~999 ms, and the default is 100 ms.
DTIM interval: This parameter is used to specify the transmission interval for the Delivery
Traffic Indication Message (DTIM). DTIM interval is used to decide the frequency of beacon
frames containing Traffic Indication Map (TIM) to be transmitted. TIM will issue a warning
to the sites entering into the sleep status, by indicating that the data is to be received. DTIM is
usually the multiple of beacon interval. Its use range is 1~255, and its default value is 1;
Enable Short Preamble: Enables or disables Short Preamble.
When enabled, the short preamble type will be used; the short preamble type can
provide better performance. Because the use of short preamble can minimize costs,
thus maximizing the network data throughput;
When disabled, the long preamble type (Long Preamble) will be used; the long
preamble type will be able to provide more viable connections and a large range of
connections;
Enable WMM: Allows you to enable or disable the WMM support. WMM (Wi-Fi
Multimedia) is a subset of the 802.11e standard. WMM allows wireless traffic to have a
priority range based on the data type. Time-sensitive information, such as video or audio, will
have a higher priority than the normal traffic. To use the WMM function properly, wireless
clients must also support WMM.
Status of wireless host
This section describes the Wireless Configuration -> Wireless host status page. Through the
"List of the wireless host status information", you can view the status information of the wireless
hosts currently connected to the device. In addition, through the "List of the wireless host status
information", you can also easily set the MAC address filtering function.

50
Figure 7-16 Status of wireless host
ID: Serial number;
MAC address: The MAC address of the wireless host;
Filter: Selecting it to indicate that the current MAC address has been added into the "List of
MAC address filter information" (which can be viewed in theWireless configuration -->
Wireless MAC address filteringpage), while not selecting it means that the current MAC
address filtering is not set;
Channel bandwidth: The theoretical data transfer rate of the data channel;
All filter: Click <All filter>, to conduct the MAC address filtering for all wireless hosts
whose filtering is not enabled in the current list, and to add all the MAC addresses to the
"MAC address filtering list";
Refresh: Click <Refresh>, to view the latest wireless host status and statistical information.
51
Chapter 8 System management
In the System Management main menu, you can enter the Administrator configure, clock
management, configuration management, software upgrade, and scheduled task pages. This
chapter mainly describes how users set the device clock; how to back up and import the
configuration files; how to upgrade device, etc.
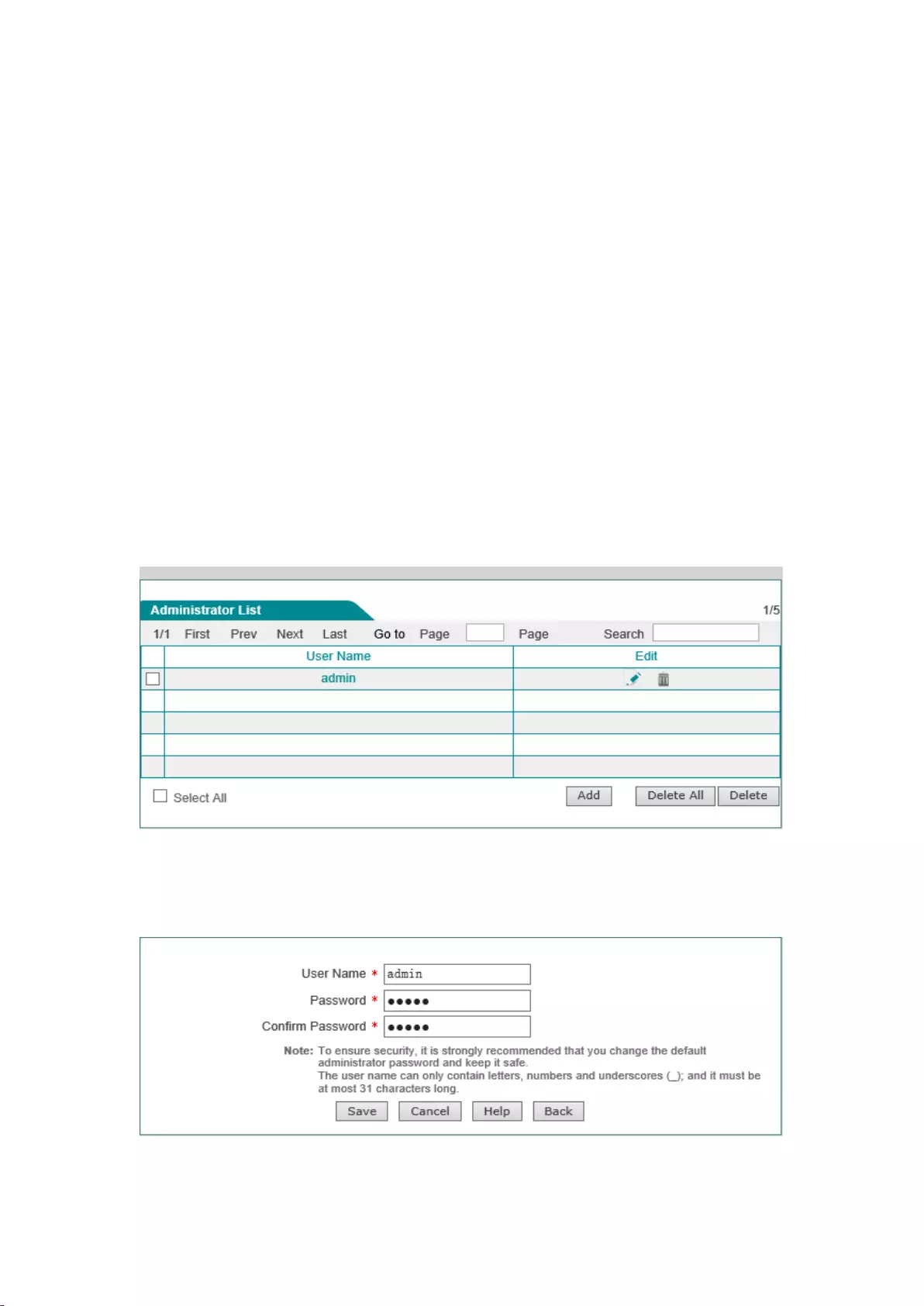
8.1 Administrator configuration
Enter into the System Management-> Administrator configuration page, to view and configure
the device administrator's user name and password.
1) Administrator configuration information list
Figure 8-1 Status of wireless host
2) Description of administrator configuration parameters
Figure 8-2 Status of wireless host

52
User name: Customize the user name of the administrator who logs in the WEB interface;
Password, confirm password: Customize the password of the administrator who logs in the
WEB interface;
3) Modification of administrators' factory user name, password
For security reasons, we strongly recommend to modify the initial administrator user name and
password, and to keep them with care.
Enter into the System Management-> Administrator configuration page, click on the Edit icon
with the user name as "admin", enter into the configuration page to modify the factory user name
and password. After modification, you must use the new user name and password to log into the
device.
8.2 Clock management
This section describes the System Management-> Clock management page.
In order to guarantee that the functions of the device relating to time work normally, the clock of
the device needs to be accurately set, to make it synchronize with the local standard time.
The device provides two ways of setting system time, "Manual setup time" and "Network time
synchronization". It is recommended to use the "Network time synchronization" function to obtain
the standard time, and the device will automatically get the standard time from the Internet after it
connects Internet in bootup.
Figure 8-3 Clock management

53
Current system time: Displays the current date and time information of the device (unit:
Y-M-D, H:M:S).
Time zone selection: Selects the international time zone in which the device resides. Only
choosing a correct time zone can the network time synchronization function work properly.
Manual time setting: Manually enters the current date and time (unit: Y-M-D, H:M:S);
Network time synchronization: After using the network time synchronization function to set
up the right NTP server, and when the device is connected to the Internet, it will
automatically synchronize the time with the set NTP server. The addresses of two NTP
servers preset by the system by default are 192.43.244.18, 129.6.15.28, which generally
requires no change. If you need to know more about the NTP knowledge and the server, just
visit http://www.ntp.org.
8.3 Configuration management
This section describes the configuration methods of System management -> Configuration
management. In this page, you can back up the current configuration file to a local PC, import the
new configuration file to the device and restore the factory configuration of the device.
Figure 8-4 Configuration management
1) Backup configuration files
Click on the <Save> button in the above figure, to back up the configuration file to the local PC,
with the format of the configuration file as .xml.
2) Import configuration file
In the previous figure, click < Browse ... >, and select the configuration file saved on the local PC.
Then click <Import> again. If you have checked the check box "Restore factory configuration
before import", click the <Import> button, and the device will be restore to the factory settings.
54
3) Restore to factory settings of device
If users need to restore the device to its factory settings, enter into the Systems management ->
Configuration management page, and click <Restore>.
Tip:
1) Do not cut off the device power supply in loading configuration, in order to avoid unexpected
errors.
2) Restoring the device's factory settings will delete all the custom settings. It is strongly
recommended that before restoring the factory configuration, first back up its configuration
files.
3) The user name and password of the device's factory administrator are as follows: admin, and
the default LAN port IP address/subnet mask is: 192.168.1.253/ 255.255.255.0.
4) After clicking <Restore>, the device needs to be rebooted before restoring its factory settings.
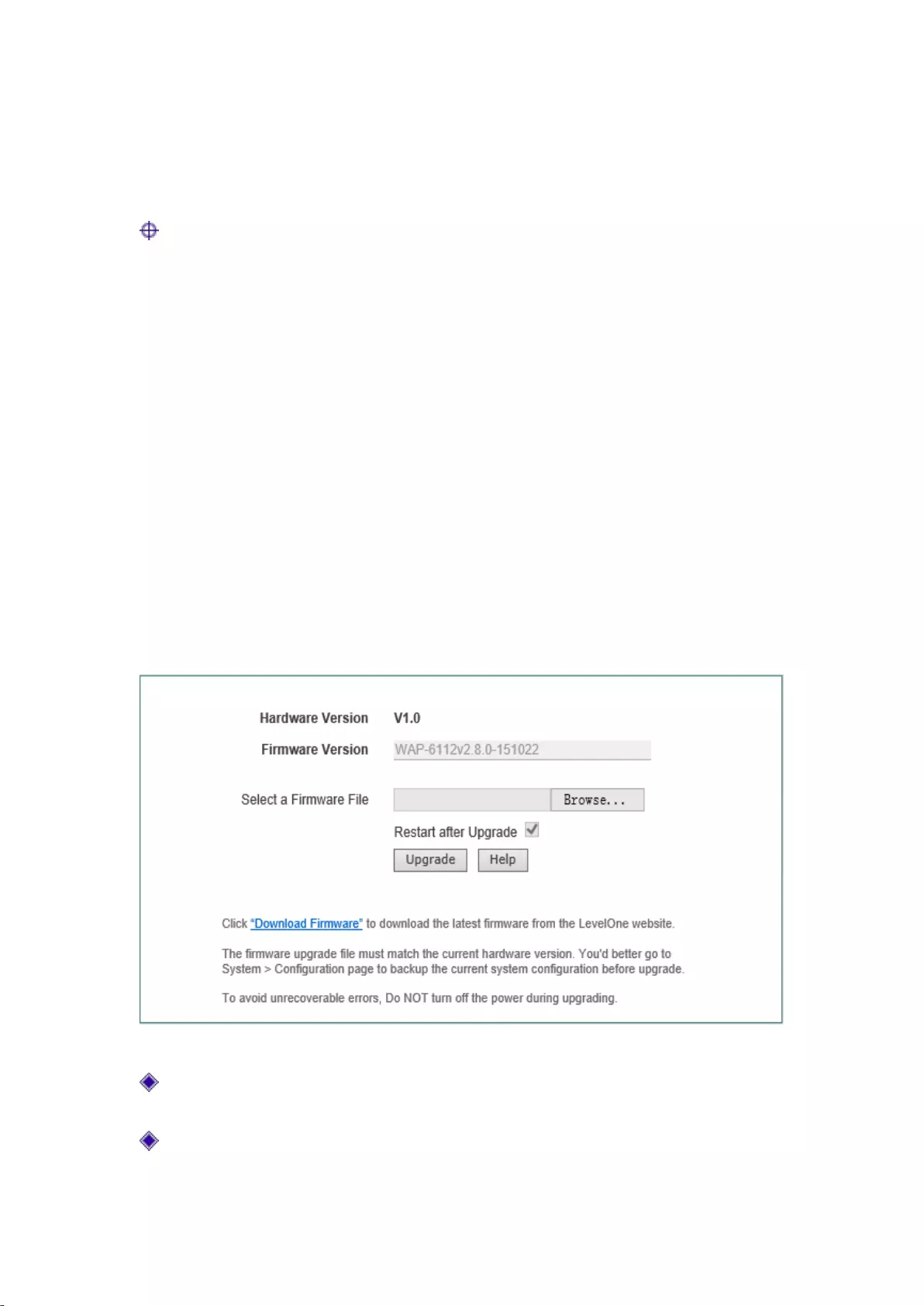
8.4 Software upgrade
This section describes the System management-> Software upgrade page and the software
upgrade procedure. In this page, you can view the information of the currently running version,
and download the latest software from the LevelOne web site.
Figure 8-5 Software upgrade
Version information: Displays the information of the current hardware version, software
version;
Download the latest version: Goes to the official website of LevelOne to download the latest
version of the software.

55
Upgrading steps:
Step 1: Download the latest software
Click on the hyperlink "Download the latest version" and go to the official site of LevelOne to
download the latest version of the software to your local PC.
Step 2: Select the upgrade path
In the "Select the upgrade file" text box, enter the path for upgrading the software on the local PC,
or select the new software on the local PC by clicking < Browse ... >.
Step 3: Update device software
After selecting software, click on the <Upgrade> button, to update the device software.
Tip:
1) Please select an appropriate type of the latest software: The hardware version for the
downloaded software must be consistent with the hard versions of the current products;
2) It is recommended that before upgrading, enter into Systems management -> Configuration
management to back up the current configuration of the system.
3) It is strongly recommended to upgrade when the device load is low (less users).
4) Upgrading device software on a regular basis enables the device to get more functions or to
have a better working performance. The right software upgrading will not change the current
device settings.
5) During the upgrading process, the device's power supply cannot be cut off, otherwise it will
cause unpredictable errors and even irreversible damages to the hardware.
6) After the completion of upgrading, the software will automatically restart to take effect,
without the need of human intervention.
8.5 Scheduled task
This section describes the System management-> Scheduled task page. By configuring
scheduled tasks, administrators can predefine the actions completed by the device at a specified
time.
1) List of scheduled tasks
The scheduled task list is an editable list. You can operate the instances in the list.

56
Figure 8-6 List of scheduled tasks
2) Description of scheduled task parameters
Figure 8-7 Configuration of scheduled tasks
Task name: Name of the custom tasks;
Startup type: Indicates time cycle, and the options are: every week, every day, every hour,
every minute;
Running time: Means the specific time for implementation of these tasks, whose setting
varies based on the startup types;
Task content: Selects the appropriate task content.

57
Chapter 9 System status
In System status, you can easily view the running state of the device, and the system information
and history of the device.
9.1 Running status
The running status described in this section is the same as Start-> Running status page, please
refer to the section: Running Status.
9.2 System information
In the System status -> System information page, network administrators can understand
system-related information and view system history; through information systems, network
administrators can understand network problems or potential problems, which helps improve the
network performance and enhance network security.
Figure 9-1 System information
Current system time: Displays the current date and time information of the device (Unit:
Y-M-D, H:M:S);
System running time: Displays the time from starting of the device at this time to viewing the
time;
CPU utilization: Shows the percentage of the current CPU utilization.
Memory usage: Shows the percentage of the current memory usage.

58
Serial number: Shows the internal serial number of product (which may be different from the
surface serial number);
Device model: Displays the product model of the device;
Hardware version: Displays the hardware version number of the device. When the device
hardware version is V1.0, it is not described in the software;
Software version: Displays the software version number of the device.
Refresh: Click < Refresh >, and you can view the latest system information.
Tip:
Figure 9-1 The usage of CPU, memory is different and the displayed colors are different:
Green when the usage is [0, 50%);
Orange when the usage is [50%, 70%);
Red when the usage is [70%, 100].

59
Appendix A FAQ
Q1. How to connect a Windows XP PC to the Device wirelessly?
Step 1: Configuring TCP/IP Settings
1. Right-click Network Neighborhood and select Properties.
2. Right-click Wireless Network Connection and select Properties.
3. Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) to open the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties window.
4. Do one of the following:
1) If a DHCP server is available on your network, and you want IP settings to be
assigned automatically, select Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain
DNS server address automatically.
2) If you want to set the IP address and other settings manually, do the following:
Select Use the following IP address, enter the static IP address (a free IP
address in 192.168.1.0/24) in IP address box, 255.255.255.0 in Subnet
mask box, and enter the IP address of your default gateway in Default
Gateway box.
Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the IP addresses
of DNS servers in Preferred DNS Server and Alternate DNS Server
(optional) boxes. If the primary DNS server is unreachable, the secondary
DNS server is used.
5. Click OK to finish the configuration.
Step 2: Connecting the PC to Your Wireless Network
1. Make sure your wireless network adapter is enabled.
2. Right-click the wireless network icon in the lower right corner of your screen,
and click View Available Wireless Networks.
3. In the list of wireless networks that appears, click the network you want to connect to,
and then click Connect.
4. If prompted, enter the network security key, and then click Connect.
5. If the connection is successful, the word Connected appears to the right of your
network name.

60
Q2. A-2 How to connect a Windows 7 PC to the Device wirelessly?
1. Step 1: Configuring TCP/IP Settings
2. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing
Center > Change Adapter Settings.
3. Right-click Wireless Network Connection and select Properties.
4. Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) to open the Internet Protocol
Version 4(TCP/IPv4) Properties window.
5. Do one of the following:
6. If a DHCP server is available on your network, and you want IP settings to be
assigned automatically, select Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server
address automatically.
7. If you want to set the IP address and other settings manually, do the following:
8. Select Use the following IP address, enter the static IP address (a free IP address in
192.168.1.0/24) in IP address box, 255.255.255.0 in Subnet mask box, and enter the IP
address of your default gateway in Default Gateway box.
9. Select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the IP addresses of DNS
servers in Preferred DNS Server and Alternate DNS Server (optional) boxes. If the primary
DNS server is unreachable, the secondary DNS server is used.
10. Click OK to finish the configuration.
11. Step 2: Connecting the PC to Your Wireless Network
12. Make sure your wireless network adapter is enabled.
13. Click the wireless network icon in the lower right corner of your screen.
14. In the list of wireless networks that appears, click the network you want to
connect to, and then click Connect.
15. If prompted, enter the network security key, and then click OK.
16. If the connection is successful, the word Connected appears next to your network name.
Q3. How to reset the Device to factory default settings?
Note
The reset operation will clear all custom settings on the Device, so do it with caution.
1. Remember the administrator password
Normally, you can reset the Device to factory default settings via the Web UI. The
operation is as follows: Go to the System > Configuration page, click Reset, and
restart the Device after the reset operation is complete.

61
2. Forget the administrator password
If you forget the administrator password, you cannot login to the Device’s Web UI. However, you can
use the Reset button to reset the Device to factory default settings. The operation is as follows: With
the Device powered on, press and hold the Reset button for more than 5 seconds, and then release the
button. The Device will restart with factory default settings.
62
Appendix B Hex ASCII Codes
Appendix A Table of ASCII Codes in Hexadecimal Form
Character
Enter
ESC
Space
!
"
#
$
%
&
’
(
)
*
+
,
Hex Code
0D
1B
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2A
2B
2C
Character
-
.
/
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
:
;
Hex Code
2D
2E
2F
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
3A
3B
Character
<
=
>
?
@
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
Hex Code
3C
3D
3E
3F
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
4A
Character
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Hex Code
4B
4C
4D
4E
4F
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
Character
Z
[
\
]
^
-
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
Hex Code
5A
5B
5C
5D
5E
5F
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
Character
j
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
Hex Code
6A
6B
6C
6D
6E
6F
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
Character
y
z
{
|
}
~
Hex Code
79
7A
7B
7C
7D
7E

63
Appendix C LICENSE STATEMENT / GPL
CODE STATEMENT
This product resp. the here
(http://global.level1.com/downloads.php?action=init) for
downloading offered software includes software code
developed by third parties, including software code subject to
the GNU General Public License Version 2 (“GPLv2”) and
GNU Lesser General Public License 2.1 („LGPLv2.1“).
WRITTEN OFFER FOR GPL/LGPL
SOURCE CODE
We will provide everyone upon request the applicable GPLv2
and LGPLv2.1 source code files via CDROM or similar
storage medium for a nominal cost to cover shipping and
media charges as allowed under the GPLv2 and LGPLv2.1.
This offer is valid for 3 years. GPLv2 and LGPLv2 inquiries:
Please direct all GPL and LGPL inquiries to the following
address:
Digital Data Communications GmbH
Zeche-Norm-Str. 25
44319 Dortmund
Deutschland
Phone: +49 231 9075 - 0
Fax: +49 231 9075 - 184
Email: support@level1.com

64
Web: www.level1.com
NO WARRANTY
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied
warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public
License for more details. IN NO EVENT UNLESS
REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN
WRITING WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY
OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY AND/OR
REDISTRIBUTE THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE,
BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO
USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED
INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR
THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO
OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS), EVEN IF
SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 2, June 1991
Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301,
USA
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
Preamble
The licenses for most software are designed to take away
your freedom to share and change it. By contrast, the GNU

65
General Public License is intended to guarantee your
freedom to share and change free software--to make sure the
software is free for all its users. This General Public License
applies to most of the Free Software Foundation's software
and to any other program whose authors commit to using it.
(Some other Free Software Foundation software is covered
by the GNU Lesser General Public License instead.) You can
apply it to your programs, too.
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom,
not price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make
sure that you have the freedom to distribute copies of free
software (and charge for this service if you wish), that you
receive source code or can get it if you want it, that you can
change the software or use pieces of it in new free programs;
and that you know you can do these things.
To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that
forbid anyone to deny you these rights or to ask you to
surrender the rights. These restrictions translate to certain
responsibilities for you if you distribute copies of the software,
or if you modify it.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program,
whether gratis or for a fee, you must give the recipients all the
rights that you have. You must make sure that they, too,
receive or can get the source code. And you must show them
these terms so they know their rights.
We protect your rights with two steps: (1) copyright the
software, and (2) offer you this license which gives you legal
permission to copy, distribute and/or modify the software.
Also, for each author's protection and ours, we want to make
certain that everyone understands that there is no warranty
for this free software. If the software is modified by someone
else and passed on, we want its recipients to know that what
they have is not the original, so that any problems introduced
by others will not reflect on the original authors' reputations.

66
Finally, any free program is threatened constantly by
software patents. We wish to avoid the danger that
redistributors of a free program will individually obtain patent
licenses, in effect making the program proprietary. To
prevent this, we have made it clear that any patent must be
licensed for everyone's free use or not licensed at all.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution
and modification follow.
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR
COPYING, DISTRIBUTION AND
MODIFICATION
0. This License applies to any program or other work which
contains a notice placed by the copyright holder saying it may
be distributed under the terms of this General Public License.
The "Program", below, refers to any such program or work,
and a "work based on the Progra m" means either the
Program or any derivative work under copyright law: that is to
say, a work containing the Program or a portion of it, either
verbatim or with modifications and/or translated into another
language. (Hereinafter, translation is included without
limitation in the term "modification".) Each licensee is
addressed as "you".
Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are
not covered by this License; they are outside its scope. The
act of running the Program is not restricted, and the output
from the Program is covered only if its contents constitute a
work based on the Program (independent of having been
made by running the Program). Whether that is true depends
on what the Program does.
1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the
Program's source code as you receive it, in any medium,
provided that you conspicuously and appropriately publish on
each copy an appropriate copyright notice and disclaimer of

67
warranty; keep intact all the notices that refer to this License
and to the absence of any warranty; and give any other
recipients of the Program a copy of this License along with
the Program.
You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a
copy, and you may at your option offer warranty protection in
exchange for a fee.
2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any
portion of it, thus forming a work based on the Program, and
copy and distribute such modifications or work under the
terms of Section 1 above, provided that you also meet all of
these conditions:
a) You must cause the modified files to carry prominent
notices stating that you changed the files and the date of any
change.
b) You must cause any work that you distribute or publish,
that in whole or in part contains or is derived from the
Program or any part thereof, to be licensed as a whole at no
charge to all third parties under the terms of this License.
c) If the modified program normally reads c ommands
interactively when run, you must cause it, when started
running for such interactive use in the most ordinary way, to
print or display an announcement including an appropriate
copyright notice and a notice that there is no warranty (or
else, saying that you provide a warranty) and that users may
redistribute the program under these conditions, and telling
the user how to view a copy of this License. (Exception: if the
Program itself is interactive but does not normally print such
an announcement, your work based on the Program is not
required to print an announcement.)
These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If
identifiable sections of that work are not derived from the

68
Program, and can be reasonably considered independent
and separate works in themselves, then this License, and its
terms, do not apply to those sections when you distribute
them as separate works. But when you distribute the same
sections as part of a whole which is a work based on the
Program, the distribution of the whole must be on the terms
of this License, whose permissions for other licensees extend
to the entire whole, and thus to each and every part
regardless of who wrote it.
Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or
contest your rights to work written entirely by you; rather, the
intent is to exercise the right to control the distribution of
derivative or collective works based on the Program.
In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on
the Program with the Program (or with a work based on the
Program) on a volume of a storage or distribution medium
does not bring the other work under the scope of this
License.
3. You may copy and distribute the Program (or a work based
on it, under Section 2) in object code or executable form
under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above provided that you
also do one of the following:
we use this doubled UL to get the sub-sections indented,
while making the bullets as unobvious as possible.
a) Accompany it with the complete corresponding
machine-readable source code, which must be distributed
under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium
customarily used for software interchange; or,
b) Accompany it with a written offer, valid for at least three
years, to give any third party, for a charge no more than your
cost of physically performing source distribution, a complete
machine-readable copy of the corresponding source code, to

69
be distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on
a medium customarily used for software interchange; or,
c) Accompany it with the information you received as to the
offer to distribute corresponding source code. (This
alternative is allowed only for noncommercial distribution and
only if you received the program in object code or executable
form with such an offer, in accord with Subsection b above.)
The source code for a work means the preferred form of the
work for making modifications to it. For an executable work,
complete source code means all the source code for all
modules it contains, plus any associated interface definition
files, plus the scripts used to control compilation and
installation of the executable. However, as a special
exception, the source code distributed need not include
anything that is normally distributed (in either source or
binary form) with the major components (compiler, kernel,
and so on) of the operating system on which the executable
runs, unless that component itself accompanies the
executable.
If distribution of executable or object code is made by offering
access to copy from a designated place, then offering
equivalent access to copy the source code from the same
place counts as distribution of the source code, even though
third parties are not compelled to copy the source along with
the object code.
4. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the
Program except as expressly provided under this License.
Any attempt otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense or
distribute the Program is void, and will automatically
terminate your rights under this License. However, parties
who have received copies, or rights, from you under this
License will not have their licenses terminated so long as
such parties remain in full compliance.

70
5. You are not required to accept this License, since you
have not signed it. However, nothing else grants you
permission to modify or distribute the Program or its
derivative works. These actions are prohibited by law if you
do not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or
distributing the Program (or any work based on the Program),
you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and all
its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying
the Program or works based on it.
6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based
on the Program), the recipient automatically receives a
license from the original licensor to copy, distribute or modify
the Program subject to these terms and conditions. You may
not impose any further restrictions on the recipients' exercise
of the rights granted herein. You are not responsible for
enforcing compliance by third parties to this License.
7. If, as a consequence of a court judgment or allegation of
patent infringement or for any other reason (not limited to
patent issues), conditions are imposed on you (whether by
court order, agreement or otherwise) that contradict the
conditions of this License, they do not excuse you from the
conditions of this License. If you cannot distribute so as to
satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this License
and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence
you may not distribute the Program at all. For example, if a
patent license would not permit r oyalty-free redistribution of
the Program by all those who receive copies directly or
indirectly through you, then the only way you could satisfy
both it and this License would be to refrain entirely from
distribution of the Program.
If any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable
under any particular circumstance, the balance of the section
is intended to apply and the section as a whole is intended to
apply in other circumstances.

71
It is not the purpose of this section to induce you to infringe
any patents or other property right claims or to contest
validity of any such claims; this section has the sole purpose
of protecting the integrity of the free software distribution
system, which is implemented by public license practices.
Many people have made generous contributions to the wide
range of software distributed through that system in reliance
on consistent application of that system; it is up to the
author/donor to decide if he or she is willing to distribute
software through any other system and a licensee cannot
impose that choice.
This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is
believed to be a consequence of the rest of this License.
8. If the distribution and/or use of the Program is restricted in
certain countries either by patents or by copyrighted
interfaces, the original copyright holder who places the
Program under this License may add an explicit geographical
distribution limitation excluding those countries, so that
distribution is permitted only in or among countries not thus
excluded. In such case, this License incorporates the
limitation as if written in the body of this License.
9. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or
new versions of the General Public License from time to time.
Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present
version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or
concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
Program specifies a version number of this License which
applies to it and "any later version", you have the option of
following the terms and conditions either of that version or of
any later version published by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Program does not specify a version number of this
License, you may choose any version ever published by the
Free Software Foundation.

72
10. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Program into other
free programs whose distribution conditions are different,
write to the author to ask for permission. For software which
is copyrighted by the Free Software Foundation, write to the
Free Software Foundation; we sometimes make exceptions
for this. Our decision will be guided by the two goals of
preserving the free status of all derivatives of our free
software and of promoting the sharing and reuse of software
generally.
NO WARRANTY
11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF
CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE
PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED
IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR
OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS"
WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND
PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU.
SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU
ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING,
REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
12. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE
LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING WILL ANY COPYRIGHT
HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY
AND/OR REDISTRIBUTE THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED
ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING
ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE
OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING
RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY

73
YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE
PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER
PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER
PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
How to Apply These Terms to Your
New Programs
If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the
greatest possible use to the public, the best way to achieve
this is to make it free software which everyone can
redistribute and change under these terms.
To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is
safest to attach them to the start of each source file to most
effectively convey the exclusion of warranty; and each file
should have at least the "copyright" line and a pointer to
where the full notice is found.
one line to give the program's name and an idea of what it
does.
Copyright (C) yyyy name of author
This program is free software; you can redistribute it
and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License
as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version
2
of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be
useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty
of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See
the
GNU General Public License for more details.

74
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public
License
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston,
MA 02110-1301, USA.
Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and
paper mail.
If the program is interactive, make it output a short notice like
this when it starts in an interactive mode:
Gnomovision version 69, Copyright (C) year name of author
Gnomovision comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details
type `show w'. This is free software, and you are welcome
to redistribute it under certain conditions; type `show c'
for details.
The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should
show the appropriate parts of the General Public License. Of
course, the commands you use may be called something
other than `show w' and `show c'; they could even be
mouse-clicks or menu items--whatever suits your program.
You should also get your employer (if you work as a
programmer) or your school, if any, to sign a "copyright
disclaimer" for the program, if necessary. Here is a sample;
alter the names:
Yoyodyne, Inc., hereby disclaims all copyright
interest in the program `Gnomovision'
(which makes passes at compilers) written
by James Hacker.
signature of Ty Coon, 1 April 1989
Ty Coon, President of Vice
This General Public License does not permit incorporating
your program into proprietary programs. If your program is a
subroutine library, you may consider it more useful to permit
linking proprietary applications with the library. If this is what
you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General Public License
instead of this License.

75
Notification of Compliance
Europe - EU Declaration of Conformity
For complete DoC please visit
http://global.level1.com/downloads.php?action=init
GPL License Agreement
GPL may be included in this product, to view the GPL license agreement goes to
http://download.level1.com/level1/gpl/GPL.pdf
For GNU General Public License (GPL) related information, please visit
http://global.level1.com/downloads.php?action=init