SilverNet SIL 73416MP User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for SIL 73416MP by SilverNet which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

V1.1 www.silvernet.com
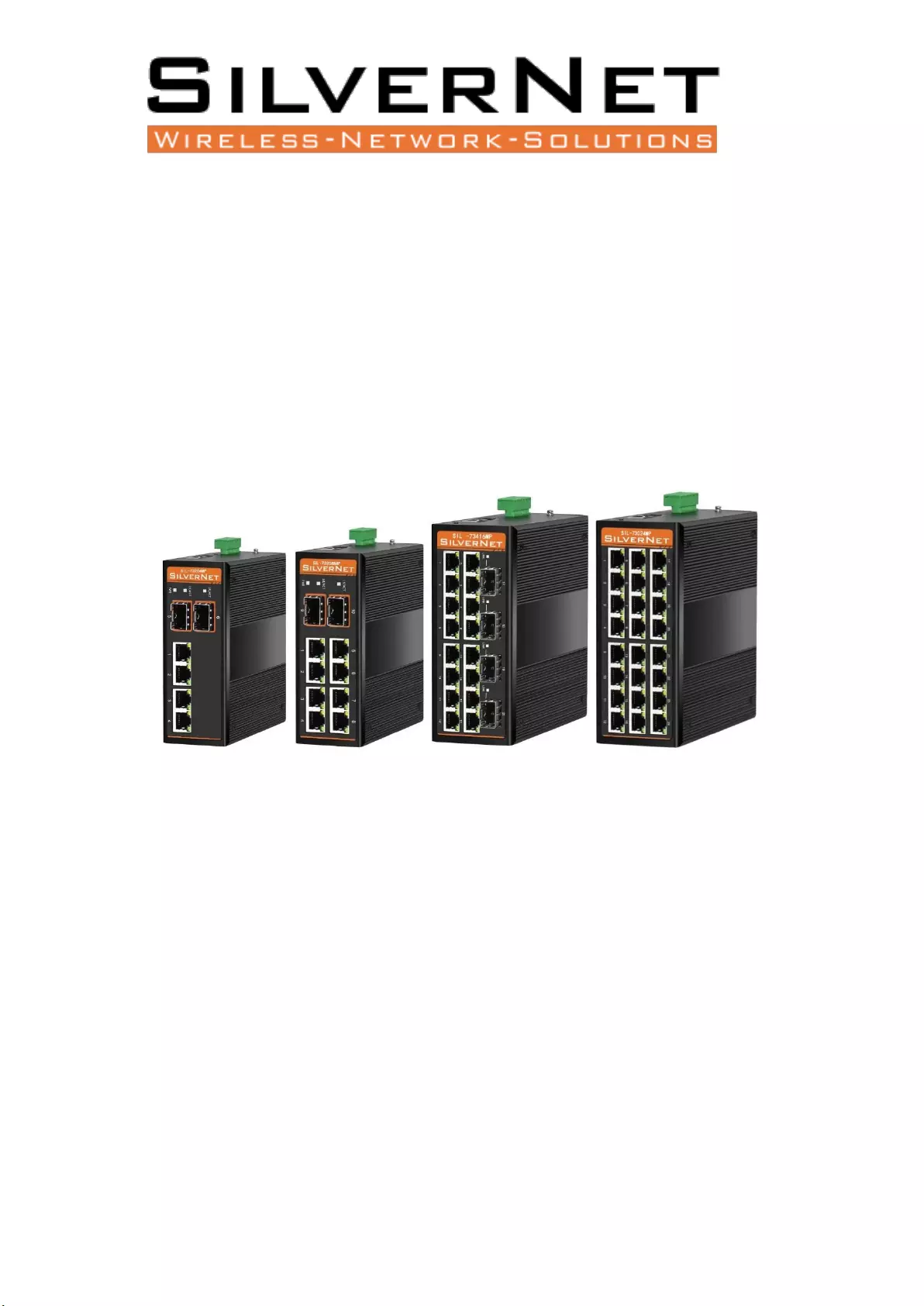
SERIES 7 INDUSTRIAL GIGABIT POE+ MANAGED
SWITCHES
SIL 73204MP SIL 73208MP SIL 73416MP SIL 73024MP
Configuration Manual
Pro Range User Manual Table of Contents 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Table of Contents ....................................................................................................................... 2
Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 7
Support Products ................................................................................................................................ 7
System Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 7
Packing List ................................................................................................................................. 7
The Panels and LED indicators ................................................................................................... 8
SIL 73204MP and SIL 73208MP ........................................................................................................... 8
SIL 73416MP and SIL 73024MP ........................................................................................................... 9
Installation ............................................................................................................................... 10
DIN-rail installation ........................................................................................................................... 10
Wall-mounted installation ................................................................................................................ 10
Power ................................................................................................................................................ 11
Product Dimension .................................................................................................................. 11
Copper cable connection ......................................................................................................... 12
Standard RJ45 connector .................................................................................................................. 12
Fibre cable connection ............................................................................................................. 13
Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 13
Getting Started .................................................................................................................................. 13
Navigation ......................................................................................................................................... 14
Device Panel ...................................................................................................................................... 16
Universal Buttons .............................................................................................................................. 16
Logout ............................................................................................................................................... 18
Device Status ..................................................................................................................................... 18
Pro Range User Manual Table of Contents 3
Port Configuration ................................................................................................................... 19
Port Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 19
Port Statistics .................................................................................................................................... 21
FDB Table ................................................................................................................................. 23
Aging time ......................................................................................................................................... 23
Static MAC ......................................................................................................................................... 23
Port Learning Ability.......................................................................................................................... 25
FDB Table .......................................................................................................................................... 26
Delete Entries .................................................................................................................................... 26
VLAN ......................................................................................................................................... 28
VLAN Port Configuration ................................................................................................................... 29
QoS ........................................................................................................................................... 31
802.1p Priority (CoS) ......................................................................................................................... 31
DSCP Priority ..................................................................................................................................... 32
Local Priority ..................................................................................................................................... 32
QOS Port Configuration .................................................................................................................... 33
Port Priority Settings ........................................................................................................ 33
Port Rate Limit .................................................................................................................................. 35
ACL ........................................................................................................................................... 36
ACL Group Setting ............................................................................................................................. 36
ACL Rules ........................................................................................................................................... 37
RSTP ......................................................................................................................................... 40
Global Configuration ......................................................................................................................... 40
Port Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 41
Path Overhead .................................................................................................................................. 42
STP Information ................................................................................................................................ 42
Port Information ............................................................................................................................... 43
Pro Range User Manual Table of Contents 4
ERPS ......................................................................................................................................... 45
ERPS Setting ...................................................................................................................................... 45
Ring Information ............................................................................................................................... 48
LLDP .......................................................................................................................................... 48
LLDP Global Setting ........................................................................................................................... 48
LLDP Port Configuration ................................................................................................... 49
802.1X ...................................................................................................................................... 52
Authentication Server ....................................................................................................................... 52
Global Settings .................................................................................................................................. 53
Port Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 54
User Authentication Information ...................................................................................................... 56
Loopback .................................................................................................................................. 56
Port Configurations ........................................................................................................................... 57
Multicast Management ............................................................................................................ 58
VLAN settings .................................................................................................................................... 60
IP Group ............................................................................................................................................ 61
MAC Groups ...................................................................................................................................... 62
Storm Filtering ......................................................................................................................... 63
Storm Filter Settings ......................................................................................................................... 63
Port Mirroring .......................................................................................................................... 64
Link Aggregation ...................................................................................................................... 65
Link Aggregation Port Setting ........................................................................................................... 67
Link Aggregation Information ........................................................................................................... 69
SNMP ........................................................................................................................................ 70
Base Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 70
Trap Setting ....................................................................................................................................... 71
Pro Range User Manual Table of Contents 5
IP interface ............................................................................................................................... 73
IP Address ......................................................................................................................................... 73
Base Configuration ........................................................................................................... 74
DHCP Client Configuration ................................................................................................................ 75
DHCP ........................................................................................................................................ 76
Global Setting .................................................................................................................................... 76
Port Setting ...................................................................................................................... 77
Binding Table..................................................................................................................................... 77
Administration ......................................................................................................................... 78
User Management ............................................................................................................................ 78
Online User ....................................................................................................................................... 81
Login Timeout Setting ....................................................................................................................... 82
System Configuration ............................................................................................................... 83
System Log ........................................................................................................................................ 83
View Logs .......................................................................................................................................... 85
Configurations ................................................................................................................................... 86
Import Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 87
Export Configuration ......................................................................................................................... 87
Restore Factory Configuration .......................................................................................................... 88
Date and Time ................................................................................................................................... 88
Software Upgrade ............................................................................................................................. 90
Software Restart ............................................................................................................................... 90
Accessories ............................................................................................................................... 91
Technical parameters ............................................................................................................... 92
Standards ................................................................................................................................. 93
Warnings .................................................................................................................................. 93
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 94
Pro Range User Manual 6
Responsibility Note .................................................................................................................. 94
Warranty .................................................................................................................................. 94
Contact SilverNet ..................................................................................................................... 94
Copyright Information ............................................................................................................. 94
Other SilverNet Products ......................................................................................................... 95
Pro Range User Manual Introduction 7
INTRODUCTION
This manual covers the firmware version x.x.x.x which is loaded onto all SilverNet 7 Series Switches.
SUPPORT PRODUCTS
This manual covers all 7 Series products listed below:
• 73204MP
• 73208MP
• 73416MP
• 73024MP
For more information, visit http://www.silvernet.com
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
• Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Linux, or Mac OS X
• Web Browser: Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Google Chrome, or Microsoft Internet Explorer 9 (or
above)
PACKING LIST
Please check the following items in the package before installing the device
Network Switch 1 piece
Quick Start Guide 1 copy
DIN Rail Mount Kit 1 piece
Wall Mount Kit 1 piece
Serial Cable 1 piece
Please contact your distributor immediately for any missing or damaged items.
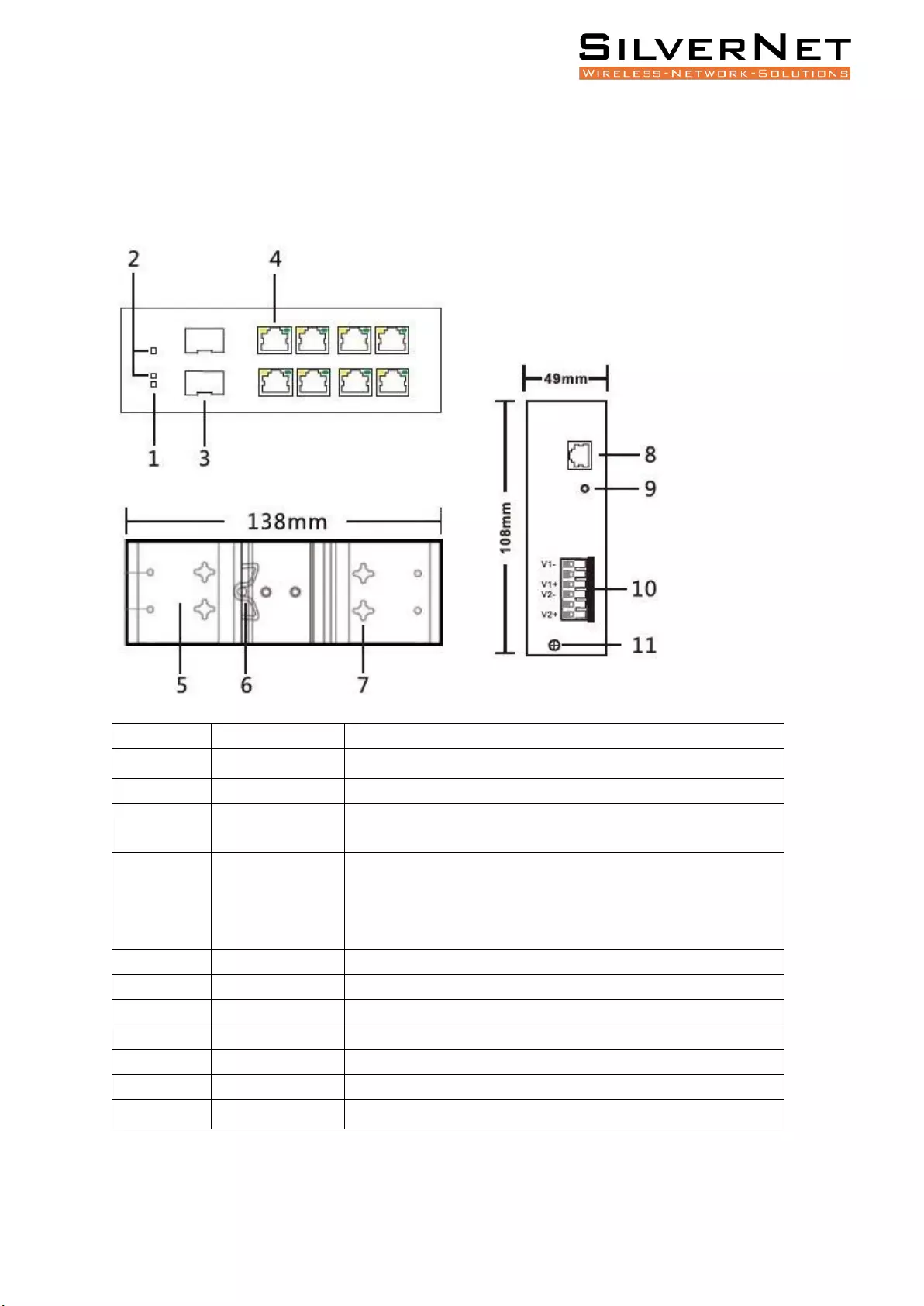
Pro Range User Manual The Panels and LED indicators 8
THE PANELS AND LED INDICATORS
SIL 73204MP AND SIL 73208MP
Mark
Name
Function
1
Power LED
“On”: Power is on and normal
2
System LED
“On”: System is on and normal
3
SFP Port
“On”: Fibre connection is present
“Blinking”: Data being transmitted
4
RJ45 Ports
Yellow LED “On”: PoE connection is present
Yellow LED “Blinking”: Data being transmitted
Green LED “On”: Ethernet connected at 1000M
Green LED “Off”: Ethernet connected at 10/100M
5
Wall kit
Wall mounting bracket
6
DIN kit
DIN-rail mounting bracket
7
Wall kit
Wall mounting holes
8
Console Port
Connection port to access CLI
9
Reset
Reset button
10
Terminal block
Power input Terminal
11
Ground
Grounding screw
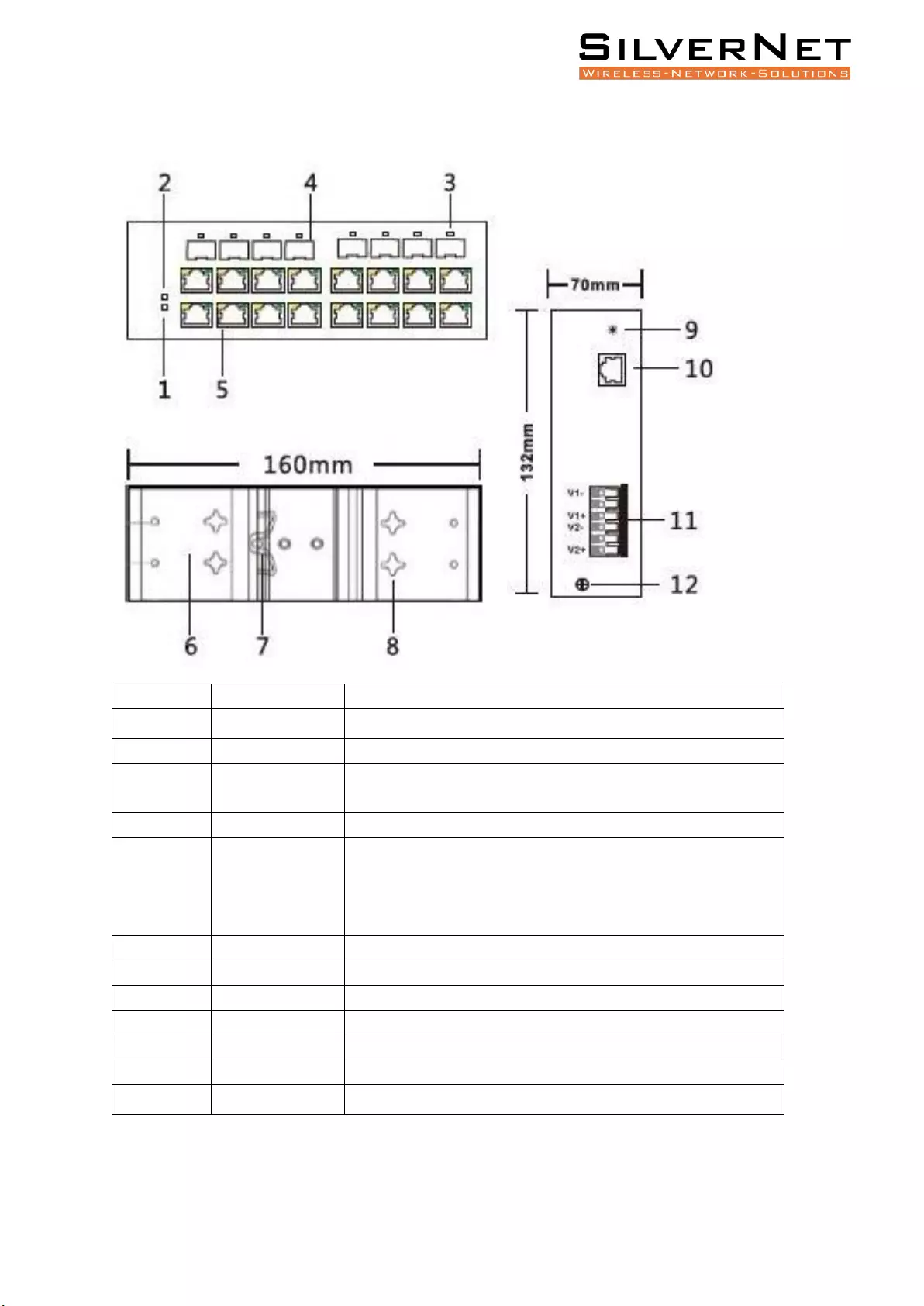
Pro Range User Manual 9
SIL 73416MP AND SIL 73024MP
Mark
Name
Function
1
Power LED
“On”: Power is on and normal
2
System LED
“On”: System is on and normal
3
SFP Port LED
“On”: Fibre connection is present
“Blinking”: Data being transmitted
4
SFP Port
SFP Port
5
RJ45 Ports
Yellow LED “On”: PoE connection is present
Yellow LED “Blinking”: Data being transmitted
Green LED “On”: Ethernet connected at 1000M
Green LED “Off”: Ethernet connected at 10/100M
6
Wall kit
Wall mounting bracket
7
DIN kit
DIN-rail mounting bracket
8
Wall kit
Wall mounting holes
9
Reset
Reset button
10
Console Port
Connection port to access CLI
11
Terminal block
Power input Terminal
12
Ground
Grounding screw
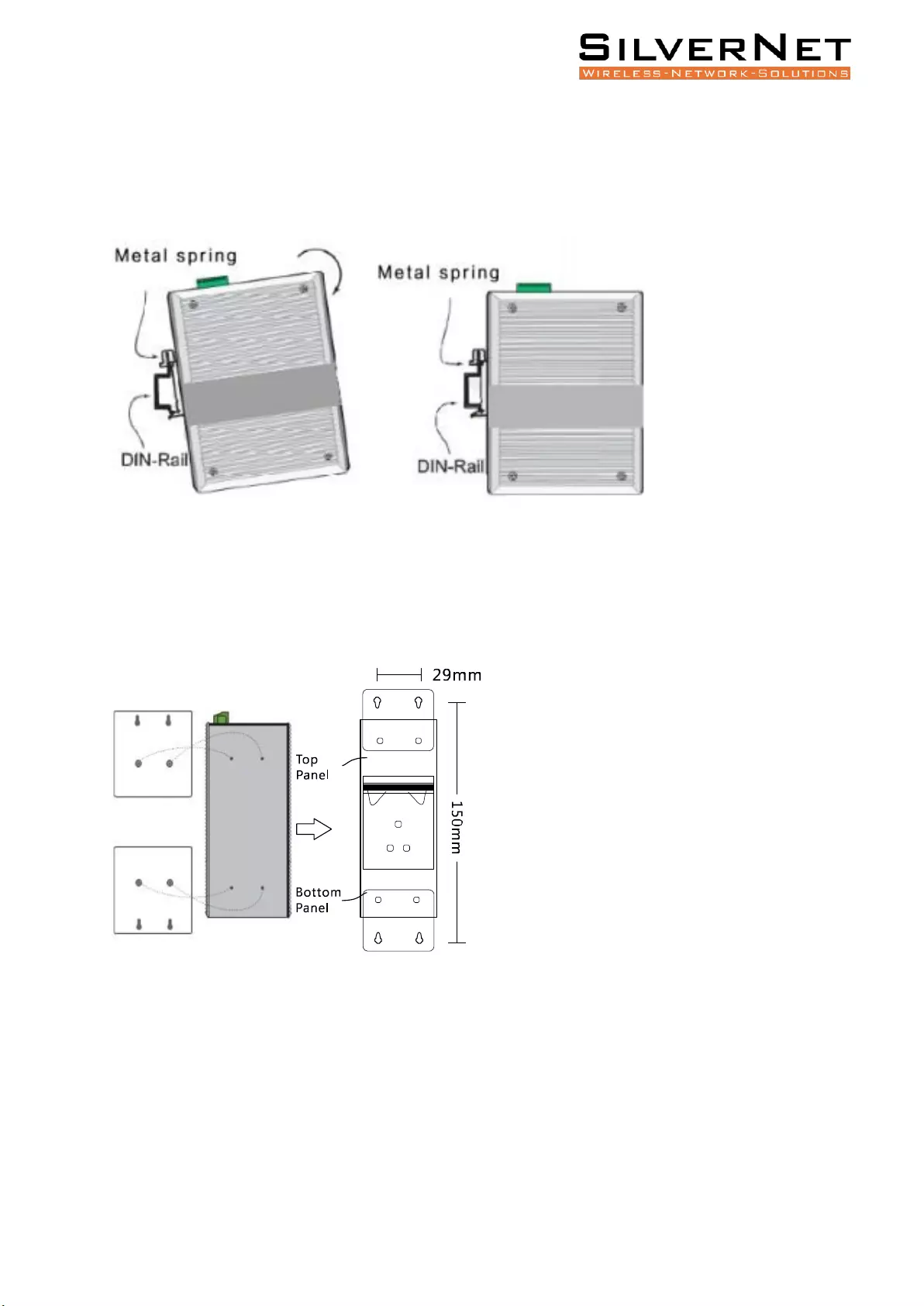
Pro Range User Manual Installation 10
INSTALLATION
DIN-RAIL INSTALLATION
Pic 1 Pic 2
The DIN-rail installation is based on Pic 1 and Pic 2.
WALL-MOUNTED INSTALLATION
The wall mount kit is fixed to the back of the switch. Remove and re-attach the wall mounting kit as
shown in the image above.
Attach the switch and bracket to the wall using appropriate screws. Do not completely tighten the
screws, allow approximately 2mm of space.
Place the screw head through the large holes in the wall bracket then pull down to secure, tighten
screws once in place.
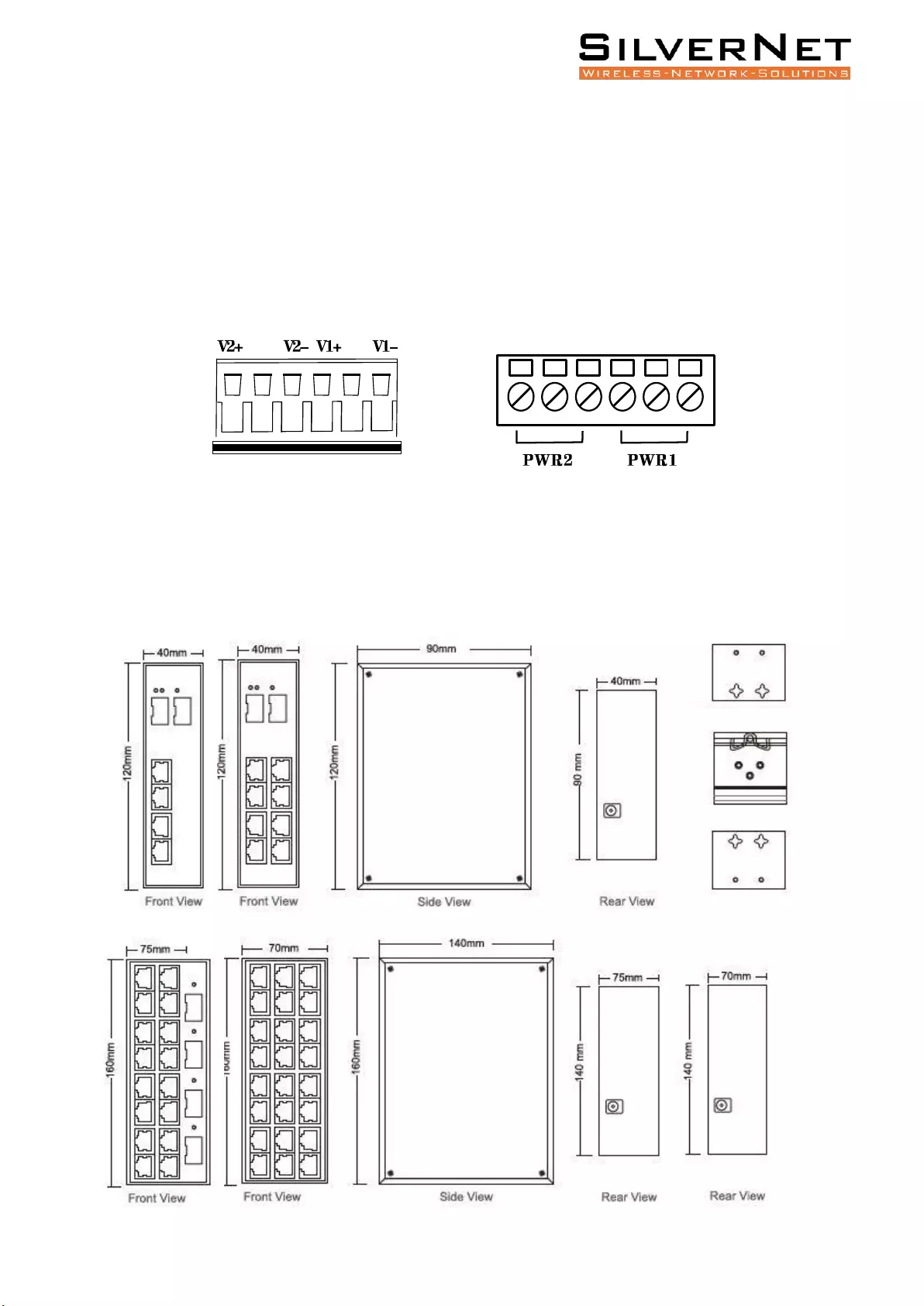
Pro Range User Manual Product Dimension 11
POWER
The input terminal of the switch is for 6 PIN plug type terminals, V1+ and V1- is for power supply 1
(PWR1), V2 + and V2- is for power supply 2 (PWR2) and GND for the earthing terminal, as shown in
image below.
The input voltage range for power 1 and power 2 is 12VDC ~ 56VDC,V1+, and V2+ are positive, V1-
and V2- are negative.
The switch can be powered by two power supplies simultaneously allowing the switch to continue
functioning even if one of the power supplies fails.
PRODUCT DIMENSION
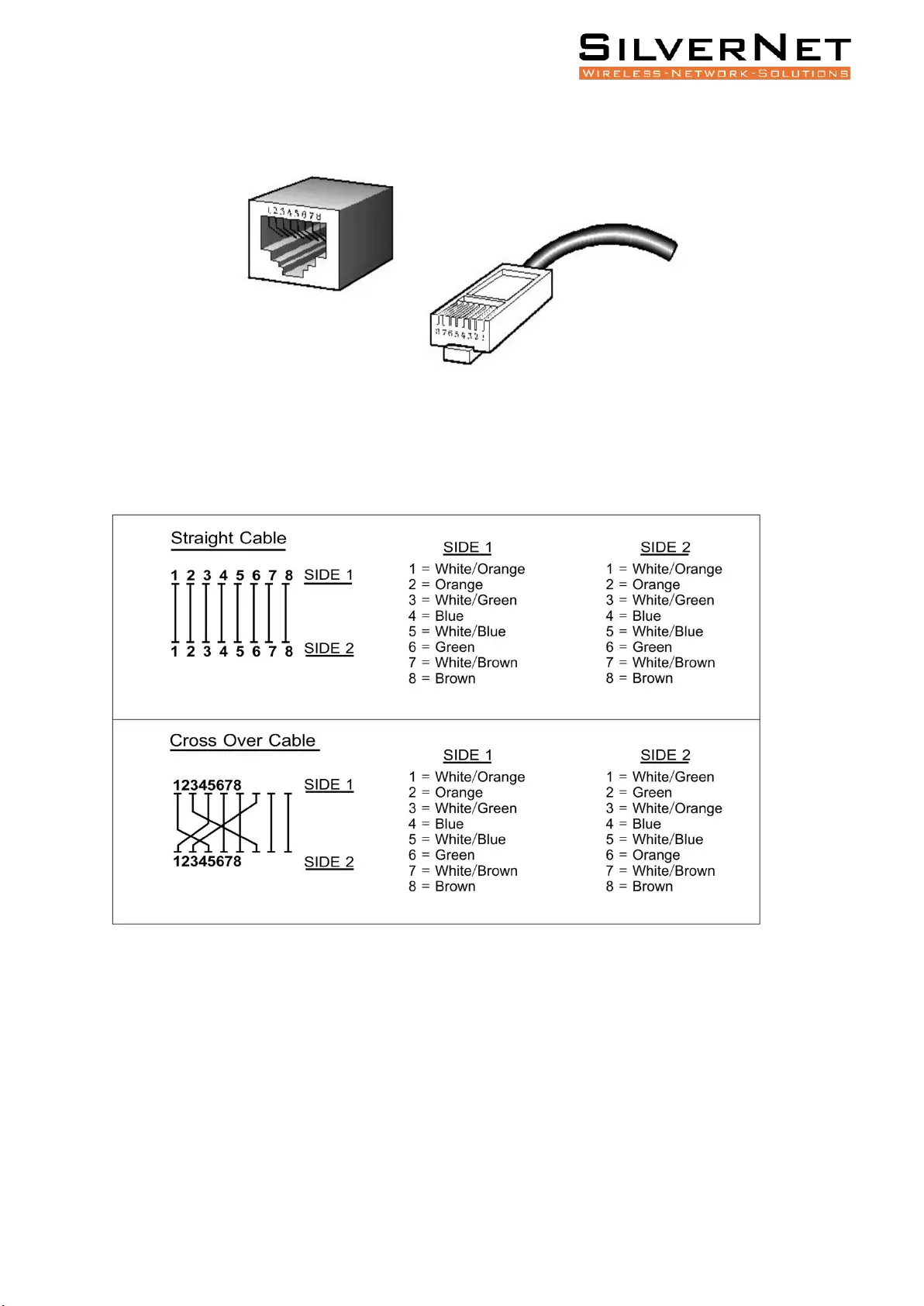
Pro Range User Manual Copper cable connection 12
COPPER CABLE CONNECTION
STANDARD RJ45 CONNECTOR
There are 8 wires on a standard UTP/STP cable, and each wire is colour coded. The following shows
the pin allocation and colour of a straight through cable and crossover cable:
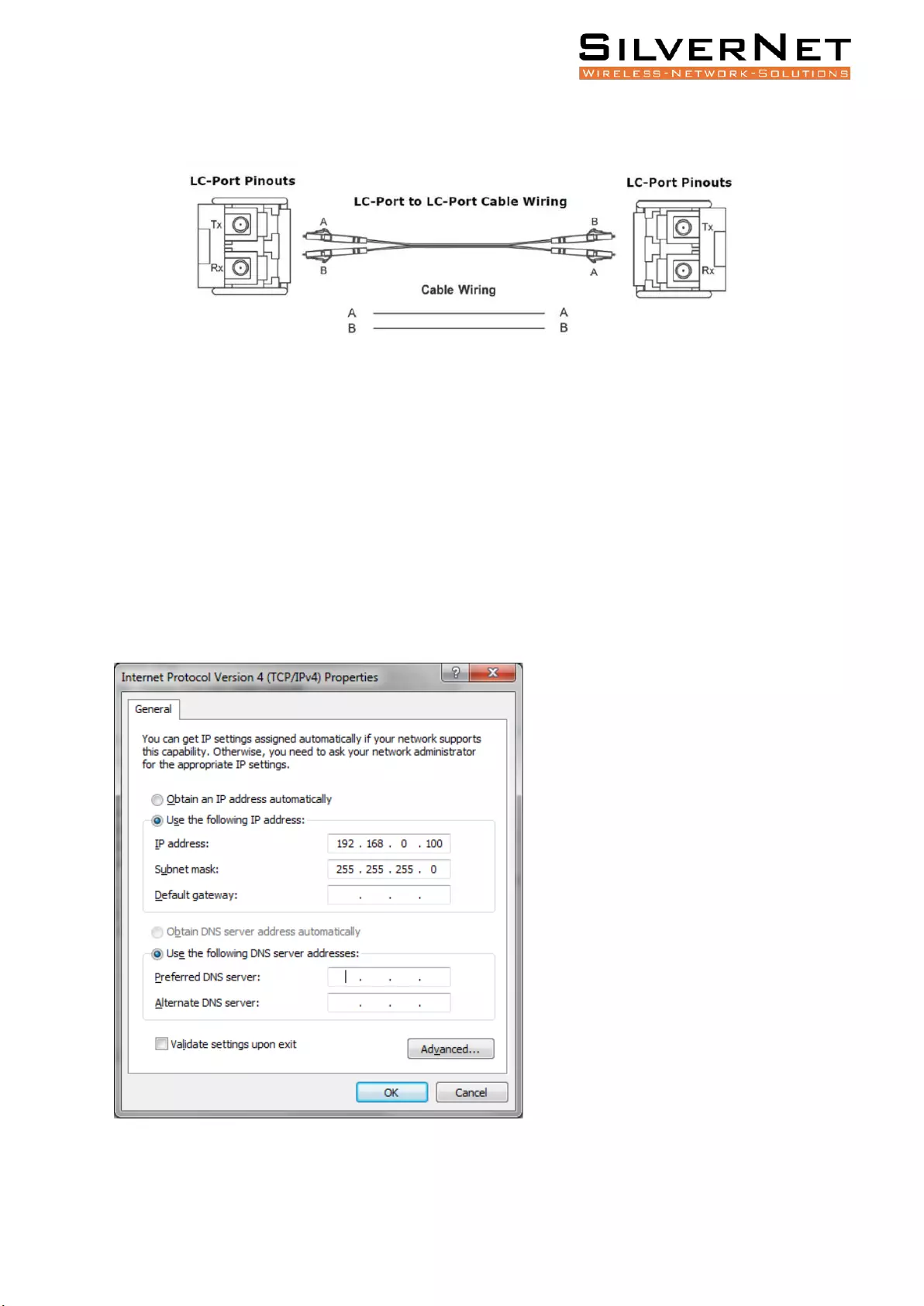
Pro Range User Manual Fibre cable connection 13
FIBRE CABLE CONNECTION
CONFIGURATION
GETTING STARTED
To access the 7 Series equipment management interface, perform the following steps:
To access the Pro Range Configuration Interface, perform the following steps:
1. Configure the Ethernet adapter on your computer with a static IP address on the 192.168.0.x
subnet (for example, IP address: 192.168.0.100 and subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Launch your web browser and enter the default IP address of your device in the address field. IP
Address
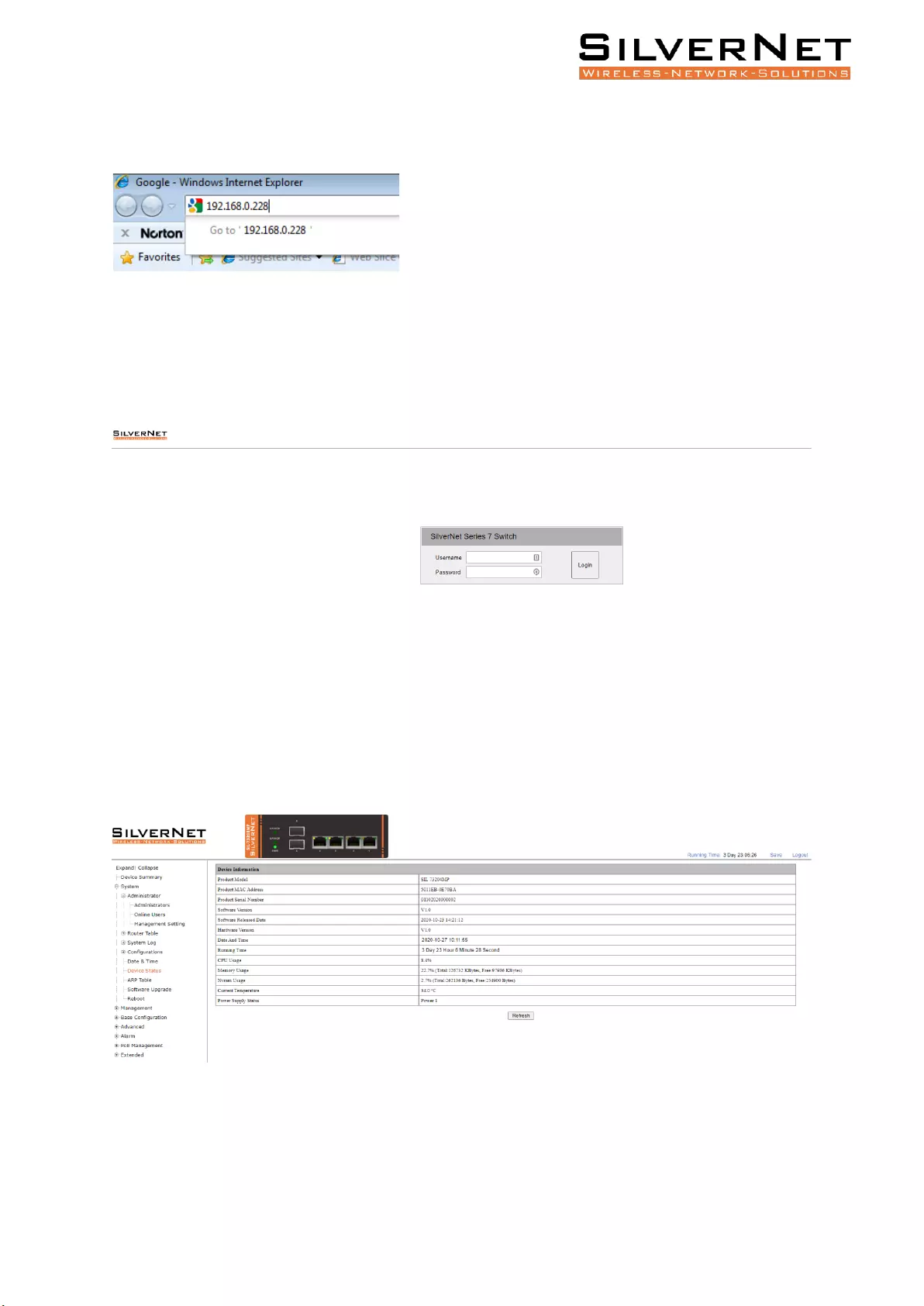
Pro Range User Manual Configuration 14
Pro Range products are pre-configured to IP address 192.168.0.229/192.168.0.228
If the unit has been reset, it will go to the default IP address of 192.168.1.6. You will need to
change your Ethernet adapter IP address to 192.168.1.x subnet.
3. Enter admin in the Username field and admin in the Password field and click Login.
Figure 1.1 Login Page
NAVIGATION
The 7 Series management interface contains seven main groups, each with their groups which
provide a web-based management page to configure a specific aspect of the SilverNet device:
Figure 1.2 Web Management Interface
Please see Table 1.2 for a description of the areas as shown in Figure 1.2

Pro Range User Manual Configuration 15
• System The “System” group allows configuration of general system-wide settings such as;
Administrator Settings, Router Table, System Logs, Configuration Management, Date & Time, Device
Status Check, ARP Table, Firmware Upgrade and Reboot.
• Management The “Management” group allows configuration of management protocols such as; IP
Interfaces, SNMP Configuration and LLDP Configuration.
• Base Configuration The “Base Configuration” group allows configuration of general managed
switch settings such as; Port Settings and Statistics, VLAN Configuration, QOS, FDB Table, Port
Mirroring, Port Isolation, Storm Control.
• Advanced The “Advanced” group allows configuration of more advanced network switch settings
such as; Port Security, ACL Groups and Rules Settings, DHCP Snooping, DHCP Server Settings,
Multicast Options, GMRP Configuration, GVRP Configuration, 802.1X Settings, Link Aggregation,
Loopback Settings, STP Settings and ERPS Configuration.
• Alarm The “Alarm” group allows configuration of alarm warnings such as; Relay Settings,
Temperature Settings, Trap Settings and Power Settings.
• PoE Management The “PoE Management” group allows configuration of PoE such as; Port PoE
Configurations, Smart Power Configuration, Time Range Configuration, Timing Supply Configuration.
• Extended The “Extended” group allows configuration of diagnostics such as; Port Cable Testing
and Ping Testing.
Web Management Interface Descriptions Table 1.2
Configuration Interface
Description
Navigation Bar
Groups which enable navigation of the web management interface.
Selected Page
The currently selected configuration page.
Device Panel
Displays a quick overview of connectivity for ports on the switch.
Running Time
The uptime of the device since last full reboot.
Device Model
Displays the name of the 7 Series switch.
Common Functions
Save: Save the current configuration to the system. This button will blink
from blue to amber when there is a configuration which hasn’t been
committed to memory.
Logout: Logout the current user.

Pro Range User Manual Configuration 16
DEVICE PANEL
You can view the current connection status of each port interface via the Device Panel, as displayed
in Figure 1.3 below.
Figure 1.3 Device Panel
See below Table 1.3 for the Device Panel Interface Descriptions.
Table 1.3 Device Panel Interface Description
Port
Instructions
GREEN and YELLOW LED: Copper Port, Enabled, Connected
NO LED INDICATOR: Copper Port, Enabled, not Connected
SFP SLOT IN: Fibre Port, Enabled, Connected
SFP SLOT OUT: Fibre Port, Enabled, not Connected
UNIVERSAL BUTTONS
The 7 Series switch has multiple Universal buttons across the entire management interface.
Please find a description of these buttons on the next page.
Buttons
Instructions
Expand all groups in the navigation bar.
Close all groups in the navigation bar.
Apply your configuration changes.
Pro Range User Manual Configuration 17
Refresh the interface information.
Add a new item.
Modify the selected item.
Delete the selected item.
Return to the previous page.
Go to the next page.
Go to the specified page.
Navigate to the home page.
Go back to the last page.
Apply the configuration to the device.
Cancel the current configuration changes.
Clear the specified information.
Save system configuration.
Logout from the current user.
After you have finished making your configuration changes, click Apply to apply the configuration to
the system. However, it is only stored in the memory and not saved in the configuration file. If you
do not press Save, the configuration will be lost after the device is powered off or restarted.
After all configurations are complete, click Save. The configuration will be saved to the configuration
file and will not be lost after the device is powered off or restarted.
Pro Range User Manual Configuration 18
LOGOUT
After completing the configuration on the web interface, press Save first to avoid loss of the
configuration. Then click Exit to exit the Web management interface.
Directly closing the browser will not logout the user from Web management interface. If you reopen
your browser within the login timeout frame, the user can directly enter the Web configuration
interface.
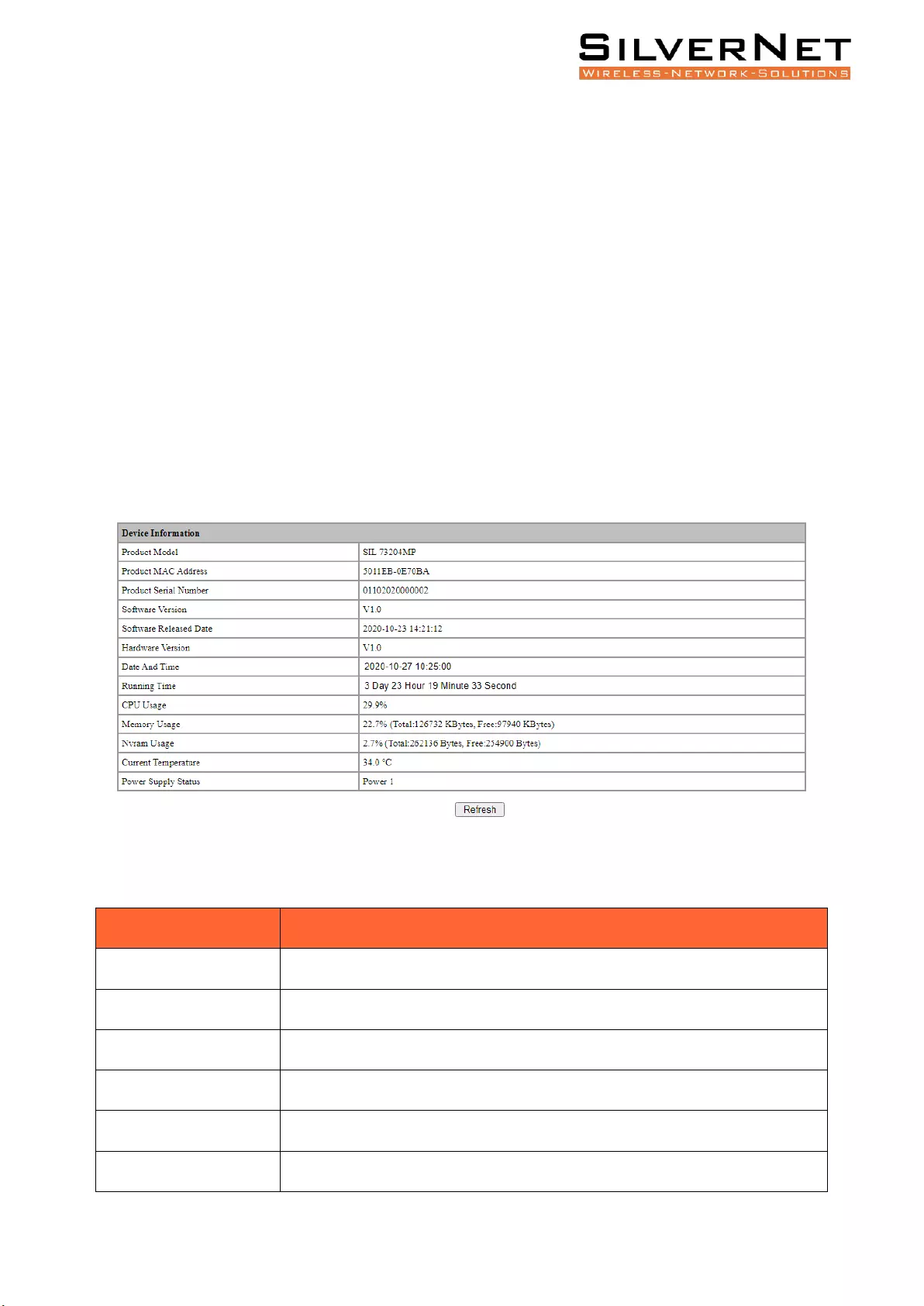
DEVICE STATUS
Expand the System group and enter the Device Status page to view information regarding your
connected network switch. The results here will vary depending on what model of 7 Series switch you
have, for example, the Product Model listed as SIL 73208MP. Please see figure 1.4 and Table 1.4 for a
view of and descriptions of the Device Status Page.
Figure 1.4 – Device Status Interface
Table 1.4 Device Status Descriptions
Item
Description
Product Model
The devices model, For Example: SIL 73208MP.
Product MAC Address
The devices MAC address.
Product Serial Number
The devices serial number.
Software Version
The current software version.
Software Release Date
The release date of your current software.
Hardware Version
The hardware version of the device.
Pro Range User Manual Port Configuration 19
Date and Time
The device system time.
Running Time
The systems running time.
CPU Usage
The systems CPU usage.
Memory Usage
The memory usage of the system.
NVRAM Usage
Configuration space usage of the system.
Current Temperature
Current temperature of the switch.
Power Supply Status
Current terminal block wiring.
PORT CONFIGURATION
This chapter describes the port configuration in detail, including the following:
• Port Configuration (Admin Status, Copper Mode, Flow Control, EEE)
• Port Statistics (Detailed Statistics, SFP Statistics, Traffic Statistics)
PORT CONFIGURATION
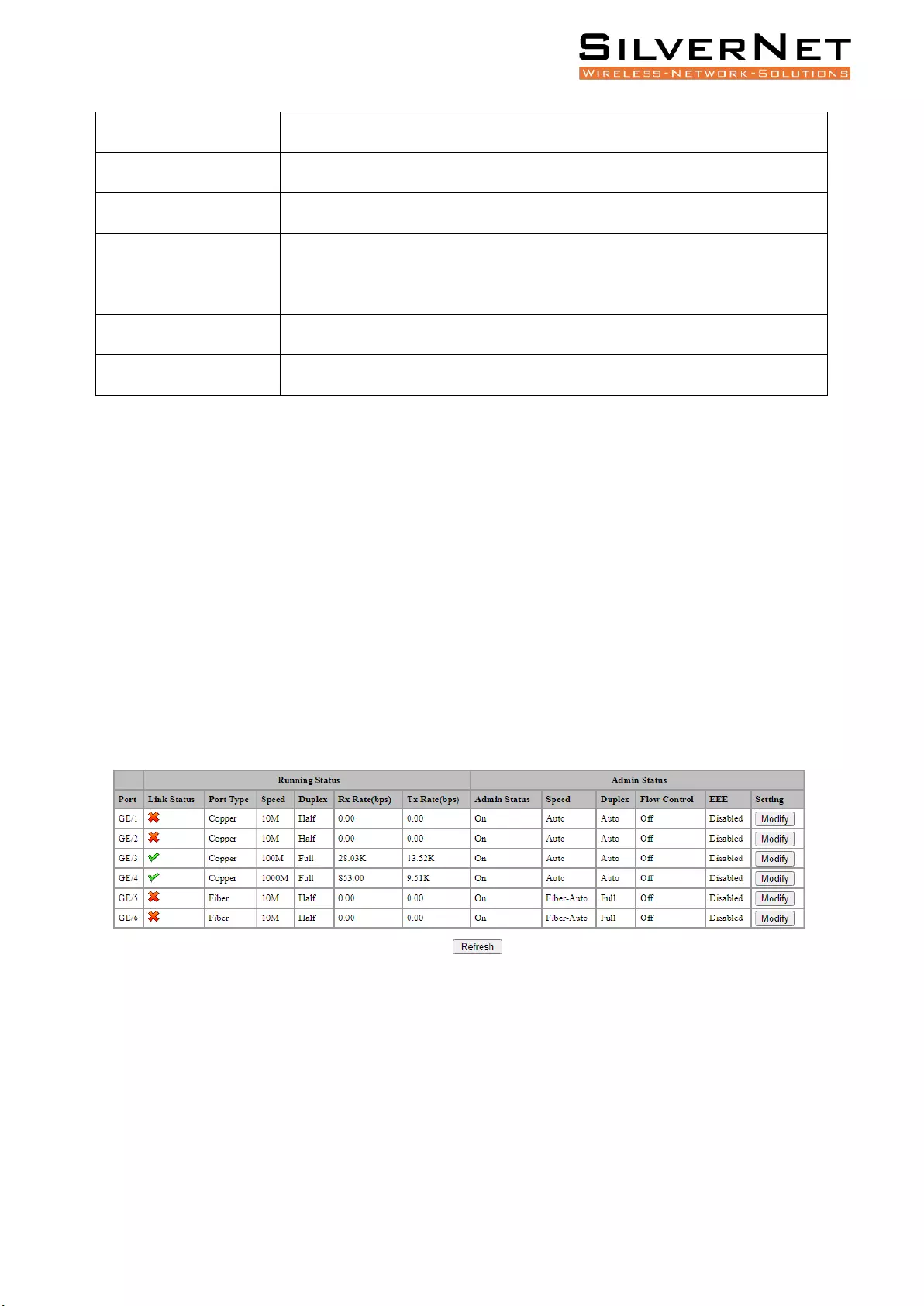
Select Base Configuration / Ports / Status and Setting in the navigation bar to enter the Status and
Setting interface.
The Status and Settings interface (Figure 2.1) shows the operating status and configuration information
for each port. Table 2.1 Explains this interface.
Figure 2.1 Port Status and Settings Interface
Table 2.1 Port Configuration Description
Pro Range User Manual Port Configuration 20
Item
Description
Port
The name and number of the port.
Link Status
GREEN TICK: Indicates that the port is connected.
RED CROSS: Indicates that the port is disconnected.
Port type
Copper or Fibre Port.
Speed
The ports working speed, a disconnected port is always displayed as 10M.
Duplex Mode
The ports duplex mode, a disconnected port always shows half duplex.
Admin Status
Current condition of the Admin Status of the port.
Flow Control
Current status of Flow Control on the port.
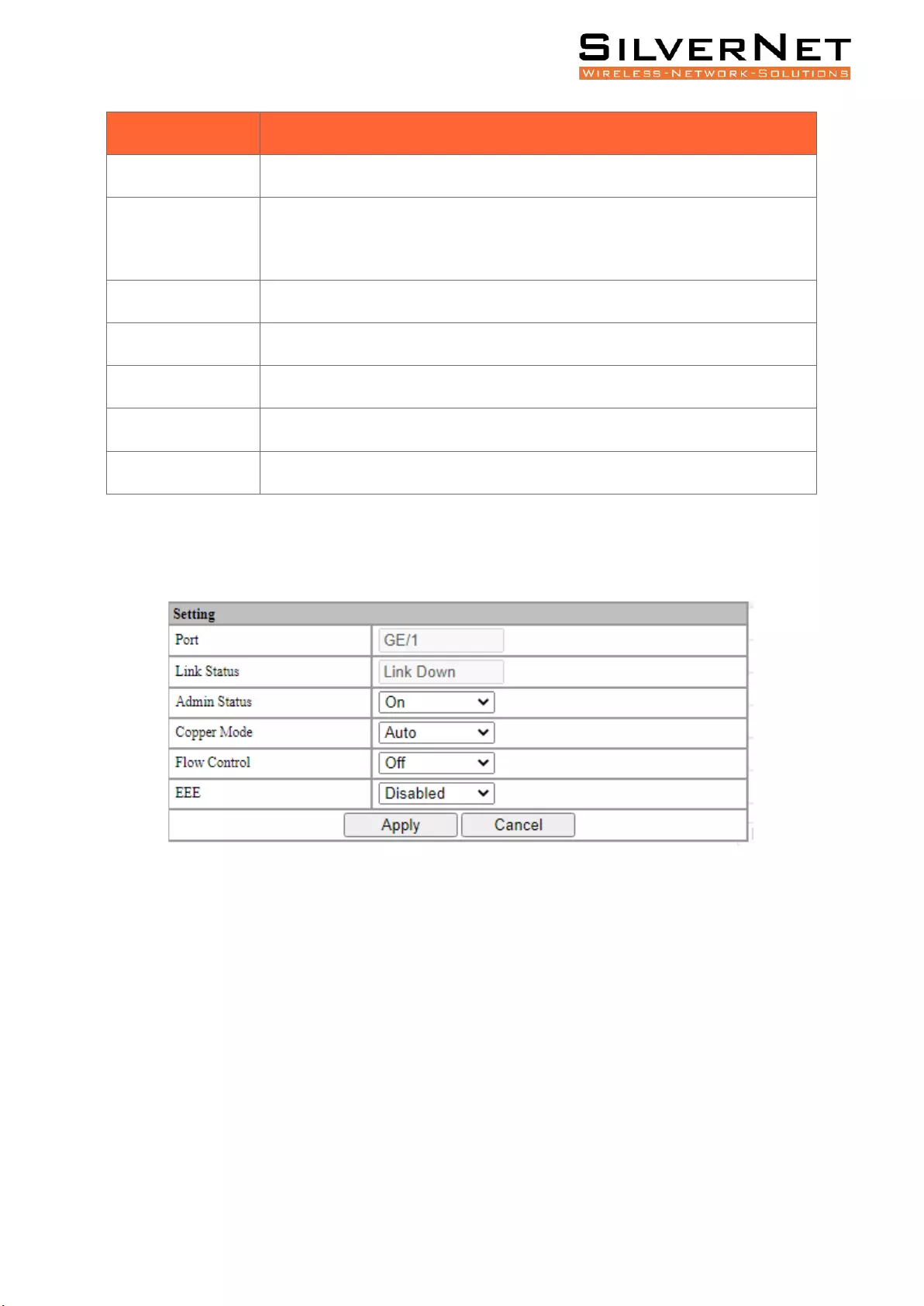
Click the modify button to enter the port configuration page as seen in Figure 2.2. Click the Apply
button to complete the configuration and click the Cancel button to cancel the configuration.
Figure 2.2 Port Configuration
Pro Range User Manual Port Configuration 21
Table 2.2 Port Configuration Descriptions
Item
Configuration
Description
Admin Status
On
Off
Turn the port on or off. When set to Off, the
port will be inaccessible until turned back On.
Default setting for all ports is On.
Copper Mode
Auto
10M Half
10M Full
100M Half
100M Full
1000M Full
The configurable duplex and data rate, such as
10M / 100M / 1000M / Auto. Only one
communication is permitted in half-duplex
mode and simultaneous two-way
communication in full-duplex mode. Default
setting is Auto.
Flow Control
On
Off
The Layer 2 port flow control function can
effectively prevent network congestion when
turned on. Flow control is a peer-to-peer
function. It is implemented by pause frames.
When the ports of the PVRP system are
enabled, the peer port must be also enabled.
Default setting is Disabled.
EEE
Enabled
Disabled
Enable Energy-Efficient Ethernet protocol. This
will reduce power consumption during periods
of low data activity. Default setting is Disabled.
PORT STATISTICS
Select Base Configuration / Ports / Statistics to enter the port Statistics page (as shown in Figure 2.3).
The Statistics shows each ports statistical information. You can expand the corresponding port
statistics by clicking the button and click the Clear button to clear the statistics of the port. Table
2.3 explains this statistical information in more detail.
Click the Refresh button to update the statistics of all ports. Click Clear All to clear the statistics for
all ports.
Pro Range User Manual 22
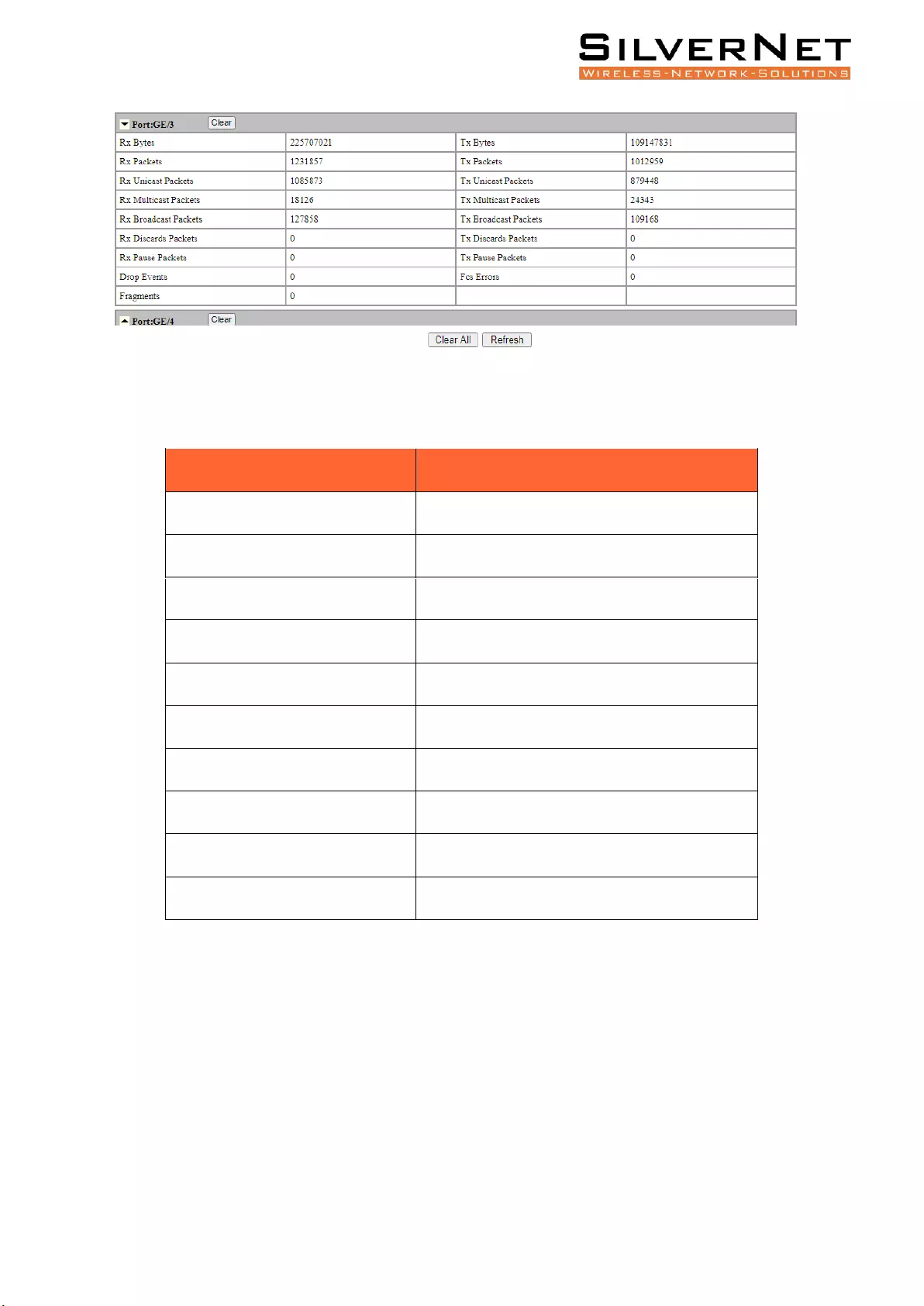
Figure 2.3 Port Statistics Information
Table 2.3 Port Statistics Descriptions
Port Statistics Type
Description
Rx / Tx Bytes
Total received / sent bytes.
Rx / Tx Packets
Total received / sent packets.
Rx / Tx Unicast Packets
Total received / sent unicast packets.
Rx / Tx Multicast Packets
Total received / sent multicast packets.
Rx / Tx Broadcast Packets
Total received / sent broadcast packets.
Rx / Tx Discards Packets
Total received / sent discarded packets.
Rx / Tx Pause Packets
Total received / sent flow control packets.
Drop Events
Drop messages (interval sampling).
FCS Errors
FCS error packet.
Fragments
Fragment packets (less than 64 bytes).
Pro Range User Manual FDB Table 23
FDB TABLE
This chapter describes the FDB Table in detail, including the following:
• Base Configuration (Aging Settings, Static MAC Entry, Port Learning Ability)
• FDB Table Information
• Deletion
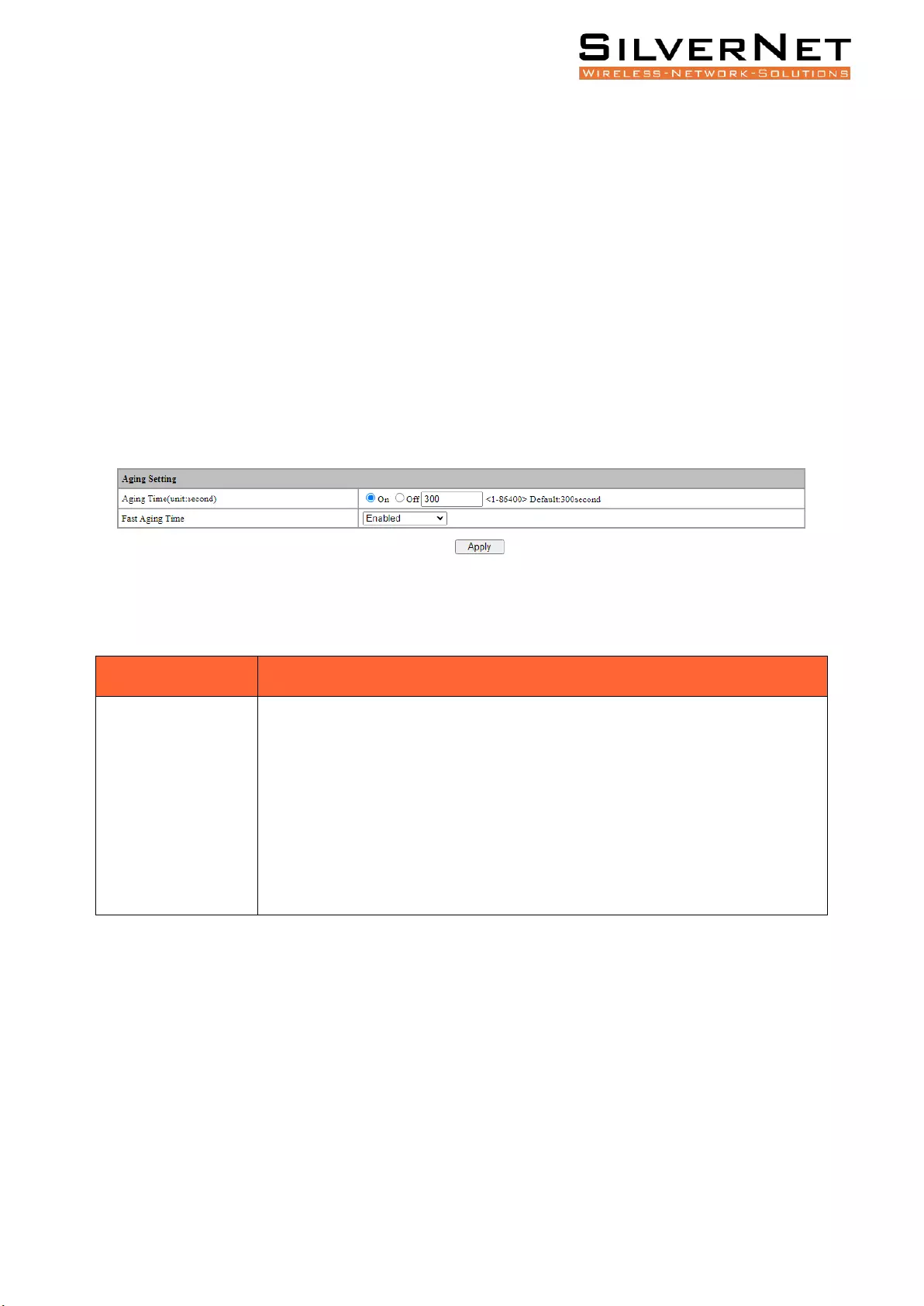
AGING TIME
Select Base Configuration / FDB Table / Configuration / Aging Setting to enter the Aging Setting
interface. Table 3.1 explains this setting.
If you need to modify the aging time configuration of the FDB Table, you can modify this in the aging
time configuration box and click Apply, as shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1 Aging Time Configuration
Table 3.1 The FDB Table Aging Time Description
Configuration Item
Description
Aging time
The FDB Table Aging Time describes the period dynamic entries are stored in the
FDB table based on the last reception of a frame. The FDB Table aging time can
be configured as below:
ON: Aging Time is on. Range 1-86400 seconds, default value 300 seconds before
dynamic forwarding entries are discarded.
OFF: The FDB Table never ages, but the system resetting could clear the dynamic
forwarding entries.
STATIC MAC
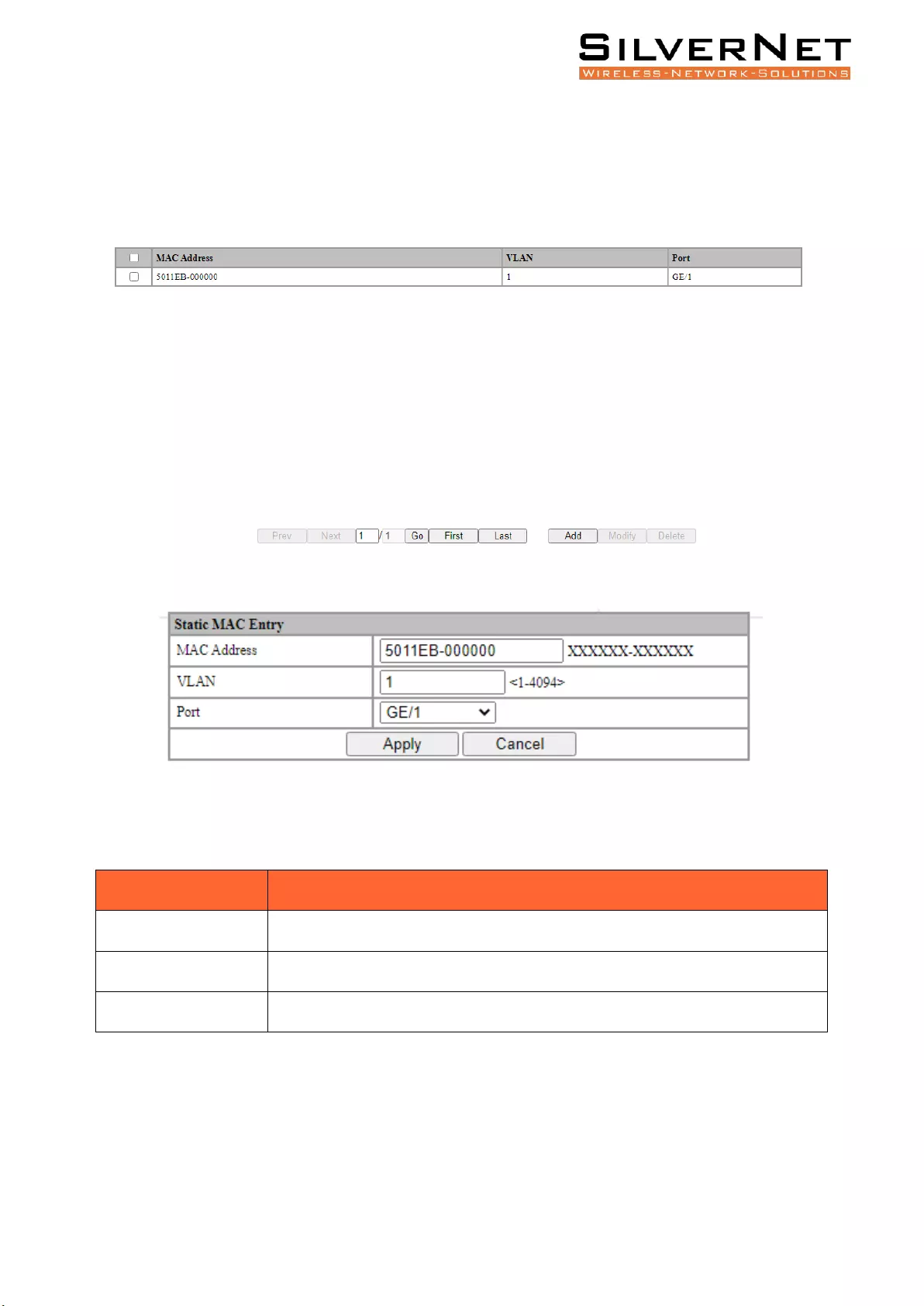
Select Base Configuration / FDB Table / Configuration / Static MAC Entry to enter the Static MAC
Entry configuration interface.
On the FDB Table Static MAC Entry interface, you can view the static MAC related configuration
information of the FDB Table, as shown in Figure 3.2.
To add a new static MAC address, click Add. Fill in the corresponding configuration items and click
Apply to complete. There will be error prompts if the configuration setting is filled in incorrectly.
Table 3.2 explains Static MAC Entry in more detail.
Pro Range User Manual FDB Table 24
If modifying the static MAC address, click Modify to enter Static MAC Entry interface. Click Apply to
complete the configuration. There will be error prompts if the configuration setting is filled in
incorrectly.
To delete a static MAC, select the corresponding static MAC and click Delete.
Figure 3.2 Static MAC Interface
Figure 3.2 Static MAC Configuration
Table 3.2 FDB Table Static MAC Description
Configuration Item
Description
MAC address
A valid unicast MAC address, format XXXXXX-XXXXXX.
VLAN
A valid VLAN ID, range 1-4094.
Port
Select a port.
Pro Range User Manual FDB Table 25
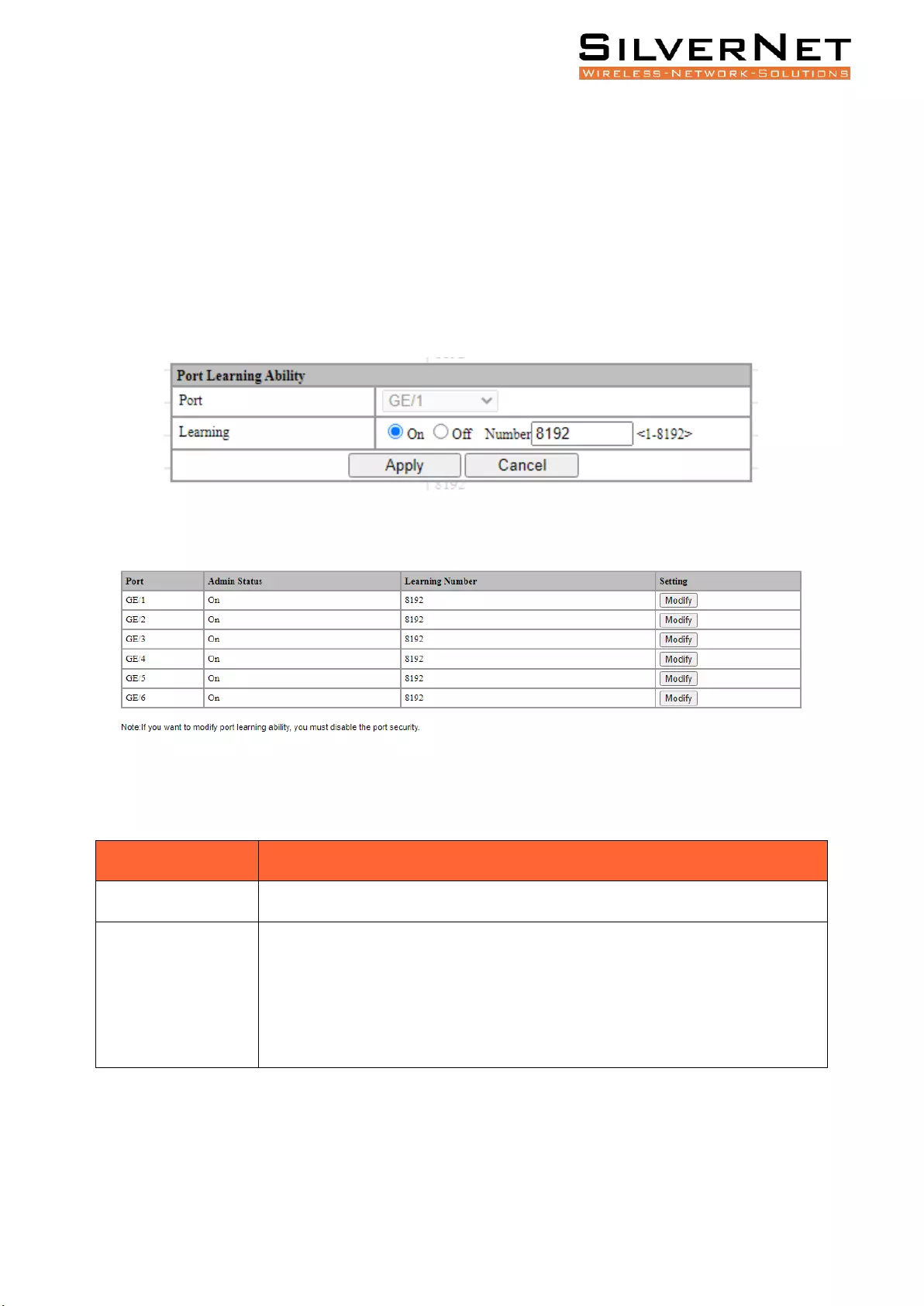
PORT LEARNING ABILITY
Select Base Configuration / FDB Table / Configuration / Port Learning Ability to enter the Port
Learning Ability interface.
To modify the Port Learning Ability configuration, click Modify in the corresponding port column to
enter the port configuration interface, as shown in Figure 3.3.
Select or fill in the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply. There will be
prompts if the configuration item is filled in incorrectly. Table 3.3 describes this in more detail.
Figure 3.3 Port Learning Ability Configuration
Figure 3.4 Port Learning Ability Statistics
Table 3.3 FDB Table Port Learning Ability Description
Configuration item
Description
Port
Port name, selected modified port.
Learning
Functional configuration of port learning. This allows the Switch to dynamically
add learned FDB Entries.
ON: The Port Learning Ability is on. IS3000 / IS2000 series range is 1-8192;
OFF: Closes the Port Learning Ability.
Note: The number of address learning is shared by all ports.
Pro Range User Manual FDB Table 26
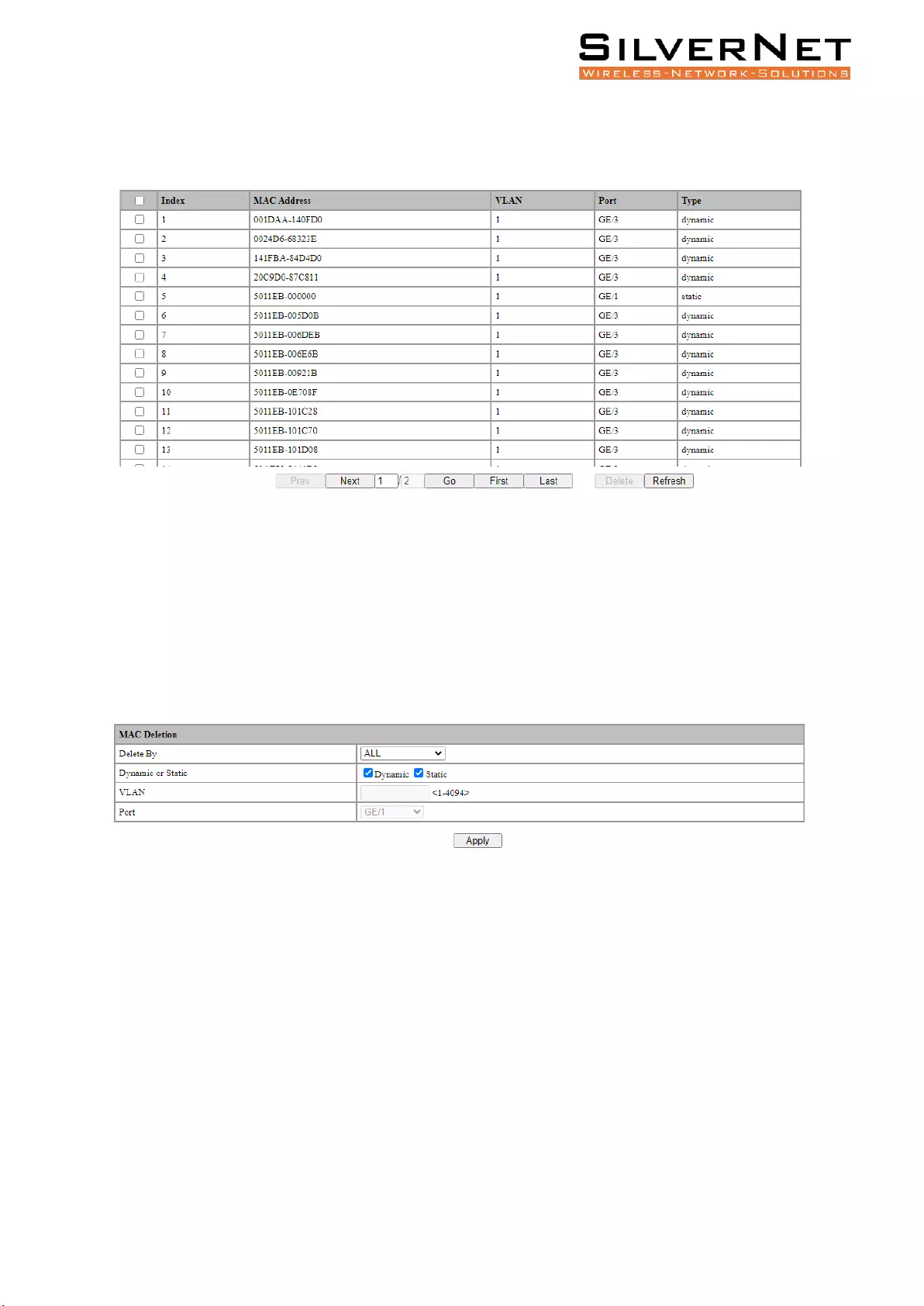
FDB TABLE
Select Base Configuration / FDB Table / FDB Table to enter FDB Table interface as shown in figure 3.5.
Figure 3.5 FDB Table
If deleting a forwarding entry, select the corresponding forwarding entry or select it all and click Delete
to delete the entry.
DELETE ENTRIES
Select Base Configuration / FDB Table / Delete Entries to enter the Deletion interface. Please see
Figure 3.6 and Table 3.4 for an overview of this section.
Figure 3.6 FDB Table Deletion
Pro Range User Manual FDB Table 27
Table 3.4 FDB Table Deletion Description
Configuration Item
Description
Delete By
Select the type of delete operation.
ALL: Deletes all FDB Table entries.
VLAN Only: Specifies the VLAN ID to delete FDB Table entries.
Port Only: Specify the port number to delete FDB Table entries.
Dynamic or static
Select the delete type, dynamic or static:
Dynamic: Delete the dynamic FDB Table entries that have been learned.
Static: Delete manually added static FDB Table entries.
VLAN
Delete the forwarding entry of the specified VLAN. The range is 1-4094.
Port
Delete the forwarding entry of the specified port.
Pro Range User Manual VLAN 28
VLAN
This chapter describes VLAN Configuration, including the following:
• VLAN Port Settings
• Basic VLAN Information
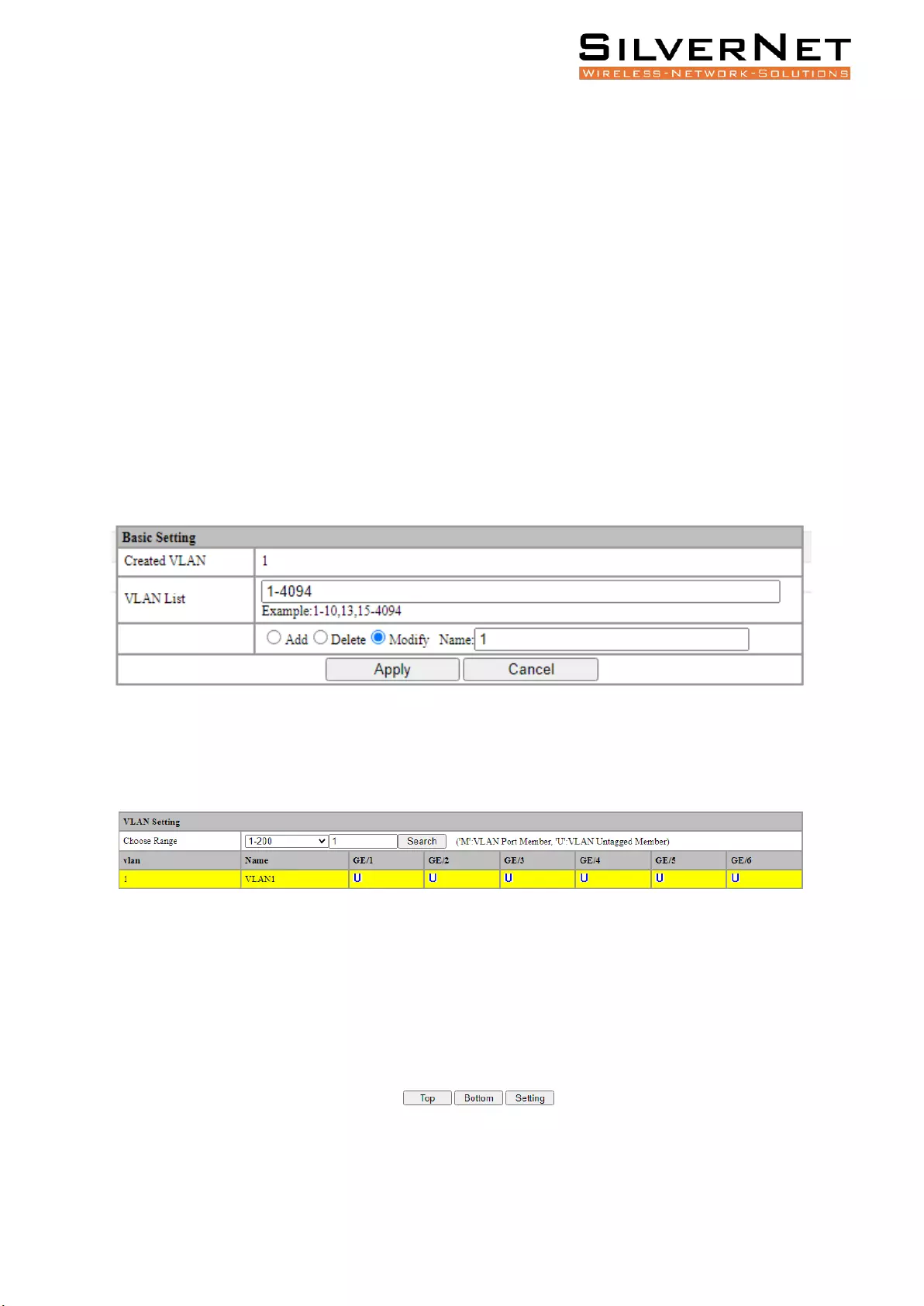
Select Base Configuration / VLAN / Basic Setting to enter the VLAN Basic Setting interface.
On the Basic Setting interface, you can view information of each VLAN. If you want to find
information about a specific VLAN ID, select the range of the VLAN ID in the drop-down box, enter
the specified VLAN ID in the input box and click Search.
To add, modify, or delete VLANs, click Setting. Enter the VLAN to be added, modified, or deleted in
the <VLAN list> box on setup interface. Then select Add, Modify, or Delete. Click Apply. The setting
and modification options can only modify the VLAN name, as shown in Figure 4.1. Table 4.1 explains
this in more detail.
Figure 4.1 VLAN Basic Setting
Figure 4.2 VLAN Search Function
Pro Range User Manual VLAN 29
Table 4.1 VLAN Basic Setting Configuration
Configuration Item
Description
Search
Search for a VLAN ID. If there is a matching VLAN ID to your search query then it
will be highlighted YELLOW, as shown above in Figure 4.2.
Top
Display the first page of VLAN information.
Bottom
Display the last page of VLAN information.
Setting
Enter the VLAN Basic Setting Configuration
Table 4.2 VLAN Basic Setting Description
Configuration item
Instructions
Created VLAN
Used to input a VLAN ID onto the VLAN List, also supports multi-VLAN batch
input, such as 1,2,3,4-10.
VLAN List
VLANs to be added, deleted or modified, supports batch input. VLAN 1 is the
default VLAN. It already exists and does not need to be created.
Add
Add the selected VLAN into the VLAN list box. VLAN 1 is the default VLAN. It
already exists and does not need to be created.
Delete
Delete the selected VLAN in the VLAN list box. VLAN 1 is the default VLAN and
cannot be deleted.
Modify
Modify the selected VLAN in the VLAN list box. The VLAN name can be modified.
The new name needs to be entered in the name box.
VLAN PORT CONFIGURATION
Select Base Configuration / VLAN / Port Setting to enter the VLAN Port Setting interface.
On the Port Setting interface, you can view the VLAN related configuration information of each port
as shown in Table 4.4
To modify the VLAN configuration of a port, click Modify in the corresponding port display field to
enter the port setting interface, as shown in Figure 4.3.
Select or fill in the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply. There will be
prompts if the configuration item is filled in incorrectly.
Pro Range User Manual VLAN 30
Figure 4.3 VLAN Port Overview
Figure 4.4 VLAN Port Setting
Table 4.3 VLAN Port Setting Configuration
Configuration Item
Description
Modify
Modify the VLAN configuration of the corresponding port.
Refresh
Refresh the VLAN configuration information of all ports.
Table 4.4 Modify Interface Configuration of VLAN Port Setting
Configuration Item
Description
Port
Port name information.
VLAN Mode
Port VLAN Mode:
Access Mode: Set the port onto Access Mode. This means the port will only
communicate on specified VLANS.
Trunk mode: Set the port to Trunk Mode. This means the port will be able to
communicate on all VLANS simultaneously (unless a VLAN has been restricted).
Hybrid mode: Allow the port to decide between Trunk or Access Mode.
Pro Range User Manual QoS 31
PVID
Port VLAN ID.
Permitted VLANs
for Trunk / Tagged
VLANs For Hybrid
List of VLANs allowed to pass through the port. It supports batch input of
multiple VLANs. For example: 1,2,3,4-10.
Add: Add the tagged VLAN to the port via the VLAN ID.
Delete: Delete the VLAN from the tagged VLAN of the port.
Replace: Replace the original tagged VLAN of the port with a new VLAN ID.
All created VLANs: All the created VLANs will be added, even if they are created
later, they will be automatically added to the tagged VLAN of the port.
Untagged VLAN
Port untagged VLAN list, supports multi-VLAN batch input, such as: "1,2,3,4-10".
Add: Add a VLAN ID to the untagged VLAN of the port.
Delete: Delete a VLAN ID from the untagged VLAN of the port.
Replace: Replace the original untagged VLAN of the port with a new VLAN ID.
QOS
This chapter describes Quality of Service features (QoS), including the following:
• QoS Mapping Settings
• QoS Port Settings
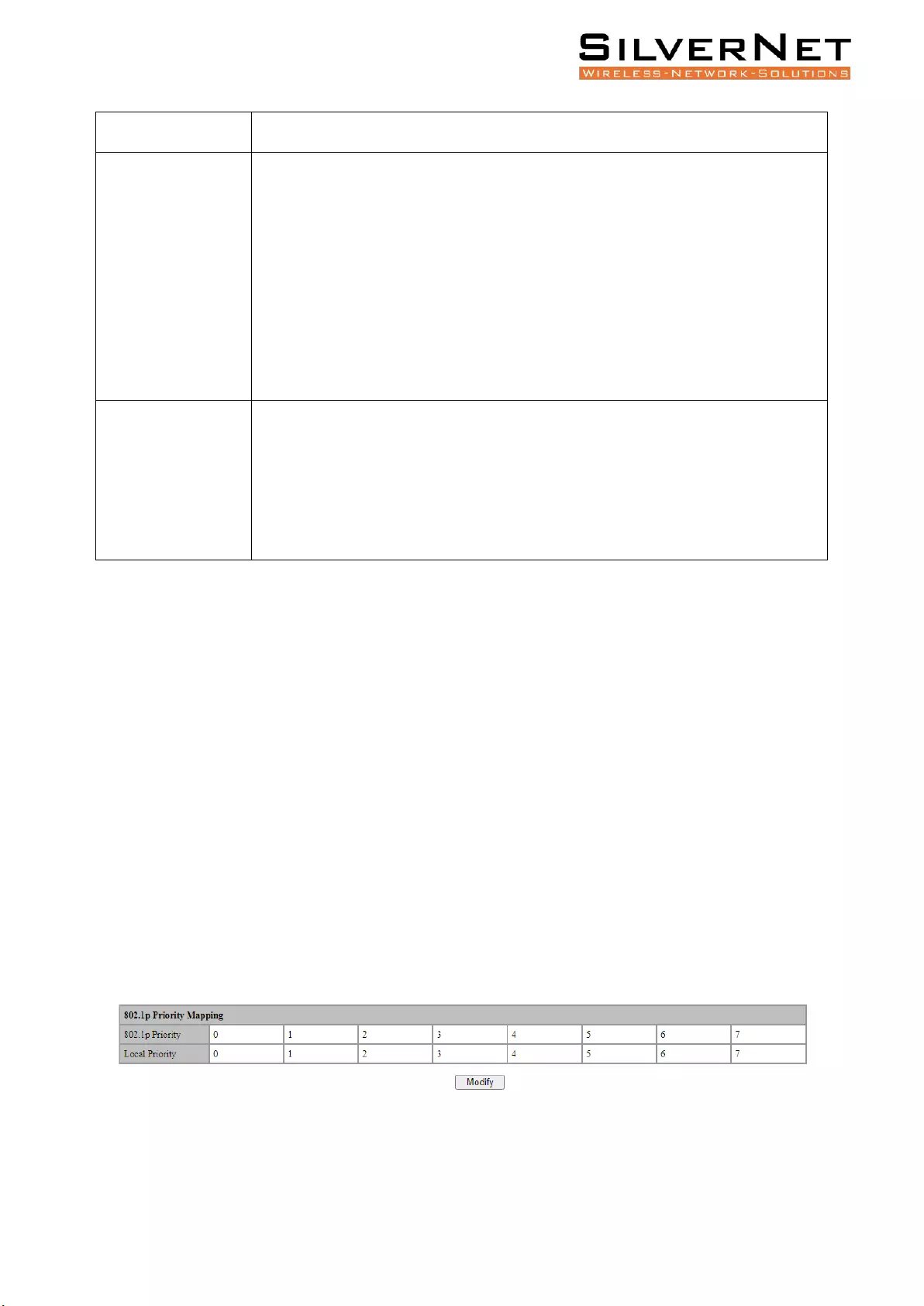
802.1P PRIORITY (COS)
Select Base Configuration / QOS / Mapping / 802.1p Priority in the navigation bar to enter the QOS
802.1p Priority interface.
On the QOS 802.1p Priority interface, you can view the mapping from 802.1p priorities to local
priorities.
To modify the mapping relationship, click Modify and select the mapped local priority for the
corresponding 802.1p priority in drop-down list box, as shown in Figure 5.1.
Figure 5.1 QOS 802.1p Priority Mapping Setting
Pro Range User Manual QoS 32
Table 5.1 QOS 802.1p Priority Description
Configuration item
Description
Modify
Modify the mapping between 802.1p priorities and local priorities.
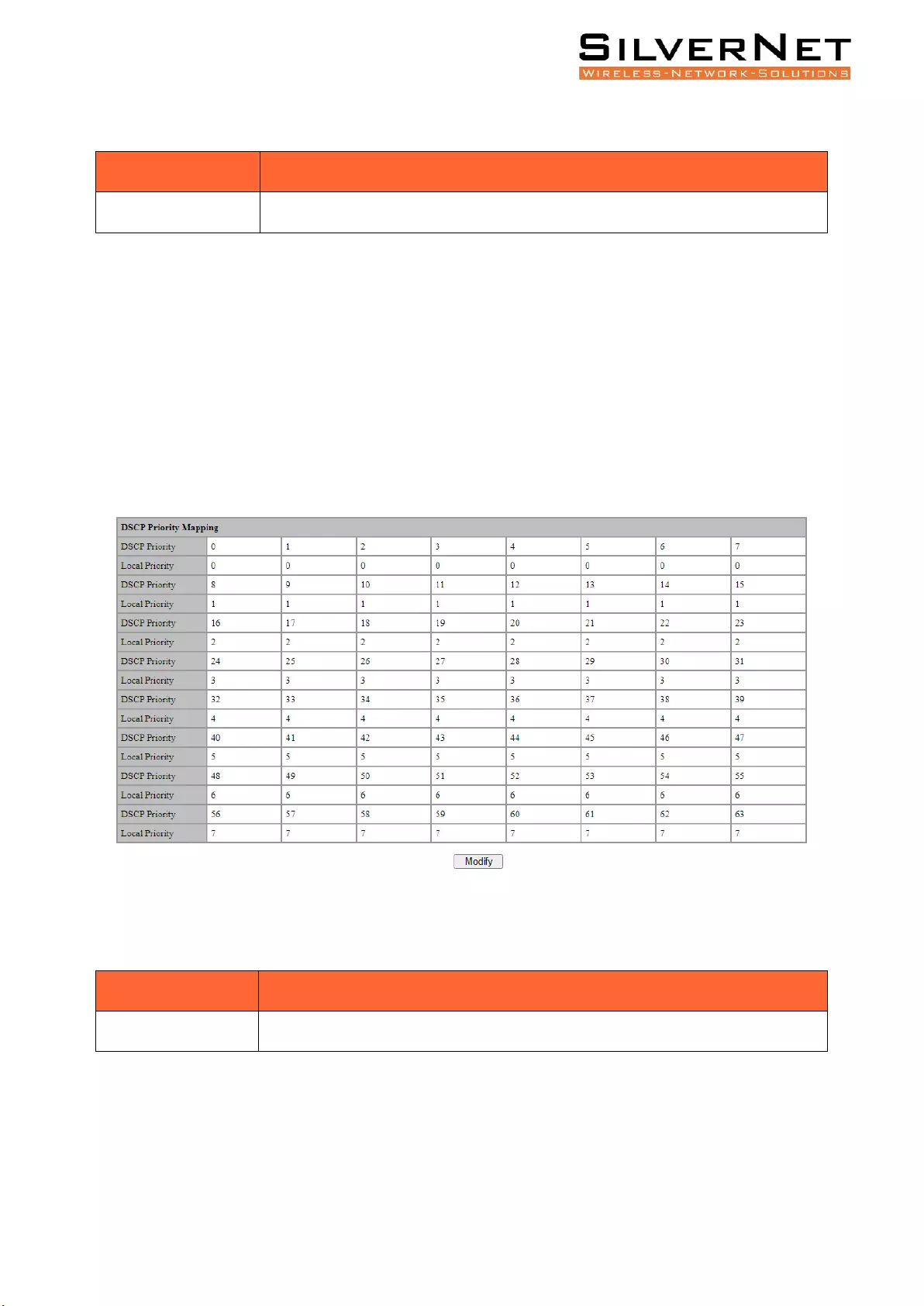
DSCP PRIORITY
Select Base Configuration / QOS / Mapping / DSCP Priority in the navigation bar to enter the QOS
DSCP Priority Mapping interface.
On the QOS DSCP Priority interface, you can view the mapping from DSCP priorities to local
priorities.
To modify the mapping relationship, click Modify and select the mapped local priority for the
corresponding DSCP priority in drop-down list box, as shown in Figure 5.2.
Figure 5.2 QOS DSCP Priority Mapping Setting
Table 5.2 QOS DSCP Priority Description
Configuration Item
Instructions
Modify
Modify the mapping between DSCP priorities and local priorities.
LOCAL PRIORITY
Select Base Configuration / QOS / Mapping / Local Priority in the navigation bar to enter the QOS
Local Mapping.
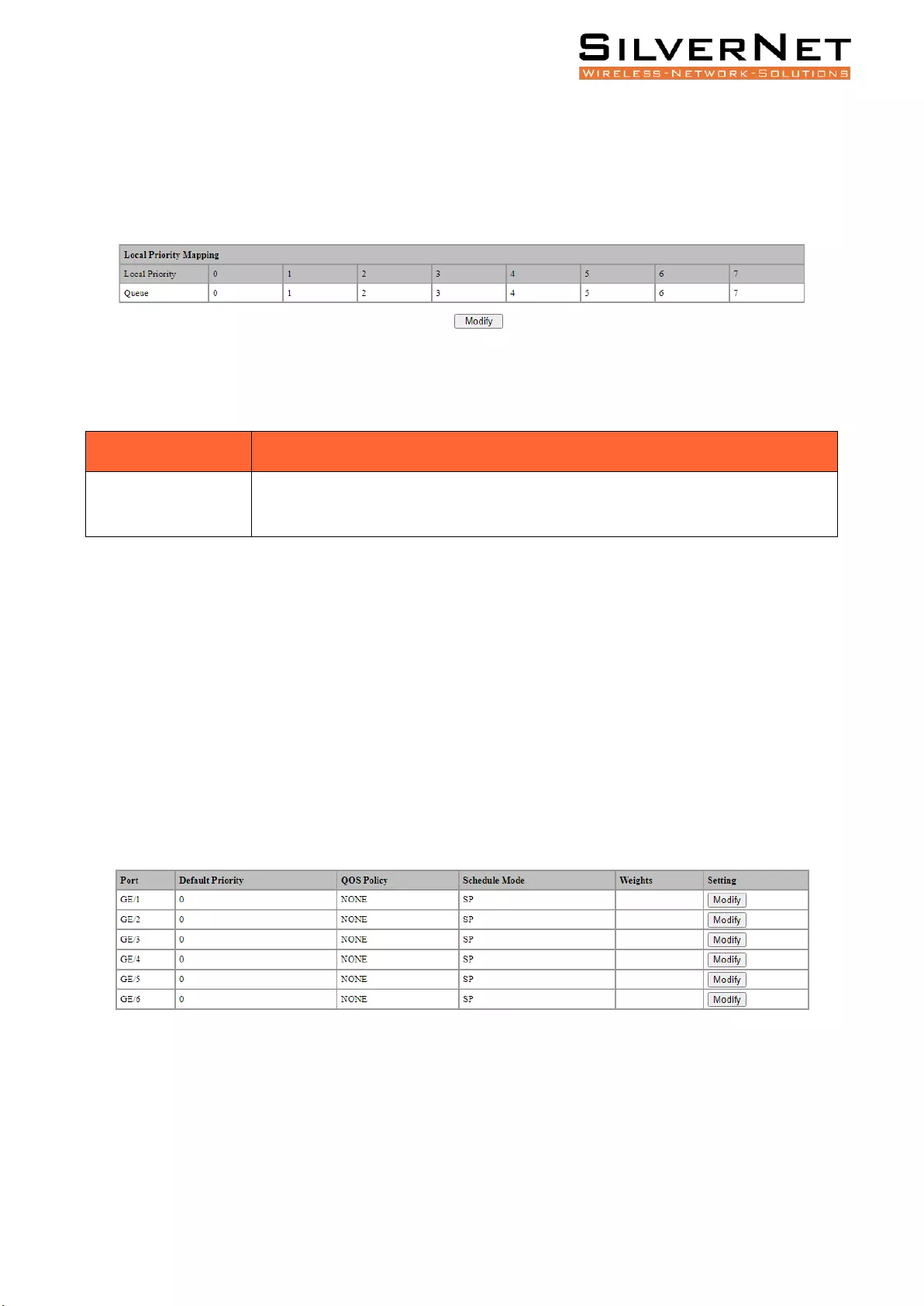
Pro Range User Manual QoS 33
You can view the mapping from the local priority to the egress queue on the QOS Local Priority
interface.
To modify the mapping relationship, click Modify and select the mapped egress queue for the
corresponding local priority in drop-down list box, as shown in Figure 5.3.
Figure 5.3 QOS Local Priority Mapping Setting
Table 5.3 QOS Local Priority Description
Configuration Item
Description
Modify
Modify the mapping relationship between the local precedence and the egress
queue
QOS PORT CONFIGURATION
PORT PRIORITY SETTINGS
Select Base Configuration / QOS / Ports / Port Priority in the navigation bar to enter the QOS Port
Priority interface.
To modify the QOS configuration of a port, click Modify on the corresponding port to enter the port
setting interface, as shown in Figure 5.5 and Table 5.4.
Select or fill in the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply to confirm. There
will be prompts if the configuration item is filled in incorrectly.
Figure 5.4 QOS Port Overview
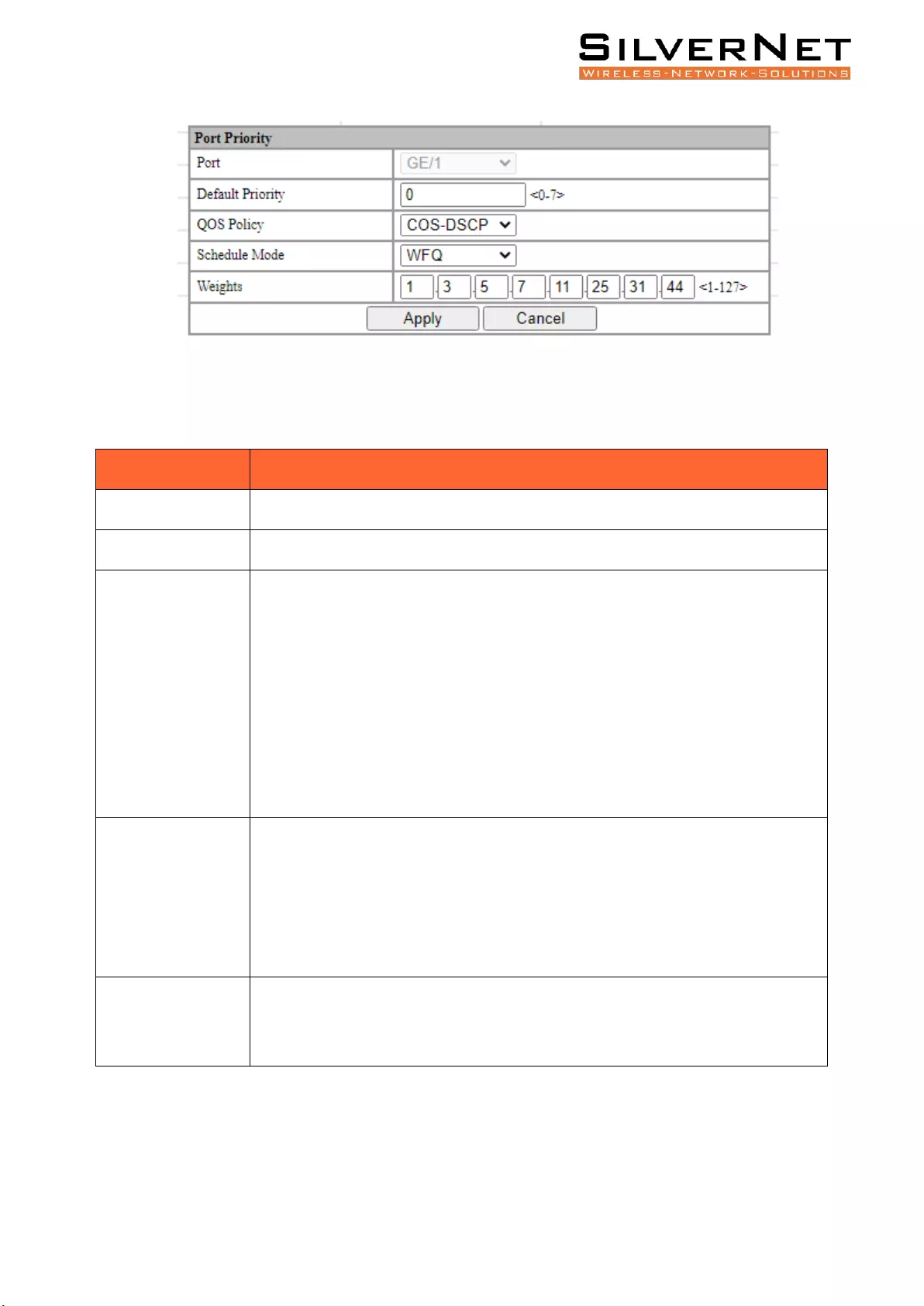
Pro Range User Manual QoS 34
Figure 5.5 QOS Port Settings
Table 5.4 QOS Port Priority Modifying Description
Configuration Item
Description
Port
Specified Port.
Default Priority
The port with Priority, range <0-7>.
QOS Policy
Port QOS policy:
NONE: Indicates no policy. The port does not have a policy by default.
COS: Class Of Service priority policy. This is an algorithm that compares CoS tags
to classify packets and to assign to queues of different priority.
DSCP: Differentiated Services Code Point priority policy. This is used to
determine traffic classifications for network data.
COS-DSCP: Hybrid of both COS-DSCP Priorities.
Schedule Mode
QOS Scheduling strategy:
SP: Strict Priority scheduling strategy
WRR: Weighted Round Robin scheduling strategy
WFQ: Weighted Fair Queue scheduling strategy
Weights
If the selected scheduling mode is WRR or WFQ, you need to configure the
weight of each queue, total 8 queues. To set 8 weights, the weight of all queues
must be 127.
Pro Range User Manual QoS 35
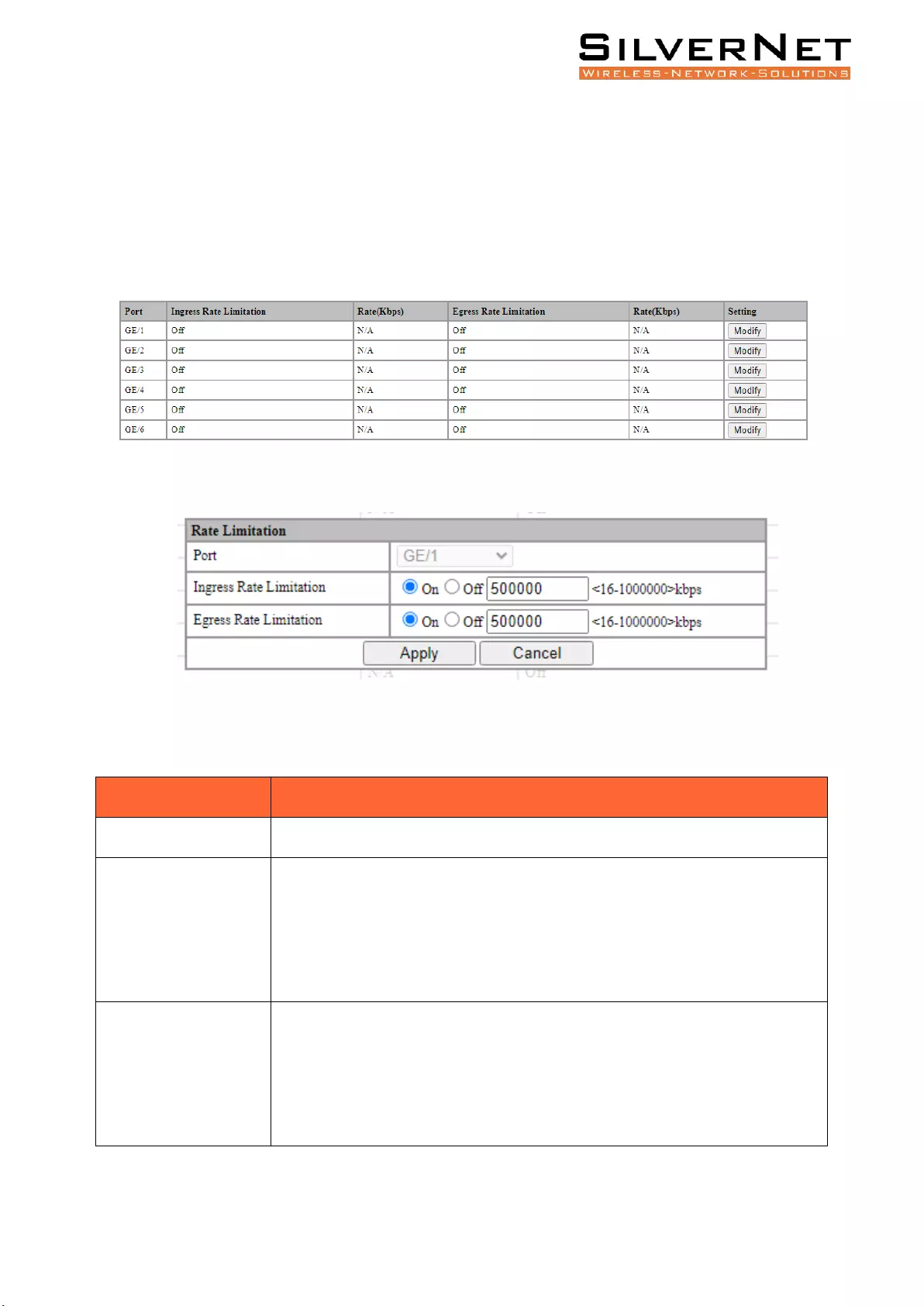
PORT RATE LIMIT
Select Base Configuration / QOS / Port / Rate Limitation in the navigation bar to enter the QOS Rate
Limitation interface.
To modify the ports speed limit configuration, click Modify in the port display column to enter the
Rate Limitation setting interface, as shown in Figure 5.5.
Figure 5.5 QOS Rate Limitation Overview
Figure 5.6 QOS Port Speed Setting
Table 5.7 QOS Port Rate Limit Modifying Description
Configuration Item
Description
Port
Port name information.
Ingress Rate
Limitation
Set the ports entry speed limit:
On: Enables the port to limit the rate of ingress. The rate limit ranges from
<16-1000000>kbps.
Disabled: Close the ports ingress rate limit
Egress Rate Limitation
Set the ports output speed limit:
On: Enables the port to limit the rate of egress. The rate limit ranges from
<16-1000000>kbps.
Disabled: Close the ports egress rate limit
Pro Range User Manual ACL 36
ACL
This chapter describes Access Control List rules which describes the following:
• ACL Filtering Rule Settings
• ACT Group Settings
ACL GROUP SETTING
Select Advanced / ACL / ACL Group Setting in the navigation bar to enter the ACL interface.
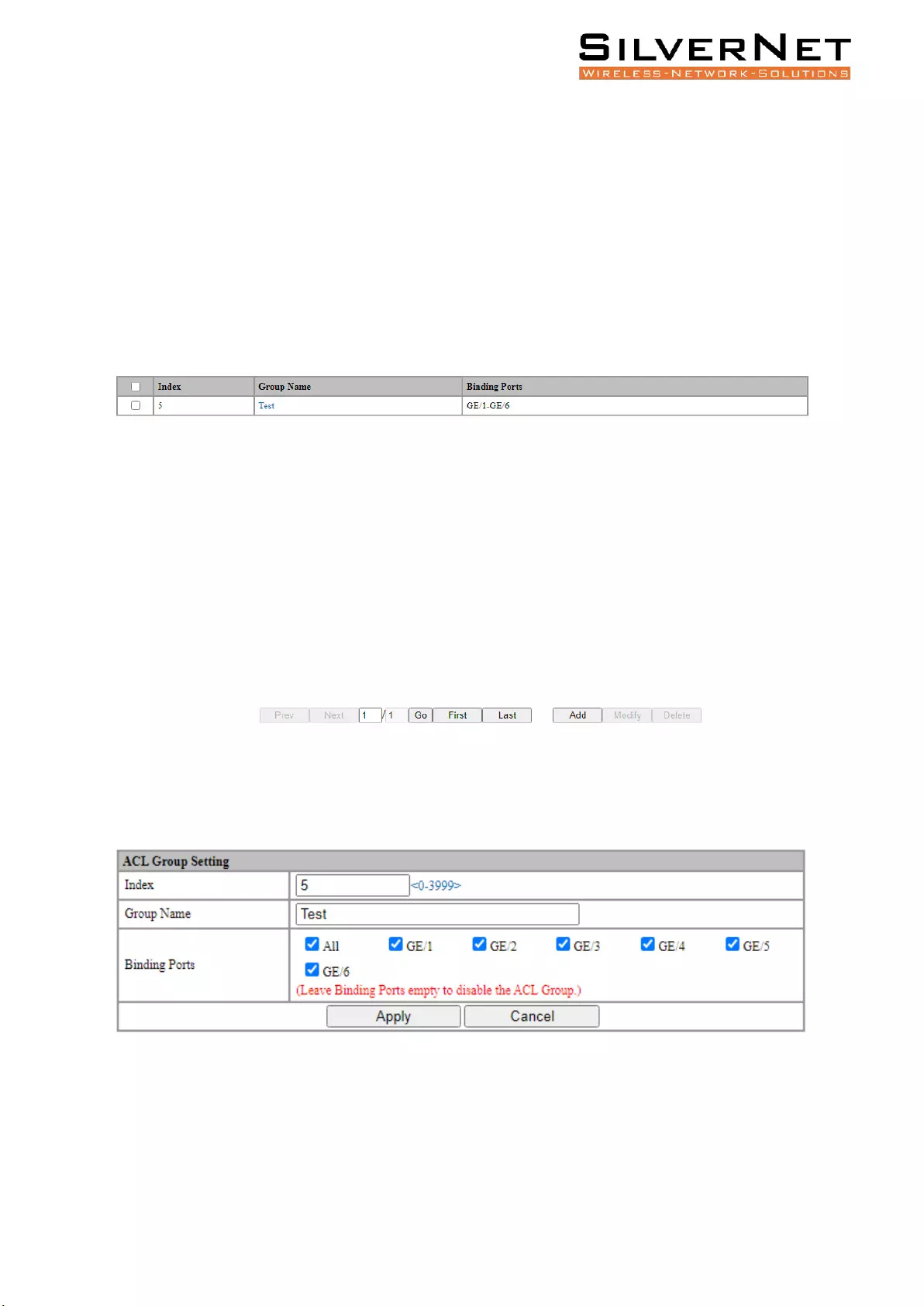
The ACL information will be added in ACL Group Setting interface, as shown in figure 6.1.
Figure 6.1 ACL Group Information
Click Add to enter ACL Group Setting interface, as shown in figure 6.2. An ordinal number (0-3999) is
assigned to the group. Set a name for the group, non-repeatable, then select the port and bind to the
group. It is not workable if port binding is not done. Click Apply to complete the configuration.
Figure 6.2 ACL Group Setting
Select an ACL group and click Modify to enter the ACL Group Setting interface. Fill in the required
configuration items and click Apply to complete the configuration.
Select an ACL group and click Delete to delete the configuration.

Pro Range User Manual ACL 37
Table 6.1 ACL Group Description
Configuration
Description
Index
ACL group index, range <0-3999>, divided into 4 matching groups L2, L3 / L4, Source
L2 / L3 / L4, Destination L2 / L3 / L4. The matching items supported by each
matching group are as follows:
L2: Source MAC, Destination MAC, Ethernet type, VLAN, IP protocol, range 0-999.
L3 / L4: VLAN, Source IP, Destination IP, Source IP port, Destination IP port, IP
protocol, range 1000-1999.
Source L2 / L3 / L4: Source MAC, Ethernet type, VLAN, Source IP, Source IP port, IP
protocol, range 2000-2999.
Destination L2 / L3 / L4: Destination MAC, Ethernet type, VLAN, Destination IP,
Destination IP port, IP protocol, range 3000-3999.
ACL Group
Name
The Group name must be unique and string format, ASCII code A-Z, a-z, 0-9, _, no
more than 32 characters.
Binding Ports
An ACL is applied to a certain port or some ports, then the bound ACL Port becomes
active.
ACL RULES
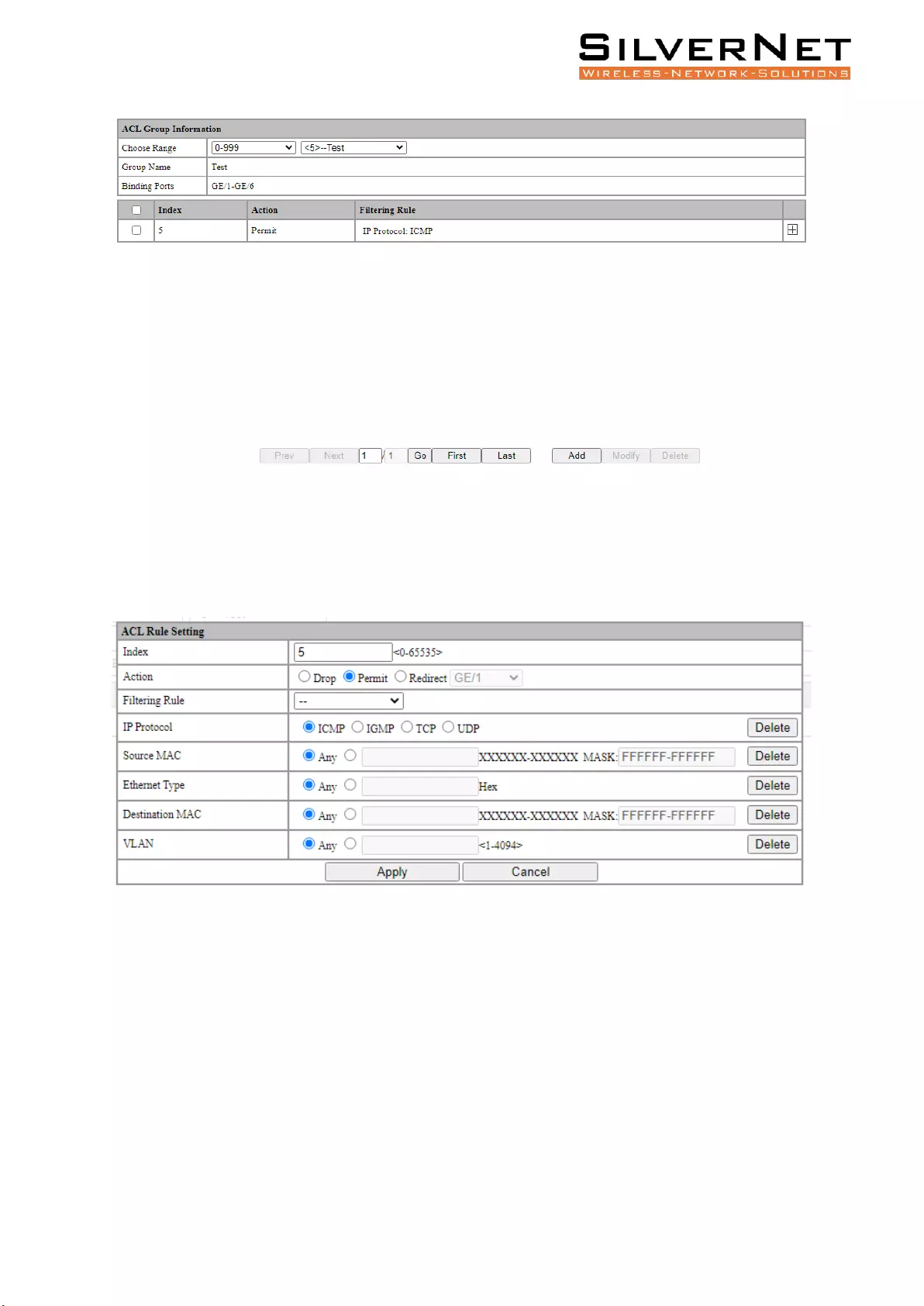
Select Advanced / ACL / ACL Rule Setting in the navigation bar to enter the ACL Rule view interface,
as shown in figure 6.3.
In the Choose Range field, select the range of the group in the first drop-down list and select a
specific group within the second drop-down list. The next two lines show the selected group name
and the port that the group binds. The table shows the ACL rules that the group has configured. Click
the icon in the filter rule bar to expand and view the specific content of the filter rule, the icon
will change to to collapse the group.
Pro Range User Manual ACL 38
Figure 6.3 ACL Rule View
Click Add to enter the ACL rule setting interface. One of the filtering rules can be selected by selecting
different filters via the drop-down list, and then the corresponding filtering items will be automatically
generated for users to fill in. You can also remove the filter items by the Delete on the right side. Fill
in the required configuration items and click Apply to complete the configuration.
Figure 6.4 ACL Rule Setting
Select an ACL and click Modify to enter the ACL Rule Setting interface. Fill in the required
configuration items, click Apply to complete the configuration.
Select an ACL and click Delete to delete the configuration.
Pro Range User Manual 39
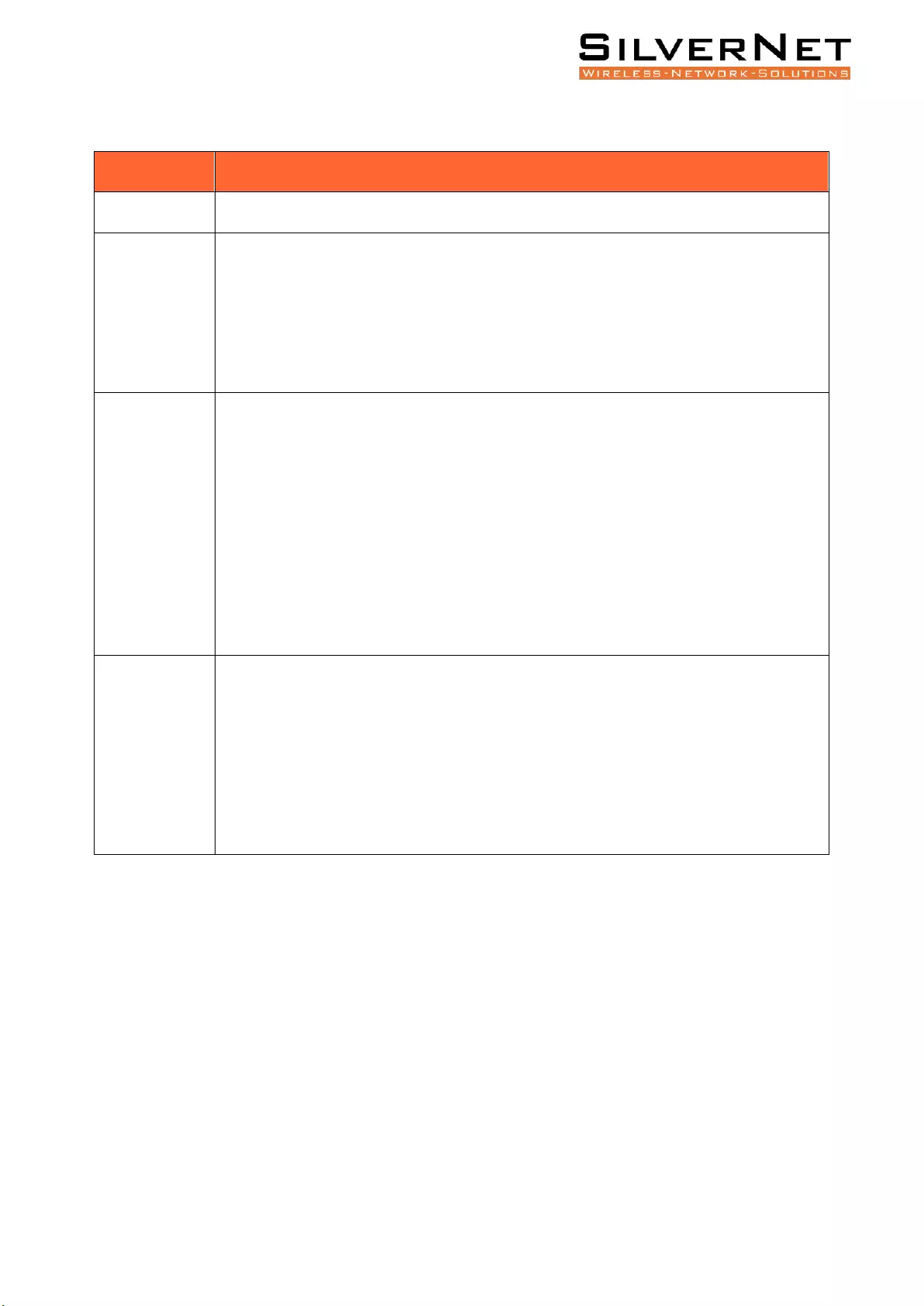
Table 6.2 ACL Rule Description
Configuration
Description
Index
ACL Rule Index
Action
When the message conforms to the filter rule, the action includes:
Drop: Drops the traffic.
Permit: Permits the traffic.
Redirect: Redirects the traffic to a specified port.
Filtering Rule
ACL filtering rules include:
Source MAC: Filters based on the source MAC Address.
Destination MAC: Filters based on the destination MAC Address.
IP Protocol: Filters based on the type of IP Protocol used.
Ethernet Type: Filters based on the Ethernet Type used.
VLAN: Filters based on input VLAN IDs.
Matching
Description
Source MAC: Format xxxxxx-xxxxxx, default mask ffffff-ffffff.
Destination MAC: Format xxxxxx-xxxxxx, support the mask, default mask ffffff-ffffff
IP Protocol: Currently only supports TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP.
Ethernet Type: Hexadecimal format, default mask FFFF.
VLAN: VLAN ID.
Pro Range User Manual RSTP 40
RSTP
This chapter describes Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) which includes the following:
• RSTP Global Configuration
• RSTP Port Configurations
• STP Information
• Port Information
GLOBAL CONFIGURATION
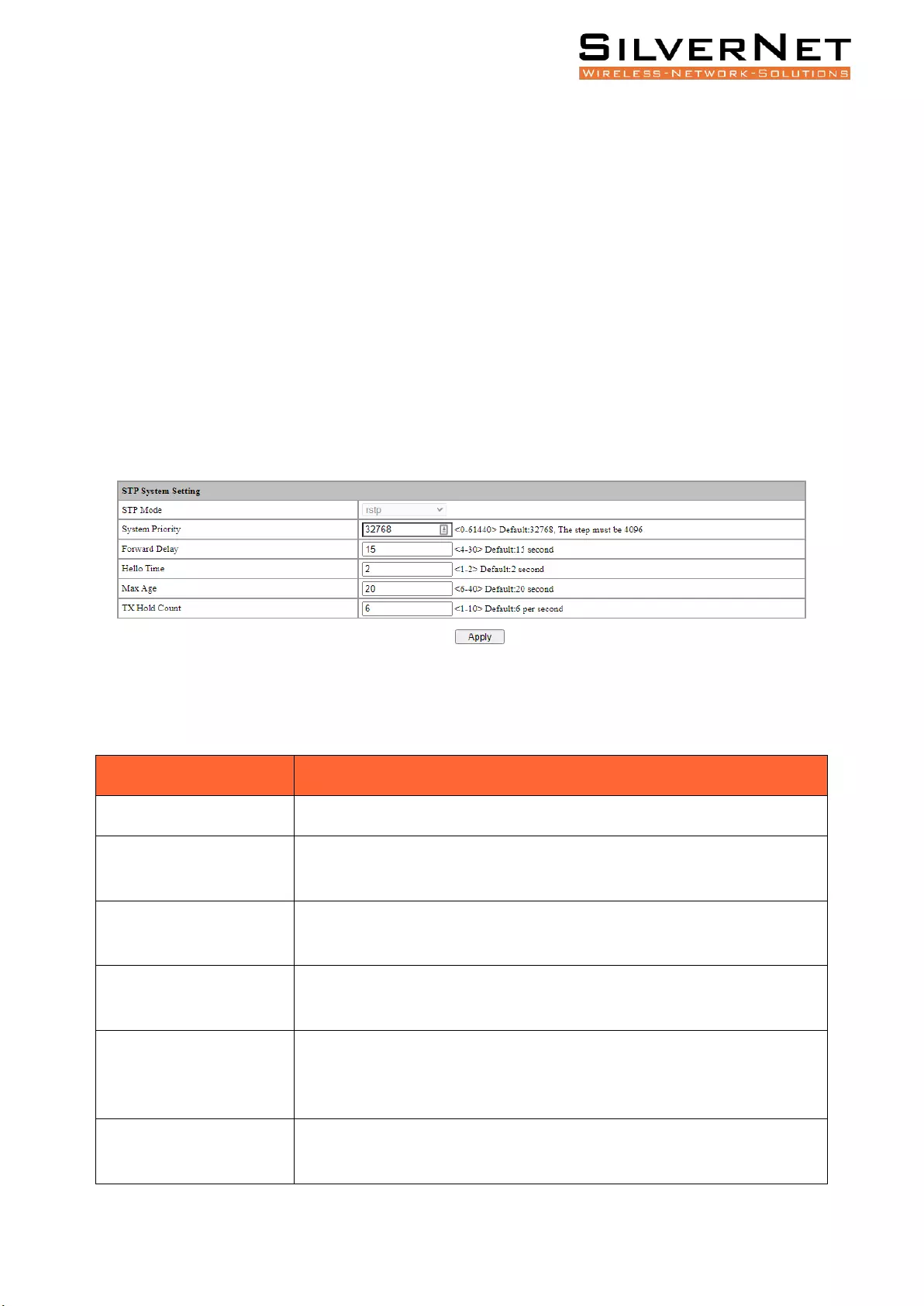
Select Advanced / STP / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the STP Global Setting interface.
To modify the configuration, you can enter the values that need to be configured directly in
corresponding configuration item, as shown in figure 7.1.
Figure 7.1 STP System Setting
Figure 7.1 STP Global Setting Description
Configuration
Description
STP Mode
Supports RSTP, compatible with STP
System Priority
STP System priority, default is 32768. Increments must increase or
decrease by 4096.
Forward Delay
Delay in seconds for port to change its states between disabled / listening
/ learning / forwarding modes. Default is 15 seconds.
Hello Time
The time interval in seconds sent by STP protocol message in stable state.
Default is 2 seconds.
Max Age
The maximum survival time in seconds of the STP protocol packet
received by the bridge. If no new protocol packets received at this time,
the packet will be discarded. Default is 20 seconds.
TX Hold Count
The maximum number of STP protocol packets sent by Port per second.
Default is 6 per second.
Pro Range User Manual RSTP 41
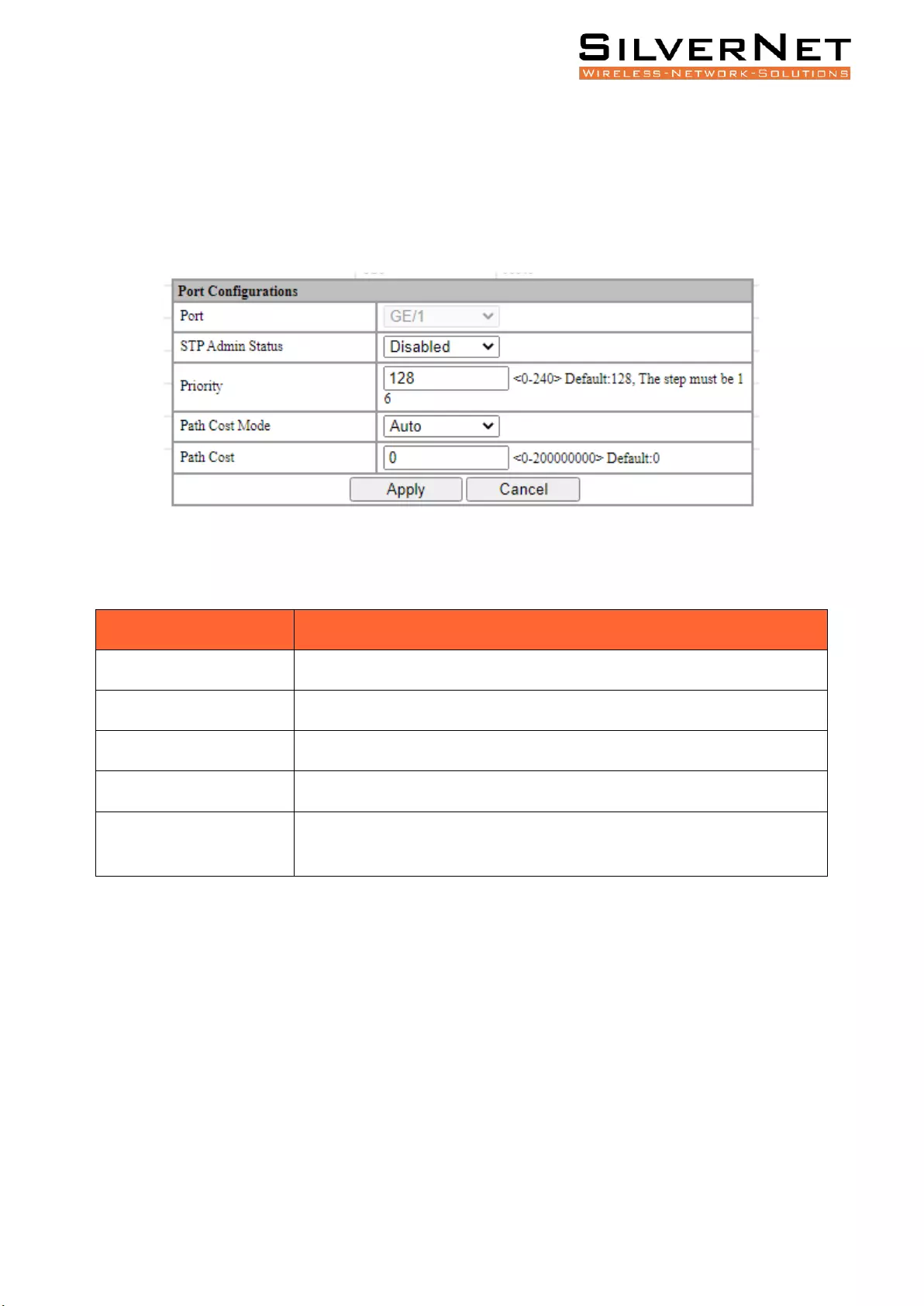
PORT CONFIGURATION
Select Advanced / STP / Port Configurations in the navigation bar to enter the STP Port Configurations
interface.
To modify the port configuration, you can click Modify on the right side of the corresponding port to
enter the port configuration interface of the STP, as shown in figure 7.2.
Figure 7.2 STP Port Configurations
Figure 7.2 STP Port Configurations Description
Configuration
Description
Port
Port Name.
STP Admin Status
Disable or Enable, default is Disable.
Priority
STP Priority, default is 128. Increments must be done in 16.
Path Cost Mode
The calculation of STP port path overhead, Auto or Admin, default is Auto.
Path Cost
When the path overhead is calculated in Admin mode, the ports cost
overhead takes effect as the configured value. Default is 0.
Pro Range User Manual RSTP 42
PATH OVERHEAD
The STP BPDU message requires a certain Path overhead for each Root port. The Path overhead of
each bridge is cumulative, and this value is called Root Path Cost. To calculate the Path Overhead for
RTSP you will need to divide 20Tbits/s by your required bandwidth. Figure 7.3 shows some examples
of this calculation:
Figure 7.3 Path Overhead of Different Port Rate
Port Rate
Path Overhead
10Mbps
2,000,000
100Mbps
200,000
1000Mbps
20,000
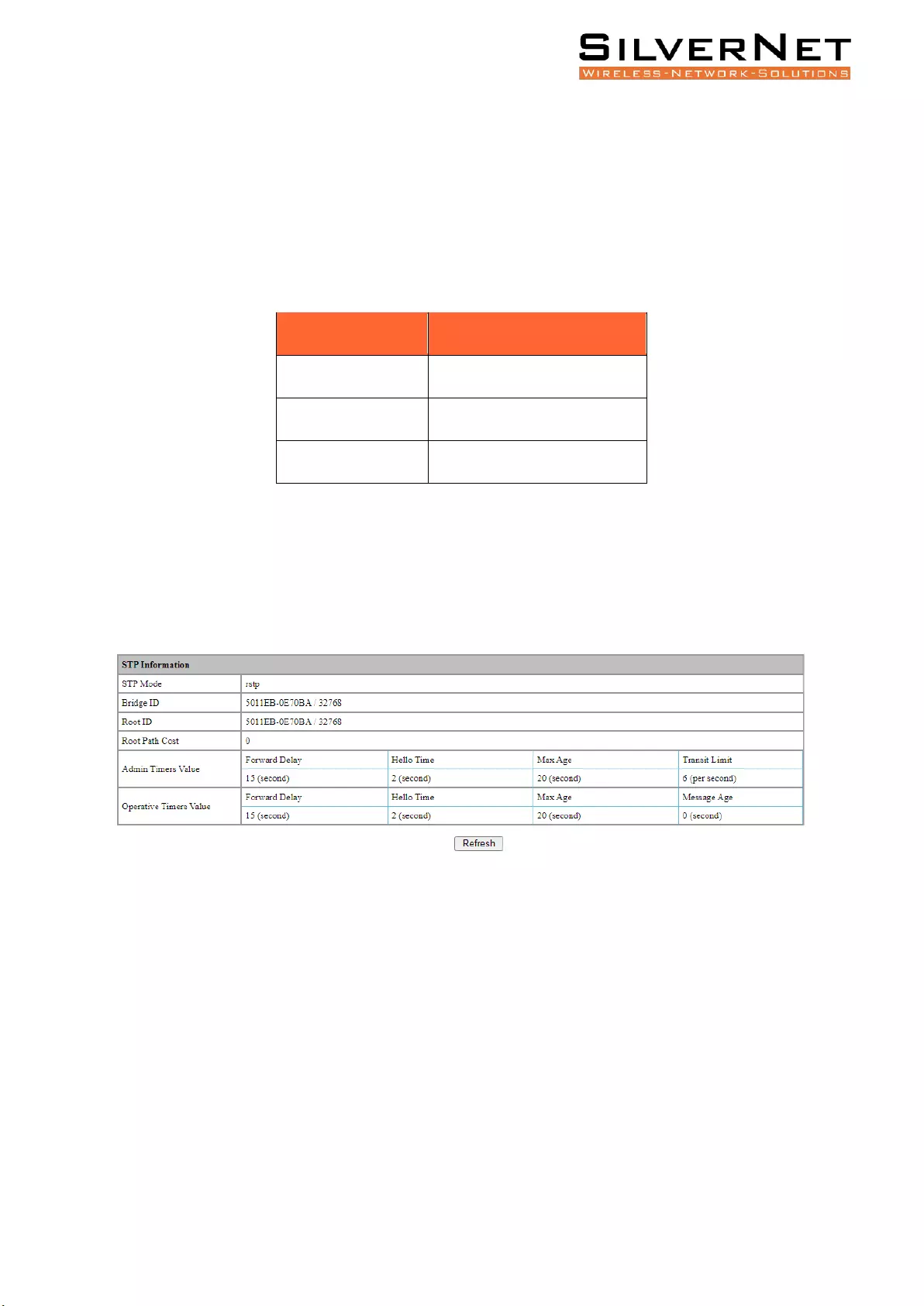
STP INFORMATION
Select Advanced / STP / STP Information in the navigation bar and enter the STP information interface
as shown in figure 7.3.
Click Refresh to show the latest running information.
Figure 7.3 STP Information Interface
Pro Range User Manual RSTP 43
Table 7.4 STP Information Description
Configuration
Description
STP Mode
Current STP mode running.
Bridge ID
Current Bridge ID running.
Root ID
Current Root ID Running.
Root Path Cost
Current cumulative Root Path Cost
Admin Timers Value
Admins statistics on STP configurations, see above Table 7.1 for
further explanations.
Operative Timers Value
Users statistics on STP configurations, see above Table 7.1 for
further explanations.
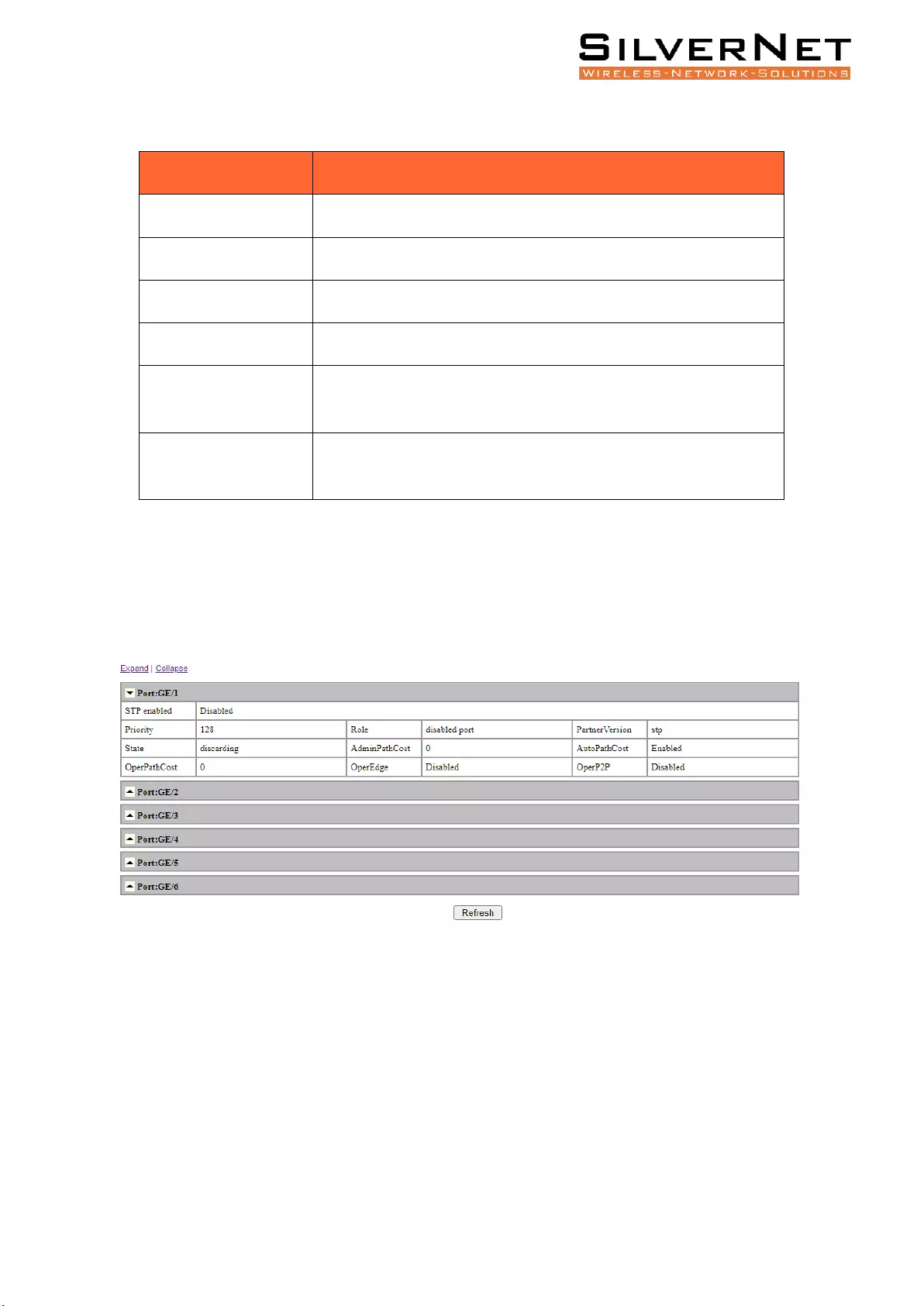
PORT INFORMATION
Select Advanced / STP / Port Information in the navigation bar and enter the STP Port information
interface as shown in figure 7.4.
Click Refresh to show the latest running information.
Figure 7.4 RSTP Port Information Interface
Pro Range User Manual RSTP 44
Table 7.5 RSTP Port Information Description
STP Port Information
Description
STP Enabled
Disabled: STP is currently disabled on the port.
Enabled: STP is currently enabled on the port.
Priority
Port Priority for STP.
Role
Root Port: Connect the Root Bridge Port, provide lowest path cost.
Designated Port: Connect with the Root Port, provide lowest path cost.
Disable Port: Disabled Port. Not responsible for message forwarding/blocking
status.
Alternate Port: Provides an alternate path for the current Root Port to the Root
Bridge
Backup Port: Provides a backup path for the designated port.
Partner Version
STP Mode: STP / RSTP.
State
Forwarding or Block.
Admin Path Cost
Path cost configuration values.
Auto Path Cost
Disable automatic computing path cost.
Enable automatic computing path cost.
Operate Path Cost
Operate Path Cost.
Operate Edge
Disable non-edge port.
Enable edge port.
Operate P2P
Disable non-point-to-point mode.
Enable point-to-point mode.
Pro Range User Manual ERPS 45
ERPS
This chapter describes Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) in detail, including the following:
• ERPS Configuration
• ERPS Information
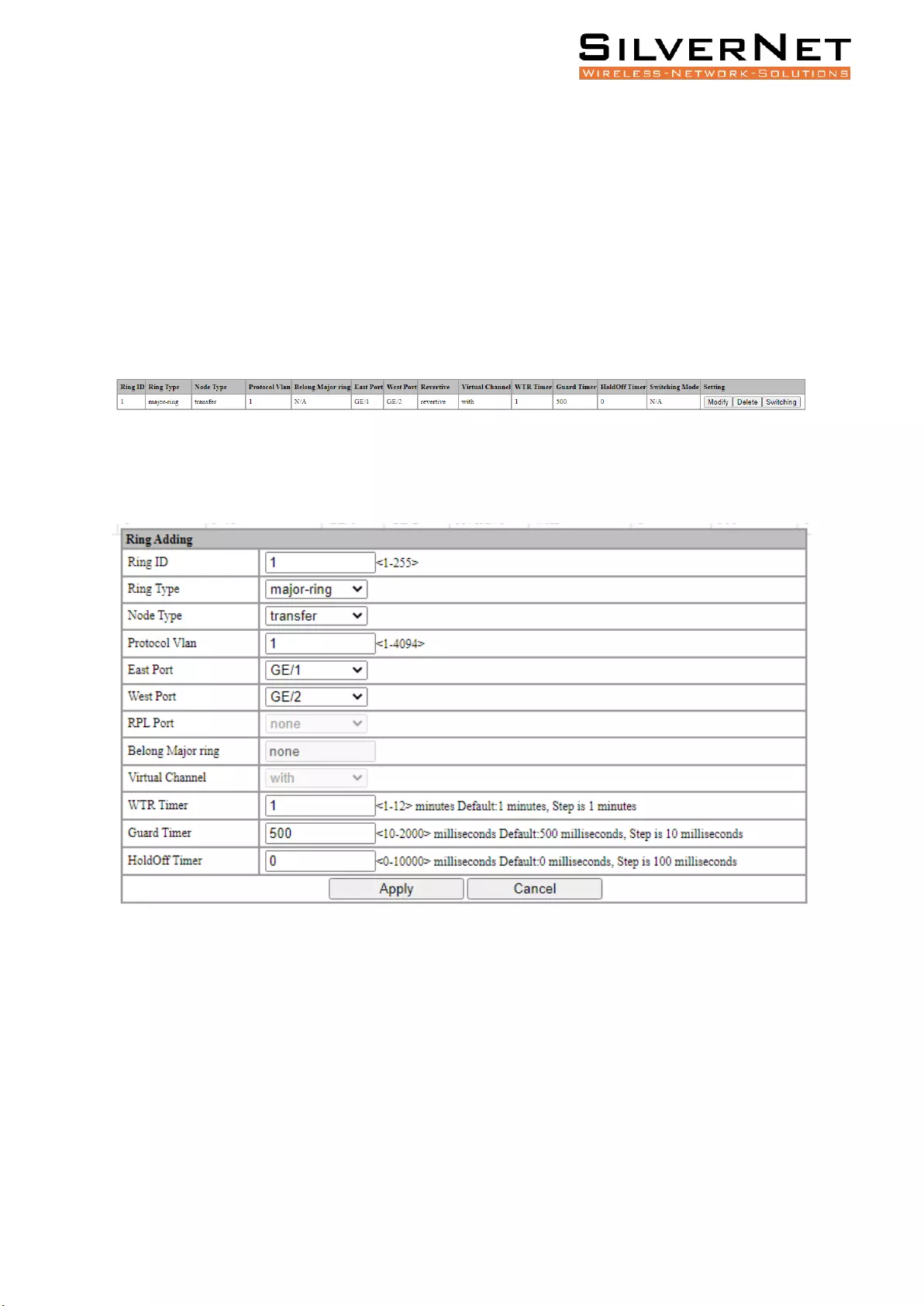
ERPS SETTING
Select Advanced / ERPS / Ring Setting in the navigation bar and enter the ERPS Ring Setting interface,
as shown in Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1 ERPS Setting
Click the Add button, enter the Ring Adding interface as shown in figure 8.2, enter a valid configuration
parameter and click Apply to submit the changes. Click Cancel to discard the modification.
Figure 8.2 ERPS Ring Adding
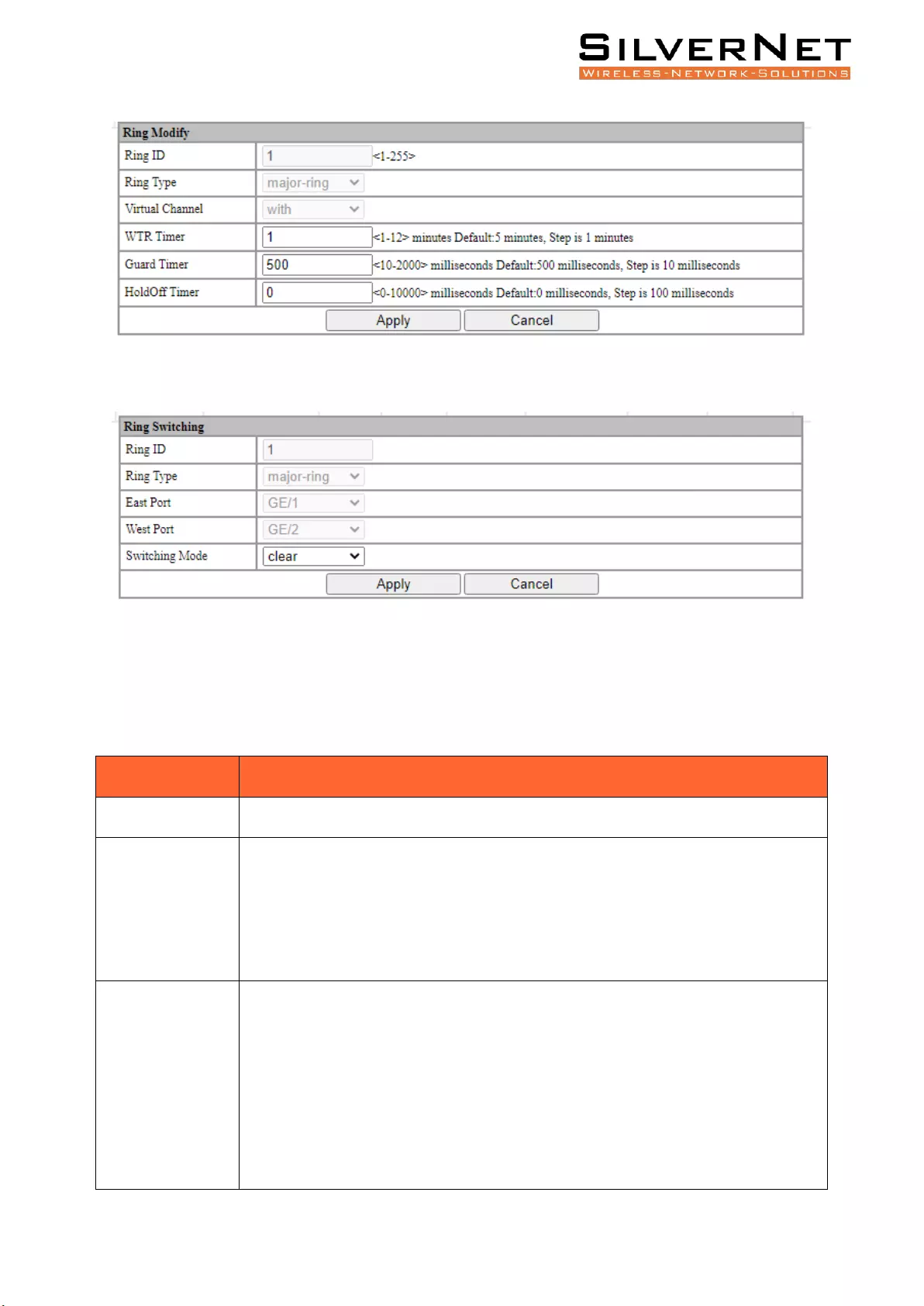
Click Modify , enter the Ring Modification interface, as shown in figure 8.3
Pro Range User Manual ERPS 46
Figure 8.3 ERPS Ring Modification
Click Switching button to enter Ring Flow Switching Configuration Interface, as shown in Figure 8.4
Figure 8.4 ERPS Flow Switching Configuration
Click the Delete button to delete the corresponding Ring
Figure 8.1 ERPS Ring Setting Ring Description
Configuration
Description
Ring ID
Input new Ring ID.
Ring Type
Select the type of Ring protocol.
Major-Ring: Set the current Ring ID as a fully closed topology of at least 2 Nodes.
Sub-Ring: Set the current Ring ID as a partial ring either connected to a major-ring
or another sub-ring.
Node Type
Select the role of the Node within the ring.
Transfer: The node will transfer data between links.
RPL-Owner: Set the node to RPL-Owner Mode. This means traffic will not flow
into the selected RPL-Owner Port.
RPL-Neighbour: Set the node to RPL-Neighbour Mode. This means traffic will not
flow out of the selected RPL-Neighbour Port.
Pro Range User Manual ERPS 47
Protocol VLAN
Select the VLAN ID associated with the new Ring ID.
East Port
Select the port you with to use for the East Interface.
West Port
Select the port you with to use for the West Interface.
RPL Port
Select the Port which you would like the Node Type setting to apply to.
Belong Major
Ring
Does the setting belong to a major ring.
Virtual Channel
To transmit sub-ring protocol information in the main ring you will need to
configure use of a VLAN Virtual Channel.
WTR Timer
Configure the value of WTR Timer. WTR (Wait to Restore) is used to ensure a
signal failure is not intermittent. This is only used when the RPL-Owner is trying to
restore the ring. Default is 1 Minute.
Guard Timer
Configure the value of Guard Timer. Guard Timer is the amount of time that an
ERP instance discards most R-APS (Ring Automatic Protection Switching) messages
before being allowed to process them. Default is 0ms. Default is 500ms.
Hold Off Timer
Configure the value of Hold Off Timer. Hold Off Timer allows any other underlying
protection schemes to recover before ERPS reacts to its defect, giving time for the
ERPS defect to clear.
Table 8.2 ERPS Global Setting Flow Switching Description
Configuration
Description
Ring ID
Current Ring ID
Ring Type
Current Ring type
East Port
Current East Port Ring Interface on this Node.
West Port
Current West Port Ring Interface on this Node.
Switching Mode
FS and MS are commands which result in a block being applied at an Interface
(and an unblock on the opposite interface), and an R-APS Forced Switch (FS)
message to flow around the ring. MS is nearly identical to FS other than only one
MS can be issued on the ring and it has lower priority than FS.
Clear: Clear any FS or MS messages on the Ring.
FS East Port: Force the Node to switch on the East Port.
FS West Port: Force the Node to switch on the West Port.
Pro Range User Manual LLDP 48
MS East Port: Manually force the Node to switch on the East Port.
MS West Port: Manually force the Node to switch on the West Port.
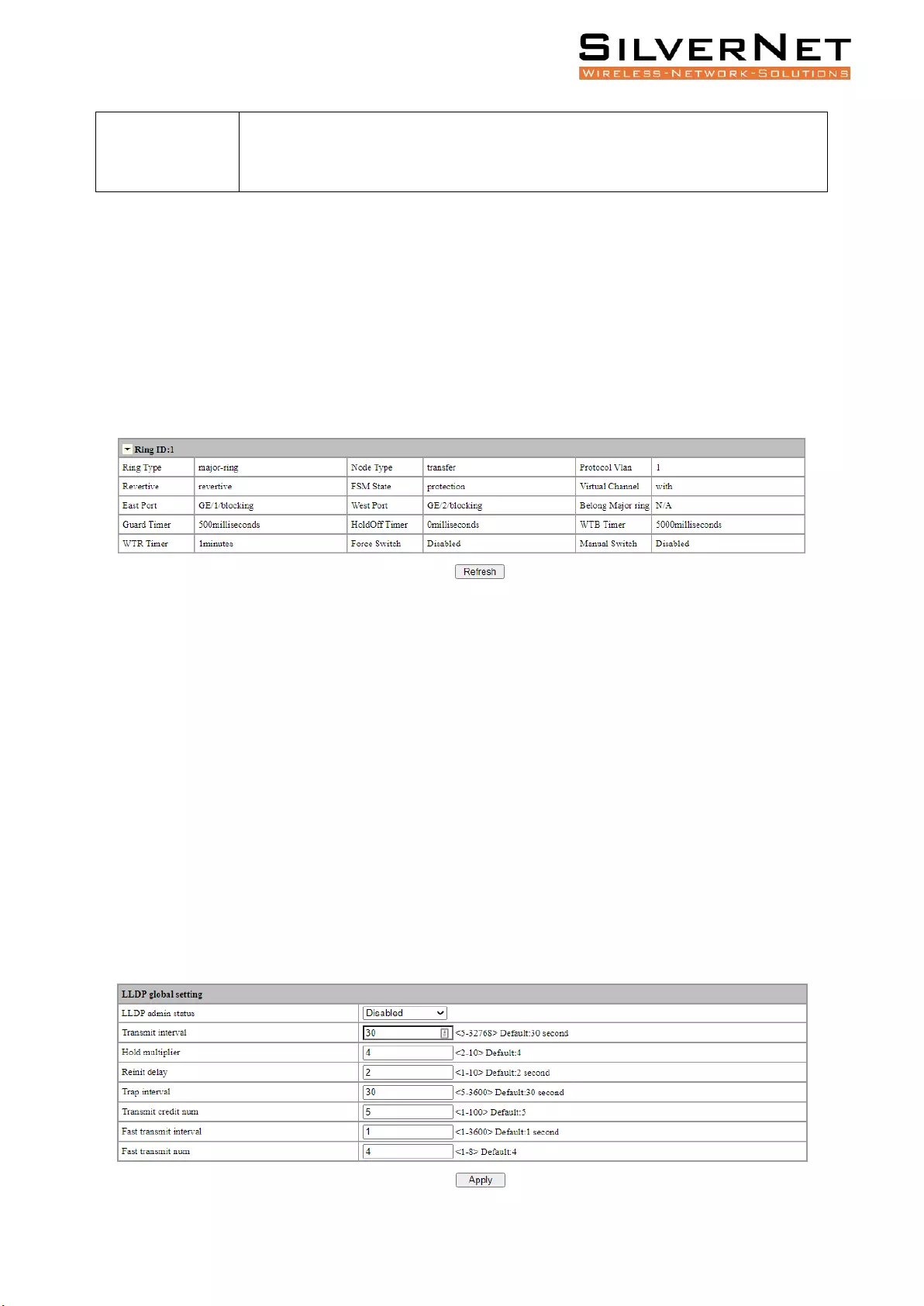
RING INFORMATION
Select Advanced / ERPS / Ring Information in the navigation bar to enter the interface of ERPS Ring
Network Information.
The ERPS current running information can be viewed in the Ring Information interface, as shown in
figure 8.5.
Click Refresh to show the latest running information.
Figure 8.5 ERPS Information
LLDP
This chapter discusses Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) in detail, including the following:
• LLDP Global Configuration
• LLDP Port Configuration
LLDP GLOBAL SETTING
Select Management / LLDP / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the LLDP Global Setting
interface as shown in Figure 9.1.
Modify the corresponding LLDP configuration in the LLDP Global Setting interface, and then click
Apply.
Pro Range User Manual LLDP 49
Figure 9.1 LLDP Global Setting
Table 9.1 LLDP Global Setting Description
Configuration
Description
LLDP Admin Status
LLDP is a protocol used by devices to advertise their identity, capabilities
and neighbours on a LAN network.
Enable: Enable LLDP function.
Disable: Disable LLDP function.
Transmit Interval
LLDP transmit period in seconds. Range is 0-32768, default is 30
seconds.
Hold Multiplier
LLDP Holding Multiplier. Range is 2-10, default is 4.
Reinit Delay
LLDP Reinit Delay, Range is 1-10, default is 2 seconds.
Trap Interval
LLDP Trap Interval in seconds, Range is 5-3600, default is 30 seconds.
Transmit Credit Num
LLDP transmit volume, range 1-100, default is 5
Fast Transmit Interval
LLDP fast transmit interval, range 1-3600, default 1 second.
Fast Transmit Num
LLDP fast transmit number, range 1-8, default 4
LLDP PORT CONFIGURATION
Select Management / LLDP / Port Configuration in the navigation bar to enter the LLDP Port
Configuration interface as shown in Figure 9.3.
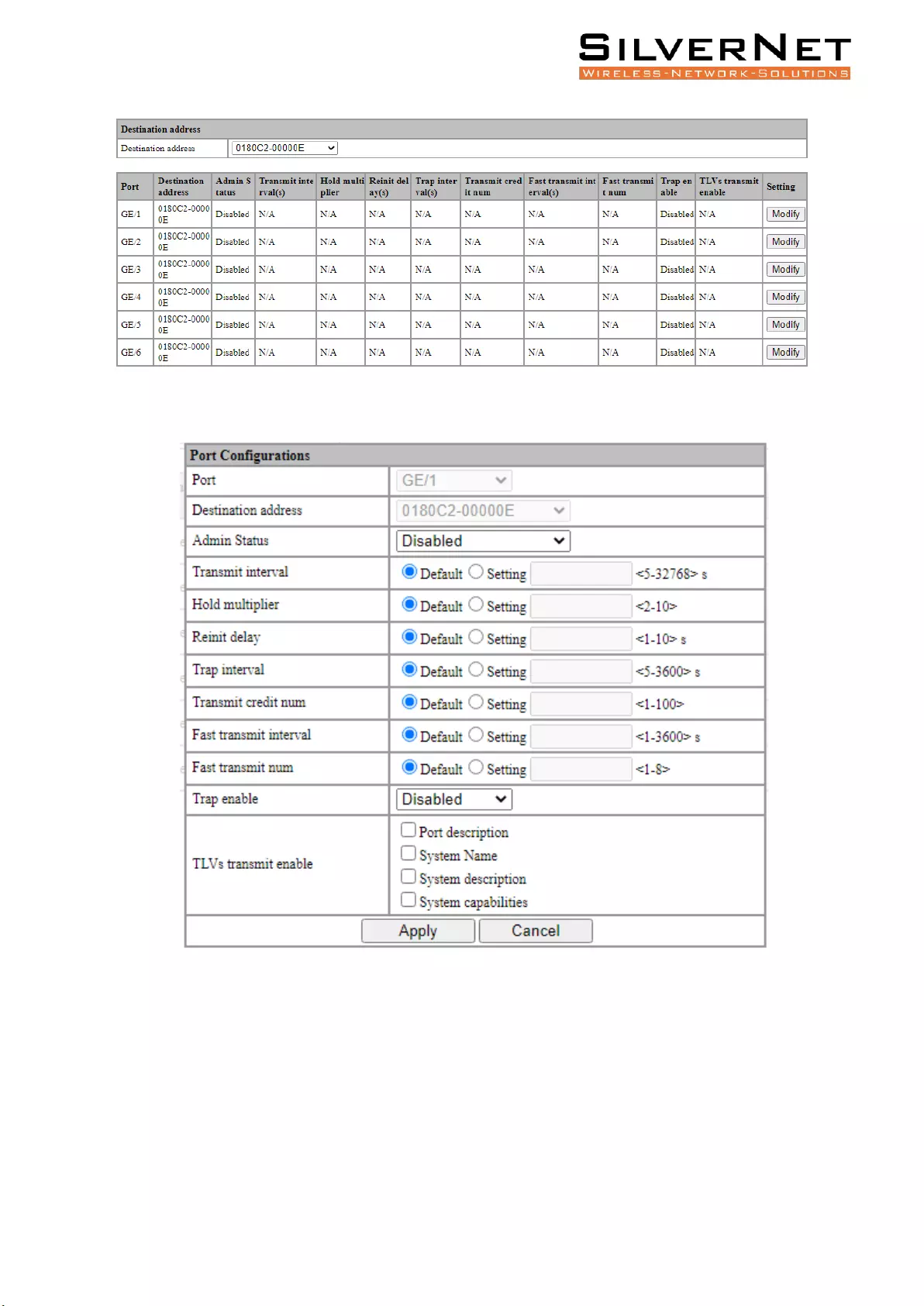
Choose the LLDP configuration of all ports corresponding to any destination address 0180C2-00000E,
0180C2-000003, 0180C2-000000 in the LLDP Port Configuration interface, as shown in figure 9.2
Select or fill out the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply to make effective.
There will be a corresponding prompt if the configuration item is incorrectly filled.
Pro Range User Manual LLDP 50
Figure 9.2 LLDP Destination Address
Figure 9.3 LLDP Port Configuration
Pro Range User Manual LLDP 51
Figure 9.2 LLDP Port Description
Configuration
Description
Port
Port name information
Destination Address
LLDP destination address 0180C2-00000E, 0180C2-000003, 0180C2-000000
Admin Status
LLDP Port Status
Transmit Only: Enable LLDP port transmit function
Receive Only: Enable LLDP port receive function
Transmit and Receive: Enable LLDP port transmit and receive function
Disable: Disable LLDP port transmit and receive function
Transmit Interval
Default: Use Global Setting transmit Interval
Setting: Set transmit period range 5-32768 in seconds.
Hold Multiplier
Port Multiplier
Default: Use Global Setting neighbour aging coefficient
Setting: Neighbour aging coefficient, range 2-10
Reinit Delay
Port Reboot Delay Time
Default: Use Global Setting reboot delay time
Setting: Set reboot delay time, range 1-10
Trap Interval
Port Warning Period
Default: Use Global Setting warning period
Setting: Set warning period range 5-3600
Transmit Credit
Num
Port Transmit Volume
Default: Use Global Setting transmit volume
Setting: Set transmit volume range 1-100
Fast Transmit
Interval
Port Quick Transmit Period
Default: Use Global Setting quick transmit period
Setting: Set quick transmit period range 1-3600
Fast Transmit Num
Port Quick Transmit Quantity
Pro Range User Manual 802.1X 52
Default: Use Global Setting quick transmit quantity
Setting: Set quick transmit quantity range 1-8
Trap Enable
Port Warning Enable
Enable: Enable LLDP port warning function
Disable: Disable LLDP port warning function
TLVs
Transmit Enable
Support one or more TLVs transmit enable selection of port description, system
name, system description and system capability
802.1X
This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1X Standard, including the following:
• 802.1X Server Configuration
• 802.1X Port Configuration
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control. It provides an authentication
mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN or WLAN.
AUTHENTICATION SERVER
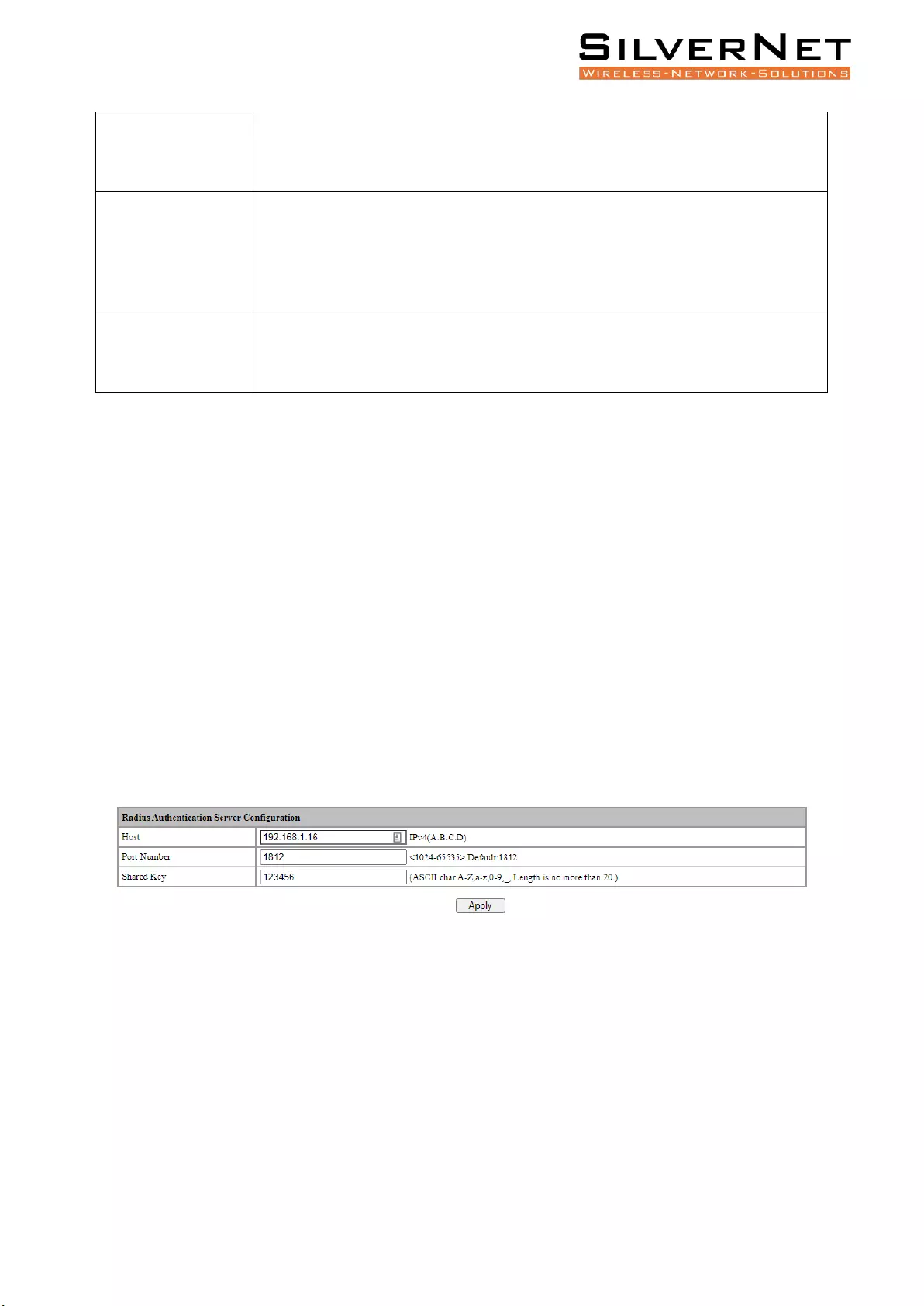
Select Advanced / 802.1X / Authentication Server in the navigation bar to enter Radius Authentication
Server Configuration.
To modify the Authentication Server configuration, click Modify in the Authentication Server
configuration box, as shown in Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1 Radius Authentication Server Configuration
Pro Range User Manual 802.1X 53
Table 10.1 802.1X Authentication Server Description
Configuration Item
Description
Host
The IP of Radius Authentication Server, IPv4 and Dotted decimal format.
Port Number
The port of Radius Authentication Server, range <1024-65535>
Shared Key
Shared key used to access the server. Must be consistent with Radius server,
otherwise it cannot pass authentication. String format, only contain letters,
numbers, underscores, and the length cannot be more than 20 bytes.
GLOBAL SETTINGS
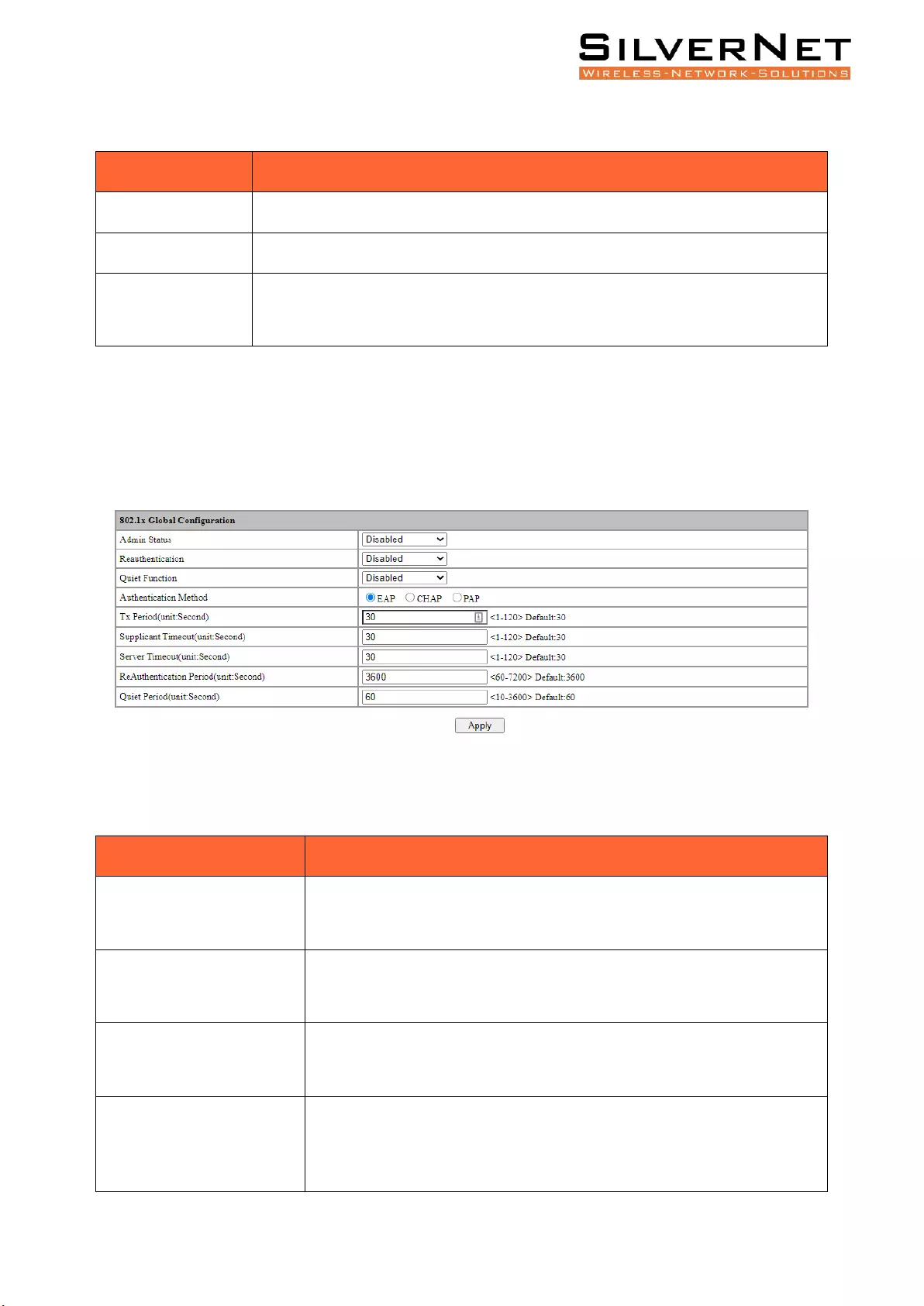
Select Advanced / 802.1X / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the Global Setting interface.
To modify the global configuration in the Global Configuration box, click Apply as shown in Figure
10.2
Figure 10.2 802.1x Global Configuration
Table 10.2 802.1X Description
Configuration Item
Description
Admin Status
Disable: Prohibit Global 802.1X
Enable: Enable Global 802.1X
Reauthentication
Disable: Prohibit reauthentication to the server.
Enable: Enable reauthentication to the server.
Quiet Function
Disable: Prohibit the silent function.
Enable: Enables the silent function.
Authentication Method
Check the respective box to select the type of Authentication Method
used for 802.1x
Pro Range User Manual 802.1X 54
EAP: Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication
framework frequently used in network and internet connections. EAP is
an authentication framework, not a specific authentication mechanism. It
provides some common functions and negotiation of authentication
methods called EAP methods
PAP: Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is a password-based
authentication protocol used by Point to Point Protocol (PPP) to validate
users. PAP authentication is only done at the time of the initial link
establishment and verifies the identity of the client using a two-way
handshake. Client sends username and password. This is sent repeatedly
until a response is received from the server. Server sends authentication-
ack (if credentials are OK) or authentication-nak (otherwise).
CHAP: CHAP is an authentication scheme used by Point-to-Point Protocol
(PPP) servers to validate the identity of remote clients. CHAP periodically
verifies the identity of the client by using a three-way handshake. This
happens at the time of establishing the initial link (LCP), and may happen
again at any time afterwards. The verification is based on a shared secret
(such as the client's password). After the completion of the link
establishment phase, the authenticator sends a "challenge" message to
the peer. The peer responds with a value calculated using a one-way hash
function on the challenge and the secret combined. The authenticator
checks the response against its own calculation of the expected hash
value. If the values match, the authenticator acknowledges the
authentication; otherwise it should terminate the connection. At random
intervals the authenticator sends a new challenge to the peer and repeats
steps 1 through 3.
Tx Period (unit:Second)
Integer 1-120, default 30
Supplicant Timeout
(unit:Second)
Integer 1-120, default 30
Server-Timeout
(unit:Second)
Integer 1-120, default 30
Re-authentication Period
Integer 60-7200, default 3600
Quiet Period (unit:Second)
Integer 10-3600, default 60
PORT CONFIGURATION
Select Advanced / 802.1X / Port Configurations in the navigation bar to enter the Port Configurations
interface as shown in Figure 10.3.
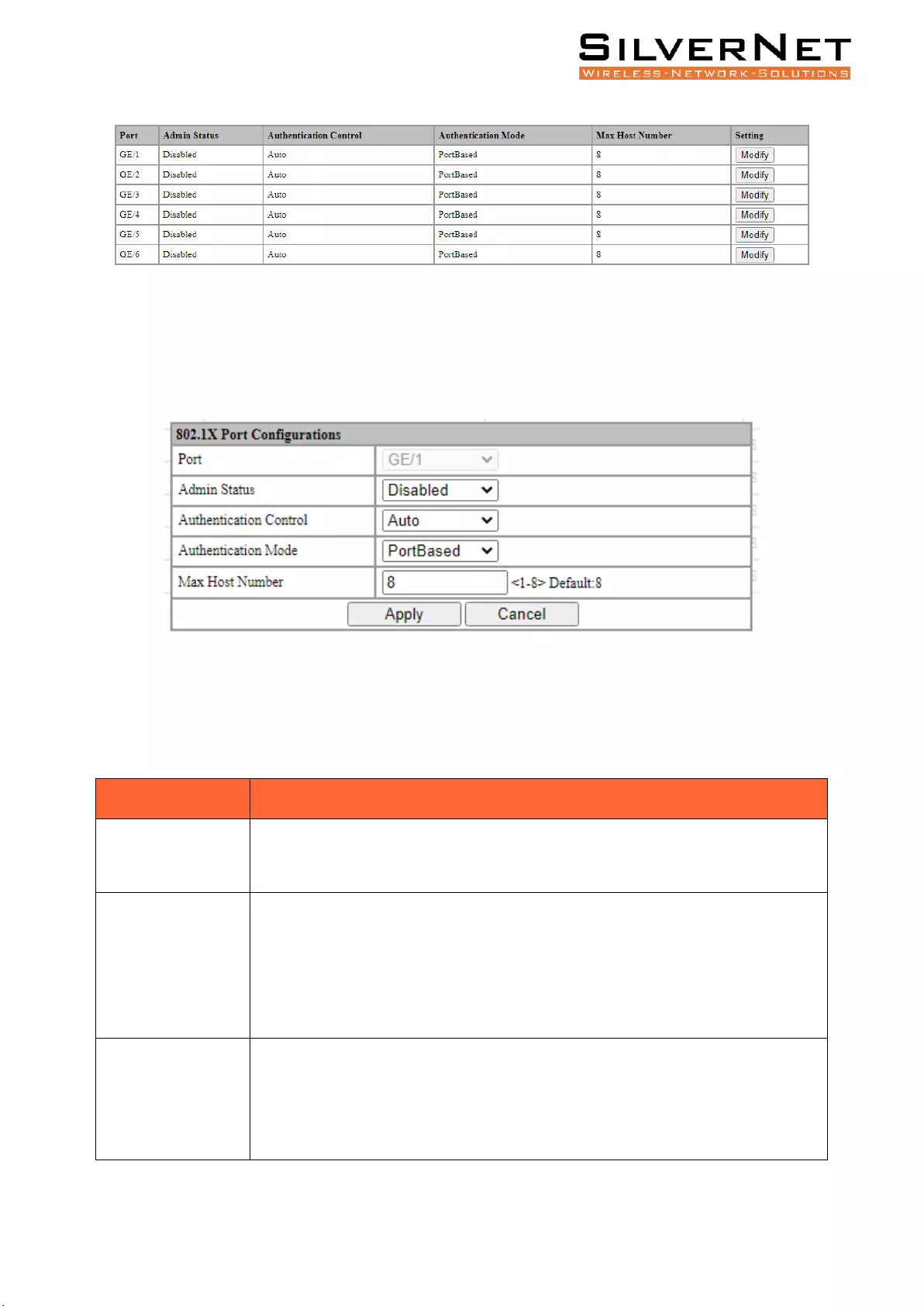
Pro Range User Manual 802.1X 55
Figure 10.3 802.1X Port Configuration
To modify the configuration of a port, simply click the Edit in corresponding entry to enter
modification interface, as shown in Figure 10.4. Modify the corresponding configuration item, click
the Apply to complete the modification, and click the Cancel to cancel the modification.
Figure 10.4 802.1X802.1X Port Configuration
Precautions: When the 802.1X port is configured to authentication mode, all authenticated users will
go offline, and re-authentication is required to access the network.
Table 10.3 802.1X Port Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Disabled: Disable 802.1x on the port
Enabled: Enable 802.1x on the port
Authentication
Control
Automatic: You cannot access the network before authentication. You can access
the network after passing the authentication.
Forced Authorization: Always have access to the network
Forced-Unauthorization: Always cannot access the network
Authentication
Mode
Port-based: After a user is authenticated on a specific port, all users will be able
to access on the same port.
MAC-Based: All users need to be authenticated individually to access the
network.

Pro Range User Manual Loopback 56
Max Host Number
There is maximum number of authenticated hosts supported by the port.
Authentication will fail if this number is exceeded. Integer 1-8, default 8
USER AUTHENTICATION INFORMATION
Select Advanced / 802.1X / User Authentication Information in the navigation bar to enter the User
Authentication Information interface.
Click Expand in the upper left corner to expand the user authentication information for all ports and
click Close to close the user authentication information for all ports. Click the icon to expand the
user authentication information for the corresponding port and click the icon to close the user
authentication information for the corresponding port.
The authentication information of the user can be viewed on this interface: username, client MAC
address, and the time the authentication passed.
Click Refresh to refresh the current user authentication information.
LOOPBACK
This chapter describes Loopback configuration, including the following:
• Loopback Global Configuration
• Loopback Port Configuration
Loopback is the routing of electronic signals, digital data streams, or flows of items back to their
source without intentional processing or modification. It is primarily a means of testing the
communications infrastructure.
Select Advanced / Loopback / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter Global Setting interface.
To modify the global configuration, modify the corresponding configuration in the Global
Configuration box and click Apply, as shown in Figure 11.1.
Figure 11.1 Loopback Global Configuration
Pro Range User Manual Loopback 57
Table 11.1 Loopback Global Item Description
Item
Description
Detection
Timer(unit:Second)
Loop detection packet sending interval, range <1-32767>. The default value is 5
Resume
Timer(unit:Second)
Port auto recovery period, range <10-65535>, must not be less than 2x detection
timer
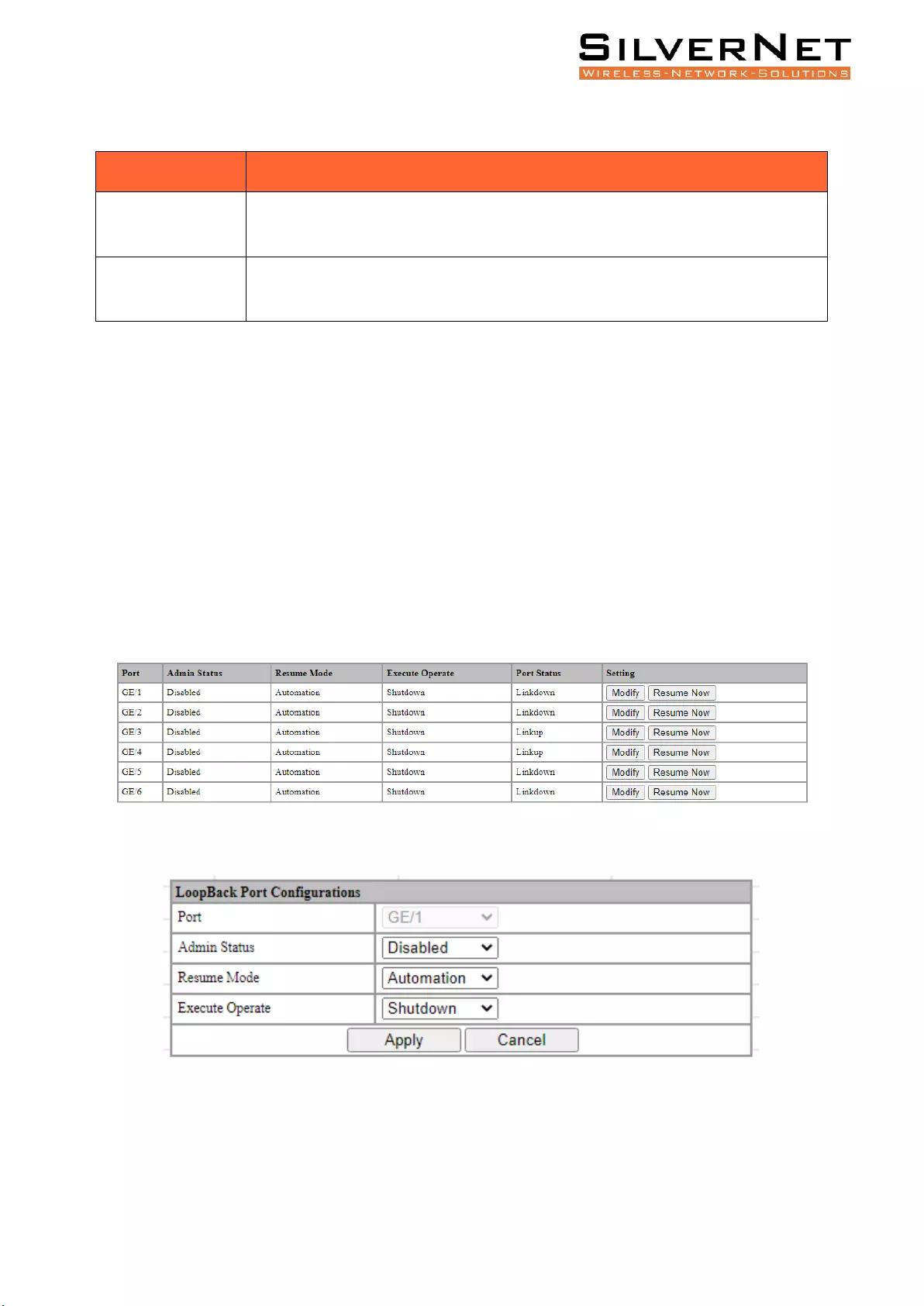
PORT CONFIGURATIONS
Select Advanced / Loopback / Port Configuration in the navigation bar to enter the Port
Configuration interface as shown in Figure 11.2.
To modify the configuration of a port, simply click the Edit on the right side of the corresponding
entry to enter the modification interface, as shown in Figure 11.3. Modify the corresponding
configuration item, click the Apply to complete the modification, and click the Cancel to cancel the
modification.
After a loop occurs on a port and the port is shut down or blocked by a specified action, if you want
to restore it immediately, you can click the Restore Now on the right side of the corresponding
entry.
Figure 11.2 Loopback Port Configuration and Operating Status
Figure 11.3 Loopback Port Configuration
Pro Range User Manual Multicast Management 58
Table 11.2 Loopback Port Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Disabled: Disable loop detection
Enabled: Enable loop detection
Resume Mode
Select the mode of resumption after loopback completes.
Automatic: After the loop occurs, the port is closed or blocked, and the port
automatically recovers.
Manual: After a loop occurs, the port is closed or blocked, need to manually restore
the port.
Execute
Operate
Select the action of the loopback operation.
Shutdown: After the loopback occurs, the port is shutdown.
Block: After a loopback occurs, the port is blocked.
MULTICAST MANAGEMENT
This chapter describes Multicast Management, including the following:
• IGMP Snooping
• Multicast Table
• Multicast Manual Address Setting
Multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination
computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution.
Select Advanced / Multicast / IGMP snooping / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the
Global Setting.
If you need to modify the global configuration of IGMP snooping, you can modify the corresponding
configuration in the configuration box, and then click Apply, as shown in Figure 12.3.
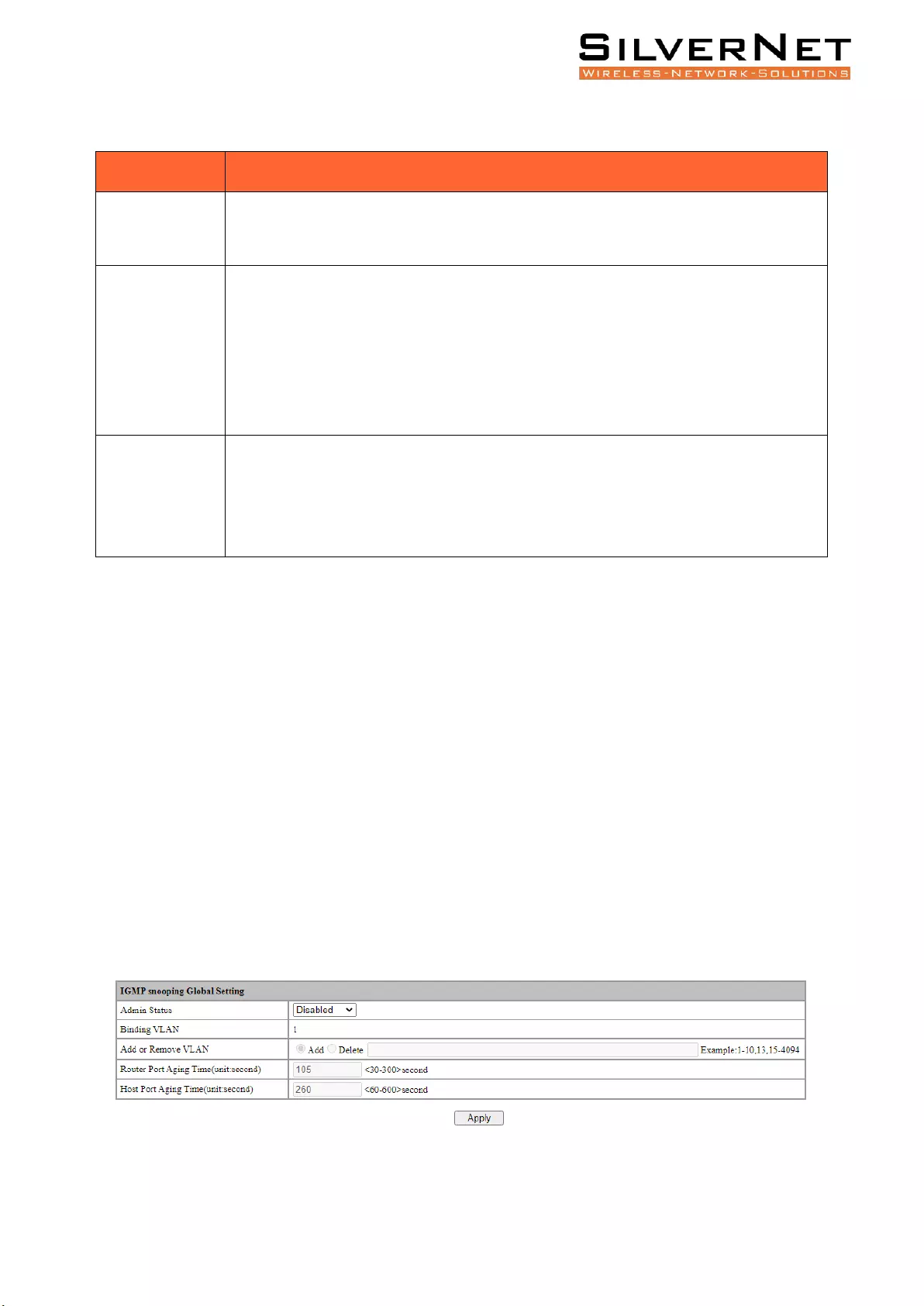
Figure 12.1 IGMP Snooping Global Settings
Pro Range User Manual Multicast Management 59
Table 12.1 IGMP Snooping Global Settings Description
Item
Description
Admin status
IGMP snooping is the process of listening to Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) network traffic to control delivery of IP multicasts. Network
switches with IGMP snooping listen in on the IGMP conversation between hosts
and routers and maintain a map of which links need which IP multicast
transmission. Multicasts may be filtered from the links which do not need them,
conserving bandwidth on those links.
Select the global enable state of IGMP Snooping:
Enabled: Enable the IGMP snooping function.
Disabled: Disable IGMP snooping.
Binding VLAN
List of VLANs to be bound.
Add or Remove
VLANs
Select the operation for the VLAN and enter the list of VLANs to add or remove:
Add: Add a VLAN. The format is as follows: 1-10,13,15-4094;
Delete: Delete the VLAN. The format is as follows: 1-10,13,15-4094.
Router Port Aging
Time
Valid aging time of routed ports, range 30-300. The default is 105. The unit is
seconds.
Host Port Aging
Time
Effective host port aging time, range 60-600. The default is 260. The unit is second
Pro Range User Manual Multicast Management 60
VLAN SETTINGS
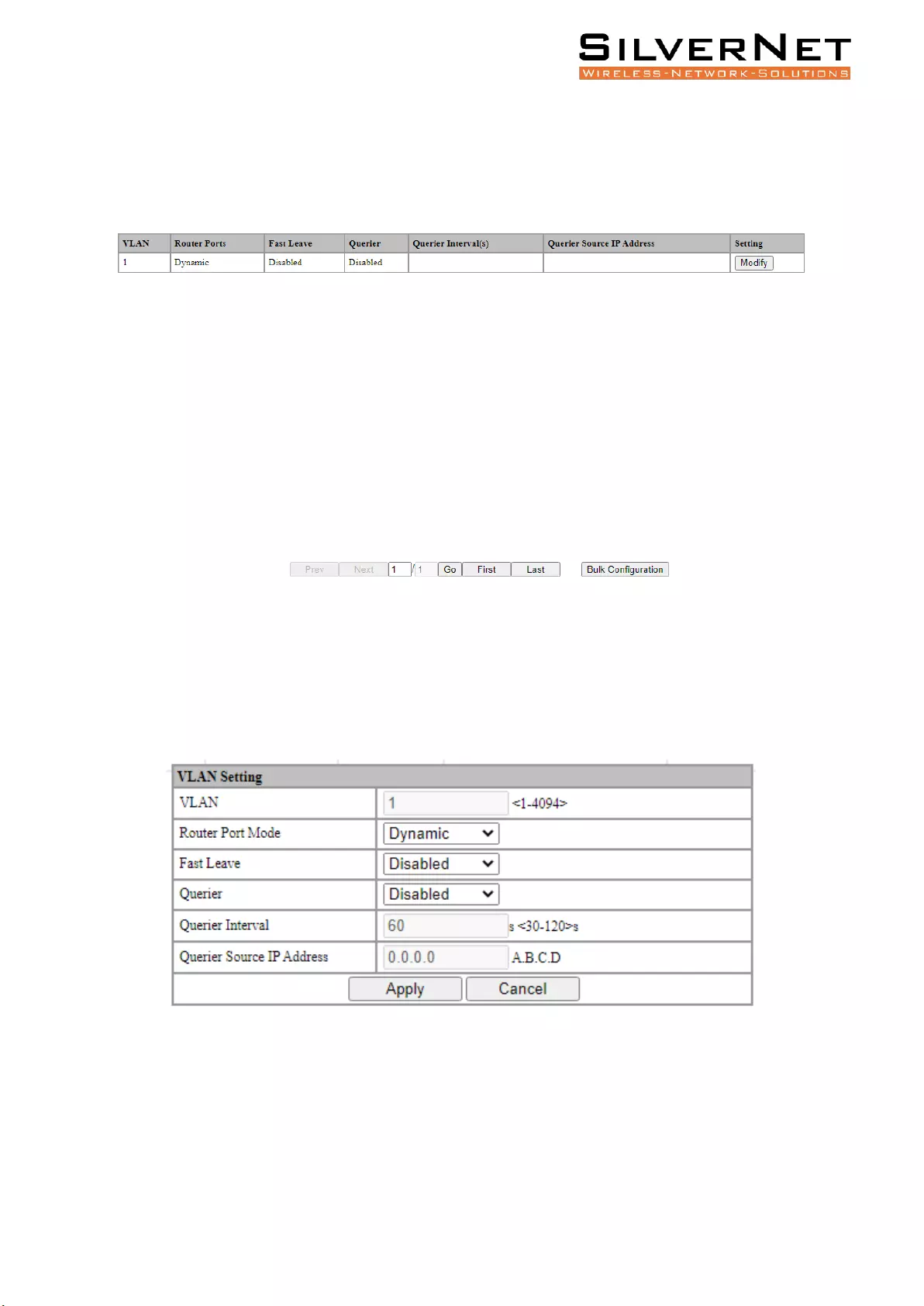
Select Advanced / IGMP Snooping / VLAN Settings to enter the VLAN Settings, as shown in Figure
12.2.
Figure 12.2 IGMP Snooping VLAN Setting
Modify individual bound VLAN configuration information. After entering the VLAN Settings interface,
click the Modify to enter the modification interface, as shown in Figure 12.2. Enter valid
configuration parameters and click Apply to submit the modification. Click Cancel to abandon the
modification.
Figure 12.2 IGMP Snooping VLAN Configuration
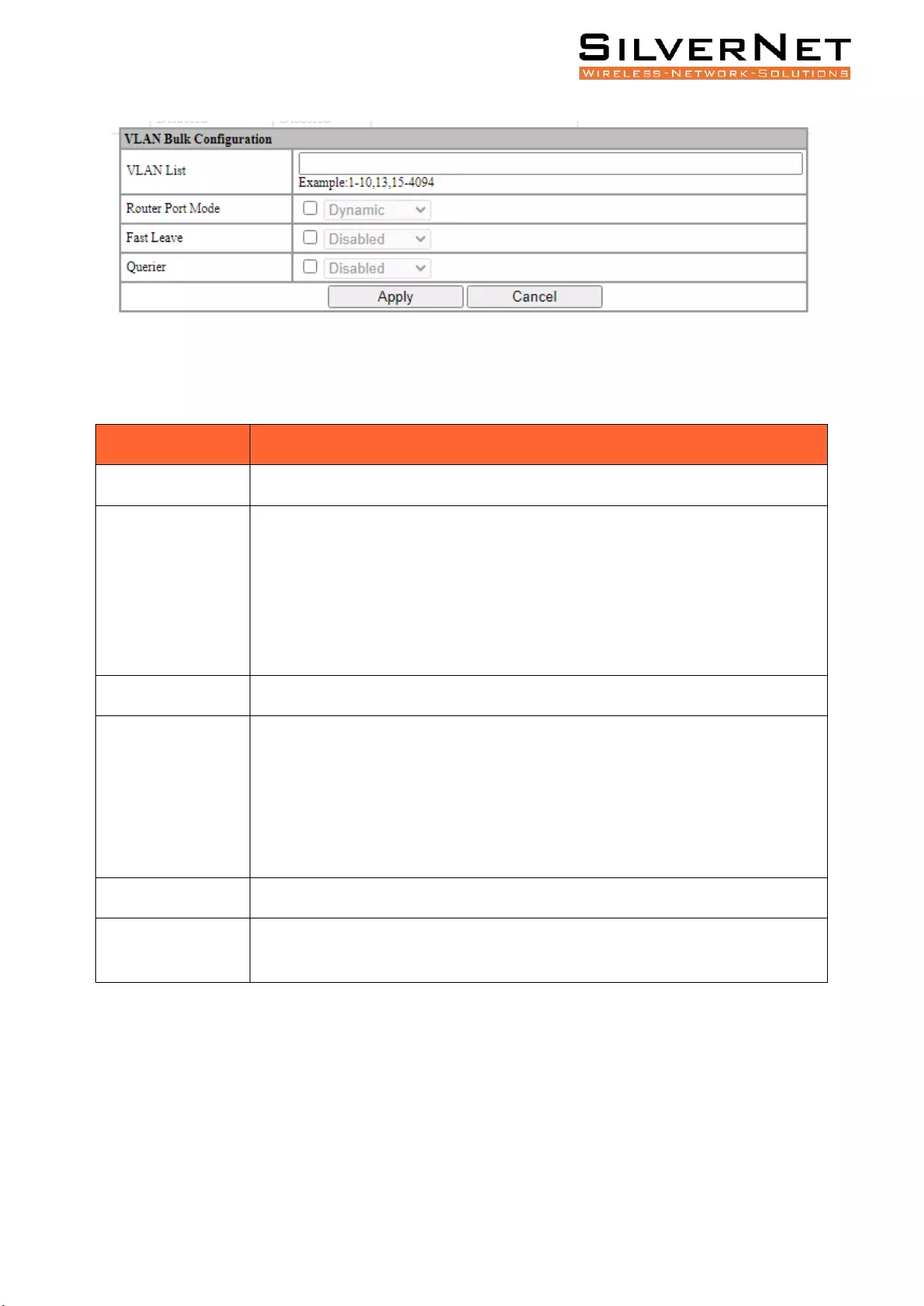
Bind VLAN configuration information in batches. After entering the VLAN Setting, click the Bulk
Configuration at the bottom of the page to enter the VLAN Bulk Configuration, as shown in Figure 12.3.
Enter valid configuration parameters and click Apply to submit the modification. Click Cancel to
abandon the modification.
Pro Range User Manual Multicast Management 61
Figure 12.3 IGMP Snooping VLAN Bulk Configuration
Table 12.3 Configuration Items on IGMP Snooping
Item
Description
VLAN
VLAN ID configured.
Router Port Mode
Select the mode of the routed port in this VLAN. Use the drop-down box to modify
it.
Dynamic: This will dynamically select routing ports.
Static: If you choose the static routing port mode, you still need to select specific
routing ports.
Fast Leave
Select whether to enable the quick leave mode under this VLAN.
Querier
Select whether to enable the querier function in this VLAN. Use the drop-down
box to modify it.
Disabled: Disable the querier function.
Enabled: If the querier is enabled, you need to set the corresponding querier
interval and query source IP address.
Querier Interval
The query interval of the querier is 30-120 seconds.
Querier Source IP
Address
Set the source IP address of the query message sent by the querier. The valid
unicast address is “192.168.1.11”. "0.0.0.0" is also available
IP GROUP
Select Advanced / IGMP snooping / IP Group in the navigation bar to enter the IP Group interface, as
shown in Figure 12.4.

Pro Range User Manual Multicast Management 62
Figure 12.4 IGMP Snooping IP Group
The IGMP snooping IP group interface displays the IP group information maintained by IGMP Snooping
and can be refreshed by clicking Refresh.
MAC GROUPS
Select Advanced / IGMP Snooping / MAC Group in the navigation bar to enter the MAC Group
interface, as shown in Figure 12.5.
Figure 12.5 IGMP snooping MAC group interface
The IGMP snooping MAC Group interface displays the MAC group information maintained by IGMP
Snooping. Click the Refresh button to refresh.
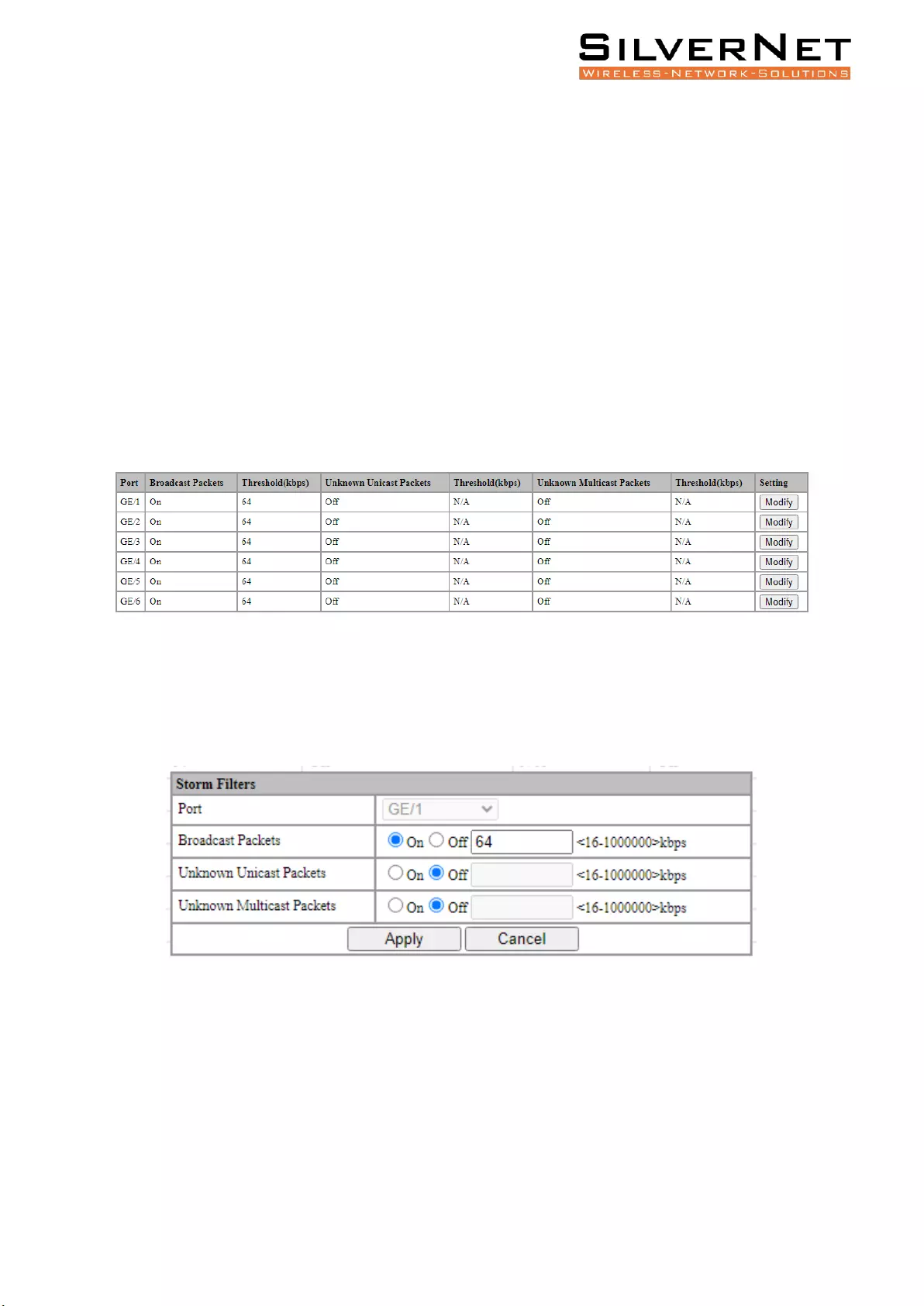
Pro Range User Manual Storm Filtering 63
STORM FILTERING
This chapter describes Storm Filtering, including the following:
• Storm Filter Configuration
Broadcast Storm is the accumulation of broadcast and multicast traffic on a computer network.
Extreme amounts of broadcast traffic constitute a broadcast storm. A broadcast storm can consume
sufficient network resources so as to render the network unable to transport normal traffic.
STORM FILTER SETTINGS
Select Base Configuration / Storm Filters in the navigation bar to enter Storm Filters configuration
interface, as shown in Figure 13.1.
Figure 13.1 Storm Filter
To modify the port storm filtering configuration information, click the Modify as shown in Figure
13.2. Enter valid configuration parameters and click Apply to submit the changes. Click Cancel to
cancel the modification
Figure 13.2 Storm Filter Modify
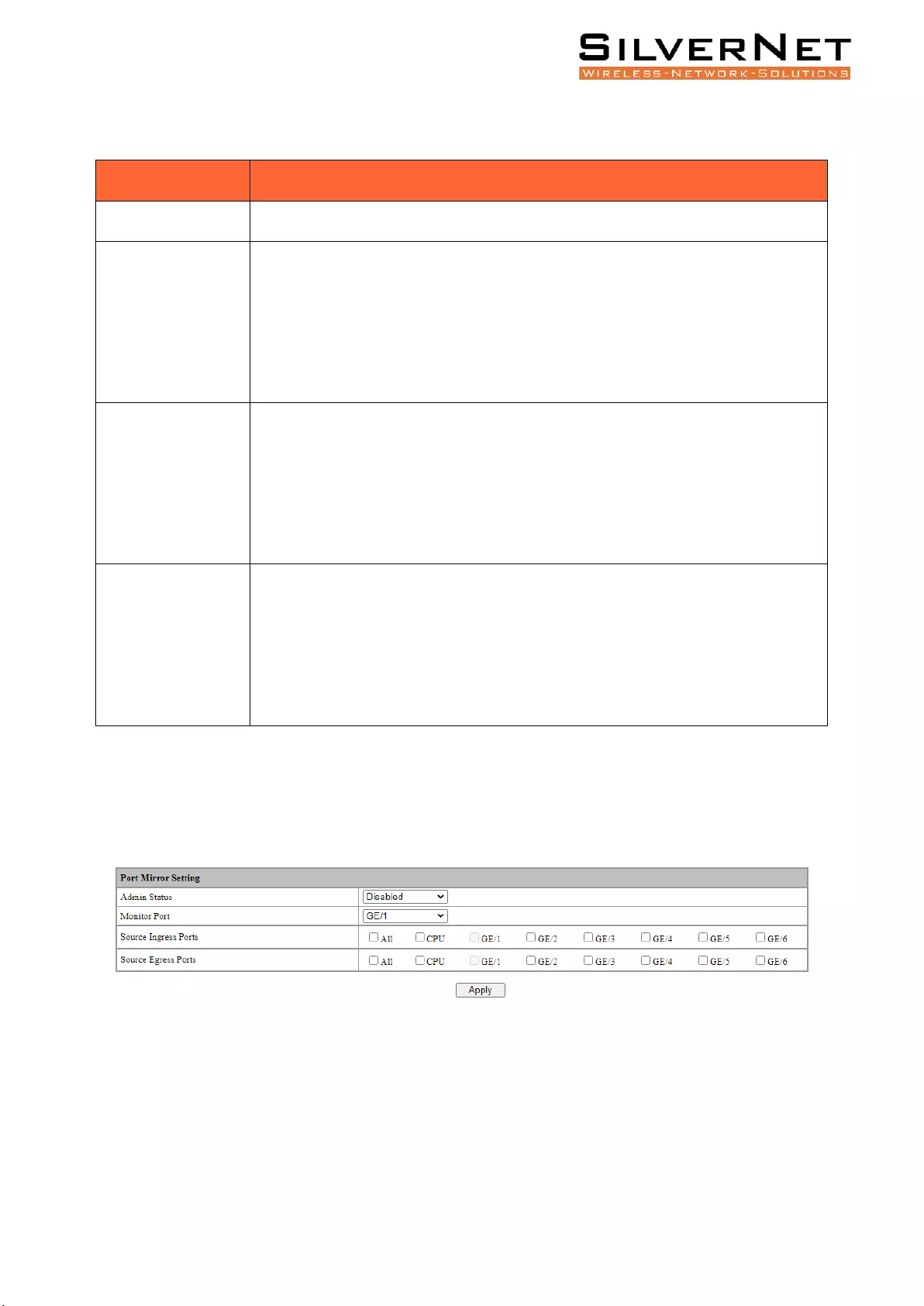
Pro Range User Manual Port Mirroring 64
Table 13.1 Storm Filters Description
Item
Description
Port
The currently selected port.
Broadcast Packets
Select whether to enable rate suppression on broadcast packets, selected by
radio button.
ON: If you choose to enable, enter the corresponding rate suppression value,
<16-1000000>, and enter 16, unit is kbps
OFF: Turn off Rate Suppression of Broadcast Packets.
Unknown
Unicast Packets
Select whether to enable rate suppression for unknown unicast packets,
selected by radio button.
ON: If you choose to enable, enter the corresponding rate suppression value,
<16-1000000>, enter 16, unit is kbps
OFF: Turn off Rate Suppression of Unknown Unicast Packets
Unknown
Multicast Packet
Select whether to enable rate suppression for unknown multicast packets,
selected by radio button.
ON: If you choose to enable, enter the corresponding rate suppression value,
<16-1000000>, enter 16, unit is kbps
OFF: Turn off Rate Suppression for Unknown Multicast Packets
PORT MIRRORING
Select Base Configuration / Port Mirror in the navigation bar to enter the Port Mirror configuration
interface, as shown in Figure 13.3.
Figure 13.3 Port Mirror Setting
Modify the port mirroring configuration information. Pull down and select to disable or enable
mirroring, select the mirroring destination port, check the ingress port and egress port, the ingress or
egress cannot contain the destination port, and click apply to submit the modification
Pro Range User Manual Link Aggregation 65
Table 13.2 Port Mirroring Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Select whether to enable or disable port mirroring.
Monitor Port
Select the destination port for port mirroring.
Source Ingress Port
Select the source port list in the ingress direction. It can be selected with the check
button. (The source port list cannot contain the destination port).
Source Egress Port
Select the source port list in the egress direction. It can be selected with the
check button. (The source port list cannot contain the destination port).
LINK AGGREGATION
This chapter describes Link Aggregation, including the following:
• Link Aggregation Global Settings
• Link Aggregation Port Settings
• Link Aggregate Information
Link Aggregation refers to various methods of combining (aggregating) multiple network
connections in parallel in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could
sustain, and to provide redundancy in case one of the links should fail. A link aggregation group
(LAG) is the collection of physical ports combined together.
Select Advanced / Link Aggregation / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the Link
Aggregation / Global Setting interface.
To modify the global configuration of link aggregation, modify the corresponding configuration in
the LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) configuration box, and then click Apply, as shown in
figure 14.1.
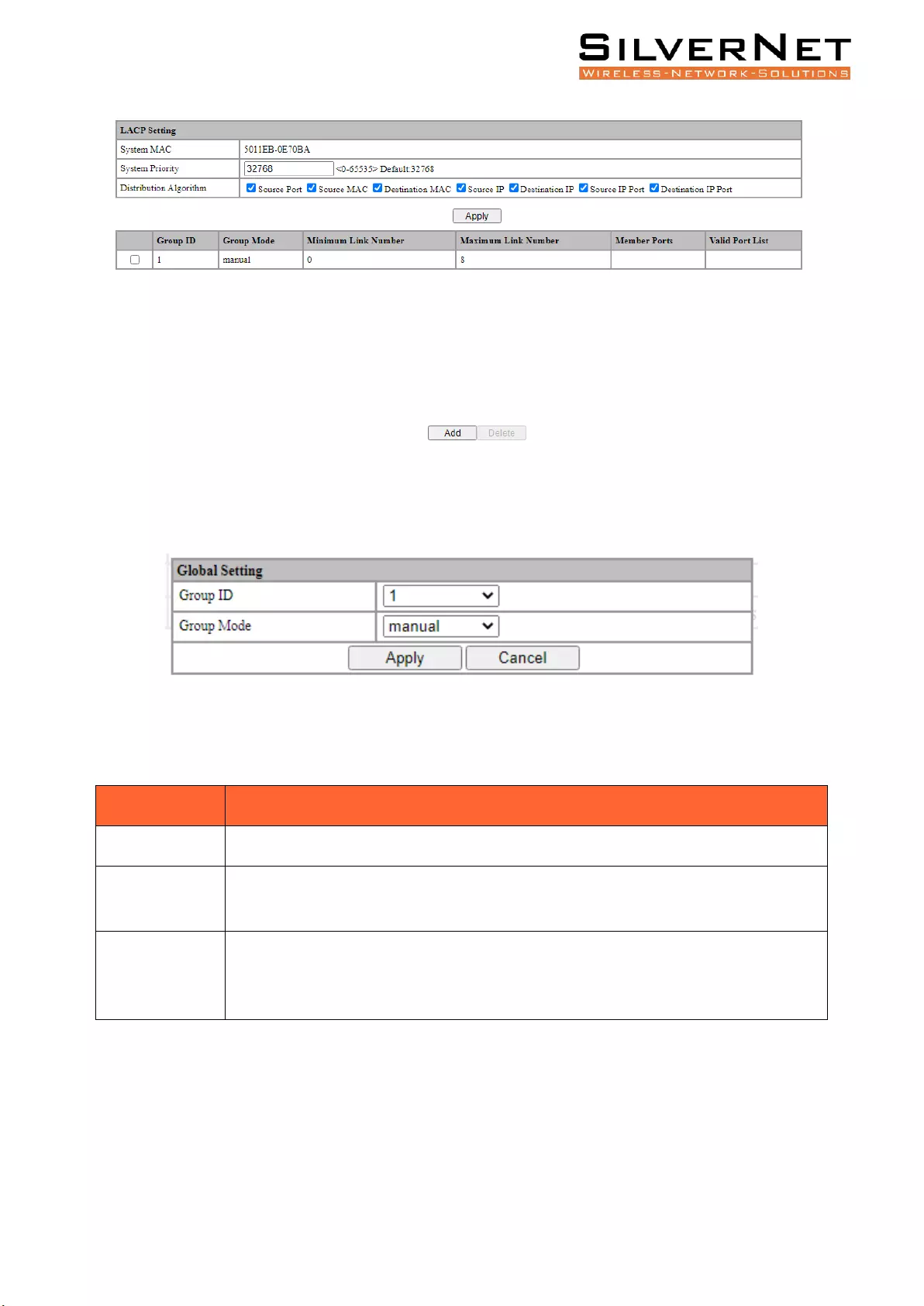
Pro Range User Manual Link Aggregation 66
Figure 14.1 LACP Global Setting
If you want to add an aggregation group, click set, as shown in figure 14.2. click Apply.
Figure 14.2 Add Aggregation Group
Table 14.1 Link Aggregation Global Setting Description
Item
Description
System MAC
The current system MAC Address.
System Priority
Set the link aggregation system priority, range 0-65535, default value 32768, the
smaller the better.
Distribution
Algorithm
The system supports one or more to compute the load ports according to the
source port, source MAC, destination MAC, source IP, destination IP, source IP port
and destination IP port in the message.
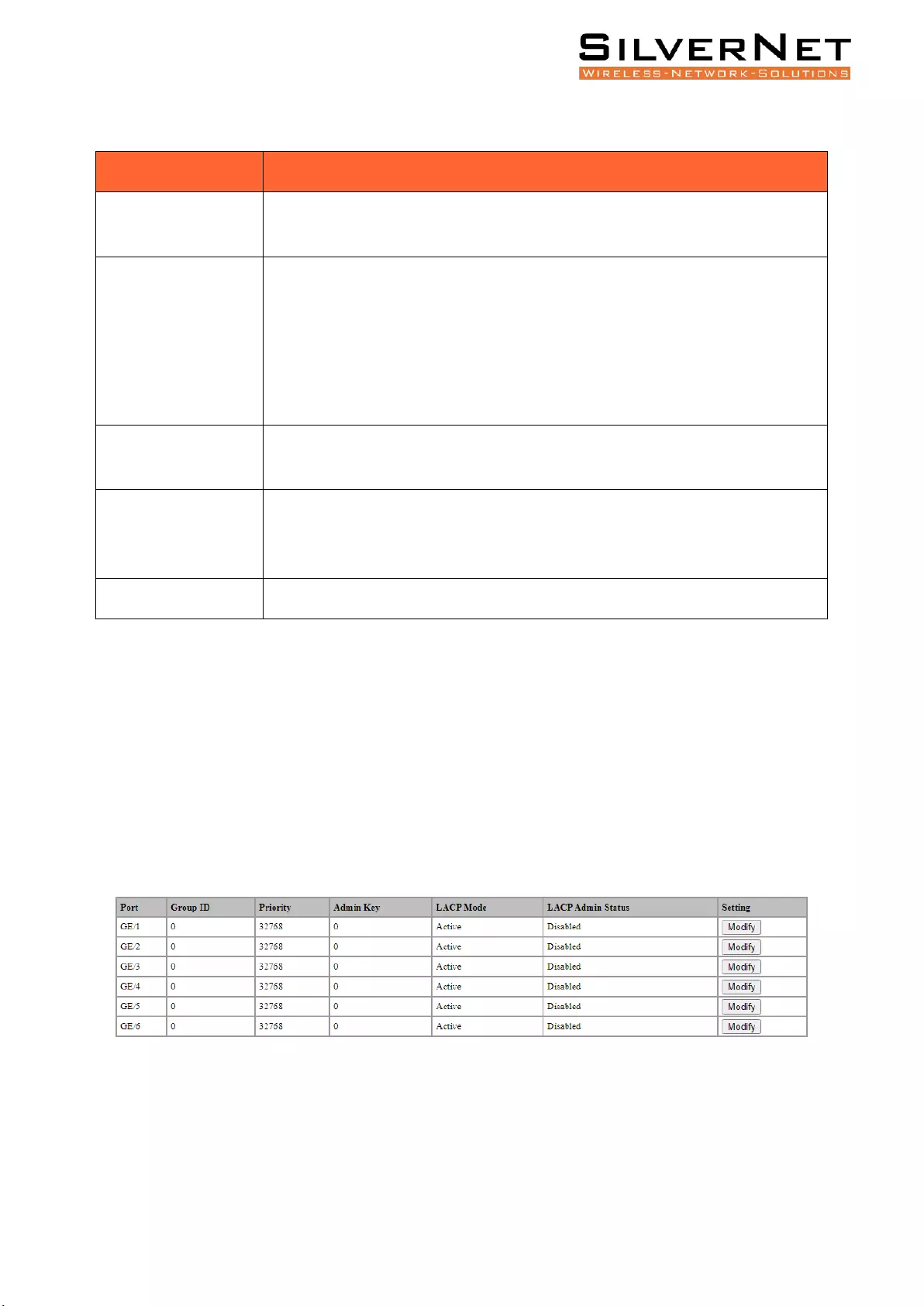
Pro Range User Manual Link Aggregation 67
Table 14.2 Link Aggregation Global Setting Description
Item
Description
Aggregation Group
ID
Aggregation Group ID information
Aggregation
Group Mode
Set Aggregation Group Mode:
Manual: Manual mode, the port of the aggregation group member is manually
configured and the port LACP protocol is closed.
Static: Static mode, the port of the aggregation group member is manually
configured and the port LACP protocol is on.
Minimum Port
The active ports minimum number of aggregation group configuration, ranging
<0-8>, and the value cannot exceed the maximum number of links.
Maximum Port
The active ports maximum number of aggregation group configuration,
ranging <0-8>, and the value cannot be less than the minimum number of
links.
Member Port List
Member port of aggregation group configuration
LINK AGGREGATION PORT SETTING
Select Advanced / Link Aggregation / Port Configurations in the navigation bar to enter the link
aggregation Port Configurations interface, as shown in figure 14.3.
If the link aggregation configuration of the port needs to be modified, click the Modify to enter the
port configuration interface, as shown in figure 14.4.
Select or fill in the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply to make effective. If
the configuration items are incorrectly filled, there will be corresponding prompts.
Figure 14.3 Link Aggregation Port Information
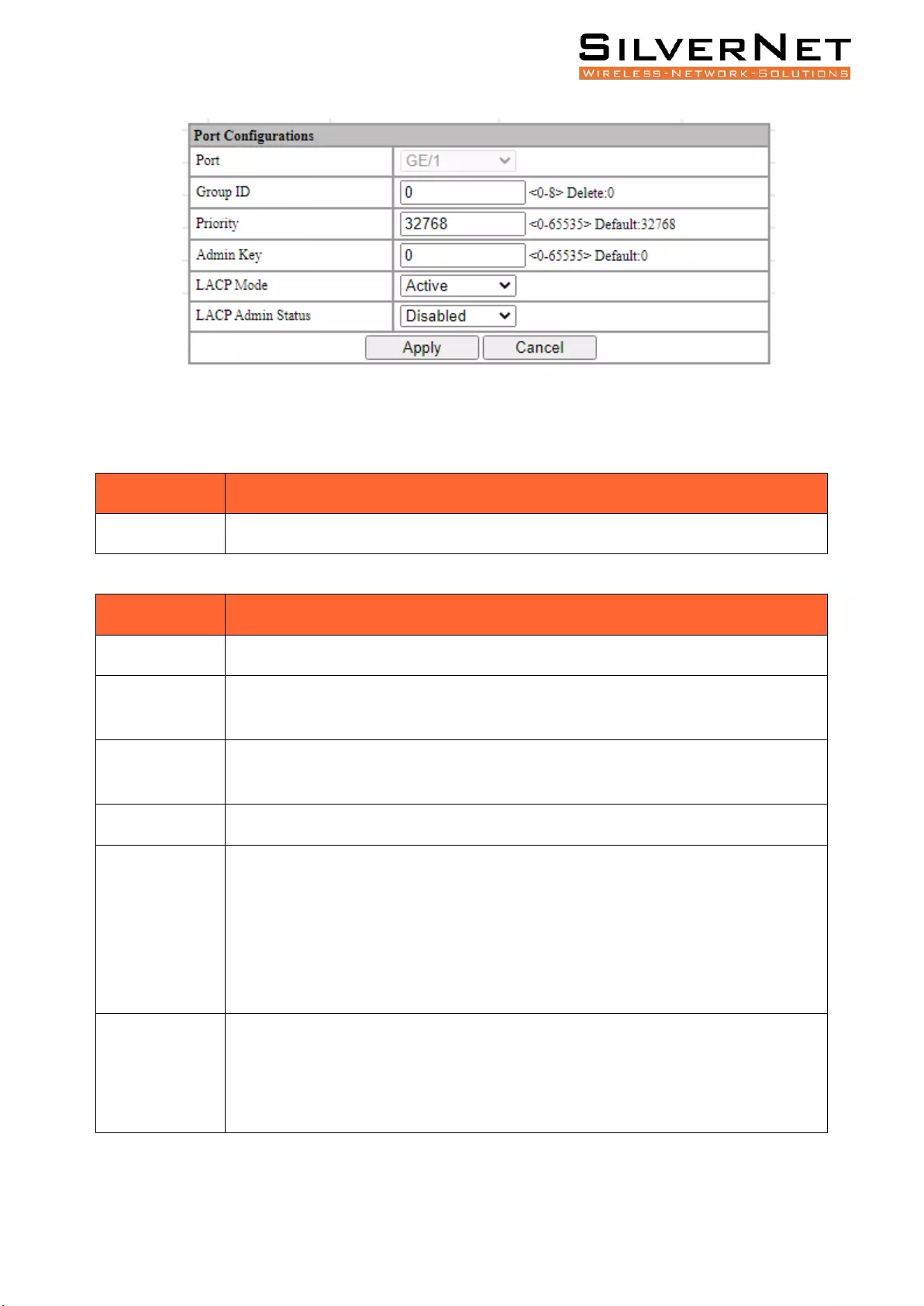
Pro Range User Manual Link Aggregation 68
Figure 14.4 Link Aggregation Port Configuration
Table 14.3 Link Aggregation Port Description
Item
Description
Modify
Modify the port configuration of link aggregation
Table 14.4 Link Aggregation Port Description
Item
Description
Port
Port name
Aggregation
Group ID
The port ID of aggregation group
Priority
Port link aggregation priority, range <0-65535>, default value 32768, the smaller the
better
Admin Key
Select Admin Key numeric, range is 0-65535, default is 0.
LACP
Port Mode
Port master-slave mode in LACP protocol
Active: Active mode, the port sends protocol messages automatically when LACP
protocol enabled.
Passive: Passive mode, the port will not send protocol messages automatically, but
only send when received protocol messages.
LACP
Mode
Port timeout mode in LACP protocol
Active: Quick timeout mode, timeout 1 second
Passive: Slow timeout mode, timeout 30 seconds
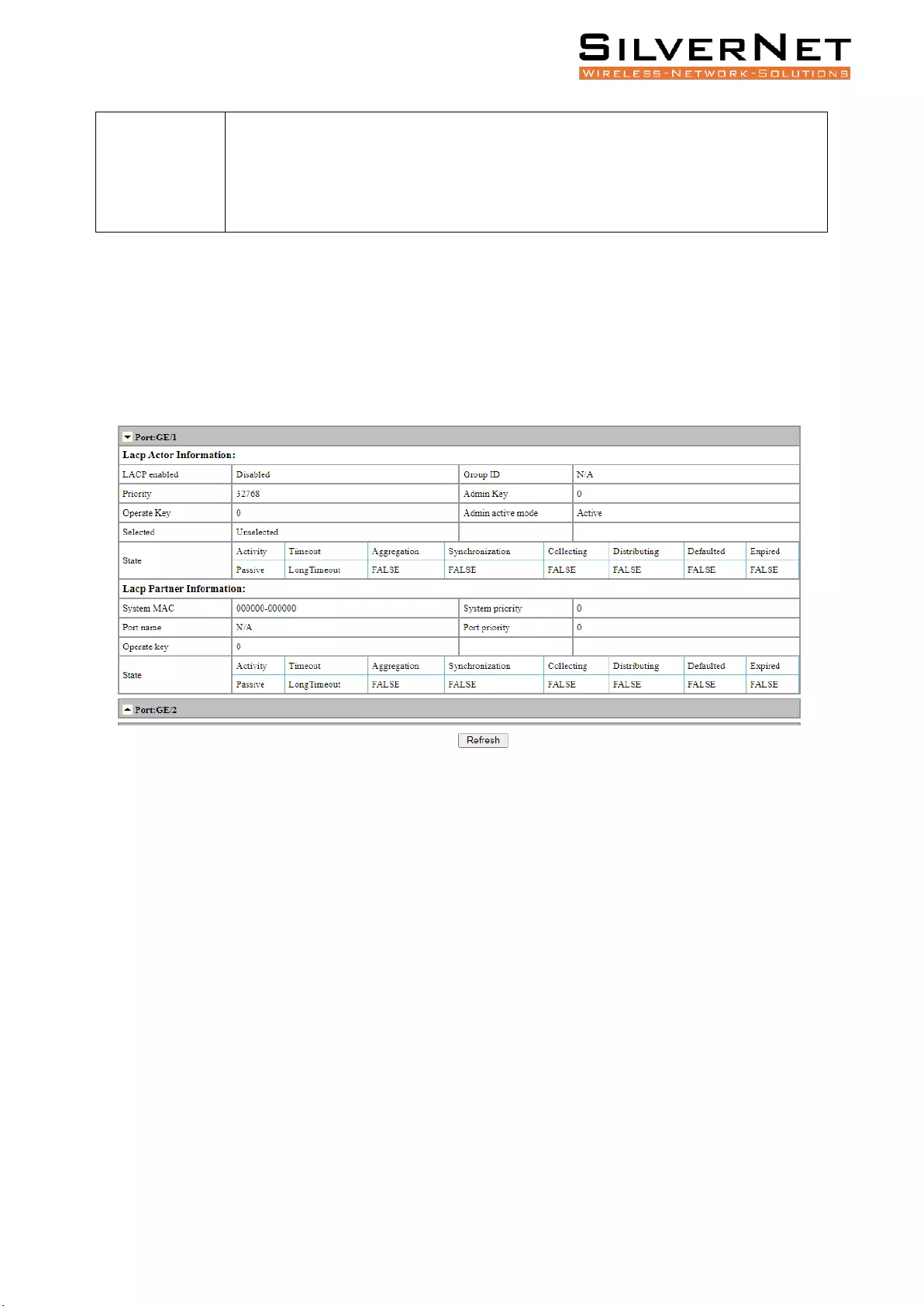
Pro Range User Manual Link Aggregation 69
LACP
Enable Status
Port LACP Enable Status
Enabled: Turn on port LACP
Disabled: Close port LACP
LINK AGGREGATION INFORMATION
Select Advanced / Link Aggregation / Aggregatee Information in the navigation bar to enter the Link
Aggregation / Aggregation Information interface.
In the link aggregation Aggregate Information interface, all port link aggregation related information
can be viewed as shown in figure 14.4.
Click Refresh to see the latest aggregation information for each port.
Figure 14.5 Port Aggregation Information
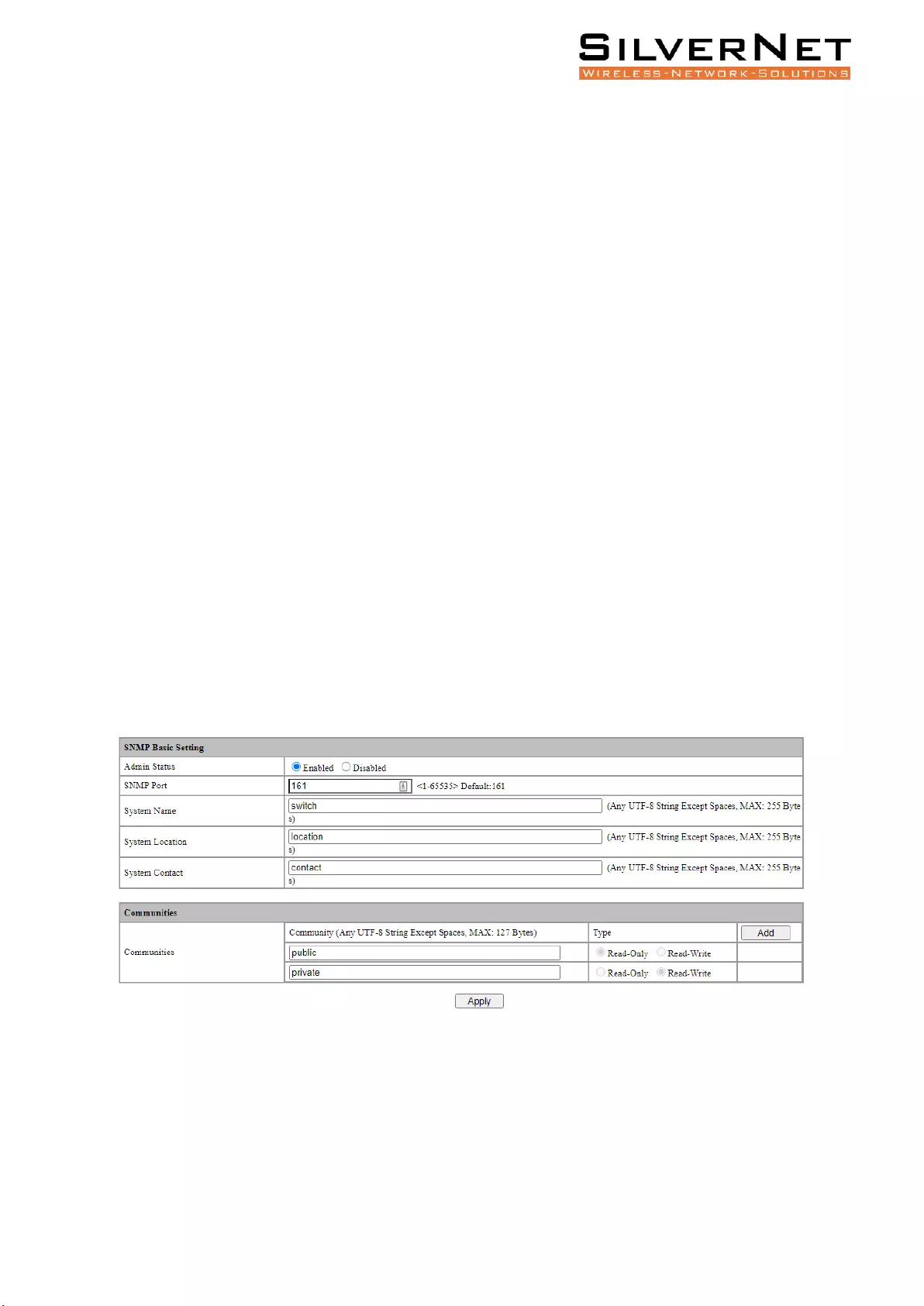
Pro Range User Manual SNMP 70
SNMP
This chapter covers SNMP in detail, including the following:
• SNMP Configuration (V1 / V2 / V3 Setting)
• Trap Setting
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and
organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to
change device behaviour. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers,
switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more.
BASE CONFIGURATION
Select Management / SNMP / V1/V2 Setting in the navigation bar to enter the SNMP Base Setting
interface.
To modify the Base Configuration, modify the corresponding configuration in the configuration box,
and then click Apply to make effective, as shown in figure 15.1.
If you want to add a group word, click Add and a group word is added to set the group word name
and type. The system supports up to eight group characters, with the first and second being the
default, so you can add up to six more. Click Apply to make effective.
To delete a group word, click Delete on the right corresponding entry (the first and second are the
system default, cannot be deleted), and click Apply to make effective.
Figure 15.2 SNMP Base Configuration
Pro Range User Manual SNMP 71
Table 15.2 SNMP Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
SNMP Global Enable Status:
Enabled: Enable SNMP function
Disabled: Disable SNMP function
SNMP Port
SNMP port with range <1-65535>, default 161.
System Name
System name, any legal character other than a space can be entered
with a maximum length of 255.
System Location Information
System location information, any legal character other than a space can
be entered with a maximum length of 255.
System Contact
System contact information, any legal character other than a space can
be entered with a maximum length of 255.
Communities
SNMP Communities:
Name: Any legal character other than a space can be entered with a
maximum length of 127
Type: Read and write
Note: The system supports a maximum of 8 group characters and
requires at least two group characters. The default two group
characters can only change the group name, cannot change the type or
delete. Click Add to add a group character, add a group character can
change the name and type, and delete.
TRAP SETTING
Select Management / SNMP / Trap Setting in the navigation bar and enter the SNMP Trap Setting
interface.
If you need to modify the Trap Setting, modify the corresponding configuration in the configuration
box, and then click Apply, as shown in figure 15.3.
If you want to add a Trap server, click Add and the Trap server entry will occur. The system supports
up to 4 groups of Trap servers, the first group is the default of the system and cannot be deleted, so
you can add up to 3 groups of Trap servers.
If you want to delete the Trap server, click Delete on the right of the corresponding entry (group 1 is
the default of the system and cannot be deleted), and click Apply.
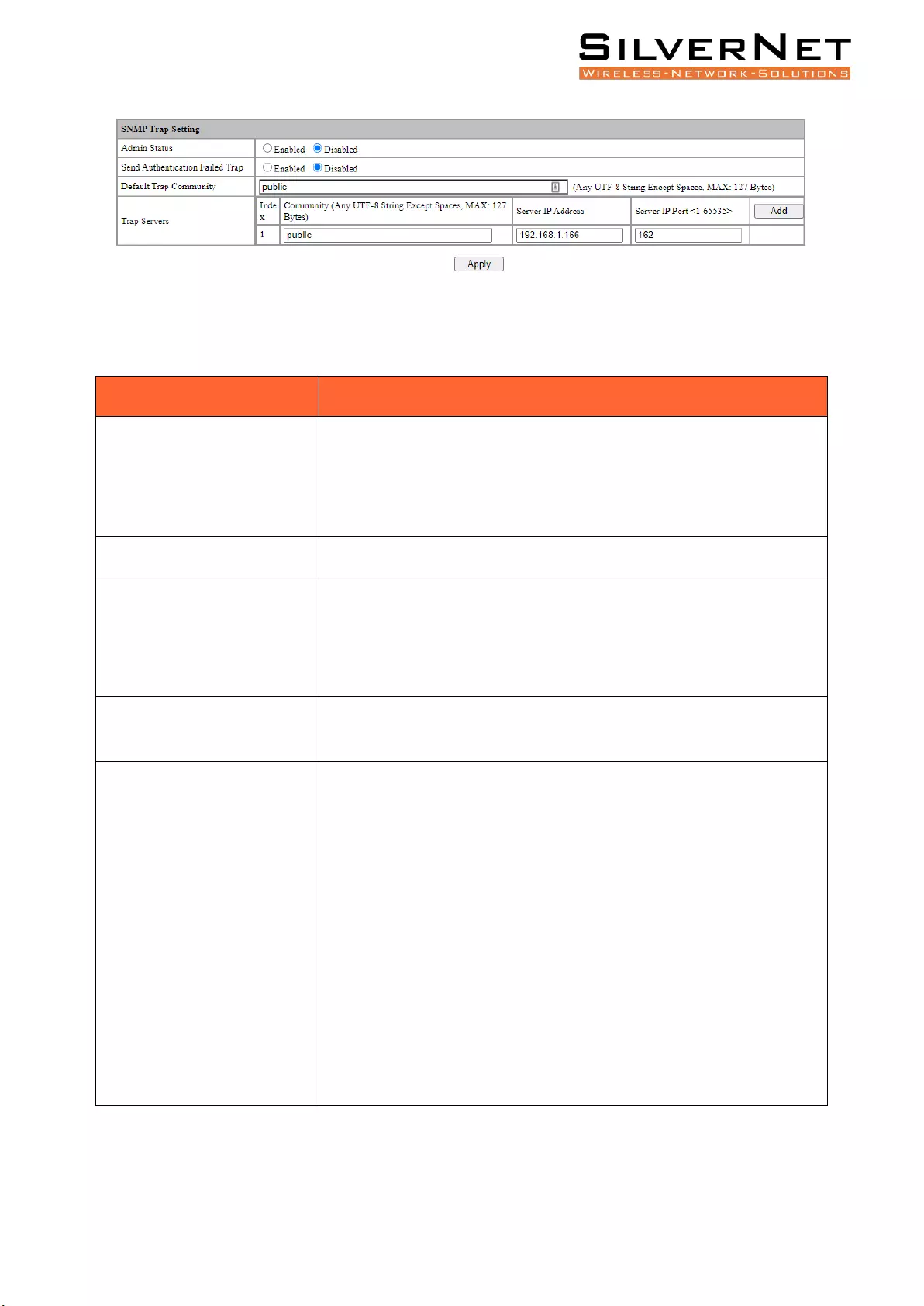
Pro Range User Manual 72
Figure 15.3 SNMP Trap Setting
Table 15.3 SNMP Trap Setting Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Trap Global Enable Status:
Enabled: Turn on Trap function
Disabled: Close Trap function
Trap Version
Trap version support V1 and V2
Send Authentication Failed
Trap
Enable or Disable the Sending SNMP Authentication Failed Trap:
Enabled: Enable the Sending SNMP Authentication Failed Trap
Disabled: Close the Sending SNMP Authentication Failed Trap
Default Trap Community
Default trap group characters, any legal character other than a space
can be entered with a maximum length of 127.
Trap Server
Set Trap Server:
Group Characters: Any legal character other than a space can be
entered with a maximum length of 127
Server IP Address: The IP address of trap server, IPv4, dot decimal
format.
Server IP Port: The IP port of trap server, range <1-65535>, default
162
Note: The system supports up to 4 servers. Click the Add to add. The
system default server number: 1, group character: public, IP address:
192.168.1.200, IP port: 162. The default server cannot be deleted, but
the added server can be deleted.
Pro Range User Manual IP interface 73
IP INTERFACE
This chapter describes the IP interface in detail, mainly including the following contents:
• IP Address
• DHCP Client Configuration
IP ADDRESS
IP (Internet Protocol Address) is short for IP Address. IP address is a unified address format provided
by the IP protocol, which assigns a logical address to each network and host on the Internet to mask
physical address differences.
IP address consists of two parts: network address (Net-id) and Host address (Host-id).
Network address is to distinguish between different networks, and host address is to distinguish
between different hosts within a network.
IP address is classified into five categories, as detailed in the following table:
IP Address Type
IP Address Range
Description
A
0.0.0.0-127.255.255.255
The IP address 0.0.0.0 is only used for
temporary communication between the host
and the current host when the system is
started.
127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255 is used for loop
testing. Groups sent to this address are not
output to the link and are treated internally as
input groups.
B
128.0.0.0-191.255.255.255
-
C
192.0.0.0-223.255.255.255
It is for small scale LAN, and each network can
only contain 254 computers at most.
D
224.0.0.0-239.255.255.255
Multicast address.
E
240.0.0.0-255.255.255.255
255.255.255.255 is for broadcast address,
other address is reserved for future use.
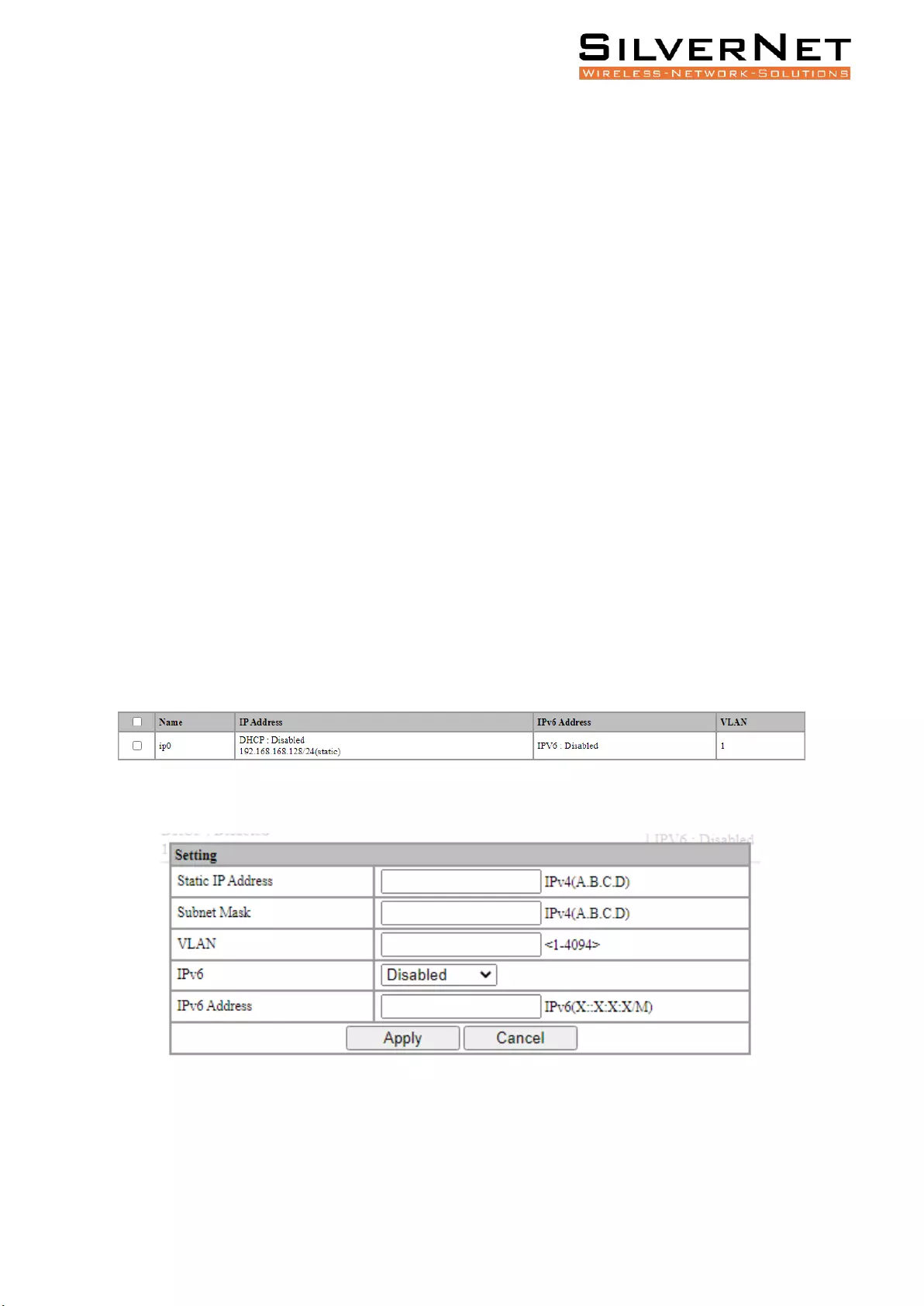
Pro Range User Manual IP interface 74
Some IP addresses are reserved for special purposes.
Users cannot configure IP interfaces as host addresses: The address with each byte being 0
("0.0.0.0") corresponds to the current host; Each IP address that is 1 ("255.255.255.255") is the
broadcast address of the current subnet;
Any class E IP address starting with 11110 shall be reserved for future and experimental use; An IP
address cannot begin with a decimal 127. Change the address number 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255
is for loop testing, such as: 127.0.0.1 can represent the local IP address, and http://127.0.0.1 can be
used to test the local Web server.
The first 8-bit group network ID cannot be fully set to 0, 0 indicates the address; In IP network, the
same network address can be directly communicated, while the address of different networks
cannot.
BASE CONFIGURATION
Select Management / IP Interface / Setting in the navigation bar to enter the IP interface Setting as
shown in figure 16.1.
To add a new IP interface, click Add, then fill in the relevant configuration, and click Apply, as shown
in figure 16.2.
To modify an IP interface, check the corresponding IP interface, click modify, then modify the
configuration, and click Apply, the IP interface is shown in figure 16.2.
To delete an IP interface, check the appropriate IP interface and click Delete.
Figure 16.1 IP Interface Viewing
Figure 16.2 IP Interface Setting
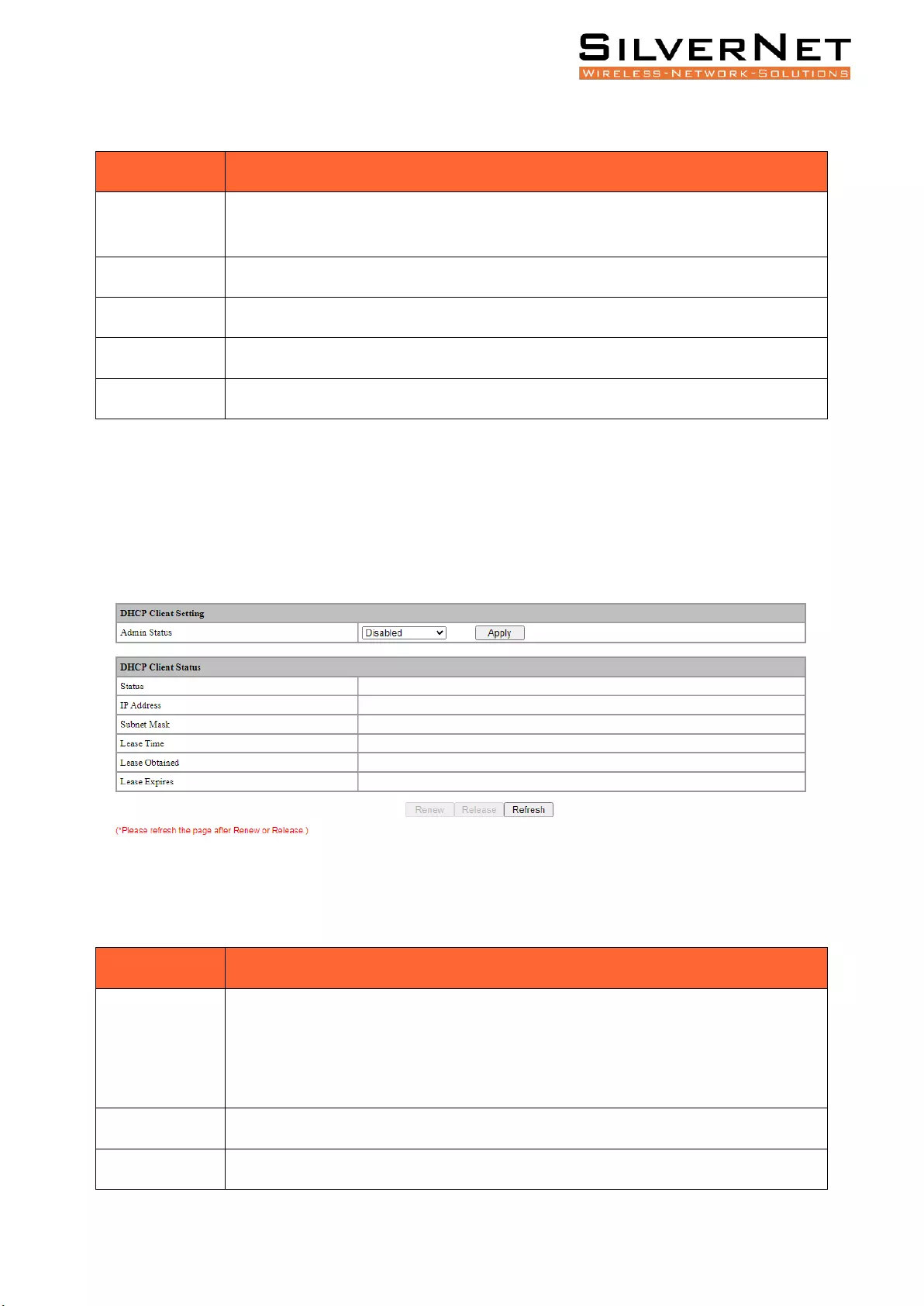
Pro Range User Manual IP interface 75
Table 16.1 IP Interface Setting Description
Item
Description
Static IP
Address
Static IPv4 address, the format is dot decimal system, each interface IPv4 address
cannot be in the same network segment.
Subnet Mask
Subdivision of IP address network.
VLAN
VLAN bound by assigned IP interface.
IPv6
Enable or Disable IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 Address
Input valid static IPv6 address. Format is hexadecimal.
DHCP CLIENT CONFIGURATION
Note: DHCP functions are described in detail in the next chapter.
Select Management / IP Interface / DHCP Client in the navigation bar to enter the DHCP Client
interface.
Figure 16.3 DHCP Client Configuration
Table 16.2 DHCP Client Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Enable or Prohibit DHCP Client
Enabled: Enable DHCP Client
Disabled: Prohibit DHCP Client
Renew
DHCP Client renews the configuration.
Release
DHCP Client releases the current configuration.
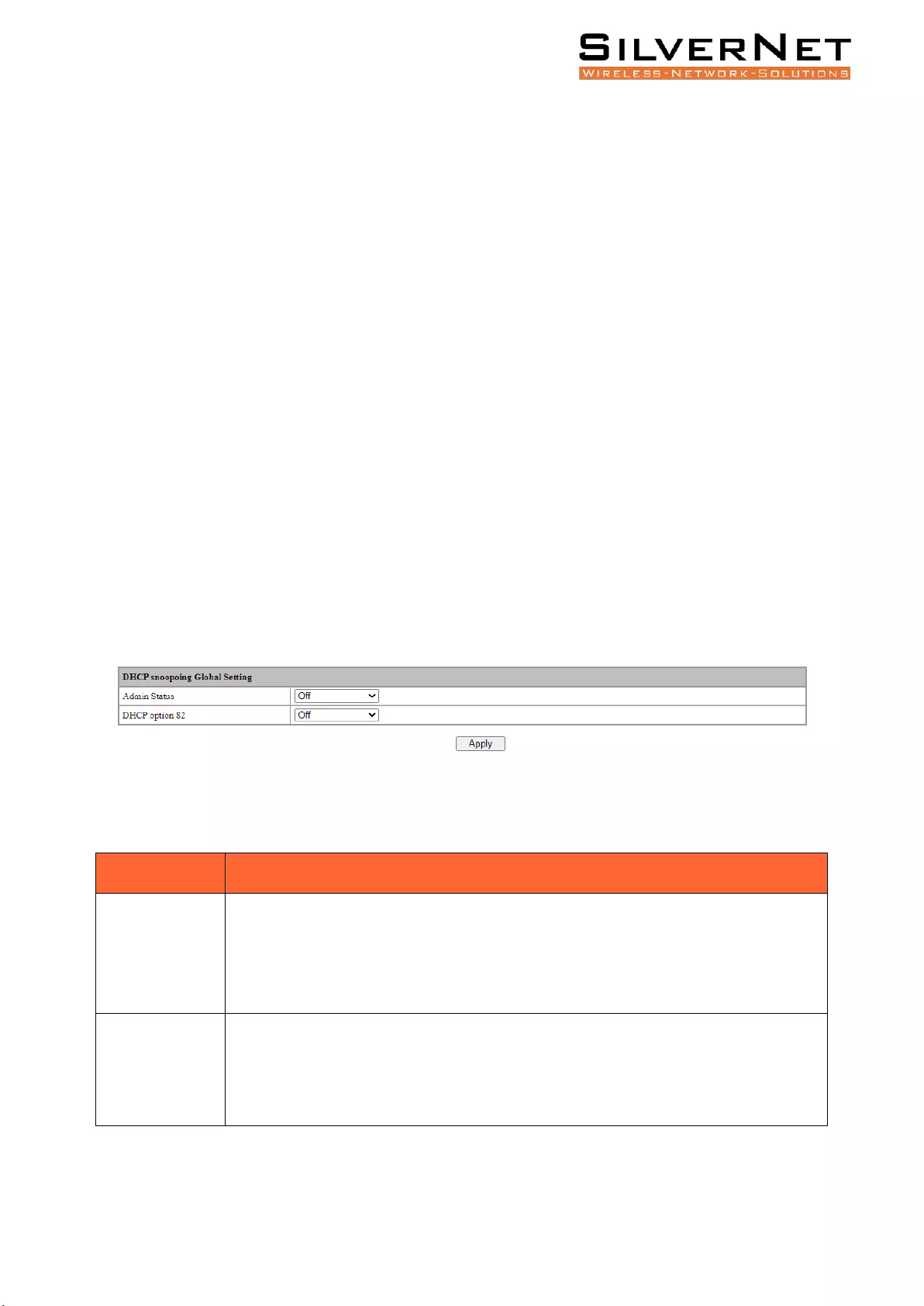
Pro Range User Manual DHCP 76
DHCP
This chapter discusses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol in detail, including the following:
• DHCP Snooping
• DHCP Configuration
• DHCP Information
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on
Internet Protocol (IP) networks, whereby a DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other
network configuration parameters to each device on the network, so they can communicate with
other IP networks. A DHCP server enables computers to request IP addresses and networking
parameters automatically from the Internet service provider (ISP), reducing the need for a network
administrator or a user to manually assign IP addresses to all network devices.
GLOBAL SETTING
Select Advanced / DHCP Snooping / Global Setting in the navigation bar to enter the Global Setting
interface of DHCP snooping.
To modify the global configuration of DHCP snooping in the DHCP snooping global configuration box,
click Apply, as shown in figure 17.1.
Figure 17.1 DHCP Snooping Global Setting
Table 17.1 DHCP Snooping Global Setting Description
Item
Description
Management
Status
DHCP Snooping Global Enable Switch
ON: Enable DHCP snooping function
OFF: Disable DHCP snooping function
DHCP Option 82
DHCP Option 82 is organized as a single DHCP option that contains information
known by the relay agent. This feature provides additional security when DHCP is
used to allocate network addresses, and enables the switch to act as a DHCP relay
agent to prevent DHCP client requests from untrusted sources.
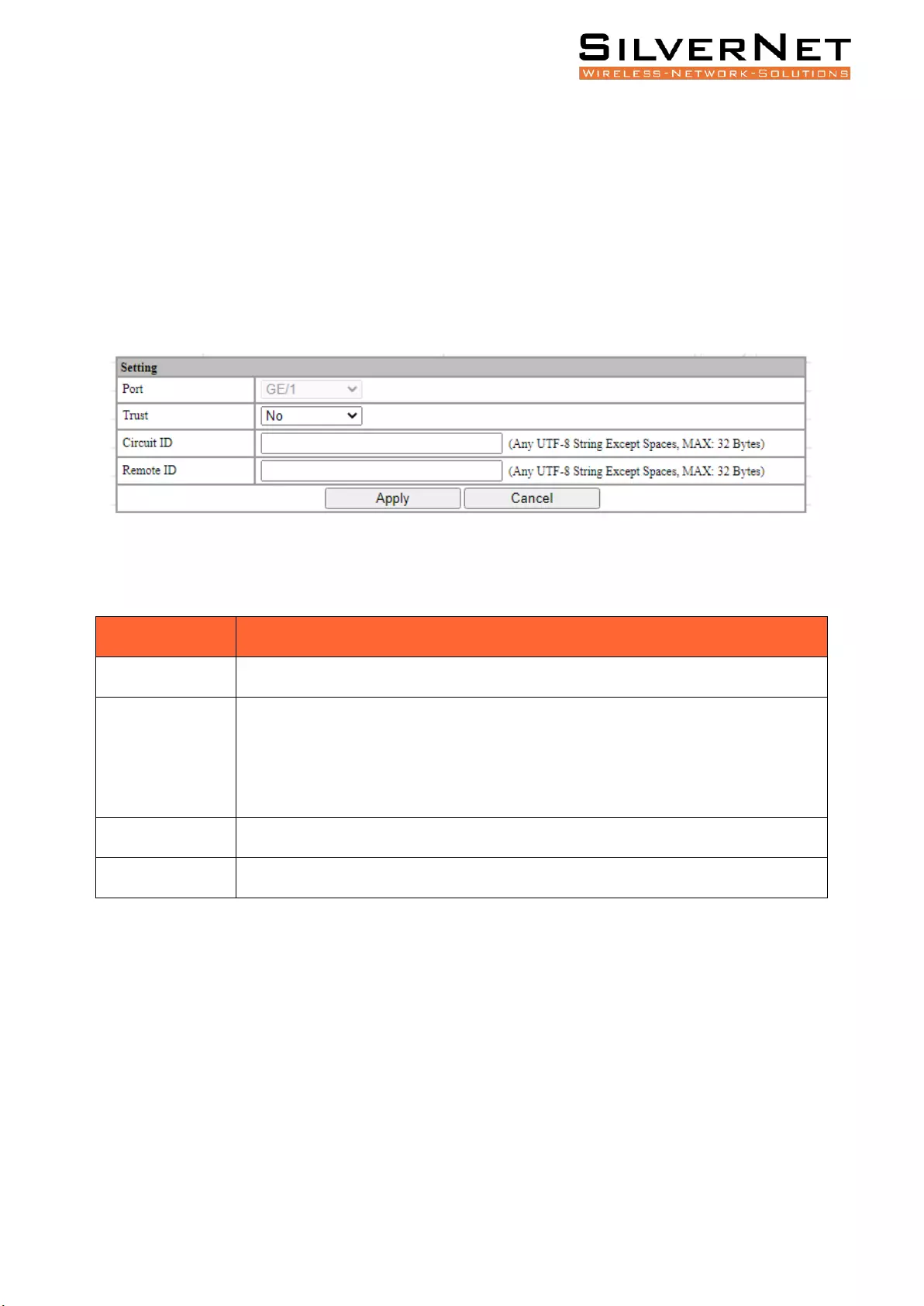
Pro Range User Manual DHCP 77
PORT SETTING
Select Advanced / DHCP Snooping / Port Setting in the navigation bar to enter the DHCP snooping
Port Setting interface.
To modify the DHCP snooping configuration for a port, click the modify to enter the port
configuration interface, as shown in figure 17.2.
Select or fill in the configuration items that need to be modified and click Apply to make effective.
There will be prompts if the configuration items are incorrectly filled.
Figure 17.2 DHCP Snooping Port Setting
Table 17.2 DHCP Snooping Port Setting Description
Item
Description
Port
Currently selected port.
Trust
Port Trust:
YES: Set as trusted port to avoid DHCP Snooping.
NO: Set as non-trusted port.
Circuit ID
Default by global agent circuit ID
Remote ID
Default by global agent remote ID
BINDING TABLE
Select Advanced / DHCP Snooping / Binding Table in the navigation bar to enter the DHCP snooping
Binding Table interface as shown in figure 17.3.
Click Refresh to update all DHCP snooping bind list information

Pro Range User Manual Administration 78
Figure 17.3 DHCP Snooping Binding Table
ADMINISTRATION
This chapter describes Administration in detail, including the following:
• User Management
• Online User
• Login Timeout Setting
USER MANAGEMENT
Select System / Administrator / Administrators in the navigation bar to enter the Administrators
interface.
The current user configuration information can be viewed in the Administrators interface, as shown
in figure 18.1.
To add a new user, click Add to enter the administrator configuration interface, fill in the
corresponding configuration items, click Apply to finish adding the user, and add the user interface
as shown in Figure 18.2.
If need to modify the user information, select the corresponding user firstly, and then click Modify to
enter the user configuration modification interface and modify the corresponding configuration
item. Click Apply to complete the configuration modification and modify the user interface as shown
in Figure 18.3
To delete a user, firstly select the corresponding user and click Delete to delete the user.

Pro Range User Manual Administration 79
Figure 18.1 Administration
Figure 18.2 Add a User
Figure 18.3 Modify User Interface
Pro Range User Manual Administration 80
Table 18.1 Administration Description
Item
Description
Username
Username information.
Password
User password.
Status
User activation status:
Green Tick: Active
Red Cross: Inactive
By default, new users are activated.
Level
User level: Super Administrator, Senior Administrator, Junior Administrator, Guest
User.
Description
User description.
Table 18.2 User Management Description
Item
Description
Username
Username information, valid characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, _, length 1-32 bytes
Password
User login password, any printable ASCII characters, length 1-16 bytes.
Confirm
Password
Re-enter the login password to confirm.
Level
Set the users level, including:
Super Administrator: User has complete control over every aspect of the
managed switch.
Senior Administrator: User has most control over the management, however, user
is unable to remove or supersede the Super Administrator.
Junior Administrator: User has control over some aspects of the management,
cannot supersede the Senior Administrator.
Guest users: User can view management settings but is unable to change
anything.
Status
User activation status, including
On: Active
Off: Inactive
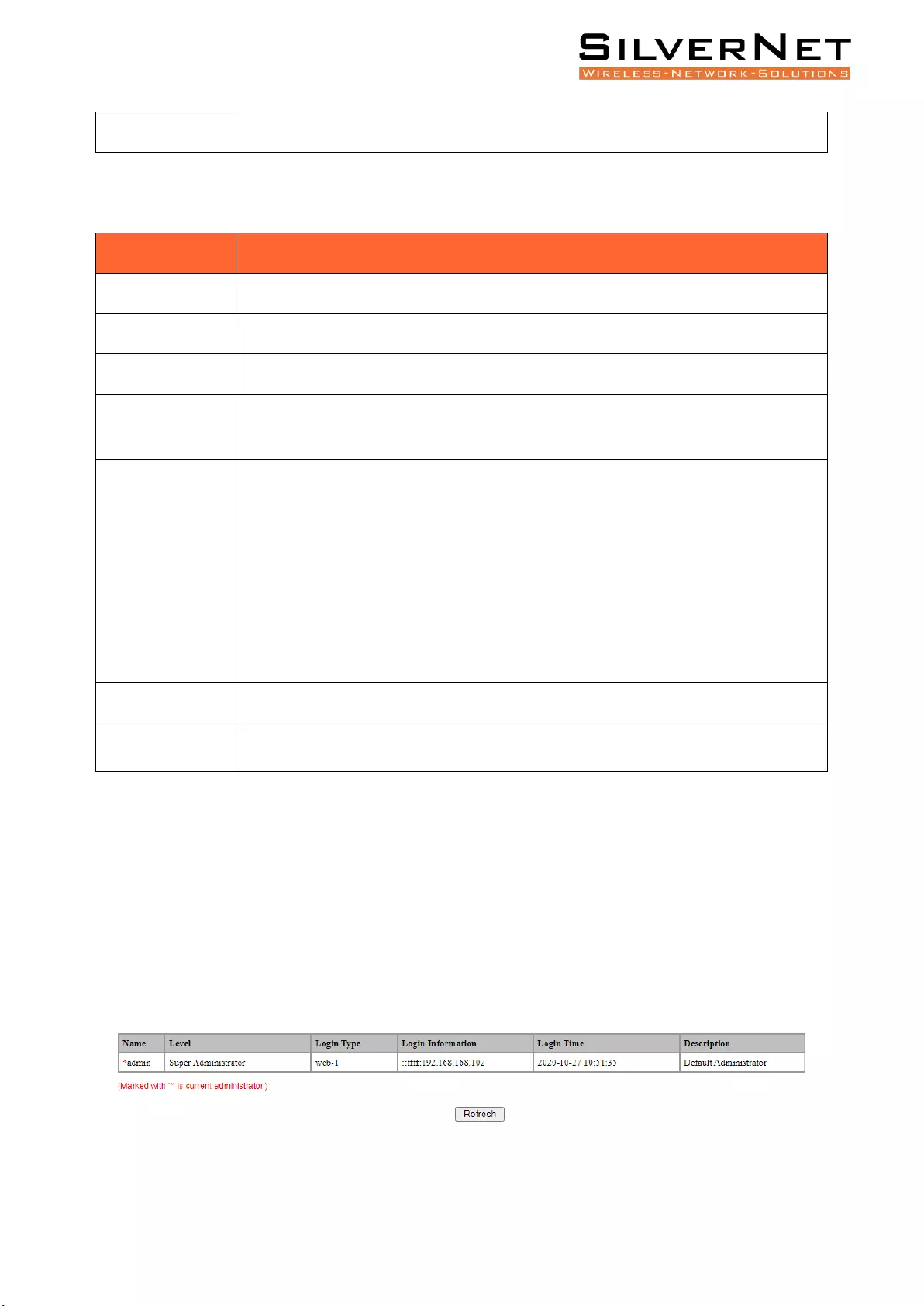
Pro Range User Manual Administration 81
Description
User description information, any printable ASCII character, length 1-128 bytes.
Table 18.3 User Management Description
Item
Description
Username
Username information, valid characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, _, length 1-32 bytes.
Old Password
The password for the user to log in to the web interface.
Password
New password set by the user, any printable ASCII character, length 1-16 bytes.
Confirm
Password
Re-enter the new password set by the user and confirm the password.
Level
Set the users level, (see table 18.2 for detailed descriptions on user levels)
including:
Super administrator
Senior Administrator
Junior Administrator
Guest users
Status
User activation status, including ON and OFF.
Description
User description information, any printable ASCII character, length 1-128 bytes.
The device has a super administrator (username admin) by default and cannot be deleted. The user
level cannot be changed. Extra 15 users can be added in addition to this user.
ONLINE USER
Select System / Administrator / Online Users in the navigation bar to enter the Online Users
interface.
In the interface of Online Users, you can view the user information of the current logged in device
Figure 18.4 Online User Information
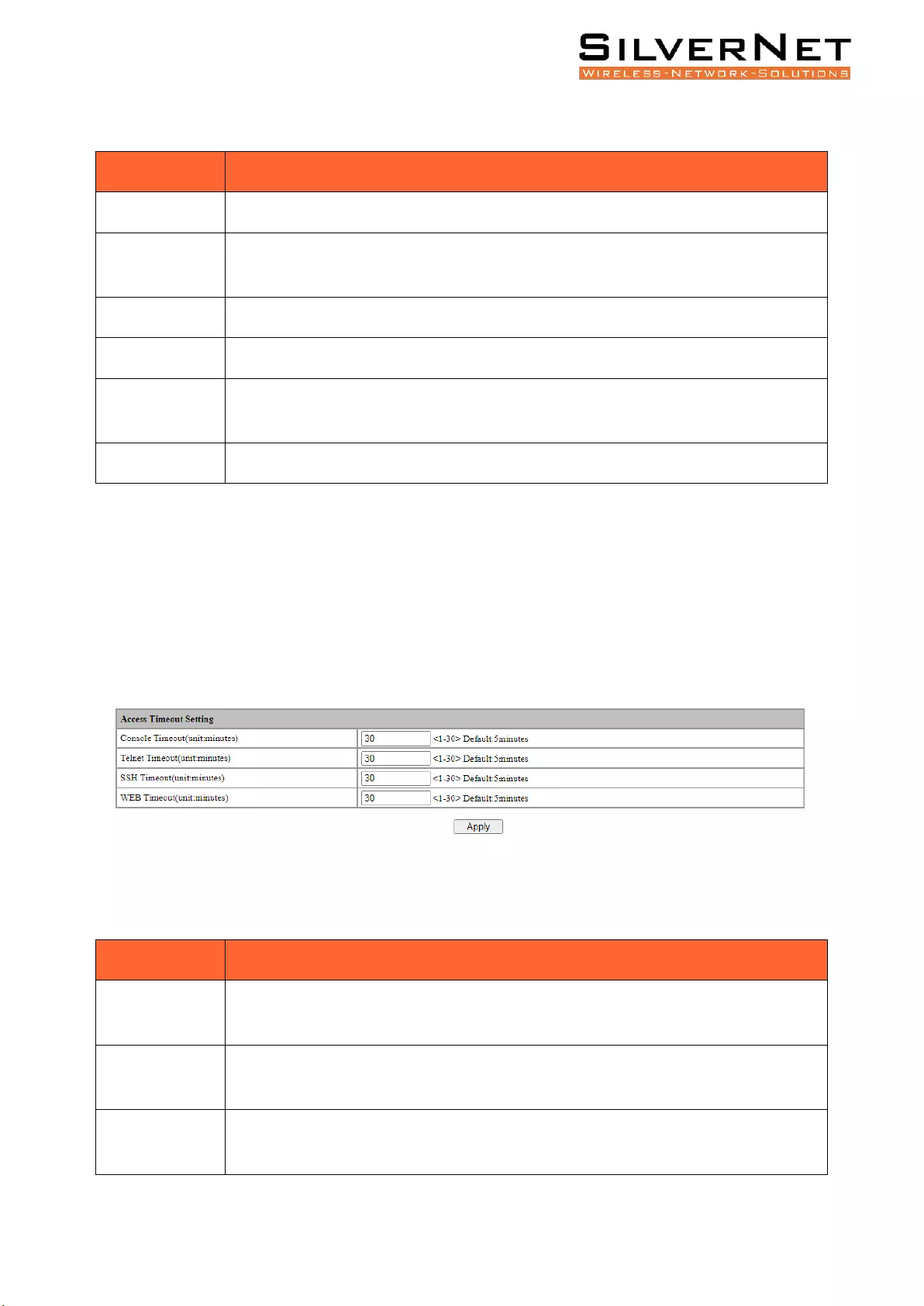
Pro Range User Manual Administration 82
Table 18.4 Online User Description
Item
Description
Username
Username information
Level
User level, including: Super Administrator, Senior Administrator, Junior
Administrator, Guest User.
Description
User description information.
Login Method
Web, console, telnet.
Login IP
Address
The client IP address of user login, except the console mode login.
Login Time
The time that the user logs in to the device.
LOGIN TIMEOUT SETTING
Select System / Administrator / Management Setting in the navigation bar to enter the Login
Timeout Setting interface.
To change the login timeout period, fill in the timeout period of the corresponding login mode and
click Apply to complete the configuration modification, as shown in Figure 18.5.
Figure 18.5 Login Timeout Setting
Table 18.5 Login Timeout Description
Item
Description
Console
Timeout
The login timeout period via console port, range 1 to 30. The default value is 5 and
the unit is in minutes.
Telnet Timeout
The login timeout period via telnet, range 1 to 30. The default value is 5 and the unit
is in minutes.
SSH Timeout
The login timeout period via SSH, range 1 to 30. The default value Is 5 and the unit is
in minutes.
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 83
Web Timeout
The login timeout period via web, range 1 to 30. The default value is 5 and the unit
is in minutes.
The setting can only take effect in next login after setting the timeout period for different login
methods.
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter describes the system configuration in detail, including the following:
• System Log
• Configurations
• Date and Time
• Software Upgrade
• Software Restart
After the device is configured, you need to save the configuration information to the device. The
newly saved configuration information will overwrite the original configuration information. After
the configuration is complete, if you do not perform the save operation, the new configuration will
be lost when the device is restarted, and the original configuration will continue to be executed.
When the device fails, you can try to solve the problem by restarting the device according to the
actual situation. In system configuration, you can manage the configuration of the system, including
erasing the configuration, saving the configuration, and restarting the device. Users can also view
and configure the corresponding system start-up management according to needs.
SYSTEM LOG
Select System / System Log / Setting in the navigation bar to enter the System Log Setting interface as
shown in Figure 19.1.
To modify the system log configuration, set the corresponding configuration in the System Log Settings
box and click Apply to complete the configuration, as shown in Figure 19.1.
To add a remote log server, click Add, fill in the corresponding configuration items in the Remote Log
Server Setting interface and click Apply to complete the configuration. Maximum 4 remote servers can
be added.
To modify the remote log server, first select the corresponding remote log server, and then click Modify
to enter the remote log server setting interface. Modify the corresponding configuration item and click
Apply to complete the configuration modification.
To delete a remote log server, first select the corresponding remote log server and click Delete to delete
the remote log server.
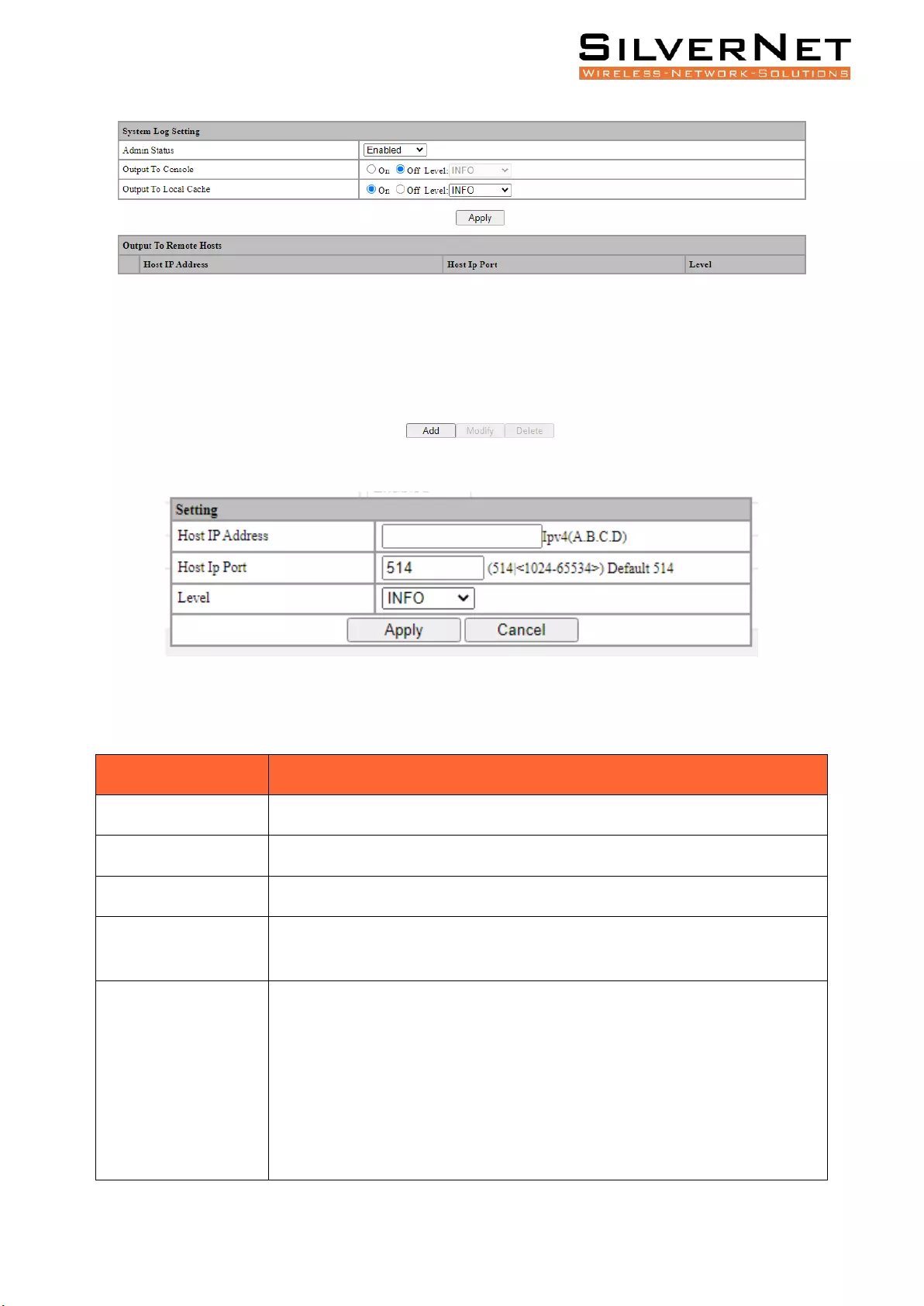
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 84
Figure 19.1 System Log Setting
Figure 19.2 Remote Log Server Setting
Table 19.1 System Log Setting Configuration Description
Item
Description
Admin Status
Turn ON / OFF the System Logging Status.
Output to Console
Turn ON / OFF logging output to the console port.
Output to Local Cache
Turn ON / OFF logging output to the Local Cache.
Output to Remote
Host
System log output to remote log server.
Level
System log level divided into 8 levels according to severity.
EMERG: level 0, system cannot be used.
ALERT : Level 1, need to be processed immediately.
CRIT: Level 2, Severe State.
ERR : Level 3, Error Status.
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 85
WARNING : Level 4, Warning Status.
NOTICE : Level 5, normal but important state.
INFO : Level 6, Notification Event.
DEBUG : Level 7, debugging information.
Table 19.2 Remote Log Server Description
Item
Description
Host IP address
Remote log host IP address, in dotted decimal format, valid host IP address, up to 4
groups.
Host IP port
Remote log host port, range 514, 1024-65534, default is 514.
Level
System log level, divided into 8 levels according to severity
EMERG: level 0, system cannot be used
ALERT : Level 1, need to be processed immediately
CRIT: Level 2, severe status
ERR : Level 3, error Status
WARNING : Level 4, warning status
NOTICE : Level 5, normal but important status
INFO : Level 6, notification event
DEBUG : Level 7, debugging information
The smaller the log level value, the higher the level. Only logs with a level equal to or greater than
the set level will be output. For example, if you set the logging level to the console to 5 (NOTICE),
only logs with level 0 to 5 will be output to the console.
VIEW LOGS
Select System / System Log / View in the navigation bar to enter the system log View interface as
shown in Figure 19.3.

Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 86
Figure 19.3 System Log View
Table 19.3 System Log View Description
Item
Description
Refresh
Refresh the system log content.
Ordinal
Display in chronological order.
Reversed
New to old display in chronological order.
Export
Export the contents of the system log
Clear
Clear the contents of the system log.
CONFIGURATIONS
Select System / Configurations / View in the navigation bar to enter the View interface.
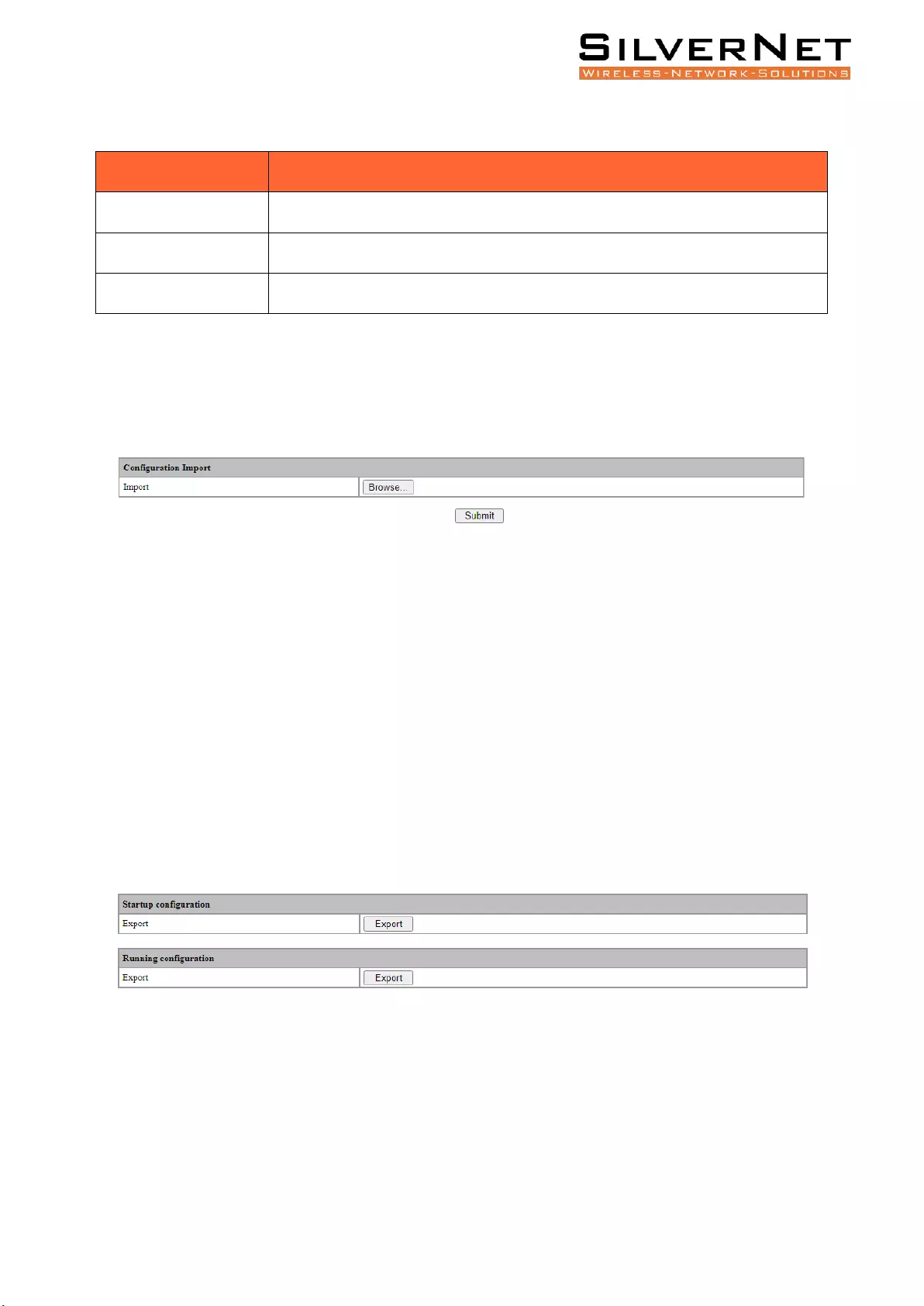
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 87
Table 19.4 Configurations View Description
Item
Description
Running Configuration
View system running configuration file, text style
Startup Configuration
Check the system startup configuration file, text style.
Reload
Reload the running or startup configuration file.
IMPORT CONFIGURATION
Select System / Configurations / Import in the navigation bar to enter the Import interface of
Configurations, as shown in Figure 19.4.
Figure 19.4 Configurations Import
In the Configurations Import interface, click Browse, select the configuration file to import, and click
Submit to start the import.
EXPORT CONFIGURATION
Select System / Configurations / Export in the navigation bar to enter the Configurations Export
interface, as shown in Figure 19.5.
Export configuration is divided into startup configuration and running configuration. Click Export in
the corresponding project to prompt up the "File Save" dialog box (different browsers may differ,
here take the IE11 browser as an example), click Save to export the corresponding configuration file
to the local.
Figure 19.5 Export Configuration
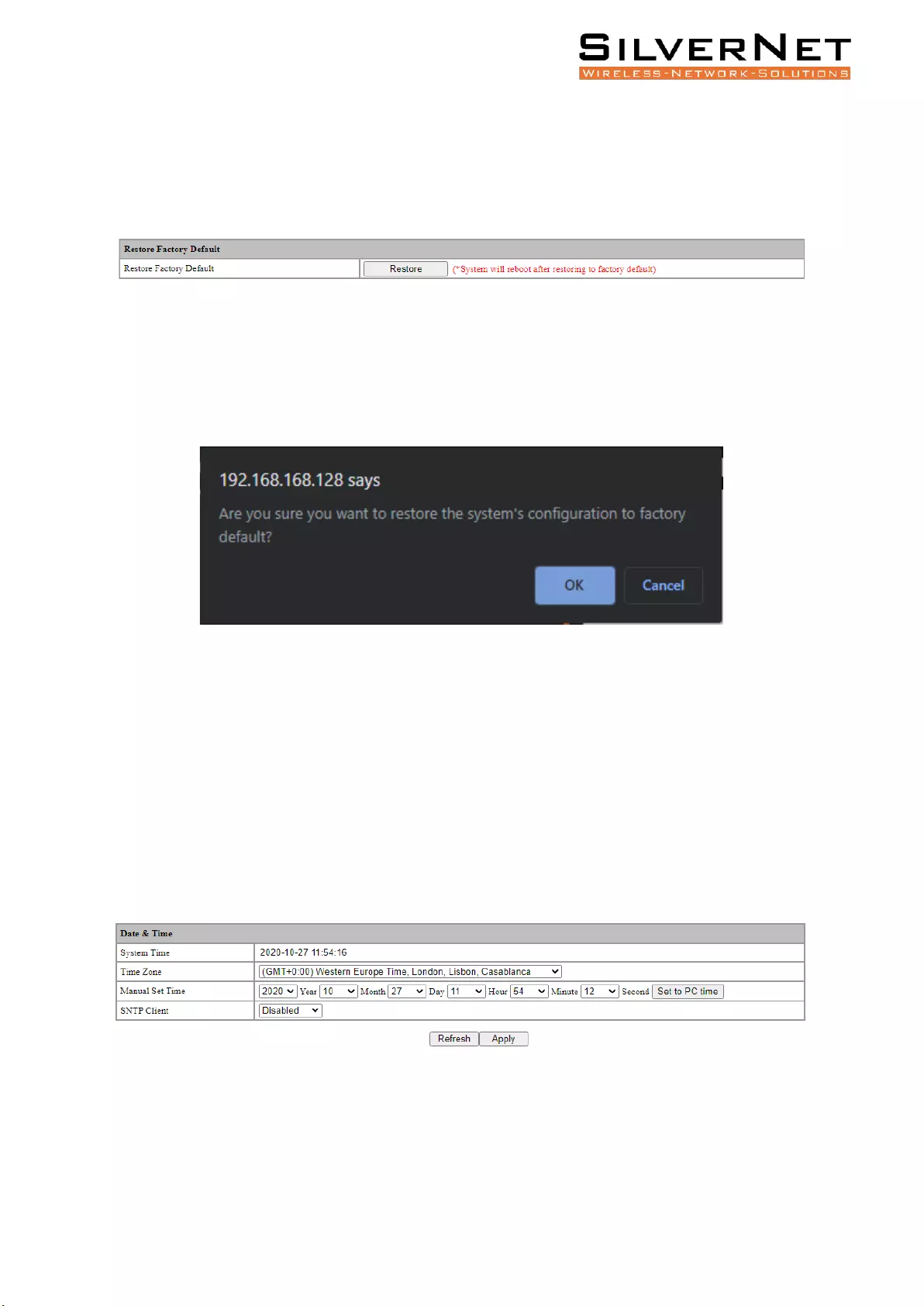
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 88
RESTORE FACTORY CONFIGURATION
Select System / Configurations / Restore Factory Default in the navigation bar to enter the Restore
Factory Default interface, as shown in Figure 19.6.
Figure 19.6 Restore Factory Setting
Click Restore and then click OK in the confirmation dialog box to restore the factory configuration.
Click Cancel to cancel the factory configuration restoration. After a successful factory reset, the
system automatically restarts to take effect to the factory configuration, as shown in Figure 19.7.
Figure 19.7 Restore Factory Configuration Confirmation Dialog Box
DATE AND TIME
Select System / Date and Time in the navigation bar to enter the system setting Date and Time
interface. The system time can be manually set, or automatically synchronized through the SNTP
client.
To set the system time manually, the SNTP client must be disabled. Select the corresponding time
zone in the Time Zone column and set the system time in the Time Setting column. Click Apply to
complete the system time setting, as shown in Figure 19.8.
Figure 19.8 System Time Setting by Manual
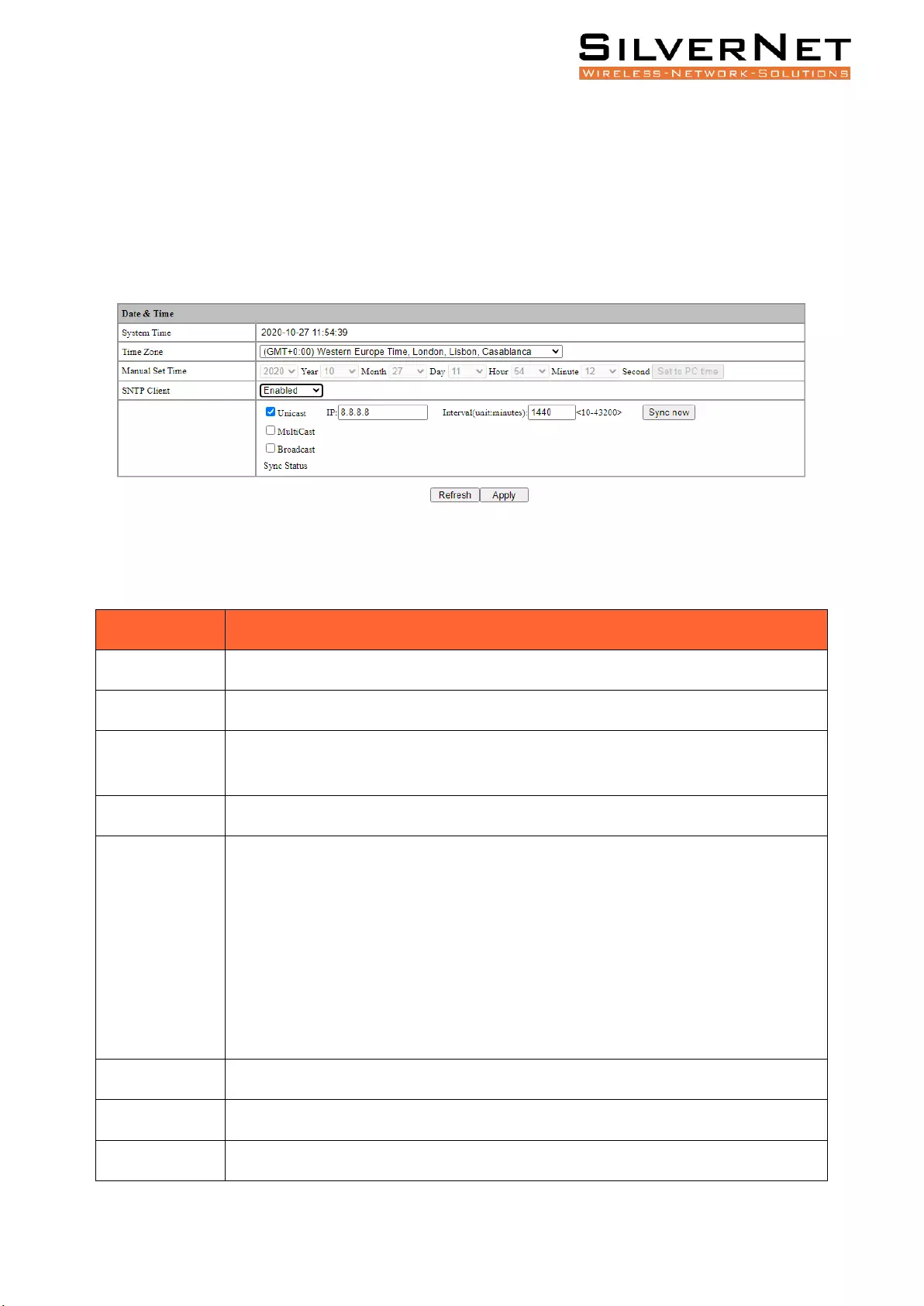
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 89
Synchronize system time automatically via SNTP client. The SNTP client time synchronization mode is
divided into unicast, multicast, and broadcast. These three modes can be selected, but at least one
mode must be selected. When the unicast mode is selected, the IP address of the time server
(8.8.8.8 by default) and the synchronization interval (1440 minutes by default) must also be set. Sync
Now button means SNTP client requests time synchronization immediately, otherwise it will be
synchronized once at the set synchronization interval. Click Apply to complete the SNTP client time
synchronization setting, as shown in Figure 19.9.
Figure 19.9 SNTP client setting interface
Table 19.5 Date and Time Description
Item
Description
System Time
Displays the actual effective system time.
Time Zone
System time zone setting, select any time zone from the drop-down list.
Time Setting
It can be set after the SNTP client is disabled. The year range is 1970-2037. Others
are the same as the common settings.
SNTP Client
Turn ON / OFF the SNTP Client function.
Synchronous
Mode
The SNTP client synchronization mode is divided into:
Unicast Mode: default IP address 8.8.8.8; interval range 10-43200, and default
value 1440.
Multicast Mode:
Broadcast Mode:
These three modes are multi-selectable, but at least one must be selected.
IP
IP address of SNTP server, only for unicast mode.
Interval
SNTP client time synchronization interval, only for unicast mode.
Synchronize
SNTP client immediate synchronizes time, only for unicast mode.
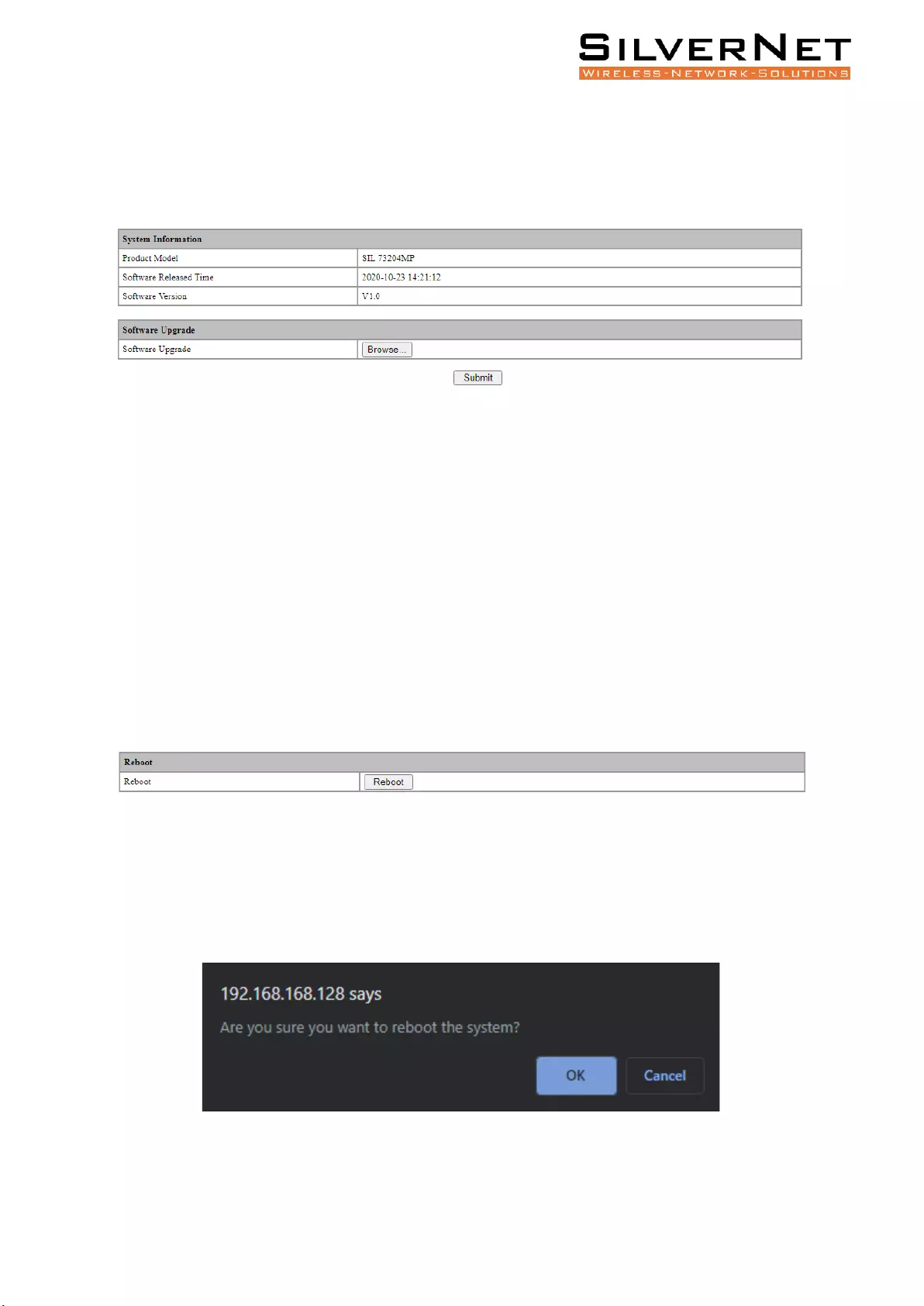
Pro Range User Manual System Configuration 90
SOFTWARE UPGRADE
Select System / Software Upgrade in the navigation bar to enter the Software Upgrade interface, as
shown in Figure 19.10.
Figure 19.10 Software Upgrade
On the Software Upgrade interface, click Browse to select the upgrade file to be imported. (The
upgrade files are generally of the form .ub and .urk. Marked with "b" for BOOT files and "r" for "File
System". The file is marked with k for the file with the kernel. Click Submit. The system starts
uploading the upgrade file. After the upload is complete, the device automatically restarts to update
the software after the upgrade is complete.
Note: During the software upgrade, make sure that the device is powered up until the upgrade is
completed.
SOFTWARE RESTART
Select System / Reboot in the navigation bar to enter the Reboot interface, as shown in Figure 19.11.
Figure 19.11 Restart
Click Reboot and the Confirm Restart dialog box will pop up. Click OK to restart the device. A restart
progress bar is displayed. Click Cancel to cancel the restart of the device. The restart confirmation is
shown in Figure 19.12, and the restart progress is shown in Figure 19.13.
Figure 19.12 Restart Confirmation

Pro Range User Manual Accessories 91
Figure 19.13 Restart Progress
ACCESSORIES
1Gbps Fibre transmission
Part Code
Description
SIL-SFP0-01-25-X850-0-5D
1G Multimode 850nm SFP, 550m
SIL-SFP0-01-25-X131-10XD
1G Singlemode 1310nm SFP, 10km
SIL-SFP0-01-25-X131-40XD
1G Singlemode 1310nm SFP, 40km
SIL-SFP0-01-25-X155-80XD
1G Singlemode 1550nm SFP, 80km
1Gbps BiDi
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B131-10XD
1G SM 1310nm TX FP 10km with DDM, 1550nm RX
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B155-10XD
1G SM 1550nm TX FP 10km with DDM, 1310nm RX
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B139-10XD
1G SM 1310nm TX FP 10km with DDM, 1490nm RX
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B149-10XD
1G SM 1490nm TX FP 10km with DDM, 1310nm RX
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B131-40XD
1G SM 1310nm TX DFB 40km with DDM, 1550nm RX
SIL-SFP0-01-25-B155-40XD
1G SM 1550nm TX DFB 40km with DDM, 1310nm RX
SFP to Ethernet
SIL-SFP0-01-25-XXXT-0-1
1G RJ45 Copper SFP, 100m
Power supplies
Part Code
Description
SIL NDR-120-48 (48V 2.5A)
120W 48V 2.5A Industrial Din Rail Power Supply
SIL NDR-240-48 (48V 5A)
240W 48V 5A Industrial Din Rail Power Supply
SIL NDR-480-48 (48V 10A)
480W 48V 10A Industrial Din Rail Power Supply
Pro Range User Manual Technical parameters 92
TECHNICAL PARAMETERS
Power supply
Input voltage: 12V~56V (redundant dual power)
PSE Power: 0~30W
POE Pin: 1/2+,3/6-
Copper Port
Connector: RJ-45 connector
Data Rate: 10/100MbpsAuto, 10/100/1000Mbps Auto
Twisted Pair cable: Cat5 UTP cable
Transmission distance: 100 metres
Fibre Port
Connector: SC (default), FC/ST/SFP (optional)
Data Rate: 155Mbps,1.25Gbps
Fibre Type: SM 9/125μm,MM 50/125μm、62.5/125μm
Transmission distance: 20km ~ 120km
Environment
Storage temperature: -40~85℃
Operating temperature: -40~75℃
Relative humidity: 5%-90%
Mechanism
Enclosure: IP40, Black, Metal shell
Mounting: DIN-rail, Wall
Agreement
IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3z, IEEE 802.3x
IEEE 802.3af, IEEE 802.3at
Pro Range User Manual Standards 93
STANDARDS
EMI FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A
EN61000-4-2(ESD)
EN61000-4-3(RS)
EN61000-4-4(EFT)
EN61000-4-5(Surge)
EN61000-4-6(CS)
EN61000-4-8
EN61000-4-11
IEC60068-2-27
IEC60068-2-32
IEC60068-2-6
EN60950-1
WARNINGS
This product is only suitable for indoor applications.
Ensure that the dust caps are placed over the Fibre interface connectors when not in use.
Do not stare directly into the fibre transmitter as this is very dangerous and can cause serious
damage to your eyes.
Optical fibre transceivers must be used in pairs.
Single optical fibre transceivers must be used in pairs (A, B)
A: TX1310/RX1550nm B: TX1550/RX1310nm.
Pro Range User Manual Troubleshooting 94
TROUBLESHOOTING
If you have no connection then please check that the corresponding network devices are using the
same transfer rate as the Ethernet Switch (10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps).
If you have excessive power loss in the fibre, please check and clean the fibre connectors and ports.
RESPONSIBILITY NOTE
1. SilverNet Ltd will repair or replace any product that fails within the terms of the limited
warranty in effect at the time of purchase.
2. If the product has been purchased via one of our distribution partners, it should be
returned to the place of purchase as their terms may differ from ours.
3. If you use a Power Supply that is not provided by SilverNet and the device is damaged, then
this is not covered under the product warranty.
4. Please follow this manual when using our power supply.
5. We will not cover any damage to our equipment or persons that is caused by any changes
to this equipment without prior authorisation from us.
6. We will replace any defective equipment which fails within the warranty period.
WARRANTY
The Series 7 industrial gigabit PoE+ managed switches come with a 5-year warranty as standard. For
full terms and conditions of warranty please go to www.silvernet.com/terms-and-conditions/
CONTACT SILVERNET
Email us at support@silvernet.com
Call our support team on 08712233067
www.silvernet.com
COPYRIGHT INFORMATION
Copyright ©2019 all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, adapted, stored
in a retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any means
without the written permission of the supplier.

Pro Range User Manual Other SilverNet Products 95
OTHER SILVERNET PRODUCTS
Pro Range
Industrial Network Transmission
Intelligent Wi-Fi Solutions
Industry Leading Technical Support