Salicru 699CC000001 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 699CC000001 by Salicru which is a product in the Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPSs) category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals
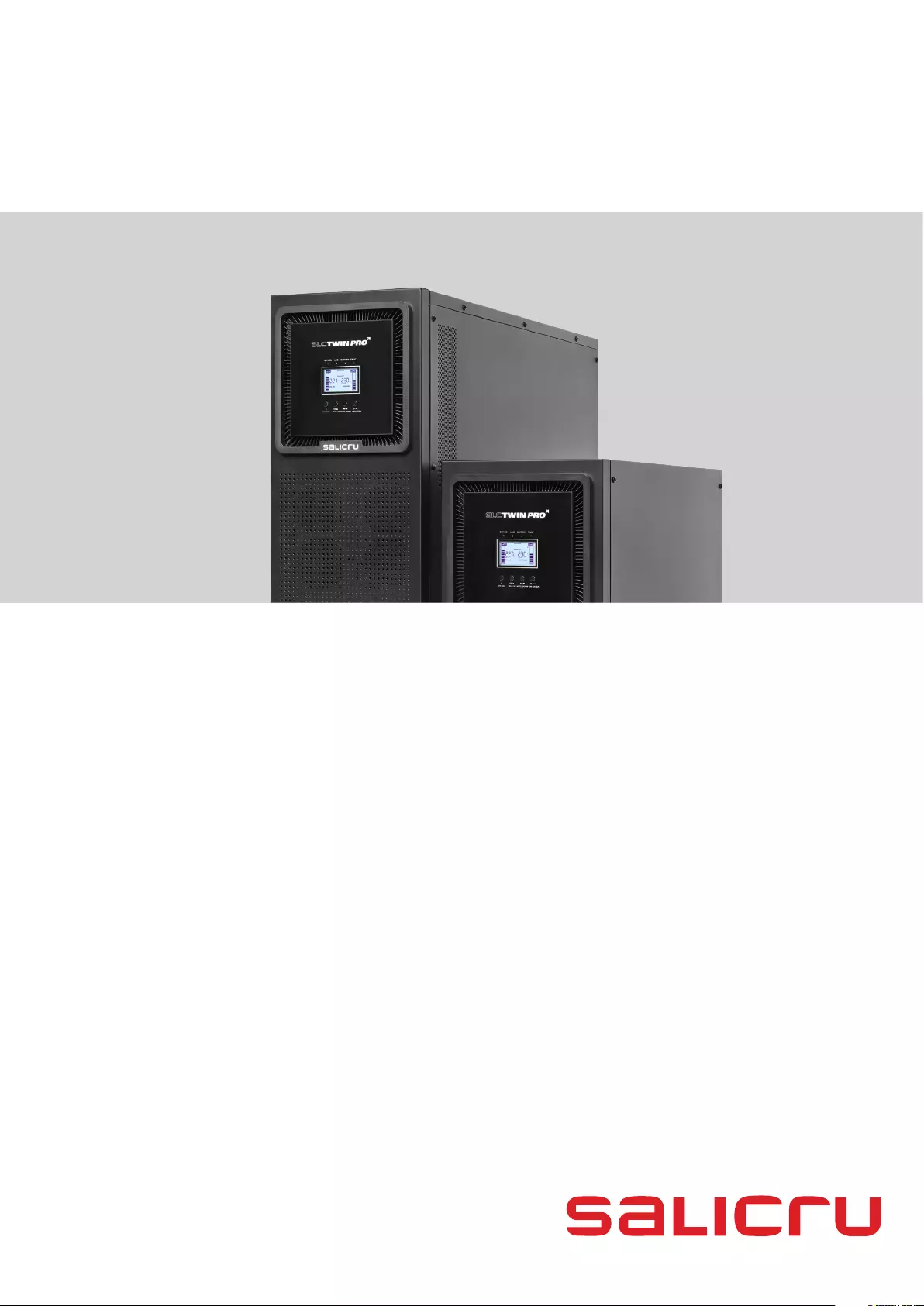

SLC TWIN PRO2
4.. 20 kVA
UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)
USER'S MANUAL

2SALICRU
General index
1. INTRODUCTION.
1.1. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT LETTER.
2. INFORMATION FOR SAFETY.
2.1. USING THIS MANUAL.
2.1.1. Conventions and used symbols.
3. QUALITY AND STANDARD GUARANTEE.
3.1. DECLARATION OF THE MANAGEMENT.
3.2. STANDARD.
3.2.1. First and second environment.
3.2.1.1. First environment.
3.2.1.2. Second environment.
3.3. ENVIRONMENT.
4. PRESENTATION.
4.1. VIEWS.
4.1.1. Views of the equipment.
4.2. PRODUCT DEFINITION.
4.2.1. Nomenclature.
4.3. OPERATING PRINCIPLE.
4.3.1. Main features.
4.4. OPTIONS.
4.4.1. Isolation transformer.
4.4.2. External manual bypass manual.
4.4.3. Communication card.
4.4.3.1. Integration into IT networks by means of the SNMP
adaptor.
4.4.3.2. RS485 Modbus.
4.4.3.3. Dry contacts.
5. INSTALLATION.
5.1. EQUIPMENT RECEPTION.
5.1.1. Reception, unpacking and contents.
5.1.2. Storage.
5.1.3. Unpacking.
5.1.4. Transport till its location.
5.1.5. Location, immobilising and considerations.
5.1.5.1. Location for single units.
5.1.5.2. Location for parallel systems.
5.1.5.3. Immobilising the equipment.
5.1.5.4. Preliminary considerations, before connecting the
equipment.
5.1.5.5. Preliminary considerations for batteries and their
protections before connecting the equipment.
5.1.5.6. Connection parts.
5.2. CONNECTION.
5.2.1. Connection of the input terminals to AC power supply.
5.2.2. Connection of load/s to the output terminals or output 1.
5.2.3. Connection of the load/s to the output terminals 2
(TWIN/3 PRO2 from 8 to 20 kVA only).
5.2.4. Connection with the external battery module and
extended back up times.
5.2.5. AC power supply for the battery charger built in the
battery module.
5.2.6. Connection of the main protective earth and
bonding earth .
5.2.7. EPO terminals (Emergency Power Off).
5.2.8. Terminals for digital Input and Output.
5.2.9. Terminals for the manual bypass auxiliary contact.
5.2.10. Parallel connection.
5.2.10.1. Introduction to the redundancy.
5.2.10.2. Parallel installation and operating.
5.2.11. Communication port.
5.2.11.1. RS232 and USB ports.
5.2.12. Intelligent slot to insert the communication card.
5.2.13. Software.
5.2.14. Considerations before commissioning with the loads.
6. OPERATING.
6.1. COMMISSIONING.
6.1.1. Checking before commissioning.
6.2. START UP AND SHUTDOWN OF THE UPS.
6.2.1. UPS start up with AC mains present.
6.2.2. UPS start up with no AC mains (Cold start).
6.2.3. UPS shutdown with AC mains present.
6.2.4. UPS shutdown with no AC mains.
6.3. MANUAL BYPASS SWITCH (MAINTENANCE).
6.3.1. Shifting to maintenance bypass.
6.3.2. Shifting to normal mode.
6.4. PARALLEL SYSTEM OPERATING
6.5. HOW UPGRADE THE PARALLEL SYSTEM WITH A NEW
UPS OR DOWNGRADE TO SINGLE MODE.
6.6. HOW TO REPLACE A FAULTY UPS FROM THE PARALLEL
SYSTEM.

3
7. CONTROL PANEL WITH LCD.
7.1. CONTROL PANEL.
7.2. TABLE 6 SHOWS THE INDIVIDUAL FUNCTION OF EACH
ONE OF THEM OR THEIR INTERACTION WITH OTHERS,
AS REGARDS TO THE UPS STATUS. LED FUNCTIONS.
7.2.1. Acoustic alarms.
7.2.2. Messages shown in the LCD.
7.3. MEANING OF THE ABBREVIATIONS DISPLAYED IN THE
LCD OF THE CONTROL PANEL.
7.4. SETTINGS IN THE LCD CONTROL PANEL.
7.4.1. Setting menu views, depending on the parameter 1
code.
7.5. OPERATING MODES / STATUS DESCRIPTION.
7.6. WARNING CODES.
7.7. ERROR O FAULT CODES.
7.8. WARNING INDICATORS.
8. MAINTENANCE, WARRANTY AND
SERVICE.
8.1. BATTERY MAINTENANCE.
8.1.1. Notes to replace and install the batteries.
8.2. UPS TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE.
8.2.1. Troubleshooting guide.
8.3. WARRANTY CONDITIONS.
8.3.1. Warranty terms.
8.3.2. Out of scope of supply.
8.4. TECHNICAL SERVICE NETWORK.
9. ANNEXES.
9.1. GENERAL TECHNICAL FEATURES.
9.2. GLOSARIO.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

4SALICRU
SALICRU
1. INTRODUCTION.
1.1. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT LETTER.
We would like to thank you in advance for the trust you have
placed in us by purchasing this product. Read this instruction
manual carefully in order to be familiarized with its contents,
because, as much as you know and understand the equipment
the highest will be your satisfaction and safety levels and their
features will be optimized too.
We remain at you entire disposal for any further information or
any query you should wish to make.
Yours sincerely.
•The equipment here described can cause important
physical damages due to wrong handling. This is why,
the installation, maintenance and/or fixing of itself must
be done by our staff or qualified personnel exclusively.
•Although we have made every effort to guarantee a com-
plete and accurate information in this user’s manual, we
are not responsible for any errors or omissions that may
exist.
The images included in this document are mere illustrations
and they could not represent the part of the equipment ex-
actly, therefore they are not contractual. Nevertheless, dif-
ferences that could exist will be alleviated or solved with
the correct labelling of the equipment.
•According to our policy of constant evolution, we reserve
the right to modify the specifications, operating or
described actions in this document without fore-
warning.
Any reproduction, copy or third party concession,
modification or partial or in whole translations of this
manual or document, in any format or media, is prohibited without
the previous written authorization of our firm, being reserved
the full and exclusive ownership right over it.

5
2. INFORMATION FOR SAFETY.
2.1. USING THIS MANUAL.
The documentation of any standard equipment can be down-
loaded from our website by the client (www.salicru.com).
•Those equipments «supplied by power cord with plug», this
is is the website to get the user’s manual and the «Safety
instructions» EK266*08.
•Those equipments «with permt connection», hardwired,
can be supplied together with a CD-ROM or Pen Drive,
which includes any information needed for its erection
and commissioning, including the «Safety instructions»
EK266*08.
Before doing any action over the equipment regarding installa-
tion or commissioning, change of location, setting or handling,
read them carefully.
This user’s manual is intended to provide information regarding
the safety and to give explanations about the procedures for
the installation and operating of the equipment. Read them
carefully and follow the stated steps in the established order.
Compliance as regards to «Safety instructions» is
mandatory, being the user the legal responsible
regarding to its observance and application.
The equipments are delivered duly labelled for the correct iden-
tification of any their parts, which combined with the instruc-
tions described in this user’s manual, allows the end-user to
make any operating of both installation and commissioning, in
an easy and ordered way without doubt.
Finally, once the equipment is commissioned and in operation,
it is recommended to keep the downloaded documentation
from the WebSite, or the CD-ROM or Pen Drive in a safe place
and with easy access, for further questions that could arise.
The following terms are used in the document indistinctly to
be referred to:
•«SLC TWIN PRO2, TWIN PRO2, TWIN, PRO2, equip-
ment, unit o UPS».- Uninterruptible Power Supply.
Depending on the context of the sentence, it can be re-
ferred either to the own equipment or to the equipment
with batteries, although all is assembled in one cabinet or
metallic enclosure.
•«Batteries or accumulators».- Group or set of elements
that store the electron flow through electrochemical means.
•«T.S.S.».- Technical Service & Support.
•«client, fitter, operator or end-user».- are used indis-
tinctly and by extension, to be referred to the fitter and/or
operator which will make the corresponding actions, being
responsible the same person about the actions to take on
behalf of himself.
2.1.1. Conventions and used symbols.
Some symbols can be used and shown in the equipment and/or
in the description of this user’s manual.
For more information, see section 1.1.1 of EK266*08 document
as regards to «Safety instructions».
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

6SALICRU
3. QUALITY AND STANDARD GUARANTEE.
3.1. DECLARATION OF THE MANAGEMENT.
Our target is the client’s satisfaction, therefore this Manage-
ment has decided to establish a Quality and Environmental
policy, by means of installation a Quality and Environmental
Management System that becomes us capable to comply the
requirements demanded by the standard ISO 9001 and ISO
14001 and by our Clients and concerned parts too.
Likewise, the enterprise Management is committed with the
development and improvement of the Quality and Environ-
mental Management System, through:
•The communication to all the company about the impor-
tance of satisfaction both in the client’s requirements and
in the legal and regulations.
•The Quality and Environmental Policy diffusion and the fixa-
tion of the Quality and Environment targets.
•To carry out revisions by the Management.
•To provide the needed resources.
3.2. STANDARD.
The SLC TWIN PRO2 product is designed, manufactured and com-
mercialized in accordance with the standard EN ISO 9001 of
Quality Management Systems. The marking shows the con-
formity to the EEC Directive by means of the application of the fol-
lowing standards:
•2014/35/EU. - Low Voltage Directive [LVD].
•2014/30/EU. - Electromagnetic Compatibility [EMC].
•2011/65/EU. - Restriction of Hazardous Substances in elec-
trical and electronic equipment [RoHS).
In accordance with the specifications of the harmonized stand-
ards. Standards as reference:
•EN-IEC 62040-1. Uninterruptible power supply [UPS]. Part
1-1: General and safety requirements for UPS’s used in ac-
cessible areas by end users..
•EN-IEC 60950-1. IT equipments. Safety. Part 1: General
requirements.
•EN-IEC 62040-2. Uninterruptible power supply [UPS]. Part
2: EMC requirements.
The manufacturers responsibility is excluded in the event of
any modification or intervention in the product by the cus-
tomer’s side.
ADVERTENCIA!:
SLC TWIN PRO2 4.. 20 kVA. This is a category C3 UPS
product. This is a product for commercial and industrial
application in the second environment; installation re-
strictions or additional measures may be needed to pre-
vent disturbances
The use of this equipment is not suitable for life sup-
port applications, where the failure of it can leave out
of service the life support device or could affect to its
safety or efectiveness. Likewise, it is not recommended
its use in those medical applications, commercial trans-
port, nuclear power stations and other applications or
loads, where the failure of this product can reverse in
personal injuries and material damages.
Declaration of conformity CE of the product is at the
client disposal under previous request to our headquar-
ters offices.
3.2.1. First and second environment.
The following examples of environment cover the majority of
UPS installations.
3.2.1.1. First environment.
Environment that includes residential, commercial and light
industrial premises directly connected without intermediate
transformers to a public low-voltage mains supply.
3.2.1.2. Second environment.
Environment that includes all commercial, light industry and in-
dustrial establishments other than those directly connected to
a low-voltage mains that supplies buildings used for residential
purposes.
3.3. ENVIRONMENT.
This product has been designed to respect the environment and
has been manufactured in accordance with the standard ISO
14001.
Equipment recycling at the end of its useful life:
Our company commits to use the services of authorised so-
cieties and according to the regulations, in order to treat the
recovered product at the end of its useful life (contact your dis-
tributor).
Packaging:
To recycle the packaging, follow the legal regulations in force,
depending on the particular standard of the country where the
equipment is installed.
Batteries:
The batteries mean a serious danger for health and environ-
ment. The disposal of them must be done in accordance with
the standards in force.

7
4. PRESENTATION.
4.1. VIEWS.
4.1.1. Views of the equipment.
Figures from 1 to 3 show the equipment illustrations according
to the format of the case and its power rate. Nevertheless, as
the product is in constant evolution, some discrepancies or
slight contradictions can arise. In case of any doubt, the label-
ling in the own equipment will always prevail
In the nameplate of the equipment, the most important
parameters and features can be checked. Proceed with
the installation accordingly.
Standard and B1, from 4 to 10 kVA. Single phase input and output.
Standard and B1, from 8 to 10 kVA. Three phase input and single
phase output.
B1, from 15 and 20 kVA. Three phase input and single phase output.
Standard, 15 and 20 kVA. Three phase input and single phase
output.
Size 2
Size 1
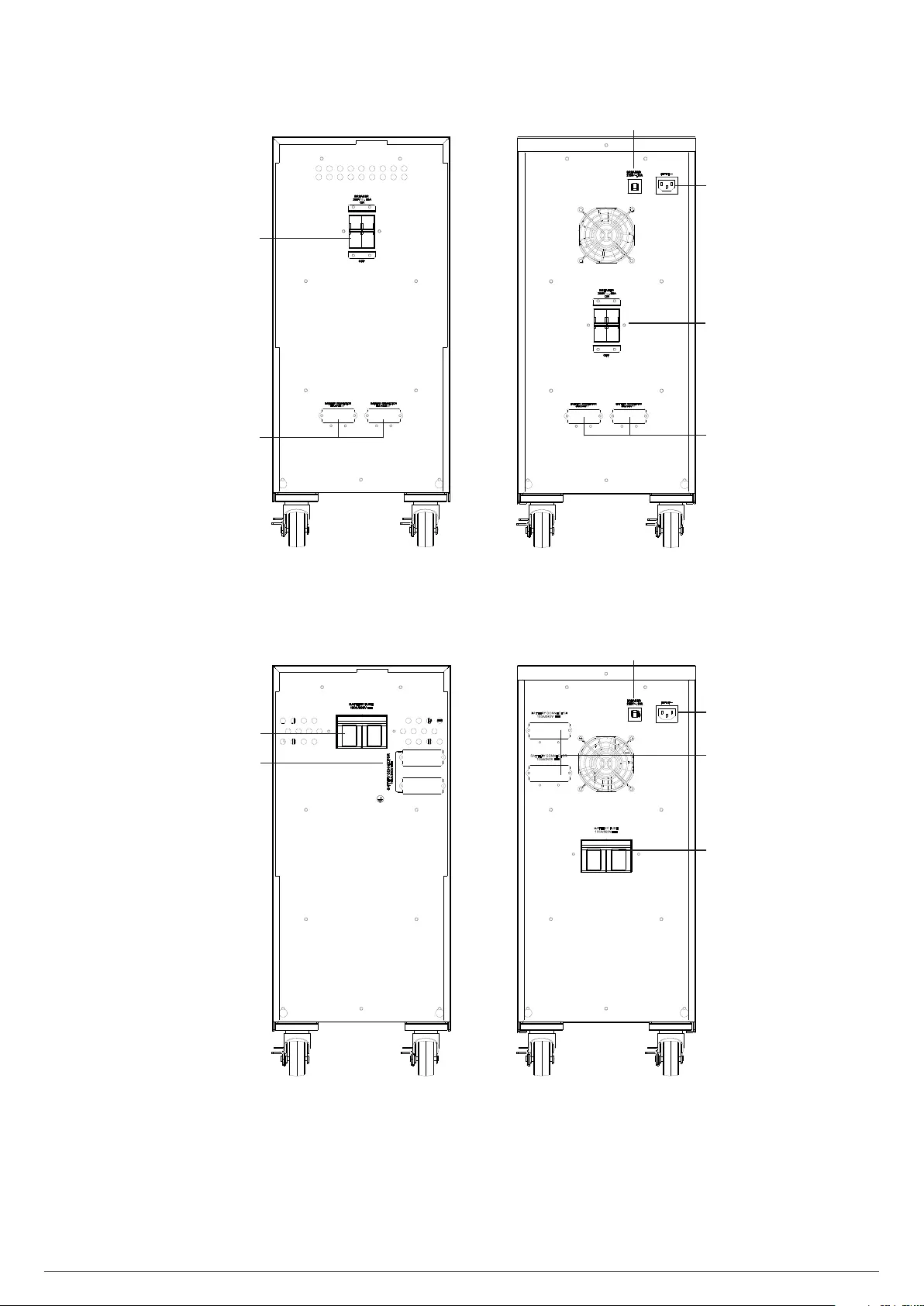
Fig. 1. Front view for 4 to 20 kVA equipments.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

8SALICRU
Standard and B1, from 4 to 10 kVA. Single phase input and output.
Digital input-output
RS232
USB
EPO
Manual Byp aux.
contact
Bat. connector cover
Battery connector
Manual bypass screw
locking
Manual bypass lock
Manual Bypass -BM-
Input protection
Output 1 breaker
Output 1, connected to
critical loads
Terminal cover, see
Fig. 17
Swivel casters
Caster brake
Digital input-output
RS232
USB
EPO
Smart Slot
Communication bus
Current sharing signal,
under the cover
Manual bypass screw
locking
Manual bypass lock
Manual byp. aux.
contact
Manual Bypass -BM-
Input protection
Output 1 breaker
Output 1, connected to
critical loads
Terminal cover, see
Fig. 17
Swivel casters
Caster brake
Communication bus
Current sharing signal,
under the cover
Smart Slot
Bat. connector cover
Battery connector
Standard and B1, from 8 to 10 kVA. Three phase input and single phase output.
Digital input-output
RS232
USB
EPO
Manual bypass screw
locking
Manual bypass lock
Contacto auxiliar BM
Manual Bypass -BM-
Input protection
Terminal cover, see
Fig. 17
Swivel casters
Caster brake
Digital input-output
RS232
USB
EPO
Current sharing signal,
under the cover
Communication bus
Manual bypass screw
locking
Smart slot
Manual byp. aux.
contact
Manual Bypass -BM-
Manual bypass lock
Input protection
Terminal cover, see
Fig. 17
Terminal cover, PE
terminals
Swivel casters
Caster brake
Communication Bus
Current sharing signal
under the cover
Smart slot
B1, from 15 and 20 kVA. Three phase input and single phase output. Standrd from 15 and 20 kVA. Three phase input and single phase output.
-BM- letters means Manual Bypass.
Fig. 2. Rear view for 4 to 20 kVA models.
9
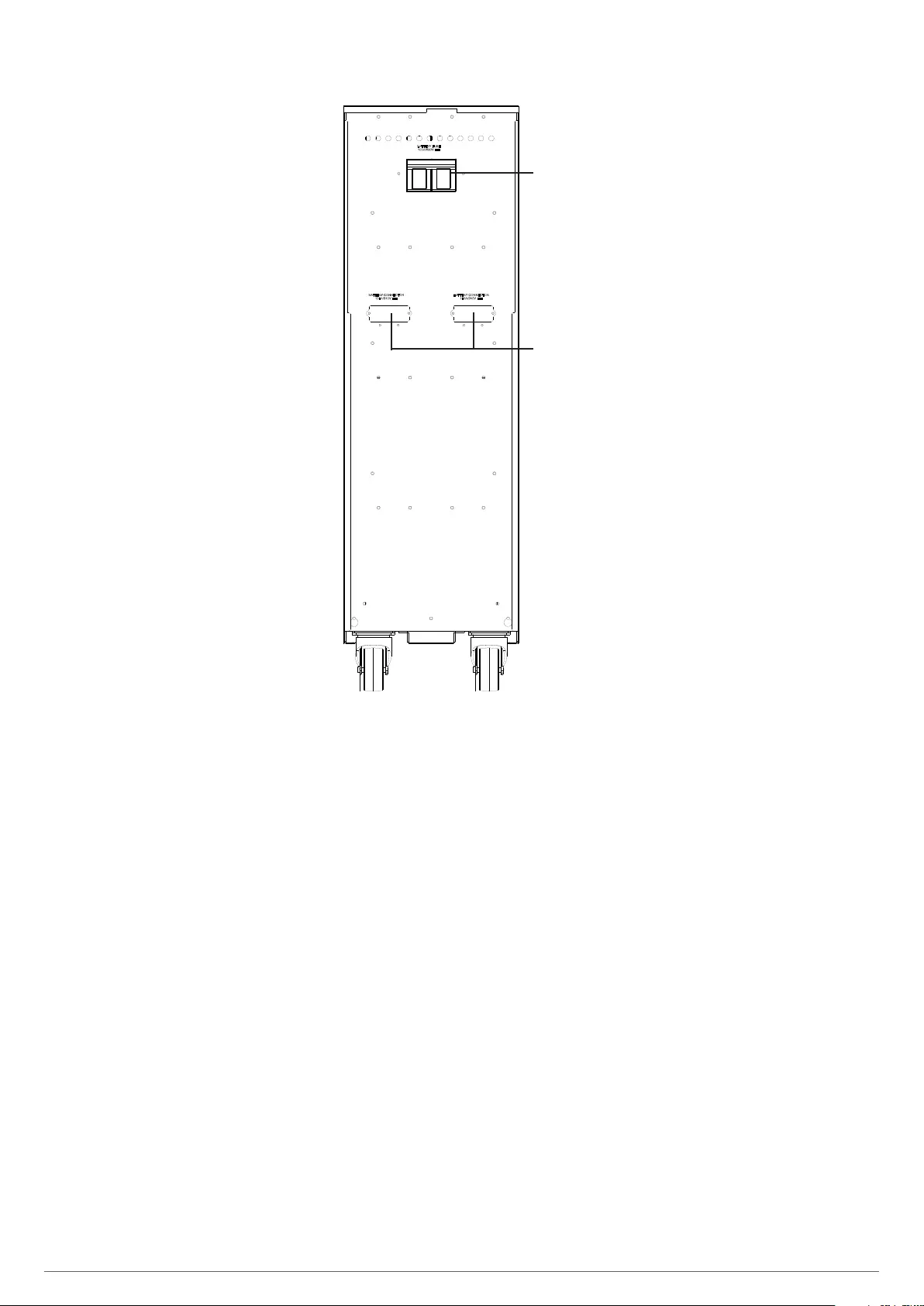
Battery switch
Terminal cover
Conector IEC para alimen-
tación AC
Batery switch
Terminal cover
Térmico de protección
Battery module, size 1, with 2x20 batteries
and 50 A protection.
Battery module, size 1, with 3x20 batteries
and 50 A protection.
Battery fuses
Terminal cover
IEC inlet for AC power
supply
Terminal cover
Battery switch
Protection breaker
Battery module, size 1, with 2x20 batteries
and 100 A protection.
Battery module, size 1, with 3x20 batteries
and 100 A protection.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
10 SALICRU
Battery switch
Terminal cover
Battery module, size 2 with 4x20 batteries
and 100 A protection
Fig. 3. Rear view of the battery module.
11
4.2. PRODUCT DEFINITION.
4.2.1. Nomenclature.
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2 B1 WCO 0/AB147 208/208V EE521925
MOD BAT TWIN PRO2 2x3AB147 3x40A WCO EE521925
EE521925 Particular specifications of the client.
208V Output voltage if it is not 220/230/240V AC.
208V Input voltage if it is not 220/230/240V AC.
147 Last three characters of the battery code.
AB Family of the battery according to Salicru's code.
0/ Equipment with no batteries but with the needed
accessories to fit them in.
CO “Made in Spain” marking in the UPS and packaging
(custom issues).
W Neutral equipment brand.
B0 No batteries and no space to install them.
B1 External batteries to the UPS enclosure and extra charger.
TWIN PRO2 Single phase input - output configuration.
TWIN/3 PRO2 Three phase input / single phase output equipment.
8000 Power in VA.
SLC Brand acronym.
CF Frequency converter (equipment with no batteries).
EE* Particular specifications of the client.
CO “Made in Spain” marking in the UPS and packaging
(custom issue).
W Neutral equipment brand.
40A Protection size.
3x Quantity of fuses in parallel. Omitted for only one.
147 Last three characters of the battery code.
AB Family of the battery according to Salicru's code..
3 Quantity of batteries in one string.
2x Quantity of strings in parallel. Omitted for only one.
0/ Battery module with no batteries, but with the needed
accessories to fit them in.
TWIN PRO2 Battery module series.
MOD BAT Battery module.
Note concerning batteries:
B0 and B1 acronyms, stated in the nomenclature are re-
lated with the batteries:
B0 The equipment is supplied with no batteries and no
accessories (screws and electrical cables). Batteries
belong to the client and they will be installed externally
to the UPS enclosure. Under request, it is possible to
supply these accessories, which are needed to inter-
connect them with the own the equipment.
B1 Equipment with extra battery charger. The UPS
is supplied with no batteries and no accessories
(screws and electrical cables).Under request, it is pos-
sible to supply these accessories, which are needed to
interconnect them with the own the equipment.
Those equipments requested with no batteries, their pur-
chasing, installation and connection will be borne by the
client and under his responsibility.
Data concerning batteries in respect of quantity, capacity
and voltage are stated in the battery label sticked beside
the nameplate of the equipment, respect this data and
their polarity strictly when connecting them.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

12 SALICRU
4.3. OPERATING PRINCIPLE.
This manual describes the commissioning and operating of
the Uninterruptible Power Supplies -UPS- from SLC TWIN
PRO2 series as equipments that can operate in parallel or
single configurations, without needing a centralised bypass.
The UPS's from SLC TWIN PRO2 series assure an optimal
protection for any critical load, keeping the power supply to
the loads inside the stated parameters, with either no break
in case of mains failure nor fluctuations. The wide range of
available models (from 4kVA up to 20kVA), allows adapting
the model to the end-user needs.
Thanks to the used technology, PWM (Pulse Width Modula-
tion) and the double conversion, the UPS's from SLC TWIN
PRO2 series are compact, cold, silent and with high efficiency.
The double conversion principle cancels any fluctuations from
the electrical mains. A rectifier converts the alternating cur-
rent from mains in to direct current, and it keeps the optimal
charge level to the batteries and at the same time feeds the
inverter; the inverter generates a alternating current sin-
ewave, which is ready to feed the loads constantly. In case
of power outage at the UPS input, the batteries supply the
energy to the inverter.
The UPS design and manufacturing from SLC TWIN PRO2
series has been done in accordance with the international
standards.
These equipments allow their upgrading by connecting addi-
tional equipments of the same power rate in parallel, in order
to get redundancy -i.e.: N+1- or increasing the power of the
system.
Therefore, this series has been designed to maximize the
availability of the critical loads in order to protect them
against voltage fluctuations, power outages and blackouts,
which are present in the energy distribution lines. This is the
main aim of the UPS's from de SLC TWIN PRO2 series.
This manual applies to the standardised models stated in Tab. 1.
4.3.1. Main features.
•True on-line technology of double conversion and inde-
pendent output frequency from mains.
•Output power factor 1 in single phase input equipments and
0.9 in three phase input ones. Pure sinewave shape, suit-
able for almost all type of loads.
•Input power factor > 0.99 and high efficiency (> 0.94 for
single phase input or > 0.92 for three phase input). So, it
is got a high economy saving and lower installation cost
-wiring-, as well as low input current distortion, so the per-
turbances to mains are reduced.
•Great adaptability to the worst conditions of input mains.
Wide input voltage range, frequency range and wave
shape, so it is avoided the excessive use of the battery,
which has limited energy.
•Available battery charger up to 8 A in order to decrease the
battery recharge time.
•Parallel redundant N+X connection, in order to increase
the reliability and flexibility. 3 equipments in parallel as
maximum.
•Selectable of the High Efficiency Mode > 0.97 -ECO-MODE-.
Energy saving, which means economic saving for the end-
user.
•Possibility to start it up with no mains or discharged bat-
teries. Be careful, with this last point, because the back up
time will be reduced, as much as they are more discharged.
•The smart battery management technology is very useful
to extend the lifetime of the batteries and to optimise their
recharging time.
•RS232 or USB communication ports as standard.
•Digital input to start up-shutdown the equipment.
•Digital output for «Error or fault».
•Remote emergency power off -EPO-.
•User-friendly interface between user and equipment by
means of the control panel with LCD and LED.
•Optional available cards to improve the communication ca-
pabilities.
Model Type Input/output topology
SLC-4000-TWIN PRO2
Standard
Single phase in/out
SLC-5000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-6000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-8000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-10000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-15000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-20000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2
Three phase in / Single
phase out
SLC-10000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-15000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-20000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-4000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
No batteries
Single phase in/out
SLC-5000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-6000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-8000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-10000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-15000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-20000-TWIN PRO2 (B0)
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B0)
Three phase in / Single
phase out
SLC-10000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B0)
SLC-15000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B0)
SLC-20000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B0)
SLC-4000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
Extended back up time
Single phase in / out
SLC-5000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-6000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-8000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-10000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-15000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-20000-TWIN PRO2 (B1)
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B1)
Three phase in / Single
phase out
SLC-10000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B1)
SLC-15000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B1)
SLC-20000-TWIN/3 PRO2 (B1)
Tab. 1. Standardized models.

13
4.4. OPTIONS.
Depending on the selected configuration, the equipment can
include any of the following options:
4.4.1. Isolation transformer.
The isolation transformer, provides a galvanic isolation that al-
lows isolating the output from input completely and/or even
change the neutral regime.
The fact of having an electrostatic shield between the primary
and secondary windings of the transformer provides a high at-
tenuation level of the electrical noise.
Physically, the isolation transformer can be located at the input
or output of the UPS, depending on the particular specifications
of the installation (equipment power supply and/or loads, type
of loads,...).
In parallel systems, it is not possible to operate with separate
isolation transformers for each UPS. So it is necessary to have
only one transformer for the complete parallel system of the
suitable power rate.
In any case, it will always be supplied as a separate item to the
own UPS enclosure.
4.4.2. External manual bypass manual.
The purpose of this option is to isolate electrically the equip-
ment from mains and critical loads with no break. Therefore the
maintenance or reparation tasks can be done in the equipment
with no breaks in the power supply of the protected system and
at the same time undue risks to the technical staff are avoided.
The basic difference, between this option and the integrated manual by-
pass in the own UPS enclosure is its better operability, because it allows
the total disconnection of the UPS from the installation.
4.4.3. Communication card.
In the rear side of the UPS there is a slot, which allows in-
serting any of the following communication cards.
4.4.3.1. Integration into IT networks by means of the SNMP
adaptor.
The large-scale IT systems based in LANs and WANs, which
integrates servers with different operating systems, must in-
clude an easy control by the management of the system. This
feature is get by the use of the SNMP adaptor, which is ac-
cepted by the main manufacturers of software and hardware.
The connection of the UPS with the SNMP is internal, mean-
while the connection between the SNMP and the IT network is
done by means of a RJ45 10 base connector.
4.4.3.2. RS485 Modbus.
Many times, the large-scale IT systems based in LANs and
WANs require communication by means of a industrial standard
protocol with any part or component integrated inside the IT
network.
One of the most used industrial protocols in the market is the
MODBUS protocol. The SLC TWIN PRO2 series is ready to be
integrated in this kind of environments either by means of the
“SNMP mini card” adaptor or the RS485 Modbus card which is
described in the documentation of the optional.
4.4.3.3. Dry contacts.
•As an option, the UPS has a dry contact card, which pro-
vides digital signals, with maximum applicable voltage and
current of 240 V AC or 30 V DC and 1A.
•This port provides a dialogue between the equipment and
other machines or devices, thanks to the supplied dry con-
tacts, which includeds a terminal strip located in the own
card, with only one common terminal for all of them.
All the dry contacts are normally opened, preset from fac-
tory, being able to set them independently, according to the
information supplied with the option.
•The most common use of these type of ports is to provide
the needed information to the closing file software.
•For information, contact with our T.S.S. or our closest dis-
tributor.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

14 SALICRU
5. INSTALLATION.
•Read and respect the Safety Information, described
in section 2 of this document. The fact of ignoring
any of the indications described in it, can cause serious ac-
cidents or very serious injuries to the persons in the vicini-
ties in direct contact, as well as damages to the equipment
and/or loads connected to itself.
•A part from the own user's manual of the equipment, the
CD-ROM or Pen Drive contents other documents, which
have to consulted and followed strictly.
•Unless otherwise indicated, any action, indications, notes
and other ones are applicable to the equipments, never
mind if they belong to a parallel system or not.
5.1. EQUIPMENT RECEPTION.
•It is dangerous to handle the equipment over the pallet
with no caution, because it could tip over or cause se-
rious injuries to the operators due to the impact of the fall and/or
entrapment. Pay attention to section 1.2.1. from Safety Intruc-
tions -EK266*08- regarding handling, moving and location of the
equipment.
•Use the most suitable medium to move the UPS meanwhile
it is still packaged, by means of pallet jack or forklift.
•Any equipment handling will be done keeping in mind the
weights and technical features of the model, stated in sec-
tion «9. Annexes».
5.1.1. Reception, unpacking and contents.
•Reception. Check the following:
Data in the labelling of the packaging are the same as
the stated in the purchase order. Once the UPS is un-
packed, check previous data with the nameplate of the
equipment.
In case of discrepancies, make the non-conformity as
soon as possible by quoting the serial number of the
equipment and the delivery note reference.
No damage during transport (packaging and impact in-
dicator correct).
Otherwise, follow the stated protocol in the labelling
beside the impact indicator, located in the packaging.
•Unpacking.
To check the contents, the packaging must be removed.
Complete the unpacking procedure according to
section 5.1.3.
•Contents.
The own equipment.
User's manual in IT support: [CD-ROM] or [Pen Drive].
1 communication cable.
2 cables for parallel connection, current bus and control
signal.
1 female connector to connect into the external EPO. It in-
cludes an isolated cable as a «bridge» mode to close the
circuit (already fitted in).
•Once the reception is finalised, it is better to pack the UPS
again till its commissioning in order to protect it against pos-
sible mechanical impacts, dust, dirt, etc...
•The equipment packaging has wooden pallet, cardboard
or wooden enclosure depending on the requirements, ex-
panded polystyrene corners, plastic bag and polyethylene
wrap, all of them are recyclable materials. When they has
to be disposed proceed in accordance with the laws in
force.
It is advised to keep the packaging, for 1 year at least.
5.1.2. Storage.
•The storage of the equipment will be done in a dry and
cool room, protected from rain, dust, water jets or chemical
agents. It is advisable to keep each equipment and battery
unit inside their original packaging, because they have
been designed to assure the maximum protection during
transport and storage.
•Those equipments, which include Pb-Ca batteries,
the recharging period of time according to the storage
temperature, stated in Tab. 2 from EK266*08 document, must
be respected. Otherwise the warranty will be cancelled.
•After this period of time, connect the equipment with the
batteries unit,if any, and start it up according to the instruc-
tions described in this user's manual and charge them for
12 hours.
In parallel systems, to charge only the batteries, it is not needed
to make the connection among the equipments. Proceed as com-
plete single equipments to charge them.
•Later on, shutdown the equipment, disconnect it and pack
the UPS and batteries in their original packaging again, by
writing down the new recharging battery date in any docu-
ment or over the own packaging as a record mode.
•Do not store the devices, where the temperature exceeds
over 50º C or below –15º C, because the electrical features
of the batteries can be affected.
5.1.3. Unpacking.
•The equipment packaging has wooden pallet, cardboard
or wooden enclosure depending on the requirements, ex-
panded polystyrene corners [EPS] or polyethylene foam
[EPE], plastic bag and polyethylene wrap, all of them are
recyclable materials. When they has to be disposed pro-
ceed in accordance with the laws in force.
It is advised to keep the packaging, in case it was to be
used in future.
•Equipments with single phase input TWIN PRO2 or three
phase input TWIN/3 PRO2 up to 10 kVA.
To unpack the equipment follow the sequence from
figure 4 to 7 (cut the wraps of the cardboard enclosure
and remove it from the top as it was a cover or in case
of wooden packaging, dismantle it with the needed
tools; remove the corners and plastic bag. The UPS will
be naked over the pallet.
With the help of one or two people in each side of the
UPS, download it from the wooden pallet.
15
Fig. 4. Fig. 5. Fig. 6. Fig. 7.
Fig. 8. Fig. 9. Fig. 10. Fig. 11.
5.1.4. Transport till its location.
•All the equipments have four casters (with mechanical
lock), so it is easy to move it till its right location once it
is unpacked.
Nevertheless, if the reception area is far from the installa-
tion location, it is recommended to move the UPS by means
of a pallet jack or the most suitable transport medium,
keeping in mind the distance between both points.
In case of long distances, it is recommended to move the
equipment with its packaging till the installation location
and finally unpack it there.
5.1.5. Location, immobilising and considerations.
5.1.5.1. Location for single units.
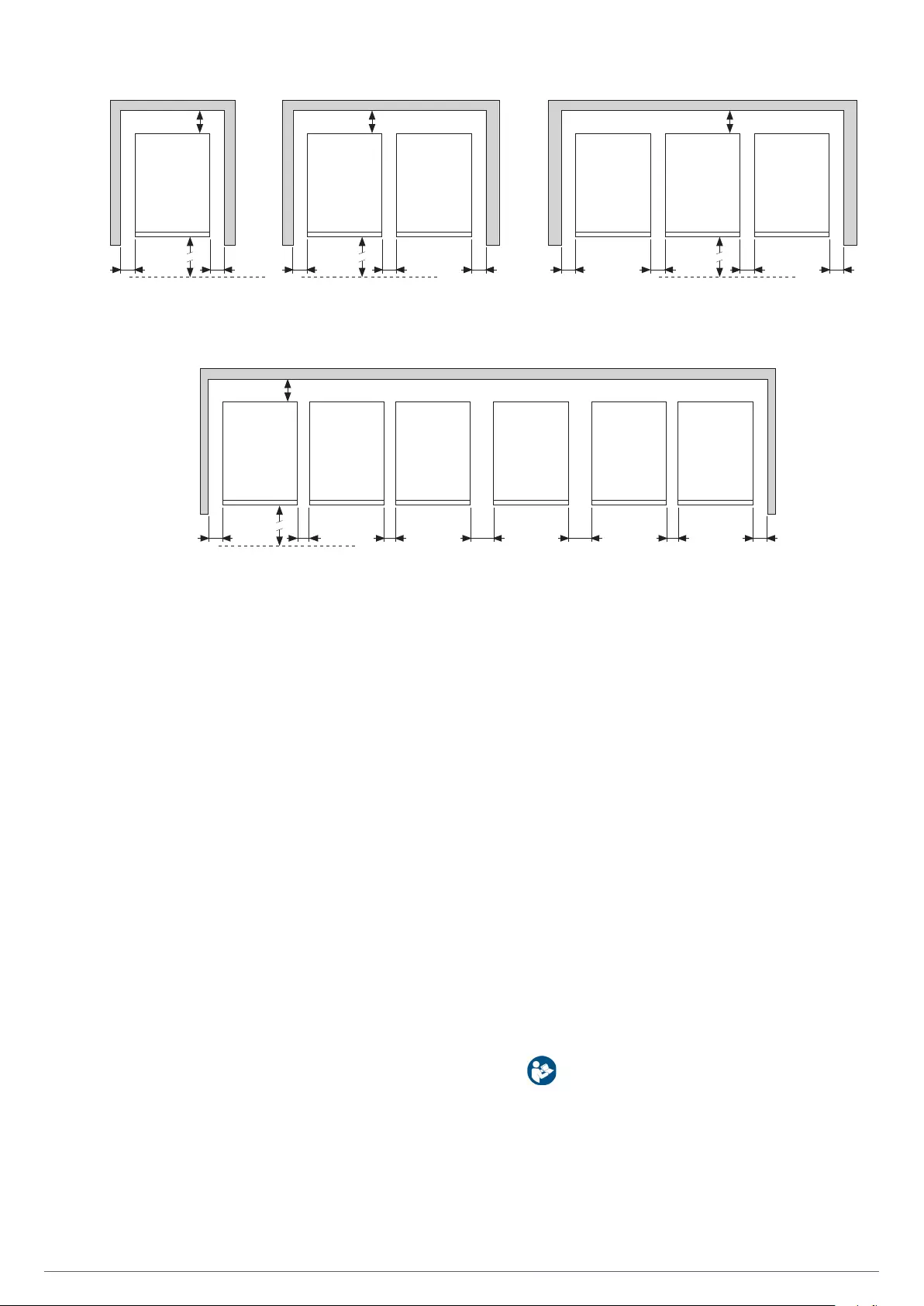
•As an example, Fig. 14 shows the typical case depending
on the model. The equipment based on one single phase
(UPS with batteries fitted in) and UPS with the batteries in
a separate case or extended back up times.
For a correct cooling, the space around the equipment
must be free of obstacles. Respect the minimum dis-
tances stated in Tab. 1 from section 1.2.1 of the docu-
ment EK266*08 (Safety Instructions), where the figures
of each dimension A, B, C and D are stated according to
the power rate of each equipment.
For the battery cases, keep the same distances as the
same UPS enclosure.
It is recommended to leave 75 cm additional free in each
side, for the possible tasks of the (T.S.S.) or the needed
power cable length to facilitate the movement of the
equipment to the front.
For extended back up times, with more than one case, it
is recommended to put one at each side of the equipment
and in case of a higher quantity proceed in the same way
alternately.
•Equipments with three phase input TWIN/3 PRO2
To unpack the equipment, follow the sequence of figures
8 to 10 (cut the wraps of the cardboard enclosure and
remove it from the top as it was a cover or in case of
wooden packaging use the needed tools; remove the
corners and plastic bag. The UPS will be naked over the
pallet.
The equipment is fixed to the wooden pallet by means
of metallic support with «L» shape (stabilising support),
fixed at each side of the equipment.
Remove the screws that fix the equipment to the pallet
by means of the support [see Fig. 12 and 13].
Before downloading the equipment from the
pallet, the stabilising supports have to be removed
first, otherwise they will make difficult the downloading
procedure and they will be bent when impacting with
the wooden ramp, being able to cause damages to the
own structure of the equipment.
Put the ramp as figure 11 shows and download the
equipment from the pallet.
Fig. 12.
Fig. 13.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
16 SALICRU
B
AA
UPS cabinet
with
batteries
D
B
AA A
UPS cabinet Battery UPS
cabinet
D
B
AA A
Battery
cabinet UPS
nr 1
Battery
cabinet UPS
nr 2
A
UPS cabinet
D
Fig. 14. Minimum distances for a correct UPS cooling.
D
B
AA A Ax2Ax2 A A
Battery
cabinet UPS
nr 1
Battery
cabinet UPS
nr 2
UPS cabinet
nr 1
UPS cabinet
nr 2
UPS cabinet
nr 3
Battery
cabinet UPS
nr 3
Fig. 15. Minimum distances for a correct UPS system
cooling.
5.1.5.2. Location for parallel systems.
•As an example of three equipments in parallel, Fig. 15
shows them with their battery case. For systems with two
equipments in parallel and/or more battery modules pro-
ceed accordingly in the same way.
Likewise, obviate the illustration of the battery modules
when they are not available.
The numbering of the equipments in Fig. 15 doesn't have
any purpose less than number each unit in the illustration.
•For a correct cooling, the space around equipment must be
free of obstacles. Respect the minimum distances stated in
Tab. 1 from section 1.2.1 of the document EK266*08 (Safety
Instructions), where the figures of each dimension A, B, C
and D are stated according to the power rate of each equip-
ment.
For the battery cases, keep the same distances as the UPS
enclosure.
5.1.5.3. Immobilising the equipment.
•The equipment has casters with brakes. Once the equip-
ment is placed in its final location, to immobilise the equip-
ment is recommended to lock them.
5.1.5.4. Preliminary considerations, before connecting the
equipment.
•In the description of this manual, there is reference to con-
nect terminals and manoeuvring switches, which are only
available in some models or equipments with extended
back up times. Ignore those operations related with your
unit in case it does not have them.
•Regarding the installation instructions of a single equip-
ment or parallel system, follow and respect them.
•The switchgear or external manual bypass panel:
At least, the installation will have one protection for
the short-circuit in the power supply line of the UPS.
For single equipments, it is recommended to install an
external manual bypass panel, equipped with input,
output and manual bypass protections.
For parallel systems, it is essential to install a switch-
gear or manual bypass panel. The switches of the panel
must allow isolating one UPS from the system, in case
of any failure and allow feeding the loads with the rest
ones, either during the preventive maintenance tasks or
during the failure and its reparation.
•An external manual bypass panel for a single unit or parallel
system can be purchased under request.
Also, it can be manufactured by yourself by keeping in mind
the version and configuration of the available equipment
or system and the attached documentation in the CD-ROM
or el Pen Drive as regards to «Recommended installation
diagram».
•The documentation delivered together with this us-
er's manual and/or CD-ROM or Pen Drive, includes
information regarding the «Recommended installation dia-
gram» for each input and output configuration. This docu-
mentation shows the wiring circuit diagrams, as well as the
protection and cross cable sizes that are connected to the
equipment, considering the nominal voltage. All the figures
are calculated for a total maximum cable length of 30 m
between the switchgear panel, equipment and loads.
For longer lengths, correct the cross cable sections in
17
accordance with the Regulations or standards of the
country, in order to avoid dropping voltages.
In the own documentation and for each configuration,
it is available the information for «N» equipments in
parallel, as well as the features of the «Backfeed pro-
tection».
•In parallel systems, the length and cross cable sec-
tion that connect the switchgear or manual bypass
panel with each UPS must be the same for all of them, with
no exception.
•The cross cable section must be always according to the size
of the own terminals of the switches, in such way that the
wire is embraced properly, in order to guarantee an optimal
contact between both parts.
•The data in the nameplate of the equipment states the
nominal current only, as the safety standard EN-IEC
62040-1 states. To calculate the input current, it has been
considered the power factor and the own efficiency of the
equipment.
The overload conditions are considered as a non-perma-
nent and exceptional operating mode, so it will not be kept
in mind when sizing the protections. Do not connect devices
to the UPS terminals or outlets that could overload it, like
motors.
•TWIN/3 PRO2 models (three phase input and single
phase output), the input current of R phase and Neutral
is higher than the other two lines/phases when the UPS
works on bypass mode (loads supplied from mains directly). Pay
attention to the nameplate data to size the two corresponding
cables.
•In case of adding peripheral parts at the UPS or parallel
system input or output, like transformers or autotrans-
formers, the stated currents in their own nameplates
must be also considered, in order to use the suitable cross
cable section, by respecting the Local and/or National Low
Voltage Electrotechnical Regulation.
•When a UPS or parallel system, as standard, as an option
or installed by yourself, at the input line or at the output or
in both, include a galvanic isolation transformer, a Residual
Current Device must be installed at its output, in order to
protect against electrical shocks and indirect contacts, be-
cause its intrinsic feature of isolation will prevent the trip-
ping of the protections fitted in the primary winding of the
transformer.
•As a reminder, all the isolation transformers installed or
supplied from factory has the output neutral connected to
the protective earth by means of a cable bridge between
the neutral and PE terminals. In case of requiring an iso-
lated output neutral, remove this cable bridge, by taking
the stated cautions in the local and/or national low voltage
regulations.
•This equipment is ready to be installed in grids with
power distribution systems TT, TN-S, TN-C or IT,
keeping in mind the particular features of each neutral re-
gime and the electrical regulations of the destination
country.
•The switches, RCD and circuit breaker of a three phase input
equipment connected to an IT power distribution system
must break the NEUTRAL apart from the three phases.
•TWIN PRO2 has a terminal strip to install an external emer-
gency power off button -EPO-. Only one device has to be
fitted in, in order to break the energy to the loads in any
operating mode.
5.1.5.5. Preliminary considerations for batteries and their
protections before connecting the equipment.
•All the standard UPSs include batteries in the same enclo-
sure, less those models called B0 and B1. For the standard
UPSs, the battery protection is done by internal fuses and
they are not accessible by the end-user.
Also, the battery modules have protection and in this case they
are doubled. Once are internal by means of fuses and not ac-
cessible by the end-user and the second ones by means of a
two poles circuit breaker or fuses.
•IMPORTANT FOR THE SAFETY: In case of installing the
batteries by yourself, the battery set must have a two
poles circuit breaker or fuses switch, with the size stated in
Tab. 2.
•Inside the battery module there are DANGEROUS VOLT-
AGES with the risk of electrical shock it involves, so it is
classified as RESTRICTED ACCESS AREA.
•Do not handle the battery fuse holder or circuit breaker
switch when the equipment is turned ON. These
switches cannot be turned ON/OFF with load.
•When the power supply to the equipment or parallel
system is broken and it is foreseen an out of service of
the equipment for long time, the equipment must be shutdown
completely.
•The battery circuit is not isolated from the input
voltage. So, dangerous voltages can be found be-
tween the battery terminals and the earth. Check that there
is not any kind of voltage, before doing any action over the
terminals.
5.1.5.6. Connection parts.
•Any electrical connection of the equipment is done through
the rear side of the equipment:
Input and output connection terminals. Remove the
fixing screws of the protection cover and the own cover,
to have access to the terminals.
Connect the UPS with the battery modules. Depending
on the power rate of the UPS, it has a connector or ter-
minals.
–Equipment and battery module with connector. Re-
move the screws and the «BATTERY CONNECTOR»
cover. These covers will not be put back again,
keep them.
–Equipment with battery terminals. They are beside
the AC power terminals.
–Battery module with terminals. Remove the screws
and protection cover.
Communication connectors:
–DB9 type for RS232.
–USB type for communication as a peripheral.
–Digital input and output.
–Terminal strip for external EPO button.
–Auxiliary contact for manual bypass switch.
Control connections for parallel systems, by DB15 connec-
tors and analogical signal for current sharing. Remove the
screws and the protection cover to have access to them.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
18 SALICRU
Slot to insert one of the optional communication cards.
Remove the fixing screws and the plastic cover to allow its
inserting.
•When finalising the connection tasks, the cover or
covers and their fixing screws will be put back be-
fore commissioning the equipment, in order to avoid acci-
dents due to direct contacts.
•It is recommended the use of crimping pin terminal in all
the cable ends connected to terminals, in particular the
power ones (input, output and batteries).
•Check the correct torque in the screws of the terminals.
5.2. CONNECTION.
•The terminal protection cover leaves a slot for the cable
entering to the power terminal strip. The cover and/or en-
closure frame has drills that allows fixing the connection
cables in order to avoid unexpected cable pulling due to the
consequences that it could have.
5.2.1. Connection of the input terminals to AC power
supply.
•As this is an equipment with protection against elec-
trical shocks of class I, it is essential to connect the
main protective earth cable [ ]. Connect this cable to the
terminal before supplying voltage to the input terminals.
•Pay attention to the «Recommended installation» document
in section 5.1.5.4., which states the cross cable section,
protection size and features, etc, ...
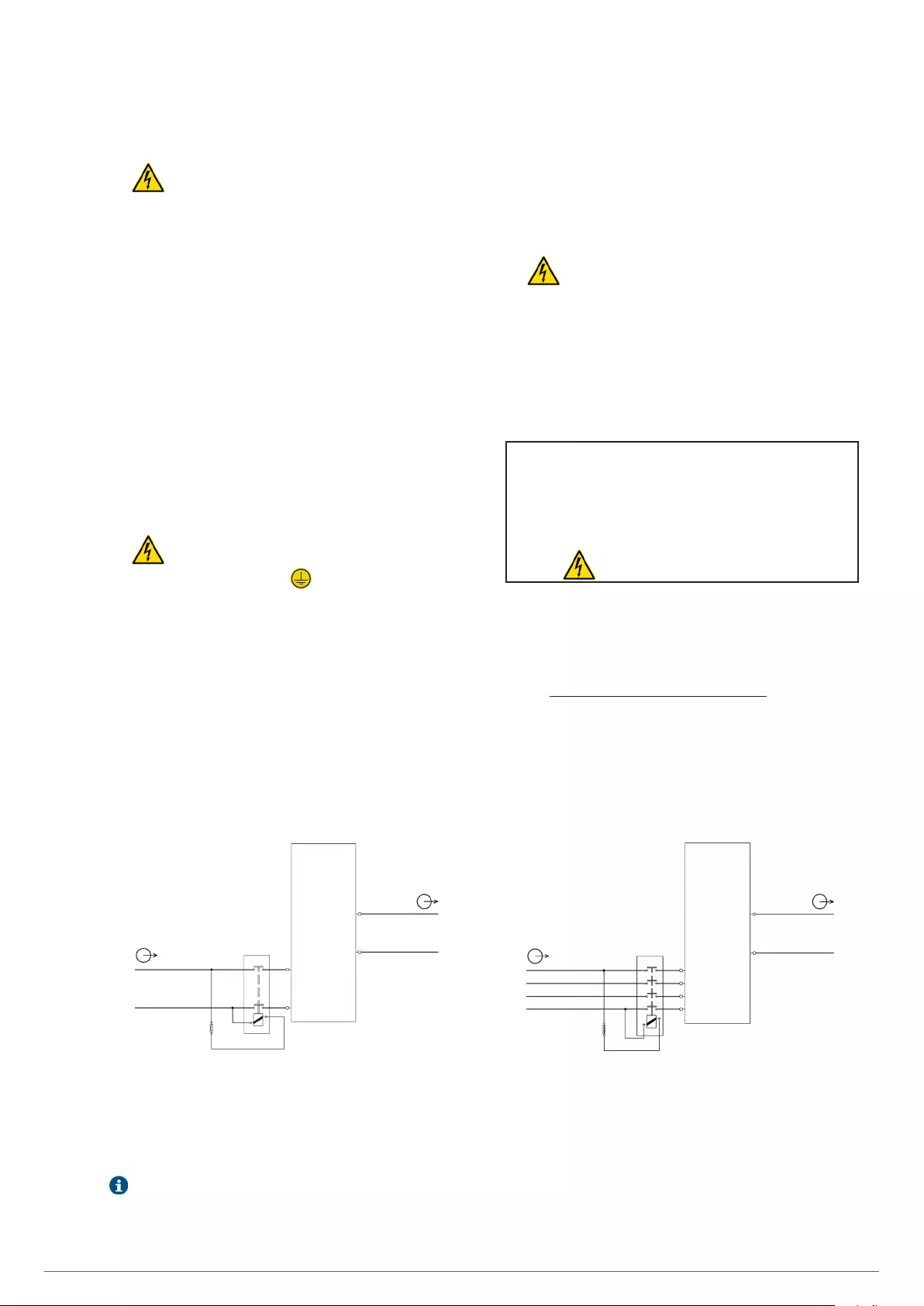
«Backfeed protection» connection for TWIN PRO2.
(BP) Automatic «Backfeed protection» system, external to the UPS (EN-IEC 62040-1).
(1) General purpose fuse or fuses with size 600V AC and 1A of type F.
(2) Two or four poles contactor of 400V AC with minimum distance among the contacts of 1.4 mm and230V ACcoil, with minimum current size of the stated one in
the UPS namopete .
For parallel systems, each equipment must have its own "Backfeed protection" separately.
Conexión «Backfeed protection» para TWIN/3 PRO2.
R
N
(2)
Input
Output
UPS
U
N
(1)
(BP) R
S
T
N
U
N
(BP)
(2)
Salida
Entrada
(1)
SAI
Fig. 16. «Backfeed protection» circuit diagram.
•In accordance with the EN-IEC 62040-1 safety standard the
installation must have an automatic «Backfeed protection»
system, i.e.: a contactor, which prevents power supply or
dangerous energy at the UPS input during a power outage
[seer Fig. 16].
The standard applies to single or three phase input equip-
ments as well as both single units and UPSs in a parallel
systems.
•Do not connect any line between the «Backfeed pro-
tection» and UPS, because the safety standard
would not be met.
•Warning labelling must be placed in all the primary power
switches, installed far from the equipment, in order to warn
the electrical maintenance staff about the presence of a
UPS in the electrical circuit.
The labelling will include the following text or an equiva-
lent one:
Before operating in the circuit.
•Isolate the Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS).
•Check that the voltage among the terminals, PE
included.
Risk of UPS voltage backfeed.
•Connect the input cables to the respective power terminal
strip depending on the available equipment [see Fig. 17].
For parallel systems, it will be needed to repeat the connec-
tions that go from the switchgear panel to each equipment.
Connection to a single phase input:
Connect the power supply cables to the R and N input ter-
minals, by respecting the phase rotation of the neu-
tral and phase stated in the labelling of the equipment
and this manual. Otherwise it can be damaged.

19
In 15 and 20 kVA equipment, the R phase cable will be
connected to the plate and the neutral cable to terminal N.
Connection to a three phase input:
Connect the power supply cables to the R, S T and N input
terminals, by respecting the phase rotation of the
phases and neutral stated in the labelling of the equip-
ment and this manual. Otherwise it can be damaged.
In case of discrepancies between the labelling and the in-
structions of this manual, the first ones will always prevail.
5.2.2. Connection of load/s to the output terminals or output 1.
•As this is an equipment with protection against elec-
trical shocks of class I, it is essential to connect the
main protective earth cable [ ]. Connect this cable to the
terminal before supplying voltage to the input terminals.
•Pay attention to the «Recommended installation» document
in section 5.1.5.4., which states the cross cable section,
protection size and features, etc, ...
•Connect the loads to the output power terminals or output
1, U and N, by respecting the rotation of the phase and
neutral stated in the labelling of the equipment and this
manual [see Fig. 17]. Otherwise the UPS and/or load/s can
be damaged.
•For parallel systems, it will be needed to repeat the connec-
tions that go from the switchgear panel to each equipment.
In case of discrepancies between the labelling and the in-
structions of this manual, the first ones will always prevail.
•As regards to the output protection to be fitted in the
switchgear or manual bypass panel, it is recommended to
split the output power into four different lines. Each one of
them will have a circuit breaker sized to the suitable figure.
This type of energy distribution at the output will allow that
in case of tripping one of them due to a problem in one of the
connected loads in that line, will not affect to the other ones.
Because the rest of loads will have their power supply con-
tinuously, because the only protection that will trip will be
the affected one by the short-circuit in their loads.
•The single phase input equipments up to 10 kVA, apart from
the power terminal strip, also has two IEC outlets protected
by a 10 A breaker.
These outlets are connected in parallel with the output ter-
minals, so it is important to pay attention to the following
consideration:
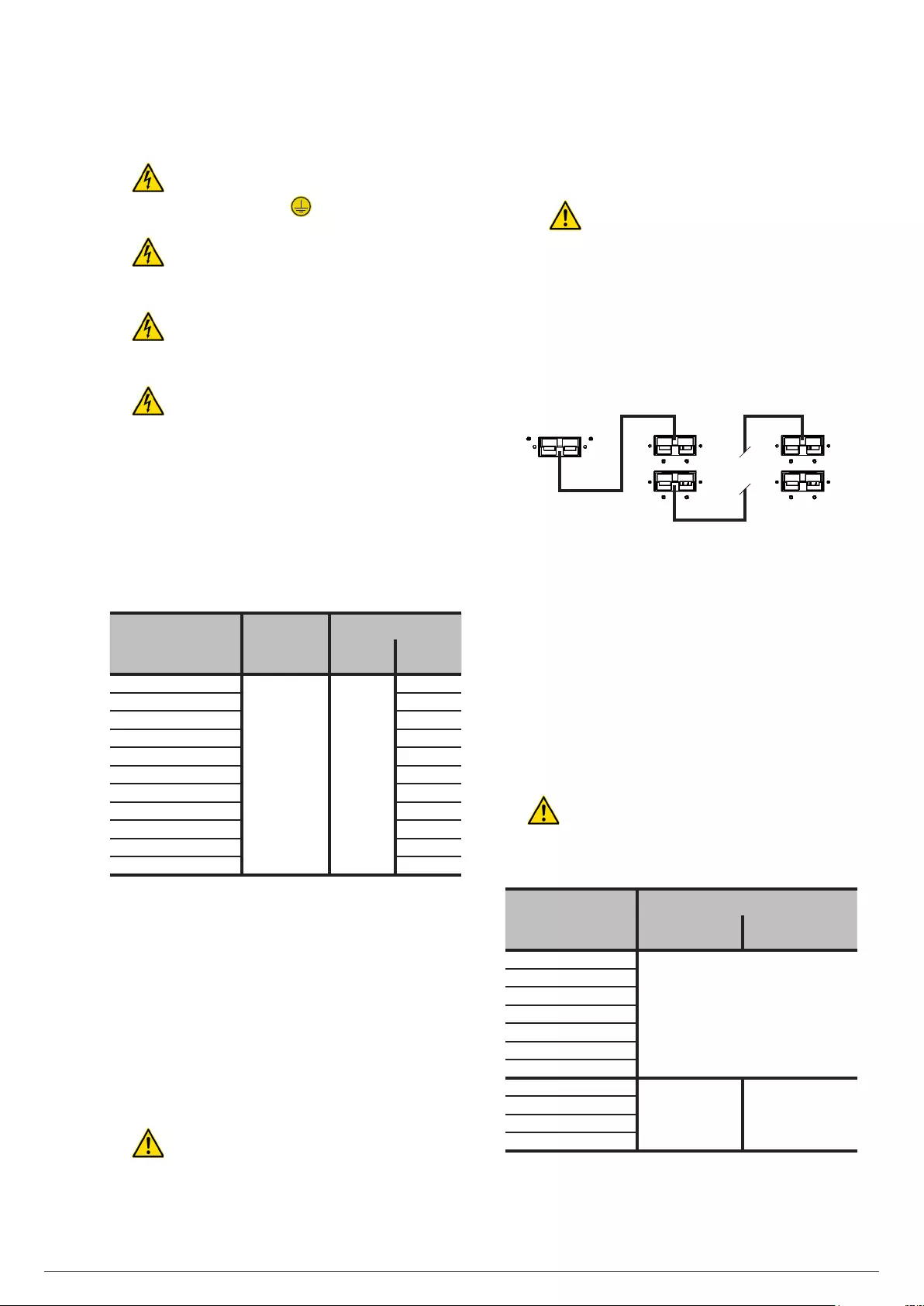
Bonding PE stud
U output phase
Output neutral
Main PE stud
Input neutral
R phase input
Bonding PE stud
U phase output 1
Output neutral 1
U phase output 2
Output neutral 2
(*) + Battery
Main PE stud
Input neutral
T input phase
S input phase
R input phase
– Battery (*)
TWIN/3 PRO2 8.. 20 kVA power terminal stripTWIN PRO2 4.. 10 kVA power terminal strip
(*) Special features of these terminals according to models:
Not available in models of up to 10 kVA.
Not useful in models of 15 and 20 kVA III / II standard.
Implied connection in models of 15 and 20 kVA III / II B1.
Fig. 17. Power terminal strip.
The size of the output protection stated in the rec-
ommended installation document, is done for
the loads connected at the output power terminals.
This protection will be adapted by the fitter or end-user
to the installation in case part of the power is con-
nected to the IEC outlets, otherwise it is possible that
the input of the UPS will not trip, although the overload
alarm in the UPS is triggered.
5.2.3. Connection of the load/s to the output terminals 2
(TWIN/3 PRO2 from 8 to 20 kVA only).
•Models from 8 to 20 kVA with three phase input has a
second set of output power terminals labelled as output
2, which supply voltage from the same source of output 1,
from the inverter or static bypass.
By means of the control panel the output 2 can be set as
Non-critical loads (set to «On»).
•When setting the output 2 to Non-critical loads, the
back up time is reserved for the most critical loads,
which are connected to output 1, by breaking the power
supply of the output 2 during power outages.
• The size of the output protection stated in the recom-
mended installation document, is the sum of both
output 1 and 2, which does not exceed the power rate of
the UPS in any case.
In case of using both terminal strips, the installer or
end-user will fit the suitable protection at each output,
otherwise the input protection of the equipment could
trip, apart from triggering the overload alarm.
•In parallel systems check that the Output 2 is set to the
same figure in all of them, in order to avoid problems.
•Connect the loads to the output power terminals 2, U and
N, by respecting the rotation of the phase and neutral
stated in the labelling of the equipment and this manual [see
Fig. 17]. Otherwise the UPS and/or load/s can be damaged.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
20 SALICRU
5.2.4. Connection with the external battery module and
extended back up times.
•As this is an equipment with protection against elec-
trical shocks of class I, it is essential to connect the
main protective earth cable [ ]. Connect this cable to the
terminal before supplying voltage to the input terminals.
•Respect the instructions stated in this section and
those ones referred to the batteries in the EK266*08
safety instructions, section 1.2.3, because risk of electrical
shock exists, which can cause even the death.
•Before starting the connection procedure between
the battery module or modules and the equipment,
check that the UPS input switch and the battery protection in
the module or modules are turned « Off».
•The battery module has been designed for its equip-
ment. Do not modify the battery capacity or quantity
that makes it.
Also, it exists risk of electrical or electrocution shock due to
the high internal DC voltage, which can cause serious inju-
ries for the health and life.
•Do not connect the battery modules between them or with
UPSs with different DC voltage (figure stated in the rear side
of each equipment).
•Tab. 3 states the physical connection between the UPS and
the battery module or modules.
Model
Batteries
(U bat. block x Nº) =
U nominal / U floating
Two poles switch
DC
voltage(V) Current (A)
SLC-4000-TWIN PRO2
(12 V x 20) =
240 V / 275 V 440
20
SLC-5000-TWIN PRO2 25
SLC-6000-TWIN PRO2 32
SLC-8000-TWIN PRO2 40
SLC-10000-TWIN PRO2 50
SLC-15000-TWIN PRO2 63
SLC-20000-TWIN PRO2 100
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2 40
SLC-10000-TWIN/3 PRO2 50
SLC-15000-TWIN/3 PRO2 63
SLC-20000-TWIN/3 PRO2 100
Tab. 2. Features of the protection to install in the battery
set belonging to the end-user.
•All the standard UPSs include batteries in the same enclo-
sure, less those models called B0 and B1. For the standard
UPSs, the battery protection is done by internal fuses and
they are not accessible by the end-user.
Also, the battery modules have protection and in this case they
are doubled. Once are internal by means of fuses and not ac-
cessible by the end-user and the second ones by means of a
two poles circuit breaker or fuses
•IMPORTANT FOR THE SAFETY: In case of installing the
batteries by yourself, the battery set must have a two
poles circuit breaker or fuses switch, with the size stated in
Tab. 2.
•The connection of the UPS with the battery module will
be done with the supplied cable bundle. First connect one
cable end to the UPS terminals or connector and then the
other cable end to the battery module terminal or con-
nector. See Fig. 18, as an example.
Equipments with connectors, there is not any possi-
bility of wrong polarity connection.
For the equipments with terminals, respect the
polarity and the colour of the cables (red for
positive, black for negative and green-yellow for PE)
stated in the labelling of each module and this
manual.
•When more than one battery module for the UPS is sup-
plied, the connection among them will be in parallel.
• • •
Connector at the
rear side of the UPS
Connectors at the rear side of the
battery modules
Battery
module 1
Battery
module «n»
Fig. 18. Example of connection between a UPS and bat-
teyr modules with connectors.
•In extended back up times, to make easier the connection
between the UPS and the battery modules in parallel, all
the battery modules have two connectors or terminal strips.
•Models with terminals, the polarity and colour of the cables
(red for positive and black for negative) must always be
respected.
•Each battery module is totally independent for
each equipment. It is completely prohibited to
connect two equipments to the same battery
module.
Model
Connection mode with the batteries
In the UPS In the external
battery module
SLC-4000-TWIN PRO2
Connector
SLC-5000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-6000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-8000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-10000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-8000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-10000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-15000-TWIN PRO2
Terminal strip Connector
SLC-20000-TWIN PRO2
SLC-15000-TWIN/3 PRO2
SLC-20000-TWIN/3 PRO2
Tab. 3. Connection between the UPS and battery module
or modules.

21
5.2.5. AC power supply for the battery charger built in
the battery module.
•Some battery modules have an additional charger, which
means making some additional work.
They can be identified, because they include an IEC male
connector, circuit breaker and cooling grid
•Together with the module, it is supplied a power cord with
an IEC female connector in one end and Schuko plug in the
other end.
•The installation must have a wall outlet, schuko type, pro-
tected by a circuit breaker of 6 A, in order to feed the charger
with 230 V AC.
•Those equipments with more than one battery module of
this type, each one of them must have the Schuko wall
output with its corresponding protection.
•Insert the cable into the IEC connector of the battery module
and the schuko plug into the wall outlet of 230 V AC.
5.2.6. Connection of the main protective earth and
bonding earth .
•As this is an equipment with protection against elec-
trical shocks of class I, it is essential to connect the
main protective earth cable [ ]. Connect this cable to the
terminal before supplying voltage to the input terminals.
•Make sure that all the loads connected to the UPS are only
connected to its bonding earth stud . The fact of not lim-
iting the connection this bonding earth of the load or loads
and battery module or modules to this single point, will
break backfeed loops of earth that will decrease the quality
of the energy supplied.
•Those terminals labelled as bonding earth , are joined
among them to the main protective earth stud and to the
ground of the equipment.
•Never and under no circumstances disconnect the
protective earth cable from the building and/or UPS.
5.2.7. EPO terminals (Emergency Power Off).
•The UPSs has two terminals to install a remote Emergency
Power Off button -EPO-.
•The equipment is delivered from factory with the EPO circuit
closed -NC-. So, the UPS will break the output when the
emergency power off button opens the circuit:
Or by removing the own female connector from the
equipment, because this connector includes a cable as
a bridge mode, which closes the electrical circuit [see
Fig. 19-A].
Or when pressing the external button, which belongs to
the end-user and it is installed between the terminals
of the connector [see Fig. 19-B]. The connection of the
button will be normally closed -NC-, so it will open the
electrical circuit when pressing it.
•By means of the communication software, the inverse func-
tion can be set.
Less particular cases, it is better to not use this type of con-
nection, because in case of one of the cables were cut, the
EPO will not break the output voltage.
On the other hand, the use of the normally closed contact ,
the cut cable would be detected immediately, because the
power supply to the loads would be broken.
•To restore the normal operating of the UPS, it is needed to in-
sert the connector with the cable as a bridge mode again in the
equipment or deactivate the EPO button. The equipment will
be turned ON automatically.
A B
Fig. 19. Connector for the external EPO.
5.2.8. Terminals for digital Input and Output.
•The equipment has a terminal strip of four terminals for a
digital input and output [see Fig. 20].
The «Start up-Shutdown» digital input. When the equipment
is turned ON, when applying a voltage between 5 and 12 V
DC, it is shutdown.
The static bypass is enabled from factory. In this
situation, when the inverter is shutdown the
output terminals will supply voltage through the in-
ternal static bypass.
Disable the bypass function through the control panel,
when it is required to break the output when the shut-
down order has been triggered.
Error or fault dry contact. Any error or fault of the UPS
will trigger the digital output (-NO- dry contact of 24V
DC 1A). (ATTENTION to the applied voltage and current
to the contact).
– Digital input
+ Digital input
Error or fault dry
contact output
Fig. 20. Digital input and output connector.
5.2.9. Terminals for the manual bypass auxiliary
contact.
•The manual bypass switch of the equipment has a micros-
witch located under its mechanical lock. This contact is nor-
mally opened and it is extended till a terminal strip located
in the rear side of the equipment [see Fig. 21] and internally
connected with the own UPS control.
•The manual bypass panels supplied under request, they
include a terminal strip with two terminals connected in
parallel with the normally opened auxiliary contact of the
manual bypass switch of the own panel. The auxiliary con-
tacts of the manual bypass are advanced to its closing.
•The connection between the auxiliary contact of the panel
and the UPS or UPSs must be in parallel. Therefore, in case
any of the auxiliary contacts closes the circuit will trigger
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

22 SALICRU
the command to shutdown the inverter, so the equipment
will supply output voltage through the static bypass, unless
it is disabled by means of the control panel, which in that
case would break the load feeding.
•In parallel systems, the manual bypass switch of the
switchgear panel will have a terminal strip for each
equipment. Under no circumstances joint the contacts
of the different UPSs among them, because the ground of
the UPS control would be joined.
•In case of buying the manual bypass panel from
other sources, check that it has the stated auxiliary
contact and connect it to the terminal strip of the UPS or
UPSs in parallel systems. The auxiliary contact type must
be advanced to its closing.
•As safety measures, it is ESSENTIAL, to connect
the terminals strips of the UPS, and even for the
loads, with the ones of the manual bypass panel with the
same function. Therefore, it will be avoided any wrong han-
dling of the manual bypass switch/es when the UPS or
UPSs are turned ON, which could cause a total or partial
failure of the installation and/or loads.
Fig. 21. Auxiliary contact connector of the UPS manual
bypass.
5.2.10. Parallel connection.
5.2.10.1. Introduction to the redundancy.
N+X is usually the most reliable power structure. N means the
minimum quantity of equipments that the total load needs; X
means the quantity of redundant equipments, that is to say, the
quantity of faulty UPSs that the system can allow at the same
time. As higher is the X, the more reliable will be the system.
For those situations, where the reliability is the most important,
N+X will the optimal mode.
Up to 3 equipments can be connected in parallel to set a shared
output and redundant in power.
5.2.10.2. Parallel installation and operating.
•The communication line -COM- means a low safety
voltage circuit.
To preserve the quality of them, they must be installed
separate from other lines with dangerous voltages (energy
distribution line).
Parallel connection bus
Current sharing signal bus
UPS nr 1 UPS nr 3UPS nr 2
Communication bus
Current sharing signal bus
Fig. 22. Connection of the communication bus and current
sharing signal.
Input circuit breaker switches
Output circuit breaker switches
Man ual Bypass
SAI nº 1 SAI nº 2 SAI nº "3"
Input
To loads
Fig. 23. Parallel UPS installation with a switchgear panel
with manual bypass.
•Parallel connection bus. Use the 15 pins DB15 connectors
and shielded cable bundle to joint 3 equipments maximum.
Each bundle has a male and female connectors at its end,
which have to be connected between two correlative equip-
ments. It is essential to close the loop of the parallel bus
among the equipments.
23
The length of the parallel cable is 1.5 metres and it can't be
extended under no circumstances, due to the risk of interfer-
ences that it would mean.
Fig. 22 shows an installation of two equipments in parallel.
For three UPSs proceed in the same way to close the com-
munication bus and current sharing circuits.
•Bus connection of the signal of current. Joint the equip-
ments, by using the cable bundle with connectors in both
ends and connecting them in the connectors of both correla-
tive equipments as Fig. 22 shows. Finally, close the bus loop
between the last and first equipment.
The length of the cable is 1.5 metres and it can't be extended
under no circumstances, due to the risk of interferences that
it would mean.
Fig. 22 shows an installation of two equipments in parallel.
For three UPSs proceed in the same way to close the com-
munication bus and current sharing circuits.
•Parallel installations must have a switchgear panel with sep-
arate input and output protections for each UPS, apart from
a manual bypass switch with mechanical lock, see Fig. 23.
For more information, about the descriptions referred to the
manual bypass and the indications of the «Recommended
installation» see section 5.1.5.4.
•Respect the stated procedures in the previous sections, for
the input and output connections of each equipment.
•For those equipments with extended back up time, respect
the stated procedures for the battery modules, which are de-
scribed in the previous sections.
•In parallel systems, where the length and cross sec-
tion of the cables that go from the switchgear panel
to each UPS and from the UPS to the switchgear panel will
be the same for all them, with no exception.
In the worst conditions, the following deviations must be
strictly respected:
When the distance between the parallel UPSs and the
switchgear panel is less than 20 metres, the length
difference among the input and output cables of each
equipment must be lower than 20%.
When the distance between the parallel UPSs and the
switchgear panel is over 20 metres, the length difference
among the input and output cables of each equipment
must be lower than 10%.
5.2.11. Communication port.
5.2.11.1. RS232 and USB ports.
• The communication line -COM- means a low safety
voltage circuit. To preserve the quality of them, they
must be installed separate from other lines with dangerous
voltages (energy distribution line).
•The RS232 and USB interface are used by the monitoring
software and firmware updating.
•It is not possible to use both ports (RS232 and USB) at the
same time.
•Tab. 4 shows the pin-out of the RS232 signal in the DB9
female connector. The RS232 is a serial data port, so an
important amount of information can be sent through a
communication cable of 3 wires.
•The USB communication port is compatible with the USB
1.1 protocol for the monitoring software.
5 1
9 6
2 1
3 4
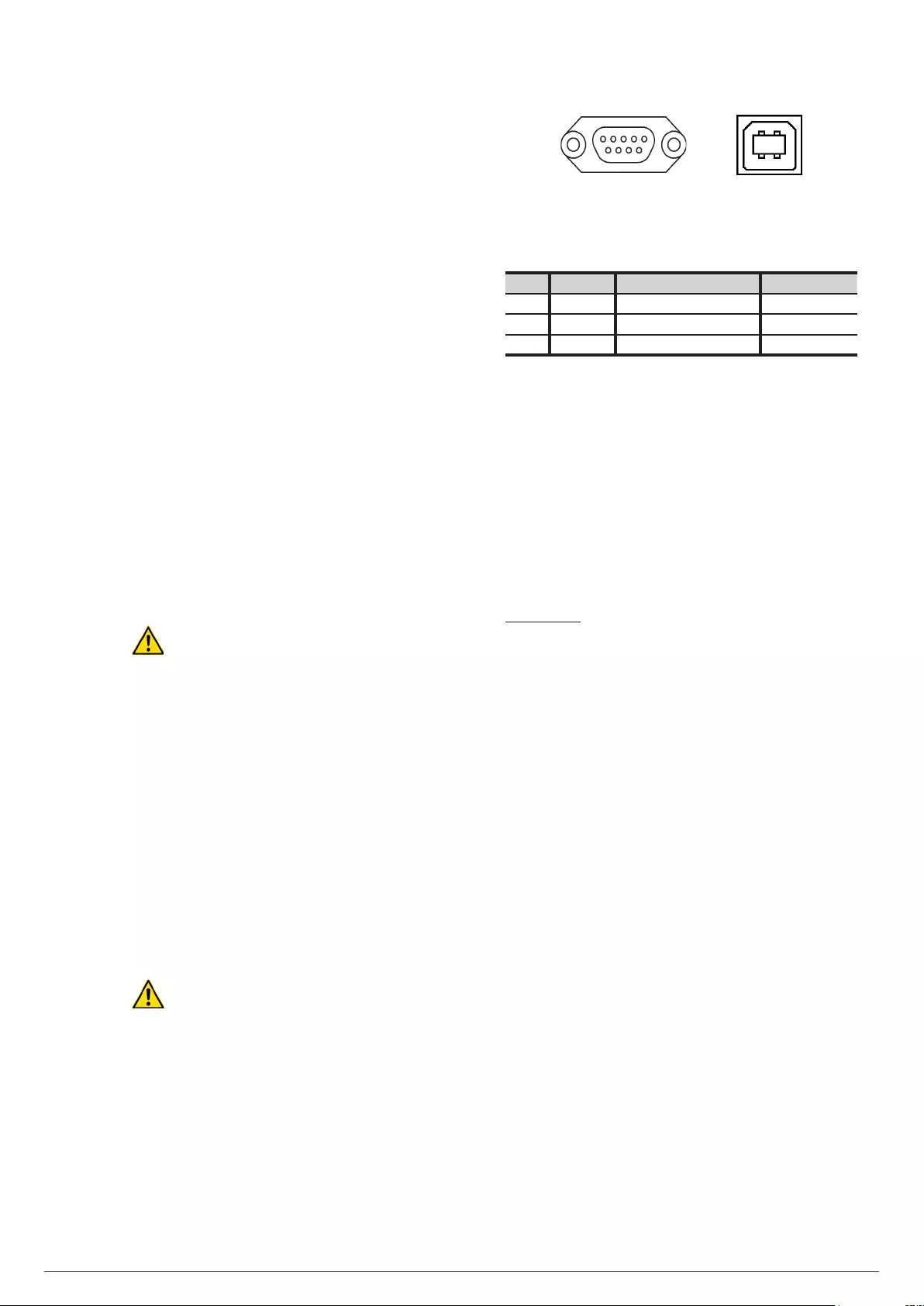
Fig. 24. DB9 connectors for RS232 and USB.
Pin # Ref. Description Input / Output
2 RS232 TXD (serial data transmission) Output
3 RS232 RXD (serial data reception) Input
5 RS232 RS232 ground signal GND
Tab. 4. DB9 connector pinout, RS232.
5.2.12. Intelligent slot to insert the communication card.
•Different communication cards can be inserted into the slot:
Programmable dry contacts.
SNMP adaptor.
RS485 Modbus adaptor.
•Each option card is supplied with its own particular docu-
mentation. Read it before installing them.
Installation.
•Remove the protection cover from the slot of the equip-
ment.
•Take the corresponding card and insert it into the reserved
slot. Make sure that it is well connected, to do it the resist-
ance that own connector faces when it inserted into the
slot has to be overcome.
•Make the needed connections of the terminal strips or con-
nectors depending on each case.
•Put the new protection cover supplied with the option cards
and fix it by means of the same screws that previously fixed
the original one.
•For more information, contact with our T.S.S. or our nearest
distributor.
5.2.13. Software.
•Download the free software - Viewpower.
Viewpower is a UPS monitoring software, which has a user
friendly interface for monitoring and control. This software,
in case of power outage provides an auto Shutdown for a
system based on several computers. With this software,
the end-users can monitor and control any UPS hosted in
the same IT network, by means of the communication port
(RS232 or USB), no matter the distance among them.
•Installation procedure:
Go to the website:
http://support.salicru.com
Choose the operating system that you need and follow
the instructions described in the website to download
the software.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

24 SALICRU
Fig. 25. Screen shot of the main screen of ViewPower
monitoring software.
5.2.14. Considerations before commissioning with the
loads.
•It is recommended to charge the batteries for 12
hours at least before using the UPS for first time.
To do it, supply the input of the equipment and turn the
input switch «On». The battery charger will be auto-
matically started up.
For battery modules.
Those models with extended back up times with one or
more battery modules, the fuse or battery switch has to
be turned «On» too.
•Although the equipment can work without charging the bat-
teries for stated 12 h, the risk of a long power outage for
the first operating hours must be evaluated, because the
back up time of the UPS will be lower.
•Do not start up the equipment and loads before section 6
states it.
Nevertheless, when it is started up, it will be done gradu-
ally, in order to avoid possible issues, at least in the first
UPS start up.
•In case of connecting inductive loads with high consump-
tion, apart from the sensitive loads, like laser printers or
CRT monitors; their worst inrush current will be kept in
mind in order to avoid blocking the equipment.
Depending on the equipment, for this type of loads, which
are considered NON-CRITICAL, the equipment has a pro-
grammable terminal strip. Depending on the setting of that
terminal strip, the power supply will be broken or not in
case of power outage.

25
6. OPERATING.
6.1. COMMISSIONING.
6.1.1. Checking before commissioning.
•Make sure that all connections have done properly with the
correct torque, by respecting the labelling of the equipment
and the instructions of section 5.
•Check that the UPS switch and battery module or modules
are turned -«Off»-.
•Make sure that all the loads are turned «Off».
Shutdown the loads before starting up the UPS and
turn on the loads one by one when the UPS is started
up only. Before shutting down the UPS, check that all the
loads are turned «Off» and out of service.
•It is very important to proceed in the established order.
•See figures 1 to 3 for UPS views.
•Fig. 23 shows a conceptual switchgear panel with manual
bypass for a parallel system, which illustrates only one
equipment by adapting the quantity of switches.
6.2. START UP AND SHUTDOWN OF THE UPS.
6.2.1. UPS start up with AC mains present.
•Check that the power supply connection is correct.
•Supply AC voltage to the equipment (turn the input switch
from switchgear or manual bypass panel to «On». In case
the panel includes output switch turn it «On» too.
•Turn the battery switch «On» (models B0 and B1).
•Turn the input switch of the UPS «On».
The output terminals will be supplied through the
internal static bypass of the equipment.
The fan or fans, depending on the model, will be turned on.
Next the main start screen will be displayed after the initial
equipment test.
•Press over the start up key for more than 0.5 seconds,
the acoustic alarm will beep for 1 sec. and the UPS will be
started up.
•After a few seconds, the UPS will be on «Normal mode». If
the input AC voltage is wrong, the UPS will shift to «Battery
mode», with no break in the power supply to the output
terminal strip.
•Start up the load or loads, without exceeding the nominal
power rate of the equipment.
6.2.2. UPS start up with no AC mains (Cold start).
•If the switchgear panel is available turn the input and
output switches «On».
•Turn the battery switch «On» (models B0 and B1).
•Turn the input switch of the UPS «On».
•Press over the start up key for more than 0.5 seconds,
the acoustic alarm will beep for 1 sec. and the UPS will be
started up
The fan or fans, depending on the model, will be turned on.
Next the main start screen will be displayed after the initial
equipment test.
It is necessary to press the ‘ON’ button for a second time,
about 5 to 7 seconds after the first press, for longer than
0.5 seconds.
•After a few seconds, the UPS will be on «Battery mode».
so it has to be considered: their charge level, the remaining
back up time and the risk that means to operate on this
operating mode.
If the AC mains is restored, the UPS will shift to «Normal
mode», with no break at the power supply of the output
terminals.
•Start up the load or loads, without exceeding the nominal
power rate of the equipment.
6.2.3. UPS shutdown with AC mains present.
•Shutdown the load or loads.
•Press the key for more than 0.5 seconds to shutdown the
inverter. The acoustic alarm will be for 1 sec. The equip-
ment will shift to «Bypass mode».
The output terminals will be supplied through the
internal static bypass stage of the equipment.
•To break the UPS output voltage, turn «Off» the input switch
of the UPS or turn «Off» the input and output protections
located in the switchgear distribution panel.
After a few seconds, the LCD panel is off and the equip-
ment will be out of service.
6.2.4. UPS shutdown with no AC mains.
•Shutdown the load or loads.
•Press the key for more than 0.5 seconds to shutdown the
inverter. The acoustic alarm will beep for 1 sec. The equip-
ment will break the power supply of the output terminals.
After a few seconds, the LCD panel is off and the equip-
ment will be out of service.
•To leave the equipment completely isolated, turn the input
and output switches from switchgear panel «Off».
6.3. MANUAL BYPASS SWITCH (MAINTENANCE).
The internal manual bypass in the SLC TWIN PRO2 UPS is
very useful, but a wrong handling can cause irreversible con-
sequences for both UPS and connected loads. Therefore, it is
important to respect the manoeuvring on the switches as it is
described in the following sections.
In case of mains failure, it is not possible to operate on this
mode.
6.3.1. Shifting to maintenance bypass.
•The procedure to shift from normal mode to maintenance
bypass is the same for single unit and parallel system, less
in the quantity of actions to make:
In case of handling the switches in the different
order as the stated, it will break the power
supply to the loads and even can cause damage
to the UPSs.
For a single equipment.
–Press the start up key for than 0.5 sec. in order to
shutdown the inverter. The acoustic alarm will beep
1 sec. The equipment will shift to «Bypass mode».
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

26 SALICRU
For a parallel system.
–Press the start up key for than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs
in order to shutdown the inverter. The acoustic
alarm will beep 1 sec. The equipments of the par-
allel system will shift to «Bypass mode».
Shift the equipment or equipments to manual bypass
as follows:
1. Remove the mechanical lock from bypass manual
switch from switchgear panel and turn it «On».
2. Remove the manual bypass switch cover, located
in the rear side of the UPS and turn it to «BYPASS»
position.
In parallel systems proceed in the same way in all
the equipments.
Keep in mind that on «Bypass mode» or with the
manual bypass switch on «BYPASS» position,
the loads will remain exposed to the voltage and fre-
quency fluctuations from mains, blackouts and power
outages, so it was possible choose a day with the lowest
failure probability (days with no fluctuations, days with
no storms,...) and speed up the process.
Turn the input circuit breaker switch of the equipment
to «Off».
In parallel systems proceed in the same way in all the
equipments.
Turn all the input and output circuit breakers of the
switchgear panel to «Off».
The system is completely shutdown and out of service
and loads are supplied by means of the manual bypass
switchgear panel.
Make the needed maintenance tasks.
6.3.2. Shifting to normal mode.
•The procedure to shift from maintenance bypass to normal
mode is the same for single unit and parallel system, less
in the quantity of actions to make:
In case of handling the switches in the different
order as the stated, it will break the power
supply to the loads and even can cause damage
to the UPSs.
Turn the input and output circuit breaker switches from
switchgear panel to «On».
Turn the input switch of the own equipment to «On».
In parallel systems proceed in the same way in all the
equipments.
Turn the manual bypass switch, located in the rear side
of each equipment to «UPS» position and put back their
protection covers.
In parallel systems proceed in the same way in all the
equipments.
Turn the manual bypass switch of the switchgear panel
to «Off» and put back its mechanical lock.
In order to avoid wrong handling, the mechan-
ical lock, protection covers of the manual by-
pass and their fixing screws have to put back.
For a single equipment.
–Press the start up key for more than 0.5 sec, the
acoustic alarm will beep 1 sec. The equipment will
start up.
For a parallel system.
–Press the start up key for more than
0.5 sec. in all UPSs and each one of them will be
started up, finally the parallel system will be on
«Normal mode».
Load or loads are protected by the parallel system
again.
6.4. PARALLEL SYSTEM OPERATING
•To operate with parallel systems, in order to avoid prob-
lems, check that the output 2 of each UPS is set to the same
parameter in all of them.
•The operating described hereafter, is for equipments with
the standard setting preset from factory.
•Check that the load or loads and/or the output circuit
breaker switches are turned «Off».
•Turn the input circuit breaker switches from switchgear
panel or manual bypass to «On» and the own input switches
in each UPS too.
The UPSs supply AC voltage by means of their internal
static bypass of each unit. Check if any alarm has been trig-
gered in the LCD panel. Measure the output voltage at the
output terminals of each UPS separately, in order to check
if the voltage difference is lower than 1 V among them. In
case the voltage difference is higher than 1 V, check the
wiring and the previous installation instructions.
•If the difference voltage is lower than 1 V, press over the
start up key for more than 0.5 seconds in all UPSs and
each one of them will be started up and all the UPSs will
shift to «Normal mode».
Measure the output voltage a the output terminals of each
UPS separately, in order to check if the voltage difference is
lower than 0.5 V among them. In case the voltage difference
is higher than 1 V, the UPSs must be set (contact with the
T.S.S.).
•Continue with the procedure if everything is correct only.
Press the start up key for than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs and
each one of them will be shutdown.
Turn all the output switches from switchgear or manual by-
pass panel to «On». The output terminals of the switchgear
panel will be supplied by means of the internal static by-
pass of the equipment.
•Press the start up key for more than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs and
each one of them will be started up and all the UPSs will
shift to «Normal mode».
•Start up the load or loads.
•Do not leave one of the UPSs with no neutral con-
nection as regard to the rest one. The neutral of all
UPSs must be joined among them, either through the input
or through the output. Do not open the input and output
circuit breakers of the switchgear panel of one UPS at the
same when the parallel system is turned On, otherwise the
UPS can be damaged and the loads will be shutdown.
6.5. HOW UPGRADE THE PARALLEL SYSTEM WITH A
NEW UPS OR DOWNGRADE TO SINGLE MODE.
•To do this manoeuvring, the parallel system must have a
manual bypass panel for a parallel system.
In case of not having it, it has to be foreseen a complete

27
shutdown of the system and loads connected to it.
•The steps here stated are to add an equipment in a parallel
system of two units. To upgrade a single unit to a parallel
system of two equipments proceed in the same way.
•The switchgear panel will have the corresponding input and
output switches for each UPS apart from the manual bypass
one. Otherwise it will be needed to adapt the panel or pur-
chase a new one, if it has not been foreseen previously.
•Due that the own parallel bus communication has to be
changed in order to integrate the new UPS into the par-
allel system (cable bundle with DB15 connectors), it will be
needed to shift the power supply of the loads to manual by-
pass.
Proceed as follows:
Press the start up key for than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs in
order to shutdown the inverter. The acoustic alarm will
beep 1 sec. The equipments of the parallel system will
shift to «Bypass mode».
Transfer the equipments to manual bypass as follows:
1. Remove the mechanical lock of the manual bypass
switch from switchgear panel and turn it «On».
2. Remove the protection cover of the manual bypass
switch, which is located in the rear side of the
equipment. Put all the manual bypass switches
from UPS to «BYPASS» position.
Keep in mind that on «Bypass mode» or with the
manual bypass switch on «BYPASS» position,
the loads will remain exposed to the voltage and fre-
quency fluctuations from mains, blackouts and power
outages, so if it was possible choose a day with the
lowest failure probability (days with no fluctuations, days
with no storms,...) and speed up the process.
Turn the own input circuit breaker switches of each
equipment to «Off».
Turn all the input and output switches from switchgear
panel to «Off».
•Before adding the new TWIN PRO2 UPS to the system,
make the needed steps, in order to leave it in the same
situation as the rest ones (input switch turned «Off» and
manual bypass switch with no cover and turned to «BY-
PASS»).
•Add the new UPS to the system, by attending the procedure
stated in section 5.2.10.2, for the parallel connection.
•Disconnect the communication bus between the first and
last equipment, and reconnect it by including the new UPS.
It is compulsory to close the loop of the communication bus
for its correct operating.
Carry out the same operation for the current signal bus.
•Turn the input circuit breaker switch of each UPS from
switchgear panel to «On».
•Turn the input circuit breaker switches from each UPS to
«On».
Turn the internal manual bypass switch of each UPS to UPS
position.
The output switches of each UPS from switchgear panel
must be turned off.
Put the locking cover of the manual bypass switch of each
UPS.
The UPSs supplies output voltage by means of the internal
static bypass of each unit. Check if any alarm has been
triggered in the LCD panel in any UPS. Measure the output
voltage a the output terminals of each UPS separately, in
order to check if the voltage difference is lower than 1 V
among them. In case the voltage difference is higher than 1
V, check the wiring and the previous installation instructions.
•If the difference voltage is lower than 1 V, press over the
start up key for more than 0.5 seconds in all UPSs and
each one of them will be started up and all the UPSs will
shift to «Normal mode».
Measure the output voltage a the output terminals of each
UPS separately, in order to check if the voltage difference is
lower than 0.5 V among them In case the voltage difference
is higher than 1 V, the UPSs must be set (contact with the
T.S.S.).
•Continue with the procedure if everything is correct only.
Press the start up key for than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs and
each one of them will be shutdown.
Turn all the output switches from switchgear or manual
bypass panel to «On». The output terminals of the switch-
gear panel will be supplied by means of the internal static
bypass of the equipment, the same voltage as the manual
bypass line
•Turn the manual bypass switch from switchgear panel to
«Off» and put the mechanical lock back to avoid possible
accidents.
•To avoid inappropriate manoeuvring, it is better to
put back the mechanical lock and the manual bypass
covers and their fixing screws.
•Press the start up key for more than 0.5 sec. in all UPSs and
each one of them will be started up and all the UPSs will
shift to «Normal mode».
•The load or loads are protected by the parallel system
again.
6.6. HOW TO REPLACE A FAULTY UPS FROM THE
PARALLEL SYSTEM.
•The steps to follow for replacing a UPS in a parallel system
based on two or three equipments are exactly the same as to
upgrade the system, less bridging the gaps of the type of action
to make. Proceed as it is described in section 6.4.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
28 SALICRU
7. CONTROL PANEL WITH LCD.
7.1. CONTROL PANEL.
Fig. 26. Control panel view.
Button Description
/ o
«ON / ENTER»
ON. Press this key for more than 0.5 sec. to start up the
UPS [inverter of the equipment].
ENTER. Press this key to confirm a selection in the setting
menu.
o
«OFF / ESC»
OFF. Press this key for more than 0.5 sec. to shutdown the
equipment, when the equipment is started up previously.
ESC. Press this key to escape and go back to the previous
setting menu.
/ o
«TEST / UP»
TEST. Press this key for more than 0.5 sec. to make a
battery test when the equipment works on AC or FC (*)
UP. Press this key to show the next setting menu screen .
/ o
«MUTE / DOWN»
ALARM SILENT. Press it for more than 0.5 sec. to silent
the acoustic alarm (see section 6.2.3.2).
DOWN. Press this key to show the previous setting menu
screen.
/ o
«TEST / UP» +
/ o
«MUTE / DOWN»
UP + DOWN. Press boht keys simultaneously for more
than 1 sec. to enter and escape from setting menu .
(*) CF. Operating mode as Frequency Converter. With this operating
mode the static bypass is disabled.
Tab. 5. Control panel keypad functions.
•The UPS has a control panel, which has the following parts:
Four buttons with the functions described in table 5.
A backlight LCD with the messages displayed as text or
graphics form, with black letter and blue backgrounds.
Four led indicators, which provides the following in-
formation:
–Bypass (yellow).
–Line (green).
–Battery (yellow).
–Fault (red).
7.2. TABLE 6 SHOWS THE INDIVIDUAL FUNCTION
OF EACH ONE OF THEM OR THEIR INTERACTION
WITH OTHERS, AS REGARDS TO THE UPS
STATUS. LED FUNCTIONS.
UPS status Leds
Bypass Line Battery Fault
UPS ON
No output mode
Bypass mode
AC mode
Battery mode
FC mode
ECO mode
Battery test
Fault
: Led permanent lighting.
: Led off.
Tab. 6. Led optical indicators function.
7.2.1. Acoustic alarms.
Description Modulation or alarme tone Silent
UPS status
Bypass mode Beep every 2 minutes.
YesBattery mode Beep every 4 seconds.
Fault Continuous.
Warning
Overload 2 Beeps every second. Yes
Other Beep every 1 second.
Faults
All Continuous. Yes
Tab. 7. Acoustic alarms. Condition and modulation or
tone.
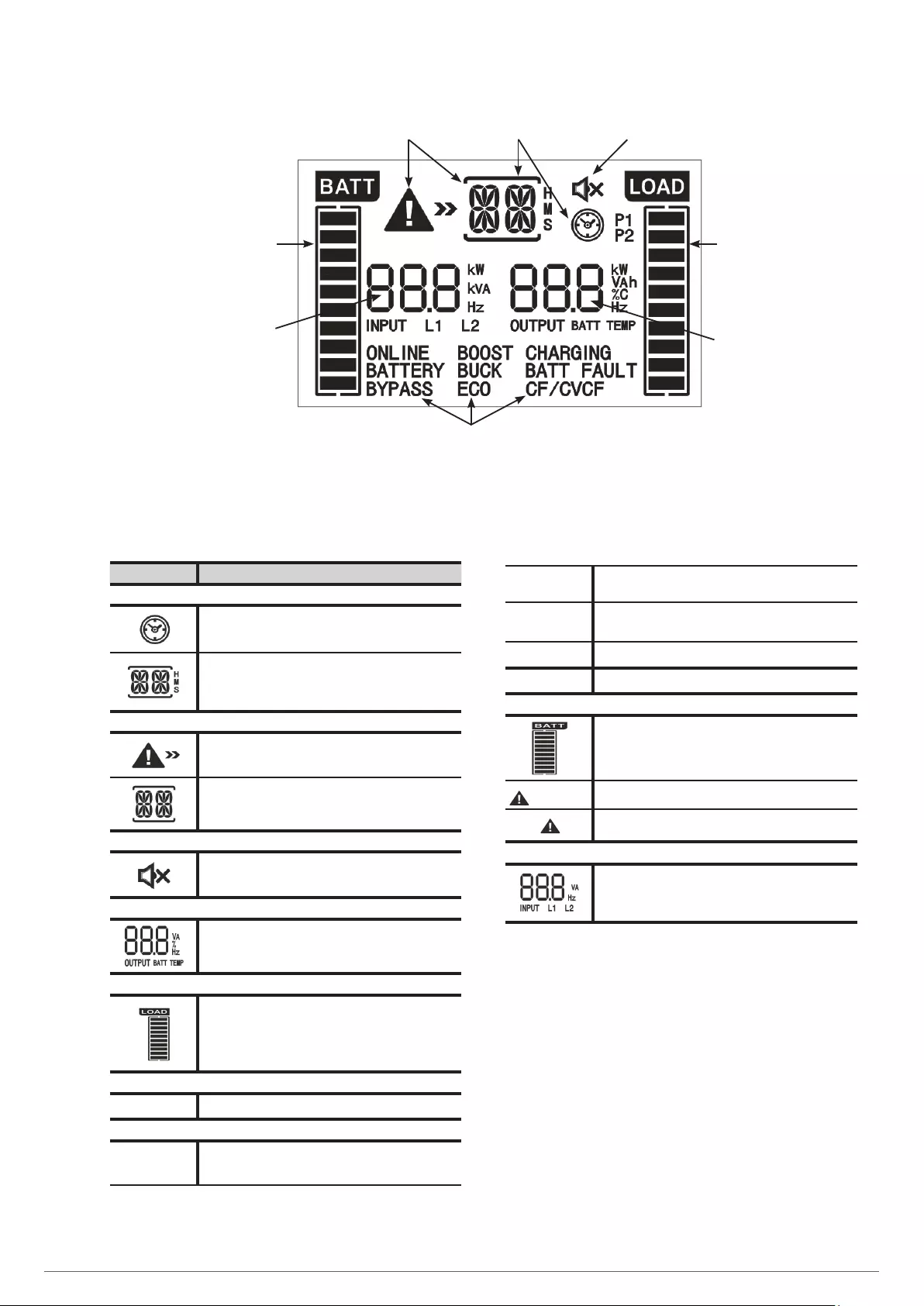
29
Information of input
and battery voltage
Information of the
fault
Information of battery
charge level
Information of the
remaining time
Information of
the load level
connected at the
output
Information about the operating mode of the equipment
Information of
the load level
connected at the
output
Acoustic alarm
disabled
Fig. 27. Control panel with LCD.
7.2.2. Messages shown in the LCD.
Display Function
Information of the back up time.
It states the remaining back up time in analogical clock
mode.
It states the remaining back up time in a digital clock
mode.
H.- Hours, M.- Minutes, S.- Seconds.
Information of the fault.
As a warning mode indicates that there is a fault.
Numerical code from setting menu. See table 9 from
section 7.5.
Information of the acoustic alarm.
It indicates that the acoustic alarm has been disabled.
Information of the output voltages.
It indicates the output voltage or output frequency.
V AC.- output voltage, Hz.- Output frequency.
Information of the load level connected to the output.
It indicates the load connected at the output in %, by
means of four segments, which are equivalent to the
following proportion: 0-25 %, 26-50 %, 51-75 % and 76-
100 %.
Information of the programmable outputs
P1 It indicates that the programmable outputs are activated.
Information about the operating mode of the equipment.
BATTERY
It indicates that the equipment is supplying output voltage
from the battery (battery mode).
BYPASS It indicates that the equipment is activated in ECO mode.
ECO It indicates that the equipment is supplying output voltage
by means of the bypass (ECO mode).
ONLINE It indicates that the inverter is working.
P1 It indicates that the output is activated.
Information of the battery charge level.
It indicates the battery charge level in %, by means of
four segments, which are equivalent to the following
proportion: 0-25 %, 26-50 %, 51-75 % and 76-100 %.
BATT FAULT It indicates that the battery is not connected.
It indicates that the battery voltage is low.
Information of the input and battery voltage.
It indicates the input voltage, input frequency or battery
voltage. V AC.- Input voltage, V DC.- Battery voltage, Hz.-
Input frequency.
Tab. 8. Indications shown in the LCD of the control panel.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

30 SALICRU
7.3. MEANING OF THE ABBREVIATIONS DISPLAYED IN
THE LCD OF THE CONTROL PANEL.
Code LCD message Meaning
ENA A
U
EEnabled.
DIS d1S Disabled.
ATO AtO Automatic.
BAT bAt Battery.
NCF CF
U
Normal mode (not available for FC).
CF CF Frequency converter mode.
SUB SUb Down.
ADD Add Up.
ON ON Start up.
OFF OFF Shutdown.
FBD Fbd Not allowed.
OPN OP
U
Allowed.
RES RES Reserved.
N.L
U
.LNeutral lost.
CHE CHE Checking.
OP.V OP.UOutput voltage
PAR PAR Parallel, 001 is the first one.
EPO EP Emergency power off.
FR FR Frequency.
OPL OPL Load percentage.
RRPhase R.
SSPhase S.
TTPhase T.
Tab. 9. Abbreviations shown in the LCD.
7.4. SETTINGS IN THE LCD CONTROL PANEL.
Parameter 1
Parameter 2 Parameter 3
Fig. 28. Parameter layout in the LCD panel.
•Parameter 1: Code of setting menu. Consult table 9 for its
description.
•Parameter 2 and 3 are the options of the figures for each
setting menu.
Select the «Down» or «Up» keys to change the menu
or parameters.
Any parameter setting is only saved when the UPS
is shutdown on normal mode and internal or ex-
ternal batteries are connected, depending on the case. (It is
understood as shutdown on normal mode to turn off the
input circuit breaker switch when the equipment is on by-
pass or no voltage -depending if the static bypass is ena-
bled or disabled-).
31
Code
Decription Bypass
mode/ No
output
mode
AC mode ECO
mode FC mode Battery
mode
Battery
test
TWIN PRO2 TWIN/3 PRO2
01 Output voltage. YES - - - - -
02 Output frequency. YES - - - - -
(*) 03 Bypass voltage range. YES - - - - -
(*) 04 Bypass frequency range. YES - - - - -
05 Enable / disable ECO mode. YES - - - - -
(*) 06 ECO mode voltage range. YES - - - - -
(*) 07 ECO mode frequency range. YES - - - - -
08 Bypass mode setting. YES YES - - - -
09 Maximum battery discharge time setting.- YES YES YES YES YES YES
10 Reserved. -- Reserved for future options.
- Programmable output setting. YES YES YES YES YES YES
11 Reserved. - Reserved for future options.
- Programmable level shutdown. YES YES YES YES YES YES
12
Start-up without bateries
(HOT STANDBY FUNCTION). - YES YES YES YES YES YES
- Reservedo /Neutral lost. YES YES YES YES YES YES
(*) 13 Battery voltage setting. YES YES YES YES YES YES
(*) 14 Charger voltage setting. YES YES YES YES YES YES
(*) 15 Inverter voltage setting. - - YES - YES YES -
(*) 16 Output voltage setting. - YES - YES YES -
17 External MOD BAT setting. - YES - - - - -
- Input phase shifting. SI
18 -Battery capacity and quantity of
strings setting. SI
19 Back up time setting. SI
(*) WARNING with regard to codes from 3, 4, 6, 7, 13, 14, 15 and 16!:
DEPENDING ON THE FIRMWARE VERSION OF THE EQUIPMENT, THE ORIGINAL FACTORY SETTINGS CAN BE CHANGED.
DO NOT CHANGE THEM, BECAUSE DEPENDING ON THE SETTING THE UPS, LOADS OR BOTH COULD BE DAMAGED.
Tab. 10. Code list for parameter 1. Description and setting de-
pending on the operating mode.
7.4.1. Setting menu views, depending on the parameter
1 code.
•Code 01 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). Output voltage.
Fig. 29.
Parameter 3 setting: Output voltage.
It is possible to select one of the following output voltage
figures, phase to neutral value:
–208, 220, 230 or 240 V.
•Code 02 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). Output frequency.
Fig. 30.
Parameter 2 setting: Output frequency.
It is possible to select one of the following figures:
–50 Hz, 60 Hz or ATO.
When ATO is selected, the output frequency is automatic
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
32 SALICRU
set to the frequency input detection, when the equipment
is supplied from mains.
If the frequency is between 46 and 54 Hz, the output
frequency will be set to 50 Hz and if it is between 56
and 64 Hz, it will be set to 60 Hz. The preset parameter
from factory is ATO.
Parameter 3 setting: Frequency mode.
Output frequency setting on FC mode or no FC mode. Two
options can be selected:
–FC. Set the UPS as FC mode. With this option ac-
tivated, the output frequency is set to 50 or 60 Hz
depending on the parameter 2 selection. The input
frequency range can be from 46 to 64 Hz.
–NCF. Set the UPS to normal mode [No FC mode]. With
this option activated, the output frequency is set to 50 or
60 Hz synchronised with the input frequency depending
on the selection in parameter 2 and its range.
If the parameter 2 selection is set to 50 or 60 Hz,
it will shift to battery mode (to supply the loads),
when the frequency is not between 46 and 54 Hz or
56 and 64 Hz respectively.
Fig. 31.
(*) If parameter 2 is set to ATO, then the parameter
3 shows the current frequency.
•Code 03 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). By-
pass voltage range.
Fig. 32.
Parameter 2 setting: It states the minimum acceptable
voltage limit for bypass. The setting range is from 110 to
209 V and the preset factory figure is 110 V.
Parameter 3 setting: It states the maximum acceptable
voltage limit for bypass. The setting range is from 231 to
276 V and the preset factory figure is 264 V.
•Code 04 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). By-
pass frequency range.
Fig. 33.
Parameter 2 setting: Minimum limit of the acceptable
input frequency range.
–For nominal 50 Hz, the setting range is from 46 to 49 Hz.
–For nominal 60 Hz, the setting range is from 56 to 59 Hz.
The preset factory figures are 46 / 56Hz, for 50 and
60Hz respectively.
Parameter 3 setting: Maximum limit of the acceptable
input frequency range.
–For nominal 50 Hz, the setting range is from 51 to 54 Hz.
–For nominal 60 Hz, the setting range is from 61 to 64 Hz.
The preset factory figures are 54 / 64Hz, for 50 and
60Hz respectively.
•Code 05 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). ECO mode, enabled
/ disabled.
Fig. 34.
Parameter 3 setting: Enable or disable the ECO mode.
–DIS. ECO mode disabled.
–ENA. ECO mode enabled.
If the ECO mode is disabled, the voltage and frequency
ranges can be set, although it does not have so much
sense because the own operating mode is disabled.
•Code 06 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). ECO
mode voltage range.
Fig. 35.
33
Parameter 2 setting: Low voltage threshold for ECO
mode. The regulation range is between –5 and –10 % of
the nominal voltage.
Parameter 3 setting: High voltage threshold for ECO
mode. The regulation range is between +5 and +10 % of
the nominal voltage.
•Code 07 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). ECO
mode frequency range.
Fig. 36.
Parameter 2 setting: The low frequency threshold in ECO
mode. The regulation range is between –5 and –10 % of
the nominal frequency.
–setting range from 46 to 49, for 50 Hz nominal .
–setting range from 56 to 58, for 60 Hz nominal.
The preset factory figures are 48 / 58 Hz, for 50 and
60Hz respectively.
Parameter 3 setting: The high frequency threshold in
ECO mode. The regulation range is between +5 and +10
% of the nominal frequency.
–setting range from 51 to 54, for 50 Hz nominal .
–setting range from 62 to 64, for 60 Hz nominal.
The preset factory figures are 52 / 62 Hz, for 50 and
60Hz respectively.
•Code 08 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). Bypass mode set-
ting.
Fig. 37.
Parameter 2 setting.
–OPN. Bypass allowed. When selecting this op-
tion, the UPS will operate on bypass mode, but
depending on the bypass setting, if it is enable or
disable (parameter 3).
–FBD. When selecting this option, it is not allowed the
bypass mode operating under no circumstances.
Parameter 3 setting.:
–ENA. Bypass enable. When selecting this option,
the bypass mode is enabled.
–DIS. Bypass disabled. When selecting this option,
the automatic bypass is allowed but not the manual
bypass shifting.
Bypass shifting is understood as that one that the
end-users make it over the own UPS. I.e.: when
pressing the OFF key at the front of the equipment
when it is on normal mode, then the load is shifted
to the static bypass.
•Code 09 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). Maximum battery
discharge time setting.
Fig. 38.
Parameter 3 setting:
–DIS, default value. It disables the maximum battery
discharge time of the batteries, so the back up time
will depend on the capacity of themselves.
–000 ~ 999. It states the maximum back up time.
The UPS will be automatically shutdown once the
time is exceeded. In some III / II models and ac-
cording to firmware version it may be set to 990
minutes [16.5 h] instead of DIS.
•Code 10 (TWIN PRO2). Reserved.
Fig. 39.
Reserved for future options.
•Code 10 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Programmable output setting
Fig. 40.
Parameter 3 setting: Set the programmable output. It
is allowed to select one of the following three options:
–ON: the programmable output is activated perma-
nently.
–OFF: the programmable output is deactivated. Nev-
ertheless, if the UPS is re-start up, this setting will
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

34 SALICRU
change automatically to “ATO” selection.
–ATO: the programmable output is automatically
activated or deactivated, depending on the status
of the battery or load. The programmable output
will be shutdown either when the battery voltage
is lower than the entered value or the shutdown is
done. When the input mains is restored, the output
will be activated automatically. In case of overload,
the programmable output will be shutdown auto-
matically. If the last situation would happen 3 times
in less than 30 minutes, the programmable output
will be shutdown till be activated manually.
•Code 11 (TWIN PRO2). Reserved.
Fig. 41.
Reserved for future options.
•Code 11 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Programmable output shutdown.
Fig. 42.
Parameter 2 setting: 001.
Setting for shutdown time of the programmable output.
Parameter 3 setting: Time to shutdown, stated in min-
utes.
Setting range is from 0 and 300. When the setting time is
achieved, the programmable output will be shutdown. The
preset factory value is 30 minutes.
Fig. 43.
Parameter 2 setting: 002.
Setting for voltage shutdown of the programmable output.
Parameter 3 setting: Shutdown voltages in V.
The setting range is from 11,2 to 13,6 V. If the battery
voltage is lower than the entered figure, the program-
mable output will be shutdown. The preset factory figure
is 11,2 V.
•Code 12 (TWIN PRO2). Hot standby function enable / dis-
able.
Fig. 44.
Parameter 2 setting. HS.H
–Enabling or disabling the Hot standby function.
Parameter 3 setting:
–YES: The Hot standby function is enabled after mains
is restored even with no batteries connected to the
UPS.
–NO: The Hot standby function is disabled. The UPS op-
erates on normal mode. It will not be re-started up if
the batteries are not connected to the UPS.
•Code 12 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Neutral lost detection. By de-
fault, AUTO.
In case of neutral lost, this screen will change to input neu-
tral lost during its checking, option CHE.
AUTO
Fig. 45.
Parameter 2 setting.
–It is displayed when the option input neutral lost is
selected. It is not allowed to be set by the end-user.
Parameter 3 setting:
–In this screen the end-user can check if the input neu-
tral is connected or not.
•Code 13 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2). Bat-
tery voltage calibration.
Fig. 46.
35
Parameter 2 setting.
–Select «Add» or «Sub» to set the battery voltage to
the real figure.
Parameter 3 setting:
–The voltage range is from 0 to 9,9 V and the preset
factory figure is 0 V.
•Code 14 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2).
Charger voltage setting.
Fig. 47.
Parameter 2 setting.
–It can be selected «Add» or «Sub» to set the charger
voltage.
Parameter 3 setting:
–Voltage range is from 0 to 9.9 V and the preset fac-
tory figure is 0 V.
Before doing any voltage setting, check that the bat-
teries are disconnected before setting the charger
voltage.
The setting must be according to the battery specifications.
•Code 15 (TWIN PRO2). Inverter voltage set-
ting.
Fig. 48.
Parameter 2 setting.
–Select «Add» or «Sub» to set the inverter voltage.
Parameter 3 setting:
–The voltage range is from 0 to 9.9 V and the preset
factory figure is 0 V.
•Code 15 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Inverter voltage
setting.
Fig. 49.
Parameter 2 setting.
–Select «Add» or «Sub» to set the inverter voltage.
Parameter 3 setting:
–The voltage range is from 0 to 6 V and the preset
factory figure is 0 V
•Code 16 (TWIN PRO2, TWIN/3 PRO2).
Output voltage setting.
Fig. 50.
Parameter 3 setting:
–It is displayed the measured internal output voltage
figure. It can be set by pressing the Up or Down keys
according to an external voltmeter. The calibration will
be effective once the Enter key has been pressed. The
calibration range limit is +/-9V. This function is usually
used in parallel systems.
WARNING with regard to codes from 13 to 16!:
DEPENDING ON THE FIRMWARE VERSION OF
THE EQUIPMENT, THE ORIGINAL FACTORY SET-
TINGS CAN BE CHANGED.
DO NOT CHANGE THEM, BECAUSE DEPENDING
ON THE SETTING THE UPS, LOADS OR BOTH
COULD BE DAMAGED.
•Code 17 (TWIN PRO2). External MOD BAT setting.
Fig. 51.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
36 SALICRU
Parameter 3 setting: Set the quantity of the external
MOD BAT.
–0-7: The setting allow figures between 0-7. The preset
factory figure is 0
•Code 17 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Input phase shifting enable / dis-
able.
Fig. 52.
Parameter 3 setting: Enabling / Disabling phase shifting
function. It is possible to selected between two options:
–DIS: phase shifting is disabled. Pay attention to the
phase rotation of the phases by respecting the label-
ling of the equipment -R, S, T-.
–ENA: phase shifting is enabled. It makes possible to
connect the phases without respecting their rotation.
This option will be selected, when the three input
terminals -R, S, T- are supplied with the same phase
(single phase mains).
•Code 18 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Battery capacity and MOD BAT
quantity setting.
Fig. 53.
Parameter 2 setting.
–It allows setting the battery capacity.
Parameter 3 setting:
–It allows setting the MOD BAT quantity.
•Code 19 (TWIN/3 PRO2). Back up time setting.
Fig. 54.
Parameter 3 setting:
–It allows setting the back up time to the preset factory
figure or other ones.
7.5. OPERATING MODES / STATUS DESCRIPTION.
Table 10 shows the displayed screens in the LCD of the control
panel [status] for all the operating modes.
1. If the UPS is on normal mode, there will be five screens
for the following measurements: three phases to neutral
input voltages [R, S, T], input frequency, output frequency
and output load.
2. Those parallel systems, which are properly set, instead of
displaying the parameter 2, it will be displayed the «PAR»
acronym and parameter 3 will be displayed the number of the
UPS corresponding to the equipment in the parallel system.
«MASTER» UPSs will be assigned by default as «001» and
the slaves as «002» and «003» respectively. The assigned
numbers can change during their operation.
Fig. 55. Parallel system screen.
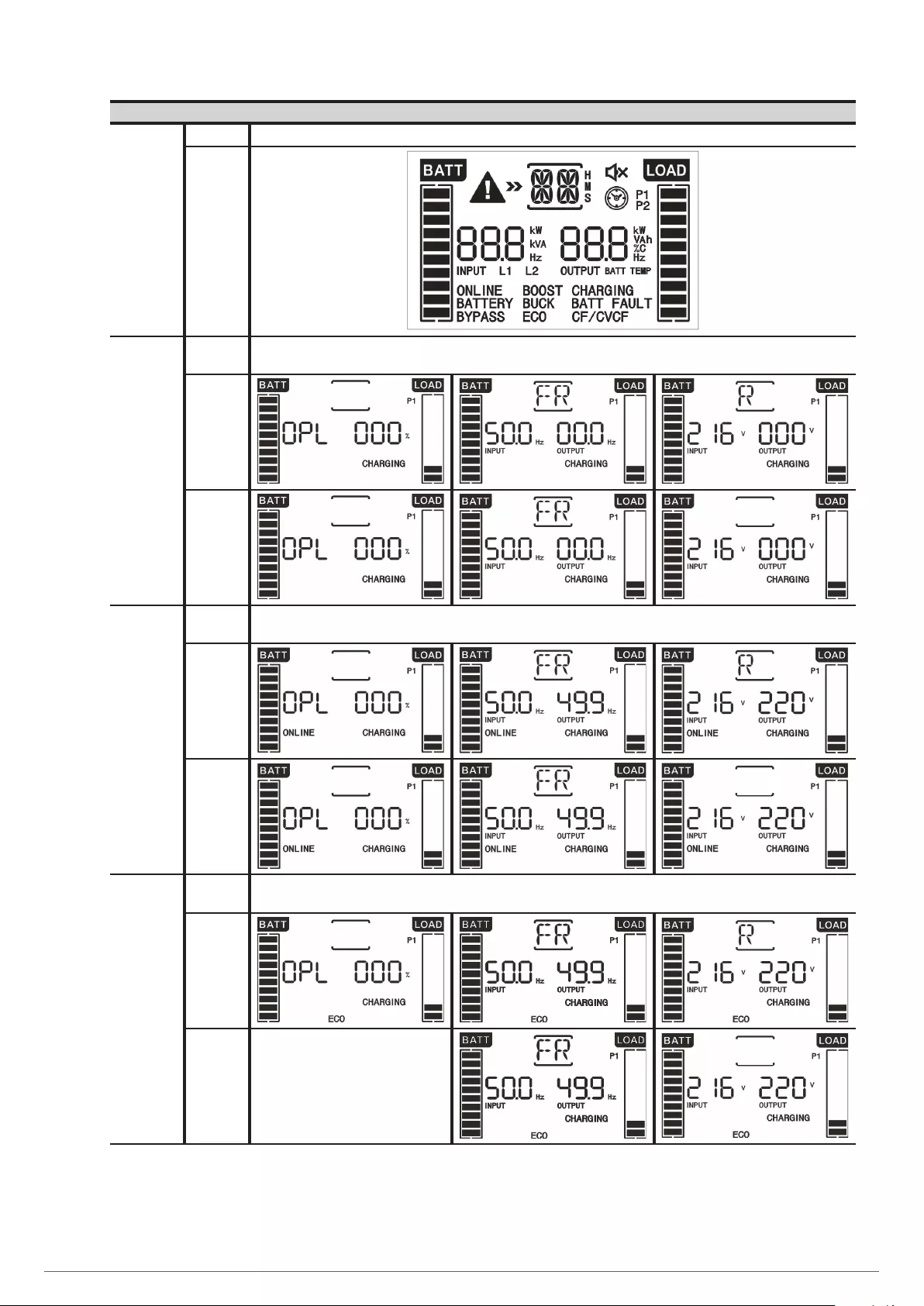
37
Operating mode / status
UPS start up
Description. When starting up the UPS, it is displayed this screen for a few seconds in order initialize the CPU and system.
LCD panel.
No output mode
Description. If the bypass voltage / frequency are out of range or the bypass is disabled (or not allowed), the UPS will shift to no output mode
with the inverter on or when shutdown it. The UPS does not supply output voltage. The acoustic alarm beeps every two minutes .-
TWIN/3
TWIN
AC mode
Description. If the input voltage is inside the range,the UPS will supply sinewave and stable AC energy to the load or loads, and batteries will be
charged .
TWIN/3
TWIN
ECO mode
Description. If the input voltage is inside the range and the ECO mode is activated, the UPS supplies output voltage through its bypass (energy
saving).
TWIN/3
TWIN
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
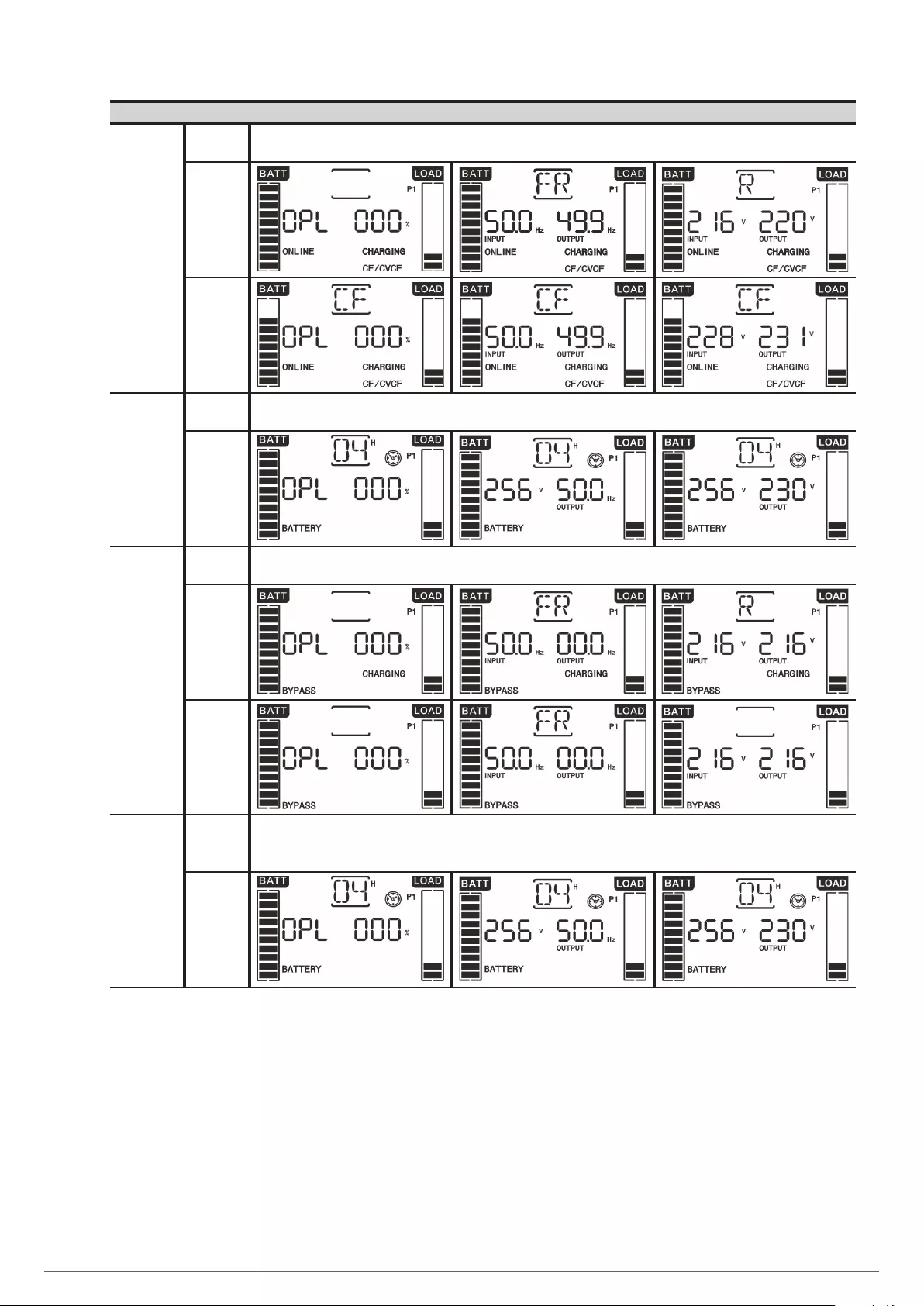
38 SALICRU
Operating mode / status
FC mode
Description. When the output frequency is selected as FC in parameter 3 from code 02 of setting menu, the inverter supplies a constant output
frequency (50 or 60 Hz). Therefore, the UPS does not supply output voltage from bypass, but batteries will be charged.
TWIN/3
TWIN
Battery mode
Description. When the input voltage / frequency are not inside their preset ranges or there is a power outage, the UPS supplies the loads from batteries for
a limited time , which will depend on their capacity, also the acoustic alarm beeps every 4 sec..
TWIN/3
TWIN
Bypass mode
Description. When the input voltage is inside the preset range and the bypass is enabled, when the UPS is shutdown, the equipment shifts to
bypass mode. The acoustic alarm beeps every two minutes.
TWIN/3
TWIN
Battery test
Description.
If the UPS is on AC or FC modes, when pressing the «TEST» key for more than 0.5 sec.. The acoustic buzzer will beep as an informative
mode and the battery test is started. In the energy flow diagram of the LCD panel, the line between the input and the inverter icon
blinks with a dashed line. This test is very useful to check the battery status.
TWIN/3
TWIN
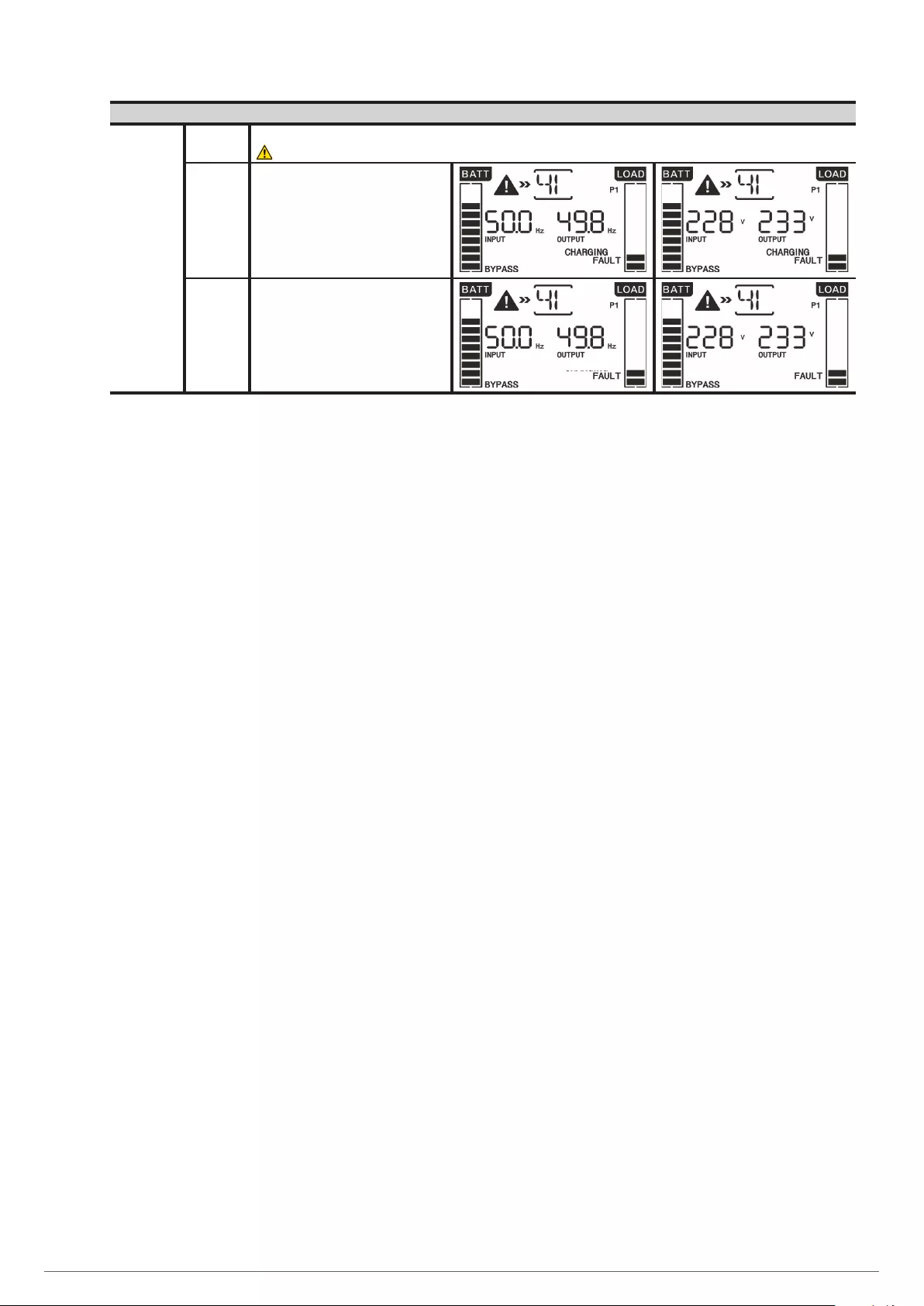
39
Operating mode / status
Error or fault
status
Description. When the UPS detects an error or fault, the inverter will be blocked. And the fault code will be displayed in the LCD panel and the icon
will light. Table 13 shows the error or fault codes and their description.
TWIN/3
TWIN
Tab. 11. Operating modes.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
40 SALICRU
7.6. WARNING CODES.
Code Warning description
TWIN TWIN/3
01 Battery disconnected.
02 - Input neutral lost or L2/L3 input
fuse blown.
04 - Input phases out of range
05 - Bypass phase fault.
07 Battery overcharged.
08 Low battery.
09 Output overload.
0A Fan failure.
0B EPO activated.
0D Over temperature.
0E Charger fault.
10 L1 input fuse blown.
21 Output voltages of the equipments connected in parallel are
different
22 Bypass voltages of the equipments connected in parallel are
different.
33 After 3 overloads in less than 30 minutes, the equipment is
blocked on bypass
34 - Unbalanced converter current
35 - Battery fuse blown
36 - Unbalanced inverter current
3A Maintenance switch cover opened
3B - Phase shifting function failure
3C - Unbalanced input mains
3D Bypass not available
3E Start up fault -
Tab. 12. Warning code.
7.7. ERROR O FAULT CODES.
Code Error or fault description
TWIN TWIN/3
01 DC bus start up fault.
02 DC bus overvoltage.
03 DC bus undervoltage.
04 Unbalanced DC bus.
06 - Converter overcurrent
11 Inverter soft start fault
12 High inverter voltage
13 Low inverter voltage
14 Inverter output short-circuited
1A Negative output power fault.
21 Battery thyristor short-circuited.
24 Inverter relay short-circuited.
29 - Battery fuse blown when
running on battery mode
31 Canbus communication fault -
35 - Parallel communication failure
36 Unbalanced output current in a
parallel system Short-circuited output
41 Over temperature
42 CPU communication fault -
43 Output overload
46 - UPS fault
60 Inverter over current -
63 Wrong inverter wave shape -
6A Battery start up fault -
6B PFC current fault when running
on battery mode -
6C Too fast DC bus voltage change -
Tab. 13. Error or fault code.
7.8. WARNING INDICATORS.
Code Icon (blinking) Acoustic alarm
Low battery voltage. Beep every 1 sec.
Overload
Beep twice x 1 sec.
Disconnected battery BATT FAULT Beep every 1 sec.
Battery overcharged
Beep every 1 sec.
Activated EPO. Beep every 1 sec.
Fan failure /
Overtemperature TEMP Beep every 1 sec.
Charger fault CHARGING
BATTERY
Beep every 1 sec.
Tab. 14. Warning indicators.
41
8. MAINTENANCE, WARRANTY AND
SERVICE.
8.1. BATTERY MAINTENANCE.
•Pay attention to any safety instructions stated in EK266*08
manual section 1.2.3 referred to batteries.
•The useful lifetime of the batteries depends on the ambient
temperature and other factors like the quantity of charging
and discharging cycles and the deep discharges done.
Its design lifetime is between 3 and 5 years if the ambient
temperature is between 10 and 20 ºC. Under request, other
typology and/or design lifetime batteries can be supplied.
•The UPS from SLC TWIN PRO2 series only needs a min-
imum maintenance. The used batteries in standard models
are lead acid, sealed, VRLA and maintenance free. The only
requirement is to charge them regularly in order to extend
their lifetime.
Meanwhile, the UPS is connected to mains, started up or
not, it will keep the batteries charged and will guarantee a
protection against overcharge and over discharge.
8.1.1. Notes to replace and install the batteries.
•In case of replacing any interlink wire, purchase original
parts through the authorised distributors or service centres
in order to avoid over heating or sparks due to the risk that
would entail the use of not enough size.
•Do not short both battery poles + and -, exists risk of elec-
trocution or fire.
•Make sure that there is not any voltage before handling the
batteries. The battery circuit is not isolated from the input,
so dangerous voltages between battery and earth can exist.
•Although the input circuit breaker is turned off, the internal
parts of the UPS are still connected to the batteries, so dan-
gerous voltages are present.
So, before doing any maintenance or reparation, the in-
ternal battery fuse must be removed and/or the connectors
between them and the own UPS too.
As the battery circuit is not isolated from the input, so dan-
gerous voltages between battery and earth or ground (any
metallic part of the cabinet, supports and accessories in-
cluded) can exist.
•Batteries have dangerous voltages. The maintenance and
battery replacement must be done by qualified personnel
and familiarized with them. No other persons must manipu-
late them.
8.2. UPS TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE.
If the UPS doesn't work properly, check the information dis-
played in the LCD panel.
Try to solve the problems by following the steps described in
table 15. If the problem persists, consult with our Technical Ser-
vice and Support T.S.S..
When necessary contact with our Technical Service and Sup-
port T.S.S., and provide the following information:
•UPS model and serial number.
•Date of the problem.
•Complete description of the problem, including the informa-
tion supplied by the LCD or leds or alarm status.
•Power supply condition, type of load and load percentage,
ambient temperature, cooling conditions.
•Battery information (capacity and quantity) and if the equip-
ment is a (B0) or (B1).
•Other informations considered as important.
8.2.1. Troubleshooting guide.
Symptom Possible cause Solution
Neither alarms nor indications in the LCD panel and
normal mains voltage. The input cables are not connected properly. Check if the input cables are firmly connecte to
mains.
The icon and warning code blink in
the LCD panel and the acoustic alarm beep every
second.
EPO function is activated. Close the EPO circuit to deactivate it.
The icon and BATT FAULT message
blink in the LCD panel and the acoustic alarm beep
every second.
The internal or external battery are not properly
connected. Check if all the batteries are properly connected.
The and icons blink in the LCD panel
and the acoustic alarm beep twice every second.
The UPS is overloaded. Remove/shutdown the exceeding loads connected
at the UPS output.
The UPS is overloaded. The connected devices to the
UPS are directly supplied from mains through the
internal Bypass.
Remove/shutdown the exceeding loads connected
at the UPS output.
After several overloads, the UPS is blocked on Bypass
mode. The connected devices to the UPS are supplied
directly from mains.
First remove/shutdown the exceeding loads
connected at the UPS output. Then shutdown the
UPS and reboot it .
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
42 SALICRU
Symptom Possible cause Solution
Code fault 43 is displayed. The icon lights
in the LCD panel and the acoustic alarm beeps
continuously.
The UPS has been overloaded for long time and
their equipment is blocked. The UPS is shutdown
automatically.
Remove/shutdown the exceeding loads connected
at the UPS output and reboot it.
Code fault 14 is displayed, the acoustic alarm
beeps continously .
The UPS is automatically shutdown due a short-circuit
at its output.
Check the output wiring and/or connected devices
to its output are short-circuited.
One of the following codes are displayed in the
LCD panel 01, 02, 03, 04, 11, 12, 13, 14,1A, 21, 24,
35, 36, 41, 42 or 43 and the acoustic alarm beeps
continously.
An itnernal fault has ocurred. Two possible situations:
1. The load is still supplied, but through the UPS bypass.
2. The load is not supplied. Contact with the distributor.
The back up time is lower than the expected
Batteries are not fully charged
Charge the batteries for 7 hours at least and
then check their capacity. If the problem persists,
contact with the distributor.
Batteries are damaged Contact with the distributor to replace the battery.
The icon and the TEMP message blink in
the LCD panel and the acoustic alarm beeps every
second.
The fan is blocked or it does not work ; or the UPS
temperature is very high. Check the fans and contact with the distributor .
Tab. 15. Troubleshooting guide.
8.3. WARRANTY CONDITIONS.
8.3.1. Warranty terms.
The warranty conditions for this product can be found in our
website, register the product in it. It is recommended to do it
as soon as possible in order to include it in the database of
our Technical Service and Support (T.S.S.). Among other advan-
tages, it will be easier to make any proceeding, in case it was
needed an intervention from T.S.S..
8.3.2. Out of scope of supply.
Our company is not forced by the warranty in case it is de-
tected that the defect was caused by wrong use, negligence,
not suitable installation and/or checking, reparation by non-au-
thorised personnel, accident, fire, lightning or any other cause
far from the foreseen use. In all these cases, no compensation
will be covered by damaged or injuries.
8.4. TECHNICAL SERVICE NETWORK.
The coverage, both national and international, of the Technical Service
and Support (T.S.S.), can be found in our website.
43
9. ANNEXES.
9.1. GENERAL TECHNICAL FEATURES.
Models: TWIN PRO TWIN/3 PRO
Available powers (kVA / kW) (**) 4 / 4 5 / 5 6 / 6 8 / 8 10 / 10 15 / 13.5 20 / 18 8 / 7.2 10 / 9 15 / 13.5 20 / 18
Technology On-line double conversion, PFC, double DC bus
Rectifier
Input typology Single phase Three phase
Quantity of wires 3 wires - Phase R (L) + Neutral (N) and PE 5 wires - 3 Phases R (L1), S (L2), T (L3) +
Neutral (N) and PE
Nominal volage 208 / 220 / 230 / 240 V AC 220 / 230 / 240 V AC 3 x 360 /3 x 380 / 3 x 400 / 3 x 415 V AC
Input voltage range wirh 100 % load 176.. 276 V AC 3 x 305.. 478 V AC
Input voltage range with 50 % load 110.. 300 V AC 3 x 190.. 520 V AC
Voltage range of transference: At full load
- Low mains voltage 176 V AC (±3 %) 305 V AC (± 3 %)
- Low mains voltage returned 186 V AC (±3 %) 322 V AC (± 3 %)
- High mains voltage 276 V AC (±3 %) 478 V AC (± 3 %)
- High mains voltage returned 266 V AC (±3 %) 460 V AC (± 3 %)
Frequency 50 / 60 Hz (autosensing)
Input frequency range ± 4 Hz (46.. 54 / 56.. 64 Hz)
Power factor > 0.99 (at full load)
Inverter
Technology PWM
Wave shape Pure sinewave
Nominal voltage 208 / 220 / 230 / 240 V AC 220 / 230 / 240 V AC
Output voltage accuracy ± 1 %
Voltage THD with linear load < 1 % < 2 %
Voltage THD with non-linear load < 4 % < 5 %
Frequency With mains , synchronised with nominal input (46.. 54 / 56.. 64 Hz)
Free running, battery mode 50 / 60 ±0.1 Hz Free running, battery mode 50 / 60 ±0.05 Hz
Slew rate 1 Hz/sec.
Power factor 1 (by default) 0.9 (by default)
Permissible load power factor 0.5.. 1 lagging
Transfer time, inverter to battery 0 ms.
Transfer time, inverter to bypass 0 ms.
Transfer time, inverter to ECO 0 ms.
Transfer time, ECO to inverter < 10 ms.
Efficiency at full load, on normal mode with battery
100% charged > 93 % > 90 %
Efficiency at full load, on ECO mode > 99 % > 96 %
Overload on normal mode
100.. 110 %, 10 min.
> 110.. 130 %, 60 sec.
> 130 %, 1 sec.
Overload on battery mode
100.. 110 %, 30 sec.
> 110.. 130 %, 10 sec.
> 130 %, 1 sec.
Crest factor 3:1
Quantity of parallel equipments Up to 3 UPSs
Static Bypass
Type Hybrid (thyristors in antiparallel + relay)
Nominal voltage 208 / 220 / 230 / 240 V AC 220 / 230 / 240 V AC
Nominal frequency 50 / 60 Hz ±4 Hz
Overload < 130 %, constant
> 130 %, 60 sec.
Batteries
Voltage / capacity 12 V DC / 7 Ah 12 V DC / 9 Ah
Quantity of batteries per string / set voltage 20 / 240 V DC
Quantity of battery strings 1 2 1 2
Low battery voltage, battery block / string 11.4 V DC / 228 V DC
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL
44 SALICRU
Models: TWIN PRO TWIN/3 PRO
Available powers (kVA / kW) (**) 4 / 4 5 / 5 6 / 6 8 / 8 10 / 10 15 / 13.5 20 / 18 8 / 7.2 10 / 9 15 / 13.5 20 / 18
Internal battery charger
Type of load I / U (Constant current / constant voltage)
Constant current / constant voltage 1/2/4 A depending on the model / 273 V DC
(13.65 V DC bat. block.)
2/4/6/8 A / 288 V DC
(14.4 V DC bat. block)
1/2/4 A depending on
the model / 273 V DC
(13.65 V DC bat. block.)
2/4/6/8 A / 288 V DC
(14.4 V DC bat. block)
Floating voltage, battery block / string 13,65 V CC / 273 V CC 13,65 V CC / 288 V CC 13,65 V CC / 273 V CC 13,65 V CC / 288 V CC
Maximum charge current 4 A 8 A 4 A 8 A
Recharging time 7 houras at 90% 9 hours at 90%
Voltage / temperature compensation – 20 mV / ºC per battery from 25 ºC
Internal battery charger, option (B1)
Maximum charge current 4 A 8 A 4 A 8 A
Generals
Communication ports RS232 -DB9- and USB, mutually exclusive
Monitoring software Viewpower (free download)
Noise level at 1 m. < 58 dB < 60 dB < 58 dB < 60 dB
Operating temperature 0.. 40 ºC
Storage temperature 0.. 35 ºC
Storage temperature with no batteries – 15.. + 60 ºC
Operating altitude 2.400 m a.s.l.
Relative humidity 0.. 95 % non-condensing
Protection degree IP20
Dimensions -Depth x Width x Height- (mm) 592 x 250 x 576 815 x 250 x 826 592 x 250 x 576 815 x 250 x 826
Dimensions -Depth x Width x Height- (mm) B1 592 x 250 x 576
Weight (kg) -Standard equipment- 81 82 83 84 85 164 166 84 85 164 166
Weight (kg) -Equipment B0- 14 15 16 26 28 37 38 27 28 37 38
Weight (kg) -Equipment B1- 16 17 18 29 30 37 38 29 30 37 38
Safety EN-IEC 62040-1; EN-IEC 60950-1
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) EN-IEC 62040-2
Marking CE
Quality System ISO 9001 and ISO 140001
(**) As frequency converter, the supplied power will be 70 %
of the nominal one.
Tab. 16. General technical specifications.
9.2. GLOSARIO.
•AC.- Se denomina corriente alterna (abreviada CA en
español y AC en inglés) a la corriente eléctrica en la que
la magnitud y dirección varían cíclicamente. La forma de
onda de la corriente alterna más comúnmente utilizada
es la de una onda senoidal, puesto que se consigue una
transmisión más eficiente de la energía. Sin embargo,
en ciertas aplicaciones se utilizan otras formas de onda
periódicas, tales como la triangular o la cuadrada.
•Bypass.- Manual o automáticamente, se trata de la unión
física entre la entrada de un dispositivo eléctrico con su
salida.
•DC.- La corriente continua (CC en español, en inglés DC, de
Direct Current) es el flujo continuo de electrones a través
de un conductor entre dos puntos de distinto potencial. A
diferencia de la corriente alterna (CA en español, AC en in-
glés), en la corriente continua las cargas eléctricas circulan
siempre en la misma dirección desde el punto de mayor
potencial al de menor. Aunque comúnmente se identifica la
corriente continua con la corriente constante (por ejemplo
la suministrada por una batería), es continua toda corriente
que mantenga siempre la misma polaridad.
•DSP.- Es el acrónimo de Digital Signal Processor, que significa
Procesador Digital de Señal. Un DSP es un sistema basado
en un procesador o microprocesador que posee un juego de
instrucciones, un hardware y un software optimizados para
aplicaciones que requieran operaciones numéricas a muy alta
velocidad. Debido a esto es especialmente útil para el proce-
sado y representación de señales analógicas en tiempo real: en
un sistema que trabaje de esta forma (tiempo real) se reciben
muestras (samples en inglés), normalmente provenientes de un
conversor analógico/digital (ADC).
•Factor de potencia.- Se define factor de potencia, f.d.p.,
de un circuito de corriente alterna, como la relación entre la
potencia activa, P, y la potencia aparente, S, o bien como el
coseno del ángulo que forman los factores de la intensidad
y el voltaje, designándose en este caso como cos f, siendo f
el valor de dicho ángulo.
•GND.- El término tierra (en inglés GROUND, de donde
proviene la abreviación GND), como su nombre indica, se
refiere al potencial de la superficie de la Tierra.
•Filtro EMI.- Filtro capaz de disminuir de manera notable la
interferencia electromagnética, que es la perturbación que
ocurre en un receptor radio o en cualquier otro circuito eléc-
trico causada por radiación electromagnética proveniente
de una fuente externa. También se conoce como EMI por

45
sus siglas en inglés (ElectroMagnetic Interference), Radio
Frequency Interference o RFI. Esta perturbación puede in-
terrumpir, degradar o limitar el rendimiento del circuito
•IGBT.- El transistor bipolar de puerta aislada (IGBT, del inglés
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) es un dispositivo semicon-
ductor que generalmente se aplica como interruptor con-
trolado en circuitos de electrónica de potencia. Este dispositivo
posee la características de las señales de puerta de los tran-
sistores de efecto campo con la capacidad de alta corriente y
voltaje de baja saturación del transistor bipolar, combinando
una puerta aislada FET para la entrada e control y un transistor
bipolar como interruptor en un solo dispositivo. El circuito de
excitación del IGBT es como el del MOSFET, mientras que las
características de conducción son como las del BJT.
•Interface.- En electrónica, telecomunicaciones y hard-
ware, una interfaz (electrónica) es el puerto (circuito físico)
a través del que se envían o reciben señales desde un sis-
tema o subsistemas hacia otros
•kVA.- El voltampere es la unidad de la potencia aparente
en corriente eléctrica. En la corriente directa o continua es
prácticamente igual a la potencia real pero en corriente
alterna puede diferir de ésta dependiendo del factor de
potencia.
•LCD.- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) son las siglas en inglés
de Pantalla de Cristal Líquido,dispositivo inventado por
Jack Janning, quien fue empleado de NCR. Se trata de un
sistema eléctrico de presentación de datos formado por 2
capas conductoras transparentes y en medio un material
especial cristalino (cristal líquido) que tienen la capacidad
de orientar la luz a su paso.
•LED.- Un LED, siglas en inglés de Light-Emitting Diode
(diodo emisor de luz) es un dispositivo semiconductor
(diodo) que emite luz casi monocromática, es decir, con un
espectro muy angosto, cuando se polariza en directa y es
atravesado por una corriente eléctrica. El color, (longitud de
onda), depende del material semiconductor empleado en
la construcción del diodo, pudiendo variar desde el ultra-
violeta, pasando por el espectro de luz visible, hasta el in-
frarrojo, recibiendo éstos últimos la denominación de IRED
(Infra-Red Emitting Diode).
•Magnetotérmico.- Un interruptor magnetotérmico, o
disyuntor magnetotérmico, es un dispositivo capaz de in-
terrumpir la corriente eléctrica de un circuito cuando ésta
sobrepasa ciertos valores máximos.
•Modo On-Line.- En referencia a un equipo, se dice que
está en línea cuando está conectado al sistema, se en-
cuentra operativo, y normalmente tiene su fuente de ali-
mentación conectada.
•Inversor.- Un inversor, también llamado ondulador, es un cir-
cuito utilizado para convertir corriente continua en corriente
alterna. La función de un inversor es cambiar un voltaje de
entrada de corriente directa a un voltaje simétrico de salida de
corriente alterna, con la magnitud y frecuencia deseada por el
usuario o el diseñador.
•Rectificador.- En electrónica, un rectificador es el el-
emento o circuito que permite convertir la corriente alterna
en corriente continua. Esto se realiza utilizando diodos
rectificadores, ya sean semiconductores de estado sólido ,
válvulas al vacío o válvulas gaseosas como las de vapor de
mercurio. Dependiendo de las características de la alimen-
tación en corriente alterna que emplean, se les clasifica
en monofásicos, cuando están alimentados por una fase de
la red eléctrica, o trifásicos cuando se alimentan por tres
fases. Atendiendo al tipo de rectificación, pueden ser de
media onda, cuando solo se utiliza uno de los semiciclos de
la corriente, o de onda completa, donde ambos semiciclos
son aprovechados.
•Relé.- El relé o relevador (del francés relais, relevo) es un
dispositivo electromecánico, que funciona como un inter-
ruptor controlado por un circuito eléctrico en el que, por
medio de un electroimán, se acciona un juego de uno o
varios contactos que permiten abrir o cerrar otros circuitos
eléctricos independientes.
•SCR.- Abreviatura de «Rectificador Controlado de Silicio»,
comúnmente conocido como Tiristor: dispositivo semicon-
ductor de 4 capas que funciona como un conmutador casi
ideal.
•THD.- Son las siglas de «Total Harmonic Distortion» o «Dis-
torsión armónica total». La distorsión armónica se produce
cuando la señal de salida de un sistema no equivale a la señal
que entró en él. Esta falta de linealidad afecta a la forma de
la onda, porque el equipo ha introducido armónicos que no es-
taban en la señal de entrada. Puesto que son armónicos, es
decir múltiplos de la señal de entrada, esta distorsión no es tan
disonante y es menos fácil de detectar.
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

46 SALICRU
: .............................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................

47
: .............................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................
SLC TWIN PRO2 UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY (UPS)USER'S MANUAL

Avda. de la Serra 100
08460 Palautordera
BARCELONA
Tel. +34 93 848 24 00
Fax +34 93 848 22 05
services@salicru.com
SALICRU.COM
www.linkedin.com/company/salicru
@salicru_SA
Product Range
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
Lighting Flow Dimmer-Stabilisers
DC Power Systems
Static Inverters
Photovoltaic Inverters
Voltage stabilisers
The Technical Service and Support (T.S.S.) network, Com-
mercial network and warranty information are available in
website:
www.salicru.com
REF. EL082D01 REV. D CODE 401*