Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- Get to Know About Your Router
- Connect the Hardware
- Log in to Your Router
- Set Up Internet Connection
- Guest Network
- USB Application
- Parental Controls
- QoS
- Network Security
- NAT Forwarding
- VPN Server
- Customize Your Network Settings
- 12. 1. Change the LAN Settings
- 12. 2. Set Up Link Aggregation
- 12. 3. Configure to Support IPTV Service
- 12. 4. Specify DHCP Server Settings
- 12. 5. Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account
- 12. 6. Create Static Routes
- 12. 7. Specify Wireless Settings
- 12. 8. Use WPS for Wireless Connection
- 12. 9. Schedule Your Wireless Function
- Manage the Router
- 13. 1. Set Up System Time
- 13. 2. Test the Network Connectivity
- 13. 3. Upgrade the Firmware
- 13. 4. Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
- 13. 5. Change the Administrator Account
- 13. 6. Password Recovery
- 13. 7. Local Management
- 13. 8. Remote Management
- 13. 9. System Log
- 13. 10. Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
- 13. 11. Control LEDs
- FAQ
TP-Link Archer C5400 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for Archer C5400 by TP-Link which is a product in the Wireless Routers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

REV2.0.0 1910011896
Archer C5400
User Guide
AC5400 Wireless Tri-Band MU-MIMO Gigabit Router

Contents
About This Guide ...............................................................................................1
Chapter 1. Get to Know About Your Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1. 1. Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1. 2. Appearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1. 2. 1. The Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1. 2. 2. The Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Chapter 2. Connect the Hardware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2. 1. Position Your Router. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2. 2. Connect Your Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 3. Log in to Your Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 4. Set Up Internet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4. 1. Use Quick Setup Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4. 2. Manually Set up Your Internet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4. 3. Set Up an IPv6 Internet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Chapter 5. Guest Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5. 1. Create a Network for Guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5. 2. Set Portal Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5. 3. Customize Guest Network Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 6. USB Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6. 1. Local Storage Sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6. 1. 1. Access the USB disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6. 1. 2. Customize Your Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6. 2. Remote Access via FTP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6. 2. 1. Access the USB Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6. 2. 2. Customize Your Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
6. 3. Media Sharing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6. 3. 1. Access the USB Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37

6. 3. 2. Customize Your Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6. 4. Printer Sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Chapter 7. Parental Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Chapter 8. QoS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8. 1. Prioritize Internet Traffic with QoS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8. 2. Update the Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chapter 9. Network Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
9. 1. Protect the Network from Cyber Attacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
9. 2. Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
9. 3. IP & MAC Binding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Chapter 10. NAT Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10. 1. Share Local Resources on the Internet by Virtual Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
10. 2. Open Ports Dynamically by Port Triggering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
10. 3. Make Applications Free from Port Restriction by DMZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
10. 4. Make Xbox Online Games Run Smoothly by UPnP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Chapter 11. VPN Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
11. 1. Use OpenVPN to Access Your Home Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Step1. Set up OpenVPN Server on Your Router. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Step 2. Configure OpenVPN Connection on Your Remote Device . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
11. 2. Use PPTP VPN to Access Your Home Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Step 1. Set up PPTP VPN Server on Your Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Step 2. Configure PPTP VPN Connection on Your Remote Device . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Chapter 12. Customize Your Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
12. 1. Change the LAN Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12. 2. Set Up Link Aggregation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12. 3. Configure to Support IPTV Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
12. 4. Specify DHCP Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
12. 5. Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
12. 6. Create Static Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
12. 7. Specify Wireless Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
12. 8. Use WPS for Wireless Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80

12. 8. 1. Set the Router’s PIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
12. 8. 2. Use the WPS Wizard for Wi-Fi Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
12. 9. Schedule Your Wireless Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Chapter 13. Manage the Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
13. 1. Set Up System Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
13. 2. Test the Network Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
13. 3. Upgrade the Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
13. 3. 1. Online Upgrade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
13. 3. 2. Manual Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
13. 3. 3. Restore Interrupted Upgrade after Power Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
13. 4. Backup and Restore Configuration Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
13. 5. Change the Administrator Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
13. 6. Password Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
13. 7. Local Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
13. 8. Remote Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
13. 9. System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
13. 10. Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
13. 11. Control LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
FAQ .....................................................................................................................98
1
About This Guide
This guide is a complementation of Quick Installation Guide. The Quick Installation
Guide instructs you on quick Internet setup, and this guide provides details of each
function and shows you the way to configure these functions appropriate to your
needs.
When using this guide, please notice that features of the router may vary slightly
depending on the model and software version you have, and on your location, language,
and Internet service provider. All screenshots, images, parameters and descriptions
documented in this guide are used for demonstration only.
Conventions
In this guide the following conventions are used:
Convention Description
Blue Italic Hyperlinks are in blue italic. You can click to redirect to a website or a specific section.
Blue Contents to be emphasized and texts on the web page are in blue, including the
menus, items, buttons, etc.
>
The menu structures to show the path to load the corresponding page. For example,
Advanced > Wireless > MAC Filtering means the MAC Filtering function page is under
the Wireless menu that is located in the Advanced tab.
Note: Ignoring this type of note might result in a malfunction or damage to the device.
Tips: Indicates important information that helps you make better use of your device.
symbols on the web
page
• click to edit the corresponding entry.
• click to delete the corresponding entry.
• click to enable or disable the corresponding entry.
• click to view more information about items on the page.
More Info
The latest software, management app and utility can be found at Download Center at
www.tp-link.com/support.
The Quick Installation Guide can be found where you find this guide or inside the
package of the router.
Specifications can be found on the product page at http://www.tp-link.com.
A Technical Support Forum is provided for you to discuss our products at
http://forum.tp-link.com.
Our Technical Support contact information can be found at the Contact Technical
Support page at www.tp-link.com/support.
3
Chapter 1 Get to Know About Your Router
1. 1. Product Overview
The TP-LINK router is designed to fully meet the need of Small Office/Home Office
(SOHO) networks and users demanding higher networking performance. The powerful
antennas ensure continuous Wi-Fi signal to all your devices while boosting widespread
coverage throughout your home, and the built-in Ethernet ports supply high-speed
connection to your wired devices.
Moreover, it is simple and convenient to set up and use the TP-LINK router due to its
intuitive web interface and the powerful Tether app.
1. 2. Appearance
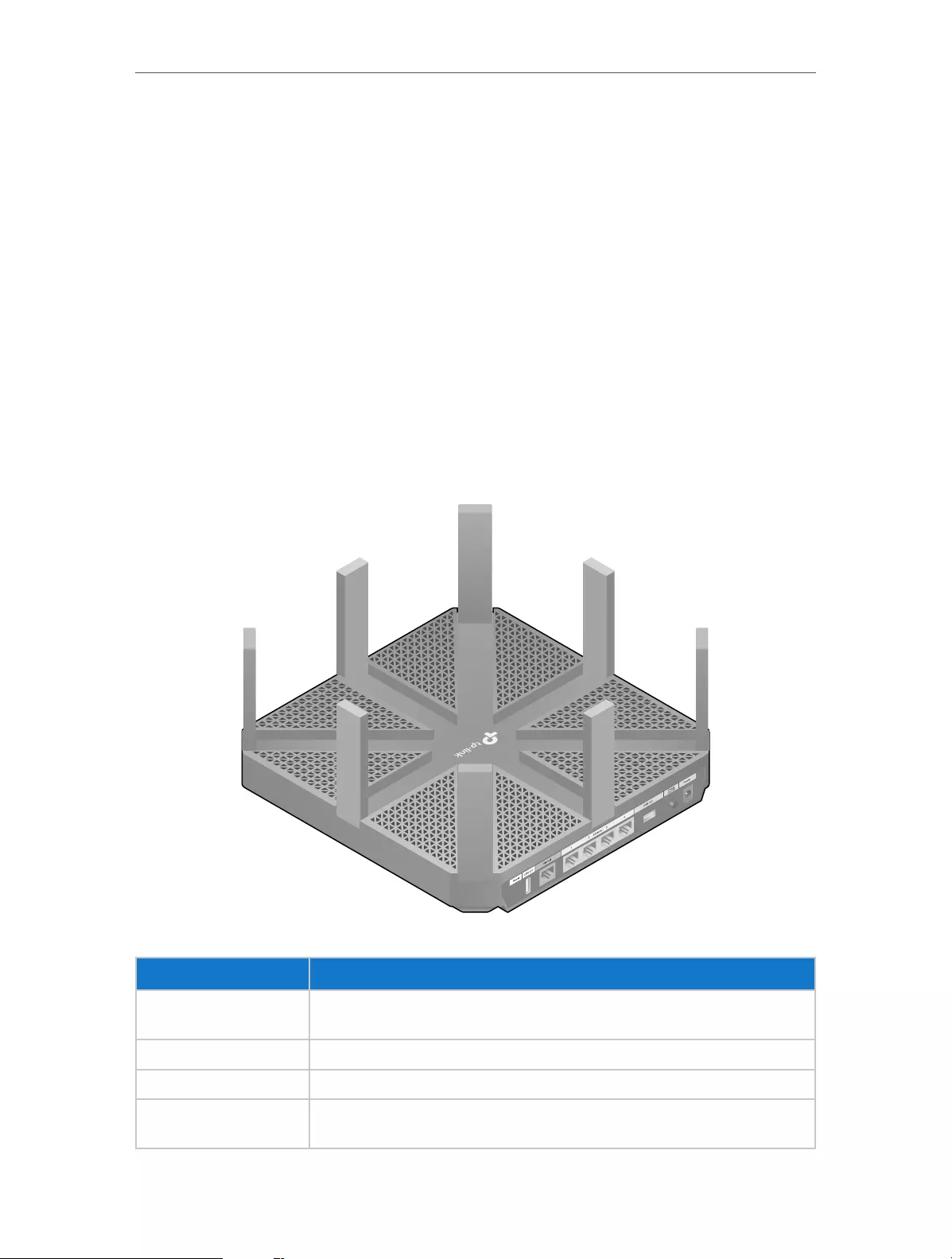
1. 2. 1. The Back Panel
The router’s ports (view from left to right) are located on the rear panel.
Item Description
Reset Button Press this button for more than 5 seconds to reset the router to its factory default
settings.
USB 2.0 Port For connecting to a 2.0 USB storage device or a 2.0 USB printer.
Internet Port For connecting to the DSL/Cable modem, or an Ethernet.
Ethernet Ports (1/2/3/4) For connecting the router to the Ethernet network devices, such as PCs, smart TVs
and game consoles.

4
Chapter 1 Get to Know About Your Router
Item Description
USB 3.0 Port For connecting to a 3.0 USB storage device or a 3.0 USB printer. It is also compatible
with USB 2.0 devices.
Power On/Off Button Press this button to power on or off the router.
Power Port For connecting the router to power socket via the provided power adapter.
Antennas Used for wireless operation and data transmit. Upright them for the best Wi-Fi
performance.
1. 2. 2. The Front Panel
The router’s LEDs and buttons (view from left to right) are located on the front panel.
You can check the router’s working status by following the LED Explanation table.
LED Explanation
Name Status Indication
(Power)
On System initialization completes.
Flashing System initialization or firmware upgrade is in progress. Do not
disconnect or power off the router.
Off Power is off.
(2.4GHz Wireless)
On The 2.4GHz wireless band is working properly.
Off The 2.4GHz wireless band is disabled.
(5GHz-1 Wireless)
On The 5GHz-1 wireless band is working properly.
Off The 5GHz-1 wireless band is disabled.
(5GHz-2 Wireless)
On The 5GHz-2 wireless band is working properly.
Off The 5GHz-2 wireless band is disabled.
(Ethernet)
On At least one Ethernet port is connected.
Off No Ethernet port is connected.
(Internet)
Blue On The Internet is available.
Orange On The router’s Internet port is connected, but the Internet is not available.
Off The router’s Internet port is unplugged.
5
Chapter 1 Get to Know About Your Router
Name Status Indication
(WPS)
On/Off Turns on when WPS connection is established, and goes off about 5
minutes later.
Flashing A wireless device is trying to connect to the network via WPS. This
process may take up to 2 minutes.
(USB)
On The USB device is identified and ready to use.
Flashing The USB device is being identified.
Off No USB device is plugged into the USB port or the USB device is not
identified or USB device has been safely ejected.
Button Explanation
Item Description
(WiFi Button) Press the WiFi button for about 2 seconds to turn on or off the wireless function of
your router.
(WPS Button)
Press this WPS button, and immediately press the WPS button on your device.
The WPS LED of the router should change from flashing to solid on, indicating
successful WPS connection.
(LED Button) Press the LED button for about 1 second to turn on or off the LEDs of your router.
7
Chapter 2 Connect the Hardware
2. 1. Position Your Router
• The product should not be located in a place where it will be exposed to moisture or
excessive heat.
• Place the router in a location where it can be connected to multiple devices as well as
to a power source.
• Make sure the cables and power cord are safely placed out of the way so they do not
create a tripping hazard.
• The router can be placed on a shelf or desktop.
• Keep the router away from devices with strong electromagnetic reference, such as
Bluetooth devices, cordless phones and microwaves.
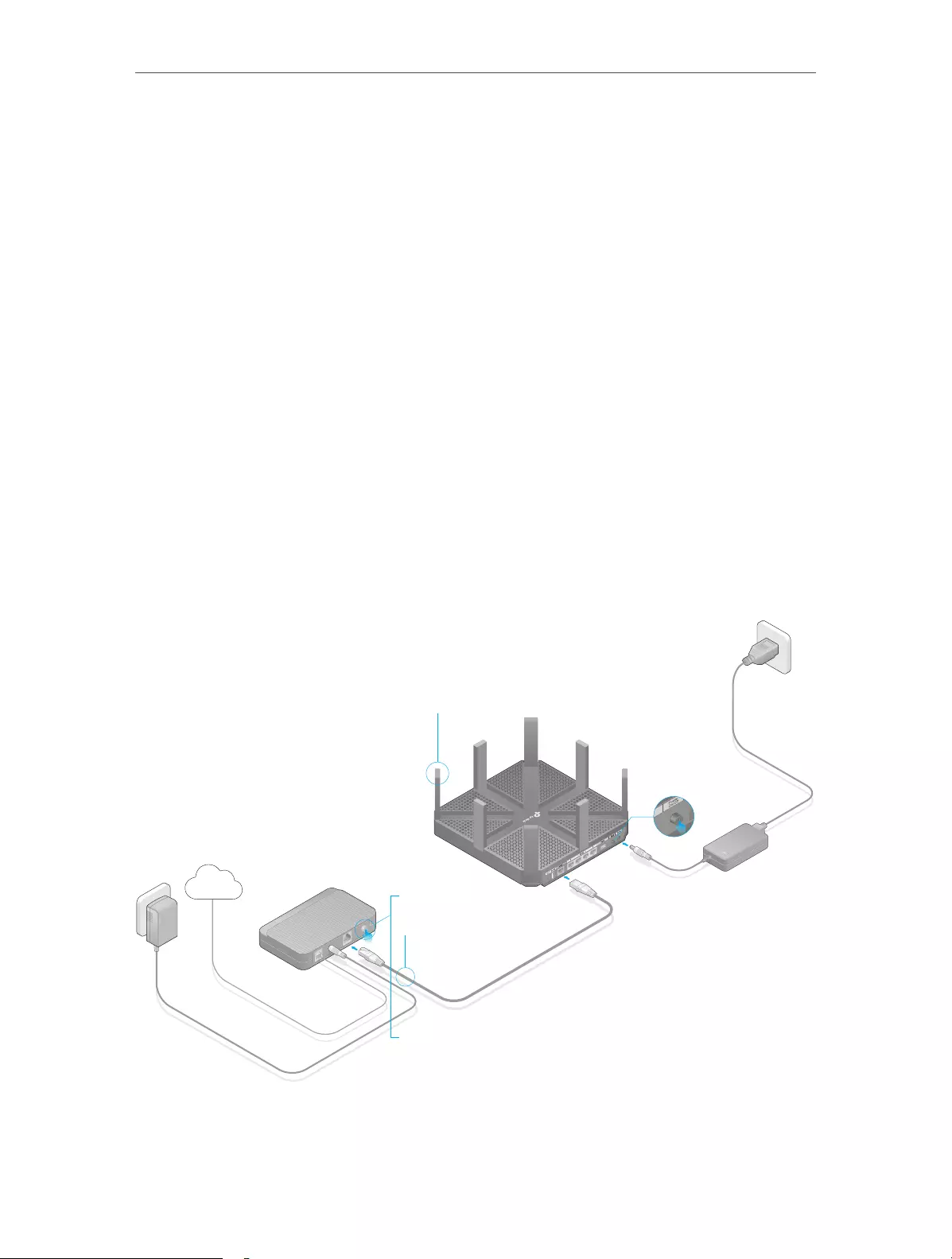
2. 2. Connect Your Router
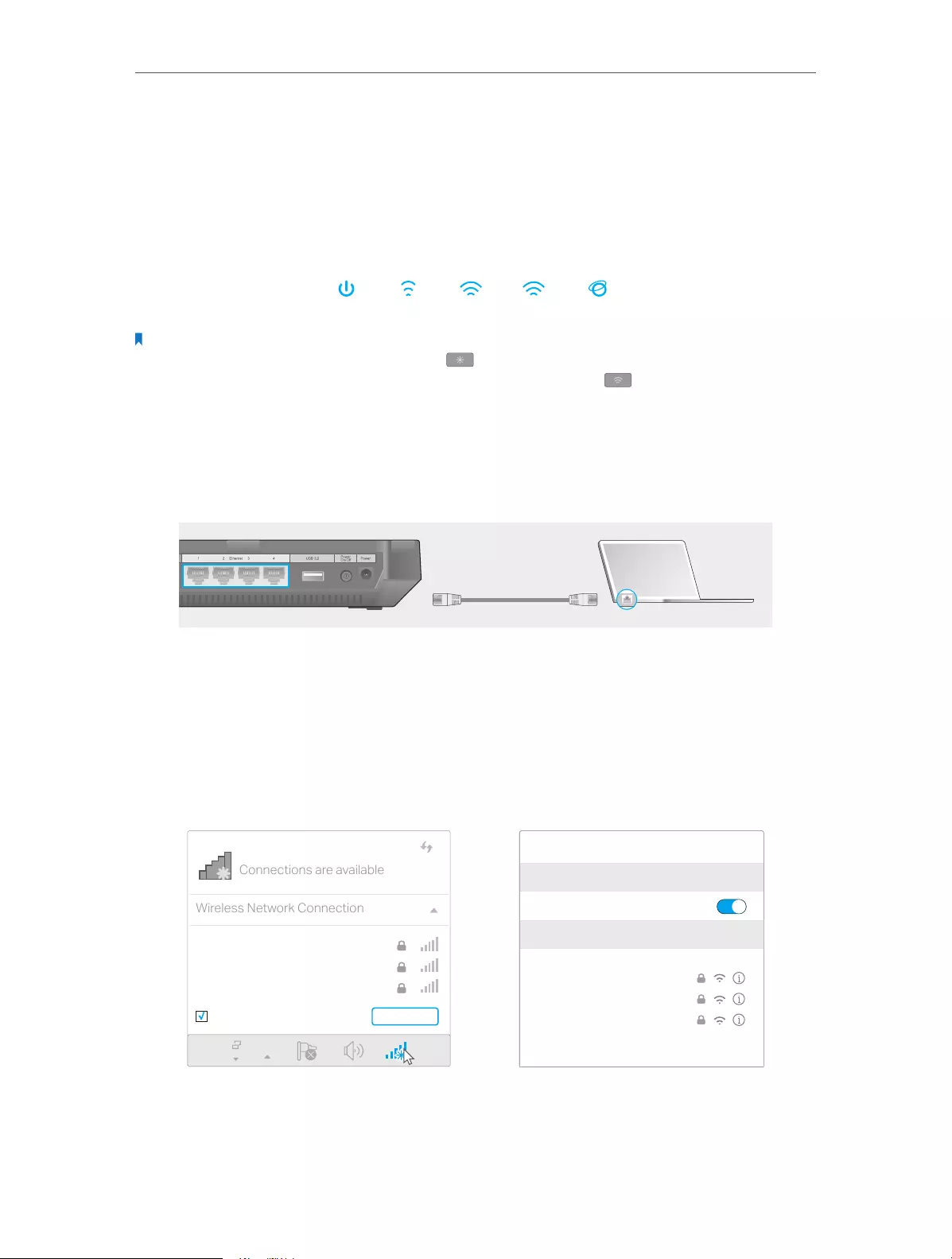
Follow the steps below to connect your router.
If your Internet connection is through an Ethernet cable from the wall instead of through
a DSL / Cable / Satellite modem, connect the Ethernet cable directly to the router’s
Internet port, and then follow Step 1, 5 and 6 to complete the hardware connection.
Router
5
Power adapter
Modem
Power adapter
2
3
4
1
Internet
1. Install the antennas.
2. Turn off the modem, and remove the backup battery if it has one.
8
Chapter 2 Connect the Hardware
3. Connect the modem to your router’s Internet port with an Ethernet cable.
4. Turn on the modem, and then wait about 2 minutes for it to restart.
5. Connect the power adapter to the router and turn on the router.
6. Confirm that the following LEDs are on and solid to verify the hardware is connected
correctly.
On
Internet
5GHz-1
On
5GHz-2
On
Power
On
2.4GHz
On
Note:
• If all the LEDs are off, press the LED On/Off button for about 1 second, and then check the LEDs again.
• If the 2.4GHz, 5GHz-1, and 5GHz-2 LEDs are off, press the Wi-Fi On/Off button for about 2 seconds and all the
three LEDs should turn solid on in a few seconds.
7. Connect your computer to the router.
• Method 1: Wired
Turn off the Wi-Fi on your computer and connect the devices as shown below.
Ethernet cable
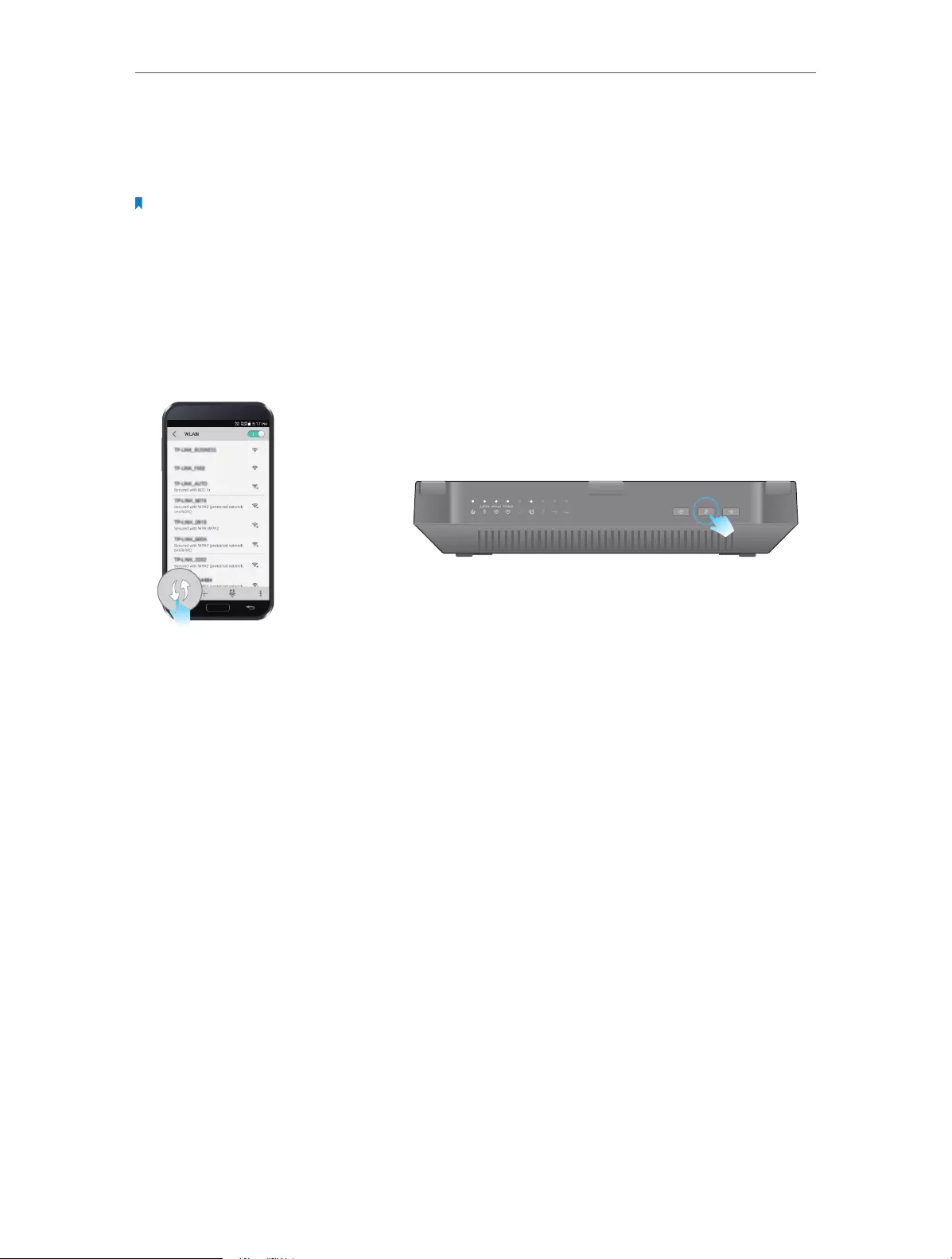
• Method 2: Wirelessly
1 ) Find the SSID (Network Name) and Wireless Password printed on the label at
the bottom of the router.
2 ) Click the network icon of your computer or go to Wi-Fi Settings of your smart
device, and then select the SSID to join the network.
Connections are available
Wireless Network Connection
Connect automatically Connect
TP-LINK_XXXX
TP-LINK_XXXX_5G_2
TP-LINK_XXXX_5G_1
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
TP-LINK_XXXX
TP-LINK_XXXX_5G_2
TP-LINK_XXXX_5G_1
CHOOSE A NETWORK...
Other...
< Settings
Smart DeviceComputer
9
Chapter 2 Connect the Hardware
• Method 3: Use the WPS button
Wireless devices that support WPS, including Android phones, tablets, most USB
network cards, can be connected to your router through this method.
Note:
• WPS is not supported by iOS devices.
• The WPS function cannot be configured if the wireless function of the router is disabled. Also, the WPS function will
be disabled if your wireless encryption is WEP. Please make sure the wireless function is enabled and is configured
with the appropriate encryption before configuring the WPS.
1 ) Tab the WPS icon on the device’s screen. Here we take the Android phone for
instance.
2 ) Within two minutes, press the WPS button on your router.
close to

Chapter 3
Log in to Your Router
11
Chapter 3 Log in to Your Router
With a web-based utility, it is easy to configure and manage the router. The web-based
utility can be used on any Windows, Macintosh or UNIX OS with a Web browser, such as
Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox or Apple Safari.
Follow the steps below to log in to your router.
1. Set up the TCP/IP Protocol in Obtain an IP address automatically mode on your
computer.
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router. The default one is admin for both username and password.
Note:
If the login window does not appear, please refer to the FAQ Section.

Chapter 4
Set Up Internet Connection
This chapter introduces how to connect your router to the Internet. The router is
equipped with a web-based Quick Setup wizard. It has necessary ISP information built
in, automates many of the steps and verifies that those steps have been successfully
completed. Furthermore, you can also set up an IPv6 connection if your ISP provides
IPv6 service.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Use Quick Setup Wizard
• Manually Set up Your Internet Connection
• Set Up an IPv6 Internet Connection
13
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
4. 1. Use Quick Setup Wizard
The Quick Setup Wizard will guide you through the process to set up your router.
Tips:
If you need the IPv6 Internet connection, please refer to the section of Set Up an IPv6 Internet Connection.
Follow the steps below to set up your router.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Click Quick Setup on the top of the page. Then follow the step-by-step instructions
to connect your router to the Internet.
Note:
During the quick setup process:
• If you are not sure of the Internet Connection Type, please click Auto Detect or contact your ISP for Internet
connection information.
• If you have changed the preset wireless network name (SSID) and wireless password, all your wireless devices
must use the new SSID and password to connect to the router.
4. 2. Manually Set up Your Internet Connection
In this part, you can check your current Internet connection settings. You can also
modify the settings according to the service information provided by your ISP.
Follow the steps below to check or modify your Internet connection settings.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Basic > Internet.
3. Select your Internet connection type from the drop-down list.
Note:
If you are unsure of what your connection type is, click Auto Detect. Since different connection types need different
cables and connection information, you can also refer to the demonstrations in Step 4 to determine your connection
type.
4. Follow the instructions on the page to continue the configuration. Parameters on
the figures are just used for demonstration.
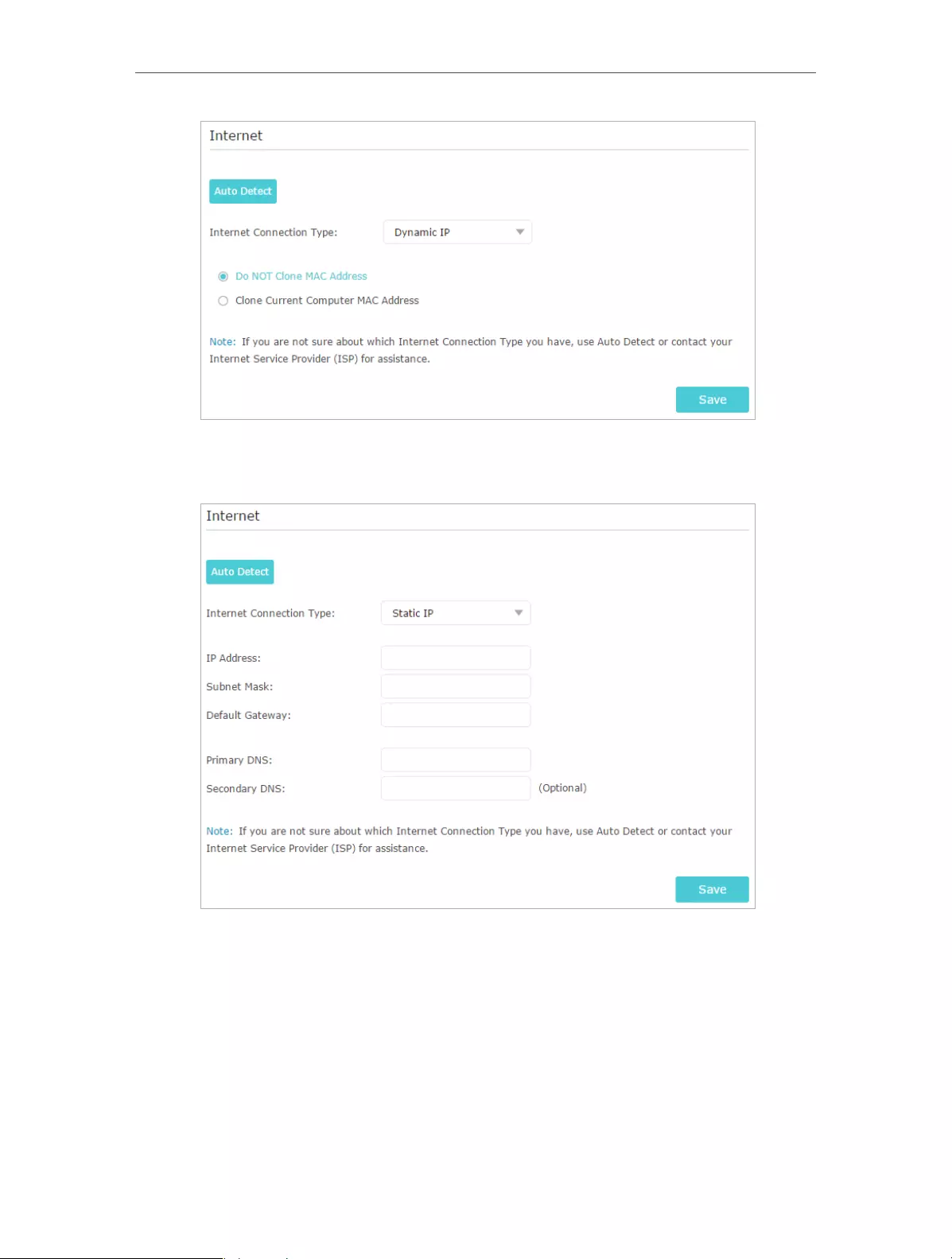
1 ) If you choose Dynamic IP, you need to select whether to clone the MAC address.
Dynamic IP users are usually equipped with a cable TV or fiber cable.
14
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
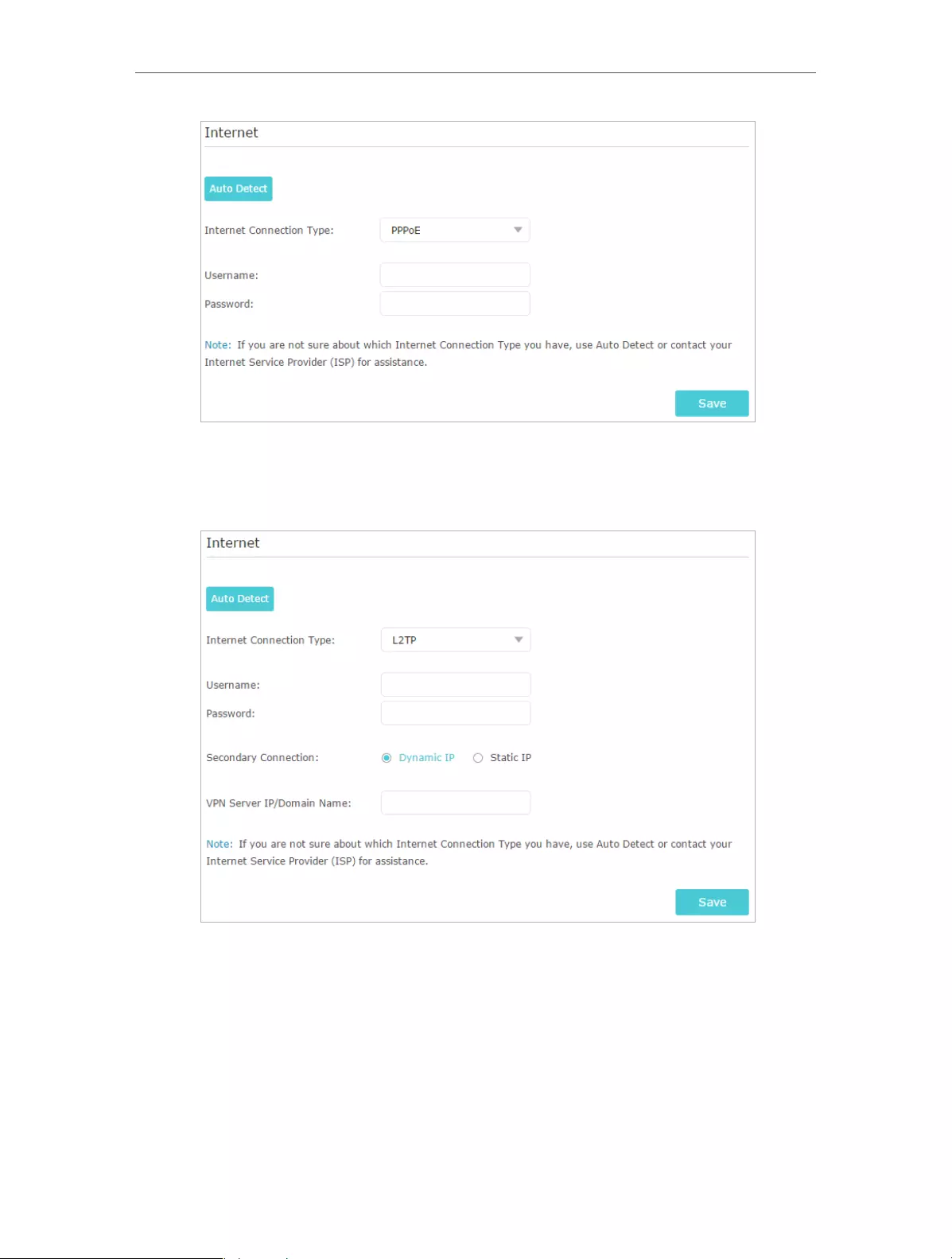
2 ) If you choose Static IP, enter the information provided by your ISP in the
corresponding fields.
3 ) If you choose PPPoE, enter the username and password provided by your ISP.
PPPoE users usually have DSL cable modems.
15
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
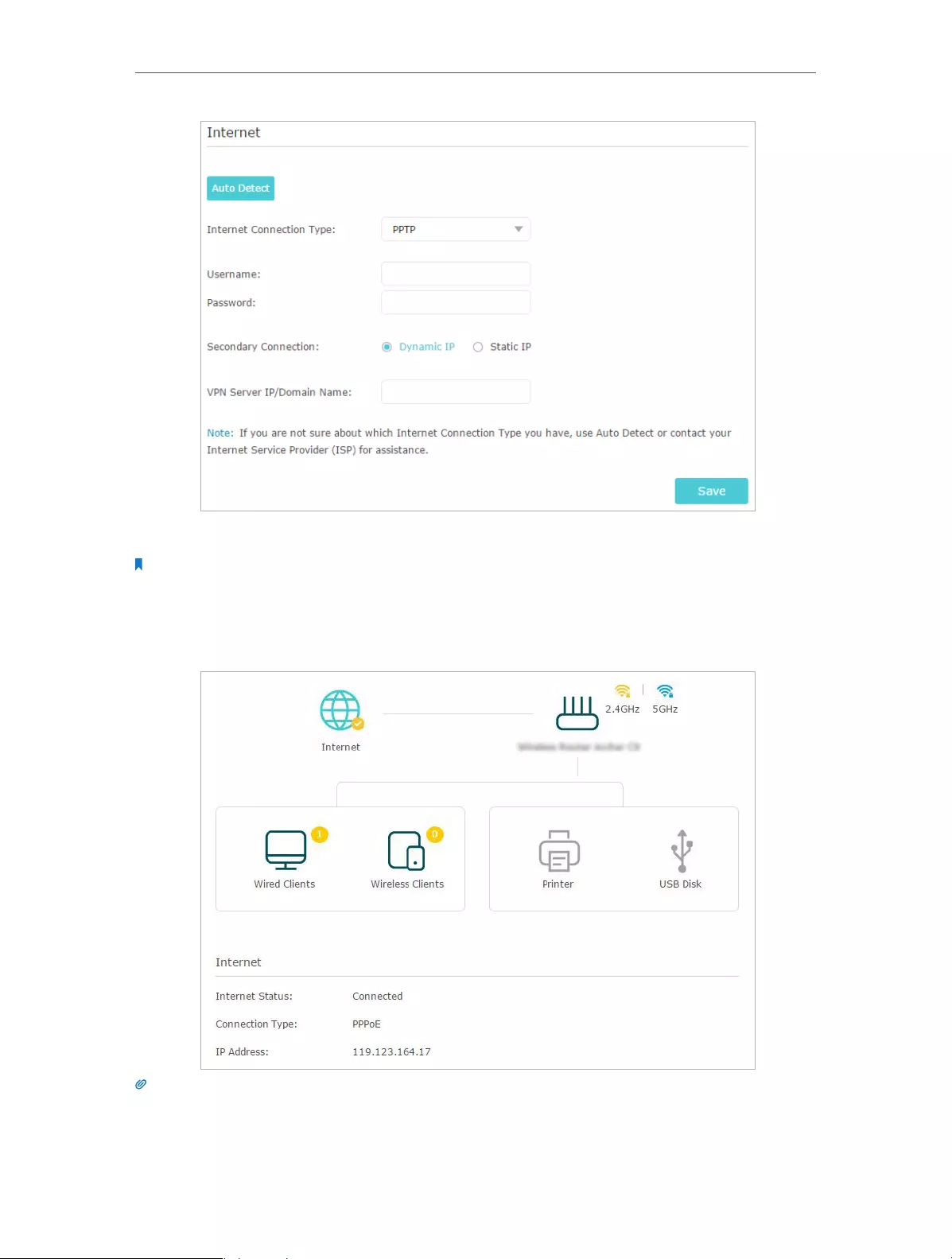
4 ) If you choose L2TP, enter the username and password and choose the Secondary
Connection provided by your ISP. Different parameters are needed according
to the Secondary Connection you have chosen.
5 ) If you choose PPTP, enter the username and password, and choose the
Secondary Connection provided by your ISP. Different parameters are needed
according to the Secondary Connection you have chosen.
16
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
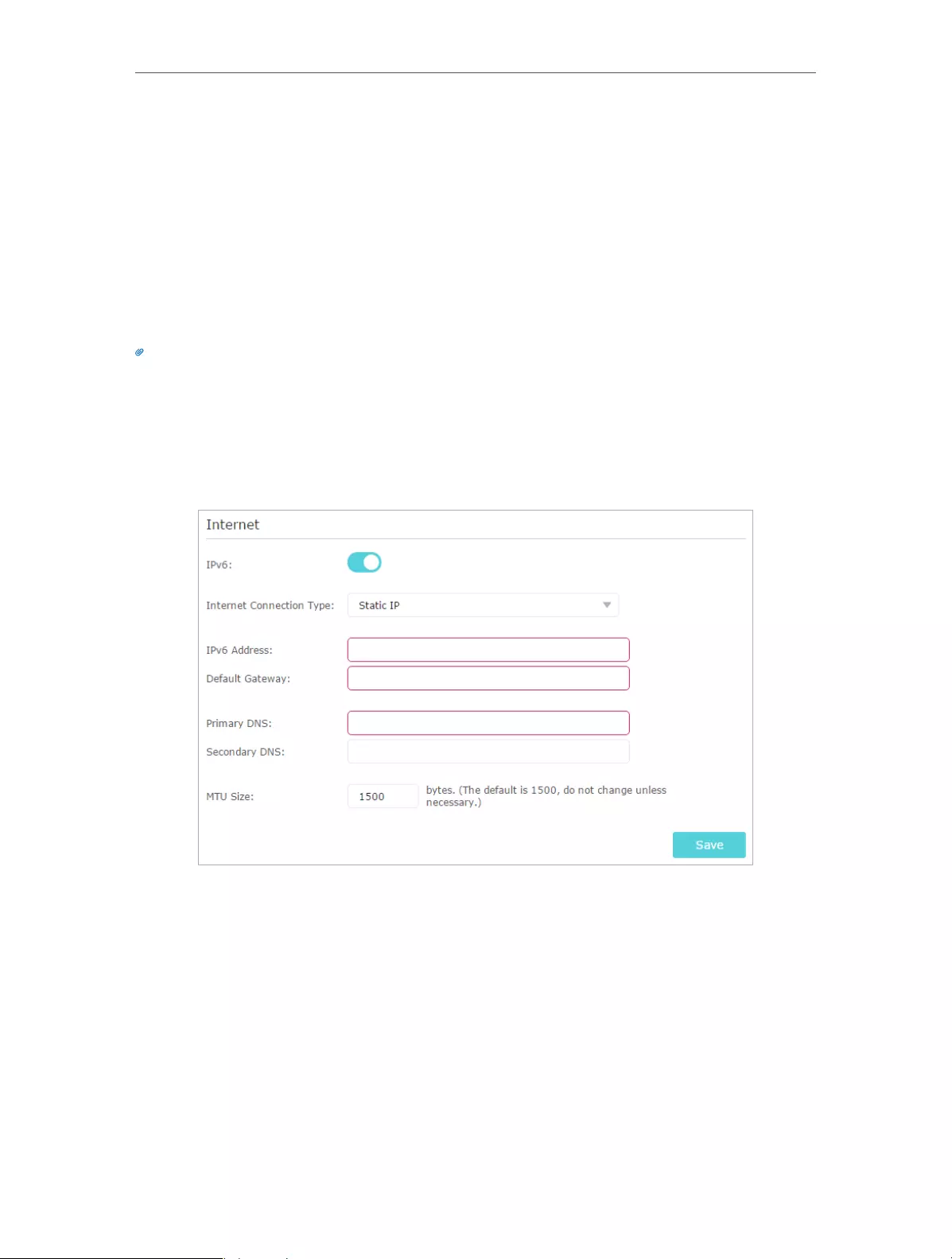
5. Click Save.
Note:
It may take 1-2 minutes to make the settings valid.
6. After the connection succeeds, the screen will display as follows. Here we take
PPPoE as an example.
Tips:
• If your Internet connection type is BigPond Cable, please go to Advanced > Network > Internet to set your router.
• If you use Dynamic IP and PPPoE and you are provided with any other parameters that are not required on the
page, please go to Advanced > Network > Internet to complete the configuration.
• If you still cannot access the Internet, refer to the FAQ for further instructions.
17
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
4. 3. Set Up an IPv6 Internet Connection
Your ISP provides information about one of the following IPv6 Internet connection
types: PPPoE, Dynamic IP(SLAAC/DHCPv6), Static IP, 6to4 tunnel, Pass-Through (Bridge).
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > IPv6.
3. Enable IPv6 and select the Internet connection type provided by your ISP.
Tips:
If you do not know what your Internet connection type is, contact your ISP or judge according to the already known
information provided by your ISP.
4. Fill in information as required by different connection types. Red blanks must be
filled in.
1 ) Static IP: Fill in blanks and click Save.
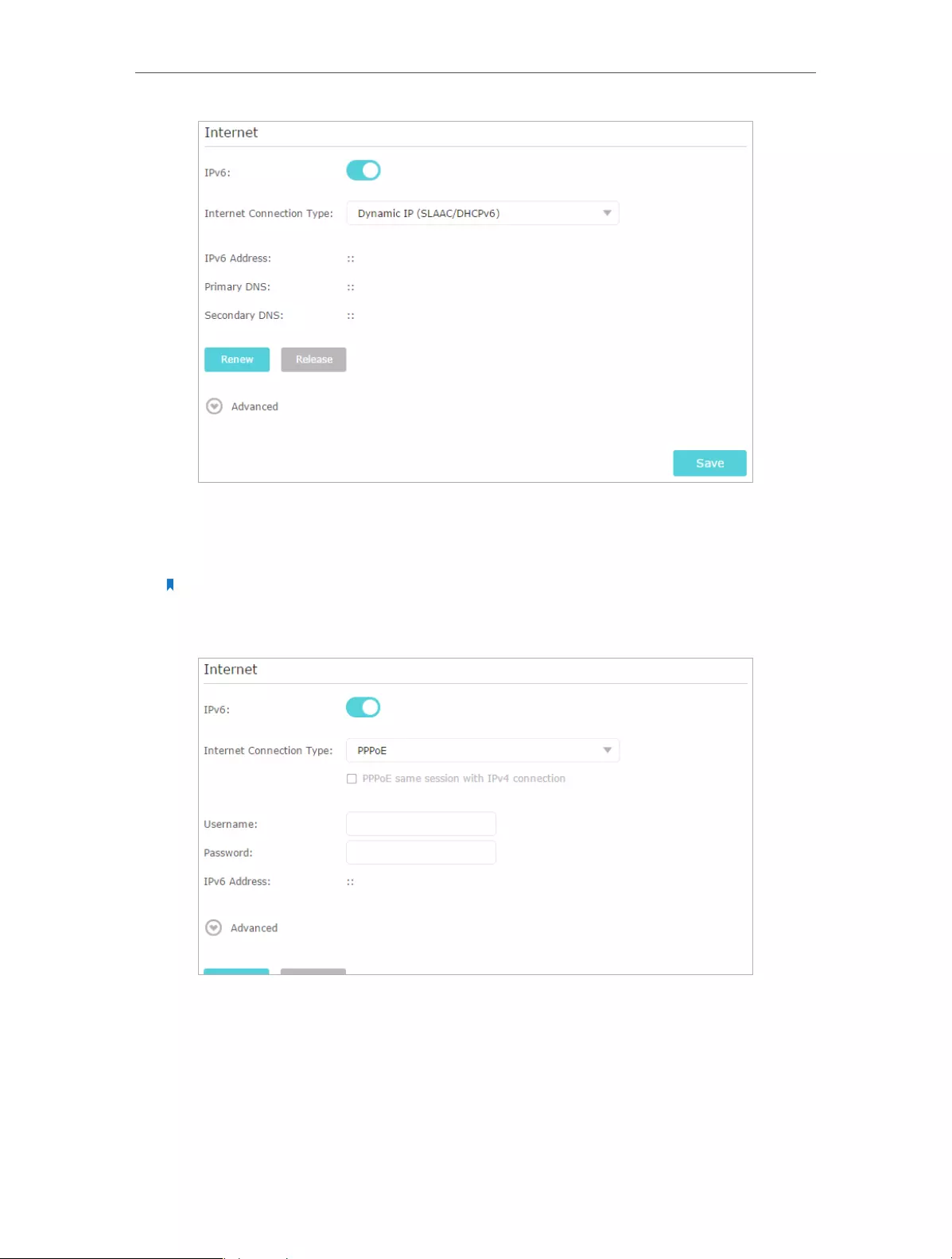
2 ) Dynamic IP(SLAAC/DHCPv6): Click Advanced to input further information if
your ISP requires. Click Save and then click Renew.
18
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
3 ) PPPoE: By default, the router uses the IPv4 account to connect to the IPv6
server. Click Advanced to input further information if your ISP requires. Click
Save and then click Connect.
Note:
If your ISP provides two separate accounts for the IPv4 and IPv6 connections, please uncheck the box for Use the
same session with IPv4 connection and manually enter the username and password for the IPv6 connection.
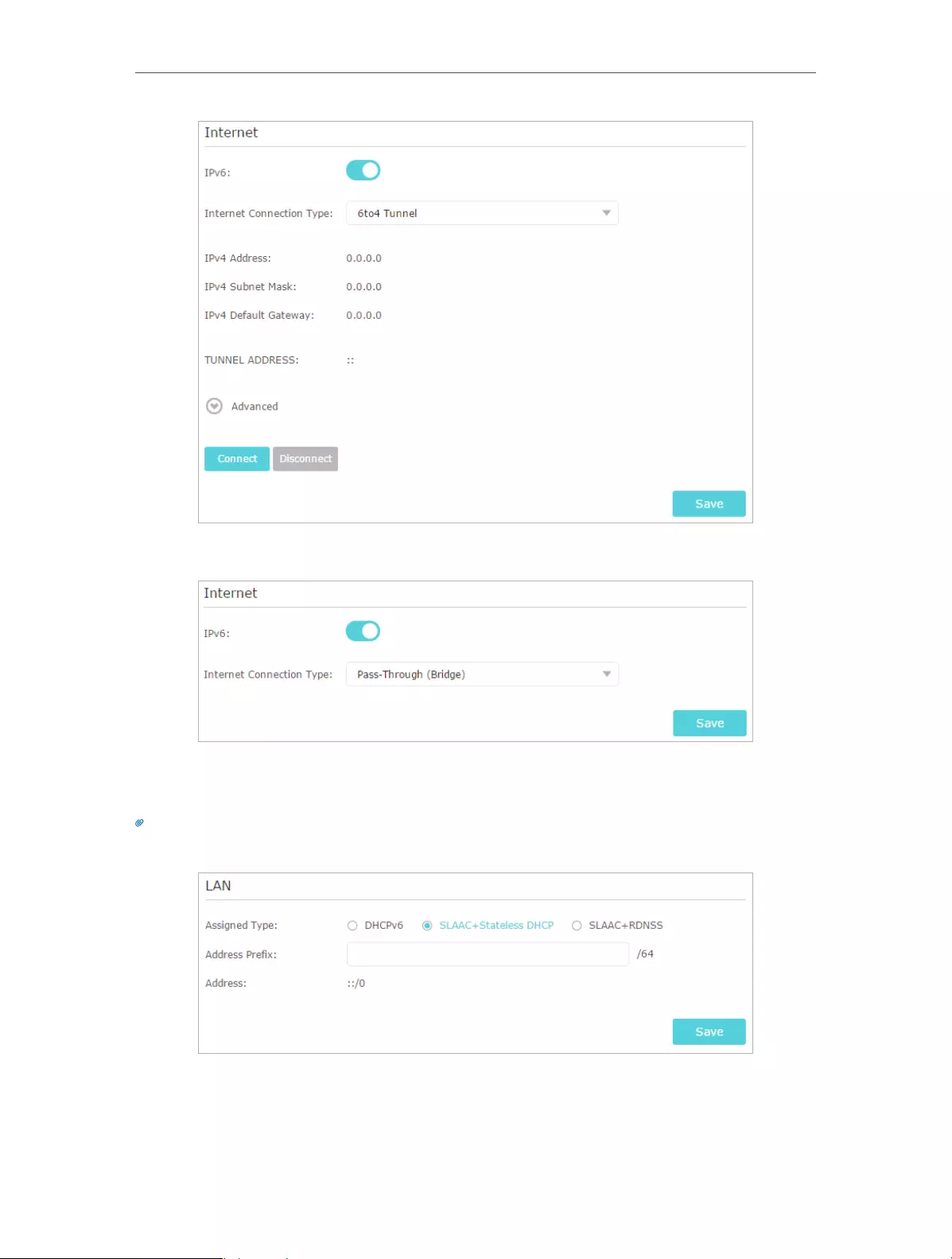
4 ) 6to4 Tunnel: An IPv4 Internet connection type is a prerequisite for this
connection type (Manually Set up Your Internet Connection). Click Advanced to
input further information if your ISP requires. Click Save and then click Connect.
19
Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
5 ) Pass-Through (Bridge): Click Save and skip to step 6.
5. Configure LAN ports. Windows users are recommended to choose from the first two
types. Fill in Address Prefix provided by your ISP, and click Save.
Tips:
Find Help on the management interface to know more about items.
6. Click Status to check whether you have successfully set up an IPv6 connection. The
following figure is an example of a successful PPPoE configuration.

Chapter 5
Guest Network
This function allows you to provide Wi-Fi access for guests without disclosing your
main network. When you have guests in your house, apartment, or workplace, you can
create a guest network for them. In addition, you can customize guest network options
to ensure network security and privacy.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Create a Network for Guests
• Customize Guest Network Options
22
Chapter 5 Guest Network
5. 1. Create a Network for Guests
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Guest Network. Locate the Wireless section.
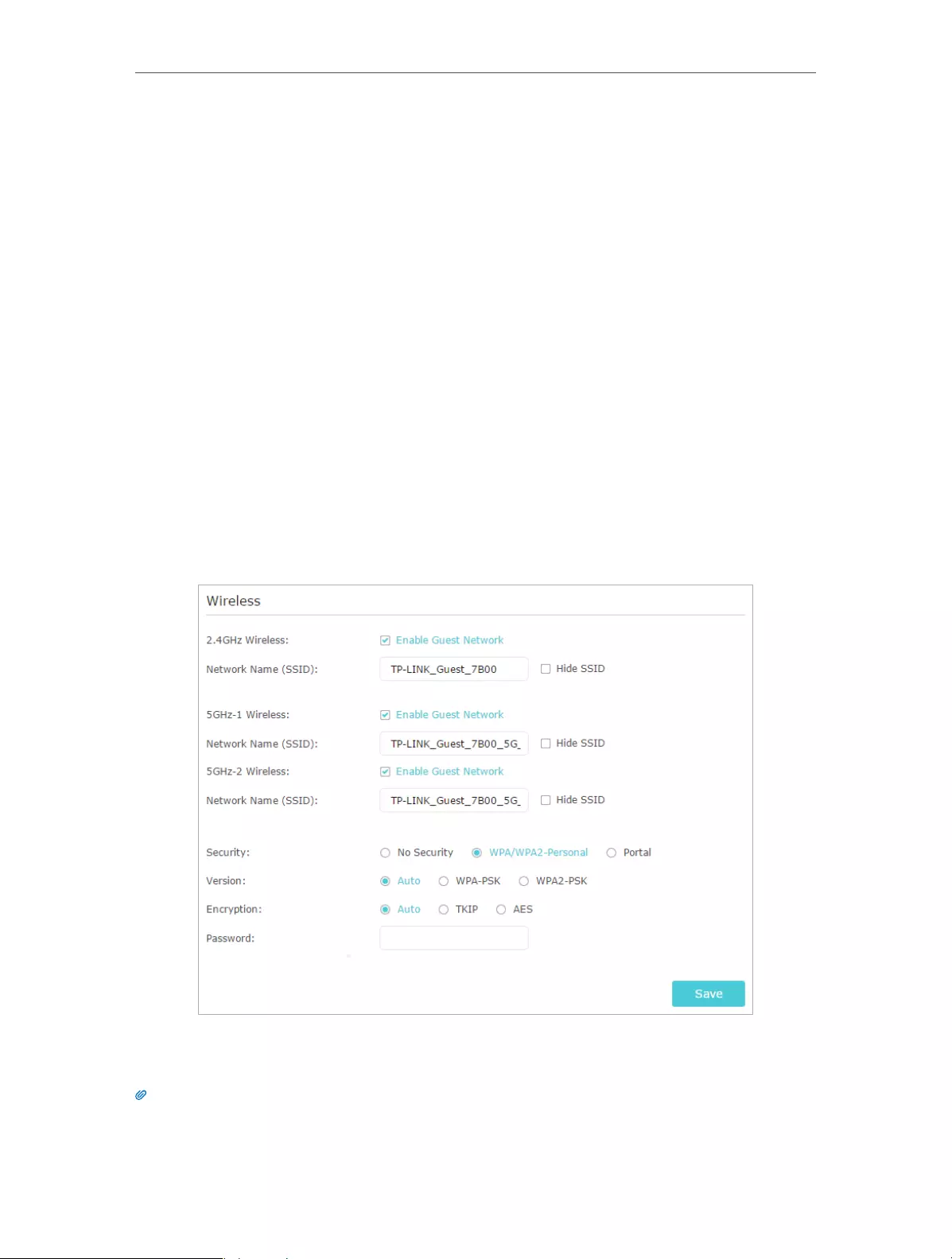
3. Create a guest network as needed.
1 ) Enable 2.4GHz Wireless network, 5GHz-1 Wireless or 5GHz-2 Wireless network.
2 ) Customize the SSID. Don‘t select Hide SSID unless you want your guests to
manually input the SSID for guest network access.
3 ) Select the Security type.
• If No security is selected, no password is needed to access your guest
network.
• If WAP/WPA2-Personal is selected, keep the default Version and Encryption
values, and customize your own password.
• If Portal is selected, please refer to Set Portal Authentication to personalize
the anthentication login page for your guests.
4. Click Save. Now your guests can access your guest network using the SSID and
password you set!
Tips:
To view guest network information, go to Advanced > Status and locate the Guest Network section.
23
Chapter 5 Guest Network
5. 2. Set Portal Authentication
Imagine that you run a small shop and provide a guest network for your customers.
You want to seize every opportunity to promote your shop, which makes portal
authentication an excellent choice. Customers will be directed to a web page for access
verification, on which your personalized promotion is displayed. Moreover, you can
specify a web link so that the newly connected guest will be redirected to, for example,
the official website of your shop.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
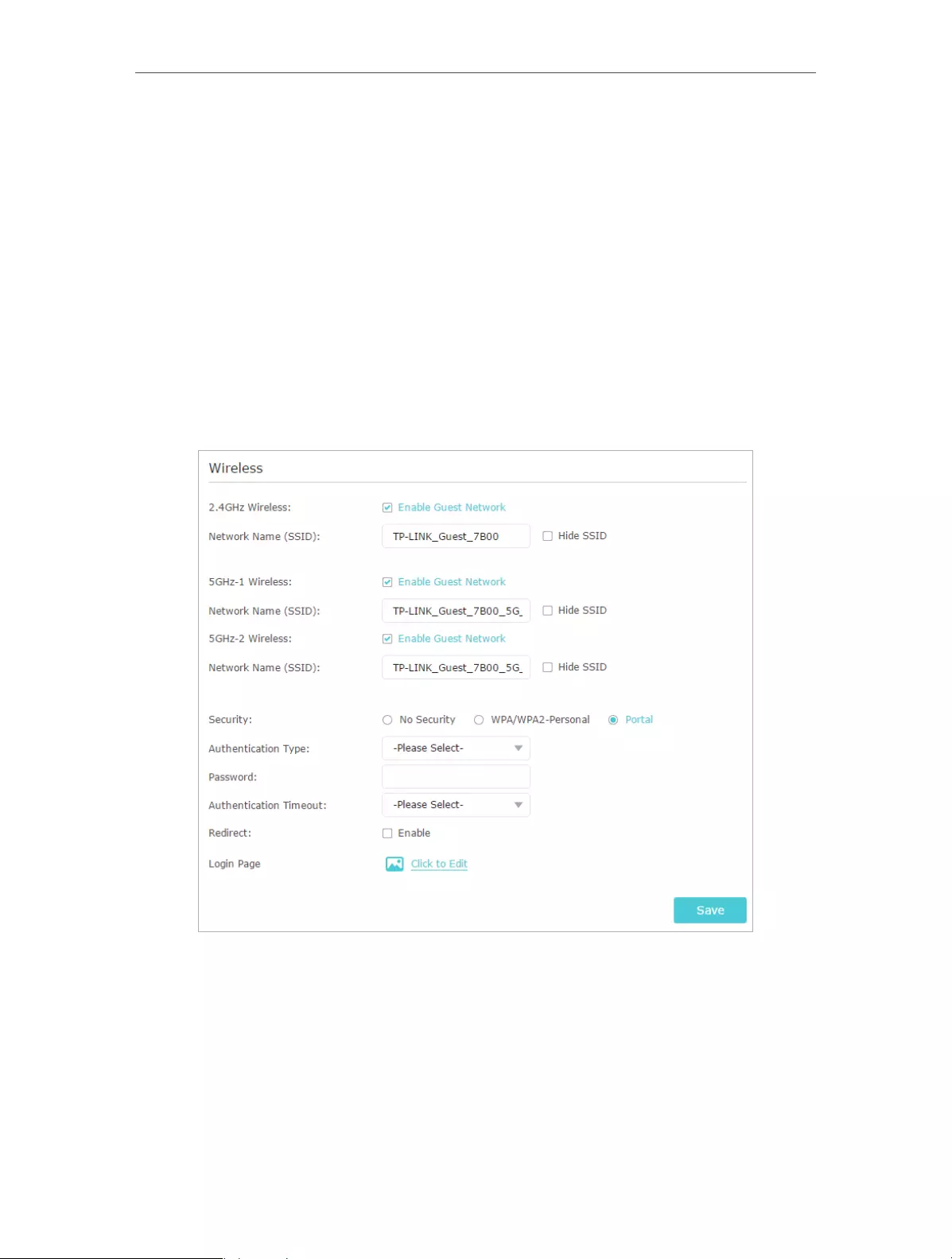
2. Go to Advanced > Guest Network. Focus on the Wireless section, and select Portal
for Security.
3. Select the Authentication Type.
• Simple Password – Specify a password for authentication (8-16 alphanumeric
or “_” characters are allowed).
• No Authentication – Guests can access the network without any authentication.
4. Specify the Authentication Timeout. When a guest’s authentication expires, they
have to reconnect to the network.
5. (Optional) Enable Redirect and enter the desired web link. The newly connected
guest will be redirected to the website you have specified.
24
Chapter 5 Guest Network
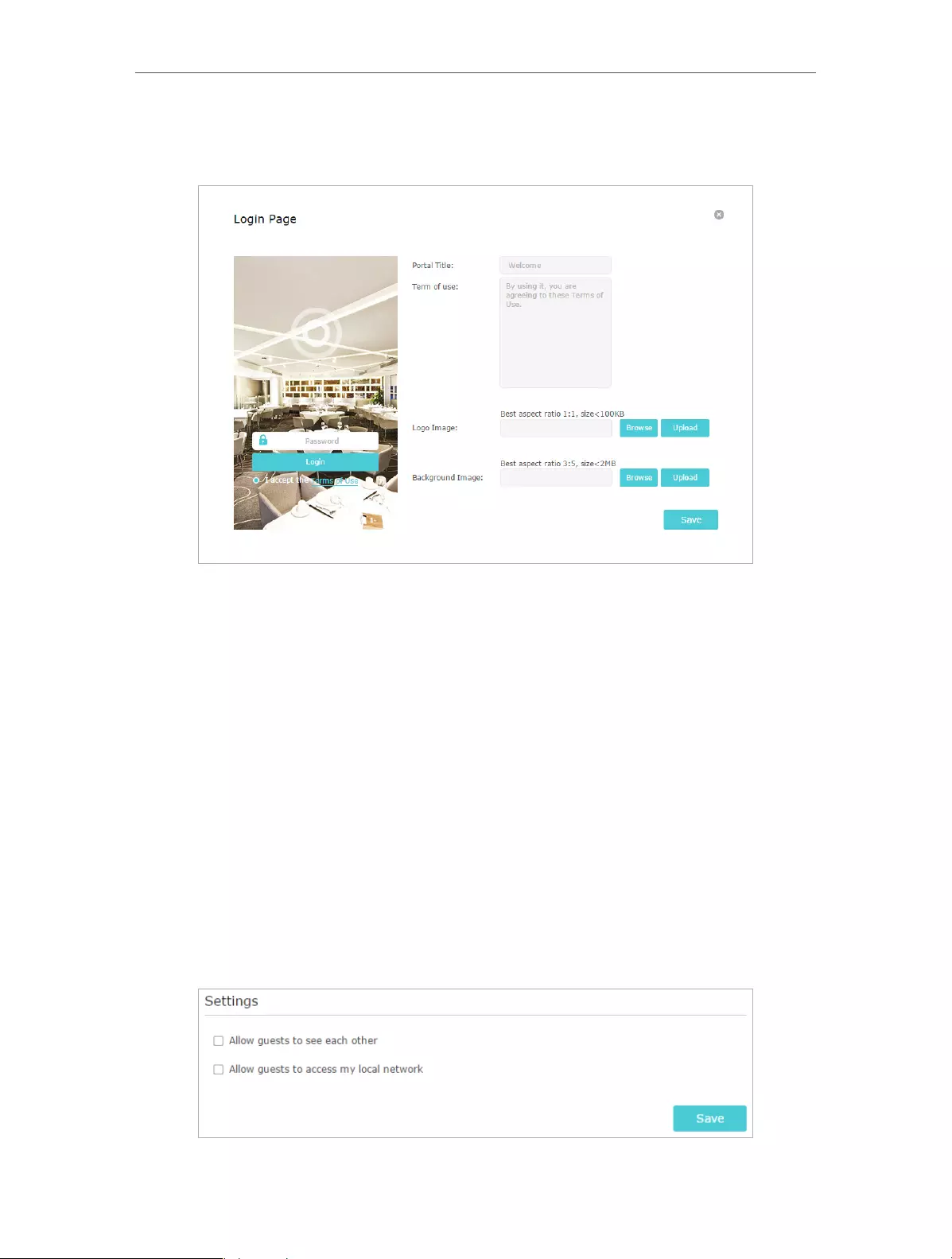
6. (Optional) You can click Click to Edit to personalize the authentication page, and click
Save.
• Portal Title – Up to 31 characters.
• Terms of Use – Up to 1023 characters.
• Logo Image – Upload a JPG or PNG image (less than 100KB) to customize the
logo.
• Background Image – Upload a JPG or PNG image (less than 2MB) to customize
the background.
7. Click Save.
5. 3. Customize Guest Network Options
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Guest Network. Locate the Settings section.
3. Customize guest network options according to your needs.
• Allow guests to see each other

25
Chapter 5 Guest Network
Check this box if you want to allow the wireless clients on your guest network to
communicate with each other via methods such as network neighbors and Ping.
• Allow guests to access my local network
Check this box if you want to allow the wireless clients on your guest network
to communicate with the devices connected to your router’s LAN ports or main
network via methods such as network neighbors and Ping.
4. Click Save. Now you can ensure network security and privacy!
Tips:
To view guest network information, go to Advanced > Status and locate the Guest Network section.

Chapter 6
USB Application
This chapter describes how to share and access USB devices connected to the router
among different clients. The router only supports USB external flash drives, hard drives
and USB printers.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Local Storage Sharing
• Remote Access via FTP Serverr
• Media Sharing
• Printer Sharing
27
Chapter 6 USB Application
6. 1. Local Storage Sharing
Share your USB storage devices with different users on the network.
6. 1. 1. Access the USB disk
1. Connect Your USB Disk
Insert your USB storage device into the router’s USB port directly or using a USB
cable. Wait several seconds until the USB LED becomes solid on.
Tips:
• If you use USB hubs, make sure no more than 4 devices are connected to the router.
• If the USB storage device requires using bundled external power, make sure the external power has been
connected.
• If you use a USB hard drive, make sure its file system is FAT32, exFat, NTFS or HFS+.
• Before you physically disconnect a USB device from the router, safely remove it to avoid data damage: Go to
Advanced > USB Settings > Device Settings and click .
2. Access Your USB Disk
By default, all the network clients can access all folders on your USB disk. Refer
to the following table for access instructions. You can also customize your sharing
content and set a sharing account by referring to Customize Your Settings.
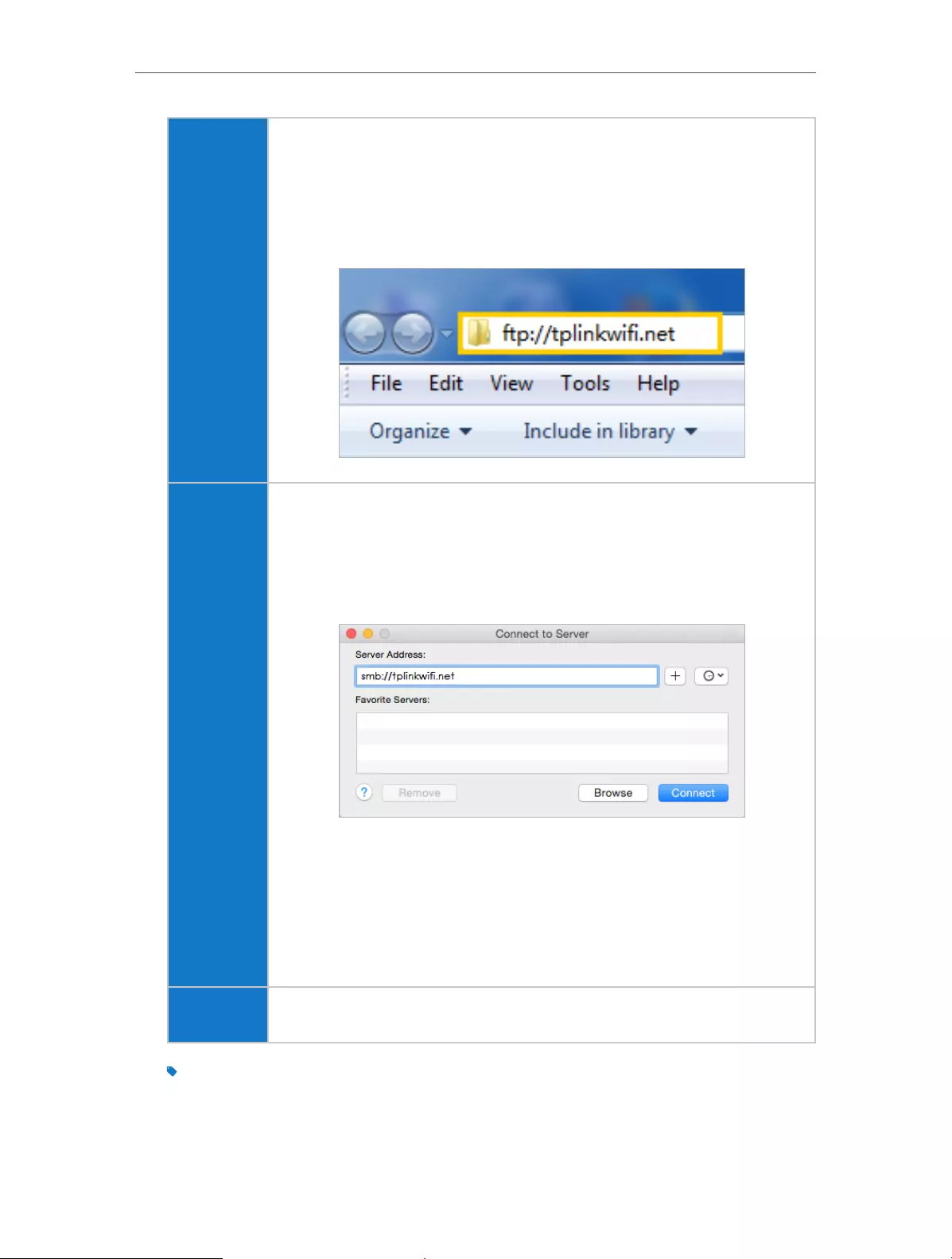
Windows
computer
¾Method 1:
Go to Computer > Network, then click the Network Server Name
(TP-SHARE by default) in the Computer section.
Note:
Operations in different systems are similar. Here we take Windows 7 as an example.
28
Chapter 6 USB Application
Windows
computer
¾Method 2:
Open the Windows Explorer (or go to Computer) and type the
server address \\tplinkwifi.net or ftp://tplinkwifi.net in the address
bar, then press [Enter].
Mac
1 ) Go to Go > Connect to Server.
2 ) Type the server address smb://tplinkwifi.net.
3 ) Click Connect.
4 ) When prompted, select the Guest radio box. (If you have set up
a username and a password to deny anonymous access to the
USB disks, you should select the Registered User radio box. To
learn how to set up an account for the access, refer to To Set up
Authentication for Data Security.)
pad Use a third-party app for network files management.
Tips:
You can also access your USB disk by using your Network/Media Server Name as the server address. Refer to To
Customize the Address of the USB Disk to learn more.
29
Chapter 6 USB Application
6. 1. 2. Customize Your Settings
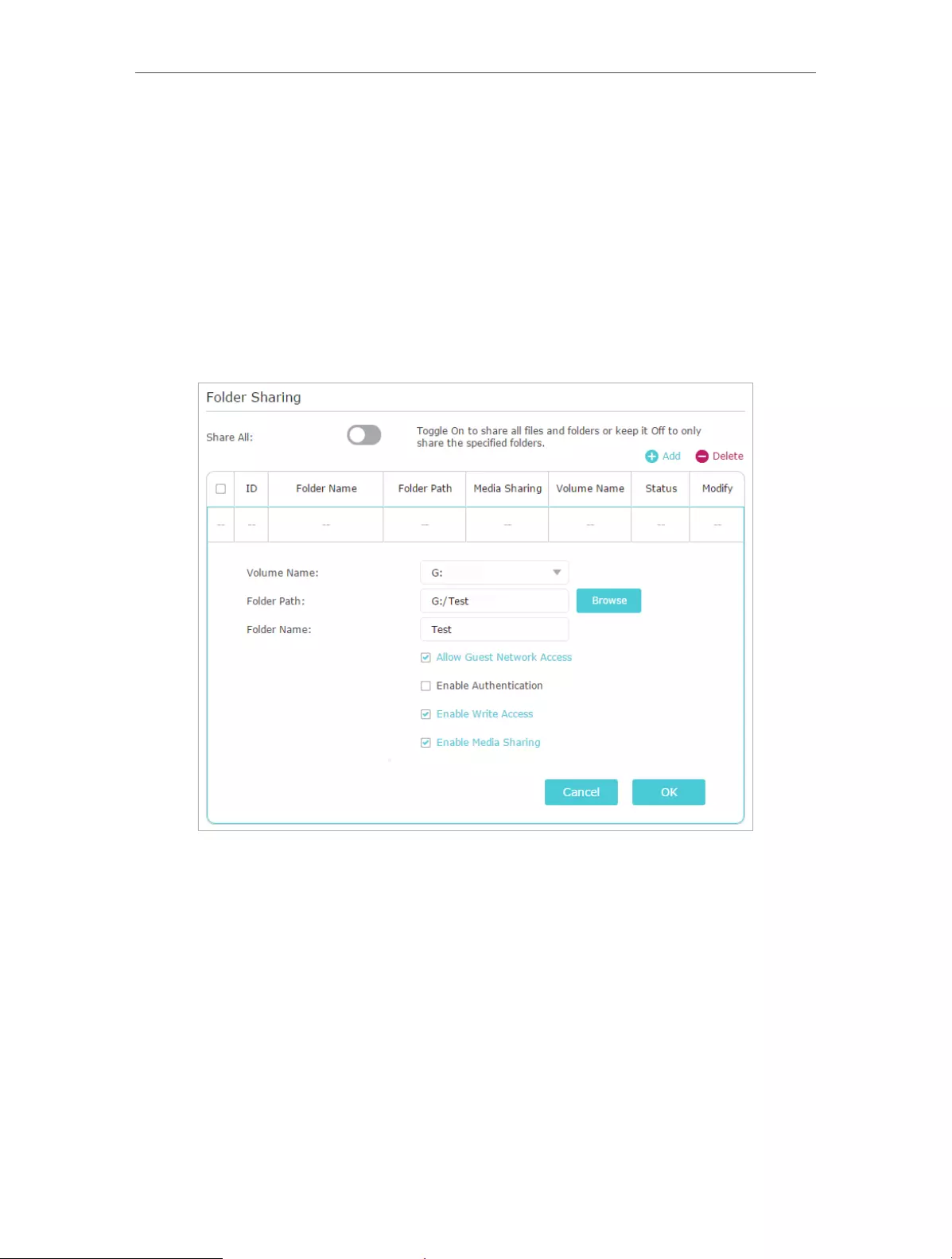
¾To Only Share Specific Content
By default, Share All is enabled so all content on the USB disk is shared. If you want to
only share specific folders, follow the steps below:
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
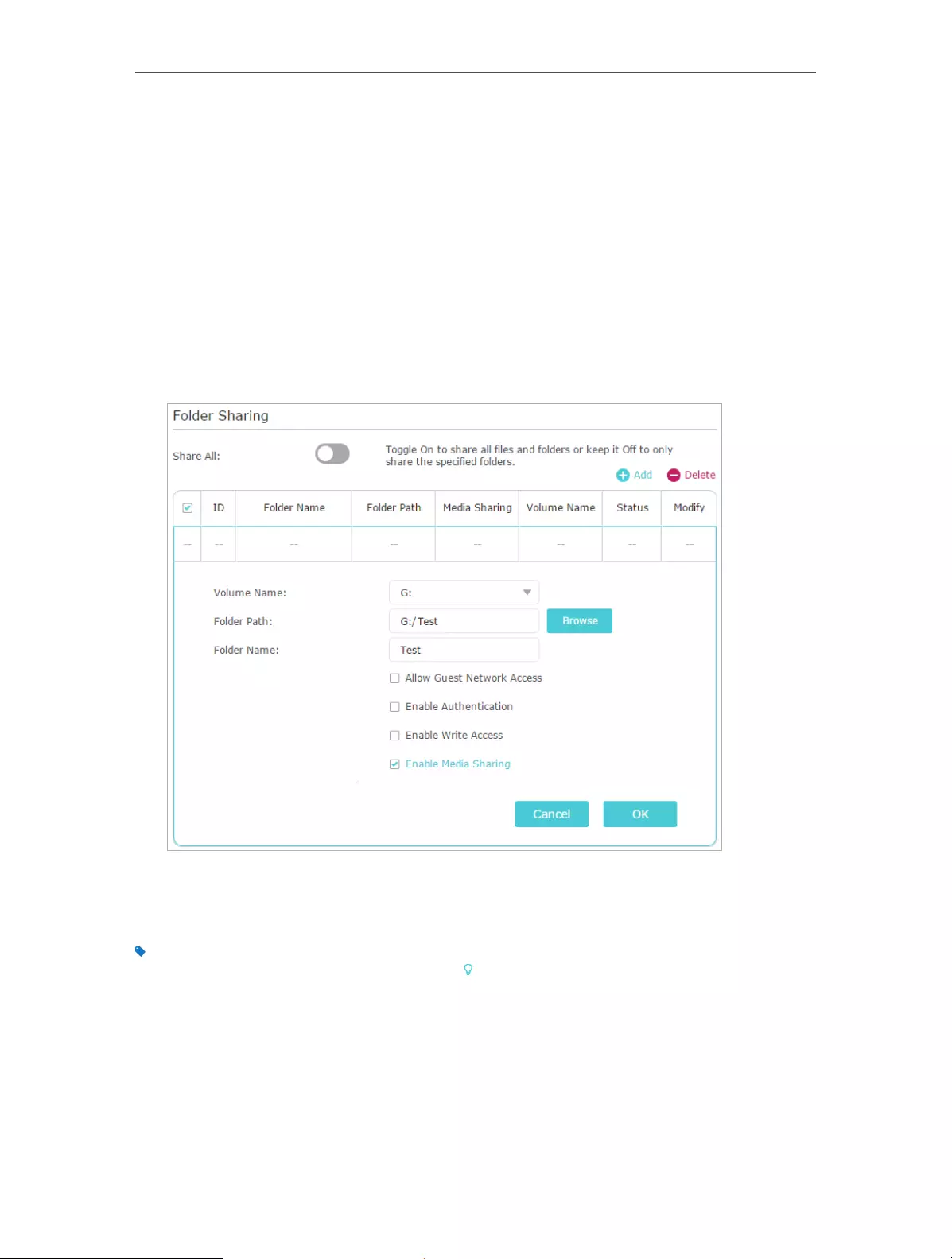
2. Go to Basic > USB Settings > Sharing Access. Focus on the Folder Sharing section.
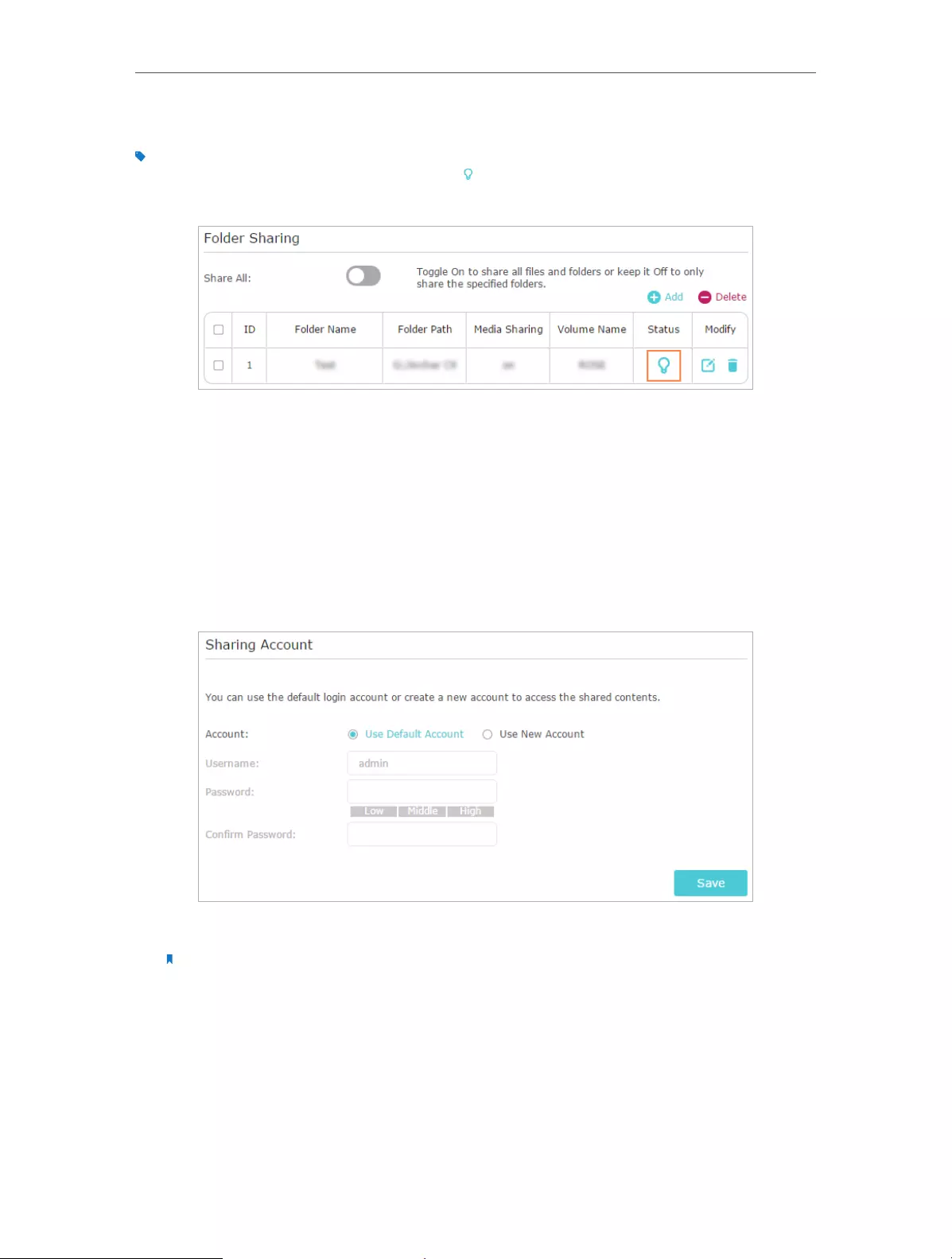
Click the button to disable Share All, and then click Add to add a new sharing folder.
3. Select the Volume Name and Folder Path, and then enter a Folder Name as you like.
4. Decide the way you share the folder:
• Allow Guest Network Access: If you check this box, guest network users can
access the folder.
• Enable Authentication: If you check this box, you will be required to use a
username and password to access the folder. Refer to To Set up Authentication
for Data Security to learn more.
• Enable Write Access: If you check this box, network clients can modify the folder.
• Enable Media Sharing: If you check this box, you can view photos, play music
and watch movies in the folder directly from DLNA-supported devices. Click
Media Sharing to learn more.
30
Chapter 6 USB Application
5. Click OK.
Tips:
The router can share 32 volumes at most. You can click on the page to detach the corresponding volume you do
not need to share.
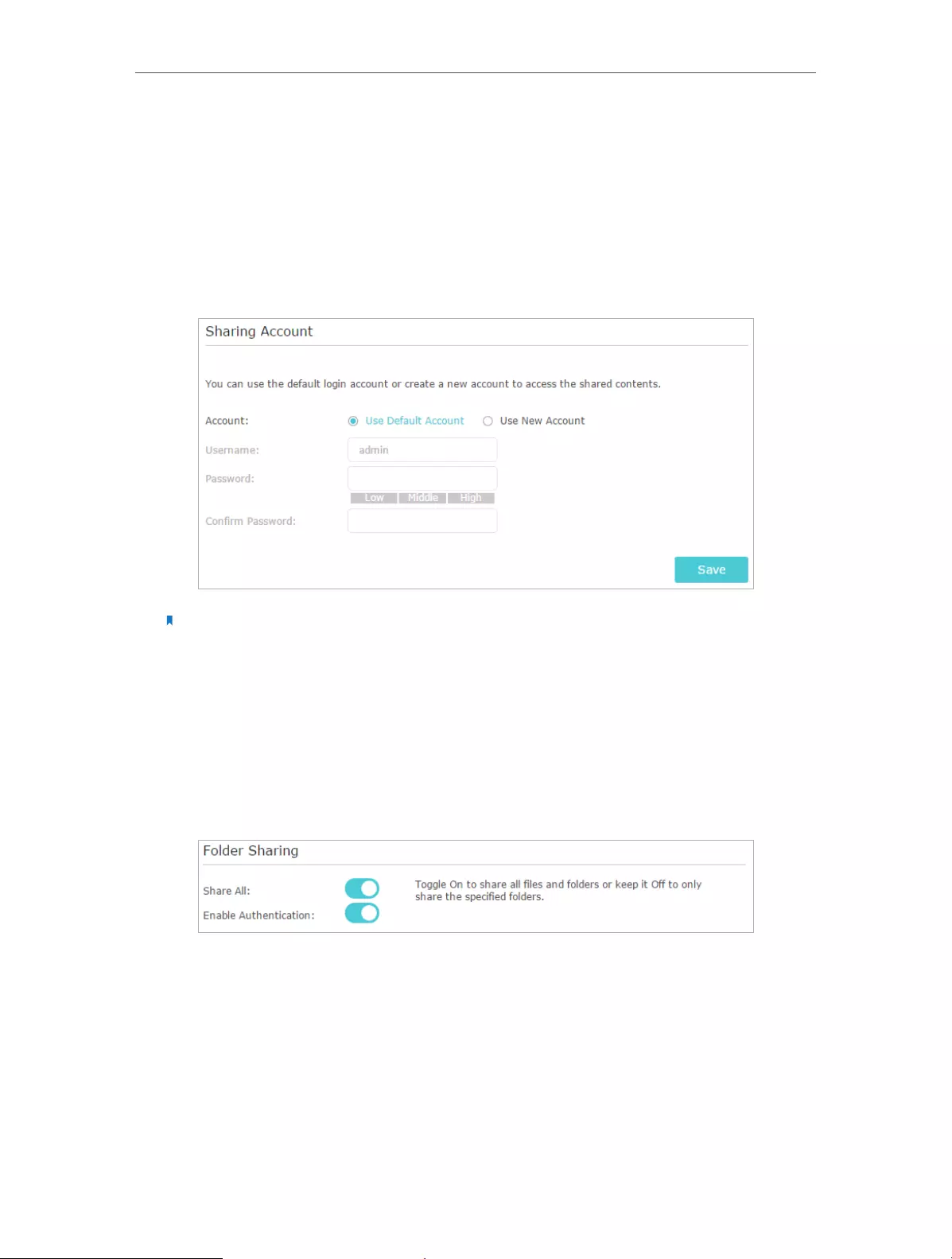
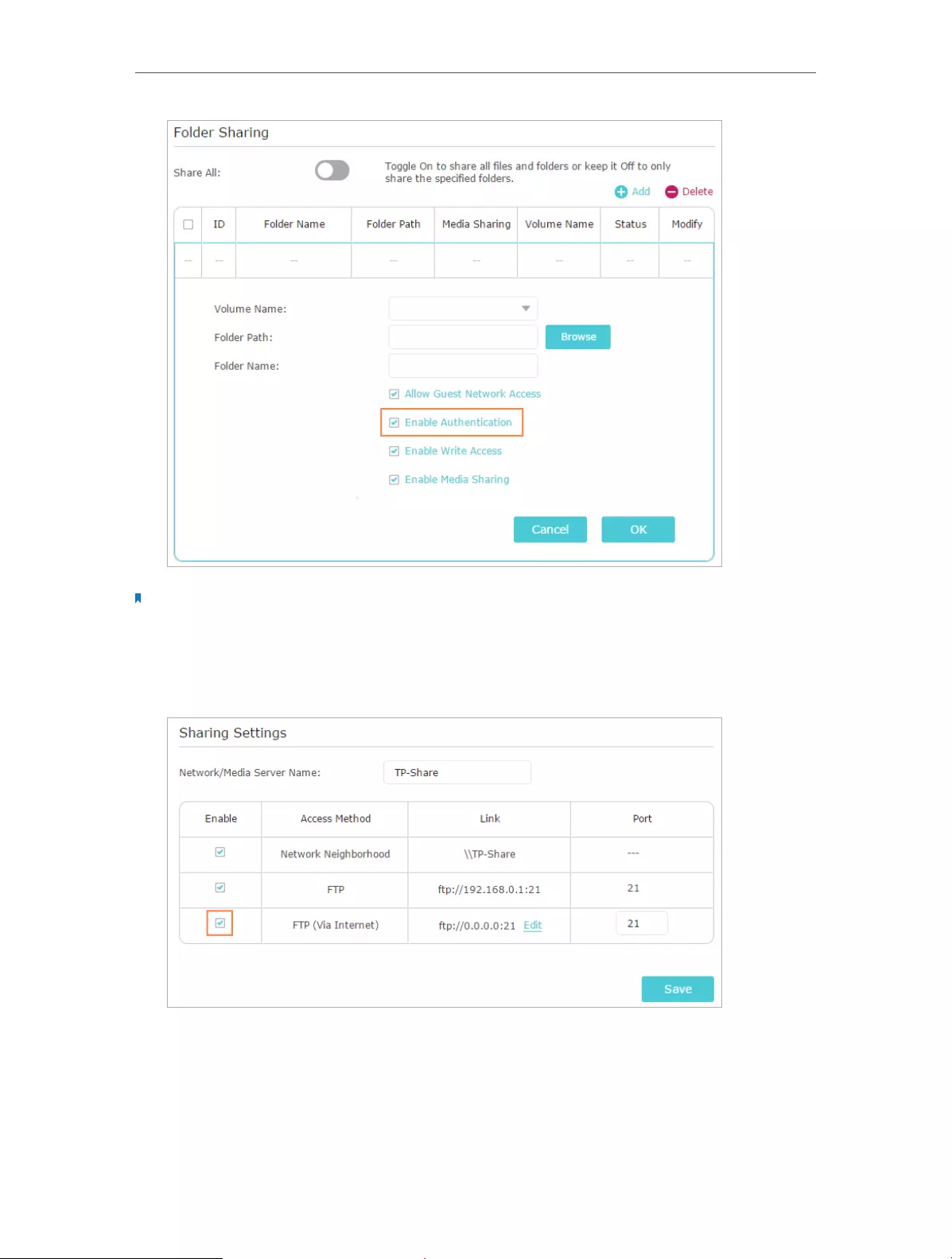
¾To Set up Authentication for Data Security
If you enable Authentication, network clients will be required to enter the username
and password you set when accessing the USB disk.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > USB Settings > Sharing Access. Focus on the Sharing Account
section.
3. Choose Use Default Account (admin) or Use New Account and click Save.
Note:
For Windows users, do not set the sharing username the same as the Windows username. Otherwise, Windows
credential mechanism may cause the following problems:
• If the sharing password is also the same as the Windows password, authentication will not work since the
Windows will automatically use its account information for USB access.
• If the sharing password is different from the Windows password, the Windows will be unable to remember
your credentials and you will always be required to enter the sharing password for USB access.
4. Enable Authentication to apply the account you just set.
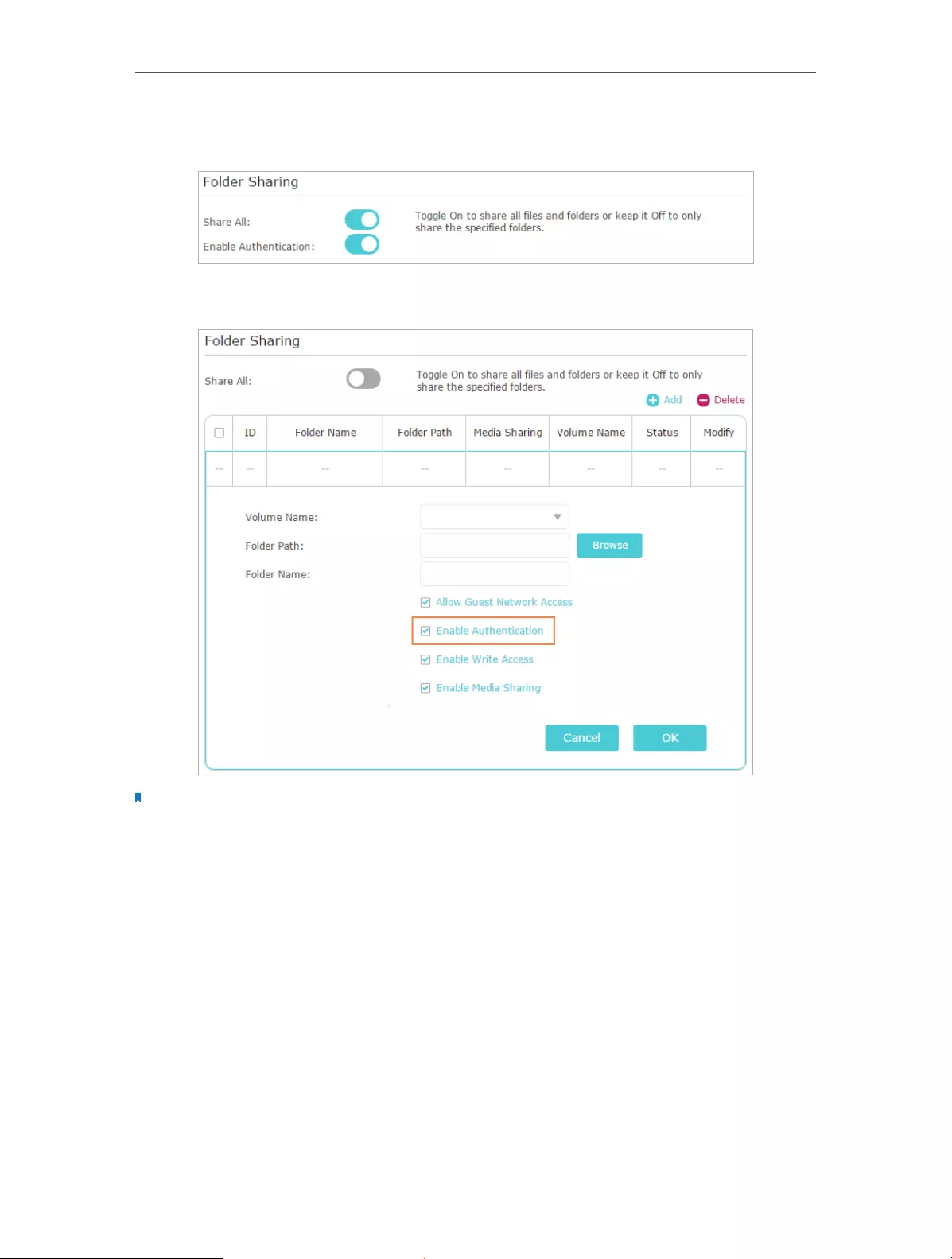
31
Chapter 6 USB Application
• If you leave Share All enabled, click the button to enable Authentication for all
folders.
• If Share All is disabled, enable Authentication for specific folders.
Note:
Due to Windows credential mechanism, you might be unable to access the USB disk after changing Authentication
settings. Please log out from Windows and try to access again. Or you can change the address of the USB disk by
referring to To Customize the Address of the USB Disk.
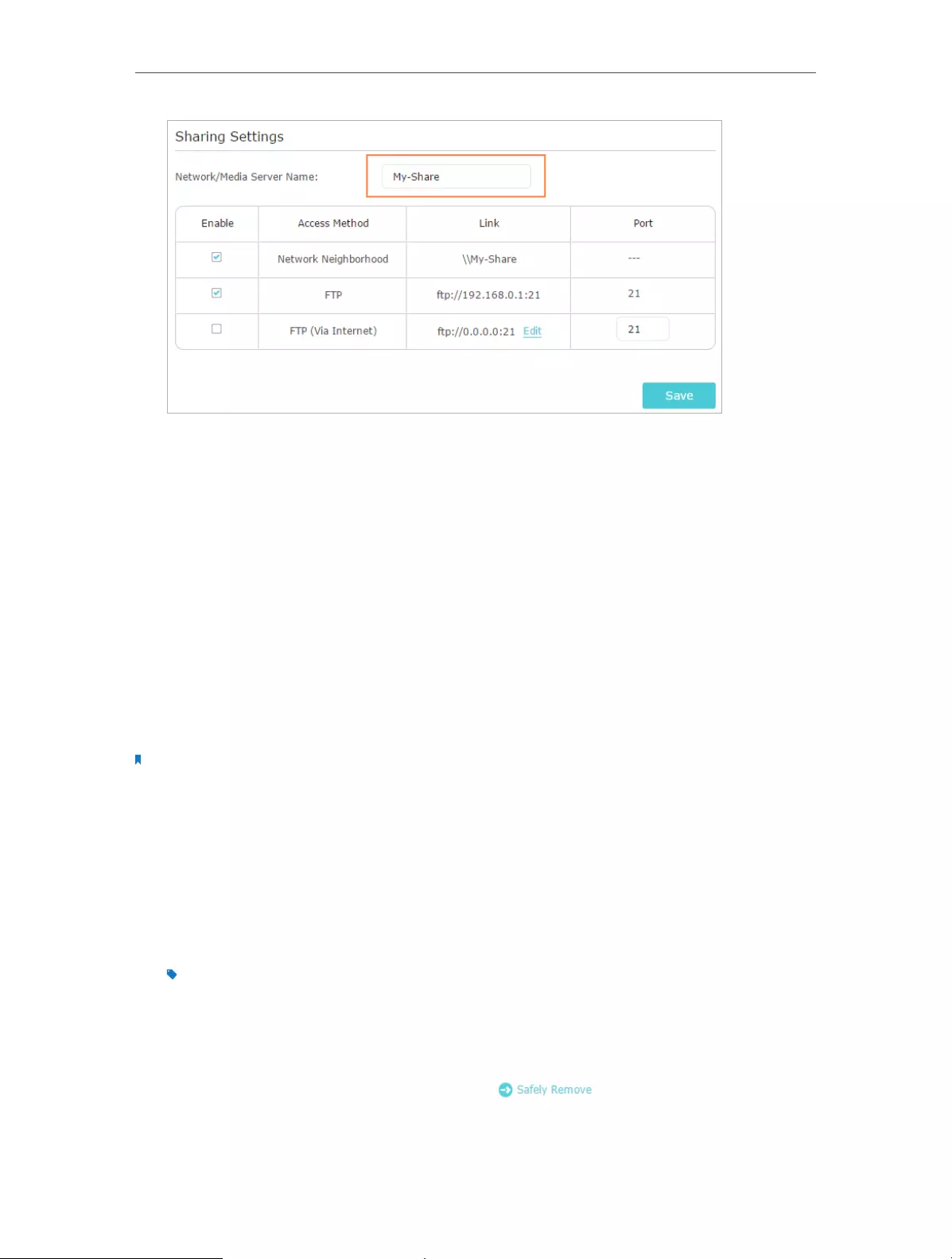
¾To Customize the Address of the USB Disk
You can customize the server name and use the name to access your USB disk.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > USB Settings > Sharing Access. Focus on the Sharing Settings
section.
3. Make sure Network Neighborhood is ticked, enter a Network/Media Server Name
as you like, such as My-Share, and then click Save.
32
Chapter 6 USB Application
4. Now you can access the USB disk by visiting \\My-Share (for Windows) or
smb://My-Share (for Mac).
6. 2. Remote Access via FTP Server
You can access your USB disk outside the local area network.
For example:
• Share photos and other large files with your friends without logging in to (and paying
for) a photo-sharing site or email system.
• Get a safe backup for the materials for a presentation.
• Remove the files on your camera’s memory card from time to time during the journey.
Note:
If your ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x), you cannot use this feature because
private addresses are not routed on the Internet.
6. 2. 1. Access the USB Disk
1. Connect Your USB Disk
Insert your USB storage device into the router’s USB port directly or using a USB
cable. Wait several seconds until the USB LED becomes solid on.
Tips:
• If you use USB hubs, make sure no more than 4 devices are connected to the router.
• If the USB storage device requires using bundled external power, make sure the external power has been
connected.
• If you use a USB hard drive, make sure its file system is FAT32, exFat, NTFS or HFS+.
• Before you physically disconnect a USB device from the router, safely remove it to avoid data damage: Go to
Advanced > USB Settings > Device Settings and click .
33
Chapter 6 USB Application
2. Enable Authentication for Data Security
It is strongly recommended that you set and apply a sharing account for data
security.
1 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you
set for the router.
2 ) Go to Advanced > USB Settings > Sharing Access.
3 ) Choose Use default Account (admin) or Use New Account and click Save.
Note:
For Windows users, do not set the sharing username the same as the Windows username. Otherwise, Windows
credential mechanism may cause the following problems:
• If the sharing password is also the same as the Windows password, authentication will not work since the
Windows will automatically use its account information for USB access.
• If the sharing password is different from the Windows password, the Windows will be unable to remember
your credentials and you will always be required to enter the sharing password for USB access.
4 ) Enable Authentication to apply the sharing account.
• If you leave Share All enabled, click the button to enable Authentication for all
folders.
• If Share All is disabled, enable Authentication for specific folders.
34
Chapter 6 USB Application
Note:
Due to Windows credential mechanism, you might be unable to access the USB disk after changing Authentication
settings. Please log out from Windows and try to access again.
3. Enable the FTP (via Internet)
Check this box to enable FTP(via Internet) and click Save.
4. Access Your USB Disk via Internet
Now different clients with Internet connection can access the USB disk:
35
Chapter 6 USB Application
Computer
1 ) Open the Windows Explorer (or go to Computer, only for
Windows users) or open a web browser.
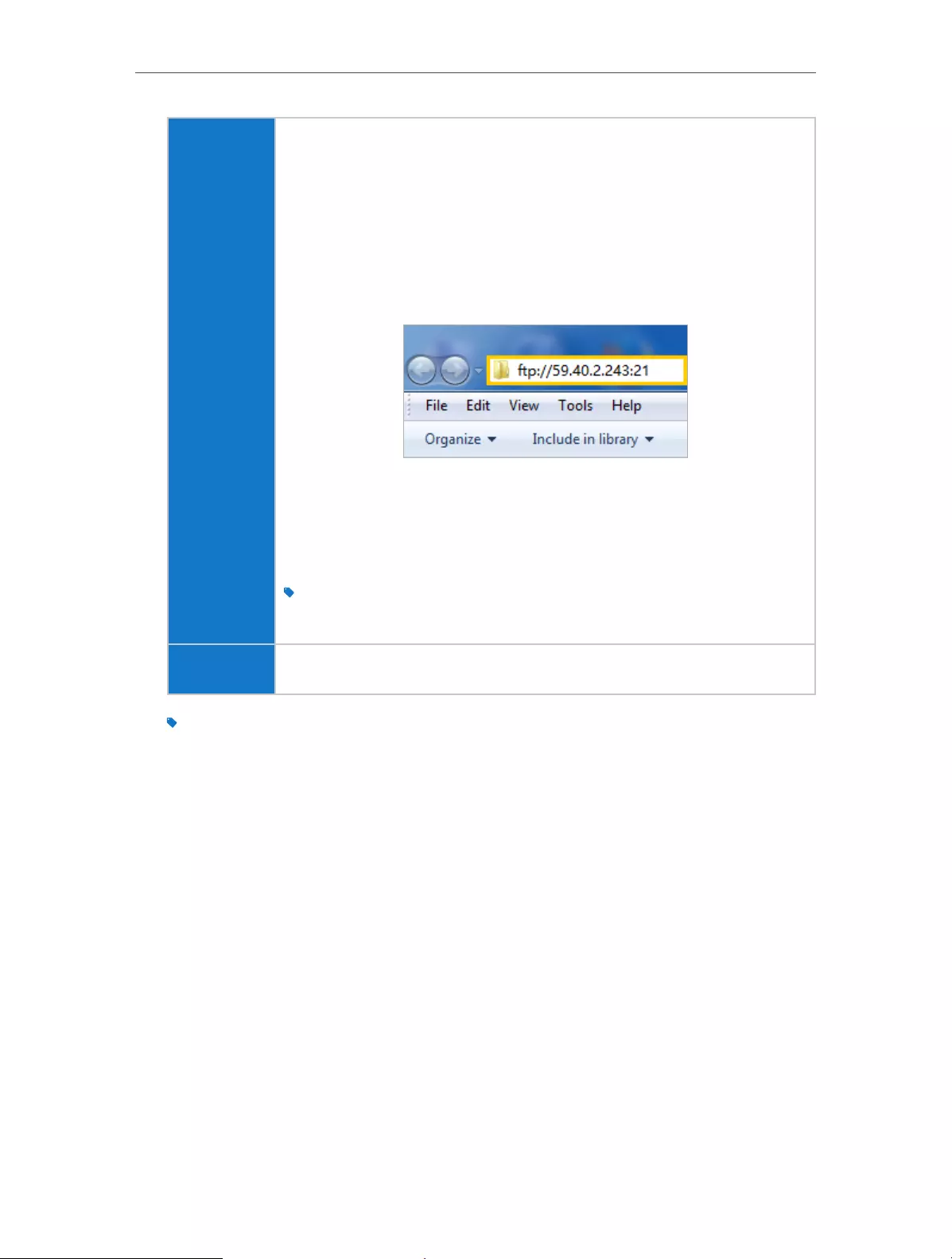
2 ) Type the server address in the address bar:
Type in ftp://<WAN IP address of the router>:<port number>
(such as ftp://59.40.2.243:21). If you have specified the domain
name of the router, you can also type in ftp://<domain
name>:<port number> (such as ftp://MyDomainName:21)
The Address Bar the Windows Explorer (Windows 7)
3 ) Press [Enter] on the keyboard.
4 ) Access with the username and password you set in Step 2
Enable Authentication for Data Security.
Tips:
You can also access the USB disk via a third-party app for network files management,
which can resume broken file transfers.
Pad Use a third-party app for network files management.
Tips:
Click Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account to learn how to set up a domain name for you router.
6. 2. 2. Customize Your Settings
¾To Only Share Specific Content
By default, Share All is enabled so all content on the USB disk is shared. If you want to
only share specific folders, follow the steps below:
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
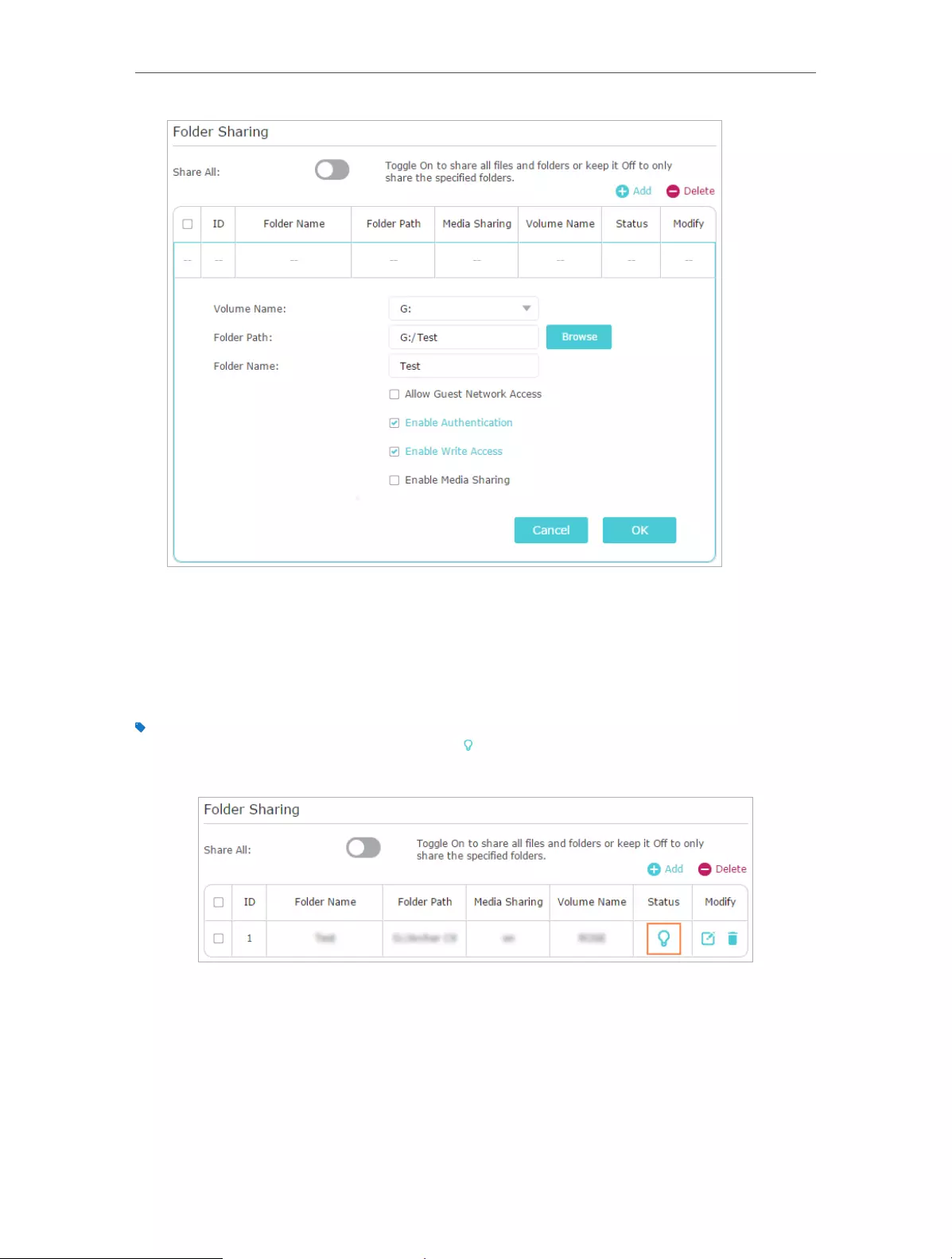
2. Go to Basic > USB Settings > Sharing Access. Focus on the Folder Sharing section.
Click the button to disable Share All, then click Add to add a new sharing folder.
36
Chapter 6 USB Application
3. Select the Volume Name and Folder Path, then specify the Folder Name as you like.
4. Tick Enable Authentication. If you allow network clients to modify this folder, tick
Enable Write Access.
5. Click OK.
Tips:
The router can share 32 volumes at most. You can click on the page to detach the corresponding volume you do
not need to share.
6. 3. Media Sharing
The Media Sharing feature allows you to view photos, play music and watch movies
stored on the USB disk directly from DLNA-supported devices, such as your computer,
pad and PS2/3/4.
37
Chapter 6 USB Application
6. 3. 1. Access the USB Disk
1. Connect Your USB Disk
Insert your USB storage device into the router’s USB port directly or using a USB
cable. Wait several seconds until the USB LED becomes solid on.
Tips:
• If you use USB hubs, make sure no more than 4 devices are connected to the router.
• If the USB storage device requires using bundled external power, make sure the external power has been
connected.
• If you use a USB hard drive, make sure its file system is FAT32, exFat, NTFS or HFS+.
• Before you physically disconnect a USB device from the router, safely remove it to avoid data damage: Go to
Advanced > USB Settings > Device Settings and click .
2. Access the Media Files on Your USB Disk
Now the DLNA-supported devices (such as your computer and pad) connected to
the router can detect and play the media files on the USB disks.
Windows
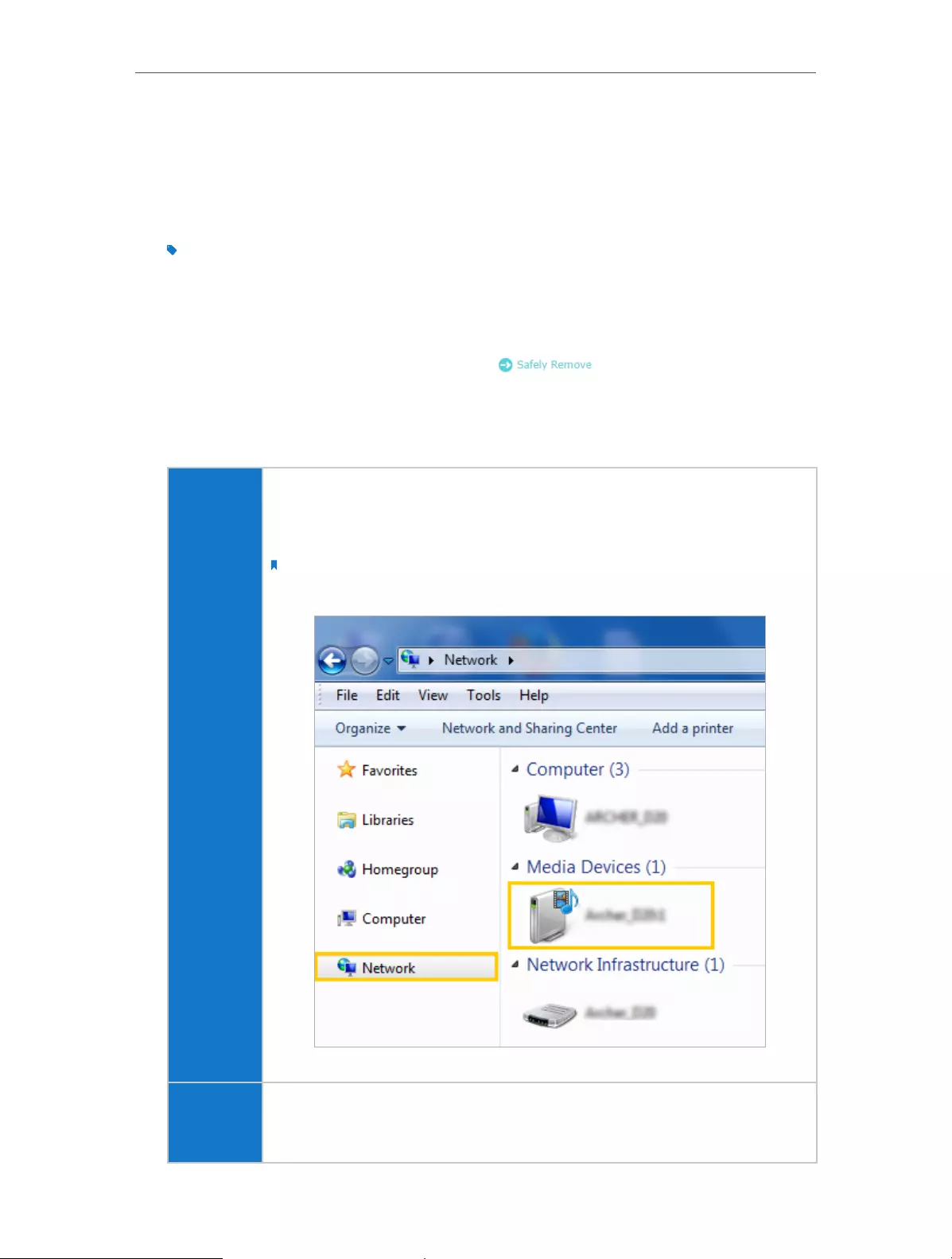
computer
• Go to Computer > Network, then click the Media Server Name (Model number-
share by default) in the Media Devices section.
Note:
Here we take Windows 7 as an example.
Pad • Use a third-party DLNA-supported player.
38
Chapter 6 USB Application
6. 3. 2. Customize Your Settings
¾To Only Share Specific Content
By default, Share All is enabled so all content on the USB disk is shared. If you want to
only share specific folders, follow the steps below:
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and then log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
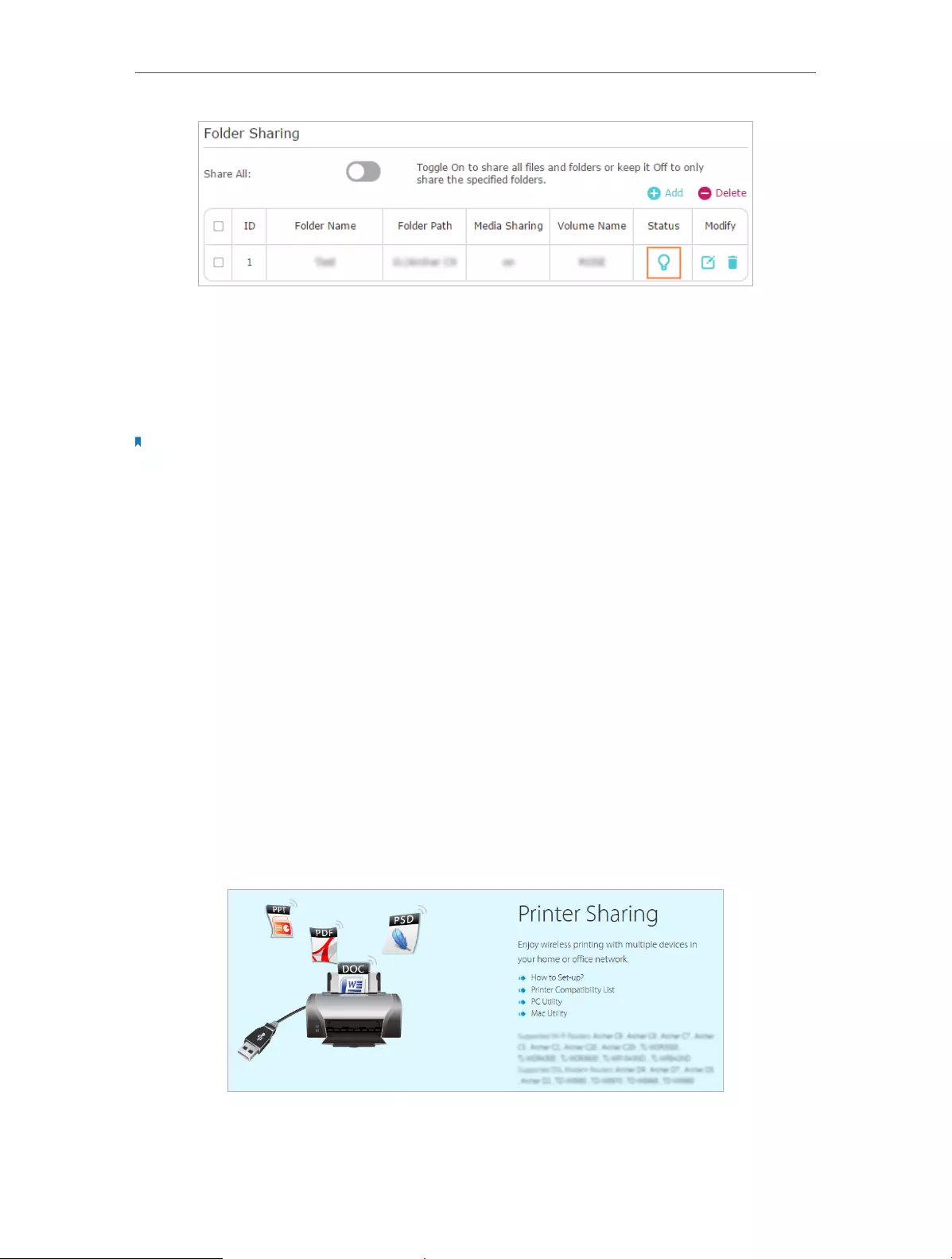
2. Go to Basic > USB Settings > Sharing Access.
3. Focus on the section of Folder Sharing. Click the button to disable Share All, and
then click Add to add a new sharing folder.
4. Select the Volume Name and Folder Path, and then enter a Folder Name as needed.
5. Tick Enable Media Sharing and click OK.
Tips:
The router can share 32 volumes at most. You can click on the page to detach the corresponding volume you do
not need to share.
39
Chapter 6 USB Application
6. 4. Printer Sharing
The Printer Sharing feature helps you share a printer with different computers connected
to the router.
Note:
Printers unlisted on this page may be incompatible with the router:
http://www.tp-link.com/common/compatible/print-server/.
1. Install the Driver of the Printer
Make sure you have installed the driver of the printer on each computer that needs
printer service.
If you do not have the driver, contact the printer manufacturer.
2. Connect the Printer
Cable a printer to the USB port with the USB cable. Wait several seconds until the
USB LED becomes solid on.
3. Install the TP-LINK USB Printer Controller Utility
TP-LINK USB Printer Controller Utility helps you access the shared printer. Download
and Install the utility on each computer that needs printer service.
1 ) Visit http://www.tp-link.com/app/usb/.
2 ) Click PC Utility (for Windows users) or Mac Utility to download the installation
file and uncompress it.
40
Chapter 6 USB Application
3 ) Open the uncompressed folder, then click TP-LINK USB Printer Controller Setup
(for Windows users) or TP-LINK UDS Printer Controller Installer (for Mac users)
to install the utility.
4. Access the Printer
You should set the shared printer as Auto-Connect Printer on every computer that
needs printer service.
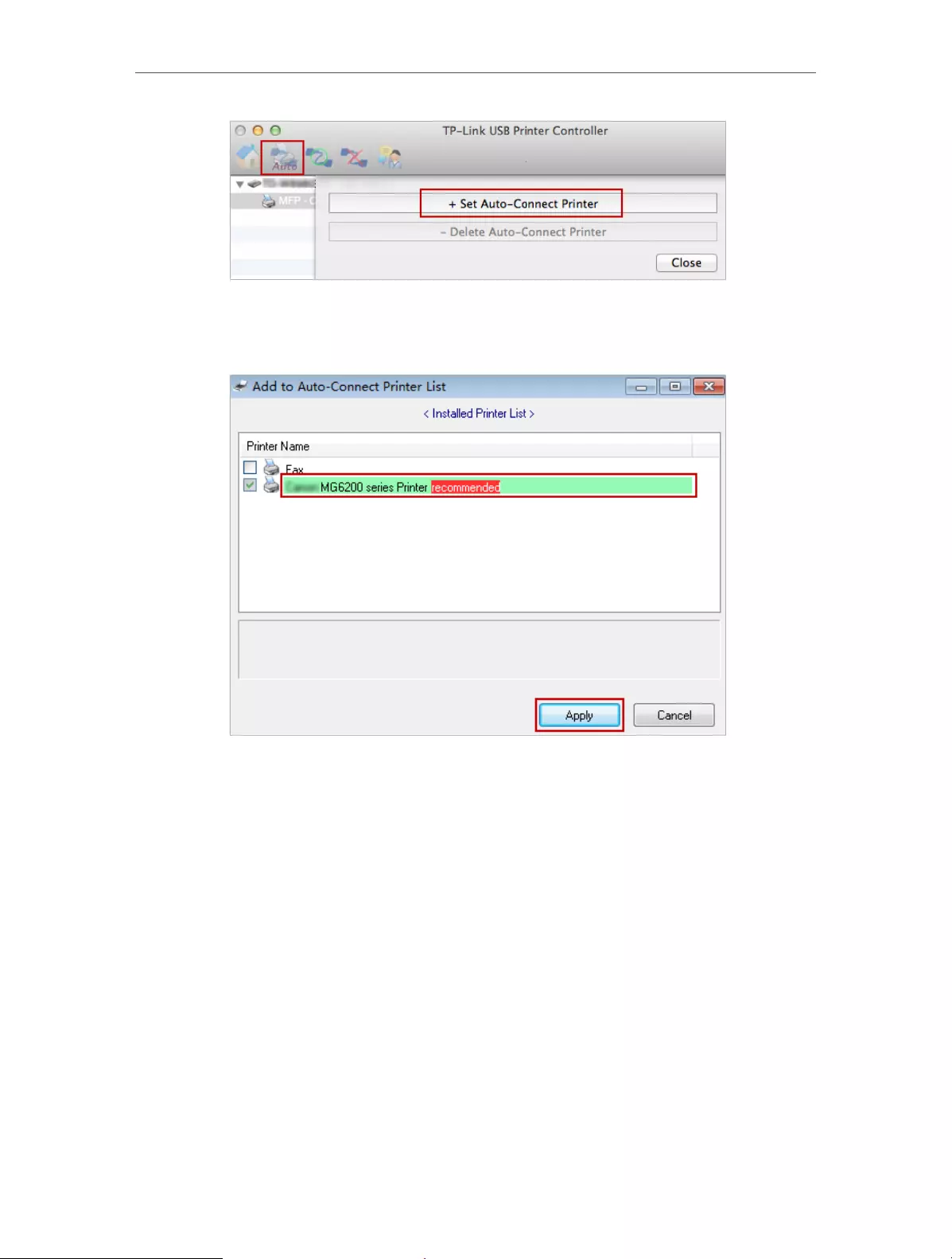
1 ) Double-click the icon on your desktop to launch the USB Printer Controller.
2 ) Highlight the printer you share.
Windows
Mac
3 ) Click the Auto-Connect for printing tab to pull down a list, and then select Set
Auto-Connect Printer.
Windows
41
Chapter 6 USB Application
Mac
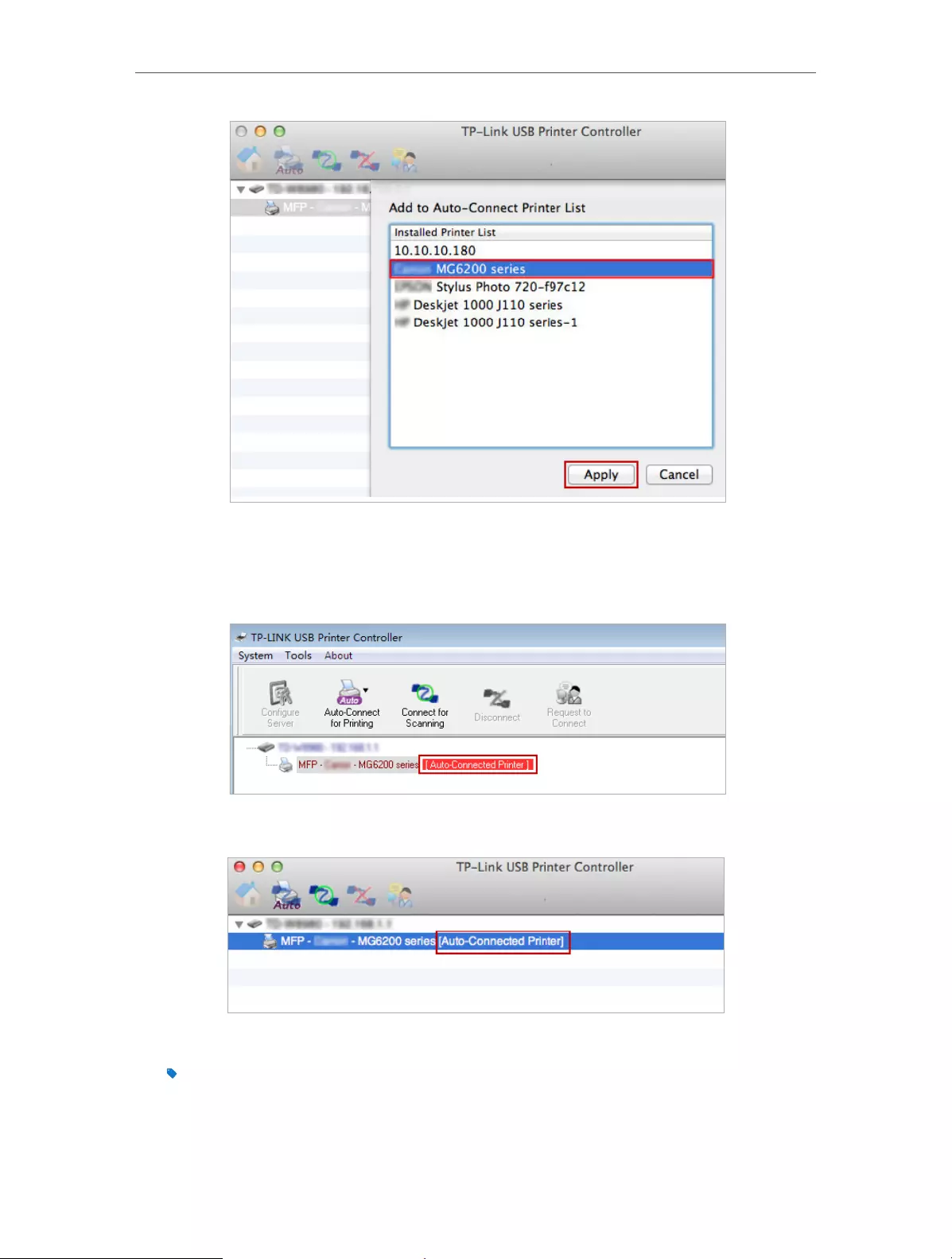
4 ) Select the printer you share, and then click Apply.
Windows
42
Chapter 6 USB Application
Mac
5 ) You will see the printer marked as Auto-Connect Printer. Now you can print
with this printer.
Windows
Mac
Tips:
The Print Server also allows different clients to share the scan feature of MFPs (Multi-Function Printers). To
scan with TP-LINK USB Printer Controller, right-click the printer and select Network Scanner. Then, a scanning
window will pop up. Finish the scanning process by following on-screen instructions.

Chapter 7
Parental Controls
This function allows you to block inappropriate, explicit and malicious websites, and
control access to specified websites at specified time.
44
Chapter 7 Parental Controls
Control the times of day my children or other home network
users are allowed to access the Internet and even types of
websites they can visit.
For example, I want to allow my children’s devices (e.g. a
computer or a tablet) to access only www.tp-link.com and
Wikipedia.org from 18:00 (6PM) to 22:00 (10PM) at the weekend
and not other times.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > Parental Controls and enable Parental
Controls.
3. Click Add. And then Click View Existing Devices, and select
the access device. Or, input the Device Name and MAC
Address manually.
4. Click the icon to set the Internet Access Time. Drag the
cursor over the appropriate cell(s) and click OK.
I want to:I want
How can I
do that?
45
Chapter 7 Parental Controls
5. Enter a Description for the entry, check the box for Enable
This Entry, and then click OK.
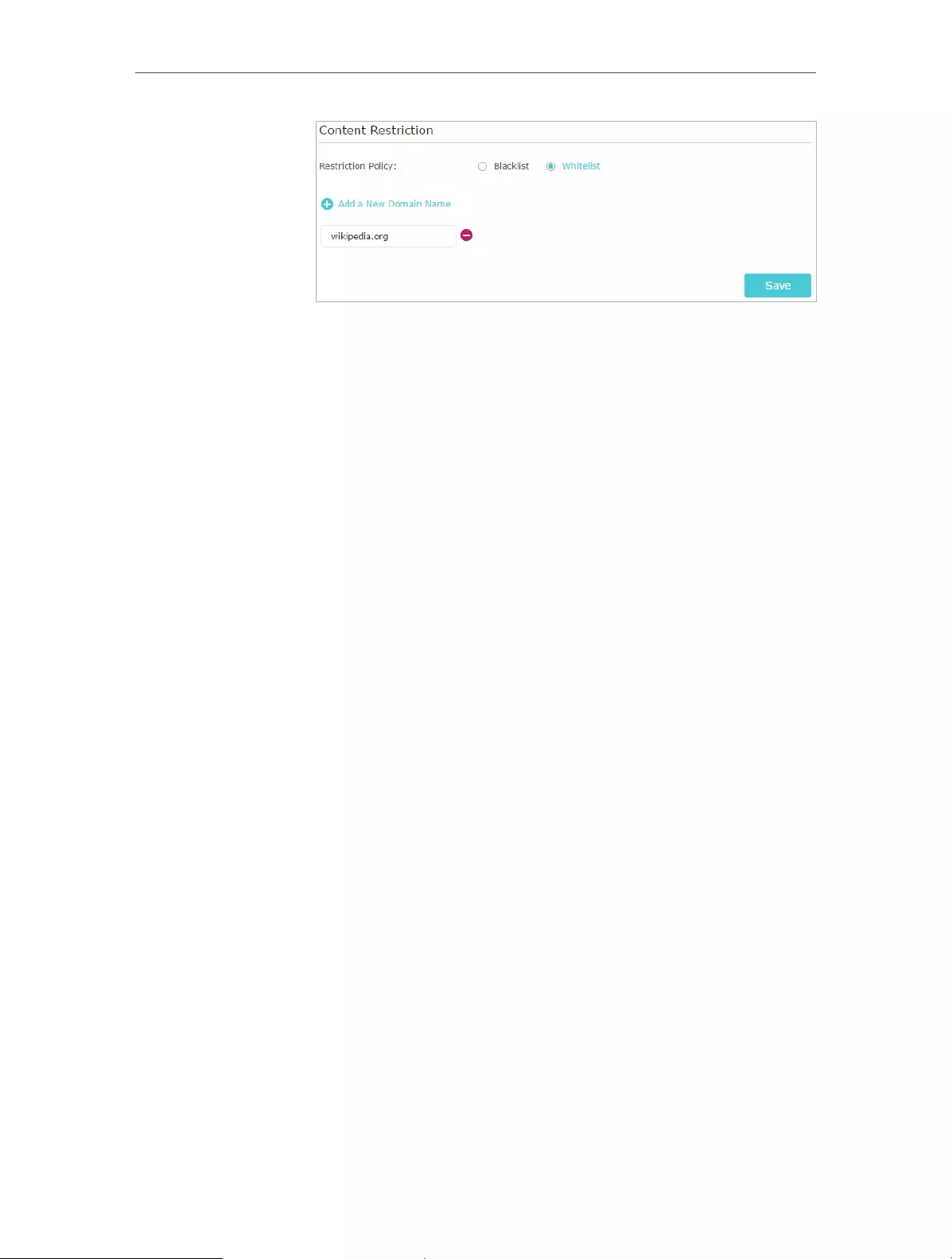
6. Select Whitelist as the restriction policy.
Tips:
• With Blacklist selected, the controlled devices cannot access any websites
containing the specified keywords during the Internet Access Time period.
• With Whitelist selected, the controlled devices can only access websites containing
the specified keywords during the Internet Access Time period.
7. Click . Enter a website and click Save.
You can add up to 32 keywords for either Blacklist or Whitelist.
Below are some sample entries to allow access.
• For Whitelist: Enter a web address (e.g. wikipedia.org)
to allow access only to its related websites. If you wish
to block all Internet browsing access, do not add any
keyword to the Whitelist.
• For Blacklist: Specify a web address (e.g. wikipedia.org), a
web address keyword (e.g. wikipedia) or a domain suffix
(eg. .edu or .org) to block access only to the websites
containing that keyword or suffix.
46
Chapter 7 Parental Controls
Now you can control your children’s Internet access as needed.
Done!
48
Chapter 8 QoS
8. 1. Prioritize Internet Traffic with QoS
QoS (Quality of Service) is designed to ensure the efficient operation of the network
when come across network overload or congestion.
Specify priority levels for some devices or applications.
For example, I have several devices that are connected to my
wireless network. I would like to set an intermediate speed on
the Internet for my phone.
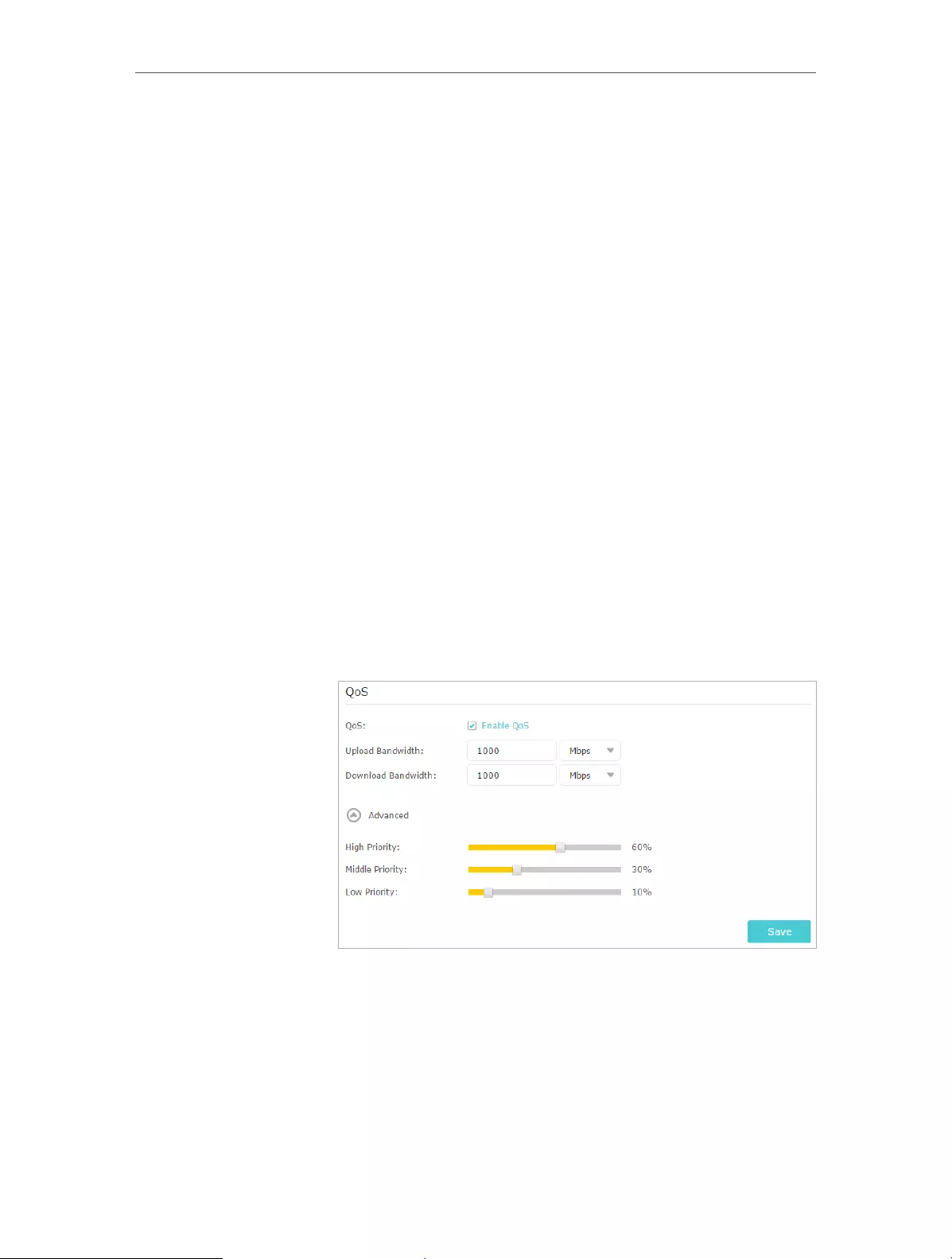
1. Enable QoS and set bandwidth allocation.
1 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username
and password you set for the router.
2 ) Go to Advanced > QoS > Settings.
3 ) Select Enable QoS.
4 ) Input the maximum upload and download bandwidth
provided by your Internet service provider. 1Mbps equal
s to 1000Kbps.
5 ) Click Advanced and drag the scroll bar to set the
bandwidth priority percentage.
6 ) Click Save.
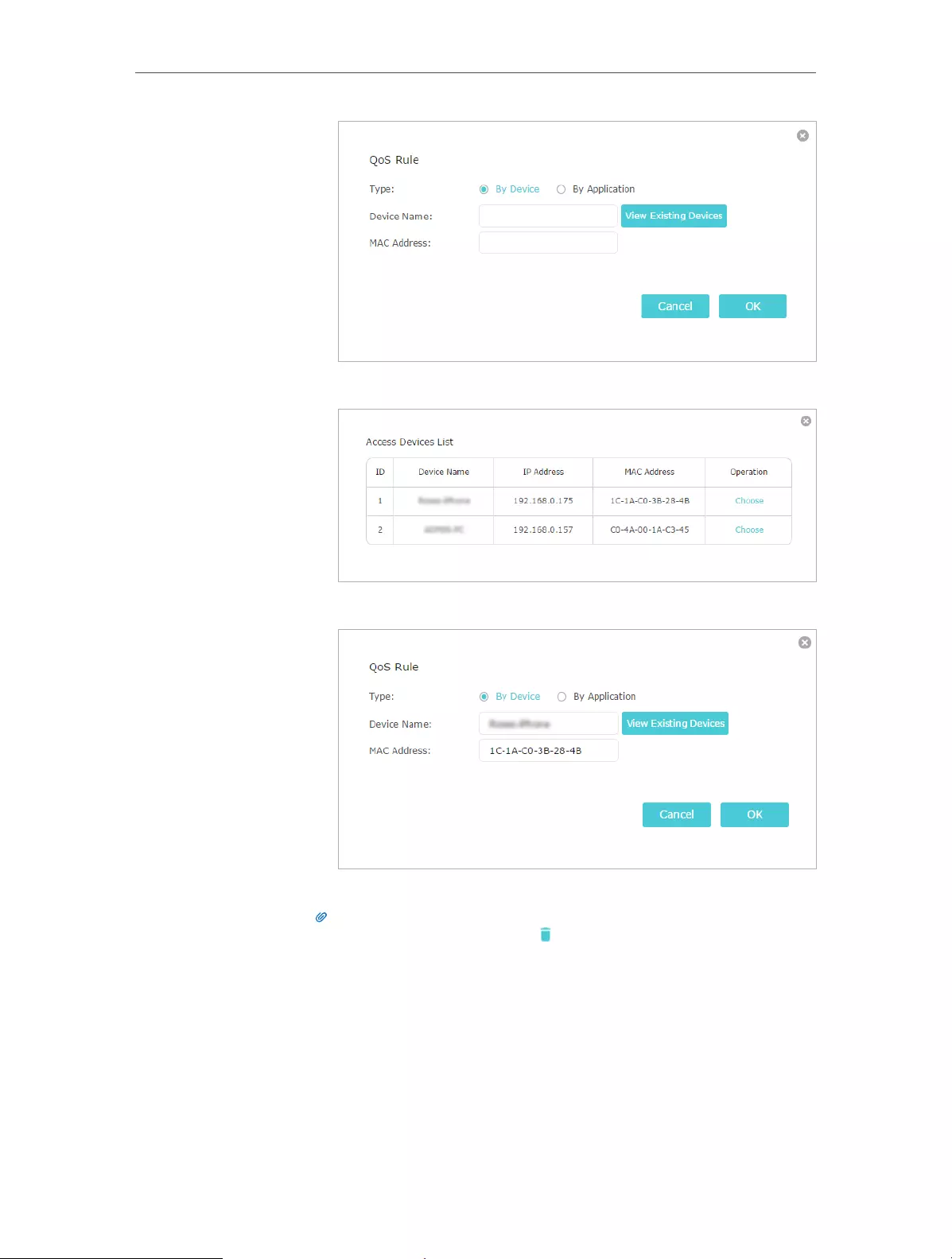
2. Add a middle priority QoS rule for the phone.
1 ) Select By Device and then click View Existing Devices.
I want to:
How can I
do that?
49
Chapter 8 QoS
2 ) Choose the respective device from the list.
3 ) Click OK.
3. Refer to the steps above to apply other QoS rules if any.
Note:
If you want to delete a QoS rule, click to remove the responding rule from the list.
Now QoS is implemented to prioritize Internet traffic.
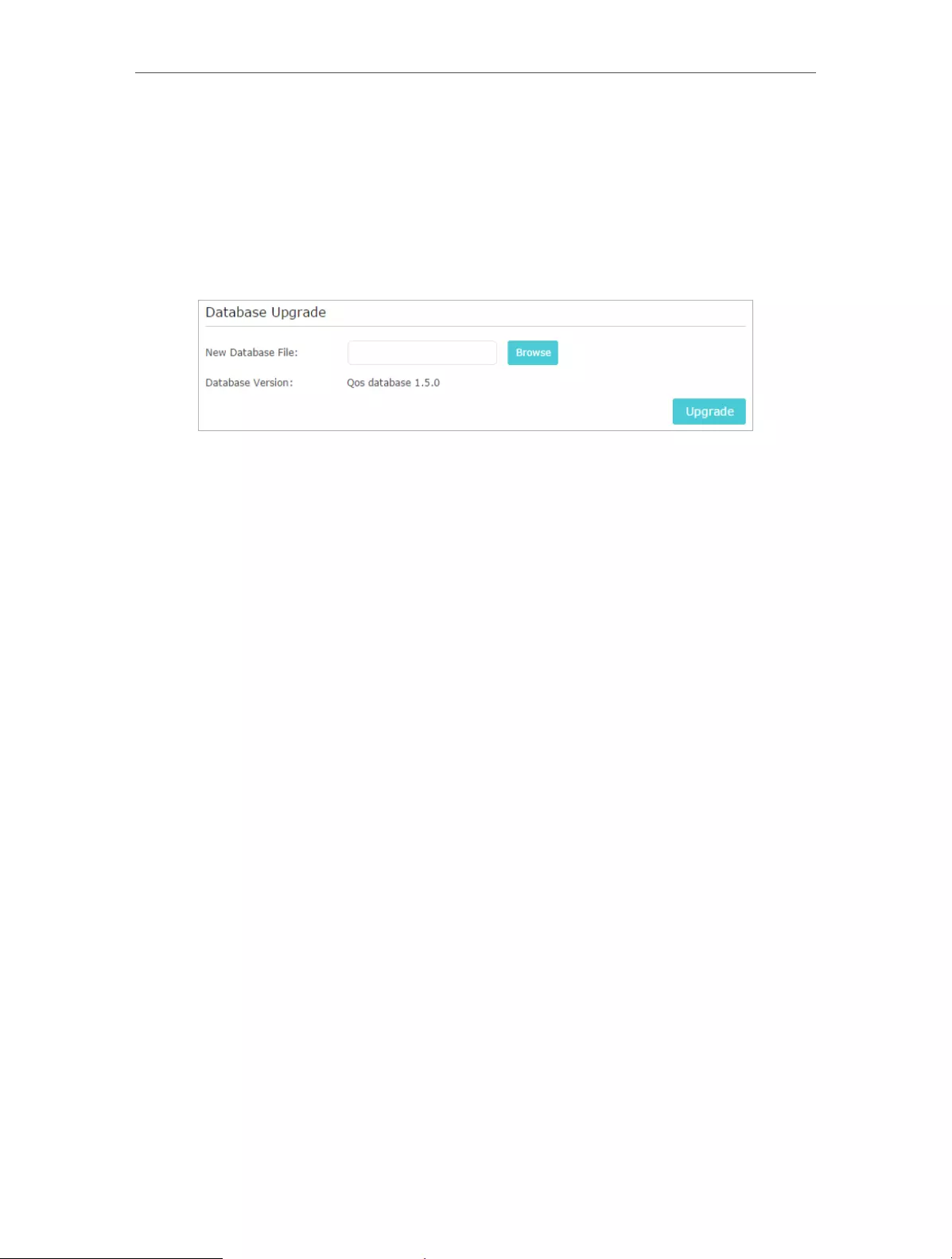
8. 2. Update the Database
This function can help to add or update the applications the router supports. If the
applications you need are not listed in the Application list, you can try to download
the new version and upgrade the datebase. New database versions are posted at
www.tp-link.com and can be downloaded for free.
Done!
50
Chapter 8 QoS
1. Download the latest QoS database from our website (www.tp-link.com).
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
3. Go to Advanced > QoS > Database. Click Browse to select the database upgrade file,
and then click Upgrade. Wait until the upgrade is completed and do not operate
during the process.

Chapter 9
Network Security
This chapter guides you on how to protect your home network from cyber attacks
and unauthorized users by implementing these three network security functions. You
can protect your home network against DoS (Denial of Service) attacks from flooding
your network with server requests using DoS Protection, block or allow specific client
devices to access your network using Access Control, or you can prevent ARP spoofing
and ARP attacks using IP & MAC Binding.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Protect the Network from Cyber Attacks
• Access Control
• IP & MAC Binding
52
Chapter 9 Network Security
9. 1. Protect the Network from Cyber Attacks
The SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) Firewall and DoS (Denial of Service) Protection
protect the router from cyber attacks.
The SPI Firewall can prevent cyber attacks and validate the traffic that is passing
through the router based on the protocol. This function is enabled by default, and it’s
recommended to keep the default settings.
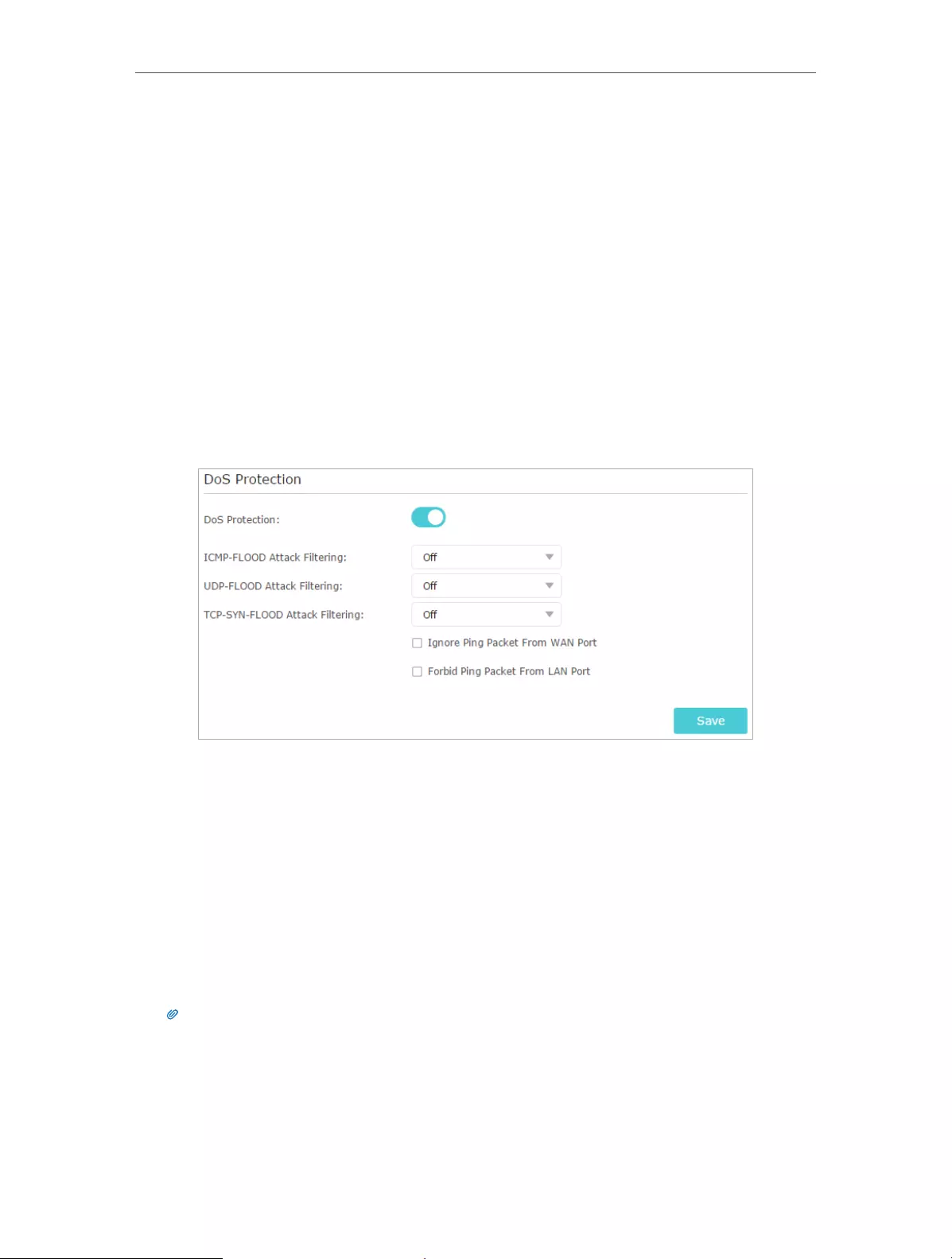
DoS Protection can protect your home network against DoS attacks from flooding your
network with server requests. Follow the steps below to configure DoS Protection.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for
the router.
2. Go to Advanced > Security > Settings.
3. Enable DoS Protection.
4. Set the level (Off, Low, Middle or High) of protection for ICMP-FLOOD Attack
Filtering, UDP-FlOOD Attack Filtering and TCP-SYN-FLOOD Attack Filtering.
• ICMP-FLOOD Attack Filtering - Enable to prevent the ICMP (Internet Control
Message Protocol) flood attack.
• UDP-FlOOD Attack Filtering - Enable to prevent the UDP (User Datagram
Protocol) flood attack.
• TCP-SYN-FLOOD Attack Filtering - Enable to prevent the TCP-SYN (Transmission
Control Protocol-Synchronize) flood attack.
Tips:
The level of protection is based on the number of traffic packets. The protection will be triggered immediately
when the number of packets exceeds the preset threshold value (the value can be set on Advanced > System
Tools > System Parameters > DoS Protection Level Settings), and the vicious host will be displayed in the
Blocked DoS Host List.
53
Chapter 9 Network Security
5. If you want to ignore the ping packets from the WAN port, select Ignore Ping Packet
From WAN Port; if you want to ignore the ping packets form the LAN port, select
Ignore Ping Packet From LAN Port.
6. Click Save.
9. 2. Access Control
Access Control is used to block or allow specific client devices to access your network
(via wired or wireless) based on a list of blocked devices (Blacklist) or a list of allowed
devices (Whitelist).
Block or allow specific client devices to access my network (via
wired or wireless).
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > Security > Access Control.
3. Enable Access Control.
4. Select the access mode to either block (recommended) or
allow the device(s) in the list.
To block specific device(s)
1 ) Select Blacklist and click Save.
2 ) Select the device(s) to be blocked in the Online Devices
table by ticking the box.
I want to:
How can I
do that?
54
Chapter 9 Network Security
3 ) Click Block above the Online Devices table. The selected
devices will be added to Devices in Blacklist automatically.
To allow specific device(s)
1 ) Select Whitelist and click Save.
2 ) Click Add in the Devices in Whitelist section. Enter the
Device Name and MAC Address (You can copy and paste
the information from the Online Devices list if the device
is connected to your network).
3 ) Click OK.
Now you can block or allow specific client devices to access your
network (via wired or wireless) using the Blacklist or Whitelist.
9. 3. IP & MAC Binding
IP & MAC Binding, namely, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Binding, is used to bind
network device’s IP address to its MAC address. This will prevent ARP Spoofing and
other ARP attacks by denying network access to an device with matching IP address in
the Binding list, but unrecognized MAC address.
Done!
55
Chapter 9 Network Security
Prevent ARP spoofing and ARP attacks.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > Security > IP & MAC Binding.
3. Enable ARP Binding.
4. Bind your device(s) according to your need.
To bind the connected device(s):
Click to add the corresponding device to the Binding List.
To bind the unconnected device
1 ) Click Add in the Binding List section.
2 ) Enter the MAC address and IP address that you want to
bind. Enter a Description for this binding entry.
3 ) Check the box for Enable This Entry and click OK.
Now you don’t need to worry about ARP spoofing and ARP
attacks!
I want to:
How can I
do that?
Done!

Chapter 10
NAT Forwarding
The router’s NAT (Network Address Translation) feature makes devices on the LAN use
the same public IP address to communicate with devices on the Internet, which protects
the local network by hiding IP addresses of the devices. However, it also brings about
the problem that an external host cannot initiatively communicate with a specified
device on the local network.
With the forwarding feature the router can penetrate the isolation of NAT and allows
devices on the Internet to initiatively communicate with devices on the local network,
thus realizing some special functions.
The TP-LINK router supports four forwarding rules. If two or more rules are set, the
priority of implementation from high to low is Virtual Servers, Port Triggering, UPNP
and DMZ.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Share Local Resources on the Internet by Virtual Servers
• Open Ports Dynamically by Port Triggering
• Make Applications Free from Port Restriction by DMZ
• Make Xbox Online Games Run Smoothly by UPnP
57
Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
10. 1. Share Local Resources on the Internet by Virtual
Servers
When you build up a server on the local network and want to share it on the Internet,
Virtual Servers can realize the service and provide it to Internet users. At the same time
Virtual Servers can keep the local network safe as other services are still invisible from
the Internet.
Virtual Servers can be used for setting up public services on your local network, such
as HTTP, FTP, DNS, POP3/SMTP and Telnet. Different services use different service ports.
Port 80 is used in HTTP service, port 21 in FTP service, port 25 in SMTP service and port
110 in POP3 service. Please verify the service port number before the configuration.
Share my personal website I’ve built in local network with my
friends through the Internet.
For example, the personal website has been built on my home
PC (192.168.0.100). I hope that my friends on the Internet can
visit my website in some way. The PC is connected to the router
with the WAN IP address 218.18.232.154.
Personal Website
Home
Router
WAN: 218.18.232.154LAN
1. Assign a static IP address to your PC, for example
192.168.0.100.
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
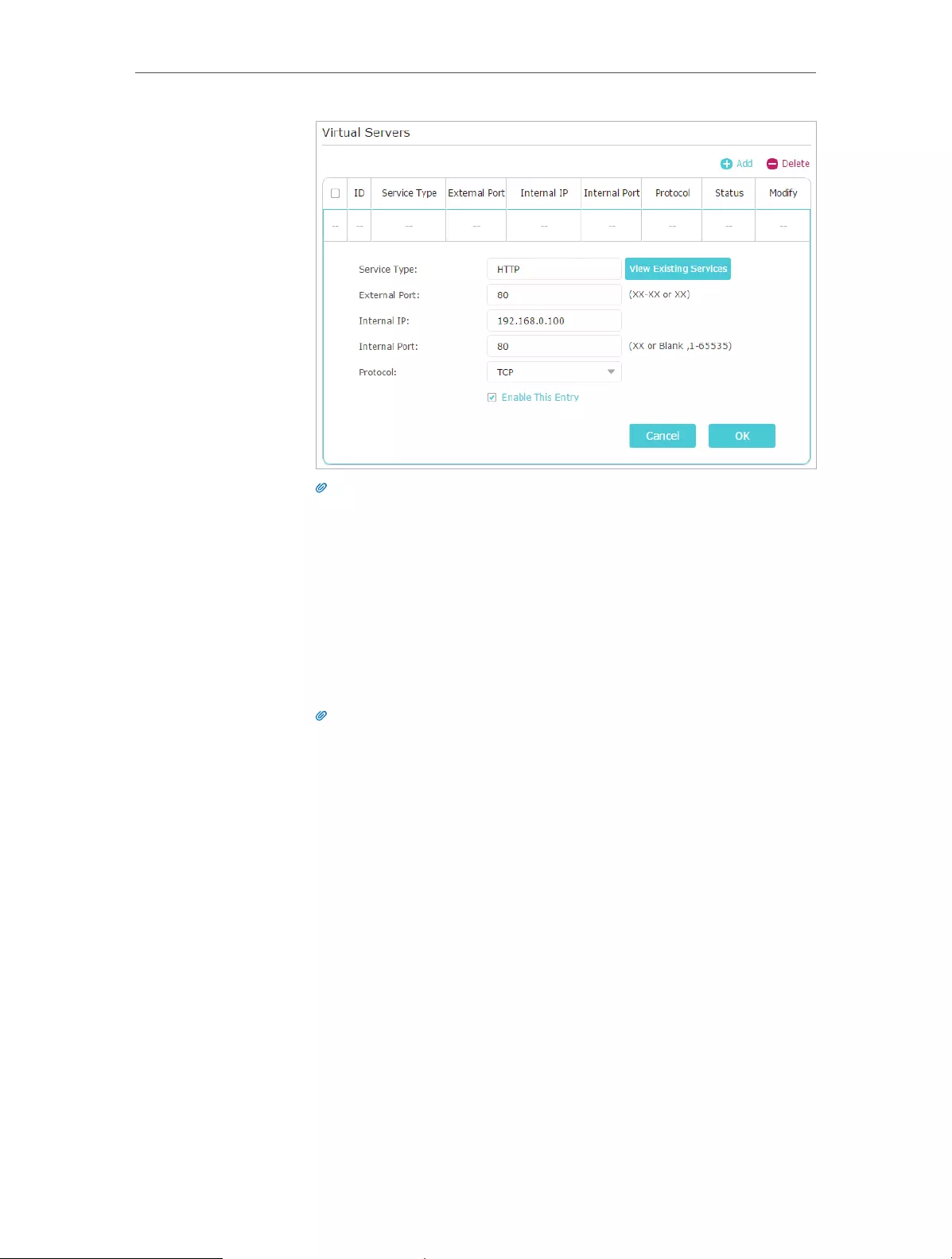
3. Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > Virtual Servers.
4. Click Add. Click View Existing Services and select HTTP. The
External Port, Internal Port and Protocol will be automatically
filled in. Enter the PC’s IP address 192.168.0.100 in the
Internal IP field.
5. Click OK.
I want to:
How can I
do that?
INTERNET
58
Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
Tips:
• It is recommended to keep the default settings of Internal Port and Protocol if you
are not clear about which port and protocol to use.
• If the service you want to use is not in the Service Type, you can enter the
corresponding parameters manually. You should verify the port number that the
service needs.
• You can add multiple virtual server rules if you want to provide several services in
a router. Please note that the External Port should not be overlapped.
Users on the Internet can enter http:// WAN IP (in this example:
http:// 218.18.232.154) to visit your personal website.
Tips:
• The WAN IP should be a public IP address. For the WAN IP is assigned dynamically
by the ISP, it is recommended to apply and register a domain name for the WAN
referring to Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account. Then users on the Internet can use
http:// domain name to visit the website.
• If you have changed the default External Port, you should use
http:// WAN IP: External Port or http:// domain name: External Port to visit the
website.
10. 2. Open Ports Dynamically by Port Triggering
Port Triggering can specify a triggering port and its corresponding external ports.
When a host on the local network initiates a connection to the triggering port, all the
external ports will be opened for subsequent connections. The router can record the IP
address of the host. When the data from the Internet return to the external ports, the
router can forward them to the corresponding host. Port Triggering is mainly applied to
online games, VoIPs, video players and common applications including MSN Gaming
Zone, Dialpad and Quick Time 4 players, etc.
Follow the steps below to configure the Port Triggering rules:
Done!
59
Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
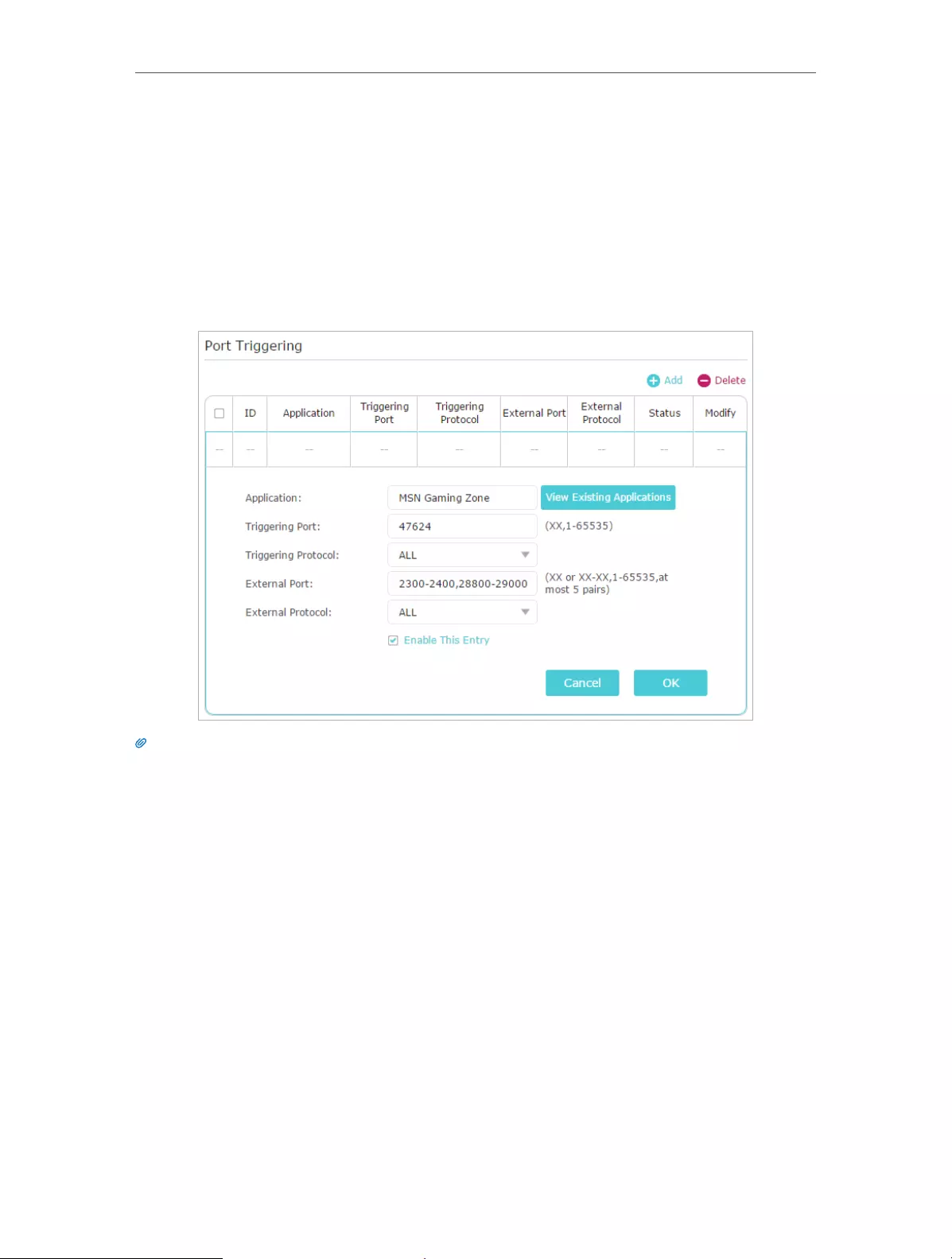
2. Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > Port Triggering and click Add.
3. Click View Existing Applications, and select the desired application. The External Port,
Internal Port and Protocol will be automatically filled in. The following picture takes
application MSN Gaming Zone as an example.
4. Click OK.
Tips:
• You can add multiple port triggering rules according to your network need.
• The triggering ports can not be overlapped.
• If the application you need is not listed in the Existing Applications list, please enter the parameters manually.
You should verify the external ports the application uses first and enter them into External Port field according
to the format the page displays.
10. 3. Make Applications Free from Port Restriction by
DMZ
When a PC is set to be a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) host on the local network, it is totally
exposed to the Internet, which can realize the unlimited bidirectional communication
between internal hosts and external hosts. The DMZ host becomes a virtual server with
all ports opened. When you are not clear about which ports to open in some special
applications, such as IP camera and database software, you can set the PC to be a DMZ
host.
60
Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
Note:
When DMZ is enabled, the DMZ host is totally exposed to the Internet, which may bring some potential safety
hazards. If DMZ is not in use, please disable it in time.
Make the home PC join the Internet online game without port
restriction.
For example, due to some port restriction, when playing the
online games, you can login normally but cannot join a team
with other players. To solve this problem, set your PC as a DMZ
host with all ports open.
1. Assign a static IP address to your PC, for example
192.168.0.100.
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
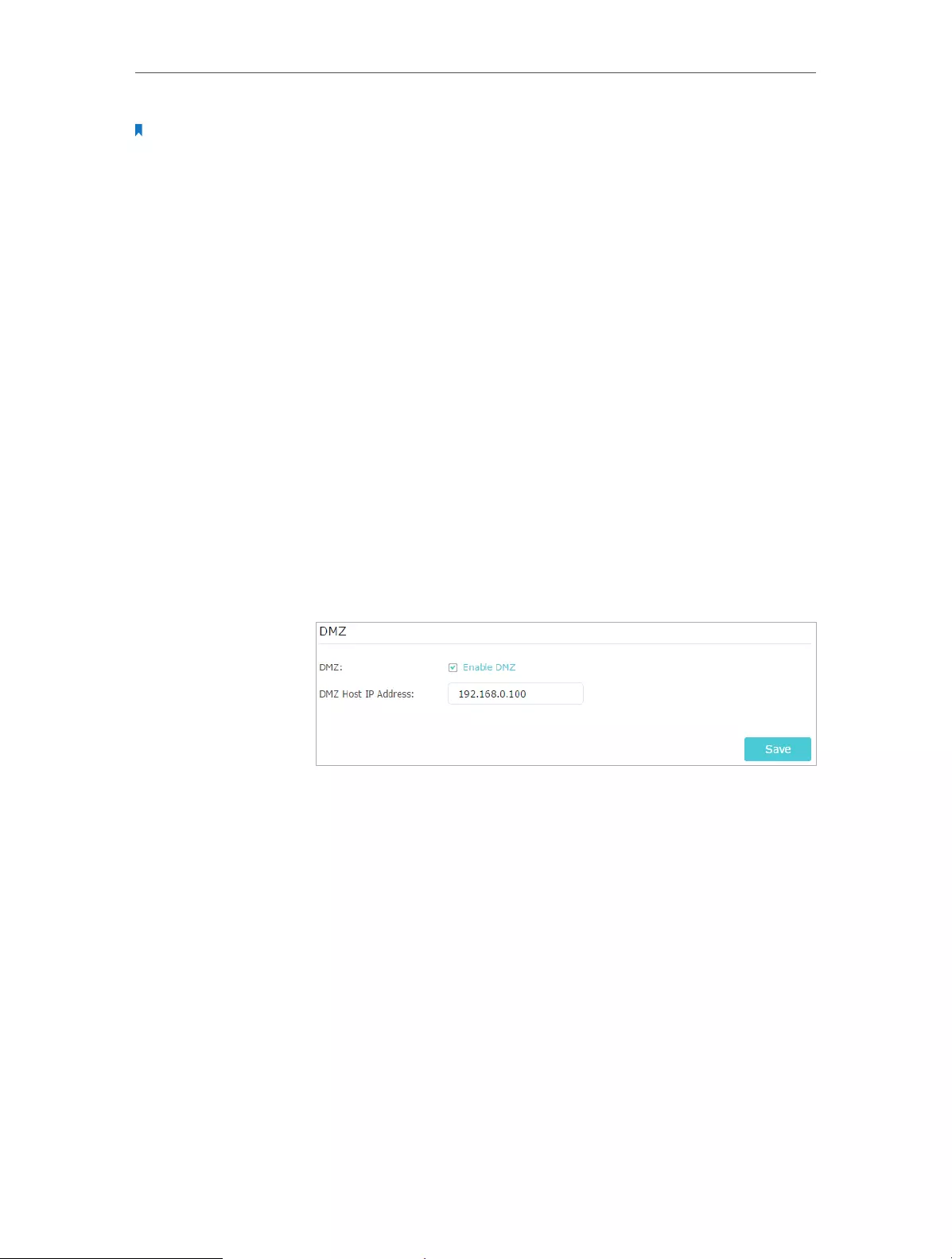
3. Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > DMZ and select Enable
DMZ.
4. Enter the IP address 192.168.0.100 in the DMZ Host IP
Address filed.
5. Click Save.
The configuration is completed. You’ve set your PC to a DMZ
host and now you can make a team to game with other players.
10. 4. Make Xbox Online Games Run Smoothly by UPnP
The UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) protocol allows applications or host devices
to automatically find the front-end NAT device and send request to it to open the
corresponding ports. With UPnP enabled, the applications or host devices on the local
network and the Internet can freely communicate with each other thus realizing the
seamless connection of the network. You may need to enable the UPnP if you want
to use applications for multiplayer gaming, peer-to-peer connections, real-time
communication (such as VoIP or telephone conference) or remote assistance, etc.
I want to:
How can I
do that?
Done!
61
Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
Tips:
• UPnP is enabled by default in this router.
• Only the application supporting UPnP protocol can use this feature.
• UPnP feature needs the support of operating system (e.g. Windows Vista/ Windows 7/ Windows 8, etc. Some of
operating system need to install the UPnP components).
For example, when you connect your Xbox to the router which has connected to
the Internet to play online games, UPnP will send request to the router to open the
corresponding ports allowing the following data penetrating the NAT to transmit.
Therefore, you can play Xbox online games without a hitch.
XBOX Router
INTERNET
LAN WAN
If necessary, you can follow the steps to change the status of UPnP.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > NAT Forwarding > UPnP and toggle on or off according to your
needs.

Chapter 11
VPN Server
The VPN (Virtual Private Networking) Server allows you to access your home network in
a secured way through Internet when you are out of home. The router offers two ways
to setup VPN connection: OpenVPN and PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol) VPN.
OpenVPN is somewhat complex but with greater security and more stable. It is suitable
for restricted environment, such as campus network and company intranet.
PPTP VPN is more easily used and its speed is faster, it’s compatible with most operating
systems and also supports mobile devices. Its security is poor and your packets may be
cracked easily, and PPTP VPN connection may be prevented by some ISP.
This chapter contains the following sections, please choose the appropriate VPN server
connection type according to your needs.
• Use OpenVPN to Access Your Home Network
• Use PPTP VPN to Access Your Home Network
63
Chapter 11 VPN Server
11. 1. Use OpenVPN to Access Your Home Network
In the OpenVPN connection, the home network can act as a server, and the remote
device can access the server through the router which acts as an OpenVPN Server
gateway. To use the VPN feature, you should enable OpenVPN Server on your router,
and install and run VPN client software on the remote device. Please follow the steps
below to set up an OpenVPN connection.
Step1. Set up OpenVPN Server on Your Router
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
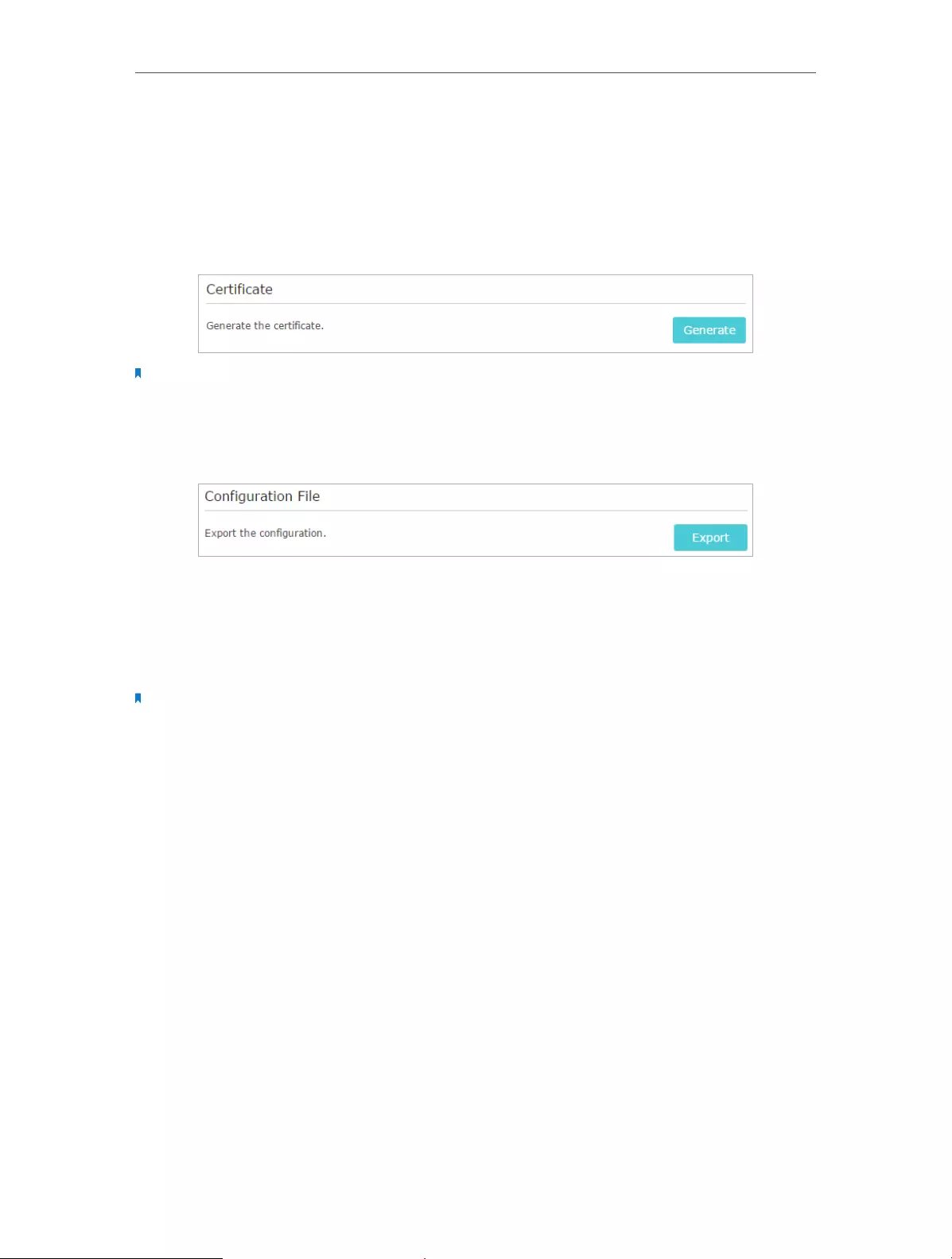
2. Go to Advanced > VPN Server > OpenVPN, and select Enable VPN Server.
Note:
• Before you enable VPN Server, we recommend you configure Dynamic DNS Service (recommended) or assign a
static IP address for router’s WAN port and synchronize your System Time with Internet.
• The first time you configure the OpenVPN Server, you may need to Generate a certificate before you enable the
VPN Server.
3. Select the Servive Type (communication protocol) for OpenVPN Server: UDP, TCP.
4. Enter a VPN Service Port to which a VPN device connects, and the port number should
be between 1024 and 65535.
5. In the VPN Subnet/Netmask fields, enter the range of IP addresses that can be leased
to the device by the OpenVPN server.
64
Chapter 11 VPN Server
6. Select your Client Access type. Select Home Network Only if you only want the
remote device to access your home network; select Internet and Home Network if
you also want the remote device to access Internet through the VPN Server.
7. Click Save.
8. Click Generate to get a new certificate.
Note:
If you have already generated one, please skip this step, or click Generate to update the certificate.
9. Click Export to save the OpenVPN configuration file which will be used by the remote
device to access your router.
Step 2. Configure OpenVPN Connection on Your Remote Device
1. Visit http://openvpn.net/index.php/download/community-downloads.html to
download the OpenVPN software, and install it on your device where you want to
run the OpenVPN client utility.
Note:
You need to install the OpenVPN client utility on each device that you plan to apply the VPN funxtion to access your
router. Mobile devices should download a third-party app from Google Play or Apple App Store.
2. After the installation, copy the file exported from your router to the OpenVPN client
utility’s “config” folder (for example, C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config on Windows).
The path depends on where the OpenVPN client utility is installed.
3. Run the OpenVPN client utility and connect it to OpenVPN Server.
11. 2. Use PPTP VPN to Access Your Home Network
PPTP VPN Server is used to create a VPN connection for remote device. To use the VPN
feature, you should enable PPTP VPN Server on your router, and configure the PPTP
connection on the remote device. Please follow the steps below to set up a PPTP VPN
connection.
Step 1. Set up PPTP VPN Server on Your Router
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
65
Chapter 11 VPN Server
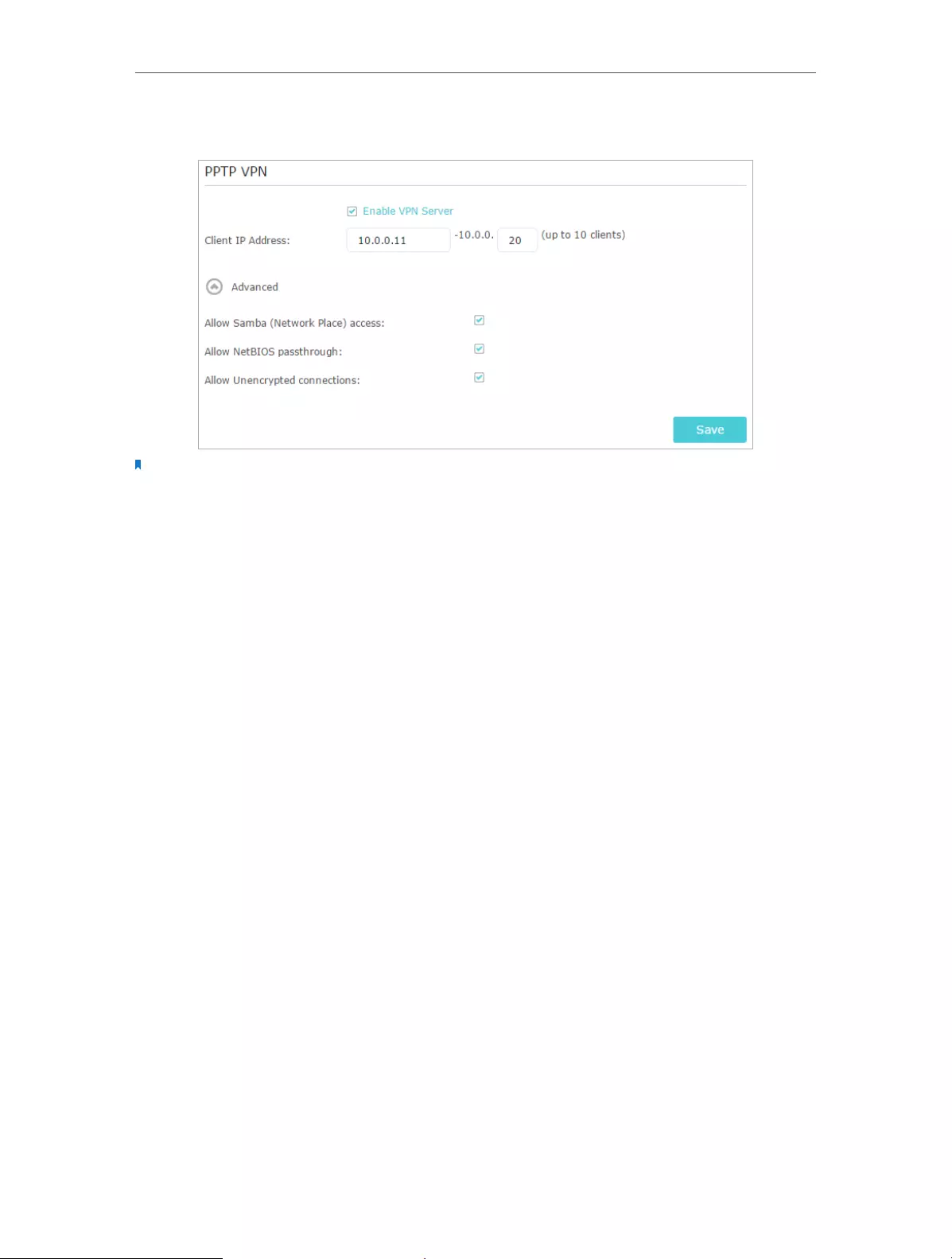
2. Go to Advanced > VPN Server > PPTP VPN, and select Enable VPN Server.
Note:
Before you enable VPN Server, we recommend you configure Dynamic DNS Service (recommended) or assign a
static IP address for router’s WAN port and synchronize your System Time with Internet.
3. In the Client IP Address filed, enter the range of IP addresses (up to 10) that can be
leased to the devices by the PPTP VPN server.
4. Click Advanced to set the PPTP connection permission according to your needs.
• Select Allow Samba (Network Place) access to allow your VPN device to access
your local Samba server.
• Select Allow NetBIOS passthrough to allow your VPN device to access your
Samba server using NetBIOS name.
• Select Allow Unencrypted connections to allow unencrypted connections to
your VPN server.
5. Click Save.
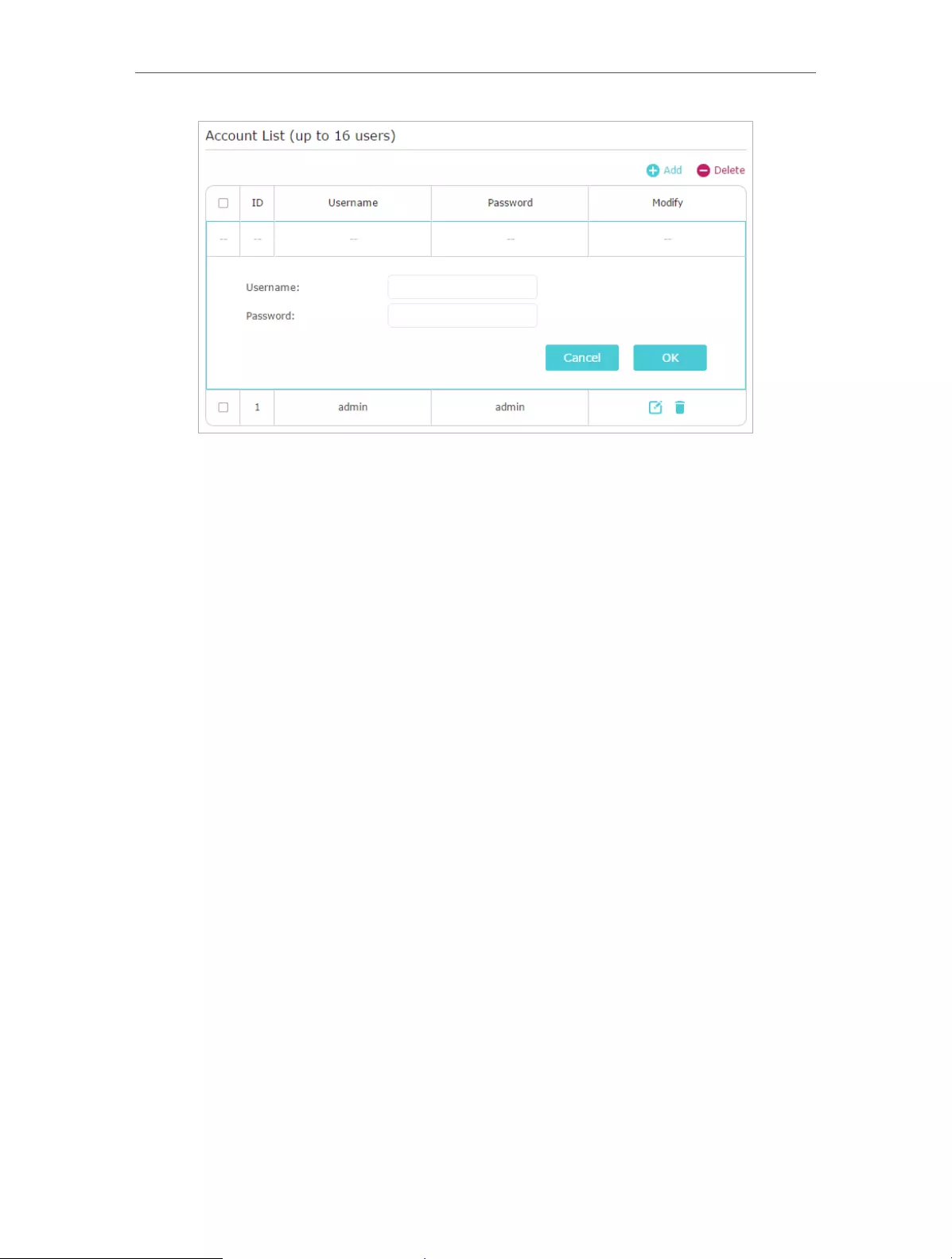
6. Configure the PPTP VPN connection account for the remote device, you can create
up to 16 accounts.
66
Chapter 11 VPN Server
1 ) Click Add.
2 ) Enter the Username and Password to authenticate devices to the PPTP VPN
Server.
3 ) Click OK.
Step 2. Configure PPTP VPN Connection on Your Remote Device
The remote device can use the Windows built-in PPTP software or a third-party PPTP
software to connect to PPTP Server. Here we use the Windows built-in PPTP software
as an example.
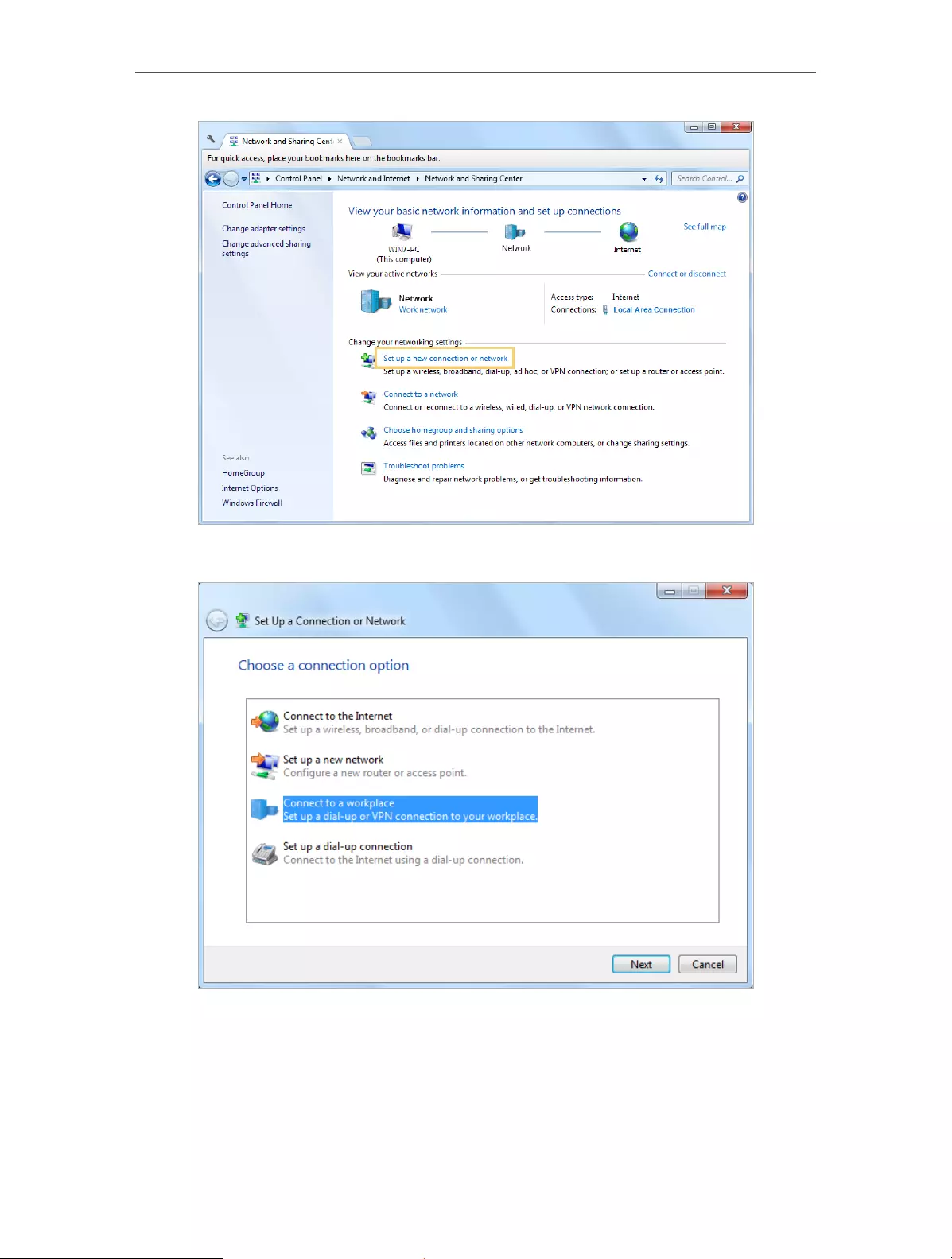
1. Go to Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
2. Select Set up a new connection or network.
67
Chapter 11 VPN Server
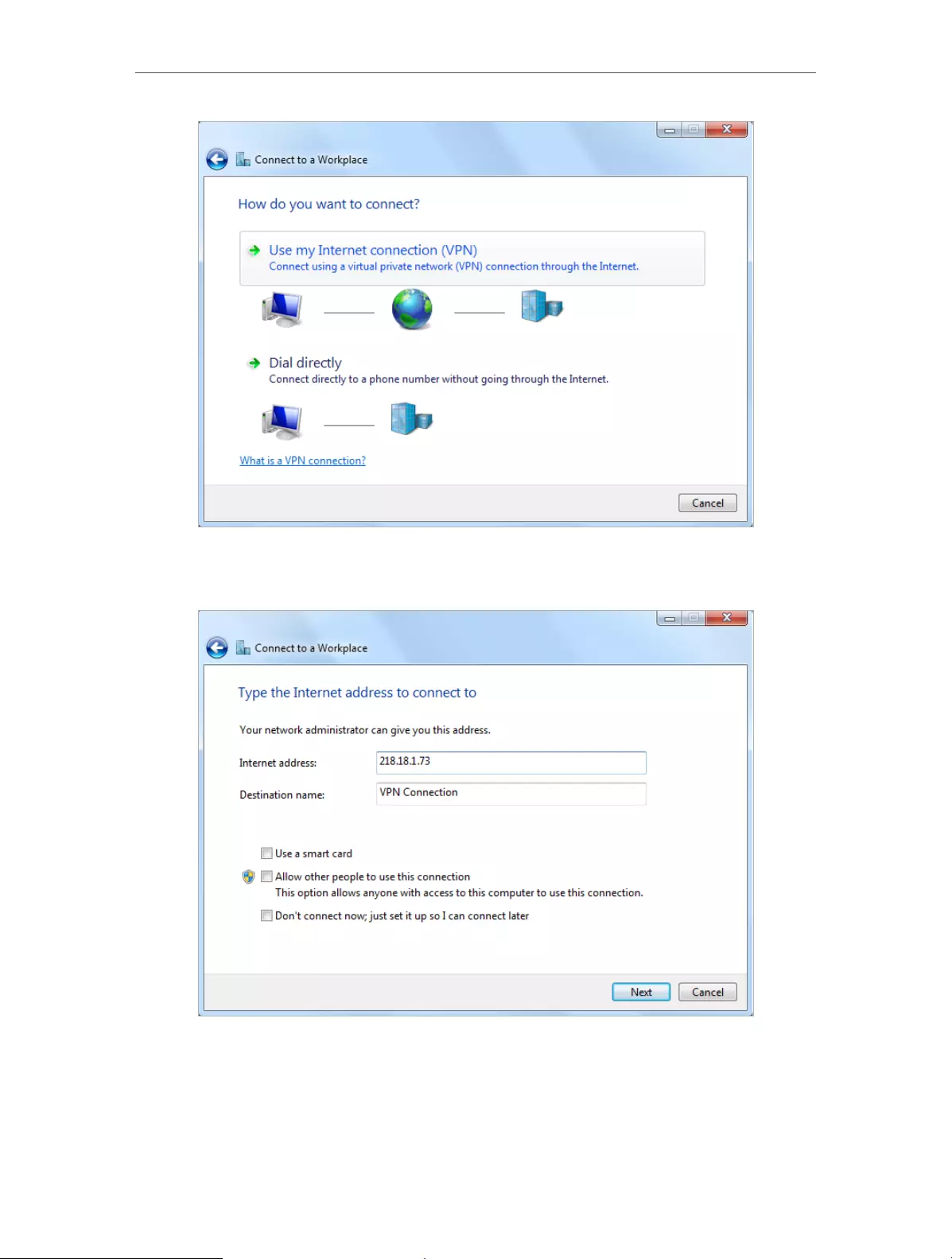
3. Select Connect to a workplace and click Next.
4. Select Use my Internet connection (VPN).
68
Chapter 11 VPN Server
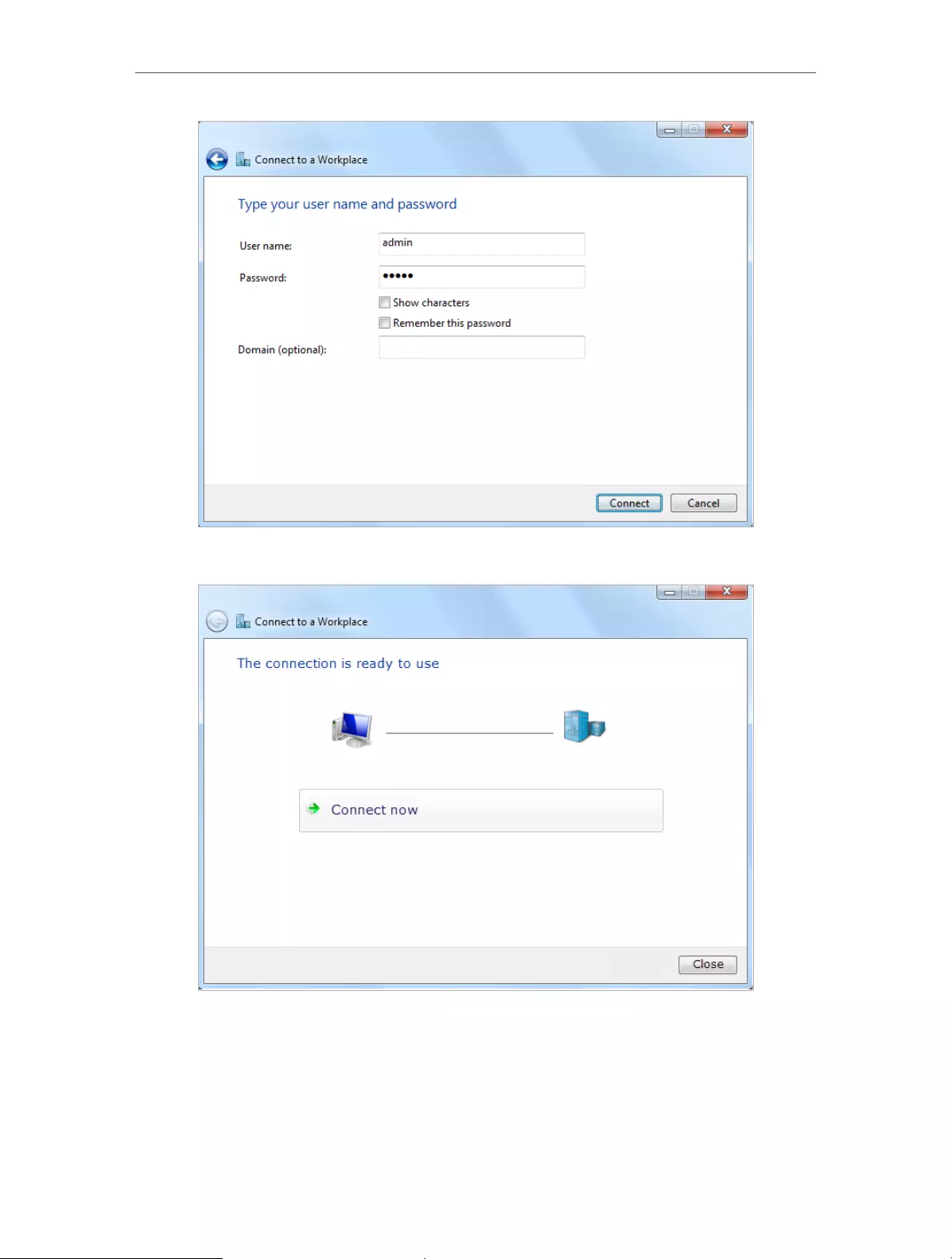
5. Enter the Internet IP address of the router (for example: 218.18.1.73) in the Internet
address field. Click Next.
6. Enter the User name and Password you have set for the PPTP VPN server on your
router, and click Connect.
69
Chapter 11 VPN Server
7. The PPTP VPN connection is created and ready to use.

Chapter 12
Customize Your Network
Settings
This chapter guides you on how to configure advanced network features.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Change the LAN Settings
• Configure to Support IPTV Service
• Specify DHCP Server Settings
• Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account
• Create Static Routes
• Specify Wireless Settings
• Use WPS for Wireless Connection
• Schedule Your Wireless Function
71
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
12. 1. Change the LAN Settings
The router is preset with a default LAN IP 192.168.0.1, which you can use to log in to
its web management page. The LAN IP address together with the Subnet Mask also
defines the subnet that the connected devices are on. If the IP address conflicts with
another device on your local network or your network requires a specific IP subnet, you
can change it.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Network > LAN.
3. Type in a new IP Address appropriate to your needs. And leave the Subnet Mask as
the default settings.
4. Click Save.
Note:
If you have set the Virtual Server, DMZ or DHCP address reservation, and the new LAN IP address is not in the same
subnet with the old one, then you should reconfigure these features.
12. 2. Set Up Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation feature combines two ports together to make a single high-
bandwidth data path, thus sustaining a higher-speed and more stable wired network.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Network > LAN.
3. Enable Link Aggregation.
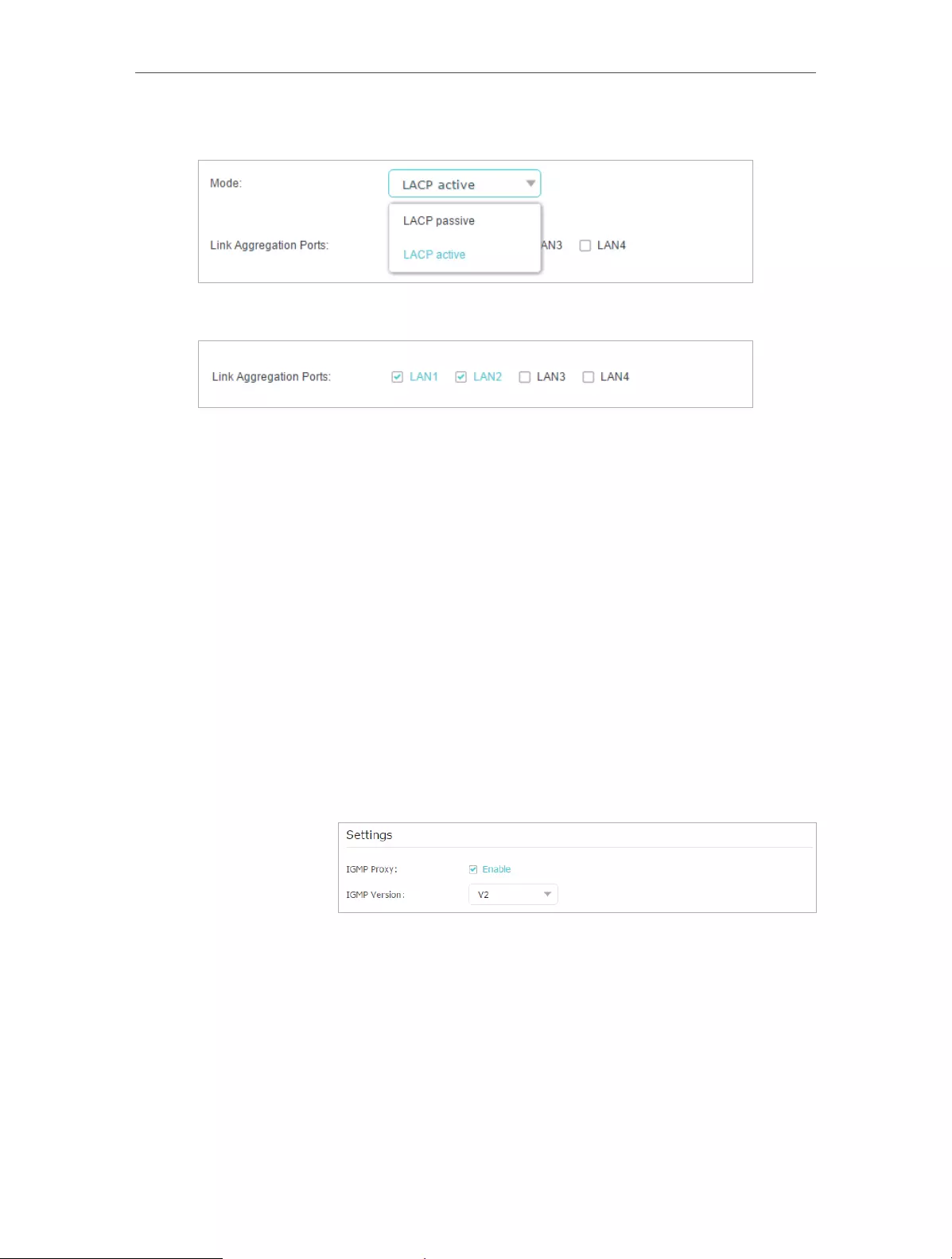
4. Select LACP active or LACP passive for Mode.
• LACP active: enables LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) unconditionally.
72
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
• LACP passive: enables LACP only when an LACP device is detected.
5. Specify two ports for link aggregation.
6. Click Save.
12. 3. Configure to Support IPTV Service
Configure IPTV setup to enable Internet/IPTV/Phone service
provided by my Internet Service Provider (ISP).
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for the router.
2. Go to Advanced > Network > IPTV.
3. If your ISP provides the networking service based on IGMP
technology, e.g., British Telecom(BT) and Talk Talk in UK:
1 ) Check the box for IGMP Proxy and select the IGMP
Version, either V2 or V3, as required by your ISP.
2 ) Click Save.
3 ) After configuring IGMP proxy, IPTV can work behind your
router now. You can connect your set-top box to any of
the router’s Ethernet port.
If IGMP is not the technology your ISP applies to provide
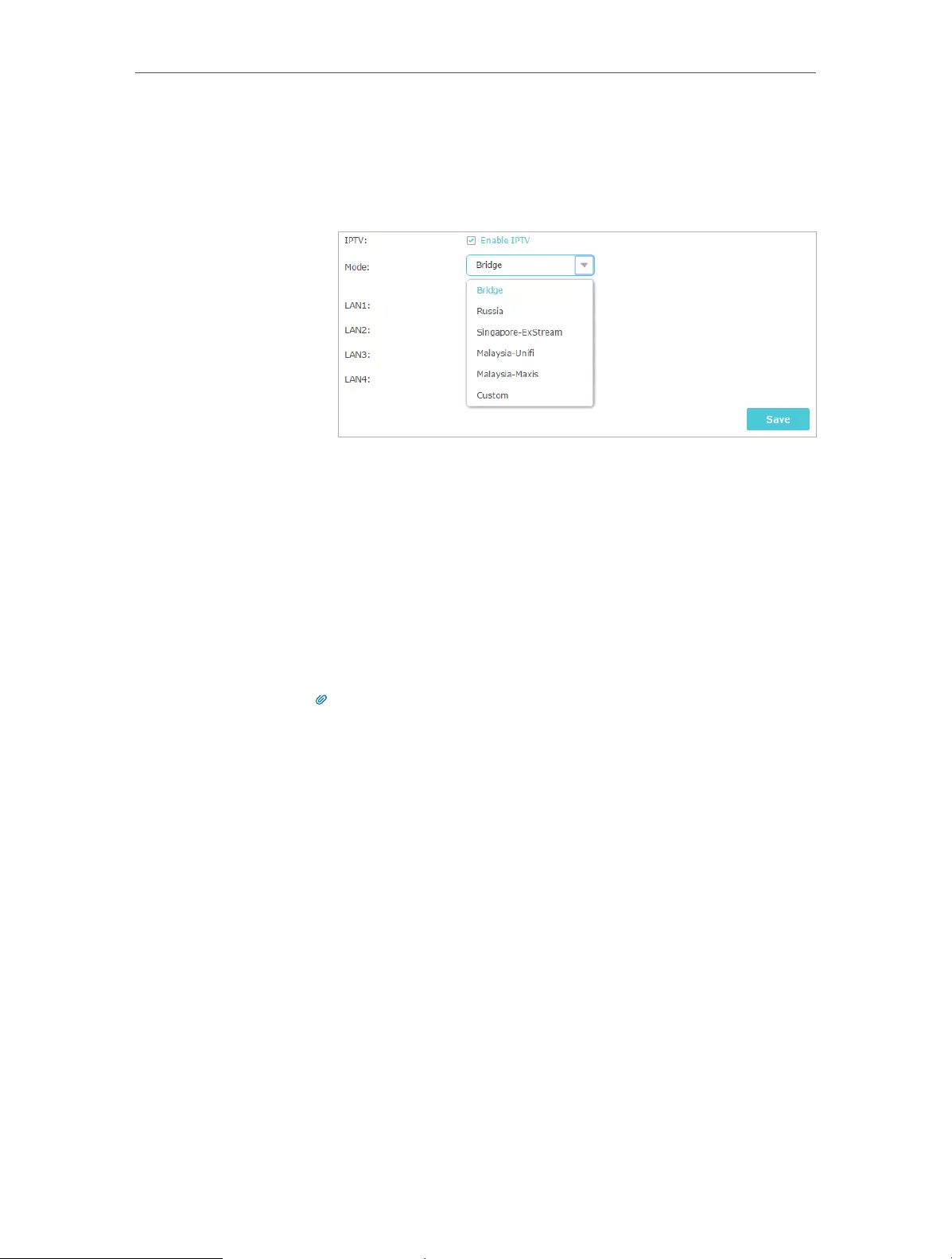
IPTV service:
1 ) Tick Enable IPTV.
2 ) Select the appropriate Mode according to your ISP.
I want to:
How can
I do that?
73
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
• Select Bridge if your ISP is not listed and no other
parameters are required.
• Select Custom if your ISP is not listed but provides
necessary parameters.
3 ) After you have selected a mode, the necessary
parameters, including the LAN port for IPTV connection,
are predetermined. If not, select the LAN type to
determine which port is used to support IPTV service.
4 ) Click Save.
5 ) Connect the set-top box to the corresponding LAN port
which is predetermined or you have specified in Step 3.
Your IPTV setup is done now! You may need to configure your
set-top box before enjoying your TV.
Tips:
Qos and IPTV cannot be enabled at the same time.
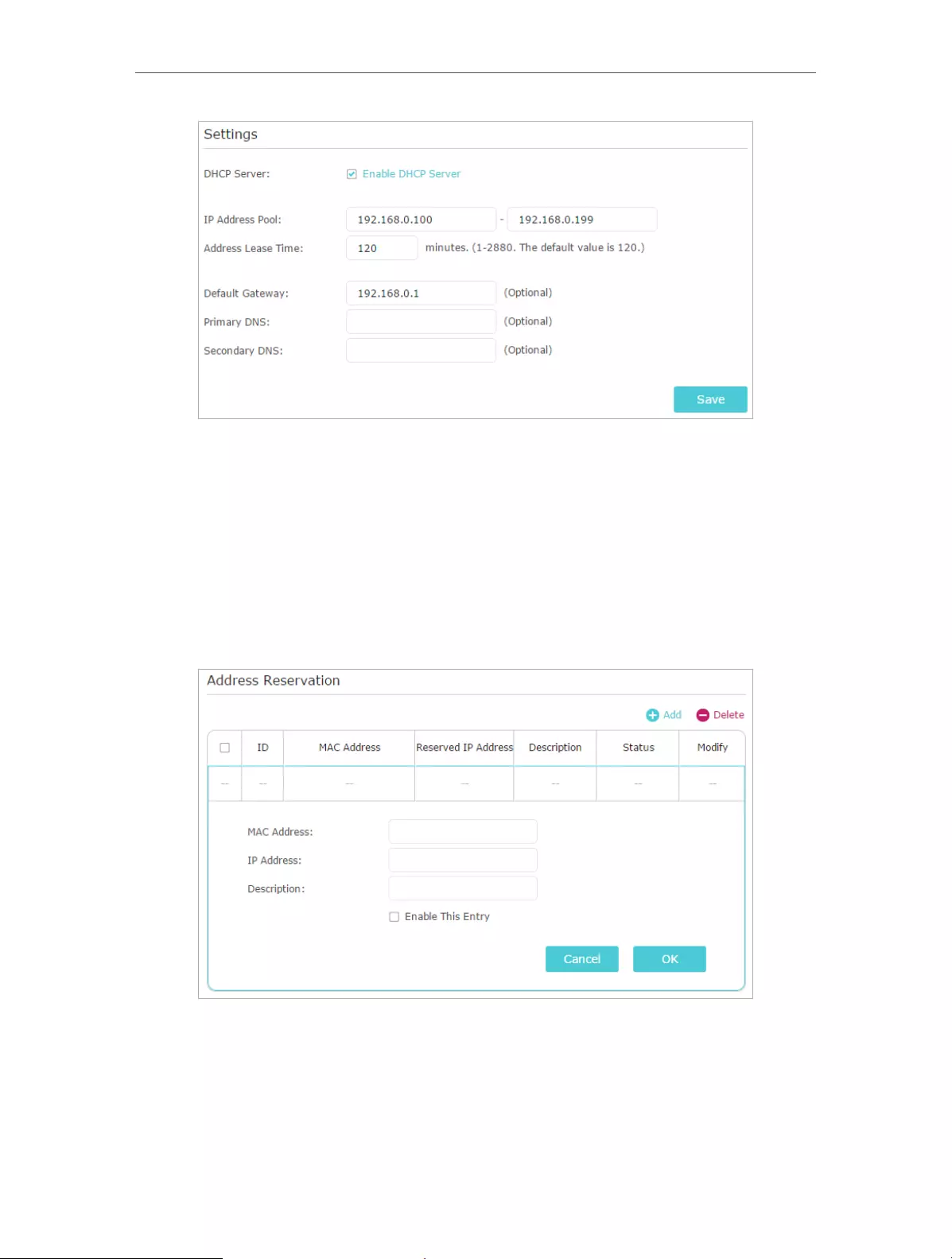
12. 4. Specify DHCP Server Settings
By default, the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server is enabled and the
router acts as a DHCP server; it dynamically assigns TCP/IP parameters to client devices
from the IP Address Pool. You can change the settings of the DHCP Server if necessary,
and you can reserve LAN IP addresses for specified client devices.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Network > DHCP Server.
¾To specify the IP address that the router assigns:
Done!
74
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
1. Check the box for Enable DHCP Server.
2. Enter the starting and ending IP addresses in the IP Address Pool.
3. Enter other parameters if the ISP offers. The Default Gateway is automatically filled in
and is the same as the LAN IP address of the router.
4. Click Save.
¾To reserve an IP address for a specified client device:
1. Click Add in the Address Reservation section.
2. Click View Exsiting Devices or enter the MAC address of the client device.
3. Enter the IP address to reserve for the client device.
4. Enter the Description for this entry.
5. Check the box for Enable This Entry and click OK.
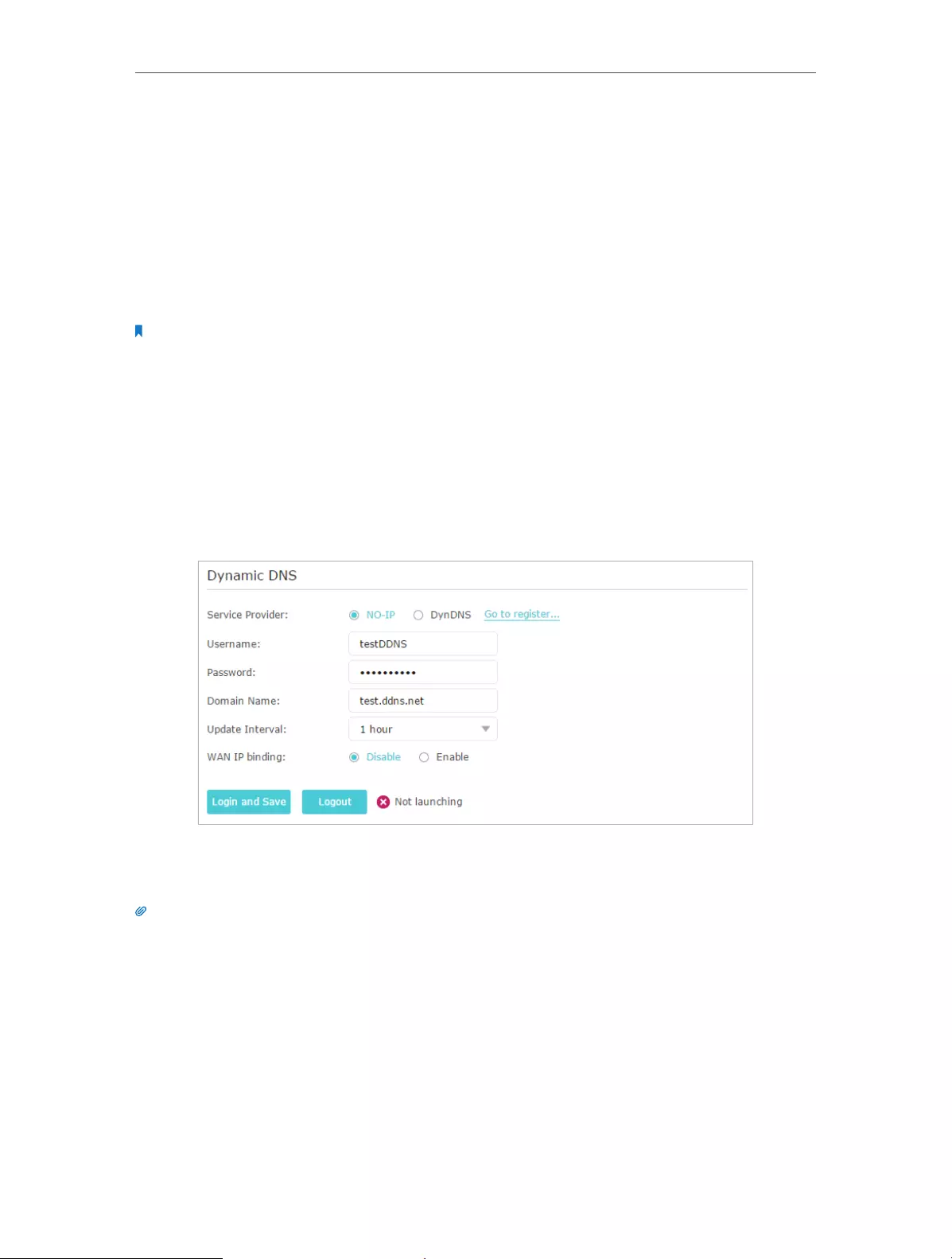
75
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
12. 5. Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account
Most ISPs assign a dynamic IP address to the router and you can use this IP address
to access your router remotely. However, the IP address can change any time and
you don’t know when it changes. In this case, you might apply the DDNS (Dynamic
Domain Name Server) feature on the router to allow you and your friends to access
your router and local servers (FTP, HTTP, etc.) using domain name without checking and
remembering the IP address.
Note:
DDNS does not work if the ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.1.x) to the router.
To set up DDNS, please follow the instructions below:
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Network > Dynamic DNS.
3. Select the DDNS Service Provider (NO-IP or DynDNS). If you don’t have a DDNS
account, select a service provider and click Go to register.
4. Enter the username, password and domain name of the account.
5. Click Login and Save.
Tips:
If you want to use a new DDNS account, please logout first, and then login with the new account.
12. 6. Create Static Routes
Static routing is a form of routing that is configured manually by a network administrator
or a user by adding entries into a routing table. The manually-configured routing
information guides the router in forwarding data packets to the specific destination.
Visit multiple networks and servers at the same time.
I want to:
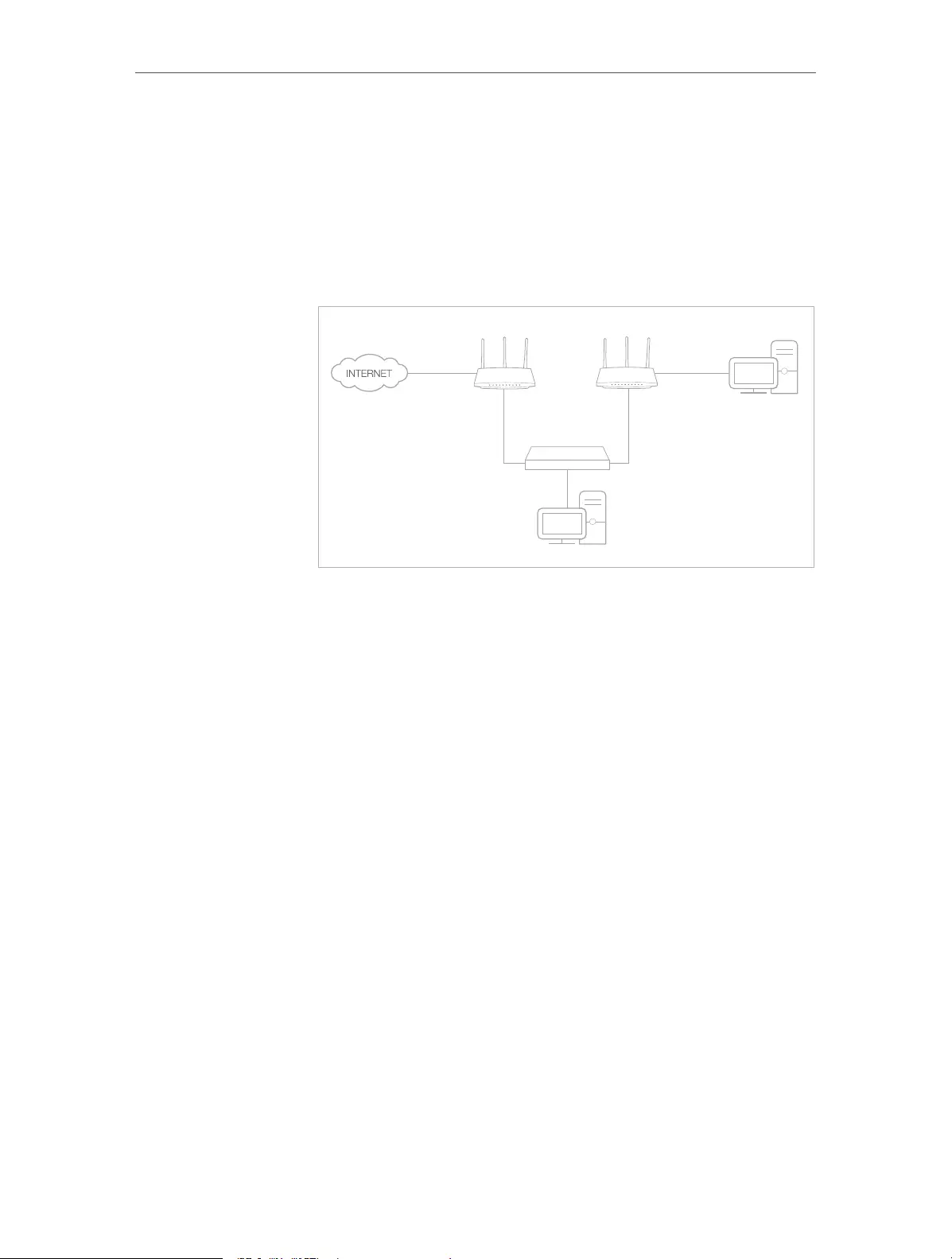
76
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
For example, in a small office, my PC can surf the Internet
through Router A, but I also want to visit my company’s network.
Now I have a switch and Router B. I connect the devices as
shown in the following figure so that the physical connection
between my PC and my company’s server is established. To surf
the Internet and visit my company’s network at the same time, I
need to configure the static routing.
Company’s server
PC
Router B
Router A
Switch
LAN: 192.168.0.1
192.168.0.100
LAN: 192.168.0.2
WAN: 172.30.30.100
172.30.30.1
1. Change the routers’ LAN IP addresses to two different IP
addresses on the same subnet. Disable Router B’s DHCP
function.
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and
password you set for Router A.
3. Go to Network > Advanced Routing.
4. Click Add and finish the settings according to the following
explanations:
How can
I do that?
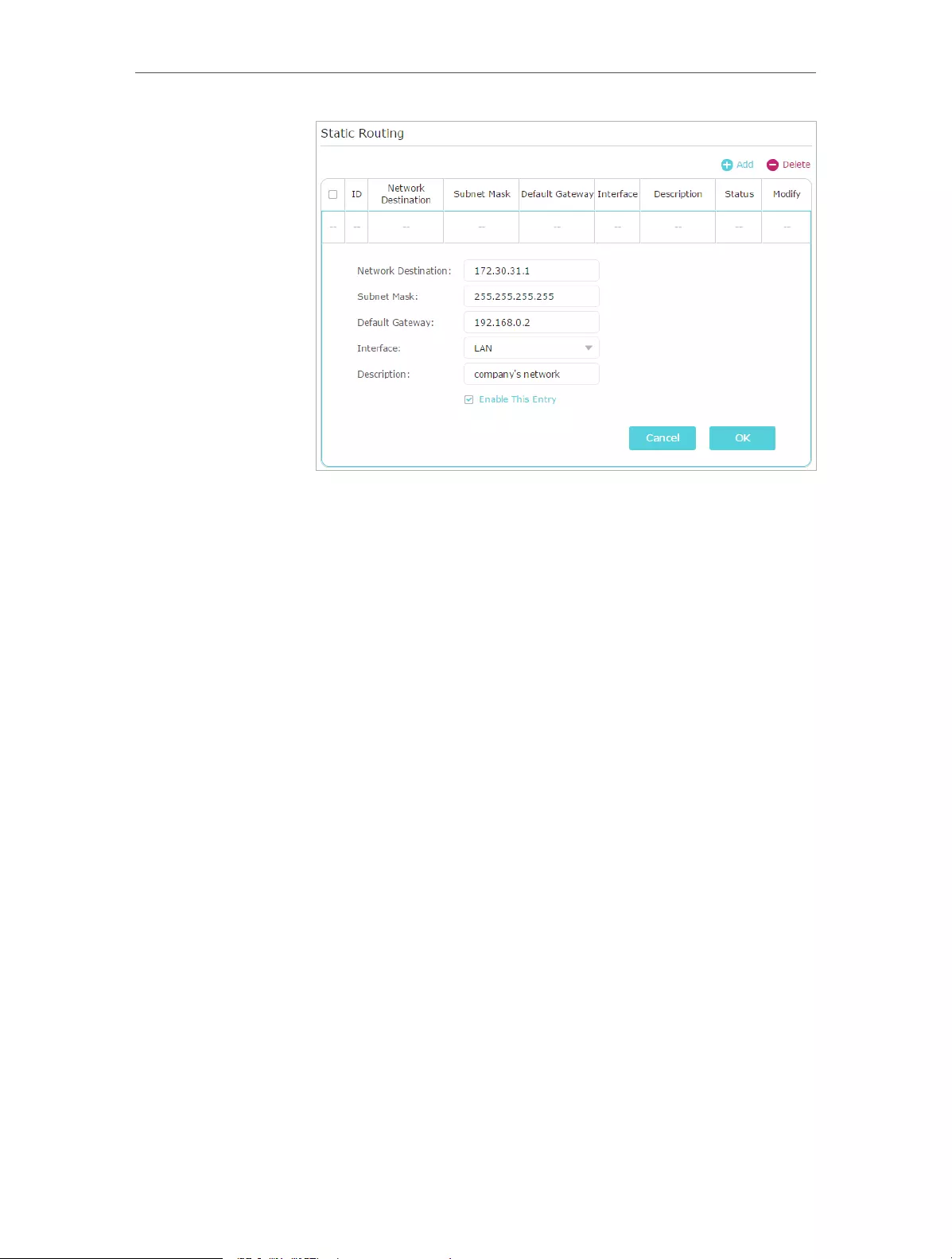
77
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
Network Destination: The destination IP address that you want
to assign to a static route. This IP address cannot be on the same
subnet with the WAN IP or LAN IP of Router A. In the example,
the IP address of the company network is the destination IP
address, so here enter 172.30.30.1.
Subnet Mask: Determines the destination network with the
destination IP address. If the destination is a single IP address,
enter 255.255.255.255; otherwise, enter the subnet mask of
the corresponding network IP. In the example, the destination
network is a single IP, so here enter 255.255.255.255.
Default Gateway: The IP address of the gateway device to which
the data packets will be sent. This IP address must be on the
same subnet with the router’s IP which sends out data. In the
example, the data packets will be sent to the LAN port of Router
B and then to the Server, so the default gateway should be
192.168.0.2.
Interface: Determined by the port (WAN/LAN) that sends out
data packets. In the example, the data are sent to the gateway
through the LAN port of Router A, so LAN should be selected.
Description: Enter a description for this static routing entry.
5. Click OK.
6. Check the System Routing Table below. If you can find the
entry you’ve set, the static routing is set successfully.
78
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
Open a web browser on your PC. Enter the company server’s IP
address to visit the company network.
12. 7. Specify Wireless Settings
The router’s wireless network name (SSID) and password, and security option are preset
in the factory. The preset SSID and password can be found on the label of the router.
You can customize the wireless settings according to your needs.
Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
¾To enable or disable the wireless function:
1. Go to Basic > Wireless.
2. The wireless radio is enabled by default. If you want to disable the wireless function
of the router, just uncheck the box for Enable Wireless Radio. In this case, all the
wireless settings will be invalid.
¾To change the wireless network name (SSID) and wireless password:
1. Go to Basic > Wireless.
2. Create a new SSID in Network Name (SSID) and customize the password for the
network in Password. The value is case-sensitive.
Note:
If you change the wireless settings with a wireless device, you will be disconnected when the settings are effective.
Please write down the new SSID and password for future use.
¾To hide SSID:
1. Go to Basic > Wireless.
2. Select Hide SSID, and your SSID won’t display when you scan for local wireless
networks on your wireless device and you need to manually join the network.
¾To change the security option:
1. Go to Advanced > Wireless > Wireless Settings.
Done!
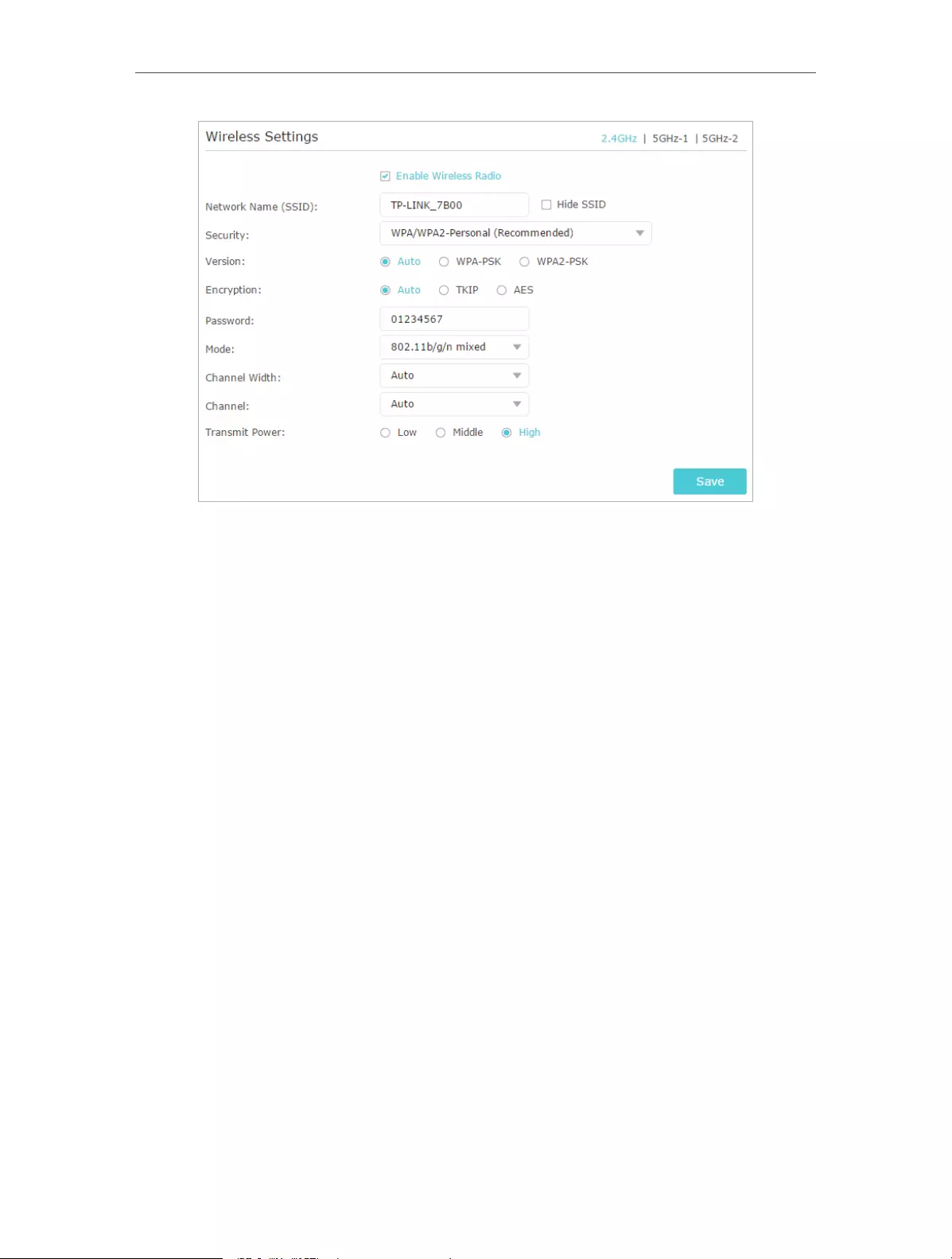
79
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
2. Select the wireless network 2.4GHz, 5GHz-1 or 5GHz-2.
3. Select an option from the Security drop-down list. We recommend you don’t change
the default settings unless necessary. If you select other options, configure the
related parameters according to the help page.
In addition
• Mode - Select a transmission mode according to your wireless client devices. It is
recommended to just leave it as default.
• Channel Width - Select a channel width (bandwidth) for the wireless network.
• Channel - Select an operating channel for the wireless network. It is recommended
to leave the channel to Auto, if you are not experiencing the intermittent wireless
connection issue.
• Transmit Power - Select either High, Middle or Low to specify the data transmit power.
The default and recommended setting is High.
¾To enable the Airtime Fairness feature
The Airtime Fairness feature can improve the overall network performace by sacrificing
a little bit of network time on your slow devices. Enable Airtime Fairness when you
wish to sacrifice some of the networking time from the slow devices, so that your faster
devices can achieve better quality of service.
For example, you have a gaming computer next to the router in the living room, and
a slower family computer upstairs. Enable the airtime fairness feature so that your
gaming computer can perform as optimally as possible.
1. Go to Advanced > Wireless > Wireless Settings.
2. Select the wireless network 2.4GHz, 5GHz-1 or 5GHz-2.
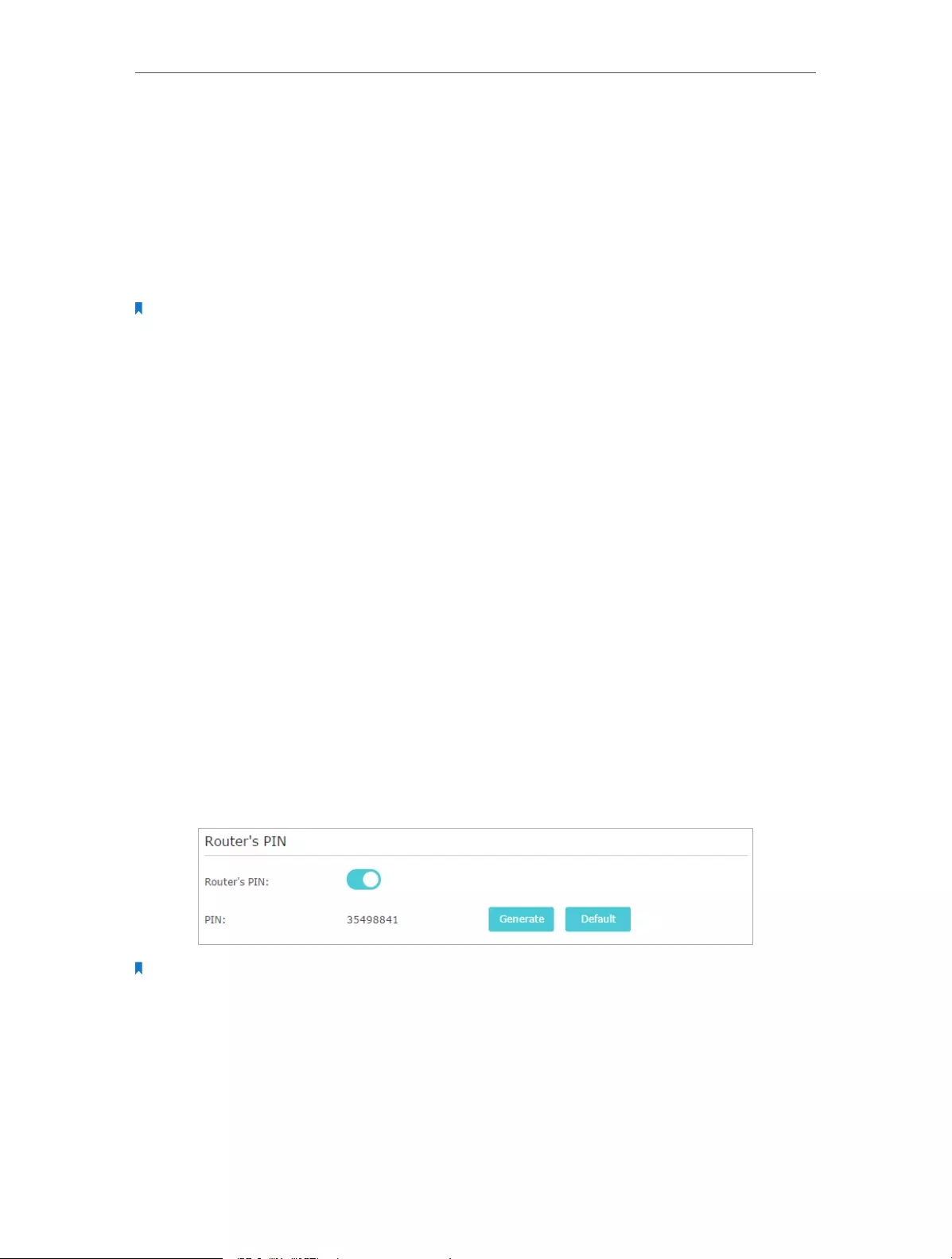
80
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
3. Check the box for Enable Airtime Fairness.
4. Click Save.
¾To enable the Multi-User MIMO feature
A router with the Multi-User MIMO feature serves 4 devices simultaneously while
a traditional router serves only one user at a time. That means Multi-User MIMO can
provide a faster, more efficient Wi-Fi network for multiusers.
Note:
Devices supporting 5GHz wireless band can enjoy the Multi-User MIMO service.
1. Go to Advanced > Wireless > Wireless Settings.
2. Select the wireless network 5GHz-1 or 5GHz-2.
3. Check the box for Enable Multi-User MIMO.
4. Click Save.
12. 8. Use WPS for Wireless Connection
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) provides an easier approach to set up a security-protected
Wi-Fi connection.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Wireless > WPS .
12. 8. 1. Set the Router’s PIN
Router’s PIN is enabled by default to allow wireless devices to connect to the router
using the PIN. You can use the default one or generate a new one.
Note:
• If you want to enable/disable the WPS feature, go to System Tools > System Parameters > WPS, check or uncheck
the box for Enable WPS.
• PIN (Personal Identification Number) is an eight-character identification number preset to each router. WPS
supported devices can connect to your router with the PIN. The default PIN is printed on the label of the router.
12. 8. 2. Use the WPS Wizard for Wi-Fi Connections
1. Select a setup method:
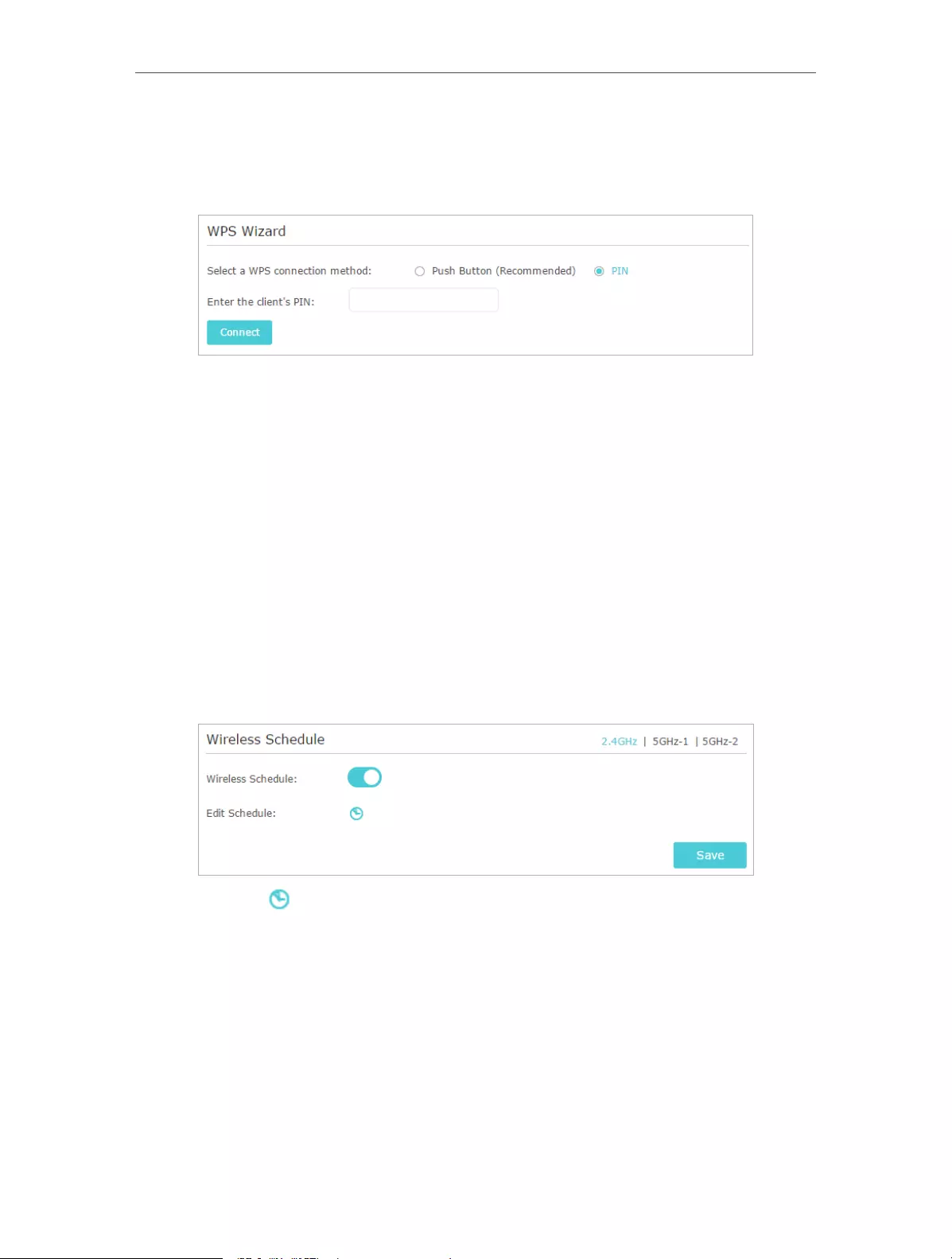
81
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
• Push Button(Recommended): Click Connect on the screen. Within two
minutes, press the WPS button on the client device.
• PIN: Enter the client’s PIN, and click Connect.
2. Success will appear on the above screen and the WPS LED on the router will keep on
for five minutes if the client has been successfully added to the network.
12. 9. Schedule Your Wireless Function
The wireless network can be automatically off at a specific time when you do not need
the wireless connection.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > Wireless > Wireless Schedule.
3. Select 2.4GHz, 5GHz-1 or 5GHz-2 to change the corresponding settings.
4. Enable the Wireless Schedule feature.
5. Click the icon to set the Effective Time. Drag the cursor over the cells to choose
the period during which you need the wireless off automatically, and click OK.
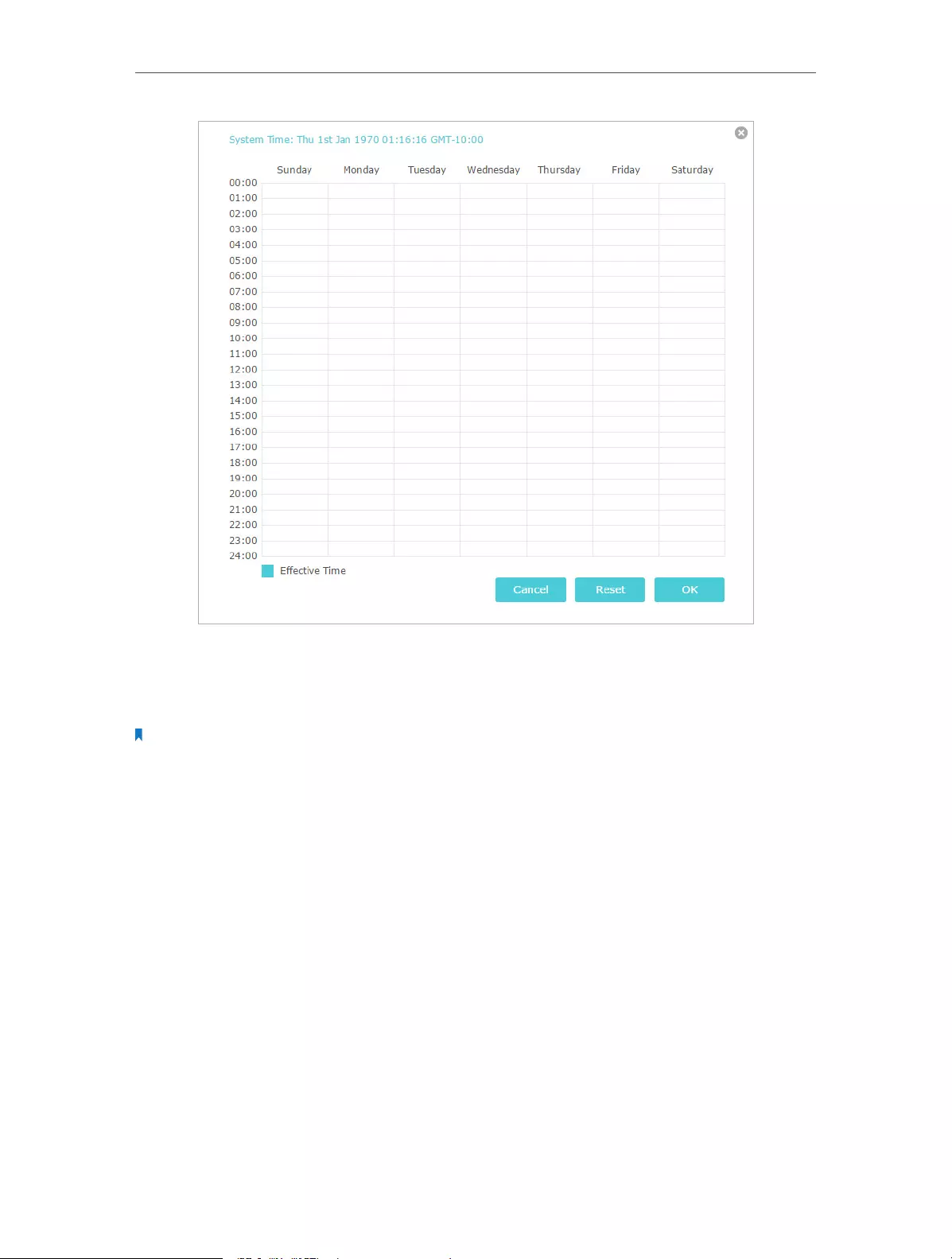
82
Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
6. Click Save.
7. If you also want to set wireless off time for other band(s), please repeat the steps
above.
Note:
• The Effective Time Schedule is based on the time of the router. You can go to Advanced > System Tools > Time
Settings to modify the time.
• The wireless LED will be off if the corresponding wireless network is disabled.
• The wireless network will be automatically turned on after the time period you set.

Chapter 13
Manage the Router
This chapter will show you the configuration for managing and maintaining your router.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Set Up System Time
• Test the Network Connectivity
• Upgrade the Firmware
• Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
• Change the Administrator Account
• Password Recovery
• Local Management
• Remote Management
• System Log
• Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
• Control LEDs
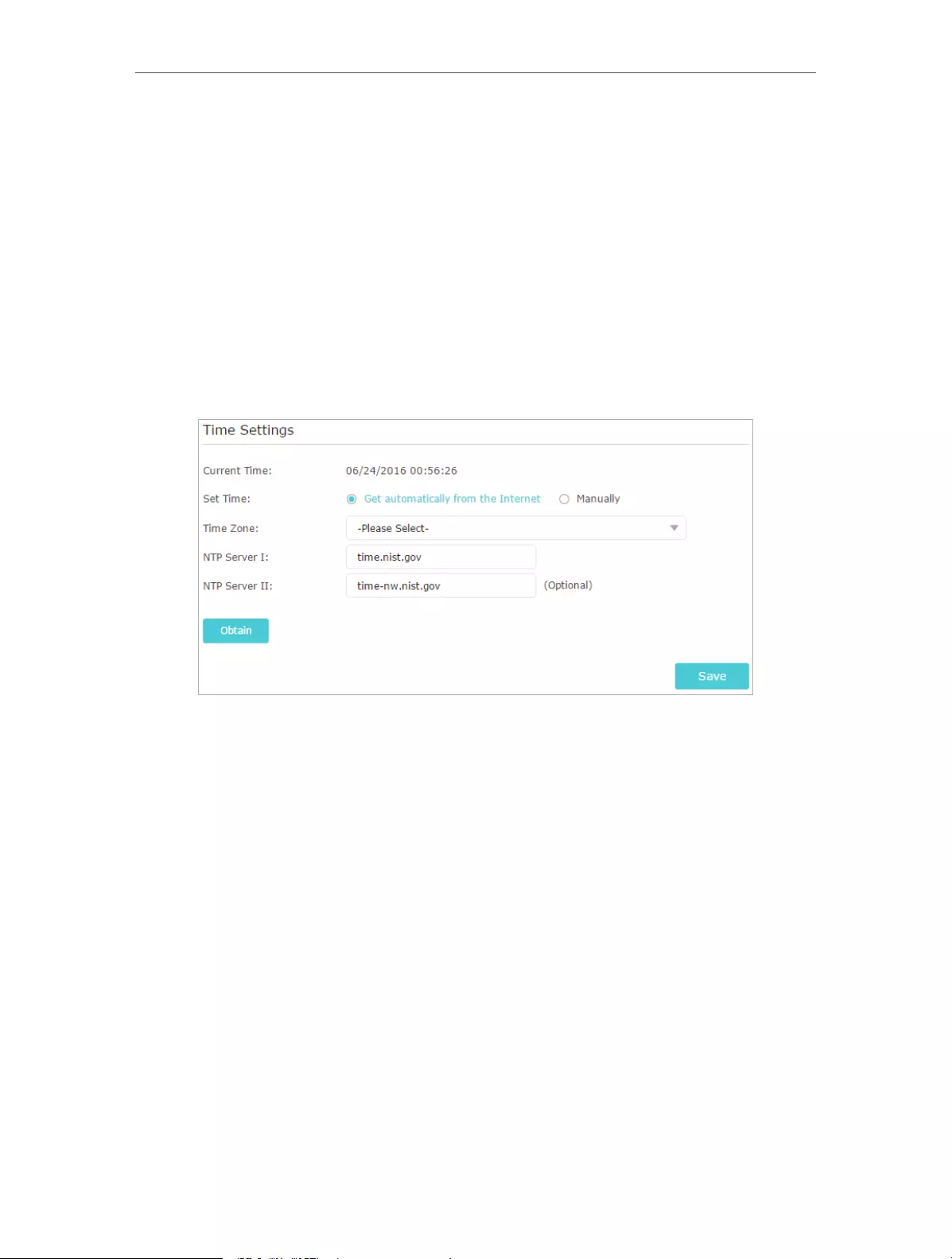
84
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
13. 1. Set Up System Time
System time is the time displayed while the router is running. The system time you
configure here will be used for other time-based functions like Parental Controls. You
can choose the way to obtain the system time as needed.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Time Settings.
¾To get time from the Internet:
1. In the Set Time field, select Get automatically from the Internet.
2. Select your local Time Zone from the drop-down list.
3. In the NTP Server I fileld, enter the IP address or domain name of your desired NTP
Server.
4. (Optional) In the NTP Server II fileld, enter the IP address or domain name of the
second NTP Server.
5. Click Obtain to get the current Internet time and click Save.
¾To manually set the date and time:
1. In the Set Time field, select Manually.
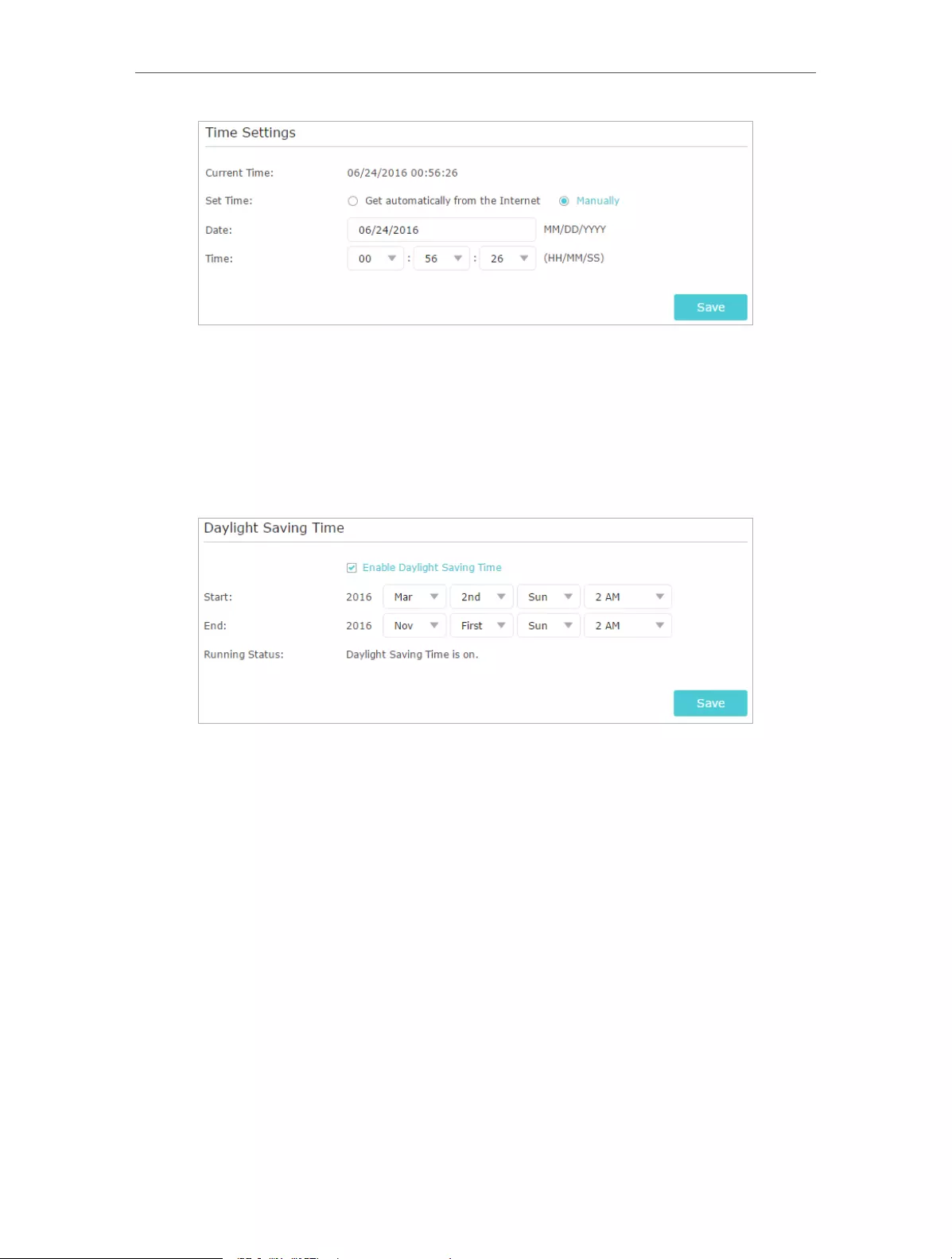
85
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
2. Set the current Date (In MM/DD/YYYY format).
3. Set the current Time (In HH/MM/SS format).
4. Click Save.
¾To set up Daylight Saving Time:
1. Select Enable Daylight Saving Time.
2. Select the correct Start date and time when daylight saving time starts at your local
time zone.
3. Select the correct End date and time when daylight saving time ends at your local
time zone.
4. Click Save.
13. 2. Test the Network Connectivity
Diagnostics is used to test the connectivity between the router and the host or other
network devices.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Diagnostics.
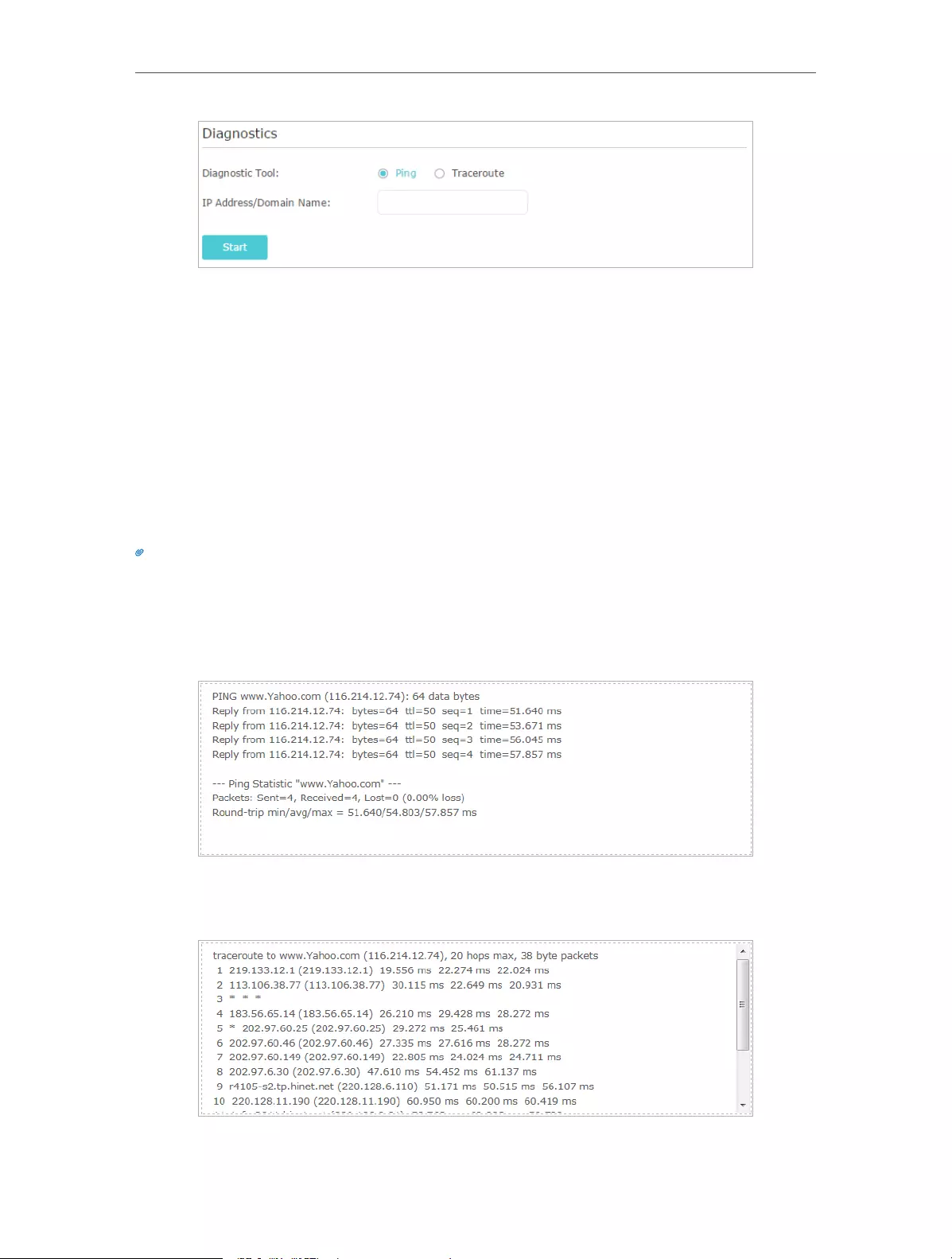
86
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
3. Enter the information with the help of page tips:
1 ) Choose Ping or Traceroute as the diagnostic tool to test the connectivity;
• Ping is used to test the connectivity between the router and the tested host,
and measure the round-trip time.
• Traceroute is used to display the route (path) your router has passed to reach
the tested host, and measure transit delays of packets across an Internet
Protocol network.
2 ) Enter the IP Address or Domain Name of the tested host.
4. Click Start to begin the diagnostics.
Tips:
Click Advanced, you can modify the ping count, ping packet size or the Traceroute Max TTL. It’s recommended to
keep the default value.
The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo
server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Ping.
The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo
server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Traceroute.
87
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
13. 3. Upgrade the Firmware
TP-LINK aims at providing better network experience for users.
We will inform you throught the web management page if there’s any update firmware
available for your router. Also, the latest firmware will be released at the TP-LINK official
website www.tp-link.com, and you can download it from the Support page for free.
Note:
• Make sure you remove all attached USB devices from the router before the firmware upgrade to prevent data
loss.
• Backup your router configuration before firmware upgrade.
• Do NOT turn off the router during the firmware upgrade.
13. 3. 1. Online Upgrade
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you’ve set for
the router.
2. When the latest firmware is available for your router, the update icon will display
in the top-right corner of the page. Click the icon to go to the Firmware Upgrade
page.
Alternatively, you can go to Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade, and click
Check for upgrade to see whether the latest firmware is released.
3. Focus on the Online Upgrade section, and click Upgrade.
4. Wait a few minutes for the upgrade and reboot to complete.
Tips:
If there’s a new and important firmware update for your router, you will see the notification (similar as shown below)
on your computer as long as a web browser is opened. Click Upgrade now, and log into the web management page
with the username and password you set for the router. You will see the Firmware Upgrade page.
88
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
13. 3. 2. Manual Upgrade
1. Download the latest firmware file for the router from www.tp-link.com.
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
3. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade.
4. Focus on the Device Information section. Make sure the downloaded firmware file is
matched with the Hardware Version.
5. Focus on the Manual Upgrade section. Click Browse to locate the downloaded new
firmware file, and click Upgrade.
6. Wait a few minutes for the upgrade and reboot to complete.
13. 3. 3. Restore Interrupted Upgrade after Power Failure
If your router cannot start up after an upgrade interruption due to power failure, follow
the steps below to restore the interrupted upgrade. Otherwise, your router cannot
work again.
1. Make sure you have the latest firmware file in your computer. If not, try another way
to connect your computer to the Internet and download the latest firmware file from
www.tp-link.com.
2. Connect your computer to the router with an Ethernet cable.
3. Visit 192.168.0.1 and you will see the following upgrade page.
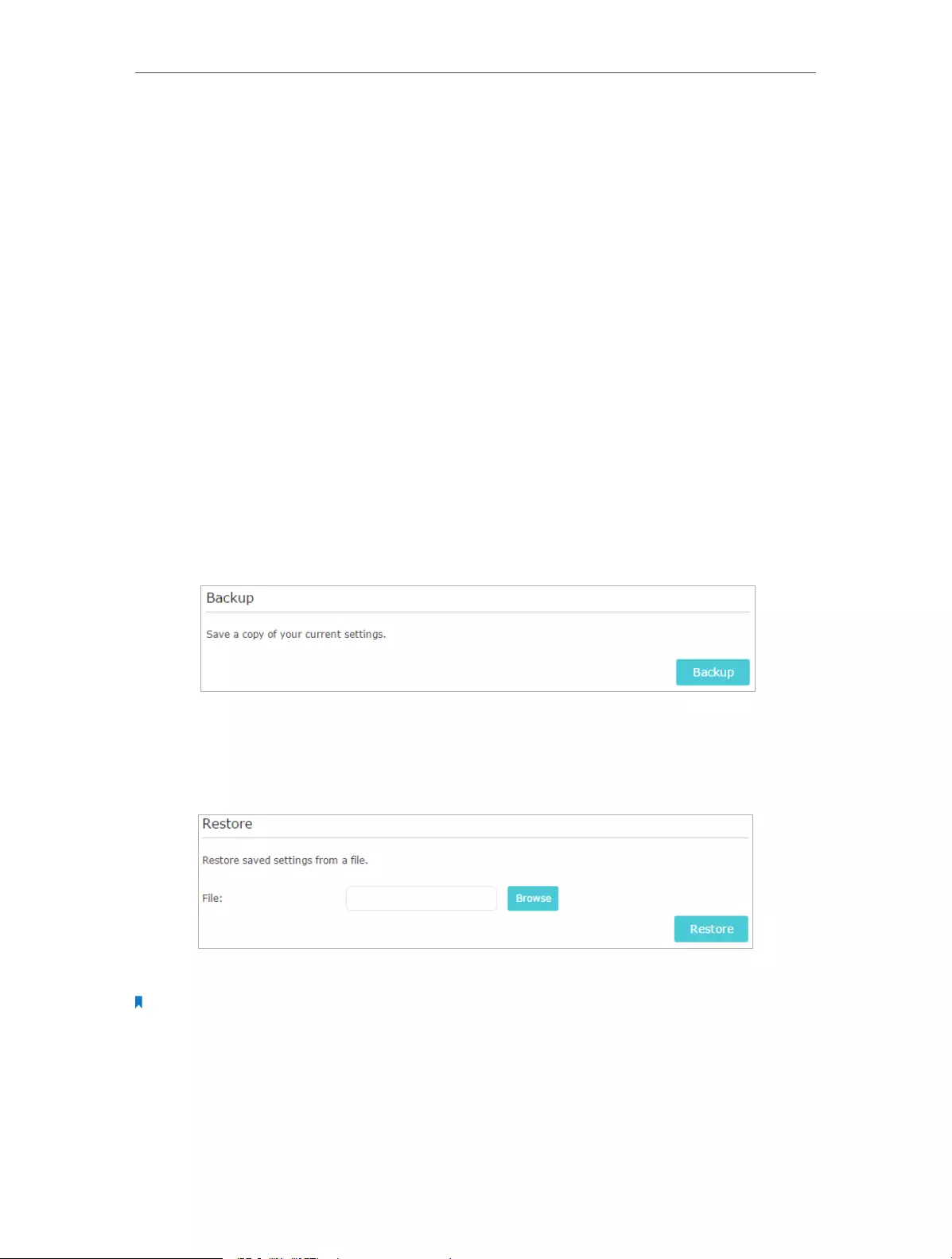
89
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
4. Click Browse and select the downloaded firmware file.
5. Click Upgrade and wait for a few minutes until the router completes the upgrading
and restarts.
13. 4. Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
The configuration settings are stored as a configuration file in the router. You can
backup the configuration file to your computer for future use and restore the router to
a previous settings from the backup file when needed. Moreover, if necessary you can
erase the current settings and reset the router to the default factory settings.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Backup & Restore.
¾To backup configuration settings:
Click Backup to save a copy of the current settings to your local computer. A ‘.bin’ file of
the current settings will be stored to your computer.
¾To restore configuration settings:
1. Click Browse to locate the backup configuration file stored on your computer, and
click Restore.
2. Wait a few minutes for the restoring and rebooting.
Note: During the restoring process, do not turn off or reset the router.
¾To reset the router to factory default settings:
1. Click Factory Restore to reset the router.
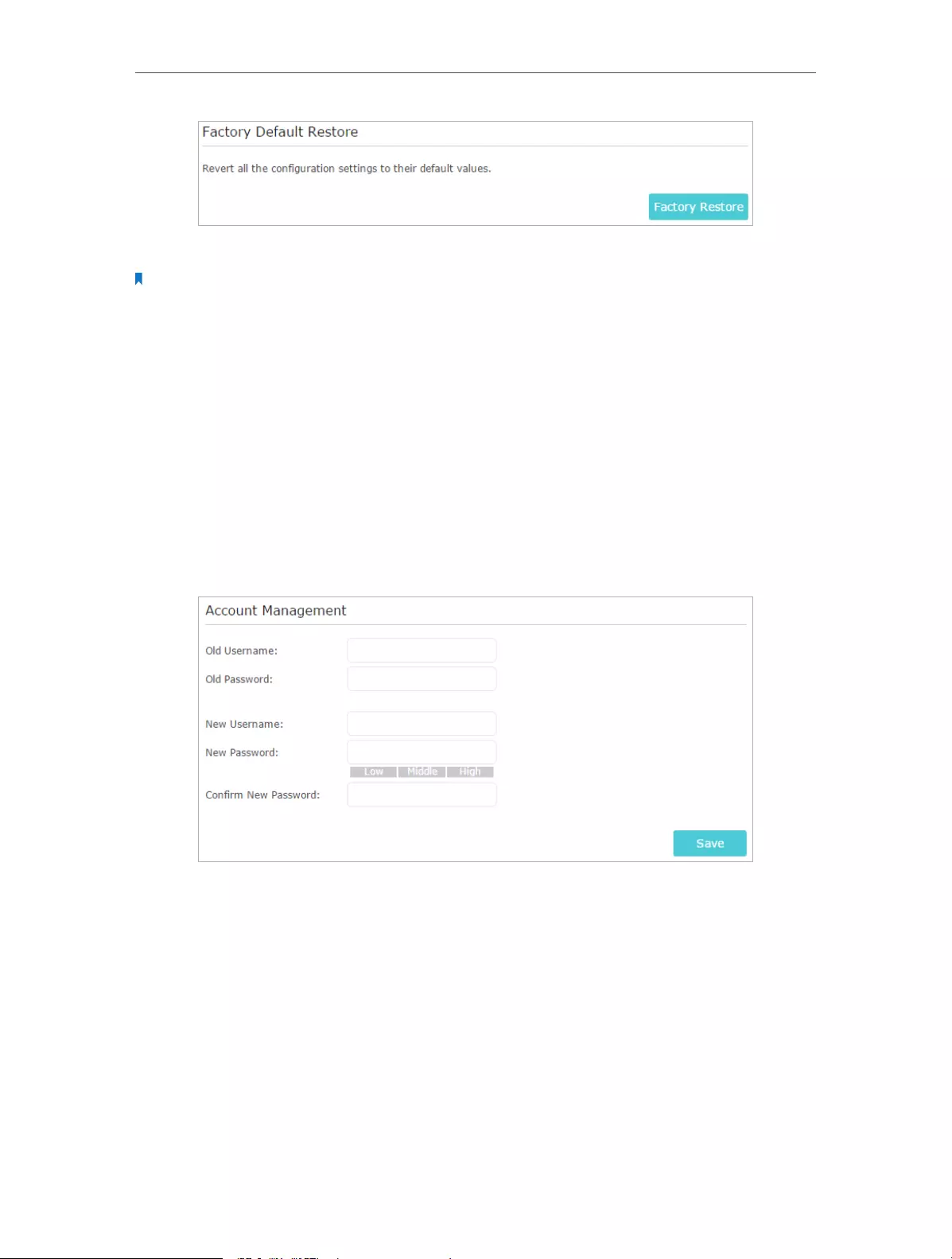
90
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
2. Wait a few minutes for the resetting and rebooting.
Note:
• During the resetting process, do not turn off or reset the router.
• We strongly recommend you backup the current configuration settings before resetting the router.
13. 5. Change the Administrator Account
The account management feature allows you to change your login username and
password of the web management page.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and focus on the Account
Management section.
3. Enter the old username and old password, then a new username and a new password
twice (both case-sensitive). Click Save.
4. Use the new username and password for the following logins.
13. 6. Password Recovery
This feature allows you to recover your default login username and password in case
you forget them.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
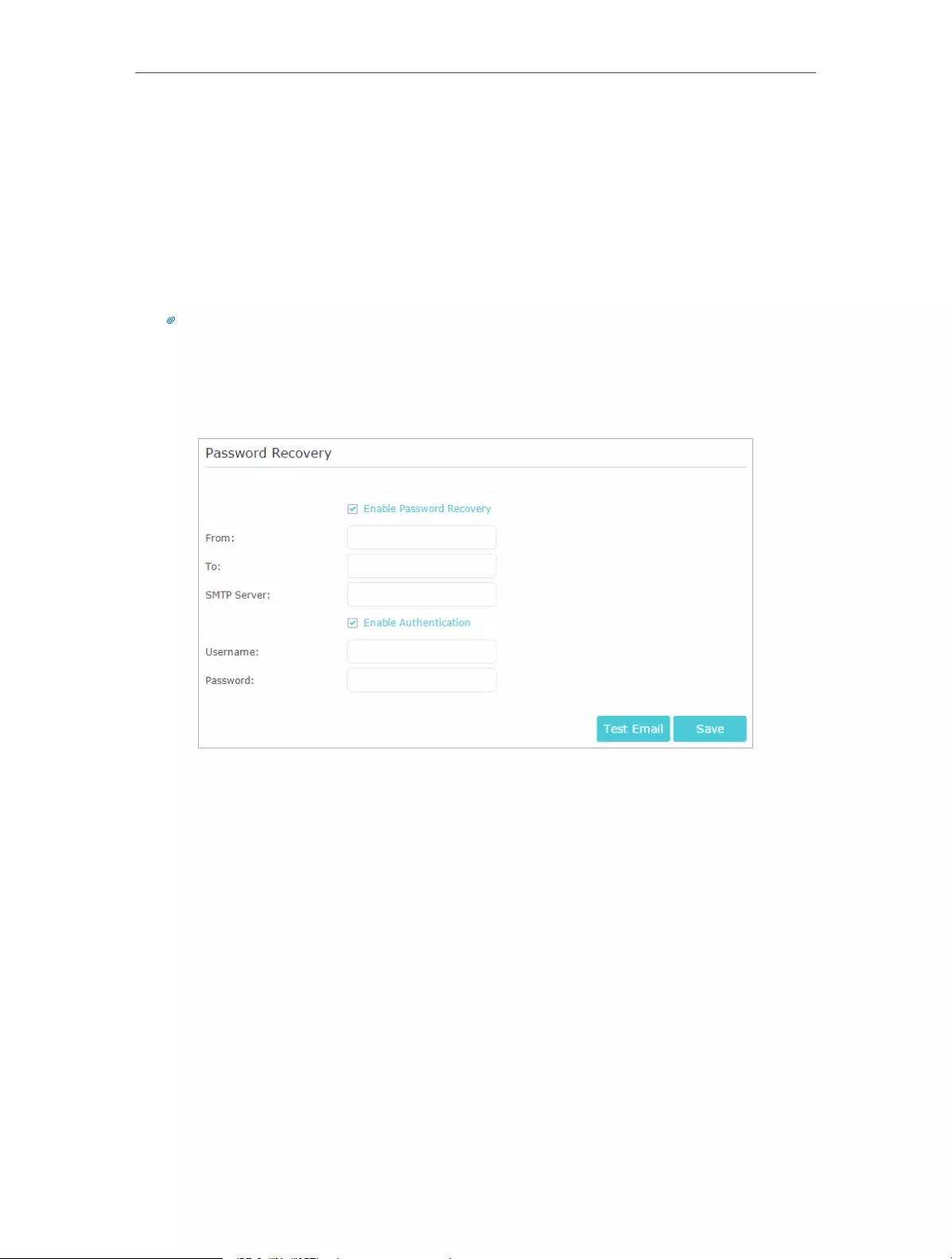
91
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and focus on the Password Recovery
section.
3. Check the box for Enable Password Recovery.
4. Specify a mailbox (From) for sending the recovery letter and enter its SMTP Server
address. Specify a mailbox (To) for receiving the recovery letter. If the mailbox (From)
to send the recovery letter requires encryption, select Enable Authentication and
enter its username and password.
Tips:
• SMTP server is available for users in most webmail systems. For example, the SMTP server address of Gmail
is smtp.gmail.com. You can refer to their Help page to learn the SMTP server address.
• Generally, Enable Authentication should be selected if the login of the mailbox requires username and
password.
5. Click Save.
You can click Test Email to test whether the configuration is successful. To recover the
default login username and password, please refer to FAQ.
13. 7. Local Management
This feature allows you to limit the number of client devices on your LAN from accessing
the router by using the MAC address-based authentication.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and complete the settings In Local
Management section according to your needs.
• Allow all LAN connected devices to manage the router:
Toggle on Access for All LAN Connected Devices.
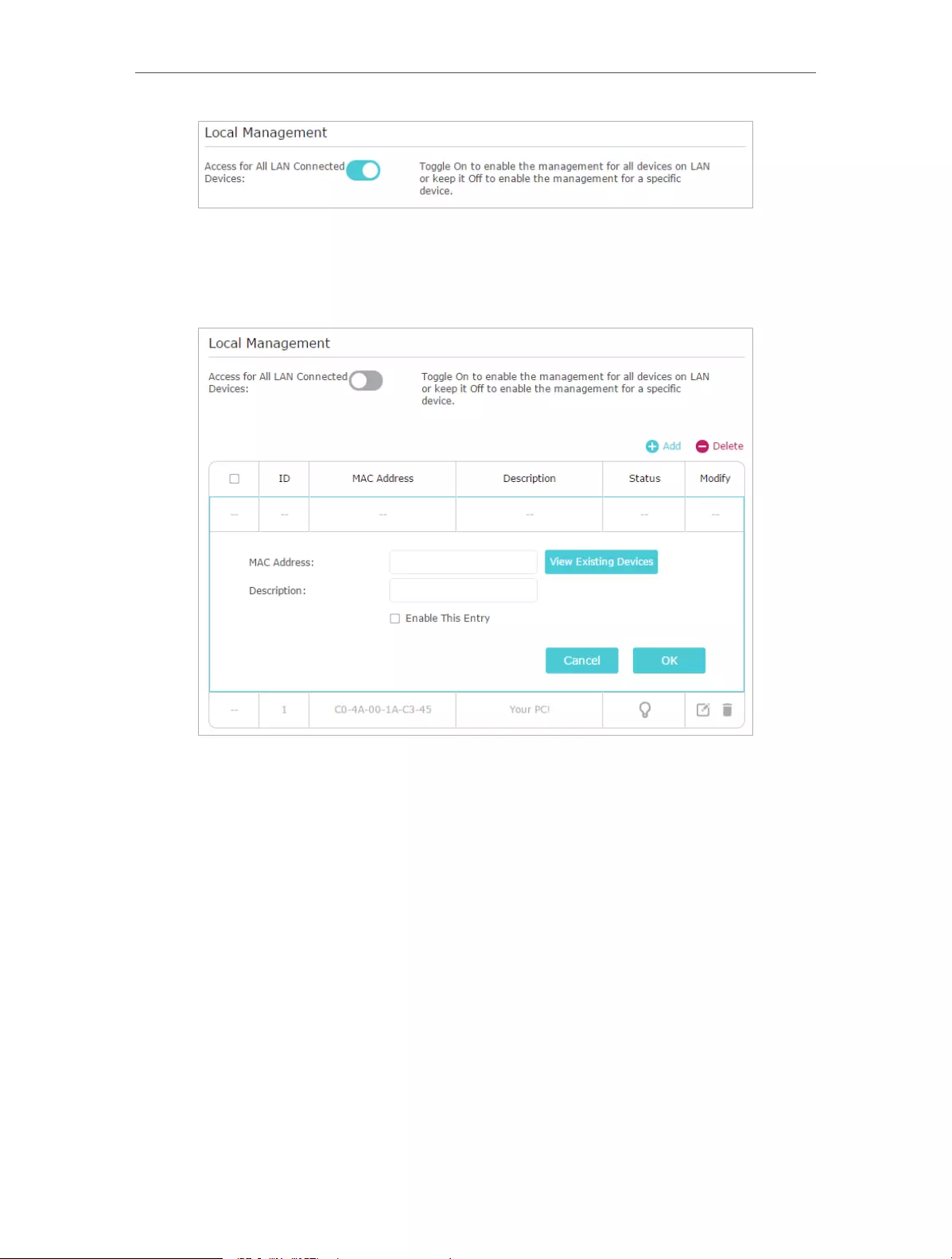
92
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
• Allow specific devices to manage the router:
1 ) Toggle off Access for All LAN Connected Devices.
2 ) Click Add.
3 ) Click View Existing Devices and select the device to manage the router from
the Existing Devices list, or enter the MAC address of the device manually.
4 ) Specify a Description for this entry.
5 ) Check the box for Enable This Entry.
6 ) Click OK.
13. 8. Remote Management
This feature allows you to control remote devices’ authority to manage the router.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and complete the settings in
Remote Management section according to your needs.
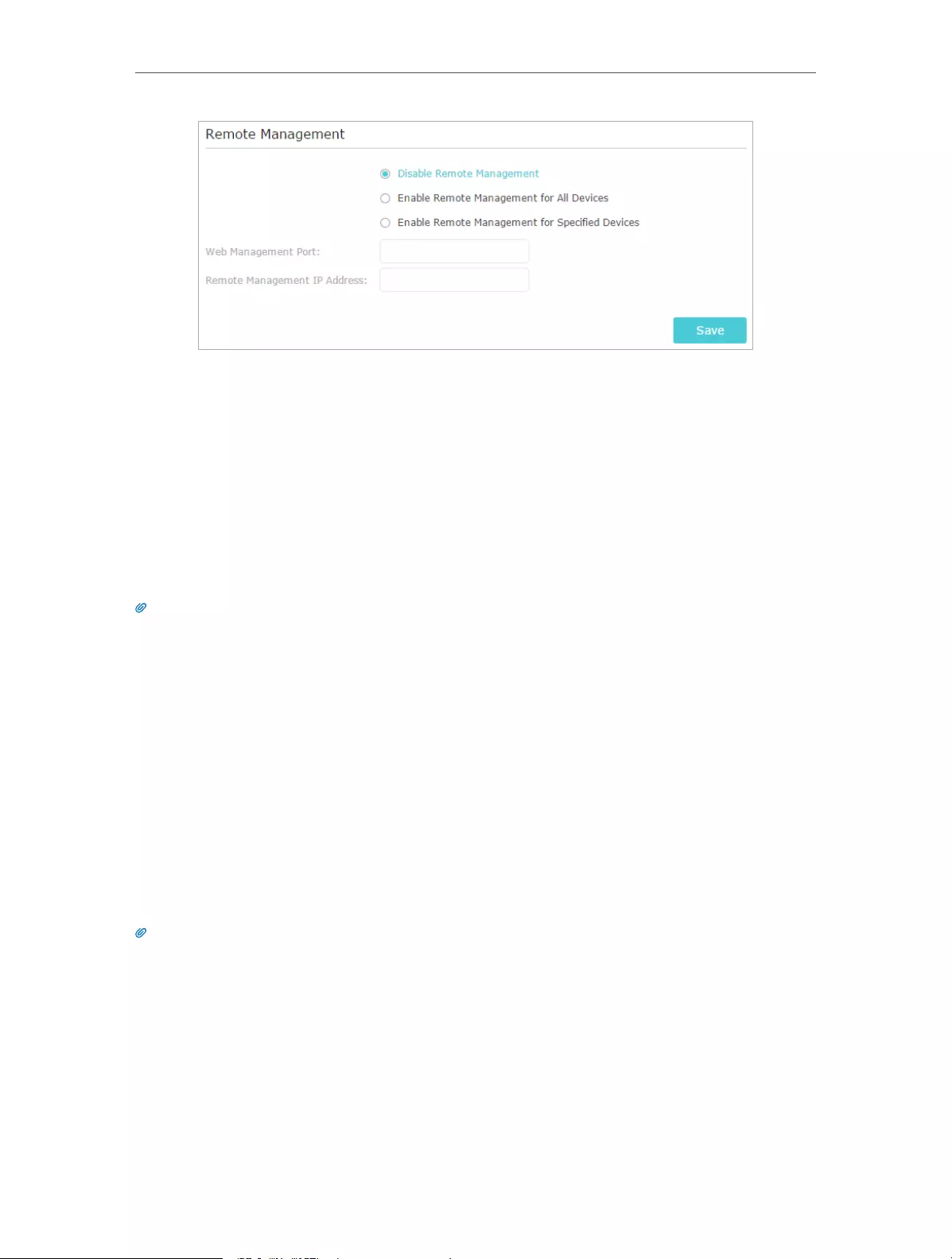
93
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
• Forbid all devices to manage the router remotely: Select Disable Remote
Management and click Save.
• Allow all devices to manage the router remotely:
1 ) Select Enable Remote Management for All Devices.
2 ) Enter Web Management Port (1024-65535 or 80).
3 ) Click Save.
Devices on the Internet can log in to http://Router’s WAN IP address:port number (such as
http://113.116.60.229:1024) to manage the router.
Tips:
• You can find the WAN IP address of the router on Basic > Network Maps > Internet.
• The router’s WAN IP is usually a dynamic IP. Please refer to Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account if you want to log
in to the router through a domain name.
• Allow specific devices to manage the router remotely:
1 ) Select Enable Remote Management for Specified Devices.
2 ) Enter Web Management Port (1024-65535 or 80).
3 ) In Remote Management IP address, enter the IP address of the remote device
to manage the router.
4 ) Click Save.
Devices using this WAN IP can manage the router by logging in to http://Router’s WAN
IP:port number (such as http://113.116.60.229:1024).
Tips:
The router’s WAN IP is usually a dynamic IP. Please refer to Set Up a Dynamic DNS Service Account if you want to log
in to the router through a domain name.
13. 9. System Log
When the router does not work properly, you can save the system log and send it to the
technical support for troubleshooting.
¾To Save the System Log in Local:
94
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Log.
3. Choose the type and level of the system logs according to your need.
4. Click Save Log to save the system logs to local.
¾To Send the System Log to a Mailbox at a Fixed Time:
For example, I want to check my router’s working status at a fixed time every day,
however, it’s too troublesome to log in to the web interface every time I want to go
checking. It would be great if the system logs could be sent to my mailbox at 8 a.m.
every day.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Log.
3. Click Mail Settings.
4. Enter the information with the help of page tips:
95
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
1 ) From: Enter the email address used for sending the system log.
2 ) To: Enter the recipient’s email address, which can be the same as or different
from the sender’s email address.
3 ) SMTP Server: Enter the SMTP server address.
Tips: SMTP server is available for users in most webmail systems. For example, the SMTP server address of
Hotmail is smtp-mail.outlook.com. You can refer to their Help page to learn the SMTP server address.
4 ) Select Enable Authentication.
Tips: Generally, Enable Authentication should be selected if the login of the mailbox requires username and
password.
5 ) Username: Enter the email address used for sending the system log.
6 ) Password: Enter the password to login the sender’s email address.
7 ) Select Enable Auto Mail.
Tips: The router will send the system log to the designated email address if this option is enabled.
8 ) Set a fixed time. The recipient will receive the system log sent at this time every
day.
5. Click Save.
13. 10. Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics page displays the network traffic of the LAN, WAN and WLAN sent
and received packets, allowing you to monitor the volume of Internet traffic statistics.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router.
2. Go to Advanced > System Tools > Traffic Statistics.
96
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
3. Toggle on Traffic Statistics, and then you can monitor the traffic statistics in Traffic
Statistics List section.
Click Refresh to update the statistic information on the page.
Click Reset All to reset all statistic values in the list to zero.
Click Delete All to delete all statistic information in the list.
Click to reset the statistic information of the specific device.
Click to delete the specific device item in the list.
13. 11. Control LEDs
The router‘s LEDs indicate router’s activities and status. You can turn on or turn off the
LEDs either from the web management page or by pressing the LED button.
¾ To turn on or off the LEDs:
• Press the LED button on the router (if available) about 2 seconds to turn on or off the
LEDs.
• Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the
router. Click the LED icon in the top right corner of the page.
¾To turn off LEDs during Night Mode Period:
1 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
2 ) Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters.
3 ) In the LED Control section, check the box for Enable Night Mode.
4 ) Specify a time period in the Night Mode Period as needed, and the LEDs will be
off during this period.
5 ) Click Save.
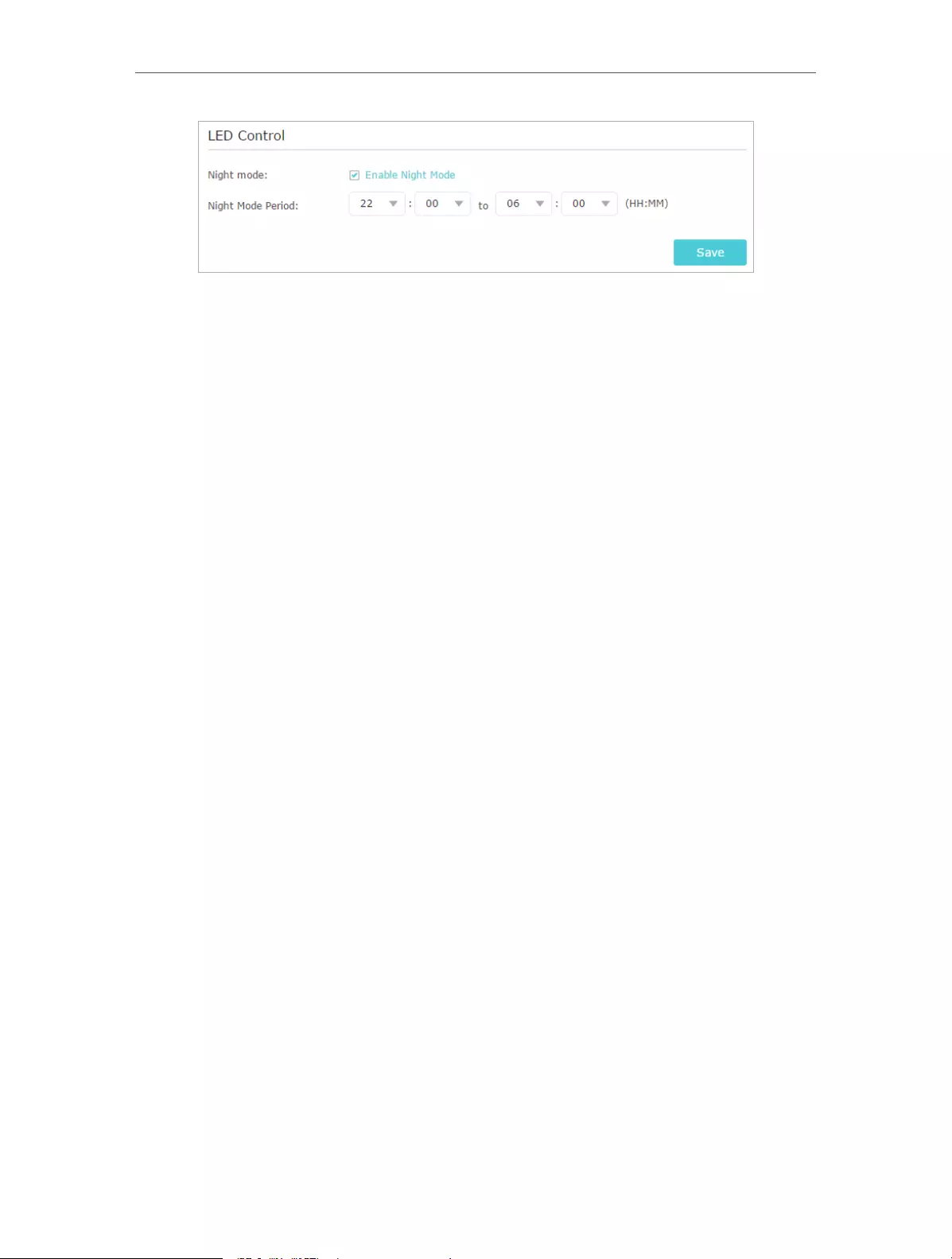
97
Chapter 13 Manage the Router

98
FAQ
Q1. What can I do if I forgot my wireless password?
The default wireless password is printed on the label of the router. If the password has
been altered, please connect your computer to the router using an Ethernet cable and
follow the steps below:
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net.
2. Go to Basic > Wireless to retrieve or reset your wireless password.
Q2. What can I do if I forgot my login password of the web management
page?
The default username and password of the web management page are admin (in
lowercase). If your router supports Password Recovery and you have enabled it,
please follow the steps below to reset the password without resetting the router:
Note: Make sure the Internet access is available before using this method.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net.
2. Click Forgot password > Send Code, and the verification code will be sent to the
mailbox you set.
3. Log into your mailbox to copy the verification code.
4. Paste the verification code on the window which pops up in Step 2.
5. Click Confirm (the default login username and password will be reset as admin after
the click).
6. Use admin (in lowercase) as both username and password to login.
Tips: Please refer to Password Recovery to learn how to configure Password Recovery.
If you have altered the username and password but Password Recovery is disabled:
1. Reset the router to factory default settings: press and hold the Reset button for about
7 seconds and then release;
2. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and enter admin (in lowercase) as both username and
password to login.
Note: You’ll need to reconfigure the router to surf the Internet once the router is reset, and please mark down your
new password for future use.
Q3. What can I do if I cannot log into the router’s web management
page?
This can happen for a variety of reasons. Please try the methods below to login again.
• Make sure your computerthe is connected to the router correctly and the
corresponding LED indicator(s) light up.
99
• Make sure the IP address of your computer is configured as Obtain an IP address
automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically.
• Make sure you enter the correct IP address to login: http://tplinkwifi.net.
• Check your computer’s settings:
1 ) Go to Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet, and click View network status
and tasks.
2 ) Click Internet Options on the bottom left.
3 ) Click Connections and select Never dial a connection.
4 ) Click LAN settings and deselect the following three options and click OK.
100
5 ) Go to Advanced > Restore advanced settings, click OK to save the settings.
• Use another web browser or computer to login again.
• Reset the router to factory default settings and try again. If login still fails, please
contact the technical support.
Note: You’ll need to reconfigure the router to surf the Internet once the router is reset.
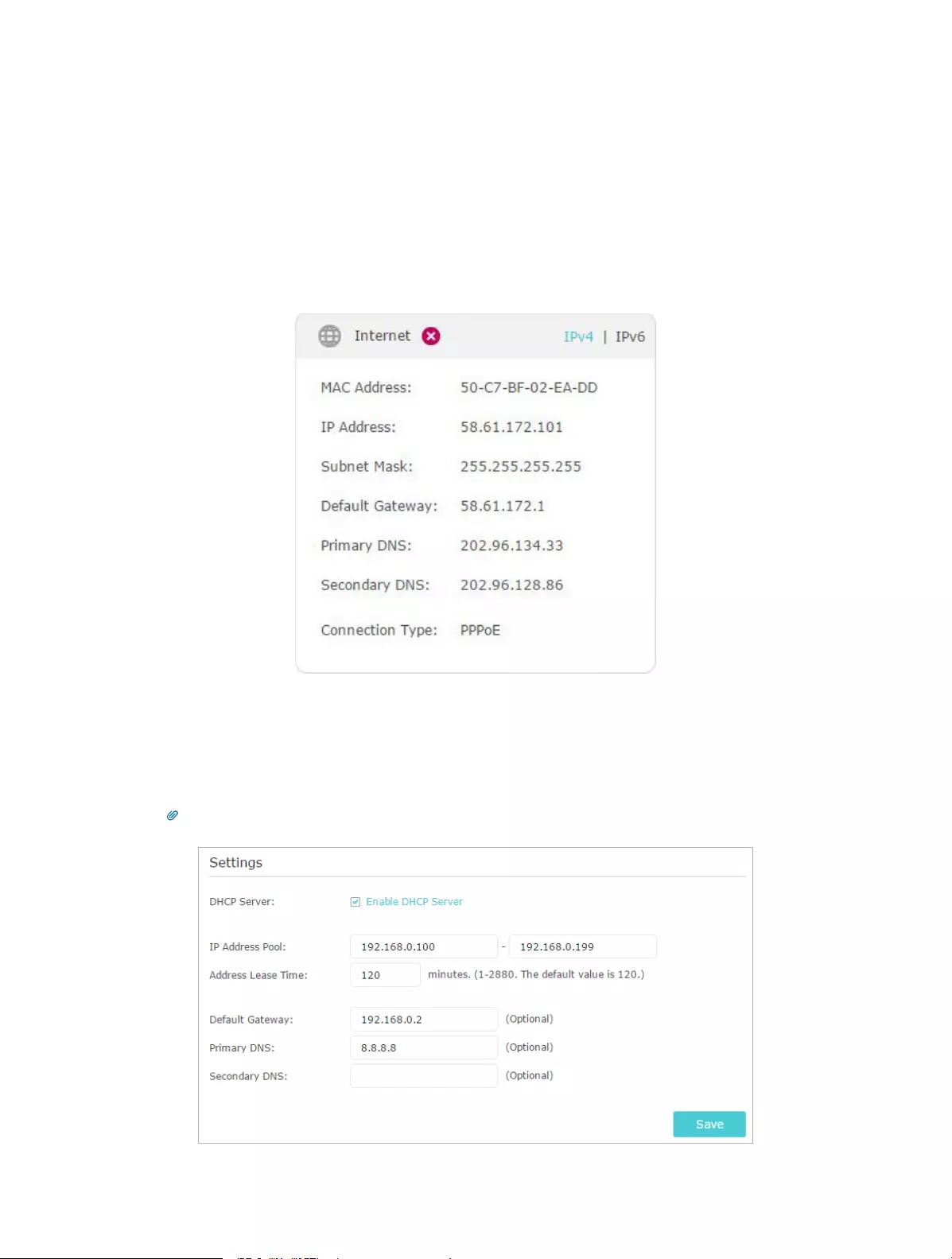
101
Q4. What can I do if I cannot access the Internet even though the
configuration is finished?
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net.
2. Go to Advanced > Status to check Internet status:
As the follow picture shows, if IP Address is a valid one, please try the methods
below and try again:
• Your computer might not recognize any DNS server addresses. Please manually
configure the DNS server.
1 ) Go to Advanced > Network > DHCP Server.
2 ) Enter 8.8.8.8 as Primary DNS, click Save.
Tips: 8.8.8.8 is a safe and public DNS server operated by Google.
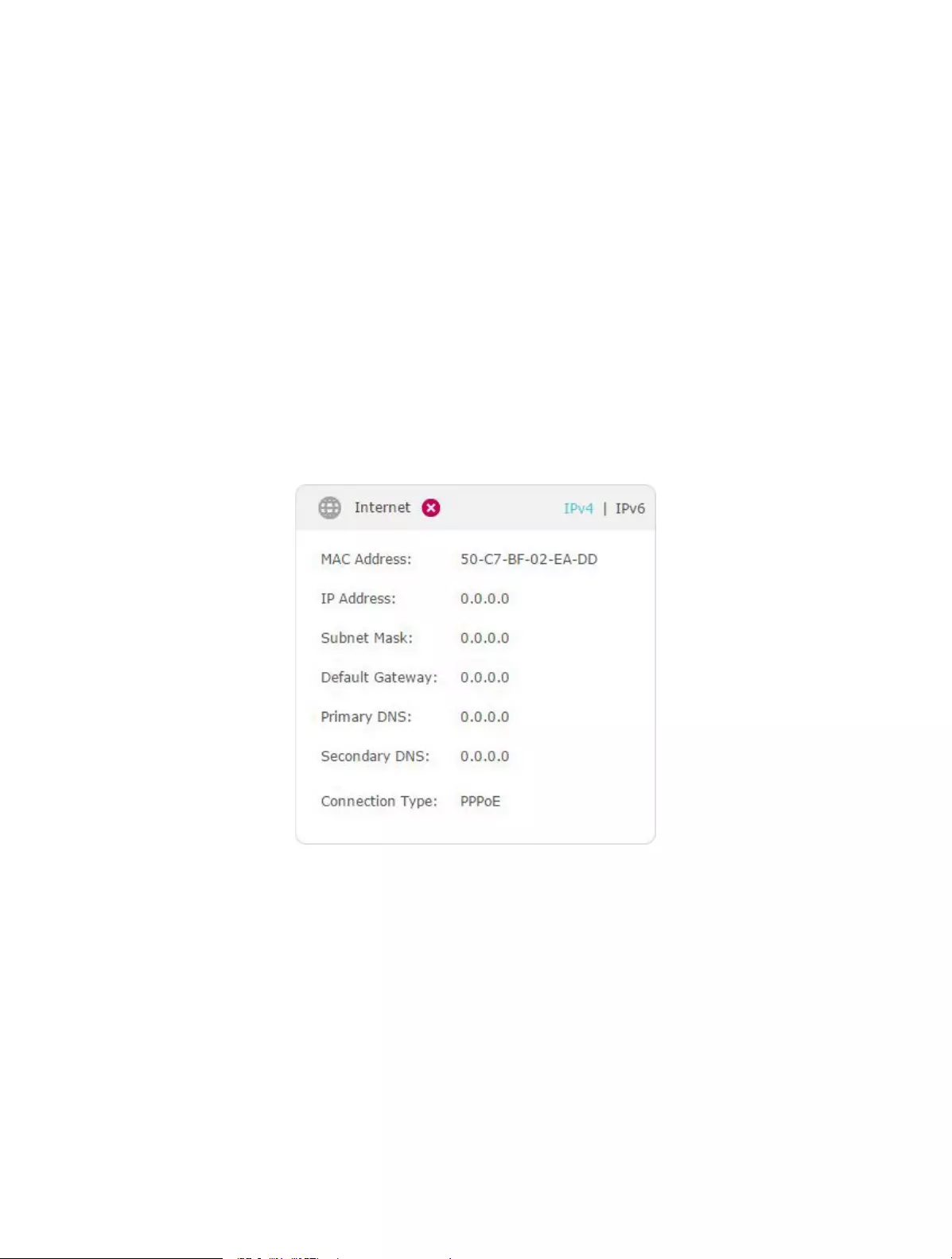
102
• Restart the modem and the router.
1 ) Power off your modem and router, and leave them off for 1 minute.
2 ) Power on your modem first, and wait about 2 minutes until it gets a solid cable
or Internet light.
3 ) Power on the router.
4 ) Wait another 1 or 2 minutes and check the Internet access.
• Reset the router to factory default settings and reconfigure the router.
• Upgrade the firmware of the router.
• Check the TCP/IP settings on the particular device if all other devices can get Internet
from the router.
As the picture below shows, if the IP Address is 0.0.0.0, please try the methods below
and try again:
• Make sure the physical connection between the router and the modem is proper.
• Clone the MAC address of your computer.
1 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
2 ) Go to Advanced > Network > Internet and focus on the MAC Clone section.
3 ) Choose an option as needed (enter the MAC address if Use Custom MAC
Address is selected), and click Save.
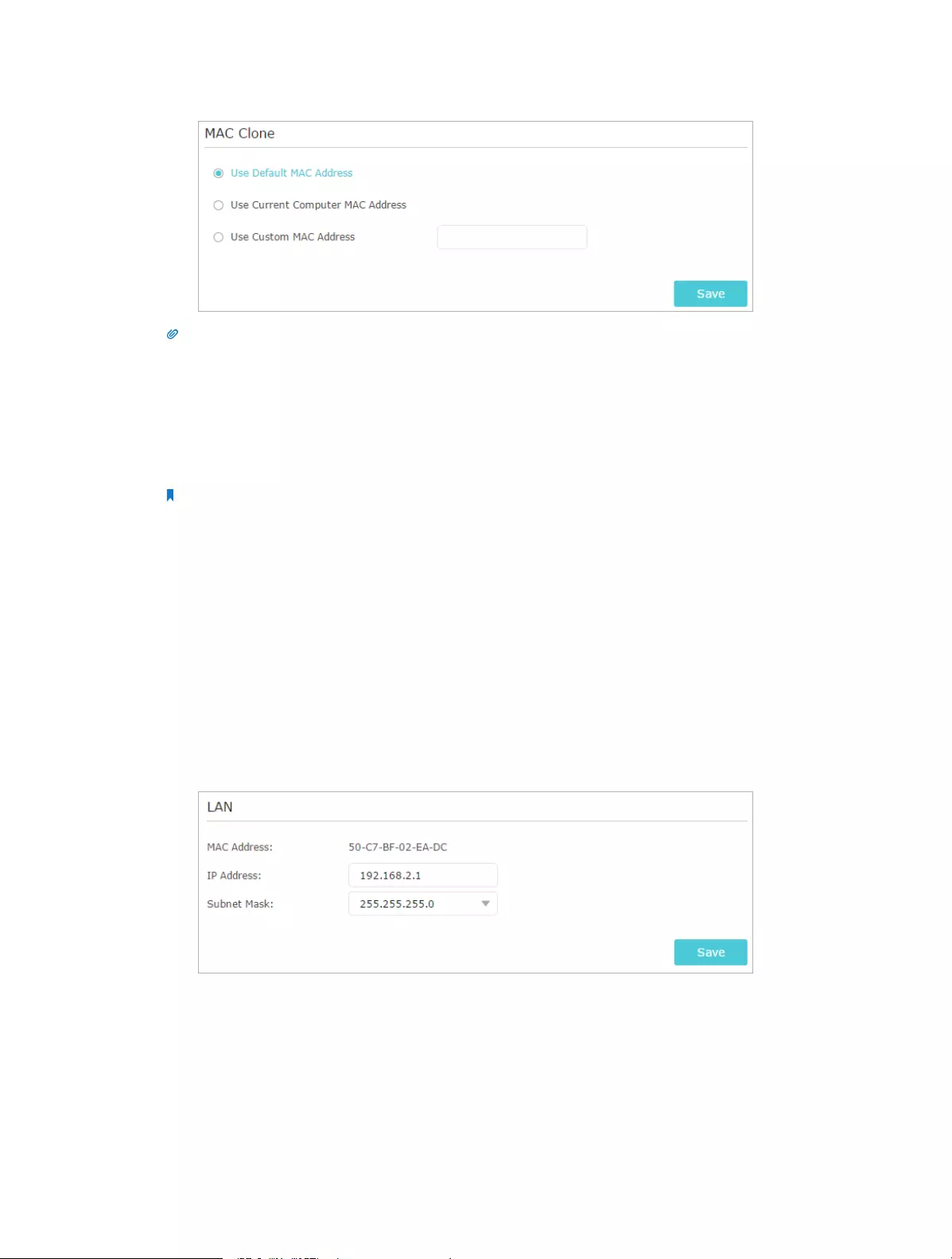
103
Tips:
• Some ISP will register the MAC address of your computer when you access the Internet for the first time
through their Cable modem, if you add a router into your network to share your Internet connection, the
ISP will not accept it as the MAC address is changed, so we need to clone your computer’s MAC address to
the router.
• The MAC addresses of a computer in wired connection and wireless connection are different.
• Modify the LAN IP address of the router.
Note:
Most TP-LINK routers use 192.168.0.1/192.168.1.1 as their default LAN IP address, which may conflict with the
IP range of your existing ADSL modem/router. If so, the router is not able to communicate with your modem
and you can’t access the Internet. To resolve this problem, we need to change the LAN IP address of the router
to avoid such conflict, for example, 192.168.2.1.
1 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
2 ) Go to Advanced > Network > LAN.
3 ) Modify the LAN IP address as the follow picture shows. Here we take 192.168.2.1
as an example.
4 ) Click Save.
• Restart the modem and the router.
1 ) Power off your modem and router, and leave them off for 1 minute.
2 ) Power on your modem first, and wait about 2 minutes until it get a solid cable
or Internet light.
3 ) Power on the router.
4 ) Wait another 1 or 2 minutes and check the Internet access.
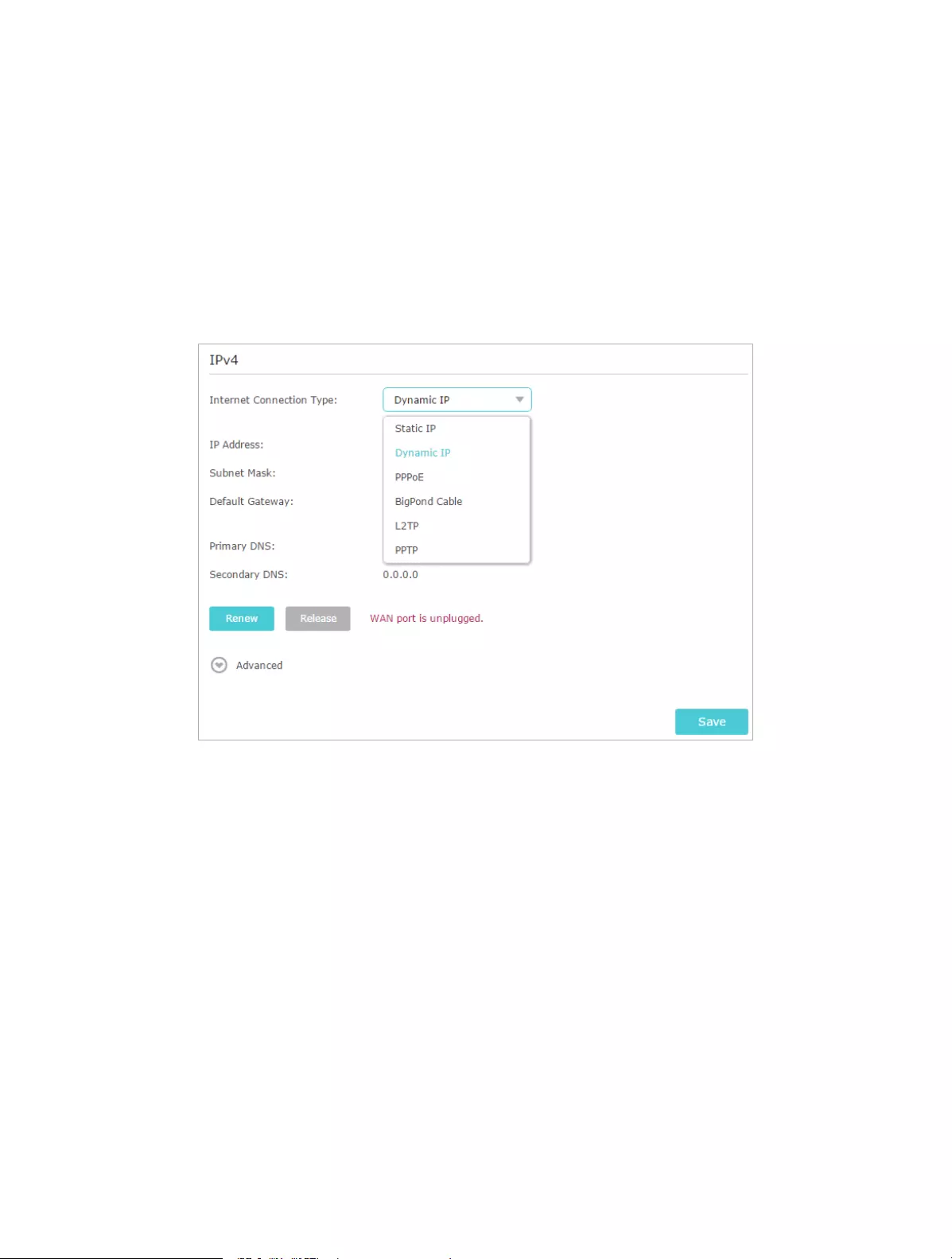
104
• Double check the Internet Connection Type.
1 ) Confirm your Internet Connection Type, which can be learned from the ISP.
2 ) Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set
for the router.
3 ) Go to Advanced > Network > Internet.
4 ) Select your Internet Connection Type and fill in other parameters.
5 ) Click Save.
6 ) Restart the modem and the router again.
• Please upgrade the firmware of the router.
If you’ve tried every method above but still cannot access the Internet, please contact
the technical support.
Q5. What can I do if I cannot find my wireless network or I cannot connect
the wireless network?
If you fail to find any wireless network, please follow the steps below:
• Make sure the wireless function of your device is enabled if you’re using a laptop
with built-in wireless adapter. You can refer to the relevant document or contact the
laptop manufacturer.
• Make sure the wireless adapter driver is installed successfully and the wireless adapter
is enabled.
• On Windows 7
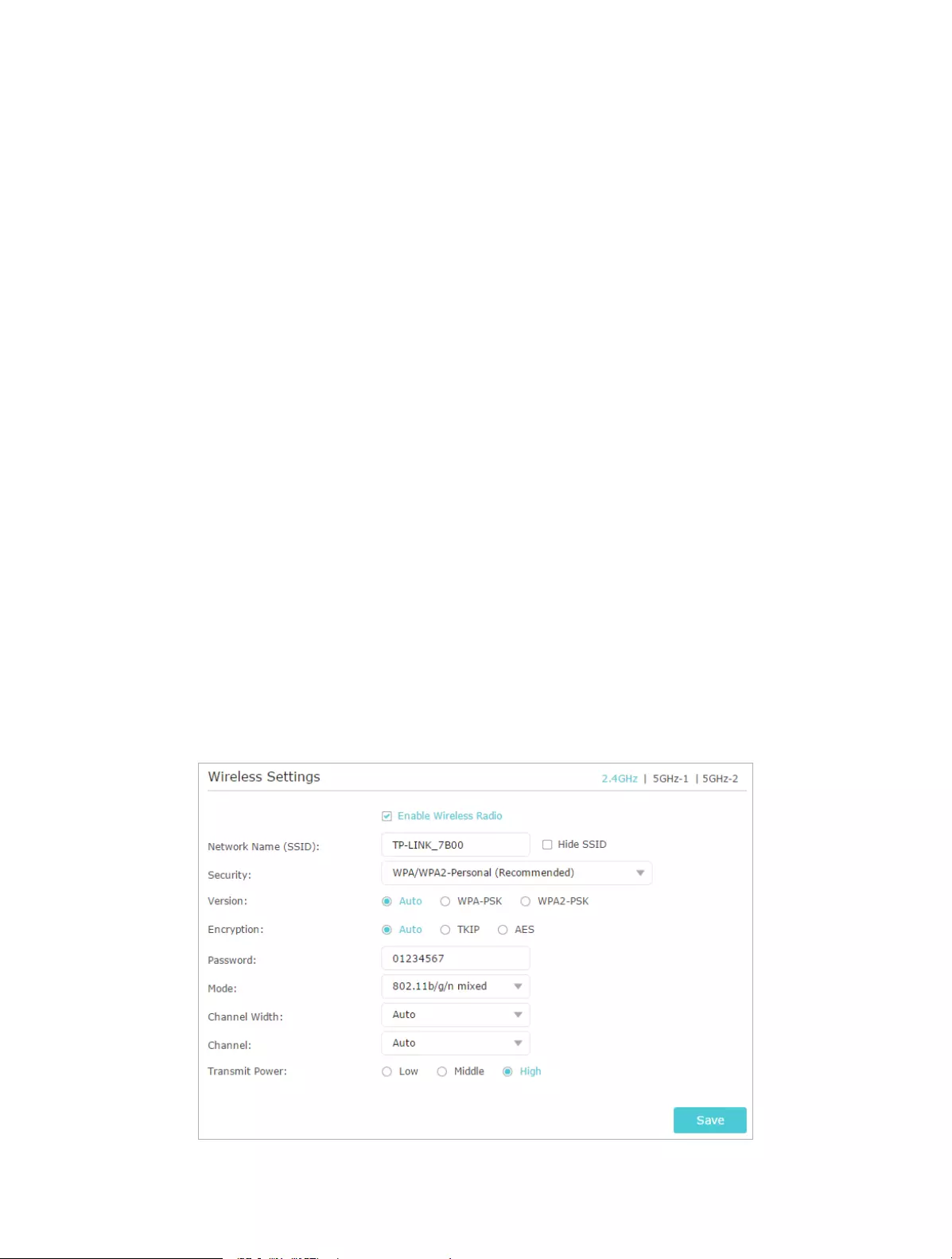
105
1 ) If you see the message No connections are available, it is usually because the
wireless function is disabled or blocked somehow.
2 ) Click Troubleshoot and windows might be able to fix the problem by itself.
• On Windows XP
1 ) If you see the message Windows cannot configure this wireless connection, this
is usually because windows configuration utility is disabled or you are running
another wireless configuration tool to connect the wireless.
2 ) Exit the wireless configuration tool (the TP-LINK Utility, for example).
3 ) Select and right click on My Computer on desktop, select Manage to open
Computer Management window.
4 ) Expand Services and Applications > Services, find and locate Wireless Zero
Configuration in the Services list on the right side.
5 ) Right click Wireless Zero Configuration, and then select Properties.
6 ) Change Startup type to Automatic, click on Start button and make sure the
Service status is Started. And then click OK.
If you can find other wireless network except your own, please follow the steps
below:
• Check the WLAN LED indicator on your wireless router/modem.
• Make sure your computer/device is still in the range of your router/modem. Move it
closer if it is currently too far away.
• Go to Advanced > Wireless > Wireless Settings, and check the wireless settings.
Double check your Wireless Network Name and SSID is not hided.
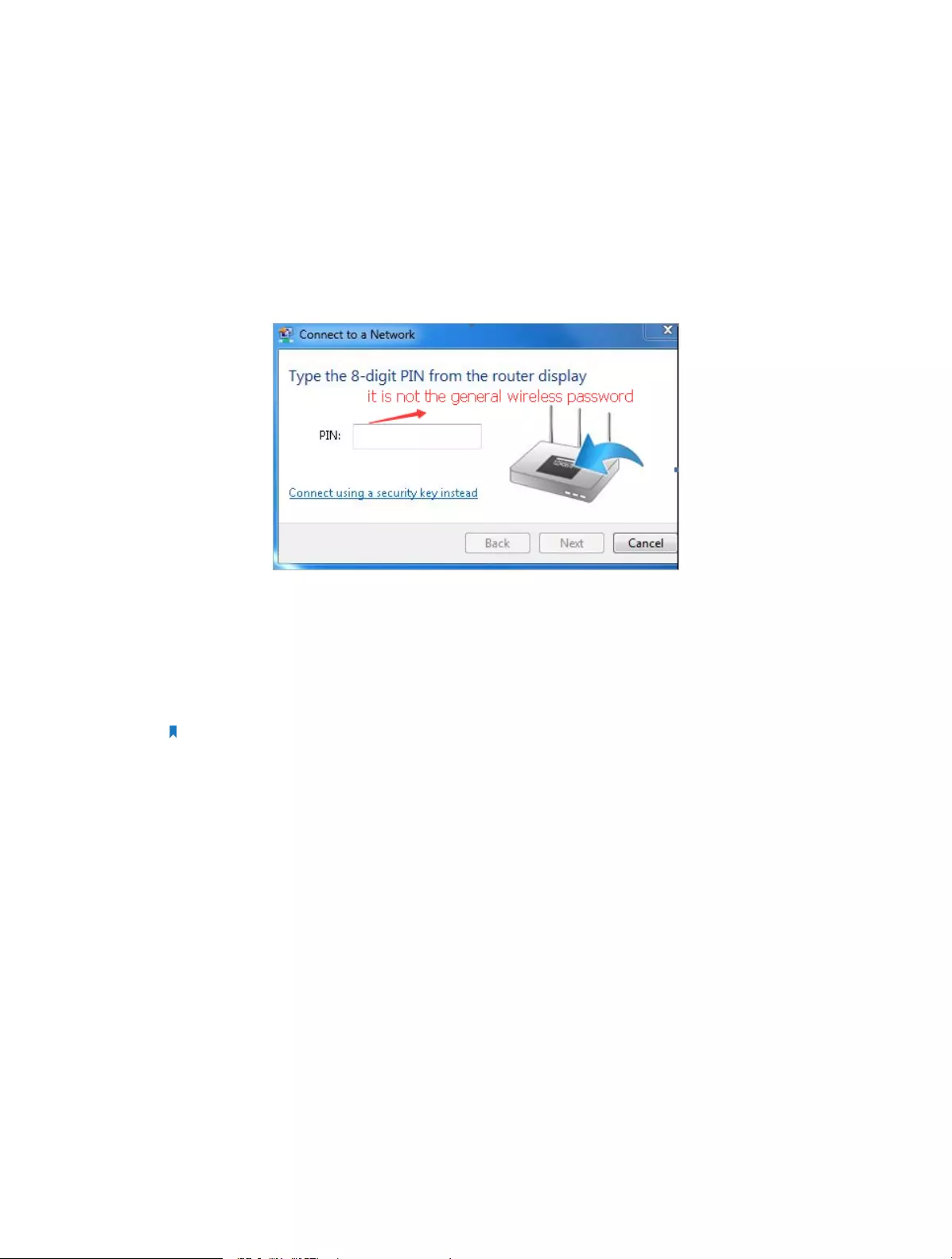
106
If you can find your wireless network but fail to connect, please follow the steps
below:
• Authenticating problem/password mismatch:
1 ) Sometimes you will be asked to type in a PIN number when you connect to
the wireless network for the first time. This PIN number is different from the
Wireless Password/Network Security Key, usually you can only find it on the
label of your router.
2 ) If you cannot find the PIN or PIN failed, you may choose Connecting using a
security key instead, and then type in the Wireless Password/Network Security
Key.
3 ) If it continues to show note of Network Security Key Mismatch, it is suggested
to confirm the wireless password of your wireless router.
Note: Wireless Password/Network Security Key is case sensitive.
• Windows unable to connect to XXXX / Can not join this network / Taking longer
than usual to connect to this network:
• Check the wireless signal strength of your network. If it is weak (1~3 bars),
please move the router closer and try again.
• Change the wireless Channel of the router to 1,6,or 11 to reduce interference
from other networks.
• Re-install or update the driver for your wireless adapter of the computer.

107
COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark
of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other brands and product names are trademarks
or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any means or
used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or adaptation
without permission from TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Copyright © 2016 TP-LINK
TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
108
FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Note: The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by
unauthorized modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device and its antenna must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
“To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, this grant is applicable to
only Mobile Configurations. The antennas used for this transmitter must be installed to
provide a separation distance of at least 31 cm from all persons and must not be co-
located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.”
The device is restricted in indoor environment only.

109
CE Mark Warning
This is a class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
RF Exposure Information
This device meets the EU requirements (1999/5/EC Article 3.1a) on the limitation of
exposure of the general public to electromagnetic fields by way of health protection.
The device complies with RF specifications when the device used at 20 cm from your
body.
Restricted to indoor use.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils
radio exempts de licence. L’exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1. l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage;
2. l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, meme si
le brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le fonctionnement
This radio transmitter (IC: 8853A-C5400/ Model: Archer C5400) has been approved by
Industry Canada to operate with the antenna types listed below with the maximum
permissible gain indicated. Antenna types not included in this list below, having a gain
greater than the maximum gain indicated for that type, are strictly prohibited for use
with this device.
Le présent émetteur radio (IC: 8853A-C5400/ Model: Archer C5400) a été approuvé
par Industrie Canada pour fonctionner avec les types d’antenne énumérés ci-dessous
et ayant un gain admissible maximal. Les types d’antenne non inclus dans cette liste
ci-dessous et dont le gain est supérieur au gain maximal indiqué, sont strictement
interdits pour l’exploitation de l’émetteur.
Antenna
Four 1.8dBi External Non-detachable Omni-Directional Antennas @2.4G
& 5GHz
Four 1.8dBi External Non-detachable Omni-Directional Antennas @5GHz

110
Caution:
1. The device for operation in the band 5150–5250 MHz is only for indoor use to reduce
the potential for harmful interference to co-channel mobile satellite systems;
2. For devices with detachable antenna(s), the maximum antenna gain permitted for
devices in the band 5725-5850 MHz shall be such that the equipment still complies
with the e.i.r.p. limits specified for point-to-point and non-point-to-point operation
as appropriate.
Avertissement:
1. Le dispositif fonctionnant dans la bande 5150-5250 MHz est réservé uniquement
pour une utilisation à l’intérieur afin de réduire les risques de brouillage préjudiciable
aux systèmes de satellites mobiles utilisant les mêmes canaux;
2. Le gain maximal d’antenne permis pour les dispositifs avec antenne(s) amovible(s)
utilisant la bande 5725-5850 MHz doit se conformer à la limitation P.I.R.E spécifiée
pour l’exploitation point à point et non point à point.
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
30cm between the radiator & your body.
Déclaration d’exposition aux radiations:
Cet équipement est conforme aux limites d’exposition aux rayonnements IC établies
pour un environnement non contrôlé. Cet équipement doit être installé et utilisé avec
un minimum de 30 cm de distance entre la source de rayonnement et votre corps.
Industry Canada Statement
CAN ICES-3 (B)/NMB-3(B)
Korea Warning Statements:
당해 무선설비는 운용중 전파혼신 가능성이 있음.
NCC Notice & BSMI Notice:
注意!
依據 低功率電波輻射性電機管理辦法
第十二條 經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均
不得擅自變更頻率、加大功率或變更原設計之特性或功能。
第十四條 低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通行;經發現有干
擾現象時,應立即停用,並改善至無干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依
電信規定作業之無線電信。低功率射頻電機需忍受合法通信或工業、科學以及醫
療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
111
電磁波曝露量MPE 標準值1mW/cm²,本產品使用時建議應距離人體:20 cm。
安全諮詢及注意事項
• 請使用原裝電源供應器或只能按照本產品注明的電源類型使用本產品。
• 清潔本產品之前請先拔掉電源線。請勿使用液體、噴霧清潔劑或濕布進行
清潔。
• 注意防潮,請勿將水或其他液體潑灑到本產品上。
• 插槽與開口供通風使用,以確保本產品的操作可靠並防止過熱,請勿堵塞
或覆蓋開口。
• 請勿將本產品置放於靠近熱源的地方。除非有正常的通風,否則不可放在
密閉位置中。
• 請不要私自打開機殼,不要嘗試自行維修本產品,請由授權的專業人士進
行此項工作。
Продукт сертифіковано згідно с правилами системи УкрСЕПРО на відповідність
вимогам нормативних документів та вимогам, що передбачені чинними
законодавчими актами України.
Safety Information
• When product has power button, the power button is one of the way to shut off the
product; when there is no power button, the only way to completely shut off power
is to disconnect the product or the power adapter from the power source.
• Don’t disassemble the product, or make repairs yourself. You run the risk of electric
shock and voiding the limited warranty. If you need service, please contact us.
• Avoid water and wet locations.
• Adapter shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily accessible.
• The plug considered as disconnect device of adapter.
• Use only power supplies which are provided by manufacturer and in the original
packing of this product. If you have any questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
For EU/EFTA, this product can be used in the following countries:
AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK
EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU
IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MT
NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK

112
Explanations of the symbols on the product label
Symbol Explanation
DC voltage
RECYCLING
This product bears the selective sorting symbol for Waste electrical and electronic equipment
(WEEE). This means that this product must be handled pursuant to European directive 2012/19/
EU in order to be recycled or dismantled to minimize its impact on the environment.
User has the choice to give his product to a competent recycling organization or to the retailer
when he buys a new electrical or electronic equipment.



