Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About This Guide
- 1 Product Introduction
- Switch Description
- Front Panel Description
- LED Indicators
- Rear Panel Description
- Side Panel Description
- Gigabit Fiber Ports
- Connecting the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to the RPS Port (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME only)
- Installing the RPS into a Rack-mount Chassis (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME only)
- 2 Hardware Installation
- 3 Getting Started
- 4 Configuration
- Web-based Management
- Tool Bar > Save Menu
- Tool Bar > Tool Menu
- Tool Bar > Online Help
- Function Tree
- Device Information
- System > System Settings
- System > Firmware Information
- System > Serial Port Settings
- System > IP Interface
- System > Static ARP Settings
- System > IPv6 System Settings
- System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
- System > DHCP Auto Configuration
- System > DHCP Auto Image
- System > Port Configuration > Port Settings
- System > Port Configuration > Port Description
- System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
- System > Port Configuration > Port Media Type
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID
- System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings
- System > User Accounts
- System > MAC Address Aging Time
- System > ARP Aging Time Settings
- System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings
- System > Web Settings
- System > Telnet Settings
- System > Password Encryption
- System > Ping Test
- System > MAC Notification Settings
- System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
- System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server
- System > Time Profile
- System > Power Saving
- System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings
- System > SMTP Service > SMTP Server Settings
- System > SMTP Service > SMTP Service
- System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings
- Configuration > Jumbo Frame
- Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
- Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Settings
- Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Trunk
- Configuration > VLAN Status
- Configuration > MAC-Based VLAN Settings
- Configuration > GVRP Settings
- Configuration > GVRP Timer Settings
- Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings
- Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation CVID Entry Settings
- Configuration > Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings
- Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol Group Settings
- Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings
- Configuration > VLAN Trunk Settings
- Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings
- Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
- Configuration > BPDU Protection Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > ISM VLAN Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IP Multicast Profile Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Limited Multicast Range Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Max Multicast Group Settings
- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
- Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
- Configuration > Port Mirroring
- Configuration > Loopback Detection
- Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
- Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings
- Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings
- Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings
- Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
- Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings
- Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings
- Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information
- Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings
- Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
- Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
- Configuration > DULD > DULD Global Settings
- Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
- Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filtering
- Configuration > ERPS Setting
- QoS > Traffic Control
- QoS > Bandwidth Control
- QoS > CoS Scheduling Mechanism
- QoS > CoS Output Scheduling
- QoS > 802.1p Default Priority
- QoS > 802.1p User Priority
- QoS > DSCP Priority Settings
- QoS > Priority Settings
- RMON > RMON Basic Settings
- RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
- RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
- RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration
- RMON > RMON Event Configuration
- Security > Trusted Host
- Security > Safeguard Engine
- Security > CPU Protect
- Security > Gratuitous ARP
- Security > Port Security
- Security > SSL Settings
- Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
- Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
- Security > Smart Binding > White List
- Security > Smart Binding > Black List
- Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS
- Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN
- Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC
- Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table
- Security > MAC Address Table > Auto Learning Vlan Settings
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Policy Settings
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Application Authentication Settings
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Login Method Lists
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Enable Method Lists
- Security > Access Authentication Control > Local Enable Password Settings
- Security > Traffic Segmentation
- Security > DoS Prevention Settings
- Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening Port Settings
- Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening Vlan Settings
- Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCP Server
- Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCPv6 Server
- Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter ICMPv6
- Security > SSH Settings > SSH Settings
- Security > SSH Settings > SSH Authmode and Algorithm Settings
- Security > SSH Settings > SSH User Authentication Lists
- Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Settings
- Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Local Settings
- Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Authentication State
- Monitoring > Statistics
- Monitoring > Session Table
- Monitoring > CPU Utilization
- Monitoring > Memory Utilization
- Monitoring > Port Utilization
- Monitoring > Packet Size
- Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX)
- Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX)
- Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX)
- Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX)
- Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX)
- Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
- Monitoring > System Log
- Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
- Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
- Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
- Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
- Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
- Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
- Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
- Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
- Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Global Settings
- Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Analyzer Server Settings
- Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Flow Sampler Settings
- Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Counter Poller Settings
- ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
- ACL > Access Profile List
- ACL > ACL Finder
- ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
- ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
- ACL > CPU Filter Finder
- ACL > ACL Flow Meter
- PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only)
- PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only)
- Time-Based PoE > Time Range Settings
- LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
- LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings
- LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
- LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
- LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
- LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
- LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
- LLDP > LLDP-MED Settings
- L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
- L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder
- L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
- L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder
- Appendix A - Ethernet Technology
- Appendix B - Ethernet Technology
D-Link DGS-1210-10P/ME User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for DGS-1210-10P/ME by D-Link which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

User Manual
Product Model : DGS-1210/ME Series
Metro Ethernet Switches
Release 2.10
©Copyright 2016. All rights reserved.

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
i
i
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ............................................................................................................................................. i
About This Guide ............................................................................................................................................. 1
Terms/Usage .................................................................................................................................................. 1
Copyright and Trademarks ............................................................................................................................ 1
1 Product Intr o du ction ................................................................................................................................... 2
Switch Description .......................................................................................................................................... 2
Front Panel Description.................................................................................................................................. 2
LED Indicators ................................................................................................................................................ 6
Rear Panel Description .................................................................................................................................. 8
Side Panel Description ................................................................................................................................. 10
Gigabit Fiber Ports ....................................................................................................................................... 10
Connecting the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to the RPS Port (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME
only).............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Installing the RPS into a Rac k-mount Chassis (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME only) ..... 12
DPS-800 Rac k-mount Chassis ................................................................................................................. 12
2 Hardware Installation ................................................................................................................................ 13
Step 1: Unpacking ........................................................................................................................................ 13
Step 2: Switch Installation ............................................................................................................................ 13
Desktop or Shelf Installation ..................................................................................................................... 13
Rack Installation ....................................................................................................................................... 13
Step 3 – Plugging in the AC Power Cord ..................................................................................................... 14
Power Failure ........................................................................................................................................... 15
3 Getting Started ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Management Options ................................................................................................................................... 16
Using Web-based Management Interface ................................................................................................... 16
Supported Web Browsers ........................................................................................................................ 16
Connectin g to the Sw itch .......................................................................................................................... 16
Accessing the Web-based Management Interface .................................................................................. 17
Web-based Management ............................................................................................................................. 17
D-Link Network Assistant (DNA) .................................................................................................................. 17
4 Configuration ............................................................................................................................................. 19
Web-based Management ............................................................................................................................. 19
Tool Bar > Save Menu ................................................................................................................................. 20
Save Configuration ................................................................................................................................... 20
Save Log .................................................................................................................................................. 20
Tool Bar > Tool Menu .................................................................................................................................. 20
Reset System ........................................................................................................................................... 20
Reboot Device .......................................................................................................................................... 21
Configuration Backup & Restore .............................................................................................................. 21
Firmware Backup & Upgrade ................................................................................................................... 22
Flash Information ...................................................................................................................................... 23
Tool Bar > Online Help ................................................................................................................................. 23
Function Tree ............................................................................................................................................... 23
Device Information.................................................................................................................................... 24
System > System Settings ....................................................................................................................... 24
System > Firmware Information ............................................................................................................... 25
System > Serial Port Settings................................................................................................................... 26
System > IP Interface ............................................................................................................................... 26

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
i
ii
i
System > Static ARP Settings .................................................................................................................. 27
System > IPv6 System Settings ............................................................................................................... 27
System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings ............................................................................................................ 28
System > DHCP Auto Configuration ........................................................................................................ 29
System > DHCP Auto Image .................................................................................................................... 29
System > Port Configuration > Port Settings ........................................................................................... 29
System > Port Configuration > Port Descripti on ...................................................................................... 30
System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled ................................................................................. 30
System > Port Configuration > Port Media Type ...................................................................................... 31
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State ..................................................................................... 31
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table ........................................................................................ 31
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table ..................................................................................... 32
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table ....................................................................................... 33
Sy stem > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table ............................................................................. 33
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table ........................................................................................ 33
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID ......................................................................................... 34
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings .................................................................................... 34
System > User Accounts .......................................................................................................................... 35
System > MAC Address Aging Time ........................................................................................................ 35
System > ARP Aging Time Settings ......................................................................................................... 36
System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings ......................................................................................... 36
System > Web Settings ............................................................................................................................ 37
System > Telnet Settings ......................................................................................................................... 37
System > Password Encryption................................................................................................................ 37
System > Ping Test .................................................................................................................................. 37
System > MAC Notification Settings ........................................................................................................ 38
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings .................................................................. 38
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server ..................................................................... 39
System > Time Profile .............................................................................................................................. 39
System > Power Saving ........................................................................................................................... 40
System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings ...................................................................................................... 40
System > SMTP Service > SMTP Server Settings .................................................................................. 41
System > SMTP Service > SMTP Service ............................................................................................... 41
System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings ............................................................................................ 42
Configuration > Jumbo Frame .................................................................................................................. 43
Configura tio n > 802.1Q VL AN .................................................................................................................. 43
Configura tio n > Privat e VL AN > Private VL AN Sett in g s .......................................................................... 45
Configura tio n > Privat e VL AN > Private VL AN T runk .............................................................................. 46
Configuration > VLAN Status ................................................................................................................... 47
Configuration > MAC-Based VLAN Settings ............................................................................................ 48
Configura tio n > GVRP Sett i ngs ................................................................................................................ 48
Configuration > GVRP Timer Settings ..................................................................................................... 49
Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings ..................................................................................................... 49
Configura tio n > QinQ > VLAN Tr ans lation C VID Entr y Settings .............................................................. 50
Configuration > Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings ............................................................................... 51
Configuration > 802.1v Prot oc ol VL AN > 802.1 v Protoc ol Grou p Settings .............................................. 52
Configura tio n > 802.1 v Prot oc ol VLAN > 802.1v Prot oc ol VL AN Sett ings............................................... 52
Configuration > VLAN Trunk Settings ...................................................................................................... 53
Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings ................................................................................. 53

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
iii
Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings.......................................................................... 54
Configuration > BPDU Protection Settings ............................................................................................... 54
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping ................................................................................. 55
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings .......................................................... 57
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > ISM VLAN Settings ........................................................................... 58
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table ......................................................................................... 59
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IP Multicast Profile Settings .............................................................. 59
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Limited Multicast Range Settings ...................................................... 60
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Max Multicast Group Settings ........................................................... 60
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings .............................................. 61
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings ...................................................................... 62
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table .................................................................................. 63
Configuration > Port Mirroring .................................................................................................................. 63
Configuration > Loopback Detection ........................................................................................................ 63
Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings ...................................................................................... 64
Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings .............................................................................. 65
Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings ...................................... 66
Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings .................................. 67
Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings ............................................................................................ 68
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings .................................................................................................. 68
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Settings .................................................................................. 69
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings ................................................................ 69
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings ............................................................................... 71
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification ......................................................... 72
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings ........................................................................ 73
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information ....................................................................... 74
Configura tio n > Ethern et O AM > Ether net O AM Port S etti ngs ................................................................ 74
Configura tio n > Ethern et O AM > Ether net O AM Event Configuratio n ..................................................... 75
Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings ..................................................................................................... 76
Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Threshold Settings .............................................................. 76
Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Set tin gs Thr eshold Set tin gs ......................................................... 77
Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings ............................................................... 78
Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings ................................................................... 78
Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings ................................................................... 79
Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table .............................................................................................. 79
Configuration > DULD > DULD Global Settings ....................................................................................... 80
Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings .......................................................................................... 80
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filtering ..................................................... 80
Configuration > ERPS Setting .................................................................................................................. 81
QoS > Traffic Control ................................................................................................................................ 82
QoS > Bandwidth Control ......................................................................................................................... 83
QoS > CoS Scheduling Mechanism ......................................................................................................... 84
QoS > CoS Output Scheduling ................................................................................................................ 84
QoS > 802.1p Default Priority................................................................................................................... 85
QoS > 802.1p User Priority ...................................................................................................................... 85
QoS > DSCP Priority Settings .................................................................................................................. 86
QoS > Priorit y Settings ............................................................................................................................. 86
RMON > RMON Basic Set ti ngs ................................................................................................................ 87
RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration ................................................................................... 87

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
i
iv
v
RMON > RMON History Control Configuration ........................................................................................ 87
RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration ...................................................................................................... 88
RMON > RMON Event Configuration ....................................................................................................... 88
Security > Trusted Host ............................................................................................................................ 89
Securit y > Safegu ard Eng in e.................................................................................................................... 89
Securit y > CPU Protect ............................................................................................................................ 89
Security > Gratuitous ARP ....................................................................................................................... 90
Securit y > Port Security ............................................................................................................................ 91
Securit y > SSL Settings ............................................................................................................................ 91
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings ................................................................................. 92
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding ............................................................................................... 93
Security > Smart Binding > White List ...................................................................................................... 94
Security > Smart Binding > Black List ...................................................................................................... 94
Securit y > Sm art Binding > DHCP Snoop ing List .................................................................................... 95
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings ....................................................................................................... 95
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User ............................................................................................................. 97
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS ............................................................................... 97
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN ................................................................................................ 98
Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC .......................................................................................... 98
Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table ................................................................. 99
Security > MAC Address Table > Auto Learning Vlan Settings ............................................................. 100
Securit y > Access Authent i c ation Contr ol > Authent ic a tion Policy Settings .......................................... 100
Security > Access Authentication Control > Application Authentication Settings .................................. 100
Security > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group ............................................ 101
Securit y > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server ....................................................... 102
Securit y > Access Authent i c ation Contr ol > Login Met h od Lis ts ............................................................ 103
Security > Access Authent i c ation Contr ol > Enabl e Me thod List s ......................................................... 103
Securit y > Access Authent i c ation Contr ol > Local Ena ble Password Settings ...................................... 104
Security > Traffic Segmentation ............................................................................................................. 104
Securit y > DoS Preven tio n Sett ings ....................................................................................................... 105
Securit y > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng Port Sett in gs ...................................... 105
Securit y > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng Vlan Sett in gs ...................................... 106
Security > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng > Filter DHC P Ser v er .................................................................... 106
Securit y > DHCP Ser ver Scr eeni ng > Filter DHC P v6 Ser ver ................................................................ 106
Securit y > DHCP Ser ver Scr eening > Filter ICMPv6 ............................................................................. 107
Security > SSH Settings > SSH Settings ............................................................................................... 108
Security > SSH Settings > SSH Authmode and Algorithm Settings ...................................................... 109
Security > SSH Settings > SSH User Authentication Lists .................................................................... 110
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Settings ........................ 110
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Local Settings .............. 111
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Authentication State .... 112
Monitori ng > Statis tics ............................................................................................................................ 112
Monitori ng > Sessio n T able .................................................................................................................... 113
Monitoring > CPU Utilization .................................................................................................................. 113
Monitori ng > Mem ory Utili z atio n ............................................................................................................. 114
Monitori ng > Port Util izat ion ................................................................................................................... 114
Monitori ng > Packet Size ........................................................................................................................ 115
Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX) .............................................................................................. 116
Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX) .................................................................................................. 117

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
v
Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) ................................................................................................. 118
Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX) ..................................................................................................... 119
Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX).................................................................................................. 120
Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics ............................................................................................................. 122
Monitori ng > Syst em Log ........................................................................................................................ 122
Monitori ng > Bro wse ARP T able ............................................................................................................ 123
Monitori ng > Ether net O AM > Browse Ether net O AM Even t Log .......................................................... 123
Monitori ng > Ether net O AM > Bro wse Ether net O AM St atist ic s ............................................................ 124
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group ........................................................................ 124
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host ........................................................................... 124
Monitori ng > MLD Snoop in g > MLD Snooping Group ............................................................................ 125
Monitori ng > Port Acc es s Control > RADIUS Au the ntication ................................................................. 125
Monitori ng > Port Acc es s Control > RADIUS Ac count Client ................................................................ 126
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Global Settings .......................................................................................... 127
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Analyzer Server Settings ........................................................................... 128
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Flow Sampler Settings .............................................................................. 129
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Counter Poller Settings ............................................................................. 129
ACL > ACL Configur ati on Wizard ........................................................................................................... 130
ACL > Access Profile List ....................................................................................................................... 131
ACL > ACL Finder .................................................................................................................................. 132
ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard ................................................................................................. 132
ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List ..................................................................................................... 133
ACL > CPU Filter Finder ......................................................................................................................... 134
ACL > ACL Flow Meter ........................................................................................................................... 134
PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only) ............................. 136
PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only) ........................ 138
Time-Based PoE > Time Range Settings .............................................................................................. 138
LLDP > LLDP Global Settings ................................................................................................................ 139
LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Sett ings .......................................................................................................... 139
LLDP > 802.1 Extensi on LL D P Port Sett ings ......................................................................................... 140
LLDP > 802.3 Extensi on LL D P Port Sett ings ......................................................................................... 141
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings ....................................................................................... 141
LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table ................................................................................................................ 142
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table ........................................................................................... 143
LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table .............................................................................................................. 143
LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table .......................................................................................................... 144
LLDP > LLDP-MED Set t ing s .................................................................................................................. 146
L3 Functions > IP v4 Static Route ........................................................................................................... 146
L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder ............................................................................................. 147
L3 Functions > IP v6 Static Route ........................................................................................................... 147
L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder ............................................................................................. 148
Appendix A - Ethernet Technology ............................................................................................................ 149
Gigabit Ethernet Technology ..................................................................................................................... 149
Fast Ethernet Technology .......................................................................................................................... 149
Switching Technology ................................................................................................................................ 149
Appendix B - Ethernet Technology ............................................................................................................ 150
Features ..................................................................................................................................................... 150
L2 Features ............................................................................................................................................ 150
VLAN ...................................................................................................................................................... 150

Table of Contents DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
v
vi
i
L3 Features ............................................................................................................................................ 150
QoS (Quality of Service) ......................................................................................................................... 150
Security ................................................................................................................................................... 151
OAM ....................................................................................................................................................... 151
Management ........................................................................................................................................... 151

About This Guide DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
About This Guide
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how install the D-Link DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet
Switches, how to use the Web Utility, and how to perform web-based management functions.
Note: The model you have purch
ased may
appear slightly different from the illustrations
shown in the document. Refer to the Product
Instruction and Technical Specification sections
for detailed in
formation about your switch, its
components , network connections, an d technical
specifications.
This guide is mainly divided into three parts:
1. Hard ware Ins ta lla ti on: Ste p -by-step hardware installation procedures.
2. Getting Started: A startup guide for basic switch installation and settings.
3. Configuration: Information about the function descriptions and configuration settings.
Terms/Usage
In this guide, the term “Switch” (first letter capitalized) refers to DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch, and
“switch” (f irst letter lower case) refer s to other Ethernet s witches. Som e technologies r efer to terms “switch”,
“bridge” and “switching hubs” interchangeably, and both are commonly accepted for Ethernet switches.
A NOTE indicates important information that
helps a better use of the device.
A CAUTION indicates pote ntial prop ert y damage
or persona l injury.
Copyright and Trademarks
Information in this document is subjected to change without notice.
© 2016 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of D-Link Corporation is strictly
forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-LINK logo are trademarks of D-Link Corporation; Microsoft
and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other tradem arks and trade nam es may be used in this docum ent to refer to either the entities claiming the
mark s and names or their pr oducts. D-Link Corporation discl aims any propri etary interest i n trademark s and
trade names other than its ow n.

1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
1 Product Introduction
Switch Description
Front Panel Description
LED Indicators
Rear Panel Description
Side Panel Description
Connecting the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to the RPS Port (for DGS-1210-
10/12TS/20/28X/28XS/52/ME only)
Installing the RPS into the Rack-mount Chassis (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28X/28XS/52/ME only)
Switch Description
The DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch is equipped with Copper ports (10/100/1000Mbps) and SFP
ports (1000Mbps) that can be used to attach various networking devices to the network like Computers,
Notebooks, Print Servers, Network Attached Storage devices, IP Cameras, VoIP PBX devices, and other
Switches . T he Small Form Factor Porta ble (SFP) ports can be us ed t oget her with f iber -optic a l trans c eiver s i n
order to connect various other networking devices, using a fiber-optic connection, to the network at Gigabit
Ethernet speeds over great distances.
This DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch provides unsurpassed performance, fault tolerance, scalability,
robust security, standard-based interoperability and impressive technolog y to future-proof departmental and
enterprise network deployments.
It allows IGMP Snooping and Authentication, QoS, Bandwidth Control, ACL and many security functions. It
can be managed by Web UI, or commands via Telnet.
The DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switches have different port configuration (10/100/1000Base-T or SFP
ports) that may be used in to uplink various network devices to the Switch, including PCs, hubs and other
switches to provide a gigabit Ethernet uplink in full-duplex mode. The SFP (Small Form Factor Portable)
ports are used with fiber-optical transceiver cabling in order to uplink various other networking devices for a
gigabit link that may span great distances.
Front Panel Description
The front panel of the DGS-1210-10/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 8 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 2 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, RPS, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 10
Figure 1.1 – DGS-1210-10/ M E F ront Pane l
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
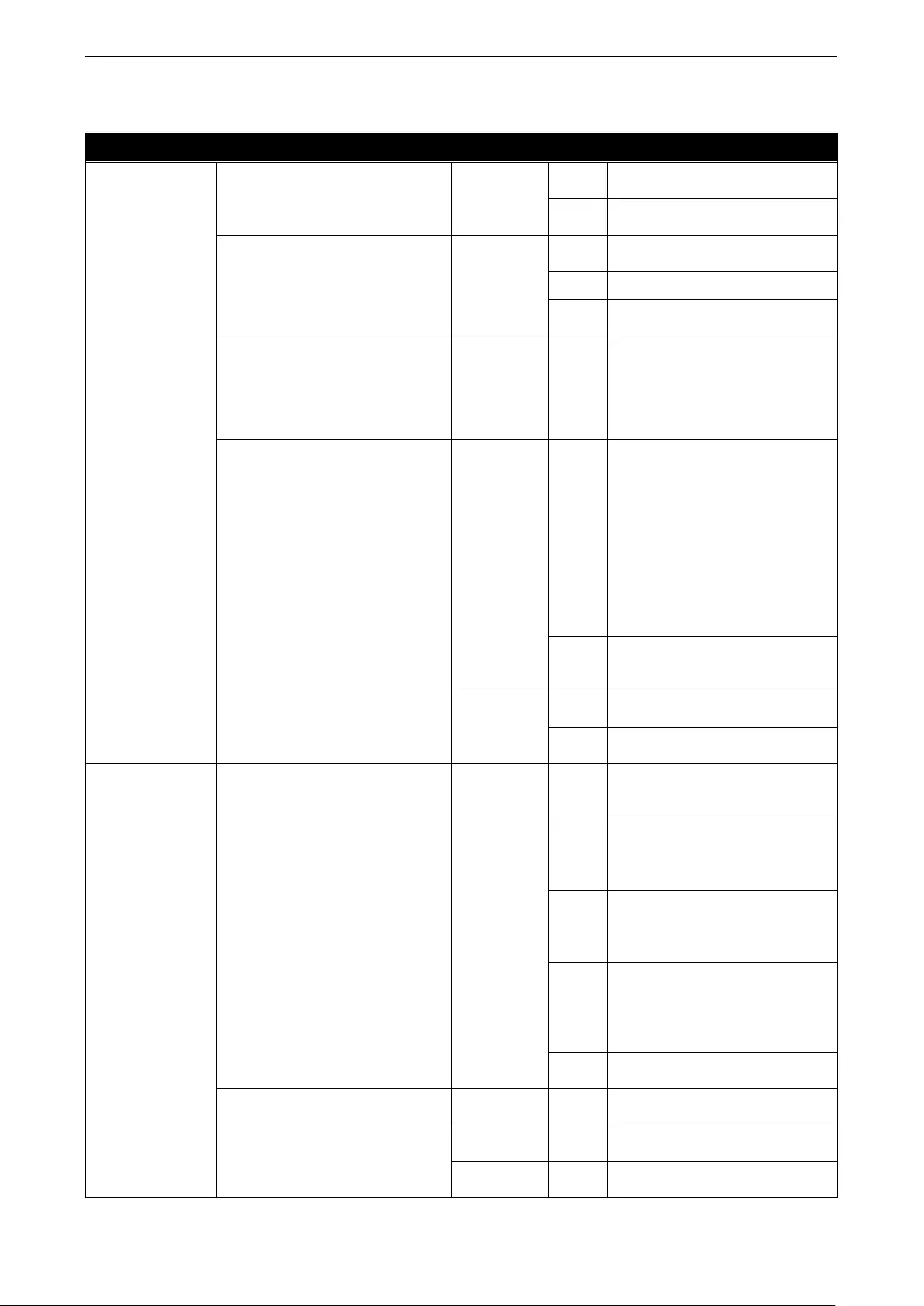
The front panel of the DGS-1210-10P/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 8 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 2 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, PoE Max, Console, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 10
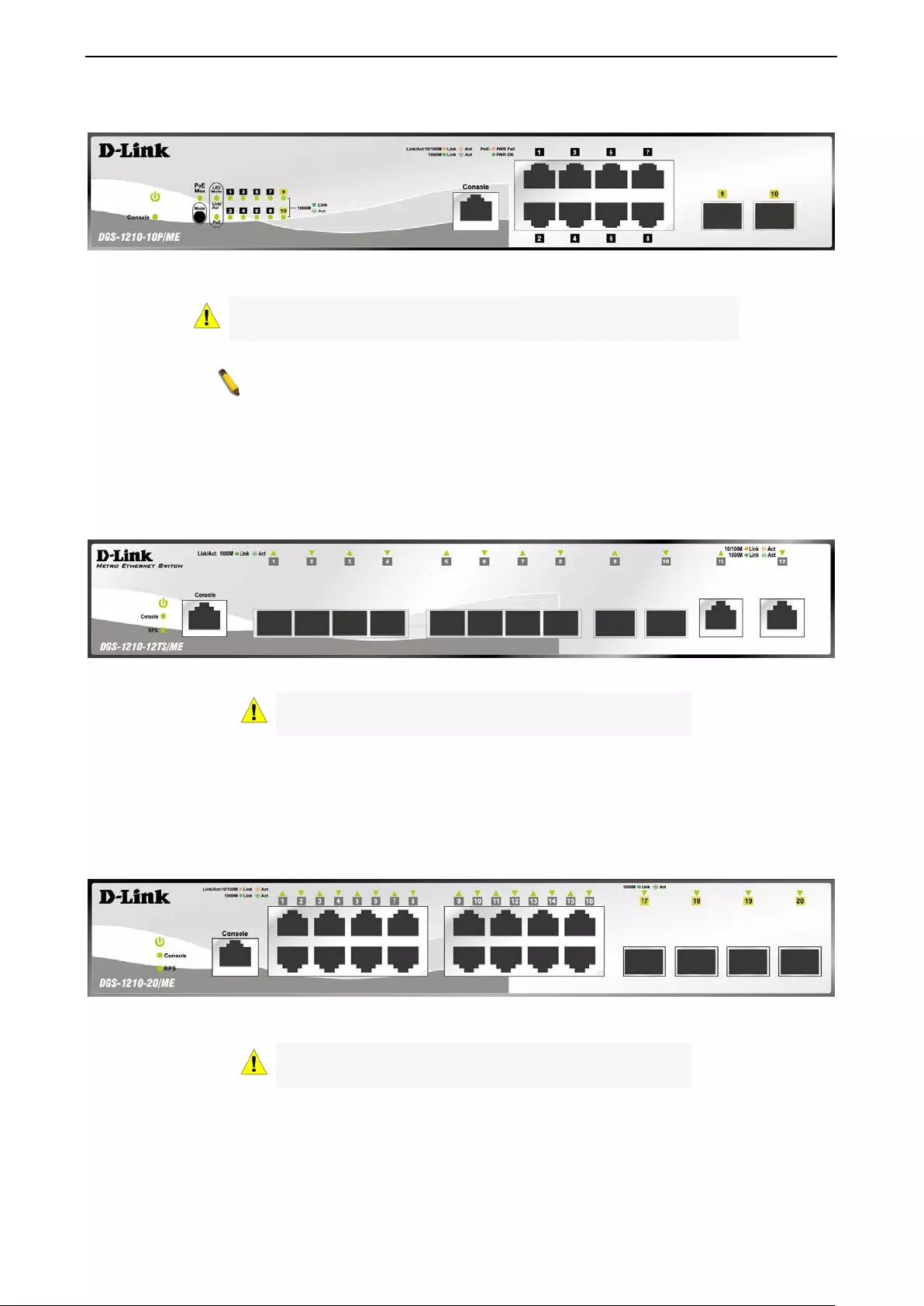
1 Product Introduc tion DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
3
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes.
Figure 1.2 – DGS-1210-10P/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 78 Watts for DGS-1210-10P/ME.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-12TS/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 10 1000Mbps SFP por t
• 2 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, RPS, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 12
Figure 1.3 – DGS-1210-12TS/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-20/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 16 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, RPS, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 20
Figure 1.4 – DGS-1210-20/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-28/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 24 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
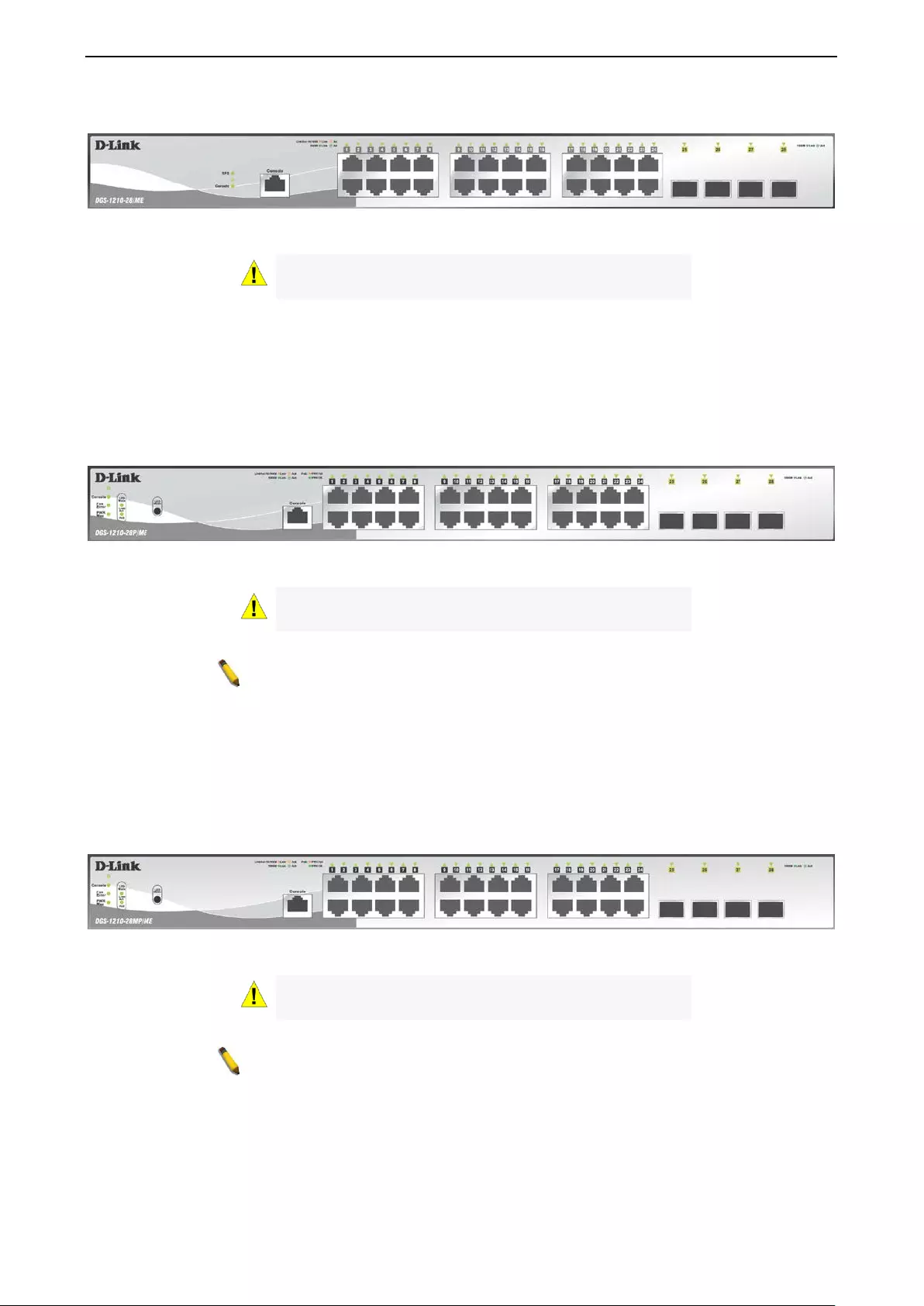

1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
• LEDs for Power, RPS, Con s ole, Link /Act for port 1 ~ 28
Figure 1.5 – DGS-1210-28/ M E F r ont Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-28P/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 24 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, Pwr Max, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 28
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes
Figure 1.6 – DGS-1210-28P/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 193 Watts for DGS-1210-28P/ME.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-28MP/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 24 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP port
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, Pwr Max, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 28
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes
Figure 1.7 – DGS-1210-28MP/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 370 Watts for DGS-1210-28MP/ME.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-28X/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 24 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps/10G SFP+ port
• One RJ-45 Console Port
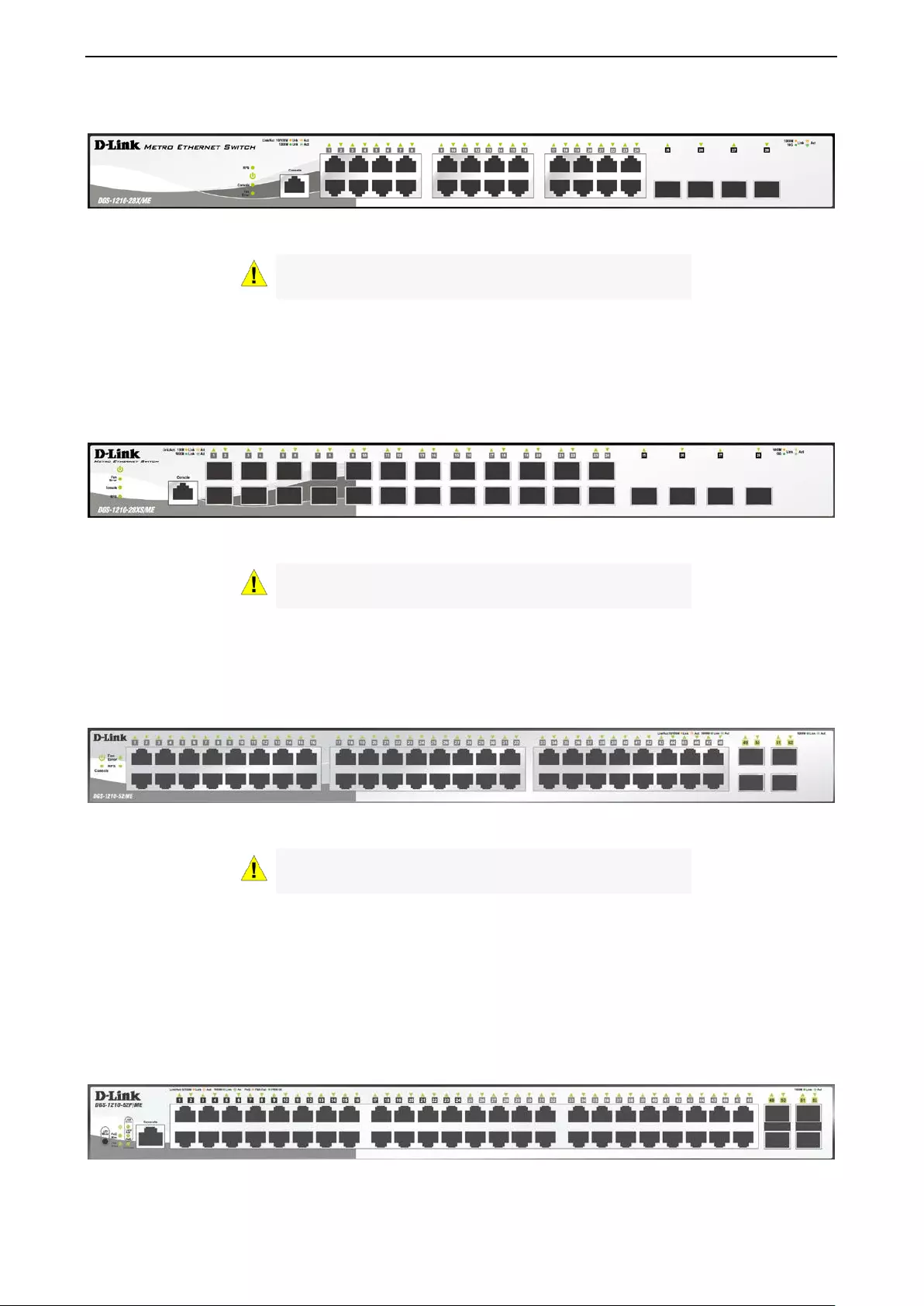
1 Product Introduc tion DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
5
• LEDs for RPS, Power, Console, Fan Error, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 28
Figure 1.8 – DGS-1210-28X/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-28XS/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 24 100/1000Mbps SFP port
• 4 1000Mbps/10G SFP+ ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, RPS, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 28
Figure 1.9 – DGS-1210-28XS/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-52/ME switch consists o ut of the following:
• 48 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error , RPS, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 52
Figure 1.10 – DGS-1210-52/ME Front Panel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL listed
Optical Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-52P/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 48 10/100/1000Mbps Copper Ports
• 24 10/100/1 000 Mbps Po E por ts
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, PoE Max, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 52
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes
Figure 1.11 – DGS-1210-52P/ ME Front Pan el
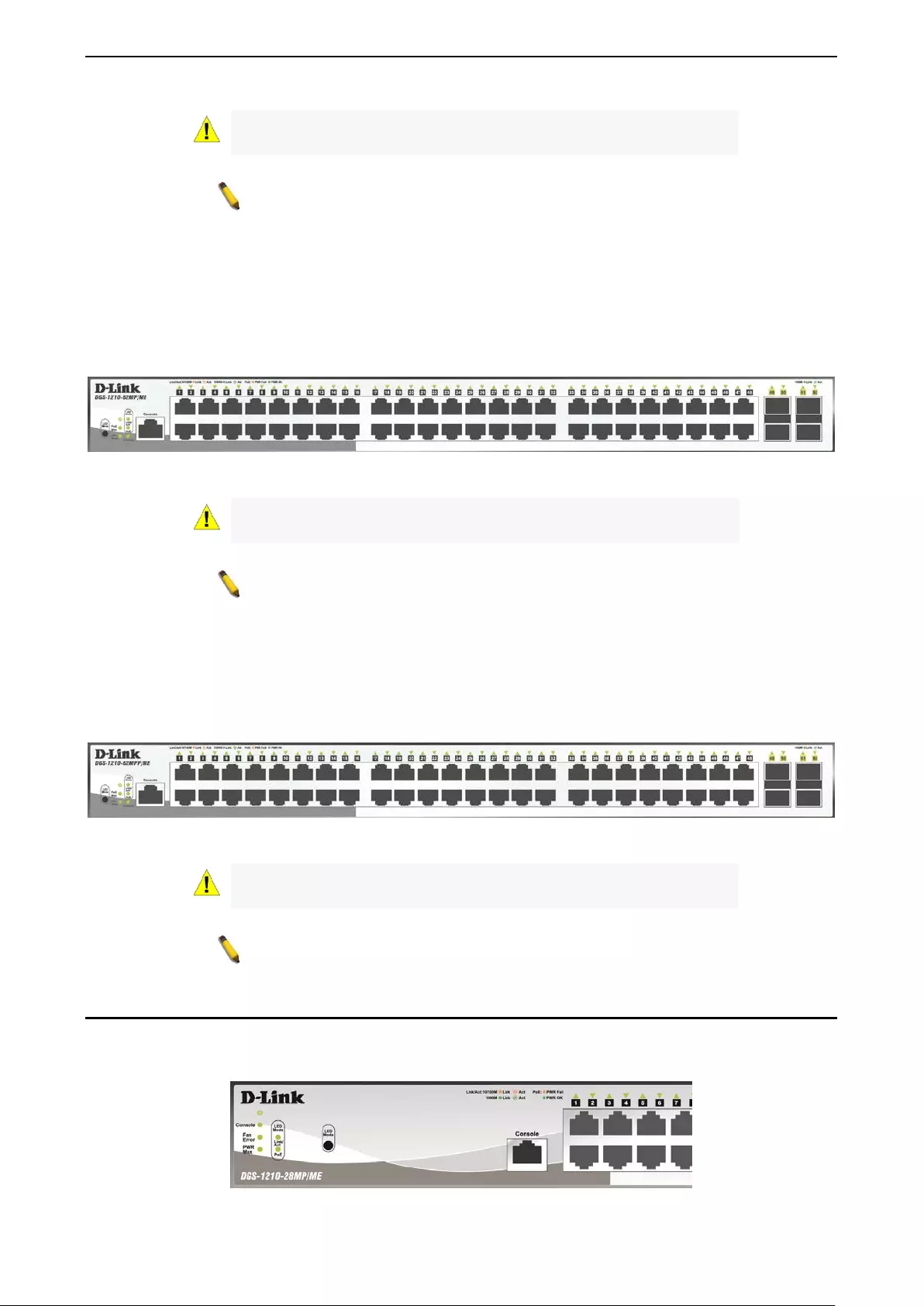
1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 193 Watts for DGS-1210-52P/ME.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-52MP/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 48 10/100/1000Mbps Copper and PoE Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, PoE Max, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 52
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes
Figure 1.12 – DGS-1210-52MP/ME Front Pan el
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 370 Watts for DGS-1210-52MP/ME.
The front panel of the DGS-1210-52MPP/ME switch consists out of the following:
• 48 10/100/1000Mbps Copper and PoE Ports
• 4 1000Mbps SFP ports
• One RJ-45 Console Port
• LEDs for Power, Console, Fan Error, PoE Max, Link/Act for port 1 ~ 52
• Mode: By pressing the Mode button, the Port LED will switch between Link/Act and PoE modes
Figure 1.13 – DGS-1210-52MPP/ME Front P anel
CAUTION: The MiniGBIC ports should use UL
listed Optical
Transceiver product, Rated Laser Class I. 3.3Vdc.
NOTE: The power budget is 740 Watts for DGS-1210-52MPP/ME.
LED Indicators
The Switch supports LED indicators for Power, Console, Fan, and Link/Act for each port. The following
shows the LED indicators for the DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch along with an explanation of each
indicator.
Figure 1.14 –LED Indicators on DGS-1210/ME SERIES
1 Product Introduc tion DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
7
Location LED Indicative Color Status Description
Per Device
Power Green
Solid
Light
Power on.
Light
off
Power off .
Console Green
Solid
Light
Console on.
Blinking
POST is in progress.
Light
off
Console off.
Fan Error
(for DGS-1210-28P/ME,
28MP/ME, 28X/ME, 28XS/ME,
52/ME, 52P/ME, 52MP/ME,
52MPP/ME)
Red Solid
light The fan has runtime failure and
is brought offline.
Pwr/PoE Max.
(for DGS-1210-10P/ME,
28P/ME, 28MP/ME 52P/ME,
52MP/ME, 52MPP/ME)
Red
Solid
light
The Pwr/PoE Max LED lights up
when the total Po E output of
Switch reached or exceeded 71
Watts for DGS-1210-10P/ME,
186 Watts for DGS-1210-
28P/52P/ME, 363 Watts for
DGS-1210-28MP/52MP/ME,
and 733 Watts for DGS-1210-
52MPP/ME.
In the meantime, no
additional PoE device can be
supported.
Light
off
When the system power usage
does not reach the guard band
range.
RPS
(DGS-1210-
10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME)
Green
Solid
Light
RPS power on.
Light
off
RPS power off.
LED Per
10/100/1000
Mbps
Copper Port
Link/Act Green/Amber
Solid
Green
When there is a secure
1000Mbps Ethernet connection
(or link) at any of the ports.
Blinking
Green
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act)
of data occurring at a 1000Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
Solid
Amber
When there is a secure
10/100Mbps Ethernet
connection (or link) at any of the
ports.
Blinking
Amber
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act)
of data occurring at a
10/100Mbps Ethernet connected
port.
Light
off
No link.
PoE Mode
Green
Solid
Light
Power feeding
Amber
Solid
Light
Error Condition
Off
Solid
Off
No Power feeding
1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
LED Per SFP
Port Link/Act
Green
Solid
Green
When there is a secure
1000Mbps Ethernet connection
(or link) at any of the ports.
Blinking
Green
When there is reception or
transmission (i.e. Activity—Act)
of data occurring at a 1000
Mbps
Ethernet connected port.
Amber
Solid
Light
When there is a secure
100Mbps connection at the port.
(For DGS-1210-28XS/ME only)
Blinking
Amber
When there is reception or
transmission occurring at the
port. (For DGS-1210-28XS/ME
only)
Off
Solid
off
No link.
LED Per 10G
SFP+ Port
(for DGS-1210-
28X/ME,
28XS/ME)
Link/Act
Green
Solid
Light
When there is a secure 10Gbps
connection at the port.
Blinking
Green
When there is reception or
transmission occurring at the
port.
Amber
Solid
Light
When there is a secure
1000Mbps connection at the
port.
Blinking
Amber
When there is reception or
transmission occurring at the
port.
Off
Solid
off
No link.
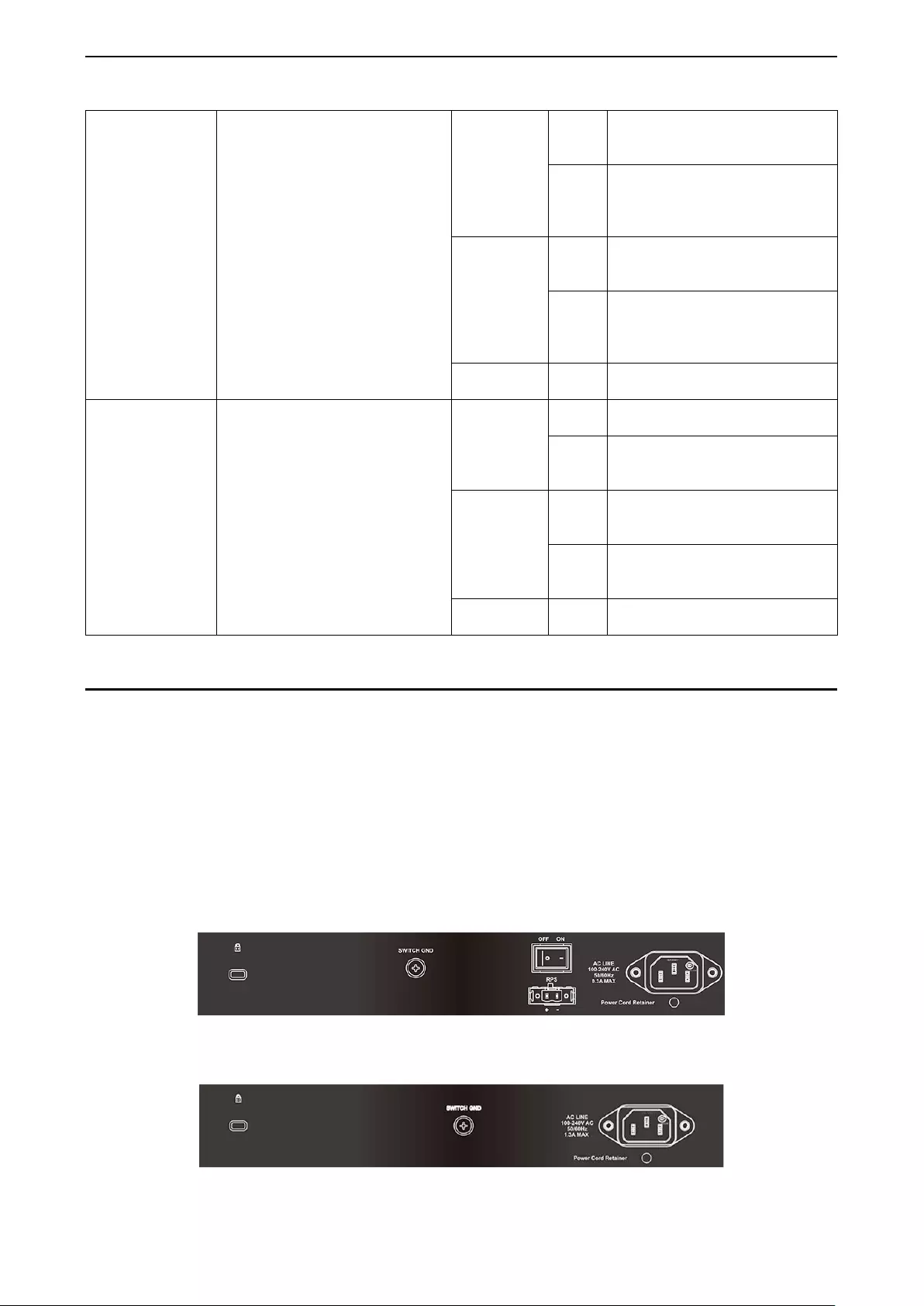
Rear Panel Description
The rear panel of the Switc h conta ins an AC po wer co nnector. T he AC po wer co nnector is a s tandar d three-
pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug-in the female connector of the provided power cord
into this s ocket, and the male s ide of t he c ord int o a power o utl et. The Switch automatically adj usts its po wer
setting to any supply voltage in the range from 100 to 240 VAC at 50 to 60 Hz. Connect the Kensington-
compatible security lock, at the rear of the switch, to a secure immovable device. Insert the lock into the
notch and turn the key to secure the lock.
The rear panel also includes an outlet for an optional external power supply and one RJ-45 console port.
When a power failure occurs, the optional external RPS will immediately and automatically assume the
power supply for the Switch.
DGS-1210-10/ME
Figure 1. 15
-
DGS-1210-10/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-10P/ME
Figure 1. 16
-
DGS-1210-10P/ME Rea r Panel

1 Product Introduc tion DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
9
DGS-1210-12TS/ME
Figure 1. 17
-
DGS-1210-12TS/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-20/ME
Figure 1. 18
-
DGS-1210-20/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-28/ME
Figure 1. 19
-
DGS-1210-28/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-28P/ME
Figure 1. 20
-
DGS-1210-28P/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-28MP/ME
Figure 1. 21
-
DGS-1210-28MP/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-28X/ME
Figure 1. 22
-
DGS-1210-28X/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-28XS/ME
Figure 1. 23
-
DGS-1210-28XS/ME Rear Panel
1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
10
DGS-1210-52/ME
Figure 1. 24
-
DGS-1210-52/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-52P/ME
Figure 1. 25
-
DGS-1210-52P/ME Rear Panel
DGS-1210-52MP/ME
Figure 1. 26
-
DGS-1210-52MP/ME Rear P anel
DGS-1210-52MPP/ME
Figure 1. 27
-
DGS-1210-52MPP/ME R ear Pan el
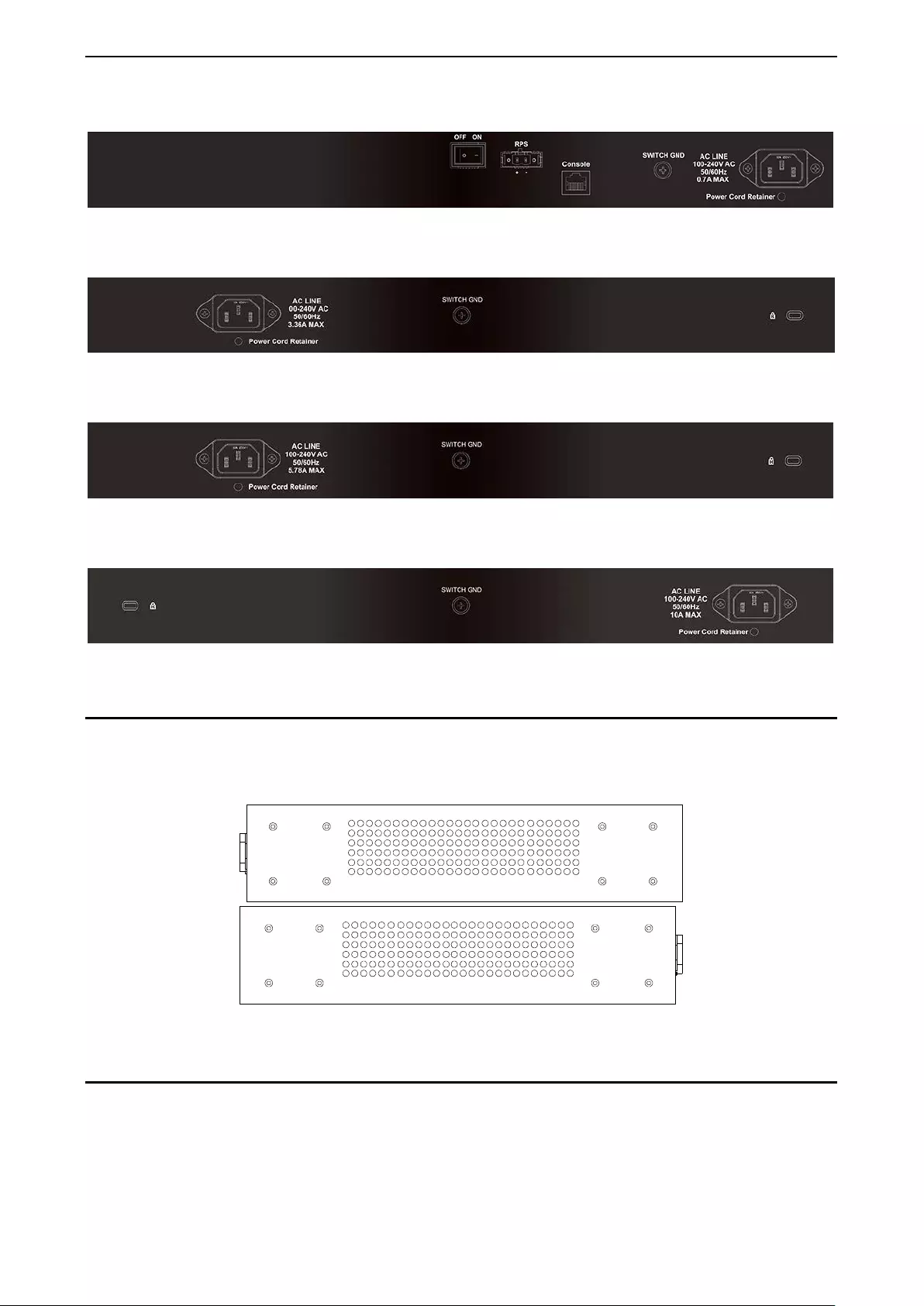
Side Panel Description
The lef t- and right-h and pa nels of th e S witc h ha ve he at v ents t o d iss ipat e h eat. D o no t b lock these op eni ng s ,
and leave at least 6 inches of space at the rear and sides of the Switch for proper ventilation. Be rem inded
that witho ut proper heat dis sipat ion and a ir circ ulatio n, s ystem components m ight overheat, which c ould lea d
to system failure.
Figure 1.28 - Side panels of the DGS-1210/ M E SERIES
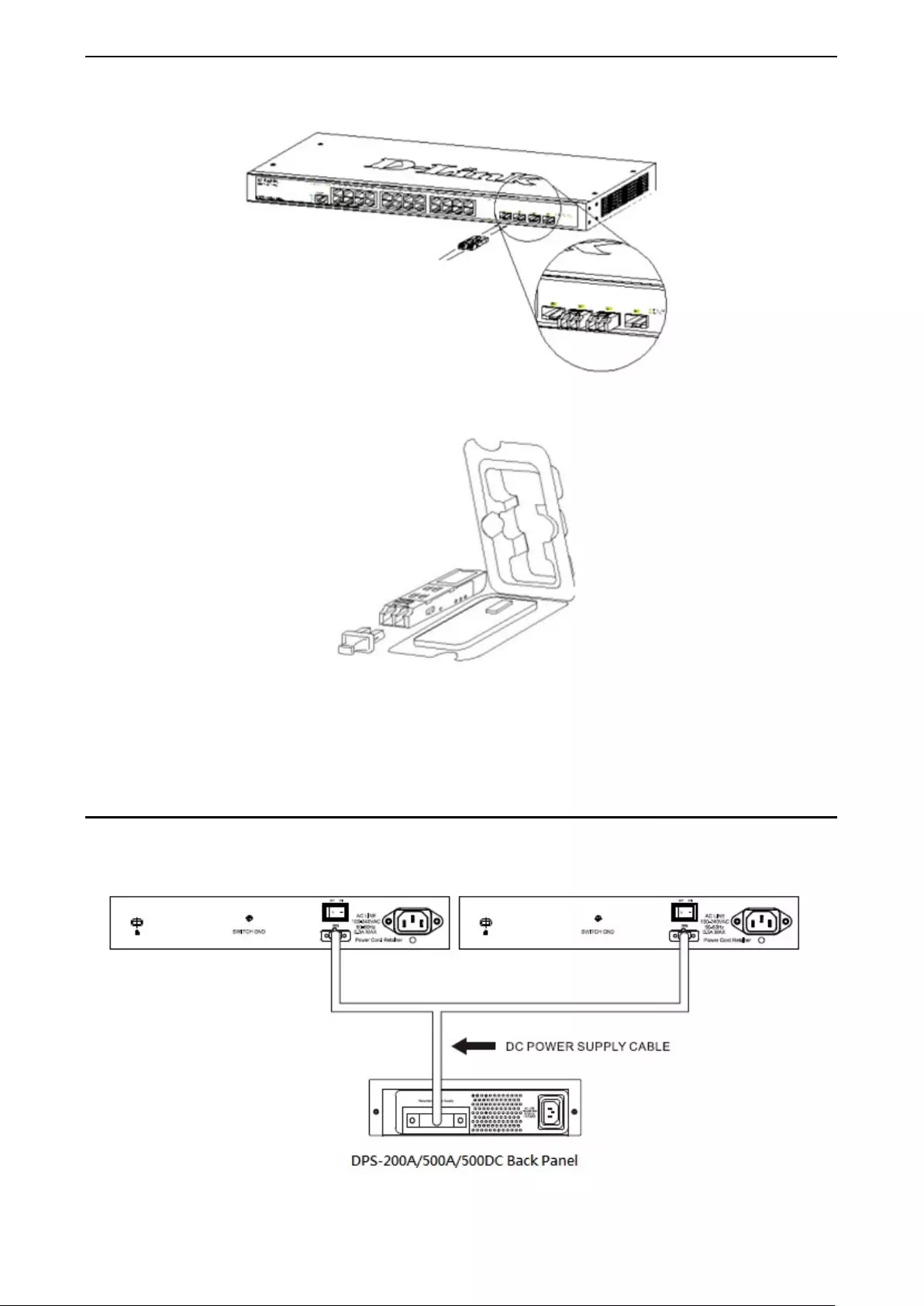
Gigabit Fiber Ports
The DGS-1210/ME Series features support four Sm all Form Factor Porta ble (SFP) por ts (optional). See the
diagram below to view the four SFP port modules being plugged into the Switch.
1 Product Introduc tion DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
1
Figure 1.29 - Inserting the SFP modules into the Switch
Figure 1.30 - Installing the SFP Module
The Switch is equ ipped with SFP ports, which ar e to b e used with fib er-optical tra nsc eiver cabl ing in order to
uplink various other networking devices for a gigabit link that may span great distances.
Connecting the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to the RPS Port (for DGS-1210-
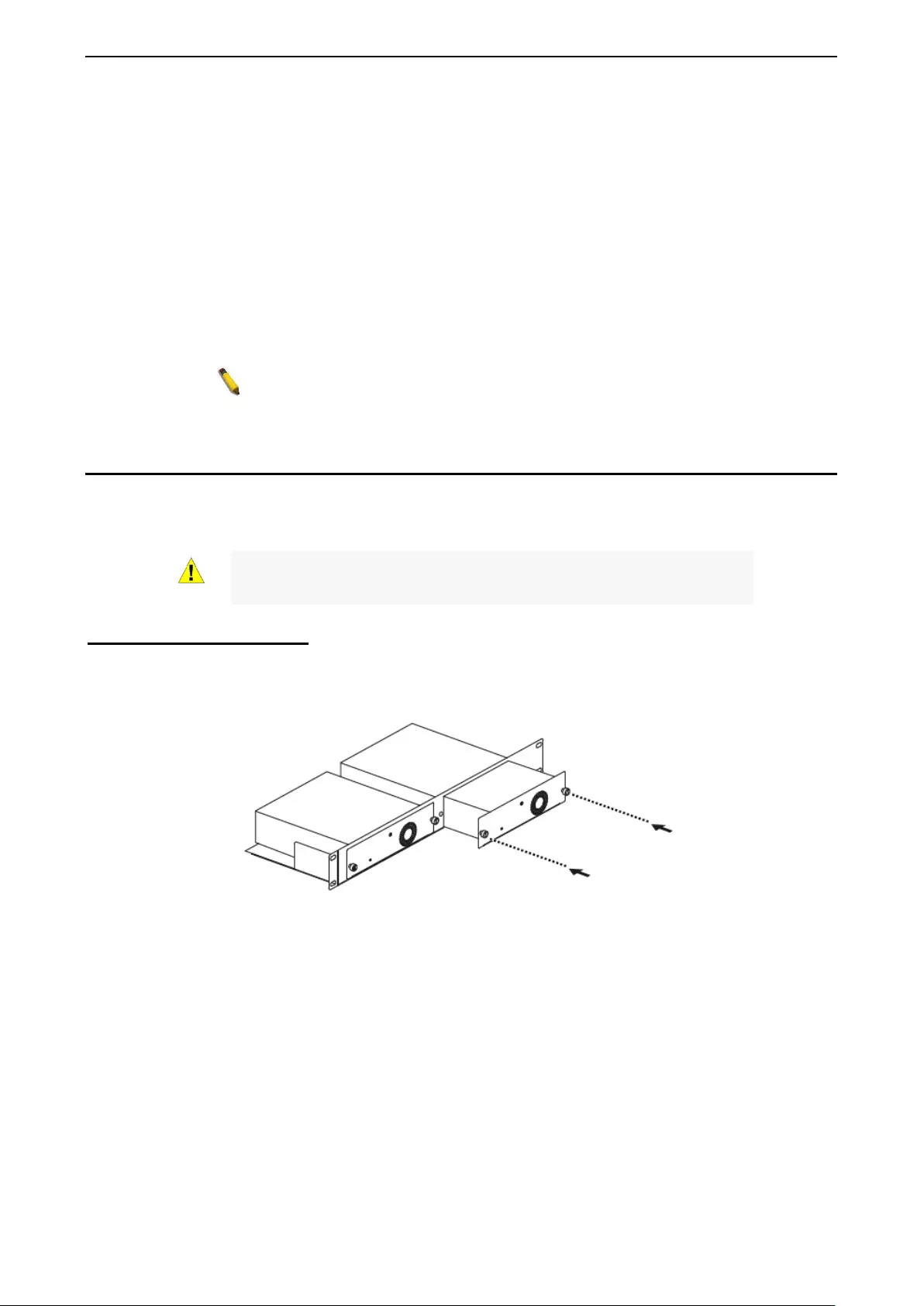
10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME only)
The DPS-200A/500A/500DC redundant po wer suppl y can be c onnected to t he RPS port of the Switch us ing
the DC power supply cord, called the DPS-CB150-2PS. It is important to notice that the DPS-
200A/500A/500DC can supply power to one or two DGS-1210-10/ME at the same time.
Figure 1.31 – Connecting two Swi tches to the DPS-200A/500A/500DC
1 Product Introduction DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
12
The following section explains how to connect the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to the Switch.
• Disconnect the Switch from the main AC power source.
• Insert the 14-pin end of the DPS-CB150-2PS into the DPS-200A/500A/500DC and the 2-pin end into
the receptacle of the RPS port on the Switch.
• Using a s tand ar d AC po we r c ord, c o nnec t the DPS-200A/500A/500DC to th e main AC po wer sour c e.
A green LED on the front panel of the DPS-200A/500A/500DC wi ll illuminate to indicat e a
successful connection.
• Make sure that the ON/OFF toggle switch on the rear panel of the Switch is turned on.
• Re-connect the Switch to the AC power source and power on the DPS-200A/500A/500DC.
No configuration is needed in the Switch software for this installation.
NOTE: See the DPS-200A/500A/500DC Quick Installation Guide for
more information.
Installing the RPS into a Rack-mount Chassis (for DGS-1210-10/12TS/20/28/28X/28XS/52/ME
only)
The DPS-200A/500A/500DC are the redundant power supply unit designed to conform to the voltage
requirements of the RPS port of the Switch being supported. The DPS-200A/500A/500DC can be installed
into a DPS-800 rack-mount chassis unit.
CAUTION: DO NOT connect the RPS to the AC power before the DC
power cable is connected. Connecting the AC power before the DC
power is connected might damage the internal power supply.
DPS-800 Rac k-mount Chassis
The DPS-800 is a standard-size rack-mount (1 standard unit in height) designed to hold up to three DPS-
200A/500A/500DC redundant power supplies.
Figure 1.32 –Installing the DPS-200A/500A/500DC in the DPS-800
The DPS-800 rack-mount chassis can be mounted into a standard 19" rack. Use the following diagram to
guide you.
2 Hardware Installation DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
3
2 Hardware Installation
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the D-Link DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet
Switch.
Step 1: Unpacking
Open the shipping carton and carefully unpack its contents. Please consult the packing list located in the
User Manual to m ak e sure all i tems are present a nd u ndamaged. If an y item is m issing or dam aged, please
contact your local D-Link reseller for replacement.
One D-Link Metro Ethernet Switch
One multi-language Getting Started Guide
One CD
One RJ-45 console cable
Power cord clip
Power cord
Rack mount kit
Rubber feet
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact the local reseller for replacement.
Step 2: Switch Installation
For safe switch installation and operation, it is recommended that you:
Visually inspect the power cord to see that it is secured fully to the AC power connector.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation and adequate ventilation around the switch.
Do not place heavy objects on the switch.
Desktop or Shelf Installation
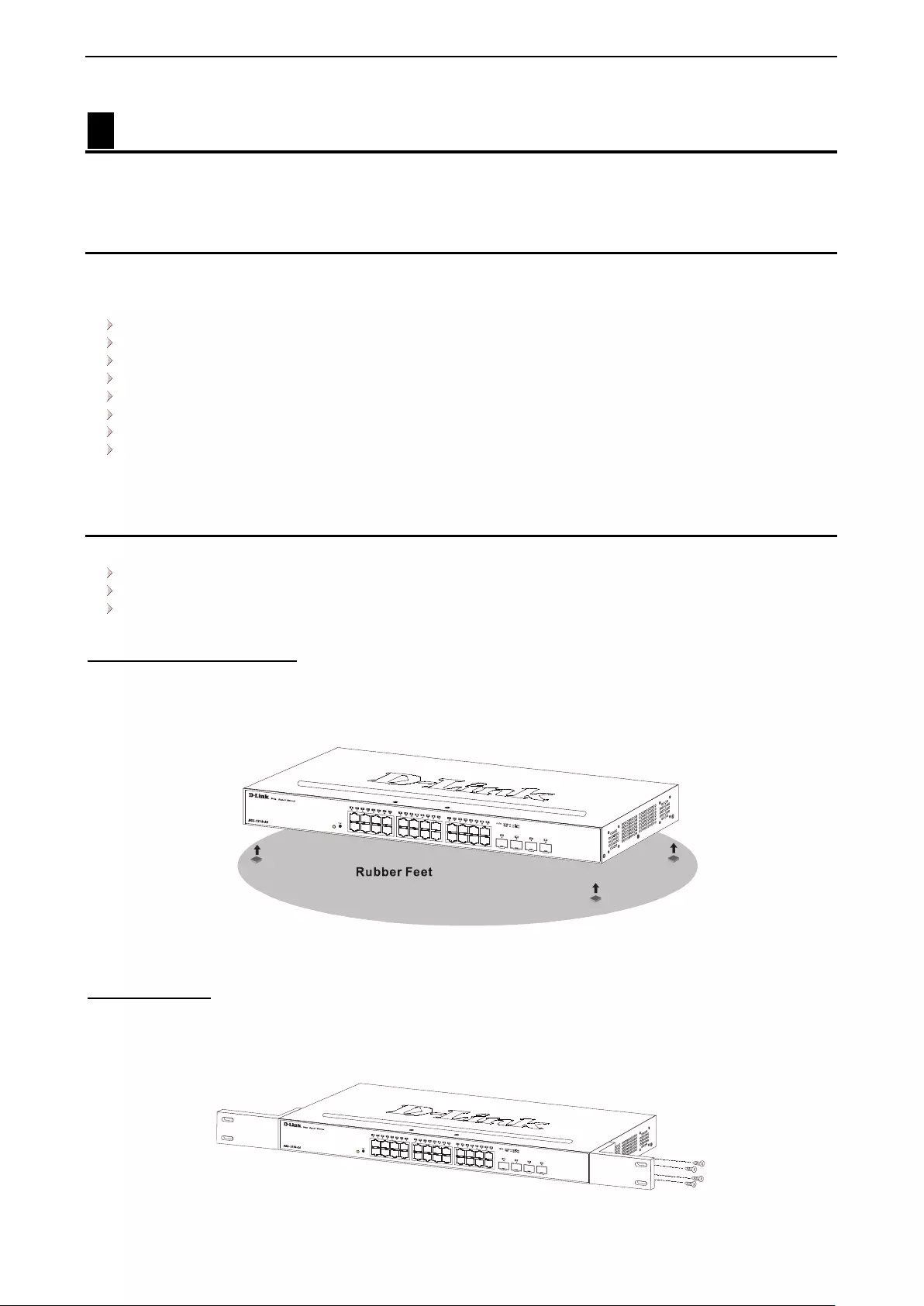
The DG S-1210/ME ser ies s witches c om e with a strip of four adhes ive rub ber pa ds that can be p lace d on the
bottom of the device to pre vent the device from dam aging the desk top or shelf it is places on. To att ach the
rubber pads, simply remove them from the adhesive strip and stick one pad on each corner on the bottom
panel of the Switch.
Figure 2.1 – Attach the adhesi ve rubber pads to the bottom
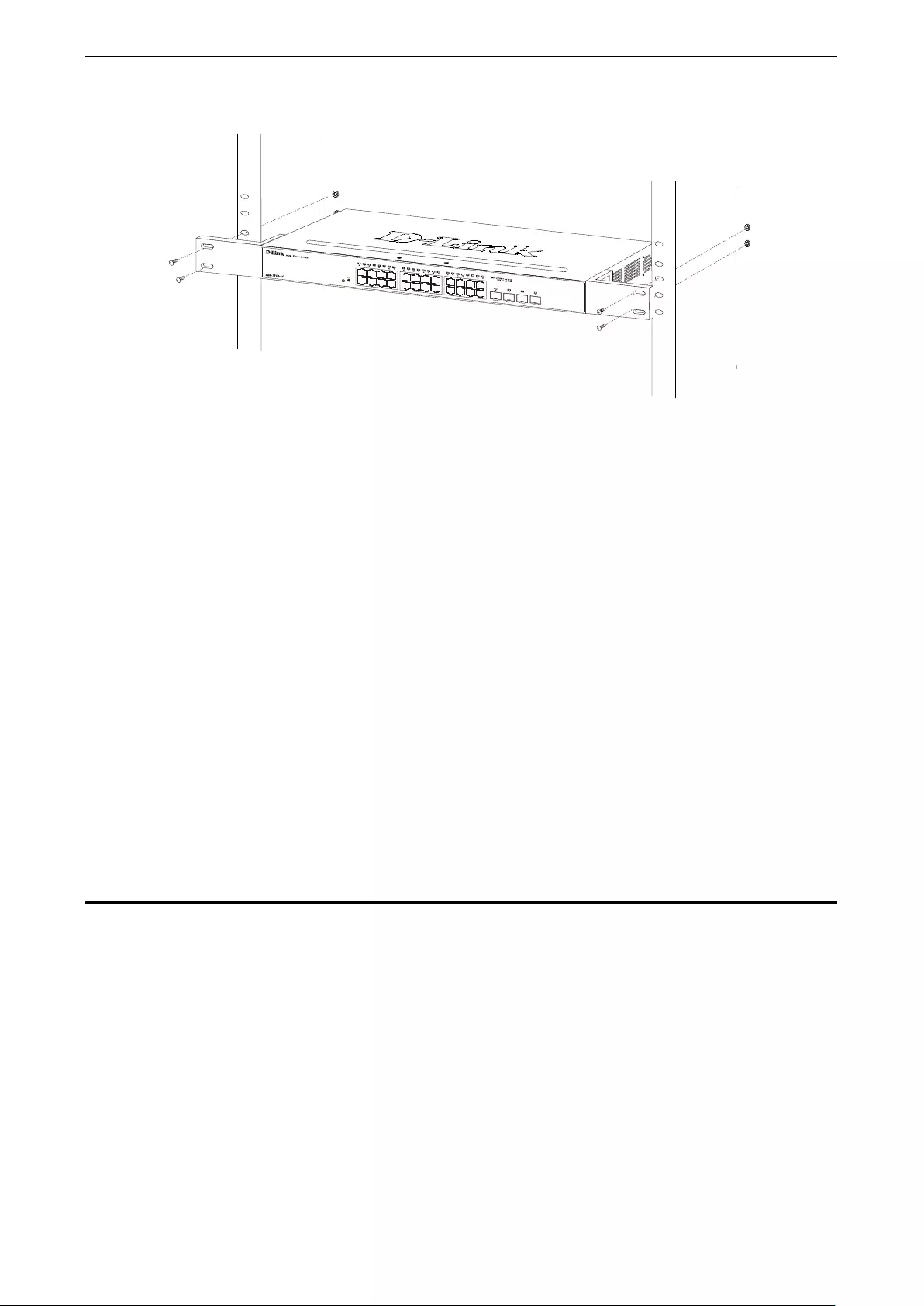
Rack Install at ion
The s witch c a n be mounte d i n an EI A standard size 1 9-inch r ac k , which c a n be p lac ed i n a wir ing closet with
other equ ipment. T o install, attach the m ounting brackets t o the switc h’s side p anels (one on each s ide) and
secure them with the screws provided (please note that these brackets are not designed for palm size
switches).
Figure 2.2 – Attach the mounting brackets to the Switch
2 Hardware Installation DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
14
Then, use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the switch in the rack.
Figure 2.3 – Mount the Switch in the rack or chassis
Please be aware of following safety Instructions when installing:
A) Elevated Operating Ambient - If installed in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating ambient
tem perature of the rac k environm ent ma y be great er than room ambient. T herefor e, considera tion should b e
given to installing the equ ip ment in an enviro nment compatible w ith th e maxim um ambient tem per ature ( Tma)
specified by the manufacturer.
B) Reduced Air Flow - Installation of the equipment in a rack should be such that the amount of air flow
required for safe operation of the equipment is not compromised.
C) Mechan ical Load ing - Mount ing of the e quipm ent in the rack should be suc h that a ha zardous conditio n is
not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
D) Circuit Overloading - Consideration should be given to the connection of the equipment to the supply
circuit, a nd the eff ect that over loading of the circu its m ight have on over current pr otection a nd suppl y wiring.
Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate ratings should be used when addressing this concern.
E) Reliable Earthing - Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained. Particular
attention should be given to suppl y connections other than direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. use
of power strips)."
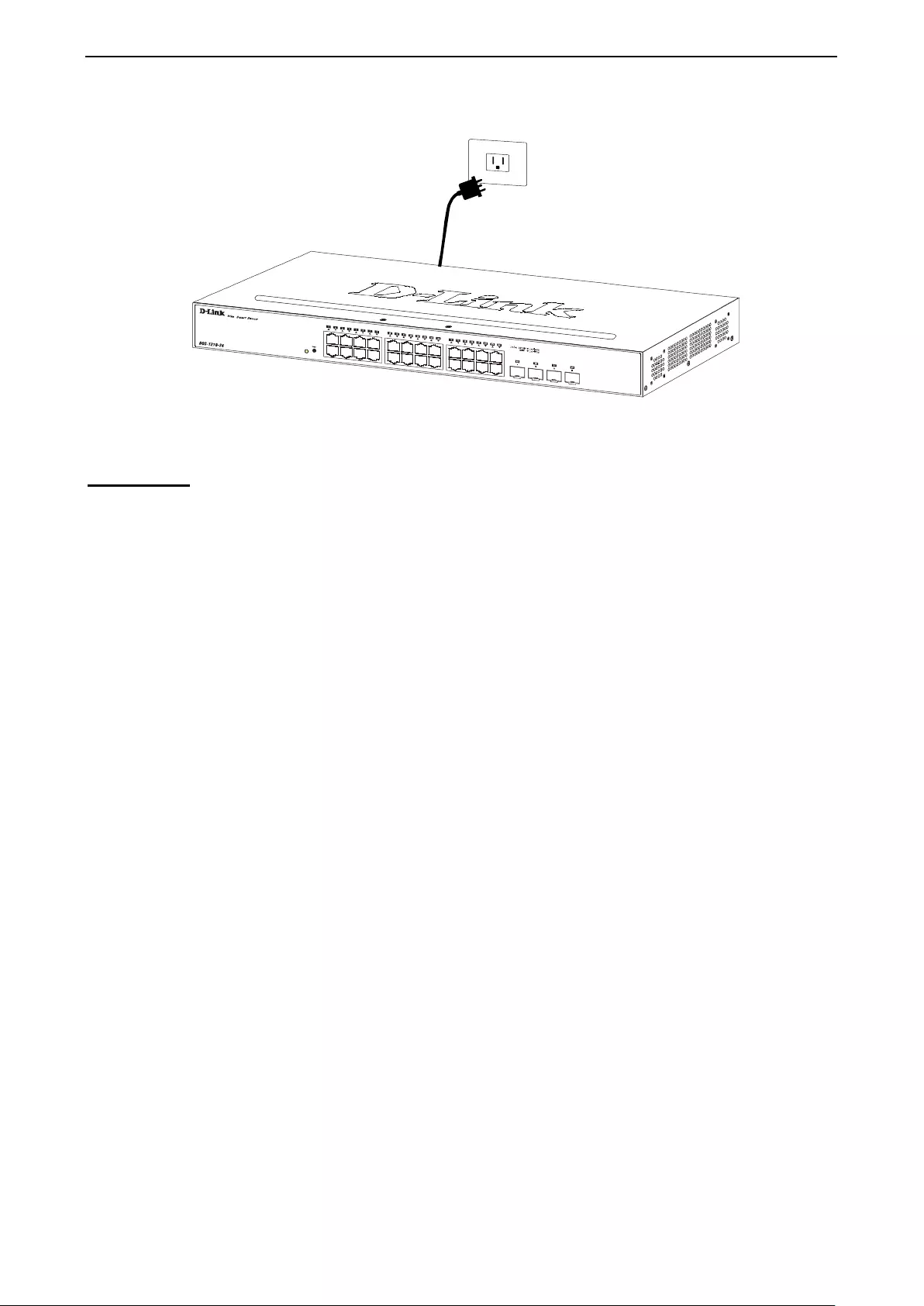
Step 3 – Plugging in the AC Power Cord
Users may now connect the AC power cord into the r ear of the switch and to an electrical outlet (preferably
one that is grounded and surge protected).
2 Hardware Installation DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
15
5
Figure 2.4 – Plugging the switch into an outlet
Power Failu re
As a prec aution, th e switch should be u nplugged in ca se of po wer failure. When po wer is resum ed, plug t he
switch back in.
3 Getting Started DGS-1210 series Metro Eth ernet Managed Switch User Manual
16
3 Getting Started
This chapter introduces the management interface of D-Link DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch.
Management Option s
Using Web-based Managem ent
Connecting to the Console Por t
Management Options
The D-Link DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch can be m anaged through any port on the device b y using
the web-based management interface, or the D-Link Network Assistant (DNA).
Each switch must be assigned its own IP address, which is used for communication with the web-based
management interface or a SNMP net work manager. The PC should have an I P address in the sam e range
as the Switch. Each Switch allows up to four users to access the web-based management interface
concurrently.
However, if you want to manage multiple D-Link Smart Managed Switches, the D-Link Network Assistant
(DNA) is a more convenient choice. By using the D-Link Network Assistant (DNA), you do not need to
change the IP address of your PC, making it easier to simultaneously initialize multiple D-Link Managed
Switches.
Please refer to the following installation instructions for the W eb interface and th e D-Link Network Assistant
(DNA).
Using Web-based Management Interface
After successfully instal ling the S w itch, you ca n configure the S witc h, monitor th e n et work status , and disp lay
statistics using a web browser.
Supported Web Browsers
The embedded Web-based Management currently supports the following web browsers:
Microsoft Internet Ex plor er 10/11
Microsoft Edge 25
Chrome 51
Safari 5.1.7
Connecting to the Switch
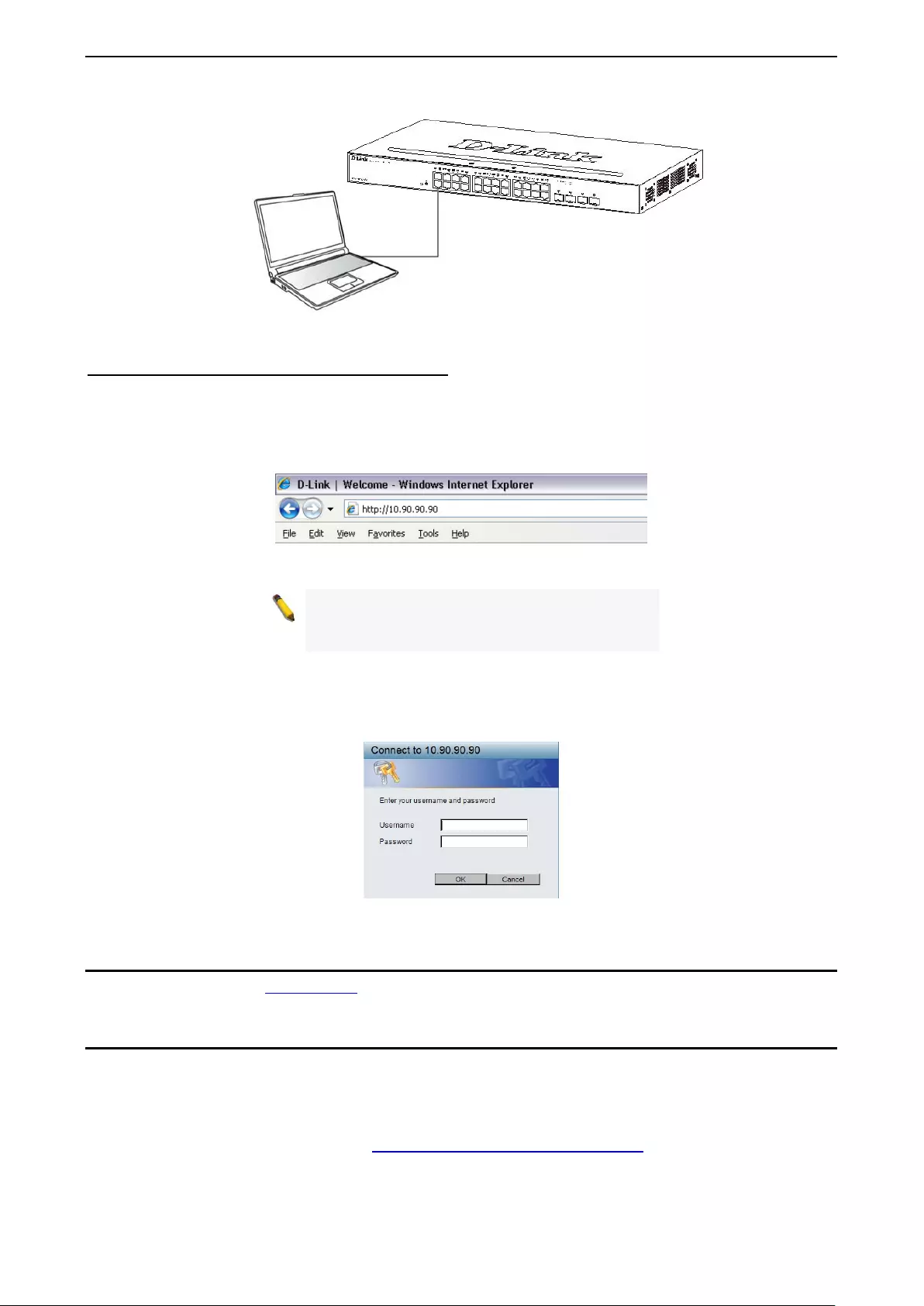
The access the web interface you will need the following equipment:
1. A PC with a RJ45 Ethernet port.
2. A standard Ethernet cable
Connect on end of the Ethernet cable to any of the ports on the front panel of the Switch and connect the
other end of Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the PC.
3 Getting Started DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
17
7
Figure 3.1 – C onnected Ethernet cable
Accessing the Web-based Management Interface
In order to access the management interface, the PC must have an IP address in the same subnet as the
switch. For example, if the switch has an IP address of 10.90.90.90, the PC should have an IP address of
10.x.y.z (wher e x /y is a num ber betwee n 0 ~ 254 and z is a number bet ween 1 ~ 254), and a subnet mask of
255.0.0.0. T o launch the web inter fac e, simply open a ny com patible web bro wser and enter 10.90.90.90 (the
factory-default IP address) in the address bar. Then press <Enter>.
Figure 3.2 –Enter the IP address 10.90.90.90 in the web brow ser
NOTE: T he switch's f actor y default IP addres s is
10.90.90 .90 with a subne t m ask of 255.0.0 .0 and
a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
When the following logon dialog box appears, enter the password and choose the language of the Web-
based Management interface then click OK.
By default, the Username and Password are empty.
Figure 3.3 – Logon Dia log Box
Web-based Management
Please refer to Chapter 4 Configuration for detailed instructions.
D-Link Network Assistant (DNA)
D-Link Net work Assistant ( DNA) is a progr am that is used t o disc over s witches whic h are in the sam e La yer
2 network segment as your PC. You c an download th e DNA App f rom the Chr ome web store an d insta ll it in
a Chrome web browser.
1. Go to the Chrome web store at: https://chrome.google.com/webstore, and search the store for
Network Assistant.

3 Getting Started D-Link DGS-1210-52/ME-28/ME User
Manual
18
Figure 3.4 – D-LINK Network Assistant
2. Click ‘ADD TO CHROME’ button on the right hand side of the search results.
3. Click ‘Add app’ button in the pop-up window to install the D-Link Network Assistant in Chrome.
4. When the installation process has finished:
(Option 1) Click the ‘LAUNCH APP’ button in the upper-right corner of the window to start DNA.
(Option 2) Click the ‘Apps’ icon in the upper-lef t corner of the Chrome browser and click the DNA icon
to start the app.
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
19
4 Configuration
The features and functions of the D-Link DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch can be configured through
the web-based management interface.
Web-based Management
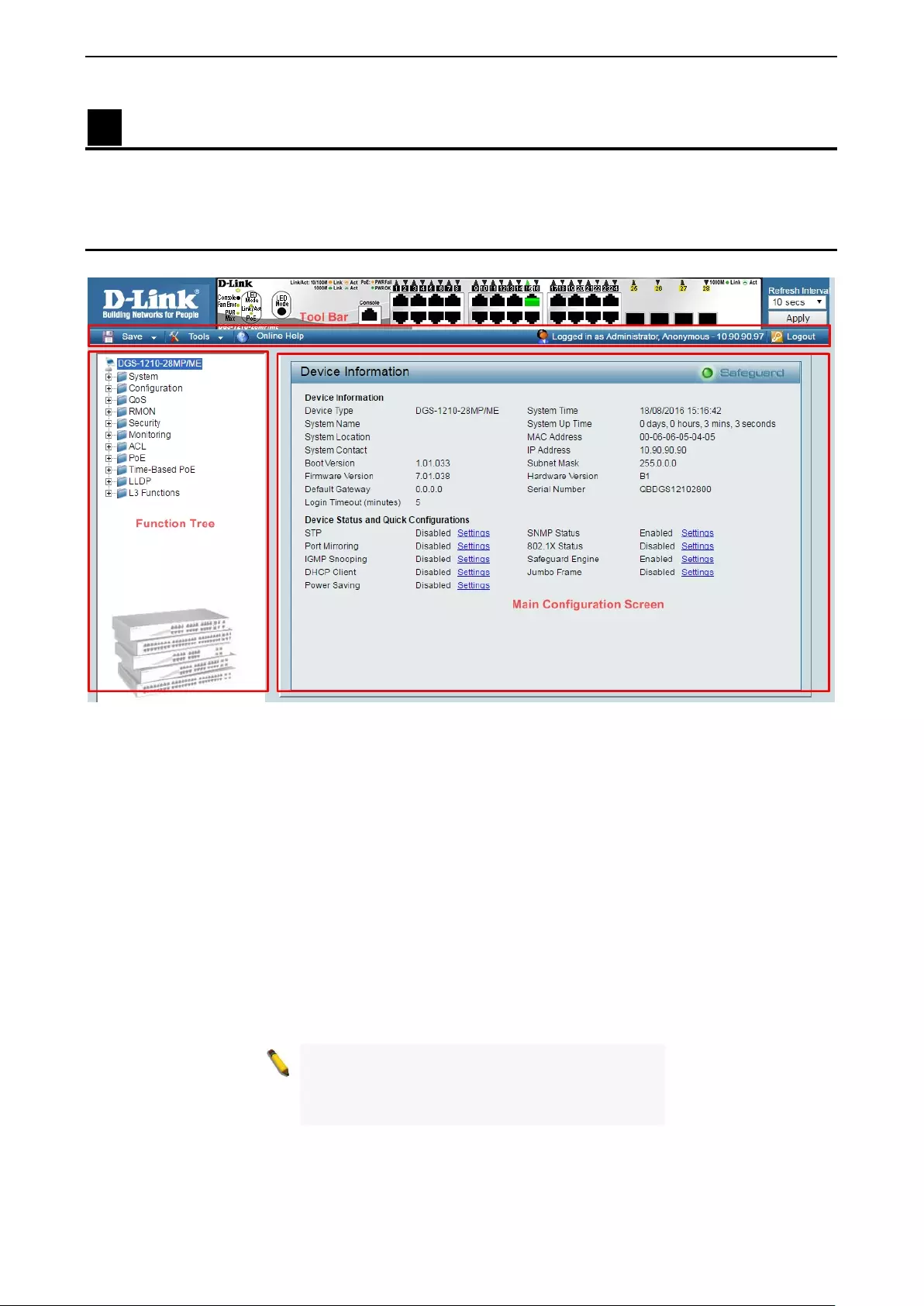
After press the OK butt on i n Logon Dialog Box, you will see the screen below:
Figure 4.1 – Web-based Management
The three m ain areas are the Tool Bar on t op, the Function Tree on t he left, and t he Main Configuration
Screen.
The Tool Bar provides a quick and convenient way for accessing essential functions such as firmware
upgrades and basic settings.
Clicking on a section or subs ection in the func tion tree will d isplay all the sett ings of that s ection in the main
configuration screen. The main configuration screen will show the current status of your Switch by clicking
the model name on top of the function tree.
In the upper-right corner of the screen the username and current IP address will be displayed.
Under the username is the Logout button. Click this to end this session.
NOTE:
If you close the web browser without
clicking the Logout butto n first, then it wil l b e seen
as an abnormal exit and the login session will still
be occupied.
Fina ll y, by c lick ing on t he D -Link logo at the up per-left corner of the screen you wi ll be redirected t o th e local
D-Link website.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
20
Tool Bar > Save Menu
The Save Menu provides Save Configuration and Save Log functions.
Figure 4.2 – Save Menu
Save Configuration
Select to save the entire configuration changes you have made of the device to switch’s non-volatile RAM
then click Save Config button to t ake effect . Or select to boot up t he device fr om which configur ation of the
device then click the Apply button to take effect.
Figure 4.3 – Save Configuration
Save Log
Save the log e ntries to your loc al drive and a pop-up mes sage will prom pt you for the f ile path. You can vie w
or edit the log file by using text editor (e.g. Notepad).
Figure 4.4 – Save L og
Tool Bar > Tool Menu
The T ool Menu offer s global function c ontrols such as Reset System, Reboot De vice, C onfiguration Backup
and Restore, Firmware Backup and Upgrade and Flash Information.
Figure 4.5 – Tool Menu
Reset System
Provide another safe reset option for the Switch. All configuration settings in non-volatile RAM will reset to
factory default and the Switch will reboot.
Figure 4.6 – Tool Menu > Reset System
Select the different reset method then click Apply to reset the system.
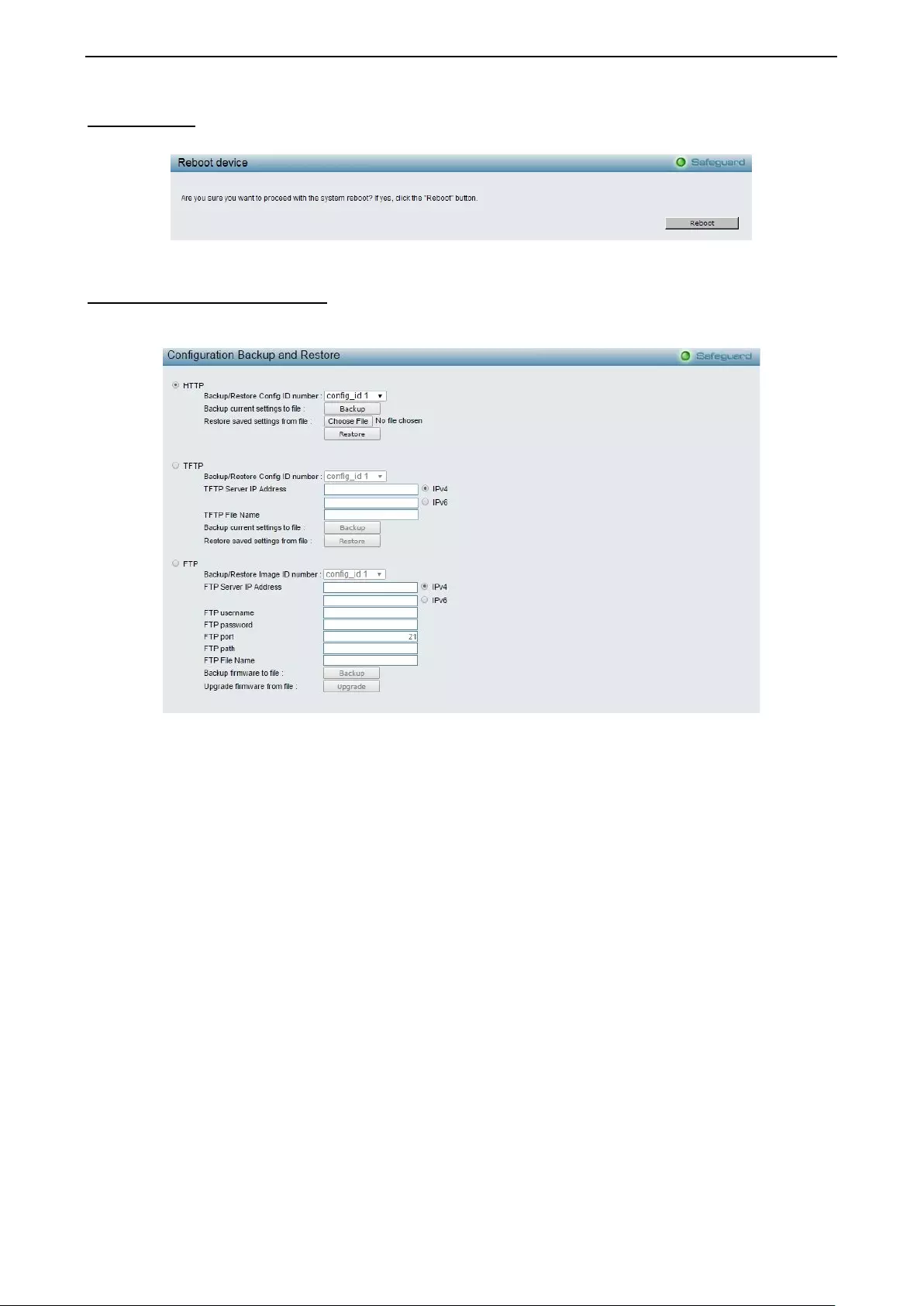
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
21
1
Reboot Device
Provide a safe way to reboot the system. Click Reboot to restart the switch.
Figure 4.7 – Tool Menu > Reboot Device
Configuration Backup & Restore
Allow the current configuration settings to be saved to a file (not including the password), and if necessary,
you can restore configuration settings from this file. Three methods can be selected: HTTP, TFTP or FTP.
Figure 4.8 – Tool Menu > Configuration Backup and Restore
HTTP: Backup or restore the configuration file to or from your local drive.
Backup/Restore Config ID number: Specify the configuration ID number to be backup or restored.
Click Backup to save the current settings to your disk.
Click Choose File to browse your inventories for a saved backup settings file.
Click Restore after selecting the backup settings file you want to restore.
TFTP: TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a file transfer protocol that allows you to transfer files to a
remote TFTP server. The maximum Telnet Server co nnec tion is 4.
Backup/Restore Config ID number: Specify the configuration ID number to be backup or restored.
TFTP Server IP Address: Specif y the IPv4 or IPv6 addr ess .
TFTP File Name: Enter the file name which you want to save/restore from for the configuration.
Click Backup to save the current settings to the TFTP server.
Click Restore after selecting the backup settings file you want to restore.
FTP: FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a file transfer protocol that allows you to transfer file to a remote FTP
server.
Backup/Restore Image ID number: Specify to image ID number to be updated on the Switch.
FTP Server IP Address: Specify the IPv4 or IPv6 address.
FTP username: Enter the user name for the FTP server.
FTP password: Enter the user password for the FTP server.
FTP port: Enter the FTP port number. The default is 21.
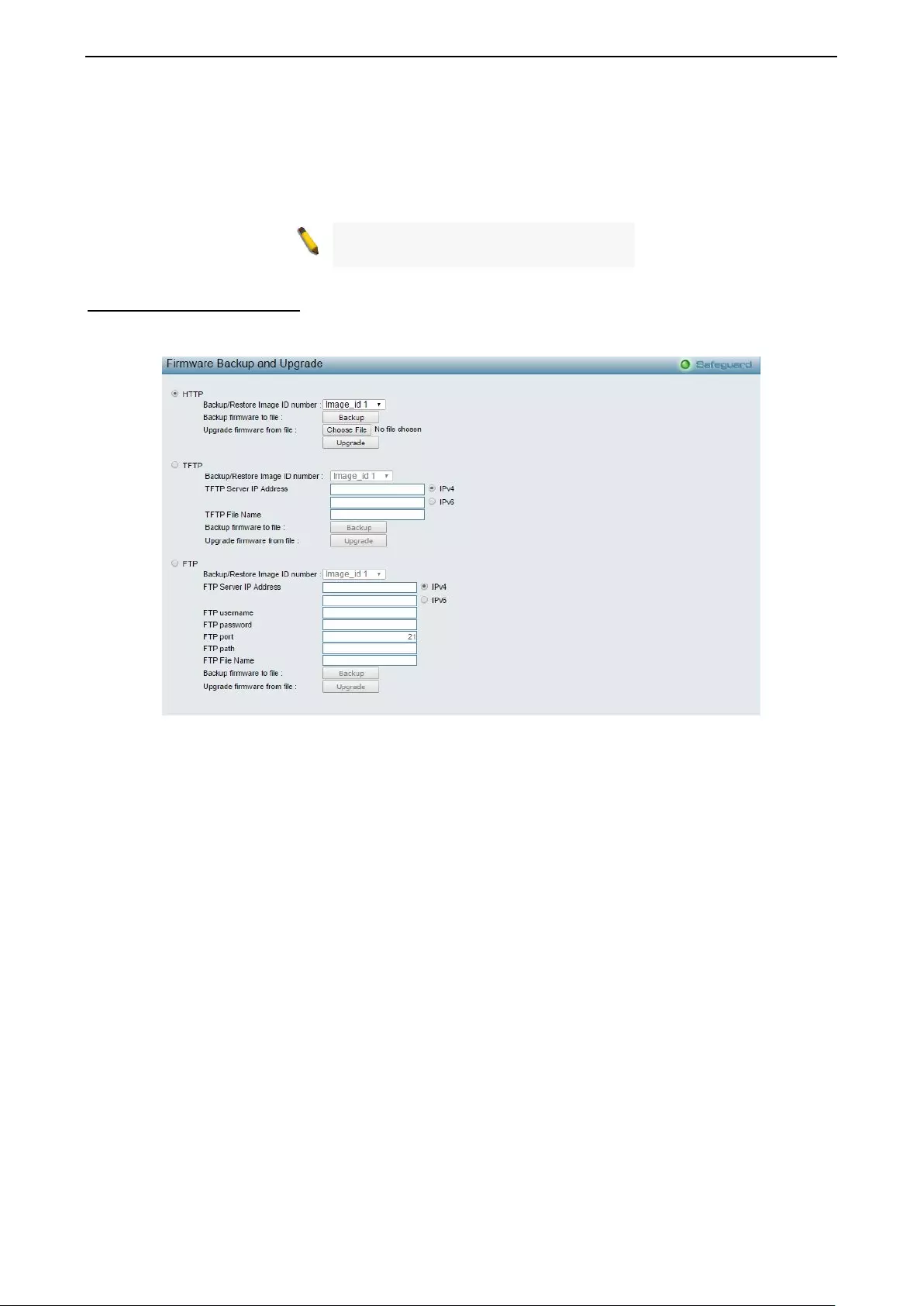
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
22
FTP path: Specify the FTP path where the configuration file locat ed.
FTP File Name: Enter the file name which to be updated on the FTP server.
Click Backup to save the current settings to the FTP server.
Click Restore after selecting the backup settings file you want to restore.
Note: Switch will reboot after restore, and
all current config ur at ions wi ll be lost.
Firmware Backup & Upgrade
Allow for the firmware to be saved, or for an existing firmware file to be uploaded to the Switch. Two methods
can be selected: HTTP or TFTP.
Figure 4.9 – Tool Menu > Firmware Backup and Upgrade
HTTP: Backup or upgrade the firmware to or from your local PC drive.
Backup/Restore Image ID number: Specify the firmware image ID number to be backup or restored.
Click Backup to save the firmware to your disk.
Click Choose File to browse your inventories for a saved firmware file.
Click Upgrade after selecting the firmware file you want to restore.
TFTP: Backup or upgrade the firmware to or from a remote TFTP server. The maximum Telnet Server
connection is 4.
Backup/Restore Image ID number: Specify the firmware image ID number to be backup or restored.
TFTP Server IP Address: Specify the IPv4 or IPv6 addres s.
TFTP File Name: Enter the file name which you want to save/restore from for the firmware.
Click Backup to save the firmware to the TFTP server.
Click Upgrade after selecting the firmware file you want to restore.
FTP: Backup or restore the firmware to or from a FTP server.
Backup/Restore Image ID number: Specify to image ID number to be updated on the Switch.
FTP Server IP Address: Specify the IPv4 or IPv6 address.
FTP username: Enter the user name for the FTP server.
FTP password: Enter the user password for the FTP server.
FTP port: Enter the FTP port number. The default is 21.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
23
3
FTP path: Specify the FTP path where the firmware file located.
FTP File Name: Enter the file name which to be updated on the FTP server.
Click Backup to save the current firmware to the FTP server.
Click Restore after selecting the backup firmware file you want to restore.
CAUTION: Do not disconnect the PC or remove
the power cord from device until the upgrade
completes. The Switch may crash if the
Firmware upgrade is incomplete.
Flash Information
The Flash Information page displays the detail information of flash on the Switch.
Figure 4.10 – Tool Menu > Flash Information
Tool Bar > Online Help
The Online Help provides two ways of online support:
Figure 4.11 – Online Help
D-Link Support Site: This will lead you to the D-Lin k website w here you c an find on line resour ces suc h as
updated firmware images.
User Guide: This can offer an immediate reference for the feature definition or configuration guide.
Click Apply to make configuration take effect.
Function Tree
All config ur ati on opt ions o n the switch are ac c ess ed th r ough t he function menu on the lef t s ide of the scr een .
Click on the setup item that you want to configure. The following sections provide more detailed description
of each feature and function.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
24
Figure 4.12 –Function Tree
Device Information
The Dev ice Infor mation pro vides a n overv iew of the switch, includ ing essen tial inf ormation s uch as f irm ware
& hardware information, and IP address.
It also offers an overall status of common software features:
STP: Click Settings to link to Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings. Default is
disabled.
Port Mirroring: Click Settings to link to Configuration > Port Mirrorin g. D ef ault is dis ab led .
IGMP Snooping: Click Settings to link to Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping. Default is
disabled.
DHCP Client: Click Settings to link to System > System Settings. Default is disabled.
Power Saving: Click Settings to link to System > Power Saving. Default is disabled.
SNMP Status: Click Settings to link to System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State. Default is enabled.
802.1X Status: Click Settings to link to Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings. Default is disabled.
Safeguard Engine: Click Settings to link to Security > Safeguard Engine. Default is enabled.
Jumbo Frame: Click Settings to link to Configuration > Jumbo Frame. Default is disabled.
Figure 4.13 – Device Information
System > System Settings
The System Setting allows the user to configure the IP address and the basic system information of the
Switch.
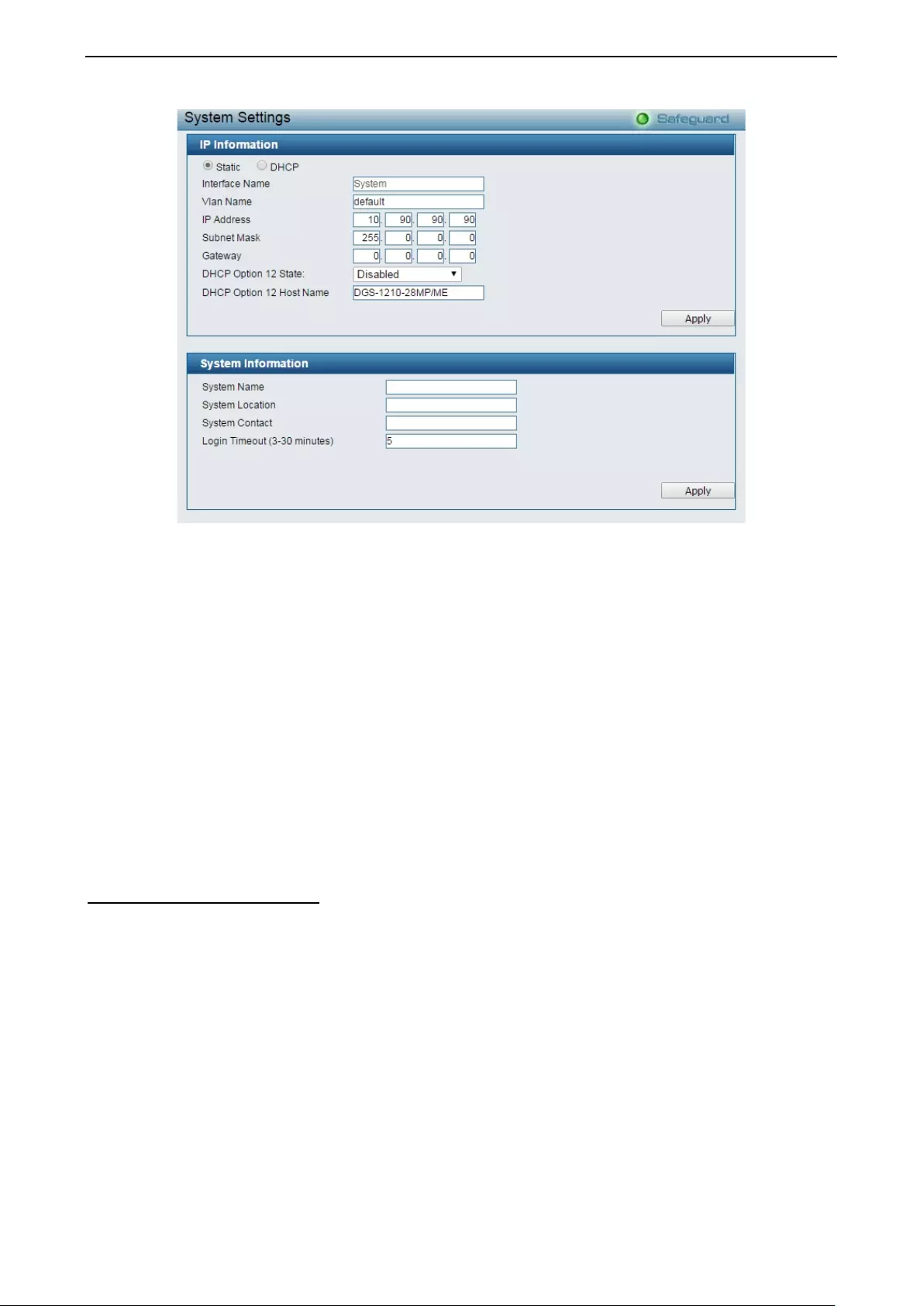
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
25
5
Figure 4.14 – System > System Setting s
IP Information: There are two wa ys for the s witch to obtain an IP address: S tati c and DHC P (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol).
When using static mode, the IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, DHCP Option 12 State and DHCP
Option 12 Host Name can be m anually co nfigured. W hen using DHCP m ode, the Switc h will f irs t look f or a
DHCP serv er to pro vide it with an IP a ddress (incl uding net work mask and default g atewa y) bef ore using t he
default or previo usly enter ed sett ings. B y default the I P settin g is static m ode with IP addr ess is 10.90.90.90
and subnet mask is 255.0.0.0.
System Information: By entering a System Name and System Location, the device can more easily be
recognized.
Login Timeout: The Login Timeout controls the idle time-out period for security purposes, and when there is
no action f or a specific tim e span in the Web-bas ed Management. If the current s ession times out ( expires),
the user is required a re-login before using the Web-based Mana gement agai n. Select ive range is f rom 3 to
30 minutes, and the default setting is 5 minutes.
System > Firmware Information
The F irmware Inf ormation page displa ys the inform ation of f irmware. T he user c an specif y configurat ion and
image file to boot up when power on the Switch next time.
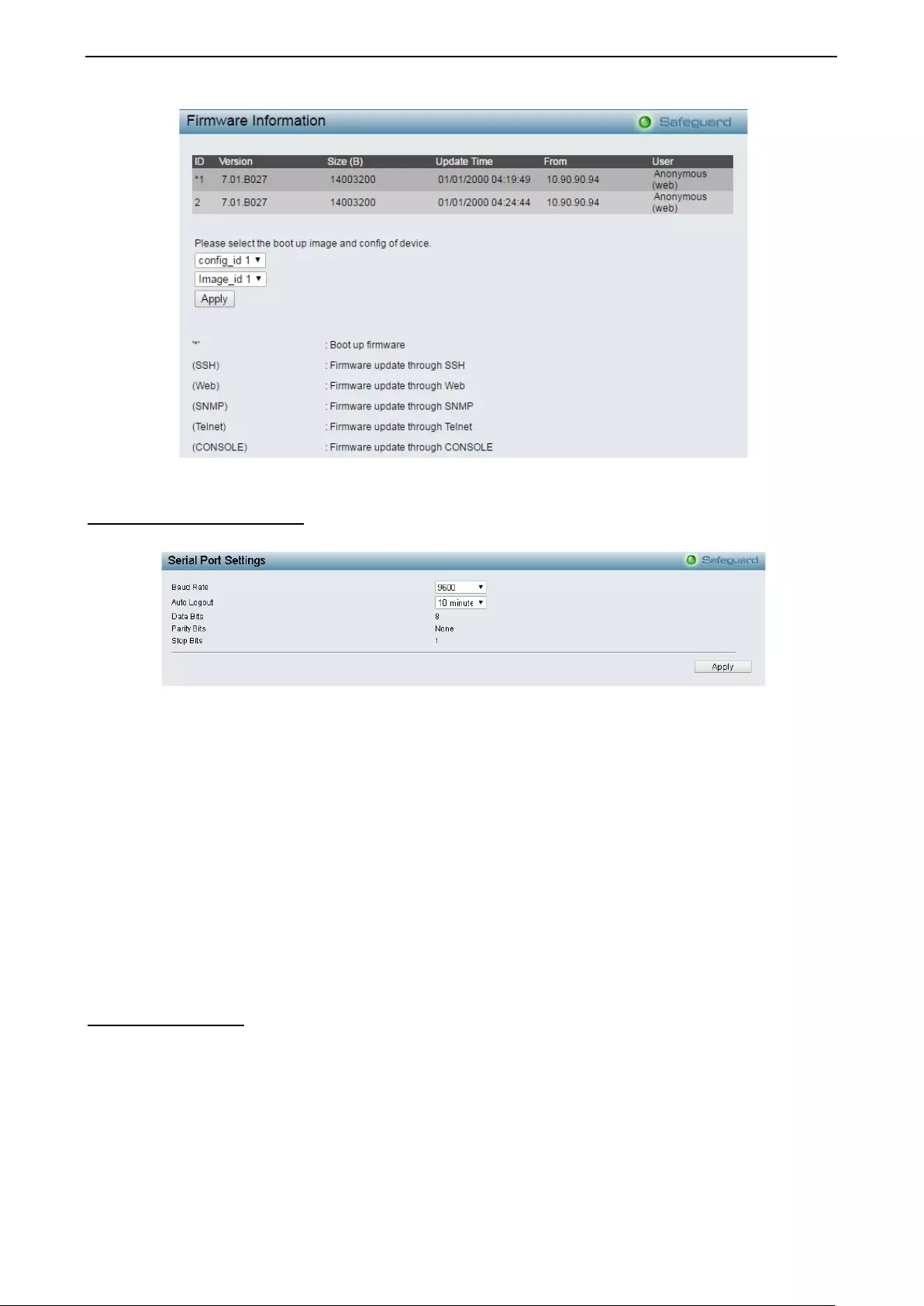
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
26
.
Figure 4.15 – System > Firmware Information
System > Serial Port Settings
The Serial Port Sett ings allows the user to adjust the Baud Rate and the Auto Logout values.
.
Figure 4.16 – System > Firmware Information
Baud Rate: Specify the baud rate for the serial port on the Switch. There are four possible baud rates to
choose from, 9600, 19200, 38400 and 115200. For a connection to the Switch using the console port, the
baud rate must be set to 9600, which is the default setting.
Auto Logout: Select the logout time used for the console interface. This automatically logs the user out after
an idle period of time, as defined. Choose from the following options: 2, 5, 10, 15 minutes or Never. The
default setting is 10 minutes.
Date Bits: Display the date bits used for the serial port connection.
Parity Bits: Display the parity bits used for the serial port connection.
Stop Bits: Display the stop bits used for the serial port connection.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > IP Interface
The IP Interface page allow user to configure the IPv6 system settings.
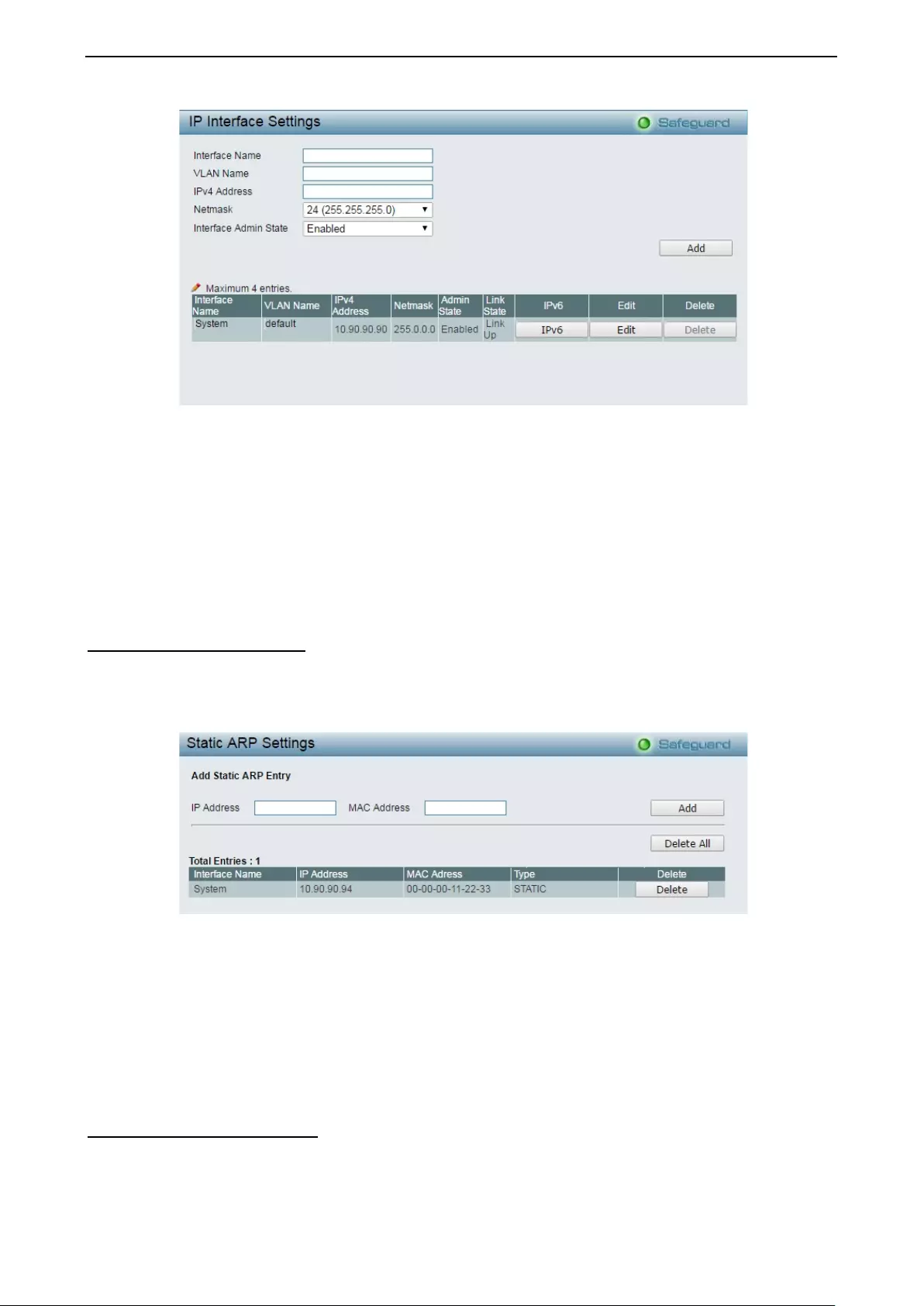
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
27
7
.
Figure 4.17 – System > IP Interf ace
Interface Name: Specifies the name of IP interface.
VLAN Name: Specifies the VLAN name of IP interface.
IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address for the interface.
Netmask: Select the netmask of IP address.
Interface Admin State: Enables or disables the interface administration state.
Click Add for the settings to take effect.
System > Static ARP Settings
The Address Resolution Protocol is a TCP/IP protocol that converts IP addresses into physical addresses.
This table allo ws net work m anager s to vie w, def ine, m odif y, and delete A RP inf orm ation f or spec ific device s.
Static entr ies c an be def ine d in the ARP tab le. W hen static e ntries are def ined, a perm anent entr y is enter ed
and is used to translate IP addresses to MAC addresses.
.
Figure 4.18 – System > Static ARP Settings
Add Static ARP Entry: Allows user to add a static ARP entry.
IP Address: Specifies the IP address of ARP entry to be created.
M AC Add ress: Specifies the MAC address of ARP entry to be created.
Click Add to create a new ARP entry.
Click Delete to remove the specified ARP entry.
System > IPv6 System Settings
The IPv6 System Settings page allow user to configure the IPv6 system information.
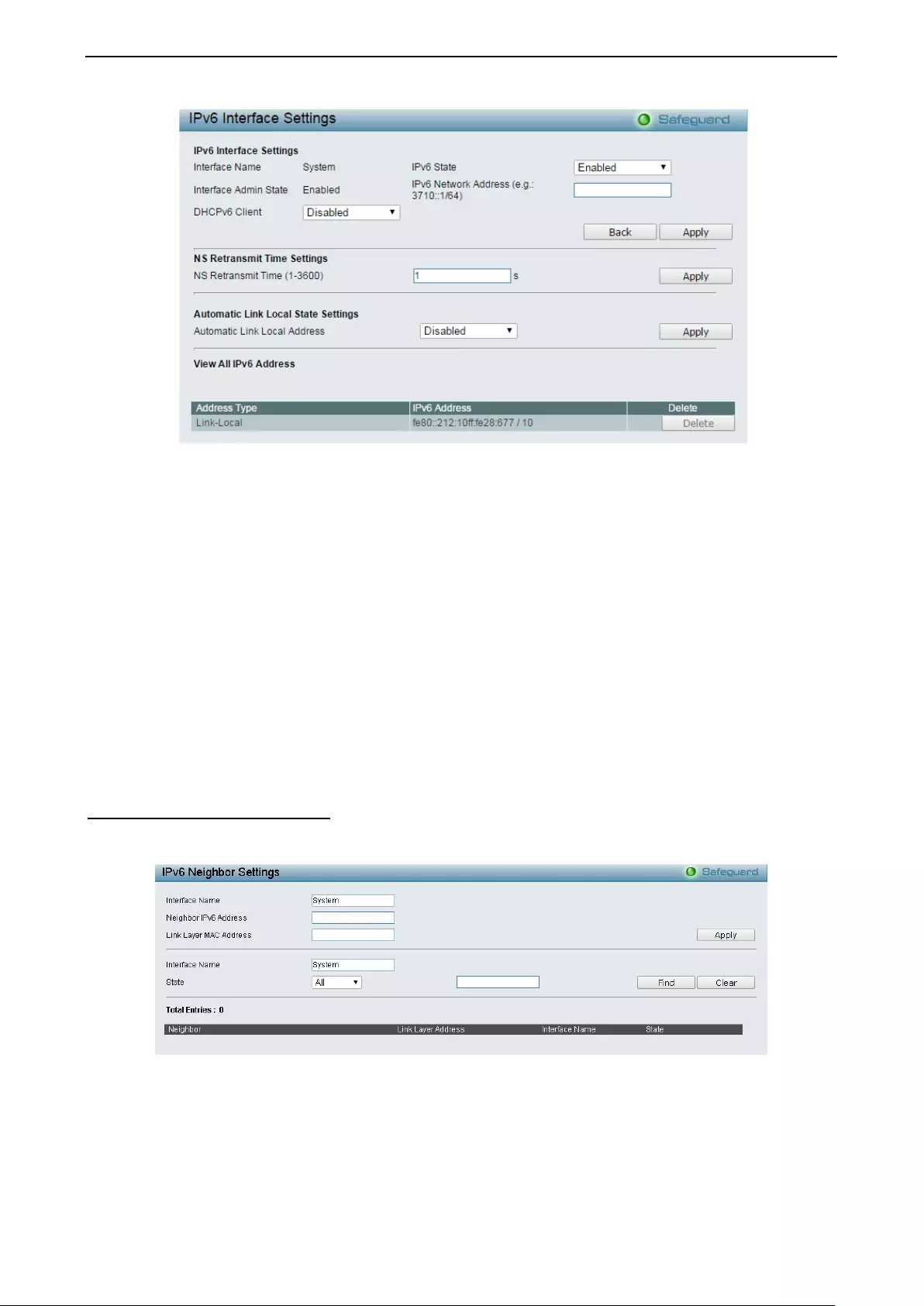
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
28
.
Figure 4.19 – System > IPv6 System Settings
IPv6 System Settings:
Interface Name: Displays the interface name of IPv6.
IPv6 State: Specifies the IPv6 to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Client: Specifies the DHCPv6 client to be enabled or disabled.
IPv6 Network Address: Specifies the IPv6 Network Address.
NS Retransmit Time Settings:
NS Retransmit Time (1-3600): Enter the Neighbor solicitation’s retransmit timer in second here. Specifies
the NS retransmit time for IPv6. The field range is 1-3600, and default is 1 second.
Automatic Link Local State Settings:
Automatic Link Local Address: Specifies the automatic link is enabled or disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
The user can c onfigure the Switch’s IPv 6 neighbor s ettings. The Switch’s current IPv6 nei ghbor settings will
be displayed in the table at the bottom of this window.
Figure 4.20 – System > IPv6 Neighbor Settings
Interface Name: Enter the interface name of the IPv6 neighbor.
Neighbor IPv6 Address: Specifies the neighbor IPv6 address.
Link Layer MAC Address: Specifies the link layer MAC address.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
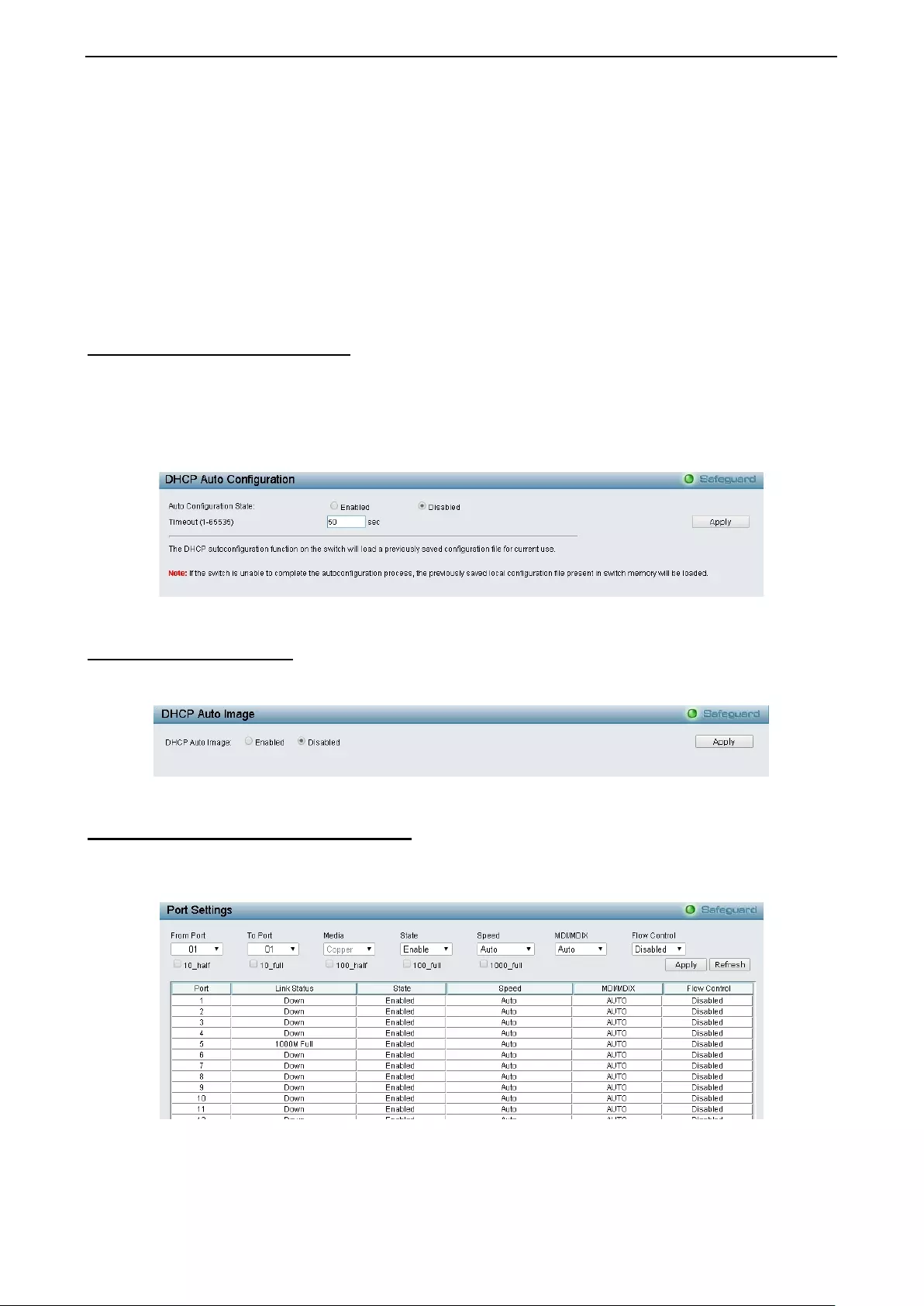
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
2
29
9
Interface Name: Specifies the interface name of the IPv6 neighbor. To search for all the current interfaces
on the Sw itch, go to th e s e c ond I nterface N ame field i n th e middle part of the win do w, tick the All chec k box.
Tick the Hardware option to display all the neighbor cache entries which were written into the hardware table.
State: Use the drop-down menu to select All, Address, Static or Dynamic. When the user selects address
from the drop-down menu, the user will be able to enter an IP address in the space provided next to the state
option.
Click Find to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click Clear to clear all the information entered in the fields.
System > DHCP Auto Configura tion
The DHCP Auto Configuration page allows user to enable the DHCP Auto Configuration feature on the
Switch. When enabled, the Switch becomes a DHCP client and gets the configuration file from a TFTP
server automatically o n next boot up. T o accomplish this , the DHCP ser ver mus t del iver the TFT P server IP
address and c onf igurat ion file nam e inf orm ation in the D HCP rep ly pack et. T he TFT P server m ust be up and
running and st ore t he nec es sar y configur ation file i n it s bas e dir ector y when th e reques t is r eceive d fr om the
Switch.
Figure 4.21 – System > DHCP Auto Configuratio n
System > DHCP Auto Image
The DHCP Auto Image page allows user to automatically download FW Image and upgrade the different
firmware version image into the Switch.
Figure 4.22 – System > DH CP Auto Image
System > Port Configuration > Port Settings
In the Por t Setting pa ge, the s tatus of all por ts can be monitor ed and adjuste d for optim um configuration. B y
selecting a range of ports ( From Port and To Port), the Speed can be set for all selected ports by click ing
Apply. Press the Refresh button to view the latest information.
Figure 4.23 – System > Port Configuration > P or t S ettings
Media: Depending on the selected port type, two options for user. Copper and Fiber_1G.
State: Enable or disable the state of specified ports.
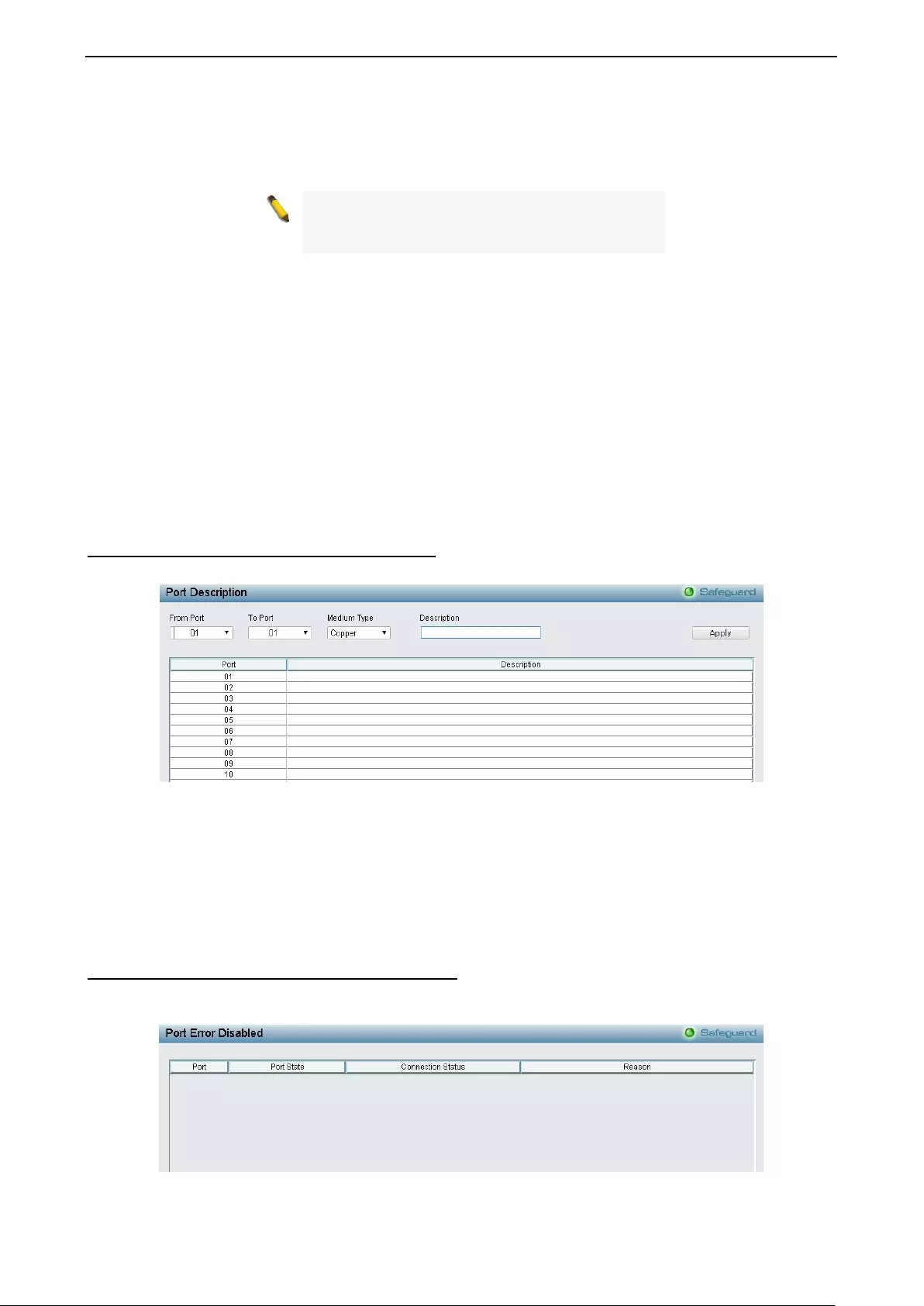
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
30
Speed: Gigabit Fiber connections can operate in 1000M Full Force Mode, Auto Mode or Disabled. Copper
connections can operate in Forced Mode settings (1000M Full, 100M Full, 100M Half, 10M Full, 10M Half),
Auto, or Disabled. The default setting for all ports is Auto.
NOTE:
Be sure to adjust port speed settings
appropriately after changing the connected cable
media types.
MDI/MDIX:
A medium dependent interface (MDI) port is an Ethernet port connection typically used on the Network
Interface Card (NIC) or Integrated NIC port on a PC. Switches and hubs usually use Medium dependent
interface crossover (MDIX) interface. When connecting the Switch to end stations, user have to use
straight through Ethernet cables to make sure the Tx/Rx pairs match up properly. When connecting the
Switch to other networking devices, a crossover cable must be used.
This switch provides a co nfigurabl e MDI/MDIX function f or users . The switches can be s et as an MDI port i n
order to connect to other hubs or switches without an Ethernet crossover cable.
Auto is designed on the switch t o detect if the connection is backwards, and automatically chooses MDI or
MDIX to properly match the connection. The default setting is “Auto” MDI/MDIX.
Flow Control: You can enabl e this f unction to m itigat e the tr aff ic conges tion. P orts c onfigur ed for full-duplex
use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex ports use backpressure flow control. The default setting is Disabled.
System > Port Configuration > Port Description
In the Port Description page, the user may name various ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.24 – System > Port Configuration > Port Description
From Port / To Port: Specify the range of ports to describe.
Medium Type: Depending on the selected port type, two options for user. Copper and Fiber_1G.
Description: Specify the description of ports.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
The Port Error Disabled page displays the information about ports that have had their connection status
disabled, for reasons such as STP loopback detection or link down status.
Figure 4.25 – System > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled
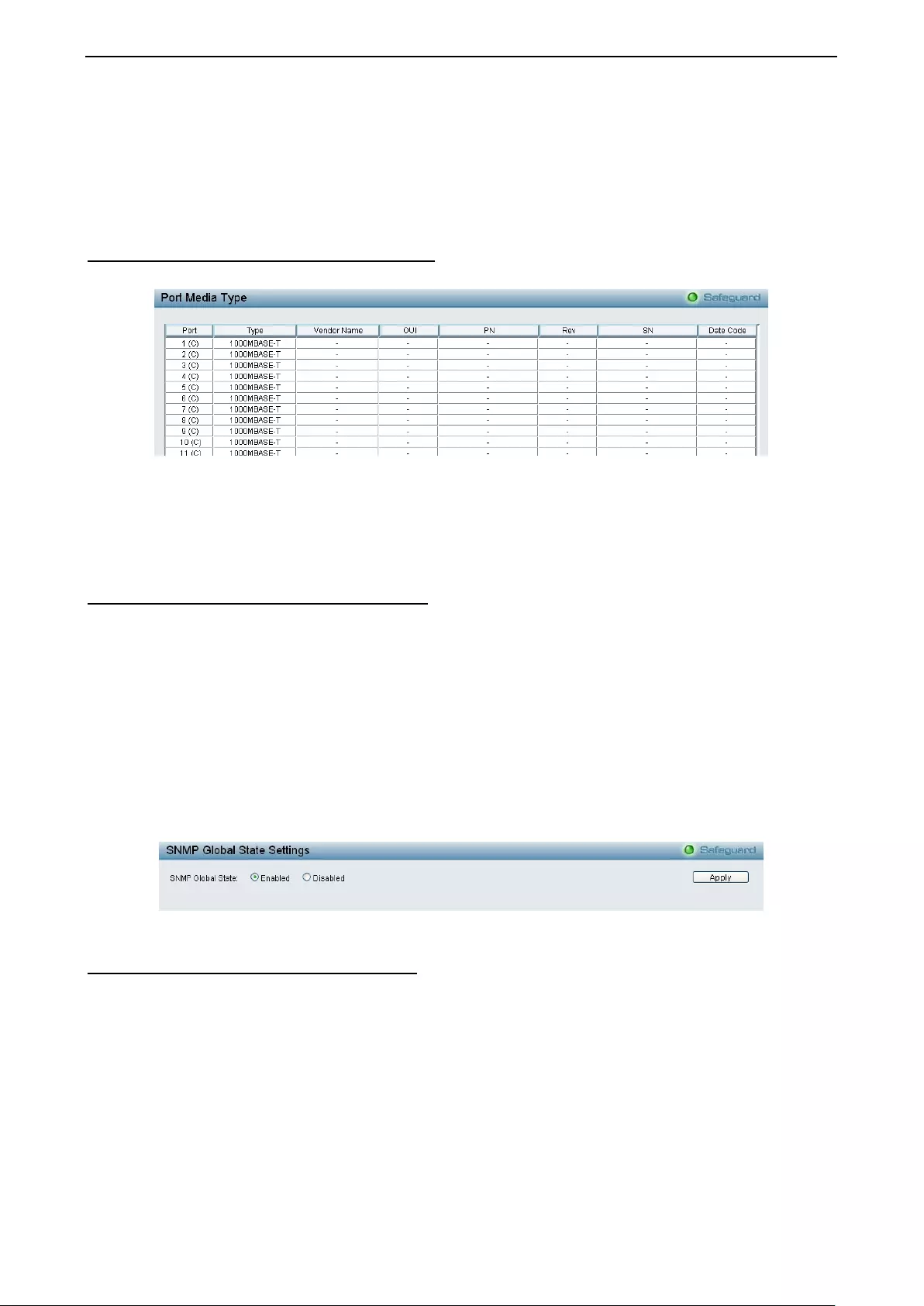
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
31
1
Port: Displays the port that has been error disabled.
Port State: Describes the current running state of the port, whether Enabled or Disabled.
Connection Status: This field wil l read the u pl ink s tatus of the ind iv id ual por ts , wheth er Ena bl ed or Disabled .
Reason: Describes the reason why the port has been error-disabled, such as a STP loopback occurrence.
System > Port Configuration > Port Media Type
The Port Media Type page displays the information about the port media type.
Figure 4.26 – System > Port Configuration > Port Media Type
Port: Displays the port number.
Type: Displays the port media type. The media types are 1000MBASE-T, 1000MBASE-X, 100MBASE-T,
100MBASE-X, 10MBASE-T and 10MBASE-X.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) protocol designed
specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to
read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to
configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the
Switch or LAN.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the
device. A def ined set of var iables (m anaged objects ) is m aintained by th e SNM P agen t and used t o m anage
the device. These objects are defined in a Management Inform ation Base (MIB), which provides a standard
presentat io n of the inf ormation contr ol led by the on-bo ard SNMP agent. SNM P de f ines both th e f ormat of the
MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network.
The default SNMP global state is disabled. Select Enable and click Apply to enable the SNMP function.
Figure 4.27 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Global State
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
This page is used t o maintain the SNM P user tab le f or the use of SNM Pv3. SN MP v3 a llows or r estr icts us er s
using the MIB OID, and also encrypts the SNMP messages sent out between users and Switch.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
32
Figure 4.28 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table
User Name: Enter a SNMP user name of up to 32 characters.
Group Name: Specify the SNMP group of the SNMP user.
SNMP Version: Specify the SNMP version of the user. Only SNMPv3 encrypts the messages.
Encrypt: Specifies the Encrypt is enabled or disabl ed when the SN MP Vers i on is V3.
Auth-Protocol/Password: Specify either HMAC-MD5-96 or HMAC-SHA to be the authentication protocol.
Enter a password for SNMPv3 encryption in the righ t c olumn.
Priv-Protocol/Password: Specify either no authorization or DES 56-bit encryption and then enter a
password for SNMPv3 encryption in the right column.
Click Apply to create a new SNMP user account, and click Delete to remove any existing data.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
This page is used to maintain the SNMP Group Table associating to the users in SNMP User Table.
SNMPv3 can control MIB access policy, security policy for a user group directly.
Group Name: Specify the SNMP user group of up to 32 characters.
Read View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that are allowed SNMP read privileges to the
Switch's SNMP agent.
Write View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that are allowed SNMP write privileges to the
Switch's SNMP agent.
Security Model: Select the SNMP security model.
SNMPv1 - SNMPv1 does not support the security features.
SNMPv2 - SNMPv2 supports both centralized and distributed network management strategies. It
includes improvements in the Structure of Management Information (SMI) and adds some security
features.
SNMPv3 - SNMPv3 pr ovides sec ure access to devices through a com bination of authentic ation and
encrypting packets over the network.
Security Level: T his funct ion is only available whe n you select SNMPv3 security level.
NoAuthNoPriv - No author i zation a nd no encr ypti on for packets sent bet ween the S witch and SNMP
manager.
AuthNoPriv - Authorization is required, but no encryption for packets sent between the Switch and
SNMP manager.
AuthPriv – Both authorization and encr yption are required f or packets sent between the S witch and
SNMP manger.
Notify View Name: Specify a SNMP group name for users that can receive SNMP trap messages gene rated
by the Switc h's SNMP age nt.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
33
3
Figure 4.29– System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
This page allows you to maintain SNMP views to community strings that define the MIB objects whic h can be
accessed by a remote SNMP manager.
Figure 4.30 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table
View Name: Name of the view, up to 32 characters.
Subtree OID: The Object Identifier (OID) Subtree for the view. The OID identifies an object tree (MIB tree)
that will be included or excluded from access by an SNMP manager.
OID Mask: The mask of the Subtree OID. 1 means this object number is concerned, 0 means do not
concerned. For example 1.3.6.1.2.1.1 with mask 1.1.1.1.1.1.0 means 1.3.6.1.2.1.X.
View Type: Specify the configured OID is Included or Excluded that a SNMP manager can access.
Click Apply to create a new view, Delete to remove an existing view.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
This page is used to maintain the SNMP community string of the SNMP managers using the same
community string are permitted to gain access to the Switch's SNMP agent.
Community Name: Name of the community string
User Name (View Policy): Specify the read/write or read-only level permission for the MIB objects
accessible to the SNMP community.
Figure 4.31 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Community Table
Click Apply to create a new SNMP community, Delete to remove an existing community.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table
This page is to configure the SNMP trap recipients.
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
34
Host IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and specify the IP address of SNMP management host.
SNMP Version: Specify the SNMP version to be used to the management host.
Community String/SNMPv3 User Name: Specify the community string or SNMPv3 user name for the
management host.
Figure 4.32– System > SNMP Settings > S NMP Host Table
Click Apply to creat e a new SNMP host, Delete to remove an existing host.
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Engine ID
The Engine ID is a unique identifier used to identify the SNMPv3 eng ine on the Switch.
Input the Engine ID then click Apply to apply the changes and click Default resets to default value.
Figure 4.33 – System > SNMP Settings > SNMP E ngine ID
System > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Settings
The SNMP Trap Settings page provide user to Specify whether the device can send SNMP notifications.
Figure 4.34 – System > SNMP Settings > SNM P Trap Settings
SNMP Authentication Traps: Specifies the device to send authentication failure notifications.
System Coldstart Traps: Specifies the device to send SNMP coldstart notifications.
System Warmstart Traps: Specifies the device to send SNMP warmstart notifications.
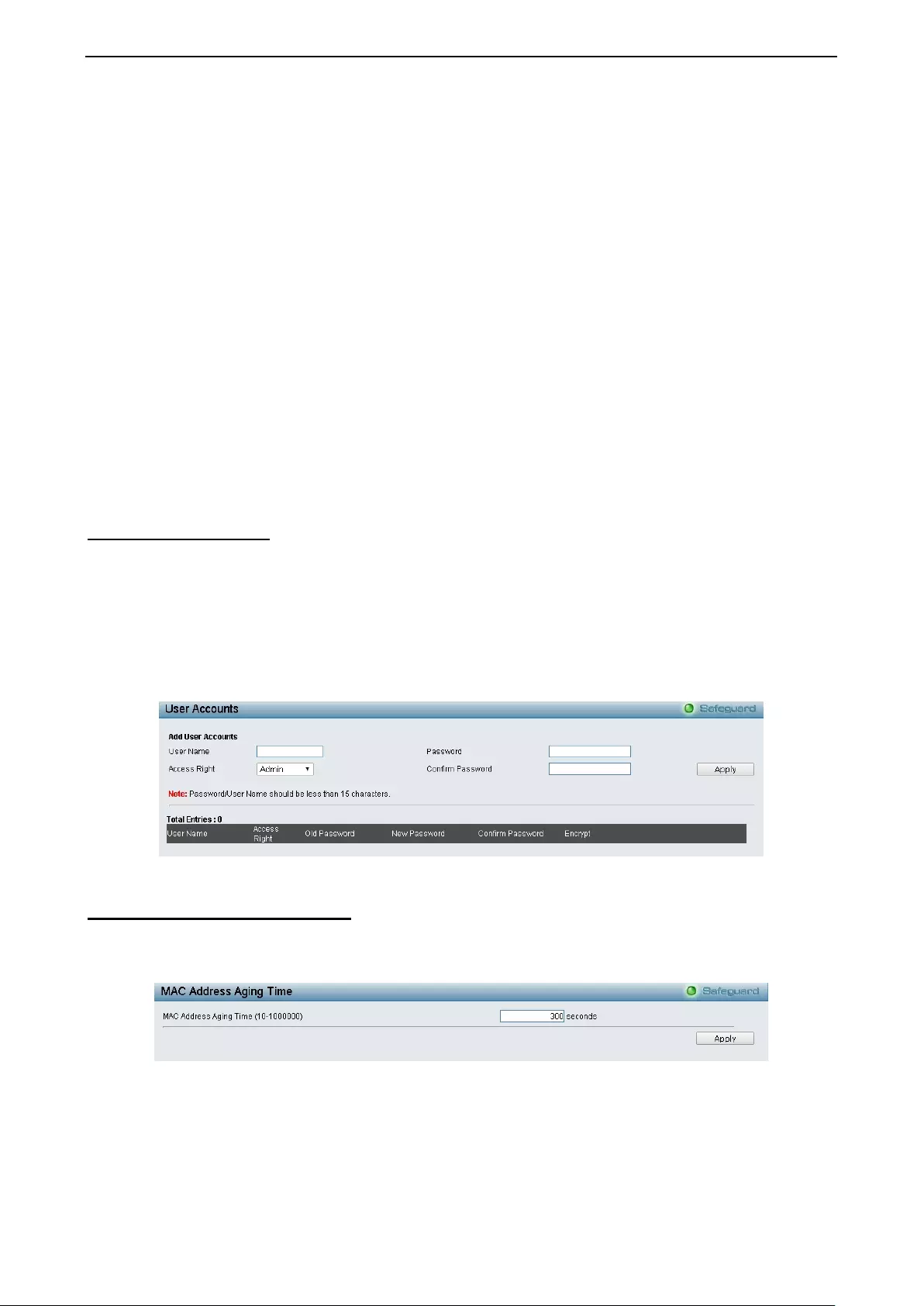
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
35
5
Port Link Up / Link Down: Port connection information.
RSTP Port State Change: Events of a RSTP port state changes.
Firmware Upgrade State: Information of firmware upgrade - success or failure.
Trap notification if PoE Power On / Off: Specifies the de vic e t o s end tra p not if ic atio n when P oE p o wer On
or Off.
Trap notification if PoE Power Error: Specifies the device to send trap notification when PoE power error.
Trap notification if over max power budget: Specifies the device to send trap notification when the device
over the PoE max power budget.
Port Security Violation: Information of Port Security Violation.
IMPB Violation: IMPB Violation information.
Loopback Detection occurring / recovery: Specify the device to send SNMP Trap when Loopback
Detection occurring and recovery.
DHCP Se rv er Sc r een in g: Information of DHCP Server Screening.
Duplicate IP Detected: Information of Duplicate IP Detected.
DHCPv6 Server Screening: Information of DHCPv6 Server Screening.
ICMPv6 RA All Node Filter: Information of ICMPv6 RA all node filter.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > User Accounts
The User Accounts page provides user to control user privileges. To add a new user by typing in a User
Name, Password and retype the same password in the Confirm Password and choose the level of
privilege(Admin, Operator, PowerUser or User) from the Access Right drop-down menu, then click the
Apply button.
User can m odify exist ing user ac count in the Us er Account T able. To chan ge the pass word, type in the Old
Password, New Password and retype it in the Confirm New Password entry field and select the Encrypt,
then click the Edit button. To delete the user account, click on the Delete button.
Figure 4.35– Syst em > User Accounts
System > M AC Add ress Aging Time
The MAC Address Aging Time page specifies the length of time a learned MAC Address will remain in the
forwardi ng tab le wit hout be i ng ac ces s ed (that is, h o w l ong a l earn ed MAC ad dres s is al lo wed t o r emain idl e).
To change this, type in a different value representing the MAC address age-out time in seconds.
Figure 4.36 – System > MAC Address Aging Time
MAC Address Aging Time (10-1000000): Specifies the aging time of MAC address on the Switch. The
range is from 10 to 1000000, and the default is 300 seconds.
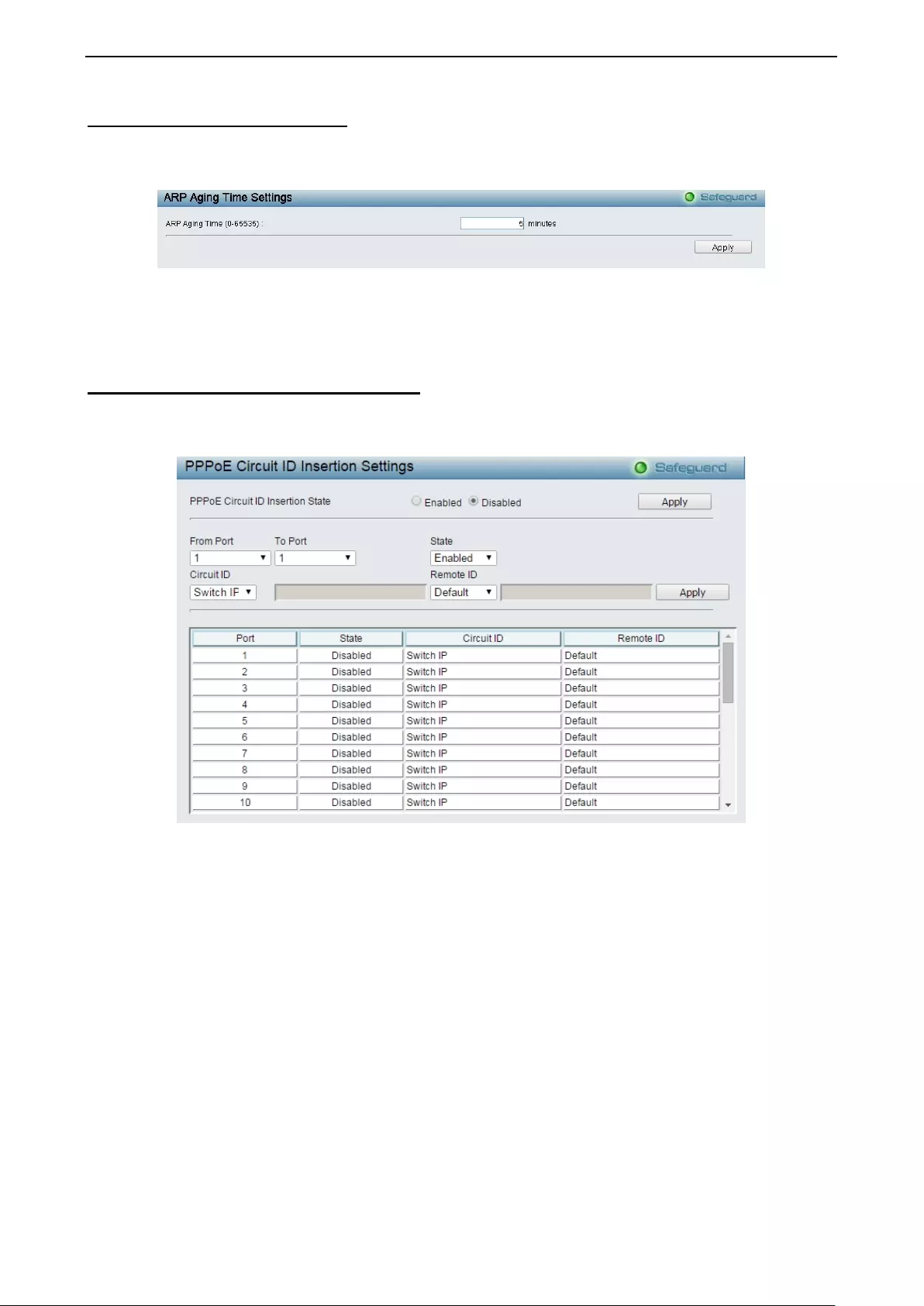
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
36
System > ARP Aging Time Settings
The ARP Aging Time Settings page provides user to globally set the maximum amount of time, in minutes,
and Addr es s R eso lut ion Protocol (AR P) e ntry can r em ain in t h e S witch’s AR P t ab le, wit hout bein g acc es s ed,
before it is dropped from the table.
Figure 4.37 – System > ARP Ag ing Time Settings
ARP Ag ing Time (0-65535): Spec if ies th e ARP a gin g time on the Switch. The ran ge is from 0 t o 6 553 5 with
a default setting of 5 minutes.
System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Se ttings
The PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings page specifies the configuration of settings. When enabled, the
system will insert the c ircui t tag to the recei ved PPPoE d iscover request a nd the request p acket if the tag is
absent. It will remove the circuit ID tag from the received PPPoE offer and session confirmation packet.
Figure 4.38 – System > PPPoE Circuit ID Insertion Settings
PPPoE Circuit Insertion State: Enable or disable the PPPoE circuit insertion state, and Click Apply to make
the configurations take effect.
From Port/ To Port: Specifies the ports to be configured.
State: Enable or disable the state of specified ports.
Circuit ID: Specifies the Circuit ID is Switch IP, Switch MAC, UDF String, Vendor2 and Vendor3.
Switch IP – The Switch’s IP address will be used to encode the circuit ID option. This is the default.
Switch MAC – The MAC address of the Switch will be used to encode the circuit ID option.
UDF String – A user specified string to be used to encode the circuit ID option. Enter a string with
the maximum length of 32.
Remote ID: Specifies the Remote ID is Deafult, Vendor2 or Vendor3.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
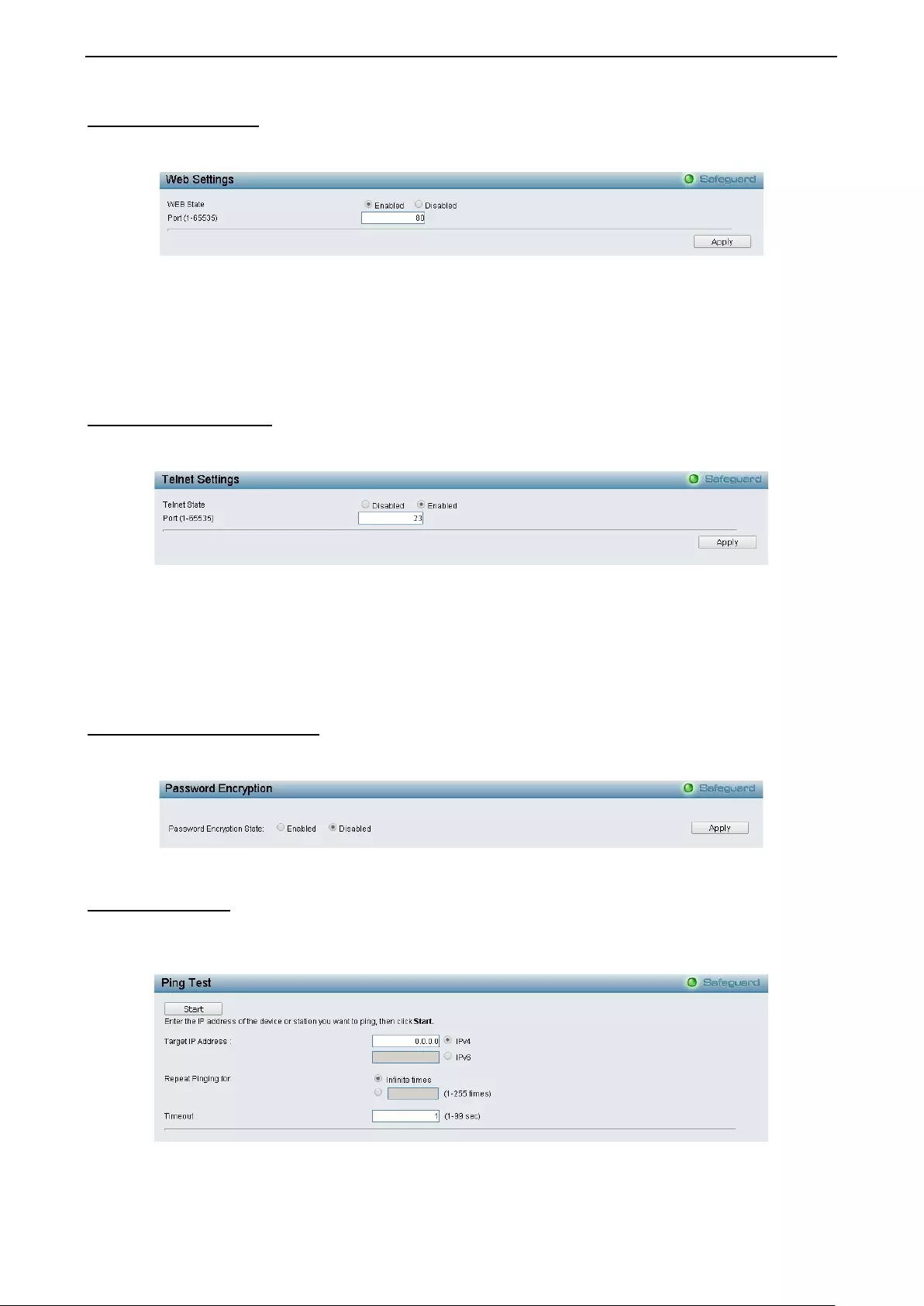
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
37
7
System > Web Setting s
The WEB State is Enabled by default. If us er c hoos es to disab le th is by selecting Disabled, us er will los e th e
ability to configure the system through the web interface as soon as these settings are applied.
Figure 4.39– Syst em > Web Settings
Port (1-65535): S pec ifies t he P or t number. T he r ange is between 1 and 6 55 35 with t he well-known def ault is
80.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > T elnet Settings
Telnet conf iguration is Enabled by def ault. If user does not want to allo w the T elnet configuration, they only
need to disable the Tel net Stat e.
Figure 4.40 – System > Telnet Settings
Port (1-65535): The TCP port number. TCP ports are numbered between 1 and 65535. The well-known TCP
port for the Telnet protocol is 23.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System > Password Encryption
The Pass word Encr yption page is used to en able or dis able the p assword encr yption state. Select Enabled
and click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Figure 4.41 – System > Password Encryp tion
System > Ping Test
The Ping Test is a small program that sends ICMP Echo packets to the IP address you specify. The
destination node then responds to or “echoes” the packets sent the Switch. This is very useful to verify
connectivity between the Switch and other nodes on the network.
Figure 4.42 – System > Ping Test
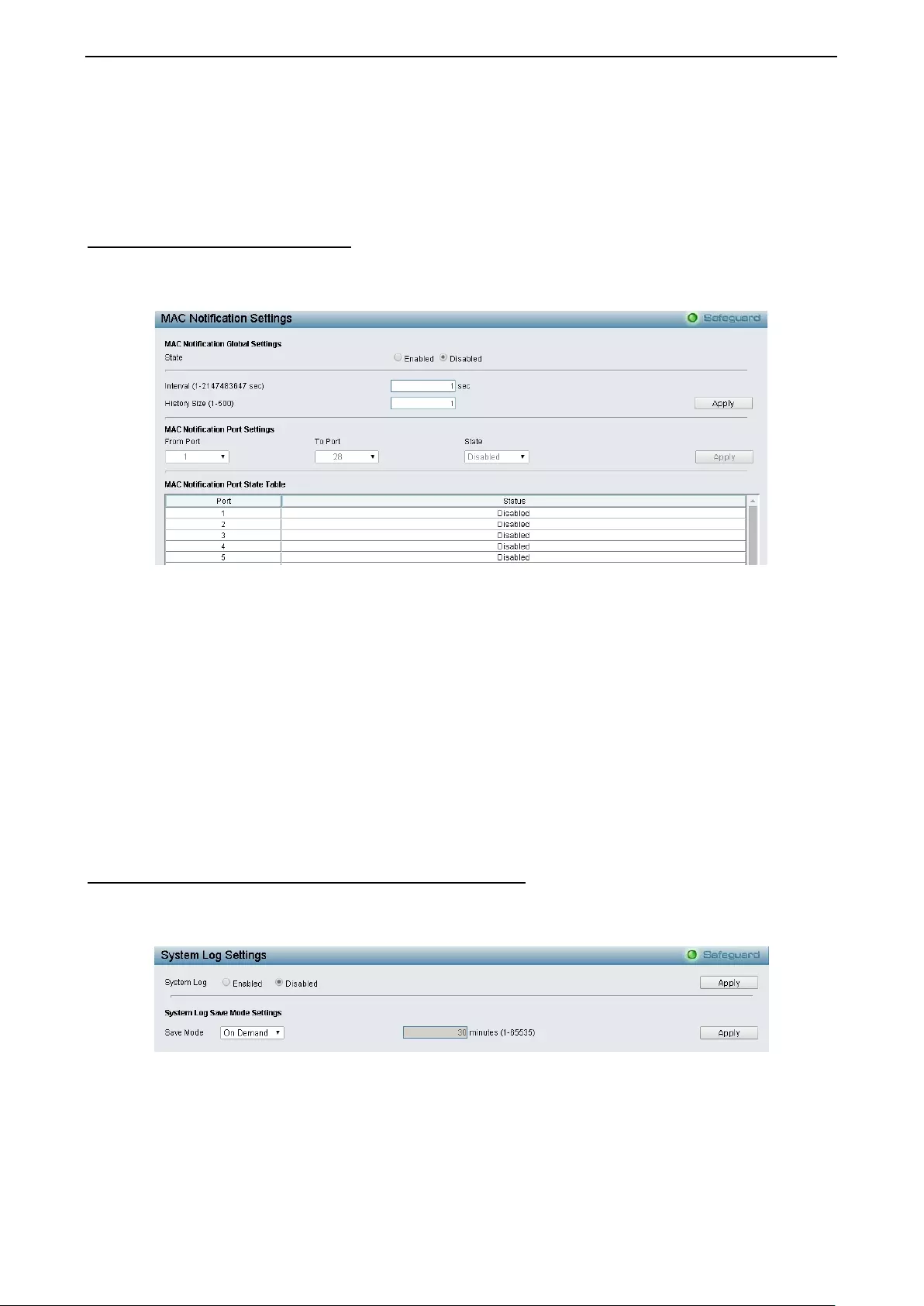
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
38
The us er m a y use Inf in ite ti mes radio butto n, i n th e Re peat Pinging for fie ld, wh i c h w il l te ll the pi ng program
to keep s ending ICMP Ech o pack ets to the specif ied IP a ddress u ntil the progra m is s topped. T he user m ay
opt to choose a specific number of times to ping the T arget IPv4 o r IPv 6 Address by clicking its radio button
and entering a number between 1 and 255. Cl ic k Start to initiate the Ping Program
Timeout: Specify the timeout time of Ping test. The range is between 1 and 99 seconds.
System > MAC Notification Settings
MAC Notif ication p age is us ed to m onitor MAC ad dres ses learned and e ntere d into the f orwardin g databas e.
To globally set MAC notification on the Switch, user should enabled or disabled state, input the Time Interval
between notification and History Size then click the Apply button.
Figure 4.43 – System > MAC Notific ation Setti ngs
State: Enabled or Disabled MAC notification globally on the Switch.
Interval (1-2147483647 sec): The time in seconds between notifications.
History Size (1-500): The maximum number of entries listed in the history log used for notification. Up to
500 entries can be specified.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
To change MAC notification settings for a port or group of ports on the Switch, configure the following
parameters. , then click the Apply button.
From Port / To Port: Select a port or group of ports to enable for MAC notification using the pull-down
menus.
State: E nab le MAC Notif icatio n for the ports sel ect ed using the pu ll-down menu.
System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
System Logs record and manage events, as well as report errors and informational messages. Message
severity determines a set of event message will be sent. Click Enable so you can start to configure the
related settings of remote system log server, then press Apply for the changes to take effect.
Figure 4.44 – System > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings
Save Mode: Use this drop-down menu to choose the method that will trigger a log entry. You can choose
between On Demand, Time Interaval and Log Trigger .
Minutes: Enter a time intervel, in minutes, for which user would like a log entry to be made.
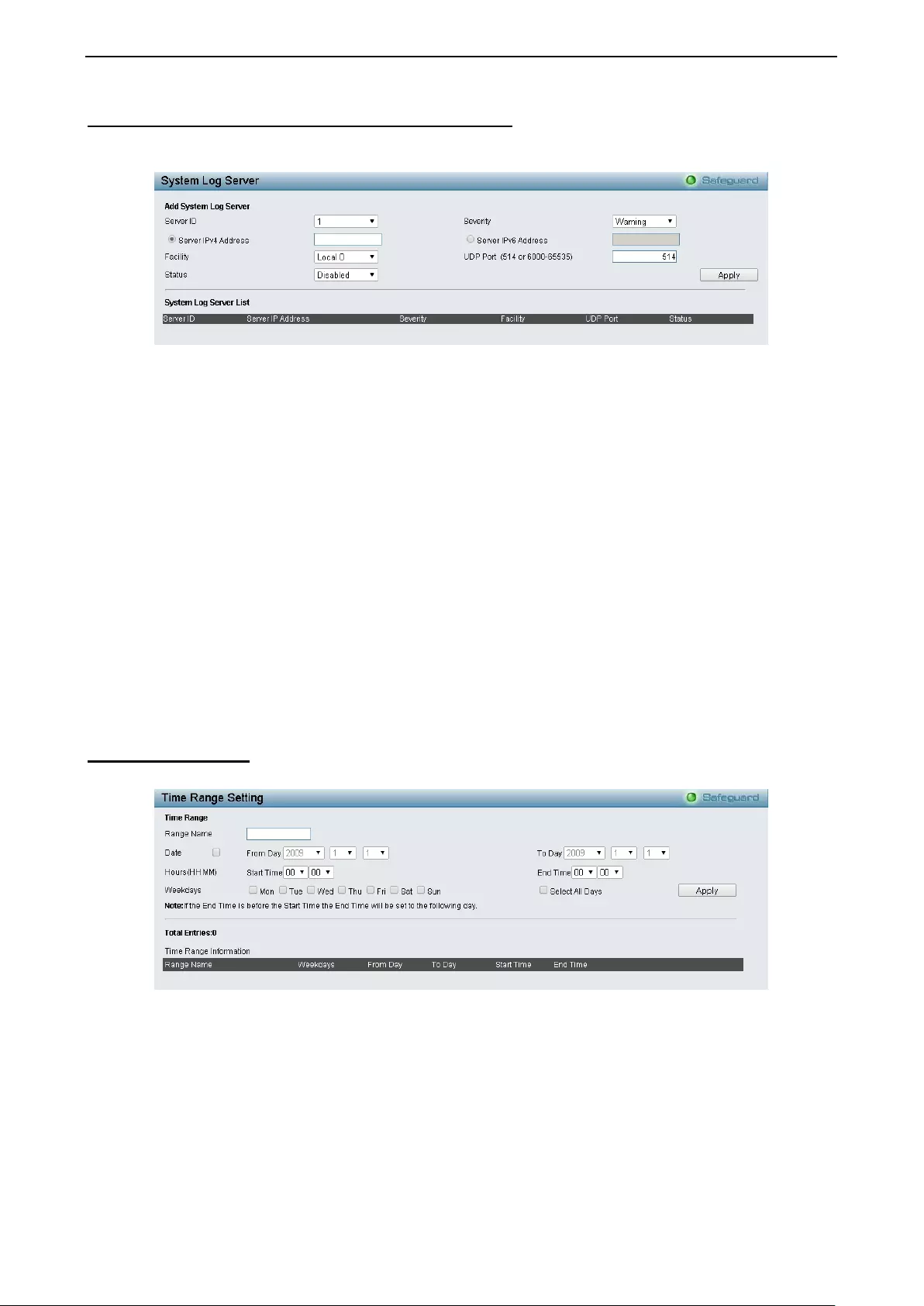
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
3
39
9
Syste m > Syste m L og Configuration > System Log Server
The user can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers using the System Log Server. It
supports maximum 500 system log entries. To set the System Log Server configuration, click Apply.
Figure 4.45 - System > System Log Configuration > System Log Server
Server ID: Specifies the Server ID. The field range is 1-4.
Severity: Specifies the minimum severity from which warning messages are sent to the server. There are
three levels. When a severity level is selected, all severity level choices above the selection are selected
automatically. The possible levels are:
Warning - The lowest level of a device warning. The device is functioning, but an operational
problem has occurred.
Informational - Provides device information.
All - Displays all levels of system logs.
Server IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address of the system log server.
Server IPv6 Address: Specifies the IPv6 address of the system log server.
Facility: Spec ifies an appli cation f rom which s ystem logs are sent to t he rem ote s erver. Onl y one f acilit y can
be assigned to a single ser ver. If a second fac ility level is ass igned, the firs t facility is over written. There are
up to eight facilities can be assigned (Local 0 ~ Local 7).
UDP Port: Specifies the UDP port to which the server logs are sent. The possible range is 6000 – 65535,
and the default value is 514.
Status: Specifies the status is enable or disable.
System > T im e Profile
The Time Profile page allows users to configure the time profile settings of the device.
Figure 4.46 – System > Time Profile Settings
Range Name: Specifies the profile name for the time profile to be configured.
Date: Se lec t Date and specifies the From Day and To Day of the time profile.
Hours (HH MM): Specifies the Start Time and End Time.
Weekdays: Specif ies th e work da y for the t im e profile. Or tick Select All Days to s elect al l da ys for th e tim e
profile.
Click Apply to create a new time profile or click Delete to delete a time profile from the table.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
40
NOTE: The time must be set after current time,
otherwise it will take effect on the next cycle time.
System > Power Saving
The Po wer Sav ing mode feature reduces po wer cons u mption aut omaticall y whe n the RJ-4 5 p or t is l ink down
or the connected devices are turned off. Less power will be consumed also when the short cable is used
(less than 20 meters).
By reducing power consumption, less heat is produced, resulting in extended product life and lower
operatin g costs. By defaul t, the Cable Le ngth Detect ion and Link Status Detection ar e enabled. Clic k Apply
to make the change effective.
Figure 4.47 – System > Power Saving
Advanced Power Saving Settings:
Type: Specifies the Power Saving type to be LED Shut-off, Port Shut-off, Port Standby or System
Hibernation.
LED Shut-off - The LED Shut-off gets high priority. If the user select LED Shut-off, the profile
function will not take ef fect. It m eans the LED cann ot be turned on af ter T ime Profile tim e’s up when
the state is disabled. On the contrary, if the LED is enabled, the Time Profile function will work.
Port Shut-off - The Port Shut-off state has high priority (the priority rule is the same as LED.)
Therefore, if the Port Shut-off sate is already disabled the Time Profile function will not take effect.
System Hibernation - In this mode, switches get most power-saving figures since main chipsets
(both MAC and PHY) are disabled for all ports, and energy required to power the CPU is minimal.
State: Specifies the power saving state to be Enabled or Disabled.
Time Profile 1: Specifies the time profile or None.
Time Profile 2: Specifies the time profile or None.
Port: Specifies the ports to be configure of the Power Saving.
Click Select All configure all ports, or click Clear to uncheck all port. Then Click Apply to make the
configurations take effect.
System > IEEE802.3az EEE Settings
The IEEE 802.3 EEE standard defines mechanisms and protocols intended to reduce the energy
consumption of network links during periods of low utilization, by transitioning interfaces into a low-power
state without interrupting the network connection. The transmitted and received sides should be
IEEE802.3az EEE compliance. By default, the s witch enabled the 802.3az EEE function. Users can disable
this feature by individual port via the IEEE802.3az EEE setting page.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
41
1
Figure 4.48 – System > I EEE802.3az EEE Settings
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
State: Enabled or Disabled the IEEE802.3az EEE for the specified ports. By default, all ports are enabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
If the con necti on sp eed dro ps do wn f rom 1000M to 1 0 0M, or th e f irst link up t ak es longer t im e, please f ollo w
below steps and check again:
1. Upgrade drivers of your Ethernet adapter or LAN controller for the host PC.
2. Disable EEE function on the switch port
System > SMTP Service > SMTP Server Settings
The SMTP Service Settings page is used to configure the fields to set up the SMTP server for the switch,
along with setting e-mail addresses to which switch log file can be sent when a problem arises on the Switch.
User c an Enabled or Disabled the S MTP State , then inp ut the SMT P Server Address, SMT P Server Port,
Self Mail Address and Mail Receiver Address then click Apply button to configure.
Figure 4.49 - System > SMTP Service > SMTP Server Settings
SMTP State: Enabled or Disabled the SMTP service on this device.
SMTP Server Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP address of the SMTP server on a remote
device. This will be the device that sends out the mail for user.
SMTP Server Port: En ter the v irtual port number that the Switch will connec t with on the SMTP ser ver. T he
common port number for SMTP is 25, yet a value between 1 and 65535 can be chosen.
Self M ail Address: Enter the e-mail address from which mail messages will be sent. This address will be the
“from” address on the e-mail message sent to a recipient. Only one self mail address can be configured f or
this Switch. This string can be no more that 64 alphanumeric characters.
Mail Receiver Address: Enter a list of e-mail addresses so recipients can receive e-mail messages
regarding Switch functions. Up to 8 e-mail addresses can be added per Switch. Do delete these addresses
from the Switch, click Delete button from the Mail Receiver Address Table.
System > SMTP Service > SMTP Service
The SMT P Service is used to s end test messages to all mail recipients c onf igured on the S witch , thus testing
the configurations set and the reliability of the SMTP server.
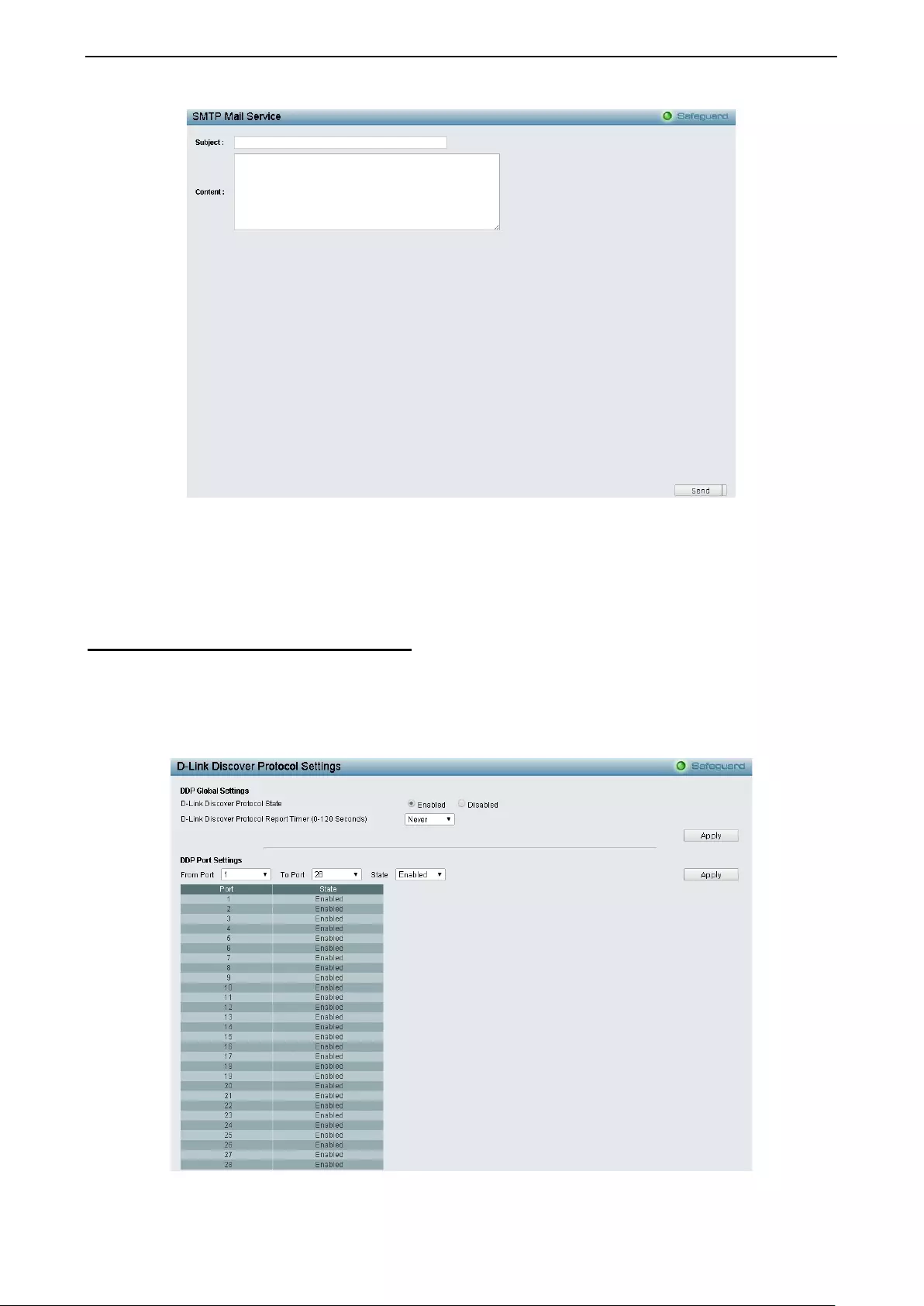
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
42
Figure 4.50 - System > SMTP Service > SMTP Service
Subject: Enter the subject of the test e-mail.
Content: Enter the content of the test e-mail.
Once the message is ready, click Send to send this mail to all recipients configured on the Switch for SMTP.
System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings
For the D-L ink Discover y Protoc ol (DDP) suppor ted device, th is page is an o ption for you to dis able DDP or
configure the DDP packet report timer.
D-Link Discover Protocol State: The default setting is Enabled. Select Disabled then click Apply to turn
off D-Link Discover Protocol State.
Figure 4.51 – System > D-Link Discover Protocol Settings

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
43
3
D-Link Discover Protocol Report Timer (Seconds): Configure the report timer of D-Link Discover Protocol
in seconds. The values are 30, 60, 90, 120 or Never. The default is 30 seconds.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Jumbo Frame
Jumbo Frame support is designed to enhance Ethernet networking throughput and significantly reduce the
CPU utilization of large file transfers like large m ultimedia files or large data files by enabling more efficient
larger pa yloads per packet. The Jum bo Fram e page allows network managers to enable Jum bo Frames on
the device.
The Jumbo Frame default is disabled, Select Enabled then click Apply to turn on the jumbo frame support.
Figure 4.52 – Configuration > Jumbo Frame Settings
Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they were in
the same area.
VLANs c an b e eas ily or gani zed to ref lect dep artm ent g roups (suc h as R &D, Mark eting) , usage gro ups (s uch
as e-mail), or multicast groups (multimedia applications such as video conferencing), and therefore help to
simplify network management by allowing users to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change
any physical connections.
The IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Configuration page provides powerful VID management functions. The original
settings have the VID as 1, no default name, and all ports as “Untagged”
Rename: Click to rename the VLAN group.
Delete VID: Click to delete the VLAN group.
Figure 4.53 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN
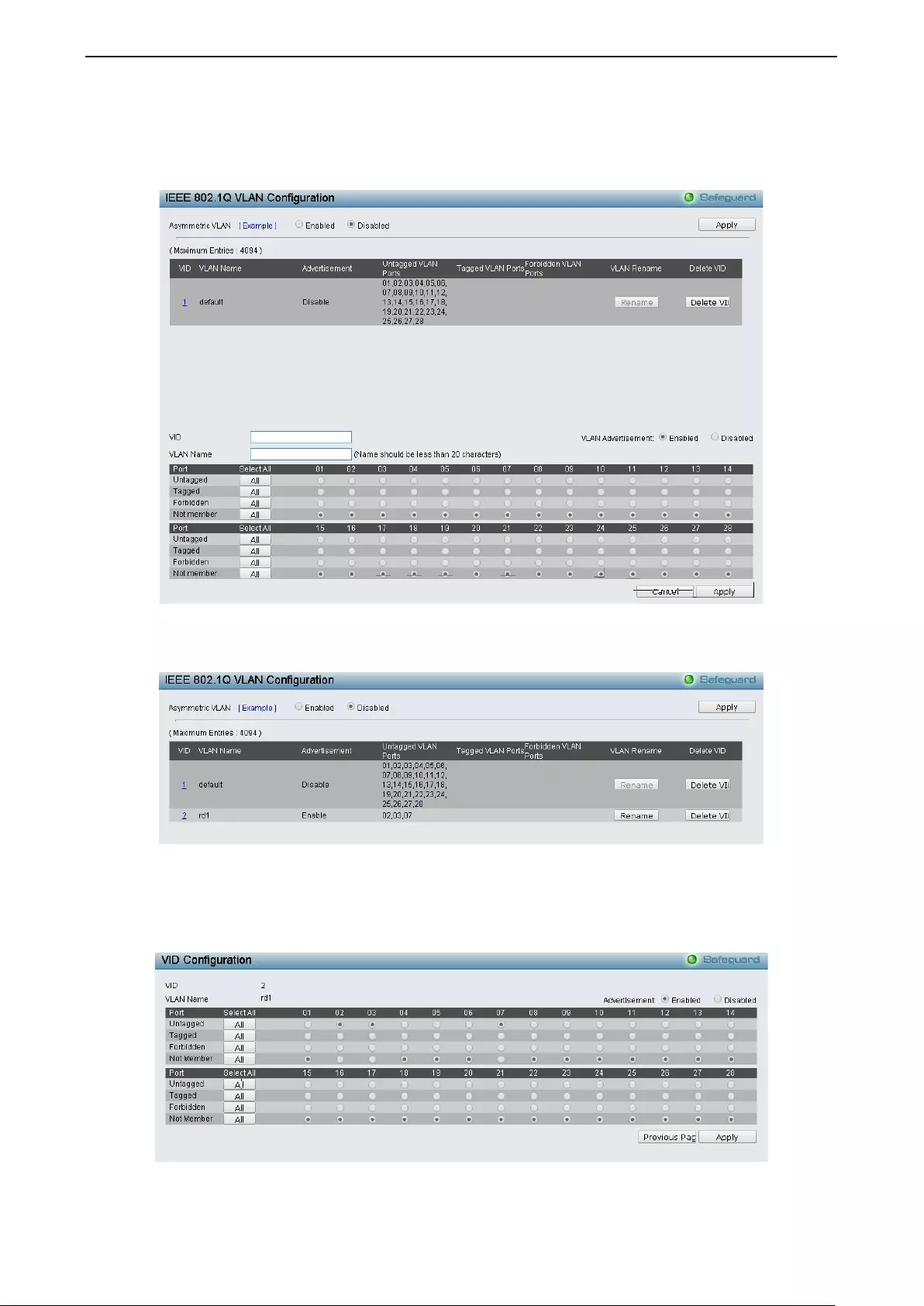
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
44
Click Add VID to create a new VID group, assigning ports from 01 to 10 as Untag, Tag, Forbidden or Not
Member. Enab le or d isable the VLAN Advertisement. A port can be untagge d in onl y one VID. T o s ave the
VID group, click Apply.
Figure 4.54 – Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Add VLAN
After click Apply, the 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Table will displayed with updates.
Figure 4.55 - Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > Example VIDs
Click the VID number, the configuration of VLAN group which selected by user will displayed.
Change the port assignment then Clic k Apply to make the c onfigurations take effect. User can also click the
Previo us Page to the go back to the previous page.
Figure 4.56 - Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > VID Assignments
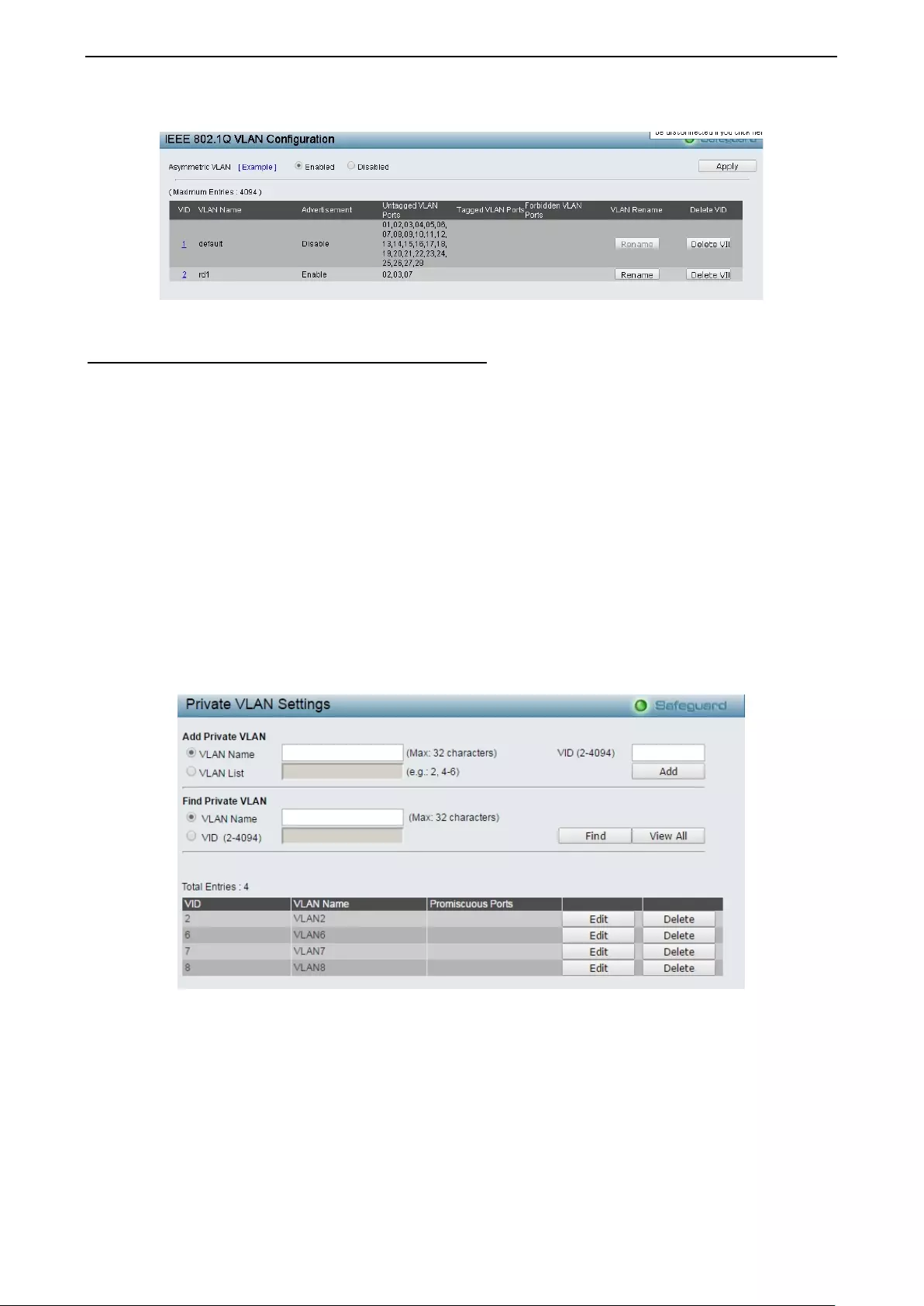
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
45
5
Select Enabled of Asymmetric VLAN and click Apply to change to Asymmetric VLAN mode:
Figure 4.57 - Configuration > 802.1Q VLAN > VID Assignments
Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Settings
A private VLAN is comprised of a primary VLAN, up to one isolated VLAN, and a number of community
VLANs. A private VLAN ID is presented by the VLAN ID of the primary VLAN. The command used to
associate or deas soc iate a s econdary VLAN with a primary VLAN.
A secondary VLAN cannot be associated with multiple primary VLANs. The untagged member port of the
prim ar y VLAN is named as the pr omiscuous por t. The tagge d member por t of the pr im ary VLAN is nam ed as
the trunk port. A promiscuous port of a private VLAN cannot be promiscuous port of other private VLANs.
The primary VLAN member port cannot be a secondary VLAN member at the same time, or vice versa. A
secondar y VLAN can only have the untagged member port. T he member port of a secondary VLAN can not
be member port of other secondary VLAN at the same time. When a VLAN is associated with a primary
VLAN as the secondary VLAN, the promiscuous port of the primary VLAN will behave as the untagged
mem ber of the secondar y VLAN, and the tru nk port of the pr im ary VLAN will behave as th e tagged mem ber
of the second ary VLAN. A secondar y VLAN cannot b e s pecified with ad vertisement. Onl y the primar y VL AN
can be co nf igure d as a layer 3 inter f ac e. The privat e VL AN member por t cann ot be configured with the traf f ic
segmentation function.
The Private VLAN Settings page allows the user to configure the Private VLAN settings.
Figure 4.58 - Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Se ttings
Add Priva te VLAN: Spec if y to add a private VLAN of the Switch.
VL AN Nam e: Enter a VLA N name for the pr ivat e VLA N to be cr eate d. T his name can be up to 32 characters
in length.
VID (2-4094): Enter a VLAN ID for the private VLAN to be created. The value ranges between 2 and 4094.
VLAN List: Enter a list of VLAN ID for the private VLAN to be created.
Click Add to add a new entry based on the information entered.
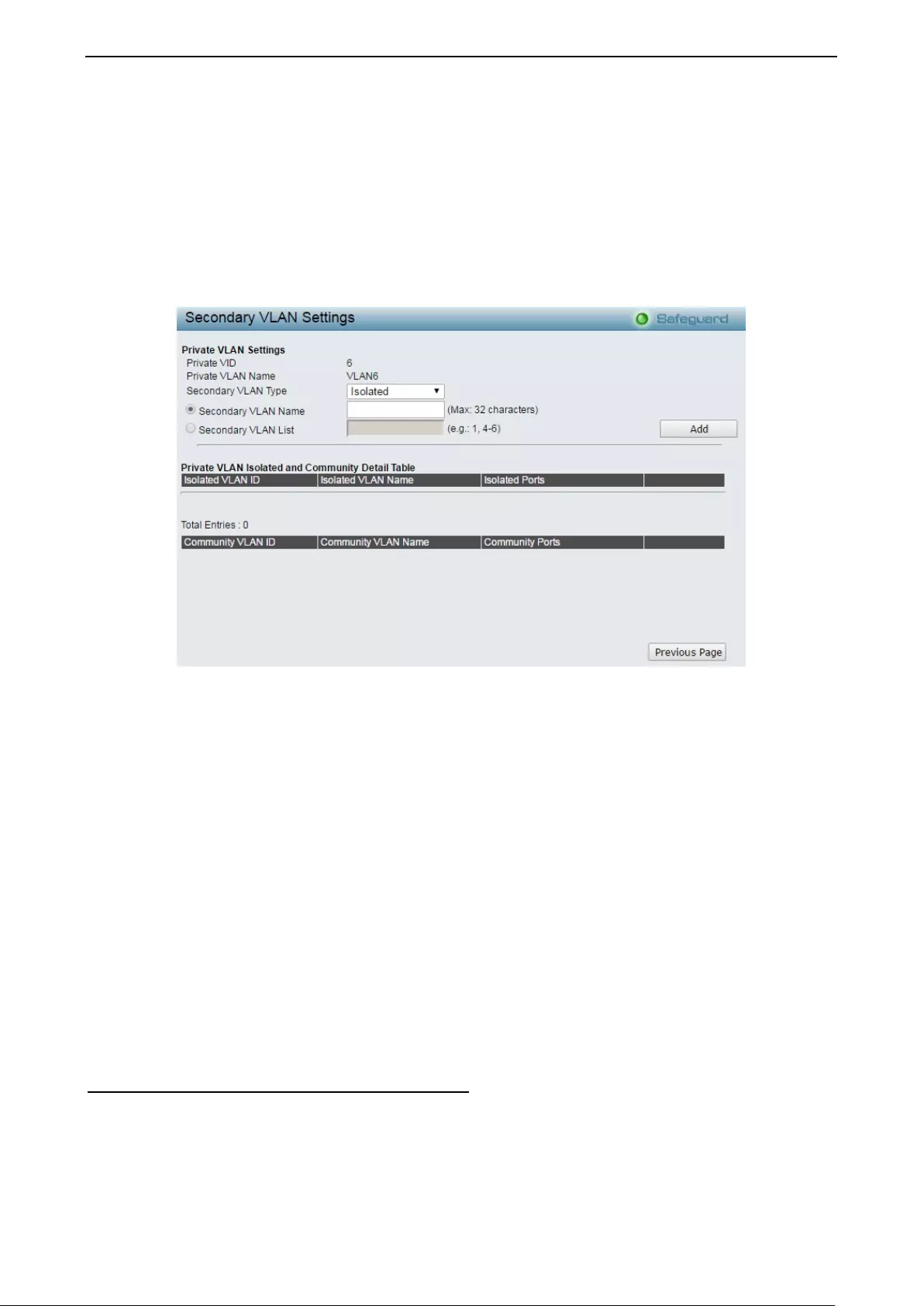
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
46
Find Private VLAN: Specify to display a private VLAN information.
VLAN Name: Enter a VLAN name for the private VLAN to be displayed. This name can be up to 32
characters in length.
VID (2-4094): Enter a VLAN ID for the private VLAN to be displayed. The value ranges between 2 and 4094.
Click Find to locate a specific entry absed on the information entered.
Click View All to display all the existing entries.
Click Edit to configure the secondary VLAN as below:
Figure 4.59 - Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Se ttings – Secondary VLAN Settings
Secondary VLAN Typ e: To specify the secondary VLAN type to be Isolated or Community.
Isolated – The ports within an isolated VLAN cannot communicate with each other at the Layer 2
level. Isolated ports are typically used for those endpoints that only require access to a limited
number of outgoing interfaces on a Private VLAN enabled device. An endpoint connected to an
isolated port will only possess the ability to communicate with those endpoints connected to
promiscuous ports. Endpoints connected to isolated ports cannot communicate with one another.
Community – The ports within a community VLAN can communicate with each other but cannot
comm unicate with ports in other comm unities at the Layer 2 leve l. W ithin a communit y, endpo ints can
communicate with one another and can also communicate with any configured promiscuous port.
Endpoints belonging to one community cannot communicate with endpoints belonging to a different
community or with endpoints connected to isolated ports.
Secondary VLAN Name: Enter a VLAN name for the secondary VLAN. This name can be up to 32
characters in length.
Secondary VLAN List: Enter a list of secondary VLAN ID. The value ranges between 2 and 4094.
Click Add to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click Previous Page to the go back to the previous page.
Configuration > Private VLAN > Priva te VLAN Trun k
The Private VLAN Trunk setting page allows user to configure the trunk ports settings.
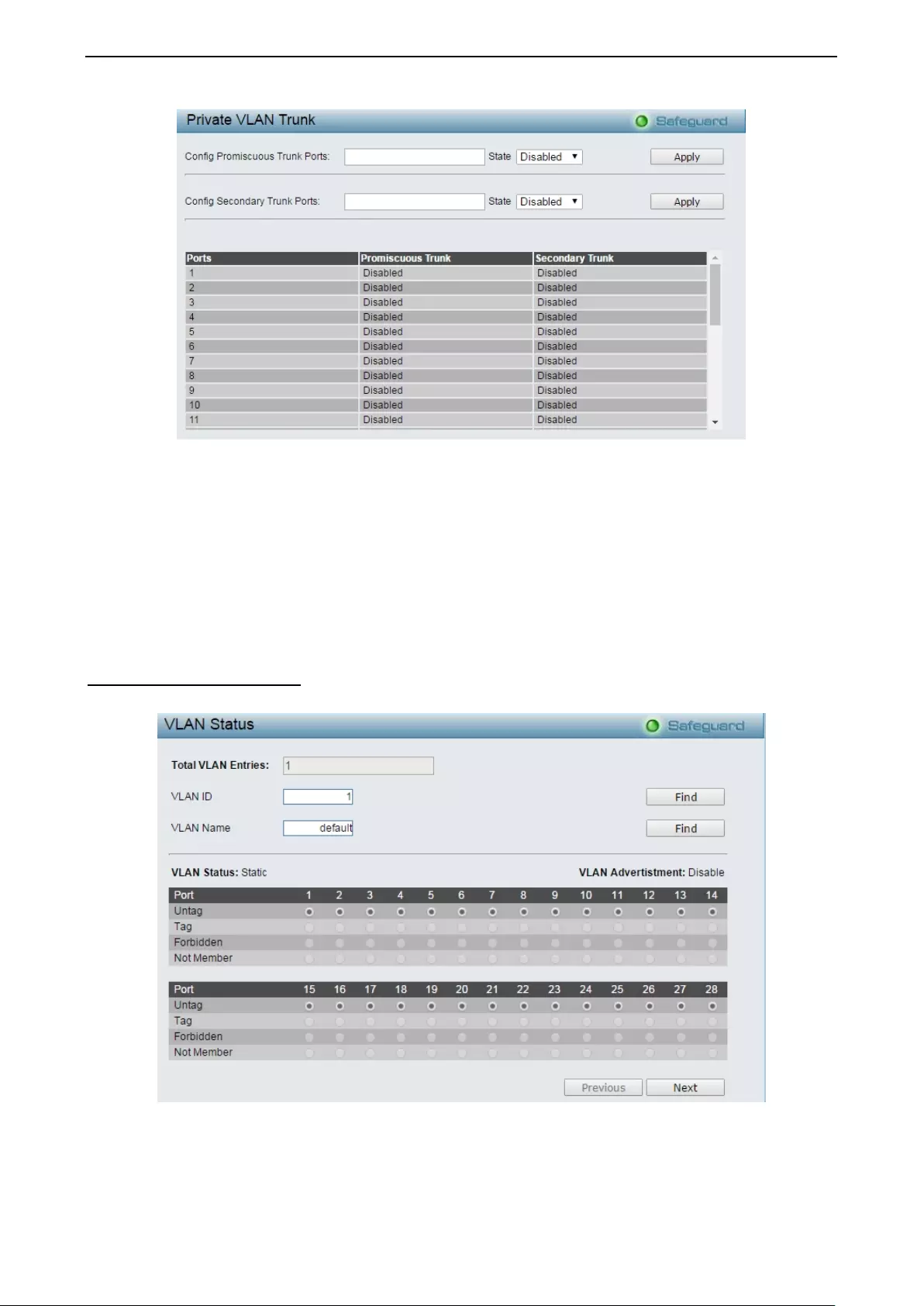
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
47
7
Figure 4.60 - Configuration > Private VLAN > Private VLAN Trunk
Config Promiscuous Trunk Ports: To spec ify the pr om iscuous trunk por ts to the spec ified pr ivate VLAN to
be enabled or disabled. A promiscuous port belongs to the primary VLAN and can communicate with all
interfaces, including the community and isolated host ports and private VLAN trunk ports that belong to the
secondary VLANs assoc iat ed with the pr im ary VLAN.
Config Secondary Trunk Ports: To specify the secondary trunk ports to the specified private VLAN to be
enabled or disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > VLAN Status
The VLAN Status page is for user to search the VLAN which has already existed on the Switch.
Figure 4.61 - Configuration > VLAN Status
Enter the VLAN ID or VLAN Name then click Find to show the existed VLAN.
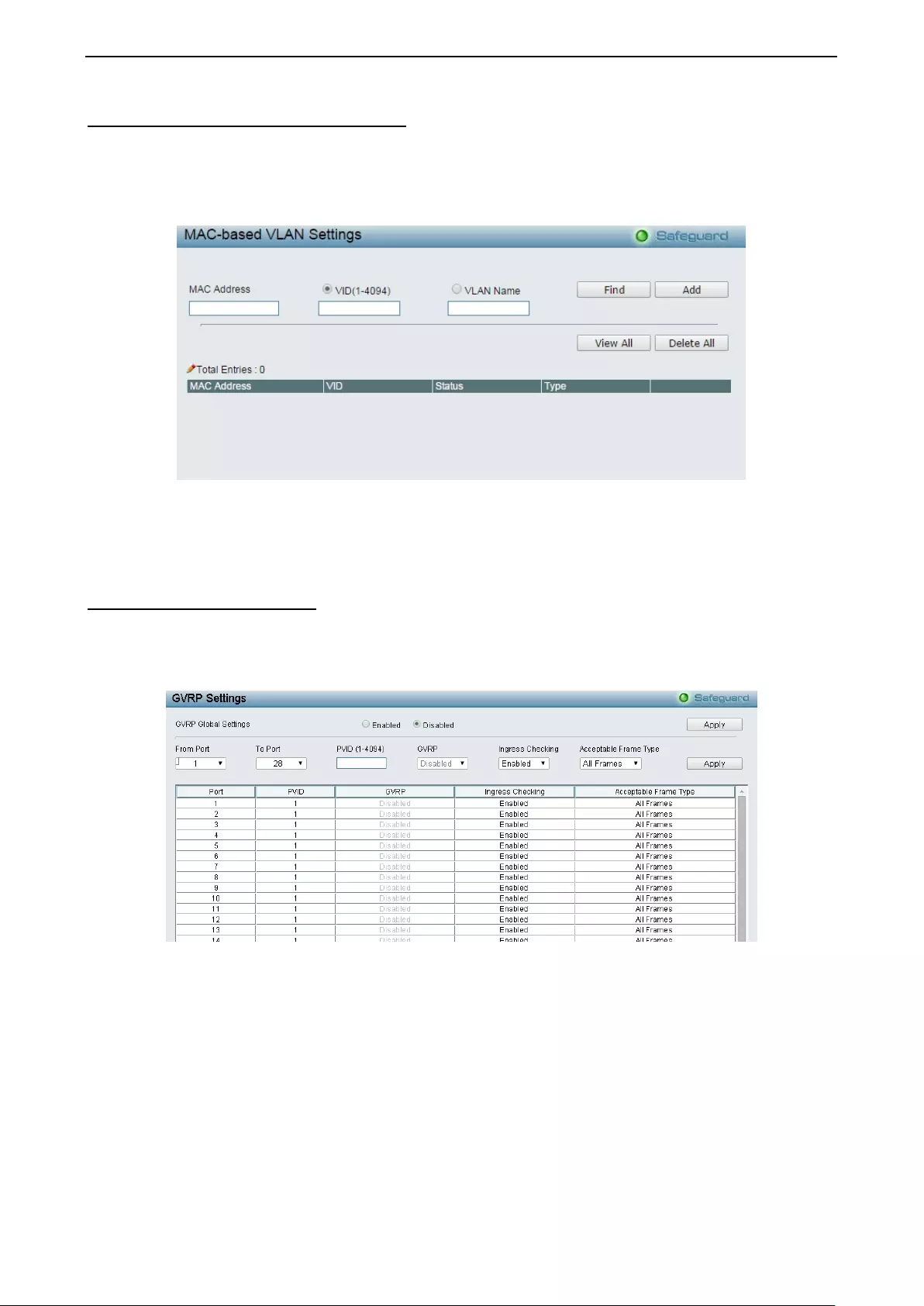
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
48
Configuration > MAC-Based VLAN Settings
The table is us ed to create MAC-bas ed VLAN entri es on the switch. A MAC address can be mapped to an y
existing static VLAN and multiple MAC addresses can be m apped to the same VLAN. When a static MAC-
based VLAN entry is created for a user, the traffic from this user is able to be serviced under the specified
VLAN regardless of the authentication function operated on the port. Therefore each entry specifies a
relationship of a source MAC address with a VLAN.
Figure 4.62 - Configuration > MAC-based VLAN
M AC Add ress: Specify the MAC address to be reauthenticated by entering it into the MAC Address field.
VID (1-4094) / VLAN Name: Enter the VID or VLAN name of a previously configured VLAN.
Configuration > GVRP Settings
The GVRP Settings page allows user to determine whether the Switch will share its VLAN configuration
information with other GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enabled switches. In addition, Ingress
Checking can be used to limit traffic by filtering incoming packets whose PVID does not m atch the PVID of
the port. Results can be seen in the table under the configuration settings, as seen below.
Figure 4.63 - Configuration > GVRP Settings
From Port/To Port: These two fie lds allow user to s pe cify the range of por ts t hat wil l be inc lu ded in th e P ort -
based VLAN that user is creating using the 802.1Q Port Settings page.
PVID (1-4094): The read-only field in the 802.1Q Port Table shows the current PVID assignment for each
port, whic h ma y b e m anually assigne d to a VLAN when cr eated in the Sett ings table. T he Switch's default is
to assign all ports to the default VLAN with a VID of 1. The PVID is used by the port to tag outgoing,
untagged packets, and to m ake filtering decisions about incom ing packets. If the port is specified to accept
only tagged fram es - as tagging, and an untag ged packet is forwarded to the port for transmission, the port
will add an 8 02.1Q tag usi ng the PVID t o write the V ID in the tag. W hen t he packet arrives at its dest ination,
the receivi ng dev ice will us e the PVID to mak e VLAN forwar ding dec isions. If the port rec eives a pack et, and
Ingress filtering is enabled, the port will compare the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are
unequal, the port will drop the packet. If the two are equal, the port will receive the packet.
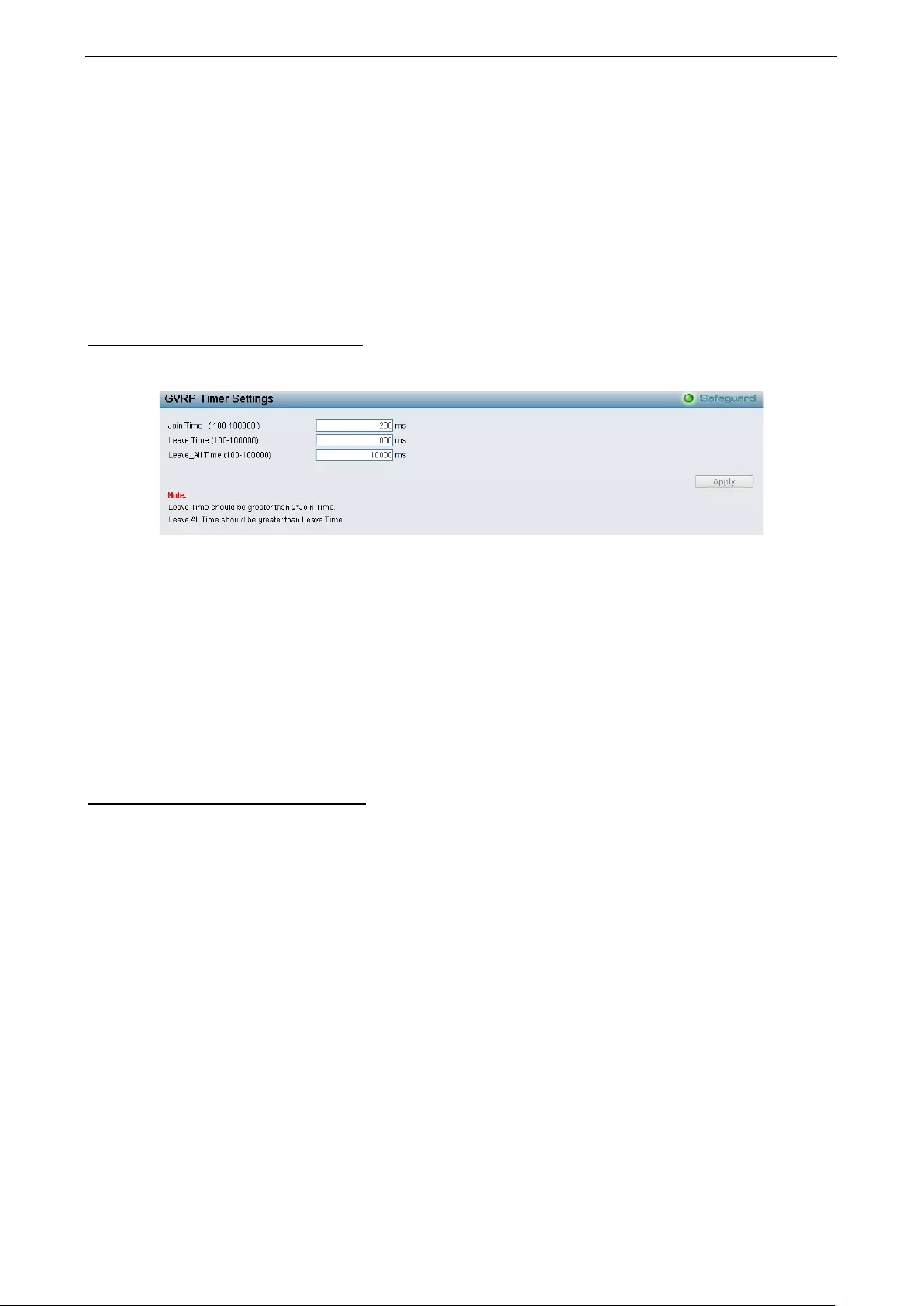
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
4
49
9
GVRP: The Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to dynamically become a member
of a VLAN. GVRP is Disabled by default.
Ingress Checking: This field can be toggled using the space bar between Enabled and Disabled. Enabled
enables t he por t t o c ompare th e V ID t ag of an incoming packet with t he PV ID number ass igned t o th e p or t. I f
the two are different, t he port filters ( drops) the p acket. Disabled disab les ingress filtering. Ingr ess Checking
is Disabled by default.
Acceptable Frame Type: This field denotes the type of frame that will be accepted by the port. The user
may choose between T agged Only, which m eans only VLAN ta gge d f r am es will be ac c epte d, an d Admit_All,
which mean both tagged and untagged frames will be accepted. Admit_All is enabled by default.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > GVRP Timer Settings
The GVRP Timer Settings page allows user to configure the GARP timer values for application join, leave,
and leave_all GARP timer values.
Figure 4.64 - Configuration > GVRP Timer Settings
Join Time (100-100000): Indicates the tim e in milliseconds that PDUs are tra nsmitted. The def ault value is
200ms.
Leave Time (100-100000): Ind icates th e amount of tim e in milliseconds that the device waits befor e leaving
its GAR P state. T he leave t ime is activated b y a lea ve all tim e message s ent/recei ved, and c ancelled by the
Join message. The default value is 600ms.
Leave_All Time (100-100000): Us ed to c onfirm the port within the VLAN. T he ti me in m illiseconds betwee n
messages sent. The default value is 10000ms.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > QinQ > QinQ Settings
The Q inQ Settings page allows us er to enable or disable the Q-in-Q f unction. Q-in-Q is des igned f or service
providers to carry traffic from multiple users across a network.
Q-in-Q is used t o maintain c ustomer s pec if ic VLA N an d L a yer 2 pro t oco l c o nf igurations e ve n when the s am e
VLAN ID is being used by different customers. This is achieved by inserting SPVLAN tags into the
customer’s frames when they enter the service provider’s network, and then removing the tags when the
frames leave the network.
Customers of a service provider may have different or specific requirements regarding their internal VLAN
IDs and the number of VLANs that can be supported. Therefore customers in the same service provider
network m ay have VLAN ra nges t hat ov erlap, which m ight ca use traf fic to bec om e mixed up. So as signin g a
unique range of VLAN IDs to each customer might cause restrictions on some of their configurations
requiring intense processing of VLAN mapping tables which may exceed the VLAN mapping limit. Q-in-Q
uses a s ingle serv ice provider VLAN (SPVL AN) for cu stomers who have m ultiple VLANs. Customer ’s VL AN
IDs are segregated within the service provider’s network even when they use the same customer specific
VLAN ID . Q -in-Q expands t he VLAN s pac e av ai lable whil e pr eser v ing t he cus tomer ’s origi nal t ag ged p ac kets
and adding SPVLAN tags to each new frame. Select Enabled or Disabled then click Apply to enable or
disable the Q-in-Q Global Settings.
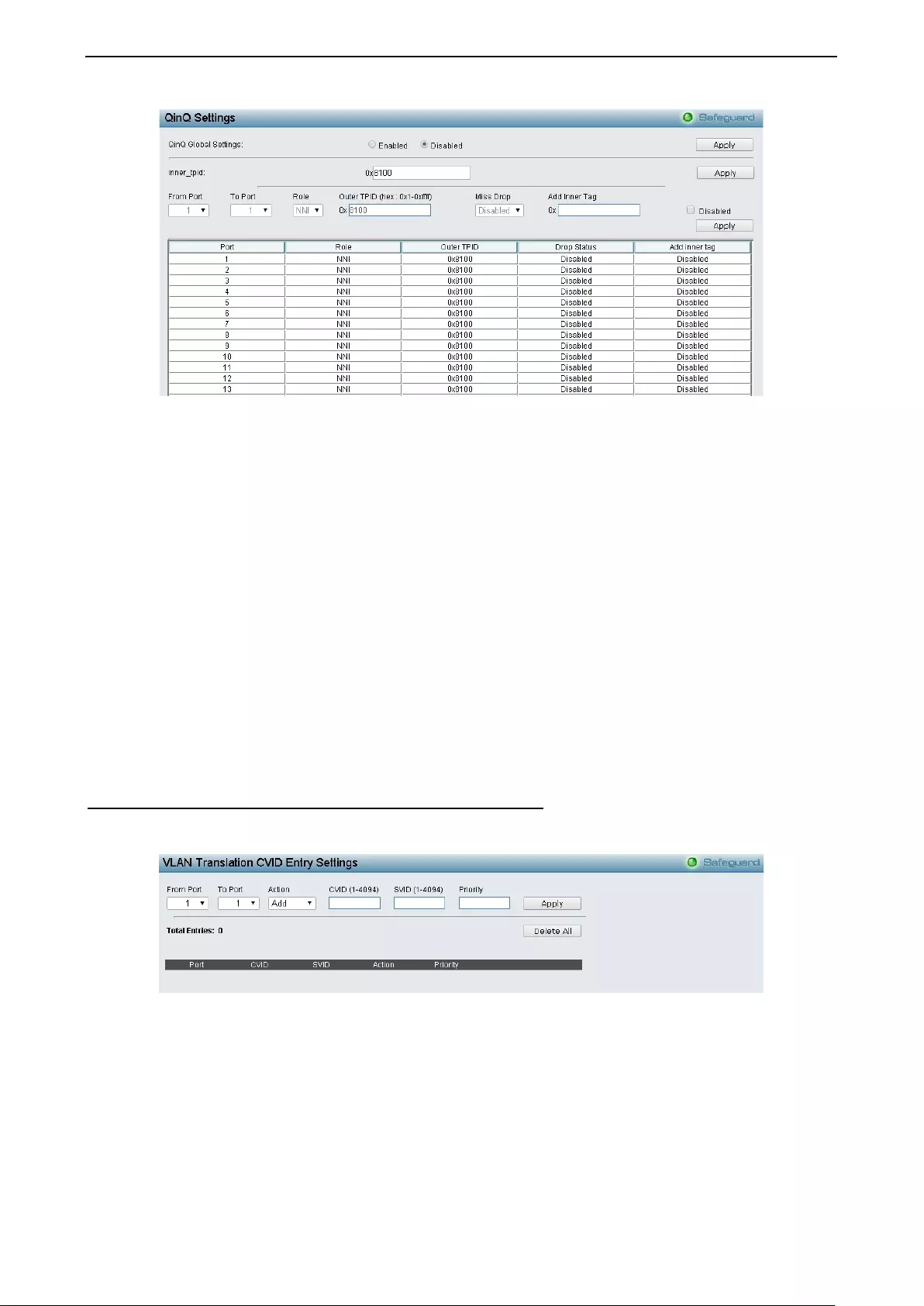
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
50
Figure 4.65 - Configuration > Qin Q > QinQ Sett ing s
From Port / To Port: A consecuti ve group of ports that are part of t he VLAN co nfiguration s tarting with t he
selected port.
Role: The user can choose between UNI or NNI role.
UNI – To select a user-net work interface which specifies that communication between the specified
user and a specified network will occur.
NNI – To select a network-to-network interface specifies that com munication between two specified
networks will occur.
Outer TPID (hex: 0x1-0xffff): The Outer TPID is used for learning and switching packets. The Outer TPID
constructs and inserts the outer tag into the packet based on the VLAN ID and Inner Priority.
Mi ss Drop: Specifies to en abl e or dis a ble t he M is s Dr op. If Miss Dr op is ena bl ed, t he packet does not match
any assignment rule in t he VL AN tr ansl ati on a nd Q -in-Q pr of ile will be dropped. If dis ab led , the pac k et w ill be
forwarded and will be assigned to the PVID of the received port.
Add Inner Tag: Unselect the Disable check box and enter an entry that an Inner T ag will be added to the
entry.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation CVID Entry Settings
The VLAN Translation translates the VLAN ID carried in the data packets it receives from private networks
into those used in the Service Providers network.
Figure 4.66 - Configuration > QinQ > VLAN Translation CVID Entry Settings
From Port / To Port: A consec utive group of ports that ar e part of the VLAN c onfiguration starting w ith t he
selected port.
Action: Specify for SPVID packets to be added or replaced.
CVID List (1-4094): The customer VLAN ID List to which the tagged packets will be added.
SVID (1-4094): This configures the VLAN to join the Service Providers VLAN as a tagged member.
Priority: Specifies the CVID entry priority.
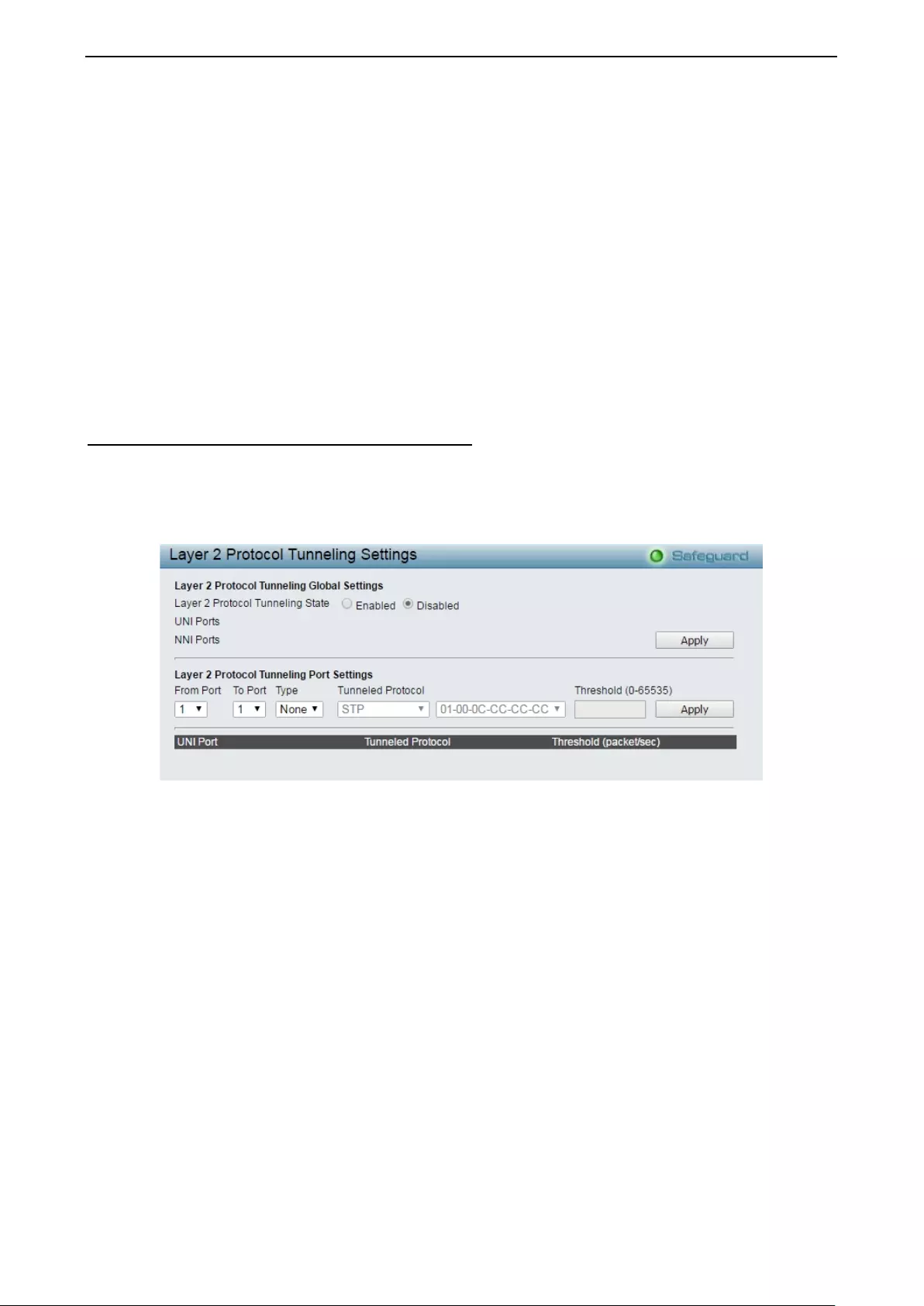
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
51
1
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. Click Delete All to remove all the CVID entries.
Q-in-Q and VLAN Translation Rules:
For Ingress untagged packets at UNI ports:
1. The Switch does not reference the VLAN translation table.
2. Check the Switch VLAN tables. The Sequence is MAC-based VLAN -> subnet-based VLAN ->
protocol-based VLAN -> po rt-based VLAN. If m atched, the m atched VLAN wi ll becom e this pack et’s
SPVLAN.
For Ingress tagged packets at UNI ports:
1. The Switch looks up the VLAN translation table. If matched, the VLAN tag will be translated
(replace CEVLAN with SPVLAN, or add SPVLAN).
2. Or, check the Switch VLAN tables. The sequence is the same as above. The matched VLAN
becomes this packet’s SPVLAN.
Configuration > Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings
The layer 2 protocol tunneling is used to tunnel the layer 2 protocol packets. When the device is operating
with the Q-in-Q enabled, DA will be replaced b y the tunnel multicast address, and the BPDU will be tagged
with the t unnel VLAN b ased on t he QinQ VLAN conf iguratio n and the tu nnel/upl ink setting. W hen the d evice
is operating with the Q-in-Q disabled, the BPDU will have its DA replaced by the tunnel multicast address
and is transmitted out based on the VLAN configuration and the tunnel/uplink setting.
Figure 4.67 - Configuration > Layer2 Protocol Tunneling Settings
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling State: Specify to enable or disable the layer 2 Protocol Tunneling of ports.
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports that are part of the configuration starting with the selected
port.
Type: Specify the layer 2 protocol tunnel type which wi ll app ly on the spec ified por ts .
UNI – Specify the port is UNI port.
NNI – Specify the port is NNI port.
None – Disable the tunneling function.
Tunneled Protocol: Specify tunneled protocols on this UNI port.
STP – Specify the BPDU received on these UNI will be tunneled.
GVRP – Specify the GVRP PDU received on these UNI will be tunneled.
Protocol MAC – Specify the destination MAC address of the L2 protocol packets that will tunneled
on these UNI ports. The MAC address can be 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC or 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CD.
All – Specify all supported.
Threshold (0-65535): Specif y the dro p thres h old f or p ackets-per-second accepted on this U NI p or t. T he por t
drops the PDU if the protocol’s threshold is exceeded. The range of the threshold value is 0 to 65535
(packet/second). The value 0 means unlimited. By default, the value is 0.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
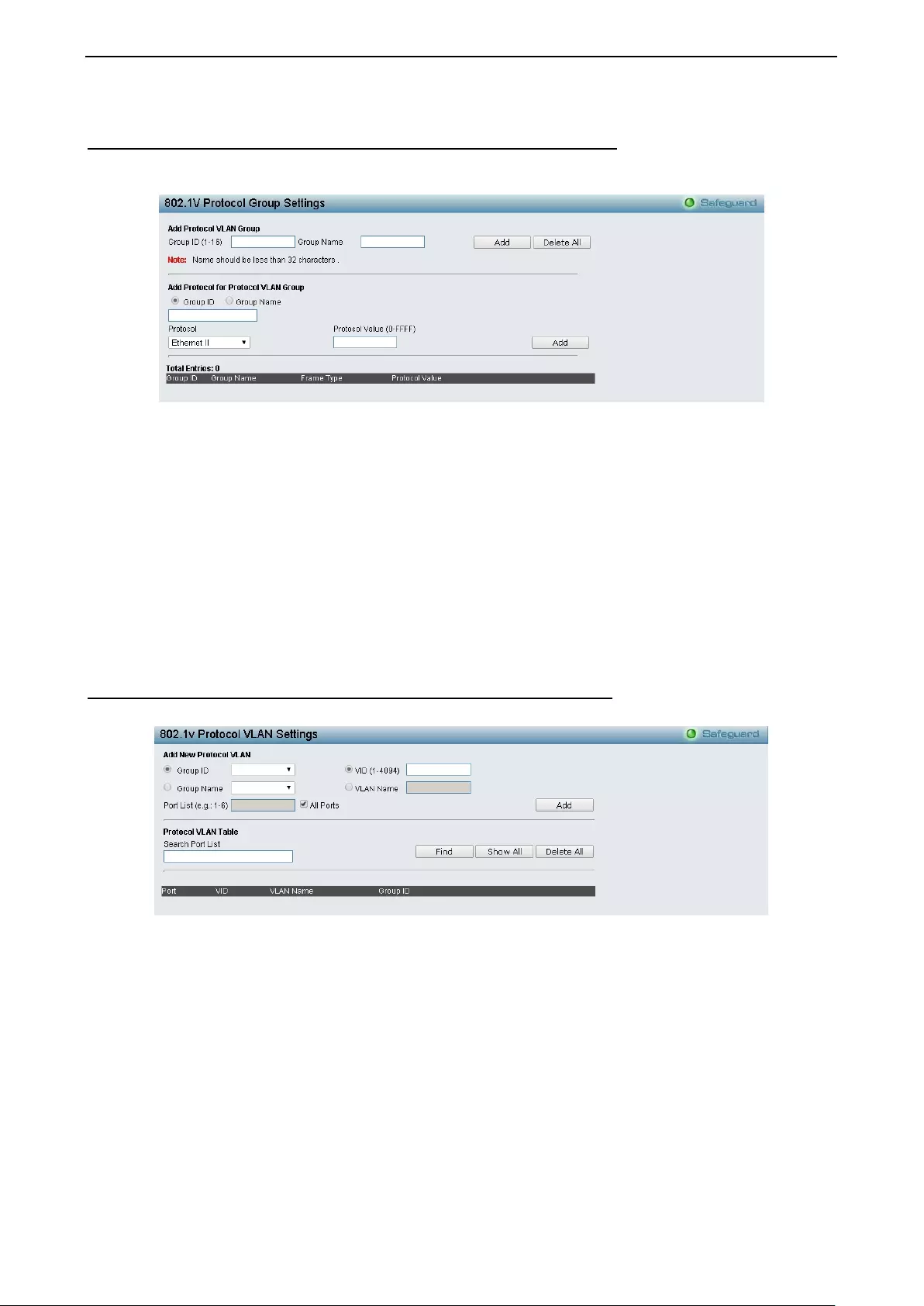
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
52
Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol Group Settings
The 802.1v Protocol Group Settings page allows user to configure the untagged ports of different protocols
on the same physical port.
Figure 4.68 - Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol Group Settings
Group ID (1-16): Select an ID number for the group. The value is between 1 and 16.
Group Name: Specifies the group name for the 802.1v protocol group.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Click the Delete All button to remove all the entries based on the information entered.
Protocol: Specifies the packets to protocol-defined VLANs by examining the type octet within the packet
header to discover the type of protocol associated with it. The types are Ethernet II, IEEE802.3 SNAP, and
IEEE802.3 LLC.
Protocol Value: Enter a value for the group. The protocol value is used to identify a protocol of the frame
type specified. The form of the input is 0x0 to 0xffff.
Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings
The 802.1 v Protoc o l VL AN Sett ings page allows user to configure the Protocol VLAN settings.
Figure 4.69 - Configuration > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings
Group ID: Select a previously configured Group ID from the drop-down menu.
VID (1-4094): Specifies the VID to be created.
Group Name: Select a previously configured Group Name from the drop-down menu.
VLAN Name: Specifies the VLAN name to be created.
Port List: Enter the specified ports to be configured or tick the All Port s check box.
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered.
Search Port List: Specifies t he port to be sear ched.
Click the Find button to view the information with specified ports.
To display all previously configured port lists on the button half of the screen click the Show All button.
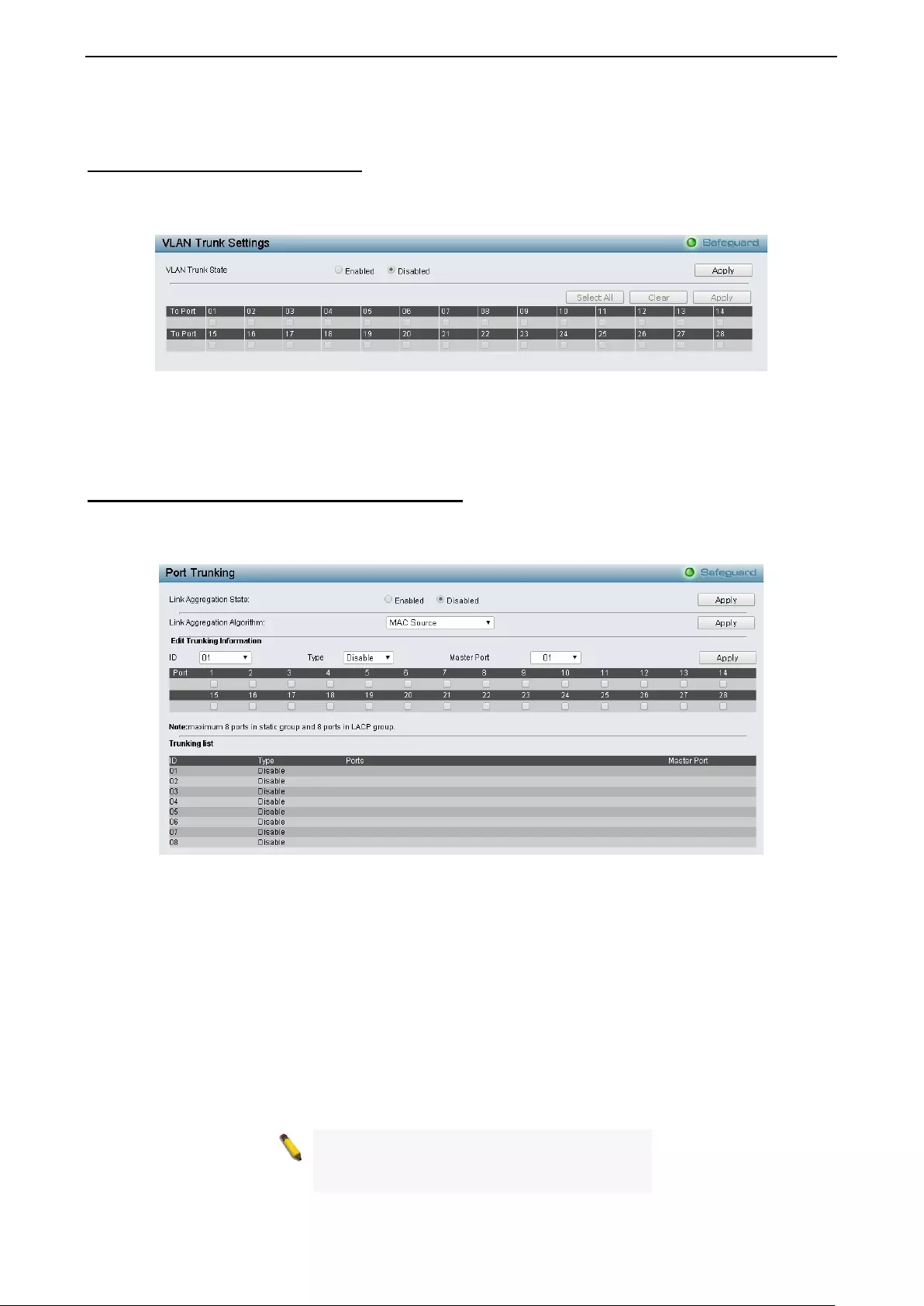
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
53
3
To clear all previously configured lists click the Delete All button.
Configuration > VLAN Trunk Settings
The VLAN Trunk Settings is used to combine a number of VLAN ports together to create VLAN trunks. To
create Vlan Trunk Port settings on the Switch, enter the ports to be configured, change the state to Enabled
and click Apply, the new settings will appear in the VLAN Trunk Port Settings Table below.
Figure 4.70 - Configuration > VLAN Trunk Settings
Click Select All to check all ports or click Clear to remove ports then click Apply.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Link Aggregation > Port Trunkings
The Port Trunk ings f unction e nables the com bining of two or m ore ports t ogether to incr ease bandwidth. Up
to eight Trunk groups ma y be created, and e ach group consists up to e ight ports . Select Enabled and click
Apply to active the Link Aggregation State.
Figure 4.71 – Configuration > L in k Agg regation > Por t Tr u n kings
Link Aggregation Algorithm: Specify the algorithm to be MAC Source, MAC Destination, MAC Source
Destination, IP Source, IP Destination or IP Source Destination, and then Click Apply to make the
configurations take effect.
Edit Trunking Information:
Specif y th e ID, Type and Master Port then select the ports to be gr ouped together, and then click Apply to
activate the selected Trunking groups. Two types of link aggregation can be selected:
Static - Static link aggregation.
LACP - LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is enabled on the device. LACP allows for the
automatic detection of links in a Port Trunking Group.
Disable - Remove all members in this trunk group.
NOTE:
Each combined trunk port must be
connected to devices within the same VLAN
group.
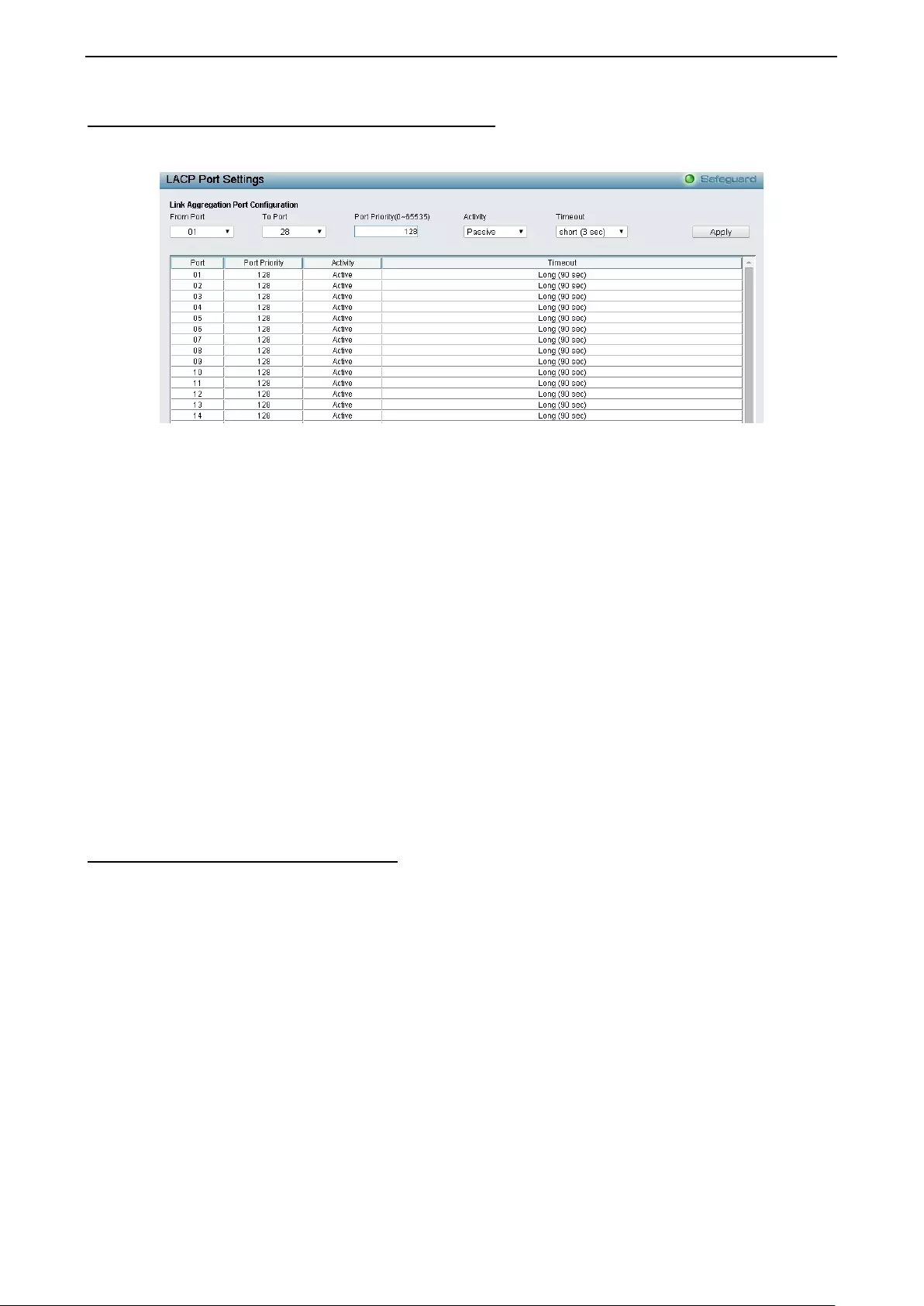
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
54
Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
The LACP Port Set tings is used to cr eate port trunk ing groups on the Switch. T he user m ay set which ports
will be active and passive in processing and sending LACP control frames.
Figure 4.72 – Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port Settings
From Port: The beginning of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
To Port: The ending of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Port Prio rity (0-65535): D i s plays the LACP priorit y value for the port. Def ault is 128.
Activity: There are two different roles of LACP ports:
Active - Active LACP p orts ar e c apa ble of proc es s ing and sending L AC P co ntr o l f r ames. This allows
LACP com pliant devices t o negotiate t he aggregate d link so the grou p may be chang ed dynamically
as needs require. In or der to utili ze the abilit y t o change an aggregated por t group, th at is, to add or
subtract por ts f rom the group, at leas t one of the par tic ipating dev ices m us t designat e LACP p orts as
active. Both devices must support LACP.
Passive - LACP ports that are designated as passive cannot initially send LACP control frames. In
order to allow the linked port group to negotiate adjustments and make changes dynamically, one
end of the connection must have "active" LACP ports.
Timeout: Specif y the administrati ve LACP timeout. The possible field values are:
Short (3 Sec) - Defines the LACP timeout as 3 seconds.
Long (90 Sec) - Defines the LACP timeout as 90 seconds. This is the default value.
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Configuration > BPDU Protection Settings
The BPDU Protection Settings page allows user to configure the BPDU protection function for the ports on
the Switc h. In genera lly, there are two states in BPDU protect ion function. O ne is norm al state, an d another
is under attack state. The under attack state have three modes: drop, block, and shutdown. A BPDU
protecti on enabled por t will enter and under attac k state wh en it receives one STP BPDU packet. A nd it will
take action based on the configuration. Thus, BPDU protection can only be enabled on the STP-disabled
port. Select Enabled or Disabled and click Apply to enabled or disable the BPDU attack protection state.
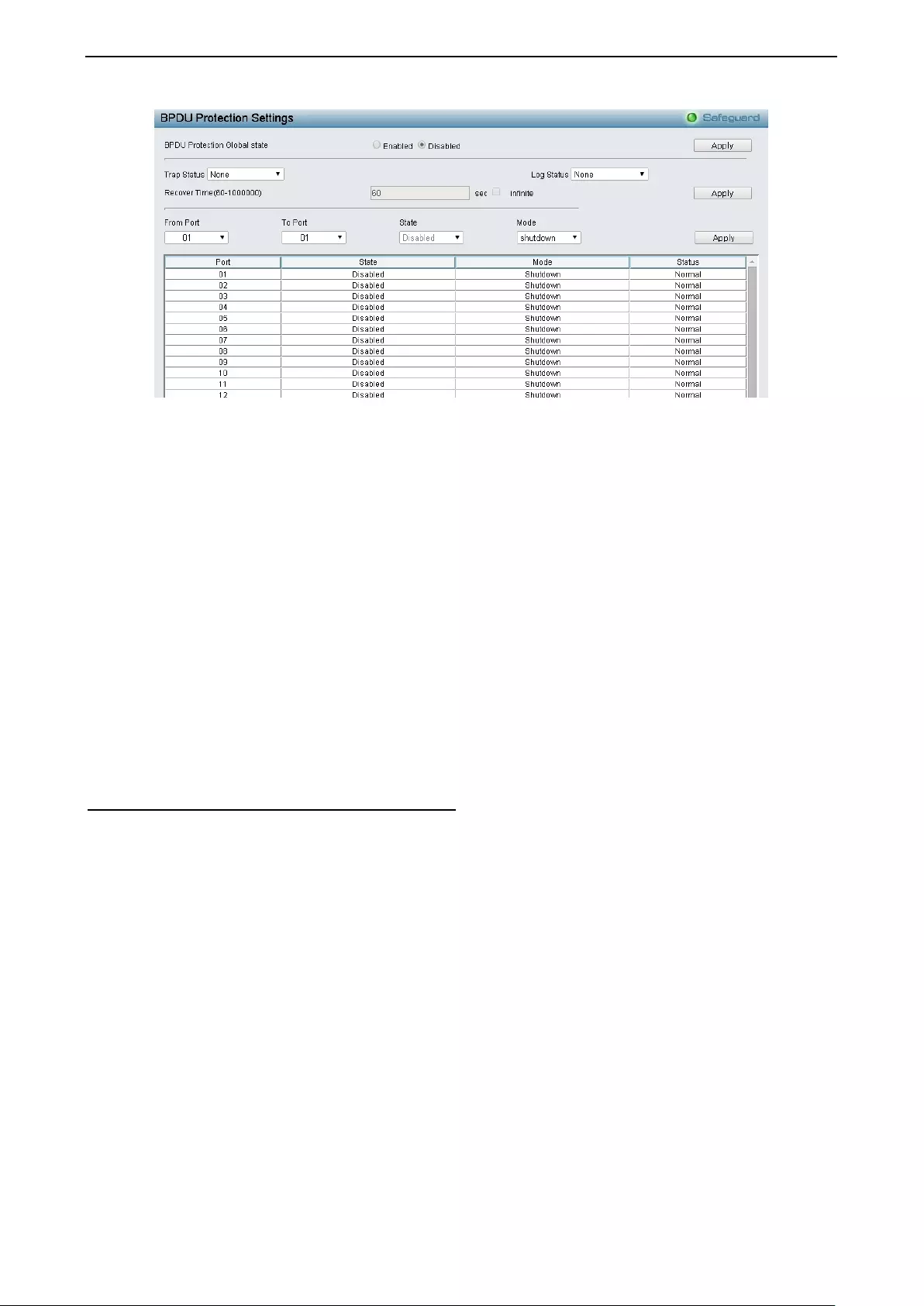
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
55
5
Figure 4.73 – Configuration > BPDU Protec tion Settings
Trap Status: S pecify to send trap packet when Attack Detected, Attack Cleared, None or Both.
Log Status: Specify the Log Status when Attack Detected, Attack Cleared, None or Both.
Recover Time (60-1000000): Specify the BPDU protection Auto-Recovery timer, the range is from 60 to
1000000 and default is 60 seconds. Or select infinite.
Click Apply for changes to take effect.
From Port / To Port: Specify the port ranges to be configured.
State: To enabled or disable the protection mode for a specific port.
Mode: Specify the BPDU protection mode. The default mode is shutdown.
Drop – Drop all received BPDU packets when the port enters under attack stats.
Block – Drop all packets (includes BPDU and normal packets) when the port enters under attack
state.
Shutdown – Shut down the port when the port enters under attack state.
Click Apply for changes to take effect.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
With Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping, the DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch can
make intelligent multicast forwarding decisions by examining the contents of each frame’s Layer 2 MAC
header.
IGMP snooping can help reduce cluttered traffic on the LAN. With IGMP snooping enabled globally, the
DGS-1210/ME Metro Ethernet Switch will forward multicast traffic only to connections that have group
members attached.
The settings of IGMP snooping is set by each VLAN individually.
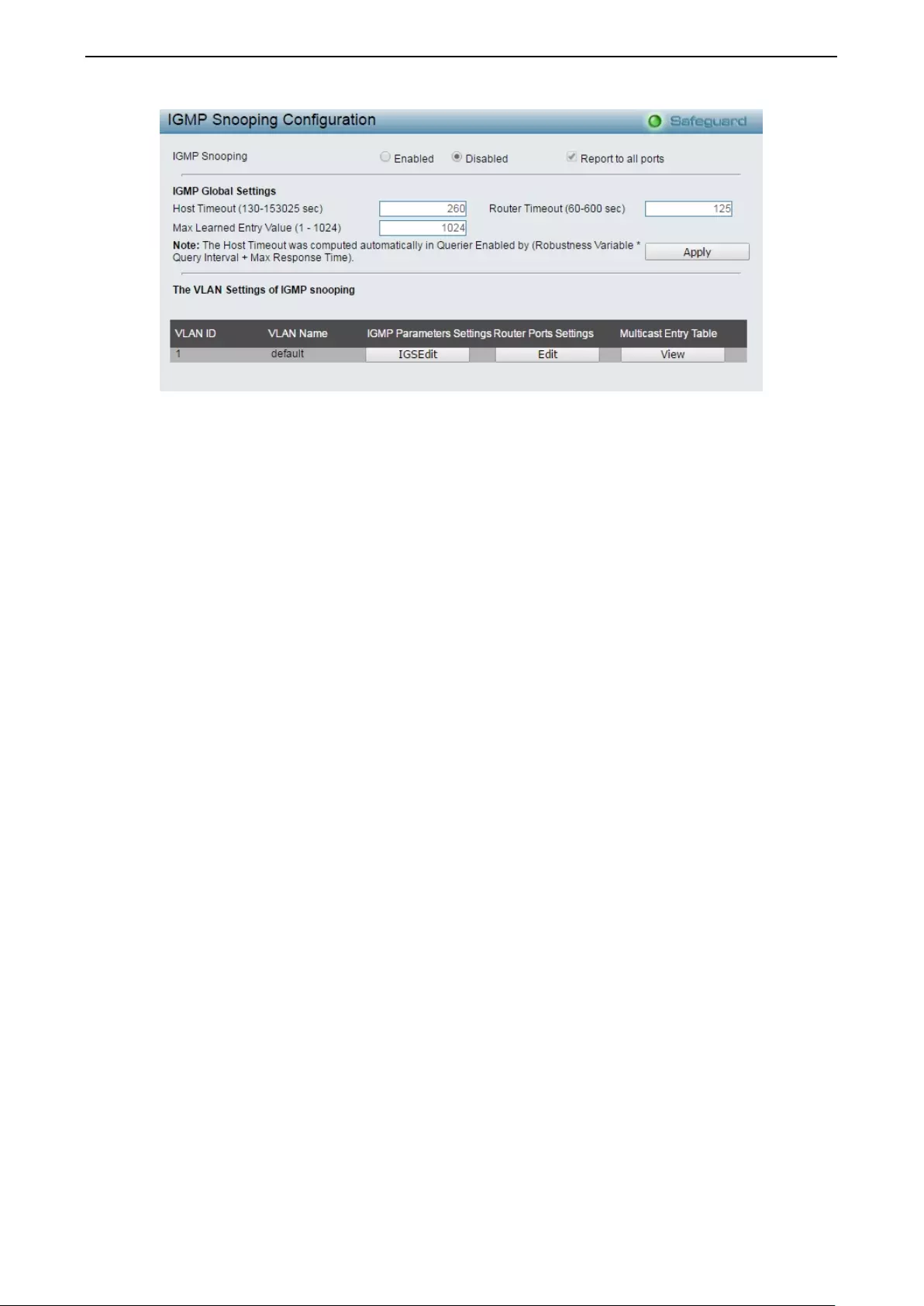
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
56
Figure 4.74 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping
By default, IGM P is disabled. If enabled, the IGMP Global Settings will need to be entered:
Host Timeout (130-1530 25 sec): This is the interval after which a learned host port entry will be purged. For
each host port learned, a 'Port Purge Timer' runs for 'Host Port Purge Interval'. This timer will be restarted
whenever a repor t mess age f r om hos t is r ec eived ove r that port. I f no rep or t messages are r ecei ve d f or 'Hos t
Port Purge Interv al' tim e, the learned hos t entr y will be purged fr om the m ulticast group. The defau lt value is
260 seconds.
Robust ness Variable ( 2-255 sec) : The Robustness Variable allows adjustment for the expected packet loss
on a subnet. If a subnet is expected to be loss y, the Robustness Variable may need to be increased. The
Robustness Variable cannot be set to zero, and it SHOULD NOT be. Default is 2 seconds.
Query Interval (60-600 sec): The Query Inter val is th e interva l bet ween G enera l Q ueries sent. B y adjusting
the Quer y Interval, the number of IGMP messages can be increased or decreased; larger values will cause
IGMP Queries to be sent less often. Default value is 125 seconds.
Max L earned Entry Value (1-1024): The Max L ear ne d Entry Value a ll o ws adjus t ment for t he value. Default
value is 256.
Router Timeout (60-600 sec): T his is the inter val after wh ich a learned ro uter port entr y will be purg ed. For
each ro uter port learned, a 'Router Port Purge Tim er' runs for 'Router Port Purge Inter val'. This t imer will be
restarted whenever a Query control message is received over that port. If there were no Query control
mess ages received f or 'Rout er Port Purge Inter val' tim e, the learn ed router p ort entr y will be pur ged. Defa ult
is 260 seconds.
Last Member Query Interval (1-25 sec): The Last Member Query Interval is the Max Response Time
inserted int o Group-Specif ic Queries sent in res ponse to Leave Gro up mess ages, and is also th e amount of
time between Group-Specific Query messages. This value may be adjusted to m odify the "leave latenc y" of
the network. A reduced value results in reduced time to detect the loss of the last member of a group. Default
is 1 second.
Max Response Time (10-25 sec): The Max Response Time specifies the maximum allowed time before
sending a respon ding r eport m essage. Adjus ting th is sett ing ef fects the " leave la tency", or the tim e bet ween
the moment the last host leaves a group and when the multicast server is notified that there are no more
mem bers. It also all ows adjustm ents for contr olling the frequency of IGMP traf fic on a subnet. D efault is 1 0
seconds.
Select the State, Q uerier State, Fa st Leave and Data Driv en Learni ng to be enabled or disabled then click
Apply for changes to take effect.
Click IGSEdit button to enter the IGMP Parameters Settings page.
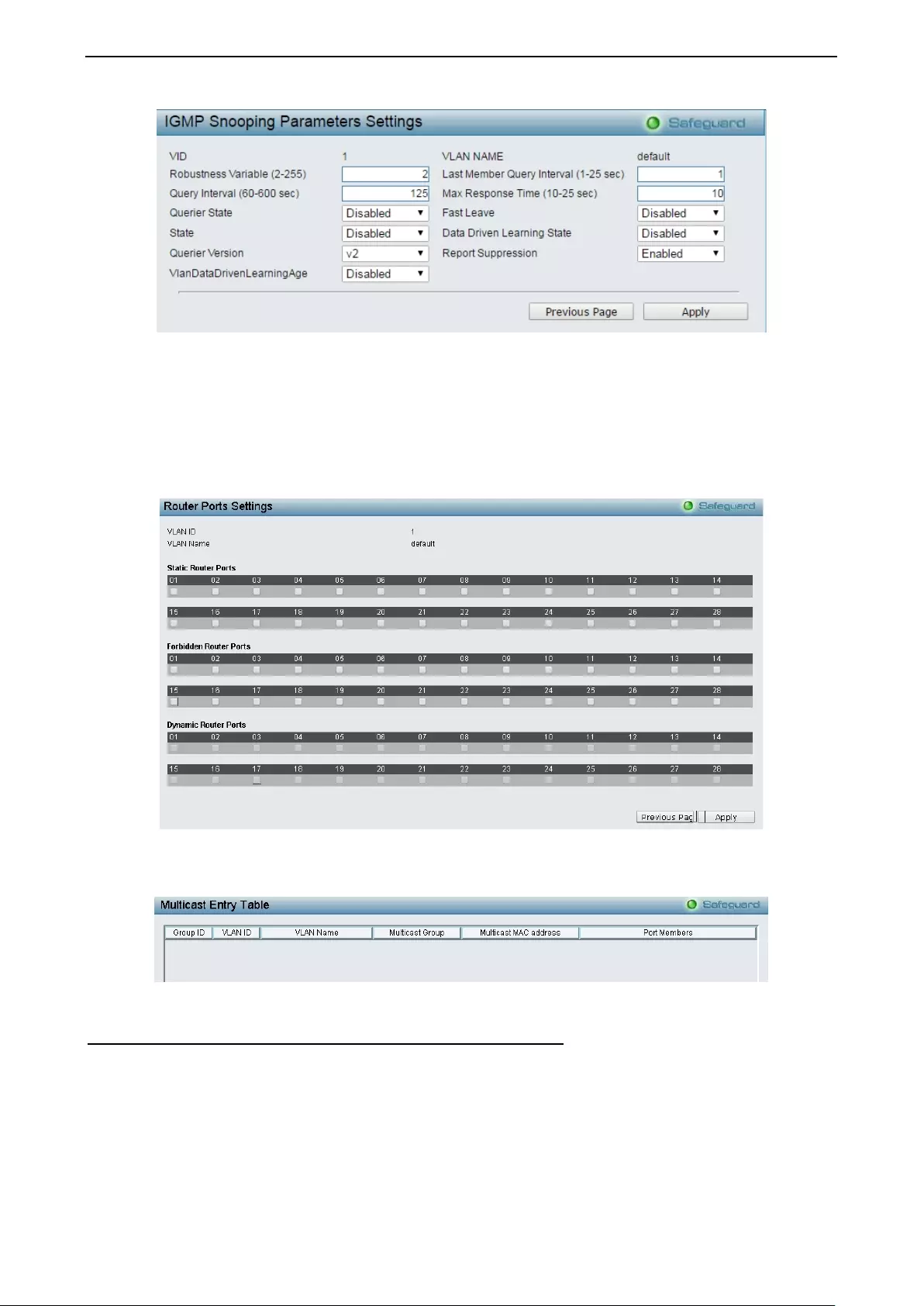
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
57
7
Figure 4.75 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping-Parameters Settings
Click Edit button to enter the Router Port Settings page, and the ports to be assigned as router ports for
IGMP snooping for the VLAN.
A router port configured manually i s a Static Router Port, a Forbidden Router Port and a Dyn amic Router
Port is dynamically configured by the Switch when a query control message is received. Press Apply for
changes to take effect.
Figure 4.76 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping-Router Port Settings
To view the Multicast Entry Table for a given VLAN, press the View button.
Figure 4.77– Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snoo ping-Multicast Entr y Table
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
The IGMP Access Control Settings page is used to enable or disable the IGMP access control of selected
ports.
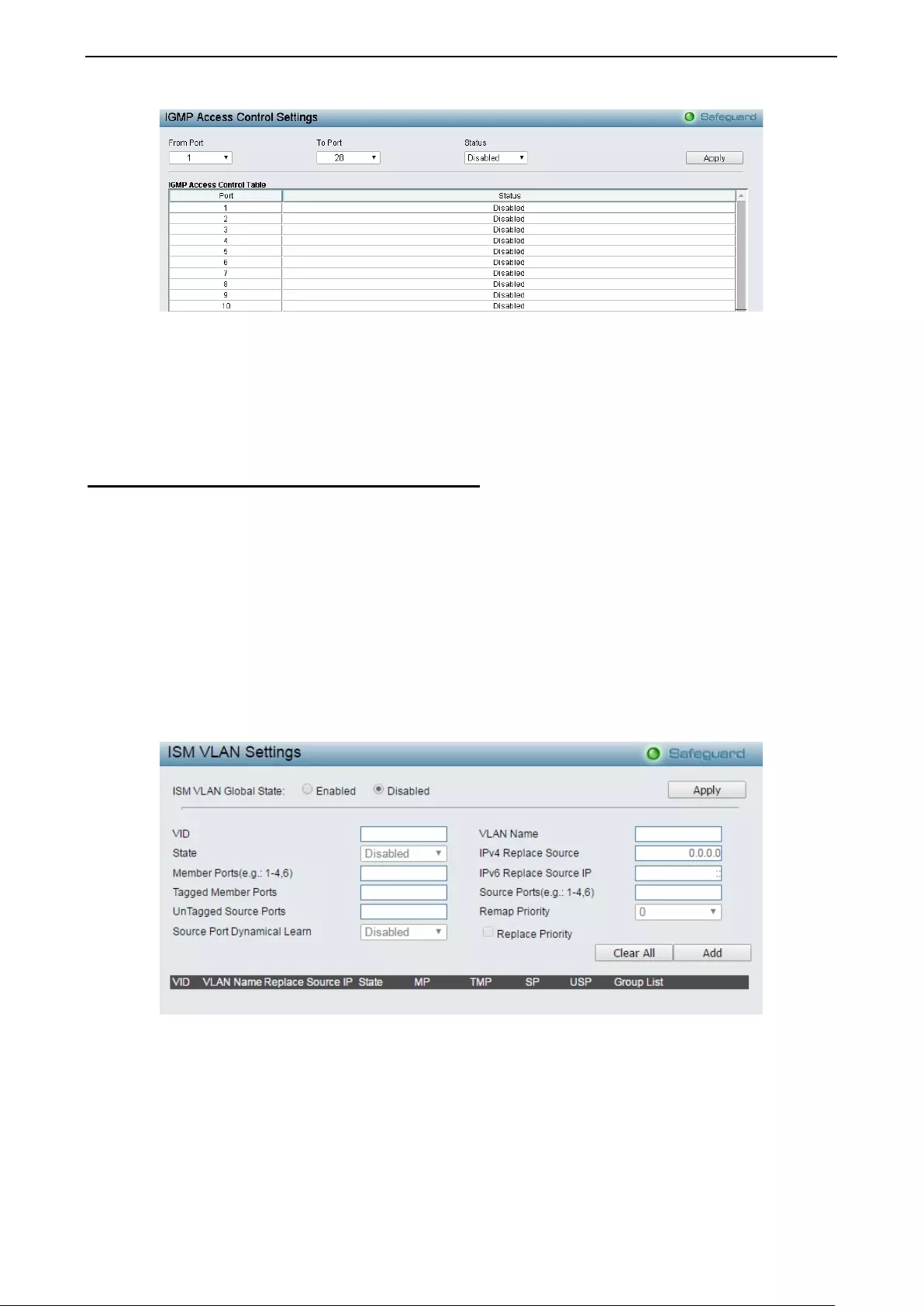
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
58
Figure 4.78 – Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Access Control Settings
From Port/To Port: Select the port ranges to be configured.
Status: Enable or disable the IGMP Access Control of specified ports.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > ISM VLAN Settings
In a switching environment, multiple VLANs may exist. Every time a multicast query passes through the
Switch, the s witch m ust forward s eparate diff erent cop ies of the data t o each VLAN on the s ystem, which, in
turn, incr eases data tr affic and m ay clog up t he traffic pat h. To lighten the traff ic load, multicas t VLANs m ay
be incorp orated. Thes e multicast VLANs will allow the Switch to f orward this m ulticast tr affic as on e copy to
recipients of the multicast VLAN, instead of multiple copies.
Regardless of other normal VLANs that are incorporated on the Switch, users may add any ports to the
multicast VLAN where they wish multicast traffic to be sent. Users are to set up a source port, where the
multic ast traff ic is enter ing t he s witc h, an d the n s et the por ts wher e the incoming multicast traf f ic is to be s ent.
The source port cannot be a recipient port and if configured to do so, will cause error messages to be
produce d b y the sw itch. O n c e proper ly configure d, the s tream of multicas t data wil l be rel a yed to th e r ecei ver
ports in a much more timely and reliable fashion.
The ISM VLAN Settings page allows the user to configure the ISM VLAN.
Figure 4.79 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > I SM VLAN Settings
ISM VLAN Gl o bal State: Enable or disable the IGMP Snoop ing Multic ast (ISM) VLAN Glob al Sta te.
Click Apply button to confirm the ISM VLAN Global State.
VID: Add the corresponding VLAN ID of the Multicast VLAN. Users may enter a value between 2 and 4094.
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the selec ted Mu lticas t VL AN .
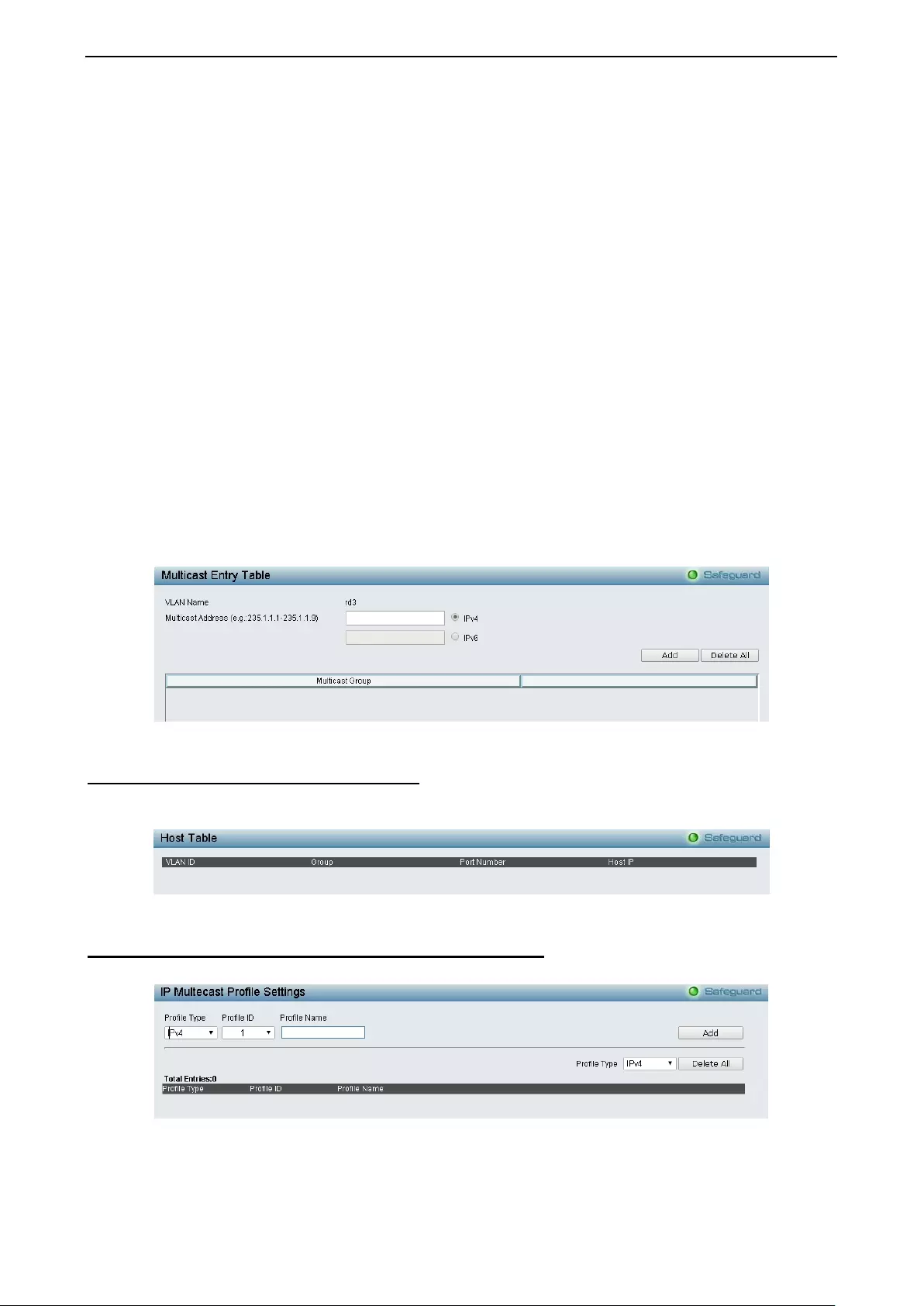
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
5
59
9
Member Ports: Enter a port or list of ports to be added to the Multicast VLAN. Member ports shall be the
untagged members of the multicast VLAN.
Tagged Member Ports: Enter a port or list of ports that will become tagged members of the Multicast VLAN.
UnTagged Source Ports: Enter a port or list of ports that will become untagged members of the Multicast
VLAN.
Source Port Dy namical Learn: Specify the source port dynamical learning to be enabled or disabled.
VLAN Name: Enter the name of the new Multicast VLAN to be created. This name can be up to 32
characters in length.
IPv4 Replace Source: T hi s field is used t o repl ac e th e s ourc e IP v4 addr ess of in c om ing packets s ent by the
host before being forwarded to the source port.
IPv6 Replace Source IP: This field is used to replac e the sourc e IPv6 addr ess of incoming pack ets s ent by
the host before being forwarded to the source port.
Source Ports: Enter a port or list of ports to be added to the Multicast VLAN. Source ports shall be the
tagged members of the multicast VLAN.
Remap Priority: Specif y the rem ap pr iority (0 t o 7) t o be ass ociated with th e data traf fic to be forwar ded on
the multicast VLAN. Specify None, the packet’s original priority is used. The default setting is None.
Click Add to add the ISM VLAN which will appear in the table, or click Clear All to clear all fields.
Click Edit button to modify the parameters and update the ISM VLAN Setting or click Delete to delete the
ISM VLAN.
Click View to display the detail information of ISM VLAN.
Figure 4.80 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > I SM VLAN Settings
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host Table
The Host Table page displays the information of Host Table. Including VLAN ID, Group, Port Number and
Host IP.
Figure 4.81 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Host T ab le
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IP Multicast Profile Settings
The IP Multicast Profile Settings page allows user to configure the IP Multicast Profile.
Figure 4.82 - Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IP Multicast Profile Settings
Profile ID: Specify the Profile ID.
Profile Name: Sp ec ify the Profile Nam e.
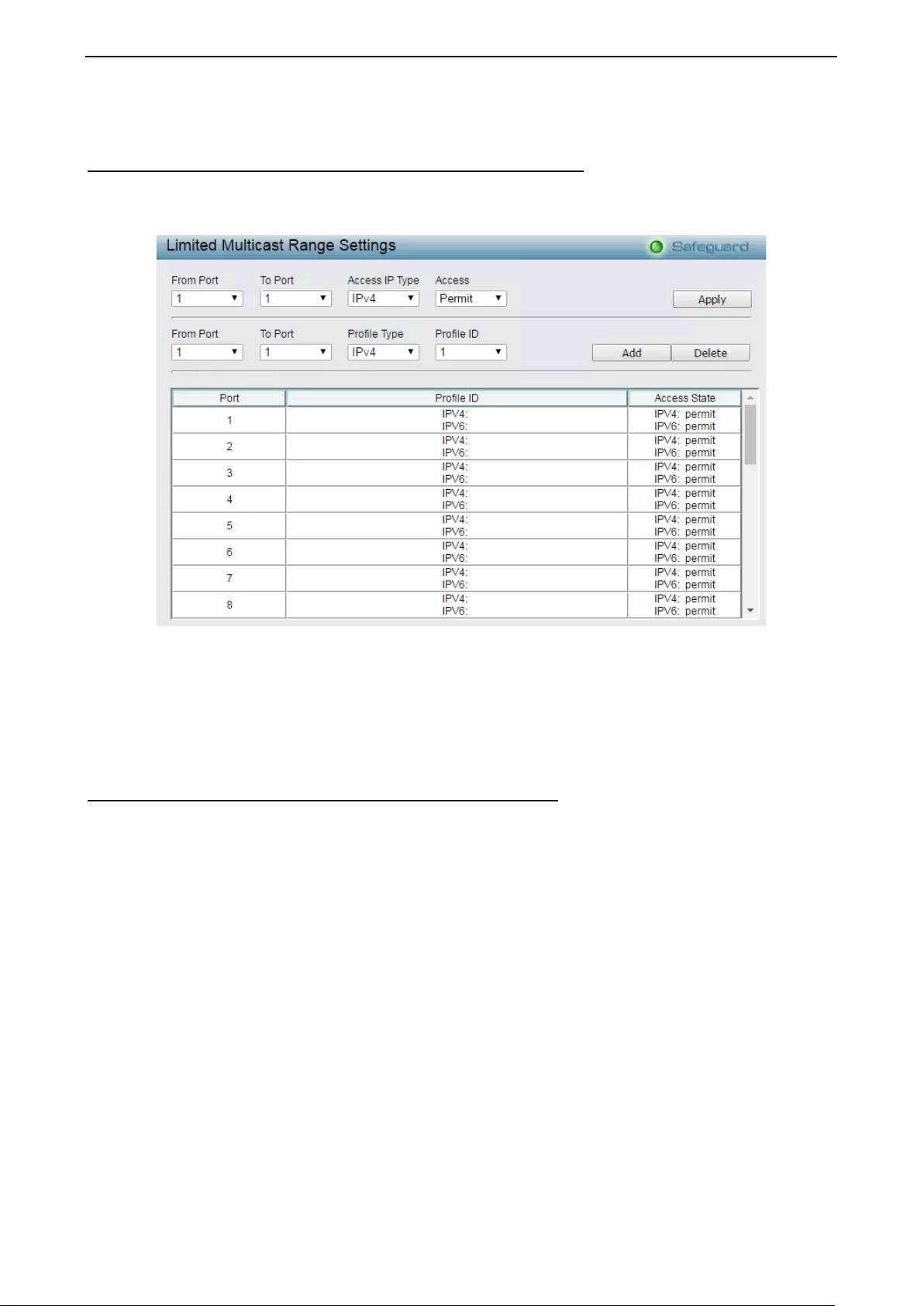
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
60
Click Add to create a new IP Multicast Profile or click Delet e All to clear all the entries.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Limited Multicast Ra ng e Settings
The Limited Multicast Range Settings page allows user to configure the Limited Multicast. Specify the port
range, select Access IP Type is IPv4 or IPv6 and select the Access is Deny or Permit then Click Apply to
make the configurations take effect.
Figure 4.83- Config uration > IGMP Snooping > Limited Multicast Range Settings
From Port / To Port: Specify the port ranges to be configured.
Profil e Type: Specify the profile type is IPv4 or IPv6.
Profile ID: Specify the Profile ID.
Click Add to create the Profile ID with specified ports or click Delete to remove the ports.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Max Multicast Group Settings
The Max Multicas t Group Setti ngs pa ge a ll o ws user to c onf igure the m ax m ulticas t group for IGM P S noo pin g.
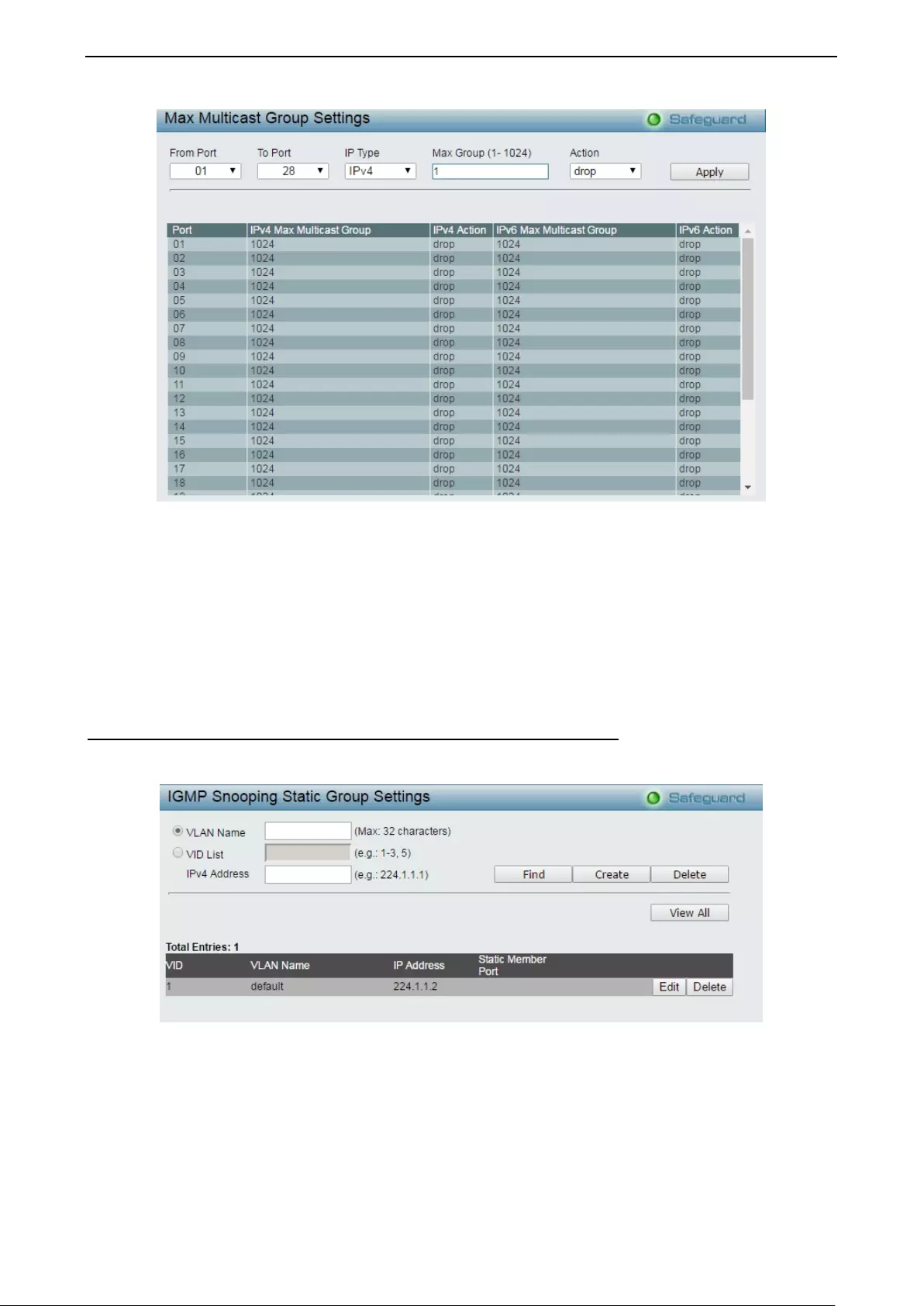
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
61
1
Figure 4.84- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > Max Multicast Group Settings
From Port / To Port: Specify the port ranges to be configured.
IP Type: Specify the IP type is IPv4 or IPv6.
Max Group (1-512): Specify the Max Group to be configured.
Action: Use the drop-down m enu to select the appropriate action for this rule. The user can select Drop to
initiate the drop action or the user can select Replace to initiate the replace action.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
The IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings page allows the Switch to read the Multicast Group IP address
and the corresponding MAC address from IGMP packets that pass through the Switch.
Figure 4.85- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings
VLAN Name: Specifies the VLAN name of the multicast group.
VID List: Specifies the VID list or of the multicast group.
IPv4 Address: Specifies the IPv4 address.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Create button to add a new entry based on the information entered.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
62
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry based on the information entered.
Click the Vi ew All button to display all the existing entries.
Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry.
After clicking the Edit button, the following page will appear:
Figure 4.86- Configuration > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Static Group Setting s - Edit
Click the S elect All button to select all the ports for configuration.
Click the Cle ar All button to unselect all the ports for configuration.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Click the <<Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
The MLD Snooping Settings page allows user to configure the max multicast group for IGMP Snooping.
Figure 4.87- Configur ation > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings
MLD Snooping: Enable or disable the MLD Sn oop in g.
MLD Global Settings:
Host Timeout (130-153025 sec): Specifies the time interv al in s ec onds after wh ic h a por t is r emoved fr om a
Multicast Group. Ports are removed if a Multicast group MLD report was not received from a Multicast port
within the defined Host Timeout period. The possible field range is 130 - 153025 seconds. The default
timeout is 260 seconds.
Router Timeout (60-600): Specifies the time interval in seconds the Multicast router waits to receive a
message before it times out. The possible field range is 60 - 600 seconds. The default timeout is 125
seconds.
Max Learned Entry Value (1-1024): Specifies the max learned entry value for MLD Snooping. The field
range is 1-1024. The default is 256.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. Press the Edit button under Router Port Setting, and

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
63
3
select the ports to be assigned for MLD snooping for the VLAN, and press Apply for changes to take effect.
Configuration > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
The MLD Host Table page displays the MLD Snooping information.
Figure 4.88- Configur ation > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table
Configuration > Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming and/or
outgoing packet f rom one port of the Switch to another port, where the pack et can be studi ed. This enab les
network managers to better monitor network performances.
Figure 4.89 – Configuration > Port Mirroring
Port Mirror ing: Enables or Disables the port mirroring feature.
Target Port: Specifies the target port.
Selection options for the Source Ports are as follows:
TX (transmit) mode: Duplicates the dat a tr ansmitted f rom the s ourc e port and forw ards it to the T arget Port.
Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
RX (receive) mode: Duplicates the data that is received from the source port and forwards it to the Target
Port. Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
Both (TX and RX) mode: Duplicate both the data transmitted from and data sent to the source port, and
forwards all the data to the assigned Target Port. Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
None: Turns off the mirroring of the port. Click “all” to remove all ports from mirroring.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Loopback Detection
The Loopback Detection function is used to detect the loop created by a specific port while Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP) is not enabled in the network, especially when the down links are hubs or unmanaged
switches. The Switch will automatically shut down the port and sends a log to the administrator. The
Loopback Detection port will be unlocked when the Loopback Detection Recover Time times out. The
Loopback Detection function can be implemented on a range of ports at the sam e tim e. You may enable or
disable this function using the pull-down menu.
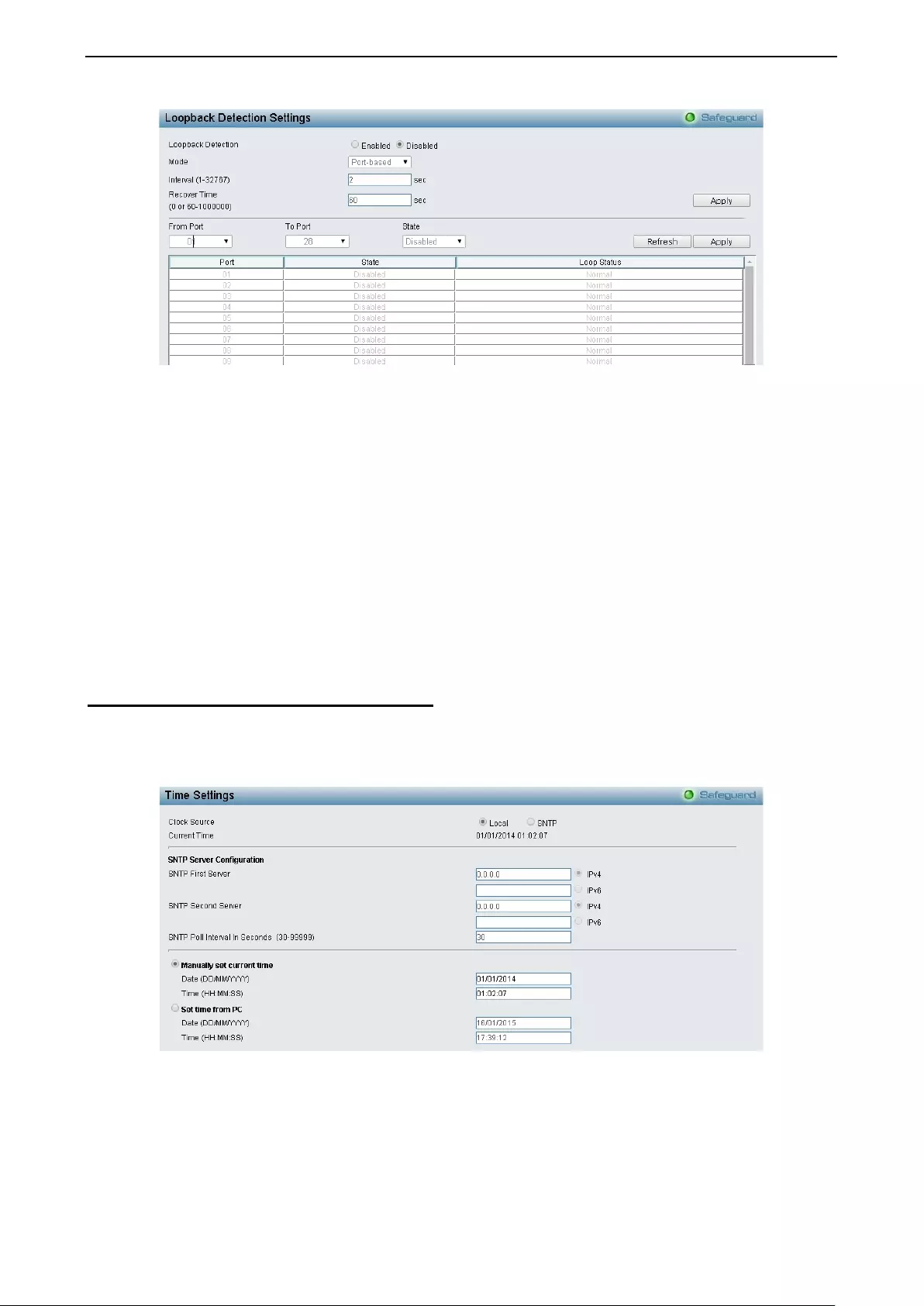
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
64
Figure 4.90 – Configuration > Lo opback Detection
Loopback Detection State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable loopback detection. The default
is Disabled.
Mode: Specify the Loopback Detection to be Port-based or VLAN-based.
Interval (1-32767): Set a Loop detection Interval between 1 and 32767 sec on ds . The default is 2 seconds.
Recover Time (0 or 60-1000000): Time allowed (in seconds) for recovery when a Loopback is detected.
The Loop Detection Recover Time can be set at 0 seconds, or 60 to 1000000 seconds. Entering 0 will
disable the Loop Detection Recover Time. The default is 60 seconds.
From Port: The beginning of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
To Port: The ending of a consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
State: Use the drop-down menu to toggle between Enabled and Disabled. Default is Disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
SNTP or Sim ple Net work Tim e Protoc ol is used b y the S witch to s ynchro nize th e c lock of the c om puter. The
SNTP sett ings folders contain two win dows: Tim e Settings and T imeZone Setti ngs. Users can configure the
time settings for the switch, and the following parameters can be set or are displayed in the Time Settings
page.
Figure 4.91 – Configuration > SNTP Settings > Time Settings
Clock Sourc e: Specify the clock source by which the system time is set. The possible options are:
Local - Indicates that the system time is set locally by the device.
SNTP - Indicates that the system time is retrieved from a SNTP server.
Current Time : Di splays the current date and time for the switch.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
65
5
If choosing SNTP for the clock source, then the following parameters will be available:
SNTP First Server: Sel ect IPv4 or I Pv6 and spec ify the IP address of the primar y SNT P server fr om whic h
the system time is retrieved.
SNTP Second Server: Select IPv4 or I Pv6 and specify the IP address of the secondary SNTP server from
which the system time is retrieved.
SNTP Poll Interval in Seconds (30-99999): Defines the interval (in seconds) at which the SNTP server is
polled for Unicast information. The Poll Interval default is 30 seconds.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
When selecting Local for the clock source, users can select from one of two options:
Manually set current time: Users input the system time manually.
Set time from PC: The system time will be synchronized from the local computer.
Configuration > SNTP Settings > TimeZone Settings
The TimeZone Setting Page is used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings time settings for SNTP.
Figure 4.92 – Configuration > SNTP > TimeZo n e Sett ings
Dayligh t Saving Time State: Enable or disable the DST Settings.
Daylight Saving Time Offset: Use this drop-down menu to specify the amount of time that will constitute
your local DST offset - 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes.
Time Zone Offset GMT +/- HH:MM: Use these drop-down menus to specify your local time zone's offset
from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT.)
DST Repeati n g Settings:
From: Which Wee k of the Month: Enter the Week of Month will start on, each year.
From: Day o f the Week: Enter the Day DST will start on, each year.
From: Month: Enter the m onth DST will start on, each year.
From: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will start on, each year .
To: Which Week of the Month: Enter the Week of Month will end on, each year.
To: Day of the Week: Enter the day of week that DST will end on, each year.
To: Month: Enter the month DST and date DST will end on, each year.
To: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
DST Annual Settings:
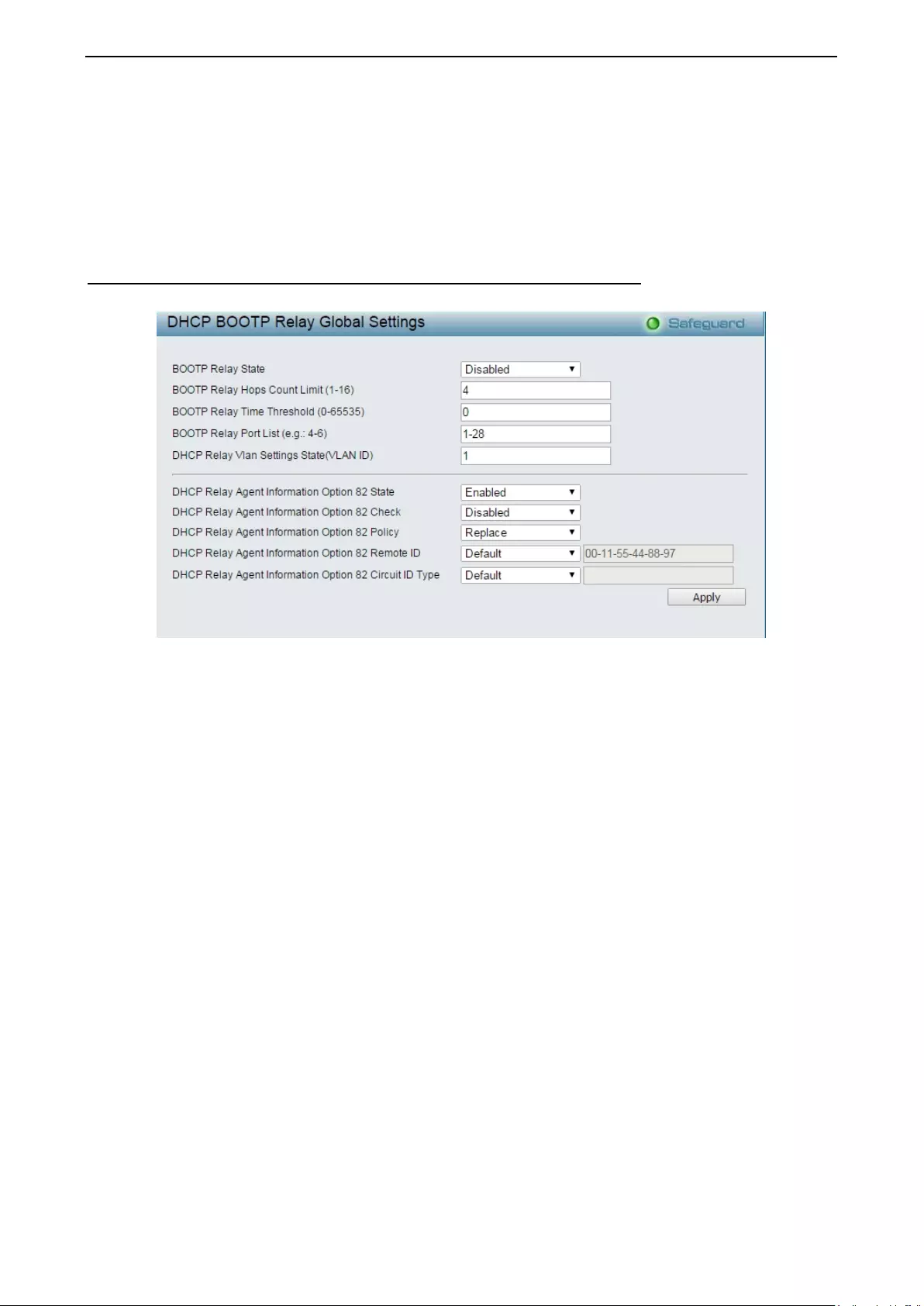
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
66
From: Month / Day: Enter the month DST and date DST will start on, each year.
From: Time In HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will start on, each year.
To: Month / Day: Enter the month DST and date DST will end on, each year.
To: Time HH:MM: Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings
User can enable and configure DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings on the Switch.
Figure 4.93 - Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings
BOOTP Relay State: This f ield can be to ggled bet ween Enab led and Disa bled us ing the pull-d own m enu. It
is used to enable or disable the DHCP/BOOTP Relay service on the Switch. The default is Disabled.
BOOTP Relay Hops Count Limit (1-16): This field allows an entry between 1 and 16 to define the
maximum number of router ho ps DHCP/ BOOT P messages ca n be for warded across. The defau lt hop c ount
is 4.
BOOTP Relay Time Threshold (0-65535): Allows an entr y between 0 and 65535 sec onds, and defines the
maximum time lim it for routing a DHC P/BOOT P pack et. If a value of 0 is enter ed, the S witch will not pr ocess
the value in th e seconds field of the BOOT P or DH C P pac ket. If a non-zero val ue is ent ered, the S witch wil l
use that value, along with the hop count to determine whether to forward a given BOOTP or DHCP packet.
BOOTP Relay Port List: Specify the ports for BOOTP relay.
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 State: This field can be to ggl ed b et w een Enabled and Disabled
using the pull-down menu. It is used to enable or disable the DHCP Agent Information Option 82 on the
Switch. The default is Disabled.
Enabled – W hen this field is toggled to Enabled the relay agent will insert and rem ove DHCP relay
inform ation (option 82 field) in messages between DHC P servers and clients. W hen the relay agent
receives the DHCP request , it adds the optio n 82 inform ation, and the IP address of the relay agent
(if the relay agent is configured), to the packet. Once the option 82 information has been added to
the packet it is sent on to the DHCP server. When the DHCP server receives the packet, if the server
is capable of opt ion 82, it c an im plem ent policies l ik e restricting the num ber of IP address es that ca n
be assigne d to a sin gle rem ote ID or circuit ID . Then the D HCP server echoes t he option 82 f ield in
the DHCP reply. The DHCP server unicasts reply to the back to the relay agent if the request was
relayed to the server by the relay agent. The switch verifies that it originally inserted the option 82
data. Finally, the relay agent rem oves the option 82 field and forwards the packet to the switch port
that connects to the DHCP client that sent the DHCP request.
Disabled - If the field is toggled to Disabled the relay agent will not insert and remove DHCP relay
information (option 82 field) in messages between DHCP servers and clients, and the check and
polic y settings will have no ef f ec t.
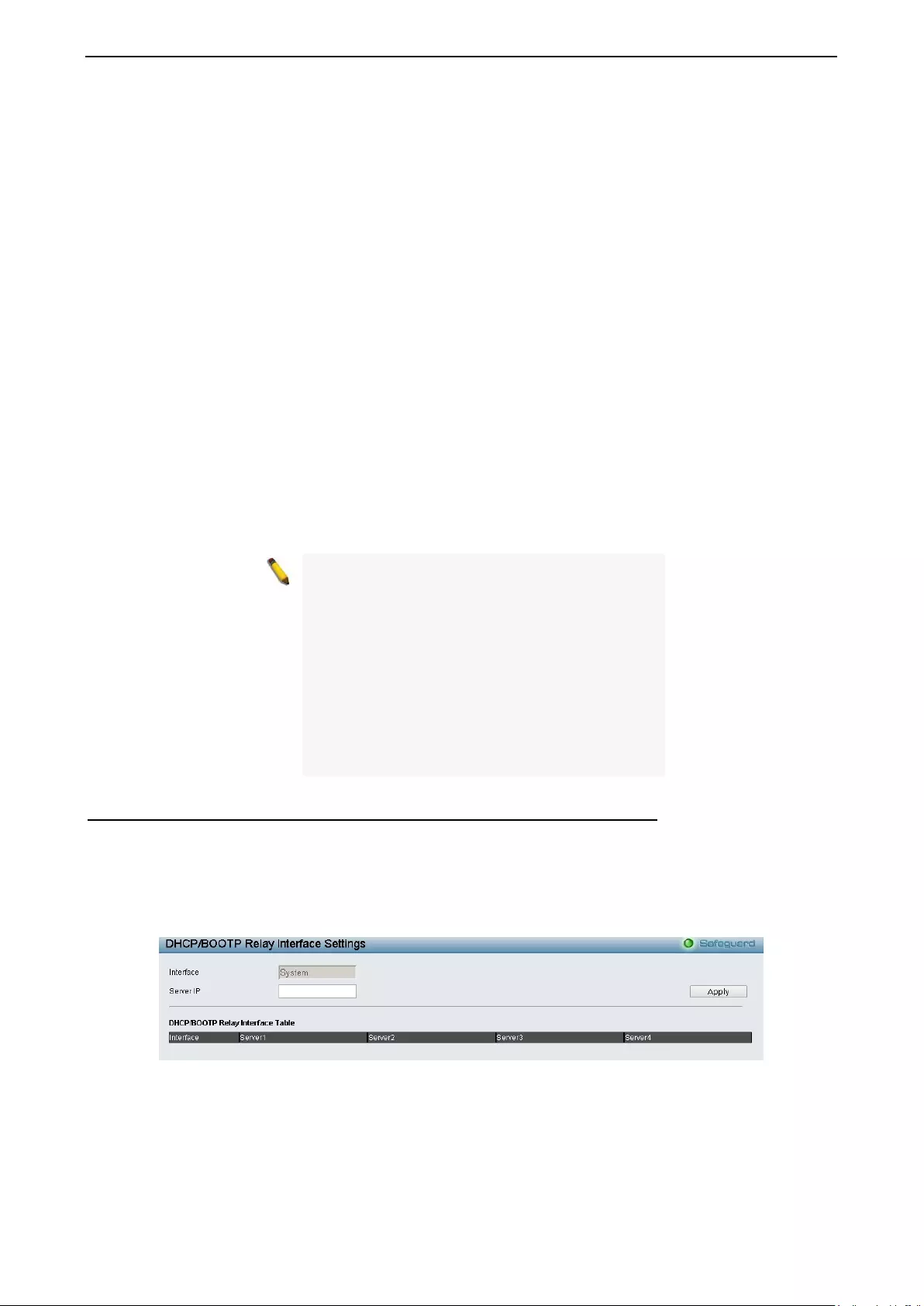
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
67
7
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 Check: This field can be toggled between Enabled and
Disabled using t he p ul l-do wn menu. It is us ed to e nab l e or dis ab le t he S witch es a bil ity to check the va lidity of
the packet’s option 82.
Enabled – When the field is toggled to Enabled, the relay agent will check the validity of the packet’s
option 82 fields. If the s witch recei ves a pac ket tha t contai ns the option-82 f ield fr om a DHC P client,
the switch drops t he packet beca use it is invalid. In packets received from DHCP servers, the rela y
agent will drop invalid messages.
Disabled - When the field is toggled to Disabled, the relay agent will not check the validity of the
packet’s option 82 fields.
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 Policy: T his field can be t oggled bet ween Replace, Drop, and
Keep b y using the pull-down menu. It is used to set the Switches policy for handling packets when the DHCP
Agent Information Option 82 Check is set to Disabled. The default is Replace.
Replace - The option 82 field will be replaced if the option 82 field already exists in the packet
received from the DHCP client.
Drop - The packet will be dropped if the option 82 field already exists in the packet received from the
DHCP client.
Keep -The option 82 field will be reta ined if the opt ion 82 field already exists in the pack et received
from the DHCP client.
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 Remote ID: This field can be toggled between Default and User
Define.
DHCP Relay Agent Information Option 82 Circuit ID Type: This field can be toggled between Default,
User Define, User Define Hex, vendor1, vendor2, vendor3, vendor4, vendor5 and vendor6.
NOTE: If the Switch r
eceives a packet that
contains the option-82 field from a DHCP client
and the information-checking feature is enabled,
the switch drops the packet because it is invalid.
However, in some instances, you might configure
a client with the option-82 field. In this situation,
you should disable the information-check feature
so that the switch does not remove the option-82
field fr om the packet. You can conf igur e t he ac ti on
that the switch takes when it receives a packet
with existing option-82 information by configuring
the DHCP Agent Information Option 82 Policy.
Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings
This page allows the user to set up a server, by IP address, for relaying DHCP/BOOTP information the
switch. T he user m ay enter a prev iously c onfigured IP inter face on t he Sw itch that will be c onnected directl y
to the DH CP/BO OT P serve r using the f ollo wing window. Pro perl y conf igure d sett ings will be displ ayed in the
BOOTP Relay Table at the bottom of the following window, once the user clicks the Add button under the
Apply heading. The user may add up to four server IPs per IP interface on the Switch. Entries may be
deleted by clicking Delete button.
Figure 4.94 - Configuration > DHCP/BOOTP Relay > DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings
Interface: The IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to the Server.
Server IP: Enter the IP addres s of the DHC P/ BOOT P server. Up to f our s erver I Ps can be c onfigure d per IP
Interface.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
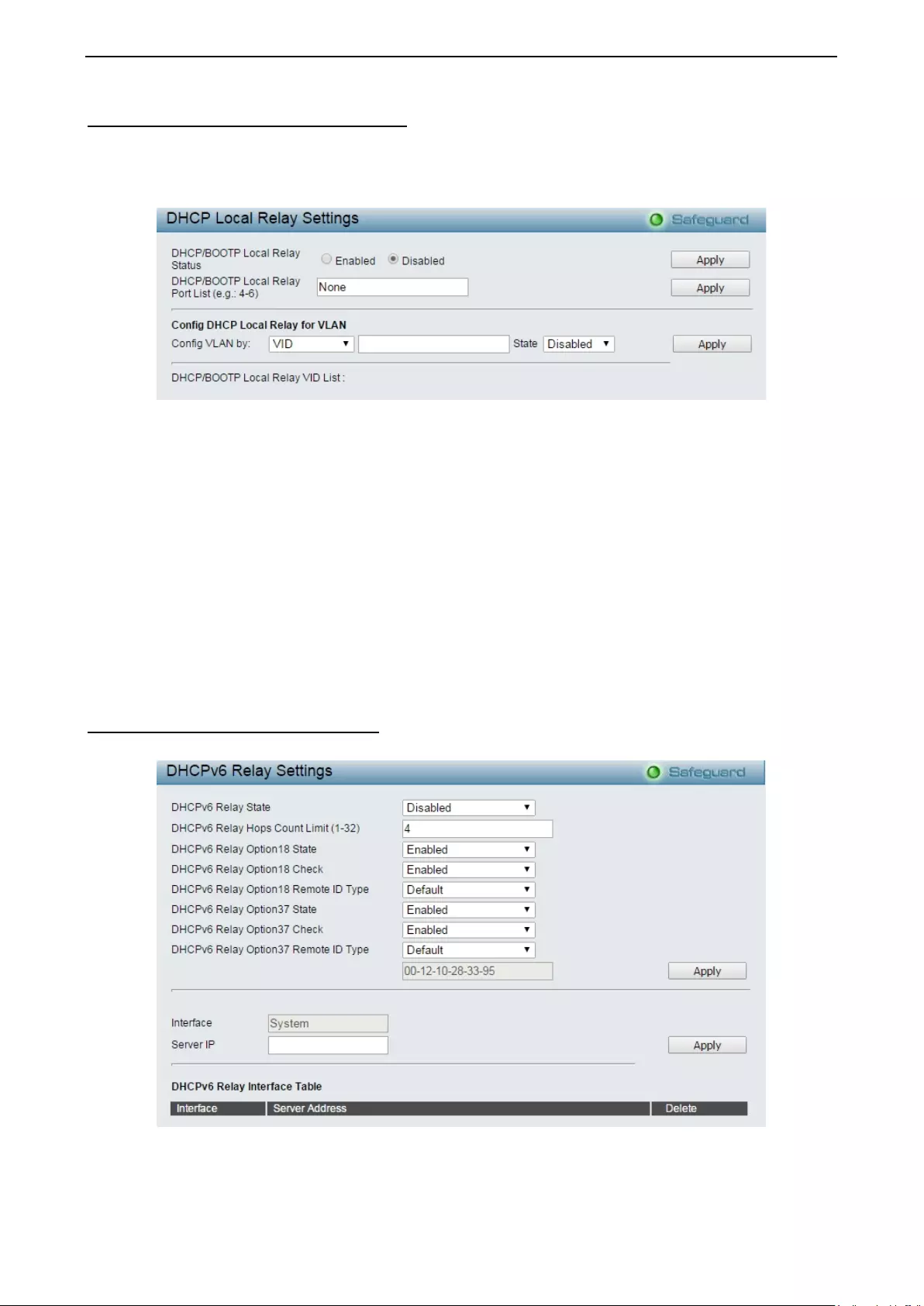
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
68
Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
The DHCP Local Relay Settings page allows the user to configure DHCP Local Relay. DHCP broadcasts are
trapped by the switch CPU, and replacement broadcasts are forwarded with Option 82. Replies from the
DHCP servers are trapped by the switch CPU, the Option 82 is removed and the reply is sent to the DHCP
Client.
Figure 4.95 - Configuration > DHCP Local Relay Settings
DHCP/BOOTP Local Relay Status: Specifies whether DHCP Local Relay is enabled on the device.
Enabled – Enab les DHCP Loc al Rel a y on the device .
Disabled – Disables DHCP Local Relay on the device. This is the default value.
DHCP/B OOTP Loc al Relay Port List: Specifies the port or ports for DHCP/BOOTP local relay port.
Config VLAN by: Configure the VLAN by VID or VLAN Name of drop-down menu.
State: Specifies whether DHCP Local Relay is enabled on the VLAN.
Enabled – Enab les DHCP Loc al Rel a y on the VLAN.
Disabled – Disables DHCP Local Relay on the VLAN.
DHCP Local Relay VID List: Displays the list of VLANs on which DHCP Local Relay has been defined.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Se ttings
The DHCPv6 R elay Setting s page allows user to configure the DHCPv6 settings.
Figure 4.96 - Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Settings
DHCPv6 Relay Status: Specifies whether DHCPv6 Relay is enabled on the device.
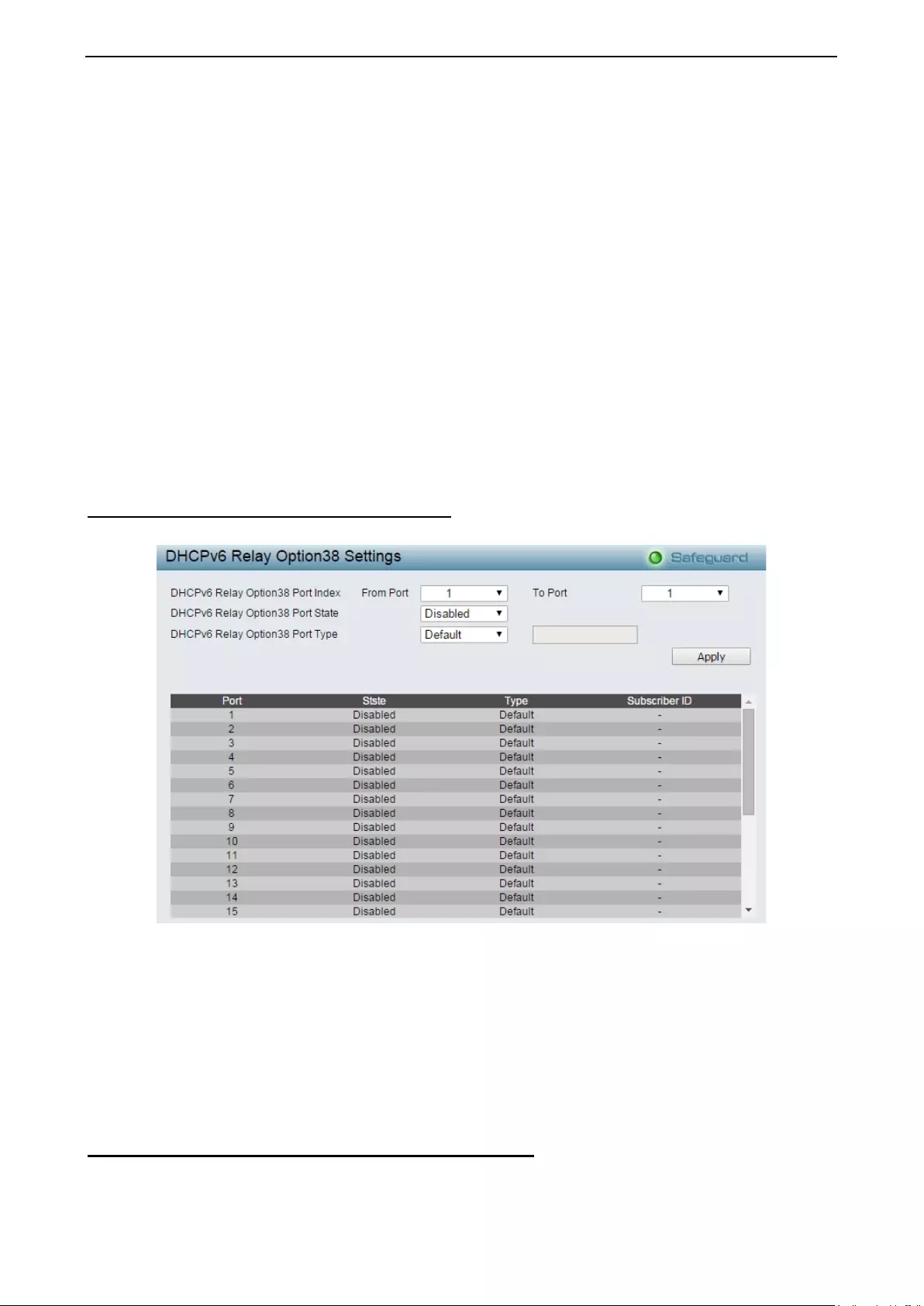
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
6
69
9
Enabled – Enables DHCPv6 Relay on the device.
Disabled – Disables DHCPv6 Relay on the device. This is the default value.
DHCPv6 Relay Hops Count Limit (1-32): The field allows and entry between 1 and 32 to define the
maximum number of router hops DHCPv6 messages can be forwarded. The default hop count is 4.
DHCPv6 Relay Option18 State: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option18 State to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option18 Check: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option18 Check to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option18 Remote ID Type: Sp ecifies the DH CPv6 Rela y Opt ion18 Rem ote ID type is CID
with User Defined, User Defined or VENDOR1.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 State: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option37 State to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Check: Specifies the DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Check to be enabled or disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option37 Remote ID Type: Spec ifies the DH CPv6 Relay O ption37 Rem ote ID type is CID
with User Defined, User Defined or Default.
Interface: Enter a name of the interface.
Server IP: Enter the server IP address.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Settings
The DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Settings page allows user to configure the DHCPv6 relay option38 settings.
Figure 4.97 - Configuration > DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Settings
DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Port Index: Specify the port range to be configured.
DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Port State: Specify the port state of DHCPv6 relay option38 to be enabled or
disabled.
DHCPv6 Relay Option38 Port Type: Specify the port type of DHCPv6 relay option38 to be enabled or
disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
The Switch implements three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol, the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
(RSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1w specification and a version compatible with the IEEE 802.1D STP
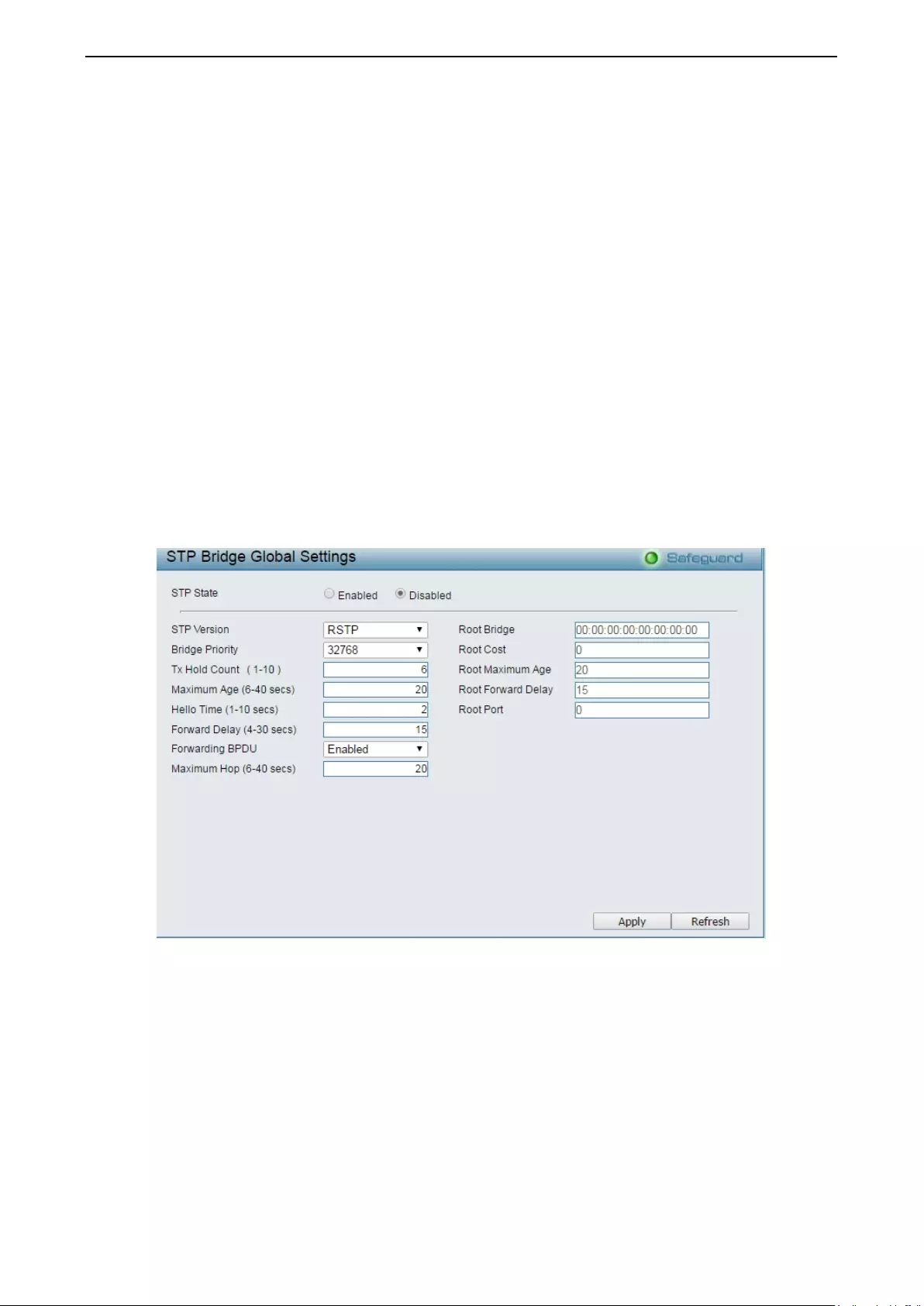
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
70
and Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) as defined by the IEEE802.1 specification. R STP can operate
with legacy equipment implementing IEEE 802.1D, however the advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802. 1 w Rapid Sp anning T ree Protoc ol (RST P) evo lved f rom the 802. 1D STP s tandard. R STP was
developed in order to overcome some limitations of STP that impede the function of some recent switching
innovations. The basic function and much of the terminology is the same as STP. Most of the settings
configured f or STP ar e also used f or RSTP. T his section intr oduces s ome new Spann ing Tr ee concepts and
illustrates the main differences between the two protocols.
The IEEE 802.1 Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) provides various load balancing scenarios by allowing
multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance, providing multiple pathways across the
network. For example, while port A is blocked in one STP instance, the same port can be placed in the
Forwarding state in another STP instance.
By default, Rapid Spanning Tree is disabled. If enabled, the Switch will listen for BPDU packets and its
accompanying Hello packet. BPDU packets are sent even if a BPDU packet was not received. Therefore,
each link between bridges is sensitive to the status of the link. Ultimately this difference results in faster
detection of failed links, and thus faster topology adjustment.
By default Multiple Spanning Tree is enabled. It will tag BPDU packets to receiving devices and distinguish
spanning tree ins ta nc es , spanning tree regions and the VLANs associated with them.
After enabling STP, setting the STP Global Setting includes the following options:
Figure 4.98 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Bridge Global Settings
STP State: Specify the Spanning Tr ee Protoc ol to be Enabled or Disabled.
STP Version: You can choose MSTP, RSTP or STP Compatible. The default setting is MSTP.
Bridge Priority: This value betwee n 0 and 61410 s pecifies the prior ity for f orwarding p ack ets: the low er the
value, the higher the priority. The default is 32768.
TX Hold Count (1-10): Used to set the maximum number of Hello packets transmitted per interval. The
count can be specified from 1 to 10. The default is 6.
Maximum Age (6-40 sec): T his va lue ma y be set to ensur e th at old i nf ormation does not e nd less l y circ ul ate
through redundant paths in the network, preventing the effective propagation of the new inform ation. Set by
the Root Bridge, this value will aid in determining that the Switch has spanning tree configuration values
consistent with other devices on the bridged LAN. If the value ages out and a BPDU has still not been
received from the Root Bridge, the Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other switches for permission
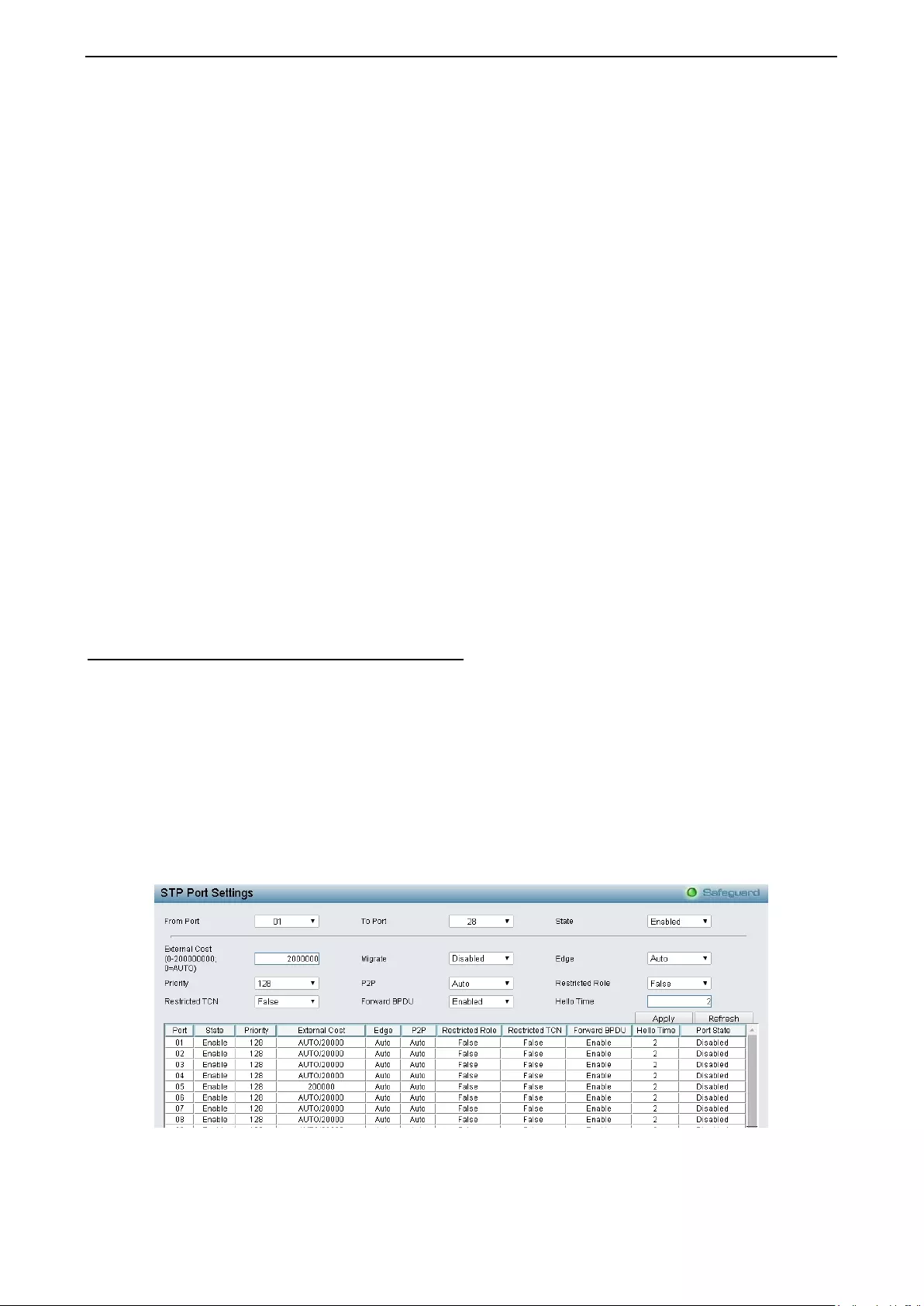
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
71
1
to become the Root Bridge. If it turns out that the Switch has th e lowest Bridge Identifier, it will becom e the
Root Bridge. A time interval may be chosen between 6 and 40 seconds. The default value is 20. (Max Age
has to have a value bigger than Hello Time)
Hello Tim e (1-10 se c): The user may set the time interval between transmissions of configuration messages
by the root device, thus stating that the Switch is still functioning. The default is 2 seconds.
Forward Delay (4-30 sec): This sets the maximum amount of time that the root device will wait before
changing states. The default is 15 seconds.
Forwarding BPDU: Bridges use Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) to provide spanning tree information.
STP BPDUs filtering is useful when a bridge interconnects two regions; each region needing a separate
spanning tree. BPDU filtering functions only when STP is disabled either globally or on a single interface.
Enabled - BPDU filtering is enabled on the port.
Disabled - BPDU forwarding is enabled on the port (if STP is disabled).
Maximum Hop (6-40 secs ): Specifies the number of hops between devices in a spanning tree region before
the BPDU (bridge protocol data unit) packet sent by the Switch will be discarded. Each switch on the hop
count wi ll reduce t he hop count by one u ntil the val ue reaches zero. The Switch wil l then disc ard the BPDU
packet and the information held for the port will age out. The user may set a hop count from 6 to 40. The
default is 20.
Root Bridge: Displays the MAC address of the Root Bridge.
Root Cost: Defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list.
Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto).
Root Maximum A ge: Displays the Maximum Age of the Root Bridge. The default is 20.
Root Forward Delay: Displays the Forward Delay of the Root Bridge. The default is 15.
Root port: Displays the root port.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect. Click Refresh to renew the page.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP P o rt Settings
STP can be set up on a port per port basis. In addition to setting Spanning Tree par ameters for use on the
switch le vel, the S witch al lows f or the conf iguration of the grou ps of ports, eac h port-gr oup of whic h will hav e
its own spanning tree, and will require some of its own configuration settings.
An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge
concept is replace d with a root port concept. A root port is a port of the group th at is elected based on port
priorit y and port c ost, t o be the con necti on to th e net work for t he group. R edun dant l inks will be bloc k ed, just
as redundant links are blocked on the switch level.
The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices). The
port level STP will block redundant links within an STP Group.
It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports.
Figure 4.99 – Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
72
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable STP by per-port based. It will be selectable after the
global STP is enabled.
External Cost: This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified
port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. Thedefault value is 0 (auto).
0 (auto) - Settin g 0 f or t h e ext ernal c ost will aut omatically set the spee d for for war ding packets to the
specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency. Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit
port = 20000.
Value 1-200000000 - Def ine a value between 1 and 2000000 00 to determ ine the extern al cost. T he
lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
Migrate: Setting this parameter as Yes will set the ports to send out BPDU packets to other bridges,
requesting inform ation on their STP setting. If the Switch is configured for RSTP, the port will be capable to
migrate from 802.1d STP to 802.1w RSTP. Migration should be set as yes on ports connected to network
stations or segments that are capable of being upgraded to 802.1w RSTP on all or some portion of the
segment.
Edge: Selecting the True parameter designates the port as an edge port. Edge ports cannot create loops,
however a n edge por t can lose edg e port status if a topol ogy change c reates a p otential f or a loop. A n edge
port normally should not receive BPDU packets. If a BPDU packet is received, it automatically loses edge
port status. Selecting the False parameter indicates that the port does not have edge port status. Selecting
the Auto parameter indicates that the port have edge port status or not have edge port status automatically.
Priority: Specify the priority of each port. Selectable range is from 0 to 240, and the default setting is 128.
The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen as a root port.
P2P: Choosing the True parameter indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shared link. P2P ports are similar to edge
ports, however they are restricted in that a P2P port must operate in full-duplex.
Like edge ports , P2P port s transition to a f orward ing state rap idly thus benef iting from RSTP. A p2p valu e of
false indicates that the port cannot have p2p status. Auto allows the port to have p2p status whenever
possible and operate as if t he p2p st at us were tru e. If the por t cannot maintain th i s stat us, ( f or ex ample if the
port is forced to half-duplex operation) the p2p status changes to operate as if the p2p value were False. The
default setting for this parameter is Auto.
Restricted Role: T oggle bet ween True and False to s et th e restr icted r ole stat e o f the pack et. I f set t o True,
the port will never be selected to be the Root port. The default value is False.
Restricted TCN: T oggle b etween True and False to set the restricte d TCN of the p acket. T opolog y Cha nge
Notification (TCN) is a BPDU that a bridge sends out to its root port to signal a topology change. If set to
True, it stops the port from propagating received TCN and to other ports. The default value is False.
Forwarding BPDU: Bridges use Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) to provide spanning tree information.
STP BPDUs filtering is useful when a bridge interconnects two regions; each region needing a separate
spanning tree. BPDU filtering functions only when STP is disabled either globally or on a single interface.
The possible field values are:
Disabled – BPDU filtering is enabled on the port.
Enabled – BPDU forwarding is enabled on the port (if STP is disabled).
Hello Time: The inter val bet ween t wo trans m issions of BPDU p ack ets sent by the Ro ot Bridg e to ind icate to
all other switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge. The default value is 2.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Click Refresh to renew the page.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identifi cation
The MST Configuration Identification page allows user to configure a MSTI instance on the switch. These
settings will uniquely identify a multiple spanning tree instance set on the switch. The Switch initially
possesses one CIST or Common Internal Spanning Tree of which the user may modify the parameters for
but cannot change the MSTI ID for, and cannot be deleted.
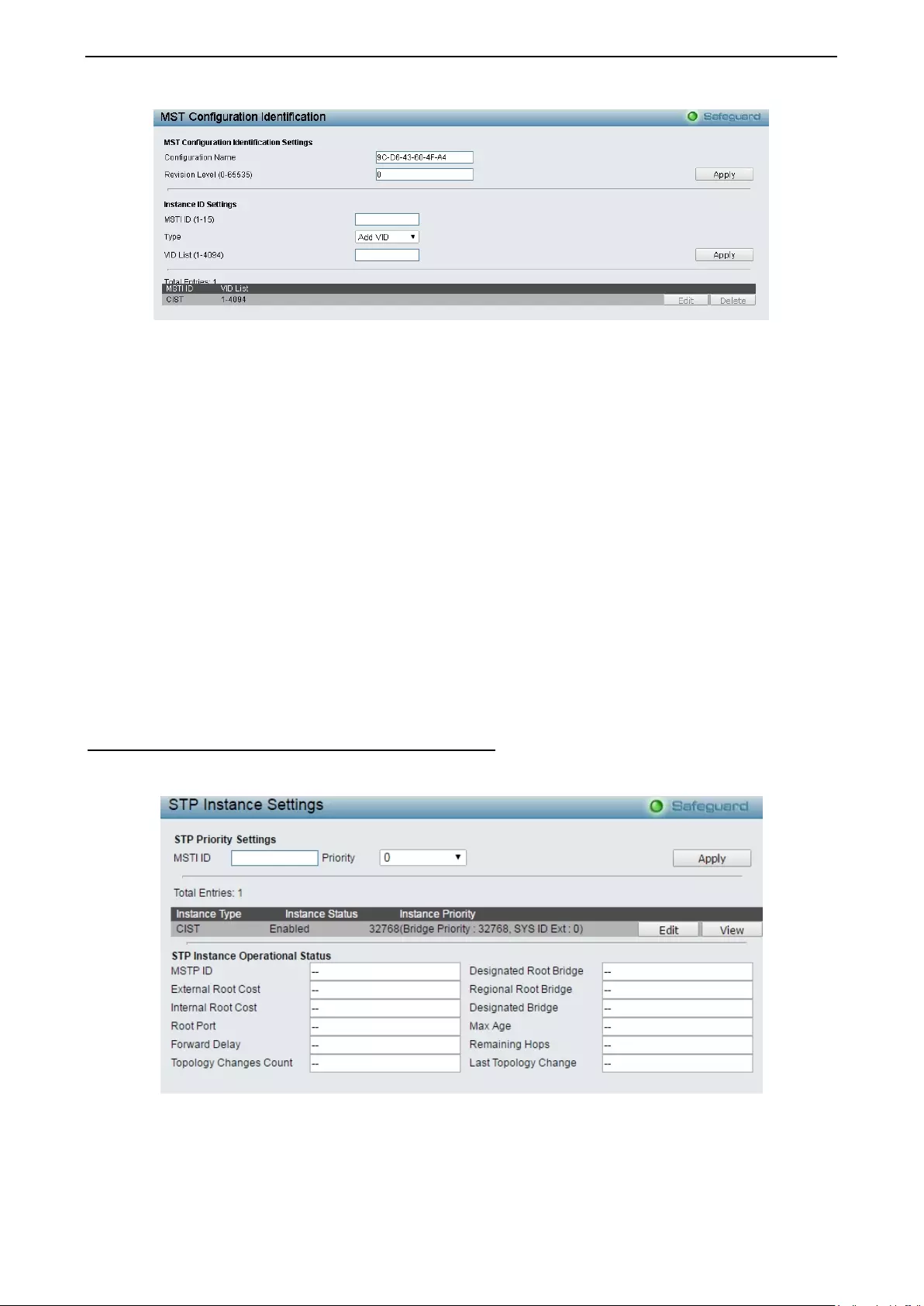
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
73
3
Figure 4.100 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Configuration Identification
MST Configuration Id entification Settings :
Configuration Name: A previously configured name set on the Switch to uniquely identify the MSTI (Multiple
Spanning Tree Instance). If a configuration name is not set, this field will show the MAC address to the
device running MSTP. This field can be set in the STP Bridge Global Set-tings window.
Revision Level: T his value, along with the C onfiguration Nam e will identify the MST P region configured on
the Switch. The user may choose a value between 0 and 65535 with a default s ett ing of
0
.
MSTI ID (1-15): Enter a number between 1 and 15 to set a new MSTI on the Switch.
Type: This field allows the user to choose a desired method for altering the MSTI settings.
Add VID - Select this parameter to add VIDs to the MSTI ID, in conjunction with the VID List
parameter.
Remote VID – Select this parameter to r emove VID s fr om the MST I ID, in con-ju nction with the VID
List parameter.
VID List (1-4094): This field displays the VLAN IDs associated with the specific MSTI.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Settings
The STP Instance Settings page display MSTIs currently set on the Switch and allows users to change the
Priorit y of the MSTPs.
Figure 4.101 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance Setting s
To modify an entr y on the tabl e, cl ick the Edit button. T o view m ore infor m ation about and en tr y on the t able
at the top of the window, click the view button.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
74
The window above contains the f oll o wing inf or mation:
MSTI ID: Enter the MSTI ID in this field. An entry of 0 denotes the CIST (default MSTI).
Priority: Enter the new priority in the Priority field. The user may set a priority value between 0-61440.
Click Apply to implement the new priority setting.
Configuration > Spanning Tree > MSTP Port Information
The MSTP Port Information page can be used to update the port configuration for an MSTI ID. If a loop
occurs , the MSTP f unction wil l use the por t priorit y to selec t an interf ace to put i nto the f orwardin g state. Set
a higher pr ior ity value f or i n terfaces to b e s e lec ted f or f orw ardi ng f irs t. In insta nc es where th e pr iori t y val ue is
identical, the MSTP function will implement the lowest MAC address into the forwarding state and other
interfac es will be blocked.
To View the MSTI s ettings f or a particular port, selec t the Port number and click Find butt on. To m odify the
settings for a particular MSTI Instance, click Edit button, then modify the MSTP Port Setting and click Apply.
Figure 4.102 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port Information
Instance ID: Displays the MSTI ID of the instance being configured. An entry of 0 in this field denotes the
CIST (default MSTI).
Internal Path Cost (0=Auto): This parameter is set to represent the relative cost of forwarding packets to
specified ports when an interface is selected within a STP instance. The default setting is 0 (auto).
0 (Auto) - Selecting this parameter for the internal Cost will set quickest route automatically and
optimally for an interface. The default value is derived from the media speed of the interface.
Value 0-2000000 - Selecting this parameter with a value in the range of 0 to 2000000 will set the
quickest route then a loop occurs. A lower internal cost represents a quicker transmission.
Priority: Enter a value between 0 and 240 to set the priority for the port interface. A higher priority will
designate the interface to forward packets first. A lower number denotes a higher priority.
Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Settings
The Ethern et OA M Port Set tings page allows user to configure the Ethernet OAM settings.
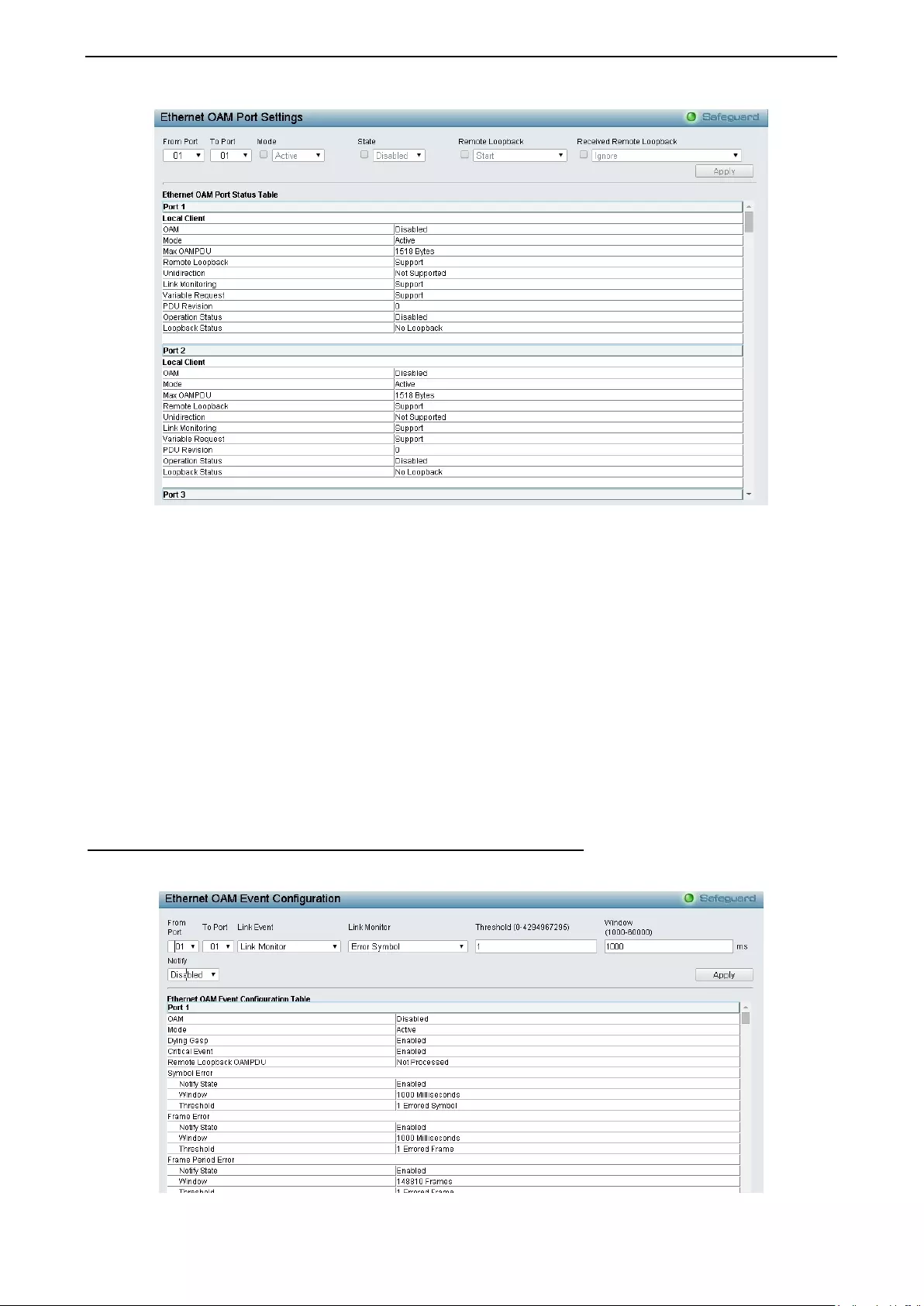
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
75
5
Figure 4.103 - Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Port Setting s
From Port/To Port: Select a range of ports to be configured.
Mode: Use the drop-down menu to select to operate i n either Active or Passive. The default mode is Active.
State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the OAM function.
Remote Loopba ck: Specifies the Ethernet OAM remote loopback is None or Start.
None – Select to disable the remote loopback.
Start – Select to request the peer to change to the remote loopback mode.
Received Remote Loopback: To configure the client to process or to ignore the received Ethernet OAM
remote loopback command.
Process – Select to process the received Ethernet OAM remote loopback command.
Ignore – Select to ignore the received Ethernet OAM remote loopback command.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
The Ethernet OAM Event Configuration page allows user to configure the Ethernet OAM configuration
settings.
Figure 4.104 - Configuration > Ethernet OAM > Ethernet OAM Event Configuration
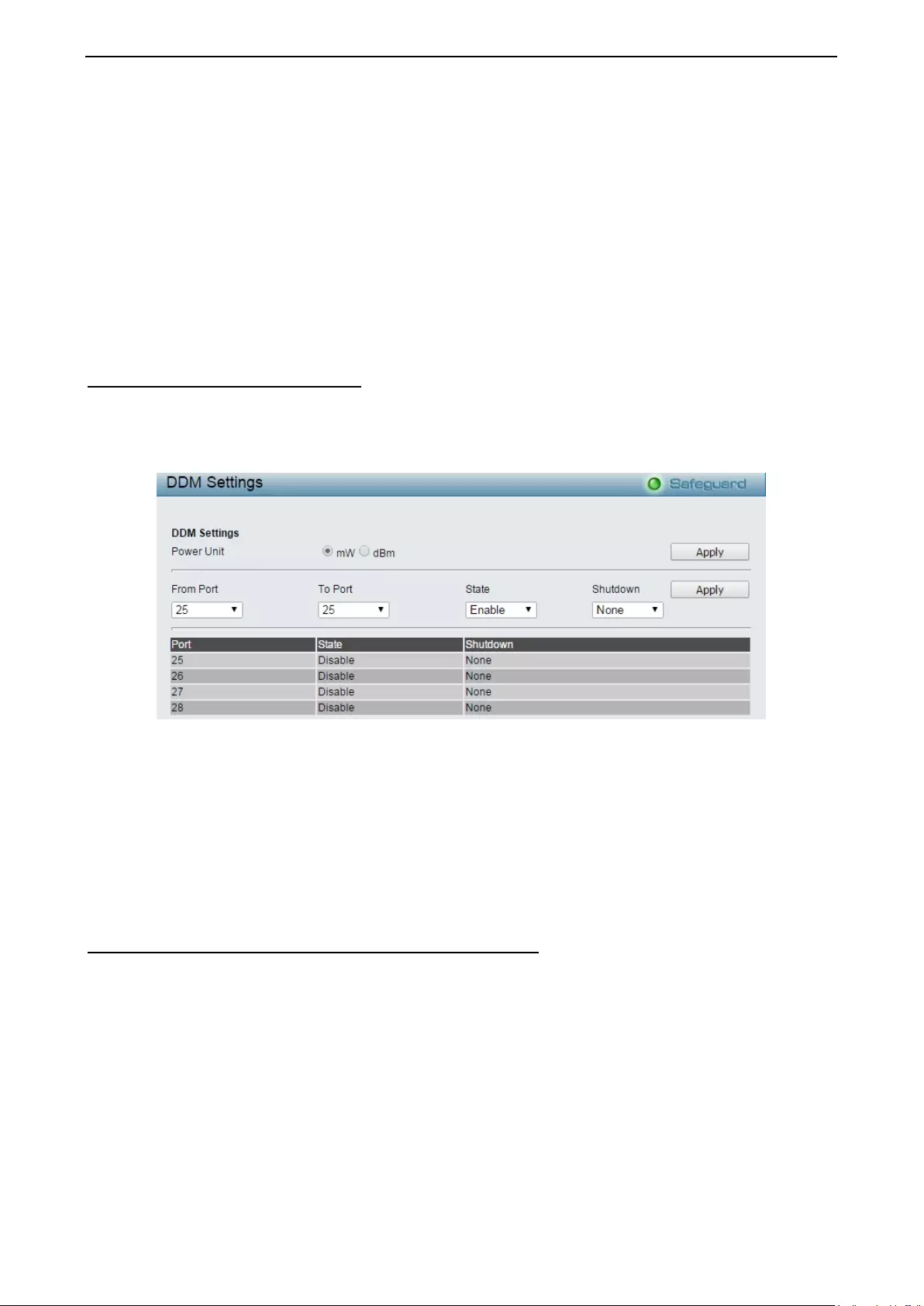
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
76
From Port / To Port: Select a range of ports to be configured.
Link Event: Select the link event, Link Monitor or Criti cal Link Event.
Link Monitor: Select the link monitor. Avaliable options are Error Symbol, Error Frame, Error Frame
Period, and Error Frame Seconds.
Threshold (0-4294967295): Enter the num ber of er ror f rame or s ymbol in the period is require d to be e qual
to or greater than in order for the event to be generated.
Window (1000-60000): Enter the period of error frame or symbol in milliseconds summary event.
Notify: Select the notification to be enabled or disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
The Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) functions allow the user to view the digital diagnostic monitoring
status of SFP modules inserting to the Switch and to configure related settings.
The DDM Settings page allows user to configure the action that will occur for specific ports when an
exceeding alarm threshold or warning threshold event is encountered.
Figure 4.105 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Settings
Power Unit: Specifies the power unit for DDM. The options are mW (milliwatts) and dBm (decibel-milliwatts).
From Port / To Port: Specifies a port or range of ports to be configured.
State: Specifies to enable or disable the DDM settings state.
Shutdown: Specifies whet her or n ot t o shutdown th e por t, w hen the op er ati ng pa rameter ex c eeds t he Alarm
or Warning threshold.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Tempera ture Threshold Settings
The DDM T em perature T hreshol d Setti ngs pag e allow s us er to conf igure the D DM temperatur e thresho ld for
specific ports on the Switch.
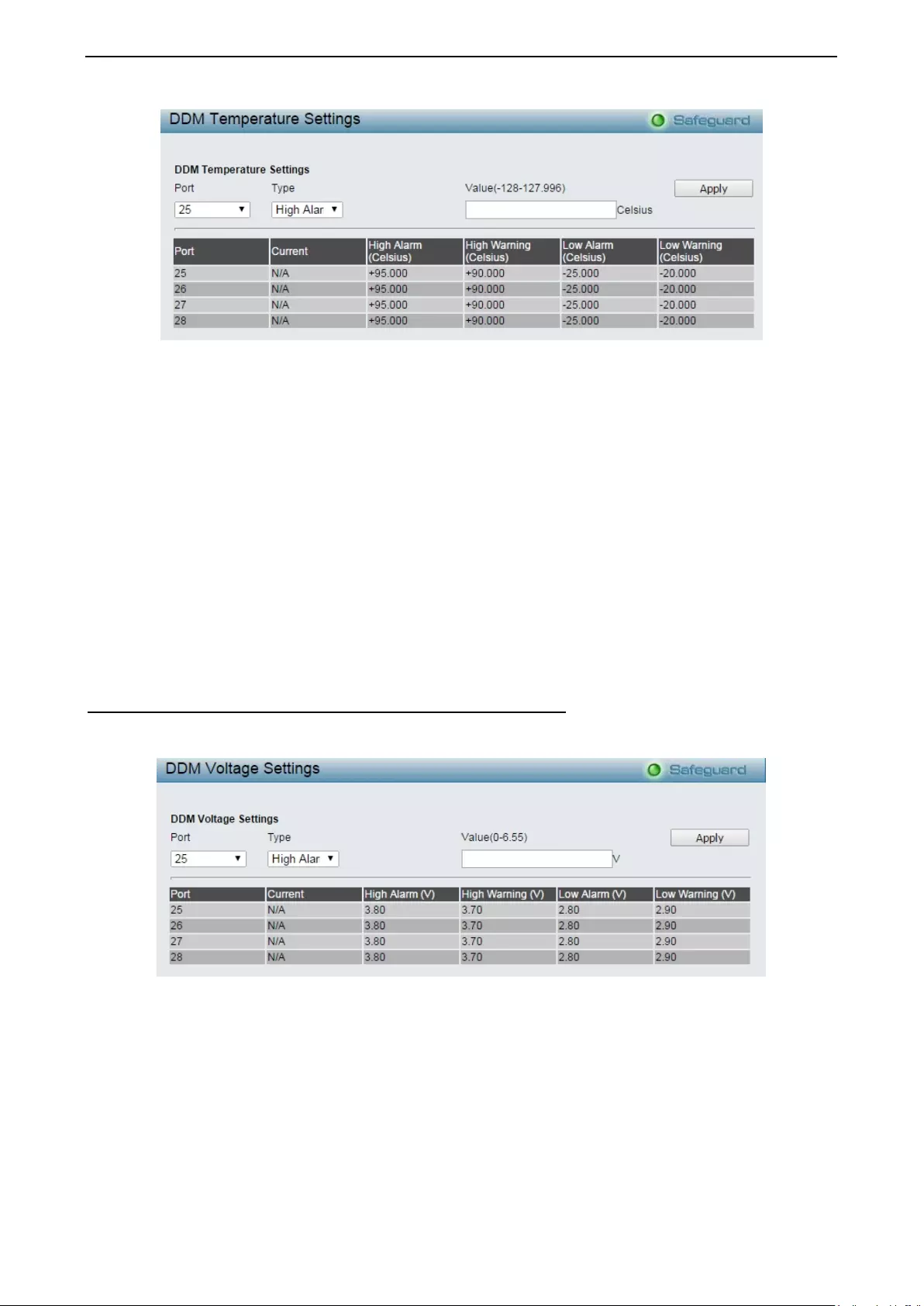
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
77
7
Figure 4.106 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Temperature Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the t ype for the operati ng param eter, t he options are Hig h Alarm , Low Alar m, High W arning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high thr es ho ld f or t he alar m . When the operat ing t emperature rises abo ve
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the operating temperature falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the operating temperature rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the operating temperature falls
below the config ur ed value , the actio n ass ociat ed with the w arni ng is taken.
Vaule (-128 – 127.996): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings
The DDM Voltage Settings Threshold Settings page is used to configure the DDM voltage threshold for
specific ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.107 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Voltage Settings Thr eshold Setting s
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the t ype for the operati ng param eter, the options are Hig h Alarm , Low Alarm , High W arning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specif ies th e hig h thres hold f or t he al arm . W hen the op erati ng V oltage rises a bo ve the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the operating Voltage falls below the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the operating Voltage rises
above the configured value, the action assoc ia ted wit h the warni ng is tak en.
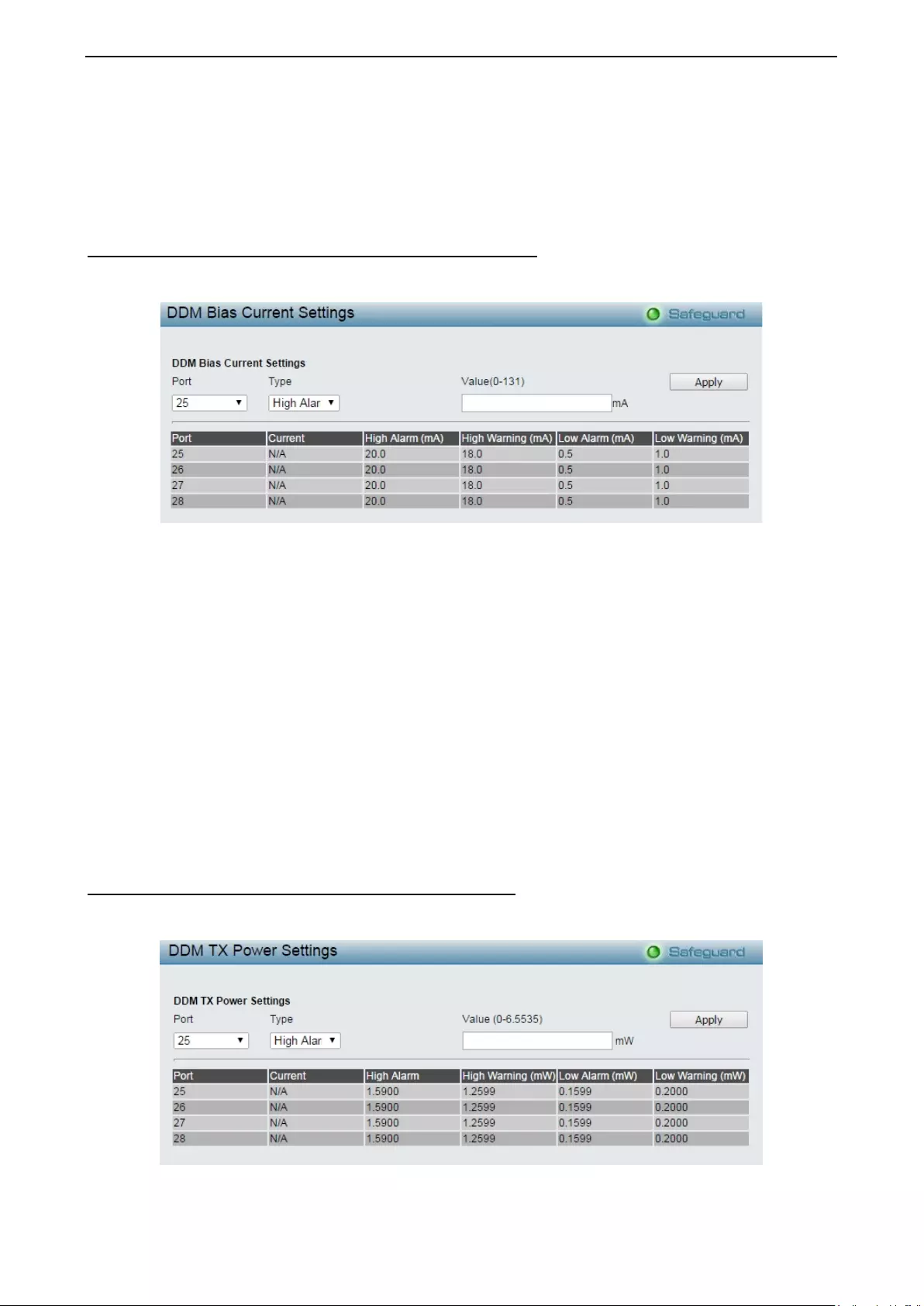
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
78
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. W hen the operating Voltage falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.55): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
The DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings page is used to configure the DDM Bias current threshold for
specific ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.108 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Bias Current Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the t ype for the operati ng param eter, the options are Hig h Alarm , Low Alarm , High W arning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: S pec if ies t he hig h thr es h ol d f or the alarm. When the B ias c urr ent threshold r ises a bo ve
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the low threshold for the alarm. When the Bias current threshold falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the Bias current threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the Bias current threshold falls
below the config ur ed value , the actio n ass ociat ed with the w arni ng is taken.
Vaule (0 – 131): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
The DDM TX Power Threshold Settings page is used to configure the threshold of TX power for specific
ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.109 - Configuration > DDM > DDM TX Power Threshold Settings
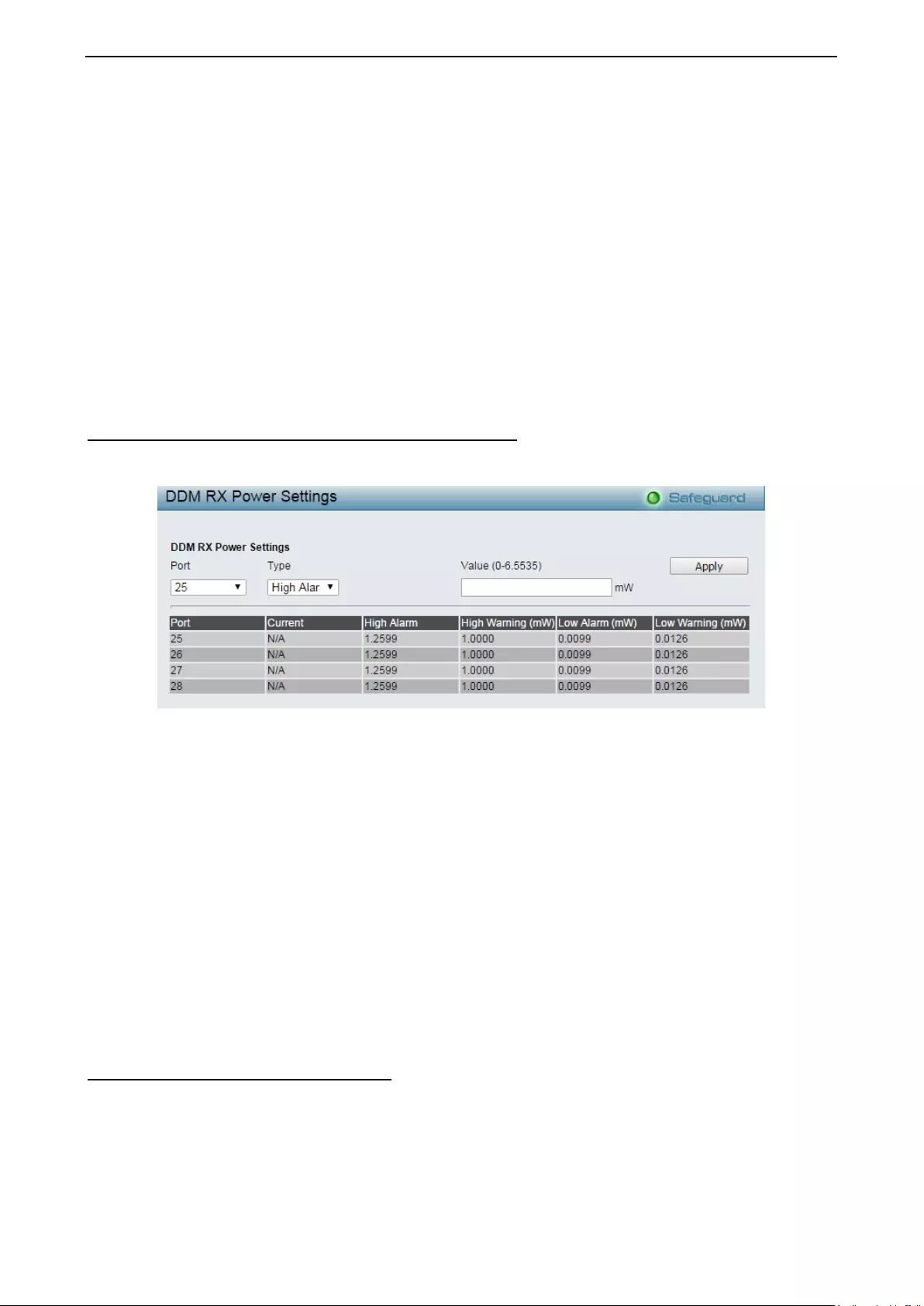
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
7
79
9
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the t ype for the operati ng param eter, the options are Hig h Alarm , Low Alarm , High W arning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the TX power threshold rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specif ies the low thr eshold for the al arm. W hen the T X power threshol d falls b elow the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the TX power threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies th e lo w thr eshold for the w ar nin g. When the TX power threshol d f alls b elo w
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.5535): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
The DDM RX Power Threshold Settings page is used to configure the threshold of RX power for specific
ports on the Switch.
Figure 4.110 - Configuration > DDM > DDM RX Power Threshold Settings
Port: Specifies the port to be configured.
Type: Specifies the t ype for the operati ng param eter, the options are Hig h Alarm , Low Alarm , High W arning
and Low Warning.
High Alarm: Specifies the high threshold for the alarm. When the RX power threshold rises above
the configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
Low Alarm: Specifies the lo w threshold for the alarm . W hen the RX power thres hold falls be low the
configured value, the action associated with the alarm is taken.
High Warning: Specifies the high threshold for the warning. When the RX power threshold rises
above the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Low Warning: Specifies the low threshold for the warning. When the RX power threshold falls below
the configured value, the action associated with the warning is taken.
Vaule (0 – 6.5535): Specifies the value for the specified type of port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
The DDM Status Table page displays the current operating digital diagnostic monitoring parameters and their
values on the SFP module for specified ports.
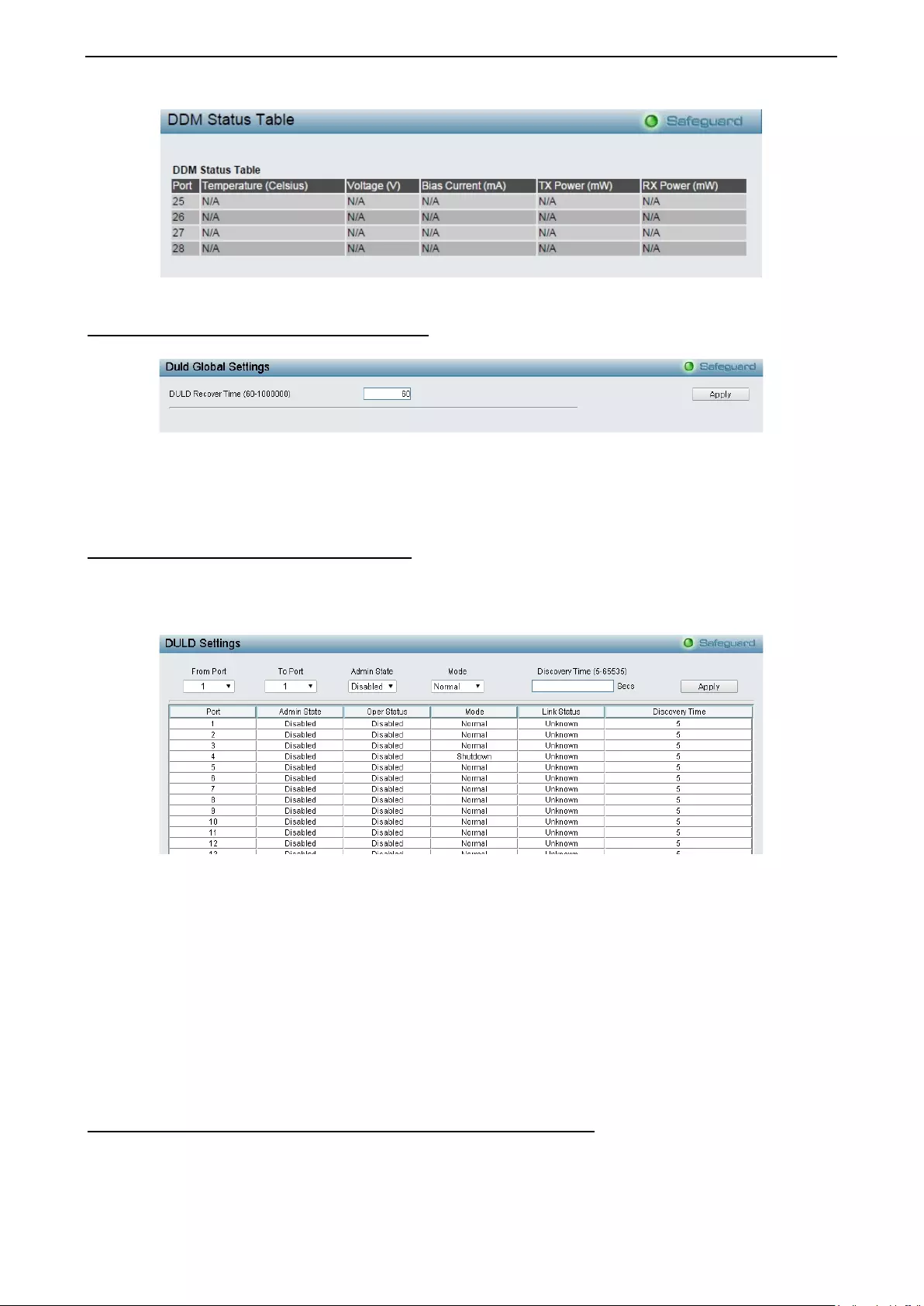
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
80
Figure 4.111 - Configuration > DDM > DDM Status Table
Configuration > DULD > DULD Global Settings
The DULD Global Settings page allows user to configure the DULD recover time.
Figure 4.112 - Configuration > DULD > DULD Global Settings
DULD Recover Time (60-1000000): Specifies the DULD recover time.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
The DULD Port Settings page allows user to configure the unidirectional link detection on ports.
Unidirectional link detection provides discovery mechanism based on 802.3ah to discovery its neighbor. If
the OAM discovery can complete in configured discovery time, it concludes the link is bidirectional.
Otherwise, it starts detecting task to detect the link status.
Figure 4.113 - Configuration > DULD > DULD Port Settings
From Port / To Port: Specifies a range of ports to be configured.
Admin State: Enable or disable the port uni directional link detection status. The default is disabled.
Mode: Speci fies the mode of DULD.
Normal – Only log and event when a unidirectional link is detected.
Shutdown – If any unidirectional link is detected, disable the port and log an event.
Discovery Time (5-65535): Specifies these ports neighbor discovery time. If the discovery is timeout, the
unidirectional link detection will start. The default discovery time is 5 seconds.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Configuration > Multicast Forwarding & Filtering > Multicast Filtering
The Multicast Filtering Mode page allows user to set up the filtering mode.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
81
1
Figure 4.114 - Configuration > Multicast Forw arding & Filtering > Multicast Filtering
From Port / To Port: Specify the ports of the VLAN on which the corresponding MAC address belongs to.
Multicast Filtering Mode: This dr op-down m enu allo ws you to select th e actio n the S witch will t ake when it
receives a multicast packet that is to be forwarded to one of the ports in the range specified above.
Forward Unregistered Groups - This will instruct the Switch to forward a multicast packet whose
destination is an unregistered multicast group residing within the range of ports specified above.
Filter Unregistered Groups - This will instruct the Switch to filter any multicast packets whose
destination is an unregistered multicast group residing within the range of ports specified above.
Configuration > ERPS Settin g
ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) is the first industry standard (ITU-T G.8032) for Ethernet ring
protection switching. It is achieved by integrating mature Ethernet operations, administration, and
maintenance (OAM) functions and a simple automatic protection switching (APS) protocol for Ethernet ring
networks. ERPS provides sub-50ms protection for Ethernet traffic in a ring topology. It ensures that there are
no loops formed at the Ethernet layer. One link within a ring will be blocked to avoid Loop (RPL, Ring
Protection Link). When the failure happens, protec t ion s witching blocks the failed link and unblocks the RPL.
When the failure clears, protection switching blocks the RPL again and unblocks the link on which the failure
is cleared.
RPL (Ring Protection Link) – Link designated by mechanism that is blocked during Idle state to prevent loop
on Bridged ring RPL Owner – Node connected to RPL that blocks traffic on RPL during Idle state and
unblocks during Protected state R-APS (Ring – Automatic Protection Switching) - Protocol messages defined
in Y.1731 and G.8032 used to coordinate the protection actions over the ring through RAPS VLAN (R-APS
Channel). RAPS VLAN (R-APS Channel) – A separate ring-wide VLAN for transmission of R-APS messages
Protected VLAN – The service traffic VLANs for transmission of normal network traffic.
The ERPS Setting page allows user to configure the settings of ERPS.
Figure 4.115 - Configuration > ERPS Setting
ERPS Global Settings:
ERPS Sta te : To enable or disable the ERPS state.
ERPS Log: To enable or disable the ERPS log.
ERPS Trap: To enable or disable the ERPS trap.
R-APS VLAN Settings:
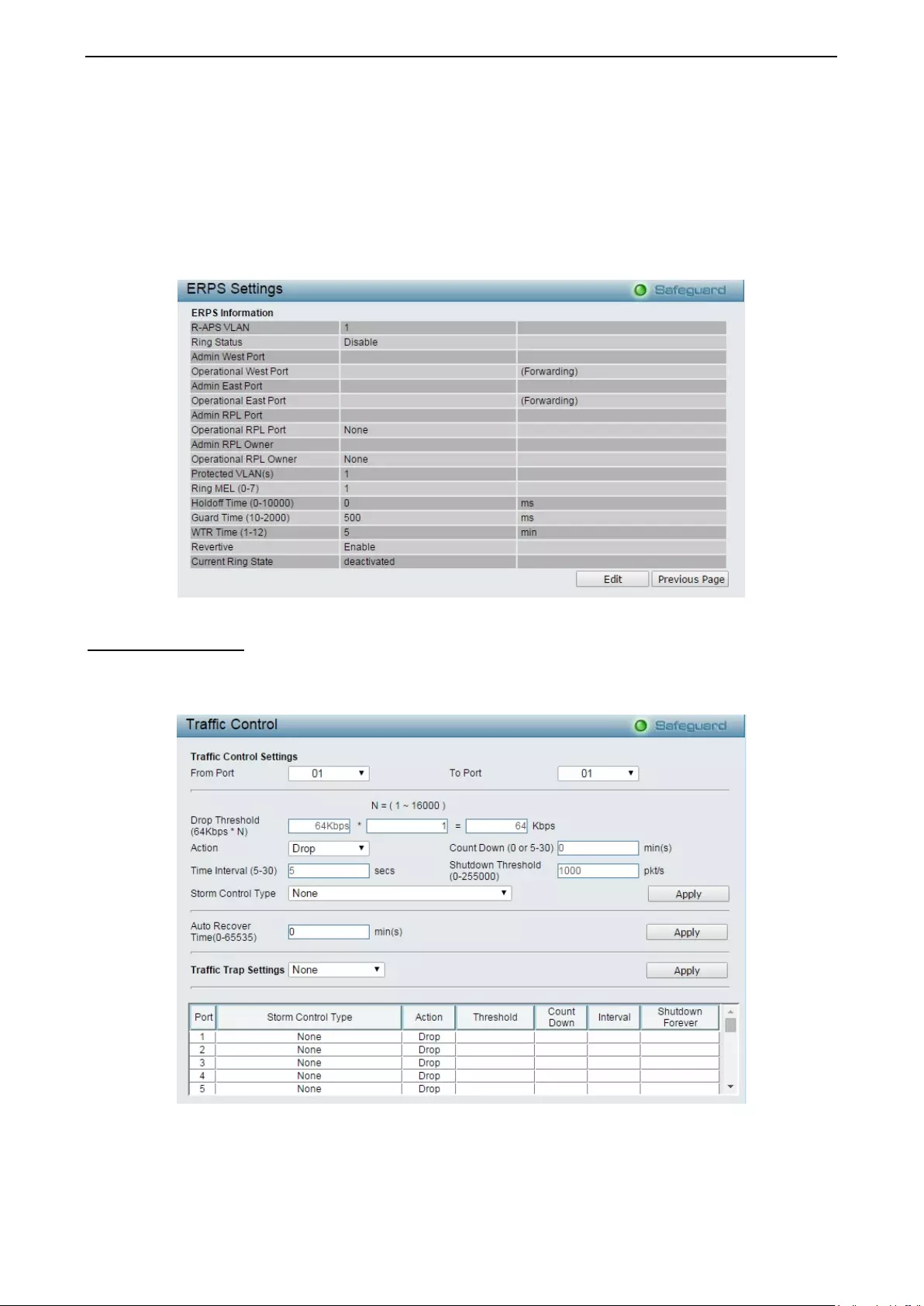
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
82
R-APS VLAN (1-4094): To configure the R-APS VLAN ID.
Click Apply or Clear All to implement changes made.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry.
Click the Detail Information link to view detailed information of the R-APS entry.
Click the Sub-Ring Information link to view the Sub-Ring information of the R-APS entry.
After clicking the Detail Information link, the followin g wind o w will appe ar :
Figure 4.116 - Configuration > ERPS Setting - Detail
QoS > Traffic Control
The Traffic Control feature provides the ability to control the receive rate of broadcast, multicast, and
unknown un icast pack ets. Once a pac ket storm has been detec ted, the S witch will dr op pack ets com ing into
the Switch until the storm has subsided.
Figure 4.117 – QoS > Traffic Control
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Drop Threshold (64Kbps * N): If storm control is en able d (default is dis abled), t he thres hold is f rom of 64 ~
1,024,000 Kbit per second, with steps (N) of 64Kbps. N can be from 1 to 16000.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
83
3
Action: Select the method of traffic control from the pull down menu. The choices are:
Drop – Utilizes the hardware Traffic Control mechanism, which means the Switch’s hardware will
determ ine the Pack et Stor m based on th e Thr eshold value s tate d and dr op p ackets until t he iss ue is
resolved.
Shutdown – Utilizes the S witch’s sof tware Tr affic Control m echanism to determine the Pack et Storm
occurring. Once detected, the port will deny all incoming traffic to the port except STP BPDU packets,
which are essential in keeping the Spanning T ree operational on the Switch. If the countdown tim er
has exp ired an d yet th e Pa ck et Stor m continues , the p ort will be p lac e d in r es t mode and if no ac t ion
is taken will enter auto-recover y mode after a five minute period. Choosing this option obligates the
user to configure the interval setting as well, which will provide packet count samplings from the
Switch’s chip to determine if a Packet Storm is occurring.
Count Down (0 or 5-30): The countdown timer is set to determine the amount of time, in minutes, that the
Switch will wait before shutting down the port that is experiencing a traffic storm. This parameter is only
useful for ports configured as Shutdown in their Action field and therefore will not operate for Hardware
based Traffic Control implementations. The possible time settings for this field are 0, 5-30 minutes. 0 denotes
that the port will never shutdown.
Time In terval (5-30): T he interv al w ill s et the t ime between M ult icas t an d Broa dc as t pac ket counts s ent f rom
the Switch’s chip to the Traffic Control function. These packet counts are the determining factor in deciding
when incoming packets exceed the Threshold value. The interval may be set between 5 and 30 seconds with
the default setting of 5 seconds.
Shutdown Threshold (0-255000): Specify the shutdown threshold for traffic threshold.
Storm Control Type: User can select the different Storm type from Broadcast, Multicast, Broadcast +
Multicast, Unknown U nicast, Bro adcast + Unk nown Unicast, Multicast + U nknown Unicas t, and Broa dcast +
Multicast + Unk no wn Unica s t.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
Auto Recover Time (0-65535): Specify the auto recover time. The value is from 0 to 65535.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
Traffic Trap Settings: Specify the traffic trap is None, Storm Occurred, Storm Cleared or Both.
Click Apply for the settings to take effect.
NOTE: Traffic Control cannot be implemented on
ports that are set for Link Aggregation.
NOTE: Ports that are in the rest mode will be
seen as Discarding in Spanning Tree windows
and implementations though these ports will still
be forwarding BPDUs to the Switch’s CPU.
NOTE: Ports that ar e i n res t m ode will be seen as
link down in all windows and screens until it
enters the auto-
recovery mode or the user
recovers these ports by configuring the port state.
QoS > Bandwidth Control
The Ban dwidth Contr ol pag e allows netw ork manager s to d efine the ba ndwidt h se ttings for a s pecif ied p ort’s
transmitting and receiving data rates.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
84
Figure 4.118 – QoS > Bandwidth Control
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Type: T his dr op-down menu allo ws you to selec t b et ween RX (receive), TX (trans mit), and Both. T h is setting
will determine whether the bandwidth ceiling is applied to receiving, transmitting, or both receiving and
transmitting packets.
No Limit: This drop-down menu allows you to specify that the selected port will have no bandwidth limit.
Enabled disables the limit.
Rate (63-1024000): This field allows you to enter the data rate, in Kbits per second, will be the limit for the
selected port. The value is between 63 and 102 400 0.
Click Apply to set the bandwidth control for the selected ports.
NOTE: The TX rate for Gigabit ports can only be
configured in multiples of 1850kbps. If any other
value is used, the system automatically rounds it
down to the lower multiple of 1850.
QoS > CoS Scheduling Mechanism
The CoS Scheduling Mechanism page allows user to select between a WRR and a Strict mechanism for
emptying the priority classes.
Figure 4.119 - QoS > CoS Scheduling Mechanism
Strict Priority: Denoting a Strict scheduling will set the highest queue to be emptied first while the other
queues will follow the weighted round-robin scheduling scheme
WRR: Use the weighted round-robin (WRR) algorithm to handle packets in an even distribution in priority
classes of service.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > CoS Output Scheduling
CoS can be customized by changing the output scheduling used for the hardware classes of service in the
Switch. As with any changes to CoS implementation, careful consideration should be given to how network
traffic in lower priority classes of service is affected. Changes in scheduling may result in unacceptable levels
of packet loss or significant transmission delay. If you choose to customize this setting, it is important to
monitor network perf orm anc e, es peciall y durin g peak dem and, as bot t le necks c an quickly devel op if th e CoS
settings are not suitable.
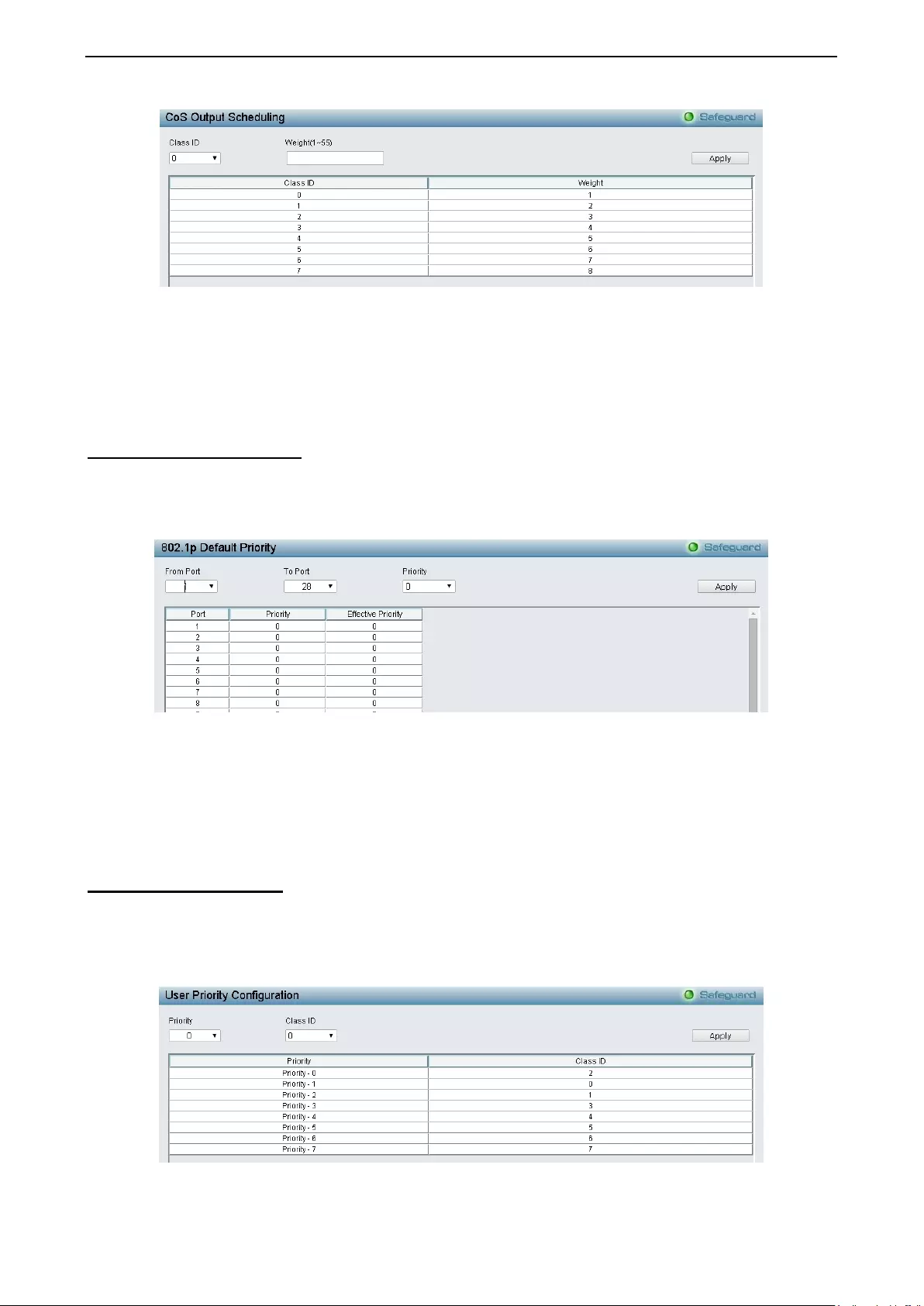
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
85
5
Figure 4.120 - QoS > CoS Output Scheduling
Class ID: Specify the priority queue for the switch. The value is from 0 to 7.
Weight (1-55): Specify the weight for a CoS. The value is from 1 to 55.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > 802.1p Default Priority
QoS is an implementation of the IEEE 802.1p standard that allows network administrators to reserve
bandwidt h f or important f unc tions th at r equ ire a larg er band wid th or t hat might have a hi gher pr iority, such as
VoIP (voice-over Internet Protocol), web browsing applications, file server applications or video conferencing.
Thus with larger bandwidth, less critical traffic is limited, and therefore excessive bandwidth can be saved.
Figure 4.121 - QoS > 802.1p Default Priority
From Port / To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Priority: Def in es the prior it y assigned to the port. T he pr iority are 0~7.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > 802.1p User Priority
When using 802.1p priority mechanism, the packet is examined for the presence of a valid 802.1p priority tag.
If the tag is present, the packet is assigned to a programmable egress queue based on the value of the
tagged priority. The tagged priority can be designated to any of the available queues.
The Switch allows the assignment of a class of service to each of the 802.1p priorities.
Figure 4.122 - QoS > 802.1p User Priority
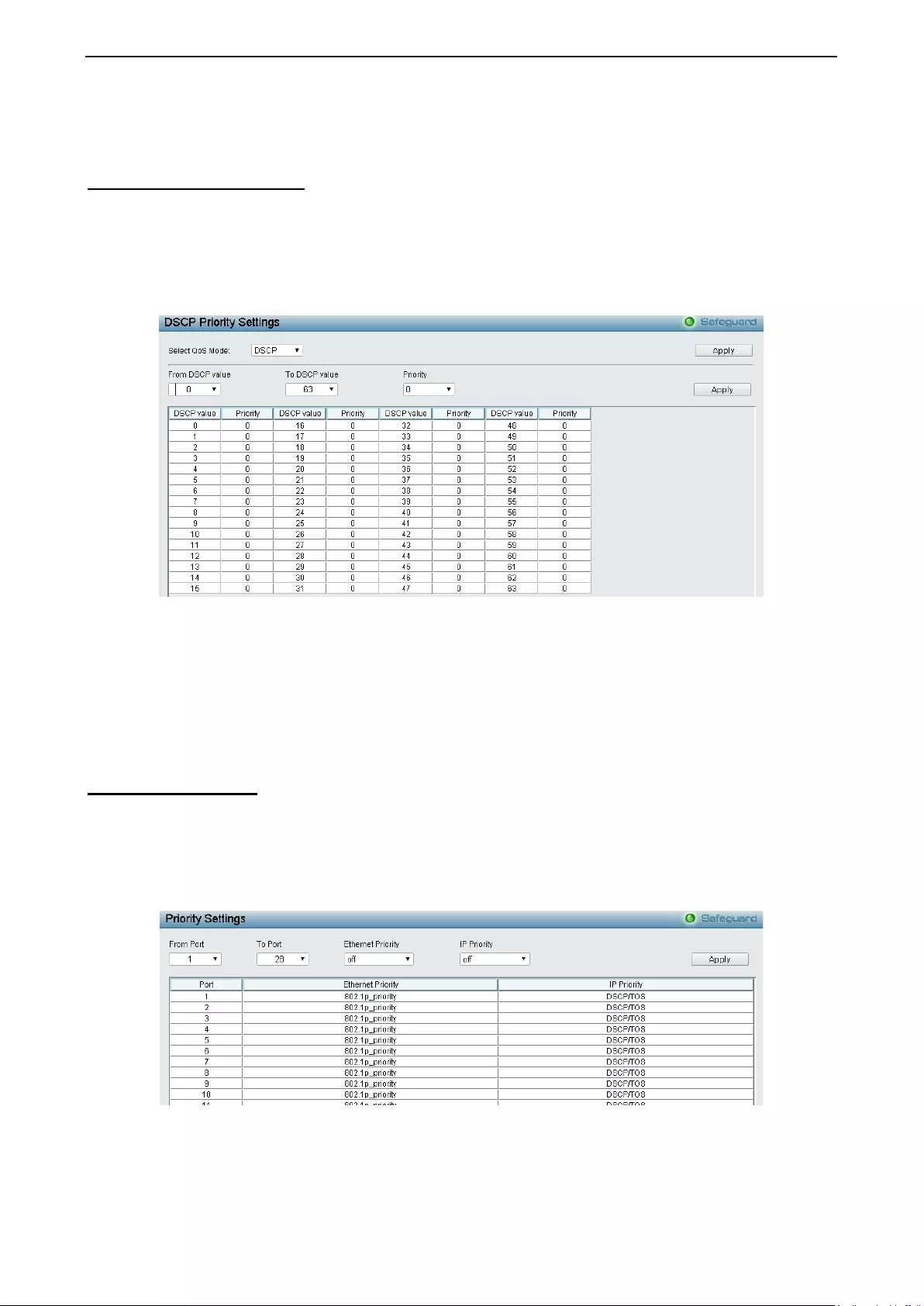
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
86
Once the user had assigned a priority to the port groups on the Switch, you can then assign this Class to
each of the four levels of 802.1p priorities. Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > DSCP Pri orit y Sett i n gs
W hen using the D SCP priorit y m ec hanism, the pack et is clas sif ied bas ed o n the D SCP f ie ld in t he IP hea der.
If the tag is present, the packet is assigned to a programmable egress queue based on the value of the
tagged priority. The tagged priority can be designated to any of the available queues. When a packet is
received containing this DSCP tag, it will be mapped to the CoS queue configured here. T hese settings will
only tak e effect if at least one of the priority settings per port is configured for DSCP. W hen DSCP is set to
enable, TOS cannot be used, and when TOS is set to enable, DSCP cannot be used.
Figure 4.123 - QoS > DSCP Priority Settings
Select QoS Mode: Specify the mode to be DASP or TOS.
From DSCP val ue / To DSCP value: Specify the range of DSCP values.
Priority: Specify the priority queue for the switch. The value is from 0 to 7.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
QoS > Prio rity Settin gs
The Priority Setting page allow users to configure the CoS priority settings on a port or ports. When CoS
tagged packets arrive on t he s witch, the y are m apped to the se ttings conf igured h ere. For exam ple, if a port
has been assigned a MAC priority, the packet that has the CoS priority assigned to a MAC address will be
sent to t he Co S queue conf igured for t hat MAC addre ss. Once th e conf iguratio n has been com pleted, us ers
may see the results in the Priority Settings Table seen here. After configuring the port priorities, users may
adjust the individual CoS settings on the other windows located in the CoS folder of the Switch.
Figure 4.124 - QoS > Priority Settings
From Port/To Port: Users may select a port or group of ports to assign the priority settings.
Port Priority: Spec ify the Port Priority is Off or On on the port.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
87
7
Ethern et Pr iorit y: Specify the Ethernet Priority is Off or 802.1p on the port.
IP Priority: Specify the IP Priority is Off or DSCP on the port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON Basic Settings
Users can enable and disable remote monitoring (RMON) status for the SNMP function on the Switch. In
addition, RMON Rising and Falling Alarm Traps can be enabled and disabled. Click Apply to make effects.
Figure 4.125 - RMON > RMON Basic Settings
RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
The RMON Statistics Configuration page displays the information of RMON Ethernet Statistics and allows
the user to configure the settings.
Figure 4.126 - RMON > RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration
The RMON Ethernet Statistics Configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates the RMON Ethernet Statistics entry number.
Port: Specifies the port from which the RMON information was taken.
Owner: Displays the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
The RMO N His tor y Contro l Conf igur ation pa ge contai ns inf orm ation abo ut sam pl es of data t ak en fr om ports .
For example, the samples may include interface definitions or polling periods.
Figure 4.127 - RMON > RMON History Control Configuration
The History Control Configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates the history control entry number.
Port: Specifies the port from which the RMON information was taken.
Buckets Requested (1 ~ 50): Specifies the number of buckets that the device saves.
Interval (1 ~ 3600): Indicates in seconds the time period that samplings are tak en from the ports. T he field
range is 1-3600. The default is 1800 seconds (equal to 30 minutes).
Owner: Displays the RMON station or user that requested the RMON information.
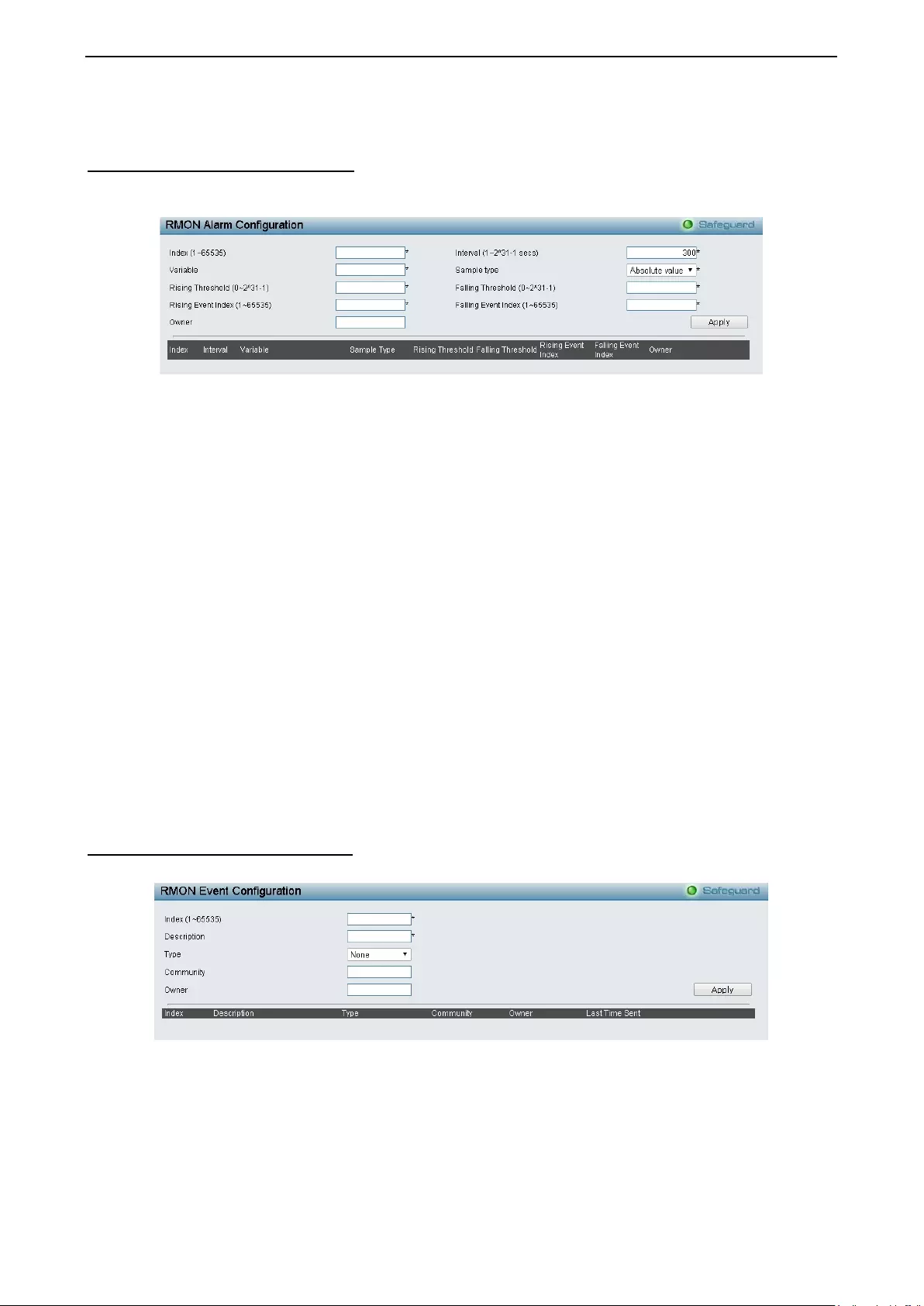
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
88
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON Alarm Configuration
The RMO N Alarm Conf iguratio n pa ge a llo ws t he us er t o c onf igur e th e network alarms. Network alarms oc cur
when a network problem, or event, is detected.
Figure 4.128 - RMON > RMON Alarm S ettings
The configuration contains the following fields:
Index (1 - 65535): Indicates a specific alarm.
Variable: Specify the selected MIB variable valu e.
Rising Threshold (0 ~ 2^31-1): Displays the rising counter value that triggers the rising threshold alarm.
Rising Event Index (1 ~ 65535): Displays the event that triggers the specific alarm. The possible field values are
user defined RMON events.
Owner: Displays the devic e or user that def ined the alarm.
Interval (1 ~ 2^31-1): Defines the alar m int erv al time in se cond s.
Sample type: Defines the sampling method for the selected variable and comparing the value against the
thresholds. The possible field values are:
Delta value – Subtracts the last sampled value from the current value. The difference in the values
is compared to the threshold.
Absolute value – Compares the values directly with the thresholds at the end of the sampling
interval.
Falling Threshold (0 ~ 2^31-1): Displays the falling counter value that triggers the falling threshold alarm.
Falling Event Index (1 ~ 65535): Displays the event that triggers the specific alarm . The possible field values are
user defined RMON even ts.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
RMON > RMON Event Configuration
The RMON Event page contains fields for defining, modifying and viewing RMON events statistics.
Figure 4.129 - RMON > RMON Event Configuration
The RMON Events Page contains the following fields:
Index (1~ 65535): Displays the event.
Description: Specifies the user -def ined event des c ript ion.
Type: Specifies the event type. The possible values are:
None – Indicates that no event occurred.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
8
89
9
Log – Indicates that the event is a log entry.
SNMP Trap – Indicates that the event is a trap.
Log and Trap – Indicates that the event is both a log entry and a trap.
Community: Specifies the community to which the event belongs.
Owner: Specifies the time that the event occurred.
Click Apply to add a new RMON event.
Securi ty > Trusted Host
Use Trusted Host f unction to manage the switch from a rem ote station. You can enter up to ten designated
management stations networks by defining the IP address/Subnet Mask as seen in the figure below.
Figure 4.130 - Security > Trusted Host
To def ine a m anagement statio n IP s ett ing , c lick the Add Host button and type in the IP addr es s and S ubn et
mask. Click the Apply button to save your settings. You m ay permit only single or a range of IP addresses
by dif ferent IP mask settings, the f ormat can either be 192. 168.1.1/255.25 5.255.0 or 192.1 68.0.1/24. Ple ase
see the example below for permitting the IP range
IP Address Subnet Mask Permitted IP
192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1~192.168.0.255
172.17.5.215 255.0.0.0 172.0.0.1~172.255.255.255
To delete the IP address, simply click the Delete button. Check the unwanted address, and then click Apply.
Security > Safeguard Engine
D-Link’s Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology that automatically throttles the impact of
packet flooding into the switch's CPU. This function helps protect the Switch from being interrupted by
malicious viruses or worm attacks. This option is enabled by default.
Figure 4.131 – Security > Safeguard Engine
Securi ty > CPU Protect
The CPU Protect setting page allows user to view and configure the CPU protection type settings.
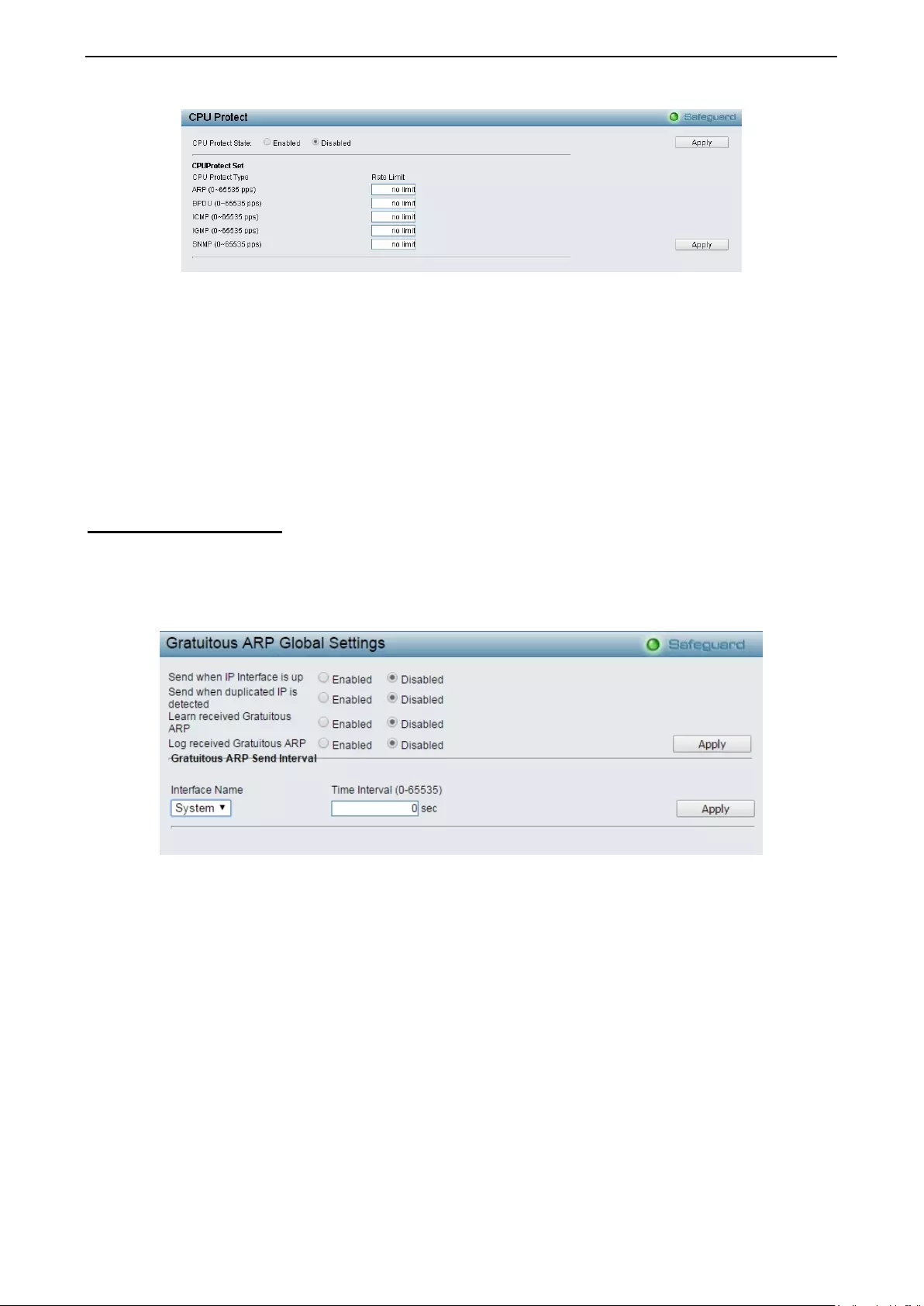
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
90
Figure 4.132 – Security > CPU Protect
CPU Protect State: Specifies the CPU protect state to be enabled or disabled.
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
The CPU Pro tect Types are ARP, BPDU, ICMP, IGMP and SNMP. Select the CPU Protect Type and enter
the Rate limit which the value is between 0 and 65535 pps. The default value is no limit.
Click the Apply button to save your settings.
Securi ty > Gratuitous AR P
The Gratuitous ARP page shows the settings on the Switch. An ARP announcement (also known as
Gratuitous ARP) is a packet (usually an ARP Request) containing a valid SHA (Sender Hardware Address)
and SPA (Sender Protocol Address) for the host which sent it, with TPA (Target Protocol Address) equal to
SPA. Such a request is not intended to solicit a reply, but merely update the ARP caches of other hosts
which receive the packet and determine if there are any IP conflicts.
Figure 4.133 – Security > Gratuitous ARP
Send when IP Interface is up: This is used to enable/disable the sending of gratuitous ARP request
packets while an IP interface comes up. This is used to automatically announce the interface’s IP address to
other nodes. By default, the state is Disabled, and only one ARP packet will be bro adc as t.
Send when duplic ated IP is detec ted: This is used to enable/disable the sending of gratuitous ARP
request packets while a duplicate IP is detected. By default, the state is Disabled. Duplicate IP detected
means that the system received an ARP request packet that is sent by an IP address that matches the
system’s own IP addres s.
Learn recei ved Gratuitous ARP: This is used to enable/disable updating ARP cache based on the received
gratuitous ARP packet. If a switch receives a gratuitous ARP packet and the sender’s IP address in its ARP
table, it should update the ARP entry. This is Disabled by default.
Gratuitous ARP Send Interval: Specify the interval value.
Interface Name: Specify the Interface Name. The default is System.
Time In terval (0-65535): Specify the time interval, the range is from 0 to 65535, and the default is 0 seconds.
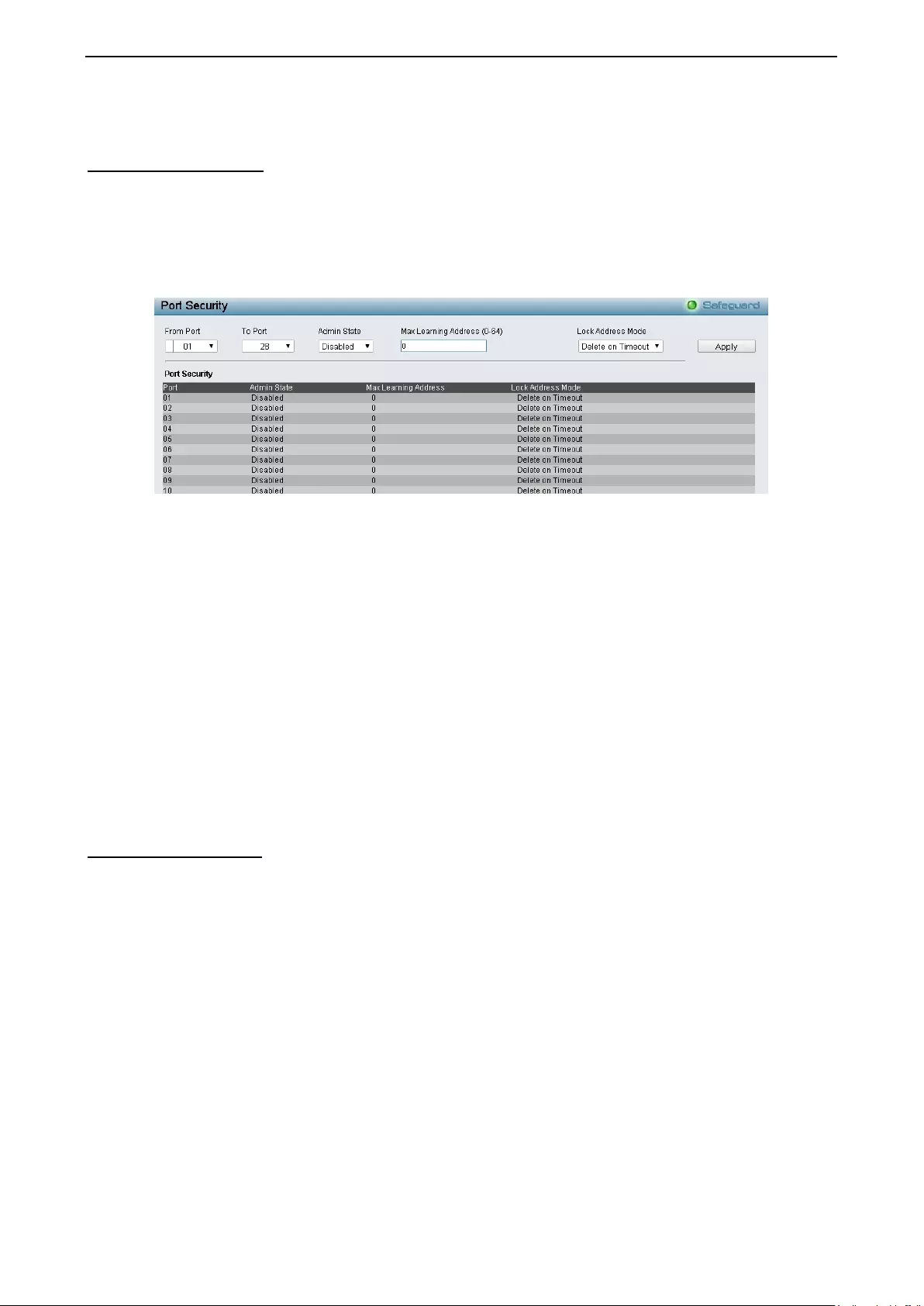
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
91
1
Click Apply to make configurations make effects.
Security > Port Security
Port Security is a security feature that prevents unauthorized computers (with source MAC addresses)
unknown to the Switch prior to stopping auto-learning processing from gaining access to the network.
A given ports’ (or a range of ports') dynamic MAC address learning can be stopped such that the current
source MAC addresses entered into the MAC address forwarding table cannot be changed once the port is
enabled.
Figure 4.134 - Security > Port Security
The Port Security page contains the following fields:
From Por t/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Admin State: This pull-down menu allows users to enable or disable Port Security (locked MAC address
table for the selected ports).
Max. Learning Address (0-64): T he number of MAC addr esses t hat will be in the M AC ad dress-forwarding
table for the selected switch and group of ports.
Lock Address Mode: This pull-do wn menu allo ws yo u to selec t how the MAC address tab le locking w ill be
implemented on the Switch, for the selected group of ports. The options are:
Delete On Reset – The locked addresses will not age out until the Switch has been reset.
Delete On Timeou t – The locked addresses will age out after the aging timer expires.
Permanent – The locked addresses will not age out af ter the ag ing tim er expires .
Click Apply to make configurations make effects.
Security > SSL Settings
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security feature that provides a secure communication path between a Web
Management host and the Switch W eb UI by using authentication, digital signatures and encryption. These
security functions are implemented by Ciphersuite, a security string that determines the cryptographic
parameters, encryption algorithms and key sizes.
This page allows you to configure the SSL global state and the Ciphersuite settings. Select Enable or
Disable an d then click Apply to change the SSL state or the Ciphersuite settings of the Switch. By default,
SSL is Disabled and all Ciphersuites are Enabled.
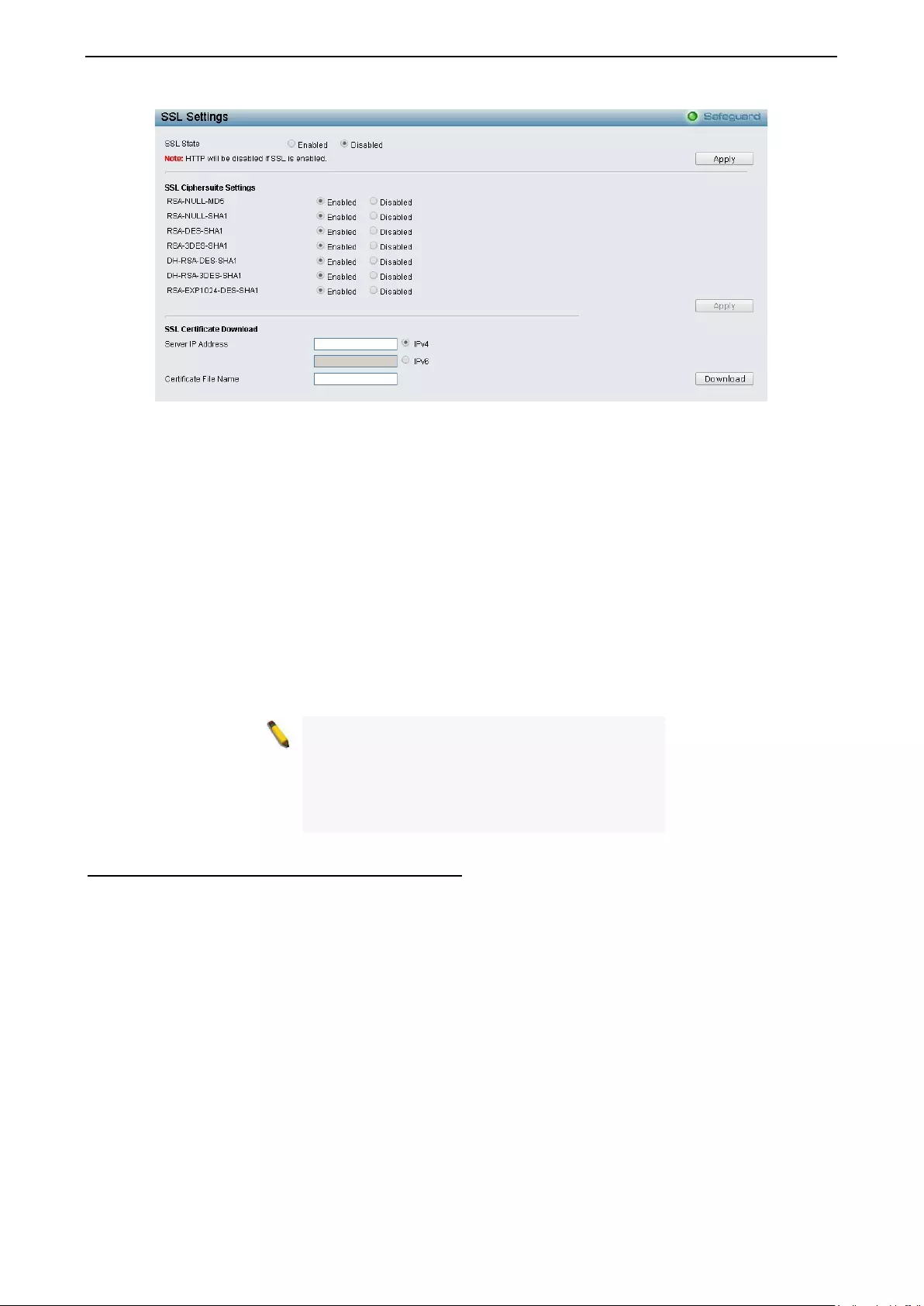
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
92
Figure 4.135 - Security > SSL Settings
The SSL Settings page allows users to download a certificate file for the SSL function on the Switch from a
TFTP server. The certificate file is a data r ecord used for authent icating devices on the net work. It contains
inform ation on the owner, keys for authentication and digital signatures. Both the server and the client must
have consis tent certificat e files for opt imal use of t he SSL f unction. The Switch only suppor ts certificate f iles
with .der file extensions. The Switch is shipped with a certificate pre-loaded though the user may need to
download more, depending on user circumstances.
Server IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP address of the TFTP server where the certificate
files are located.
Certificat e File Name: En ter the pat h an d th e f ile nam e of the c ert ific at e f ile to d o wnlo ad. This f ile must have
a .der extension. (Ex. c:/cert.der)
Click Download to download the certificate file.
NOTE: Enabling the SSL command will disable
the web-based switch management. To log on to
the Switch again, the header of the URL must
begin with https://. Entering anything else into the
address field of the web browser will result in an
error and no authentication will be granted.
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
The primary purpose of Smart Binding is to restrict client access to a switch by enabling administrators to
configure pairs of client MAC and IP addresses that are allowed to access networks through a switch.
The Smart Binding function is port-based, meaning that a user can enable or disable the function on any
individual port. Onc e Sm ar t Bindin g is enab led on a switch port, th e switc h will r estrict or allow c lient acc ess
by check ing th e pair of IP-MAC ad dress es with the pr e-configur ed da tabas e, als o k nown as the “ IMP B whit e
list”.
Users can enable or disable the Packet Inspection and DHCP Snooping on the Switch.
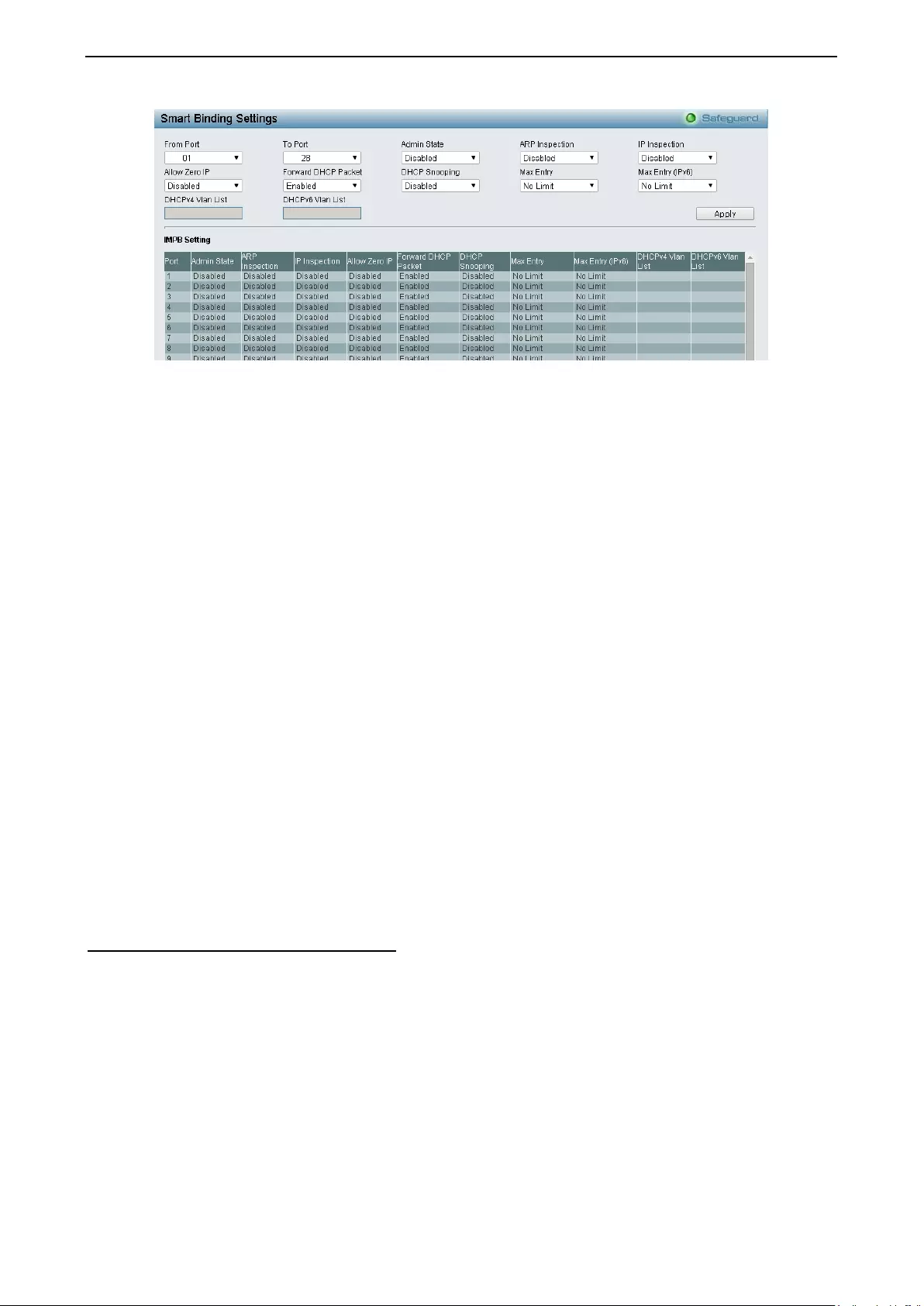
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
93
3
Figure 4.136 – Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding Settings
The Smart Binding Settings page contains the following fields:
From Por t/ To Port: Select a range of ports to set for IP-MAC-port binding.
Admin State: Use the dr op -down menu to enable or disable these ports for Smart Binding.
Enabled –Enable Smart Binding with related configurations to the ports
Disabled –Disable Smart Binding.
ARP Inspection: If ARP inspection is enabled, the Switch will inspect incoming ARP packets and compare
them with the Switch’s Smart Binding white list entries. If the IP-MAC pa ir of an ARP packet is not found in
the white list, t he Switch will bloc k the M AC addres s. A m ajor benef it of Lo ose st ate is that it uses less C PU
resourc es. Ho wever, it ca nnot b lock m alicious users who send o nl y unicast IP pack ets. An ex am ple of this is
that a malicious user can perform DoS attacks by statically configuring the ARP table on their PC. In this
case, the Switch cannot block such attacks because the PC will not send out ARP packets.
IP Inspection: When IP Inspection is enabled, and ARP Inspection is disabled, all non-IP packets are
forwarded by default. If ARP Inspection and IP Inspection mode are enabled, the Switch will inspect all
incoming ARP and IP packets and compare them to the IMPB white list. If the IP-MAC pair find a match in
the white list, the packets from that MAC address are unblocked. If not, the MAC address will stay block ed.
While the mode examines every ingress ARP and IP packet, it enforces better security.
Allow Zero IP: Enable or disable to allow zero IP to configure the state which allows ARP packets with
0.0.0.0 source IP to bypass.
Forward DHCP Packet: Enable or disable to forward DHCP packet.
DHCP Snooping: By enable DHCP Snooping, the switch will snoop the packets sent from DHCP Server and
clients, and update information to the White List.
Max Entry: Specifies the max entries of Smart Binding. The range is between 1 and 10, or No Limit.
Max Entry (IPv6): Specifies the IPv6 m ax entries of Smart Binding. T he range is between 1 and 10, or No
Limit.
Click Apply to make configurations make effects.
Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
The Smart Binding page allows the user to create Static IP-MAC-Port Binding entries on the Switch.
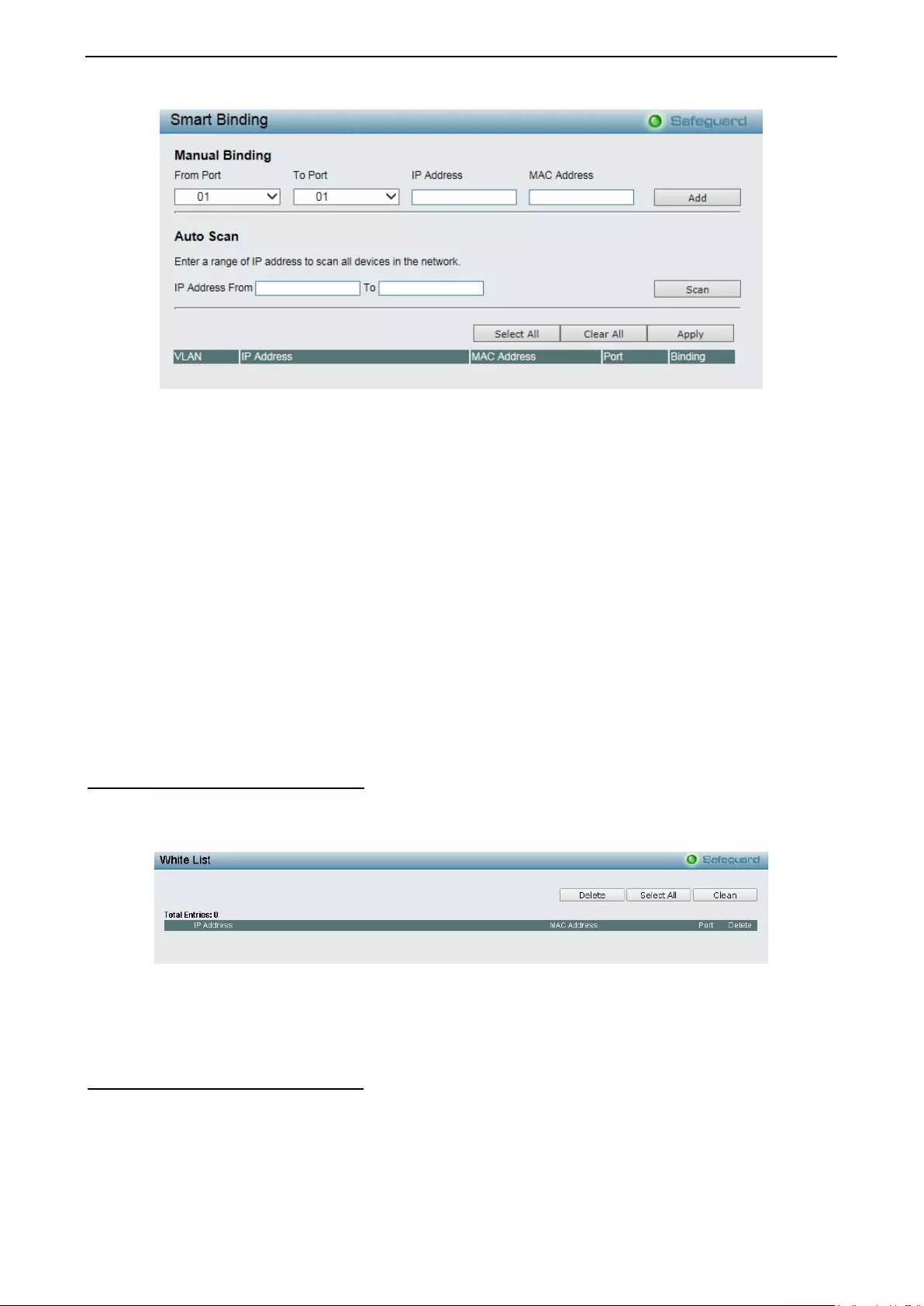
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
94
Figure 4.137 – Security > Smart Binding > Smart Binding
The Manu al Bind ing Settings contains the following fields:
From Port / To Port: Specifies the port ranges for MAC address to bind to the IP address of Binding list.
IP Address: Specifies the IP address to bind to the MAC address set below.
M AC Add ress: Specifies the MAC address to bind to the IP address set above.
Click Add to add a new entry.
Auto Scan: Specifies to scan connected devices in a range of IP address.
IP Address Fr o m /To: Specifies the range of IP Address to scan all devices in the network.
Click Scan and the search results will be listed in below table.
Binding: check the box to select desired bi nding devices .
Apply: click Apply to set IP-MAC-Port Bind ing entr ie s .”
Select All: to check the boxes of Binding for all found devices.
Clear All: to cancel the box of Binding.
Security > Smart Binding > White Lis t
When IP+ARP Inspection Mode were selected, the White List page displays finished IP-MAC-Port Binding
entries from page Smart Binding. Only IP packets or ARP packets carrying matched IP-MAC-Port
information can access to the switch. You can cancel a device’s authorization by deleting it from the table.
Figure 4.138 – Security > Smart Binding > White List
Click Select All to select all entries of the table or click Clean to select none entries. Please keep at least
one management host in the White List.
Security > Smart Binding > Black List
The Black List page shows unauthorized accesses. When ARP Inspection is selected and a device sends
out an ARP packet containing unmatched IP-MAC-Port information, the device will be forbidden and listed
here.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
95
5
Figure 4.139 – Security > Smart Binding > Black List
By givin g conditions , desired d evices infor mation can be screened out belo w then click Find to search for a
list of the entry:
VID: Enter the VLAN ID number of the device.
IP Address: Enter the IP Address of the device.
M AC Add ress: Enter the MAC Address of the device.
Port: Enter the port number which the device connects.
Check a box of Delete colum n to release an entr y from the for bidden list t hen cl ick Apply to de lete an entry
from the list.
Click Select All to select all entries, or click Clean to select none of the entries.
Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
The DHCP Snoop ing List p age shows the DHCP Snooping list.
Figure 4.140 – Security > Smart Binding > DHCP Snooping List
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
Network switc hes provide easy and open access to res ources b y sim ply attachin g a client PC. Unf ortunate ly
this autom atic configur ation also al lows u nauthori zed p ersonne l to eas il y intrud e and p ossibl y gain ac cess to
sensitive dat a.
IEEE-80 2.1X provides a secur ity standard f or network access contr ol, especiall y in W i-Fi wireless net works.
802.1X holds a network port disconnected until authentication is completed. The switch uses Extensible
Authentication Protocol over LANs (EAPOL) to exchange authentication protocol client identity (such as a
user name) with the client, and forward it to another remote RADIUS authentication server to verify access
rights. The EAP packet from the RADIUS server also contains the authentication method to be used. The
client can r eject t he authen tication m ethod and r eques t another, dependin g on the conf iguratio n of the c lient
software and the RADIUS server. Depending on the authenticated results, the port is either made available
to the user, or the user is denied access to the network.
The RADIUS ser vers m ak e the network a lot easier to m anage f or the adm inistrator by gather ing and s toring
the user lists.
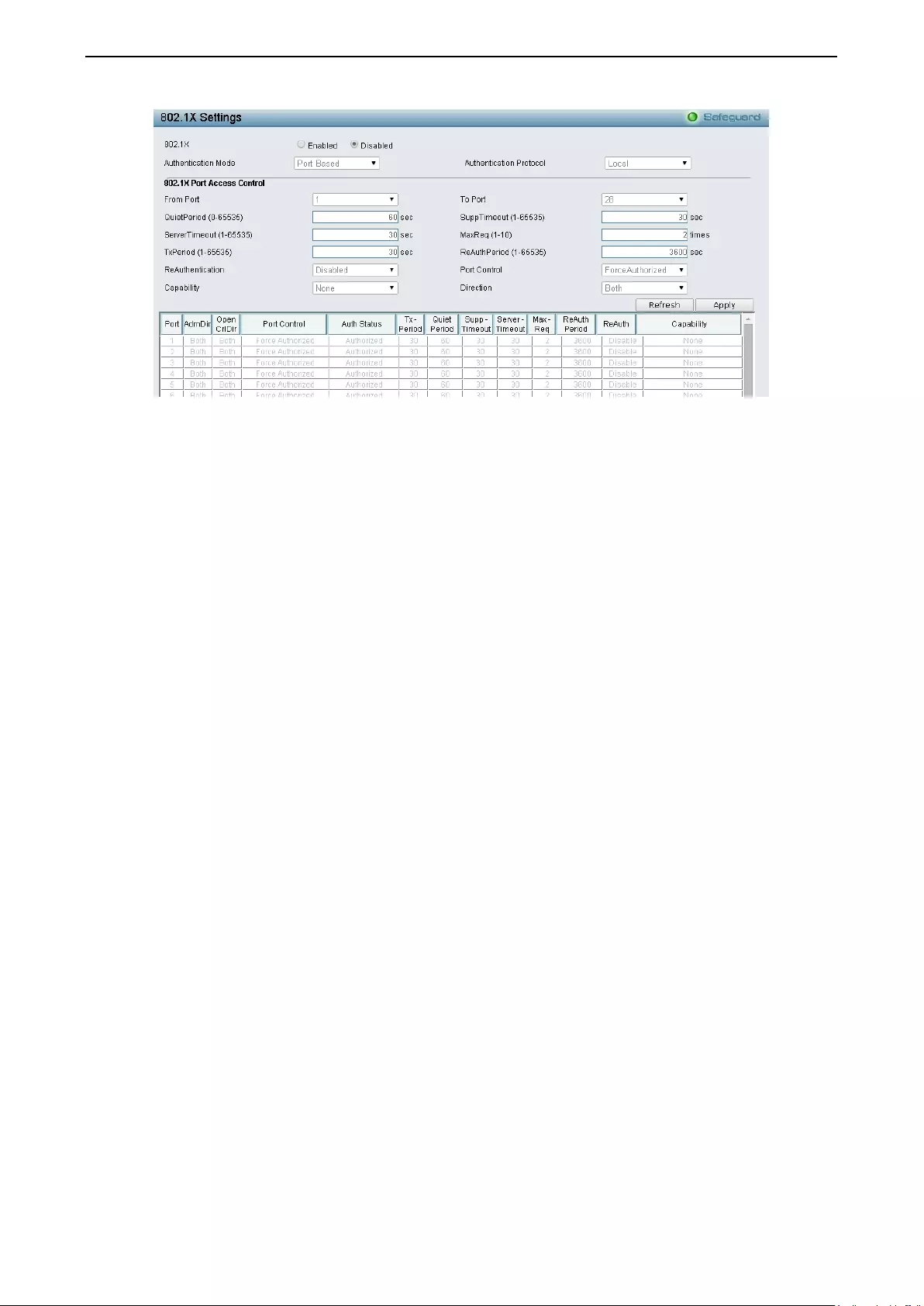
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
96
Figure 4.141 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Settings
By default, 802.1X is disabled. To use EAP for security, select enabled and set the Authentication Mode
and Authentication Pro tocol then click Apply.
Authentication Mode: Indicates the 802.1X mode enabled on the device. The possible field values are:
Port Based – Enables 802.1X on ports. This is the default value.
MAC Based – Enables 802.1X on MAC addresses.
Authentication Protocol: Indicates the 802.1X Protocol on the device. The possible field values are Local
and RADIUS EAP.
From Port/To Port: Enter the port or ports to be set.
QuietPeriod (0 – 65535 sec): Sets the number of seconds that the switch remains in the quiet state
following a failed authentication exchange with the client. Default is 60 seconds.
ServerTimeout (1 – 65535 sec): Sets the amount of time the switch waits for a response from the client
before resending the response to the authentication server. Default is 30 seconds.
TxPeriod (1 – 65535 sec): This sets the TxPeriod of time for the authenticator PAE state machine. This
value determines the period of an EAP Request/Identity packet transmitted to the client. Default is 30
seconds.
ReAuthentication: Determines whether regular reauthentication will take place on this port. The default
setting is Disabled.
Capability: Indicates the capability of the 802.1X. The possible field values are:
Authenticator – Specify the Authenticator settings to be applied on a per-port basis.
None – Disable 802.1X functions on the port.
SuppTimeout (1 – 65535 sec): This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the
Authenticator and the client. Default is 30 seconds.
MaxReq (1 – 10): This parameter specifies the maximum number of times that the switch retransmits an
EAP request (md-5challnege) to the client before it times out the authentication session. Default is 2 times.
ReAuthPeriod (1 – 65535 sec): A constant that defines a nonzero number of seconds between periodic
reauthentication of the client. The default setting is 3600 seconds.
Port Control: This allows user to control the port authorization state.
Select ForceAuthorized to disable 802.1X and cause the port to transition to the authorized state
without any authentication exchange required. This means the port transmits and receives normal
traffic without 802.1X-based authentication of the client.
If ForceUnauthorized is selected, the port will remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all
attem pts by the client to a ut hent ic ate. The Switch c a nn ot pr o vid e aut he ntication se r vices to th e c lient
through the interface.
If Auto is selected, it will enable 802.1X and cause the port to begin in the unauthorized state,
allowing only EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port. The authentication process
begins when the li nk state of the por t transitions from down to up, or when an EAPOL-s tart frame is
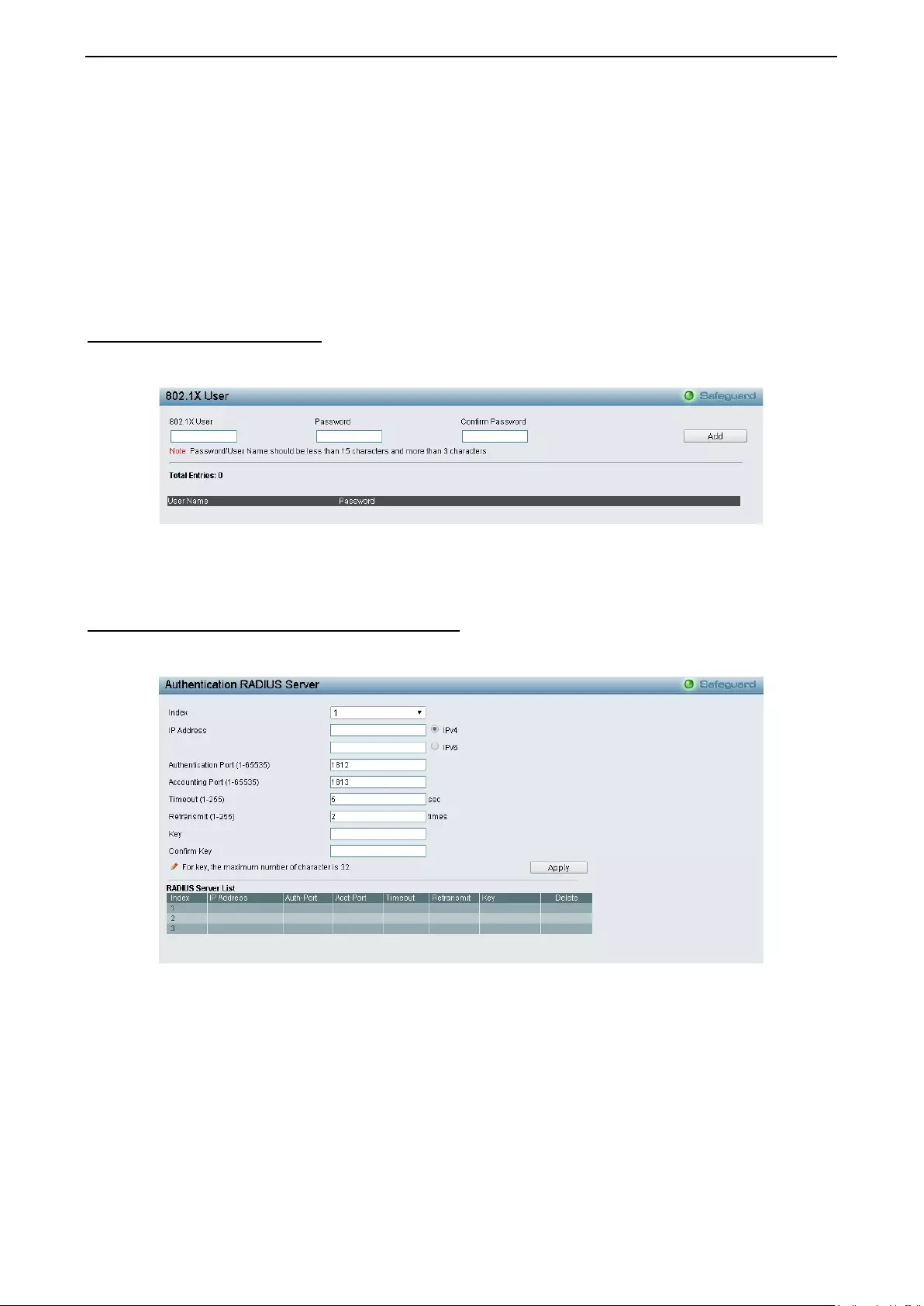
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
97
7
received. The Switch then requests the identity of the client and begins relaying authentication
messages between the client and the authentication server.
The default setting is Auto.
Direction: Sets the administrative-controlled direction on the port. The possible field values are:
Both – Specif y the control is exerted over both incom ing and outgoing traff ic through the controlled
port selected in the first field.
In – Disables the support in the present firmware release.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
The 802.1X User page allows user to set different local users on the Switch. Enter a 802.1X User name,
Password and Confirm Password. Properly configured local users will be displayed in the table.
Figure 4.142 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X User
Click Add to add a new 802.1X user.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RADIUS
The 802.1X Auth ent ication RUAIUS of the Switch allows you to facilitate centralized user administration as
well as providing protection against a sniffing, active hacker.
Figure 4.143 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Authentication RUDIUS
Index: Choose the desired RADIUS server to configure: 1, 2 or 3.
IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP address.
Authentication Port (1 - 65535): Set the RADIUS authentic server(s) UDP port. The default port is 1812.
Accounting Port (1 - 65535): Set the RADIUS account server(s) UDP port. The default port is 1813.
Timeout (1 – 255 sec): T his field will s et the tim e the Switch w ill wait for a r esponse of authentication f rom
the user. The user may set a time between 1 and 255 seconds. The default setting is 5 seconds.
Retransmit (1 – 255 times): This command will configure the maximum number of times the Switch will
accept authentication attempts. Users failing to be authenticated after the set amount of attempts will be
denied access to the Switch and will be locked out of further authentication attempts. Command line
interfac e user s will h av e t o w ait 6 0 sec o nds b ef or e a n other authen tic at io n a ttempt. T elne t and web us ers will

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
98
be disconnected from the Switch. The user may set the number of attempts from 1 to 255. The default
setting is 2.
Key: Set the key the same as that of the RADIUS server.
Confirm Key: Confirm the shared key is the same as that of the RADIUS server.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Guest VLAN
The 802. 1X Guest V LAN page allo ws user to s et a G uest VLAN, an d the user m ust firs t configure a norm al
VLAN which can be enabled here for Guest VLAN status.
Enter the pre-configured VLAN name to create as a Guest 802.1X VLAN and select the port or ports. Click
Apply to implement the settings.
Figure 4.144 - Security > 802.1X > 802.1X Gu es t VL AN
Security > MAC Address Table > Static MAC
This f eature pr ovides t wo dis tinct f unctions . T he Disable Auto Learning table allo ws turn ing of f the f unction
of learning MAC address automatically, if a port isn't specified as an uplink port (for example, connects to a
DHCP Server or Gateway). By default, this feature is Off (disabled).
Figure 4.145 - Security > MAC Address Table > Sta tic Mac Addre ss
To initiate the removal of auto-learning for any of the uplink ports, click On to enable this feature, and then
select the port(s) for auto learning to be disabled.
The Static M AC Address List table displays th e s tat i c MAC addres s es con nec te d, as we ll as the V ID . Cl ick
Ad d M a c to add a n e w M A C address, you a ls o ne ed t o s elect the as s ign ed Port number, enter b oth the Mac
Address an d VID and Click Apply. Clic k Delete to r emove one entr y or click Delete all to clear the list. You
can also copy a learned MAC address from Dynamic Forwarding Table (please refer to Security > MAC
Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table for details).
By disabling Auto Learning capability and specify the static MAC addresses, the network is protected from
potential threats like hackers because traffic from illegal MAC addresses will not be forwarded by the Switch.
Click Ad d MAC button, select the Port, VID and enter the MAC add ress then click Apply to add a new MAC
address.
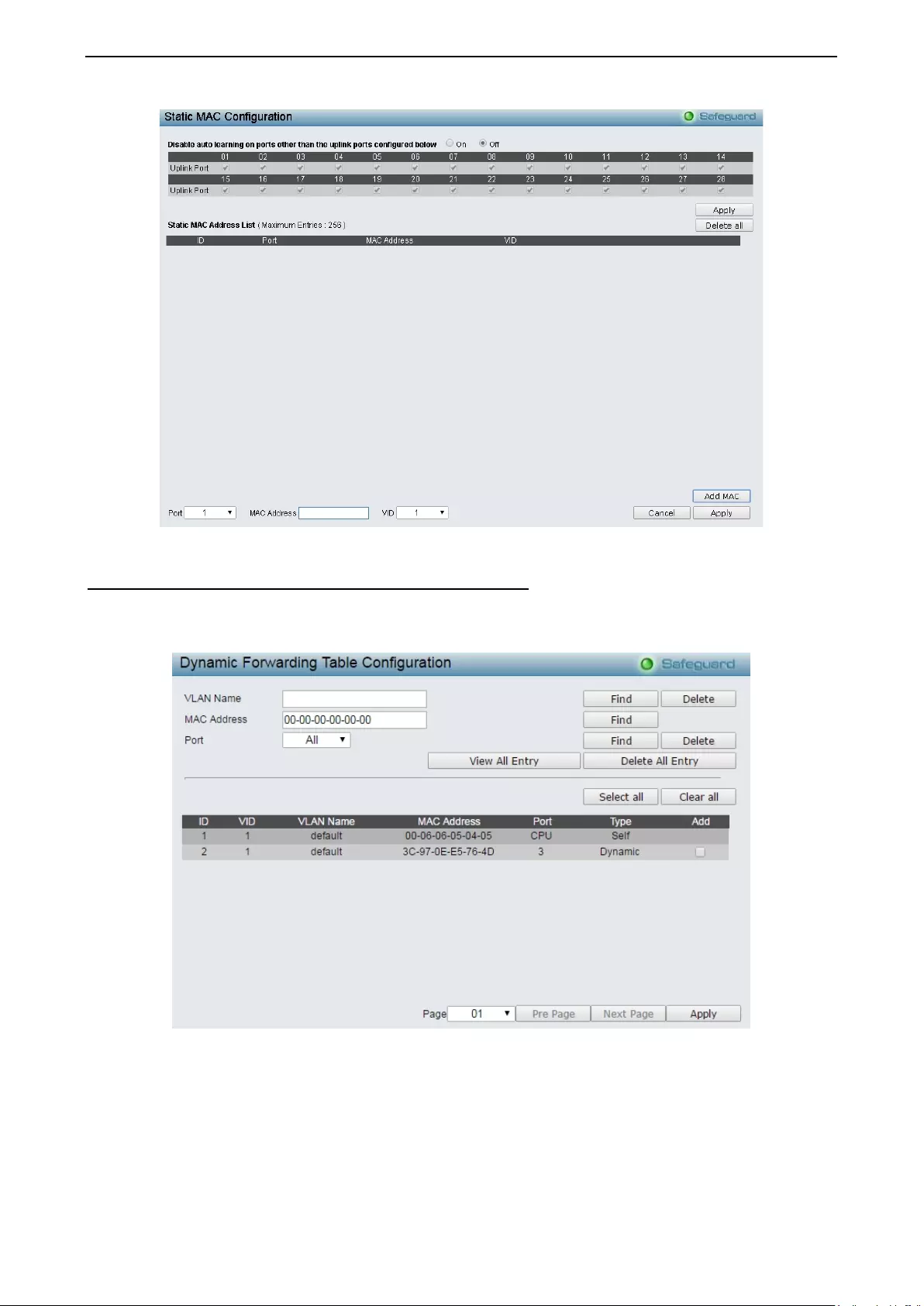
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
9
99
9
Figure 4.146 - Security > MAC Address Table > Static Mac Addres s -add MAC
Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forwarding Table
This allows the Switch’s dynamic MAC address forwarding table to be viewed. When the Switch learns an
association between a MAC address and a port number, it makes an entry into its forwarding table. These
entries are then used to forward packets through the Switch.
Figure 4.147 - Security > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Forw ar d ing Table
VLAN Name: Enter a VLAN Name by which to browse the forwarding table.
M AC Add ress: Enter a MAC address by which to browse the forwarding table.
Port: S elec t the port or all ports by using the corresponding pull-down menu.
Find: Allows the user to move to a sector of the database corresponding to a user defined port, VLAN or
MAC addres s.
VID: The VLAN ID of the VLAN of which the port is a member.
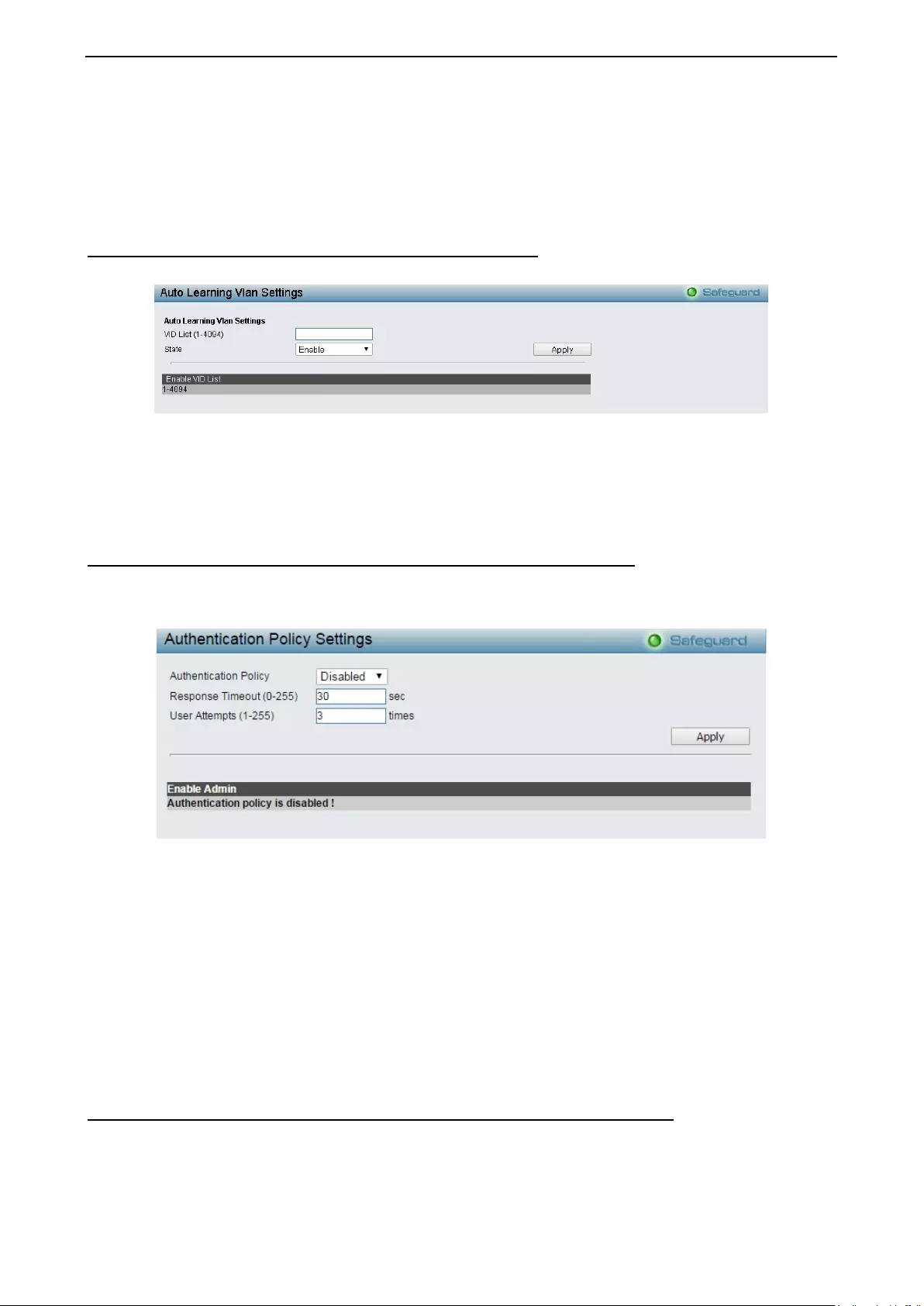
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
100
M AC Add ress: The MAC address entered into the address table.
Port: The port to which the MAC address above corresponds.
Type: Describes the method which the Switch discovered the MAC address. The possible entries are
Dynamic, Self, and Static.
View All Entry: Clicking this button will allow the user to view all entries of the address table.
Security > MAC Address Table > Au to L earning Vlan Settings
The Auto Learning Vlan Settings page allows you to enable or disable the auto learning VLAN feature.
Figure 4.148 - Security > MAC Address Ta ble > Auto Learning Vlan Settings
VLAN List (1-4094): Enter the VID.
State: Specifies to enable or disable the auto learning VLAN state.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Authentica tion Policy Settings
This feature will enable an administrator-defined authentication polic y for users trying to access the Switch.
When enabled, the device will check the Login Method List and choose a technique for user authentication
upon login.
Figure 4.149 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Policy Se ttings
Authentication Policy: Use the pull-down menu to enable or disable the Authentication Policy on the Switch.
Response Timeout (0 - 255): This f ield will set the t im e the Switc h will w ait for a r esponse of authent icati on
from the user. The user may set a time between 0 and 255 seconds. The default s etti ng is 30 seconds.
User attempts (1 - 255): This comm and will conf igure the m aximum number of times the Switc h will acc ept
authentication attempts. Users failing to be authenticated after the set amount of attempts will be denied
access to the Switch and will be lock ed out of f urther authenticat ion attem pts. Comm and line interf ace users
will have to wait 60 seconds before another authentication attempt. Telnet and web users will be
disconnec ted from t he S wit ch. T he us er m a y set the n umber of attempts from 1 to 255. T he d efault setting is
3.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Application Authentication Settings
The Application Authentication Settings page allows user to configure switch configuration applications
(Console, Telnet, SSH, HTTP) for login at the user level and at the administration level (Enable Admin
)
utilizing a previously configured method list.
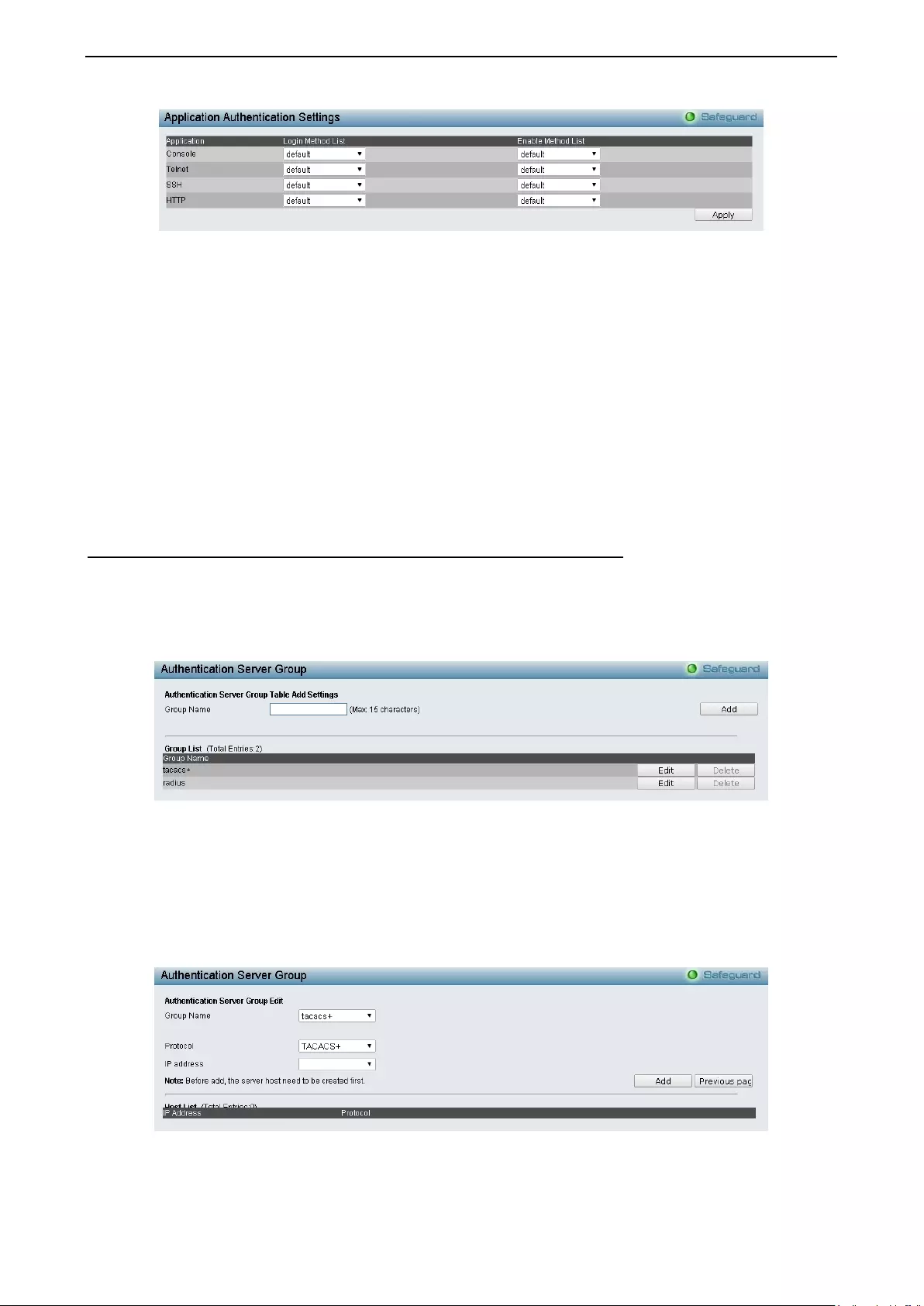
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
10
01
1
Figure 4.150 – Security > Access Authentication control > Application Authentication Settings
Application: Lists the configuration applications on the Switch. The user may configure the Login Method
List and Enable Method List for authentication for Console, Telnet application, SSH and the WEB (HTTP)
application.
Login Method List: Using the pull-down menu, configure an application for normal login on the user level,
utilizing a previously conf igured m ethod list. The user m ay use the default Method List or other Method List
configured by the user.
Enable Method List: Using the pull-down m enu, configur e an ap plication f or norm al login on t he user level,
utilizing a previously conf igured m ethod list. The user m ay use the default Method List or other Method List
configured by the user.
Click Apply to implement configuration changes.
Securit y > Access Authentication Control > Authentication Server Group
A server group is a technique used to group TACACS+ and RADIUS server hosts into user-defined
categories for auth entic atio n using m ethod lis ts. T he u ser m a y define t he t ype of s erver group by prot ocol or
by previously defined server group. The Switch has three built-in Authentication Server Groups that cannot
be removed but can be modified.
To add a user-defined group to the list, click the Add button in the Authentication Server Group page.
Figure 4.151 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server Group
Simply enter a group name of no more than 15 alphanumeric characters to define the user group to add.
After c lic king Apply, the new user-def ine d gr o up wil l b e disp layed in th e Server Group table. Here, it can b e
configured as the user desires.
F
The Switch has two built-in Authentication Server Groups that cannot be removed but can be modified. To
modify a particular group, click Edit button, which will then disp lay the following window.
Figure 4.152 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server Group-Edit
Select Group Name, Protocol and IP address then click Add to implement the changes.
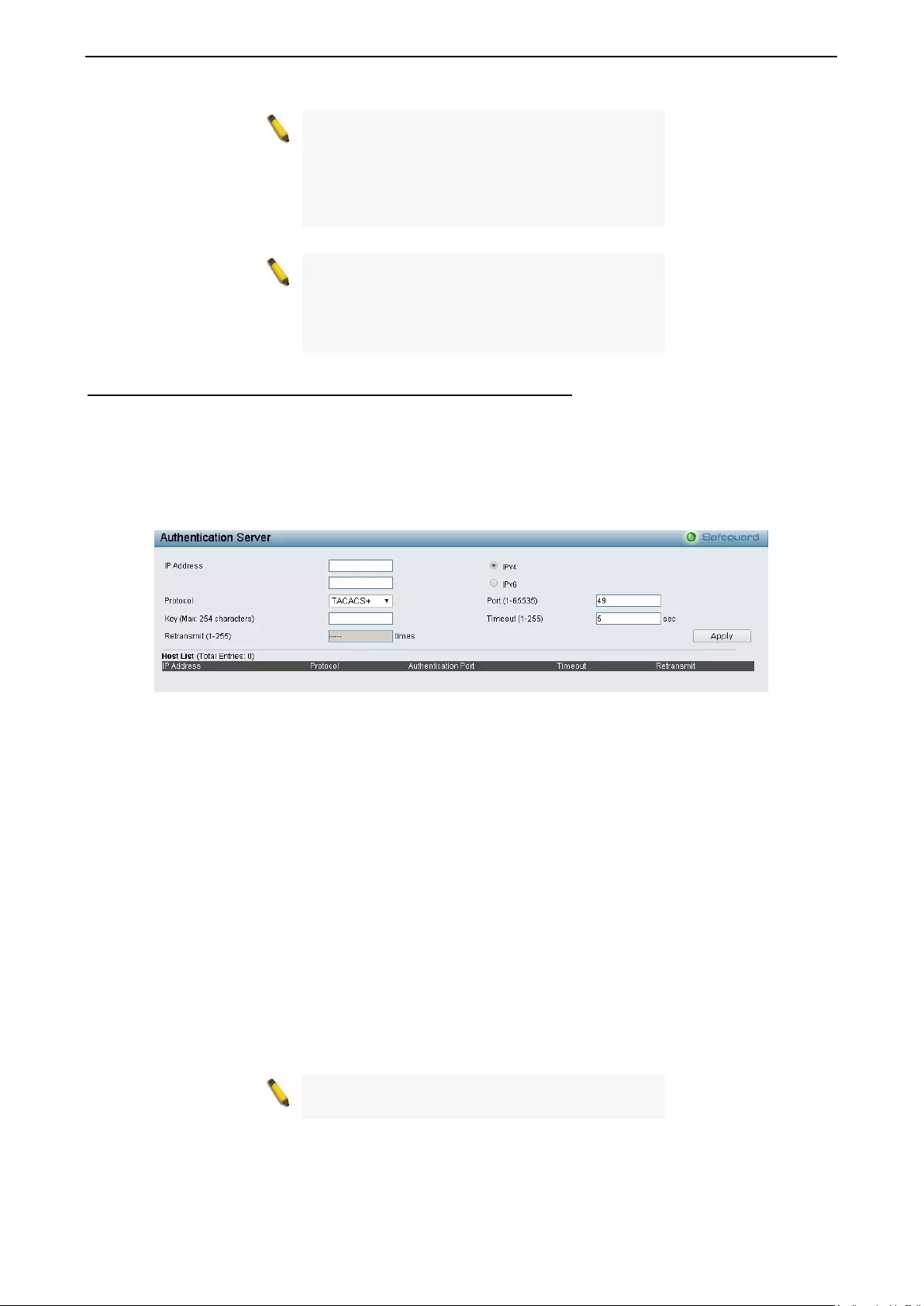
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
102
NOTE:
The user must configure Authentication
Server
Hosts using the Authentication Server
Hosts page
before adding hosts to the list.
Authentication Server Hosts must be configured
for their specific protocol on a remote centralized
server before this function can work properly.
NOTE: The two built in server groups can only
have server hosts running the same TACACS
daemon. The TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols
are separate entities and are not compatible with
each other.
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Authentica tion Server
This Authentication Server page will set user-defined Authentication Server Hosts for the TACACS+ and
RADIUS security protocols on the Switch. When a user attempts to access the Switch with Authentication
Policy enabled, the Switch will send authentication packets to a remote TACACS+ or RADIUS server host on
a remote host. The TACACS+ or RADIUS server host will then verify or deny the request and return the
appropriat e mess age to the Switch. Mor e than one a uthentication pr otocol can be run on the s ame physic al
server host but, remember that TACACS+ and RADIUS are separate entities and are not compatible with
each other. The maximum supported number of server hosts is 16.
Figure 4.153 – Security > Access Authentication control > Authentication Server
To add an Authentication Server Host:
IP Address: Select IPv4 or IPv6 and enter the IP addr es s .
Protocol: The protocol used by the server host. The user may choose one of the following:
TACACS+ – Enter this parameter if the server host utilizes the TACACS+ protocol.
RADIUS – Enter this parameter if the server host utilizes the RADIUS protocol.
Key: Authentication key to be shared with a configured TACACS+ or RADIUS servers only. Specify an
alphanumeric string up to 254 characters.
Port (1 - 65535): Enter a number between 1 and 65535 to define the virtual port number of the
authentication protocol on a server host. The default port number is 49 for TACACS+ server and 1813 for
RADIUS servers but the user may set a unique port number for higher security.
Timeout (1 - 255): Enter the time in seconds the Switch will wait for the server host to reply to an
authentication request. The default value is 5 seconds.
Retransmit (1 - 255): Enter the value in the retransmit field to change how many times the device will resend
an authentication request when the TACACS server does not respond.
Click Apply to add a new Authentication Server Host.
NOTE: More than one authentica tion pr otocol can
be run on the same physical server host.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
10
03
3
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Login Method Lists
This feature will configure a user-defined or default Login Met hod List of auth entication tech niques for us ers
logging on t o the Switch . Succes sful login us ing any of these techniq ues will gi ve the user a "User" pri vilege
only. To upgrade his or her status to the administrator level, the user must use the Enable Admin windo w, in
which the user must enter a previously configured password, set by the administrator.
The Switch contains one Method List that is set and cannot be removed, yet can be modified. To delete a
Login Metho d L is t def ine d b y the us er, c l ick Delete button. T o modif y the Login M etho d Lis t, c l ick Edit button.
Figure 4.154 – Security > Access Authentication control > Login Method Lists
To define a Login Method List, set the following parameters and click Apply:
Method List Name: Enter a method list name defined by the user of up to 15 characters.
Priority 1, 2, 3, 4: The user may add one, or a combination of up to four of the following authentication
methods to this method list:
none – Adding this parameter will require an authentication to access the Switch.
local – Adding this p arameter will require the user to be authenticated using the local user account
database on the Switch.
tacacs+ – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the TACACS+
protocol from a remote TACACS+ server.
radius – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the RADIUS protocol from a
remote RADIUS server.
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Enable Method Lists
The Enable Method Lists page is used to set up Method Lists to promote users with user level privileges to
Administrator (Admin) level privileges using authentication methods on the Switch. Once a user acquires
normal user level privileges on the Switch, he or she must be authenticated by a method on the Switch to
gain administrator privileges on the Switch, which is defined by the Administrator. A maximum of eight
Enable Method Lists can be implemented on the Switch, one of which is a default Enable Method List. This
default Enab le Meth od Lis t c annot be delet e d but can be config ur ed.
To delete an Enable Method List defined by the use, click Delete button to the entry desired to be deleted.
To modify and Enable Method List, click Edit button to make the changes and click Apply.
Figure 4.155 – Security > Access Authentication control > Enable Method Lists
To define an Enable Login Method List, set the following parameter and click Apply:
Method List Name: Enter a method list name defined by the user of up to 15 characters.
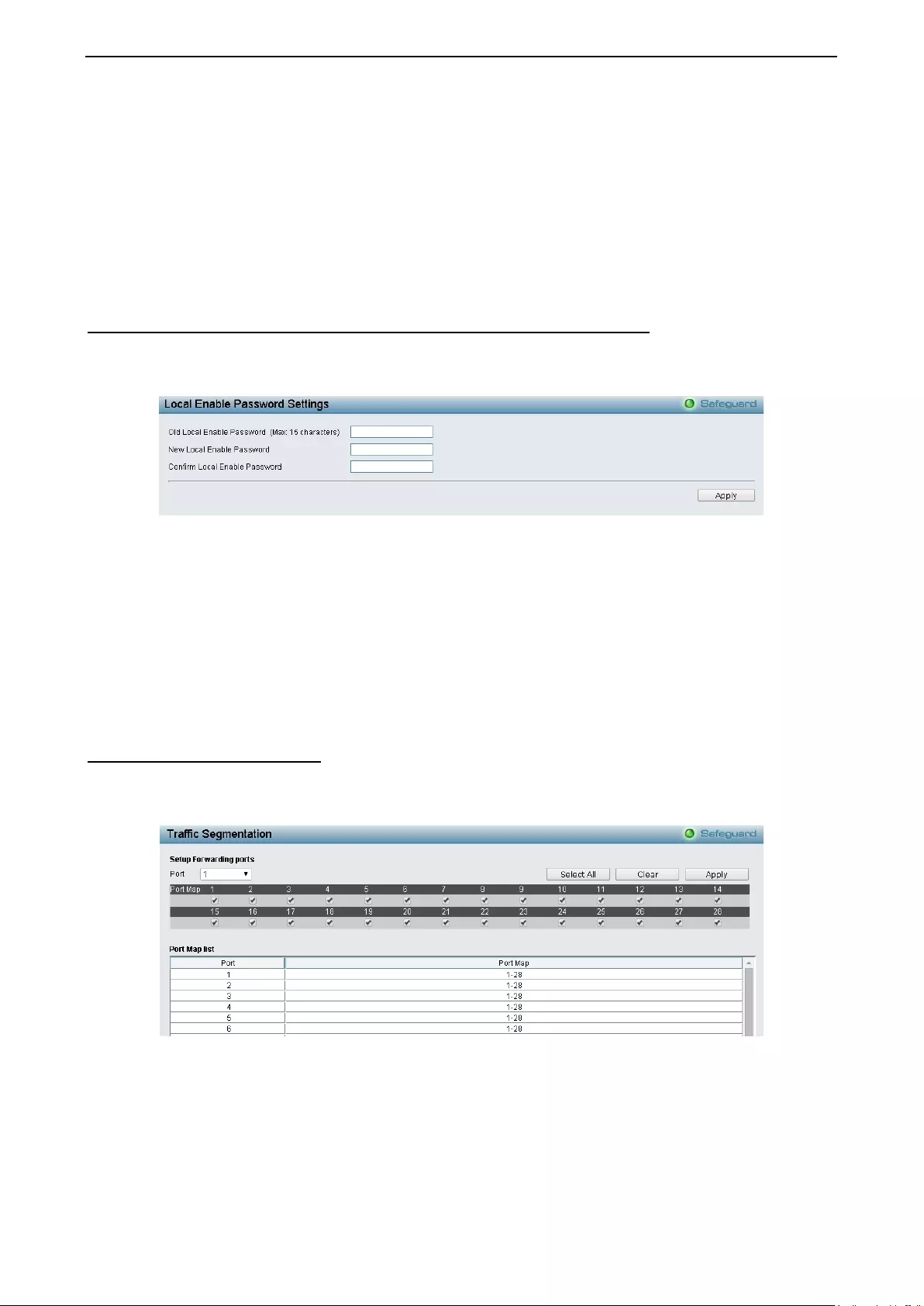
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
104
Priority 1, 2, 3, 4: The user may add one, or a combination of up to four of the following authentication
methods to this method list:
none – Adding this parameter will require an authentication to access the Switch.
local – Adding this p arameter will require the user to be authenticated using the local user account
database on the Switch.
tacacs+ – Adding this parameter will require the user to be authenticated using the TACACS+
protocol from a remote TACACS+ server.
radius – Ad ding this para meter will require th e user to be authe nticated using t he RADIUS protoco l
from a remote RADIUS server.
Securi ty > Access Authenticati o n Control > Local Enable Password Settings
The Local Enable Password Settings page allows user to configure the locally enabled password. When a
user chooses the "local_enable" method to promote user level privileges to administrator privileges, he or
she will be prompted to enter the password configured here that is locally set on the Switch.
Figure 4.156 – Security > Access Authentication control > Local Enable Password Settings
To set the Local Enable Password, set the following parameters and click Apply:
Old Local En able Passw ord: If a pass word w as pr e vi ously configure d f or this entry, ent er it h er e i n order t o
change it to a new password.
New Local Enable Password: Enter the new password that you wish to set on the Switch to authenticate
users attemptin g to acces s A dm inistrator Level priv ileges on t he S witch. The use r m a y set a passwor d of up
to 15 characters.
Confirm Local Enable Password: Confirm the new pass wor d ent er ed ab ov e. E nterin g a dif f er ent pas s wor d
here from the one set in the New Local Enabled field will result in a fail message.
Securi ty > Traffi c Segmentation
This feature provides administrators to limit traffic flow from a single port to a group of ports on a single
Switch. This method of segmenting the flow of traffic is similar to using VLANs to limit traffic, but is more
restrictive.
Figure 4.157 – Security > Traffic Segmentation
To conf igure traffic segmentation specif y a port or All ports from the switch, using the Port pull-down menu
and select Port Map then click Apply to enter the settings into the Switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
Click Select All to select all port maps or click Clear button to uncheck port maps.
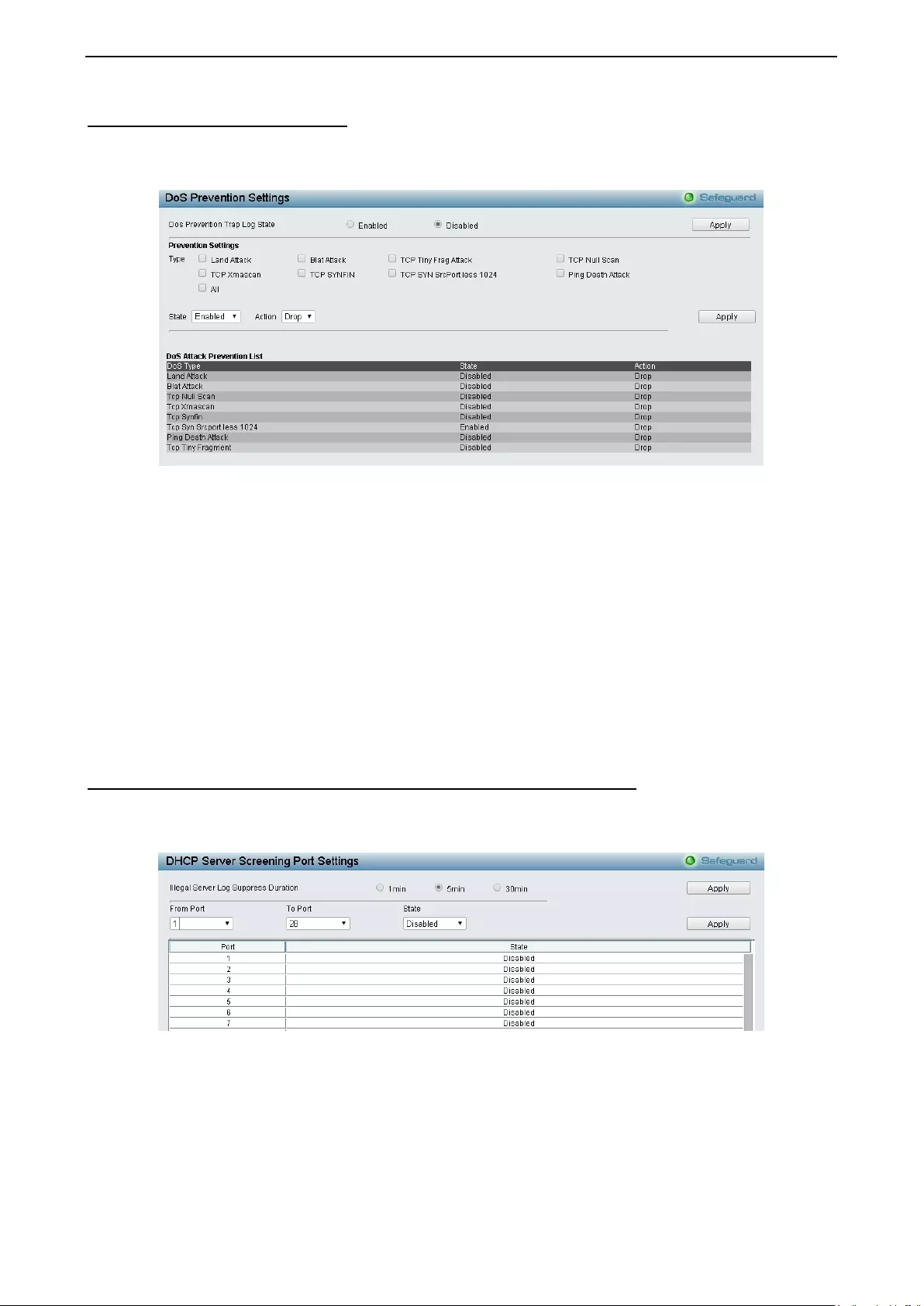
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
10
05
5
Securi ty > DoS Prevention Settin gs
The DoS is a malicious attack against a net work . This attack is designed to st op a netw ork from f unctioning
by floodi ng it with use less traff ic. S ymptom s of a m alicious a ttack includ e the inab ility to acces s an y web site
or a particular web site being unavailable and network performance slowing down.
Figure 4.158 – Security > DoS Prev ent ion Settings
Prevention Settings:
Type: Selec t the attac k types to be prevente d. The t ypes are Land Attack, TCP Tine Frag Attack, TC P Null
Scan, TCP Xmascan, TCP SYNFIN, TCP SYN SrcPortless 1024, Ping Death Attack or All.
Action: Set actio n to Drop or Mirr or the selec ted types of attacks. W hen Mirror was selecte d, also spec ifies
the mirror port.
Mirror Port: Specifies the mirror port to be active.
Priority (0-7): Specifies the priority. The priority range is between 0 and 7.
Rx Rate (64-1024000): Specifies the RX rate. The range is between 64 and 1024000.
State: Specify the state to be enabled or disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > DHC P Se rver Screen i ng > DHCP Server Scre eni ng Po rt Se tt in g s
DHCP Server Screening function allows user to restrict the illegal DHCP server by discarding the DHCP
service from distrusted ports. This page allows you to configure the DHCP Server Screening state for each
port and designed trusted DHCP server IP address.
Figure 4.159– Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening Port Settings
Illegal Server Log Suppress Duration: Specifies the illegal server log suppres s duration for DHCP server
screening port.
From Port/ To Port: Specifies a range of ports to be DHCP server screening port.
State: Specifies the DHCP server screening port to be enabled or disabled.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
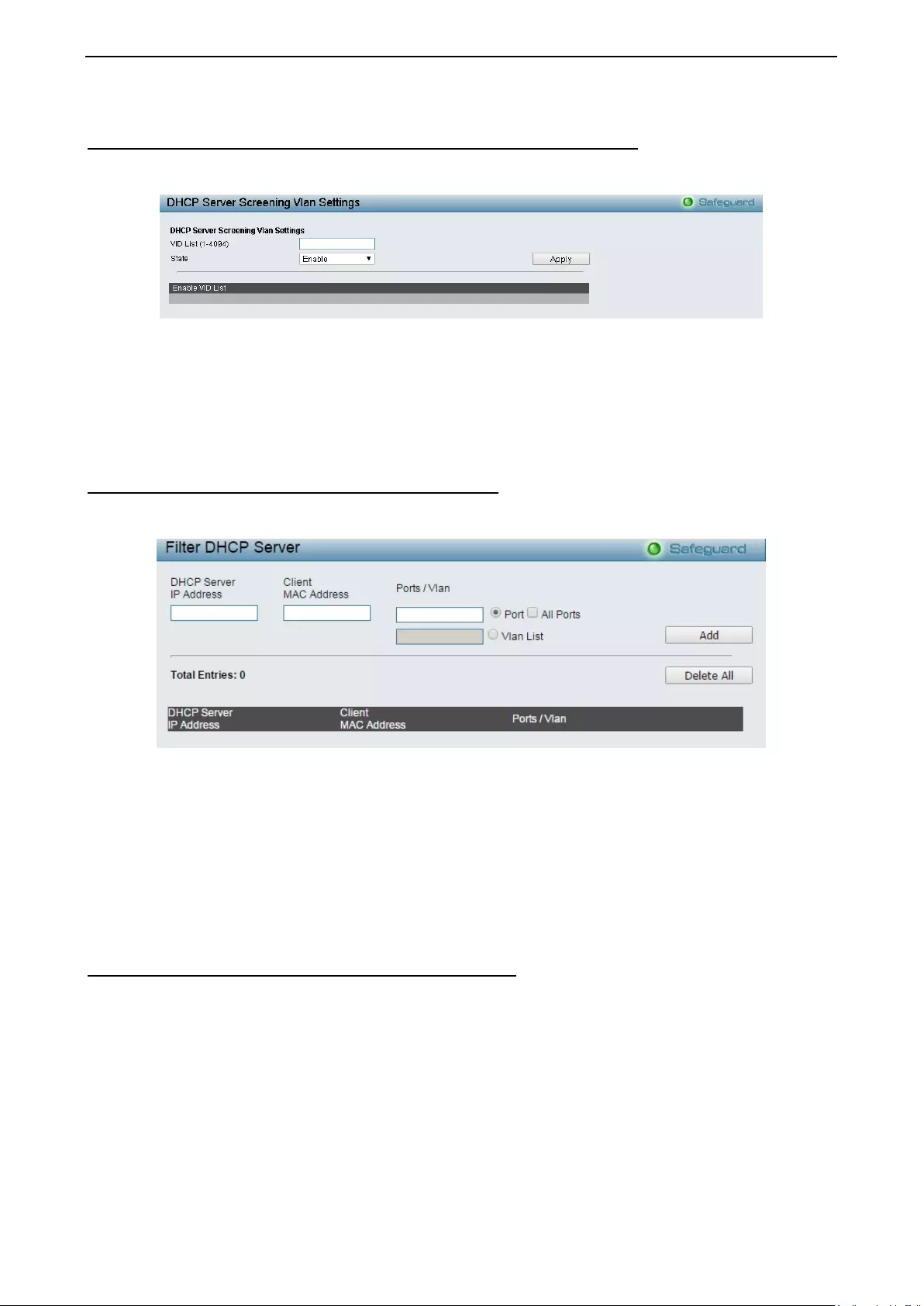
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
106
Security > DHC P Serv er Screen in g > DHCP Server Scr een ing Vlan Sett in gs
The DHCP Server Screening VLAN Settings page allows the user to view and configure the VLAN state for
the DHCP Server Screening.
Figure 4.160– Security > DHCP Server Screening > DHCP Server Screening VLAN Settings
VID List (1-4094): Specifies the VLAN ID to be configured.
State: Specifies to enable or disable the DHCP Server Screening for the specified VLAN.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCP Server
This Filter DHCP Server page allows you to designed trusted DHCP Server IP address and Client MAC
Address.
Figure 4.161 – Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCP Server
To add the DHCP Trusted DHCP Server, set the following fields and click Add. Or click Delete All to remove
all DHCP Server IP Address.
DHCP Se rv er I P Address: Specifies the IP address of the DHCP server to be trusted.
Client MAC Address: Specif y the MAC address of the client which allowed the requested IP address from
the DHCP Address server.
Ports/VLAN: Enter th e l ist of ports to us e th e g iv en f i lt er D HC P s erv er entry. Tick the All Ports chec k box to
select all ports. Or click the VLAN List and enter the VLAN.
Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCPv6 Server
This Filter DHCPv6 Server page allows you to designed trusted DHCPv6 Server IP address.
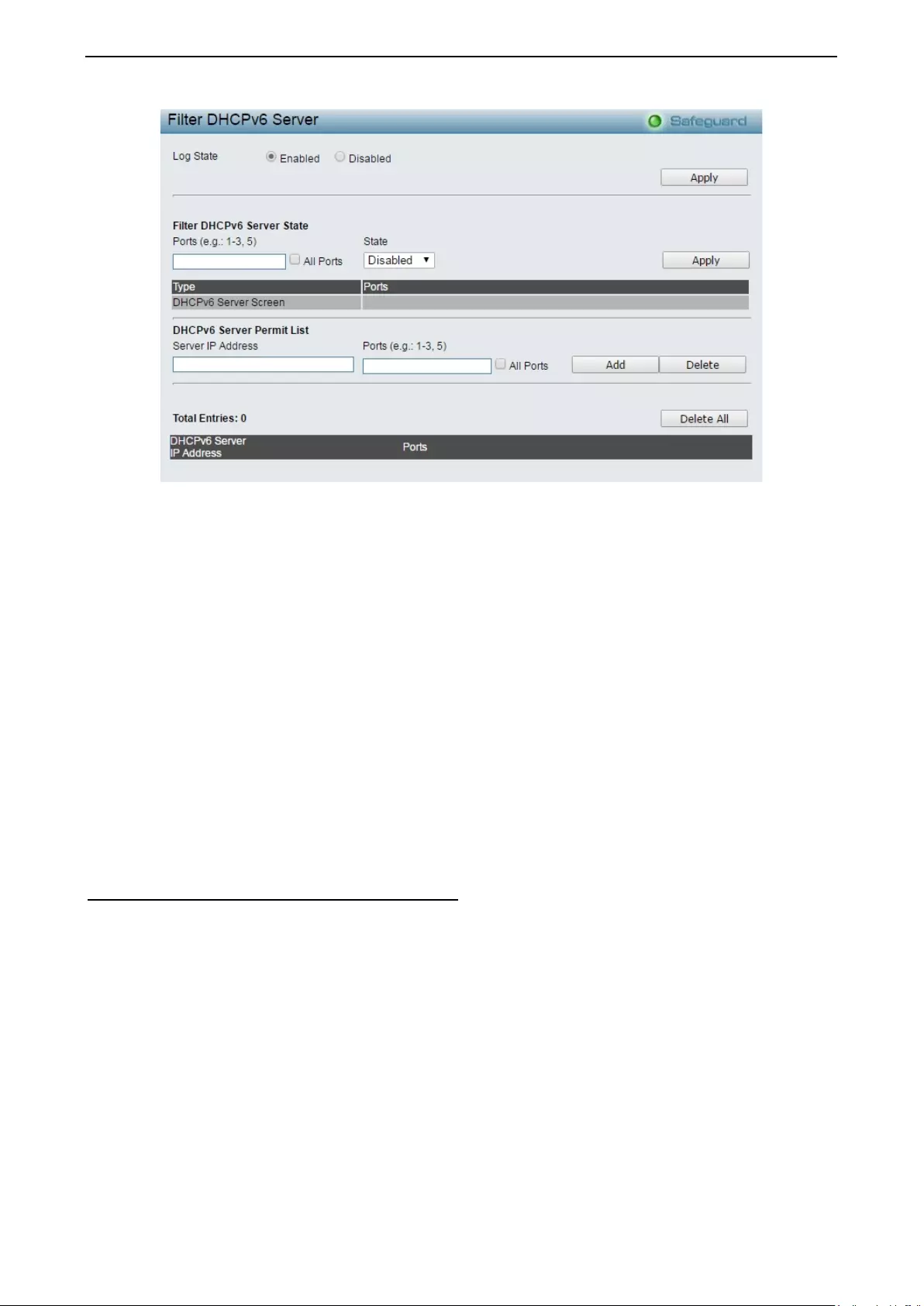
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
10
07
7
Figure 4.162 – Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter DHCPv6 Server
Log State: Specify to enable or disable the log state for filter DHCPv6 server.
Click Apply to makes effects.
Filter DHCPv6 Server State:
Ports: Specify the ports, or select All Ports.
State: Specify to enable or disable the filter DHCPv6 server state for the specified ports.
Click Apply to makes effects.
DHCPv6 Server Permit List:
Server IP Address: Specify the IP address for the DHCPv6 server.
Ports: Specify the ports, or select All Ports.
Click the Add button to add a DHCPv6 server permit list or click the Delete button to remove a DHCPv6
server permit list.
Click the Del ete All button to remove all DHCPv6 server permit list.
Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter ICMPv6
This Filter ICMPv6 page al lo ws you to designed trusted ICMPv6 Server IP address.
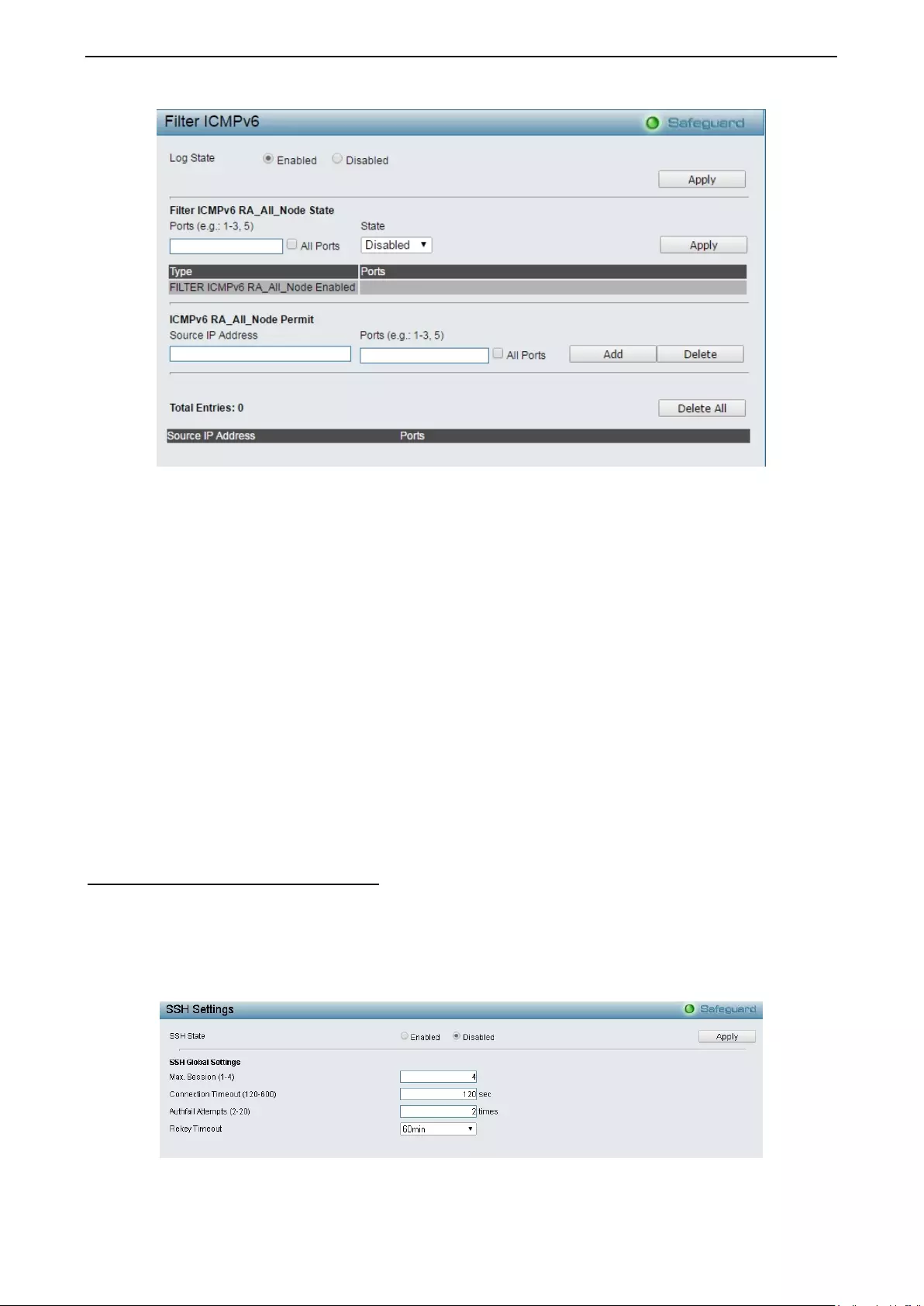
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
108
Figure 4.163 – Security > DHCP Server Screening > Filter ICMPv6
Log State: Specify to enable or disable the log state for filter ICMPv6 server.
Click Apply to makes effects.
Filter ICMPv6 RA_All_Node State:
Ports: Specify the ports, or select All Ports.
State: Specify to enable or disable the filter ICMPv6 RA_All_Node state for the specified ports.
Click Apply to makes effects.
ICMPv6 R A_All_Node Permit:
Server IP Address: Specify the IP address for the ICMPv6 RA_All_Node Permit.
Ports: Specify the ports, or select All Ports.
Click the Add button to add an ICMPv6 RA_All_Node permit list or click the Delete button to remove a
ICMPv6 RA_All_Node permit list.
Click the Del ete All button to remove all ICMPv6 RA_All_Node permit list.
Security > SSH Settings > SSH Settings
SSH is an abbreviation of Secure Shell, which is a program allowing secure remote login and secure network
services over an insecure network. It allows a secure login to remote host computers, a safe method of
executing commands on a remote end node, and will provide secure encrypted and authenticated
communication between two non-trusted hosts. SSH, with its array of unmatched security features is an
essentia l t ool in to day’s net wor king enviro nment. It is a po werf ul guard ia n a gai ns t numerous existing sec ur ity
hazards that now threaten network communications.
Figure 4.164 – Security > SSH Settings > SSH Setti ngs

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
10
09
9
To configure the SSH server on the Switch, modify the following parameters and click Apply:
SSH State: Enabl ed or Disabl ed SSH on the Switch. The default is Disabled.
Max Session (1 - 4): Enter a value between 1 and 4 to set the number of users that may simultaneously
access the Switch. The default setting is 1.
Connection Timeout (120 - 600): Allows the user to set the connection timeout. The use may set a time
between 120 and 600 seconds. The default setting is 120 seconds.
Authfail Attempts (2 - 20): Allows the Administrator to set the maximum number of attempts that a user
may tr y to log on t o th e SSH Server ut ilizing t he S SH auth ent ication. Aft er the m ax im um num ber of attem pts
has been exceeded, the Switch will be disconnected and the user must reconnect to the Switch to attempt
another login. The number of maximum attempts may be set between 2 and 20. The default setting is 2.
Rekey Timeout: Using the pull-down menu us es this field to set the time per iod that the Switch will change
the security shell encryptions. The available options are Never, 10 min, 30 min, and 60 min. The default
setting is 60 min.
Security > SSH Settings > SSH Authmode and Algorithm Settin gs
The SSH Authentication and Algorithm Settings page allows user to configure the desired types of SSH
algorithms used for authentication encryption.
Figure 4.165 – Security > SSH Settings > SSH Authmode and Algorithm Settings
SSH Authentication Mode Settings:
Password: Allows user to use a locally configured password for authentication on the Switch.
Public Key: This par ameter may be en ab led if the a dm inistr ator wish es to us e a pub lic k e y c onf igur at ion s et
on a SSH server, for authentication on the Switch.
Host Based: This parameter may be enabled if the administrator wishes to use a host computer for
authentication. This parameter is intended for Linux users requiring SSH authentication techniques and the
host computer is running the Linux operating system with a SSH program previously installed.
Encryption Algorithm:
3DES-CBC: Use the check box to enable or disable the Triple Data Encryption Standard encryption
algorithm with Cipher Block Chaining. The default is enabled.
Data Inte g rity Algorithm:
HMAC-MD5: Use the check box to enable the supports of hash for message Authentication Code (HMAC)
MD5 Message Digest (MD5) mechanism.
HMAC-SHA1: Use th e check box to enable the suppo rts of hash f or message Authent ication Code (H MAC)
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) mechanism.
Public Key Algorithm:
HMAC-RSA: Use the check box to enable the supports of Hash for Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
mechanism utilizing the RSA encryption algorithm.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
110
Security > SSH Settings > SSH User Authentication Lists
The SSH User Auth entication L ists page is used t o configure par ameters for us ers attempting to acc ess the
Switch through SSH.
Figure 4.166 – Security > SSH Settings > SSH User Authentication Lists
The user may view the following parameters:
User Name: A name of no more than 15 characters to identify the SSH user. This User Name must be a
previously configured user account on the Switch.
Auth. M ode: The administrator may choos e o ne of the f ollo win g t o s et th e a uth or i zat ion for user s attem pting
to access the Switch.
Host Based – This parameter should be chosen if the administrator wishes to use a remote SSH
server for authentication purposes.
Password – This parameter should be chosen if the administrator wishes to use an administrator-
defined password for authentication. Upon entry of this parameter, the Switch will prompt the
administrator for a password, and then to re-type the password for confirmation.
Public Key – This param eter should be c hosen if the administrator wishes to us e the public key on
an SSH server for authentication.
Host Name: Enter an alphanumeric string of no more than 32 characters to identify the remote SSH user.
This parameter is only used in conjunction with the Host Based choice in the Auth. Mode field.
Host IP: Enter the corresponding IP address of the SSH user. This parameter is only used in conjunction
with the Host Based choice in the Auth. Mode field.
MAC-based Access Control (MAC)
MAC-based Access Control is a m et hod t o a uthe ntic a t e an d a uthorize acc es s us i ng e ith er a port or hos t. For
port-based MAC, the method dec ides p ort access rights, while f or host-based MAC, the m ethod determ ines
the MAC access rights.
A MAC us er m ust be aut henticat ed befor e be ing grant ed access to a networ k. Both local authent ication and
remote RADIUS server authentication methods are supported. In M AC-based Access Control, M AC user
information in a local database or a RADIUS server data base is searched for authentication. Following the
authentication result, users achieve different levels of Authorization.
Notes about MAC-based Access Control
There are certain limitations and regulations regarding MAC-based Access Control:
1. Once this feature is enabled for a port, the Switch will clear the FDB of that port.
2. If a port is granted clearance for a MAC address in a VLAN that is not a Guest VLAN, other MAC
addresses on that port must be authenticated for access and otherwise will be blocked by the Switch.
3. A por t ac cepts a maximum of two hundr e d auth enticated M AC address es per p hysical por t of a VL AN that
is not a Guest VLAN. Othe r MAC addresses attem pting authentication on a port with the m aximum number
of authenticated MAC addresses will be blocked.
4. Ports that have been enabled for Link Aggregation, Port Security, or GVRP authentication cannot be
enabled for MAC-based Authentication.
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Settings
The MAC-based Access Control Settings page is used to configure the MAC Settings for the MA C-based
Access Control function on the Switch. The user can set the running state, method of authentication, RA
DIUS password, view the Guest VLAN configuration to be associated with the MAC-based Access Control
function of the Switch, and configure ports to be enabled or disabled for the MAC-based Access Control
feature of the Switch. Please rem ember, ports enabled for certain other features, listed previously, cannot
be enabled for MAC-based Access Control.
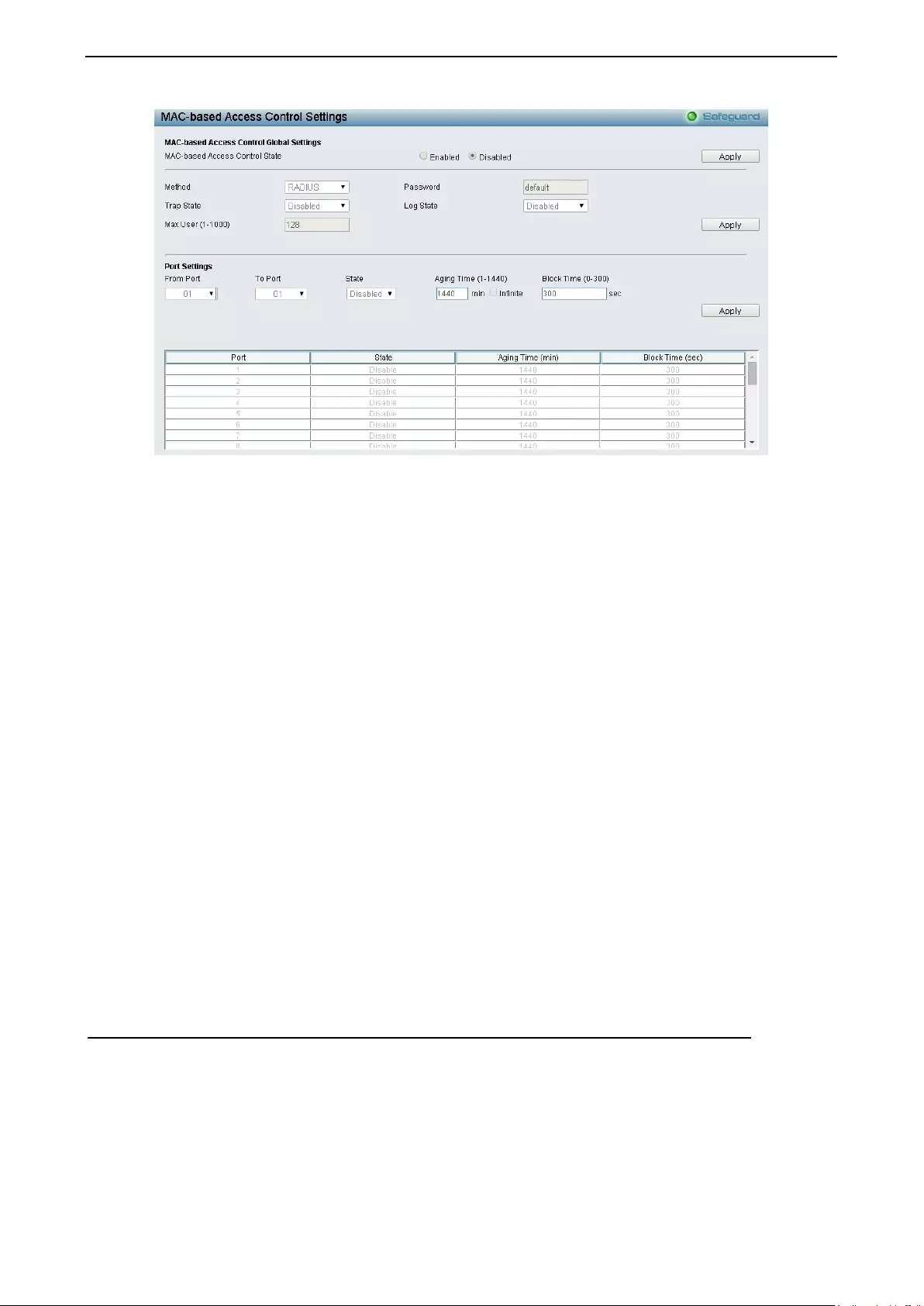
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
11
1
Figure 4.167 – Security > MAC-based Access Contr ol (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Settings
MAC-based Access Control Global Settings:
MAC-based Access Control State: Enable or disable the MAC-based Access Control function on the
Switch. Click Apply button to take effect.
Configuring the MAC Authentication Method:
Method: Specify the type of authentication to be used.
Local – Use this method to utilize the locally set MAC address database as the authenticator for
MAC-based Access Control.
RADIUS – Use this method to utilize a remote RADIUS server as the authenticator for MAC-based
Access Control.
Password: Enter the password for the RADIUS server, which is to be used for packets being sent
requesting authentication. The default password is "default".
Trap State: Enab le or disa ble the MA C-based Access Control trap state. The default is disabled.
Log State: Enable or disable the MAC-based Access Control log state. The default is disabled.
Max User (1-1000): Specify the max users. The value is between 1~1000, and the default is 128.
Click the Apply button to implement the configuration changes.
Port Settings:
From Port / To Port: The ports of range to be configured for MAC-based Access Control.
State: Enable or disable MAC-based Access Control on the port or range of ports.
Aging Time (1-1440): Specify the aging time. The default is 1440.
Block Time (0-300): Specify the block time. The default is 300 and the value is between 1 to 300 seconds.
Click the Apply button to implement the configuration changes.
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Local Settings
Users can set a list of M AC addresses, along with their corresponding target VLAN, which will be
authenticated for the Switch. Once a queried MAC address is matched in this window, it will be placed in the
VLAN associated with it he re. The Switch administrator may enter up to 128 MAC addresses to be
authenticated using the local method configured here.
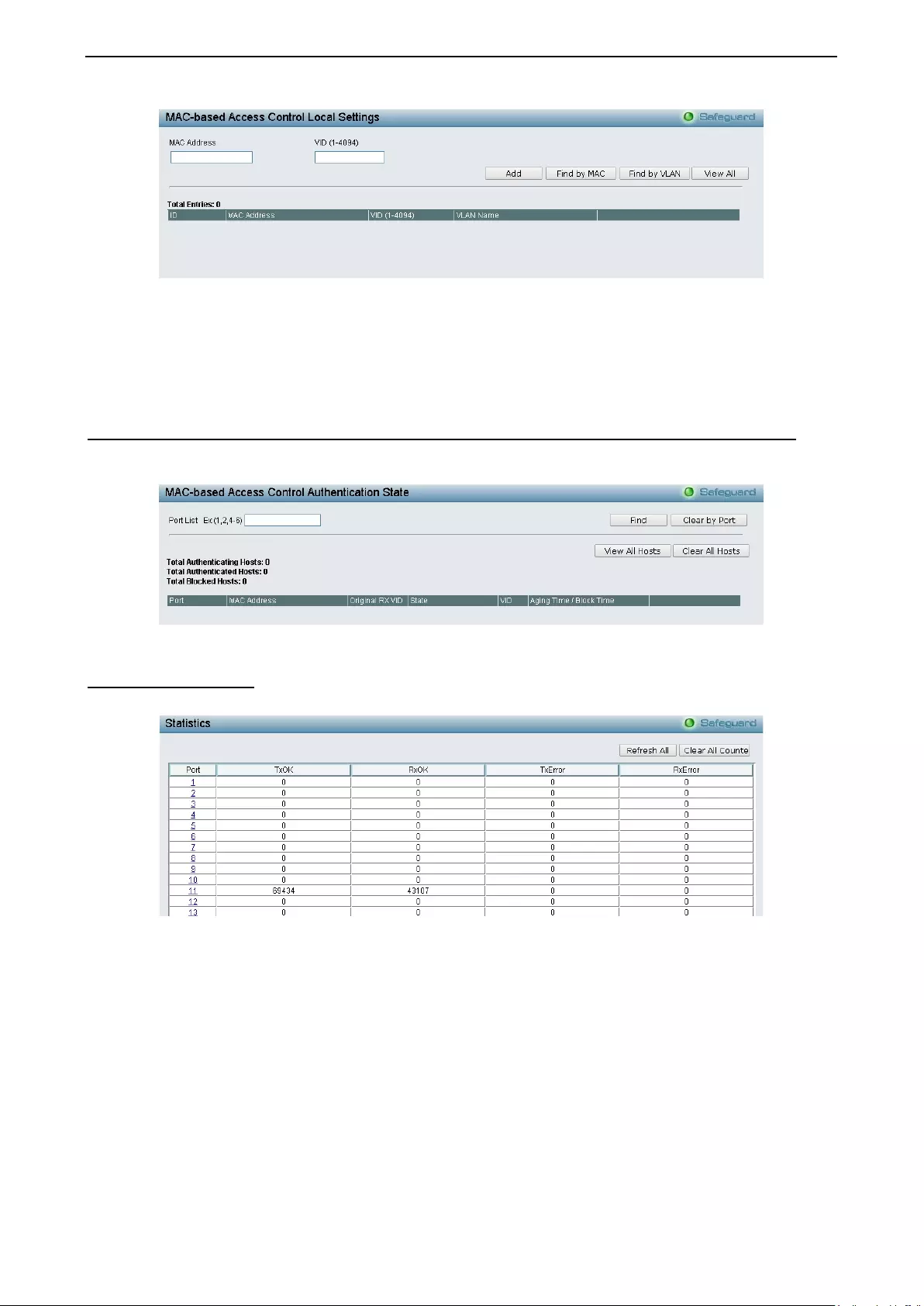
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
112
Figure 4.168 – Security > MAC-based Access Control (M AC) > MAC-based Access Control Local Settings
To add a MAC address to the local authentication list, enter the MAC address and the target VLAN ID into
their appropr ia te fields and click Add. To search for a specific MAC Address, enter the MAC address in the
first field and then click the Find By MAC button. To search for a specific VLAN Name, enter the VID in the
second field and then click the Find By VLAN button.
Security > MAC-based Access Control (MAC) > MAC-based Access Control Authentication State
The MAC-based Access Control Authentication State page allows user to configure the authentication state
of ports.
Figure 4.169 – Security > MAC-based Access Control (M AC) > MAC-base d Access Control Authentication State
Monitoring > Statistics
The Statistics screen displays the status of each port packet count.
Figure 4.170 – Monitori ng > Statistics
Refresh All: Renews the details collected and displayed.
Clear All: To reset the details displayed.
TxOK: Number of packets transmitted successfully.
RxOK: Number of packets received successfully.
TxError: Number of transmitted packets resulting in error.
RxError: Number of received packets resulting in error.
To view the statistics of individual ports, click one of the linked port numbers for details.
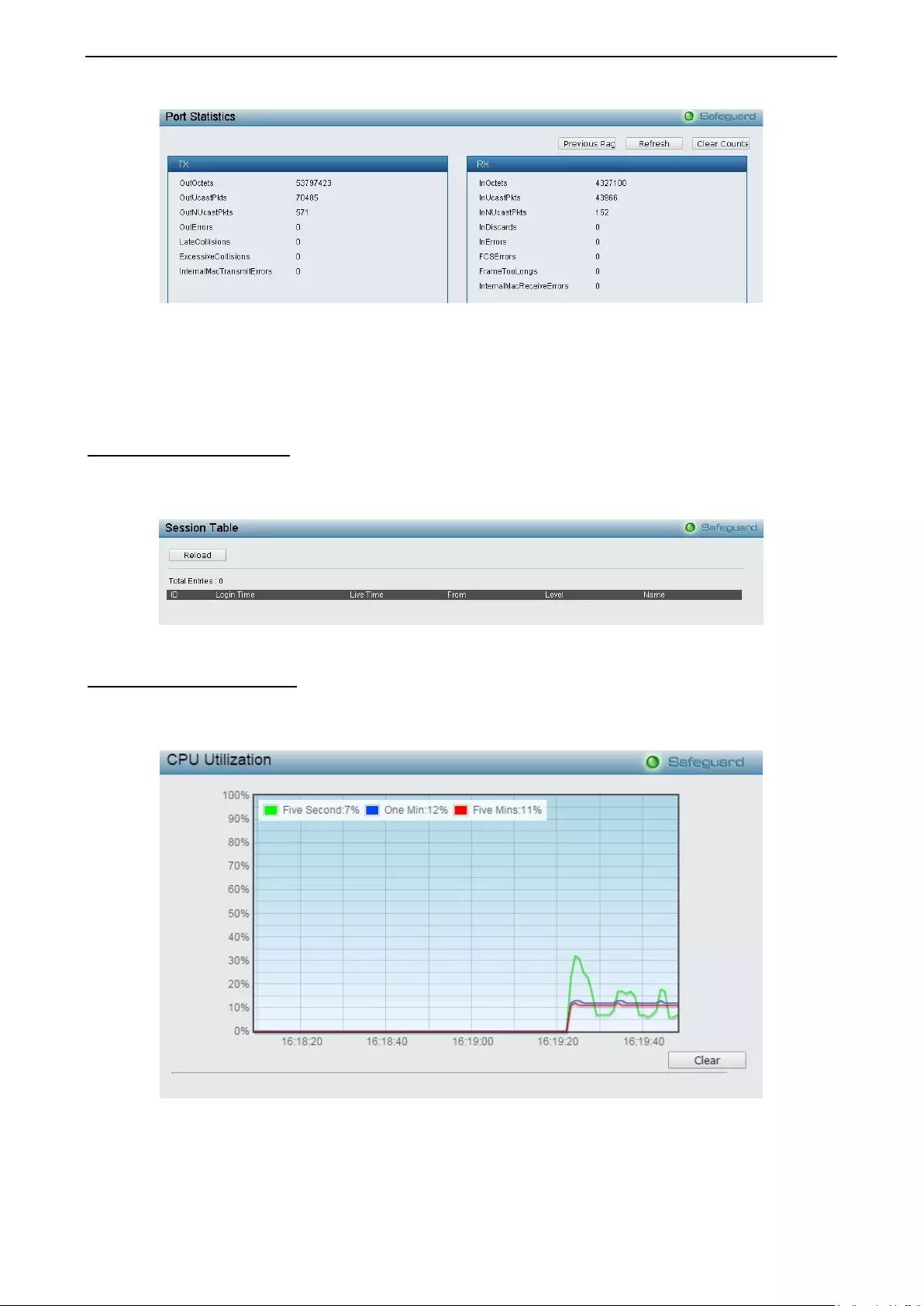
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
13
3
Figure 4.171 – Monitoring > Port Statistics
Previo us Page : Go back to the Statistics main page.
Refresh: To renew the details collected and displayed.
Clear Counter: To reset the details displayed.
Monitoring > S ession Table
The Session Table allows the user to view detailed information on the current configuration session of the
Switch. Information such as the Session ID of the user, initial Login Time, Live Time, configuration
connection From the Switch, Level and Name of the user are displayed. Click Reload to refresh this window.
Figure 4.172 – Monitoring > Session Table
Monitoring > CPU Utilization
The CPU Utilization displays the percentage of the CPU being used, expressed as an integer percentage
and calcul ated as a s im ple avera ge b y tim e interva l. The w indow will autom aticall y refr esh with n e w updated
statistics.
Figure 4.173 – Monitoring > CPU Utilization
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
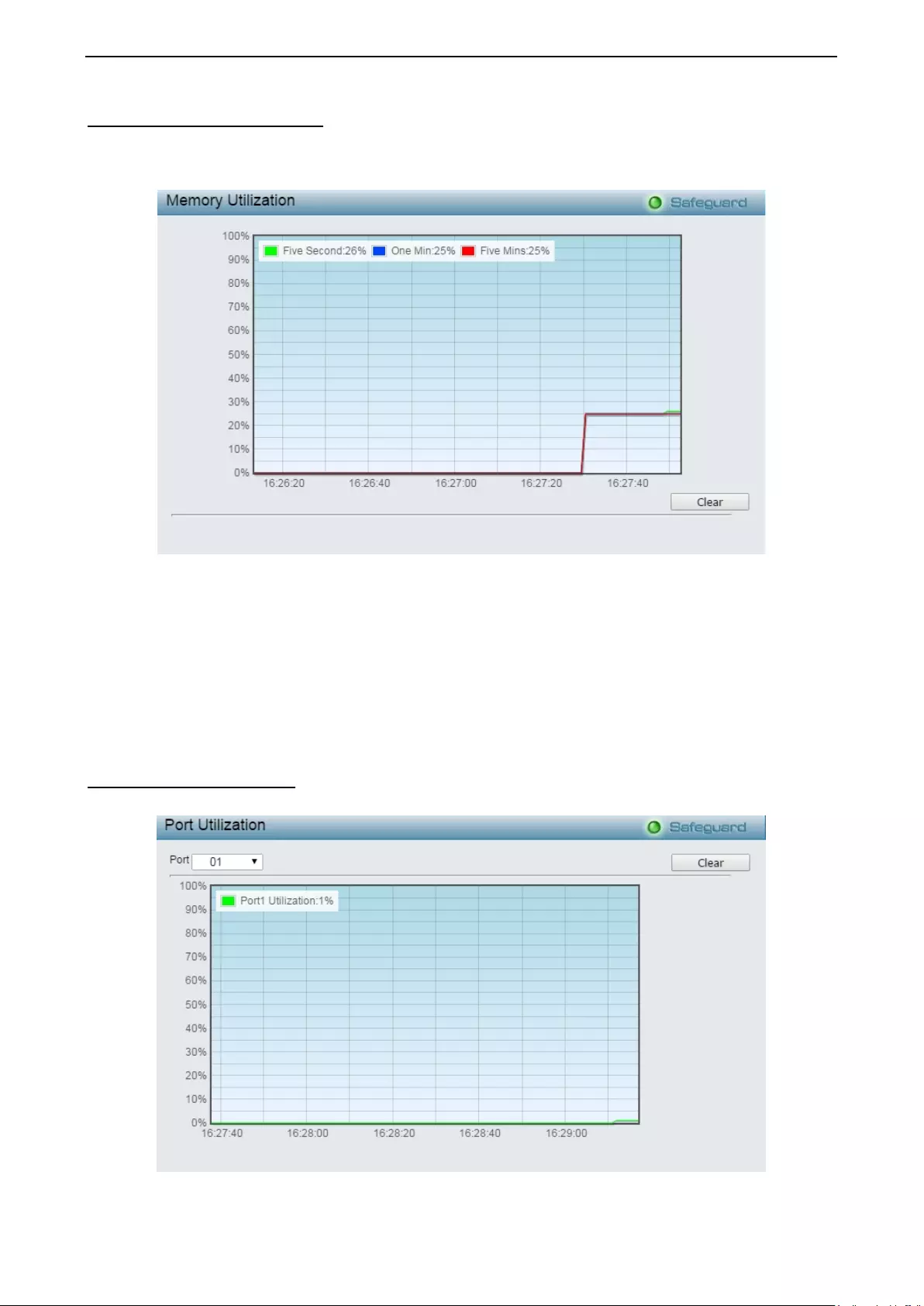
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
114
Monitoring > Memory Utilization
The Memory Utilization displays the percentage of the memory being used, expressed as an integer
percentage and calculated as a simple average by time interval. Click Apply to implement the configured
settings. The window will automatically refresh with new updated statistics.
Figure 4.174 – Monitoring > Memory Utilization
The information is described as follows:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where "s" stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. The def ault value i s
200.
Show/Hide: Check whether to display Five Secs, One Min, and/or F iv e Min s .
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
Monitoring > Port Utilization
The Port Utilization page displays the percentage of the total available bandwidth being used on the port.
Figure 4.175 – Monitori ng > Port Utilization
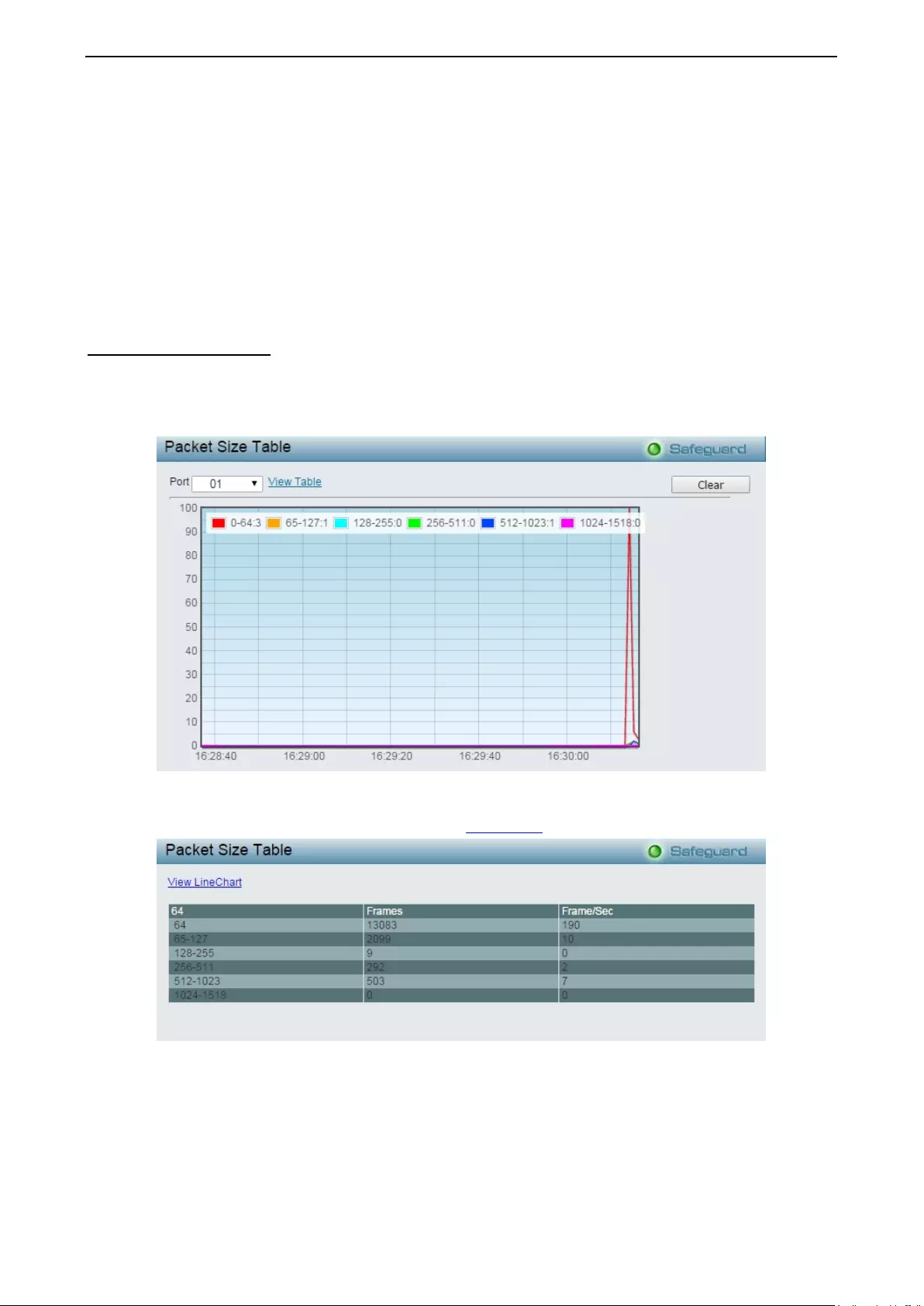
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
15
5
The user may use the r eal-time graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page to view utilization statistics
per port by clicking on a port. Click Apply to make the configurations take effect. The following field can be
set:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where "s" stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be p olled bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
Show/Hide: Check whether to display Utilization.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
Monitoring > Packet Siz e
The W eb Manager all ows pack ets received by the S witch, arra nged in six groups and c lassed b y size, to be
viewed as ei ther a l ine gr ap h or a table. T wo w indows are of fered. T o s elect a port to vie w thes e s t atistics f or,
select t he port b y using the Port pull-do wn m enu. T he us er m ay als o use t he real-tim e graphic of the S witch
at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.176 – Monitoring > Packet Size
To view the Packet Size Analysis Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.177 – Monitoring > Packet Size Table
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led betw een 20 and 200. The def ault value is
200.
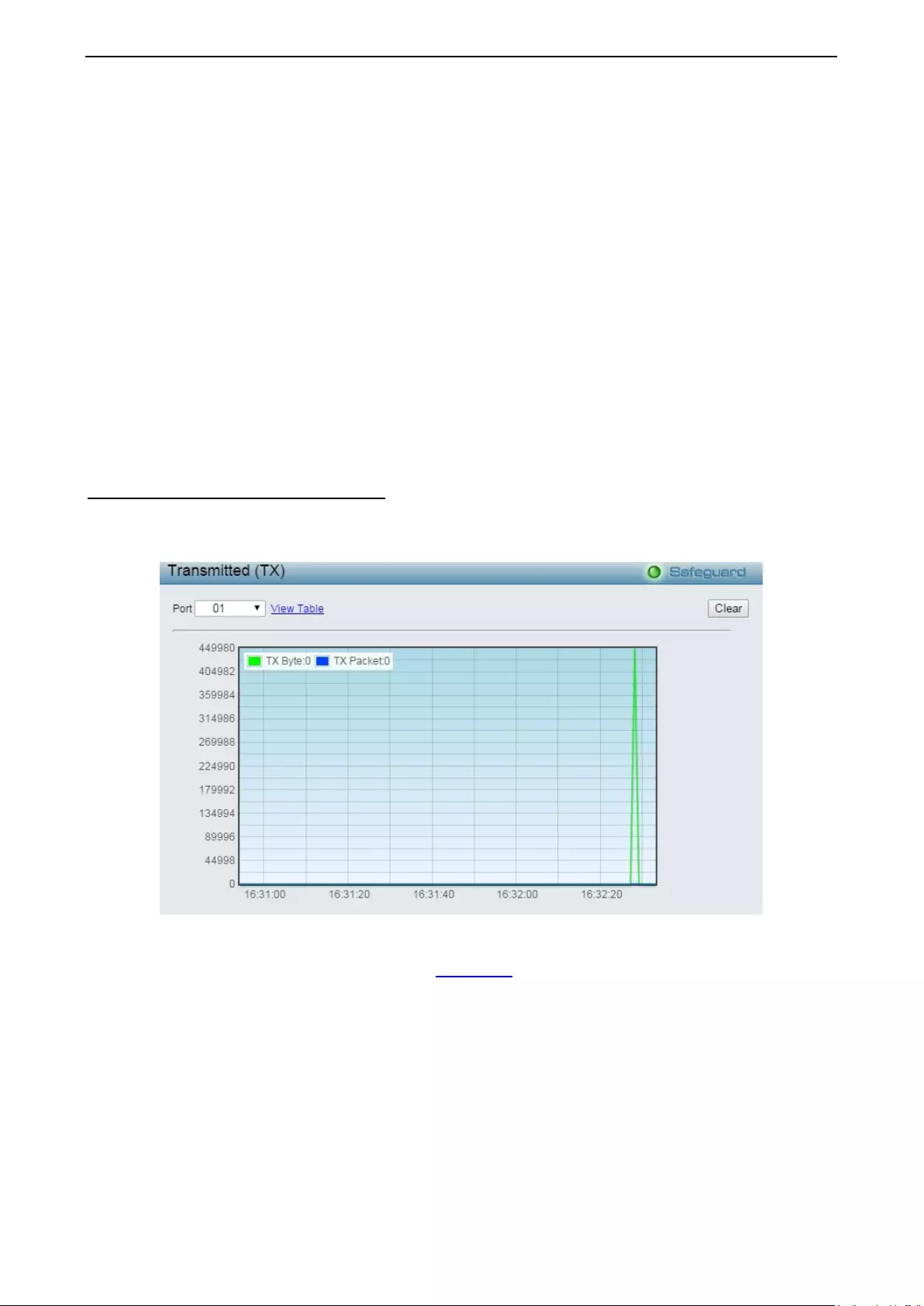
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
116
64: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were 64 octets in length (excluding
framing bits but including FCS octets).
65-127: T he total num ber of pack ets (including bad pack ets) received that were between 65 and 127 octets
in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
128-255: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 128 and 255
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
256-511: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 256 and 511
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
512-1023: The total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were between 512 and 1023
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
1024-1518: T he total n um ber of pac kets (includin g ba d pack ets) r eceived tha t we re betw een 1024 and 1518
octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display 64, 65-127, 128-255, 256-511, 512-1023, and 1024-1518
packets received.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX)
The Transmitted (T X) page displays the following graph of packets transmitted from the Switch. To select a
port to vie w thes e statistics for, use the Port pull-do wn menu. The user m a y also us e the r eal-t ime graphic of
the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.178 - Monitoring > Packets > Transmitted (TX) (line graph for Bytes and Packets)
To view the Transmitte d (TX) Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
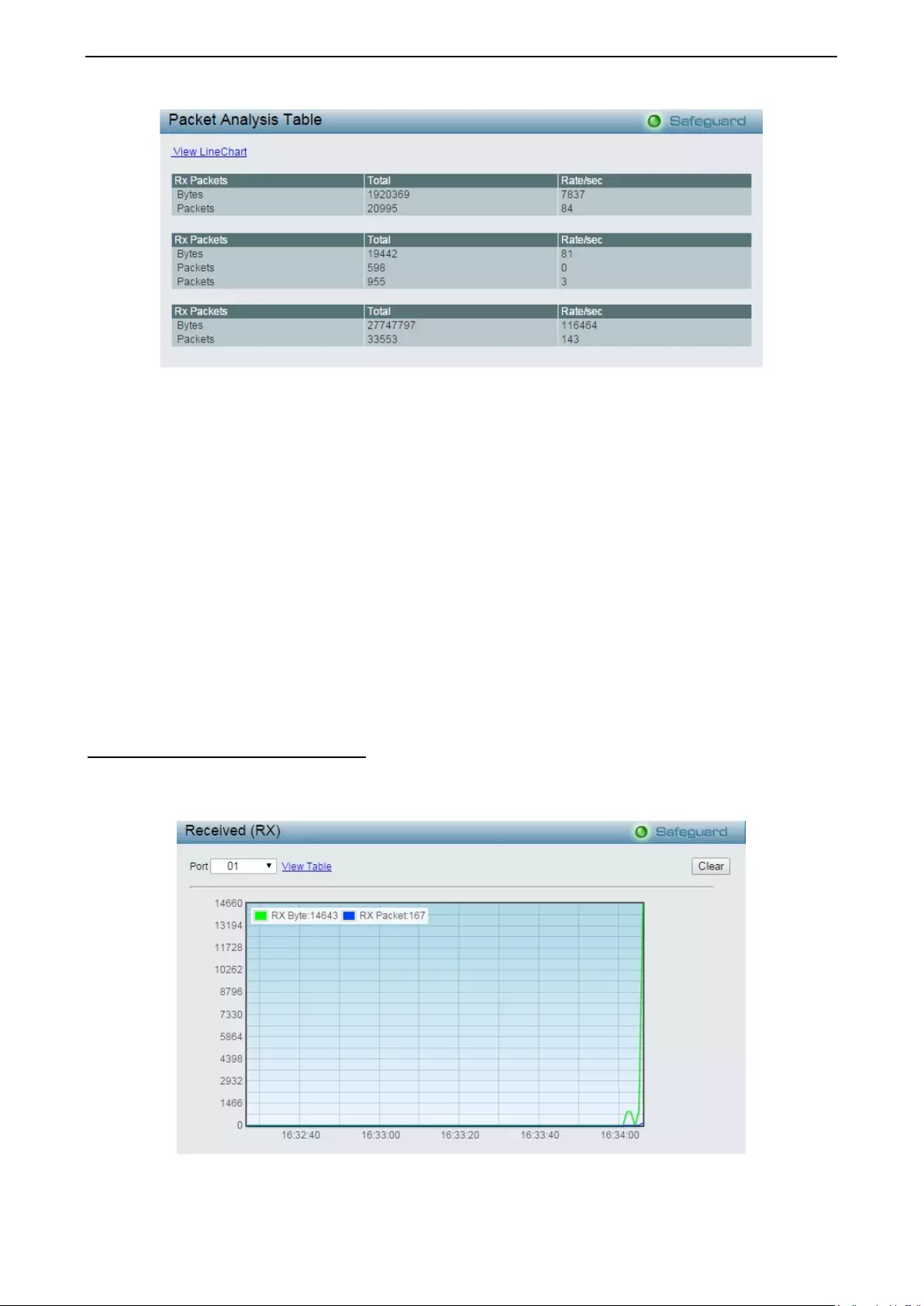
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
17
7
Figure 4.179 - Monitoring > Packet s > Transmitted (TX) (table for Bytes and Packets)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
Bytes: Counts the number of bytes successfully sent from the port.
Packets: Counts the number of packets successfully sent on the port.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were transmitted by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Bytes and Packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX)
The Rec eived (RX) pag e displa ys the follo wing gr aph of pack ets received on the Switch . To select a port to
view these statistics for, use the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time graphic of the
Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.180 - Monitoring > Packets > Received (RX) (line graph for Bytes and Pa ckets)
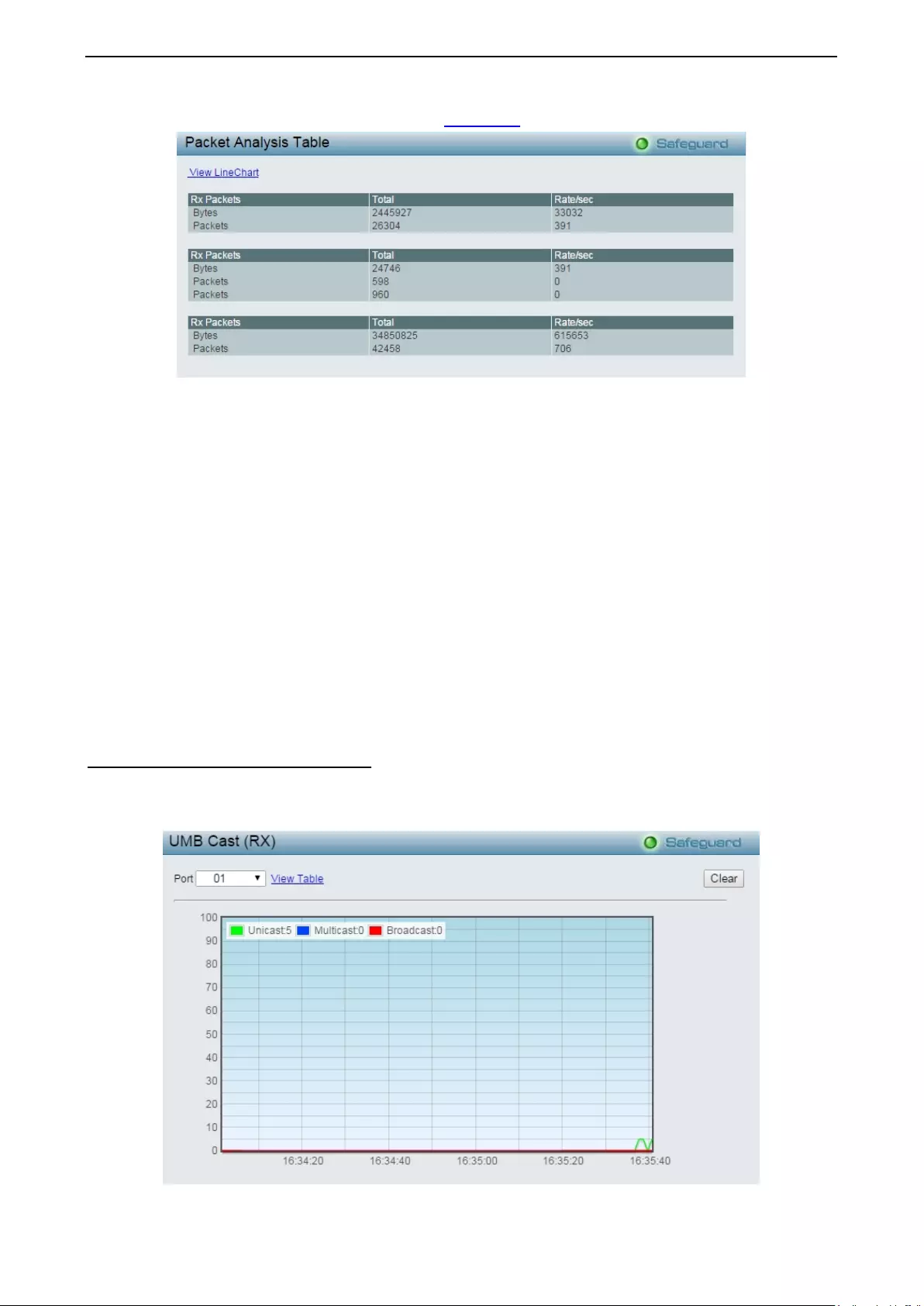
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
118
To view the Received Packets Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.181 - Monitoring > Packet s > Received (RX) (table for Bytes and Packets)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
Bytes: Counts the number of bytes received on the port.
Packets: Counts the number of packets received on the port.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Bytes and Packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX)
The UMB Cast (RX) page displays the following graph of UMB cast packets received on the Switch. To
select a port to view these statistics for, use the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time
graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.182 - Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) (line graph for Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast Packets)
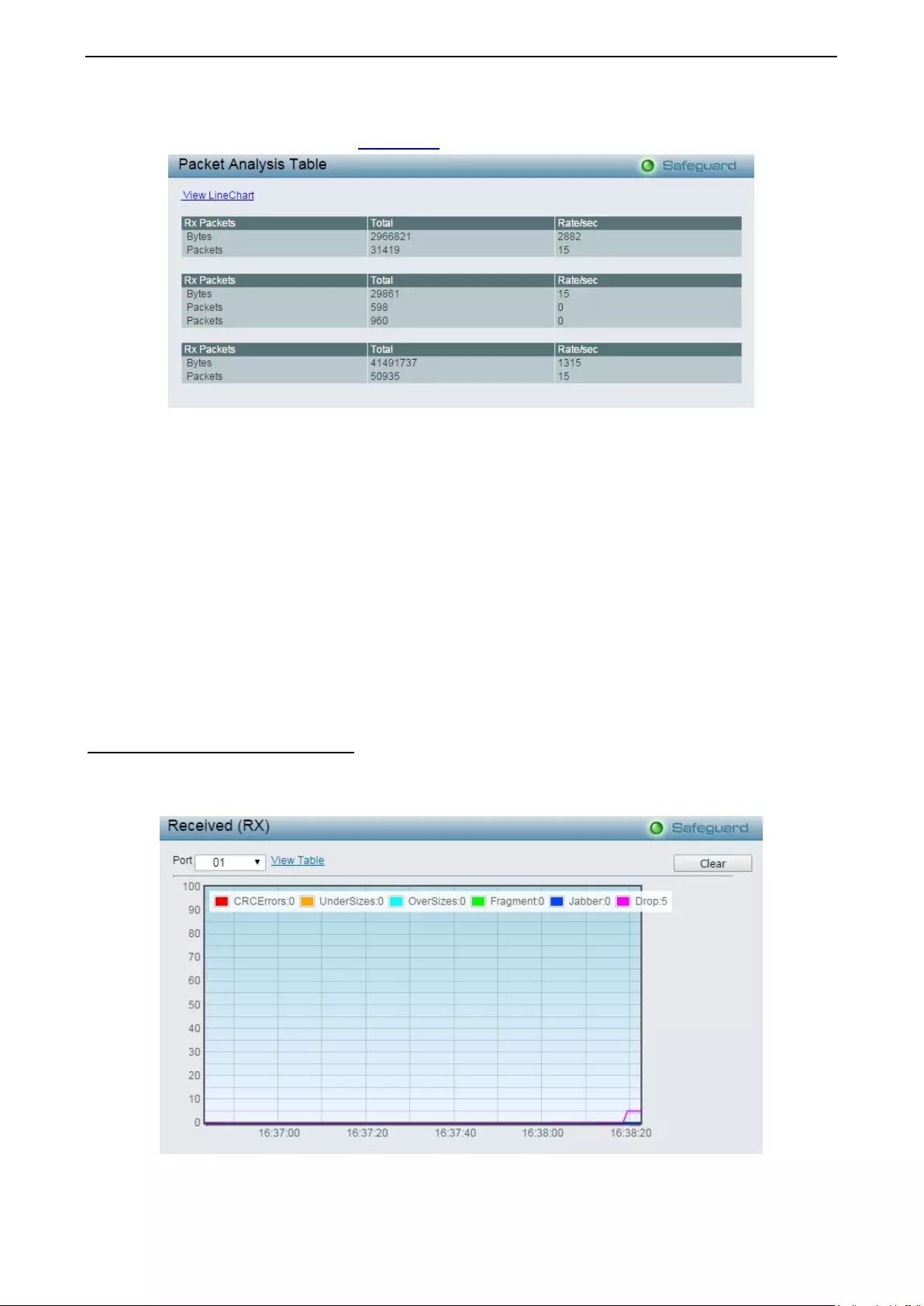
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
11
19
9
To view the UMB Cast Table, click the View Table link, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.183 - Monitoring > Packets > UMB Cast (RX) (table for Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast Packets)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
Unicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a unicast address.
Multicast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a multicast address.
Broadcast: Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a broadcast address.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display Multicast, Broadcast and Unicast packets.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX)
This page dis p lays the following graph of err or packets receive d on th e S witc h. T o s elect a port to v ie w thes e
statistics for, sel ect the p ort b y using the Port pull-down m enu. T he user m ay also use the rea l-time gr aphic
of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
Figure 4.184 - Monitoring > Errors > Received (RX) (line g raph)

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
120
To view the Received Error Packets Table, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.185 - Monitoring > Erro rs > Received (RX) (table)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
CRC Error: Counts otherwise valid packets that did not end on a byte (octet) boundary.
UnderSize: The number of packets detected that are less that the minimum permitted packets size of 64
bytes and have a good CRC. Undersize packets usually indicate collision fragments, a normal network
occurrence.
OverSize: Counts packets received that were longer that 1518 octets, or if a VLAN frame is 1522 oc tets, and
less that the MAX_PKT_LEN. Internally, MAX_PKT_LEN is equal to 1522.
Fragment: The number of packets less than 64 bytes with e ither bad fr aming or an invalid CRC. These are
normally the result of collisions.
Jabber: The number of packets with lengths more than the MAX_PKT_LEN bytes. Internally,
MAX_PKT_LEN is equal to 1522.
Drop: The number of packets that are dropped by this port since the last Switch reboot.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display CRC Error, Under Size, Over Size, Fragment, Jabber, and
Drop errors.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.
Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX)
This page displays the following graph of error packets transmitted on the Switch. To select a port to view
these statistics for, select the port by using the Port pull-down menu. The user may also use the real-time
graphic of the Switch at the top of the web page by simply clicking on a port.
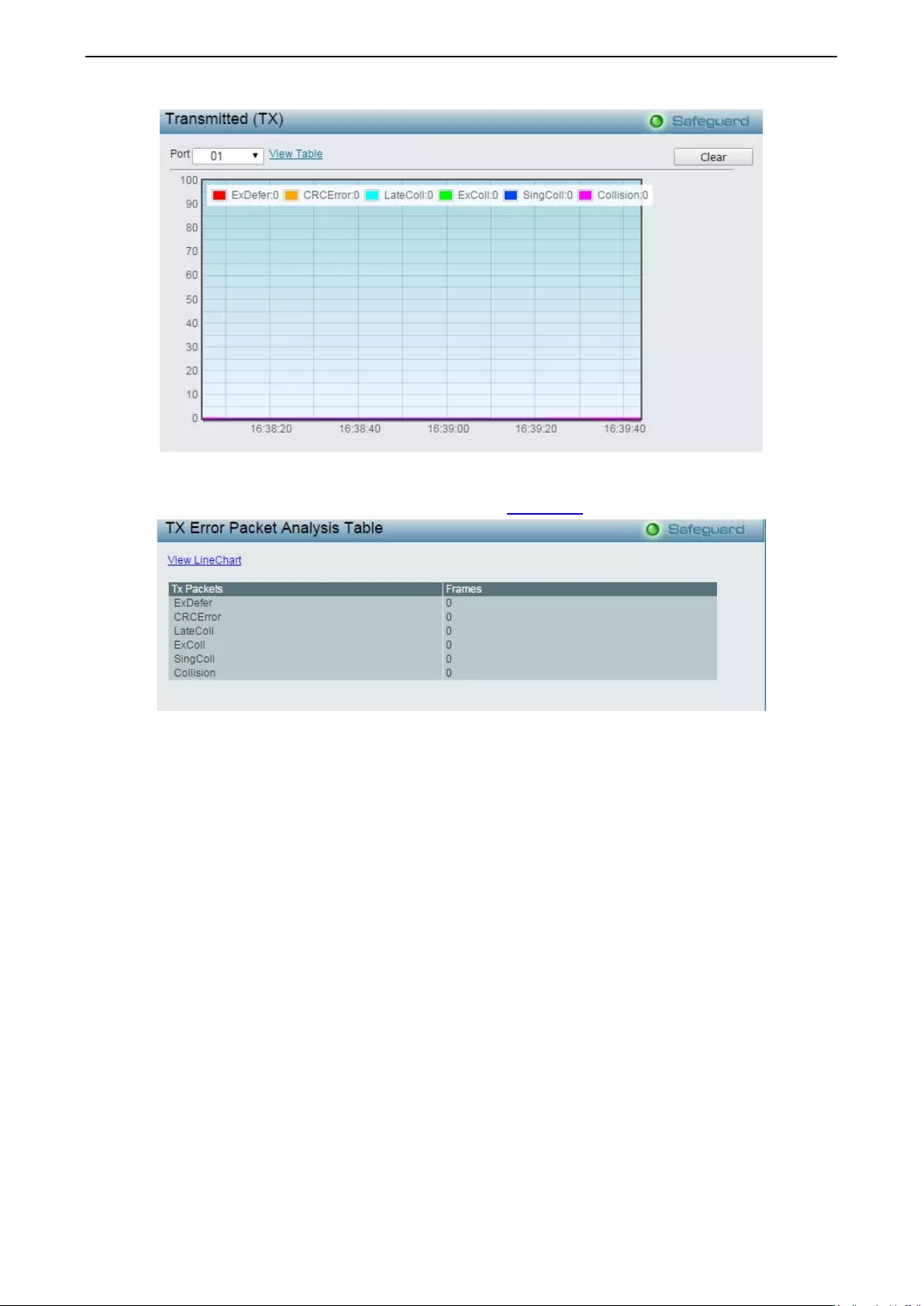
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
12
21
1
Figure 4.186 - Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX) (li ne graph)
To view the Transmit ted E rror Pa ckets T abl e, click the link View Table, which will show the following table:
Figure 4.187 - Monitoring > Errors > Transmitted (TX) (tabl e)
The following fields can be set or viewed:
Time Interval: Select the desired setting between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default
value is one second.
Record Number: Select n um ber of times the Switch will be pol led bet ween 20 and 200. T he def ault value i s
200.
ExDefet: Counts t he num ber of pack ets for which t he f irst tr ansm ission attem pt o n a par ticular interf ace was
delayed because the medium was busy.
CRC Error: Counts otherwise valid packets that did not end on a byte (octet) boundary.
LateColl: Counts the number of times that a collision is detected later than 512 bit-times into the
transmission of a packet.
ExColl: Excessive Collisions. The number of packets for which transmission failed due to excessive
collisions.
SingColl: Sin g l e Collis i on F r am es. T he number of s uc ces sf ully tr ans mitted pac kets f or whic h trans miss ion is
inhibited by more than one collision.
Coll: An estimate of the total number of collisions on this network segment.
Show/Hide: Check whether or not to display ExDefer, LateColl, ExColl, SingColl, and Coll errors.
Clear: Clicking this button clears all statistics counters on this window.
View Table: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a table rather than a line graph.
View Line Chart: Clicking this button instructs the Switch to display a line graph rather than a table.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
122
Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
The Cable Diagnostics is designed primarily for administrators and customer service representatives to
examine of the copper cable quality. It rapidly determines the type of cable errors occurred in the cable.
Select a port and then click the Test Now button to start the diagnosis.
Figure 4.188 - Monitoring > Cable Diagnostics
Test Result: The description of the cable diagnostic results.
•
OK means the cable is good for the connection.
•
Short in C able means the wires of the RJ45 cable may be in contact somewhere.
•
Open in Cable means the wires of RJ45 cable may be broken or the other end of the cable is simply
disconnected.
•
Test Failed m eans some ot her error s occ urred during c able dia gnost ics. P lease s elect t he sam e port a nd
test again.
Cable Fault Distance (meters): Indicates t he d istanc e of the c able f au lt from the Switch por t, if the c able i s
less than 2 meters, it will show “No Cable”, whether the fiber is connected to the port or not.
Cable Length (meter): If the test res ult shows O K, then cable length will be i ndicated f or the total leng th of
the cabl e. T he cab le le ngth s are c ateg ori zed into four types : <50 m eters , 50~80 m eter s, 80~100 m eter s a nd
>100 m eter s. Deviat ion is + /-2 m eter s, ther ef or e "No C abl e" may be d is pla yed un der "T es t Res ult, " whe n the
cable used is less tha n 2 m in le ngth. T his tes t can only be p erf ormed whe n the port is up and oper atin g at 1
Gbps.
NOTE: Cable length detection is effe
ctive on Gigabit
ports only.
The definition of cable pair is listed below:
Pair1: PIN4, PIN5
Pair2: PIN1, PIN2
Pair3: PIN3, PIN6
Pair4: PIN7, PIN8
Monitoring > Sy stem Log
The System Log page provides information about system logs, including information when the device was
booted, how the ports are operating, when users logged in, when sessions timed out, as well as other
system information.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
12
23
3
Figure 4.189 - Monitoring > System Log
ID: Displays an incremented counter of the Sy stem Log entry. The Maximum entries are 500.
Time: Displays the time in days, hours, and minutes the log was entered.
Log Description: Displays the description of event recorded.
Severity: Displays a severity level of the event recorded.
Click Refresh to renew the page, and click Clear to clean out all log entries.
Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
The Browse ARP Table page provides information regarding ARP VLANs, including which IP address was
mapped to what MAC address. To clear the ARP Table, click C lear All.
Figure 4.190 - Monitoring > Browse ARP Table
Click Find, The table updates and displays the values required.
Interface Name: Defines the name of ARP mappings.
IP Address: Defines the station IP address, which is associated with the MAC address.
M AC Add ress: Displays the MAC addres s ass oc iated w ith the IP addres s .
Type: Indicates how the MAC was assigned. The possible values are:
Dynamic – Indicates that the MAC address is dynamically created.
Static – Indicates the MAC address is a static IP address.
Port: Defines the ARP mapping ports.
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
The Browse Ethern et OAM Ev ent Log page displays the ports Ethernet OAM event log information.
Figure 4.191 - Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Event Log
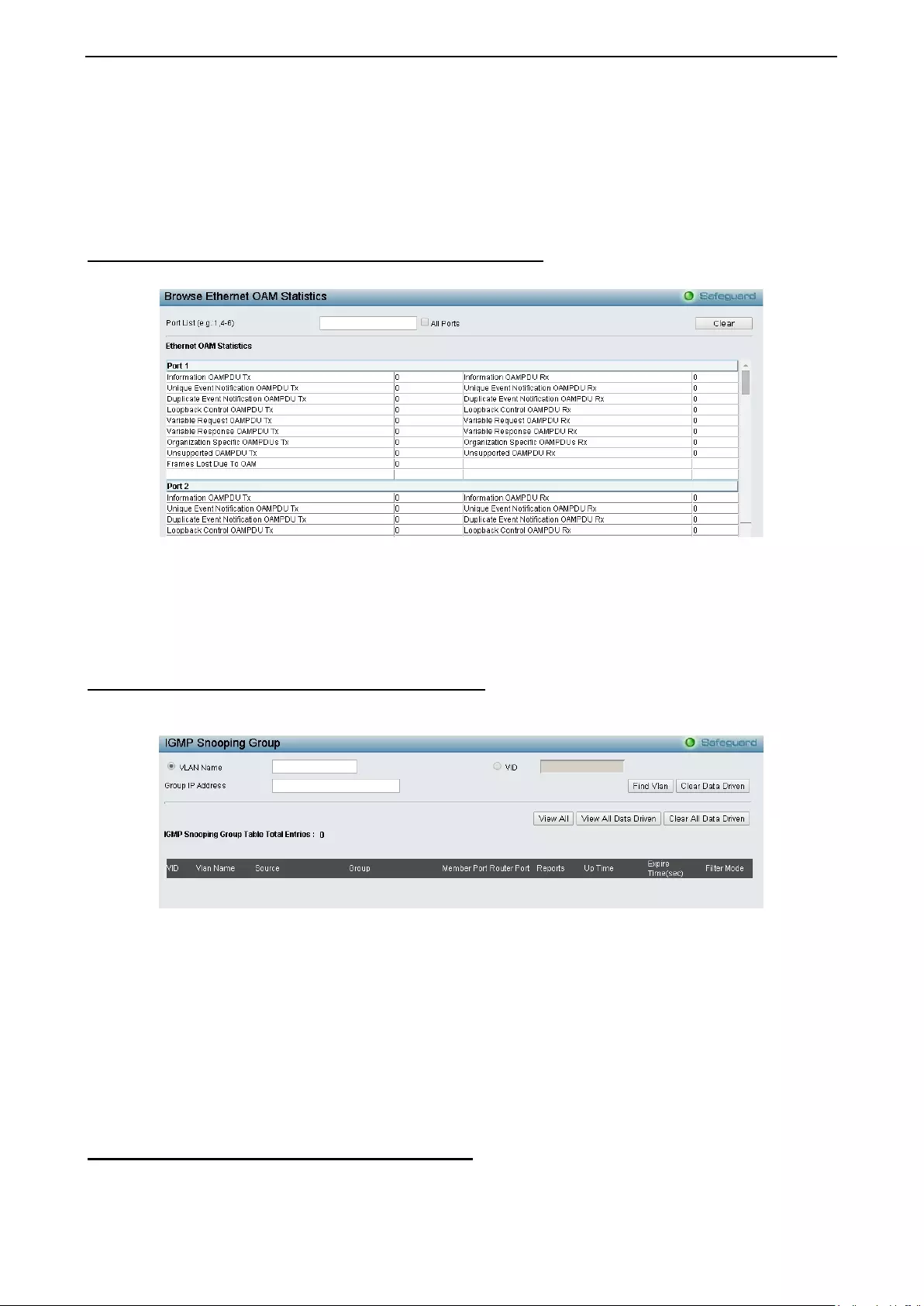
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
124
Port: Select the port to be viewed.
Port List: Enter a list of ports. Tick the All Ports check box to select all ports.
Click Find to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click Clear to clear all the information entered in the fields.
Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
The Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics page displays the ports Ethernet OAM statistics information.
Figure 4.192 - Monitoring > Ethernet OAM > Browse Ethernet OAM Statistics
Port List: Enter a list of ports. Tick the All Ports check box to select all ports.
Click Clear to clear all the information entered in the fields.
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
The IGMP Snooping Group page is used to display the current IGMP snooping static group information on
the Switch.
Figure 4.193 - Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group
VLAN Name: Specify the name of the VLAN for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Group
information.
VID: Spec ify the list of the VLAN IDs for whic h to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Group information.
Group IP Address: Specify the static group address for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping static
group information.
Click Find VLAN to dis pla y the IGM P gr oup inf orm ation or clic k Clear Data Driven to clear the I GMP gr oup
information.
Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
The IGMP Snooping Host page allows user to display the information of IGMP Snooping Host.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
12
25
5
Figure 4.194 - Monitoring > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Host
VLAN Name: Specify the nam e of the VLAN for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Host information.
VID (1-4094): Specify the list of the VLAN IDs for which to be displayed the IGMP Snooping Host information.
Port: Specify the ports of IGMP Snooping Host information to be displayed.
Group: Specify the group of IGMP Snooping Host information to be displayed.
Click Find to display the information.
Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
The MLD Snooping Group page allows user to configure the MLD Snooping group settings.
Figure 4.195 - Monitoring > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group
VLAN Name: Specify the VLAN name for MLD Snooping group.
VID: Specify the VID for MLD Snooping group.
Group IP Add re ss: Specify the IP address for the specified VLAN.
Click Find Vlan to locate a specific entry based on the information entered.
Click View All to display all the existing entries.
Click View All Data Driv en to display all existing entire entries.
Click Clear All Data Driven to clear data driven information for all entries.
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
This table contains inf ormation conc erning the ac tivity of the RA DIUS authentic ation client on the client si de
of the RADI US authenticat ion protocol. It has one row f or each RADIUS authen tication ser ver that the cli ent
shares a secret with.
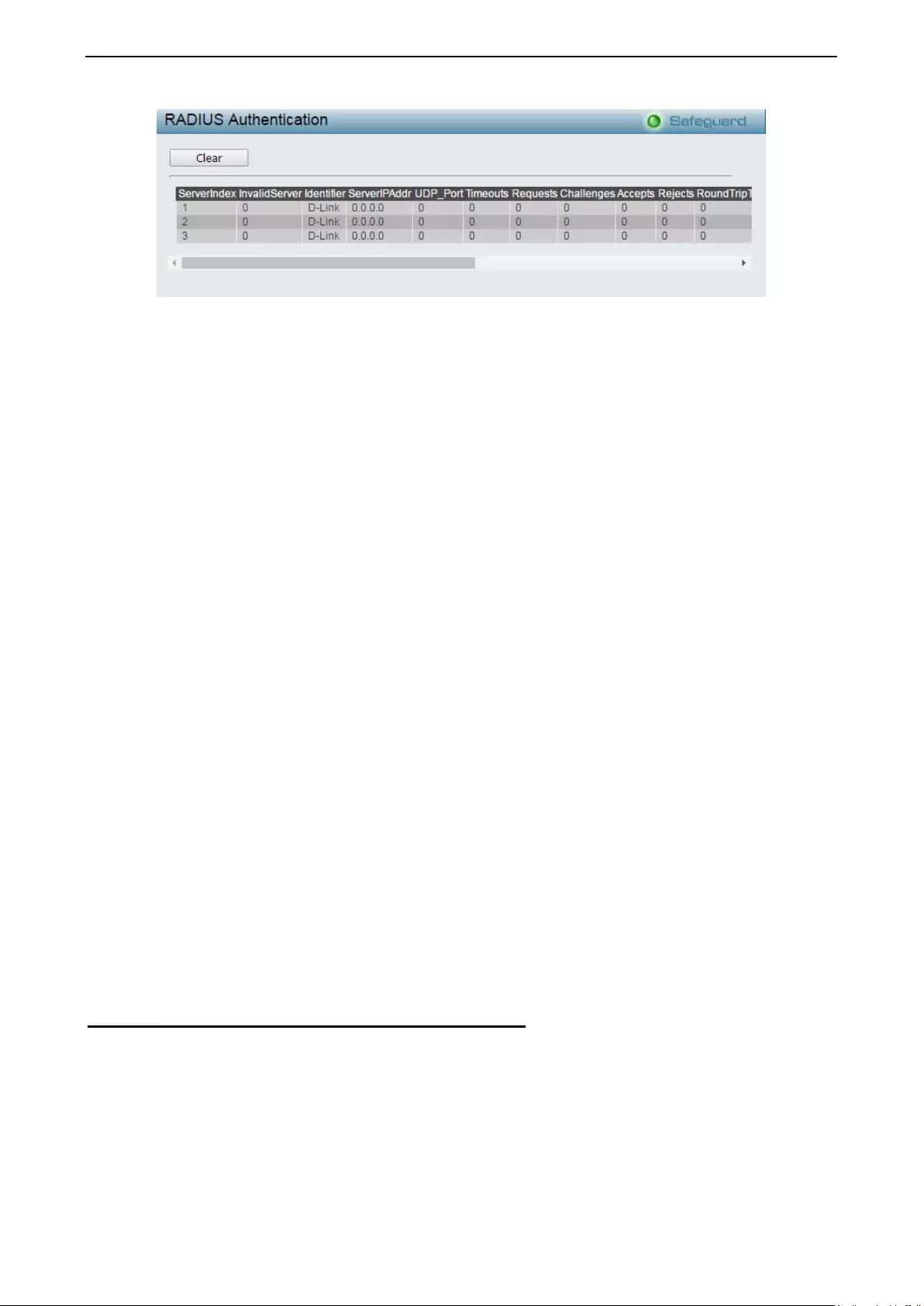
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
126
Figure 4.196 - Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Authentication
The user may also select the desired time interval to update the statistics, between 1s and 60s, where “s”
stands for seconds. The default value is one second. To clear the current statistics shown, click the Clear
button in the top left hand corner.
The following fields can be viewed:
Server Index: The identification number assigned to each RADIUS Authentication server that the client
shares a secret with.
UDP Port : The UDP port the client is using to send requests to this server.
Timeouts: The number of authentication timeouts to this server. After a timeout the client may retry to the
same s erver, send to a d ifferent ser ver, or give up. A retry to the same ser ver is counted as a r etransmit as
well as a timeout. A send to a different server is counted as a Request as well as a timeout.
Requests: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets sent to this server. This does not include
retransmissions.
Challenges: The number of RADIUS Access-Challenge packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
Accepts: The number of RADIUS Access-Accept packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
Rejects: The number of RADIUS Access-Reject packets (valid or invalid) received from this server.
RoundTripTime: The time interval (in hundredths of a second) between the most recent Access-
Reply/Access-Challenge and the Access-Request that matched it from this RADIUS authentication server.
AccessRetrans: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets retransmitted to this RADIUS
authentication server.
PendingRequests: The number of RADIUS Access-Request pack ets destined for this server that have not
yet timed out or received a response. This variable is incremented when an Access-Request is sent and
decremented due to receipt of an Access-Accept, Access-Reject or Access-Challenge, a timeout or
retransmission.
AccessResponses: The number of malformed RADIUS Access-Response packets received from this
server. Malfor med pack ets include pac kets with a n invalid length. Bad authenticator s or Signatur e attributes
or known types are not included as malformed access responses.
BadAuthenticators: The num ber of RADIUS Acc ess-Res ponse pack ets containi ng invalid aut henticator s or
Signature attributes received from this server.
UnknownTypes: The num ber of RAD IUS pack ets of unk nown t ype whic h were rec eived f rom this ser ver o n
the authentication port.
PacketsDropped: The number of RADIUS packets of which were received from this server on the
authentication port and dropped for some other reason.
Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
This RADIUS Account Client page shows managed objects used for managing RADIUS accounting clients,
and the current statistics associated with them. It has one row for each RADIUS authentication server that
the client shares a secret with.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
12
27
7
Figure 4.197 - Monitoring > Port Access Control > RADIUS Account Client
The user may also select the desired time interval to update the statistics, between 1s and 60s, where “s”
stands for seconds. The default value is one second. To clear the current statistics shown, click the Clear
button in the top left hand corner.
The following fields can be viewed:
Serve r IP Addr: The IP ad dres s as s igned t o each R A DIUS Ac coun t ing s er ver th at the client s hares a s ec re t
with.
Server Port Number: The UDP port the client is using to send requests to this server.
Timeouts: The num ber of account ing tim eouts to t his s erver . Af ter a tim eout the c lient ma y retr y to the s am e
server, s end to a dif ferent ser ver, or give u p. A retr y to the sam e ser ver is counted as a r etransm it as well as
a timeout. A send to a different server is counted as an Accounting-Request as well as a timeout.
Requests: The number of RADI U S Ac c ounting-Request packets sent. This does not include retransmissions.
Responses: The number of RADIUS packets received on the accounting port from this server.
RoundTripTime: The time interval between the most recent Accounting-Response and the Accounting-
Request that matched it from this RADIUS accounting server.
AccessRetrans: The number of RADIUS Access-Request packets retransmitted to this RADIUS
authentication server.
PendindRequests: The number of RADIUS Accounting-Request packets sent to this server that have not
yet tim ed out or rece ived a response. T his variable is incr emented when an Accounti ng-Request is sent a nd
decremented due to receipt of an Accounting-Response, a timeout or a retransmission.
MalformedResponses: The number of malformed RADIUS Accounting-Response packets received from
this server. Malformed packets include packets with an invalid length. Bad authenticators and unknown types
are not included as malformed accounting responses.
BadAuthenticators: The number of RADIUS Accounting-Response packets, which contained invalid
authenticators, received from this server.
UnknownTypes: The num ber of RADIUS p ack ets of unknown t ype which were recei ved from this server on
the accounting port.
PacketsDropped: The num ber of RADIUS p ackets , which were rec eived from this server on t he account ing
port and dropped for some other reason.
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Global Settings
sFlow (RF C31 76) is a tec h nol ogy for m onitori ng traff ic in dat a net wor k s c ontaini n g sw itches a nd r o uters . The
sFlow monitoring system consists of an sFlow Agent (embedded in a switch or router or in a standalone
probe) and a central sFlow Collector. The architecture and sampling techniques used in the sFlow monitoring
system were designed for providing continuous site-wide (and enterprise-wide) traffic monitoring of high
speed switched and routed networks.
This sFlow Global Se tti ngs page allows user to configure the sFlow Global configuration.
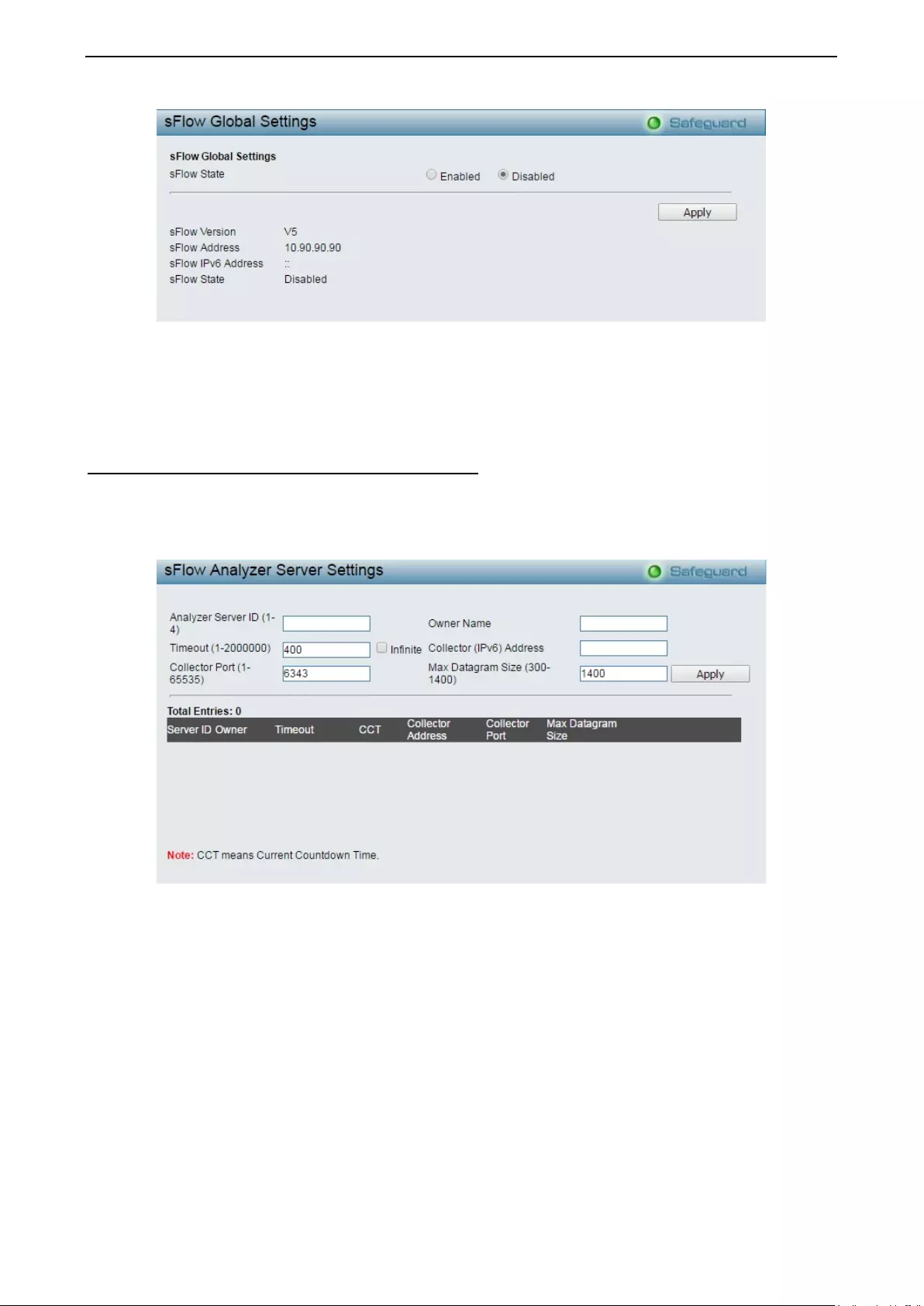
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
128
Figure 4.198 - Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Global Settings
sFlow State: Specify to enable or disable the sFlow feature.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Analyzer Server Settings
The Switch c an support 4 d iff erent Analyzer Ser vers at the s ame tim e and each sam pler or poller can se lect
a collector t o s en d th e s amples. We c an send dif ferent samples f r om diff erent s amplers or poll ers to dif f er ent
collectors.
This sFlow Analyzer Server Settings page allows user to configure the sFlow analyzer server configuration.
Figure 4.199 - Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Analyzer Server Settings
Analyzer Server ID (1-4): The anal yzer server ID spe cifies the ID of a s erver an al yzer where th e pack et will
be forwarded.
Owner Name: The entity making use of this sFlow analyzer server. When owner is set or modified, the
timeout value will become 400 automatically.
Timeout (1-2000000): The length of time before the server times out. When the analyzer server times out,
all of the flow samplers and counter pollers associated with this analyzer server will be deleted. If not
specified, its default value is 400. Tick the Infinite check box to have unlimited time.
Collector (IPv6) Address: The IP address of the analyzer server. If not specified or set a 0 address, the
entry will be inact ive.
Collector Port (1-65535): The destination UDP port for sending the sFlow datagrams. If not specified, the
default value is 6343.
Max D atagram Size (300-1400): T he maxim um number of data bytes that c an b e packed in a sing le sample
datagram. If not specified, the default value is 1400.
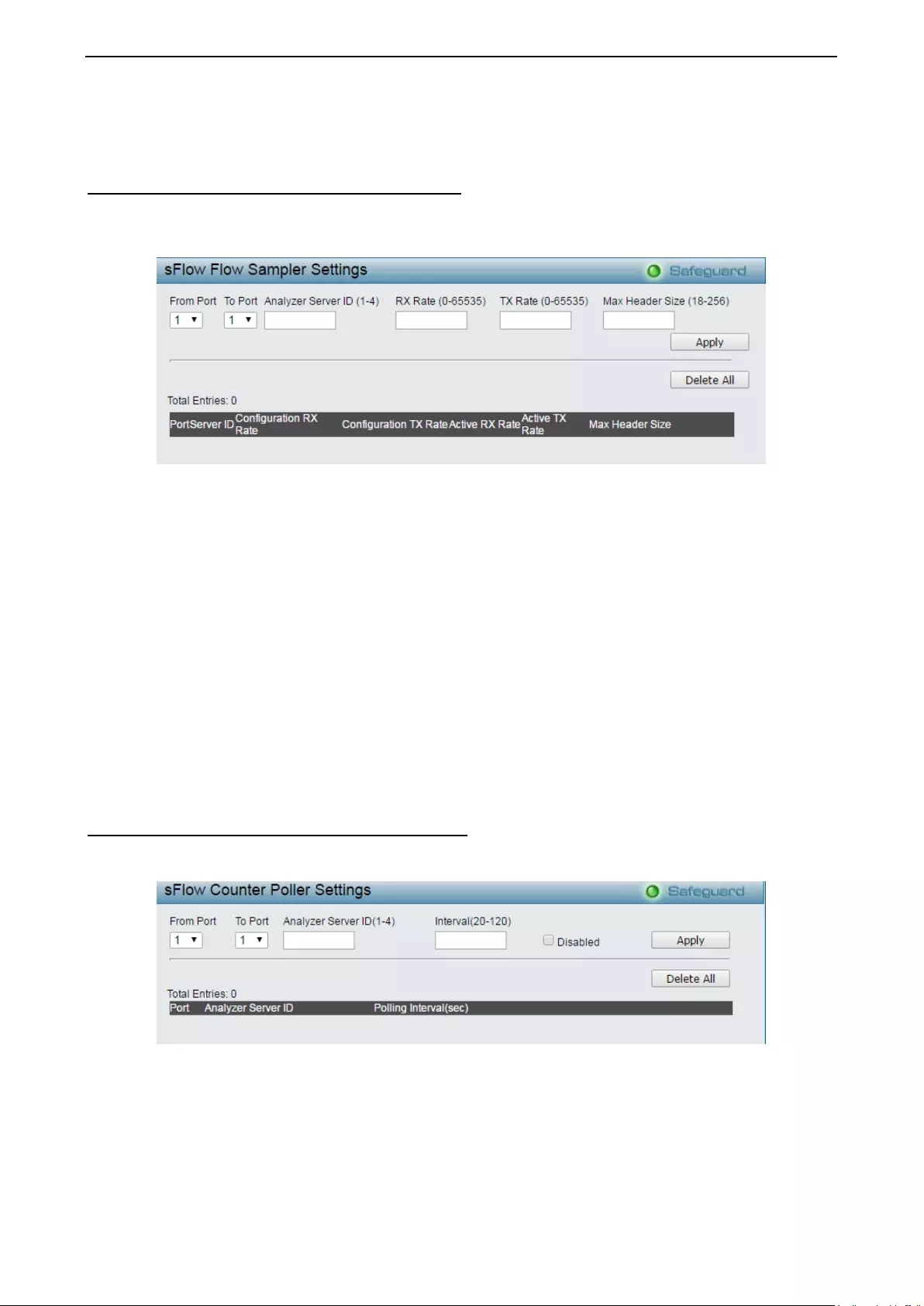
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
12
29
9
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Flow Sampler Settings
This sFlow Flow Sampler Settings page allows user to configure the sFlow flow sampler parameters. By
configuring the sam pling function for a port, a sample packet received by this port will be encapsulated an d
forwarded to the analyzer server at the specified interval.
Figure 4.200 - Monitoring > sFlow > sF low Flow Sample r Settings
From Port / To Port: User the drop-down to specify the list of ports to be configured.
Analyzer Server ID (1-4): The anal yzer server ID spe cifies the ID of a s erver an al yzer where th e pack et will
be forwarded.
RX Rate (0-65535): The sampling rate for packet Rx sampling. The configured rate value multiplied by 256 is
the actual rate. For example, if the rate is 20, the actual rate 5120. One packet will be sampled from every
5120 packets. If set to 0, the sampler is disabled. If the rate is not specified, its default value is 0.
TX Rate ( 0-65535): T he sampling rate f or packet Tx sam pling. T he c onf igur ed rat e va lue multiplied by 256 is
the actual rate. For example, if the rate is 20, the actual rate 5120. One packet will be sampled from every
5120 packets. If set to 0, the sampler is disabled. If the rate is not specified, its default value is 0.
Max Header Size (18-256): The maximum number of leading bytes in the packet which has been sam pled
that will be encapsulated and forwarded to the server. If not specified, the default value is 128.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
Click Delete All to remove all entries.
Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Counter Poller Settings
This sFlow Counter Poller Settings page allows user to configure the sFlow counter poller settings. If the
user wants to change the analyzer server ID, he needs to delete the counter poller and create a new one.
Figure 4.201 - Monitoring > sFlow > sFlow Counter Poller Settings
From Port / To Port: Use the drop-down menus to specify the list of ports to be configured.
Analyzer Server ID ( 1-4): The anal yzer server ID s pe cif ies the ID of a serv er anal yzer wher e the p ack et will
be forwarded.
Interval (20-120): The maximum number of seconds between successive samples of the counters.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
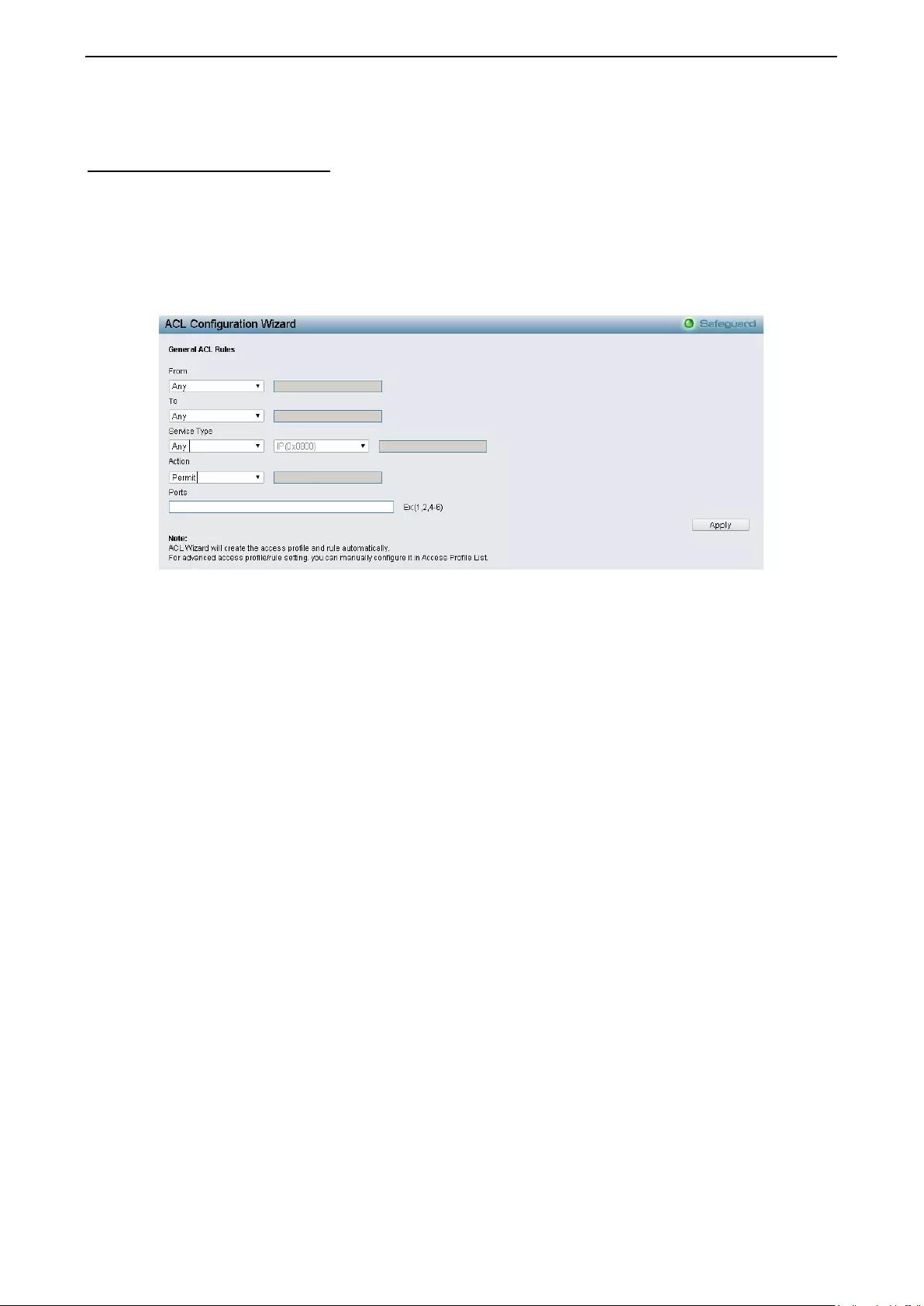
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
130
Click Delete All to remove all entries.
ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
Access Contro l List (AC L) all ows you t o es tablish crit eria t o de term ine w hether or no t the Switc h will f orwar d
packets based on the information contained in each packet's header. These criteria can be specified on a
basis of MAC address, or IP address.
The ACL Configuration Wizard will aid with the creation of access profiles and ACL Rules. The ACL Wizard
will create the ac c es s r ule and profile automatical l y. The maxim um us able prof ile s are 50 a nd with 2 40 Rule s
in total for the switch.
Figure 4.202 - ACL > ACL Configuration Wizard
From: Specify the origin of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any source.
M AC Add ress - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this MAC address.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv6 sourc e addres s
To: Specify the destination of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any source.
MAC Address - Indica tes ACL action w ill be on p ackets f rom this MAC addres s. The f ield of f ormat
is xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 Addresses - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from this IPv6 sourc e addres s .
Service Type: Specify the type of service. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from any service type.
Ether type - Specifies an Ethernet type for filtering packets.
ICMP All - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from ICMP packets.
IGMP - IGMP packets can be filtered by IGMP message type.
TCP All - Indicates ACL ac tion will be on packets from TCP Pack ets .
TCP Source Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Source Port.
TCP Destination Port - Matches the packet to the TCP Destination Port.
UDP All - Indicates ACL action will be on packets from UDP Packets.
UDP Source Port - Matches the packet to the UDP Source Port.
UDP Destination Por t - Matches the packet to the UDP Destination Port.
Action: Specify the ACL forwarding action matching the rule criteria.
Permit - Forwards packets if all other ACL criteria are met.
Deny - Drops packets if all other ACL criteria is met.
Mirror - Mirrors packets if all other ACL criteria is met.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
31
1
Rate Limit - Rate limiting is activated if all other ACL criteria is met.
Replace DSCP - Reassigns a new DSCP value to the packet if all other ACL criteria are met.
Ports: Enter a range of ports to be configured.
Press Apply for the settings to take effect.
NOTE: Once the ACL rules conflict, rul
es with
smaller rule ID will take higher priority.
NOTE: Be car eful when c onfigurin g ACL rules , an
inappropriate may cause management access
failed.
AC L > Access Profile List
The Access Profile L is t pr o vides i nf ormation for c onf ig ur ing ACL Profi les manual ly. ACL pr of iles are attac he d
to interfaces, and define how packets are forwarded if they match the ACL criteria.
Figure 4.203 - ACL > Access Profile List
The contents of Access Profile List table include:
Profile ID: Indicates the profile Identification number. The possible configured profile IDs are 1~50, and
profile ID 51~55 are reserved for the pre-defined features.
Owner Type: The owner type of ACL profile; it can be normal ACL, Voice VLAN or Survei ll anc e VLAN .
Profile Su m m a r y: Displays the profile summary.
Show Details: To displa y an AC L’s pr of ile details. The ACL profile details are d is played below th e AC L tab le .
Show Rules: To show the access rule in this profile.
To add a new rule, please see Access Rule List in the next section.
Delete: To delete an access profile.
To manually add a profile, click Add ACL Profile:
Figure 4.204 - Add ACL Profile
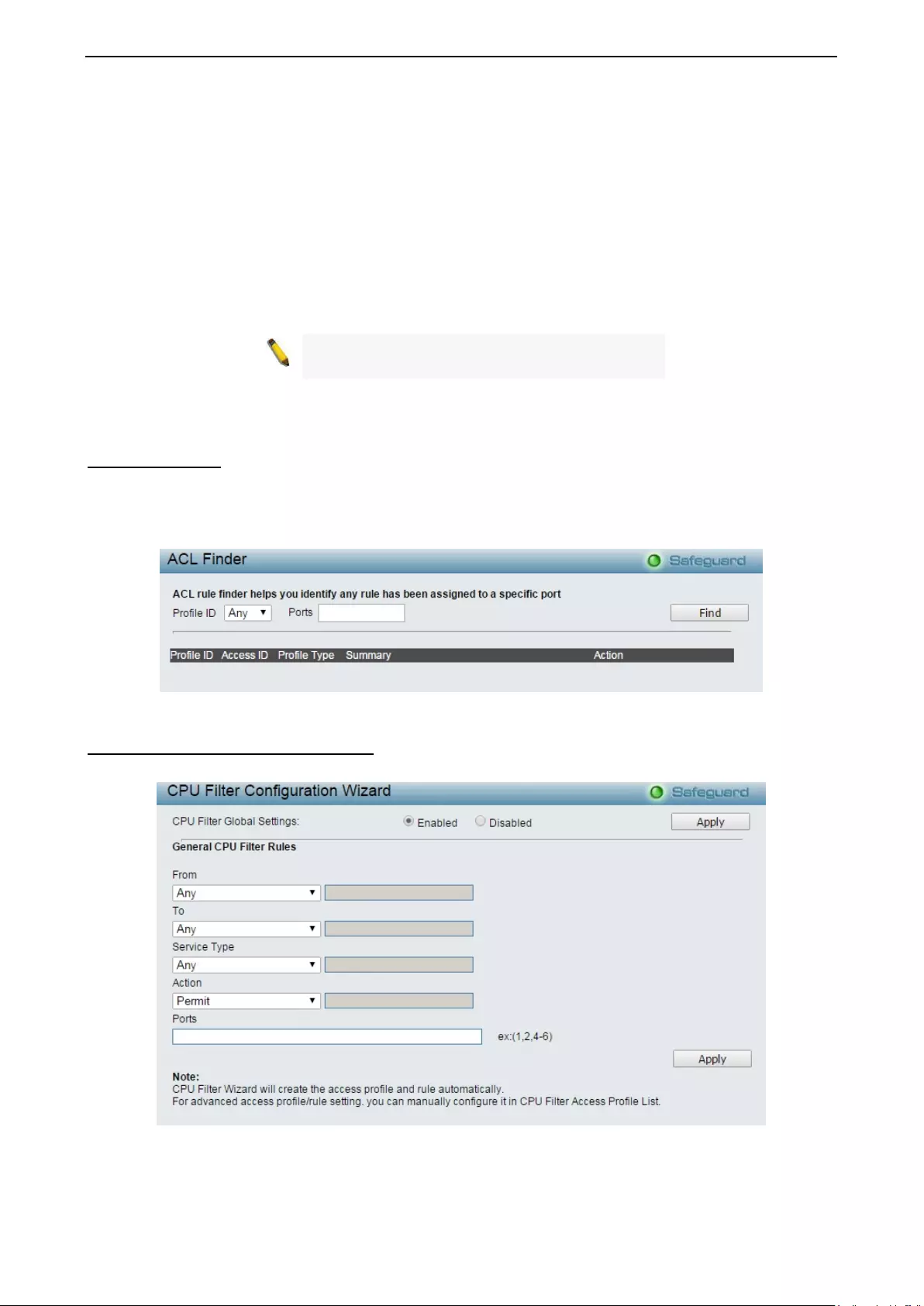
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
132
The steps of adding an access profile is like below:
1) After selecting the Profile ID and Frame Type (MAC, IPv4, IPv6 or Packet content ACL), specify
attributes like Untagged/Tagged (for MAC), ICMP/IGMP/TCP/UDP/Protocol ID (for IPv4), or
ICMPv6/TCP/UDP (for IPv6), then click Select and a simplified frame diagram will be displayed.
2) Select the field of interest and related columns will be displayed in lower part of the page. Enter the
filtering m ask and clic k Create when d one. A filter ing m ask is to spec ify the d igit that you wa nt to check . For
example, if you want to check a network of 192.168.1.0/24, then you should enter the IP mask as
255.255.255.0.
NOTE: You cannot select Pa yload in a MAC ACL,
or L2 Header in IP ACL.
3) After the Profile ID has been created, it will go back to the main Access Profile List page.
ACL > ACL Finder
The ACL Finder page is us ed to h elp user to find a prev iously conf igured ACL entr y. To sear ch for an entr y,
enter the Profile ID from the drop-down menu, select a port that you wish to view and click Find. The table
on the lower half of the screen will display the entries. To delete an entry click the corresponding Delete
button.
Figure 4.205 - ACL > ACL Finder
ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
The CPU Filter C onf igur ati on Wizard will aid with the cr eation of CPU Filter Rules.
Figure 4.206 - ACL > CPU Filter Configuration Wizard
CPU Filter Global Settings: To enable or disable the CPU filter feature.
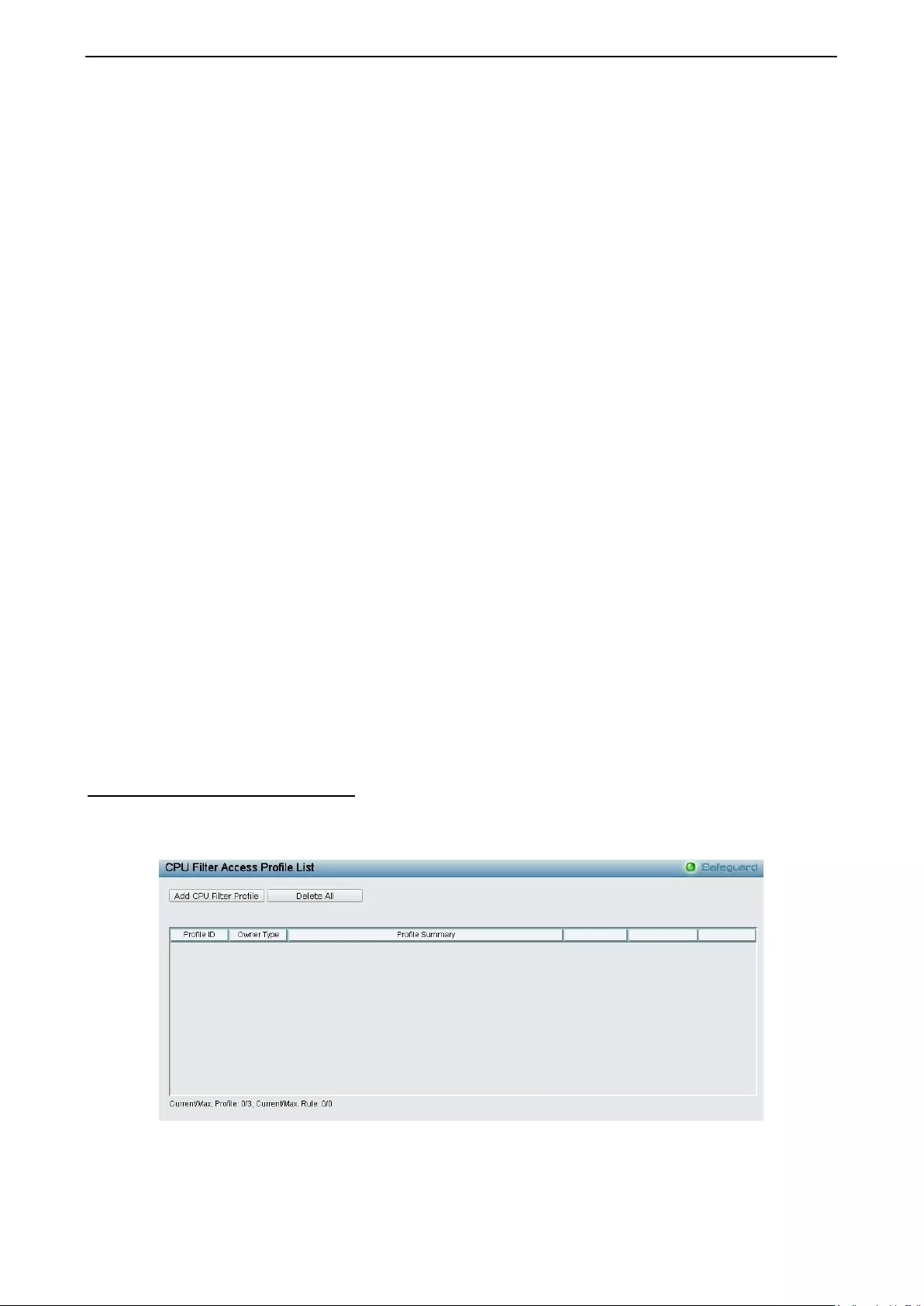
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
33
3
Press Apply for the settings to take effect.
From: Specify the origin of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from any source.
MAC Address - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from this MAC address.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets from this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 - Indicates CPU Filter ac tion will be on packets from this IPv6 source address.
To: Specify the destination of accessible packets. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to any source.
MAC Address - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to this MAC address. The field of
format is xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
IPv4 Addresses - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets to this IPv4 source address.
IPv6 - Indicates CPU Filter ac tion will be on packets to this IPv6 source address.
Service Type: Specify the type of service. The possible values are:
Any - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on packets of any service type.
Ether type - Specifies an Ethernet type for filtering packets.
ICMP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all ICMP packets.
IGMP - IGMP packets can be filtered by IGMP message type.
TCP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all TCP Packets.
TCP Source Port - Take effect if TCP Source Port matches.
TCP Destination Port - Take effect if TCP Destination Port matches.
UDP All - Indicates CPU Filter action will be on all UDP Packets.
UDP Source Port - Take effect if UDP Source Port matches.
UDP Destination Por t - Take effect if UDP Destination Port matches.
Action: S pecify the CPU Filter forwarding action matching the rule criteria.
Permit - Forwards packets if all other CPU Filter criteria are met.
Deny - Drops packets if all other CPU Filter criteria is met.
Press Apply for the settings to take effect.
ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
The CPU Filter Access Profile List provides information for configuring CPU Profiles manually. CPU Filter
Access profiles are attached to interfaces, and define how packets are forwarded if they match the CPU
Filter criteria.
Figure 4.207 - ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List
The contents of CPU Filter Access Profile List table include:
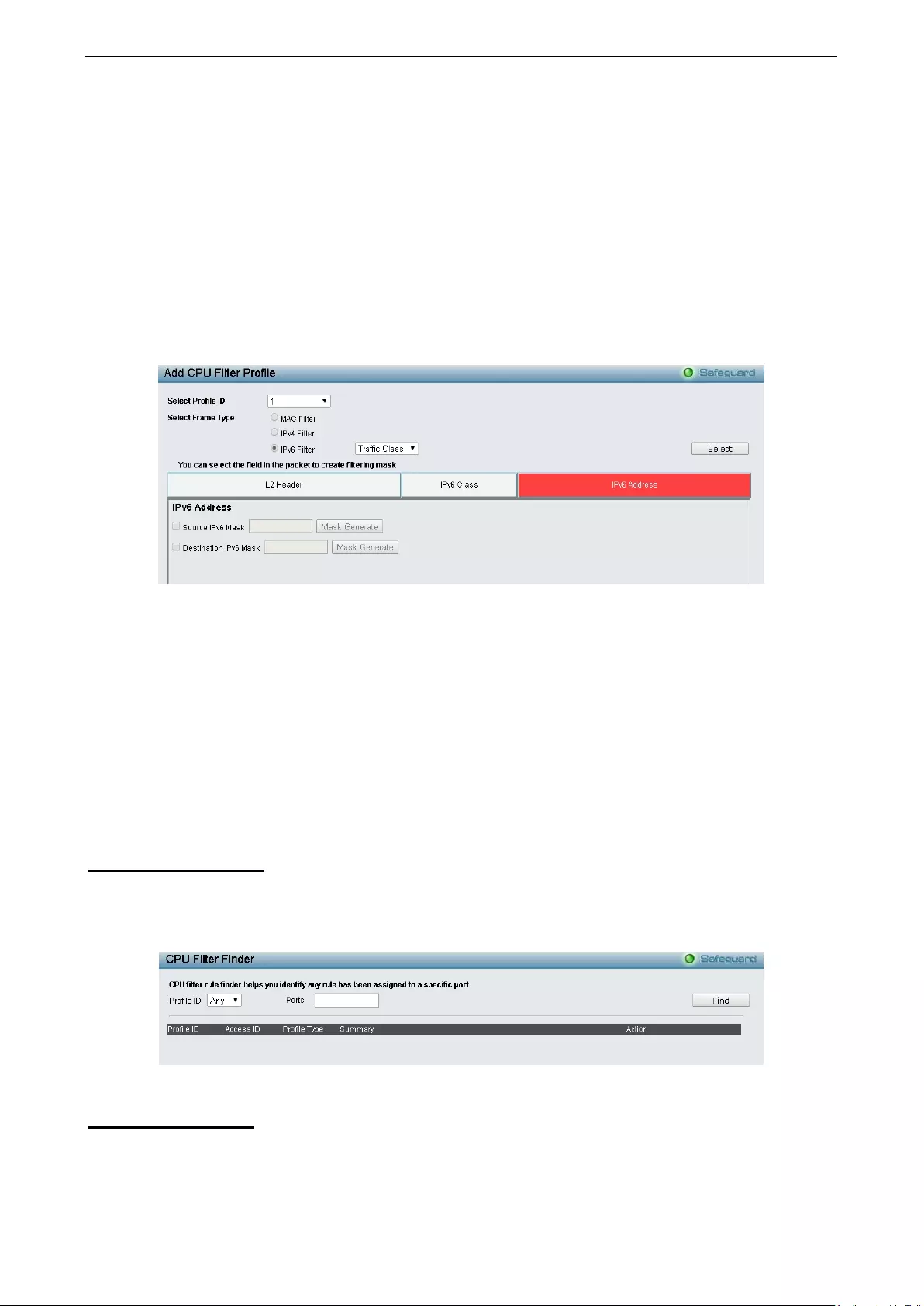
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
134
Profile ID: Indicates the profile Identification number. The possible configured profile IDs are 1~50, and
profile ID 51 is reserved for Voice VLAN.
Owner Type: T he ow ner t ype of C PU F ilte r profile, it can be nor m al CPU Filter, Voic e VLAN or Surveillance
VLAN.
Profile Su m m a r y: Displays the profile summary.
Show Details: To display a CPU Filter’s profile details. The CPU Filter profile details are displayed below the
CPU Filter table.
Edit/New Rules: To configure or add the CPU access rule in this profile.
To add a new rule, please see Add CPU Filter Profile in the next section.
Delete All: To delete all access profile.
To manually add a profile, click Add CPU Filter Profile.
Figure 4.208 - ACL > CPU Filter Access Profile List -Add CPU Filter Profile
The steps of adding a CPU Filter profile is like below:
1) After selecting the Profile ID and Frame Type (MAC, IPv4 or IPv6), specify attributes like
Untagged/Tagged (for MAC), or ICMP/IGMP/TCP/UDP/Protocol ID (for IPv4), or Traffic Class (for IPv6), then
click Select and a simplified frame diagram will be displayed.
2) Select the field of interest and related columns will be displayed in lower part of the page. Enter the
filtering m ask and clic k Create when d one. A filter ing m ask is to spec ify the d igit that you wa nt to check . For
example, if you want to check a network of 192.168.1.0/24, then you should enter the IP mask as
255.255.255.0.
3) After the Profile ID has been created, it will go back to the main CPU Filter Access Profile List page.
ACL > CPU Filter Finder
The CPU F ilter Finder page is us ed to help user to fin d a previous ly config ured CPU e ntry. To sear ch for an
entry, en ter the Prof ile ID from the drop-down m enu, select a p ort that yo u wish to vie w and click Find. The
table on the lower half of the screen will display the entries. To delete an entry click the corresponding
Delete button.
Figure 4.209 - ACL > CPU Fil ter Finder
A CL > ACL Flow Meter
ACL Flow Metering table is a per flow bandwidth control used to limit the bandwidth of the ingress traffic.
When the users create an ACL rule to filter packets, a metering rule can be created to associate with this
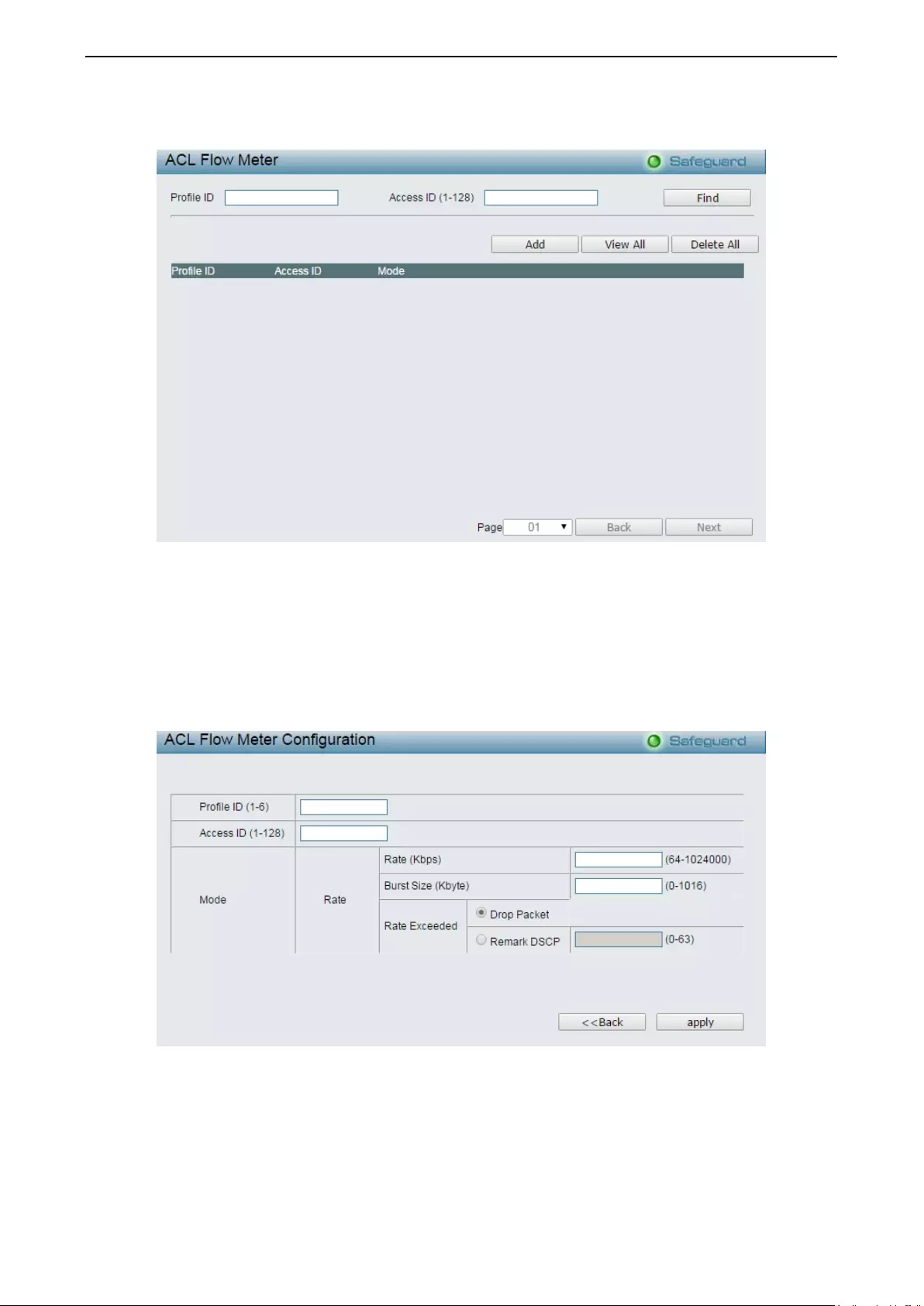
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
35
5
ACL rule t o lim it traff ic. T he step of band width is 64k bps. Due to limited m et ering rules , not a ll ACL rules can
associate with a metering rule.
Figure 4.210 - ACL > ACL Flow Meter
Profile ID: The pre-configured Profile ID for which to configure the Flow Metering parameter.
Access ID (1-128): The pre-configured Access ID for which to configure the Flow Metering parameters.
Enter the appropriate information and click Find the entries will be displayed on the lower half of the table.
To edit and entry click the corresponding Modify button, to delete an entry click the corresponding Delete
button, to add a new entry click the Add button which will display the following window for the user to
configure.
Figure 4.211 - ACL > Add ACL Flow Meter
Profile ID (1-6): Specify the profile ID.
Access ID (1-128): Specify the Acces s ID that w i ll be us ed to c onf ig ure the Flow Metering parameters , enter
a value between 1 and 128.
Mode: To be used the corresponding information.
- Rate: Specify the committed information Rate of the packet. The range is from 64 to 1024000
kbyte.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
136
- Burst Size: Specify the committed Burst Size of the packet. The range is from 0 to 1016 kbyte.
Rate Exceed: Specifies the action when the packet is in yellow color mode.
- Drop Packet: Drops the packet.
- Replace DSCP: Allow user to change the DSCP of the packet.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
PoE > PoE Port Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only)
DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) as defined by the
IEEE specification.DGS-1210-10 P/ME s upplies p ower to P D device up to 30W, DGS-1210-28P/ME supplies
power to PD de vic e u p to 1 5.4W for port 5~24 and 30 W for port 1~4, DGS-1210-28MP/M E s upp li es power to
PD device up to 30W for port 1~24, DGS-1210-52P/ME supplies power to PD device up to 15.4W for port
9~24 and 30W for port 1~8, DGS-1210-52MP/ME supplies power to PD device up to 15.4W for port 9~48
and 30W for port 1~8, and DGS-1210-52MPP/ME supplies power to PD device up 30W for port 1~48,
meeting IEEE802.3af standards and pr e-802.3at standards.
DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME works with all D-Link 802.3af or 802.3at capable devices.
The Switch also works in PoE mode with all non-802.3af capable D-Link AP, IP Cam and IP phone
equipment via the Po E splitter DWL-P50.
IEEE 802.3at defined that the PSE provides power acc or ding to the following classification:
Class Usage Output power limit by PSE
0 Default 15.4W
1 Optional 4.0W
2 Optional 7.0W
3 Optional 15.4W
4 Reserved 30W
The PoE port tab le will display the PoE status including, Port Enable, Power Limit, Power (W), Voltage (V),
Current (mA), Clas s ific at ion , Port Status. You ca n s e le c t From Port / T o Port to c ontr ol th e Po E f unc ti ons of
a port. DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME will auto disable the ports if port current is over
375mA in 802.3af mode or 625mA in pre-802.3at mode.
Note:
The PoE Status information of Power
current, Power Voltage, and Current is the power
usage information of the connected PD; please
"Refresh" to renew the information.
Note: For DGS-1210-10P/ME, the port 1 ~ port 8 are compliance
with 802.3at. The total PoE budget is 78 Watts.
For DGS-1210-
28P/ME, the port 1 ~ port 4 are compliance with
802.3at, and the port 5 ~ port 24 are compliance with 802.3af. The
total PoE budget is 193 Watts.
For DGS-1210-28MP/ME, the port 1 ~ port 24 are compliance with
802.3at and 802 .3af. The total PoE budget is 370 Watts.
For DGS-1210-
52P/ME, the port 1 ~ port 8 are compliance with
802.3at, and the port 9 ~ port 24 are compliance with 802.3af. The
total PoE budget is 193 Watts.
For DGS-1210-52MP/ME, the port 1 ~ port 8 are compliance with
802.3at, and the port 9 ~ port 48 are compliance with 802.3af. The
total PoE budget is 370 Watts.
For DGS-1210-52MPP/ME, the port 1 ~ port 48 are compliance with
802.3at. The total PoE budget is 740 Watts.
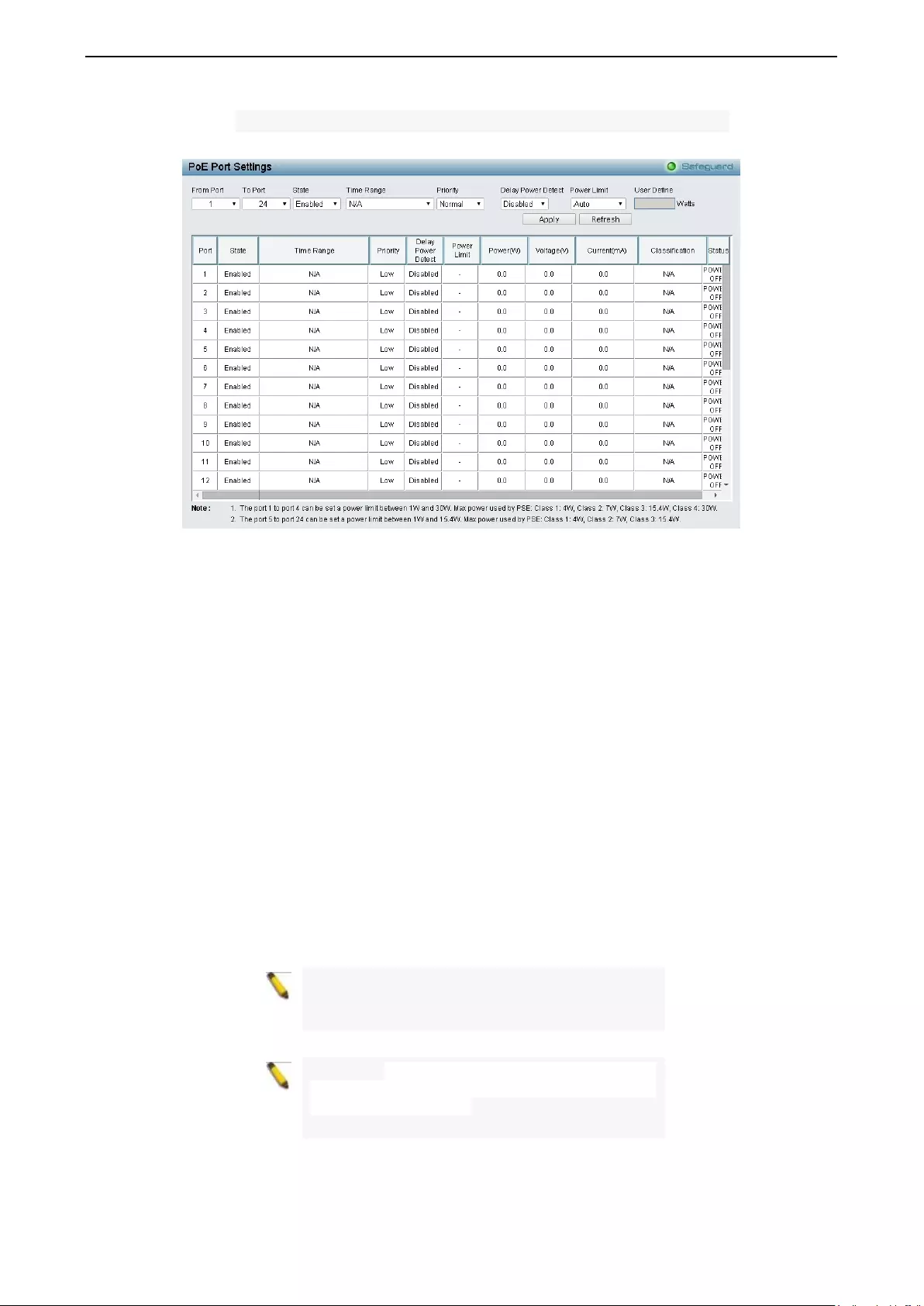
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
37
7
Figure 4.212 – PoE > PoE Port Settings
From Port/To Port: Specifies the PoE function of a port or ports.
State: Select “Enabled” or “Disabled” to configure PoE function for designated port(s). Default is Enabled.
Time R ange: Select the P oE t ime prof ile conf igur e d f rom Time-Bas ed Po E > T ime R an ge Sett ings to enab le
the time-based PoE function on designated port(s). Default setting is N/A.
Priority: C onfigure t he pow er suppl y priorit y as “Low”, “Normal” , or “ High” on design ated por t(s). Def ault i s
Normal.
Delay Power Detect: Configure the delay power detection. Default is Disabled. This switch conforms to
IEEE 802.3 af and 8 02.3at standar ds. T he IEE E PoE standard re qu ires a s witch to s hut off power to a port if
the po wer dra w is less than 10m A within a 400m s tim e interval. To s upport som e non-s tandar d de vices t hat
may take longer, you may enable this feature to extend the time interval to 500ms. If the PD is still not
powering on, pl eas e con tac t the vendor of your device for support.
Power Limit: This function allows you to manually set the port power current limitation to be given to the PD.
To protect the DGS-1210-28P/ME and the connected devices, the power limit function will disable the PoE
function of the port when the power is overloaded. Select from "Class 1", "Class 2", "Class 3", “Class 4”,
User Define and "Auto" for the power limit. "Auto" will negotiate and follow the classification from the PD
power current based on the 802.3at standard. Select User Define then input the power budget (from 1 to
30W) to manually assign an upper limit of port power budget on designated port(s).
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect or click Refresh to redisplay the table.
Note:
For the PoE Port Settings table, if the
classif ication w as sho wn as “Legac y PD”, it will b e
classified to non-AF PD or Legacy PD.
Note: The ports 1-4 are capable of feeding power
up to 30 watts to devices with the LLDP-Med
function is enabled of the connected PD. Or the
ports can only feeding power up to 15.4 watts.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
138
PoE > PoE System Settings (DGS-1210-10P/28P/28MP/52P/52MP/52MPP/ME only)
This PoE System Settings page will display the PoE status including System Bud get Pow er, Support Total
Power, Remainder Power, and The ratio of system power supply.
Figure 4.213 – PoE > PoE System Settings
System Power Threshold: Manually configure the system power budget 7.1 ~ 193.0 watts for DGS-1210-
28P/ME.
System Setting Disconnect Method: Defines the m ethod us ed to den y power t o a port onc e the thr eshold
is reached. The possible fields are:
Deny next port: When the power budget is exceeded, the next port attempting to power up is
denied, regardless of the port priority.
Deny low priority port: The port with th e lower priori ty will be shut d own to allow the hi gher priority
port to power up.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
System Power Status: Displays the system power status of device.
Syste m Budget Power: D i splays the total PoE power budg et of this switch.
Support Total Power: Displays the current used power of the switch.
Remainder Power: Displays the spare power of the switch.
The ratio of system power supplied: Displays the percentage of system power supplied of the
switch.
Time-Based PoE > Time Range Settings
The Time Profile page allows users to configure the time profile settings of the device
Figure 4.214 – Time-Based PoE > Time Range Settings
Range Name: Specifies the range name.
Date: Specifies the From Day and To Day.
Hours(HH MM): Specifies the Start Time and End Time.
Weekdays: Specifies the work day.
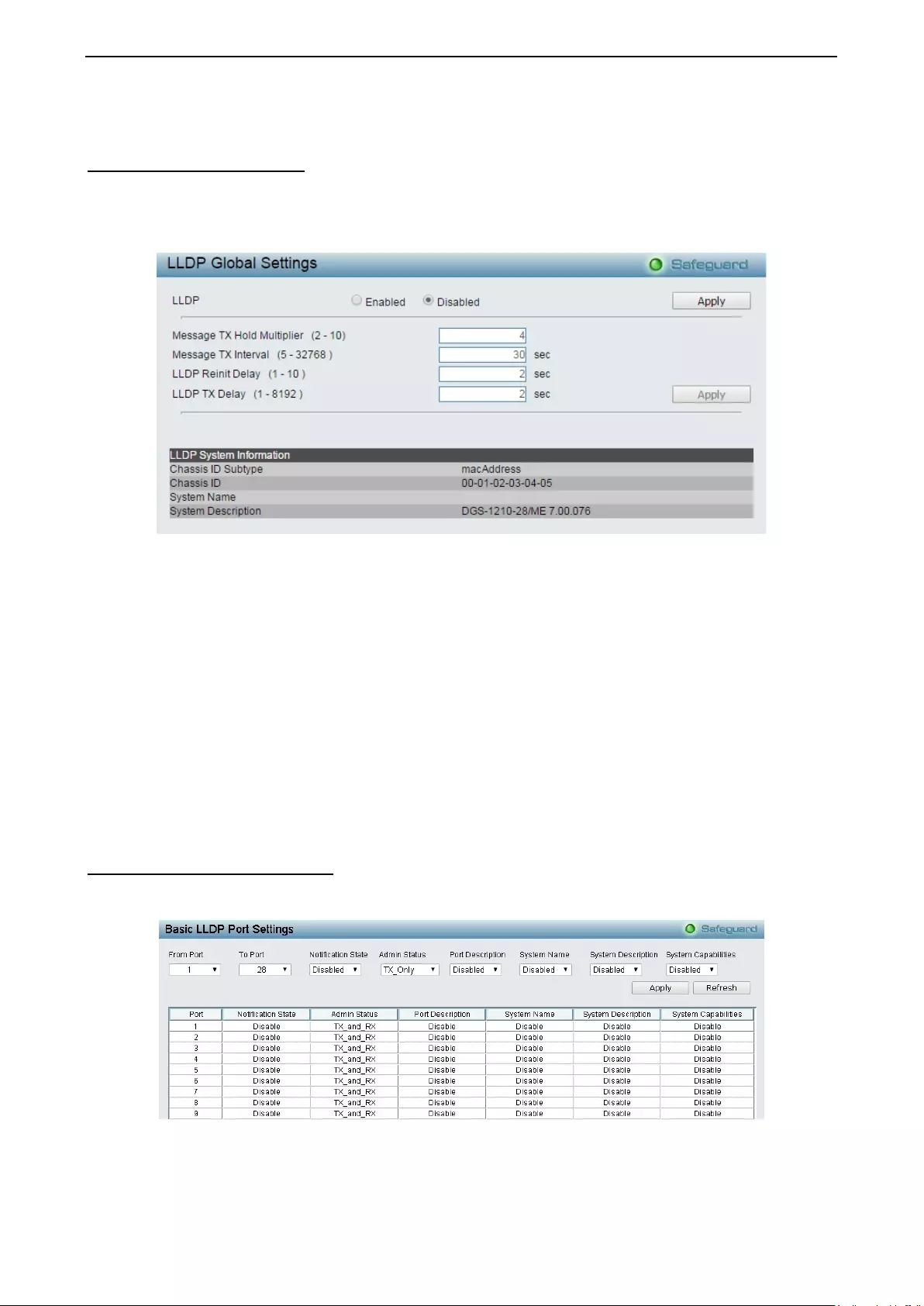
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
13
39
9
Click Apply to create a new time range or click Delete to delete a time profile from the table.
LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) provides IEEE 802.1AB standards-based method for switches to
advertise themselves to neighbor devices, as we ll as to learn about neighbor LLDP devices. The switch will
keep the information in the Management Information Base (MIB). SNMP utilities can learn the network
topology by obtaining the MIB information in each LLDP device. The LLDP function is enabled by default.
Figure 4.215 – LLDP > LLDP Global Settings
LLDP: When this function is Enabled, the switch can start to transmit, receive and process the LLDP packets.
For the a dvertisem ent of LLDP pac kets, the s witch an nounces the i nformation to its neig hbor through ports.
For the receiving of LLDP packets, the switch will learn the information from the LLDP packets advertised
from the neighbor in the neighbor table. Click Apply to make the change effective.
Message TX Hold Multiplier (2-10): This parameter is a multiplier that determines the actual TTL value
used in an LLDPDU. The default value is 4.
Messag e TX Interval ( 5-32768): This parameter indic ates the interval at whic h L LDP f r ames are tr ansmitted
on behalf of this LLDP agent. The default value is 30 seconds.
LLDP Reinit Delay (1-10): This parameter indicates the amount of delay from the time adminStatus
becomes "disabled" until re-initialization is attempted. The default value is 2 seconds.
LLDP TX Delay (1-8192): This parameter indicates the delay between successive LLDP frame
transmissions initiated by value or status changes in the LLDP local systems MIB. The value for txDelay is
set by the following range formula: 1 < txDelay < (0.25 °— msgTxInterval). The default value is 2 seconds.
LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
The Basic LLDP Port Setti ngs page displ ays LLDP por t information a nd contains parameters for configuring
LLDP port settings.
Figure 4.216– LLDP > Basic LLDP Port Settings
From Port/ To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
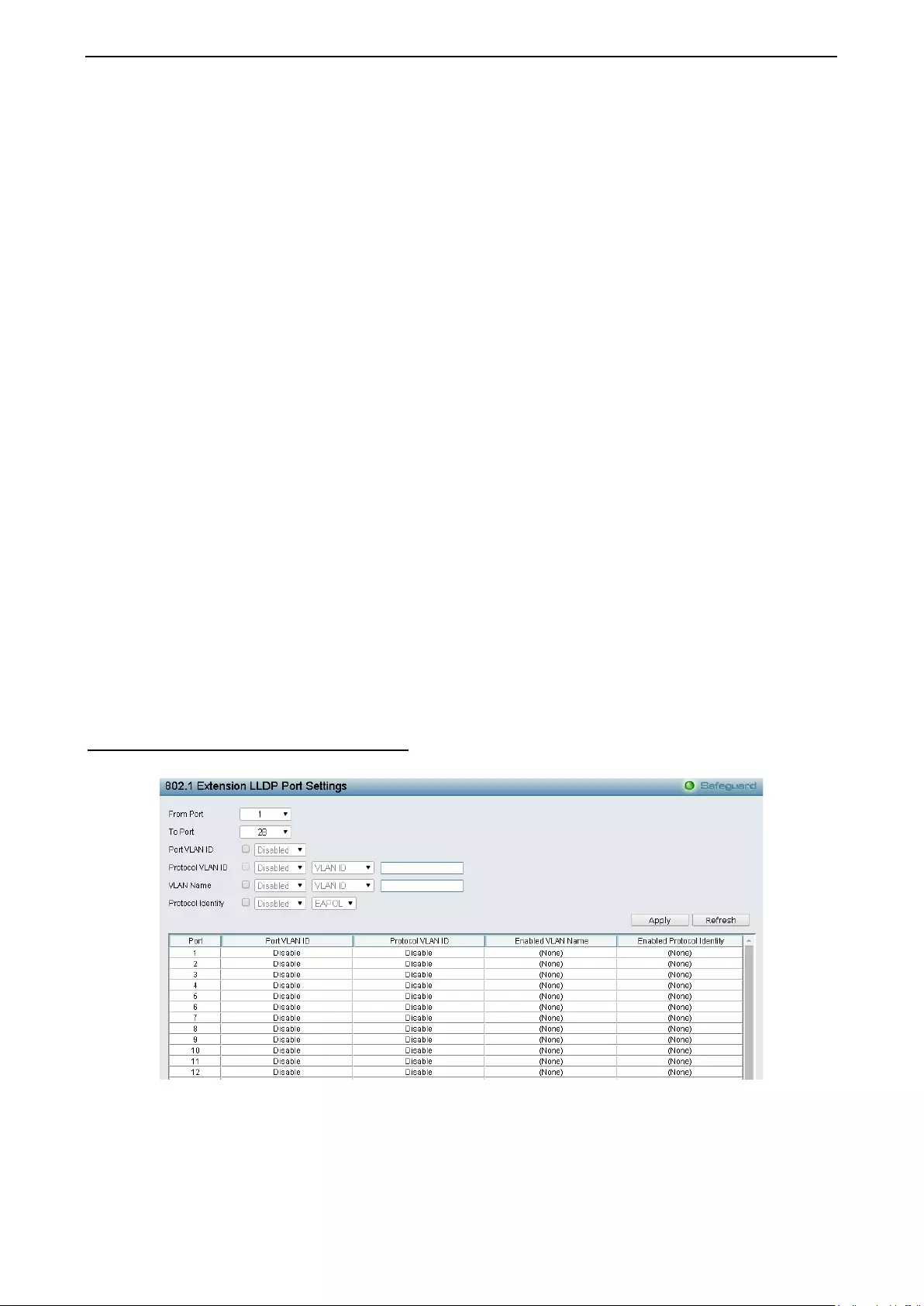
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
140
Notification State: Specif i es whet her n otif ication is sent when an LLDP t opo lo g y change occ ur s on t he p ort.
The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables LLDP notification on the port.
Disabled – Disables LLDP notification on the port. This is the default value.
Admin Status: Specifies the LLDP transmission mode on the port. The possible field values are:
TX_Only – Enables transmitting LLDP packets only.
RX_Only – Enables receiving LLDP packets only.
TX_and_RX – Enables transmitting and receiving LLDP packets. This is the default.
Disabled – Disables LLDP on the port.
Port Description: Specifies whether the Port Description TLV is enabled on the port. The possible field
values are:
Enabled – Enables the Port Description TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the Port Description TLV on the port.
System Name: Specifies whether the System Name TLV is enabled on the port. The possible field values
are:
Enabled – Enables the System Name TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Name TLV on the port.
System Description: Specifies whether the System Description TLV is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the System Description TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Description TLV on the port.
System Capabilities: Specifies whether the System Capabilities TLV is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the System Capabilities TLV on the port.
Disabled – Disables the System Capabilities TLV on the port.
Define these parameter fields. Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the
table information.
LLDP > 80 2.1 Ext en si on LLDP Port Settings
This 802.1 Extens ion LLDP Port Settings page is used to configure the LLDP Port settings.
Figure 4.217 – LLDP > 802.1 Extension LLDP Port Settings
From Port / To Port : A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the sel ec ted por t.
Port VLAN ID : Specifies the Port VLAN ID to be enabled or disabled.
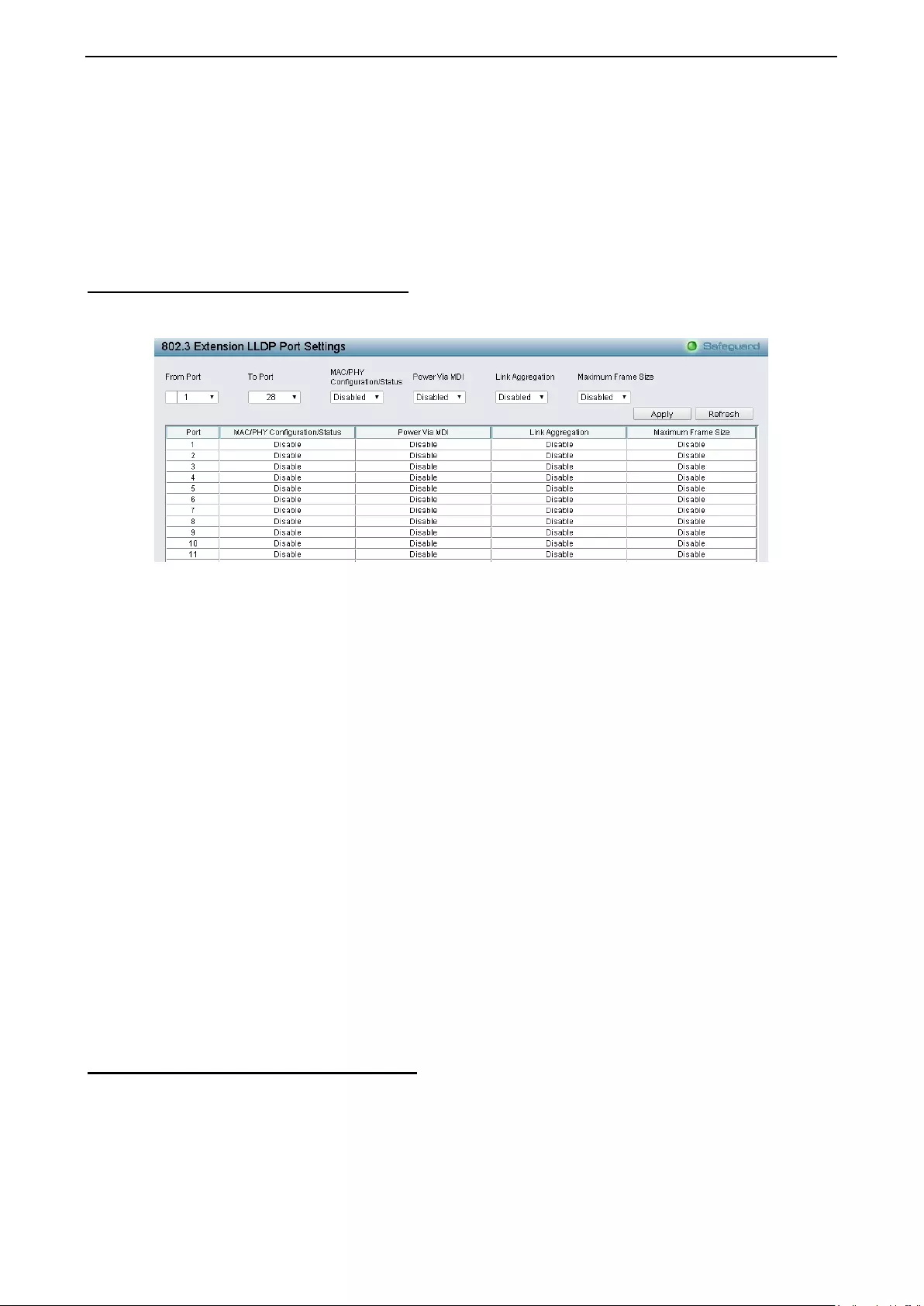
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
14
41
1
Protocol VLAN ID : Specifies the VLAN ID to be enabled or disabled in the LLDP port. If select Enabled,
users can specifies the content of VLAN ID.
VL AN N am e : Specif ies t h e VL AN n ame to be e nab le d or dis a bl ed in t h e LL DP p or t. If s elect En ab led, us er s
can specifies the content of VLAN Name.
Protocol Identity : Specifies the Protocol Identity to be enabled or disabled in the LLDP port. If select
Enabled, users can specifies the EAPOL, LACP, GVRP, STP or ALL.
Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the table information.
LLDP > 802.3 Extension LLDP Port Settings
The 802.3 Ext ension LLD P Port Set tings page displays 802.3 Extens ion LLDP po rt inform ation and conta ins
parameters for configuring 802.3 Extension L LD P port s ettin gs .
Figure 4.218 – LLDP > 802. 3 Extension LLDP Port S ettings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
MAC/PHY Configuration/Status: Specifies whether the MAC/PHY Configuration Status is enabled on the
port. The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables the MAC/PHY Configuration Status on the port.
Disabled – Disables th e MAC/PHY Config urat ion Sta tus on the port.
Power Via MDI: Advertises the Power via MDI implementations supported by the port. The possible field
values are:
Enabled – Enables the Power via MDI configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the Power via MDI configured on the port.
Link Aggregation: Specifies whether the link aggregation is enabled on the port. The possible field values
are:
Enabled – Enables the link aggregation configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the link aggregation configured on the port.
Maximum Frame Size: Specifies whether the Maximum Frame Size is enabled on the port. The possible
field values are:
Enabled – Enables the Maximum Frame Size configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the Maximum Frame Size configured on the port.
Define these parameter fields. Click Apply to implement changes made and click Refresh to refresh the
table information.
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
The LLDP Management Address Settings allows the user to set management address which is included in
LLDP information transmitted.
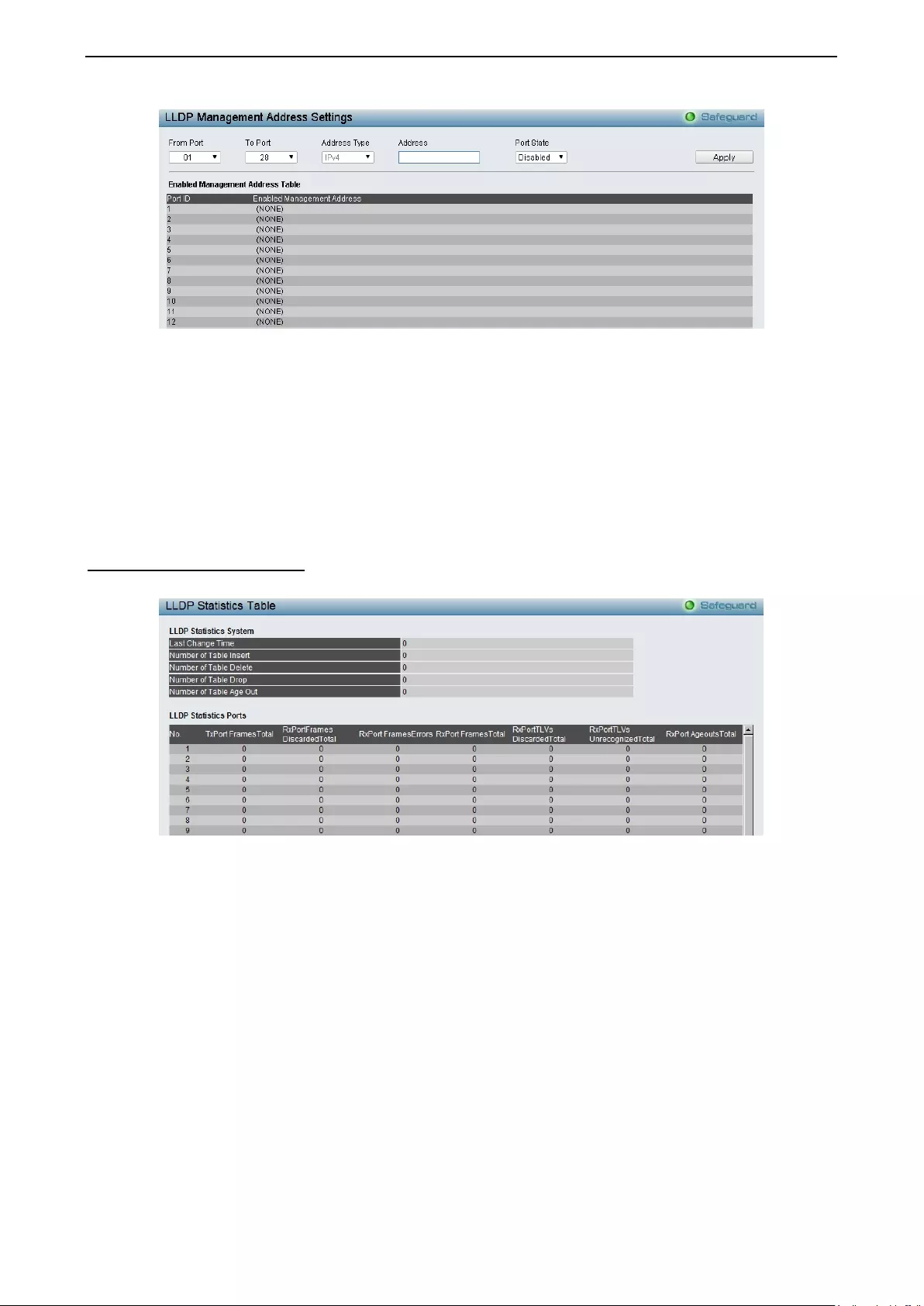
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
142
Figure 4.219 – LLDP > LLDP Management Address Settings
From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Address Type: Specify the LLDP address type on the port. The value is always IPv4.
Address: Specify the address.
Port State: Specify whether the Port State is enabled n the port. The possible field values are:
Enabled – Enables the port state configured on the port.
Disabled – Disables the port state configured on the port.
Click Apply to make the configurations take effect.
LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
The LLDP Statistics page displays an overview of all LLDP traffic.
Figure 4.220 – LLDP > LLDP Statistics Table
The following information can be viewed:
LLDP Statistics System: Displays the counters that refer to the whole switch.
Last Change Time – Displays t he tim e for when t he last c hange entr y was las t deleted or added. It
is also displays the time elapsed since last change was detected.
Number of Table Insert – Displays the number of new entries inserted since switch reboot.
Number of Table Delete – Displays the number of new entries deleted since switch reboot.
Number of Table Drop – Displays the number of LLDP frames dropped due to that the table was
full.
Number of Table Age Out – Displays the number of entries deleted due to Time-To-Live expiring.
LLDP Port S tatistics: Disp lays the counters that refer to the ports.
TxPort Fram esTotal – Displays the total number of LLDP frames transmitted on the port.
RxPort F ramesDisc arded – Displays the total discarded frame number of LLDP frames received on
the port.
RxPort FramesErrors – Displays the Error frame number of LLDP frames received on the port.
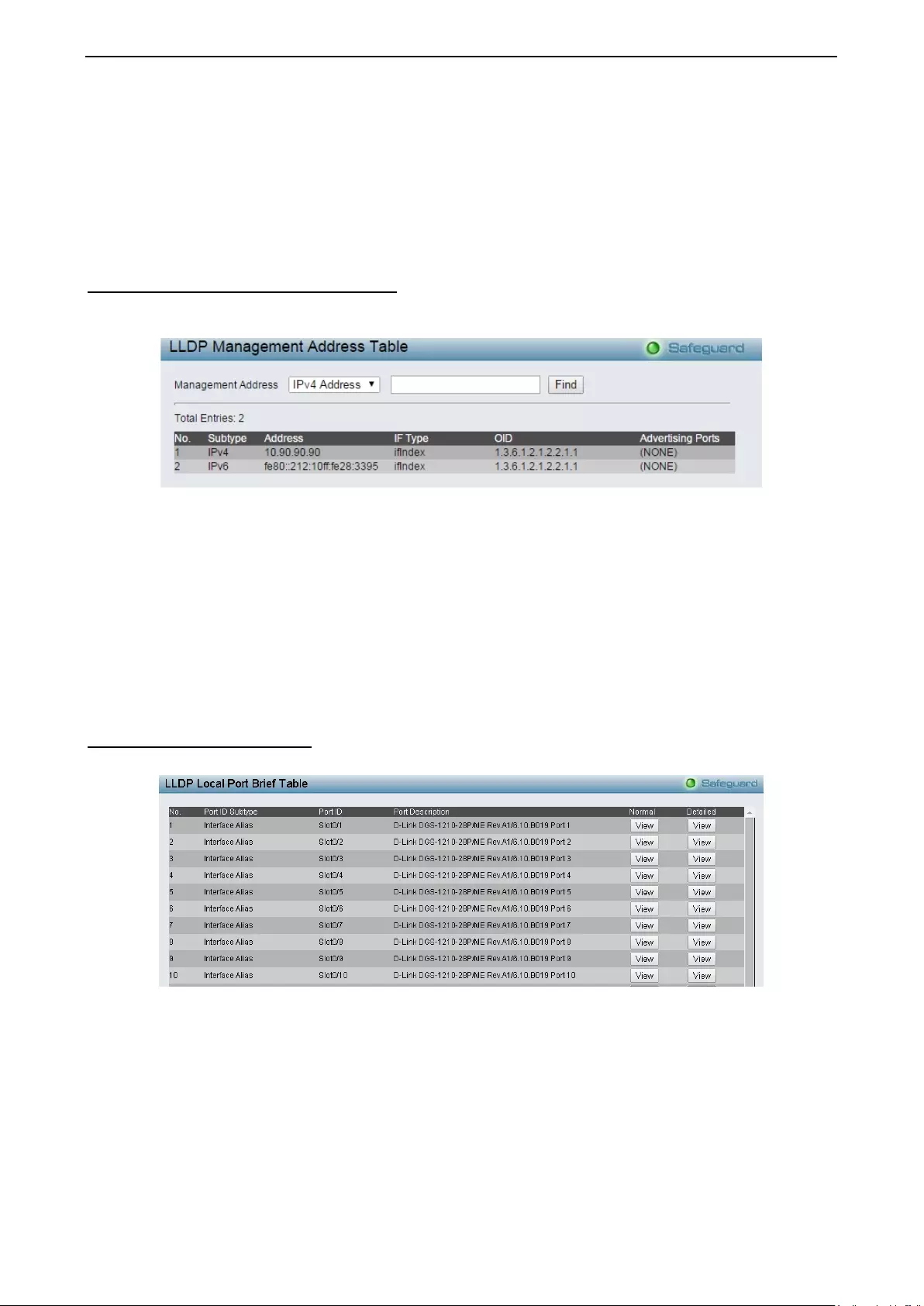
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
14
43
3
RxPort Frames – Displays the total number of LLDP frames received on the port.
RxPortTLVsDiscarded – Each LLDP frame can contain multiple pieces of information, known as
TLVs. If a TLV is malformed, it is counted and discarded.
RxPortTLVsUnrecognized – Displays the number of well-formed TLVs, but with a known type value.
RxPort Ageouts – Eac h L LDP f r am e c ontains inf or m atio n abo ut ho w lon g time the LLD P inf ormation is vali d.
If no ne w LLDP f r ame is received with in th e ag e out t i me, the LLDP inf or mation is r em oved, a nd th e A ge-Out
counter is incremented.
LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
The LLDP Management Address T able page displays the detailed m anagement address information for the
entry.
Figure 4.221 – LLDP > LLDP Management Address Table
Management Address: Specifies IPv4 or IPv6 address then enter the address. Click Search and the t able
will update and display the values required.
Subtype: Displays the managed address subtype. For example, MAC or IPv4.
Management Address: Di s plays the IP address.
IF Type: Displays the IF Type.
OID: Displays the SNMP OID.
Advertising Ports: Displays the advertising ports.
LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
The LLDP Local Port Table page displays LLDP local port information.
Figure 4.222 –LLDP > LLDP Local Port Table
No: Displays the port number.
Port ID Subtype: Displays the port ID subtype.
Port ID: Displays the port ID (U nit number/Port number).
Port Descrip tion: Displays the port description.
Click View of Normal column to d is p lay more information.
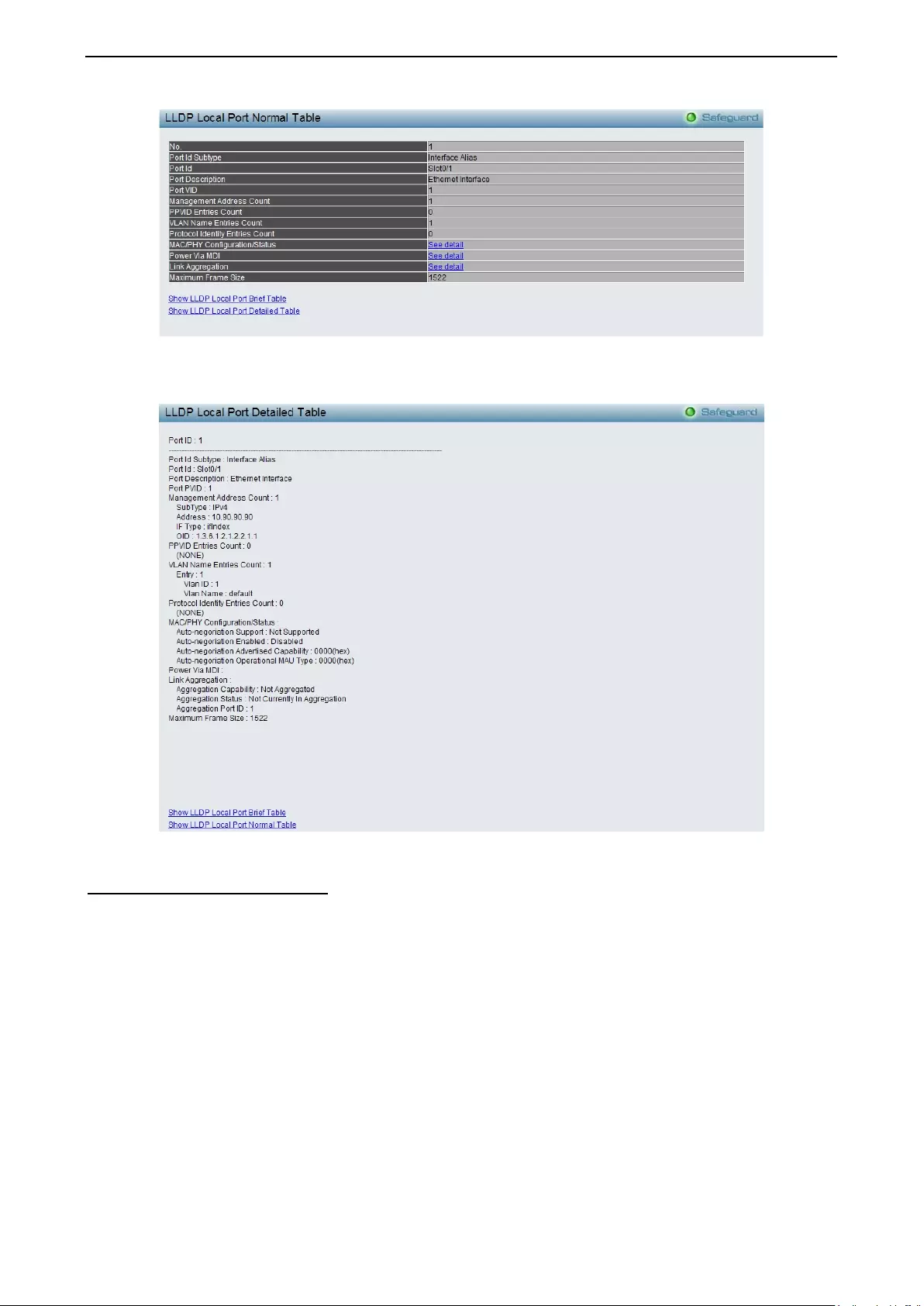
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
144
Figure 4.223 – LLDP > LL DP Local Port Normal Table
Click View of Detailed column to display detail information.
Figure 4.224 – LLDP > LLDP Local Port Det aile d Ta ble
LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
This LLDP Remote Port Table page is used to display the LLDP Remote Port Brief Table. Select port
number and click Search to display additional information.
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
14
45
5
Figure 4.225 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Table
To view the settings for a remote port, click View Normal and the following page displays.
Figure 4.226 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Normal Table
To view the detail settings for a remote port, click View Detailed and the following page displays.

4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
146
Figure 4.227 – LLDP > LLDP Remote Port Detail ed Tab le
LLDP > LLDP-MED Settings
By selecting a range of ports (From Port and To Port), the power PSE TLV type can be enabled for all
selected ports to indicate t h e po wer sour c e equ ipment (PSE) sw itc h t o transmit high p o wer (1 5.4 to 30 W atts)
to the pre-s tandard of 802.3at power devices via LLD P MDI TLV. Thr ough this featur e, the P SE can pr ovide
precise output power to the pre-standard of 802.3at power devices and achieve optimal power management.
Figure 4.228 – LLDP > LLDP –MED Setti ngs
L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
The Switch supports static routing for IPv4 formatted addressing. User can create up to 256 static route
entries for IPv4. For IPv4 static routes, once a static route has been set, the Switch will send an ARP request
packet to the next hop router that has been set by the user. Once an ARP response has been retrieved by
the Switch f r om that nex t hop, the r o ute bec omes ena ble d. Ho wever , if the ARP entry alread y exis ts, an AR P
request will not be sent.
The Switch also supports a floating static route, which means that the user may create an alternative static
route to a d if ferent next ho p. This sec o ndary next hop de v ice r o ute is consid er ed as a back up s tat ic ro ute for
when the primar y static route is down. If the primary route is lost, the backup route will up link and its status
will becom e active. E ntries into the S witch’s for wardin g table c an be made usi ng both an IP address subne t
mask and a gateway.
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
14
47
7
Figure 4.229 – L3 Functions > IPv4 Static Route
IPv4 Address: Specifies an IPv4 address to be assigned to the static route.
Netmask: Specifies a subnet mask to be applied to the corresponding subnet mask of the IPv4 address.
Gateway: Specifies the entry of a Gateway IP address to be applied to the corresponding gateway of the
IPv4 address.
Metric (1-65535): Represents the metric value of the IP interface entered into the table. The value ranges
between 1 and 65535.
Backup State: Each IP address can o nly have one primar y r oute, while other routes should be as signed to
the backup state. When the primary route failed, Switch will try the backup routes according to the order
learnt by the routing table until route success. The field represents the Backup state that the Static and
Default Route is configured for.
Click Add to create a new IPv4 static route entry.
L3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finder
The IPv4 routing table stores all the external routes information of the Switch. The IPv4 Routing Table
Finder page displays all the routing information on the Switch.
Figure 4.230 – L 3 Functions > IPv4 Routing Table Finde r
Network Address; Specifies the destination network address of the route to be displayed.
Click Search to display the information of specified route entry.
L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
A static entry of an IPv6 address can be entered into the Switch’s routing table for IPv6 formatted addresses.
4 Configuration DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
148
Figure 4.231 – L3 Functions > IPv6 Static Route
IPv6 Address / Prefix Length: Specifies an IPv6 address to be assigned to the static route.
Nexthop Address: Specifies the corresponding IPv6 address for the next hop gateway address in IPv6
format.
Metric (1-65535): Specifies a metric of the IPv6 interface into the table representing the number of routers
between the Switch and the IPv6 address above. The value ranges between 1 and 65535.
Backup State: Each IPv6 address can only have one prim ary route, while other routes should be assigned
to the backup state. When the primary route failed, the Switch will try the backup routes according to the
order learnt by the routing table until route success. This field represents the backup state for the IPv6
configured. This field may be Primary or Backup.
Click Add to create a new IPv6 static route entry.
L3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finder
The IPv6 routing table stores all the external routes information of the Switch. The IPv6 Routing Table
Finder page displays all the routing information on the Switch.
Figure 4.232 – L 3 Functions > IPv6 Routing Table Finde r
Network Address; Specifies the destination network address of the route to be displayed.
Click Search to display the information of specified route entry.
Appendi x A - Ethernet Technology DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
149
Appendix A - Ethernet Tec hnology
This chapter will describe the features of the D-Link and provide some background information about
Ethernet/Fas t Et her net /Gigabit Ethernet switching technology.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format, and
support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex, and management objects, but with a tenfold increase in
theoretical throughput of over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a hundredfold increase over 10-Mbps Ethernet.
Since it is compatible with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit Ethernet provides a
straightf or ward upgr a de wit hout was ti ng existing investments in hardware, software, or trained personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet is essential in solving network
bottlenecks, which frequently develops as more advanced computer users and newer applications continue
to demand greater network resources. Upgrading key components, such as backbone connections and
servers to Gigabit Ethernet technology, can greatly improve network response times as well as significantly
speed up the traffic between subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enabl es fast optica l fiber connecti ons to suppor t video conferenc ing, com plex imaging, and
similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet,
servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to perform 10 times the number of operations in the
same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet is the most cost-effective method to
take advantage of today and tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technolog ies. With expec ted ad vanc es i n the c oming years in sil icon technology and digit al si gna l proc es s in g ,
which will enable Gigabit Ethernet to eventually operate over unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling, a flexible
foundation for the next generation of network technology products will be created. This will outfit your
network with a powerful 1000-Mbps-capable backbone/server connection.
Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs, and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications are
fueling the need for high performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies have been
propose d t o pr ovid e gr eate r ban d width a nd improve cli ent/s er v er r esponse t im es . Among t hem, 100B AS E-T
(Fast Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the current 10BASE-T technology. The
non-disruptive and smooth evolution nature, and the dominating potential market base, virtually guarantees
cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3 LAN committee. It is an extension of the
10Mbps Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while maintaining the
CSMA/CD Ethern et protoc ol. S ince the 100M bps F ast Etherne t is com patible with a ll ot her 10Mbps Ether net
environm ents, it provides a straightforward upgrade and utilizes existing investments in hardware, software,
and personn el trai nin g.
Switching Technology
Another approach to push beyond the limits of Ethernet technology is the development of switching
technology. A s witch br i dge s Ethern et p ac kets at the M AC a ddr es s le ve l of the Et h er net pr ot oco l tr ans mitting
among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-effective way of increasing the total network capacity available to users on a local area
network. A switch increases capacity and decreases network loading by dividing a local area network into
different segments, which won’t compete with each other for network transmission capacity.
The switch acts as a high-speed selective bridge between the individual segments. The switch, without
interfering with any other segments, automatically forwards traffic that needs to go from one segment to
another. By doing this the total network capacity is multiplied, while still maintaining the same network
cabling and ad apter cards .

Appendi x B - Ethernet Technology DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
150
Appendix B - Ethernet Technology
Features
L2 Features
Supports up to 16K MAC address
Supports 256 static MAC
IGMP snooping:
- Supports 1024 multicast groups shared
with MLD
- Supports at least 256 static multicast
groups
Limited IP Multicast:
- Support up to 24 profiles and each
profile can add up to 1024 multicast
groups
- Able to c onf igure the maximum multicast
group number for a port, ranging from 1-
256
MLD Snooping:
- Supports 1024 M LD sn oo ping grou ps
shared with IGMP
- Supports 256 static multicast
addresses
802.1D Spanning Tree
802.1w RSTP
802.1s MSTP: up to 64 instances
Loopback Detection
802.3ad Link Aggregation: Sup port max 8
groups per device, 8 ports per group
Port mirroring
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery:
- Supports Max 512 ND entries
- Support up to 64 static ND entries
SNTP
LLDP
L2 Multicast Filtering
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN standard (VLAN Tagging)
Total 4094 VLAN groups
Asymmetric VLAN
Management VLAN
ISM VLAN
Private VLAN
GVRP: Support 256 dynamic VLANs
VLAN Trunking
Supports Port-based Q-in-Q
L3 Features
ARP:
- Max 256 AR P entr i es
- Support 255 static ARP
- Support Gratuitous ARP
IPv4 / IPv6 Static Route
QoS (Quality of Service)
Be able to classify packets according to
follow contents:
- Switch port
- 802.1p priority
- VID
- MAC address
- IP address
- IPv6 Traffic Class
- TCP/UDP Port
- DSCP
- TOS
- Protocol type
- TCP/UDP port number Up to 8 queues
per port
Supports Strict / WRR mode in queue
handling
Support Port and Flow based bandwidth
control
AAA
802.1X Local/RADIUS/TACACS+ server
802.1X port-based/MAC-based access
control
RADIUS Accounting: Support Network
accounting (for 802.1x user)
User Account Privilege for Management
Access:
- Support 4 level user accounts
- Operator (Read/Write)
- Administrator (Read/Write)
- Power user (for account
management and service)
- User (read only)
ACL
Max 6 ingress ACL profile, 128 ingress
ACL rules per AC: profile, total 768
ingress ACL rules
Each rule can be associated to a single
port, multiple ports
Support different ACL policy packet
contents:
- Switch port
- MAC address
- Ether type
- IPv4 address
- IPv6 address
- TOS
- 802.1p
- DSCP
- Protocol type

Appendi x B - Ethernet Technology DGS-1210 series Metro Ethernet Managed Switch User Manual
1
15
51
1
- TCP/UDP port number
- IPv6 traffic class
Security
Trusted Host
Port Security: Support 64 MACs per port
Traffic Segmentation
D-Link Safeguard Engine
Broadcast Storm Control
DHCP Server Sc r eening: A ble to
configure IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for
DHCP server.
SSH: Support v2 and IPv6
SSL: Support v3, IPv4 and IPv6
Smart Binding
- Supports D-Link IMPB
- Sup por t s ARP pac ket Inspect ion as d ef ault ,
ARP and IP packet Inspection as option.
- Supports DHCP Snooping
Dos Attack Prevention
OAM
Cable Diagnostics: Detect and show
cable length and status
802.3ah
- Support 802.3ah link layer remote
loopback and discovery
- 802.3ah D-Link extension: D-link
Undirectional Link Detection (DULD)
Management
Web-based GUI
D-Link proprietary CLI
Telnet Server
SNMP support
DHCP client
DHCP Relay: Support DHCP local relay,
option 82 and 12.
DHCPv6 Relay: Support DHCP local relay
and option 37
SNMP Trap
System Log: Support log server with IPv4
or IPv6 address
RMON v1/v2
Password access control
Password Enc r yptio n
Web-based configuration backup /
restoration
Reset, Reboot

140