Vertiv Geist GU30010L User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for Geist GU30010L by Vertiv which is a product in the Power Distribution Units (PDUs) category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Geist™
Intelligent Rack PDU
Installer/User Guide
Switched, Unit and Outlet Monitored Upgradeable

Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
Technical Support Site
If you encounter any installation or operational issues with your product, check the pertinent
section of this manual to see if the issue can be resolved by following outlined procedures.
Visit https://www.VertivCo.com/en-us/support/ for additional assistance.
The information contained in this document is subject to change
without notice and may not be suitable for all applications. While every
precaution has been taken to ensure the accuracy and completeness
of this document, Vertiv assumes no responsibility and disclaims all
liability for damages resulting from use of this information or for any
errors or omissions. Refer to other local practices or building codes as
applicable for the correct methods, tools, and materials to be used in
performing procedures not specifically described in this document.
The products covered by this instruction manual are manufactured
and/or sold by Vertiv. This document is the property of Vertiv and
contains confidential and proprietary information owned by Vertiv.
Any copying, use or disclosure of it without the written permission of
Vertiv is strictly prohibited.
Names of companies and products are trademarks or registered
trademarks of the respective companies. Any questions regarding
usage of trademark names should be directed to the original
manufacturer.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Overview 1
1.1 Environmental 1
1.2 Electrical 2
1.3 Networking 2
1.3.1 Ethernet 2
1.3.2 Protocols 2
1.3.3 User interfaces 2
1.3.4 Regulatory compliance 3
2 Installation 5
2.1 Mounting 5
3 Setup 17
3.1 Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD-3E) 17
3.1.1 Enhanced Switched Monitored 17
3.1.2 Enhanced Switched Monitored with RS-232 19
3.1.3 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 20
3.2 Network Setup 21
3.3 Web Interface 25
3.3.1 Home page 25
3.3.2 Sensors tab 26
3.3.3 System tab 32
3.3.4 Help tab 47
4 Vertiv Intelligence Director 49
4.1 Aggregation 49
4.2 Master rPDU 49
4.3 Network Configuration 50
4.3.1 Downstream Devices 50
4.4 Views 52
4.4.1 Summary 53
4.4.2 Groups 54
4.4.3 List 55
4.4.4 Group Configuration 56
4.5 Interfaces 57
4.5.1 Group SNMP data 58
i

4.5.2 Tips and troubleshooting 58
5 Appendices 59
Appendix A: Technical Support 59
Appendix B: Visible Light Communication (VLC) 63
Appendix C: Vertiv Mobile App 65
Appendix D: Available Sensors 72
Appendix E: Outlet LEDs 73
Appendix F: IMD Display Codes 74
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
ii
1 OVERVIEW
The Upgradeable second generation (GU2) product is a high tier rack level power distribution unit (rPDU)
with input and output monitoring, outlet level switching, remote network access via an embedded Vertiv
API, and with external sensor support via built-in Enhanced Communications (EC) card. The embedded
web based Graphical User Interface (GUI) provides access to user product configuration and data logging.
GU2 PDUs are available in a wide range of SKUs to support all standard global input voltages, enterprise
and hyperscale rack loads of over 20 kVA, and single-phase and three-phase Delta or Wye building wiring
configurations.
INPUT POWER
MONITORING
OUTLET LEVEL POWER
MONITORING
OUTLET LEVEL
SWITCHING
Switched Input Level Monitoring
EC x x
Outlet Level Monitoring EC x x
Switched Outlet Level Monitoring
EC xxx
Table 1.1 GU2 Families
1.1 Environmental
The operational environmental limits pertaining to temperature, humidity and elevation are as defined in
the following tables.
DESCRIPTION MINIMUM MAXIMUM
Operating 10°C (50°F) 60°C (140°F) UL Listed Models
50°C (122°F) CE Marked Models
Storage -40°C (-40°F) 70°C (158°F) max
Table 1.2 Temperature Limits
DESCRIPTION MINIMUM MAXIMUM
Operating 5% 95% (non-condensing)
Storage 5% 95% (non-condensing)
Table 1.3 Humidity Limits
1
DESCRIPTION MINIMUM MAXIMUM
Operating 0 m (0 ft) 3,050 m (10,000 ft)
Storage 0 m (0 ft) 15,240 m (50,000 ft)
Table 1.4 Elevation Limits
1.2 Electrical
Electrical product characteristics and performance are defined in the following table. Also, please see the
product nameplate for additional rating limits.
TYPE RATINGS
NEMA 5-15R or L5-15R 125Vac, 12A
NEMA 5-20R or L5-20R 125Vac, 16A
NEMA 6-20R or L6-20R 250Vac, 16A
NEMA L5-30R 125Vac, 24A
NEMA L6-30R 250Vac, 24A
IEC-60320 C13 250Vac, 10A (UL & CSA 12A, 250Vac)
IEC-60320 C19 250Vac, 16A (UL & CSA 16A, 250Vac)
U-Lock Locking IEC-60320 C13 250Vac, 10A (UL & CSA 12A, 250Vac)
U-Lock Locking IEC-60320 C19 250Vac, 16A (UL & CSA 16A, 250Vac)
Table 1.5 Receptacle Ratings
1.3 Networking
The product communications requirements are defined in the next sections.
1.3.1 Ethernet
The Ethernet link speed for this product is: 10/100 Mb; full duplex.
1.3.2 Protocols
The communications protocols supported by this product include: ARP, IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, NDP,
TCP, UDP, RSTP, STP, DNS, HTTP, HTTPS (TLSv1.2), SMTP, SMTPS, DHCP, SNMP (v1/v2c/v3), LDAP,
TACACS, RADIUS, NTP, SSH, RS232 and Syslog.
1.3.3 User interfaces
This product supports the following user interfaces: SNMP, JSON-based Web GUI, JSON API and
Command-line interface using SSH or serial (RS232).
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
2

1.3.4 Regulatory compliance
Vertiv products are regulated for Safety, Emissions and Environment Impact per the following agencies
and policies.
Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
UL Standards are used to assess products; test components, materials, systems and performance; and
evaluate environmentally sustainable products, renewable energies, food and water products, recycling
systems and other innovative technologies.
The UL standards specific to this equipment are as noted on the device nameplate.
CE
The placement of the CE mark on a product signifies a manufacturer's declaration that the product
complies with the applicable European (EU) health, safety, and environmental protection requirements,
including EU legislation and product directives. The CE mark is required for products offered for sale
within the European Economic Area (EEA).
The specific regulations, directives, and standards applicable to each product are specified on the
Declaration of Conformity.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates interstate and international communications
by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable in all 50 states, the District of Columbia and U.S. territories. An
independent U.S. government agency overseen by Congress, the commission is the United States'
primary authority for communications laws, regulation and technological innovation.
The FCC standards specific to this equipment are:
This Class A device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
WARNING! Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
1 Overview 3

ROHS/WEEE
RoHS, also known as Lead-Free, stands for Restriction of Hazardous Substances. RoHS, also known as
Directive 2002/95/EC, originated in the European Union and restricts the use of six hazardous materials
found in electrical and electronic products. All applicable products in the EU market after July 1, 2006
must pass RoHS compliance. RoHS impacts the entire electronics industry and many electrical products
as well.
WEEE stands for Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment. WEEE Directive 2002/96/EC mandates
the treatment, recovery and recycling of electric and electronic equipment (90% ends up in landfills). All
applicable products in the EU market must pass WEEE compliance and carry the Wheelie Bin sticker.
See product label for RoHS/WEEE compliance marks.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
4
2 INSTALLATION
Using the images in the mounting section, install your rack PDU.
NOTE: Please visit http://www.VertivCo.com/ComplianceRegulatoryInfo for important safety
information prior to installation.
To install your unit:
1. Using appropriate hardware, mount unit to rack.
2. Plug the rPDU into an appropriately-rated and protected branch-circuit receptacle.
3. Plug in the devices to be powered by the rPDU.
4. Turn on each device connected to the rPDU.
NOTE: Sequential power-up is recommended to avoid high inrush current.
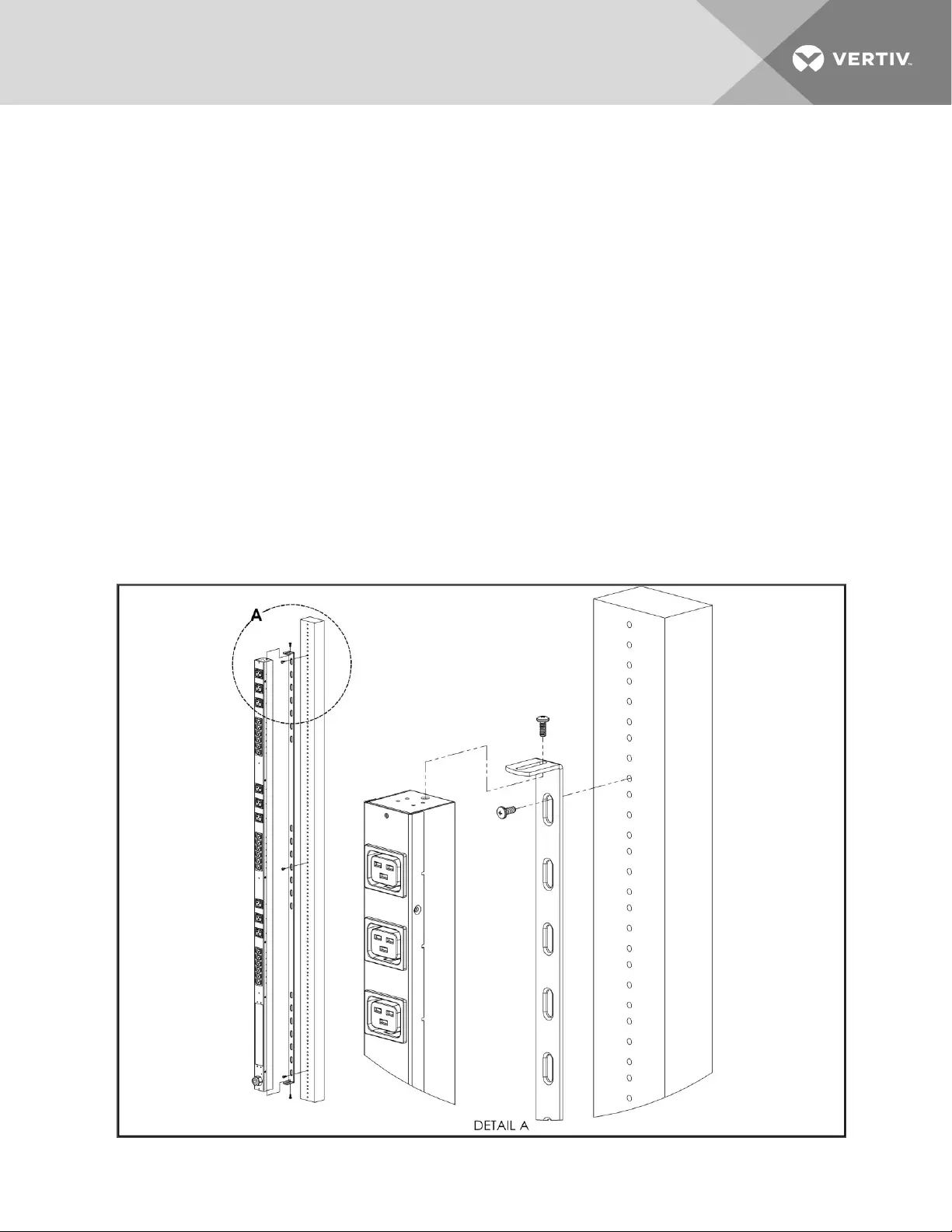
2.1 Mounting
Optional brackets are sold separately.
Figure 2.1 Full-length brackets
5
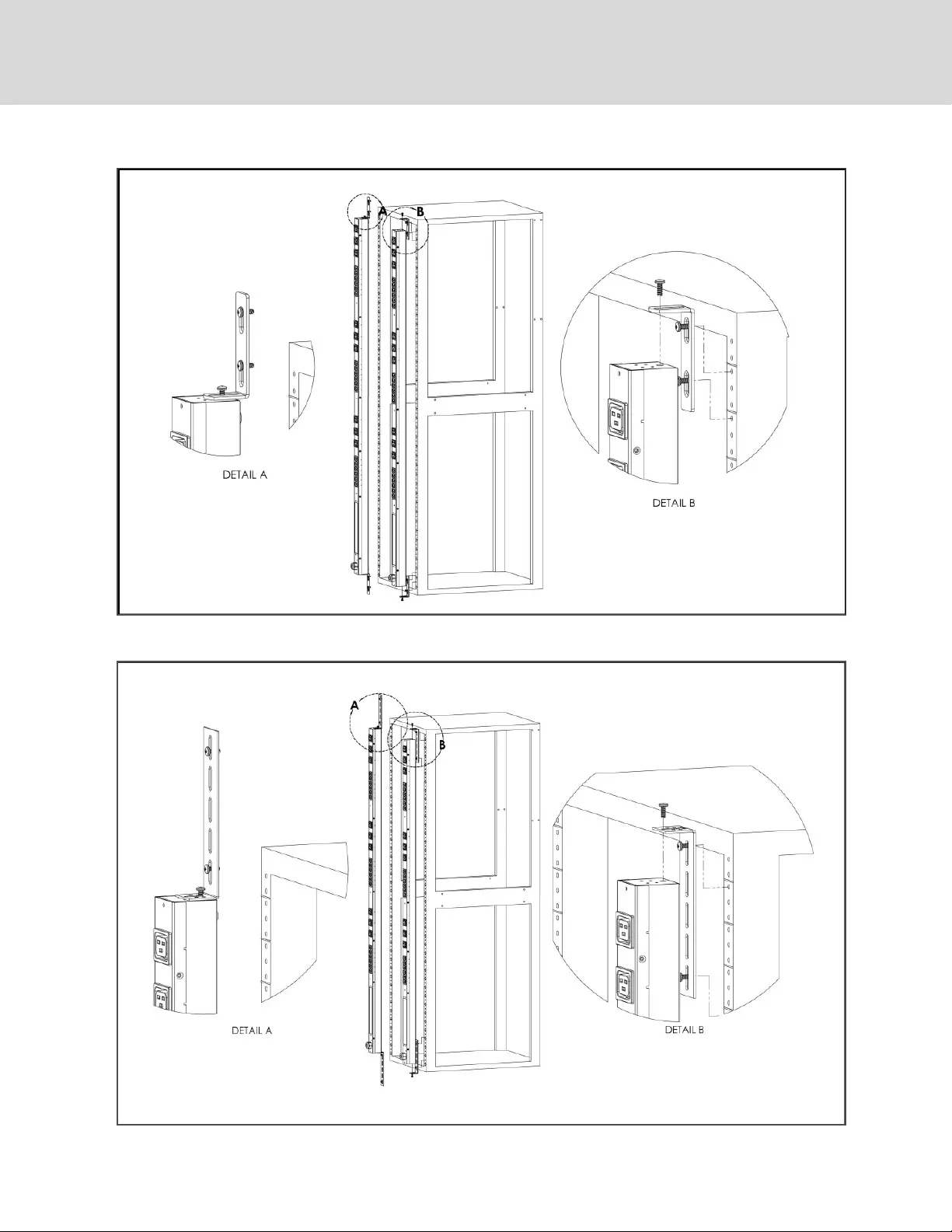
Figure 2.2 Mini L Brackets
Figure 2.3 Vertical Extension Brackets
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
6

Figure 2.4 Toolless Mounting Hardware
2 Installation 7
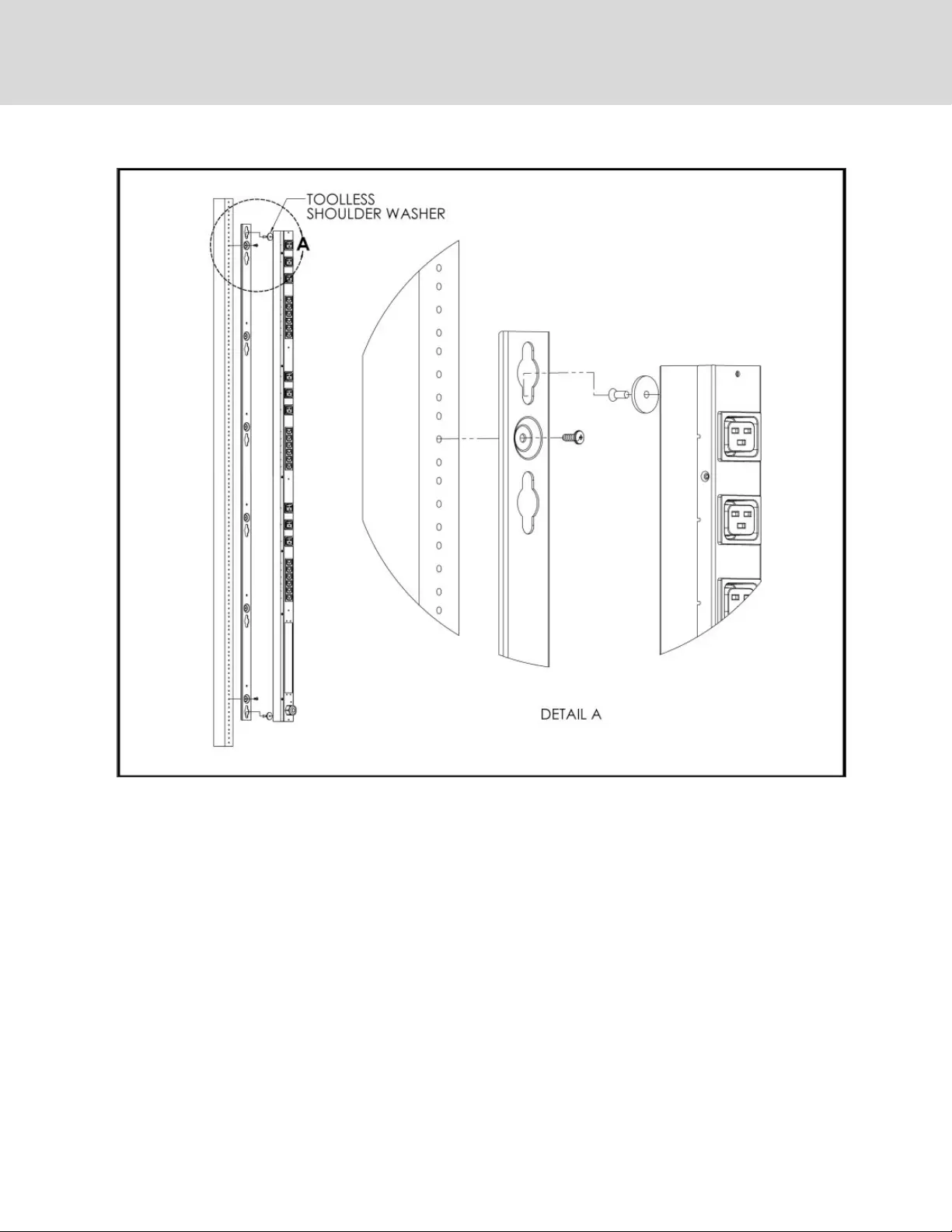
Figure 2.5 Toolless Full Length Brackets
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
8
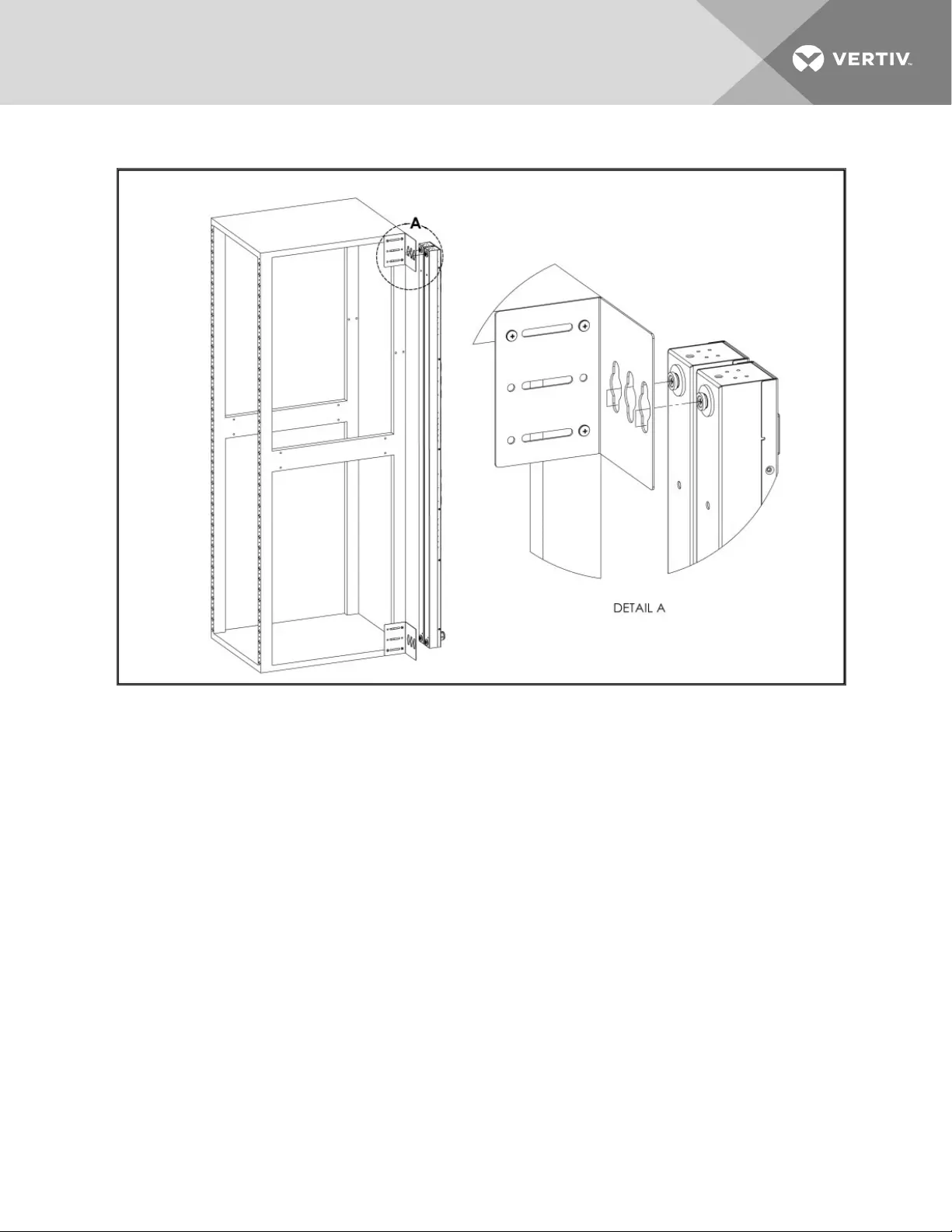
Figure 2.6 Single Side Mount 2 Units Brackets
2 Installation 9
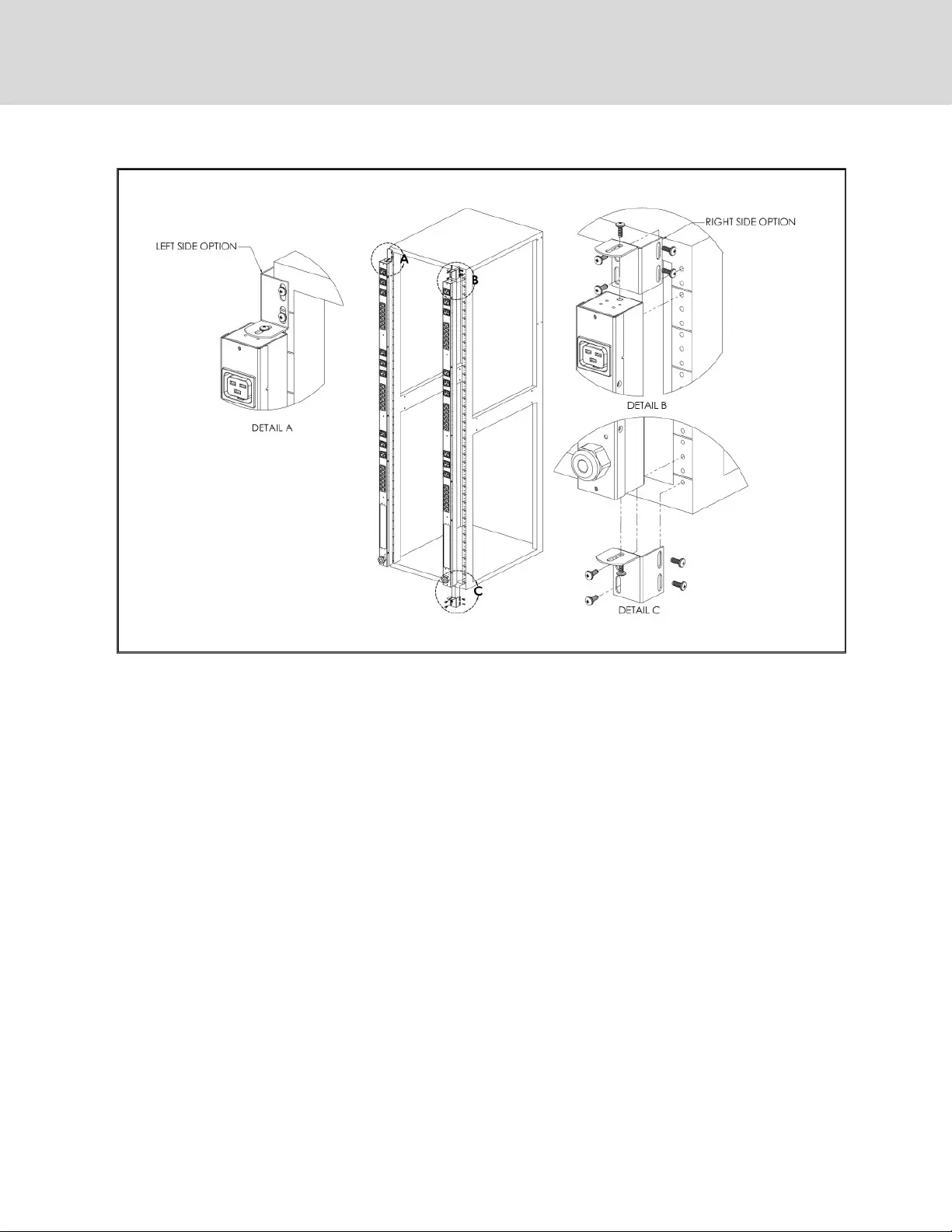
Figure 2.7 Offset/Side Mount Brackets
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
10
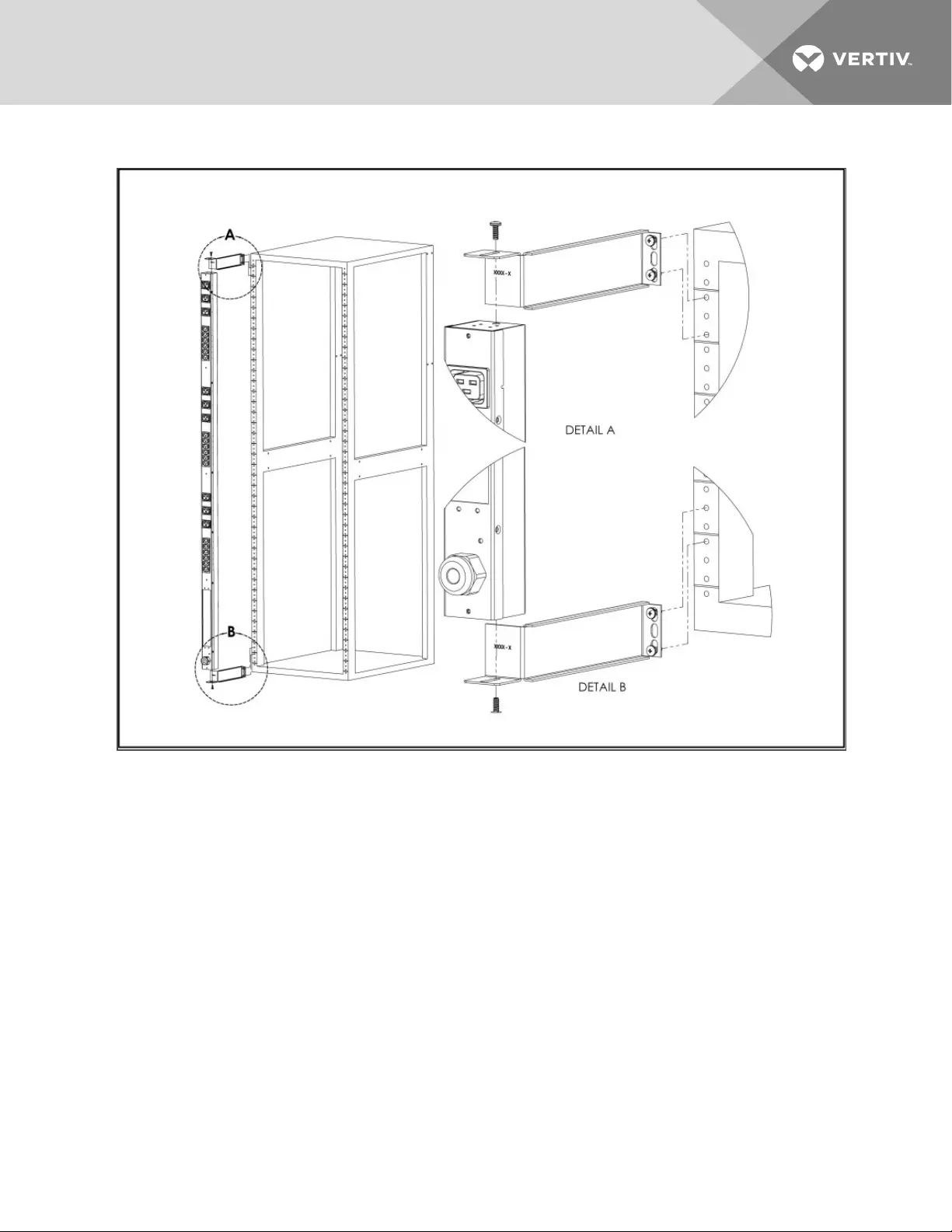
Figure 2.8 7" Extension Brackets
2 Installation 11
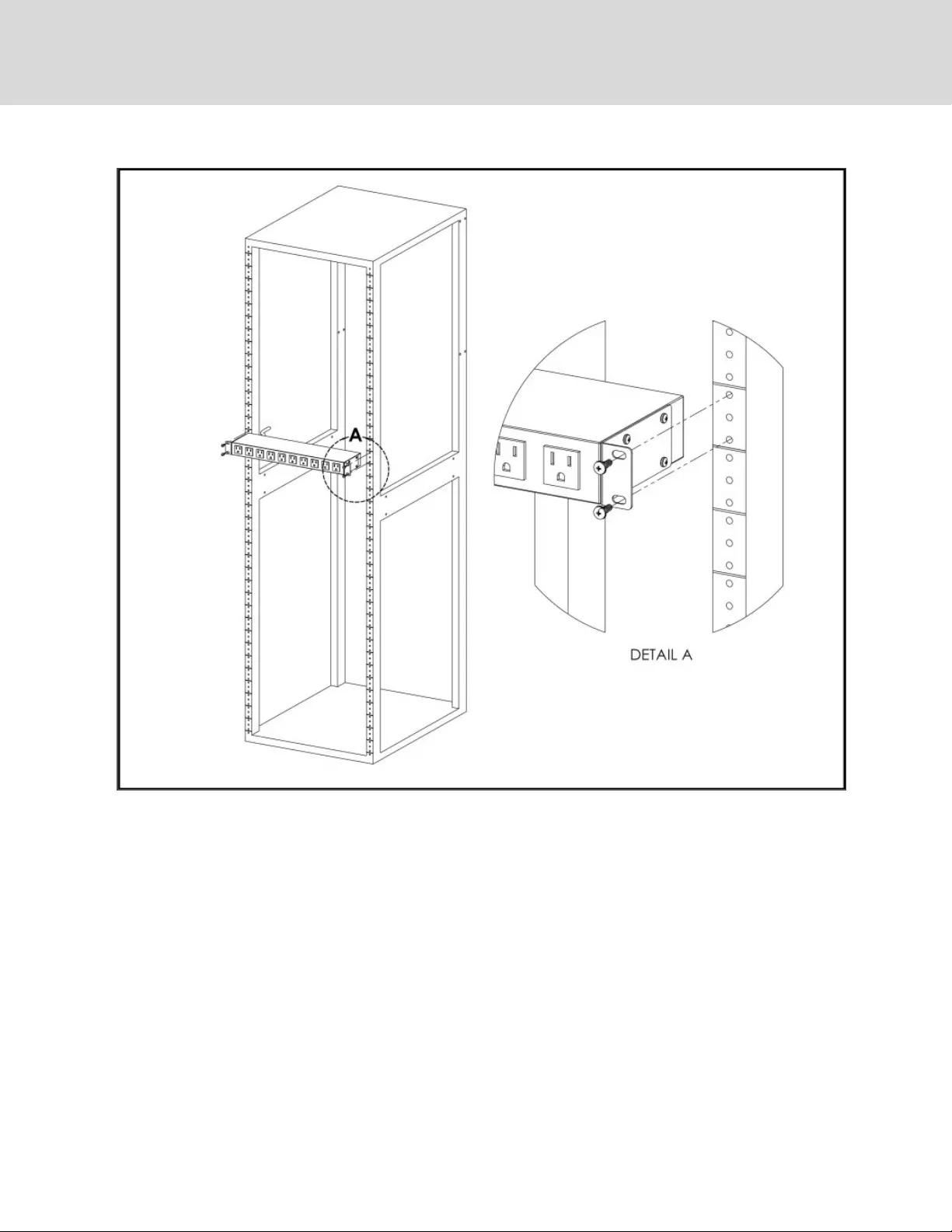
Figure 2.9 Flush Mount Bracket
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
12
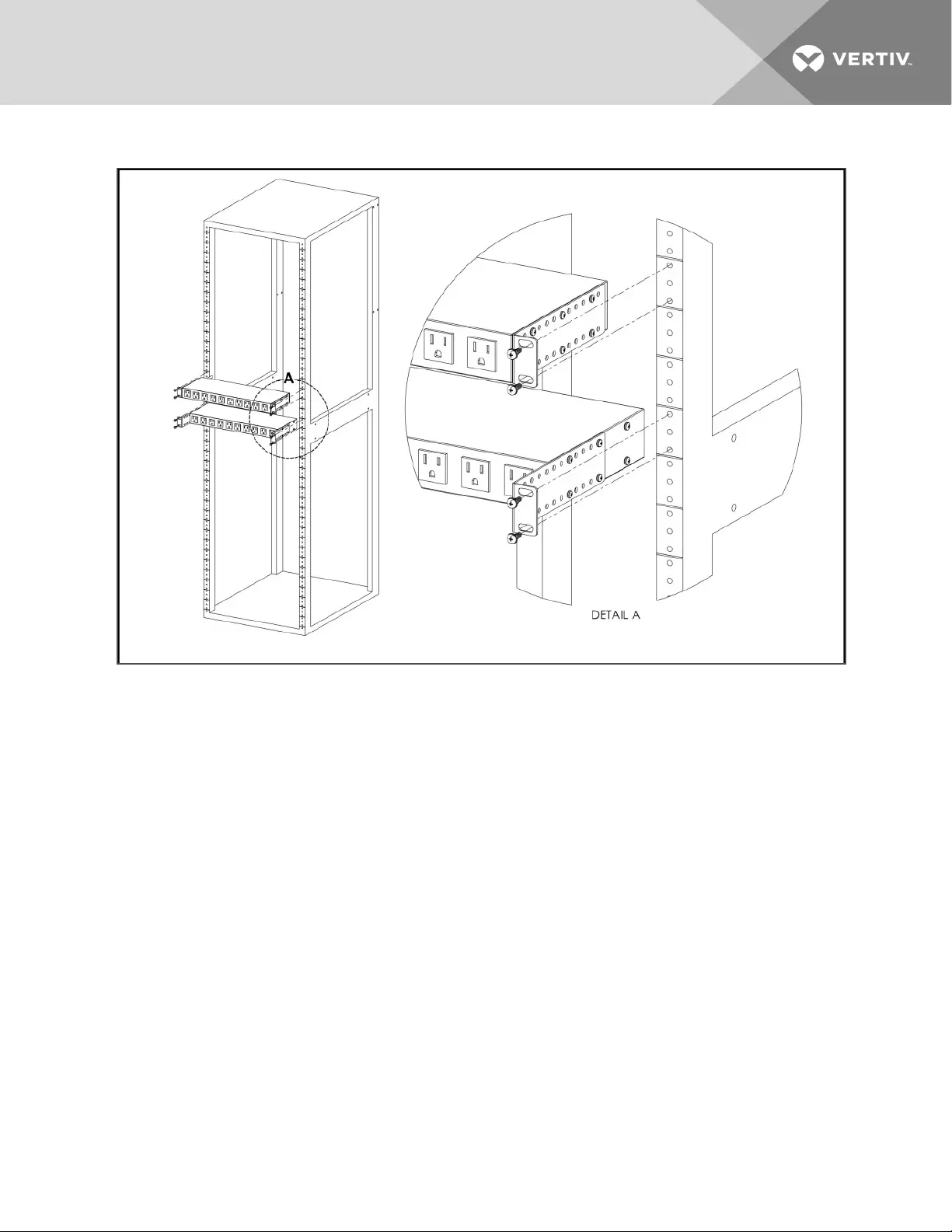
Figure 2.10 Adjustable Mount Bracket
2 Installation 13
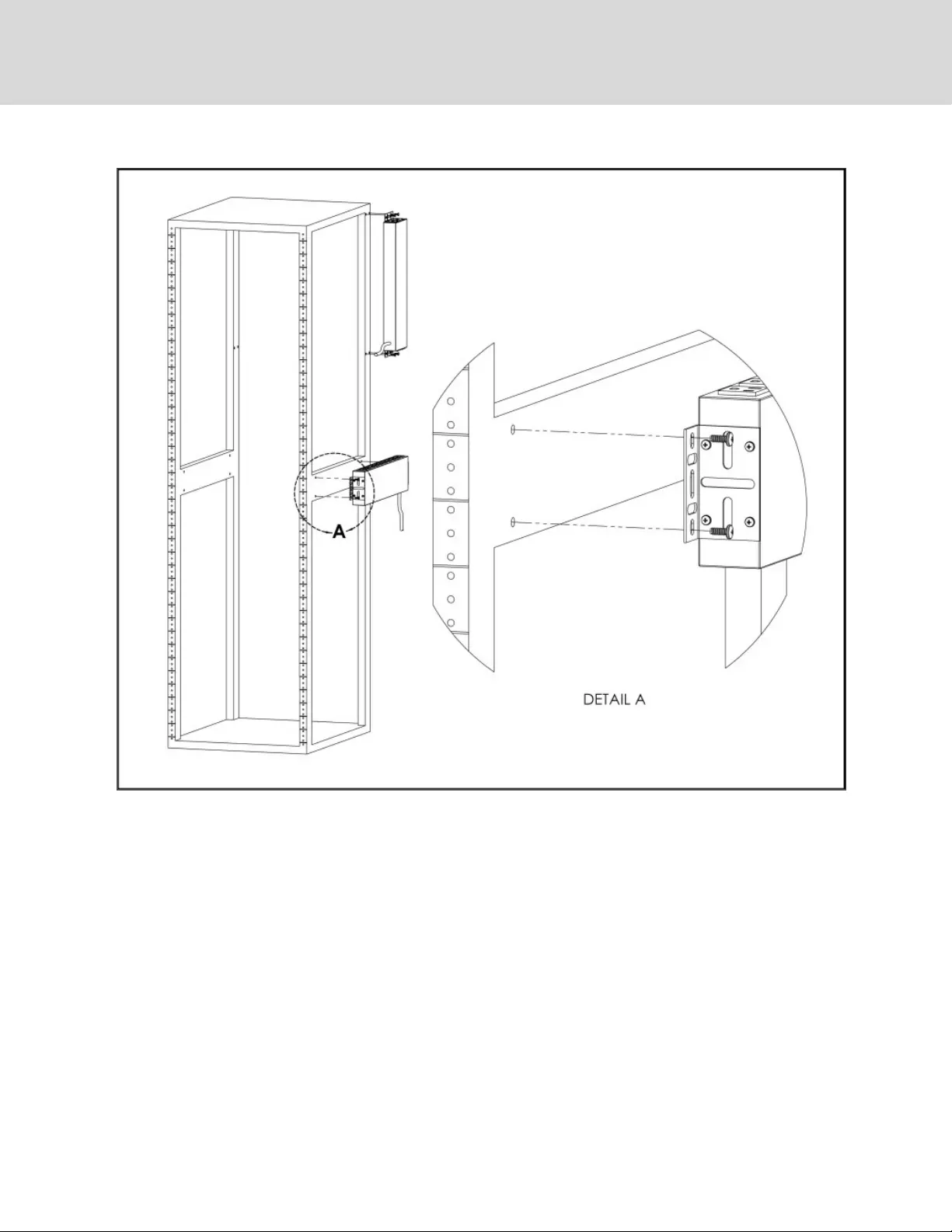
Figure 2.11 Panel Mount Bracket
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
14
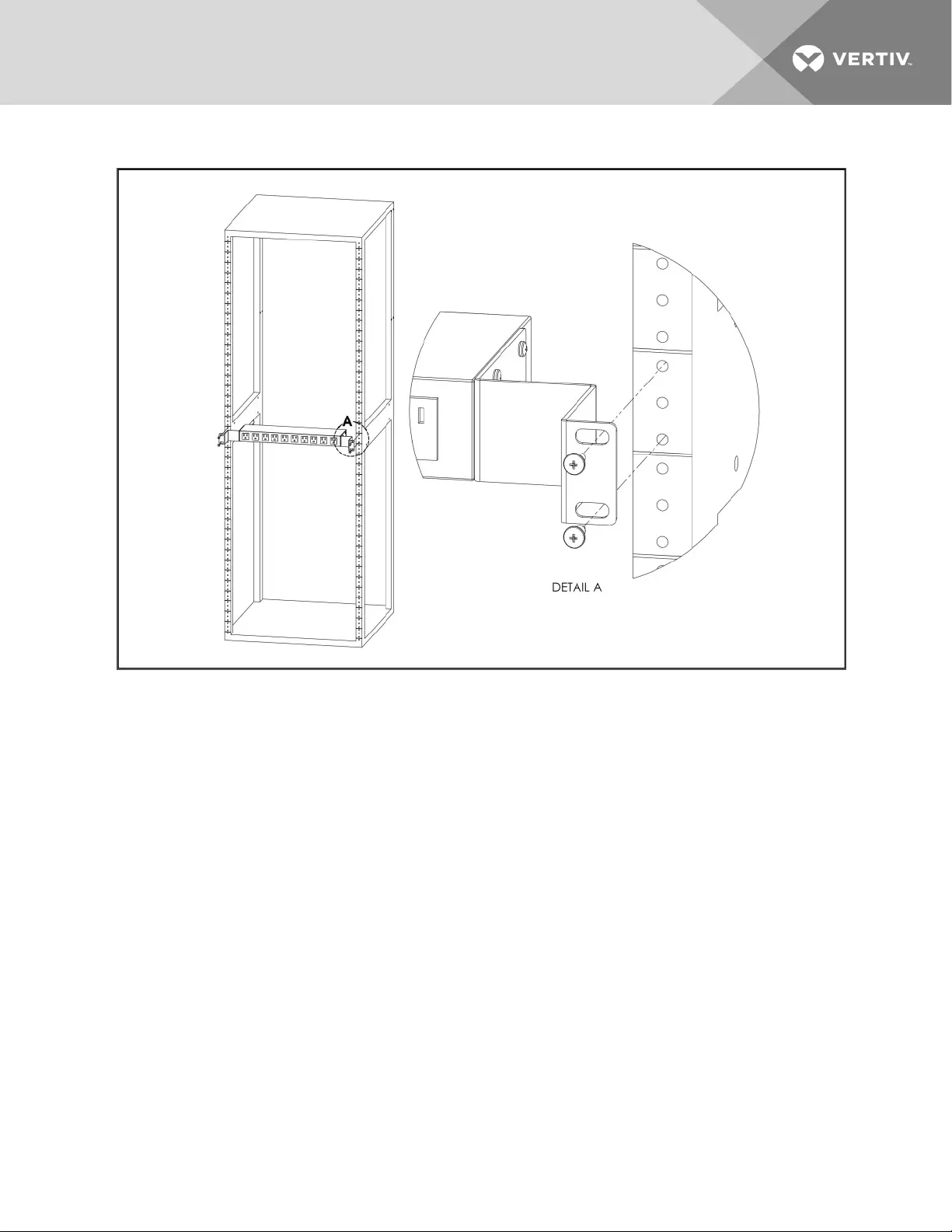
Figure 2.12 23" Conversion Mounting Brackets
2 Installation 15
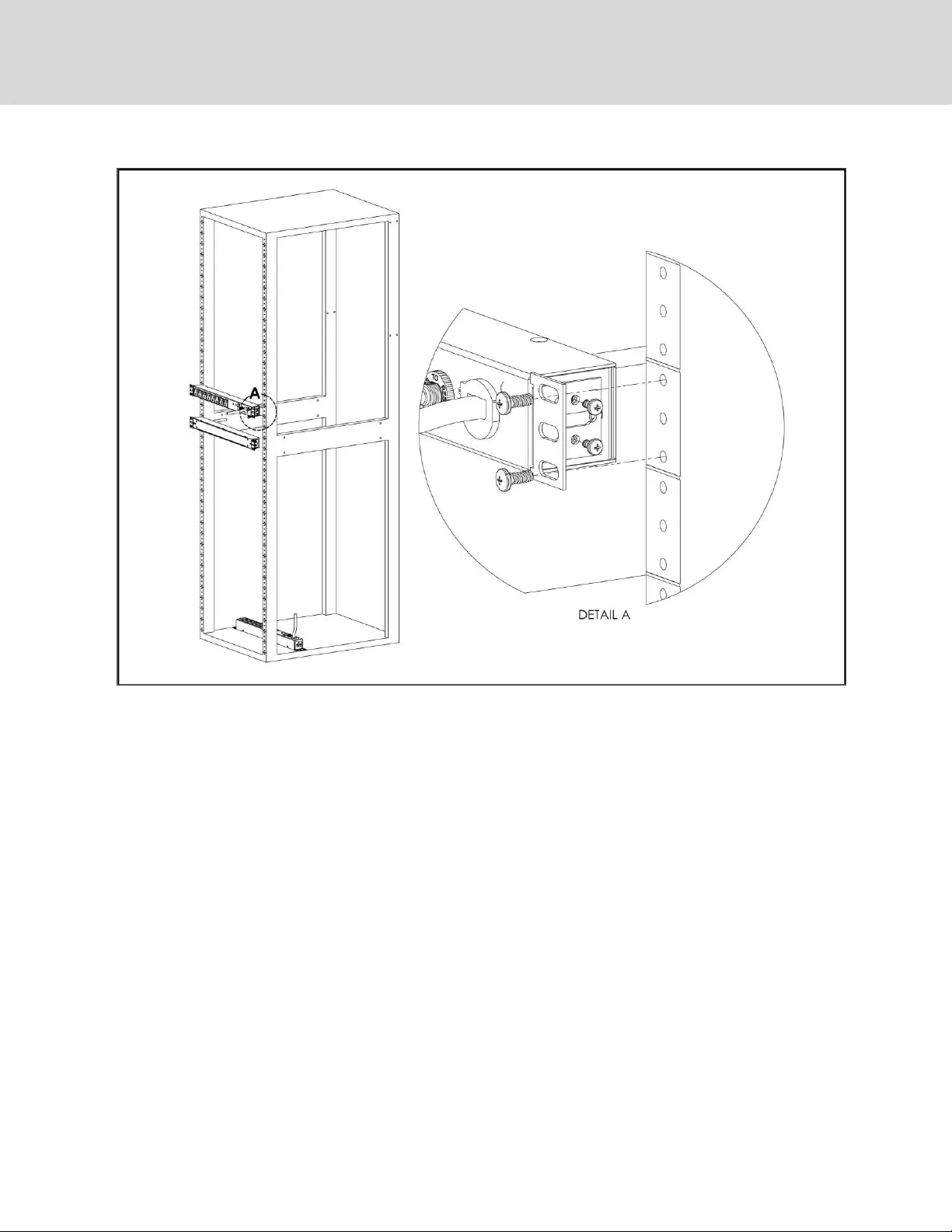
Figure 2.13 19" Horizontal/Panel Mount Brackets
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
16

3 SETUP
3.1 Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD-3E)
The Interchangeable Monitoring Device (IMD) is the controller for the GU2 line of power products. The
IMD can be replaced and upgraded to allow datacenters to future-proof their rPDU installation.
3.1.1 Enhanced Switched Monitored
The Enhanced Switched Monitored Vertiv Upgradable rPDU is a more advanced option for data centers
that need full remote switching, monitoring, alarms and remote sensors. It is built with the IMD-3E module,
which provides dual Ethernet ports, a local display, USB port and a RJ-12 port for remote sensors.
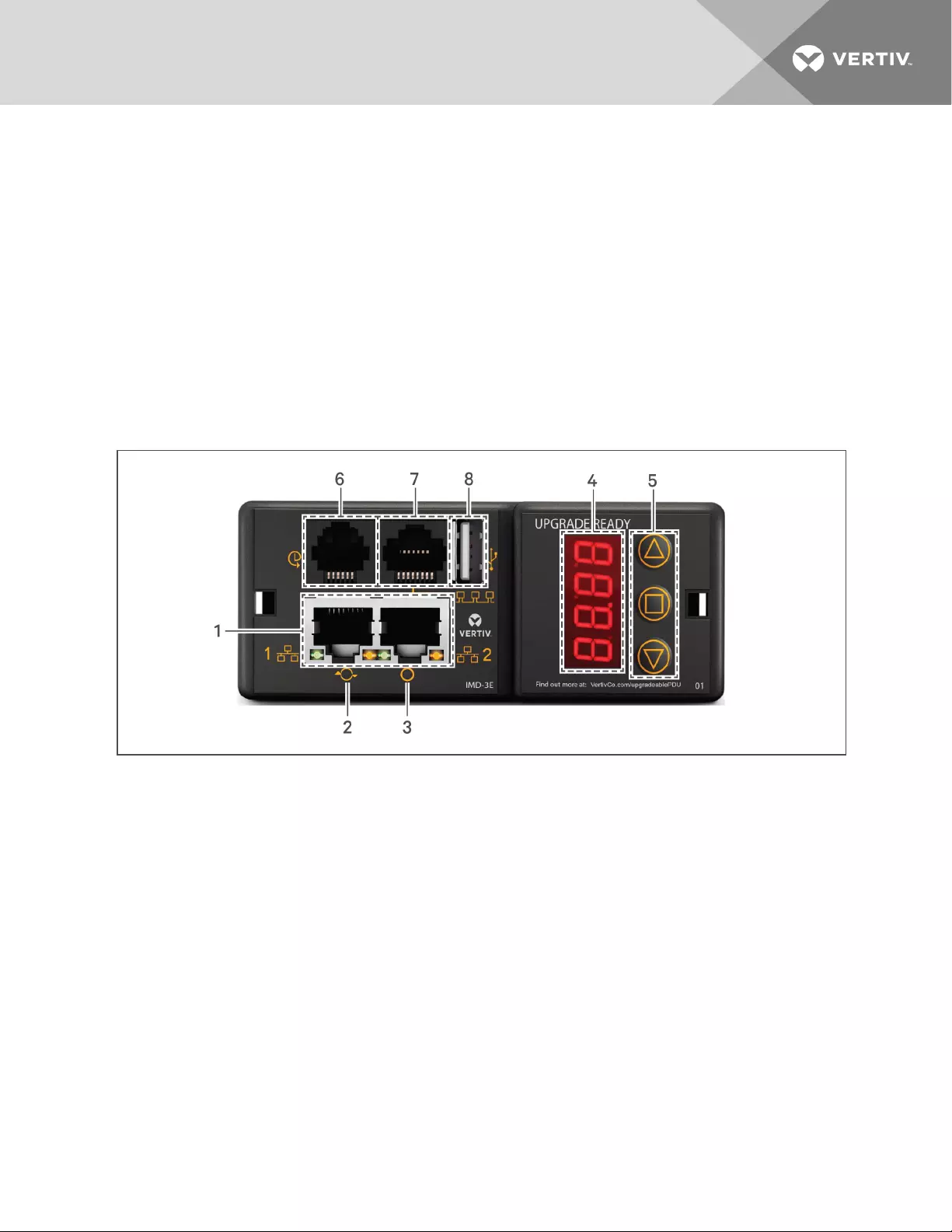
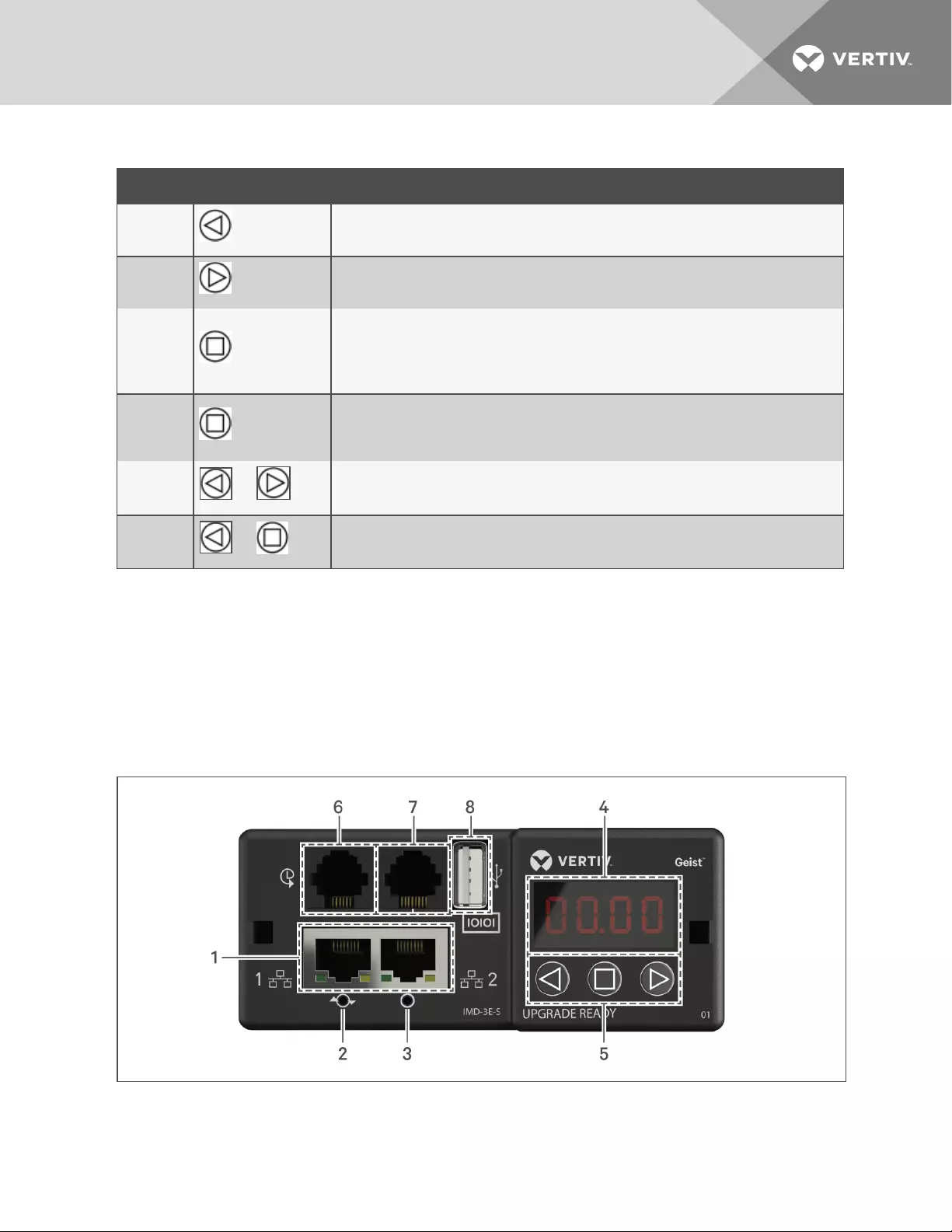
Figure 3.1 IMD-3E Module
17
NUMBER NAME DESCRIPTION
1
Dual
Ethernet
Ports
The Dual Ethernet ports act as a2-port Ethernet switch, allowing for multiple devices to be daisy-
chained.
2
Hard-
Reboot
Button
Pressing the hard-reboot button reboots the IMD. This acts as apower-cycle for the IMD, and does not
change or remove any user information.
3
Network
Reset
Button
Holding the network-reset button for 5 seconds during normal operation will restore the default IP
address and reset the user accounts. Holding the network-reset button during power-up will reset allof
the unit's settings back to factory-default values.
4Local
Display The local display shows the phase, line, and circuit current values (in Amperes).
5Display
Buttons
There are three buttons near the IMD display; a back button, a forward button, and a center button. The
functions of these buttons are described in the following table.
6Remote
Sensor Port
RJ-12 port for connecting a Vertiv plug-and-play remote digital sensors (sold separately). Each digital
sensor has a unique serial number and is automatically discovered. GU2 PDUs support up to 16 sensors.
The optional Vertiv A2D Converter can be added to support analog sensing. See Available Sensors on
page 72 for more information.
7Proprietary
Connectivity RJ-45 port for future expansion.
8 USB Port USB Port used to upload firmware, backup/restore device configuration, or expanded logging capacity
viaUSB storage device. Provides up to 500mA power capacity for USB connected devices.
Table 3.1 IMD-3E Module Descriptions
NOTE: GU2 PDUs support the use of USB MSC devices such as thumb drives or external hard drives.
USB Storage Devices must be formatted as FAT32.
Display Buttons
There are three buttons near the IMD display; a back button, a forward button and a center button. The
functions of these buttons are described in the following table.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
18
BUTTON SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Back
Button Decrement to the previous channel.
Forward
Button Increment to the next channel.
Center
Button
Toggle between scrolling and static display modes. Holding this button for 10 seconds will
perform a network reset, restoring the default IP address and resetting user account
information.
Center
Button x3
Pressing this button three times within two seconds enables VLC mode. Pressing the button
while VLC mode is active returns the unit to the standard current display. For more
information, see Visible Light Communication (VLC) on page 63.
and Pressing both buttons at the same time flips the display 180 degrees.
and Pressing both buttons at the same time displays the primary IPv4 address of the unit.
Table 3.2 Display Button Functions
NOTE: Display Button functionality may vary based on unit configuration.
3.1.2 Enhanced Switched Monitored with RS-232
All Vertiv Geist Switched Unit Level Monitoring, Outlet Level Monitoring, and Switched Outlet Level
Monitoring rPDUs ship with the IMD-3E-S module. This module provides all of the same features as the
IMD-3E, with the addition of a RS232 serial port via RJ-45.
Figure 3.2 IMD-3E-S Module
3 Setup 19
NUMBER NAME DESCRIPTION
1
Dual
Ethernet
Ports
The Dual Ethernet ports act as a2-port Ethernet switch, allowing for multiple de- vices to be daisy- chained.
2
Hard-
Reboot
Button
Pressing the hard-reboot button reboots the IMD. This acts as apower-cycle for the IMD, and does not
change or remove any user information.
3
Network
Reset
Button
Holding the network-reset button for 5 seconds during normal operation will restore the default IP address
and reset the user accounts. Holding the network-reset button during power-up will reset all of the unit's
settings back to factory-default values.
4Local
Display The local display shows the phase, line, and circuit current values (in Amperes).
5Display
Buttons
There are three buttons near the IMD display; a back button, a forward button, and a center button. The
functions of these buttons are described in the Displaybuttons table.
6
Remote
Sensor
Port
RJ-12 port for connecting a Vertiv plug-and-play remote digital sensors (sold separately). Each digital sensor
has a unique serial number and is automatically discovered. GU2 PDUs support up to 16 sensors. The optional
Vertiv A2D Converter can be added to support analog sensing. For more information see, Available Sensors
on page 72.
7Serial
Port RS-232 via RJ-45 port.
8USB
Port
USB Port used to upload firmware, backup/restore device configuration, or expanded logging capacity via
USB storage device. Provides up to 500mA power capacity for USB connected devices.
Table 3.3 IMD-3E-S Module Descriptions
NOTE: GU2 PDUs support the use of USB MSC devices such as thumb drives or external hard drives.
USB Storage Devices must be formatted as FAT32.
3.1.3 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
GU2 devices, include two Ethernet ports which work together as an internal Ethernet bridge. One of these
ports can be used to connect the IMD to an existing network, or both ports can be used at the same time
to connect one IMD to another in a daisy-chain configuration.
When both network interfaces are connected, the IMD implements a network bridging protocol called the
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). RSTP is an IEEE standard that is implemented by all managed
bridges. Using RSTP, bridges in the network exchange information to find redundant paths, or loops.
When a loop is detected, the bridges in the network work together to temporarily disable the redundant
paths. This allows the network to avoid broadcast storms caused by the loops. In addition, RSTP regularly
checks for changes in the network topology. When a connection is lost, RSTP allows the bridges to quickly
switch to a redundant path.
NOTE: RSTP protocol imposes a limit of 40 links between bridges, including IMDs.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
20

3.2 Network Setup
The Upgradeable IMD has a default IP address for initial setup and access. Once you have assigned an IP
address, the default IP address is no longer active.
To restore the default IP address and reset all user-account information:
If the user-assigned address or passwords are lost or forgotten, press and hold the network-reset button
located below the Ethernet port for 15 seconds. Holding the center button of the LED display for 10
seconds also resets the network and user account information.
To erase all user settings and restore the unit back to its factory-default state:
1. Disconnect power from the rPDU.
2. Press and hold the network-reset button while powering up the rPDU.
The Network page, located under the System Tab, allows you to assign the network properties manually,
or use DHCP to connect to your network. Access to the unit requires the IP address to be known. Use of a
static IP or a reserved DHCP is recommended. The default address is displayed on the front of the unit.
•IPAddress: 192.168.123.123
•Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
•Gateway: 192.168.123.1
To access the unit for the first time, you must temporarily change your computer's network settings to
match the 192.168.123. xxx subnet. To set up the unit, connect it to your computer's Ethernet port, then
follow the appropriate instructions for your computer's operating system.
To setup the network for a Window operating system:
1. Access the network settings for your operating system.
•Using Windows 2000, XP or Server 2003, click Start - Settings - Network Connections.
•Using Windows 7 or Server 2008, click Start - Control Panel - Adjust your Computer's
Settings - View Network Status and Tasks - Change Adapter Settings or click Start -
Settings - Control Panel - Network and Sharing Center - Change Adapter Settings.
•Using Windows 8 or Server 2012, move the mouse to the bottom or top right corner, click
Settings - Control Panel - Large or Small Icons - Network and Sharing Center - Change
Adapter Settings.
•Using Windows 10, click Start - Network and Internet - Change Adapter Settings.
2. Locate the entry under LAN, High-Speed Internet or Local Area Connection which
corresponds to the network card (NIC). Double-click on the network adaptor's entry in the
Network Connections list.
NOTE: Most computers will have a single Ethernet NIC installed, but a WiFi or 3G adaptor also shows as
a NIC in this list. Be sure to choose the correct entry.
3. Click Properties to open the Local Properties window.
3 Setup 21
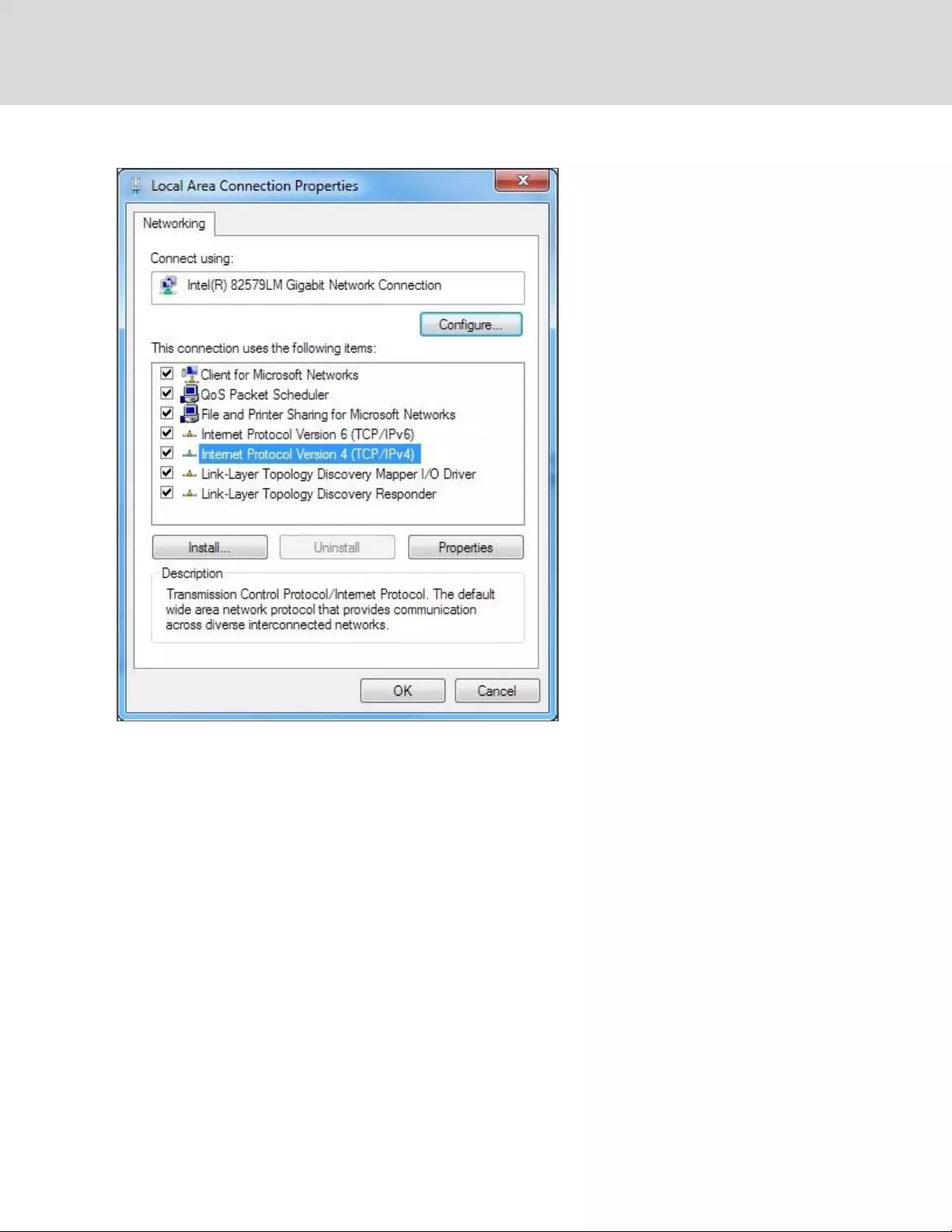
Figure 3.3 Local Area Connection Properties
4. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) from the list, then click Properties.
NOTE: If you see more than one TCP/IP entry, as in the example above, the computer may be
configured for IPv6 support as well as IPv4; make sure to select the entry for the IPv4 protocol. Write
down the current NIC card settings so you can restore them to normal after you have completed the
setup procedure.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
22
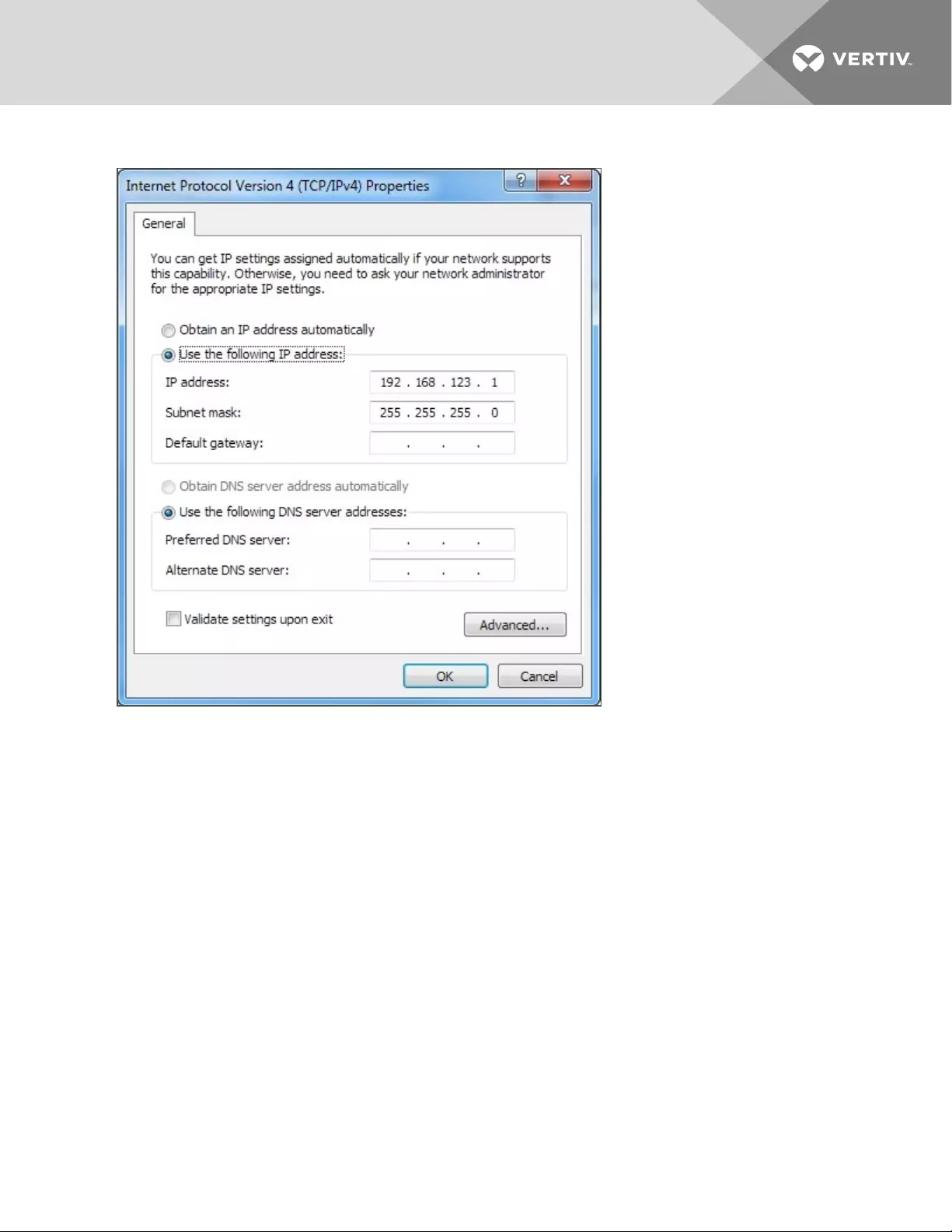
Figure 3.4 Internet Protocol Version 4
5. Choose Use the following IP address, set IP address to 192.168.123.1 and Subnet Mask to
255.255.255.0. For initial setup, Default Gateway and the DNS Server entries can be left blank.
Select OK - OK to close both the Internet Protocol Properties and Local Properties windows.
6. In a web browser, enter http://192.168.123.123 to access the unit. If you are setting up the unit
for the first time, or if the unit has been reset back to factory defaults via the network-reset
button, the unit requires you to create an Admin account and password before you can
proceed.
7. After the admin account is created, log in to the unit.
8. By default, the default sensors page is displayed. Navigate to the System tab, then the Network
page to configure the device's network properties. The unit's IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Gateway and DNS settings can either be assigned manually, or acquired via DHCP.
9. Click Save.
NOTE: After the changes are saved, the browser will no longer be able to reload the web page from the
192.168.123.123 address and displays "Page not Found" or "Host Unavailable" message; this is normal.
After you are finished configuring the unit's IP address, repeat the steps above changing the
computer's Ethernet NIC card settings to the ones you wrote down prior to changing them.
3 Setup 23
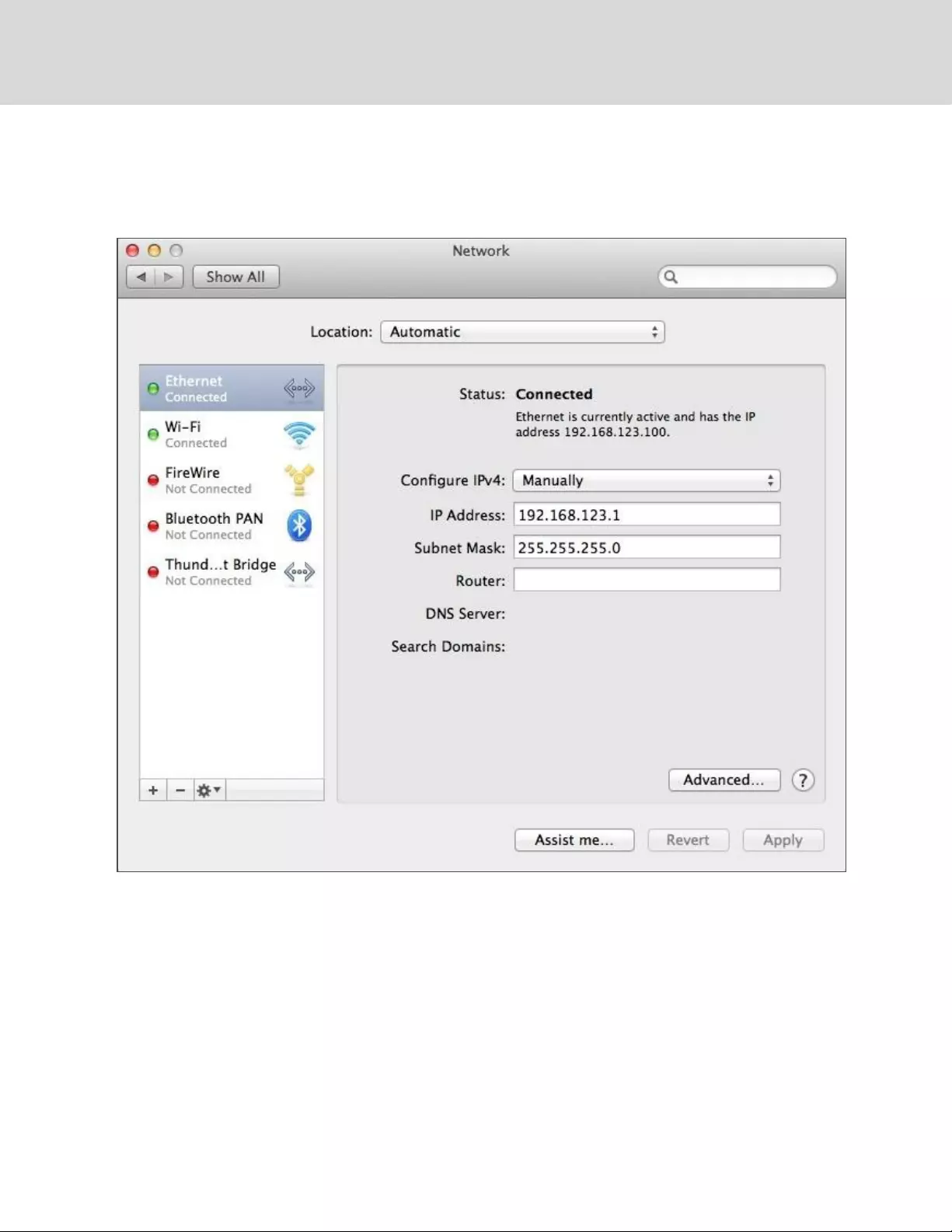
To setup the network for a MAC:
1. Click the System Preferences icon on the Dock, and choose Network.
Figure 3.5 MAC System Preferences
2. Ensure Ethernet is highlighted on the left side of the NIC window. In most cases, there will be
one Ethernet entry on a Mac. Write down the current settings so you can restore them to
normal after you have completed the setup procedure.
3. Select Manually from the Configure IPv4 drop-down list, then set IP Address to 192.168.123.1
and Subnet Mask to 255.255.255.0 and click Apply.
NOTE: The Router and DNS Server settings can be left blank for this initial setup.In a web browser,
enter http://192.168.123.123 to access the unit. If you are setting up the unit for the first time, or if the
unit has been reset back to factory defaults via the network-reset button, the unit requires you to
create an Admin account and password before you can proceed.
4. After the admin account is created, log in to the unit.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
24

5. By default, the default sensors page is displayed. Navigate to the System tab, then the Network
page to configure the device's network properties. The unit's IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Gateway and DNS settings can either be assigned manually, or acquired via DHCP.
6. Click Save.
NOTE: After the changes are saved, the browser will no longer be able to reload the web page from the
192.168.123.123 address and displays "Page not Found" or "Host Unavailable" message; this is normal.
After you are finished configuring the unit's IP address, repeat the steps above changing the
computer's Ethernet NIC card settings to the ones you wrote down prior to changing them.
3.3 Web Interface
The unit is accessible via a standard, unencrypted HTTP connection as well as an encrypted HTTPS
(TLS) connection.
NOTE: An administrator account (username and password) must be created when logging in the
device the first time.
3.3.1 Home page
The Home Page gives both current and historical views of the unit’s data. Real-time readings are provided
for all rPDU data and individual circuits' data.
Figure 3.6 Home Page
3 Setup 25
NUMBER NAME DESCRIPTION
1
Sensors,
System and
Help Tab
Mouse over to show sub-menus: Sensors, System and Help
2Log In/Log
Out
Click to log in or log out of the unit.
NOTE: Both username and password are case sensitive and no spaces are allowed. Prohibited
characters for username are: $&`:<>[ ] { }"+%@/ ; =?\^|~',
3Alarms and
Warnings Indicates the number of Alarms and Warnings currentlyoccurring, if any.
4 Device ID Unique product identification and cannot be changed. May be required for technical support.
5
Total and
Individual
Phase
Monitor
Displays AC current, voltage and power statistics for each individual phase, and for the totalof allphases
combined.
6Current
Monitor Displays AC current draw statistics for each individual circuit on the rPDU.
7Outlet
Monitor
Displays AC current, voltage and power statistics for each circuit and outlet. (Outlet Level Power
Monitoring and Switched Outlet Level Monitoring Only). Displays outlet status. (Switched and Switched
Outlet Level Monitoring Only)
8Operation
Icon Modify settings.
9Configuration
Icon Modify label name.
10 Device Label Displays the user-assigned label of this unit.
11 Vertiv Logo Clicking on this logo from any page will reload the home page.
Table 3.4 Home Page Descriptions
3.3.2 Sensors tab
Click the Sensors tab to access the Overview, Alarms and Warnings and Logging page from the drop-
down menu.
Overview
You must log in before making any changes. Only users with Control-level authorizations have access to
these settings.
To change a device label:
1. Click the Configuration icon for the rPDU and change the label. The Name is the rPDU's factory
name or model and cannot be changed.
2. Click Save.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
26

To change device operation:
1. Click the Operation icon.
2. Select the operation to perform:
•On/Off - turns on or off all outlets.
•Reboot - for outlets currently on, reboot cycles the outlets off, then back on after the
reboot hold delay. For outlets currently off, reboot turns the outlets on.
•Cancel - cancels the current operation if it has not been completed.
•Reset Energy - resets the total energy measured in kWh.
•Reset Min Max Values - resets all Min and Max values for current and voltage
measurements.
•Restore Defaults - restores device settings to their factory default. This includes Labels,
Delays and Power-On Actions for the device.
NOTE: These actions affect the entire device.
3. For operations involving the state of the outlets, setting Delay to True uses the current Delay
configuration for each outlet when performing the selected operation.
4. Select Submit to issue the action.
NOTE: Power-on action delays reference the time since the unit was plugged in, not the time since it
fully booted. They may execute before the unit fully boots.
To change phase operation:
1. Click the Operation icon.
2. Select the operation to perform.
•Reset Energy - resets the total Energy measured in kWh for the selected phase.
•Reset Min Max Values - resets Min and Max values for voltage and current.
3. Select Submit to issue the action.
To configure an outlet:
1. Click the outlet configuration icon.
2. Change the configurations, as needed.
a. Label of the outlet.
b. State - the outlet's current state (On or Off).
c. Pending State - the state the outlet is currently transitioning to.
d. Time To Action - the time left before the pending action takes place. This is adjusted
using Delays.
e. On Delay - the time, in seconds, the unit waits before switching an outlet on.
f. Off Delay - the time, in seconds, the unit waits before switching an outlet off.
g. Reboot Delay - the time, in seconds, the unit waits before rebooting an outlet.
3 Setup 27

h. Reboot Hold Delay - the time, in seconds, the unit waits after switching the outlet off,
before switching an outlet back on during a reboot.
i. Power-On Action - describes the state the outlet will start when powered on (On, Off or
Last).
j. Power-On Delay - the time, in seconds, the unit waits after being powered on before
powering on the outlet.
3. Click Save.
To change circuit operation:
1. Click the Operation icon.
NOTE: For Circuit operation only the Reset Min Max Values operation is available.
2. Click Submit to reset the Min Max Values of the Circuit.
To change outlet operation:
1. Click the desired Outlet Operation icon.
2. Select the operation to perform.
•On/Off - turns the selected outlet on or off.
•Reboot - for outlets currently on, reboot cycles the outlets off, then back on after the
reboot hold delay. For outlets currently off, reboot turns the outlets on.
•Cancel - cancels the current operation if it has not been completed.
•Reset Energy - resets the total Energy measured in kWh for the selected outlet.
•Reset Min Max Values - resets Min and Max values for voltage and current.
3. For operations involving the state of the outlets, setting Delay to True uses the current Delay
configuration for each outlet when performing the selected operation.
4. Select Submit to issue the action.
Alarms and warnings
The alarms and warnings page allows you to establish alarm or warning conditions (events) for each
power and circuit reading. Events are triggered when a measurement exceeds a user-defined threshold,
either going above the threshold (high-trip) or below it (low-trip). Events are displayed in different
sections, based on the device or measurement the event is associated with. Each event can have one or
more actions to be taken when the event occurs.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
28
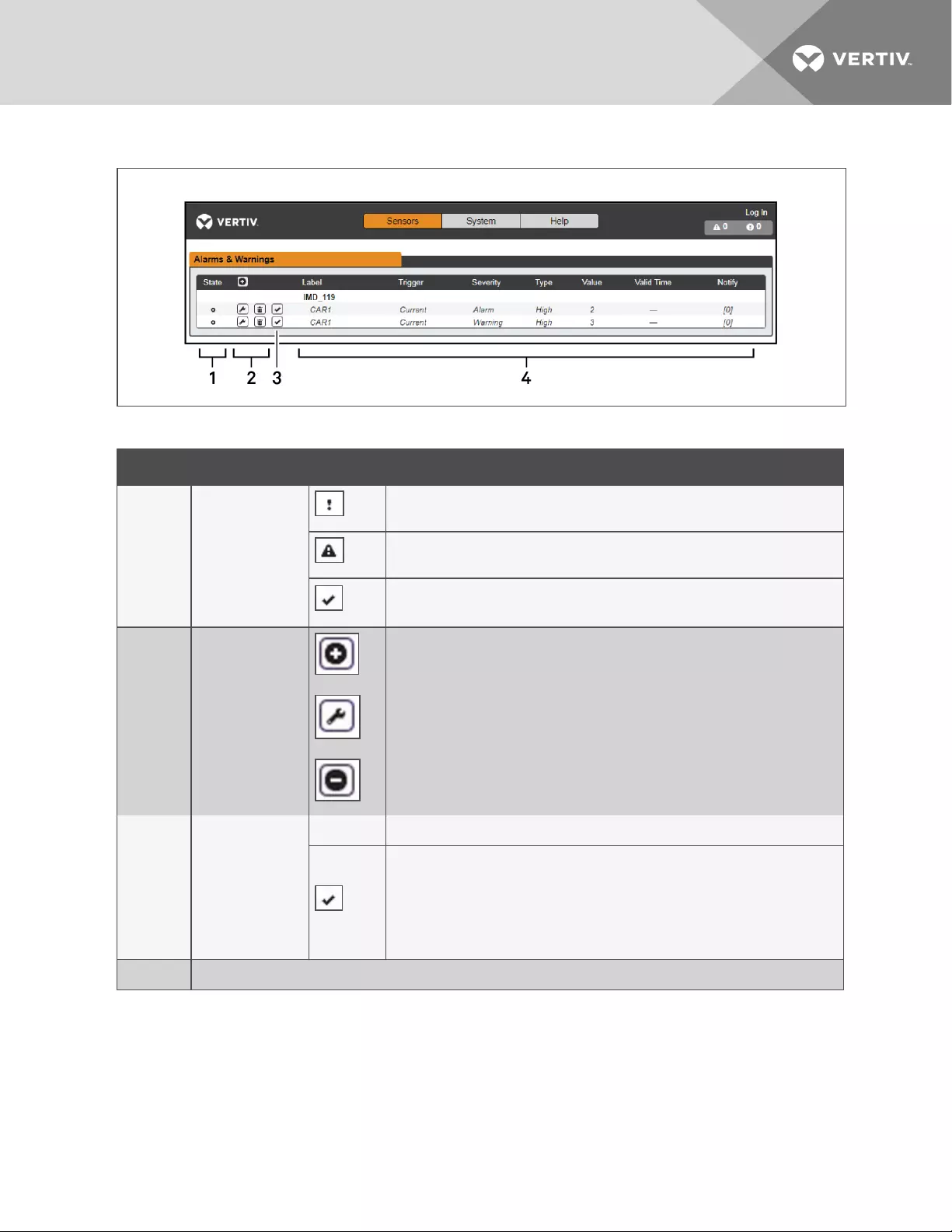
Figure 3.7 Alarms and Warnings Page
NUMBER DESCRIPTION SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1Status of each
event.
Warning symbol. Event is displayed orange.
Alarm symbol. Alarm is displayed in red.
Acknowledged event symbol. Symbol remains until the condition measured
returns to normal.
2
Add/Delete/Modify
alarms and
warnings.
Add new alarms and warnings.
Modify existing alarms and warnings.
Delete existing alarms and warnings.
3
Notify user of
tripped Events and
request
acknowledgment.
n/a Empty if there is no alert condition.
When a warning or alarm event occurs, you can click on this symbol to
acknowledge the event and stop the unit from sending any more notifications
about it.
NOTE: Clicking this symbol does not clear the warning or alarm event, it just
stops the notifications from repeating.
4 Displays the conditions for the alarms and warnings settings
Table 3.5 Alarms and Warnings Descriptions
To add a new Alarm or Warning Event:
1. Click the Add/Modify alarms and warnings button.
2. Set the desired conditions for this event as follows:
a. From the drop-down lists, select the name of the phase or circuit, the trigger
measurement, the severity and the Type.
3 Setup 29

NOTE: High trips if the measurement goes above the threshold and low trips if the measurement goes
below the threshold.
b. Enter the desired Threshold Value (any number between -999.0 through 999.0).
c. Enter the desired Clear Delay time in seconds. Any value other than 0 means once this
event is tripped, the measurement must return to normal for this many seconds before
the event will clear and reset. Clear Delay can be up to 14400 seconds (4 hours).
d. Enter the desired Trip Delay time in seconds. Any value other than 0 means that the
measurement must exceed the threshold for this many seconds before the Event will be
tripped. Trip Delay can be up to 14400 seconds (4 hours).
e. Latching Mode: If enabled, this event and its associated actions remain active until the
event is acknowledged, even if the measurement subsequently returns to normal.
f. To specify where the alert notifications are sent when this alarm or warning event occurs,
click the Add icon to create a new action.
g. Select the desired options from the drop-down menu:
•Target is the email address or SNMP manager to which notifications should be
sent when the event is tripped. For more information on configuring a target email
address see Email on page 43.
NOTE: Target Delays and Repeats are shared across all alarms. If multiple delay or repeat values are
needed for specific targets, each one must be added to the target list and then the appropriate Enabled
box checked on each alarm.
•Delay determines how long this Event must remain tripped for before this
Action's first notification is sent. This is different from the Trip Delay above. Trip Delay
determines how long the threshold value has to be exceeded before the Event itself is
tripped. This delay determines how long the Event must remain tripped before this
Action occurs. Delay can be up to 14400 seconds (4 hours). A Delay of 0 will send the
notification immediately.
•Repeat determines whether multiple notifications will be sent for this Event
Action. Repeat notifications are sent at the specified intervals until the Event is
acknowledged, or until the Event is cleared and re- set. The Repeat interval can be up to
14400 seconds (4 hours). A Repeat of 0 disables this feature, and only one notification will
be sent.
3. Click Save to save this notification action.
NOTE: More than one action can be set for an alarm or warning; to add multiple actions, just click the
Add icon again and set each one as desired. Each alert can have up to 32 Actions associated with it.
To change an existing alarm or warning event:
1. Click the Modify icon next to the alarm or warning event you wish to change.
2. Modify the settings as needed and click Save.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
30

3. After an action is added, it has a checkbox in the enabled column at the far left. By default
when an action is added it is is unchecked (disabled). Click the checkbox to enable it. This
allows you to selectively turn different actions on and off for testing.
To delete an existing alarm or warning event:
1. Click the Delete icon next to the alarm or warning event you wish to remove.
2. Click Delete and Save to confirm.
Logging
The Logging page allows you to access the historical data recorded by the rPDU by selecting the desired
sensors and time range to be logged.
Figure 3.8 Logging Page
3 Setup 31

NUMBER NAME DESCRIPTION
1Data log
download
Clicking the JSON link downloads the data log in JSON format.
Clicking the CSV downloads the data log in .csv format for use in spreadsheet software.
2 Log interval The frequency at which data is written to the log file. The logging interval can be 1-600 minutes with the
default setting being 15 minutes.
3Clear log
data Delete the log file.
4 Logging Click measurement value to select or deselect desired logging parameters. By default, all measurements
are selected. Press Save to save changes.
Table 3.6 Logging Page Descriptions
NOTE: Maximum loggable time frame is determined by number of measurements being logged and the
interval at which data is written to the log file.
3.3.3 System tab
NOTE: You must be logged in as Admin to modify settings in the System tab.
Users
The Users page in the System menu allows you to manage or restrict access to the unit's features by
creating accounts for different users.
Figure 3.9 User Account Page
NUMBER DESCRIPTIONS
1 Add new user account
2 Modify user account
3 Delete user account
Table 3.7 User Account Page Descriptions
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
32

NOTE: Only an Administrator-level account can add, modify, or delete users. Control-level and View-
Only accounts can change their own passwords via the Modify button, but cannot add or delete
accounts, or Modify other accounts. The Guest account cannot add, delete, or modify any account,
not even itself.
To add or modify a user account:
1. Click the Add or Modify User icon.
2. Create or modify the account information as needed.
a. Username: The name of the account. User names may be up to 24 characters long, are
case-sensitive, and may not contain spaces or any of these prohibited characters: $&`:<>[
] { }"+%@/ ; =?\^|~',
NOTE: A username cannot be changed after the account is created.
b. Administrator: If set to True, this account has Administrator-level access to the unit, and
can change any setting.
c. Control: If set to True, this account has Control-level access. Setting Administrator to
True will automatically set Control to True as well. Setting this to False makes the account
a View-Only account.
d. New Password: Account passwords may be up to 24 characters long, are case-sensitive,
and may not contain spaces.
e. Account Status: Set the account to Enabled or Disabled. Disabling an account prevents it
from being used to log in, but does not delete it from the account list.
3. Click Save.
User account types
•Administrator: Administrator accounts (accounts with both administrator and control
authority set to True, as above) have full control over all available functions and settings on the
device, including the ability to modify system settings and add, modify, or delete other users'
accounts.
•Control: Control accounts (accounts with only control set to True) have control over all
settings pertaining to the device's sensors. They can add, modify, or delete alarms & warning
events and notification actions, and can change the names or labels of the device and its
sensors. Control accounts cannot modify system settings or make changes to other users'
accounts.
•View: If both administrator and control are set to False, the account is a view-only account. The
only changes a view-only account is permitted to make are changing their own account's
password, and changing the preferred language for their own account. View-Only accounts
cannot change any device or system settings.
3 Setup 33
•Guest: Any user that views the unit's web page without logging in is automatically viewing the
unit as Guest. By default, the guest account is a view-only account, and cannot make changes
to any settings, although the administrator can elevate the guest account to control-level
access if desired, allowing anyone to make changes to names, labels, alarm events, and
notifications without logging in. The guest account cannot be deleted but can be disabled to
require login for viewing system status.
To change a user password:
1. Log in to your account.
2. Click your username in the top right corner of the page.
3. Enter a new password and click Save.
Figure 3.10 Change User Password Page
Network
The unit’s network configuration is set on the Network tab of the System menu. Settings pertaining to the
unit’s network connection are:
•Hostname: The hostname may be used as a method for device identification on the network.
•Interfaces: Used to configure the IP address of the rPDU, enable/disable DHCP and to view Link
State and Uptime. The device supports up to 8 user configured IP address entries.
•Ports: Used to view and/or modify Ethernet port settings and RSTP status of each port on the
rPDU.
•Routes: Displays configured routes and is where you will set your Gateway address for the
rPDU. Default routes are distinguished by a "destination" of "0.0.0.0" or "::", with a Prefix of "0" and
Interface of "all". Only one default route can exist for IPv4 and one for IPv6.
•DNS: Allows the unit to resolve host names for email, NTP, and SNMP servers.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
34
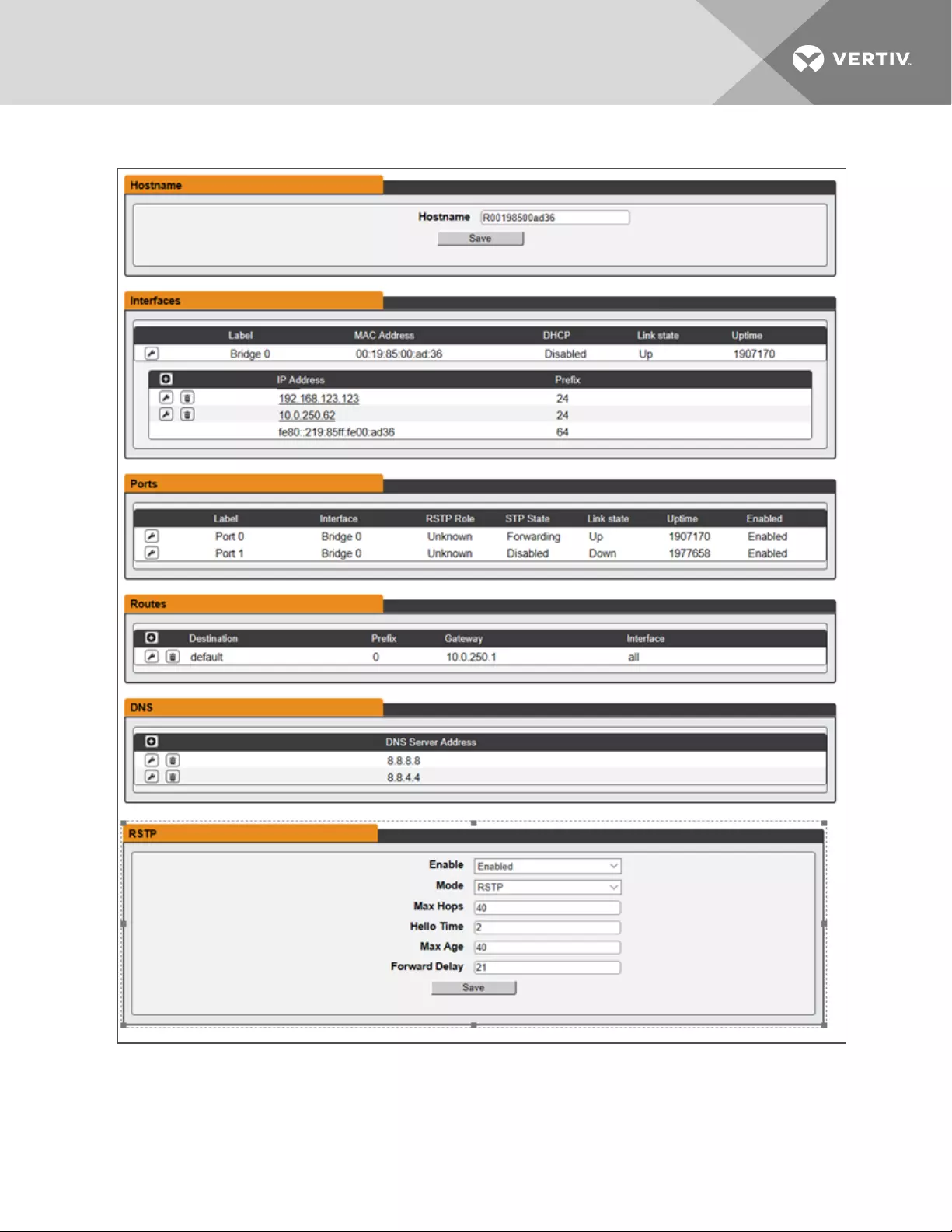
Figure 3.11 Network Configuration Page
To edit the interfaces parameters:
1. Click the Modify icon
2. Modify desired fields.
3 Setup 35

a. Label - change the desired name of the selected interface.
b. Enable - enable/disable the selected interface. If only one interface is available, disabling
the interface restricts access to the device requiring a network reset.
c. DHCP - enable/disable DHCP on the selected interface.
3. Click Save.
NOTE: Any changes made to the network interface settings take effect once the Save button is
clicked. If you have changed the IP address it will appear as if the unit is no longer responding because
the browser will not be able to reload the web page. Close the browser window, type the new IP address
into the browser's address bar and the unit will be accessible.
To add a new IP Address:
1. Click the Add icon.
2. Enter the IPv4 or IPv6 Address and Prefix/Subnet Mask into appropriate fields. Up to 8 IP
addresses can be statically assigned.
3. Click Save.
To modify an existing IP Address:
1. Click the Modify icon.
2. Edit the IP Address and Prefix/Subnet Mask fields as needed.
3. Click Save.
To modify port settings:
1. Click the Modify icon.
2. Enter the appropriate information.
a. Change port label if desired.
b. Enable/Disable port.
c. Assign STP cost. This designates this interface's contribution to the root path cost, when
it serves as the root port.
3. Click Save.
To add a new route:
1. Click the Add icon.
2. Enter the appropriate information.
a. Destination IP address for desired route.
b. Enter Prefix for desired route
c. Enter Gateway IP address.
d. Select Interface that route applies.
3. Click Save.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
36

To modify an existing route:
1. Click the Modify icon
2. Edit the desired fields.
3. Click Save.
To add a new DNS Server Address:
1. Click the Add icon.
2. Enter the IP of the desired DNS server. Up to two DNS servers can be added.
3. Click Save.
To modify an existing DNS Server Address:
1. Click the Modify icon.
2. Edit the DNS Server Address field as required.
3. Click Save.
To change RSTP settings:
1. Change the settings, as desired.
a. Enable: Enable or Disable RSTP protocol
b. Mode: RSTP. RSTP mode supports falling back to STP when necessary.
c. Max Hops: Used when mode enabled to RSTP.
d. Hello Time: The interval, in seconds, between periodic transmissions of configuration
messages by designated ports.
e. Max Age: The maximum age, in seconds, of the information transmitted by this interface,
when it serves as the root bridge. Set at 2 seconds.
f. Forward Delay: The delay, in seconds, used by bridges to transition the root bridge and
designated ports into forwarding mode. Set at 21 seconds
2. Click Save.
Web server
The unit’s Web Server configuration can be updated on the Web Server tab of the System menu.
•HTTP Interface: Enables/disables access via HTTP. HTTPS interface is always enabled.
Available options are, enabled or disabled. It is not possible to disable the web interface
completely.
•HTTP/HTTPS Server Port: Allows you to change the TCP ports which the HTTP and HTTPS
services listen to for incoming connections. The defaults are port 80 for HTTP and 443 for
HTTPS.
3 Setup 37
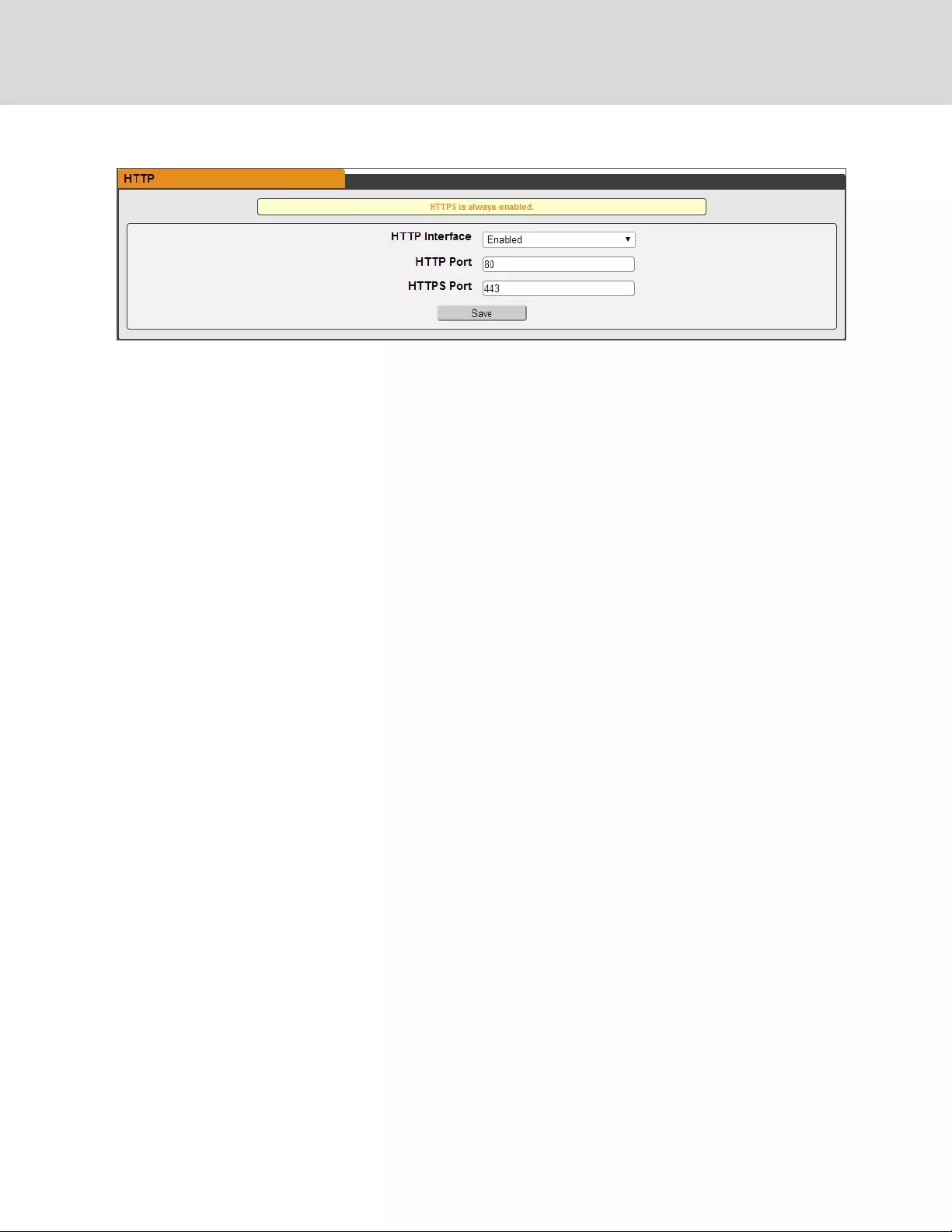
Figure 3.12 HTTP Configuration Page
•SSL Certificate: Allows you to upload your own signed SSL Certificate file to replace the default
one. The certificate can be either self-signed or signed from a Certification Authority.
Certificate must be in either PEM or PFX (PKCS12) format
•PEM Format
•The public certificate and private key must reside in the same file.
•The certificate must follow standard x.509.
•The private key must be generated with the RSA algorithm and in PEM format
•The PEM RSA private key may be password secured.
•PFX Format - Support is also available for the PKCS12 standard (.pfx) which is a binary
encrypted combination of a PEM public certificate and its PEM private key. When generating a
PFX certificate you are prompted for an optional password.
Reports
The Reports page allows you to schedule the device to send recurring status reports.
NOTE: SMTP email must be set-up on the device via the email page.
To Add or Modify a scheduled report:
1. Click the Add or Modify icon.
2. Select the Days the report is to be sent.
3. Select the time of the day to Start sending reports.
4. Set the interval (in hours).
5. Select the Target email address for the reports to be sent.
6. Click OK to save changes.
To Delete a scheduled Report:
1. Click on the Delete icon next to the report to delete.
2. Click OK on the pop-up window to confirm.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
38

Remote Authentication
The Remote Authentication page allows you to designate one of three authentication protocols for
remote access to the device.
To change Remote Authentication settings:
1. Select the mode from the drop-down menu.
•Disabled
•LDAP - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
•TACACS+ - Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
•RADIUS - Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) can be setup through this menu.
Configuration for remote authentication using LDAP.
•Enable: Enabling or Disabling LDAP.
•LDAP Server Address: Specify the host address for LDAP. The "HOST" can be an IPv4 address,
an IPv6 address in brackets (ie. [2001:0DB8:AC10:FE01::]), or a host name.
•LDAP Server Port: Used to set the LDAP port number. The default port for LDAP is 389.
•LDAP Mode: Available LDAP modes are Active Directory or OpenLDAP.
•Bind Password: Password used to bind to the directory server.
•Base DN: DN to use for the search base.
The remaining fields come from the NIS schema, defined in RFC2307. They are used to authenticate us-
ers in LDAP. Leaving them blank will use the default value.
•User Filter: LDAP filter for selecting users.
•"uid" Mapping: Name of the server attribute that corresponds to the "uid" attribute in the
schema.
•"uidNumber" Mapping: Name of the server attribute that corresponds to the "uidNumber"
attribute in the schema.
•Group Filter: LDAP filter for selecting groups.
•"gid" Mapping: Name of the server attribute that corresponds to the "gid" attribute in the
schema.
•"memberUid" Mapping: Name of the server attribute that corresponds to the "memberUid"
attribute in the schema.
•Enabled Group: Users in this group will have access to unit and permissions based on Control
Group and Admin Group settings.
3 Setup 39
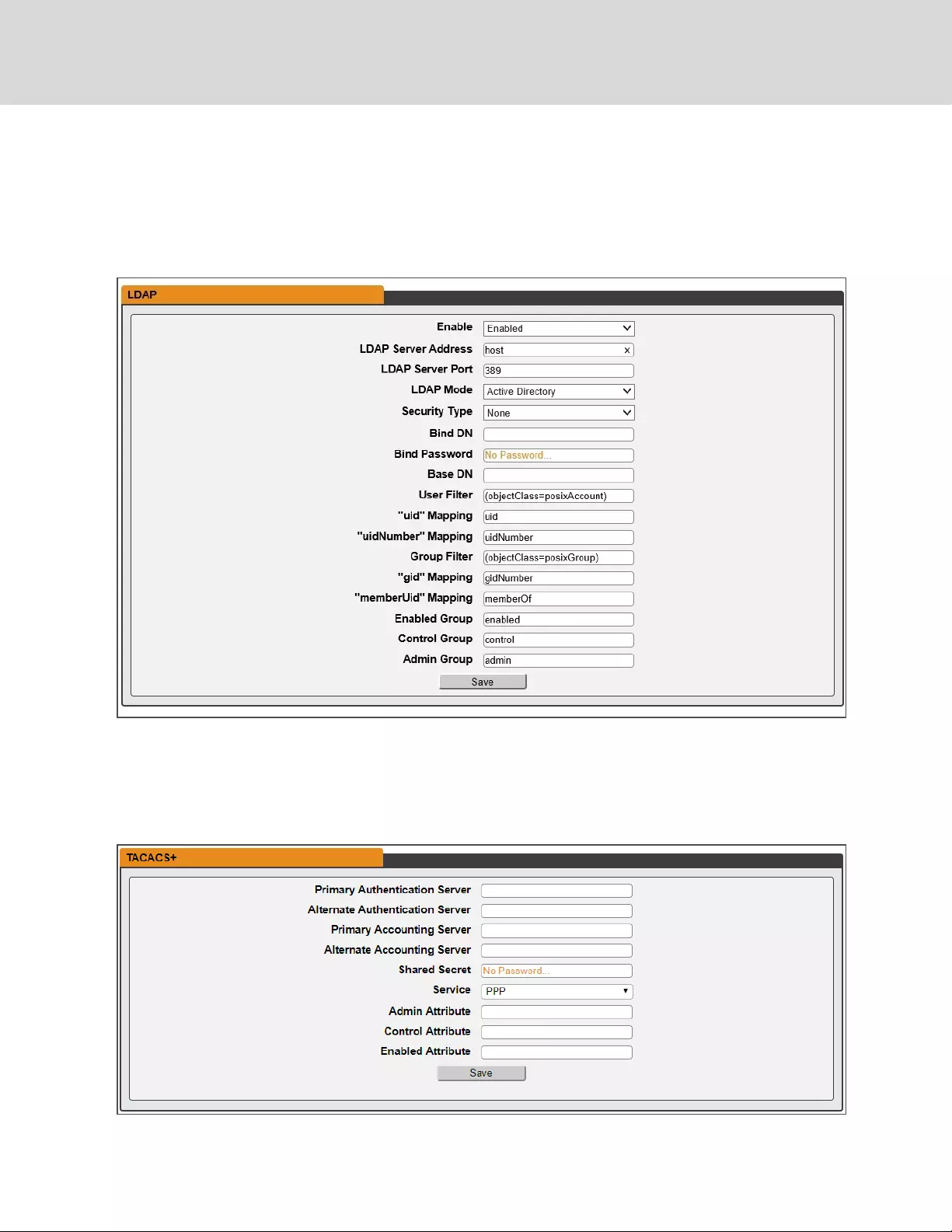
•Control Group: Users in this group have control privileges as described in the Users section of
this manual.
•Admin Group: Users in this group have admin privileges as described in the Users section of
this manual. LDAP users do not count toward minimum number of required admin users.
Figure 3.13 LDAP Menu
TACACS+
Configuration for remote authentication using TACACS+.
Figure 3.14 TACACS+ Menu
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
40

•Primary Authentication Server: The primary authentication/authorization server which can be
an IPv4 address, an IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Primary
Authentication Server is used for both authentication and authorization and is required.
•Alternate Authentication Server: The alternate authentication/authorization server which can
be an IPv4 address, an IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Secondary
Authentication Server is used for both authentication and authorization.
•Primary Accounting Server: The primary accounting server which can be an IPv4 address, an
IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Primary Accounting Server is optional. If
configured, the server is notified when a user is authorized.
•Alternate Accounting Server: The alternate accounting server which can be an IPv4 address,
an IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Secondary Accounting Server is
optional. If configured, the server is notified when a user is authorized.
•Shared Secret: The secret shared by client and server. The Shared Secret is required.
•Service: The value to use for the service field in TACACS requests. Valid options are "ppp" and
"raccess".
•Admin Attribute: A user with this attribute will have "admin" privileges as described in the Users
section of this manual. TACACS+ users do not count toward minimum number of required
admin users.
•Control Attribute: Users with this attribute will have control privileges as described in the Users
section of this manual.
•Enabled Attribute: Users with this attribute will have view -only privileges as described in the
Users section of this manual.
RADIUS
Configuration for remote authentication using RADIUS.
Figure 3.15 RADIUS Menu
•Primary Authentication Server: Enter the IP address of the primary
authentication/authorization/accounting server. The Primary Authentication Server can be an
IPv4 address, an IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Primary Authentication
Server is used for authentication, authorization and accounting, and is required.
3 Setup 41
•Alternate Authentication Server: If applicable, enter the IP address of the alternate
authentication/authorization/accounting server. The Alternate Authentication Server can be
an IPv4 address, an IPv6 address in square brackets, or a host name. The Secondary
Authentication Server is used for authentication, authorization and accounting.
•Shared Secret: Enter a secret word or passphrase in the Shared Secret field (applies to both
primary and secondary authentication and accounting servers). The Shared Secret is
required.
•Group Attribute: Identifies the Attribute-Value Pair (AVP) that tells which access group the
user belongs to. Valid values are "filter-id" and ""management-privilege-level".
•Admin Group: A user belonging to this group has “admin” privileges as described in the Users
section of the manual.
•Control Group: A user belonging to this group has “control” privileges as described in the Users
section of the manual.
•Enabled Group: A user belonging to this group has view-only privileges as described in the
Users section of the manual.
Display
The unit's display configuration can be changed via the Display tab of the System menu. Settings
pertaining to the unit’s display are:
•Display Mode: Sets the unit to display current or total power (displayed as kW) on the local LED
display.
•VLC: Allows user to enable or disable VLC mode from GUI (default is disabled).
Figure 3.16 Display Mode/VLC Configuration Page
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
42
Time
The unit's time and date are set on this page.
Figure 3.17 Time Configuration Page
There are two mode available: Network Time Protocol (NTP) and Manual.
•NTP synchronizes the unit's time and date to the specified time zone using listed NTP Servers.
NTP servers can be reconfigured.
•In Manual mode, the date and time must be typed as indicated on the left of the field.
USB
The USB menu allows you to configure settings for the USB port on the unit.
•USB : Enables/disables port.
SSH
The SSH menu allows you to configure settings for SSH access to the device.
Figure 3.18 SSH Configuration Page
•SSH Access: Enables/disables access via SSH.
•SSH Port: Allows you to change the port which the SSH service listen to for incoming
connections. The default is port 22.
Email
The unit is capable of sending email notifications to up to five email addresses when an alarm or warning
event occurs.
3 Setup 43
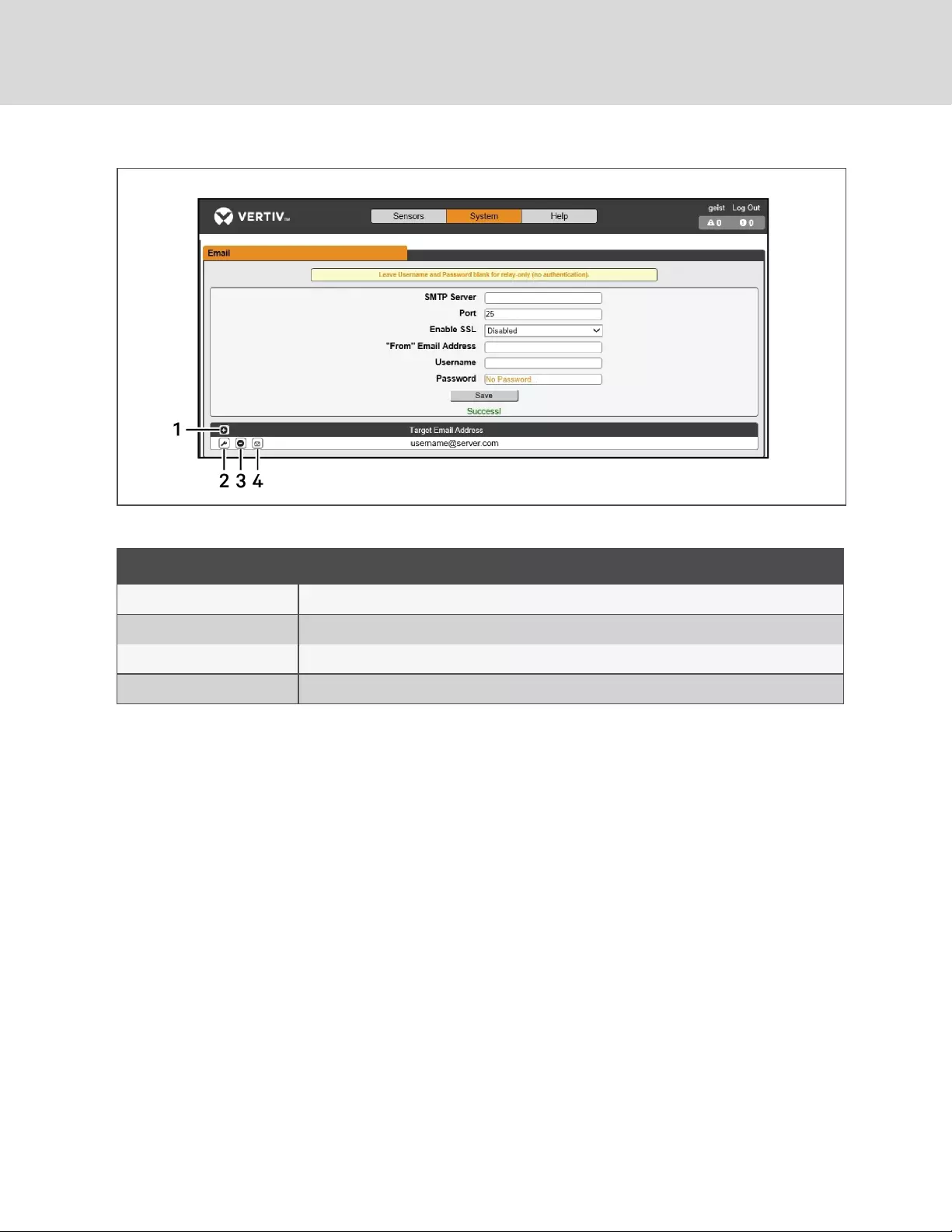
Figure 3.19 Email Configuration Page
NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Add new target email address
2 Modify existing target email address
3 Delete existing target email address
4 Send test email
Table 3.8 Email Configuration Page Descriptions
To send emails, the unit must be configured to access the mail server, as follows:
•SMTP Server: The name or IP address of a suitable SMTP or ESMTP server.
•Port: The TCP port which the SMTP Server uses to provide mail services. Typical values would
be port 25 for an unencrypted connection, or 465 and 587 for a TLS/SSL-encrypted
connection, but these may vary depending on the mail server's configuration.
•From Email Address: The address which the unit's emails appear to come from. Many hosted
email services, such as Gmail, require this to be the email account of a valid user.
•Username and Password: The login credentials for the email server. If your server does not
require authentication (open relay), these can be left blank.
Microsoft Exchange servers must be set to allow SMTP relay from the IP address of the unit. In addition,
the Exchange server must be set to allow Basic Authentication, so the unit is able to log in with the AUTH
LOGIN method of sending its login credentials. Other methods, such as AUTH PLAIN and AUTH MD5 are
not supported.
To add or modify a target email address:
1. Click the Add or Modify icon.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
44
2. Enter the email address and then click Save.
To delete a target email address:
1. Click the delete icon next to the address you wish to delete.
2. Click delete on the pop-up window to confirm.
To send a test email:
1. Click the test email icon next to the address you wish to test.
2. A pop-up window indicates the test email is being sent, click OK to dismiss the pop-up.
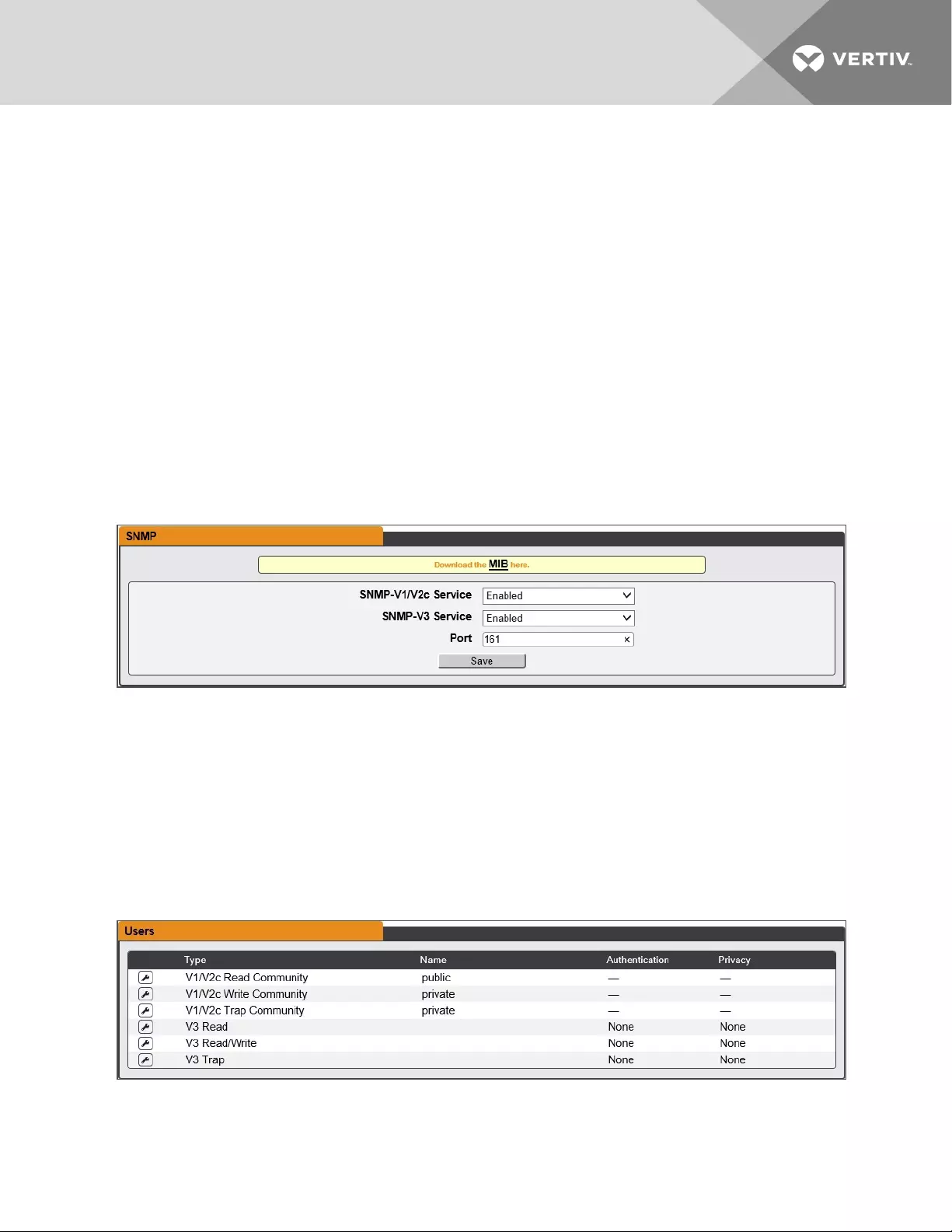
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can be used to monitor the unit's measurements and
status, if desired. SNMP v1, v2c and v3 are supported. In addition, alarm traps can be sent to up to two IP
addresses.
Figure 3.20 SNMP Configuration Page
The SNMP-V1/V2c and SNMP-V3 Service can be enabled or disabled independently as desired. The
service listens for data-read requests on port 161, which is the usual default for SNMP services; this can
also be changed if desired.
The Management Information Base (MIB) can be downloaded from the unit, if needed, via the MIB link at
the top of the web page. Clicking this link downloads a .zip archive containing both the MIB file itself, and a
CSV-formatted spreadsheet describing the available OIDs in a human-readable form to assist you in
setting up your SNMP manager to read data from the unit.
Figure 3.21 SNMP Users Configuration Page
3 Setup 45

The Users section allows you to configure the various Read, Write, and Trap communities for SNMP
services. You can also configure the authentication types and encryption methods used for the SNMP v3
if desired. Click the modify icon to change settings.
Traps allows you to define the IP addresses and SNMP types that you wish the traps to be sent.
To configure a trap destination:
1. Locate the Traps section of the SNMP page, and click the Add icon.
2. Enter the IP Address which the trap should be sent to in the Host field.
3. Change the Port number if required.
4. Select the trap version to be used (v1, v2c or v3) and click Save.
A test trap may be sent by clicking on the test icon next to the Host IP address. Trap settings can also be
updated/changed by clicking the modify icon next to the Host IP address.
SYSLOG
Syslog data can be captured remotely but must first be setup and enabled via the Syslog page.
NOTE: This function is primarily only useful for diagnostic purposes, and should normally be left
disabled unless advised to enable it by Vertiv technical support for troubleshooting a specific issue.
Admin
The Admin page allows the administrator of the device to save their contact information along with the de
vice description and location. Once the info is saved by an administrator, other (non-administrator) users
can view the information. Also, the System Label can be modified on this page. This label is typically shown
in the title bar of the web browser's window, and/or on the browser tab(s) currently viewing the device.
Locale
The Locale page sets the default language and temperature units for the device. These settings will
become the default viewing options for the device, although individual users can change these options for
their own accounts. The guest account will only be able to view the device with the options set here.
Utilities
The Utilities page in the System menu provides the ability to restore defaults, reboot the communication
system and perform firmware updates.
The Restore Defaults section allows you to restore the unit's settings to the factory defaults. There are two
options:
•All Settings: Erases all of the unit's settings, including all network and user accounts settings,
effectively reverting the entire unit back to its original out-of-the-box state.
•All Non-Network Settings: Erases all settings except the Network and User Accounts.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
46

The Reboot section allows the user to perform a system reboot. This function will not affect power delivery
to connected equipment. Use the Firmware Update section to load firmware updates into the unit.
Firmware updates, when available, can be found on the Vertiv website: VertivCo.com/Firmware-Support.
You can also subscribe to a mailing list, to be notified of when firmware updates become available.
Firmware updates typically comes in a .zip archive file containing several files including the firmware
package itself, a copy of the SNMP MIB, a "readme" text file explaining how to install the firmware, and
various other support files as needed. Be sure to un-zip the archive and follow the included instructions.
NOTE: Firmware updates can be performed via HTTP interface only. Updates over the HTTPS interface
are not currently supported.
3.3.4 Help tab
Info
The Info Page displays the unit's current configuration information, including the device name and ID, the
type of IMD installed, the unit's current firmware versions, and network information. Manufacturer support
information is also here.
Figure 3.22 Info Page
3 Setup 47

Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
48
This page intentionally left blank
4 VERTIV INTELLIGENCE DIRECTOR
Vertiv Intelligence Director brings a single unified viewing layer for small deployments of Vertiv Geist
rPDUs, Vertiv UPSs, and environmental sensors. When deployed, Vertiv Intelligence Director offers
enhanced functionality, using the rack PDU not as a standalone device but as a gateway to understand
the broader device ecosystem in which it’s installed.
4.1 Aggregation
The initial element of Veritiv Intelligence Director, available with Vertiv Geist rPDUs running firmware 5.3.0
or later, is called Aggregation. This single element allows you to:
•Use a single IP address assigned to the Master rPDU to monitor up to fifty (50) devices, the
master and (49) downstream devices.
•Allow rPDUs downstream from the master to self-configure network settings.
•Create aggregated measurements like total rack power and total row power, including
averages, minimums and maximums.
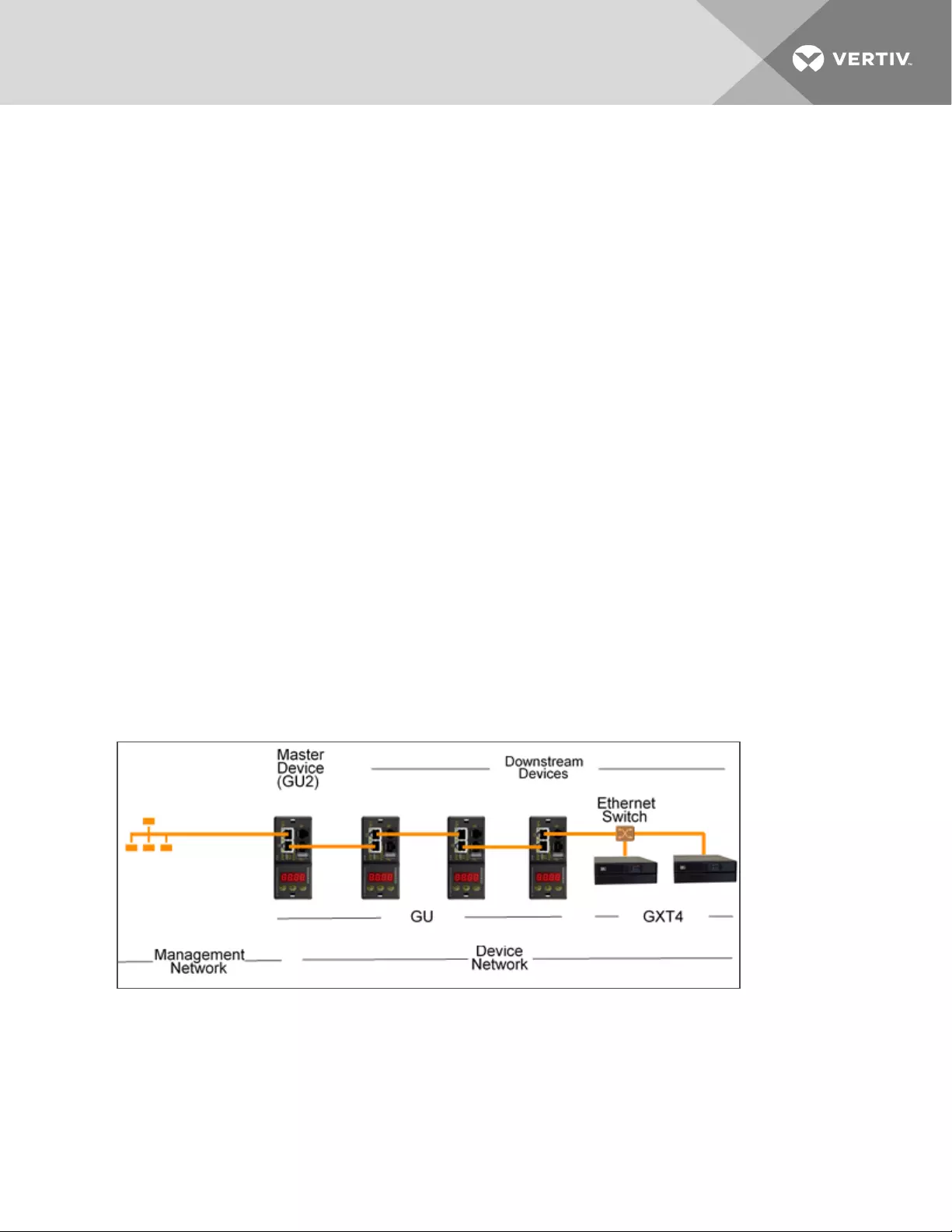
4.2 Master rPDU
Aggregation requires the designation of a Master rPDU, deployed with IMD model IMD-3E. The IMD of the
master device facilitates and configures the device network, the interconnected array of Vertiv Geist
rPDUs, Vertiv UPS, and environmental sensors, while aggregating select data points from these devices. It
also interacts with the management network for monitoring and management of it and its downstream
devices.
Figure 4.1 Sample Configuration
The IMD-3E is the default intelligence card for Vertiv Geist GU2 rPDUs, which include switched (model
numbers beginning with MNS), outlet monitored (model numbers beginning with MNR), and switched
plus outlet monitored (model numbers beginning with MNU) products. To serve as the master rPDU,
rPDUs with a legacy intelligence card must first upgrade to the IMD-3E
49

4.3 Network Configuration
Aggregation is enabled on the master rPDUs only. As each master can support up to 49 downstream
devices, the number of masters depends on the overall size of the installation and the preferred network
architecture.
The master rPDU must be commissioned before it’s connected to the primary management network or to
the downstream device network. This commissioning is typically accomplished via a laptop or local
machine connected directly to port 1 on the IMD.
After local connectivity is established, you can commission the master rPDU.
To commission the master rPDU:
1. Use the top drop-down menu to navigate to System - Locale.
2. Select the appropriate Default Language and Temperature Units from the drop-down menus.
These settings are pushed to the downstream devices in its network.
3. Browse to System - Utilities. Change the settings as desired.
a. Aggregation: Choose Enabled from the drop-down menu.
b. Managed Device Username: Defines the username configured on all downstream devices.
c. Managed Device Password: Defines the password configured on all downstream devices.
4. Enter the new password, verify the password and click OK.
5. Click Submit. If Aggregation is enabled, the Device tab appears next to the Sensors tab on the
top navigation bar.
After aggregation is enabled on the master rPDU, configure the remaining master rPDU settings. Connect
the master rPDU to management network (port 1) on the IMD and the device network (port 2).
NOTE: The master rPDU has a built-in DHCP network to assign addresses to its downstream devices.
This DHCP network uses 192.168.124.0/24 addresses and they cannot be used for the management
network.
4.3.1 Downstream Devices
In the initial release of aggregation, downstream devices are defined as rPDUs within the GU1 and GU2
product platforms as well as GXT4 UPS. All GU1 rPDUs must be running firmware version 3.3.3 or later; GU2
rPDUs must be running version 5.3.0 or later. If the rPDUs are newly-ordered and have never been
configured with network settings, they are ready for aggregation out-of-the-box. If the rPDUs have been
deployed in a computing environment and commissioned with local LAN settings and user accounts, the
rPDUs must be reset to factory defaults. The master rPDU then pushes configuration data to the
downstream devices, including:
•Network settings
•Default Language and Temperature Units
•Username
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
50

•Password
To setup a new installation with one master rPDU:
1. Install downstream rPDUs in racks and power on the racks.
2. Daisy-chain the downstream PDUs to one another where appropriate using ports labeled 1 and
2 on the IMD.
•If daisy-chaining, ensure no more than 40 rPDUs are chained together.
•A star network or other design is also acceptable in lieu of a daisy-chain.
•If connecting daisy-chains to a network switch, no daisy-chain should be longer than 20
rPDUs
3. Install the master rPDU in rack location. Using a laptop or a local machine, connect to port 1 to
configure aggregation..
4. Connect the master rPDU to the management network using port 1
5. Connect the master rPDU to the downstream network using port 2.
To setup an existing installation with one master rPDU:
NOTE: Use the following instructions if existing Geist rPDUs are connected in a daisy-chain.
1. Designate a master rPDU and disconnect it from the management network.
2. Reset all downstream rPDUs to factory default settings. The physical ethernet connections in
the daisy-chain can remain the same; however, if previously connected in a looped
configuration, the final PDU in the chain should be disconnected from the network switch.
3. Enable Aggregation on the master rPDU.
4. Connect the master rPDU to the management network using port 1
5. Connect the master rPDU to the downstream network using port 2.
Multiple master rPDUs
For installations with multiple master rPDUs, keep in mind that each device network must operate as a
standalone, isolated network. Consider a 200 rPDU example, represented in the following diagram. This
installation would require a minimum of 4 master rPDUs, each operating its own standalone device
network. Each master is visible on the management network and acts as a DHCP server for its downstream
devices. A user on the management network can navigate through each master to reach the interface of
a downstream device. Other considerations may affect the quantity of master rPDUs. If you have a row
network architecture, you may prefer a master at the start of each row, as opposed to a master that
traverses several rows. Depending on how these 200 cabinets are divided into rows, you may have more
than four master rPDUs. When the configuration is decided, follow the appropriate process for
aggregation.
4 Vertiv Intelligence Director 51
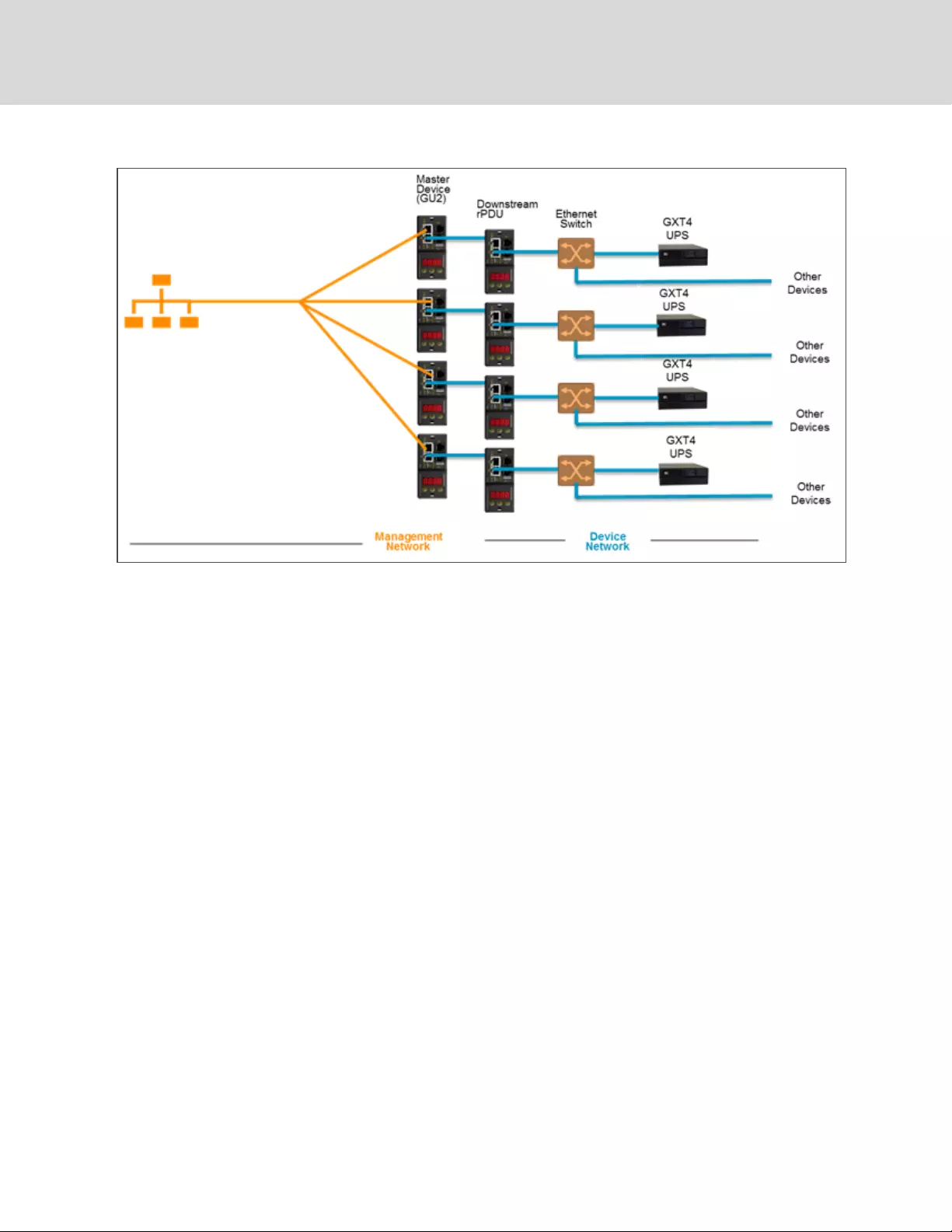
Figure 4.2 Sample Network Configuration
NOTE: RSTP is disabled by default in GU1 rPDUs running 3.4.0 or later and GU2 rPDUs running 5.3.3 or
later. In previous firmware, RSTP is enabled on both platforms. Aggregation does not support RSTP.
Leaving RSTP enabled limits a rPDU daisy-chain within aggregation to forty. Disabling RSTP on
downstream devices will remove the forty device limitation.
4.4 Views
When communication is established between the master and downstream devices, several views are
automatically populated within the user interface. The new views are under the Device tab in the top
navigation bar are:
•Summary
•Groups
•List
•Group Configuration
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
52

Figure 4.3 Device Tab
4.4.1 Summary
The summary view aggregates data from all downstream devices, presenting a concise outline of relevant
power, environmental and alarm details.
Rack PDUs
The rPDU network is summarized by the following data points:
•Energy: The total PDU energy within the device network.
•Power Sum: The total PDU power load within the device network.
•Power Minimum: The lowest group PDU power load within the device network.
•Power Maximum: The highest group PDU power load within the device network.
•Power Average: The average group PDU power load within the device network.
NOTE: These readings are repeated per phase (shown when only 3-phase PDUs present).
UPS
The UPS network is summarized by the following data points:
•Power Maximum: The highest group UPS power load within the device network.
•Power Average: The average group UPS power load within the device network.
•Battery Autonomy Minimum: The lowest UPS battery runtime within the device network.
•Battery Autonomy Average: The average UPS battery runtime within the device network.
•Battery Charge Minimum: The lowest UPS battery charge within the device network.
•Battery Charge Average: The average UPS battery charge within the device network.
4 Vertiv Intelligence Director 53

Environmental (Sensors)
The Environmental category is summarized by the following data points:
NOTE: Humidity values are blank when temperature-only sensors are used.
•Temperature Minimum: The lowest temperature within the device network.
•Temperature Maximum: The highest temperature within the device network.
•Temperature Average: The average temperature within the device network.
•Humidity Minimum: The lowest humidity within the device network.
•Humidity Maximum: The highest humidity within the device network.
•Humidity Average: The average humidity within the device network.
Notifications
Notifications shows outstanding alarms from devices in the device network.
4.4.2 Groups
After groups are established within the Group Configuration, the Groups view summarizes power and
environmental data. The available data points are as follows:
Group rPDU
•Energy: The total PDU energy within the group.
•Power Sum: The total PDU power load within the group.
•Power Minimum: The lowest PDU power load within the group.
•Power Maximum: The highest PDU power load within the group.
•Power Average: The average PDU power load within the group.
NOTE: These readings are repeated per phase (shown when only 3-phase PDUs present).
Group UPS
•Power Maximum: The highest UPS power load within the group.
•Power Average: The average UPS power load within the group.
•Battery Autonomy Minimum: The lowest UPS battery runtime within the group.
•Battery Autonomy Average: The average UPS battery runtime within the group.
•Battery Charge Minimum: The lowest UPS battery charge within the group.
•Battery Charge Average: The average UPS battery charge for the group.
Group Environmental
•Temperature Minimum: The lowest temperature within the group.
•Temperature Maximum: The highest temperature within the group.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
54

•Temperature Average: The average temperature within the group.
•Humidity Minimum: The lowest humidity within the group.
•Humidity Maximum: The highest humidity within the group.
•Humidity Average: The average humidity within the group.
4.4.3 List
The list view presents an inventory of all devices within the master’s Device network.
The inventory is subdivided into in the following categories:
Rack PDUs
All rPDUs in the device network roll into this category and present the following data points:
•State: The status of the rPDU. Status is either normal or unavailable (loss of connectivity).
•Name: rPDU label. Clicking on the name opens a browser tab for device access.
•Group: The group name. If there is no user created group, the group name is Unassigned.
•Energy: rPDU energy.
•Power: Total rPDU power load.
UPS
All UPS devices in the device network roll into this category and present the following data points:
•State: The status of the UPS. Status is either normal or unavailable (loss of connectivity).
•Name: UPSlabel. Clicking on the name opens a browser tab for device access.
•Group: The group name. If there is no user created group, the group name is Unassigned.
•Input Voltage: UPS input voltage.
•Output Source: The UPS operating mode which can be: Normal, Bypass, Battery, Booster,
Reducer, Off or Other.
•Status: The battery status which can be: Normal , Low, Depleted or Unknown
•Battery Autonomy: UPS battery runtime.
•Charge: UPS battery charge.
ENV (Environmental Sensors)
All environmental sensors in the device network roll into this category and present the following data
points:
•State: The status of the Sensor. Status is either normal or unavailable (loss of connectivity).
•Name: Sensor label. Clicking on the name opens a browser tab for device access.
•Group: The group name. If there is no user created group, the group name is Unassigned.
•Device: Displays the sensor parent PDU label and MAC address.
4 Vertiv Intelligence Director 55
•Temperature: Temperature reading (main temperature only with GT3HD sensors).
•Humidity: Humidity reading. This field is blank if only SRT temperature sensors are deployed.
Environmental sensors, report their values through the MIB of the rPDUs to which they are connected.
They are not standalone sensors with their own IP addresses. In this release, the only valid sensors are
rPDU-connected Geist-brand SRT, GTHD or GTHD3 sensors.
NOTE: The Name of any device can be customized by logging into the device and editing through the
configuration icon.
NOTE: To delete a device which has been removed from the network, select the trash icon next to the
device. Selecting Delete deletes the device and any environmental sensors connected to it.
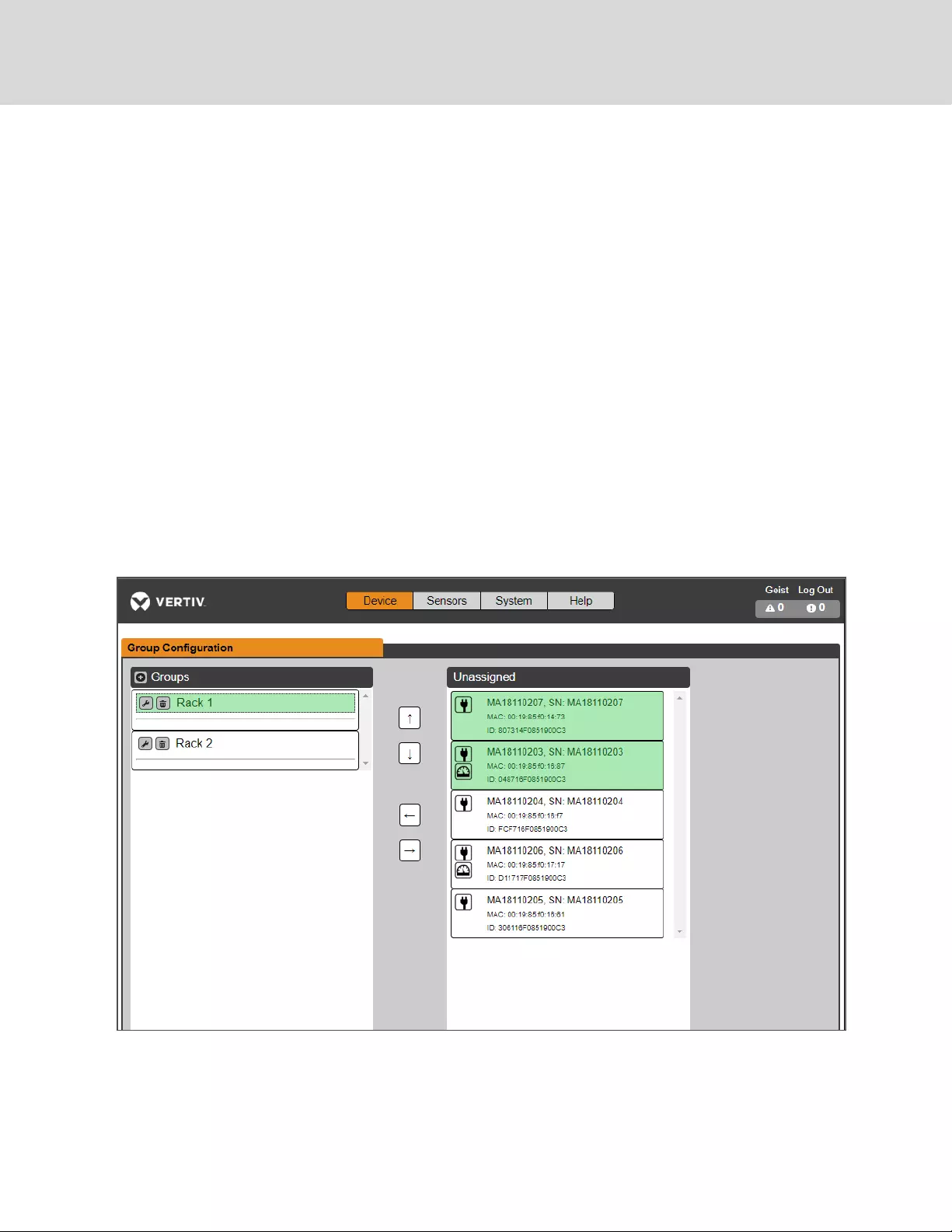
4.4.4 Group Configuration
On the Group configuration page, you can define groups of devices for data aggregation and analytic
purposes. A group often refers to a unit of measure within a computing environment that includes
multiple downstream devices, such as a rack with two rPDUs, UPS devices and environmental sensors or a
row within a facility that includes multiple racks.
Figure 4.4 Group Configuration
The Group Configuration page lists the automatically discovered devices under the “Unassigned” column
showing:
•One or more icons defining the type of device such as, rPDU, environmental sensor or UPS.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
56

•Device label
•Serial number
•MAC address
•ID
Configured groups of devices (typically representing racks) are shown on the left.
Figure 4.5 To create a new group:
1. Click the + to the left of Groups. A new group, is displayed under Groups.
2. Click the configuration icon to change the name of the group label.
3. Edit the label, if desired, and click Save.
4. To assign devices to the group, highlight the desired group (within Groups category) and
highlight the desired devices within the Unassigned category.
5. Click the right arrow to assign the devices to the group.
6. Repeat the process for other groups, as needed.
NOTE: Groups can be reordered by clicking the up or down arrows.
To remove devices from a group:
Highlight the devices and click the right arrow.
Figure 4.6 To delete a group:
Click the trash icon next to the group name.
NOTE: Deleting a group returns all of its devices to the unassigned group.
4.5 Interfaces
Downstream devices are combined to form groups, each device retains its own standalone user interface
and SNMP data.
To access the downstream device user interface:
1. From the List view, use your mouse to hover over the entries in the table. A yellow highlight and
text box appear as you pause on the devices. The text box reveals the IP address of the device.
2. Navigating to IP address to access the web server interface of the device.
-or-
Click the name of the device to access the hyperlink to the web server.
Figure 4.7 To access downstream device SNMP data:
SNMP data is available using port mapped access through the master device IP address using the geist_
v5 MIB. The MIB file is downloadable from the master device SNMP page.
4 Vertiv Intelligence Director 57
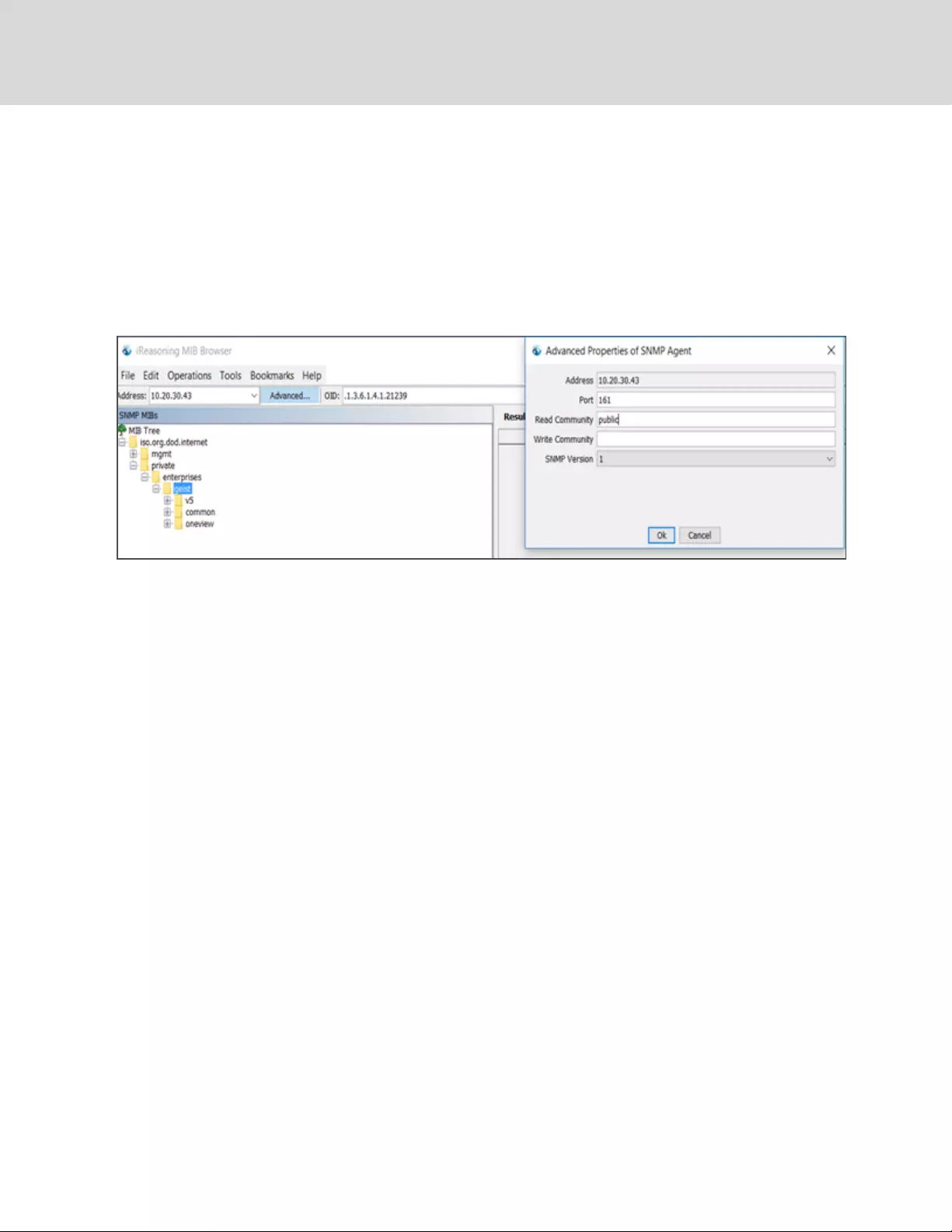
1. From the List view, use your mouse to hover over the entries in the table. A yellow highlight and
text box appear as you pause on the devices. The text box reveals the SNMP port of the
device.
2. In the MIB browser, enter the SNMP port listed.
NOTE: Monitoring software intended to monitor individual downstream devices must be capable of
accepting a unique SNMP port number per monitored device.
Figure 4.8 MIBBrowser
4.5.1 Group SNMP data
Aggregated data, both summary (such as total kWh and maximum kW) and group data is available
through the master rPDU IP address and default SNMP port 161. Within the MIB structure, the folders
differentiate the data points available from the master rPDU:
•v5: Contains data points for the individual master rPDU.
•Oneview: Contains data points for aggregated data across all downstream devices.
4.5.2 Tips and troubleshooting
•Summary and Group aggregated data cannot be used to generate SNMP traps.
•SNMP community names are configured on each device. Follow the device links displayed on
the List page under the Devices menu and logging into each device to configure SNMP.
•Do not change the default SNMP port number when logged into a downstream device.
•SNMP traps and alarms are routed from a device to the management network through the
master device.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
58

5 APPENDICES
Appendix A: Technical Support
A.1 Resetting rPDU
If the rPDU loses communication, the processor may be manually rebooted without affecting power to the
outlets. Pressing the reboot button on the face of the IMD will cause the processor to reboot. The web
interface will remain off-line during boot up. For more information, see Interchangeable Monitoring Device
(IMD-03X)
A.2 Service and maintenance
No service or maintenance is required. Do not attempt to open the rPDU or you may void the warranty.
There are no serviceable parts inside the rPDU other than the field replaceable Interchangeable
Monitoring Device (IMD). It is recommended that power be removed from the unit before installing or
removing any equipment.
The Interchangeable Monitoring Device is designed to be field replaceable by qualified service personnel
only. The IMD is designed to be replaced while the rPDU is still connected to AC Mains power. Please refer
the Geist™ PDU IMD Modules Replacement Guide for more information.
A.3 More technical support
Technical support can be found at www.VertivCo.com/support.
Americas
•Website: www.VertivCo.com/geist
•Email: support@VertivCo.com
•Telephone: 1-888-630-4445
Europe and Middle East
•Technical Support: www.VertivCo.com/en-emea/support
•Email: eoc@VertivCo.com
•Telephone: 1-800-1155-4499
Asia
•Telephone (English): 1-888-630-4445 (US number)
•Telephone (Chinese): +86 755 8663 9505
59

A.4 Using Microsoft Exchange as an SMTP server
If your facility uses a Microsoft Exchange email server, it can be used by the IMD rPDU to send Alarm and
Warning notification emails if desired. However, the Exchange server may need to be configured to allow
SMTP connections from the unit first, as later version of Exchange often have SMTP services or basic au-
thentication disabled by default. If you encounter difficulties in getting your IMD rPDU to send emails
through your Exchange server, the following notes may be helpful in resolving the problem.
NOTE: These suggestions only apply if you are using your own, physical Exchange server. Microsoft’s
hosted Office365 service is not compatible with the IMD rPDU using firmware versions prior to v3.0.0,
as Office365 requires a StartTLS connection. Firmware versions 3.0.0 and beyond have support for
StartTLS and are compatible with Office365.
First, since the IMD rPDU cannot use IMAP or Microsoft’s proprietary MAPI/RPC Exchange/Outlook proto-
cols to send messages, you will need to enable SMTP by setting up an SMTP Send Connector in the
Exchange server. More information on setting up an SMTP Send Connector in Exchange can be found at
this Microsoft TechNet article: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997285.aspx
Next: Your Exchange server may also need to be configured to allow messages to be relayed from the
monitoring unit. Typically, this will involve turning on the Reroute incoming SMTP mail option in the
Exchange server’s Routing properties, then adding the IMD rPDU’s IP address as a domain which is
permitted to relay mail through the Exchange server. More information about enabling and configuring
SMTP relaying in Exchange can be found at this Microsoft TechNet article:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/library/dd277329.aspx
The SMTP AUTH PLAIN and AUTH LOGIN authentication methods for logging in to the server are often
no longer enabled by default in Exchange; only Microsoft’s proprietary NTLM authentication method is
enabled.
To re-enable the AUTH LOGIN method:
1. In the Exchange console select Server Configuration - Hub Transport.
2. Right-click the client server, and select Properties.
3. Select the Authentication Tab and click the Basic Authentication checkbox.
4. Deselect the Offer Basic only after TLS checkbox.
5. Apply or Save and click Exit.
NOTE: You may need to restart the Exchange service after making these changes.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
60

Finally, once you have enabled SMTP, relaying, and the AUTH LOGIN Basic Authentication method, you
may also need to create a user account specifically for the IMD rPDU to log into. If you have already cre-
ated an account prior to enabling the SMTP Send Connector, or you are trying to use an already-existing
account created for another user, and the IMD rPDU still cannot seem to connect to the Exchange server,
the account probably did not properly inherit the new permissions when you enabled them as above. This
tends to happen more often on Exchange servers that have been upgraded since the account(s) you are
trying to use were first created, but can sometimes happen with accounts when new connectors and
plug- ins are added regardless of the Exchange version. Delete the user account, then create a new one
for the monitoring unit to use, and the new account should inherit the SMTP authentication and mail-
relaying permissions correctly.
If none of the above suggestions succeed in allowing your IMD rPDU to send mail through your Exchange
server, then you may need to contact Microsoft’s technical support for further assistance in configuring
your Exchange server to allow SMTP emails to be sent from a 3rd-party, non-Windows device through
your network.
5 Appendices 61

Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
62
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix B: Visible Light Communication (VLC)
The VLC feature on Upgradeable PDUs allows the user to unobtrusively upload product information into a
database management system via the embedded LED display. This product feature provides new
opportunities to monitor and enable larger amounts of rPDU power data to be obtained via the unit’s
display, and all without physically connecting to the rPDU.
Using a smart device, such as a smart phone or tablet with the Vertiv Mobile app installed, it is possible to
capture data from the LED display when running in VLC mode, which can be enabled/disabled easily by
using the display buttons on the device, or using the GUI on monitored units.
By default, the Upgradeable LED display will provide the Current (Amps) per input and circuit/breaker. By
enabling the VLC feature, the LED Display will scroll through a set of alpha-numeric characters. Utilizing
the Vertiv Mobile app the user can scan the LED display and retrieve additional power metrics which
include Volts, Amps, Watts, Volt-Amps and Kilowatt Hours. Before VLC, the power data was only available
on network connected PDUs by viewing the GUI, or using external software to collect and display the data.
The VLC feature provides this data on local metered only devices, as well as on monitored units without
the need to connect them to the network.
WARNING! This feature, when enabled, causes the unit to emit flashing lights, text, or number
sets at frequencies that can induce adverse reactions. Persons susceptible to adverse
reactions as a result of such emissions or persons who have been diagnosed with epilepsy
should not utilize or enable this feature.
To enable VLC:
Press the center button three times in under two seconds.
NOTE: With the release of firmware version 3.3.0, Vertiv has added support for the VLC feature to all
standard Metered and Monitored Upgradeable products, as well as a significant majority of its
engineered-to-order range. Certain custom models of Upgradeable PDUs may not have VLC support
within the Vertiv Mobile application. If your custom product is not supported by the Vertiv Mobile app
it will be noted in the product specification sheet. Please contact your sales representative if you would
like assistance with this. The latest firmware updates can be found at VertivCo.com/Firmware-Support.
Vertiv Mobile app is available via the App Store for iOS devices.
63

Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
64
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix C: Vertiv Mobile App
The Home screen allows the user to initiate a device scan or export data via .csv file.
•Scan: Turns on scan mode to allow the app to capture VLC data from Upgradeable rPDU.
•Export: Pressing the export button will launch the smart device's email app and attach the
Database .csv file to be emailed to desired recipients.
Figure C.1 Mobile App Home Screen
To scan an rPDU
1. Press Scan on the Home screen to load the Vertiv Mobile app scanning engine.
65
Figure C.2 Mobile App Scanning Screen
2. Position the smart device so that the characters on the LED display are between the lines on
the screen. The LED characters should be clear and in-focus. If the characters appear too
bright or too dark, the exposure setting can be adjusted by using the sliding bar at the bottom
of the screen. The app captures data as soon as it can see the LED characters inside the
horizontal lines. Scan progress is displayed as a percentage. If the scan percentage is
increasing slowly, or resetting, the device is having trouble reading the data properly. In this
case, try repositioning the device to improve results. After the scan reaches 100% the app loads
the Readings page.
NOTE: When a device is scanned for the first time, the Vertiv Mobile app recognizes the serial number
as being new and ask if it should be added to the database as shown in the following image. If added to
the database, all future scanned data is added to the device serial number record.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
66
Figure C.3 Mobile App New Device Screen
C.1 Scanning tips
The VLC feature relies upon light for its communication. If the lighting around the display or the lighting
going through the lens of the smart device is not optimal then the OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
will struggle to capture the data. When looking at the smart device screen during capture, you can see if
the characters of the LED display are in focus and bright, if they are blurred, with a surrounding glow or
are faint then the VLC capture will fail to work quickly and may be unable to scan at all.
Proper capture methods
•High Contrast between LED display and background
•No glow around LED display characters
•LED display characters between horizontal guidelines
Improper capture methods
•Blurry image
•Over-exposed image
•Glow around LED display characters
•LED display characters not between horizontal guidelines
67
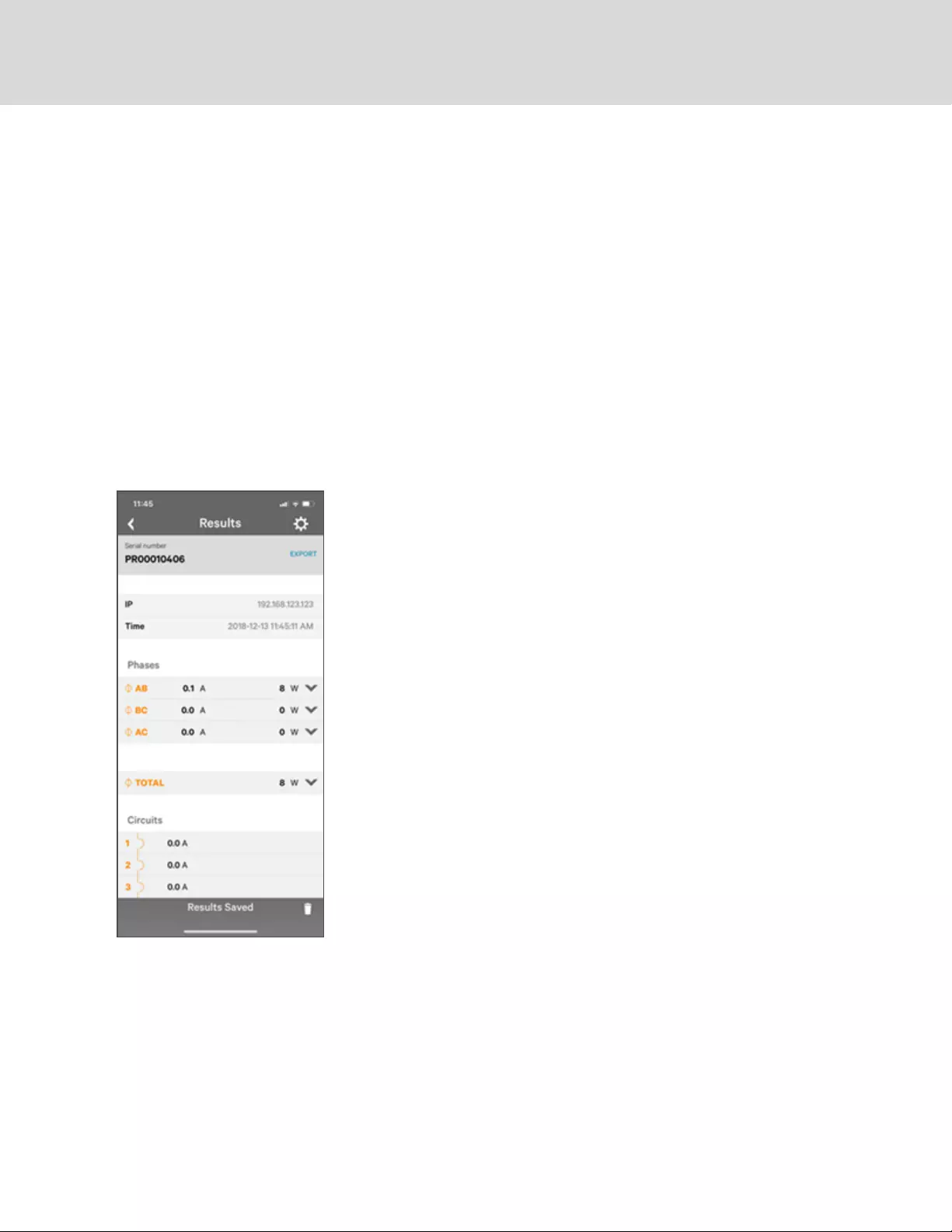
C.2 Failure modes and Errors
The Vertiv Mobile App retries a scan two times if the scan cannot be completed. The scan fails if the smart
device is unable to correctly capture all the VLC data correctly. One of the following messages is
displayed:
•Scan failed: Incorrect set configuration
•Scan failed: Incorrect data sequence
•Scan failed: Please adjust your position or the exposure and try again
Press Cancel to return to the Home screen or Retry to return to the Scan page.
C.3 Readings
The Readings page displays scan results for each rPDU scanned using VLC.
Figure C.4 Mobile App Readings Screen
NOTE: The unit serial number is displayed in the title bar of the Readings page. This serial number
matches the serial number located on the surface of the rPDU.
Pressing the Settings icon enables the user to customized the data that is displayed in the scan results.
•Collapse Rows: Allows user to collapse or expand the Readings page to help properly display
data on smart devices with smaller screens.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
68
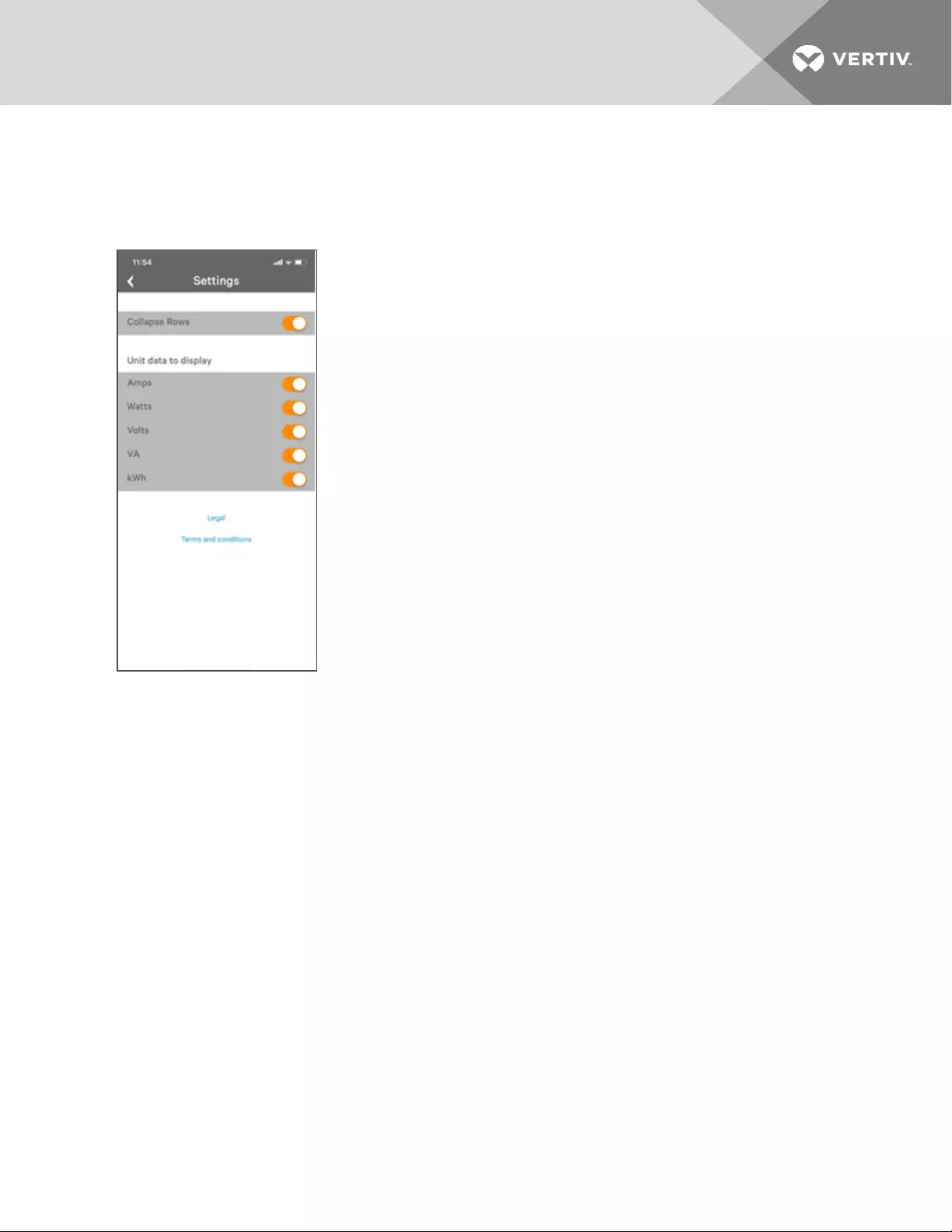
•Unit Data to Display: Selects which data is shown on the Readings page. All data is stored
within the database regardless of settings here. These settings are global and will apply to any
scanned unit.
Figure C.5 Mobile App Settings Screen
C.4 Export
The Export button on the Home screen opens the smart device's default email app to send the database
of scanned devices in .csv format to the desired recipients.
69
Figure C.6 Mobile App Export Screen
NOTE: An email app must be properly configured on the smart device to utilize the Export function.
The Vertiv Mobile app does not directly support email functionality. Vertiv cannot troubleshoot email
errors as this would be an issue with either the device, or email service being used.
Each rPDU you scan adds a new entry to the database, there is no limit to the number of individual rPDU’s
that can be added but the database has a limit of 10 scans per rPDU. Additional scans of the unit will
overwrite the oldest data for that unit.
The .csv data output organizes data first by serial number and then by date & time. You can further
organize the data by using the filter option in Excel. The data structure is split into two sections, rPDU
configuration and Power data.
rPDU configuration data includes:
•Serial Number
•Frame Definition
•Date/Time stamp
•IPv4 address
Power Data includes:
•Power Readings
•Totals
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
70
SERIAL NUMBER FRAMEDEF YYYY-MM-DD-
HH-MM-SS IP ADD
Products unique serial number. This is the
same serial number present on the units
label.
Part of the VLC con-
figuration data and used for
debugging.
Timestamp of
when the scan
occurred.
The IPv4 address of the unit. Locally
Metered units will show Null IP
address.
Table C.1 rPDU Configuration Data
VOLTS AMPS WATTS VA KWH
1 volt 1 amp 1 watt 1 va 1 kwh
Input Phase for Single Phase units. Phase A or Phase AB if 3 Phase Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
2 volts 2 amps 2 watts 2 va 2 kwh
Phase B or Phase BC if 3 Phase Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
3 volts 3 amps 3 watts 3 va 3 kwh
Phase C or Phase AC if 3 Phase Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
4 volts 4 amps 4 watts 4 va 4 kwh
Secondary Input Phase for Single Phase units. Phase A or Phase
AB if 3 Phase
Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
5 volts 5 amps 5 watts 5 va 5 kwh
Secondary Phase B or Phase BC if 3 Phase Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
6 volts 6 amps 6 watts 6 va 6 kwh
Secondary Phase C or Phase AC if 3 Phase Phase
Amperes
Phase Real
Power
Phase
Apparent
Power
Phase
Kilowatt-
Hours
Table C.2 Power Data
NOTE: Some GU models have Dual Inputs with Monitoring or Dual Inline Monitoring, these units can
have up to three additional Power readings.
BREAKER 1 BREAKER 2 BREAKER 3 BREAKER 4 BREAKER 5 BREAKER 6
Breaker / Circuit 1
Amps
Breaker / Circuit 2
Amps
Breaker / Circuit 3
Amps
Breaker / Circuit 4
Amps
Breaker / Circuit 5
Amps
Breaker / Circuit 6
Amps
Table C.3 Breakers/Circuits
71

TOTAL WATTS (REAL POWER) TOTAL VA (APPARENT POWER) TOTAL KWH
The total of Watts shown in sec- tions 1-6 The total of VA shown in sections 1-6 The total kWh shown in sections 1-6
Table C.4 Totals
NOTE: The tables above are an outline of data that is present in the database .csv file as is not
representative of the actual format of the .csv file. Data stored will vary based on product
configuration.
Appendix D: Available Sensors
D.1 Remote sensors
•SRT: Stainless Remote Temperature
•GTHD: Temperature/Humidity/Dew Point
•GT3HD: Temperature/Humidity/Dew Point with two SRT sensors
•RTAFHD3: Temperature/Air Flow/Humidity/Dew Point
•A2D: Converts analog I/O Sensors to Remote Digital Sensors
D.2 Analog I/O sensors
•FS-15: Flood (Water) Sensor
•PFS-100 US / PFS-100 UN: Power Failure Sensor
•RPDS: Door Switch Kit
D.3 Connecting remote sensors
Up to sixteen plug-and-play remote sensors can be attached to the unit at any time via the RJ-12
connectors on the front of the unit. In some cases splitters may be required to add additional sensors.
Each sensor has a unique serial number and is automatically discovered and added to the web page. The
display order of the sensors on the web, is determined by the serial number of each sensor. You can
customize names of each sensor on the Sensors Overview page.
NOTE: Sensors use cat 5, CMP wire and RJ-12 connectors. Wiring must be straight-through. Reverse
polarity temporarily disables all of the sensors until corrected. Sensors use a serial communication
protocol and are subject to network signaling constraints dependent on shielding, environmental noise
and length of wire. Typical installations allow runs of up to 600 feet of sensor wire.
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
72
Appendix E: Outlet LEDs
Outlet LEDs provide a visual indication of outlet power status (On, Off or Error). The LEDs are sequentially
numbered with easy-to-read white numbers on black background. Depending on outlet power status, the
LEDs illuminate in solid colors or blinking colors.
LED DESCRIPTION
Green Outlet Voltage is present and above minimum threshold limit
Red Outlet Voltage is not present
Amber Power output error condition has been detected
Table D.1 LED Outlets
MEASURED VOLTAGE RELAY STATE STATE LED
On On or Unknown Solid Green
Off Off or Unknown Solid Red
Off On Blinking 1> Amber Red
On Off Blinking 2Amber Green
Table D.2 LED Status Description
1. Outlet is sensed to be off but should be on.
2. Outlet is sensed to be on but should be off.
Error Codes
LEDs illuminate in solid amber during the following:
•Power failure (all relays are forced open in the event of power failure to allow for power-on
sequencing)
•Circuit breaker open
•No input voltage detected
73
Appendix F: IMD Display Codes
DISPLAY IMD
TYPE EXPLANATION
“Err1”
IMD-01
(Metered
only)
The IMD discovered either 0 or more than 1 input boards. This may be caused by internal cabling
issues or an unresponsive input board. This is also displayed if there is a measurement error
reported by the input board.
“8888”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
IMD is booting and has yet to discover the simple display and shows “boot” on it. If this is
displayed for more than a few seconds there is either a problem with the display board or internal
cabling.
“ --” (Two dashes on
the right most display
position)
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
The IMD cannot communicate with the input board. This may also be shown intermittently for
individual measurements. There is either a problem with the input board or internal cabling.
“boot” IMD-01 IMD is booting and discovering the input board.
“boot”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
Firmware is initializing. This will be displayed while firmware is being updated in slave boards.
“updt”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
Firmware update in progress.
“rset dflt”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
Following user action, rset (reset) will appear during a parameter reset sequence. During a
parameter reset, dflt (default) will appear briefly
“bcup”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
Bcup (backup) will appear during a configuration backup
“rest conf”
IMD-02,
IMD-03,
IMD-3
Rest (restore) and Conf (configuration) will appear during a configuration restore
Table D.3 IMD Display Codes
Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide
74

Vertiv | Intelligent Rack PDU Installer/User Guide

VertivCo.com | Vertiv Headquarters, 1050 Dearborn Drive, Columbus, OH, 43085, USA
© 2019 Vertiv Co. All rights reserved. Vertiv and the Vertiv logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Vertiv Co. All other names and logos referred to
are trade names, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. While every precaution has been taken to ensure accuracy and
completeness herein, Vertiv Co. assumes no responsibility, and disclaims all liability, for damages resulting from use of this information or for any errors or
omissions. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
VM1221/590-2196-501A