Table of Contents
- User Manual
- Chapter 1 Getting Started
- Chapter 2 Configuration
- Chapter 3 File Sharing
- Chapter 4 Storage Management
- Chapter 5 Backup
- Chapter 6 Remote Access
- Chapter 7 Advanced Features
- Antivirus Software
- Email Notification
- Sleep Mode
- Wake-on-LAN
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
- Power Supply Failure
- Port Trunking
- Offline Files
- Accessing from an NFS Client
- Encrypting Data Transmission
- SNMP
- Saving and Applying Settings
- Transferring Another TeraStation’s Settings
- Restoring Factory Defaults
- Resetting the Administrator Password
- Logs
- Updating the Firmware
- Configuring Update Notification
- Name, Date, Time, and Language
- Beep Alerts
- LCD and LEDs
- Proxy Server
- Jumbo Frames
- Changing the IP Address
- Boot Authentication
- Chapter 8 Drive Replacement
- Chapter 9 Utilities
- Chapter 10 Appendix
- Chapter 11 Regulatory Compliance Information
Buffalo 5410DN User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 5410DN by Buffalo which is a product in the NAS & Storage Servers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Network Attached Storage
TeraStation 5010
User Manual
Please make sure to read this manual before using and follow the procedures. If you have any inquiries about
the product, contact the number on the warranty statement or the packing box. Do not discard the included
documentations, the warranty statement, or the packing box.
Americas: www.buffaloamericas.com
Europe: www.buffalo-technology.com
Asia Pacific: www.buffalo-asia.com
35021131-16
June, 2018

Contents
Chapter 1 Getting Started .............................................9
Diagrams ...........................................................................................9
2-Bay, 4-Bay, 8-Bay Desktop Model .......................................................... 9
4-Bay Rackmount Model .........................................................................12
12-Bay Rackmount Model ....................................................................... 14
Turning the TeraStation On and Off............................................. 16
Creating an Initialization Drive .................................................... 18
Chapter 2 Configuration ............................................. 19
Running the Setup Wizard ............................................................ 19
Setting Up Through Setup Wizard ..........................................................19
Opening Setup Wizard ............................................................................22
Opening Settings .......................................................................... 23
Checking the Device Information from Dashboard ..............................25
Chapter 3 File Sharing ................................................. 26
Configuring Shared Folders ......................................................... 26
Adding a Shared Folder ...........................................................................26
Recycle Bin ................................................................................................28
Read-Only Shares .....................................................................................28
Hidden Shares ..........................................................................................29
Configuring Users ......................................................................... 29
Adding a User ........................................................................................... 29
Importing User Information ....................................................................32
Adding a Group ............................................................................. 32
1

Configuring Access Restrictions for Shared Folders .................. 34
Local Users and Groups ...........................................................................35
Active Directory .......................................................................................36
Configuring Access Restrictions for Subfolders ......................... 39
Enabling Subfolders’ Access Restrictions ..............................................39
Restoring Owner and Permission Settings ............................................41
Chapter 4 Storage Management ................................ 44
RAID Modes ................................................................................... 44
Working with RAID Arrays ............................................................ 45
Using JBOD ...............................................................................................45
Changing RAID Mode ..............................................................................46
Shutting Down the TeraStation Automatically If Error Occurred.........47
Rebuilding the RAID Array Automatically .............................................49
Configuring Actions If A Drive Used for the RAID Array Has Not Been
Discovered ................................................................................................ 50
Configuring a Hot Spare ..........................................................................52
RMM (RAID Mode Manager) ....................................................................54
RAID Scanning..........................................................................................56
Adding an External Drive ............................................................. 57
Connecting an External Drive .................................................................57
Compatibility ...........................................................................................57
Dismounting Drives ...................................................................... 58
Dismounting with the Function Button .................................................58
Dismounting from Settings ....................................................................58
Checking Drives ............................................................................ 59
SSD Trimming ................................................................................ 60
Data Protection Mode on the TS5210DF Series .......................... 61
2

S.M.A.R.T. ....................................................................................... 62
Displaying S.M.A.R.T. Information .........................................................62
Checking Drive Condition .......................................................................63
Formatting Drives ......................................................................... 64
Encrypting Drives .......................................................................... 65
Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely .............................. 65
Drive Quotas .................................................................................. 66
Quotas for Users .......................................................................................66
Quotas for Groups ...................................................................................67
Size Limits .................................................................................................68
Using the TeraStation as an iSCSI Device .................................... 70
Introduction .............................................................................................70
Creating an iSCSI Volume ........................................................................ 71
Connecting or Disconnecting Volumes ..................................................73
Using with Multiple Computers .............................................................. 74
Configuring Access Restrictions .............................................................74
Expanding Volume Sizes .........................................................................77
Deleting Volumes .....................................................................................78
Chapter 5 Backup ........................................................ 80
Backing Up to a Buffalo NAS Device ............................................ 80
Preparing a Backup Destination .............................................................80
Configuring a Backup Job .......................................................................81
Backing Up to rsync-Compatible Devices ................................... 85
Preparing a Backup Destination .............................................................85
Configuring a Backup Job .......................................................................85
Backing Up from rsync-Compatible Devices .............................. 88
Backup Logs .................................................................................. 89
3

Replication ..................................................................................... 92
Preparing a Replication Destination ......................................................92
Configuring a Replication Job ................................................................93
Synchronizing between Source and Destination TeraStations
Periodically ...............................................................................................96
Failover .......................................................................................... 97
Before Configuring Failover ....................................................................98
Usage Restrictions ...................................................................................99
Configuring Failover ..............................................................................100
Replacing to the Backup TeraStation Manually ..................................102
Reconfiguring After Failover Occurs ....................................................102
Synchronizing between Main and Backup TeraStations Periodically 104
Backing Up Your Mac with Time Machine ................................. 105
Chapter 6 Remote Access .......................................... 111
WebAccess ................................................................................... 111
FTP ................................................................................................ 113
Cloud Storage .............................................................................. 114
Configuring Cloud Storage ...................................................................114
Uploading Files to Cloud Storage .........................................................117
Dropbox Sync .............................................................................. 120
Configuring a New Job ..........................................................................120
Changing Dropbox Job Settings ...........................................................122
Creating a Shared Link (Windows Only) ...............................................126
Microsoft Azure Storage Sync .................................................... 126
Creating a New Backup Job ...................................................................126
Creating a New Restore Job ..................................................................132
Changing Job Settings ..........................................................................136
4

Chapter 7 Advanced Features .................................. 139
Antivirus Software ...................................................................... 139
Activating Virus Scanning .....................................................................139
Configuring Security Settings ..............................................................140
Licenses ..................................................................................................142
Connecting Through a Proxy Server ....................................................143
Updating Antivirus Pattern Files ..........................................................143
Configuring Folders as Virus Scanning Targets ...................................144
Virus Scanning .......................................................................................145
Checking the Log ...................................................................................146
Online Help .............................................................................................147
Email Notification ....................................................................... 148
Sleep Mode .................................................................................. 150
Wake-on-LAN .............................................................................. 152
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) ......................................... 153
One PSU Device Is Installed ...................................................................153
Two PSU Devices Are Installed ..............................................................154
Power Supply Failure .................................................................. 156
Port Trunking ............................................................................... 157
Offline Files .................................................................................. 159
Accessing from an NFS Client ..................................................... 160
Encrypting Data Transmission ................................................... 165
Encrypting Settings Data ......................................................................165
Encrypting FTP Transfer Data ...............................................................165
SSL Keys ..................................................................................................165
SNMP ............................................................................................ 166
Saving and Applying Settings .................................................... 167
Saving Settings ......................................................................................167
5

Applying Settings ..................................................................................168
Transferring Another TeraStation’s Settings ............................. 169
Creating a Config File (.nas_config) ......................................................170
Transferring Settings .............................................................................170
Restoring Factory Defaults ......................................................... 171
Initializing from Settings ......................................................................171
Initializing with the USB Initialization Drive .......................................172
Resetting the Administrator Password ..................................... 173
Logs .............................................................................................. 173
Displaying TeraStation’s Logs ...............................................................173
Transferring Logs to the Syslog Server ................................................174
Creating a Link to the Logs in the Shared Folder ................................175
Changing Archive Rules for File Access Logs .......................................177
Updating the Firmware ............................................................... 178
Updating Manually ................................................................................178
Updating Automatically ........................................................................179
Configuring Update Notification ............................................... 180
Name, Date, Time, and Language .............................................. 182
Beep Alerts .................................................................................. 184
LCD and LEDs ............................................................................... 184
Proxy Server ................................................................................ 185
Jumbo Frames ............................................................................. 186
Changing the IP Address ............................................................ 188
Boot Authentication ................................................................... 189
Notes Before Use .................................................................................... 190
Important Notice ...................................................................................190
Setting Up the Authentication Server on a Windows PC ....................190
Configuring Boot Authentication on the TeraStation ......................... 191
6

If the TeraStation Cannot Be Accessed .................................................192
Chapter 8 Drive Replacement ................................... 195
Replacing Drives on the TS51210RH Series .............................. 195
LEDs ........................................................................................................195
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is On .........195
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is Off ........197
Using RAID 0 ........................................................................................... 197
Using a Hot Spare ...................................................................................198
Replacing Drives on Another Unit Series Other Than the
TS51210RH Series ....................................................................... 199
LEDs ........................................................................................................199
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is On .........199
Using a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is Off .......................202
Using RAID 0 ........................................................................................... 202
Using a Hot Spare ...................................................................................203
Replacing SSDs on the TS5210DF Series When Data Protection
Mode Is Enabled .......................................................................... 204
Using RAID 1 ........................................................................................... 204
Using RAID 0 ........................................................................................... 205
Using JBOD .............................................................................................206
Replacing a Non-Malfunctioning Drive ..................................... 206
Chapter 9 Utilities ...................................................... 208
NAS Navigator2 for Windows ..................................................... 208
Mounting as a Network Drive ...............................................................211
Changing the IP Address .......................................................................211
NAS Navigator2 for macOS ........................................................ 212
Mounting as a Network Drive ...............................................................213
7

Changing the IP Address .......................................................................213
NovaBACKUP ............................................................................... 214
Chapter 10 Appendix ................................................ 215
TeraStation Does Not Work Properly ......................................... 215
Power LED Keeps Blinking ....................................................................215
Booting the TeraStation in Emergency Mode ......................................216
Cleaning the Dustproof Filter .................................................... 216
LCD Panel ..................................................................................... 219
Modes .....................................................................................................219
Errors .......................................................................................................220
Status ......................................................................................................221
Default Settings .......................................................................... 223
Specifications .............................................................................. 224
Chapter 11 Regulatory Compliance Information .... 227
For Customers in All Regions ..................................................... 227
For Customers in the United States ........................................... 227
For Customers in Europe ............................................................ 228
For Customers in Taiwan ............................................................. 231
8
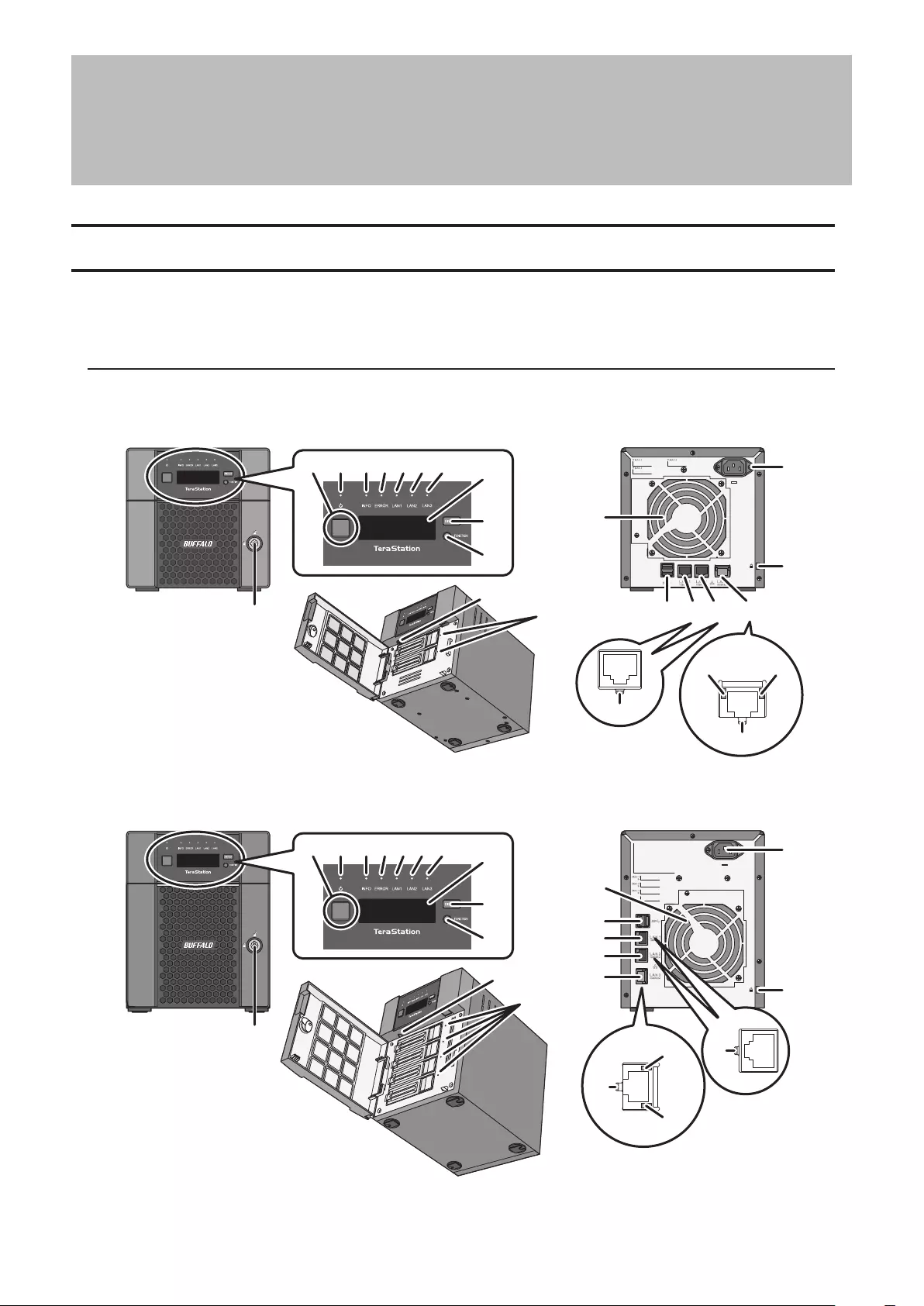
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Diagrams
Depending on the number or type of drives in the unit, the model name will be different. Check the sticker on the
packing box for your unit’s model name.
2-Bay, 4-Bay, 8-Bay Desktop Model
TS5210DN, TS5210DF
11
14
19
20
15 16 17 18
21
12
13
24
22 23
12345678
9
10
TS5410DN
13
12
19
20
14
15
16
17
18
11 21
22
23
24
12345678
9
10
9
TS5810DN
11
14 19
20
15
16
17
18
21
12 13
12345678910
15
24
22
23
1 Power Button ( )
To power on, connect the power cable and wait for 10 seconds, then press the power button. To power off,
press and hold the power button for 3 seconds.
If the TeraStation beeps, pressing this button for a short period will stop the beeping.
2 Power LED
When the TeraStation is on, the LED glows green.
3 Info LED
If there is a status message, the amber info LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the status message.
4 Error LED
If there is an error, the red error LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the error message.
5 LAN1 LED
When LAN port 1 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
6 LAN2 LED
When LAN port 2 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
7 LAN3 LED
When LAN port 3 is connected, this LED glows blue. It blinks when the connection is active.
8 LCD Panel
This display shows the status of many TeraStation settings. It also displays errors and messages when available.
9 Display Button
Switches between the different display modes. Also, if the TeraStation is beeping, press this button to stop it.
10 Function Button
Use this button for dismounting USB devices, rebuilding RAID arrays, configuring failover, stopping the
TeraStation’s beeping, and initializing settings using a USB drive.
11 Drive Lock ( )
Open the front panel with the key to replace drives or access the init button.
10

12 Init Button
Press and hold this button to initialize the TeraStation’s admin username and password, IP settings, SSL, and
service port restriction settings to their factory default values. The effects of this button can be changed in
Settings.
13 Status LEDs
Normally, these LEDs blink green when drives are accessed. If a drive fails, its LED will turn red.
14 Fan
Spins to avoid overheating inside. Do not block the fan.
15 USB 3.0 Port ( )
Compatible Buffalo USB drives, USB memory devices, and USB UPS connections can be connected. USB hubs
are not compatible.
On the TS5810DN series TeraStations, the USB 3.0 port in front is covered by a protector. Remove it before use.
16 LAN Port 1 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
17 LAN Port 2 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
18 LAN Port 3 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 10 Gbps
if using the included Ethernet or category 6A cable.
Note: To communicate at up to 10 Gbps, all network devices must be compatible with 10GbE.
19 Power Connector
Use the included power cable to connect to a UPS, surge protector, or outlet.
20 Anti-Theft Security Slot ( )
Use this slot to secure your TeraStation with a cable lock (not included).
21 Link LED
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network.
22 Link LED on 100 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps, and 5 Gbps
Glows amber when the unit is connected to a network at 100 Mbps or 2.5 and 5 Gbps.
23 Link LED on 1000 Mbps
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network at 1000 Mbps.
24 Link LED on 10 Gbps
Glows blue when the unit is connected to a network at 10 Gbps.
11
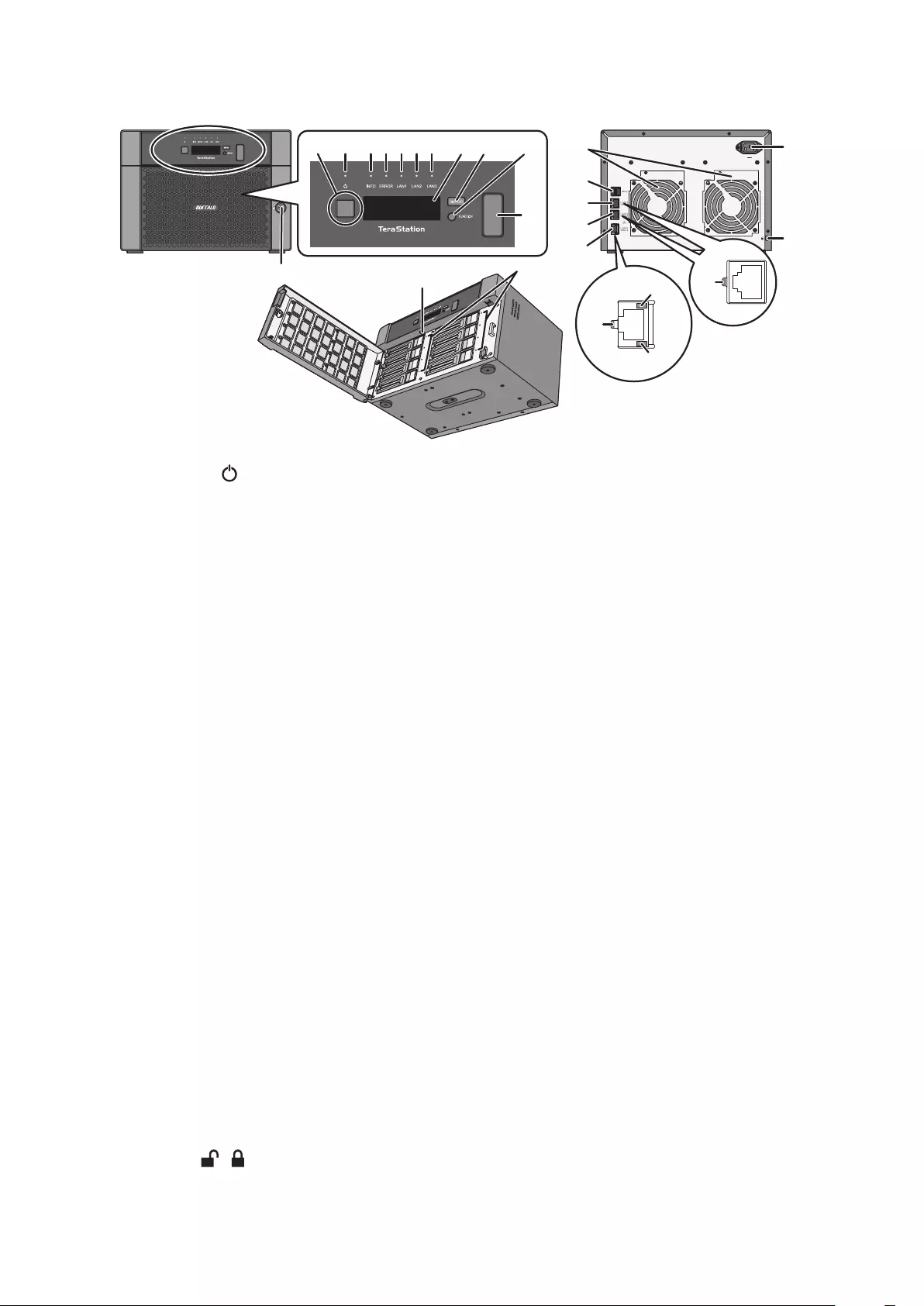
4-Bay Rackmount Model
TS5410RN
11 19 11 20 2345 11 1911 10 136 78
12 20 13 18 17 121614 15
21
24
22 23
1 Power Button ( )
To power on, connect the power cable and wait for 10 seconds, then press the power button. To power off,
press and hold the power button for 3 seconds.
If the TeraStation beeps, pressing this button for a short period will stop the beeping.
2 Info LED
If there is a status message, the amber info LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the status message.
3 Error LED
If there is an error, the red error LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the error message.
4 LAN1 LED
When LAN port 1 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
5 LAN2 LED
When LAN port 2 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
6 LAN3 LED
When LAN port 3 is connected, this LED glows blue. It blinks when the connection is active.
7 LCD Panel
This display shows the status of many TeraStation settings. It also displays errors and messages when available.
8 Display Button
Switches between the different display modes. Also, if the TeraStation is beeping, press this button to stop it.
9 Function Button
Use this button for dismounting USB devices, rebuilding RAID arrays, configuring failover, stopping the
TeraStation’s beeping, and initializing settings using a USB drive.
12
10 Init Button
Press and hold this button with something pointed to initialize the TeraStation’s admin username and
password, IP settings, SSL, and service port restriction settings to their factory default values. The effects of this
button can be changed in Settings.
11 Status LEDs
Normally, these LEDs blink green when drives are accessed. If a drive fails, its LED will turn red.
12 Fan
Spins to avoid overheating inside. Do not block the fan.
13 USB 3.0 Port ( )
Compatible Buffalo USB drives, USB memory devices, and USB UPS connections can be connected. USB hubs
are not compatible.
14 LAN Port 1 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
15 LAN Port 2 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
16 LAN Port 3 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 10 Gbps
if using the included Ethernet or category 6A cable.
Note: To communicate at up to 10 Gbps, all network devices must be compatible with 10GbE.
17 Power Connector
Use the included power cable to connect to a UPS, surge protector, or outlet.
18 Anti-Theft Security Slot ( )
Use this slot to secure your TeraStation with a cable lock (not included).
19 Serial Number
This sticker shows the TeraStation’s serial number.
20 UID Button
Press the UID button on the front or the back of the unit to cycle the blue LED on and off.
21 Link LED
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network.
22 Link LED on 100 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps, and 5 Gbps
Glows amber when the unit is connected to a network at 100 Mbps or 2.5 and 5 Gbps.
23 Link LED on 1000 Mbps
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network at 1000 Mbps.
24 Link LED on 10 Gbps
Glows blue when the unit is connected to a network at 10 Gbps.
13

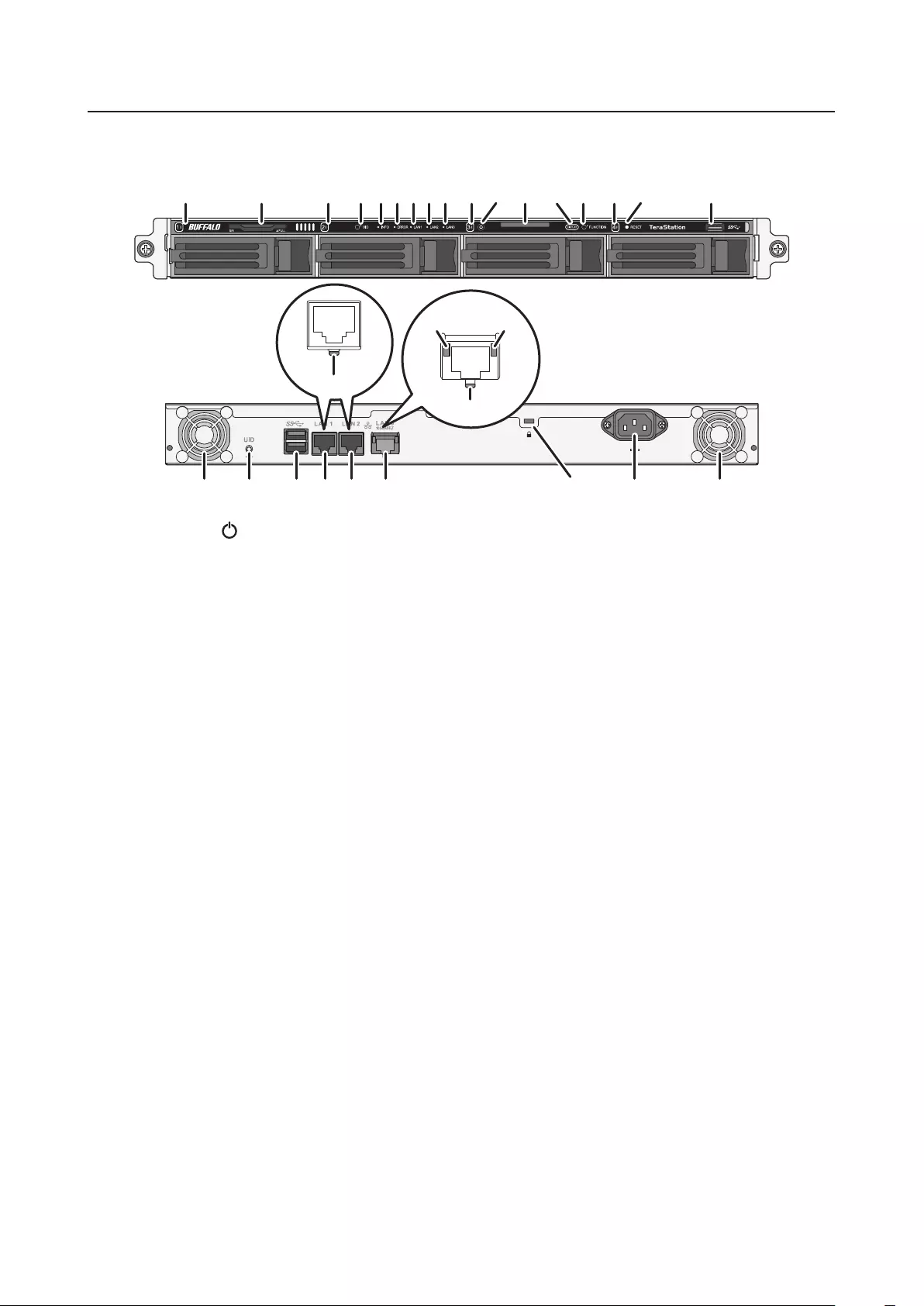
12-Bay Rackmount Model
TS51210RH
10
1
3
7
6
5
4
2
8
9
1211 14 15 16 17 1813
19
22
2120
1 Power Button ( )
To power on, connect the power cable and wait for 10 seconds, then press the power button. To power off,
press and hold the power button for 3 seconds.
If the TeraStation beeps, pressing this button for a short period will stop the beeping.
2 Power LED ( )
When the TeraStation is on, the LED glows green.
3 Error LED ( )
If there is an error, the red error LED will light up. Check the Settings interface or NAS Navigator2 to see the
error message.
4 Reset Button
Press and hold this button with something pointed to initialize the TeraStation’s admin username and
password, IP settings, SSL, and service port restriction settings to their factory default values. The effects of this
button can be changed in Settings.
5 Function Button
Use this button for rebuilding RAID arrays, configuring failover, stopping the TeraStation’s beeping, and
initializing settings using a USB drive.
14

6 LAN LED ( )
When any LAN ports are connected, this LED glows blue. It blinks when the connection is active.
7 Info LED ( )
If there is a status message, the amber info LED will light up. Check the Settings interface or NAS Navigator2 to
see the status message.
8 Drive Status LED ( )
This LED blinks blue when drives are accessed.
9 Drive Error LED ( )
Normally, this LED is extinguished. If a drive fails, its LED will turn red.
10 USB 2.0 Port ( )
Compatible Buffalo USB drives, USB memory devices, and USB UPS connections can be connected. USB hubs
are not compatible.
11 Power Connector
Use the included power cable to connect to a UPS, surge protector, or outlet.
12 Fan
Spins to avoid overheating inside. Do not block the fan.
13 Micro-USB Port
Factory use only.
14 USB 3.0 Port ( )
Compatible Buffalo USB drives, USB memory devices, and USB UPS connections can be connected. USB hubs
are not compatible.
15 LAN Port 1 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
16 LAN Port 2 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 1000
Mbps.
17 LAN Port 3 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 10 Gbps
if using the included Ethernet or category 6A cable.
Note: To communicate at up to 10 Gbps, all network devices must be compatible with 10GbE.
18 LAN Port 4 ( )
Connect an Ethernet cable to use this port for your network. It is available for communicating at max. 10 Gbps
if using the included Ethernet or category 6A cable.
Note: To communicate at up to 10 Gbps, all network devices must be compatible with 10GbE.
19 Link/Act LED
Glows and blinks green when the unit is connected to a network.
20 Link LED on 100 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps, and 5 Gbps
Glows amber when the unit is connected to a network at 100 Mbps or 2.5 and 5 Gbps.
15
21 Link LED on 1000 Mbps
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network at 1000 Mbps.
22 Link LED on 10 Gbps
Glows blue when the unit is connected to a network at 10 Gbps.
Turning the TeraStation On and Off
Note: Do not disconnect or reconnect the internal drives while turning on or off the TeraStation.
Press the power button on the TeraStation to turn it on.
To turn off the TeraStation, press and hold the power button for 3 seconds. Don’t unplug the TeraStation without
turning it off first. You can also shut it down and restart it remotely from Settings.
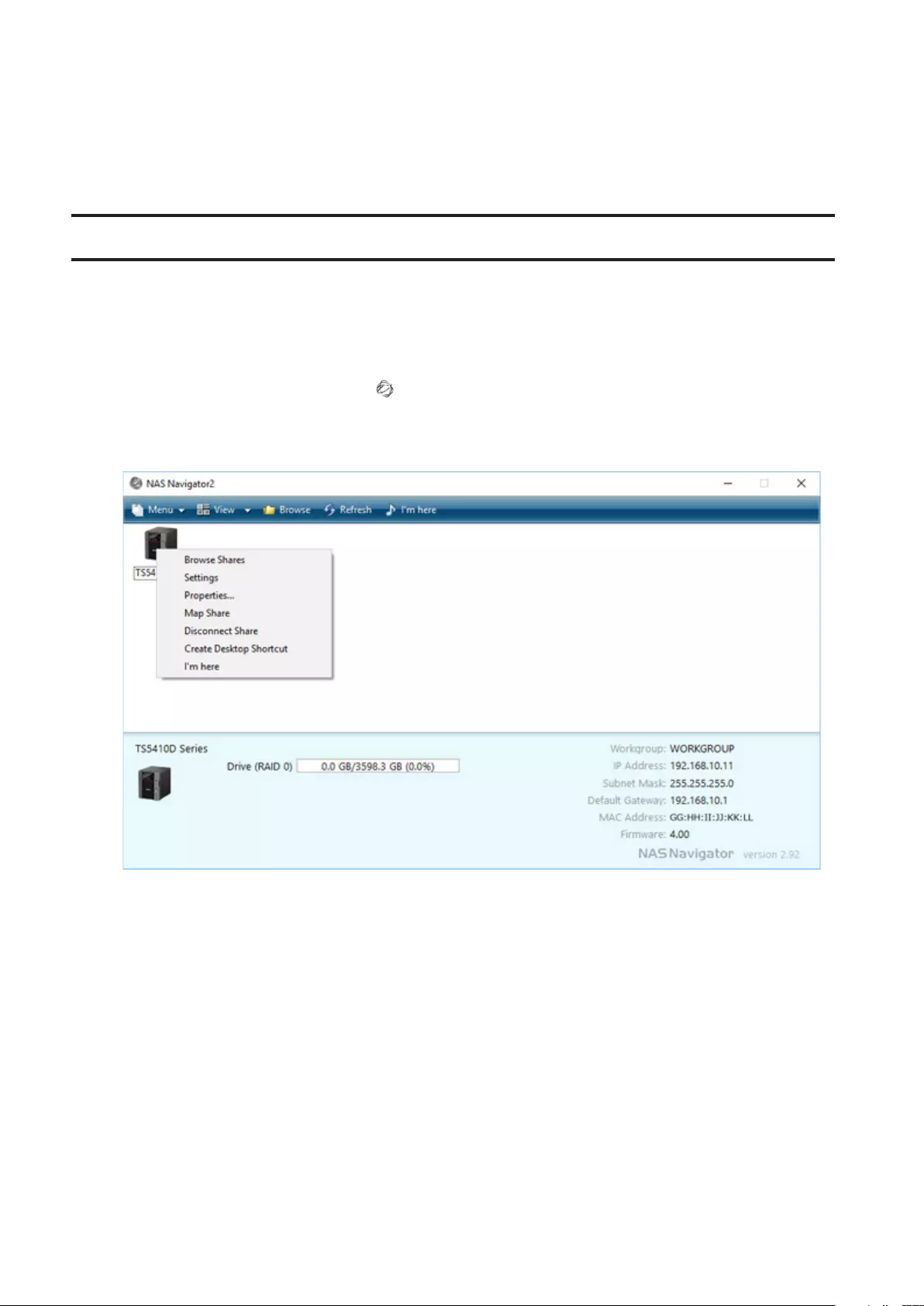
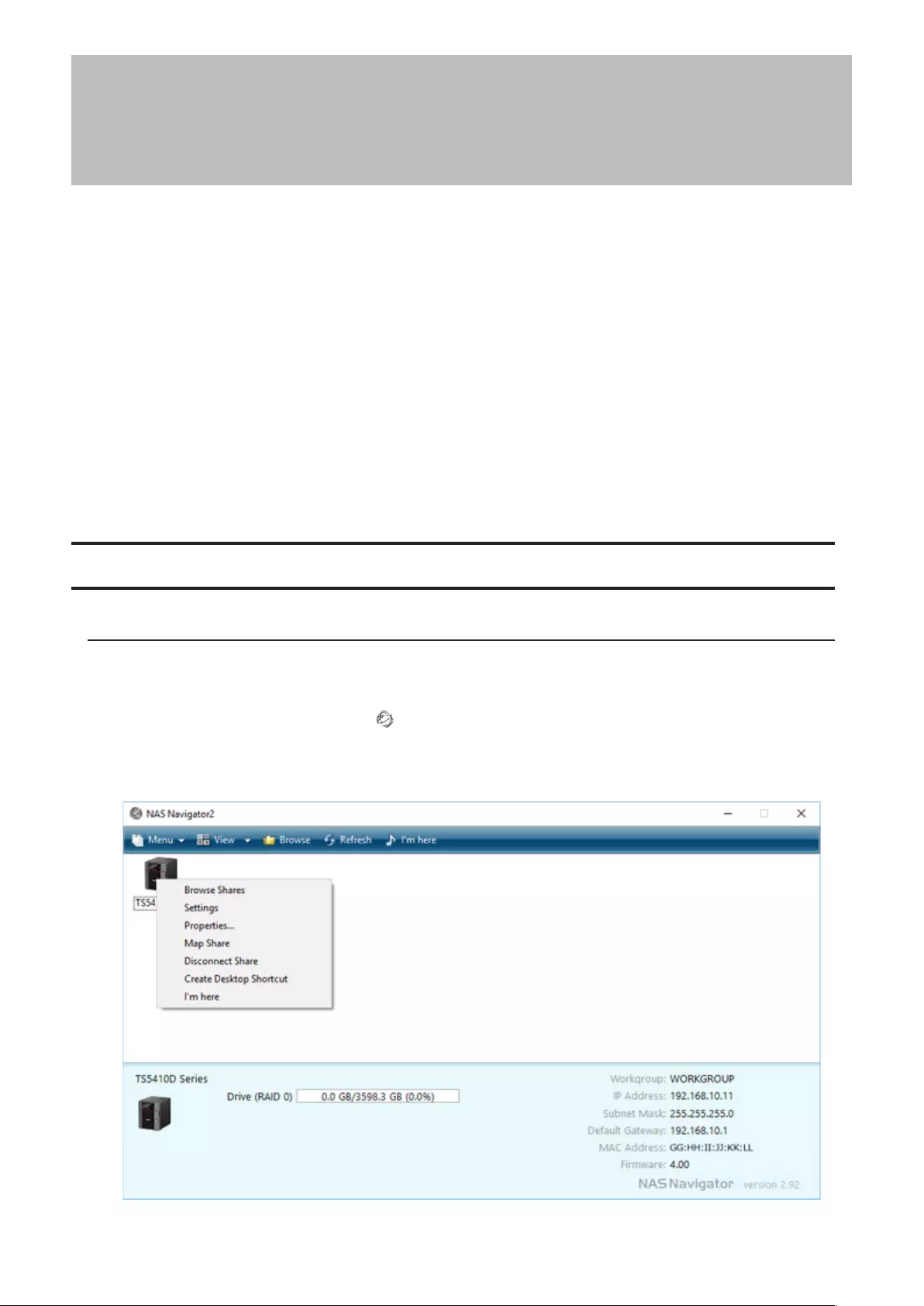
1 Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click your TeraStation’s icon and select Settings. For macOS, select the TeraStation’s icon while holding
down the control key, then select Settings.
16
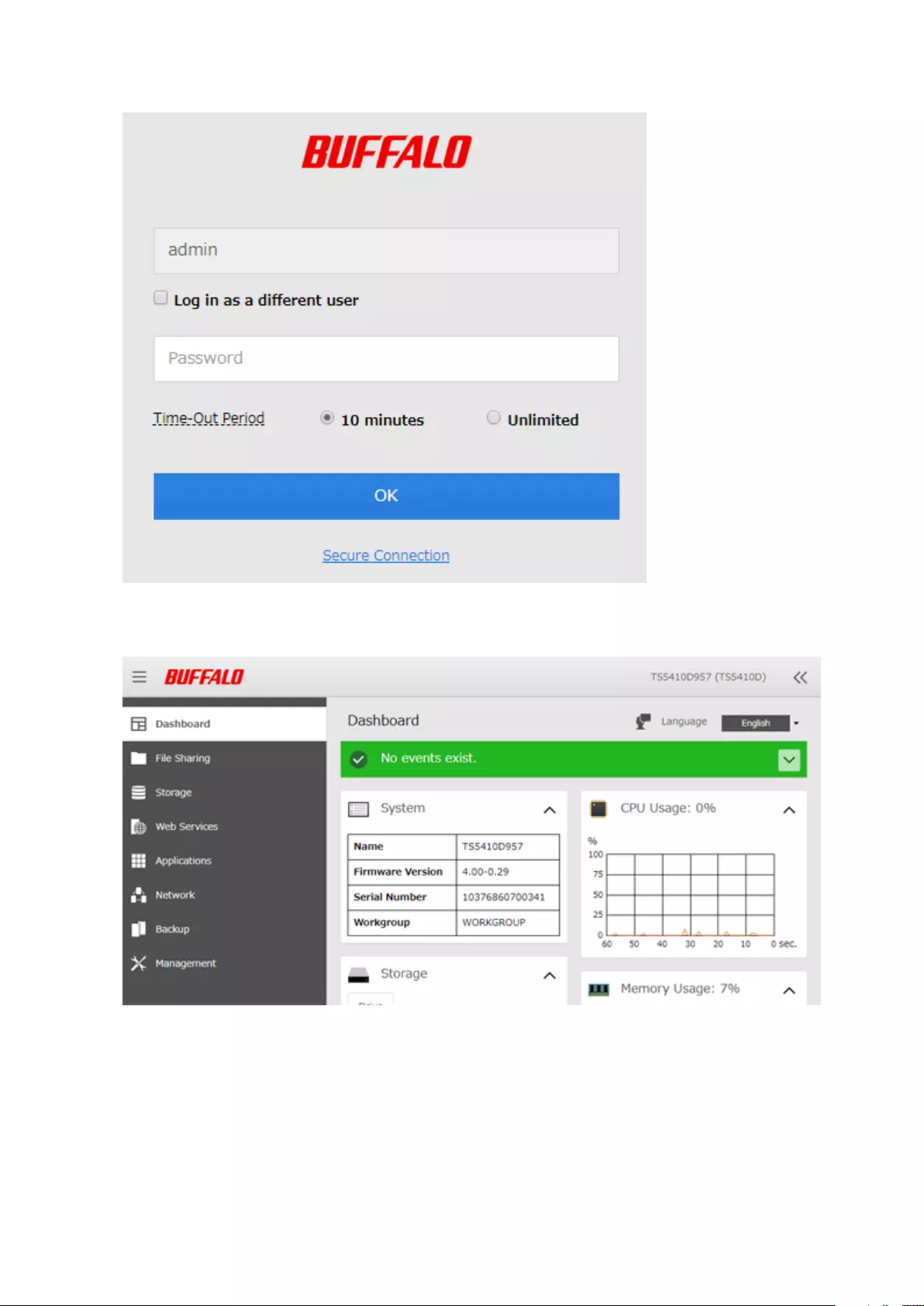
3 Enter the username and password, then click OK.
Note: The default username and password are “admin” and “password”.
4 Settings will open.
17
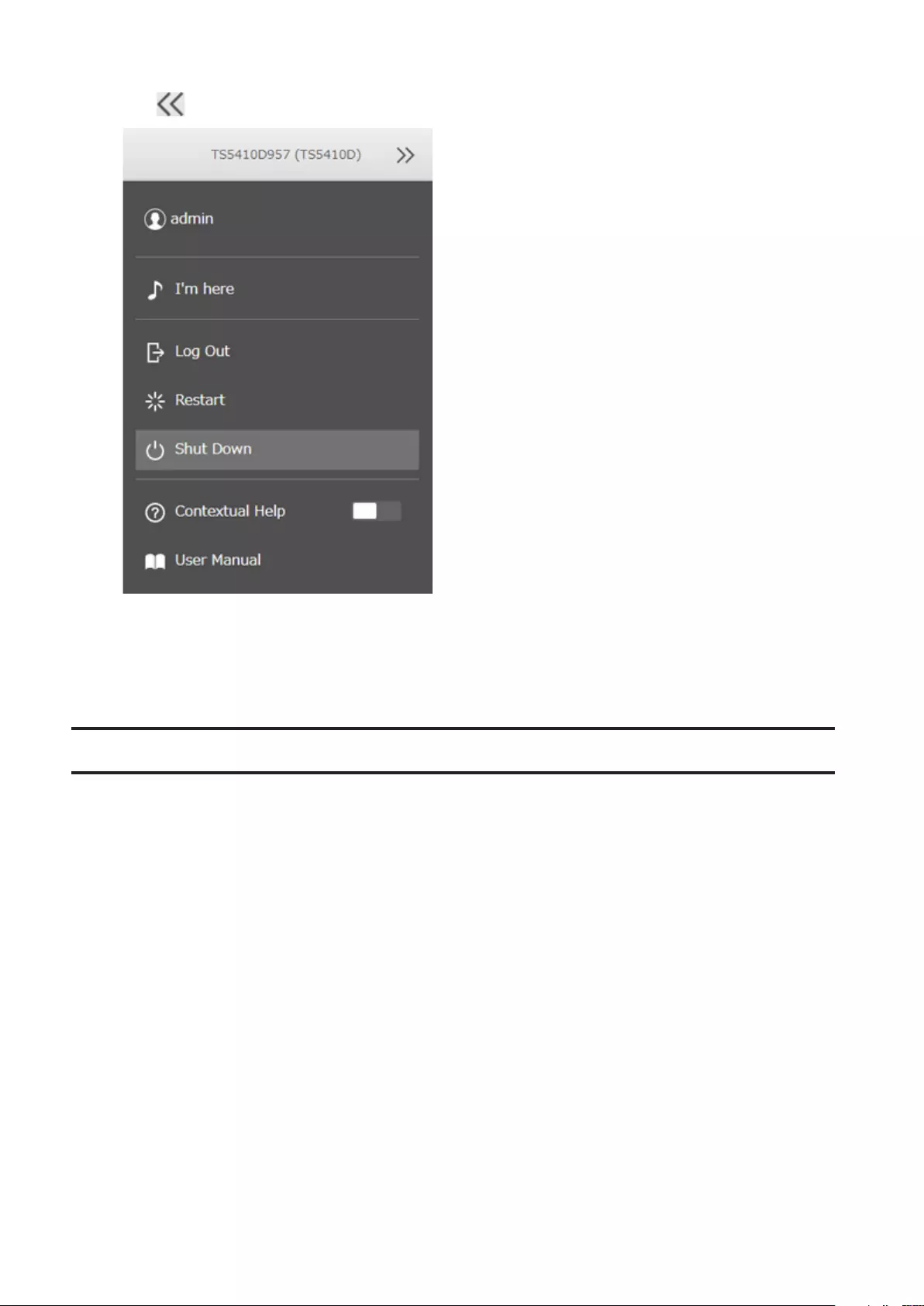
5 Click at the top-right of Settings and choose Shut Down.
6 Click Yes.
7 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
When the power LED on the front of the TeraStation turns off, the shutdown process is complete.
Creating an Initialization Drive
We recommend creating an initialization drive as soon as possible. This USB drive can be used to initialize the
TeraStation’s settings to its factory default values or recover the system if your TeraStation encounters an error that
prevents the unit from booting. For the detailed procedure, refer to the “Creating an Initialization Drive” subsection
in chapter 7.
18
Chapter 2 Configuration
Configure and manage your TeraStation using the Settings interface, accessible from a browser window. Open the
interface using the procedure below or type the TeraStation’s IP address into the URL field of your browser.
Notes:
• Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer 9 or later, and Safari 9 or later are supported. If you
have difficulty viewing Settings, check the following:
◦If there are a large number of registered users, groups, or shared folders, use another browser instead of
Internet Explorer.
◦If you have a proxy server enabled in the browser settings, configure the exception settings for Settings or
disable the proxy server.
◦With Internet Explorer, set security to Local intranet. On Windows Server operating systems, higher-level
security is configured by default. Set the security to a lower level temporarily.
• From a Mac, you can also use Bonjour to log in to Settings. Navigate to Bookmarks > Bonjour > TeraStation name
from the menu bar of Safari. If you don’t see “Bonjour” in the Bookmarks menu, click Safari > Preferences and
select “Include Bonjour in the Bookmarks menu” under “Advanced”.
Running the Setup Wizard
Setting Up Through Setup Wizard
When you access Settings for the first time, or after initializing the TeraStation’s settings, the setup wizard will
automatically be displayed. To set up the TeraStation using the wizard, follow the procedure below.
1 Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click your TeraStation’s icon and select Settings. For macOS, select the TeraStation’s icon while holding
down the control key, then select Settings.
19
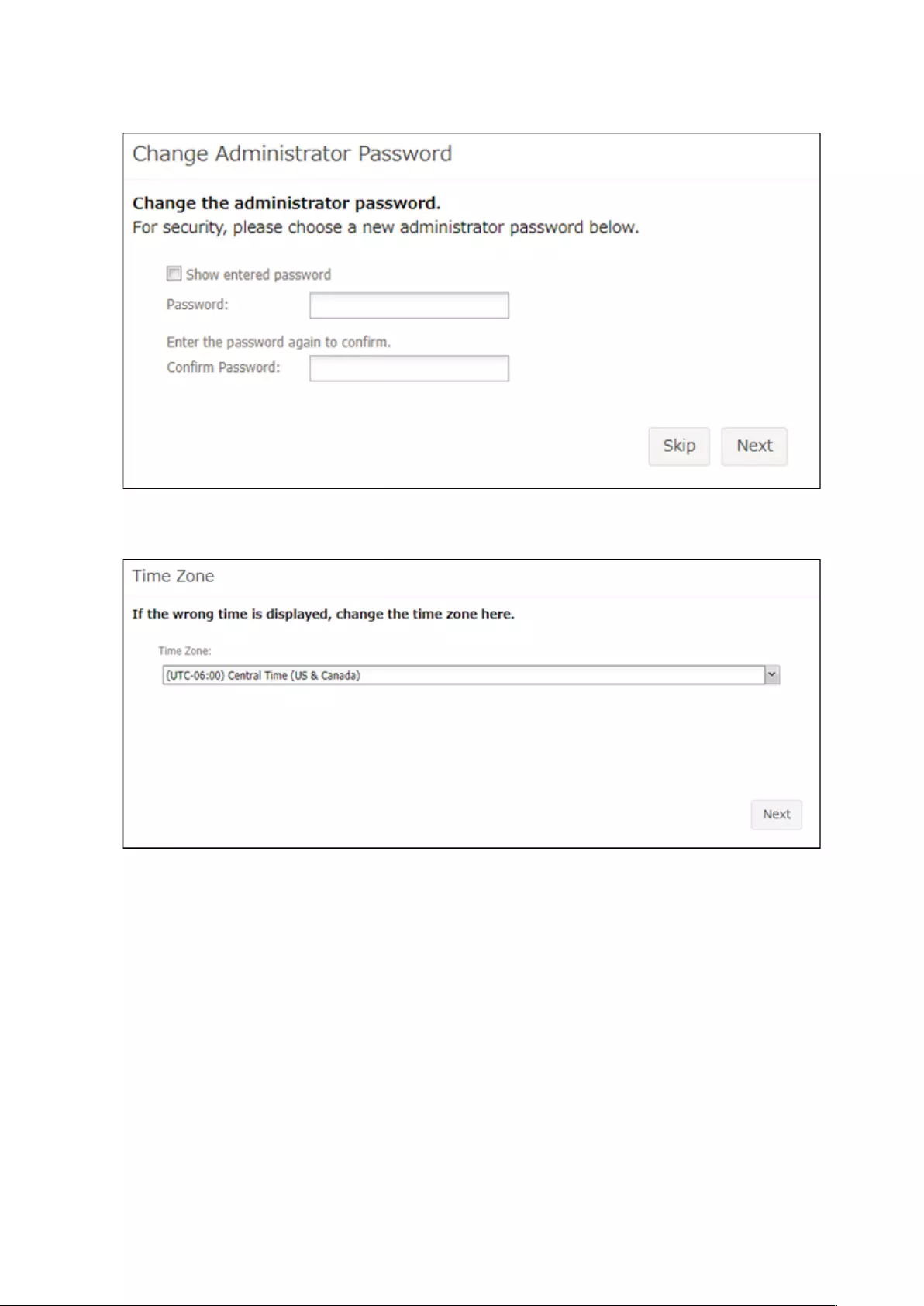
3 The password settings page will appear. Enter the desired new administrator password and click Next. If you
click Skip, the administrator password will not change from the default value (“password”).
4 The time zone settings page will be displayed. If you need to change the time zone from that which is currently
displayed on the page, select it from the drop-down list and click Next.
20
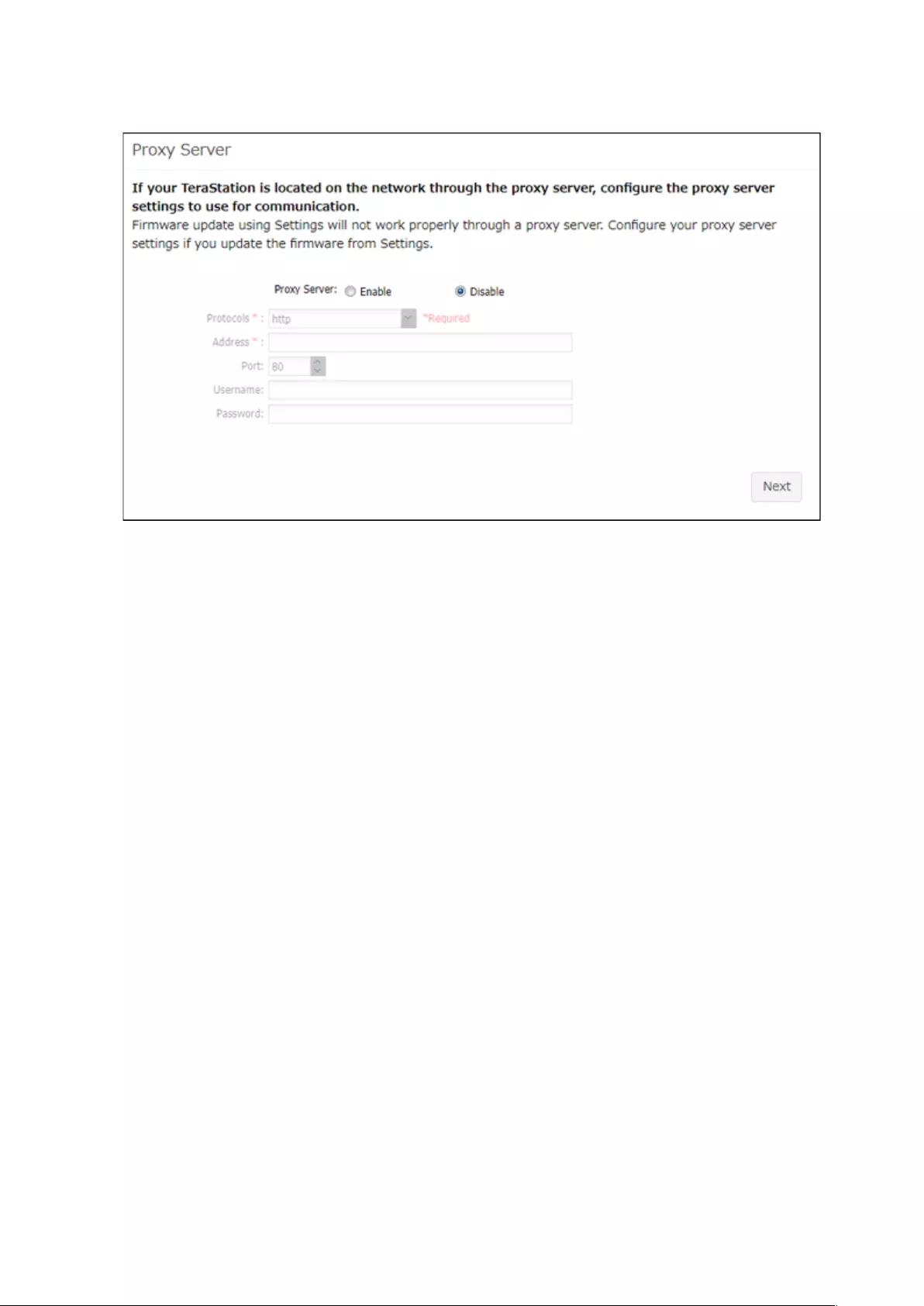
5 The proxy server settings page will be displayed. If you place the TeraStation under a proxy network, set your
proxy settings. Click Next.
6 The RAID settings page will be displayed. To change the RAID mode from the default mode, select the desired
RAID mode and click Next, then click Start on the next page. The “Confirm Operation” screen will open so enter
the confirmation number and click OK. Changing the RAID mode will begin.
21

If you want to keep the RAID mode as is, select “Keep current RAID mode” and click Next.
Note: The RAID settings page will not be displayed if using the TS5210DN series.
7 The folder path to access shared folders will be displayed and the setup will finish.
Opening Setup Wizard
You may run the setup wizard even after the initial setup or initialization. To launch the setup wizard again, follow
the procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Restore/Erase”.
22
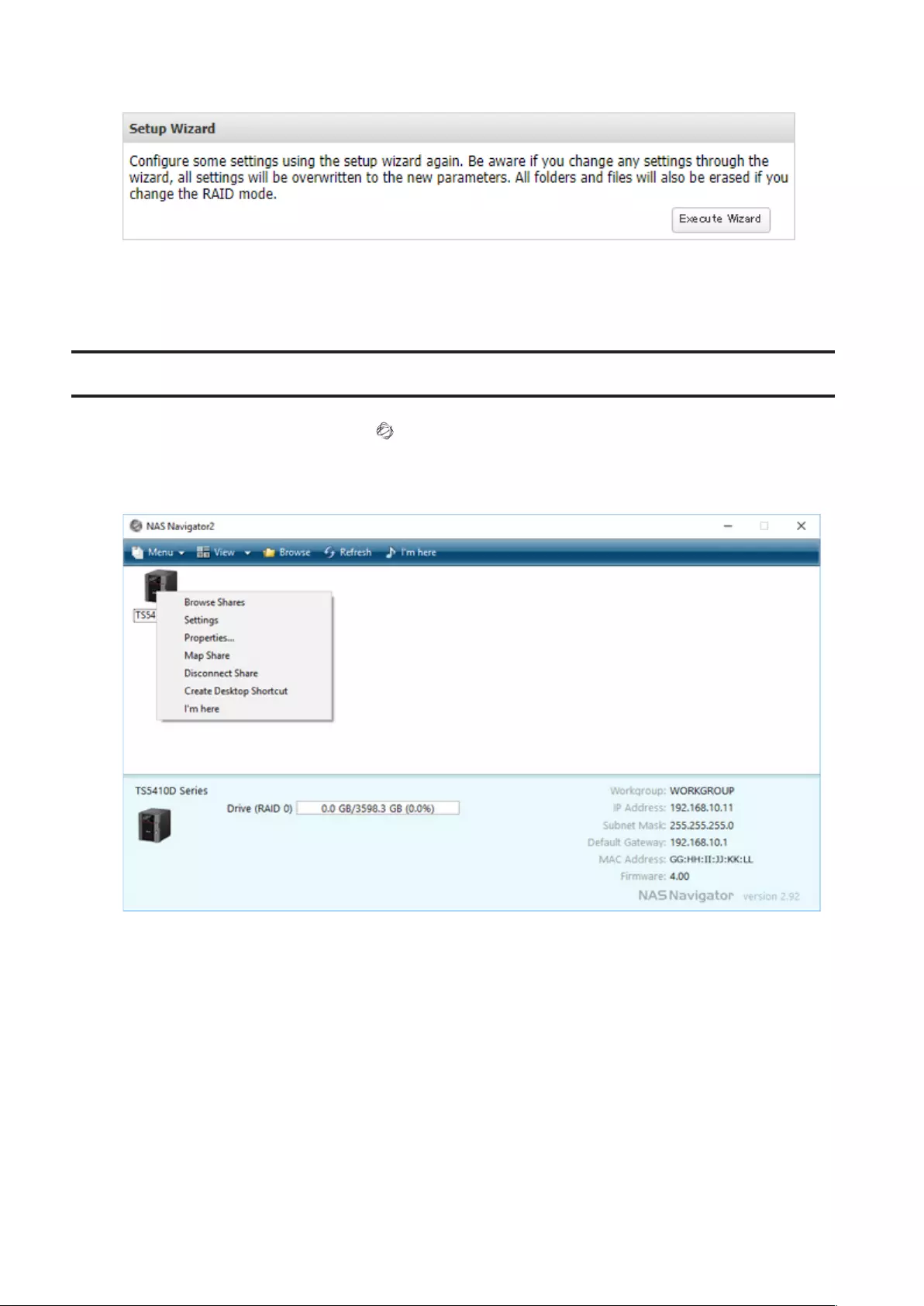
3 Click Execute Wizard.
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 Follow the instructions on the screen and finish the setup wizard.
Opening Settings
1 Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click your TeraStation’s icon and select Settings. For macOS, select the TeraStation’s icon while holding
down the control key, then select Settings.
23
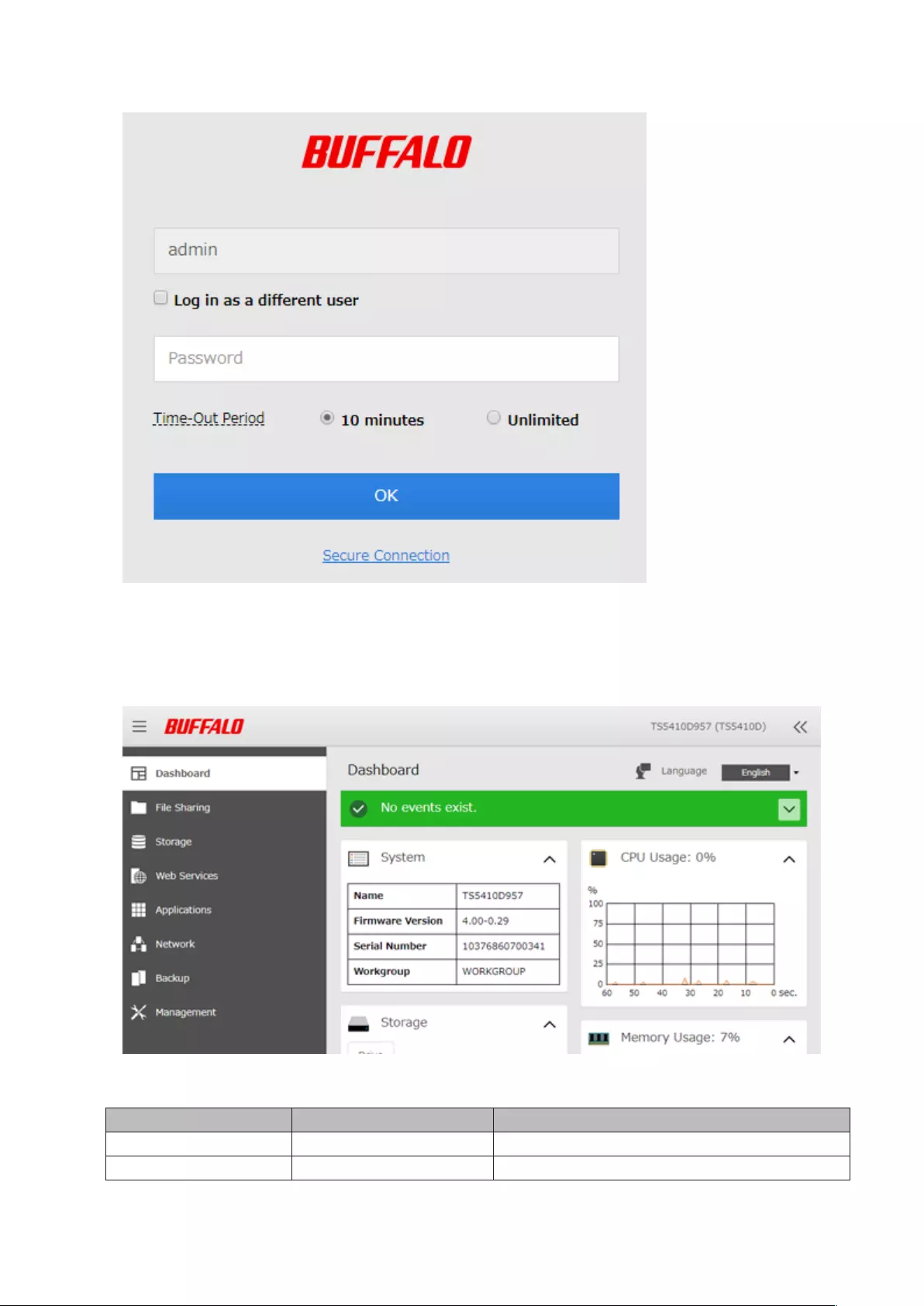
3 Enter the username and password, then click OK.
Notes:
• If the time-out period is set to “10 minutes”, you will be logged out of Settings after 10 minutes of inactivity.
• Click Secure Connection to log in using an encrypted connection.
4 Settings will open.
Notes:
• Username/Password Combinations:
Username Password Settings Available
admin (default) password (default) All
guest blank System information (read-only)
24
Username Password Settings Available
Your username Your password
If a user is assigned as an administrator, all settings
are available. If assigned to another group, only
system information (read-only) is available.
• Click at the top-right of Settings and choose I’m here to play a tone from the TeraStation for easy location.
Checking the Device Information from Dashboard
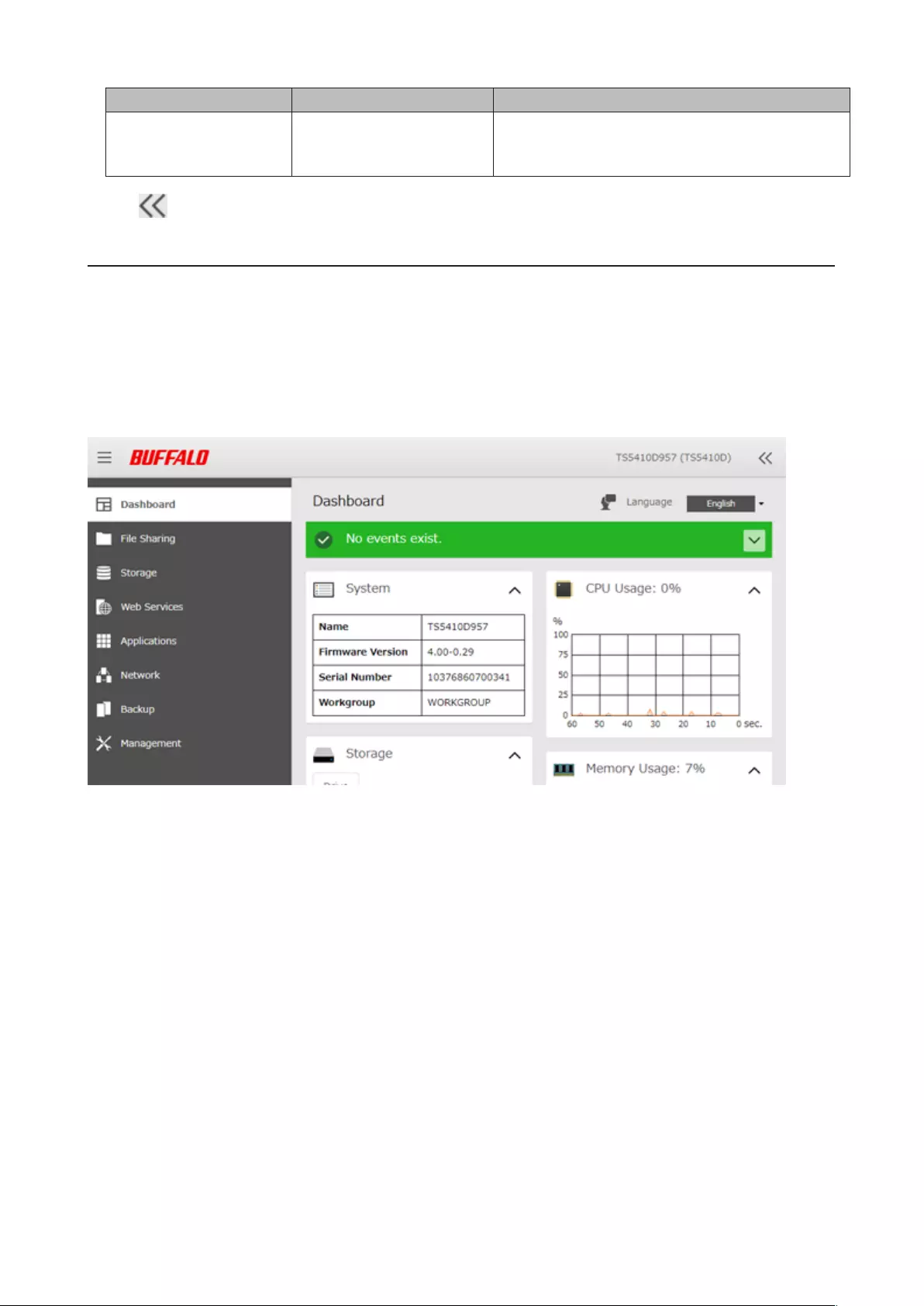
When opening the Settings interface, the Dashboard page will appear first. Dashboard will show the following
device information:
• System information, such as hostname, firmware version, IP address etc.
• Drive information, such as used capacity of internal drives, LVM volumes, iSCSI volumes etc.
• CPU usage
• System memory usage
• Network information, such as IP address, link speed, sent and received rates etc.
Note: If increasing the number of files on the TeraStation, it will raise the memory usage of the TeraStation. This
memory usage will decrease after the specific time passes. To reduce the memory usage immediately, try the
following operations:
• Restarting the TeraStation.
• Dismounting the USB drive.
25
Chapter 3 File Sharing
Configuring Shared Folders
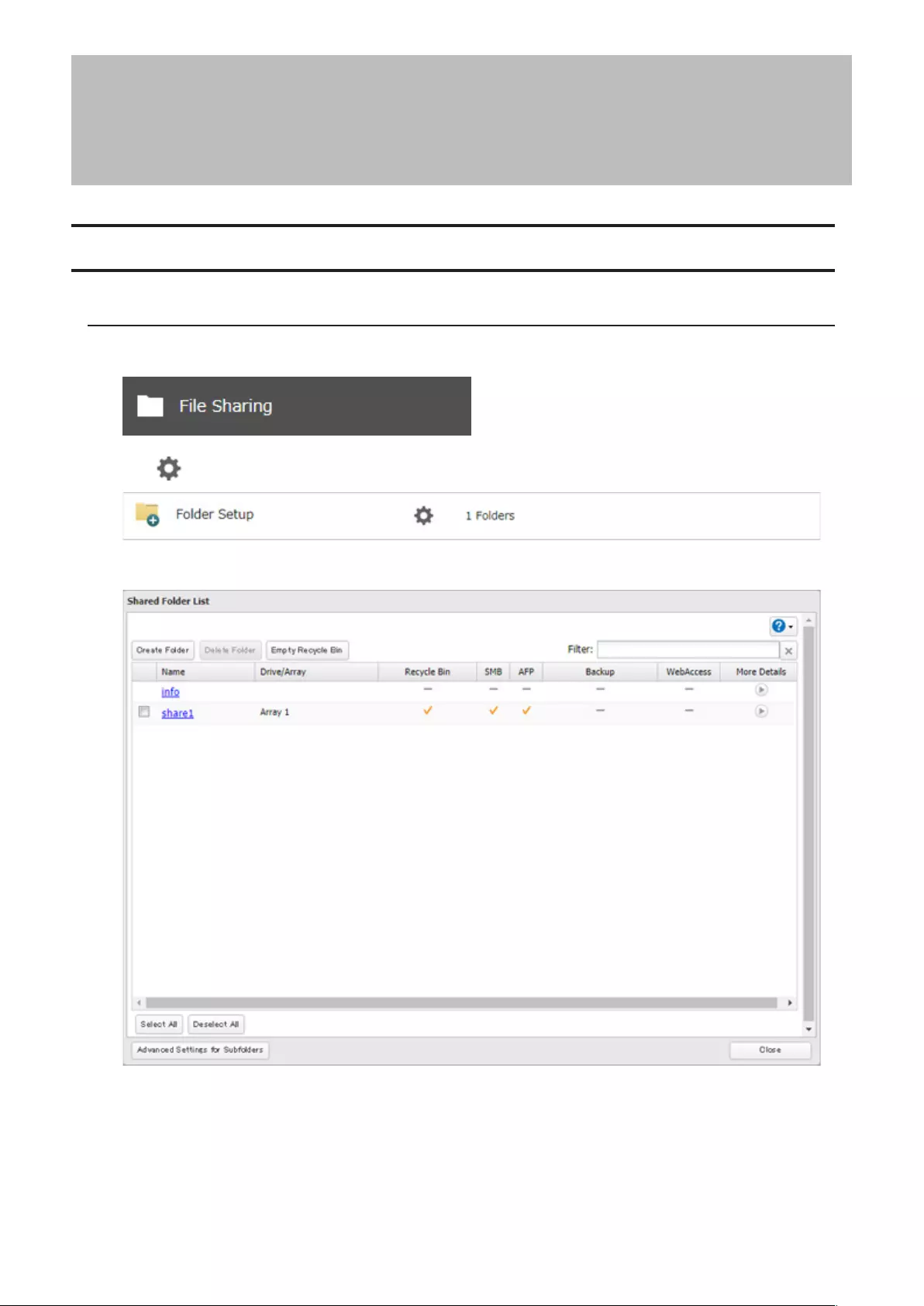
Adding a Shared Folder
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Click Create Folder.
26
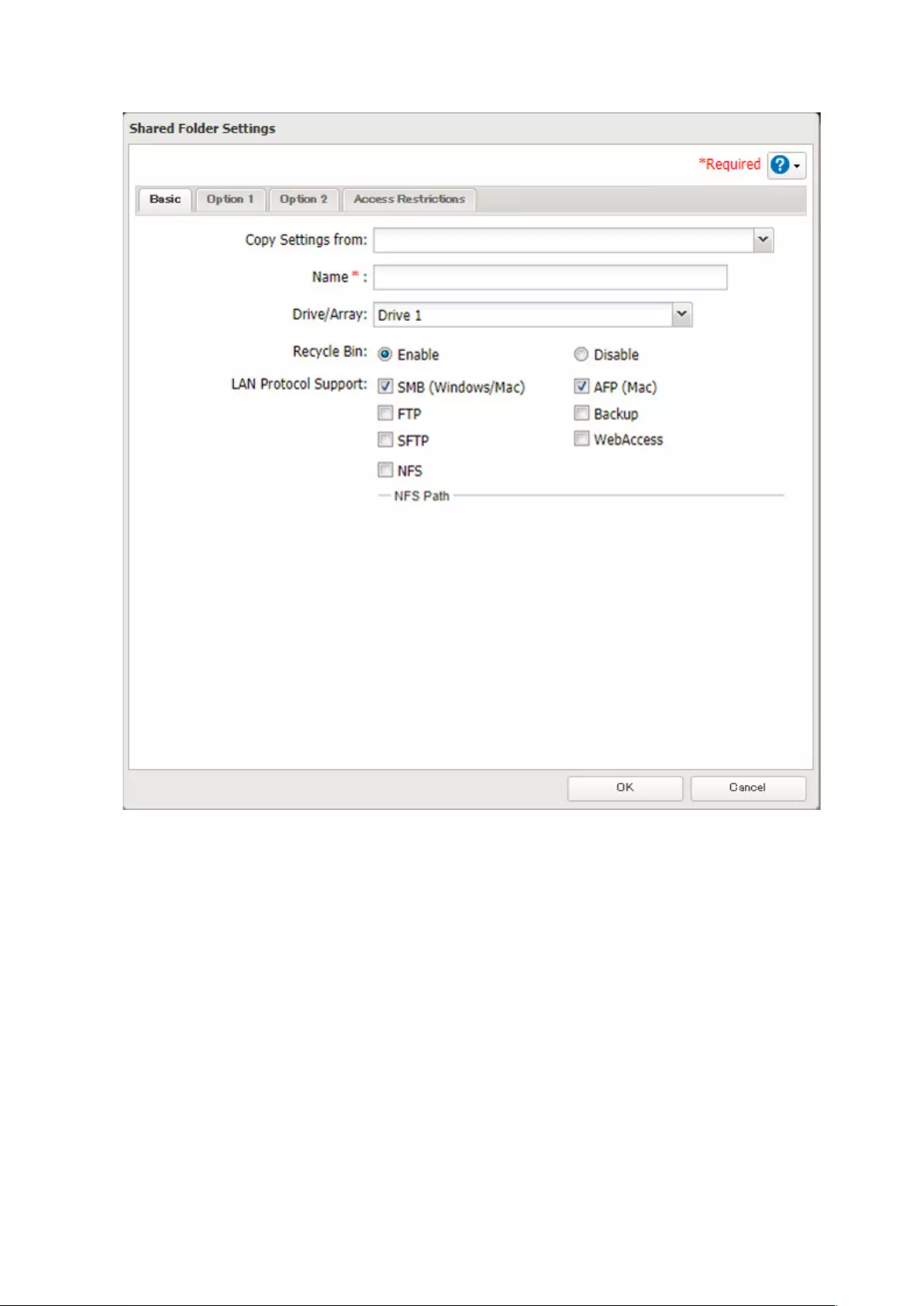
4 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Names may contain up to 27 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), and underscores (_). Multibyte characters are
supported. The first character should not be a symbol.
• When you click the Option 1 tab, you can enter the folder description. Descriptions may contain up to 75
alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces. Multibyte characters are supported. The first
character should not be a space.
• You may create up to 400 shared folders.
• If the names of shared folders accessed via AFP and FTP connections contain multibyte characters, configure the
client language in Management > Name/Time/Language to match the characters. If the setting does not match,
the shared folder name will not be displayed correctly.
• The following characters are handled differently by macOS and Windows. Avoid using these characters when
sharing data between macOS and Windows:
― ~ ∥ - ¢ £ ¬
• Windows does not support some characters that macOS and the TeraStation allow. If you create a filename on
a Mac using any of the following symbols, it will not display correctly on a Windows computer. You may have to
connect to the TeraStation via AFP in order to display or copy files that contain these symbols in their filenames.
? ] [ / \ = + > < ; : " , | *
27

• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a shared folder as these words are reserved for internal
use by the TeraStation: authtest, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, msdfs_root, mt-daapd, printers, ram, spool,
usbdisk x (where “x” is a number, for example: usbdisk1)
• Don’t use the following unsupported characters in shared folder names, workgroup names, or filenames:
①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫⑬⑭⑮⑯⑰⑱⑲⑳ⅠⅡⅢⅣⅤⅥⅦⅧⅨⅩ
ⅰⅱⅲⅳⅴⅵⅶⅷⅸⅹ㎜㎝㎞㎎㎏㏄㎡№㏍℡㊤㊥㊦㊧㊨㈱㈲㈹㍾㍽㍼㍻㍉㌔㌢㍍㌘㌧㌃㌶㍑㍗㌍㌦㌣㌫㍊
㌻¦'"〝〟∮Σ∟⊿
纊褜鍈銈蓜俉炻昱棈鋹曻彅丨仡仼伀伃伹佖侒侊侚侔俍偀倢俿倞偆偰偂傔僴僘兊兤冝冾凬刕劜劦勀勛匀匇匤
卲厓厲叝﨎咜咊咩哿喆坙坥垬埈埇﨏塚增墲夋奓奛奝奣妤妺孖寀甯寘寬尞岦岺峵崧嵓﨑嵂嵭嶸嶹巐弡弴彧德
忞恝悅悊惞惕愠惲愑愷愰憘戓抦揵摠撝擎敎昀昕昻昉昮昞昤晥晗晙晴晳暙暠暲暿曺朎朗杦枻桒柀栁桄棏﨓楨
﨔榘槢樰橫橆橳橾櫢櫤毖氿汜沆汯泚洄涇浯涖涬淏淸淲淼渹湜渧渼溿澈澵濵瀅瀇瀨炅炫焏焄煜煆煇凞燁燾犱
犾猤猪獷玽珉珖珣珒琇珵琦琪琩琮瑢璉璟甁畯皂皜皞皛皦益睆劯砡硎硤硺礰礼神祥禔福禛竑竧靖竫箞精絈絜
綷綠緖繒罇羡羽茁荢荿菇菶葈蒴蕓蕙蕫﨟薰蘒﨡蠇裵訒訷詹誧誾諟諸諶譓譿賰賴贒赶﨣軏﨤逸遧郞都鄕鄧釚
釗釞釭釮釤釥鈆鈐鈊鈺鉀鈼鉎鉙鉑鈹鉧銧鉷鉸鋧鋗鋙鋐﨧鋕鋠鋓錥錡鋻﨨錞鋿錝錂鍰鍗鎤鏆鏞鏸鐱鑅鑈閒隆
﨩隝隯霳霻靃靍靏靑靕顗顥飯飼餧館馞驎髙髜魵魲鮏鮱鮻鰀鵰鵫鶴鸙黑畩秕緇臂蘊訃躱鐓饐鷯
• File and folder names may contain up to 255 single-byte characters.
• Folder and workgroup names whose names contain non-Roman characters may not be displayed correctly.
• If shared folders are accessed from a Mac, information files for the Mac may be generated automatically. Do not
delete these files. If they are deleted using Windows, this may prevent further access from a Mac.
• The TeraStation belongs to the default zone in AppleShare; the zone cannot be specified.
• When files are copied to the TeraStation or to a USB drive connected to the TeraStation, file information such as
date created, date modified, and other date information may be updated or changed.
• During a file transfer, if settings are changed, the file transfer operation may be aborted.
• File copying to the TeraStation is protected by a journaling file system. If the Ethernet cable is disconnected or a
power outage occurs while copying data, the following may occur:
◦Preset data such as the TeraStation name, users, and groups may be erased.
◦An incomplete file may be copied and the file can no longer be deleted. If this happens, restart the
TeraStation, delete the file, and perform the copy operation again.
• If the Ethernet cable is disconnected from the LAN port during file copying, even if the cable is not in use, the
copy operation will abort. Do not disconnect or reconnect the Ethernet cable to the LAN port during file copying.
Recycle Bin
To protect your data from accidental deletion, you may configure your TeraStation to use a recycle bin instead of
deleting files immediately. The recycle bin will only work with SMB connections. To empty the recycle bin, click File
Sharing > Folder Setup > Empty Recycle Bin in Settings. The recycle bins in all shared folders will be deleted.
Notes:
• You can prevent guests and other users from emptying the trash by navigating to File Sharing > SMB and select
“Administrator only” for the “Recycle Bin Permissions” option.
• If you use macOS, select “Keep when original file is deleted” for the “macOS Temp Files” option by navigating to
File Sharing > SMB. If this setting is changed, files in the recycle bin may be corrupted.
Read-Only Shares
By default, new shares are set with read and write access, but you may change the attribute to Read only at Attribute
on the Option 2 tab. Read-only shares and HFS Plus-formatted USB drives will have “(Read Only)” added to comments
in File Explorer.
Note: Configure read-only file attribute in Settings. Configuring them from within Windows is not supported and
may cause unexpected behavior.
28
Hidden Shares
If hidden shares are enabled, shared SMB folders will not be displayed in Network, and only certain users are allowed
to access them. To hide a shared SMB folder, follow the procedure below.
1 From Settings, navigate to File Sharing > Folder Setup and choose a shared folder or a USB drive to configure
hidden shares.
2 Click the Option 2 tab and select the “Hidden share (SMB only)” checkbox, then click OK.
Notes:
• If protocols other than “SMB (Windows/Mac)” or “Backup” under “LAN Protocol Support” on the Basic tab are
enabled, the hidden shares option will be grayed out and cannot be selected.
• Configure hidden share attribute in Settings. Configuring them from within Windows is not supported and may
cause unexpected behavior.
To access a hidden folder, open File Explorer in your computer and enter “\\TeraStation name\shared folder name$\”
into the address bar. For example, if the TeraStation name is “TSXXX001” and the shared folder name is “share”, enter
“\\TSXXX001\share$\” to open it.
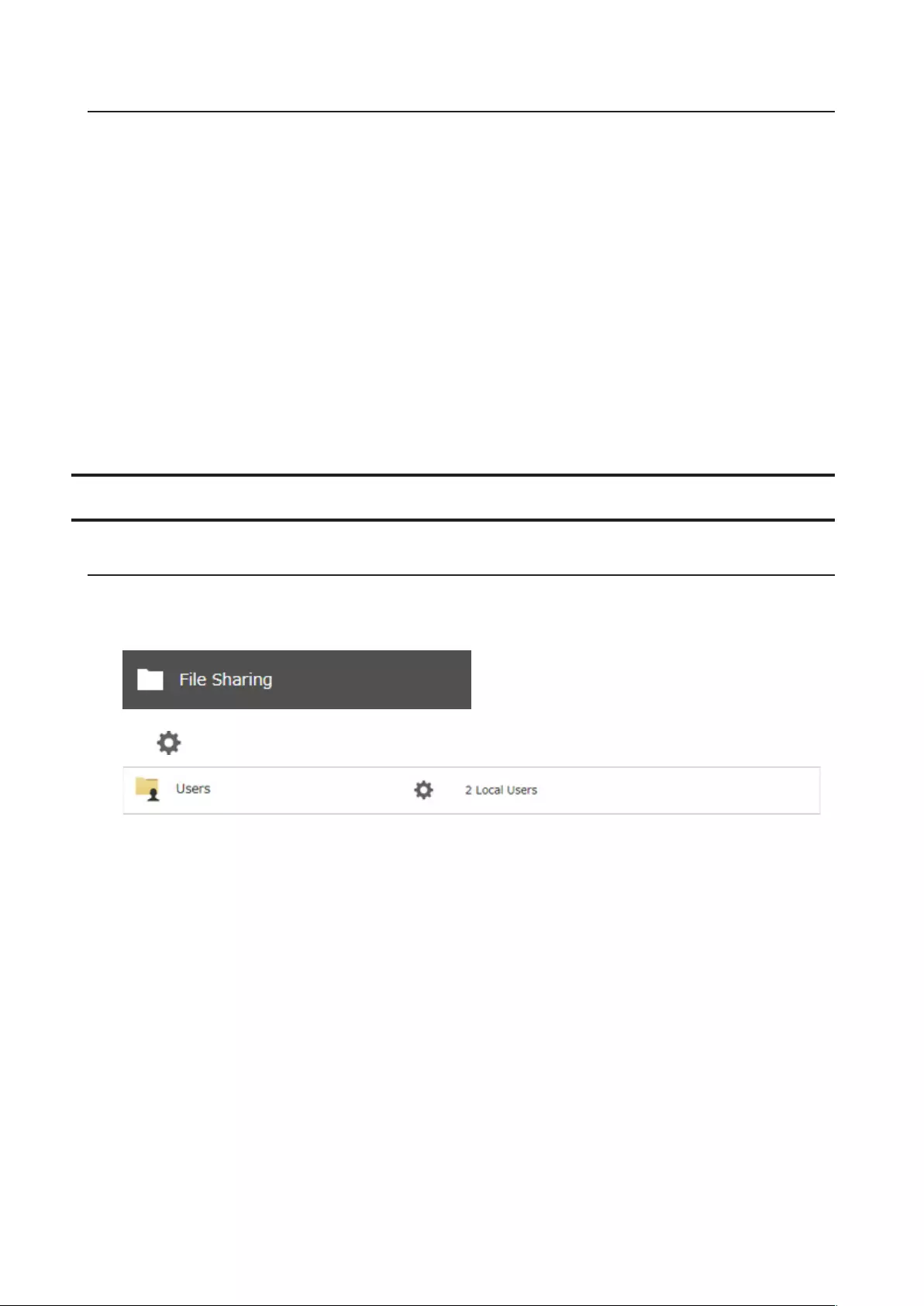
Configuring Users
Adding a User
Note: The TeraStation can register a maximum 300 of users, which include the default users “admin” and “guest”.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Users”.
29
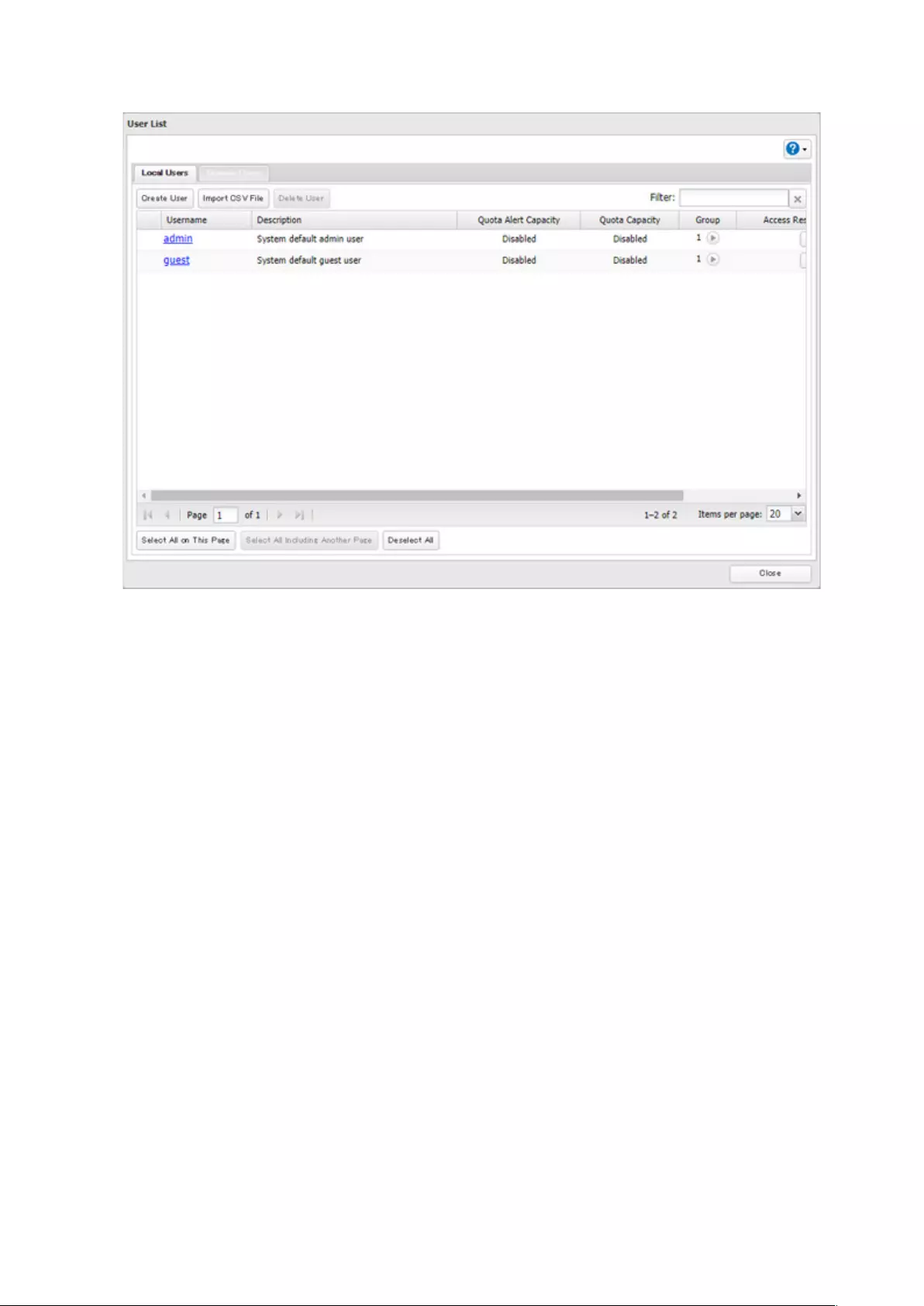
3 Click Create User.
30
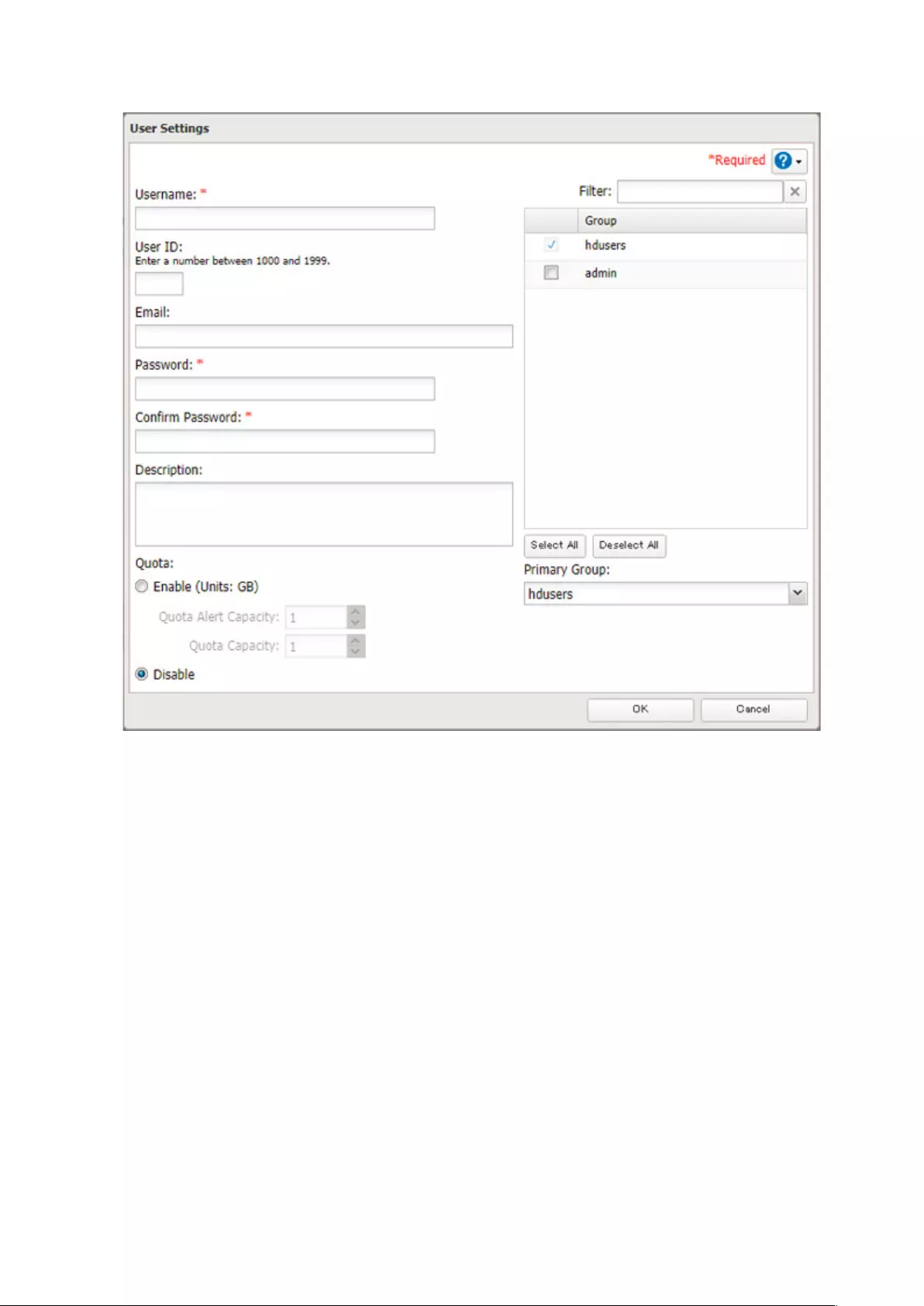
4 Enter the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Usernames may contain up to 128 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), periods (.), and the
symbols ! # & @ $ * ^ %. The first character should not be a symbol.
• The user ID should be a number from 1000 to 1999. Each user ID should be unique. If this field is left blank, a user
ID is assigned automatically.
• Do not duplicate user IDs, group IDs, usernames, or group names. Each should be distinct and unique.
• User descriptions may contain up to 75 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces.
Multibyte characters are supported. The first character should not be a symbol or space.
• Passwords may contain up to 20 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), spaces, commas (,),
periods (.), semicolons (;), tildes (~), and the symbols @ ! $ & * + : = ? ] [ ^ } { \. The first character should not be a
symbol unless it is an underscore.
• Use the same username and password for both Windows and the TeraStation or you may not be able to access
shared folders.
• Do not use a name already in use as a group; do not use any of the following words as a username as these
words are reserved for internal use by the TeraStation: _lldpd, adm, admin, administrator, admins, all, apache,
avahi, avahi-autoipd, backup, bin, crontab, daemon, dialout, dip, disk, ftp, ftpuser, fuse, gnats, guest, guests, halt,
hdusers, irc, kmem, libuuid, list, lp, mail, man, messagebus, mysql, netdev, news, nobody, nogroup, none, ntp,
openldap, operator, plugdev, proftpd, proxy, puppet, root, rpc, rpcuser, sambashare, sasl, shadow, shutdown,
snmp, splx, src, ssh, sshd, staff, statd, sudo, sync, syslog, tmhttpd, tty, users, utmp, uucp, winbindd_priv, www,
www-data
31
Importing User Information
You can import users in File Sharing > Users by clicking Import CSV File.
An example format for user data: Username (required), password (required), and user description (optional).
Example 1: Importing usernames, passwords, and comments
username1,password1,comment1
username2,password2,comment2
username3,password3,comment3
Example 2: Importing usernames and passwords
username1,password1,
username2,password2,
username3,password3,
Guidelines:
• Use commas (,) as separators. Do not put spaces before or after commas. If you don’t want user descriptions, use
a comma after the password at the end.
• If a line is in an incorrect format, the username entered on that line will not be registered.
• If an unavailable name is used by a user or if the username already exists, an error will occur and cancel the
import process. User whose usernames were entered during or after the error occurs will not be imported.
• Do not use commas (,) in the username, password, or user description.
Note: Imported users are added to the “hdusers” group automatically.
Adding a Group
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Groups”.
32
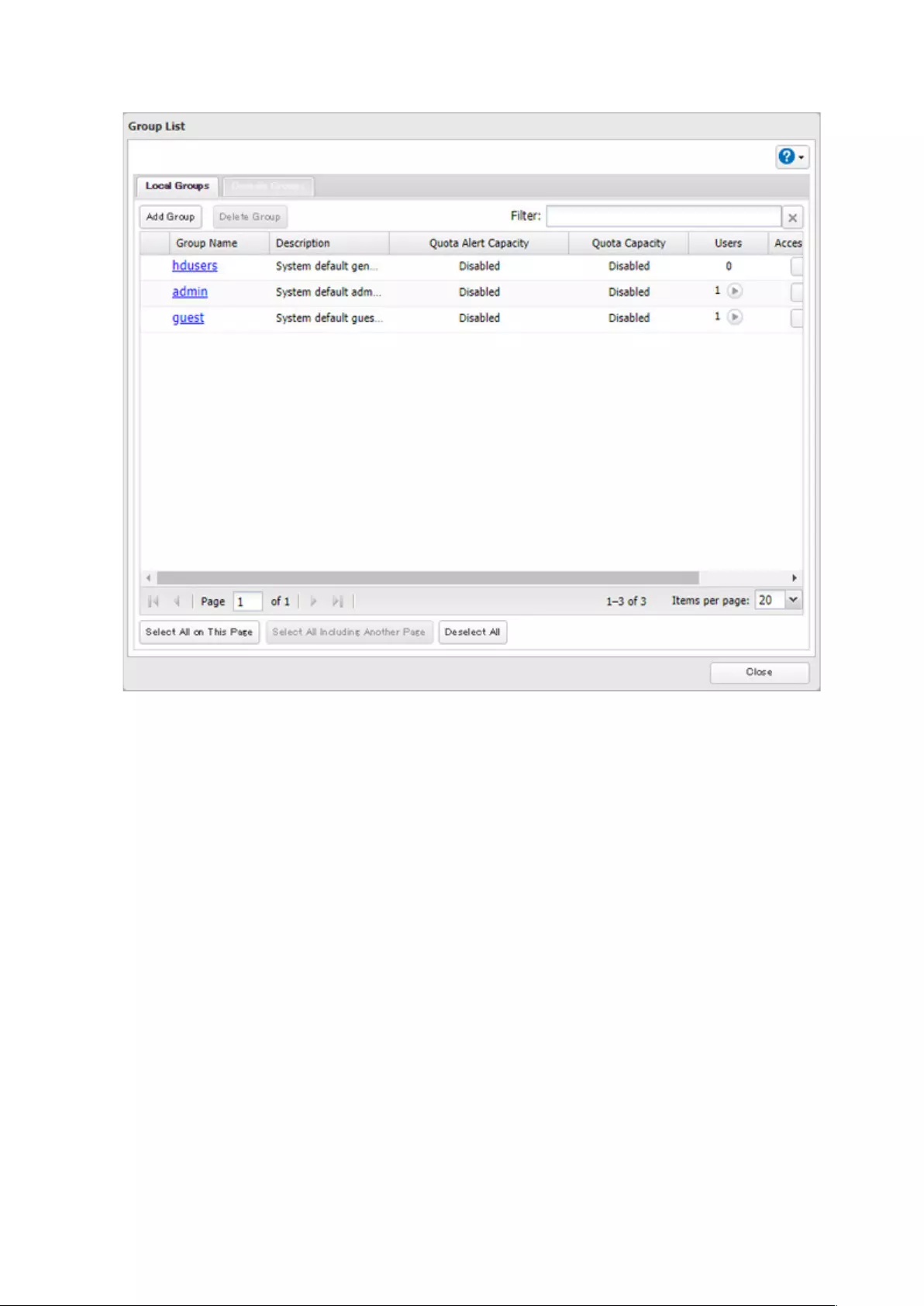
3 Click Add Group.
33
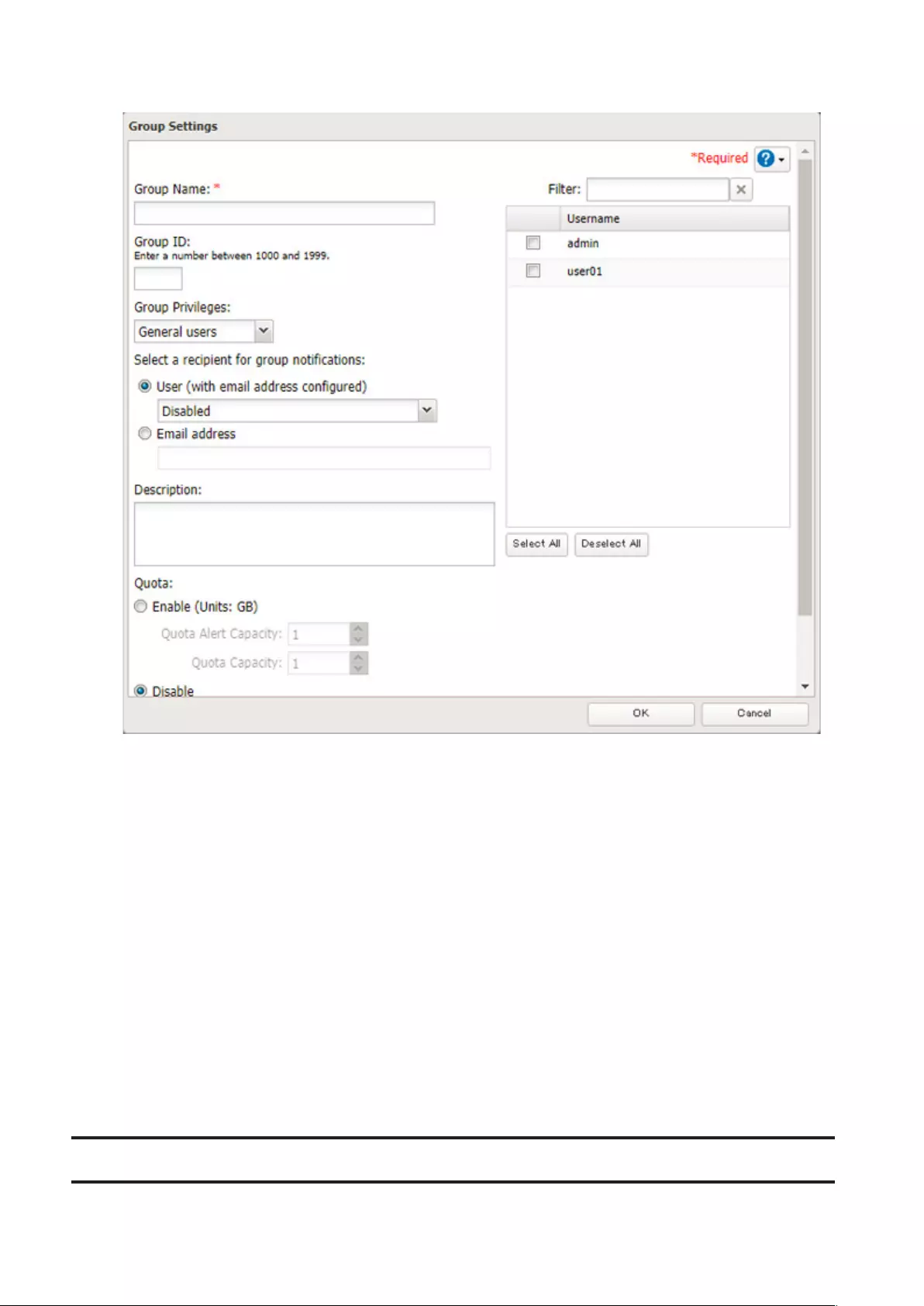
4 Enter the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Group names may contain up to 20 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and periods (.). The
first character should not be a symbol.
• Group descriptions may contain up to 75 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces.
Multibyte characters are supported. The first character should not be a symbol or space.
• If the group ID field is left blank, a group ID is automatically assigned. Use numbers between 1000 and 1999 to set
a group ID manually. Don’t use duplicate group IDs.
• You may register up to 300 groups with the TeraStation.
• If you are logged in as a member of the general users group, you can only change your own password. If you’re
logged in as an administrator, you can change any settings, including other users’ passwords. If you are logged in
as a member of the power users group, you can create and edit shared folders, users, and groups.
• Do not use a name in use as a user; do not use any of the following words as a group name as these words are
reserved for internal use by the TeraStation: _lldpd, adm, admin, administrator, admins, all, apache, avahi, avahi-
autoipd, backup, bin, crontab, daemon, dialout, dip, disk, ftp, ftpuser, fuse, gnats, guest, guests, halt, hdusers,
irc, kmem, libuuid, list, lp, mail, man, messagebus, mysql, netdev, news, nobody, nogroup, none, ntp, openldap,
operator, plugdev, proftpd, proxy, puppet, root, rpc, rpcuser, sambashare, sasl, shadow, shutdown, snmp, splx, src,
ssh, sshd, staff, statd, sudo, sync, syslog, tmhttpd, tty, users, utmp, uucp, winbindd_priv, www, www-data
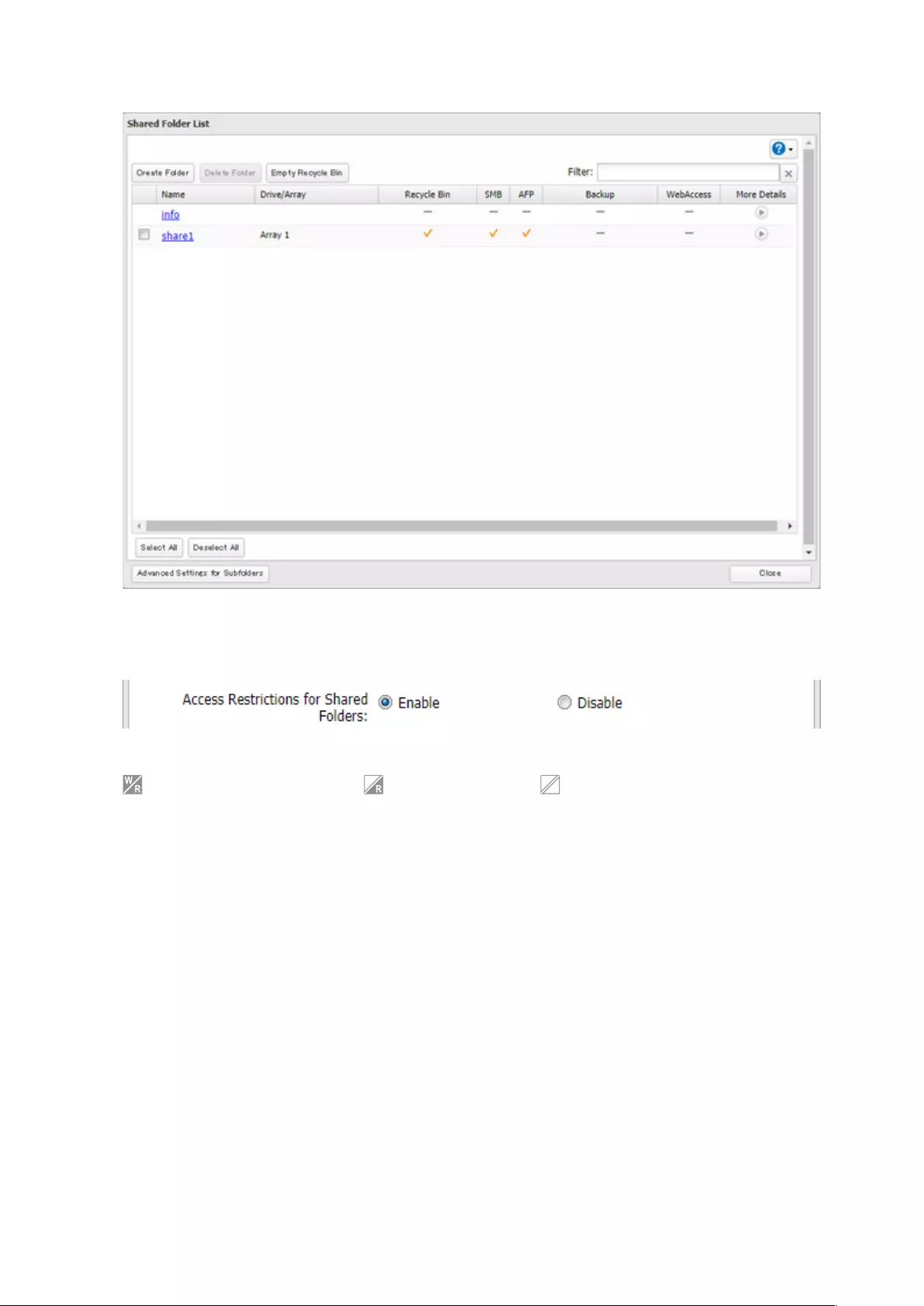
Configuring Access Restrictions for Shared Folders
You may restrict access to specific shared folders, including external USB drives.
34
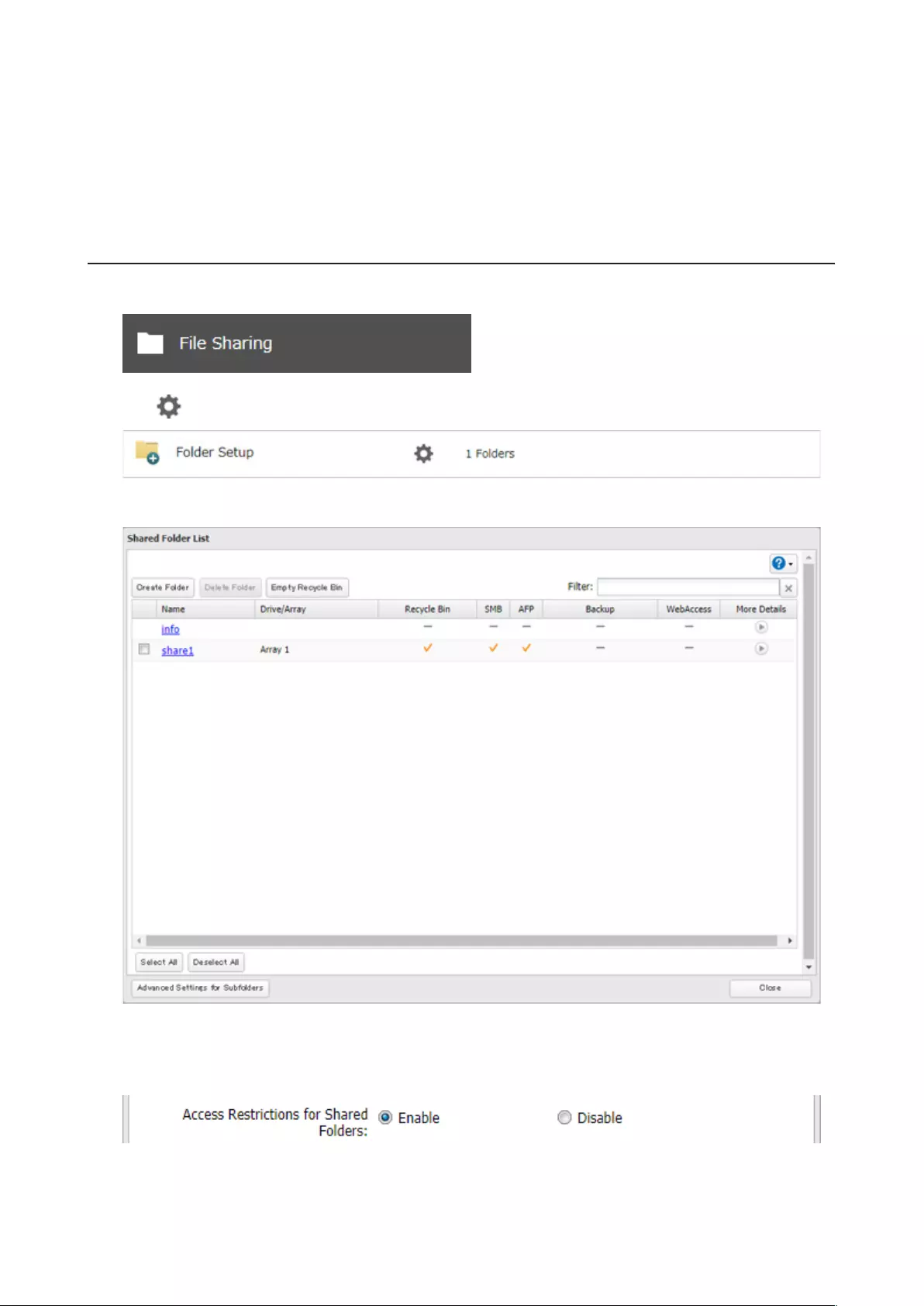
Notes:
• Configure access restrictions through Settings. Configuring access restrictions through Windows is not supported
and may cause unexpected behavior.
• Shared folders with limited access can still be used as backup destinations.
• If you change access restrictions for a user or group while they are accessing files, unexpected behavior may
result.
Local Users and Groups
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Click the shared folder that you want to set access restrictions for.
4 Click the Access Restrictions tab.
5 Enable “Access Restrictions for Shared Folders”.
6 Select the level of access for the user or group.
35
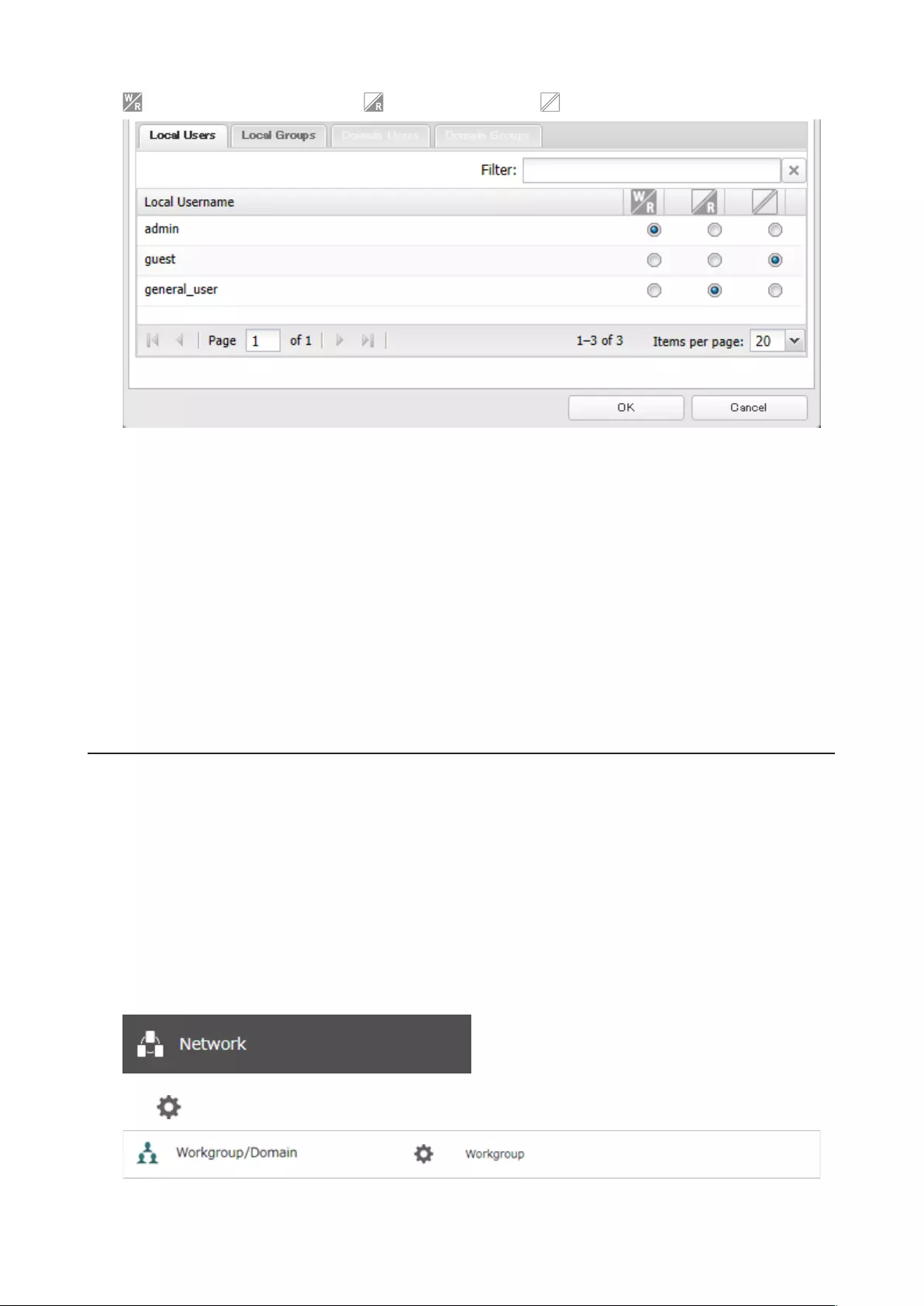
: Read and write access allowed : Read access allowed : Access prohibited
7 Click OK.
Notes:
• The example above shows access restriction by a user. To restrict access by group, click the Local Groups tab and
select group permissions.
• Under the following settings, read-only permission always applies:
◦A user joins multiple groups for which either read-only or write permissions are given.
◦A write-permitted user joins groups for which read-only permissions are given.
◦A read-only user joins joins groups for which write permissions are given.
• For an access-restricted shared folder, if you change the access restrictions of all users and groups from read and
write or read-only to access prohibited from the user or group list page in Settings, that shared folder can only be
accessed by admin users and groups.
Active Directory
If there is an Active Directory environment, the TeraStation will use account information from the Active Directory
domain controller to set access restrictions for TeraStation’s shared folders. There is no need to perform individual
account management for the TeraStation. If multiple TeraStations are installed on the network, the account
information is centrally managed in Active Directory, greatly reducing the operations required for installation and
management.
Notes:
• If usernames or group names from Active Directory include multibyte characters, you will not be able to
configure access restrictions for them.
• The TeraStation supports a domain environment with a maximum of 10,000 users and groups.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “Workgroup/Domain”.
3 Click Edit.
36
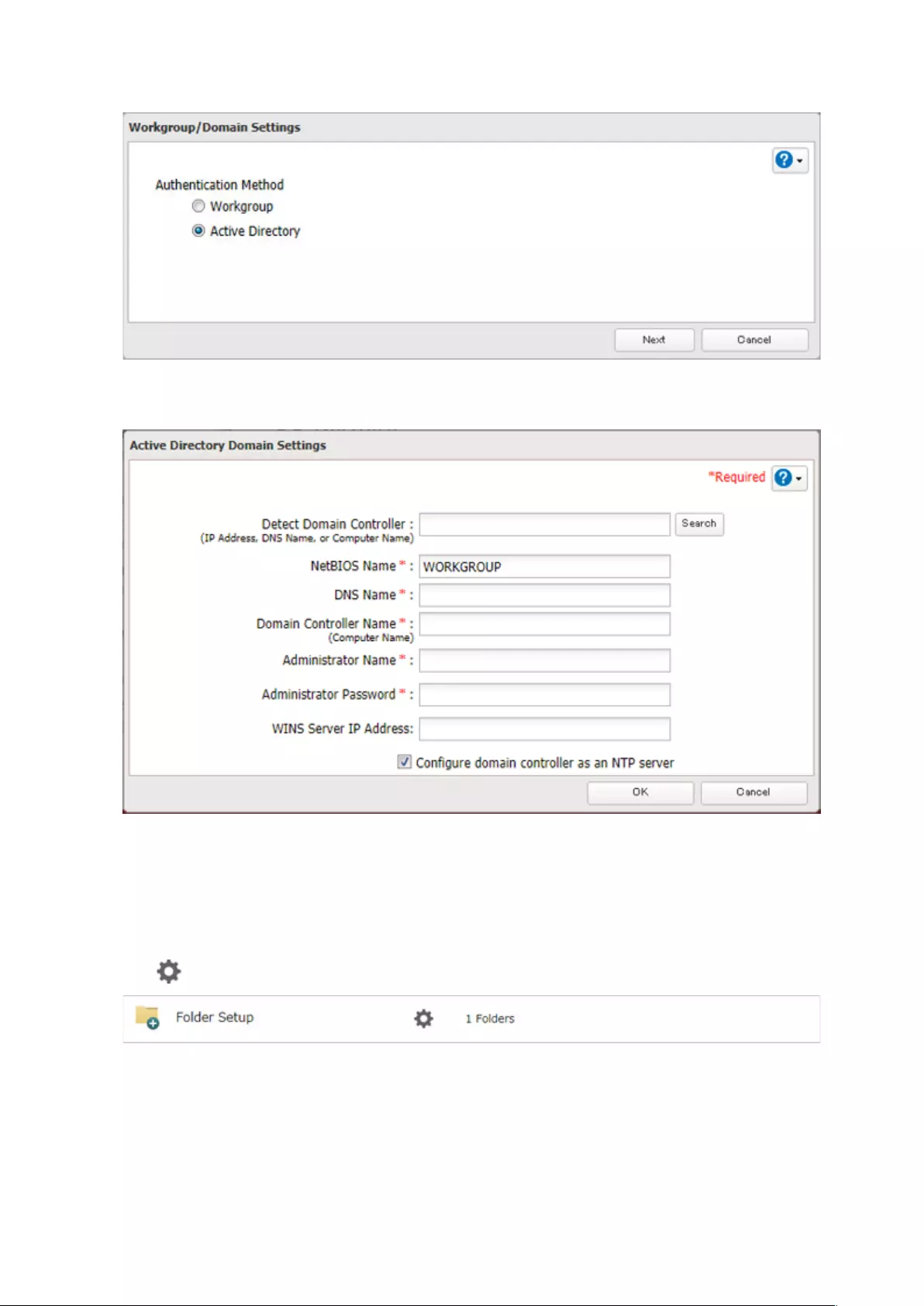
4 Select “Active Directory”, then click Next.
5 Enter the domain controller information and click Search. The domain controller on the same network will be
detected and required settings will be entered into each field automatically. Or, enter the settings manually.
6 If there is a difference of more than 5 minutes between the TeraStation’s clock and the domain controller’s
clock, joining the domain or authenticating domain users and groups may fail. For best results, select
“Configure domain controller as an NTP server” if the domain controller can function as the NTP server.
7 Click OK.
8 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
37
9 Click the shared folder that you want to set access restrictions for.
10 Click the Access Restrictions tab.
11 Enable “Access Restrictions for Shared Folders”.
12 Select the level of access for the user or group.
: Read and write access allowed : Read access allowed : Access prohibited
13 Click OK.
Notes:
• To have the TeraStation join an Active Directory domain, configure it to use a DNS server that can resolve names
for the Active Directory domain.
• After building an Active Directory domain, the administrator password for joining the domain must be changed
at least once, or joining the Active Directory domain will fail.
• The DNS name and NetBIOS name of Active Directory domains should be identical.
• Under the following settings, read-only permission always applies:
◦A user joins multiple groups for which either read-only or write permissions are given.
◦A write-permitted user joins groups for which read-only permissions are given.
◦A read-only user joins joins groups for which write permissions are given.
• To use the TeraStation as a member server in an Active Directory domain, the TeraStation should be logged in to
the domain and accessed from a computer that is not a member of the domain with a valid domain account.
• If the TeraStation is a member server of an Active Directory domain, you cannot connect as a guest user via AFP.
• If your TeraStation is a member server in an Active Directory domain and you change the authentication method
to “Workgroup”, the account on the domain controller will not be deleted automatically.
38
• If FTP is enabled, local and domain group access restrictions from the AD network do not work. Use user access
restrictions instead.
• For an access-restricted shared folder, if you change the access restrictions of all users and groups from read and
write or read-only to access prohibited from the user or group list page in Settings, that shared folder can only be
accessed by admin users and groups.
• If you allow read and write or read-only access for most users, group access restrictions are recommended.
Configuring Access Restrictions for Subfolders
You may restrict access to subfolders in shared folders by configuring access permissions from your computer using
Windows File Explorer.
Notes:
• Depending on the environment, the function may not work properly even if it’s enabled. We recommend
verifying the functionality before using.
• Access permissions configuring from File Explorer is available up to 18 files and 24 folders. This number of
available access permissions may vary if access permissions are inherited from the parent object.
The number of available access permissions are not many so using group access permissions is recommended
if the permission level is the same to the multiple users; it will save spending the number of available access
permissions.
Enabling Subfolders’ Access Restrictions
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
39
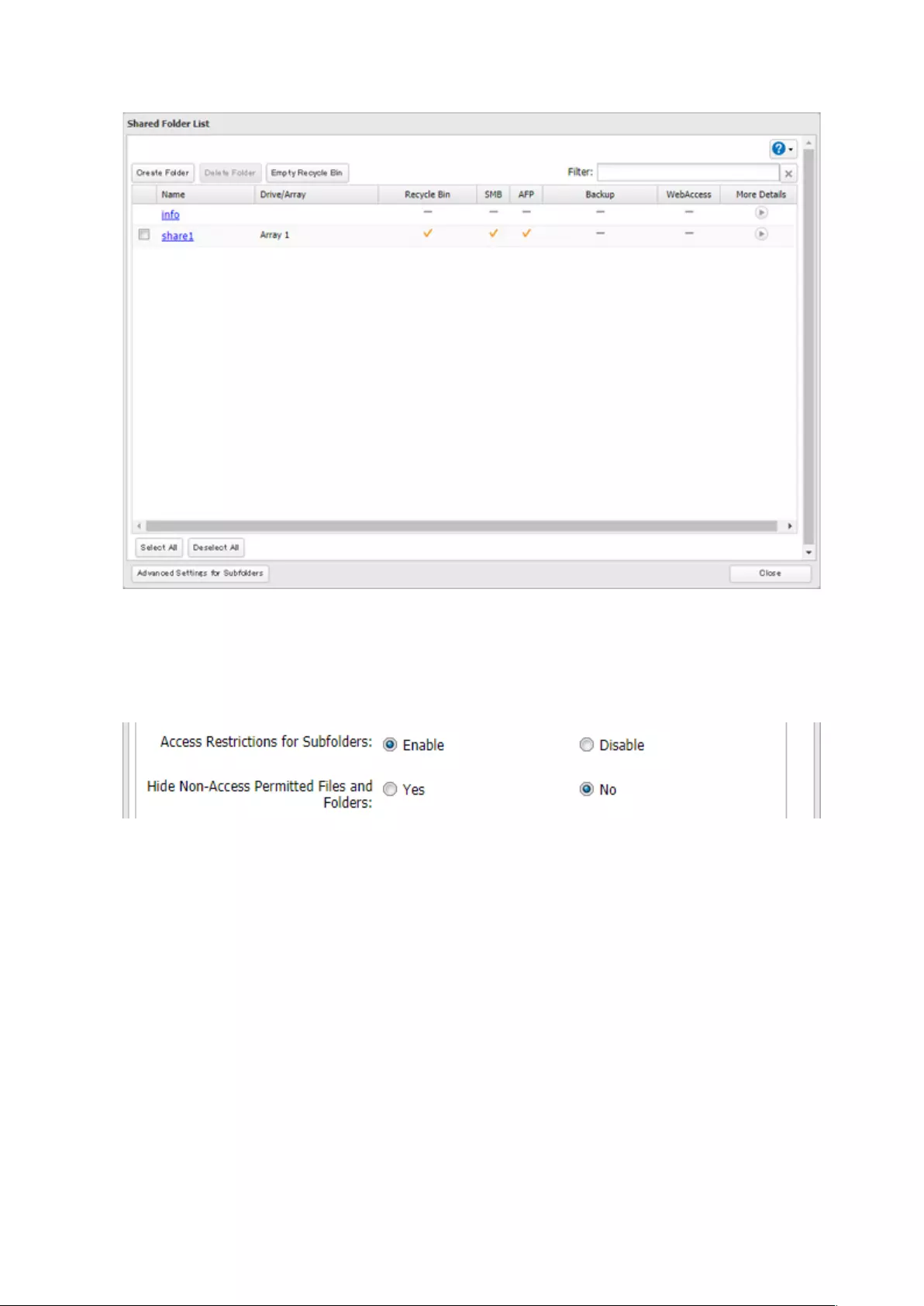
3 Click the shared folder that you want to set access restrictions for.
4 Clear all checkboxes for “LAN Protocol Support” other than “SMB (Windows/Mac)”, “Backup”, and “NFS”.
5 Click the Option 2 tab.
6 Enable “Access Restrictions for Subfolders”.
Note: If “Hide Non-Access Permitted Files and Folders” is enabled, non-access permitted sub-files and folders
will not be displayed in shared folders.
7 Click OK.
Enabling subfolders’ access restrictions finished. Next, configure access permissions for each user or group to files
and folders in subfolders from File Explorer.
40
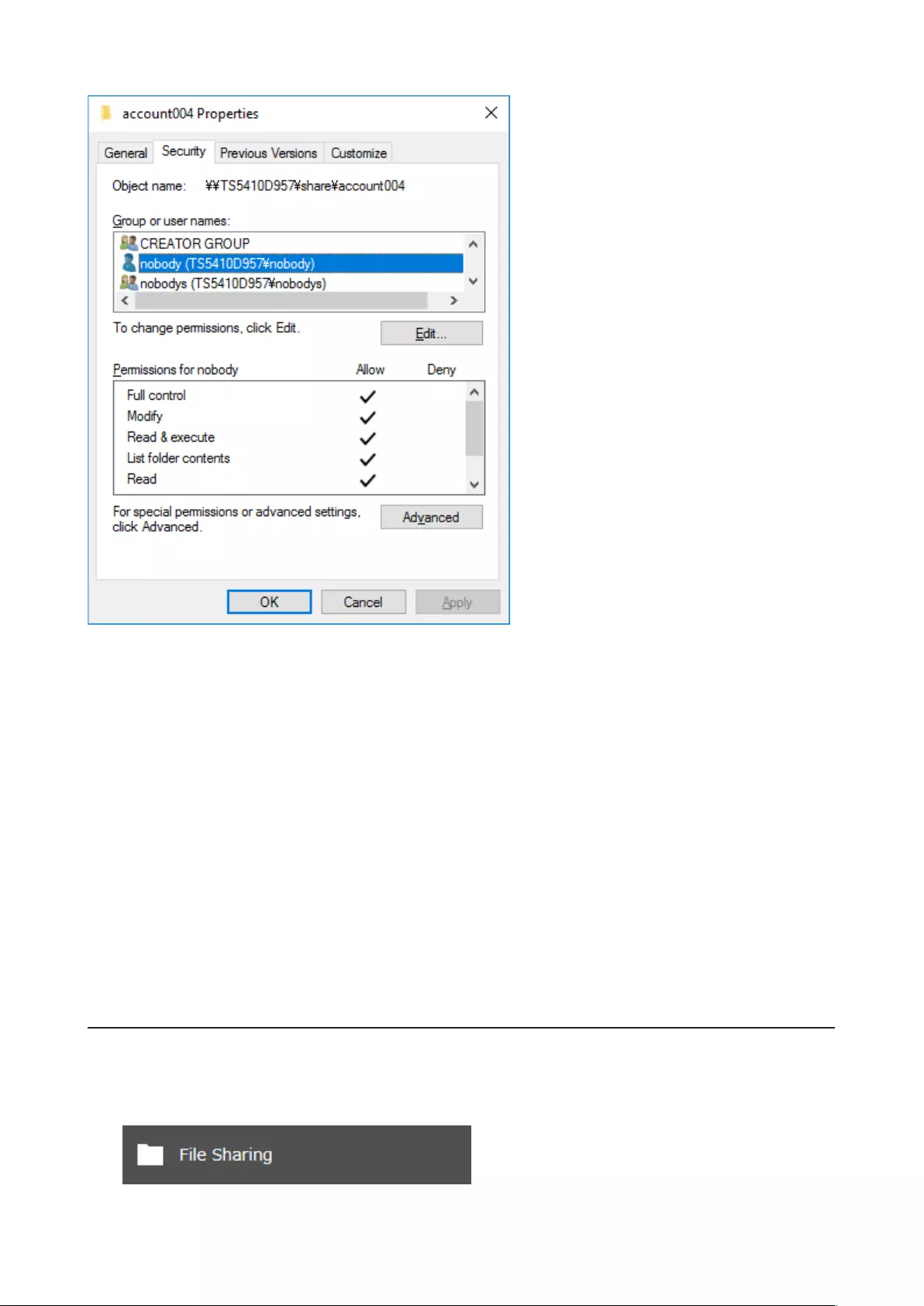
You may also configure access permissions for domain users and groups. You should have the TeraStation join your
Active Directory domain before configuring access permissions from File Explorer.
Notes:
• If enabling subfolders’ access restrictions for a USB drive, the drive should be formatted by XFS or ext3.
• The UID and GID of domain accounts should be updated before using the subfolders’ access restrictions if the
TeraStation joined the AD network while running firmware version 3.00 or earlier and has since updated to
version 3.00. To update the UID and GID, navigate to “File Sharing” > “SMB” > “Edit” in Settings and click Update.
• To back up or replicate files to backup or replication destinations with remaining access permission settings to
files and folders in subfolders, make sure that the same workgroup name, user IDs, and group IDs are configured
between backup or replication sources and destinations.
• If you enable subfolders’ access restrictions and then clear the “Read & execute” checkbox under “Allow” on File
Explorer for users or groups access permissions, these users or groups cannot be allowed to read and execute
even if subfolders’ access restrictions are disabled in Settings. If you deny reading and executing on the same
window, this will remain after disabling subfolders’ access restrictions.
• If the TeraStation’s settings have been initialized but you configure the same UID and GID for new users and
groups, access permissions to files and folders in subfolders may be inherited.
Restoring Owner and Permission Settings
If you changed the owner to an unexpected user or lost permissions to specific folder accidentally, restore them by
the procedure below.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
41
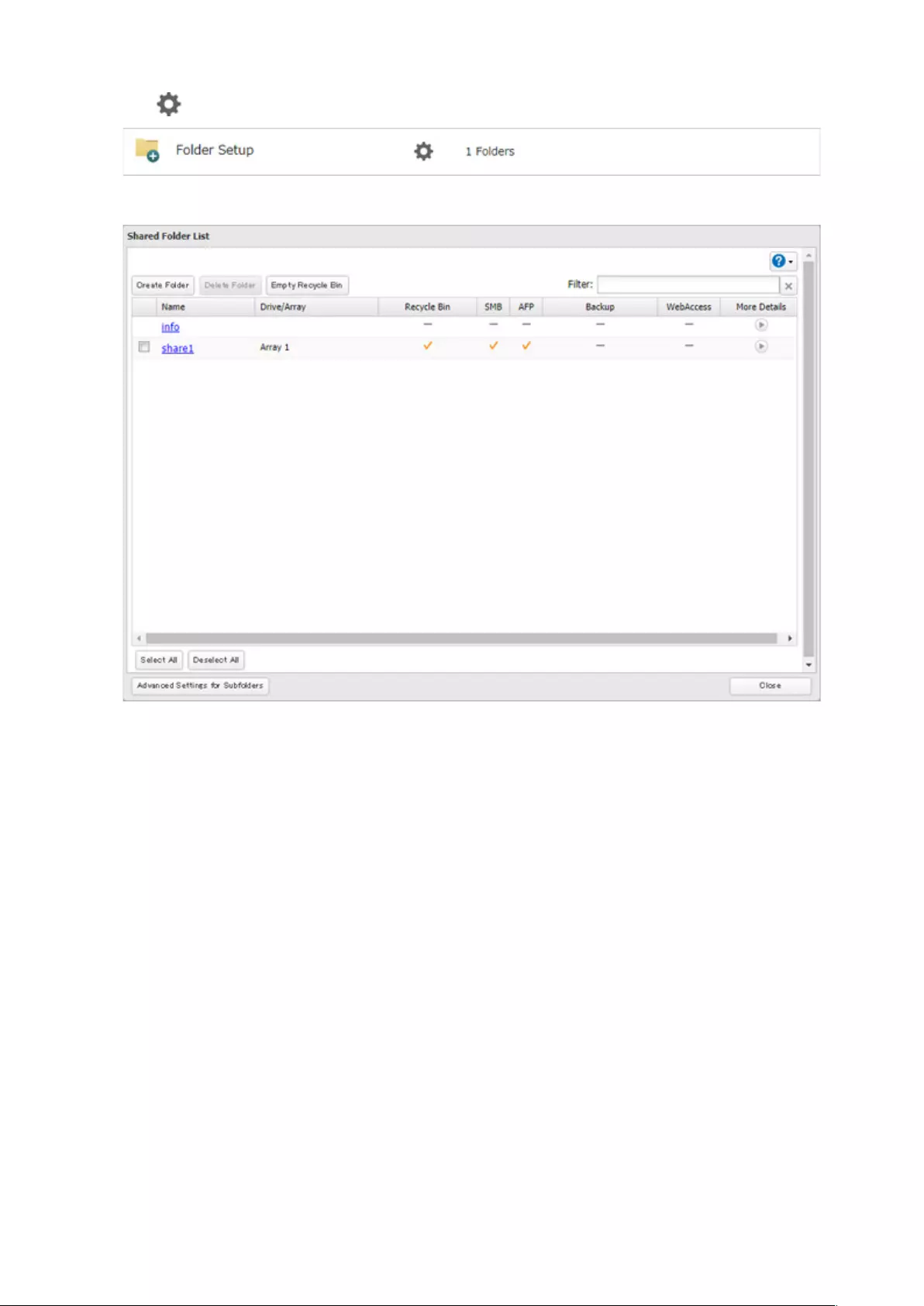
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Click Advanced Settings for Subfolders.
42
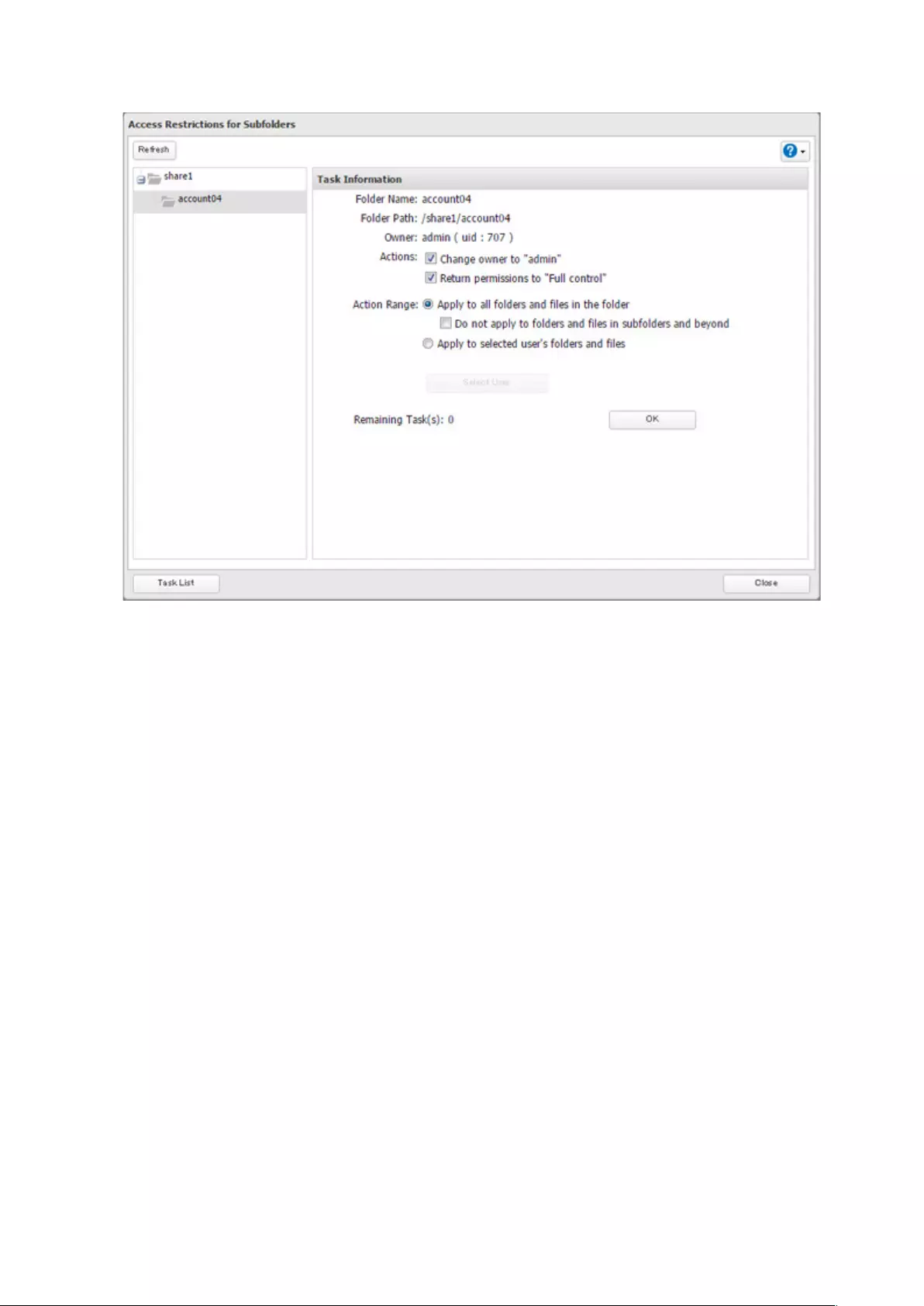
4 Select a folder to restore permissions from the tree.
Note: If you select a root shared folder from the tree, the action will not be run to the recycle bin. To run the
action, select the recycle bin instead.
5 Select actions and action range to run, then click OK.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
43

Chapter 4 Storage Management
RAID Modes
TeraStations support many types of RAID. The type of RAID arrays available for use depends on how many drives are
installed in your TeraStation.
Notes:
• If you change the RAID mode, all data on the array is deleted. This is true for every procedure in this chapter.
Always back up any important data before performing actions that affect your RAID array.
• Drive capacity is displayed in Settings in actual gigabytes. The Properties window in Windows may show GiB
instead, which will be a smaller number.
• If the TeraStation is restarted or shut down while changing the RAID mode, the message that appears on the LCD
panel will change from I46 or I47 to I18.
• RAID 5, 6, and 10 are only available for models with 4 or more drives.
RAID 6
RAID 6 arrays are available for TeraStations with 4 or more drives. RAID 6 combines 4 or more drives into a single
array. The usable space is equal to the sum of the capacity of all drives minus the capacity of two drives. For example,
if 4 drives are combined into a RAID 6 array, the usable space is the sum of the capacity of 2 drives. If 2 drives in the
array are damaged, you can recover data by replacing them. If 3 or more drives are damaged, your data is lost.
RAID 5
RAID 5 arrays are available for TeraStations with 3 or more drives. RAID 5 combines 3 or more drives into a single
array. The usable space is equal to the sum of the capacity of the drives minus the capacity of one drive. For
example, if 4 drives are combined into a RAID 5 array, the usable space is the sum of 3 drives. If one drive in the array
is damaged, you can recover data by replacing the damaged drive. If two or more drives are damaged at the same
time, your data is lost.
RAID 10
RAID 10 arrays are available for TeraStations with 4 or more drives. In this mode, mirrored pairs of drives in RAID 1
arrays are combined into a RAID 0 array. The usable space is equal to the capacity of the smallest drive multiplied by
the number of drives divided by 2.
RAID 1
Combines 2 or more drives into a mirrored array. The available space in the array is the capacity of a single drive.
Identical data is written to each drive. If a drive is damaged, data can be recovered by replacing the damaged drive.
As long as one drive in the array remains undamaged, all data in the array can be recovered.
44
RAID 0
Combines 2 or more drives into a single array. The usable drive space is the total space of all drives used. This simple
RAID mode offers faster performance than RAID modes that include parity. If a single drive in the array fails, then all
data in the array is lost.
JBOD
This mode uses the drives inside the TeraStation as individual drives. The drive space you can use is the total
capacity of all drives in the TeraStation. If any drives are damaged, then the data on that drive is lost.
Working with RAID Arrays
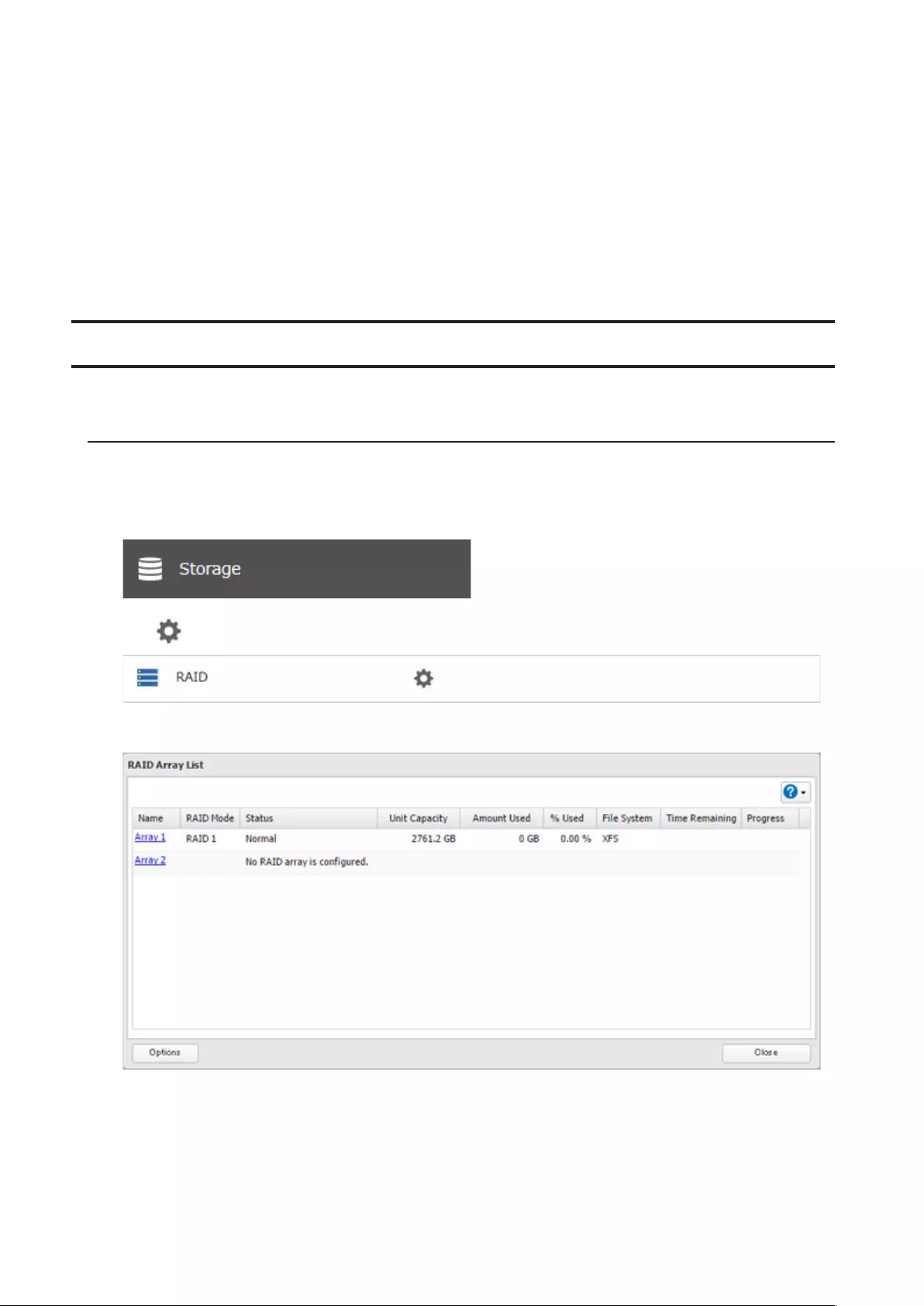
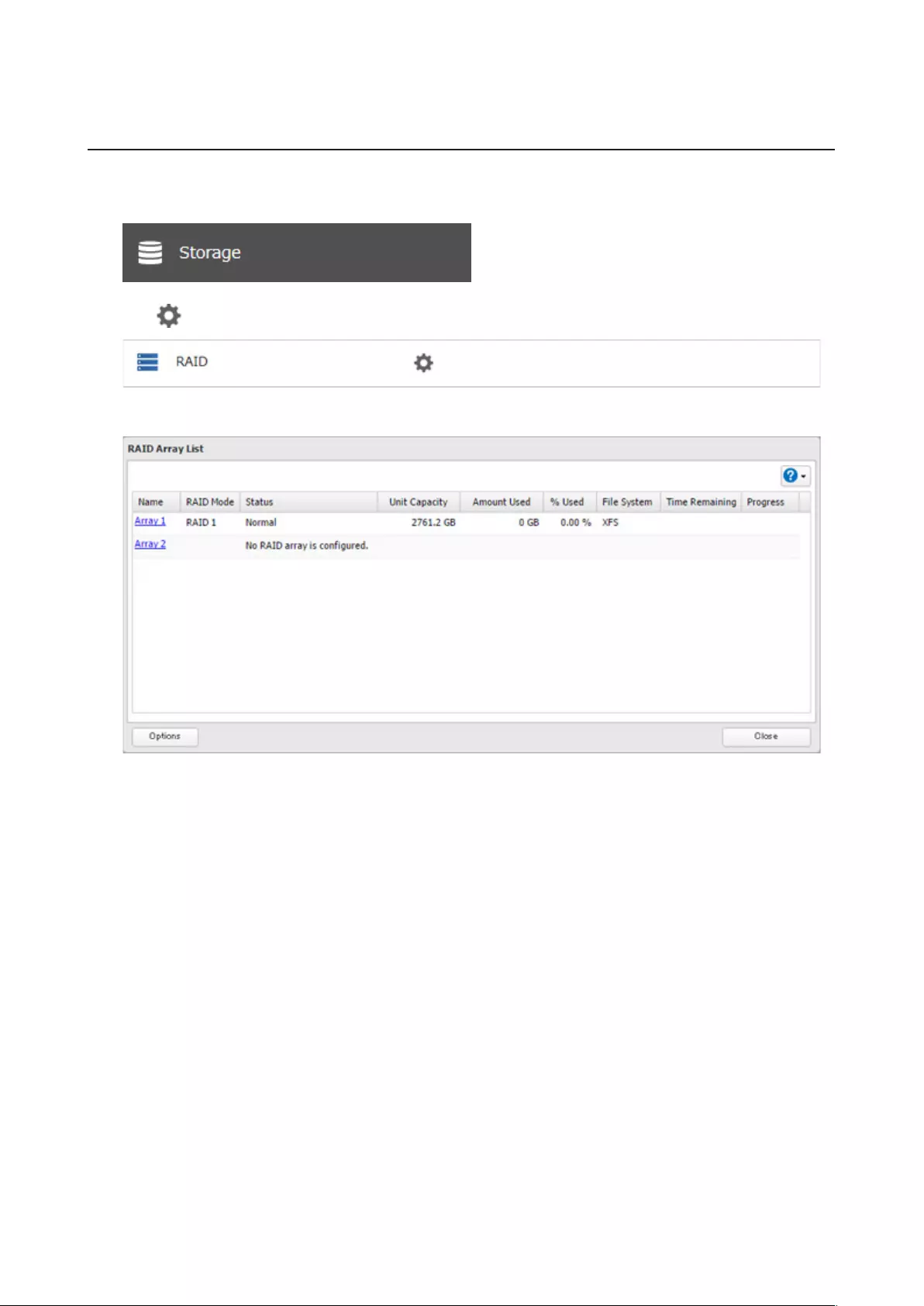
To change RAID settings, navigate to Storage > RAID in Settings.
Using JBOD
With JBOD, each drive in the TeraStation is addressed separately. To put drives from an array into JBOD, follow the
procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Click the array to delete.
4 Click Delete RAID Array.
5 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK when finished.
45
Once JBOD is configured, create shared folders on each drive to use them.
Changing RAID Mode
To change the RAID mode, first put the drives in JBOD.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Click the array to delete.
4 Click Delete RAID Array.
5 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK.
46
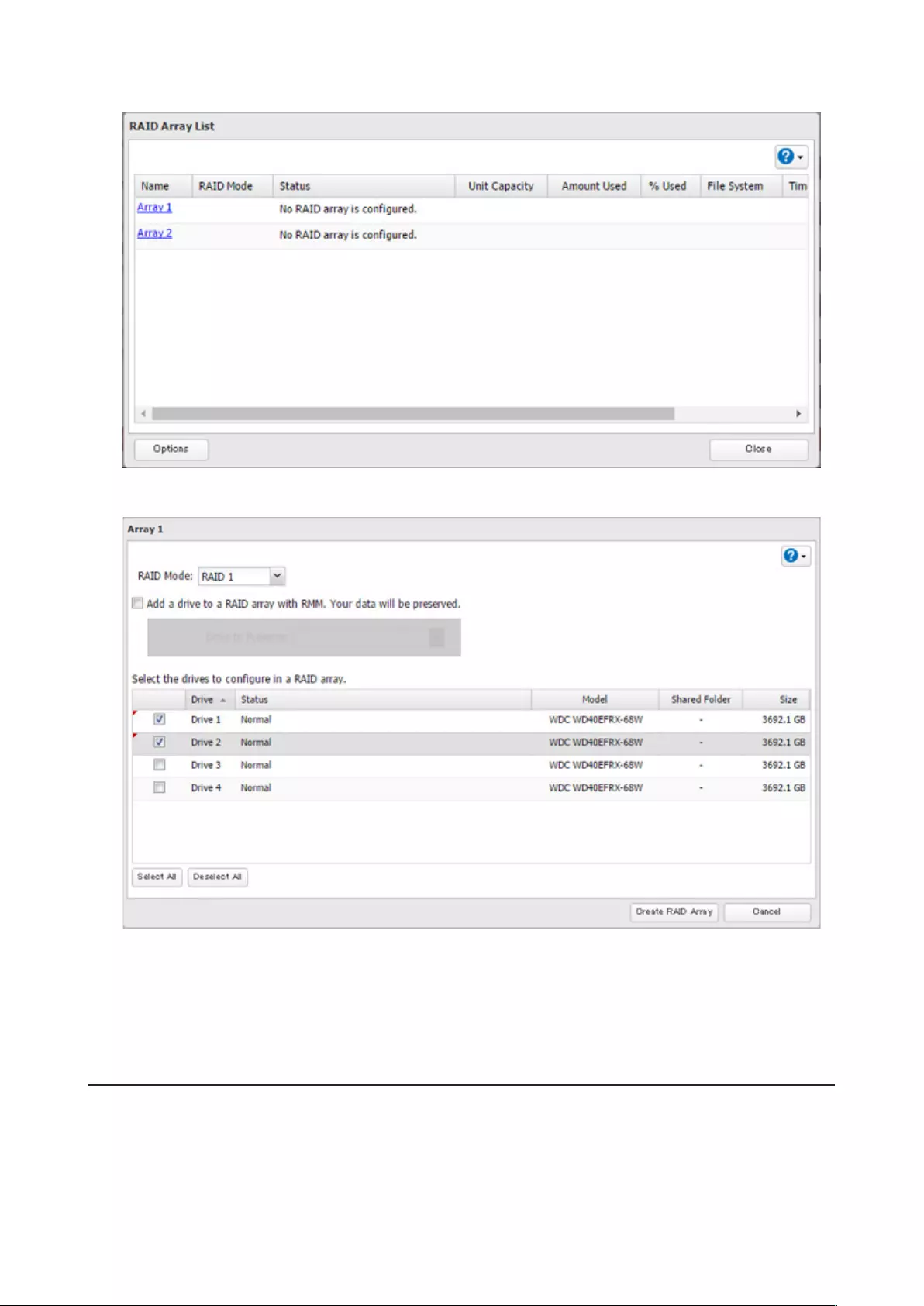
7 Choose a RAID array.
8 Select a RAID mode and the drives to be used, then click Create RAID Array.
9 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
10 Click OK when finished.
Note: After changing the RAID mode, create a shared folder.
Shutting Down the TeraStation Automatically If Error Occurred
This function will shut down the TeraStation automatically if an error occurs on a drive that is used in a redundant
RAID array.
For the TS51210RH series users, it is recommended to enable email notifications if enabling auto shutdown because
the TS51210RH series will extinguish all LEDs when shutting down and the failed drive will not be identified. In such
a case, you can confirm the failed drive number in the notification email.
47
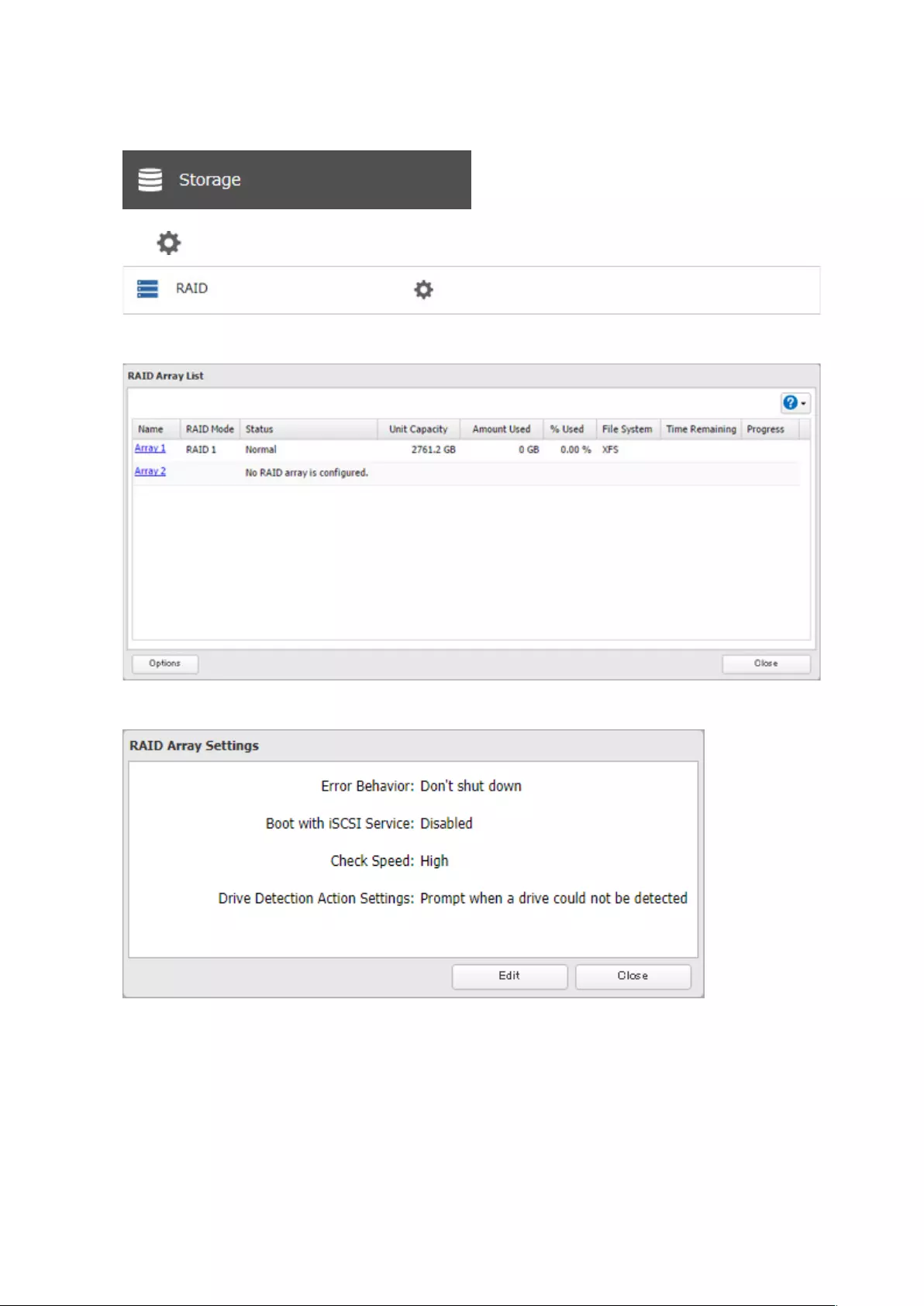
To configure auto shutdown, follow the procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Click Options.
4 Click Edit.
48
5 Select “Shut down” for “Error Behavior” and click OK.
Rebuilding the RAID Array Automatically
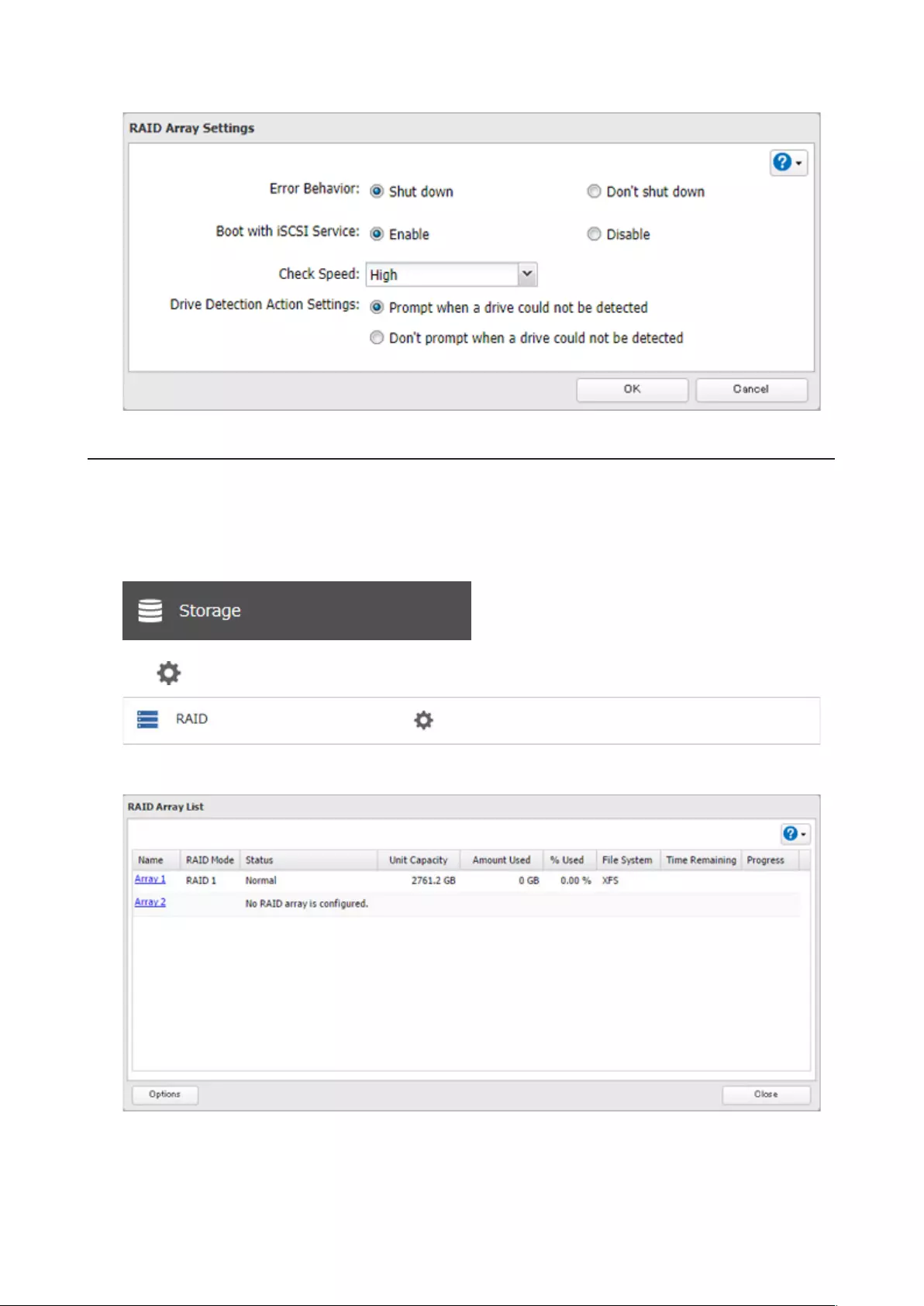
If auto RAID rebuild is enabled, RAID arrays will rebuild automatically after a failed drive is replaced. You may enable
or disable auto RAID rebuild by following the procedure below.
Note: This function is only for the TS51210RH series. Other models will not display this function in Settings.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Click Options.
49
4 Click Edit.
5 Select “Yes” for “Automatically Rebuild if New Drive Is Detected” and click OK.
Configuring Actions If A Drive Used for the RAID Array Has Not Been
Discovered
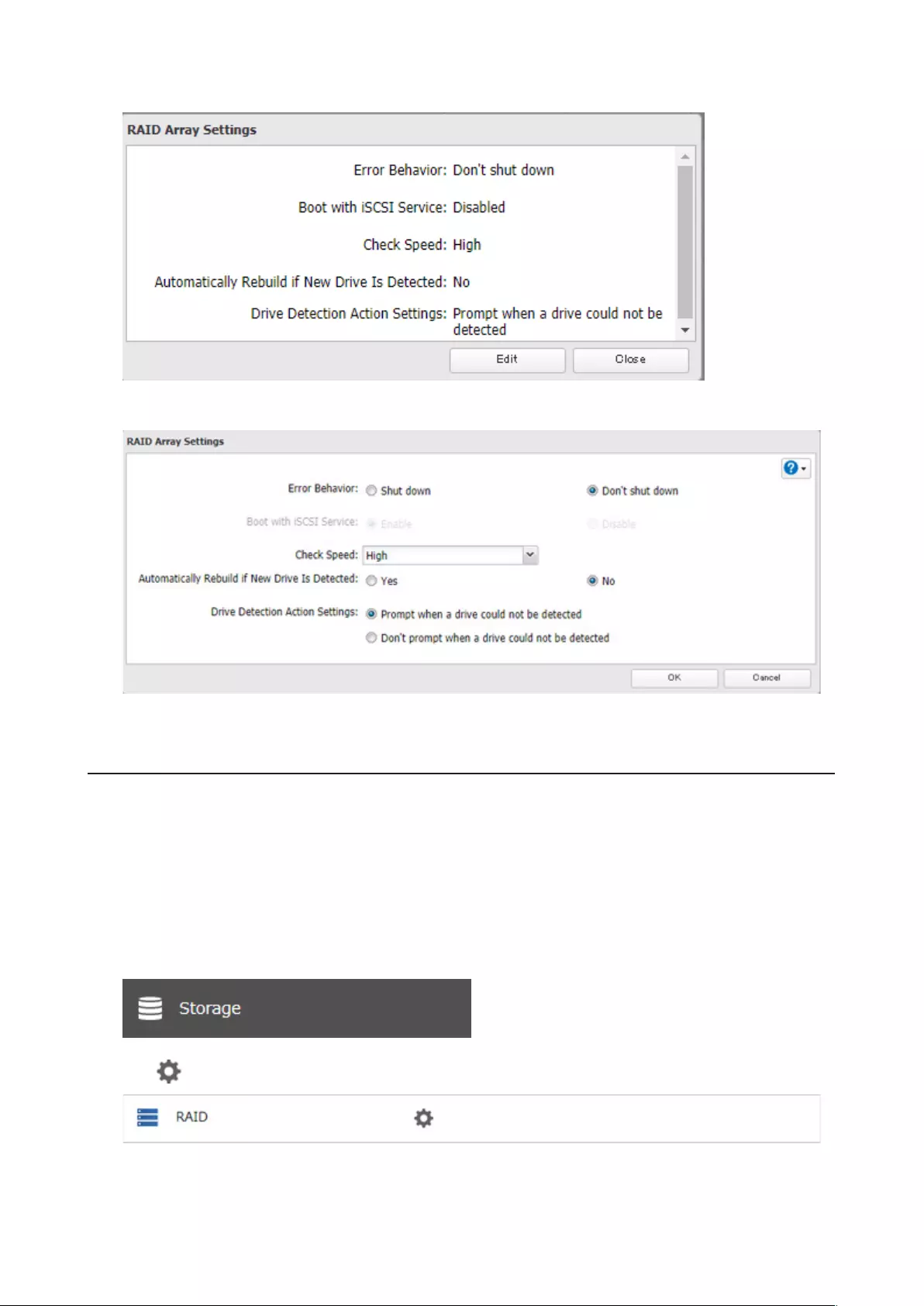
The TeraStation can configure actions if a drive used for the RAID array cannot be mounted when booting.
Displaying or Hiding the Confirmation Screen
Configure to display or hide the confirmation screen for selecting actions if a drive used for the RAID array cannot be
mounted when booting. It is configured to display the confirmation screen by default. To hide the screen, follow the
procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
50
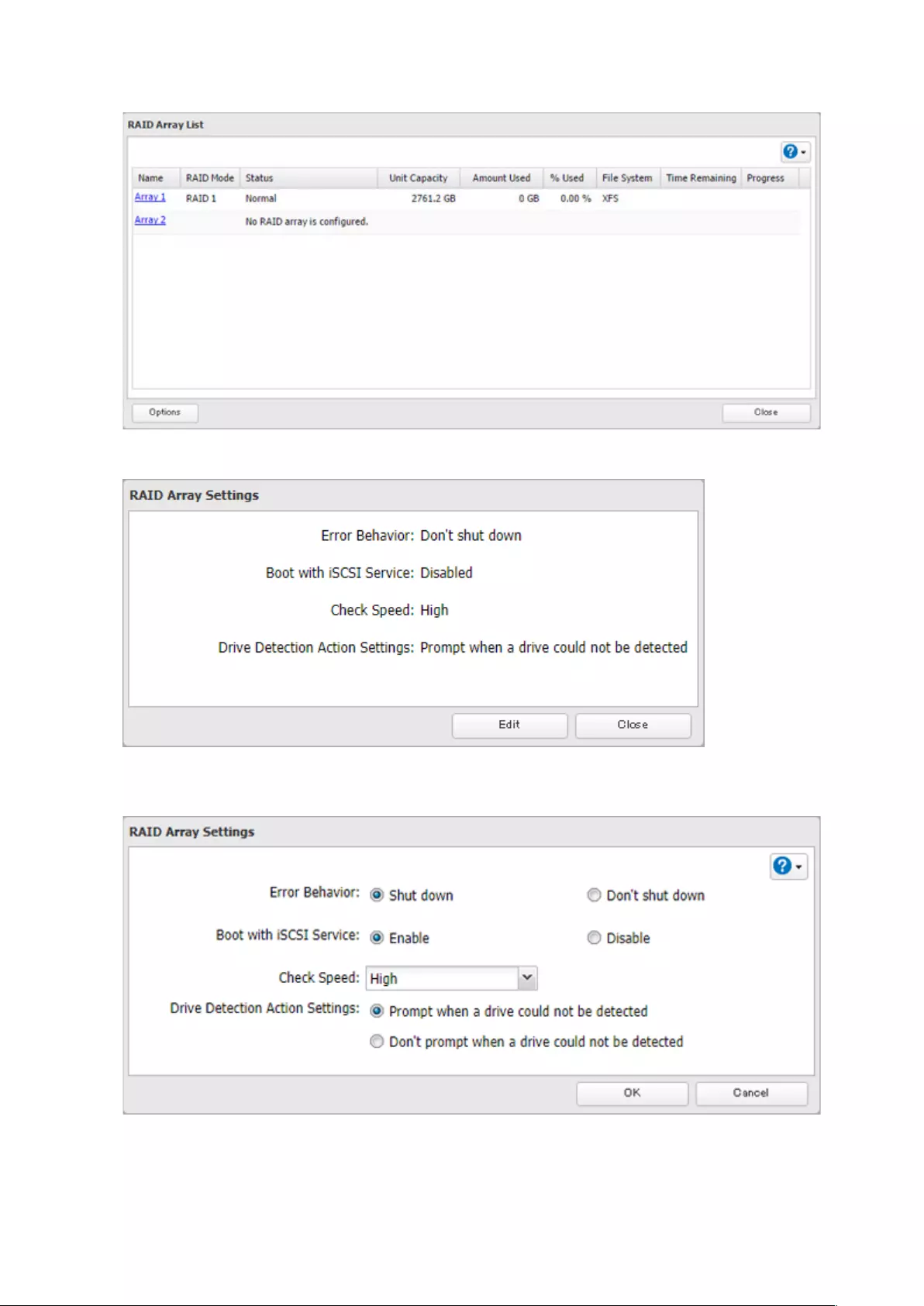
3 Click Options.
4 Click Edit.
5 Select the “Don’t prompt when a drive could not be detected” option to the right of “Drive Detection Action
Settings” and click OK.
When the confirmation screen is hidden, an undetected drive will automatically be dismounted from the TeraStation
and the TeraStation will be in degraded mode if a redundant RAID mode is configured. If RAID 0 is configured, the
51
RAID array will be corrupted so that data will be lost. It is recommended to proceed without changing settings that
the confirmation screen appears.
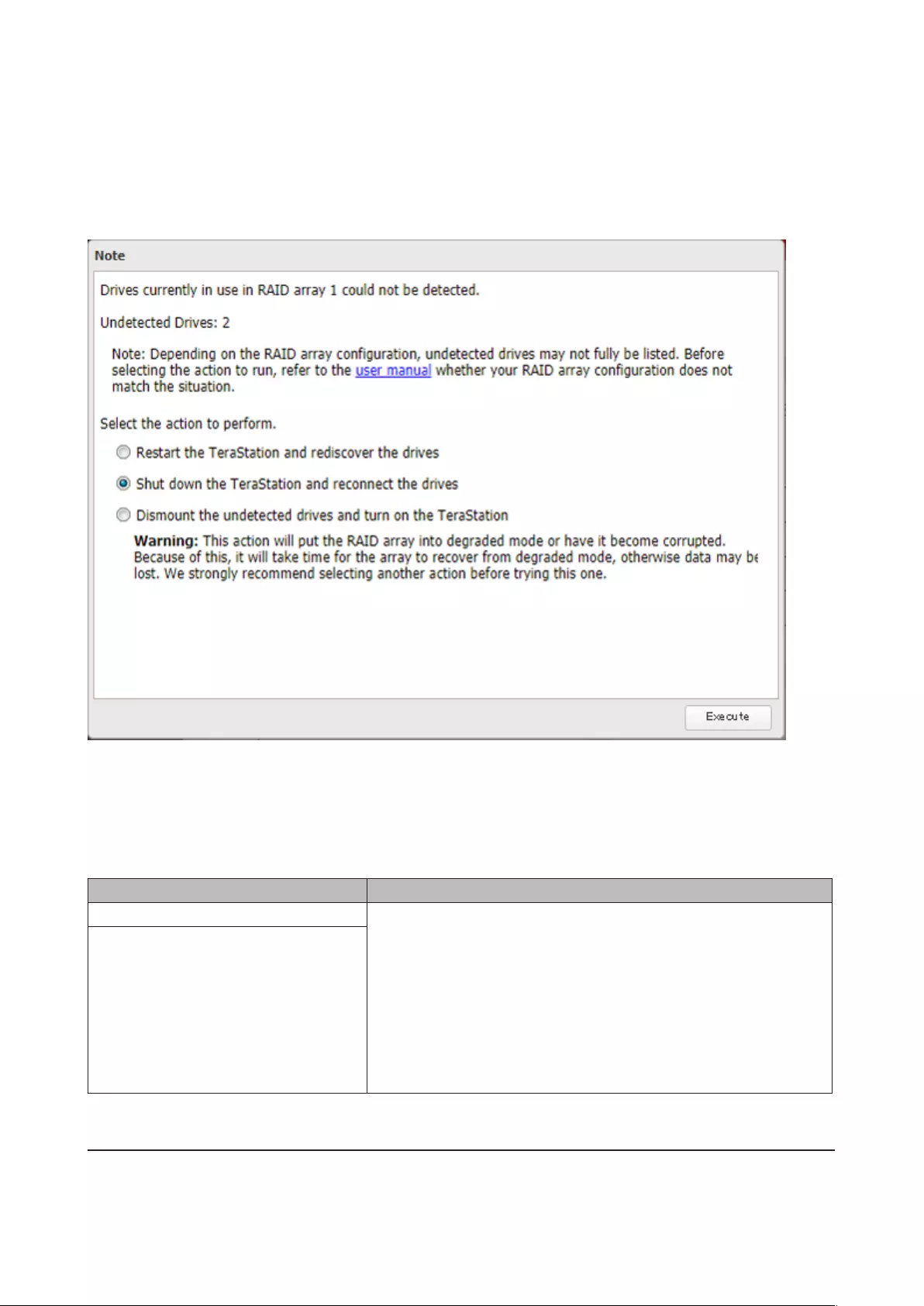
Selecting the Action on the Confirmation Screen
When having the confirmation screen displayed, the following screen will appear after logging in to Settings if the
drive used for the RAID array could not be mounted. Select the action to run when the screen appears.
Conditions and Corrective Actions If Undetected Drives Aren’t Displayed Properly
Even though you have configured to show the confirmation screen if a drive using for the RAID array cannot
be mounted, the undetected drives cannot be displayed properly under the following conditions. If you have
configured the RAID array as below, follow the procedure below for sure.
Conditions Corrective Actions
RAID 10 has been configured. 1 Select “Shut down the TeraStation and reconnect the drives” and
click Execute.
2 Confirm all drives have been inserted properly.
3 Press the power button and power on the TeraStation.
4 Log in to Settings and make sure the confirmation screen doesn’t
appear.
Multiple arrays have been configured.
Configuring a Hot Spare
If you have a hot spare configured and an array fails, the TeraStation immediately switches over to the hot spare. To
use a hot spare, you need an extra drive that’s not part of any array and a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array.
52
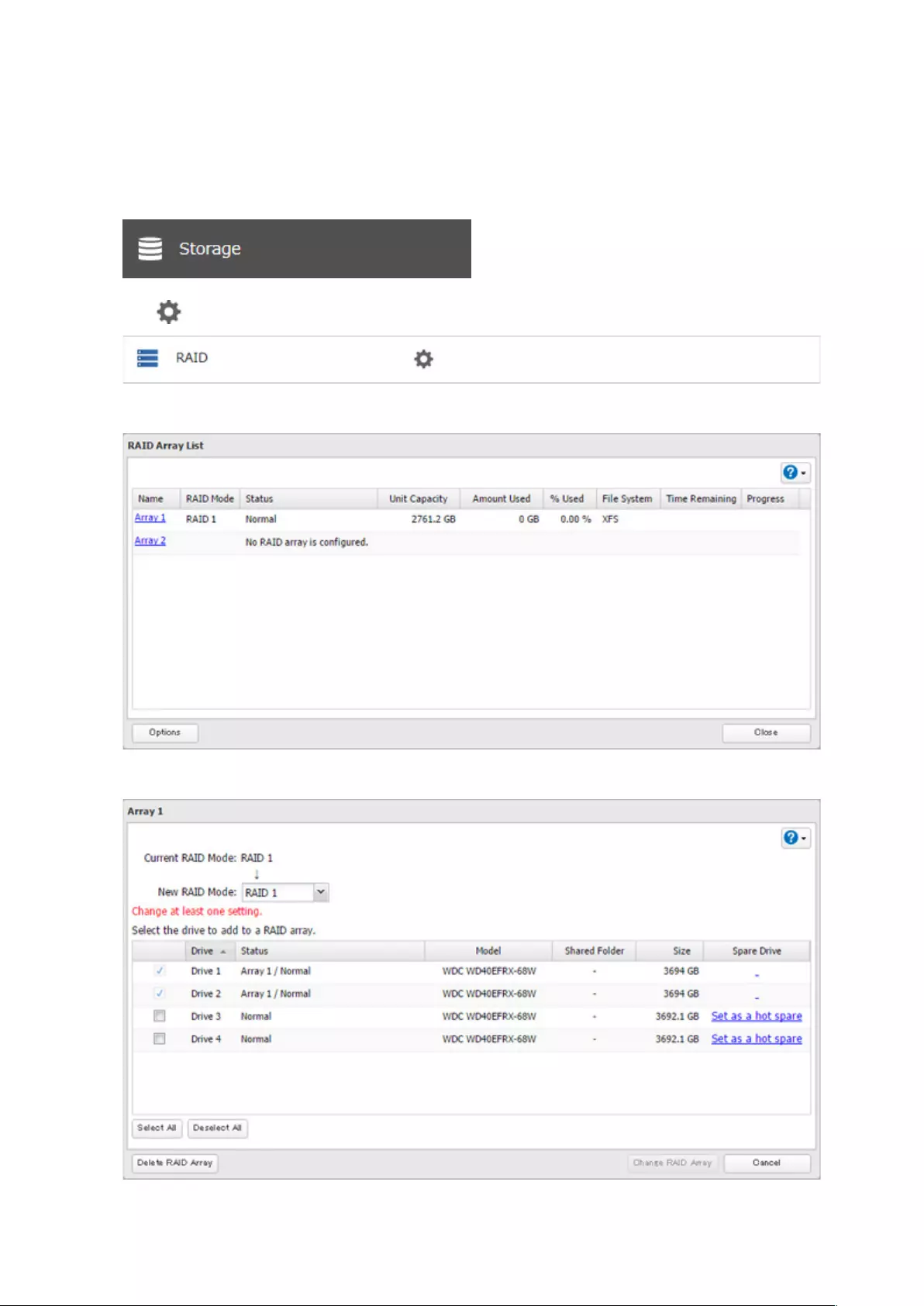
Notes:
• All data on the hot spare drive is deleted when it is configured as a hot spare and again when it changes from a
spare to a drive in the array.
• A hot spare cannot be configured for TeraStation models with only two drives.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Choose a RAID array.
4 Click Set as a hot spare.
53
5 Click Yes.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Click OK when finished.
Note: To turn the hot spare back to a normal drive, choose Set as a normal drive.
RMM (RAID Mode Manager)
With RMM, you can create or expand a RAID array without erasing the data on the drives.
Changing from JBOD to RAID 1
You must have at least two drives available in JBOD (not in a RAID array) to build the RAID 1 array with RMM.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
3 Choose a RAID array.
54
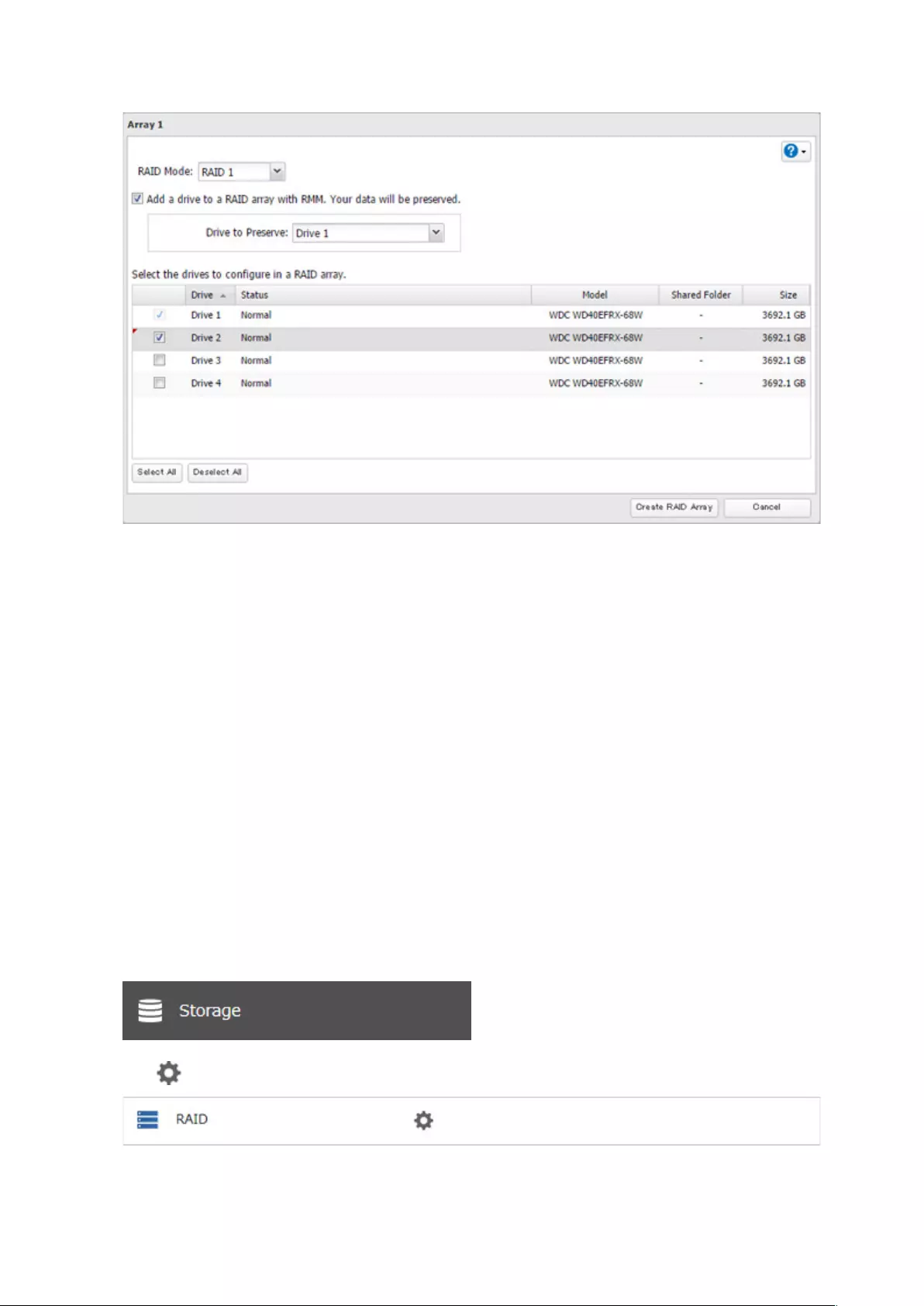
4 Set the RAID mode to “RAID 1”.
5 Select the “Add a drive to a RAID array with RMM. Your data will be preserved.” checkbox.
6 Select the drive whose data will be saved from the drop-down list.
7 Select the drive to add to the RAID array.
8 Click Create RAID Array.
9 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
10 Click OK when finished.
Adding a Drive to an Existing RAID Array or Changing the RAID Mode While Adding
a Drive
You can add a drive to a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array. Drives in JBOD can be added to the RAID array.
Note: RMM can be used to expand an array by one drive per operation. To expand by two or more drives, RMM must
be performed multiple times.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “RAID”.
55
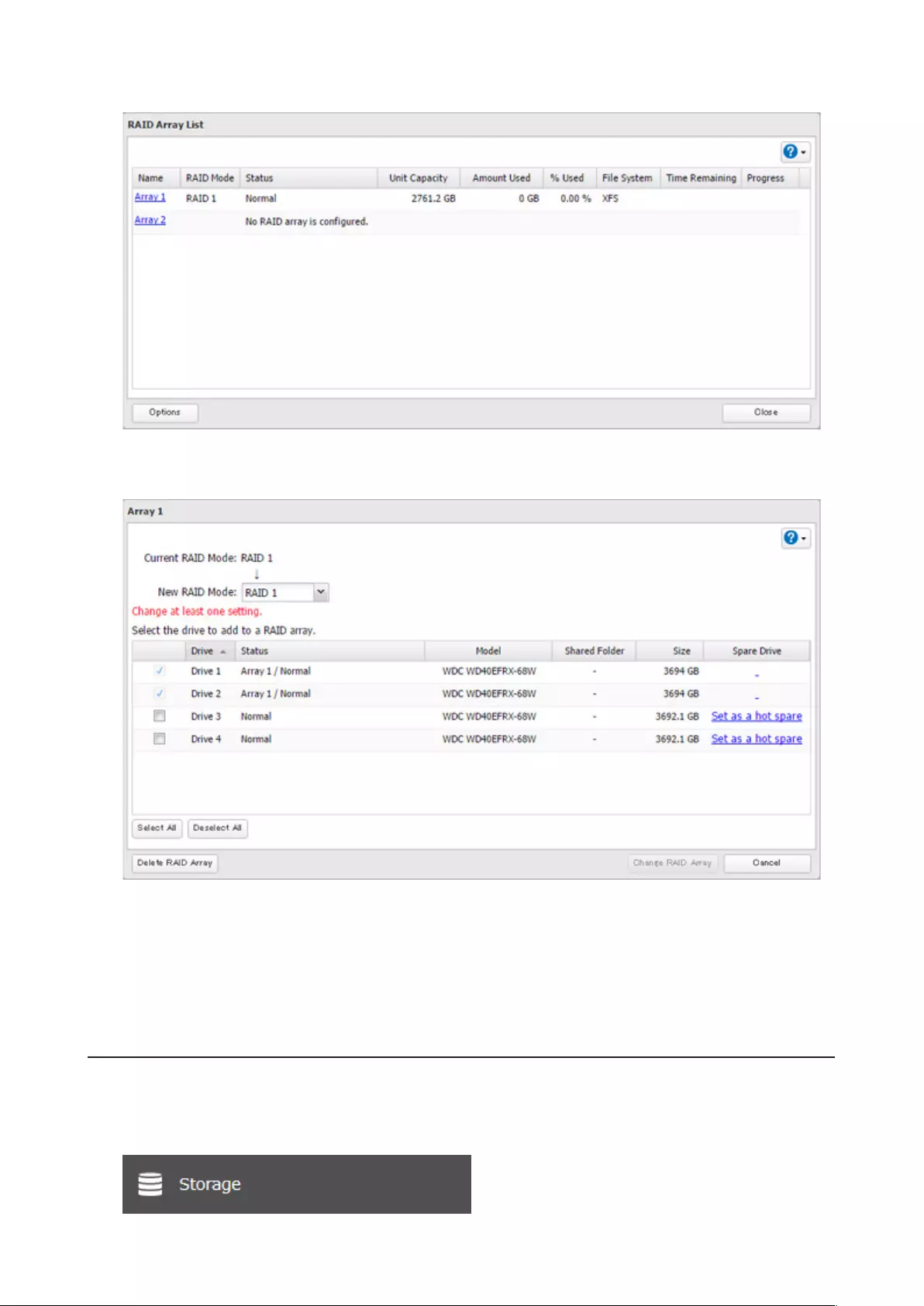
3 Choose a RAID array.
4 Select one drive to add to the RAID array. If changing the RAID mode, choose the desired mode for the array
from the drop-down list. If not, keep the current RAID mode as is.
5 Click Change RAID Array.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Click OK when finished.
RAID Scanning
A RAID scan checks you RAID array for bad sectors or blocks and if it finds any, it automatically repairs them. Arrays
other than RAID 0 are supported. For best results, run a RAID scan regularly.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
56
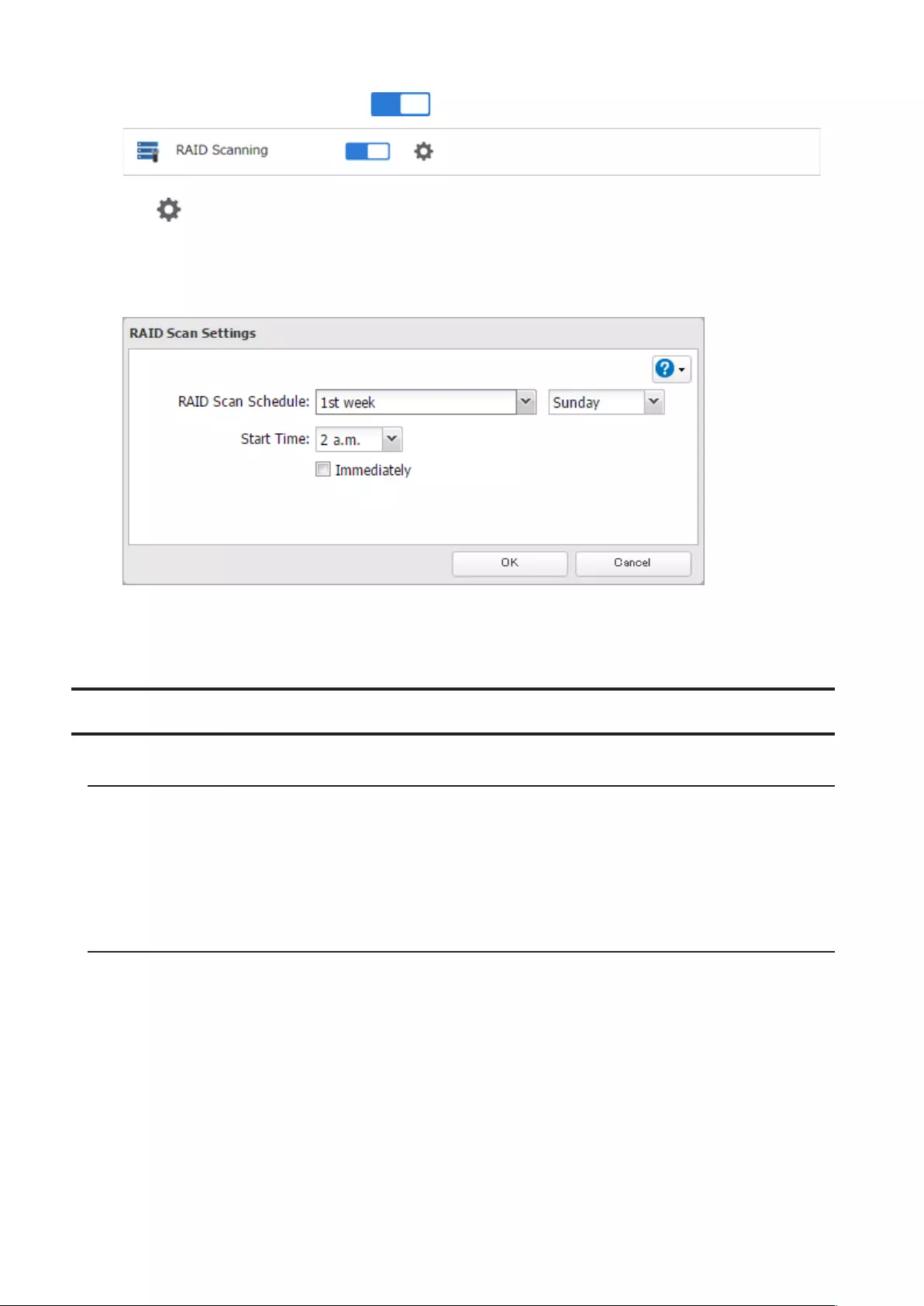
2 Move the RAID scanning switch to the position to enable RAID scanning.
3 Click to the right of “RAID Scanning”.
4 Click Edit.
5 Select when to run the scan and click OK.
Notes:
• Select the “Immediately” checkbox to run a RAID scan immediately.
• To stop a RAID scan, click Cancel RAID Scan.
Adding an External Drive
Connecting an External Drive
Your TeraStation includes USB ports (the number of ports depends on your model), and you can connect external
drives to these ports. Once connected, they appear as shared folders on the TeraStation. Formatted drives are
detected automatically. Unformatted drives should be formatted in Settings.
After a USB drive is recognized, Windows adds “usbdisk x” in File Explorer, where “x” is the USB port which the drive is
connected.
Compatibility
The following USB devices are supported by the TeraStation:
• USB storage devices
• Card readers (except for card readers that can recognize two or more memory cards)
Buffalo external USB drives are recommended.
Supported file systems for external drives are below:
• FAT32
• EXT3
• XFS
• NTFS
• HFS Plus (read-only)
• exFAT
57
Connect only one device to each USB port of the TeraStation. Note that only the first partition of a connected USB
drive is mounted. Additional partitions are not recognized.
Notes:
• Backup data from macOS may include characters that cannot be written to FAT16 or FAT32 drives such as “.DS_
Store”. For best results, reformat the drive before using it as a backup target.
• If your USB 3.0 drive is not reconfigured after rebooting the TeraStation, unplug and reconnect it.
• When copying a file that is over 100 MB to a FAT32-formatted USB drive using File Explorer, an error message may
appear. In such a case, use an FTP or SFTP connection to copy the file.
• When copying files from a shared folder to a FAT32-formatted USB drive, the progress bar may not be displayed
or the file copying may fail. Using a file system other than FAT32 is recommended for the USB drive.
Dismounting Drives
If the TeraStation is powered on, dismount drives (internal and external) before unplugging them. You may
dismount external drives using the function button, or dismount any drive from Settings. If the TeraStation is off,
then all drives are already dismounted and may be unplugged safely.
Note: Do not dismount internal drives while a RAID array is rebuilding or RMM is being configured. If you do, data on
the drives may be lost.
Dismounting with the Function Button
Note: If using the TS51210RH series TeraStations, dismount USB drives from Settings.
When you press the function button, the TeraStation will beep once. Press and hold the button until the TeraStation
beeps again and the button starts blinking blue. It will take about 6 seconds. When the dismount is finished, the
function button will stop blinking and return to glowing. You may now unplug any USB drives safely.
After 60 seconds, the function button will go out and any drives that have not yet been unplugged will be
remounted.
Dismounting from Settings
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click Drives to dismount an internal drive or USB Drives to dismount an external drive.
58
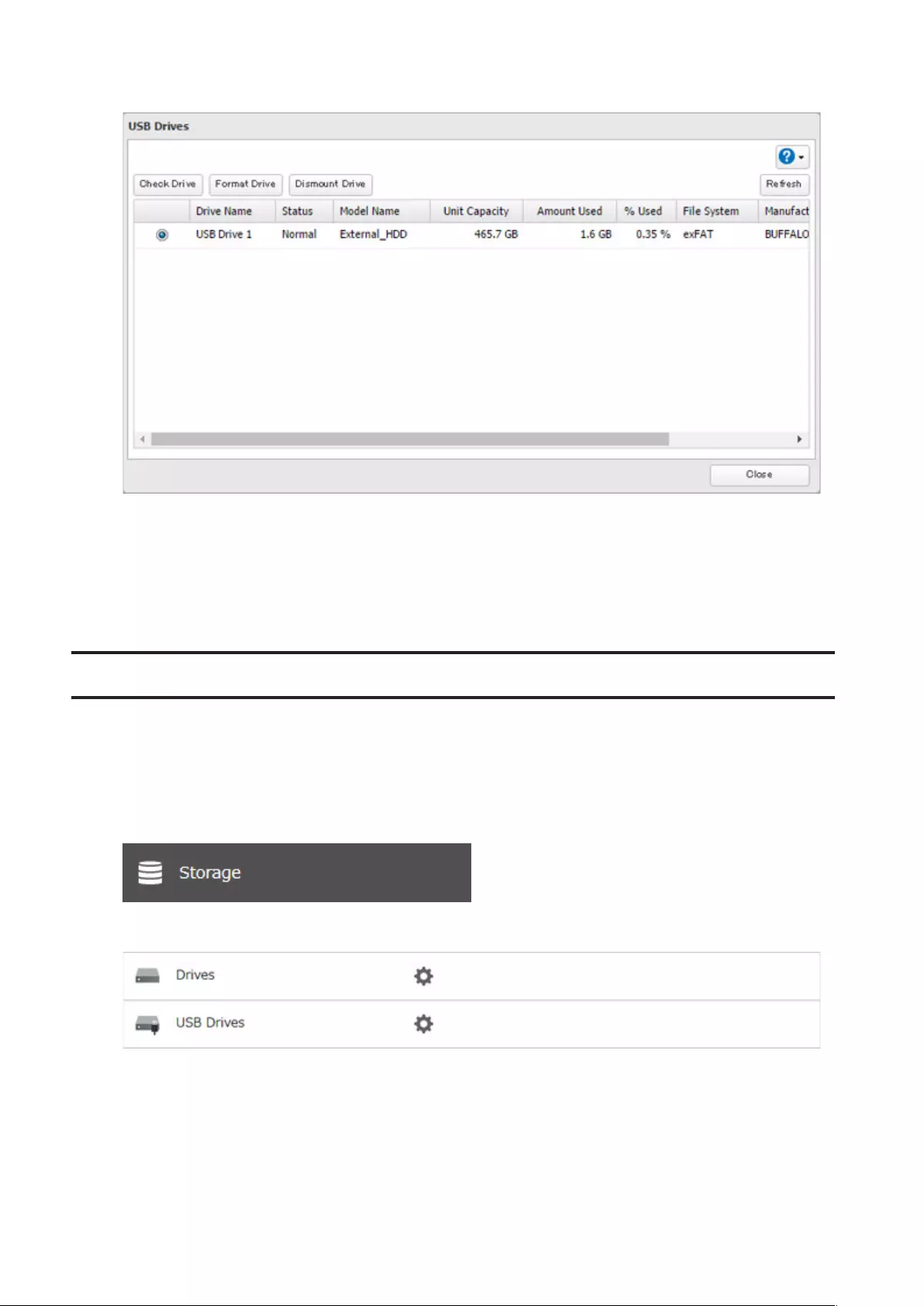
3 Select the drive to dismount and click Dismount Drive.
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 When the dismounting process is complete, it is safe to unplug the drive. Disconnect the drive from the
TeraStation.
Note: To remount the drive, unplug it and then plug it back in.
Checking Drives
A drive check tests the data on a drive in the TeraStation or one that is connected via USB for integrity. Errors are
fixed automatically. With large drives, a drive check may run for many hours. Shared folders cannot be accessed
during a drive check. Do not turn off the TeraStation until the drive check is finished. Use the procedure below to run
a drive check.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Select Drives to check an internal drive or USB Drives to check an external drive.
59
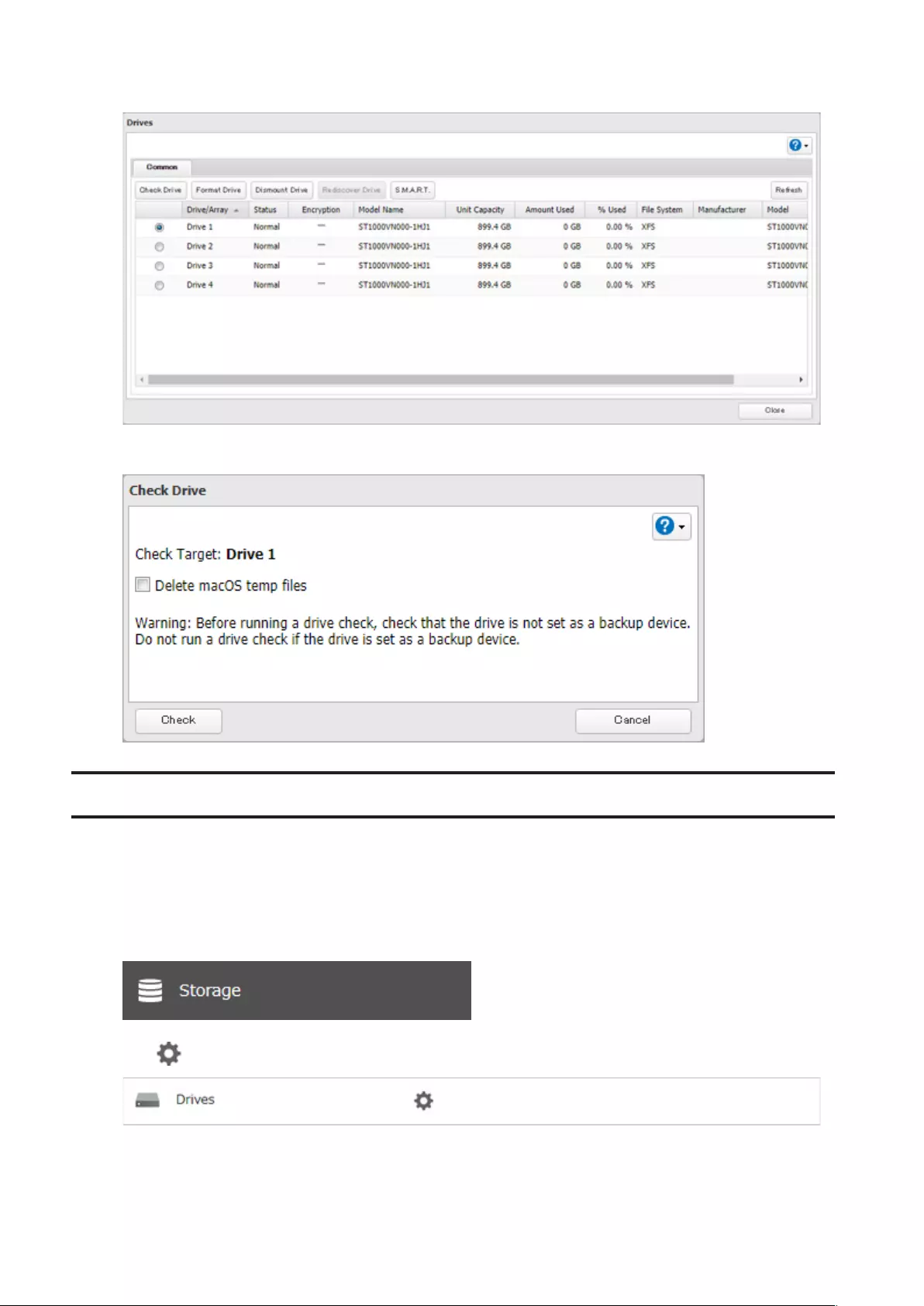
3 Select the drive or array to test, then click Check Drive.
4 Click Check. You have the option of deleting information files from macOS during the check if desired.
SSD Trimming
If an SSD has been running for a long time, drive performance may decline. To prevent this, an SSD TRIM may restore
drive performance. For best results, run SSD TRIMs regularly.
Note: This function is only available for SSD model TeraStations such as TS5210DF and may not appear on other
models.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
60
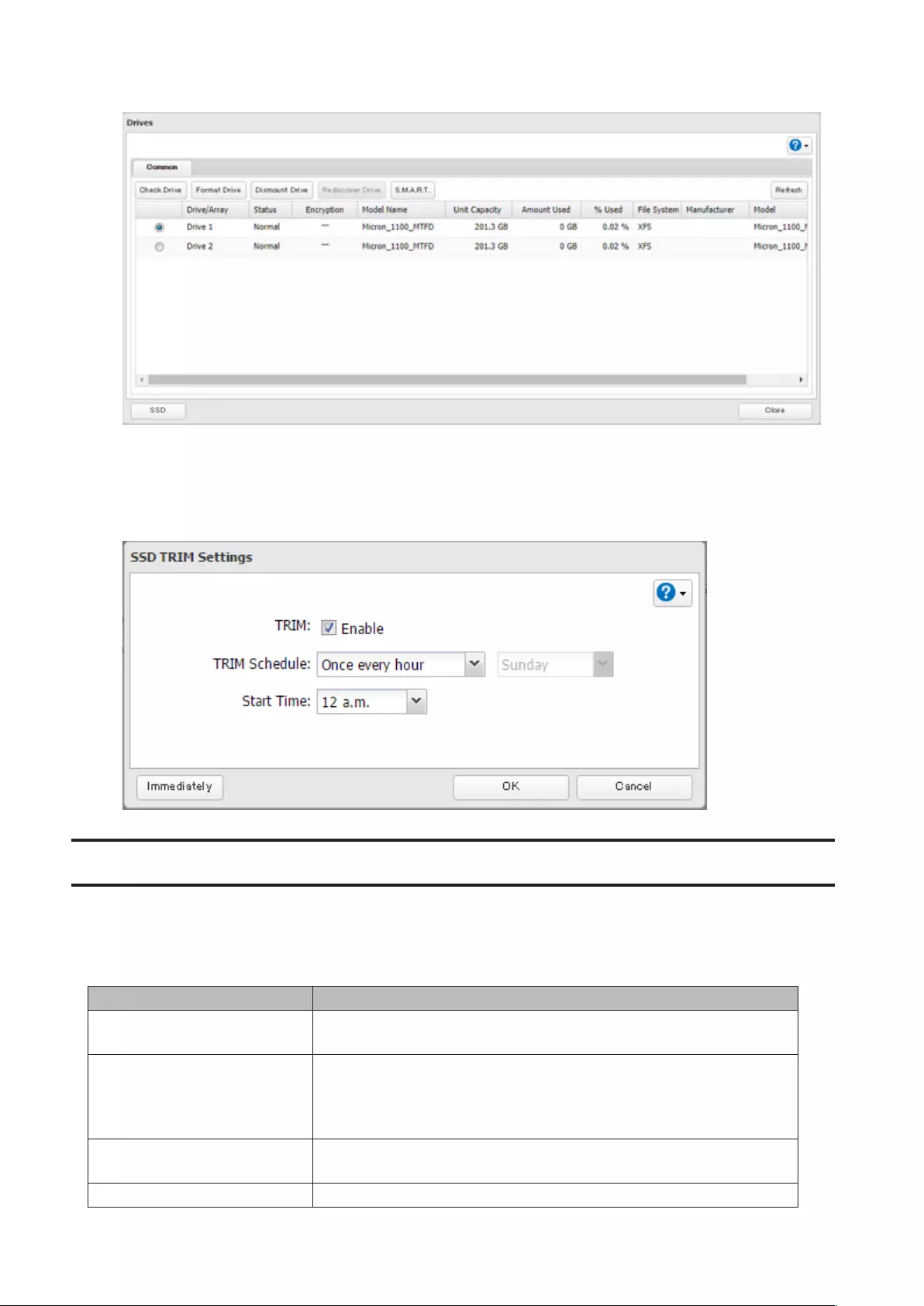
3 Click SSD at the lower left corner of the window.
4 Click Edit.
5 Select when to run the TRIM and click OK.
Note: Click Immediately to run an SSD TRIM immediately.
Data Protection Mode on the TS5210DF Series
Data protection mode will be enabled if the drives become following status.
• Two drives in RAID 1 have too many bad blocks.
• One drive in RAID 0 or as JBOD has too many bad blocks.
With this data protection mode, writing files and a part or all in the following functions are unavailable:
Category Unavailable operations
File Sharing Creating, changing, and deleting shared folders, emptying recycle bins,
enabling and disabling WebAccess
Storage
Checking and formatting drives, changing SSD TRIM settings, changing
RAID mode, changing and enabling RAID scans, enabling and disabling
LVM, deleting LVM volumes, creating, changing, and deleting iSCSI
volumes
Web Services Enabling cloud storage and Dropbox Sync, creating, changing, and
deleting jobs
Applications Enabling antivirus
61

Category Unavailable operations
Backup Configuring the device in data protection mode as a failover backup
device, enabling Time Machine, changing Time Machine settings
Management
Updating the firmware, activating and deactivating boot authentication,
changing log and boot authentication settings, changing RAID mode
using the setup wizard
Other
Recovering using drive setup, creating folders on the WebAccess
console, deleting, changing, copying, and moving files and folders on
the WebAccess console, uploading files on the WebAccess console
Notes:
• When data protection mode is enabled while computers are connected to the iSCSI volumes, this connection
may be disconnected. The iSCSI volumes can be reconnected even in data protection mode but replacing the
drives is recommended after backup.
• When data protection mode is enabled, files infected by a virus will not be inspected. When using antivirus,
configuring real-time scan is recommended. If your TeraStation enters in data protection mode, run a manual
scan before replacing the drives. To run virus scanning manually, refer to the “Virus Scanning” section in chapter 7.
• When data protection mode is enabled, and the TeraStation is configured as a backup device, the main
TeraStation will no longer detect the backup device TeraStation and the I33 message will appear. Stop failover
forcibly from the backup TeraStation’s Settings and replace the drives that have too many bad blocks.
• When data protection mode is enabled, cloud storage will be disabled.
S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) monitors internal drives to detect and report
various indicators of reliability, in the hope of anticipating failures. When a failure is anticipated by S.M.A.R.T., the
user may choose to replace the drive to avoid outages and data loss. Follow the procedure below to check S.M.A.R.T.
information for the TeraStation’s internal drives.
Note: S.M.A.R.T. information is only available for internal drives.
Displaying S.M.A.R.T. Information
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
62
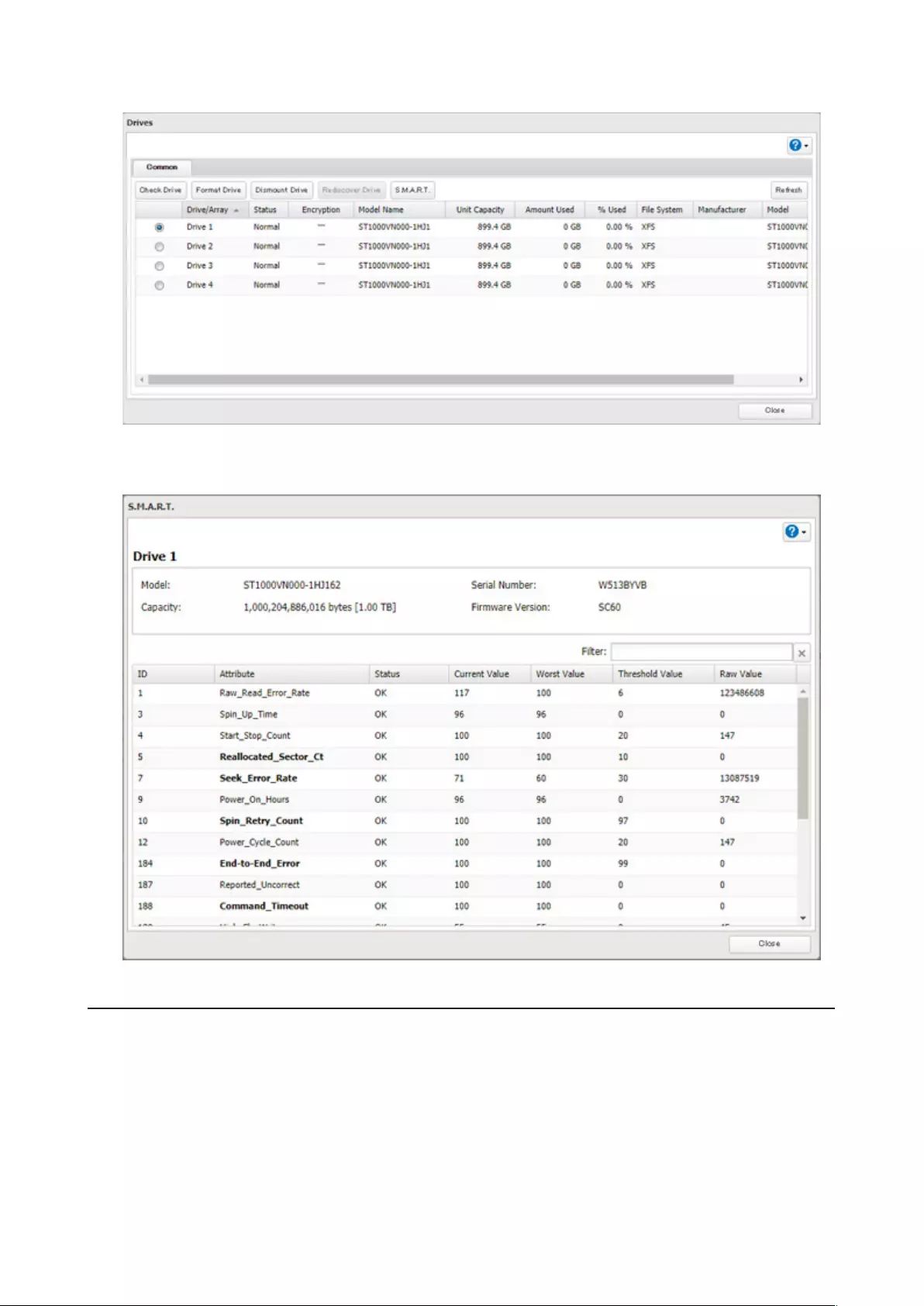
3 Select a drive to check and click S.M.A.R.T..
4 The S.M.A.R.T. information for the drive will be displayed. Different information may be displayed depending
on the brand of drives in your TeraStation. Critical attributes are displayed in bold.
Checking Drive Condition
Attributes with the worst value that is equal to or less than the threshold value may be significant. If an attribute
reports a failure, or has had one in the past, it will be displayed in the status column. In such a case, replacing that
drive is recommended.
63
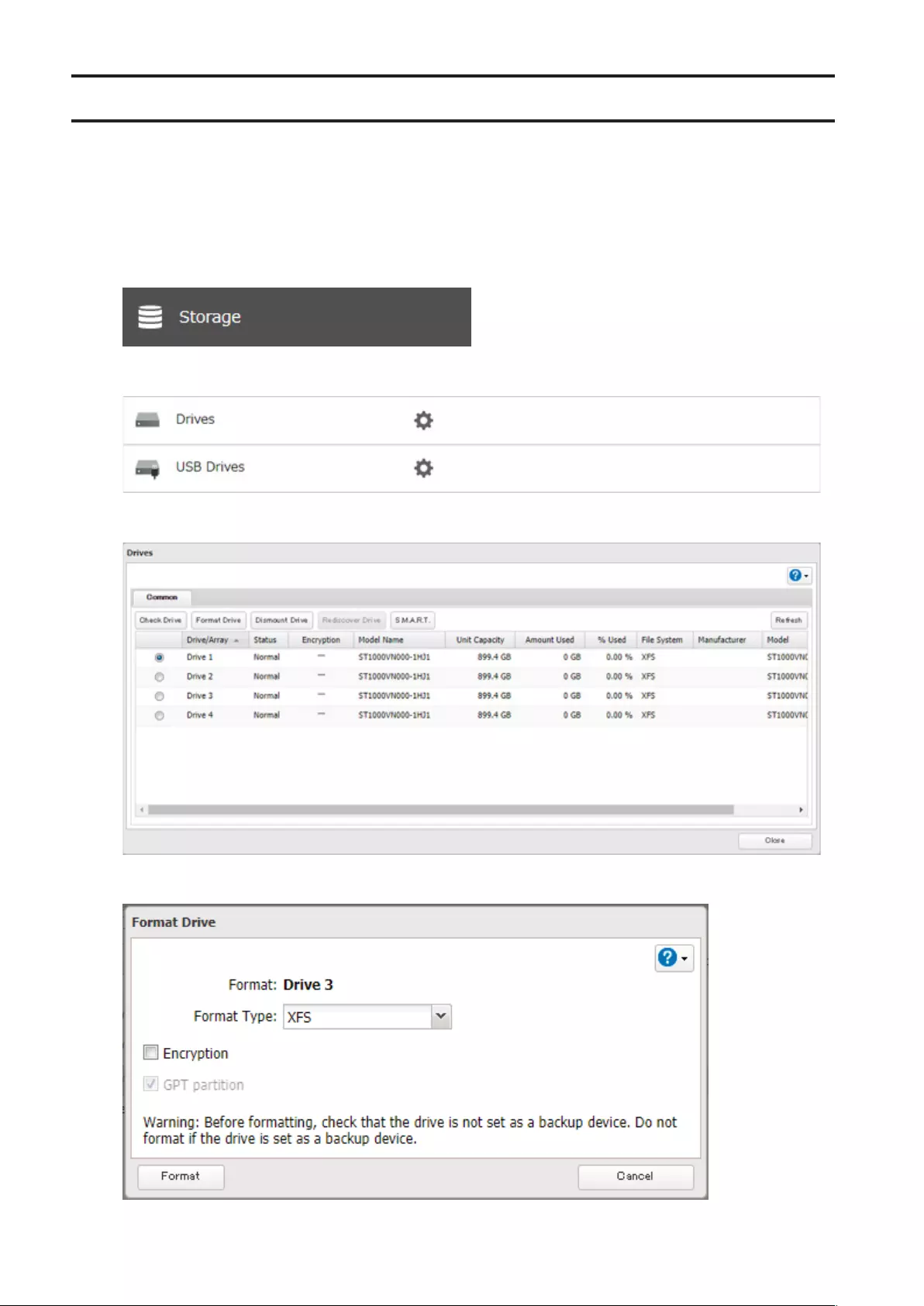
Formatting Drives
Notes:
• Under some circumstances, data deleted when a drive is formatted can be recovered. To ensure that data is “gone
forever”, a format might not be sufficient. See the “Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely” section below.
• After a drive is formatted, the “% Used” and “Amount Used” in Settings will not be 0. This is because some drive
space is used for the system area.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Select Drives to format an internal drive or USB Drives to format an external drive.
3 Select the drive or array to format, then click Format Drive.
4 Select a format type, then click Format.
64
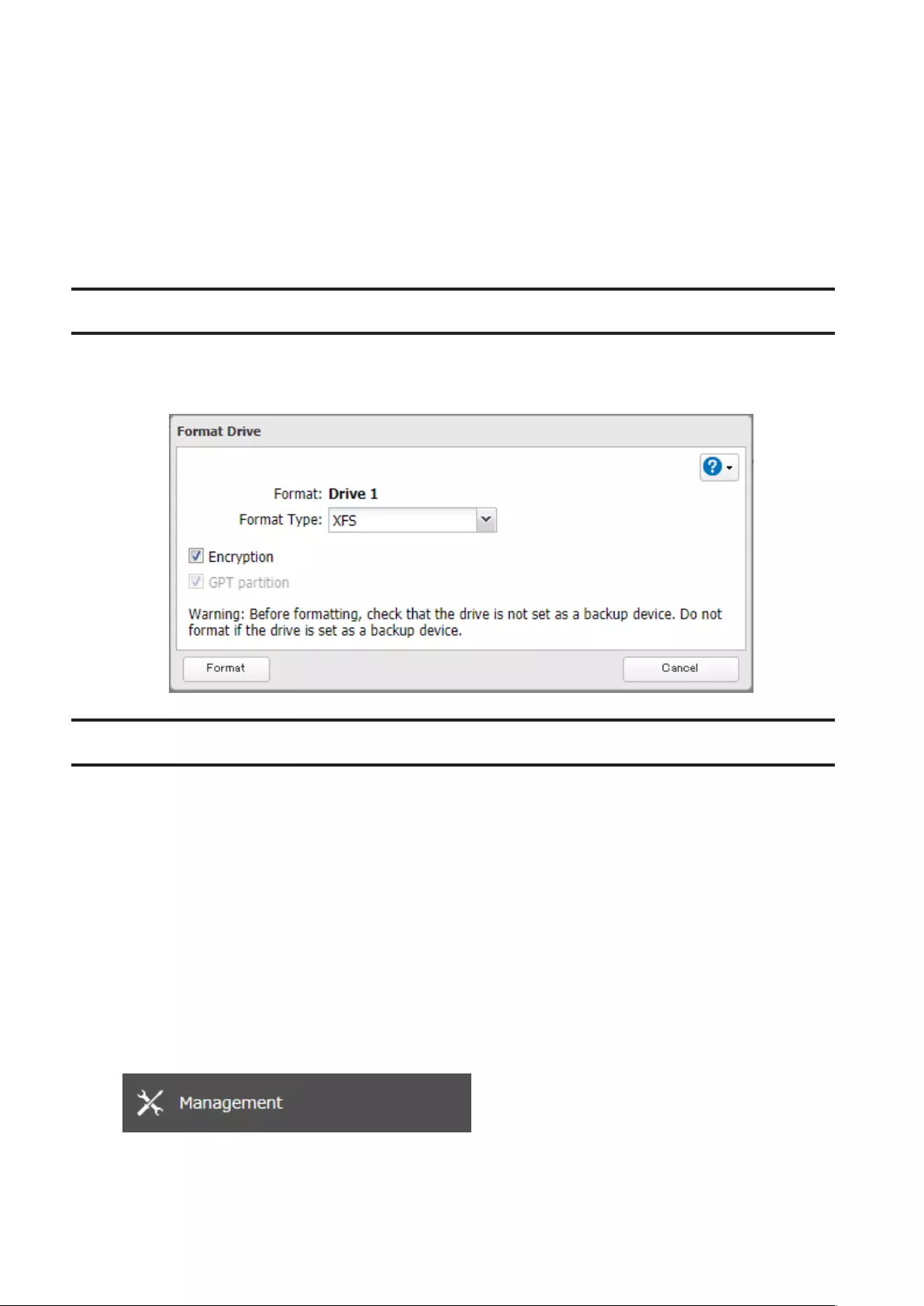
5 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Depending on the size and the formatted file system of your drive, the format may take several minutes or
several hours to complete. “Formatting” will be displayed on the LCD panel until the format is complete. Click
OK when finished.
Notes:
• Do not turn off or disconnect power to the TeraStation while formatting a drive.
• For drives of 2.2 TB or larger, make sure that the “GPT partition” checkbox is selected.
Encrypting Drives
Internal drives (and arrays) can be encrypted with 256-bit AES during formatting. Encrypted drives and arrays are
then readable only from that specific TeraStation. To decrypt a drive or array, clear the “Encryption” checkbox and
format it again.
Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely
Under some circumstances, data from formatted drives can be recovered. The drive erasure process in this section
does a much more thorough job of erasing data. This procedure is recommended for removing all data from a drive
in a way that makes it nearly impossible to recover with current tools. The TeraStation will then be in the following
state:
• All drives in JBOD
• An empty shared folder on each drive
• All settings returned to their default values
• All logs deleted
If you remove a drive and then erase all data on the TeraStation, the LCD panel will show the E22 message and the
number of the removed drive. You can still use the TeraStation.
Follow the procedure below to completely and permanently erase all data from your TeraStation.
1 From Settings, click Management.
65
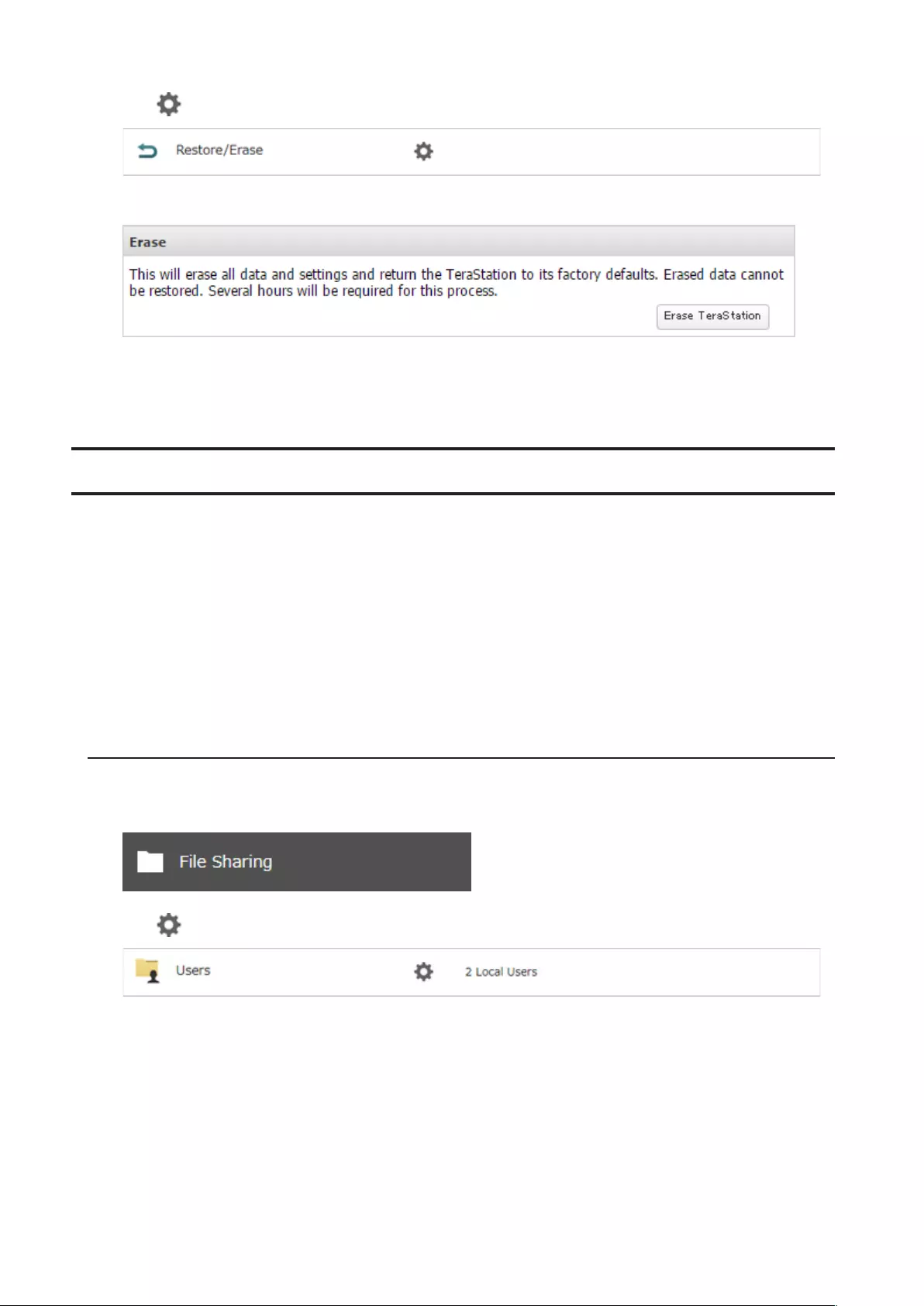
2 Click to the right of “Restore/Erase”.
3 Click Erase TeraStation.
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 All data on the TeraStation will be permanently erased.
Drive Quotas
You can set a drive quota to limit drive space for each user or group. You can also set a threshold. If the drive space
exceeds the configured threshold, an email notification will be sent. To configure email notifications for the drive
quota, refer to the “Email Notification” section in chapter 7.
Notes:
• When using quotas, disable the recycle bin or empty the trash folder often. The limited space includes the space
used for trash.
• Quotas apply per drive or per array. If a quota is set to 1 GB, each array or drive can use a maximum of 1 GB.
• Quotas cannot be set for external drives connected to the TeraStation.
• If both user and group quotas are configured for a user, the most restrictive quota will always apply.
Quotas for Users
Follow this procedure to limit the shared folder drive space available for a user.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Users”.
3 Select the user that will be given a quota and click Edit. If you want to set a quota for a new user, create a user
by referring to the “Adding a User” section in chapter 3.
66
4 Enable quotas, choose the alert and the maximum amount of space the user will be allowed to use, and click
OK.
Note: If you change the primary group, restart the TeraStation to apply the quota settings.
Quotas for Groups
Follow the procedure below to limit the space for shared folders that each group can use.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Groups”.
3 Select the group that will be given a quota and click Edit. If you want to set a quota for a new group, create a
group by referring to the “Adding a Group” section in chapter 3.
4 Enable quotas, choose the alert and the maximum amount of space the group will be allowed to use, and click
OK.
5 Click Close.
67
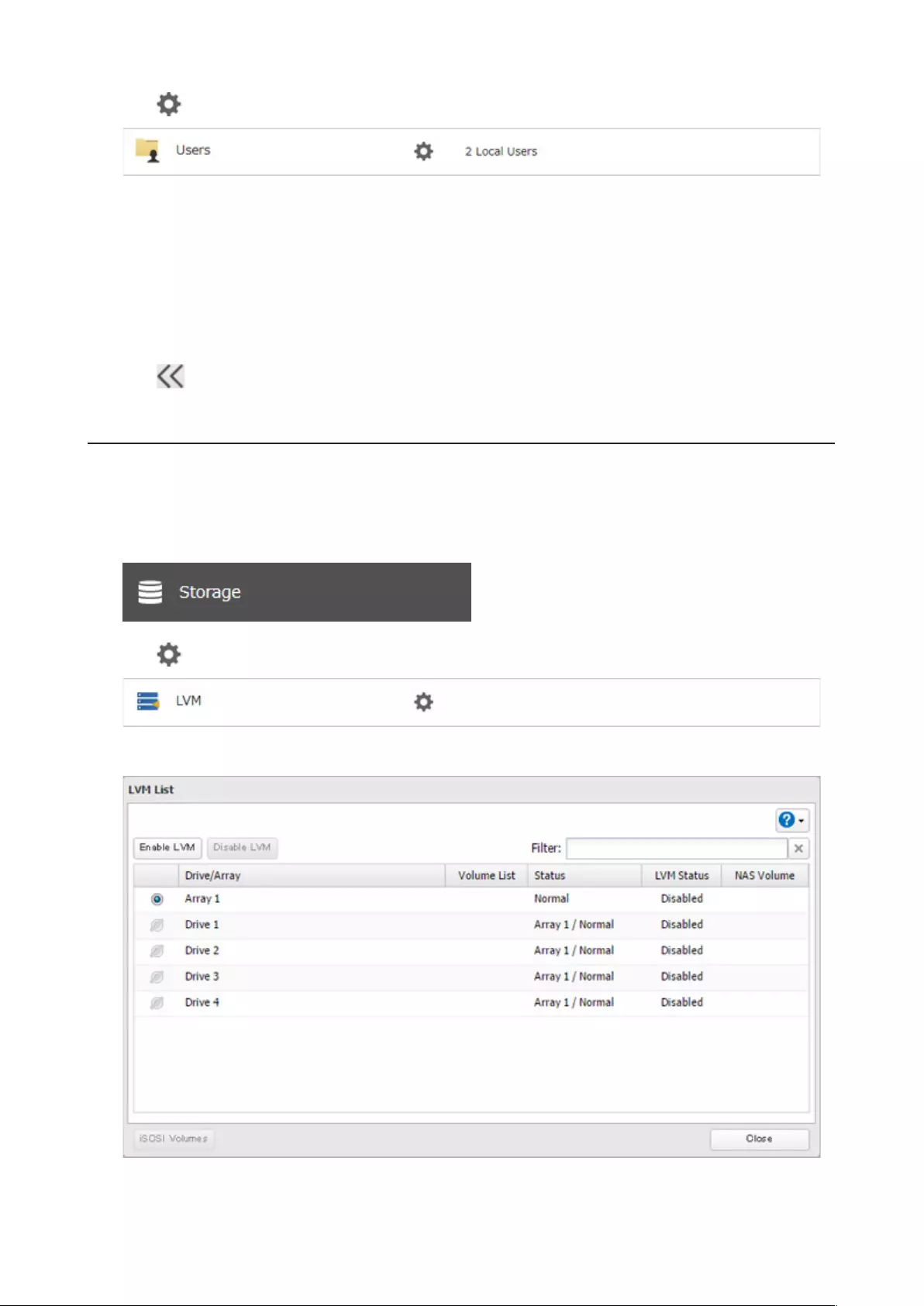
6 Click to the right of “Users”.
7 Select the user that will inherit the group quota settings and click Edit. If you want to add a new user to a
group with a quota, create a user by referring to the “Adding a User” section in chapter 3.
8 Select the group’s checkbox to join and change the user’s primary group to the group with the quota, then
click OK.
9 Click Close.
10 Click at the top-right of Settings and select Restart.
Size Limits
If LVM is enabled, volumes can be created with maximum size limits.
Note: When creating an LVM volume, all data in the area where you specified for the LVM volume will be erased.
Before changing any settings, back up any important data.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “LVM”.
3 Select the drive or array where the volume will be located and click Enable LVM.
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
68
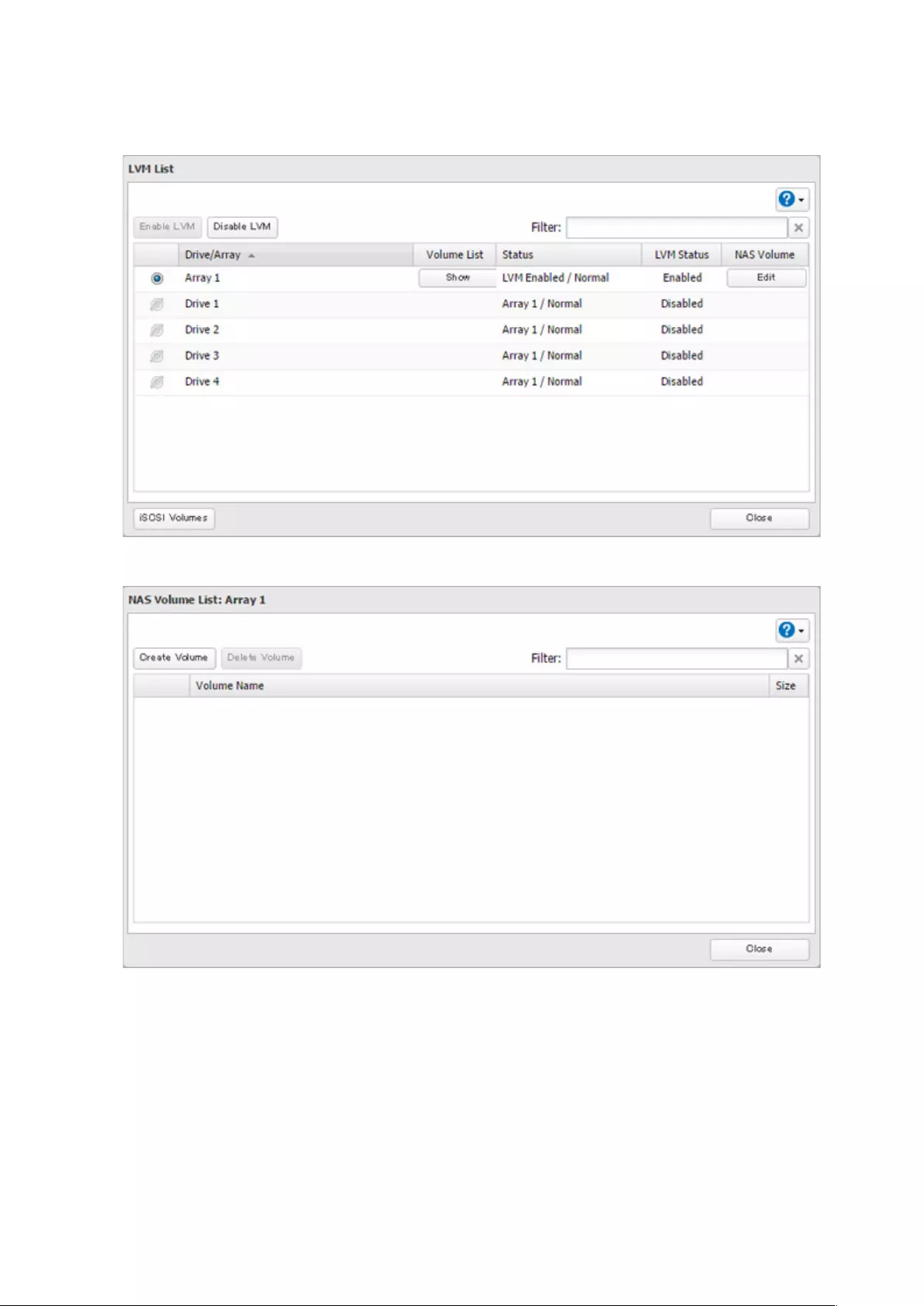
5 Click OK.
6 Click Edit under “NAS Volume”.
7 Click Create Volume.
69
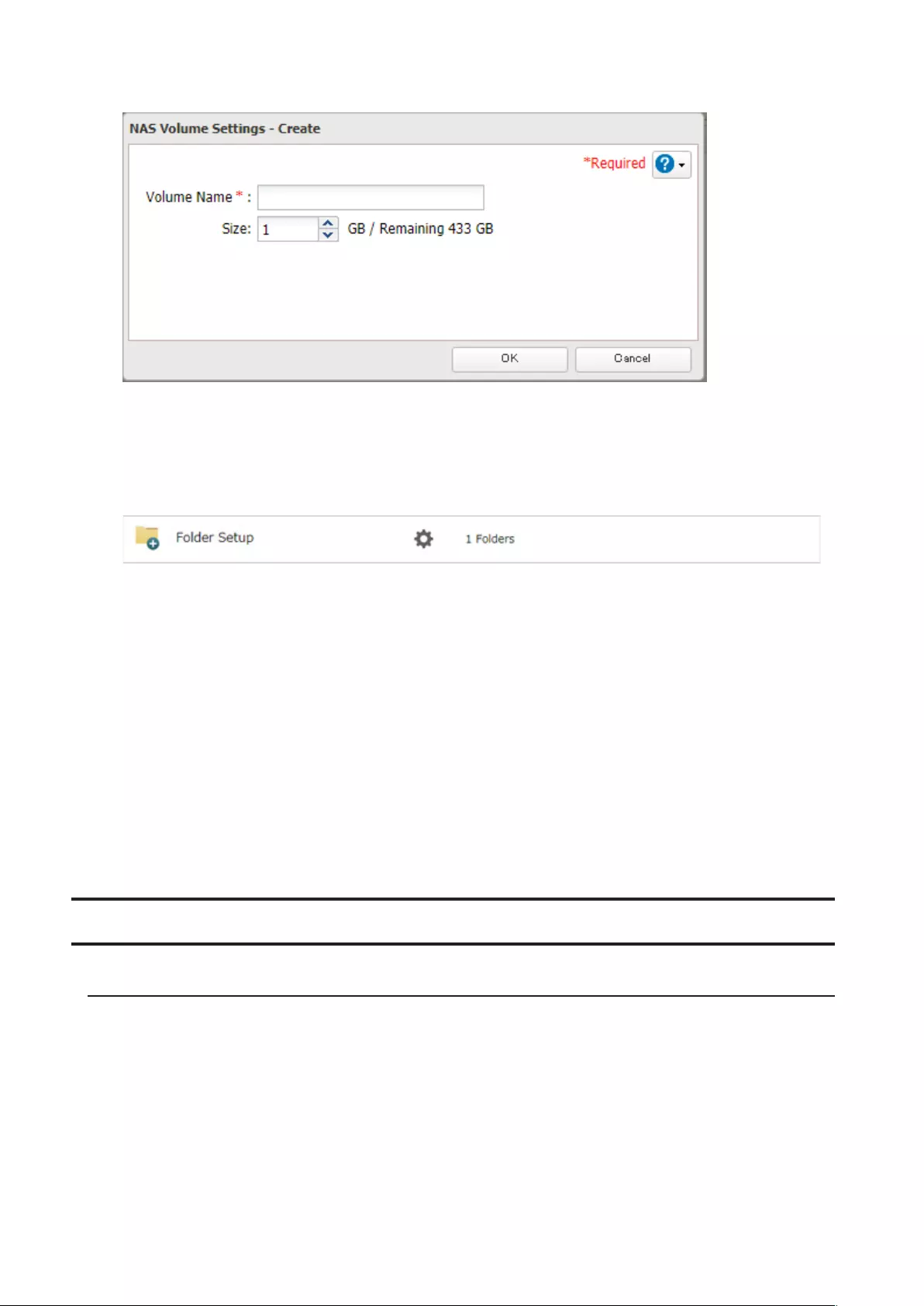
8 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
9 Click OK.
10 Click Close, then click Close again.
11 Navigate to File Sharing > Folder Setup.
12 Click Create Folder.
13 Configure the settings.
14 Select the volume that you created for “Drive/Array” on the Basic tab and click OK.
Notes:
• If you click Show under “Volume List”, the volumes will be listed on the screen and you can see if these volumes
are being used as iSCSI or NAS.
• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a volume as these words are reserved for internal use by
the TeraStation: array x, authtest, disk x, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, mediacartridge x, msdfs_root, mt-
daapd, printers, ram, spool, usbdisk x. Any instances of “x” denote a number (for example: array1 or disk3)
• If an LVM volume could not be mounted, try restarting the TeraStation. If an issue still exists, delete and recreate
the LVM volume. Deleting the LVM volume will erase data on the volume.
Using the TeraStation as an iSCSI Device
Introduction
iSCSI is a protocol for carrying SCSI commands over IP networks. Unlike traditional SAN protocols such as Fibre
Channel, which requires special-purpose cabling, iSCSI can be run over long distances using existing network
infrastructure. Normal Windows formatting such as NTFS is supported.
Differences Between NAS and iSCSI
With iSCSI, the TeraStation is connected to a single computer, such as a server. Other computers on the network
access files on the TeraStation through the computer it’s connected to. The TeraStation can be used as a local drive
from Windows Server. Features of Windows Server such as Active Directory can be used normally.
70
As a NAS, the TeraStation is a server, and computers (including other servers) on the network can access shared
folders on it directly. A separate server is not required, and features such as backup are built-in.
Network Configuration
Use gigabit or faster network equipment with iSCSI. For best results, a dedicated network for iSCSI is recommended,
separate from the regular network. By default, the IP address of the TeraStation is automatically assigned from a
DHCP server. However, in this case, if you turn off and restart the TeraStation, the IP address may be changed and
the volumes on the TeraStation may not be accessible. To avoid changing the IP address unexpectedly, using a static
IP address for the TeraStation is recommended.
Connection Tool
The Microsoft iSCSI Software Initiator is already installed on your computer. You don’t need to download and install
it.
Creating an iSCSI Volume
To use the TeraStation as an iSCSI drive, create a volume first. Configure the TeraStation as described below.
Notes:
• If the volume settings are changed, all data on the volume will be erased. Before changing any settings, back up
any important data.
• The TeraStation can have up to 255 volumes, but we recommend creating no more than 32. Exceeding this
volume amount may cause irreparable damage to the unit.
• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a volume as these words are reserved for internal use by
the TeraStation: array x, authtest, disk x, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, mediacartridge x, msdfs_root, mt-
daapd, printers, ram, spool, usbdisk x. Any instances of “x” denote a number (for example: array1 or disk3)
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Move the iSCSI switch to the position to enable iSCSI.
3 Click to the right of “iSCSI”.
71
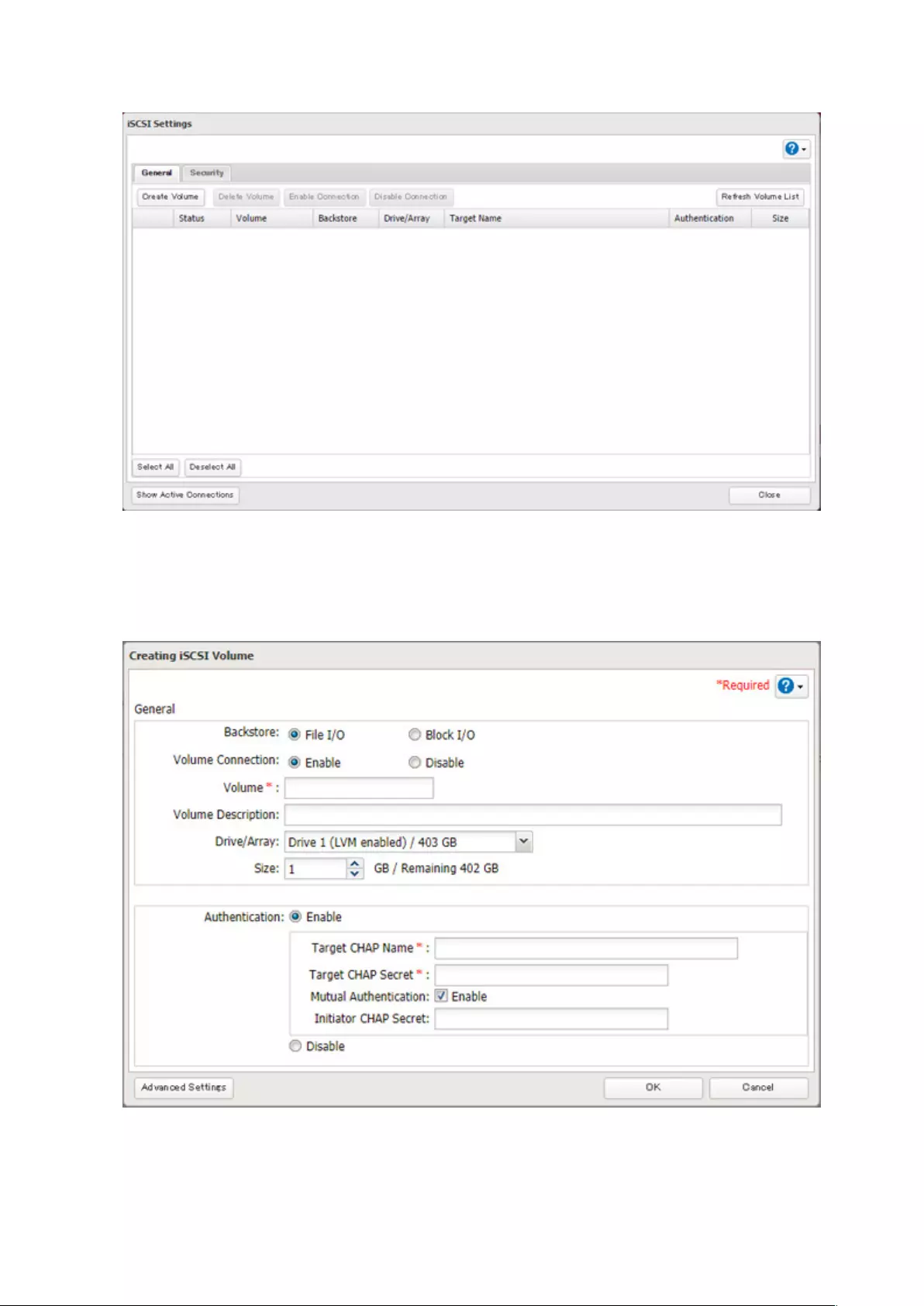
4 Click Create Volume.
5 Enter a volume name, volume description, drive or array where a volume will be created, and volume size. Click
OK when finished.
If you enabled LVM for the target drive or array, or selected “File I/O” for the “Backstore” option, the volume size
that you specify here can be changed later. To change the volume size, refer to the “Expanding Volume Sizes”
section below.
6 Click OK, then click OK again.
72
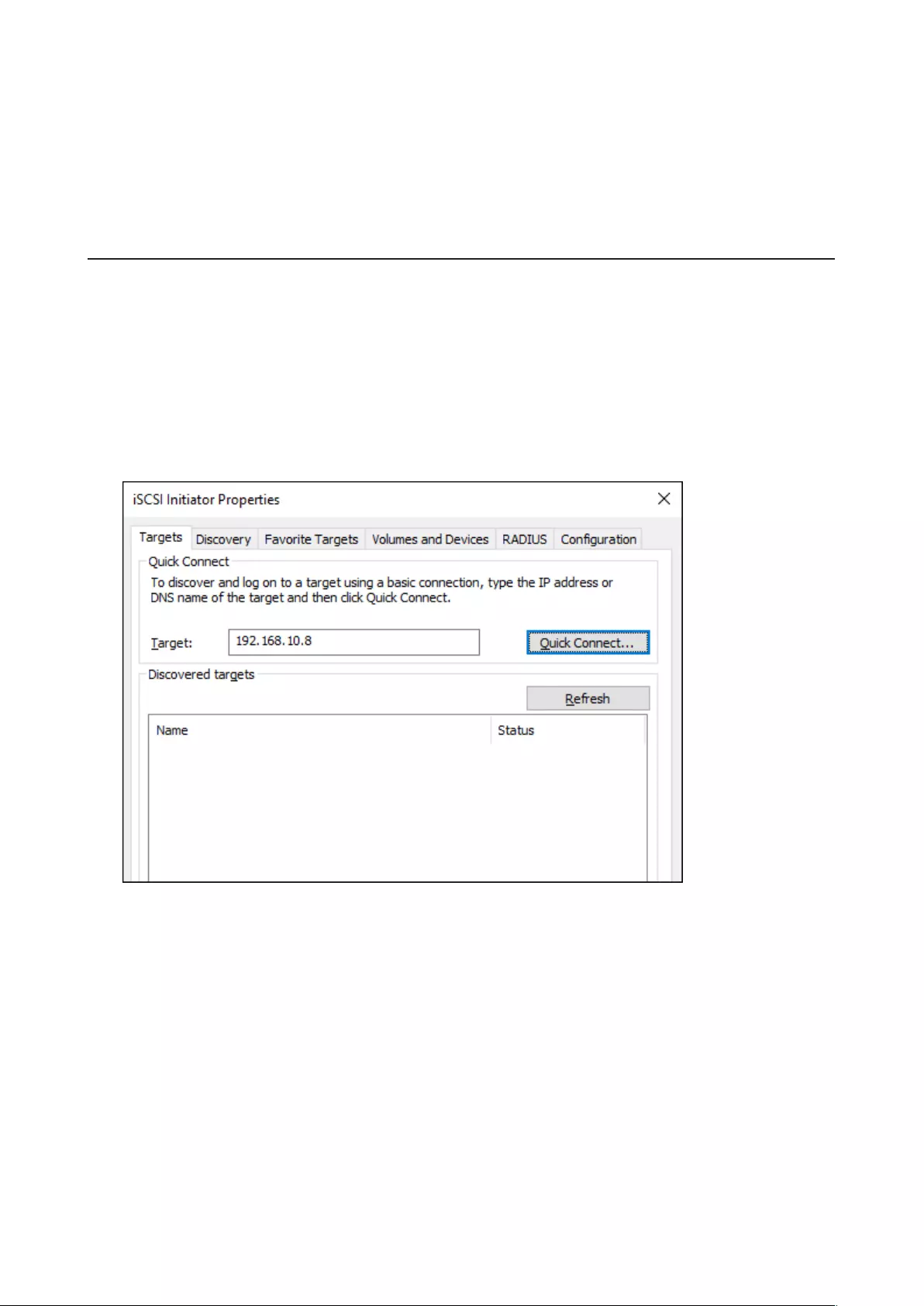
Notes:
• If you click Disable Connection for the selected volume in Storage > iSCSI in Settings, the selected iSCSI volume can
no longer be accessed. If you click Enable Connection, the volume will become accessible from the iSCSI initiator
software.
• If you selected “Block I/O” for the “Backstore” option, write cache (WCE) cannot be configured from the “Advanced
Settings” page.
Connecting or Disconnecting Volumes
Connecting Volumes
To connect a volume, follow the procedure below.
Note: Do not shut down the TeraStation while connecting to an iSCSI volume. It may cause unexpected data erasure.
Make sure all connections are disconnected before shutdown.
1 From Windows, navigate to Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > iSCSI Initiator.
2 Enter the IP address of the TeraStation into the “Target” field and click Quick Connect.
3 Confirm if the connection is established and click Done.
Formatting Volumes
If using the connected volume for the first time, the volume should be formatted to be used as a local drive. Follow
the procedure below for formatting.
1 From Windows, navigate to Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > Computer Management.
2 Click Disk Management.
When the “Initialize Disk” screen appears, click OK without changing any settings.
3 Right-click the drive volume that shows the status “Unallocated” and click New Simple Volume from the
displayed menu. Follow the screen to finish formatting.
73
When the formatting process is complete, the drive will be visible as an icon in Computer or This PC and can be used
as a normal drive on the computer.
Disconnecting a Volume
1 From Windows, navigate to Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > iSCSI Initiator.
The status of the connecting volume will be displayed as “Connected” under “Discovered targets”.
2 Select a volume to disconnect and click Disconnect.
3 Click Yes.
4 When the volume status is displayed as “Inactive”, the disconnection was carried out properly.
Using with Multiple Computers
If the TeraStation is divided into multiple volumes (or drives), it can be used with multiple computers. However,
multiple computers cannot be accessed from one volume (or one drive) at the same time.
Checking Whether iSCSI Volume Is Connected
To check whether an iSCSI volume is connected, navigate to Storage > iSCSI. Current volumes will be listed. If
“Connected” is displayed under “Status”, the volume is currently connected to the client.
Configuring Access Restrictions
A CHAP name and secret can be configured for the entire iSCSI volume or each existing volume. Access restrictions
can be configured so that entering a target CHAP name and secret is required for each connection.
The TeraStation can perform mutual authentication (two-way authentication). Dual passwords ensure that only
authorized client computers can access the volume on the TeraStation.
Follow the procedure below to enable access restrictions.
Configuring Access Restrictions for the Entire TeraStation
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “iSCSI”.
3 Click the Security tab.
74
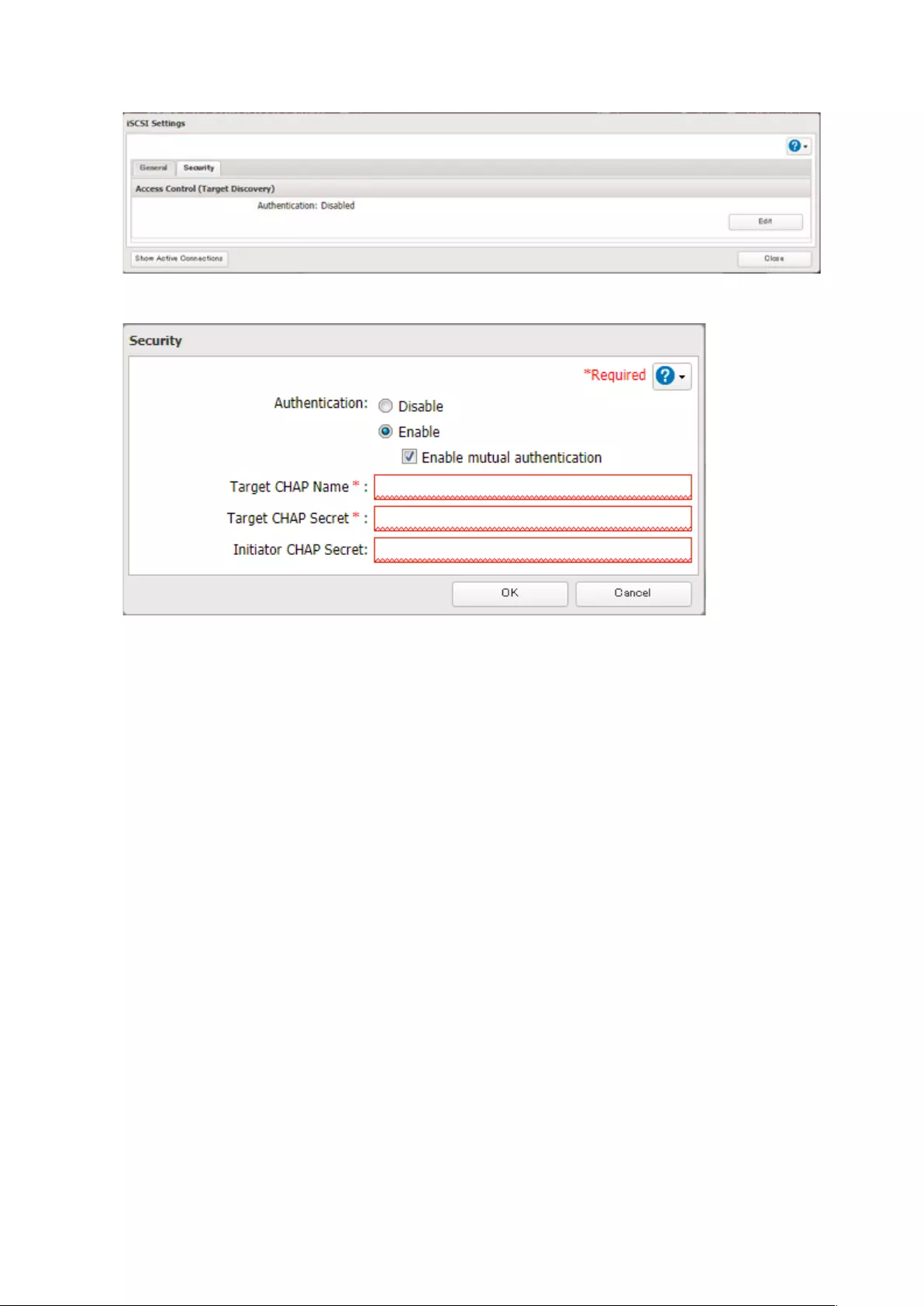
4 Click Edit under “Access Control (Target Discovery)”.
5 Enable authentication, enter the target CHAP name and secret, and click OK.
Note: To enable mutual authentication in addition to target CHAP name and secret authentication, select the
“Enable mutual authentication” checkbox and enter the initiator CHAP secret.
To search or connect the volume which has mutual authentication enabled from Microsoft iSCSI Initiator,
initiator CHAP secret settings should be configured.
6 Click OK when completed.
Connecting Volumes on the Access-Restricted TeraStation
If access restrictions are configured for the entire iSCSI volume, that volume will not be detected by Microsoft iSCSI
Initiator. To connect that volume, the target CHAP name and secret should be authenticated.
1 Open the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator.
2 Register the initiator CHAP secret to your computer first. If you didn’t enable mutual authentication, skip this
step.
Click CHAP on the Configuration tab. Enter the configured initiator CHAP secret into the “Initiator CHAP secret”
field and click OK.
3 From the Discovery tab, click Discover Portal.
4 Enter the TeraStation’s IP address into the “IP address or DNS name” field and click Advanced.
5 Select the “Enable CHAP log on” checkbox and enter the target CHAP name into the “Name” field and the
target CHAP secret into the “Target secret” field.
If mutual authentication is enabled, select the “Perform mutual authentication” checkbox.
6 Click OK, then click OK again.
75
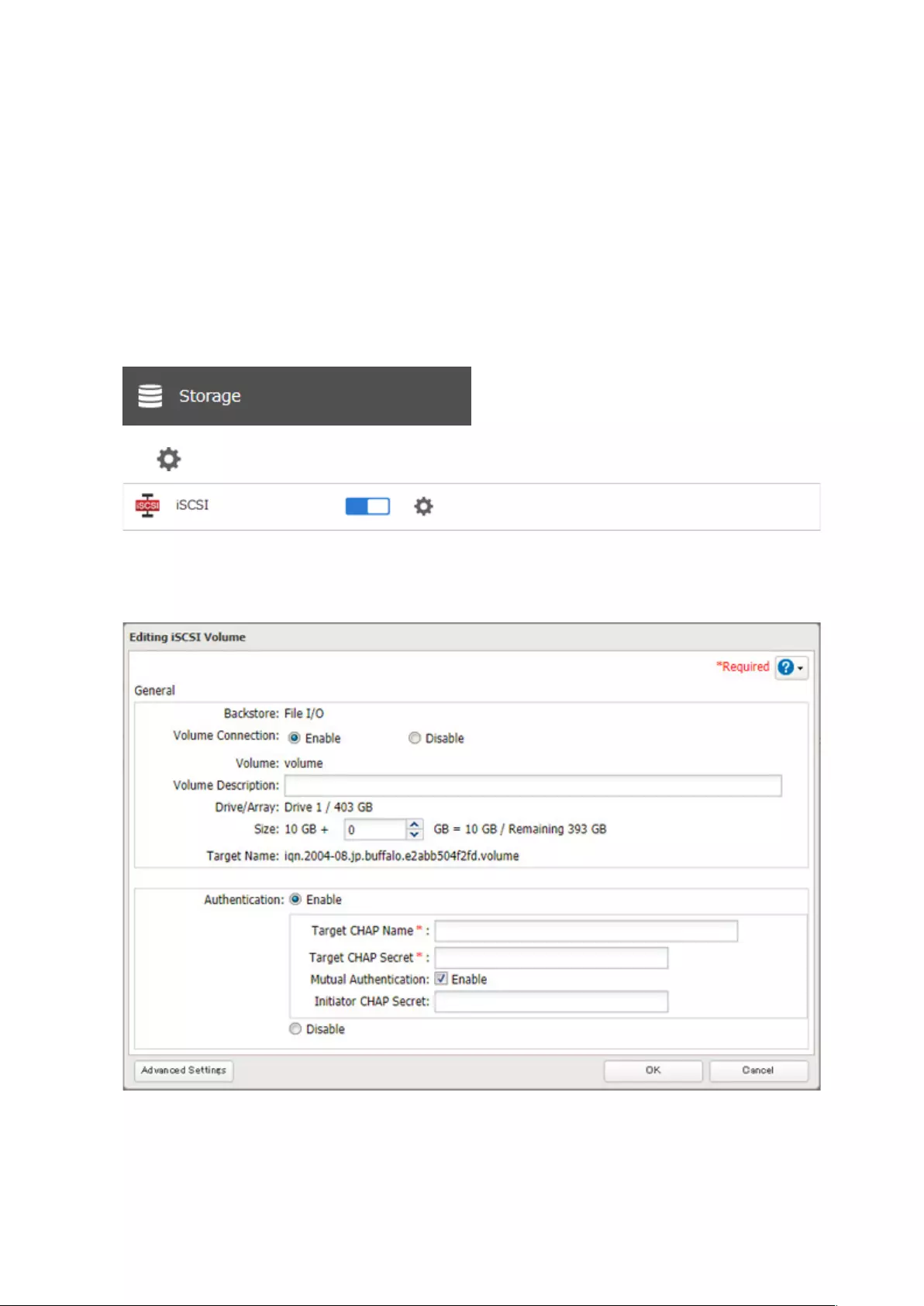
7 The iSCSI volumes on the TeraStation will be listed under “Discovered targets” on the Targets tab. Select the
desired volume to connect and click Connect.
8 Click OK.
9 When the status of the selected volume is displayed as “Connected”, the connection is established properly.
Configuring Access Restrictions for Individual Volumes
If access restrictions are configured for a volume, that volume cannot be accessed unless the target CHAP name and
secret are authenticated.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “iSCSI”.
3 Click the volume to enable access restrictions.
4 Enable authentication, enter the target CHAP name and secret, and click OK.
Note: To enable mutual authentication, select the “Enable” checkbox to the right of “Mutual Authentication”
and enter the initiator CHAP secret.
5 Click OK when completed.
76
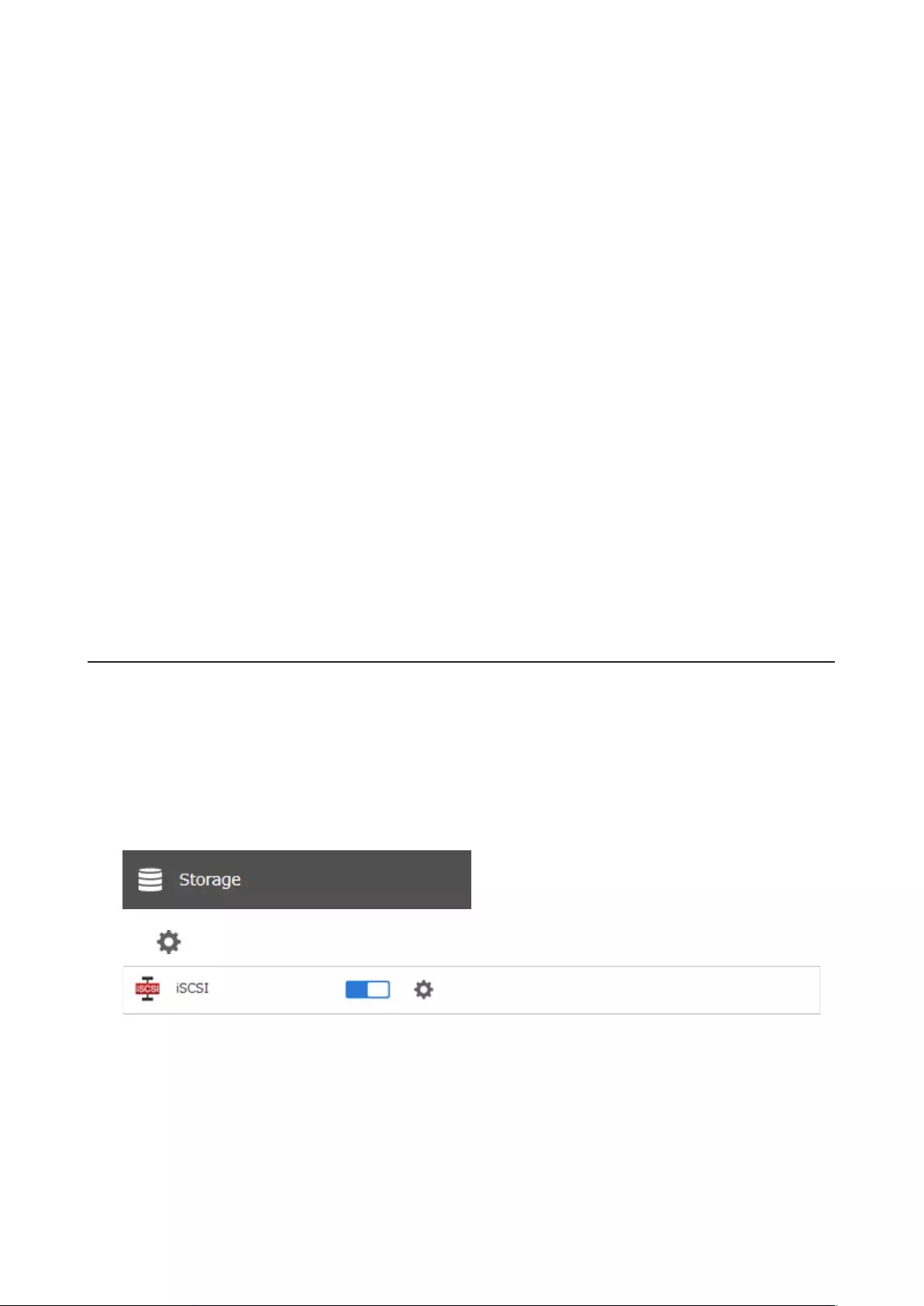
Connecting to Individual Volumes that Are Access-Restricted
1 Open the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator.
2 Register the initiator CHAP secret to your computer first. If you didn’t enable mutual authentication, skip this
step.
Click CHAP on the Configuration tab. Enter the configured initiator CHAP secret into the “Initiator CHAP secret”
field and click OK.
3 From the Discovery tab, click Discover Portal.
4 Enter the TeraStation’s IP address into the “IP address or DNS name” field and click OK.
5 The iSCSI volumes on the TeraStation will be listed under “Discovered targets” on the Targets tab. Select the
desired volume to connect and click Connect.
6 Click Advanced.
7 Select the “Enable CHAP log on” checkbox and enter the target CHAP name into the “Name” field and the
target CHAP secret into the “Target secret” field.
If mutual authentication is enabled, select the “Perform mutual authentication” checkbox.
8 Click OK, then click OK again.
9 When the status of the selected volume is displayed as “Connected”, the connection is established properly.
Expanding Volume Sizes
The volume size of the existing volumes can be expanded after they are created.
Notes:
• Expanding the volume size may erase all data on the volume depending on the formatting type. Backing up the
data before expanding the volume size is recommended.
• To expand the volume size, the volume should have “File I/O” selected for the “Backstore” option, or the volume
needs to have been created in a drive or array with LVM enabled.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “iSCSI”.
3 Select the volume to expand.
77
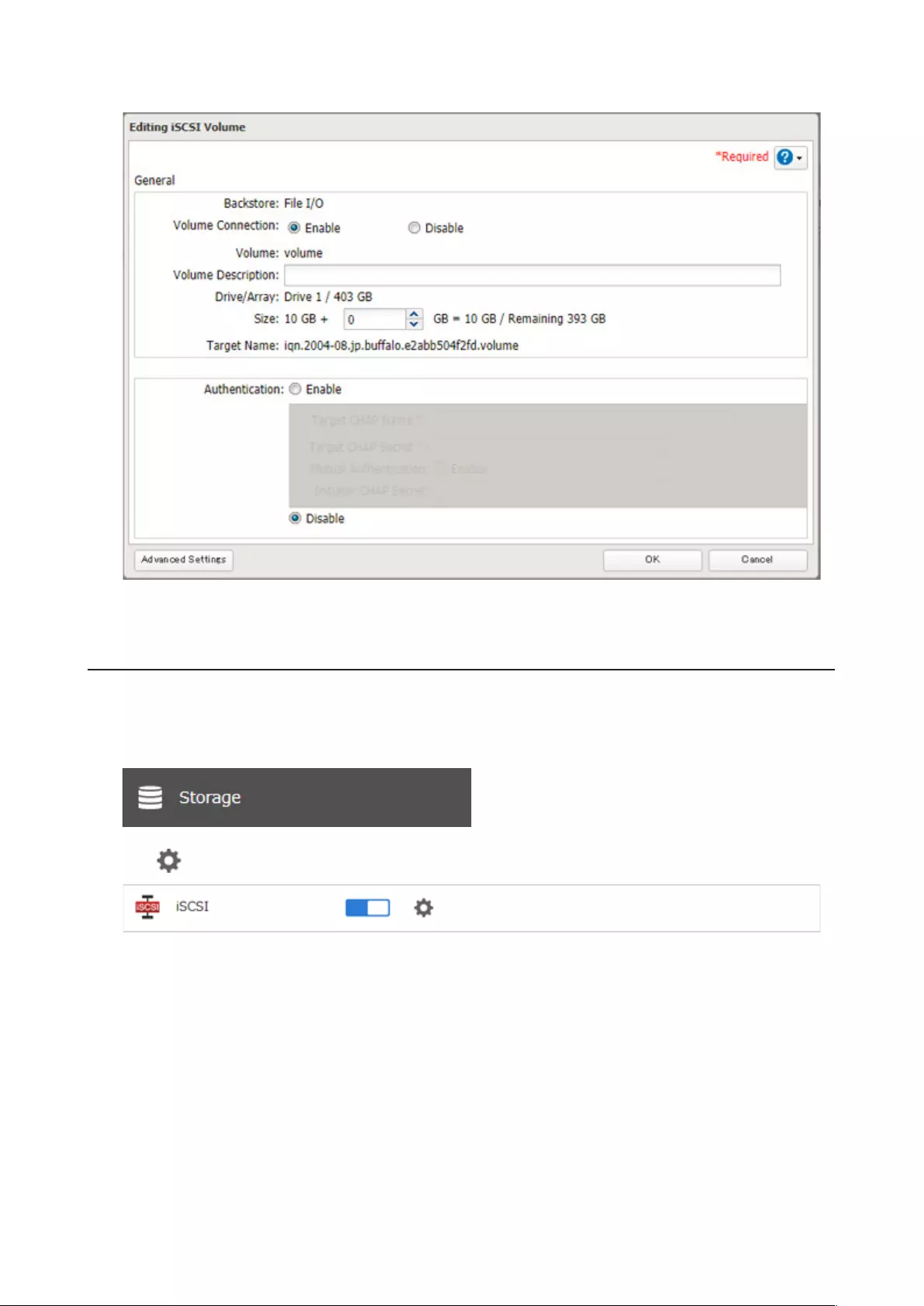
4 Enter the desired volume size to add and click OK.
5 Click OK.
Deleting Volumes
To delete an existing volume, follow the procedure below.
Note: Deleting a volume will erase all data on the volume. Back up the data before deleting the volume.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “iSCSI”.
78
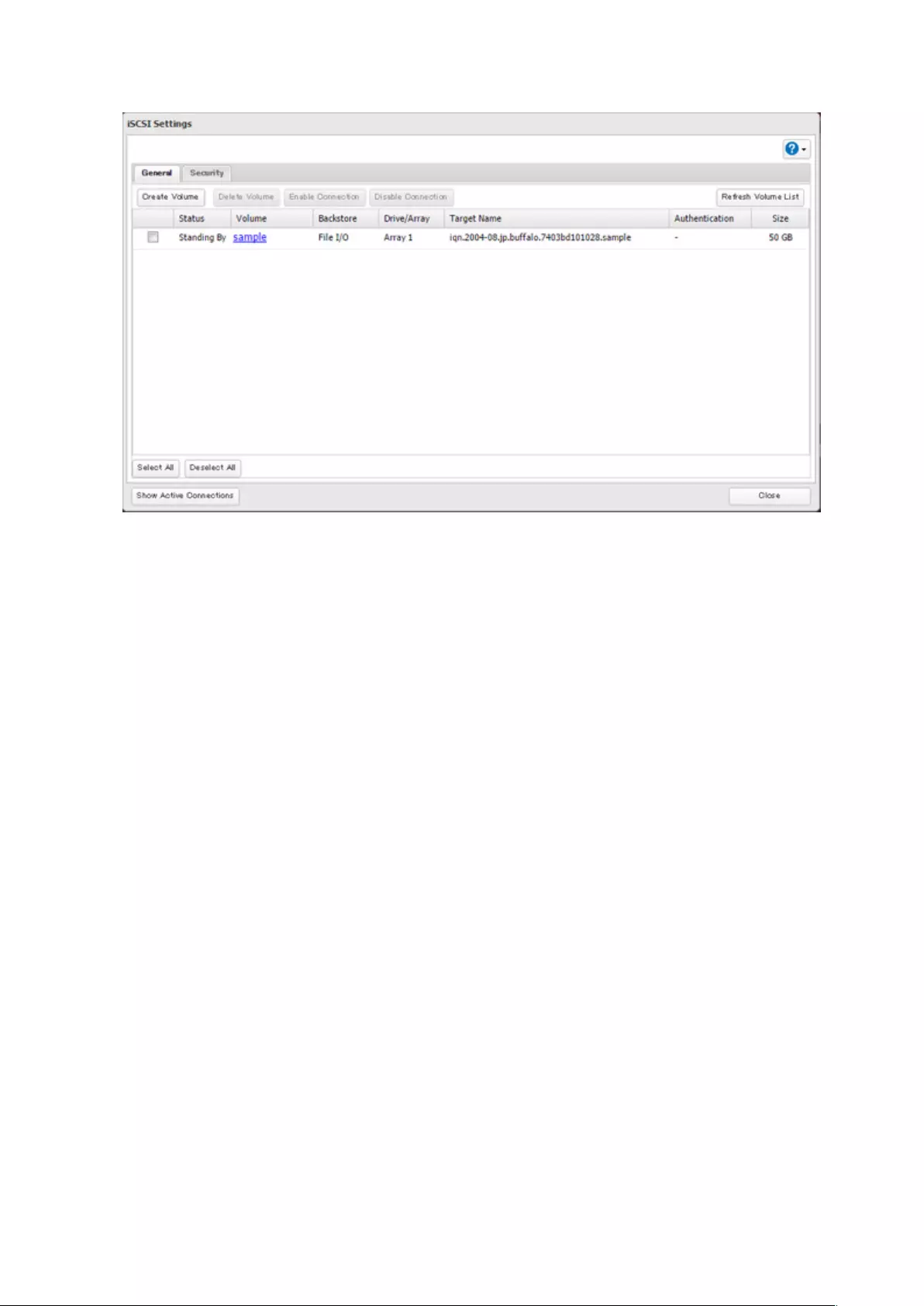
3 Select the volume to delete and click Delete Volume.
4 Confirm that the volume is correctly selected on the screen and click OK.
5 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK.
79
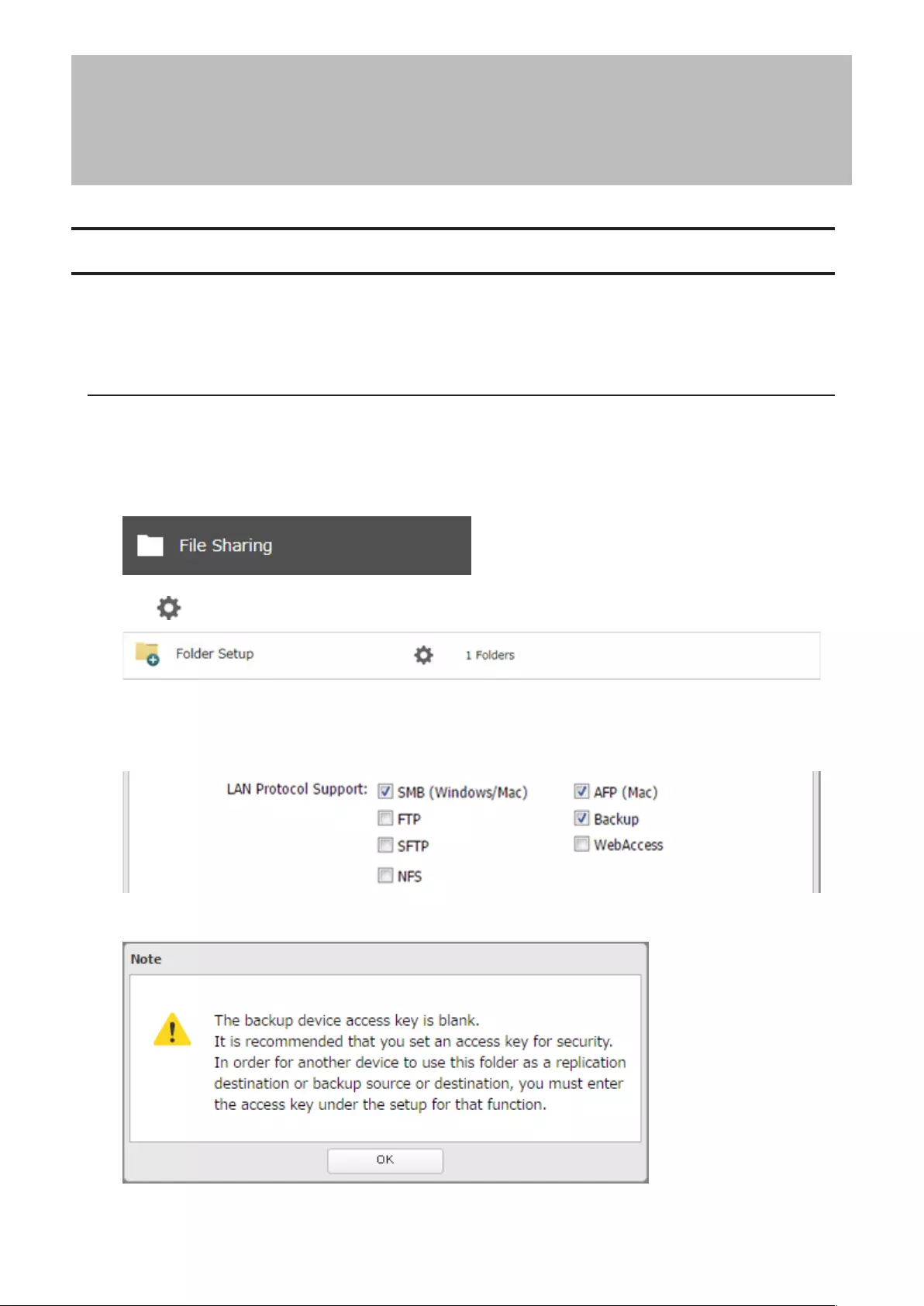
Chapter 5 Backup
Backing Up to a Buffalo NAS Device
You can back up the TeraStation folders to another shared folder on the same TeraStation, a connected USB drive, or
a shared folder on another Buffalo NAS device, either on the same network or on another network. For best results,
using a 10GbE port to connect a backup device is recommended.
Preparing a Backup Destination
First, configure a shared folder on a Buffalo NAS device or connected USB device as a backup destination. The
following procedure explains using another shared folder on a TeraStation as a backup destination. The procedure
may vary depending on which Buffalo NAS device is selected as a destination.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Choose the folder to set as a backup destination.
4 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “Backup” checkbox on the Basic tab.
5 Click OK.
80
6 Enter the desired characters into the backup device access key field and click OK.
Note: You may leave this field blank if you do not want a backup device access key, but for security reasons
we highly recommend entering one for the shared folder. If a backup device access key is configured for the
shared folder, that folder will not show up as a target for the backup source or destination when configuring a
backup job on another Buffalo NAS device unless it’s entered. You may create multiple folders using different
backup device access keys for backup and replication, but only one access key can be used on the TeraStation.
Folders that are configured with a different access key cannot be used.
Configuring a Backup Job
You can configure backup jobs by using another shared folder on the Buffalo NAS device or a USB drive connected
to the TeraStation as a destination. You can also back up to a Buffalo NAS device on another network as long as the
two networks are connected by a VPN or the route is configured properly.
Note: To back up the subfolders’ access restriction settings, the USB drive should be formatted by ext3 or XFS.
1 From Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Backup”.
3 If you had configured a backup device access key for the backup source folder on another Buffalo NAS device
or the backup destination folder, click Set. If you didn’t, skip to step 5.
81
4 Enter the backup device access key and click OK.
5 Click Add.
82
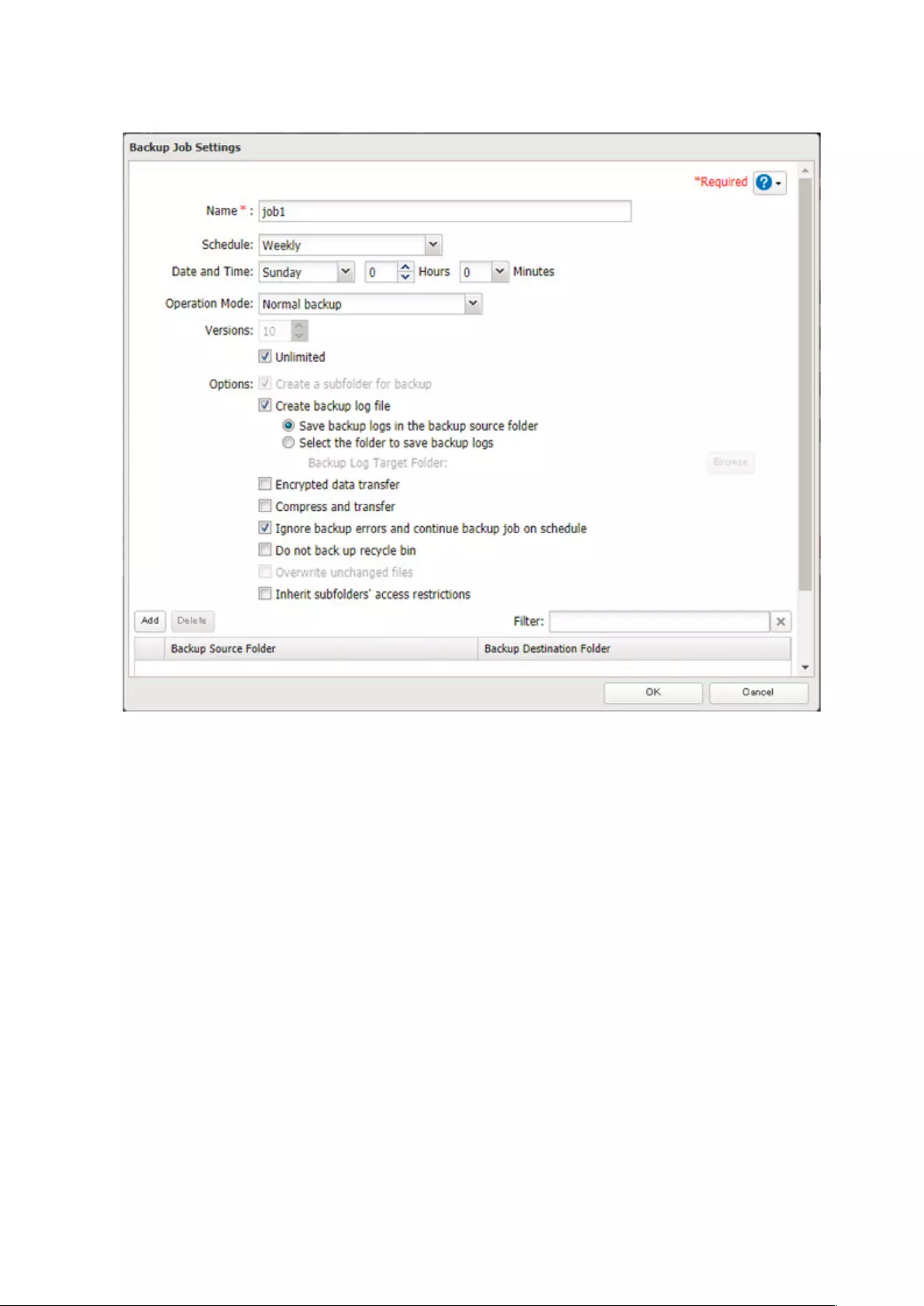
6 Select backup settings such as date and time to run. Refer to the differences between the backup modes in the
following section, “Backup Modes”.
7 Click Add.
83

8 Select the shared folder that will be the backup source and destination.
Note: If you want to back up to a Buffalo NAS device on another network, follow the procedure below to add
the Buffalo NAS device on another network before selecting the backup folders.
a. Click List of Servers.
b. Click Add; select the “Add Buffalo NAS device” option, enter the IP address or hostname of the destination
Buffalo NAS device, then click OK. Make sure the desired Buffalo NAS device has been added to the list.
c. Click Close when finished.
9 Click OK, then click OK again. Jobs will be added to the backup list.
Notes:
• Up to 8 backup jobs can be configured at a time, and 25 backup source and destination folder pairs can be used
in one backup job.
• To inherit the subfolders’ access restriction settings to the backup destination, the backup destination should also
support the subfolders’ access restrictions. Check it before creating a backup job.
• To back up data between Buffalo NAS devices on a network using jumbo frames, make sure that both devices are
configured to use identical (or similar) MTU sizes. If MTU sizes are significantly different, the backup job may not
be properly performed. In such a case, select the default MTU size (1500 bytes).
• You can also specify a hostname by a fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
• Windows-based TeraStations with multibyte characters in the hostname may not be detected as a backup
destination, and folders in these devices cannot be used as backup destination folders.
Backup Modes
The following types of backup jobs may be selected:
Type Files included
Normal backup
All files in the source will be backed up to the destination. You can specify
how many backup versions to keep from 1–400, or select “Unlimited” to keep
all backups until the drive is full. If a specific number of backup versions is
specified, the backup destination folder should be on the same TeraStation
that the backup job is configured from, or on an external USB drive attached
to that TeraStation.
84
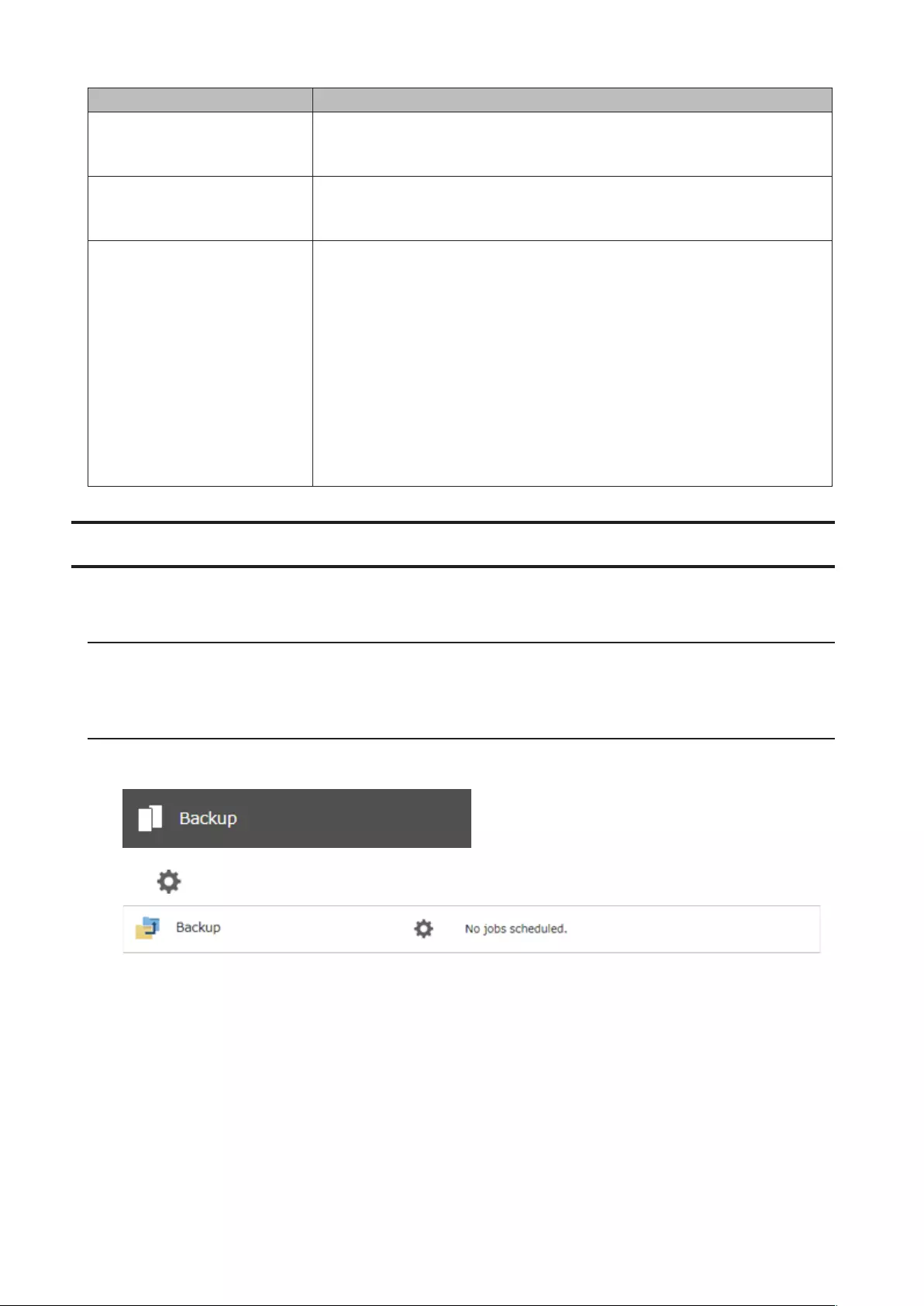
Type Files included
Overwrite (incremental)
The first backup job runs like a normal backup. In subsequent backups, files
added to the source as well as files deleted from the source are kept in the
backup folder.
Overwrite (differential)
The first backup job runs like a normal backup. As each additional backup
job runs, files are added to and deleted from the backup folder. The backup
destination folder is always the same size as the backup source folder.
Management backup
Each time a backup is executed, management information is stored, and
only files that have changed are copied or deleted. Data is retrieved from the
previous backup file for files that were not changed. This is useful for making
backups with limited space or for referencing status at a particular point in
time (for use for data snapshot applications). The destination folder for a
management backup should be a local folder on this TeraStation or on a USB
drive attached to it. The destination folder will be set to read-only. Do not use
folders from drives formatted with FAT.
You can specify how many backup versions to keep from 1–400, or select
“Unlimited” to keep all backups until the drive is full. The backup destination
folder should be on the same TeraStation that the backup job is configured
from, or on an external USB drive attached to that TeraStation.
Backing Up to rsync-Compatible Devices
You can back up TeraStation folders to other manufacturers’ rsync-compatible devices on the same network.
Preparing a Backup Destination
First, configure an rsync-compatible device as a backup destination. You should enable rsync on the destination
device. For more detailed information, refer to the device’s manual.
Configuring a Backup Job
1 From Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Backup”.
85
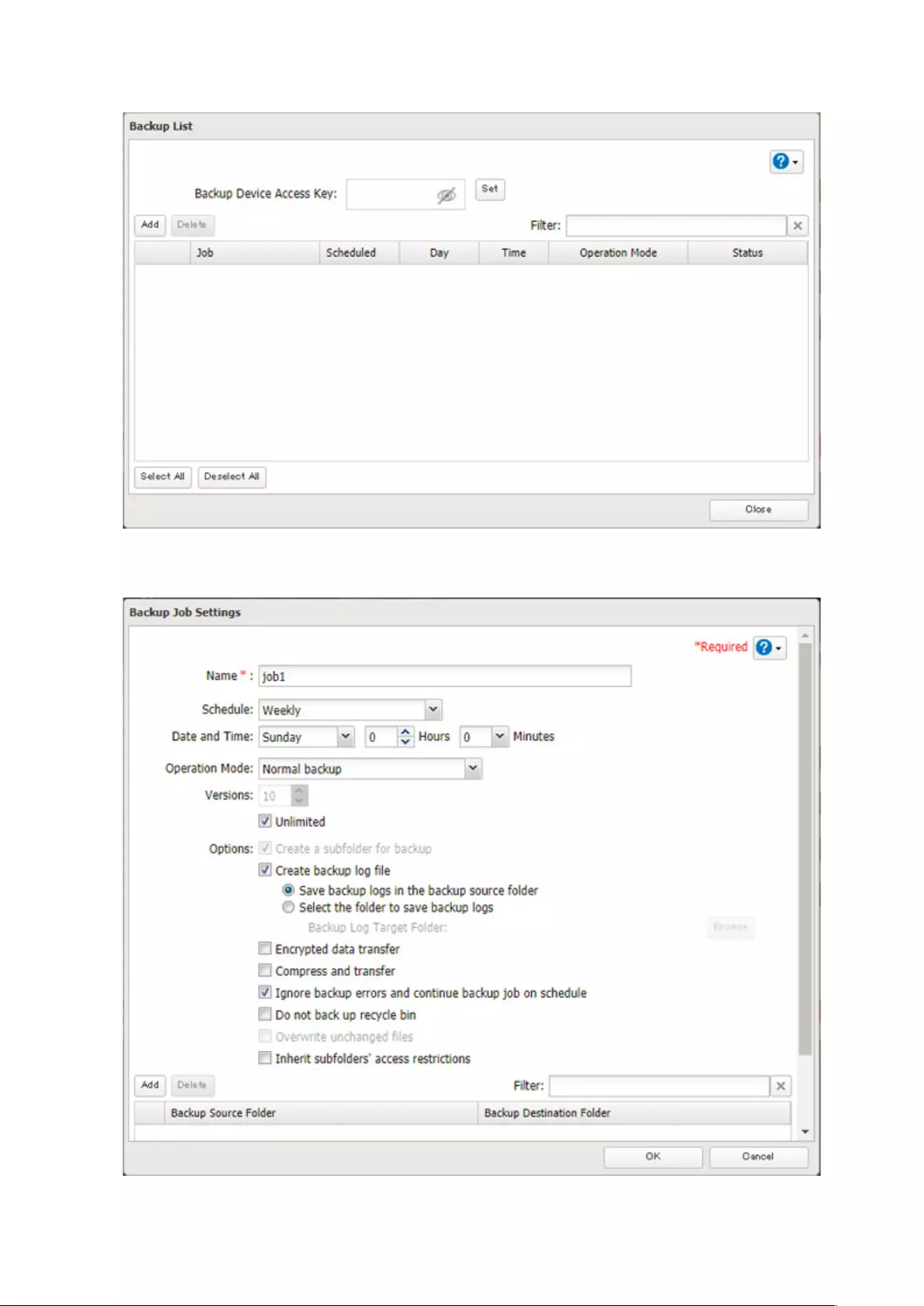
3 Click Add.
4 Select backup settings such as date and time to run. Refer to the differences between the backup modes in the
above section, “Backup Modes”.
5 Click Add.
86
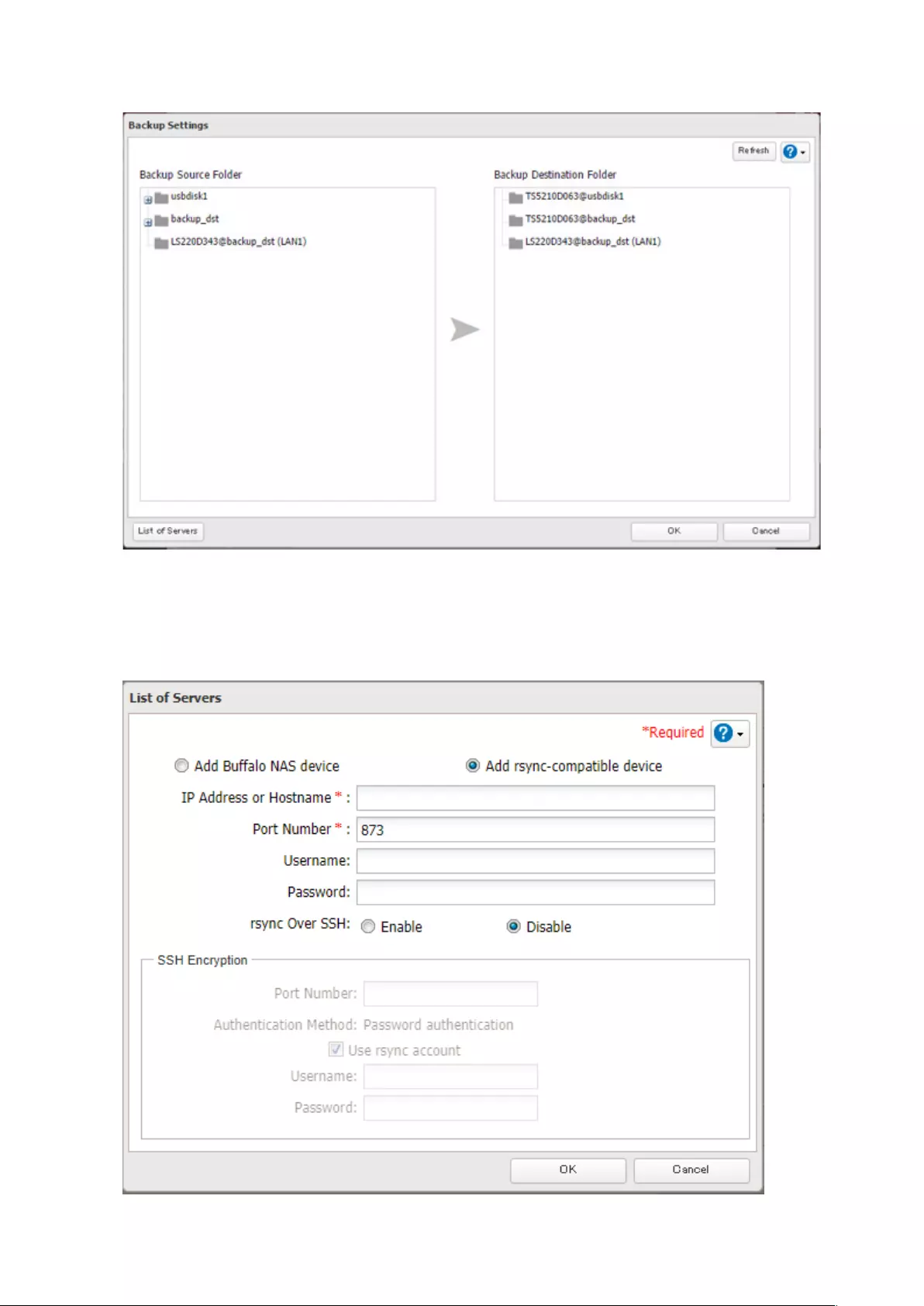
6 Click List of Servers.
7 Click Add.
8 Select “Add rsync-compatible device”; enter the IP address or hostname of the destination rsync-compatible
device and port number. If your rsync-compatible device requires the username and password for backup,
enter these values into the fields.
87
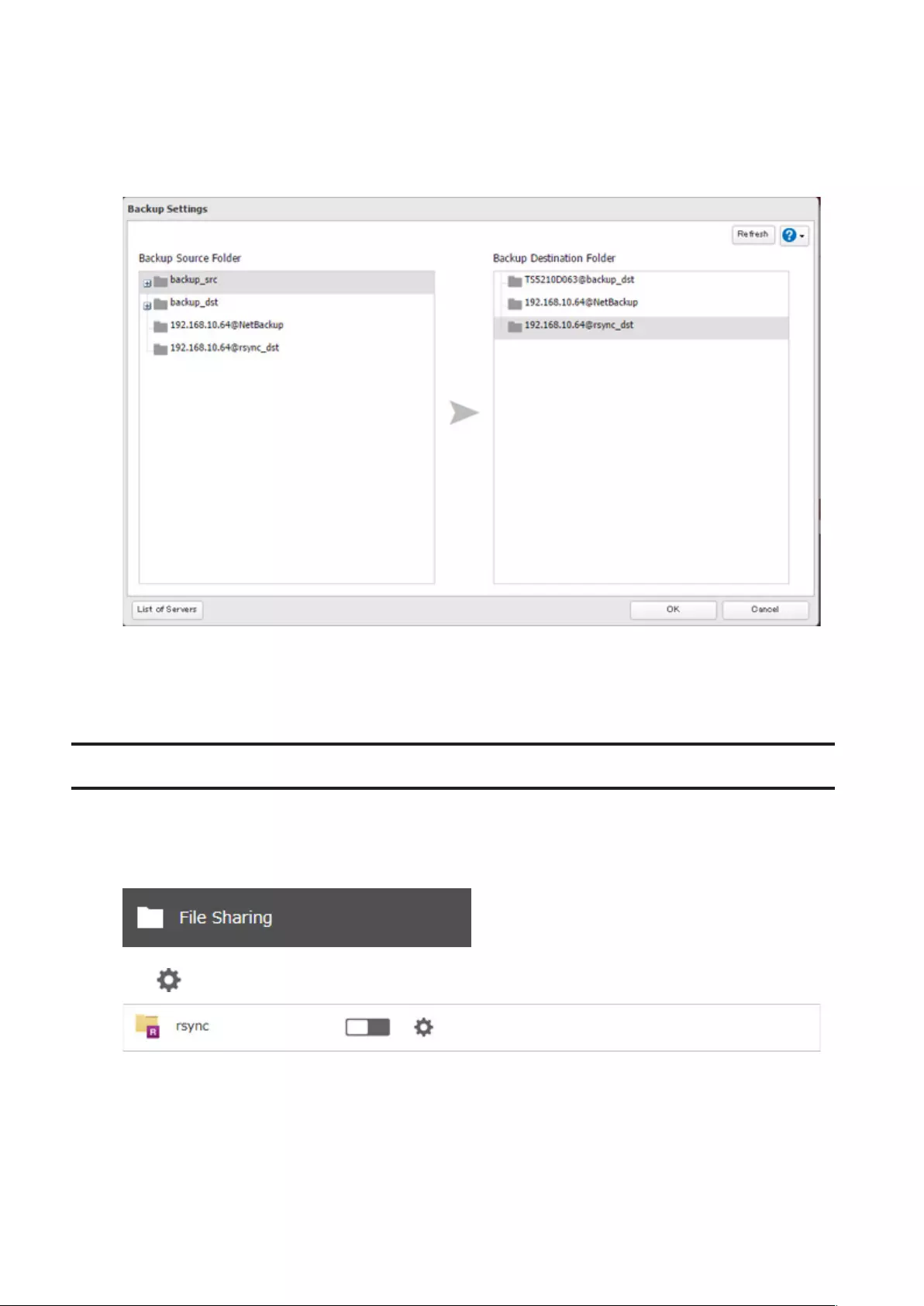
9 Click OK, then Close.
10 Click Refresh and Yes. The folder list will be updated to include the rsync-compatible device’s folders.
11 Select the shared folder that will be the backup source and destination, then click OK.
12 Click OK. Jobs will be added to the backup list.
Note: Up to 8 backup jobs can be configured at a time, and 25 backup source and destination folder pairs can be
used in one backup job.
Backing Up from rsync-Compatible Devices
To configure the TeraStation as a backup destination for other rsync-compatible devices, follow the procedure
below.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “rsync”.
88
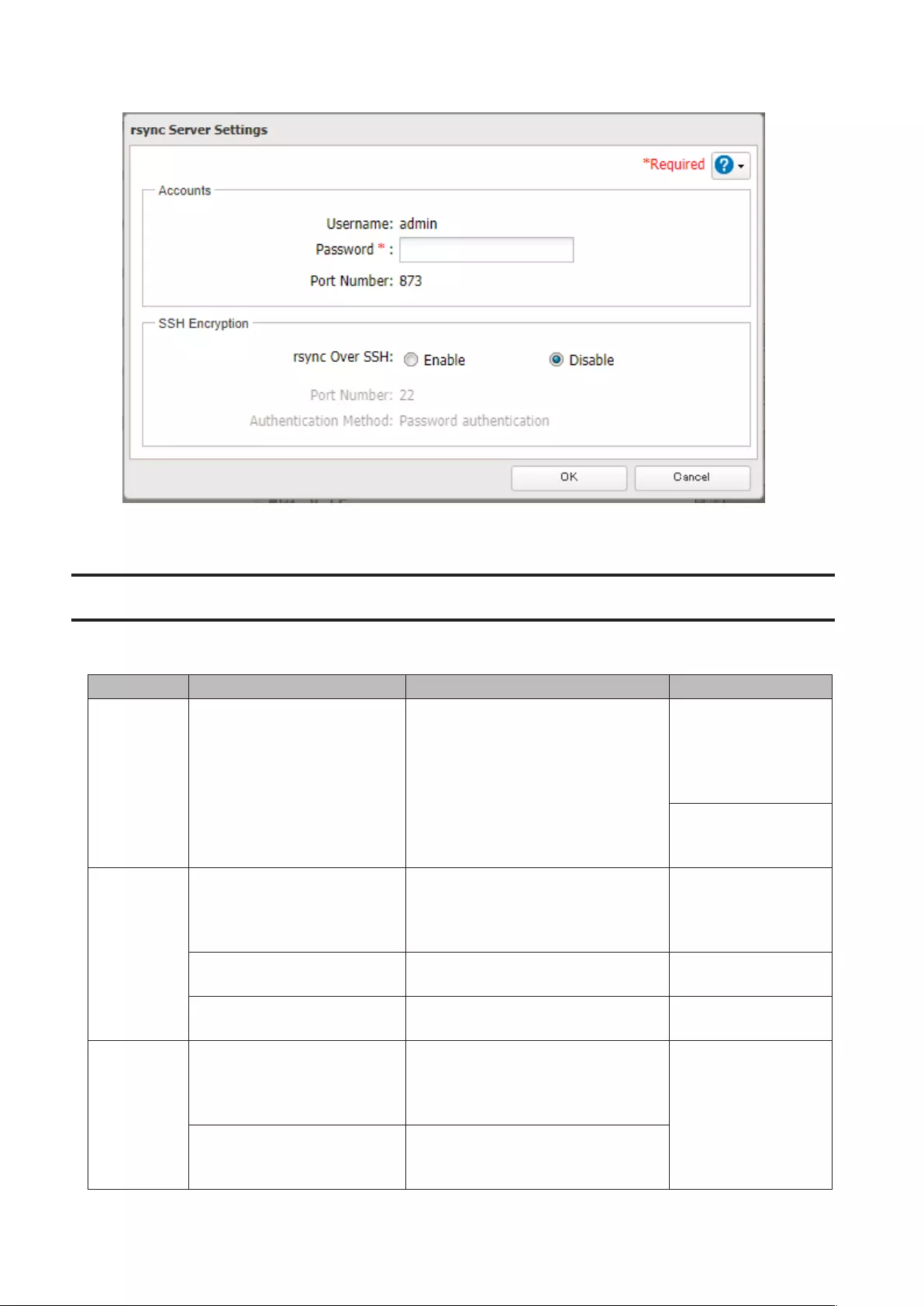
3 Enter the admin password. If you use SSH encryption during backup, enable SSH.
4 Click OK.
Backup Logs
The following backup error codes may be recorded in the backup log. Read the description and try the respective
corrective actions for each error.
Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
Code 3 The backup destination USB
drive could not be found.
Check that the backup destination
USB drive is connected to the
TeraStation properly.
rsync error: errors
selecting input/
output files, dirs (code
3) at main.c(634)
[Receiver=3.1.0]
Can’t write to backup
destination(target
disk is broken?).
Code 5
The backup destination shared
folder could not be found.
Check that the Ethernet cable is
securely connected and that the hub
or other devices on the network are
turned on.
rsync error: error
starting client-server
protocol (code 5) at
main.c(1504)
Authentication failed. Try adding the rsync-compatible NAS
device from the server list again.
@ERROR: auth failed
on module
A registered user does not
have permission to run.
Check the settings of the rsync-
compatible NAS device.
@ERROR: permission
denied
Code 10
The Ethernet cable was
disconnected from the backup
source TeraStation when the
backup job started.
Reconnect the Ethernet cable. rsync error: error in
socket IO (code 10)
at clientserver.c(128)
[sender=3.1.0pre1]
A backup destination doesn’t
support the subfolders’ access
restrictions.
Select another backup destination
or remove the subfolders’ access
restrictions.
89
Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
Code 11
The drive capacity of the
backup destination TeraStation
became full.
Delete unnecessary files and folders.
rsync error: error
in file IO (code 11)
at receiver.c(389)
[receiver=3.1.0]
Files larger than 4 GB were
backed up to the FAT32-
formatted USB drive.
Reduce the file size to 4 GB or less, or
change the file system to one other
than FAT32. Refer to the “Adding an
External Drive” section in chapter 4 for
compatible file systems.
rsync: write failed on
“filename”: File too
large (27)
Code 12
Could not communicate
between backup source and
destination TeraStations.
Check that the Ethernet cable is
securely connected and that the hub
or other devices on the network are
turned on.
rsync error: error in
rsync protocol data
stream (code 12) at
io.c(515)
The settings of the TeraStation
were changed while the
backup job was running.
Do not change the settings while the
backup job is running. If changed, the
connection is temporarily terminated
and the backup job will fail.
Code 14
Insufficient memory on the
TeraStation was not enough
so that the backup job did not
run.
Reduce the number of backup
destination files or disable any other
functions running at the same time.
ERROR: out of
memory in flist_
expand
rsync error: error
in IPC code (code
14) at main.c(655)
[receiver=2.6.8]
Code 22
rsync: fork failed in
do_recv: Cannot
allocate memory (12)
rsync error: error
allocating core
memory buffers
(code 22) at util.c(120)
[sender=2.6.8]
Code 20
The connection was
disconnected while the
backup job was running.
Do not change the settings while the
backup job is running. If changed, the
connection is temporarily terminated
and the backup job will fail.
rsync error: received
SIGINT, SIGTERM, or
SIGHUP (code 20) at
rsync.c(242)
90
Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
Code 23
Invalid characters were used in
the filename or folder name of
the backup destinations.
Change the filename or folder
name using compatible characters.
Available characters are described in
the “Adding a Shared Folder” section
in chapter 3.
rsync error: some
files could not be
transferred (code 23)
at main.c(702)
The backup destination files
were updated while the
backup job was running.
Do not overwrite the backup
destination files while the backup job
is running. If updated, the backup
destination files will not be backed up
and the backup job will fail.
The TeraStation backed up the
data to the FAT32-formatted
USB drive, then the upper- or
lowercases of filename and
folder name on the backup
source TeraStation were
changed.
Do not change the upper- or
lowercase of filenames and folder
names on the backup source
TeraStation if the backup destination
USB drive is formatted to FAT32. Linux
on the TeraStation is case-sensitive
but FAT isn’t, so the same filename
and folder name that only differs
in upper- or lowercase will not be
identified and treated as the same file
or folder. To back up properly, using
XFS or ext3 is recommended.
Code 24
The backup destination files
were updated while the
backup job was running.
Do not overwrite the backup
destination files while the backup job
is running. If updated, the backup
destination files will not be backed up
and the backup job will fail.
rsync warning:
some files vanished
before they could be
transferred (code 24)
at main.c
Code 30
The Ethernet cable was
disconnected from the
backup source or destination
TeraStations while the backup
job was running.
Reconnect the Ethernet cable.
rsync error: timeout
in data send/receive
(code 30) at io.c(195)
[sender=3.1.0]
B14 Insufficient TeraStation
memory. Restart the TeraStation and try again. -
B101
The backup destination
TeraStation does not exist.
Check that the backup destination
TeraStation is turned on, the Ethernet
cables are securely connected,
and the hostname of the backup
destination TeraStation is not
changed.
-
B102
Check that the backup destination
folders on the backup destination
TeraStation exist in the shared folder
list and the backup destination
folders are configured for backup in
Settings.
-
B103
The backup source folders on
the backup source TeraStation
do not exist.
Check that the backup source folders
on the backup source TeraStation
exist in the shared folder list.
-
91

Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
B104
The backup destination folders
on the backup destination
TeraStation do not exist.
Check that the backup destination
folders on the backup destination
TeraStation exist in the shared folder
list.
-
B105 The drives were not
recognized.
Check that the drives are recognized
properly in Settings. If you configure
the “usbdisk” folders for the backup
source or destinations, confirm if
these folders exist in the shared folder
list.
-
B106 The file systems of the USB
drive are not supported.
Check that the USB drive is formatted
to the compatible file systems. If you
configure the management backup in
the backup job, FAT format cannot be
used for the backup destination.
-
B107 The device files such as “/dev/
null” etc. does not exist. Restart the TeraStation and try again. -
B108
Credentials to access a shared
folder on the rsync-compatible
NAS device were not found.
Try adding the rsync-compatible NAS
device from the server list again. -
Replication
Replication copies all data from a share to a share on a different TeraStation. This is an easy way to configure a
reliable system to provide data protection in the event your main TeraStation fails. To configure replication, connect
an Ethernet cable to the LAN port of each TeraStation and follow the procedure below.
Notes:
• For best results, use static IP addresses and a 10GbE port for connecting both replication TeraStations (source and
destination).
• Replication source data is copied to the replication destination folder with a differential overwrite. Any data that
is not in the replication source will be overwritten.
Preparing a Replication Destination
First, configure a folder as a replication destination.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Choose the folder to set as a replication destination.
92
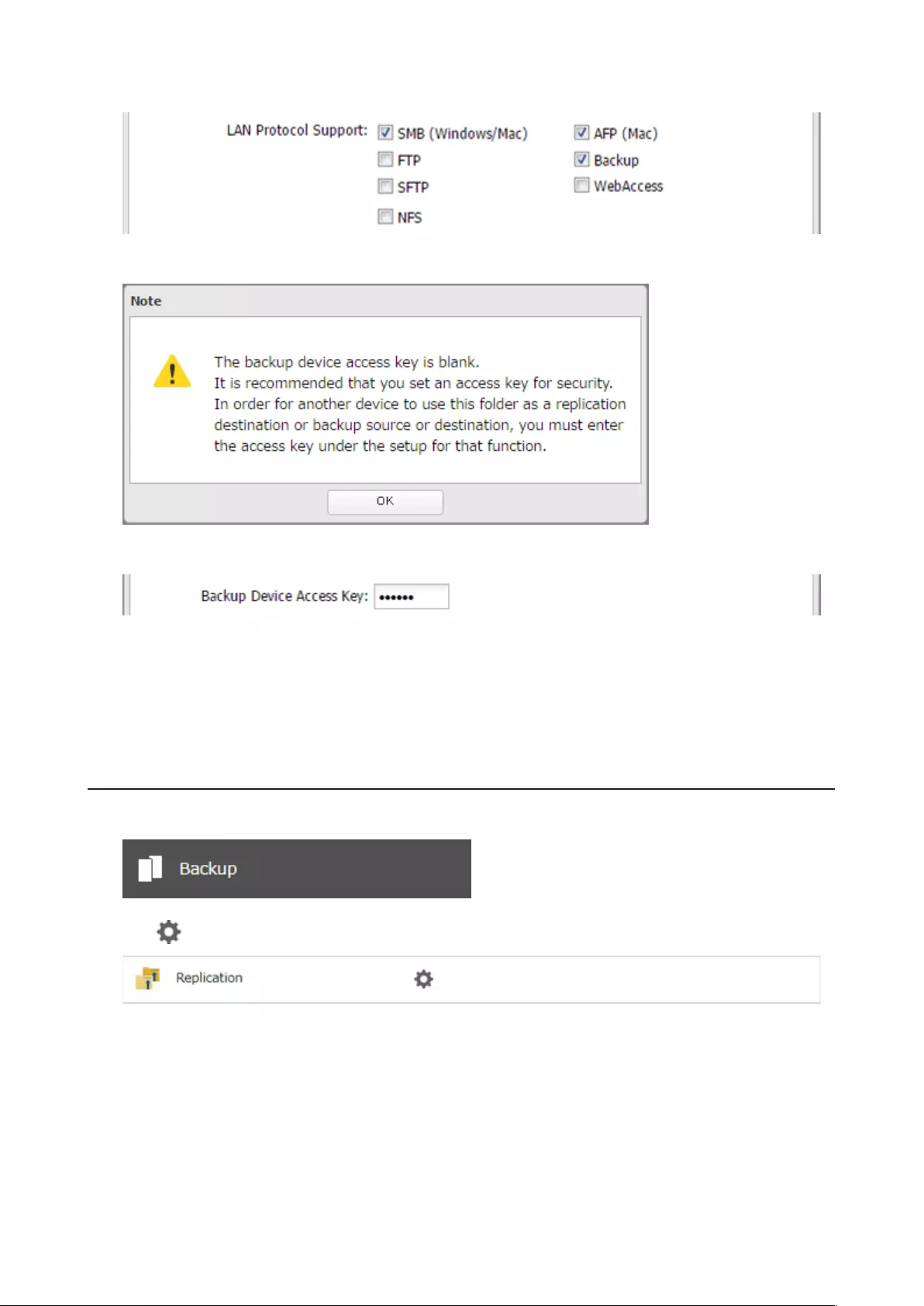
4 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “Backup” checkbox on the Basic tab.
5 Click OK.
6 Enter the desired characters into the backup device access key field and click OK.
Note: You may leave this field blank if you do not want a backup device access key, but for security reasons
we highly recommend entering one for the shared folder. If a backup device access key is configured for the
shared folder, that folder will not show up as the replication destination when configuring a replication job on
another Buffalo NAS device unless it’s entered. You may create multiple folders using different backup device
access keys for backup and replication, but only one access key can be used on the TeraStation. Folders that
are configured with a different access key cannot be used.
Configuring a Replication Job
1 From Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Replication”.
93
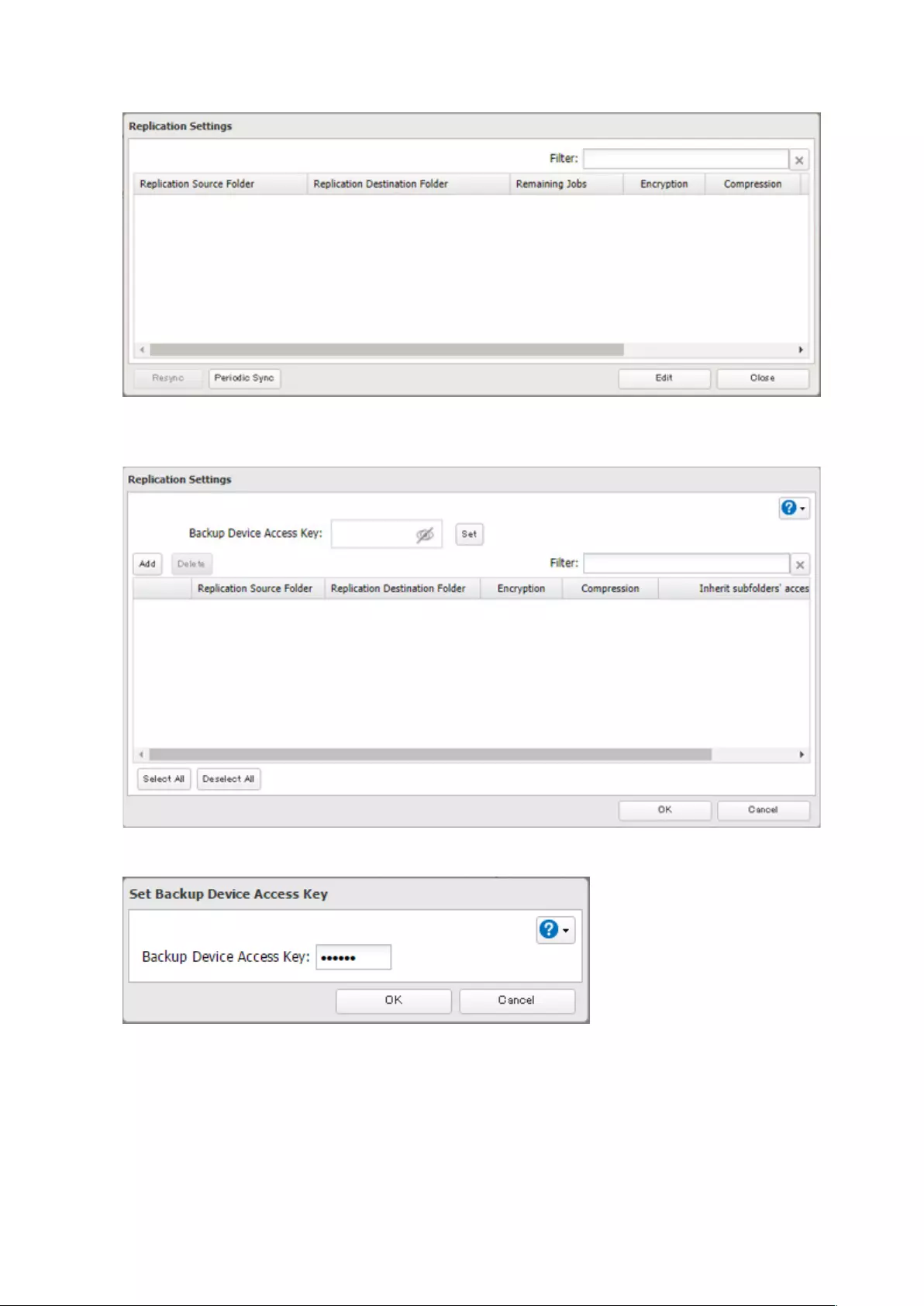
3 Click Edit.
4 If you had configured a backup device access key for the replication destination folder, click Set. If you didn’t,
skip to step 6.
5 Enter the backup device access key and click OK.
94
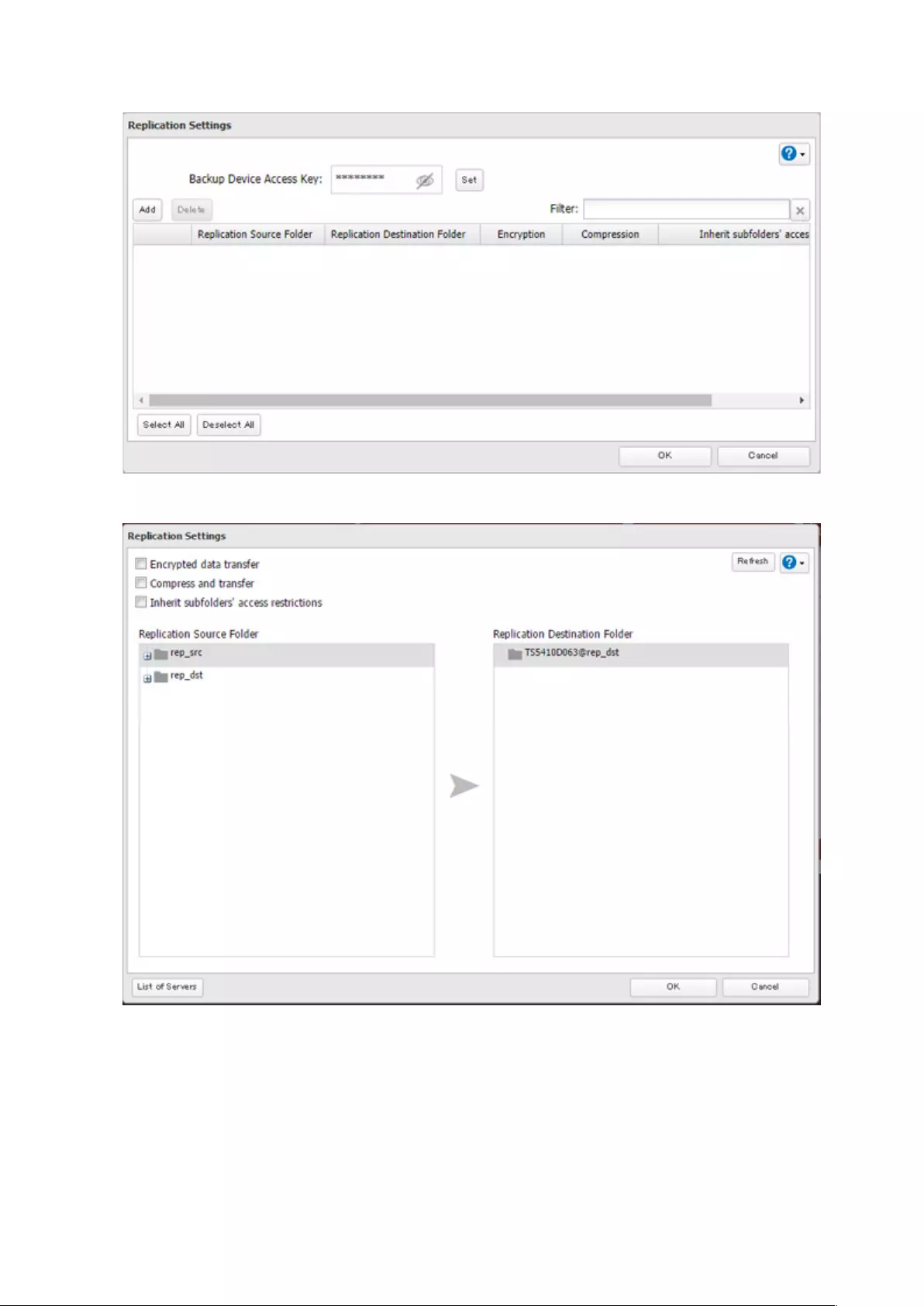
6 Click Add.
7 Select the shared folder that will be the replication source and destination, then click OK.
8 Click OK, then Yes.
Notes:
• During setup, you may choose to encrypt and/or compress replication data. Encrypted data will be transferred
securely on the network. Compressed data will ease network loading and is recommended for slow or heavily
loaded network connections. Either will increase the CPU load on the source TeraStation. Encrypted or
compressed data will be decrypted or decompressed on the destination TeraStation.
• A maximum of 64 shared folders can be configured for replication.
95
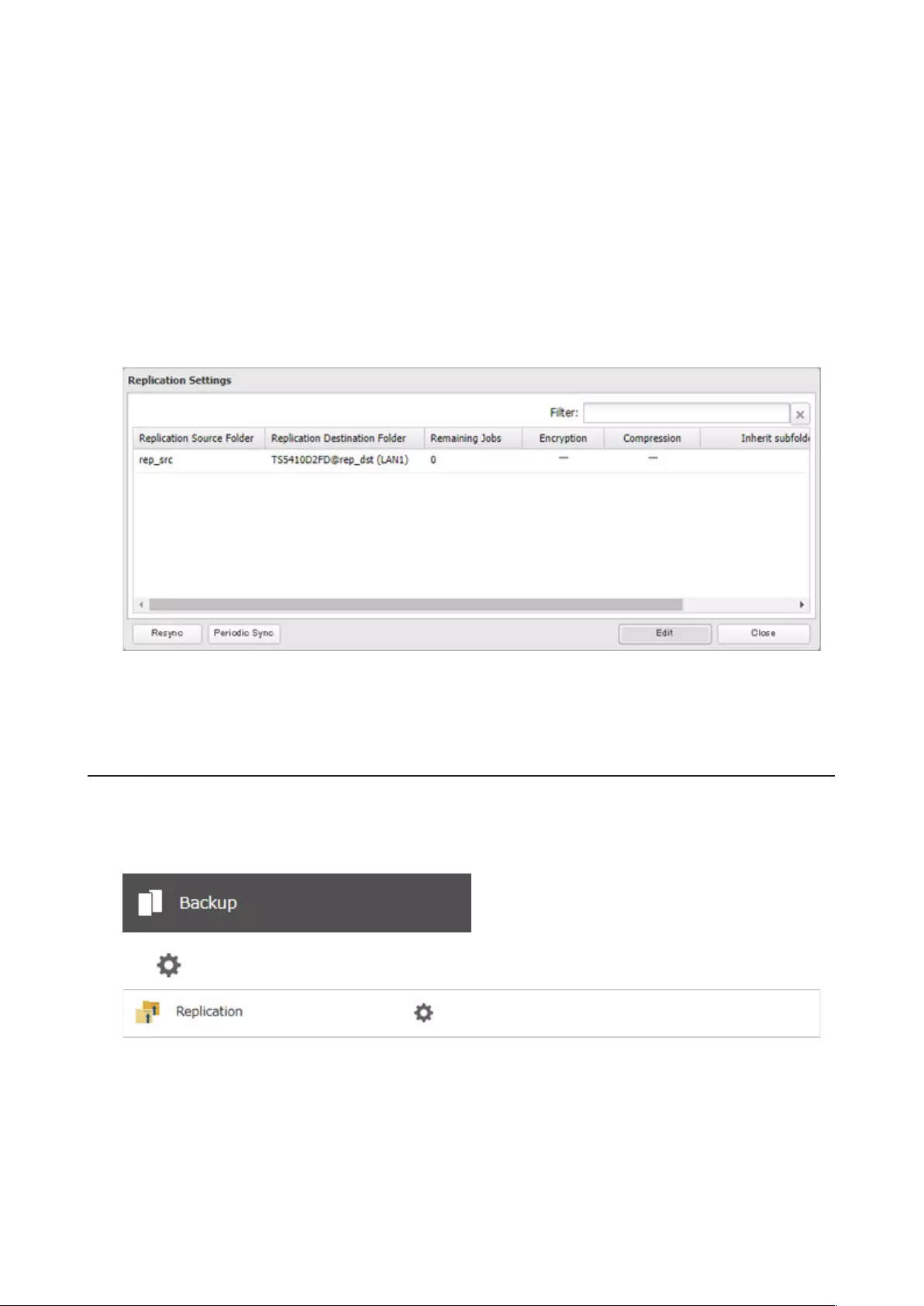
• Replication can also be used to copy all data from a share to a share on an attached external drive. Format
the drive with ext3 or XFS before using it for replication. Drives with FAT32 partitions are not supported with
replication.
• You can select the first and second levels of shared folders and USB drives connected to the TeraStation as
the replication source. Folders whose names contain more than 80 alphanumeric characters or “@” cannot be
selected.
As the replication destination, you can select the first level of shared folders, USB drives, and on/off-subnet NAS
devices’ shared folders.
• Don’t use the same TeraStation for both failover and replication, or replication and Time Machine.
• Don’t configure replication from one source folder to multiple destination folders.
• If a network problem causes a replication error, unsynced data may be shown as “0” even though replication is
incomplete. Click Resync to recover from the replication error. All files from the source folder will be copied to the
destination folder.
• To inherit the subfolders’ access restriction settings to the replication destination, the replication destination
should also support the subfolders’ access restrictions. Verify it before creating a replication job.
Synchronizing between Source and Destination TeraStations
Periodically
To copy files that are saved via other file sharing protocols such as AFP or FTP to the replication destination regularly,
configure “Periodic Sync” in Settings. Follow the procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Replication”.
96
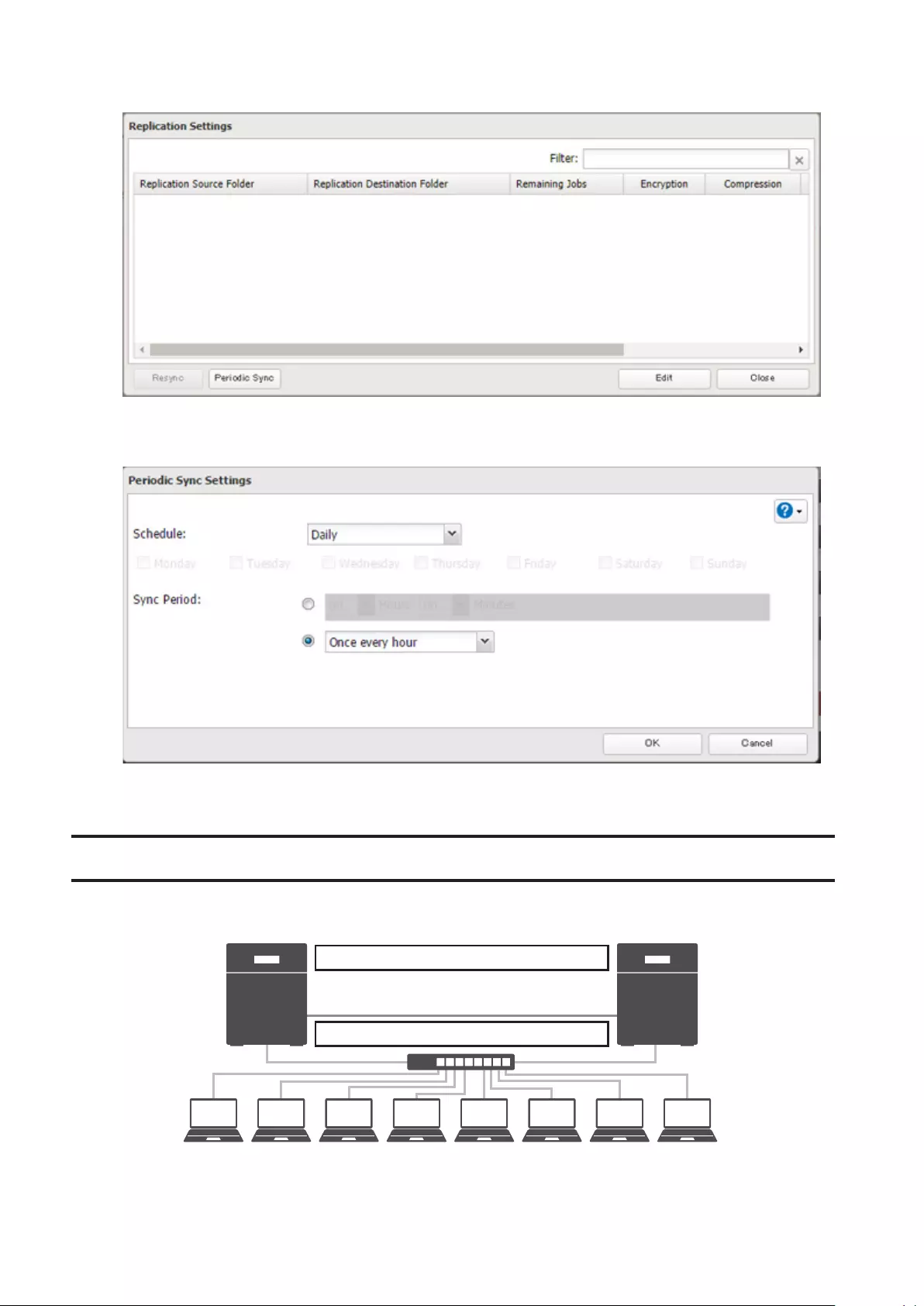
3 Click Periodic Sync.
4 Select “Daily” or “Weekly” from the “Schedule” drop-down list. If “Daily” is selected, configure the sync period. If
“Weekly” is selected, specify the weekdays and the sync period.
5 When the configuration is finished, click OK.
Failover
With failover, two TeraStations are connected to the network for redundancy. If an issue renders the main
TeraStation inaccessible, operation automatically switches to the backup TeraStation.
Switches automatically if failure occurs.
Data on both TeraStations stays up-to-date.
BackupMain
Failover will activate during any of the following situations:
• The backup TeraStation cannot detect the main TeraStation within a specified time
97
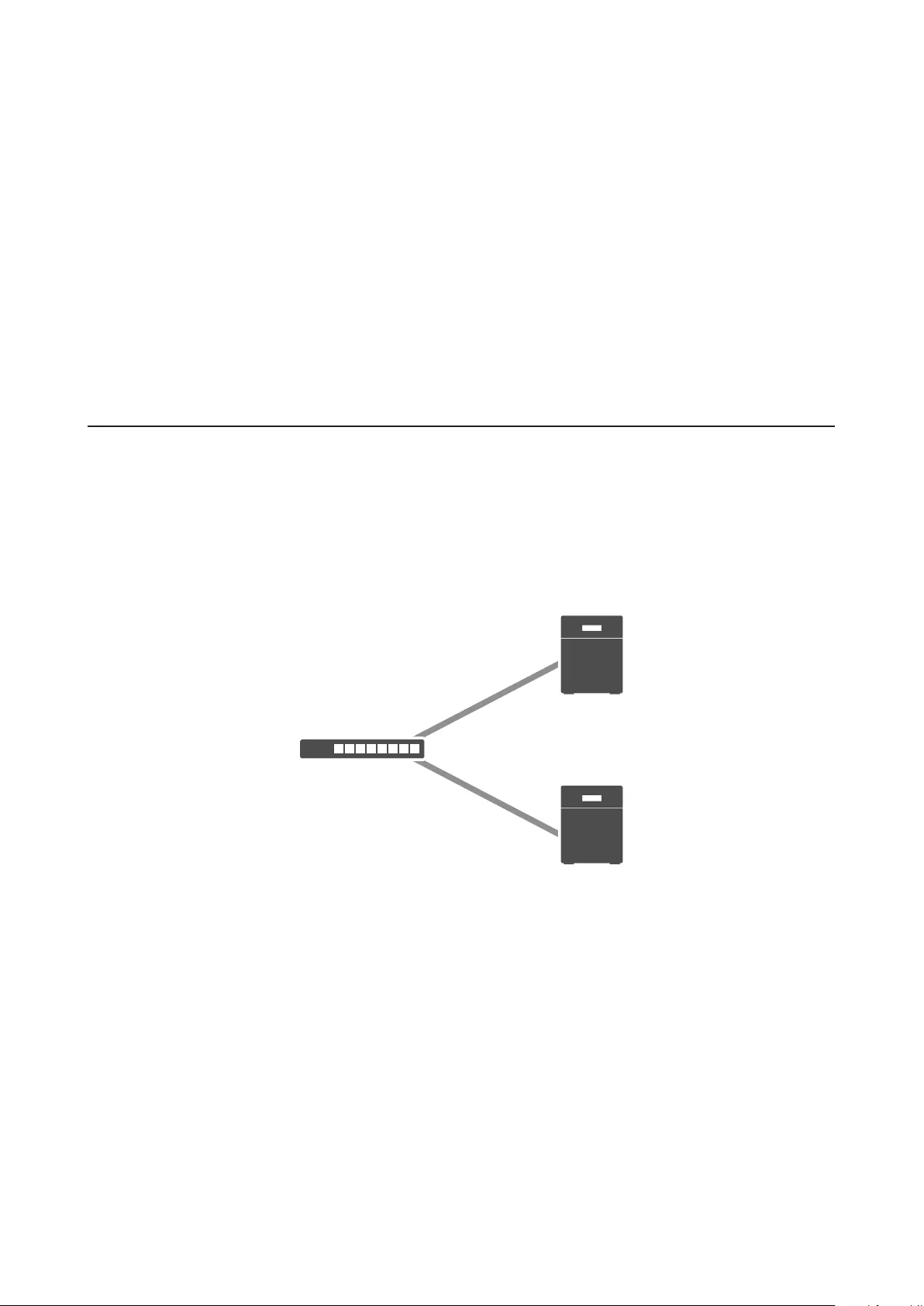
If the backup TeraStation has not received a packet from the main TeraStation within a specified time, the backup
TeraStation considers the main TeraStation to have failed. By default, it will try 5 times and wait 60 seconds. If this
is triggered by accident, reconfigure failover from the main TeraStation.
• Errors
Failover will occur if any of the following errors occur:
E12 (cooling failure), E14 (cannot mount RAID array), E16* (drive not found), E22* (cannot mount drive), E30*
(drive failure)
*When the drive is configured in JBOD.
Notes:
• Only use identical model and capacity TeraStations for failover. If the capacity of the main TeraStation is larger
than that of the backup TeraStation, an I33 replication error will occur.
• All drive bays of a TeraStation should be occupied if it will be used for failover. Failover will not work if a drive is
missing from any bay.
Before Configuring Failover
Use the same LAN ports for transferring data and configure both TeraStations with static IP addresses for the
purposes of failover. It is recommended to use a 10GbE port for failover. This section explains using an example with
LAN ports 1 and 3.
Using the Same LAN Port for Both Failover and Connecting to the Network
Using this setup, if the main TeraStation fails, the backup TeraStation will replace it completely. The backup
TeraStation will be updated over normal network traffic.
Main
Backup
Network
LAN port 3
(Static IP)
LAN port 3
(Static IP)
Using Different LAN Ports for Connecting to the Network and Failover
With this setup, the backup TeraStation and main TeraStation are connected by a second Ethernet cable connecting
their LAN 3 ports. Updating is done over this dedicated network path, so updates are quicker and don’t interfere
with normal network traffic.
98
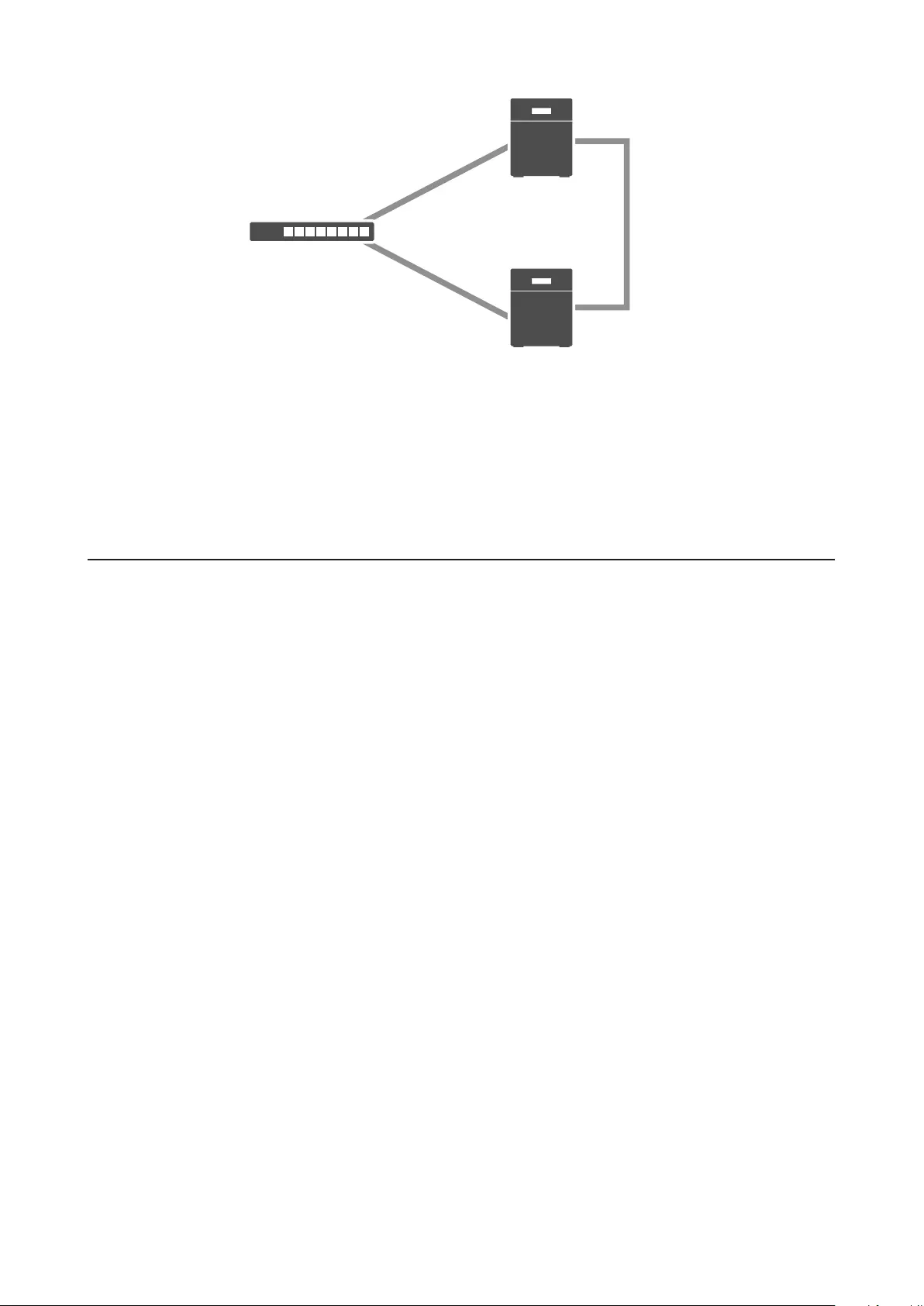
Main
Backup
Network
LAN port 1
(Static IP)
LAN port 1
(Static IP)
LAN port
3
(Static IP)
LAN port
3
(Static IP)
• LAN Port 1 for Alive Check and LAN Port 3 for Failover
Select the IP address labeled “(LAN1)” for the LAN port setting of “IP Settings for File Sharing” and select “(LAN3)”
for “Backup LAN Port” in Settings.
• LAN Port 3 for Both Alive Check and Failover
Select the IP address labeled “(LAN3)” for the LAN port settings both “IP Settings for File Sharing” and “Backup
LAN Port” in Settings.
Usage Restrictions
Functional Restrictions
Failover is not available when any of the following functions are enabled:
Replication, sleep mode, encrypted drive volume, LVM volume, iSCSI volume, port trunking, cloud storage*, Dropbox
Sync, hot spare, access restrictions by Active Directory domain
*Even if the function is disabled, the settings may remain if the settings were configured beforehand. Initialize all
settings before configuring failover.
Setting Restrictions
The following functions will not be available while failover is enabled:
Initializing settings, changing the RAID settings, formatting drives, iSCSI volume, changing the backup TeraStation’s
settings, turning the TeraStation on and off, updating the firmware
While failover is enabled, shutdown, power-on, and firmware update operations can be made available by
temporarily changing the TeraStation to maintenance mode. Maintenance mode can be enabled or disabled at
Backup > Failover in the main TeraStation’s Settings. Click Maintenance mode to enable maintenance mode, or click
Cancel maintenance mode to disable maintenance mode.
To update the firmware while in maintenance mode, the main TeraStation can be updated from Settings, but the
backup TeraStation cannot. Download the firmware updater from the Buffalo website for the backup TeraStation
and try updating the firmware on it.
Non-Transferable Settings
The settings below are not copied from the main TeraStation to the backup TeraStation. Make a note of the original
settings so that they can be configured manually if failover errors.
WebAccess*, UPS synchronization, antivirus**, the backup job settings either if specifying shared folders on the
backup TeraStation or USB drives as the backup destination, and USB drives’ shared folder settings
99
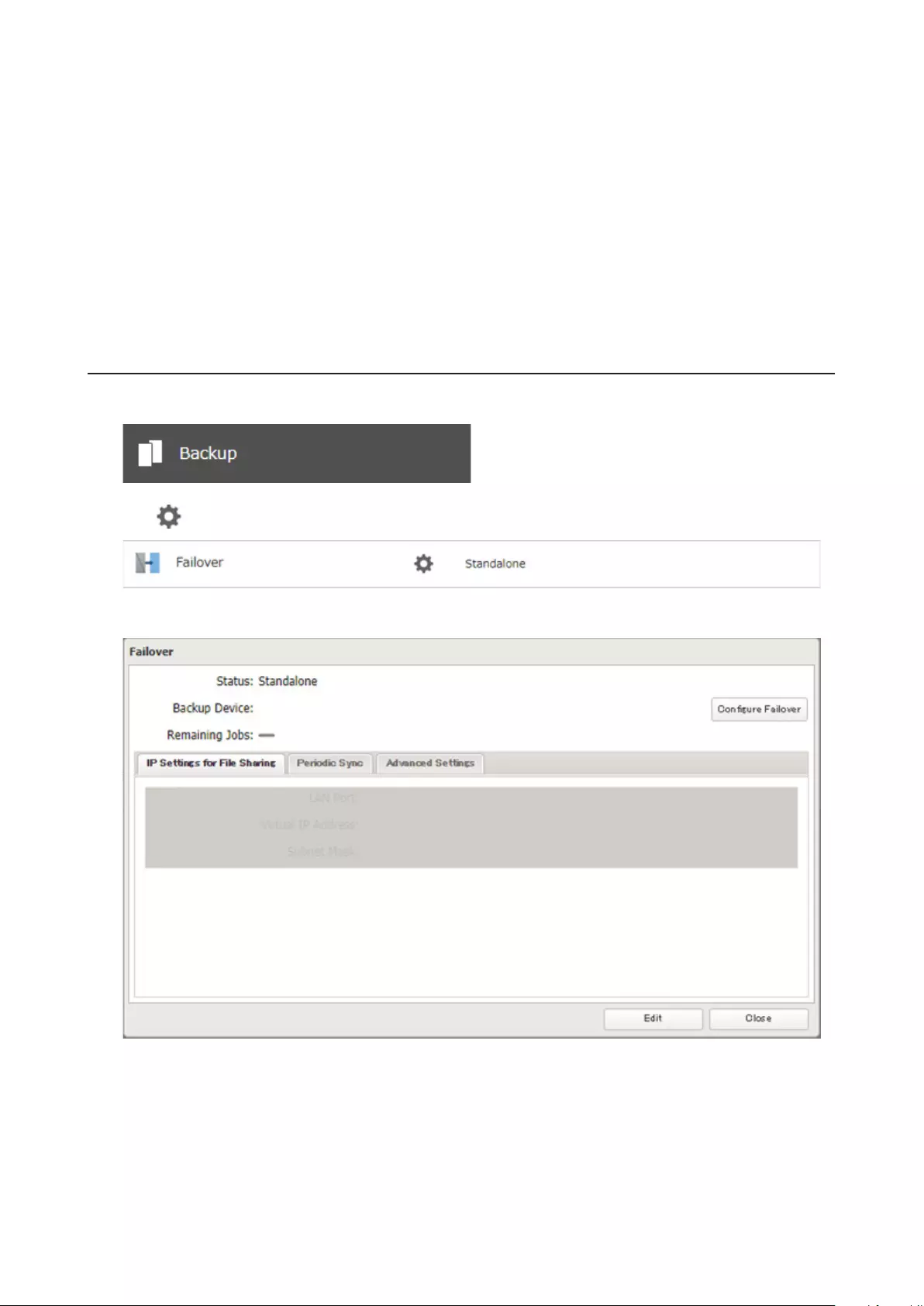
*If the backup TeraStation took over the main TeraStation’s IP address after failover, the WebAccess settings will not
be copied. Re-register your BuffaloNAS.com account for WebAccess. If the backup TeraStation kept its IP address, the
settings will be copied from the main TeraStation.
**The settings configured on the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page will not be copied to the backup
TeraStation. The settings configured on the main TeraStation’s Settings page will be copied. Only if the antivirus is
activated on the TeraStation.
Using with UPS
Once failover is configured, you cannot set up a UPS for the backup TeraStation. Configure your UPS before
configuring failover. UPS recovery can be configured for both the main and backup TeraStations.
Configuring Failover
1 From Settings for the main TeraStation, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Failover”.
3 Click Configure Failover.
100
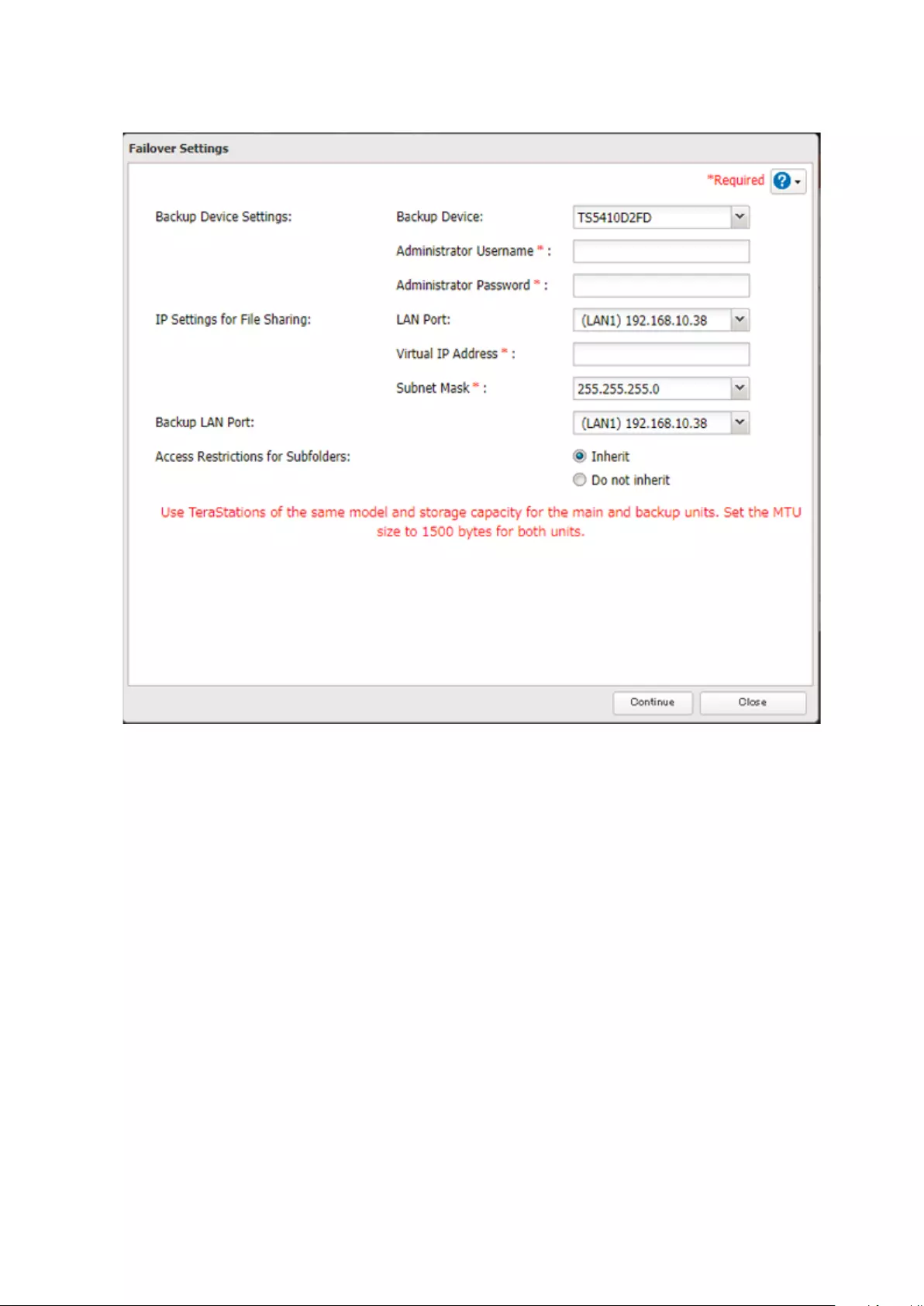
4 Select a TeraStation to be the backup destination device and enter its administrator username and password
(the username is “admin”, the password is “password” by default).
5 Select the LAN port to be used for sharing files and enter a virtual IP address and subnet mask.
About Virtual IP Address:
A virtual IP address is an IP address that will be used for file sharing while failover is configured. By assigning
a different IP address from the one to be assigned to the LAN port, you can access the TeraStation for sharing
files, as well as open Settings using the virtual IP address. This IP address will be inherited to the backup
TeraStation when failover occurs, so you can access the backup TeraStation even if you don’t know the backup
TeraStation’s static IP address.
Configure an unused IP address for the virtual IP; make sure it uses the same segment as the main and backup
TeraStations.
6 Select the LAN port to be used for transferring data via failover.
7 Configure whether or not to inherit subfolders’ access restrictions to the backup TeraStation, then click
Continue.
8 If the administrator username and password is correct, the backup TeraStation will beep. Press and hold the
function button to accept the settings from the main TeraStation. When you press the function button, the
backup TeraStation will stop beeping.
9 Hold it down until the backup TeraStation beeps again.
10 The I51 message will appear on the LCD panel and NAS Navigator2 for both TeraStations. Wait until
initialization finishes. Failover is configured after it finishes and the I51 message disappears.
101
Notes:
• If you want to cancel the failover settings while both the main and backup TeraStations are working properly,
click Force Failover to Stop on both TeraStations and restart them. After the TeraStations are restarted, make sure
that all settings such as IP address and files on the shared folders are correct.
When you cancel failover settings, attributes of the shared folders on the backup TeraStation will become read-
only. Change the attribute settings to the desired options if necessary.
• If replication is configured for more than one folder, initialize the TeraStation before configuring failover.
• The main TeraStation cannot be used as the backup location for Time Machine.
• Do not use the same TeraStation for both failover and replication, or failover and Time Machine.
• If email notification is enabled and failover occurs, navigate to Management > Email Notification > Edit in the main
TeraStation’s Settings and click OK.
• MTU size settings for main and backup TeraStations should be 1500 bytes. To change the MTU size, navigate to
Network > IP Address > Edit, and change the MTU size to “1500” bytes.
• Files whose filenames contain more than 80 alphanumeric characters will not be backed up.
• If the I33 message appears on the LCD panel, navigate to Backup > Replication and click Resync.
• The RAID array on the backup TeraStation may be reconfigured and resynchronized as part of the failover
configuration process. This is expected behavior and not an error.
Replacing to the Backup TeraStation Manually
If “Switch to backup unit manually” is selected on the Advanced Settings tab in the main TeraStation’s Settings, the
backup TeraStation will not replace the main TeraStation if the main TeraStation fails. To have the backup TeraStation
replace the main TeraStation, you can either:
• Log in to Settings for the backup TeraStation and click Set as Main Unit.
• Or, press and hold the function button on the backup TeraStation.
Note: If the main TeraStation fails but all LAN ports’ link on the backup TeraStation is up, the backup TeraStation
cannot replace to the main TeraStation from Settings. In such a case, use the function button instead.
Reconfiguring After Failover Occurs
When the backup TeraStation replaces the main TeraStation, the I49 message may appear on the backup
TeraStation’s LCD panel and NAS Navigator2. To configure failover again, follow the procedure below using the new
TeraStation unit. The following procedure is an example using the replaced backup TeraStation (“main TeraStation”)
and the new TeraStation (“backup TeraStation”).
If you don’t want to configure failover with the new TeraStation, cancel the failover settings by following the steps
1–5 below and restart both TeraStations. The I49 message will disappear.
Note: The following procedure will also work if failover occurs unexpectedly.
1 After failover occurs, log in to Settings for the main TeraStation.
If you have configured to sync with the UPS device connected to the failed TeraStation, the E10 message will
be displayed on the main TeraStation. In such a case, follow the procedure below to change the UPS settings
on the main TeraStation. If you didn’t, skip to the next step.
a. Disconnect the UPS cable from the failed TeraStation and connect it to the main TeraStation.
b. Click Management.
c. Click to the right of “Power Management”.
d. Click Edit.
e. Select “Sync with UPS connected to this TeraStation” and reconfigure the desired UPS settings.
f. Click OK when finished.
102
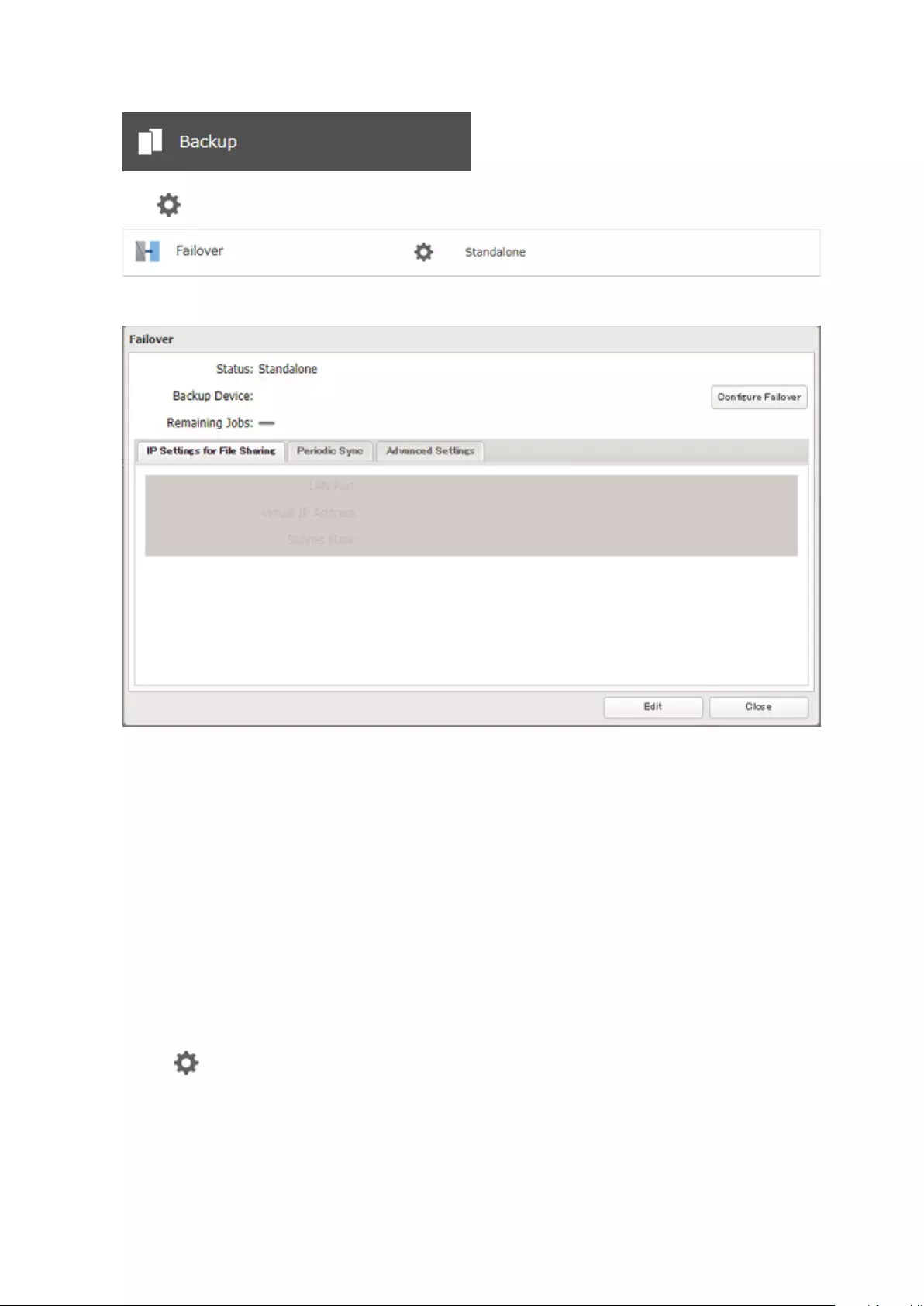
2 Click Backup.
3 Click to the right of “Failover”.
4 Click Configure Failover.
5 Click Force Failover to Stop to cancel the failover settings.
6 Shut down this main TeraStation.
7 Turn the backup TeraStation on.
8 Log in to Settings for the backup TeraStation, then rename the TeraStation’s hostname and configure the IP
address so that it has a new static IP address.
9 Power on the main TeraStation. To configure the UPS sync on the backup TeraStation, configure the settings
here. Otherwise, skip to the next step.
To sync with the UPS device connected to the main TeraStation, follow the procedure below on the backup
TeraStation.
a. Click Management.
b. Click to the right of “Power Management”.
c. Click Edit.
d. Select “Sync with UPS connected to another Buffalo NAS device on the same network” and configure the
main TeraStation as a sync source.
e. Click OK when finished.
10 Reconfigure failover by referring to the “Configuring Failover” section above.
103
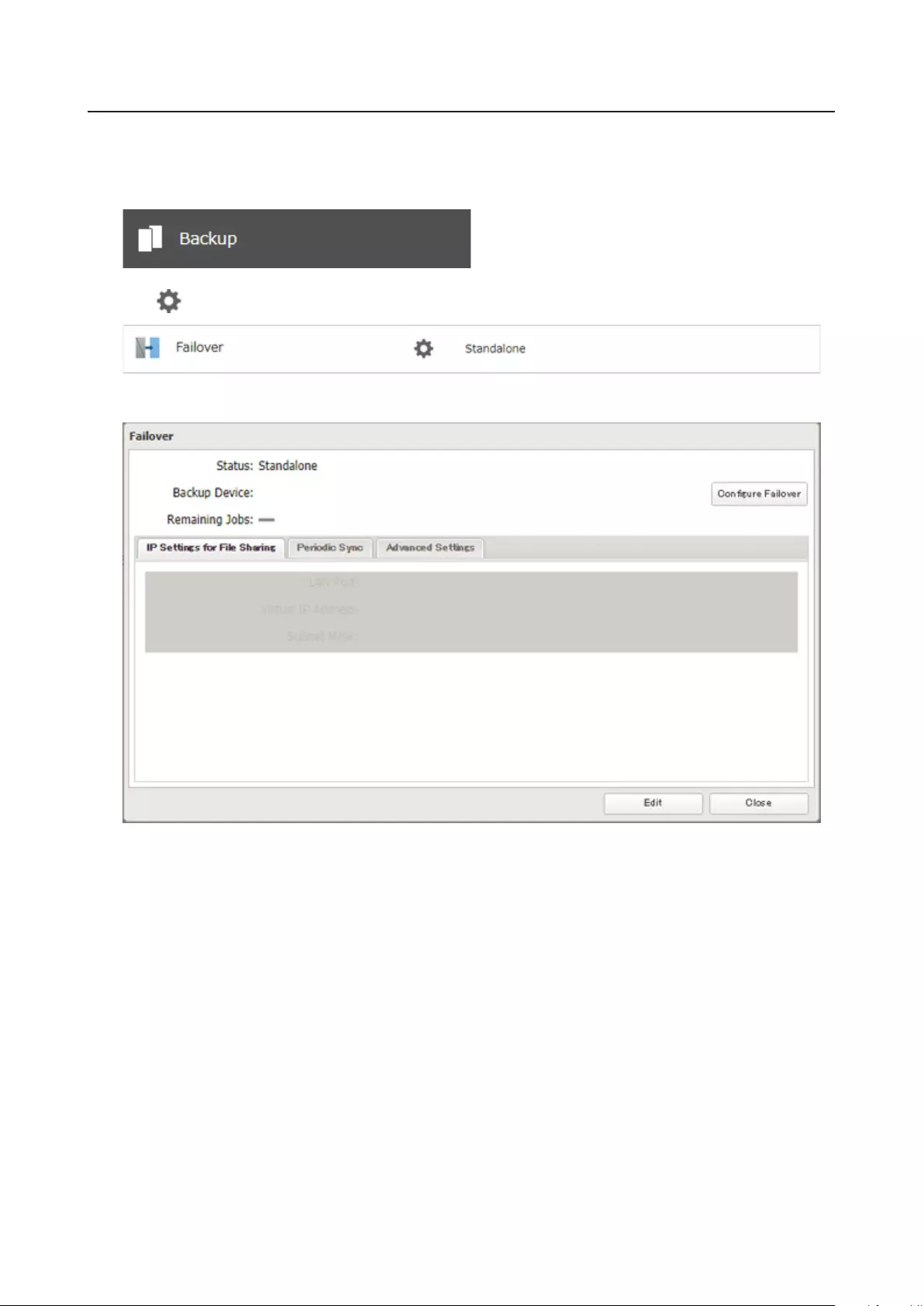
Synchronizing between Main and Backup TeraStations Periodically
To copy files that are saved via other file sharing protocols such as AFP or FTP to the backup TeraStation regularly,
configure “Periodic Sync” in Settings. Follow the procedure below.
1 From Settings for the main TeraStation, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Failover”.
3 Click the Periodic Sync tab.
104
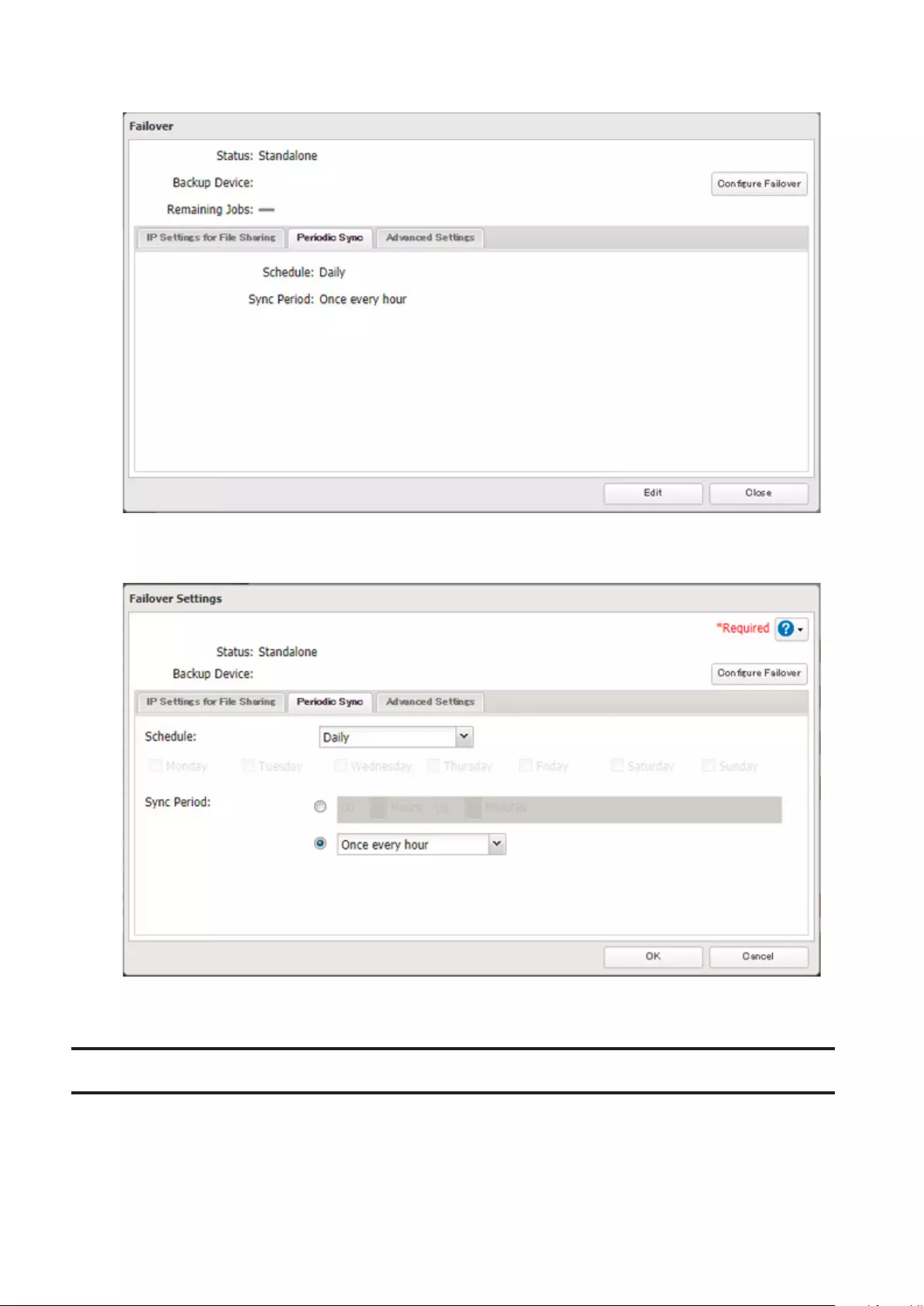
4 Click Edit.
5 Select “Daily” or “Weekly” from the “Schedule” drop-down list. If “Daily” is selected, configure the sync period. If
“Weekly” is selected, specify the weekdays and the sync period.
6 When the configuration is finished, click OK.
Backing Up Your Mac with Time Machine
Time Machine is a backup program included with macOS. Configure your TeraStation as shown below to use Time
Machine.
105
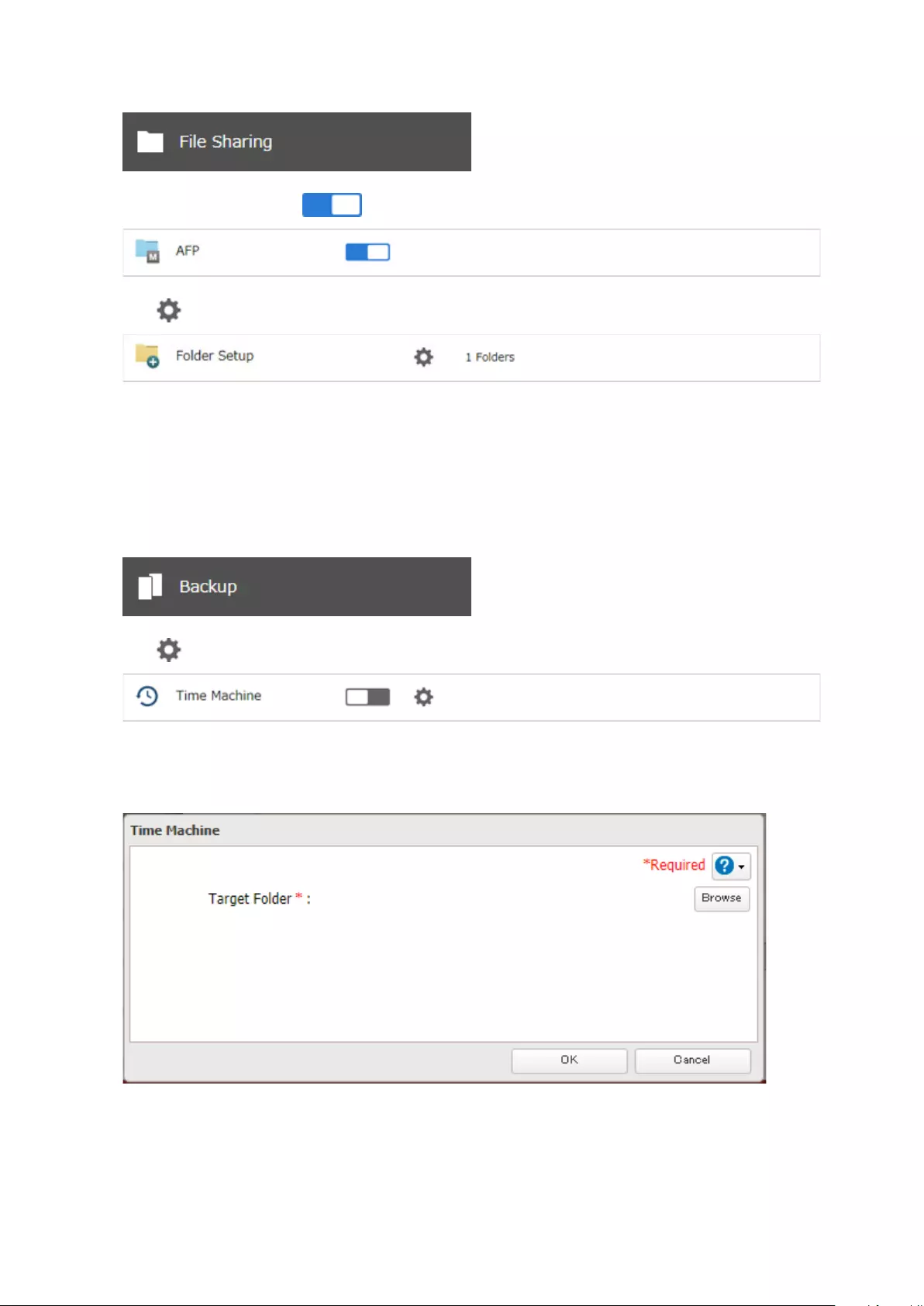
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Move the AFP switch to the position to enable AFP.
3 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
4 Choose a shared folder as your backup destination for Time Machine.
5 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “AFP (Mac)” checkbox on the Basic tab and click OK.
6 Click Close.
7 Click Backup.
8 Click to the right of “Time Machine”.
9 Click Edit.
10 Click Browse.
106
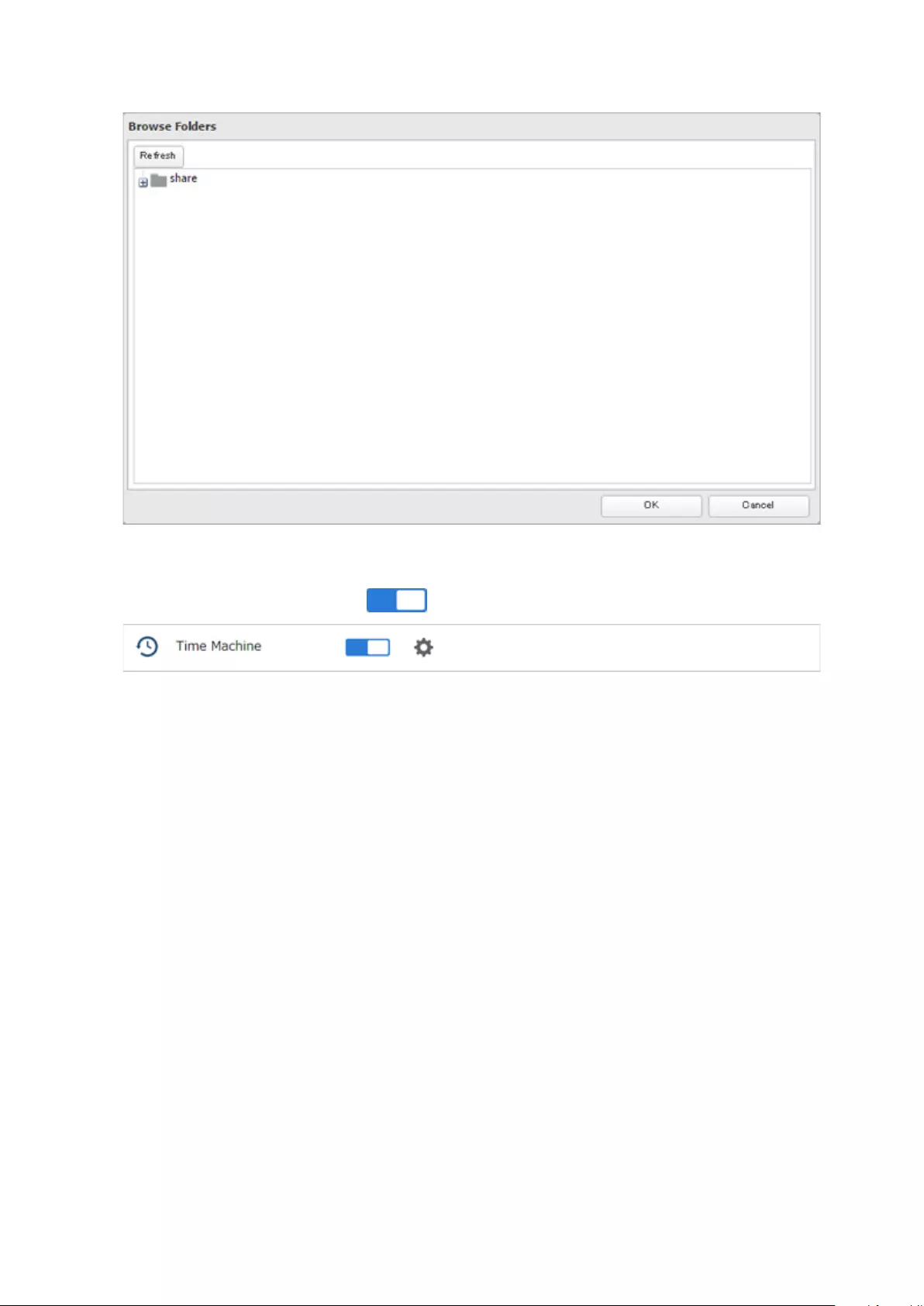
11 Select the shared folder that you enabled AFP for in the previous steps, then click OK.
12 Click OK, then click OK again.
13 Move the Time Machine switch to the position to enable Time Machine.
14 From the Mac, open System Preferences.
107
15 Click Time Machine.
108
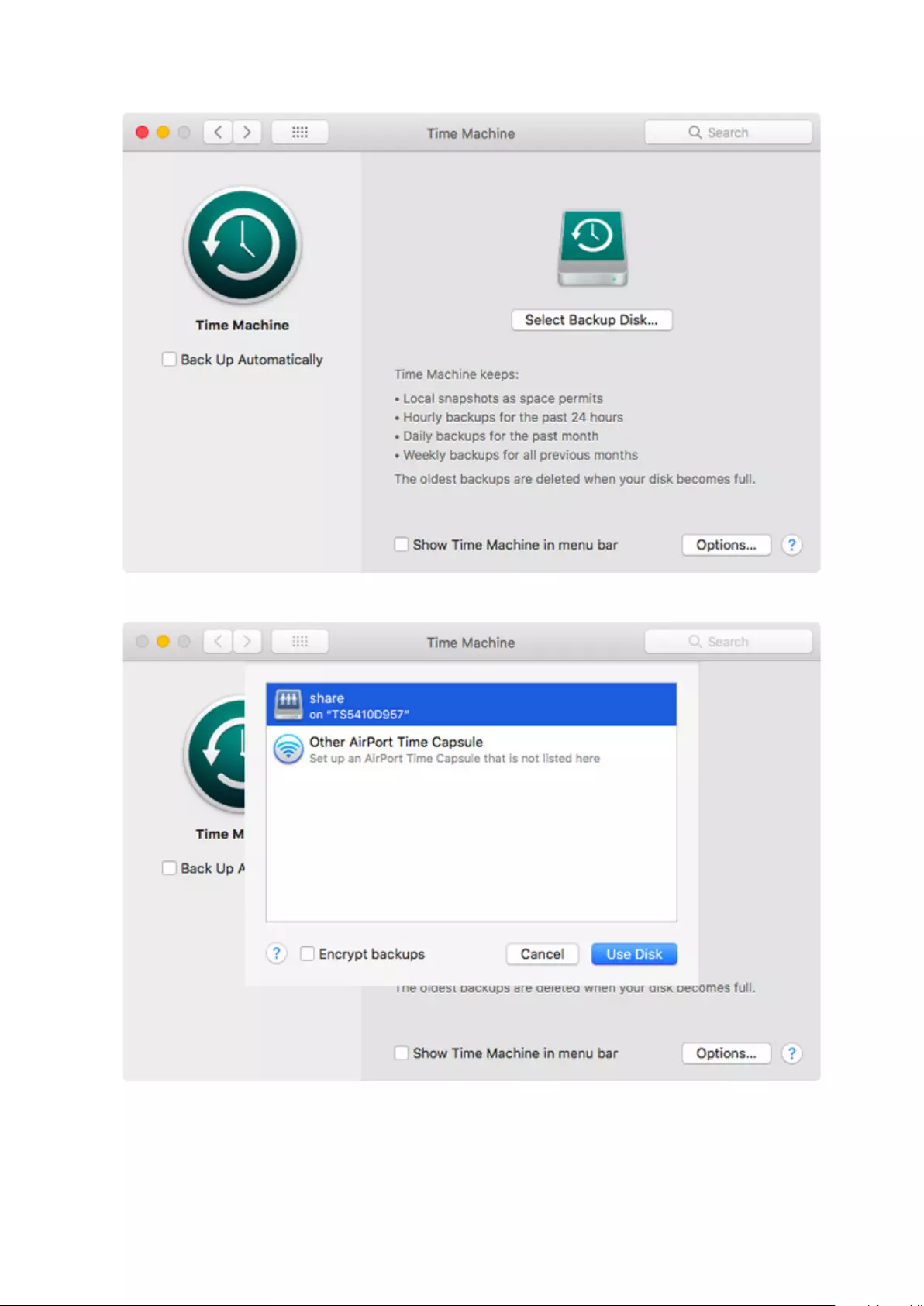
16 Click Select Backup Disk.
17 Select the TeraStation, then click Use Disk.
109
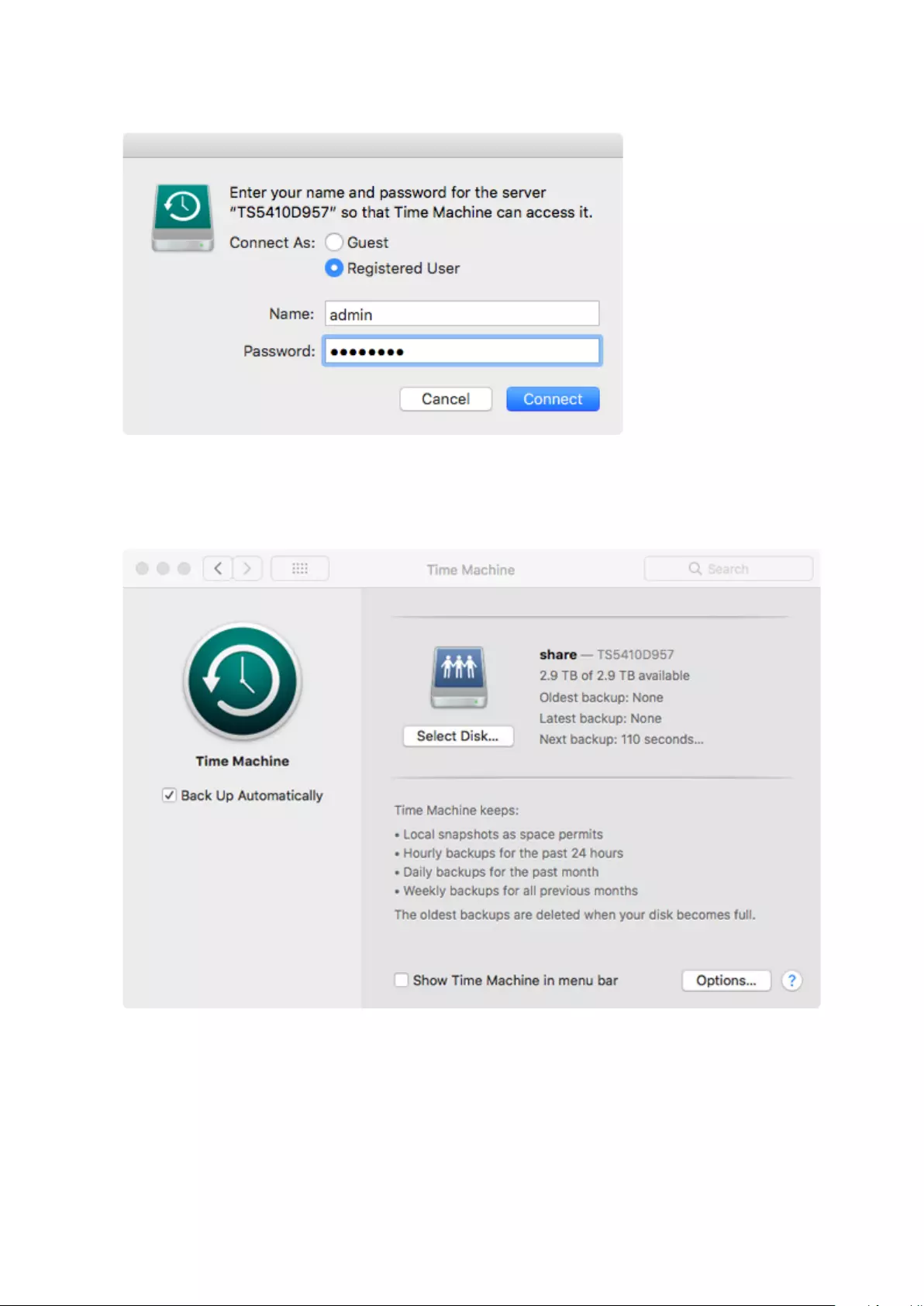
18 Enter a username and password with the rights to access the shared folder of the TeraStation, then click
Connect.
Note: If access restrictions are not configured on the destination share, log in with the administrator account.
The default username and password for the administrator account are “admin” and “password”. If access
restrictions are configured, log in with an account with write privileges.
19 Time Machine will count down from 120 seconds, then backup will begin.
110
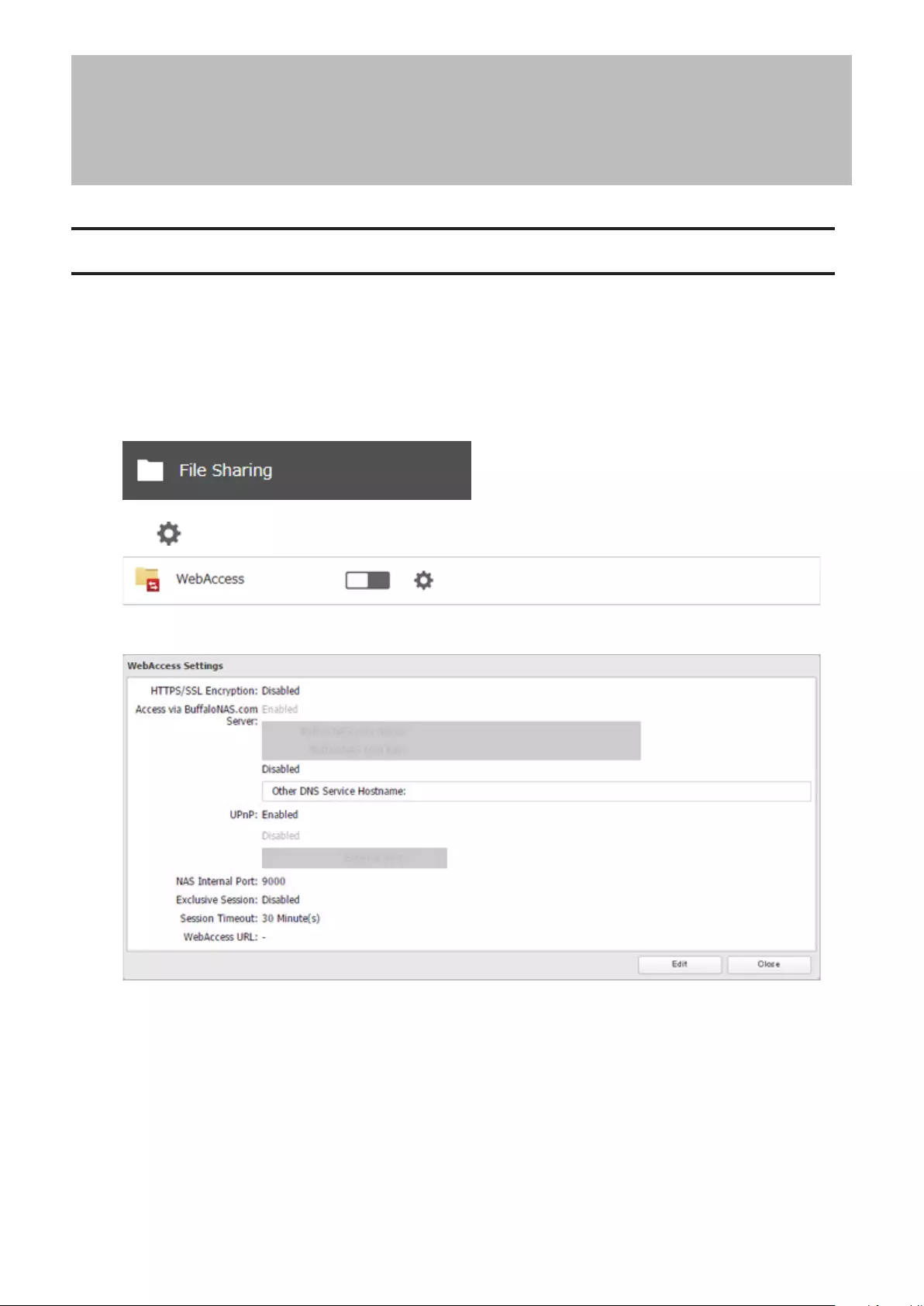
Chapter 6 Remote Access
WebAccess
WebAccess is a software utility for accessing the files in the shared folder of your TeraStation from your computer
or mobile devices through the Internet. Be careful when configuring WebAccess. Certain settings can make the
files in the shared folder available to anyone on the Internet, without any access restrictions.
Note: WebAccess supports downloading up to 60,000 files at a time. Attempting to download up to 60,000 files at a
time may result in unexpected behavior.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “WebAccess”.
3 Click Edit.
111
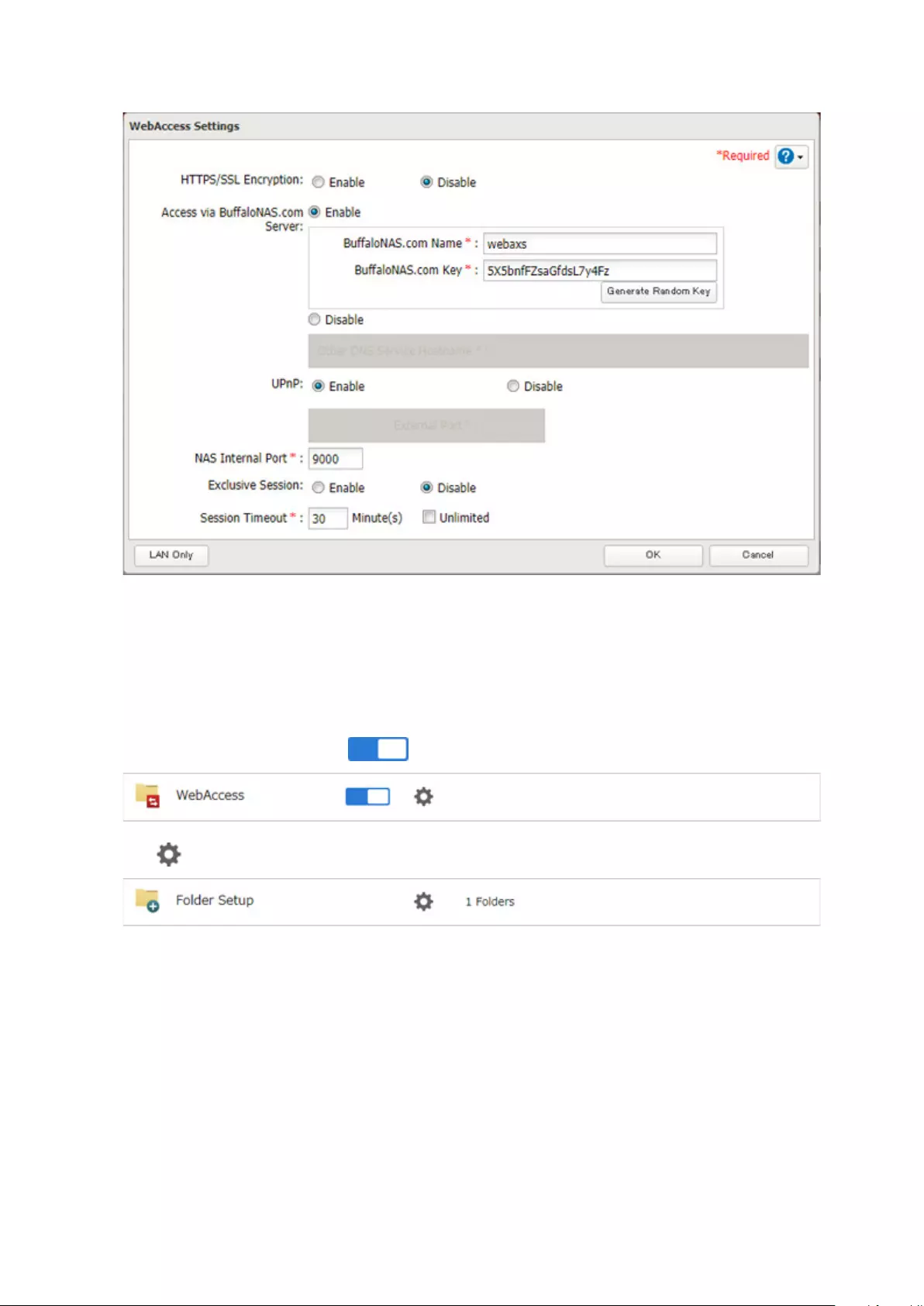
4 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
• To use SSL encryption for more secure data transfers, enable “HTTPS/SSL Encryption”.
• You may use the BuffaloNAS.com server as a DNS server, or disable it to use a different DNS server.
• Choose a “BuffaloNAS.com Name” and “BuffaloNAS.com Key” for your WebAccess account. Names and keys
may contain between 3 and 20 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
• If “Exclusive Session” is enabled, multiple users cannot be logged in to WebAccess at the same time. Only the
last login will be active.
• Enter a time in minutes (1 to 120, or “Unlimited”) before inactive users are logged out of WebAccess.
5 Move the WebAccess switch to the position to enable WebAccess.
6 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
7 Select a shared folder to publish.
Notes:
• For best results, create a new dedicated share for WebAccess.
• When accessing shared folders through WebAccess from a remote location, a username and password
may be required for certain operations. For best results, create a user account with permissions on the
WebAccess share before using WebAccess.
8 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “WebAccess” checkbox on the Basic tab.
9 Click the Option 2 tab.
10 Select the desired WebAccess security level for “WebAccess Permissions”.
112
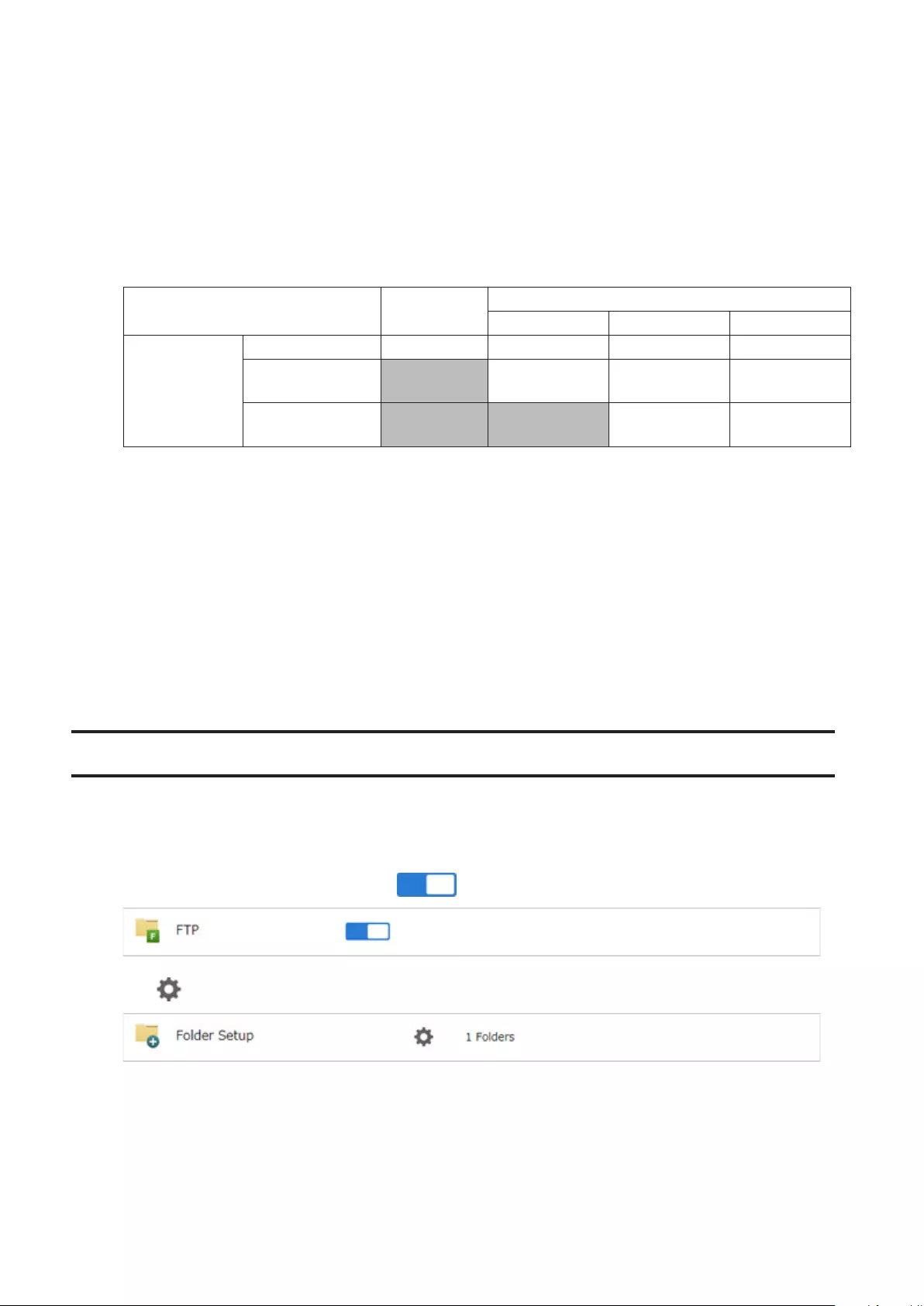
Allow anonymous: Anyone can access (view) shared folders. (Access restrictions configured for shared folders
will not work.)
Allow all groups and users: All groups and users registered on the Buffalo NAS device can use WebAccess.
(Access restrictions configured for shared folders will not work.)
Use inherited folder permissions: Users and groups have the same access permissions with WebAccess that
they do locally. If access restrictions are not set for the shared folder, then this option will not be shown.
Whether a user or group can access a folder through WebAccess depends on a combination of WebAccess
settings and the shared folder’s settings.
Not logged in Access restrictions for the logged-in users
No access Read-only Read and write
WebAccess
permissions
Allow anonymous R R/W R/W R/W
Allow all groups
and users - R/W R/W R/W
Use inherited
folder permissions - - R R/W
R: Read-only, R/W: Read and write, -: No access
11 Click OK.
There are many ways to access WebAccess folders depending on your device.
• From a computer, supported browsers include Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer 9
or later, Safari 9 or later. Refer to the help guide at the BuffaloNAS.com website after connecting with your
BuffaloNAS.com name for more detailed information.
• To access from an iOS device, install the “WebAccess i” application from the App Store. Refer to the help guide for
the app for more detailed information.
• To access from an Android device, install the “WebAccess A” application from Google Play. Refer to the help guide
for the app for more detailed information.
FTP
By default, the TeraStation’s shares are only accessible by users connected to the same network or router as the
TeraStation. The optional FTP server allows users outside the local network to access the TeraStation.
Note: FTP is intended for users who already have FTP client software and have experience with it.
1 From Settings, move the FTP switch to the position to enable FTP.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Choose a folder to enable remote FTP access on.
4 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “FTP” checkbox on the Basic tab; select read-only or read and write for
the shared folder’s attribute on the Option 2 tab and click OK.
Accessing the TeraStation with an FTP Client
113

To access the TeraStation via FTP, configure your FTP client software with the following settings:
• Hostname: IP address of the TeraStation
• Username: The TeraStation’s username
• Password: The TeraStation’s password
• Port: 21
Accessing the TeraStation with an Anonymous User
To allow anonymous access to your FTP share, disable access restrictions. Configure your FTP client software with
the following settings for anonymous FTP access:
• Hostname: IP address of the TeraStation
• Username: Anonymous
• Password: Any character string
• Port: 21
Notes:
• If the TeraStation joins a domain, domain and anonymous users cannot access it.
• Shared folders connected by FTP are available from the “/mnt” directory. The examples of default locations are:
/mnt/array1/share
/mnt/disk1/share
/mnt/usbdisk1
• If a file was created or copied by AFP, you may not be able to delete it using an FTP connection. If this occurs, use
an SMB or AFP connection instead to delete the file.
• For FTP connections, make sure that the total filename including directory path is 250 single-byte characters or
less.
Cloud Storage
The TeraStation supports Amazon S3, a fee-based online storage service provided by Amazon, and other cloud
storage services that share the Amazon S3 API. Follow the procedure below to configure your TeraStation for use
with your cloud storage service.
Notes:
• Depending on the services you have purchased, prices for operations and amount of data will vary. To avoid
being charged unexpectedly expensive fees, we recommend staying aware of the price structure for data storage
and operations and regularly checking how much have been charged.
• Set the TeraStation’s time settings to the correct time. Using NTP is recommended. To configure NTP settings on
the TeraStation, refer to the “Name, Date, Time, and Language” section in chapter 7.
Configuring Cloud Storage
1 From Settings, click Web Services.
2 Click to the right of “Cloud Storage”.
114
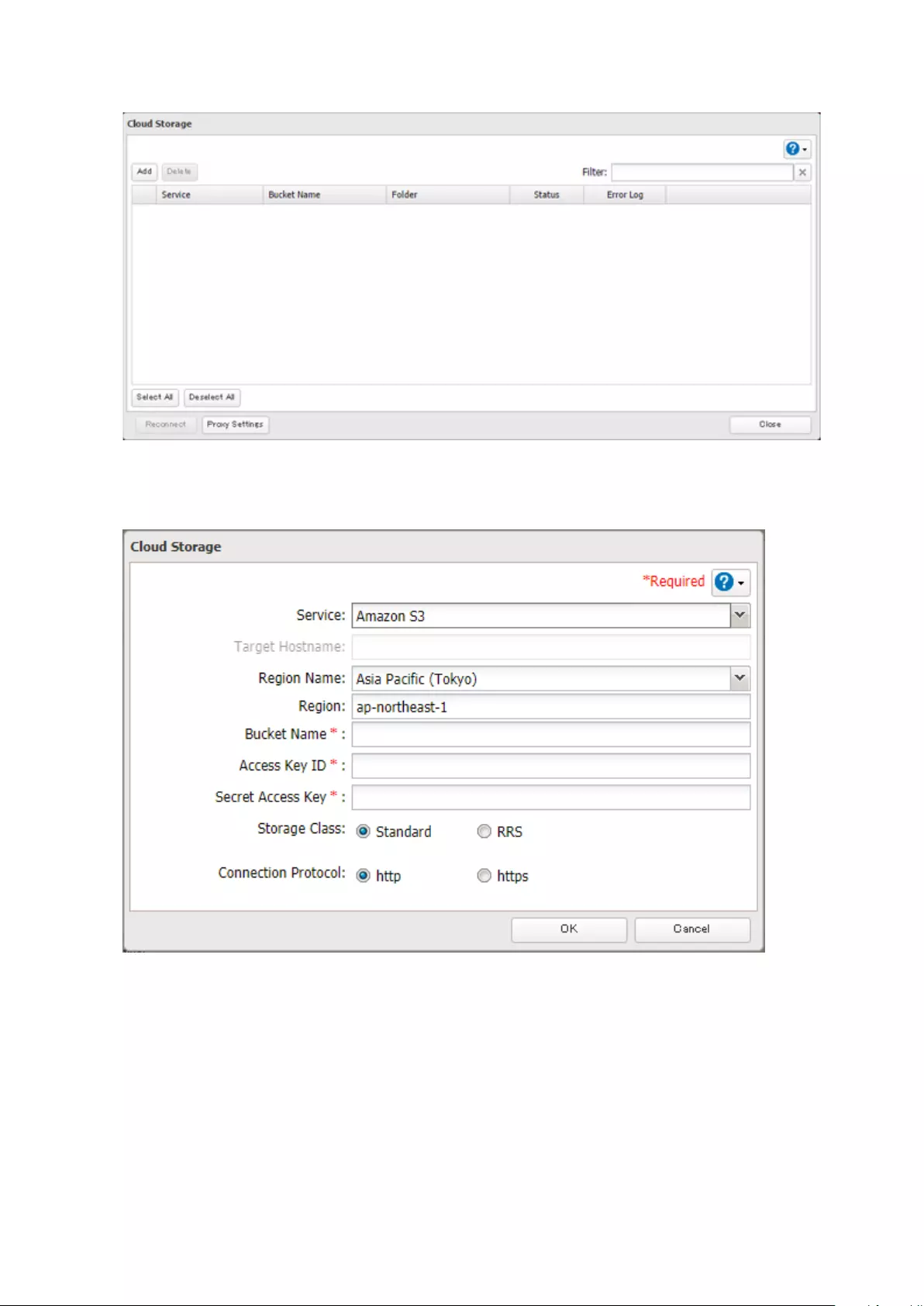
3 Click Add.
4 Select the service name and region name that you have selected when creating the bucket from the drop-
down list. Enter the bucket name, access key ID, and secret access key; select the storage class and the
connection protocol, then click OK.
115
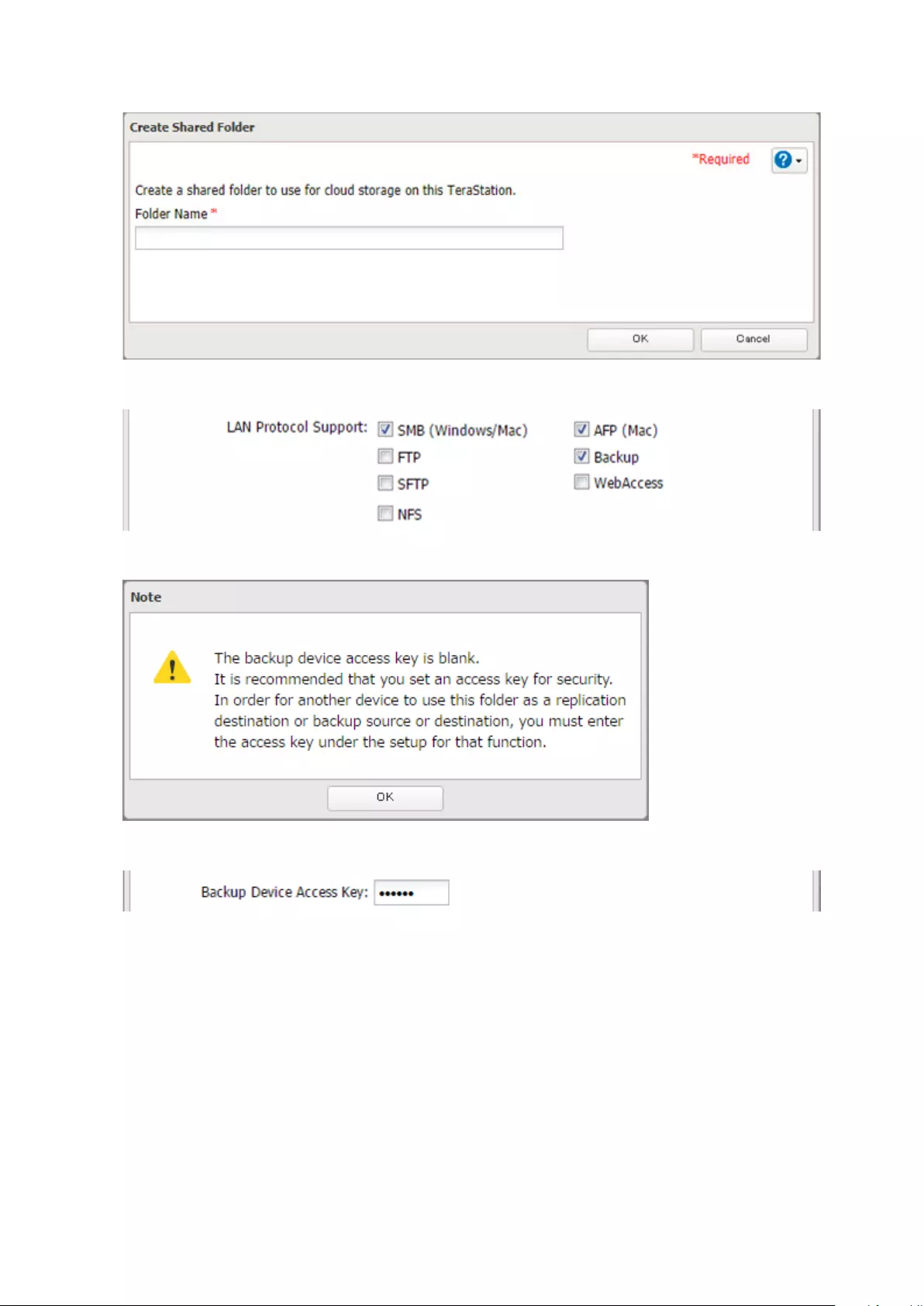
5 Enter a remote folder name to use with the cloud storage service and click OK.
6 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “Backup” checkbox on the Basic tab.
7 Click OK.
8 Enter the desired characters into the backup device access key field.
9 Configure the desired shared folder settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• If a remote folder created through this process is configured to use NFS, it cannot be mounted from an NFS client.
• Files cannot be uploaded to this remote folder using WebAccess.
• If using the cloud storage through a proxy server, click Proxy Settings. From the displayed page, you can select
whether to use the configured settings or configure an identical proxy server. If using the identical proxy server,
select “New settings” and enter the proxy server name, port number, username, and password. Consult your
network administrator for detailed proxy server settings.
• If you enter an incorrect bucket name and then cancel editing the cloud storage service settings, that wrong
bucket name may still accidentally be registered. If this happens, reconfigure the cloud storage service settings
correctly starting from step 4.
• Do not configure a folder that is created through the procedure above as replication destination folder.
116
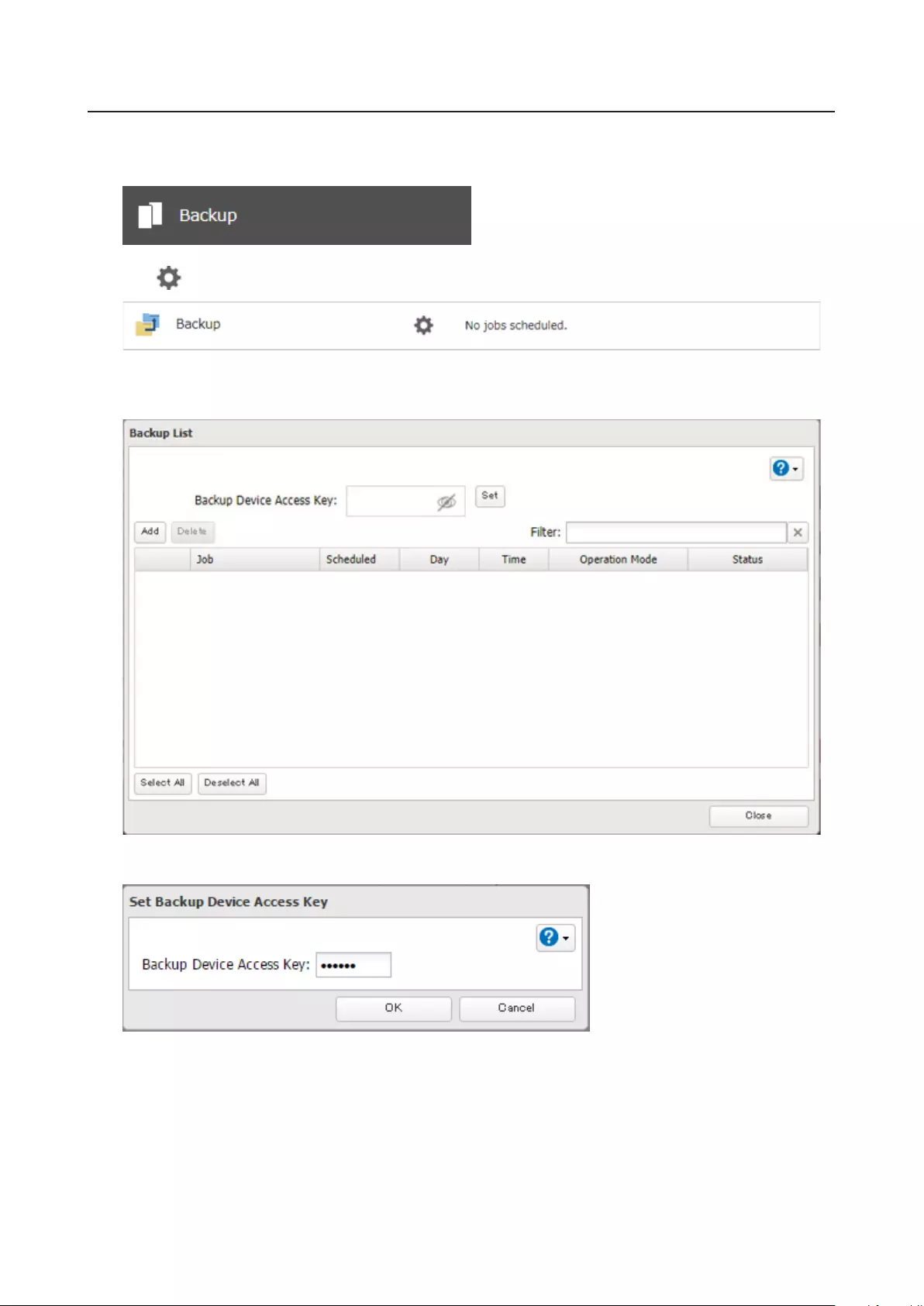
Uploading Files to Cloud Storage
To upload files to cloud storage, using backup job is recommended.
1 From Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of “Backup”.
3 If you had configured a backup device access key to the remote folder that was created through the
“Configuring Cloud Storage” section above, click Set. If you didn’t, go to step 5.
4 Enter the backup device access key and click OK.
117
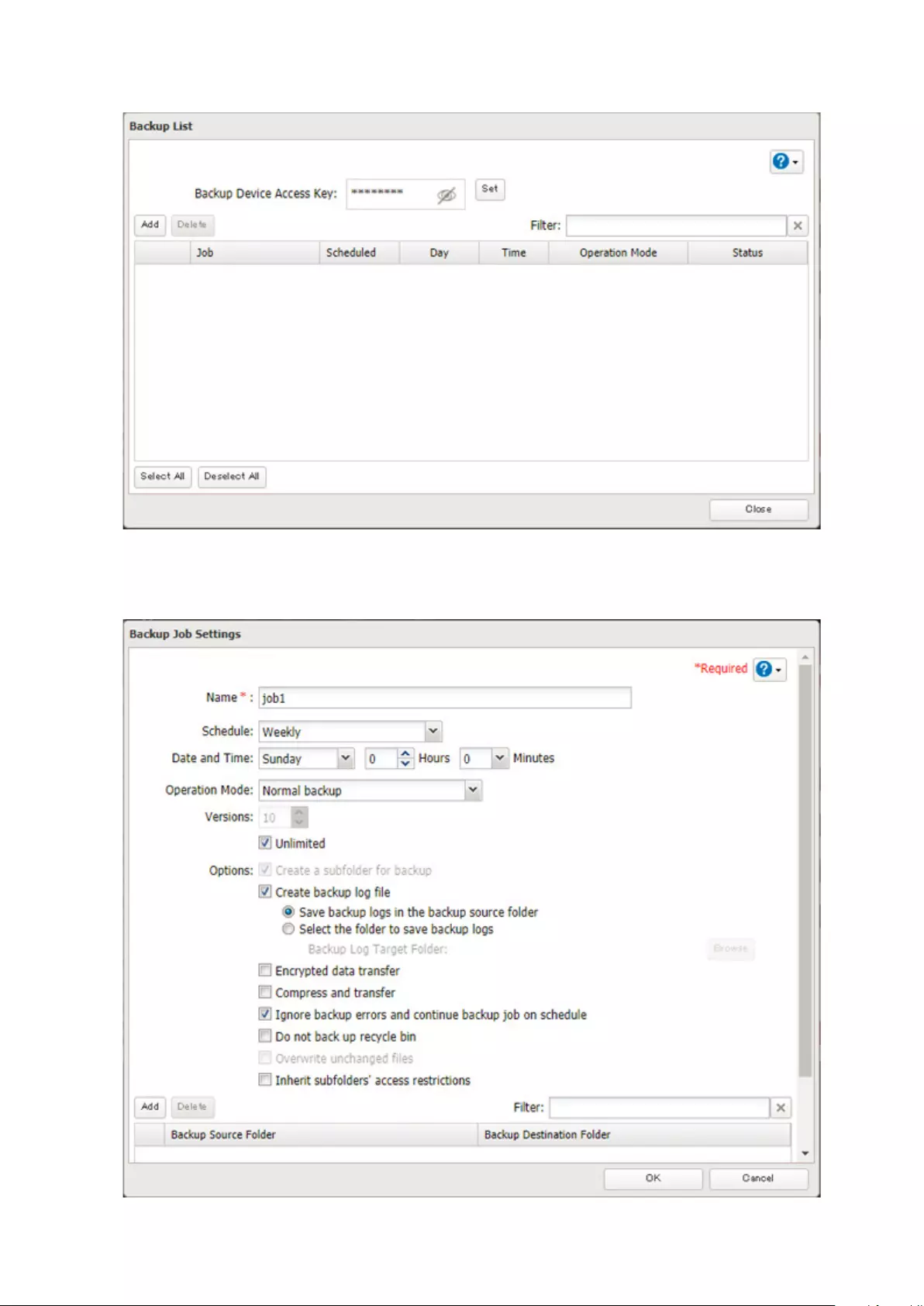
5 Click Add.
6 Select backup settings such as date and time to run. It is recommended to configure a job to run periodically.
If you create a differential backup job and there are files that only exist in the destination folder, these files will
be deleted when the job runs. Make sure that files are not saved when creating a backup job.
118
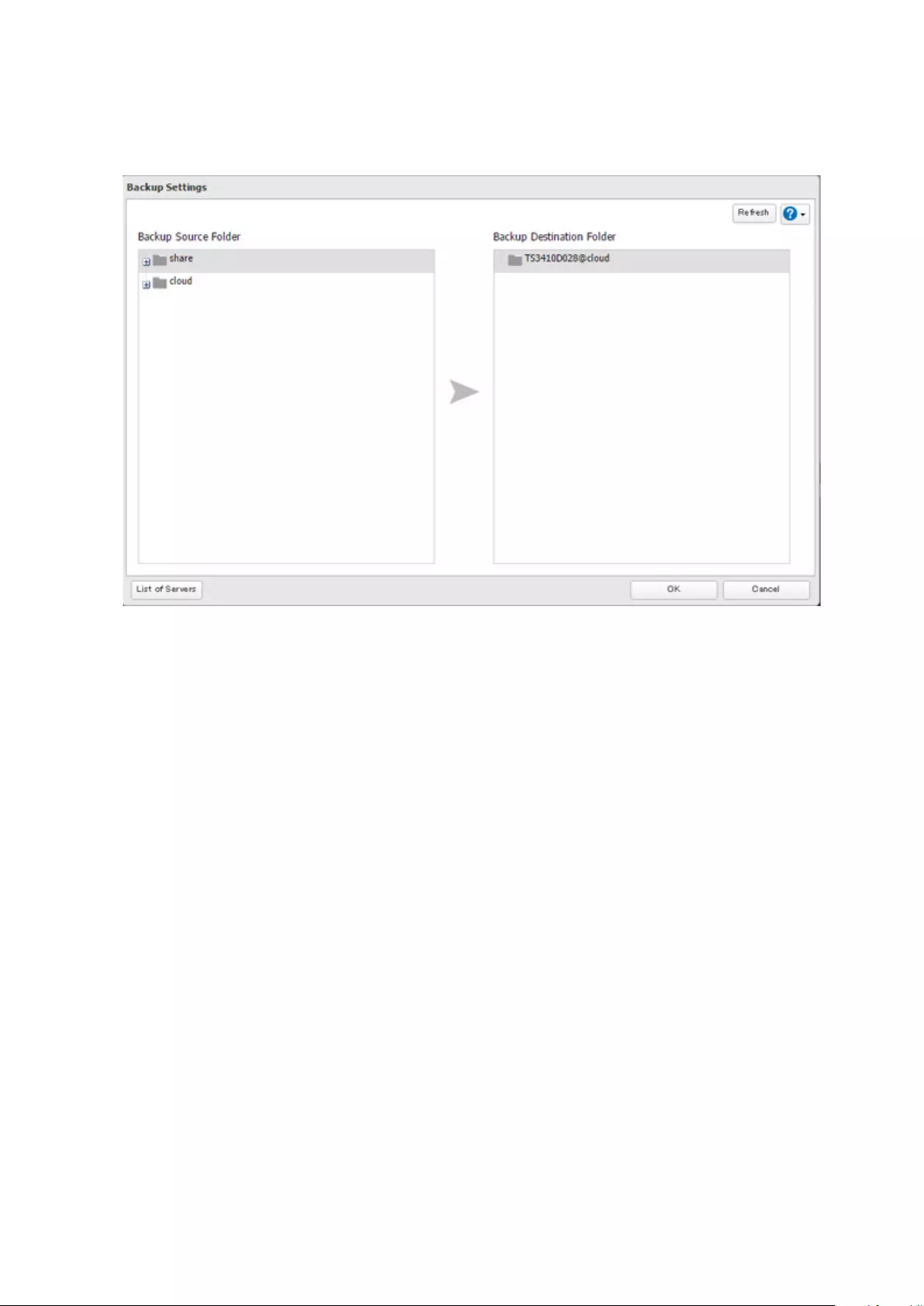
7 Click Add.
8 Select the shared folder that files will be saved to as a source, and the remote folder created through the
“Configuring Cloud Storage” section above as a destination.
9 Click OK. Jobs will be added to the backup list.
Notes:
• To use after the network was temporarily disconnected, click Reconnect.
• If a file is added to the cloud storage bucket from a folder other than the remote folder, it may take more than an
hour for the file to appear in the remote folder. However, when a file is added to the remote folder, it immediately
appears in the bucket.
• Do not copy 100,000 or more files to the backup source folder at once. If you do and uploading fails, check the
network environment speed and try again with fewer files.
• Be careful with existing files in the remote folder, as files with the same name will be overwritten even if copied
files are older.
• If you copy a file to the shared folder using File Explorer or a backup process, the file will also be uploaded
sequentially to the cloud storage bucket. This second uploading process will start in the background during the
first copying process and will not be visible. If the TeraStation is shut down or restarted immediately after copying
a file to the shared folder, changing the settings, or disconnecting and reconnecting the Ethernet cable, the file
may not be uploaded to the bucket. Try copying the file again if this occurs.
• If you encounter any upload or download errors, click Error Log. The log will display the filename and operation
during which the error occurred.
• If uploading fails, try copying the file again. If it still fails, click Reconnect or set the cloud storage switch to off and
on again, then restart the cloud storage service.
• If transferring or accessing 1 TB or more files from cloud storage, make sure there is enough free space on
the TeraStation for temporary file caching. For example, when uploading 1 TB of files to cloud storage, it is
recommended to keep at least 2 TB of free space available.
119
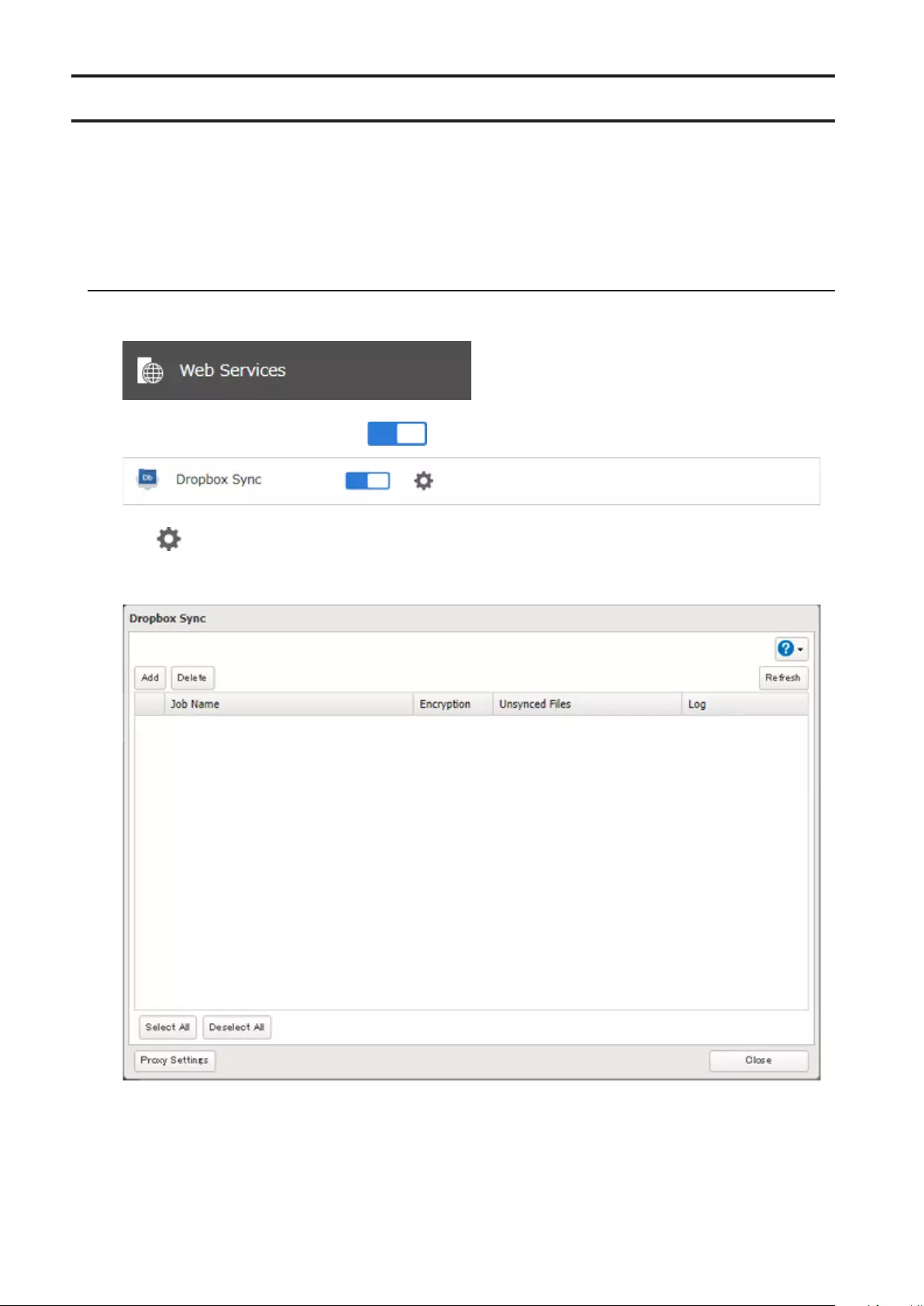
Dropbox Sync
The TeraStation supports syncing with Dropbox, the online cloud service. Once connected, you can share
TeraStation files via Dropbox (or Dropbox files via TeraStation). To link your TeraStation with your Dropbox account,
follow the procedure below.
Note: To use Dropbox Sync, you need a Dropbox account and an available empty Dropbox folder. If you don’t have a
Dropbox account, or if you need to create a new empty Dropbox folder, refer to the Dropbox website.
Configuring a New Job
1 From Settings, click Web Services.
2 Move the Dropbox Sync switch to the position to enable Dropbox Sync.
3 Click to the right of “Dropbox Sync”.
4 Click Add.
120
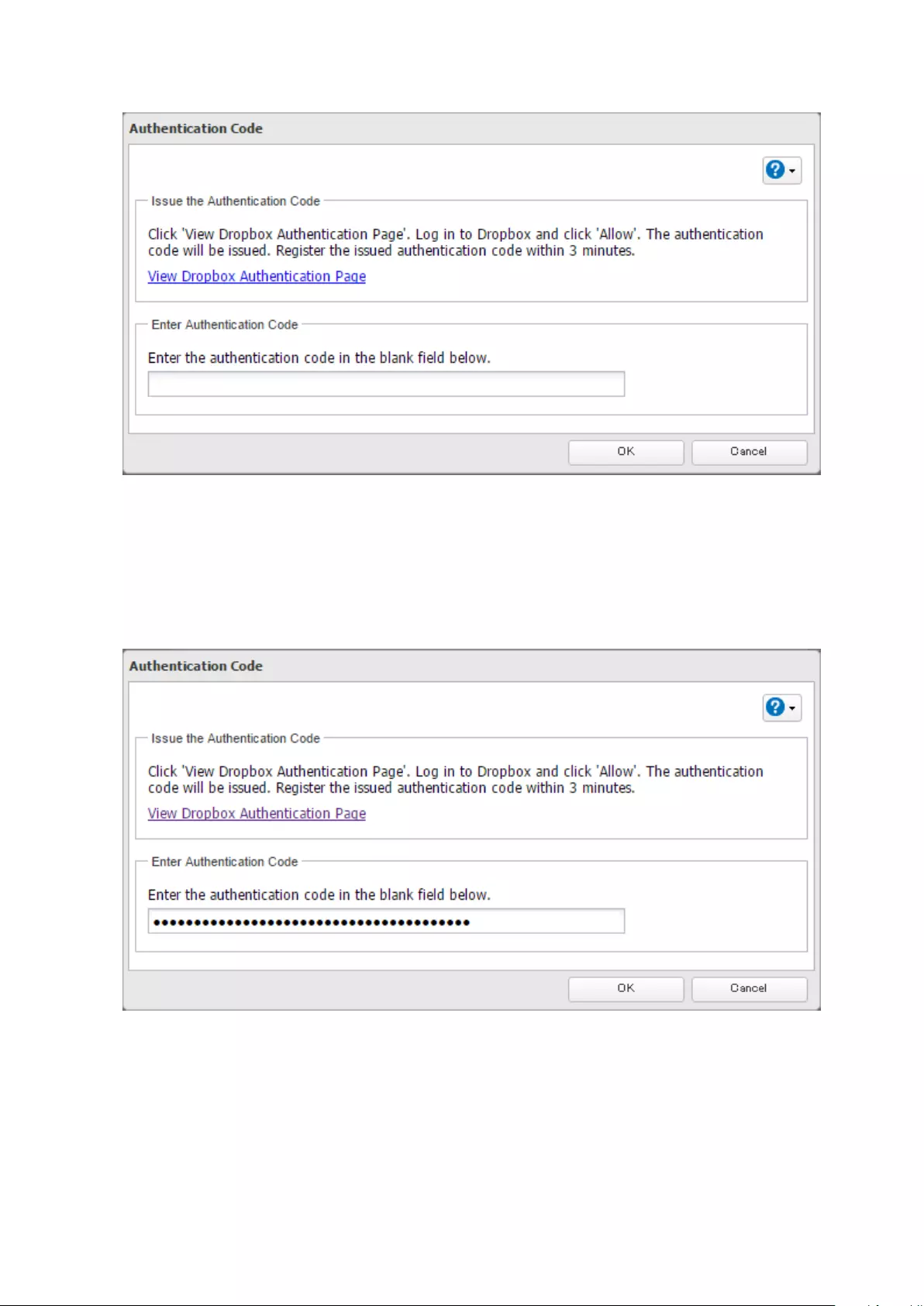
5 Click View Dropbox Authentication Page.
6 The authentication site that is offered by Dropbox will be displayed. Log in to the website with your Dropbox
account, then click Allow.
7 The authentication code will be displayed. Copy the authentication code and return to Settings.
Authentication code reregistration should be finished within 3 minutes.
8 Paste the authentication code and click OK.
9 Enter the desired job name; select the TeraStation and Dropbox folders, and configure encryption. Click OK.
121
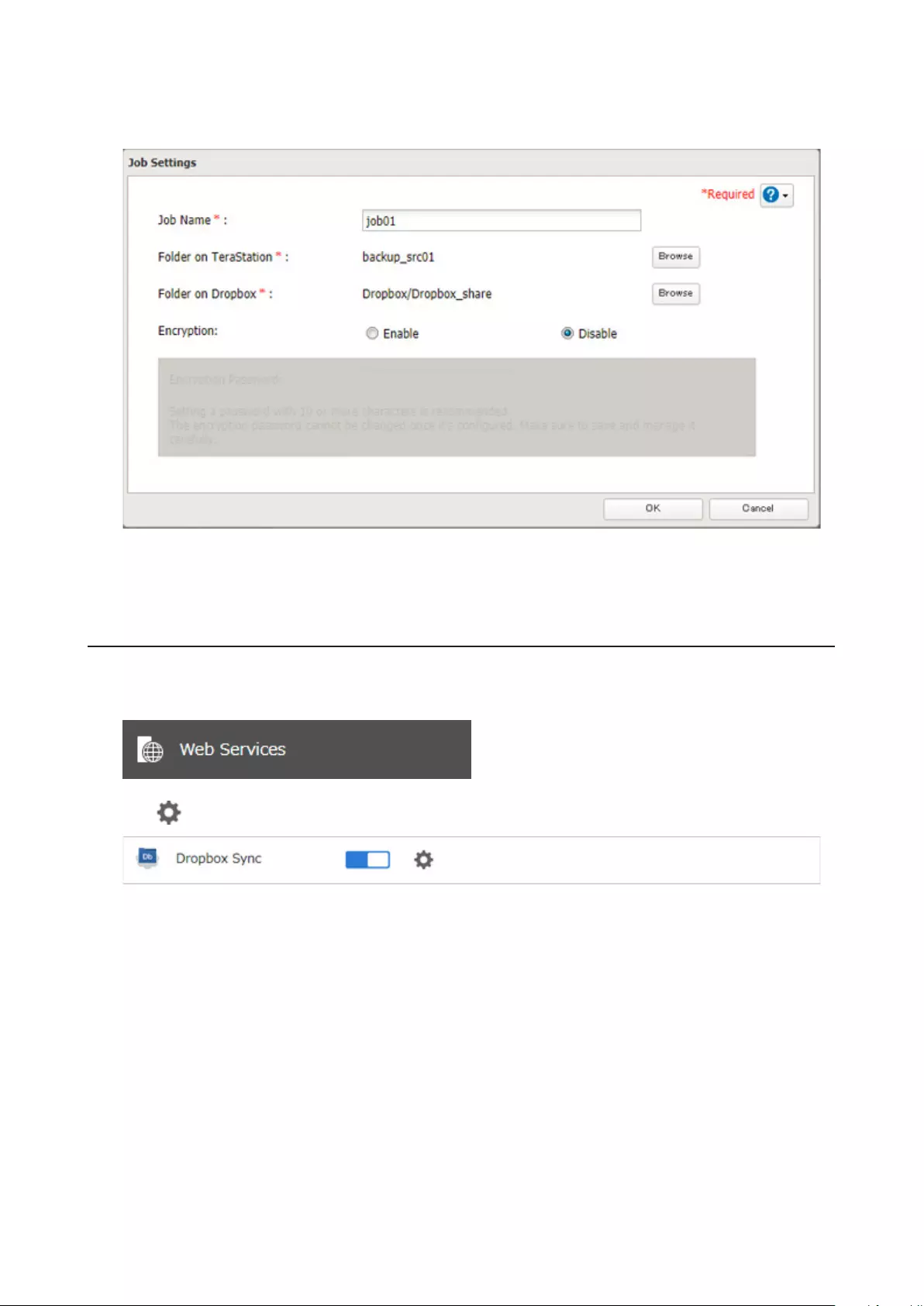
If you enable encryption, you will need to set an encryption password. The password cannot be changed once
you configure it. Please take note of the password and keep it secure. If you forget the password, create a new
job using the same Dropbox account. The old job can then be deleted.
10 Click OK.
Note: Up to 8 Dropbox jobs can be configured at a time.
Changing Dropbox Job Settings
Follow the procedure below to change any job settings you have already configured.
1 From Settings, click Web Services.
2 Click to the right of “Dropbox Sync”.
122
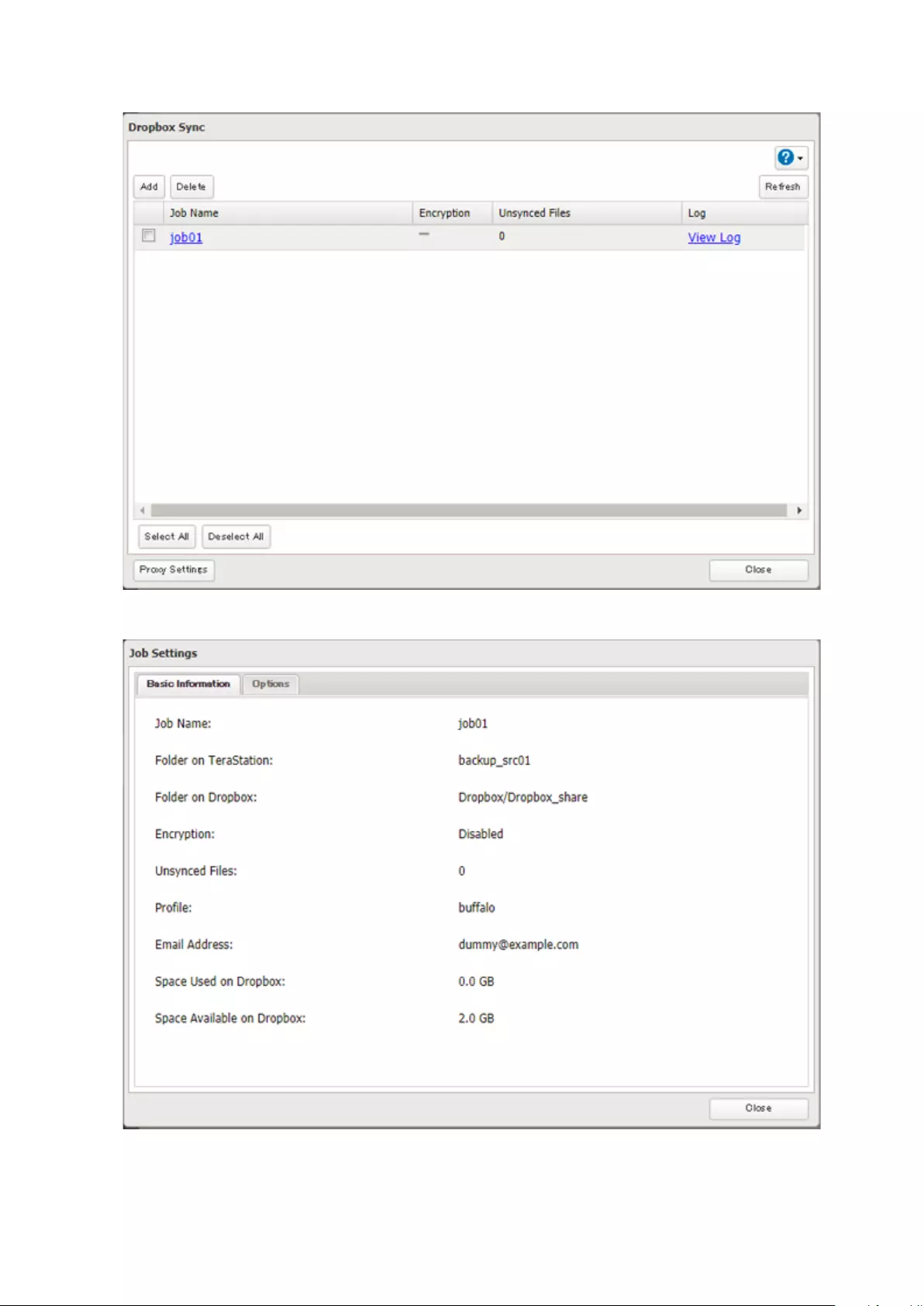
3 From the job list, click the job whose settings you want to change.
4 Click the Options tab.
123
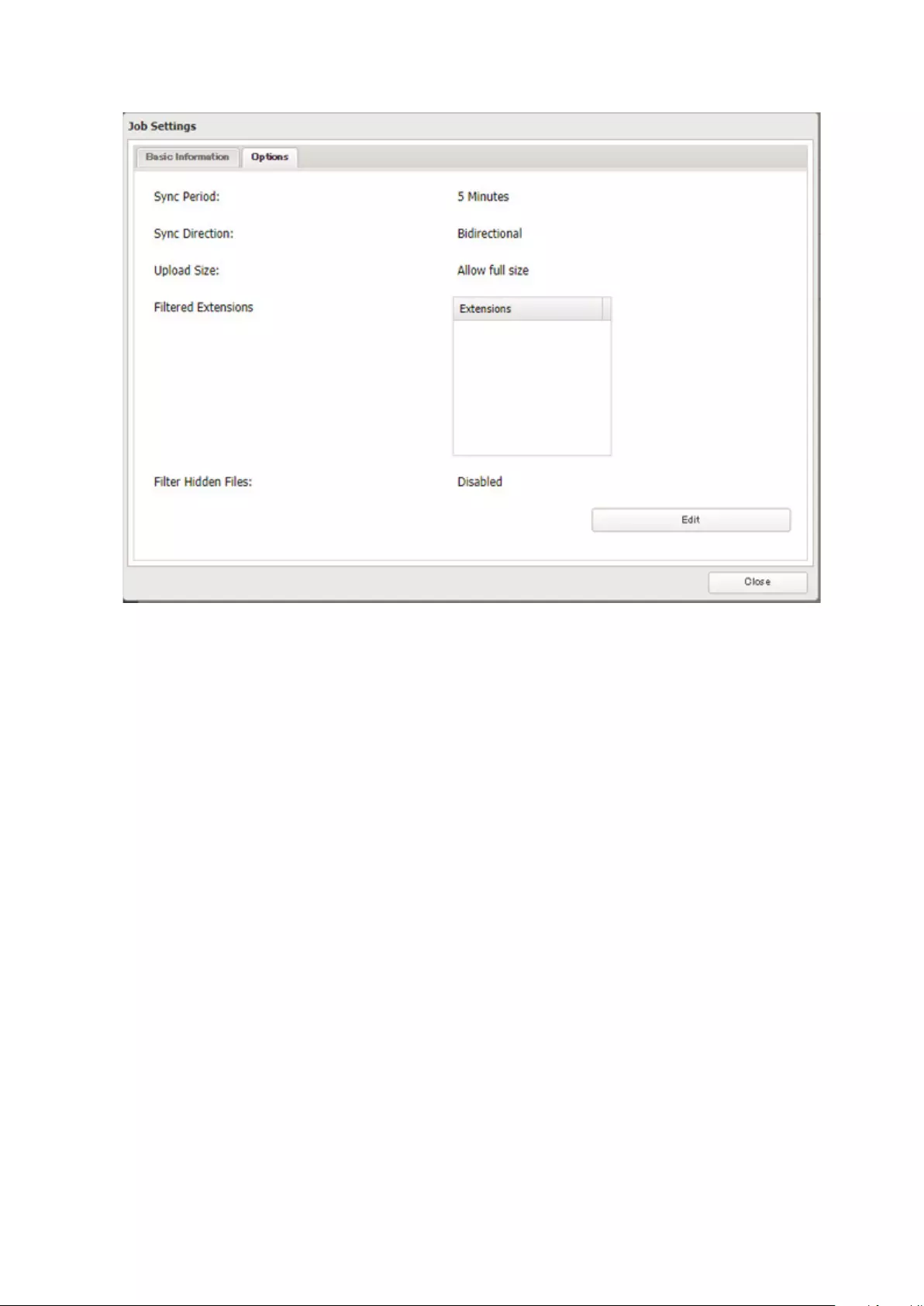
5 Click Edit.
124
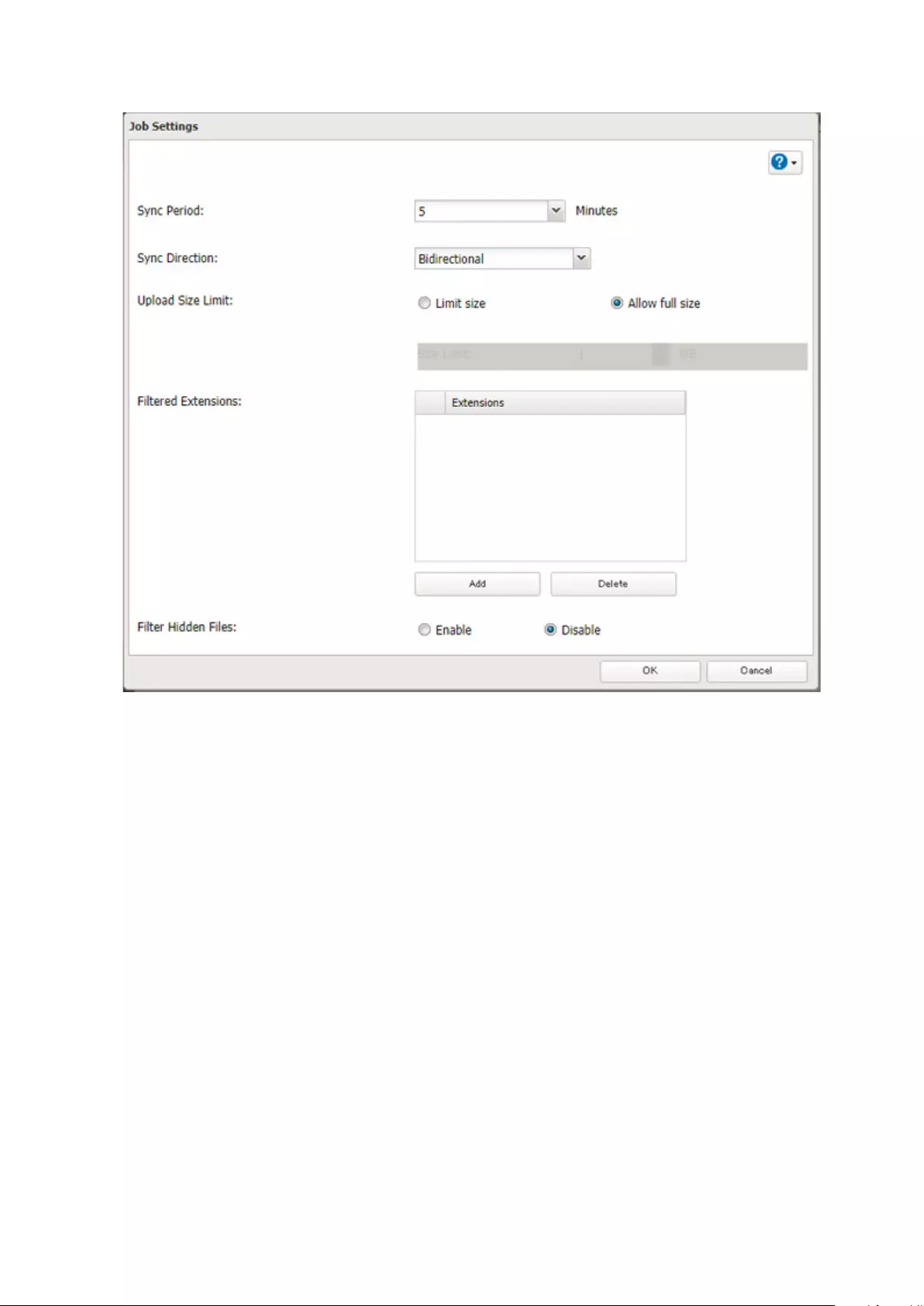
6 Configure the desired settings and click OK.
Notes:
• When encryption is enabled, files uploaded to Dropbox not using Dropbox Sync will not be downloaded to the
TeraStation even if the sync direction is configured to “Bidirectional” or “Download only”.
• Refer to the following website for synchronization restrictions between the TeraStation and Dropbox:
https://www.dropbox.com/help/145
• Folders that are configured for Dropbox Sync cannot be renamed or used for replication.
• When specific settings are changed, the changes are not applied and the files on Dropbox may not be synced to
the TeraStation. In such a case, delete the target files to be synced and upload them to Dropbox again or delete
the job and recreate it again. The following are the specific circumstances when files may not be synced:
◦Uploading or downloading fails.
◦File extensions are removed from filtering.
◦The sync direction is changed.
• If using Dropbox through a proxy server, click Proxy Settings. From the displayed page, you can select whether
to use the configured settings or configure an identical proxy server. If using the identical proxy server, select
“New settings” and enter the proxy server name, port number, username, and password. Ask your network
administrator for detailed proxy server settings.
• Files that are 900 MB or larger cannot be downloaded using Dropbox Sync. However, even if the file size is smaller
than 900 MB, downloading may fail when multiple processes are running at the same time.
• Regardless of whether file filtering was configured, the following files will not be uploaded to Dropbox:
◦desktop.ini
◦thumbs.db
◦Files whose filename contains the symbols / \ > < : " | ? *
125
◦Files whose filename ends with either a space or period
◦Files whose filename starts with either ~$ or .~
◦Files whose filename starts with ~ and have the file extension .tmp
Creating a Shared Link (Windows Only)
Buffalo offers a Windows application, “B-Sync”, that can create shared links for the files stored in the TeraStation
folders. You can download the application from the Buffalo website. Refer to the application help for the usage
procedure.
Microsoft Azure Storage Sync
The TeraStation supports syncing with Microsoft Azure, the online cloud storage service. Once connected, you can
back up data on the TeraStation to Azure Storage, or restore data from Azure Storage to the TeraStation.
Microsoft Azure offers multiple types of storage and the TeraStation is compatible with Blob Storage. There are three
types of blobs: block blobs, page blobs, and append blobs. The TeraStation only works with block blobs to store your
data.
This feature is meant for situations such as disaster recovery and not a catch-all backup function. After linking the
TeraStation and Microsoft Azure, data on the TeraStation will not be bidirectionally synchronized between the
TeraStation and an Azure container.
Notes:
• Depending on the services you have purchased, prices for operations and amount of data will vary. To avoid
being charged unexpectedly expensive fees, we recommend staying aware of the price structure for data storage
and operations and regularly checking how much have been charged.
• To access data that have been backed up to the container, use “Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer”.
• If using Azure Storage through a proxy server, click Proxy Settings. From the displayed page, you can select
whether to use the configured settings or configure an identical proxy server. If using the identical proxy server,
select “New settings” and enter the proxy server name, port number, username, and password. Ask your network
administrator for detailed proxy server settings.
To link your TeraStation with a Microsoft Azure Storage account, follow the procedure below.
Creating a New Backup Job
1 From the Azure portal, create your Azure Storage account and a container before proceeding with the
procedure.
2 From Settings, click Web Services.
3 Move the Microsoft Azure Storage Sync switch to the position to enable Microsoft Azure Storage
Sync.
4 Click to the right of “Microsoft Azure Storage Sync”.
126
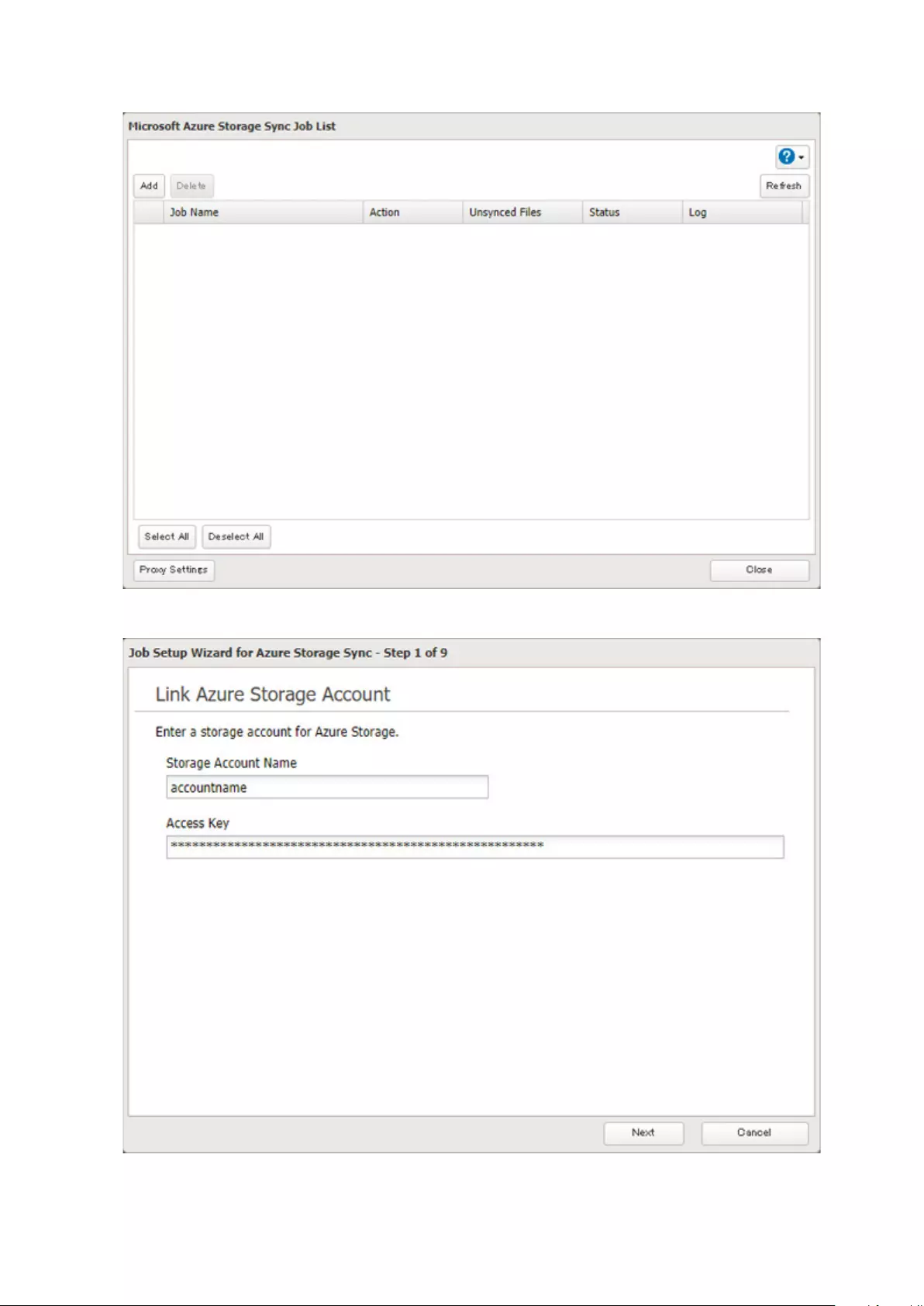
5 Click Add.
6 The job setup wizard will open. Enter your Azure Storage account name and access key, then click Next.
127
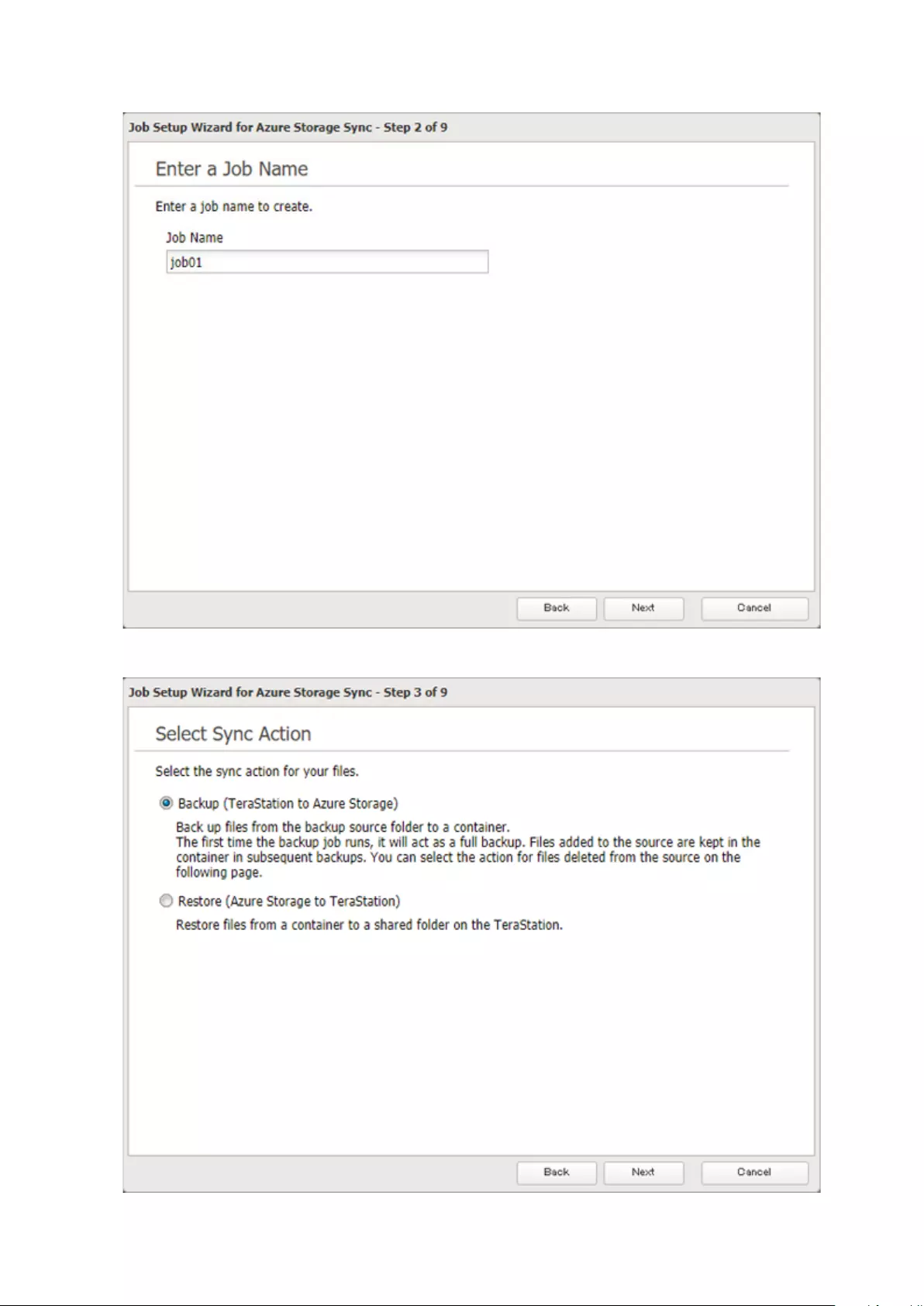
7 Enter the desired job name and click Next.
8 Select “Backup” and click Next.
128
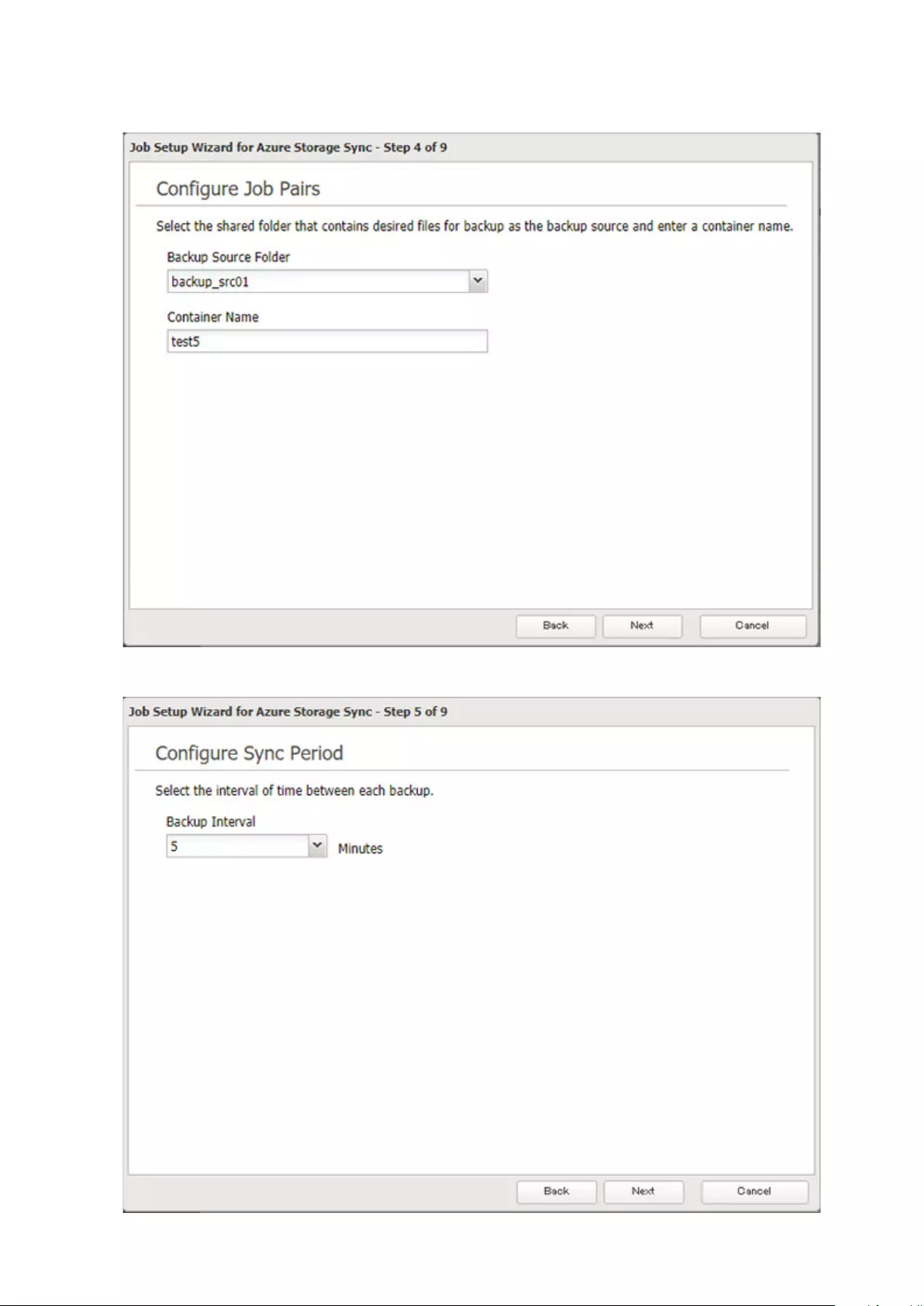
9 Select the desired shared folder on the TeraStation as the backup source folder and enter the container name
for the backup destination, then click Next.
10 Specify the sync period and click Next.
129
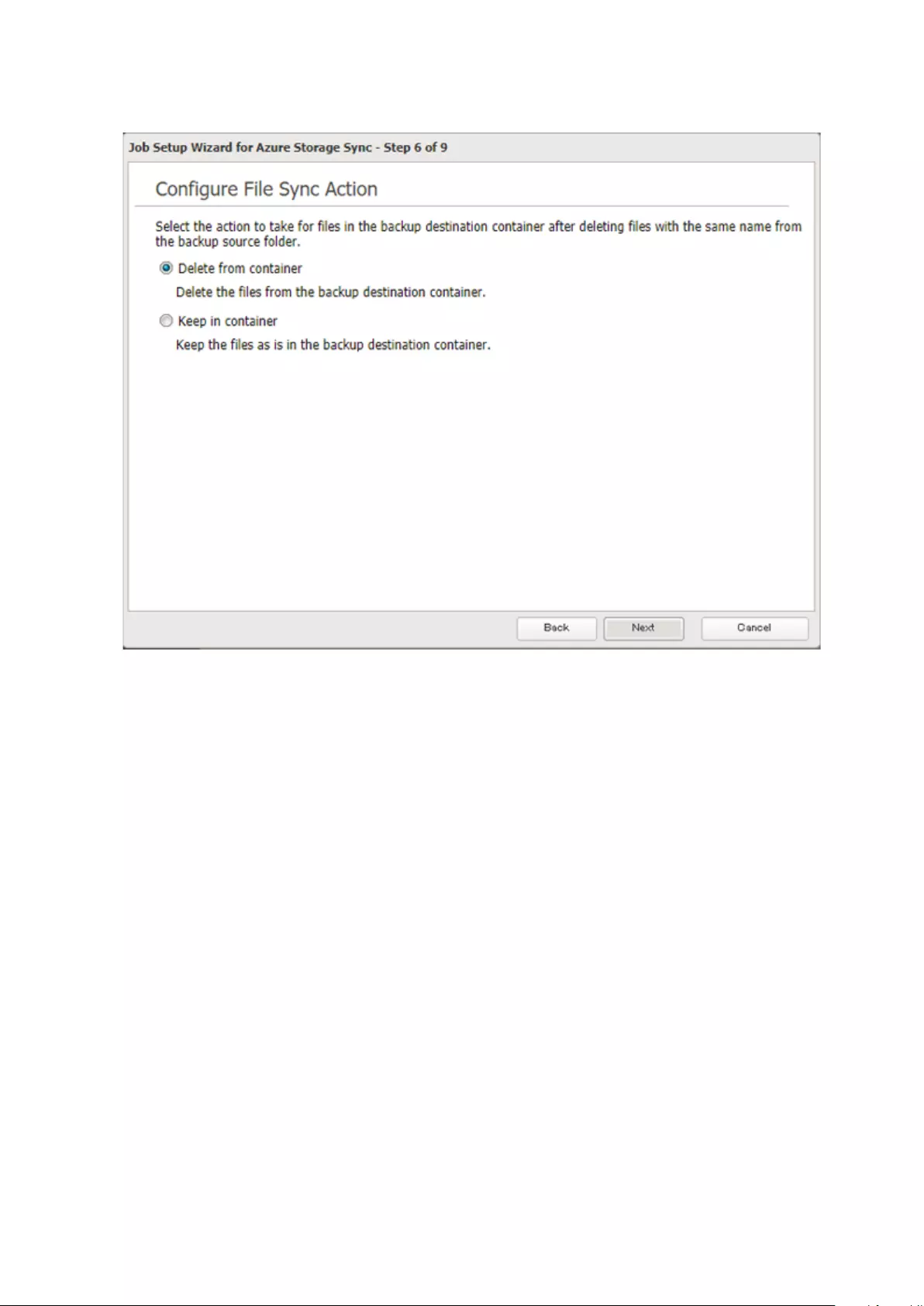
11 Select the desired action to take for files in the container that share the same name as files in the backup
source after they are deleted, then click Next.
130
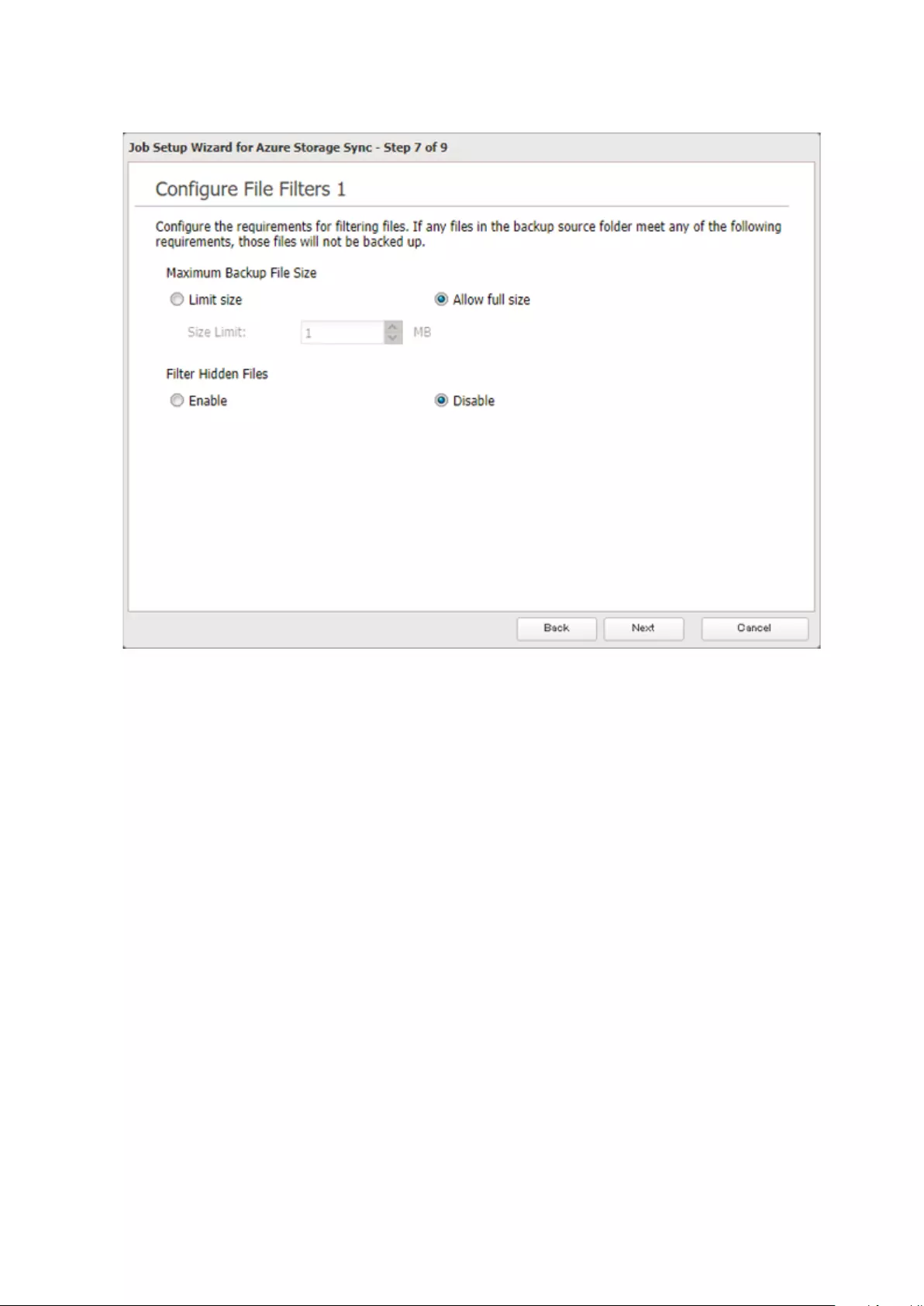
12 Configure whether to filter the backup target files. The following screen is available to configure filtering files
by file size and whether they’re hidden. Configure the desired filtering settings and click Next.
131
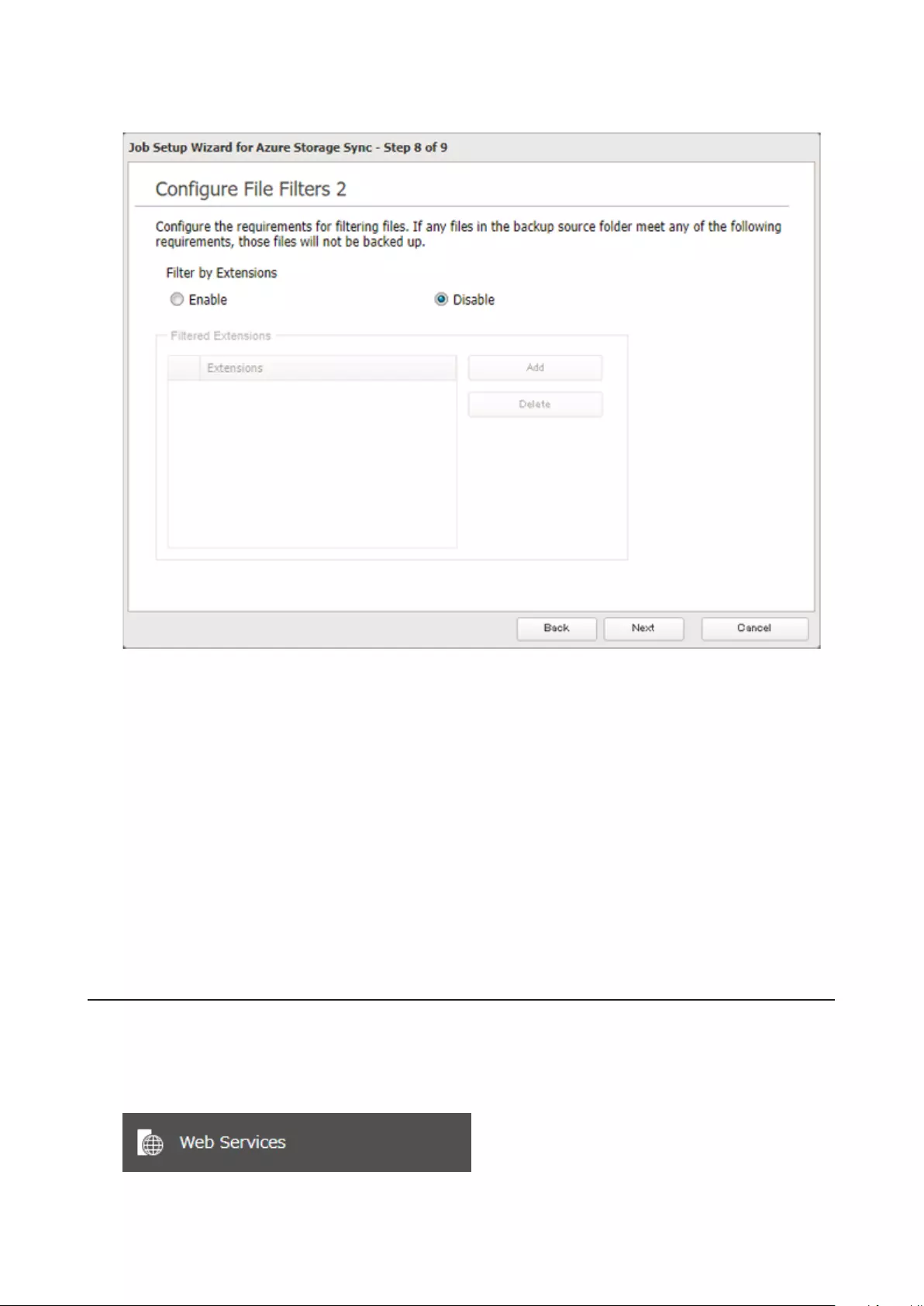
13 The following screen is available to configure filtering files by extensions. Configure the desired filtering
settings and click Next.
14 Confirm that all settings are properly configured and click OK.
Notes:
• Regardless of whether file filtering was configured, the following files will not be backed up to an Azure Storage
container:
◦desktop.ini
◦thumbs.db
◦Files whose filename contains the symbols / \ > < : " | ? *
◦Files whose filename ends with either a space or period
◦Files whose filename starts with either ~$ or .~
◦Files whose filename starts with ~ and have the file extension .tmp
• Do not copy files that are 10 GB or larger, and do not copy 100,000 or more files to the backup source folder at
once. If you do and backup fails, check the network environment speed and try again with fewer files.
Creating a New Restore Job
1 From the Azure portal, create your Azure Storage account and a container before beginning the following
procedure.
2 From Settings, click Web Services.
132
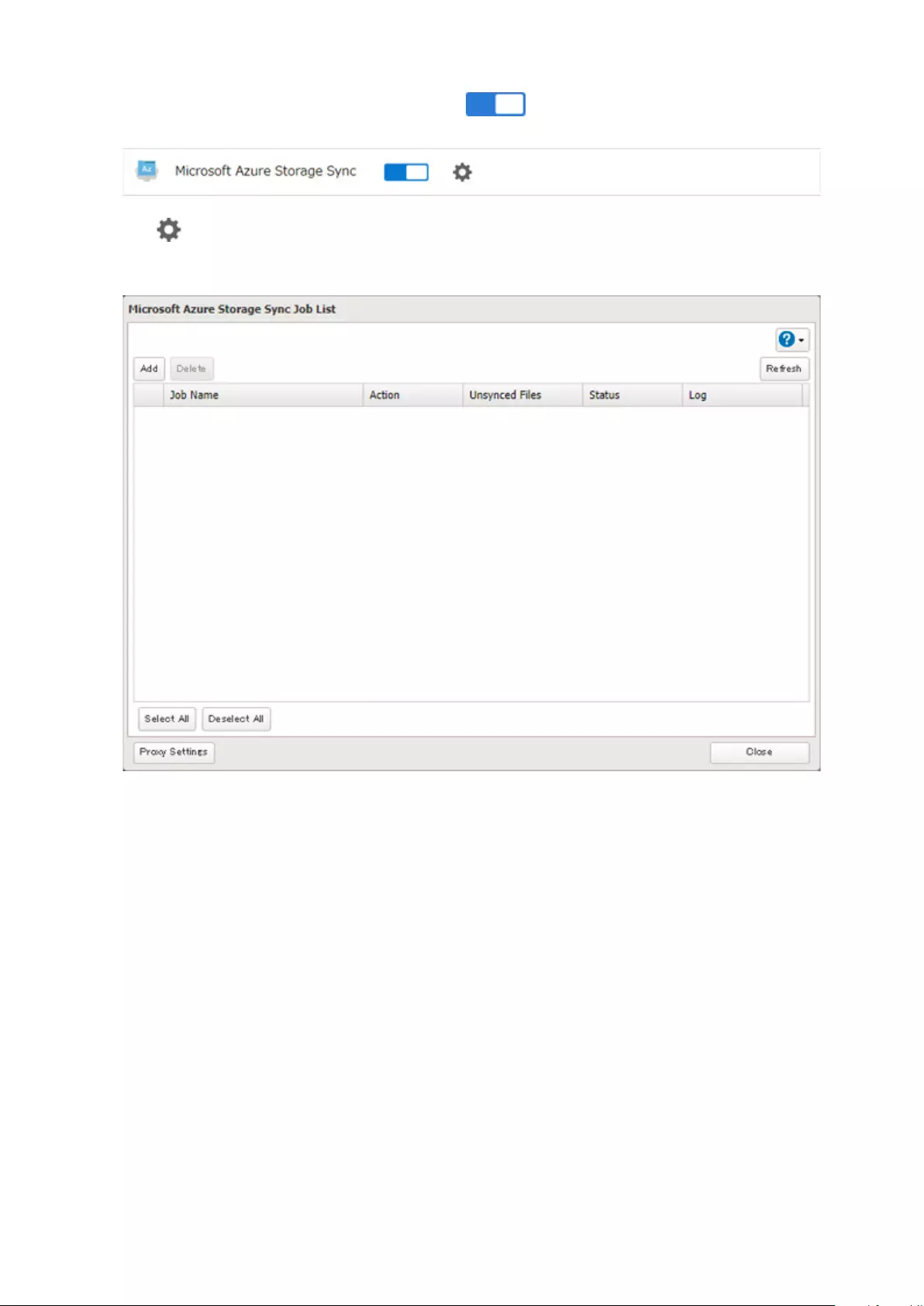
3 Move the Microsoft Azure Storage Sync switch to the position to enable Microsoft Azure Storage
Sync.
4 Click to the right of “Microsoft Azure Storage Sync”.
5 Click Add.
133
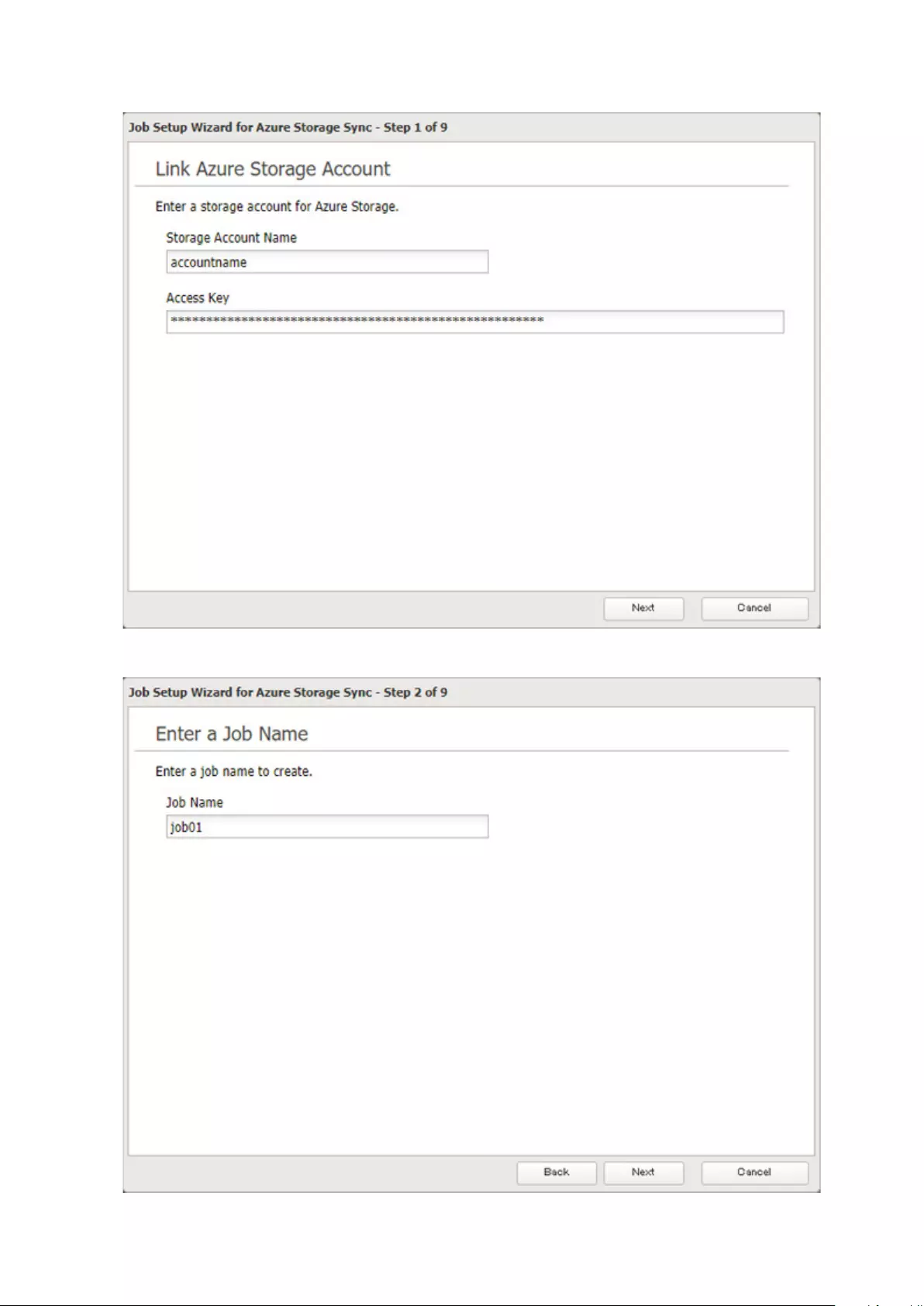
6 The job setup wizard will open. Enter your Azure Storage account name and access key, then click Next.
7 Enter the desired job name and click Next.
134
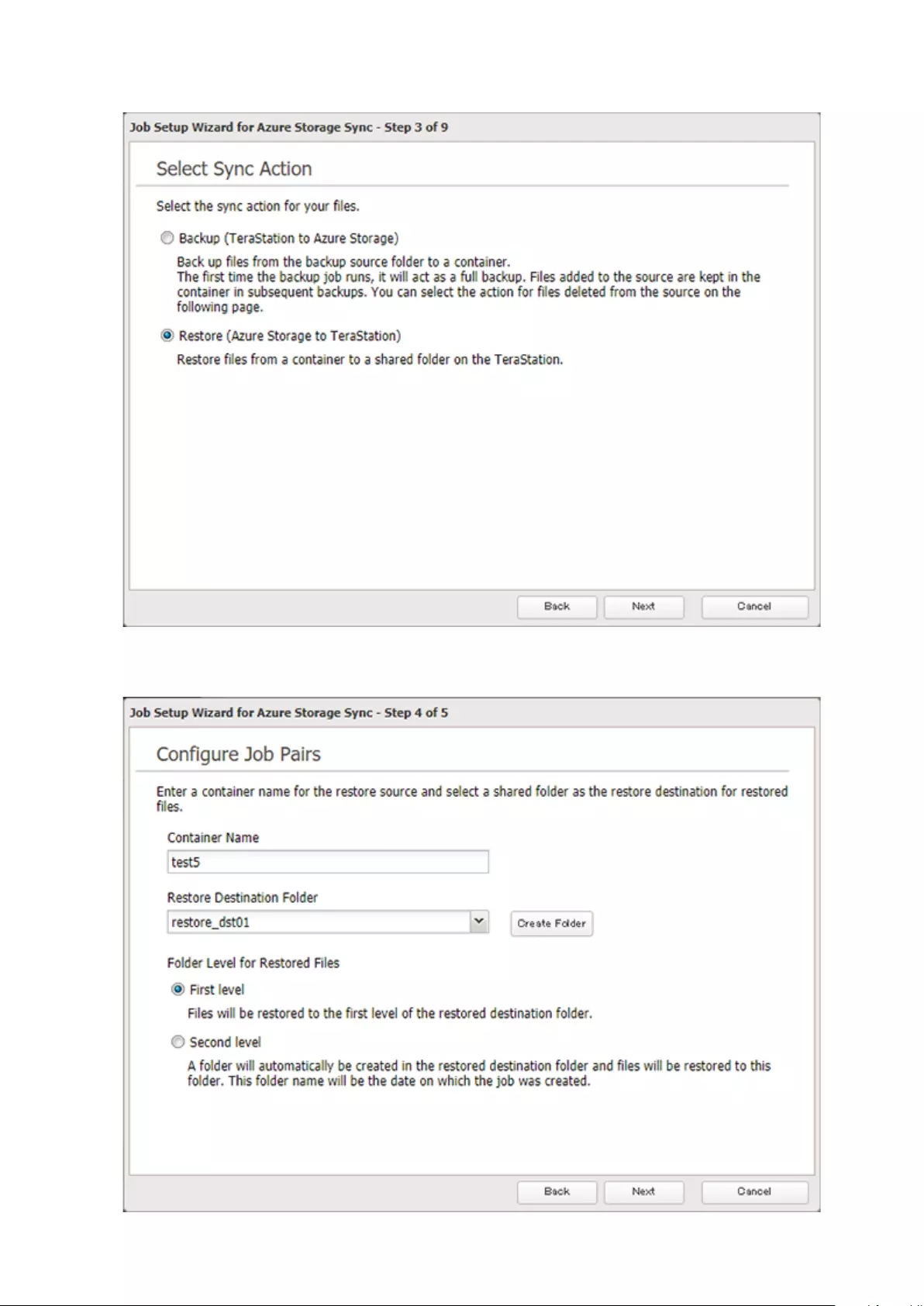
8 Select “Restore” and click Next.
9 Enter the container name for the restore source and select the desired shared folder on the TeraStation as the
restore destination.
135
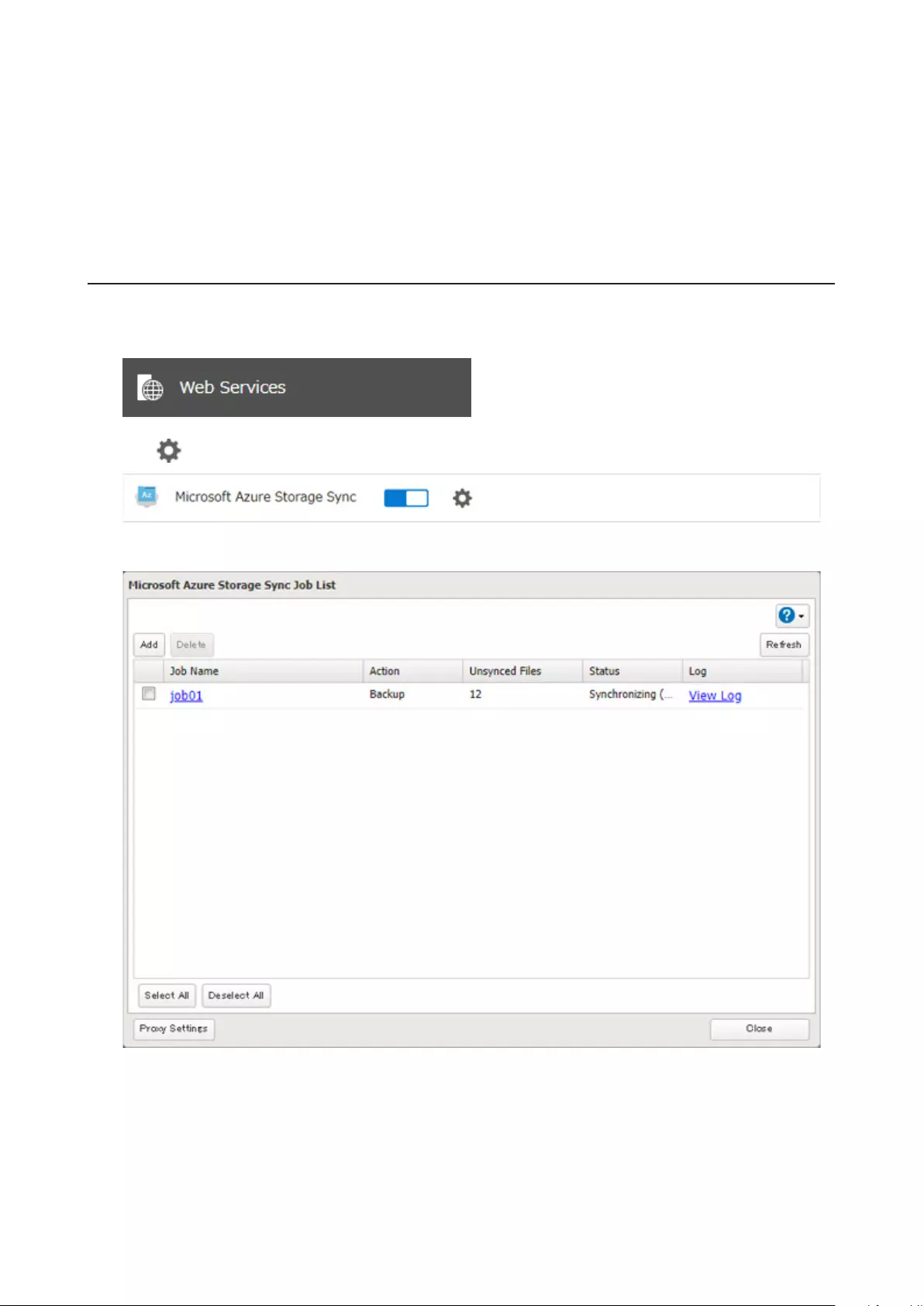
10 Select either to restore data into the first level folder (root folder) or the second level (subfolder) of the restore
destination folder, then click Next.
11 Confirm that all settings are properly configured and click OK.
Note: When deleting a completed restored job, it can be converted to a backup job. If that restore job had been
configured to restore to the second level on the shared folder, restored data will automatically move to the first
level. If there are files with the same filename in the first level folder, those files will be overwritten.
Changing Job Settings
Follow the procedure below to change any job settings you have already configured.
1 From Settings, click Web Services.
2 Click to the right of “Microsoft Azure Storage Sync”.
3 From the job list, click the job whose settings you want to change.
136
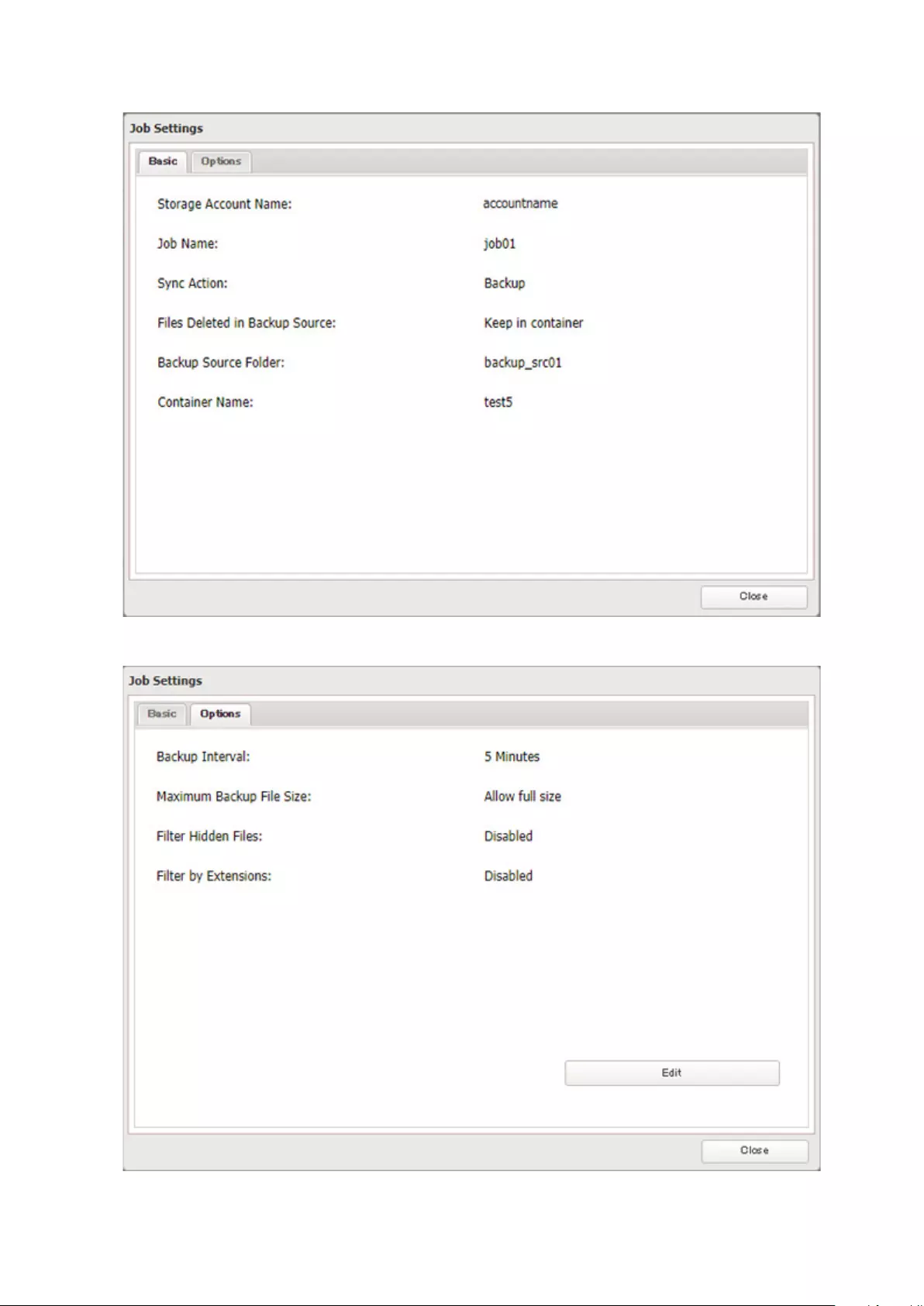
4 Click the Options tab.
5 Click Edit.
137
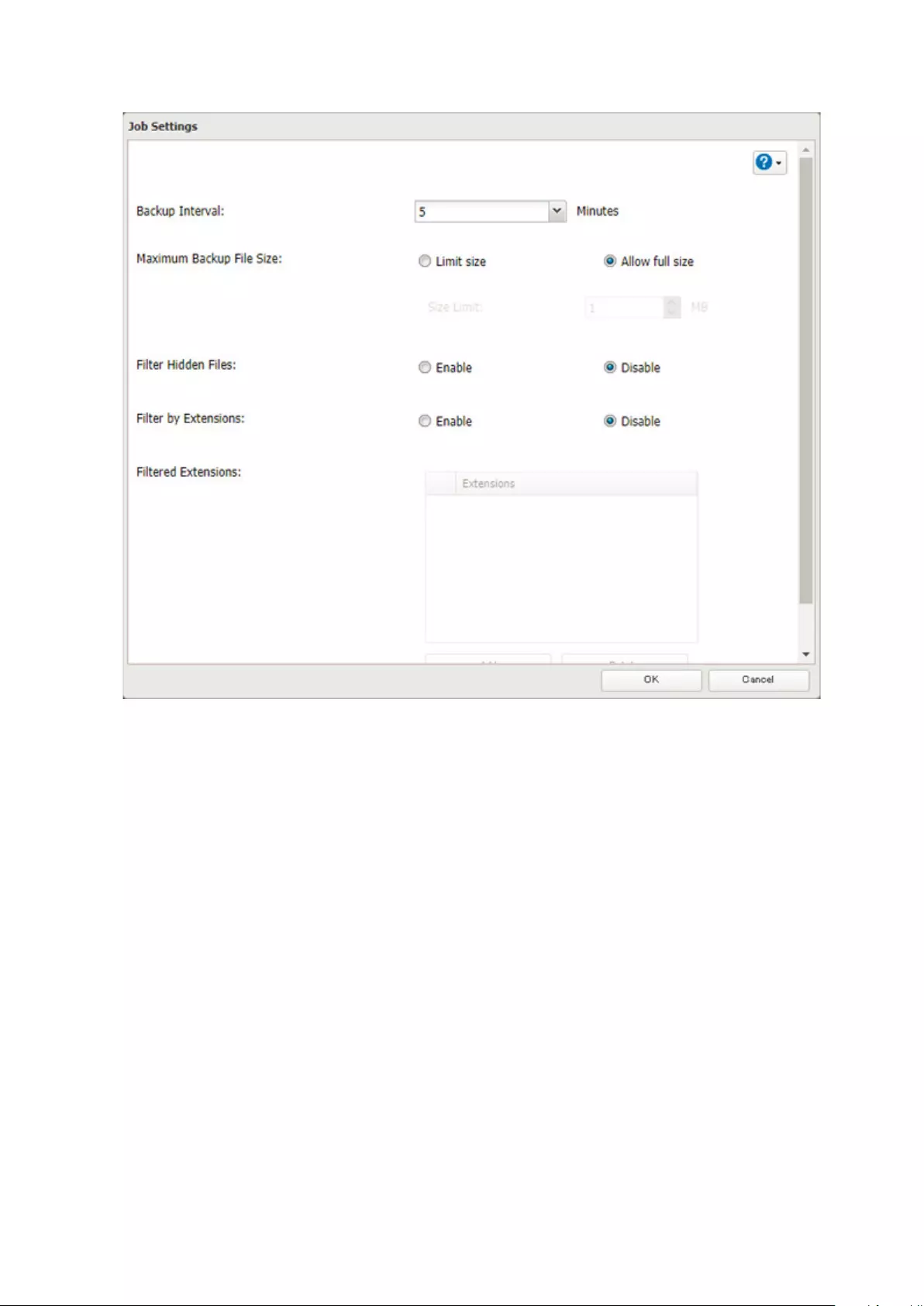
6 Configure the desired settings and click OK.
138
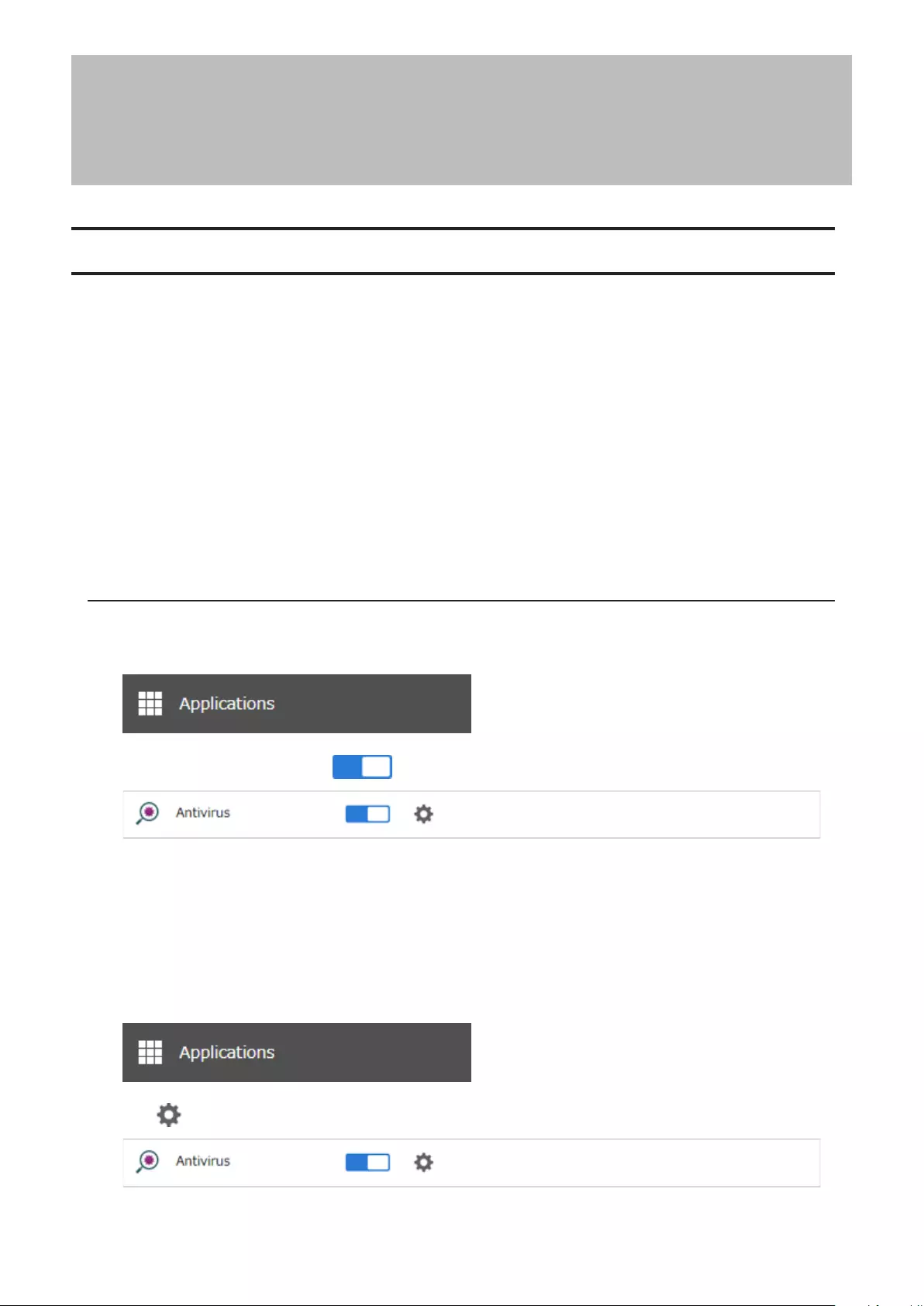
Chapter 7 Advanced Features
Antivirus Software
Trend Micro NAS Security can protect your network and data from software viruses, malware, and spyware. Virus
scan by Trend Micro NAS Security is available for files in the TeraStation’s shared folders, except for the “usbdisk”
folder.
To use Trend Micro NAS software, purchase an OP-TSVC license pack (sold separately). If your TeraStation is already
running an activated antivirus software, no license registration is necessary.
Notes:
• If LVM is enabled on the TeraStation, the antivirus software may not work properly. For best results, disable LVM
before use.
• To use the antivirus software effectively, the TeraStation should be connected to the Internet. The connection can
be routed through a proxy server if the appropriate settings are configured in Administration > Proxy Settings from
the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page.
• Trend Micro is a trademark of Trend Micro Incorporated.
Activating Virus Scanning
Follow the procedure below to activate virus scanning.
1 From Settings, click Applications.
2 Move the antivirus switch to the position to enable antivirus.
A quarantine folder named “TMNAS” is automatically created on the TeraStation. If a virus is detected, it is moved to
this folder.
If you want to configure the specific shared folder as a quarantine folder, follow the procedure below.
1 Create a new shared folder by referring to the “Adding a Shared Folder” section in chapter 3.
2 From Settings, click Applications.
3 Click to the right of “Antivirus”.
139
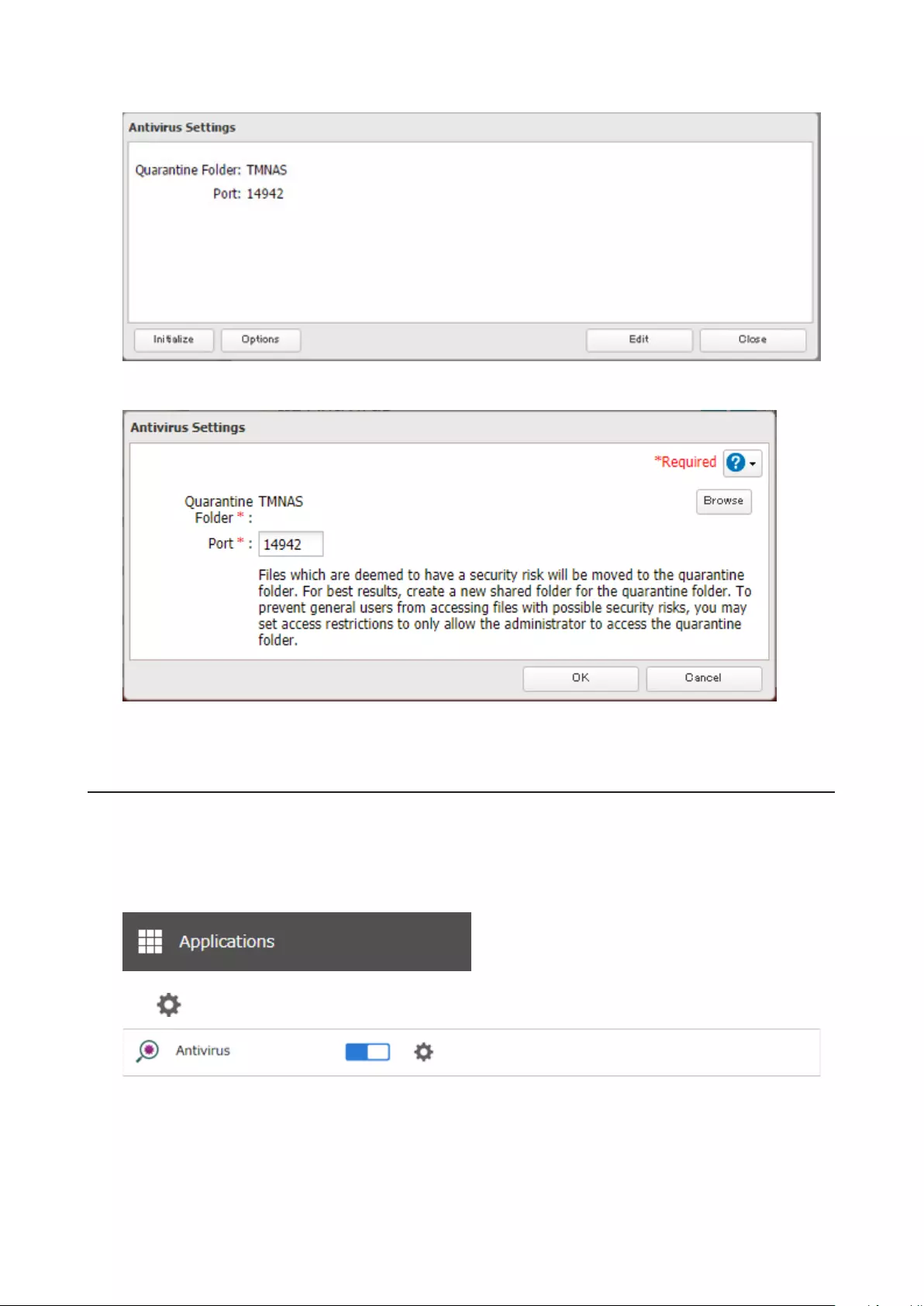
4 Click Edit.
5 Click Browse and select the quarantine folder.
6 Click OK.
Configuring Security Settings
Use the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page to configure security settings such as updating pattern files,
configuring scan schedules, and activating or expanding the license. To open the settings page, follow the
procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Applications.
2 Click to the right of “Antivirus”.
140
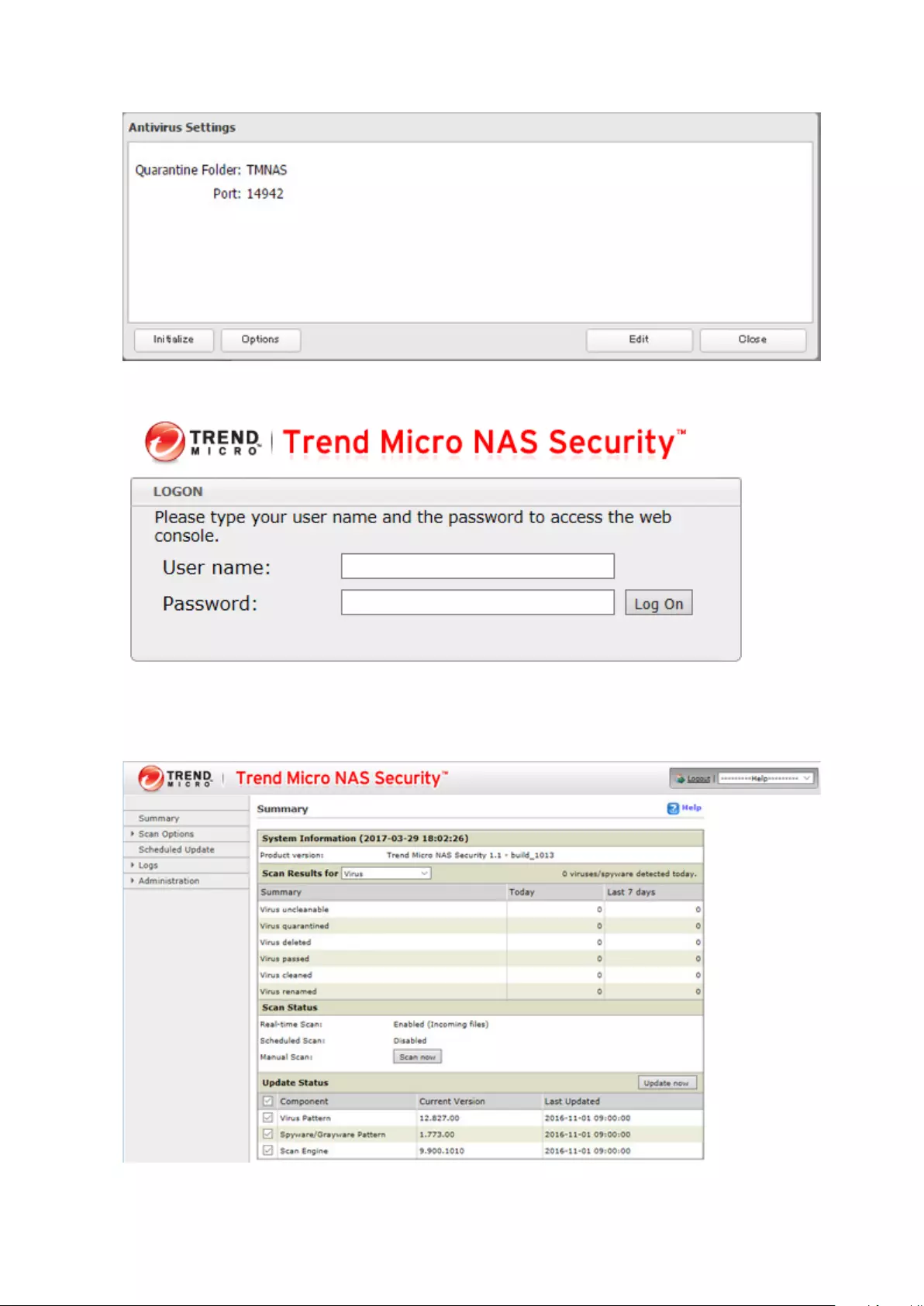
3 Click Options.
4 Enter your username and password, then click Log On.
You can log on with the TeraStation’s admin account. The default username and password are “admin” and
“password”.
5 The Trend Micro NAS Security settings page will open.
141
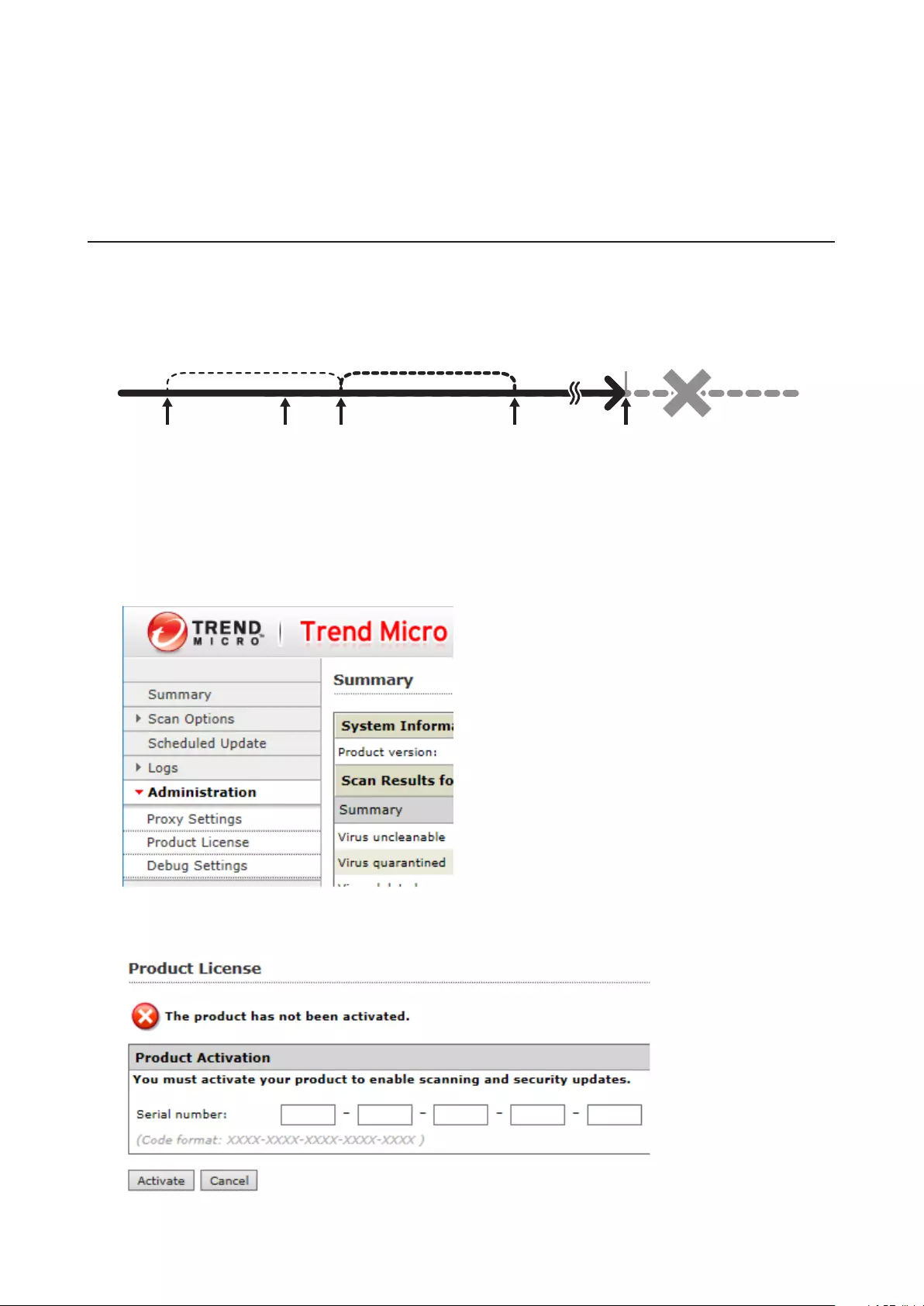
Notes:
• The Trend Micro NAS Security settings page is compatible with IE 6.0 SP2 or later (Windows) and Firefox 1.5 or
later (Windows or Mac).
• To change the display language of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, change the system language to
the desired settings by referring to the “Name, Date, Time, and Language” section below.
Licenses
If the antivirus software on your TeraStation is not activated or has expired, please purchase an OP-TSVC license pack
(sold separately). If your TeraStation includes activated antivirus software, no license registration is required. The
total period for antivirus software updates may be extended up to 5 years.
This example shows an initial 1-year period for updates extended by an additional year.
1/1/2016 1/1/2017 1/1/2018 1/1/2021
Antivirus
software
updates
activated
Extension
(9/1/2016)
License period
before extension
License period
after extension
Up to 5 years
(Cannot be extended beyond
5 years)
Note: It’s not possible to register a serial number that would extend the total license period beyond 5 years, such as
a second 3-year license after 3 years.
1 From the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, click Administration > Product License.
2 Enter the serial number from the “Trend Micro NAS Security License Pack Guide”, included in your package.
Click Activate.
142
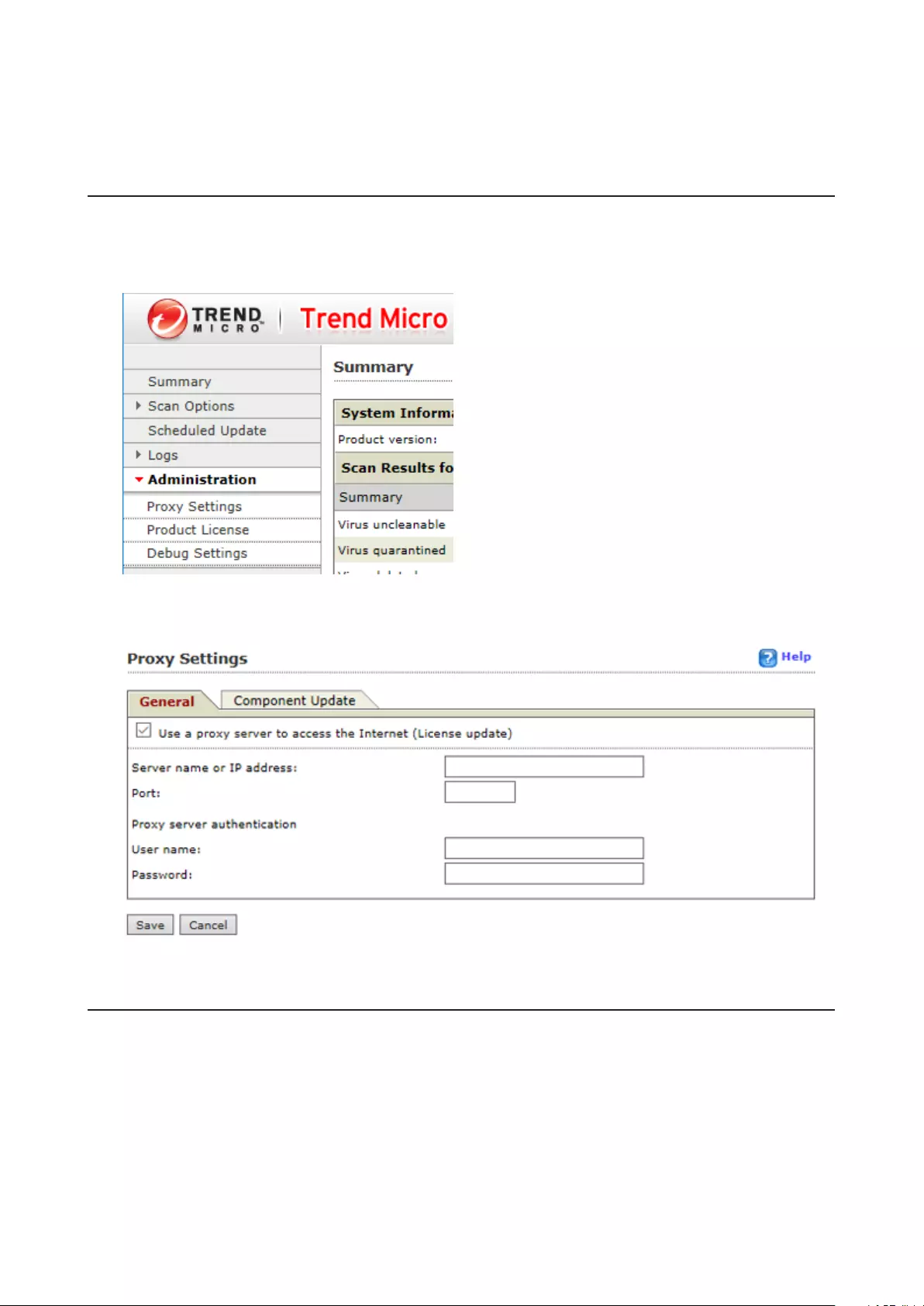
The new license is now registered.
To check the status of the current license, open the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page and navigate to
Administration > Product License on the left-side menu.
Connecting Through a Proxy Server
If you must pass through a proxy server to connect to the Internet in your network environment, follow this
procedure to set the IP address of the proxy server and other settings.
1 From the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, click Administration > Proxy Settings.
2 Select the “Use a proxy server to access the Internet (License update)” checkbox. Enter the IP address and port
of the proxy server, then click Save.
The antivirus software is now configured to use a proxy server.
Updating Antivirus Pattern Files
For best results, configure your antivirus software to update the antivirus pattern files automatically as described
below.
143
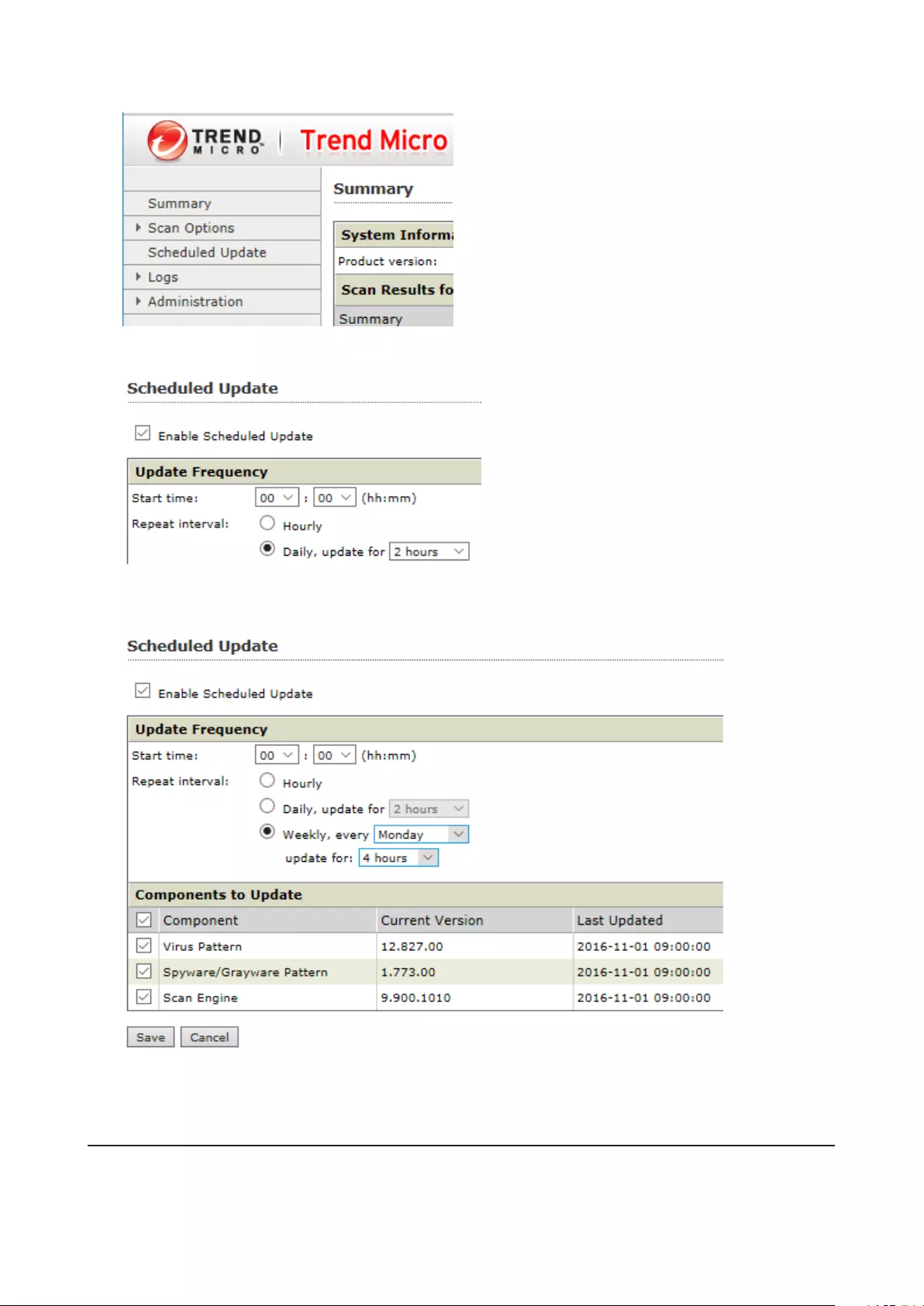
1 From the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, choose Scheduled Updates.
2 Check “Enable Scheduled Update”.
3 Select a time for updates to begin, an interval for updates, and an amount of time for updates to continue.
Select the components to update. Click Save.
The antivirus software is now configured to update automatically at the scheduled time. Updates will not be
downloaded if the TeraStation is turned off, in standby mode, or disconnected from the Internet.
Configuring Folders as Virus Scanning Targets
By default, all folders on the TeraStation (including attached USB drives) will be scanned. Follow the procedure
below to block specific shared folders from being scanned.
144
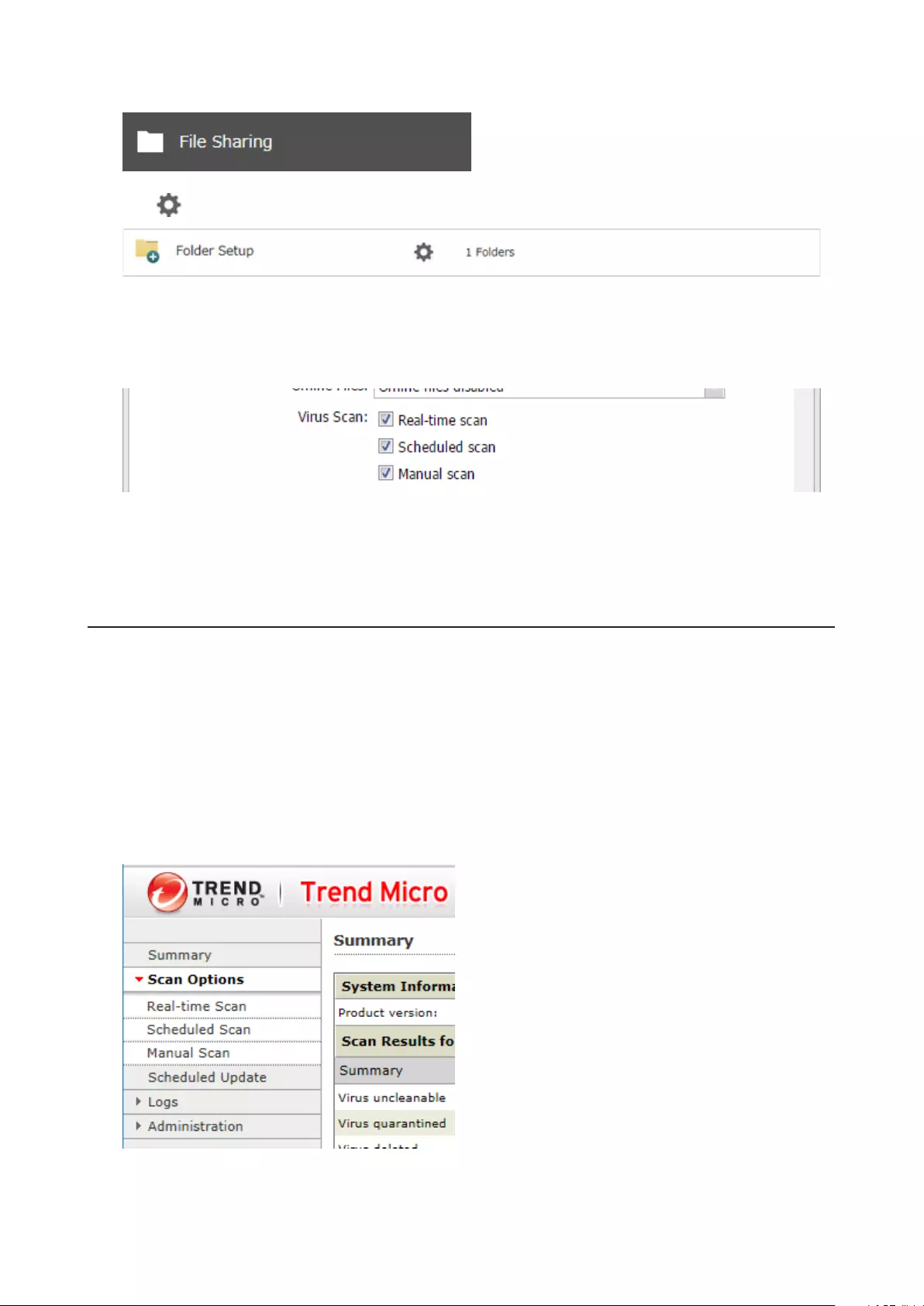
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Click the shared folder that you want to exclude from the scan.
4 If the options’ checkboxes are selected on the Option 1 tab, it means the shared folder will be scanned by those
scan options. To exclude from the scan, clear the options’ checkboxes.
5 Click OK.
Note: Even if the scan options are selected in the quarantine folder settings, the quarantine folder will be excluded
from the virus scan.
Virus Scanning
Three types of virus scans are available:
• Real-time scan
The virus scan runs in the background, scanning every file that you read or write. This is the default type of
scanning. Your TeraStation may run slower if real-time scanning is enabled.
• Scheduled scan
A scheduled scan is executed at specific regular intervals, such as every Tuesday at 3 a.m.
• Manual scan
A manual scan runs once when initiated. Initiate a manual scan as described below.
1 From the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, choose Scan Options > Manual Scan.
145
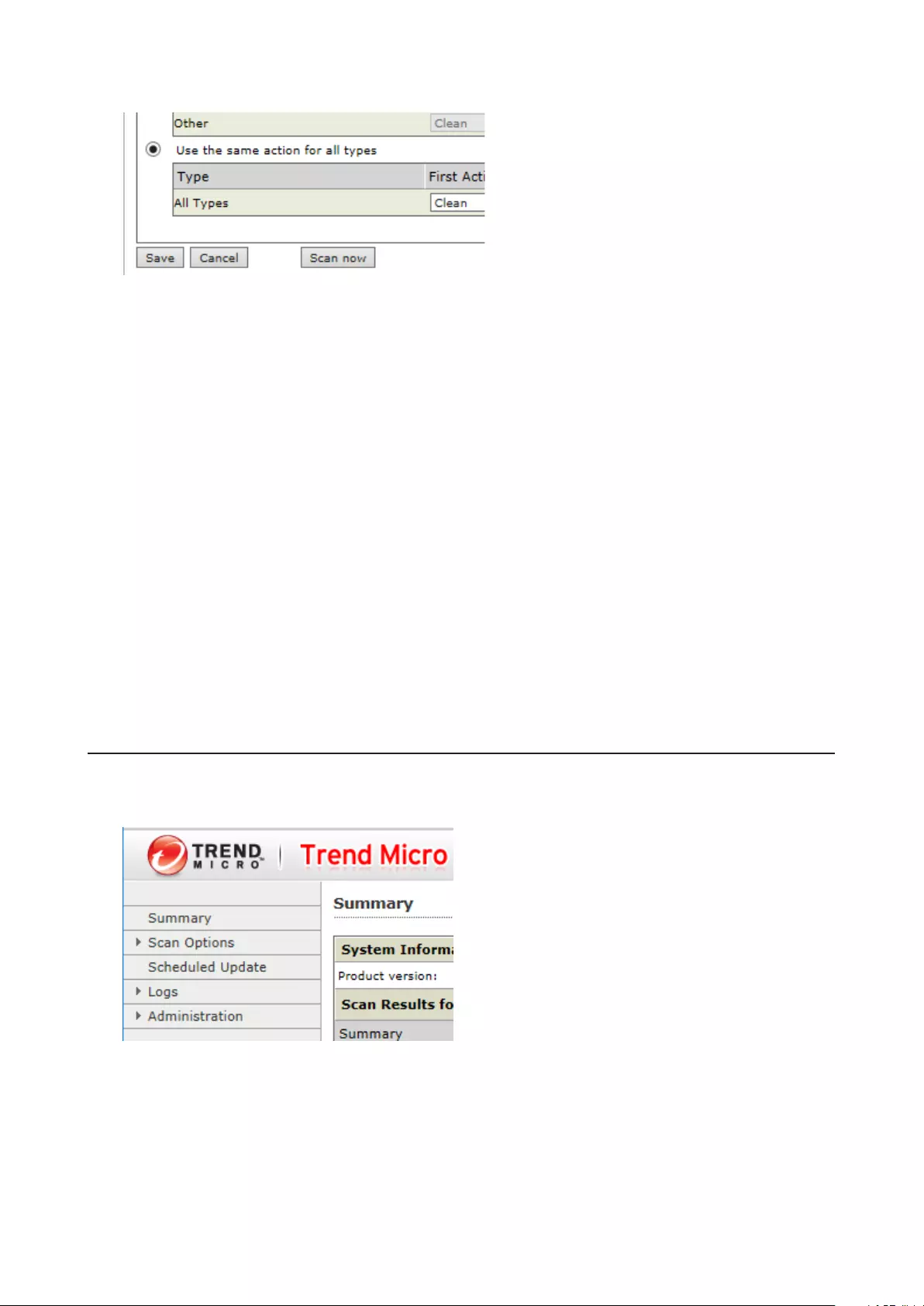
2 Click Scan now. This starts the virus scan.
If the scan finds a virus, the user can be notified in two ways:
• The I34 virus alert message is normally shown on the LCD panel. Once the virus is removed from the quarantine
folder, the message is no longer displayed. If the antivirus software is configured to delete viruses from the
quarantine folder automatically, then the I34 virus alert message will not be displayed.
• If email notification is enabled in Settings, then the antivirus software notifies the user by email if a virus is found.
Enabling email notifications is recommended.
Depending on how many files are on your TeraStation, a virus scan may take several hours. Estimated scanning
times are shown below.
10,000 files: ~ 30 minutes
100,000 files: ~ 5 hours
1,000,000 files: ~ 50 hours
Notes:
• If the quarantine folder doesn’t have enough space, the infected files may be unable to be moved to the
quarantine folder. The Trend Micro NAS security scan log may identify any infected files as quarantined even if the
quarantine did not actually occur. In such a case, remove non-essential files from the quarantine folder and try
the virus scan again.
• If the size of the infected file is large, it may not be able to be moved to the quarantine folder. In such a case,
check the scan log to see whether the quarantine succeeds, and move the infected file to the quarantine folder
manually.
Checking the Log
Follow the procedure below to check the virus scan log.
1 From the left-side menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, choose Logs.
146
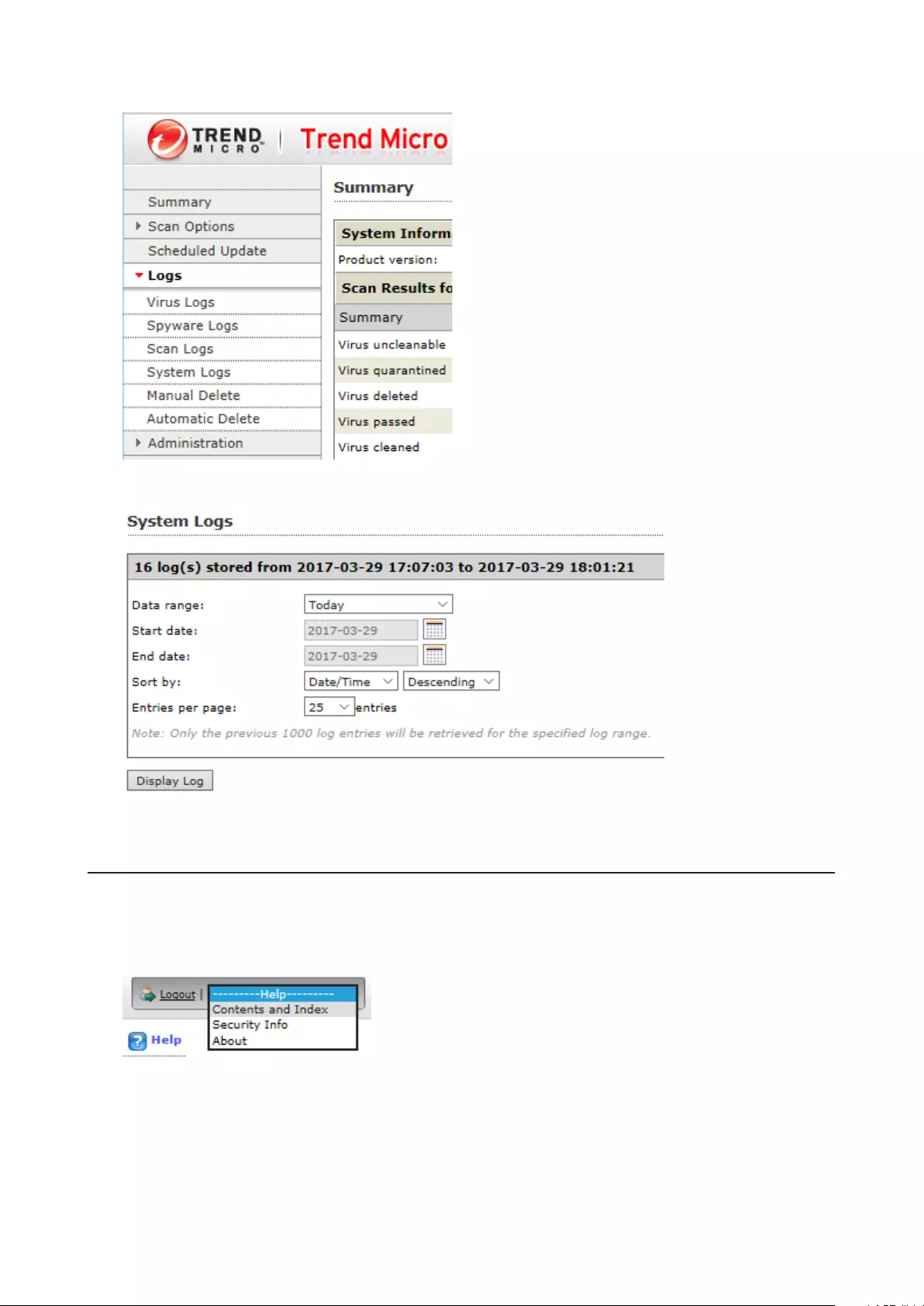
2 Click the log item that you want to check.
3 Click Display Log.
This completes the procedure for checking the log.
Online Help
For more information on the antivirus software, refer to the online help. Follow the procedure below to access the
online help.
1 From the right-top menu of the Trend Micro NAS Security settings page, choose Help > Contents and Index.
2 Online help will open.
Online help is now ready to use.
147
Email Notification
Your TeraStation can send you email reports daily, or when settings are changed or an error occurs. You can
configure the events that will trigger notifications from any of the following functions: drive quota, drives (internal,
external, or RAID array), fan, backup, replication, failover, antivirus, system alert
Refer to the contextual help in Settings for more detailed information such as when the notification email will be
sent or the differences between the notification categories.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Move the email notification switch to the position to enable email notification.
3 Click to the right of “Email Notification”.
4 Click Edit.
5 Enter your email server settings, notification email’s default subject, and configure recipients and the time
when email reports will be sent. Click OK to send a test email.
148
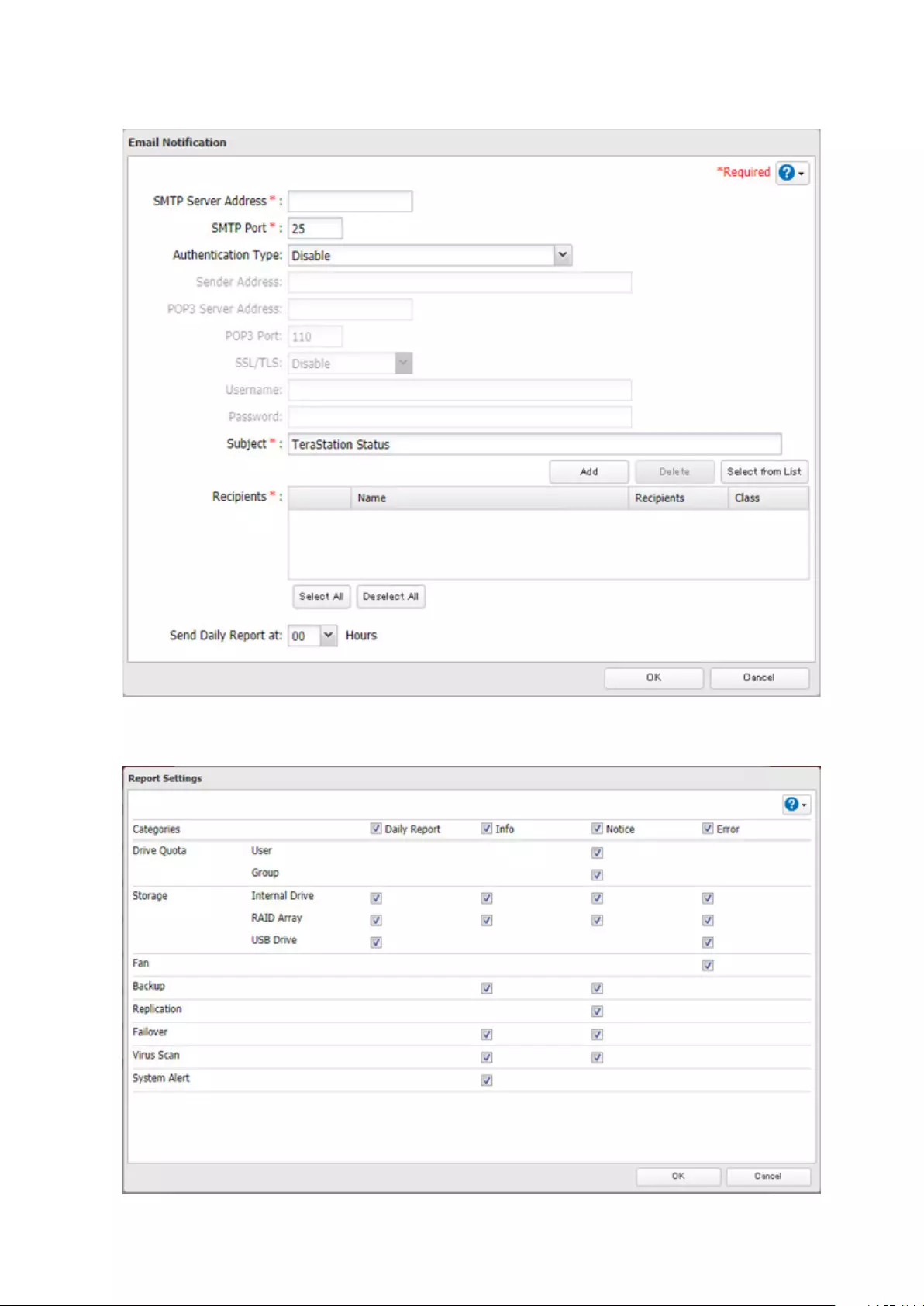
If you select an authentication type other than “Disable” from the drop-down list, you can enter the sender
email address and credentials of the email server.
6 To change the events of email reports, click Advanced Report Settings. On the displayed screen, select or clear
the category’s checkboxes.
149
The notification emails will be categorized into the following importance levels.
Levels Details
Daily Report Describes the status of the TeraStation in a daily report email.
Info Sends a notification email if an event occurs. Info reports will contain
just information such as capacity information, job starts/finishes, etc.
Notice
Sends a notification email if a non-critical error occurs. Notice reports
will contain warnings such as something has failed, but the function
or unit can continue operating as usual. It is recommended to do the
corrective action for the notice as soon as possible.
Error
Sends a notification email if a critical error occurs. Error reports
will describe critical failure which prevents a function or unit from
operating. It is recommended to do the corrective action to for the error
immediately.
Sleep Mode
To save energy, you can specify times to put the TeraStation into sleep (standby) mode, during which the drive and
LEDs are turned off.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Sleep Timer”.
3 Click Edit.
150

4 Specify the timer interval, wake-up time, and time to go into sleep mode, then click OK.
Notes:
• Up to three timers can be set.
• The time to enter sleep mode can be set from 12:00 a.m. to 3:45 a.m. of the next day. The time to wake from sleep
mode can be set from 12:00 a.m. to 11:45 p.m. If the time to enter sleep mode is after 12:00 a.m., the wake-up
time setting may be from 4:00 a.m. to 11:45 p.m.
• The time to enter sleep mode should not be set at the same time as or before the start time.
• If a timer is scheduled during a drive check, drive format, backup process, and backup job, or within 5 minutes of
the current time, the TeraStation will not change to standby mode when the configured time is reached.
• If scheduled times in the timer overlap, the operation is performed using the widest time interval.
• Examples of multiple timer settings are shown below:
◦Example 1:
If running at a current time of 10:00 a.m. Wednesday
Timer 1: Daily 12:00–24:00
Timer 2: Not used
Timer 3: Not used
No operation is performed at 12:00 p.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at 12:00 a.m.
◦Example 2:
If running at a current time of 10:00 a.m. Wednesday
Timer 1: Daily 9:00–18:00
Timer 2: Wednesday 10:00–20:00
Timer 3: Not used
On days other than Wednesday, normal operation begins at 9:00 a.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at
6:00 p.m. On Wednesday, the unit goes into sleep mode at 8:00 p.m.
◦Example 3:
If running at a current time of 10:00 a.m. Wednesday
151
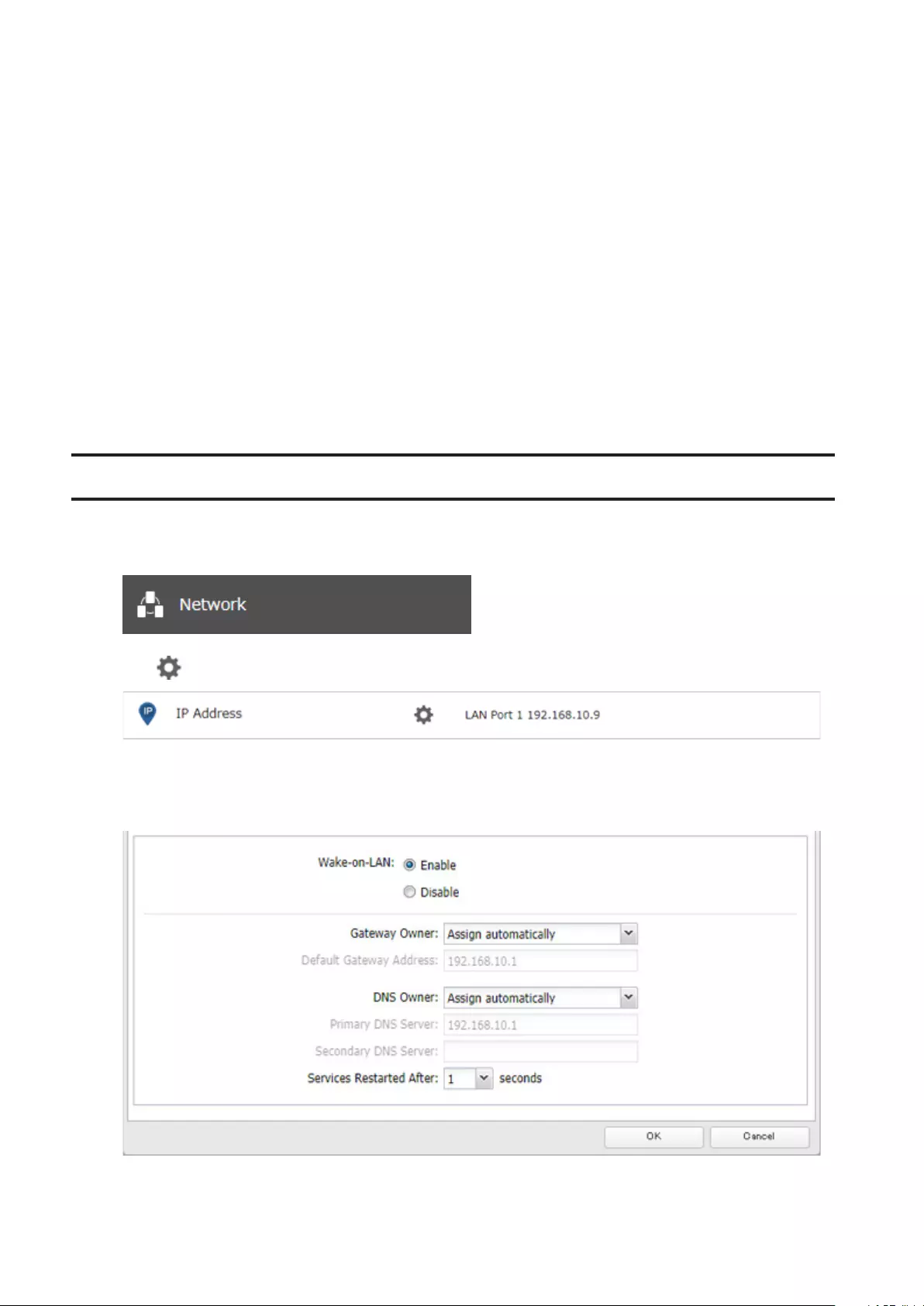
Timer 1: Daily 9:00–18:00
Timer 2: Wednesday 10:00–1:00 a.m. of the next day
Timer 3: Not used
On days other than Wednesday, normal operation begins at 9:00 a.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at
6:00 p.m. On Wednesday, normal operation begins at 10:00 a.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at 1:00
a.m. of the next day.
◦Example 4:
If running at a current time of 10:00 a.m. Wednesday
Timer 1: Daily 9:00–18:00
Timer 2: Wednesday 7:30–22:00
Timer 3: Not used
On days other than Wednesday, normal operation begins at 9:00 a.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at
6:00 p.m. On Wednesday, normal operation begins at 7:30 a.m. and the unit goes into sleep mode at 10:00
p.m.
• To wake the TeraStation from sleep mode manually, press and hold the power button for 3 seconds.
Wake-on-LAN
The TeraStation supports Wake-on-LAN, which allows it to be turned on remotely.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “IP Address”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Enable “Wake-on-LAN”, then click OK.
Wake-on-LAN is now enabled. As long as the TeraStation is connected to a power source and the network, you can
turn it on remotely.
152
Notes:
• After receiving the Wake-on-LAN packet, the TeraStation may take approximately five minutes to be ready to use.
• If a power outage occurs while Wake-on-LAN is enabled, the TeraStation will automatically start up after power is
restored.
• To use Wake-on-LAN, you’ll need Wake-on-LAN software that sends magic packets. The TeraStation does not
include Wake-on-LAN software.
• The TeraStation does not support using Wake-on-LAN and port trunking at the same time. You may use either
feature, but not both at the same time.
• If the TeraStation is connected to a Buffalo wireless router configured for remote access, then it may be turned on
from outside the local network (from the WAN side). To use this feature, connect the router to LAN port 1 or 2 on
the TeraStation.
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
If a UPS (sold separately) is attached, the TeraStation can be automatically shut down to protect data in the event of
a power outage.
The procedure to configure for a UPS device is different depending on how many power supply units are installed
on your TeraStation. Depending on your setup, follow one of the procedures below for your TeraStation.
One PSU Device Is Installed
1 Plug the power cable of the UPS to a wall socket.
2 Connect the power cable of the TeraStation to the UPS.
3 Connect the UPS and TeraStation.
4 Turn on the UPS, then the TeraStation.
5 From Settings, click Management.
6 Click to the right of “Power Management”.
7 Click Edit.
153
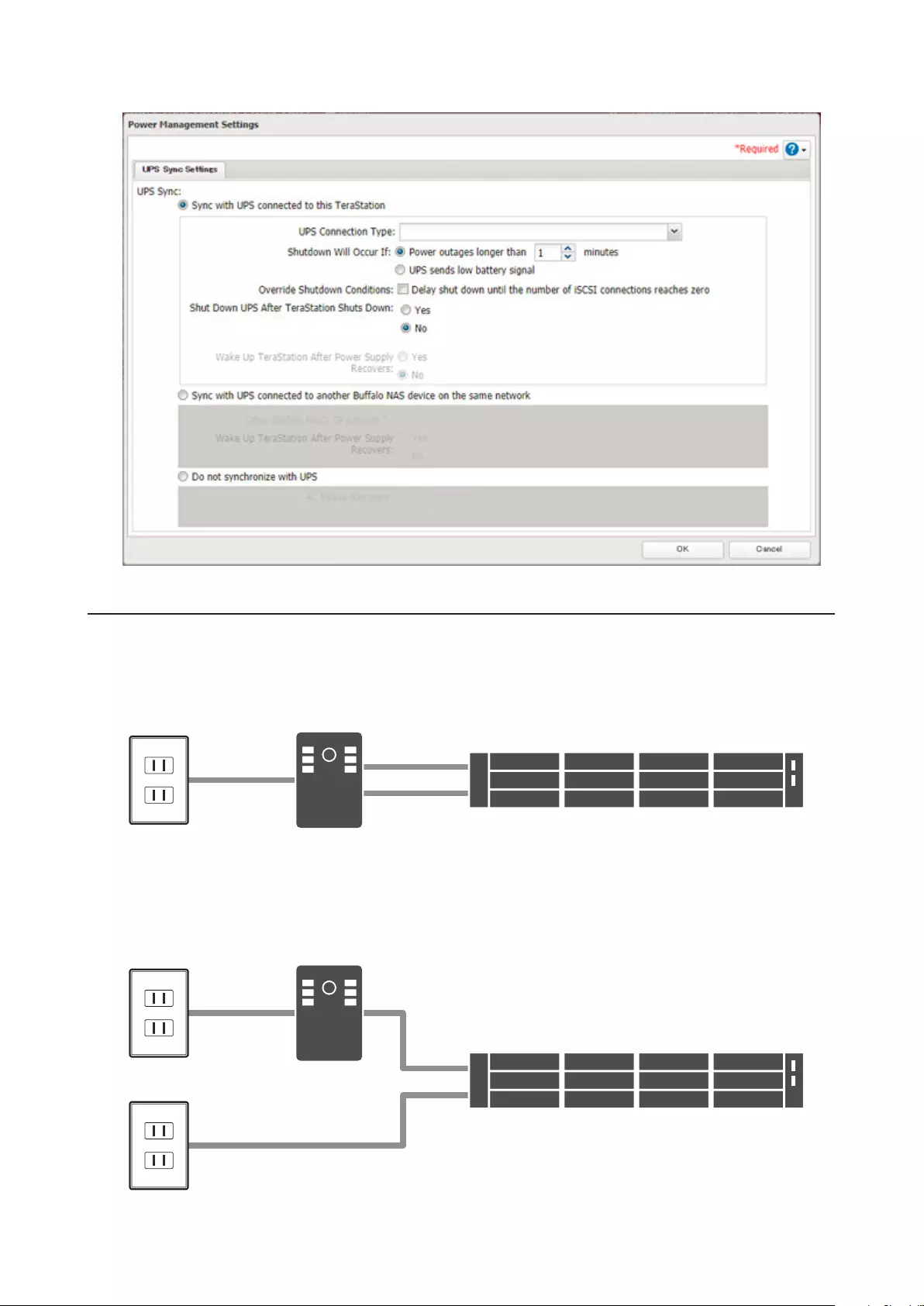
8 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
Two PSU Devices Are Installed
If you add multiple PSU devices to your TS51210RH series, the following connection setups are available.
A. To Boot the TeraStation After the Power Supply Recovers (Recommended)
Connect both power cables of the TeraStation to a single UPS device.
Wall Socket UPS TS51210RH
B. To Increase Redundancy for Power Failure
Connect one power cable of the TeraStation to the UPS device and the other to the wall socket. Use separate power
supply systems to increase redundancy.
Wall Socket 1
Wall Socket 2
UPS
TS51210RH
154
Note: With this connection setup, the option “Wake Up TeraStation After Power Supply Recovers” will not work if it’s
configured.
C. To Use Two UPS Devices
Connect a power cable to each of the UPS devices. Use separate power supply systems to increase redundancy.
With this connection setup, the UPS devices of the same connection type cannot be used. One should be a USB,
another should be a serial connection UPS device. The serial connection UPS device should be converted to a USB
connection using a USB-to-serial converter cable.
Wall Socket 1
Wall Socket 2
UPS 1
TS51210RH
UPS 2
1 Connect the UPS device and the TeraStation as described above.
2 Turn on the UPS, then the TeraStation.
3 From Settings, click Management.
4 Click to the right of “Power Management”.
5 Click Edit.
155
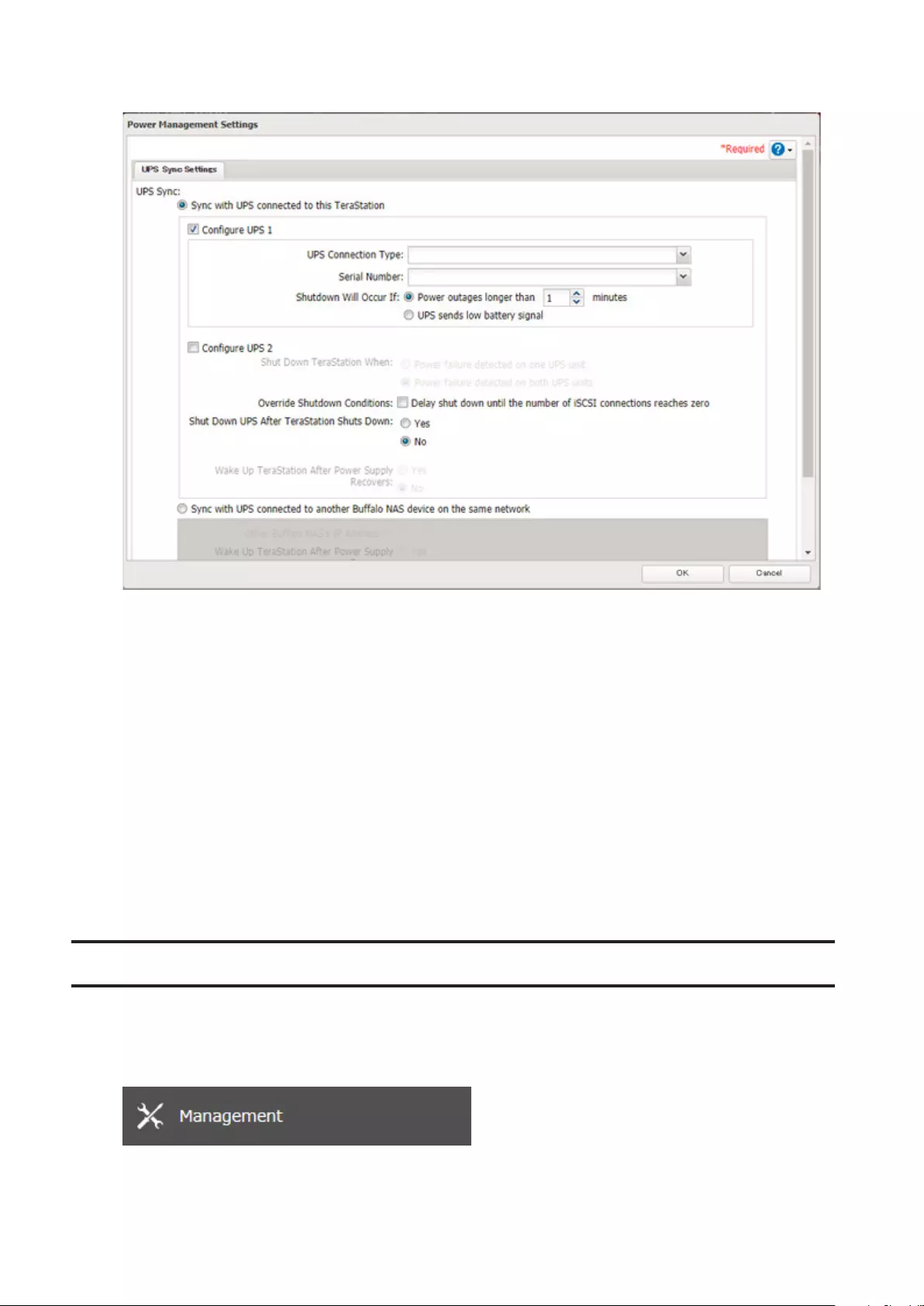
6 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• If the TeraStation is connected directly to a UPS, select “Sync with UPS connected to this TeraStation”. If a different
Buffalo NAS device is connected to the UPS, select “Sync with UPS connected to another Buffalo NAS device on
the same network”. After making this selection, enter the IP address of the Buffalo NAS device that will be the
sync source into “Other Buffalo NAS’s IP Address”.
• If you don’t want to connect any UPS devices, select “Do not synchronize with UPS” and the operation if a power
supply failure occurs. If “Use last state” at “AC Power Recovery” is selected, the TeraStation will revert to the
state before the power supply failure occurs. If “Stay off” is selected, the TeraStation will keep off even after the
TeraStation shuts down due to the power supply failure.
• When the TeraStation is restarted after an automatic shutdown such as from a power outage or power supply
problem, verify that the power supply has been restored. If the TeraStation is turned on while it is still running on
the UPS and without the power supply restored, the automatic shutdown will not be performed, even after the
specified time elapses.
• If the power supply from the UPS to the TeraStation is stopped and restarted when UPS recovery is enabled, the
TeraStation is automatically restarted.
Power Supply Failure
You may configure the TeraStation to shut down automatically if a power supply fails.
Note: This function is only for the TS51210RH series. Other models will not display this function on Settings.
1 From Settings, click Management.
156
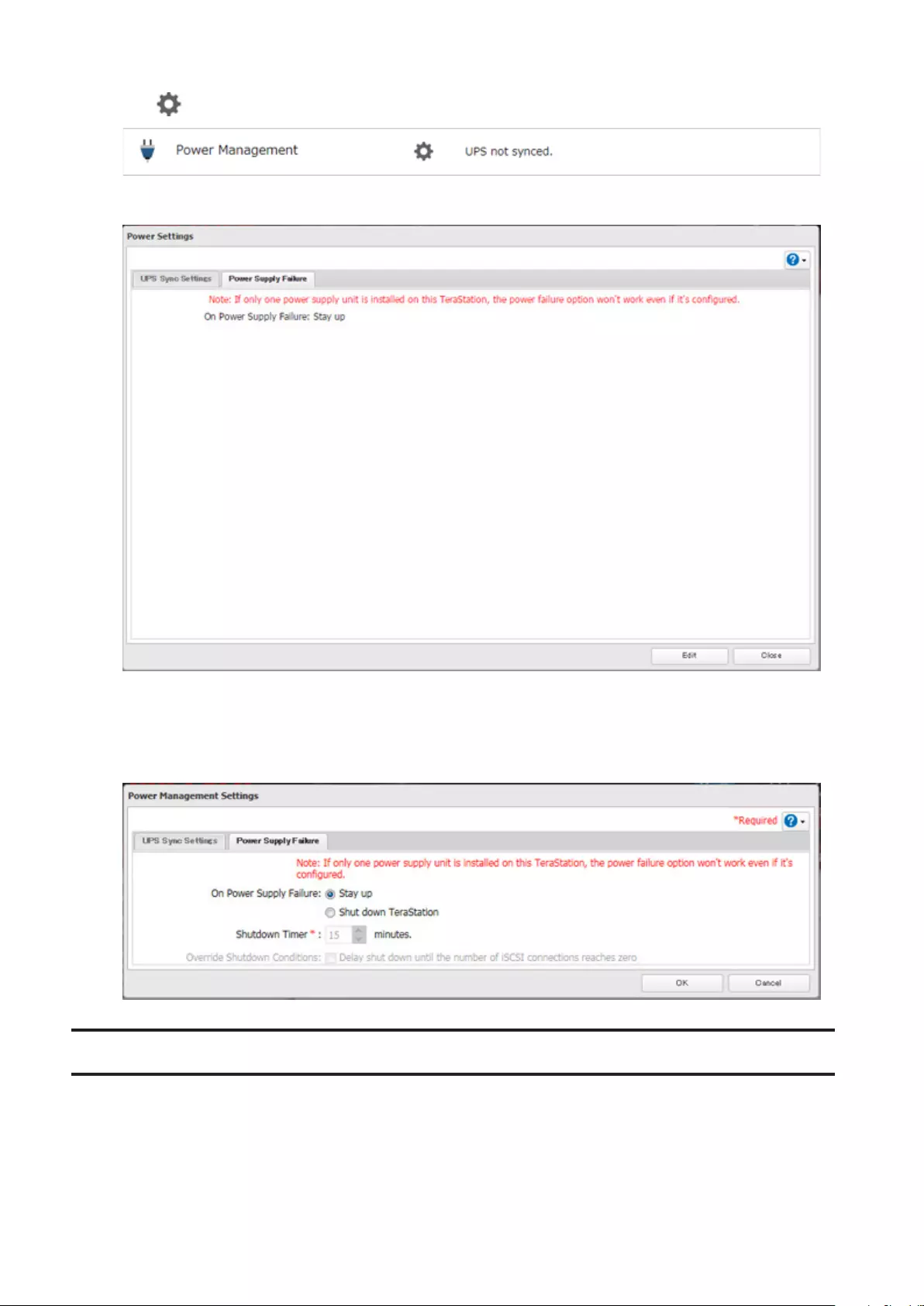
2 Click to the right of “Power Management”.
3 Click the Power Supply Failure tab.
4 Click Edit.
5 Select the number of minutes that will elapse after the power supply fails before the unit shuts down and click
OK.
Port Trunking
Two Ethernet cables can be used to establish two separate communication routes, providing LAN port redundancy
and improving communication reliability. The use of two Ethernet cables enables access to the TeraStation even if
one of the cables is disconnected.
The port trunking modes that can be set in the TeraStation are shown below.
157
Trunking Mode Characteristics
Active-backup Only one NIC slave in the bond is active. A different slave becomes
active if and only if the active slave fails.
Dynamic link aggregation
Creates aggregation groups that share the network speed and duplex
settings. Utilizes all slave network interfaces in the active aggregator
group according to the 802.3ad specification.
Note: To use this mode, a separate intelligent switch that supports
IEEE 802.3ad is required. Configure LACP on the switch first.
TLB The outgoing network packet traffic is distributed according to the
current load (relative to the speed) on each network interface slave.
ALB
The incoming and outgoing network packet traffic is distributed
according to the current load on each network interface slave. The
receive load balancing is achieved by ARP negotiation.
Note: If the TeraStation is being used as an iSCSI drive, disable iSCSI before changing network settings such as port
trunking. Navigate to Storage > iSCSI in Settings and move the iSCSI switch to the off position temporarily.
1 Use an Ethernet cable to connect the hub LAN port and TeraStation LAN port.
Notes:
• Do not connect the second Ethernet cable to the TeraStation yet.
• If using an intelligent switch, configure the LAN ports on the switch first, before connecting to the
TeraStation.
2 From Settings, click Network.
3 Click to the right of “Port Trunking”.
4 Select the LAN port that will be used and choose a port trunking bond.
158
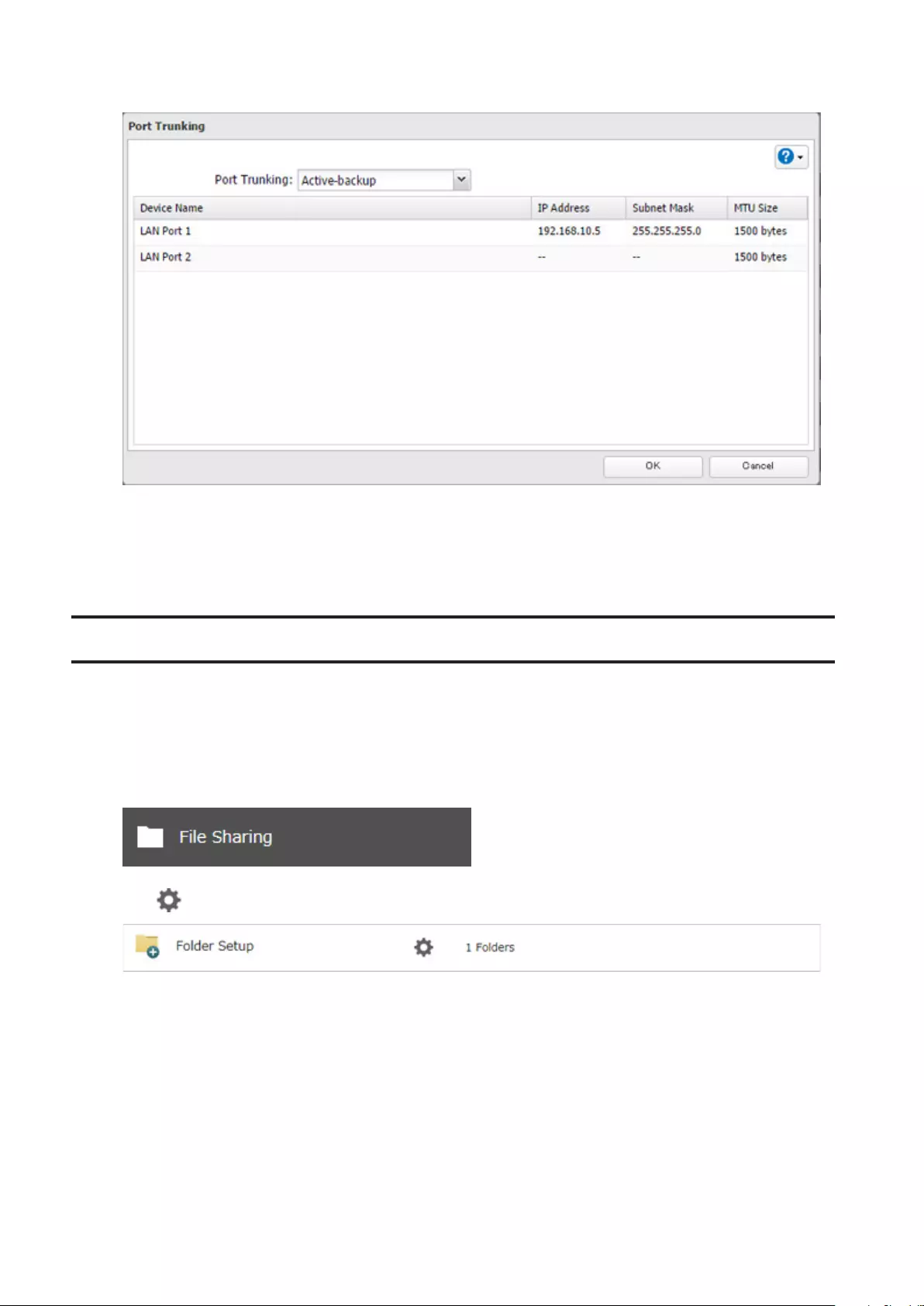
5 Select the port trunking mode and click OK.
6 Connect the hub’s LAN port and TeraStation’s LAN port using the second LAN cable. If you are using an
intelligent switch, connect to the LAN port that was previously configured for port trunking.
7 Restart the TeraStation before use.
Offline Files
The “offline files” feature that is included with many versions of Windows can be used with files on the TeraStation.
You will be able to work on files stored on the TeraStation even when your PC is disconnected from the network.
When you next connect to the network, the updated files are written and synchronized. Follow the procedure below
to configure offline files.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Click the shared folder for offline files.
4 Choose either “Manual caching of documents”, “Automatic caching of documents”, or “Automatic caching of
programs and documents” on the Option 1 tab, then click OK.
Manual caching of documents: User selects files that are cached.
Automatic caching of documents: Opened files can be cached locally for offline use. Previous versions of files
that are not synchronized are automatically replaced by the latest versions.
Automatic caching of programs and documents: Opened files can be cached locally for use offline. Previous
versions of files and applications executed on the network that are not synchronized are automatically
replaced by the latest version of the files and applications.
159
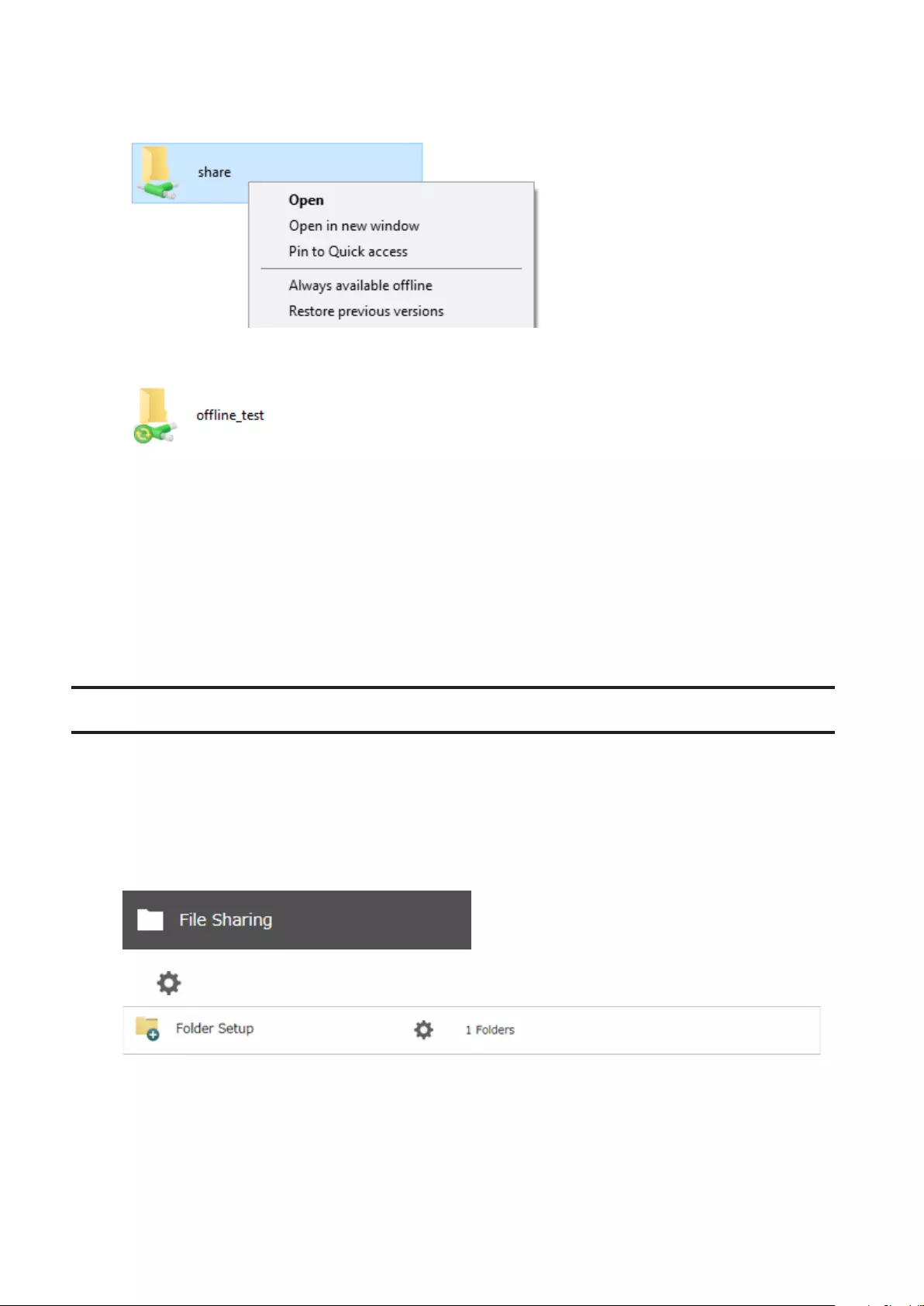
5 From File Explorer, right-click the icon of the shared folder on the TeraStation for which you have set the offline
feature, then click Always available offline. If the offline file wizard opens, follow the procedure on the screen.
6 When the offline settings and sync settings are complete, the files and folders set appear as shown:
7 If the computer is disconnected from the network after synchronization is complete, the offline file function
can be used.
Offline files can be accessed by the original Universal Naming Convention (UNC) where the data was saved.
Note: If you cannot access offline files, try the following procedure:
(1) Reconnect the computer to the network.
(2) From Control Panel, change the view to the icon view and click Sync Center. Click Sync All to synchronize all
offline files.
(3) Disconnect the computer from the network and verify that you can access offline files.
Accessing from an NFS Client
Note: (US customers only) Buffalo’s customer support will help configure the NFS settings on your TeraStation, and
will support VMware and Windows clients but will not provide support for configuring your Linux or other UNIX
clients. There are various types of UNIX and the procedures for configuring NFS with them will vary considerably.
For help configuring your NetWare, Linux, or other UNIX clients for NFS support, please consult each client’s own
documentation and support.
1 From Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of “Folder Setup”.
3 Choose the shared folder that will be accessible from the NFS client.
4 Under “LAN Protocol Support”, select the “NFS” checkbox on the Basic tab and click OK.
Note the NFS path. It will be used later for accessing data from an NFS client.
5 Click Close.
160
6 Move the NFS switch to the position to enable NFS.
7 Click to the right of “NFS”.
8 Click the Client Settings tab.
161
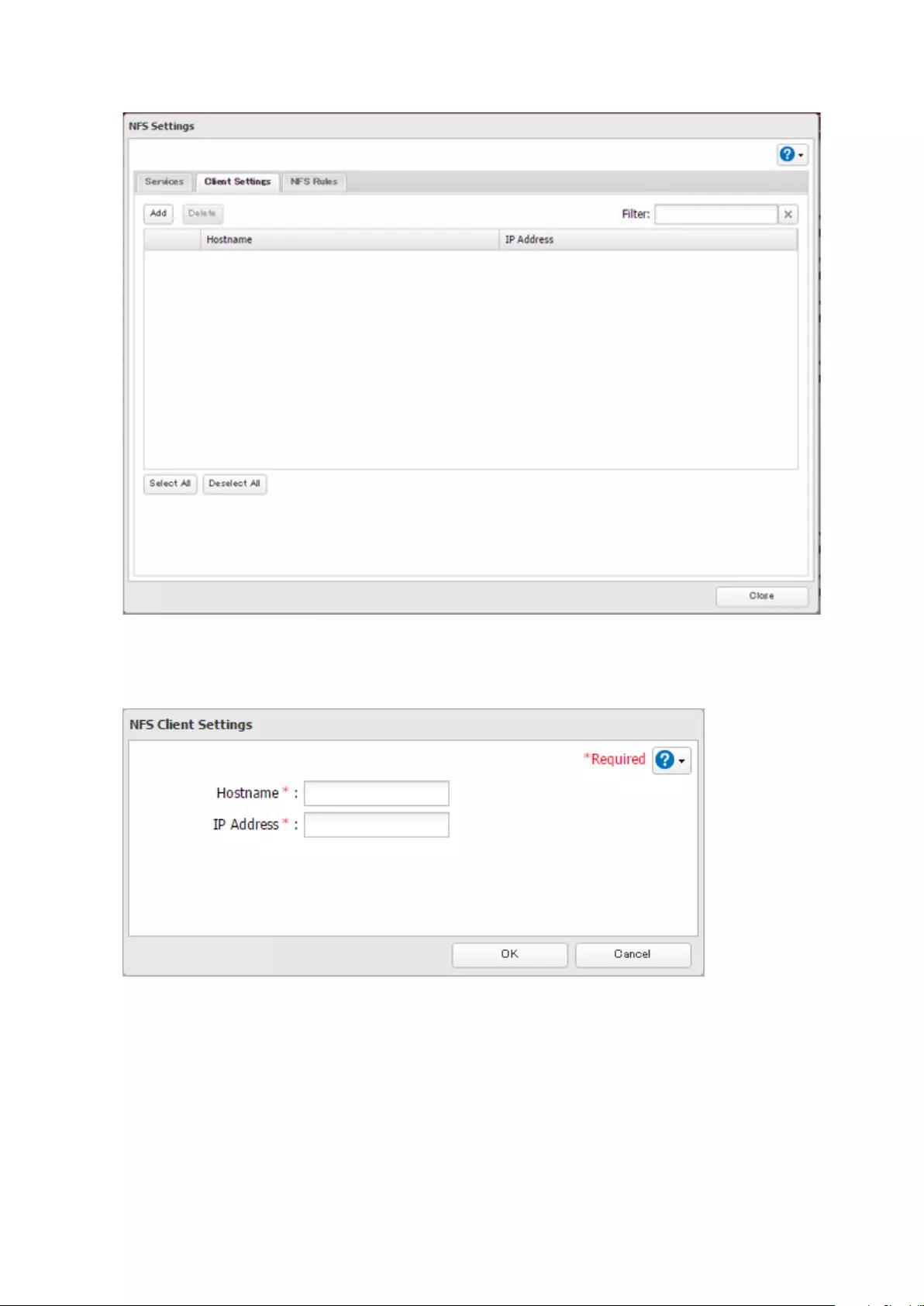
9 Click Add.
Note: To delete a client, select the checkboxes of the clients from the lists and click Delete.
10 Enter the hostname and IP address of the NFS client, then click OK. You should add all NFS clients to access the
shared folder.
162
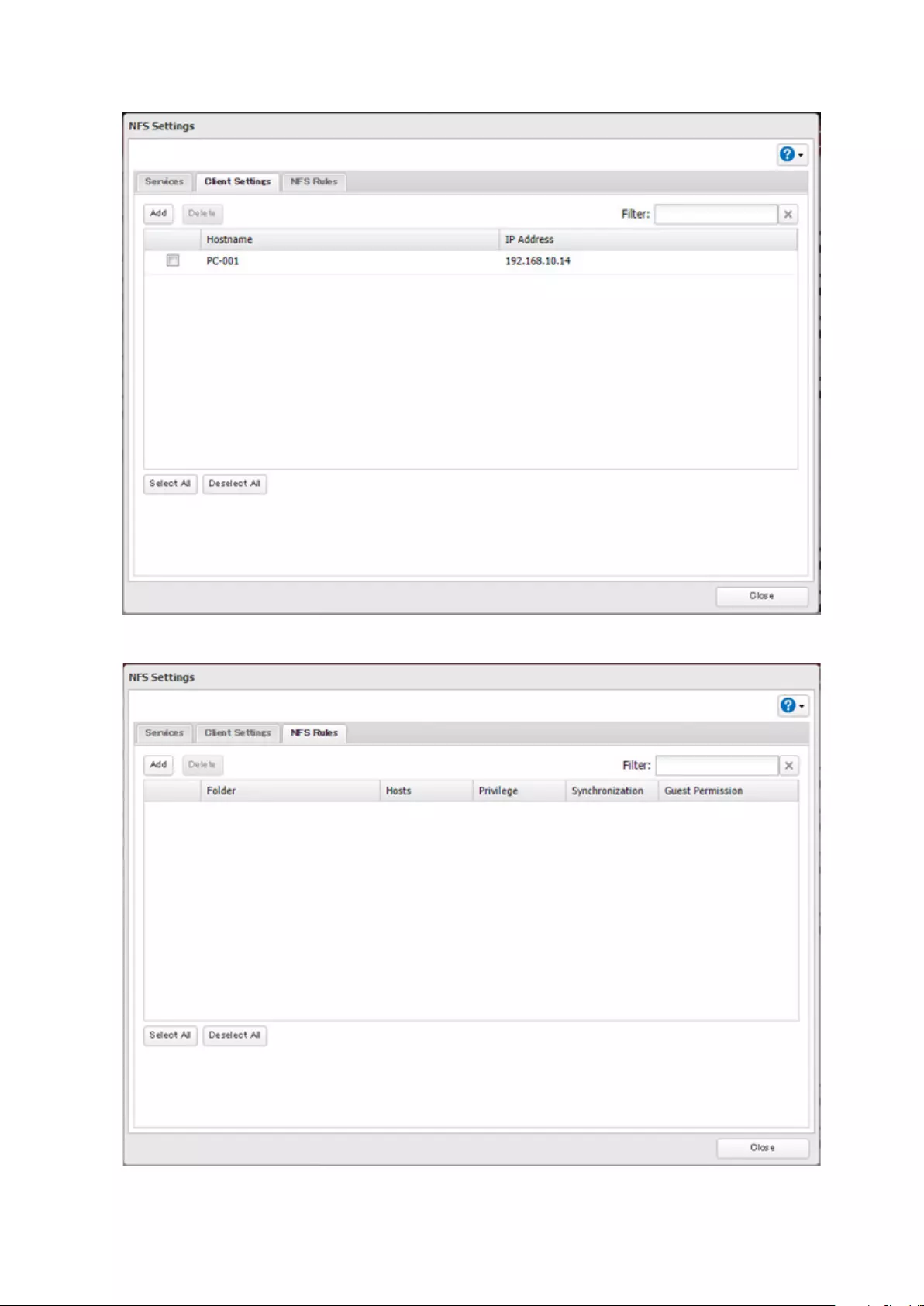
11 Click the NFS Rules tab.
12 Click Add.
163
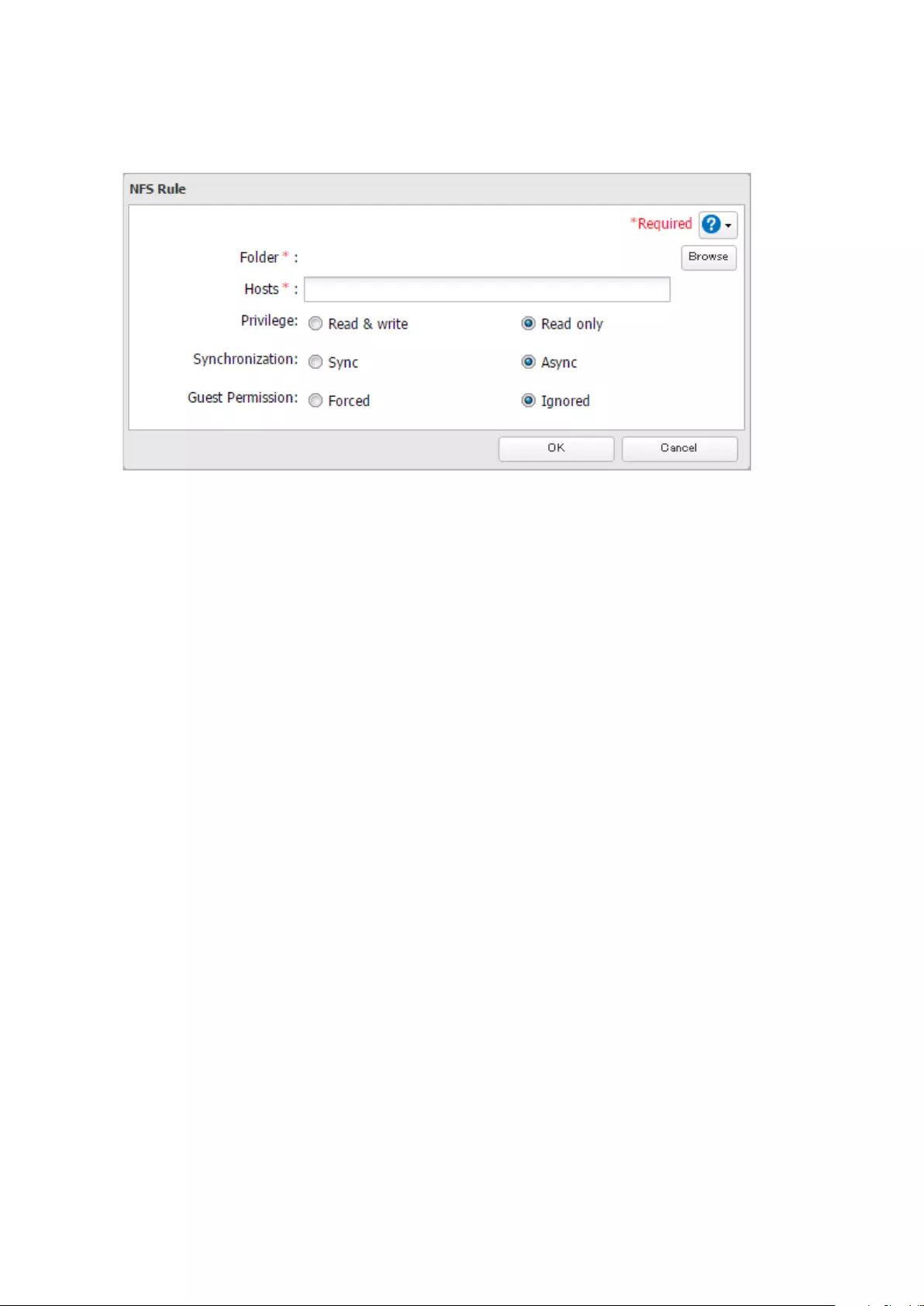
13 Choose the folder to restrict access to, and enter the clients that will have restricted access into the “Hosts”
field. Clients may be entered by hostname, IP address, or IP address range. Wildcards are supported. Separate
multiple entries with commas. You may assign read-only or read and write access to the listed clients. Rules
override any settings made from the Services tab.
14 Click OK.
Notes:
• To restrict NFS access to a specific network or client, navigate to File Sharing > NFS > Services and click Edit. Enter
the address of the network. For example, if your local network subnet has a router at 192.168.1.1 and clients
with IP addresses in the range from 192.168.1.2 through 192.168.1.48 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0, then the
“Public Network Address” would be 192.168.1.0 and the “Public Subnet Mask” would be 255.255.255.0. This would
mean that only clients on this local network would be able to access the NFS share. If the default settings are used
(0.0.0.0 for both the public network address and the public subnet mask), then access to the NFS share will not be
restricted.
• If you configure “Guest Permission” to “Forced” on the screen navigating to NFS Rules > Add, user ID and group ID
should be 65534 when the data is written from NFS clients; this is recommended for SMB or other protocols as
well. Use “Ignored” if the TeraStation only enables NFS connection.
NFS Mount Commands
Enter the mount command to access the shared folder from the NFS client. The mount command depends on your
operating system. The examples below assume that IP address of your TeraStation is 192.168.11.10, “/mnt/array1/
share” is the desired NFS path, and “/mnt/nas” or drive letter “z” is the mount point.
For Linux:
mount -t nfs 192.168.11.10:/mnt/array1/share /mnt/nas
For Windows Service for Unix 3.5:
mount 192.168.11.10:/mnt/array1/share z:
Note: A shared folder whose folder name contains multibyte characters cannot be accessed.
For Solaris 10:
mount -F nfs 192.168.11.10:/mnt/array1/share /mnt/nas
For macOS:
mount -t nfs -o resvport 192.168.11.10:/mnt/array1/share /mnt/nas
164

Encrypting Data Transmission
Encrypting Settings Data
All communication with Settings can use SSL encryption if you access the Settings page by changing “http://” to
“https://” in the browser address bar or click Secure Connection from the login window. Once you are logged in using
the HTTPS connection and wish to disable SSL encryption, click Normal Connection from the login window.
Encrypting FTP Transfer Data
You can encrypt passwords using SSH for secure FTP communication. First, open a shared folder’s settings; under
“LAN Protocol Support”, select the “SFTP” checkbox on the Basic tab and click OK. Also, you have to enable the SFTP
service by moving the SFTP switch to the on position on “File Sharing”.
SSL Keys
SSL keys are used during setup screen operations and FTP communication. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is a type of
encryption system called public key encryption. Generally, SSL is managed by the two files below.
server.crt (SSL Certificates)
The TeraStation sends the file to a computer, and the computer uses it to perform encryption. The TeraStation
receives the encrypted data and uses server.key (the private key) to decrypt the data.
In SSL, this key contains the server certificate, and depending on your computer environment, a check may be
performed to determine the trustworthiness of the certificate. The server certificate included in the TeraStation’s
default settings was created by Buffalo, and in some cases, the security certificate warning message may appear in
your browser or another security software. Disregard this message and continue.
server.key (SSL Private Key)
This file is used as a pair with server.crt (server certificate). This is required for decrypting the data that was
encrypted by the server certificate, and this is normally not revealed.
Note: The passphrase for the private key must be removed before importing to the TeraStation.
Updating SSL Key Files
To update a server certificate and a private key for SSL, follow this procedure.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click SSL.
3 Register “server.key” for “Secret Key” and “server.crt” for “Server Certificate (.crt)”, then click Import.
Notes:
• Place the SSL key files (server.key, server.crt) directly below the C root drive. The SSL key files may be unable to be
updated if it is placed in folders or paths that contain multibyte characters.
• If Settings cannot be displayed after updating, initialize the TeraStation settings.
• Updating the firmware initializes an SSL key.
165
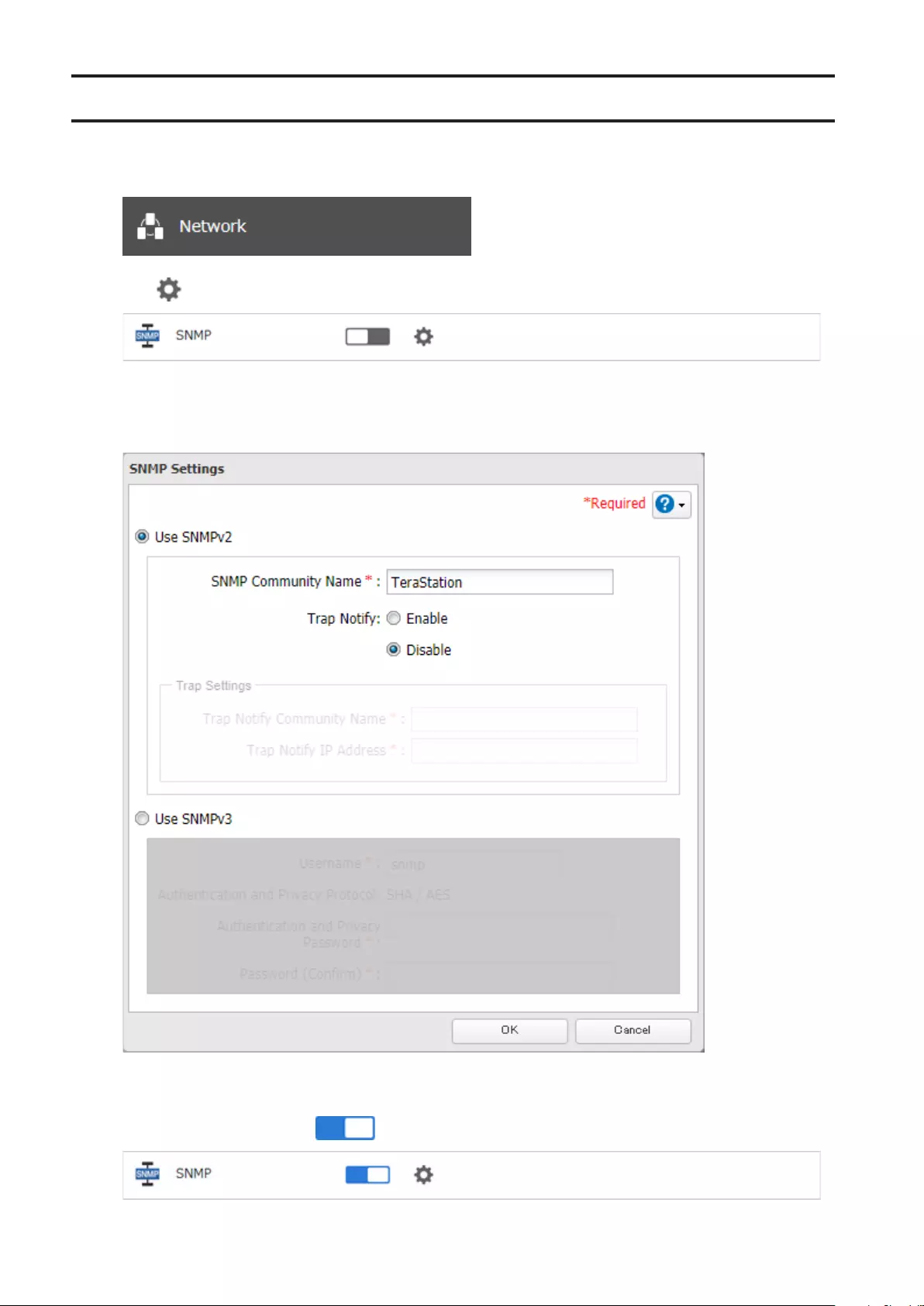
SNMP
If SNMP is enabled, you can browse your TeraStation from SNMP-compatible network management software.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “SNMP”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Select whether to use SNMP version 2 or version 3.
5 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
6 Move the SNMP switch to the position to enable SNMP.
166
7 SNMP has been configured for the TeraStation. For further use, configure your SNMP-compatible network
management software using the Buffalo-specific MIB (management information base) file. The MIB file is
available from the Buffalo website.
Depending on which SNMP client software you use, the procedure for configuring the software will differ. For
more detailed information on configuring the client software, refer to its help or included manual.
Saving and Applying Settings
The TeraStation’s settings can be saved to a USB drive and restored to another TeraStation of the same series. Use
this feature to back up and copy settings to a new TeraStation.
Save
Settings &
Firmware
Settings &
Firmware
Settings &
Firmware
Settings &
Firmware
Restore
Restore
Restore
Write down the drive configuration (number of drives, RAID, LVM, etc.) of the TeraStation whose settings were saved.
Make sure that any TeraStations that you apply these settings to have exactly the same drive configuration before
you apply the settings. If the drive configuration is different, you may get unexpected results.
The following settings are not saved or restored:
Category Settings
File Sharing
Subfolders’ access restriction settings in the shared
folders
All settings for USB drives
Storage
All settings in “Drives”
All settings in “LVM”
All settings in “iSCSI”
USB drive information
Web Services Job settings of Dropbox Sync
Network
All settings except for service port restrictions, Wake-on-
LAN, and MTU size settings in “IP Address”
All settings in “Port Trunking”
Backup All settings in “Failover”
Management
The TeraStation’s hostname
All settings in “Power Management”
All settings in “SSL”
Display language in Settings
Saving Settings
1 Insert a 1 GB or larger USB drive (not included) into a USB port on the TeraStation.
Note: All data on the USB drive will be erased!
167
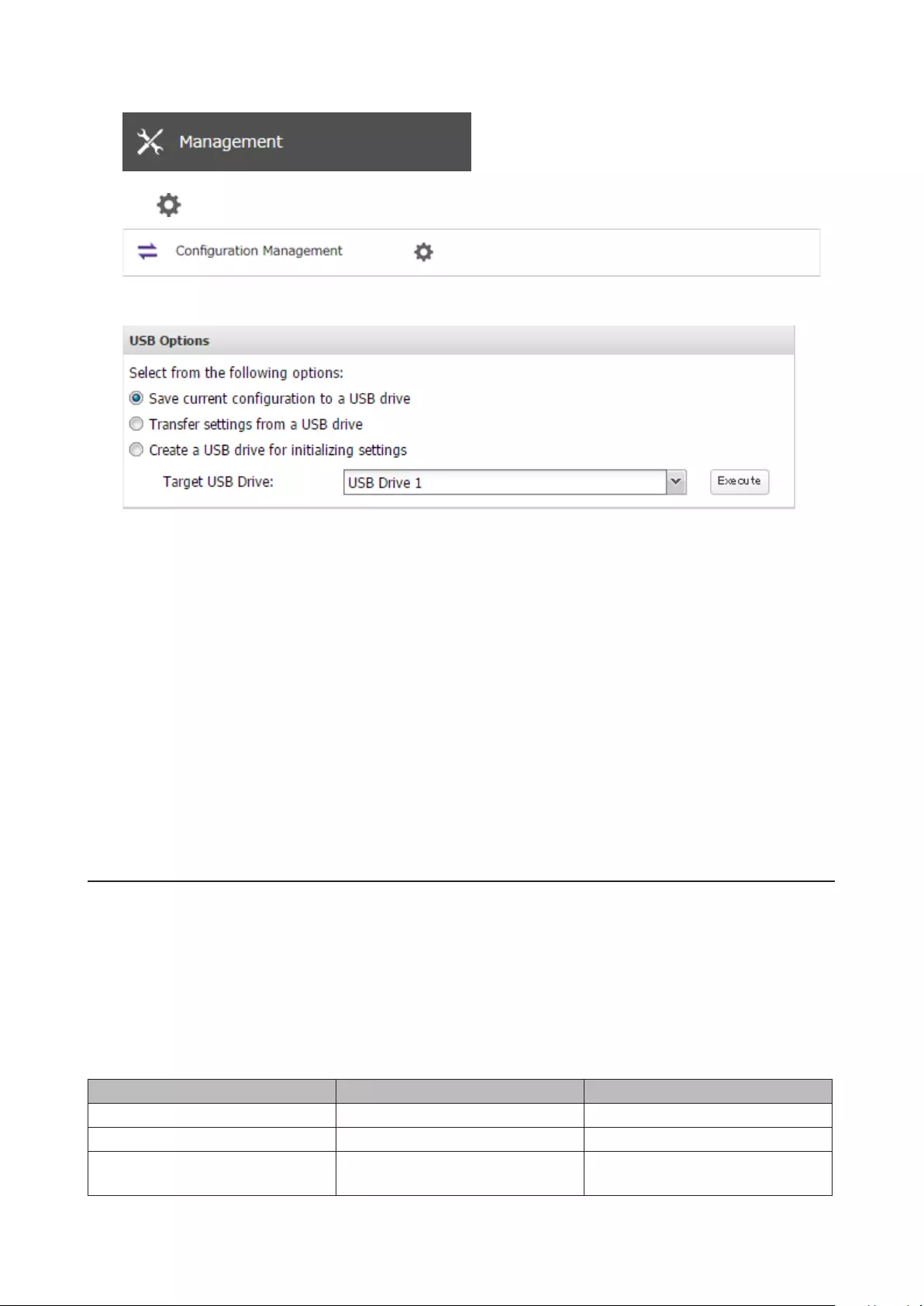
2 From Settings, click Management.
3 Click to the right of “Configuration Management”.
4 Select “Save current configuration to a USB drive”.
5 From “Target USB Drive”, select the USB drive that is connected to the USB port on the TeraStation, then click
Execute.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 The TeraStation will save the settings. When saving settings is finished, click OK.
Troubleshooting:
If the settings are not saved to the USB drive successfully, you may receive an error message such as “The specified
operation cannot be executed.”. Verify:
• The USB drive has a capacity of 1 GB or larger.
• The USB drive is not write-protected.
• Failover is configured on the TeraStation.
Applying Settings
The saved settings can be applied to a different TeraStation of the same series. If applying settings to another
TeraStation, the unit’s current firmware version will be changed to the version used to save the settings.
Note: Depending on your TeraStation model and its firmware version, saved settings cannot be applied from a USB
drive which contains saved settings from a unit that was running an earlier firmware version described below. In
such a case, create the settings restoration USB drive again using the unit running the latest firmware version.
As an example of this requirement, you have created a USB drive which contains the settings of the TS5410DN series
TeraStation running firmware version 3.00 and try to apply these settings to the TS5810DN series TeraStation, the
settings cannot be applied from the USB drive because the settings should be created from a unit running firmware
version 3.20 or later for the TS5810DN series TeraStation.
TeraStation Model Untransferable Version Transferable Version
TS5810DN series Version 3.12 or earlier Version 3.20 or later
TS51210RH series Version 3.00 or earlier Version 3.02 or later
TS5210DN, TS5210DF, TS5410DN,
TS5410RN series Version 3.00 or earlier Version 3.03 or later
168
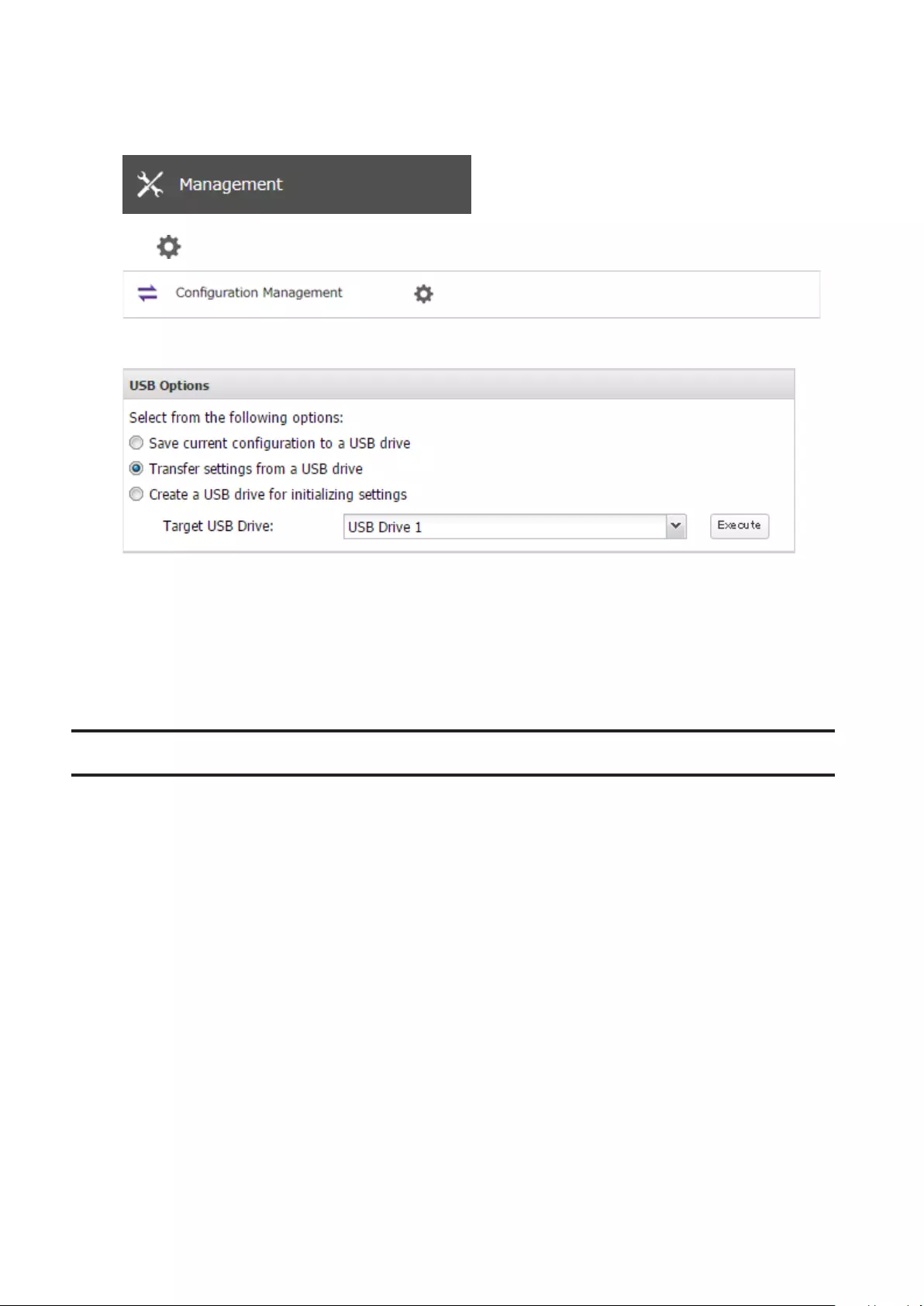
1 Insert the USB drive with the saved settings to a USB port on the TeraStation.
2 From Settings, click Management.
3 Click to the right of “Configuration Management”.
4 Select “Transfer settings from a USB drive”.
5 From “Target USB Drive”, select the USB drive that is connected to the USB port on the TeraStation, then click
Execute.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 The TeraStation will apply the settings. When applying settings is finished, click OK.
Transferring Another TeraStation’s Settings
You can transfer saved settings from another series TeraStation to your TeraStation. The following settings can be
transferred:
• Shared folders which are created from “File Sharing” > “Folder Setup”
• Access restrictions
• Users
• Groups
Note: This feature currently supports the following TeraStation series as of August 2016. The latest compatibility
information will be on the Buffalo website.
• TS-X series firmware version 1.58 or later
• TS3000 series
• TS4000 series
• TS5000 series
• TS3010 series
• TS5010 series
169
Creating a Config File (.nas_config)
Procedure for TS-X Series
To transfer settings from TS-X series TeraStations, it will use the “NS-SHFT” software to create a config file. The NS-
SHFT can be downloaded from the Buffalo website.
For the procedure on creating the config file, refer to the NS-SHFT user guide.
Procedure for TeraStations Other Than TS-X Series
Follow the procedure below to create a config file on a TeraStation that is not a TS-X series.
1 Refer to the user manual of the TeraStation that you want to transfer settings for saving settings to a USB drive.
2 Access the “usbdisk x” shared folder while connecting the USB drive to the TeraStation whose settings were
saved in the previous step. The “x” in the folder name represents the USB port number you connected the drive
to.
3 Copy and paste the .nas_config file to the desired location on your computer.
Transferring Settings
Follow the procedure below to transfer settings from another series TeraStation.
1 Before transferring access restrictions with Active Directory domain users, make sure the migration target
TeraStations are joined to the same domain controller. To have the unit join the domain network, refer to the
procedure on the “Active Directory” section in chapter 3.
If you didn’t configure access restrictions with Active Directory domain users, skip to the next step.
2 From Settings, click Management.
3 Click to the right of “Configuration Management”.
170
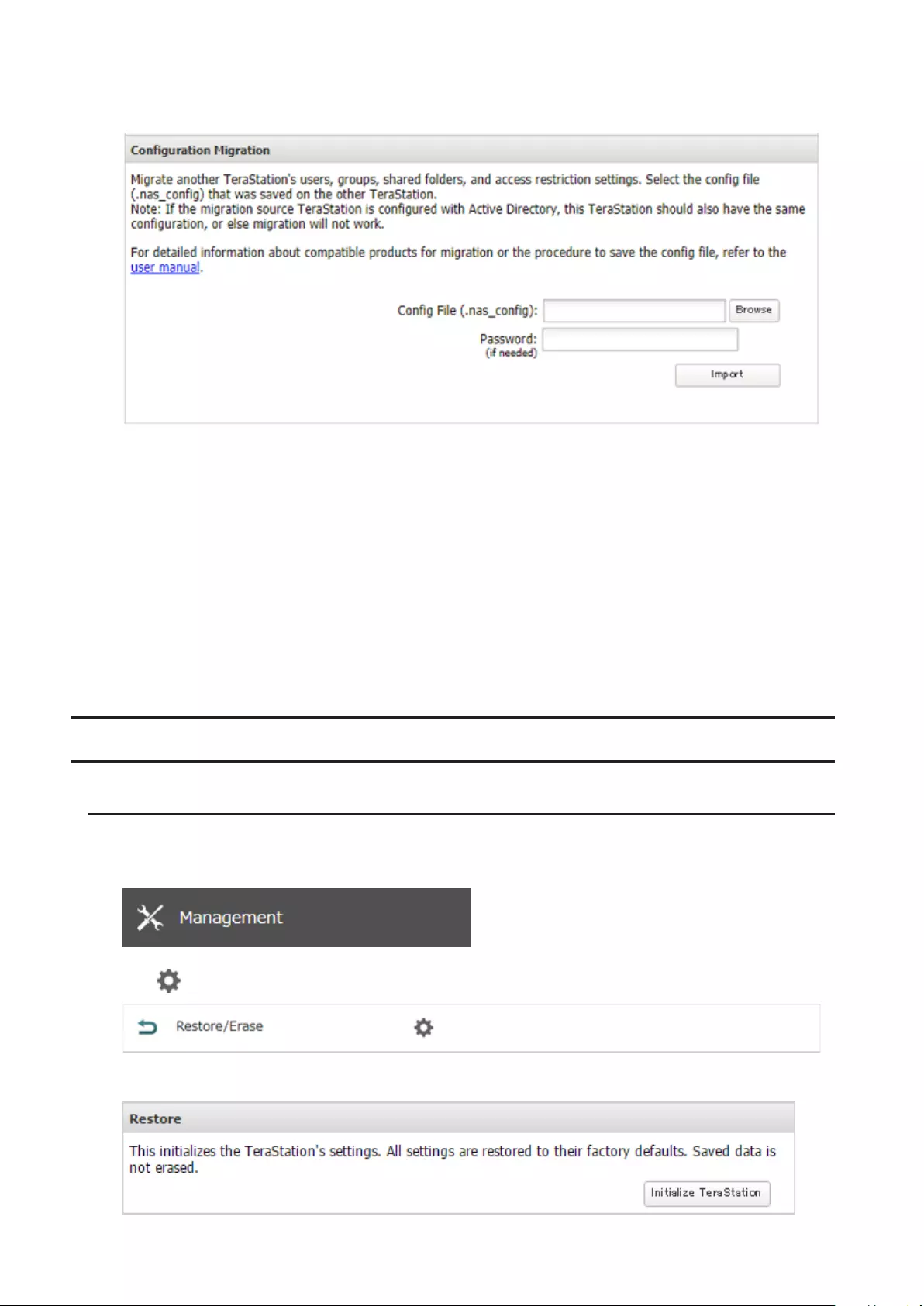
4 Click Browse and choose the config file (.nas_config) that was created with another TeraStation. If the config
file was created with a password, enter it into the “Password” field.
5 Click Import.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 The TeraStation will transfer the settings. When transferring settings is finished, click OK.
Notes:
• If the migration target TeraStation contains shared folders, users, and groups that share the same name as the
transferred settings, the existing settings will be overwritten.
• If the migration target TeraStations have already added some shared folders, users, and groups, the transferred
settings may exceed the maximum number of allowed shared folders, users, or groups. After migration finishes,
open Settings and verify that all settings were properly transferred.
Restoring Factory Defaults
Initializing from Settings
To initialize the TeraStation to its factory defaults from Settings, follow this procedure.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Restore/Erase”.
3 Click Initialize TeraStation.
171
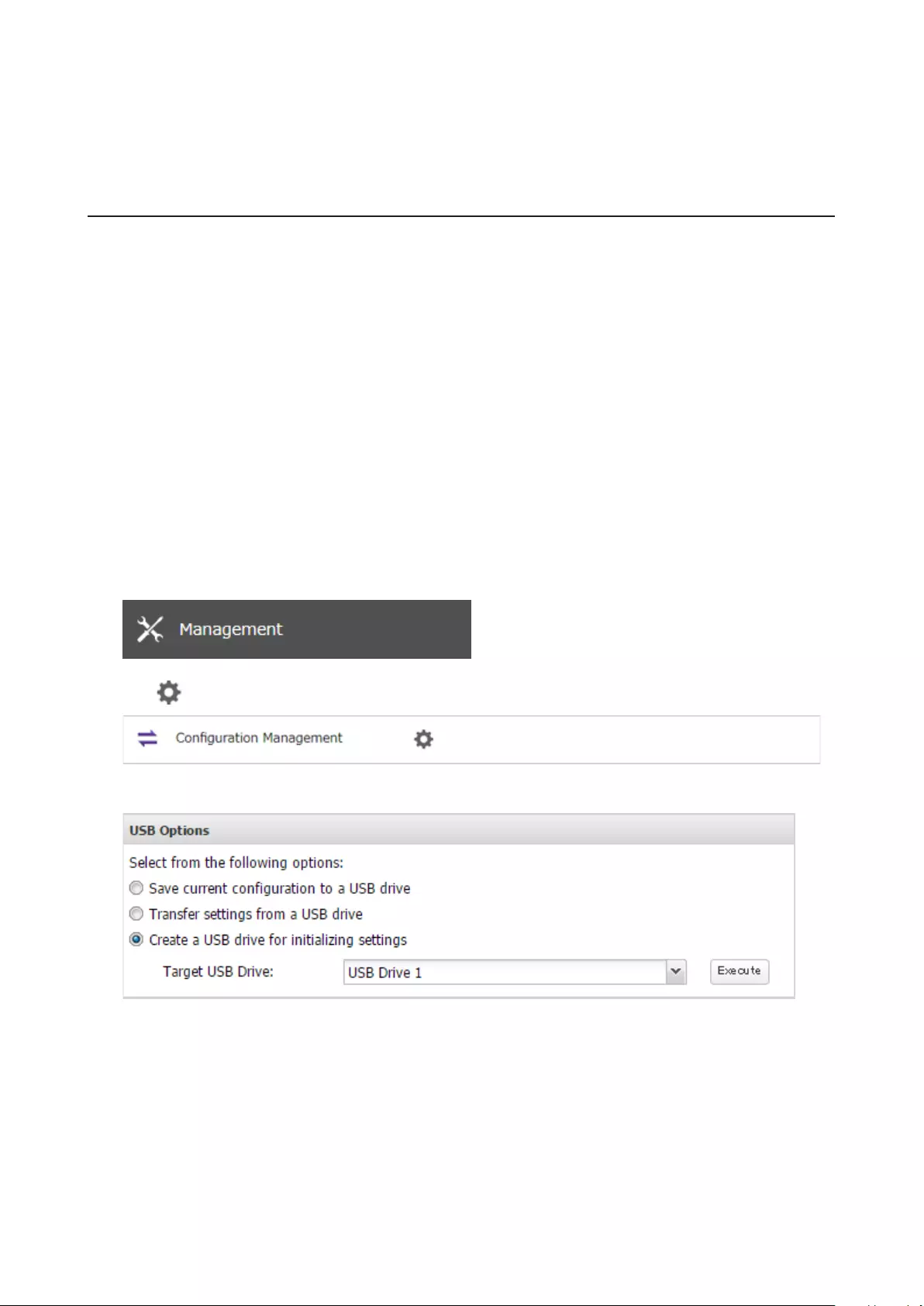
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 The TeraStation will restore its factory default settings. Close the browser and wait until the initialization is
finished.
Initializing with the USB Initialization Drive
An initialization drive will restore the settings on your TeraStation to their factory defaults. You can initialize them
without logging in to Settings. Follow the procedure below to create an initialization drive.
Notes:
• Initializing settings with the USB drive is available for the same TeraStation unit that created the initialization
drive.
• Normally, making and using an initialization drive will not affect data on the TeraStation. However, always back up
your data regularly!
• This USB drive can be used to recover the system if your TeraStation doesn’t boot at all. In this case, if the data
partition is damaged, then all your data will be deleted by the recovery process.
Creating an Initialization Drive
1 Insert a 1 GB or larger USB drive (not included) into a USB port on the TeraStation.
Note: All data on the USB drive will be erased!
2 From Settings, click Management.
3 Click to the right of “Configuration Management”.
4 Select “Create a USB drive for initializing settings”.
5 From “Target USB Drive”, select the USB drive that is connected to the USB port on the TeraStation, then click
Execute.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 The TeraStation will create the initialization drive. This will take about a minute. When creating the USB
initialization drive is finished, refresh the browser and log in to Settings again.
172
Initializing with the USB Drive
To initialize the settings on your TeraStation with the USB drive as created above, follow the procedure below.
Note: If using the initialization drive to initialize, the unit’s current firmware version will be changed to the version
used to create the initialization drive.
1 Turn off the TeraStation by pressing and holding the power button for 3 seconds.
2 Insert the USB drive into a USB port on the TeraStation. Make sure that no other USB drives are currently
connected to any USB ports on the TeraStation.
3 Power on the TeraStation while holding down the function button.
4 When the I41 message appears on the LCD panel, press the function button.
5 It will take several minutes for initializing the settings. The TeraStation will restart when it’s finished.
Dismount the USB drive before unplugging it. See the “Dismounting Drives” section in chapter 4 for the procedure
on dismounting drives.
Resetting the Administrator Password
If you forget the admin username or password and cannot log in to Settings, or wrong network settings are
configured and Settings is inaccessible, initialize these settings by holding down the init button (refer to the
TeraStation diagram in chapter 1) on the front panel for three seconds. Normally this will reset the admin username
and password, network configuration, SSL, and security port settings to their factory default values.
This button can be disabled in Settings; to do so, navigate to Management > Restore/Erase > Edit under “Init Button
Settings”, then select “Keep current admin username and password” and click OK.
Logs
Displaying TeraStation’s Logs
Follow the procedure to check the TeraStation’s logs.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Logs”.
173
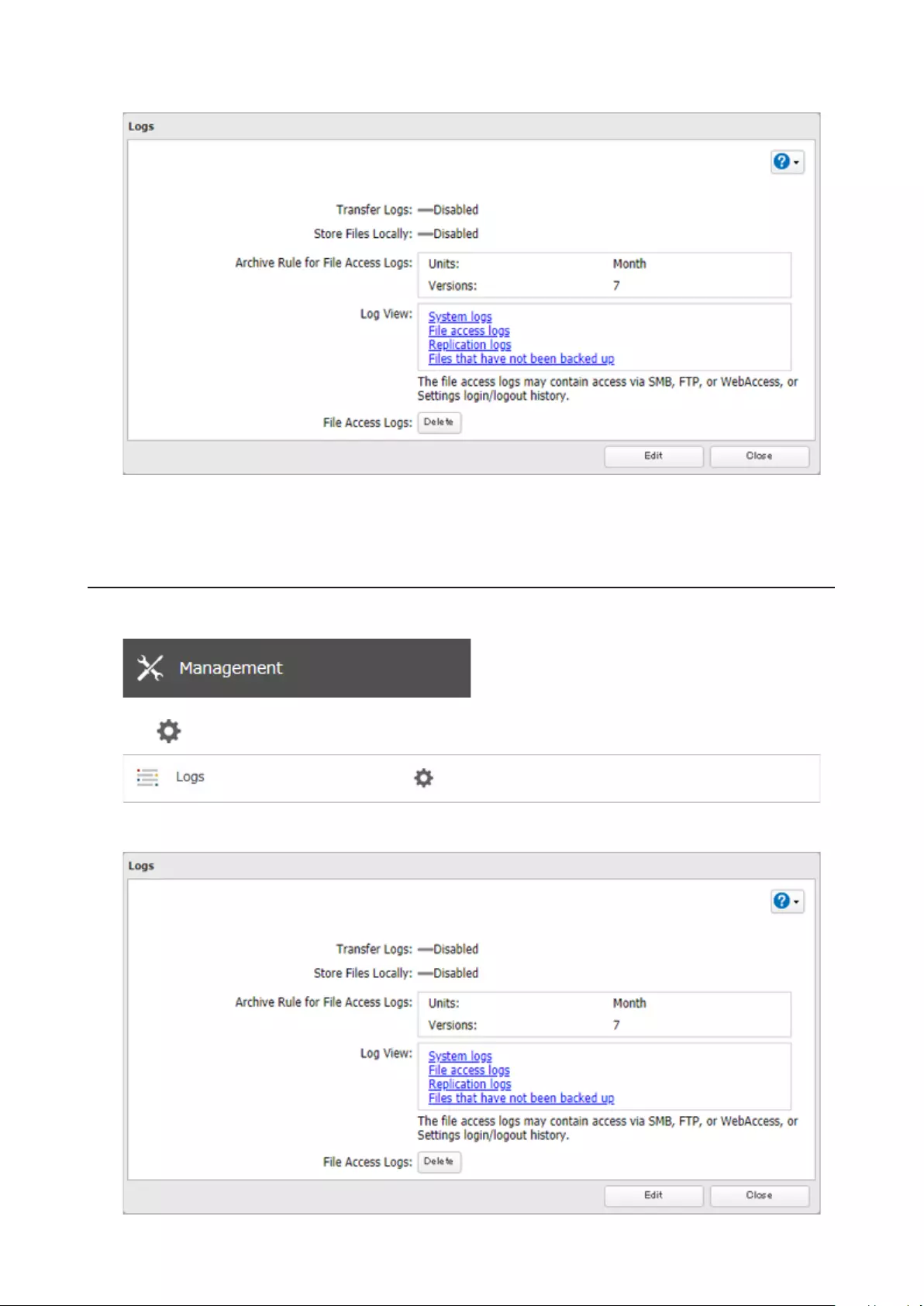
3 Select a log to view.
The file access log stores file access events that occurred on the internal drives. File access on USB drives are
not logged.
Note: All logs are encoded in UTF-8 format. To show them correctly, change the software encoding to “UTF-8”.
Transferring Logs to the Syslog Server
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Logs”.
3 Click Edit.
174
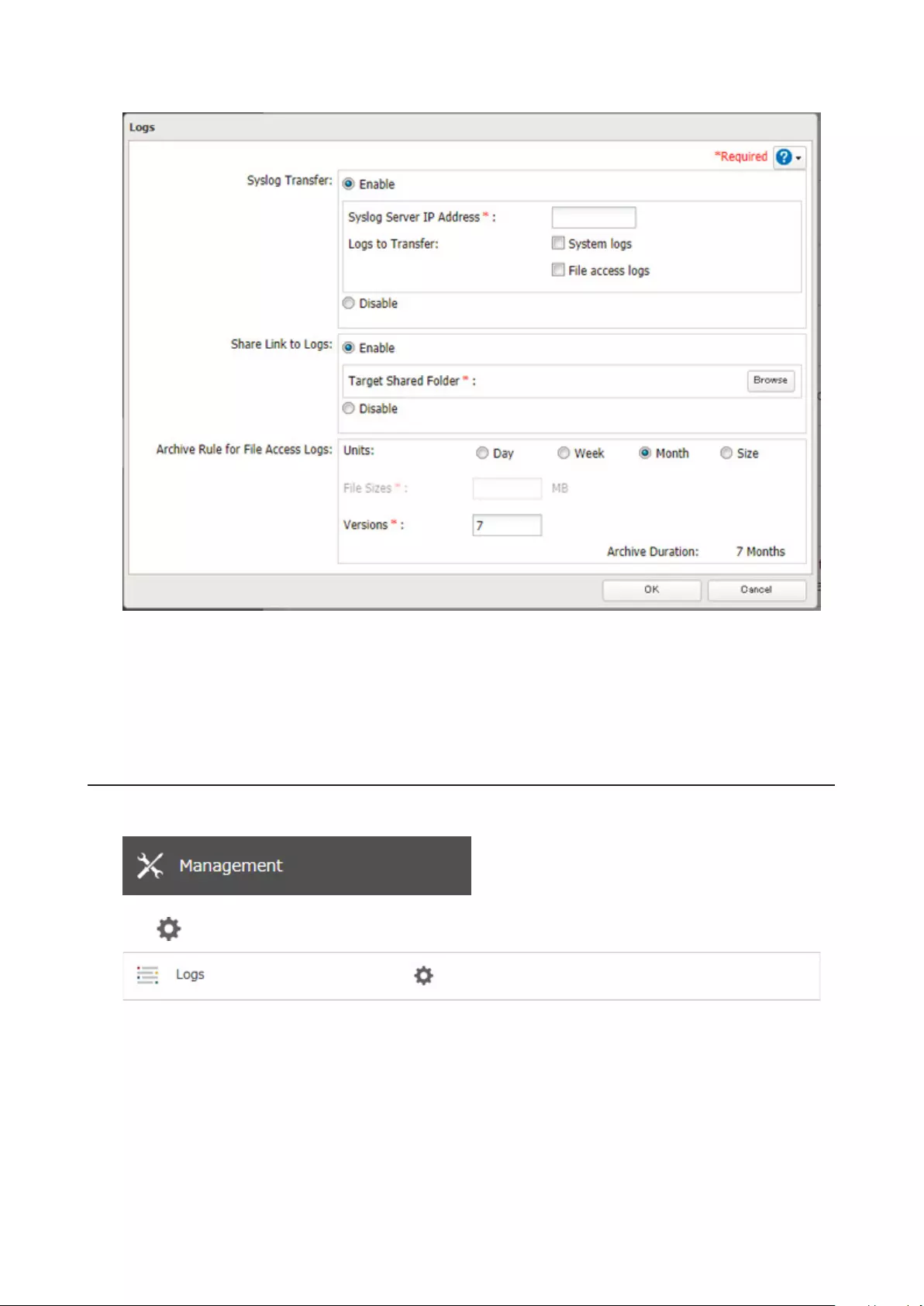
4 Enable “Syslog Transfer”.
5 Enter the IP address of the syslog server where you want to transfer the logs to.
6 Select the type of log that you want to transfer from “Logs to Transfer”.
7 Click OK.
Creating a Link to the Logs in the Shared Folder
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Logs”.
175
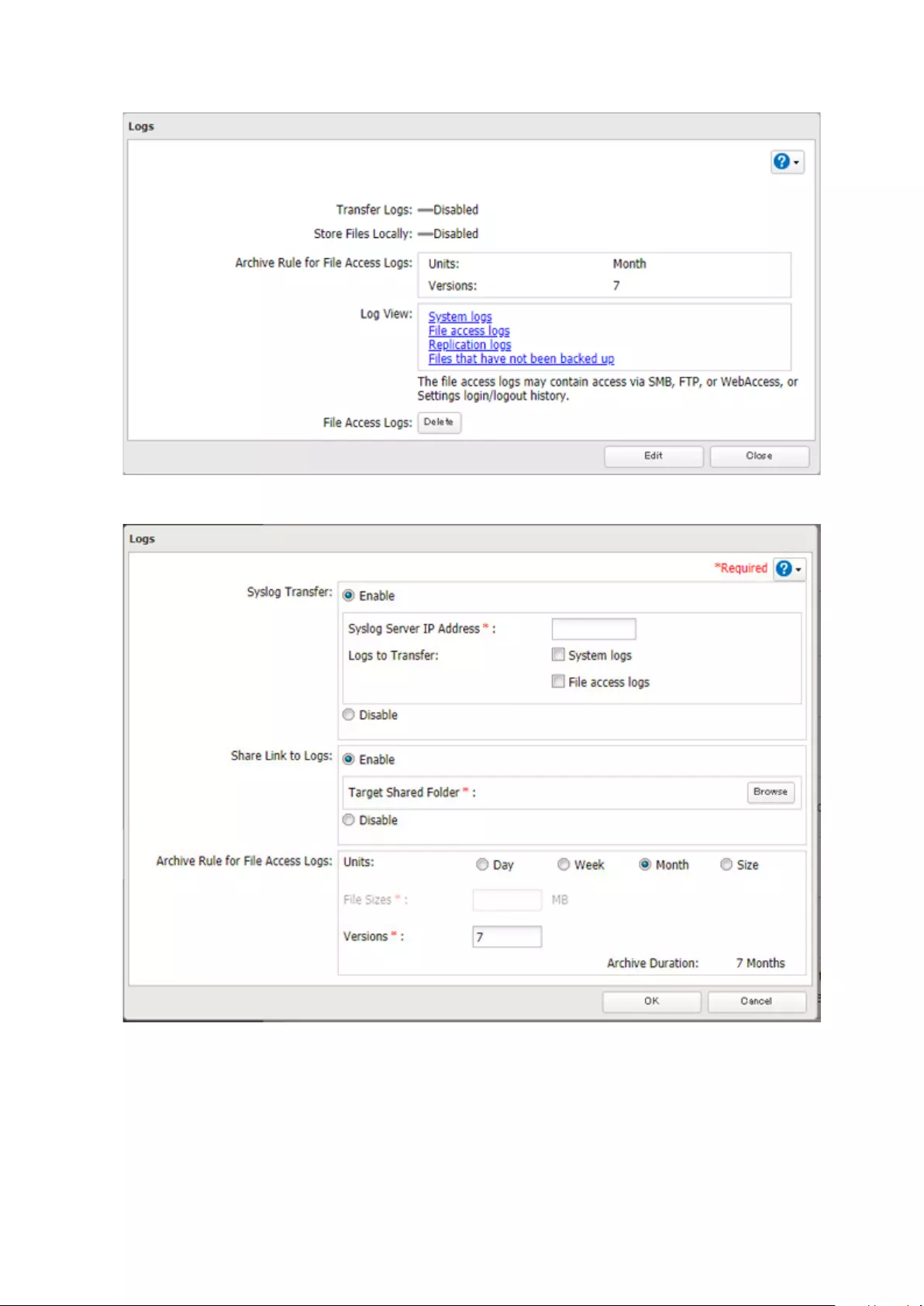
3 Click Edit.
4 Enable “Share Link to Logs”.
5 Click Browse and select the shared folder where the link will be created in “Target Shared Folder”. Click OK.
Under the selected shared folder, a folder named “system_log” will now contain the logs.
176
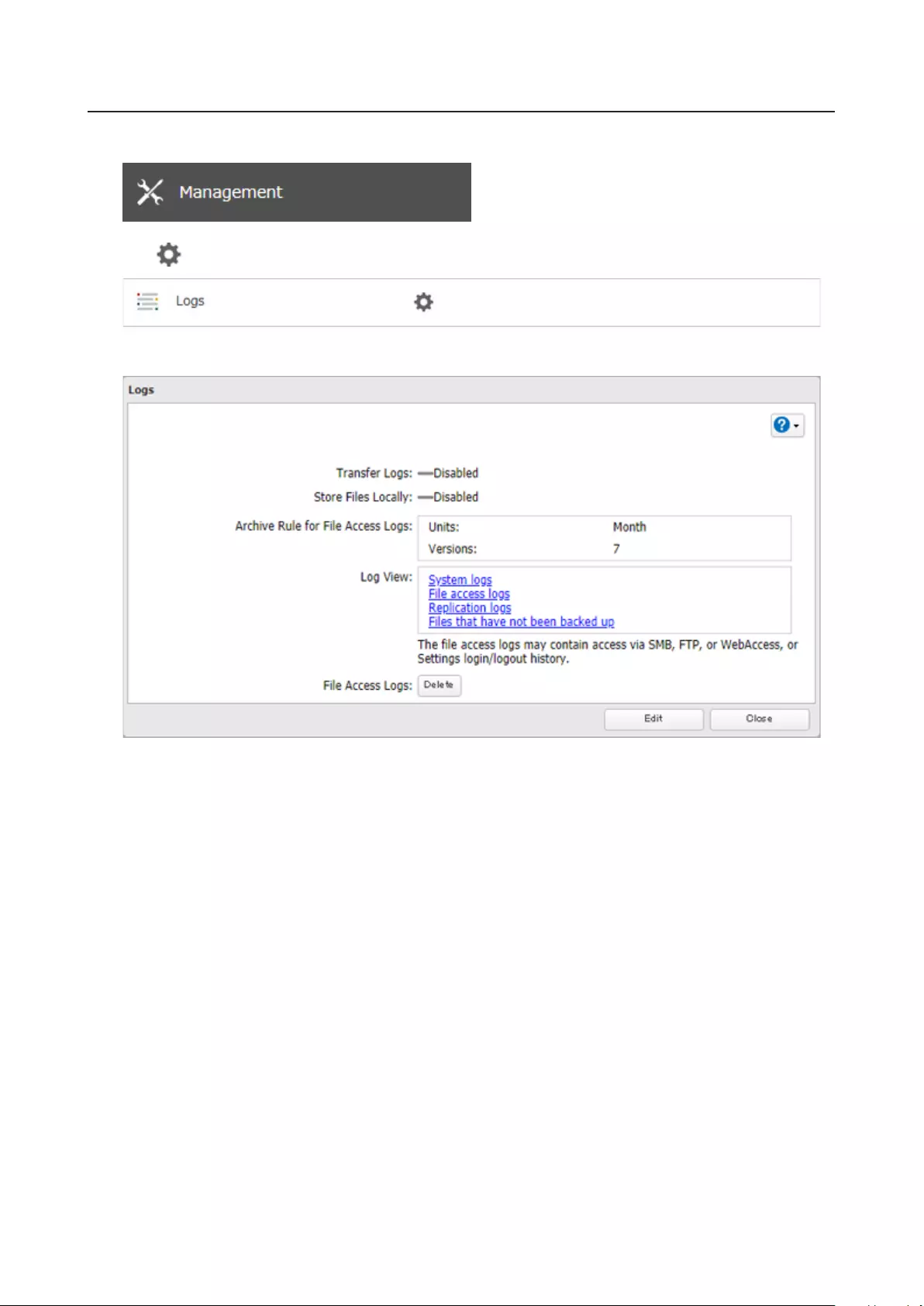
Changing Archive Rules for File Access Logs
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Logs”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Select the unit and version to save logs to the right of “Archive Rule for File Access Logs”. For example, if you
select “Month” for the unit and enter “7” for the version, the file access logs for the next 7 months will be saved
on the TeraStation.
Available duration and capacity to save logs will vary depending on the unit. The following values are
available:
Unit (Day): 1–367 for all versions
Unit (Week): 1–53 for all versions
Unit (Month): 1–13 for all versions
177
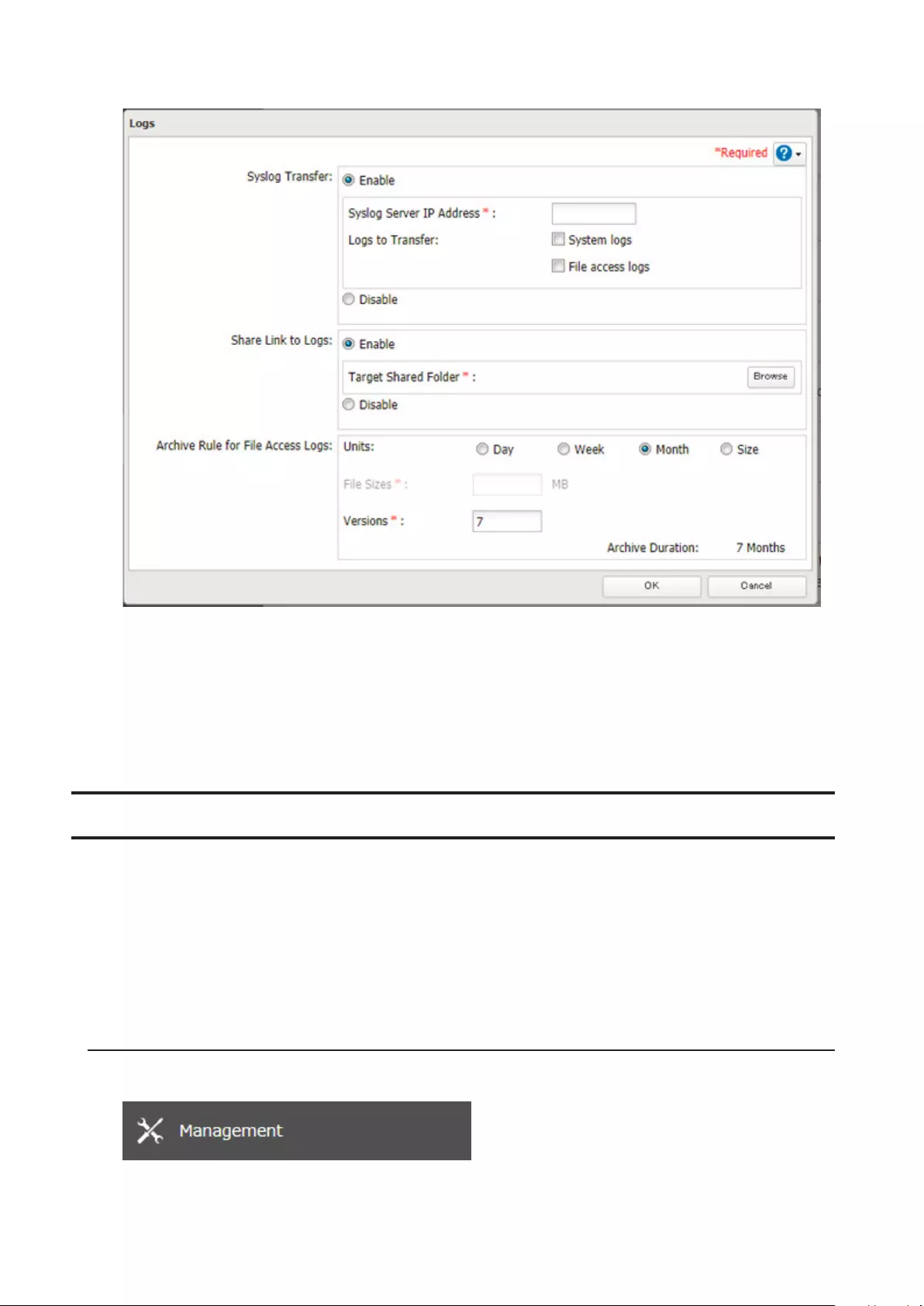
Unit (Size): 1–100 for file sizes and 1–13 for all versions
5 Click OK.
Notes:
• To delete the saved logs, click Delete at the window in step 3.
• If there is not enough space to save logs, the I70 message will appear on the LCD panel. When it appears, delete
unnecessary logs or move them to another device from the TeraStation. If no free space is available elsewhere,
older logs will automatically be deleted.
Updating the Firmware
If new firmware is available, a message is displayed when the TeraStation boots. You can update the firmware either
manually or automatically.
Notes:
• If all drives and RAID arrays on the TeraStation have LVM enabled but no LVM volumes have been created, you will
not able to update the firmware from Settings.
• Settings will not be available while the firmware is updating. Don’t try to access Settings from another computer
until the update is complete.
Updating Manually
1 From Settings, click Management.
178
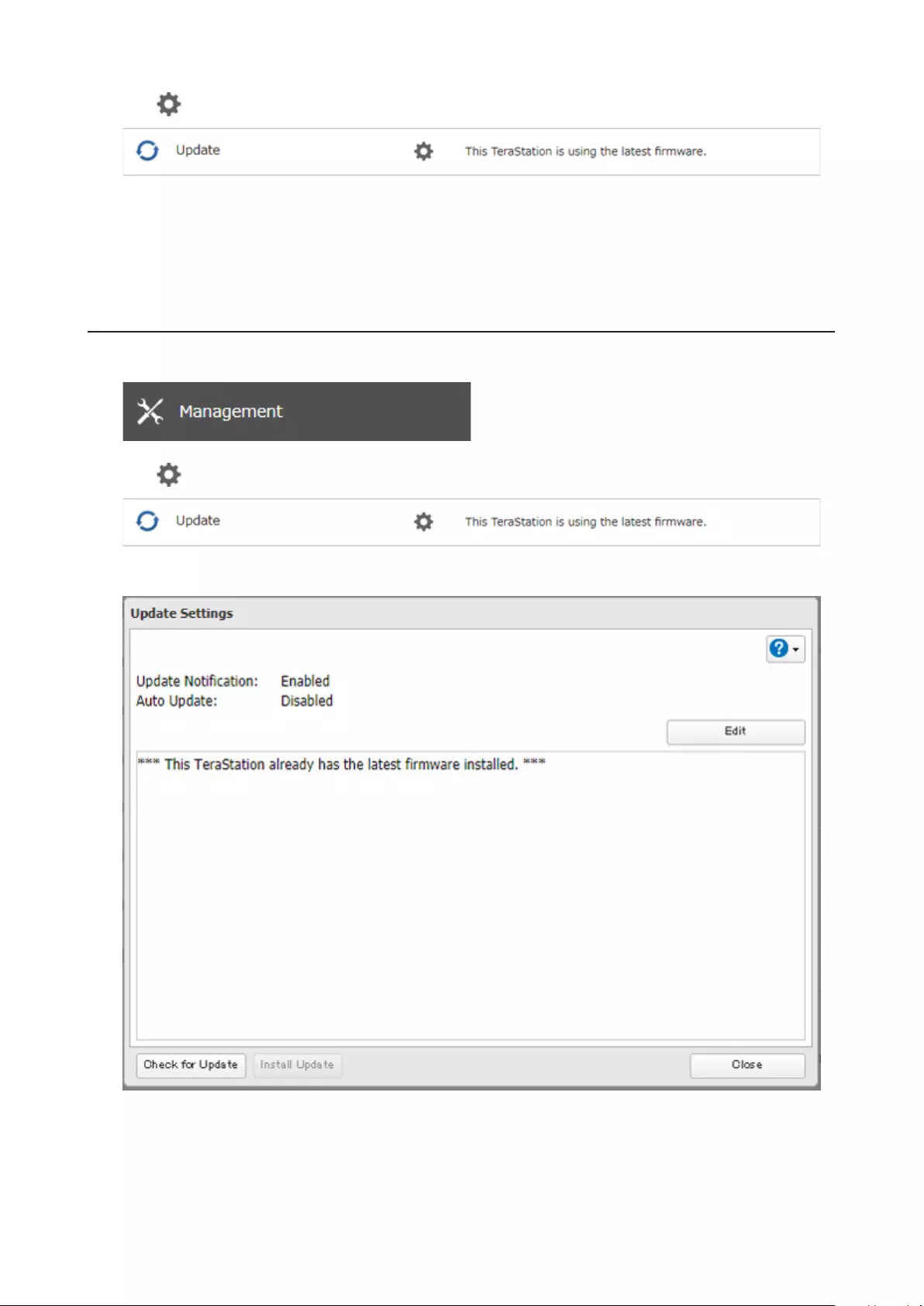
2 Click to the right of “Update”.
3 Click Install Update.
4 When updating the firmware is finished, refresh the browser and log in to Settings again.
You can also download the latest firmware from the Buffalo website.
Updating Automatically
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Update”.
3 Click Edit.
179
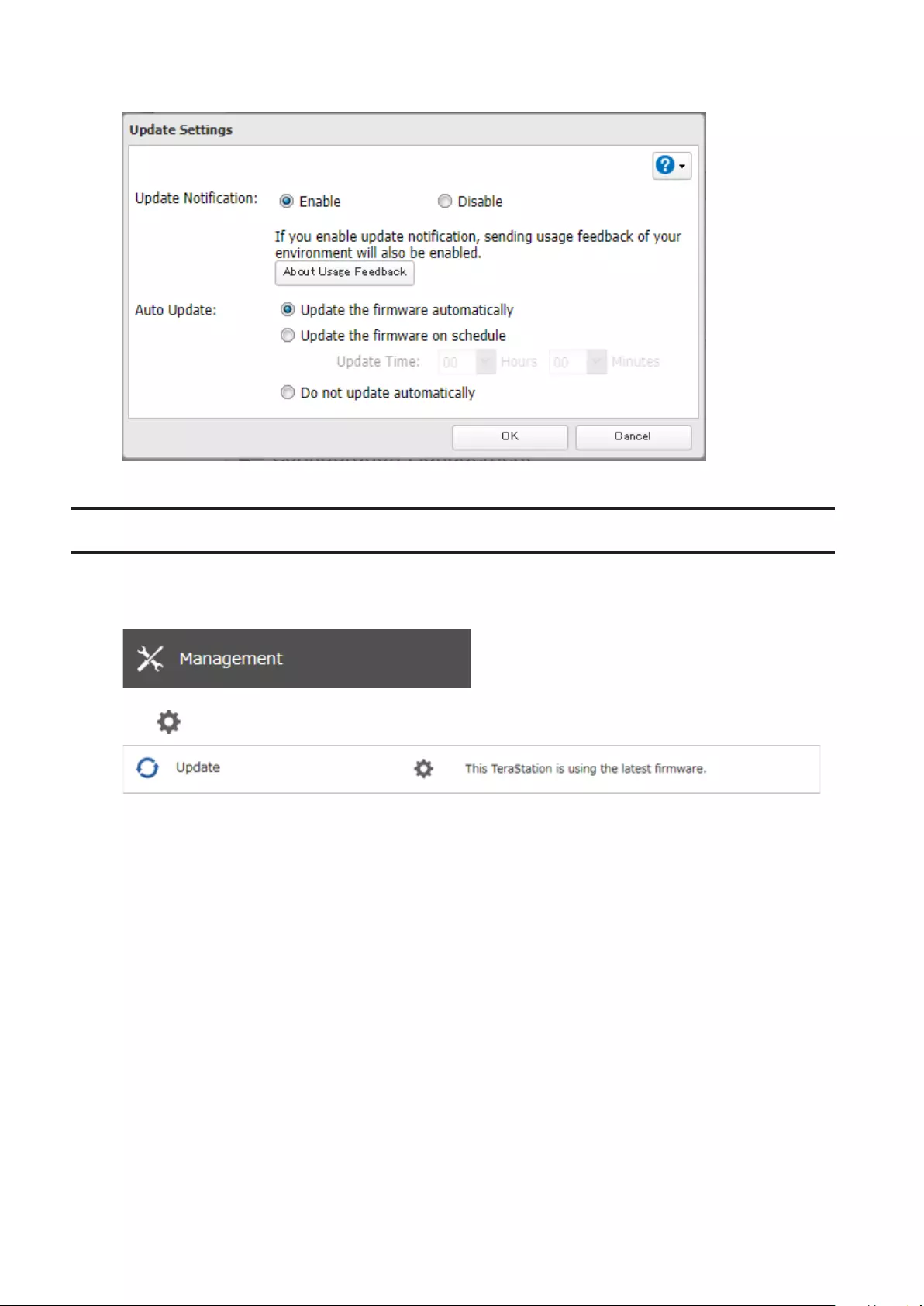
4 Select “Update the firmware automatically” and click OK.
Alternately, you may choose to schedule updates for a specific time of day.
Configuring Update Notification
Configure whether or not to receive a notification when new firmware becomes available.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Update”.
180
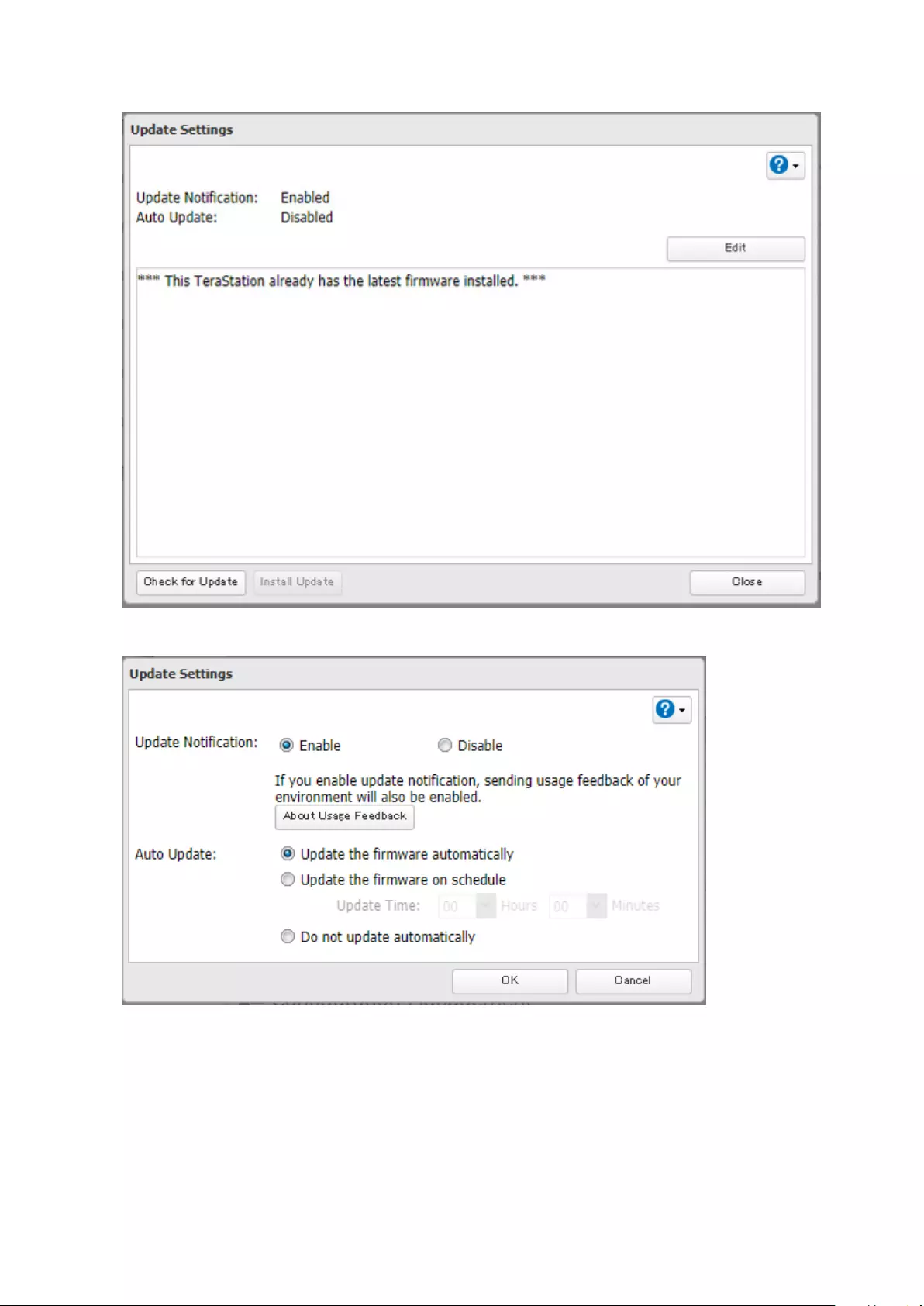
3 Click Edit.
4 Select to enable or disable update notification and click OK.
For further optimized firmware updates and product usability improvements, Buffalo may ask you to send your
usage and environment information, such as a number of shared folders and client computers, and/or S.M.A.R.T.
information. The collected information will only be used for improving future firmware stability and product
development and no other purpose.
If update notification is enabled, it will also automatically enable sending usage feedback to Buffalo. If you don’t
want to send this information to us, disable update notification.
181
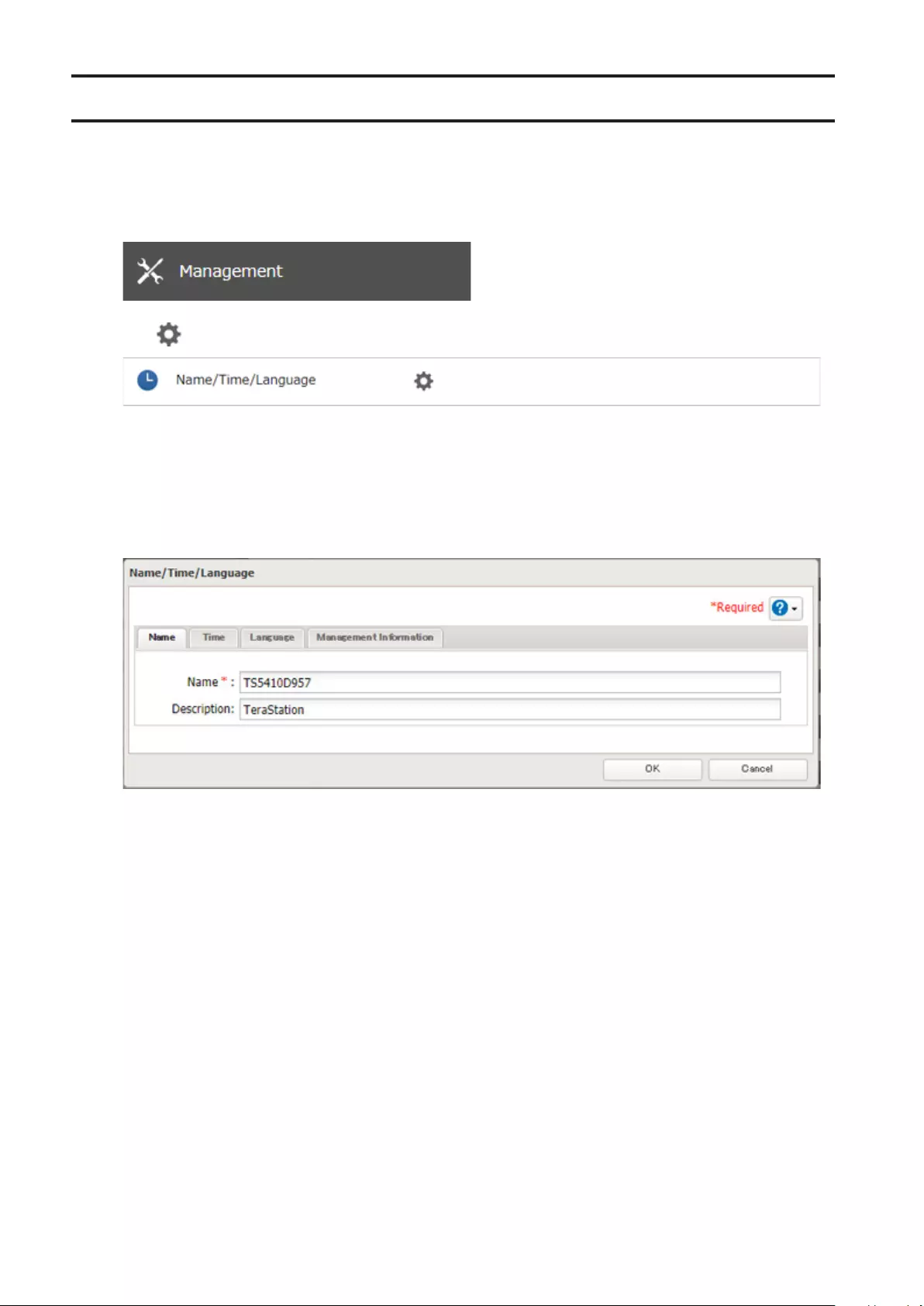
Name, Date, Time, and Language
Configure the TeraStation’s hostname, date, time, and language as shown below.
Note: If the TeraStation is being used as an iSCSI drive, to change the settings, navigate to Storage > iSCSI in Settings
and move the iSCSI switch to the off position temporarily before changing settings.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Name/Time/Language”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Click the Name tab, then configure the TeraStation’s name and description.
The name will be used for identifying your TeraStation on the network. When your TeraStation is detected,
the name will be used as the hostname. The hostname may contain up to 15 alphanumeric characters and
hyphens (-). The first and last characters should not be a hyphen.
182
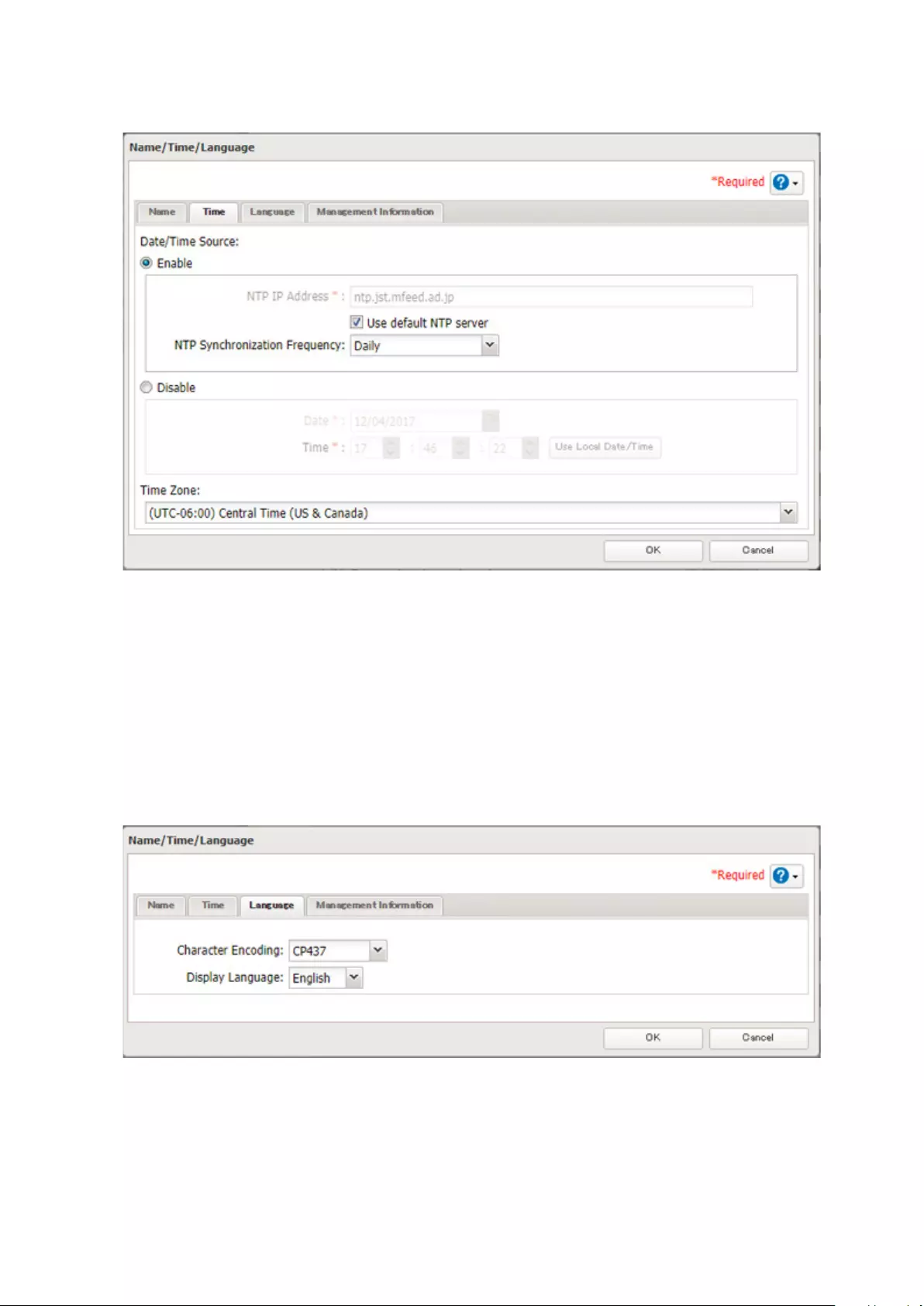
5 Click the Time tab. Enable the NTP server and select the “Use default NTP server” checkbox. If you disable the
NTP function, click Use Local Date/Time to use your computer’s time settings for the TeraStation.
By default, the TeraStation adjusts its clock automatically by using a default NTP server. This NTP server belongs
to Internet Multi Feed Inc. For more information, visit http://www.jst.mfeed.ad.jp.
To use a different NTP server, clear the “Use default NTP server” checkbox and enter a new NTP IP address or
its hostname, then click OK. If an NTP server is specified by name instead of IP address, make sure that a DNS
server is configured for the TeraStation.
Note: The internal clocks of the TeraStation and other devices on your network may run at slightly different
speeds. Over a long period of time, your network devices may show somewhat different times, which can
cause network problems. If clocks on your network vary by more than 5 minutes it may cause unexpected
behavior. For best results, keep all clocks on the network set to the same time by adjusting them regularly, or
use an NTP server to correct them all automatically.
6 Click the Language tab. Select the language to be used and click OK.
Note: This tab changes the language used by the TeraStation for email notifications and other functions. To
change the language displayed in Settings, go to Settings and click Language from the menu bar. Choose your
desired language from the drop-down list.
183
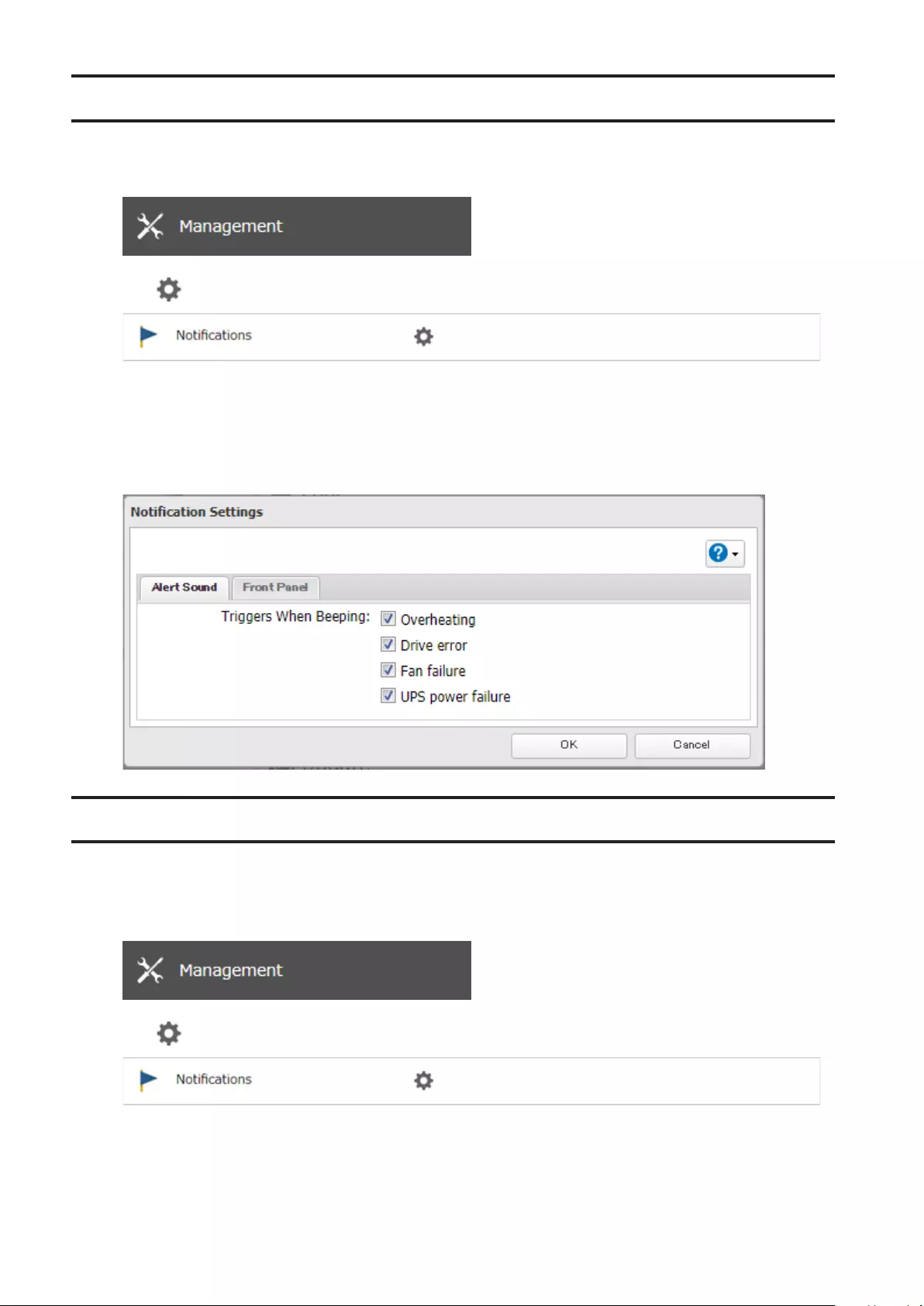
Beep Alerts
You can set the TeraStation to beep if certain errors occur.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Notifications”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Click the Alert Sound tab.
5 Select the triggers to make the alert beep, then click OK.
LCD and LEDs
You may configure options for the LCD panel and adjust the brightness of the LCD panel and LEDs on the
TeraStation.
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Notifications”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Click the Front Panel tab.
184
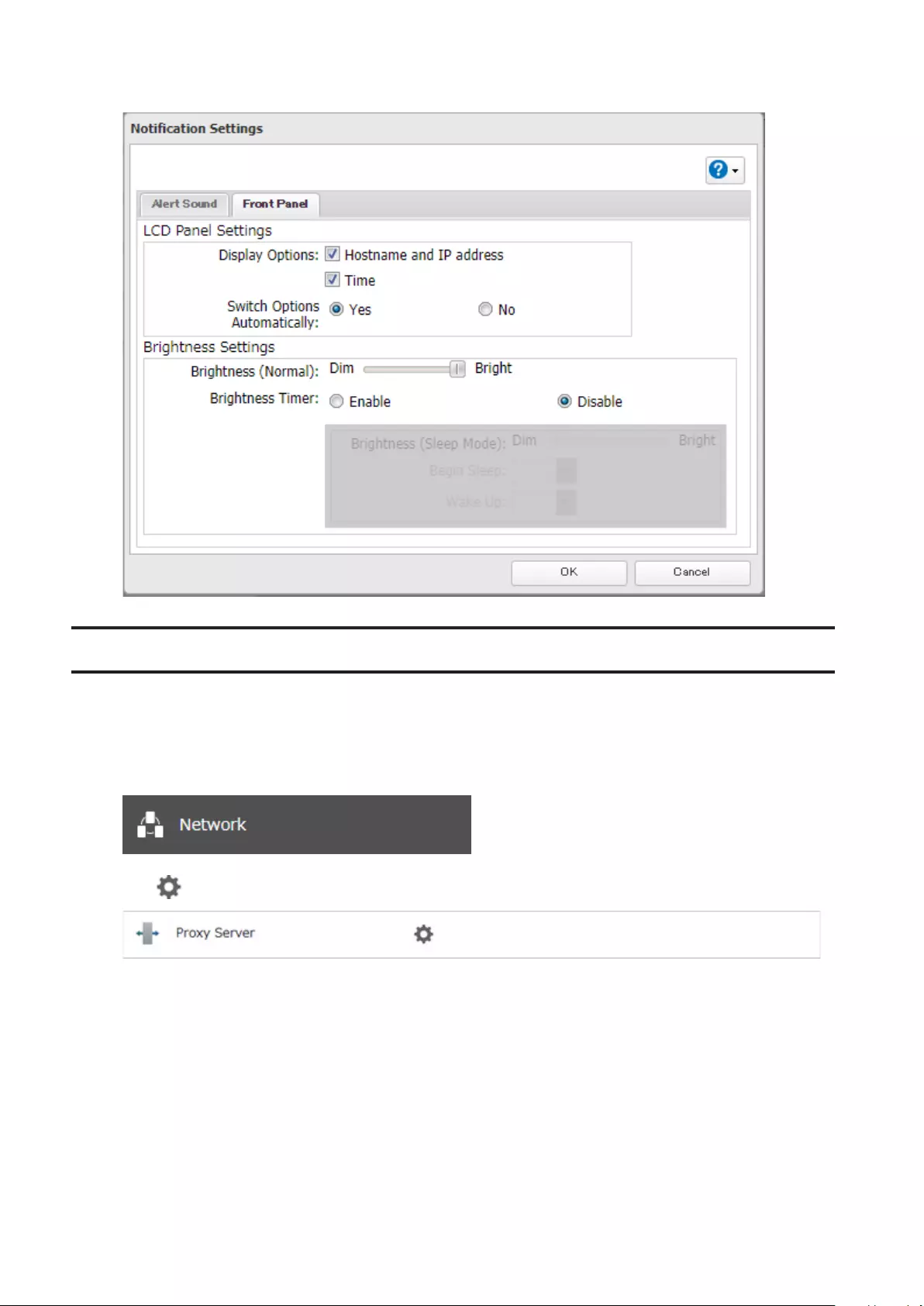
5 Configure your settings, then click OK.
Proxy Server
If you locate the TeraStation on the network that passes through a proxy server, configuring the proxy server
settings is recommended. Unless you configure the proxy settings, firmware updates in Settings will not work. To
configure the settings, follow the procedure below.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “Proxy Server”.
185
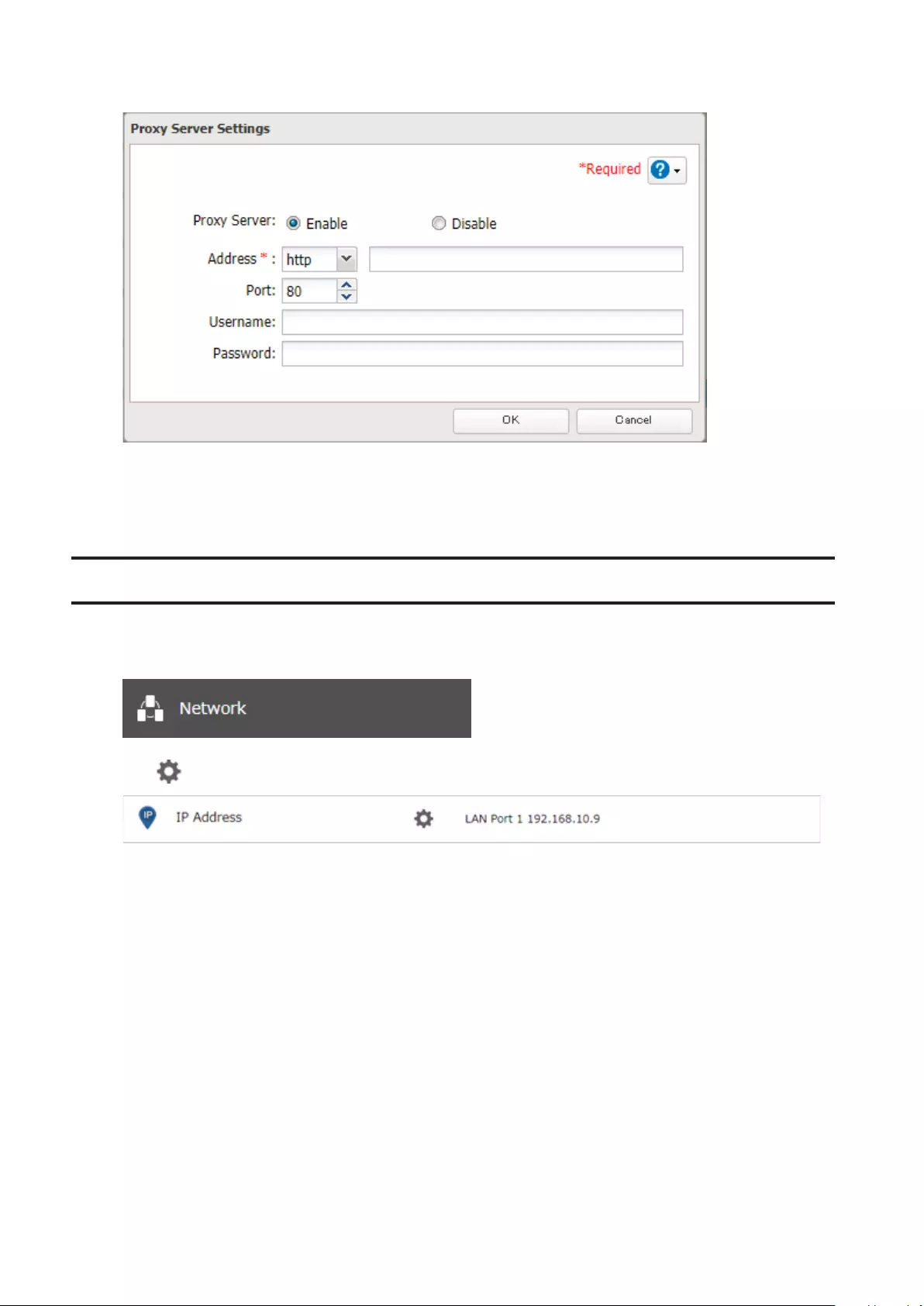
3 Enable “Proxy Server”.
4 Enter the proxy server IP address or hostname, port number, username and password, then click OK.
Once you configure the proxy server settings, you may use the settings for other web services such as cloud storage
or Dropbox Sync by selecting the “Configured settings” option on each settings page.
Jumbo Frames
If your other network devices support jumbo frames, you may be able to increase network performance.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “IP Address”.
186
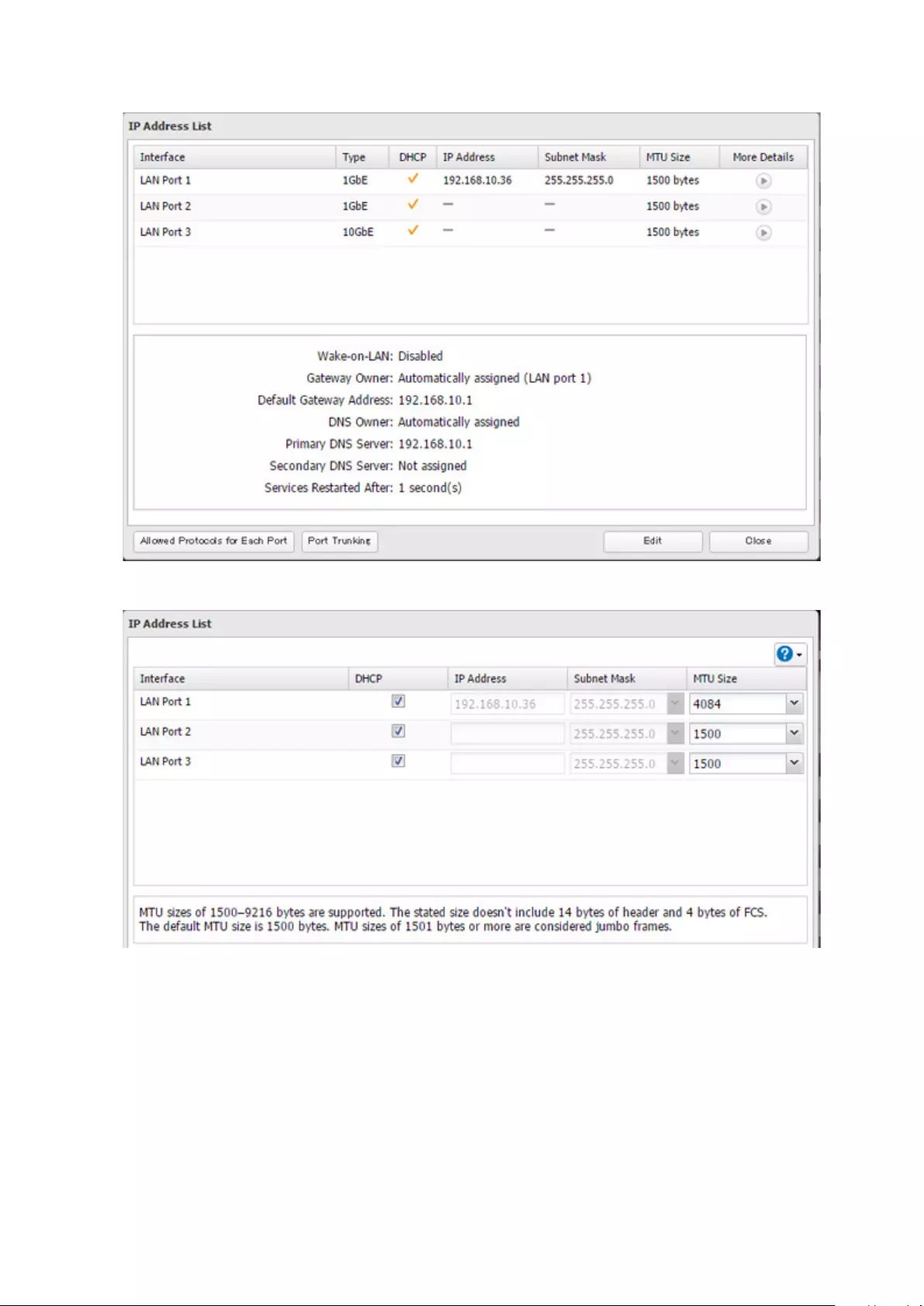
3 Click Edit.
4 Select or enter the desired MTU size and click OK.
187
Connection Transmission
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frame
Compatible Switch
Jumbo Frame
Compatible PC
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frame
Compatible Switch
Jumbo Frame
Incompatible PC
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frame
Incompatible Switch
Jumbo Frame
Incompatible PC
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frame
Incompatible Switch
Jumbo Frame
Compatible PC
Transfer data in
jumbo frames.
Transfer data not
using jumbo
frames.
Transfer data not
using jumbo
frames.
Any data cannot be
transferred.
Note: Make sure the TeraStation’s MTU size is smaller than the hub or router’s. Larger MTU sizes may not transfer the
data to the TeraStation correctly.
Changing the IP Address
Normally, the TeraStation’s IP address is set automatically from a DHCP server on your network. If you prefer, you can
set it manually. An easy way to do this is to change it on NAS Navigator2 running on a computer connected to the
same router (subnet) as the TeraStation. The procedure to change the IP address in Settings is below.
Note: If the TeraStation is being used as an iSCSI drive, to change the settings, navigate to Storage > iSCSI in Settings
and move the iSCSI switch to the off position temporarily before changing settings.
1 From Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of “IP Address”.
188
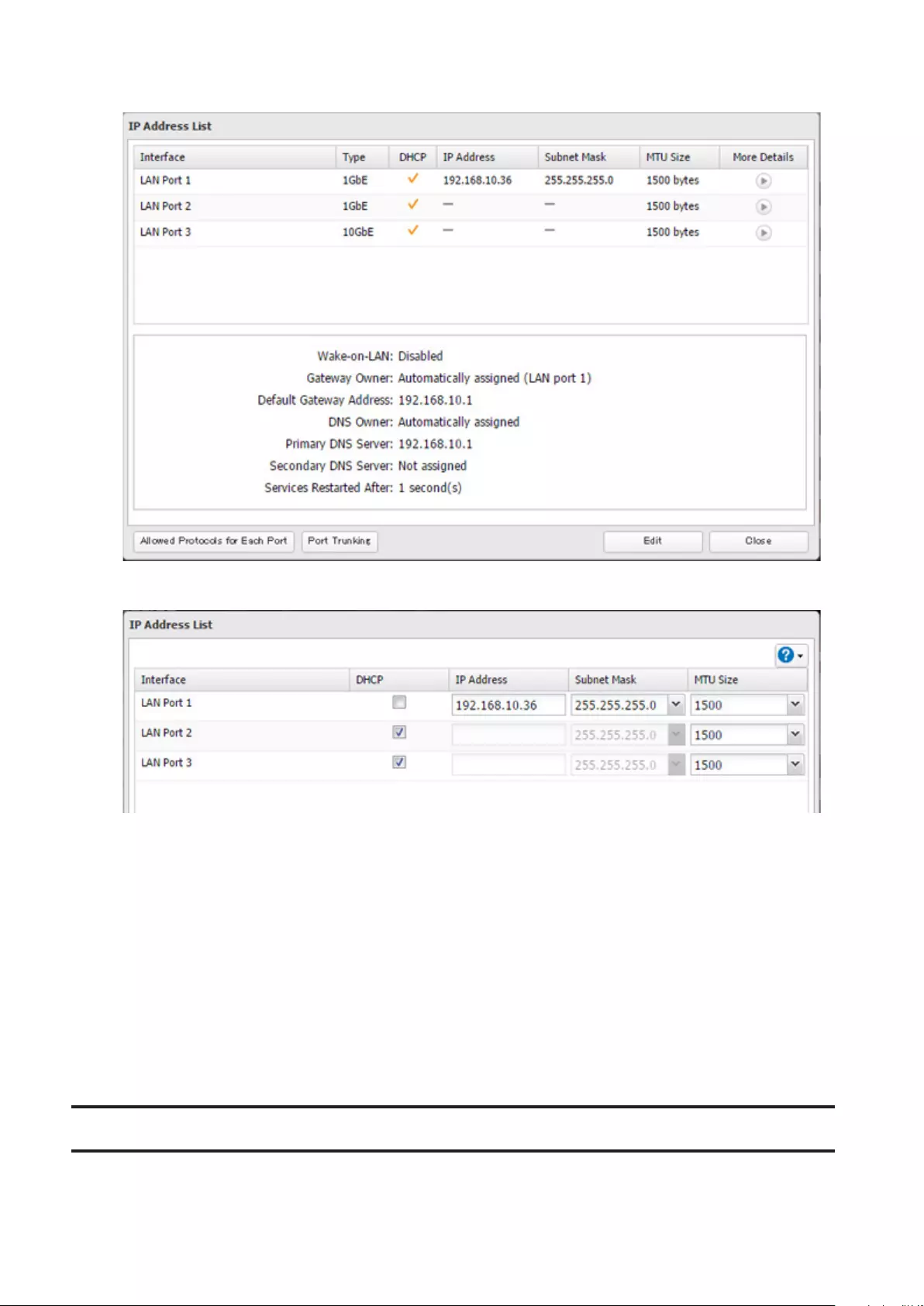
3 Click Edit.
4 Clear the “DHCP” checkbox and enter the desired IP address and its subnet mask.
5 Select “User (static)” for both “Gateway Owner” and “DNS Owner” options from the drop-down list, then enter
the desired default gateway address and DNS server addresses.
6 Click OK.
Notes:
• Only one default gateway and DNS address can be configured for all LAN ports. Different network addresses
cannot be assigned to the LAN ports.
• Do not set the IP address of the same segment for all LAN ports. This may cause unstable network
communication.
• Network services such as SMB or AFP will be restarted when the Ethernet cable is disconnected/reconnected or if
a network issue occurs. You can specify the time to delay the restart at the “Services Restarted After” option.
Boot Authentication
Boot authentication allows you to authenticate the TeraStation while it’s booting, and also to prevent the TeraStation
from being used in an unauthorized or unexpected manner, such as in cases of theft.
189
If authentication fails, the TeraStation will stay on, but all functions and services are stopped. Users will not be able
to log in to Settings to make changes or access any shares.
Notes Before Use
• To use boot authentication, a Windows PC is necessary to serve as the authentication server.
• When activating boot authentication, the drives on the TeraStation will be formatted and all data on the drives
will be erased. Back up any important data to another device. Even though the data is deleted, the RAID array
will be kept as is.
• Assigning the TeraStation a fixed IP address is recommended for boot authentication.
• When boot authentication settings finish, export the configuration file for backup. Refer to the “Exporting
Managed TeraStations to a File” section in the Boot Authentication Tool help for the procedure.
• Boot authentication cannot be enabled if any of the following functions are enabled: drive encryption, LVM,
iSCSI, and failover. Conversely, these functions cannot be enabled while boot authentication is enabled.
Important Notice
This feature was developed with the intention of preventing critical data leakage by rendering the TeraStation
unusable in cases of misoperation or missing important setting files. Before configuring boot authentication, back
up the data on the TeraStation by referring to the “Backup” section in chapter 5 and create a settings initialization
drive by referring to the “Creating an Initialization Drive” subsection above. With these preparations, a TeraStation
that is unusable may be initialized and reverted to a usable state.
If any of the situations below occur, the TeraStation will stop booting and become inaccessible.
• The TeraStation is unable to communicate with the authentication server due to the server crashing or it being
on another network.
• The TeraStation unit has been deleted from Boot Authentication Tool or the Boot Authentication Tool database
has been erased.
• Security level is configured to “High” and the wrong passcode is entered 3 times.
Setting Up the Authentication Server on a Windows PC
To set up the authentication server, follow the procedure below. The authentication server must be placed on the
local network or VPN.
Note: For proper operation, make sure that the TeraStation and the authentication server are on a network with only
one router. If there are two or more routers on the network, the authentication server may not acquire the correct
TeraStation status. For example, if the TeraStation’s IP address has been changed, its status does not change to
“Warning”.
190
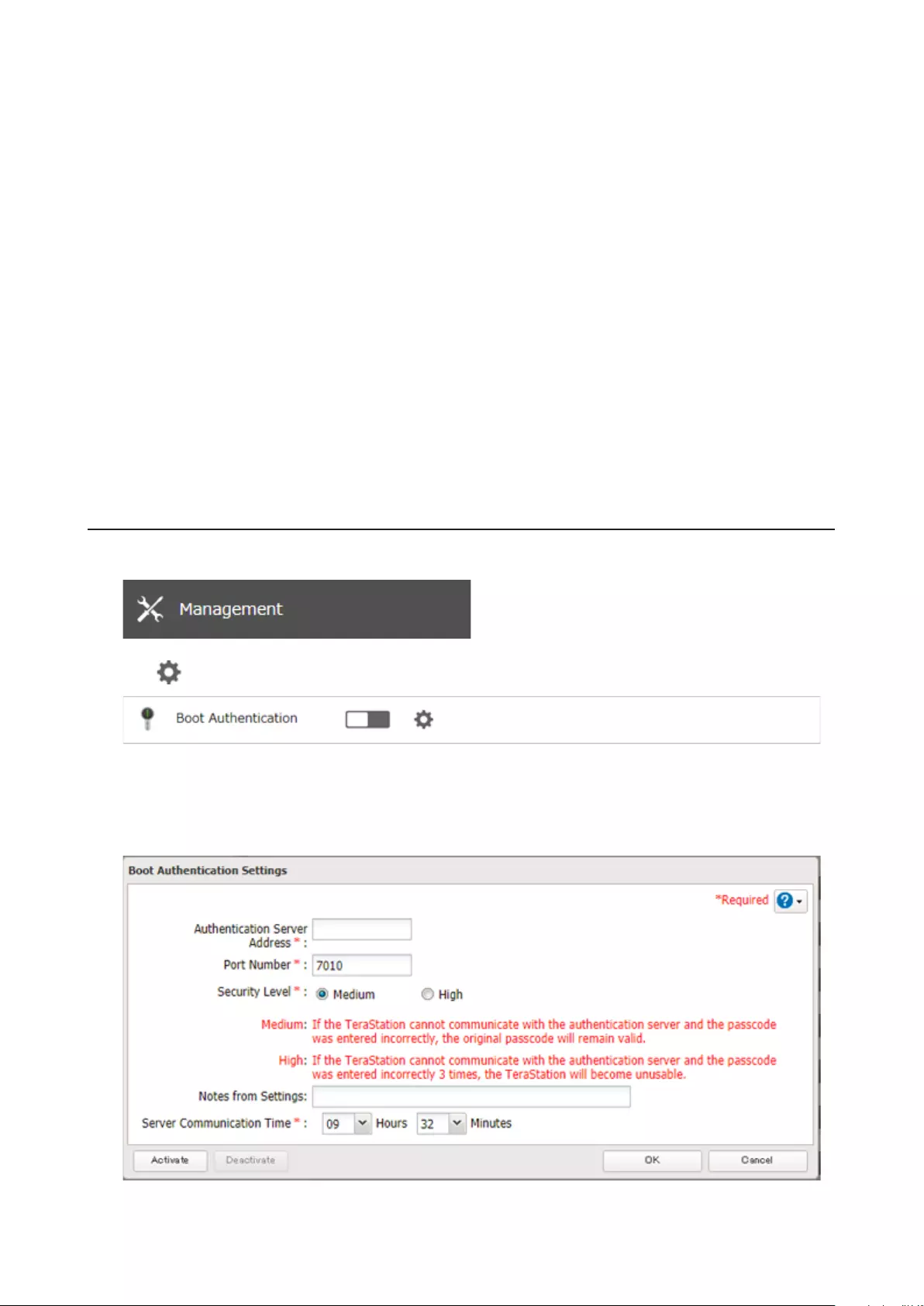
1 Download the application for the authentication server, “Boot Authentication Tool”, from the Buffalo website
and install it onto the Windows PC.
2 Register the specific port number that is used on the application as a firewall exception rule. Navigate to
Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Firewall on the authentication server.
3 Click Advanced settings.
4 Right-click Inbound Rules and click New Rule.
5 Select “Port” and click Next.
6 Select “TCP”, enter the port number that is used on the application to the right of “Specific local ports”, and click
Next. The default port number on the application is “7010”. The port number can be confirmed on the Options
tab of the application.
7 Click Next, then click Next again.
8 Enter a desired name for the setting and click Finish to complete.
Configuring Boot Authentication on the TeraStation
1 From Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of “Boot Authentication”.
3 Click Edit.
4 Enter the authentication server’s IP address or hostname and port number, specify the security level and
communication time settings, then click Activate.
191
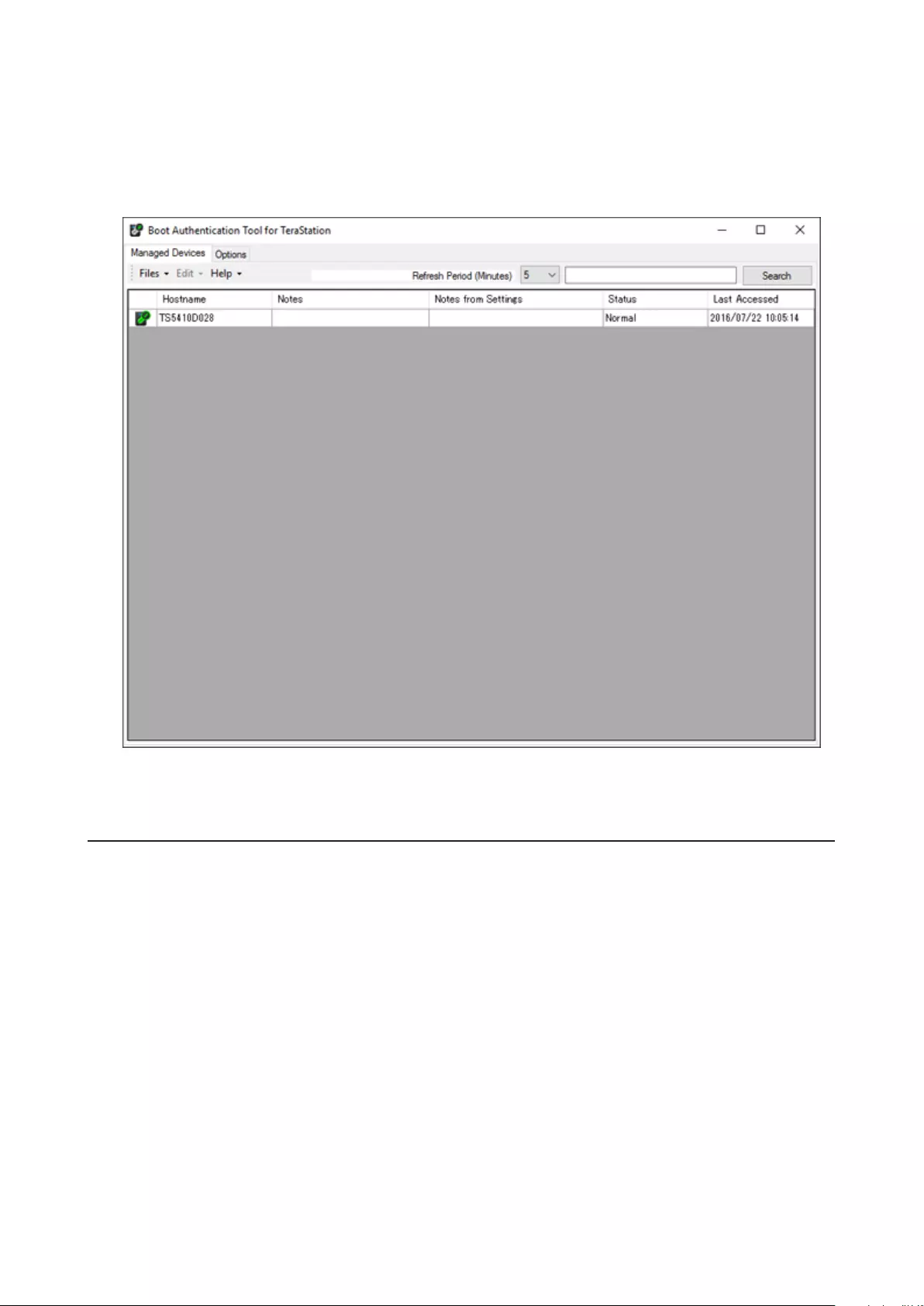
5 The drive formatting process will start. Click Yes.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 The format will begin. Wait until it finishes. When formatting finishes and the TeraStation is added to Boot
Authentication Tool, boot authentication setting is complete.
Note: To activate, deactivate, or change the boot authentication settings, the TeraStation must be communicating
with the authentication server.
If the TeraStation Cannot Be Accessed
If the TeraStation cannot communicate with the authentication server or vice versa, such as in a case of network
failure, the TeraStation will not be accessible. If the TeraStation is not accessible, manually authenticate the
TeraStation by following the procedure below.
Note: The procedure defines an “authentication server administrator” as someone who manages the authentication
server using Boot Authentication Tool, and a “user” as one attempting to access the TeraStation from a remote
location.
192
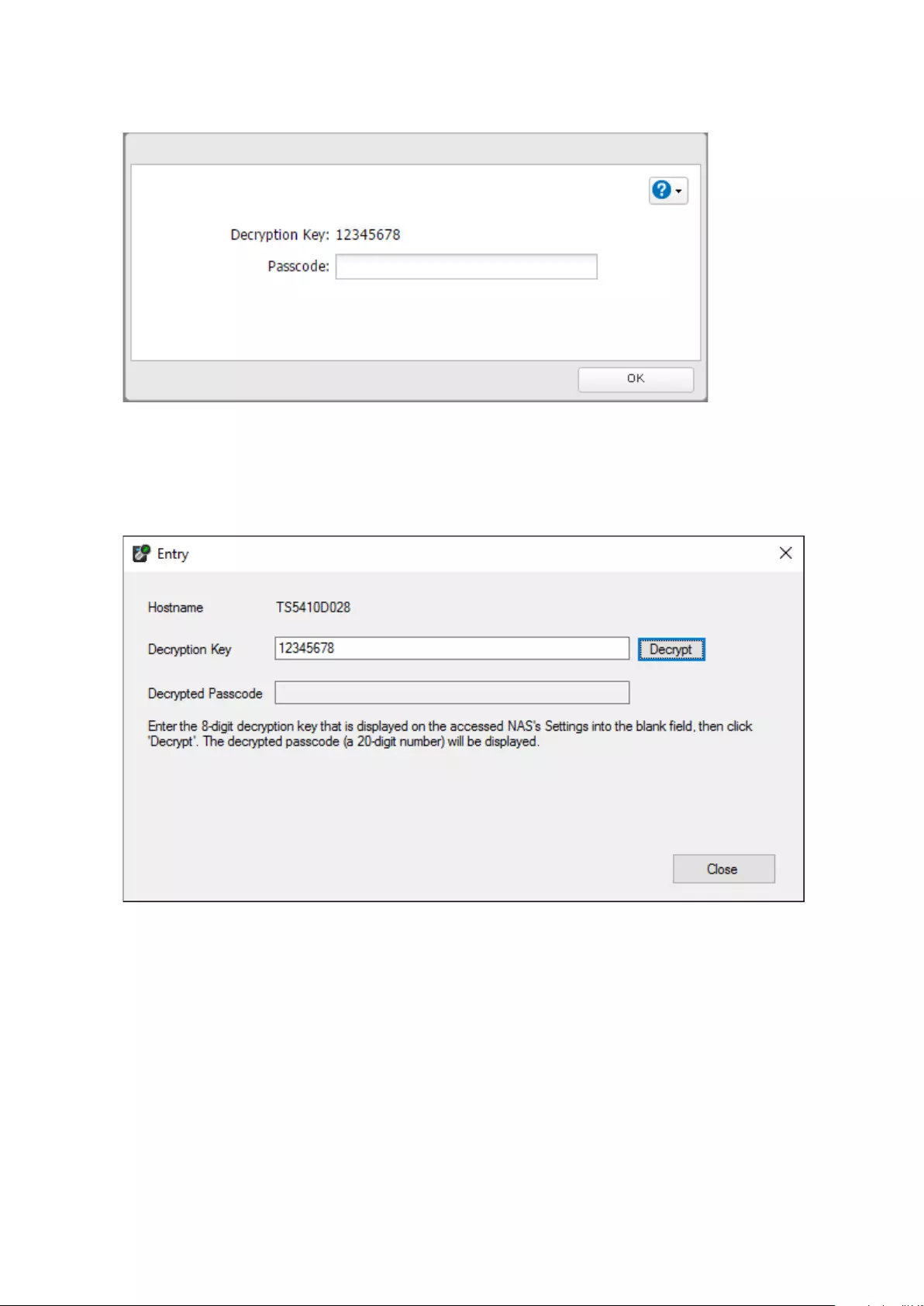
1 When the user tries to access the TeraStation’s Settings and the TeraStation is not available, the screen below
will be displayed. Have the user forward the decryption key to the authentication server administrator.
2 Open Boot Authentication Tool on the authentication server.
3 From Boot Authentication Tool, right-click the target TeraStation from the list and click Decrypt Passcode.
4 Enter the decryption key received from the user and click Decrypt.
193
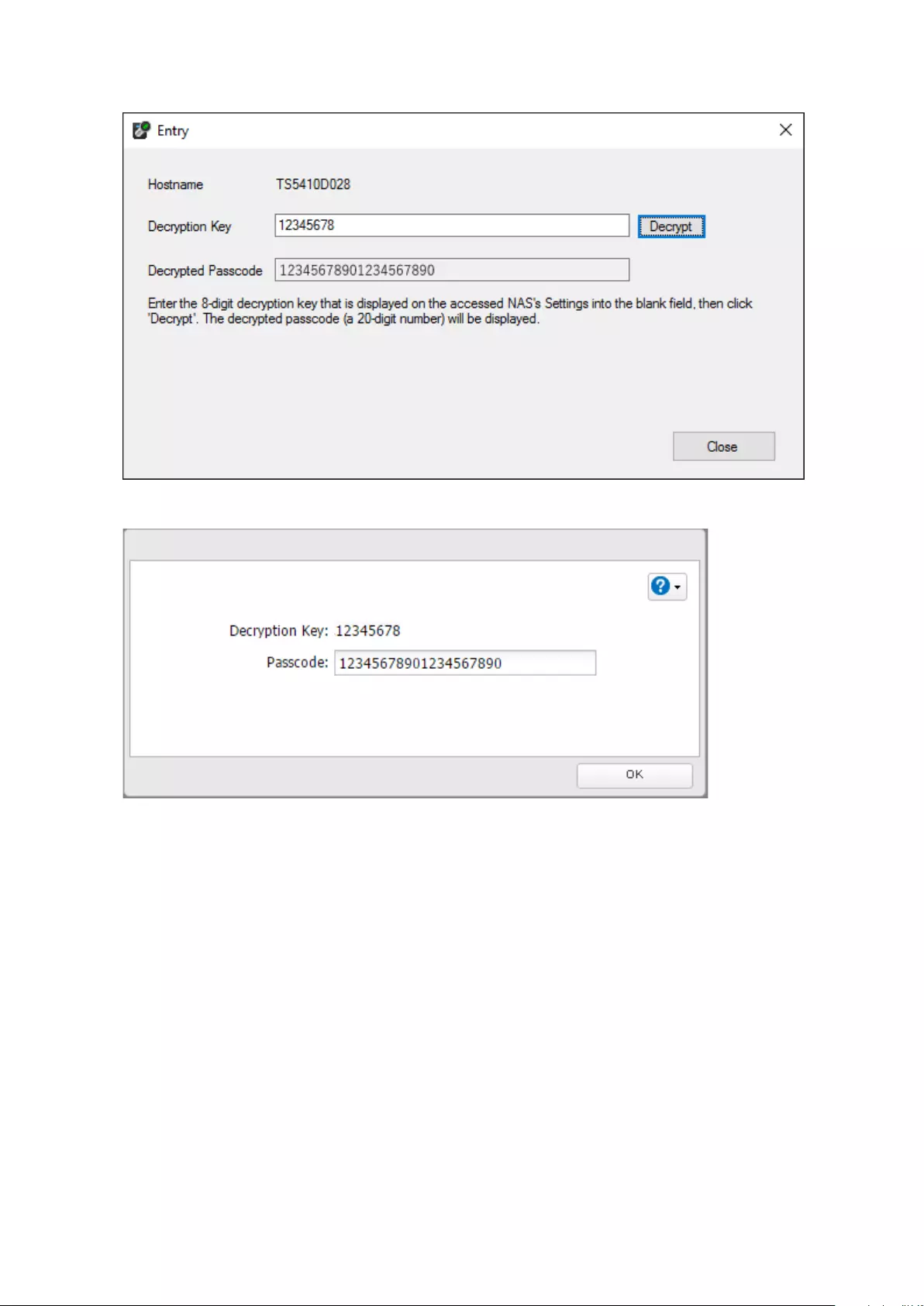
5 The decrypted 20-digit passcode will be displayed. Send the passcode to the user.
6 The user can then enter the 20-digit passcode into Settings and click OK.
If the passcode is authenticated, the TeraStation will become available. The user can click OK to log in to Settings.
194
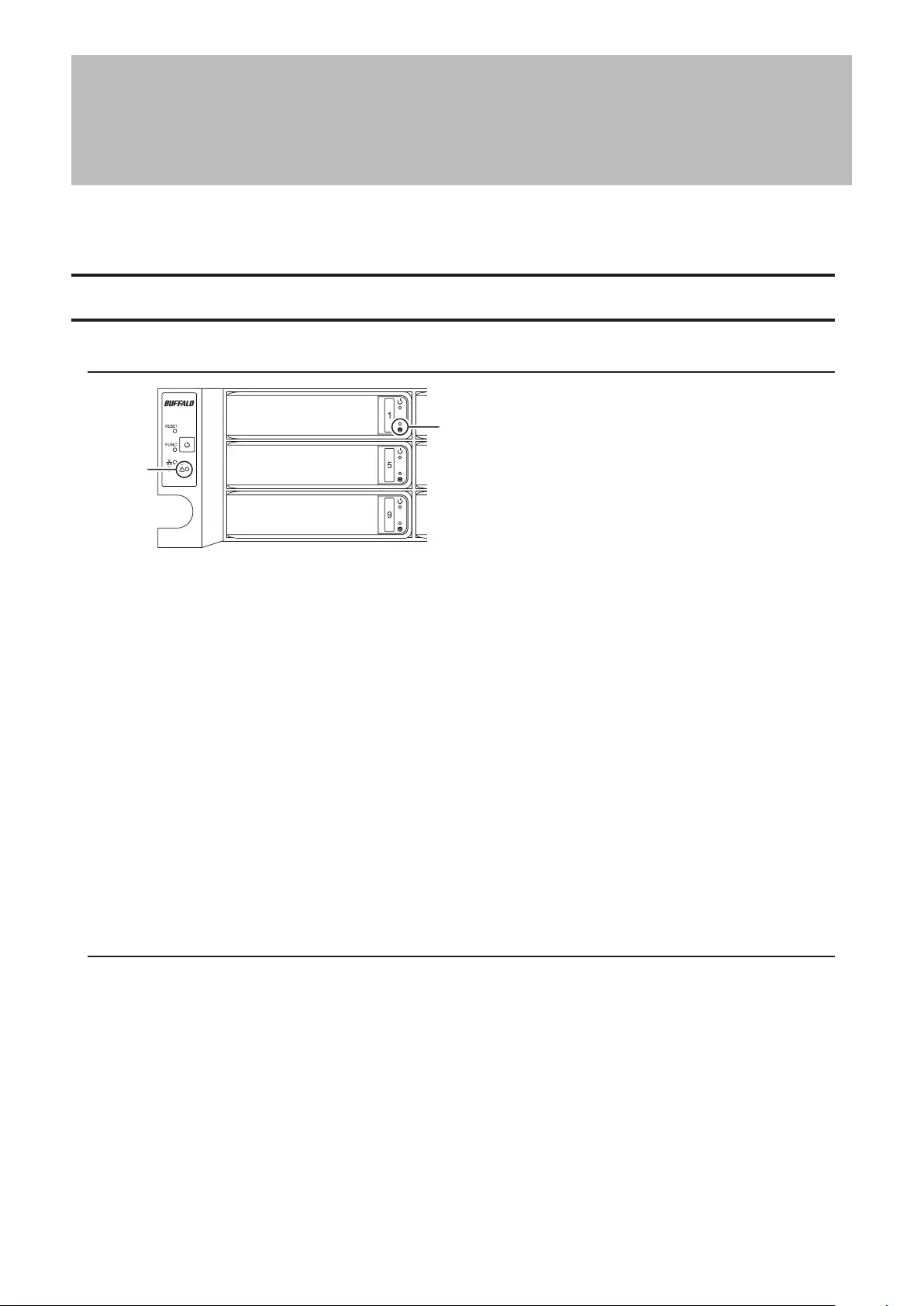
Chapter 8 Drive Replacement
Drive replacement procedures will vary depending on your TeraStation models. Refer to the replacement procedure
in the following sections corresponding to your model.
Replacing Drives on the TS51210RH Series
LEDs
1
2
1 Error LED
Glows red if a drive has failed.
2 Drive Error LED
The failed drive’s error LED will be blinking but still mounted. It will turn to be a glowing red when dismounted.
Notes:
• For the replacement drive, use a Buffalo OP-HDH2U series drive. The new drive should be the same size or larger.
If a larger drive is used, the extra space will not be usable in a RAID array.
• To avoid damaging the TeraStation with static electricity, ground yourself by touching something made of metal
before handling any sensitive electronic parts.
• After a drive is replaced, it will take about 30 minutes before normal file reading and writing are restored. Settings
may not be accessible during this period.
• Do not change the order of the drives in the TeraStation. For example, pulling out drive 1 and replacing it with
drive 2 may cause data to be corrupted or lost.
• If the LEDs do not change after a new drive is installed, click Rediscover Drive in Settings.
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is On
1 Back up the saved data to another place before replacing the failed drive. If one or more drives fail during the
drive replacement, data can no longer be retrieved from the TeraStation.
195
2 The failed drive’s error LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
Drives without red error LEDs blinking are still on. Do not unplug or remove them.
3 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
4 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
5 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
6 When the replaced drive is recognized, the error LED will flash.
7 For a redundant RAID mode:
The replaced drive will be rebuilt into the RAID array automatically when auto RAID rebuild is enabled. If not,
rebuild the RAID array manually from “Storage” > “RAID”.
For JBOD:
From Storage > Drives, click Format Drive to format the new drive. Enter the confirmation number, then click
OK. Create a shared folder before use.
196
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is Off
1 Push the failed drive’s unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out. Refer to the notification email sent by
email notifications to determine which drive has failed.
2 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
3 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
4 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
5 Press the power button on the TeraStation.
6 When the replaced drive is recognized, the error LED will flash.
7 For a redundant RAID mode:
The replaced drive will be rebuilt into the RAID array automatically when auto RAID rebuild is enabled. If not,
rebuild the RAID array manually from “Storage” > “RAID”.
For JBOD:
From Storage > Drives, click Format Drive to format the new drive. Enter the confirmation number, then click
OK. Create a shared folder before use.
Using RAID 0
Drives in a RAID 0 array do not automatically turn off in the event of a malfunction. Shut down the TeraStation
before replacing the failed drive.
This section describes the process of replacing a drive with the TeraStation on.
Note: If a drive malfunctions in RAID 0, all data on the RAID array will be lost. All of the settings for the shared folders
(such as access restrictions) are erased after replacing a drive from a RAID 0 array.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
3 Select the drive with the flashing error LED and click Dismount Drive.
4 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 The error LED will stop flashing and glow steadily.
6 Push the failed drive’s unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
7 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
8 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
9 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
10 When the replaced drive is recognized, the error LED will flash.
11 From Settings, click Storage.
12 Click to the right of “RAID”.
197

13 Select the RAID array for which the failed drive was being used and click Delete RAID Array.
14 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
15 From Storage > Drives, click Format Drive to format the new drive.
16 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
17 From Storage > RAID, choose “RAID 0” from the RAID mode drop-down lost and click Create RAID Array.
18 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
19 When creating a new RAID 0 array is completed, create a shared folder.
Using a Hot Spare
If your TeraStation’s drives are in a redundant RAID mode and you have a hot spare enabled, a malfunctioning drive
in the array is replaced by the spare drive and the RAID array is rebuilt automatically. The error LED will continue to
glow red for the failed drive even after the RAID array is rebuilt with the hot spare. After you replace the failed drive
with a new drive, follow the procedure below to configure a spare drive as a new drive.
1 The failed drive’s error LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
2 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
3 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
4 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
5 When the replaced drive is recognized, the error LED will flash.
6 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep.
7 The replacement drive is automatically registered as a hot spare.
To use the replacement drive as a normal drive rather than a hot spare, navigate to Storage > RAID and click the
RAID array, select the new drive, and click Set as a normal drive.
Note: If a drive fails in the RAID array before it is rebooted, the hot spare will not automatically replace the failed
drive. In this case, follow the procedure below to repair the array.
(1) From Settings, navigate to Storage > Drives.
(2) Click the drive that was configured as a hot spare, then click Dismount Drive.
(3) Click Rediscover Drive.
(4) Navigate to Storage > RAID.
(5) Choose the RAID array to repair.
(6) Click the drive that was previously configured as a hot spare, then click Recover RAID Array.
This will rebuild the RAID array.
198
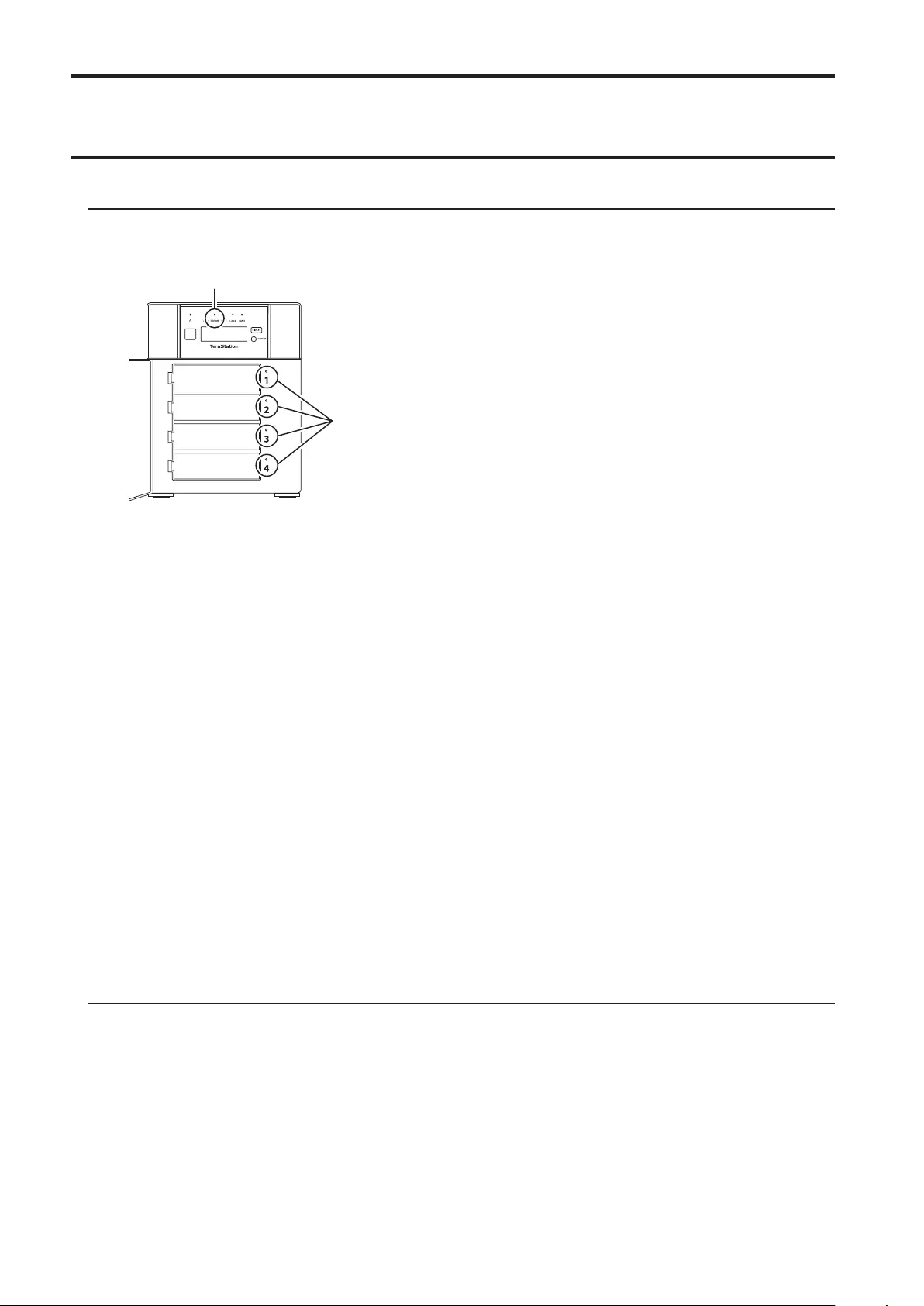
Replacing Drives on Another Unit Series Other Than the
TS51210RH Series
LEDs
Drives in the TeraStation show a green status LED during normal operation. If a drive fails, its error LED will glow red.
The following drive replacement examples use the case of the TS5410DN series.
1
2
1 Error LED
Glows red if a drive has failed.
2 Status LEDs
The failed drive’s status LED will be glowing a steady red. A drive with a red status LED is ready to hot-swap.
Notes:
• Do not unplug a drive whose status LED is green instead of red. Dismount it first or shut down the TeraStation
before swapping a working drive. If you remove the drive without properly dismounting it, data may be lost or
the TeraStation may malfunction.
• If using the TS5210DF series TeraStations, use a Buffalo OP-SSD series drive as the replacement drive. For the
replacement drive of other series TeraStations, use a Buffalo OP-HDN series drive. The new drive should be the
same size or larger. If a larger drive is used, the extra space will not be usable in a RAID array.
• To avoid damaging the TeraStation with static electricity, ground yourself by touching something made of metal
before handling any sensitive electronic parts.
• After a drive is replaced, it will take about 30 minutes before normal file reading and writing are restored. Settings
may not be accessible during this period.
• Do not change the order of the drives in the TeraStation. For example, pulling out drive 1 and replacing it with
drive 2 may cause data to be corrupted or lost.
• If the LCD panel does not change after a new drive is installed, click Rediscover Drive in Settings.
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is On
1 Back up the saved data to another place before replacing the failed drive. If one or more drives fail during the
drive replacement, data can no longer be retrieved from the TeraStation.
199
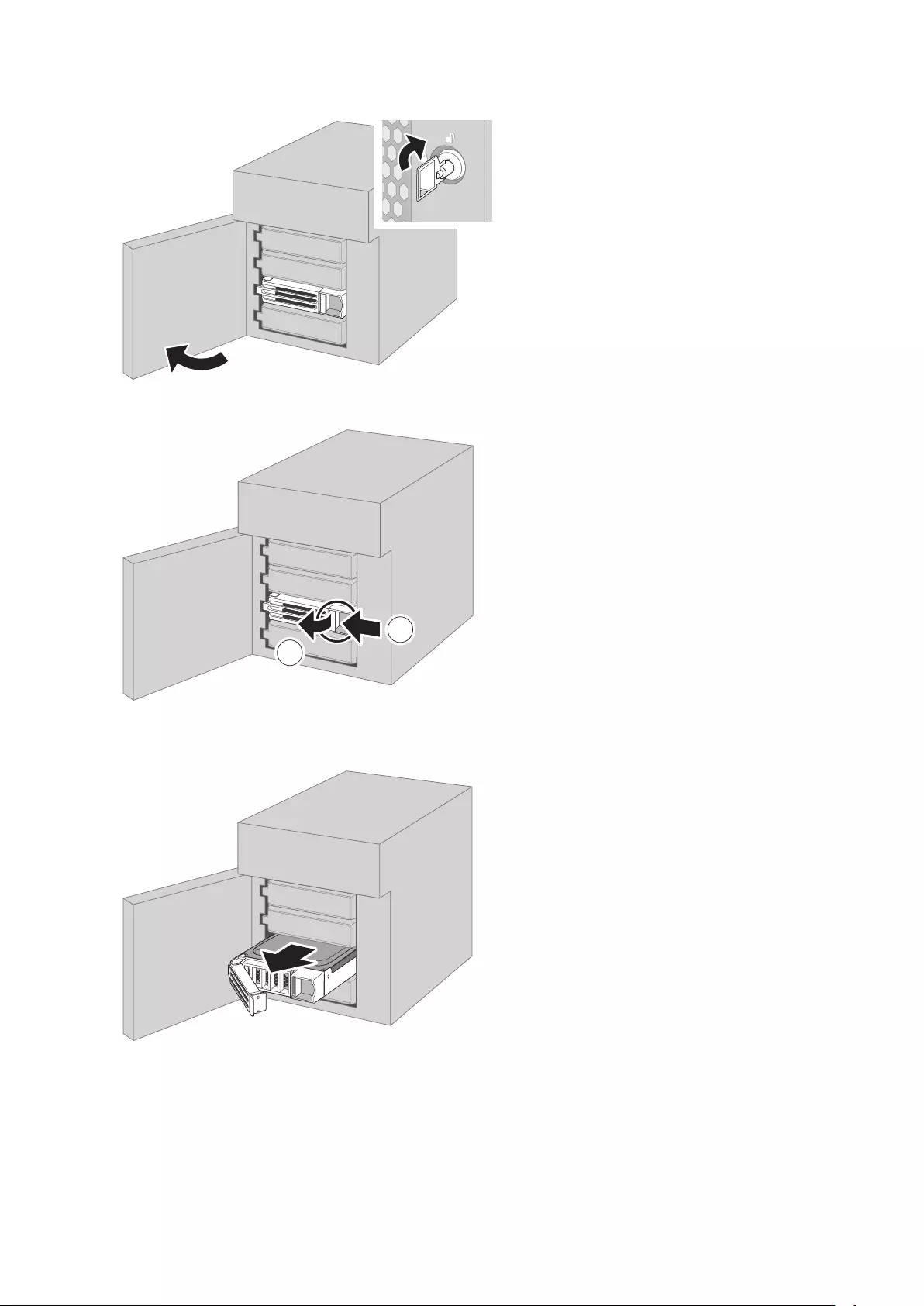
2 Open the front cover with the included key.
3 The failed drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
1
2
Drives without red status LEDs lit are still on. Do not unplug or remove them.
4 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
200
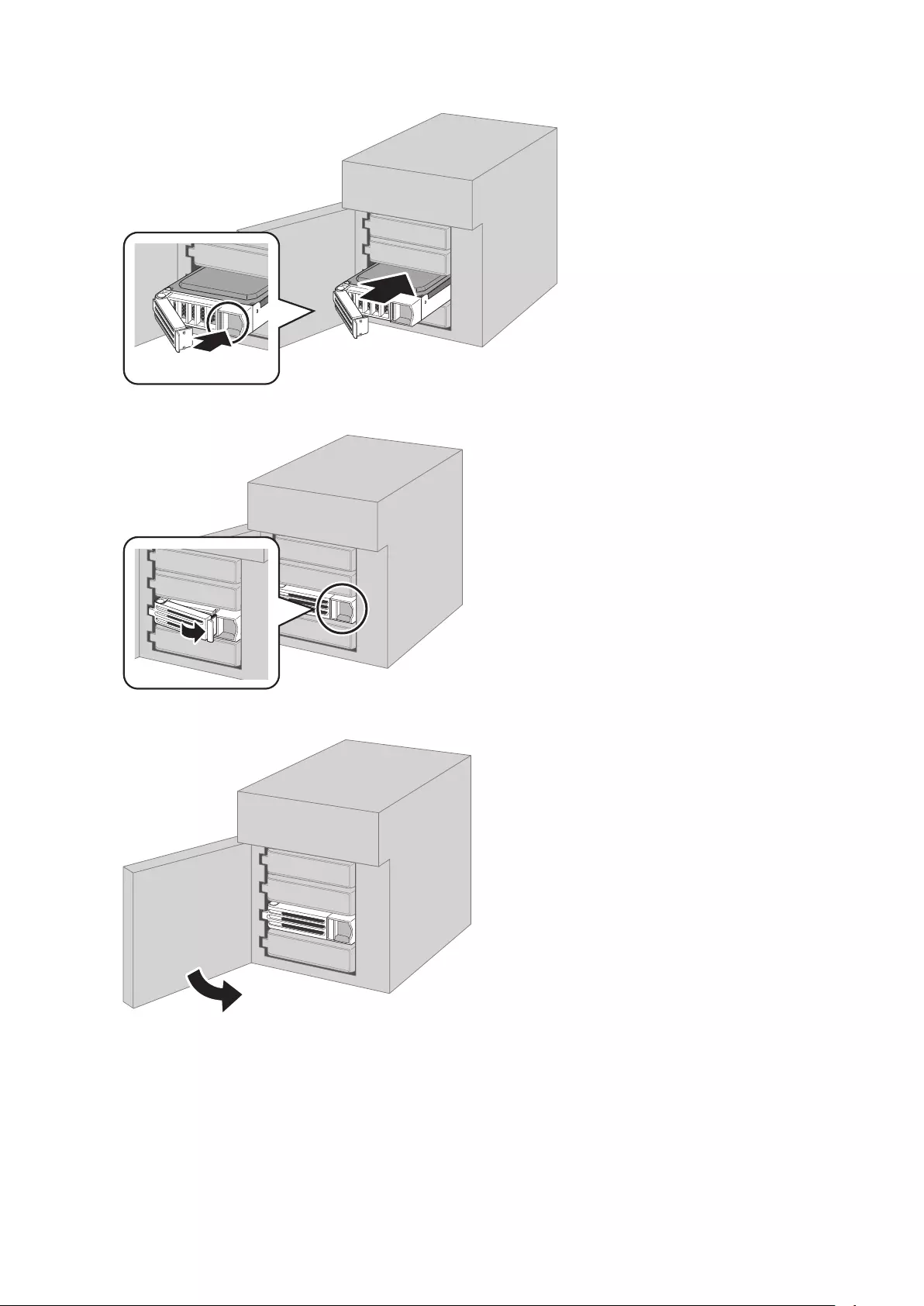
5 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
6 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
7 Close the front cover.
8 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I31 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
9 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep. If replacing multiple
malfunctioning drives at once, select the replaced drives on Settings and click Recover RAID Array.
10 For a redundant RAID mode:
201

The TeraStation will start rebuilding the RAID array automatically. After a few minutes, the I18 message will be
displayed until the array is rebuilt.
For JBOD:
The drive will be formatted as an individual drive. Create a shared folder on the drive before use.
Using a Redundant RAID Mode and TeraStation Is Off
1 Open the front cover with the included key.
2 The failed drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
3 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
4 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
5 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
6 Close the front cover.
7 Press the power button on the TeraStation.
8 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I31 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
9 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep. If replacing multiple
malfunctioning drives at once, select the replaced drives on Settings and click Recover RAID Array.
10 The TeraStation will start rebuilding the RAID array automatically. It will take about 5 minutes before the I18
message is displayed.
Using RAID 0
Drives in a RAID 0 array do not automatically turn off in the event of a malfunction. Shut down the TeraStation
before replacing the failed drive.
This section describes the process of replacing a drive with the TeraStation off.
Note: If a drive malfunctions in RAID 0, all data on the RAID array will be lost. All of the settings for the shared folders
(such as access restrictions) are erased after replacing a drive from a RAID 0 array.
1 Turn off the TeraStation.
2 Open the front cover with the included key.
3 The failed drive’s status LED will be blinking red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
4 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
5 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
6 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
7 Close the front cover.
8 Press the power button on the TeraStation.
202

9 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I32 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
10 From Settings, click Storage.
11 Click to the right of “RAID”.
12 Select the RAID array for which the failed drive was being used and click Delete RAID Array.
13 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
14 From Storage > Drives, click Format Drive to format the new drive.
15 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
16 From Storage > RAID, choose “RAID 0” from the RAID mode drop-down list and click Create RAID Array.
17 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
18 When creating a new RAID 0 array is completed, create a shared folder before use.
Using a Hot Spare
If your TeraStation’s drives are in a redundant RAID mode and you have a hot spare enabled, a malfunctioning drive
in the array is replaced by the spare drive and the RAID array is rebuilt automatically. The status LED will continue to
glow red for the failed drive even after the RAID array is rebuilt with the hot spare. After you replace the failed drive
with a new drive, follow the procedure below to configure a spare drive as a new drive.
1 Open the front cover with the included key.
2 The failed drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism out.
3 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
4 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
5 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
6 Close the front cover.
7 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I31 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
8 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep. The replaced drive is
automatically registered as a hot spare.
To use the replaced drive as a normal drive rather than a hot spare, navigate to Storage > RAID and click the
RAID array, select the new drive, and click Set as a normal drive.
Note: If a drive fails in the RAID array before it is rebooted, the hot spare will not automatically replace the failed
drive. In this case, follow the procedure below to repair the array.
(1) From Settings, navigate to Storage > Drives.
(2) Click the drive that was configured as a hot spare, then click Dismount Drive.
(3) Click Rediscover Drive.
203

(4) Navigate to Storage > RAID.
(5) Choose the RAID array to repair.
(6) Click the drive that was previously configured as a hot spare, then click Recover RAID Array.
This will rebuild the RAID array.
Replacing SSDs on the TS5210DF Series When Data
Protection Mode Is Enabled
When data protection mode is enabled, a warning message to notify you that too many bad blocks have been
detected on the drive after logging in to Settings. In such a case, back up data on the drive and replace it. When a
drive with bad blocks is replaced in a RAID 0 or JBOD array, all data on the array will be lost. The procedure
may vary depending on what RAID mode you have configured. Do not perform the following procedure unless the
bad blocks warning message appears and data protection mode is enabled. If another drive error message such as
the E30 message appears, follow the replacement procedure described at the “Replacing Drives on Another Unit
Series Other Than the TS51210RH Series” section above.
Using RAID 1
When too many bad blocks occur on both drives in the RAID array, the TeraStation will be in data protection mode. If
both drives need replacement, replace them one by one.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
3 Select a drive and click S.M.A.R.T. to check whether the current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less.
4 Click Close.
5 Select a drive whose current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less and click Dismount Drive.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 When the dismount process is complete, the TeraStation will beep and the I12 and E30 messages appear. Press
the display button to stop the TeraStation beeping.
8 Open the front panel with the included key.
9 The dismounted drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism
out.
10 Pull out the drive cartridge and remove it from the TeraStation.
11 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
12 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
13 Close the front cover.
14 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I32 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
204

15 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep and start rebuilding the
RAID array automatically. After a few minutes, the I18 message will be displayed until the array is rebuilt.
16 After the rebuilding process is complete, repeat the steps 5–14 for another drive with bad blocks.
Using RAID 0
When too many bad blocks occur on one drive in the RAID array, the TeraStation will be in data protection mode.
Make sure all data has been backed up before replacing. If both drives need replacement, replace them one by one.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
3 Select a drive and click S.M.A.R.T. to check whether the current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less.
4 Click Close.
5 Select a drive whose current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less and click Dismount Drive.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 When the dismount process is complete, the TeraStation will beep and the I14 and E30 messages appear. Press
the display button to stop the TeraStation beeping.
8 Open the front panel with the included key.
9 The dismounted drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism
out.
10 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
11 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
12 Close the front cover.
13 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I32 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
14 From Settings, click Storage.
15 Click to the right of “RAID”.
16 Select the RAID array for which the failed drive was being used and click Delete RAID Array.
17 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
18 From Storage > Drives, click Format Drive to format the new drive.
19 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
20 From Storage > RAID, choose “RAID 0” from the RAID mode drop-down list and click Create RAID Array.
205
21 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
22 When creating a new RAID 0 array is completed, create a shared folder before use.
Using JBOD
When too many bad blocks occur on a drive, the TeraStation will be in data protection mode. Make sure all data has
been backed up before replacing. If both drives need replacement, replace them one by one.
1 From Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of “Drives”.
3 Select a drive and click S.M.A.R.T. to check whether the current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less.
4 Click Close.
5 Select a drive whose current value of “Reallocated_Sector_Ct” is 99 or less and click Dismount Drive.
6 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Open the front panel with the included key.
8 The dismounted drive’s status LED will be glowing red. Push its unlock button and swing the lock mechanism
out.
9 Insert the new drive into the empty slot. Slide the drive in with the locking mechanism open.
10 Swing the lock back down until it clicks into place.
11 Close the front cover.
12 When the replaced drive is recognized, the status LED will flash red and the I32 message will appear on the
LCD panel.
13 Press the function button on the front of the TeraStation. The TeraStation will beep and start formatting the
drive.
14 After the drive is formatted as an individual drive, create a shared folder before use.
Replacing a Non-Malfunctioning Drive
Do not replace a drive that is not malfunctioning.
If you must change a drive that is not malfunctioning, either first dismount it in Settings, referring to the
“Dismounting Drives” section in chapter 4, or shut down the TeraStation before replacing the drive. If you need
to replace more than one drive at the same time, replace the drives one at a time to preserve your data. When
replacing the non-malfunctioning drive, the RAID array will function as below:
Operating in RAID 0 Mode
All data on the RAID array will be deleted after replacing the drive. You will not be able to use the TeraStation until
you delete and rebuild the RAID array with the new drive.
206

Operating in JBOD
All data on that drive will be deleted after replacing the drive. You will not be able to use the TeraStation until you
format the new drive.
Operating in a Redundant RAID Mode
If you are using a redundant RAID mode such as RAID 1, 5, or 6, the RAID array will be in degraded mode after
replacing the drive. You will not be able to use the TeraStation until you rebuild the RAID array with the new drive.
207
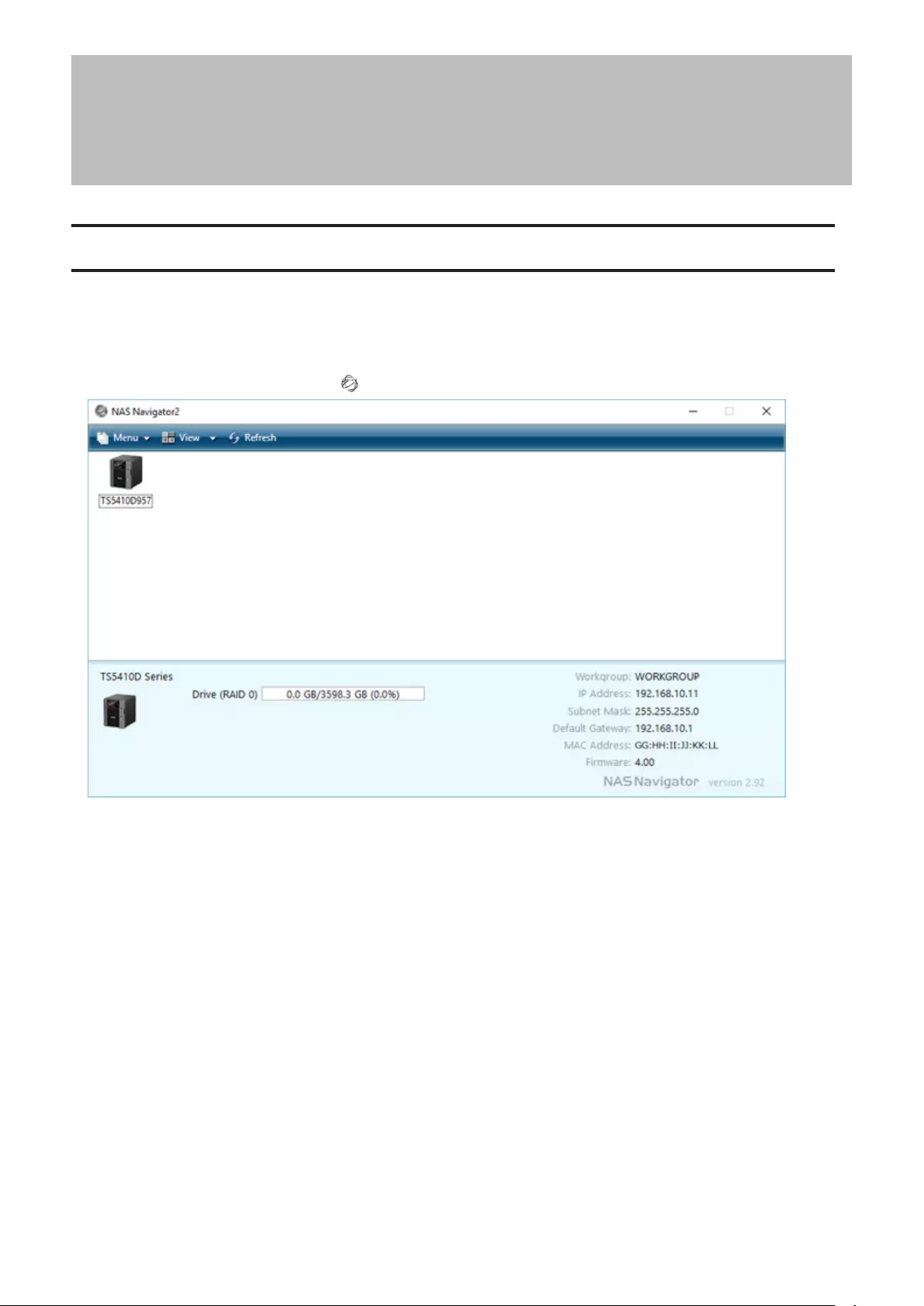
Chapter 9 Utilities
NAS Navigator2 for Windows
NAS Navigator2 is a utility program that makes it easy to display Settings, change the Buffalo NAS device’s IP
address, or check its drive. To install NAS Navigator2, download the installer from http://d.buffalo.jp/TS5010/.
NAS Navigator2 will run in the system tray when the computer is on.
Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
Click a Buffalo NAS device’s icon to display total capacity, used capacity, workgroup name, IP address, subnet mask,
default gateway, MAC address, and firmware version.
Double-click the icon to open a shared folder on the Buffalo NAS device.
208
Name Description
Menu
Map Share*Assigns the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folder as a network
drive.
Disconnect Share*Unmaps the network drive.
Map All Remote Shares to
Drive Letters
Assigns all Buffalo NAS devices’ shared folders as network
drives. This is available only when a shared folder has been
created.
Create Desktop Shortcut*Creates a desktop shortcut to the Buffalo NAS device’s
shared folders.
Launch NAS Navigator2
on Startup
Launches NAS Navigator2 in the system tray when Windows
boots.
Display Errors If an error occurs, an error message will appear from the
NAS Navigator2 icon in the system tray.
Properties*Opens the properties page that lets you configure the
Buffalo NAS device’s IP address or open Settings.
Close Closes NAS Navigator2.
View
View
Icons: Displays icons.
Details: Displays the hostname, product name, workgroup,
IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
Sort by
If you have multiple Buffalo NAS devices on the network,
you may choose to display them in order of hostname,
product name, workgroup, IP address, subnet mask, or
default gateway.
Browse*Opens the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folders.
Refresh Searches for the Buffalo NAS devices on the network again.
I’m here*Causes your Buffalo NAS device to beep.
Right-click your
device’s icon to show
these menus.
Browse Shares Opens the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folders.
Settings Opens Settings for the Buffalo NAS device.
Properties Opens the properties page that lets you configure the
Buffalo NAS device’s IP address or open Settings.
Map Share Assigns the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folder as a network
drive.
Disconnect Share Unmaps the network drive.
Create Desktop Shortcut Creates a desktop shortcut to the Buffalo NAS device’s
shared folders.
I’m here Causes your Buffalo NAS device to beep.
*Click on the Buffalo NAS device’s icon to display these options.
When NAS Navigator2 is closed, right-click the NAS Navigator2 icon in the system tray for the following options.
209
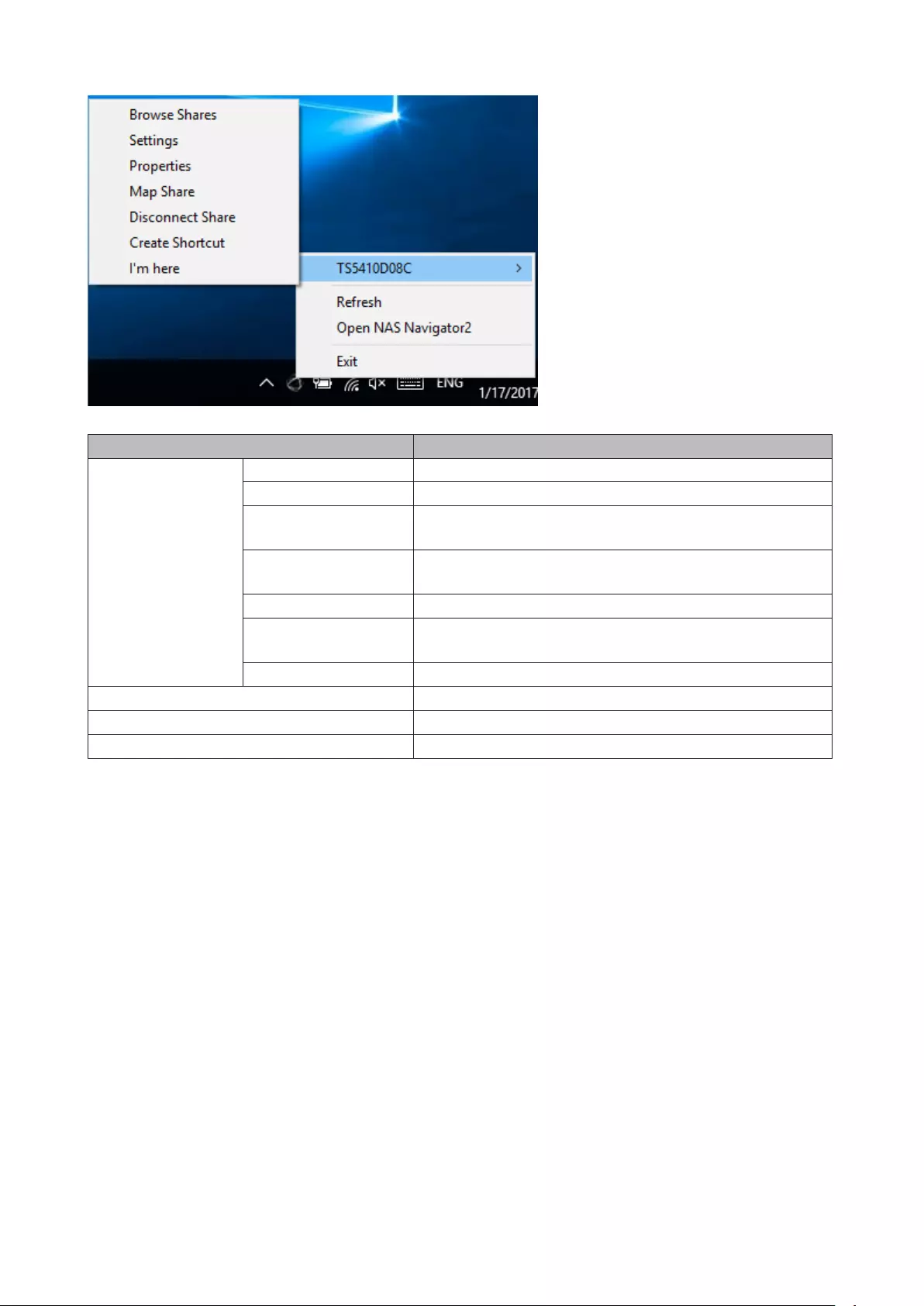
Name Description
Buffalo NAS device
name
Browse Shares Opens the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folders.
Settings Opens Settings for the Buffalo NAS device.
Properties Opens the properties page that lets you configure the Buffalo
NAS device’s IP address or open Settings.
Map Share Assigns the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folder as a network
drive.
Disconnect Share Unmaps the network drive.
Create Shortcut Creates a desktop shortcut to the Buffalo NAS device’s shared
folders.
I’m here Causes your Buffalo NAS device to beep.
Refresh Searches for the Buffalo NAS devices on the network again.
Open NAS Navigator2 Opens the NAS Navigator2 window.
Exit Exits NAS Navigator2.
The following menus may be performed from the Buffalo NAS device’s properties page.
210
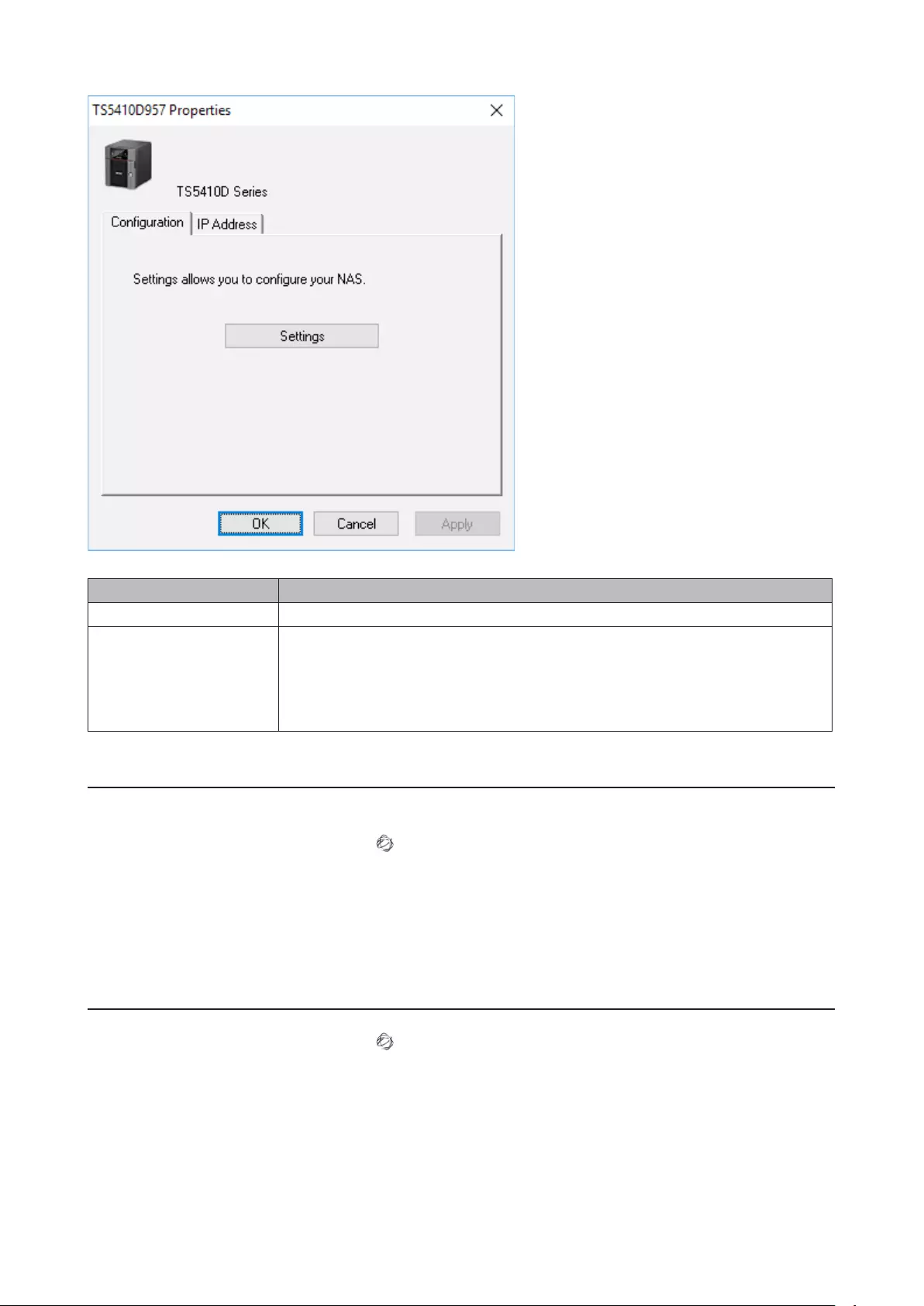
Name Description
Configuration Click Settings to open the configuration interface.
IP Address
Select the “Use DHCP” checkbox to assign an IP address from the DHCP server
automatically. If there is no DHCP server on the network, you cannot use this
function. Select the “Renew IP address” checkbox to obtain an IP address from the
DHCP server. You can manually enter a static IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway.
Mounting as a Network Drive
You can easily assign a shared folder as a network drive using NAS Navigator2.
1 Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click your Buffalo NAS device’s icon and select Map Share.
3 An icon for the mapped share will appear in Computer or This PC. You can use this network drive just like any
other drive.
Changing the IP Address
1 Double-click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click your Buffalo NAS device’s icon and select Properties > IP Address.
3 Clear the “Use DHCP” checkbox and enter the desired settings, then click OK. If the username and password
prompt appears, enter the admin username and password.
211
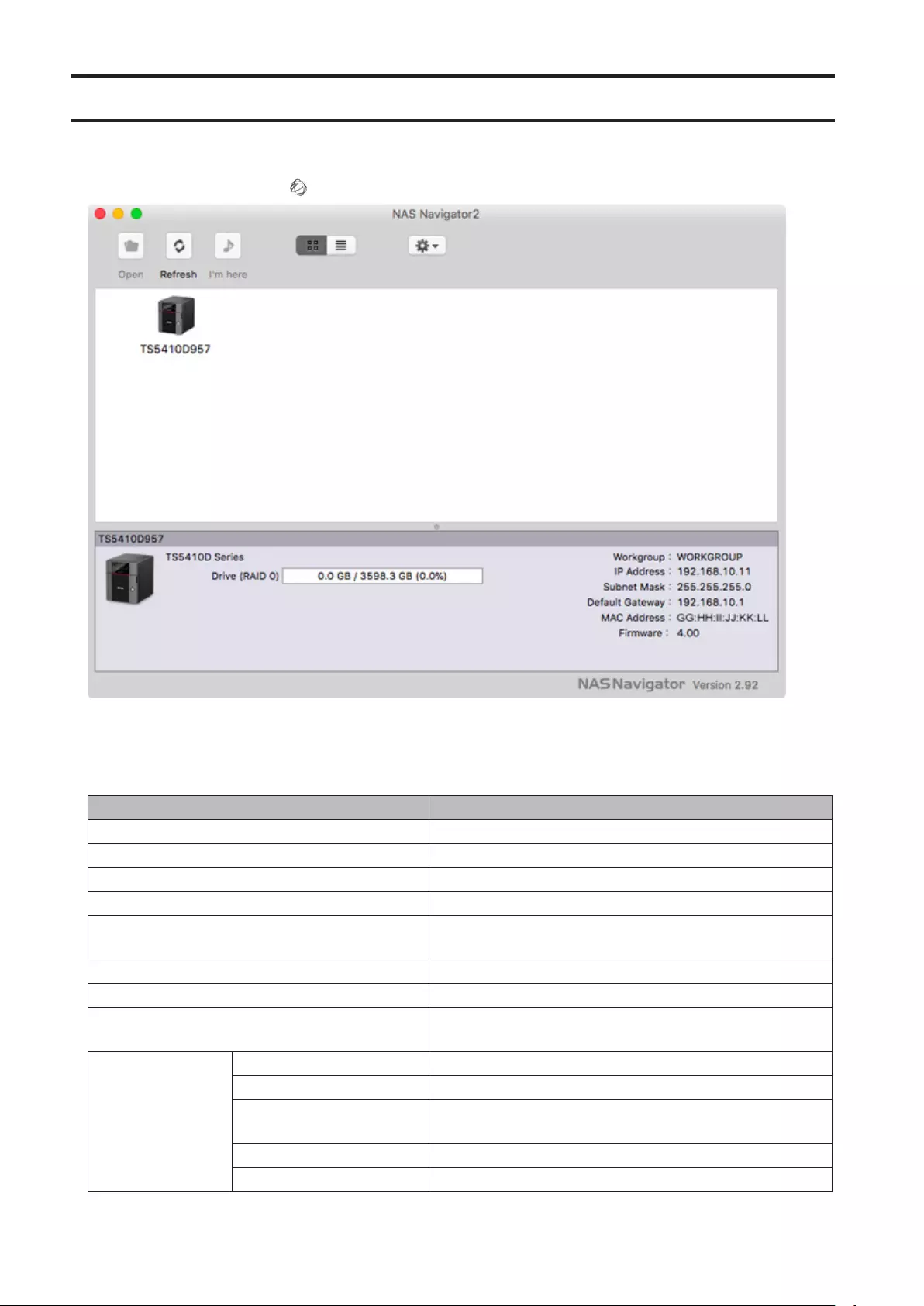
NAS Navigator2 for macOS
NAS Navigator2 is a utility program that makes it easy to display Settings, change the Buffalo NAS device’s IP
address, or check its drive. To install NAS Navigator2, download the installer from http://d.buffalo.jp/TS5010/.
Click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) in the Dock to start NAS Navigator2.
Click a Buffalo NAS device’s icon to display total capacity, used capacity, workgroup name, IP address, subnet mask,
default gateway, MAC address, and firmware version.
Double-click the icon to open a shared folder on the Buffalo NAS device.
Name Description
Open Opens the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folders.
Refresh Searches for the Buffalo NAS devices on the network again.
I’m here Causes your Buffalo NAS device to beep.
Settings Opens Settings for the Buffalo NAS device.
Configure Opens the properties page that lets you configure the
Buffalo NAS device’s IP address or open Settings.
Label Color Selects the color of the name displayed below the icon.
View Options Lets you choose icon size, position, and view mode.
Auto Power Mode Auto power mode can turn supported Buffalo NAS devices
on the network on and off automatically.
To display these
options, hold down
the control key and
click your device’s
icon.
Open Folder Opens the Buffalo NAS device’s shared folders.
Settings Opens Settings for the Buffalo NAS device.
Configure Opens the properties page that lets you configure the
Buffalo NAS device’s IP address or open Settings.
I’m here Causes your Buffalo NAS device to beep.
Label Color Selects the color of the name displayed below the icon.
212
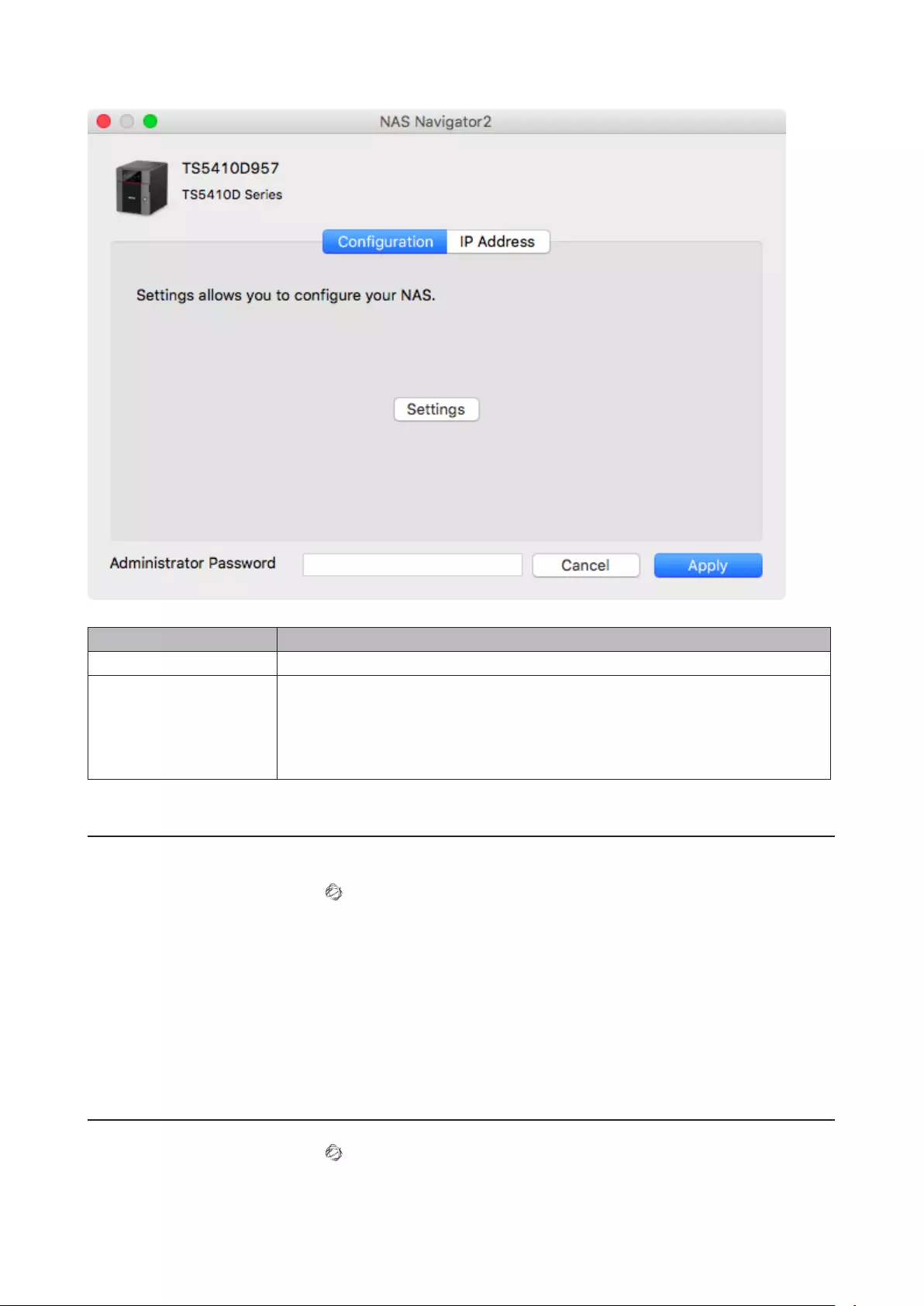
The following menus may be performed from the Buffalo NAS device’s properties page.
Name Description
Configuration Click Settings to open the configuration interface.
IP Address
Select the “Use DHCP” checkbox to assign an IP address from the DHCP server
automatically. If there is no DHCP server on the network, you cannot use this
function. Select the “Renew IP address” checkbox to obtain an IP address from the
DHCP server. You can manually enter a static IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway.
Mounting as a Network Drive
You can map a shared folder as a network drive using NAS Navigator2 on macOS.
1 Click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) in the Dock to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Double-click the Buffalo NAS device’s icon or click the Buffalo NAS device’s icon while holding down the
control key, then select Open Folder. Enter a username and password with the rights to access the shared
folder.
3 Select the shared folder that you want to mount, then click OK.
4 The shared folder is now mounted as a network drive.
Changing the IP Address
1 Click the NAS Navigator2 icon ( ) in the Dock to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Click the Buffalo NAS device’s icon while holding down the control key, then select Configure > IP Address.
213

3 Clear the “Use DHCP” checkbox; enter the desired settings and the administrator password, then click Apply.
NovaBACKUP
NovaBACKUP is a Windows utility that lets you back up data on your computer.
The NovaBACKUP installer is available from http://d.buffalo.jp/TS5010/. Select the region and model to go to your
specific model’s d.buffalo website. Download the NovaBACKUP installer and install it onto your computer.
To download the installer, you will need the serial number of your TeraStation. The serial number is printed on the
label on the back or top of the unit. For the TS5410RN series TeraStations, the serial number is located on the front as
well. Refer to the “Diagrams” section in chapter 1 for information on where to find the serial number.
214
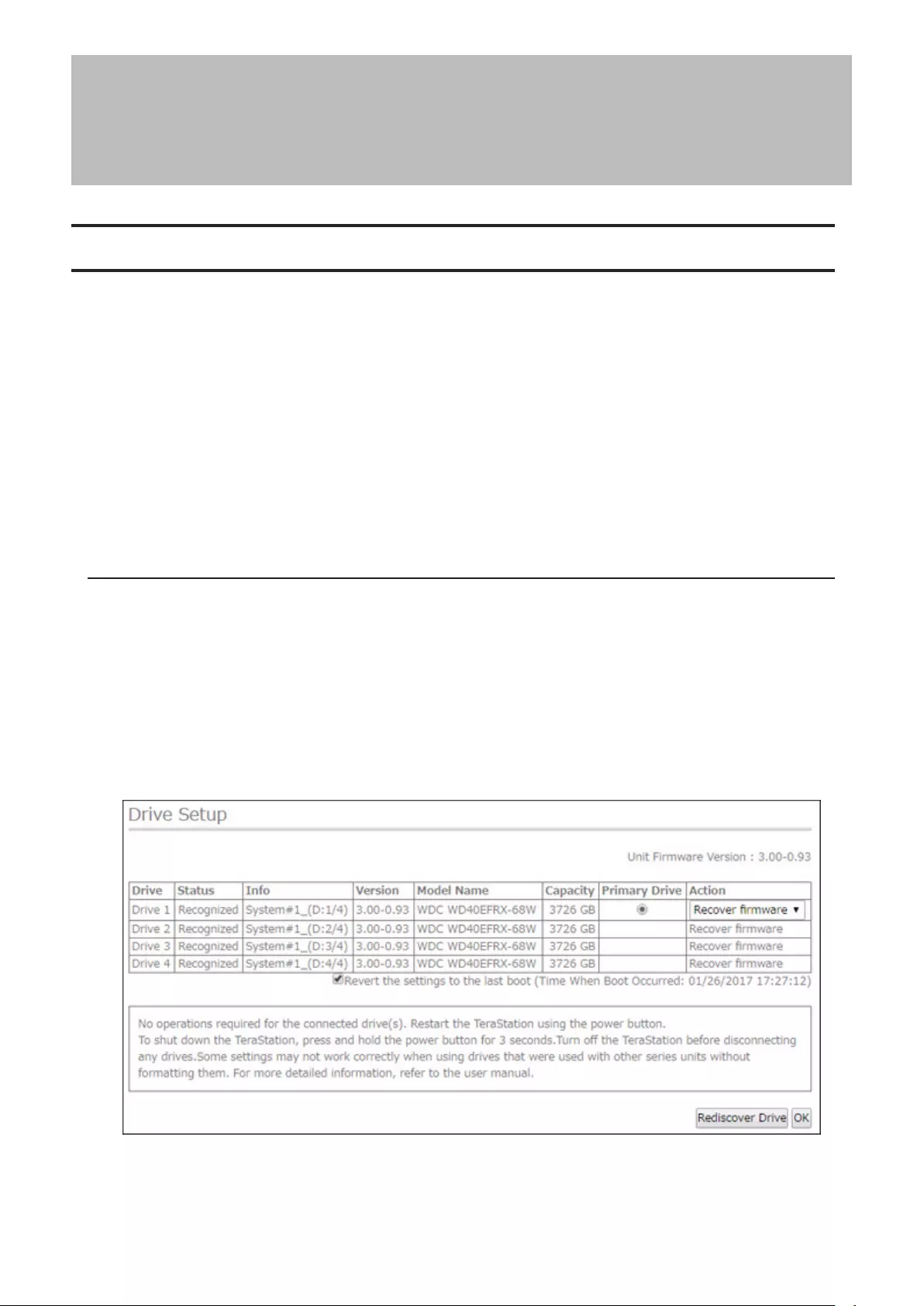
Chapter 10 Appendix
TeraStation Does Not Work Properly
If an error occurs that prevents the TeraStation from booting up properly, one or more of the following symptoms
may occur:
• The power LED keeps blinking instead of turning into a solid glow; follow the procedure at the “Power LED Keeps
Blinking” section below.
• An “i” symbol is displayed with the TeraStation icon and the I61 message appears on NAS Navigator2; follow step
3 or later at the “Power LED Keeps Blinking” section below.
• An “i” symbol is displayed with the TeraStation icon and “EM” is added to your TeraStation’s hostname on NAS
Navigator2; follow the procedure at the “Booting the TeraStation in Emergency Mode” section below.
• The LCD panel lights up in red with the “Invalid Firmware” message; follow the procedure at the “Booting the
TeraStation in Emergency Mode” section below.
If one or the above occurs, follow the appropriate procedures below to recover from the error.
Power LED Keeps Blinking
While the TeraStation’s power LED keeps blinking, you may see the I61 message on NAS Navigator2 or the LCD
panel. In such a case, follow the procedure below to recover from the message.
1 Press and hold the power button for 3 seconds to turn off the TeraStation.
2 Turn it on while holding down the function button. You should press and hold the function button for 10
seconds even after pressing the power button.
3 When the power LED changes from blinking to glowing, open Settings from NAS Navigator2.
The following screen will appear.
4 Select the drive to install the firmware as “Primary Drive” and make sure that “Recover firmware” is selected
under “Action”, then click OK.
215
5 The “Confirm Operation” screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Reinstalling the firmware will start. When the firmware is reinstalled, the TeraStation will shut down
automatically. Press the power button to turn it on.
If the error was not recovered from after trying the procedure above, try again from the first step. This time, make
sure you select the checkbox for “Revert the settings to the last boot” and click OK. This will reinstall the firmware by
reverting settings to those from the last boot.
Booting the TeraStation in Emergency Mode
If the TeraStation boots up in emergency mode, depending on your TeraStation model, an “i” symbol is displayed
with the TeraStation icon and “EM” is added to your TeraStation’s hostname, or the LCD panel lights up in red with
the “Invalid Firmware” message.
úùÛÚ×Öê
ïēěĆđĎĉÆìĎėĒĜĆėĊ
To recover from emergency mode, follow the procedure below.
1 Download the firmware updater from the Buffalo website.
2 Extract the downloaded file by double-clicking it and launch the updater.
3 Update the firmware for the TeraStation unit that is currently in emergency mode.
When the “i” symbol and “EM” disappear from the icon and the hostname on NAS Navigator2, and the LCD panel
returns to glowing blue, the TeraStation is no longer in emergency mode.
Note: If the TeraStation does not shut down properly due to a power outage or the power cable getting
disconnected while the TeraStation is on, data on the TeraStation may be corrupted when the TeraStation boots in
emergency mode. In such a case, the corrupted data may not be recoverable even if you try the procedure above.
Cleaning the Dustproof Filter
If your TeraStation has a front cover and you are trying to clean the dustproof filter on the front cover, follow the
procedure below.
216
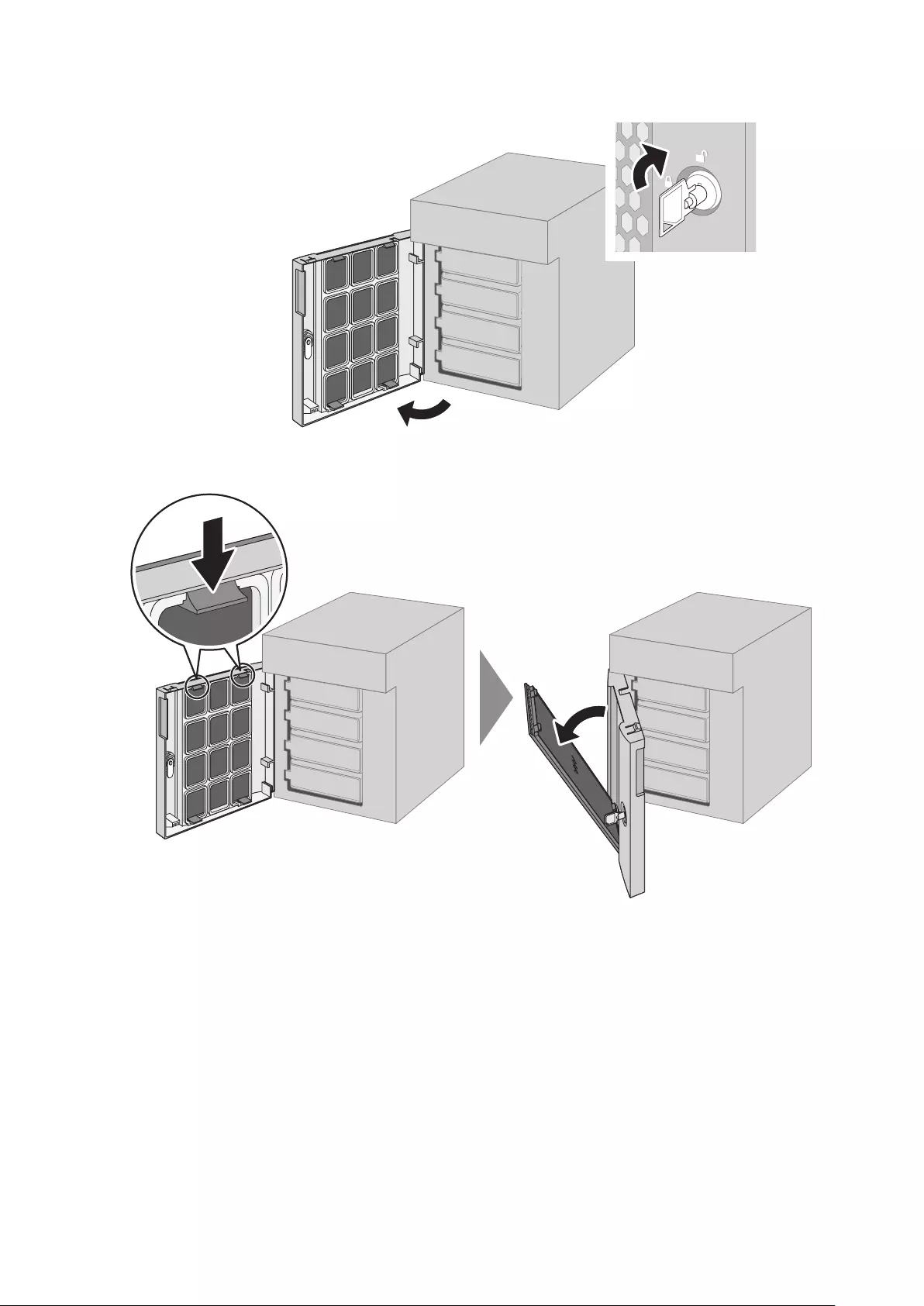
1 Open the front cover with the included key.
2 Remove the front cover while holding the hook downward.
217
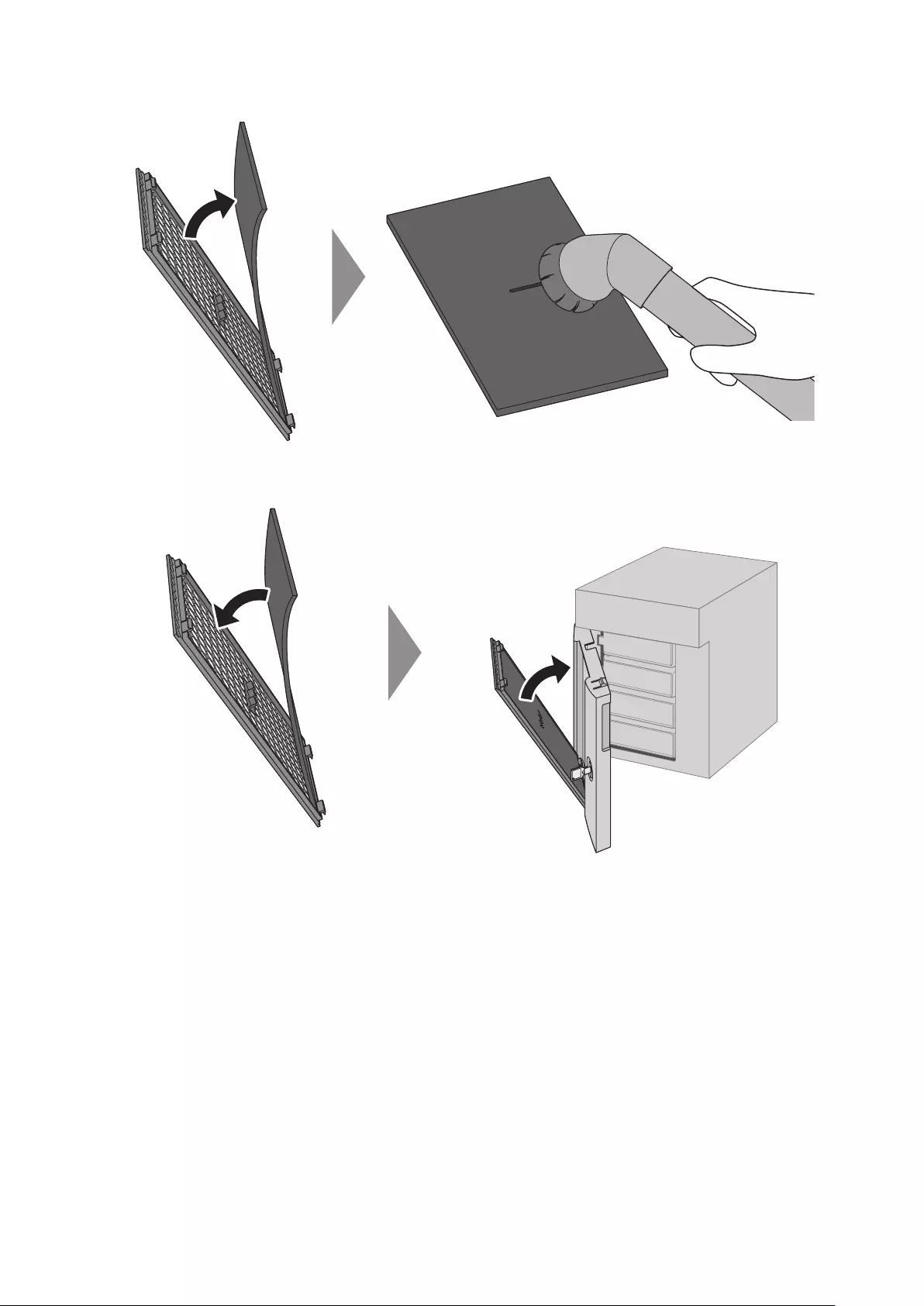
3 Remove the dustproof filter from the front cover and clear any dust, such as by using a vacuum cleaner.
4 When cleaning is finished, return the filter and the front cover.
218
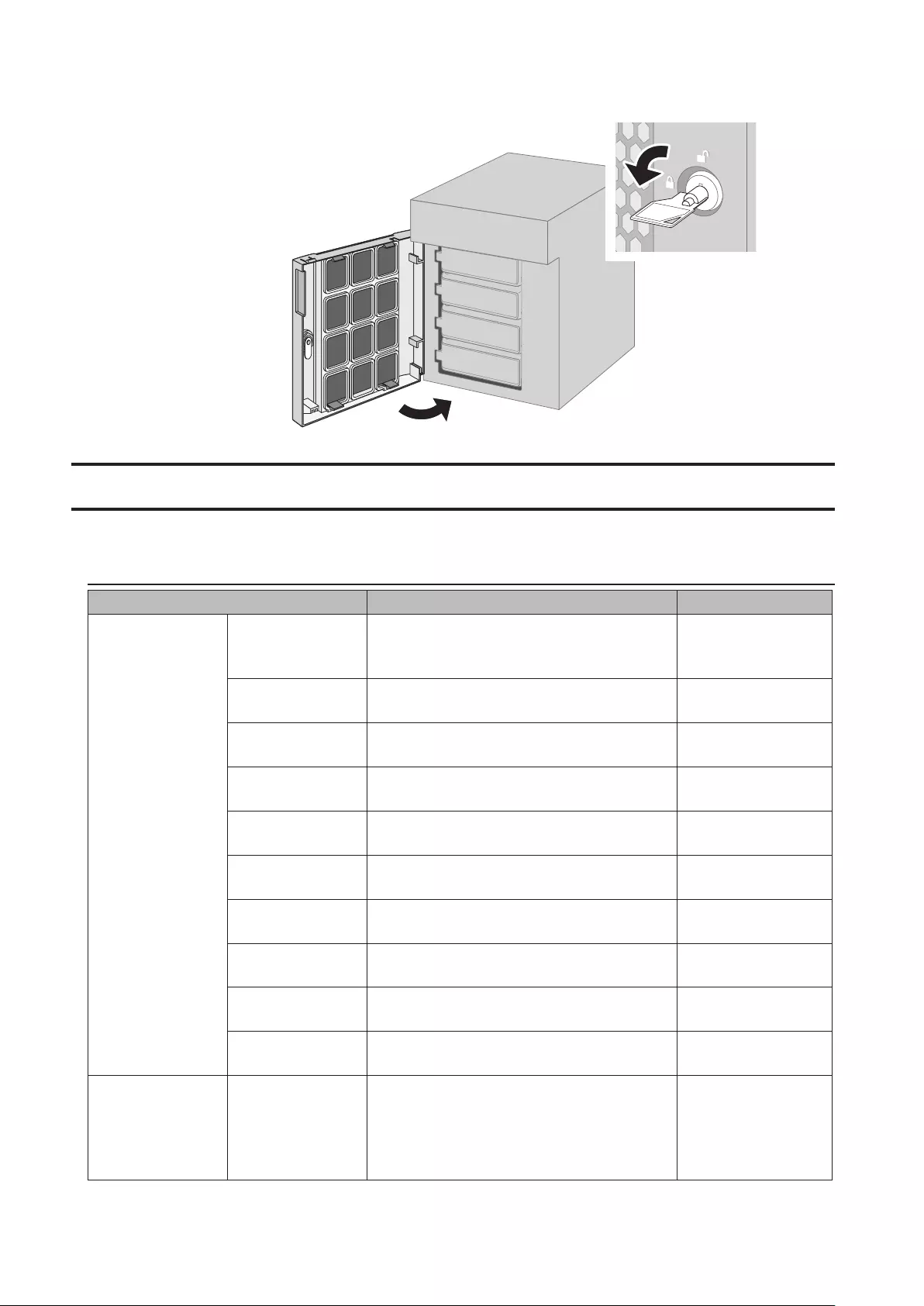
5 Close the front cover.
LCD Panel
The LCD panel can be cycled through different modes by pressing the display button on the front of the TeraStation.
Modes
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
LANx
Note: The “x”
indicates the
number of the
LAN port where
the Ethernet cable
is connected.
LANx
Not Connected Not connected to a network.
Connect an Ethernet
cable to the LAN
port.
LANx Half Duplex
10 Mbps Connected at 10 Mbps half duplex. -
LANx Full Duplex
10 Mbps Connected at 10 Mbps full duplex. -
LANx Half Duplex
100 Mbps Connected at 100 Mbps half duplex. -
LANx Full Duplex
100 Mbps Connected at 100 Mbps full duplex. -
LANx
1000 Mbps Connected at 1000 Mbps. -
LANx
2.5 Gbps Connected at 2.5 Gbps. -
LANx
5 Gbps Connected at 5 Gbps. -
LANx
10 Gbps Connected at 10 Gbps. -
LANx
Port Trunking Displays if port trunking is configured. -
Model Name/
Firmware Version
TS5410D
FW Version 1.00
Displays the model name and firmware
version of your model.
Note: This example is using a TS5410DN unit.
The numbers and letters after “TS” may vary
depending on your model.
-
219
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
Hostname Hostname:
TS5410Dxxx Displays the hostname. -
Date and Time
Date Time
YYYY/MM/DD
hh:mm
Displays the date and time set in the
TeraStation. -
IP Address
LANx DHCP
192.168.11.150
Displays the IP address. If acquiring from a
DHCP server automatically, “DHCP” will be
displayed. If configuring a static IP address,
“Static IP” will be displayed.
-
LANx
Port Trunking Displays if port trunking is configured. -
Errors
If an error occurs, the error LED will glow red. You can also confirm the current status from the LCD panel.
Note: The “x” in the LCD message is the number of the drive or array involved in the process.
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
E10 UPS Running Off
Battery
The TeraStation is running on the UPS
battery due to a power outage.
Shut down the TeraStation safely and wait
until the power outage ends. If certain
settings are configured, the TeraStation
may shut down automatically when the
error is detected.
If the setting to use the UPS connected to
this TeraStation has been configured, the
UPS cable may be disconnected. Verify that the UPS cable or LAN cable is
connected properly.
If the setting to use the UPS connected to
another TeraStation on the same network
has been configured, the LAN cable of this
TeraStation may be disconnected.
E11 Fan Failure An error occurred in the fan speed.
Check that no foreign objects or dust are
clogging the fan. If any foreign objects
or dust are found, use a pair of tweezers,
air duster, or other tools to remove them.
If the error is displayed again, contact
Buffalo technical support for assistance.
E12 Cooling Failure A rise in the system temperature may have
exceeded the allowable safety value.
Do not place objects in the area around
the TeraStation. Also, move the TeraStation
to a cool location.
E14 Can’t Mount
Array x The RAID array cannot be mounted. Run the RAID array drive check in Settings.
E16 Drive x Not
Found Unable to find the drive.
The drive may be disconnected or may
have failed. After shutting down, reinstall
the drive.
E22 Can’t Mount
Drive x Unable to mount the drive.
Format the drive. After formatting, if the
error still appears after rebooting, replace
the drive. If the error is displayed again,
contact Buffalo technical support for
assistance.
220
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
E27 Lost Failover
Target Unable to find the backup TeraStation.
From the main TeraStation’s Settings,
navigate to Backup > Failover to
reconfigure the backup TeraStation for
failover.
E30 Replace Drive x An error occurred, so the drive was
removed from the RAID array.
Replace the drive by referring to chapter 8,
“Drive Replacement”.
E32 Check Power
Supply Power supply error.
Make sure that the power cable is securely
connected. If the error still exists, replace
the failed PSU to a new OP-PU-10R2 unit.
Status
After you change settings or format a drive, the info LED will glow amber. You can also confirm the current status
from the LCD panel.
Note: The “x” in the LCD message is the number of the drive, array, or job involved in the process.
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
I01 Rebuilding
System Array Checking the system area. -
I10 System Is
Overheating
A rise in the system temperature may have
exceeded the allowable safety value.
Move the TeraStation to a cool location. Do
not place objects in the area around the
TeraStation.
I11 Bad Sectors on
Drive x The drive has too many bad sectors. Replace the drive.
I12 Degraded Mode Operating in degraded mode.
Check if the E30 message is also displayed.
In such a case, refer to the corrective action
for the E30 message.
I13 Formatting Array
x... Formatting the RAID array. -
I14 Checking Array
x... Checking the RAID array. -
I15 Scanning Array x
Data...
Examining the error status of the RAID
array.
Note: Transfer speeds are slower during
the examination process.
-
I16 Creating Array x... Creating the RAID array. -
I18 Rebuilding Array
x...
Rebuilding the RAID array.
Note: Transfer speeds are slower during
the rebuilding process.
-
I19 Filling Array x
with 0s Rewriting the RAID array. -
I20 Formatting Drive
x... Formatting the drive. -
I21 Checking Drive
x... Checking the drive. -
I22 Filling Drive x
with 0s Rewriting the drive. -
I25 Updating
Firmware...
Updating the TeraStation firmware.
Note: Do not turn off the power during the
updating process.
-
221
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
I26 Initializing
Settings... Initializing all settings. -
I27 Checking USB
Drive x... Checking the USB drive. -
I28 Formatting USB
Drive x... Formatting the USB drive. -
I31 Push Func to Use
New Drive x
Displays when pressing the function
button to rebuild the RAID array after
replacing the drive.
Press the function button to rebuild the
RAID array.
I32 New Drive x
Detected
Displays after replacing the drive when the
RAID array needs to be rebuilt in Settings
or formatting is necessary.
From Settings, either rebuild the RAID
array or format the drive.
I33 Replication
Failure
An error occurred in replication, or
synchronization between the main
TeraStation and the backup TeraStation
failed during failover configuration.
From Settings, navigate to Backup >
Replication and click Resync to execute
resynchronization.
If you configured the subfolders’ access
restrictions to be inherited to the
replication or failover destinations, disable
them or change the destinations.
If the error is displayed again, contact
Buffalo technical support for assistance.
I34 Virus
Quarantined A virus scan found a virus.
Once the virus is removed from the
quarantine folder, the message is no
longer displayed. If the antivirus software
is configured to delete viruses from the
quarantine folder automatically, then the
message will not be displayed.
I37 Recovering
System... Settings initialization in progress. -
I38 Recovery
Finished Settings initialization is complete. -
I40 All Data Will Be
Deleted
Beginning settings initialization. All data
on the drive 1 will be deleted. -
I41 Push Func to
Start Recovery
Press the function button on the front to
start the settings initialization process. -
I42 Preparing
Recovery
Preparing to start the settings initialization
process. -
I43 Unsupported
Hardware
The TeraStation was started from the
USB initialization device, but the settings
cannot be initialized from this USB
initialization device.
-
I44 Drive 1 Not
Found
Initialization from the USB initialization
device was initiated, but drive 1 was not
detected.
Make sure that drive 1 is present and fully
inserted in its slot.
I45 Recovery Failed Initialization failed. -
I46 Migrating RAID
Array x... Data migration or conversion (RAID
migration) is in progress. Do not turn off the TeraStation’s power.
I47 Don’t Power Off
System!
222
LCD Message Description Corrective Action
I48 Push Func to
Start Failover
This TeraStation is ready to become the
failover backup for the main TeraStation.
Press and hold the function button on the
front of the target TeraStation until it stops
beeping to accept failover backup status.
I49 Lost Failover
Main
The main TeraStation in the failover
configuration cannot be found.
Make sure that the main TeraStation is on,
working, and connected to the network.
I50 Failover in
Maintenance Mode Failover maintenance is in progress. Do not turn off the TeraStation’s power.
I51 Initializing
Failover... Initializing the failover configuration. Do not turn off the TeraStation’s power.
I52 New Firmware
Available A new firmware version has been released. Update the firmware.
I54 Backup Job x
Failed The backup job failed.
Make sure that the backup job is
configured correctly, and that the NAS
is on and not in standby mode. If the
backup job still fails, check the status of
NAS, network, and backup source and
destinations.
If you configured the subfolders’ access
restrictions to be inherited to the backup
destination, disable them or change the
destination.
I55 Recovery Not
Authorized
Authentication during initialization of
settings failed.
Settings can only be restored for the
TeraStation whose settings were originally
saved.
I59 Boot Auth Failed Boot authentication failed.
Open Settings, take note of the displayed
decryption key and forward the key to the
authentication server administrator.
I60 Drive x TBW
Reached
The drive has reached its guaranteed write
capacity (TBW).
Replacing the drive is recommended.
Note: Refer to the warranty statement
for more detailed information on what is
covered for the SSDs.
I61 Drive Setup
Mode The unit is in drive setup mode.
Recover from drive setup mode by
following the procedure at the “Power LED
Keeps Blinking” section.
I62 Replace Drive x
Data can no longer be written to the drive
as it has exceeded its guaranteed write
capacity (TBW).
Replace the drive.
Note: Refer to the warranty statement
for more detailed information on what is
covered for the SSDs.
I70 No Space to Save
Logs
There is not enough space to save file
access logs.
Delete unnecessary logs or move them to
another place.
I71 Old Logs
Removed
The space is occupied so older logs were
removed.
Delete unnecessary logs or move them to
another place.
Default Settings
Administrator’s Name admin
Password password
Shared Folders
“share”* and “info”** for both Windows and Mac computers.
*The recycle bin is enabled by default.
**It is a read-only share.
223
IP Address
The TeraStation will get its IP address automatically from a DHCP server
on the network. If no DHCP server is available, then an IP address will be
assigned as follows:
IP Address: 169.254.xxx.xxx (“xxx” is assigned randomly when booting the
TeraStation.)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
Registered Groups “hdusers”, “admin”, and “guest”
You cannot edit or delete these default groups.
Microsoft Network Group Settings WORKGROUP
MTU Size 1500 bytes
SMB
Enabled
SMB Protocol Auto
Recycle Bin
Permissions All users
macOS Temp Files Keep when original file is deleted
AFP Enabled
FTP Disabled
SFTP Disabled
WebAccess Disabled
NFS Disabled
rsync Disabled
RAID Scanning Disabled
iSCSI Disabled
Cloud Storage Disabled
Dropbox Sync Disabled
Microsoft Azure Storage Sync Disabled
Antivirus Disabled
SNMP Disabled
Time Machine Disabled
NTP Enabled
Email Notification Disabled
Init Button Settings Restore admin username and password to factory defaults
Boot Authentication Disabled
RAID Mode
TS5210DN, TS5210DF: RAID 1
TS5410DN, TS5410RN: RAID 5
TS5810DN, TS51210RH: RAID 6
Specifications
Check the Buffalo website for the latest product information and specifications.
224
LAN Interface
Standards Compliance
1GbE port: IEEE 802.3ab (1000BASE-T), IEEE 802.3u
(100BASE-TX), IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T)
10GbE port: IEEE 802.3an (10GBASE-T), IEEE 802.3bz
(2.5GBASE-T, 5GBASE-T), IEEE 802.3ab (1000BASE-T),
IEEE 802.3u (100BASE-TX)
Data Transfer Rates
1GbE port: 10/100/1000 Mbps (auto sensing)
10GbE port: 2.5/5/10 Gbps, 100/1000 Mbps (auto
sensing)
Number of Ports
TS5210DN, TS5210DF, TS5410DN, TS5410RN,
TS5810DN: 1 x 10GbE, 2 x 1GbE
TS51210RH: 2 x 10GbE, 2 x 1GbE
Connector Type RJ-45 8-pin (auto MDI-X)
Supported Protocols TCP/IP
Network File Services SMB/CIFS, AFP, FTP/SFTP, NFS
MTU Sizes 1500–9216 bytes
USB Interface
Standards Compliance USB 3.0/2.0
Data Transfer Rates USB 3.0: Max. 5 Gbps
USB 2.0: Max. 480 Mbps
Number of Ports
TS5210DN, TS5210DF, TS5410DN: 2 x USB 3.0
TS5410RN, TS5810DN: 3 x USB 3.0
TS51210RH: 2 x USB 3.0, 2 x USB 2.0
Connector Type Type A
Internal Hard Drives
Number of Drive Bays
TS5210DN, TS5210DF: 2
TS5410DN, TS5410RN: 4
TS5810DN: 8
TS51210RH: 12
Drive Interface SATA 6 Gbps
Supported RAID
TS5210DN, TS5210DF: 0, 1, JBOD (individual drives)
TS5410DN, TS5410RN, TS5810DN, TS51210RH: 0, 1, 5,
6, 10, JBOD (individual drives)
Replacement Drive
TS5210DF: Buffalo OP-SSD series drive
TS5210DN, TS5410DN, TS5410RN, TS5810DN: Buffalo
OP-HDN series drive
TS51210RH: Buffalo OP-HDH2U series drive
Note: The new drive should be the same size or
larger as the replaced drive. The drives listed above
are available from the Buffalo website.
225
Other
Power Supply
TS5210DN, TS5210DF, TS5410DN: AC 100–240 V, 1.5
A, 50/60 Hz
TS5410RN: AC 100–240 V, 2.5–1.25 A, 50/60 Hz
TS5810DN: AC 100–240 V, 3.0 A, 50/60 Hz
TS51210RH: AC 100–240 V, 7.0–3.5 A, 50/60 Hz
Dimensions (W x H x D,
excluding protruding parts)
TS5210DN, TS5210DF: 170 x 170 x 230 mm; 6.7 x 6.7
x 9.1 in
TS5410DN: 170 x 215 x 230 mm; 6.7 x 8.5 x 9.1 in
TS5410RN: 430 x 44.3 x 430 mm; 16.9 x 1.7 x 16.9 in
TS5810DN: 300 x 215 x 230 mm; 11.8 x 8.5 x 9.1 in
TS51210RH: 481 x 88 x 736.9 mm; 18.9 x 3.5 x 29.0 in
Weight
TS5210DN: Approx. 4.8 kg; 10.6 lb
TS5210DF: Approx. 3.5 kg; 7.7 lb
TS5410DN: Approx. 7.0 kg; 15.4 lb
TS5410RN: Approx. 8.5 kg; 18.7 lb
TS5810DN: Approx. 12.5 kg; 27.6 lb
TS51210RH: Approx. 25.0 kg; 55.1 lb
Power Consumption
TS5210DN, TS5210DF, TS5410DN: Max. 85 W
TS5410RN: Max. 100 W
TS5810DN: Max. 150 W
TS51210RH: Max. 500 W
Operating Environment Temperature: 0–40°C; 32–104°F
Humidity: 10–85% non-condensing
Compatible Devices
Windows PCs, tablets, and Mac computers with
wired or wireless Ethernet connection.
Note: The TeraStation requires an Ethernet
connection with your computer for operation. It
cannot be connected via USB.
Supported OS
Windows 10, 8.1, 7 SP1 or later
Windows Server 2016, 2012 R2, 2012, 2008 R2, 2008
macOS 10.13, 10.12, 10.11, 10.10, 10.9
226

Chapter 11 Regulatory Compliance
Information
For Customers in All Regions
IEC60950-1
WARNING:
Hazardous moving parts. Keep away from moving fan blades.
For Customers in the United States
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Only use the cables and accessories that are included in the package. Don’t use other accessories or cables unless
specifically instructed to in the documentation.
UL and MET
The socket-outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily accessible.
Proposition 65
WARNING:
This product and its components contain chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth
defects, or reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
227

For Customers in Europe
CE
Dansk
Dette er et Klasse A-produkt. I et hjemmemiljø kan dette produkt skabe radiointerferens, hvormed det kan være
nødvendigt for brugeren at tage passende forholdsregler.
Dette produkt kan forårsage interferens hvis det bruges i beboelsesområder. En sådan anvendelse skal undgås,
medmindre brugeren tager specielle foranstaltninger for at reducere elektromagnetiske emissioner for at forhindre
interferens med modtagelse af radio- og tv-udsendelser.
Der må kun bruges de kabler og det tilbehør der er inkluderet i pakken. Der må ikke bruges andet tilbehør eller
kabler, medmindre det er udtrykkeligt beskrevet i dokumentationen.
Brug ikke USB-kabler, der er 3 meter eller længere for at tilslutte USB enheder til denne TeraStation serie.
Deutsch
Dies ist ein Produkt der Klasse A. In einer häuslichen Umgebung kann dieses Produkt Funkstörungen verursachen.
Um diese zu beheben, müssen ggf. entsprechende Maßnahmen ergriffen werden.
Bei einer Nutzung in Wohngebieten können bei diesem Produkt Störungen auftreten. Eine solche Nutzung soll
vermieden werden, außer der Nutzer ergreift bestimmte Maßnahmen, um elektromagnetische Strahlung zu
reduzieren und Störungen der Radio- und Fernsehübertragung zu vermeiden.
Verwenden Sie ausschließlich die Kabel und Zubehörteile, die im Lieferumfang enthalten sind. Andere Zubehörteile
oder Kabel dürfen nur dann verwendet werden, wenn dies in der Dokumentation ausdrücklich vorgeschrieben ist.
Verwenden Sie keine USB-Kabel, die 3 Meter lang oder länger sind, um USB-Geräte an TeraStation dieser Serie
anzuschließen.
English
This is a class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
This product may cause interference if used in residential areas. Such use must be avoided unless the user takes
special measures to reduce electromagnetic emissions to prevent interference to the reception of radio and
television broadcasts.
Only use the cables and accessories that are included in the package. Don’t use other accessories or cables unless
specifically instructed to in the documentation.
Do not use USB cables that are 3 meters or longer to connect USB devices to this TeraStation series.
Español
Este es un producto de Clase A. En una situación domestica, este producto puede producir interferencias de radio,
en ese caso el usuario deberá tomar las medidas adecuadas.
Este producto puede causar interferencias al utilizarlo en áreas residenciales. Debe evitarse utilizarlo así, salvo si
el usuario adopta medidas especiales para reducir las emisiones electromagnéticas e impedir que se produzcan
interferencias con la recepción de emisiones de radio y televisión.
Utilice únicamente los cables y accesorios incluidos en el paquete. No utilice otros accesorios ni cables a menos que
así se indique en la documentación.
Utilice cables de una longitud inferior a 3 metros para conectar los dispositivos USB a este tipo de TeraStation.
Français
228

Cet appareil est un produit de Classe A. Dans un environnement domestique, ce produit est susceptible de
provoquer des interférences radio, auquel cas l’utilisateur peut être mis en demeure de prendre des mesures
appropriées.
Utilisé dans un environnement domestique, cet appareil génère des interférences. Ce type d’utilisation est donc
à éviter si l’utilisateur n’a pas pris de mesures spécifiques visant à réduire les émissions électromagnétiques pour
éviter les interférences avec la réception de programmes de radio et de télévision.
Utilisez uniquement les câbles et accessoires inclus dans ce package. N’utilisez aucun autre accessoire ou câble sauf
instruction spécifique de la documentation.
Utilisez des câbles d’une longueur de moins 3 mètres pour connecter les périphériques USB à ce type de
TeraStation.
Italiano
Questo è un prodotto di Classe A. In ambienti domestici il prodotto può causare radiointerferenza, nel qual caso
potrebbe rendersi necessaria l’adozione di opportune misure.
Questo prodotto può causare interferenze se usato in zone residenziali. Evitare l’uso in queste zone a meno che
l’utente non intraprenda azioni specifiche per ridurre le emissioni elettromagnetiche e impedire le interferenze alla
ricezione di trasmissioni radio-televisive.
Utilizzare esclusivamente i cavi e gli accessori inclusi nell’imballaggio. Non utilizzare altri accessori o cavi a meno che
non sia specificamente indicato nella documentazione.
Non utilizzare cavi USB lunghi 3 metri o più per collegare dispositivi USB a questa TeraStation.
Nederlands
Dit is een Klasse A product. Dit product kan in een huishoudelijke omgeving radiostoring veroorzaken in welk geval
de gebruiker adequate maatregelen dient te nemen.
Dit product kan storing veroorzaken wanneer gebruikt in woongebieden. Dergelijk gebruik dient te worden
vermeden tenzij de gebruiker speciale maatregelen treft om de elektro-magnetische uitstraling te beperken zodat
storing van de ontvangst van radio- en televisieuitzendingen wordt voorkomen.
Gebruik alleen de kabels en toebehoren die zich in de verpakking bevinden. Gebruik geen ander toebehoren of
kabels tenzij dit uitdrukkelijk in de handleiding wordt aangegeven.
Gebruik geen USB-kabels die 3 meter of langer zijn om USB-apparaten met deze TeraStation series te verbinden.
Norsk
Dette er et produkt i klasse A. I et hjemmemiljø kan dette produktet forårsake radiointerferens, noe som gjør at
brukeren i så fall må foreta passende tiltak.
Dette produktet kan forårsake interferens dersom det brukes i boligområder. Slik bruk må unngås med mindre
brukeren tar spesielle tiltak for å redusere elektromagnetisk stråling for å unngå interferens med mottak av radio- og
TV-sendinger.
Bruk kun kabler og tilbehør som er inkludert i pakken. Ikke bruk annet tilbehør eller kabler med mindre spesielt
instruert til å gjøre det i dokumentasjonen.
Bruk ikke USB-kabler på tre meter eller mer for å koble USB-enheter til denne TeraStation-serien.
Português
Este é um produto de Classe A. Num ambiente doméstico, este produto pode provocar interferências de rádio, pelo
que o utilizador poderá ter de tomar medidas adequadas.
Este produto poderá causar interferências se utilizado em áreas residenciais. A utilização deverá ser evitada, salvo se
o utilizador tomar medidas especiais para reduzir as emissões electromagnéticas e assim prevenir interferências na
recepção de rádio e televisão.
Utilizar apenas cabos e acessórios incluídos na embalagem. Não utilizar outros acessórios ou cabos, salvo se
especificamente indicado na documentação. 229

Não usar cabos USB de 3 metros ou mais para ligar dispositivos USB a esta série TeraStation.
Suomi
Tämä on luokan A tuote. Tämä tuote voi aiheuttaa radiohäiriöitä kotikäytössä, jolloin käyttäjän on ehkä ryhdyttävä
tarvittaviin toimenpiteisiin.
Tämä tuote saattaa aiheuttaa häirintää, jos sitä käytetään asuinalueella. Sellaista käyttöä on vältettävä, ellei
ryhdytä erityistoimenpiteisiin sähkömagneettisen säteilyn vähentämiseksi häiriöiden estämiseksi radio- ja
televisiolähetyksissä.
Käytä ainoastaan pakkauksen mukana toimitettuja kaapeleita ja varusteita. Älä käytä muita varusteita tai kaapeleita
ellei näin ole erityisesti ohjeistettu asiakirjoissa.
Älä käytä 3m tai pitempiä USB-kaapeleita USB-laitteiden liittämiseen näille TeraStation-sarjoille.
Svensk
Detta är en Klass A-produkt. I en hushållsmiljö kan denna produkt orsaka radiostörningar, och användaren kan i så
fall begäras att vidta lämpliga åtgärder.
Den här produkten kan oraka störningar om den används i bostadsområden. Sådan användning måste undvikas om
inte användaren vidtar speciella åtgärder för att minska elektromagnetiska sändningar för att förhindra störningar i
mottagningen av radio- och tv-sändningar.
Använd bara kablar och tillbehör som ingår i förpackningen. Använd inte andra tillbehör eller kablar om du inte får
uttryckliga instruktioner om det i dokumentationen.
Använd inte USB-kablar som är 3 meter eller längre för att ansluta USB-enheter till den här TeraStation-serien.
Türk
Bu, A Sınıfı bir üründür. Evde kullanım sırasında bu ürün radyo girisimine yol açabilir ve bu durumda kullanıcının
gerekli önlemleri alması gerekebilir.
Bu ürün yerleşim bölgelerinde kullanılırsa parazite neden olabilir. Kullanıcı radyo ve televizyon yayınlarında paraziti
önlemek üzere elektromanyetik salınımları azaltacak özel önlemler almadıkça bu şekilde kullanımdan kaçınılmalıdır.
Yalnızca pakette bulunan kablo ve aksesuarları kullanın. Belgelerde özellikle belirtilmedikçe başka aksesuar ve
kablolar kullanmayın.
USB aygıtları bu TeraStation serisine bağlamak için 3 metre ve daha uzun USB kabloları kullanmayın.
CB
The socket-outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily accessible.
Norsk
Utstyr som er koplet til beskyttelsesjord via nettplugg og/eller via annet jordtilkoplet utstyr – og er tilkoplet et
kabel-TV nett, kan forårsake brannfare.
For å unngå dette skal det ved tilkopling av utstyret til kabel-TV nettet installeres en galvanisk isolator mellom
utstyret og kabel- TV nettet.
Svensk
Utrustning som är kopplad till skyddsjord via jordat vägguttag och/eller via annan utrustning och samtidigt
är kopplad till kabel-TV nät kan i vissa fall medföra risk för brand. För att undvika detta skall vid anslutning av
utrustningen till kabel-TV nät galvanisk isolator finnas mellan utrusningen och kabel-TV nätet.
230

For Customers in Taiwan
BSMI
警告使用者 :
此為甲類資訊技術設備,於居住環境中使用時,可能會造成射頻擾動,在此種情況下,使用者會被要求採取某
些適當的對策。
231