QNAP VS-4116U-RP Pro+ User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for VS-4116U-RP Pro+ by QNAP which is a product in the Network Video Recorders (NVR) category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

1
VIOSTOR NVR
NETWORK VIDEO RECORDER
QVR
QNAP VIOSTOR RECORDING SYSTEM
User Manual (Version: 5.1.0)
© 2015. QNAP Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

2
Thank you for choosing QNAP products! This user manual provides detailed
instructions of using the product. Please read carefully and start to enjoy the
powerful functions of the product!
The VioStor NVR is hereafter referred to as the VioStor or the NVR.
This user manual provides the description of all the functions of the VioStor
NVR. The product you purchased may not support certain functions dedicated
to specific models.
This user manual (version 5.1.0) is applicable for the QVR version 5.1.0 only. If
the VioStor NVR is running an older firmware version, please refer to the
previous versions of the user manuals.
Legal Notices
All the features, functionality, and other product specifications are subject to change
without prior notice or obligation. Information contained herein is subject to
change without notice.
QNAP and the QNAP logo are trademarks of QNAP Systems, Inc. All other brands
and product names referred to are trademarks of their respective holders.
Further, the ® or ™ symbols are not used in the text.
LIMITED WARRANTY
In no event shall the liability of QNAP Systems, Inc. (QNAP) exceed the price paid
for the product from direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential software,
or its documentation. QNAP makes no warranty or representation, expressed,
implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this
documentation and all accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality,
performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. QNAP reserves
the right to revise or update its products, software, or documentation without
obligation to notify any individual or entity.
CAUTION
1. Back up the system periodically to avoid any potential data loss. QNAP
disclaims any responsibility of all sorts of data loss or recovery.
2. Should you return any components of the product package for refund or
maintenance, make sure they are carefully packed for shipping. Any form of
damages due to improper packaging will not be compensated.

3
Important Notice
Reading instructions
Read the safety warnings and user manual carefully before using this product.
Power supply
This product can only be used with the power supply provided by the
manufacturer.
Service
Please contact qualified technicians for any technical enquires. Do not repair
this product by yourself to avoid any voltage danger and other risks caused by
opening this product cover.
Warning
To avoid fire or electric shock, do not use this product in rain or humid
environments. Do not place any objects on this product.
4
Regulatory Notice
FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Shielded interface cables, if any, must be used in order to comply with the emission
limits.
CE NOTICE
Class B only.

5
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ........................................................................................................... 5
Safety Warning ............................................................................................................. 11
Chapter 1. Introduction .......................................................................................... 12
1.1 Overview .................................................................................................. 12
1.2 Hardware Illustration ............................................................................... 13
1.2.1 VS – 12164 / 12156 / 12148 / 12140U-RP Pro+ .............................. 13
1.2.2 VS – 12164 / 12156 / 12148 / 12140U-RP Pro ................................ 14
1.2.3 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124U-RP Pro+ ....................................... 15
1.2.4 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124U-RP Pro ......................................... 16
1.2.5 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124 Pro+ ............................................... 17
1.2.6 VS – 6120 / 6116 / 6112 Pro+ .......................................................... 18
1.2.7 VS – 6020 / 6016 / 6012 Pro ............................................................ 19
1.2.8 VS – 4116 / 4112 / 4108U-RP Pro+ .................................................. 20
1.2.9 VS – 4016 / 4012 / 4008U-RP Pro .................................................... 21
1.2.10 VS – 4116 / 4112 / 4108 Pro+ ........................................................ 22
1.2.11 VS – 4016 / 4012 / 4008 Pro .......................................................... 23
1.2.12 VS – 2212 / 2208 / 2204 Pro+ ........................................................ 24
1.2.13 VS – 2112 / 2108 / 2104 Pro+ ........................................................ 25
1.2.14 VS – 2012 / 2008 / 2004 Pro .......................................................... 26
1.2.15 VS – S2212 / S2208 / S2204 Pro + .................................................. 27
1.2.16 VS – 2108 / 2104 L ......................................................................... 28
Chapter 2. Install the NVR ...................................................................................... 29
2.1 Personal Computer Requirements ........................................................... 29
2.2 Browse CD-ROM ....................................................................................... 32
2.3 Hard Disk Drives Compatibility List .......................................................... 33
2.4 IP Cameras Compatibility List................................................................... 33
2.5 Check System Status ................................................................................ 34
2.6 System Configuration ............................................................................... 37
Chapter 3. Use the NVR by Local Display ............................................................... 40
3.1 Quick Configuration (Manual Setup or Quick Setup) ............................... 43
3.1.1 Quick Setup ...................................................................................... 43
3.1.2 Manual Setup ................................................................................... 45
3.2 Surveillance Settings ................................................................................ 48
3.3 Monitoring ............................................................................................... 51
3.4 Video Playback ......................................................................................... 63

6
3.5 Video Conversion & Export ...................................................................... 66
Chapter 4. QVR Basics and Desktop ....................................................................... 68
4.1 Introducing QVR ....................................................................................... 68
4.2 Connect to the NVR ................................................................................. 69
4.3 Using the QVR Desktop ............................................................................ 70
Chapter 5. Remote Monitoring .............................................................................. 82
5.1 Monitoring Page ....................................................................................... 83
5.1.1 Live Video Window .......................................................................... 91
5.1.2 Display Mode ................................................................................... 93
5.1.3 PTZ Camera Control Panel ............................................................... 93
5.1.4 Multi-server Monitoring .................................................................. 95
5.1.5 Monitor Settings .............................................................................. 96
5.1.6 Instant Playback ............................................................................... 99
5.1.7 Same-screen IP Camera Configurations ......................................... 100
5.1.8 Auto Cruising .................................................................................. 101
5.1.9 Qdewarp ........................................................................................ 104
5.1.10 ROI (Region of Interest) ................................................................ 106
5.2 E-map ..................................................................................................... 107
5.2.1 Icons and Description..................................................................... 108
5.2.2 Add a Map Set or an E-map ........................................................... 109
5.2.3 Edit a Map Name ........................................................................... 111
5.2.4 Delete a Map Set or an E-map ....................................................... 111
5.2.5 Indicate IP Cameras on an E-map .................................................. 112
5.2.6 Enable/Disable Event Alert ............................................................ 115
5.3 Remote Monitoring from the QNAP QVR Client for Windows .............. 118
Chapter 6. Play Video Files ................................................................................... 119
6.1 Playback Page ......................................................................................... 120
6.1.1 Play Video Files from NVR ............................................................. 124
6.1.2 Intelligent Video Analytics (IVA) .................................................... 126
6.1.3 Export NVR Videos ......................................................................... 131
6.1.4 Export Video Files with Digital Watermark ................................... 133
6.1.5 Enable Recording Video Files ............................................................ 134
6.1.6 Average Time-Divided Playback ........................................................ 135
6.2 Play Video Files in the QNAP QVR Client for Windows ......................... 136
6.3 Watermark Proof.................................................................................... 137
6.4 Access the Recording Data ..................................................................... 139
6.4.1 Microsoft Networking (SMB/CIFS) ................................................. 139
6.4.2 FTP Server (FTP) ............................................................................. 139

7
Chapter 7. Surveillance Settings ........................................................................... 141
7.1 Camera Settings ..................................................................................... 141
7.1.1 Camera Overview ........................................................................... 141
7.1.2 Camera Configuration .................................................................... 141
User Defined Multi-stream ............................................................................................................... 151
Smart Recording ............................................................................................................................... 154
Edge Recording ................................................................................................................................ 158
7.1.3 Flexible Channel Mode .................................................................. 162
7.1.4 Event Management ........................................................................ 164
Traditional Mode .............................................................................................................................. 164
Advanced Mode ................................................................................................................................ 168
7.2 System Settings ...................................................................................... 186
7.2.1 Advanced Setting ........................................................................... 186
7.2.2 Flexible Channel Mode Setting ...................................................... 187
7.1.3 Privilege Settings ............................................................................ 189
7.1.4 Protocol Management ................................................................... 190
7.3 Surveillance Logs .................................................................................... 191
7.3.1 Surveillance Logs ............................................................................ 191
7.4 Push Service ........................................................................................... 192
7.5 Recovery Management .......................................................................... 192
7.6 License Management ............................................................................. 195
7.6.1 License Activation .......................................................................... 195
Online Activation .............................................................................................................................. 195
Offline Activation ............................................................................................................................. 198
7.6.2 License Deactivation ...................................................................... 202
Online Deactivation .......................................................................................................................... 202
Offline Deactivation ......................................................................................................................... 205
7.7 On-line Users List (Only for Upgrade from Previous Version) ................ 209
8. Backup & Expansion ........................................................................................... 210
8.1 External Backup ...................................................................................... 210
8.2 One Touch Video Backup ....................................................................... 218
8.3 Remote Replication ................................................................................ 221
8.4 Storage Expansion .................................................................................. 225
9. Control Panel ...................................................................................................... 231
9.1 System Settings ...................................................................................... 231
9.1.1 General Settings ............................................................................. 231
System Administration ..................................................................................................................... 231
Time .................................................................................................................................................. 231

8
9.1.2 Storage Manager ............................................................................ 233
Volume Management ........................................................................................................................ 233
RAID 0 ............................................................................................................................................. 234
2-drive models or above.................................................................................................................... 234
RAID Management ........................................................................................................................... 237
Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T ....................................................................................................................... 253
9.1.3 Network ......................................................................................... 254
TCP/IP .............................................................................................................................................. 254
DDNS Service .................................................................................................................................. 262
9.1.4 Security .......................................................................................... 263
Security Level ................................................................................................................................... 263
Certificate & Private Key.................................................................................................................. 263
9.1.5 Hardware ....................................................................................... 265
General.............................................................................................................................................. 265
Buzzer ............................................................................................................................................... 267
Smart Fan .......................................................................................................................................... 268
9.1.6 Power ............................................................................................. 269
Power Recovery ................................................................................................................................ 269
9.1.7 Notification .................................................................................... 270
E-mail ............................................................................................................................................... 270
SMS SMSC Settings ......................................................................................................................... 271
9.1.8 Firmware Update ........................................................................... 272
Live Update ...................................................................................................................................... 272
Firmware Update .............................................................................................................................. 273
9.1.9 Backup/Restore .............................................................................. 275
Backup/Restore Settings ................................................................................................................... 275
Restore to Factory Default ................................................................................................................ 276
9.1.10 External Device ............................................................................ 277
External Storage ................................................................................................................................ 277
UPS ................................................................................................................................................... 284
9.1.11 System Status ............................................................................... 289
System Information........................................................................................................................... 289
Network Status.................................................................................................................................. 289
Hardware Information ....................................................................................................................... 289
Resource Monitor ............................................................................................................................. 290
9.1.12 System Logs .................................................................................. 293
Recording Statistics .......................................................................................................................... 293
System Connection Logs .................................................................................................................. 293

9
Online Users ..................................................................................................................................... 294
9.2 Privilege Settings .................................................................................... 296
9.3 Network Services ................................................................................... 298
9.3.1 Win ................................................................................................. 298
9.3.2 FTP .................................................................................................. 300
FTP Service ...................................................................................................................................... 300
Advanced .......................................................................................................................................... 302
10. QNAP Applications ..................................................................................... 303
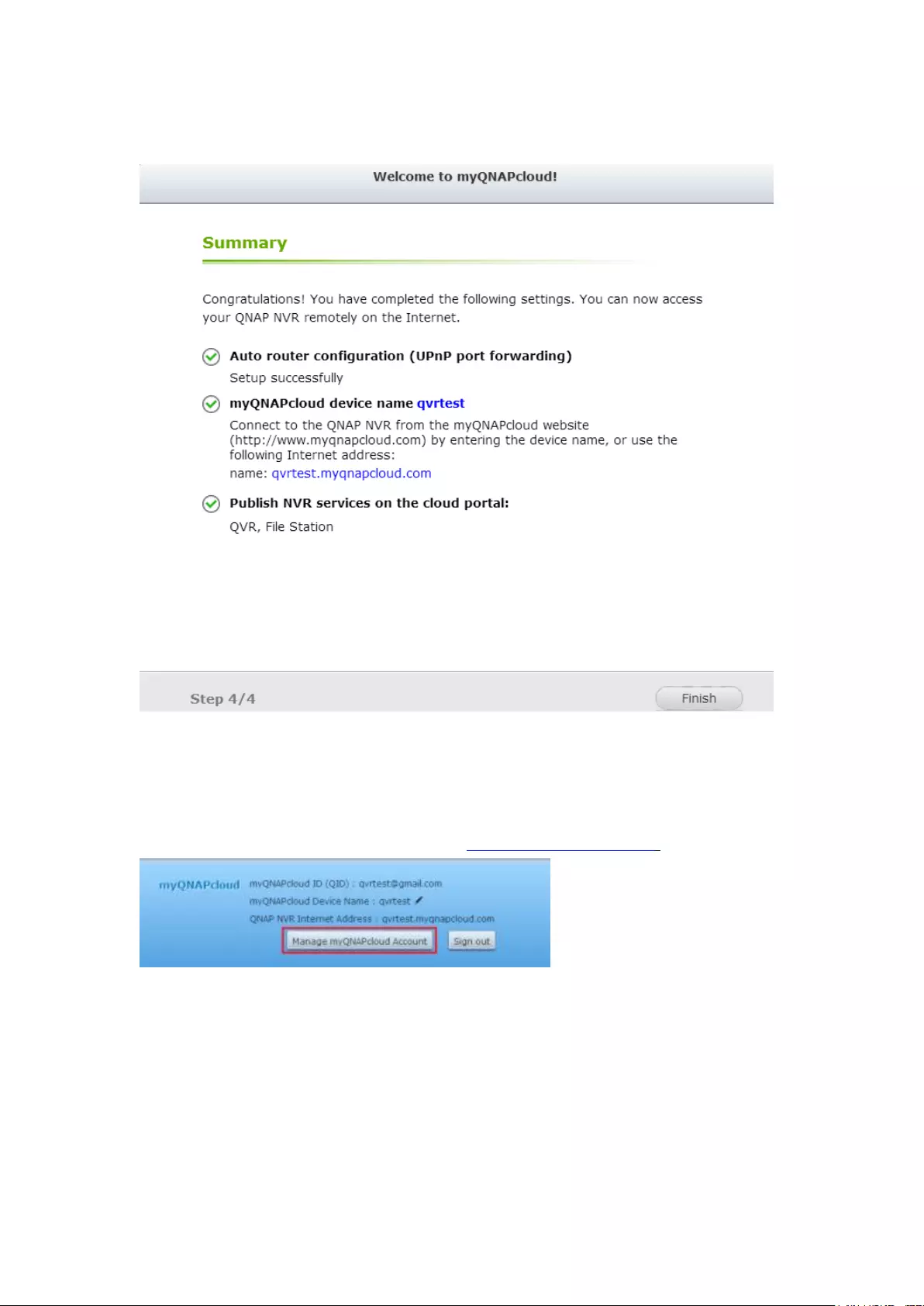
10.1 myQNAPcloud Service............................................................................ 303
10.1.1 Remote Access Services ............................................................... 303
myQNAPcloud wizard ...................................................................................................................... 303
Manage and configure your myQNAPcloud account ....................................................................... 308
Access NVR services via the myQNAPcloud website ...................................................................... 312
Auto Router Configuration ............................................................................................................... 313
My DDNS ......................................................................................................................................... 315
Cloud Portal ...................................................................................................................................... 316
10.1.2 Cloud Services .............................................................................. 320
Create your own Amazon S3 account ............................................................................................... 320
Create Remote Replication Job on Amazon S3 ................................................................................ 321
10.2 File Station ............................................................................................. 327
10.3 App Center ............................................................................................. 332
11. QNAP Surveillance Central Management (QSCM Lite) .............................. 335
11.1 Introduction ........................................................................................... 335
11.2 Install QSCM Lite to NVR Server............................................................. 335
11.2.1 App Center ................................................................................... 335
11.2.2 How to Install QSCM Lite to NVR Server ...................................... 335
Online installation ............................................................................................................................. 335
Offline installation ............................................................................................................................ 339
11.2.3 Installation Reminders and Suggestions ...................................... 343
11.3 Use QSCM Lite on NVR Client PC ........................................................... 343
11.3.1 How to use QSCM Lite on NVR client PC ..................................... 343
11.3.2 Usability Reminder and Suggestions ............................................ 347
11.3.3 QSCM Lite Client Specification ..................................................... 347
11.4 Comparison between VioStor CMS & QSCM Lite .................................. 347
12. Qstart ......................................................................................................... 349
12.1 Introduction ........................................................................................... 349
12.2 Before Using Qstart ................................................................................ 349
12.3 System Initialization ............................................................................. 349

10
12.4 Qstart Mode ........................................................................................... 352
12.5 Network Switch Control (Embedded) .................................................... 355
12.5.1 Topology: ...................................................................................... 355
12.5.2 Switch Control Chart: ................................................................... 356
12.5.3 Event Notifications: ...................................................................... 357
12.5.4 Compatibility List: ........................................................................ 358
13. LCD Panel ................................................................................................... 359
14. Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 365
Appendix A Configuration Examples ...................................................................... 368
Technical Support ....................................................................................................... 373
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE ................................................................................. 374

11
Safety Warning
1. This product can operate normally in the temperature of 0ºC–40ºC and relative
humidity of 0%–90%. Please make sure the environment is well-ventilated.
2. The power cord and devices connected to this product must provide correct
supply voltage.
3. Do not place this product in direct sunlight or near chemicals. Make sure the
temperature and humidity of the environment are in optimized level.
4. Unplug the power cord and all connected cables before cleaning. Wipe this
product with a wet towel. Do not use chemical or aerosol to clean this
product.
5. Do not place any objects on this product for the server's normal operation and
to avoid overheat.
6. Use the flat head screws in the product package to lock the hard disks in this
product when installing hard disks for proper operation.
7. Do not place this product near any liquid.
8. Do not place this product on any uneven surface to avoid falling off and damage.
9. Make sure the voltage is correct in your location when using this product. If
you are not sure about the voltage, please contact the distributor or the local
power supply company.
10. Do not place any object on the power cord.
11. Do not attempt to repair this product in any occasions. Improper disassembly
of the product may expose you to electric shock or other risks. For any
enquiries, please contact the distributor.
12. The chassis models should only be installed in the server room and maintained
by the authorized server manager or IT administrator. The server room is
locked by key or keycard access and only certified staff is allowed to enter the
server room.
Warning:
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of
used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Do NOT touch the fan inside the system to avoid serious injuries.

12
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview
The QNAP VioStor NVR (hereafter referred to as the NVR or the VioStor) is the high
performance network surveillance solution for network-based monitoring of IP
cameras, video recording, playback, and remote data access. Up to 128 channels
from multiple QNAP NVR servers can be monitored simultaneously. The NVR
supports IP-based cameras and video servers from numerous brands, for more
information please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/pro_compatibility_camera.asp.
The NVR supports video recording in H.264, MPEG-4, MJPEG, or MxPEG video
compression. The NVR offers diversified display modes and recording features, e.g.
scheduled recording, alarm recording, smart recording. The NVR also supports data
search by date and time, timeline, event, and intelligent video analytics (IVA),
including motion detection, missing object, foreign object, out of focus, and camera
occlusion. All of these functions can be configured by using your web browser.
The VioStor Pro(+) Series NVR is the world's first Linux-based NVR capable of truly
PC-less quick configuration, monitoring of IP cameras on the network, and video
playback via the HDMI or VGA connector. The NVR can be operated by connecting
to a high-definition (HD) VGA monitor or TV, and a USB mouse, USB keyboard
(optional), and a USB sound card (optional).
* The MxPEG video compression feature is not supported by VS-2008L, VS-2004L
VS-1004L.
13
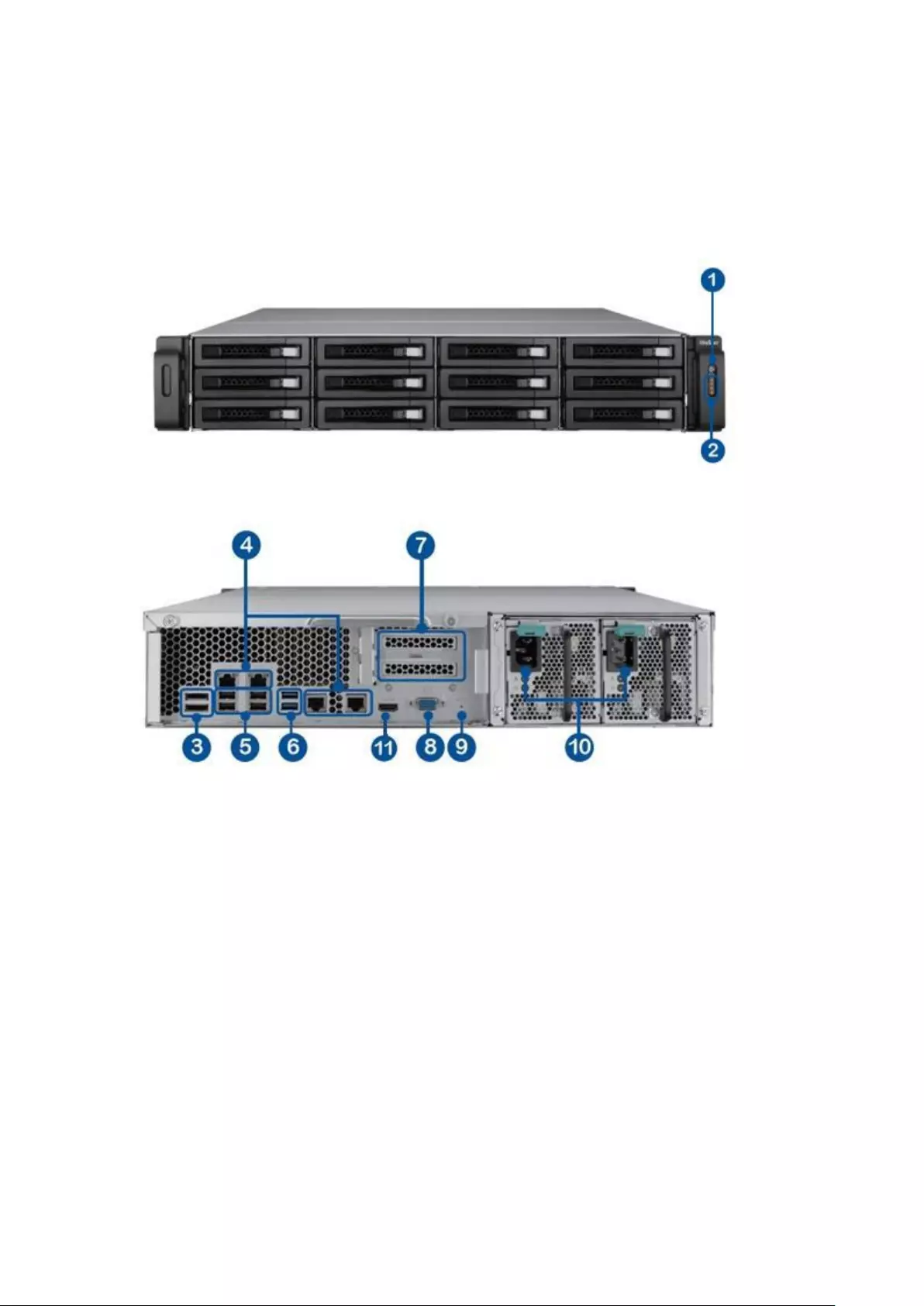
1.2 Hardware Illustration
1.2.1 VS – 12164 / 12156 / 12148 / 12140U-RP Pro+
1 Power Button
2 LED Indicators: 10 GbE, Status, LAN, eSATA (Reserved)
3 eSATA x 2 (Reserved)
4 Gigabit LAN x 4
5 USB 2.0 x 4
6 USB 3.0 x 2
7 Expansion Slot x 2 (Reserved)
8 VGA
9 Password & Network Settings Reset Button
10 Power Connector x 2
11. HDMI

14
1.2.2 VS – 12164 / 12156 / 12148 / 12140U-RP Pro
1. Power button
2. LED indicators: 10 GbE, Status, LAN, eSATA Select button(Reserved)
3. VGA
4. Expansion slot x 1 (reserved)
5. Gigabit LAN x 4
6. USB 3.0 x 2
7. USB 2.0 x 4
8. Password & network settings reset button
9. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
10. Power connector x 2

15
1.2.3 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124U-RP Pro+
1. Enter Button
2. Power Button
3. Select Button
4. LED Indicators: 10 GbE, Status, LAN, eSATA (Reserved)
5. eSATA x 2 (Reserved)
6. USB 2.0 x 4
7. Gigabit LAN x 4
8. USB 3.0 x 2
9. VGA
10. Password & Network Settings Reset Button
11. Power Connector x 2
12. Expansion Slot x 2 (Reserved)
13. HDMI

16
1.2.4 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124U-RP Pro
1. Enter button
2. Power button
3. Select button
4. LED indicators: 10 GbE, Status, LAN, eSATA(Reserved)
5. VGA
6. Expansion slot x 2 (reserved)
7. Gigabit LAN x 2
8. USB 3.0 x 2
9. USB 2.0 x 4
10. Password & network settings reset button
11. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
12. Power connector x 2

17
1.2.5 VS – 8148 / 8140 / 8132 / 8124 Pro+
1. USB 3.0
2. One-touch -video-backup button
3. Power button
4. Hard drive LEDs
5. Select button
6. Enter button
7. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, eSATA (Reserved), 10 GbE
8. Tray lock
9. Release button
10. Power connector
11. Expansion slot
12. Kensington security slot
13. VGA
14. HDMI
15. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
16. Gigabit LAN x 2
17. USB 2.0 x 4
18. USB 3.0
19. Password & network settings reset button

18
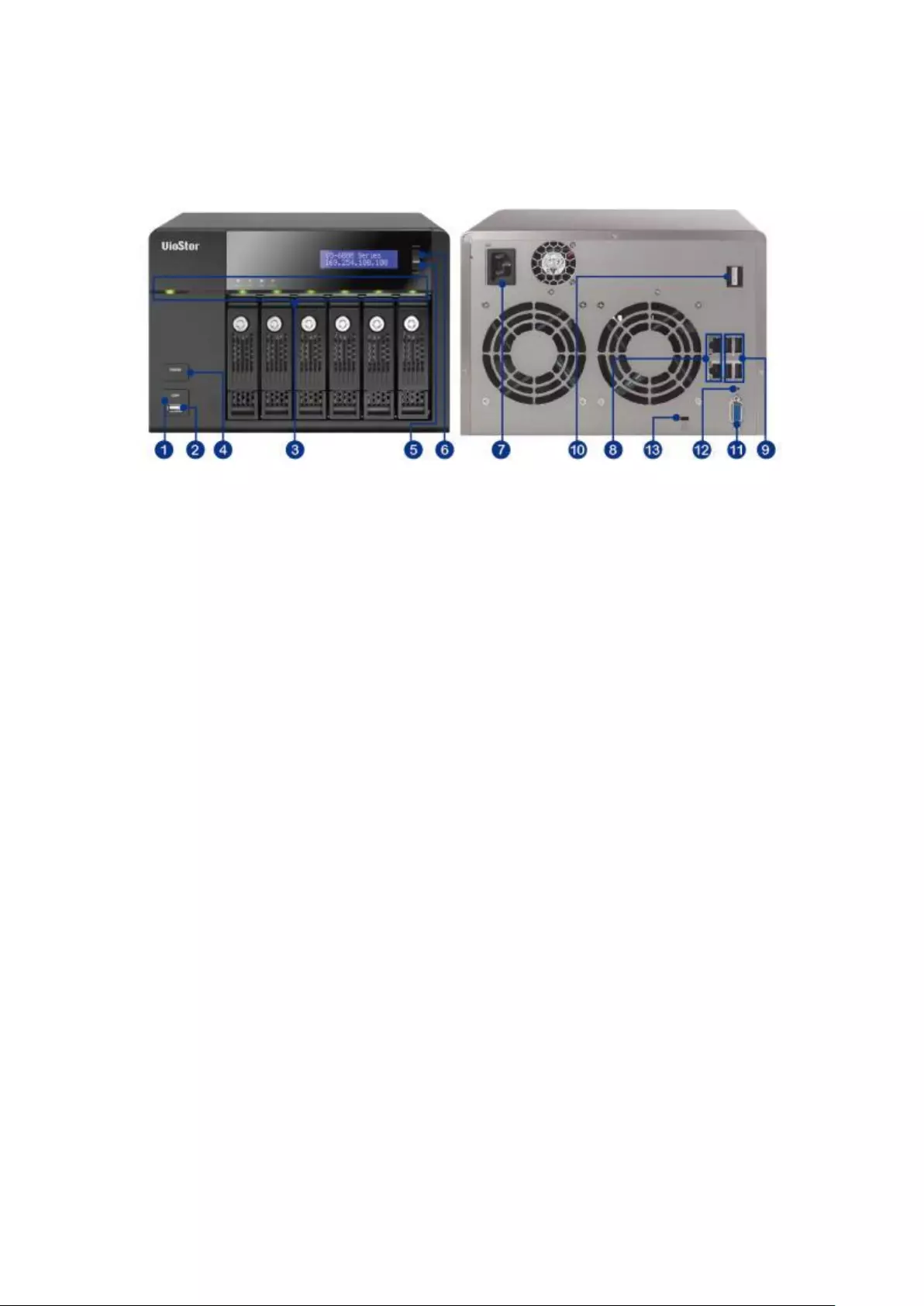
1.2.6 VS – 6120 / 6116 / 6112 Pro+
1. One-touch -video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, Power, HDD1-6
4. Power button
5. Select button
6. Enter button
7. Power connector
8. K-Lock Security Slot
9. Gigabit LAN x 2
10. Audio In/Out
11. Password & Network Settings Reset Button
12. USB 3.0 x 2
13. USB 2.0 x 4
14. HDMI

19
1.2.7 VS – 6020 / 6016 / 6012 Pro
1. One-touch -video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, eSATA(Reserved), HDD1–6
4. Power button
5. Select button
6. Enter button
7. Power connector
8. Gigabit LAN x 2
9. USB 2.0 x 4
10. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
11. VGA
12. Password & network settings reset button
13. Kensington security slot
20
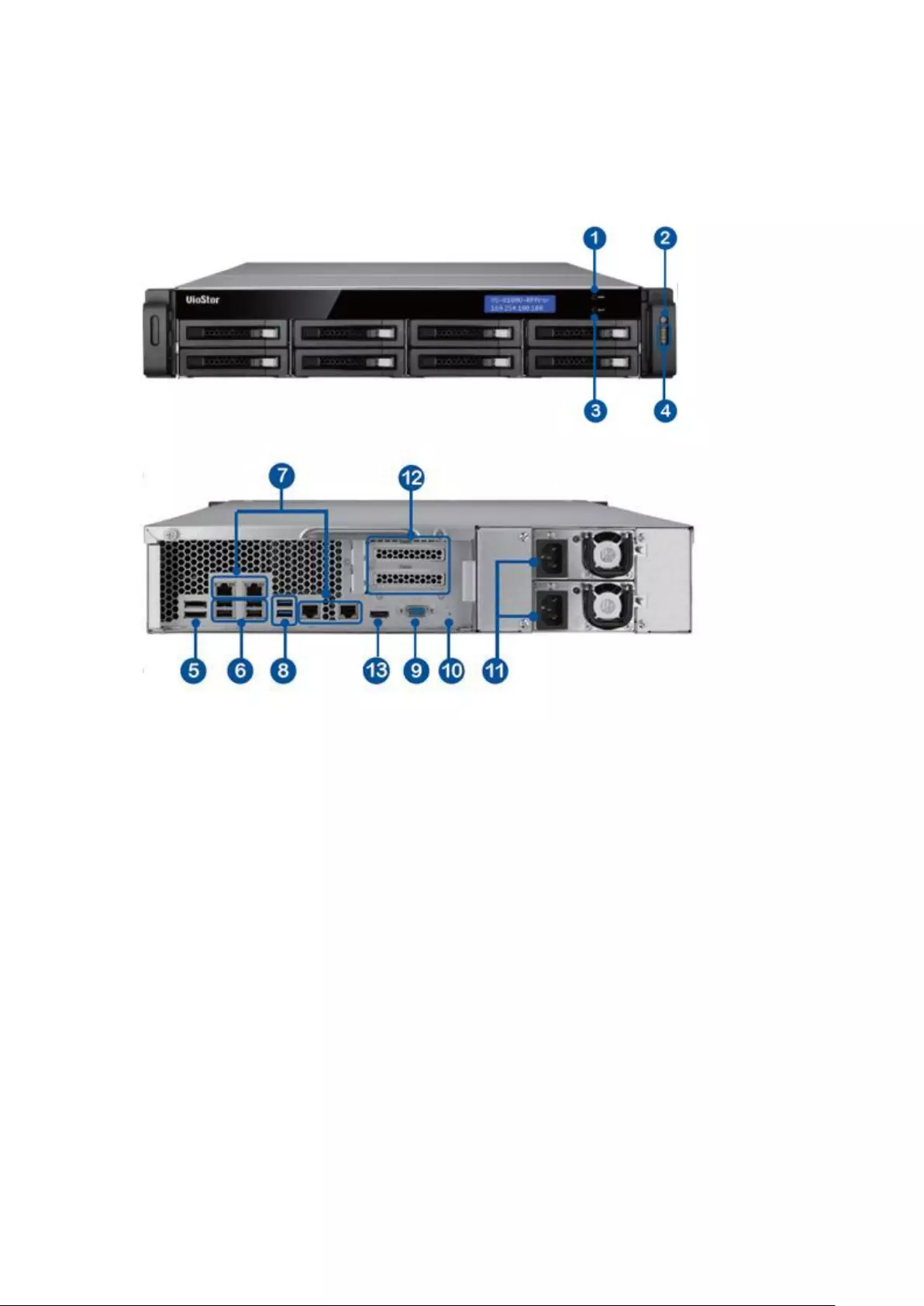
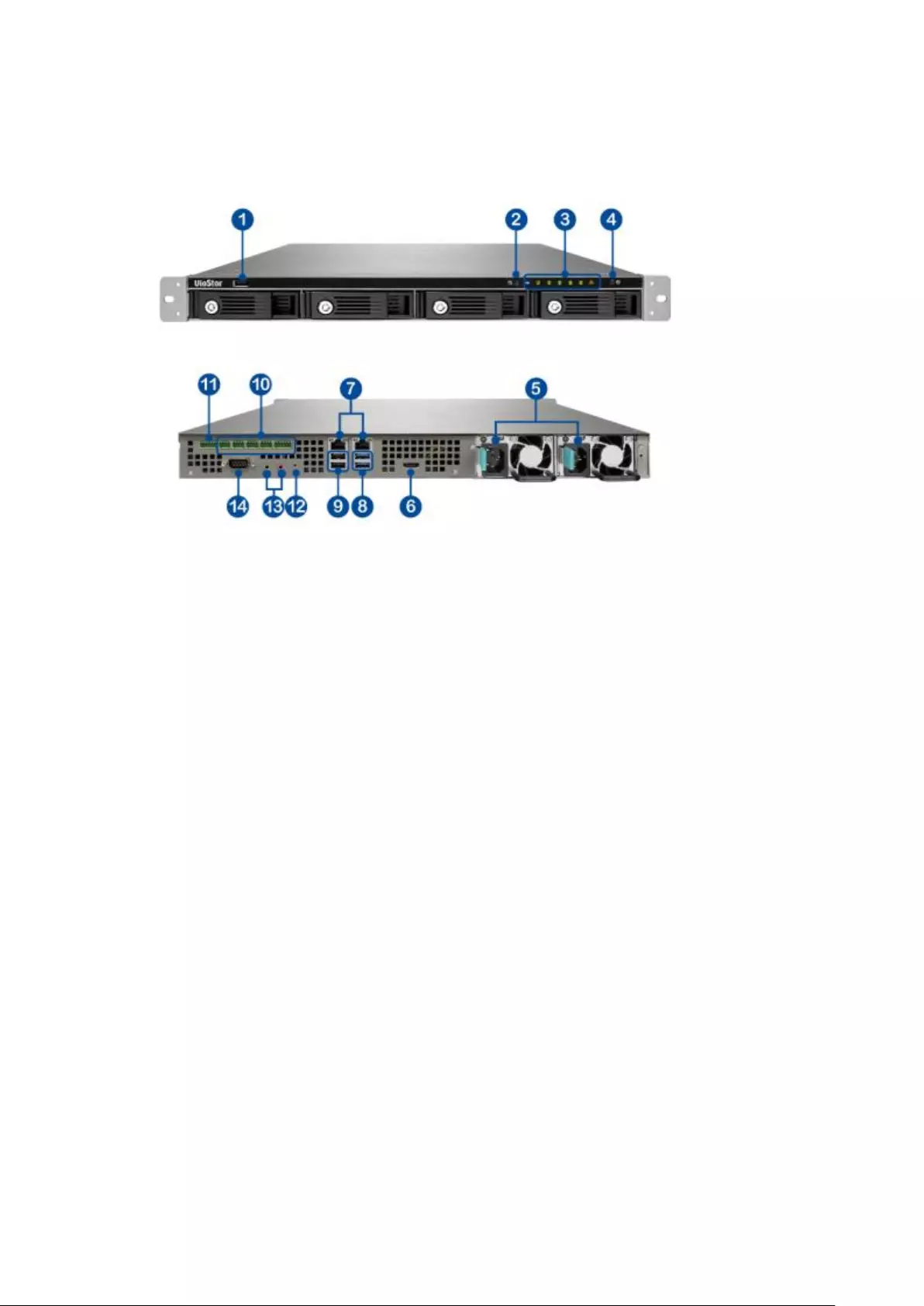
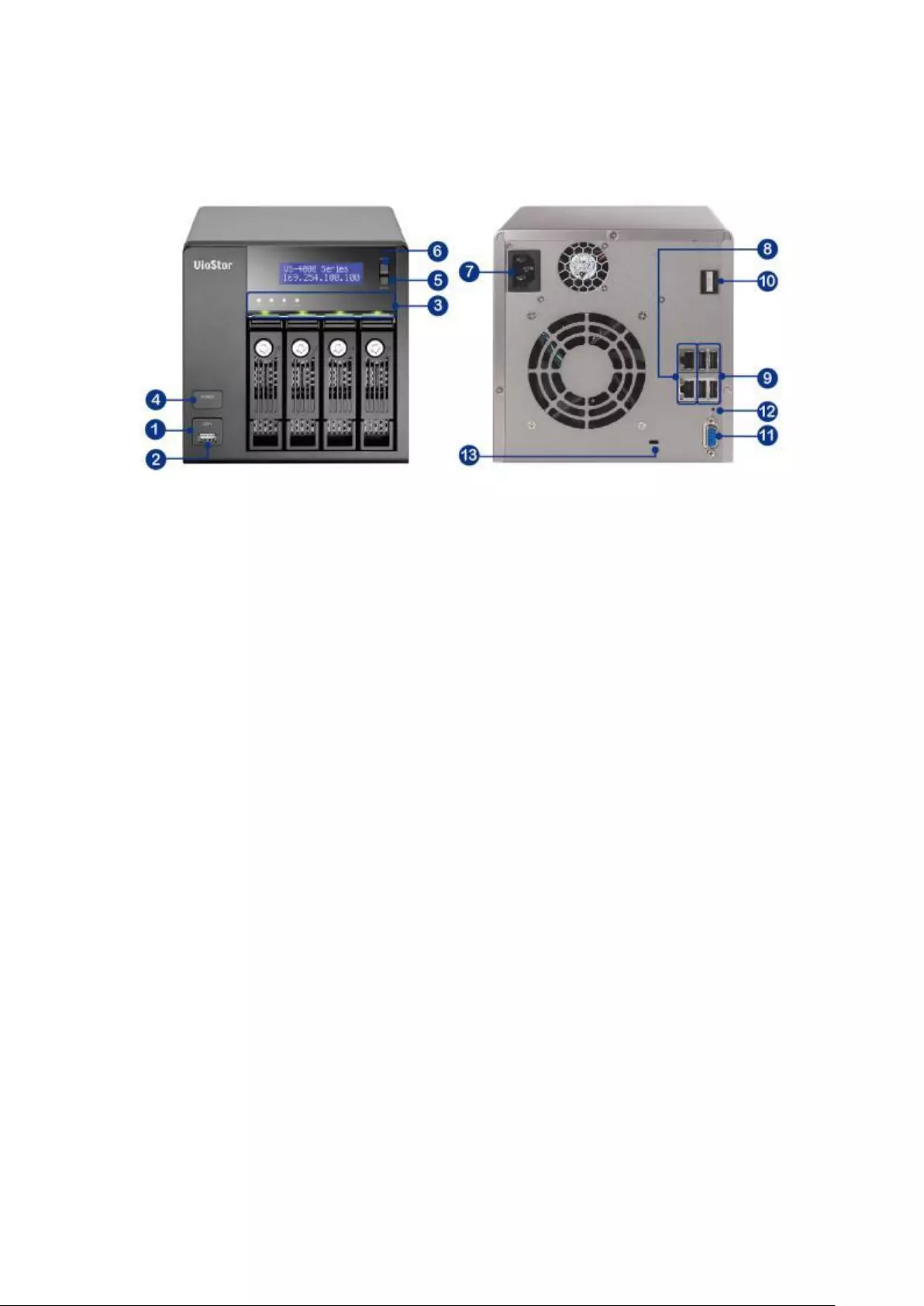
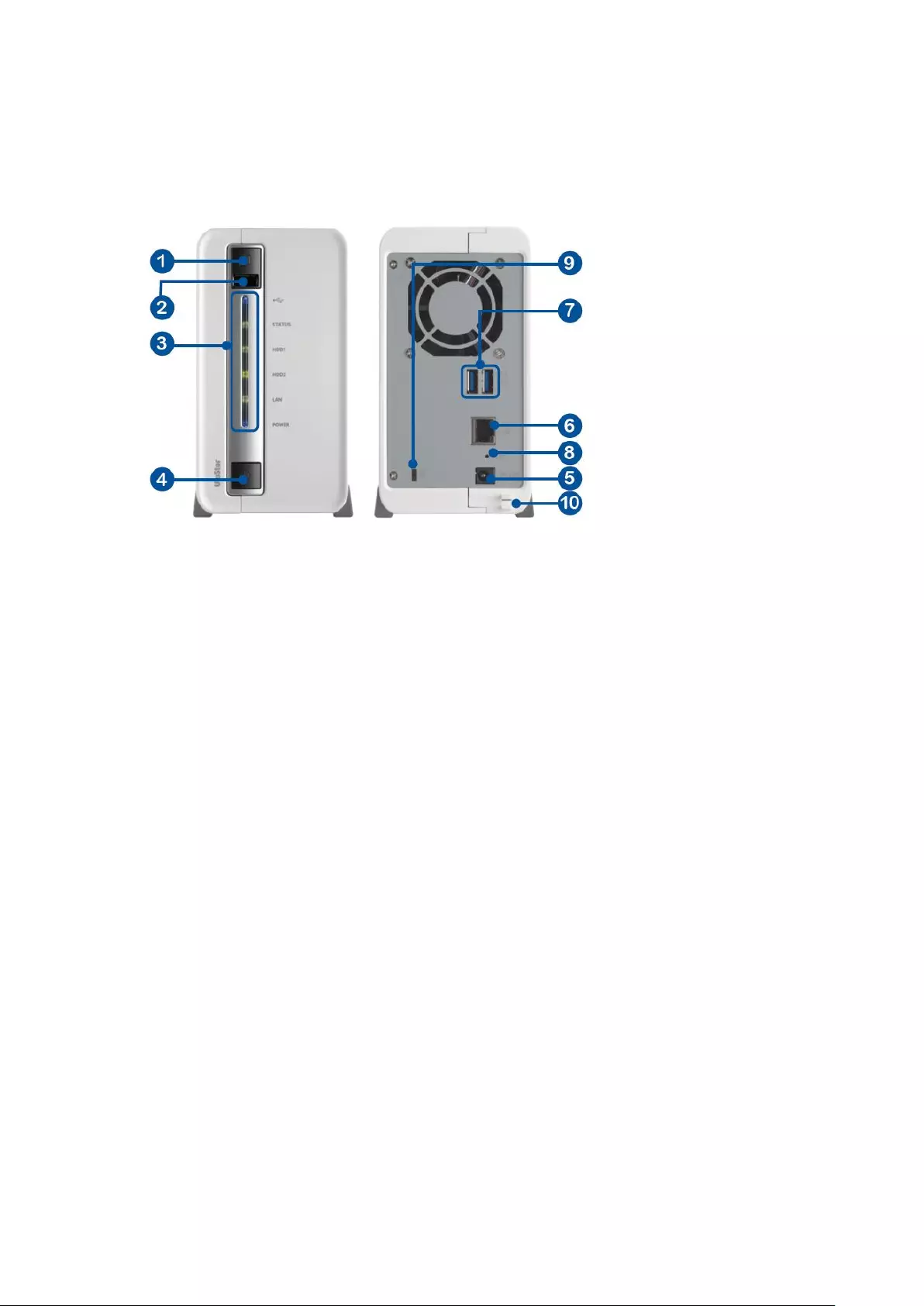
1.2.8 VS – 4116 / 4112 / 4108U-RP Pro+
1. USB 2.0
2. One-touch -video-backup button
3. LED indicators: USB, Status, HDD1–4, LAN
4. Power button
5. Power connector
6. HDMI
7. Gigabit LAN x 2
8. USB 3.0 x 2
9. USB 2.0 x 2
10. DI/DO
11. RS-485 (reserved)
12. Password & network settings reset button
13. Audio In/Out
14. RS-232 (reserved)

21
1.2.9 VS – 4016 / 4012 / 4008U-RP Pro
1. One-touch -video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, eSATA(Reserved), HDD1–4
4. Power button
5. Power connector
6. Gigabit LAN x 2
7. USB 2.0 x 4
8. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
9. VGA
10. Password & network settings reset button

22
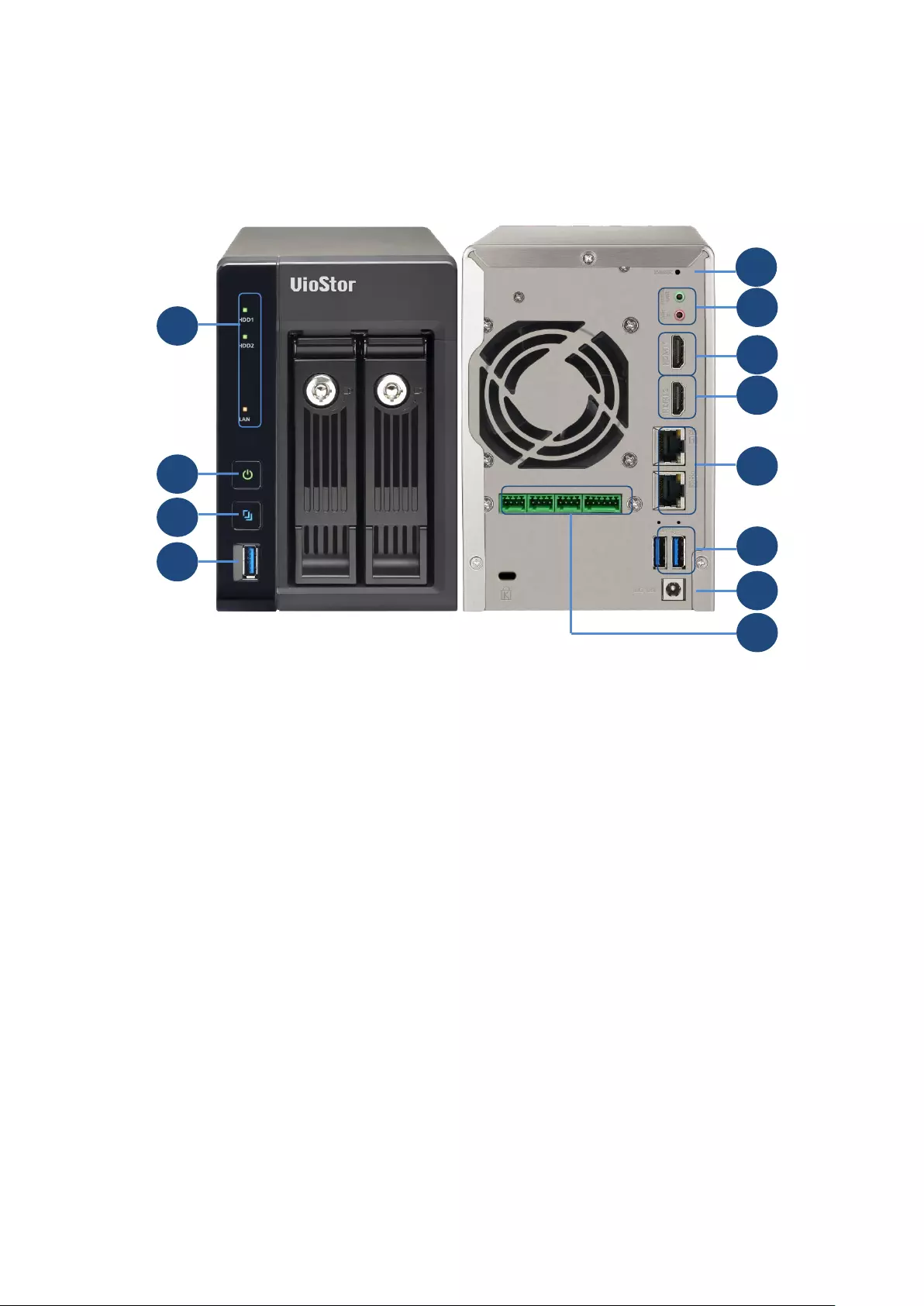
1.2.10 VS – 4116 / 4112 / 4108 Pro+
1. One-touch -video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, HDD1–4
4. Power button
5. Select button
6. Enter button
7. Power connector
8. K-Lock Security Slot
9. Gigabit LAN x 2
10. Audio In/Out
11. Password & network settings reset button
12. USB 3.0 x 2
13. USB 2.0 x 4
14. HDMI

23
1.2.11 VS – 4016 / 4012 / 4008 Pro
1. One-touch- video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: Status, LAN, USB, eSATA(Reserved), HDD1–4
4. Power button
5. Select button
6. Enter button
7. Power connector
8. Gigabit LAN x 2
9. USB 2.0 x 4
10. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
11. VGA
12. Password & network settings reset button
13. Kensington security slot

24
1.2.12 VS – 2212 / 2208 / 2204 Pro+
1. One-touch-video-backup button
2. USB 3.0
3. LED Indicators: LAN, HDD1, HDD2
4. Power Button
5. Power Connector
6. Gigabit LAN x 2
7. USB 3.0 x 2
8. Password & Network Settings Reset Button
9. K-Lock Security Slot
10. Mic Input/ audio output
11. HDMI 1
12. HDMI 2 (reserved)
13. Alarm input/ output (reserved)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
10
11
13
12

25
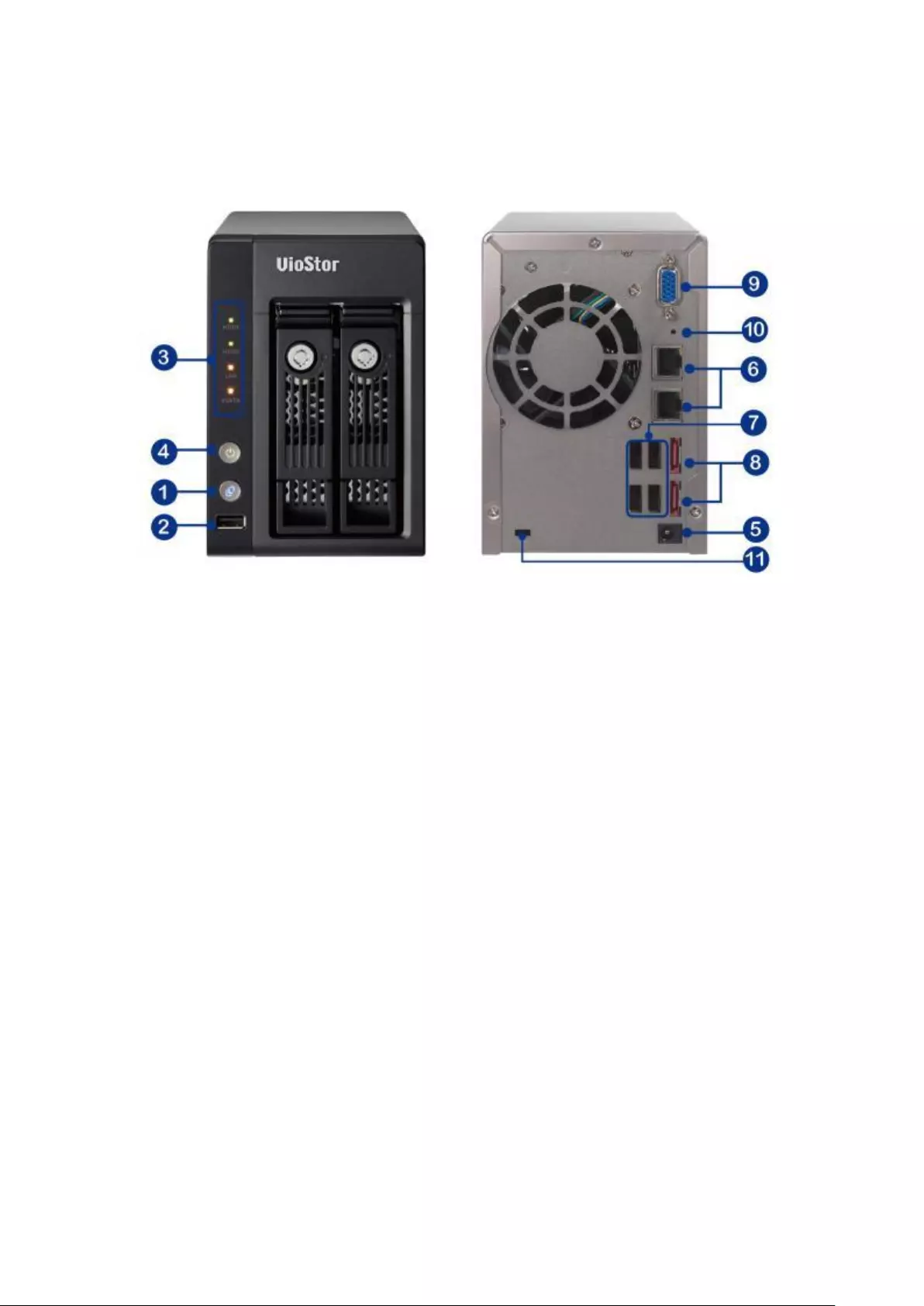
1.2.13 VS – 2112 / 2108 / 2104 Pro+
1. One-touch-video-backup button
2. USB 3.0
3. LED Indicators: LAN, HDD1, HDD2
4. Power Button
5. Power Connector
6. Gigabit LAN x 2
7. USB 2.0 x 4
8. Password & Network Settings Reset Button
9. K-Lock Security Slot
10. Audio In/Out
11. HDMI

26
1.2.14 VS – 2012 / 2008 / 2004 Pro
1. One-touch -video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED indicators: HDD1, HDD2, LAN, eSATA (Reserved)
4. Power button
5. Power connector
6. Gigabit LAN x 2
7. USB 2.0 x 2
8. eSATA x 2 (reserved)
9. VGA
10. Password & network settings reset button
11. Kensington security slot

27
1.2.15 VS – S2212 / S2208 / S2204 Pro +
1. LED indicators: Status, LAN, HDD1, HDD2, USB (Backup)
2. Power button
3. One-touch -video-backup button
4. USB 3.0 x 2
5. Password & network settings reset button
6. Mic Input/ audio output
7. USB 3.0
8. Gigabit LAN x 2
9. HDMI
10. Power connector
11. K-Lock Security Slot
28
1.2.16 VS – 2108 / 2104 L
1. One-touch-auto-video-backup button
2. USB 2.0
3. LED Indicators: USB, status, HDD1, HDD2, LAN, power
4. Power button
5. Power connector
6. Gigabit LAN
7. USB 3.0 x 2
8. Password & network settings reset button
9. K-Lock security slot
10. Power cord hook
29
Chapter 2. Install the NVR
For the information of hardware installation, see the ‘Quick Installation Guide’ (QIG)
in the product package. The QIG can also be found in the product CD-ROM or
QNAP website (http://www.qnapsecurity.com).
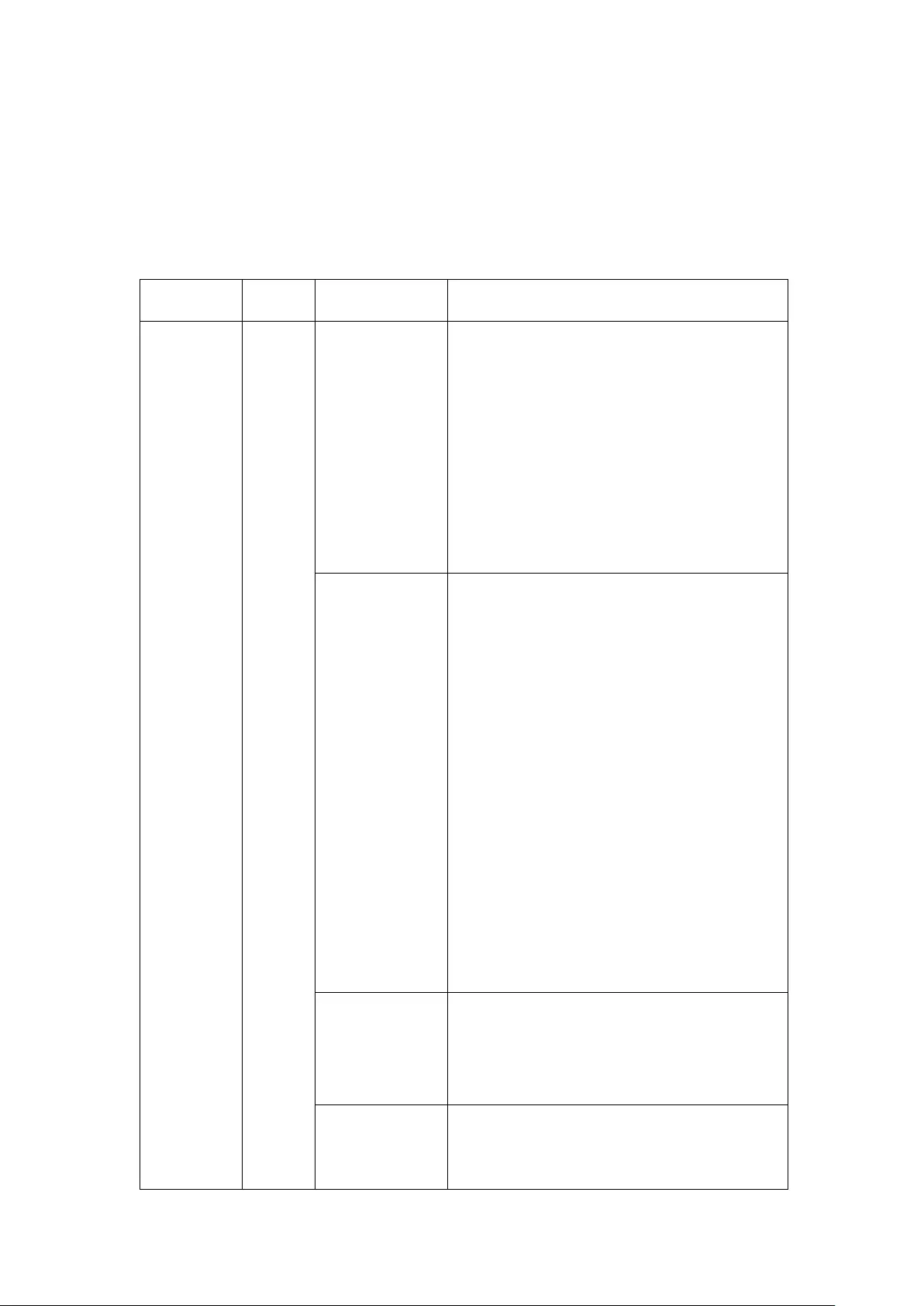
2.1 Personal Computer Requirements
For better system performance, the computer should at least fulfill the following
requirements:
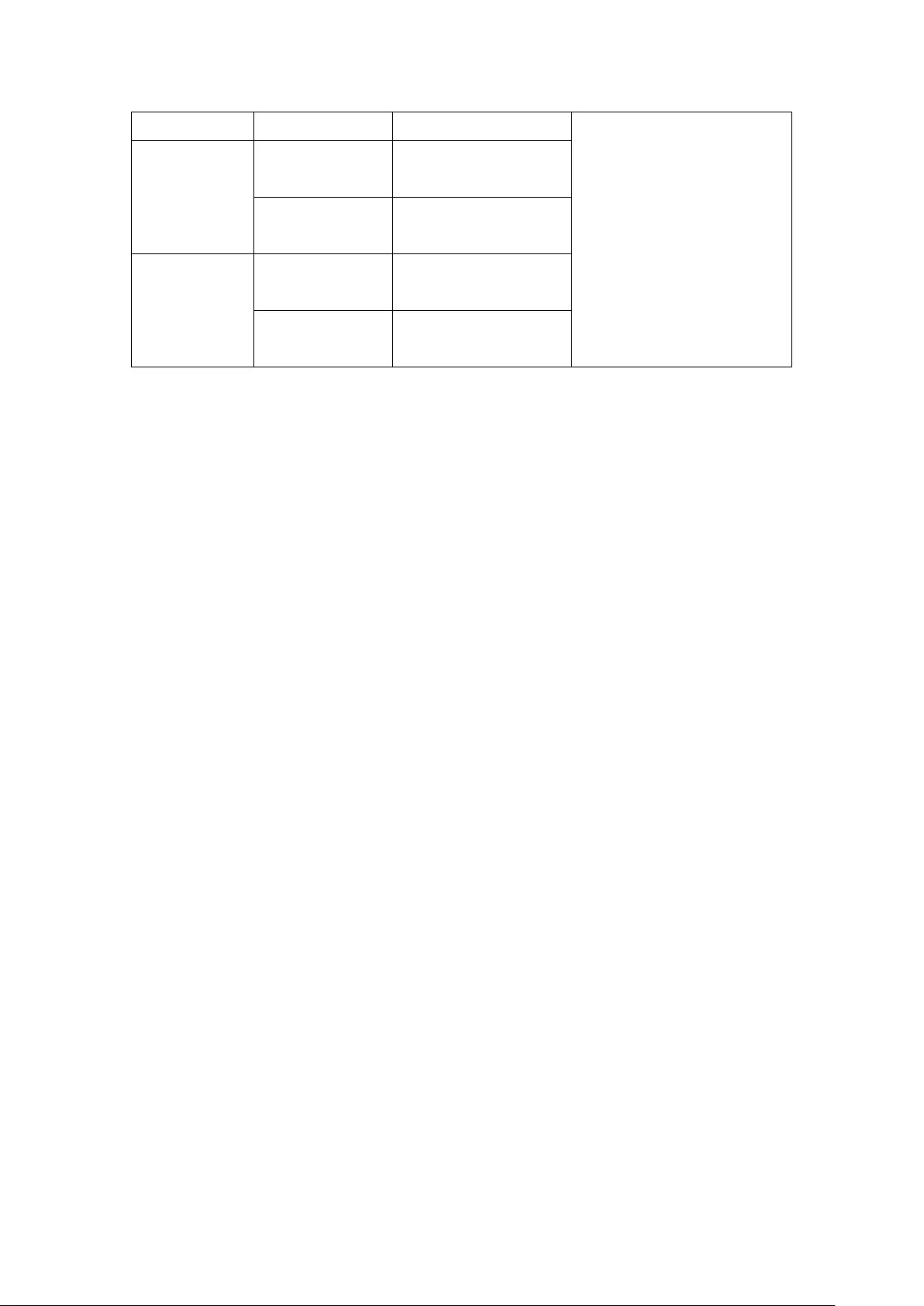
No. of
Channels
Format
CPU
Others
4
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Dual core CPU,
2.0GHz or above
Operation system:
Microsoft Windows
8, 7 Professional
Memory: 8GB or
above
Graphics Processor:
NVIDIA® GeForce®
7600 GT or ATI™
Radeon™ X800 XT or
better
Network port:
100Mbps Ethernet
port or above
Web browser: Google
Chrome
38.0.2125.104 m,
Microsoft Internet
Explorer 10/11
(desktop mode,
M-JPEG
Intel Pentium 4 CPU,
2.4GHz or above
8
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Dual core CPU,
2.4GHz or above
M-JPEG
Intel Pentium 4 CPU,
2.8GHz or above
12
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Dual core CPU,
2.8GHz or above
M-JPEG
Intel Pentium 4 CPU,
3.0GHz or above
16
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Quad core CPU,
2.33GHz or above
M-JPEG
Dual core CPU,
2.4GHz or above
20
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Quad core CPU,
2.6GHz or above
M-JPEG
Dual core CPU,
30
2.6GHz or above
32-bit), Mozilla
Firefox 33.0
CD-ROM drive or
Internet Download
Recommended
resolution: 1280 x
720 pixels or above
40
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Core i7 CPU 2.8GHz
or above
M-JPEG
Quad core CPU
2.33GHz or above
More than 48
H.264/MPEG-4/
MxPEG
Core i7 CPU 3.4GHz
or above
M-JPEG
Quad core CPU
3.0GHz or above
31
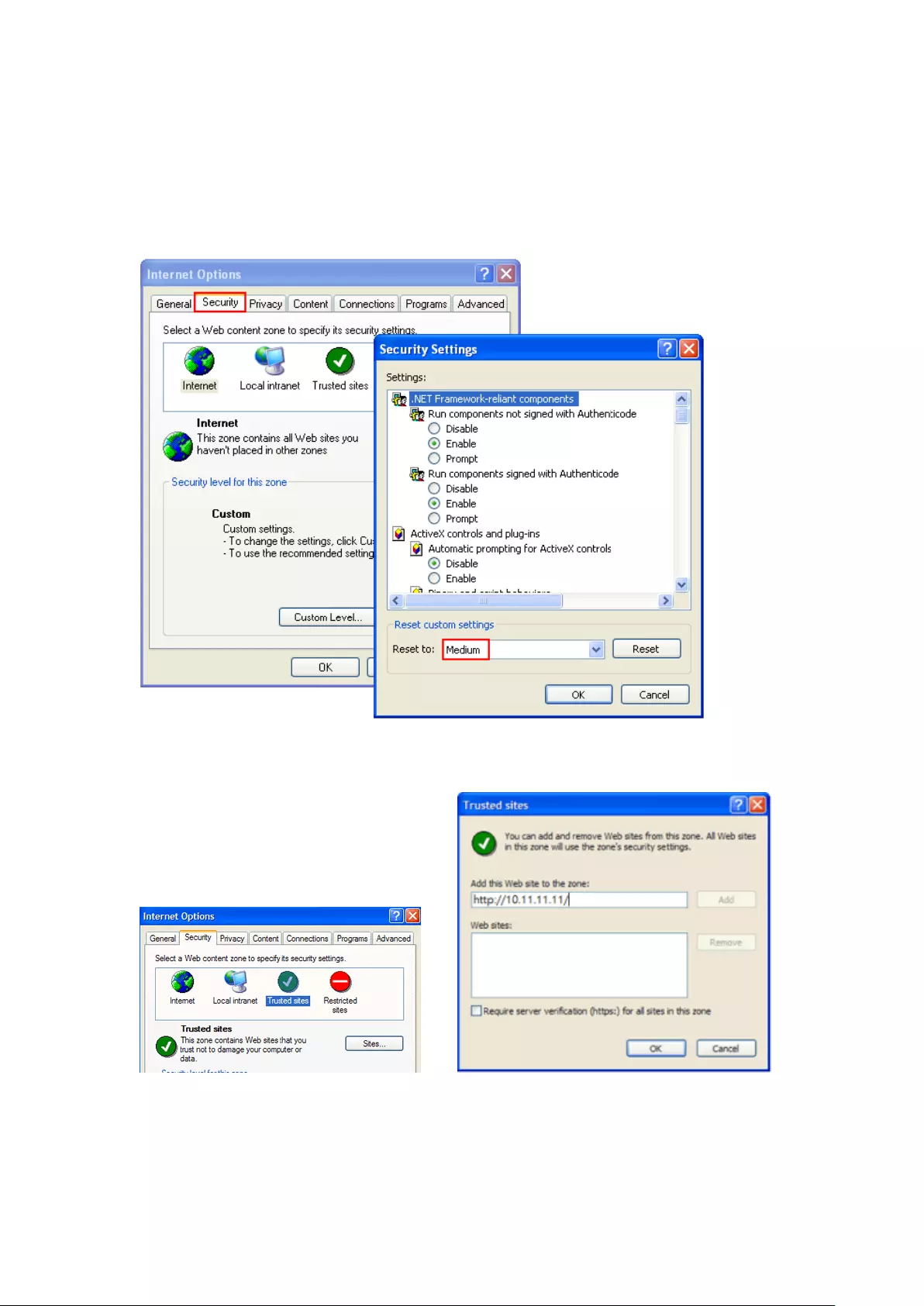
Security Settings of the Web Browser
Please make sure the security level of the IE browser in Internet Options is set to
Medium or lower.
Add your NVR’s IP address to the list of Trusted sites.
=>

32
2.2 Browse CD-ROM
Run the product CD-ROM on a Windows PC to access the Quick Start Guide and user
manual, and install the QNAP QVR Client, codec and software utilities Qfinder.
Browse the CD-ROM and access the following contents:
Codec: The codec for playing AVI videos recorded by the NVR via Windows
Media Player.
Manual: The user manuals of the NVR.
Qfinder: The setup program of QNAP Qfinder. This tool is used to discover the
NVR servers available on the local network and configure the network settings
of the NVR.
QIG: View the hardware installation instructions of the NVR.
QVR: The setup program for the QNAP QVR Client, an application to see the live
view and play videos recorded by the NVR. If you were unable to install the
QNAP QVR Client when connecting to the monitoring/playback page of the NVR,
install the plug-in from the CD-ROM.
Tool: This folder contains IPP library and monitor plug-in. If you failed to install
the ActiveX plug-in when connecting to the monitoring page of the NVR by an IE
browser, install the plug-in from the CD-ROM.
33
2.3 Hard Disk Drives Compatibility List
This product works with 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch SATA hard disk drives from popular
hard disk brands. For the hard disk compatibility list, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_x_grade/.
2.4 IP Cameras Compatibility List
For the information of supported IP camera models, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_z_g_qvr/cat_intro.php?hf=0.
QNAP disclaims any responsibility for product damage/malfunction or data
loss/recovery due to misuse or improper installation of hard disks in any occasions
for any reasons.
34
2.5 Check System Status
LED Display & System Status Overview
LED
Color
LED Status
Description
System
Status
Red/
Green
Flashes green
and red
alternately
every 0.5 sec
1. A hard drive on the NVR is being
formatted
2. The NVR is being initialized
3. The system firmware is being updated
4. RAID rebuilding is in process
5. Online RAID Capacity Expansion is in
process
6. Online RAID Level Migration is in
process
Red
1. A hard drive is invalid
2. The disk volume has reached its full
capacity
3. The disk volume is going to be full
4. The system fan is out of function
5. An error occurs when accessing
(read/write) the disk data
6. A bad sector is detected on the hard
drive
7. The NVR is in degraded read-only
mode (2 member drives fail in RAID 5
or 3 member drives fail in RAID 6
configuration, the disk data can still
be read)
8. (Hardware self-test error)
Flashes red
every 0.5 sec
The NVR is in degraded mode (one
member drive fails in RAID 1, RAID 5 or
two member drives fail in RAID 6
configuration)
Flashes green
every 0.5 sec
1. The NVR is starting up
2. The NVR is not configured
3. A hard drive is not formatted
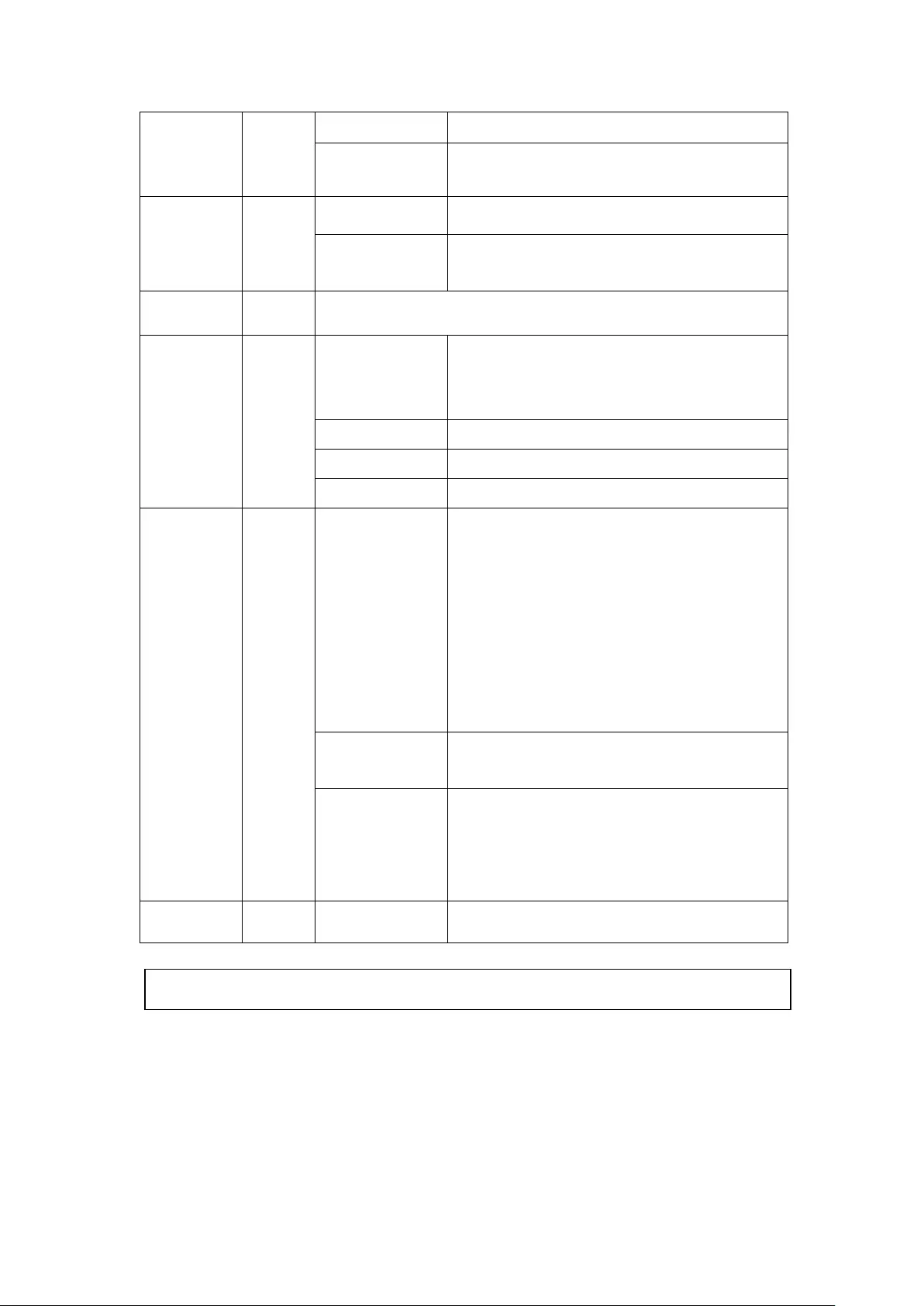
35
Green
The NVR is ready
LAN
Orange
Orange
The NVR is connected to the network
Flashes orange
The NVR is being accessed from the
network
10 GbE*
Green
(Reserved)
HDD (Hard
Drive)
Red/
Green
Flashes red
The hard drive data is being accessed and
a read/write error occurs during the
process
Red
A hard drive read/write error occurs
Flashes green
The hard drive data is being accessed
Green
The hard drive can be accessed
USB
Blue
Flashes blue
every 0.5 sec
1. A USB device is detected
2. A USB device is being removed from
the NVR
3. The USB device connected to the
front USB port of the NVR is being
accessed
4. The NVR data is being copied to the
external USB device
Blue
The USB device connected to the front
USB port of the NVR is ready
Off
1. No USB is detected
2. The NVR has finished copying the
data to the USB device connected to
the front USB port of the NVR
eSATA
Orange
Flashes
(Reserved)
*The 10 GbE network expansion function is reserved.
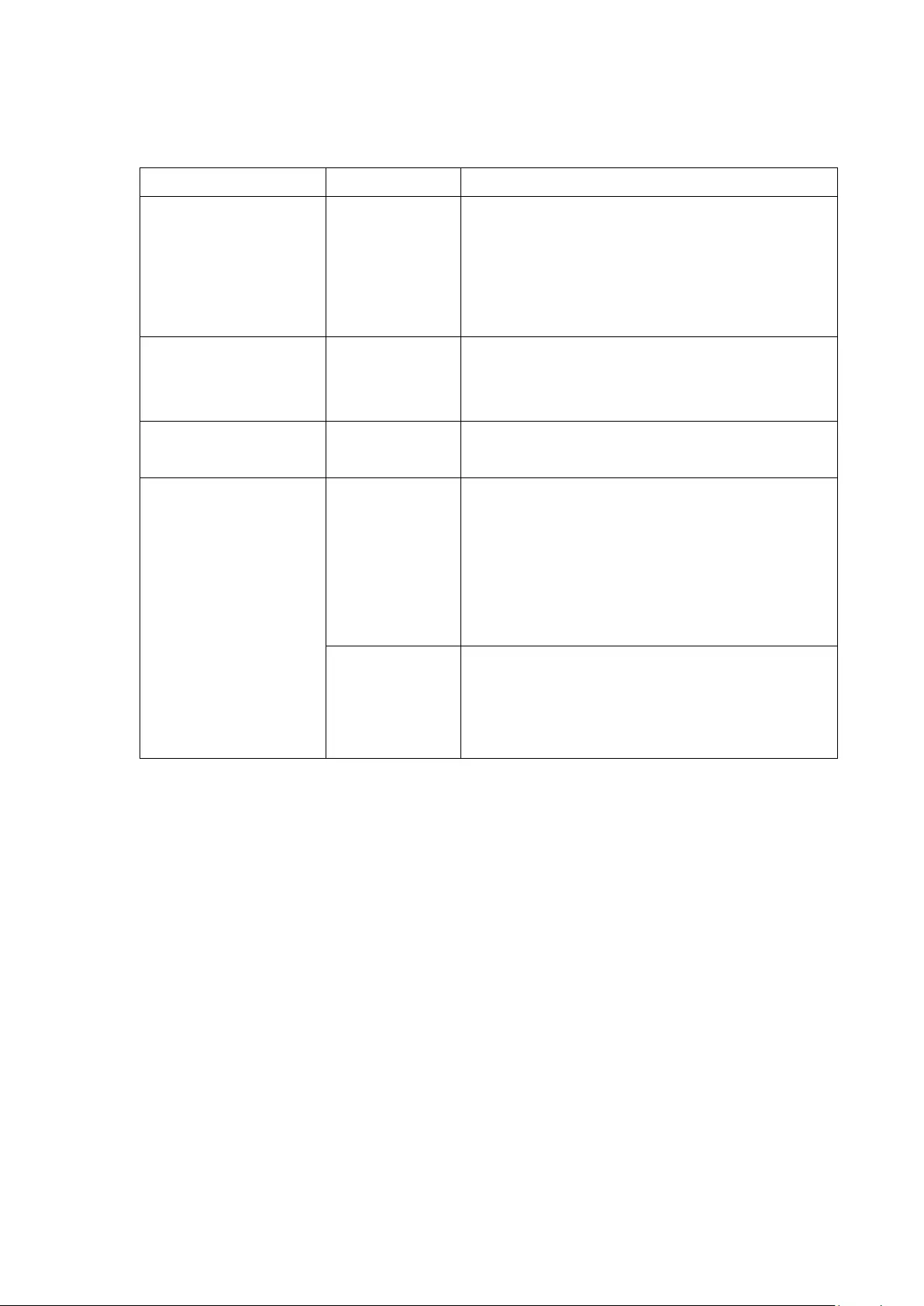
36
Buzzer (can be disabled in ‘System Settings’ > ‘Hardware’ >’Buzzer’)
Beep sound
No. of Times
Description
Short beep (0.5 sec)
1
1. The NVR is starting up
2. The NVR is being shut down (software
shutdown)
3. The reset button is pressed
4. The system firmware has been updated
Short beep (0.5 sec)
3
The NVR data cannot be copied to the external
device by pressing the
one-touch-auto-video-backup button.
Short beep (0.5 sec),
long beep (1.5 sec)
3, every 5 min
The system fan is out of function
Long beep (1.5 sec)
2
1. The disk volume is going to be full
2. The disk volume has reached its full
capacity
3. The hard drives on the NVR are in
degraded mode
4. Hard disk rebuilding process starts
1
1. The NVR is turned off by force shutdown
(hardware shutdown)
2. The NVR has been turned on successfully
and is ready
37
2.6 System Configuration
Install Qfinder
1. Run the product CD, the following menu is shown. Click ‘Install Qfinder’.
You can also download it from:
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product/app_page.php
2. Follow the instructions to install the Finder. Upon successful installation, run
the Finder. If the Finder is blocked by the firewall, unblock it.
3. The Finder detects the NVR servers on the local network. If the server has not
been initialized, you will be prompted to perform quick setup. Click ‘Yes’ to
continue.
Note: If the NVR is not found, click ‘Refresh’ to try again.
4. Enter the administrator name and password to perform quick setup. The
default administrator name and password are as below:
User name: admin
Password: admin
Note: Make sure all the IP cameras are configured and connected to the
network.
Quick Setup
1. The quick setup page will be shown. Click ‘Manual Setup’ and follow the
instructions to finish the configuration.
38
2. Click ‘Apply’ to execute the quick setup.
Add IP Cameras
Please follow the steps below to add IP cameras.
1. Go to Surveillance Settings
Please login to the NVR as an administrator and click the Surveillance Settings
shortcut on the QVR desktop.
2. Go to [Camera Configuration] -> [Camera Settings].
3. Click to add an IP camera.
4. Follow the steps to add the camera.
39
Live View
1. Click the Monitor shortcut on the QVR desktop to go to monitoring page.
2. If it is your first time connecting to the NVR monitoring page, you will need to
install the add-on.
3. The live video from the IP cameras configured on the NVR and the recording
status of each channel are shown.
40
Chapter 3. Use the NVR by Local Display
Connect a monitor or TV to the NVR via the HDMI or VGA interface to perform
PC-less quick configuration, monitoring, and video playback. To use this feature,
follow the steps below:
1. Make sure at least one hard drive has been installed on the NVR.
2. Connect the NVR to the network.
3. Make sure the IP cameras have been configured and connected to the network.
4. Connect an HDMI or a VGA monitor or TV (suggested video output resolution:
1920 x 1080)* to the HDMI or VGA interface of the NVR.
5. Connect a USB mouse and a USB keyboard (optional) to the USB ports of the
NVR.
6. Turn on the NVR.
*All Pro+ series support HDMI interface now.
Note: This feature is supported by the VioStor Pro(+) Series NVR only. The
models include VS-12164U-RP Pro(+), VS-12156U-RP Pro(+), VS-12148U-RP Pro(+),
VS-12140U-RP Pro(+), VS-8148U-RP Pro(+), VS-8140U-RP Pro(+), VS-8132U-RP
Pro(+), VS-8124U-RP Pro(+), VS-8148 Pro+, VS-8140 Pro+, VS-8132 Pro+, VS-8124
Pro+, VS-6120 Pro+, VS-6116 Pro+, VS-6112 Pro+, VS-6020 Pro, VS-6016 Pro,
VS-6012 Pro, VS-4116U-RP Pro+, VS-4112U-RP Pro+, VS-4108U-RP Pro+,
VS-4016U-RP Pro, VS-4012U-RP Pro, VS-4008U-RP Pro, VS-4116 Pro+, VS-4112
Pro+, VS-4108 Pro+, VS-4016 Pro, VS-4012 Pro, VS-4008 Pro, VS-2212 Pro+,
VS-2208 Pro+, VS-2204 Pro+, VS-2112 Pro+, VS-2108 Pro+, VS-2104 Pro+, VS-2012
Pro, VS-2008 Pro, VS-2004 Pro, VS-S2212 Pro+, VS-S2208 Pro+, and VS-S2204 Pro+.
41
When the NVR is turned on, the login screen will be shown. Select the language.
Enter the administrator name and password. If the NVR has not been configured,
skip the login page and enter Quick Configuration (refer to Chapter 3.1).
Default user name: admin
Default password: admin
42
Click to select the display language. If a USB keyboard is connected,
click to choose the keyboard layout. Click the keyboard icon to
enter the necessary information if a USB keyboard is not available.
The monitoring page will be shown upon successful login, refer to Chapter 3.3 for
details.
43
3.1 Quick Configuration (Manual Setup or Quick Setup)
If the NVR has not been configured, Quick Configuration Wizard will be shown.
Follow the instructions of the wizard to complete the system setup.
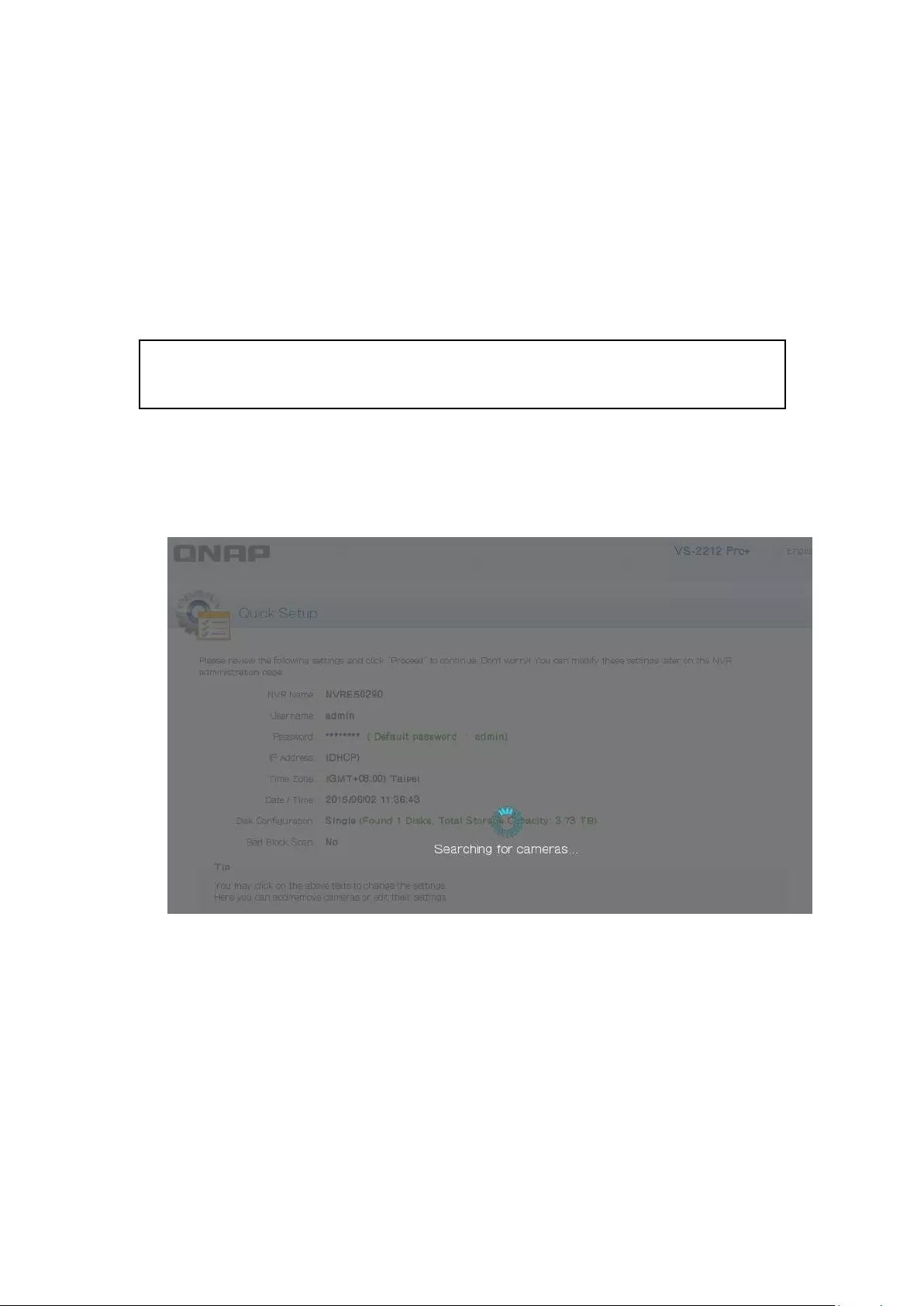
3.1.1 Quick Setup
1. In the Quick Setup page, the system will search for cameras
2. After searching for cameras, a list of discovered cameras will be displayed
Note: All the changes will be effective only after applying the settings in the last
step.
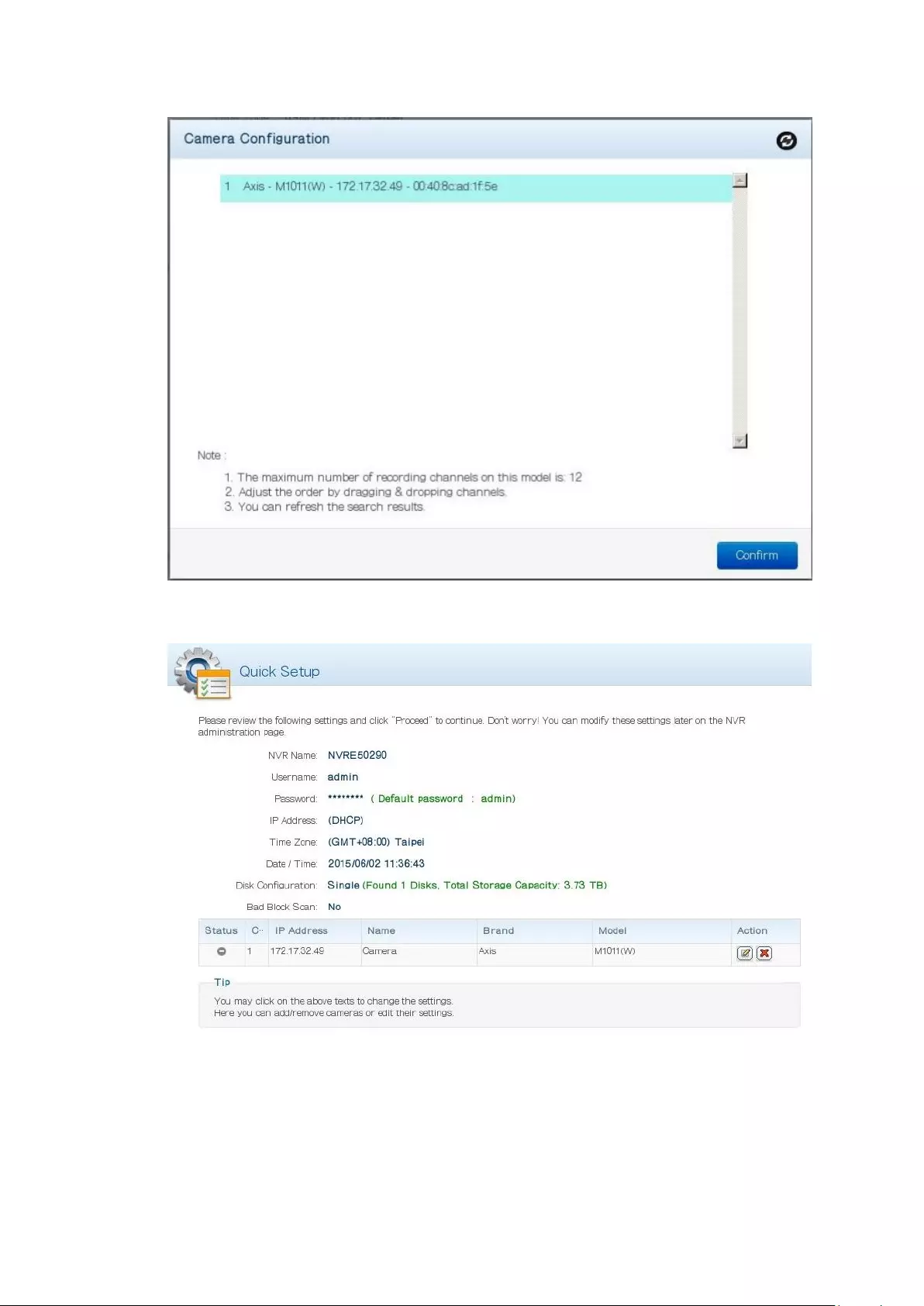
44
3. You can now check that all of the NVR and Camera settings fit your needs.
4. To start the setup process, click “Proceed”.
45
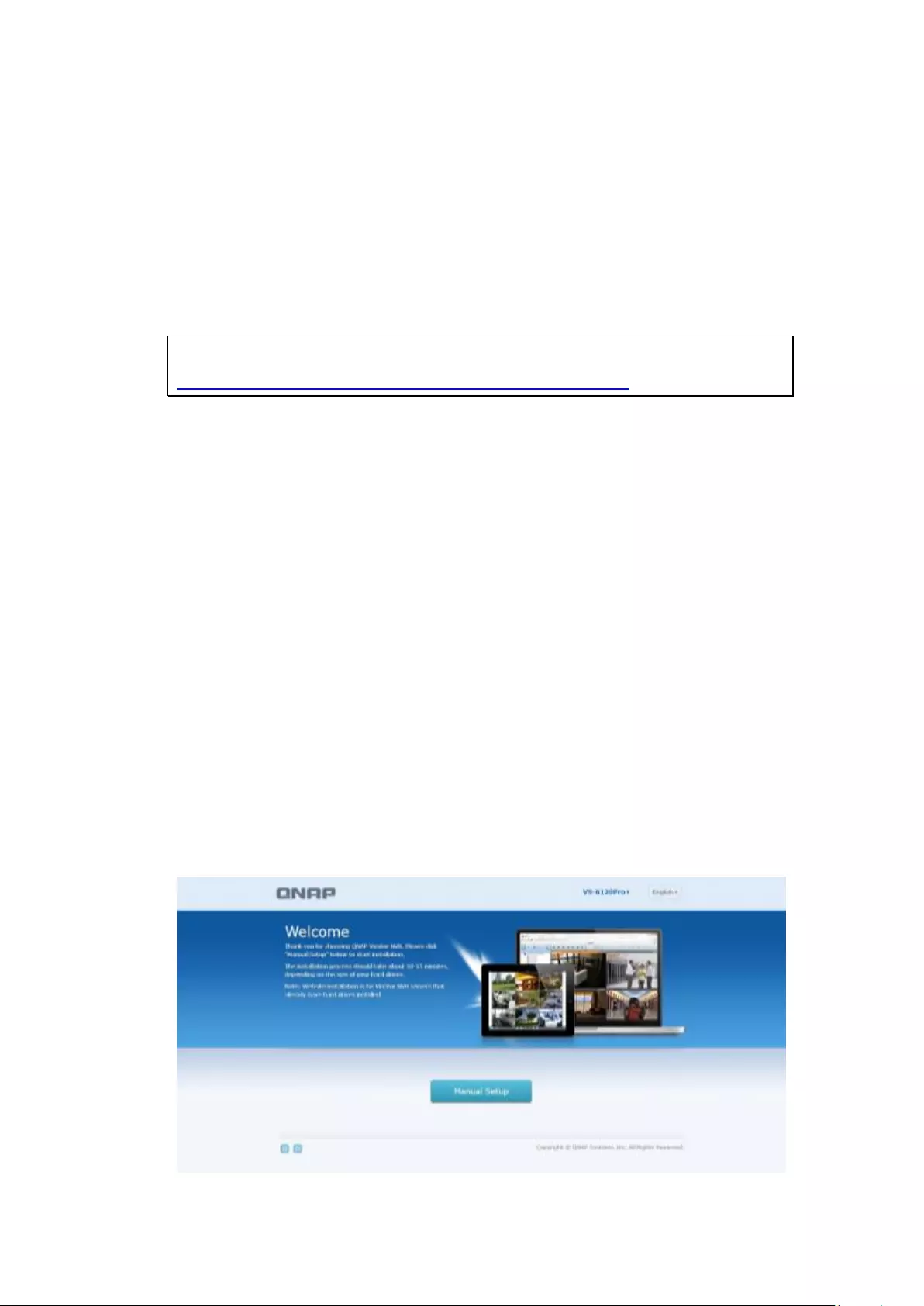
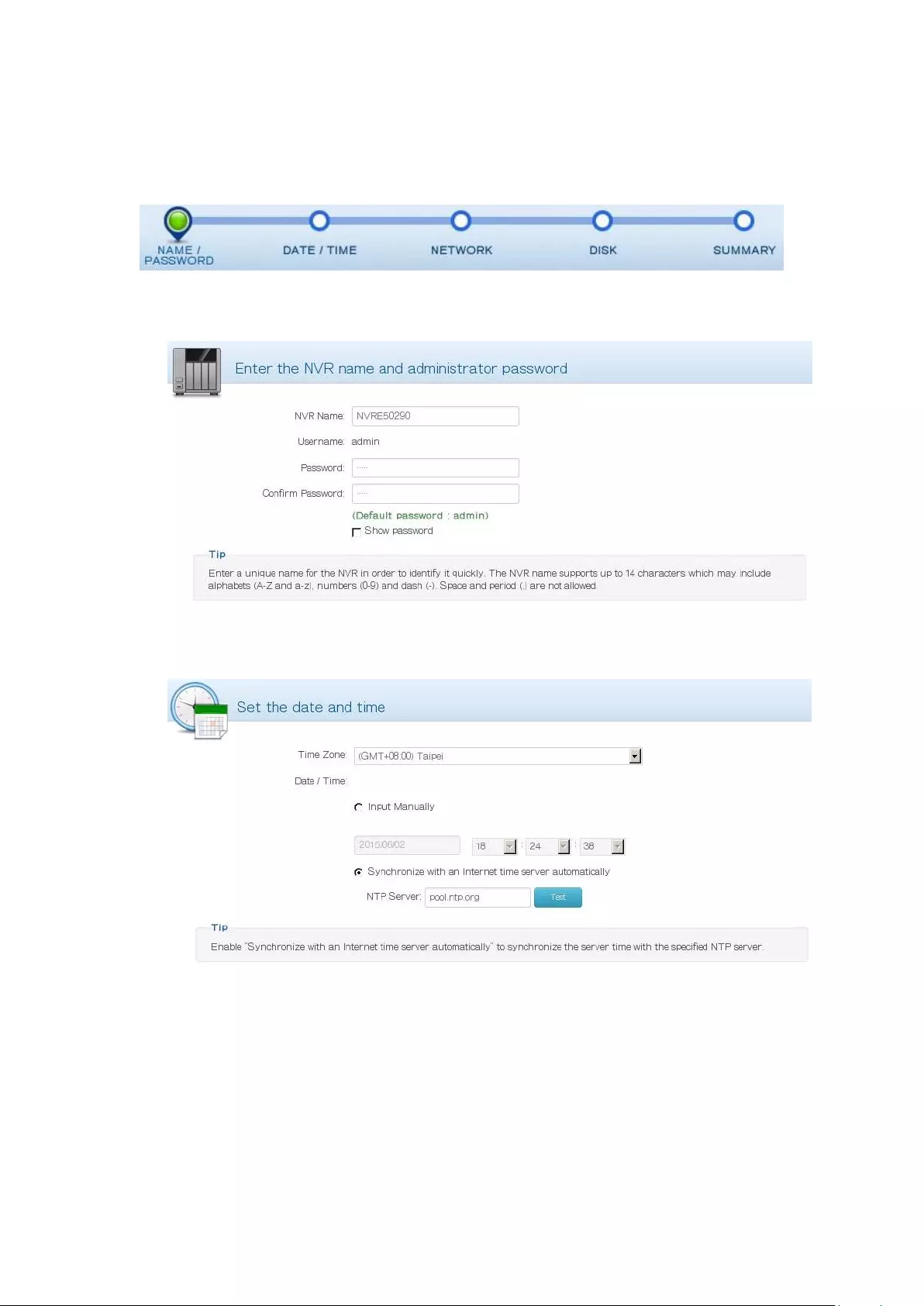
3.1.2 Manual Setup
Follow these procedures to setup the NVR.
1) Enter the NVR name and administrator password.
2) Set the time zone, date and time.
3) Configure the network settings.
46
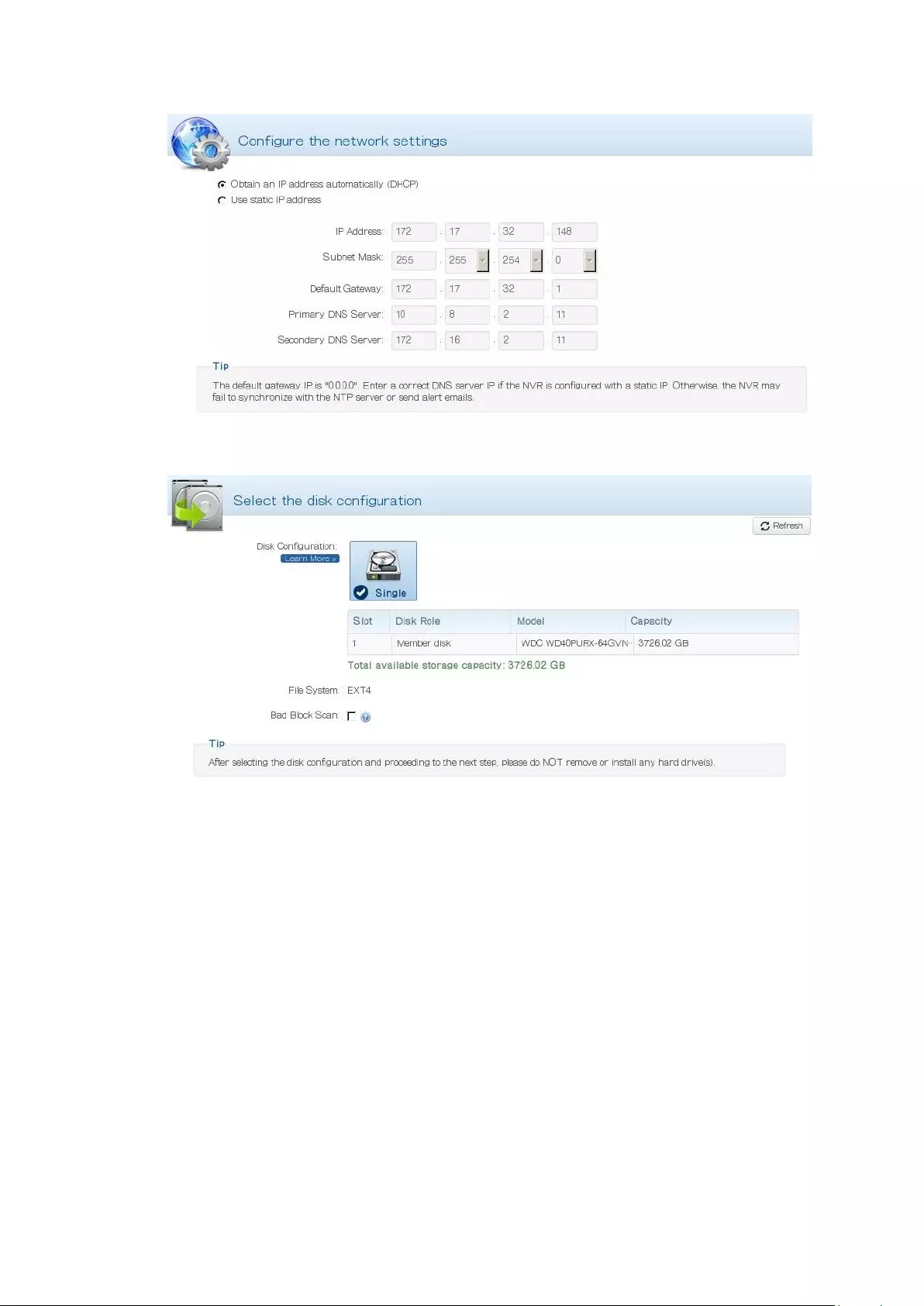
4) Select the disk configuration.
5) In the Summary, you can confirm your settings and click “Apply” to finish.

47
48
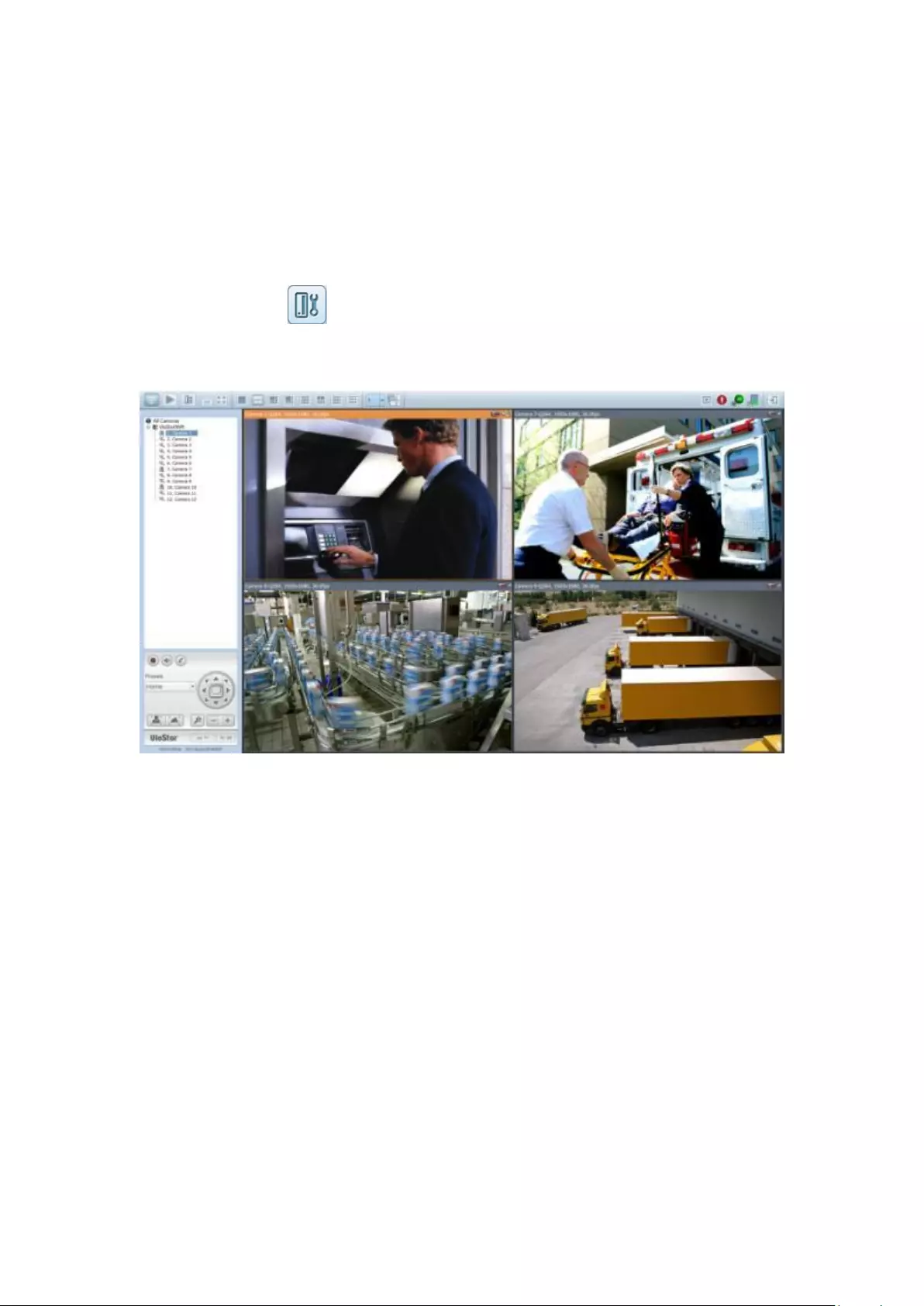
3.2 Surveillance Settings
To manage the surveillance settings such as administrator password, network and
time settings, click on the monitoring screen. Note that this button (option)
will be shown for administrator access only.
Select the language and click the icons to configure the settings.
49
50
圖示
說明
Main Menu
Back to Monitor
Control Panel
Surveillance Settings
File Station
Recording Backup and Storage Expansion
Background Tasks
External Devices
Notification
Options
Search
Help
Desktop Preferences
51
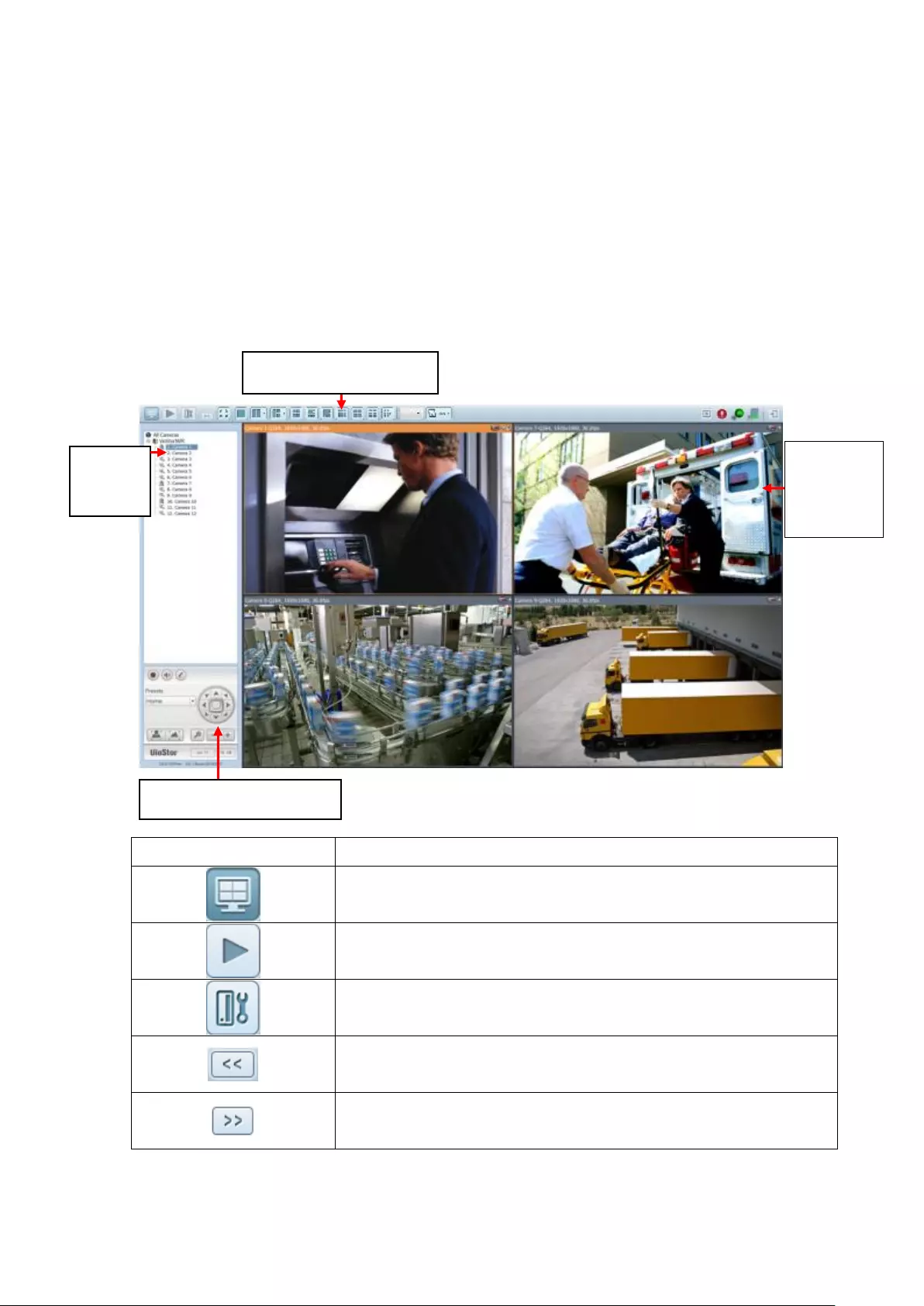
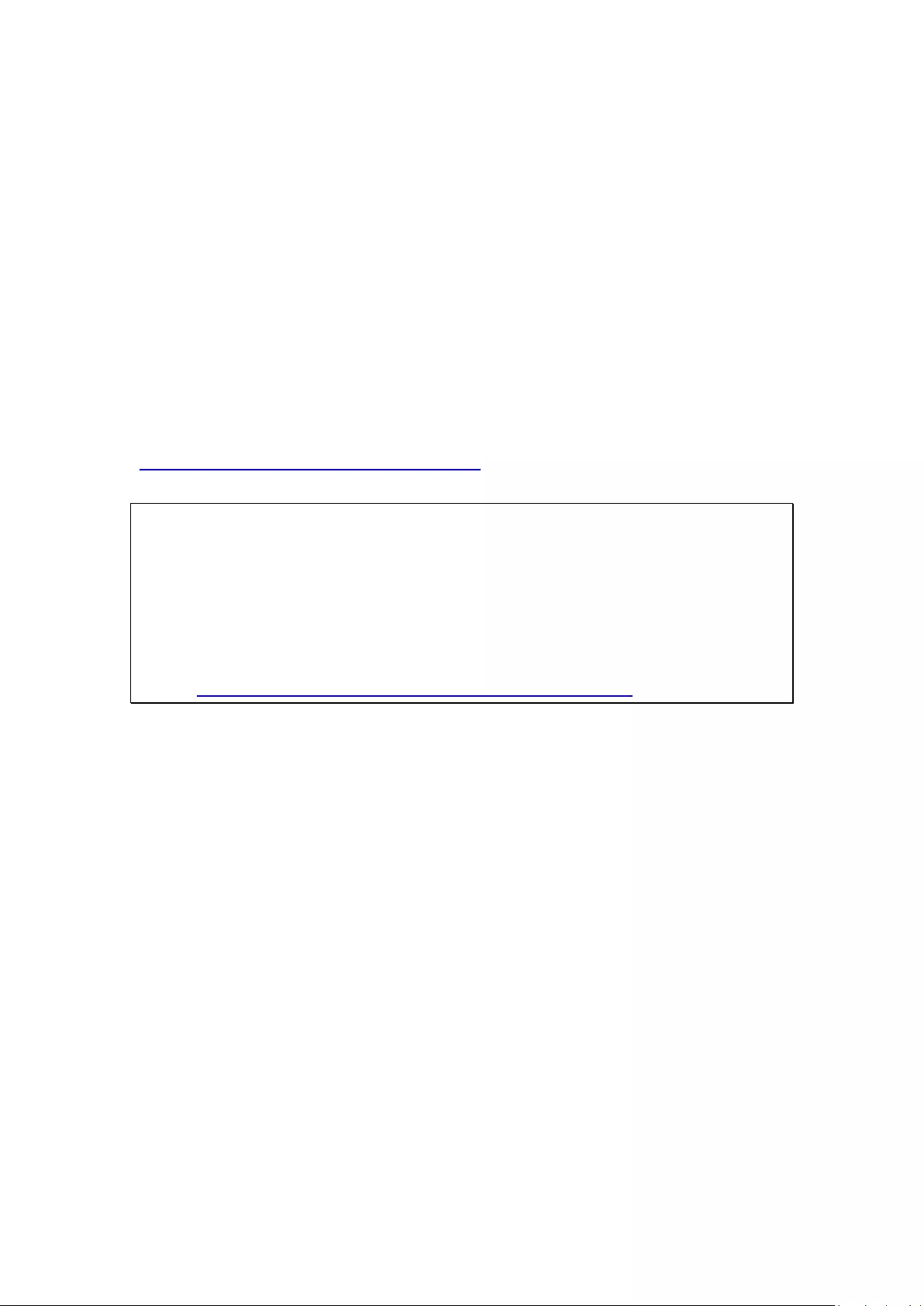
3.3 Monitoring
Upon successful login, the monitoring screen will be shown. Monitor the IP
cameras, change the display mode, enable or disable manual recording, control the
PTZ cameras, and so on.
Icon
Description
Monitor:
Enter the monitoring page.
Playback:
Enter the playback page.
Surveillance Settings:
Enter the surveillance settings page; allows admin access only.
Hide left panel:
Hide the panel on the left of the monitoring page.
Show left panel:
Show the panel on the left of the monitoring page.
View video
image and IP
camera info
Camera
list
Select monitoring mode
PTZ camera control panel
52
Options:
Configure the event notification settings, video window display
settings, screen resolution, etc.
CPU Status:
Display system CPU usage
Hard drives Status:
Display hard drive usage
About:
View the server name, NVR model, and firmware version.
Logout:
Logout the NVR.
Manual recording:
Enable or disable recording on the IP camera. The
administrator can select to enable or disable this function in
‘Camera Settings’ > ‘Recording Settings’ on the web-based
administration interface.
Audio (optional):
Turn on or off the audio support for the monitoring page.
Microphone (optional):
Toggle microphone support for the monitoring page
53
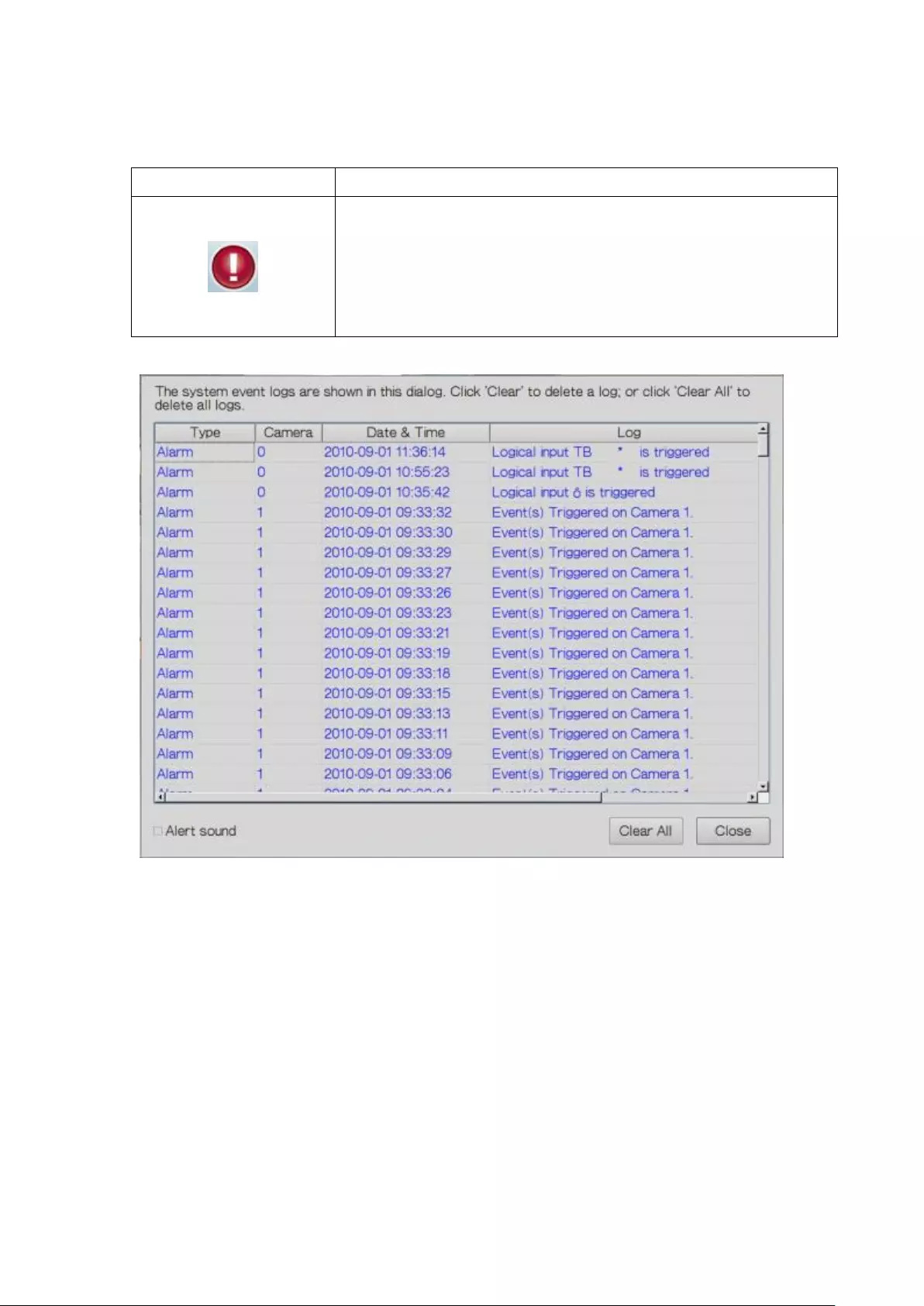
Event Notification
Icon
Description
Event notification:
When the alarm recording is enabled and an event is detected,
this icon will be shown. Click this icon to view the alert details.
The alert sound can be turned on or off. To clear all the logs,
click ‘Clear All’.

54
PTZ Control Panel
The term ‘PTZ’ stands for ‘Pan/Tilt/Zoom’. If the IP camera supports PTZ, use the
control panel on the NVR to adjust the viewing angle of the IP camera. These
functions are available depending on the camera models. Please consult the
camera's documentation for details. Note that the digital zoom function will be
disabled when the PTZ function is in use.
Icon
Description
Pan and tilt:
If the PTZ camera supports pan and tilt functions, click these
buttons to pan or tilt the camera.
Preset positions:
Select the preset positions of the PTZ camera.
Zoom out/Zoom in:
If the PTZ camera supports zooming, click these buttons to
zoom in or zoom out.
Digital zoom:
Select a channel and click this button to enable the digital zoom
function. When enabled, click ‘+’ to zoom in or ‘-’ to zoom out.
Focus control:
Adjust the focus control of the PTZ camera.
System information:
Display system time & date information
55
Display Mode
The NVR supports various display modes for monitoring. Click the correct icon to
switch the display mode.
Icon
Description
Full screen
Single-channel mode
2-channel mode (click the downwards arrow to choose another
2-channel mode)
3-channel mode (click the downwards arrow to choose another
3-channel mode)
4-channel mode
6-channel mode
8-channel mode
9-channel mode
10-channel mode
12-channel mode
4x4, 5x4, 5x5, 6x5, 8x4, 6x6 channel mode
Select the display page number
Sequential mode. This mode can be used with other display modes.
Click to enable or disable sequential mode. Click to define
the time interval of which the channels will be displayed.
There are 9 time interval types you can choose: 3 seconds, 5 seconds, 10
seconds, 15 seconds, 30 seconds, 60 seconds, 120 seconds, 150
seconds, 300 seconds.

56
Live View Screen
Upon successful configuration of the IP cameras, enter the monitoring screen to view
the live video from the cameras.
If the camera supports pan and tilt functions, click the channel on the screen and
adjust the viewing angle with a mouse. If zooming is supported, scroll the mouse
wheel to zoom in or zoom out the video. These functions are available depending
on the camera models. Please consult the camera's documentation for details.

57
Camera Status
The camera status is indicated by the icons shown below:
Icon
Camera Status
Scheduled or continuous recording is in process
This IP camera supports audio function
This IP camera supports PTZ function
Manual recording is enabled
The recording triggered by advanced event management (‘Camera Settings’
> ‘Alarm Settings’ > ‘Advanced Mode’) is in process
The alarm input 1 of the IP camera is triggered
The alarm input 2 of the IP camera is triggered
The alarm input 3 of the IP camera is triggered
Motion detection recording is in process
Digital zoom is enabled
58
Connection Message
If the NVR fails to display the video from an IP camera, a message will be shown in
the channel window to indicate the status.
Message
Description
Connecting
If the IP camera is located on remote network or the Internet, it may
take some time to establish a connection to the camera.
Disconnected
The NVR cannot connect to the IP camera. Please check the
network connection of the computer and the availability of the IP
camera. If the IP camera is installed on the Internet, open the port
on the router or gateway to connect to the IP camera. Please refer
to Appendix A.
No
Permission
You do not have access rights to view this channel. Please login as a
user with access rights or contact the system administrator.
Server Error
Check the camera settings or update the firmware of the IP camera
(if any). Contact technical support if the error persists.
Please note:
1. Enabling or disabling manual recording will not affect scheduled or alarm
recording tasks. They are independent processes.
2. Right click on the IP camera channel and select the following options:
A. Full screen
B. Keep aspect ratio
C. Deinterlace (available on particular camera models only)
D. Keep original size
E. Dewarp fisheye images
Right click on the channel and enable the function. After that, you can
select the Mount type, including wall, ceiling, and floor and then select
Dewarping mode, including Panorama (Full View), Panorama (Dual View),
and Rectangle.
Remark 1: If the selected mount type is Wall then only Panorama (Full View)
and Rectangle are supported in Dewarping mode.
Remark 2: If the selected Dewarping mode is Rectangle, you can use the
PTZ control panel to operate PTZ functions (excluding digital zoom).
F. Dewarp panomorph images: for the specific camera models with
panomorph lens
Before using this feature, you need to select the ‘Enable panomorph
support’ option in the recording settings page. Right click on the channel

59
and enable the function. After that, you can select the Mount type,
including wall, ceiling, and floor and then select Dewarping mode,
including Perimeter mode, Quad mode, and PTZ mode.
Remark 1: To see a list of camera models that support panomorph lenses,
please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/qa/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=
128.
Remark 2: This function is only available when the resolution of the video
stream is higher than 640x480 on the monitoring page.
Remark 3: If Dewarping mode is in PTZ mode, then in the channel, you can
use the PTZ control panel or mouse (by holding down the mouse left
button, and then moving the mouse or turning the mouse wheel) to
change viewing angles or to zoom in/out of the screen. If the Dewarping
mode is in Quad mode, the above methods can also be applied to operate
PTZ functions in each divided screen.
60
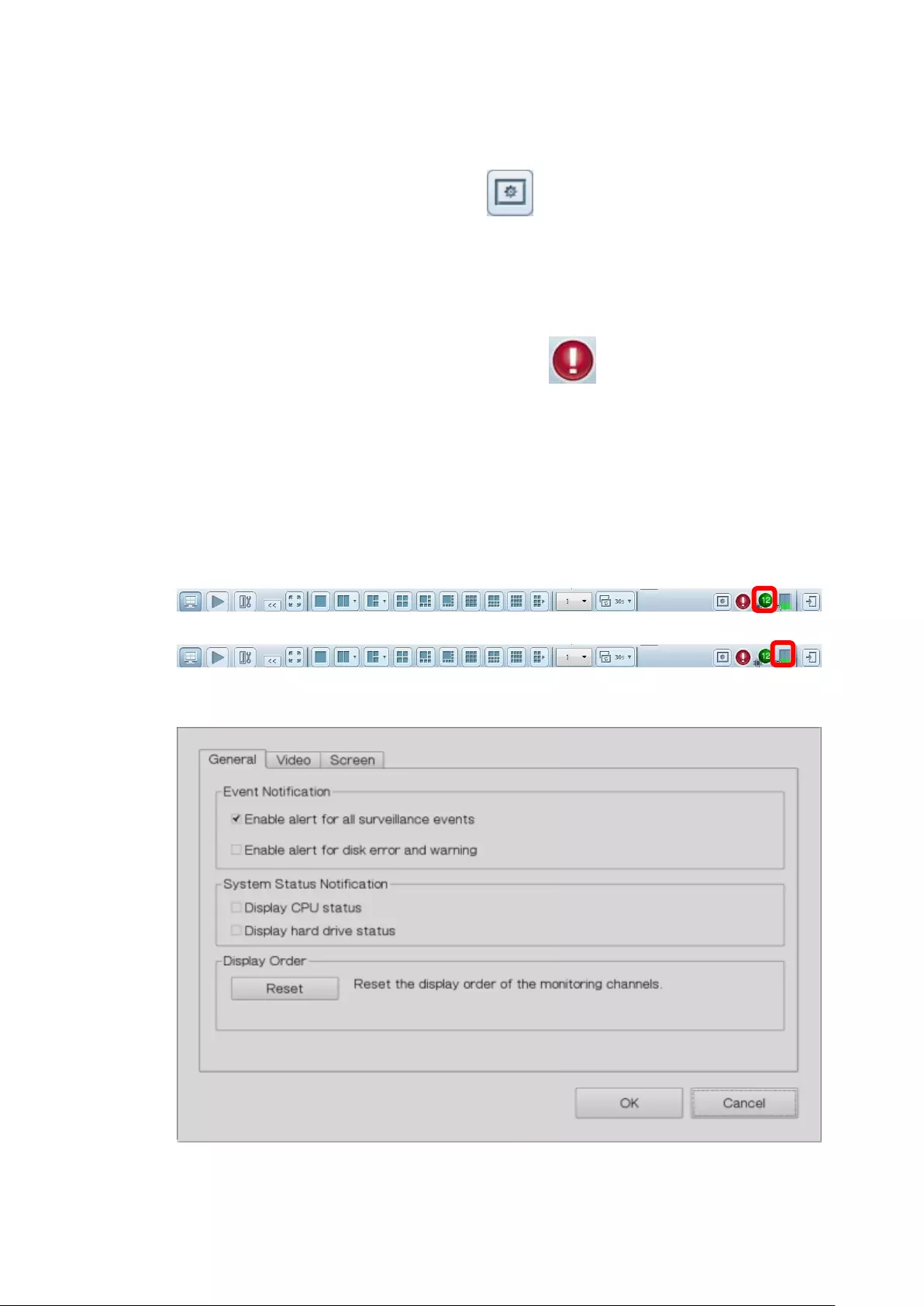
Options
To configure advanced monitor settings, click .
The following options are listed under the ‘General’ tab.
Event Notification:
When ‘Enable alert for all surveillance events’ option is enabled and a
surveillance event is triggered, the alert icon will be instantly shown
on the monitoring page. Click the icon to view the alert details.
After enabling ‘Issue notification when the disk reaches maximum
operation time set below’ in System Tools -> Hard Disk SMART, you can
then ‘Enable alert for disk error and warning’ to receive alarm
notifications if hard drive events occur.
System Status Notification:
Display CPU status: will display the CPU status as seen below
Display HDD status: will display the hard drive status as seen below
Display Order: Click ‘Reset’ to reprioritize the monitoring channels to
default.
61
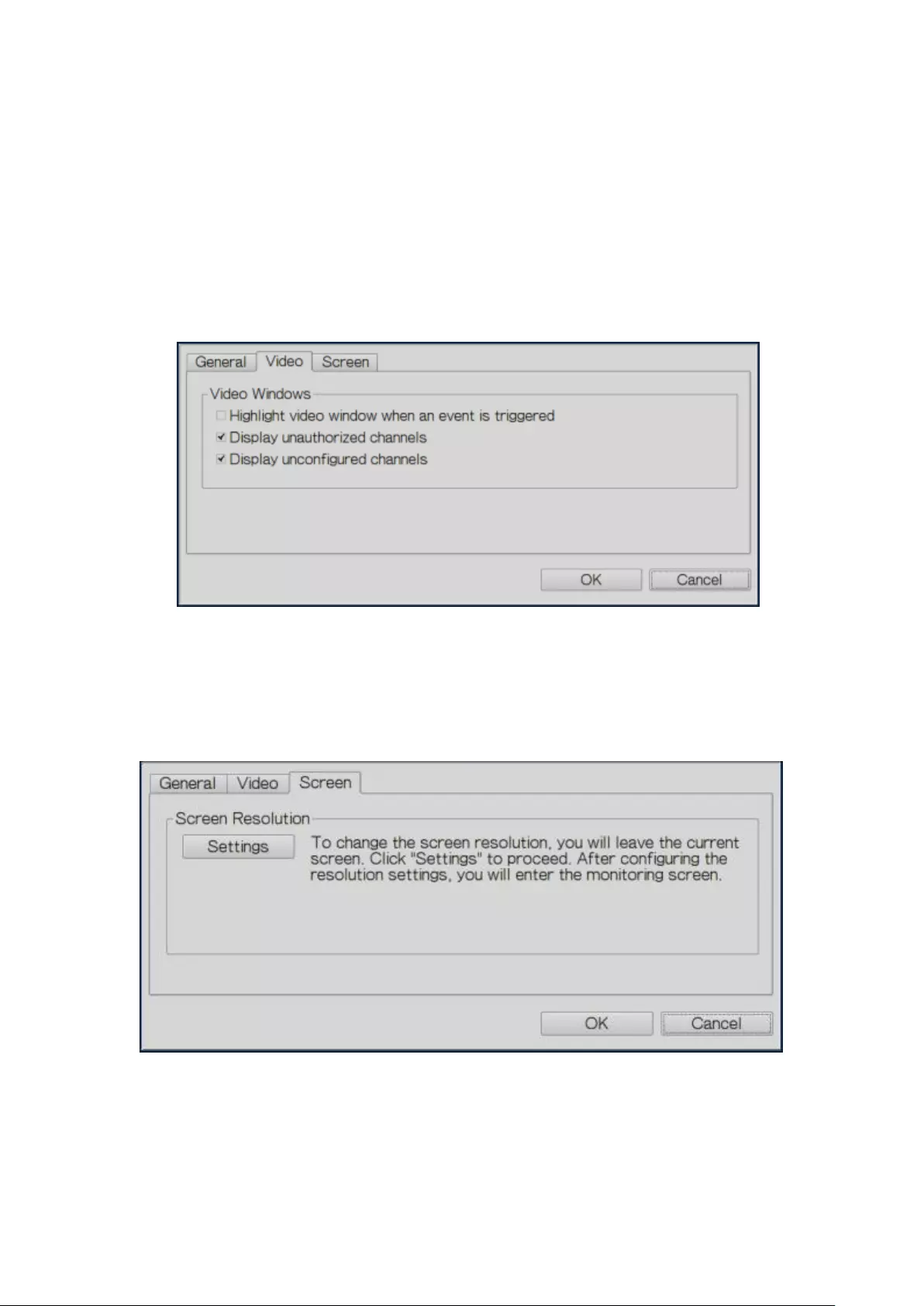
The following options are provided under the ‘Video’ tab.
Highlight the video window when an event is triggered: The video window will
flash if an event is triggered.
Display unauthorized channels: Select this option to show channels that the
user does not have the access rights to.
Display unconfigured channels: Select this option to show unconfigured
channels.
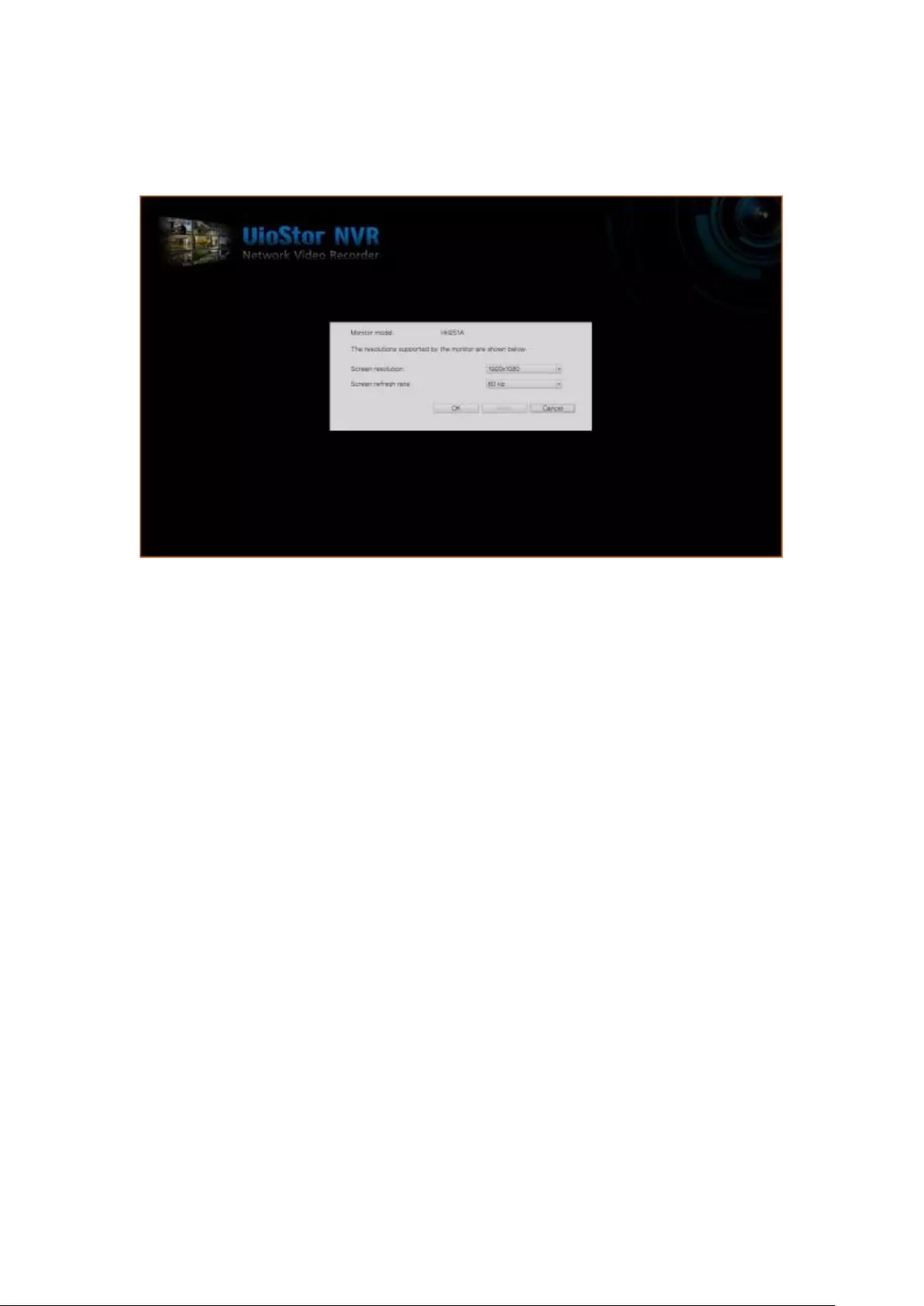
The NVR automatically detects the resolution settings supported by the connected
monitor and will use the optimum settings. To change the screen resolution, click
‘Settings’ under the ‘Screen’ tab. After configuring the resolution settings, the
monitoring screen will be shown.
62
If the monitor model cannot be detected, the NVR will provide resolution options of
1920x1080, 1400x1050, 1280x1024, and 1024x768.
63
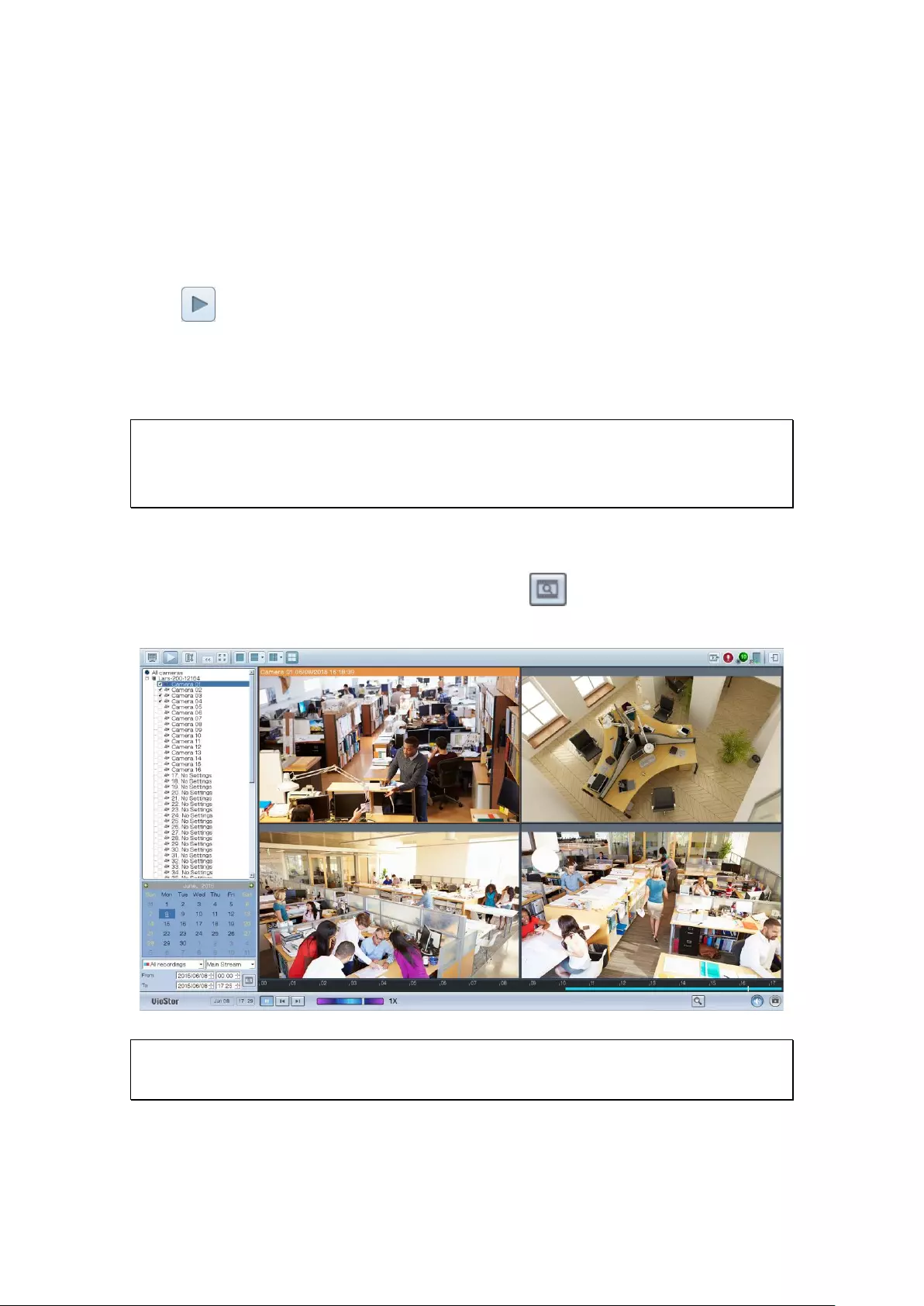
3.4 Video Playback
The videos on the NVR can be played using the local display. To use this feature,
click on the monitoring screen. Most of the icons on the playback screen are
the same as those on the monitoring screen. Please refer to Chapter 3.2 for the
icon description.
Note: The playback access rights to the IP cameras are required to play the videos.
Login to the NVR as the admin and edit the playback access rights in ‘User
Management’ using the web-based administration interface.
When the playback screen is shown, select a camera channel on the NVR. Next,
select the start and end time of the video and click to start searching. The
videos that match the search criteria will be played automatically.
Note: The number of days between the start and end dates must be less than or
equal to 2.
64
Playback Settings:
Play, pause, stop, reverse play a video file, or select to play the previous or next file.
When playing a video, use the scroll bar to adjust the playback speed or click on the
digital zoom icon to zoom in/out the video.
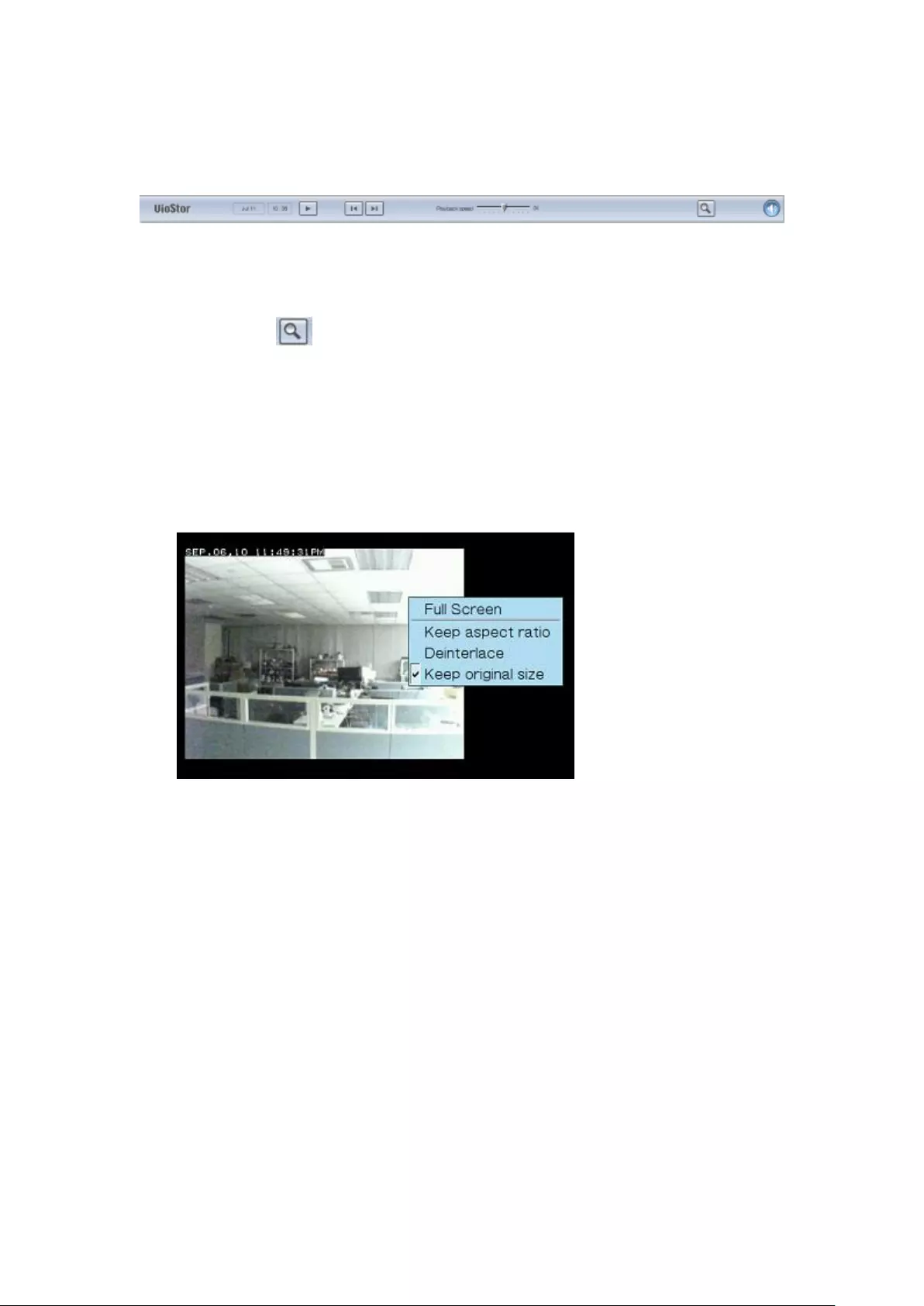
Right click on the IP camera channel to select the following options:
1. Full screen
2. Keep aspect ratio
3. Deinterlace (available on particular camera models only)
4. Keep original size
5. Dewarp fisheye images
Right click on the channel and enable the function. After that, you can select
the Mount type, including wall, ceiling, and floor and then select Dewarping
mode, including Panorama (Full View), Panorama (Dual View), and Rectangle.
Remark 1: If the Mount type is Wall, only Panorama (Full View), and Rectangle
are supported in Dewarping mode.
Remark 2: If Dewarping mode is Rectangle, you can use the PTZ control panel to
operate PTZ functions (excluding digital zoom).
6. Dewarp panomorph images: for the specific camera models with panomorph
lens
Before using this feature, you need to select the ‘Enable panomorph support’
option in the recording settings page. Right click on the channel and enable
the function. After that, you can select the Mount type, including wall, ceiling,
and floor and then select Dewarping mode, including Perimeter mode, Quad

65
mode, and PTZ mode.
Remark 1: To discover what camera models can be installed with panomorph
lenses, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/qa/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=128.
Remark 2: The function is only available when the video stream resolution is
higher than 640x480 on the monitoring page.
Remark 3: If Dewarping mode is in PTZ mode, for the channel, you can use the
PTZ control panel or mouse (by holding down the mouse left button, and then
moving the mouse or turning the mouse wheel) to change viewing angles or
zooming in/out the screen. If Dewarping mode is in Quad mode, the above
methods can also be applied to operate PTZ functions in each divided screen.

66
3.5 Video Conversion & Export
The NVR supports converting video files to AVI format and saving the files to an
external USB storage device.
Note:
To use this feature, connect a USB storage device to the front USB port of the
NVR and ensure the device has been correctly formatted.
Access rights to play the IP camera videos are required to convert the video files.
Follow the below steps to export IP camera video files from the NVR and convert the
files to an AVI file.
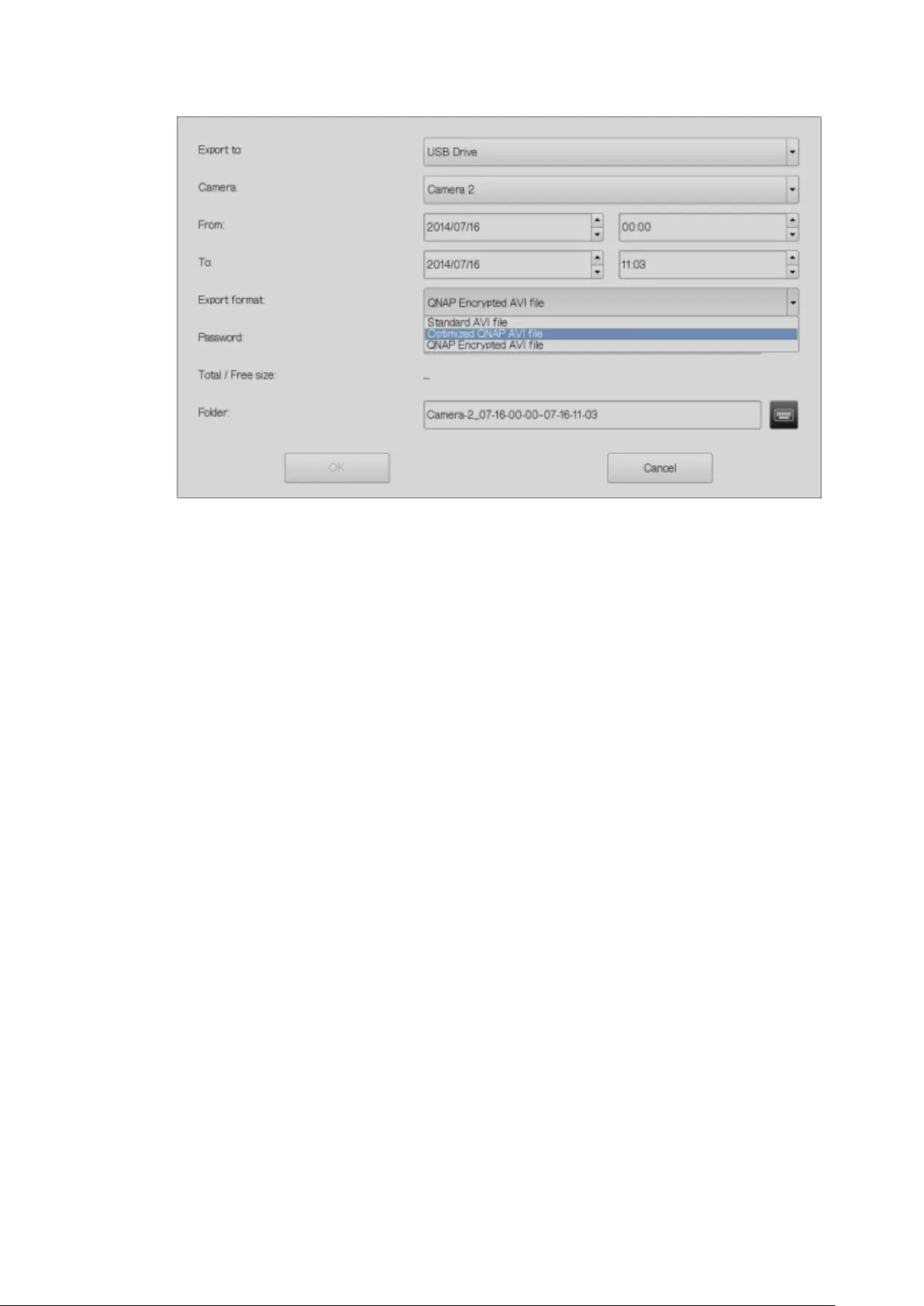
1. Enter the playback interface of the NVR. Select a camera channel on the NVR.
Click (Convert to AVI file).
2. Select the IP camera.
3. Specify the start and end times of the video files.
4. Select the export format.
Standard AVI file: Convert recording files to standard AVI file. More time is
needed to export, but no additional codecs are required.
Optimized QNAP AVI file: Convert files using an enhanced QNAP codec. Less
time is needed to export, but the QNAP codec is required.
QNAP Encrypted AVTI file: Protect the file with password protection and
encryption
67
5. Enter the file name of the video file.
6. Click ‘OK’ to convert the video files to an AVI file and save them to the external
USB storage device.

68
Chapter 4. QVR Basics and Desktop
4.1 Introducing QVR
Built on a Linux foundation, the QVR, QNAP VioStor Recording system has been
designed around an optimized kernel to deliver high-performance services satisfying
your needs in live view, recording, playback and more.
The intuitive, multi-window and multi-tasking QVR GUI makes it incredibly easy to
manage your VioStor NVR, utilize its rich surveillance applications, and install a rich
set of applications in the App Center on demand to expand your VioStor NVR
experience.
QNAP VioStor NVR has many professional features for remote monitoring, recording,
and surveillance tasks under diverse environments but also functions with great
simplicity. The QNAP VioStor NVR allows users to choose suitable network cameras
for various situations. Businesses can enjoy high flexibility in deploying their ideal
surveillance solutions with the broad-ranged offerings of compatible IP cameras.
QNAP VioStor NVR also offers:
An intuitive GUI with multi-window, multi-tasking , and multi-application
support
Real-time monitoring and recording (video/audio) from multiple IP cameras
Cross platform surveillance center
Multi-server monitoring (up to 128 channels)
Interactive control buttons
Instant playback
Same-screen IP camera configurations
Playback and speed control with shuttle bar
Preview videos with thumbnails
Intelligent video analytics (IVA)
Digital watermarking
Live monitoring, playback on Android and iOS mobile devices with Vmobile
Advanced event management
69
Real-time SMS and email alert
Install-on-demand applications via the App Center
4.2 Connect to the NVR
Follow the below steps to connect to the monitoring page of the NVR.
1. Run the Qfinder. Double click the name of the NVR, or enter the IP address of
the server in your web browser to connect to the monitoring page.
2. Enter the user name and password to login the NVR.
Default user name: admin
Default password: admin
3. To view the live video in your web browser, please add the NVR IP address to
your list of trusted sites. When accessing the NVR via Internet Explorer, you will
be prompted to install the ActiveX add-on.
4. To view the live video with Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox or by using the QNAP
QVR Client on Windows PC, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp to download and install the QNAP
QVR Client for Windows first.
5. To view the live video on Mac, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp to download and install the QNAP
QVR Client for Mac.
70
4.3 Using the QVR Desktop
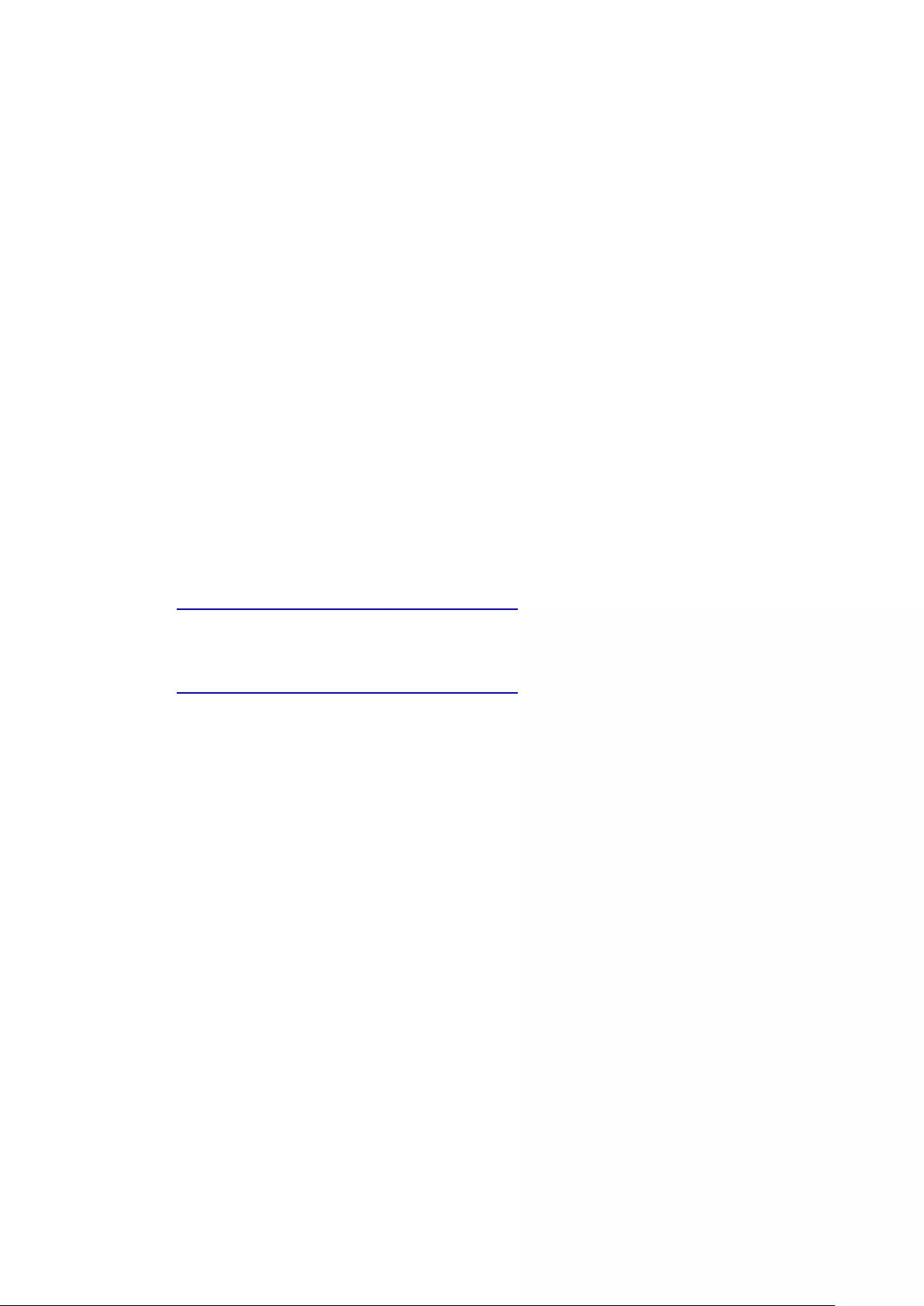
After you finish the basic NVR setup and login to the NVR, the following desktop will
appear. Each main desktop feature is introduced in the following sections.
Toolbar
Main Menu
Click to show the Main Menu. It includes three parts: 1) QNAP applications; 2)
system features and settings. Items under “APPLICATIONS” are developed by QNAP
to enhance your NVR experience. Items under “SYSTEMS” are key system features
designed to manage or optimize your NVR. These applications can add functionalities
to the NVR (for their introduction, please refer to their description at the App Center.)
Click the icon from the menu to launch the selected application.
Show Desktop
Click to minimize or restore all open windows and
Main Menu
Show Desktop
Go to Monitoring Page
Go to Playback Page
Toolbar
Notification
Personal
Settings
Desktop
Area
Next
Desktop
Dashboard
71
show the desktop.
Monitor page
Click to enter monitor page
Playback page
Click to enter playback page
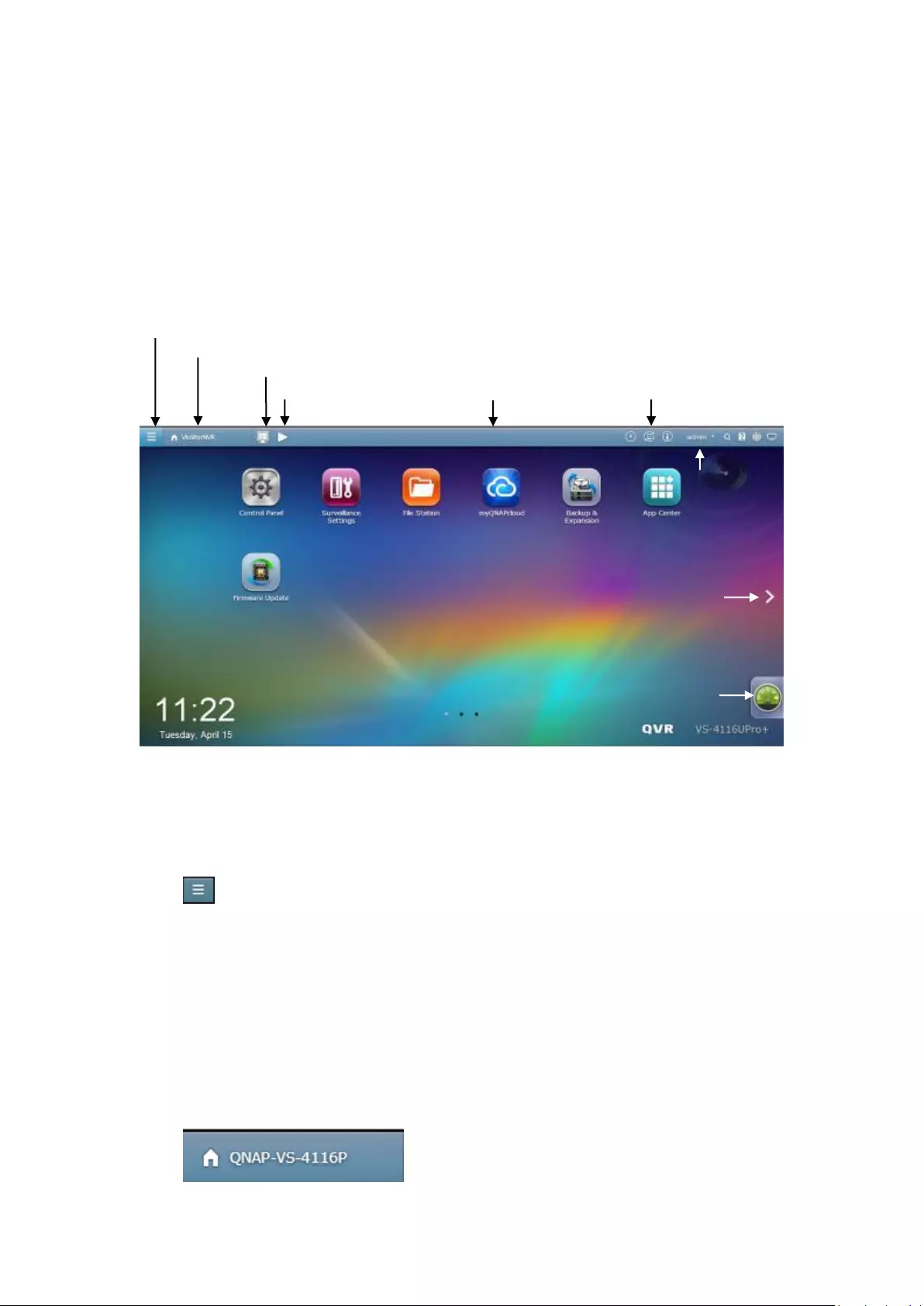
Background Task
Click to review and control all tasks running in the background (such as HDD
SMART scanning.)
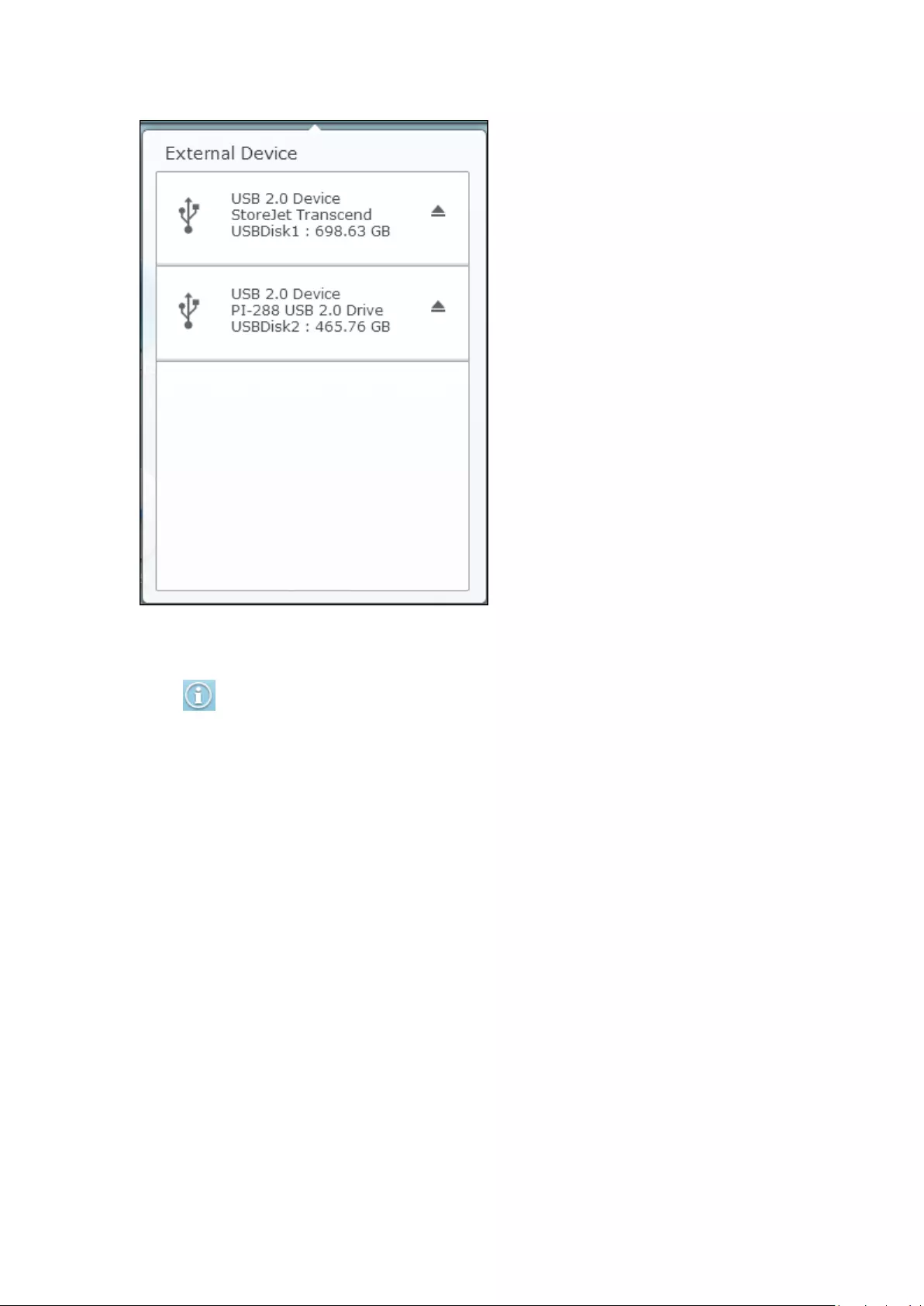
External Devices
Click to list all external devices that are connected to the NVR via its USB ports.
Click the device listed to open the File Station for that device. Click the “External
Device” header to open the External Device page for relevant settings and operations
(for details on the File Station, please refer to the chapter on File Station.) Click
to eject the external device.
72
Notification and Alerts
Click to check for recent system errors and warning notifications. Click “Clear
All” to clear all entries from the list. To review all the historical event notifications,
click the “Event Notifications” header to open the System Logs. For more details
regarding System Logs, please refer to the chapter on System Logs.
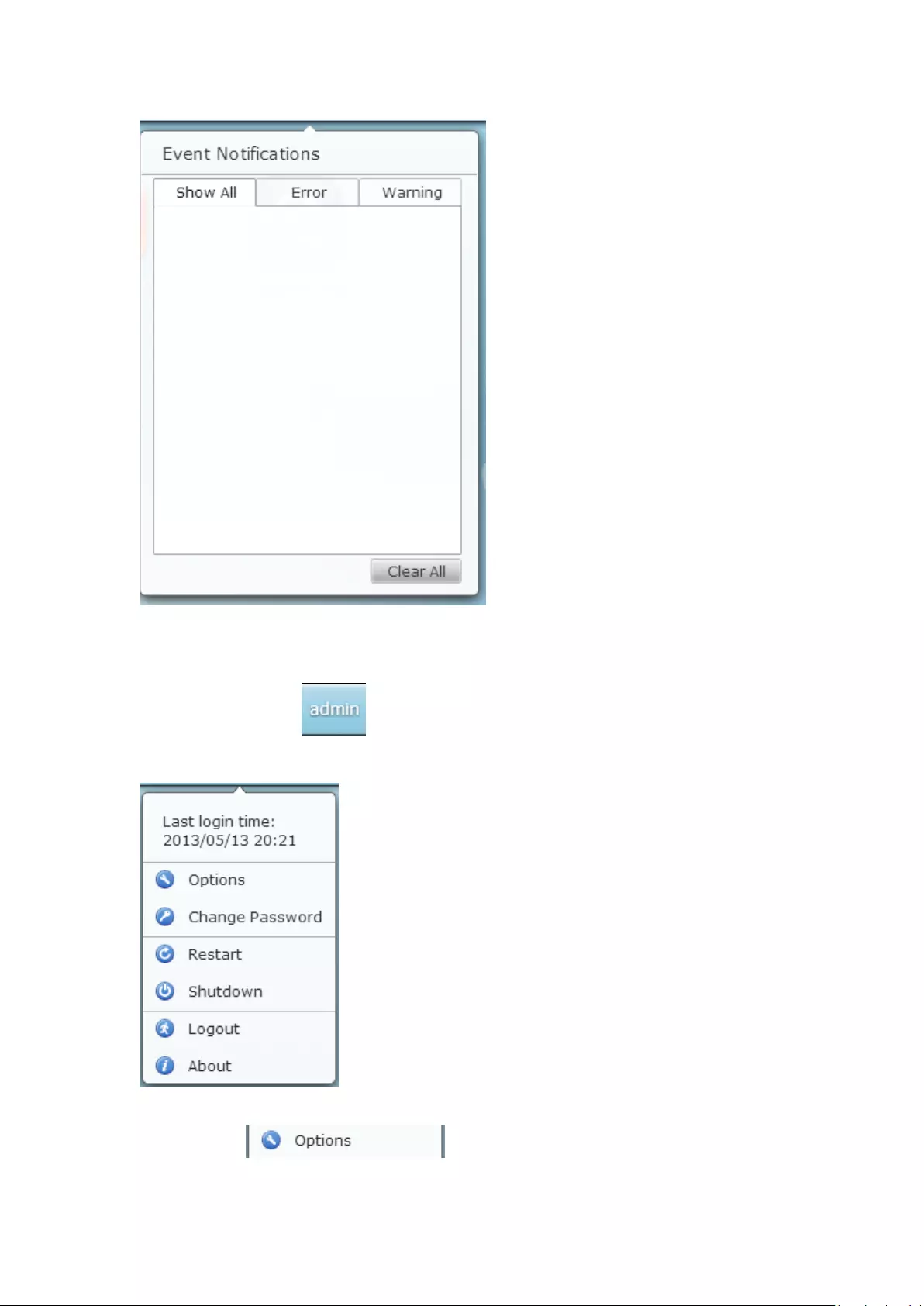
73
Personal Setting
Admin Control: Click to customize your user specific settings, change your
user password, restart/shut down the NVR or log out your user account.
1. Options ( ):
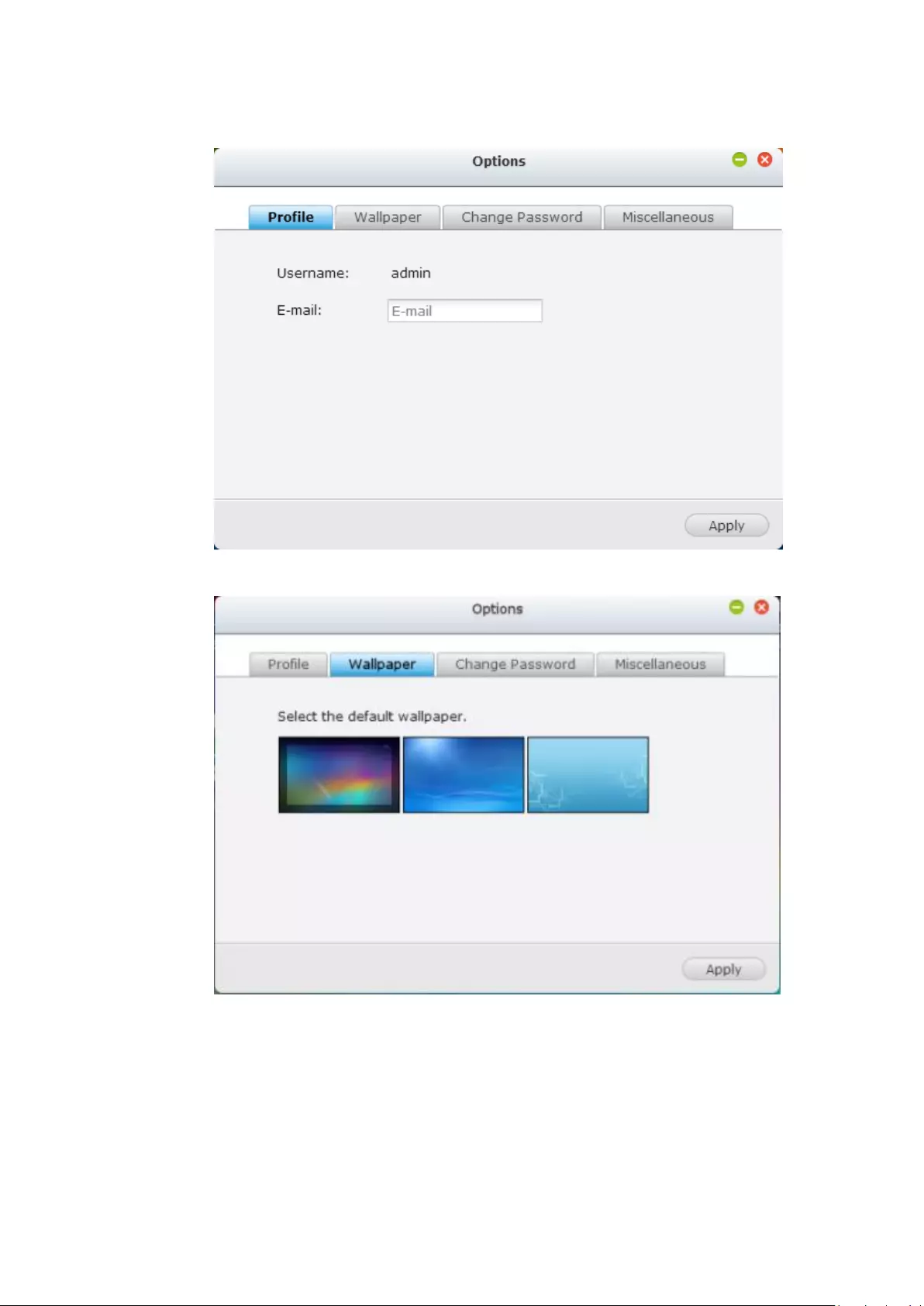
74
A. Profile: Specify your user email address.
B. Wallpaper: Change the default wallpaper or upload your own wallpaper.
C. Change Password: Change your login password.
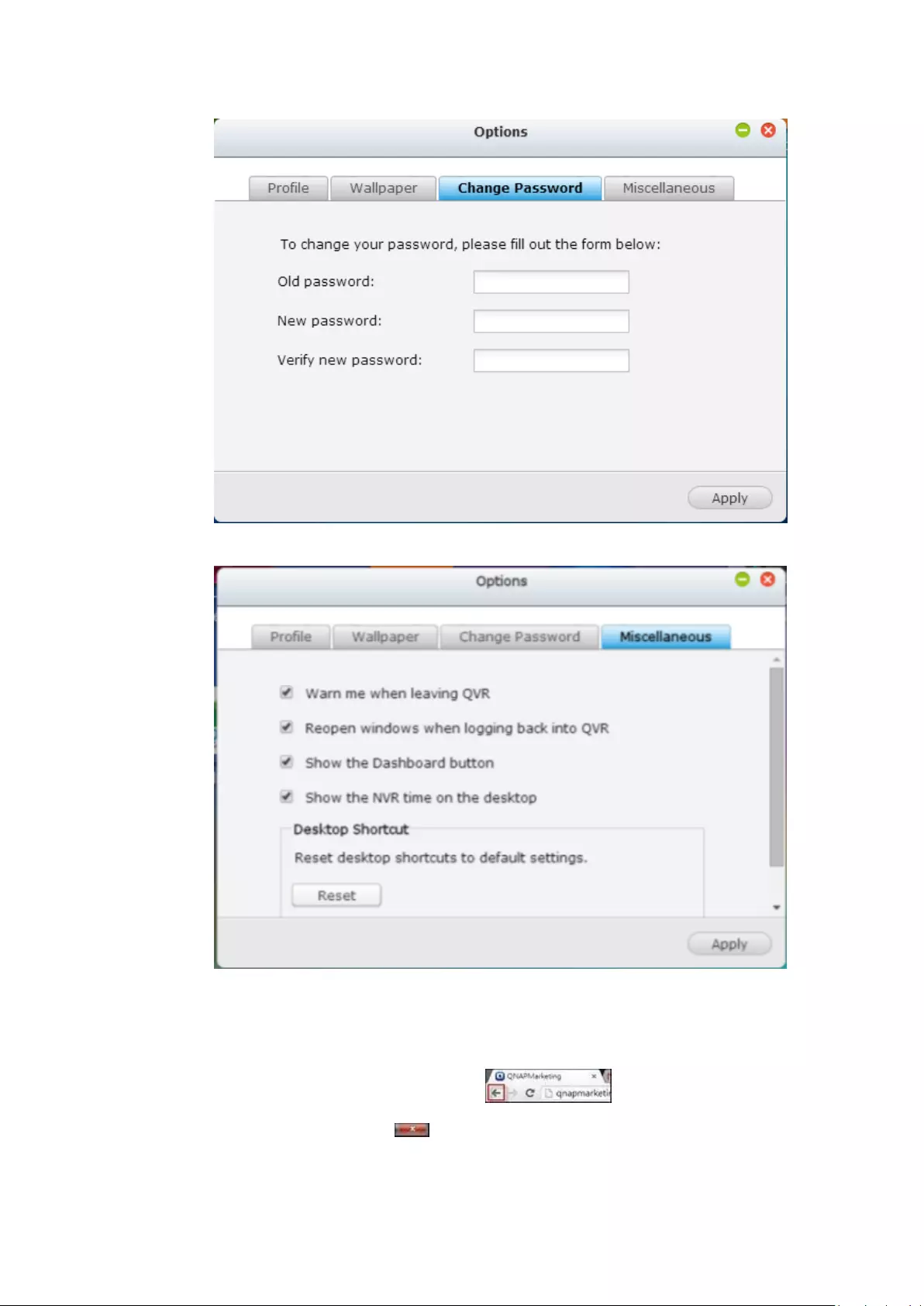
75
D. Miscellaneous:
Warn me when leaving QVR: Check this option, and users will be
prompted for confirmation each time they leave the QVR Desktop
(such as clicking the back icon ( ) in the browser or
close the browser ( ). It is recommended to check this option.
Reopen windows when logging back into QVR: Check this option, and
76
all the current desktop settings (such as the “windows opened before
your logout”) will be kept after you login the NVR the next time.
Show the desktop switching button: Check this option to hide the next
desktop button ( ) and last desktop button ( ) and only
display them when you move your mouse cursor close to the buttons.
Show the Dashboard button: If you would like to hide the Dashboard
button ( ) at the bottom right side of the NVR Desktop,
uncheck this option.
Show the NVR time on the desktop: If you prefer not to show the NVR
time at bottom left side of the desktop, uncheck this option.
Change Password: Click to change your
login password.
2. Restart: Click to restart your NVR.
3. Shutdown: Click to shut down your NVR.
4. Logout: Click to log yourself out.
5. About: Click to check the NVR model details
including, firmware version, HDDs already installed and available (empty) bays.
Search
Click and enter a feature-specific keyword in the search box to search for the
desired function and its corresponding online help. Click the result in the search box
to launch the function or open its online QVR help.
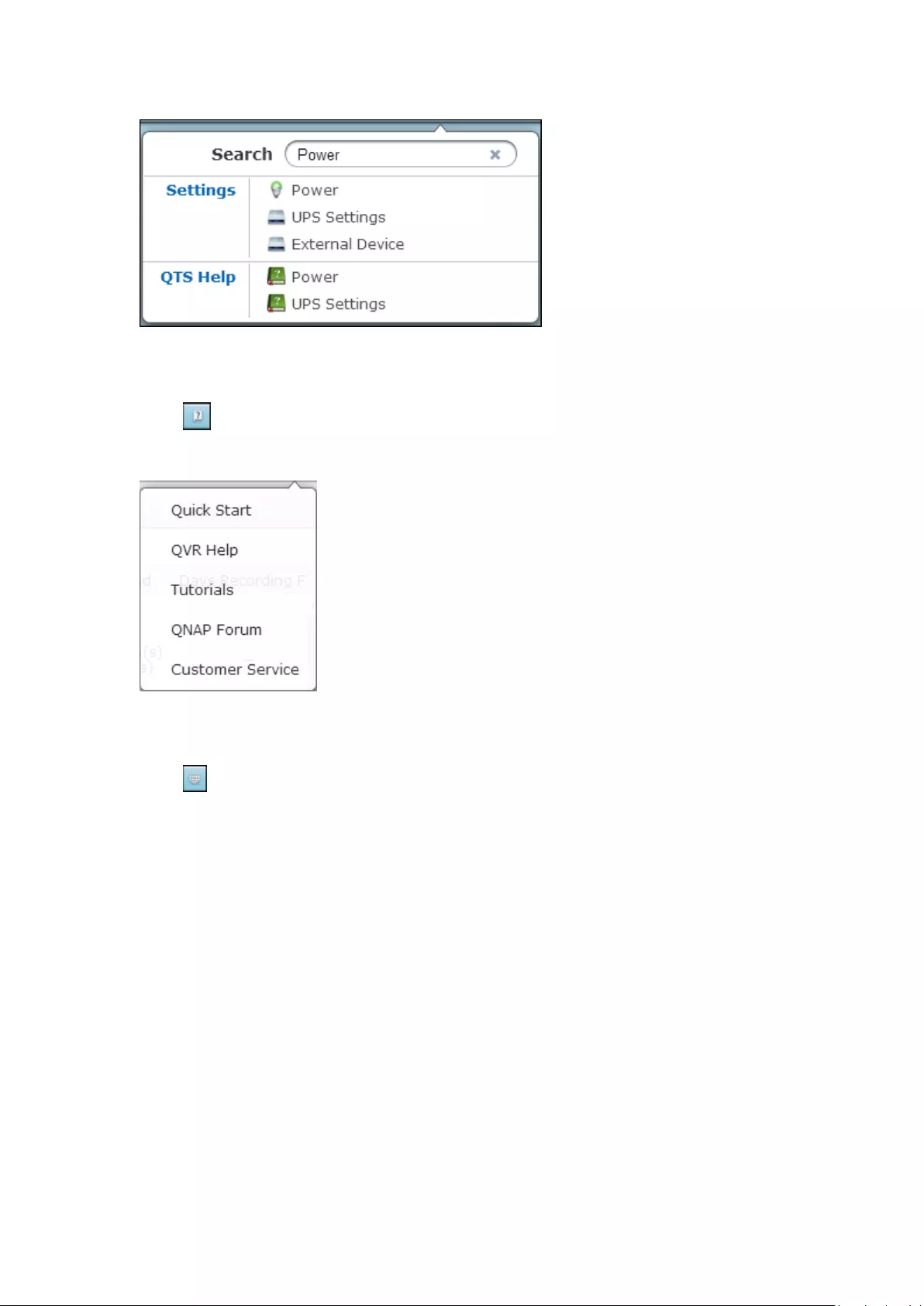
77
Online Resource
Click to display a list of online references, including the Quick Start Guide, QVR
Help, Tutorials, and QNAP Forum. Customer Service is available here.
Language
Click to choose your preferred language for the UI.
78
Desktop Preferences
Click to choose the application icon displaying style and select your preferred
application opening mode on the desktop. Application icons can be switched
between small thumbnails ( ) and detailed thumbnails
( ) and applications can be opened in the tab mode or the

79
window mode.
For the tab mode, the window will be opened to fit the entire NVR Desktop and only
one application window can be displayed at once, while in the window mode, the
application window can be resized and reshaped to a desirable style. Please note: if
you login the NVR using a mobile device, only the tab mode is available.
Desktop Area
You can remove or arrange all applications on the desktop, or drag one application
icon over the top of another to put them in the same folder ( ).
Next Desktop and Last Desktop
Click the next desktop button ( ) (right side of the current desktop) or the last
desktop button ( ) (left side of the current desktop) to switch between desktops.
The position of the desktop is indicated by the three dots at bottom of the desktop
().
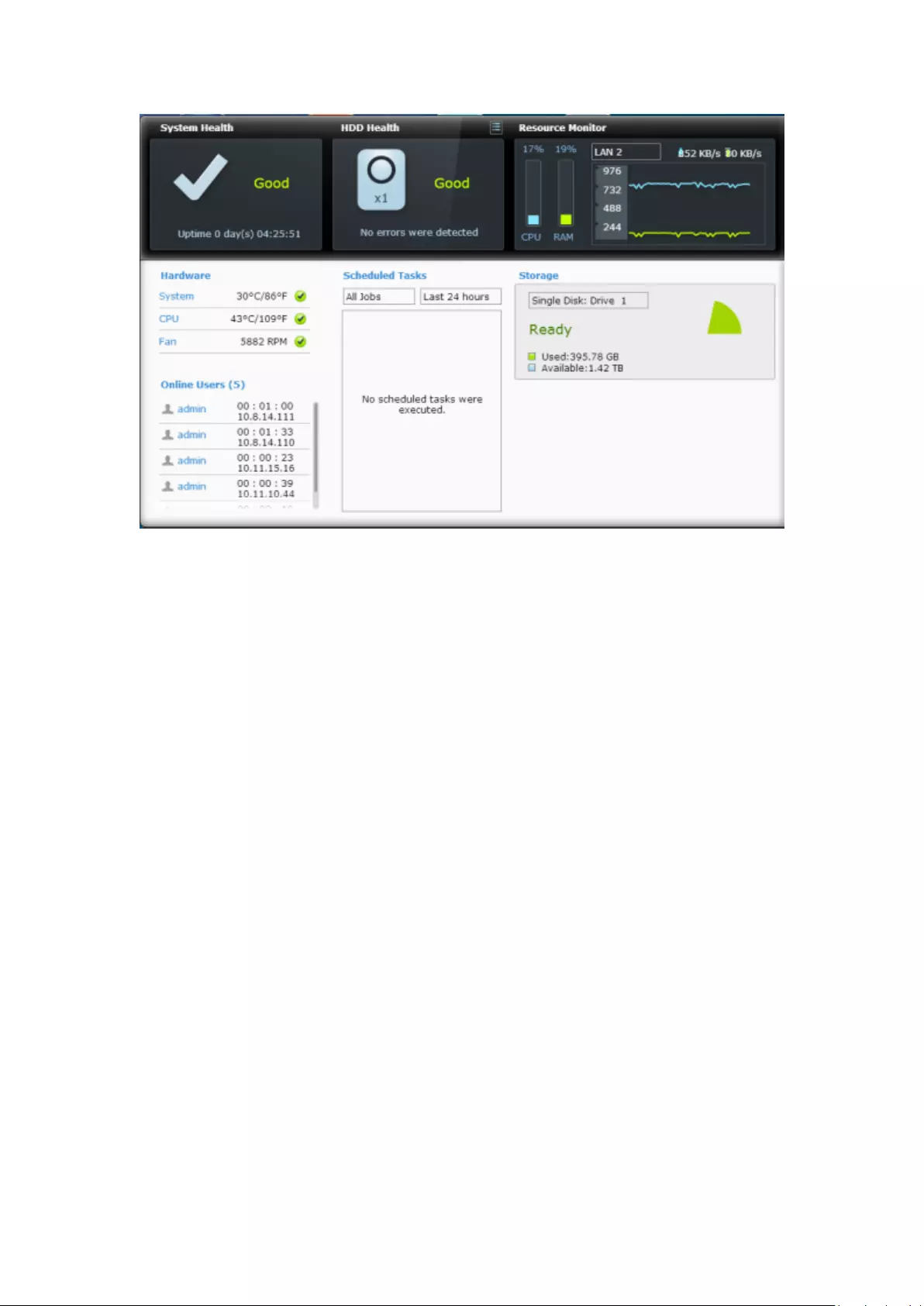
Dashboard
All important system and HDD statistics can be reviewed on the QVR Dashboard.
80
System Health: The status of the NVR system is indicated in this section. Click
the header to open the “System Status” page.
HDD Health: The status of the HDDs currently installed in the NVR will be shown
in here. X1 means that only one HDD is currently installed in the NVR. For
multiple HDDs installed in the NVR, the status indicated is only for the HDD with
the worst condition. Click the “HDD Health” header to open the “HDD SMART”
page in Storage Manager to review the status of each HDD. For details on the
Storage Manager, please refer to the chapter on Storage Manager. Click the icon
to switch between the “HDD Summary” page and the HDD status indicator.
Please note that the color of the HDD symbol will change based on HDD health.
Resource Monitor: The CPU, RAM and bandwidth usage is displayed here. Click
the “Resource Monitor” header to open the corresponding page in System
Status for details. Please note: if the port trunking feature is activated, the
bandwidth statistics are the combined usage of all NICs.
Storage: The shared folder (top five largest folders), volume and storage
statistics are summarized here. Click the “Storage” header to open the
corresponding page in System Status for details.
Hardware: The system and HDD temperatures, fan speeds and hardware usages
are summarized here. Please note: statistics listed here vary based on the NVR
model purchased. Click the “Hardware” header to open the corresponding page
in “System Status” for details.
Online Users: All users currently connected to the NVR are listed here. To
81
disconnect or block a user or IP, right click the user and choose the desired
actions. Click the “Online Users” header to open the corresponding page in
“System Logs” for details.
Scheduled Tasks: Tasks scheduled are listed here. Click the task dropdown list to
list only the chosen category and the time drop down list to specify the time
range for tasks to be listed.
Slide-in window: System-related news will be displayed on the window at bottom
right side of the desktop. Click the update to check the relevant details.
Tip:
All widgets within the Dashboard can be dragged onto the desktop for
monitoring specific details.
The Dashboard will be presented differently on different screen resolutions.
The color of the Dashboard button will change based on the status of system
health for quick recognition ( ).
82
Chapter 5. Remote Monitoring
Use Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Internet Explorer and QNAP QVR
Client to monitor the IP cameras of the NVR.
Note: QNAP QVR Client is a client application developed by QNAP Systems, inc., used
to locally or remotely access QNAP NVR servers for performing video monitoring and
playback functions. Users can find and download this application under the ‘Utility’
section of the QNAP Security website at
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp.
Important Notice:
1. Before using the NVR, install the hard disks in the server correctly and finish the
disk formatting and configuration. Otherwise, the server will not function
properly.
2. If your Windows OS is Windows Vista, Windows 7 or above, it is suggested to
turn off UAC (User Account Control) for full surveillance functions. Please refer
to http://www.qnapsecurity.com/faq_detail.asp?faq_id=503.
83
5.1 Monitoring Page
Upon successfully logging in, click on the QVR desktop to go to the monitoring
page. Select the display language. Start to configure the system settings and use
the monitoring and recording functions of the server.
The following table consists of the icons and their descriptions in the monitoring
page.
Icon
Description
QVR Desktop:
Return to the QVR desktop.
Monitor:
Enter the monitoring page. The administrator can
grant access rights to the users to see the live view.
Playback:
Enter the video playback page. The administrator
can grant access rights to the users to play back the
videos.
Event notification:
When the alarm recording is enabled and an event is
detected, this icon will be shown. Click this icon to
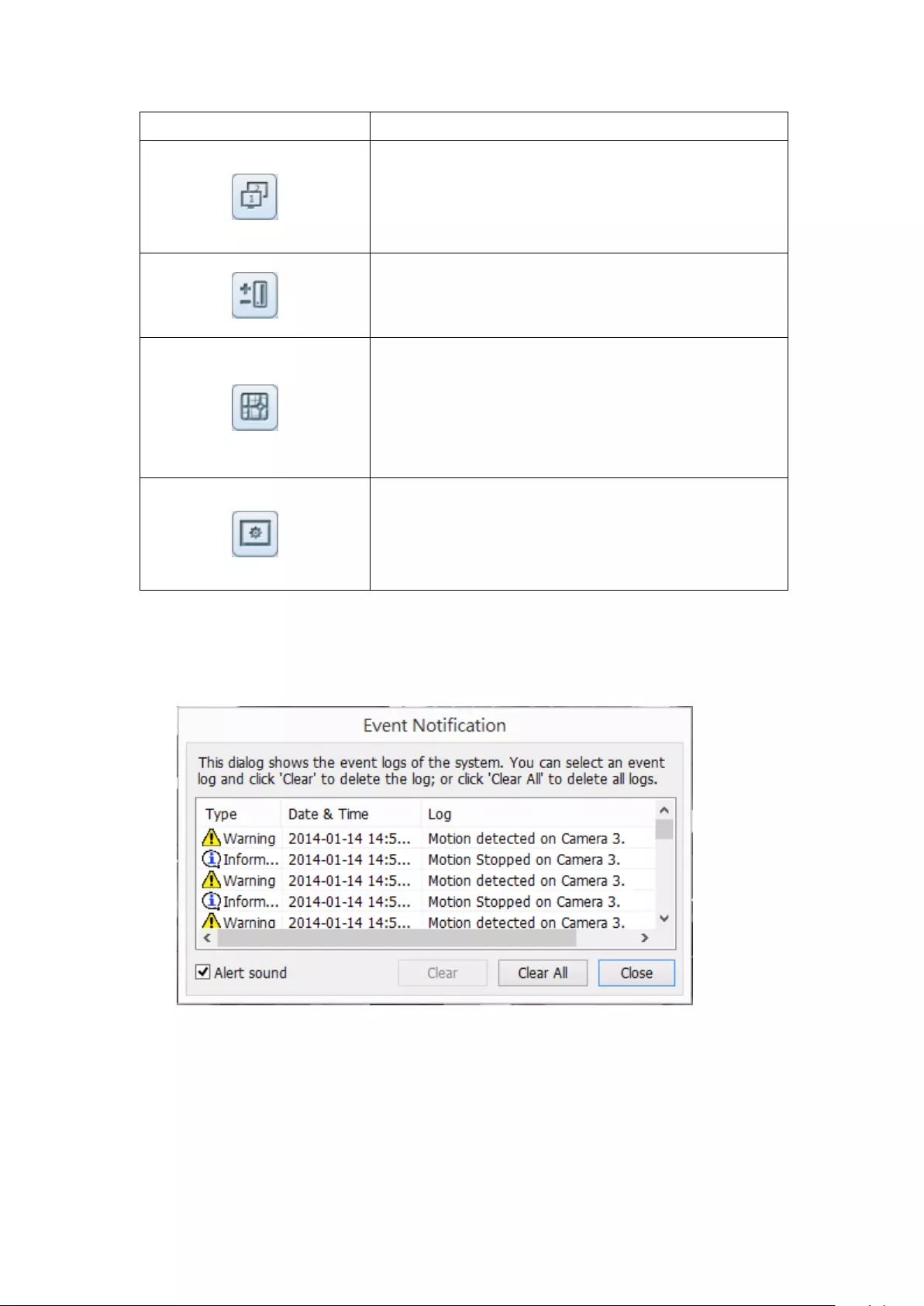
84
view the alert details.
Dual-display mode:
The NVR supports dual-display mode. (This
function can only be used when the computer or the
host is connected to multiple monitors.)
Server list:
Up to 128 channels from multiple QNAP NVR servers
can be monitored.
E-map:
Upload E-map(s) and indicate the locations of the IP
cameras. The administrators are allowed to edit
and view the E-map(s). Other users can only view
the E-map(s).
Options:
Configure the advanced settings of the monitoring
page. Specify the source of the video/audio
stream, event notification, and snapshot folder.
Note:
Click the event notification icon to view the event details, enable or disable the
alert sound or clear the event logs.
85
Interactive Control Buttons
Whenever you move the mouse cursor over a camera channel, the supported
function buttons of the camera will show up for quick access.
Icon
Description
Manual recording (Note 1):
Enable or disable manual recording on the selected channel. The
administrator can enable or disable this option on the surveillance
settings page.
Snapshot (Note 2):
Take a snapshot on the selected channel. When the picture is shown,
right click on it to save it to the computer.
Audio (optional):
Turn on/off the audio support for the monitoring page. For more
information about the compatibility of this feature, please visit
http://nvr.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_z_g_qvr/cat_intro.php?hf=ol
d.
Two-way audio (optional):
Turn on/off the two-way audio support for the monitoring page. For
more information about the compatibility of this feature, please visit
http://nvr.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_z_g_qvr/cat_intro.php?hf=ol
d.
Please note: the two-way audio function is currently only supported by
the latest version of Internet Explorer.
Dewarp fisheye images:
For specific fisheye cameras (Note 3) and the specific camera models
with panomorph lens (Note 4), you can enable/ disable the dewarping
function. After enabling the function, you can then select mount type,
dewarping mode.
PTZ mode:
1. Click & Go: Click on the camera screen at any point to align the
center of the screen using this point as the target.
2. PTZ: Pan/Tilt/Zoom camera control.
3. Auto cruising: This feature is used to configure the PTZ cameras to
cruise according to the preset positions and the staying time set for
each preset position.
4. Enable live tracking: Available on Panasonic NS202(A) cameras.
5. Disable live tracking: Available on Panasonic NS202(A) cameras.

86
Preset position: Select the preset positions of PTZ cameras.
Digital zoom (Note 5):
Enable/disable digital zoom.
Instant playback:
On the Live-view page, whenever you want to look back to check
suspicious events of a camera channel you just missed, just hit ‘Instant
Playback’ button to bring up the window to review recent feeds. While
you don’t have to switch to the playback page to do so, you can still
have full live views of other channels simultaneously.
Same-screen IP camera configurations:
On the Live-view page, you can directly configure an IP camera’s
recording schedules when needed without leaving the Live-view page,
maintaining seamless monitoring so you won’t miss any suspicious
events.
Camera information:
1. Properties (Note 6): Configure other monitoring options.
2. Locate in E-map: Highlight camera icon on E-map.
3. Connect to camera homepage.
ROI (Region of Interest):
This function provides you two kinds of magnified viewing modes to
choose from. You can choose 5-split or 7-split, then draw a square to
see an interesting region.
Click into 5-split mode.
Click into 7-split mode.
Note:
1. Enabling or disabling the manual recording feature will not affect the scheduled
or alarm recording.
2. By default, the snapshots are saved in ‘My Documents’ or ‘Documents’>
‘Snapshots’ on Windows.
If the snapshot time is inconsistent with the actual time that the snapshot is

87
taken, it is caused by the network environment but not a system error.
3. Applied to specific fisheye cameras
After enabling the feature, you can select Mount type, including wall, ceiling,
and floor and then select Dewarping mode, including Panorama (Full View),
Panorama (Dual View), and Rectangle. For more information, please refer to
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/trade_teach/con_show.php?op=showone&
cid=27.
Remark 1: If the Mount type is Wall, only Panorama (Full View), and Rectangle
are supported in Dewarping mode.
Remark 2: If Dewarping mode is Rectangle, you can use PTZ control panel to
operate PTZ functions, excluding digital zoom.
4. Applied to specific camera models with panomorph lens
Before using this feature, you need to select the ‘Enable panomorph support’
option in the camera configuration page. After enabling the feature, you can
select Mount type, including wall, ceiling, and floor and then select Dewarping
mode, including Perimeter mode, Quad mode, and PTZ mode.
Remark 1: To know the camera models that can be installed with panomorph
lens, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/qa/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=128.
Remark 2: The function is only available when the resolution of the video
stream is higher than 640x480 on the monitoring page.
Remark 3: If Dewarping mode is PTZ mode, for the channel, you can use PTZ
control panel or mouse (by clicking and holding down the mouse left button,
and then moving the mouse or turning the mouse wheel) to change viewing
angles or zooming in/out the screen. If Dewarping mode is Quad mode, the
above methods can also be applied to operate PTZ functions in each divided
screen.
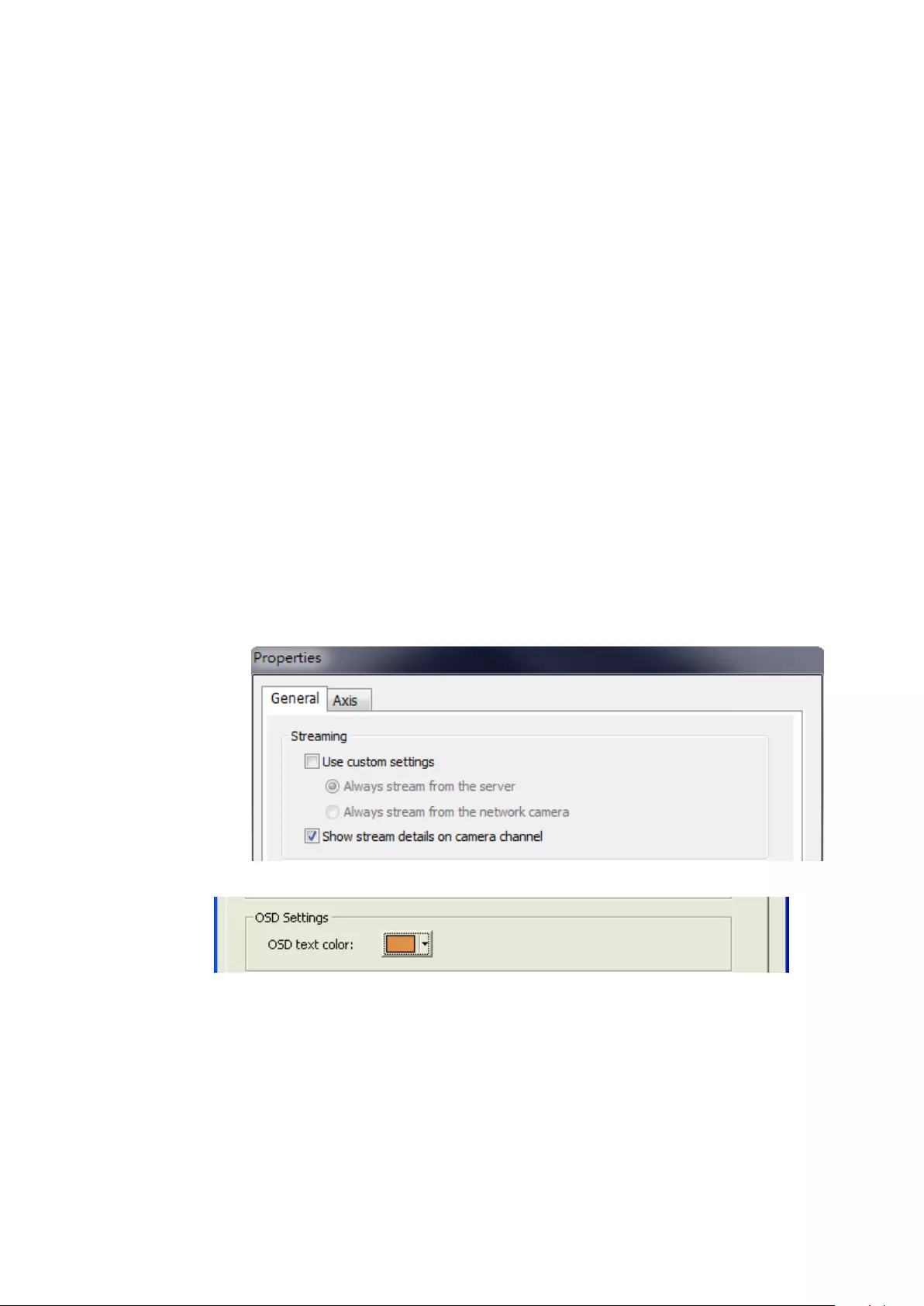
88
5. When the digital zoom function is enabled on multiple IP cameras, the zooming
function will be affected if the computer performance is not high enough.
6. Properties
A. Streaming:
I. Use custom settings
i. Always stream from the server: Select this option to stream the
audio and video data from the NVR. If the computer cannot
connect to the IP cameras, select this option to allow the NVR to
stream the data. No extra port forwarding is required; however,
the performance of the NVR may be affected.
II. Always stream from the network camera: If the NVR and the IP
cameras are connected to the same local network, select this option
to stream the video data from the IP cameras. If the NVR, the IP
cameras, and the PC are located behind a router, virtual server, or
firewall, configure port forwarding on the IP cameras to use certain
ports.
III. Show stream information
Show video codec, frame rate, bit rate, current recording days and
current recording size of this channel.
B. OSD Settings: Specify the font color of the text on the channels.
C. Display Mode:
I. Fit image to window: Select this option to fit an image to the browser
window. Specify to keep the aspect ratio or not when resizing an
image.
II. Display image in original size: Select this option to display an image in
its original size if it is smaller than the browser window. You can also
specify how an image will be resized if it is larger than the browser
89
window.
i. Shrink image to fit window, maintaining aspect ratio
ii. Shrink image by 1/2, 1/4, 1/8… and so on to fit
window
D. Video Processing: Turn on ‘Deinterlace’ when there are interlaced lines on
the video.
E. Video Resolution: Specify to adjust the resolution automatically or use a
fixed resolution. To adjust the resolution automatically, the NVR will
select the resolution setting* which best fits the size of your web browser
window. Note that ‘Stream from network camera’ will not be available if
the IP camera does not support streaming from camera or video resolution
configuration. Both options will not be available if the IP camera does not
support multiple streams.
*If an IP camera supports different resolution settings, the NVR will select
the smallest resolution larger than (or equal to) the size of the browser
window. If all the supported resolution settings of an IP camera are smaller
than the browser window, the largest resolution will be selected.
F. Let me choose other cameras to apply the same settings: Select this option
to apply the changes to other IP cameras. Note that some settings may
not be applied if the IP camera does not support the features, such as
streaming from camera or video resolution configuration.
90
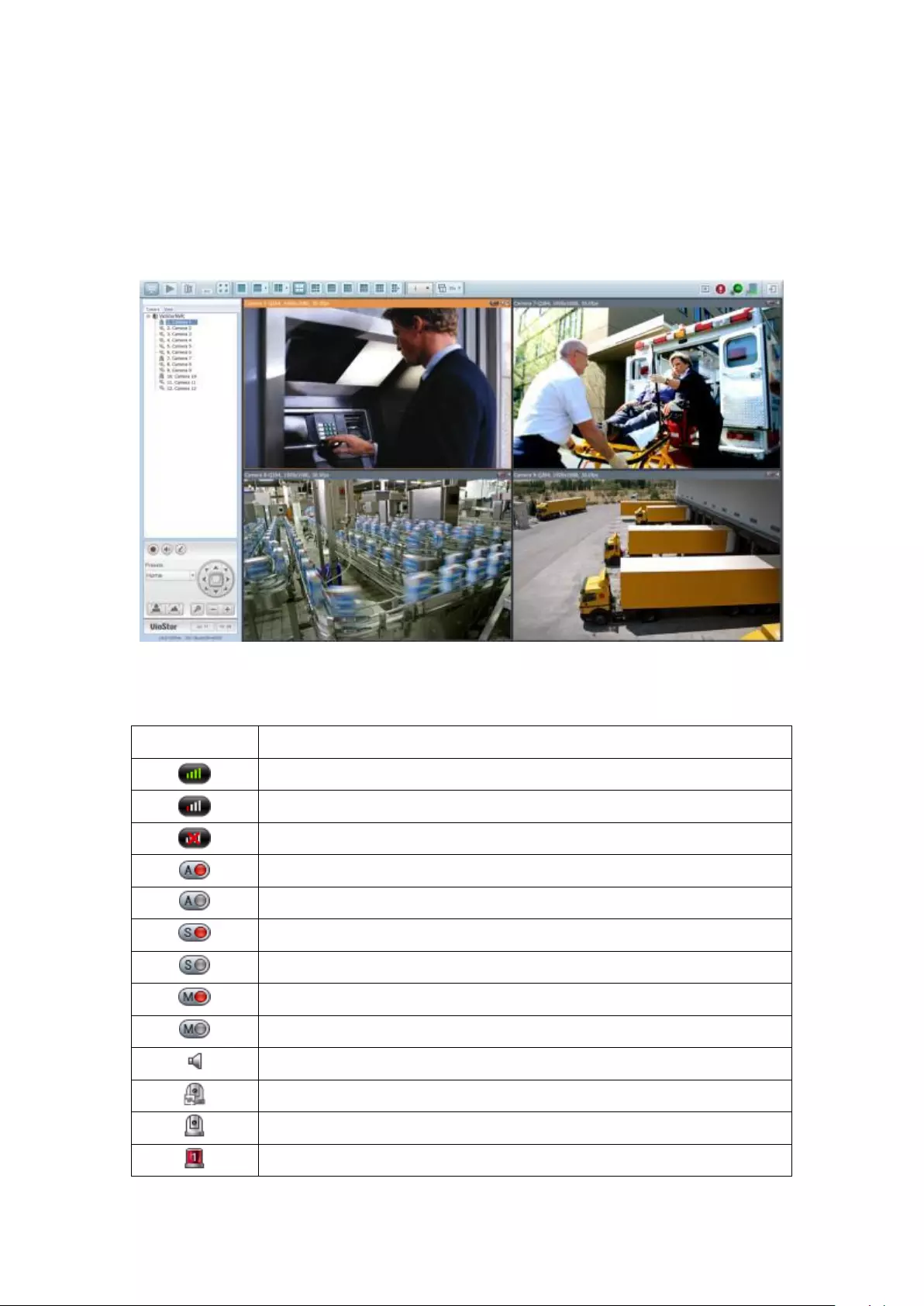
91
5.1.1 Live Video Window
The live videos of the IP cameras configured on the NVR are shown on the
monitoring page. Click the channel window to use the features supported by the IP
camera, e.g. digital zoom or pan/tilt/zoom.
Camera Status
The camera status is indicated by the icons shown below:
Icon
Camera Status
The NVR and IP camera are connected.
The NVR is trying to establish connection to the IP camera.
The NVR cannot connect to the IP camera.
The configured action triggered by alarm event is in process
Alarm settings are configured, but not in process
Scheduled or continuous recording is in process
Schedule recording is enabled, but not in process
Manual recording is enabled
Manual recording is not in process
This IP camera supports audio functions
This IP camera supports PT function with continuous PT
This IP camera supports PT function without continuous PT
The alarm input 1 of the IP camera has been triggered
92
The alarm input 2 of the IP camera has been triggered
The alarm input 3 of the IP camera has been triggered
A moving object has been detected
Digital zoom is enabled
Connection Message
When the NVR fails to display the video of an IP camera, a message will be shown in
the channel window to indicate the status.
Message
Description
No Permission
No access right to view the monitoring channel. Please login as an
authorized user or contact the system administrator.
Server Error
Please check the camera settings or update the firmware of the IP
camera (if any). Contact the technical support if the error persists.
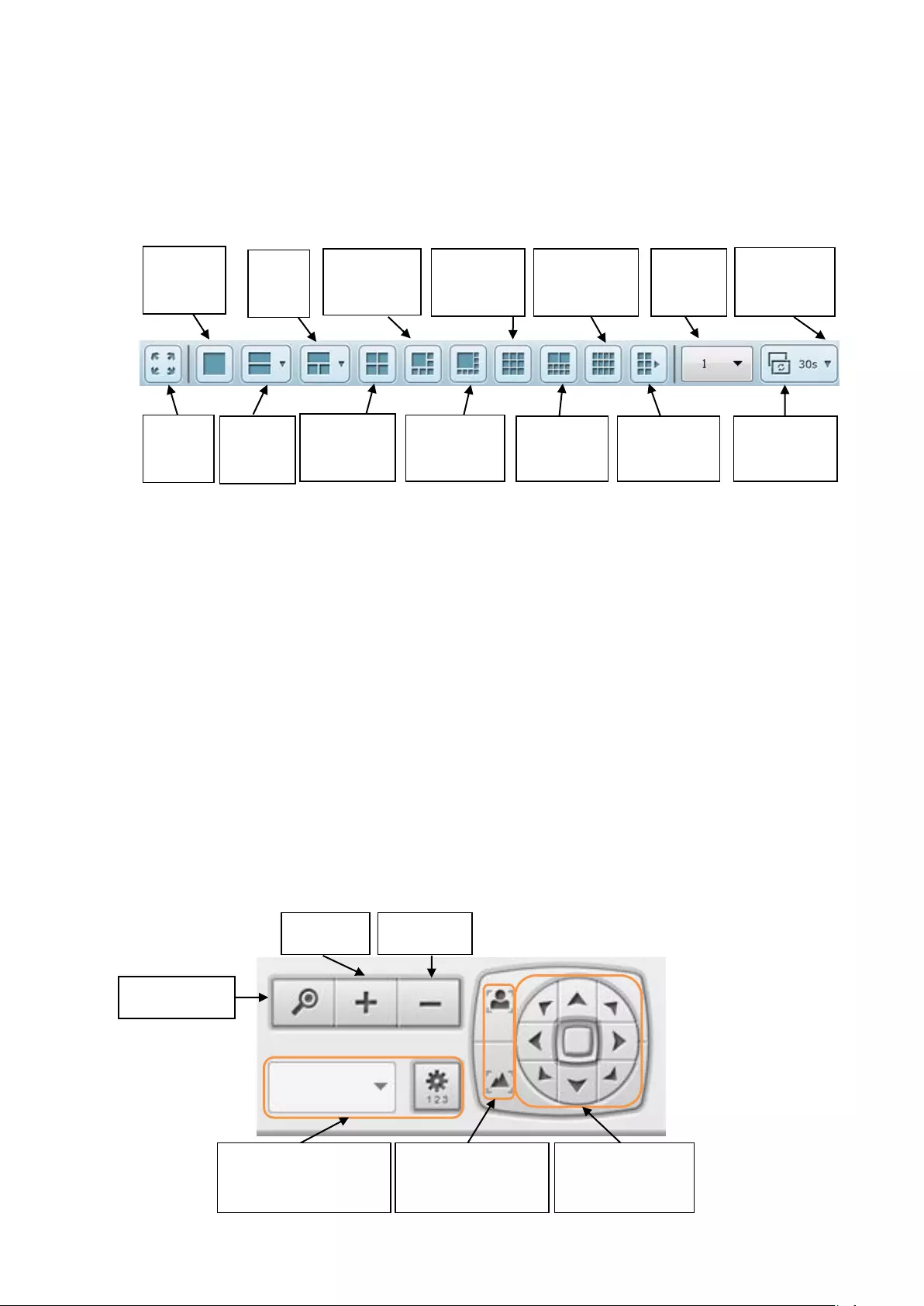
93
5.1.2 Display Mode
The NVR supports different display modes for viewing the monitoring channels.
*You can configure the sequential interval in the sequential mode settings.
5.1.3 PTZ Camera Control Panel
The term ‘PTZ’ stands for ‘Pan/Tilt/Zoom’. If an IP camera supports the PTZ feature,
use the control panel on the NVR to adjust the viewing angle of the IP camera.
These functions are available depending on the camera models. Please refer to the
user manual of the IP cameras for more information. Note that the digital zoom
function will be disabled when the PTZ function is in use.
QVR 5.0 and above hides the PTZ control panel by default. You can enable the PTZ
control panel in the options on the monitoring page.
Note: When you enable multi-display mode and the live view window is too small to
show interactive control buttons, please enable PTZ control panel to control the
camera.
Adjust PT angle of
the camera
Select and configure PTZ
camera preset positions
Focus control of the
PTZ camera
Digital zoom
Zoom in
Zoom out
Single
channel
único
mode
4-channel
mode
8-channel
mode
10-channel
mode
12-channel
mode
9-channel
mode
6-channel
mod
Sequential
mod
Multi-channe
l mode
Page
Number
Sequential
mode
Settings
2-chann
el mode
único
mode
3-cha
nnel
mod
único
mode
Full
Screen
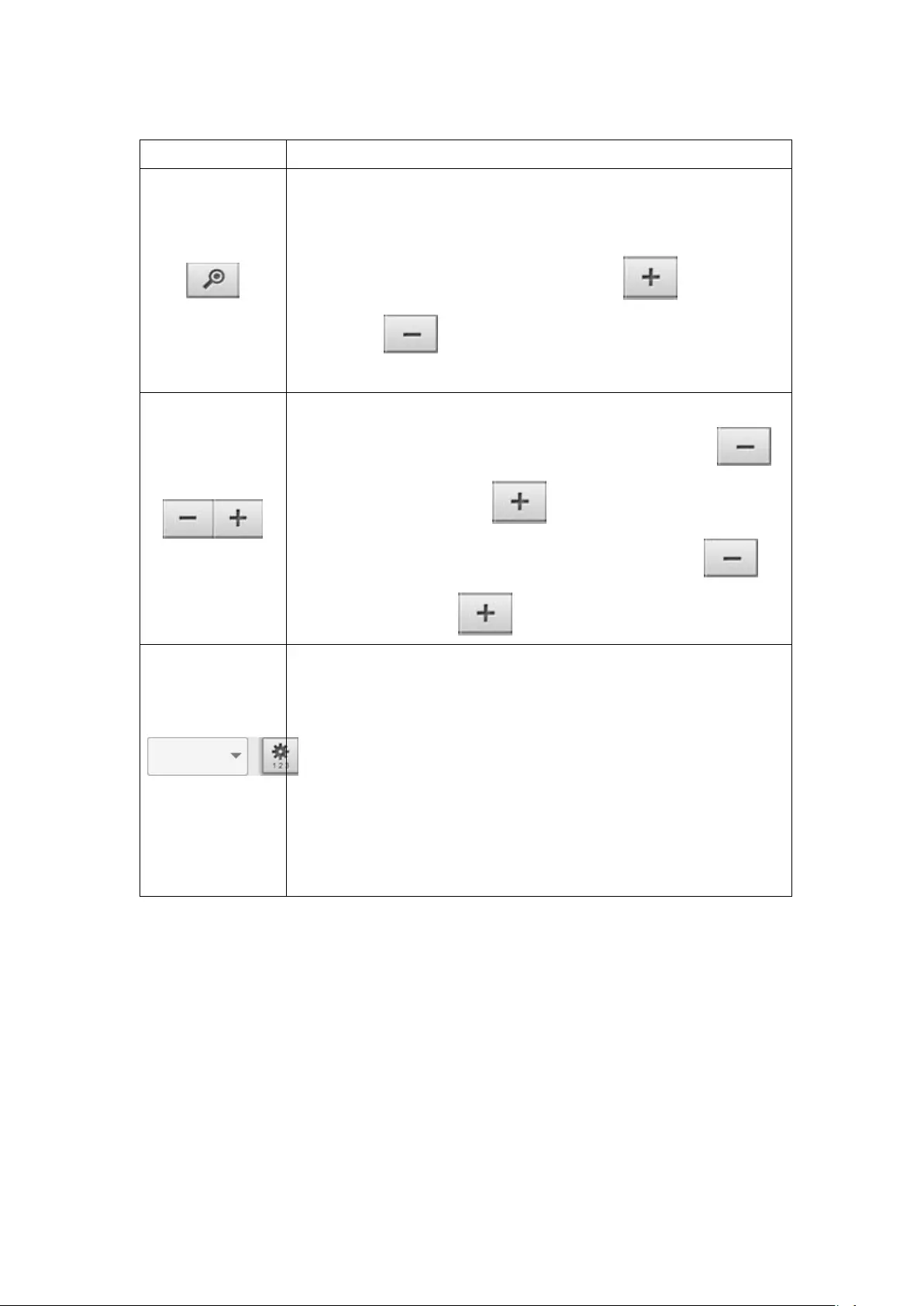
94
Icon
Description
Digital zoom:
Select a channel and click this button to enable the digital zoom
function. This function can also be enabled by right clicking the
display window of the PTZ camera. Press button to
zoom in or button to zoom out. You can also use the
mouse wheel to operate the digital zoom function.
Zoom out/zoom in:
If the PTZ camera supports optical zoom, you can press
to optically zoom out or button to optically zoom in.
When digital zoom function is enabled, you can press to
digitally zoom out or button to digitally zoom in.
Select and configure PTZ camera preset positions:
Select and view the preset positions of the IP camera from the
list. For some camera models, you can configure PTZ camera
preset positions on the monitoring page. For more information
about the compatibility of PTZ cameras for preset positions
configuration, please visit
http://nvr.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_z_g_qvr/cat_intro.ph
p?hf=old. For other PTZ camera models please refer to the
user manual of the IP camera.
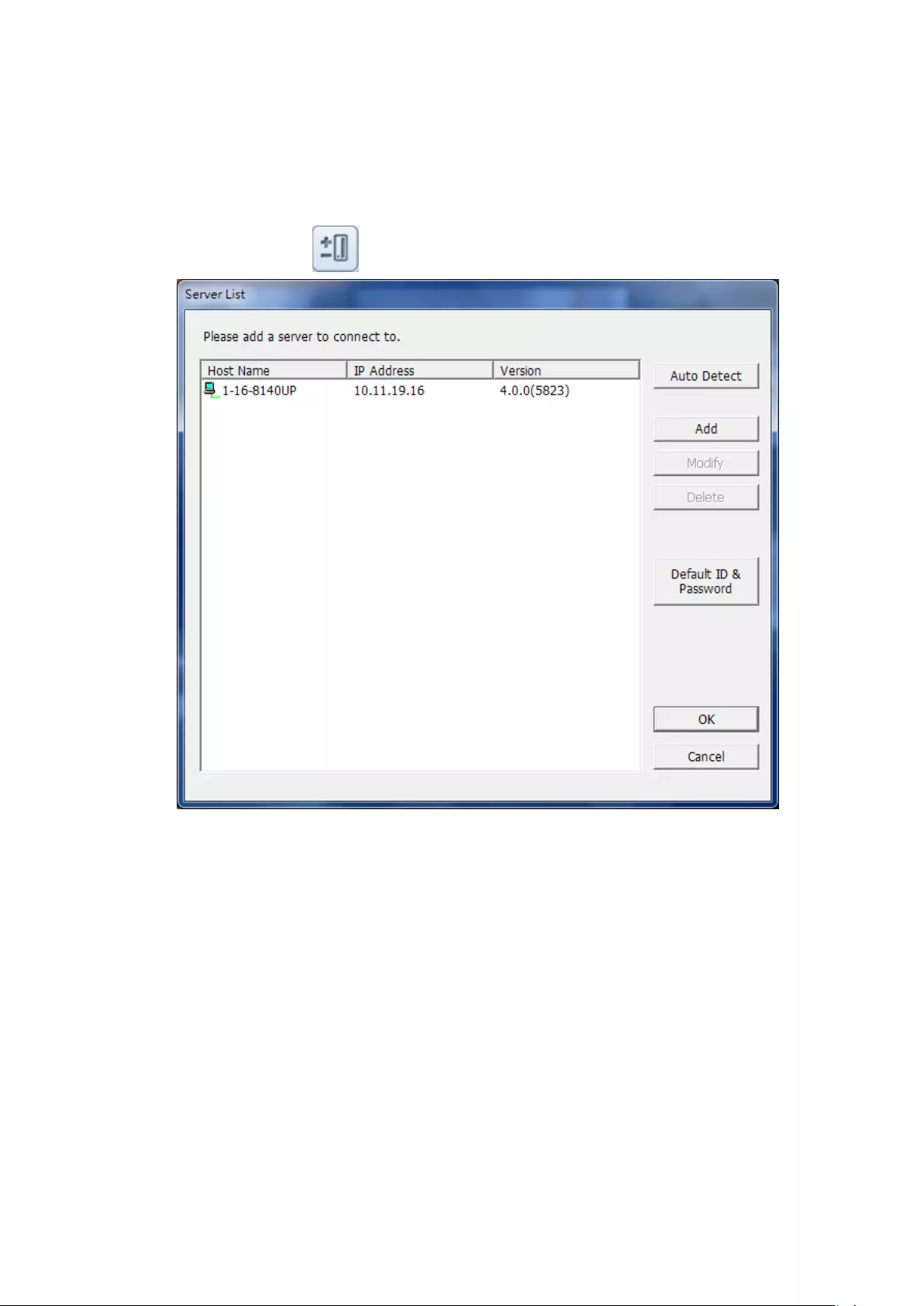
95
5.1.4 Multi-server Monitoring
Follow the steps below to use the multi-server monitoring feature of the NVR.
1. Click ‘Server List’ on the monitoring page.
A. Click ‘Auto Detect’ to search for the NVR on the LAN and add the server to
the server list.
B. Click ‘Add’ to add the NVR to the server list.
2. Up to 128 channels from multiple NVR servers can be added for monitoring.
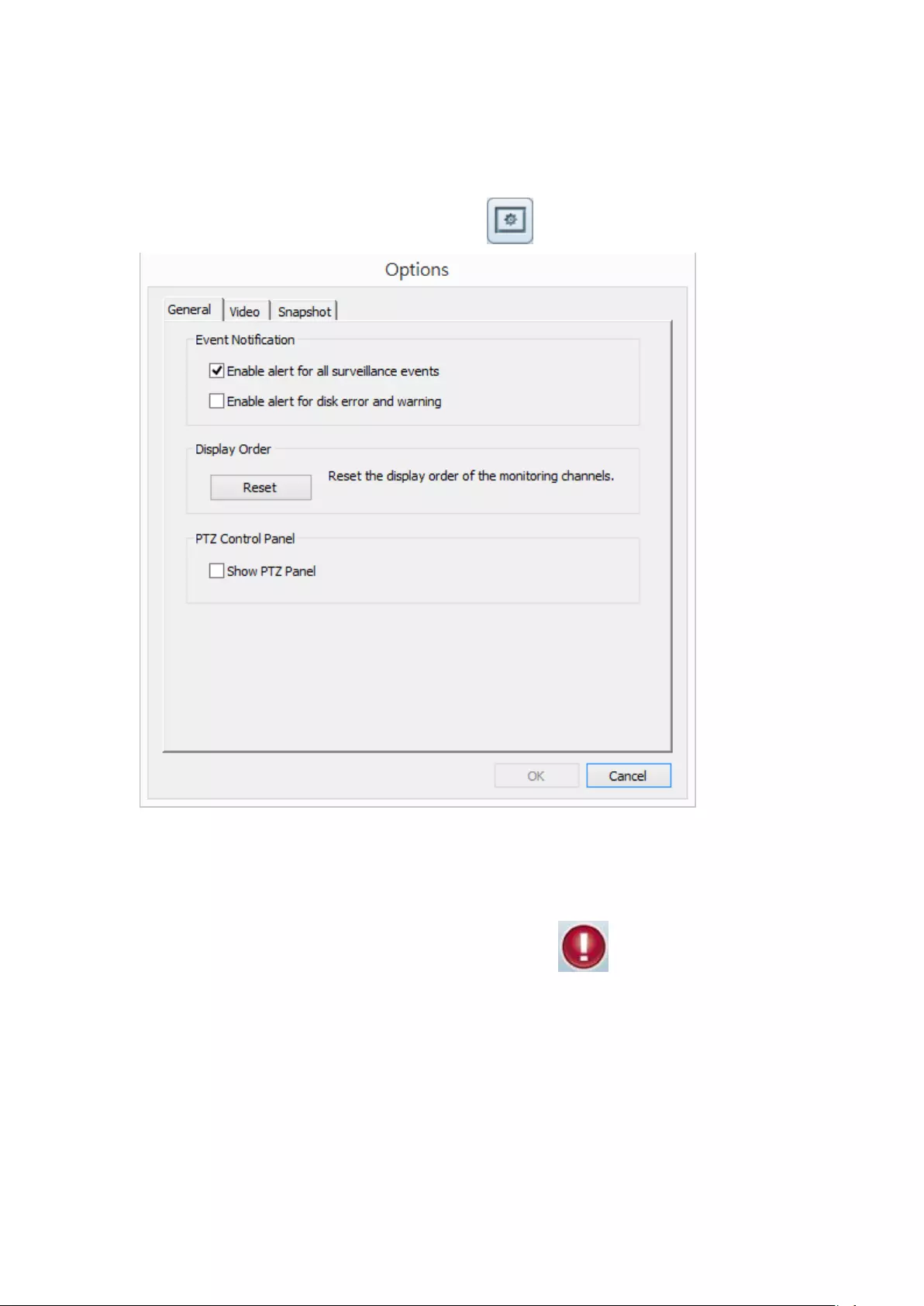
96
5.1.5 Monitor Settings
To configure advanced monitor settings, click .
The following options are provided under the ‘General’ tab.
Event Notification:
When ‘Enable alert for all surveillance events’ option is enabled and a
surveillance event is triggered, the alert icon will be shown on the
monitoring page instantly. Click the icon to view the alert details.
After enabling ‘Issue notification when the disk reaches maximum
operation time set below’ in System Tools -> Hard Disk SMART, you can
then ‘Enable alert for disk error and warning’ to receive alarm
notifications when hard drive events occur.
Display Order: Click ‘Reset’ to reprioritize the monitoring channels to the
default order.
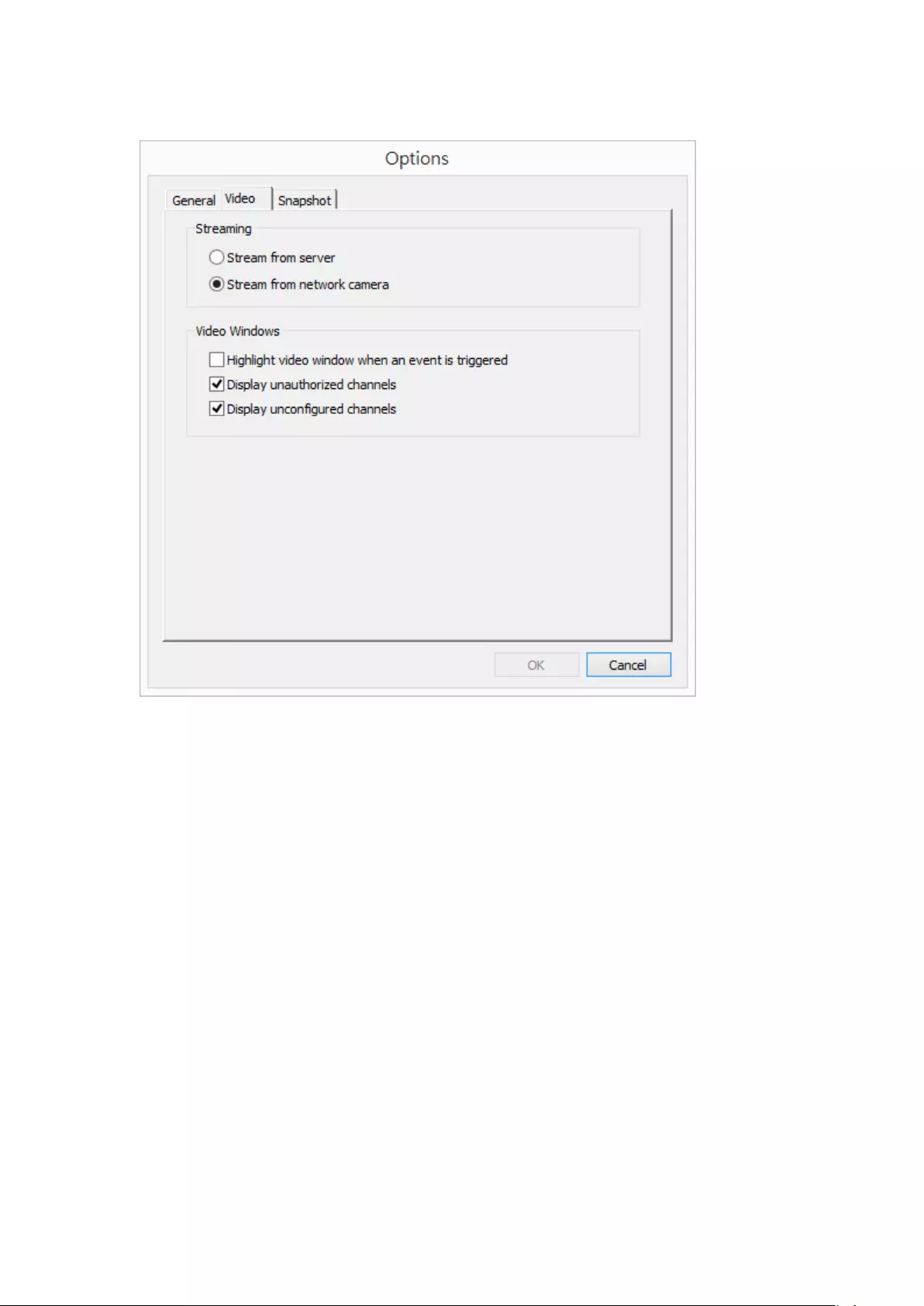
97
PTZ Control Panel: Select to show or hide the PTZ control panel.
The following options are provided under the ‘Video’ tab.
Streaming
Stream from the server: If the IP camera cannot be connected from the
computer, select this option and the video will be streamed from the NVR.
This option does not require extra port mapping configuration; but may
influence the performance of the NVR.
Stream from IP camera: If the NVR and the IP cameras are located on the
same LAN, select this option to stream the video from the IP camera.
Note that the port forwarding settings on the IP cameras must be
configured if the NVR, IP cameras, and the computer are located behind a
router, a virtual server, or a firewall.
Video Windows
Highlight the video window when an event is triggered: The video window
will flash if an event is triggered.
Display unauthorized channels: Select this option to show the channels
that the user does not have the access right to monitor.
Display unconfigured channels: Select this option to show the channels
98
that have not been configured.
The following options are provided under the ‘Snapshot’ tab.
Snapshot
1. Specify the location where the snapshots are saved and the image format
(JPEG, BMP or TIFF).
2. Show timestamp and camera name: Show the timestamp and the camera
name on the snapshot.
3. Save the snapshot as it is displayed: Select this option to save the snapshot
as it is displayed on the window. Otherwise, the snapshot will be saved in
its original size.

99
5.1.6 Instant Playback
On the Live-view page, whenever you want to look back to check suspicious events of
a camera channel you just missed, just hit the ‘Instant Playback’ button to bring up
the window to review recent feeds. While you don’t have to switch to the playback
page to do so, you can still have full live views of other channels simultaneously.
1. Please wait a moment for the system to process your request (depends on
available network bandwidth).
2. Reverse play is used by default. When playing to the event time, you can drag
the playback control button (gray part) to the right to change to normal
playback.
3. You can double click on a specific time on the timeline to change the playback
time.
Note: The range of searchable time is 24 hours.
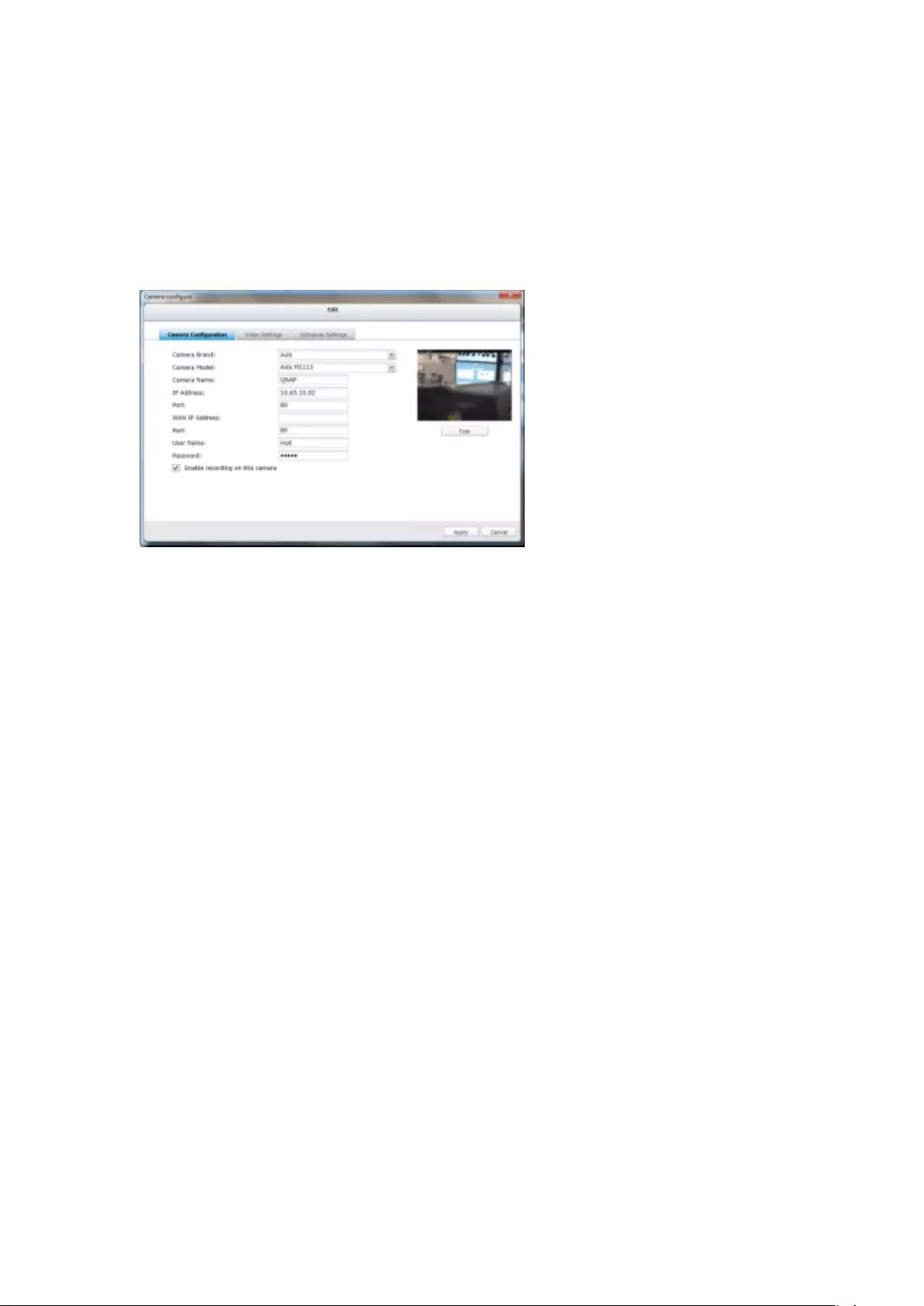
100
5.1.7 Same-screen IP Camera Configurations
On the Live-view page, you can directly configure IP camera settings when needed
without leaving the Live-view page, maintaining seamless s monitoring so you won’t
miss any suspicious events.
1. Please wait a moment for the system to process your request (depends on
available network bandwidth).
2. You can modify camera, recording and schedule settings. The settings will come
into effect after clicking ‘Apply.’
101
5.1.8 Auto Cruising
The auto cruising feature of the NVR is used to configure the PTZ cameras to cruise
according to the preset positions and the staying time set for each preset position.
To use the auto cruising feature, follow the steps below.
1. On the monitoring page of the NVR, click and select ‘Connect to
camera homepage’ to go to the configuration page of the PTZ camera.
2. Set the preset positions on the PTZ camera.
3. Return to the monitoring page of the NVR. Click to select ‘Auto
Cruising’ > ‘Configure’.
4. Click the number buttons to view the preset positions of the PTZ camera.
When this button is clicked, the name of the corresponding preset position is
shown on the ‘Preset Name’ drop-down menu.
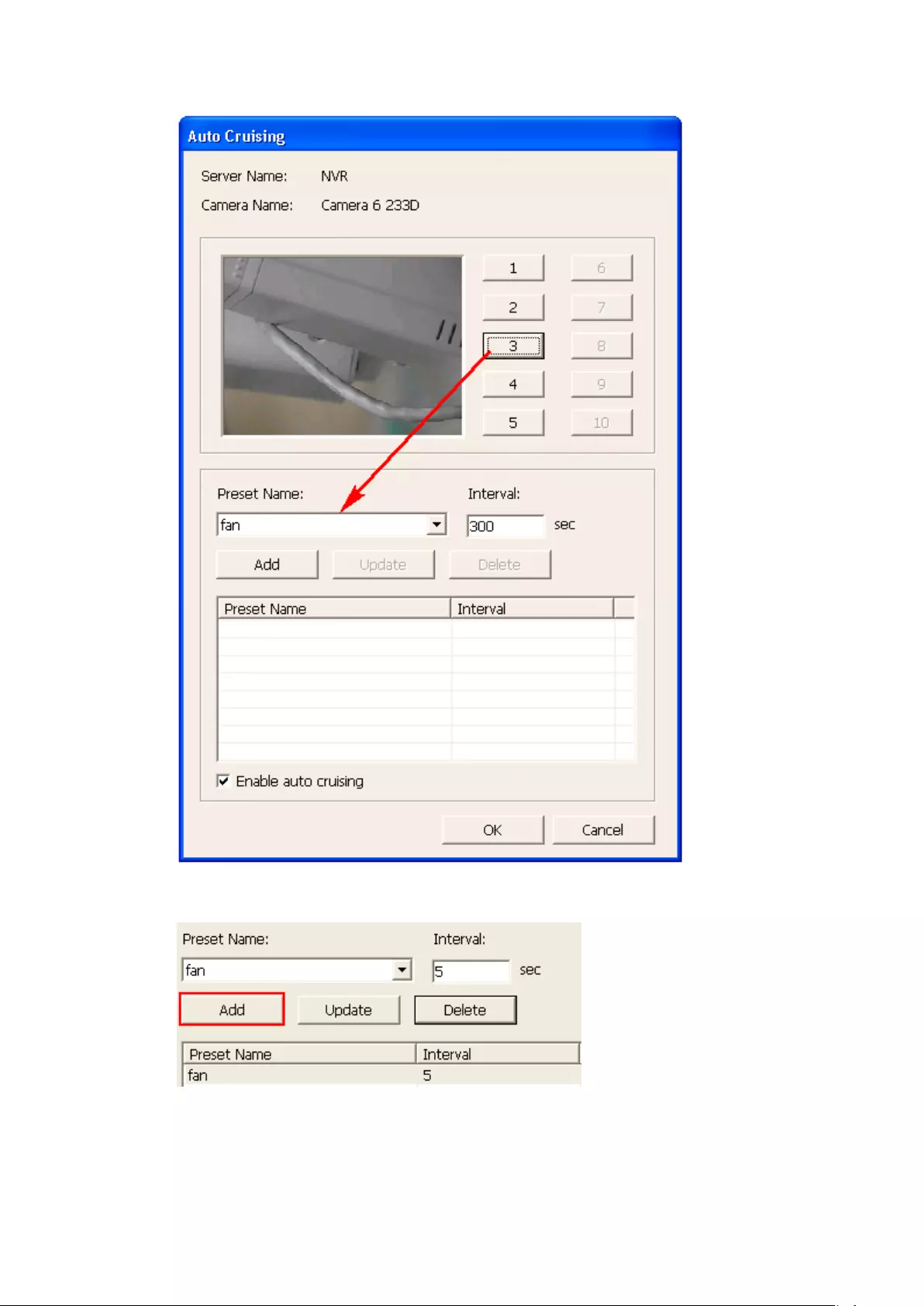
102
5. Add: To add a setting for auto cruising, select the ‘Preset Name’ from the
drop-down menu and enter the staying time (interval, in seconds). Click ‘Add’.
6. Update: To change a setting on the list, highlight the selection. Select another
preset position from the drop-down menu and/or change the staying time
(interval). Click ‘Update’.
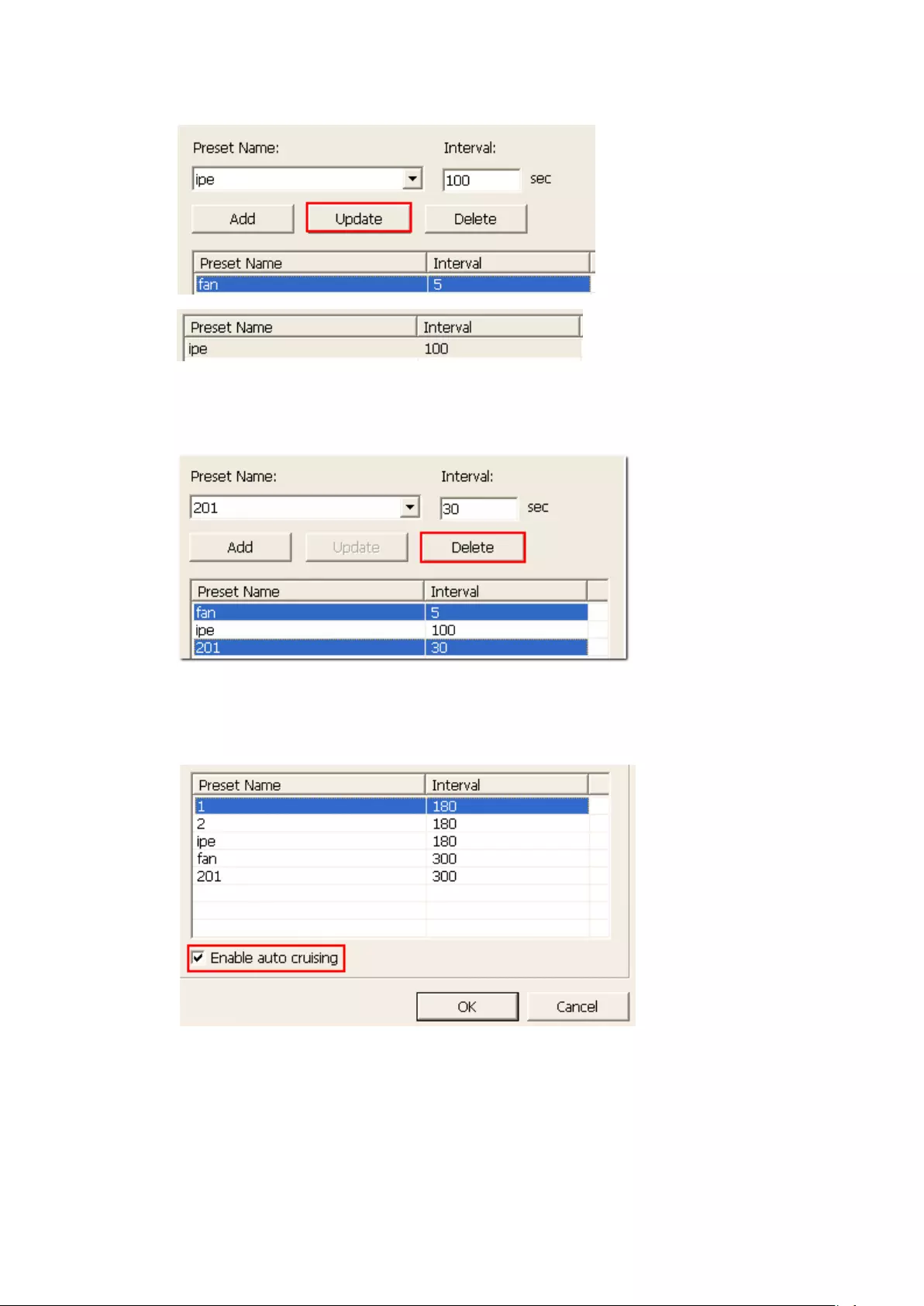
103
7. Delete: To delete a setting, highlight a selection on the list and click ‘Delete’.
To delete more than one setting, press and hold the Ctrl key and select the
settings. Then click ‘Delete’.
8. After configuring the auto cruising settings, select the option ‘Enable auto
cruising’ and click ‘OK’. The NVR will start auto cruising according to the
settings.
9. Auto cruising supports ‘snapshot’
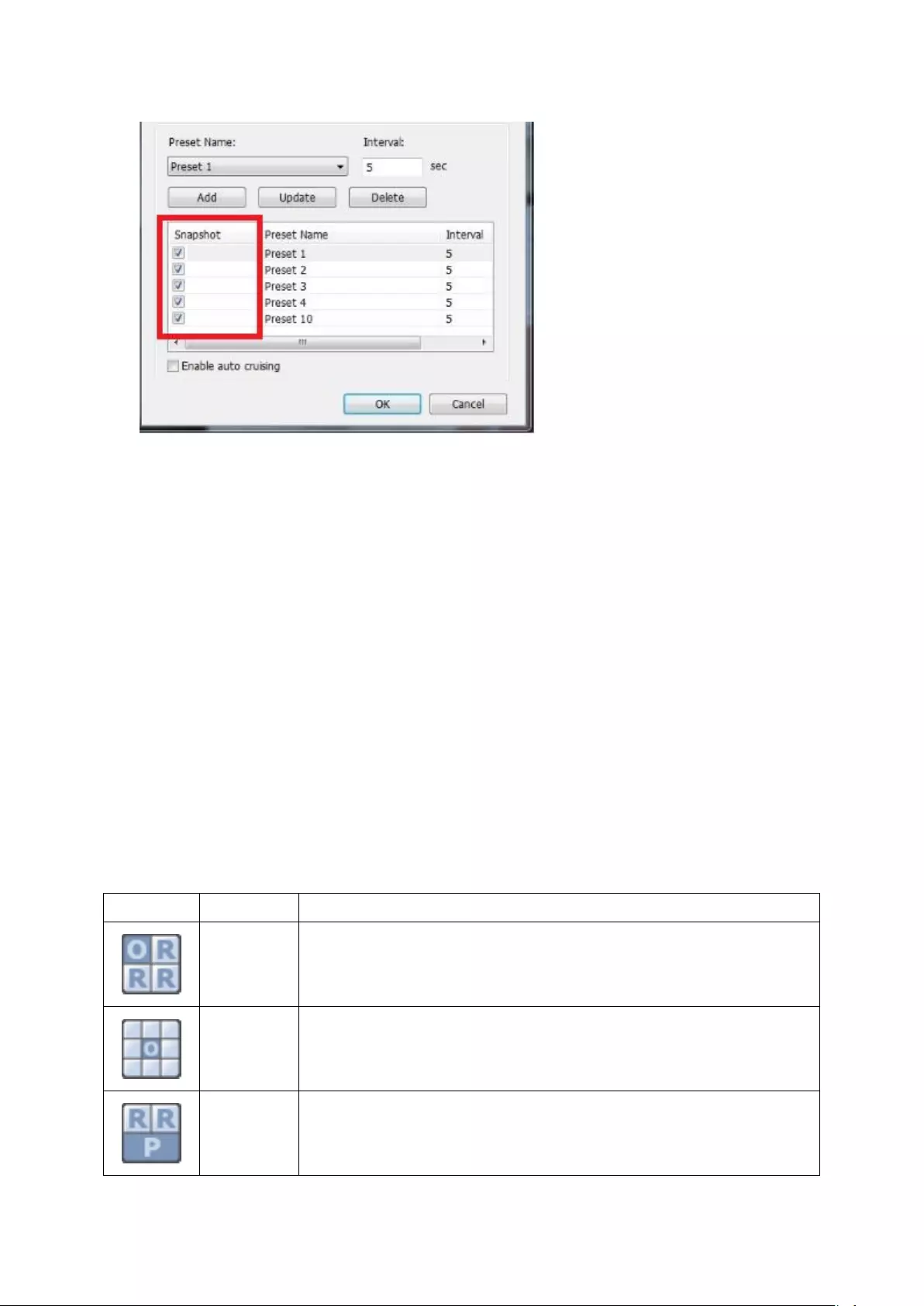
104
Note:
The default staying time (interval) of the preset position is 5 seconds. Enter
5–999 seconds for this setting.
The system supports up to 10 preset positions (the first 10) configured on the
PTZ cameras. Up to 20 settings for auto cruising can be configured. In other
words, the NVR supports maximum 10 selections on the drop-down menu and
20 settings on the auto cruising list.
5.1.9 Qdewarp
Fisheye cameras are widely used to monitor larger areas. QNAP Qdewarp allows
fisheye cameras to use their full features. You only need to configure the fisheye
camera’s installation location (ceiling, wall, or desk), then you can start using multiple
QNAP Qdewarp modes. Qdewarp is supported in the monitor and playback page.
Qdewarp mode description
Icon
Function
Description
1O3R
Provides the original screen, and 3 regional screens
1O8R
Provides the original screen in the central grid, and 8 regional
screens around the center
1P2R
Providing 2 regional screens in the upper side, and one panorama
screen in the down side
105
1P3R
Providing 3 regional screens in the upper side, and one panorama
screen in the down side
1P6R
Providing 3 regional screens in the upper side and down side
respectively, and one panorama screen in the center
=
4R
Providing 4 regional screens
=
9R
Providing 9 regional screens
=
Dual
Panorama
Providing 2 panorama screens
Full
Panorama
Providing one panorama screen
ORP
Providing one original screen one regional screen, and one
panorama screen
R
Providing one regional screen
Note: Only some dewarping modes are supported on local display.
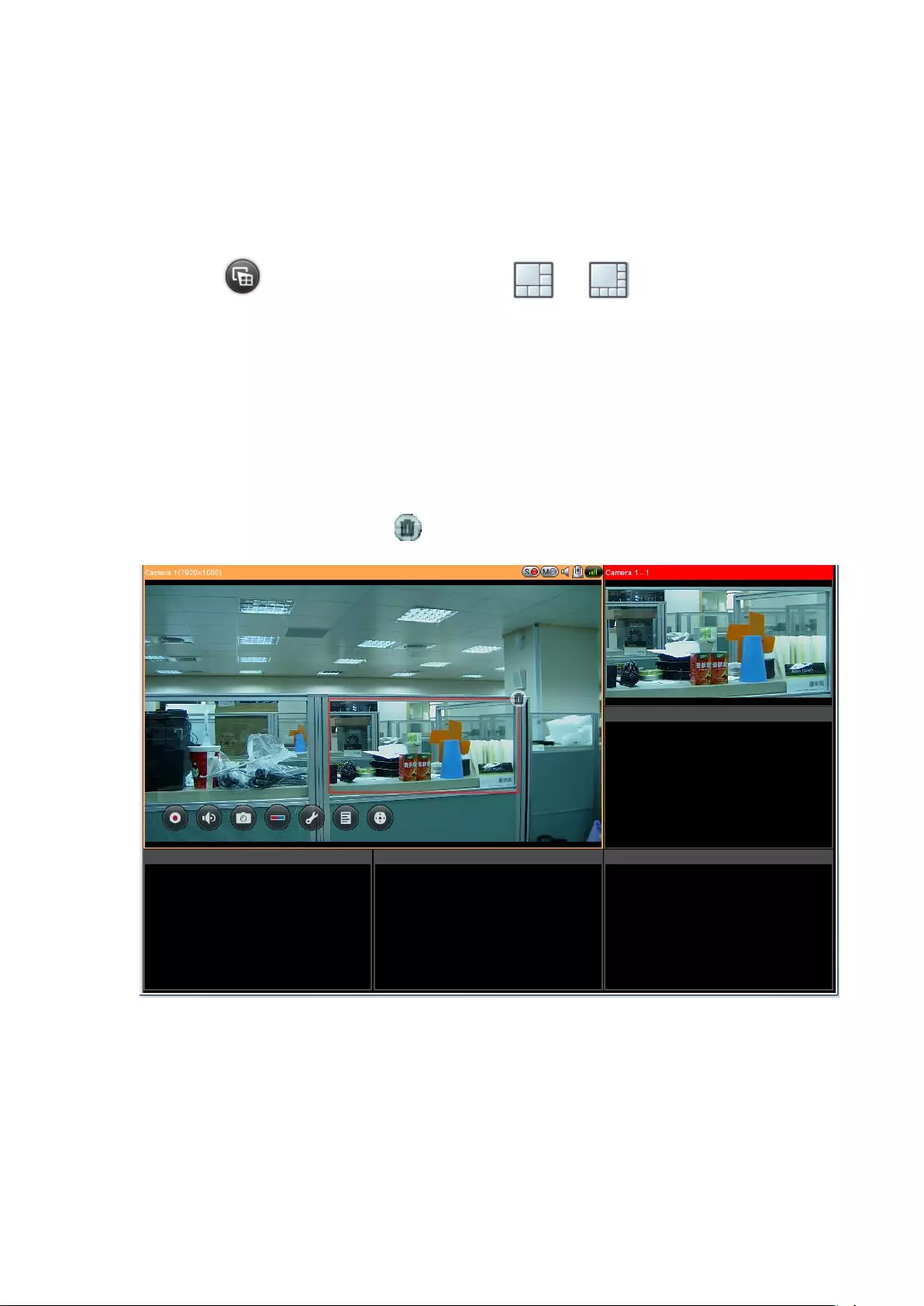
106
5.1.10 ROI (Region of Interest)
ROI monitoring mode provides 2 monitoring layouts. You can choose a 5 or 7 split
layout, and select a region of interest for monitoring.
Please follow the below steps to configure the ROI.
1. Click on the monitoring page, select or , then the system
will automatically go into the ROI monitoring mode.
2. You can select the ROI on the camera’s field of view. The system will
automatically show the ROI(s) on the side grid. You can also use the mouse to
select the ROI, and drag it to change its location or adjust the ROI’s border to
alter its size.
3. Remove the ROI by clicking on .
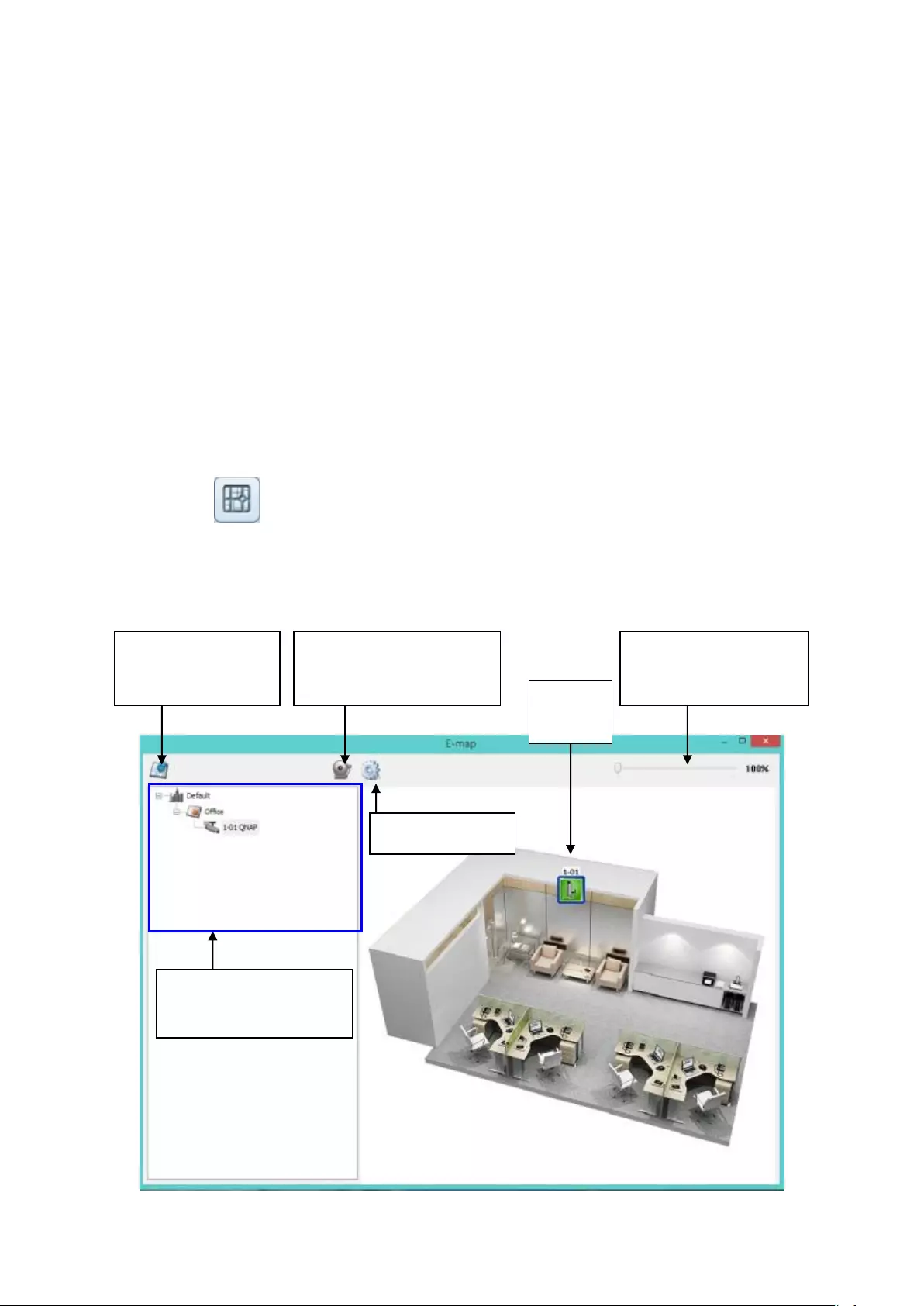
107
5.2 E-map
The E-map feature of the NVR is provided to for users to upload electronic maps to
the system to indicate the locations of the IP cameras. Users can drag and drop the
camera icons* to the E-map and enable event alert to receive instant notification
when an event occurs to the IP camera.
*The camera icons are available only when the IP cameras have been configured on
the NVR.
To use the E-map feature, login the monitoring page of the NVR as an administrator
and click .
An E-map example is shown below. The NVR provides a default E-map.
Administrators can add or remove the E-maps whenever necessary.
E-map
Enable/Disable
E-map edit mode
Enable/Disable event
alert on E-map
Tree menu of E-maps
and IP cameras
E-map Options
Zoom in/out for more
details
108
5.2.1 Icons and Description
Icon
Description
Enable E-map edit mode.
E-map edit mode in use. Click this icon to disable the
edit mode.
Add an E-map.
Edit the name of an E-map.
Remove a map or a camera icon.
Event alert not in use. Click this icon to enable event
alerts on the E-map.
Event alert in use. When an event occurs on an IP
camera, such as a moving object being detected, the
camera icon will change and flash to alert the
administrator. To disable event alerts on the E-map,
click this icon.
Note: When event alerts are enabled, the E-map
cannot be edited. The icon will become
invisible.
E-map Options. Click on this icon to change the “Icon
Size” or “Double-click” on camera icon action.
Use this control bar to zoom in/out and see more
details of E-map.
Icon for a set of E-maps.
Icon for a single E-map.
Icon for a PTZ IP camera.
Icon for a fixed body or fixed dome IP camera. After
dragging the icon to a map, right click on the camera
icon to change the icon direction or delete the icon
from the E-map.
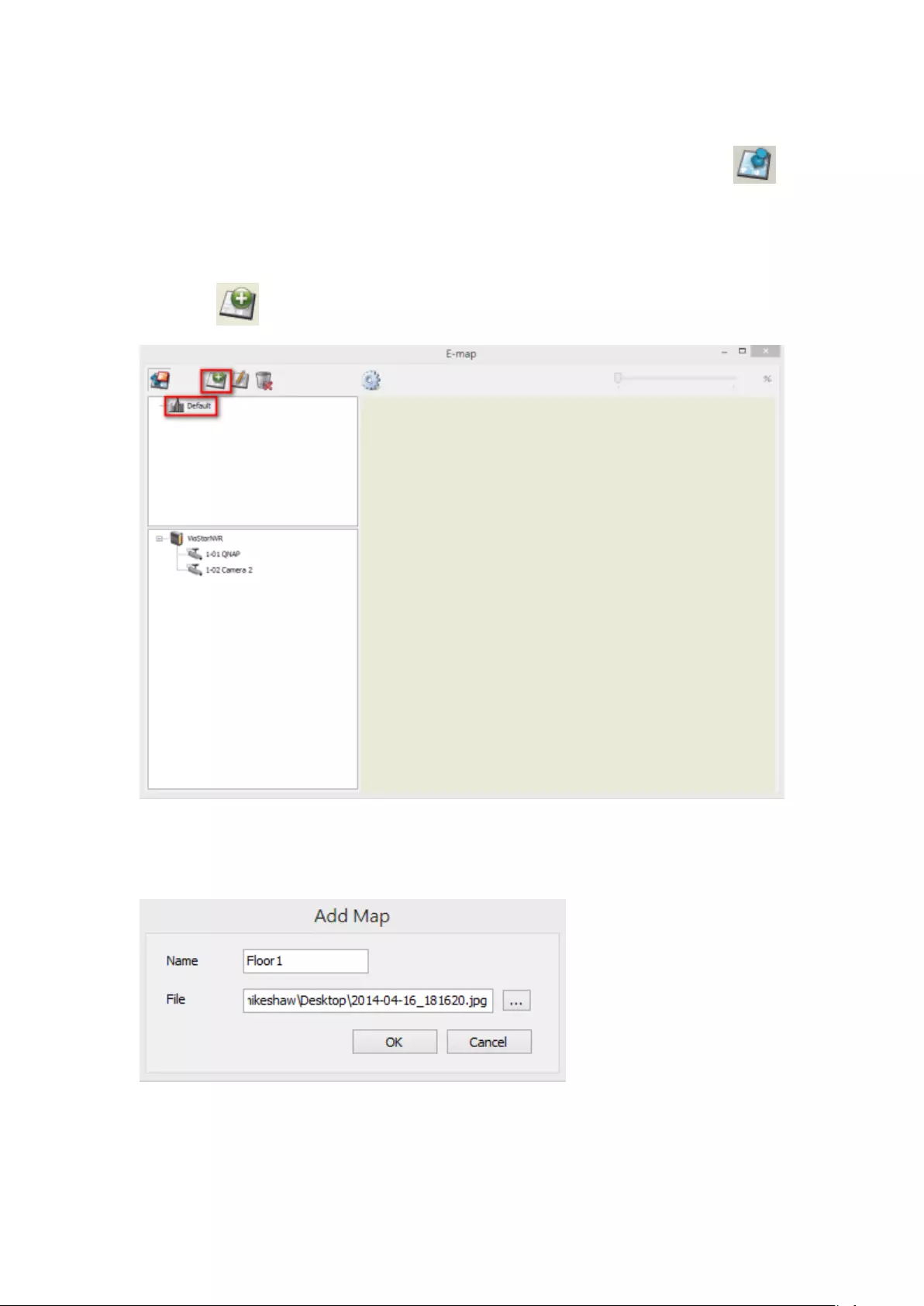
109
5.2.2 Add a Map Set or an E-map
To add a map set or an E-map to indicate the locations of the IP cameras, click
to enable Edit mode.
A list of IP cameras configured on the NVR will be shown on the left. Click ‘Default’
and then to add an E-map.
Enter the map name and select the file. The E-map image must be a JPEG format
file. Click ‘OK’.
The E-map will be shown.
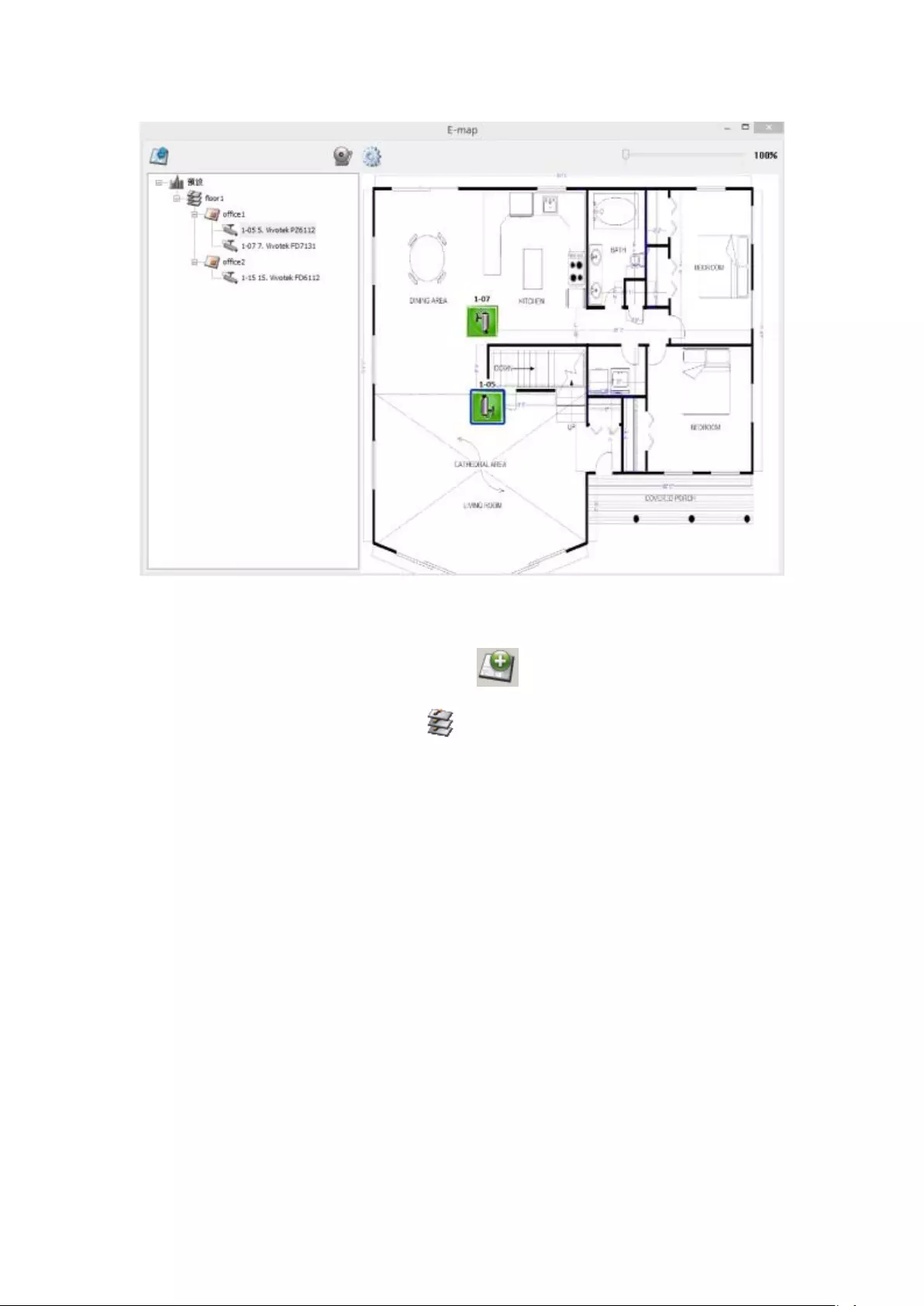
110
To add one or multiple E-maps, e.g. office1 and office2, under an E-map, e.g. floor1,
click the E-map icon of floor1 and then click to add the E-maps one by one.
The icon of floor1 will be changed to when more than one E-map is added. To
add another E-map of the same level of floor1, select ‘Default’ and add the E-map,
e.g. floor2.
To zoom in or zoom out the E-map, you can use your mouse wheel or just change the
percentage bar in upper left to enlarge or reduce the view of the E-map.
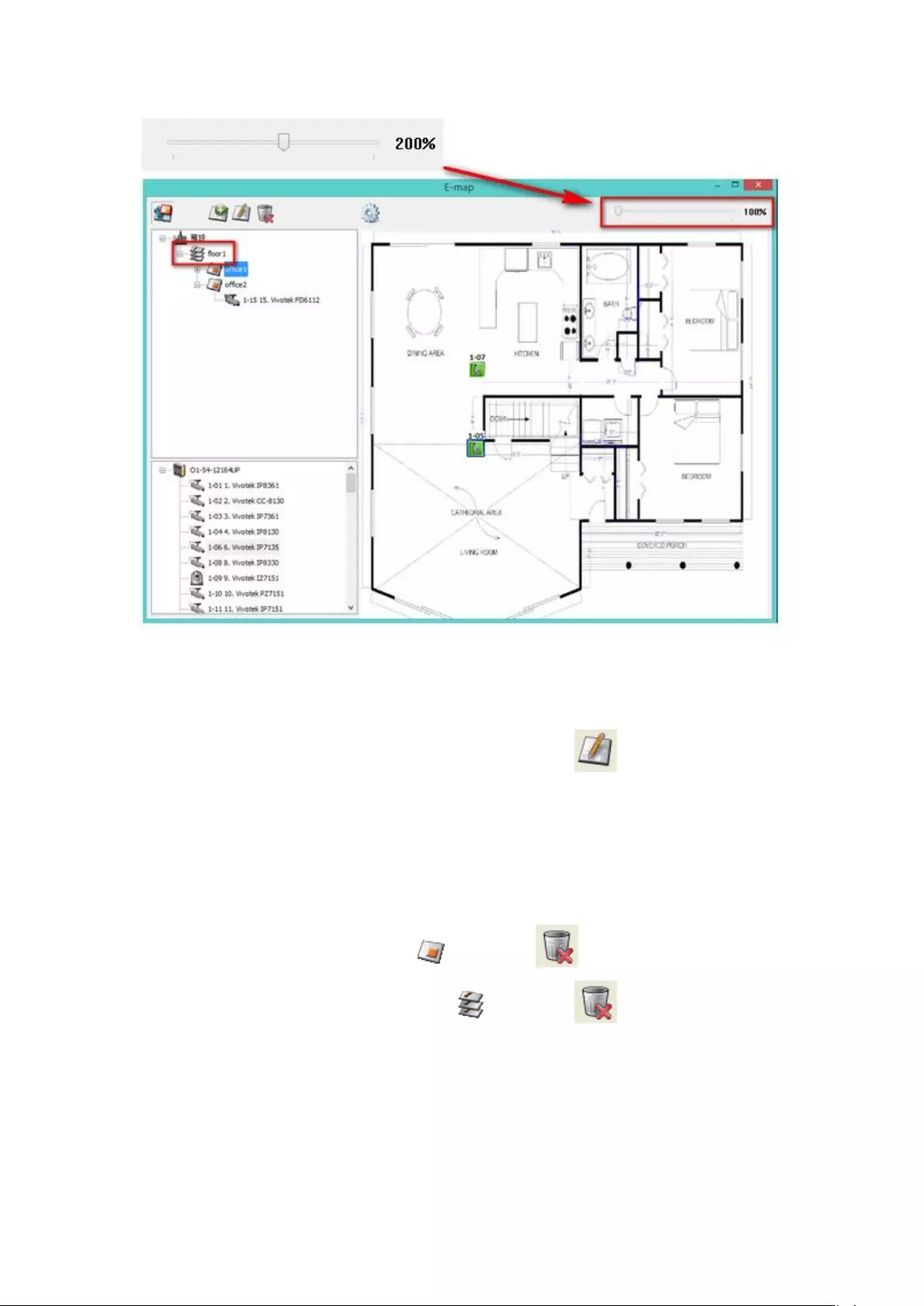
111
5.2.3 Edit a Map Name
To edit the name of an E-map, select the E-map and click . Enter the new
name and click ‘OK’. To change the picture of the E-map, delete the E-map and add
the new file.
5.2.4 Delete a Map Set or an E-map
To delete an E-map, select the map and click . To delete a set of maps
under the same level, select the map set and click .
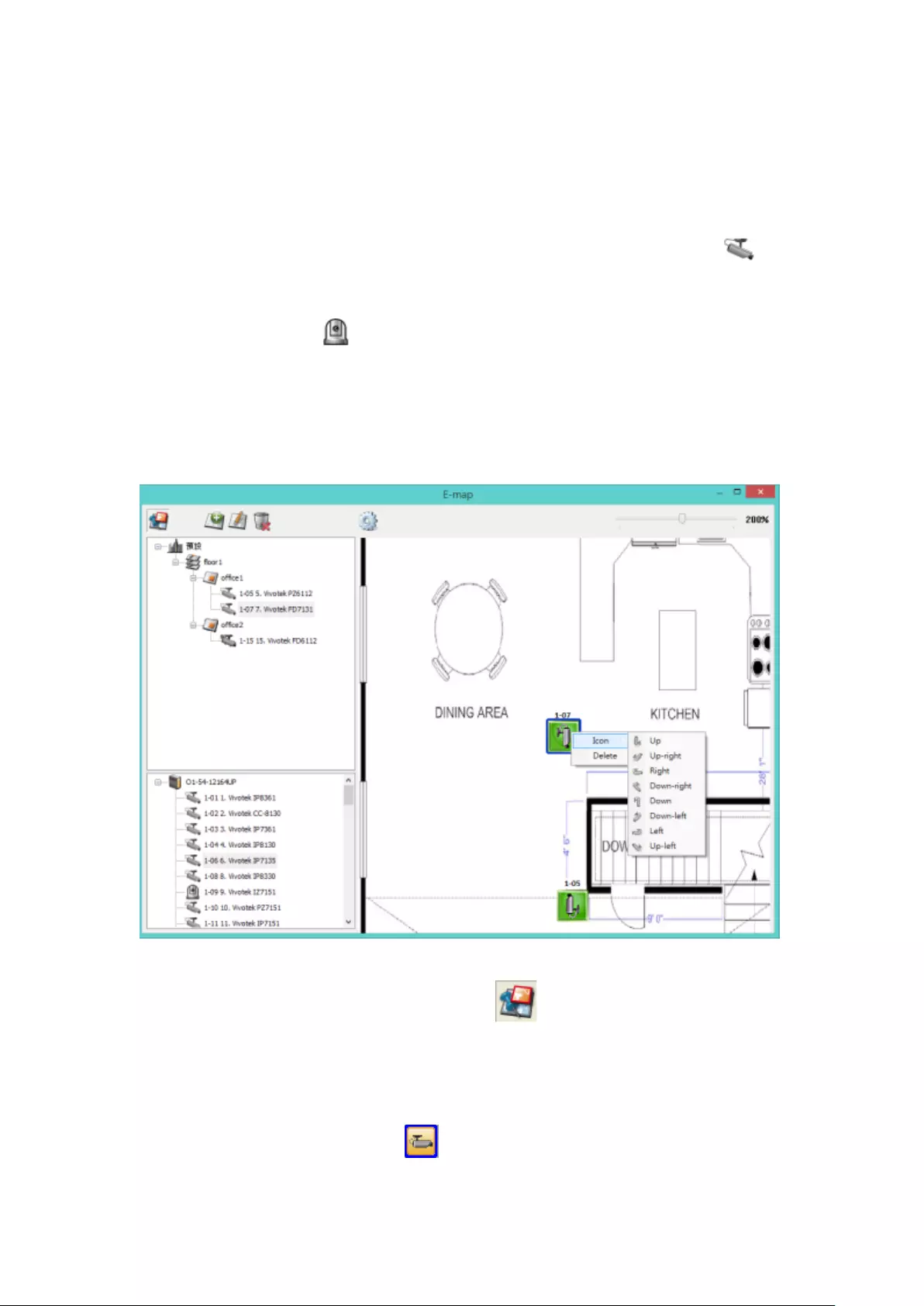
112
5.2.5 Indicate IP Cameras on an E-map
After uploading the E-maps, drag and drop the IP camera icons to the E-map(s) to
indicate the camera location. The camera name will appear under the E-map on
the top left column. When an icon of a fixed body or fixed dome IP camera is
dropped to the E-map, right click the camera icon and adjust the icon direction. The
icon of a PTZ IP camera cannot be adjusted. The naming rule of camera is as
follows: [Order of Server]-[Order of Channel][Camera Name]. For example : “1-05
Corner” means channel 5 of NVR1 and its camera name is “Corner”.
To delete a camera icon from the E-map, right click on the icon and select ‘Delete’.
To save the changes made to the E-maps, click to exit Edit mode.
When clicking an E-map or an IP camera on the left, the E-map or the E-map with the
camera icon will be shown on the right immediately. The selected camera icon will
be highlighted with a blue bracket . And the view of IP camera will be shown in
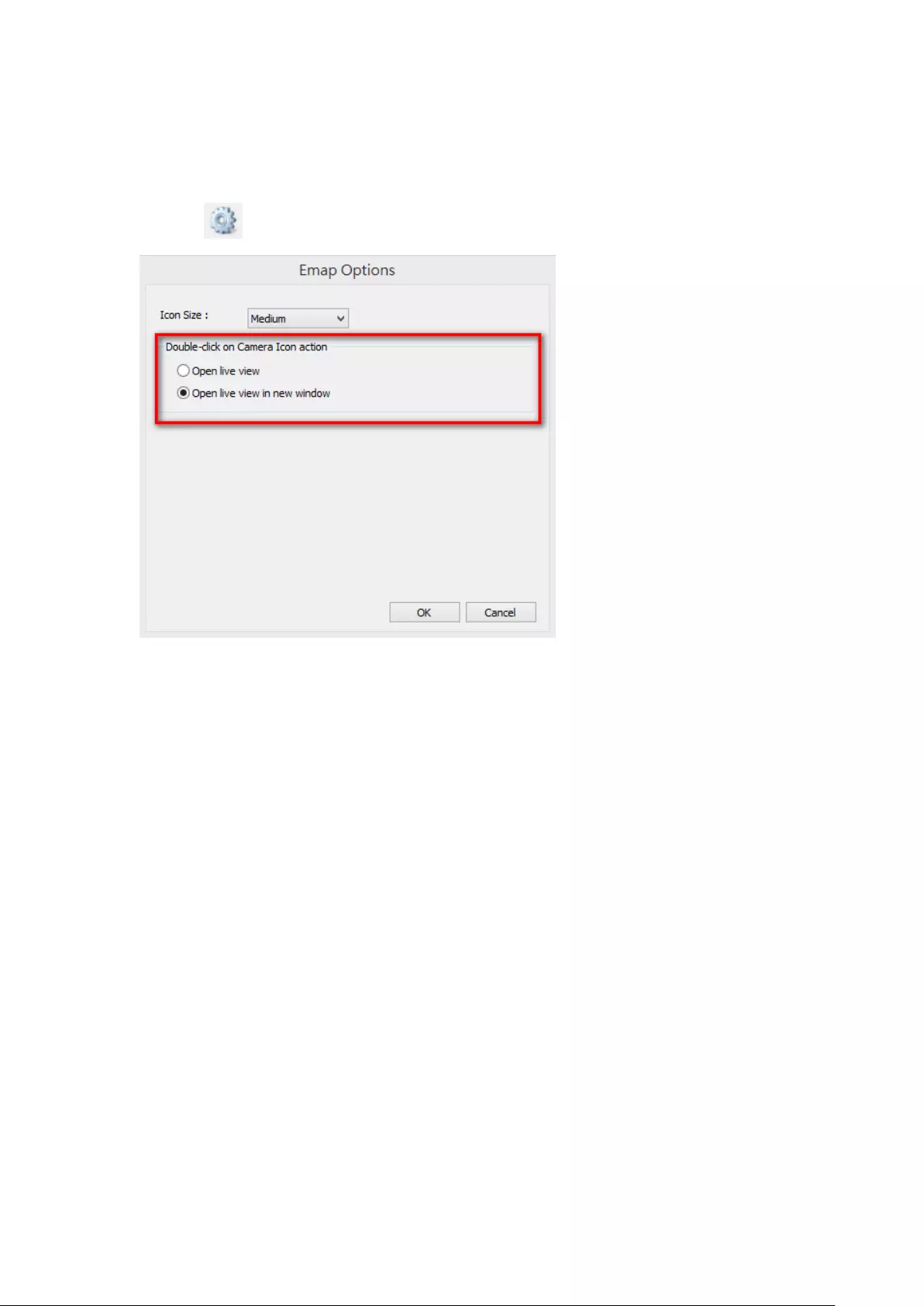
113
single-channel mode on the monitoring screen.
You can choose the Double-click action on the Camera Icon in “Emap Options” by
clicking .
Open live view: Whether or not Edit mode is enabled, the view of IP camera
will be shown in single-channel mode on the monitoring screen.
Open live view in new window:Whether or not Edit mode is enabled, the view
of IP camera will be shown on another window.
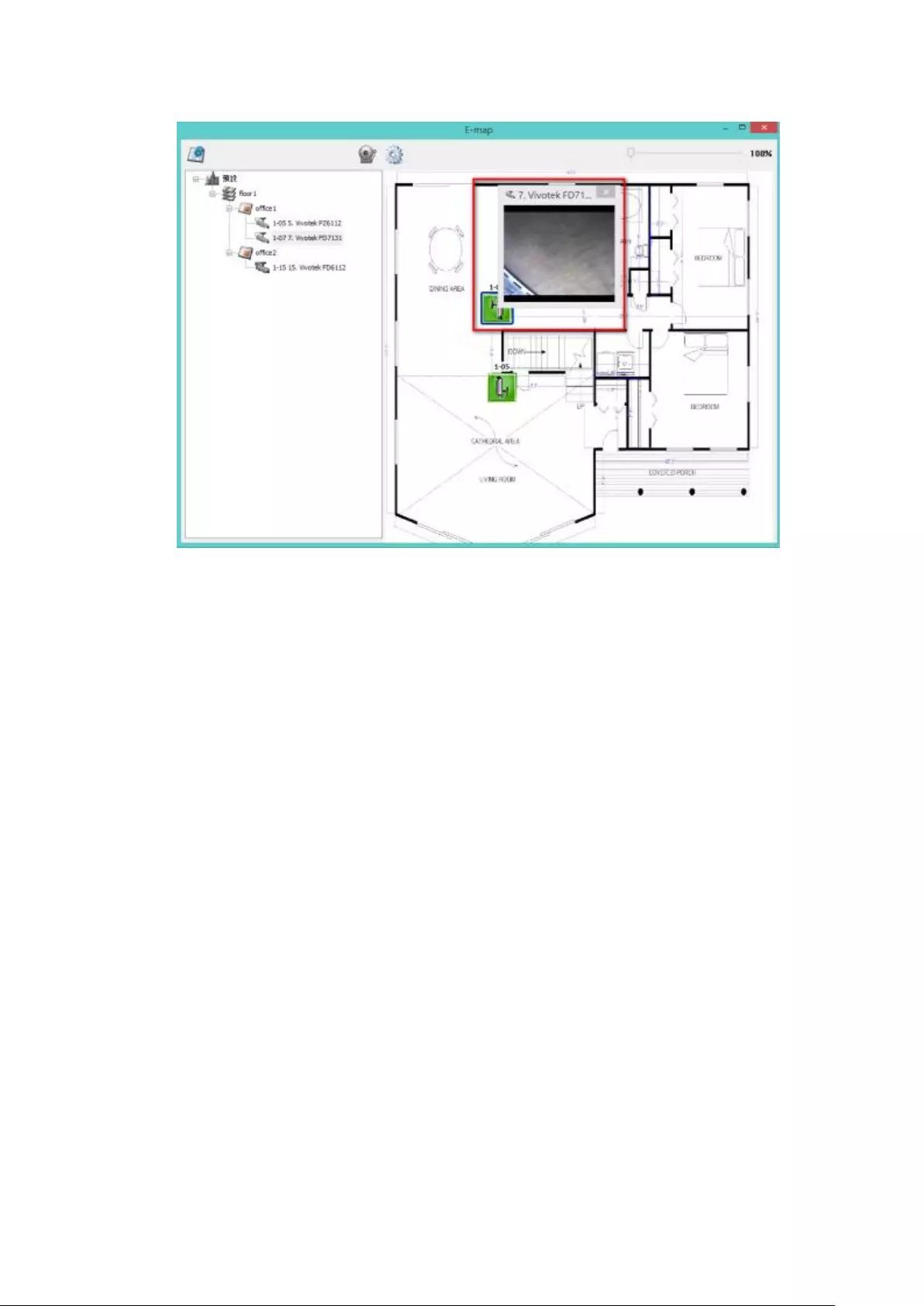
114
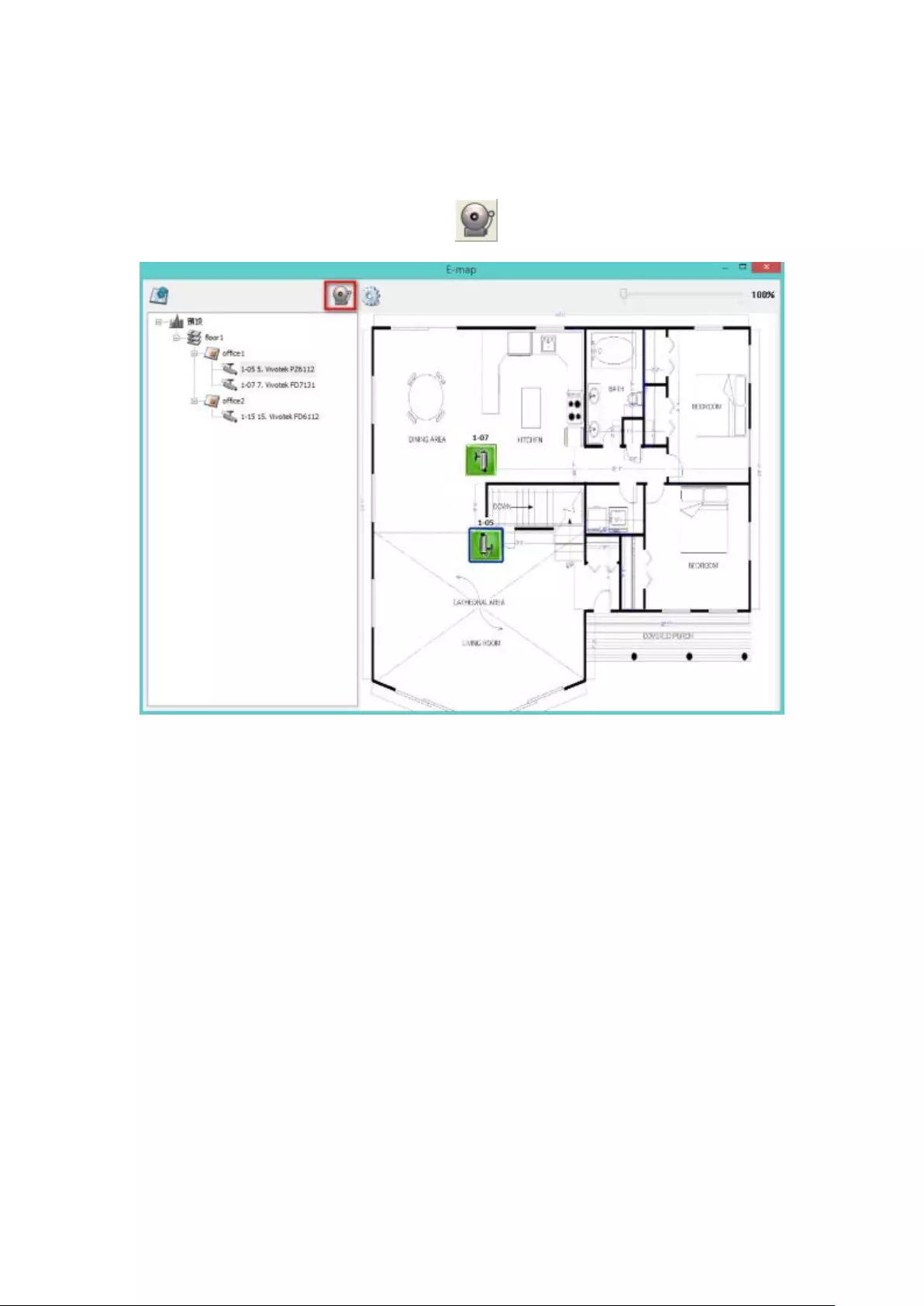
115
5.2.6 Enable/Disable Event Alert
To enable event alerts on an E-map, click .
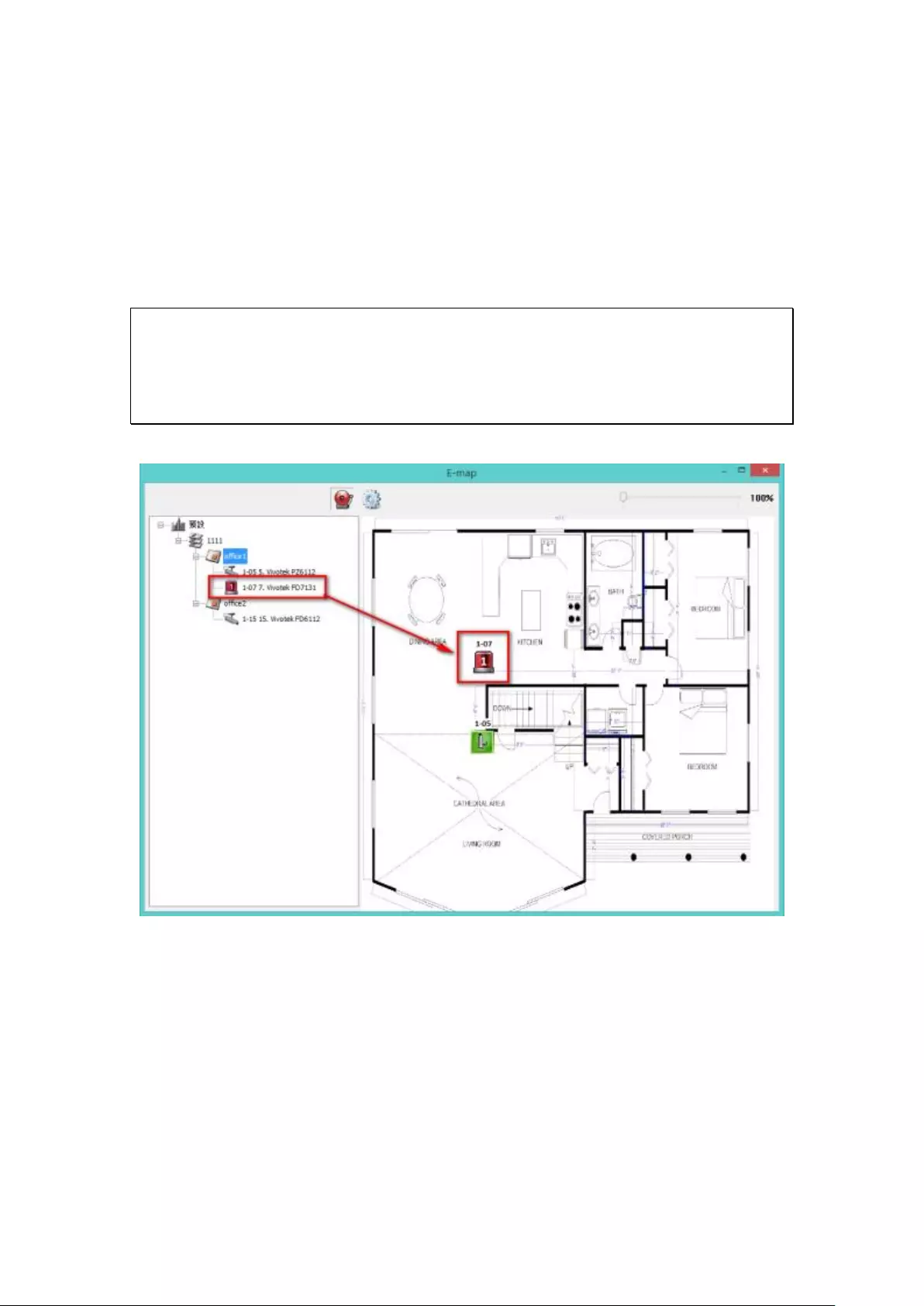
116
When an event occurs to an IP camera on the E-map, the camera icon will flash and
indicate the event type. The E-map with the IP camera on which an event is
triggered will be shown immediately*. Double click on the camera/alert icon and
the monitor screen will switch to display the alert camera channel in single-channel
view on the monitor screen automatically.
*The E-map with event alerts will not be switched to display automatically if the time
difference between the event time and the last time the user uses the E-map (clicks
the E-map window) is less than 20 seconds. In this case, refer to the tree menu on
the left to locate the IP cameras with alerts/flashing icons.
117
The event type occurring to an IP camera can be identified by the camera icon on an
E-map.
Icon
Description
A moving object has been detected
The alarm input 1 of the IP camera has been triggered
The alarm input 2 of the IP camera has been triggered
The alarm input 3 of the IP camera has been triggered
An unidentified event has been triggered
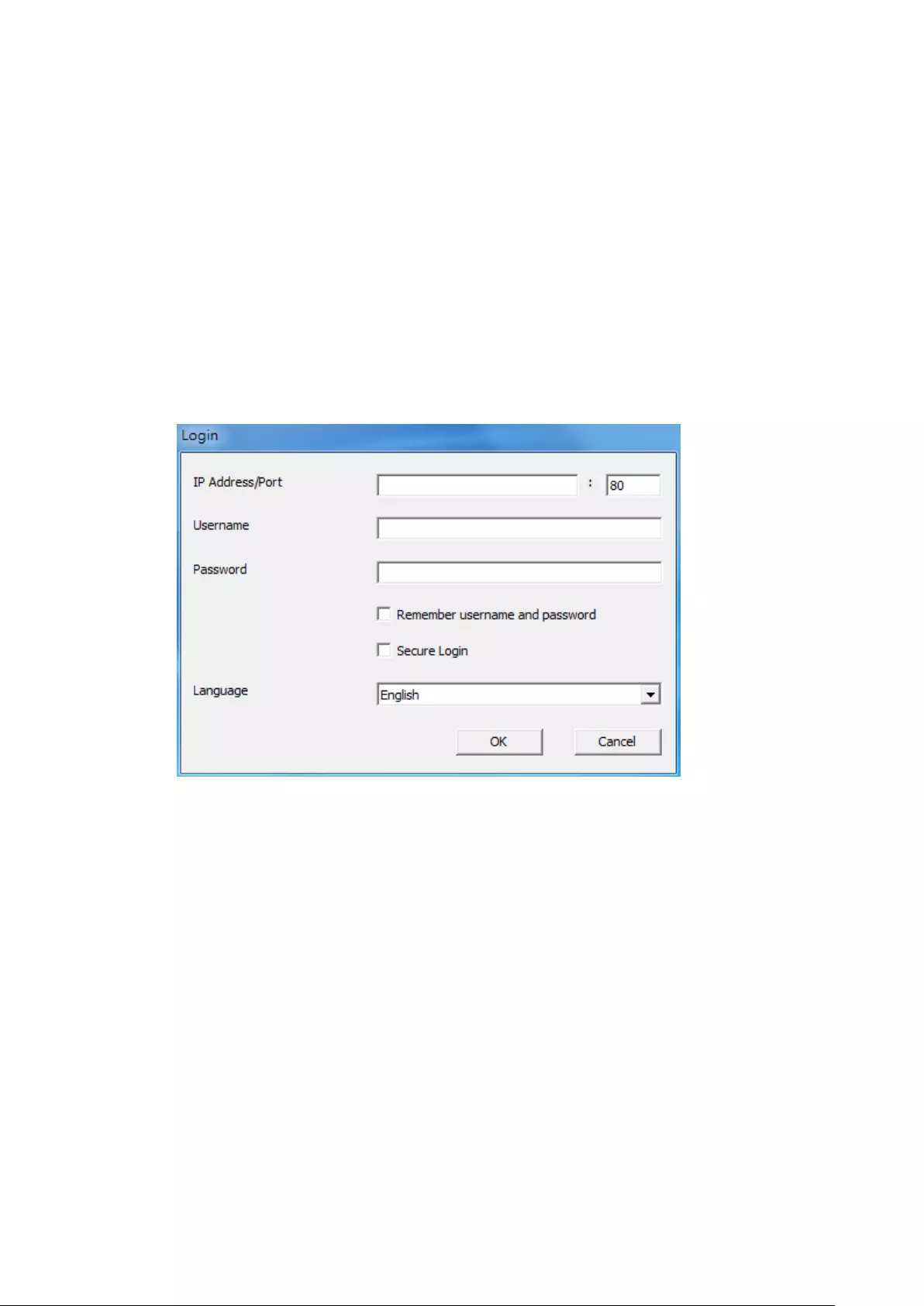
118
5.3 Remote Monitoring from the QNAP QVR Client for
Windows
1. After installing the QNAP QVR Client for Windows, click Start → All Programs
→ QNAP → QVR → Surveillance Client to open the QNAP QVR Client for
Windows.
2. The following window will be shown.
3. Enter the IP address/port, user name and password to login the NVR.
4. All the monitoring functions of the QNAP QVR Client for Windows are similar to
those of the browser-based interface. Please refer to other sections of this
chapter.
119
Chapter 6. Play Video Files
Use Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Internet Explorer and the QNAP
QVR Client to playback the files recorded by the NVR.
1. To play the recording files in Internet Explorer, please add the NVR IP address to
the list of trusted sites. When accessing the NVR via Internet Explorer, you will
be prompted to install the ActiveX add-on.
2. To play the recording files by Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox or QNAP QVR
Client on Windows PC, please visit http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp
to download and install the QNAP QVR Client for Windows.
3. To play the recording files on Mac, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp to download and install the QNAP
QVR Client for Mac.
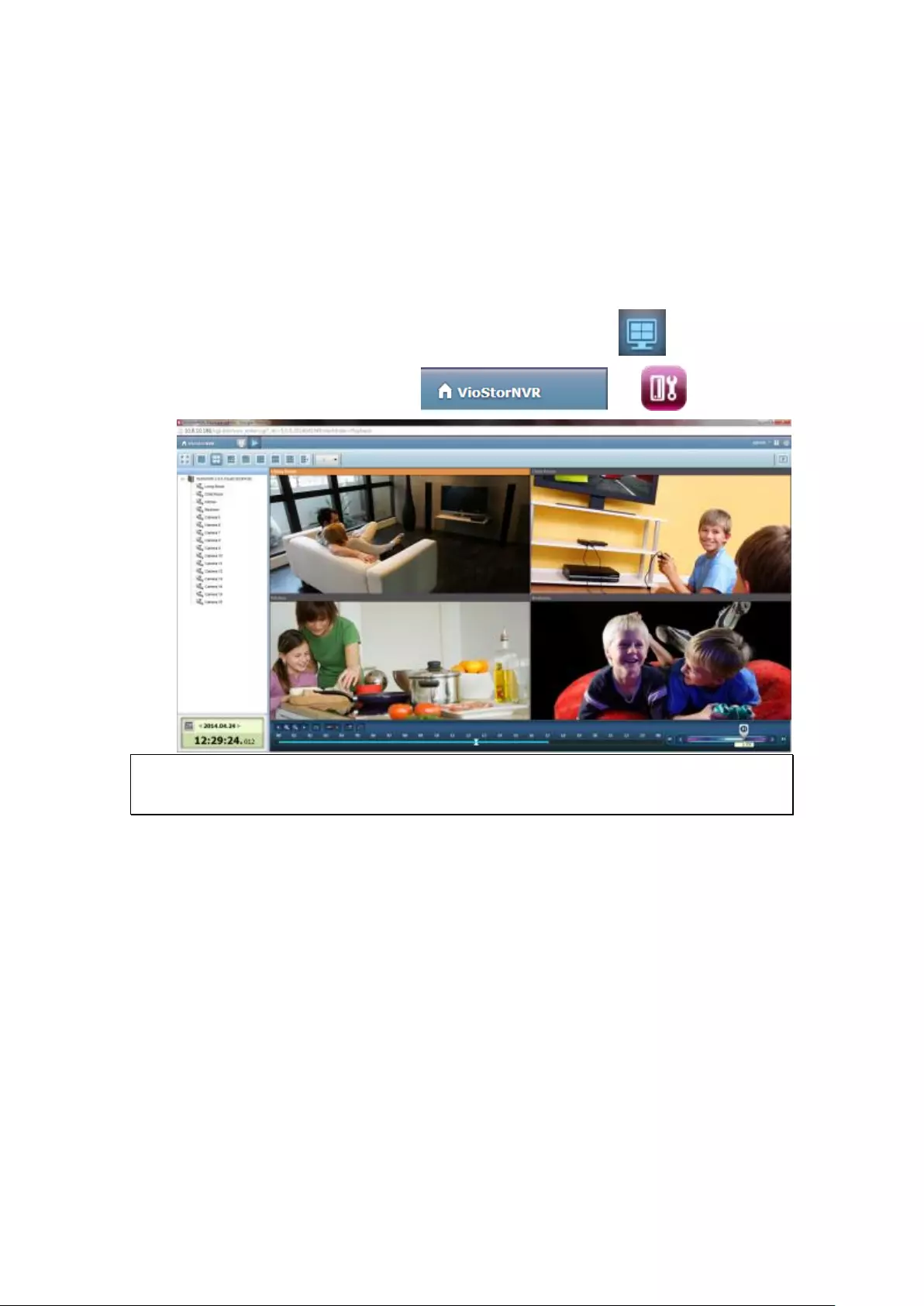
120
6.1 Playback Page
1. Click the playback button on the monitoring page or the QVR desktop.
2. The playback page will be shown. You can search and play the video files on
the NVR servers. To return to the monitoring page, click . To enter the
surveillance settings page, click -> .
Note: The playback access right to the IP cameras is required to view and play the
video files.
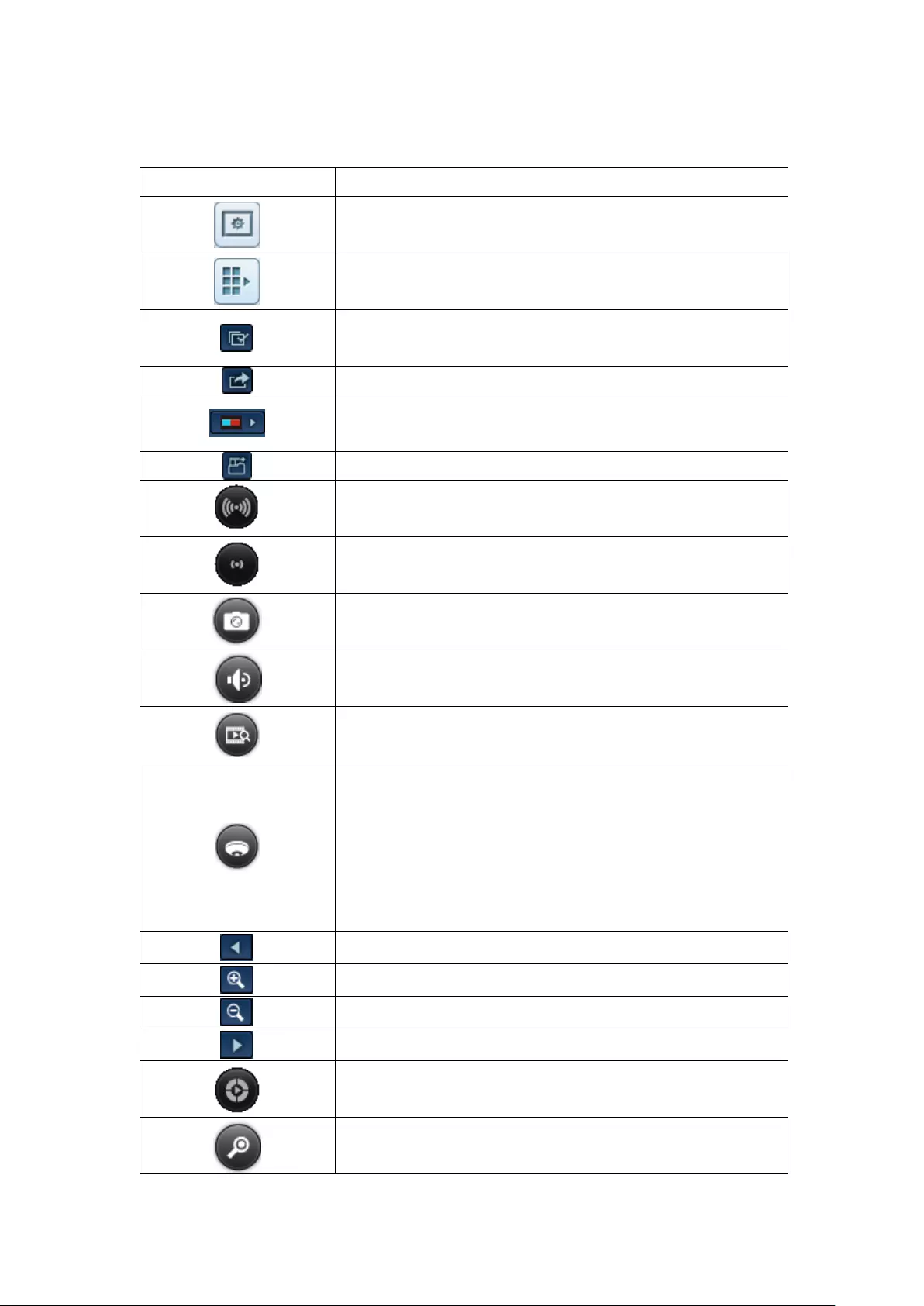
121
The following table consists of the icons and their descriptions in the playback page.
Icons
Description
Configure the options such as playing mode, snapshot
settings, and digital watermark
Multi-view mode (up to 16-view mode)
Control all views: Control the playback settings of all the
playback windows
Convert the video files on the NVR to AVI files
Select the playback video type (alarm recordings, regular
recordings, recovery recordings, etc)
Open recording files
Standard bandwidth mode
Low bandwidth mode
Take a snapshot of the video
Audio (optional): Turn on/off the audio support
Search recording files by IVA
Dewarp fisheye images:
For specific fisheye cameras (Note 1) and the specific
camera models with panomorph lens (Note 2), you can
enable/ disable dewarping function. After enabling the
function, you can then select mount type, dewarping
mode.
Last time interval
Increase the interval of scales on the timeline
Decrease the interval of scales on the timeline
Next time interval
Average Time-Divided Playback
Digital zoom: Enable/Disable digital zoom. When digital
122
zoom is enabled ( ), you can use your mouse wheel
to use digital zoom function.

123
Playback and Speed Control Shuttle Bar
Playback Control Button: Play/pause recording files
Speed up
Speed down
Last frame
Next frame
Right side of shuttle bar is
normal play, and left side of shuttle bar is reverse play.
When you drag the playback control button to right, it
will play normally. When dragging the playback control
button to left, it will reverse play. When dragging to the
center of shuttle bar, it will pause.
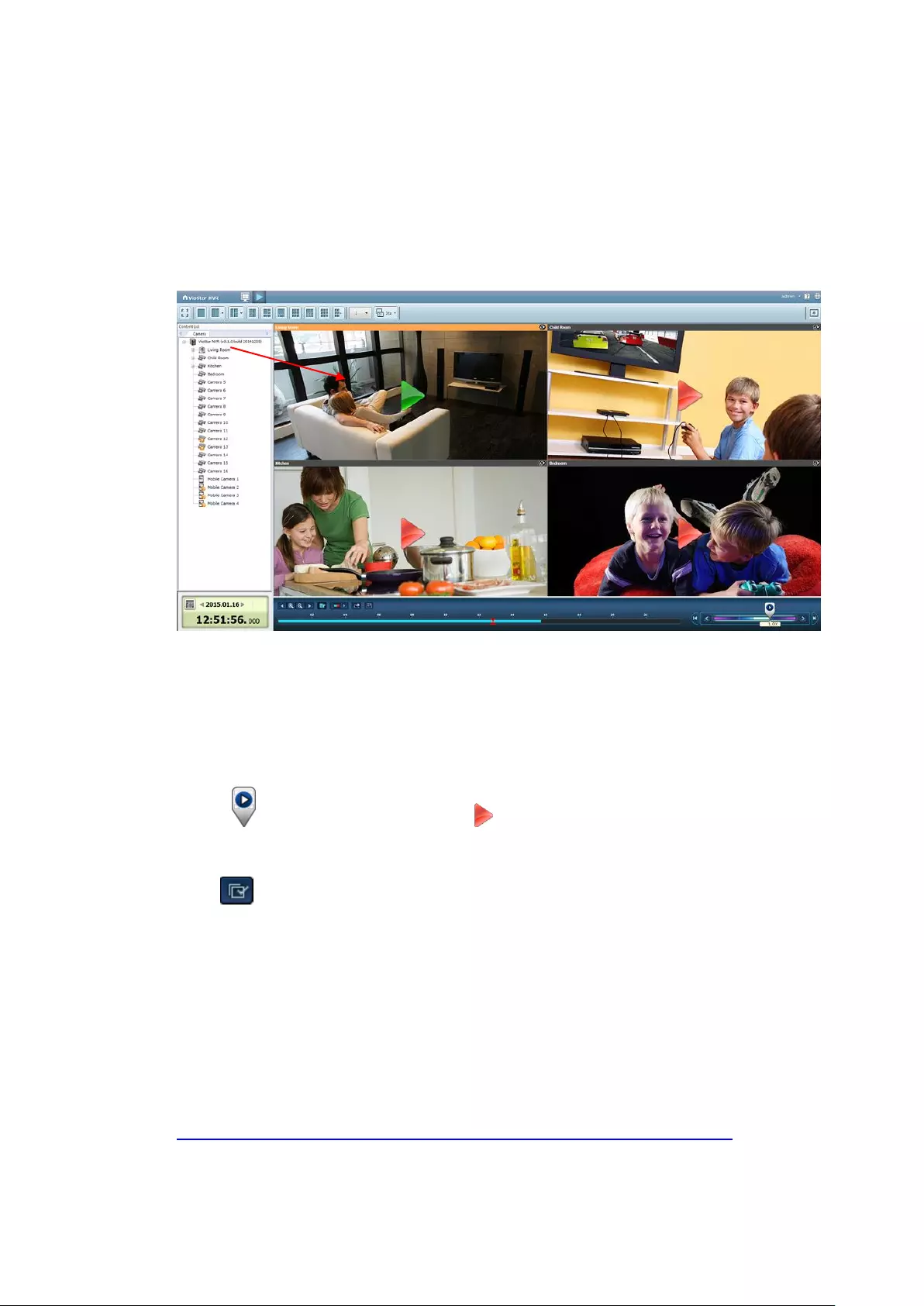
124
6.1.1 Play Video Files from NVR
Follow the steps below to play the video files on the remote NVR servers.
1. Drag and drop camera(s) from the server/camera tree to the respective
playback window(s) to select the channel(s) for playback.
2. Select the playback date from time interval. You can examine each channel to
know the time range when the files are recorded for each IP camera. The blue
cells indicate regular recording files and the red cells indicate alarm recording
files. If it is blank in the time period, it means no files are recorded at that
moment.
3. Click to start playback, or click on a channel screen.
4. Specify the time to play back the recording files at that moment.
5. Click to control all the playback windows to play back the recording files.
When this function is enabled, the playback options (play, pause, stop,
previous/next frame, previous/next file, speed adjustment) will be applied to all
the playback windows.
Note
1. Applied to specific fisheye cameras: please refer to the below camera
compatibility list
http://nvr.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/product_z_g_qvr/cat_intro.php?hf=old
After enabling the feature, you can select Mount type, including wall, ceiling,

125
and floor and then select Dewarping mode, including Panorama (Full View),
Panorama (Dual View), and Rectangle.
Remark 1: If the Mount type is Wall, only Panorama (Full View), and Rectangle
are supported in Dewarping mode.
Remark 2: If Dewarping mode is Rectangle, you can use PTZ control panel to
operate PTZ functions, excluding digital zoom.
2. Applied to the specific camera models with panomorph lens.
Before using this feature, you need to select the ‘Enable panomorph support’
option in the camera configuration page. Right click the channel and enable
the feature. After that, you can select Mount type, including wall, ceiling, and
floor and then select Dewarping mode, including Perimeter mode, Quad mode,
and PTZ mode.
Remark 1: To know the camera models which can be installed with panomorph
lens, please visit
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/n/en/qa/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=128.
Remark 2: The function is only available when the resolution of the video
stream is higher than 640x480 on the monitoring page.
Remark 3: If Dewarping mode is PTZ mode, for the channel, you can use PTZ
control panel or mouse (by clicking and holding down the mouse left button,
and then moving the mouse or turning the mouse wheel) to change viewing
angles or zooming in/out the screen. If Dewarping mode is Quad mode, the
above methods can also be applied to operate PTZ functions in each divided
screen.
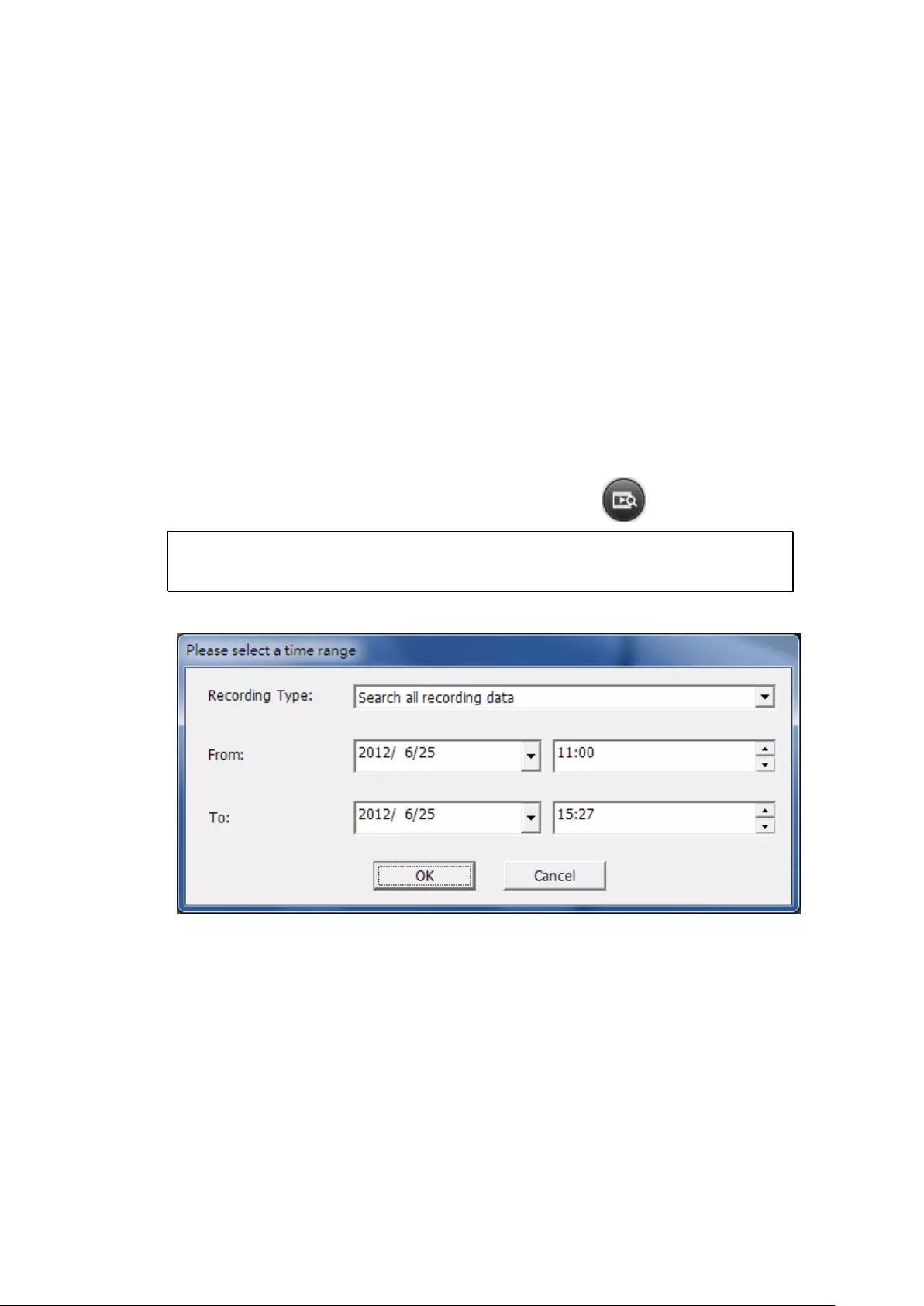
126
6.1.2 Intelligent Video Analytics (IVA)
The NVR supports intelligent video analytics for video data search.
The following features are supported:
Motion detection: Detects the movements of the objects in the video.
Foreign object: Detects new objects in the video.
Missing object: Detects missing objects in the video.
Out of focus: Detects if the camera is out of focus.
Camera occlusion: Detects if the IP camera is obstructed.
To use this function, follow the steps below:
1. Enter the playback page. Select one channel and click .
Note: The intelligent video analytics support video search on one IP camera
channel only.
2. Select recording type, start time and end time for video search.
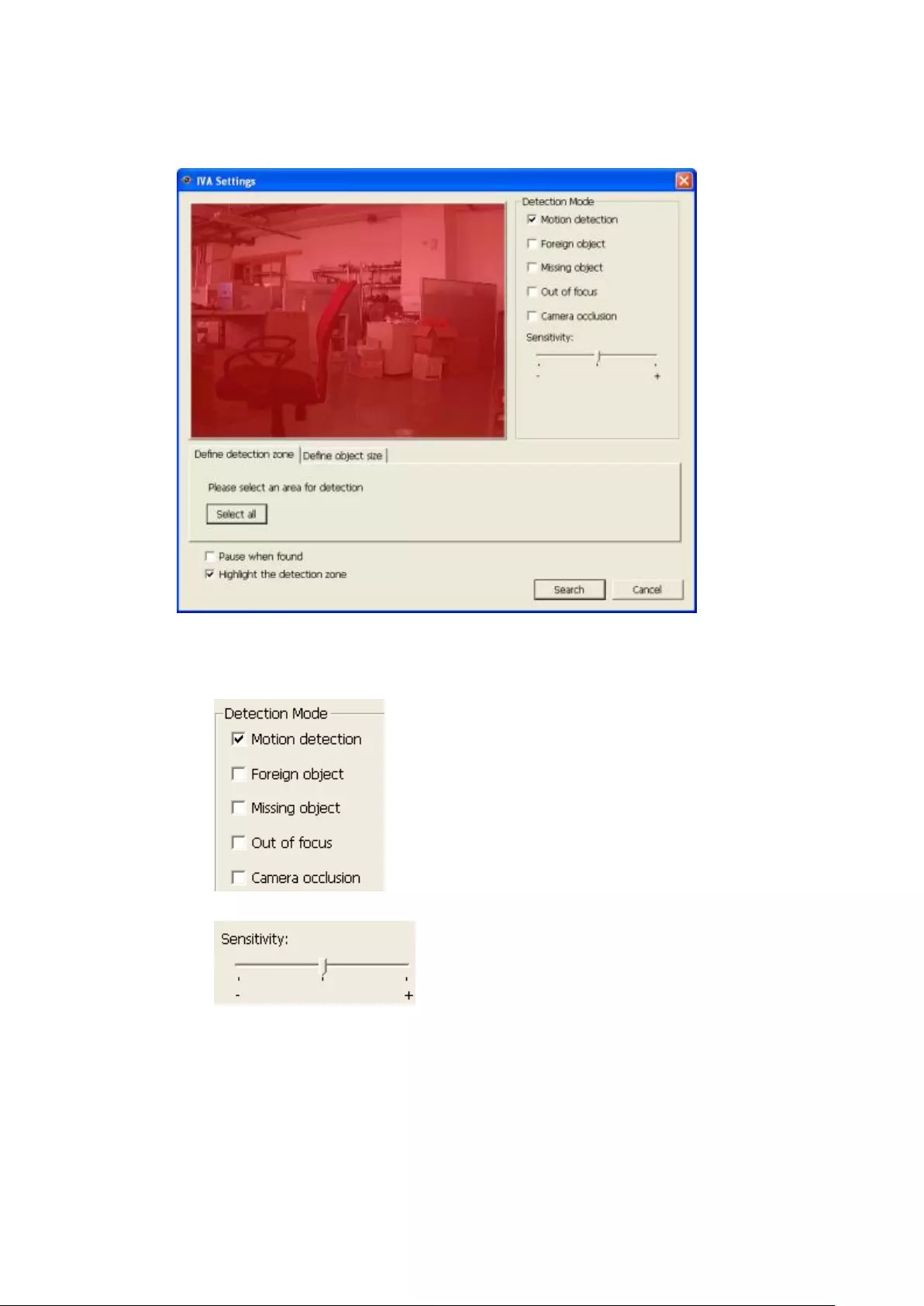
127
3. Configure the IVA settings for video search.
A. Select the detection mode: Motion detection, Foreign object, Missing
object, Out of focus, or Camera occlusion. Multiple options can be
selected.
B. Adjust the sensitivity for object detection.
C. Adjust the time interval for detecting the foreign objects and missing
objects. If a foreign object appears or a missing object disappears for a
period of time which is longer than the time interval, the NVR will record
the event.
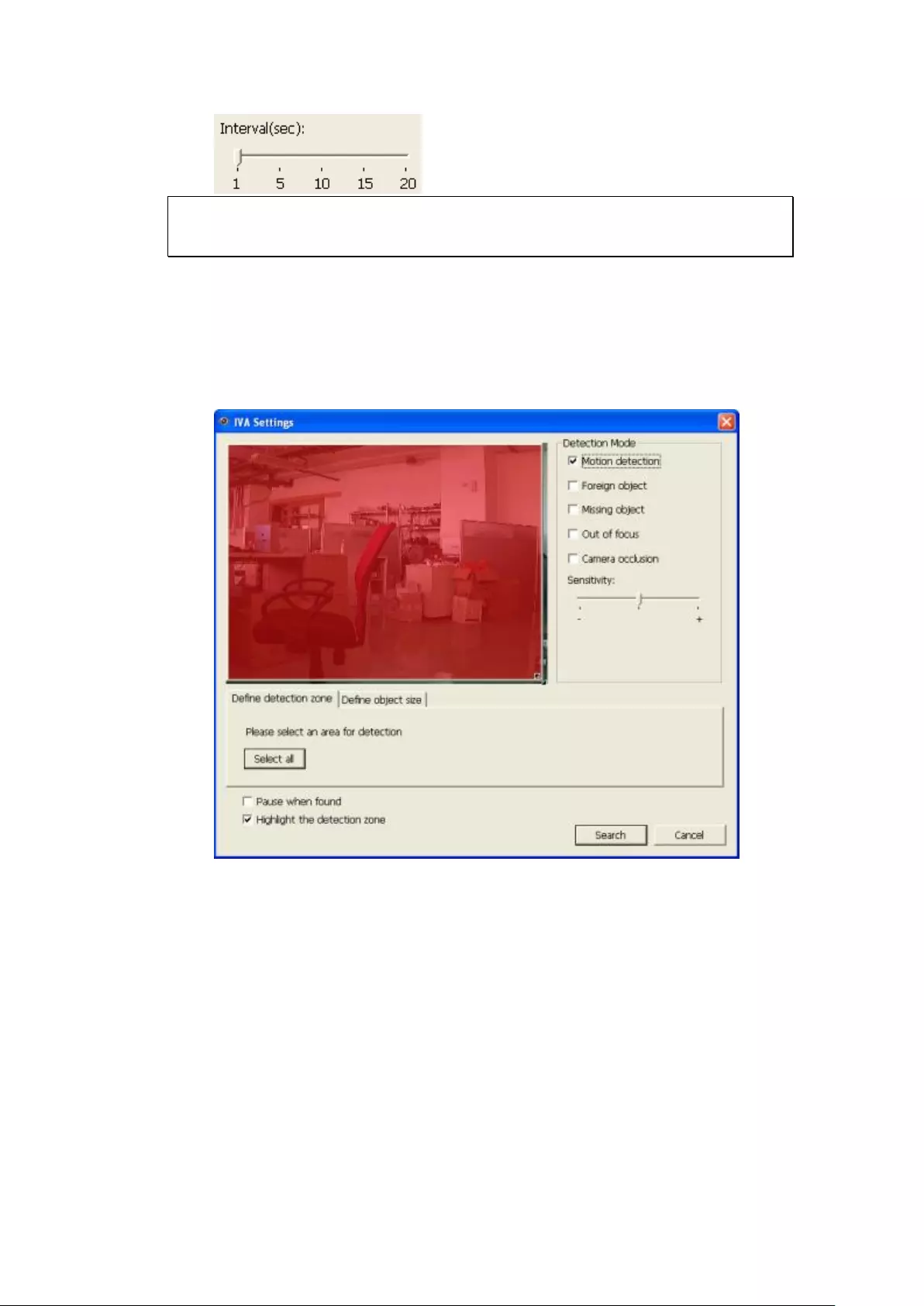
128
Note: The Interval slide bar appears only when ‘Foreign object’ or ‘Missing
object’ is selected.
D. Define the detection zone. Mouse over the edge of the red zone and use
the mouse to define the detection zone. Click ‘Select all’ to highlight the
entire area.
E. Define the object size for detection. Use the mouse to drag the yellow
zone to define the minimum object size for detection.
Ignore objects with width or height less than this setting: Enable this
option to ignore all the objects smaller than the yellow zone.
F. Enable/Disable other options for video search.
Pause when found: Enable this option and the video search will stop
when a video file matching the search criteria is found.
Highlight the detection zone: The moving objects detected in the
video will be highlighted in red boxes; the foreign or missing objects
will be highlighted in yellow boxes; the video which is out of focus or
obstructed will be displayed in transparent red.
4. Click ‘Search’ to start searching the video by IVA. The results will be shown.
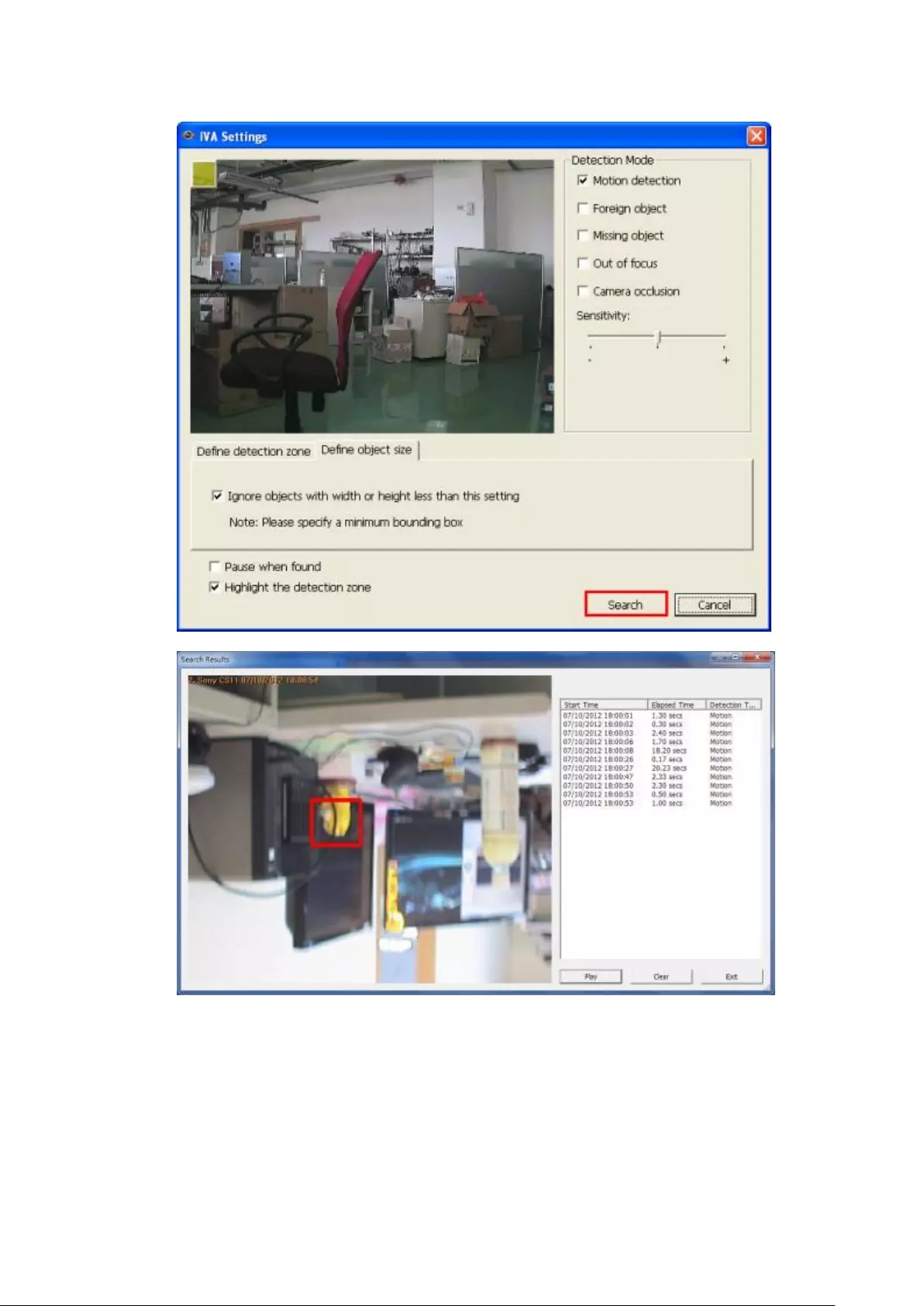
129
Other options:
Double click an entry on the search result dialog to play the video. The player
will play the video starting from 15 seconds before the event to 15 seconds after
the event.
Right click an entry on the search result dialog to export the video (AVI format)
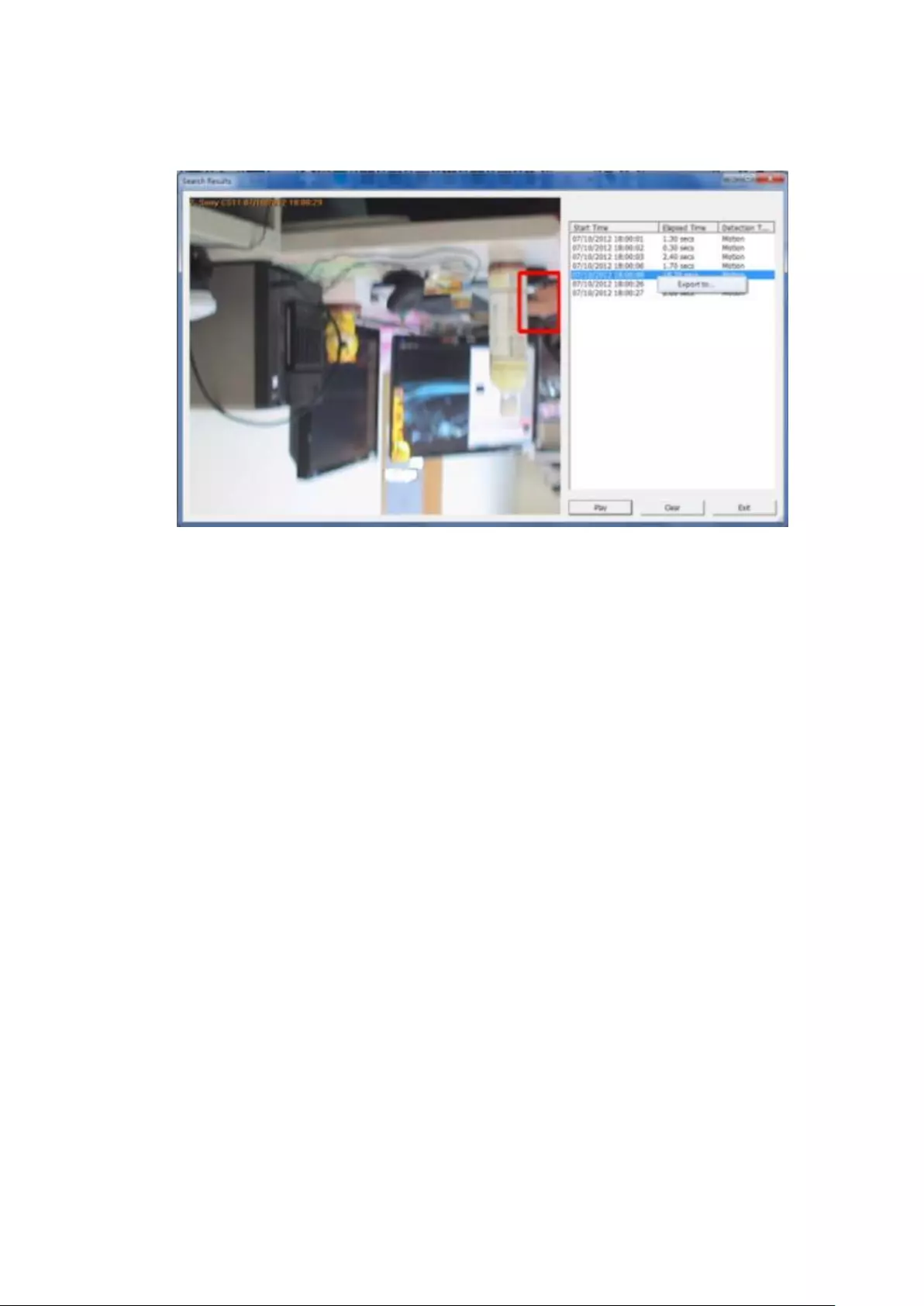
130
and save it to the computer. The exported video starts from 15 seconds before
the event to 15 seconds after the event.
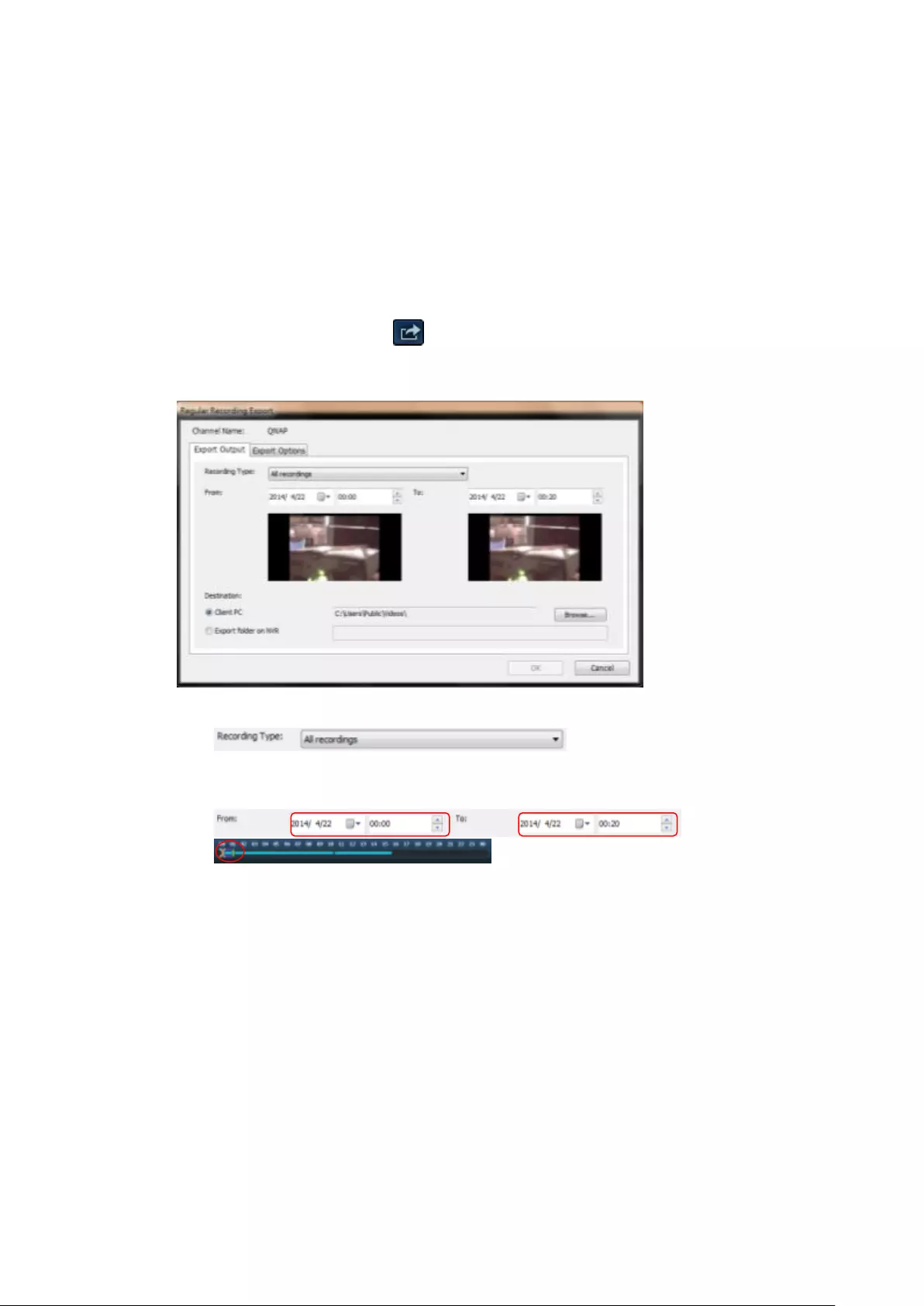
131
6.1.3 Export NVR Videos
To convert the video files on the NVR and export the file, please follow the steps
below.
1. Select an IP camera and click to ‘Convert to AVI file’.
2. Select recording type, start time and end time for video exporting.
A. Choose the recording type.
B. Specify the time range. Specify a smaller time range, or the video file will
be too large and take a long time to convert.
3. You can specify the location where the file will be saved on client PC or to the
NVR.
4. Enter the file name.
5. You can modify the export options.
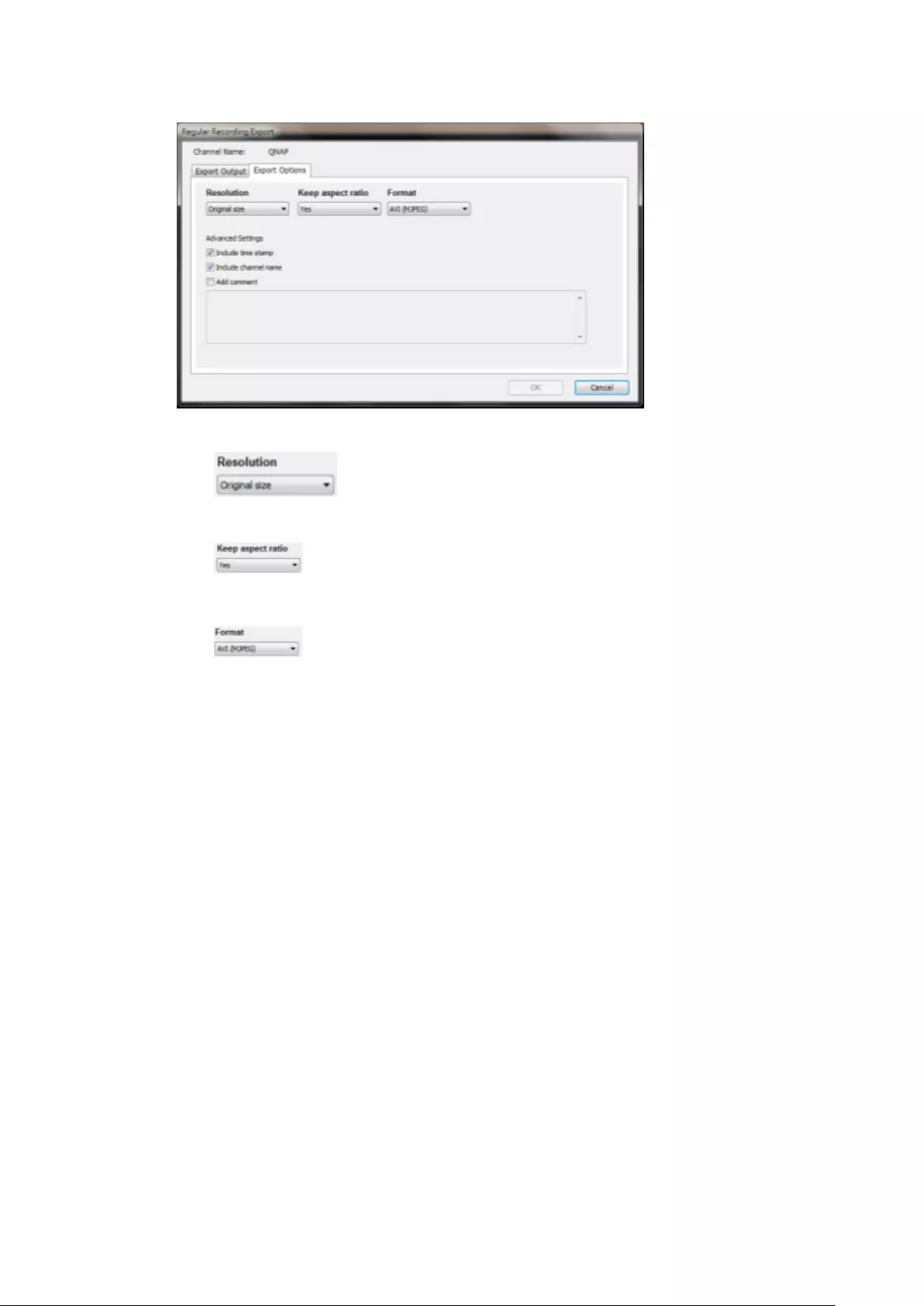
132
A. Choose the exporting resolution.
B. Select to keep the aspect ratio of exported file or not.
C. Select the file format (video compression) of the exported file.
D. You can select to include a time stamp and the channel name in the
exported file or to add comments (will have one more txt file saved as
same file name in the same folder).
6. Click ‘OK’.
7. All the video files that meet the search criteria will be converted.
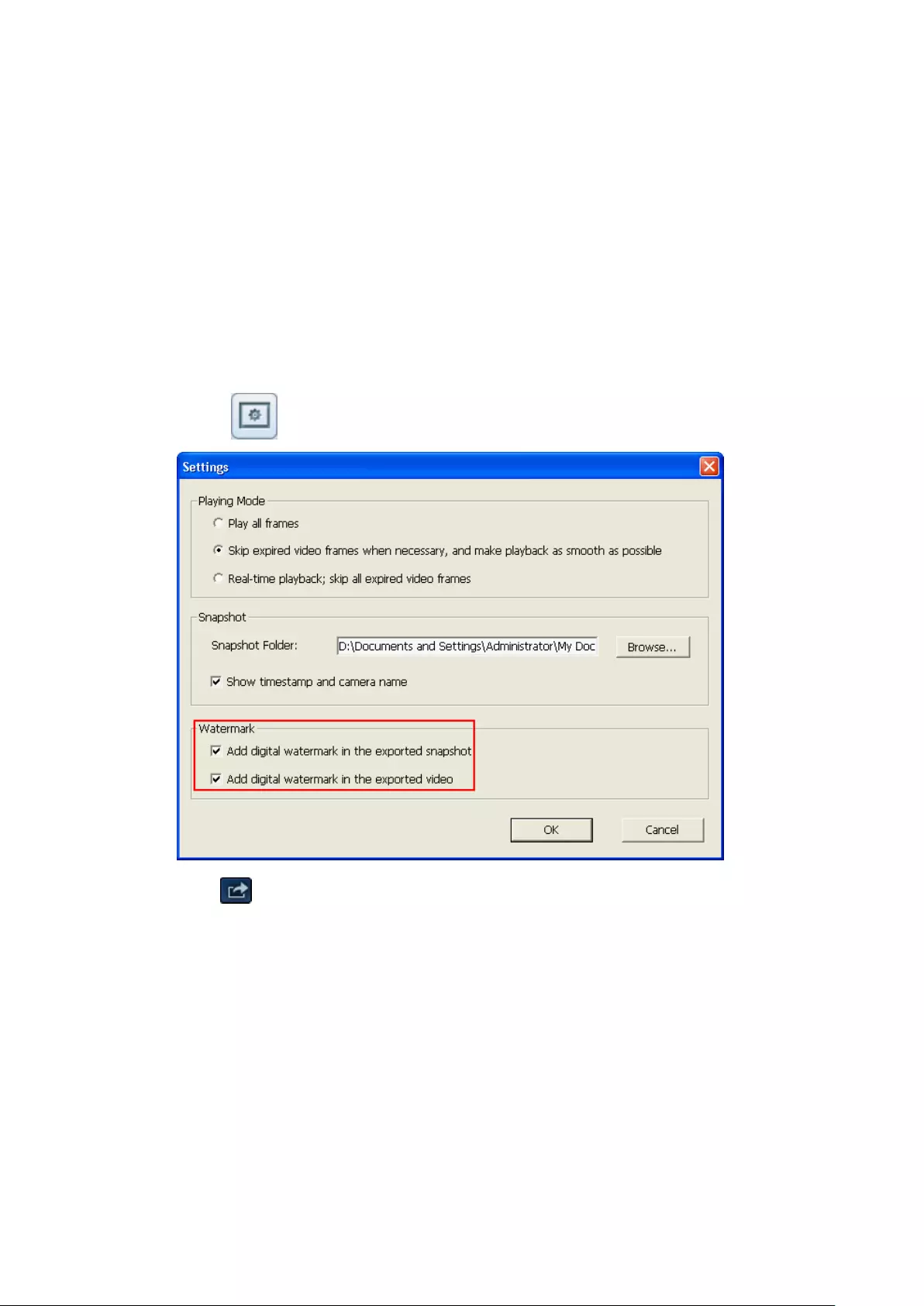
133
6.1.4 Export Video Files with Digital Watermark
The NVR supports digital watermarking to protect the videos and snapshots from
unauthorized modifications. Digital watermarks can be added to the exported
videos and snapshots in the playback page. The watermark cannot be removed and
can only be verified by the QNAP Watermark Proof software.
To use digital watermarking in the playback page, follow the steps below.
1. Enter the playback page.
2. Select to add digital watermarks in the exported snapshots or videos.
3. Click ‘Convert to AVI file’ (refer to Chapter 6.1.3). Digital watermarks will
be added to the exported video files and snapshots.
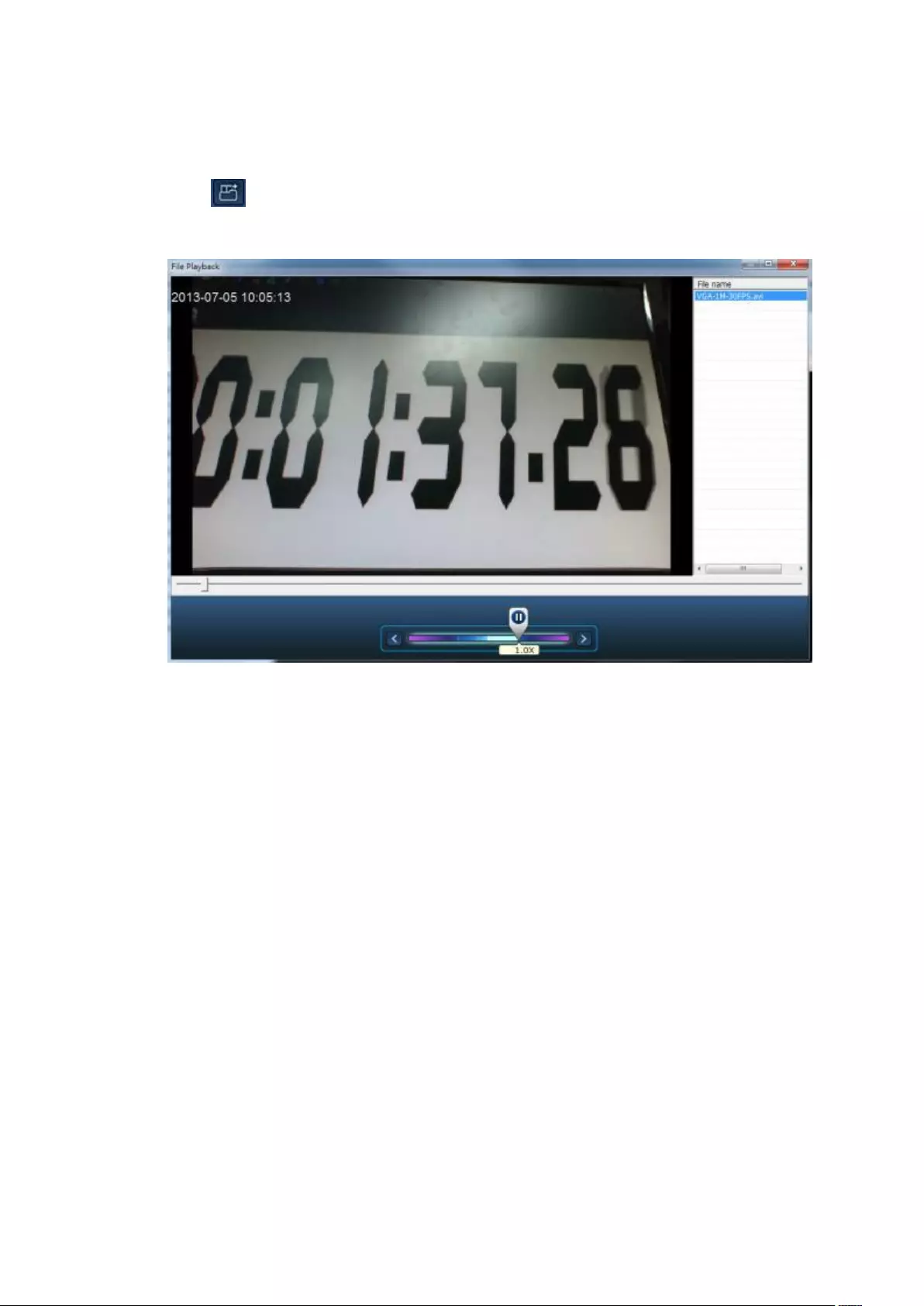
134
6.1.5 Enable Recording Video Files
Please follow the below steps to enable recording video files in the playback page.
1. Click to enable AVI files
2. Select the video files and start playback
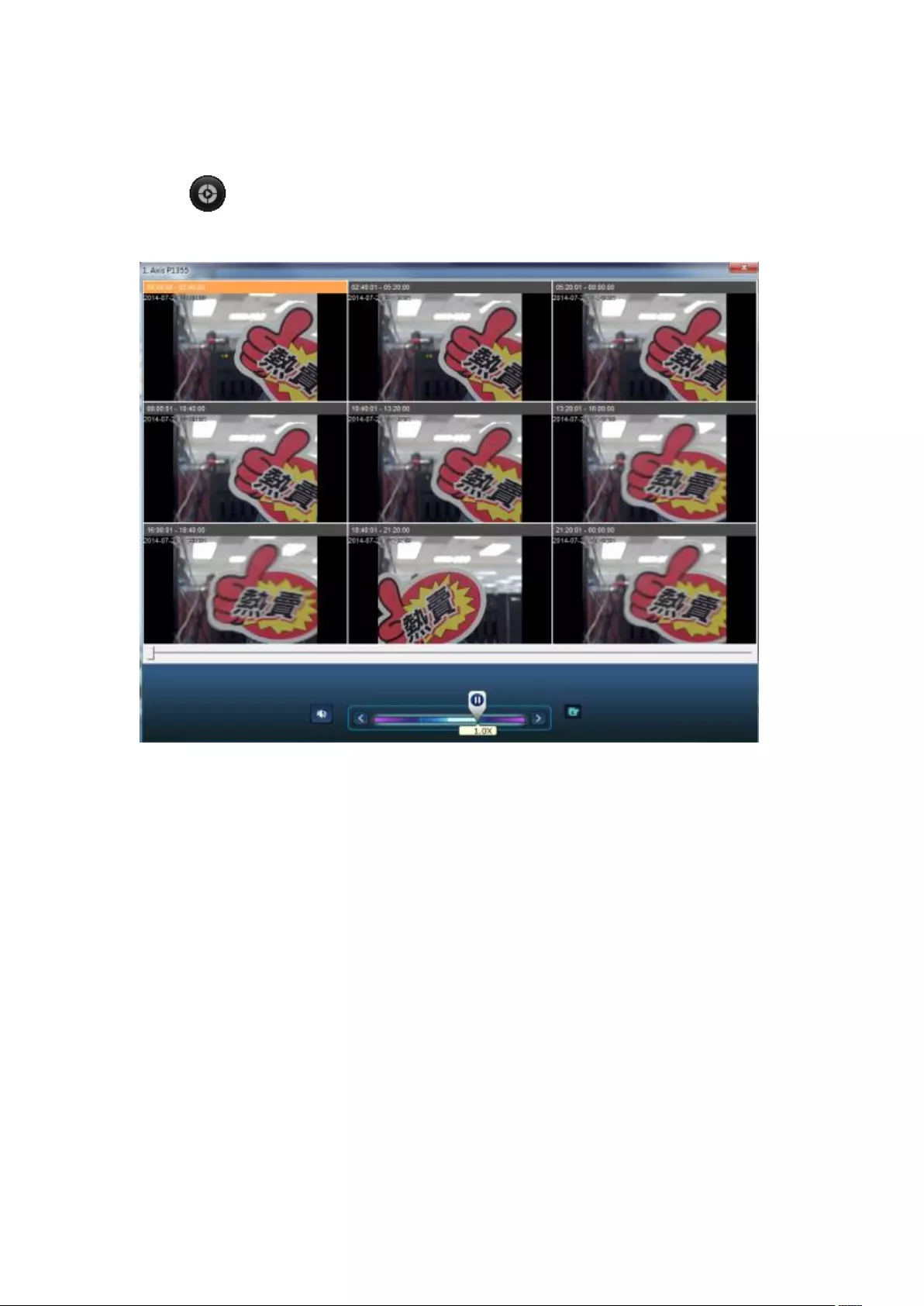
135
6.1.6 Average Time-Divided Playback
Click to designate a channel for Average Time-Divided Playback. This can be
divided for 4 channel or 9 channel display mode.
136
6.2 Play Video Files in the QNAP QVR Client for Windows
1. Click Start → All Programs → QNAP → QVR Client → Surveillance Client to
open the QNAP QVR Client for Windows.
2. The following window will be shown.
3. Enter IP address/port, user name and password to log into the NVR.
4. All the playback functions of the QNAP QVR Client for Windows are similar to
those of the browser-based interface. Please refer to other sections of this
chapter.
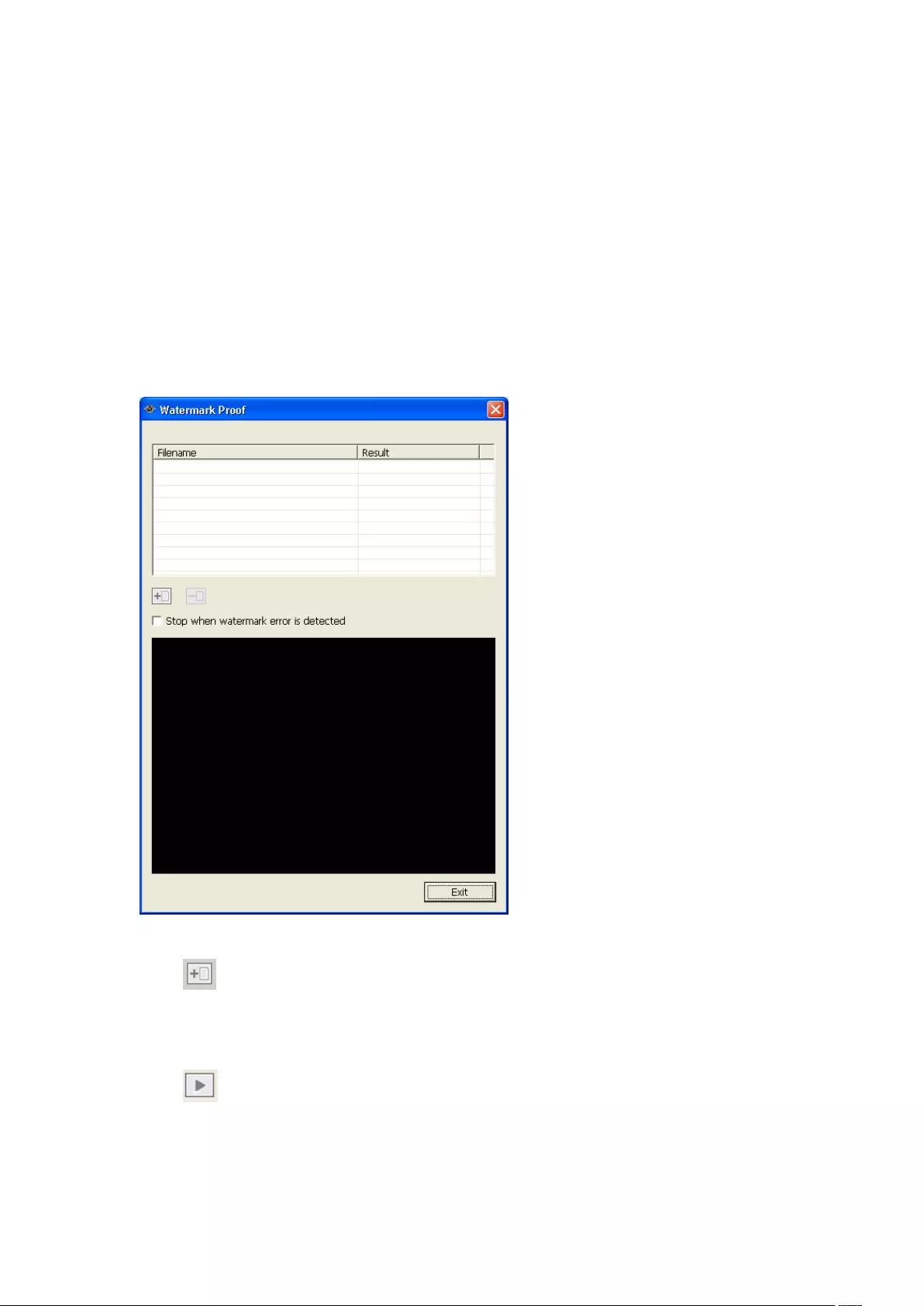
137
6.3 Watermark Proof
The Watermark Proof utility is installed automatically along with the QNAP QVR
Client for Windows. From the Windows Start menu, select ‘All Programs’ > ‘QNAP’
> ‘QVR Client’ to locate ‘Watermark Proof’.
Run Watermark Proof. The following window will be shown.
Click to browse and locate the files. Multiple files can be selected at one
time.
Click to check the files and view the proof result. When ‘Stop when
watermark error is detected’ is selected, the checking process will stop if a failed file
is detected. Otherwise the program will check all the files selected. If a video file
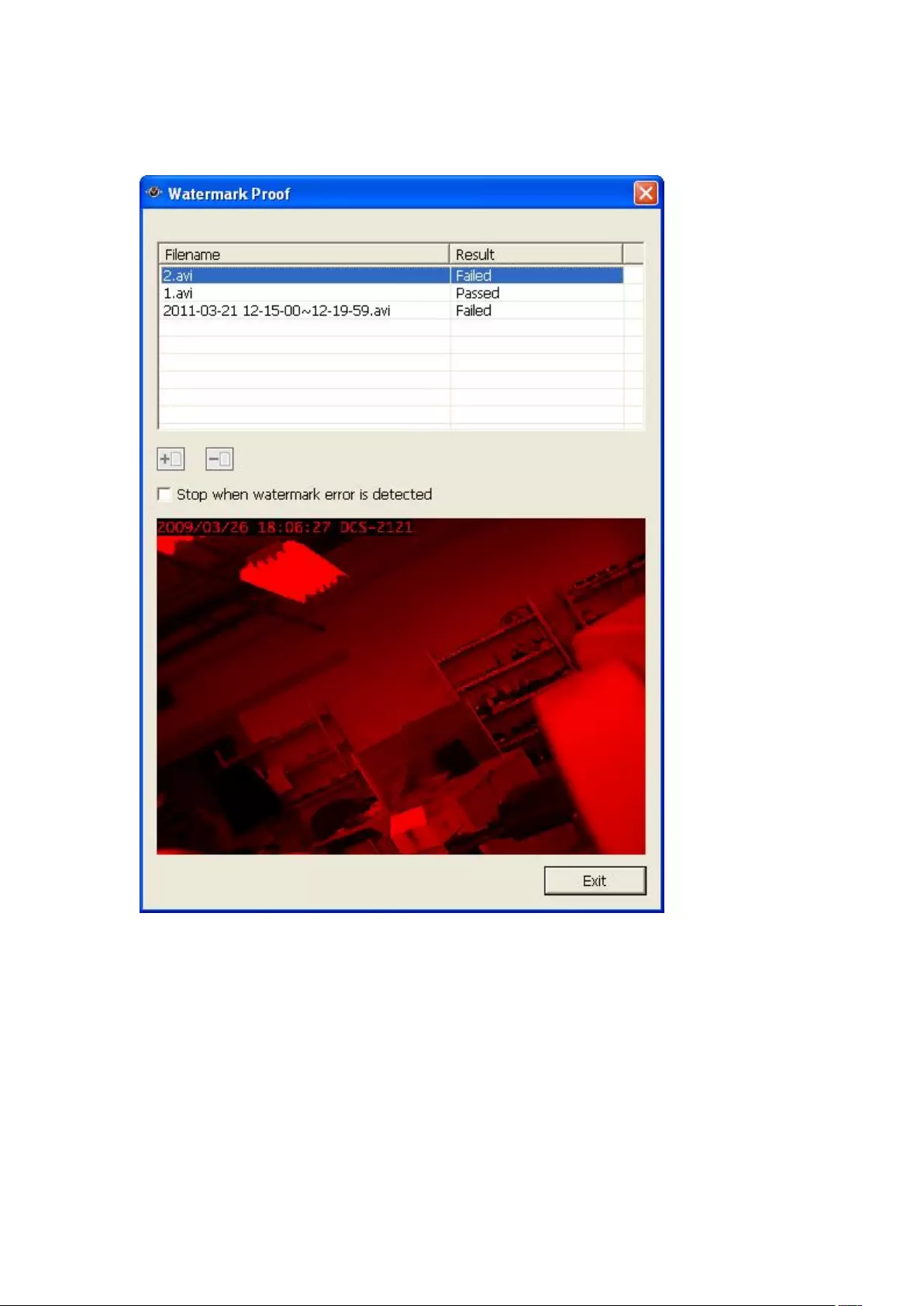
138
has been modified, or is not exported with digital watermark, or not an NVR video
file, the proof result will be shown as ‘Failed’.
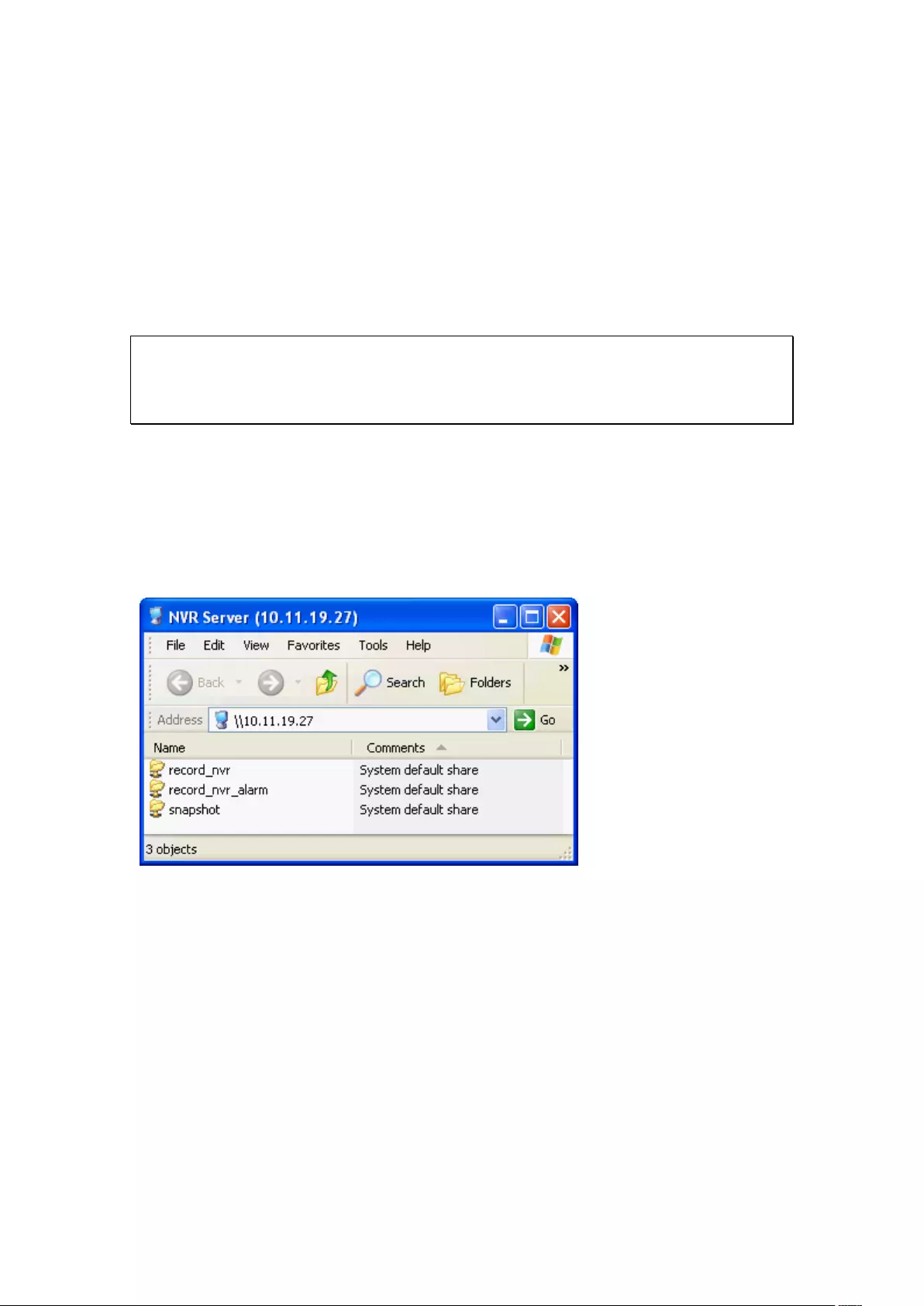
139
6.4 Access the Recording Data
The recording data on the NVR can be accessed by the following services:
Microsoft Networking (SMB/CIFS)
FTP Server (FTP)
Note:
To access the video files by these protocols, enter the user name and password
with the administrator access right.
6.4.1 Microsoft Networking (SMB/CIFS)
Access the video files by the SMB/CIFS protocol on Windows OS.
Run \\NVR_IP from the Windows Start menu. For example, if the NVR IP is
10.11.19.27, enter \\10.11.19.27.
6.4.2 FTP Server (FTP)
Access the recording data by FTP:
In Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Internet Explorer, enter
ftp://username:password@NVRIP. For example, enter
ftp://admin:admin@172.17.26.154 if the NVR IP is 172.17.26.154.
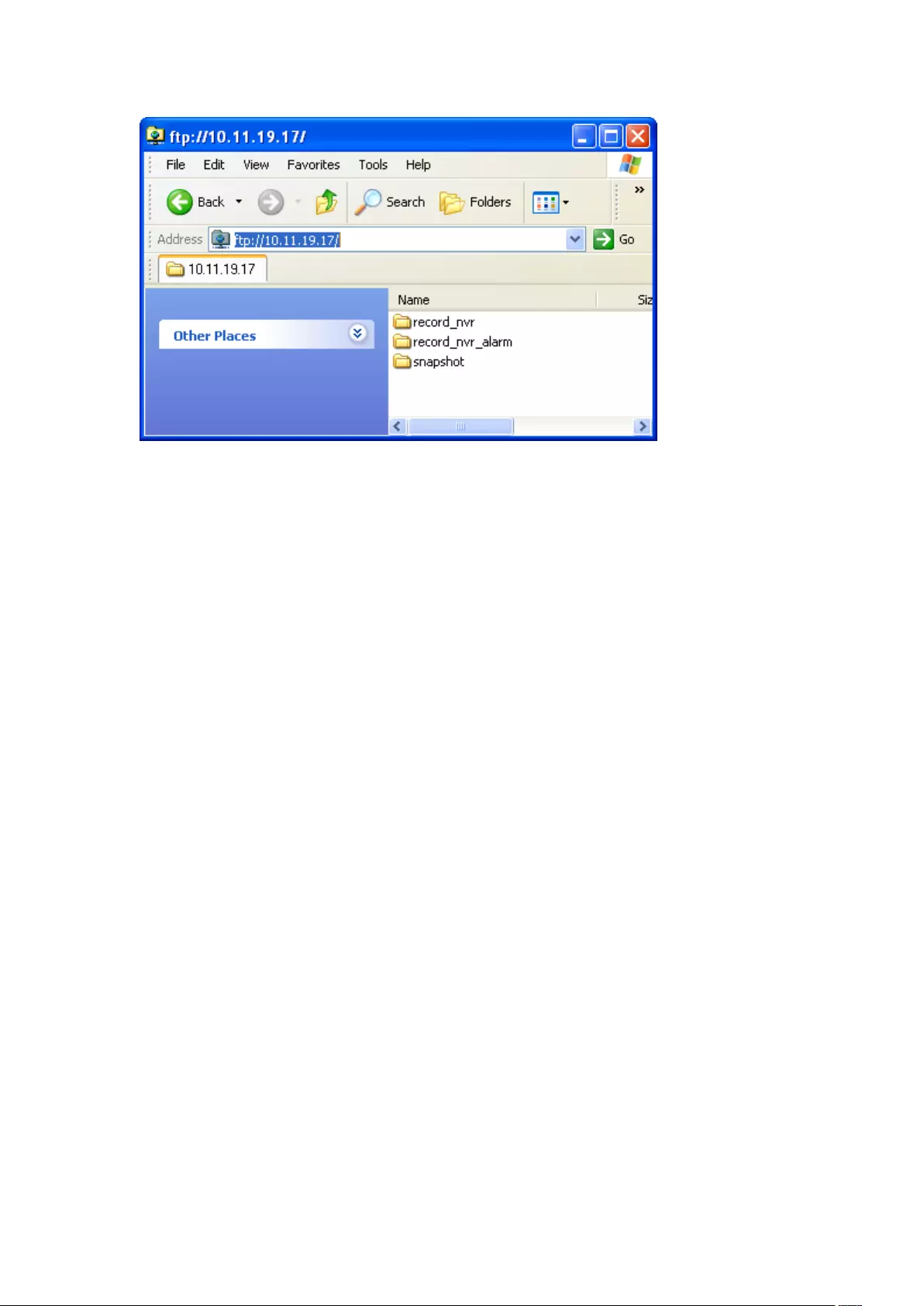
140
Note: You cannot play recording files via double click here.
141
Chapter 7. Surveillance Settings
To enter the surveillance settings page of the NVR, login to the monitoring page as an
administrator and click .
7.1 Camera Settings
7.1.1 Camera Overview
You can view a camera preview and more information, including the camera name, IP
address, connection status, recording setting, days recorded, recording file size, free
disk space, CPU usage and internet bandwidth.
7.1.2 Camera Configuration
You can add/edit a camera’s configuration, export/import a camera's configuration,
modify recording settings, and scheduled recording settings.
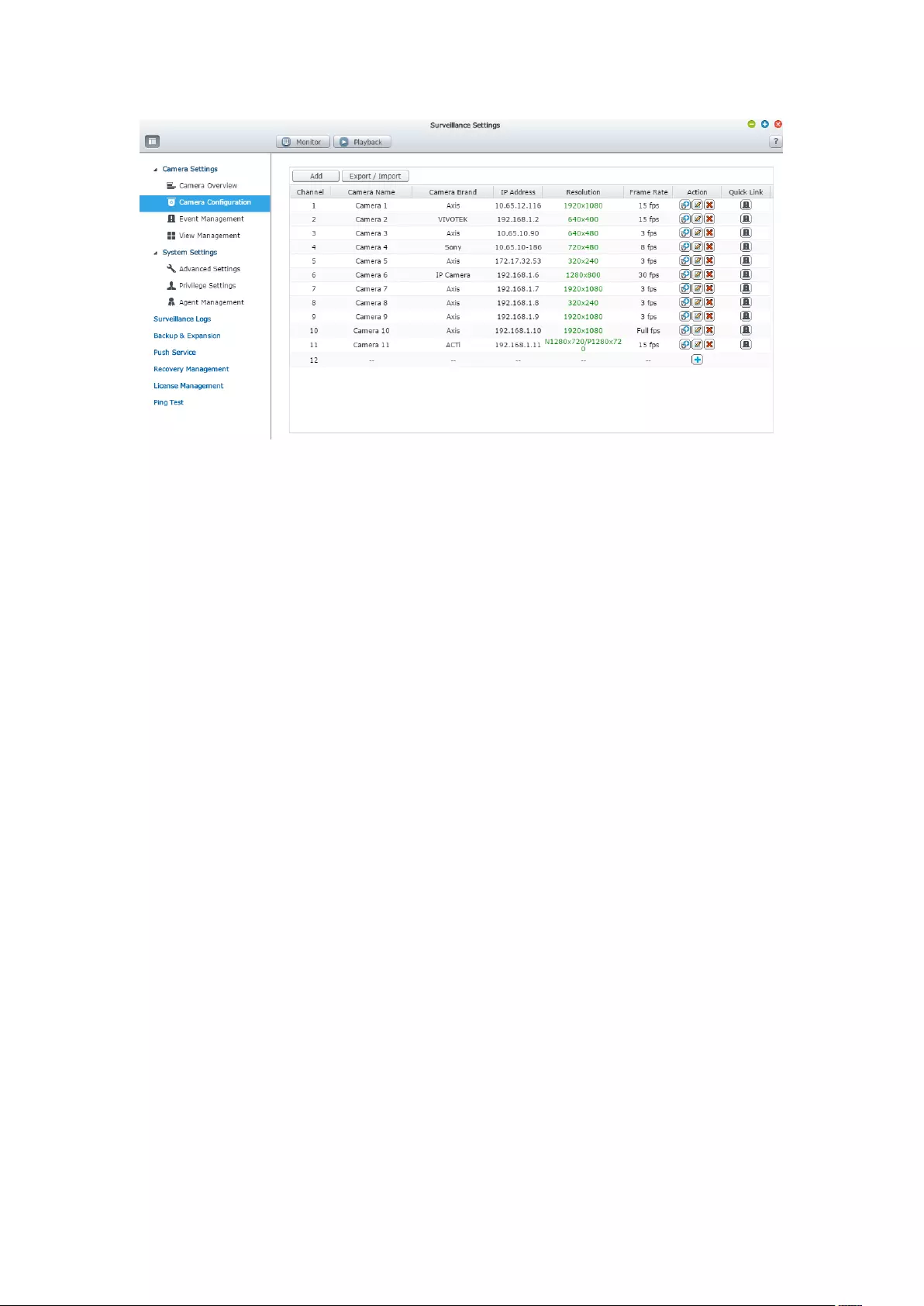
142
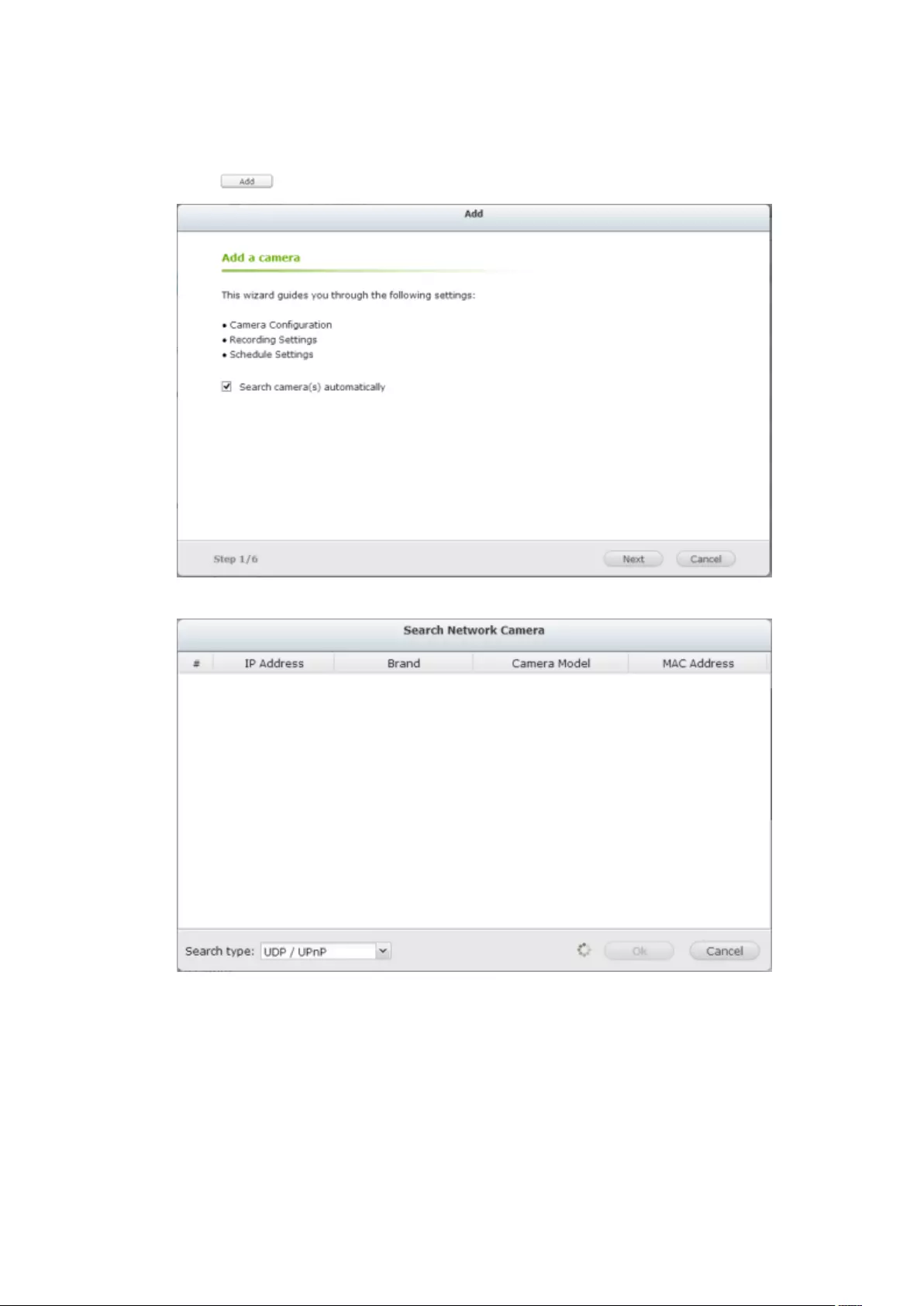
143
Please follow these steps to add a new camera.
1. Click to add a camera.
2. ‘Search camera(s) automatically’ is enabled by default.
You can select the search type: UDP/UPnP or ONVIF.
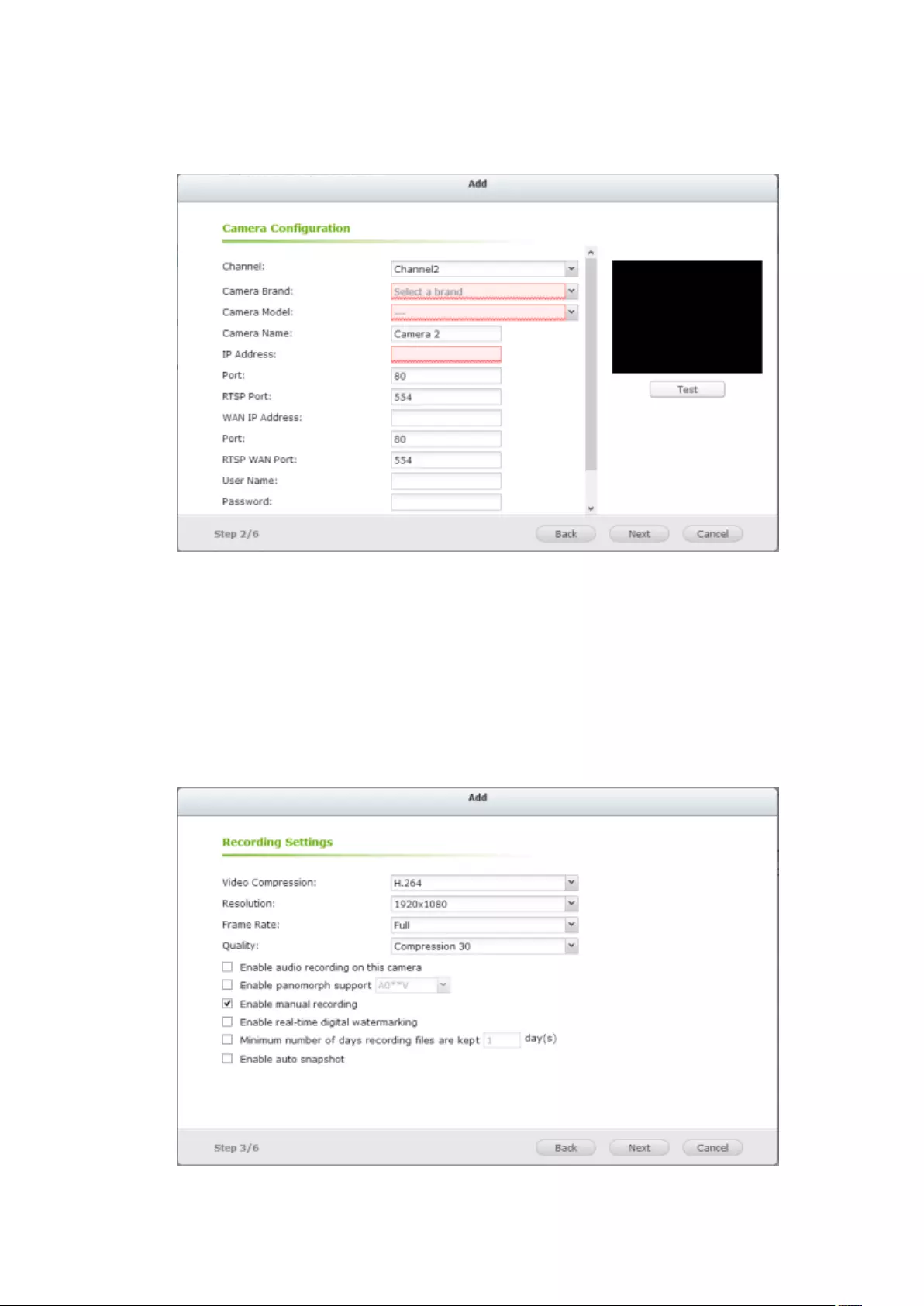
144
3. You can also cancel this search and manually add the camera.
Select the camera brand, model, name, IP address or domain name of the
camera and the user name and the password to login to the camera. And select
whether or not to enable the recording.
The NVR provides an interface for the users to enter the JPEG CGI command of
the IP cameras in order to receive the video and audio streaming data from the
IP cameras and monitor, record, and playback the video of the IP cameras on the
NVR. Please refer to Note 1 for more information.
4. Click ‘Next’ for recording settings.
145
Configure the video compression, recording resolution, frame rate, and quality.
Enable audio recording, manual recording, recording data retention, real-time
digital watermarking, and auto snapshot settings. For further information
regarding cameras that support “User defined Multi-stream” and “Smart
Recording”, please refer to the list described in that section.
A. Multi Stream: You can set the configuration of every stream.
B. Video compression: Choose a video compression format for the recording.
C. Resolution: Select the recording resolution.
D. Frame rate: Adjust the frame rate for the recording. Note that the frame
rate of the IP camera may be affected by network traffic.
E. Quality: Select the image quality for the recording. More disk space is
required to save higher quality recordings.
F. Quality Preview:
Click ‘Quality Preview’ to get a preview of how your videos will look.
You can set video compression, resolution, frame rate and quality and see a
preview picture by clicking ‘Preview’.
You can click the magnifier button to get a larger and clearer preview.
146
When you are happy with your settings, click ‘Apply’ to enable these
camera settings.
G. Audio recording (optional): To enable the audio recording, click ‘Enable
audio recording on this camera’.
H. Enable panomorph support: For the specific camera models with
panomorph lens, you can enable this option.
Note: To know the camera models which can be installed with panomorph
lens, please visit http://www.qnapsecurity.com/faq_detail.asp?faq_id=718.
I. Manual recording: To allow manual activation and deactivation of manual
recording function on the monitoring page, enable this option.
J. Real-time digital watermarking: Enable this option to add digital
watermarks to the video files as soon as they are recorded to the NVR.
Use the Watermark Proof utility to verify if the video files were maliciously
modified.
K. Enable recording data retention: Turn on this function and specify the
minimum number of days to keep the recording data. Note that the
number of days entered here must be smaller than the maximum number
of days to keep all recordings configured in ‘System Settings’ > ‘Advanced
Settings’.
L. Enable auto snapshot: Select this option and the settings will be displayed.
Configure up to 15 schedules for automatic snapshot taking or specify the
number of snapshots (max 60) the NVR should take every hour. The
snapshots are saved to the share folder of the NVR by default. Specify a
remote server to where the files will be saved. Read/write access to the
remote server is required.
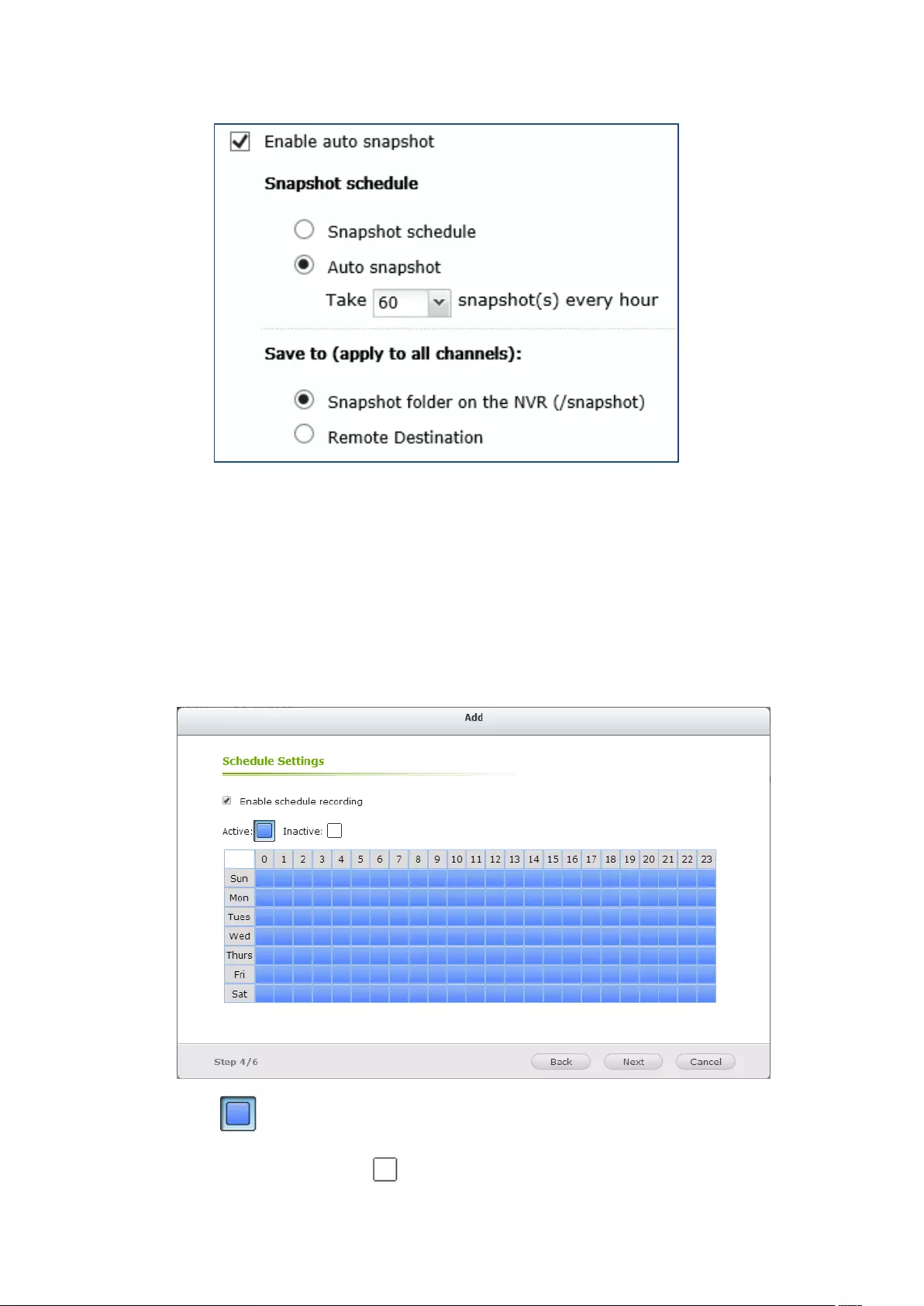
147
M. Edge Recording: When Edge Recording is enabled on VioStor NVR, the
camera can save the recording files on its local storage (such as a SD card)
even when the connection to the NVR suddenly becomes unavailable. After
the connection is resumed, the NVR will check its recording files and
compare the recording schedule set by users. If the NVR detects that
recording files are missing, it will request the camera to upload the missing
part.
5. Click ‘Next’ for schedule settings.
Click and drag on the schedule table to enable scheduled recording for
that period of time. Click and drag on the schedule table to disable
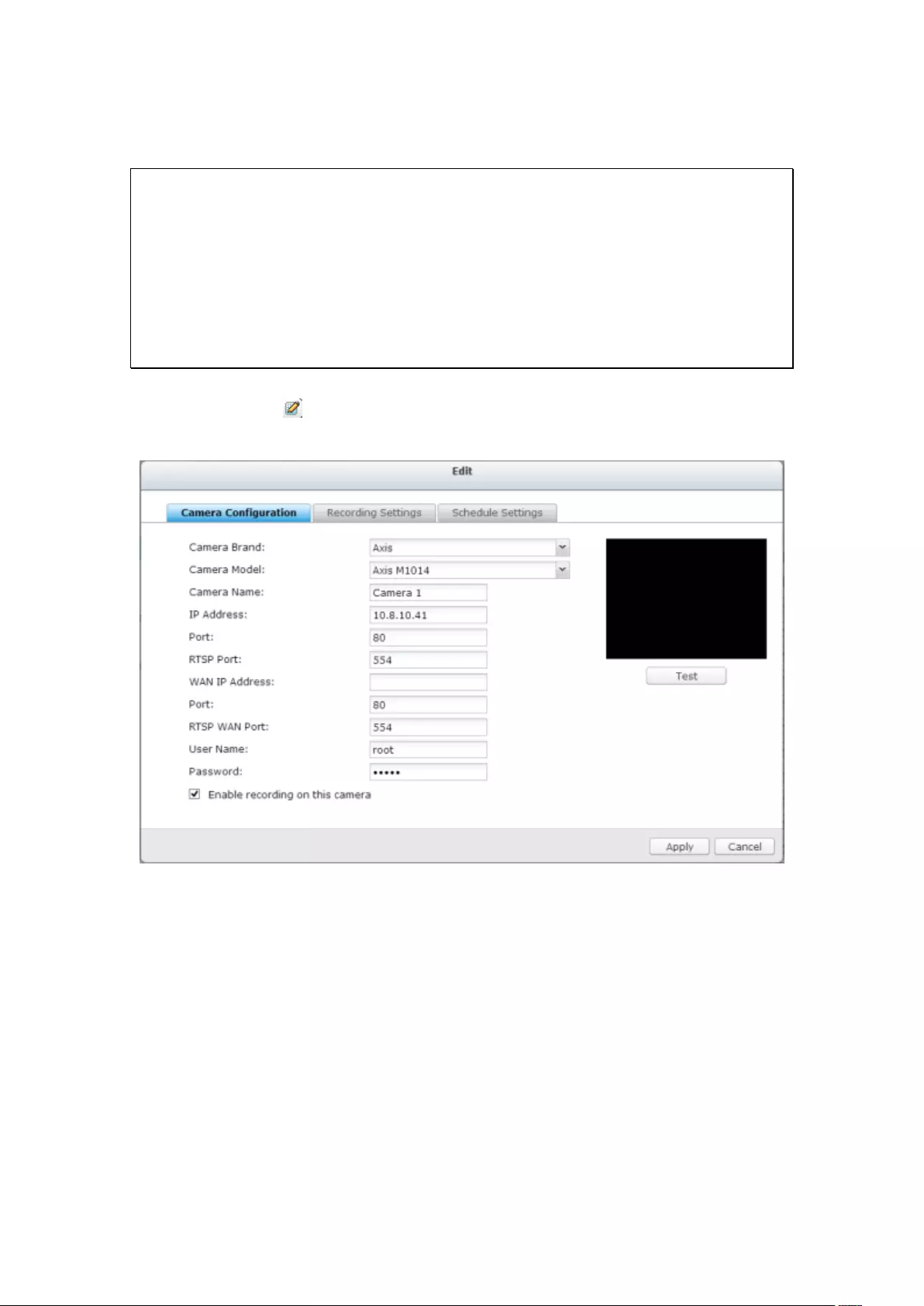
148
schedule recording for that period of time.
Note:
1. Starting and stopping manual recording will not affect scheduled or alarm
recording tasks. They are independent processes.
2. When applying the changes, the recording operation will be temporarily paused
(maximum 1 minute) and then restart.
3. The settings of the snapshot folder are global settings which will be applied to
every channel.
You can then click to edit the camera settings.
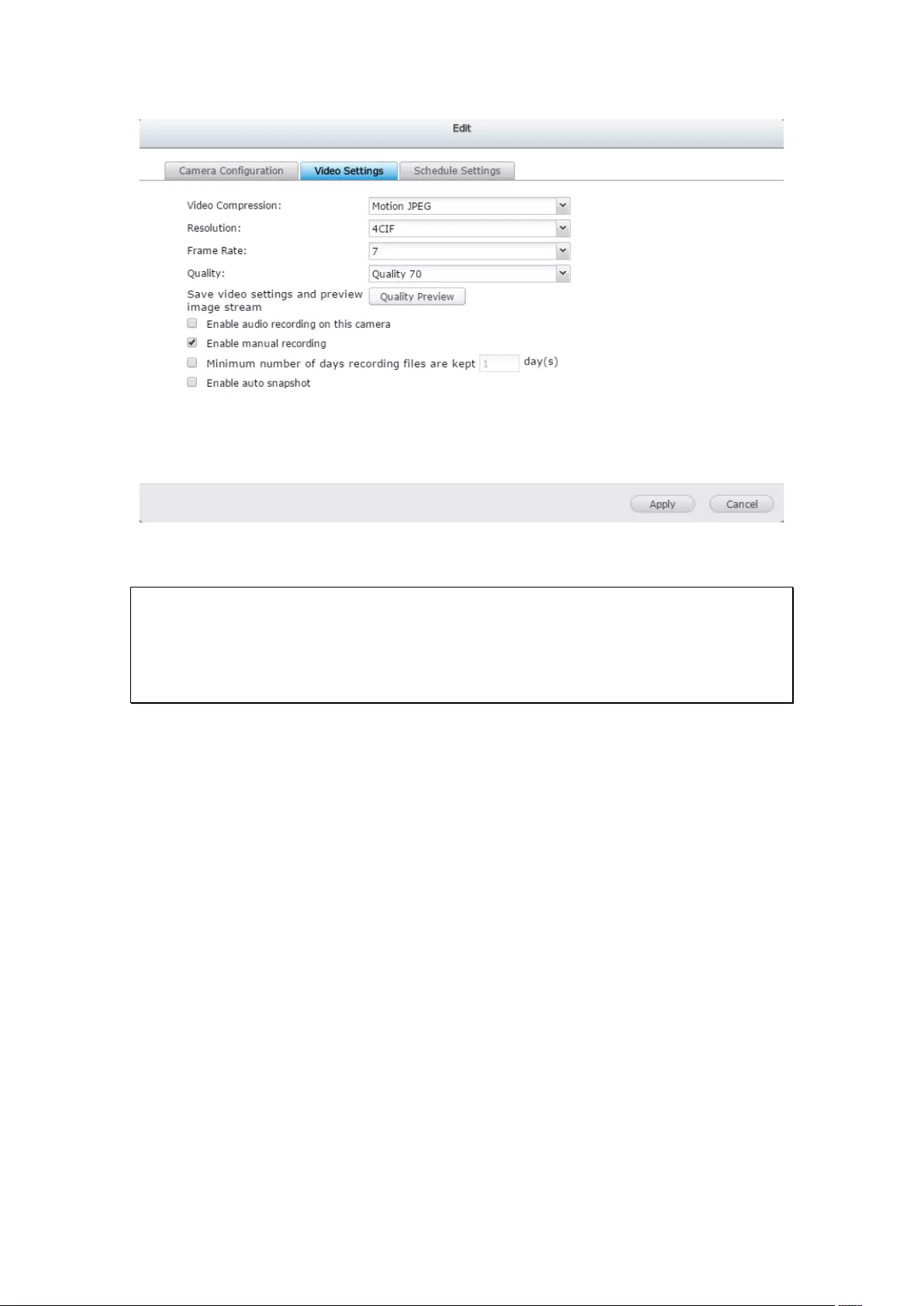
149
Click Apply to apply the settings.
Note:
4. All the settings will not take effect until ‘Apply’ is clicked. When applying the
changes, the recording operation will temporarily stop (for a maximum of one
minute) and then restart.
Export / Import camera settings
This helps you backup and replicate camera settings to another NVR (it must be the
same model).
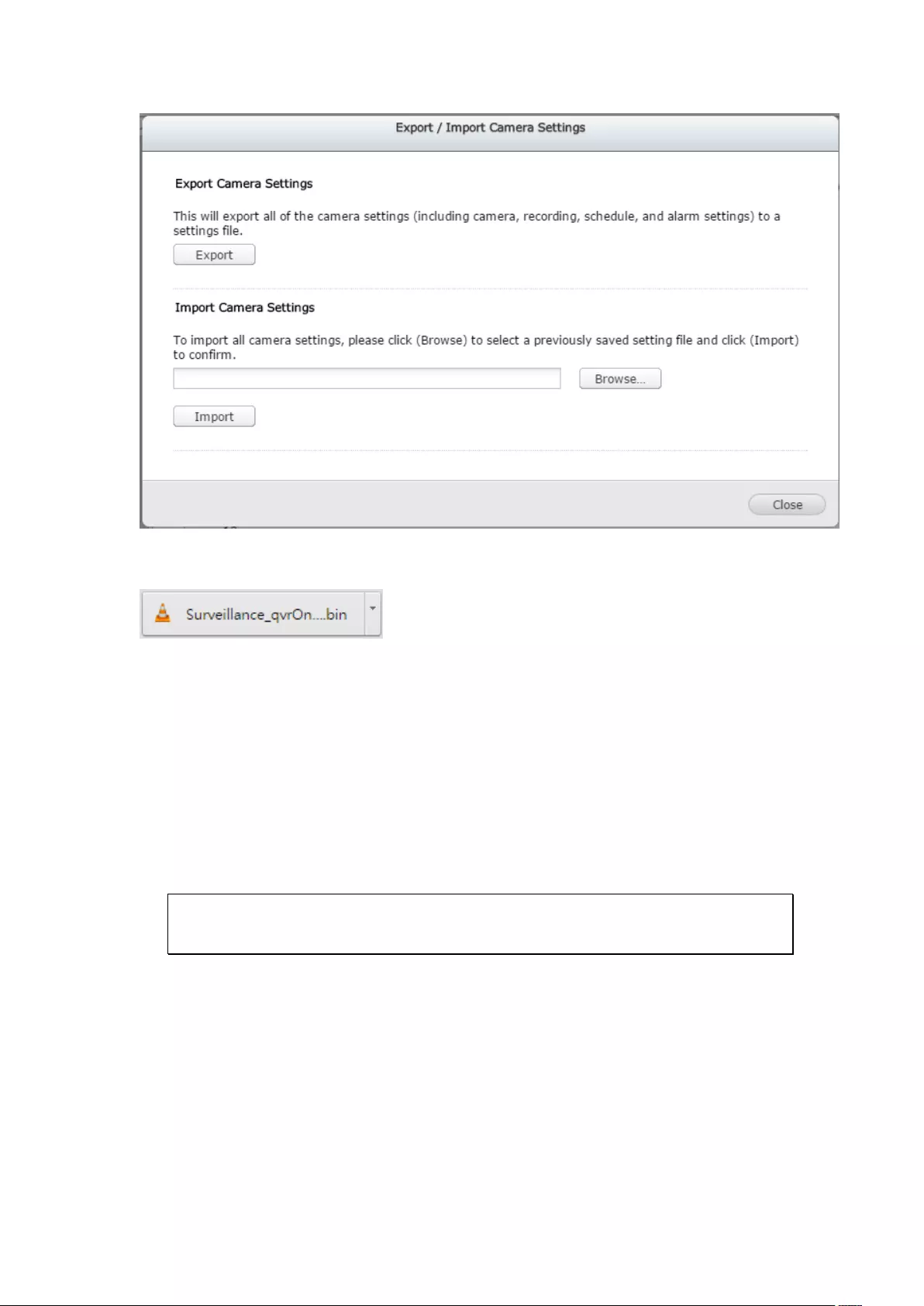
150
The export file name rule is: Surveillance_qvrOnlyBackup_[date].bin
Add generic IP camera support with a CGI command
Follow the steps below to configure the IP camera:
1. Select ‘Generic Model’ for the camera brand.
2. Select ‘Generic JPEG’ for the camera model.
3. Enter the CGI path of the IP camera in the ‘HTTP URL’ field.
4. Enter the camera name or the IP address of the camera.
5. Enter the user name and the password of the IP camera.
6. Select to enable the recording or not.
Note: The NVR only supports JPEG CGI command interface, but does not
guarantee the compatibility with all the IP camera brands.
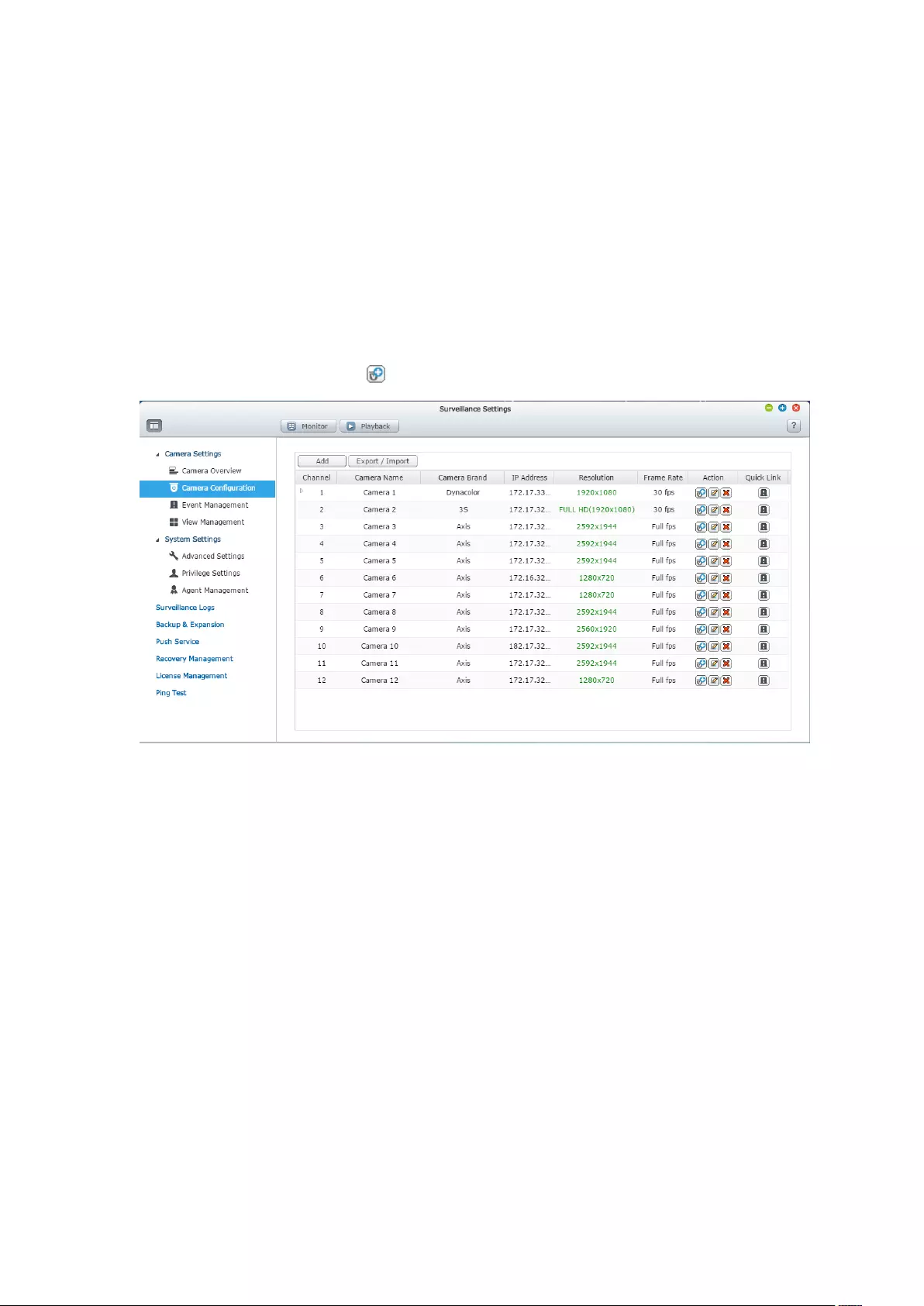
151
Virtual Camera
The era of high-megapixel cameras has come. It not only means clearer and
higher-quality videos, but also a larger coverage area for cameras. You can select an
area of a camera’s field of view as a virtual camera, and also view physical and virtual
cameras from the view management page for easier monitoring.
To add a virtual camera: click after adding a physical camera.
Configure virtual camera
1. Virtual camera name: enter a name for the virtual camera.
2. Virtual camera index: the virtual camera’s number under a physical camera
3. Virtual camera area: you can edit the virtual camera’s area and its size by dragging
the area on the “Edit Virtual Camera Area” window, or by entering values for its area
and size.
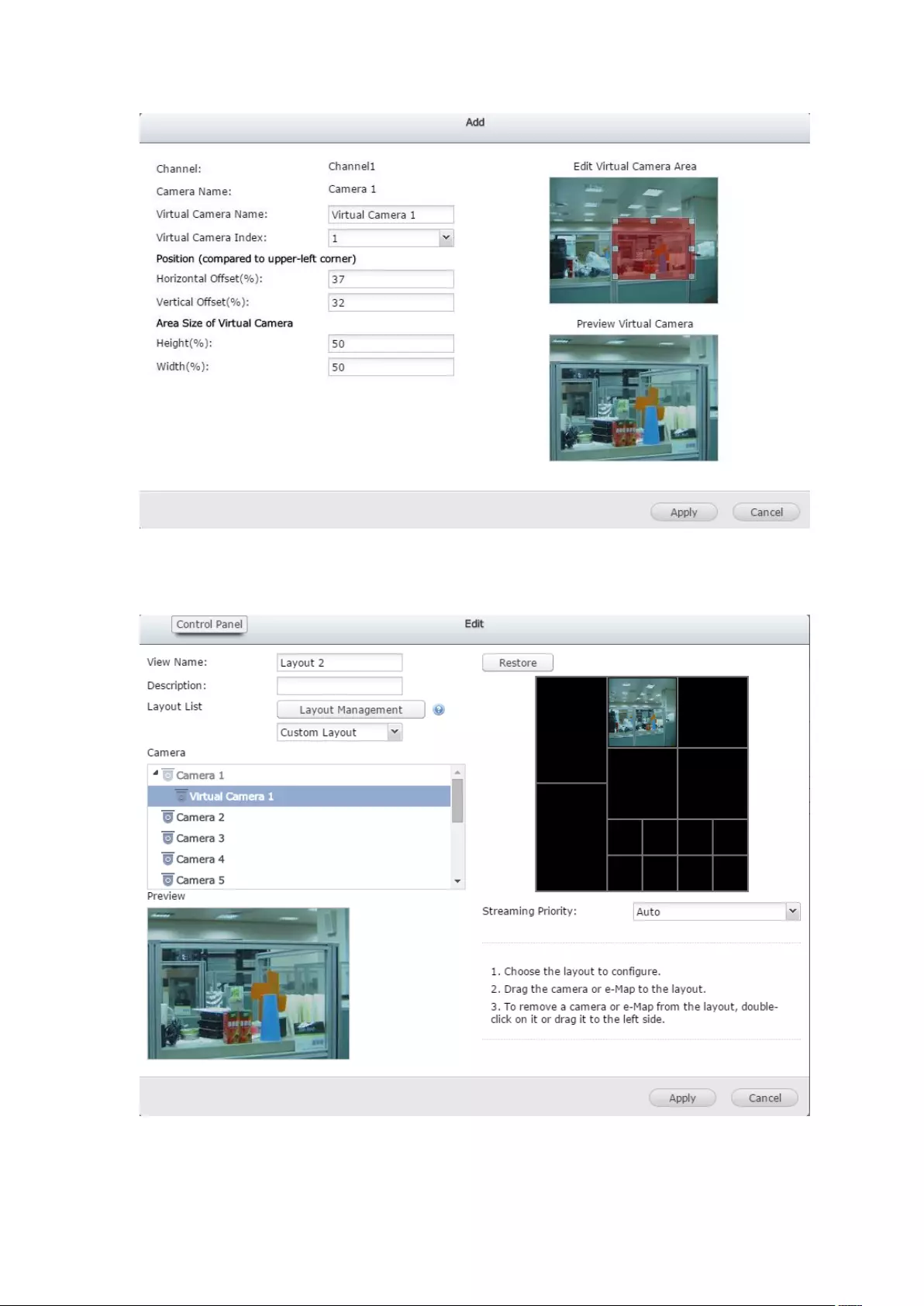
152
Virtual camera’s application
1. In the view management page, you can add a virtual camera to a view.
2. In the monitor page, you can drag virtual cameras into any window to monitor it.

153
User Defined Multi-stream
In the past, users of digital surveillance systems were forced to make a tradeoff
between the video quality of a camera stream and requested bandwidth. The same
camera stream was used for both live view and recording, and more bandwidth was
required if a high quality camera stream was selected. Fortunately, with the
introduction of multi-stream technology, users now can choose the main stream for
recording files and the sub stream for live view.
The multi-stream technology was already supported by VioStor NVR before firmware
154
v4.1.0. However, stream properties such as resolution, frame rate, and compression
mechanism could not be changed by users.
The multi-stream feature in firmware v4.1.0 has been enhanced. Users can configure
stream properties after selecting “User Defined” from the drop-down list on the user
interface, and users can choose stream properties based on their needs.
Please note that in the Multi-Stream Profile, the default value is
“System-Configured”.
Smart Recording
Smart Recording is a powerful feature in the field of digital surveillance as high
quality videos are recorded during an unexpected event, and the low quality camera
stream is used for regular recording. This is extremely beneficial as more details
about an event can be revealed from the high definition camera stream recorded
during that event, and less storage space is consumed comparing to when the high
quality camera stream is used for Round-the-clock recording.
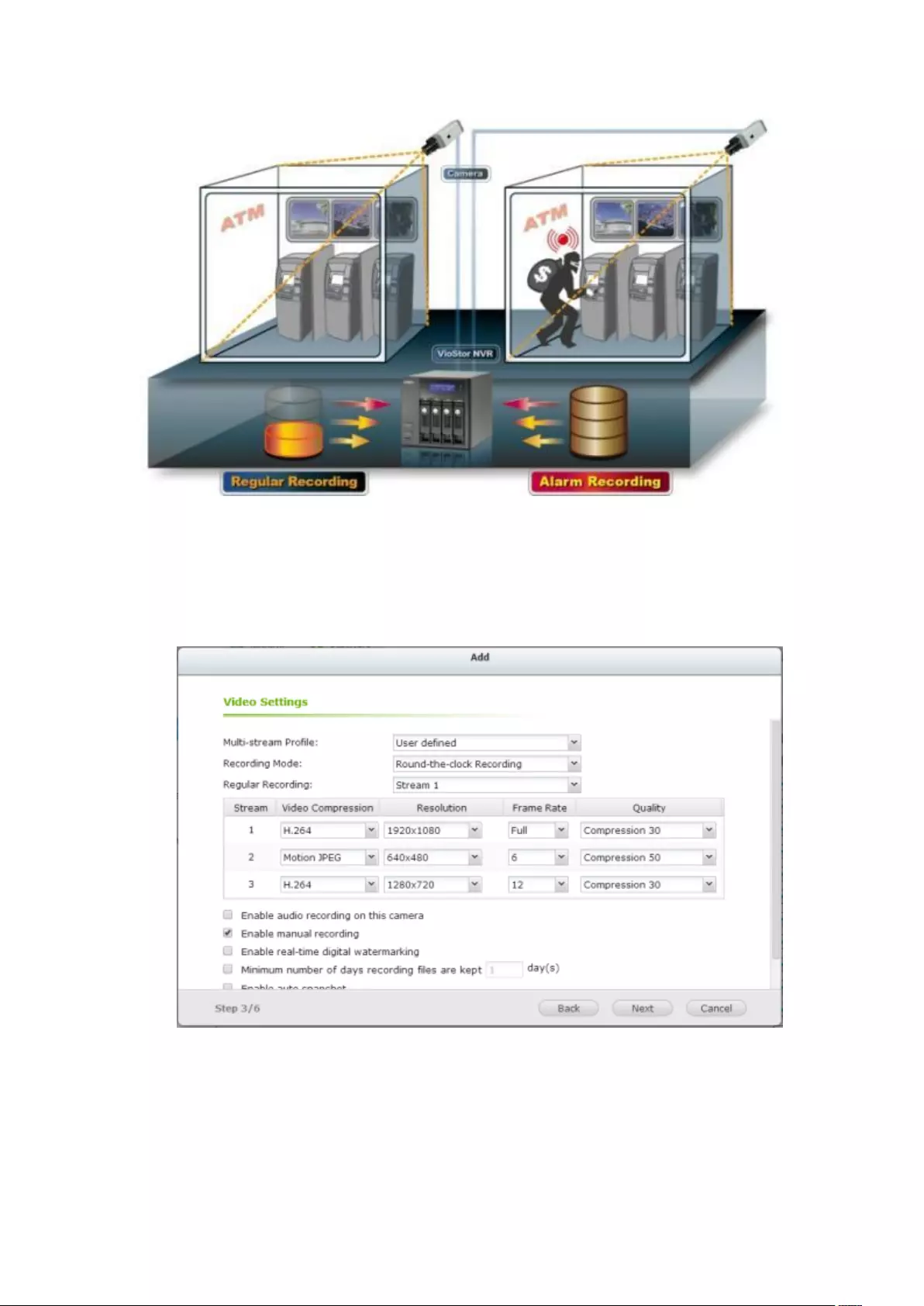
155
The VioStor NVR supports two recording modes: Round-the-clock Recording mode
and Smart Recording mode, and they are described below:
Round-the-clock Recording mode: The same stream from the camera is used for
both regular recording and alarm recording. To use this function, please select
one camera stream from the stream list.
Smart Recording mode: Different camera streams are used for regular recording
and alarm recording. To use this function, please select one camera stream for
regular recording and another for alarm recording.

156
As more cameras will be supported for Smart Recording in the future, please be sure
to check out our camera compatibility list from time to time for your camera
selection.
How to Configure Smart Recording?
1. Go to the “Camera Configure” to add a camera which supports user defined
multi-stream.
2. Click ‘Next’ for recording settings.
3. Select “User defined” from the “Multi-stream Profile” dropdown list.
4. Select “Smart Recording” from the “Recording Mode” dropdown list.
5. Select camera streams for recording modes.
6. Select one camera stream from the “Regular Recording” dropdown list.
7. Select a different camera stream from the “Alarm Recording” dropdown list.
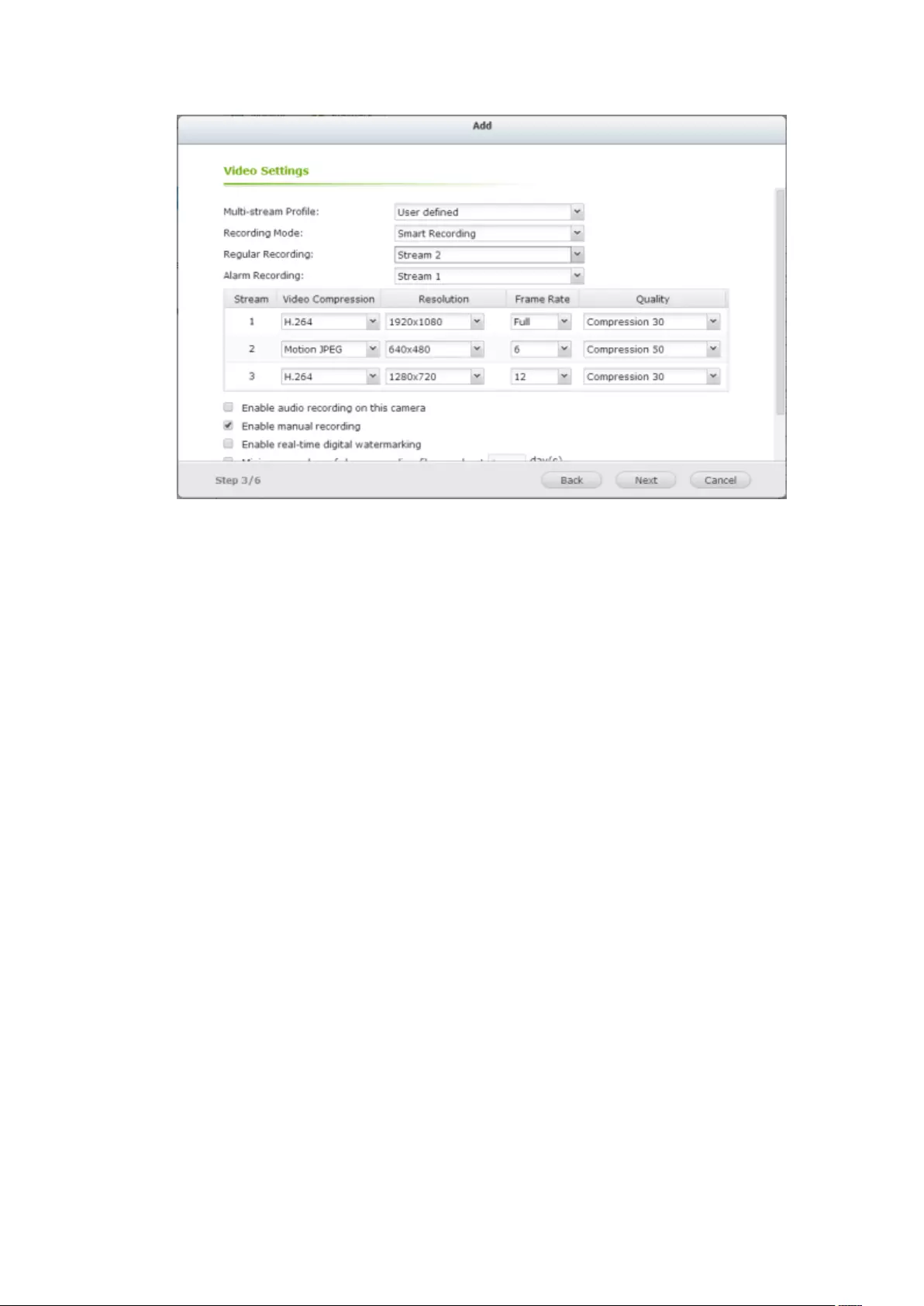
157
Please note: Scheduled Recording and Alarm Recording must be enabled first.
Limitations and Restrictions:
1. A camera stream can only be selected as for either Regular Recording or Alarm
Recording.
2. The number of streams supported and stream properties (such as codec,
resolution, frame rate and quality) vary based on camera models, and the same
property value may not be available as other properties are changed. For
example: if H.264 or Full HD is selected as the video compression setting for
stream 1, users may only be left with M-JPEG or VGA for stream 2. This is a
camera limitation.
3. Please refer to our camera compatibility list for supported camera models.
4. Because more bandwidth is required for Smart Recording, please estimate your
bandwidth usage before using this feature. Take Vivotek IP8132 for example,
this model offers three streams. Stream 1 uses 663Kbps, Stream 2 uses 1000K
bps and Stream 3 uses 3000Kbps (Please refer to Vivotek Video Transmission
Calculator for detail.) The total bandwidth required is 4663Kbps (663K + 1000K +
3000K). If 30 Vivotek IP8132 cameras are connected to a NVR for live view and
Smart Recording is used, at least 133930Kbps bandwidth is required.
158
Edge Recording
How to Configure Edge Recording?
1. Go to the camera settings page.
Before adding this camera to the NVR, please ensure that the camera time is
synchronized with that of the NVR.
The NVR will apply the settings in the edge profile to the AXIS camera
automatically.
The codec setting of videos recovered from Edge Recording is fixed as H.264.
159
After enabling Edge Recording, please check if the camera is recording videos. If
not, please enable “Continuous Recording” and make sure that the SD card is
not full or damaged.
After enabling Edge Recording, please make sure that "Recording Settings" have
been enabled on the camera page and select “NVRedgeProfile” as the stream
profile.
160
Please configure the “Remove recordings older than“ setting for the SD- card.
2. Go to the Camera Settings page.
Please enable Edge Recording.
3. Go to “Surveillance Settings” >“Recovery Management” to configure the
recovery schedule, and check the recovery status and the status of Edge
Recording attempts.
Applied models: AXIS P1343, P1344, P3343, P5534, M5013, Q1602
Limitations and Restrictions:
1. The camera audio function is not supported by Edge Recording.
2. The camera time must be synchronized with the NVR time for this feature to
work.
3. Please refer to the camera user manual to finish related settings on the camera

161
page.
4. Modification of Edge Recording related configuration is not supported on local
display
5. Please make sure that the SD card can function properly and is formatted to
VFAT and not EXT4.
6. The codec setting of videos recovered from Edge Recording is fixed as H.264.
7. Edge Recording will only check and recover recording files in the scheduled
period.
8. Please refer to our camera compatibility list for your camera selection.
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/pro_compatibility_camera.asp
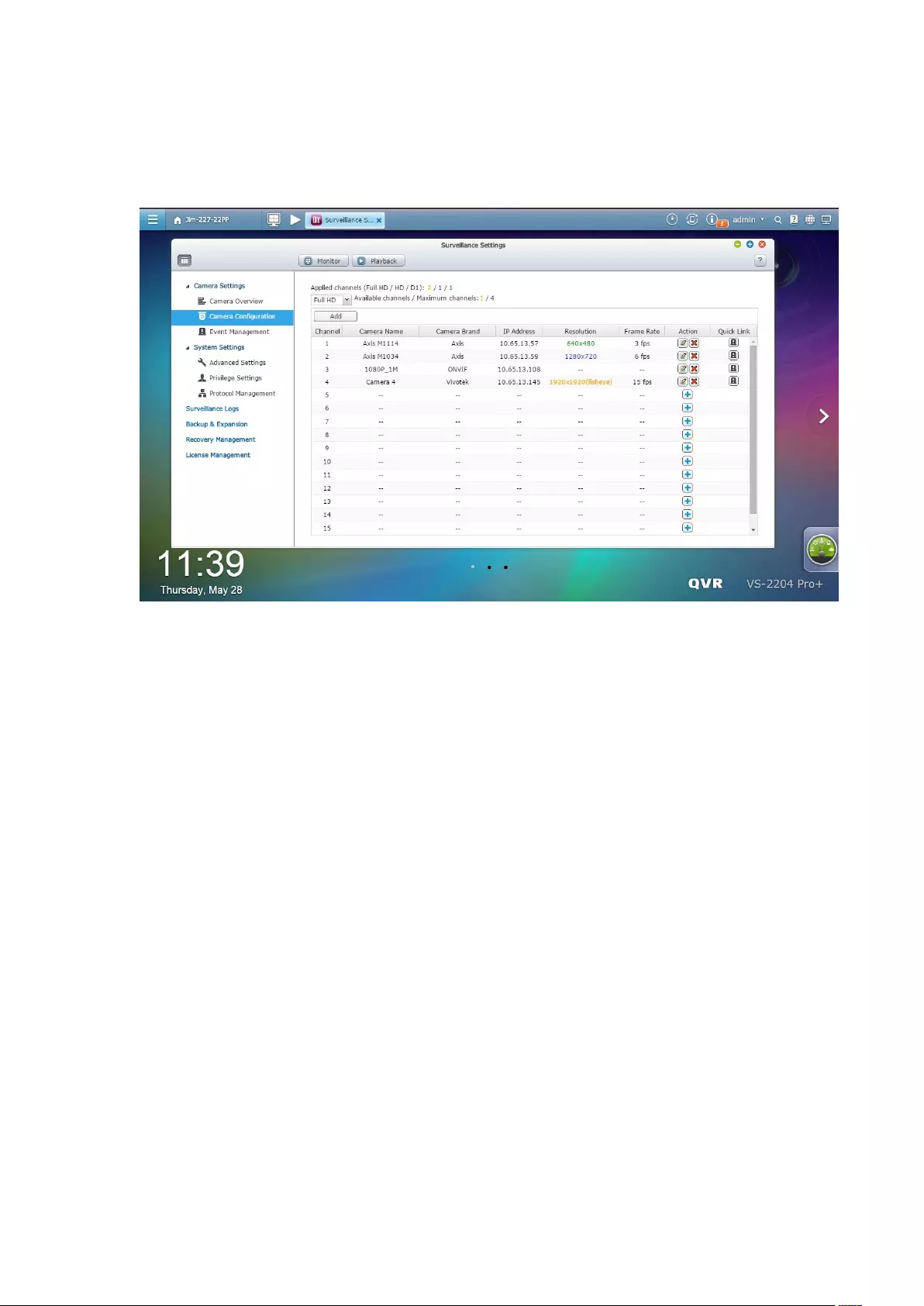
162
7.1.2.1 Flexible Channel Mode
Applicable to the VS-2200 Pro+ series (including VS-2212 Pro+, VS-2208 Pro+,
VS-2204 Pro+). Switch to the flexible channel mode on QVR desktop ->
[Surveillance Settings] -> System Settings] -> [Advanced Settings]
Definitions:
D1 here means the number of channels where the recording resolution is lower than
D1.
HD here means the number of channels where the recording resolution exceeds D1,
but is lower than HD.
Full HD here means the number of channels where the recording resolution exceeds
HD.
Applied Channels (Full HD/ HD/ D1) mean the number of channels where the
recording resolution exceeds HD, exceeds D1, but is lower than HD and will be lower
than D1 respectively
(Full HD/ HD/ D1) Available channels/ Maximum channels mean the number of (Full
HD/ HD/ D1) channels you can add and the maximum number of (Full HD/ HD/ D1)
channels.
Under the flexible channel mode, the number of actual recording channels will vary
depending on the recording resolution of added channels. The system will calculate

163
the number of actual recording channels by using the recording resolution index
automatically. The recording resolution index of Full HD channel, HD channel, and
D1 channel is 4, 2 and 1. The amount of recording resolution indexes of the device
cannot exceed 4 times the number of camera licenses. Taking VS-2212 Pro+ as an
example, after changing to the flexible channel mode, the maximum number of
recording channels will be 48. You can add up to 48 channels with (max) D1
resolution, 24 channels with (max) HD resolution, or 12 channels with Full HD
resolution. Or you can add 16 channels with (max) D1 resolution, 8 channels with
(max) HD resolution, and 4 channels with Full HD resolution.
If you change to the flexible channel mode, some advanced features will be disabled,
such as user-defined multi-stream, smart recording, dual recording, edge recording,
auto snapshot, advanced event management, auto cruising, remote replication,
storage expansion, and Qstart.
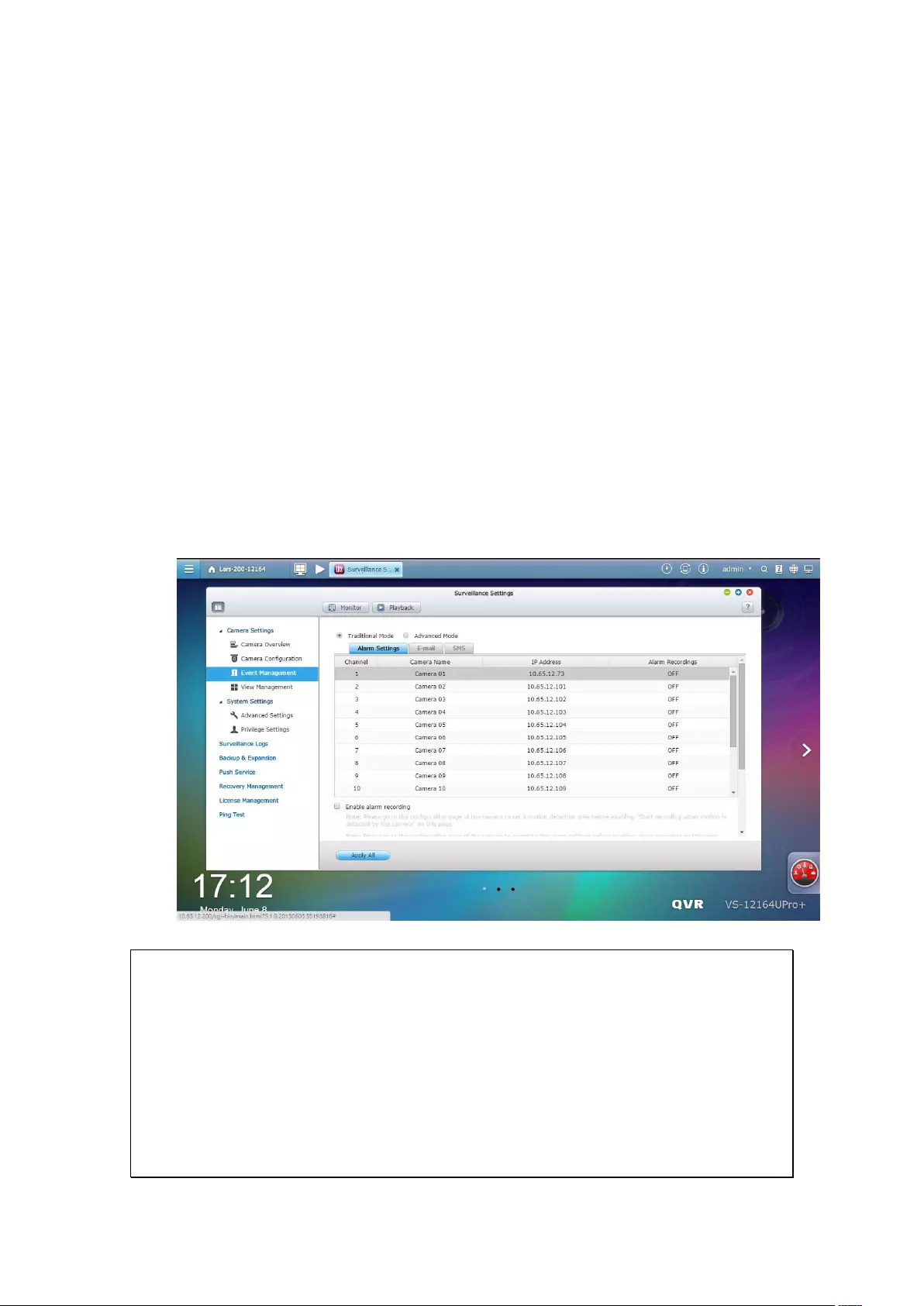
164
7.1.3 Event Management
The NVR provides ‘Traditional Mode’ and ‘Advanced Mode’ for event management.
Select ‘Traditional Mode’ to use the standard alarm settings in response to the alarm
events. To use advanced event management, select ‘Advanced Mode’.
Traditional Mode
1. Alarm Settings
Select a channel (IP camera/video server) on the list and configure the alarm
settings. The video recording will be activated when the alarm input of the
selected channel is triggered or a moving object is detected.
When the option ‘Activate alarm recording only on selected schedule’ is enabled,
the alarm recording will be activated only when the alarm input is triggered or a
moving object is detected within the schedule. To apply the same settings to
all the channels on the list, click ‘Apply to all cameras’.
Note:
All the settings will be effective after clicking ‘Apply’. When applying the
changes, the current recording process will temporarily pause (maximum 1
minute) and then restart.
To avoid blocking by the firewall, the IP cameras or the video servers configured
for alarm recording must be located on the same subnet as the NVR.
To switch from traditional mode to advanced mode, select ‘Advanced Mode’ and
click ‘Go to the settings page’.
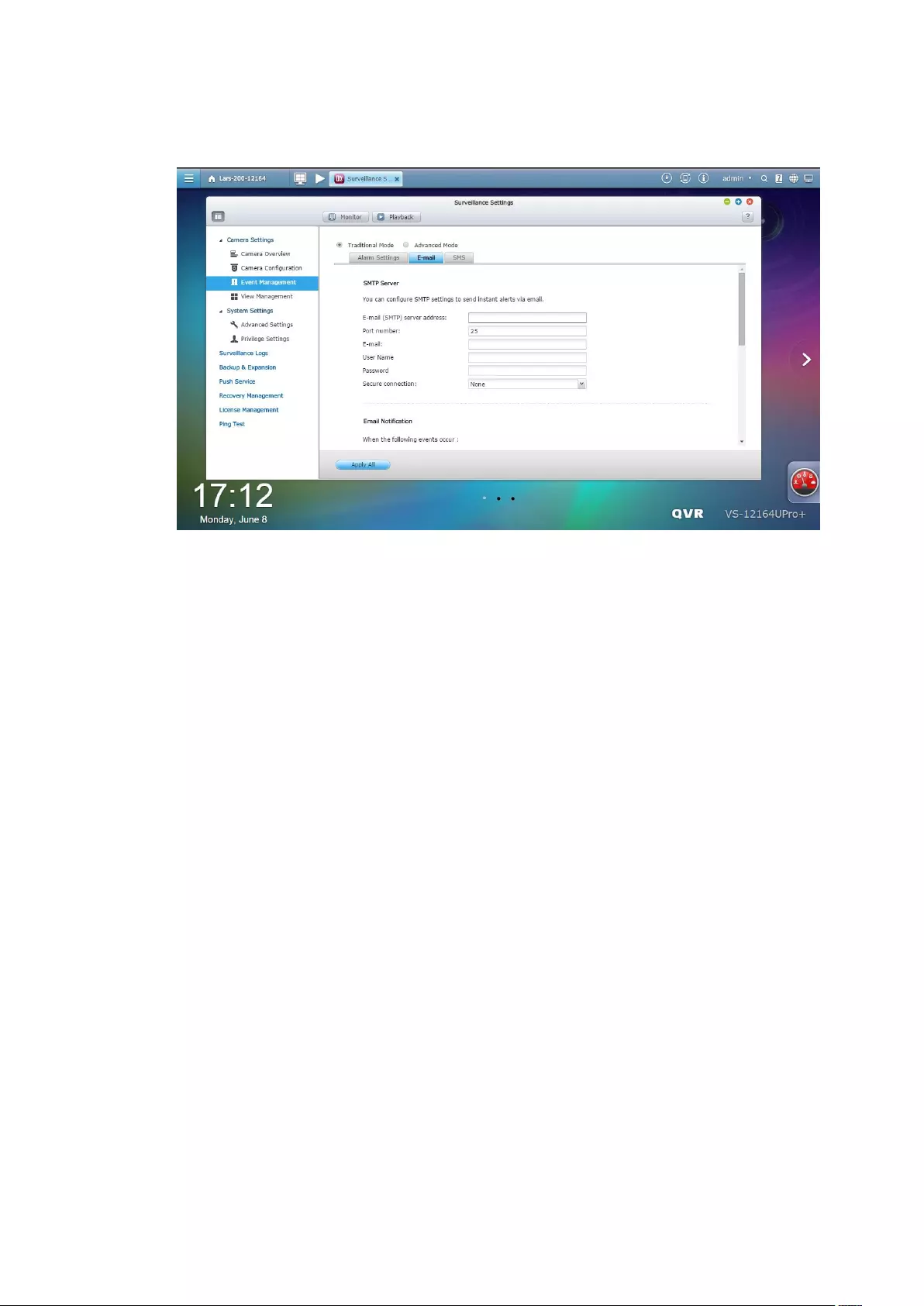
165
2. E-mail
SMTP Server
Supports sending email alerts to inform administrators of system errors and
warnings. To receive email alerts, configure the SMTP server.
E-mail (SMTP) server address: Enter the SMTP server name, for example,
smtp.gmail.com.
Port number: Enter the port number for the SMTP server. The default port
number is 25.
Email: Enter the email address of the person to receive the alerts.
User name and Password: Enter the login information of the email account.
Secure connection: Choose SSL or TLS to ensure a secure connection between
the NVR and SMTP server, or None based on your needs. It is recommended to
enable this function if the SMTP server supports it.
Email Notifications
If you enable notifications for all error alerts, you will (by default) receive
notifications when cameras disconnect and recording failure events occur. If you
enable notifications for all warning alerts, you will (by default) receive
notifications when motion detection and alarm input events occur. You can
toggle notifications for specific surveillance events here.
A maximum of five email addresses are allowed.
Advanced Settings
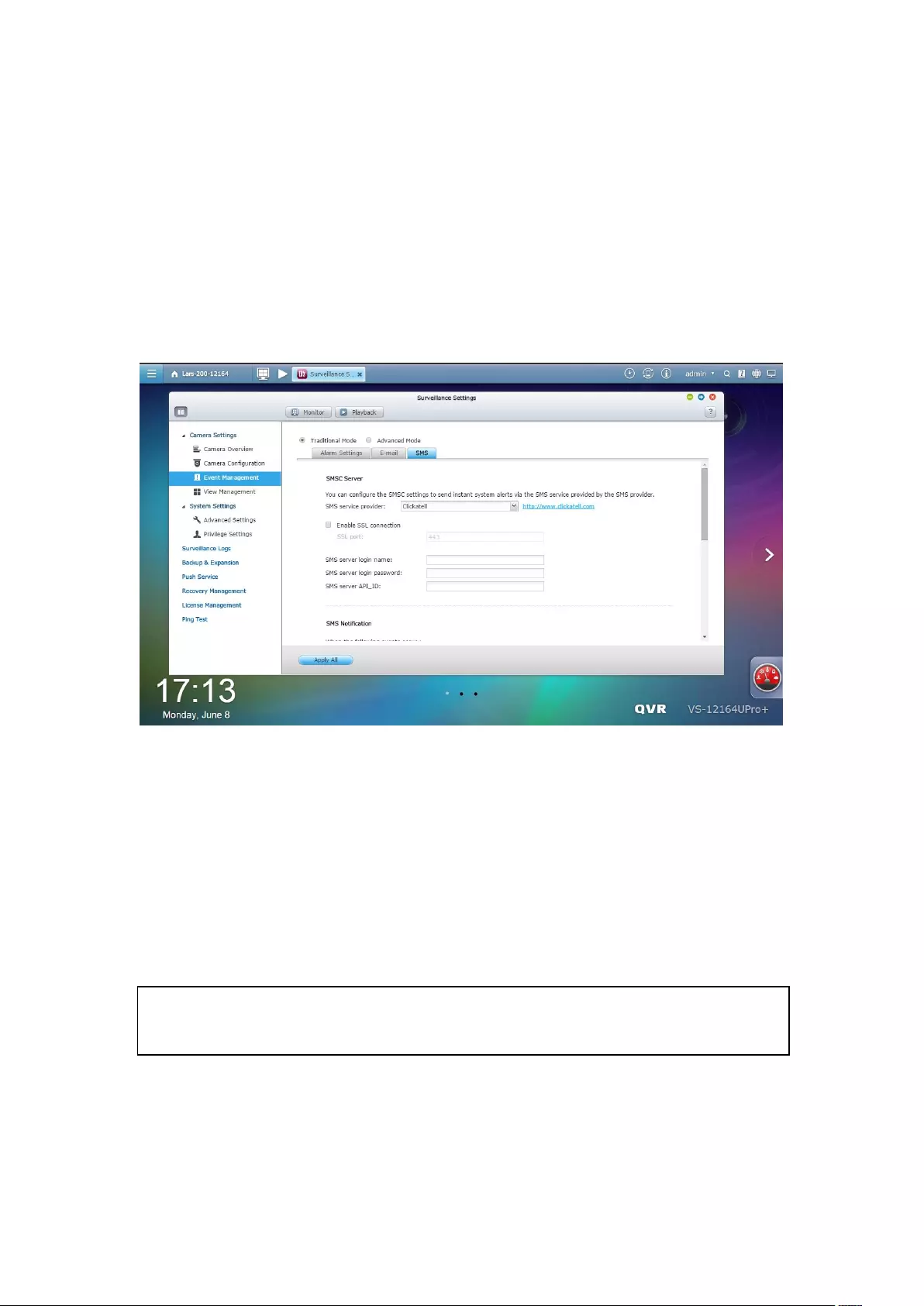
166
To avoid excessive alert emails due to similar surveillance events, you can set a
time period here. After configuration, you will not receive alert emails for
similar surveillance events in the defined period of time.
The settings here, except the notifications for specific surveillance events and
advanced settings, will be synced with [Control Panel] -> [System Settings] ->
[Notification].
3. SMS
SMSC Settings
Configure the SMSC server settings to send SMS messages to the specified
phone number(s) from the NVR. The default SMS service provider is Clickatell.
You can add your own SMS service provider by selecting “Add SMS Provider”
from the drop-down menu.
When “Add SMS service provider” is selected, enter the name of the SMS
provider and the URL template text.
SMS Notification
If you enable notifications for every error alert, you will decide whether you
receive an SMS message when cameras disconnect and recording failure events
Note: The URL template text must follow the standard of the SMS service provider
to receive the SMS alert properly.

167
occur. You can also decide whether you want to receive SMS message when
motion detection and alarm input events occur. You can toggle SMS messages
for specific surveillance events here.
A maximum of two phone numbers are allowed.
Advanced Settings
To avoid excessive SMS messages due to similar surveillance events, you can set
a time period here. After configuration, you will not receive SMS messages for
similar surveillance events in the defined period of time.
The settings here, except the notifications for specific surveillance events and
advanced settings, will be synced with [Control Panel] -> [System Settings] ->
[Notification].
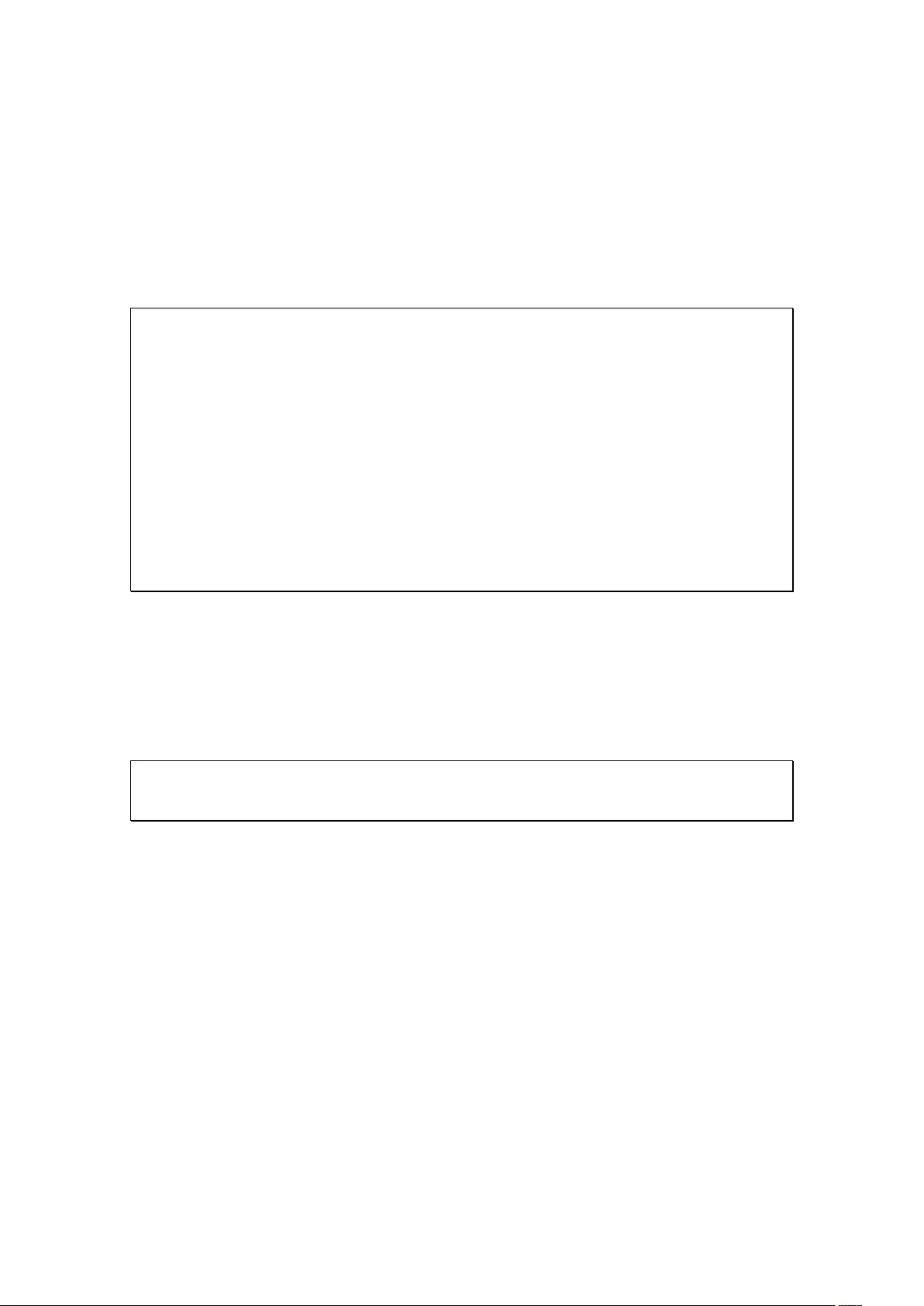
168
Advanced Mode
The advanced mode consists of the event and action sections. Define the action to
take for each event triggered on the IP cameras or the video servers connected to the
NVR.
To configure the advanced event management by the ‘Advanced Mode’, select an
event type on the left event list and configure the actions to take on the right.
Note:
Click ‘Apply’ to apply the settings or ‘Exit’ to exit the settings page. If the
‘Advanced Mode’ is selected on the ‘Alarm Settings’ page, the advanced settings
will be applied after the NVR restarts even if you have selected to exit the settings
page. The settings will be cancelled if ‘Traditional Mode’ is selected after exiting
the ‘Advanced Mode’.
To avoid blocking by the firewall, the IP cameras or the video servers configured
for the alarm recording must be located on the same subnet as the NVR.
To switch from the advanced mode to the traditional mode, select ‘Traditional
Mode’ and click ‘Apply’.
Events:
The events supported by the NVR are classified as camera events (motion detection,
alarm input, camera disconnection), NVR events (recording failure), and external
events (user-defined events).
Note: The camera events available depend on the features supported by the IP
cameras or video servers.
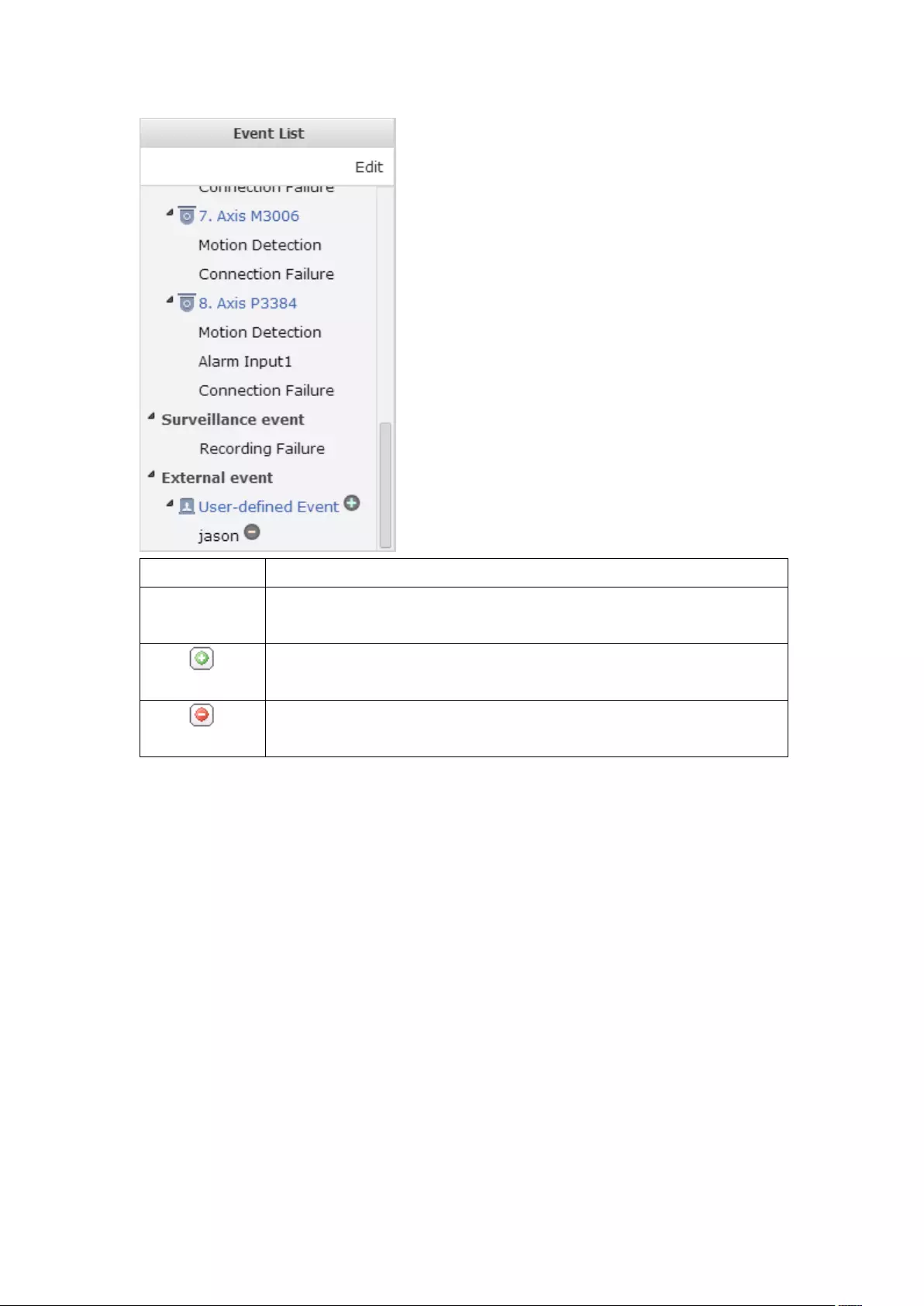
169
Button
Description
Edit
Edit an event. This button cannot be used to edit camera
disconnection.
Add an external event. This button is not applicable to the
camera events and the NVR events.
Delete an external event. This button is not applicable to the
camera events and the NVR events.
The NVR supports the following event types. Before specifying the action settings,
select the events to manage and configure the settings.
1. Motion detection
This option allows the NVR to trigger an action when a moving object is
detected by the IP camera or the video server. Select ‘Camera event’ from the
‘Event List’. Locate the channel and click ‘Motion Detection’. Next, click the
edit button, enable this option, configure the settings, and click ‘Apply’. Set
the schedule to define the active period of the alarm settings and define the
action on the right (discussed in the later sections).
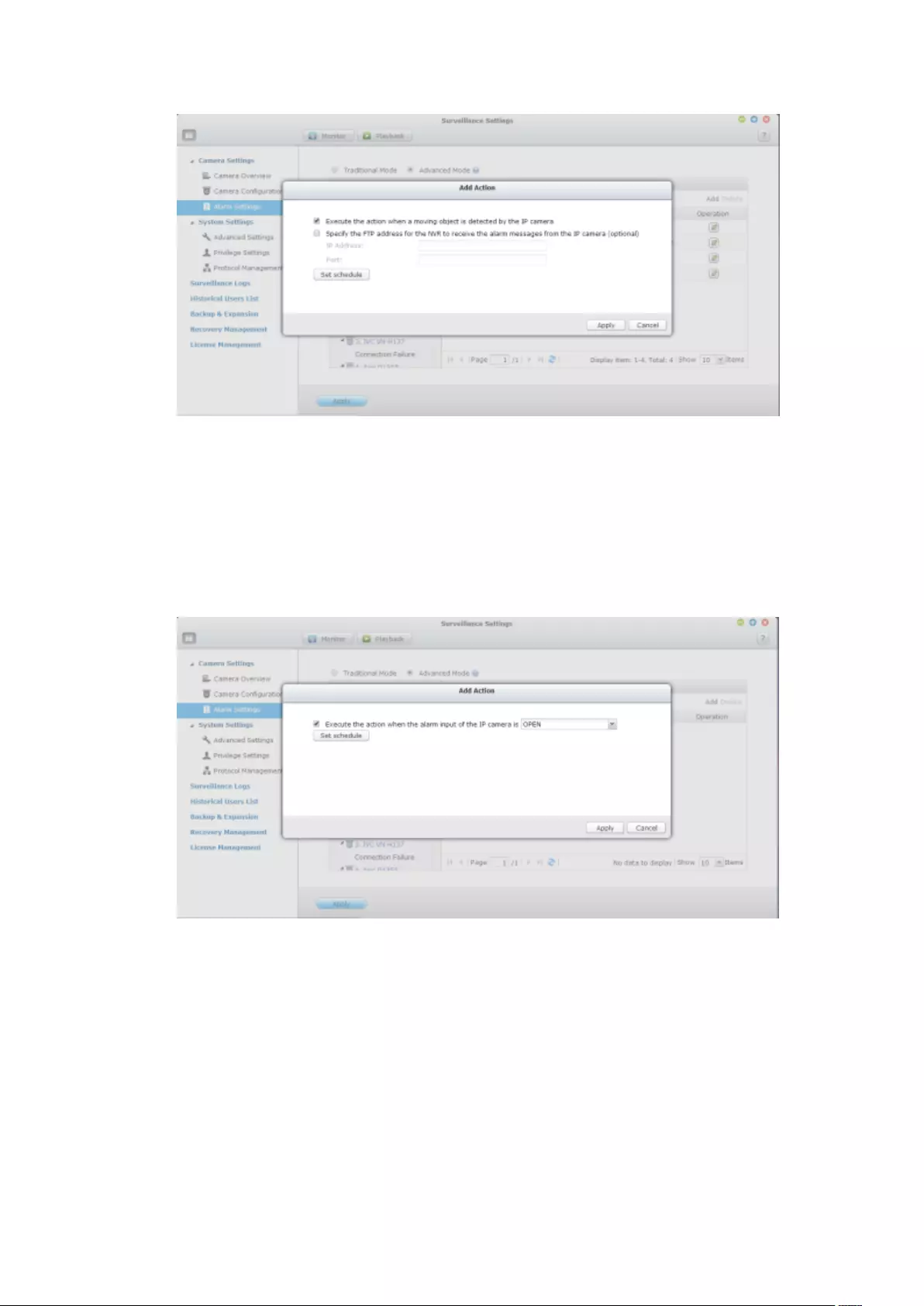
170
2. Alarm input
This option allows the NVR to trigger an action when the alarm input of the IP
camera or the video server is triggered. Select ‘Camera event’ from the ‘Event
List’. Locate the channel which supports alarm input and click ‘Alarm Input’.
Next, click the edit button, enable this option, configure the settings, and click
‘Apply’. Set the schedule to define the active period of the alarm settings.
After that, define the action on the right (discussed in the later sections).
3. Alarm event
The alarm input and the motion detection settings of some IP cameras or video
servers may be combined together and called ‘Alarm Event’ on the Event List.
Edit the event settings and define the action on the right (discussed in the later
sections).
4. Connection failure
This option allows the NVR to trigger an action when the IP camera or the video
server is disconnected. Select ‘Camera Event’ from the ‘Event List’. Locate
the channel and click ‘Connection Failure’. After that, define the action on the
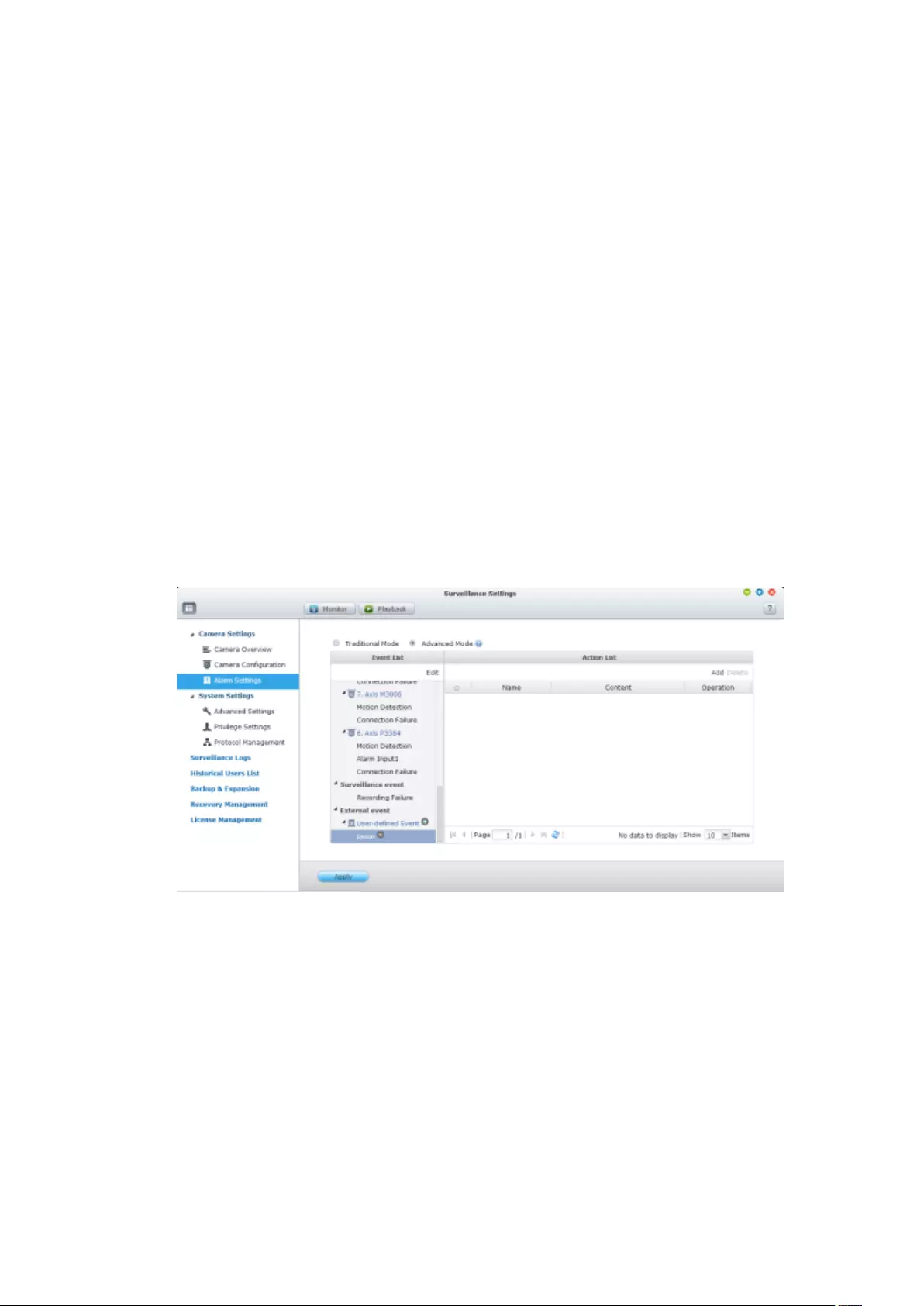
171
right (discussed in the later sections).
5. Recording failure (NVR event)
This option allows the NVR to trigger an action when the video recording of the
IP camera or the video server fails due to the hard disk bad blocks, file system
crash, or other reasons. Select ‘NVR event’ from the ‘Event List’. Click
‘Recording failure’. Then define the action settings on the right (discussed in
the later sections).
6. External event (user-defined events)
To create a self-defined event on the NVR, select ‘User-defined Event’ under
‘External event’ on the ‘Event List’. Then click the + button. Enter the event
name, for example, ‘door’.
After creating an event, click the event name and define the action on the right
(discussed in the later sections). After configuring the action settings, enter
the CGI command (including the self-defined event name) in the web browser to
trigger the action anytime. The format of the CGI command is:
http://NVRIP/cgi-bin/logical_input.cgi?name=event-name. For example,
http://10.8.12.12:80/cgi-bin/logical_input.cgi?name=door
Event schedule settings:
When editing an event (not including camera disconnection, NVR events, and
external events), click ‘Set Schedule’ to define when the alarm settings will be active.
To create a new schedule, select ‘New’ and enter a schedule name. The schedule
supports a maximum of 25 characters (double-byte characters, spaces, and symbols
are allowed). Select the day and time when the alarm settings should be active.
Click + to add a schedule; or – to delete a schedule. Up to 6 settings can be defined
for each schedule.
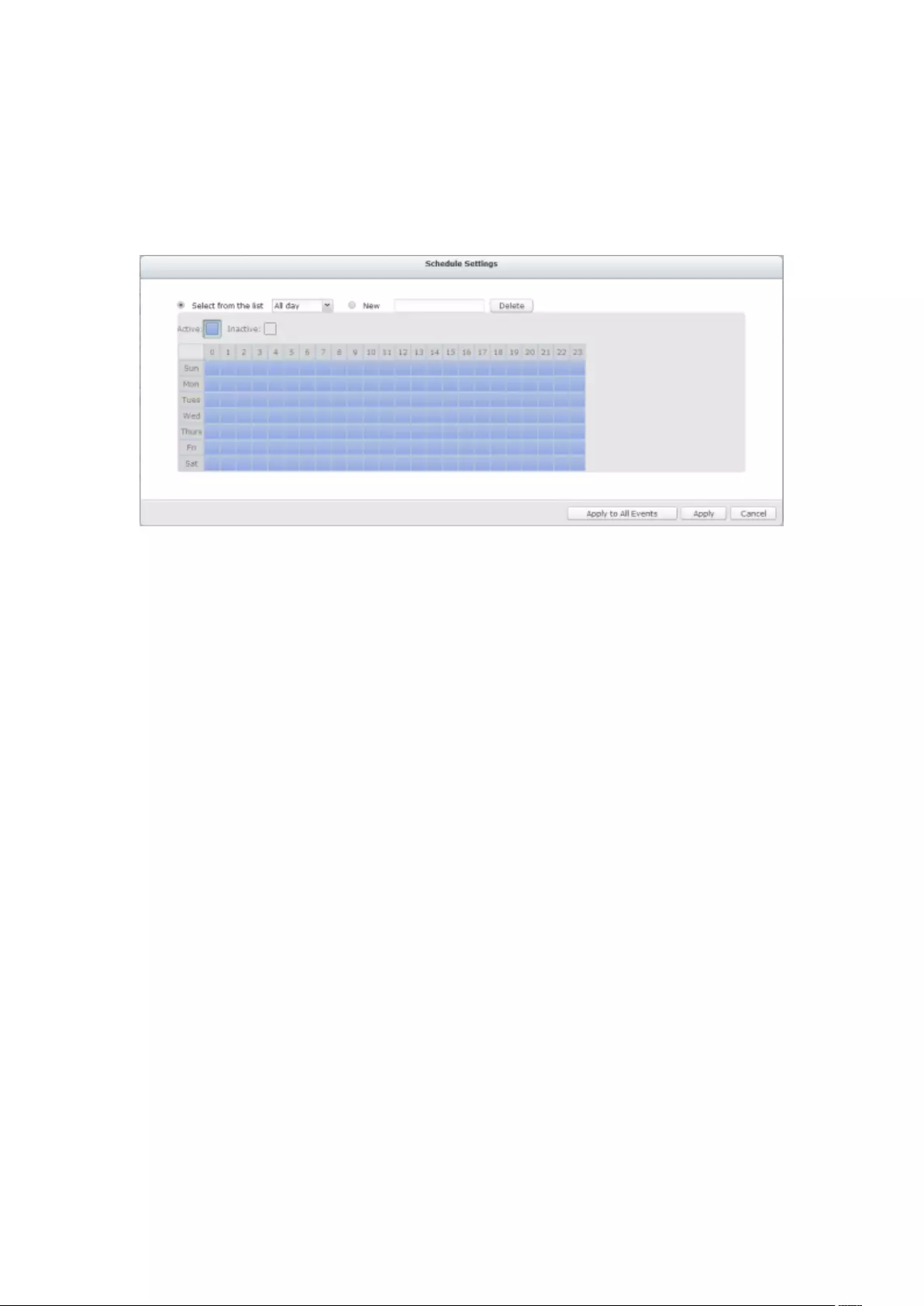
172
The settings will be shown on the graphical table. Click ‘Apply’ to save the settings.
To use the same schedule for all the events, click ‘Apply to All Events’. Select to use
the default schedule or a formerly created schedule from the list. The default alarm
settings are active all day, every day.
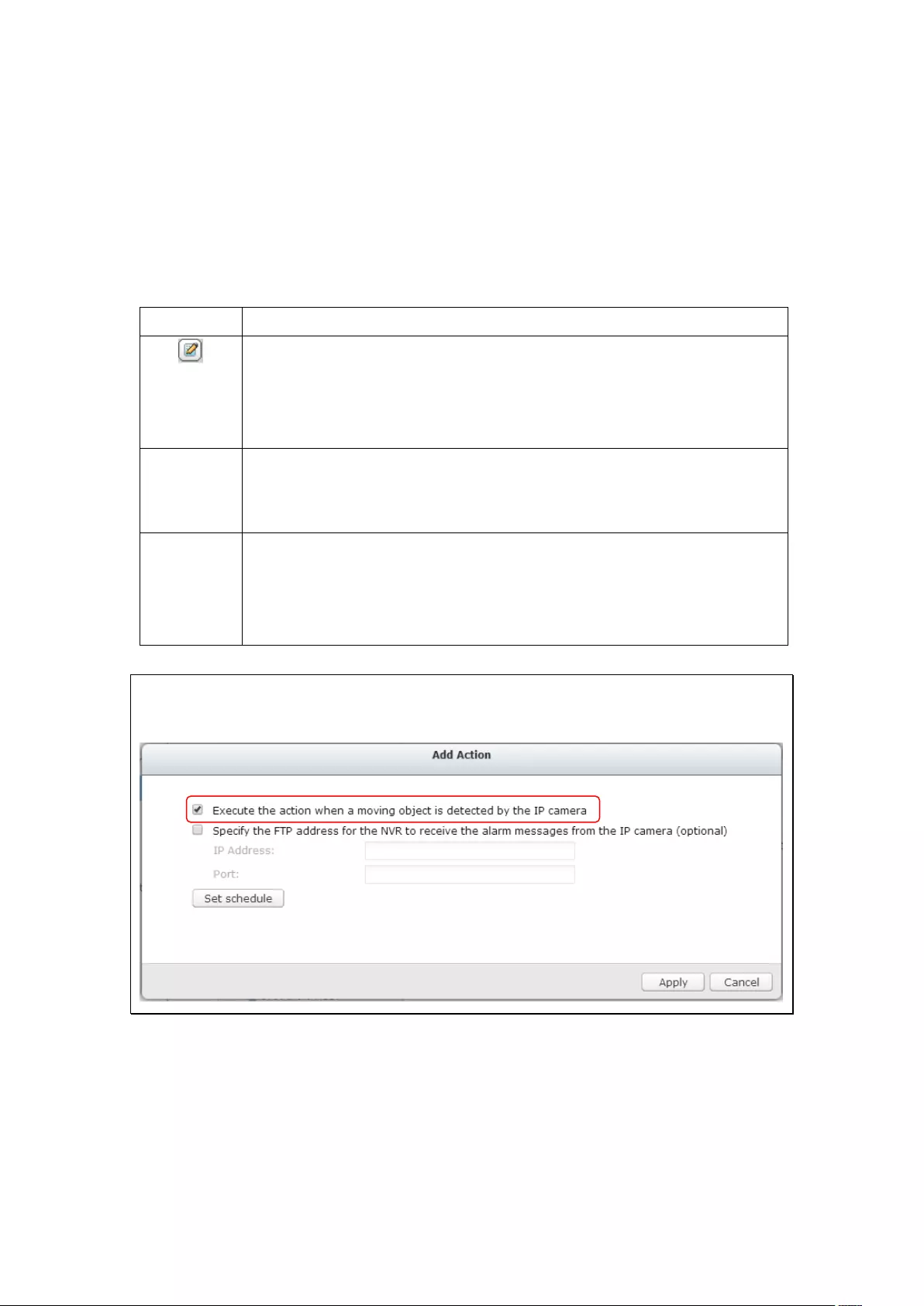
173
Actions:
The NVR supports different actions which can be activated when the selected events
are triggered on the IP cameras or the video servers. The actions include video
recording, email alert, SMS alert, buzzer, PTZ camera control, alarm output, and logic
output.
Button
Description
Edit an action:
Select an event on the left. All the actions defined for this event will
be shown. Select the box in front of the action name to edit. Then
click this button on the ‘Action’ column to edit the action settings.
Add
Add an action:
After configuring an event on the left, click ‘Add’ to create an action in
response to the event. Click ‘Apply’ to save the settings.
Delete
Delete an action:
Select an event on the left. All the actions defined for this event will
be shown. Select the box in front of the action name to delete and
click ‘Delete’. Multiple actions can be deleted.
Note: Please ensure the action in the event settings has been enabled; otherwise the
action will not be executed.
1. Recording
Select the channels (IP cameras or video servers) which will start recording
when an event occurs. The following options are also available:
A. Enter the time (in seconds) the recording should be executed after the
event has been triggered.
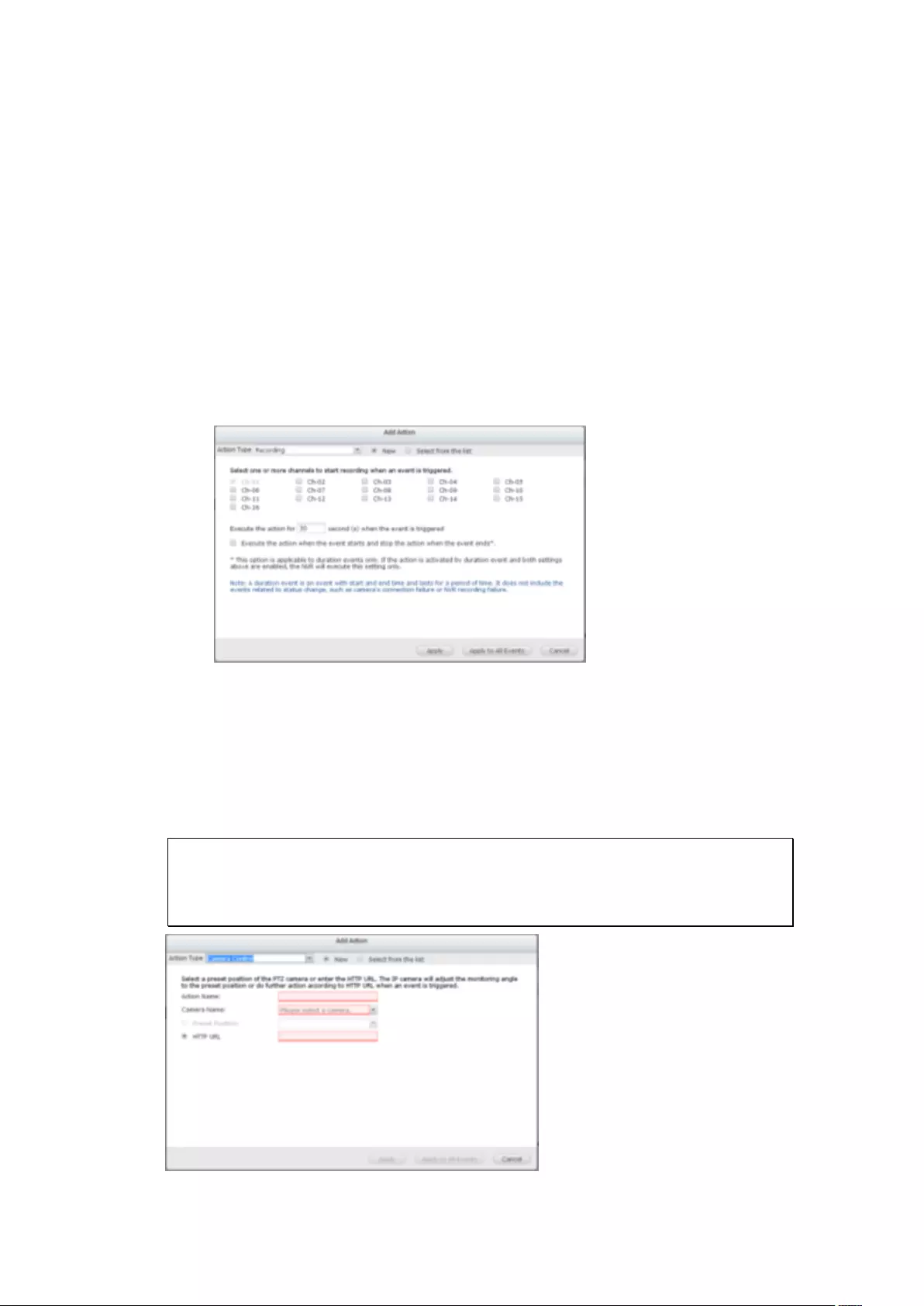
174
B. Start recording when the event starts and stop recording when the event
ends.
Option (ii) is applicable to duration events only. A duration event is an
event with a start and end time and lasts for a set period of time. It does
not include the events related to status changes, such as a camera
disconnection or NVR recording failure.
If the action is triggered by a duration event and both settings (i, ii) are
enabled, the NVR will execute the second setting (ii) only.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been
configured before.
2. Camera control
Configure the PTZ camera to adjust to the preset position for monitoring or act
according to the HTTP URL entered when an event is triggered. Select a preset
position from the drop-down menu or enter the HTTP URL.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been configured
before.
Note: The preset names will appear only after the preset settings of the PTZ
cameras have been configured.
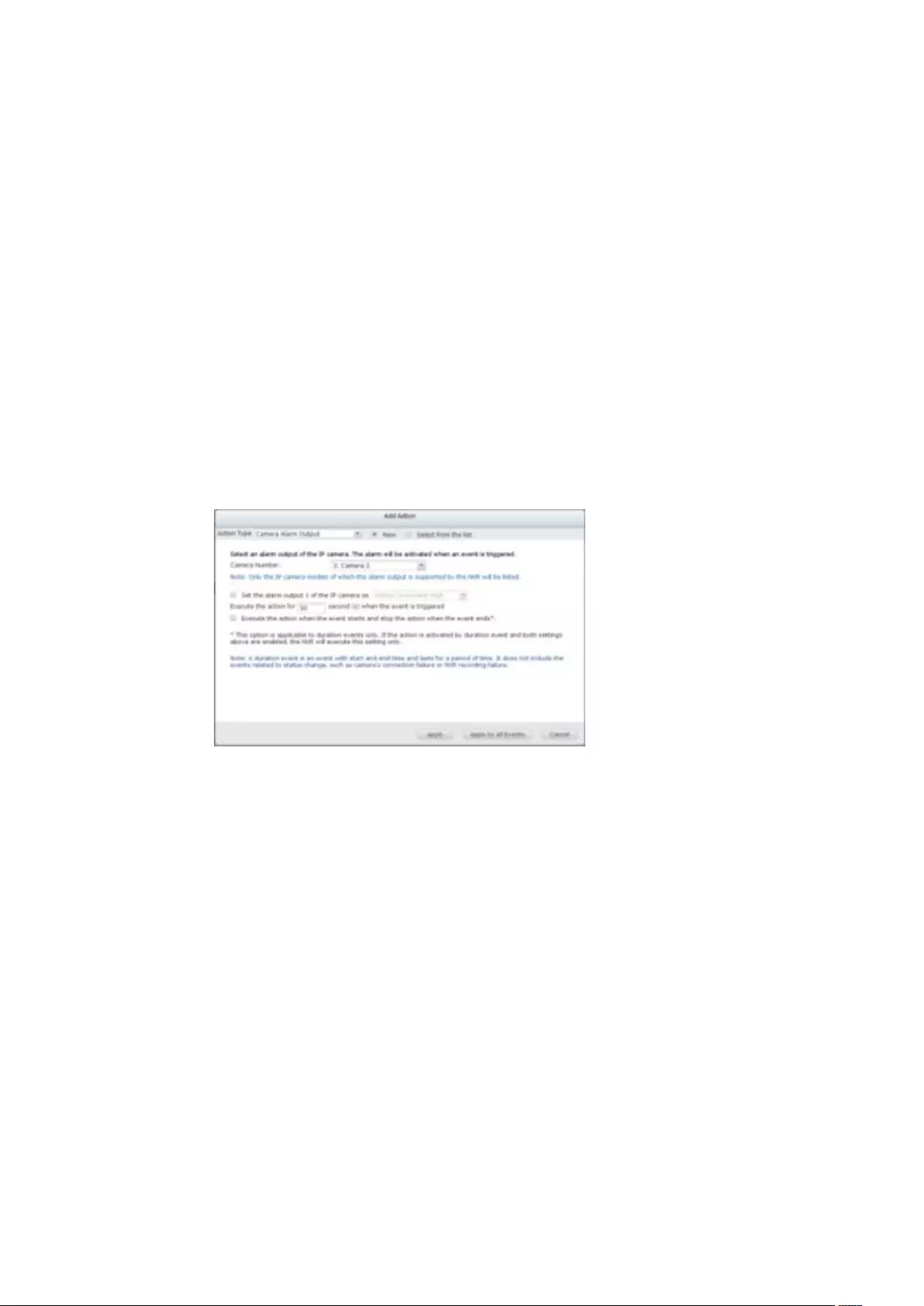
175
3. Alarm output
Select to activate the alarm device connected to the IP camera when an event is
triggered. The following options are available:
A. Enter the number of second(s) the alarm device will be active for when the
event is triggered.
B. Activate the alarm device when the event starts and stop the alarm device
when the event ends.
The option (ii) is applicable for duration events only. A duration event is
an event with a start and end time and lasts for a set period of time. It
does not include the events related to status change, such as a camera
disconnection or NVR recording failure.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been
configured before.
4. Email
To receive an instant email alert when an event is triggered, enter the SMTP
settings. Multiple email addresses can be entered as the recipients.
Snapshots of multiple channels (IP cameras/video servers) can be attached to
the alert emails.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been configured
before.
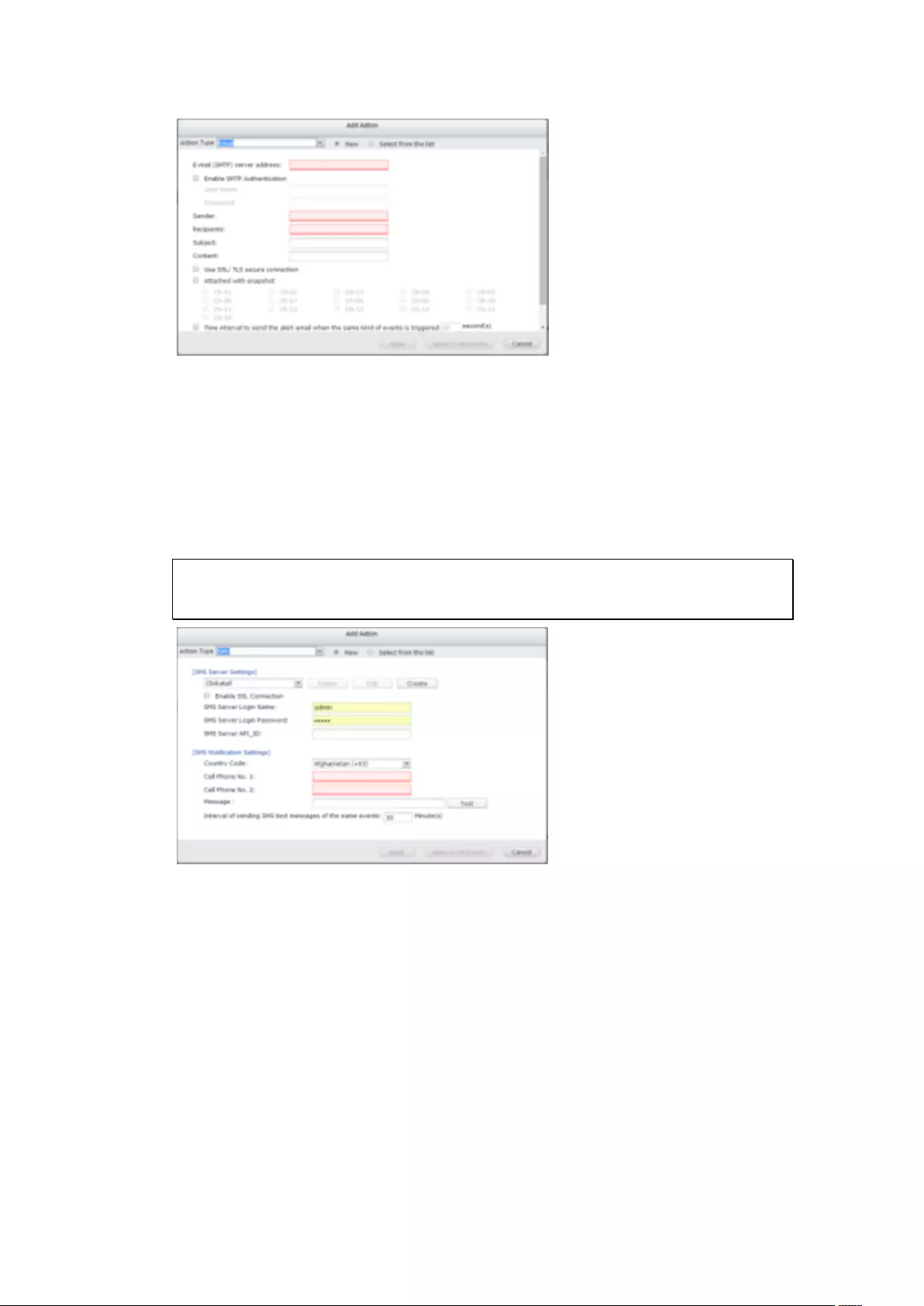
176
5. SMS
To allow the system administrator to receive an instant SMS alert when an event
is triggered, enter the SMS server settings. The default SMS service provider is
Clickatell. To add other SMS service providers, click ‘Add’ and enter the
provider's name and the URL template text.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been configured
before.
Note: Always follow the standard of the SMS service provider to receive the
SMS properly.
6. Buzzer
Enable the buzzer when an event is triggered. The following options are also
available:
A. Enter the time (in seconds) the buzzer will sound when the event is
triggered.
B. Execute the buzzer when the event starts and stop the buzzer when the
event ends.
The option (ii) is applicable to duration events only. A duration event is an
event with a start and end time and lasts for a set period of time. It does
not include the events related to status change, such as a camera
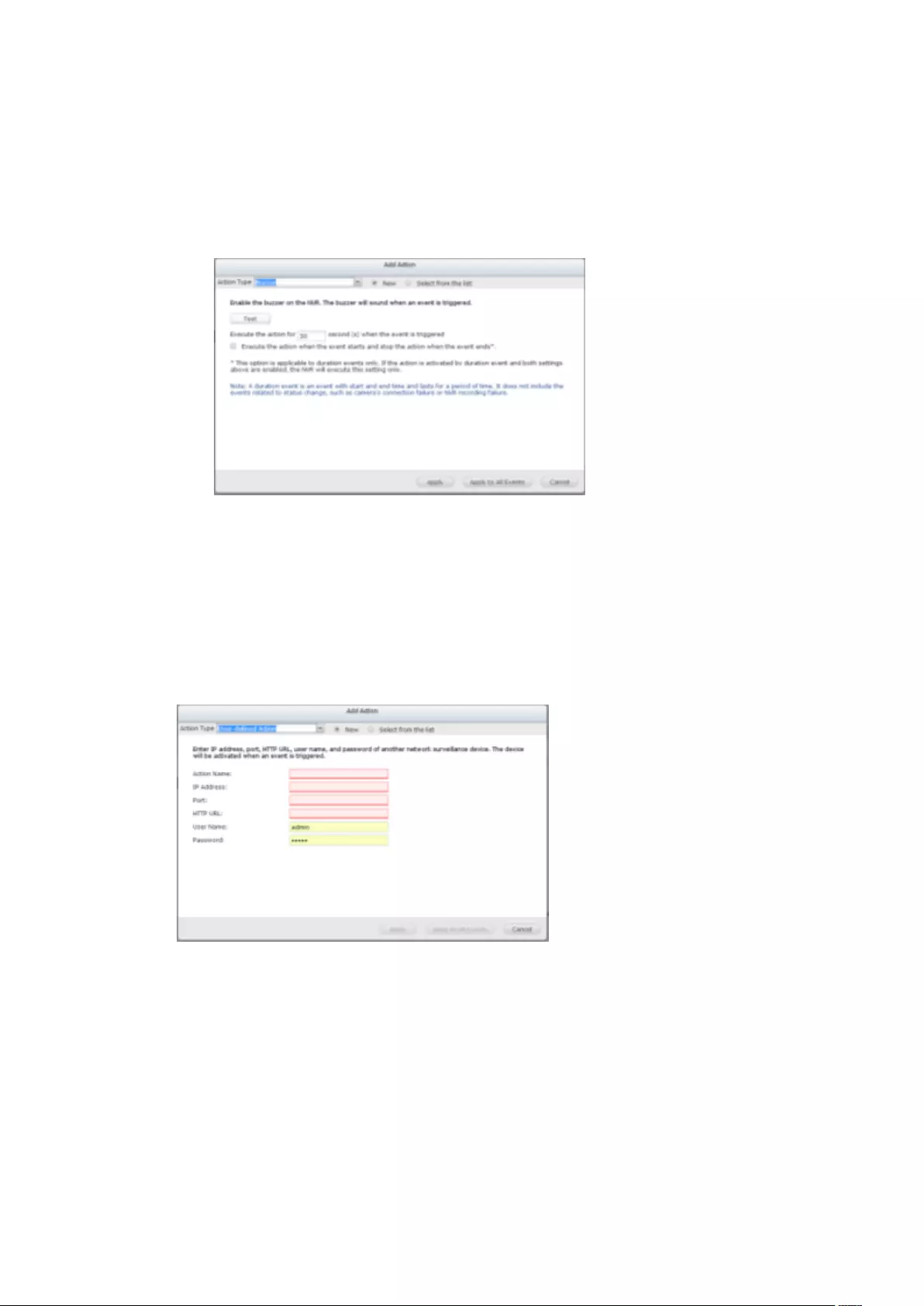
177
disconnection or NVR recording failure.
If the action is triggered by a duration event and both settings (i, ii) are
enabled, the NVR will execute the second setting (ii) only.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been
configured before.
7. User-defined Action
Add a self-defined action when an event is triggered. Enter the login account
and password, IP address, port, and the HTTP URL of other surveillance devices
to manage the devices such as fire protection devices, power controller, and air
conditioning control.
Click ‘Select from the list’ to select an action setting which has been configured
before.
7.1.4 View Management
View Management allows users to customize view layouts, and to assign cameras to specific
windows. Users can define view layouts to suit their needs. For example, when the camera
provides a corridor view, users can create a rectangle to fit the corridor view.
View Management provides two modes, normal mode is designed for non-fisheye cameras
178
and fisheye mode is designed for fisheye cameras.
Icon
Description
Edit: Edit view
Remove: Remove view.
View thumbnail:When you hover over , it will show thumbnails to
show your customized view.
Normal Mode
You can choose a customized view in the left view tree list in monitor mode.
Edit View:
1. To add a camera to a view, you can choose a view you want, then drag a camera
from the left list to the right channel screen.
2. To remove a camera from a view, you can double click on a camera snapshot or
drag it to the left camera tree list. You can also click ‘Restore’ to remove all of the
camera.
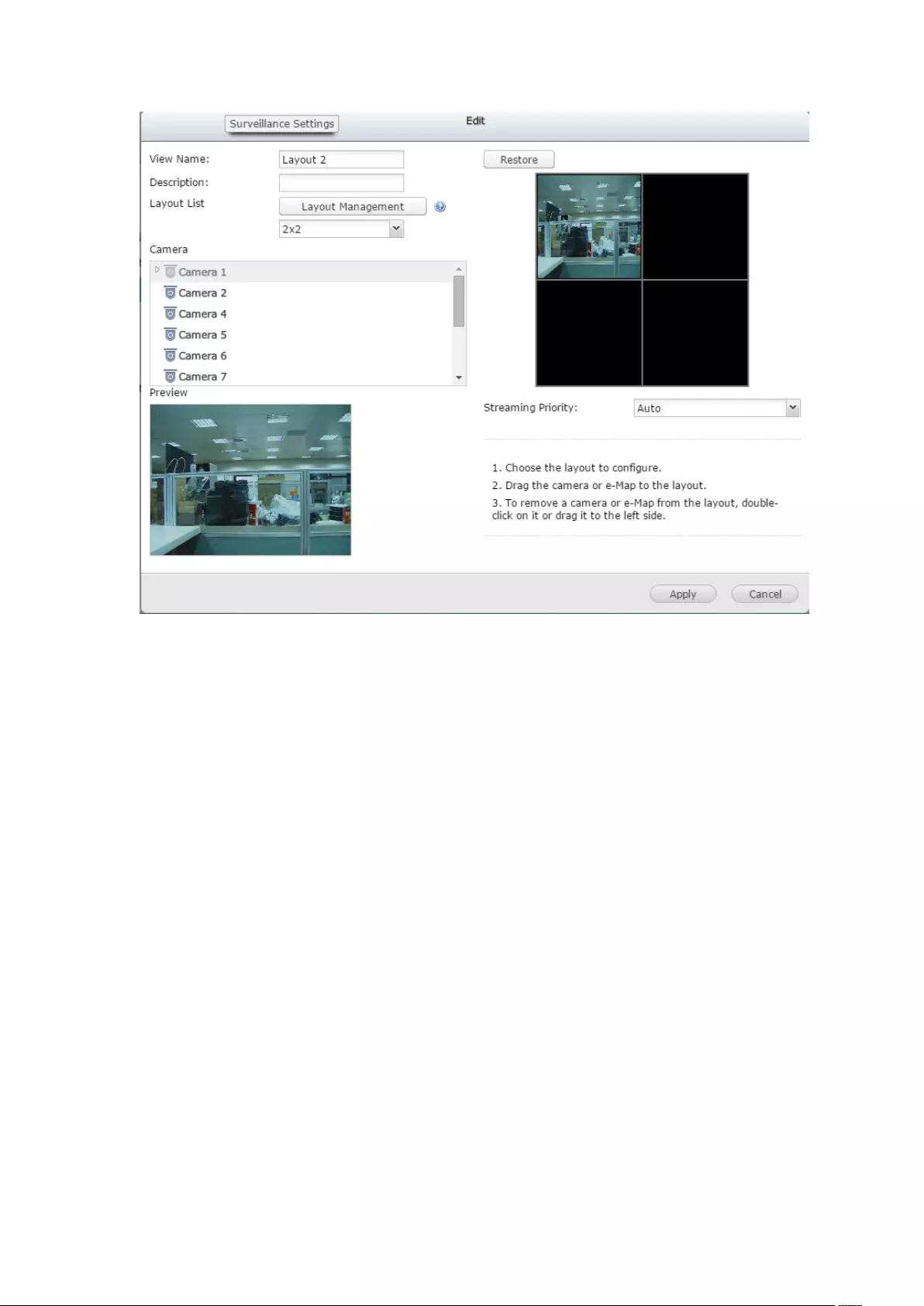
179
Add customize layout:
You can add a customized layout as a new layout
1. To choose a type of layout, for example you can choose 6x6.
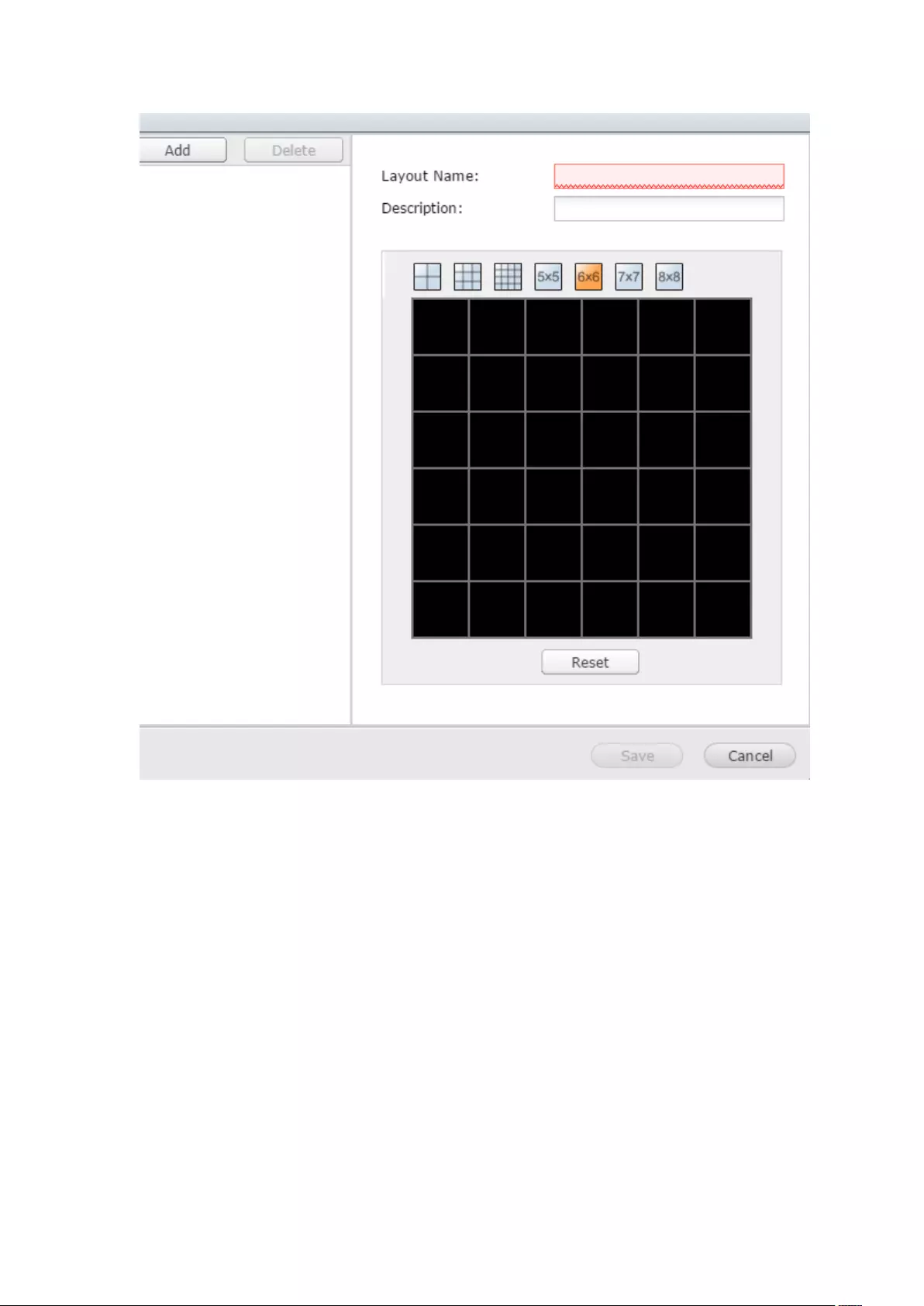
180
2. To edit the Layout, you can click a square and draw a larger square. And you can
double click the combined region to restore it. Or you can click ‘Restore’ to restore
the original layout.
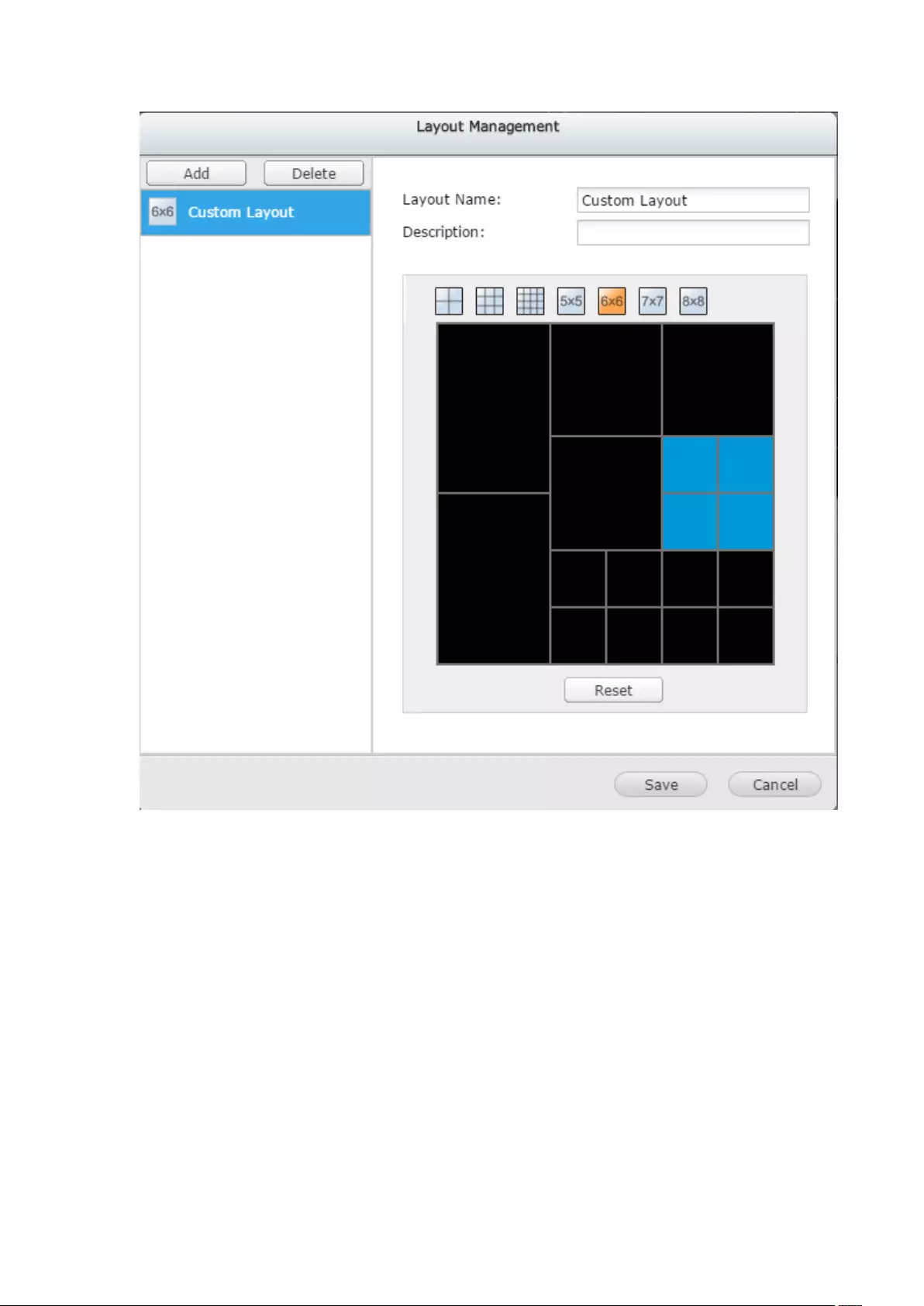
181
3. To finish, click ‘Save’ and it will show on left tree list.
4. To edit the layout, choose the layout, edit it in the right zone, then click ‘Save’.
5. To delete a layout, choose the layout then click ‘Delete’.
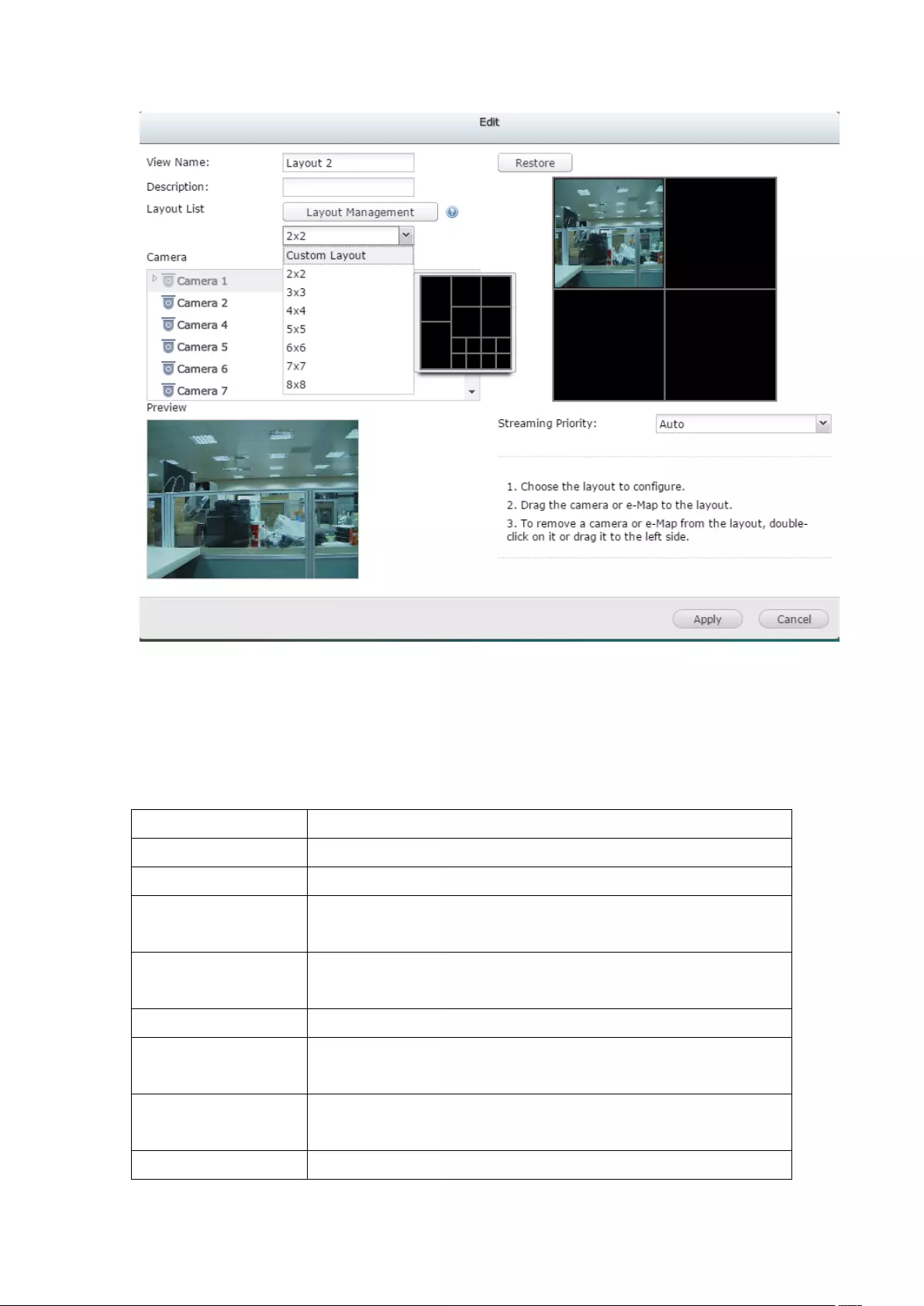
182
Fisheye Mode
Fisheye mode provides the below view modes:
View Mode
Description
9R Mode
Provides 9 regional screens
4R Mode
Provides 4 regional screens
1O8R Mode
Provides an original screen in the center, and 8 regional
screens around it
1P6R Mode
Provides an original screen in the center, and 6 regional
screens around it
Dual Panorama
Provides 2 panorama screens
1P3R Mode
Provides 3 regional screens in the upper side, and one
panorama screen below
1P2R Mode
Provides 2 regional screens in the upper side, and one
panorama screen below
OPR Mode
Provides one original screen one regional screen, and one
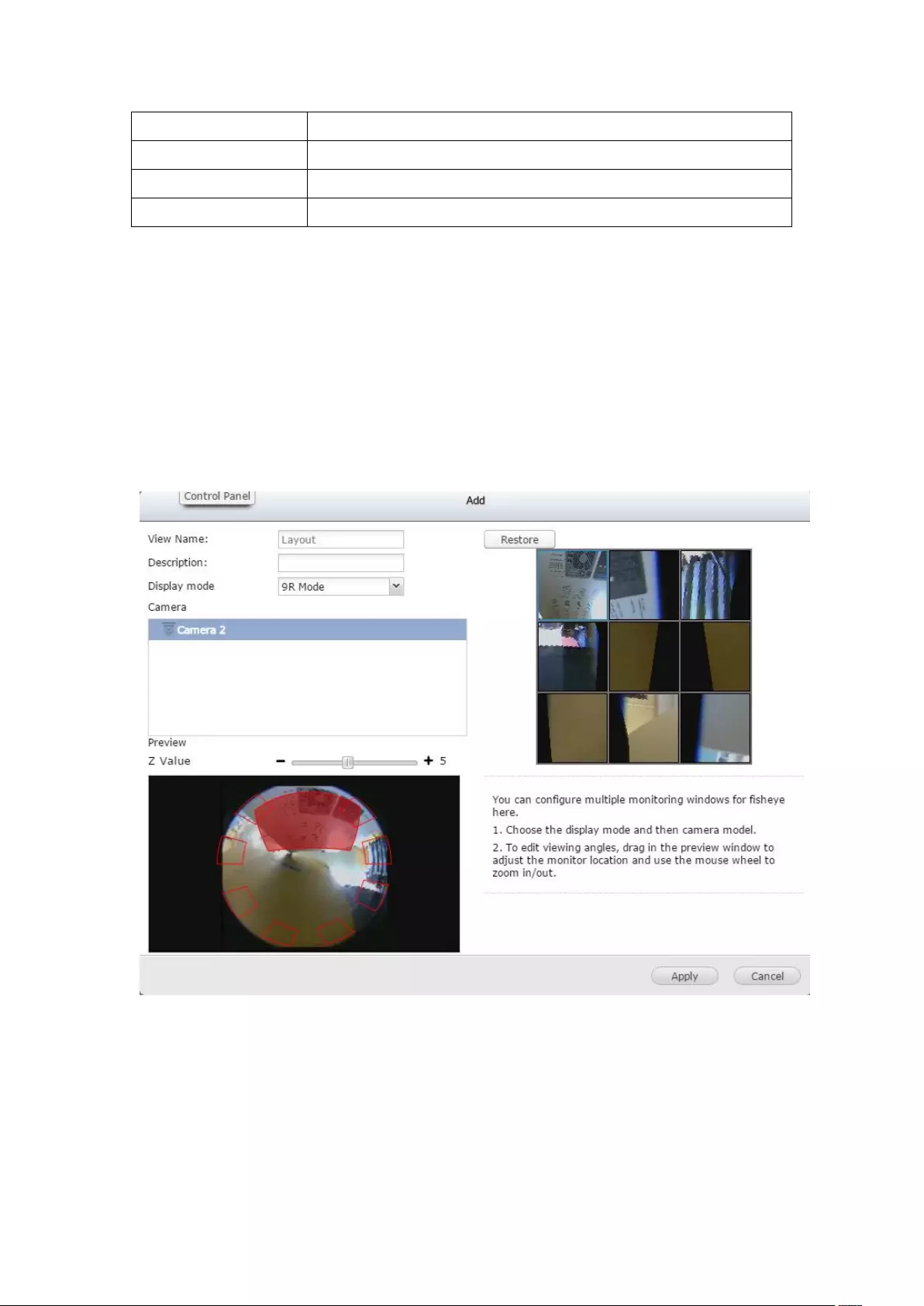
183
panorama screen
1O3R Mode
Provides an original screen, and 3 regional screens
R Mode
Provides one regional screen
Full Panorama
Provides one panorama screen
View Name:The view name cannot be duplicated. You can find your customized view
mode.
How to edit view mode:
1. Choose display mode
2. Drag a camera from left camera tree to the right preview.
3. To alter the size/drag position in preview, use the mouse wheel to zoom in/out.
Then you can see the view.
Choose View Mode to monitor
You can also choose the view mode in the left tree’s view tab on the monitor.

184

185
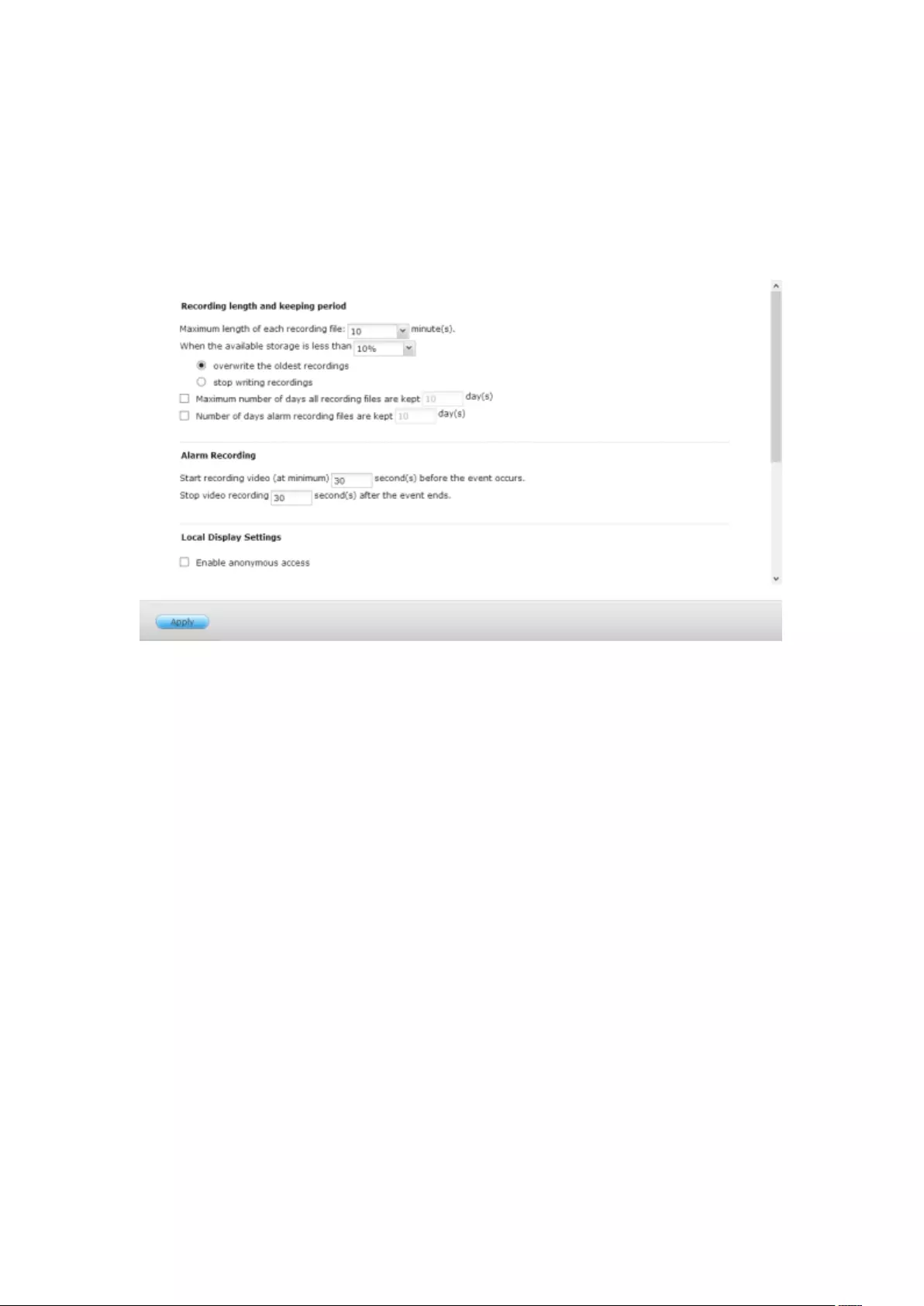
186
7.2 System Settings
7.2.1 Advanced Settings
You can configure the advanced recording settings in this section.
Maximum period for each recording file
Specify the maximum length of each recording file (maximum 15 minutes).
When the available storage is less than…%
Specify if the NVR should overwrite the oldest recordings or stop recording
when the available storage capacity is less than the specified percentage of the
total storage capacity.
Maximum number of days all recording files are kept … day(s)
Enter the number of calendar days that the NVR should keep the recording files.
Please make sure the storage capacity is enough to save the data for the
number of calendar days specified. When the recording data has reached the
expiry date, all of the expired video files will be deleted. For example, if the
NVR is configured to delete the recording data after 7 calendar days, on the 8th
day, the files recorded on the first day of each camera will be deleted so that the
NVR can start to save the data on the 8th day.
Number of days alarm recording files are kept … day(s)
Specify the number of days that alarm recordings will be retained.
187
Pre-/Post-alarm recordings
Start recording video…second(s) before the event occurs: Enter the number
of seconds to start the recording before an event occurs.
Stop video recording…second(s) after the event ends: Enter the number of
seconds to stop the recording after an event ends.
The maximum number of seconds for the above settings is 300 (5 minutes.)
Local display
To allow guest access to the monitoring screen of the NVR by local display, select
‘Enable anonymous access’.
Auto logoff
Set the timeout period to log off the users from the configuration page of the
NVR when the idling time has reached.
Note: The timeout logoff does not apply to the monitoring, playback, advanced
mode, device configuration, system update, remote replication, and logs & statistics
pages.
Network intrusion detection
The system will alert users when possible attacks on the network are detected
and give recommendations for actions to take.
Maximum number of concurrent logins (http)
You can define the maximum number of http user sessions at the same time
(maximum: 32.)
Note: All of the settings will be effective only after clicking ‘Apply’. When applying
the changes, the recording will temporarily pause (for up to 1 minute) and then
restart.
7.2.1.1 Flexible Channel Mode Settings
Applicable to the VS-2200 Pro+ series (including the VS-2212 Pro+, VS-2208 Pro+,
VS-2204 Pro+)
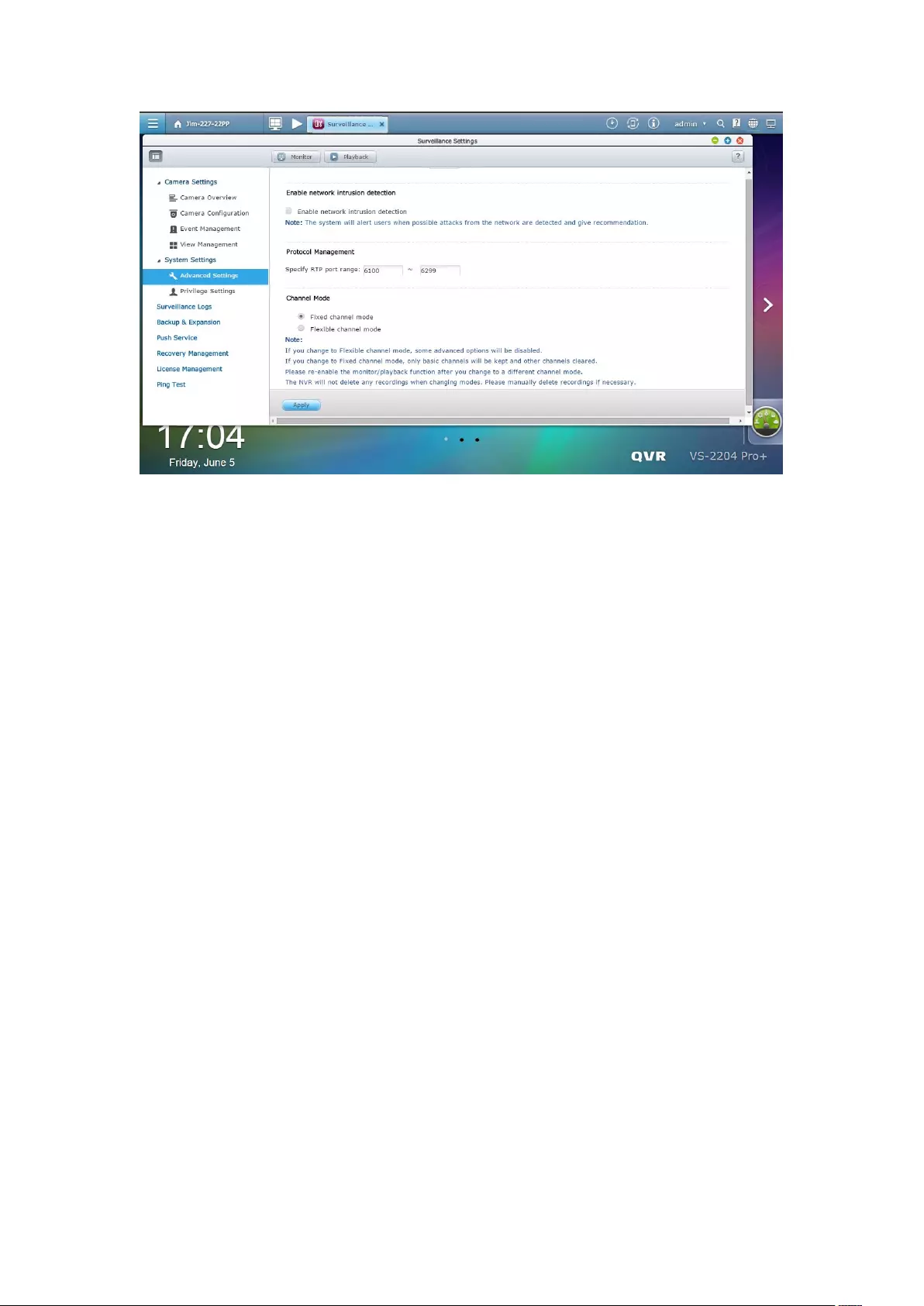
188
To change the channel mode, go to QVR desktop -> [Surveillance Settings] -> [System
Settings] -> [Advanced Settings]. There is the fixed channel mode (default) and the
flexible channel mode.
After changing to the flexible channel mode, compared with the fixed channel mode,
the maximum recording channels will become 4. Under the flexible channel mode,
the number of actual recording channels will vary depending on the recording
resolutions of added channels. The system will automatically calculate the number of
actual recording channels by the recording resolution index. The recording resolution
index of Full HD channel, HD channel, and D1 channel is 4, 2 and 1. Using the
VS-2212 Pro+ as an example, as long as the amount of recording resolution indexes
does not exceed 48 (=12 * 4), you can add more than 12 cameras.
Note:
1. If you change to the flexible channel mode, some advanced features will be
disabled, such as user-defined multi-stream, smart recording, dual recording,
edge recording, auto snapshot, advanced event management, auto cruising,
remote replication, storage expansion, and Qstart.
2. If you change to the fixed channel mode, only basic channels will be retained,
but not other channels.
The recordings of other channels will not be removed, and if necessary can be
manually deleted.
3. If you are using the QVR client to see the live view and playback recordings,
please re-enable the monitor/playback function after you change to a different
channel mode.
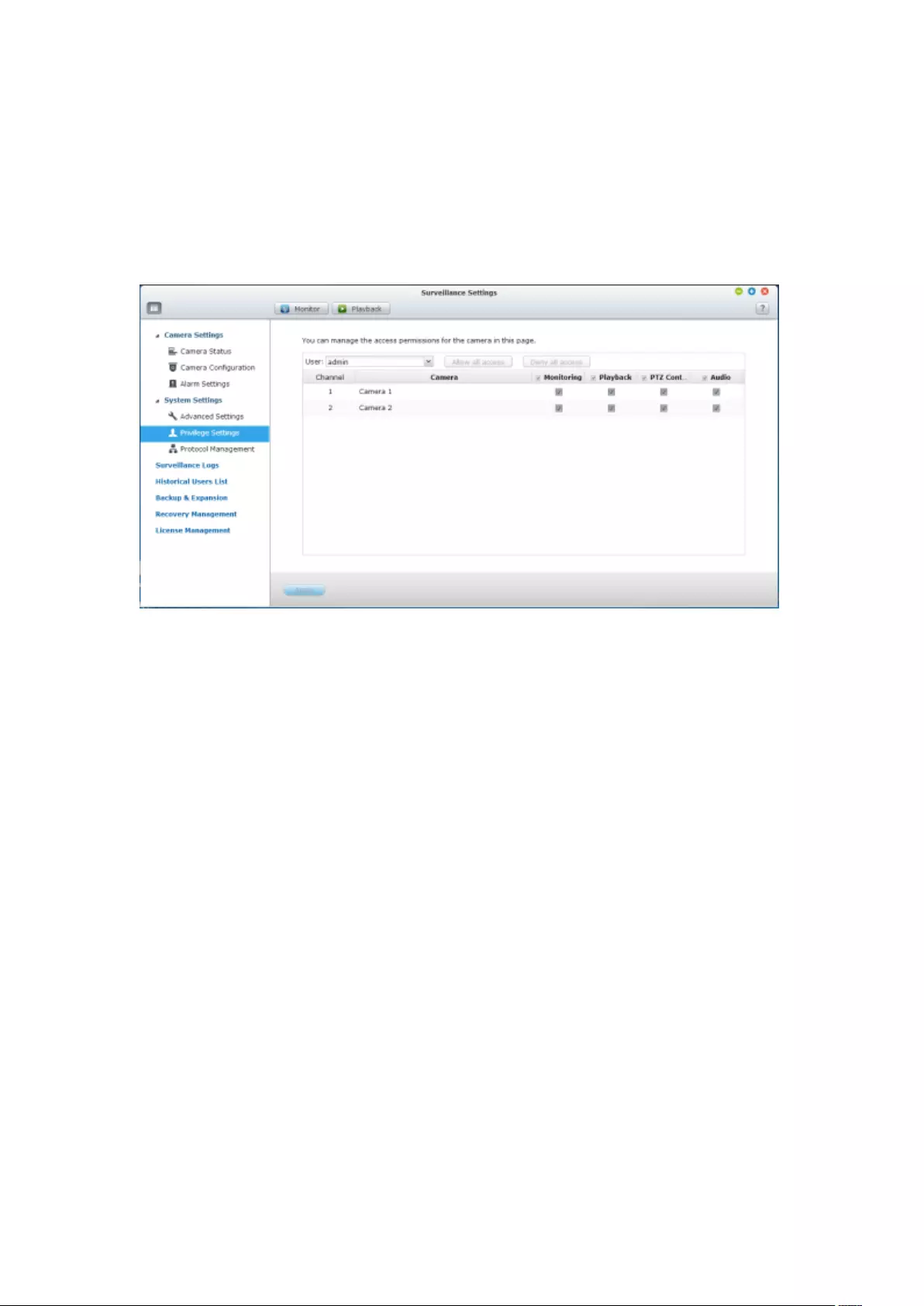
189
7.2.2 Privilege Settings
You can check the rights of camera management for all users. You can also modify
access right of monitoring, playback, PTZ control, and audio for a general user. If you
want to add a user, please go to [Control Panel] -> [Privilege Settings] -> [Users].
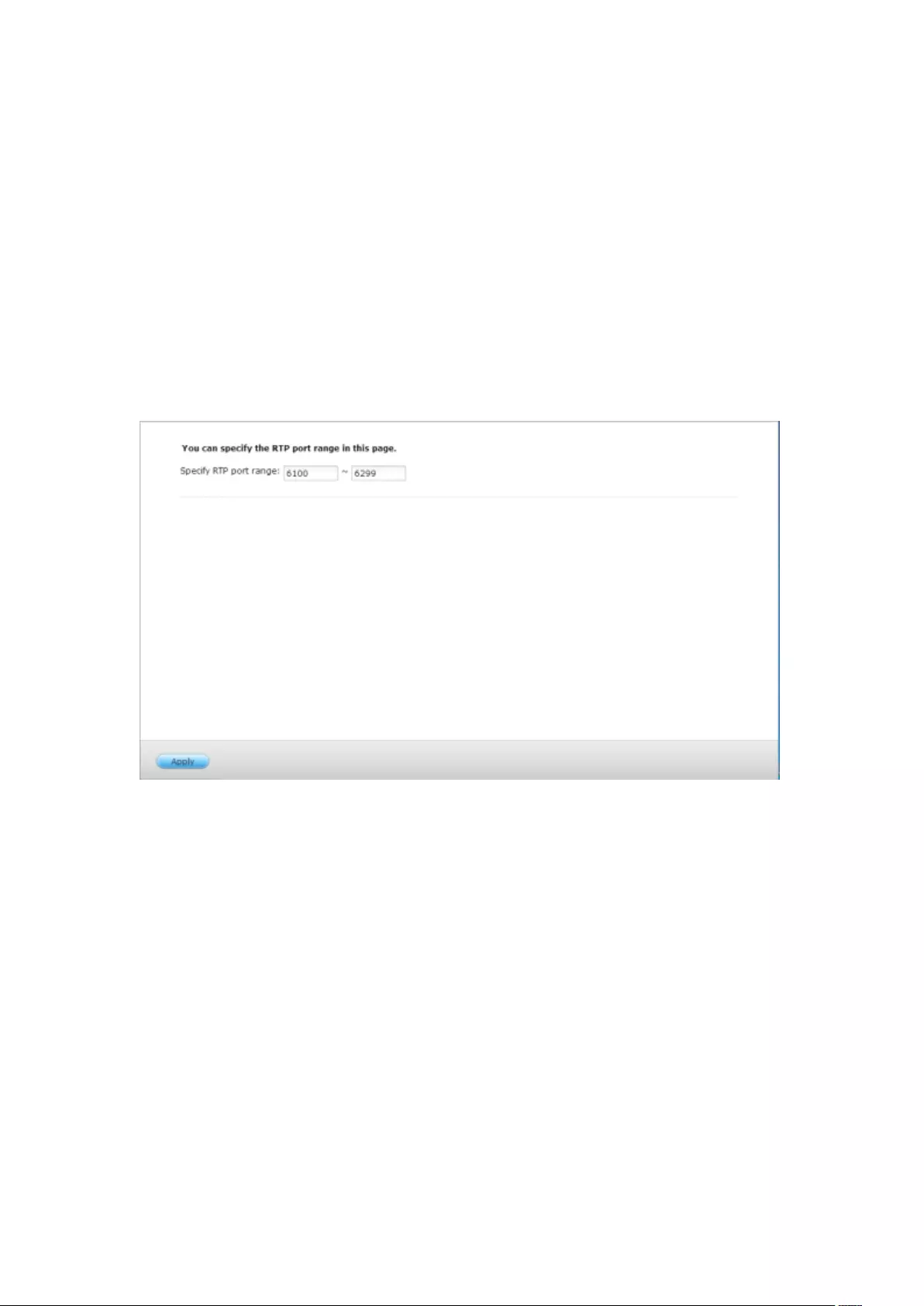
190
7.2.3 Protocol Management
RTP (Real-time Transfer Protocol) is a standardized packet format for delivering
real-time audio and video data of the IP cameras on the Internet. The real-time
data transfer is monitored and controlled by RTP (also RTCP). The default setting is
6100–6299. If the IP cameras use different RTP ports, enable ‘Specify RTP port
range’ and specify the port numbers.
Note: Make sure the ports have been opened on the router or firewall to ensure
normal monitoring and recording.
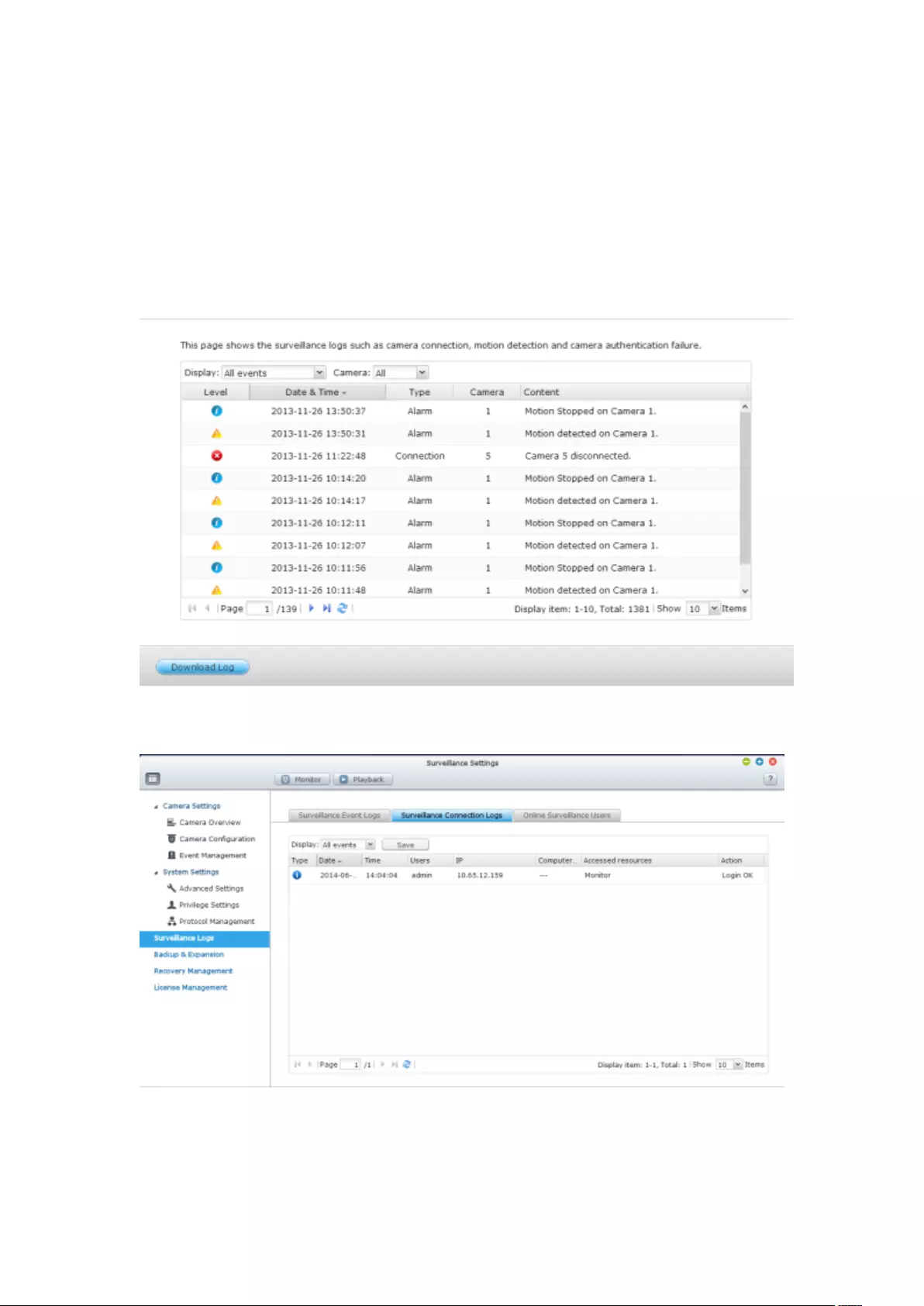
191
7.3 Surveillance Logs
This page shows the surveillance logs such as camera connection, motion detection,
and camera authentication failure.
Please Note: The logs are currently only available in English.
7.3.1 Surveillance Logs
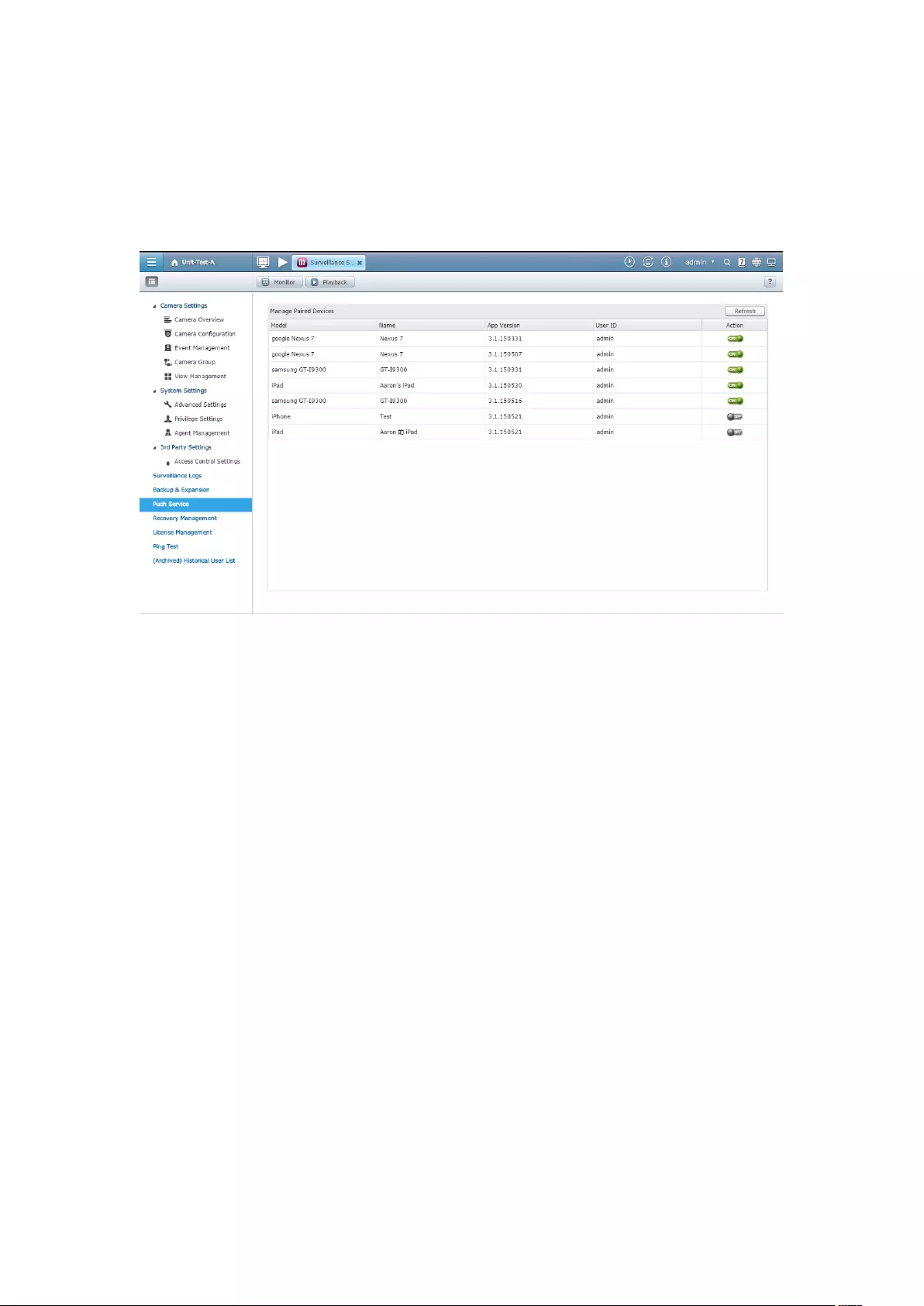
192
7.4 Push Service
The push service allows you to receive notifications on mobile devices when motion
detection or alarm events occur. To use the push service, please ensure you have the
right to receive push notifications and enable the myQNAPcloud remote access
services on the server. Use the Vmobile App on your mobile devices to add a server
for seeing the live view, playback recordings and to receive push notifications. After
being added, the information of the mobile device will be listed on the page,
including the model name, device name, version of Vmobile, and user details on the
NVR. You can also disable the push service to specific mobile devices.
7.5 Recovery Management
This page is related to the edge recording feature. You can edit the recovery schedule,
monitor the recovery status, and the edge recording status here.
1. Recovery Schedule: Schedule for recovery of recorded data. Available when edge
recording is in use.
You can edit the recovery schedule in this tab.
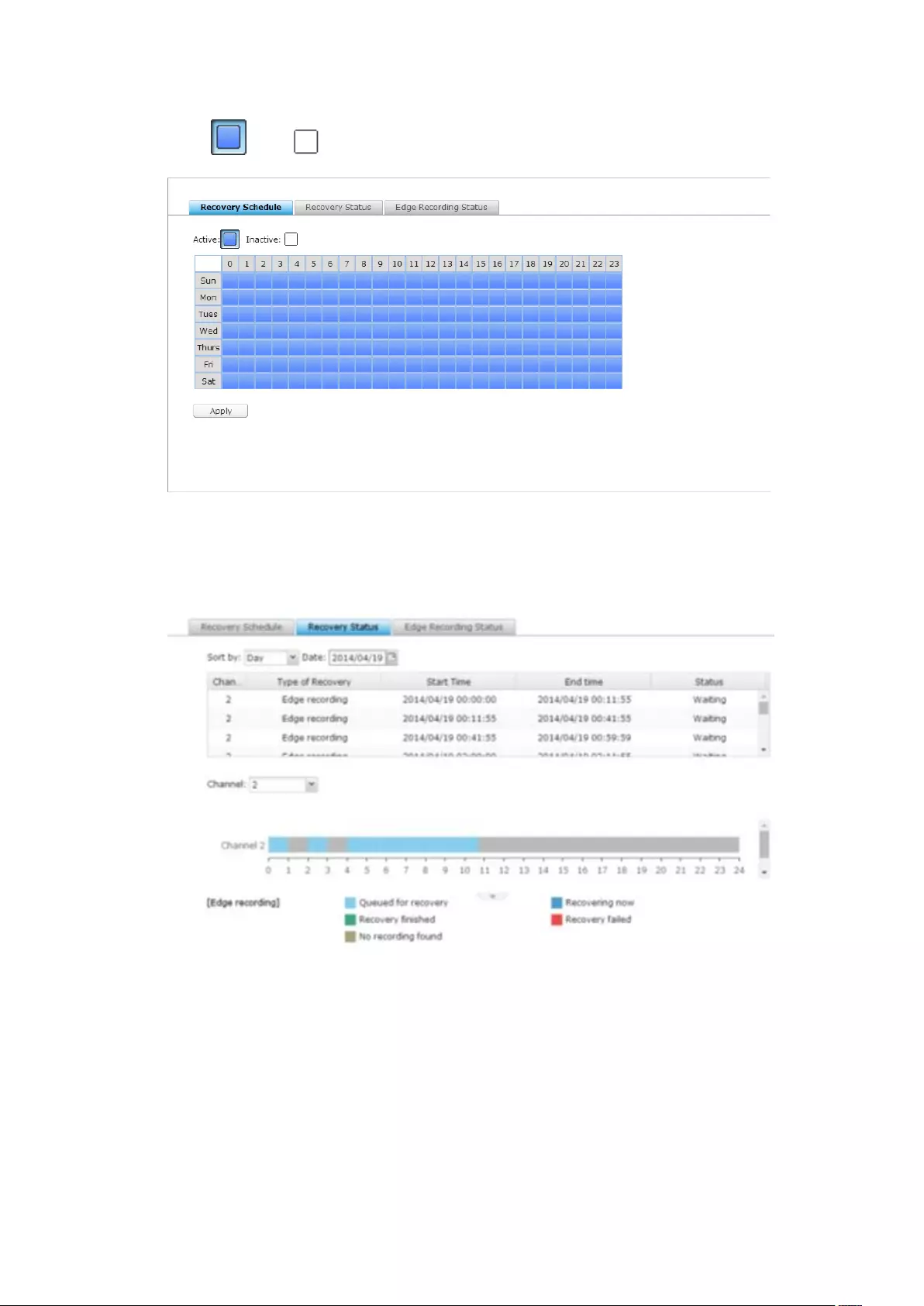
193
Click and to drag the edit recovery schedule.
2. Recovery Status: Status for the recovery of recorded data. Available when edge
recording is in use.
You can monitor the recovery status in this tab.
3. Edge Recording Status: Status of edge recording
You can check time synchronization between the NVR and cameras, the
status of cameras set up for edge recording, and the details of recording files
stored on camera’s SD
card.
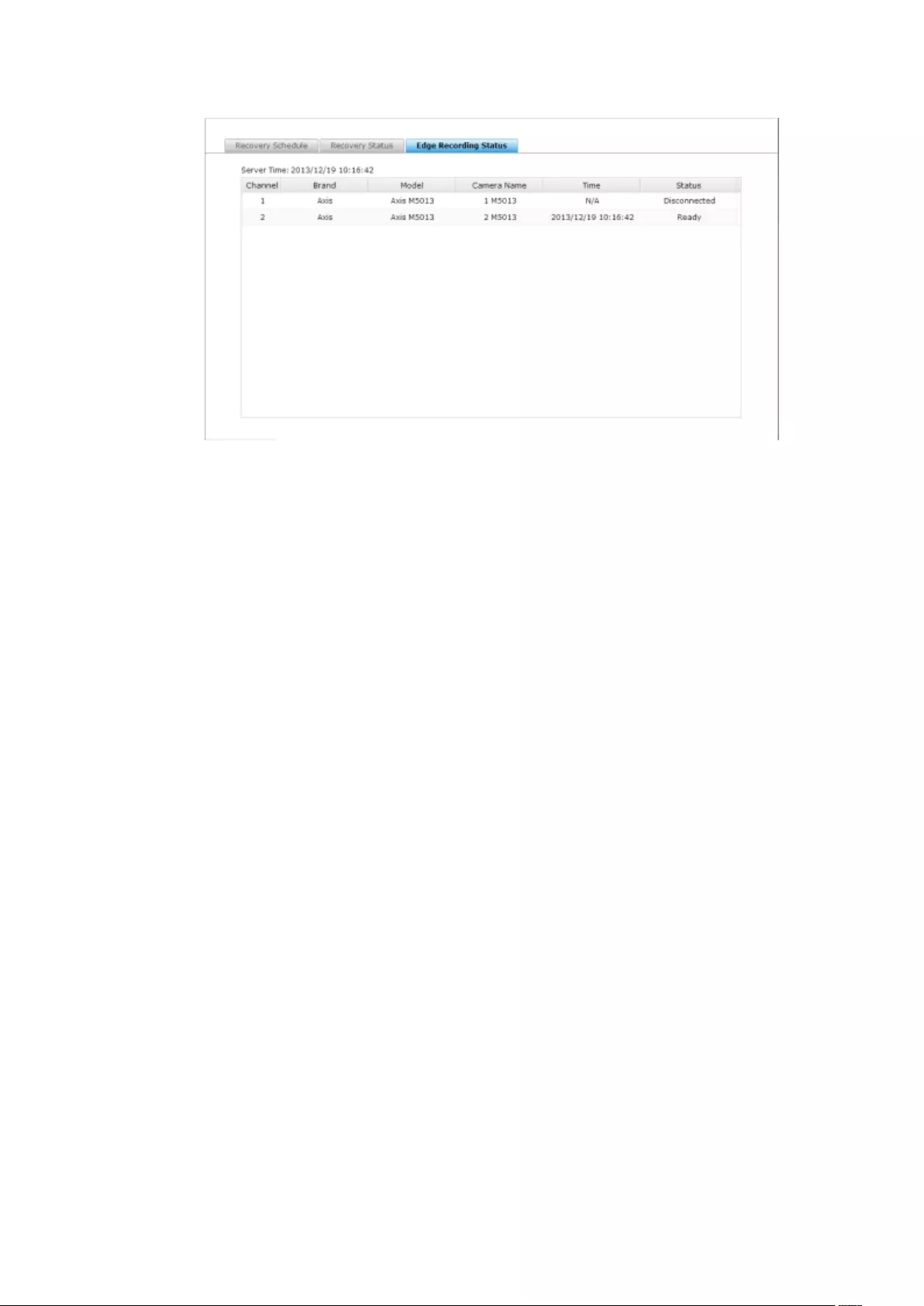
194
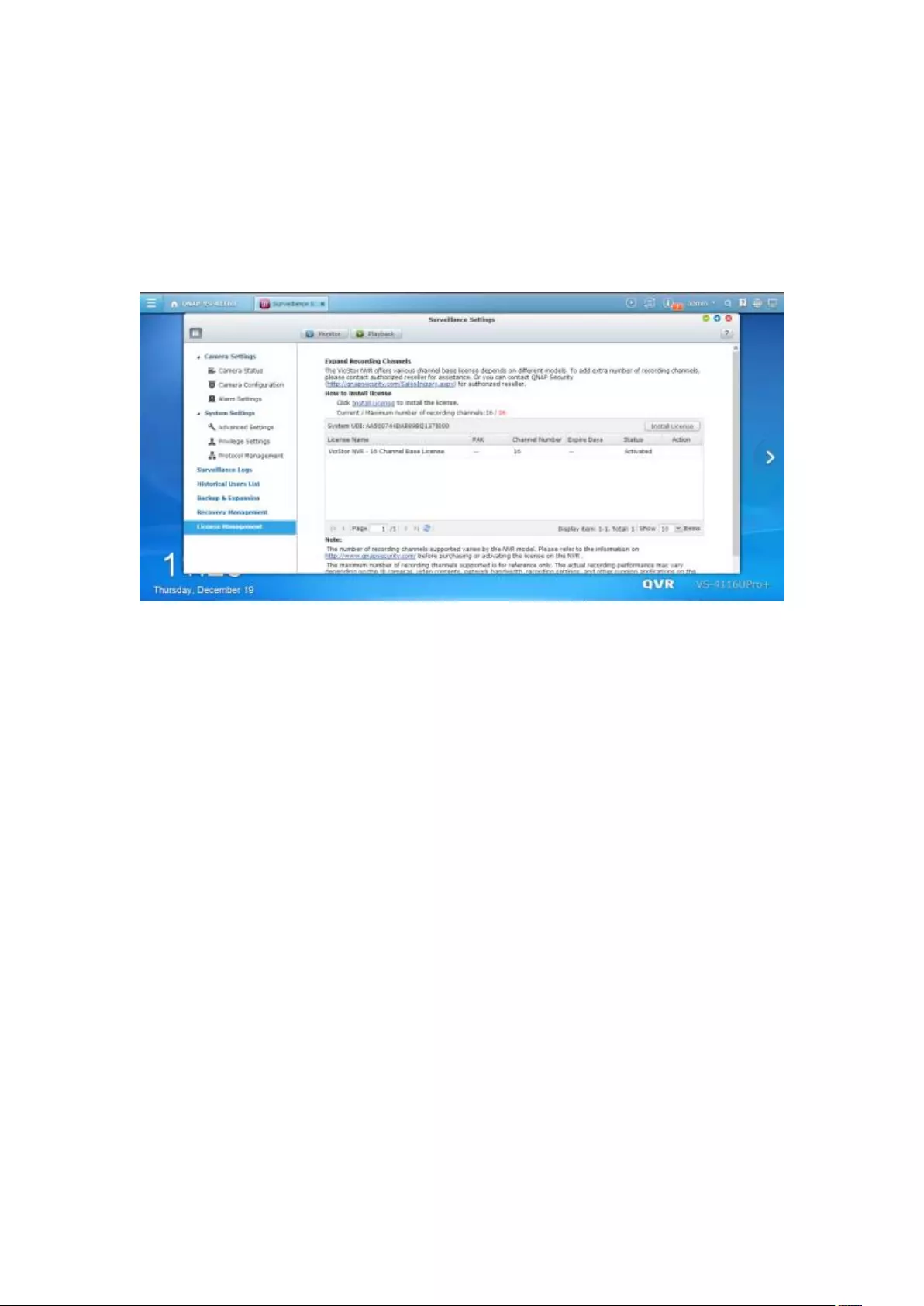
195
7.6 License Management
The VioStor NVR offers various channel base license depending on different models.
After purchasing a license, you can add extra recording channels.
You can click “Install License” to begin installing the license to the NVR.
7.6.1 License Activation
Online Activation
Step1. If your VioStor NVR is connected to the Internet, please select “Online
Activation”.
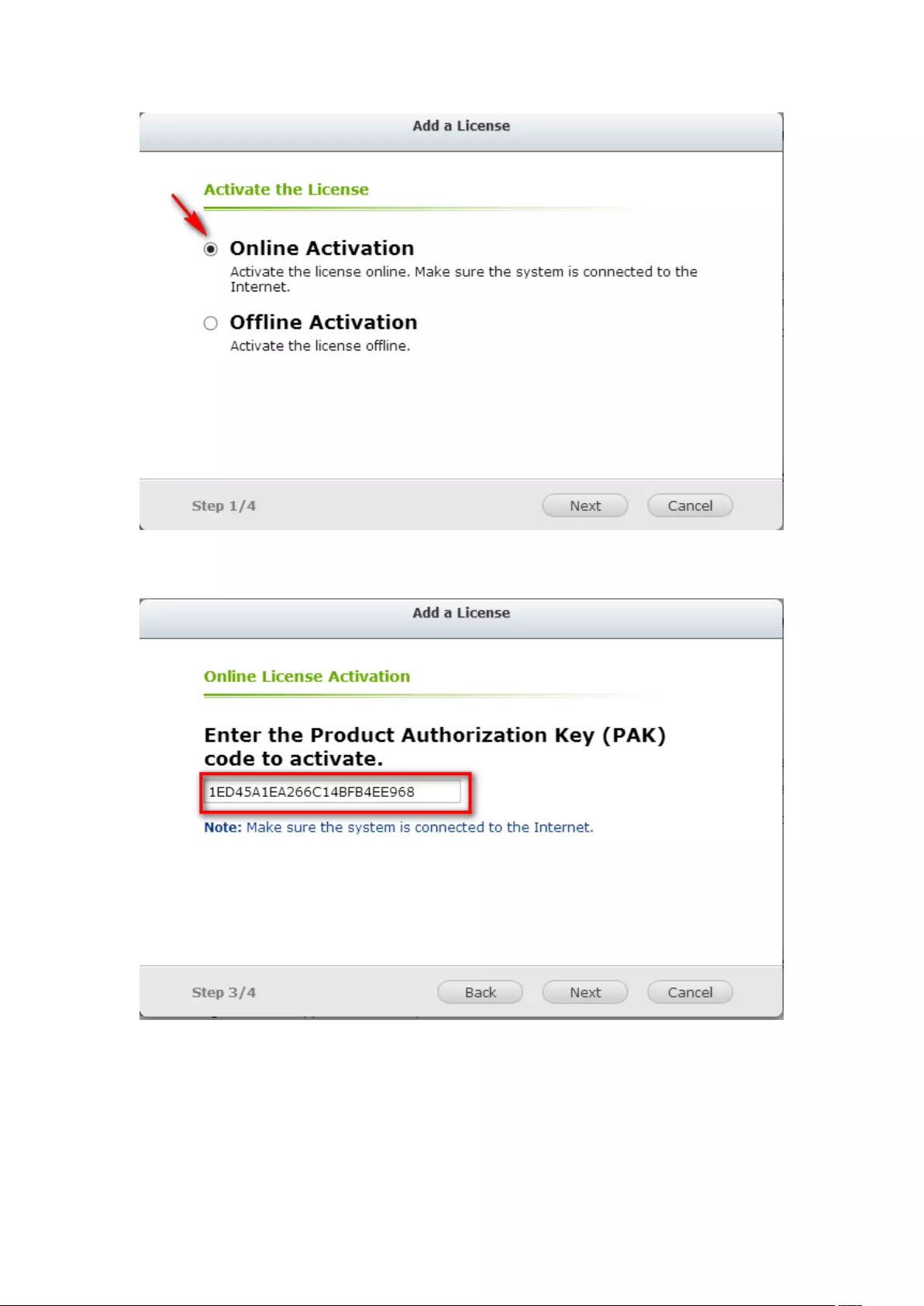
196
Step2. Enter the Product Authorization Key (PAK) code to activate the license.
197
Step3. The License has been activated. Please click [FINISH] button to close the
window.
Step4. The additional camera license will be displayed in the license management list
after the license activation.
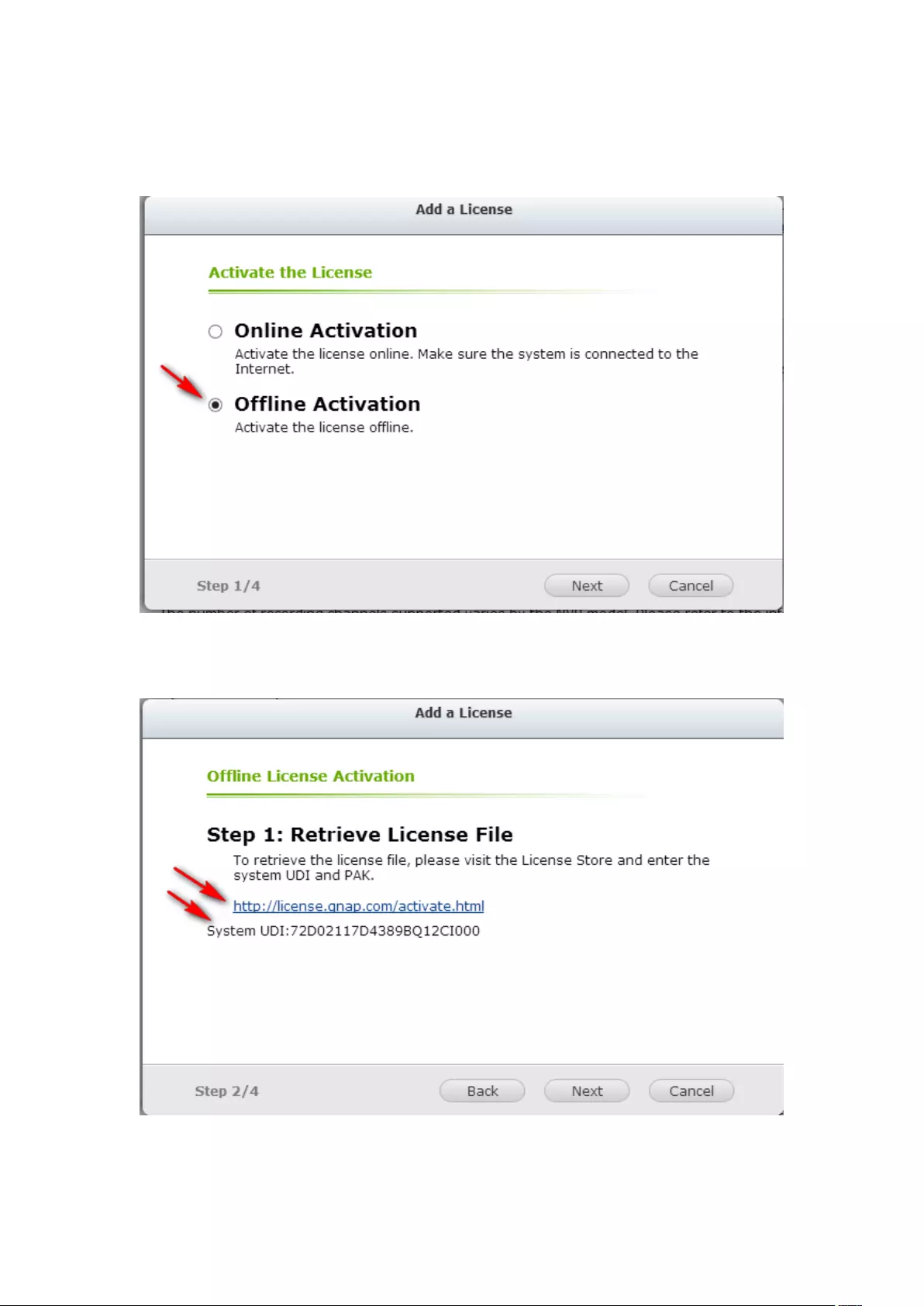
198
Offline Activation
Step1. If the VioStor NVR is behind a firewall or doesn’t have an Internet connection,
please select “Offline Activation”.
Step2. Please copy the system UDI and go to the License Store for offline license
activation.
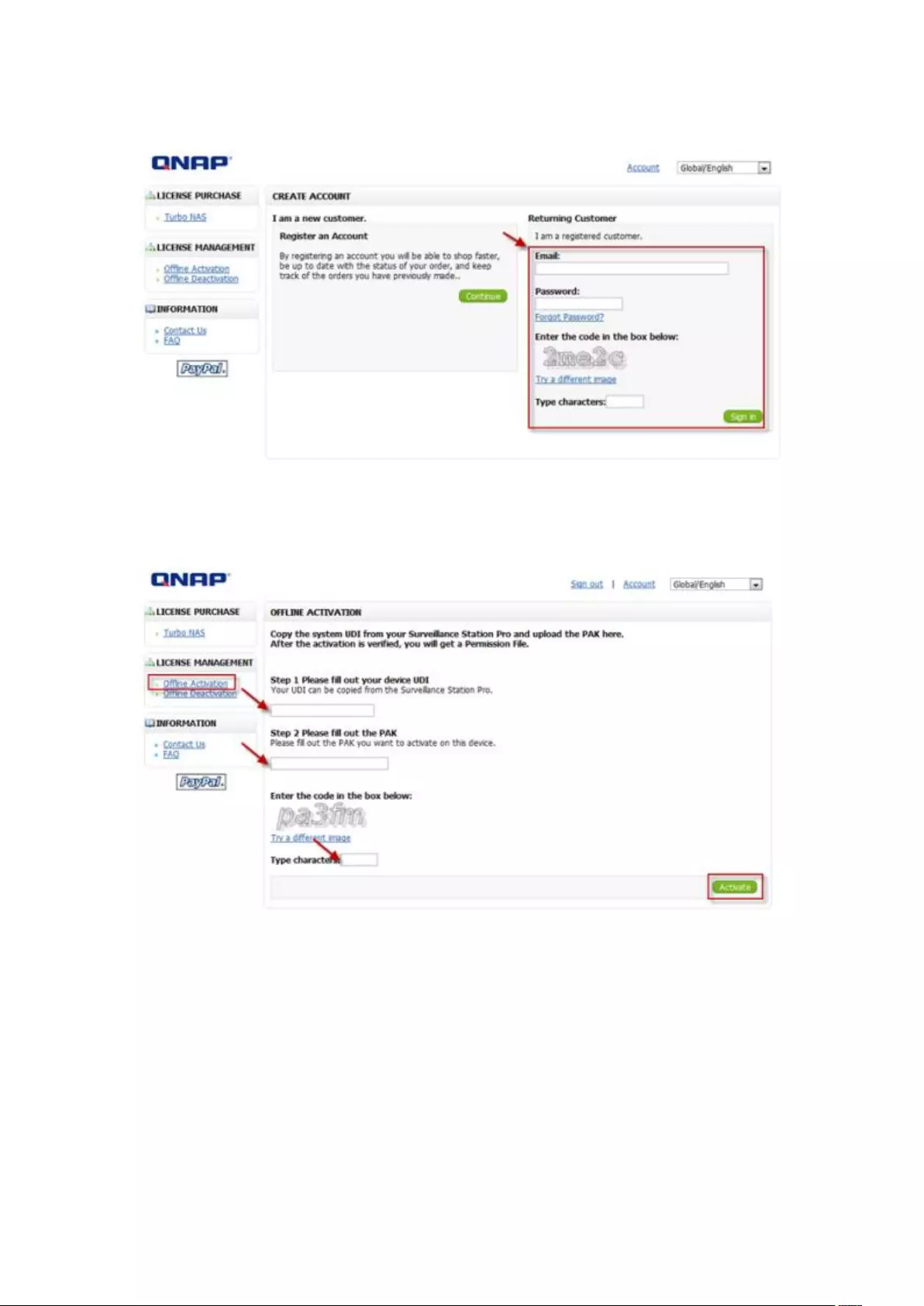
199
Step3. Please login to the License Store with your registered account.
Step4. At Offline Activation page, please fill out the UDI and PAK fields and then click
the [Activate] button.
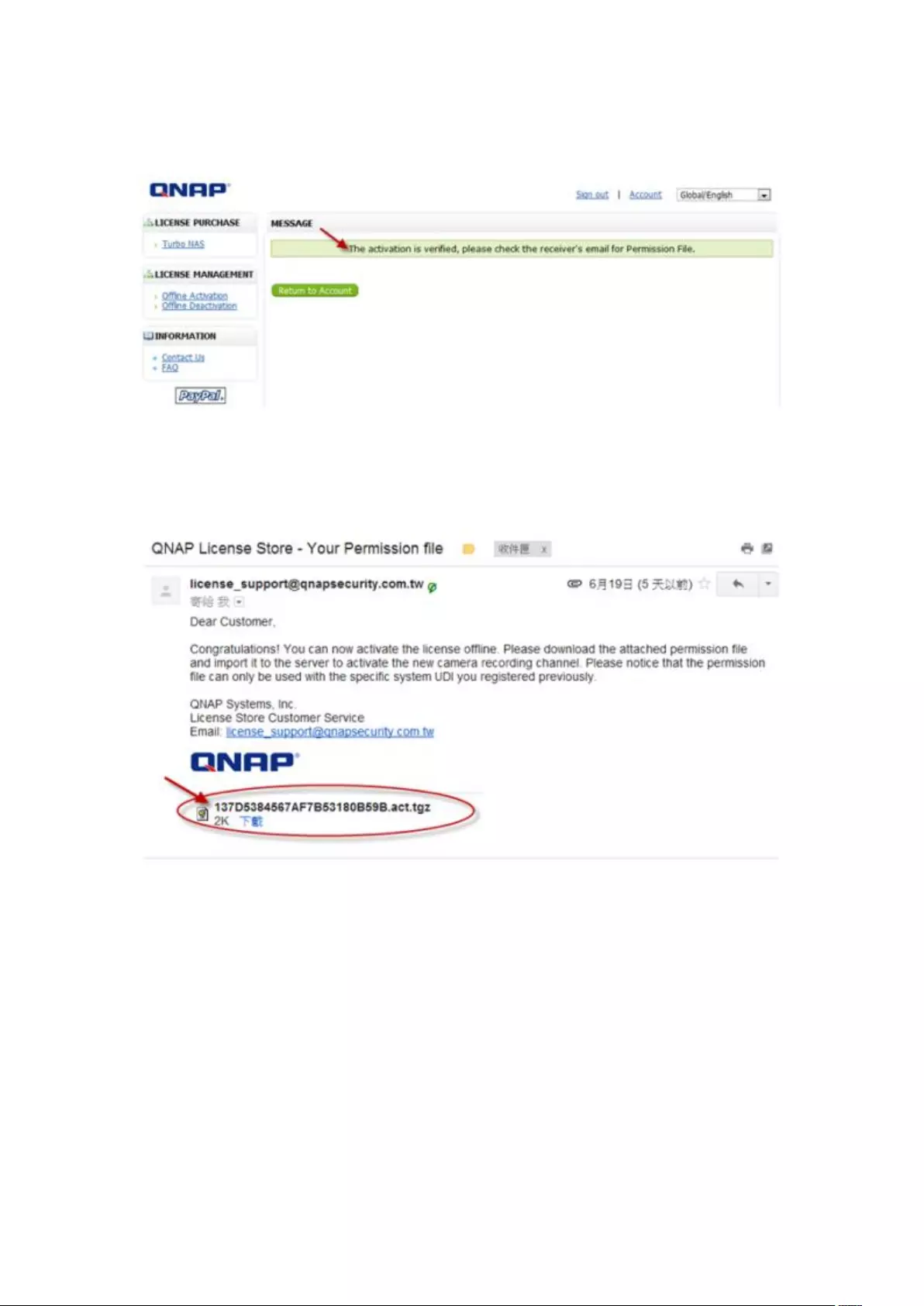
200
Step5. You will receive an email with an attached permission file after the offline
activation is verified.
Step6. Please check the email and download the permission file. The permission file
can only be used on the VioStor NVR with the UDI you specified. Please do not
decompress the permission file.
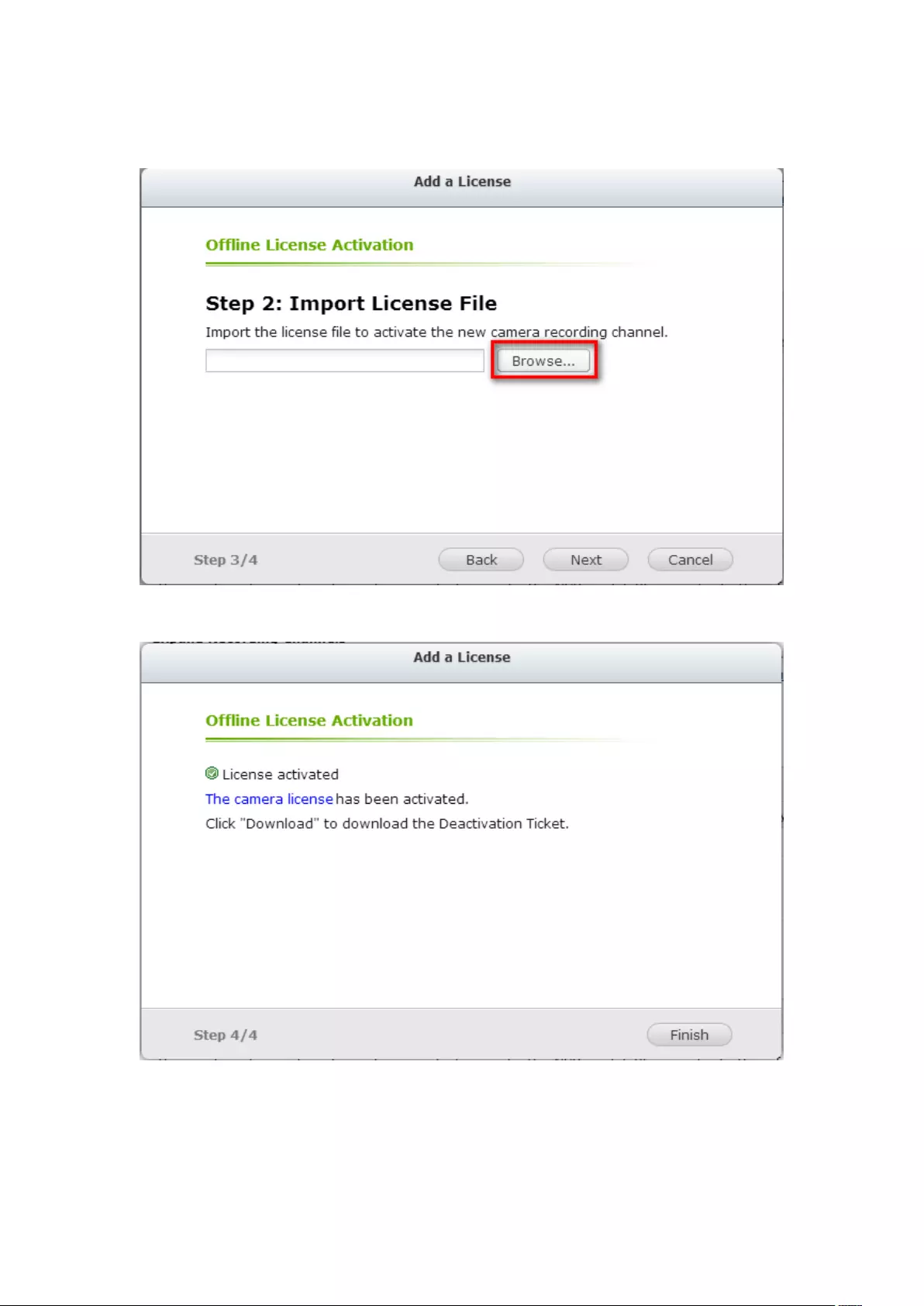
201
Step7. Please go back to the offline activation page on your VioStor NVR. You will
need import the permission file to activate the license.
Step8. The license has been activated.
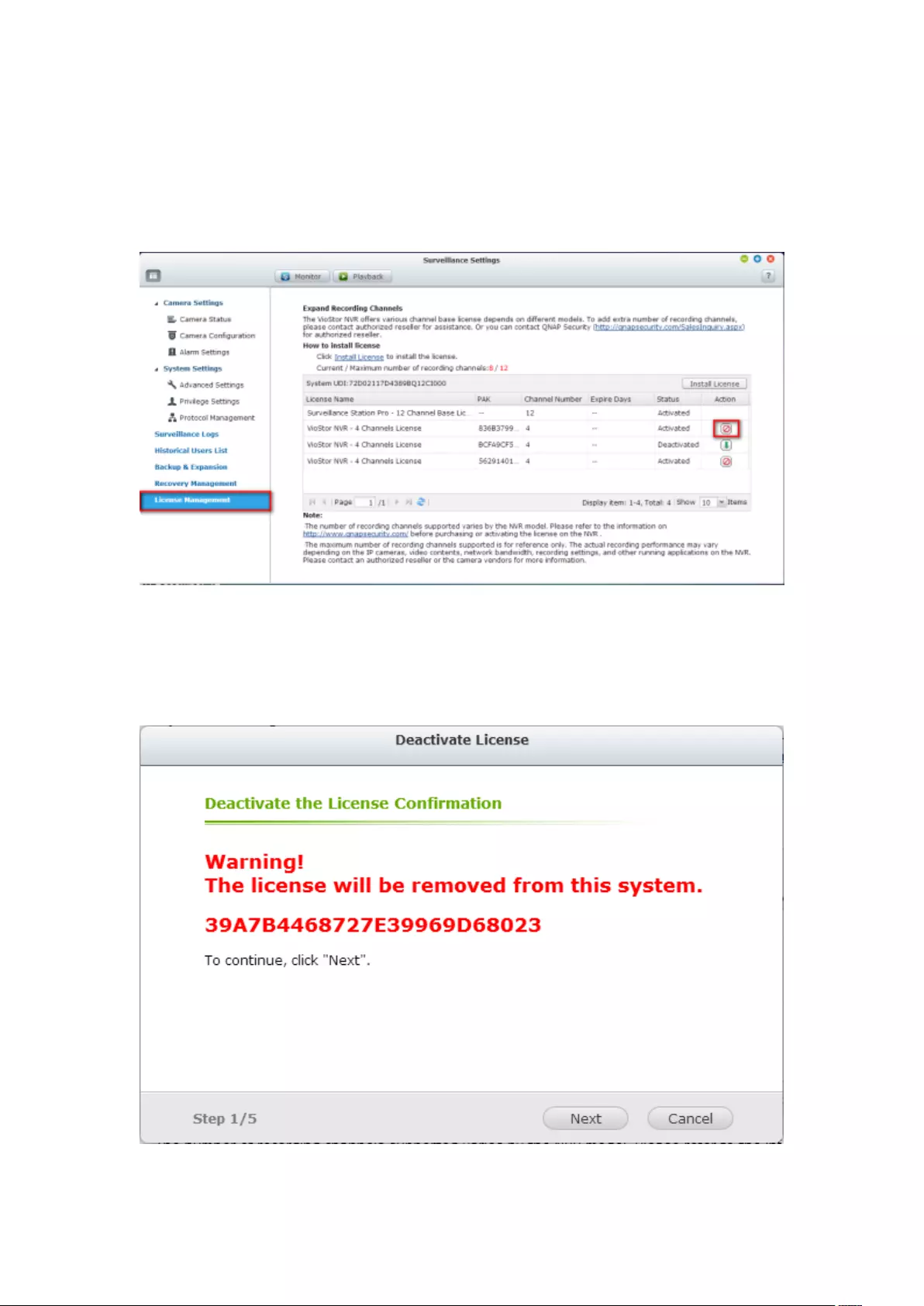
202
7.6.2 License Deactivation
Please select the “License deactivate” button to begin the process of deactivating a
license. If your VioStor NVR is connected to the Internet, please select “Online
deactivation”. If not, please select “Offline deactivation”.
Online Deactivation
Step 1: After you press the “License deactivate” button, you will be prompted to
confirm that you want to deactivate the license.
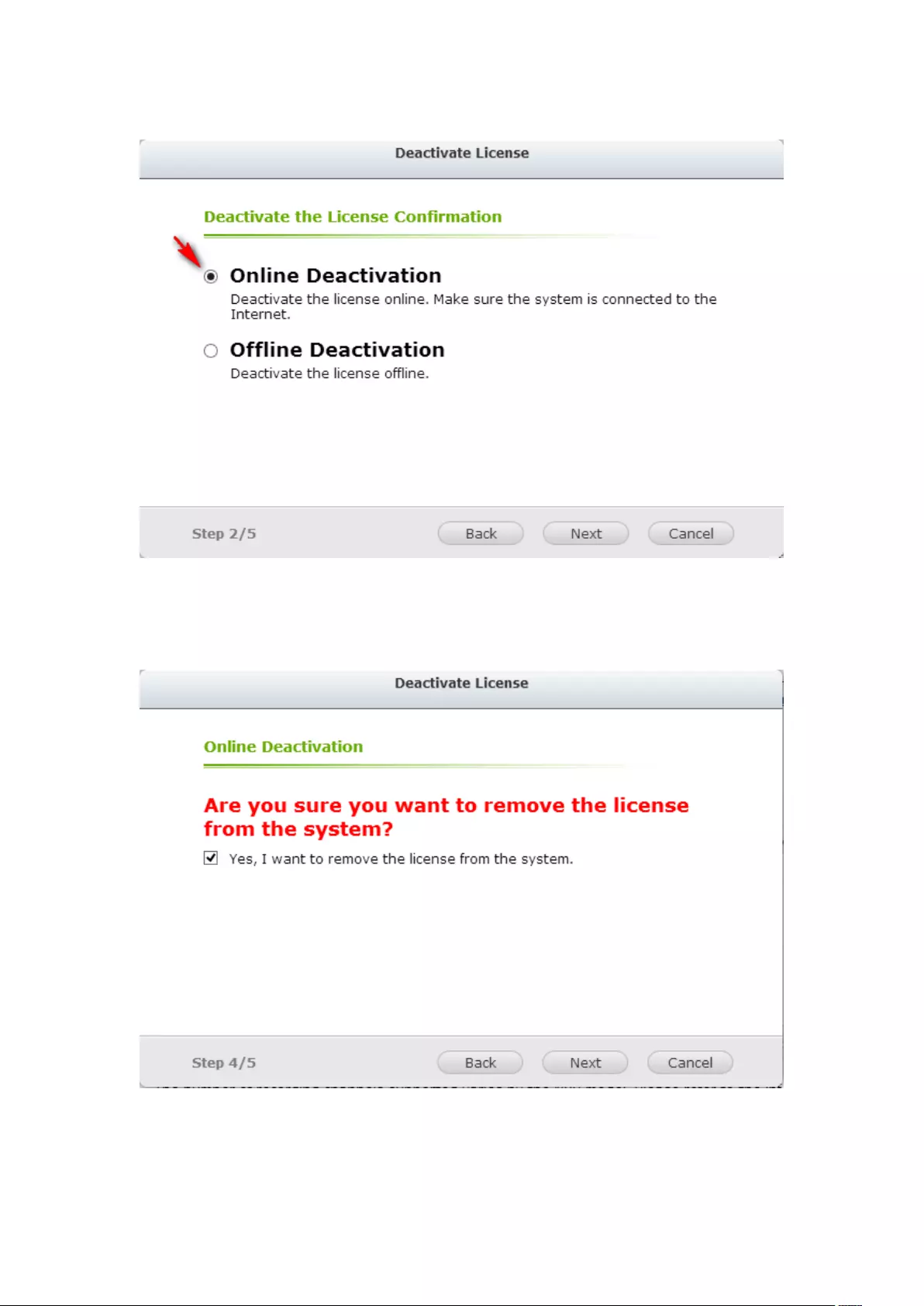
203
Step 2: Please select “Online Deactivation”.
Step 3: The system will prompt you to confirm your choice to remove the license. If
you are sure about deactivating the license, check “Yes, I want to remove the license
from the system.”
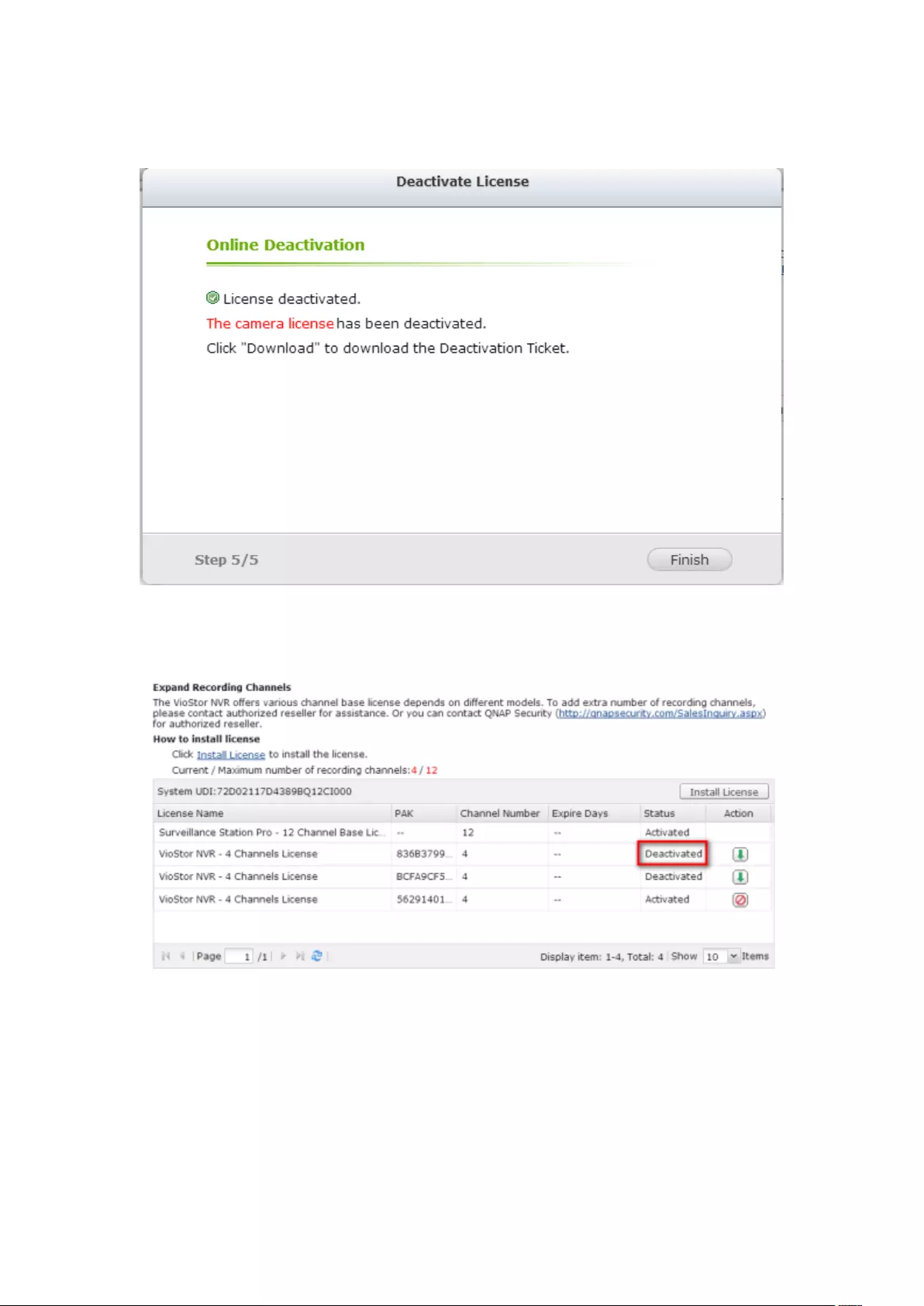
204
Step 4: The license has been deactivated. Please click [FINISH] button to close the
window.
Step 5: And now you will see that the status of the license has changed to
“Deactivated”.
Note: If you want to transfer the License to another VioStor NVR, please download
the “deactivation ticket” from the icon “” (under the “Action” column). Then contact
QNAP support for help.
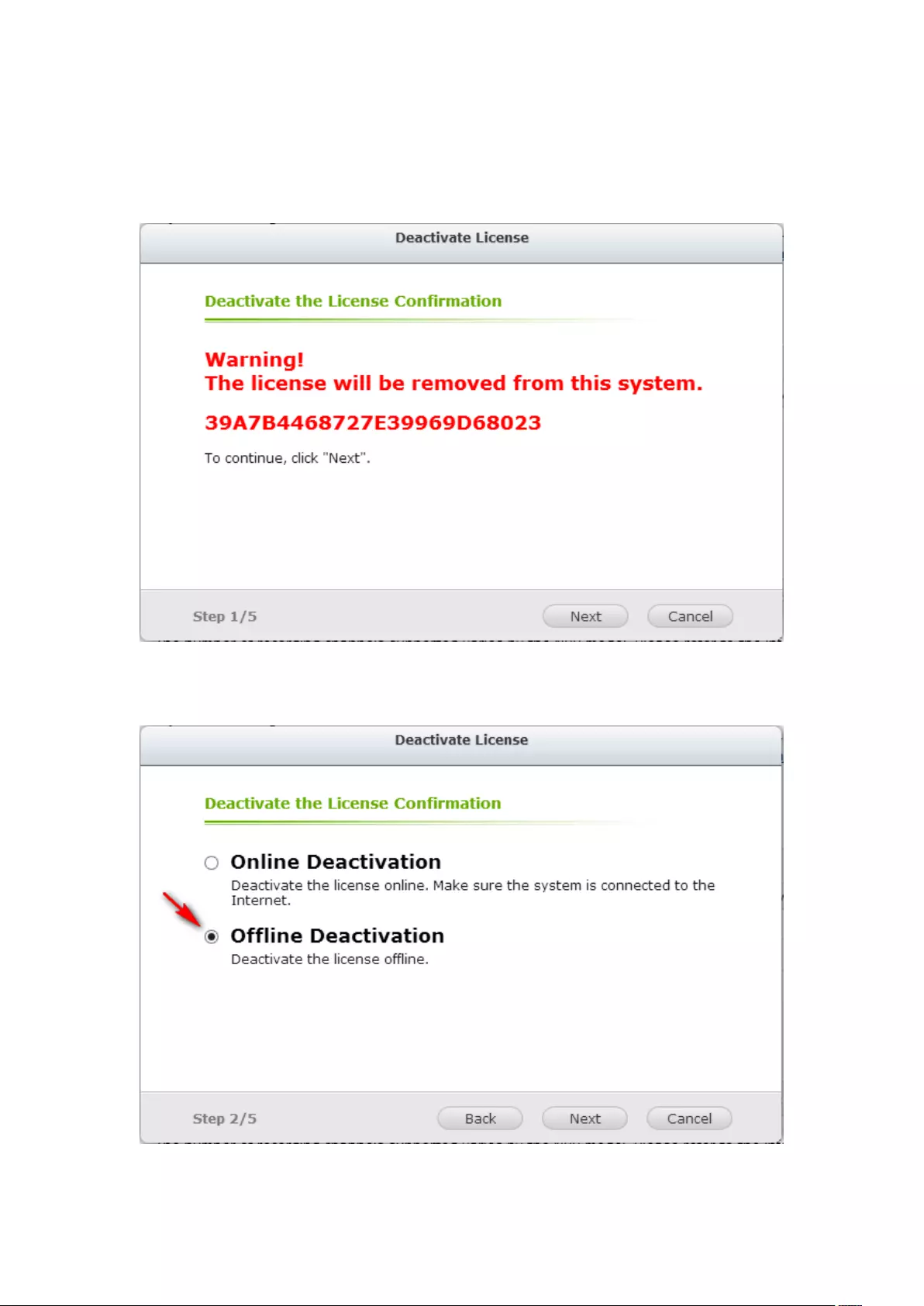
205
Offline Deactivation
Step 1: After you press the “License deactivate” button, you will be prompted to
confirm that you want to deactivate the license.
Step 2: Please select “Offline Deactivation”.
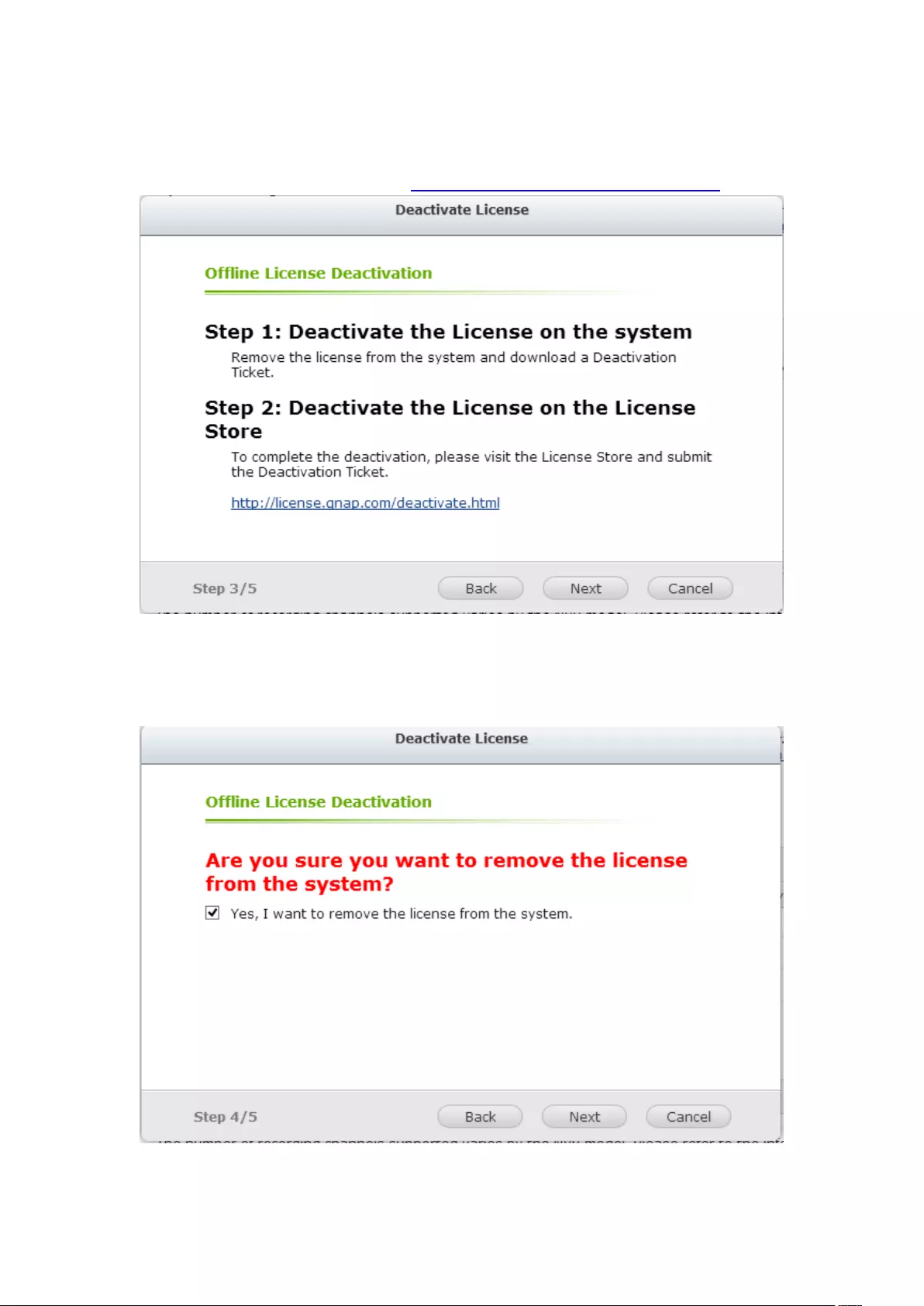
206
Step 3: Please read the instructions carefully. After you deactivate the license on the
system, you will need to download the deactivation ticket and visit the QNAP license
store to complete the deactivation. http://license.qnap.com/deactivate.html
Step 4: The system will prompt you to confirm your choice to remove the license. If
you are sure about deactivating the license, check “Yes, I want to remove the license
from the system.”
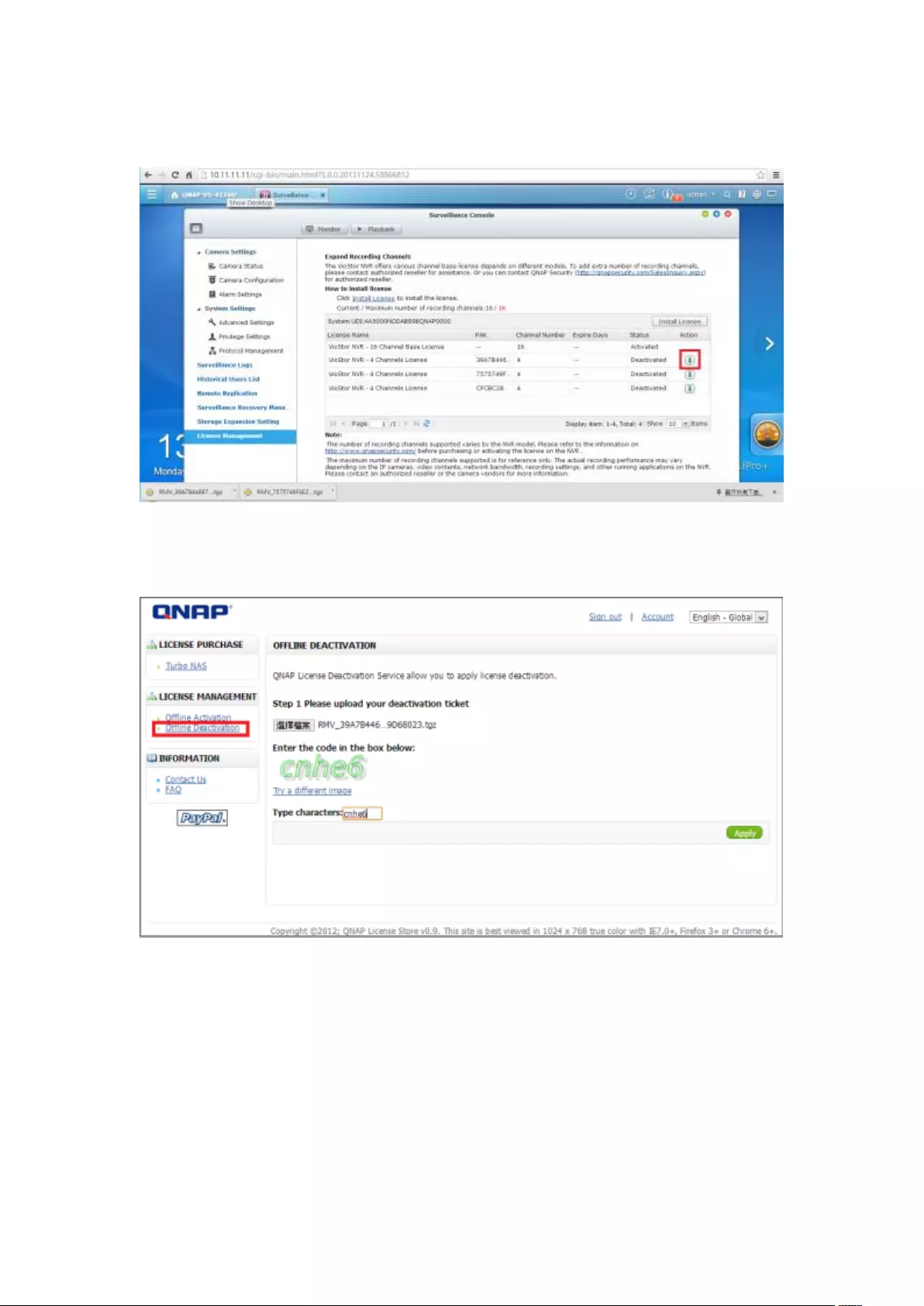
207
Step 5: The system will show that the license had been deactivated. Please download
the deactivated ticket from the column “Action”.
Step 6: Then please go to the QNAP license store, import the deactivation ticket and
then enter the code in the box. Please click “Apply” after you finish all these steps.
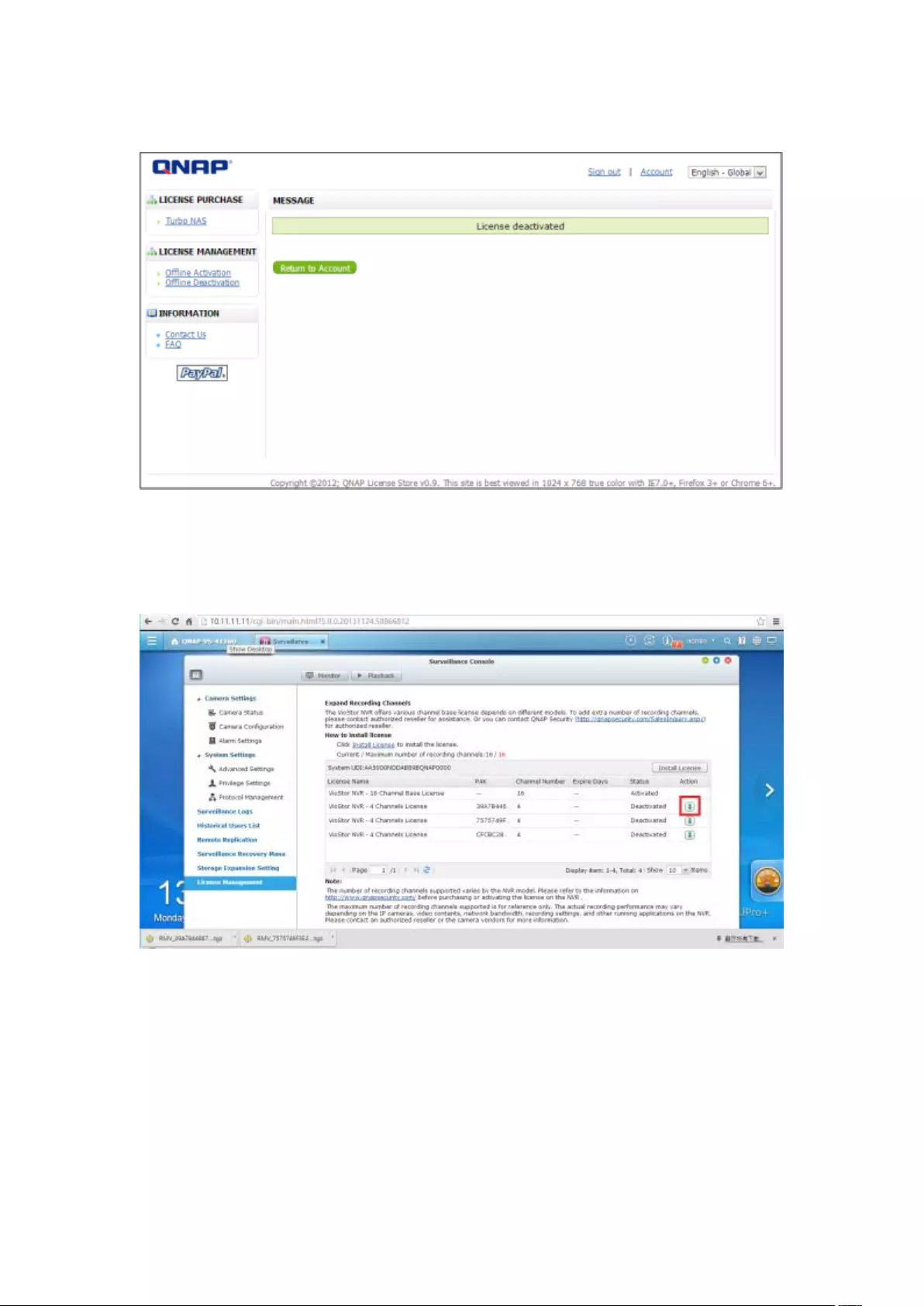
208
Step 7: The license store will show “License deactivated”.
Note: If you want to transfer the License to another VioStor NVR, please download
the “deactivation ticket” from the icon “” (under the “Action” column). Then contact
QNAP support for help.
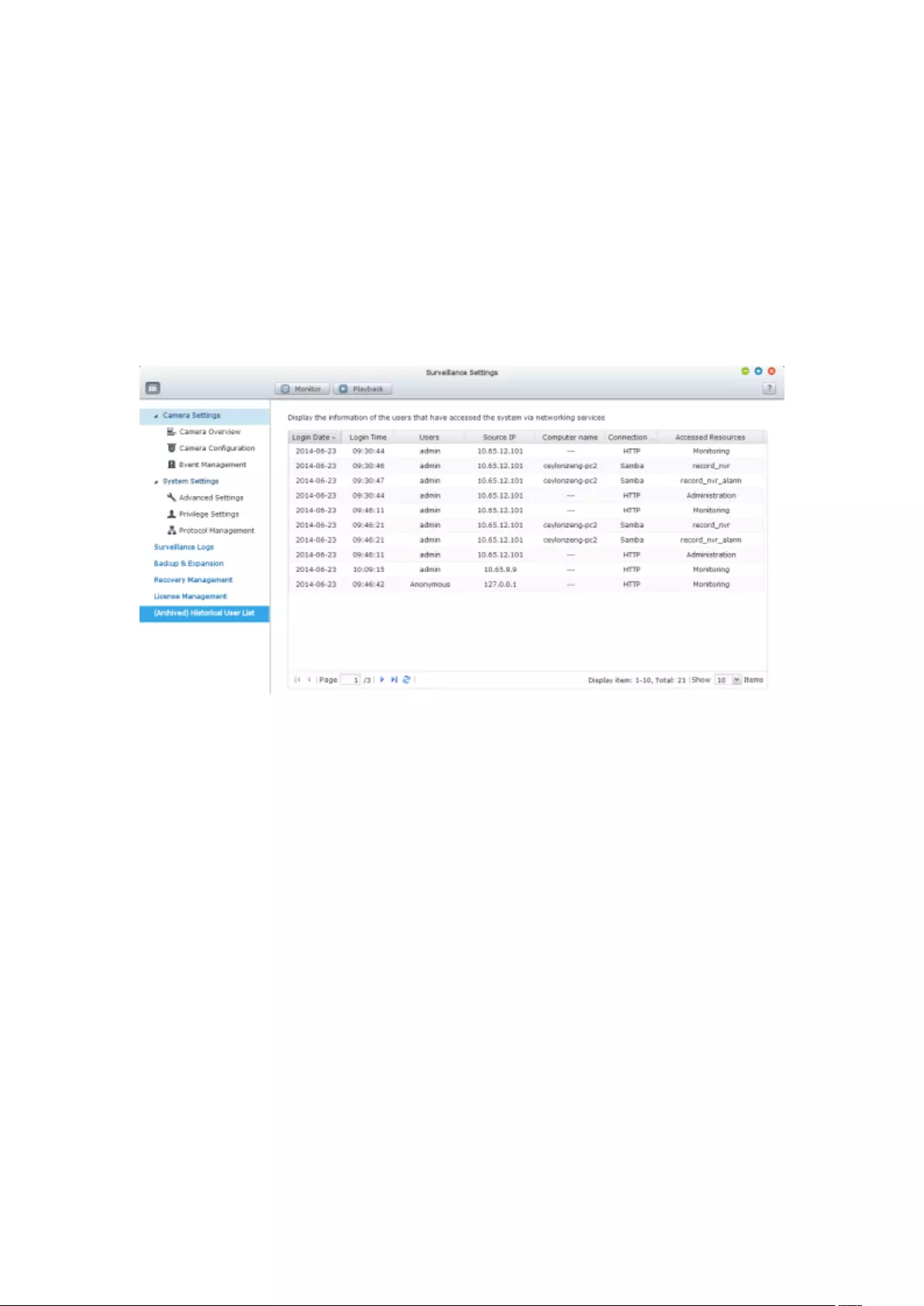
209
7.7 On-line Users List (Only for Upgrade from Previous
Version)
This page shows the information of the users before you upgraded to QVR 5.0, e.g.
the user name, IP address, and login time.
Please Note: The logs are currently only available in English.
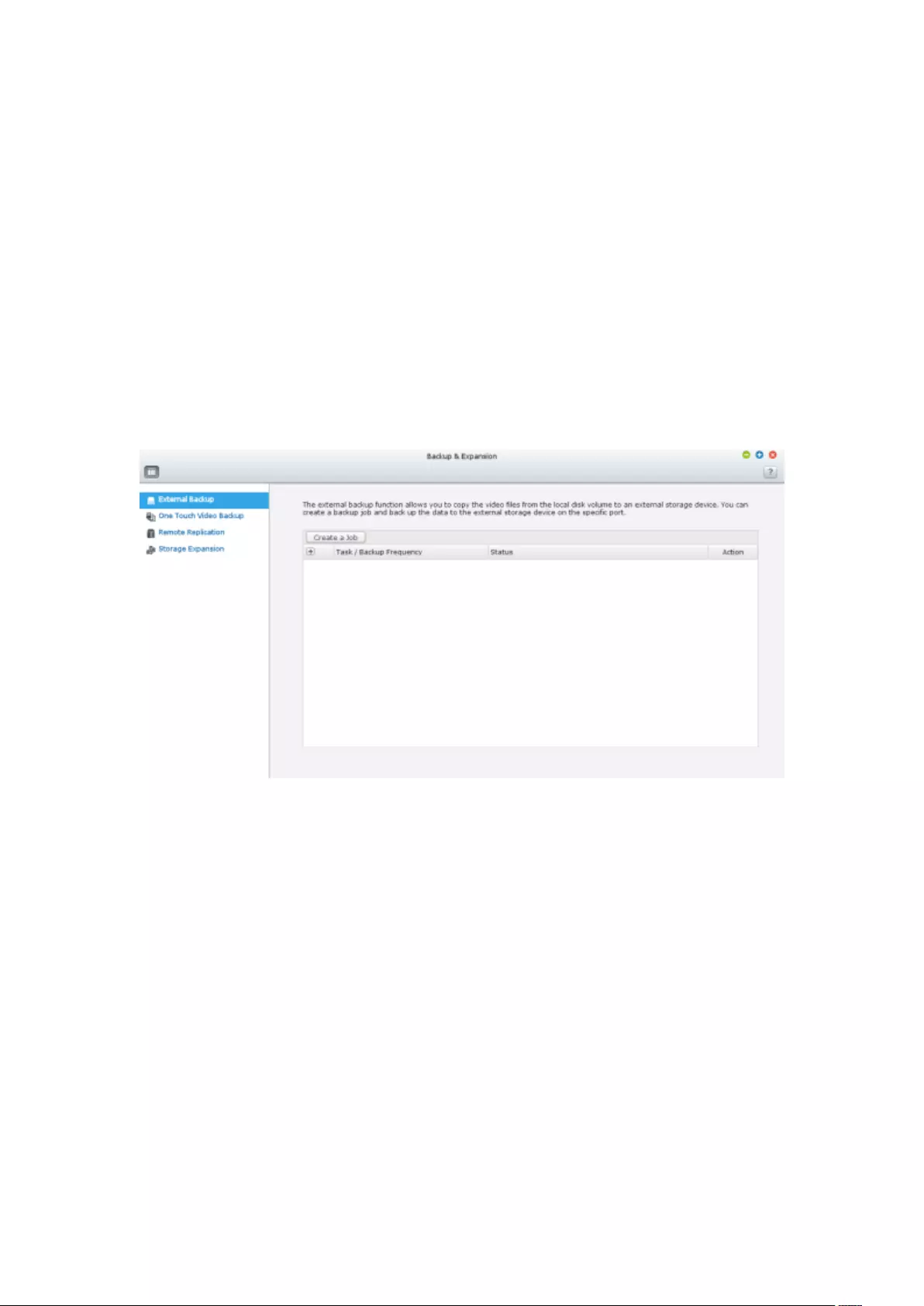
210
8. Backup & Expansion
8.1 External Backup
The NVR supports instant and scheduled data backup between the internal disk
volumes on the NVR and external USB storage devices. To use this feature, follow the
steps below.
1. Connect one or more external storage devices to the USB interfaces of the NVR.
2. Click “Create a job”.
3. When the wizard is shown, read the instructions carefully and click “Next”.
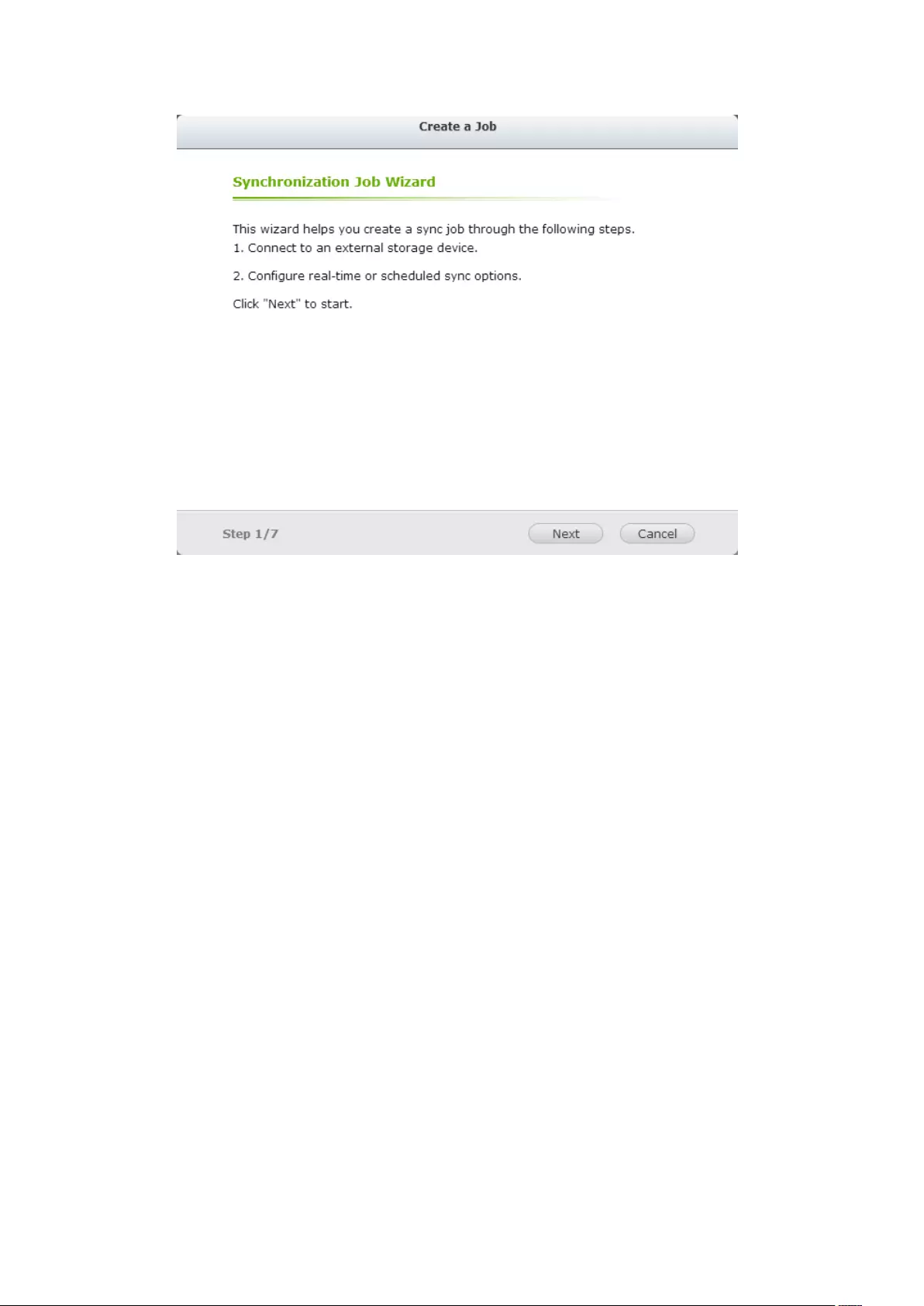
211
4. Select the backup locations.
A. Select an external disk volume* from the drop-down menu. The NVR
supports EXT3, EXT4, FAT, NTFS, and HFS+ file systems. The general
information of the storage device will be shown.
B. Click “Next”.
5. Configure the replication schedule.
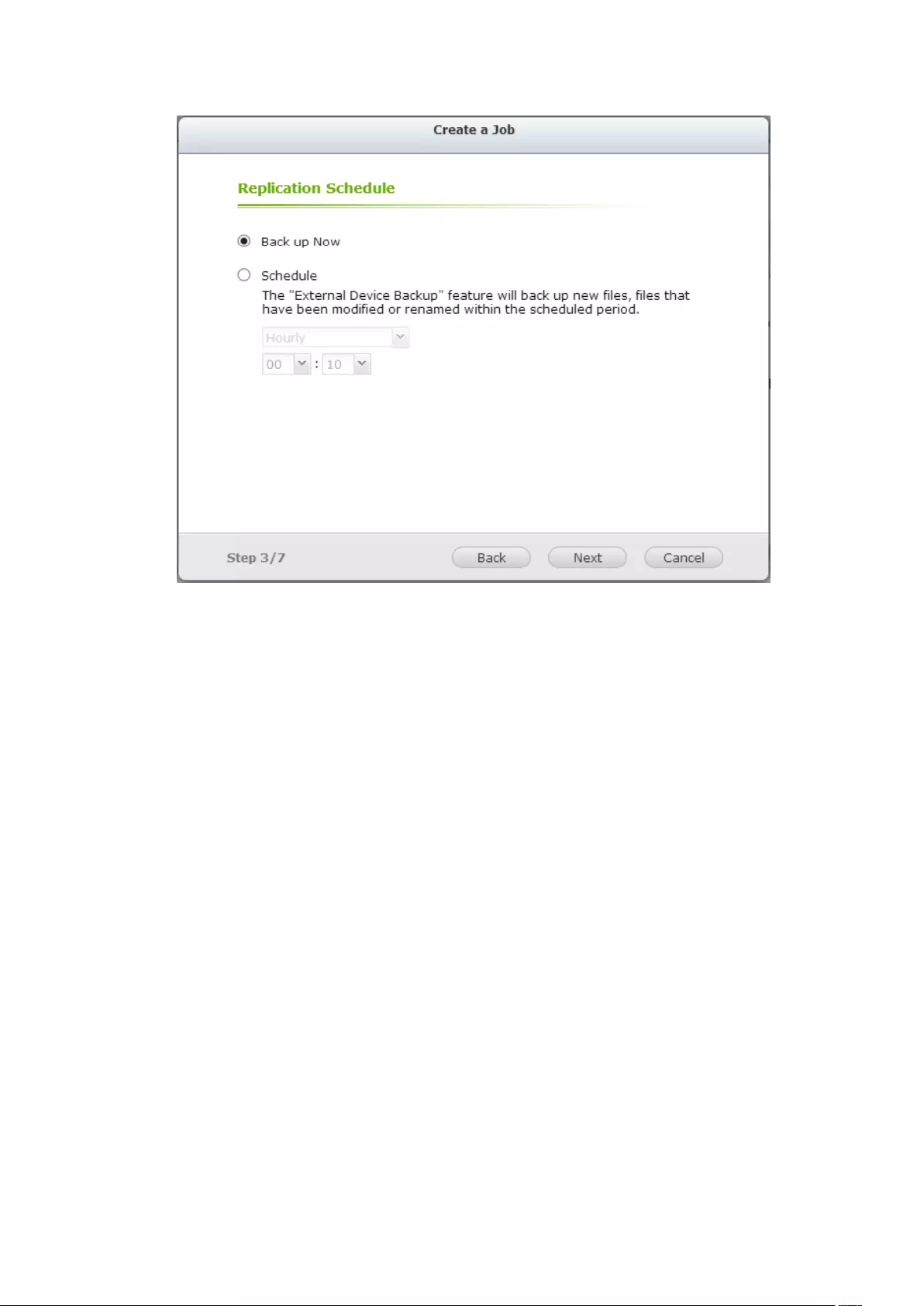
212
Choose between immediate backup and scheduled backup. The options are:
A. Back up Now: Immediately copies files that are different from the source
folder to the target folder.
B. Schedule: Copies files that are new, changed, and renamed from the source
folder to the target folder according to the schedule.
• Hourly: Select the minute when an hourly backup should be executed,
e.g. select 01 to execute the backup job every first minute of an hour, 1:01,
2:01, 3:01...
• Daily: Specify the time when a daily backup should be executed, e.g.
02:02 every day.
• Weekly: Select a day of the week and the time when a weekly backup
should be executed.
• Periodically: Enter the time interval in hour and minute that the
backup job should be executed. The minimum time interval is 5 minutes.
C. Click “Next”.
6. If you choose “Back up Now” and click “Next,” you can configure the backup
settings as below.
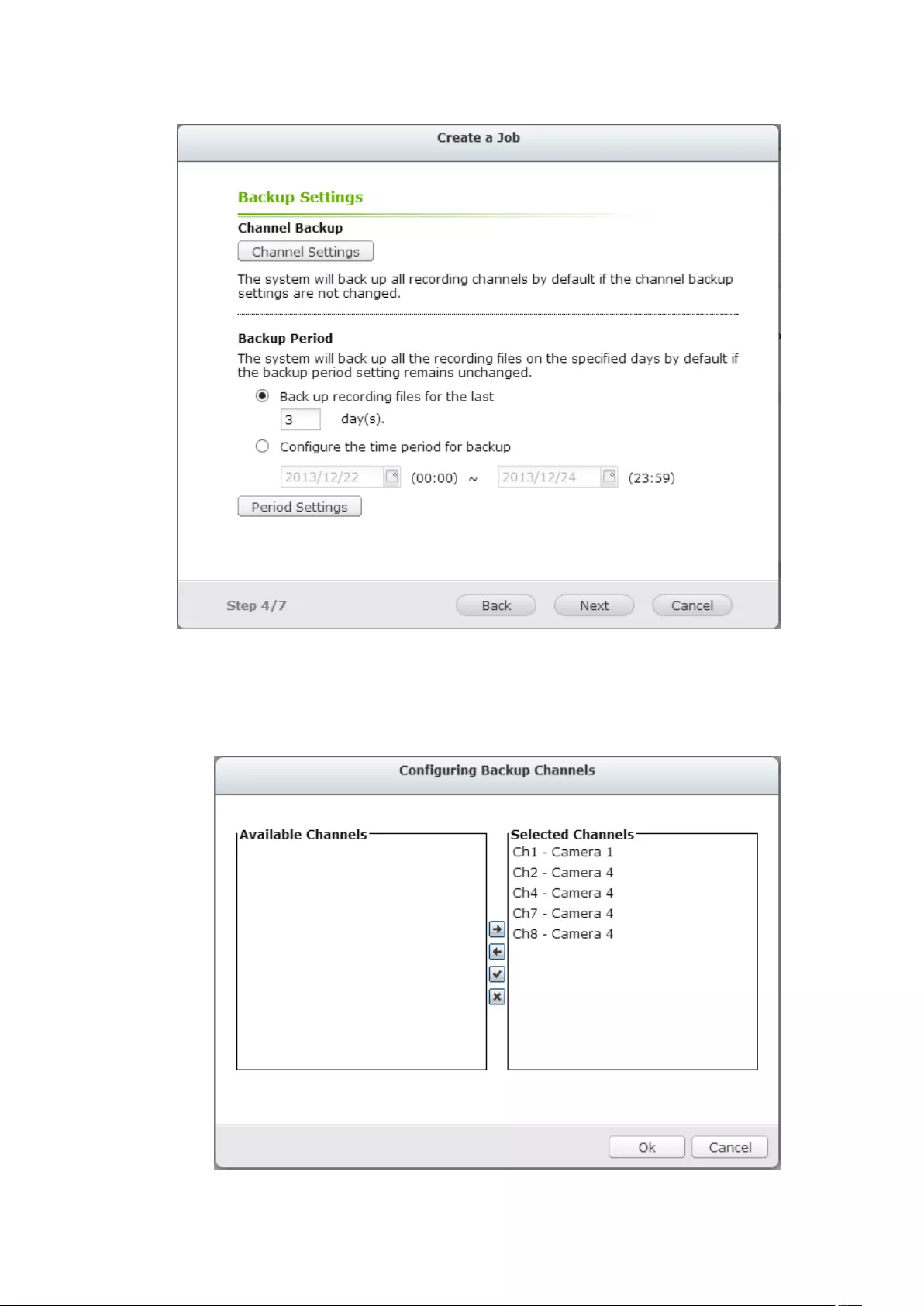
213
A. Configure backup channel.
If the backup channel settings are not changed, the system will back up all
recording channels by default.
You can click “Backup channel” to configure the backup channels.
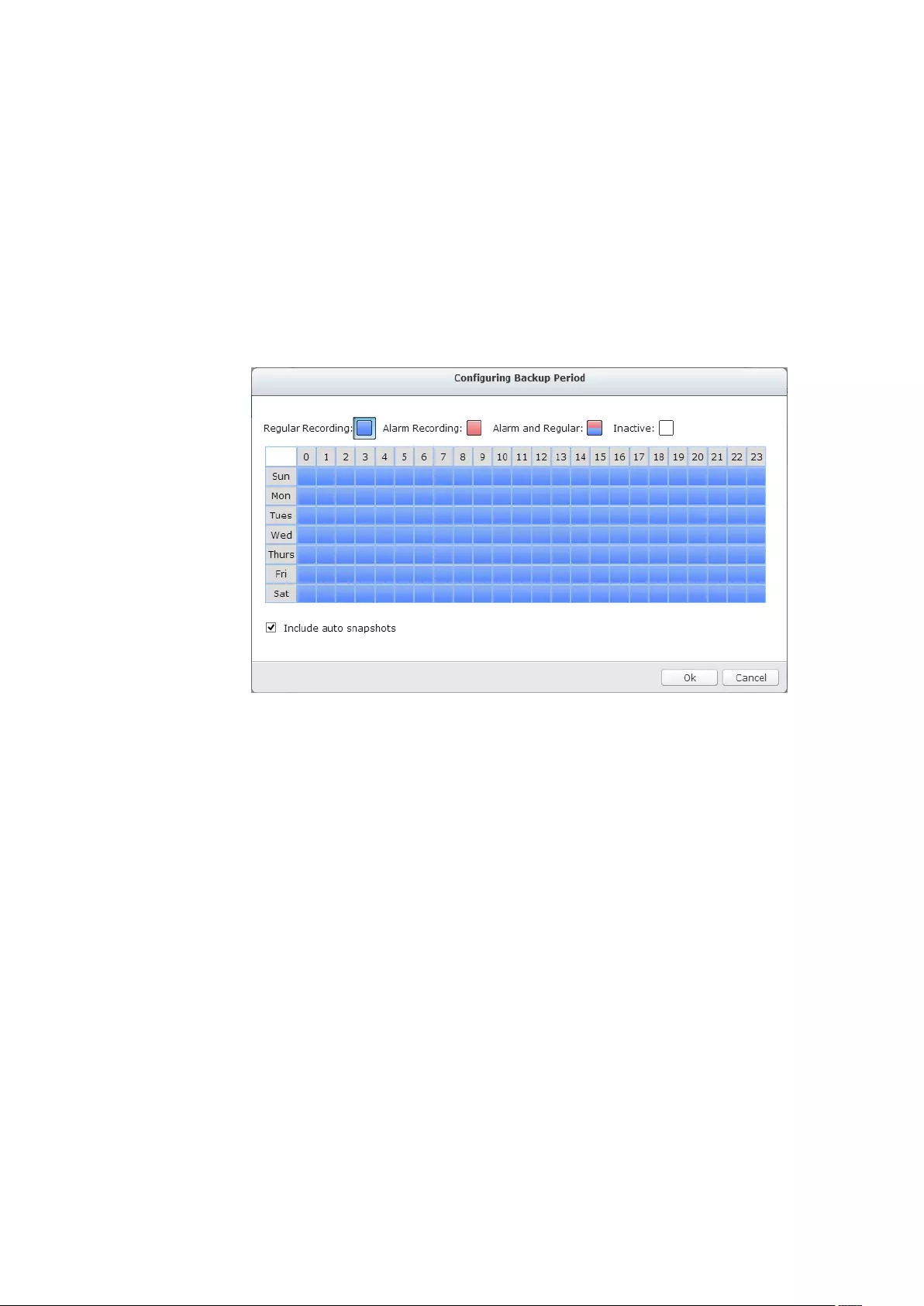
214
B. Configure backup duration and files
If the backup duration settings are not changed, the system will back up all
of the recording files on the specified days by default.
Set the number of days that the latest recordings should be backed up.
If 3 days are entered, the recordings of today, yesterday and the day
before yesterday will be backed up.
Or set the time period for backup.
You can click “Backup duration and files” to configure the backup
duration and files.
Enable “Include auto snapshots” to also copy the auto snapshot files
when the recordings are configured to back up.
C. Click “Next”.
7. If you choose “Schedule,” you can configure the backup settings as below.
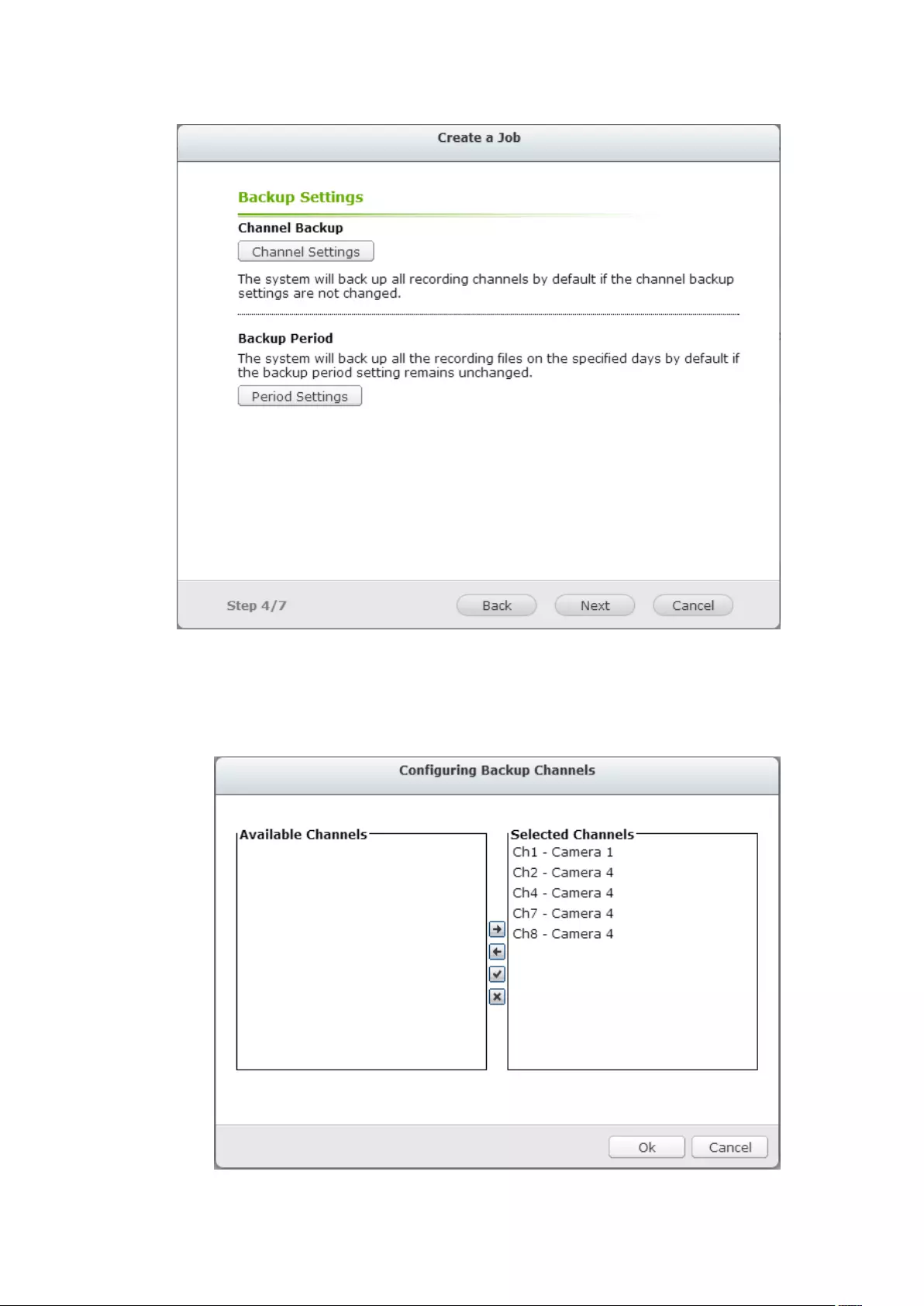
215
A. Configure backup channel.
If the backup channel settings are not changed, the system will back up all
of the recording channels by default.
You can click “Backup channel” to configure backup channels.
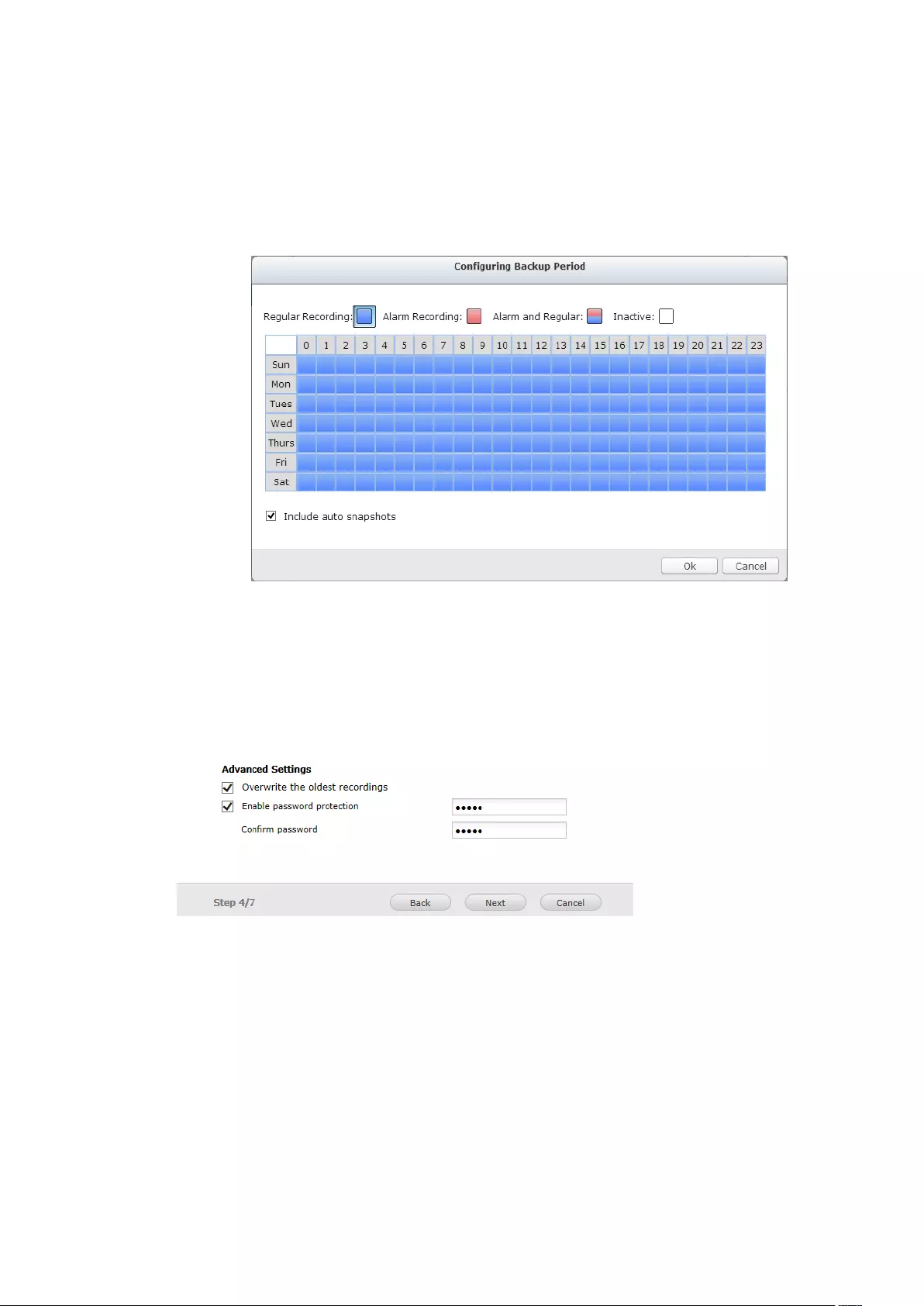
216
B. Configure backup duration
If the backup duration settings are not changed, the system will back up all
of the recording files on the specified days by default.
You can click “Backup duration and files” to configure backup duration
and files
Enable “Include auto snapshots” to also copy the auto snapshot files
when the recordings are configured to back up.
C. Click “Next”.
8. Advanced Settings include the ability to overwrite old recordings and to enable
password protection.
9. Enter a name for the backup job. A job name supports up to 63 characters; it
cannot start or end with a space. Click “Next”.
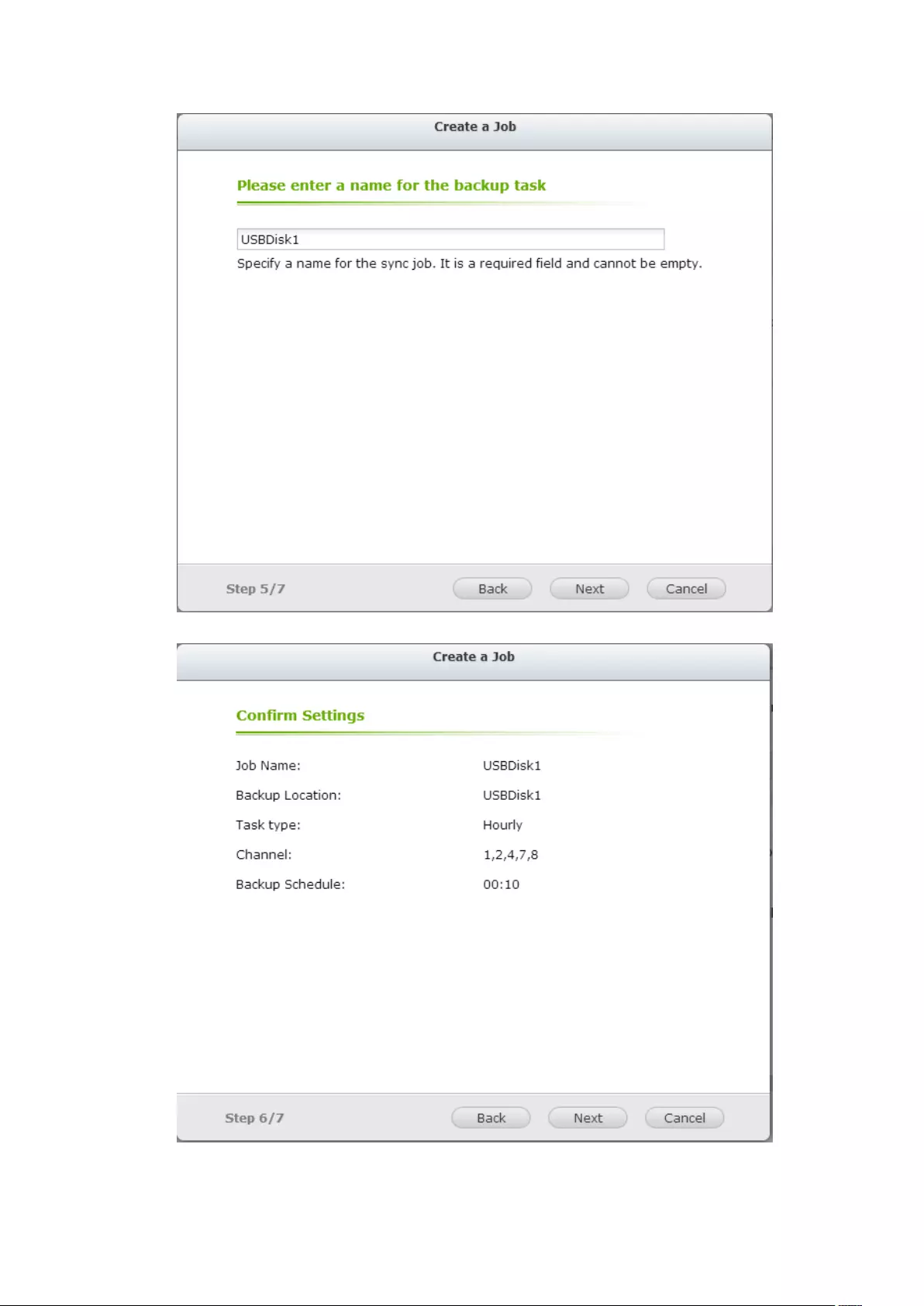
217
10. Confirm the settings and click “Next”.
11. Click “Finish” to exit the wizard.
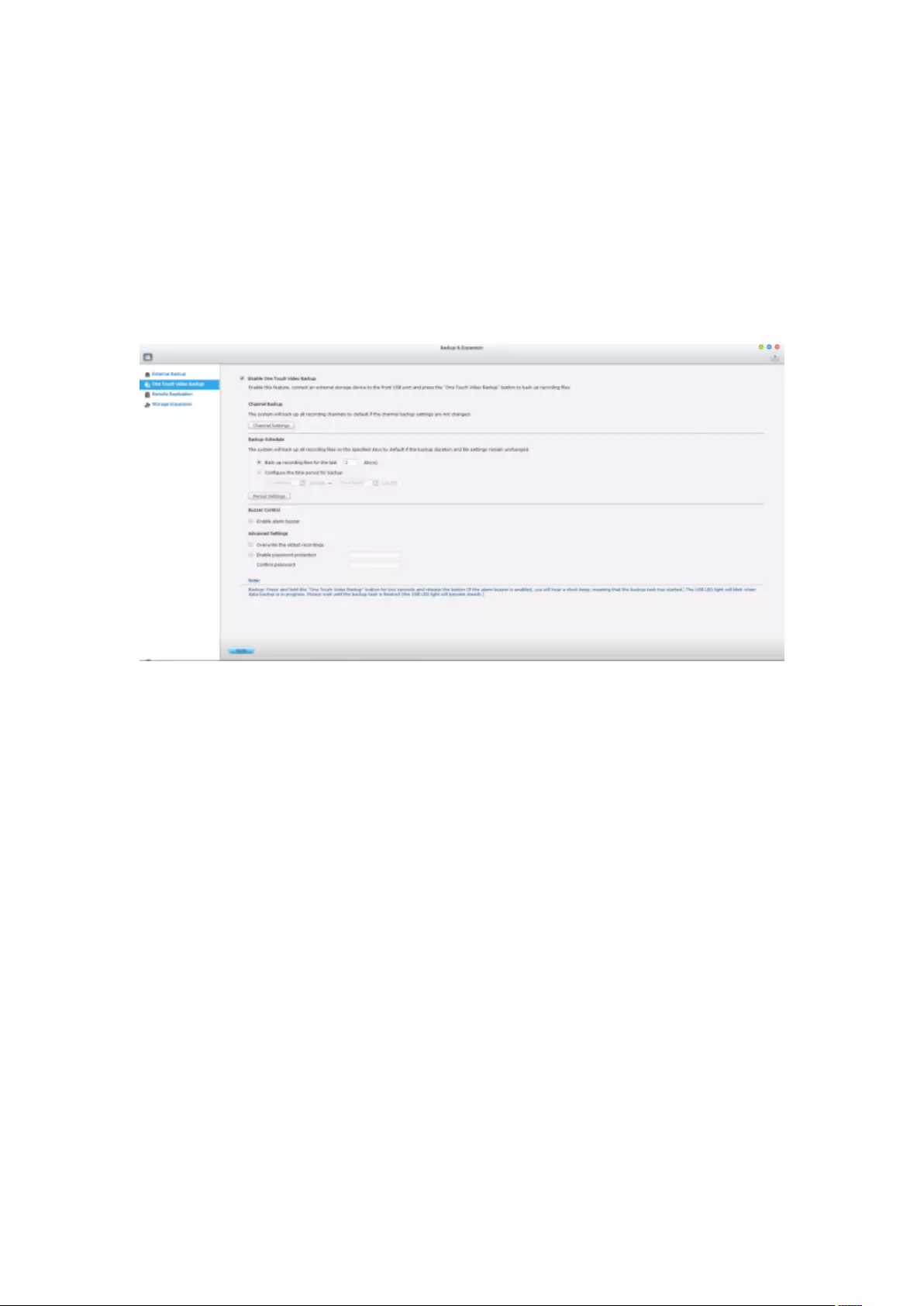
218
8.2 One Touch Video Backup
This option is valid only for series with a One Touch Video Backup button.
Enable this option to allow users to connect an external storage device to the front
USB port and press the “One Touch Video Backup” button to back up recording files.
To use this function, please follow the steps below:
1. Connect a USB storage device, for example, a USB disk drive to the front USB port
of the NVR.
2. Enable the option “Enable One Touch Video Backup.”
3. Configure backup channel.
If the backup channel settings are not changed, the system will back up all
recording channels by default.
You can click “Backup channel” to configure the backup channels.
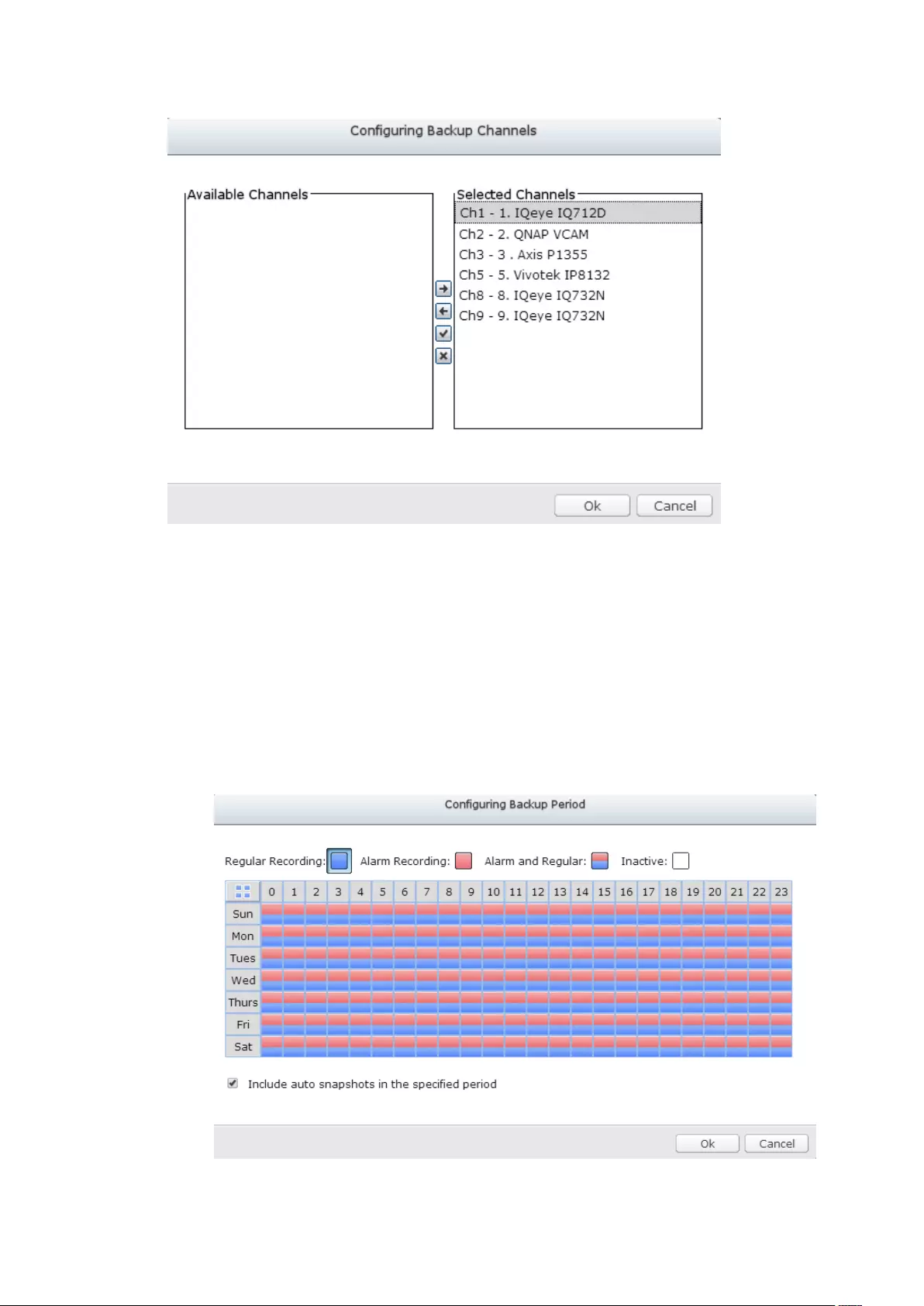
219
4. Configure backup duration and files
If the backup duration settings are not changed, the system will back up all of the
recording files on the specified days by default.
A. Set the number of days that the latest recordings should be backed up.
If 3 days are entered, the recordings of today, yesterday and the day before
yesterday will be backed up.
B. Or set the time period for backup.
C. You can click “Backup duration and files” to configure backup duration
and files.
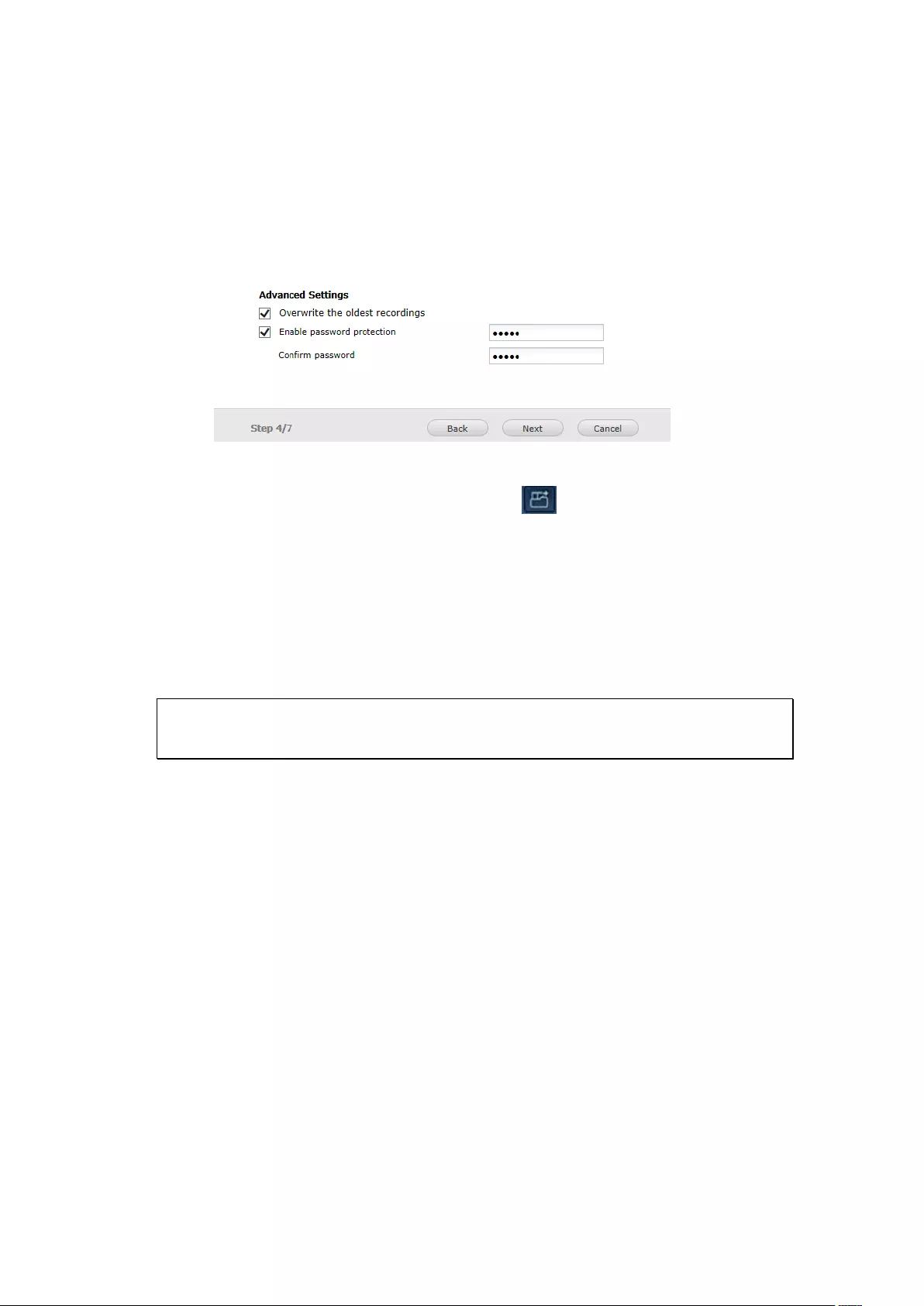
220
Enable “Include auto snapshots” to also copy the auto snapshot files when
the recordings are configured to back up.
5. Advanced Settings include the ability to overwrite old recordings and to
enable password protection.
When “Enable password protection” is applied, you will need to enter the
password to playback recording files via (Open playback files).
6. Click “Apply”.
7. Press and hold the video backup button for 3 seconds and the NVR will
immediately start copying the recording data to the USB device. If the USB
device is recognized, the USB LED will glow blue. The USB LED will flash blue
when the data is being copied. The LED will turn off after the data has been
copied. Then users can safely remove the device.
Note: Only USB devices with at least 10GB storage capacity are supported by this
video backup function.
Buzzer Control
After enabling the alarm buzzer, if you hear one short beep, it means ‘Backup has
started.
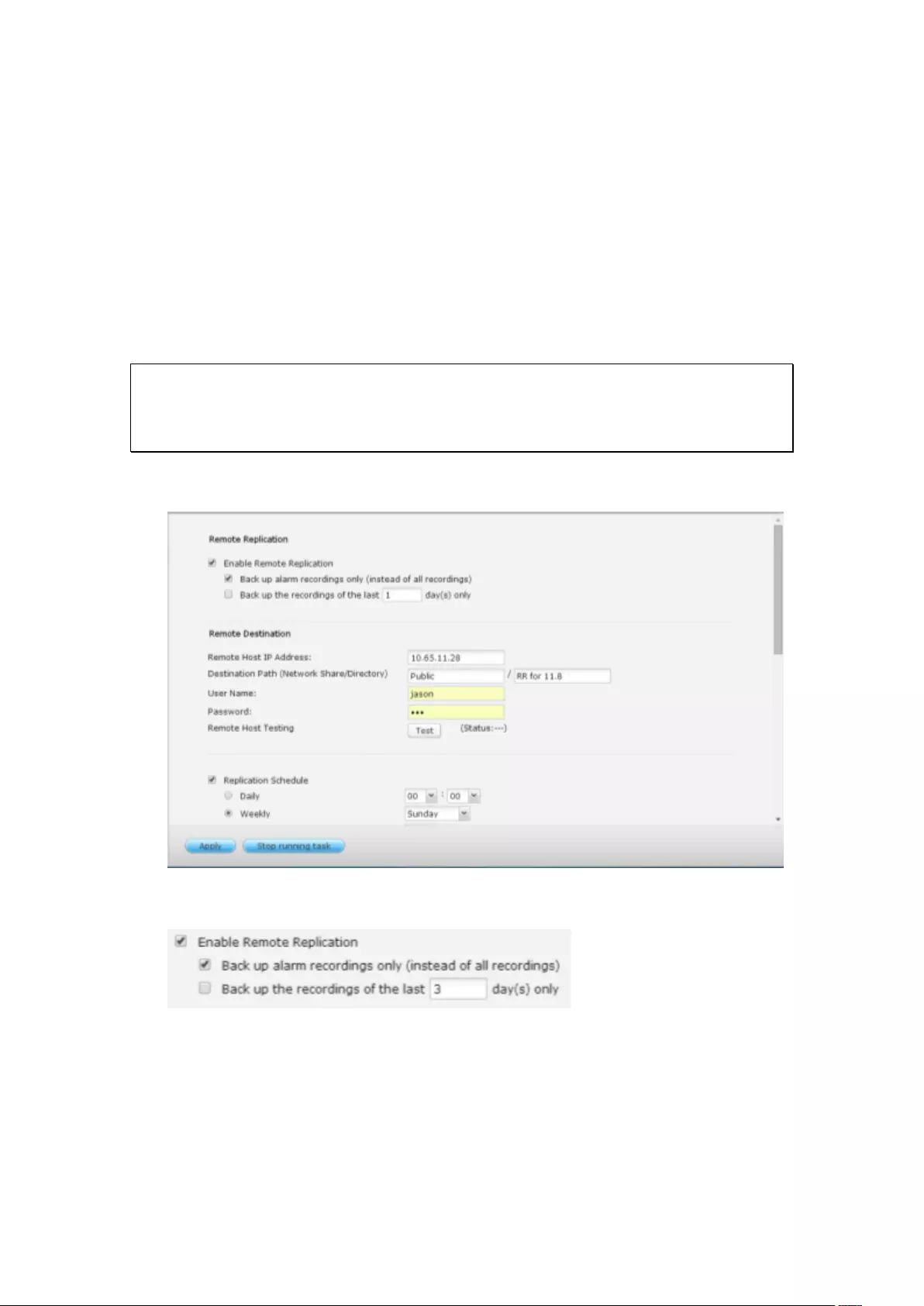
221
8.3 Remote Replication
Use the remote replication feature to copy the recording data of the local NVR to a
remote QNAP network attached storage (NAS). The remote QNAP NAS is hereafter
referred to as ‘the remote storage device’.
Note: Before using this function, make sure the Microsoft networking service of the
remote storage device is enabled, and the corresponding path and user access right
has been correctly configured.
1. Login to the QVR desktop and go to ‘Backup & Expansion’ > ‘Remote Replication’.
2. Enable remote replication (supports multiple choices)
In the above example, the NVR only copies the alarm recording data of the latest
3 days to the remote storage device.
Select ‘Enable remote replication’ to activate this feature. The NVR will execute
an automatic backup of the recording data to the remote storage device
according to the settings.

222
Select ‘Back up alarm recordings only (instead of all recordings)’, the NVR will
only copy the alarm recording data to the remote storage device. If this option
is unselected, the NVR will back up all of the recording data to the remote
storage device.
Select ‘Back up the recordings of the latest…day(s) only’ and enter the number of
days, the NVR will back up the latest recording data to the remote storage device
automatically according to the settings. If this option is unselected, the NVR will
copy all of the recording data to the remote storage device.
3. Configure the remote storage server
Enter the IP address, path, user name and password of the remote storage
device.
Note: It is recommended to execute the ‘Remote host testing’ function to verify the
connection to the remote storage device is successful.
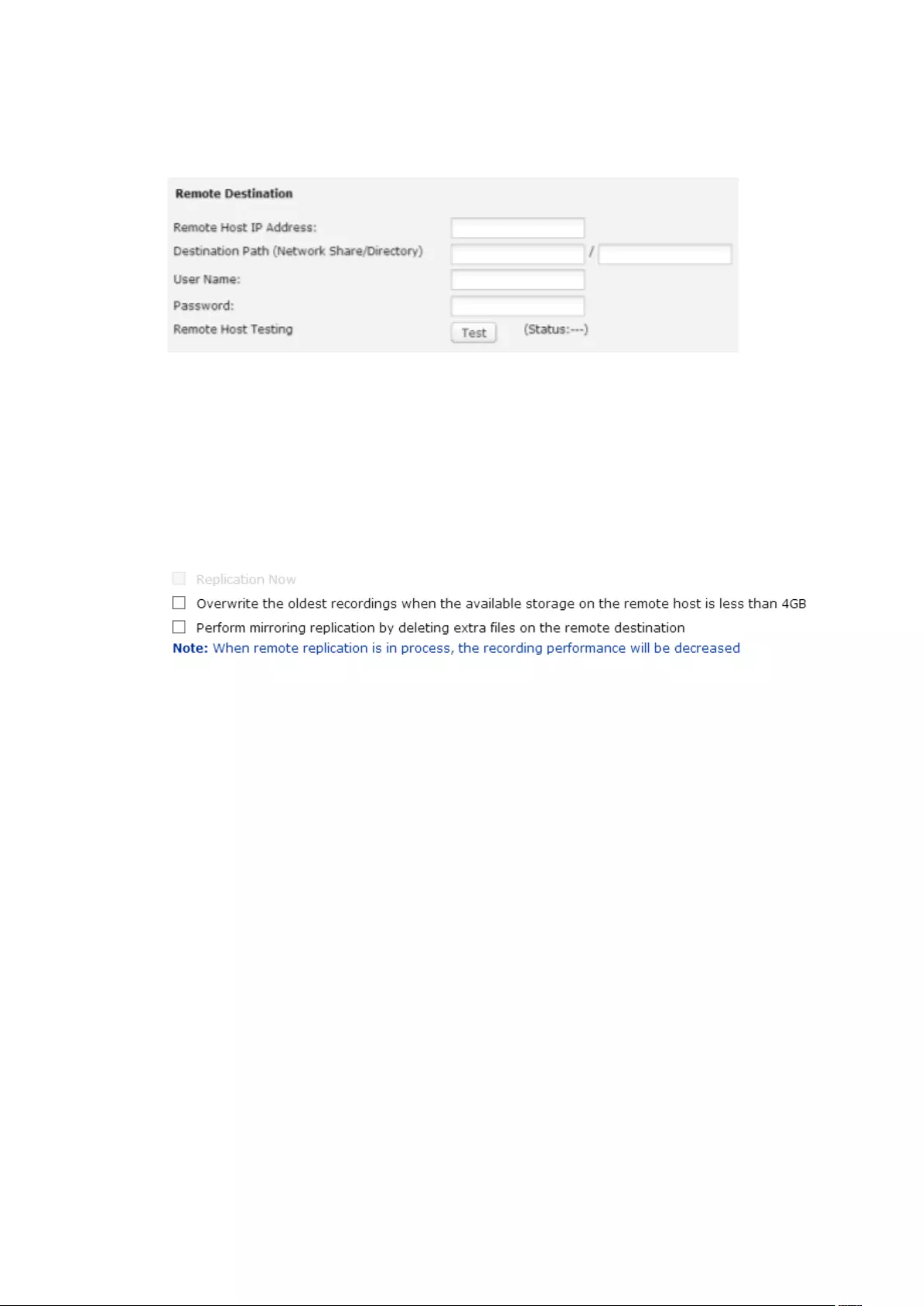
223
4. Configure the remote replication schedule
For example, to enable the NVR to copy the recording data automatically to the
remote storage device at 01:15 every Monday, please do the following:
Select ‘Replication Schedule’, select ‘Weekly’, enter 01 Hour: 15 minute, and
select ‘Monday’.
5. Select the backup options
Select ‘Replication Now’, the NVR will back up the recording data to the remote
storage device immediately.
Select ‘Overwrite the oldest recordings when the available storage on the remote
host is less than 4GB’; the NVR will overwrite the oldest recording data when the
free space on the server is less than 4GB.
Select ‘Perform mirroring replication by deleting extra files on the remote
replication’, the NVR will synchronize the recording data between itself and the
remote storage device and delete any extra files on the remote storage device.
When the above options are all selected and remote replication is executed, the NVR
will do the following:
i. The NVR checks if there are files on the remote storage device that are different
from the local source. If yes, the differentiated files will be deleted.
ii. Next, the NVR checks the free space of remote storage device. If the free space
is larger than 4GB, the remote replication will be executed immediately.
iii. If the free space of the remote storage device is less than 4GB, the NVR will
overwrite the recording data of the oldest day and then executes the remote
replication.
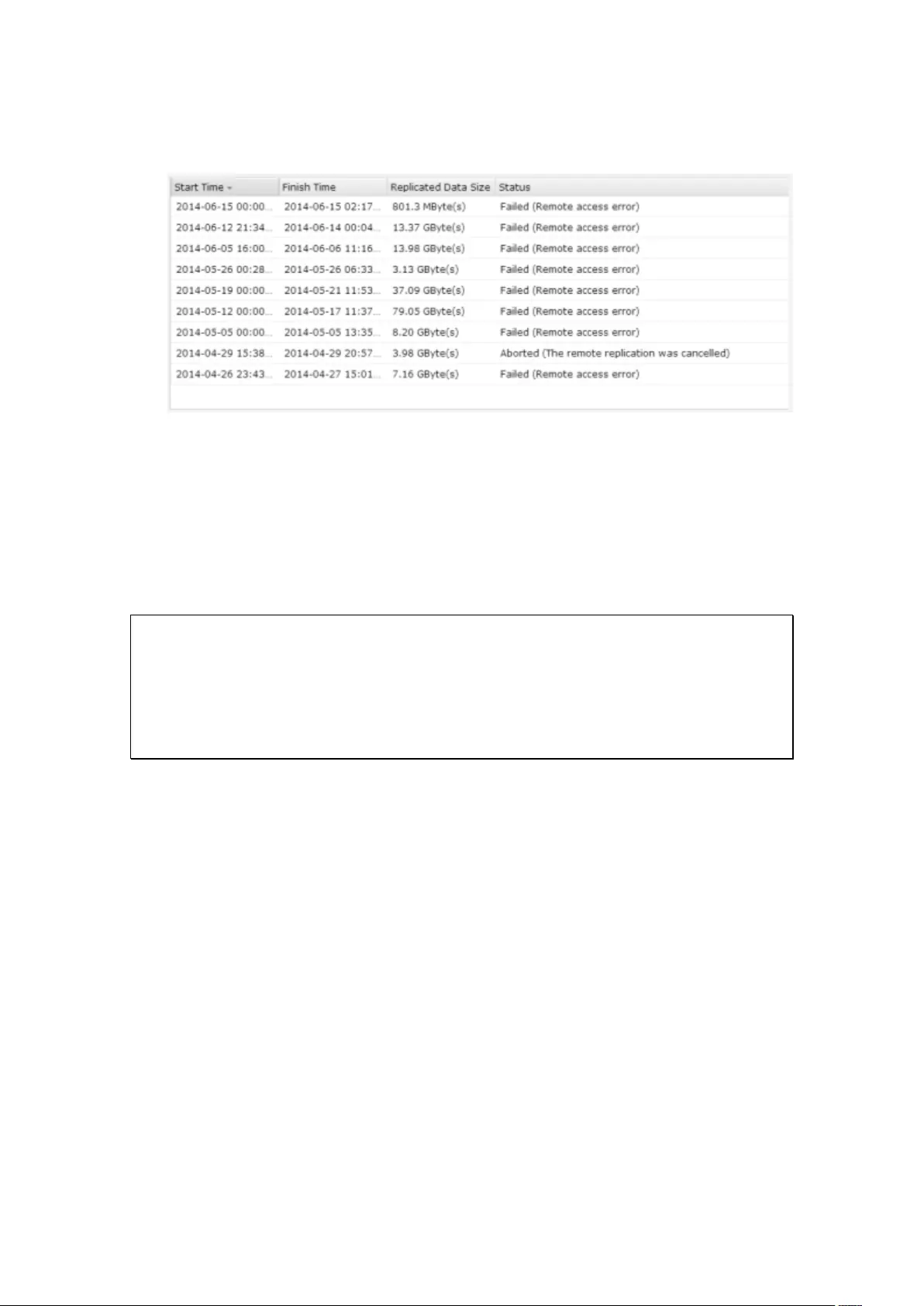
224
6. The NVR displays the latest 10 remote replication records.
In the above example:
When the status is shown as ‘Failed (Remote access error)’: Check to see if the
remote storage device is running and if the network settings are correct.
When the status is shown as ‘Failed (An internal error occurred)’: Check the hard
drive status of the NVR and view the Event Logs.
Note: The time required by the NVR to replicate the data to the remote storage
device varies depending on the network environment. If the remote replication
takes too long, some recording files may be overwritten by the NVR. To avoid this,
it is recommended to refer to the status messages to analyze the time required for
the remote replication and adjust the replication schedule accordingly.

225
8.4 Storage Expansion
Without a doubt, storage plays a significant role in the field of digital surveillance.
However, users everywhere are facing the challenge of storage capacity for long-term
recording. Now, QNAP Security has introduced the storage expansion feature to
eliminate this problem. Making the right storage decision with regard to storage
expansion is truly important to save money & time for all users. The various QNAP
Turbo NAS models are the solution that expands on the storage capacity of the NVR
to save more recording files. The storage expansion can provide up to 64TB (16-bay
model) additional space per channel, totaling more than 200TB. Integration of both
QNAP devices can help users easily save a significant amount of recording files.
Key features:
1. Addressing user needs: Users can expand their storage capacity based on their
needs.
2. Reducing expense: This is a cost-effective choice for expanding storage capacity.
3. Highly scalable for future storage expansion.
Limitations and Restrictions:
1. Currently, Storage Expansion is only supported by the VioStor Pro(+) series and
QNAP x86-based NAS models (with firmware version v4.0.2 and above), and they
are required to be set on the same LAN.
2. A gigabit switch is required for this application.
3. For NVR and NAS servers located on the same subnet, please always use static IP
addresses and the same subnet mask.
4. Modification on storage expansion related settings is not supported on local
display.
5. The file moving process between the NVR and NAS will be completed even if it is
suddenly interrupted (for example, the destination folder is deleted). For example,
the cache count is set to six hours. The destination is changed to none in the
middle of the processing. When this happens, the NVR will still move recording
files to the NAS until the entire process is finished.
Note:
In order to ensure that Storage Expansion can be executed during the recording
226
process, please be advised to estimate the limitation on network throughput for
specific VioStor NVR series.
The following is suggested limitation of the network throughput for specific NVR
models:
VS-8100 Pro+/8100U-RP Pro (+)/12100U-RP Pro (+) series: 360 Mbps.
VS-2100 Pro+/4100 Pro+/6100 Pro+ series: 160 Mbps.
VS-2000 Pro/4000 Pro/6000 Pro series: 90 Mbps.
How to configure Storage Expansion?
Step 1:
Install the StorageExpansion QPKG on the NAS
Note: Please visit our download center to download the QPKG. Before installing the
QPKG package, please make sure the QPKG is correct, read the instructions carefully
and back up all the important data on the NAS.
1. Download
and unzip the StorageExpansion package.
To install the QPKG, please click “Browse” to select the correct QPKG file and
click “INSTALL”.
Disable: disable the StorageExpansion QPKG.
Remove: remove the StorageExpansion QPKG.
2. Click the link
to connect to the webpage and configure the settings.
Check available NVRs on the list and their status on this page.
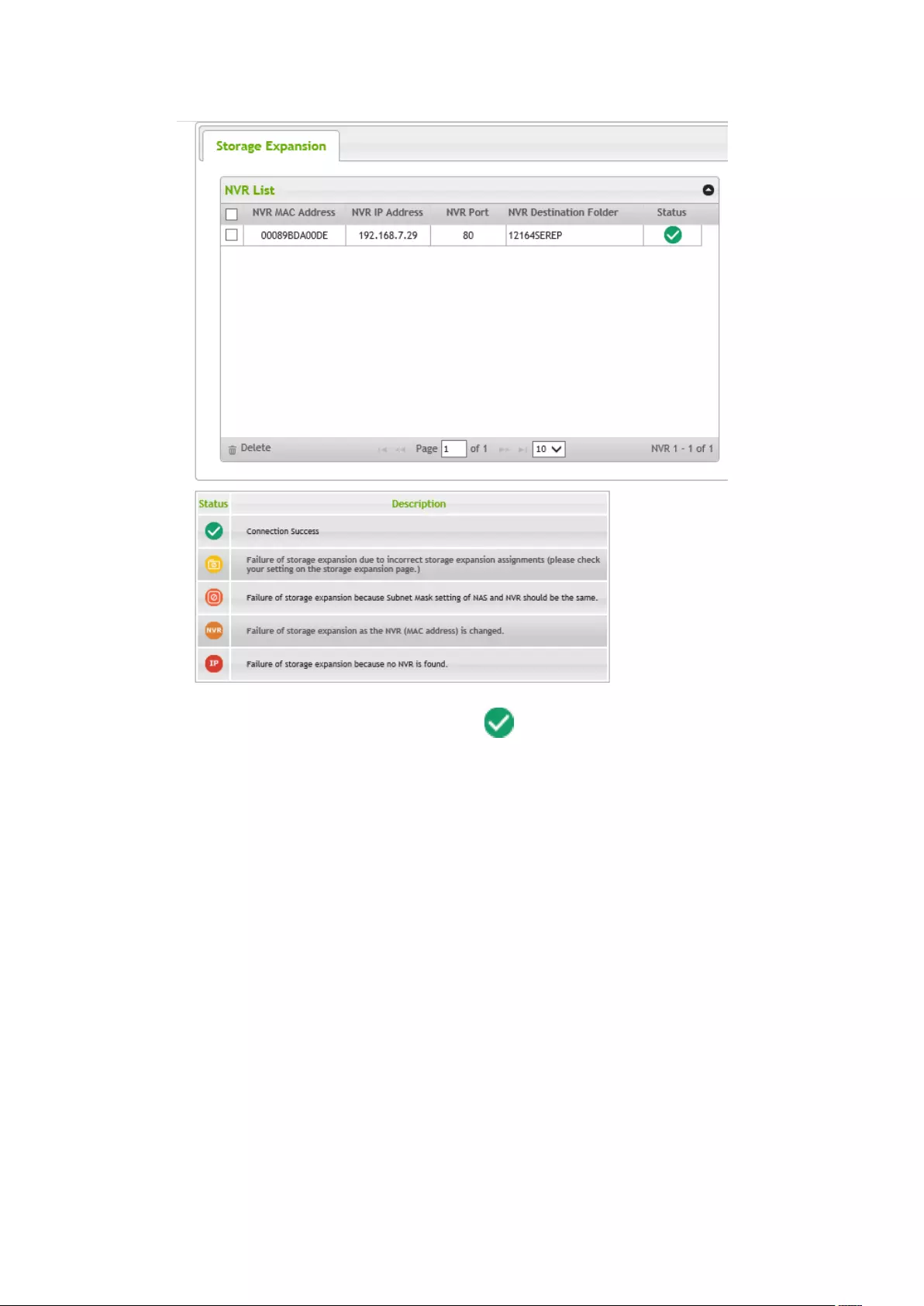
227
Note: The status of an NVR will become after storage expansion
assignment is completed.
Step2:
Please make sure that the StorageExpansion QPKG has been installed on the NAS and
enable Storage Expansion.
1. Go to
“Camera Setting” “Storage Expansion” to configure relevant settings on the
page.
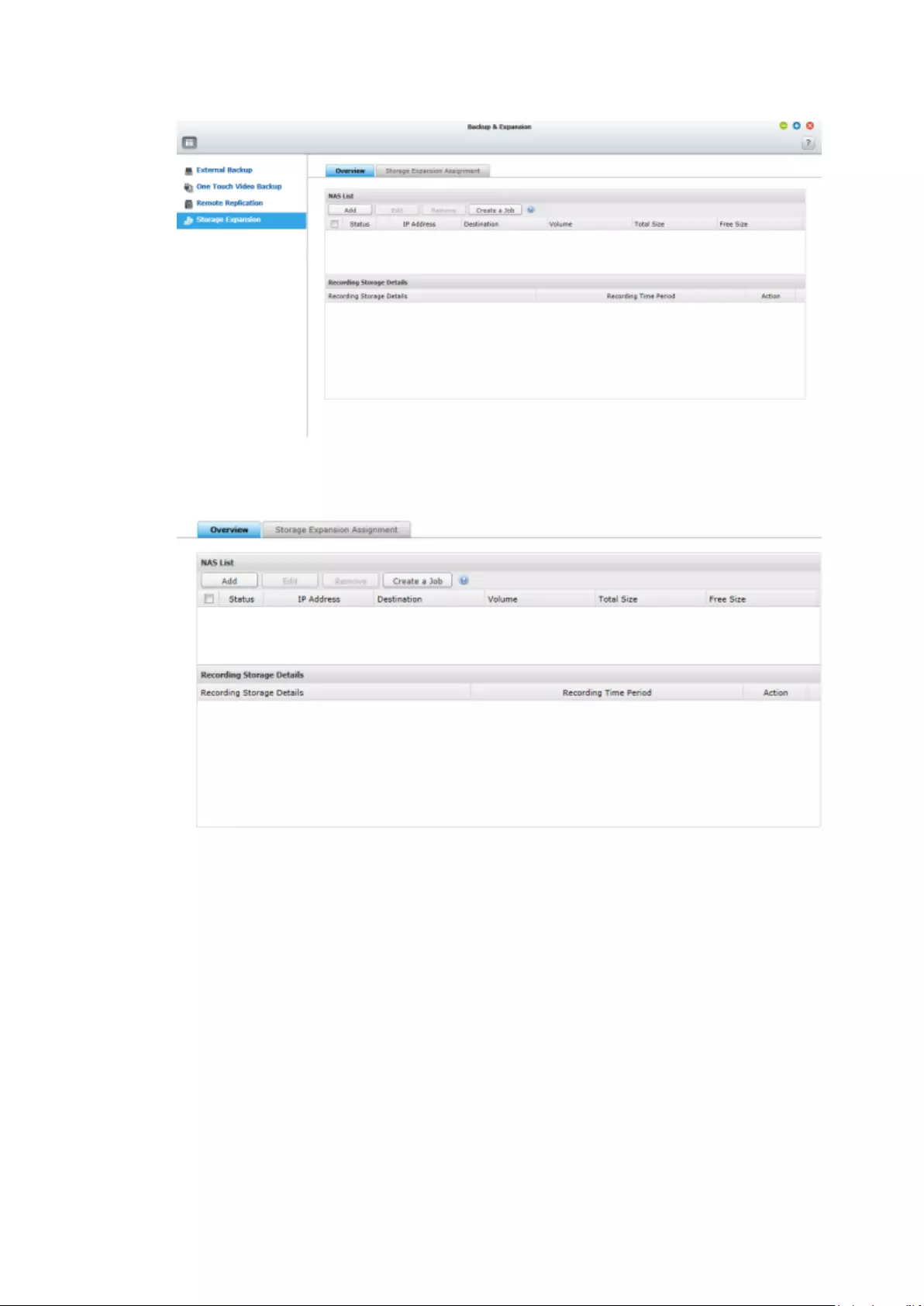
228
2. Click
“Overview” then the “Add” button.
Please enter the IP, port, username, password, destination, volume and cache
count for the NAS.
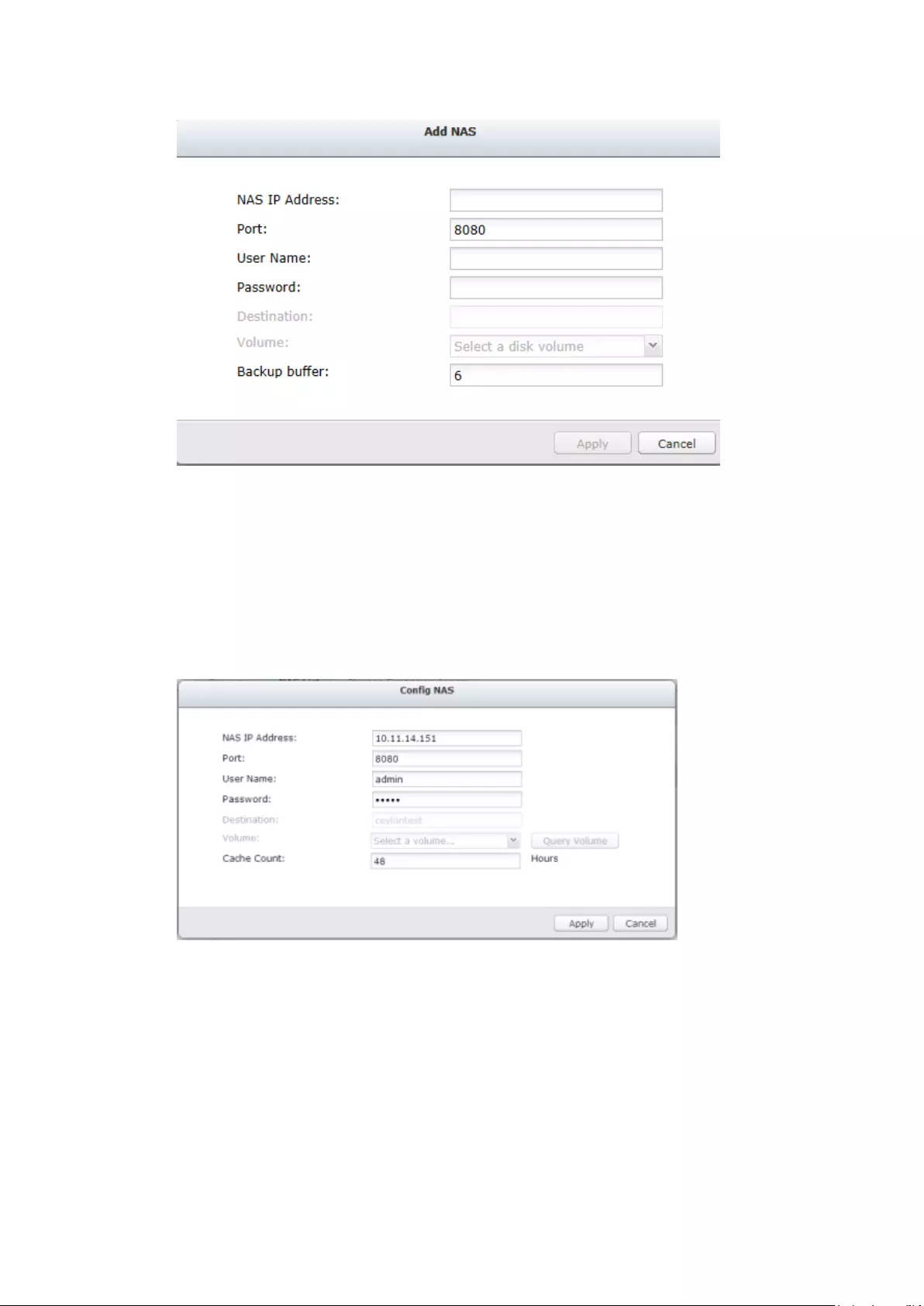
229
Note:
Destination Folder: The folder created on the NAS to save recording files.
Volume: The volume assigned for storage expansion.
Backup buffer: The time period for recording files to be moved to the NAS. The
range is from 2-48 hours.
3. Config NAS:
Modify NAS settings on this page.
4. Click “Storage
Expansion Assignment” to choose a NAS as the storage unit for each channel.
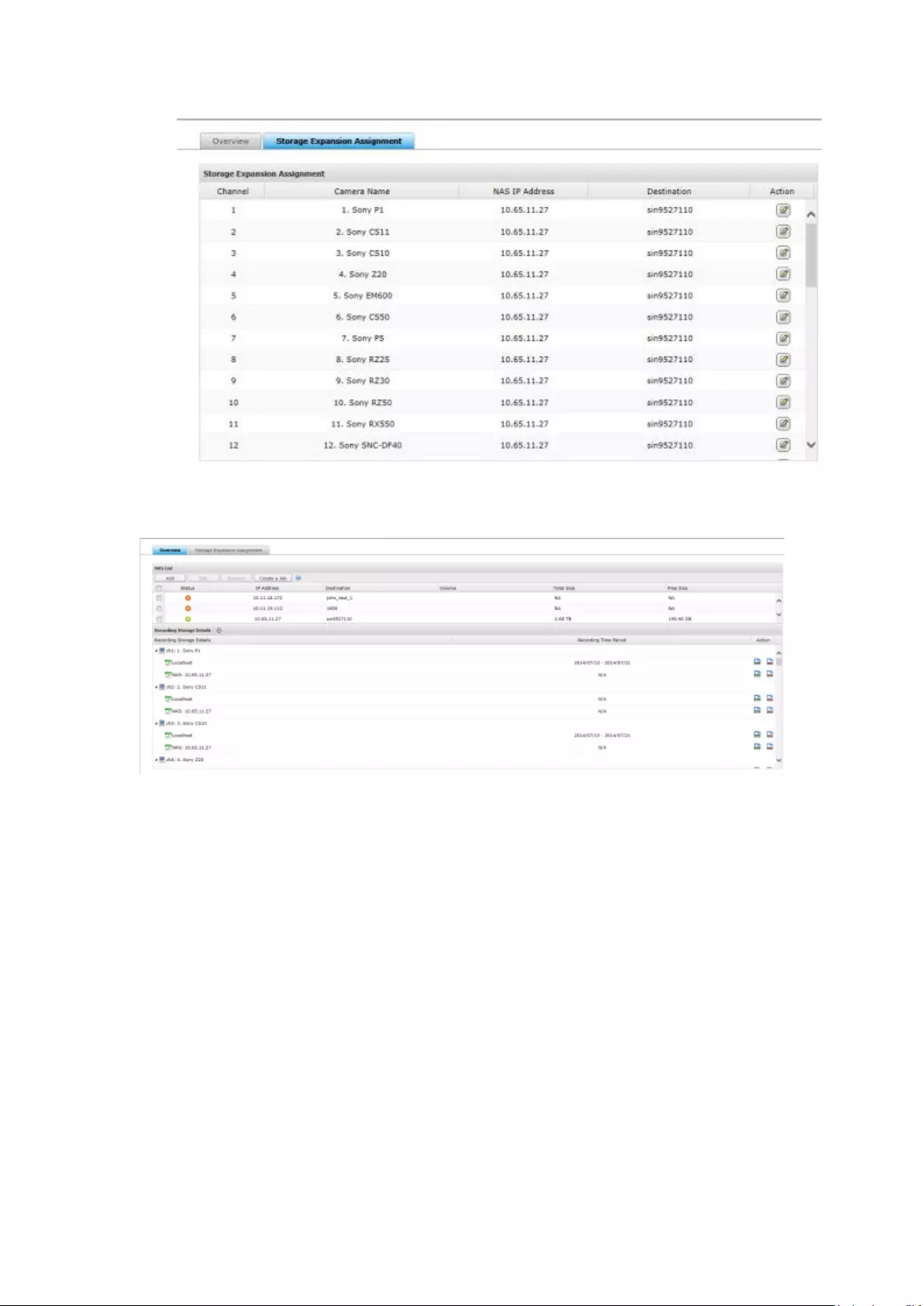
230
Review all of the configured settings and recording storage details under “Overview”.
The page will automatically refresh the status every fifteen minutes.
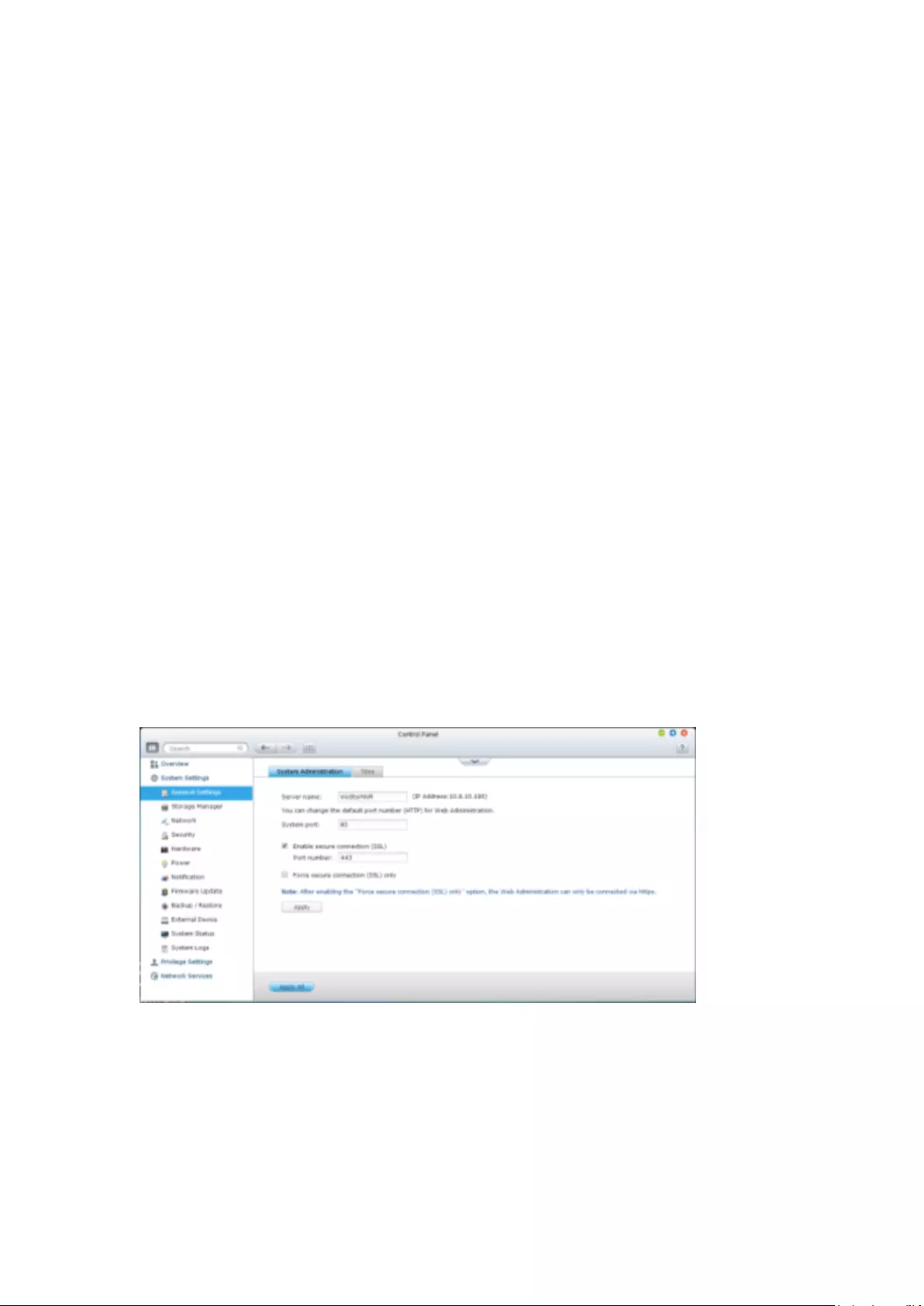
231
9. Control Panel
9.1 System Settings
9.1.1 General Settings
System Administration
Enter the name of the NVR. The NVR name supports maximum 14 characters and can
be a combination of the alphabets (a-z, A-Z), numbers (0-9), and dash (-). Space ( ),
period (.), or pure number are not allowed.
Enter a port number for the system management. The default port is 80. If you are
not sure about this setting, use the default port number.
Enable Secure Connection (SSL)
To allow the users to connect the NVR by HTTPS, turn on secure connection (SSL) and
enter the port number. If the option “Force secure connection (SSL) only” is turned
on, the users can only connect to the web administration page by HTTPS connection.
Time
Adjust the date, time, and time zone according to the location of the NVR. If the
settings are incorrect, the following problems may occur:
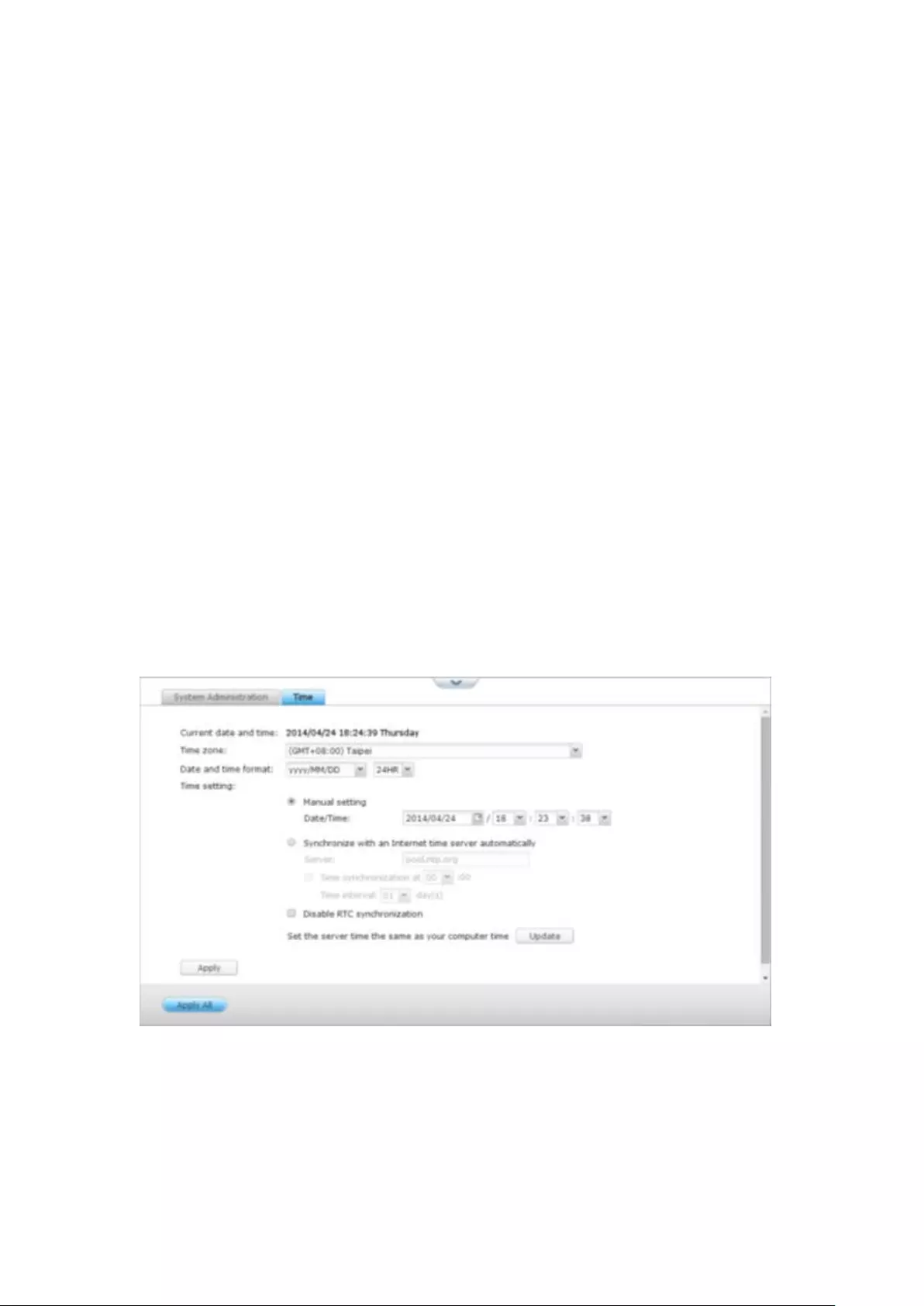
232
•
The display time of the recordings will be incorrect.
•
The time of the event log displayed will be inconsistent with the actual time when
an action occurs.
Synchronize with an Internet time server automatically
Turn on this option to synchronize the date and time of the NVR automatically with
an NTP (Network Time Protocol) server. Enter the IP address or domain name of the
NTP server, for example, time.nist.gov, time.windows.com. Then enter the time
interval for synchronization. This option can be used only when the NVR is connected
to the Internet.
Disable RTC synchronization
Disable this option to enable RTC synchronization.
Note: A real-time clock (RTC) is a computer clock (most often in the form of an
integrated circuit) that keeps track of the current time.
Set the server time the same as your computer time
To synchronize the time of the NVR with the computer time, click “Update” next to
this option.
Note: The first time synchronization may take several minutes to complete.
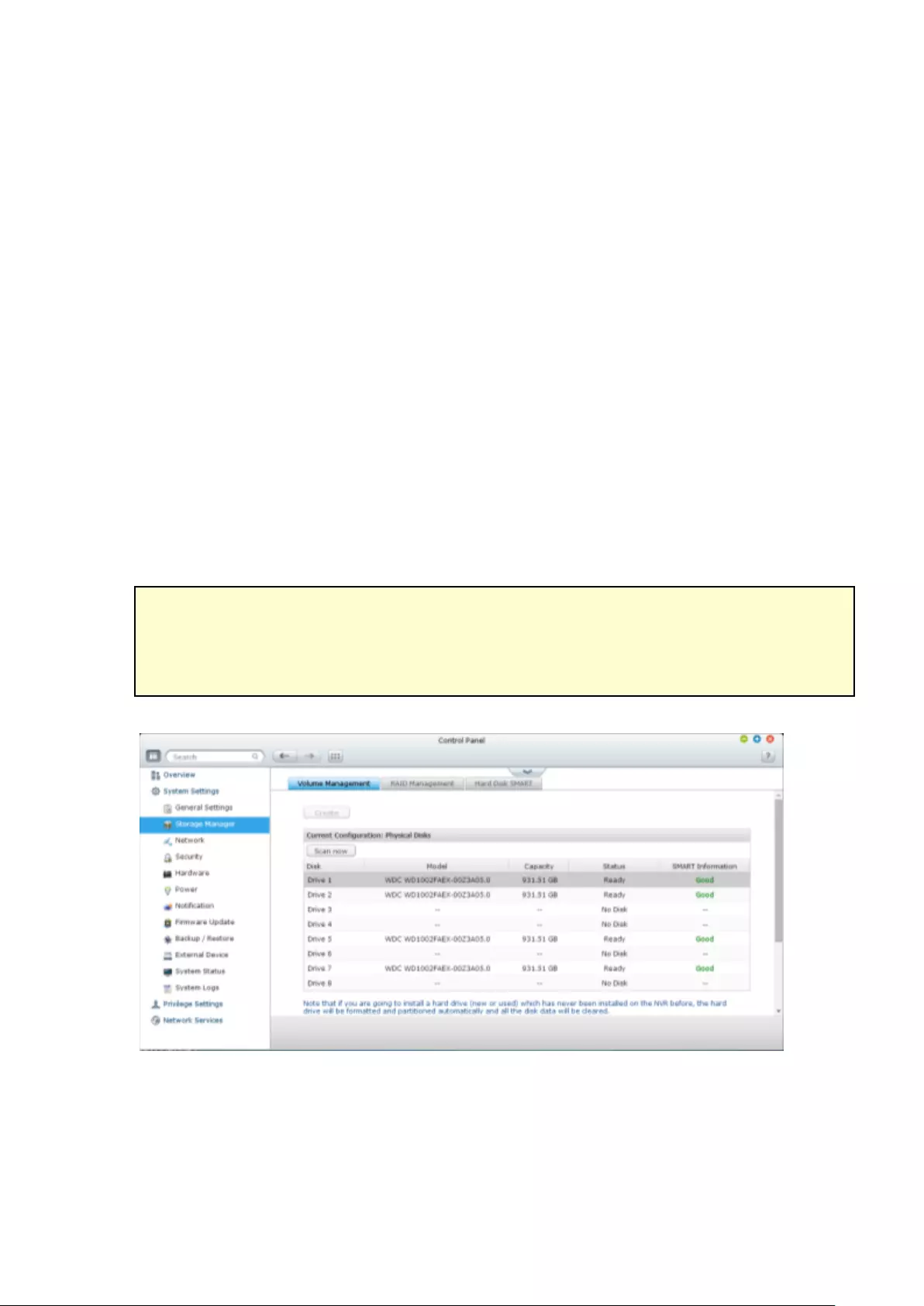
233
9.1.2 Storage Manager
Volume Management
This page shows the model, size, and current status of the hard drives on the NVR.
You can format and check the hard drives, and scan the bad blocks on the hard drives.
When the hard drives have been formatted, the NVR will create the following default
share folders:
•
mp4: The shared folder for MP4 Recordings App.
•
record_export: The shared folder for Recording Export Pro APP.
•
record_nvr: The default shared folder for regular recording files.
•
record_nvr_alarm: The default shared folder for alarm recording files.
•
snapshot: The default shared folder for auto snapshot.
Note: The default shared folders of the NVR are created on the first disk volume and the
directory cannot be changed.
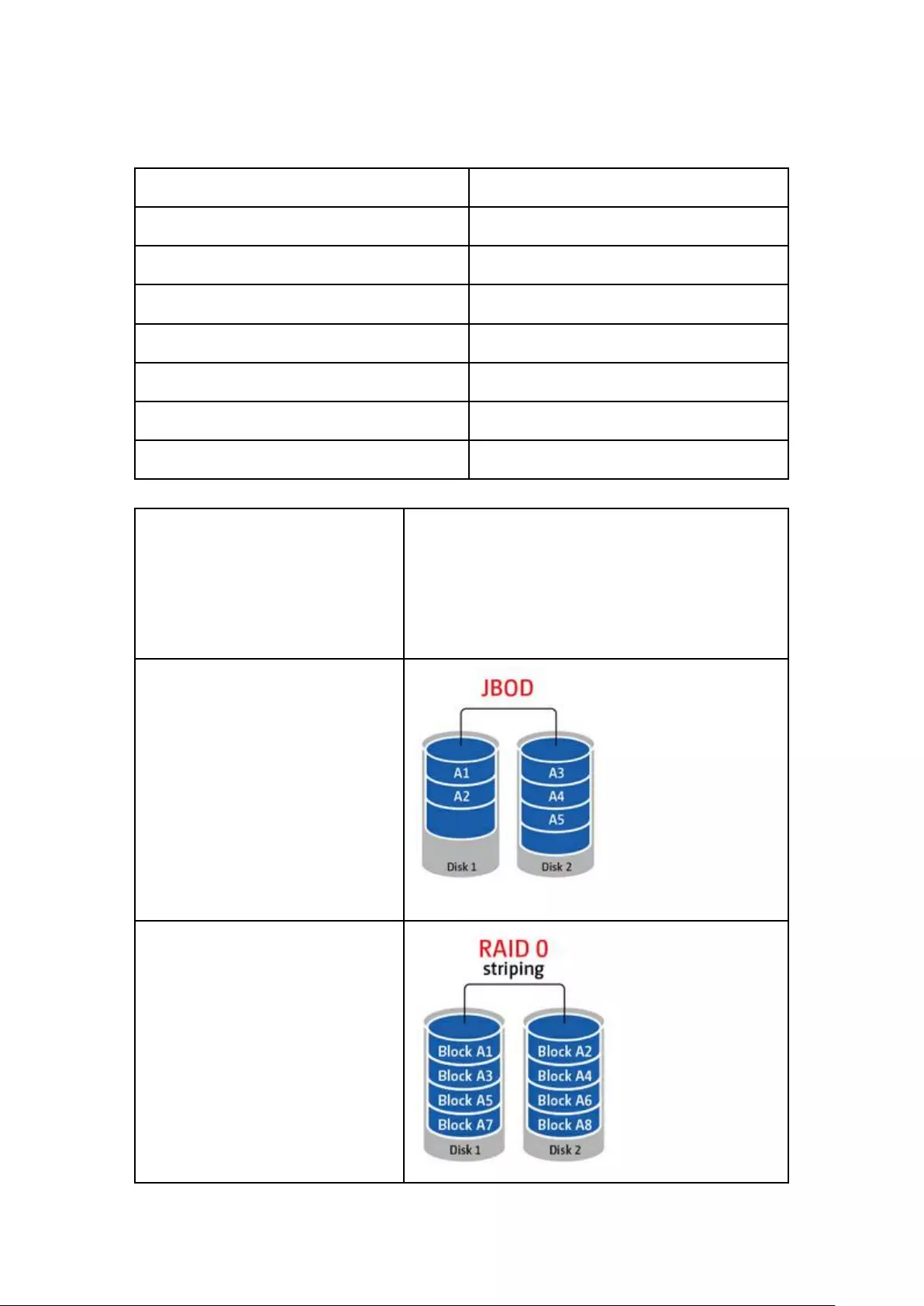
234
Disk Configuration
Applied NVR Models
Single disk volume
All models
RAID 0
2-drive models or above
RAID 1, JBOD (just a bunch of disks)
2-drive models or above
RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 5+hot spare
4-drive models or above
RAID 6+hot spare
5-drive models or above
RAID 10
4-drive models or above
RAID 10+hot spare
5-drive models or above
Single Disk Volume
Each hard drive is used as a
standalone disk. If a hard drive is
damaged, all the data will be
lost.
JBOD (Just a bunch of disks)
JBOD is a collection of hard
drives that does not offer any
RAID protection. The data are
written to the physical disks
sequentially. The total storage
capacity is equal to the sum of
the capacity of all member hard
drives.
RAID 0 Striping Disk Volume
RAID 0 (striping disk) combines 2
or more hard drives into one
larger volume. The data is
written to the hard drive without
any parity information and no
redundancy is offered.
The total storage capacity of a
RAID 0 disk volume is equal to
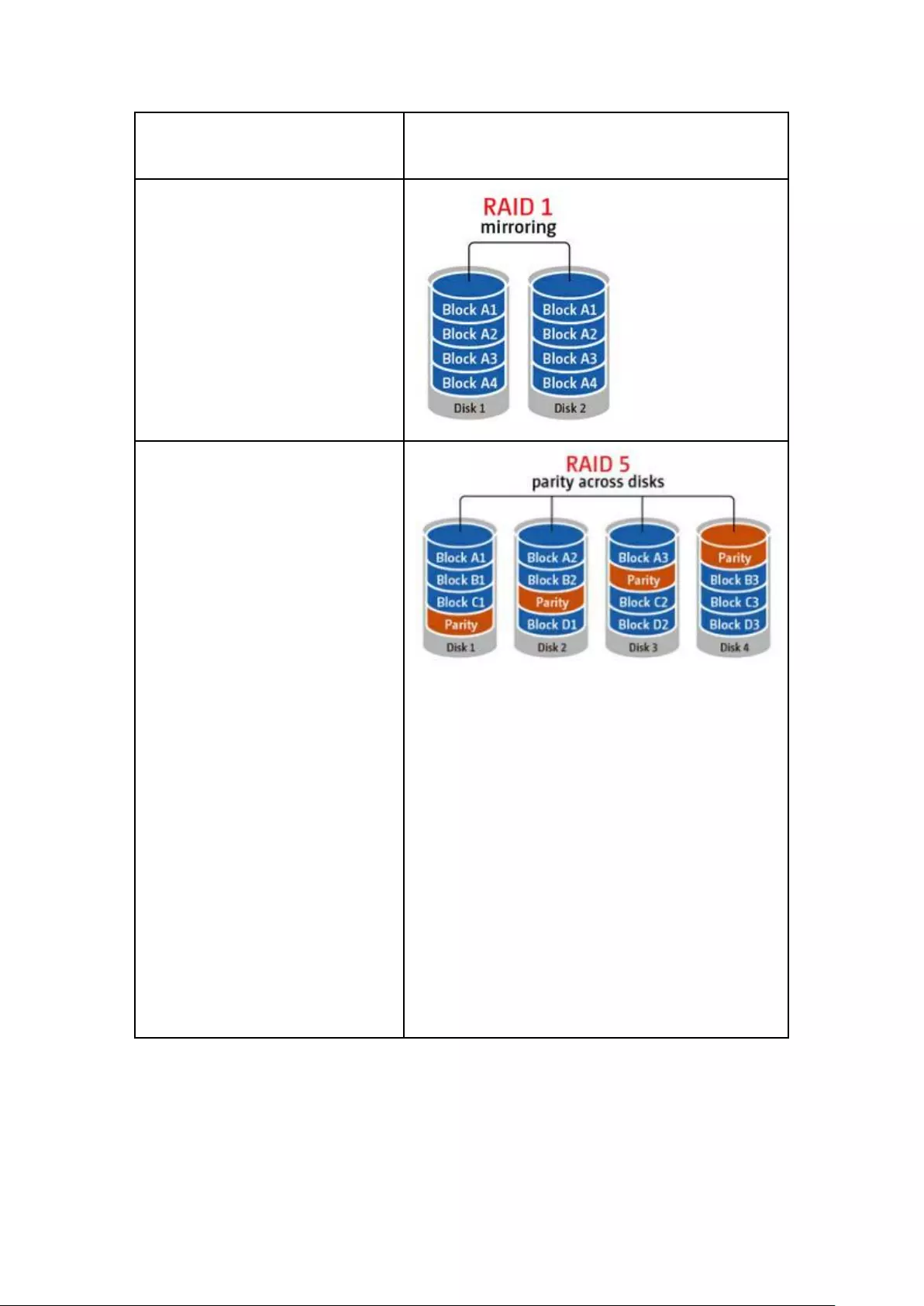
235
the sum of the capacity of all
member hard drives.
RAID 1 Mirroring Disk Volume
RAID 1 duplicates the data
between two hard drives to
provide disk mirroring. To create
a RAID 1 array, a minimum of 2
hard drives are required.
The storage capacity of a RAID 1
disk volume is equal to the size
of the smallest hard drive.
RAID 5 Disk Volume
The data are striped across all
the hard drives in a RAID 5 array.
The parity information is
distributed and stored across
each hard drive. If a member
hard drive fails, the array enters
degraded mode. After installing a
new hard drive to replace the
failed one, the data can be
rebuilt from other member
drives that contain the parity
information.
To create a RAID 5 disk volume, a
minimum of 3 hard drives are
required.
The storage capacity of a RAID 5
array is equal to (N-1) * (size of
smallest hard drive). N is the
number of hard drives in the
array.
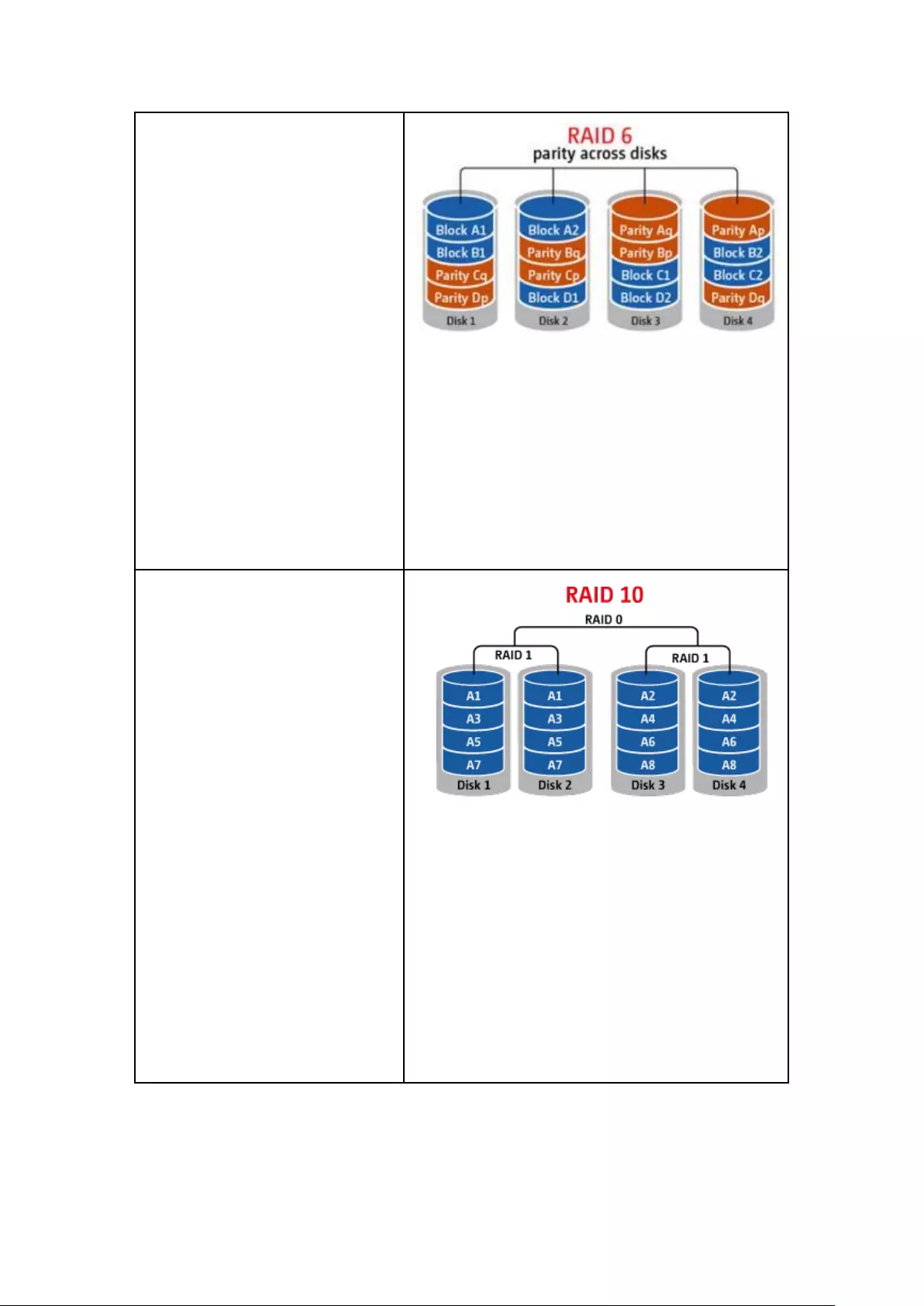
236
RAID 6 Disk Volume
The data are striped across all
the hard drives in a RAID 6 array.
RAID 6 differs from RAID 5 that a
second set of parity information
is stored across the member
drives in the array. It tolerates
failure of two hard drives.
To create a RAID 6 disk volume, a
minimum of 4 hard drives are
required. The storage capacity of
a RAID 6 array is equal to (N-2) *
(size of smallest hard drive). N is
the number of hard drives in the
array.
RAID 10 Disk Volume
RAID 10 combines four or more
disks in a way that protects data
against loss of non-adjacent
disks. It provides security by
mirroring all data on a secondary
set of disks while using striping
across each set of disks to speed
up data transfers.
RAID 10 requires an even
number of hard drives (minimum
4 hard drives). The storage
capacity of RAID 10 disk volume
is equal to (size of the smallest
capacity disk in the array) * N/2.
N is the number of hard drives in
the volume.
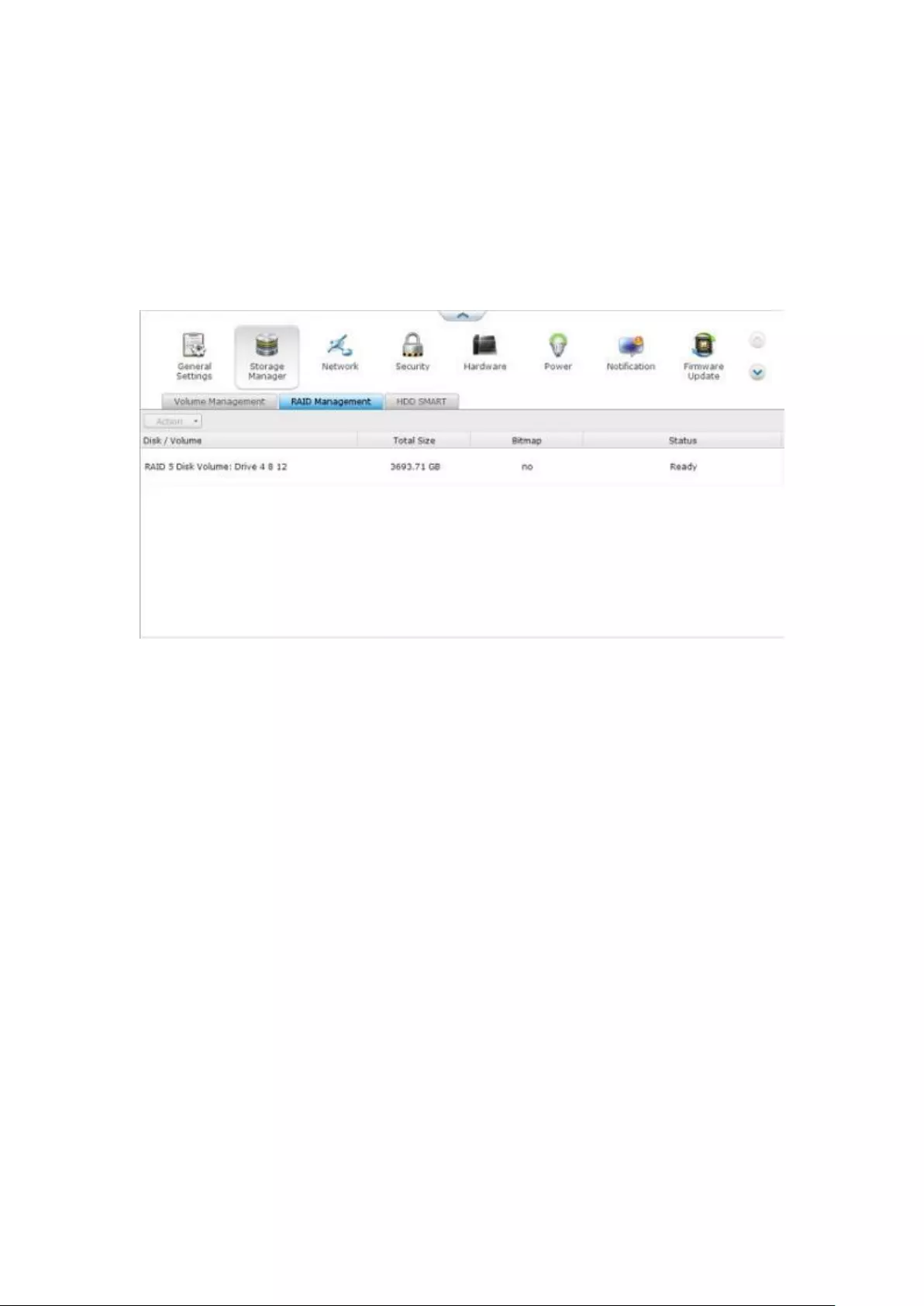
237
RAID Management
You can perform online RAID capacity expansion (RAID 1, 5, 6, 10) and online RAID
level migration (single disk, RAID 1, 5, 10), add a hard drive member to a RAID 5, 6, or
10 configuration, configure a spare hard drive (RAID 5, 6, 10) with the data retained,
enable Bitmap, recover a RAID configuration, and set a global spare on this page.
To expand the storage capacity of a RAID 10 volume, you can perform online RAID
capacity expansion or add an even number of hard disk drives to the volume.
Expand Capacity (Online RAID Capacity Expansion)
Scenario
You bought three 250GB hard drives for initial setup of a NVR and configured RAID 5
disk configuration with the three hard drives.
A half year later, the data size of the department has largely increased to 1.5TB. In
other words, the storage capacity of the NVR is running out of use. At the same time,
the price of 1TB hard drives has dropped to a large extent.
Operation procedure
In “Storage Manager” > “RAID Management”, select the disk volume for expansion
and click “Expand Capacity”.
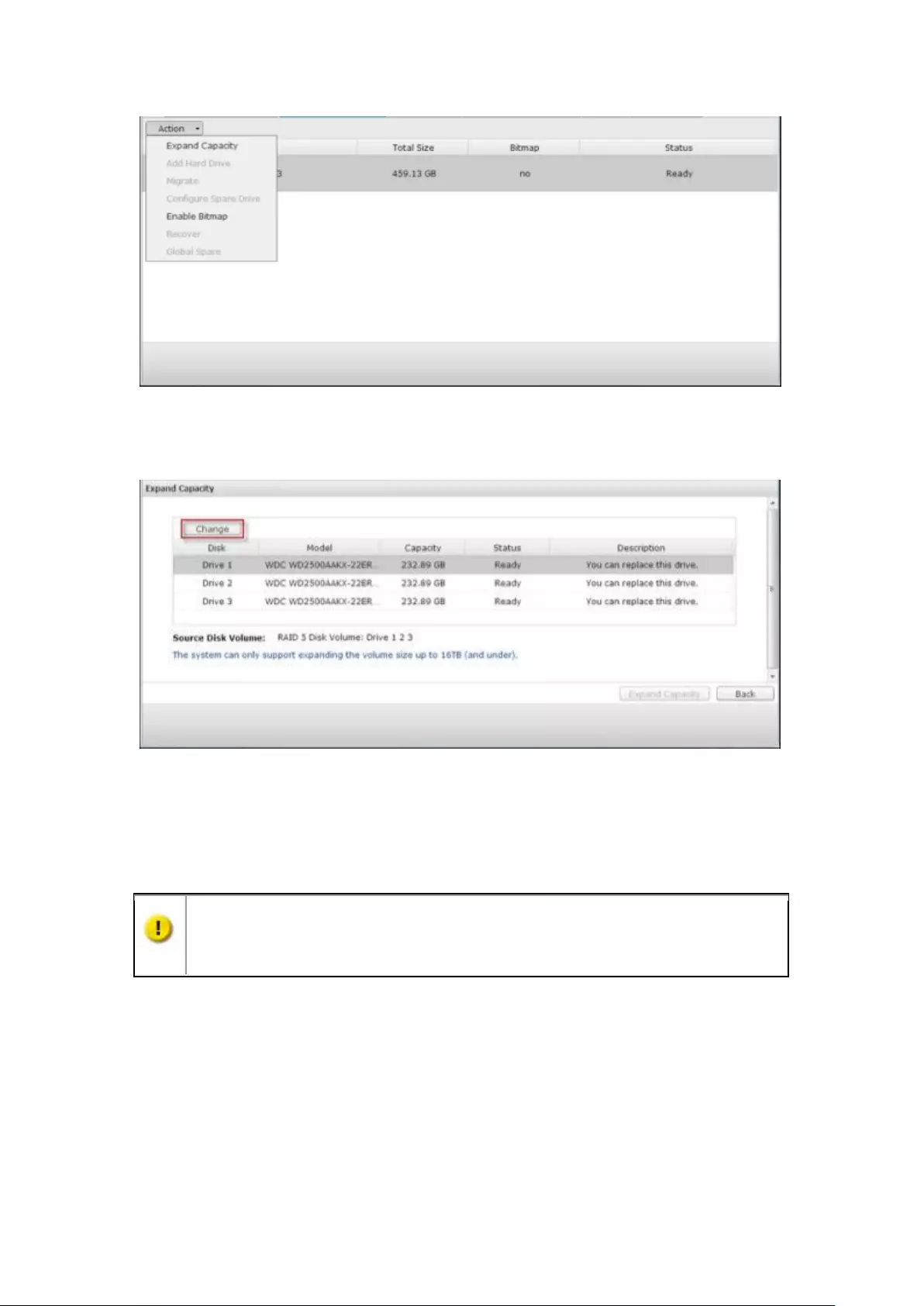
238
Click “Change” for the first hard drive to be replaced. Follow the instructions to
proceed.
Tip: After replacing the hard drive, the description field shows “You can replace this
drive”. This means you can replace the hard drive to a larger one or skip this step if
the hard drives have been replaced already.
Caution: When the hard drive synchronization is in process, do NOT turn off
the NVR or plug in or unplug the hard disk drives.
When the description displays “Please remove this drive”, remove the hard drive
from the NVR. Wait for the NVR to beep twice after removing the hard drive.
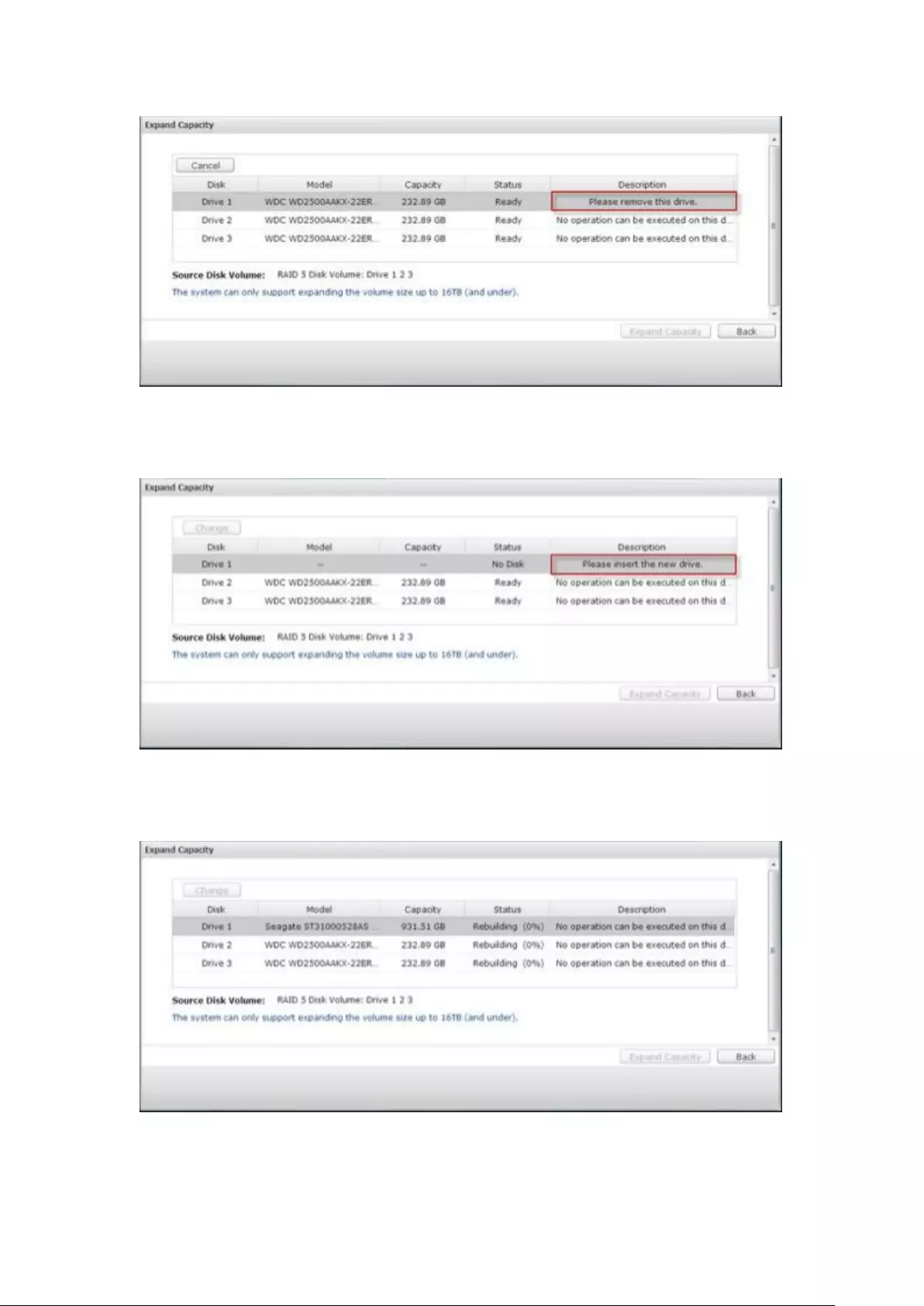
239
When the description displays “Please insert the new drive”, plug in the new hard
drive to the drive slot.
After plugging in the hard drive, wait for the NVR to beep. The system will start
rebuilding.
After rebuilding has completed, repeat the steps above to replace other hard drives.
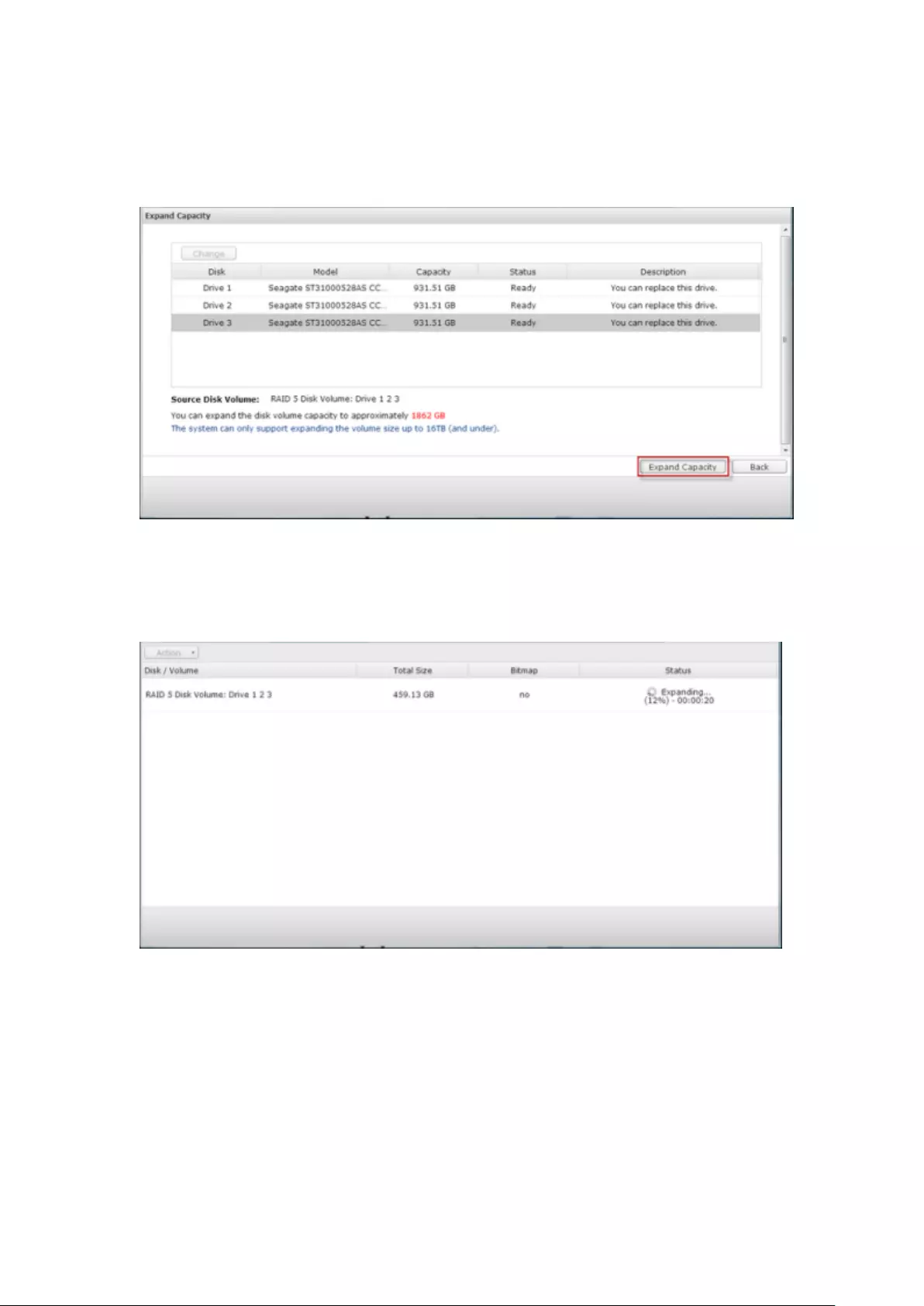
240
After changing the hard drives and disk rebuilding has completed, click “Expand
Capacity” to execute RAID capacity expansion.
Click “OK” to proceed.
The NVR beeps and starts to expand the capacity.
The process may take from hours to tens of hours to finish depending on the drive
size. Please wait patiently for the process to finish. Do NOT turn off the power of the
NVR.
After RAID capacity expansion has finished, the new capacity is shown and the status
is “Ready”. You can start to use the NVR. (In the example you have 1.8TB logical
volume.)
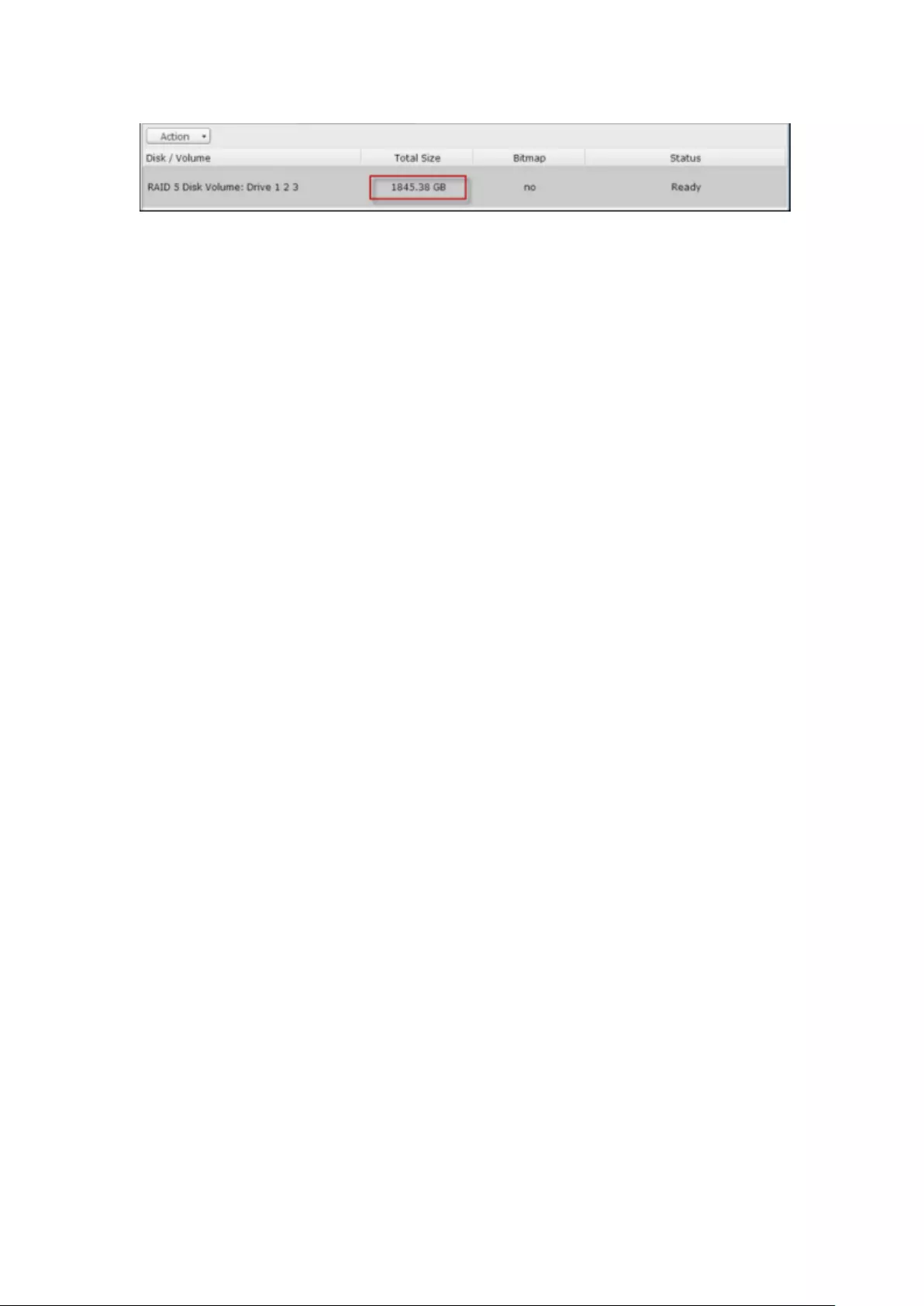
241
Tip: If the description still shows “You can replace this hard drive” and the status of
the drive volume says “Ready”, it means the RAID volume is still expandable.
Migrate (Online RAID Level Migration)
During the initial setup of the NVR, you bought a 250GB hard drive and configured it
as single disk.
After a period of time, more and more important recordings are saved on the NVR.
There is a rising concern for hard drive damage and data loss. Therefore, you planned
to upgrade the disk configuration to RAID 5.
You can install one hard drive for setting up the NVR and upgrade the RAID level of
the NVR with online RAID level migration in the future. The migration process can be
done without turning off the NVR. All the data will be retained.
You can do the following with online RAID level migration:
•
Migrate the system from single disk to RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10
•
Migrate the system from RAID 1 to RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10
•
Migrate the system from RAID 5 with 3 hard drives to RAID 6
You need to:
•
Prepare a hard drive of the same or larger capacity as an existing drive in the
RAID configuration.
•
Execute RAID level migration (migrate the system from single disk mode to RAID 5
with 4 hard drives).
Go to “Storage Manager” > “Volume Management”. The current disk volume
configuration displayed on the page is single disk (the capacity is 250GB).
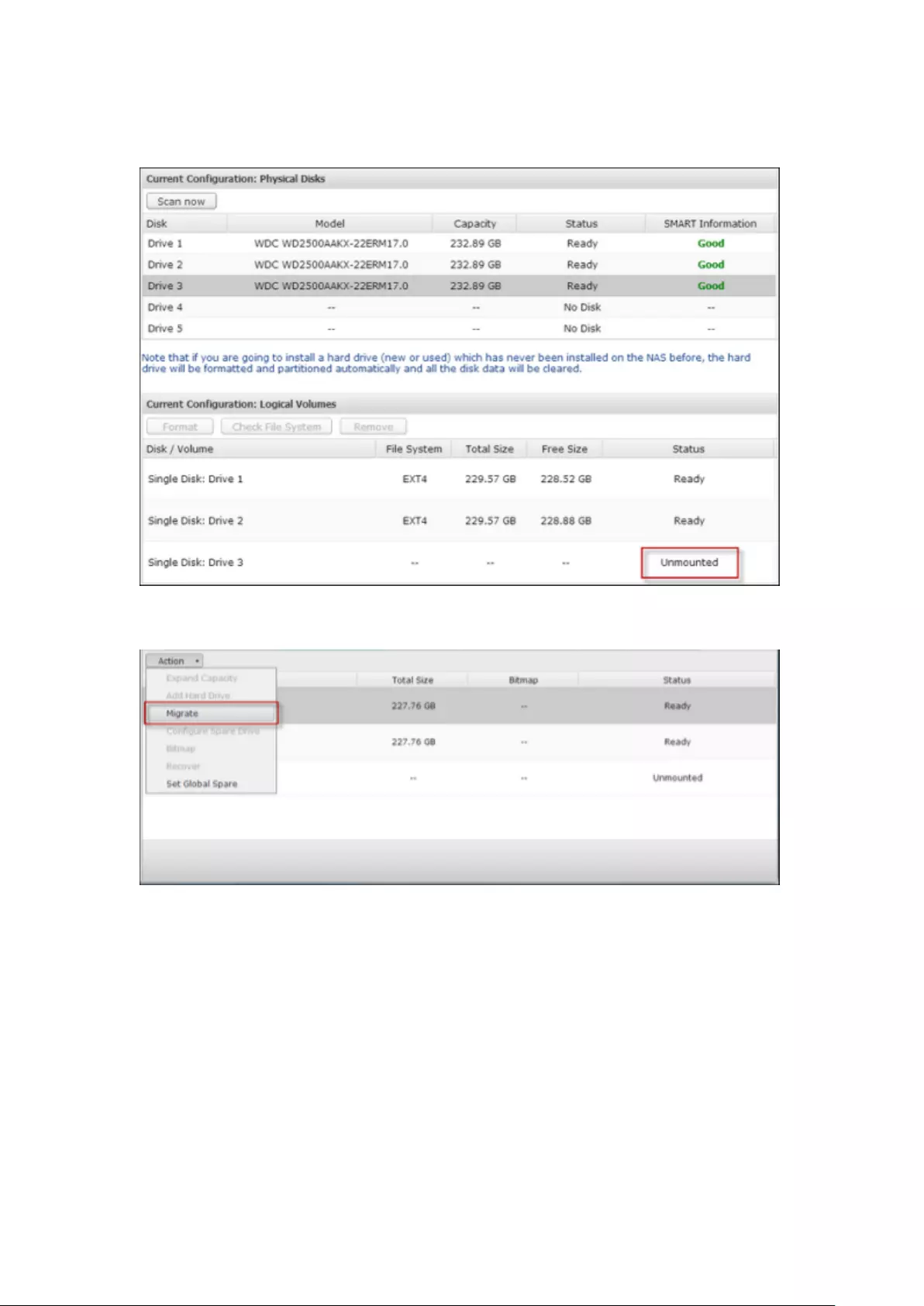
242
Plug in the new 250GB hard drives to drive slots 2 and 3 of NVR. The NVR will detect
the new hard drives. The status of the new hard drives is “Unmounted”.
Go to “Storage Manager” > “RAID Management”, click “Migrate” from the “Action.”
Select one or more available drives and the migration method. The drive capacity
after migration is shown. Click “Migrate”.

243
Note that all the data on the selected hard drive will be cleared. Click “OK” to
confirm.
When migration is in process, the required time and total drive capacity after
migration are shown in the description field.
The NVR will enter “Read only” mode when migration is in process during 11%–49%
to assure the data of the RAID configuration will be consistent after RAID migration
completes.
After migration completes, the new drive configuration (RAID 5) is shown and the
status is Ready. You can start to use the new drive configuration.
The process may take from hours to tens of hours to finish depending on the hard
drive size. You can connect to the web page of the NVR to check the status later.
Use Online RAID Capacity Expansion and Online RAID Level Migration
Add a hard drive
Follow the steps below to add a hard drive member to a RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk
configuration.
1.
Make sure the status of the RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration is “Ready”.
2.
Install a hard drive on the NVR. If you have a hard drive which has already been

244
formatted as single disk volume on the NVR, you can add this hard drive to the
RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration. You are recommended to use hard disk drives of
the same storage capacity for the RAID configuration.
3.
Select the RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration on the “RAID Management” page and
click “Add Hard Drive”.
4.
Select the new hard drive member. The total drive capacity after adding the
drive will be shown. Click “Add Hard Drive.”
5.
All the data on the new hard drive member will be deleted during this process.
The data on the original RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration will be retained. Click
“OK”. The NVR will beep twice.
To add hard drives member to a RAID 10 disk volume, repeat the above steps. Note
that you need to add an even number of hard disk drives to a RAID 10 volume.
The storage capacity of the RAID 10 volume will increase upon successful
configuration.
This process may take a few hours to tens of hours to complete depending on the
number and the size of the hard drive. Please wait patiently for the process to finish.
Do NOT turn off the NVR during this process. You can use a RAID configuration of
larger capacity after the process.
Configure Spare Drive
You can add a spare drive to or remove a spare drive from a RAID 5, 6, or 10
configuration.
Follow the steps below to use this feature.
1.
Make sure the status of the RAID 5, 6, 10 configuration is “Ready”.
2.
Install a hard drive on the NVR. If you have a hard drive which has already been
formatted as single disk volume on the NVR, you can configure this hard drive as
the spare drive. You are recommended to use hard disk drives of the same
storage capacity for the RAID configuration.
3.
Select the RAID volume and click “Configure Spare Drive.”
4.
To add a spare drive to the selected configuration, select the hard drive and click
“Configure Spare Drive.” To remove a spare drive, unselect the spare drive and
click “Configure Spare Drive.”
5.
All the data on the selected hard drive will be deleted. Click “OK” to proceed.
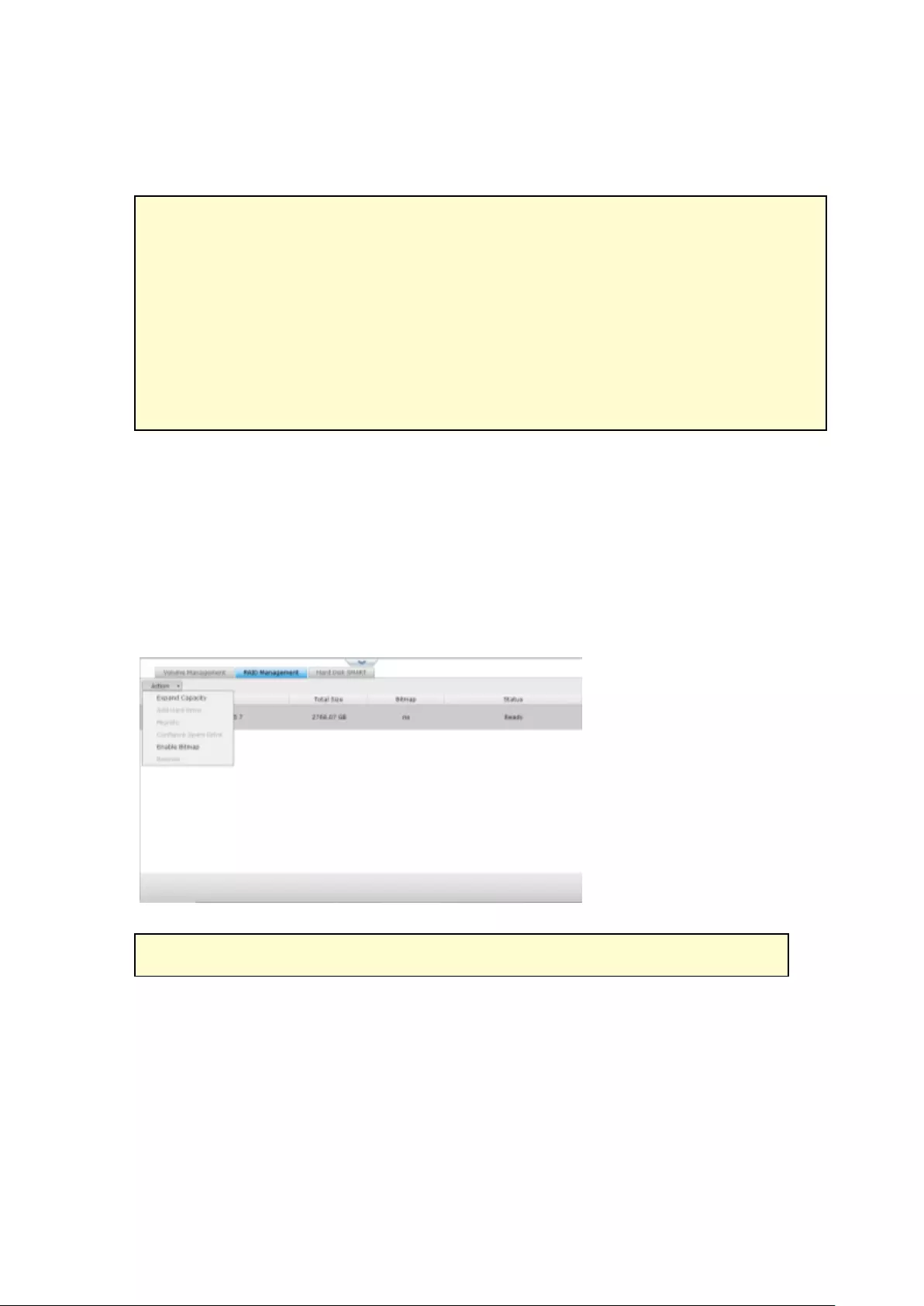
245
The original data on the RAID 5, 6, or 10 disk volume will be retained. After the
configuration completes, the status of the disk volume will become “Ready”.
Note: A hot spare drive must be removed from the disk volume before executing the
following action:
•
Online RAID capacity
expansion
•
Online RAID level
migration
•
Adding a hard drive member to a RAID 5, RAID 6
or RAID 10 volume
Bitmap
Bitmap improves the time for RAID rebuilding after an unexpected error, or removing
or re-adding a member hard drive of the RAID configuration. If an array has a bitmap,
the member hard drive can be removed and re-added and only blocks changes since
the removal (as recorded in the bitmap) will be re-synchronized. To use this feature,
select a RAID volume and click “Enable Bitmap”.
Note: Bitmap support is only available for RAID 1, 5, 6, and 10.
Recover (RAID Recovery)
RAID Recovery: When the NVR is configured as RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 and any
number of hard drives is unplugged from the NVR accidentally, you can plug in the
same hard drives into the same drive slots and click “Recover” to recover the volume
status from “Not active” to “Degraded mode”.
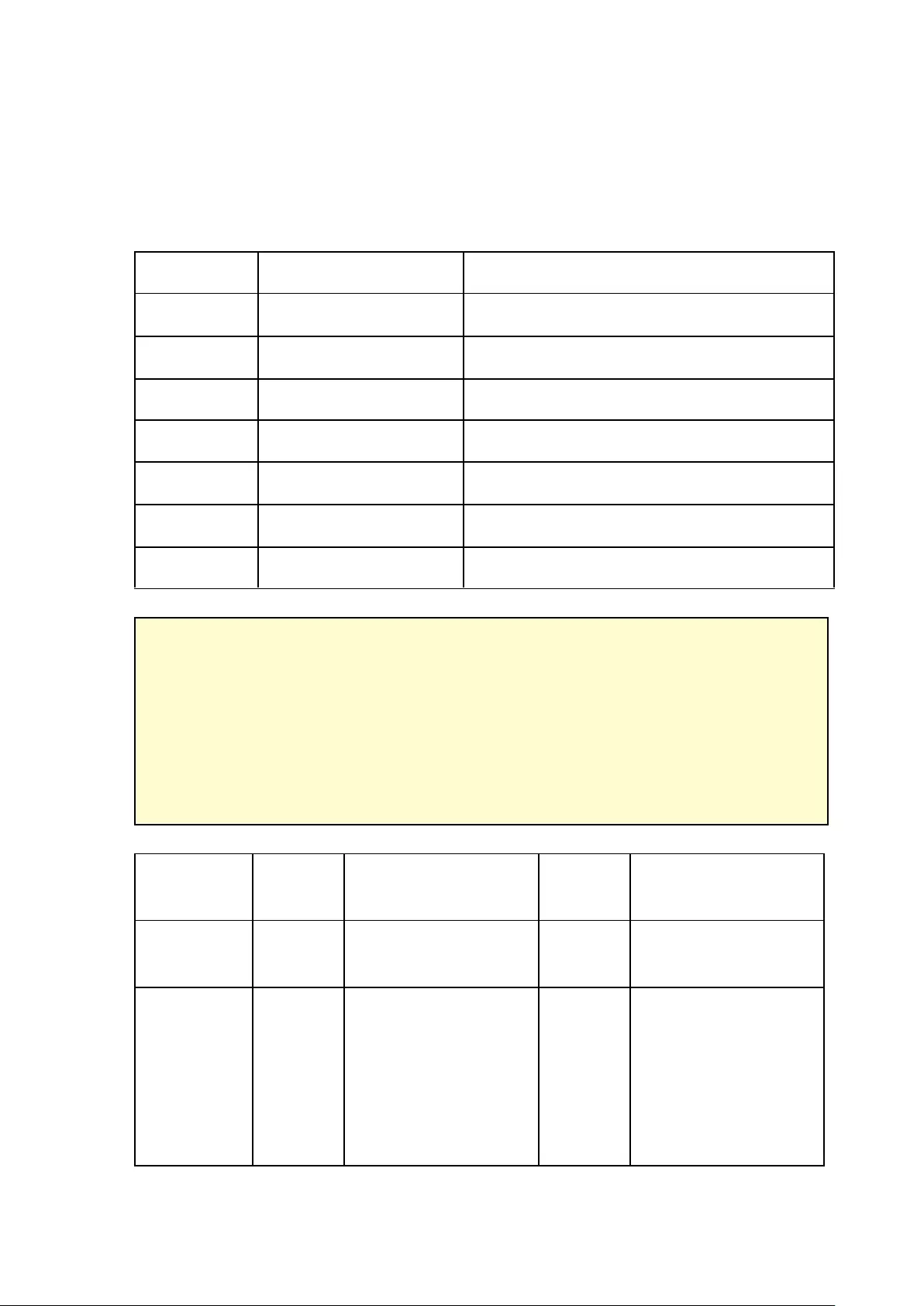
246
If the disk volume is configured as RAID 0 or JBOD and one or more of the hard drive
members are disconnected or unplugged, you can plug in the same hard drives into
the same drive slots and use this function to recover the volume status from “Not
active” to “Normal”. The disk volume can be used normally after successful recovery.
Disk volume
Supports RAID recovery
Maximum number of disk removal allowed
Single
No
-
JBOD
Yes
1 or more
RAID 0
Yes
1 or more
RAID 1
Yes
1 or 2
RAID 5
Yes
2 or more
RAID 6
Yes
3 or more
RAID 10
No
-
Note:
•
After recovering a RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk volume from
not active to degraded mode by the RAID recovery, you can read
or write the volume normally. The volume status will be
recovered to normal after synchronization.
•
If the disconnected drive member is damaged, the RAID
recovery function will not work.
Standard
RAID 5
QNAP RAID 5
Standard
RAID 6
QNAP RAID 6
Degraded
mode
N-1
N-1
N-1 &
N-2
N-1 & N-2
Read Only
Protection
(for
immediate
data backup
& hard drive
N/A
N-1, bad blocks found
in the surviving hard
drives of the array.
N/A
N-2, bad blocks found
in the surviving hard
drives of the array.
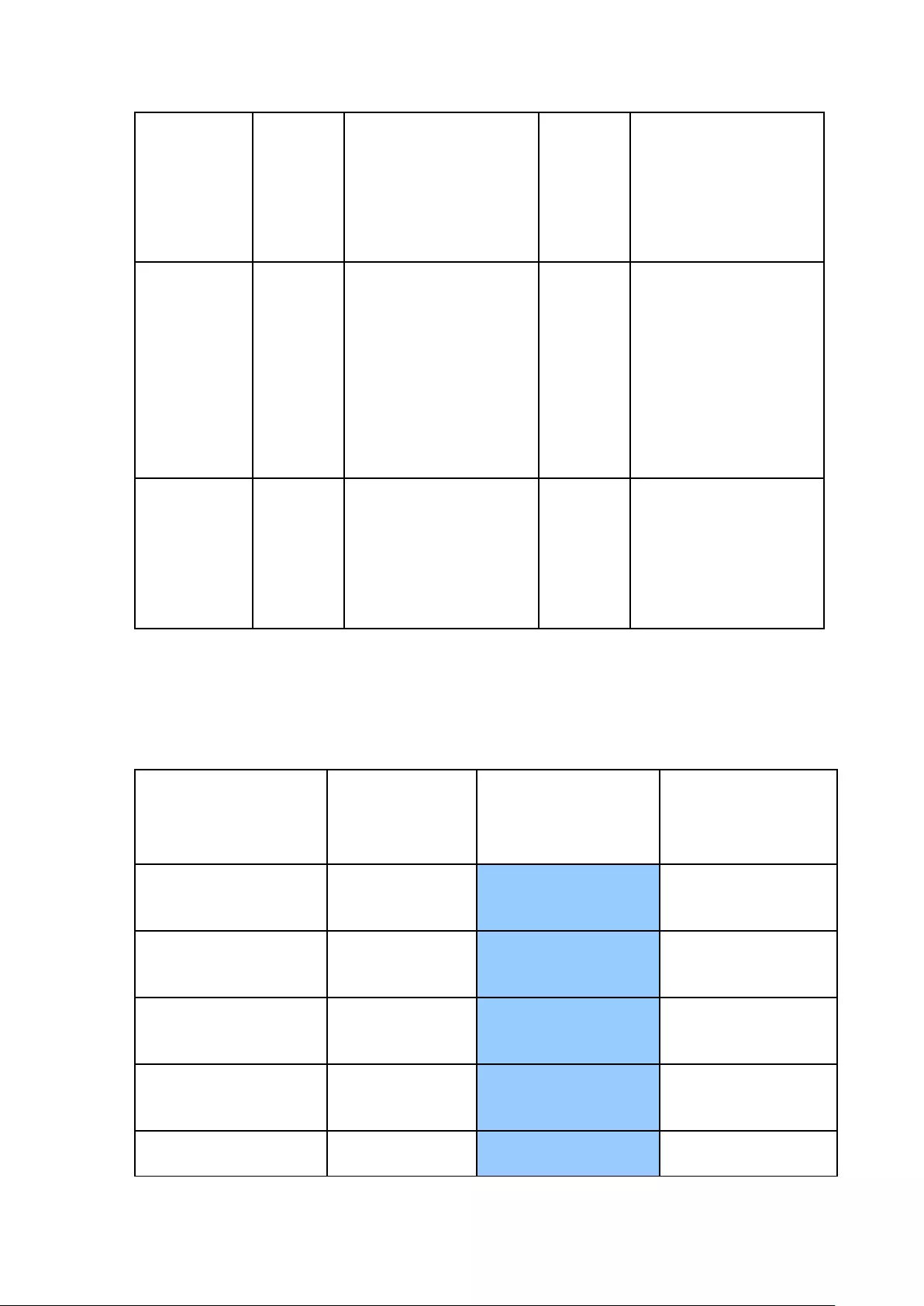
247
replacement)
RAID
Recovery
(RAID Status:
Not Active)
N/A
If re-plugging in all
original hard drive to
the NVR and they can
be spun up, identified,
accessed, and the hard
drive superblock is not
damaged.
N/A
If re- plugging in all
original hard drives to
the NVR and they can
be spun up, identified,
accessed, and the hard
drive superblock is not
damaged).
RAID Crash
N-2
N-2 failed hard drives
and any of the
remaining hard drives
cannot be spun
up/identified/accessed.
N-3
N-3 and any of the
remaining hard drives
cannot be spun
up/identified/accessed.
N = Number of hard disk drives in the array
Further information about RAID management of the NVR:
The NVR supports the following actions according to the number of hard disk drives
and disk configurations supported. Please refer to the following table for the details.
Original Disk
Configuration * No. of
Hard Disk Drives
No. of New Hard
Disk Drives
Action
New Disk
Configuration * No.
of Hard Disk Drives
RAID 5 * 3
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 5 * 3
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 3
3
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 3
4
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 3
5
Add hard drive
RAID 5 * 8
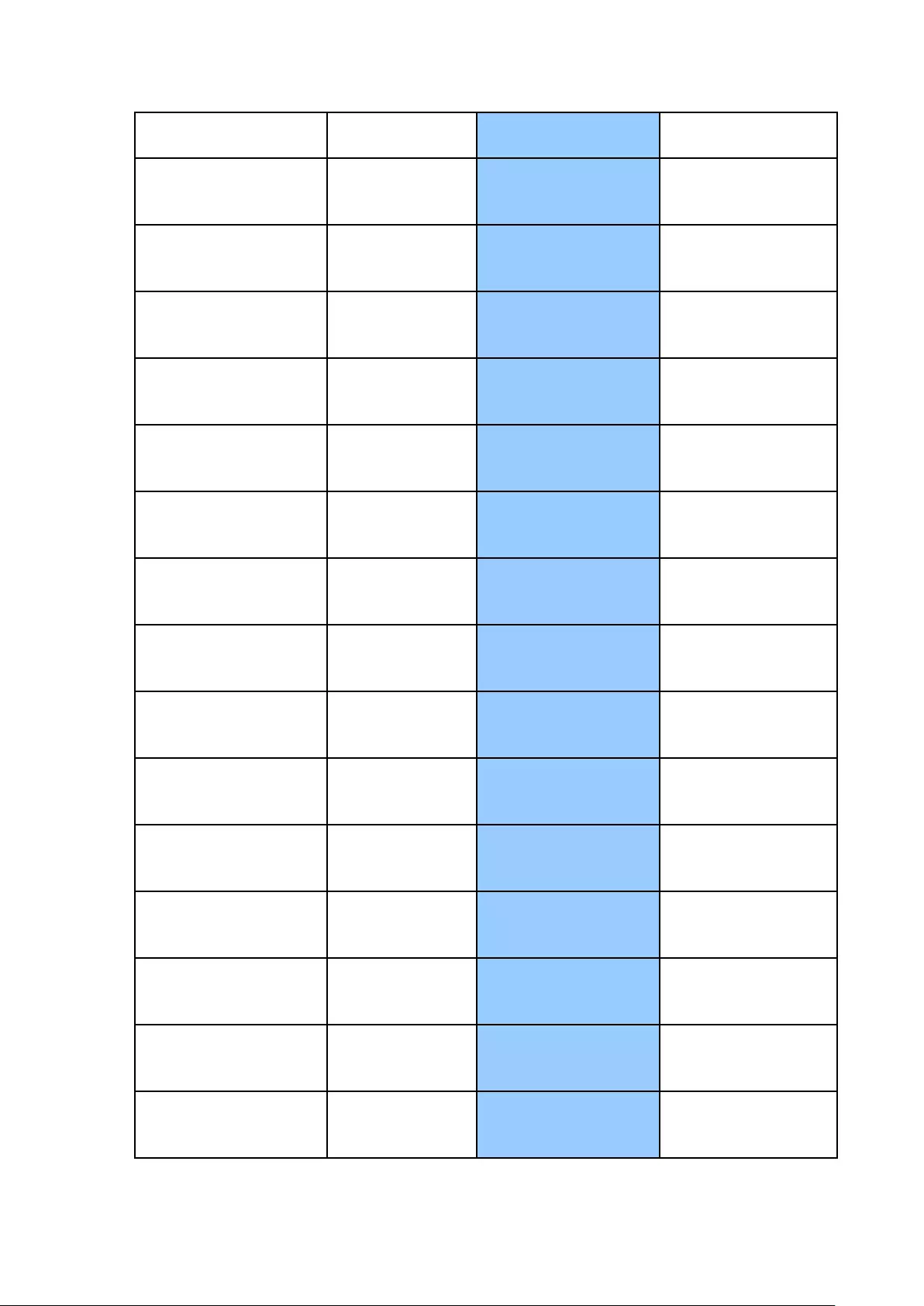
248
member
RAID 5 * 4
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 4
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 4
3
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 4
4
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 5
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 5
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 5
3
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 6
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 6
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 7
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 6 * 4
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 6 * 4
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 6 * 4
3
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 4
4
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 6 * 5
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 6
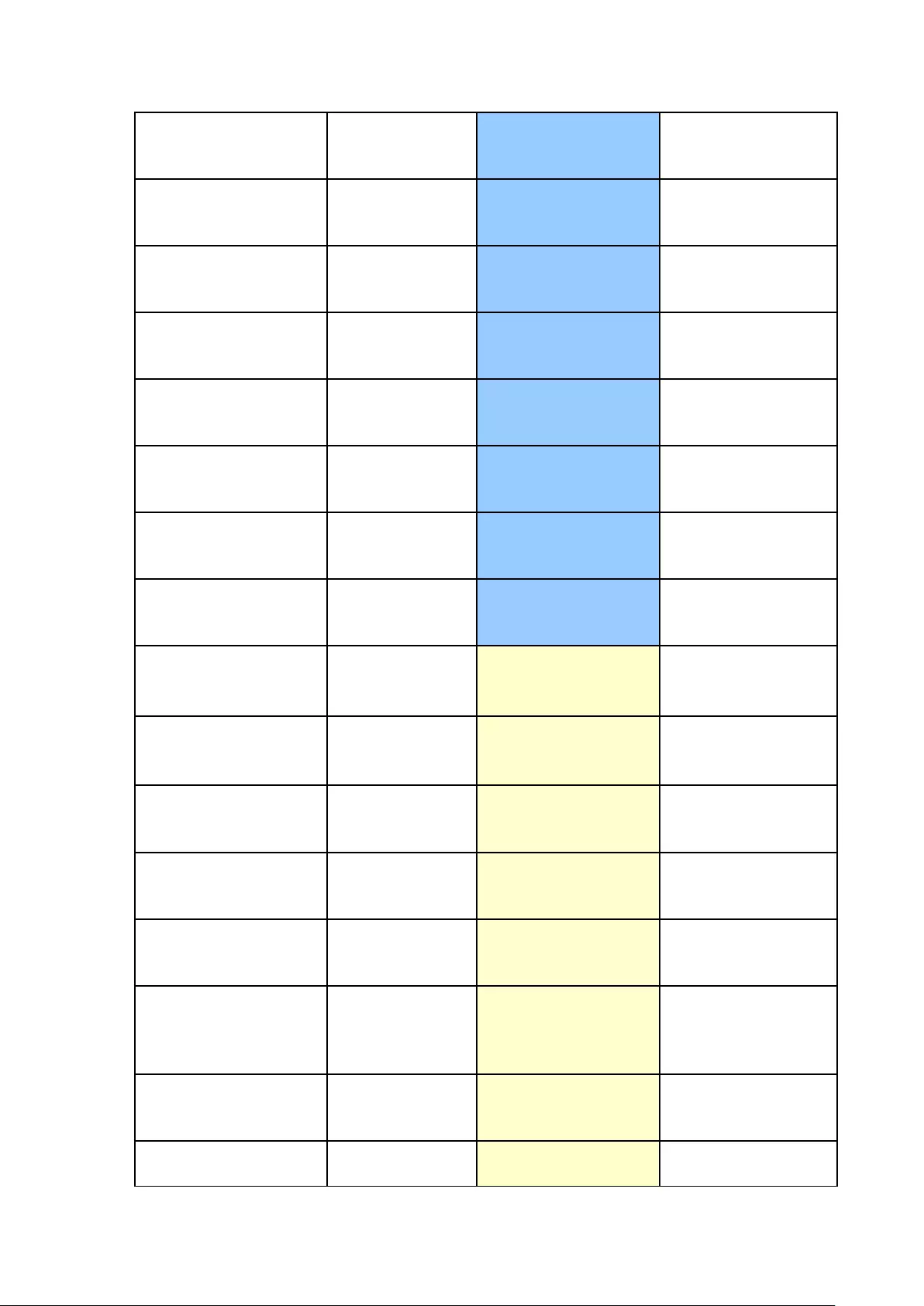
249
RAID 6 * 5
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 5
3
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 6 * 6
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 6
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 6 * 7
1
Add hard drive
member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 10 * 4
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 10 * 4
4
Add hard drive
member
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 10 * 6
2
Add hard drive
member
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 1 * 2
RAID 5 * 3
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 3
RAID 5 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 5 * 5
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 7
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 6 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
RAID 6 * 4
250
expansion
RAID 6 * 5
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 6 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 6 * 7
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 10 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 4
RAID 10 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 10 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 8
Single * 1
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 1 * 2
Single * 1
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 3
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 4
Single * 1
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 5
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 6
Single * 1
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 7
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 8
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
RAID 6 * 4
251
migration
Single * 1
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
Single * 1
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 4
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 6
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 3
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
252
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 5 * 3
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 4
RAID 5 * 3
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 5 * 3
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 5 * 3
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 5 * 3
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8
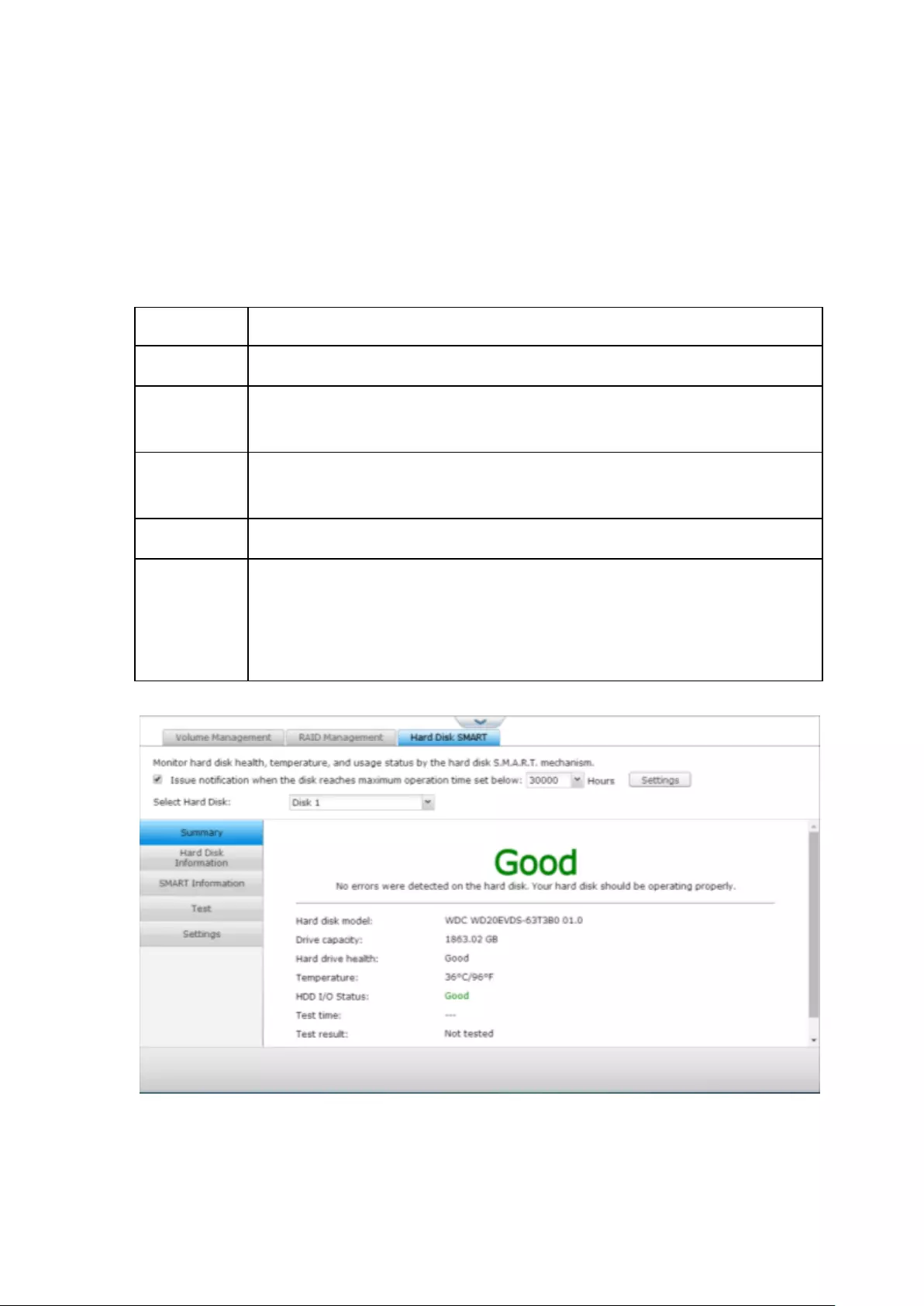
253
Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T
Monitor the hard disk drives (HDD) health, temperature, and the usage status by
HDD S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology).
The following information of each hard drive on the NVR is available.
Field
Description
Summary
Display the hard drive S.M.A.R.T. summary and the latest test result.
Hard disk
information
Display the hard drive details, for example, model, serial number, HDD
capacity.
SMART
information
Display the hard drive S.M.A.R.T. information. Any items that the values
are lower than the threshold are regarded as abnormal.
Test
Perform quick or complete hard drive S.M.A.R.T. test.
Settings
Configure temperature alarm. When the hard drive temperature is over
the preset values, the NVR records the error logs.
You can also set the quick and complete test schedule. The latest test
result is shown on the Summary page.
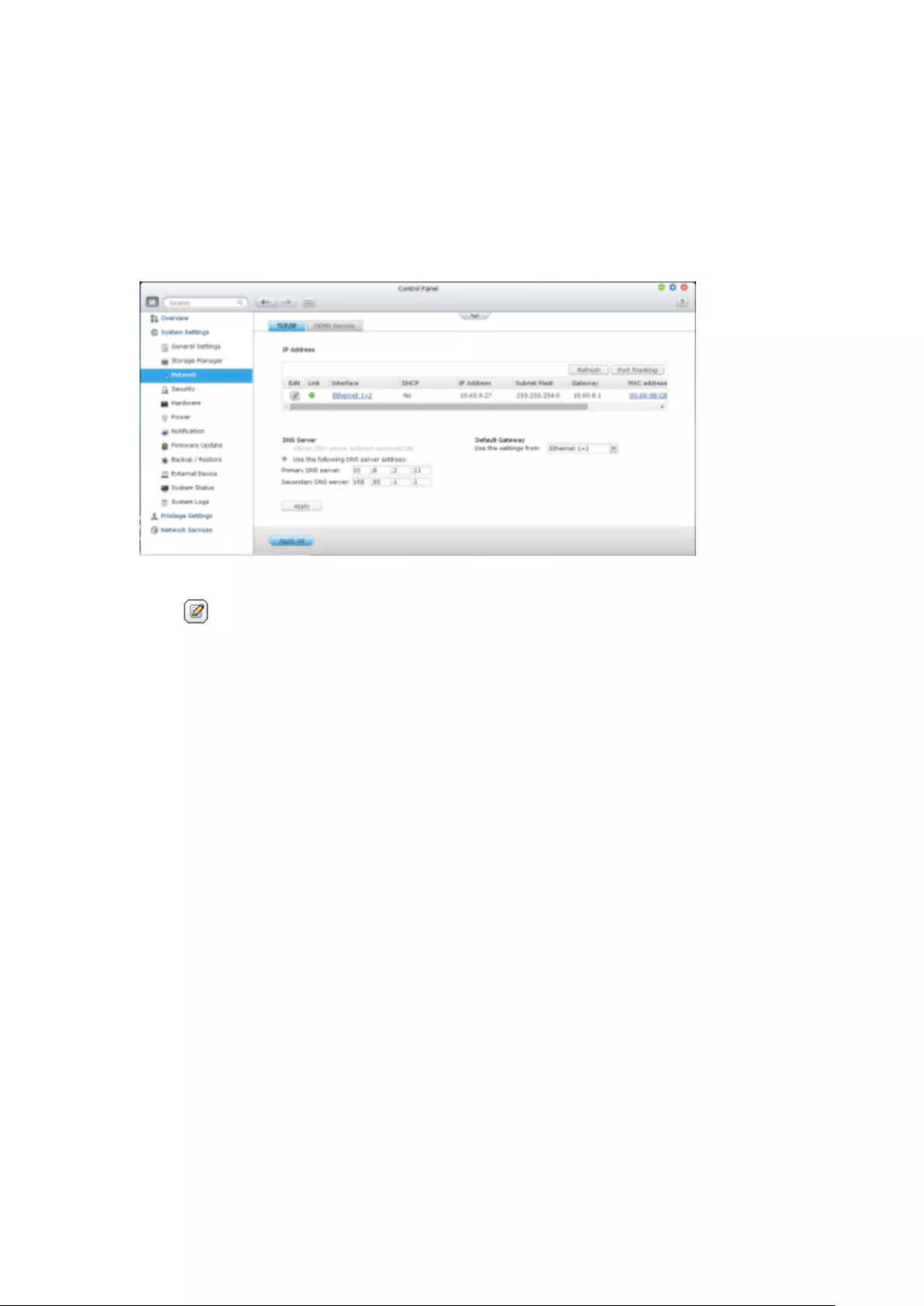
254
9.1.3 Network
TCP/IP
(i) IP Address
Configure the TCP/IP settings, DNS Server and default Gateway of the NVR on this
page.
Click to edit the network settings. For the NVR with two LAN ports, users can
connect both network interfaces to two different switches and configure the TCP/IP
settings. The NVR will acquire two IP addresses which allow access from two different
subnets. This is known as multi-IP settings*. When using the Finder to detect the
NVR IP, the IP of the Ethernet 1 will be shown in LAN 1 only and the IP of the
Ethernet 2 will be shown in LAN 2 only. To use the port trunking mode for dual LAN
connection, see section (iv).
Network Parameters
Under the Network Parameters tab on the TCP/IP Property page, configure the
following settings:
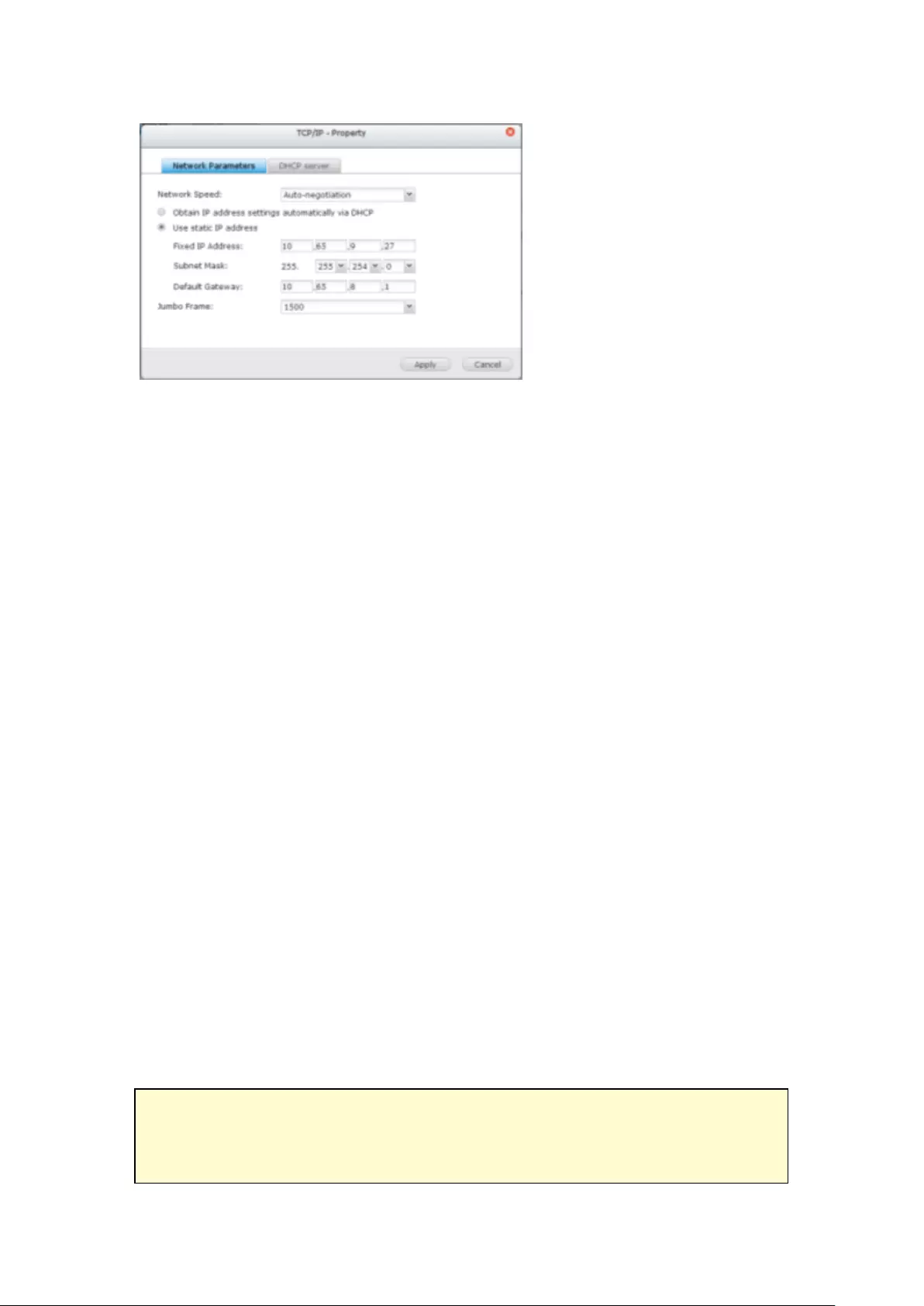
255
Network Speed
Select the network transfer rate according to the network environment to which the
NVR is connected. Select auto negotiation and the NVR will adjust the transfer rate
automatically.
Obtain the IP address settings automatically via DHCP
If the network supports DHCP, select this option and the NVR will automatically
obtain the IP address and network settings.
Use static IP address
To use a static IP address for network connection, enter the IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway.
Jumbo Frame Settings (MTU)
“Jumbo Frames” refer to the Ethernet frames that are larger than 1500 bytes. It is
designed to enhance Ethernet networking throughput and reduce the CPU utilization
of large file transfers by enabling more efficient larger payloads per packet.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) refers to the size (in bytes) of the largest packet
that a given layer of a communications protocol can transmit.
The NVR uses standard Ethernet frames: 1500 bytes by default. If the network
appliances support Jumbo Frame setting, select the appropriate MTU value for the
network environment. The NVR supports 4074, 7418, and 9000 bytes for MTU.
Note: The Jumbo Frame setting is valid in Gigabit network environment only. All the
network appliances connected must enable Jumbo Frame and use the same MTU
value.
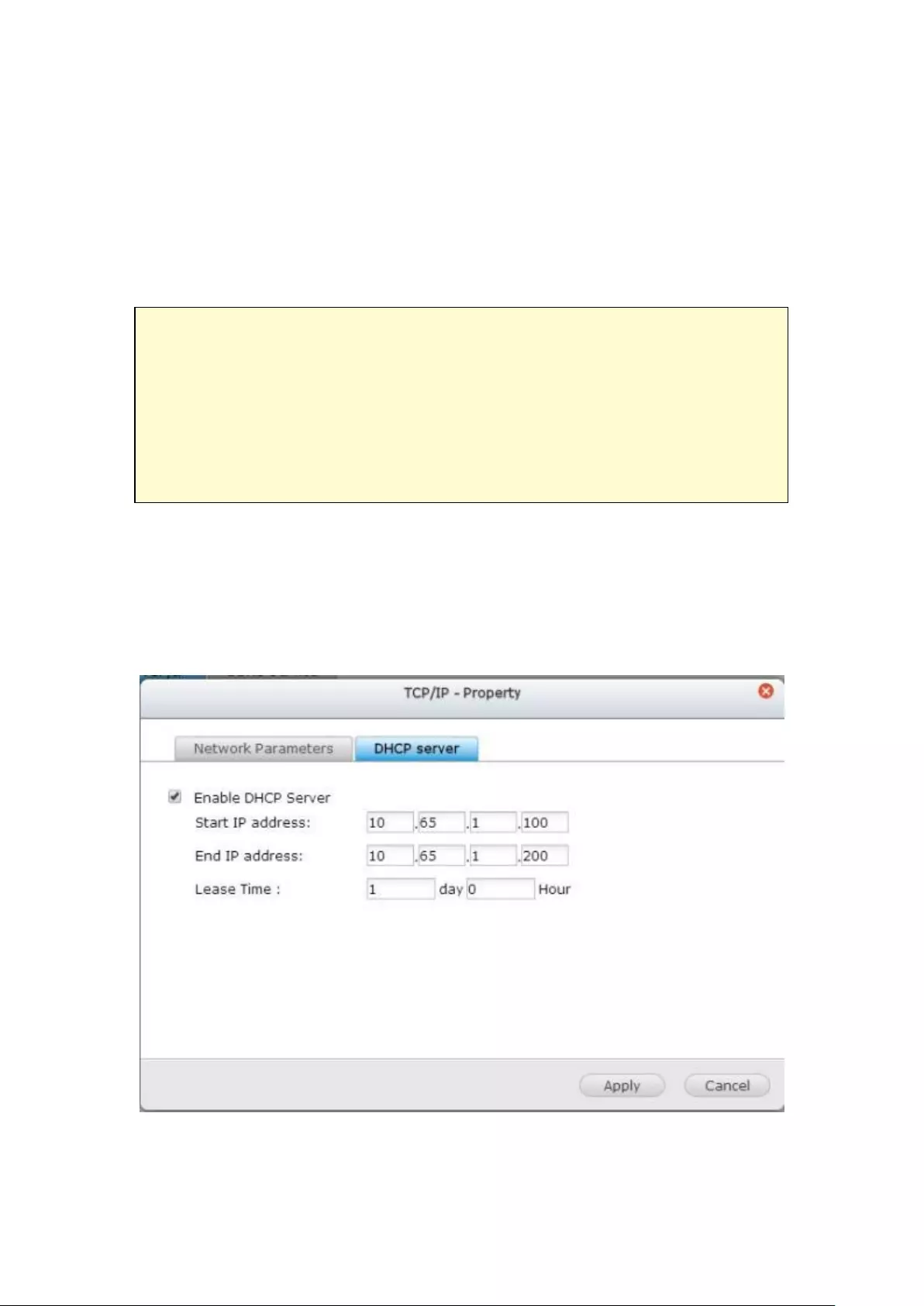
256
DHCP Server
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server assigns IP addresses to the
clients on a network. Select “Enable DHCP Server” to set the NVR a DHCP server if
there is none on the local network where the NVR locates.
Note:
•
Do not enable DHCP server if there is one the local network to avoid IP
address conflicts or network access errors.
•
The DHCP server option is available to Ethernet 1 only when both LAN ports
of a dual LAN NVR are connected to the network and Ethernet 1 is assigned
with a fixed IP.
Start IP, End IP, Lease Time: Set the range of IP addresses allocated by the NVR to the
DHCP clients and the lease time. The lease time refers to the time that an IP address
is leased to the clients. During that time, the IP will be reserved to the assigned client.
When the lease time expires, the IP can be assigned to another client.
(ii) DNS Server
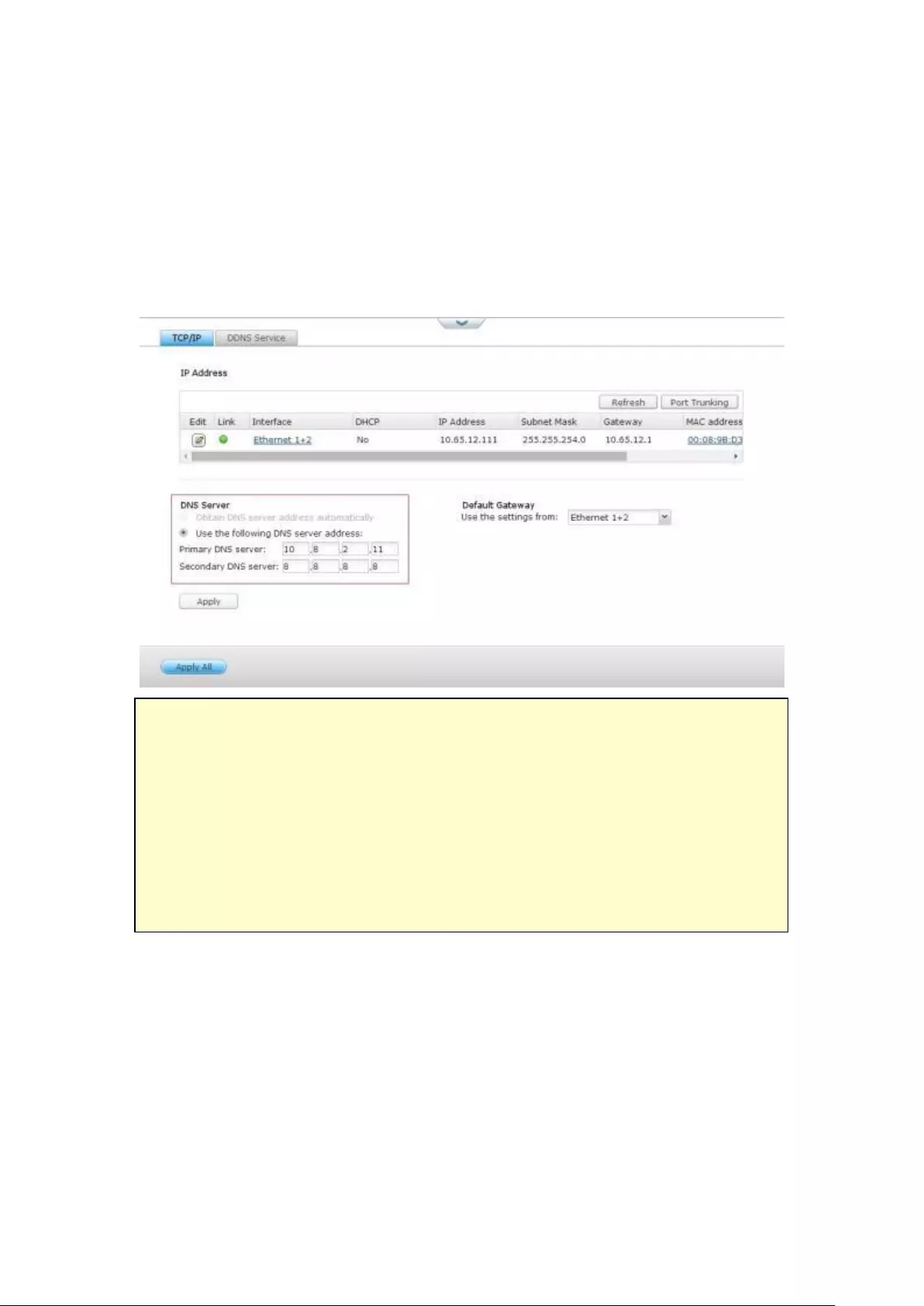
257
A DNS (Domain Name Service) server translates between a domain name (such as
google.com) and an IP address (74.125.31.105). Configure the NVR to obtain a DNS
server address automatically or specify the IP address of a DNS server.
Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
Note:
•
Please contact the ISP or network administrator for the IP address of the
primary and the secondary DNS servers. When the NVR plays the role as a
terminal and needs to perform independent connection, for example, BT
download, enter at least one DNS server IP for proper URL connection.
Otherwise, the function may not work properly.
•
If you select to obtain the IP address by DHCP, there is no need to configure
the primary and the secondary DNS servers. In this case, enter “0.0.0.0”.
(iii) Default Gateway
Select the gateway settings to use if both LAN ports have been connected to the
network (dual LAN NVR models only).
(iv) Port Trunking
Applicable to NVR models with two or more LAN ports only.
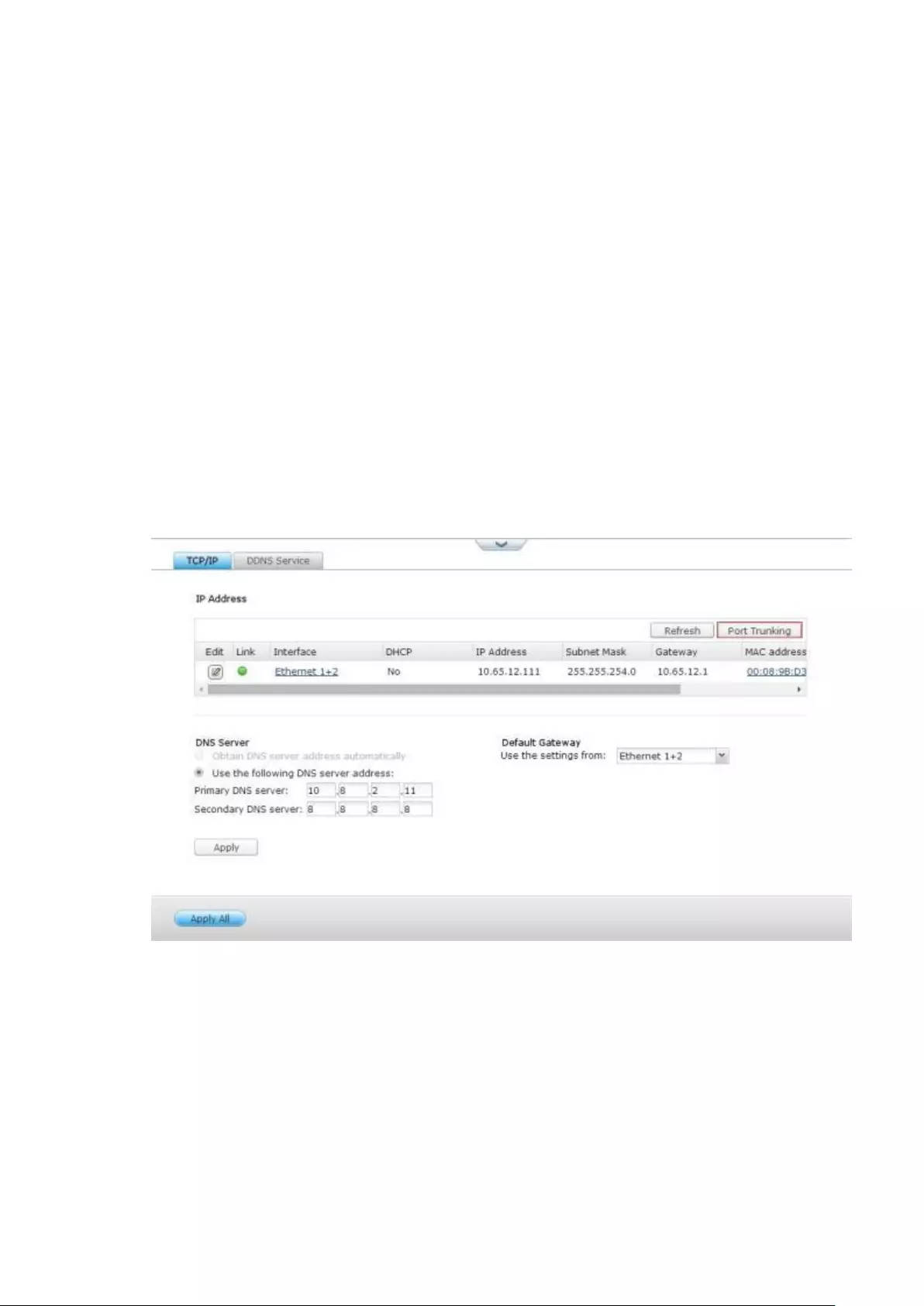
258
The NVR supports port trunking which combines two Ethernet interfaces into one to
increase the bandwidth and offers load balancing and fault tolerance (also known as
failover). Load balancing is a feature which distributes the workload evenly across
two Ethernet interfaces for higher redundancy. Failover is the capability to switch
over to a standby network interface (also known as the slave interface) when the
primary network interface (also known as the master interface) does not correspond
correctly to maintain high availability.
To use port trunking on the NVR, make sure at least two LAN ports of the NVR have
been connected to the same switch and the settings described in sections (i) and (ii)
have been configured.
Follow the steps below to configure port trunking on the NVR:
1
.
Click “Port Trunking”.
2.Select the network interfaces for a trunking group (Ethernet 1+2, Ethernet 3+4,
Ethernet 5+6, or Ethernet 7+8). Choose a port trunking mode from the drop-down
menu. The default option is Active Backup (Failover).
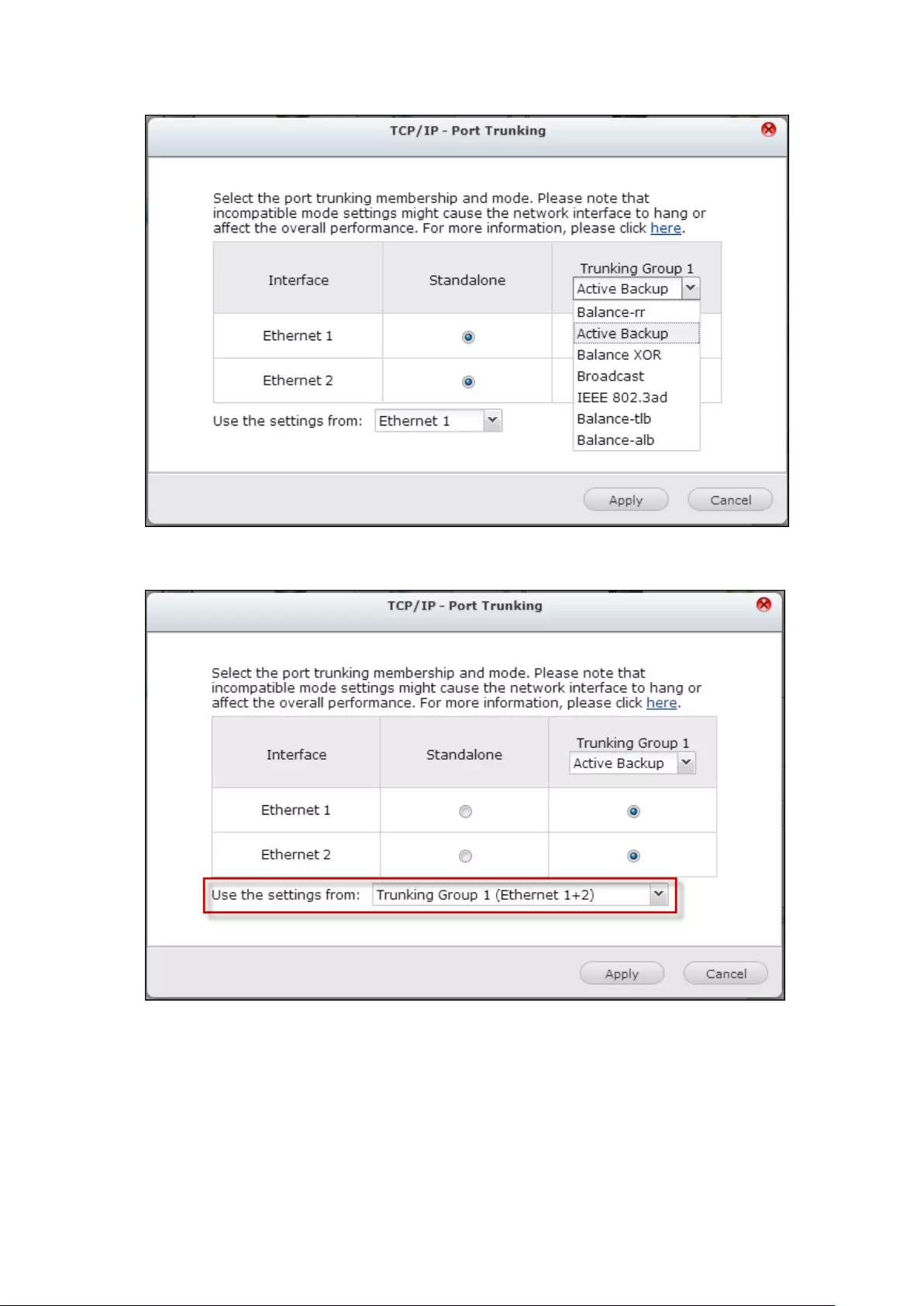
259
3.
Select a port trunking group to use. Click “Apply”.
4.
Click “here” to connect to the login page.
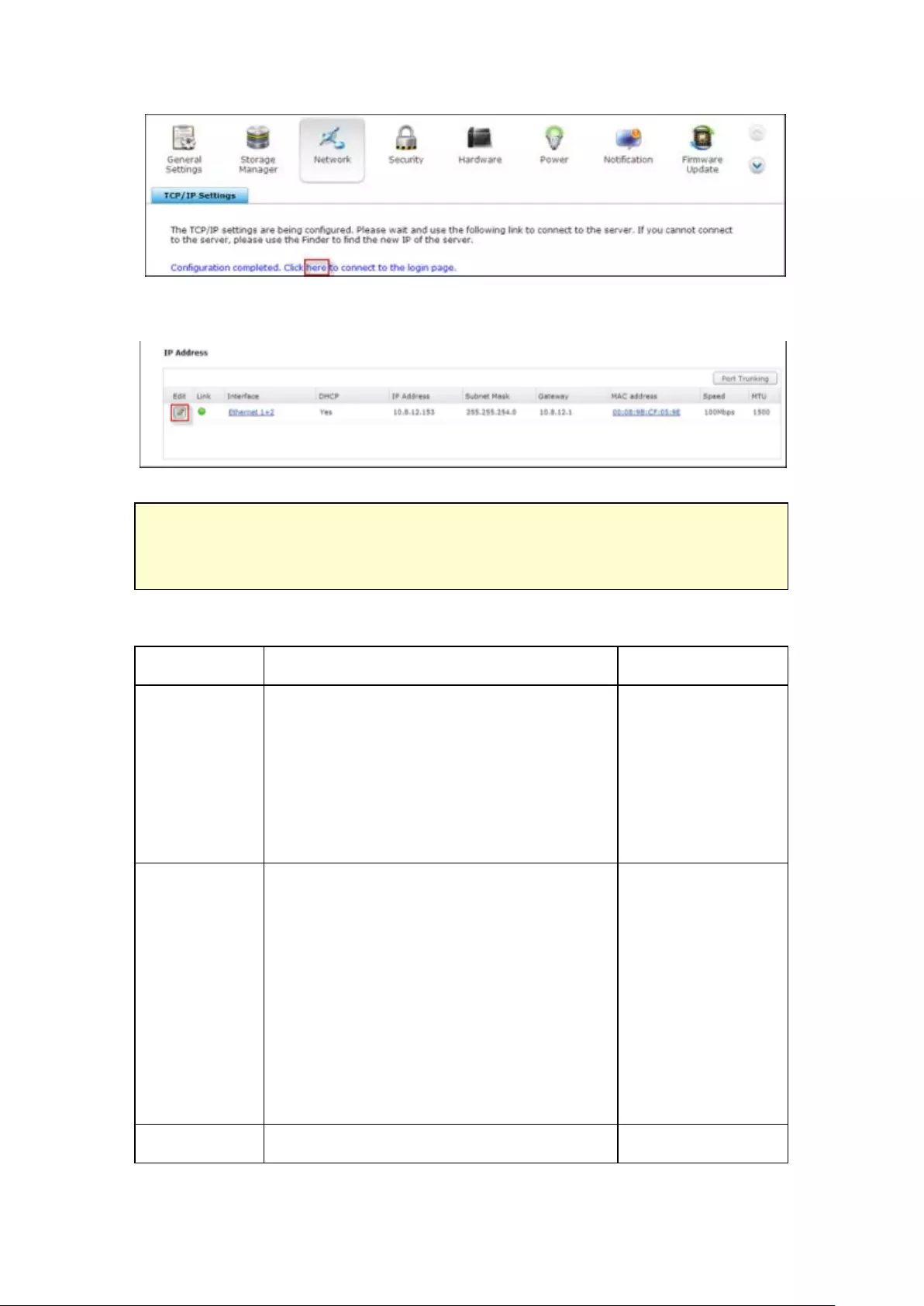
260
5.
Click the Edit button under “IP Address” to edit the network settings.
Note: Make sure the Ethernet interfaces are connected to the correct switch and the
switch has been configured to support the port trunking mode selected on the NVR.
The port trunking options available on the NVR:
Field
Description
Switch Required
Balance-rr
(Round-Robin)
Round-Robin mode is good for general
purpose load balancing between two
Ethernet interfaces. This mode transmits
packets in sequential order from the first
available slave through the last. Balance-rr
provides load balancing and fault tolerance.
Supports static
trunking. Make sure
static trunking is
enabled on the
switch.
Active Backup
Active Backup uses only one Ethernet
interface. It switches to the second Ethernet
interface if the first Ethernet interface does
not work properly. Only one interface in the
bond is active. The bond's MAC address is
only visible externally on one port (network
adapter) to avoid confusing the switch.
Active Backup mode provides fault
tolerance.
General switches
Balance XOR
Balance XOR balances traffic by splitting up
Supports static
261
outgoing packets between the Ethernet
interfaces, using the same one for each
specific destination when possible. It
transmits based on the selected transmit
hash policy. The default policy is a simple
slave count operating on Layer 2 where the
source MAC address is coupled with
destination MAC address. Alternate transmit
policies may be selected via the
xmit_hash_policy option. Balance XOR mode
provides load balancing and fault tolerance.
trunking. Make sure
static trunking is
enabled on the
switch.
Broadcast
Broadcast sends traffic on both network
interfaces. This mode provides fault
tolerance.
Supports static
trunking. Make sure
static trunking is
enabled on the
switch.
IEEE 802.3ad
(Dynamic Link
Aggregation)
Dynamic Link Aggregation uses a complex
algorithm to aggregate adapters by speed
and duplex settings. It utilizes all slaves in
the active aggregator according to the
802.3ad specification. Dynamic Link
Aggregation mode provides load balancing
and fault tolerance but requires a switch
that supports IEEE 802.3ad with LACP mode
properly configured.
Supports 802.3ad
LACP
Balance-tlb
(Adaptive
Transmit Load
Balancing)
Balance-tlb uses channel bonding that does
not require any special switch. The outgoing
traffic is distributed according to the current
load on each Ethernet interface (computed
relative to the speed). Incoming traffic is
received by the current Ethernet interface. If
the receiving Ethernet interface fails, the
other slave takes over the MAC address of
the failed receiving slave. Balance-tlb mode
provides load balancing and fault tolerance.
General switches
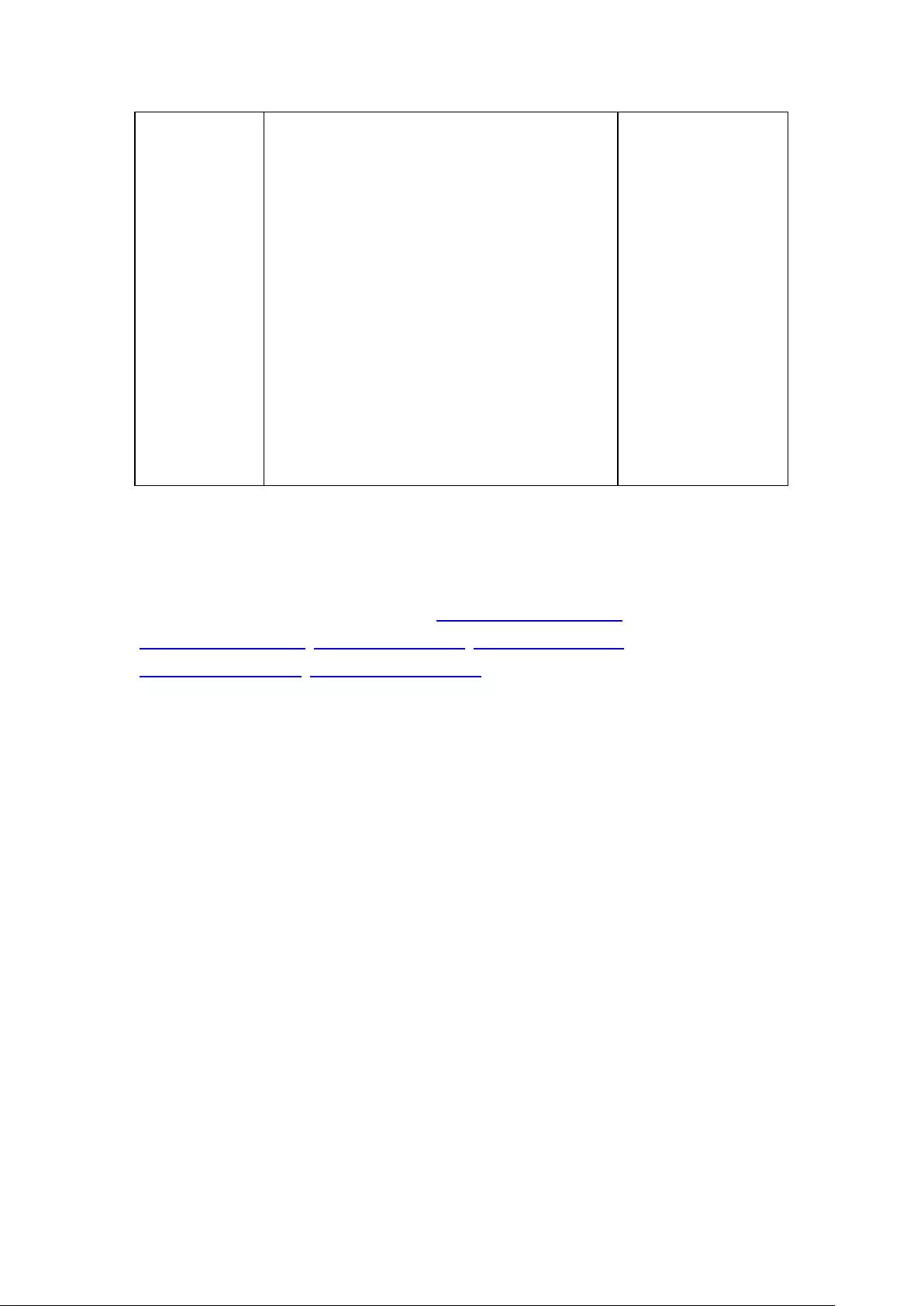
262
Balance-alb
(Adaptive Load
Balancing)
Balance-alb is similar to balance-tlb but also
attempts to redistribute incoming (receive
load balancing) for IPV4 traffic. This setup
does not require any special switch support
or configuration. The receive load balancing
is achieved by ARP negotiation sent by the
local system on their way out and overwrites
the source hardware address with the
unique hardware address of one of the
Ethernet interfaces in the bond such that
different peers use different hardware
address for the server. This mode provides
load balancing and fault tolerance.
General switches
DDNS Service
To allow remote access to the NVR using a domain name instead of a dynamic IP
address, enable the DDNS service.
The NVR supports the DDNS providers: http://www.dyndns.com,
http://update.ods.org, http://www.dhs.org, http://www.dyns.cx,
http://www.3322.org, http://www.no-ip.com.
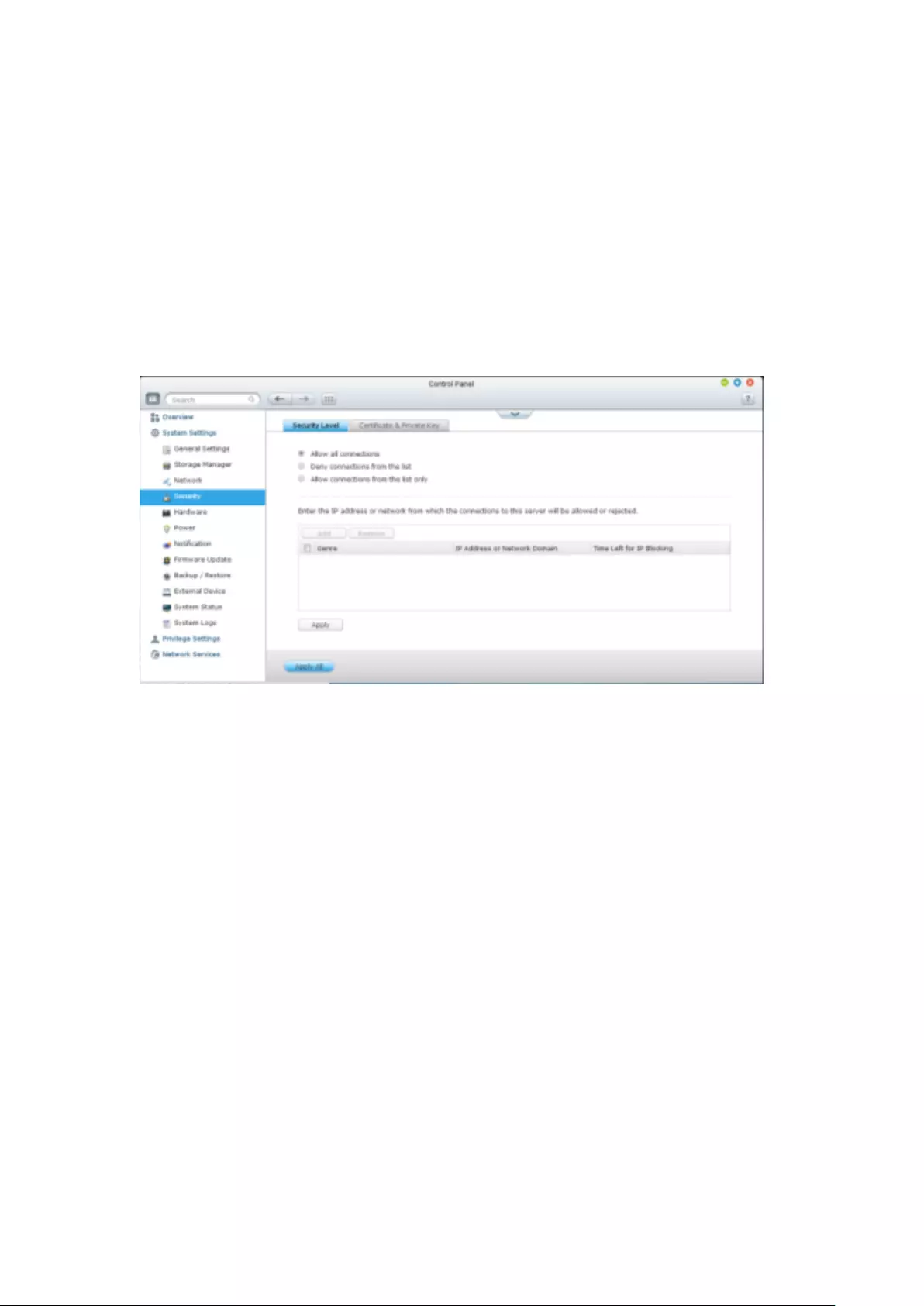
263
9.1.4 Security
Security Level
Specify the IP address or the network domain from which the connections to the
NVR are allowed or denied. When the connection of a host server is denied, all the
protocols of that server are not allowed to connect to the NVR.
After changing the settings, click “Apply” to save the changes. The network services
will be restarted and current connections to the NVR will be terminated.
Certificate & Private Key
The Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a protocol for encrypted communication between
the web servers and the web browsers for secure data transfer. You can upload a
secure certificate issued by a trusted provider. After uploading a secure certificate,
users can connect to the administration interface of the NVR by SSL connection and
there will not be any alert or error message. The NVR supports X.509 certificate and
private key only.
•
Download Certificate: To download the secure certificate which is currently in use.
•
Download Private Key: To download the private key which is currently in use.
•
Restore Default Certificate & Private Key: To restore the secure certificate and
private key to system default. The secure certificate and private key in use will be
overwritten.
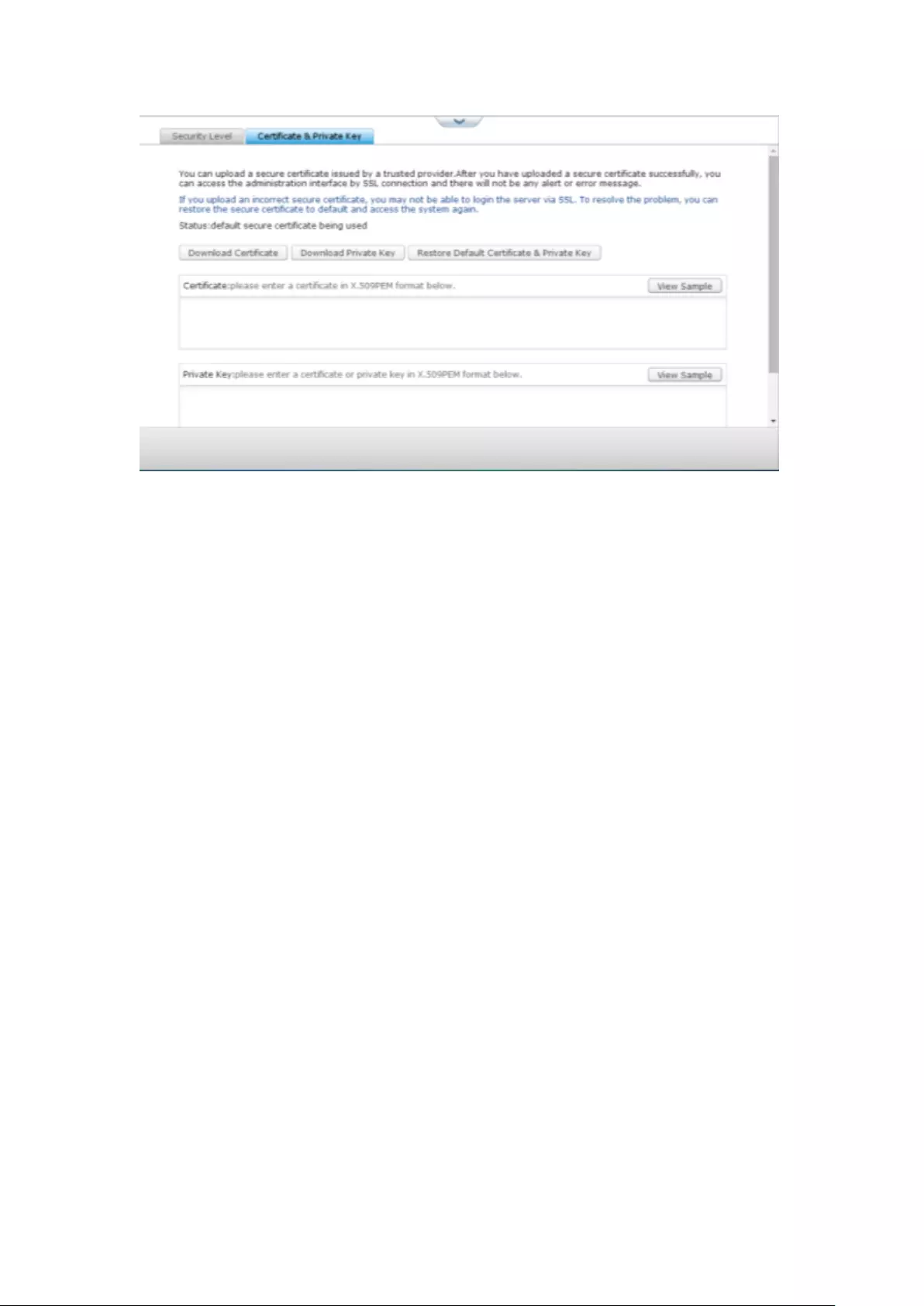
264
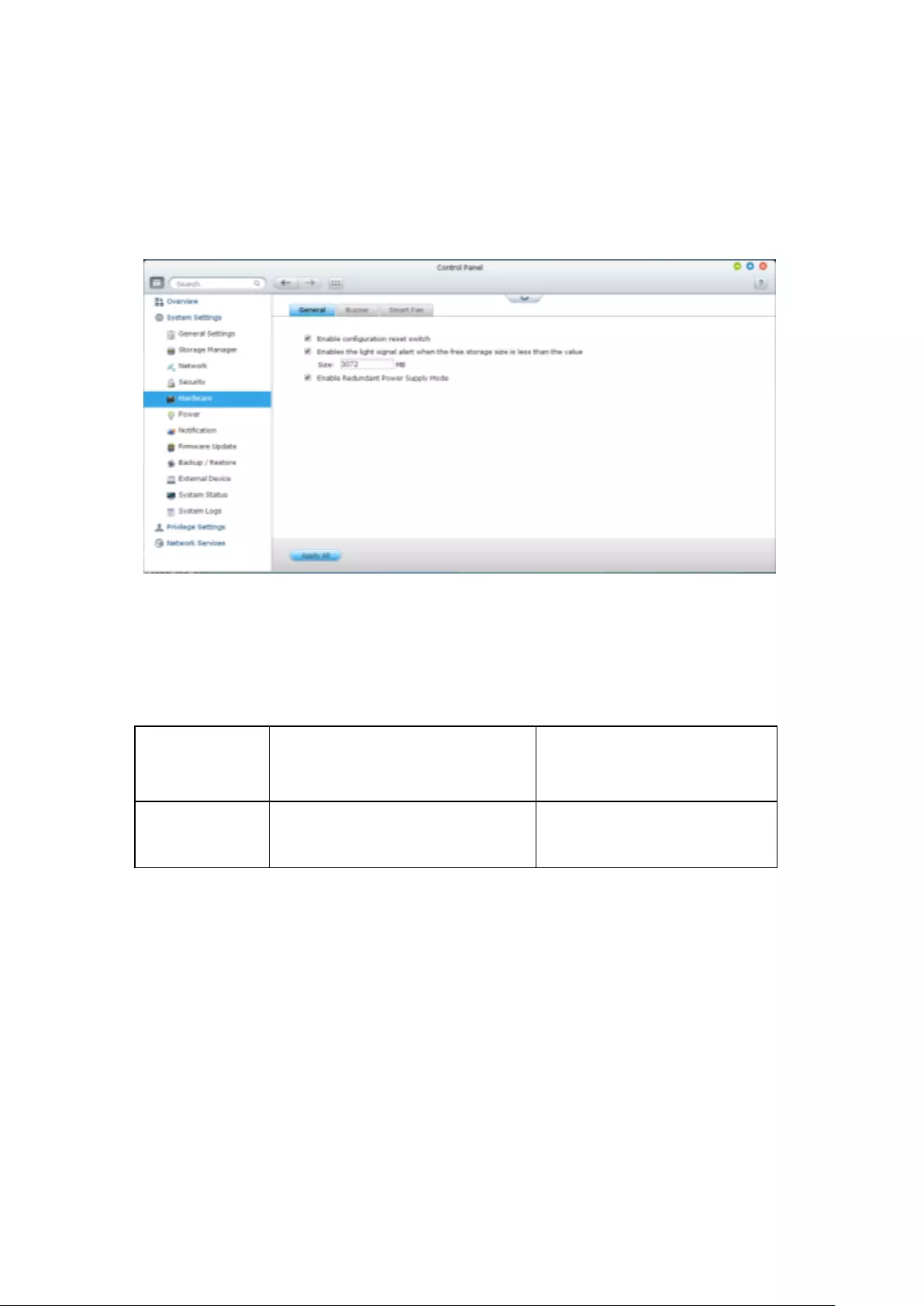
265
9.1.5 Hardware
Configure the hardware functions of the NVR.
General
Enable configuration reset switch
When this function is turned on, you can press the reset button for 3 seconds to
reset the administrator password and the system settings to default. The disk data
will be retained.
System
Basic system reset
(1 beep)
Advanced system reset
(2 beeps)
All NVR models
Press the reset button for 3 sec
Press the reset button for 10
sec
Basic system reset (3 sec)
After pressing the reset button for 3 seconds, a beep sound will be heard. The
following settings will be reset to default:
•
System administration password: admin.
•
TCP/IP configuration: Obtain IP address settings automatically via DHCP.
•
TCP/IP configuration: Disable Jumbo Frame.

266
•
TCP/IP configuration: If port trunking is enabled (dual LAN models only), the port
trunking mode will be reset to “Active Backup (Failover)”.
•
System port: 80 (system service port).
•
Security level: Low (Allow all connections).
•
LCD panel password: (blank)*.
*This feature is only provided by the NVR models with LCD panels.
Advanced system reset (10 sec)
After pressing the reset button for 10 seconds, you will hear two beeps at the third
and the tenth seconds. The NVR will reset all the system settings to default as it does
by the web-based system reset in “Administration” > “Restore to Factory Default”
except all the data are reserved. The settings such as the users, user groups, and the
shared folders previously created will be cleared.
Enable light signal alert when the free size of SATA disk is less than the value:
The status LED flashes red and green when this option is turned on and the free
space of the SATA hard drive is less than the value. The valid range of the value is
1-51200 MB.
Enable warning alert for redundant power supply on the web-based interface:
If two power supply units (PSU) are installed on the NVR and connected to the power
sockets, both PSU will supply the power to the NVR (applied to 1U and 2U models).
Turn on the redundant power supply mode in “System Settings” > “Hardware” to
receive warning alert for the redundant power supply. The NVR will sound and record
the error messages in “System Logs” when the PSU is plugged out or does not
correspond correctly.
If only one PSU is installed on the NVR, do NOT enable this option.
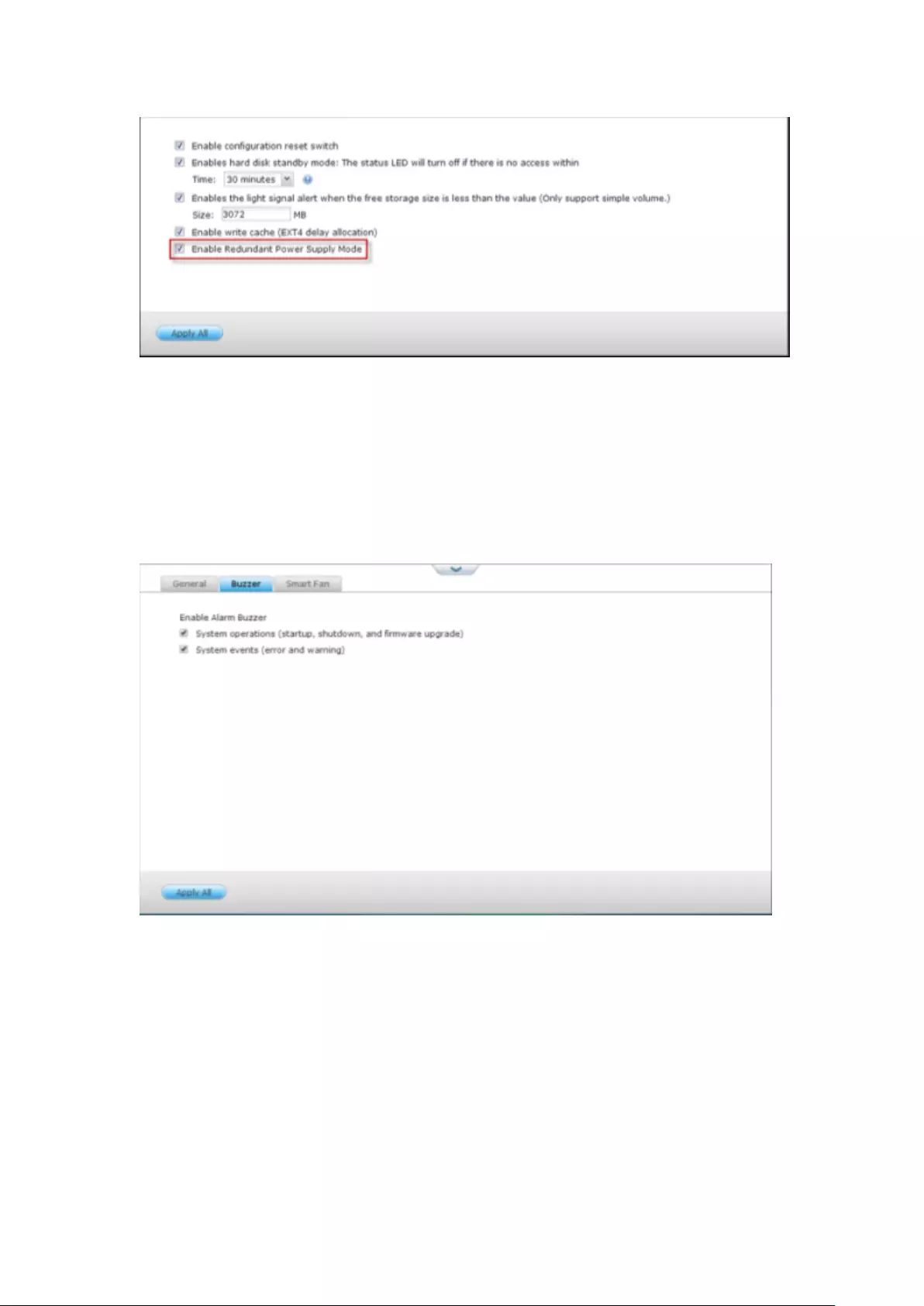
267
* This function is disabled by default.
Buzzer
Enable alarm buzzer
Turn on this option to allow the alarm buzzer to beep when certain system
operations (startup, shutdown, or firmware upgrade) are executed or system events
(error or warning) occur.
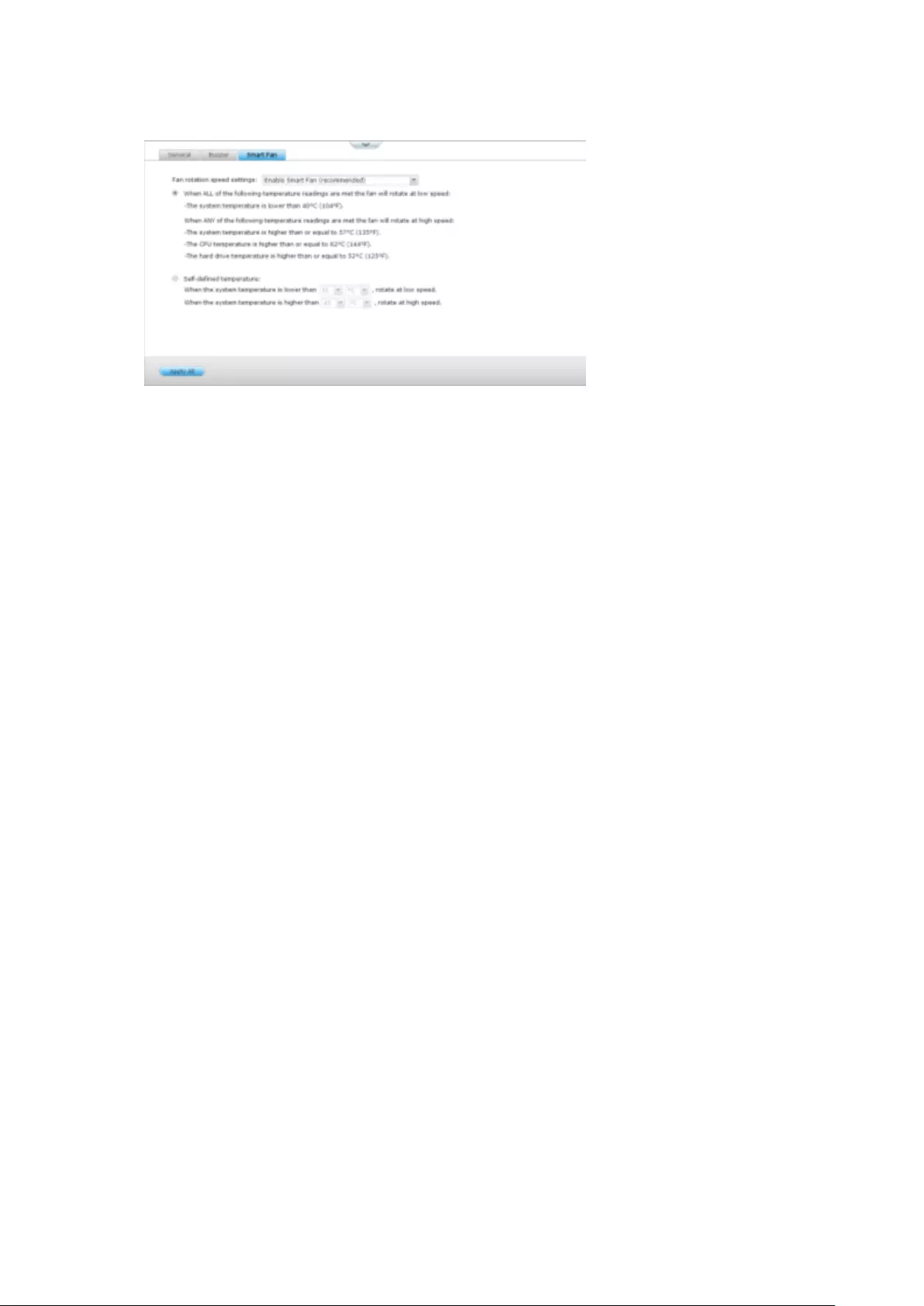
268
Smart Fan
Smart Fan Configuration:
•
Enable smart fan (recommended)
Select to use the default smart fan settings or define the settings manually. When
the system default settings are selected, the fan rotation speed will be
automatically adjusted when the NVR temperature, CPU temperature, and hard
drive temperature meet the criteria. It is recommended to enable this option.
•
Set fan rotation speed manually
By manually setting the fan rotation speed, the fan rotates at the defined speed
continuously.
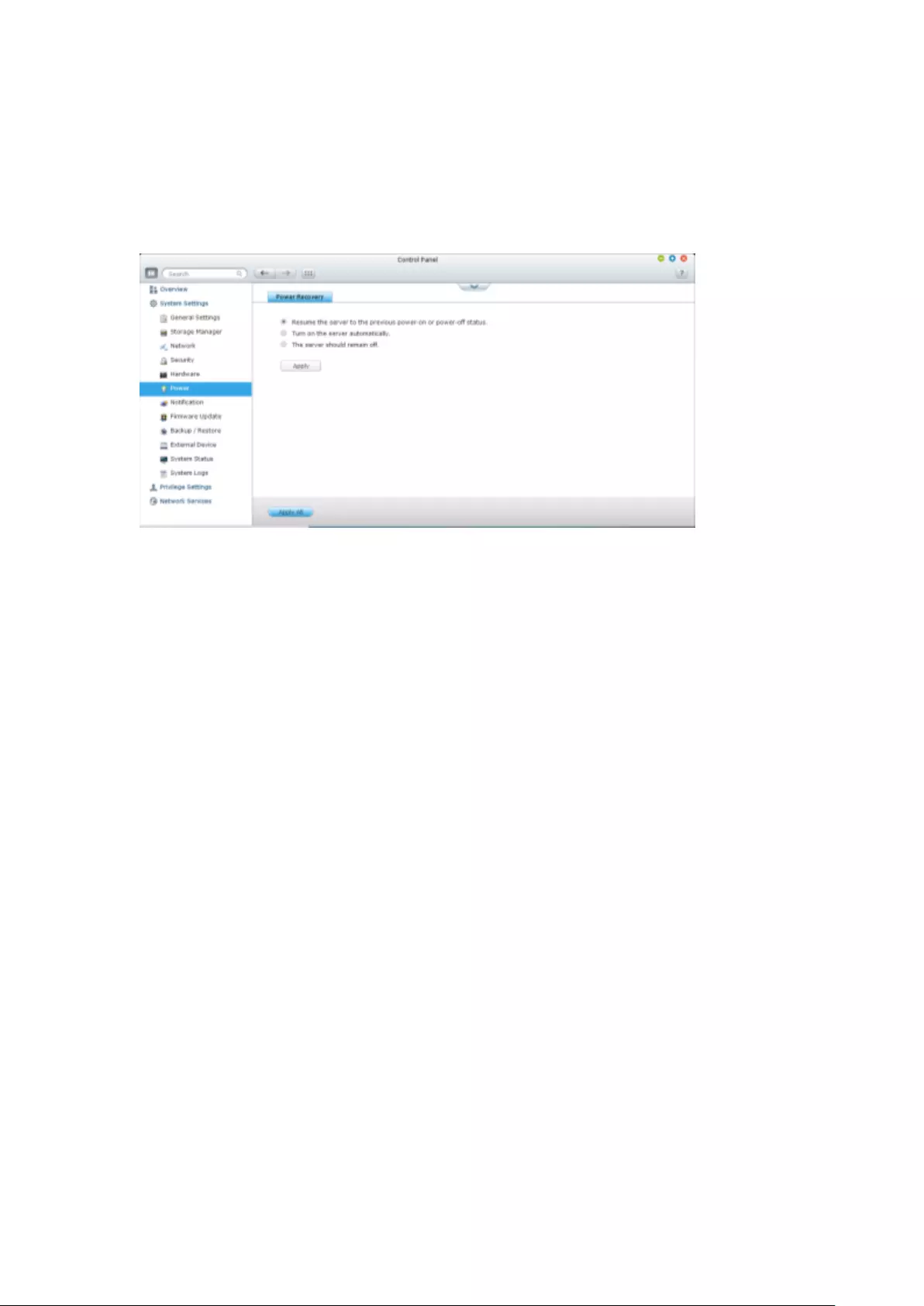
269
9.1.6 Power
Power Recovery
Configure the NVR to resume to the previous power-on or power-off status, turn on,
or remain off when the AC power resumes after a power outage.
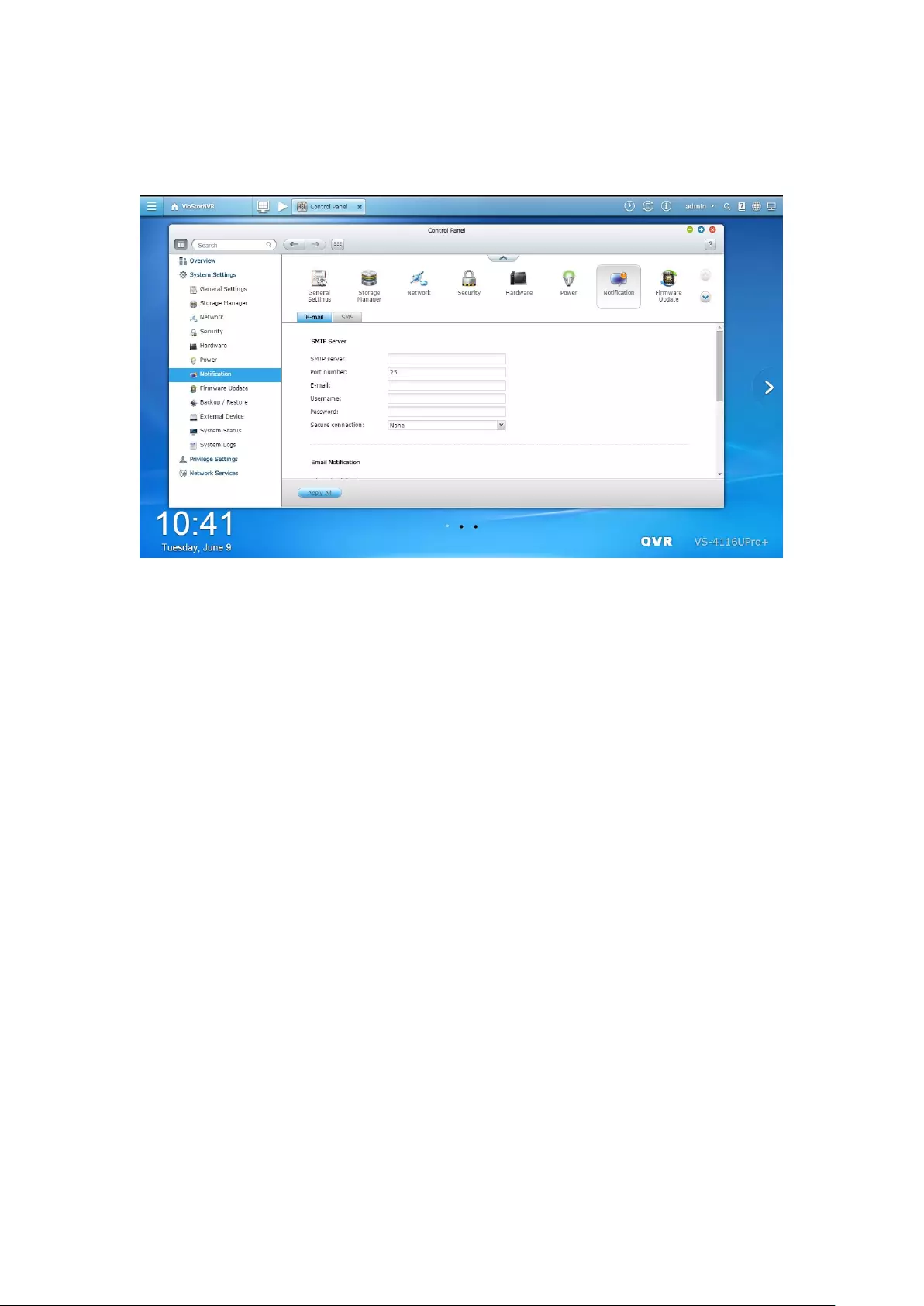
270
9.1.7 Notification
E-mail
SMTP Server
The NVR supports email alerts to inform the administrator of system errors and
warning. To receive alerts by email, configure the SMTP server.
SMTP server: Enter the SMTP server name, for example, smtp.gmail.com.
Port number: Enter the port number for the SMTP server. The default port
number is 25.
E-mail: Enter the email address of the alert recipient.
User name and Password: Enter the login information of the email account.
Secure connection: Choose SSL or TLS to ensure a secure connection between
the NVR and SMTP server, or None based on your needs. It is recommended to
enable this function if the SMTP server supports it.
Email Notification
You can toggle email notifications for all error events or warning events.
A maximum of five email addresses are allowed.
The settings here will be synced with [Surveillance Settings] -> [Camera Settings] ->
[Event Management] -> E-mail settings when choosing Traditional Mode.

271
SMS
SMSC Settings
Configure the SMSC server settings to send SMS messages to specified phone
numbers from the NVR. The default SMS service provider is Clickatell. You can add
your own SMS service provider by selecting “Add SMS Provider” from the drop-down
menu.
When “Add SMS service provider” is selected, enter the name of the SMS provider
and the URL template text.
SMS Notification
You can toggle SMS messages for all error events or warning events.
A maximum of two phone numbers are allowed.
The settings here will be synced with [Surveillance Settings] -> [Camera Settings] ->
[Event Management] -> SMS settings when choosing Traditional Mode..
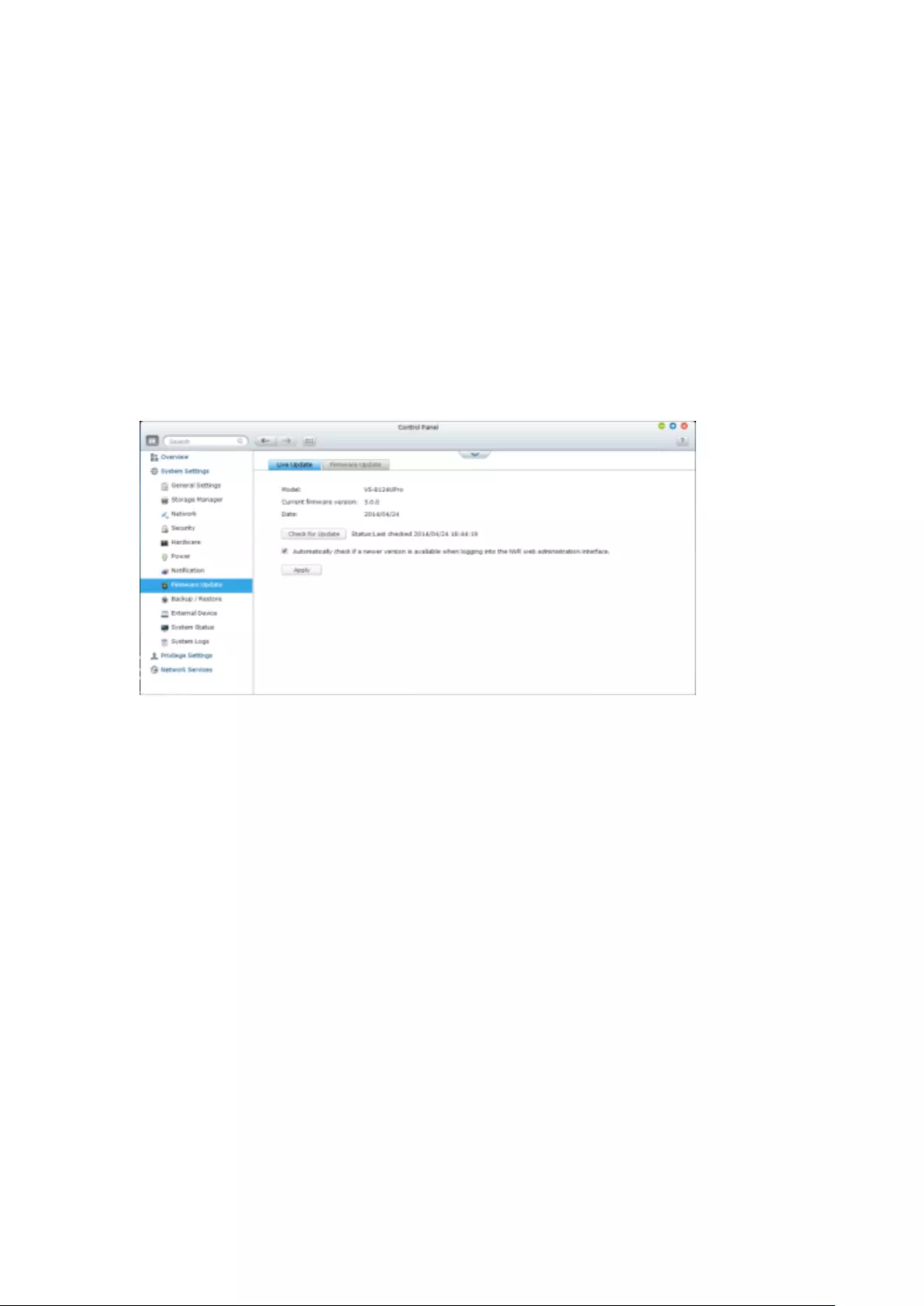
272
9.1.8 Firmware Update
Live Update
Select “Automatically check if a newer version is available when logging into the NVR
web administration interface” to allow the NVR to automatically check if a new
firmware version is available for download from the Internet. If a new firmware is
found, you will be notified after logging in the NVR as an administrator.
Click “Check for Update” to check if a firmware update is available.
Note that the NVR must be connected to the Internet for these features to work.
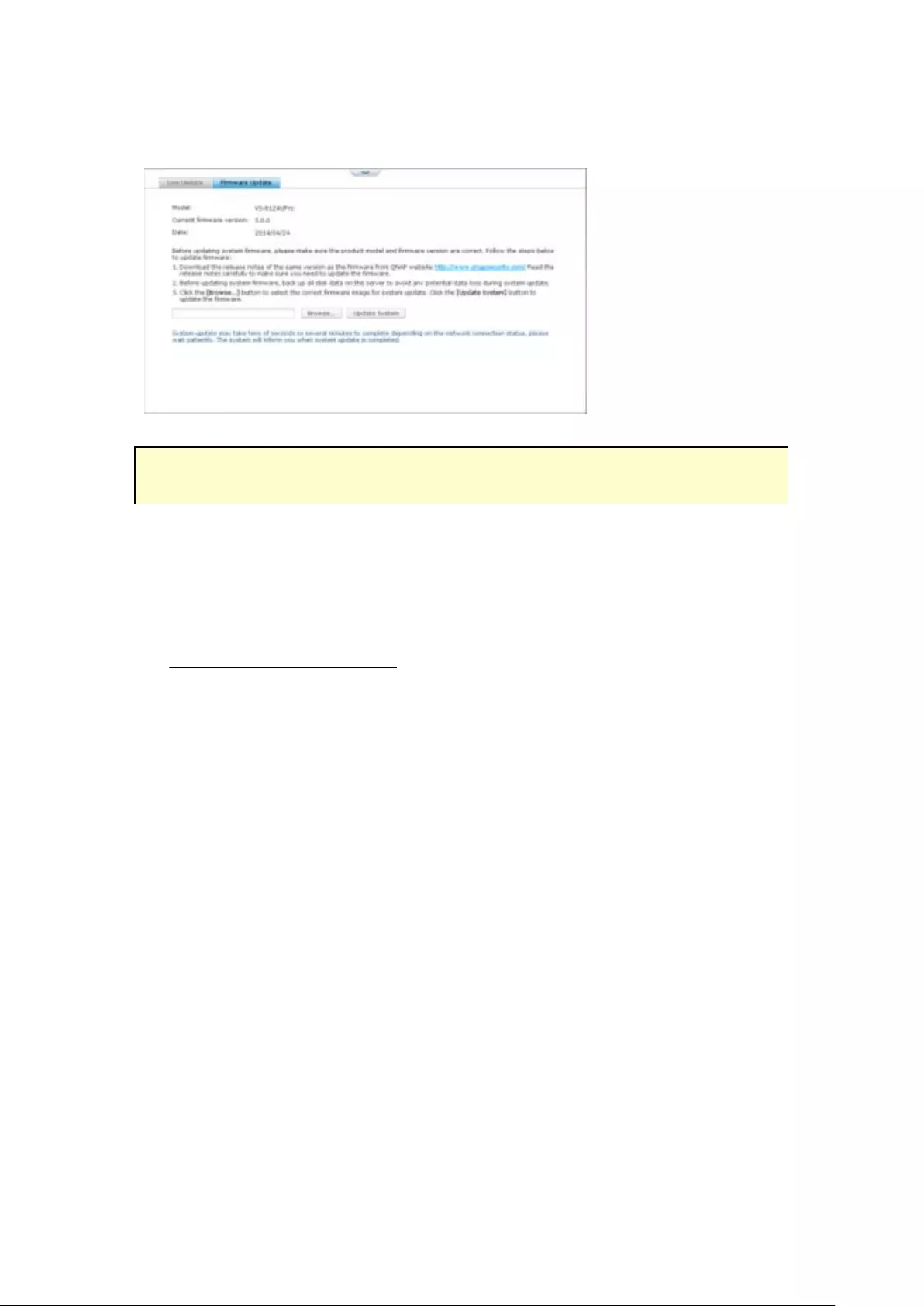
273
Firmware Update
Note: If the system is running properly, you do not need to update the firmware.
Before updating the system firmware, make sure the product model and firmware
version are correct. Follow the steps below to update firmware:
1.
Download the release notes of the firmware from the QNAP Security website
http://www.qnapsecurity.com. Read the release notes carefully to make sure it is
required to update the firmware.
2.
Download the NVR firmware and unzip the IMG file to the computer.
3.
Before updating the system firmware, back up all the disk data on the NVR to
avoid any potential data loss during the system update.
4.
Click “Browse” to select the correct firmware image for the system update. Click
“Update System” to update the firmware.
The system update may take tens of seconds to several minutes to complete
depending on the network connection status. Please wait patiently. The NVR will
inform you when the system update has completed.
Update Firmware by QNAP Qfinder
The NVR firmware can be updated by the QNAP Qfinder. Follow the steps below:
1.
Select a NVR model and choose “Update Firmware” from the “Tools” menu.
274
2.
Login the NVR as an administrator.
3.
Browse and select the firmware for the NVR. Click “Start” to update the system.
Note: The NVR servers of the same model on the same LAN can be updated by the
Finder at the same time. Administrator access is required for system update.
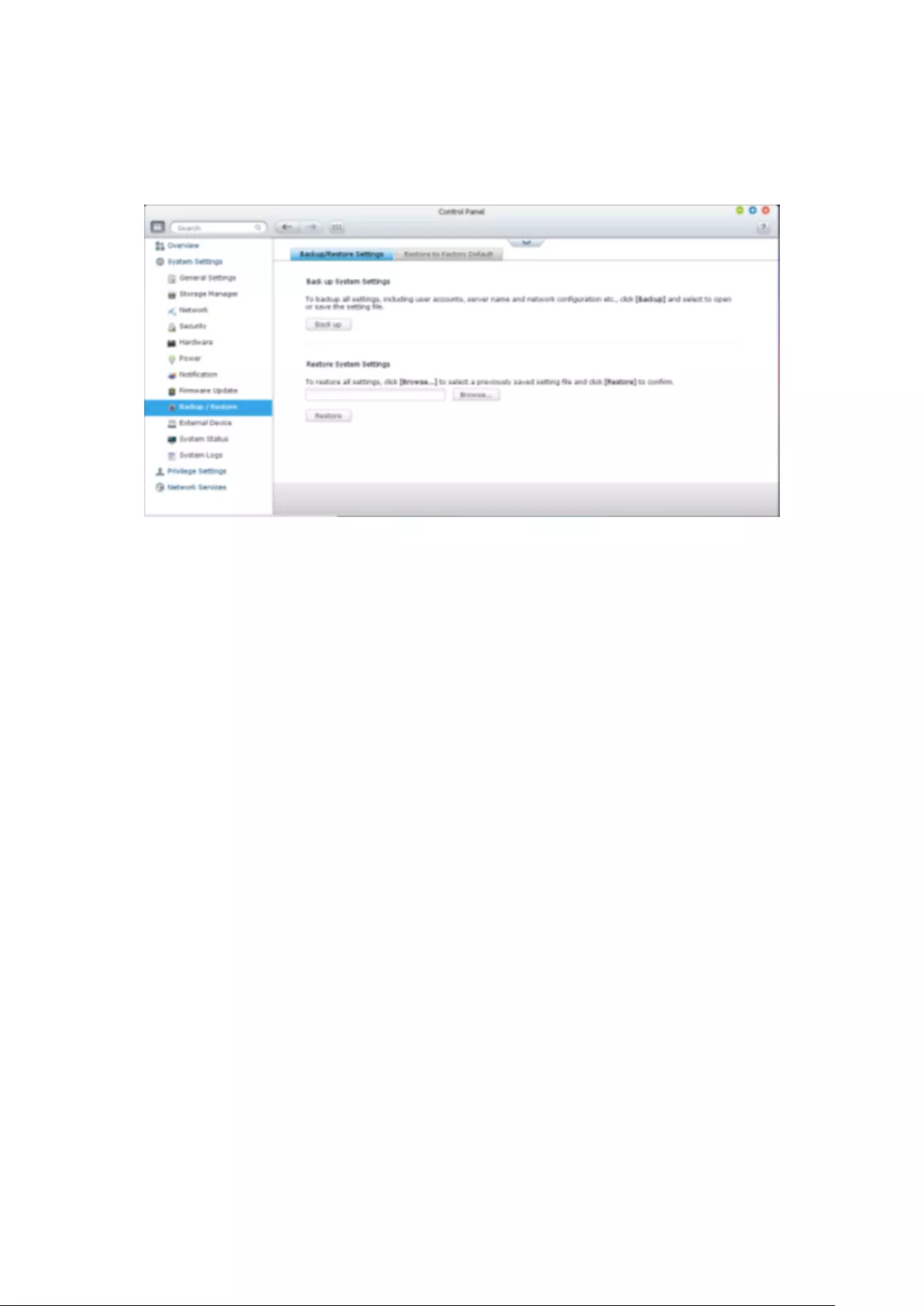
275
9.1.9 Backup/Restore
Backup/Restore Settings
Back up System Settings
To back up all the settings, including the user accounts, server name, network
configuration and so on, click “Backup” and select to open or save the setting file.
Restore System Settings
To restore all the settings, click “Browse” to select a previously saved setting file and
click “Restore”.
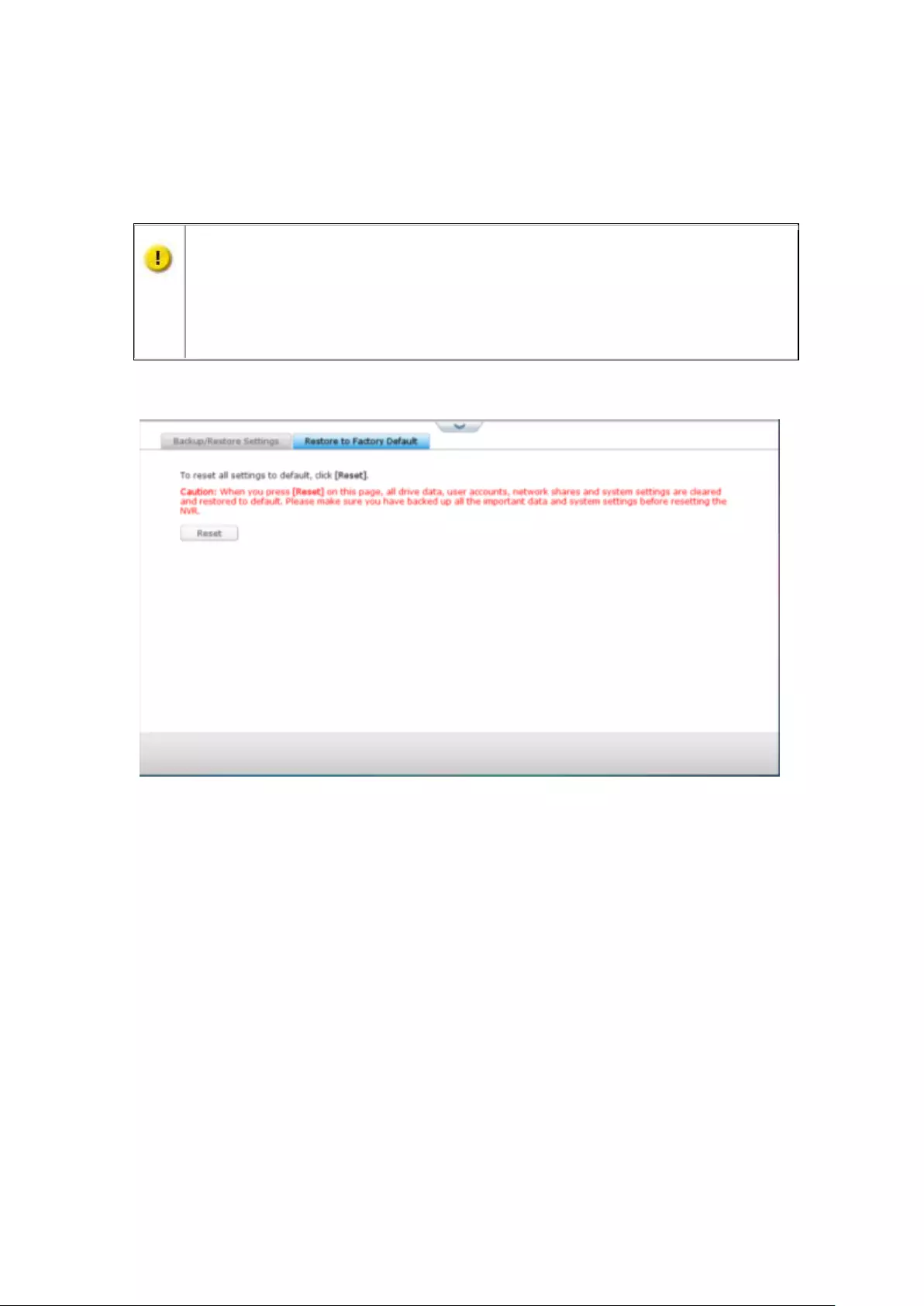
276
Restore to Factory Default
To reset all the system settings to default, click “RESET” and then click “OK”.
Caution: When “RESET” is pressed on this page, all the disk data, user accounts,
shared folders, and system settings will be cleared and restored to default.
Always back up all the important data and system settings before resetting the
NVR.
To reset the NVR by the reset button, see “System Settings” > “Hardware”.
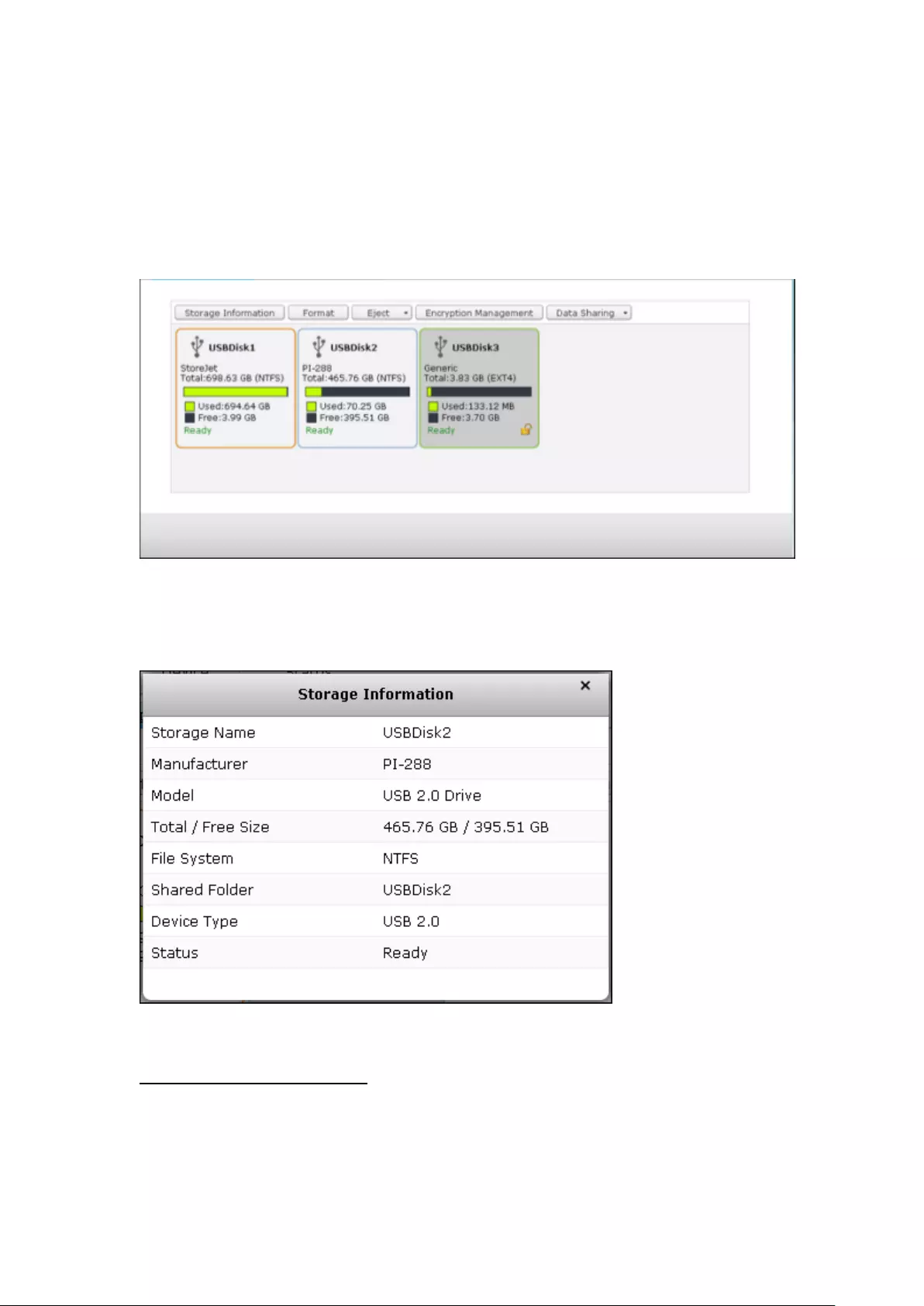
277
9.1.10 External Device
External Storage
The NVR supports external USB storage devices* for backup and data storage.
Connect the external storage device to a USB interface of the NVR, when the device
is successfully detected, the details will be shown on this page.
Storage Information
Select a storage device and click Storage Information to check for its details.
*The number of USB interfaces supported varies by models. Please refer to
http://www.qnapsecurity.com for details.
It may take tens of seconds for the NVR server to detect the external USB device
successfully. Please wait patiently.
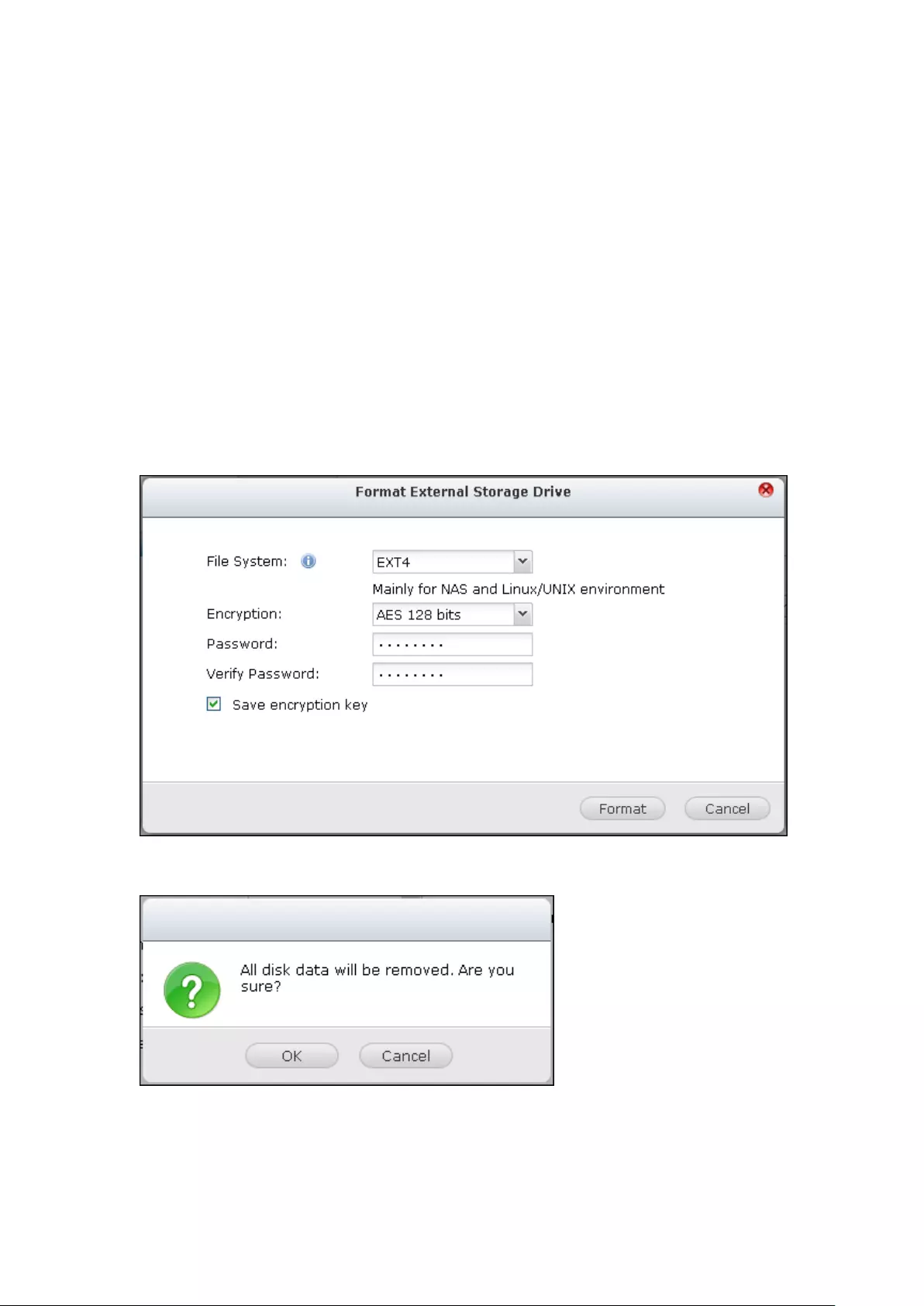
278
Format
The external storage device can be formatted as EXT3, EXT4, FAT32, NTFS, or HFS+
(Mac only) file system. Click “Format” and select the option from the drop-down
menu.
The NVR supports external drive encryption. To encrypt an external storage device,
click “Encryption”. Select the encryption method: AES 128-, 192- or 256-bit and enter
the password (8-16 characters). Select “Save encryption key” to save the password in
a hidden location on a hard drive of the NVR. The NVR will unlock the encrypted
external storage device automatically every time the device is connected. Click
Format to proceed.
Click “OK” and all the data will be cleared.
The device will be “Ready” after disk initialization.
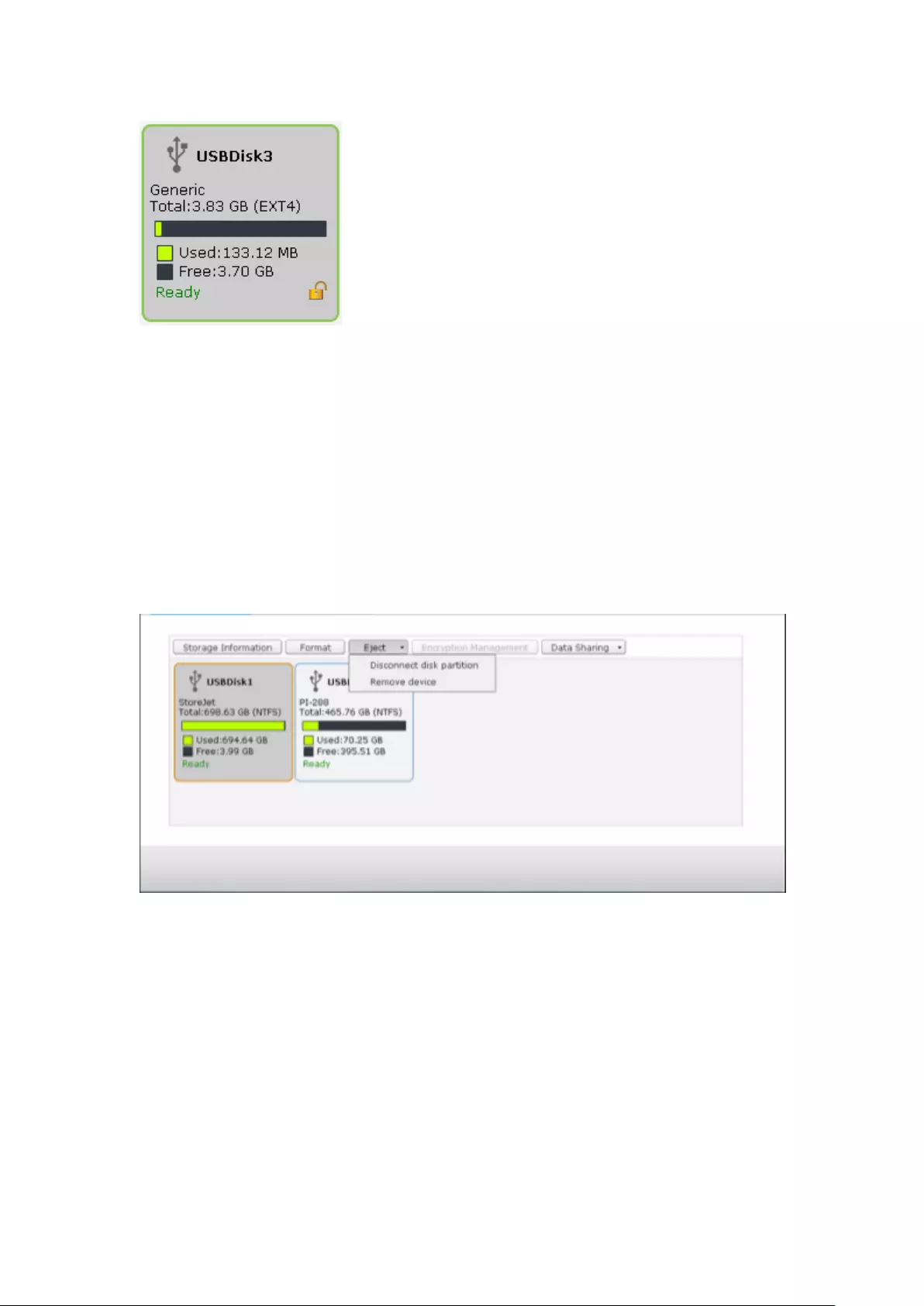
279
Eject
“Eject” offers two different options. “Disconnect disk partition” allows you to remove
a single disk partition or a disk drive in a multi-drive enclosure. “Remove external
device” allows you to disconnect external storage devices without the risk of losing
any data when the device is removed.
First choose a device to eject, click “Eject” and then to disconnect the disk partition
or remove the device.
Encryption management
If an external storage device is encrypted by the NVR, the button “Encryption
Management” will appear. Click this button to manage the encryption password/key,
or lock or unlock the device.
Lock the device
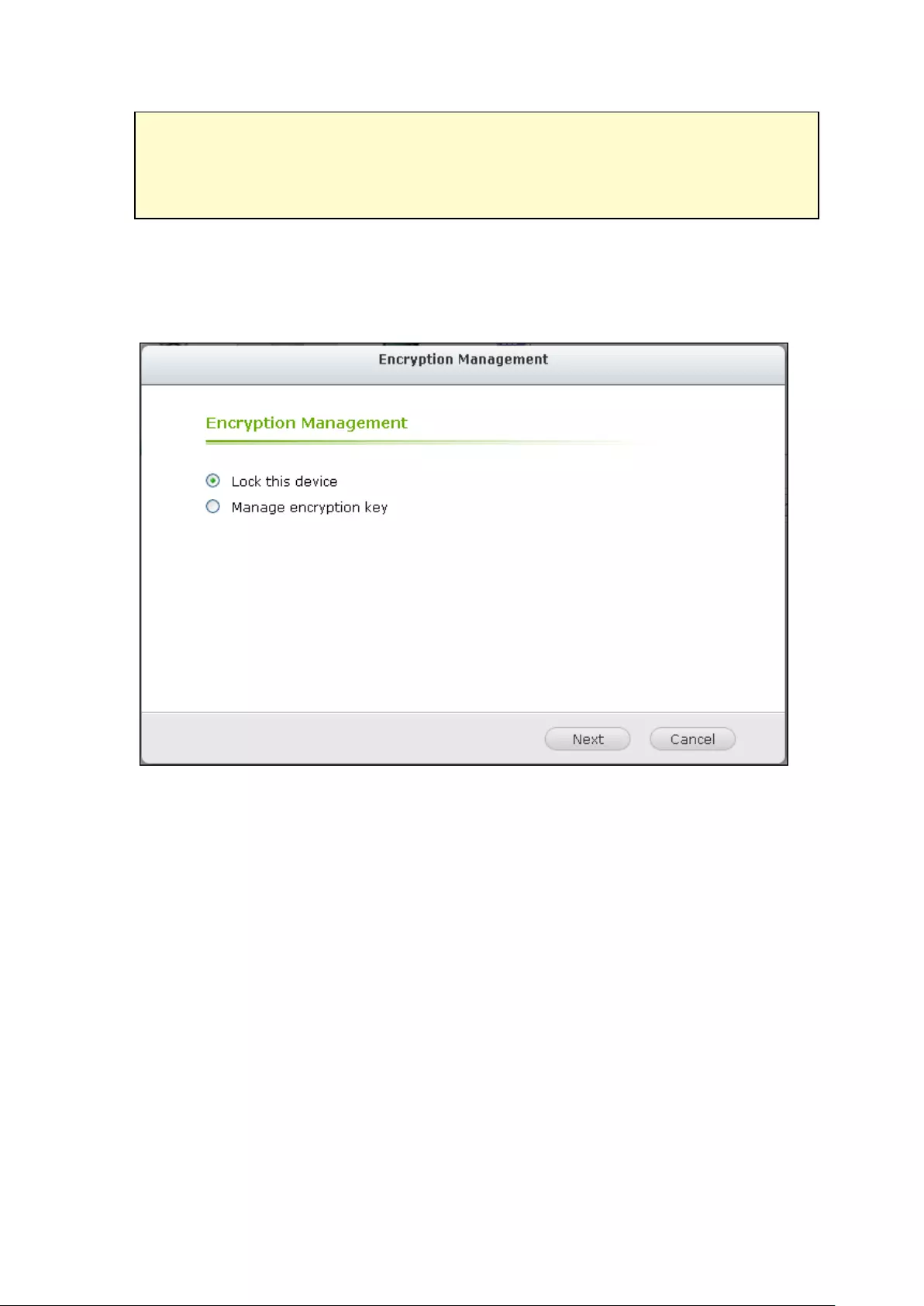
280
Note: The external storage device cannot be locked if a real-time or scheduled backup
job is running on the device. To disable the backup job, go to “Control Panel” > “External
Device” > “External Storage”
1.
To lock an encrypted external storage device, click “Encryption Management”.
2.
Select “Lock this device” and click “Next”.
3.
Click “Next” to lock the device.
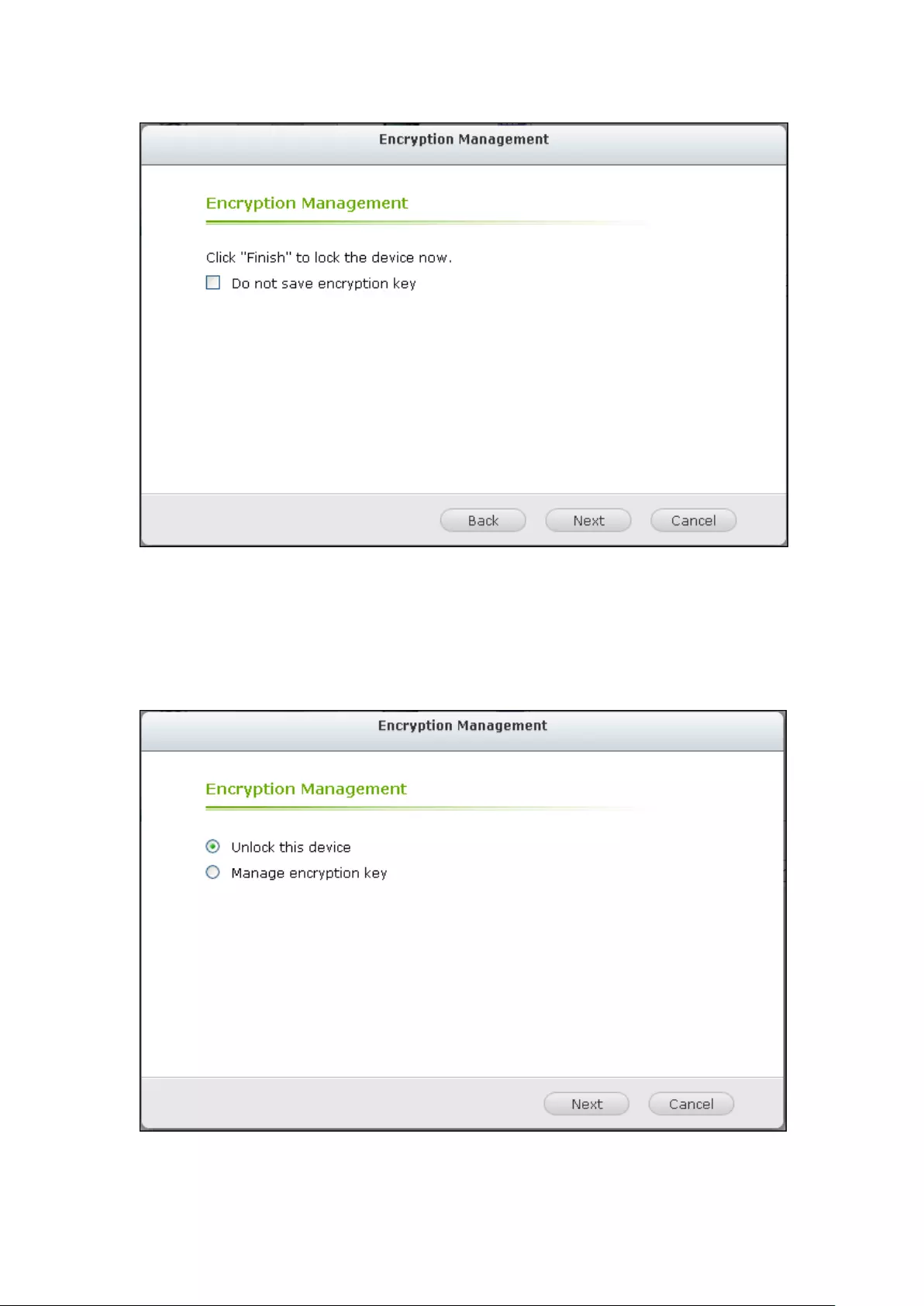
281
Unlock the device
1.
To unlock an encrypted external storage device, click “Encryption Management”.
2.
Select “Unlock this device”. Click “Next”.
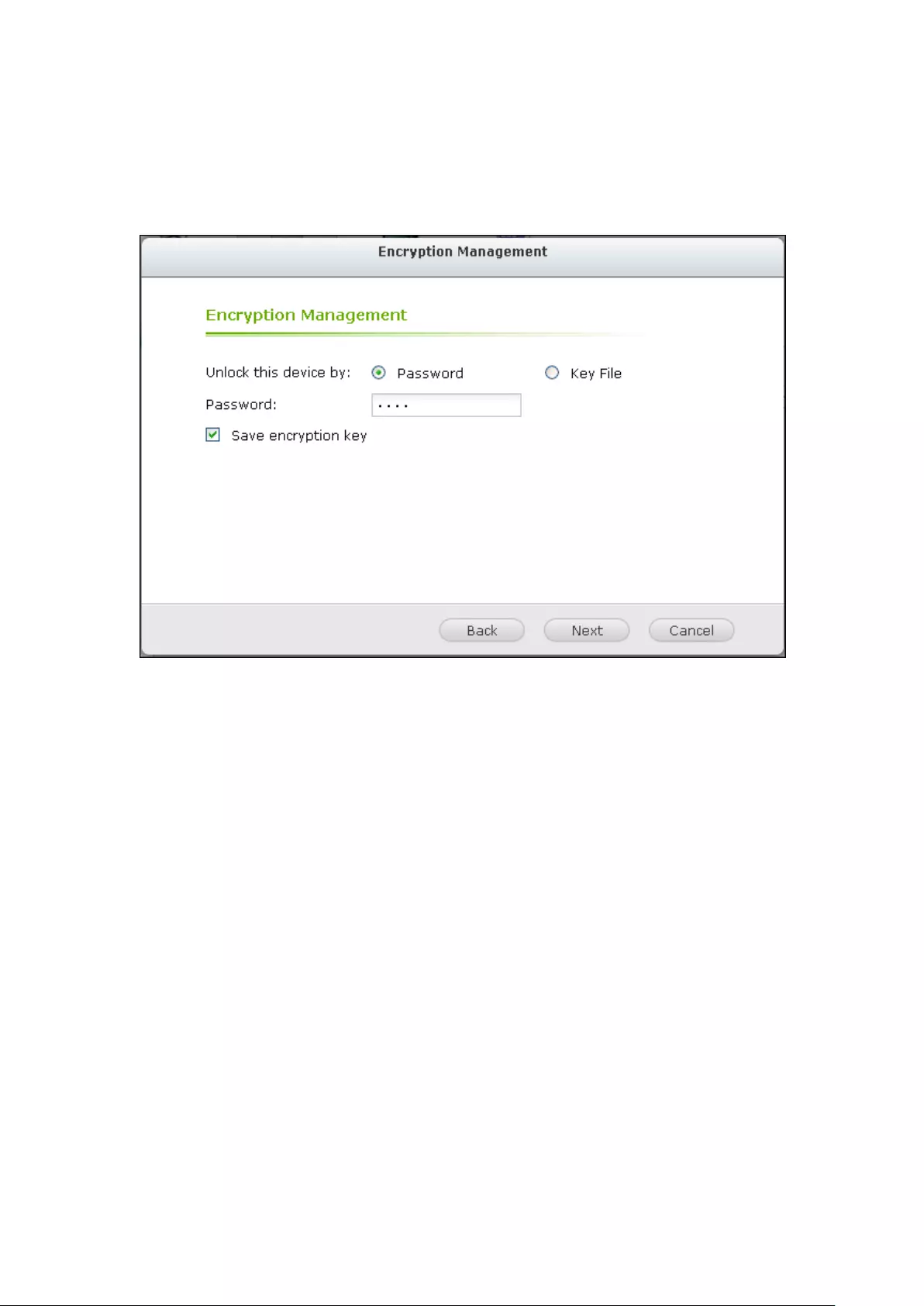
282
3.
Enter the encryption password or upload the key file. Select “Save encryption
key” to save the password in a hidden location on a hard drive of the NVR. The
NVR will unlock the encrypted external storage device automatically every time
the device is connected. Click “Next”.
Manage the encryption key
1.
To change an encryption password or download an encryption key file, click
“Encryption Management”.
2.
Select “Manage encryption key”. Click “Next”.
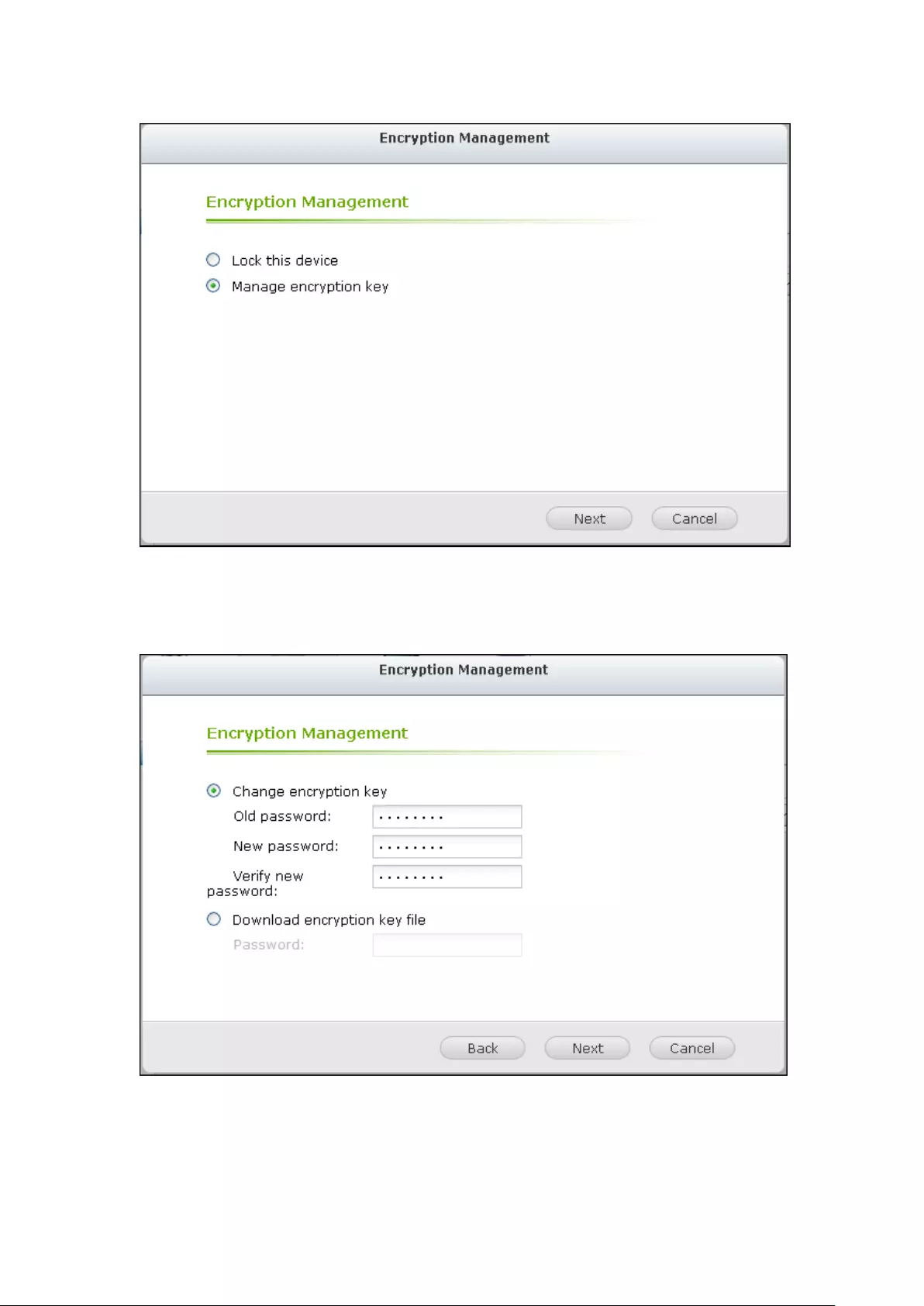
283
3.
Select to change the encryption password or download the encryption key file to
the local PC. Click “Next”.
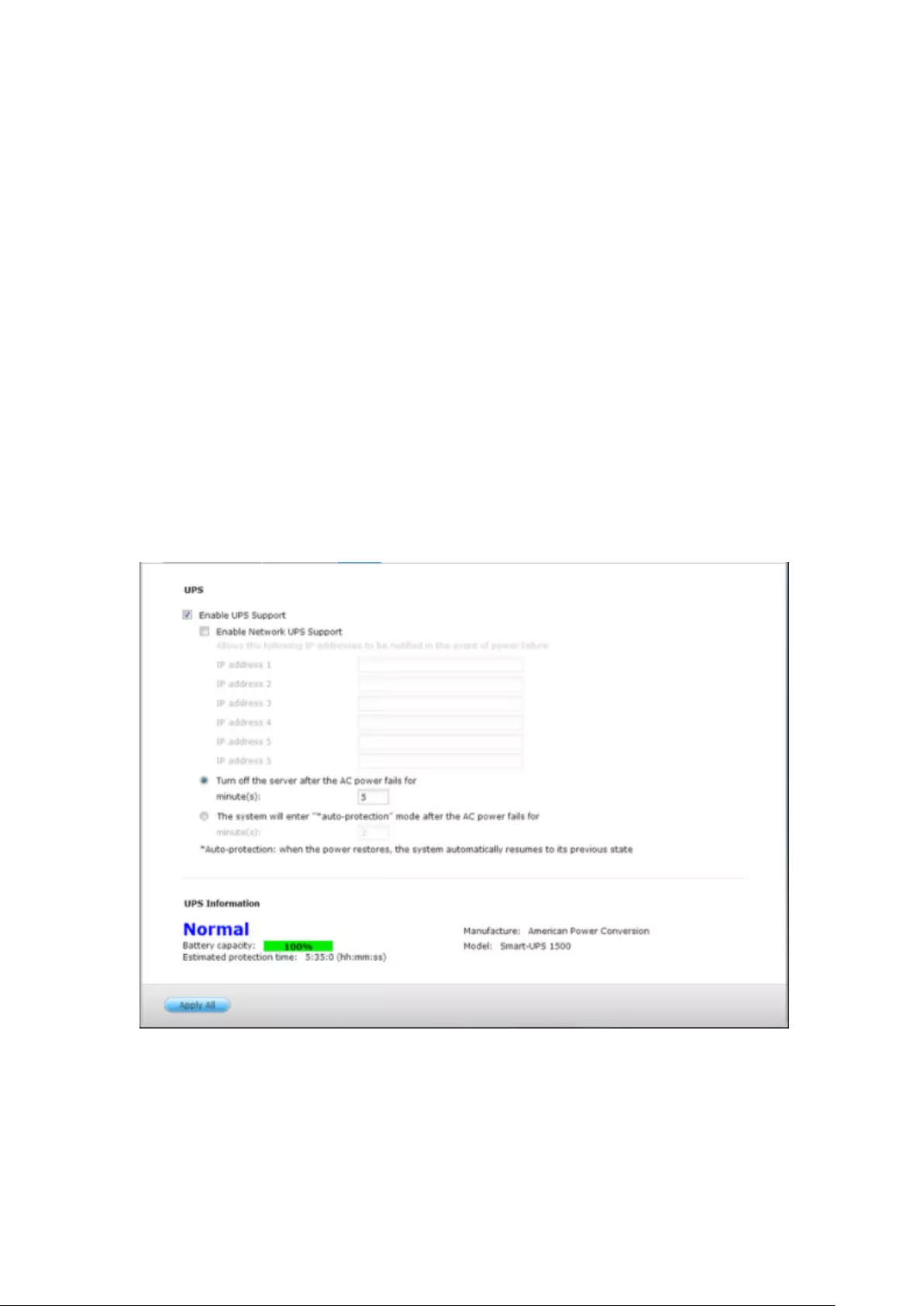
284
UPS
By enabling the UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) support, you can protect your
NVR from abnormal system shutdown caused by power disruption. In the event of a
power failure the NVR will shut down automatically or enter auto-protection mode
by probing the power status of the connected UPS unit.
Standalone mode – USB
To operate under USB standalone mode, follow the steps below:
1.
Plug in the USB cable on the UPS to the NVR.
2.
Select the option “Enable UPS Support”.
3.
Choose between whether the NVR will shut down or enter auto-protection mode
after AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NVR should wait before
executing the option you have selected. After the NVR enters auto-protection
mode, the NVR resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
4.
Click “Apply All” to confirm.
Standalone mode – SNMP
To operate under SNMP standalone mode, follow the steps below:
1.
Make sure the NVR is connected to the same physical network as the
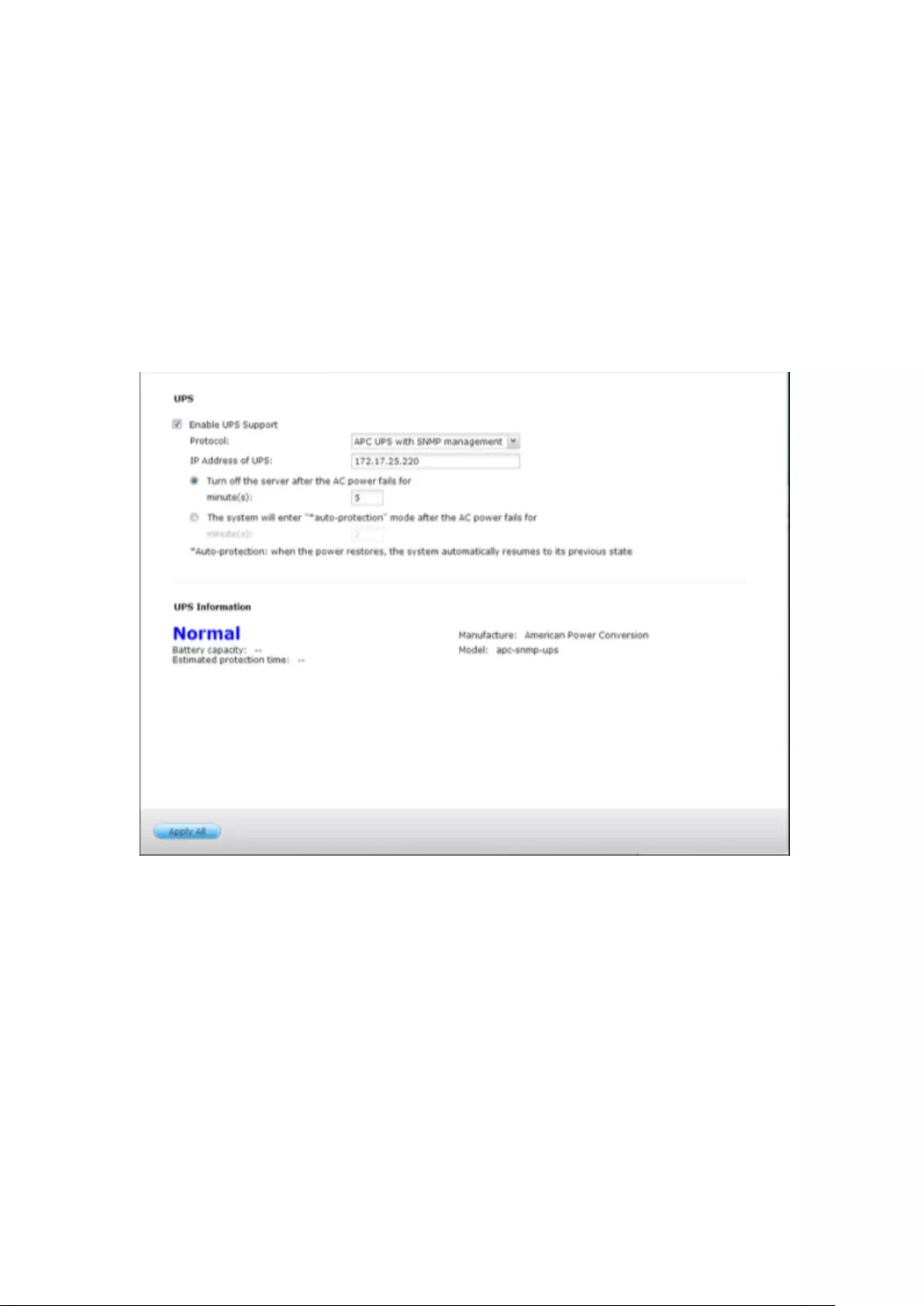
285
SNMP-based UPS.
2.
Select the option “Enable UPS Support”.
3.
Select “APC UPS with SNMP management” from the “Protocol” drop down menu.
4.
Enter the IP address of the SNMP-based UPS.
5.
Choose between whether the NVR will shut down or enter auto-protection mode
after AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NVR should wait before
executing the option you have selected. After the NVR enters auto-protection
mode, the NVR resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
6.
Click “Apply All” to confirm.
Network master mode
A network UPS master is responsible for communicating with network UPS slaves on
the same physical network about critical power status. To set up your NVR with UPS
as network master mode, plug in the USB cable on the UPS to the NVR and follow the
steps below:
1.
Make sure the NVR (the “UPS master”) is connected to the same physical
network as the network UPS slaves.
2.
Select the option “Enable UPS Support”.
3.
Click “Enable network UPS Support”. This option appears only when your NVR is
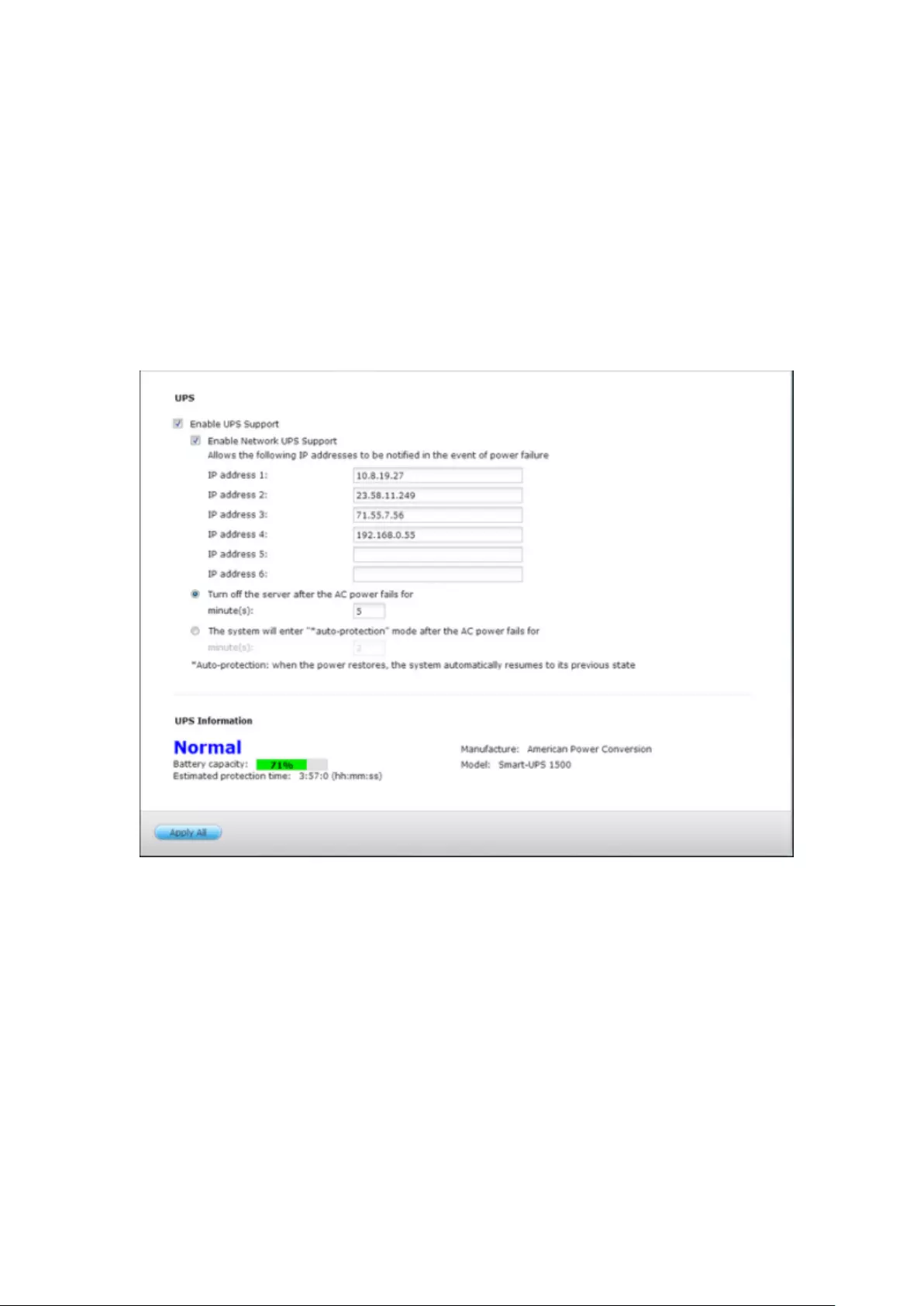
286
connected to the UPS by a USB cable.
4.
Choose between whether the NVR will shut down or enter auto-protection mode
after AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NVR should wait before
executing the option you have selected. After the NVR enters auto-protection
mode, the NVR resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
5.Enter the “IP address” of other network UPS slaves to be notified in the event
of power failure.
6.Click “Apply All” to confirm and continue the setup for the NVR systems which
operate in network slave mode below.
Network slave mode
A network UPS slave communicates with network UPS master to receive the UPS
status. To set up your NVR with UPS as network slave mode, follow the steps below:
1. Make sure the NVR is connected to the same physical network as the network
UPS master.
2. Select the option “Enable UPS Support”.
3. Select “Network UPS slave” from the “Protocol” drop down menu.
4. Enter the IP address of the network UPS server.
5. Choose between whether the NVR will shut down or enter auto-protection
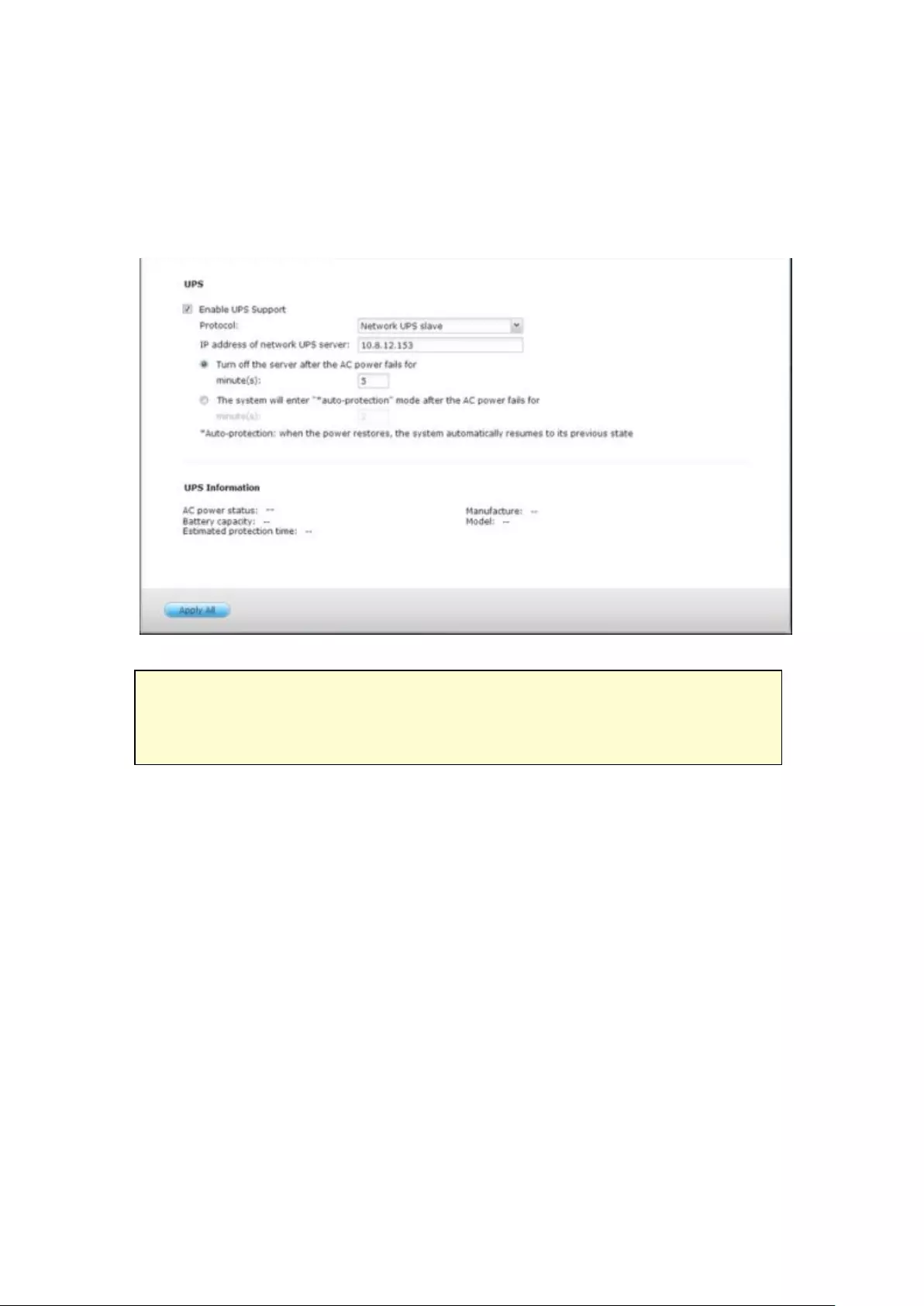
287
mode after AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NVR should wait
before executing the option you have selected. After the NVR enters
auto-protection mode, the NVR resumes the previous operation status when the
power restores.
6.
Click “Apply All” to confirm.
Note: To allow the UPS device to send SNMP alerts to the QNAP NVR in case of
power loss, you may have to enter the IP address of the NVR in the configuration
page of the UPS device.
Behavior of the UPS feature of the NVR
In case of power loss and power recovery, the events will be logged in the “System
Event Logs”.
During a power loss, the NVR will wait for the specified time you enter in the “UPS
Settings” before powering off or entering auto-protection mode.
If the power restores before the end of the waiting time, the NVR will remain in
operation and cancel its power-off or auto-protection action.
Once the power restores:
•
If the NVR is in auto-protection mode, it will resume to normal operation.
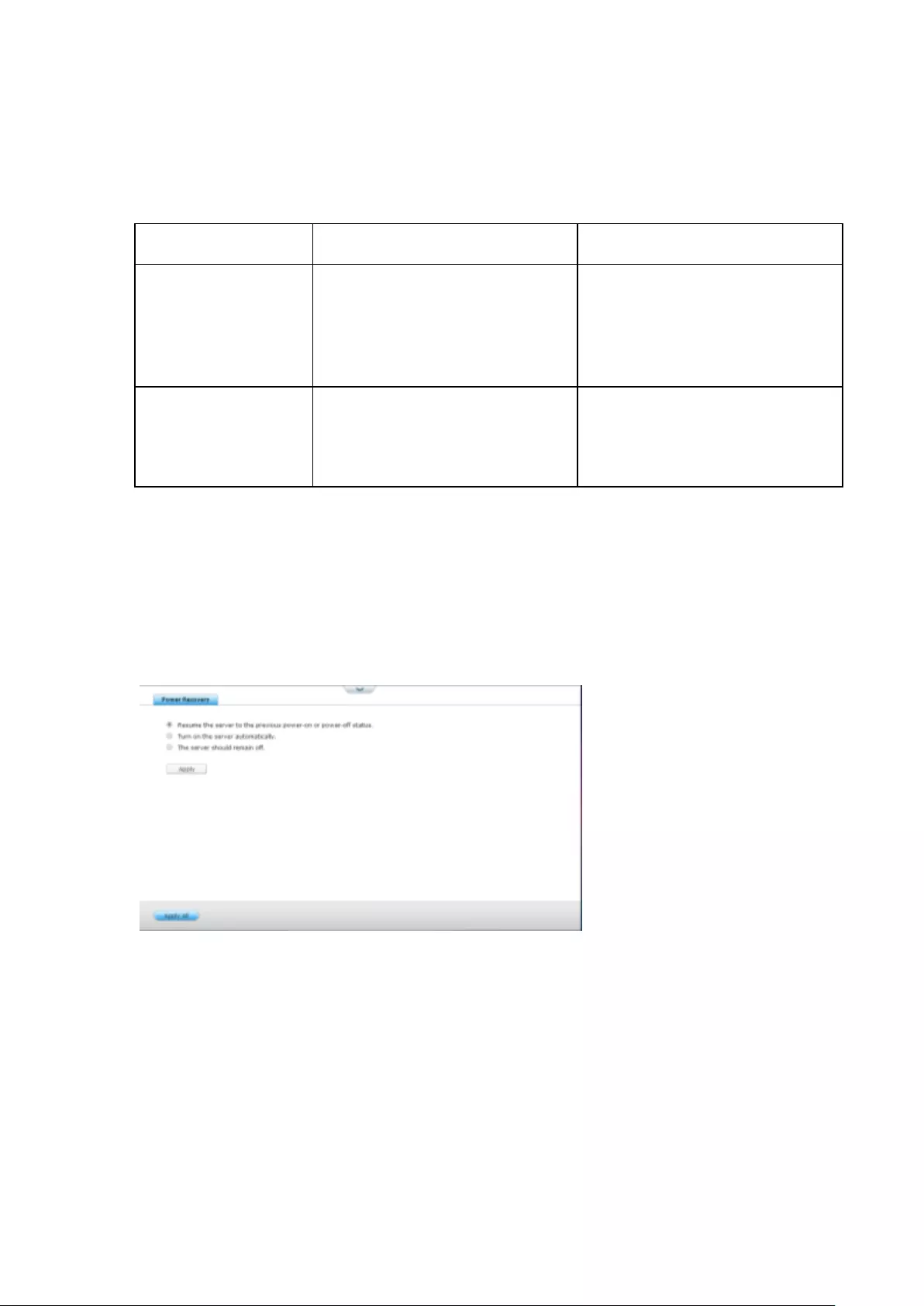
288
•
If the NVR is powered off, it will remain off.
Difference between auto-protection mode and power-off mode
Mode
Advantage
Disadvantage
Auto-protection
mode
The NVR resumes after power
recovery.
If the power outage lasts until
the UPS is turned off, the NVR
may suffer from abnormal
shutdown.
Power-off mode
The NVR will be shut down
properly.
The NVR will remain off after the
power recovery. Manual power
on of the NVR is required.
If the power restores after the NVR has been shut down and before the UPS device is
powered off, you may power on the NVR by Wake on LAN* (if your NVR and UPS
device both support Wake on LAN and Wake on LAN is enabled on the NVR).
If the power restores after both the NVR and the UPS have been shut down, the NVR
will react according to the settings in “System Settings” > “Power Recovery”.
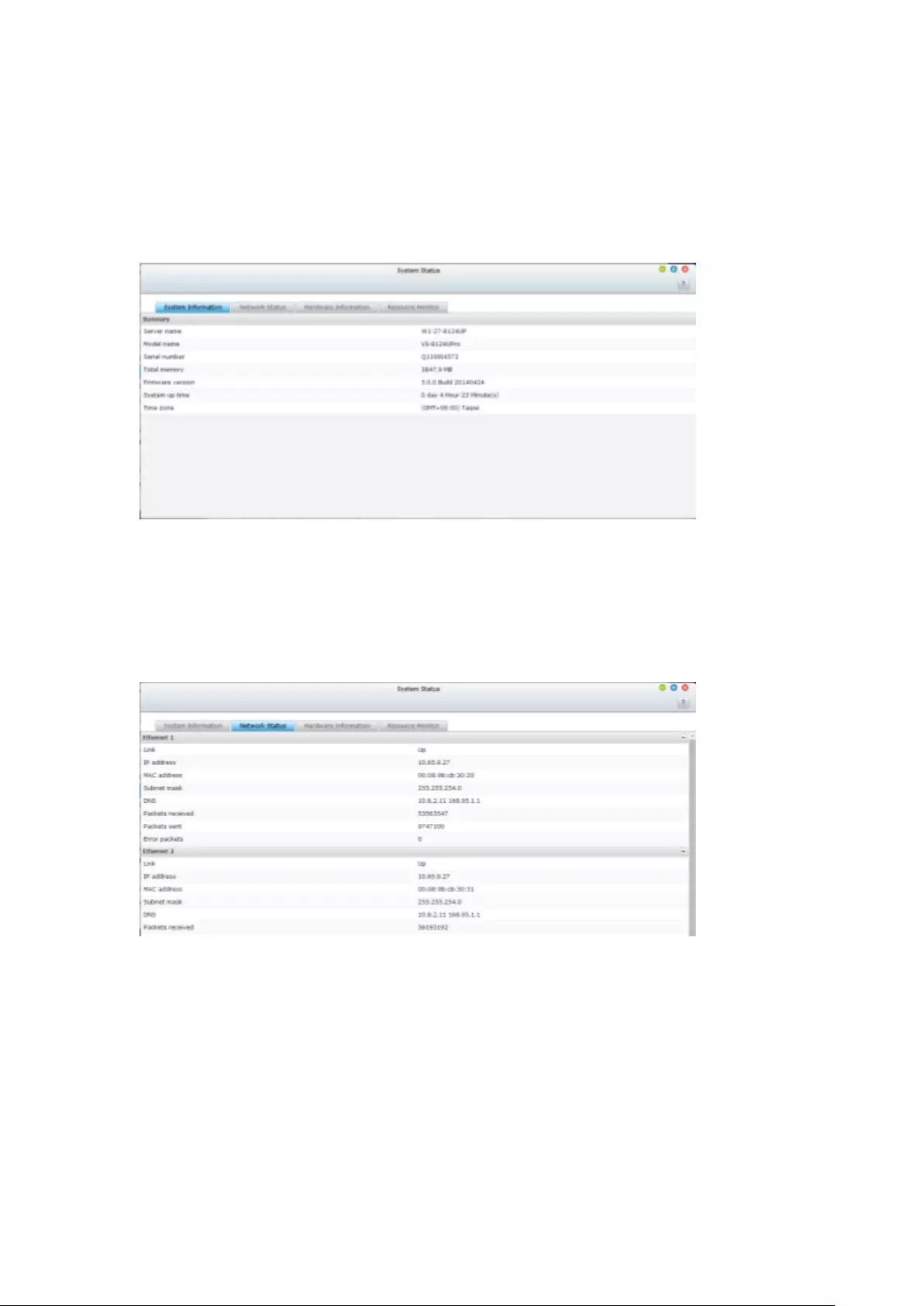
289
9.1.11 System Status
System Information
View the summary of system information such as the server name, memory,
firmware and system up time on this page.
Network Status
View the current network settings and statistics on this page and they are displayed
based on network interfaces. Click the up arrow at top right to collapse the interface
page and down arrow to expand the page.
Hardware Information
View basic hardware information of the NVR on this page.
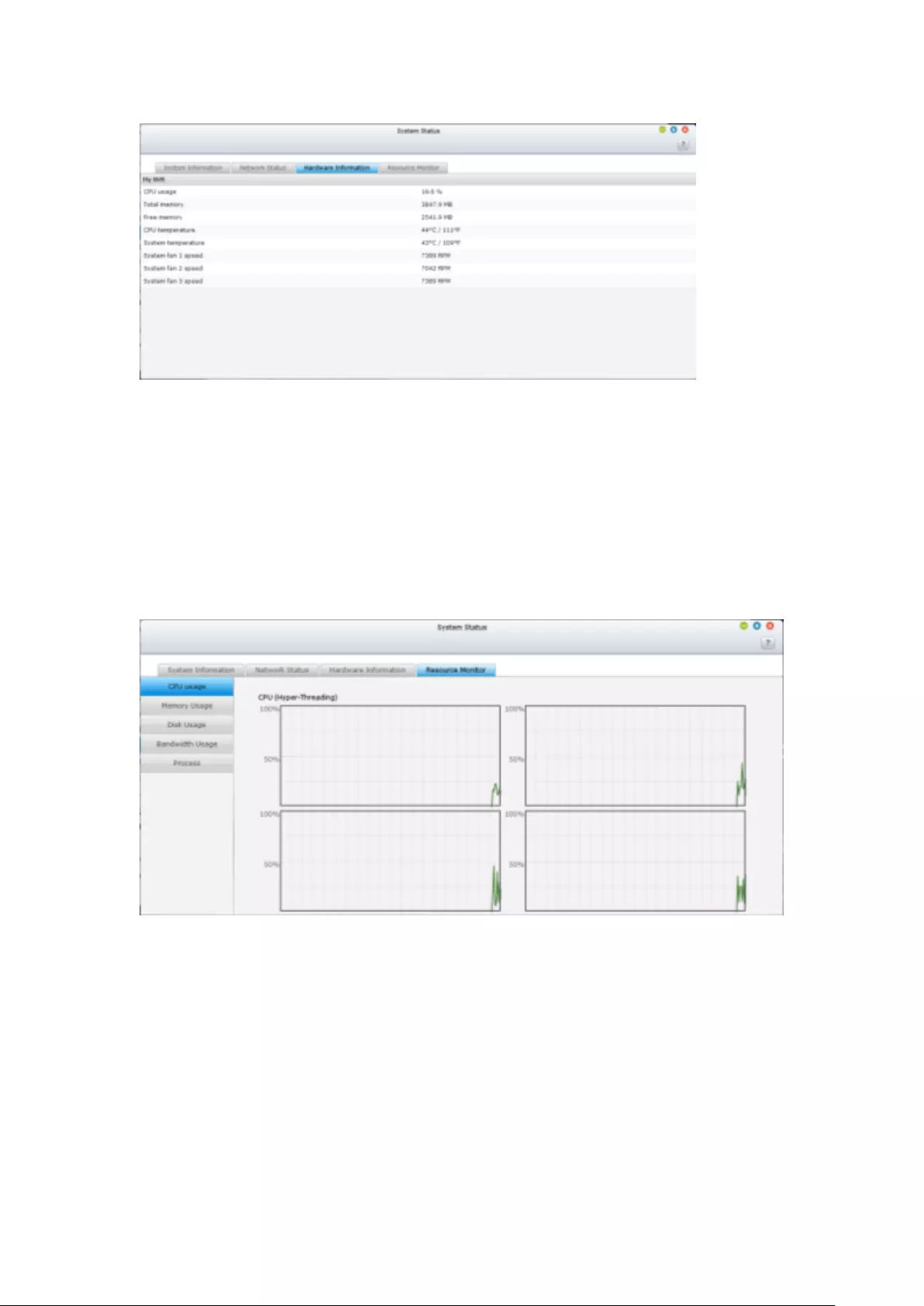
290
Resource Monitor
You can view the CPU usage, disk usage, and bandwidth transfer statistics of the NVR
on this page.
•
CPU Usage: This tab shows the CPU usage of the NVR.
•
Memory Usage: This tab shows the memory usage of the NVR by real-time
dynamic graph.
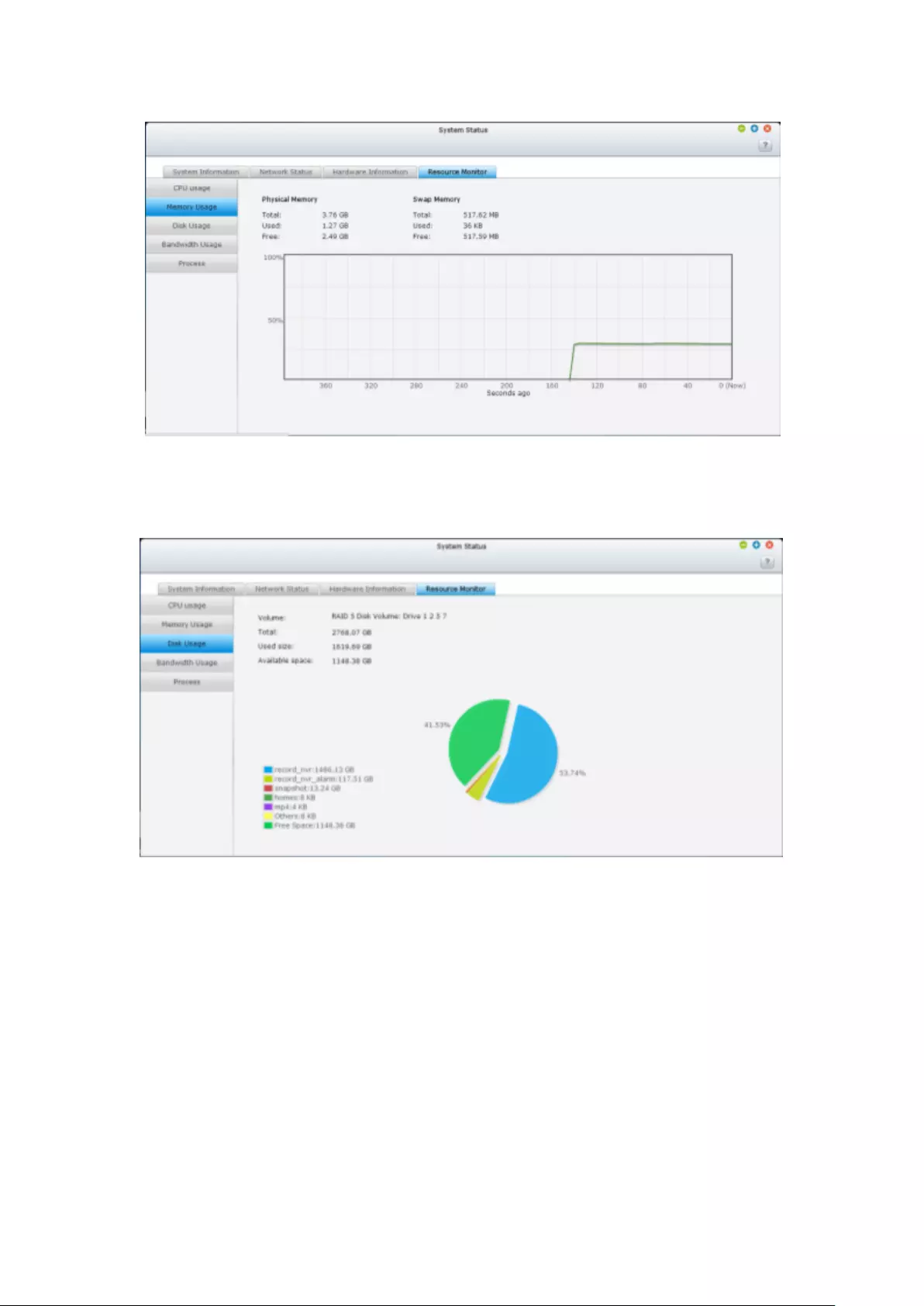
291
•
Disk Usage: This tab shows the disk space usage of each disk volume and its
shared folders.
•
Bandwidth Usage: This tab provides information about bandwidth transfer of each
available LAN port of the NVR.
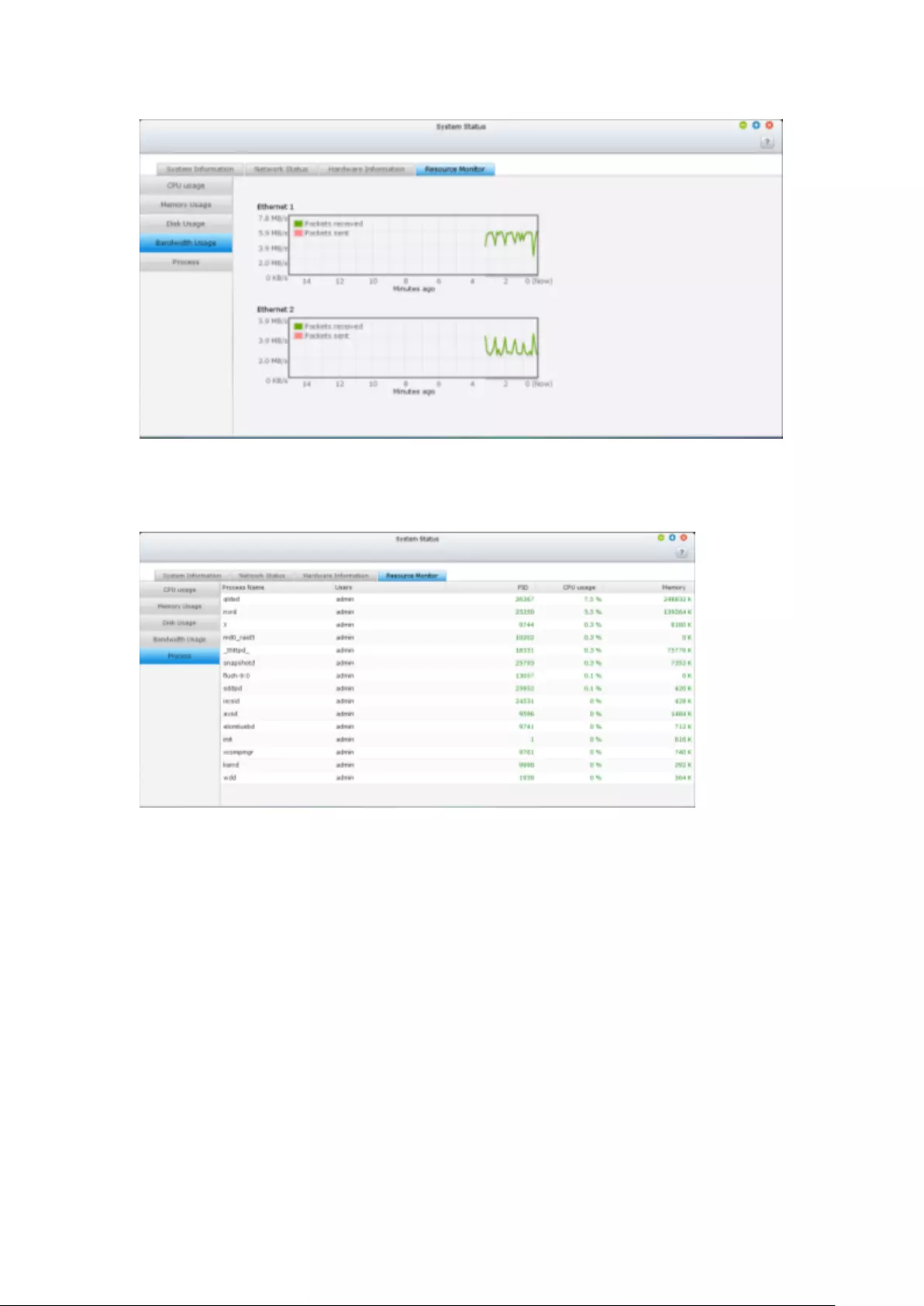
292
•
Process: This tab shows information about the processes running on the NVR.
293
9.1.12 System Logs
Recording Statistics
The NVR can store 10,000 recent event logs, including warning, error, and
information messages. If the NVR does not function correctly, refer to the event logs
for troubleshooting.
System Connection Logs
The NVR supports recording HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SSH, AFP, SAMBA, and iSCSI
connections. Click “Options” to select the connection type to be logged. The file
transfer performance can be slightly affected when this feature is turned on.
Tip: Right click a log and select to delete the record or block the IP and select how
long the IP should be blocked. To clear all the logs, click “Clear”.
294
Start Logging: Turn on this option to archive the connection logs. The NVR generates
a CSV file automatically and saves it to a specified folder when the number of logs
reaches the upper limit.
The file-level access logs are available on this page. The NVR will record the logs
when users access, create, delete, move, or rename any files or folders via the
connection type specified in “Options”.
Online Users
The information of the on-line users connecting to the NVR by networking services is
shown on this page.
295
Tip: You can disconnect the IP connection, add it to the blocked IP list and select how
long you want it to be blocked.
Advanced Log Search
Advanced log search is provided to search for system event logs, system connection
logs and online users based on user preferences. First, specify the log type, users,
computer name, date range and source IP and click “Search” to search for the desired
logs or reset to list all logs.
Please note that for online users, only the source IP and Computer name can be
specified.

296
9.2 Privilege Settings
The NVR supports 3 types of users:
1. administrator
The system default administrator accounts are ‘admin’ and ‘supervisor’ (default
password: admin). Both of them have the rights of system administration,
monitoring, and playback. The administrators cannot be deleted. They have
the rights to create and delete new administrators, system managers, and general
users, and change their passwords. Other newly created ‘administrators’ have
the rights of system administration, monitoring, and playback but some rights are
different from ‘admin’ and ‘supervisor’.
2. system manager
The default system manager account is ‘sysmgr’ (default password: admin). This
account has the right of system administration and cannot be deleted. ‘sysmgr’
can create and delete other system manager and general user accounts, and
assign monitoring, playback, and administration rights to them. Other newly
created system managers will also have the administration right but some rights
are different from ‘sysmgr’.
3. user
The general users have only the rights of monitoring and video playback. They
have no administration authority.
The following information is required to create a new user:
•
Username: The username is case-insensitive and supports multi-byte characters,
such as Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian. The maximum length is 32
characters. The invalid characters are: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < > ` '
•
Password: The password is case-sensitive and supports maximum 16 characters. It
is recommended to use a password of at least 6 characters.
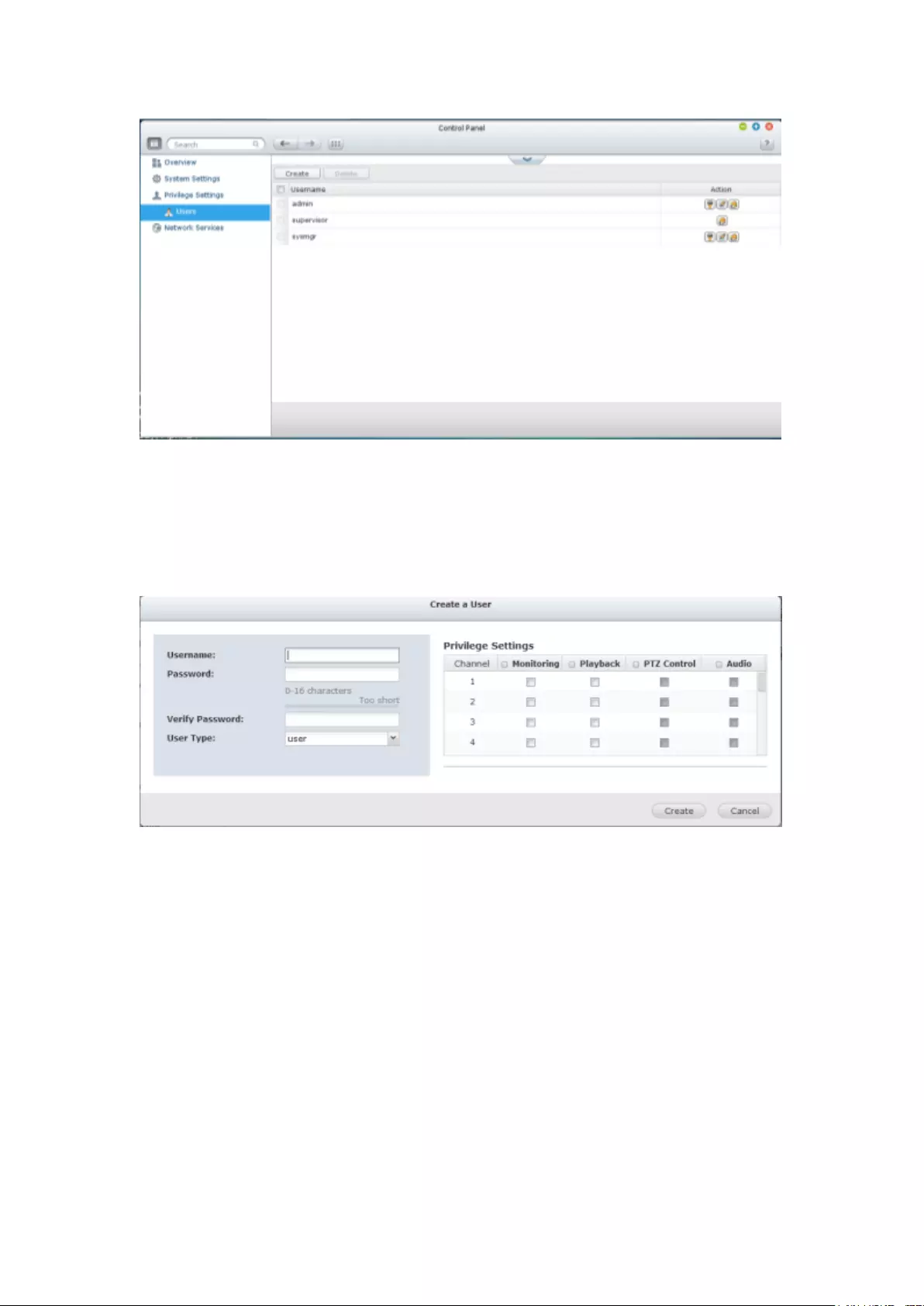
297
Create a User
To create a user on the NVR, click “Create”.
Follow the instructions of the wizard to complete the details.
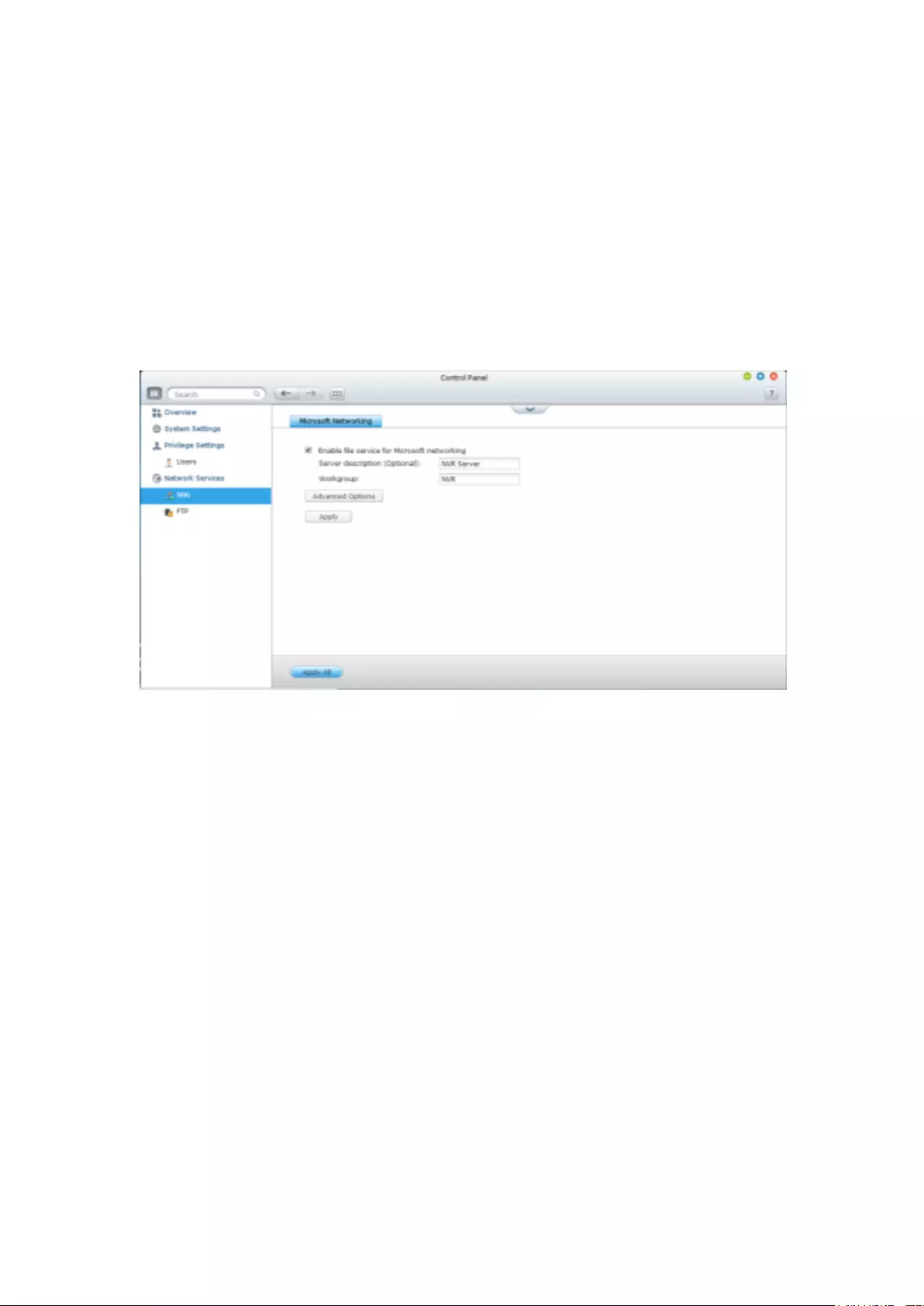
298
9.3 Network Services
9.3.1 Win
Microsoft Networking
To allow access to the NVR on Microsoft Windows Network, enable file service for
Microsoft networking. Specify also how the users will be authenticated.
Advanced Options
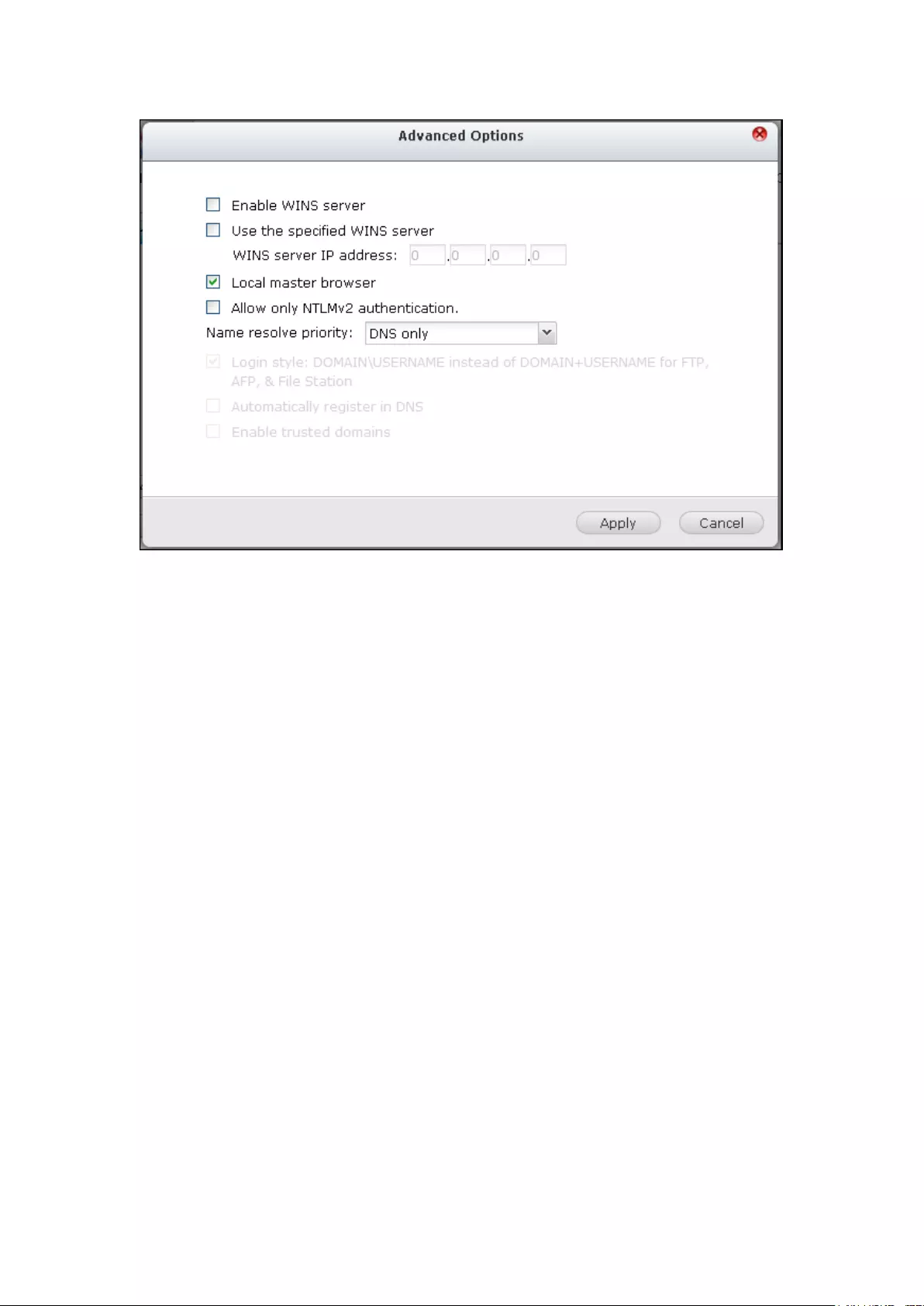
299
WINS server:
If the local network has a WINS server installed, specify the IP address. The NVR will
automatically register its name and IP address with WINS service. If you have a WINS
server on your network and want to use this server, enter the WINS server IP. Do not
turn on this option if you are not sure about the settings.
Local Domain Master:
A Domain Master Browser is responsible for collecting and recording resources and
services available for each PC on the network or a workgroup of Windows. When you
find the waiting time for connecting to the Network Neighborhood/My Network
Places too long, it may be caused by failure of an existing master browser or a
missing master browser on the network. If there is no master browser on your
network, select the option “Domain Master” to configure the NVR as the master
browser. Do not turn on this option if you are not sure about the settings.
Allow only NTLMv2 authentication:
NTLMv2 stands for NT LAN Manager version 2. When this option is turned on, login
to the shared folders by Microsoft Networking will be allowed only with NTLMv2
authentication. If the option is turned off, NTLM (NT LAN Manager) will be used by
default and NTLMv2 can be negotiated by the client. The default setting is disabled.

300
Name resolution priority:
You can select to use DNS server or WINS server to resolve client host names from IP
addresses. When you set up your NVR to use a WINS server or to be a WINS server,
you can choose to use DNS or WINS first for name resolution. When WINS is enabled,
the default setting is “Try WINS then DNS”. Otherwise, DNS will be used for name
resolution by default.
Login style: DOMAIN\USERNAME instead of DOMAIN+USERNAME for FTP, AFP, and
File Station
In an Active Directory environment, the default login formats for the domain users
are:
•
Windows shares: domain\username
•
FTP: domain+username
•
File Station: domain+username
•
AFP: domain+username
When you turn on this option, the users can use the same login name format
(domain\username) to connect to the NVR via AFP, FTP, and File Station.
Automatically register in DNS: When this option is turned on and the NVR is joined
to an Active Directory, the NVR will register itself automatically in the domain DNS
server. This will create a DNS host entry for the NVR in the DNS server. If the NVR IP is
changed, the NVR will automatically update the new IP in the DNS server.
Enable trusted domains: Select this option to load the users from trusted Active
Directory domains and specify their access permissions to the NVR in “Privilege
Settings” > “Shared Folders”. (The domain trusts are set up in Active Directory only,
not on the NVR.)
9.3.2 FTP
FTP Service
When you turn on FTP service, you can specify the port number and the maximum
number of users that are allowed to connect to the NVR by FTP at the same time.
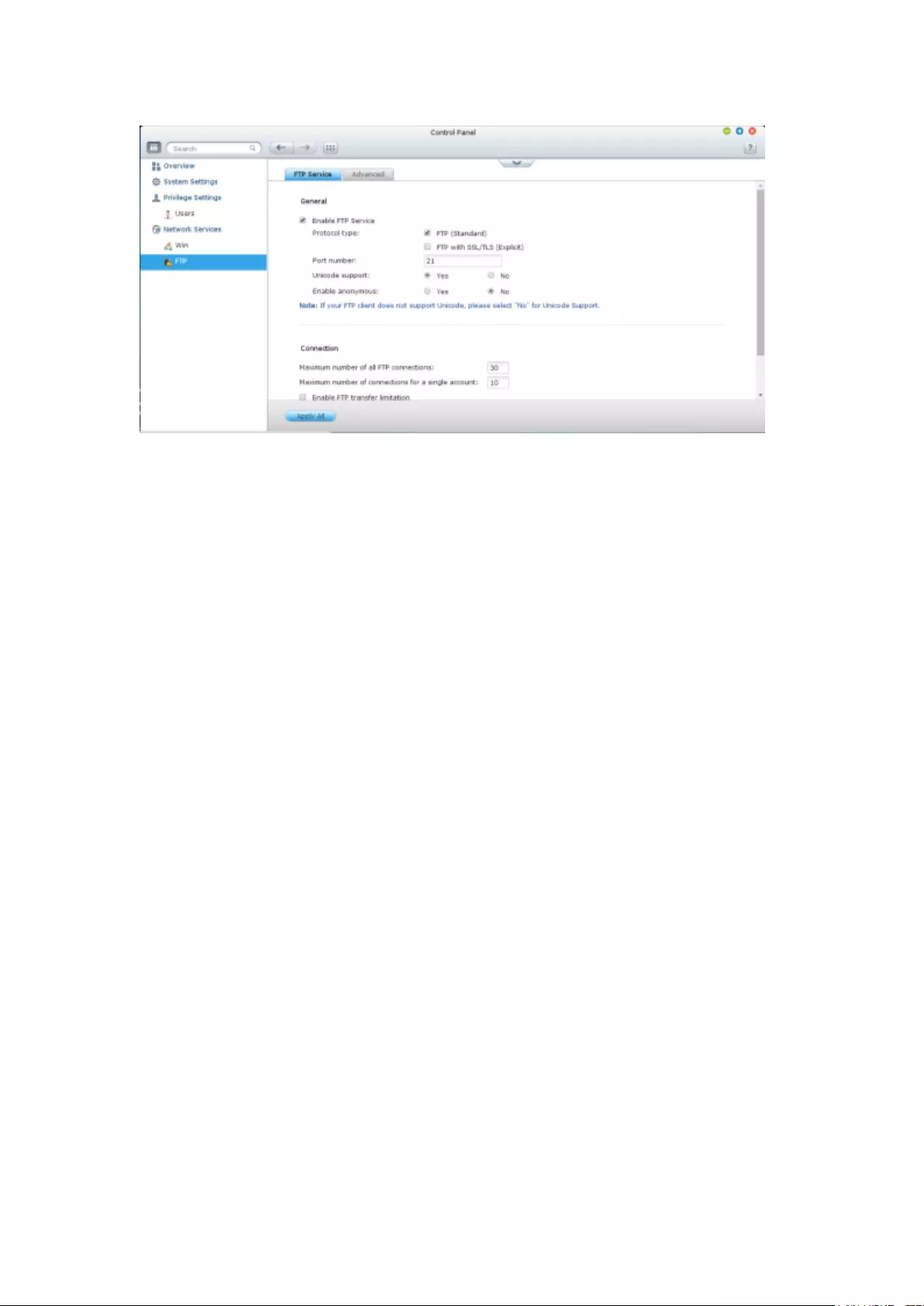
301
To use the FTP service of the NVR, enable this function. Open an IE browser and
enter ftp://NVR IP. Enter the username and the password to login the FTP service.
Protocol Type:
Select to use standard FTP connection or SSL/TLS encrypted FTP. Select the correct
protocol type in your client FTP software to ensure successful connection.
Unicode Support:
Turn on or off the Unicode support. The default setting is No. If your FTP client does
not support Unicode, you are recommended to turn off this option and select the
language you specify in “General Settings” > “Codepage” so that the file and folder
names can be correctly shown. If your FTP client supports Unicode, enable Unicode
support for both your client and the NVR.
Anonymous Login:
You can turn on this option to allow anonymous access to the NVR by FTP. The users
can connect to the files and folders which are open for public access. If this option is
turned off, the users must enter an authorized username and password to connect to
the server.
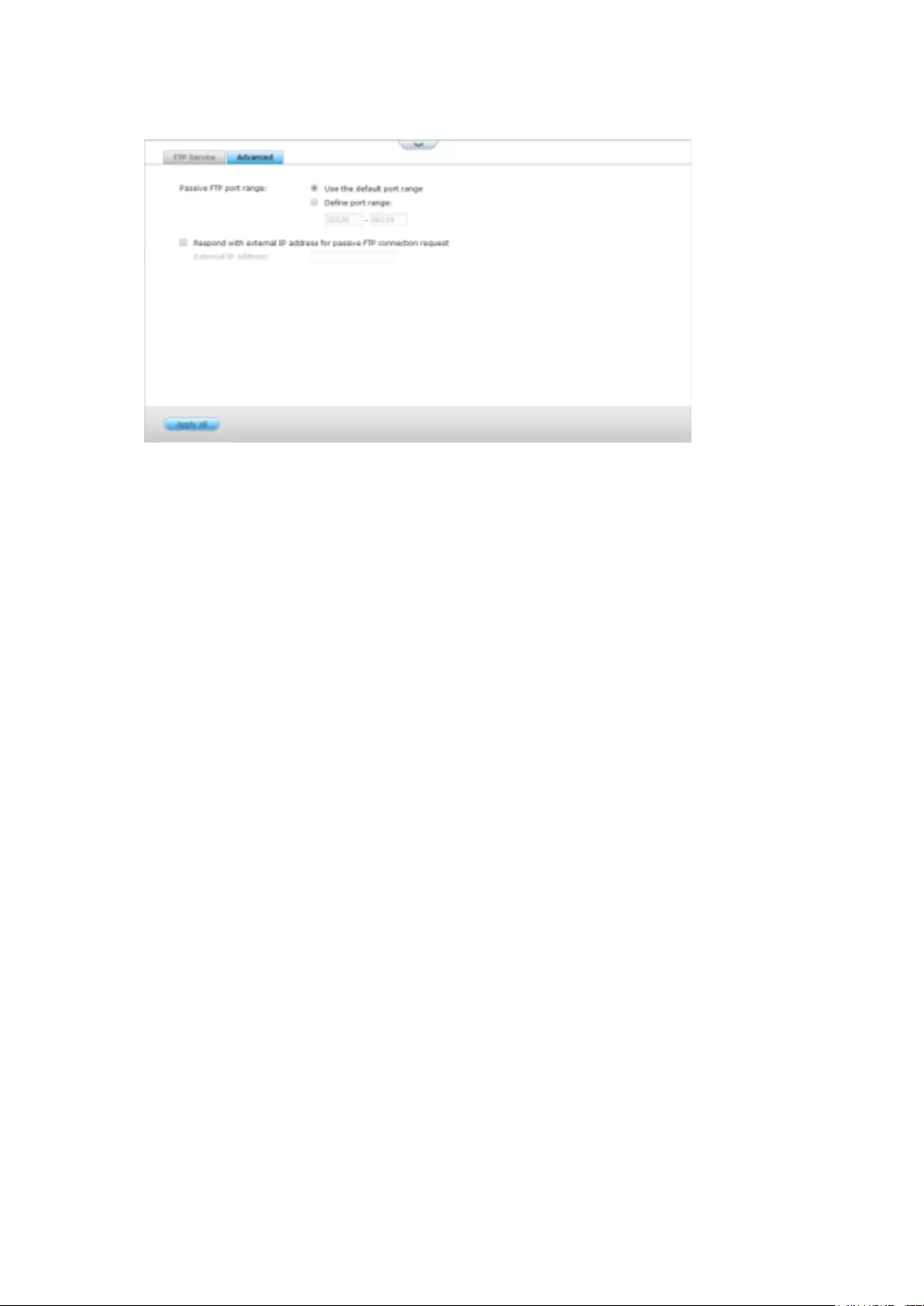
302
Advanced
Passive FTP Port Range:
You can use the default port range (55536-56559) or specify a port range larger than
1023. When using this function, make sure you have opened the ports on your router
or firewall.
Respond with external IP address for passive FTP connection request:
When passive FTP connection is in use, the FTP server (NVR) is behind a router, and a
remote computer cannot connect to the FTP server over the WAN, enable this
function. When this option is turned on, the NVR replies the IP address you specify or
automatically detects the external IP address so that the remote computer is able to
connect to the FTP server.
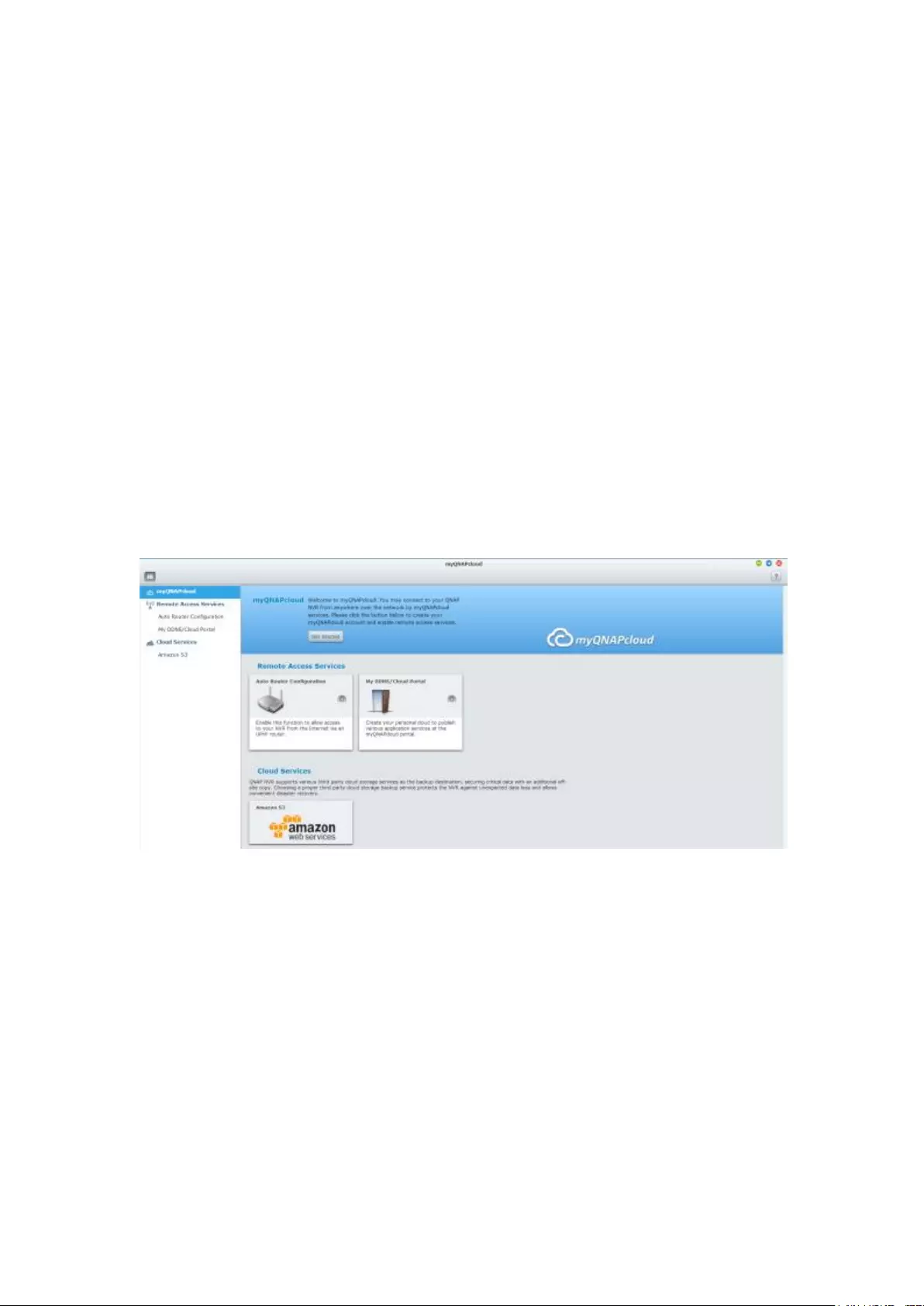
303
10. QNAP Applications
10.1 myQNAPcloud Service
The myQNAPcloud service is a function which provides host name
registration, mapping of the dynamic NVR IP to a domain name, and auto
port mapping of UPnP router on the local network. Use the myQNAPcloud
wizard to register a unique host name for the NVR, configure automatic
port forwarding on the UPnP router, and publish NVR services for remote
access over the Internet.
To use the myQNAPcloud service, make sure the NVR has been
connected to an UPnP router and the Internet and click the
myQNAPcloud shortcut from the NVR Desktop or Main Menu.
10.1.1 Remote Access Services
myQNAPcloud wizard
The first time you use the myQNAPcloud service, you are recommended to use
the myQNAPcloud wizard to complete the settings. Follow the steps below:
1.
Click “Get Started” to use the wizard.
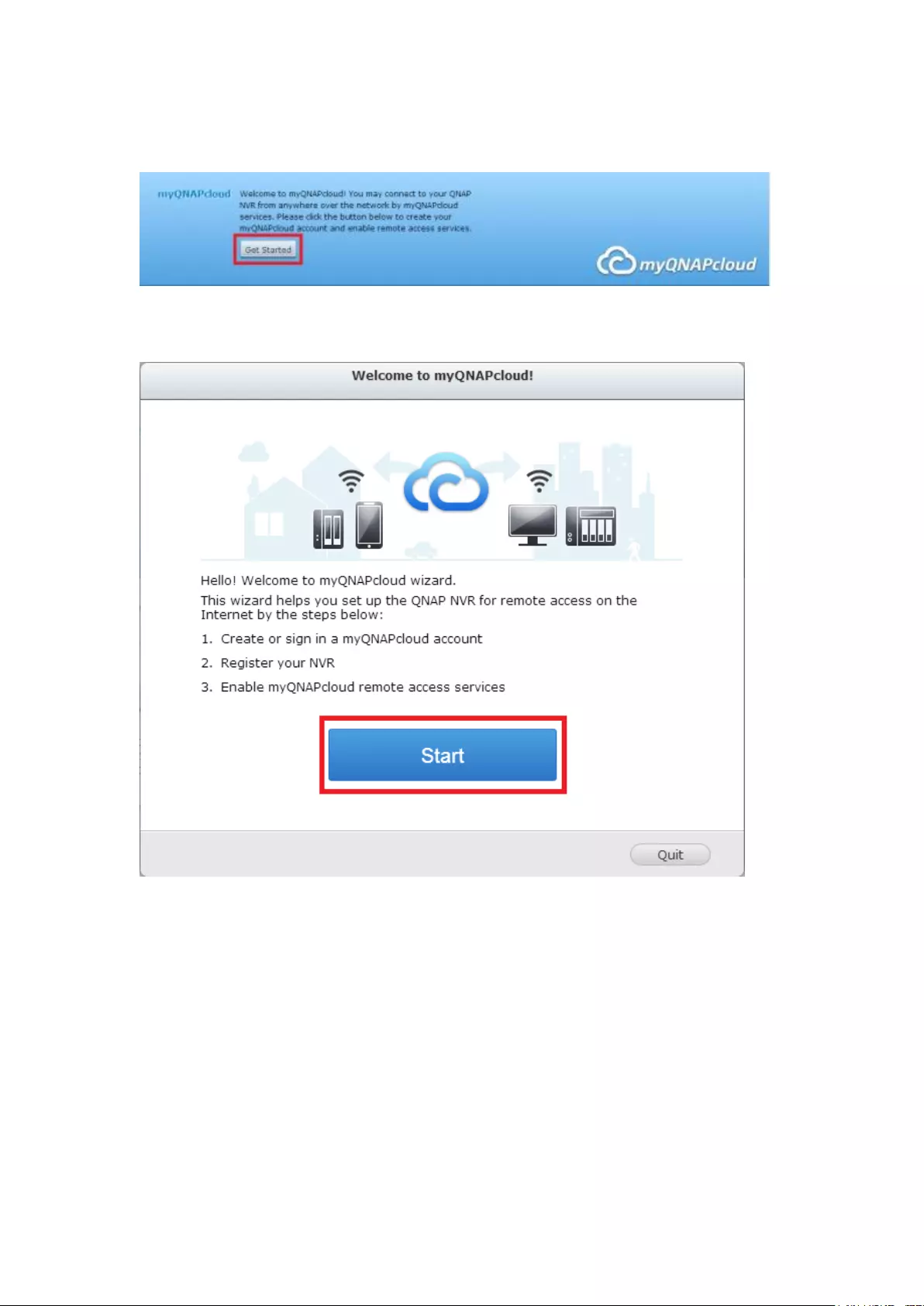
304
2.
Click “Start”.
3. Please use your myQNAPcloud ID(QID) and password to login.
(Click "Create myQNAPcloud account" if you don't have
myQNAPcloud account.)
305
4.
Enter a name to register your NVR and click “Next”.
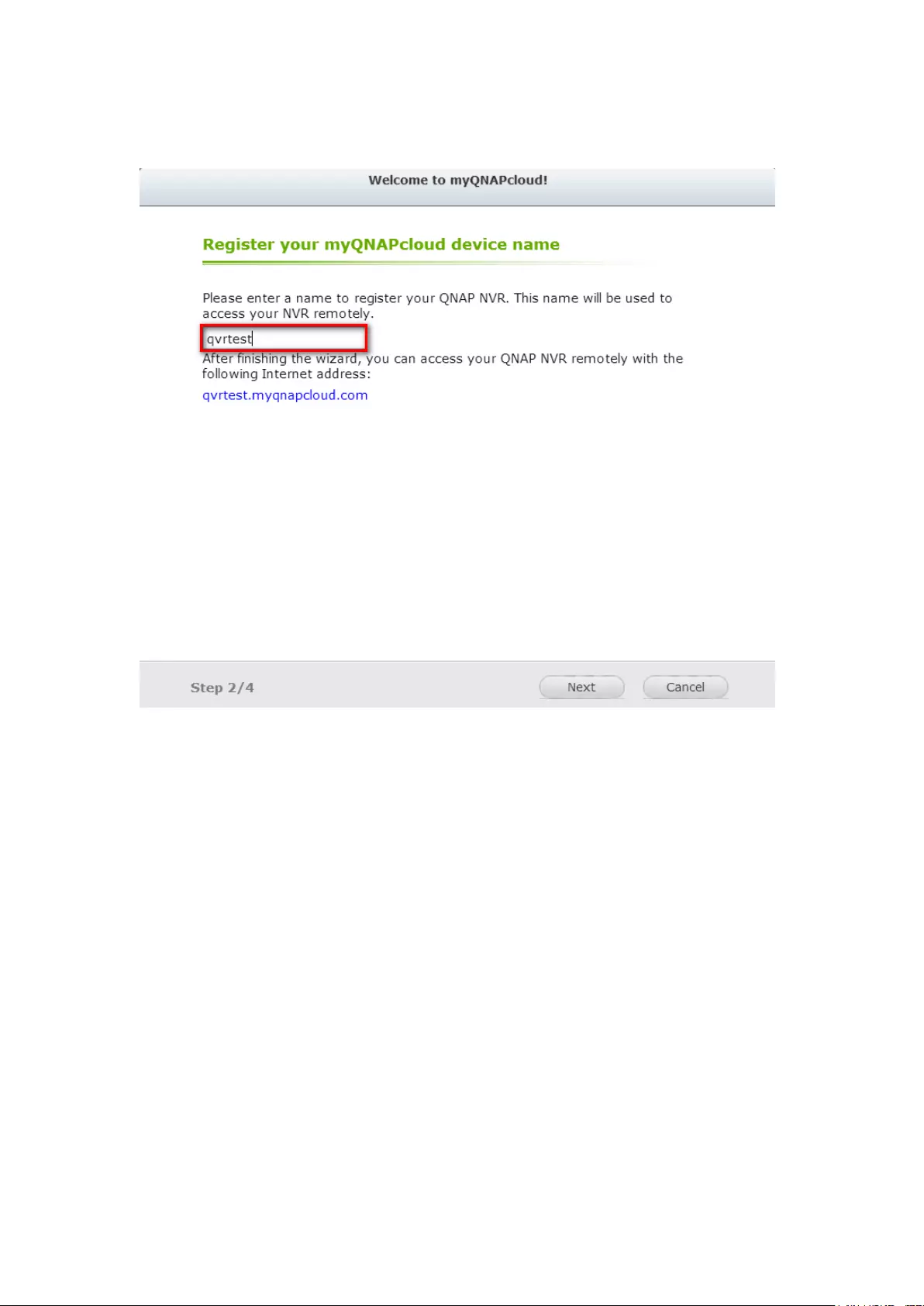
306
5.
The wizard will configure your router automatically.
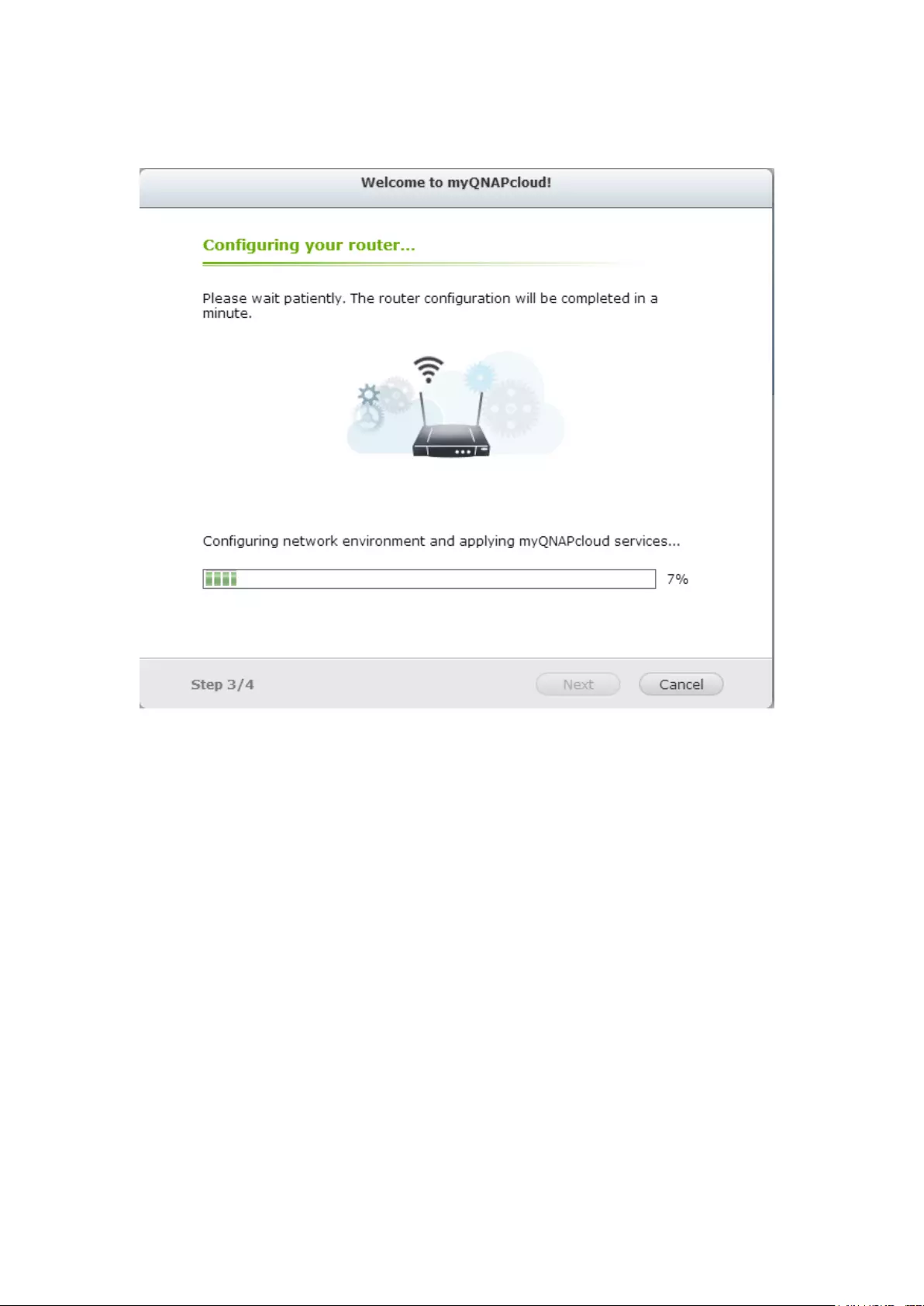
307
6.
Review the summary page and click “Finish” to complete the wizard.
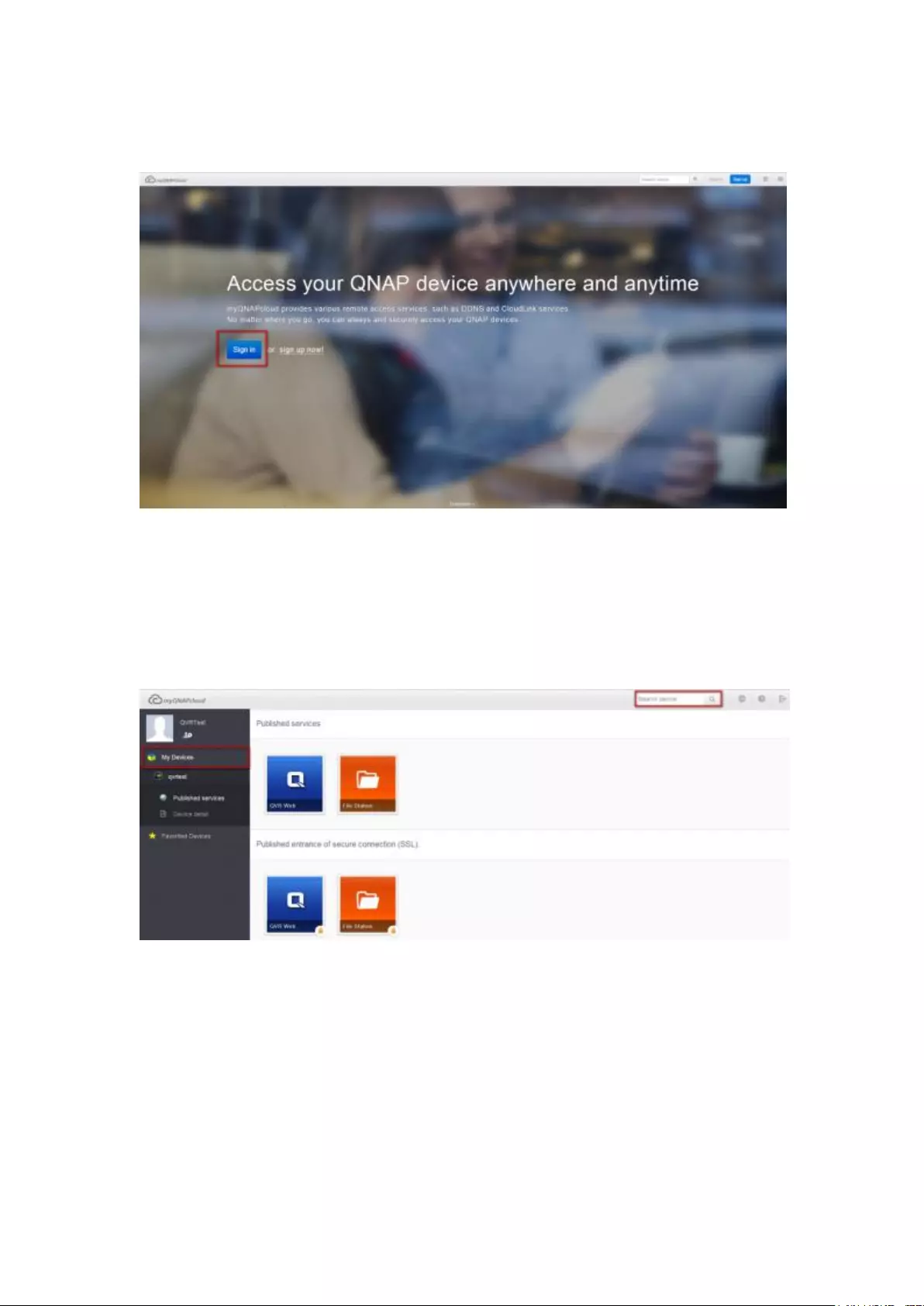
309
After click your login ID(QID) and password in “Sign in” , you can enter
your device name in “Enter device name” to search your devices. Or you
can select “My Devices” from the drop down menu in left side to review all
your device published services and details, including the name, DDNS
address, LAN and WAN IP.
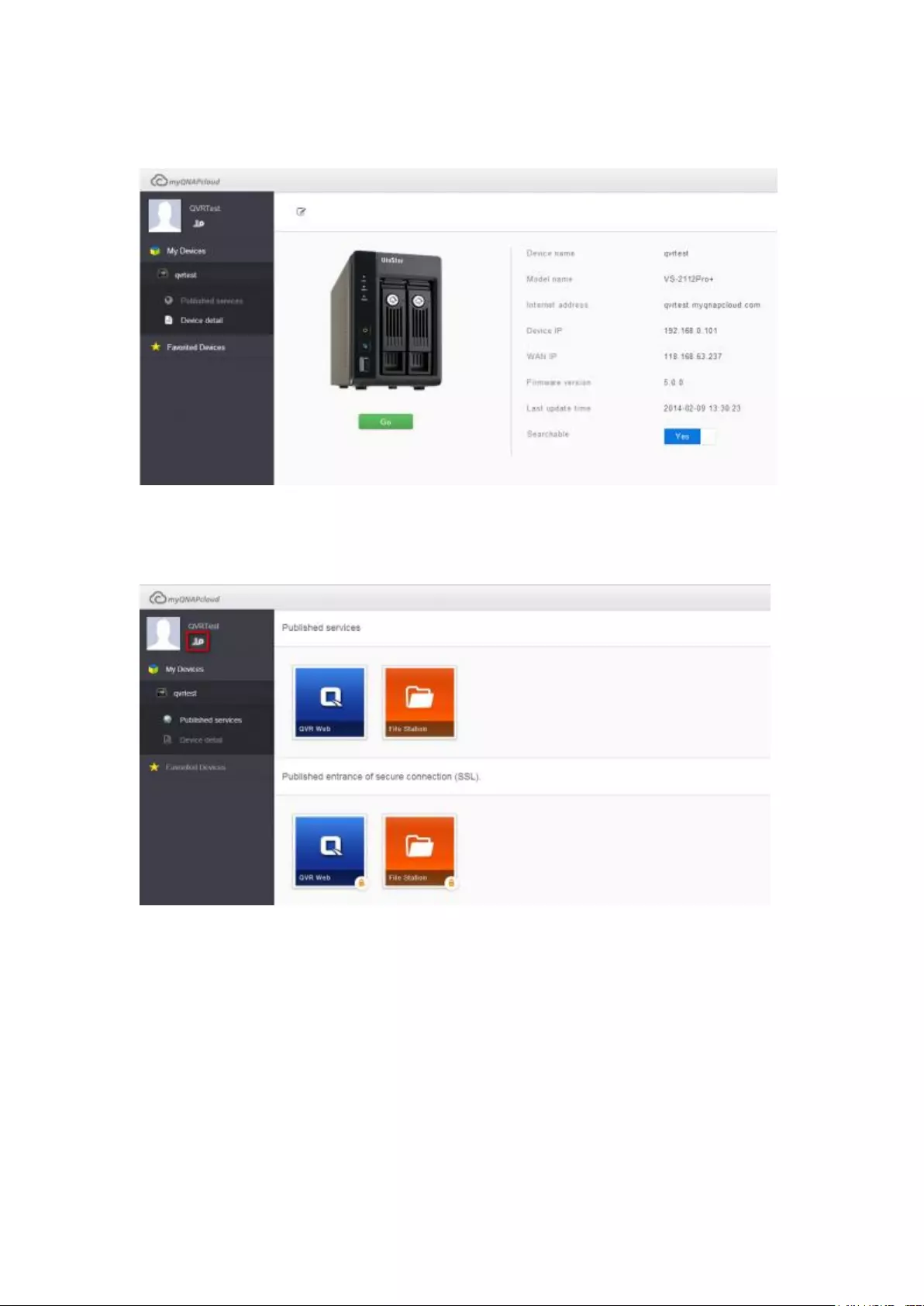
310
Or, select button “My Account” in top left corner to check your profile,
change your password and monitor your account activity.
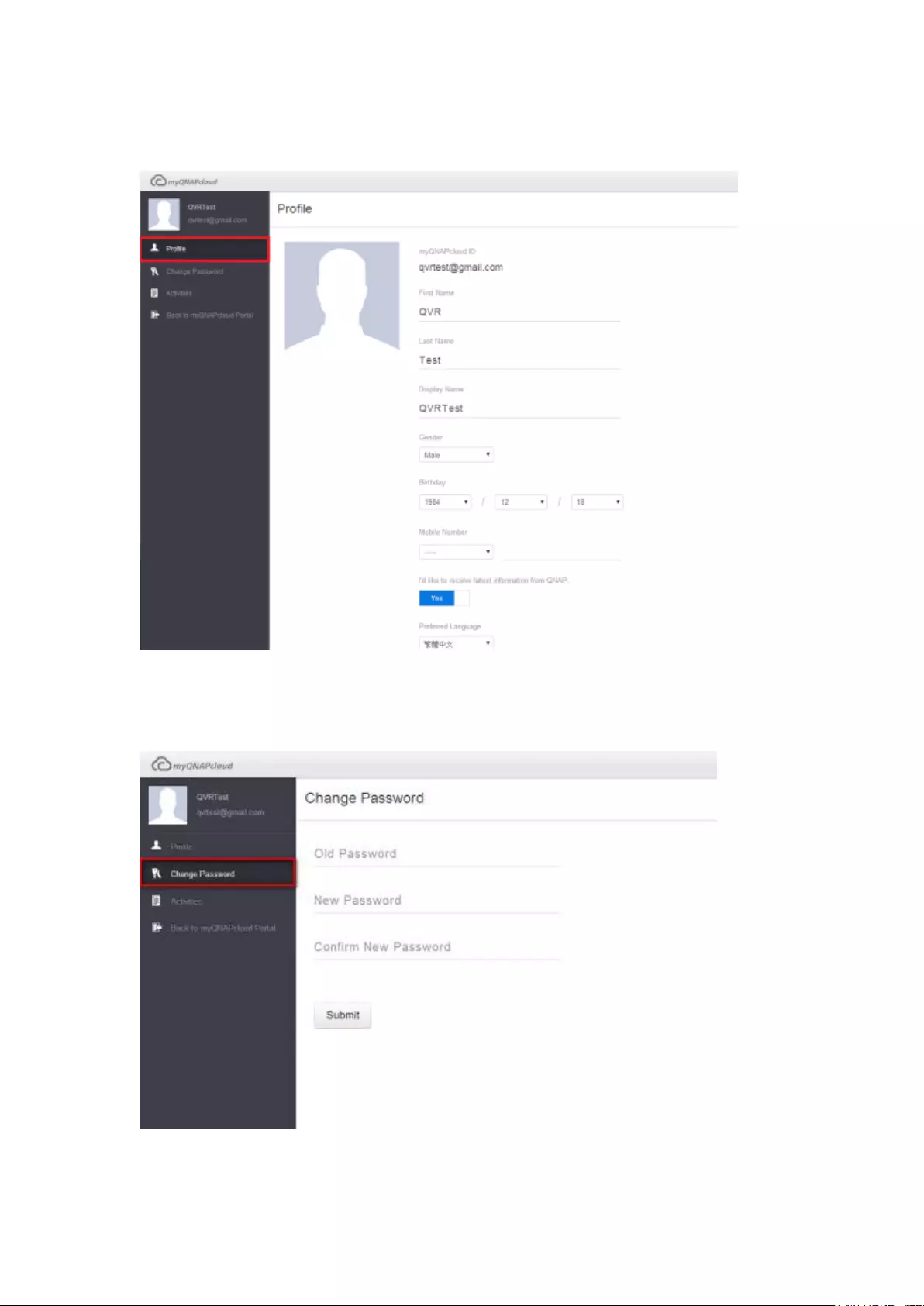
311
312
Access NVR services via the myQNAPcloud website
To access the NVR services via the myQNAPcloud website, specify the
NVR you registered with in the search box and click search button in the
right.
The published public NVR services will be listed.
313
Enter the access code to browse private services.
After entering the user name and access code, you can browse private services.
Note: For configuration on private NVR services, please refer to the DDNS/Cloud
Portal section later in this chapter.
Auto Router Configuration
In “Remote Access Services” > “Auto Router Configuration”, you can
enable or disable UPnP port forwarding. When this option is enabled, your
NVR is accessible from the Internet via the UPnP router.
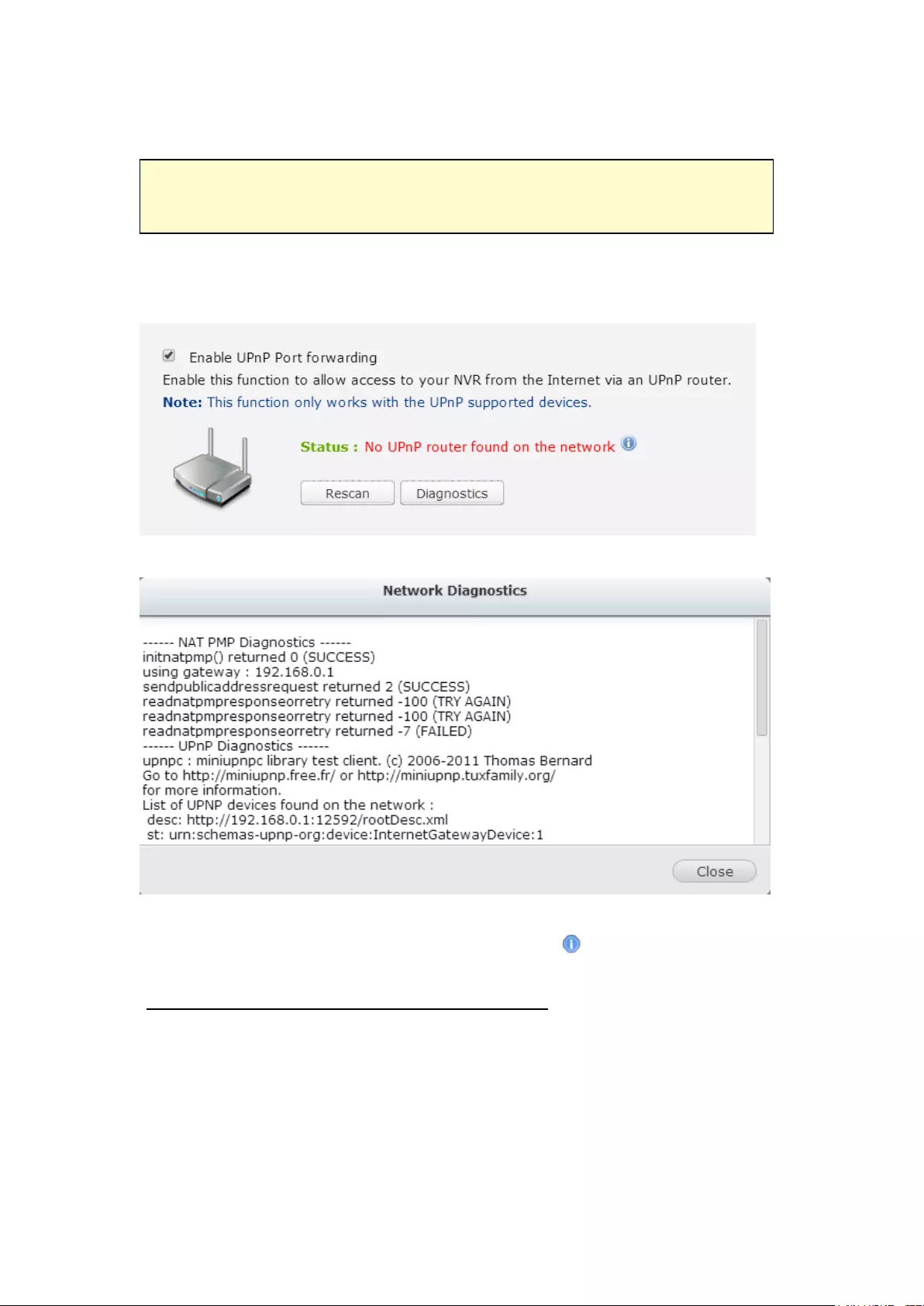
314
Note: If there is more than one router on the network, only the one which is set
as the default gateway of the NVR will be detected.
Click “Rescan” to detect the router if no UPnP router is found on the local
network and “Diagnostics” to check the diagnostic logs.
If the UPnP router is incompatible with the NVR, click and then click
“UPnP Router Compatibility Feedback...”
(http://www.qnap.com/go/compatibility_router.html) to contact the
technical support.
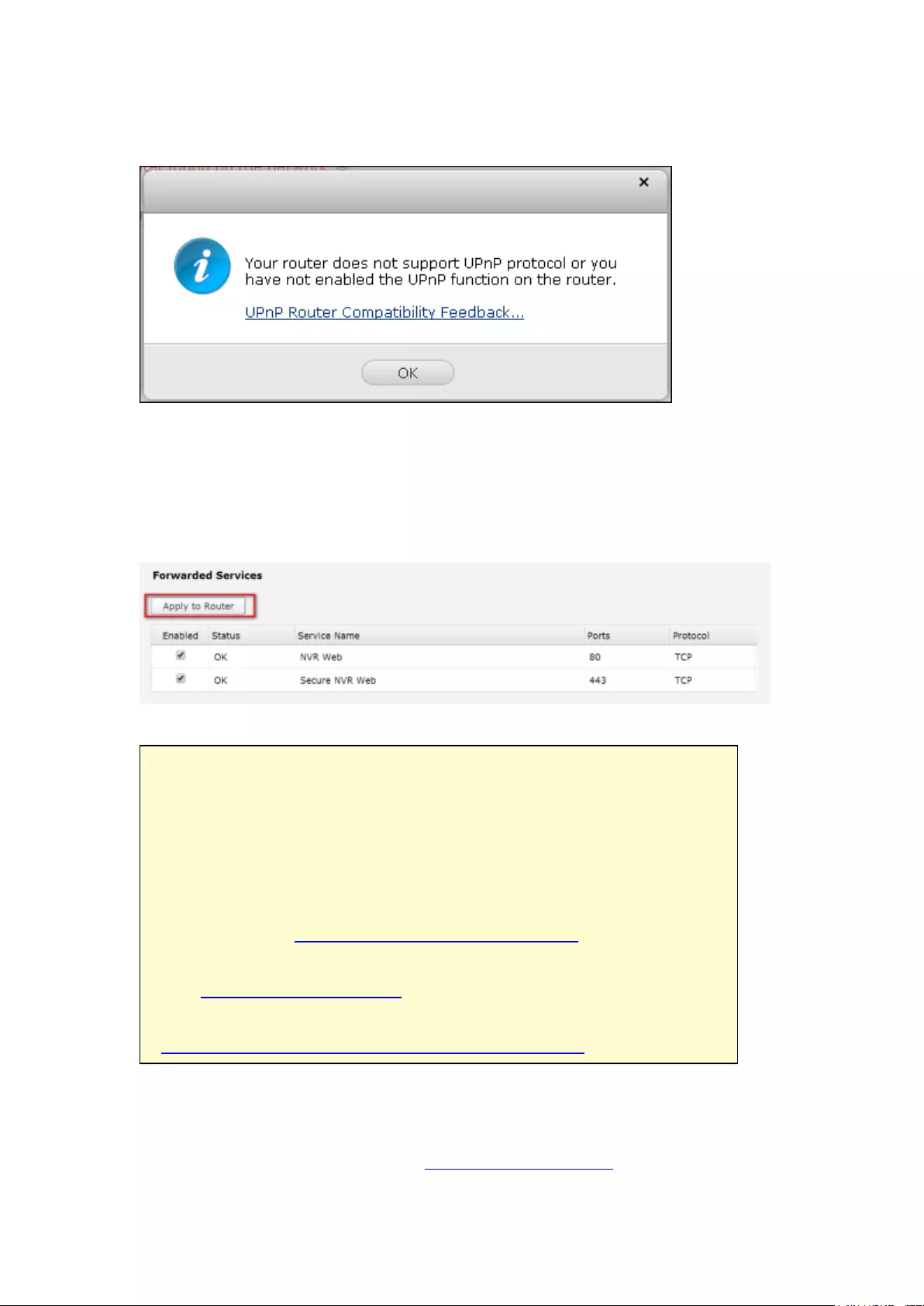
315
Select the NVR services to be allowed for remote access in section
“Forwarded Services”. Then click “Apply to Router”. The NVR will
configure the port forwarding on the UPnP router automatically. You
will then be able to access the NVR services from the Internet.
Note:
•
If more than two NVR are connected to one UPnP router, please specify a
different port for each NVR. If the router does not support UPnP, users are
required to configure port forwarding manually on the router. Please refer
to the links below:
•
Application note: http://www.qnap.com/go/notes.html
•
FAQ: http://www.qnap.com/faq
•
UPnP router compatibility list:
http://www.qnap.com/UPnP_Router_Compatibility_List
My DDNS
With the Cloud Portal, web-based NVR services such as web administration
and File Station can be published to http://www.myqnapcloud.com.
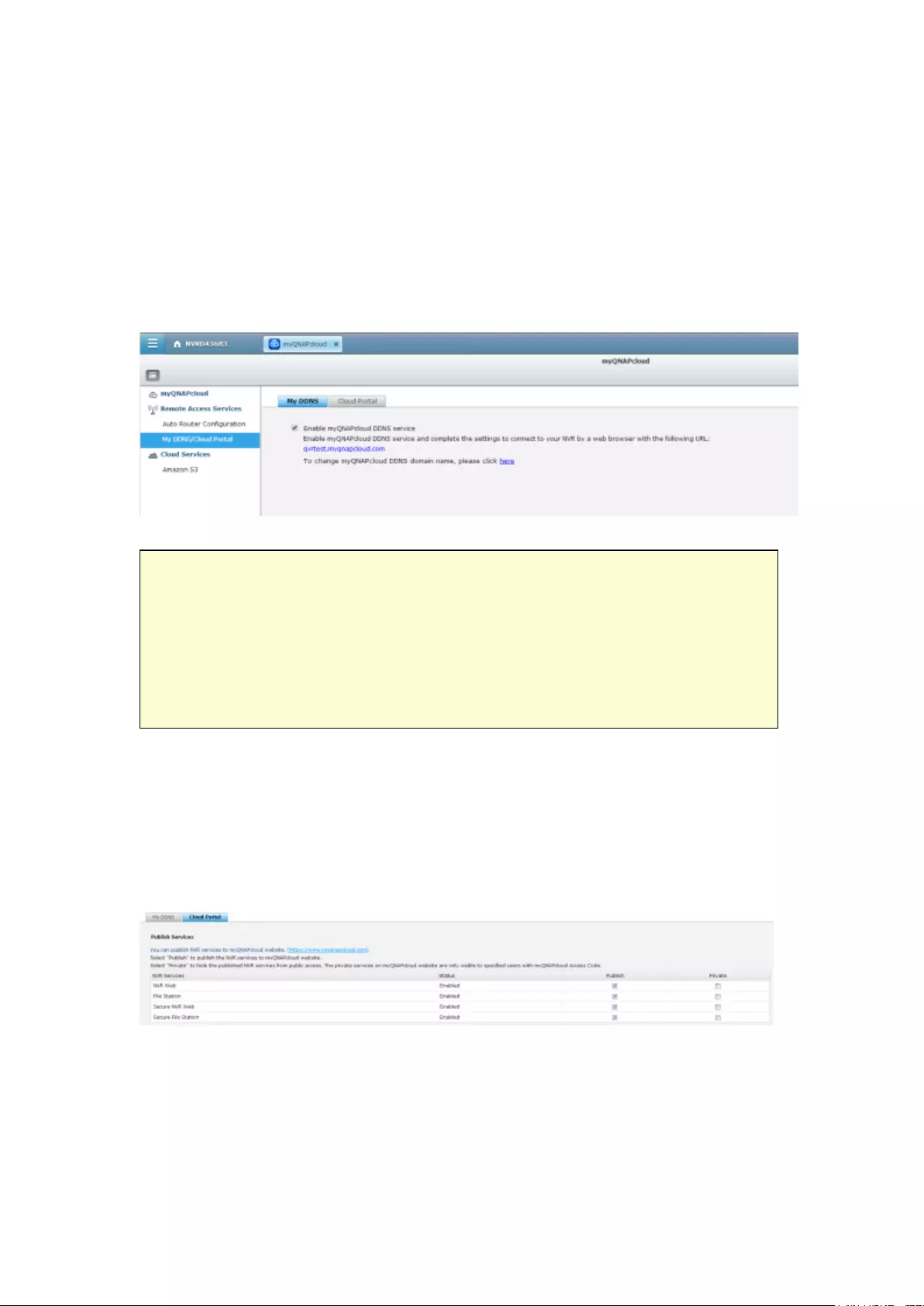
316
By enabling the NVR services in this step, they are opened for remote
access even if they are not published.
Enable the My DDNS service in “Remote Access Service” and the NVR will
notify the myQNAPcloud server automatically if the WAN IP address of the
NVR has changed. To use the myQNAPcloud service, make sure the NVR
has been connected to an UPnP router and the Internet.
Note:
•
The myQNAPcloud name of each QNAP NVR is unique. One
myQNAPcloud name can only be used with one NVR.
•
A registered myQNAPcloud name will expire in 120 days if your
NVR remains offline within the period. Once the name is
expired, it will be released for new registration by other users.
Cloud Portal
In “Remote Access Services” > “My DDNS/Cloud Portal” > “Cloud
Portal”, the web-based NVR services are shown. Select “Publish” to
publish the NVR services to myQNAPcloud website.
Select “Private” to hide the published NVR services from public access
if you don’t want every user can access this published NVR service. The
private services on the myQNAPcloud website are only visible to
specified users with the myQNAPcloud access code.
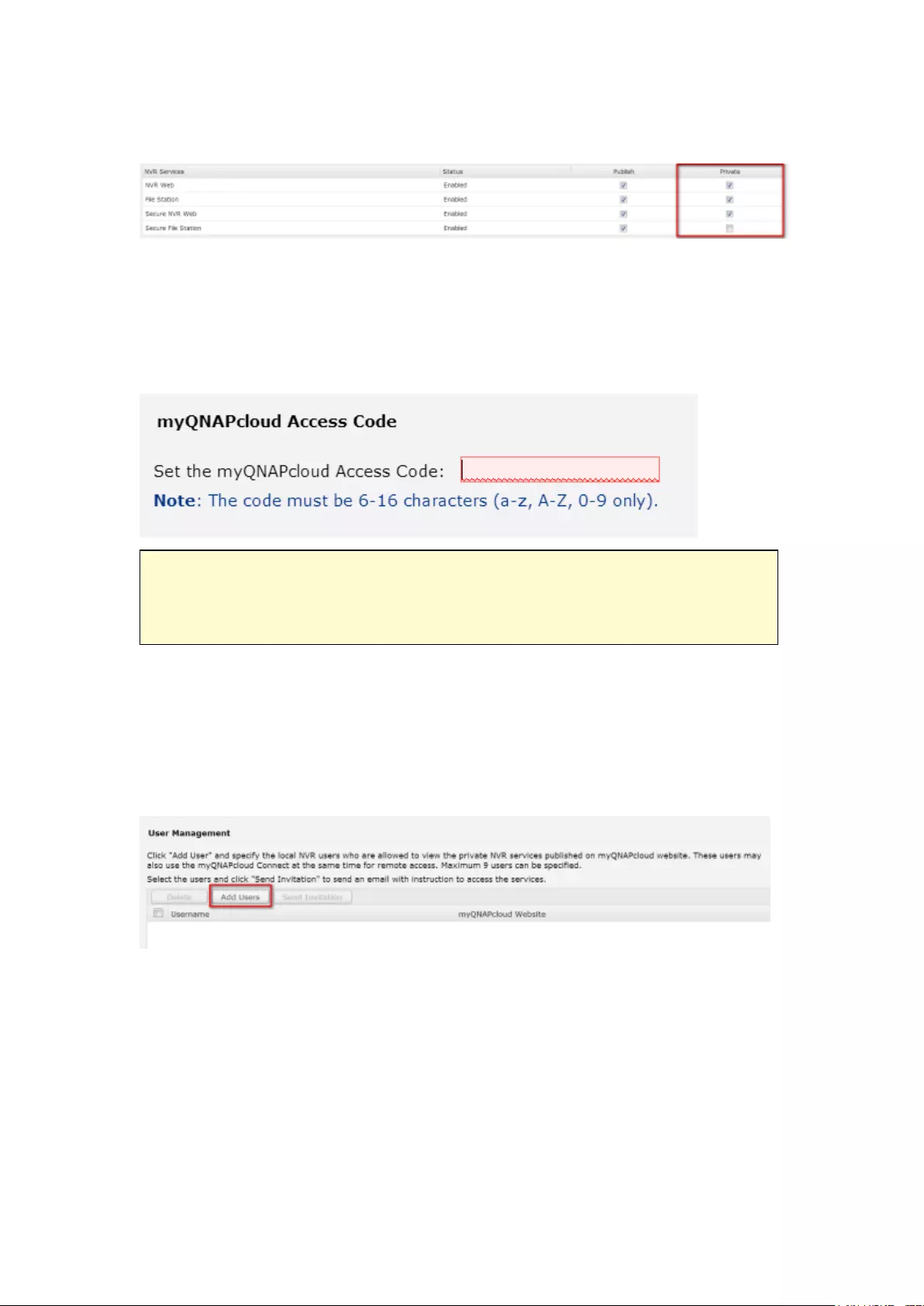
317
Set myQNAPcloud Access Code for private services: Enter a code of
6-16 characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9 only). The code is required when NVR
users attempt to view the private NVR services on the myQNAPcloud
website.
Note: If a disabled NVR service is published, the service will not be accessible even
the corresponding icon is shown on myQNAPcloud website
(http://www.myQNAPcloud.com).
Click “Add Users” and specify maximum 9 local NVR users who are
allowed to view the private NVR services published on the
myQNAPcloud website.
Select the users and connection method: myQNAPcloud website. Click
“Apply”.
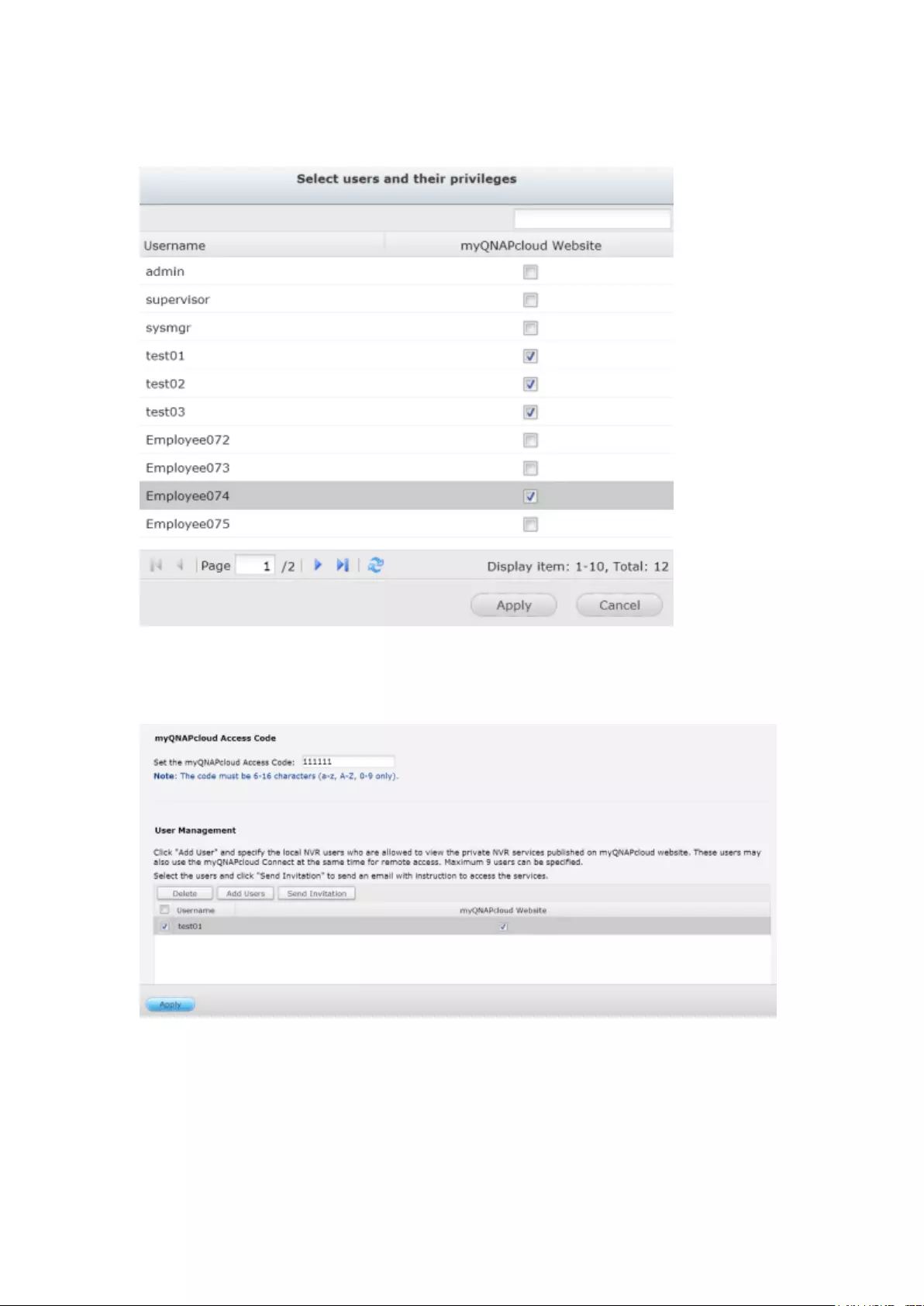
318
Then click “Apply” to save the settings.
To send the instructions of the myQNAPcloud service to users via email,
select the user(s) and click the “Send Invitation” button.
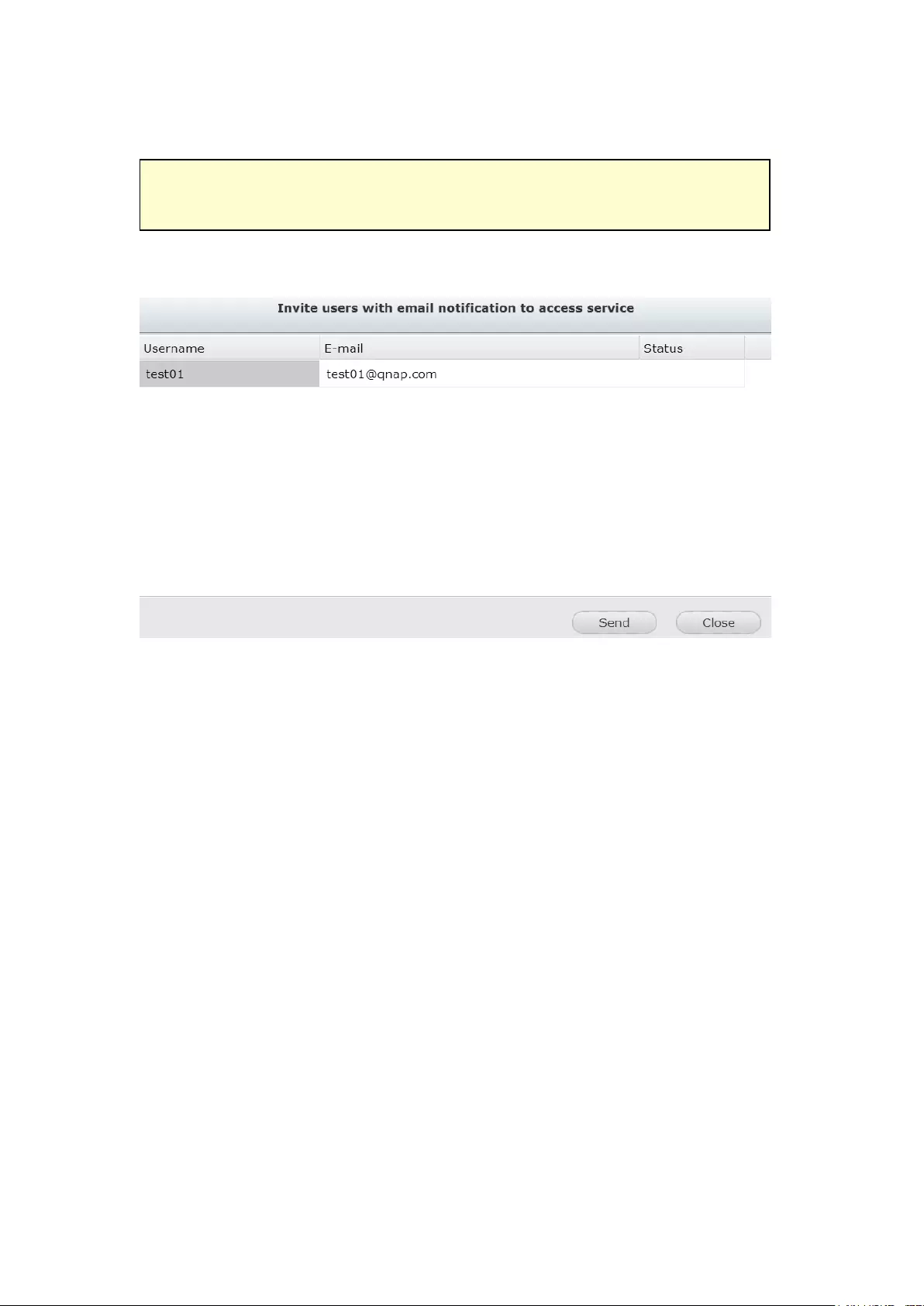
319
Note: To use this function, the mail server settings must be properly configured
in “Control Panel” > “System Settings” > “Notification” > “SMTP Server”.
Enter the email address. Click “Send”.
320
10.1.2 Cloud Services
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is an online storage web service provided by Amazon Web Services. QNAP
VioStor NVR supports Amazon S3 to allow the users to back up the data from the NVR to Amazon S3, or
download it from Amazon S3 to the NVR at anytime. Besides, the users can also create scheduled replication job
for daily, weekly, or monthly backup.
Create your own Amazon S3 account
To use the Amazon S3 feature on VioStor NVR, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Sign up/ Login Amazon Web Services Account
You need to sign up for Amazon S3 account (http://aws.amazon.com/s3/). For the price information, please refer
to the Amazon web services website.
Step 2: Get Your Access Key ID and Secret Access Key
Once you have successfully signed up an account, you will receive your Access Key ID and
Secret Access Key. Please keep your ID and key safe.
If you have missed the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key notification, click "Your Account" and
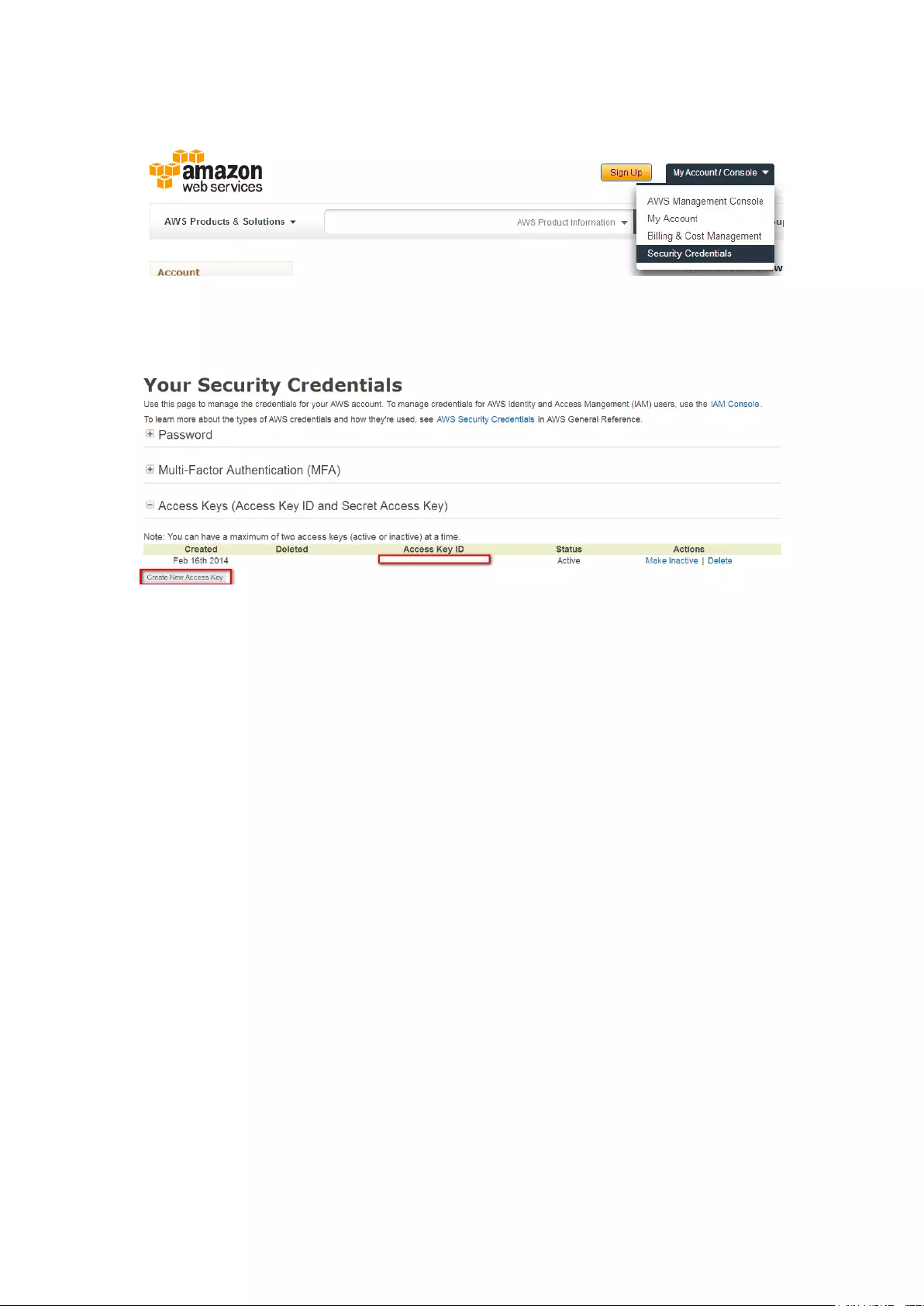
321
choose "Security Credentials" to retrieve them.
Check your Access Keys (Access Key ID and Secret Access Key). Click “Create New Access
Key” if you don’t have Access keys.
Create Remote Replication Job on Amazon S3
For using Remote Replication Job on Amazon S3, you must have one Amazon S3
account first. You can refer to section “Create your own Amazon S3 account” for
detailed information.
You can back up the NVR data to or retrieve the data from the Amazon S3. Amazon’s
services will generally accept requests that are received within 15 minutes after you
login Amazon S3. Before getting started, make sure your system clock is set
correctly according to your time zone. It is suggested to configure your NVR to
automatically synchronize with the system clock using the Network Time Protocol
(NTP).
Follow the steps below to create a remote replication job on Amazon S3.
Step 1: Login your VioStor NVR and go to "myQNAPcloud" > "Cloud Service" >
"Amazon S3". Click "Create New Replicating Job".
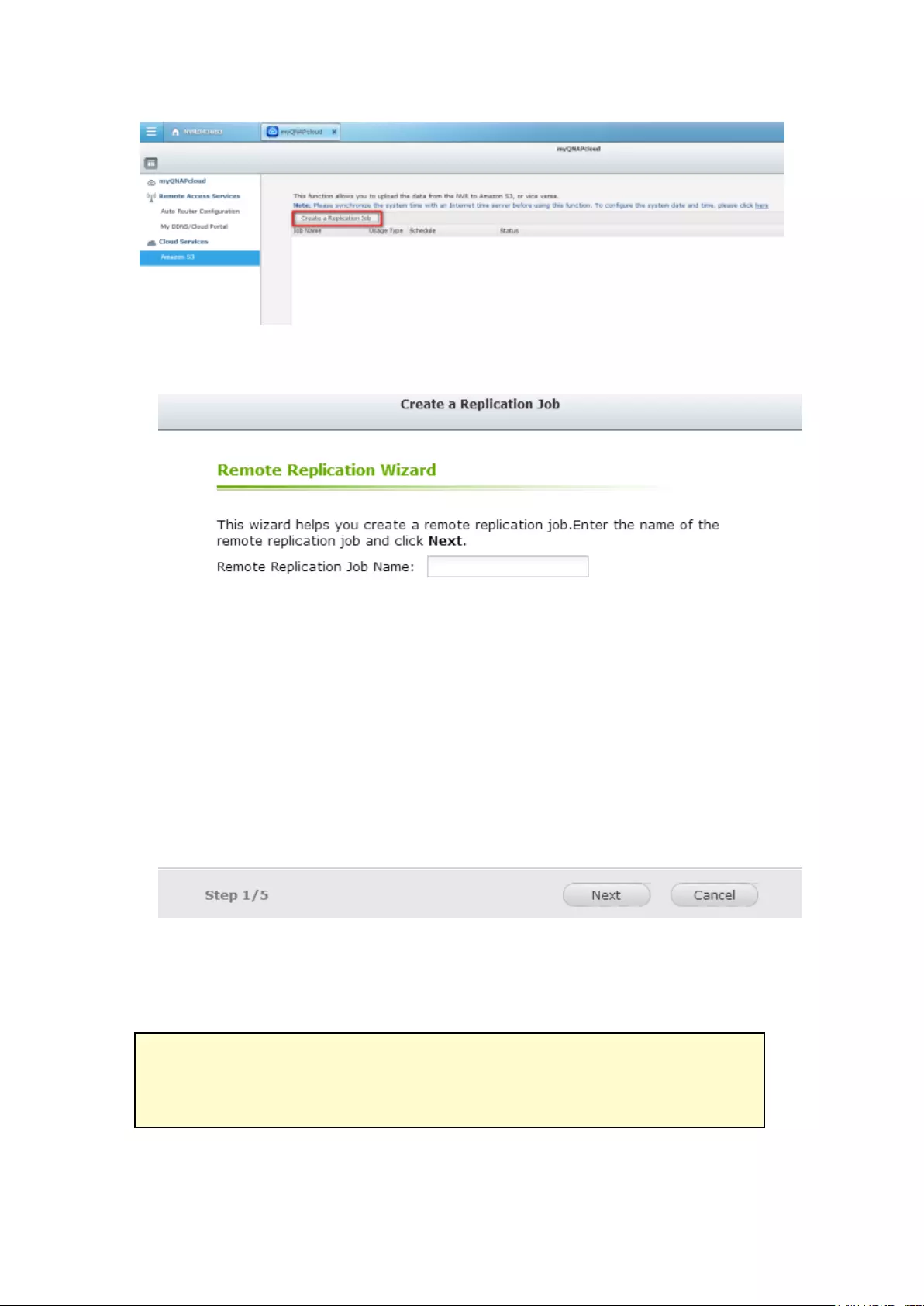
322
Step2: Enter the job name.
Step3: Select usage Type (Upload or download) from the dropdown menu. Then
input the access key, private key and remote path. A bucket is the root directory on
Amazon S3. You can do remote host testing by clicking "TEST". Other settings are
optional.
Note: To use this function, you must create at least one Bucket on Amazon S3.
Please go to Amazon S3 on website and select “Create Bucket” to create one
Bucket on your Amazon S3 account.
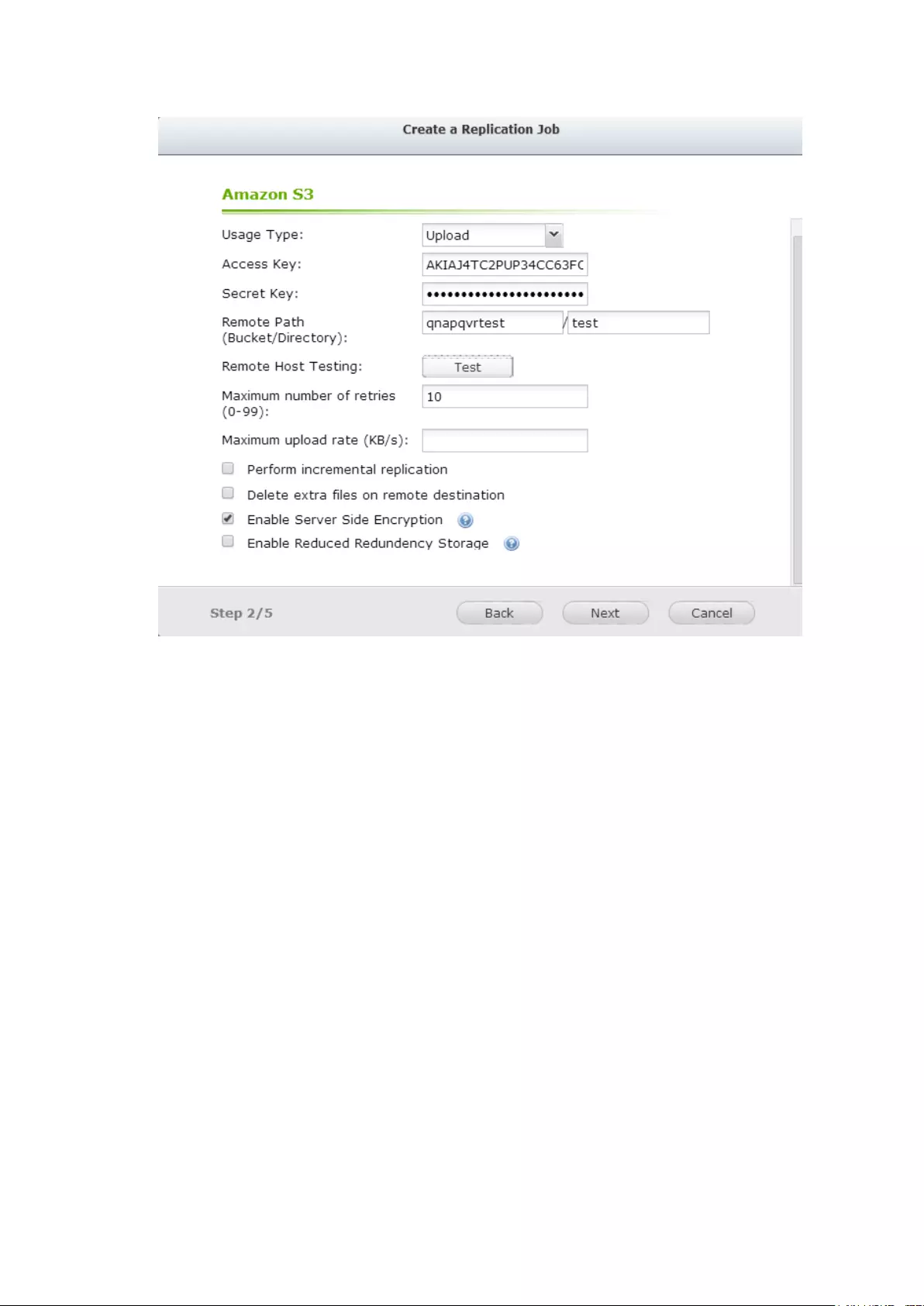
323
Step4: Specify the local path as Network Share/ Directory. Select the network share
from dropdown menu and input the directory.
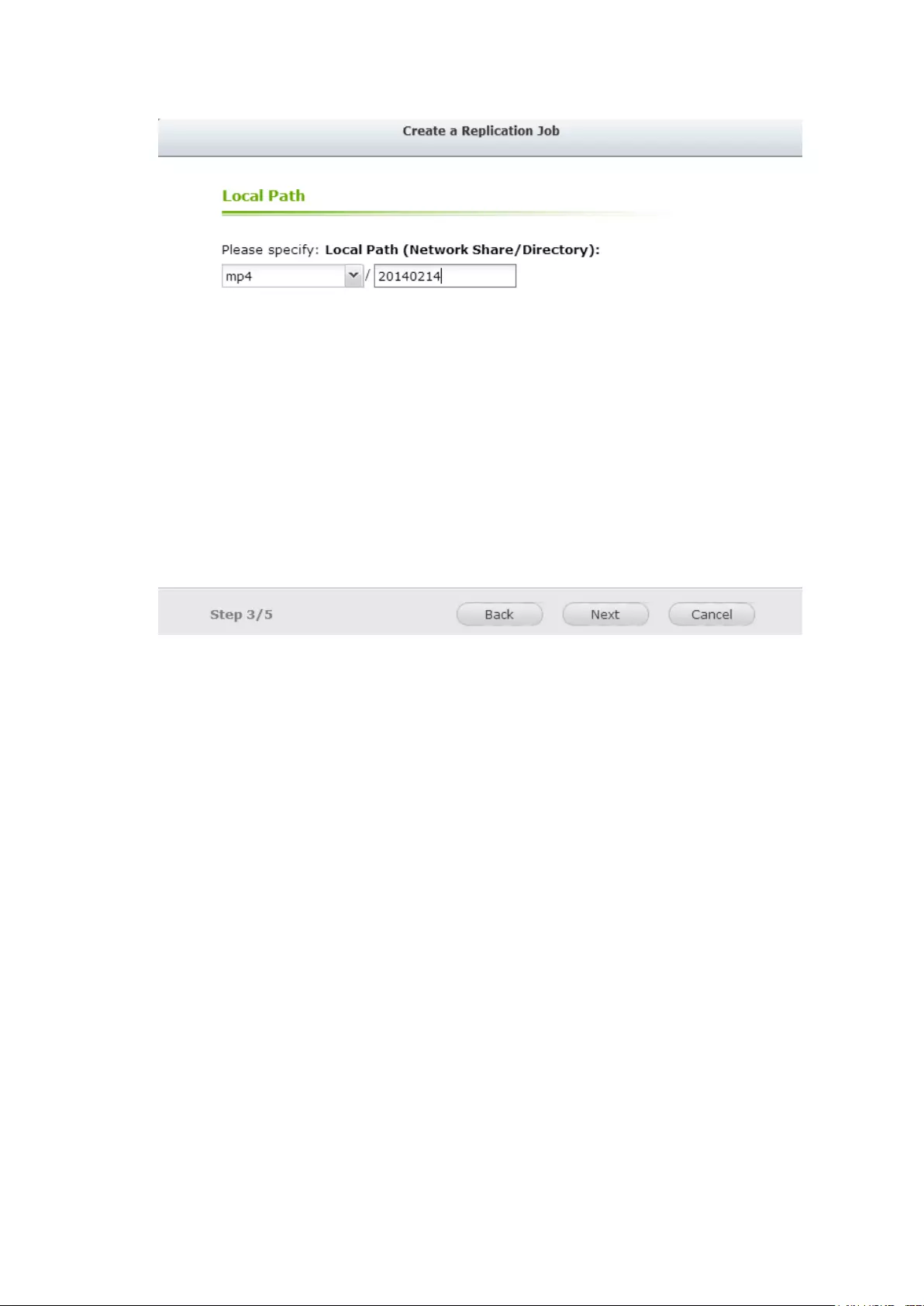
324
Step5: Specify your replication schedule.
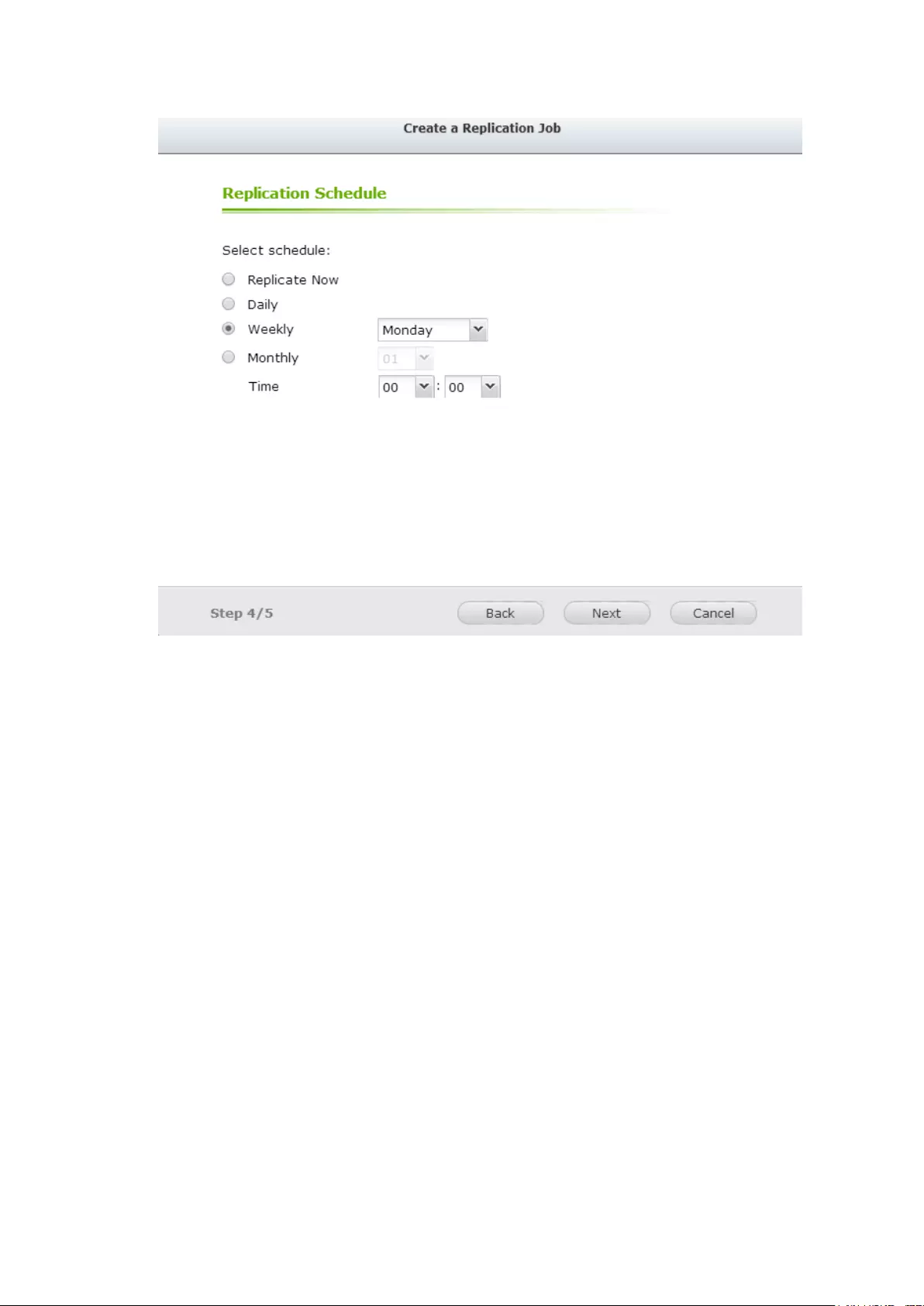
325
Step6: Click "Finish" to complete the setup.
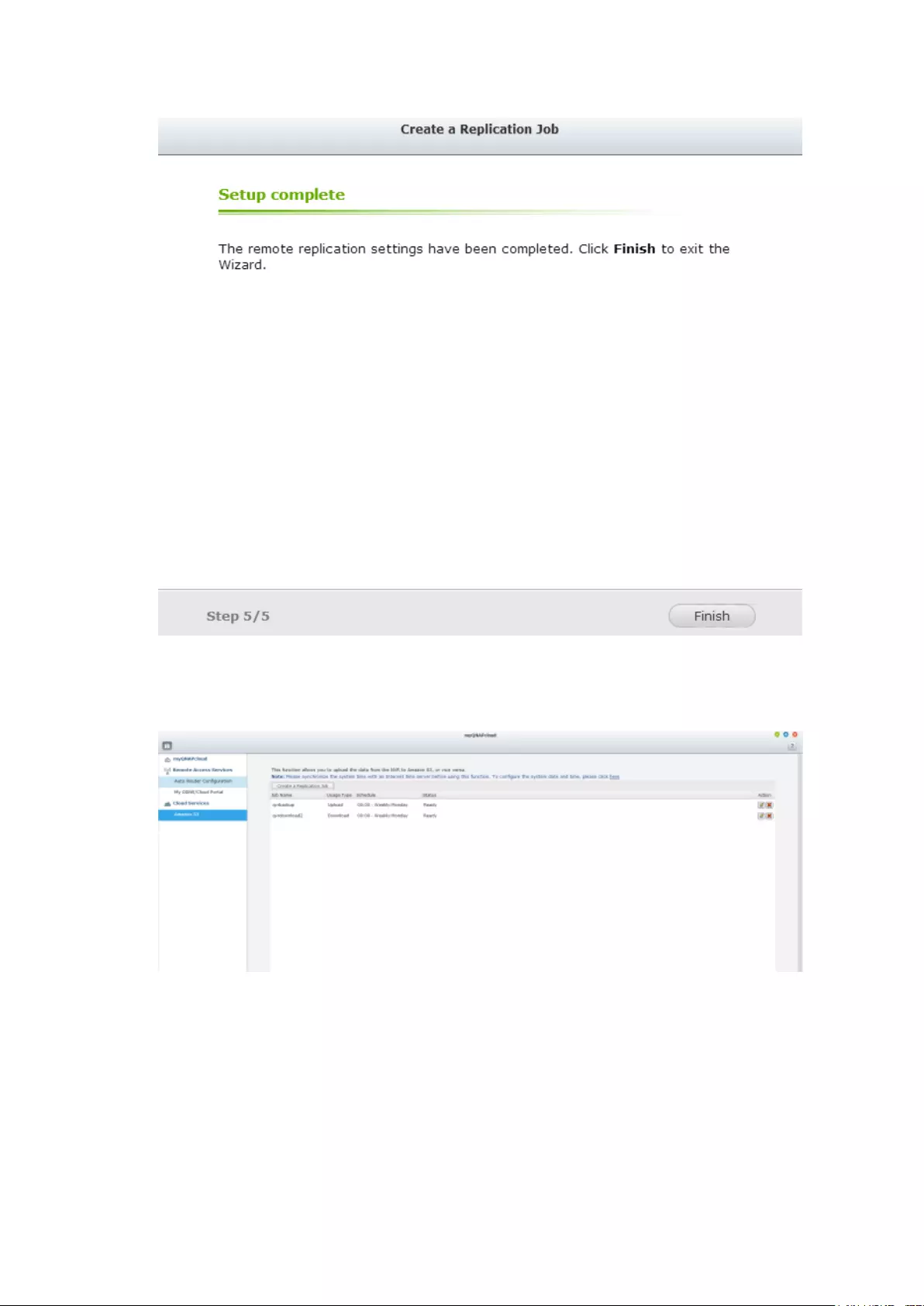
326
Upon successful job creation you will see the status of the replication job(s). You
can edit or delete them if necessary.
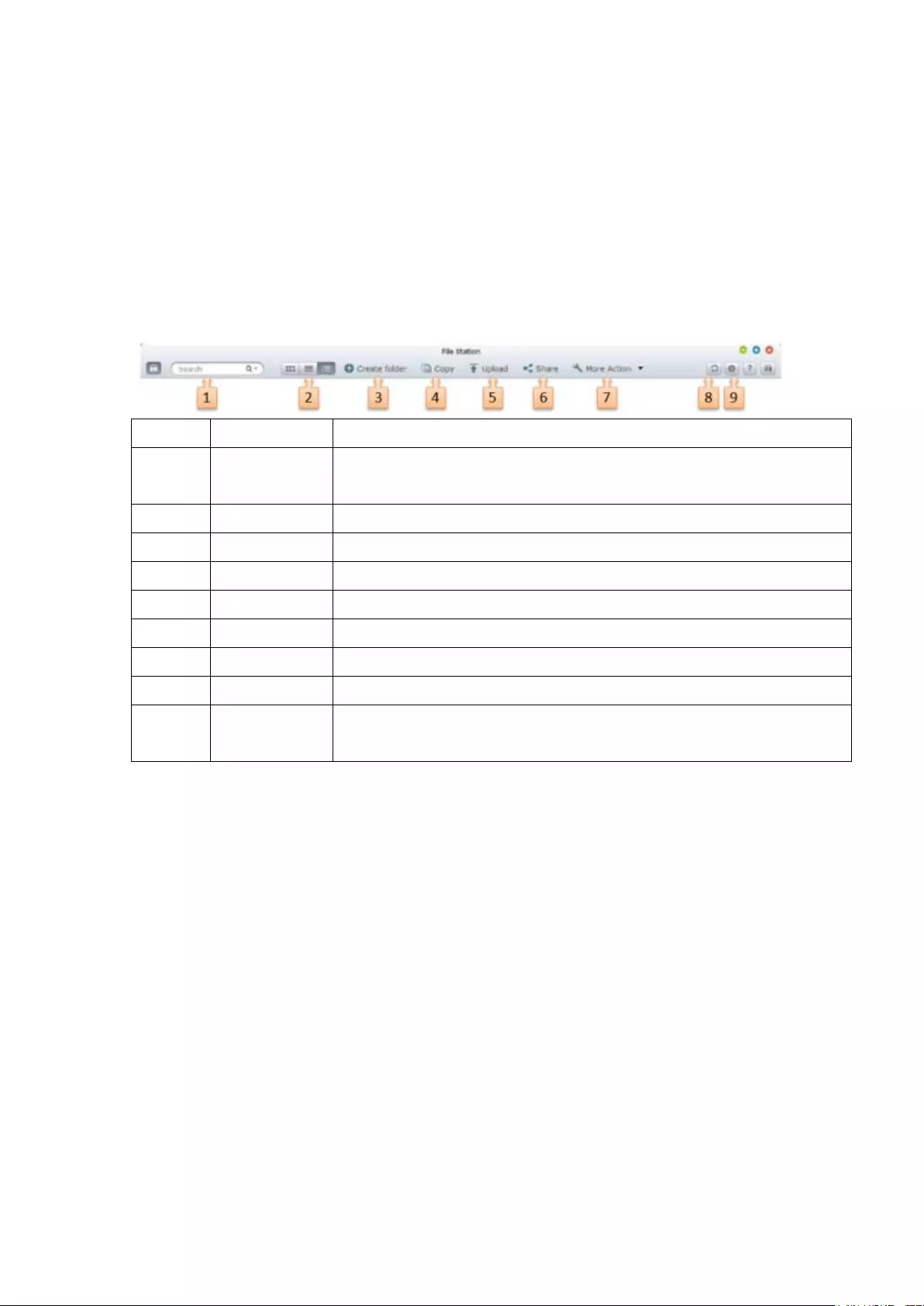
327
10.2 File Station
The File Station allows the users to access the NVR on the Internet and manage the
files by a web browser.
Number
Item
Description
1
Search
Search by name, type(music, movie, photo...) or select advanced
search
2
View mode
Change the View mode
3
Create folder
Create a folder in shared folders
4
Copy
Copy/ Paste files and folders
5
Upload
Select the folder to upload the file to
6
Share
Share a file or folder with other users using various methods
7
More Action
Add the shared folders to bookmark
8
Refresh
Refresh this page
9
Settings
• Show files and folders of my PC
• Show hidden files
Before getting started
Enable the service in “Control Panel” > “Applications” > “Station Manager”. Click the
link on the page to access the File Station.
The File Station can be launched from the Main Menu or the File Station icon on the
Desktop.
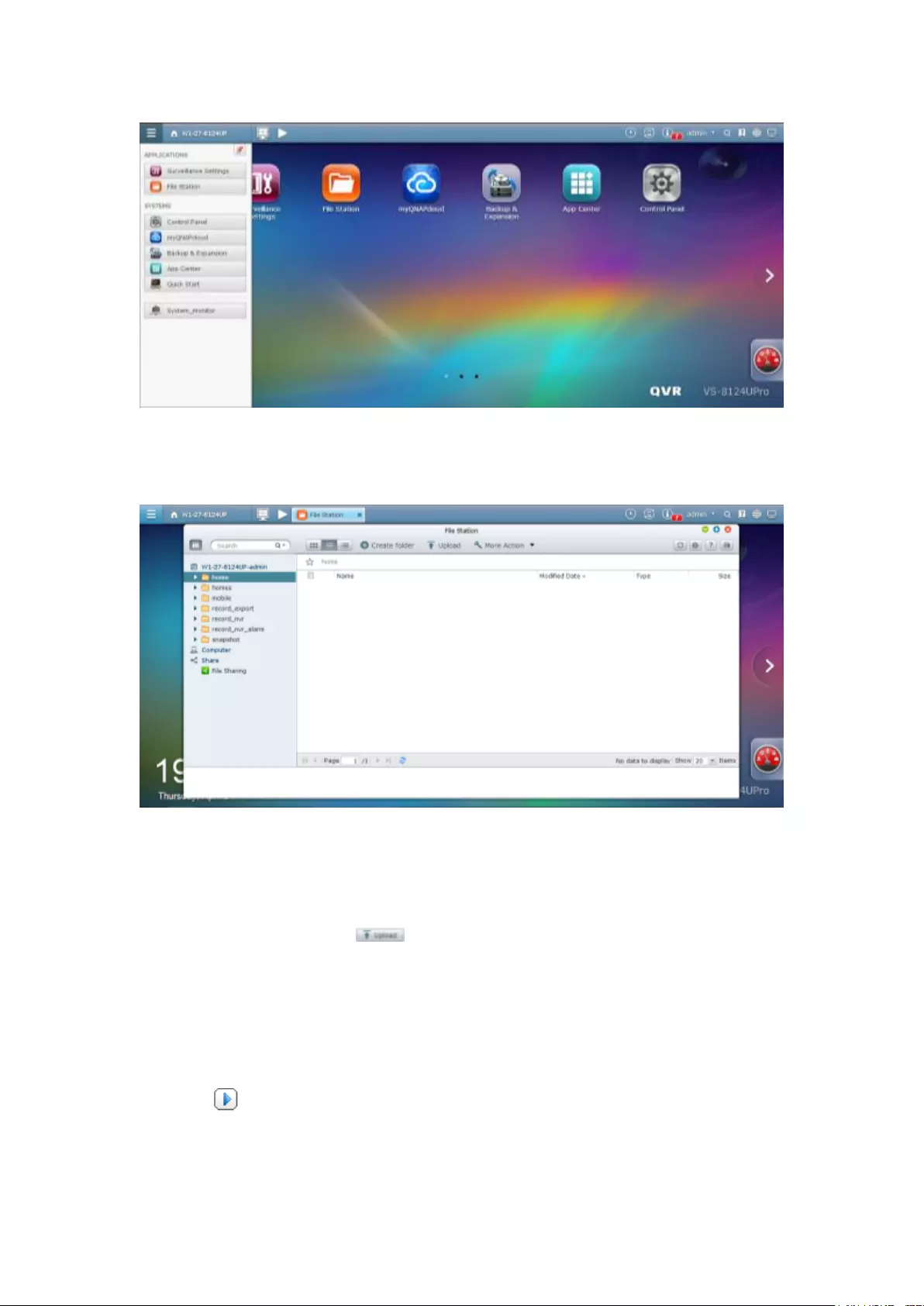
328
You can upload, download, rename, move, copy, or delete the files and folder on the
NVR.
Uploading files
To use this feature, install Adobe Flash plug-in for your web browser.
1.
Select a folder and click .
2.
Click “Browse” to select the file(s).
3.
Select to skip or overwrite the existing file(s) in the folder.
4.
Click to upload a file or “Upload All” to upload all the selected files.
329
Note: The maximum size of a file that can be uploaded to the NVR by the File
Station is 2GB without JAVA plug-in.
Downloading files
1. Select a file or folder to download.
2. Right click the mouse and select “Download” to download the file. Please note
that if all files within a folder are selected, they will be compressed and
downloaded as a zip file.
Creating folders
1.
Select a shared folder or folder in which you want to create a new folder.
2.
Click .
3.
Enter the name of the new folder and click “OK”.

330
Renaming files or folders:
1.
Select a file or folder to rename.
2.
Right click the mouse and select “Rename” to rename the file.
3.
Enter the new file or folder name and click “OK”.
Copying files or folders
1.
Select the files or folders to copy.
2.
Click .
3.
Click the destination folder.
4.
Click and confirm to copy the files or folders.
Moving files or folders
1.
Select the files or folders to move.
2.
Right click the mouse and select “Move”.
3.
Select the destination folder. Click “OK”.
Deleting files or folders
1.
Select a file or folder to delete.
2.
Right click the mouse and select “Delete”.
3.
Confirm to delete the file or folder.
File/Folder search
331
The File Station supports smart search of files, sub-folders, and folders on the NVR.
You can search a file or folder by all or part of the file or folder name, or by the file
extension.
332
10.3 App Center
The App Center is a digital platform for distribution of NVR apps. Users can search for,
install, remove and update apps developed by QNAP or third party apps through the
App Center to expand the services and add new features on the NVR.
Starting App Center
The App Center can be launched from the App Center shortcut on the Main Menu or
the QVR Desktop.
Familiarizing yourself with App Center
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Search Bar
Search apps that are available to install on the
NVR.
2
Update all
Update all apps that are currently installed on the
NVR.

333
3
Refresh
Refresh the current page
4
Install Manually
Browse to upload and install a QPKG add-on
manually.
5
Sort
Sort apps by category, name or release date.
Left Panel
• My Apps: List apps that are currently installed on the NVR.
• All Apps: List all apps that can be installed on the NVR.
Using App Center
Searching apps
To search for an app, enter the keyword in the search bar.
Installing, updating and removing apps
To install an app, click the "Add to QVR+" button and the installation process will
begin. After the installation process is complete, the "Add to QVR+" button will turn
to the "Open" button and you can directly click this button to launch this newly
installed app. This newly installed app will then show up in "My Apps".
Note:
• Make sure the NVR is connected to the Internet.
• QNAP is not responsible for troubleshooting any issues caused by the open
source software/add-ons.
• When installing an add-on which requires a prerequisite app, the prerequisite
add-on will be added to the installation queue automatically prior to the dependent
add-on.
• If the app update process is canceled before it is finished, please install the app
from the App Center again.
To update an app, click "Update" and click "OK" to confirm. Alternatively, you may
click "Update All" on the menu bar to install all updates and "Refresh" to check for
the latest updates. The button will turn to "Open" to signify that the update is
complete for an app. To remove an app, first click an installed app to open its
introduction page. Click "Remove" on the page to uninstall it from the NVR and click
"OK" to confirm.
Note:

334
• Click the on/off button in an app icon to enable or disable an app.
Offline Installation
To install apps when the NVR is offline or beta apps that are not officially available on
the QNAP App server, users can download the app application (*.qpkg) from the
QNAP security website (http://www.qnapsecurity.com/) or forum
(http://forum.qnapsecurity.com/index.php), unzip the files, and click "Install
Manually" on the menu bar to install the apps manually.

335
11. QNAP Surveillance Central Management (QSCM Lite)
11.1 Introduction
QNAP Surveillance Central Management Lite (referred to as “QSCM Lite” in the
following context) is a pioneering, powerful and free App supported by QNAP VioStor
NVR (with firmware QVR 5.0 and above), that turns your NVR into a CMS server to
manage up to 16 QNAP NVRs and 256 cameras.
No extra investment in hardware or software is required to add CMS server function
to a NVR – all you have to do is install the QSCM Lite App.
QSCM Lite can manage NVRs that are in the same private LAN with QSCM Lite.
11.2 Install QSCM Lite to NVR Server
11.2.1 App Center
To install QSCM Lite, please download it from the QVR 5.0 App Center. For more
information about the App Center, please refer to Section 10.3 App Center.
11.2.2 How to Install QSCM Lite to NVR Server
Online installation
To install QSCM Lite, please download it from the QVR 5.0 App Center. Your NVR
must be connected to the Internet to use the App Center.
Step 1: Go to the App Center on the desktop of QVR 5.0.
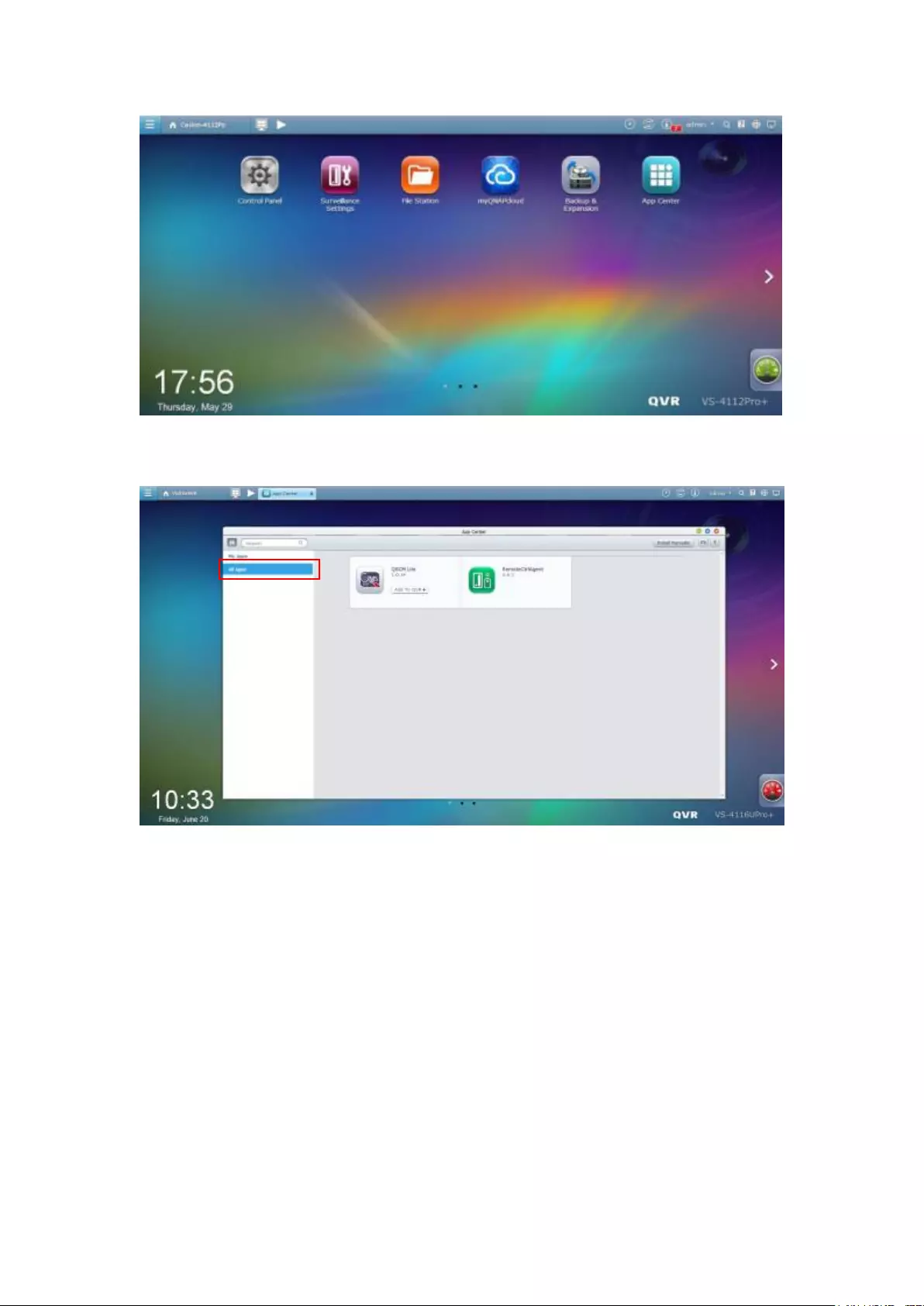
336
Step 2: Go to All Apps.
Step 3: Click “Add QSCM Lite to QVR”
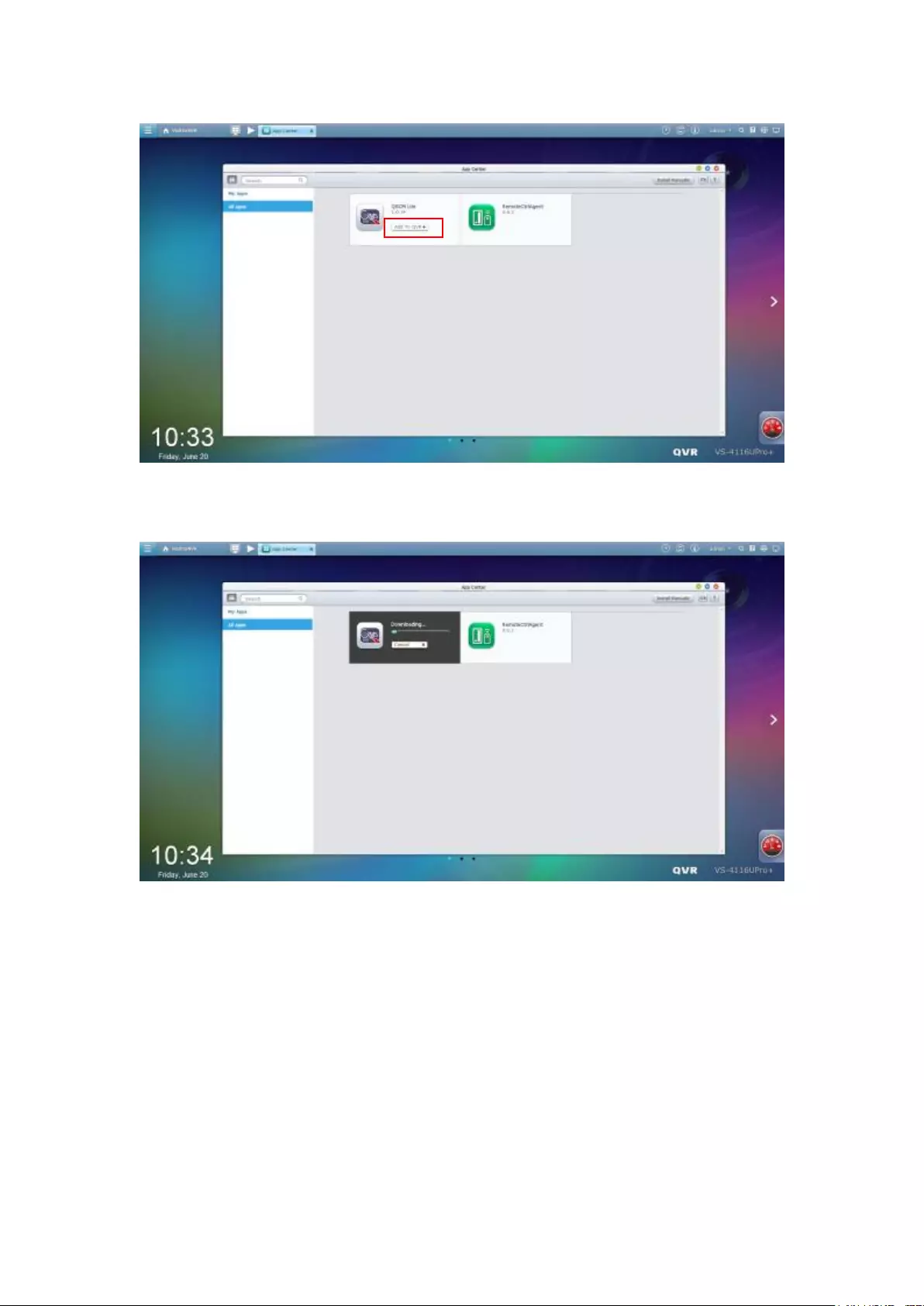
337
Step 4: Start downloading QSCM Lite
Step 5: After QSCM Lite has been downloaded, the system will automatically install
QSCM Lite.
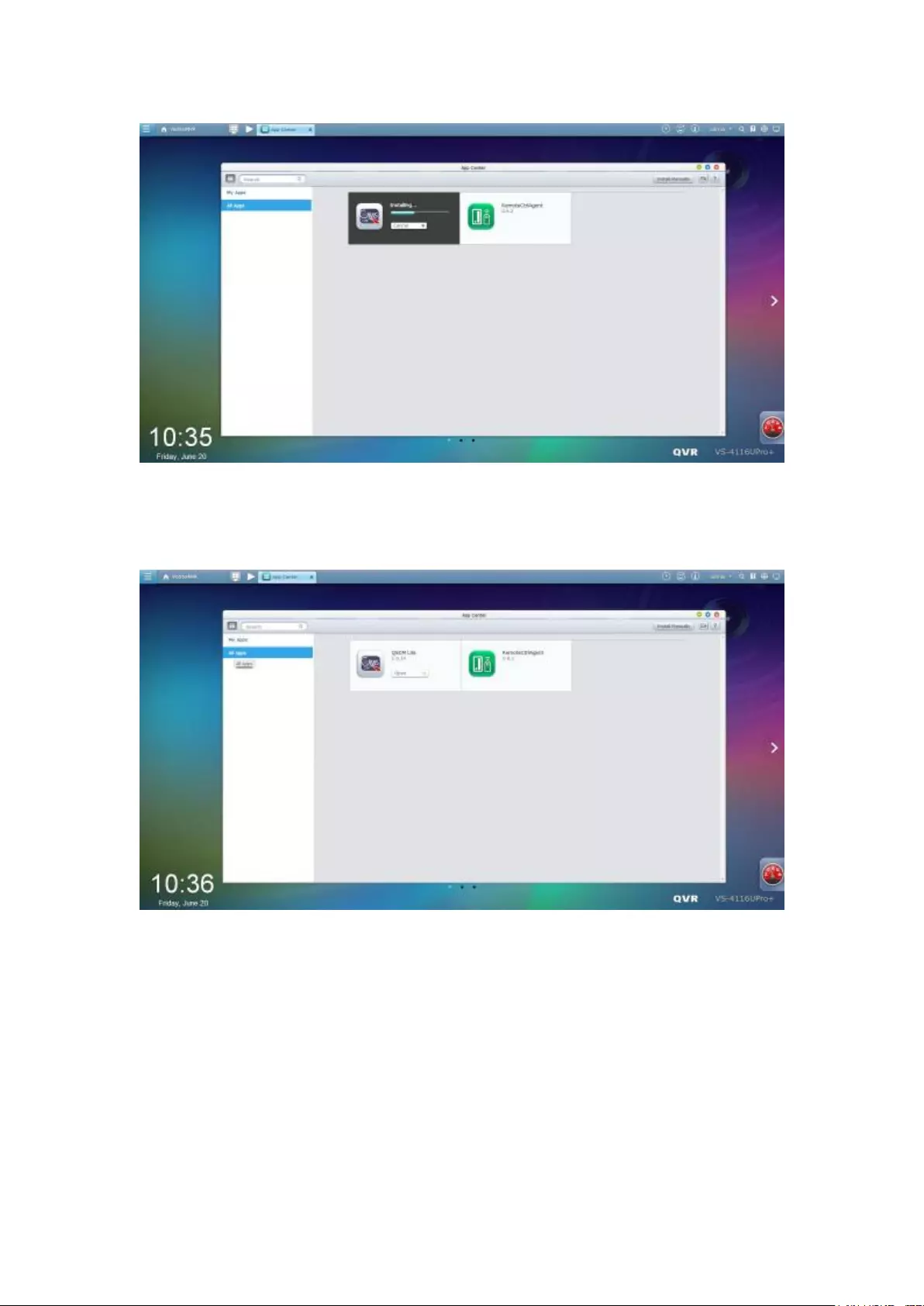
338
Step 6: When the option to “Open” appears, QSCM Lite has been successfully
installed.
Step 7: QSCM Lite will now be listed in My Apps, with the default Open status. QVR
5.0 is now a CMS server.
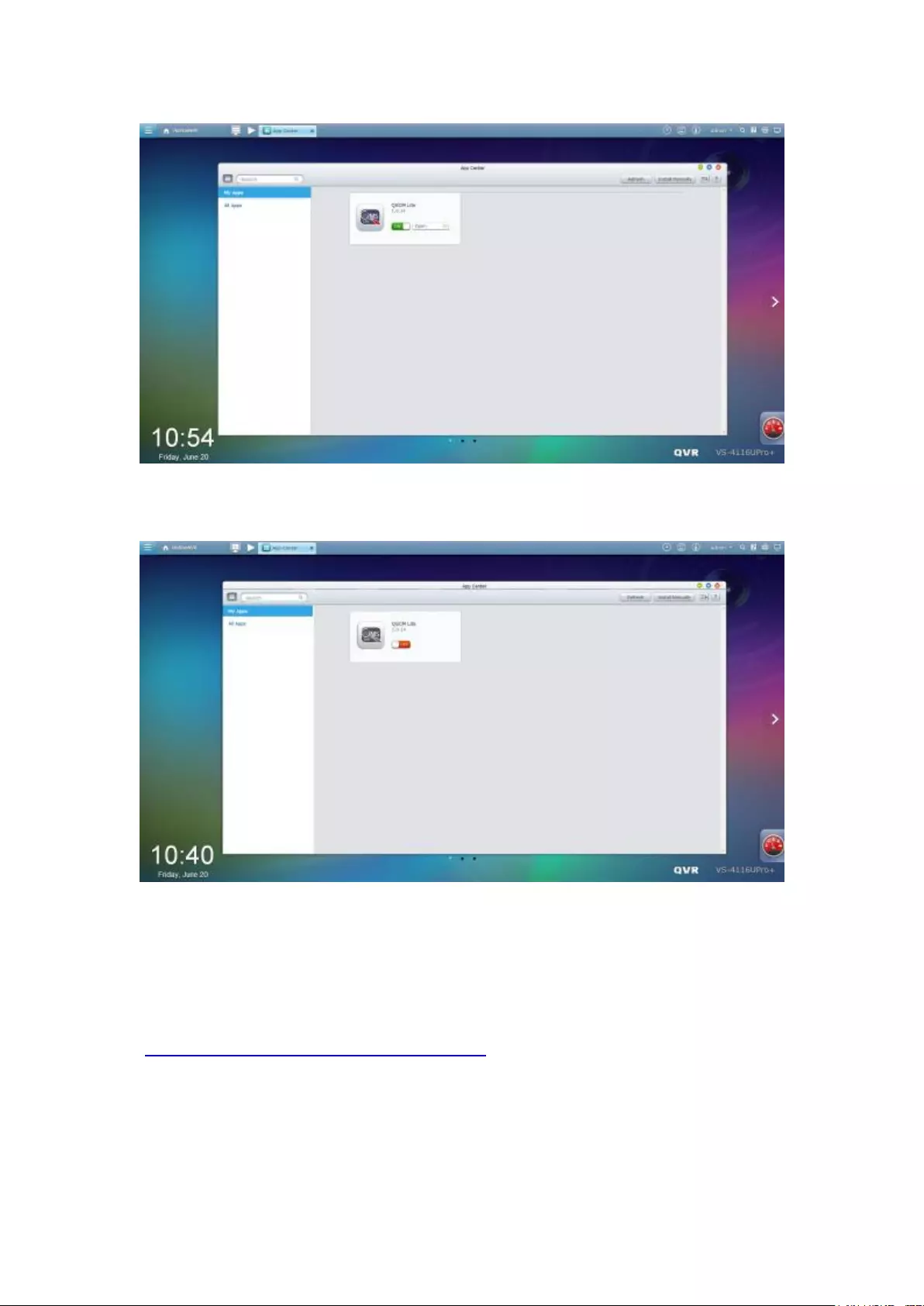
339
QSCM Lite can be turned off to disable the CMS server function if needed.
Offline installation
If the NVR is not connected to the Internet, an offline installation is available.
Step 1: Download QSCM Lite from the QNAP Security website
(http://www.qnapsecurity.com/download.asp).
Step 2: Unzip the files
Step 3: Return to the NVR and enter the App Center
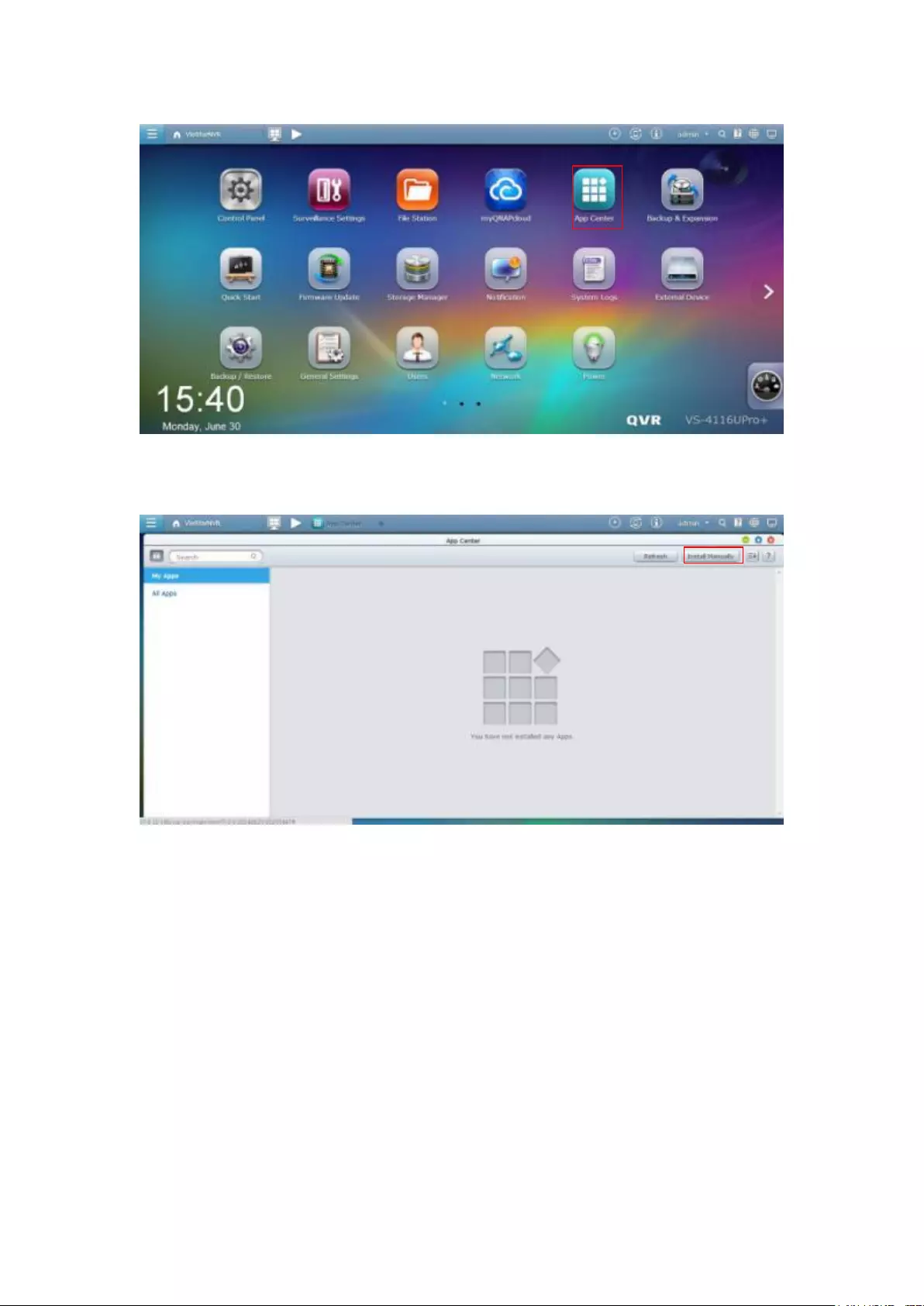
340
Step 4: Click "Install Manually"
Step 5: Find the unzipped QSCM Lite, and click [Install]
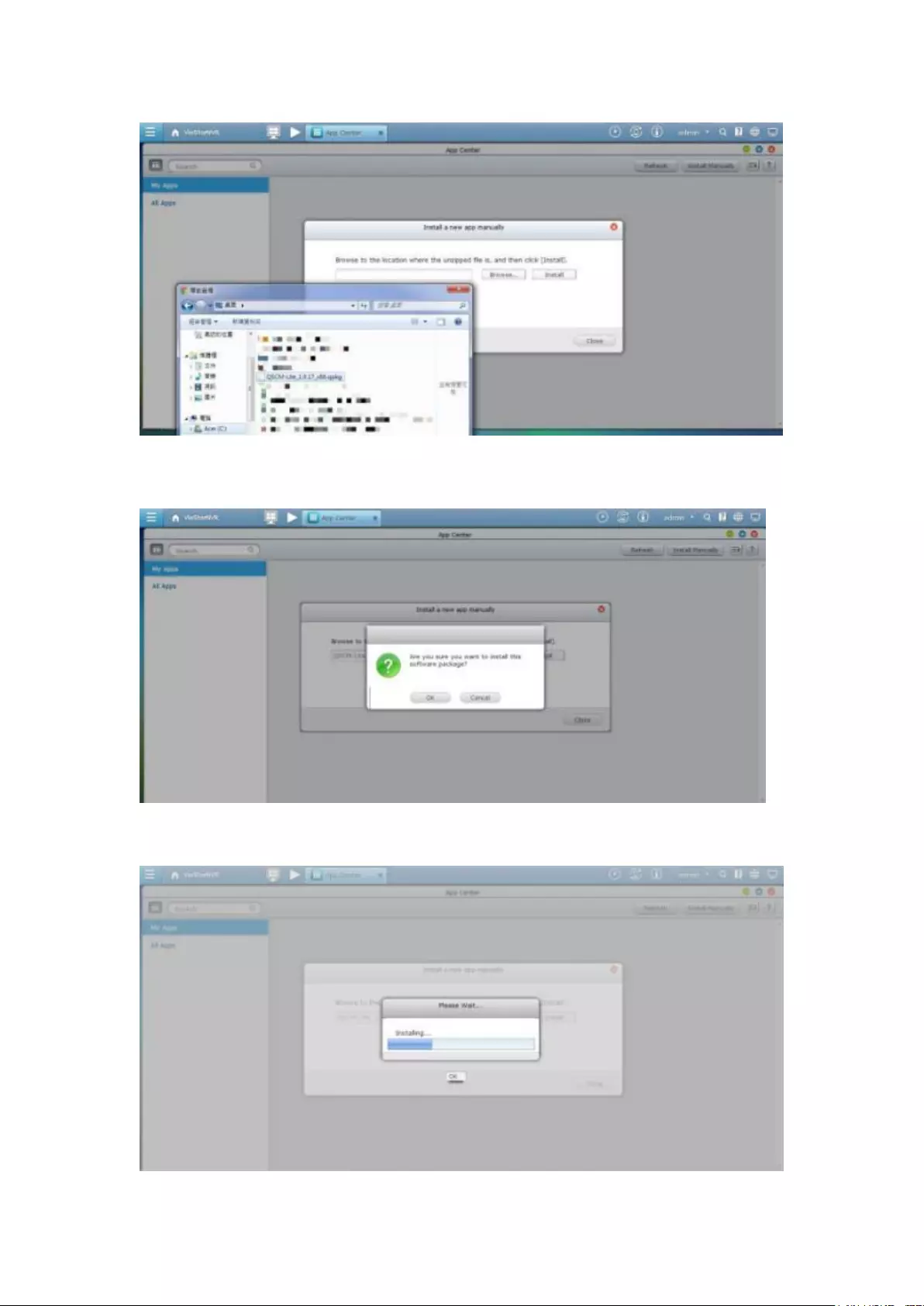
341
Step 6: Click OK
Step 7: The NVR will then install QSCM Lite
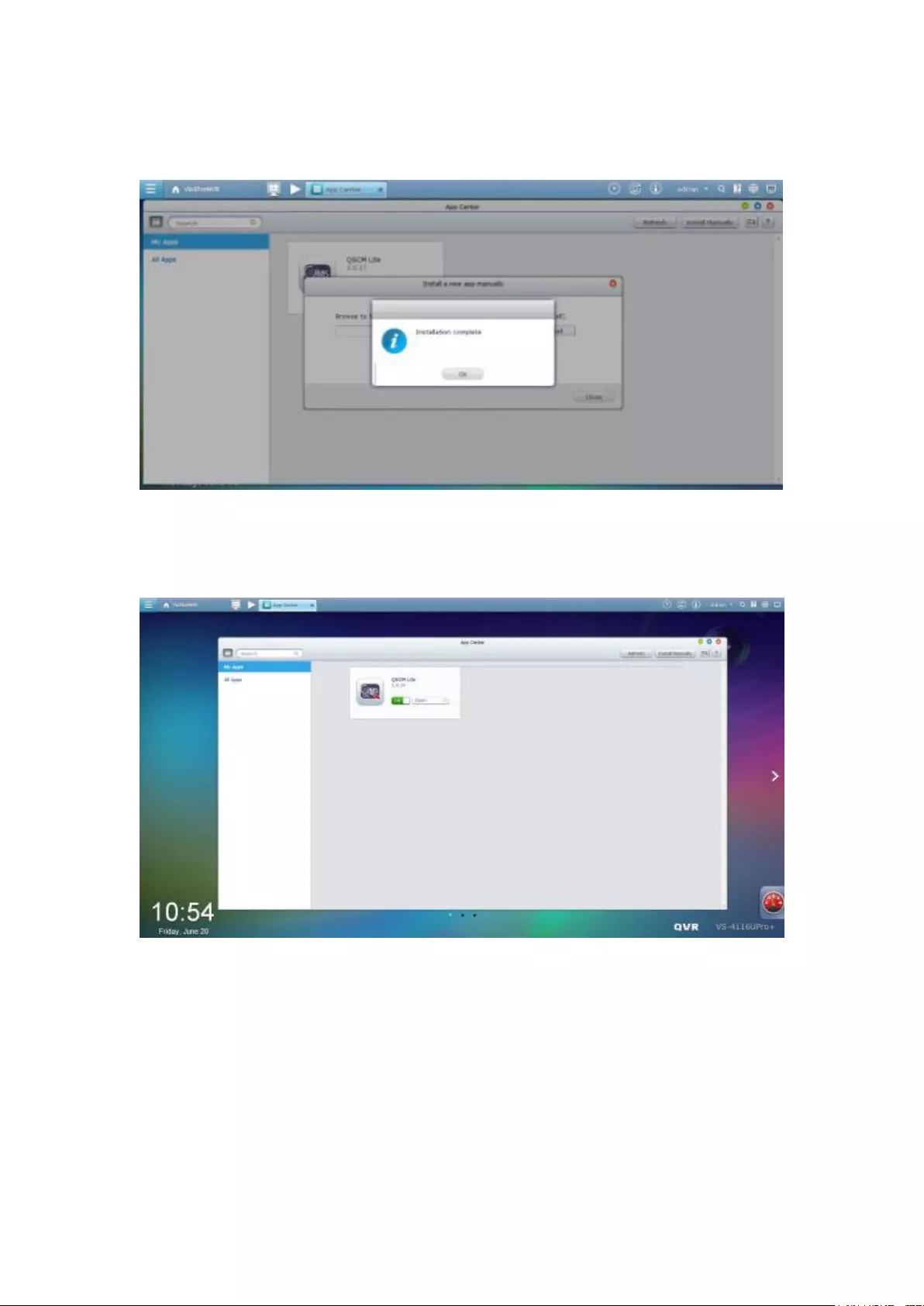
342
Step 8: Click OK
Step 9: QSCM Lite will now be listed in My Apps, with the default Open status. QVR
5.0 is now a CMS server.
If needed, QSCM Lite can be turned off to disable the CMS server function.
343
11.2.3 Installation Reminders and Suggestions
QSCM Lite can only be installed to QNAP NVR with firmware version 5.0 or
above.
When enabling QSCM Lite on QVR 5.0, you have 2 options:
1. Do not record camera footage to this server, and have it act as a pure CMS server.
2. Keep recording camera footage to this server, and have it act as both a CMS and
NVR server simultaneously.
In the second case (the server will act as both a CMS and NVR server simultaneously),
the server’s hardware resources will be shared by the NVR server service & the CMS
server service. If the CPU usage rate is more than 80%, or when the throughput is
busy, the performance of both the NVR server and CMS server will be impacted.
It is strongly recommended to enable just one QVR 5.0 as QSCM Lite to centrally
manage the NVRs in a LAN. Otherwise, the QSCM Lite event management
(including the live view event notification and event log) will be scattered to
multiple QSCM Lites.
11.3 Use QSCM Lite on NVR Client PC
11.3.1 How to use QSCM Lite on NVR client PC
Step 1: Connect to a QVR 5.0 with QSCM Lite. For instructions on how to install
QSCM Lite, please refer to 1.2.2.
344
Step 2: Go to the App Center on the QVR 5.0 desktop.
Or, the Main Menu of QVR 5.0
Step 3: Click on the QSCM Lite icon to go to the QSCM Lite login page
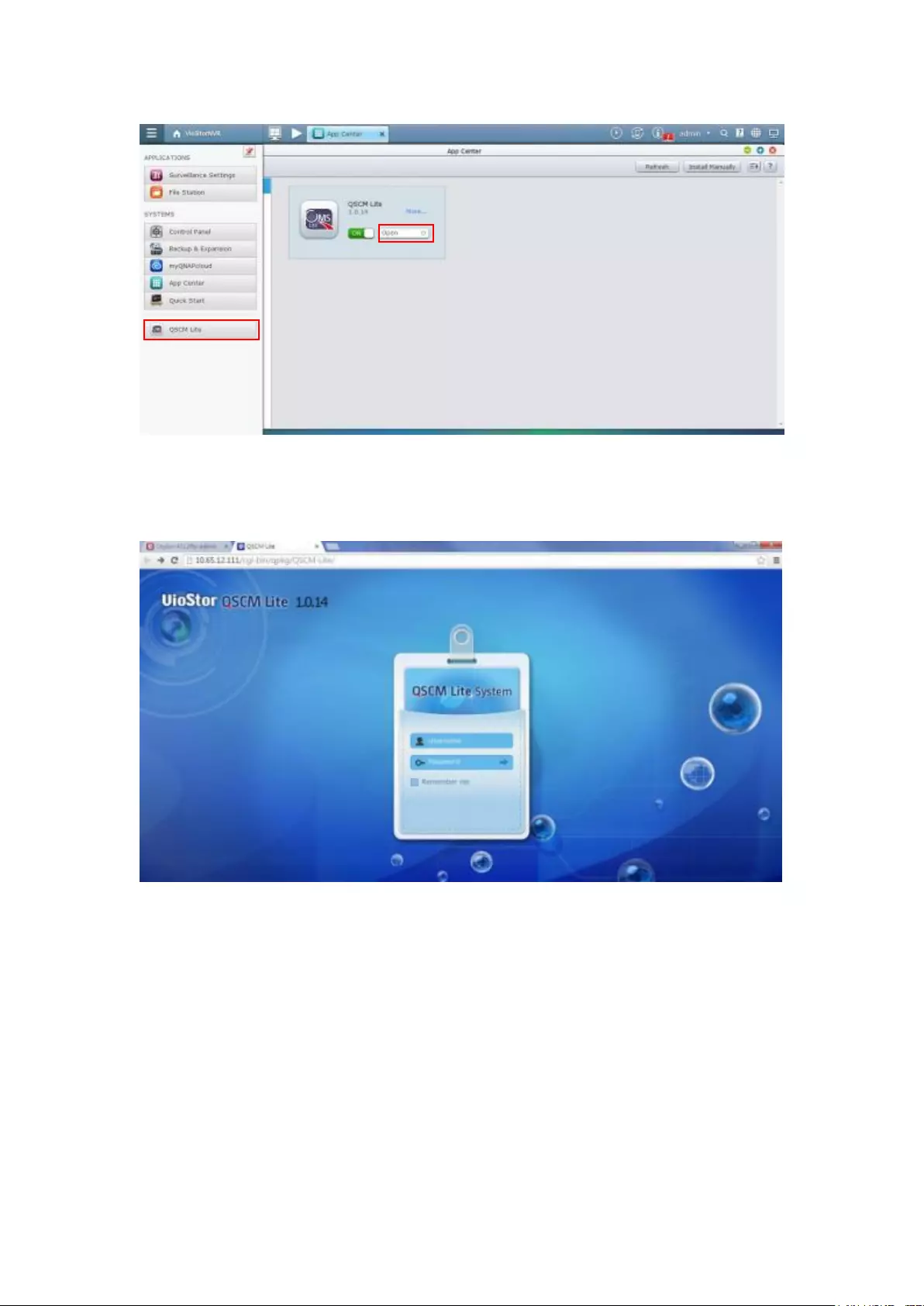
345
Step 4: The system will automatically redirect to the QSCM Lite login page, and you
can log in by using the default username/password (admin/admin).
Step 5: The first page you will see after logging into QSCM Lite is the live view page.
Before you have configured QSCM Lite, no camera feedback will be displayed.
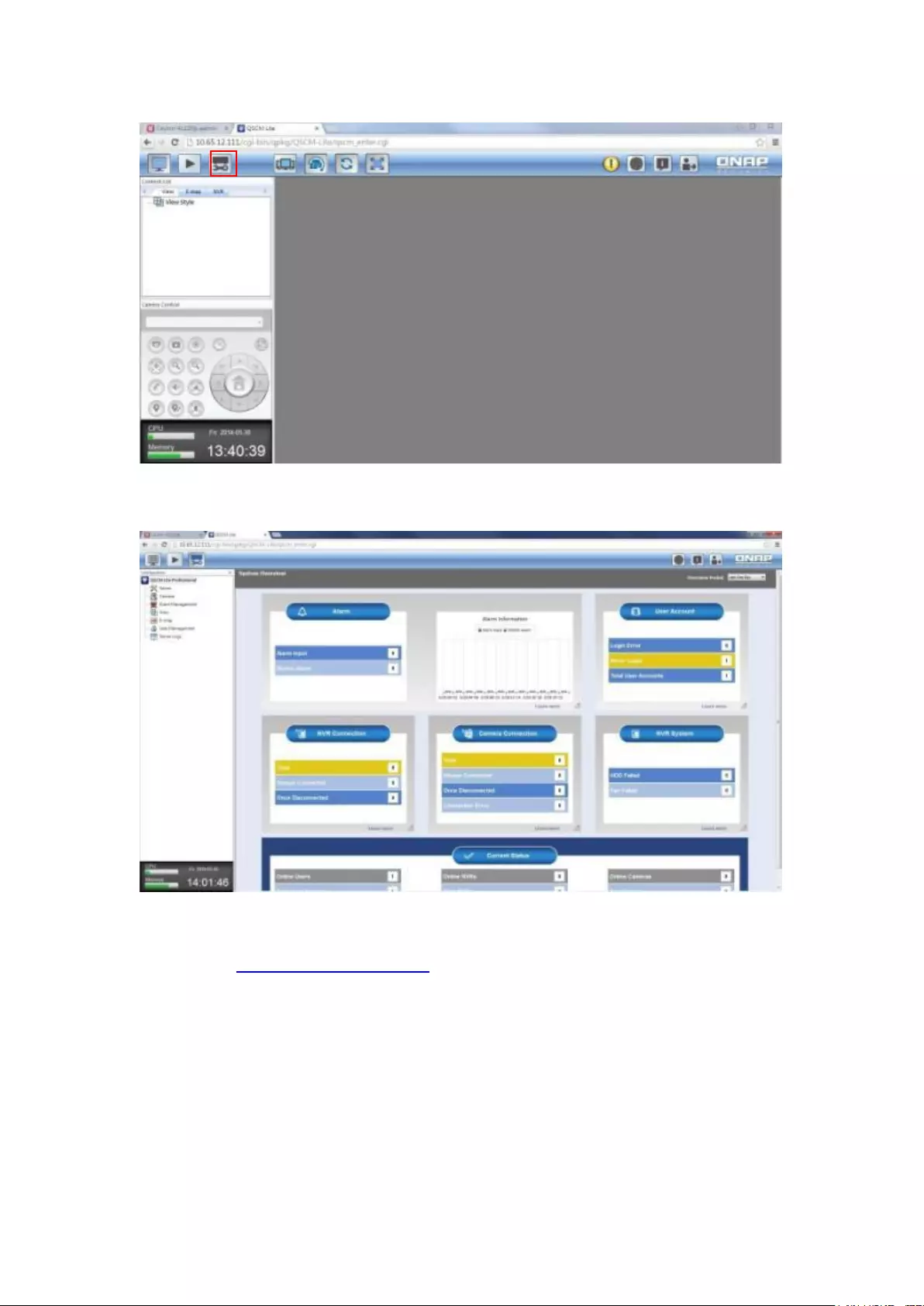
346
Step 6: To configure QSCM Lite, go to the configuration page.
Step 7: For how to configure QSCM Lite, please refer to Section 3.5 Configure CMS
Client of the VioStor CMS user manual.
Note:
VioStor CMS is a high-performance turnkey CMS solution. The CMS Server
supports up to a maximum of 128 multi-server monitoring and management.
Users can monitor up to a maximum of 1,024 IP cameras with up to 64 channels
per screen. Concurrent independent playback and display controls in four
screens are also supported. The CMS Server has the highest compatibility with
347
the QNAP VioStor NVR series and also supports a variety of brand-name IP
cameras.
For detailed VioStor CMS information, please refer to:
http://www.qnapsecurity.com/pro_detail_featurecms.asp?p_id=273
11.3.2 Usability Reminder and Suggestions
If you have the server performing as both a CMS and NVR server simultaneously,
it is strongly recommended to open just one live view page (either QVR 5.0 live
view or QSCM Lite live view) at the same time. Otherwise, the CPU and
throughput usage of the client PC will double.
For client PC requirements, please refer the Section 2.1 Personal Computer
Requirements of this user manual.
11.3.3 QSCM Lite Client Specification
The QSCM Lite client specification is mostly synchronized with the VioStor CMS
client specification.
The specification difference between the QSCM Lite client & VioStor CMS client
is subject to change without prior notification.
11.4 Comparison between VioStor CMS & QSCM Lite
Comparing Items
QSCM Lite
(App/QPKG)
VioStor CMS
Working Type
CMS solution on
QNAP VioStor NVR
(with firmware QVR
5.0 and above)
Standalone CMS server
Manageable NVR
NVR 4.1 (and above)
NVR4.1 (and above)
Number of NVRs
supported
16
128
Maximum number of
channel supported
256
1,024

348
Number of monitors
supported
4
8
Maximum number of
client registration
32
Unlimited
Key Feature
Multi-Server
Enhancement
Centralized Monitoring
and Management
The QSCM Lite client specification is mostly synchronized with the VioStor CMS
client specification
The specification difference between the QSCM Lite client & VioStor CMS client
is subject to change without prior notification.

349
12. Qstart
12.1 Introduction
Qstart brings two leading-edge innovative features: system initialization
and network switch control. It simplifies system initialization through
automatically assigning default settings with just a single click. By integrating
supported switches, Qstart provides comprehensive network topology and a
device list for users to fully manage network health and device status. Qstart
integrates the major functions of PoE switches so users can easily setup camera
IPs, manage PoE status and monitor traffic flow from the VioStor software (QVR).
The intuitive GUI also allows for precise failure detection and efficient
troubleshooting. Qstart provides users with a refreshing experience when
installing and remotely maintaining NVRs.
12.2 Before Using Qstart
1. All devices including IP cameras, Client PCs, a QNAP VioStor should be connected
to the same PoE switch. (VioStor now only supports the scenario of one PoE
switch, please avoid cascade PoE cases.)
2. Do not set your device to a static IP, including the client PC and the VioStor NVR,
DHCP settings only.
3. All IP cameras must be set to default for Qstart initialization.
12.3 System Initialization
To use Qstart, please ensure your inserted hard drives are unallocated.
Please ensure that you use a supported switch and a VioStor model (please
check the compatibility list for more information).
1. Find the VioStor’s IP address via QNAP finder.
2. Connect to the QVR web-based administration page and select Qstart.
350
3. VioStor will detect if there is a DHCP server on the same LAN.
If a DHCP server is detected, it will proceed to the Quick Setup page.
If not, users will be asked to enable the NVR’s DHCP server to start initialization.
Users can enable the DHCP server by selecting Yes.
4. TThe Quick Setup page includes basic information for both the NVR and
devices connected to the switch (including the time zone, name, IP, Disk
configuration, and more.) Confirm that this information is correct and proceed to
complete the initialization.
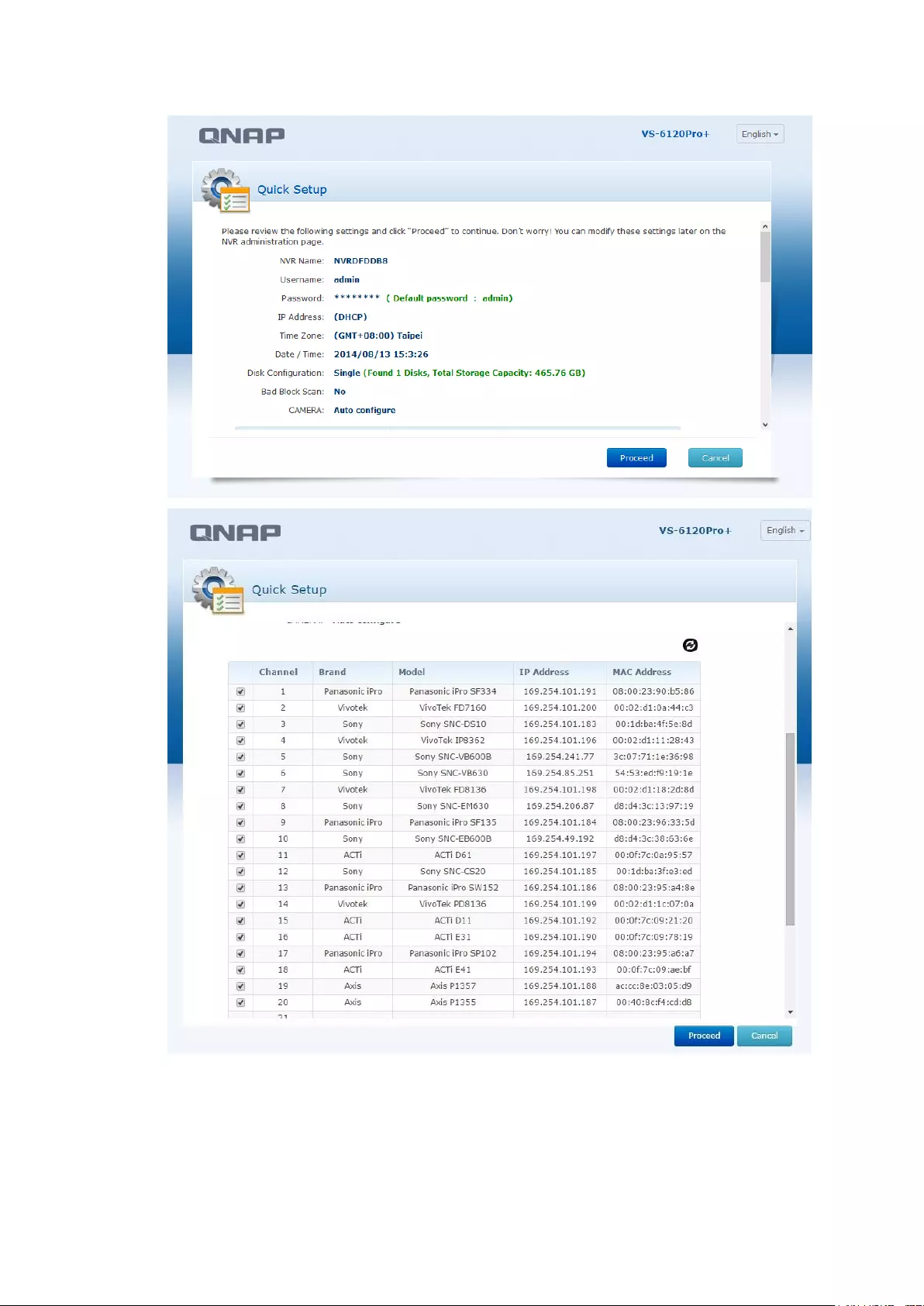
351
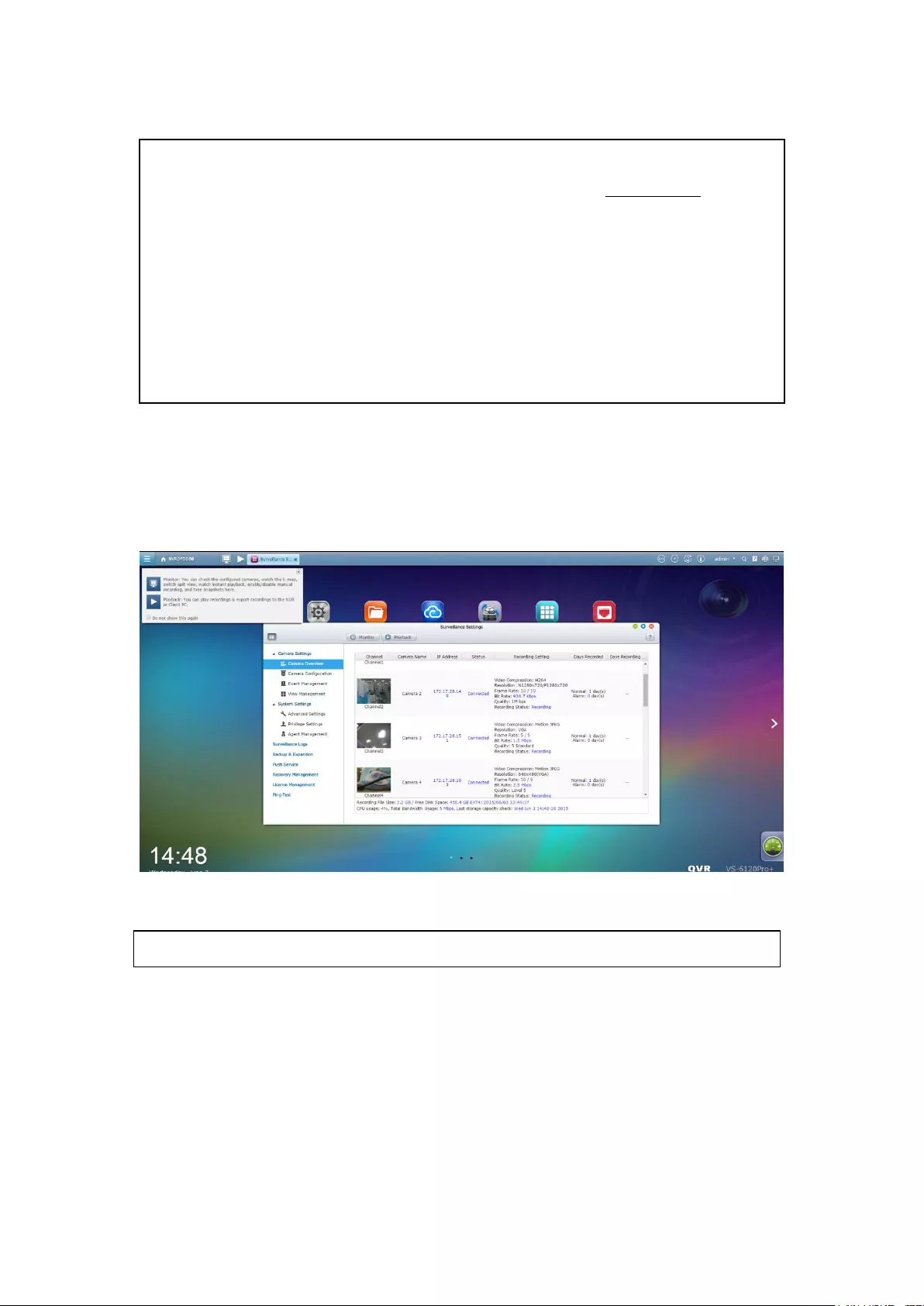
352
5. Enter the QVR desktop. The camera overview page and QVR introduction page
will appear simultaneously. (The camera overview in front, and the QVR
introduction behind it.)
Please note: The system will enable Qstart once users finish the Qstart initialization.
12.4 Qstart Mode
Main features:
Intuitive channel mapping:
The video shown on channel 1 represents the recording view of port 1 to
the switch.
Please note:
Users cannot modify network settings (DHCP/Static) in Qstart mode.
The channel number is based on the port number of the switch.
(For example, if a VS-2112 Pro+ connects to a 24-port switch, the table will
show channel 1 to channel 24 regardless of the NVR's supported
channels.)
Default settings:
1. Selects all supported cameras that are connected to the switch.
2. Auto configure
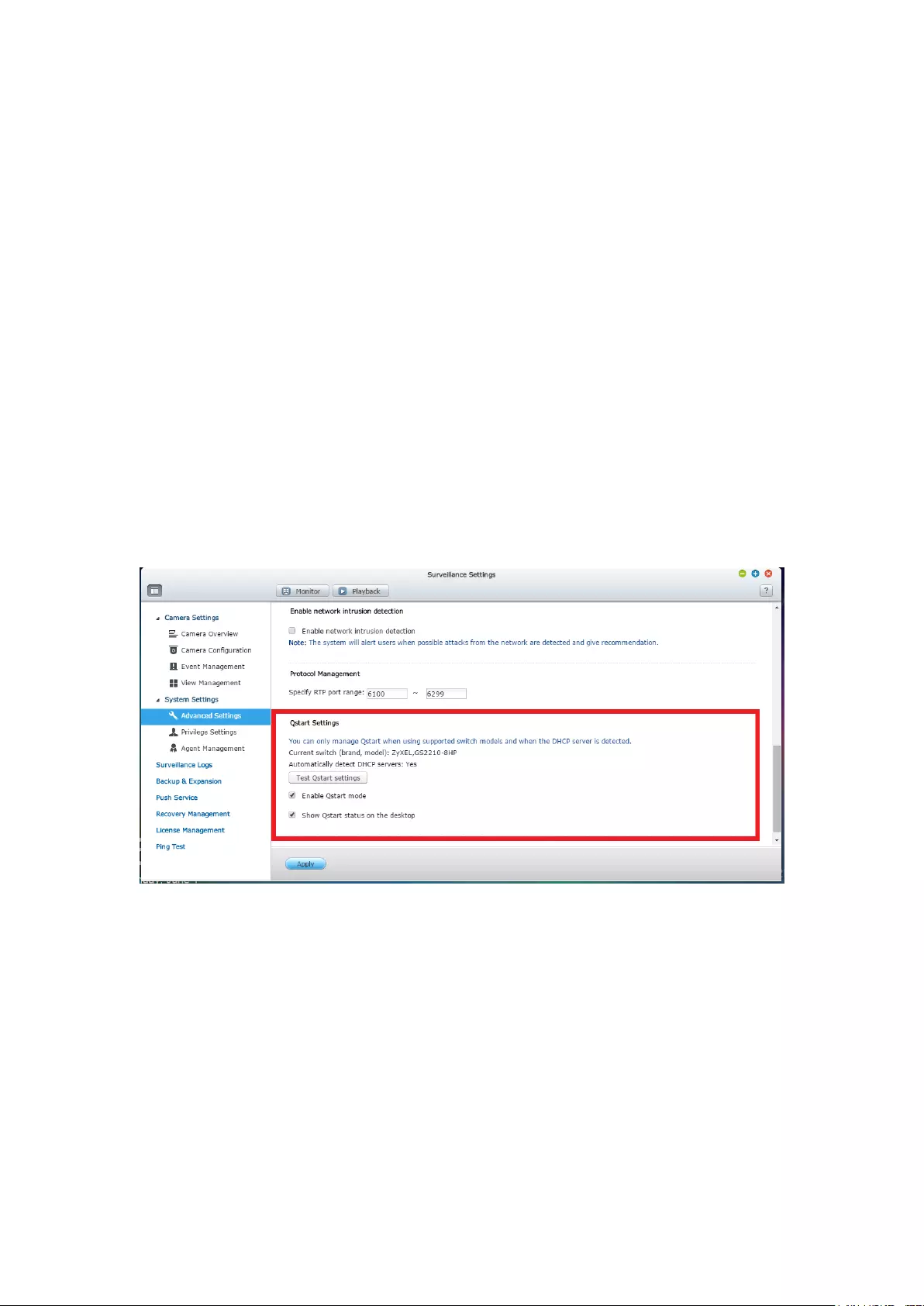
353
Auto port detection and configuration:
If devices are connected to other ports, the system will automatically
detect the change and move all settings (excluding advanced settings) to
the new ports. Users do not have to set it up all over again.
1. Add a supported camera to the port:
If it is a new camera, the NVR will automatically add it using
default settings.
If it is a camera that has been used before, the NVR will use its
previous settings.
2. Removing the camera from the port will clear the camera settings.
3. Any port changes will be saved in the system logs.
If you want to check Qstart mode, please go to [Surveillance Settings] ->[Advanced
Settings]->[ Qstart Settings]. Also be sure to use supported switches to enable Qstart
mode. The brand and model name will be shown and users can test the connection.
Qstart mode is enabled by default if users select Qstart during initialization.
Otherwise it will be disabled. Users can also choose Manual Setup for initialization if
they are not planning to use Qstart. In Qstart mode, you cannot add cameras to
specific channels. To get around this limitation, you must disable Qstart in Advanced
Settings.
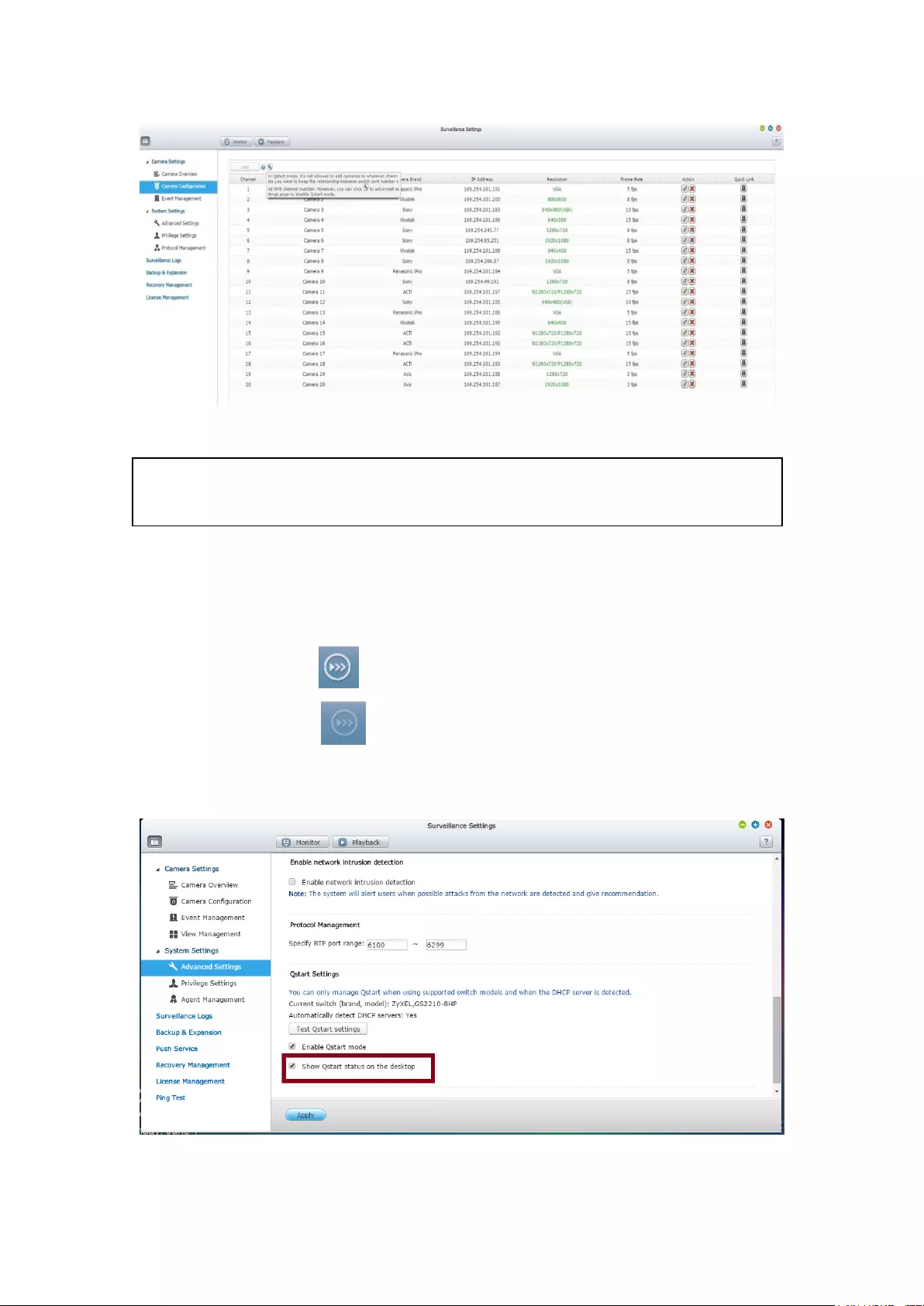
354
Qstart desktop icon
Provides users with Qstart on/off status on the VioStor desktop.
Qstart is enabled:
Qstart is disabled:
Users can decide whether to show the icon or not.
Qstart Notifications allow users to check Qstart on/off logs at the same time.
Please note:
If you enable Qstart mode again, all of your camera settings will be erased.
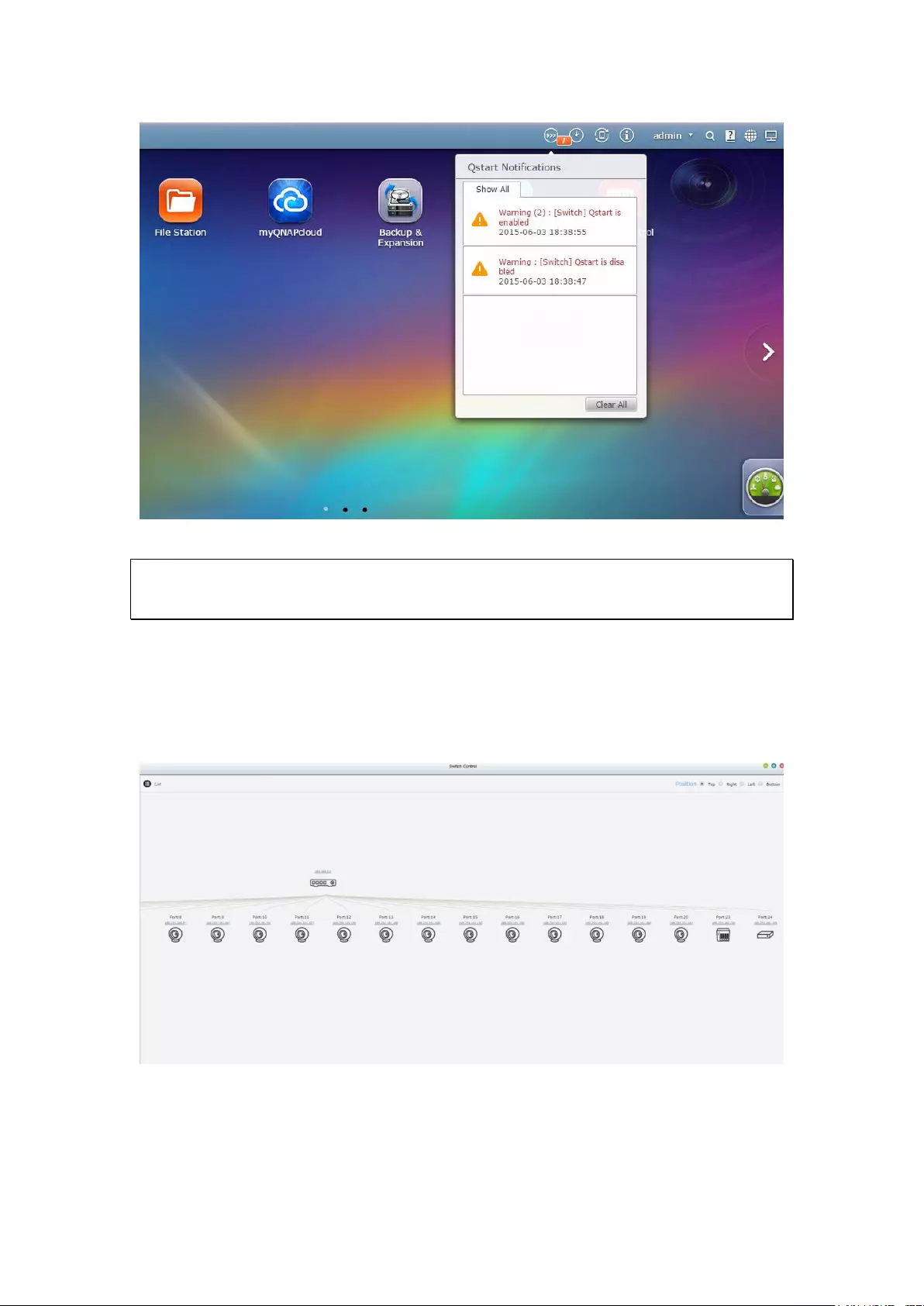
355
Please note: VioStor will not only enable Qstart mode but also show the Qstart
desktop icon once users finish initializing Qstart.
12.5 Network Switch Control (Embedded)
12.5.1 Topology:
1. Show the switch's complete connection relationship
2. The diagram will display supported switches, cameras, VioStor NVR, and
other devices (including PCs, laptops, unsupported switches, and other
unknown devices.)
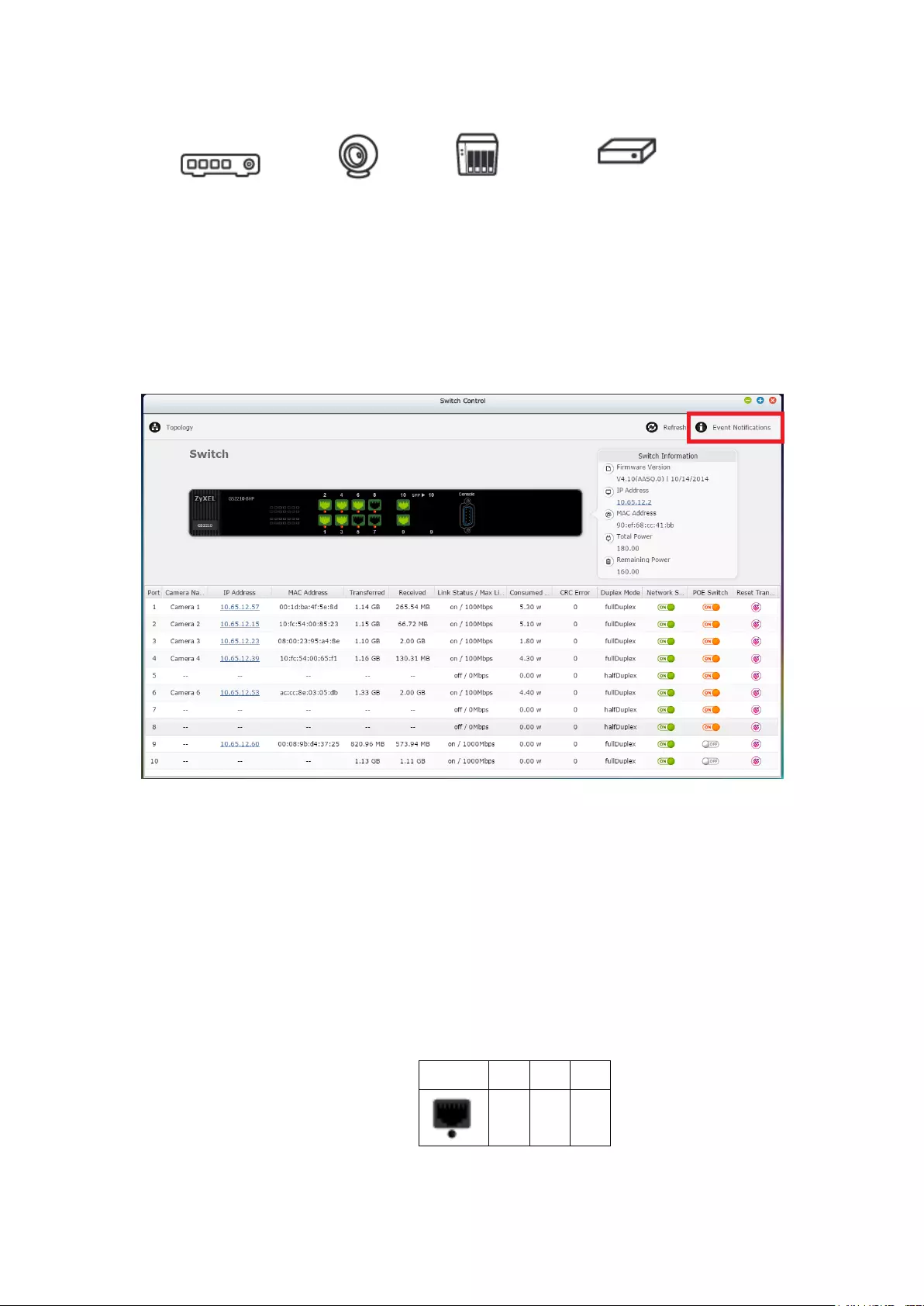
356
Switch Camera QNAP NVR Other Device
3. Users can choose different ways to display the topology
(top/right/left/bottom).
4. Clicking the device's IP address will open that IP address in your browser.
5. Clicking on a camera will open the camera's settings page.
12.5.2 Switch Control Chart:
This switch control chart includes information as follows:
1. Complete switch information table:
Firmware version, IP address, MAC, total power, and remaining power.
2. Complete port information:
Camera name, Device IP, MAC, TX/RX, power consumption, PoE ability,
Network ability.
Corresponding switch status types: 6 status types, combinations of Network,
PoE and link status. (N: Network, P: PoE, L: Link, Only N is on, then L can be
detected as on/off.)
figure
N
P
L
Off
Off
Off
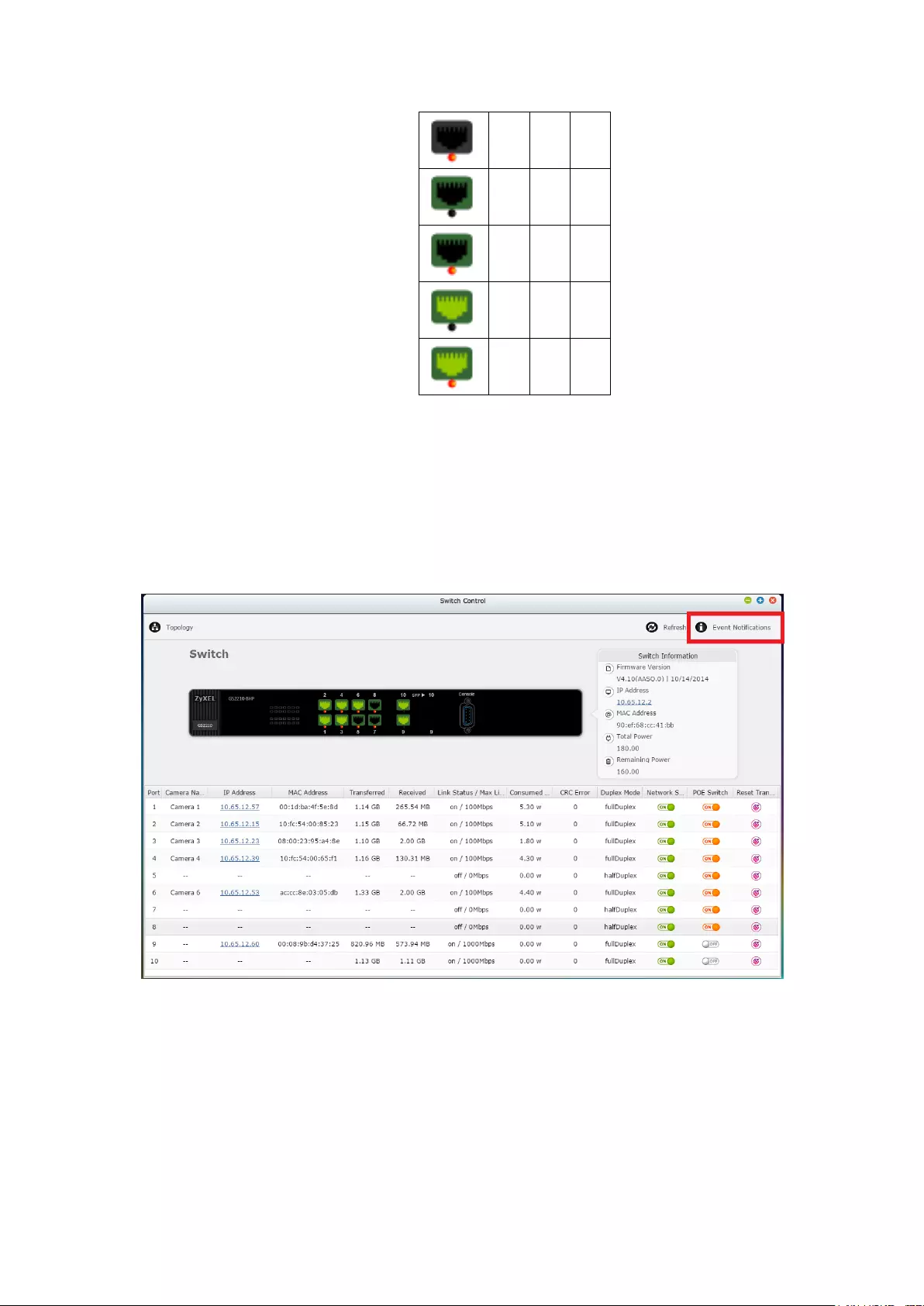
357
Off
On
Off
On
Off
Off
On
On
Off
On
Off
On
On
On
On
12.5.3 Event Notifications:
13. Enter the log list by selecting Event Notifications in Switch Control.
This table shows behaviors relevant to the switch only. Users can keep track of the
situation between the switch and the devices linked to it.

358
13.1.1 Compatibility List:
Brand
Model
NVR
QNAP
VS-6120 Pro+/ 6116 Pro+/ 6112 Pro+
VS-4116 Pro+/ 4112 Pro+/ 4108 Pro+
VS-2112 Pro+/ 2108 Pro+/ 2104 Pro+
Switch
ZyXEL
GS2210-24HP
GS2210-8HP
EtherWAN
EX76402
EX22402
eten
PSG-6010VM
PSG-6018VM
PSG-7026VM
IP Camera
AXIS、ACTi、SONY、Panasonic、VIVOTEK
Please note: The performance of Qstart will vary across different switch brands. If
you have any questions, please contact our technical support for more information.
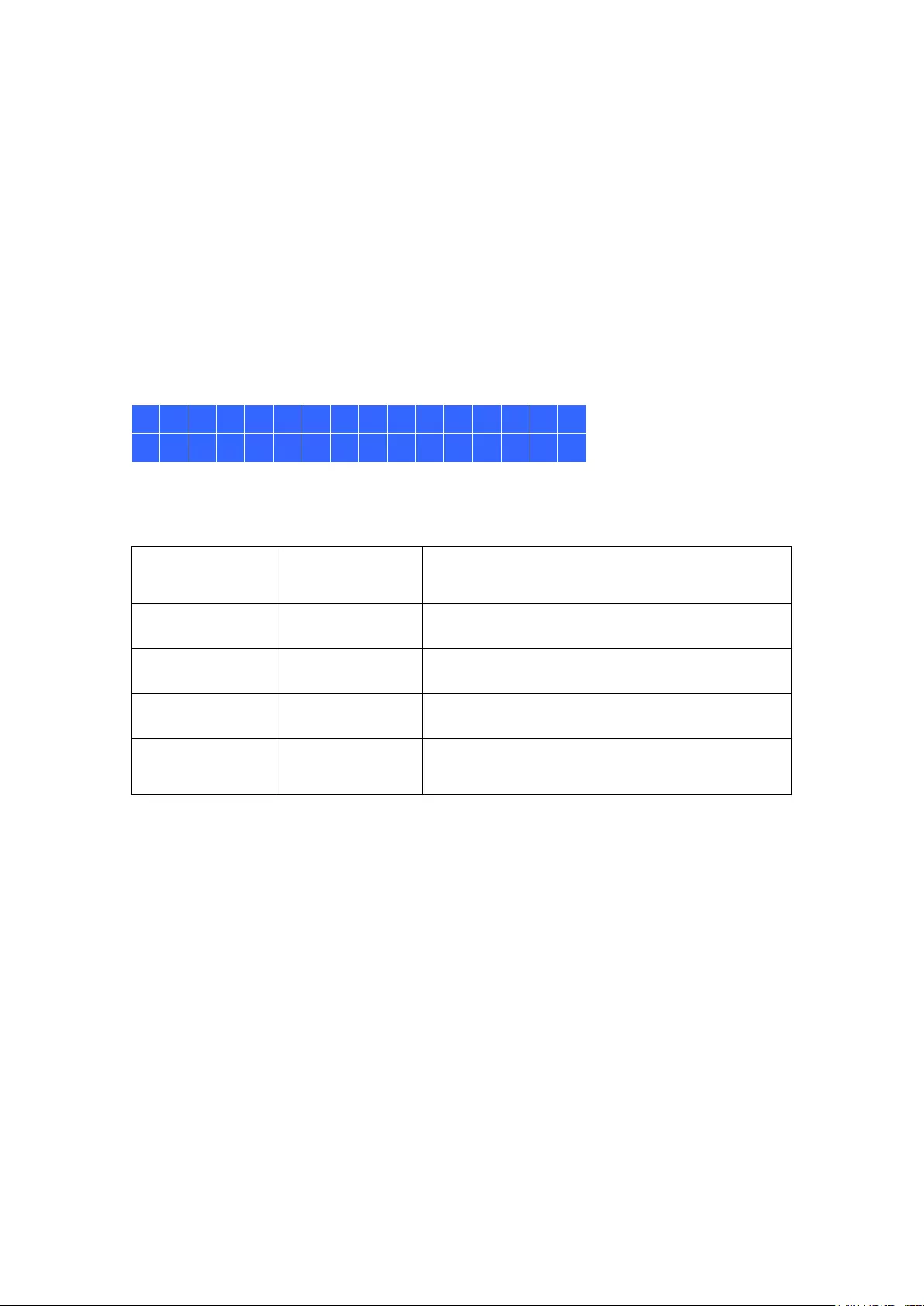
359
14. LCD Panel
* This section is applicable to the NVR models with an LCD panel only.
The NVR provides a handy LCD panel for users to perform the disk configuration and
view the system information.
When the NVR has started up, the server name and the IP address will be shown:
N
V
R
5
F
4
D
E
3
1
6
9
.
2
5
4
.
1
0
0
.
1
0
0
For the first time installation, the LCD panel shows the number of the hard disk drives
detected and the IP address. Configure the hard drives accordingly.
Number of hard
drives detected
Default disk
configuration
Available disk configuration options*
1
Single
Single
2
RAID 1
Single -> JBOD ->RAID 0 -> RAID 1
3
RAID 5
Single -> JBOD -> RAID 0 -> RAID 5
4 or above
RAID 5
Single ->JBOD -> RAID 0 -> RAID 5
-> RAID 6
*Press the ‘Select’ button to choose the option, and press the ‘Enter’ button to
confirm.
360
For example, when five hard drives have been installed, the LCD panel shows:
C
o
n
f
i
g
.
D
i
s
k
s
?
→
R
A
I
D
5
Press the ‘Select’ button to browse more options, e.g. RAID 6.
Press the ‘Enter’ button and the following message shows. Press the ‘Select’ button
to select ‘Yes’ to confirm.
C
h
o
o
s
e
R
A
I
D
5
?
→
Y
e
s
N
o
When the configuration has finished, the server name and the IP address will be
shown. If the NVR fails to create the disk volume, the following message will be
shown.
C
r
e
a
t
i
n
g
.
.
.
R
A
I
D
5
F
a
i
l
e
d

361
View the system information by the LCD panel
When the LCD panel shows the server name and the IP address, press the ‘Enter’
button to enter the Main Menu. The Main Menu consists of the following items:
1. TCP/IP
2. Physical disk
3. Volume
4. System
5. Shut down
6. Reboot
7. Password
8. Back
1. TCP/IP
In TCP/IP, the following options are available:
1.1 LAN IP Address
1.2 LAN Subnet Mask
1.3 LAN Gateway
1.4 LAN PRI. DNS
1.5 LAN SEC. DNS
1.6 Enter Network Settings
1.6.1 Network Settings – DHCP
1.6.2 Network Settings – Static IP*
1.6.3 Network Settings – BACK
1.7 Back to Main Menu
* In ‘Network Settings – Static IP’, configure the IP address, subnet mask, gateway,
and the DNS of LAN 1 and LAN 2.
362
2. Physical disk
In Physical disk, the following options are available:
2.1 Disk Info
2.2 Back to Main Menu
The disk info shows the temperature and the capacity of the hard disk drive.
D
i
s
k
:
1
T
e
m
p
:
5
0
°
C
S
i
z
e
:
2
3
2
G
B
3. Volume
This section shows the disk configuration of the NVR. The first line shows the
RAID configuration and storage capacity; the second line shows the member
drive number of the configuration.
R
A
I
D
5
7
5
0
G
B
D
r
i
v
e
1
2
3
4
If there is more than one volume, press the ‘Select’ button to view the
information. The following table shows the description of the LCD messages
for the RAID 5 configuration.
LCD Display
Drive configuration
RAID5+S
RAID5+spare
RAID5 (D)
RAID 5 degraded mode
RAID 5 (B)
RAID 5 rebuilding
RAID 5 (S)
RAID 5 re-synchronizing
RAID 5 (U)
RAID 5 is not mounted
RAID 5 (X)
RAID 5 non-activated
363
4. System
This section shows the system temperature and the rotation speed of the
system fan.
C
P
U
T
e
m
p
:
5
0
°
C
S
y
s
T
e
m
p
:
5
5
°
C
S
y
s
F
a
n
:
8
6
5
R
P
M
5. Shut down
Use this option to turn off the NVR. Press the ‘Select’ button to select ‘Yes’.
Then press the ‘Enter’ button to confirm.
6. Reboot
Use this option to restart the NVR. Press the ‘Select’ button to select ‘Yes’.
Then press the ‘Enter’ button to confirm.
7. Password
The default password of the LCD panel is blank. Enter this option to change
the password of the LCD panel. Select ‘Yes’ to continue.
C
h
a
n
g
e
P
a
s
s
w
o
r
d
Y
e
s
→
N
o
Enter a password of maximum 8 numeric characters (0-9). When the cursor
moves to ‘OK’, press the ‘Enter’ button. Verify the password to confirm the
changes.
N
e
w
P
a
s
s
w
o
r
d
:
O
K
8. Back
Select this option to return to the main menu.
364
System Messages
When the NVR encounters system error, an error message will be shown on the LCD
panel. Press the ‘Enter’ button to view the message. Press the ‘Enter’ button
again to view the next message.
S
y
s
t
e
m
E
r
r
o
r
!
P
l
s
.
C
h
e
c
k
L
o
g
s
System Message
Description
Sys. Fan Failed
The system fan fails
Sys. Overheat
The system overheats
HDD Overheat
The hard drive overheats
CPU Overheat
The CPU overheats
Network Lost
Both LAN 1 and LAN 2 are disconnected in failover
or load-balancing mode
LAN1 Lost
LAN 1 is disconnected
LAN2 Lost
LAN 2 is disconnected
HDD Failure
The hard drive fails
Vol1 Full
The volume is full
HDD Ejected
The hard drive is ejected
Vol1 Degraded
The volume is in degraded mode
Vol1 Unmounted
The volume is not mounted
Vol1 Nonactivate
The volume is not activated

365
15. Troubleshooting
1. The monitoring screen did not display.
Please check the following:
a. Check if the ActiveX add-on has been installed when logging in the
monitoring page of the NVR. Set the security level to ‘Medium’ or lower in
Internet Options of the IE browser.
b. The NVR is turned on and the network is correctly connected.
c. The IP address of the NVR does not conflict with other devices in the same
subnet.
d. Check the IP address settings of the NVR and the computer. Make sure
they are on the same subnet.
2. A channel on the monitoring page cannot be displayed.
Please check the following:
a. The IP address, the name, and the password entered on the camera
configuration page are correct. Use the ‘Test’ function to verify the
connection.
b. When the PC and the IP camera are on the same subnet, while the NVR is on
another subnet, the monitoring screen cannot be viewed from the PC.
Solve the problems by the following methods.
Method 1: Enter the IP address of the IP camera as the WAN IP on the NVR.
Method 2: Configure the router to allow internal access to the public IP
address and the mapped ports of the IP cameras.
3. The recording is not working properly.
a. Install the hard drive(s) correctly in the NVR.
b. Make sure each hard disk tray is correctly locked.
c. Check if the recording function is enabled on the Camera Configuration page
(the function is enabled by default). Make sure the IP address, the login
name, and the password of the IP camera are correct.
d. If the above items are verified to work properly while the status LED flashes
green, the hard drive may be damaged or cannot be detected. In this case,
turn off the NVR and install a new hard disk. If the problem persists, please
366
contact the technical support.
Note: When the configurations of the NVR are being updated, the recording will
be stopped temporarily and restart again shortly.
4. I cannot login the administration page of the NVR.
Please check if you have the administrator authority. Only administrators are
allowed to login the NVR.
5. The live video is not clear or smooth sometimes.
a. The image quality may be restricted and interfered by the network traffic.
b. When there are multiple connections to the IP camera or the NVR, the
image quality will be reduced. It is recommended to allow only three
simultaneous connections to the monitoring page at maximum. For higher
recording performance, do not open too many IE browsers to view the live
video.
c. The same IP camera may be shared by multiple NVR servers for recording at
the same time.
6. The alarm recording does not function.
a. Please login the NVR and go to ‘Camera Settings’ > ‘Alarm Settings’. Make
sure the alarm recording is enabled for the IP camera.
b. If the NVR is installed behind a router while the IP camera is not, the alarm
recording will not work.
c. When the alarm recording is enabled, make sure the number of days that
the alarm recordings will be retained have been specified in ‘Camera
Settings’ > ‘Advanced Settings’. Otherwise, the recordings may be
overwritten.
7. The estimated storage space for recording displayed on the ‘Recording
Settings’ page is different from the actual value.
This estimated value is a reference value only. The actual disk space may vary
according to the image contents, the network environment, and the
performance of the IP cameras.
8. The E-map cannot be displayed correctly.
Please check the file format. The NVR supports E-map in JPEG only.
9. I cannot find the NVR by the QNAP Finder.

367
a. Check if the NVR has been turned on.
b. Connect the local PC and the NVR to the same subnet.
c. Install the latest version of Finder from www.qnapsecurity.com.
d. Run Finder again to search for the NVR. Make sure all the firewall software
on the computer have been turned off; or add the Finder to the list of
allowed programs in the firewall.
e. If the NVR is not found, click ‘Refresh’ on the Finder to try again.
f. If the problem persists, contact the technical support.
10. The changes to the system configuration did not take effect.
After changing the settings on the administration page, click ‘Apply’ to apply the
changes.
11. The monitoring page cannot be fully displayed in Internet Explorer.
When using the zooming function of Internet Explorer, the page may not be
displayed properly. Please click F5 to refresh the page.
12. I cannot use the SMB, FTP, and Web File Manager services of the NVR.
a. Login the NVR as an administrator. Go to ‘Network Settings’ > ‘File
Services’ and check if these three functions are enabled.
b. If the NVR is installed behind a router, the SMB and FTP services can only be
accessed from the same subnet. Please refer to Appendix B for details.
13. The NVR takes too long to restart.
When the NVR takes more than 5 minutes to restart, turn off the power and
turn on the server again. If the problem persists, please contact the technical
support.
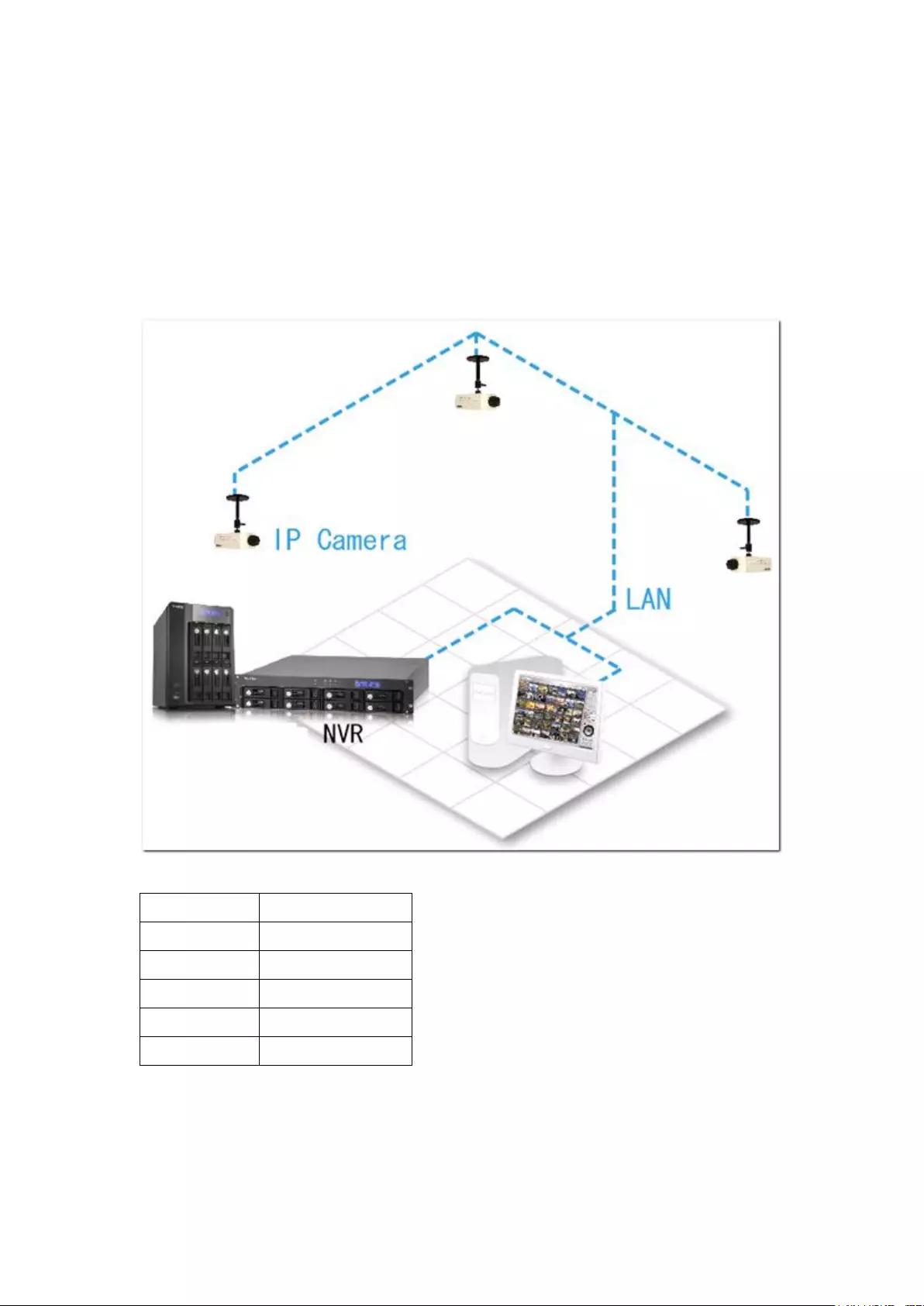
368
Appendix A Configuration Examples
Environment 1: The NVR, the IP camera, and the monitoring PC are all on the same
network
IP address
NVR
192.168.1.1
PC
192.168.1.100
Camera 1
192.168.1.101
Camera 2
192.168.1.102
Camera 3
192.168.1.103
In the example, add the IP cameras to the NVR by entering the IP addresses of the IP
cameras.
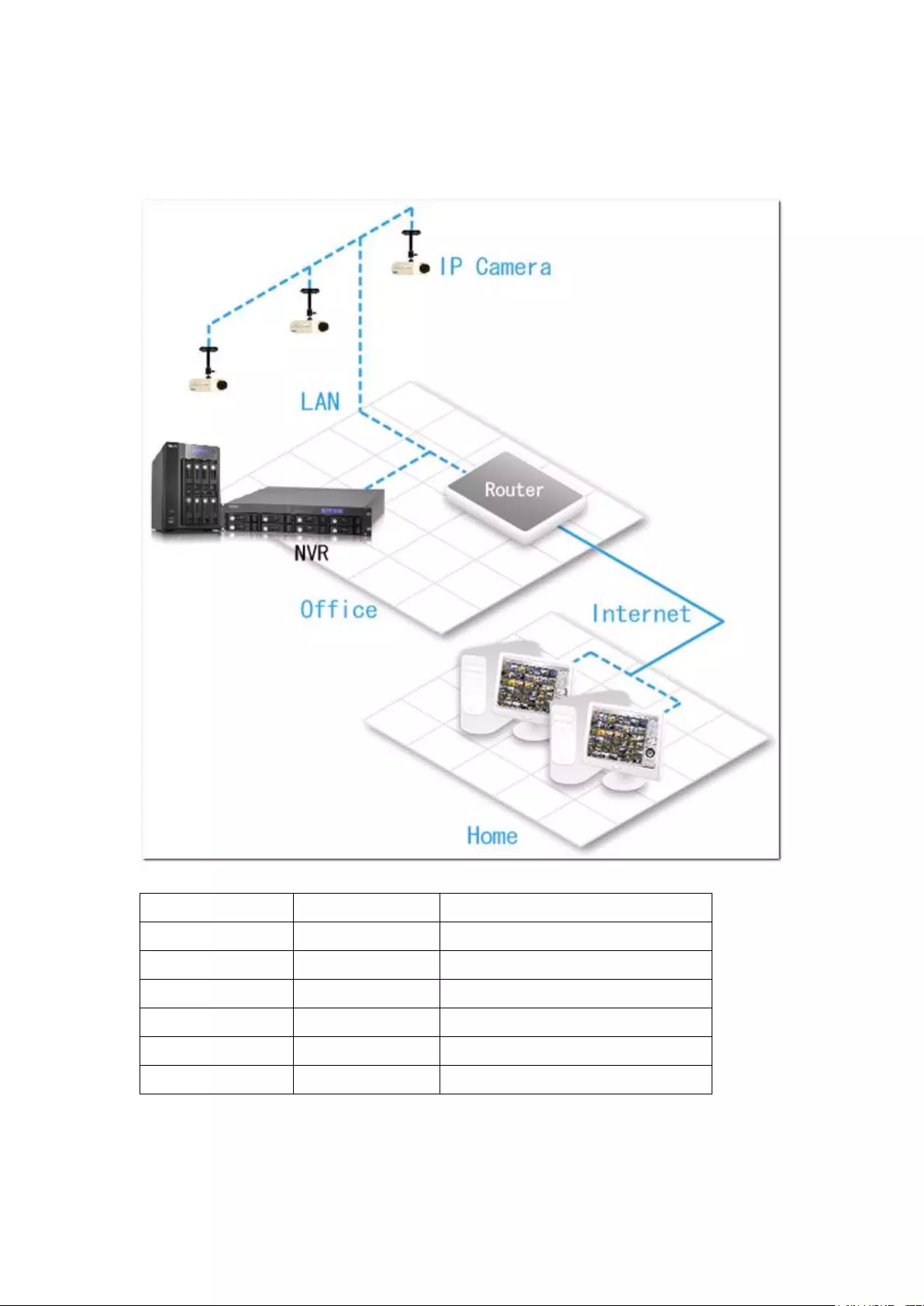
369
Environment 2: The NVR and the IP camera are installed behind the router, while the
monitoring PC is located remotely
IP address
Mapped port on the router
NVR
192.168.1.1
8000
Camera 1
192.168.1.101
8001
Camera 2
192.168.1.102
8002
Camera 3
192.168.1.103
8003
Router public IP
219.87.144.205
PC
10.8.10.100
370
To allow a remote PC to connect to the NVR and the IP cameras, do the following:
Step 1. Set up the port mapping (virtual server) on the router.
From
Forward to
219.87.144.205:8000
192.168.1.1:80
219.87.144.205:8001
192.168.1.101:80
219.87.144.205:8002
192.168.1.102:80
219.87.144.205:8003
192.168.1.103:80
Step 2. Add the IP camera to the NVR by entering the IP address of the IP camera in
the ‘IP Address’ settings. Enter the public IP address of the router and the mapped
ports of the IP camera in the ‘WAN IP Address’ settings.
Note: When configuring the IP camera, the WAN IP and LAN IP must be entered.
To open FTP (port 21) and SMB (port 445) of the NVR on WAN, configure the
following port mapping settings:
From
Forward to
219.87.144.205:21
192.168.1.1:21
219.87.144.205:139
192.168.1.1:139
219.87.144.205:445
192.168.1.1:445
After finishing the above two steps, connect to the NVR on WAN by entering the IP
address http://219.87.144.205:8000 in the IE browser. Then login the NVR with the
correct user name and password.
If the port specified to the NVR is 80, enter http://219.87.144.205 to connect to the
NVR.
Note: If the router does not use a fixed IP, configure the DDNS settings on the router.
Other configurations are the same as above.
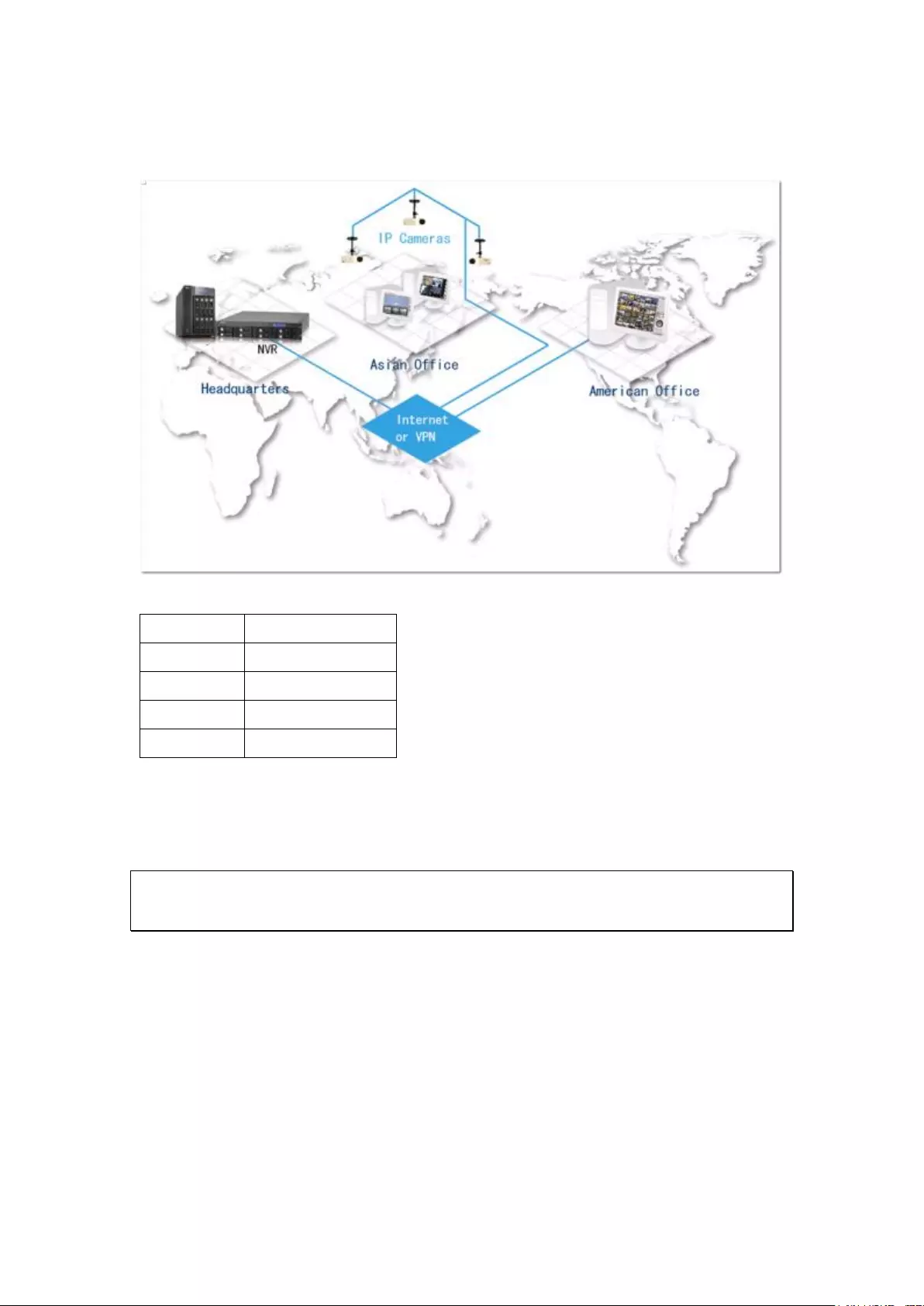
371
Environment 3: The NVR and the IP camera are all located remotely
IP address
NVR
219.87.144.205
Camera 1
61.62.100.101
Camera 2
61.62.100.102
Camera 3
61.62.100.103
In this example, add the IP camera to the NVR by adding its IP address to the ‘IP
Address’ settings.
Note: If a particular port is assigned to connect to the IP camera, specify the port in
the system configuration.
372
Environment 4: The NVR and the IP camera are installed behind the router
IP address
NVR 1
192.168.1.101
NVR 2
192.168.1.102
NVR 3
192.168.1.103
Router public IP
219.87.145.205
In the example, to allow a remote PC to connect to each NVR by FTP, do the
following:
Step 1. Set up the port mapping (virtual server) on the router
From
Forward to
NVR 1
219.87.145.205:2001
192.168.1.101:21
NVR 2
219.87.145.205:2002
192.168.1.102:21
NVR 3
219.87.145.205:2003
192.168.1.103:21
Connect to NVR 1 by ftp://219.87.145.205:2001
Connect to NVR 2 by ftp://219.87.145.205:2002
Connect to NVR 3 by ftp://219.87.145.205:2003
Step 2. Enable FTP port mapping on the NVR
To connect to each NVR via FTP by clicking ‘FTP’ on the playback page of each NVR,
enable FTP port mapping in ‘Network Settings’ > ‘File Services’ on the system
administration page and set the mapped port number.
Mapped port
NVR 1
2001
NVR 2
2002
NVR 3
2003
After finishing the above two steps, connect to the NVR via FTP by entering the IP
address in the IE browser or clicking ‘FTP’ on the playback page. Then login the NVR
by the correct user name and password.
373
Technical Support
QNAP provides dedicated online support and customer service via instant messenger.
Online Support: http://www.qnapsecurity.com/onlinesupport.asp
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/nvr.qnap
Forum: http://forum.qnapsecurity.com
Technical Support in the USA and Canada:
Email: q_supportus@qnap.com
TEL: +1-909-595-2782
Address: 168 University Parkway, Pomona CA 91768
Service Hours: 08:00-17:00 (GMT- 08:00 Pacific Time, Monday to Friday)

374
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 3, 29 June 2007
Copyright © 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <http://fsf.org/>
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license
document, but changing it is not allowed.
Preamble
The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for software and other
kinds of works.
The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed to take away
your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast, the GNU General Public
License is intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change all versions of a
program--to make sure it remains free software for all its users. We, the Free
Software Foundation, use the GNU General Public License for most of our software; it
applies also to any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
your programs, too.
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not price. Our
General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you have the freedom to
distribute copies of free software (and charge for them if you wish), that you receive
source code or can get it if you want it, that you can change the software or use
pieces of it in new free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you these rights or
asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have certain responsibilities if
you distribute copies of the software, or if you modify it: responsibilities to respect
the freedom of others.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether gratis or for a fee,
you must pass on to the recipients the same freedoms that you received. You must
make sure that they, too, receive or can get the source code. And you must show

375
them these terms so they know their rights.
Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps: (1) assert
copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License giving you legal permission
to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains that there is no
warranty for this free software. For both users' and authors' sake, the GPL requires
that modified versions be marked as changed, so that their problems will not be
attributed erroneously to authors of previous versions.
Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run modified versions of
the software inside them, although the manufacturer can do so. This is
fundamentally incompatible with the aim of protecting users' freedom to change the
software. The systematic pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for
individuals to use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those products. If
such problems arise substantially in other domains, we stand ready to extend this
provision to those domains in future versions of the GPL, as needed to protect the
freedom of users.
Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents. States should
not allow patents to restrict development and use of software on general-purpose
computers, but in those that do, we wish to avoid the special danger that patents
applied to a free program could make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the
GPL assures that patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and modification follow.
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
0. Definitions.
‘This License’ refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
‘Copyright’ also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of works, such as
semiconductor masks.
‘The Program’ refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this License. Each
licensee is addressed as ‘you’. ‘Licensees’ and ‘recipients’ may be individuals or

376
organizations.
To ‘modify’ a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work in a fashion
requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an exact copy. The
resulting work is called a ‘modified version’ of the earlier work or a work ‘based on’
the earlier work.
A ‘covered work’ means either the unmodified Program or a work based on the
Program.
To ‘propagate’ a work means to do anything with it that, without permission, would
make you directly or secondarily liable for infringement under applicable copyright
law, except executing it on a computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation
includes copying, distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
public, and in some countries other activities as well.
To ‘convey’ a work means any kind of propagation that enables other parties to make
or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through a computer network, with
no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
An interactive user interface displays ‘Appropriate Legal Notices’ to the extent that it
includes a convenient and prominently visible feature that (1) displays an appropriate
copyright notice, and (2) tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except
to the extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the work
under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If the interface presents
a list of user commands or options, such as a menu, a prominent item in the list
meets this criterion.
1. Source Code.
The ‘source code’ for a work means the preferred form of the work for making
modifications to it. ‘Object code’ means any non-source form of a work.
A ‘Standard Interface’ means an interface that either is an official standard defined
by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of interfaces specified for a particular
programming language, one that is widely used among developers working in that
language.
The ‘System Libraries’ of an executable work include anything, other than the work

377
as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of packaging a Major Component,
but which is not part of that Major Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of
the work with that Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for
which an implementation is available to the public in source code form. A ‘Major
Component’, in this context, means a major essential component (kernel, window
system, and so on) of the specific operating system (if any) on which the executable
work runs, or a compiler used to produce the work, or an object code interpreter
used to run it.
The ‘Corresponding Source’ for a work in object code form means all the source code
needed to generate, install, and (for an executable work) run the object code and to
modify the work, including scripts to control those activities. However, it does not
include the work's System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available
free programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but which
are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source includes interface
definition files associated with source files for the work, and the source code for
shared libraries and dynamically linked subprograms that the work is specifically
designed to require, such as by intimate data communication or control flow
between those subprograms and other parts of the work.
The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users can regenerate
automatically from other parts of the Corresponding Source.
The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that same work.
2. Basic Permissions.
All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of copyright on the
Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated conditions are met. This License
explicitly affirms your unlimited permission to run the unmodified Program. The
output from running a covered work is covered by this License only if the output,
given its content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not convey, without
conditions so long as your license otherwise remains in force. You may convey
covered works to others for the sole purpose of having them make modifications
exclusively for you, or provide you with facilities for running those works, provided
that you comply with the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you

378
do not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works for you
must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction and control, on terms
that prohibit them from making any copies of your copyrighted material outside their
relationship with you.
Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under the conditions
stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10 makes it unnecessary.
3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological measure under
any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article 11 of the WIPO copyright treaty
adopted on 20 December 1996, or similar laws prohibiting or restricting
circumvention of such measures.
When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid circumvention
of technological measures to the extent such circumvention is effected by exercising
rights under this License with respect to the covered work, and you disclaim any
intention to limit operation or modification of the work as a means of enforcing,
against the work's users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
technological measures.
4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you receive it, in
any medium, provided that you conspicuously and appropriately publish on each
copy an appropriate copyright notice; keep intact all notices stating that this License
and any non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code; keep
intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all recipients a copy of this
License along with the Program.
You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey, and you may
offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to produce it
from the Program, in the form of source code under the terms of section 4, provided
that you also meet all of these conditions:
a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified it, and giving a

379
relevant date.
b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is released under this
License and any conditions added under section 7. This requirement modifies the
requirement in section 4 to ‘keep intact all notices’.
c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this License to anyone who
comes into possession of a copy. This License will therefore apply, along with any
applicable section 7 additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no permission to license
the work in any other way, but it does not invalidate such permission if you have
separately received it.
d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display Appropriate Legal
Notices; however, if the Program has interactive interfaces that do not display
Appropriate Legal Notices, your work need not make them do so.
A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent works, which
are not by their nature extensions of the covered work, and which are not combined
with it such as to form a larger program, in or on a volume of a storage or
distribution medium, is called an ‘aggregate’ if the compilation and its resulting
copyright are not used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work in an
aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other parts of the aggregate.
6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms of sections 4
and 5, provided that you also convey the machine-readable Corresponding Source
under the terms of this License, in one of these ways:
a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product (including a physical
distribution medium), accompanied by the Corresponding Source fixed on a durable
physical medium customarily used for software interchange.
b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product (including a physical
distribution medium), accompanied by a written offer, valid for at least three years
and valid for as long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a copy of the
Corresponding Source for all the software in the product that is covered by this
License, on a durable physical medium customarily used for software interchange, for
a price no more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this conveying of
source, or (2) access to copy the Corresponding Source from a network server at no
charge.

380
c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the written offer to
provide the Corresponding Source. This alternative is allowed only occasionally and
noncommercially, and only if you received the object code with such an offer, in
accord with subsection 6b.
d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated place (gratis or for a
charge), and offer equivalent access to the Corresponding Source in the same way
through the same place at no further charge. You need not require recipients to
copy the Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to copy the
object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source may be on a different
server (operated by you or a third party) that supports equivalent copying facilities,
provided you maintain clear directions next to the object code saying where to find
the Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the Corresponding
Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is available for as long as needed to
satisfy these requirements.
e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided you inform
other peers where the object code and Corresponding Source of the work are being
offered to the general public at no charge under subsection 6d.
A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded from the
Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be included in conveying the
object code work.
A ‘User Product’ is either (1) a ‘consumer product’, which means any tangible
personal property which is normally used for personal, family, or household purposes,
or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation into a dwelling. In determining
whether a product is a consumer product, doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of
coverage. For a particular product received by a particular user, ‘normally used’
refers to a typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status of
the particular user or of the way in which the particular user actually uses, or expects
or is expected to use, the product. A product is a consumer product regardless of
whether the product has substantial commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses,
unless such uses represent the only significant mode of use of the product.
‘Installation Information’ for a User Product means any methods, procedures,
authorization keys, or other information required to install and execute modified
versions of a covered work in that User Product from a modified version of its
Corresponding Source. The information must suffice to ensure that the continued
functioning of the modified object code is in no case prevented or interfered with
solely because modification has been made.

381
If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or specifically for
use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as part of a transaction in which the
right of possession and use of the User Product is transferred to the recipient in
perpetuity or for a fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied by the
Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply if neither you nor any
third party retains the ability to install modified object code on the User Product (for
example, the work has been installed in ROM).
The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a requirement
to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates for a work that has been
modified or installed by the recipient, or for the User Product in which it has been
modified or installed. Access to a network may be denied when the modification
itself materially and adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the
rules and protocols for communication across the network.
Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided, in accord
with this section must be in a format that is publicly documented (and with an
implementation available to the public in source code form), and must require no
special password or key for unpacking, reading or copying.
7. Additional Terms.
‘Additional permissions’ are terms that supplement the terms of this License by
making exceptions from one or more of its conditions. Additional permissions that
are applicable to the entire Program shall be treated as though they were included in
this License, to the extent that they are valid under applicable law. If additional
permissions apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by this License
without regard to the additional permissions.
When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option remove any
additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of it. (Additional
permissions may be written to require their own removal in certain cases when you
modify the work.) You may place additional permissions on material, added by you to
a covered work, for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you add to a

382
covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of that material)
supplement the terms of this License with terms:
a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the terms of sections 15
and 16 of this License; or
b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or author attributions
in that material or in the Appropriate Legal Notices displayed by works containing it;
or
c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or requiring that
modified versions of such material be marked in reasonable ways as different from
the original version; or
d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or authors of the
material; or
e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some trade names,
trademarks, or service marks; or
f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that material by anyone who
conveys the material (or modified versions of it) with contractual assumptions of
liability to the recipient, for any liability that these contractual assumptions directly
impose on those licensors and authors.
All other non-permissive additional terms are considered ‘further restrictions’ within
the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you received it, or any part of it,
contains a notice stating that it is governed by this License along with a term that is a
further restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains a
further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this License, you may
add to a covered work material governed by the terms of that license document,
provided that the further restriction does not survive such relicensing or conveying.
If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you must place, in the
relevant source files, a statement of the additional terms that apply to those files, or
a notice indicating where to find the applicable terms.
Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the form of a
separately written license, or stated as exceptions; the above requirements apply
either way.
8. Termination.
You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly provided under
this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or modify it is void, and will

383
automatically terminate your rights under this License (including any patent licenses
granted under the third paragraph of section 11).
However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your license from a particular
copyright holder is reinstated (a) provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder
explicitly and finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means prior to 60 days
after the cessation.
Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated permanently if
the copyright holder notifies you of the violation by some reasonable means, this is
the first time you have received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from
that copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after your receipt of
the notice.
Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the licenses of
parties who have received copies or rights from you under this License. If your
rights have been terminated and not permanently reinstated, you do not qualify to
receive new licenses for the same material under section 10.
9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or run a copy of the
Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work occurring solely as a
consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission to receive a copy likewise does not
require acceptance. However, nothing other than this License grants you
permission to propagate or modify any covered work. These actions infringe
copyright if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating
a covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically receives a license
from the original licensors, to run, modify and propagate that work, subject to this
License. You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties with this
License.
An ‘entity transaction’ is a transaction transferring control of an organization, or
substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an organization, or merging
organizations. If propagation of a covered work results from an entity transaction,

384
each party to that transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives
whatever licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could give
under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the Corresponding Source
of the work from the predecessor in interest, if the predecessor has it or can get it
with reasonable efforts.
You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the rights granted or
affirmed under this License. For example, you may not impose a license fee, royalty,
or other charge for exercise of rights granted under this License, and you may not
initiate litigation (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for sale, or importing
the Program or any portion of it.
11. Patents.
A ‘contributor’ is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this License of the
Program or a work on which the Program is based. The work thus licensed is called
the contributor's ‘contributor version’.
A contributor's ‘essential patent claims’ are all patent claims owned or controlled by
the contributor, whether already acquired or hereafter acquired, that would be
infringed by some manner, permitted by this License, of making, using, or selling its
contributor version, but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For purposes of
this definition, ‘control’ includes the right to grant patent sublicenses in a manner
consistent with the requirements of this License.
Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free patent license
under the contributor's essential patent claims, to make, use, sell, offer for sale,
import and otherwise run, modify and propagate the contents of its contributor
version.
In the following three paragraphs, a ‘patent license’ is any express agreement or
commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent (such as an express
permission to practice a patent or covenant not to sue for patent infringement). To
‘grant’ such a patent license to a party means to make such an agreement or
commitment not to enforce a patent against the party.
If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license, and the

385
Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone to copy, free of charge
and under the terms of this License, through a publicly available network server or
other readily accessible means, then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding
Source to be so available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner consistent with the
requirements of this License, to extend the patent license to downstream recipients.
‘Knowingly relying’ means you have actual knowledge that, but for the patent license,
your conveying the covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered
work in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that country
that you have reason to believe are valid.
If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or arrangement, you convey,
or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a covered work, and grant a patent license
to some of the parties receiving the covered work authorizing them to use,
propagate, modify or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent
license you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered work and
works based on it.
A patent license is ‘discriminatory’ if it does not include within the scope of its
coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is conditioned on the non-exercise of one or
more of the rights that are specifically granted under this License. You may not
convey a covered work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment to the third
party based on the extent of your activity of conveying the work, and under which
the third party grants, to any of the parties who would receive the covered work
from you, a discriminatory patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered
work conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily for and in
connection with specific products or compilations that contain the covered work,
unless you entered into that arrangement, or that patent license was granted, prior
to 28 March 2007.
Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting any implied license
or other defenses to infringement that may otherwise be available to you under
applicable patent law.
12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or otherwise)
that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not excuse you from the

386
conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a covered work so as to satisfy
simultaneously your obligations under this License and any other pertinent
obligations, then as a consequence you may not convey it at all. For example, if you
agree to terms that obligate you to collect a royalty for further conveying from those
to whom you convey the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms
and this License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have permission to link or
combine any covered work with a work licensed under version 3 of the GNU Affero
General Public License into a single combined work, and to convey the resulting work.
The terms of this License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License, section 13,
concerning interaction through a network will apply to the combination as such.
14. Revised Versions of this License.
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of the GNU
General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit
to the present version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program specifies that
a certain numbered version of the GNU General Public License ‘or any later version’
applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and conditions either of that
numbered version or of any later version published by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Program does not specify a version number of the GNU General Public License,
you may choose any version ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future versions of the GNU
General Public License can be used, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of a
version permanently authorizes you to choose that version for the Program.
Later license versions may give you additional or different permissions. However,
no additional obligations are imposed on any author or copyright holder as a result of
your choosing to follow a later version.
15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT

387
HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM ‘AS IS’ WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE
OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU
ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
16. Limitation of Liability.
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR
CONVEYS THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES,
INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES
SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE
WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided above cannot be
given local legal effect according to their terms, reviewing courts shall apply local law
that most closely approximates an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection
with the Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a copy of
the Program in return for a fee.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS