Table of Contents
- Dell Latitude 5420 Rugged Service Manual
- Working on your computer
- Technology and components
- Using your computer
- AC-DC Adapters
- Battery
- Processors
- Memory features
- Graphics options
- Corning Gorilla Glass
- Pen Usage
- Media Card Readers
- UEFI BIOS
- Systems management - From on-premises to the cloud
- Trusted Platform Module
- Fingerprint Reader
- USB features
- USB Powershare
- USB Type-C
- Ethernet
- HDMI 2.0
- Software and Troubleshooting
- Chipsets
- Processor
- Verifying system memory
- Display
- Identifying the display adapter
- Identifying the display adapter
- Downloading drivers
- Adjusting brightness in Windows 10
- Adjusting brightness in Windows 7
- Changing the screen resolution
- Connecting to external display devices
- Changing the display settings in Intel HD Graphics Control Panel
- Using touch screen in Windows 8/ Windows 10
- Touchscreen Troubleshooting
- Cleaning the display
- Troubleshooting Touchpad
- Troubleshooting Your Pen
- Realtek HD audio drivers
- Camera features
- Hard drive options
- Dell Command Configure
- Intel HD Graphics drivers
- Removing and installing components
- Safety instructions
- Recommended tools
- Stylus
- SIM card
- Memory card
- Handle
- Latch Doors
- Battery
- Primary SSD carrier
- SSD
- Bottom Chassis Cover
- Keyboard
- WWAN card
- WLAN card
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Memory modules
- Coin-cell battery
- PCIe Heatsink Fan Assembly
- Primary SSD Rail
- Docking Port Assembly
- Heatsink Assembly
- Rear Input-Output Board
- Hinge Covers
- Display assembly
- LCD Bezel and Back Cover Assembly
- Microphone
- Camera
- Battery Bay
- Left I/O board
- Smart Card
- Speaker
- System board
- Bottom Base Assembly
- Diagnostics
- Getting help
DELL 5420 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 5420 by DELL which is a product in the Notebooks category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Dell Latitude 5420 Rugged
Service Manual
Regulatory Model: P85G
Regulatory Type: P85G001

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid the
problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2018 2019 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its
subsidiaries. Other trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.
2019 - 05
Rev. A01

1 Working on your computer.............................................................................................................7
Safety instructions.................................................................................................................................................................7
Safety precautions...........................................................................................................................................................7
Electrostatic discharge—ESD protection.................................................................................................................... 8
ESD field service kit ........................................................................................................................................................8
Transporting sensitive components.............................................................................................................................. 9
Turning off your computer................................................................................................................................................... 9
Turning off your — Windows........................................................................................................................................ 9
Turning off your computer — Windows 7..................................................................................................................10
Before working inside your computer................................................................................................................................10
After working inside your computer.................................................................................................................................. 10
2 Technology and components........................................................................................................ 11
Using your computer............................................................................................................................................................ 11
Open the LCD Lid............................................................................................................................................................11
Stealth mode...................................................................................................................................................................12
Using the backlit keyboard............................................................................................................................................ 12
Enabling and disabling the wireless (WiFi) feature.....................................................................................................14
Hot key definition........................................................................................................................................................... 14
AC-DC Adapters...................................................................................................................................................................16
90W..................................................................................................................................................................................16
130W.................................................................................................................................................................................17
LED and Cable................................................................................................................................................................ 18
Battery...................................................................................................................................................................................19
Battery Specifications....................................................................................................................................................19
Processors............................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Skylake processor..........................................................................................................................................................20
Kaby Lake — 7th and 8th Generation Intel Core processors...................................................................................21
Memory features................................................................................................................................................................. 22
DDR4............................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Graphics options..................................................................................................................................................................23
Graphics Specifications.................................................................................................................................................23
AMD Radeon 540 Graphics..........................................................................................................................................28
AMD Radeon RX 540 Graphics................................................................................................................................... 28
Corning Gorilla Glass........................................................................................................................................................... 29
Benefits...........................................................................................................................................................................29
Pen Usage............................................................................................................................................................................. 31
Pen Flicks........................................................................................................................................................................32
Media Card Readers............................................................................................................................................................33
UEFI BIOS.............................................................................................................................................................................34
Systems management - From on-premises to the cloud ....................................................................................34
Out-of-Band Systems Management- Intel vPro and Intel Standard Manageability.............................................35
Trusted Platform Module................................................................................................................................................... 35
Fingerprint Reader...............................................................................................................................................................36
Contents
Contents 3

USB features........................................................................................................................................................................36
USB Powershare................................................................................................................................................................. 38
USB Type-C......................................................................................................................................................................... 38
Ethernet................................................................................................................................................................................39
HDMI 2.0.............................................................................................................................................................................. 40
Software and Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................................... 41
Chipsets...........................................................................................................................................................................41
Processor........................................................................................................................................................................43
Verifying system memory ............................................................................................................................................ 44
Display............................................................................................................................................................................. 45
Troubleshooting Touchpad...........................................................................................................................................48
Troubleshooting Your Pen............................................................................................................................................ 49
Realtek HD audio drivers.............................................................................................................................................. 49
Camera features............................................................................................................................................................50
Hard drive options..........................................................................................................................................................51
Dell Command Configure..............................................................................................................................................57
Intel HD Graphics drivers..............................................................................................................................................60
3 Removing and installing components............................................................................................ 61
Safety instructions............................................................................................................................................................... 61
Before working inside your computer..........................................................................................................................61
Safety Precautions........................................................................................................................................................ 62
After working inside your computer............................................................................................................................68
Recommended tools........................................................................................................................................................... 68
Stylus ................................................................................................................................................................................... 68
Removing the stylus......................................................................................................................................................68
Installing the stylus........................................................................................................................................................ 69
SIM card............................................................................................................................................................................... 70
Removing the SIM card................................................................................................................................................ 70
Installing the SIM card....................................................................................................................................................71
Memory card........................................................................................................................................................................ 72
Installing the memory card............................................................................................................................................72
Removing the memory card......................................................................................................................................... 72
Handle................................................................................................................................................................................... 73
Removing the Handle.................................................................................................................................................... 73
Installing the Handle...................................................................................................................................................... 74
Latch Doors..........................................................................................................................................................................75
Removing the latch doors.............................................................................................................................................75
Installing the latch doors............................................................................................................................................... 75
Battery.................................................................................................................................................................................. 76
Removing the Battery................................................................................................................................................... 76
Installing the Batteries...................................................................................................................................................77
Primary SSD carrier.............................................................................................................................................................78
Removing the Primary SSD carrier..............................................................................................................................78
Installing the Primary SSD carrier................................................................................................................................ 79
SSD....................................................................................................................................................................................... 80
Removing the SSD from carrier...................................................................................................................................80
Installing the SSD in carrier........................................................................................................................................... 81
Bottom Chassis Cover.........................................................................................................................................................81
Removing the Bottom Chassis Cover......................................................................................................................... 81
4Contents

Installing the Bottom Chassis Cover........................................................................................................................... 82
Keyboard...............................................................................................................................................................................84
Removing the Keyboard............................................................................................................................................... 84
Installing the Keyboard..................................................................................................................................................85
WWAN card......................................................................................................................................................................... 87
Removing the WWAN card.......................................................................................................................................... 87
Installing the WWAN card............................................................................................................................................ 88
WLAN card...........................................................................................................................................................................89
Removing the WLAN card............................................................................................................................................89
Installing the WLAN card.............................................................................................................................................. 89
Global Positioning System (GPS)......................................................................................................................................90
Removing the GPS module.......................................................................................................................................... 90
Installing the GPS module............................................................................................................................................. 91
Memory modules................................................................................................................................................................. 93
Removing the Memory................................................................................................................................................. 93
Installing the Memory....................................................................................................................................................93
Coin-cell battery.................................................................................................................................................................. 94
Removing the Coin cell................................................................................................................................................. 94
Installing the Coin cell....................................................................................................................................................95
PCIe Heatsink Fan Assembly............................................................................................................................................. 96
Removing the PCIe Heatsink fan assembly............................................................................................................... 96
Installing the PCIe heatsink fan assembly...................................................................................................................97
Primary SSD Rail..................................................................................................................................................................99
Removing the Primary SSD rail....................................................................................................................................99
Installing the Primary SSD rail.....................................................................................................................................100
Docking Port Assembly...................................................................................................................................................... 101
Removing the Docking port assembly........................................................................................................................101
Installing the Docking Port Assembly........................................................................................................................ 102
Heatsink Assembly.............................................................................................................................................................103
Removing the Heatsink assembly.............................................................................................................................. 103
Installing the Heatsink assembly................................................................................................................................ 105
Rear Input-Output Board..................................................................................................................................................106
Removing the Rear I-O board.................................................................................................................................... 106
Installing the Rear I-O board....................................................................................................................................... 107
Hinge Covers......................................................................................................................................................................109
Removing the Hinge Covers.......................................................................................................................................109
Installing the Hinge Covers..........................................................................................................................................110
Display assembly................................................................................................................................................................. 112
Removing the Display assembly.................................................................................................................................. 112
Installing the Display Assembly....................................................................................................................................114
LCD Bezel and Back Cover Assembly..............................................................................................................................116
Removing the LCD with bezel and the display back cover assembly.................................................................... 116
Installing the LCD with bezel and the display back cover assembly.......................................................................117
Microphone..........................................................................................................................................................................119
Removing the Microphone.......................................................................................................................................... 119
Installing the Microphone............................................................................................................................................120
Camera................................................................................................................................................................................ 122
Removing the Camera.................................................................................................................................................122
Installing the Camera................................................................................................................................................... 122
Battery Bay ........................................................................................................................................................................ 123
Contents 5

Removing the Battery bay.......................................................................................................................................... 123
Installing the Battery bay ............................................................................................................................................124
Left I/O board.................................................................................................................................................................... 125
Removing the Left I/O daughterboard..................................................................................................................... 125
Installing the Left I/O Board....................................................................................................................................... 126
Smart Card..........................................................................................................................................................................128
Removing the Smart Card Reader.............................................................................................................................128
Installing the Smart Card Reader............................................................................................................................... 130
Speaker................................................................................................................................................................................132
Removing the Speaker................................................................................................................................................ 132
Installing the Speaker...................................................................................................................................................133
System board......................................................................................................................................................................134
Removing the System board...................................................................................................................................... 134
Installing the System board.........................................................................................................................................137
Bottom Base Assembly...................................................................................................................................................... 141
4 Diagnostics...............................................................................................................................144
ePSA Diagnostics............................................................................................................................................................... 144
Validation Tools ............................................................................................................................................................147
LCD Built-in Self Test .......................................................................................................................................................153
Battery Status Lights........................................................................................................................................................ 154
Diagnostic LED................................................................................................................................................................... 154
Wi-Fi power cycle.............................................................................................................................................................. 155
BIOS recovery.................................................................................................................................................................... 155
BIOS recovery using hard drive..................................................................................................................................155
BIOS recovery using USB key.................................................................................................................................... 156
Self-Heal............................................................................................................................................................................. 156
Course Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 156
Self-Heal Instruction.................................................................................................................................................... 157
Supported Latitude Models........................................................................................................................................ 157
5 Getting help............................................................................................................................. 158
Contacting Dell...................................................................................................................................................................158
6Contents

Working on your computer
Safety instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to protect your computer from potential damage and to ensure your personal safety. Unless otherwise
noted, each procedure included in this document assumes that the following conditions exist:
• You have read the safety information that shipped with your computer.
• A component can be replaced or, if purchased separately, installed by performing the removal procedure in reverse order.
NOTE: Disconnect all power sources before opening the computer cover or panels. After you finish working inside the
computer, replace all covers, panels, and screws before connecting to the power source.
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For
additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform troubleshooting and
simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or telephone service and
support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow
the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching
an unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
CAUTION: Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a card. Hold a card by
its edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as a processor by its edges, not by its pins.
CAUTION: When you disconnect a cable, pull on its connector or on its pull-tab, not on the cable itself. Some cables
have connectors with locking tabs; if you are disconnecting this type of cable, press in on the locking tabs before you
disconnect the cable. As you pull connectors apart, keep them evenly aligned to avoid bending any connector pins. Also,
before you connect a cable, ensure that both connectors are correctly oriented and aligned.
NOTE: The color of your computer and certain components may appear differently than shown in this document.
Safety precautions
The safety precautions chapter details the primary steps to be taken before performing any disassembly instructions.
Observe the following safety precautions before you perform any installation or break/fix procedures involving disassembly or reassembly:
• Turn off the system and all attached peripherals.
• Disconnect the system and all attached peripherals from AC power.
• Disconnect all network cables, telephone, and telecommunications lines from the system.
• Use an ESD field service kit when working inside any notebook to avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
• After removing any system component, carefully place the removed component on an anti-static mat.
• Wear shoes with non-conductive rubber soles to reduce the chance of getting electrocuted.
Standby power
Dell products with standby power must be unplugged before you open the case. Systems that incorporate standby power are essentially
powered while turned off. The internal power enables the system to be remotely turned on (wake on LAN) and suspended into a sleep
mode and has other advanced power management features.
Unplugging, pressing and holding the power button for 15 seconds should discharge residual power in the system board. Remove the
battery from notebooks.
1
Working on your computer 7

Bonding
Bonding is a method for connecting two or more grounding conductors to the same electrical potential. This is done through the use of a
field service electrostatic discharge (ESD) kit. When connecting a bonding wire, ensure that it is connected to bare metal and never to a
painted or non-metal surface. The wrist strap should be secure and in full contact with your skin, and ensure that you remove all jewelry
such as watches, bracelets, or rings prior to bonding yourself and the equipment.
Electrostatic discharge—ESD protection
ESD is a major concern when you handle electronic components, especially sensitive components such as expansion cards, processors,
memory DIMMs, and system boards. Very slight charges can damage circuits in ways that may not be obvious, such as intermittent
problems or a shortened product life span. As the industry pushes for lower power requirements and increased density, ESD protection is
an increasing concern.
Due to the increased density of semiconductors used in recent Dell products, the sensitivity to static damage is now higher than in
previous Dell products. For this reason, some previously approved methods of handling parts are no longer applicable.
Two recognized types of ESD damage are catastrophic and intermittent failures.
•Catastrophic – Catastrophic failures represent approximately 20 percent of ESD-related failures. The damage causes an immediate
and complete loss of device functionality. An example of catastrophic failure is a memory DIMM that has received a static shock and
immediately generates a "No POST/No Video" symptom with a beep code emitted for missing or nonfunctional memory.
•Intermittent – Intermittent failures represent approximately 80 percent of ESD-related failures. The high rate of intermittent failures
means that most of the time when damage occurs, it is not immediately recognizable. The DIMM receives a static shock, but the
tracing is merely weakened and does not immediately produce outward symptoms related to the damage. The weakened trace may
take weeks or months to melt, and in the meantime may cause degradation of memory integrity, intermittent memory errors, etc.
The more difficult type of damage to recognize and troubleshoot is the intermittent (also called latent or "walking wounded") failure.
Perform the following steps to prevent ESD damage:
• Use a wired ESD wrist strap that is properly grounded. The use of wireless anti-static straps is no longer allowed; they do not provide
adequate protection. Touching the chassis before handling parts does not ensure adequate ESD protection on parts with increased
sensitivity to ESD damage.
• Handle all static-sensitive components in a static-safe area. If possible, use anti-static floor pads and workbench pads.
• When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the component from the anti-static packing
material until you are ready to install the component. Before unwrapping the anti-static packaging, ensure that you discharge static
electricity from your body.
• Before transporting a static-sensitive component, place it in an anti-static container or packaging.
ESD field service kit
The unmonitored Field Service kit is the most commonly used service kit. Each Field Service kit includes three main components: anti-
static mat, wrist strap, and bonding wire.
Components of an ESD field service kit
The components of an ESD field service kit are:
•Anti-Static Mat – The anti-static mat is dissipative and parts can be placed on it during service procedures. When using an anti-
static mat, your wrist strap should be snug and the bonding wire should be connected to the mat and to any bare metal on the system
being worked on. Once deployed properly, service parts can be removed from the ESD bag and placed directly on the mat. ESD-
sensitive items are safe in your hand, on the ESD mat, in the system, or inside a bag.
•Wrist Strap and Bonding Wire – The wrist strap and bonding wire can be either directly connected between your wrist and bare
metal on the hardware if the ESD mat is not required, or connected to the anti-static mat to protect hardware that is temporarily
placed on the mat. The physical connection of the wrist strap and bonding wire between your skin, the ESD mat, and the hardware is
known as bonding. Use only Field Service kits with a wrist strap, mat, and bonding wire. Never use wireless wrist straps. Always be
aware that the internal wires of a wrist strap are prone to damage from normal wear and tear, and must be checked regularly with a
wrist strap tester in order to avoid accidental ESD hardware damage. It is recommended to test the wrist strap and bonding wire at
least once per week.
•ESD Wrist Strap Tester – The wires inside of an ESD strap are prone to damage over time. When using an unmonitored kit, it is a
best practice to regularly test the strap prior to each service call, and at a minimum, test once per week. A wrist strap tester is the
best method for doing this test. If you do not have your own wrist strap tester, check with your regional office to find out if they have
one. To perform the test, plug the wrist-strap's bonding-wire into the tester while it is strapped to your wrist and push the button to
test. A green LED is lit if the test is successful; a red LED is lit and an alarm sounds if the test fails.
8Working on your computer

•Insulator Elements – It is critical to keep ESD sensitive devices, such as plastic heat sink casings, away from internal parts that are
insulators and often highly charged.
•Working Environment – Before deploying the ESD Field Service kit, assess the situation at the customer location. For example,
deploying the kit for a server environment is different than for a desktop or portable environment. Servers are typically installed in a
rack within a data center; desktops or portables are typically placed on office desks or cubicles. Always look for a large open flat work
area that is free of clutter and large enough to deploy the ESD kit with additional space to accommodate the type of system that is
being repaired. The workspace should also be free of insulators that can cause an ESD event. On the work area, insulators such as
Styrofoam and other plastics should always be moved at least 12 inches or 30 centimeters away from sensitive parts before physically
handling any hardware components
•ESD Packaging – All ESD-sensitive devices must be shipped and received in static-safe packaging. Metal, static-shielded bags are
preferred. However, you should always return the damaged part using the same ESD bag and packaging that the new part arrived in.
The ESD bag should be folded over and taped shut and all the same foam packing material should be used in the original box that the
new part arrived in. ESD-sensitive devices should be removed from packaging only at an ESD-protected work surface, and parts
should never be placed on top of the ESD bag because only the inside of the bag is shielded. Always place parts in your hand, on the
ESD mat, in the system, or inside an anti-static bag.
•Transporting Sensitive Components – When transporting ESD sensitive components such as replacement parts or parts to be
returned to Dell, it is critical to place these parts in anti-static bags for safe transport.
ESD protection summary
It is recommended that all field service technicians use the traditional wired ESD grounding wrist strap and protective anti-static mat at all
times when servicing Dell products. In addition, it is critical that technicians keep sensitive parts separate from all insulator parts while
performing service and that they use anti-static bags for transporting sensitive components.
Transporting sensitive components
When transporting ESD sensitive components such as replacement parts or parts to be returned to Dell, it is critical to place these parts in
anti-static bags for safe transport.
Lifting equipment
Adhere to the following guidelines when lifting heavy weight equipment:
CAUTION: Do not lift greater than 50 pounds. Always obtain additional resources or use a mechanical lifting device.
1. Get a firm balanced footing. Keep your feet apart for a stable base, and point your toes out.
2. Tighten stomach muscles. Abdominal muscles support your spine when you lift, offsetting the force of the load.
3. Lift with your legs, not your back.
4. Keep the load close. The closer it is to your spine, the less force it exerts on your back.
5. Keep your back upright, whether lifting or setting down the load. Do not add the weight of your body to the load. Avoid twisting your
body and back.
6. Follow the same techniques in reverse to set the load down.
Turning off your computer
Turning off your — Windows
CAUTION: To avoid losing data, save and close all open files and exit all open programs before you turn off your
computer .
1. Click or tap .
2. Click or tap and then click or tap Shut down.
NOTE: Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached devices did
not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the power button for about 6
seconds to turn them off.
Working on your computer 9

Turning off your computer — Windows 7
CAUTION: To avoid losing data, save and close all open files and exit all open programs before you turn off your
computer.
1. Click Start.
2. Click Shut Down.
NOTE: Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached devices did
not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the power button for about 6
seconds to turn them off.
Before working inside your computer
1. Ensure that your work surface is flat and clean to prevent the computer cover from being scratched.
2. Turn off your computer.
3. If the computer is connected to a docking device (docked), undock it.
4. Disconnect all network cables from the computer (if available).
CAUTION: If your computer has an RJ45 port, disconnect the network cable by first unplugging the cable from your
computer.
5. Disconnect your computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
6. Open the display.
7. Press and hold the power button for few seconds, to ground the system board.
CAUTION: To guard against electrical shock unplug your computer from the electrical outlet before performing Step
# 8.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically
touching an unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
8. Remove any installed ExpressCards or Smart Cards from the appropriate slots.
After working inside your computer
After you complete any replacement procedure, ensure that you connect external devices, cards, and cables before turning on your
computer.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the computer, use only the battery designed for this particular Dell computer. Do not use
batteries designed for other Dell computers.
1. Connect any external devices, such as a port replicator or media base, and replace any cards, such as an ExpressCard.
2. Connect any telephone or network cables to your computer.
CAUTION: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network device and then plug it into the
computer.
3. Connect your computer and all attached devices to their electrical outlets.
4. Turn on your computer.
10 Working on your computer

Technology and components
This chapter details the technology and components available in the system.
Topics:
•Using your computer
•AC-DC Adapters
•Battery
•Processors
•Memory features
•Graphics options
•Corning Gorilla Glass
•Pen Usage
•Media Card Readers
•UEFI BIOS
•Systems management - From on-premises to the cloud
•Trusted Platform Module
•Fingerprint Reader
•USB features
•USB Powershare
•USB Type-C
•Ethernet
•HDMI 2.0
•Software and Troubleshooting
Using your computer
Open the LCD Lid
2
Technology and components 11

1. Press LCD latch located on the bottom chassis.
2. Lift the LCD lid at an convenient viewing angle.
NOTE: Laptops are designed to allow LCD lid movement to a maximum of 180°, however lid should not be opened more
than 140°, if the rear I/O ports are in use or when docked.
Stealth mode
Latitude rugged products come equipped with a stealth mode feature. Stealth mode allows you to turn off the display, all the LED lights,
internal speakers, the fan and all wireless radios with a single key combination.
NOTE: This mode is aimed at using the computer in covert operations. When the stealth mode is enabled, the computer
remains functional but does not emit any light or sound.
Turning stealth mode on/off
1. Press the Fn+F7 key combination (Fn key not needed if Fn lock is enabled) to turn on stealth mode.
NOTE: Stealth mode is a secondary function of the F7 key. The key can be used to perform other functions on the
computer when not used with the Fn key to enable stealth mode.
2. All the lights and sounds are turned off.
3. Press the Fn+F7 key combination again to turn off the stealth mode.
Disabling stealth mode in the system setup (BIOS)
1. Power off the computer.
2. Power on the computer and at the Dell logo, tap the F2 key repeatedly to bring up the System Setup menu.
3. Expand and open the System Configuration menu.
4. Select Stealth Mode Control.
NOTE: Stealth mode is enabled by default.
5. To disable stealth mode uncheck the Enable Stealth Mode option.
6. Click Apply changes and click Exit.
Using the backlit keyboard
The Latitude rugged series comes equipped with a backlit keyboard that can be customized. The following colors are enabled:
1. White
2. Red
3. Green
4. Blue
Alternatively, the system can be configured with two additional custom colors in the System Setup (BIOS).
Turning the keyboard backlight on/off or adjusting brightness
To turn the backlight on/off or adjust the backlight brightness settings:
12 Technology and components

1. To initialize the keyboard backlight switch, press Fn+F10 (the Fn key is not needed if function key Fn lock is enabled).
2. The first use of the preceding key combination turns on the backlight to its lowest setting.
3. Repeated pressing of the key combinations cycles the brightness settings through 25 percent, 50 percent, 75 percent and
100 percent.
4. Cycle through the key combination to either adjust the brightness or turn off the keyboard backlight.
Changing the keyboard backlight color
To change the keyboard backlight color:
1. To cycle through the available backlight colors press Fn+C keys .
2. White, Red, Green and Blue are active by default; up to two custom colors can be added to the cycle in the System Setup (BIOS).
Customizing the backlit keyboard in System Setup (BIOS)
1. Turn off the computer.
2. Turn on the computer and when the Dell logo appears, press the F2 key repeatedly to bring up the System Setup menu.
3. Under System Configuration menu, select RGB Keyboard Backlight.
You can enable/disable the standard colors (White, Red, Green and Blue).
4. To set a custom RGB value, use the input boxes on the right side of the screen.
5. Click Apply changes and click Exit to close System Setup.
Function Fn key lock features
NOTE: The keyboard has Function key Fn lock capability. When activated, the secondary functions on the top row of
keys become default and will not require use of the Fn key.
Technology and components 13

Figure 1. Fn key callouts
1. Fn lock key
2. Affected Fn keys
3. Fn key
NOTE: Fn lock affects only the above keys (F1 to F12). Secondary functions will not require the Fn key to be pressed
while enabled.
Enabling the Function (Fn) lock
1. Press the Fn+Esc keys.
NOTE: Other secondary function keys on the top row are not affected and requires the use of the Fn key.
2. Press the Fn+Esc keys again to deactivate the function lock feature.
The function keys return to the default actions.
Enabling and disabling the wireless (WiFi) feature
1. To enable wireless Networking, press Fn + PrtScr.
2. Press Fn + PrtScr again to disable wireless Networking.
Hot key definition
Fn behavior: Primary behavior is media key; Secondary behavior is F1-F12 key.
• Fn Lock only switches primary and secondary behavior on F1-F12.
• F7 is stealth –unique for rugged and semi rugged platforms. It turns off LCD, all wireless, all alerts, indicator lights, sound, fan, etc
14 Technology and components

Table 1. Keyboard shortcuts
Hot keys Function Description
Fn+ESC Fn Lock Allows the user to toggle between
locked and unlocked Fn keys.
Fn+F1 Audio Volume Mute Temporarily mutes/unmutes the
audio. The audio level before muting
is returned after unmuting.
Fn+F2 Audio Volume Down/Decrease Decreases the audio volume until
minimum/off is reached.
Fn+F3 Audio Volume Up/Increase Increases the audio volume until
maximum is reached.
Fn+F4 Microphone Mute Silences the on-board microphone so
it cannot record audio. There is an
LED on the F4 function key that
notifies the user of the state of this
feature:
• LED off = microphone capable of
recording audio
• LED on = microphone muted and
unable to record audio
Fn+F5 Num lock Allows the user to toggle between
locked and unlocked NumLock
Fn+F6 Scroll lock Used as Scroll Lock key.
Fn+F7 Stealth Mode Allows the user to toggle to and from
Stealth Mode
Fn+F8 LCD and Projector display Determines video output to LCD and
external Video devices when
attached and displays present.
Fn+F9 Search Mimics the Windows key + F
keystroke to open Windows Search
dialog box.
Fn+F10 KB Illumination/Backlight Determines the Keyboard
Illumination/Backlight brightness
level. The hot key cycles through the
following brightness states when
pressed: Disabled, Dim, Bright. For
more detail, see Keyboard
Illumination/Backlight section.
Fn+F11 Brightness Decrease Decreases the stepping of LCD
brightness for each press until
minimum is reached. For details, see
the LCD Brightness section.
Fn+F12 Brightness Increase Increases the stepping of LCD
brightness for each press until
maximum is reached. For details, see
the LCD Brightness section.
Fn+PrintScreen Radio On/Off Toggles all the wireless radios on and
off. For example, WLAN, WWAN, and
Bluetooth.
Fn+Insert Sleep Puts the system into the ACPI S3
State and does not wake the system.
Technology and components 15

Traditional programming functions like Scroll Lock are assigned to alpha keys with un-printed legends.
•Fn+S = Scroll Lock
•Fn+B = Pause
•Fn+Ctrl+B = Break
•Fn+R = Sys-Req
NOTE: For non-backlit keyboards F10 has no function and icon on function key is purged.
AC-DC Adapters
There are a two types of AC adapters offered for this platform:
• 90W 3-Pin
• 130W 3-Pin
• When you disconnect the AC adapter cable from the computer, grasp the connector, not the cable itself, and then pull firmly but
gently to avoid damaging the cable.
• The AC adapter works with electrical outlets worldwide. However, power connectors and power strips vary among countries. Using an
incompatible cable or improperly connecting the cable to the power strip or electrical outlet may cause fire or equipment damage.
How to check the status of AC Adapter in BIOS?
1. Restart / Power on your computer.
2. At the first text on the screen or when the Dell logo appears, tap <F2> until the message Entering Setup appears.
3. Under General > Battery Information, you will see AC Adapter listed.
4. The status shows the wattage of the AC adapter connected. Any errors detected with the AC adapter or the DC-In connector will
be displayed here.
90W
16 Technology and components

130W
Technology and components 17

LED and Cable
18 Technology and components

Table 2. Adapter Features
Features
1 Body shape creates a smooth base for cable wrapping.
2 Cable lock on cord for securing cable wrap.
3 90° strain relief directs the cable out the side of the adapter.
4 Adapter LED is implemented in two spots on opposite sides of the plug head. The LED illumination will be white.
Battery
Dell Latitude Rugged use the following 3-cell battery options:
• 3-cell 51 Whr (ExpressCharge)
• 3-cell 51 Whr (Long-Life Cycle, includes 3 year limited warranty)
The battery is located on the bottom of the system and is hot swap capable. This design is unlike any other Dell predecessors laptops,
where system needs to be powered off when the battery is removed, without the need to remove the bottom cover.
NOTE: Battery is categorized as a CRU (Customer Replaceable Unit) on this platform.
NOTE: Battery typically requires about 2 hours to fully charge.
Battery Specifications
What is ExpressCharge ?
For a system advertised as having the ExpressCharge feature, the battery typically will have greater than 80% charge after about an hour
of charging with the system off and fully charged in about 2 hours with the system off.
Enabling Expresscharge requires that both the system and the battery that is used on the system be ExpressCharge capable. If any of the
above requirements is missing, ExpressCharge will not be enabled.
What is BATTMAN?
BATTMAN is a computer controlled battery manager intended for typical rechargeable batteries. It has the following capabilities:
• Monitors self-discharge
• Measures internal resistance
• Automatically performs repeated discharge/charge cycles to break in new batteries
• Keeps a log of all operations performed, which can be imported
• Connects via parallel port to any PC running Microsoft Windows
• Operating software, complete with source code, is available to download
Processors
This laptop is shipped with the following Intel 6th generation i5 SkyLake or 7th and 8th Generation KabyLake processors:
• Intel Core i3, 7130U KabyLake processor
• Intel Core i5, 8350U KabyLake or 6300U SkyLake processors
• Intel Core i7, 8650U KabyLake processor series
Technology and components 19

NOTE: The clock speed and performance varies depending on the workload and other variables.
Skylake processor
Intel Skylake is the successor to the Intel® Broadwell processor. It is a microarchitecture redesign using an already existing process
technology and it will be branded as Intel 6th Gen Core. Like Broadwell, Skylake is available in four variants with suffixes SKL-Y, SKL-H,
and SKL-U.
The Skylake also includes Core i7, i5, i3, Pentium and Celeron processors.
Skylake vs Broadwell roadmap
The following illustration is a roadmap comparison between the Skylake processor vs the Broadwell processor:
Figure 2. Skylake vs Broadwell roadmap
Processor performance features
The following table illustrates the performance available on each Skylake suffix.
Table 3. Performance features
Feature Feature description SKL-Y SKL-U SKL-H
General
Features
Cores Dual Core Dual Core Dual Core
CPU/Memory/Graphic
Overclocking
No No Yes
Intel Extreme Tuning
Utility
No No Yes
Intel Hyper-Threading
Technology
Yes Yes Yes
Intel Smart Cache
Technology with last level
cache (LLC) sharing
between Processor and
GFx cores
Yes Yes Yes
Intel Smart Sound
Technology
Yes Yes Yes
Intel Turbo Boost
Technology 2.0
Yes Yes Yes
Last Level Cache (LLC) Up to 4M Up to 4M Up to 4M
Voltage Optimizer Yes TBD TBD
20 Technology and components

Feature Feature description SKL-Y SKL-U SKL-H
Display 3 Independent Display
Support
Yes Yes Yes
HDMI 2.0 Display @60Hz 3840x2160 3840x2160 3840x2160
DP/eDP Display @60Hz 3840x2160 4096x2304 4096x2304
eDP 1.3, support for
MPO, NV12
Yes Yes Yes
Media Intel Built-In Visuals Yes Yes Yes
Compute OpenCL 2.0 Yes No yes
Platform
Hardware
14nm process Yes Yes Yes
16PCIe Graphic lanes
(configurable as 1x16 or
2x8 or 1x8+2x4)
No No Yes
PCIe Gen3.0 support No No Yes
Switchable graphics
(muxless solution)
No Yes Yes
Memory Memory Type DDR4 DDR4 DDR4
Connector / Memory
Down
Memory down SODIMM SODIMM
Speed 2133MT/s for DDR4 2133MT/s for DDR4 2133MT/s for DDR4
Max Capacity 32 GB 32 GB 32 GB
OS Support Windows 10 (64-bit) Yes Yes Yes
Windows 7 (64-bit /
32bit)
Yes Yes Yes
Windows 8.1 (64-bit) Yes Yes Yes
Linux (kernel and
associated modules)
Yes Yes Yes
Chrome Yes Yes No
Android No No No
General comparison with Broadwell processor
Figure 3. Comparison with Broadwell processor
Kaby Lake — 7th and 8th Generation Intel Core processors
The 7th and 8th Gen Intel Core processor (Kaby Lake) family is the successor of Sky Lake R. It's main features include:
Technology and components 21

• Intel 14nm Manufacturing Process Technology
• Intel Turbo Boost Technology
• Intel Hyper Threading Technology
• Intel Built-in Visuals
• Intel HD graphics - exceptional videos, editing smallest details in the videos
• Intel Quick Sync Video - excellent video conferencing capability, quick video editing and authoring
• Intel Clear Video HD - visual quality and color fidelity enhancements for HD playback and immersing web browsing
• Integrated memory controller
• Intel Smart Cache
• Optional Intel vPro technology (on i5/i7) with Active Management Technology 11.6
• Intel Rapid Storage Technology
Table 4. Kaby lake specifications
Processor
number
Base Clock
Speed
Cache No. of
cores/No. of
threads
Power Memory type Graphics
Intel Dual Core
i3-7130U
2.7 GHz 3 MB 2/4 15 W DDR4-2400 Intel HD graphics
620
Intel Quad Core
i5-8350U
1.7 GHz 6 MB 4/8 15 W DDR4-2400 Intel UHD
graphics 620
Intel Quad-Core
i7-8650U
1.9 GHz 8 MB 4/8 15 W DDR4-2400 Intel UHD
graphics 620
Memory features
This laptop supports 4–32 GB DDR4 SDRAM memory, up to 2400 MHz on KabyLake processors and 2133 MHz on SkyLake processors.
DDR4
DDR4 (double data rate fourth generation) memory is a higher-speed successor to the DDR2 and DDR3 technologies and allows up to 512
GB in capacity, compared to the DDR3's maximum of 128 GB per DIMM. DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory is keyed
differently from both SDRAM and DDR to prevent the user from installing the wrong type of memory into the system.
DDR4 needs 20 percent less or just 1.2 volts, compared to DDR3 which requires 1.5 volts of electrical power to operate. DDR4 also
supports a new, deep power-down mode that allows the host device to go into standby without needing to refresh its memory. Deep
power-down mode is expected to reduce standby power consumption by 40 to 50 percent.
DDR4 Details
There are subtle differences between DDR3 and DDR4 memory modules, as listed below.
Key notch difference
The key notch on a DDR4 module is in a different location from the key notch on a DDR3 module. Both notches are on the insertion edge
but the notch location on the DDR4 is slightly different, to prevent the module from being installed into an incompatible board or platform.
Figure 4. Notch difference
Increased thickness
DDR4 modules are slightly thicker than DDR3, to accommodate more signal layers.
22 Technology and components

Figure 5. Thickness difference
Curved edge
DDR4 modules feature a curved edge to help with insertion and alleviate stress on the PCB during memory installation.
Figure 6. Curved edge
Memory Errors
Memory errors on the system display the new 2 - Amber, 3 - White failure code. If all memory fails, the LCD does not turn on.
Troubleshoot for possible memory failure by trying known good memory modules in the memory connectors on the bottom of the system
or under the keyboard, as in some portable systems.
Graphics options
Graphics Specifications
Table 5. Graphics specifications
Controller Type CPU
Dependency
Graphics
memory type
Capacity External display
support
Maximum
resolution
Intel HD 620
Graphics
UMA Intel Core i3 -
7130U
Integrated Shared system
memory
HDMI 2.0 4096×2304 @60 Hz
Intel UHD 620
Graphics
UMA Intel Core i5 -
8350U
Integrated Shared system
memory
HDMI 2.0 4096×2304 @60 Hz
Intel HD 520
Graphics
UMA Intel Core
i5-6300U Integrated Shared system
memory
HDMI 2.0 4096×2304 @60 Hz
AMD Radeon
540
Discrete Intel Core i5 -
8350U
Intel Core i7 -
8650U
Discrete Dedicated, 2 GB
DDR5
HDMI 2.0
Additional video
ports via Rear
Configurable IO
Space
• VGA
• DisplayPort
4096×2304 @60 Hz
Technology and components 23

Controller Type CPU
Dependency
Graphics
memory type
Capacity External display
support
Maximum
resolution
AMD Radeon
RX540
Discrete Intel Core i5 -
8350U
Intel Core i7 -
8650U
Discrete Dedicated, 4 GB
DDR5
HDMI 2.0
Additional video
ports via Rear
Configurable IO
Space
• VGA
• DisplayPort
4096×2304 @60 Hz
NOTE: Additional video ports via Rear Configurable IO Space is available with discrete graphics solution only.
Intel HD Graphics Integrated
Intel HD graphics 620
This system can be configured with either of the following UMA graphic options or combined with any of the AMD discrete graphics
options.
Table 6. Intel HD graphics 620 specification
Integrated Graphics Controller Intel HD Graphics 620
Bus Type Internal PCIe
Memory Interface N/A (unified memory architecture)
Graphics Level GT2
Estimated Maximum Power Consumption (TDP) 15 W (included in the CPU power)
Display Support On System:
HDMI 2.0
USB Type-C
Maximum Vertical Refresh Rate Up to 85 Hz depending on resolution
Operating Systems Graphics/ Video API Support Support for DirectX 12, OpenCL 2.0, OpenGL 4.3/4.4, OpenGL ES
Supported Resolutions and Max Refresh Rates (Hz) (Note: Analog
and/or digital)
System ports: Max Digital: (HDMI) 2560x1600, 4096x2304@24 Hz
Docked:
• Max Digital: ( DisplayPort 1.2) 3840 x2160 @60 Hz
• Max Digital: (SL-DVI) 1920x1080 @60 Hz
• Analog: (VGA) system (14 inch/15 inch) 2048x1152 @60 Hz
For 3 displays : up to max resolution each above
Numbers of Displays Supported • System Ports: 3 displays max with LCD plus 2 displays max on
each output (HDMI, USB Type-C)
• Docked: 3 displays max (combo of LCD, VGA, DP, HDMI)
Intel UHD Graphics 620
Table 7. Intel UHD Graphics 620 (8th Generation Intel Core) specification
Integrated Graphics Controller Intel UHD Graphics 620 (8th Generation Intel Core)
Bus Type Internal PCIe
Memory Interface N/A (unified memory architecture)
Graphics Level GT2
Estimated Maximum Power Consumption (TDP) 15 W (included in the CPU power)
24 Technology and components

Integrated Graphics Controller Intel UHD Graphics 620 (8th Generation Intel Core)
Display Support On System:
HDMI 2.0
USB Type-C
Maximum Vertical Refresh Rate Up to 85 Hz depending on resolution
Operating Systems Graphics/ Video API Support DirectX 11 (Windows 7/8.1), DirectX 12 (Windows 10), OpenGL 4.3
Supported Resolutions and Max Refresh Rates (Hz) (Note: Analog
and/or digital) System ports:
• Max Digital: (HDMI) 4096x2304@24 Hz
• Analog: (VGA) system (14 inches/15 inches) or docking
2048x1152 @60 Hz
Docked:
• Max Digital: (DisplayPort 1.2) 3860 x2160 @60 Hz
• Max Digital: (SL-DVI) 1920x1080 @60 Hz
• Analog: (VGA) system (14 inches/15 inches) 2048x1152 @60
Hz
For 3 displays:
• (native or docked) up to 1920x1200 max resolution each
Numbers of Displays Supported • System Ports - 3 displays max with LCD plus 1 display max on
each output (HDMI, VGA (14 inches/15 inches)
• Docked - 3 displays max (combo of LCD, VGA, DP, HDMI)
Intel HD Graphics 520
Table 8. Intel HD Graphics 520 Graphics specification
Integrated Graphics Controller Intel UHD Graphics 620 (8th Generation Intel Core)
Bus Type Internal PCIe
Memory Interface N/A (unified memory architecture)
Graphics Level GT2
Estimated Maximum Power Consumption (TDP) 15 W (included in the CPU power)
Display Support On System:
HDMI 2.0
USB Type-C
Maximum Vertical Refresh Rate Up to 85 Hz depending on resolution
Operating Systems Graphics/ Video API Support DirectX 11 (Windows 7/8.1), DirectX 12 (Windows 10), OpenGL 4.3
Supported Resolutions and Max Refresh Rates (Hz) (Note: Analog
and/or digital) System ports:
• Max Digital: (HDMI) 4096x2304@24 Hz
• Analog: (VGA) system (14 inches/15 inches) or docking
2048x1152 @60 Hz
Docked:
• Max Digital: (DisplayPort 1.2) 3860 x2160 @60 Hz
• Max Digital: (SL-DVI) 1920x1080 @60 Hz
• Analog: (VGA) system (14 inches/15 inches) 2048x1152 @60
Hz
For 3 displays:
• (native or docked) up to 1920x1200 max resolution each
Technology and components 25

Integrated Graphics Controller Intel UHD Graphics 620 (8th Generation Intel Core)
Numbers of Displays Supported • System Ports - 3 displays max with LCD plus 1 display max on
each output (HDMI, VGA (14 inches/15 inches)
• Docked - 3 displays max (combo of LCD, VGA, DP, HDMI)
Intel HD Graphics 520
The Intel HD Graphics 520 (GT2) is an integrated graphics unit, which can be found in various ULV (Ultra Low Voltage) processors of the
Skylake generation. This GT2 version of the Skylake GPU offers 24 Execution Units (EUs) clocked at up to 1050 MHz (depending on the
CPU model). Due to its lack of dedicated graphics memory or eDRAM cache, the HD 520 has to access the main memory (2x 64-bit
DDR3L-1600/DDR4-2133).
Performance
The exact performance of the HD Graphics 520 depends on various factors like L3 cache size, memory configuration (DDR3/DDR4) and
maximum clock rate of the specific model. The fastest versions Core i7-6600U should perform similar to a dedicated GeForce 820M and
handles modern games (as of 2015) in low settings.
Features
The revised video engine now decodes H.265/HEVC completely in hardware and more efficiently than before. Displays can be connected
using a DP 1.2/eDP 1.3 (max. 3840 x 2160 @ 60 Hz), whereas HDMI is limited to the older version 1.4a (max. 3840 x 2160 @ 30 Hz).
However, HDMI 2.0 can be added using a DisplayPort converter. Up to three displays can be controlled simultaneously.
Power Consumption
The HD Graphics 520 can be found in mobile processors specified at 15 W TDP and is therefore suited for compact laptops and
Ultrabooks.
Key Specifications
The following table contains the key specifications of the Intel HD Graphics 520:
Table 9. Key specifications
Specification Intel HD Graphics 520
Codename Skylake GT2
Architecture Intel Gen 6 (Skylake)
Pipelines 24 — unified
Core Speed 300 — 1050 (Boost) MHz
Memory Type DDR3/DDR4
Memory Bus Width 64/128 bit
Shared Memory Yes
Technology 14 nm
26 Technology and components

Specification Intel HD Graphics 520
Features QuickSync
DirectX DirectX 12 (FL 12_1)
Max. Displays Supported Up to 3
DP 1.2/eDP 1.3 max. resolution 3840 x 2160 @ 60 Hz
HDMI max. resolution 3840 x 2160 @ 30 Hz
Intel HD/UHD Graphics 620
The Intel HD/UHD Graphics 620 (GT2) is an integrated graphics unit, which can be found in various ULV (Ultra Low Voltage) processors
of the Skylake generation. This GT2 version of the Skylake GPU offers 24 Execution Units (EUs) clocked at up to 1050 MHz (depending
on the CPU model). Due to its lack of dedicated graphics memory or eDRAM cache, the HD 520 has to access the main memory (2x 64-
bit DDR3L-1600/DDR4-2133).
Performance
The exact performance of the HD/UHD Graphics 620 depends on various factors like L3 cache size, memory configuration (DDR3L/
DDR4) and maximum clock rate of the specific model.
Features
The revised video engine now decodes H.265/HEVC completely in hardware and more efficiently than before. Displays can be connected
using a DP 1.2/eDP 1.3 (max. 3840 x 2160 @ 60 Hz), whereas HDMI is limited to the older version 1.4a (max. 3840 x 2160 @ 30 Hz).
However, HDMI 2.0 can be added using a DisplayPort converter. Up to three displays can be controlled simultaneously.
Power Consumption
The HD Graphics 620 can be found in mobile processors specified at 15 W TDP and is therefore suited for compact laptops and
Ultrabooks.
Key Specifications
The following table contains the key specifications of the Intel HD Graphics 620:
Table 10. Key specifications
Specification Intel HD/UHD Graphics 620
Codename Skylake GT2
Architecture Intel Gen 6 (Skylake)
Pipelines 24 — unified
Core Speed 300 — 1050 (Boost) MHz
Memory Type DDR3/DDR4
Memory Bus Width 64/128 bit
Technology and components 27

Specification Intel HD/UHD Graphics 620
Shared Memory Yes
Technology 14 nm
Features QuickSync
DirectX DirectX 12 (FL 12_1)
Max. Displays Supported Up to 3
DP 1.2/eDP 1.3 max. resolution 3840 x 2160 @ 60 Hz
HDMI max. resolution 3840 x 2160 @ 30 Hz
AMD Radeon 540 Graphics
Table 11. Radeon 540 Graphics specifications
Graphics Controller AMD Radeon 540 Graphics
Graphics memory 2 GB GDDR5
Bus type PCIe x16 Gen3
Memory Interface 64-bit
Clock Speeds Up to 1124 MHz
Estimated Maximum Power Consumption (TDP) 50W TGP (GPU + frame buffer)
Display Support HDMI/mDP/eDP/USB-C
Maximum Color Depth Maximum 4:4:4 Color Depth:12 (bits per pixel)
Maximum Vertical Refresh Rate Up to 85 Hz depending on resolution
Operating Systems Graphics/ Video API Support DirectX 12, OpenGL 4.5
Supported Resolutions and Max Refresh Rates (Hz) (Note: Analog
and/or digital)
• Single DisplayPort 1.4 - 5120 x 2880 @ 60 Hz
• Dual DisplayPort 1.4 - 5120 x 2880 @ 60 Hz
Numbers of Display Support Up to five displays operating at 4096 x 2160 @60 Hz
AMD Radeon RX 540 Graphics
Table 12. Radeon RX 540 graphics specifications
Graphics Controller AMD Radeon RX 540 Graphics
Graphics memory 4 GB GDDR5
Bus type PCIe x16 Gen3
Memory Interface 128 bit
Clock Speeds Up to 1219 MHz
Estimated Maximum Power 50W TGP (GPU + frame buffer)
Display Support eDP/DVI/ DisplayPort/HDMI
Maximum Color Depth Maximum 4:4:4 Color Depth:12 (bits per pixel)
28 Technology and components

Graphics Controller AMD Radeon RX 540 Graphics
Maximum Vertical Refresh Rate Up to 395 Hz at 1920 x 1080
Up to 118 Hz at 3840 x 2160
Operating Systems Graphics/ Video API Support DirectX 12, OpenGL 4.5
Supported Resolutions and Max Refresh Rates (Hz) • Max Digital : Single DisplayPort 1.4 - 5120 x 2880 @ 60 Hz
(mDP/USB Type-C to DP)
• Max Digital : Dual DisplayPort 1.4 - 5120 x 2880 @ 60 Hz
(mDP/USB Type-C to DP)
Numbers of Display Support Up to five displays operating at 4096 x 2160 @60 Hz
Corning Gorilla Glass
Corning Gorilla Glass 5: Corning’s latest composition was formulated to address breakage the #1 consumer complaint, according to
Corning’s research. The new glass is just as thin and light as previous versions, but has been formulated to deliver dramatically improved
native damage resistance allowing improved in-field performance. Corning Gorilla Glass 5 has been tested for performance when
subjected to sharp contact damage, such as asphalt and other real-world surfaces.
Benefits
• Enhanced retained strength after use.
• High resistance to scratch and sharp contact damage.
• Improved drop performance.
• Superior surface quality.
Applications
• Ideal protective cover for electronic displays in:
• Smartphones
• Laptop and tablet computer screens
• Wearable devices
• Touchscreen devices
• Optical components
• High strength glass articles
Dimensions
Thickness: 0.7 mm
Viscosity
Table 13. Viscosity
Parameters Vectors
Softening Point (107.6 poises) 884˚C
Annealing Point (1013.2 poises) 623˚C
Strain Point (1014.7 poises) 571˚C
Properties
Table 14. Properties
Density 2.43 g/cm
Technology and components 29
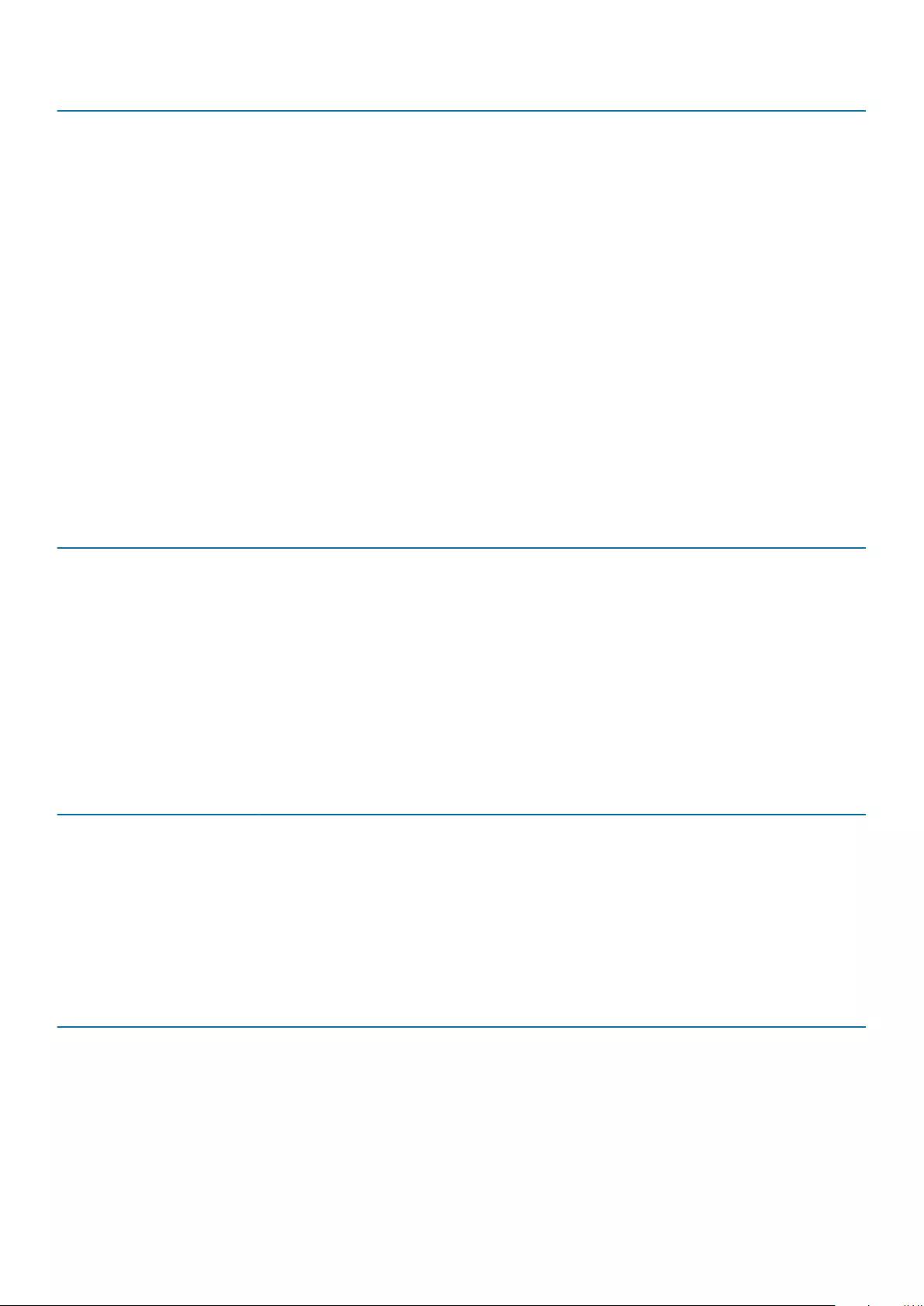
Youngs Modulus 76.7 GPa
Poissons Ratio 0.21
Shear Modulus 31.7 GPa
Vickers Hardness (200 g load)
• Un-strengthened
• Strengthened
489 kgf/mm2
596 kgf/mm2
596 kgf/mm2
Fracture Toughness 0.69 MPa m0.5
Coefficient of Expansion (0 ˚C - 300 ˚C) 78.8 x 10-7 /°C
Chemical Strengthening
Capability of >850MPa CS, at 50 µm Depth Of Layer(DOL)
Specifications subject to change
Optical
Table 15. Optical
Refractive Index (590 nm)
Core glass** 1.50
Compression layer 1.51
Photo-elastic constant 30.3 nm/cm/MPa
** Core index is used for FSM-based measurements since it is unaffected by ion-exchange conditions.
Chemical Durability
Durability is measured via weight loss per surface area after immersion in the solvents shown below. Values are highly dependent upon
actual testing conditions. Data reported is for Corning Gorilla Glass 5.
Table 16. Chemical Durability
Reagent Time Temperature (ºC) Weight Loss (mg/cm2)
HCl - 5% 24 hrs 95 5.9
NH4F:HF - 10% 20 min 20 1.0
HF - 10% 20 min 20 25.2
NaOH - 5% 6 hrs 95 2.7
Electrical
Table 17. Electrical
Frequency (MHz) Dielectric Constant Loss Tangent
54 7.08 0.009
163 7.01 0.010
272 7.01 0.011
272 7.00 0.010
490 7.99 0.010
599 7.97 0.011
30 Technology and components

Frequency (MHz) Dielectric Constant Loss Tangent
912 7.01 0.012
1499 6.99 0.012
1977 6.97 0.014
2466 6.96 0.014
2986 6.96 0.014
Terminated coaxial line similar to that outlined in NIST Technical Notes 1520 and 1355-R
Putting Corning Gorilla Glass 5 to the test.
• Greater damage resistance (upto 1.8X) with deep abrasion.
• Faster chemical strengthening with high Compressive Stress and deeper depth of compression
• Shallower check depth with higher abrasions levels
• Enables thickness reduction
Pen Usage
Your computer uses several input devices. The standard external USB keyboard and mouse are present, plus you can opt for the
electrostatic pen/stylus or use your finger as an input device.
Using the Pen as a 'Mouse'
You can use the pen the same way you use a mouse or touch pad with a laptop computer. Holding the pen near the display makes a small
cursor appear. Moving the pen moves the cursor. The following table describes how to use the pen.
Table 18. Pen functions
Action Function
Gently tap the pen tip on the screen Same as a single-click on a mouse.
Gently tap the pen tip twice in quick succession on the screen. Same as a double-click on a mouse.
Touch the pen on the screen and hold it in place momentarily until
Windows draws a complete circle around the cursor.
Same as a right-click on a mouse.
Using the Pen as a Pen
The handwriting recognition software makes it easy to enter text into your applications with the pen. Some applications, such as Windows
Journal, allow you to write with the pen directly into the application window.
Tablet PC Input Panel
When an application does not directly support pen input, you can use the Tablet PC Input Panel to enter text into your application. If you
tap in an editable area, the Tablet PC Input Panel icon appears. Tapping the icon makes the Input Panel slide out from the edge of the
display.
Technology and components 31
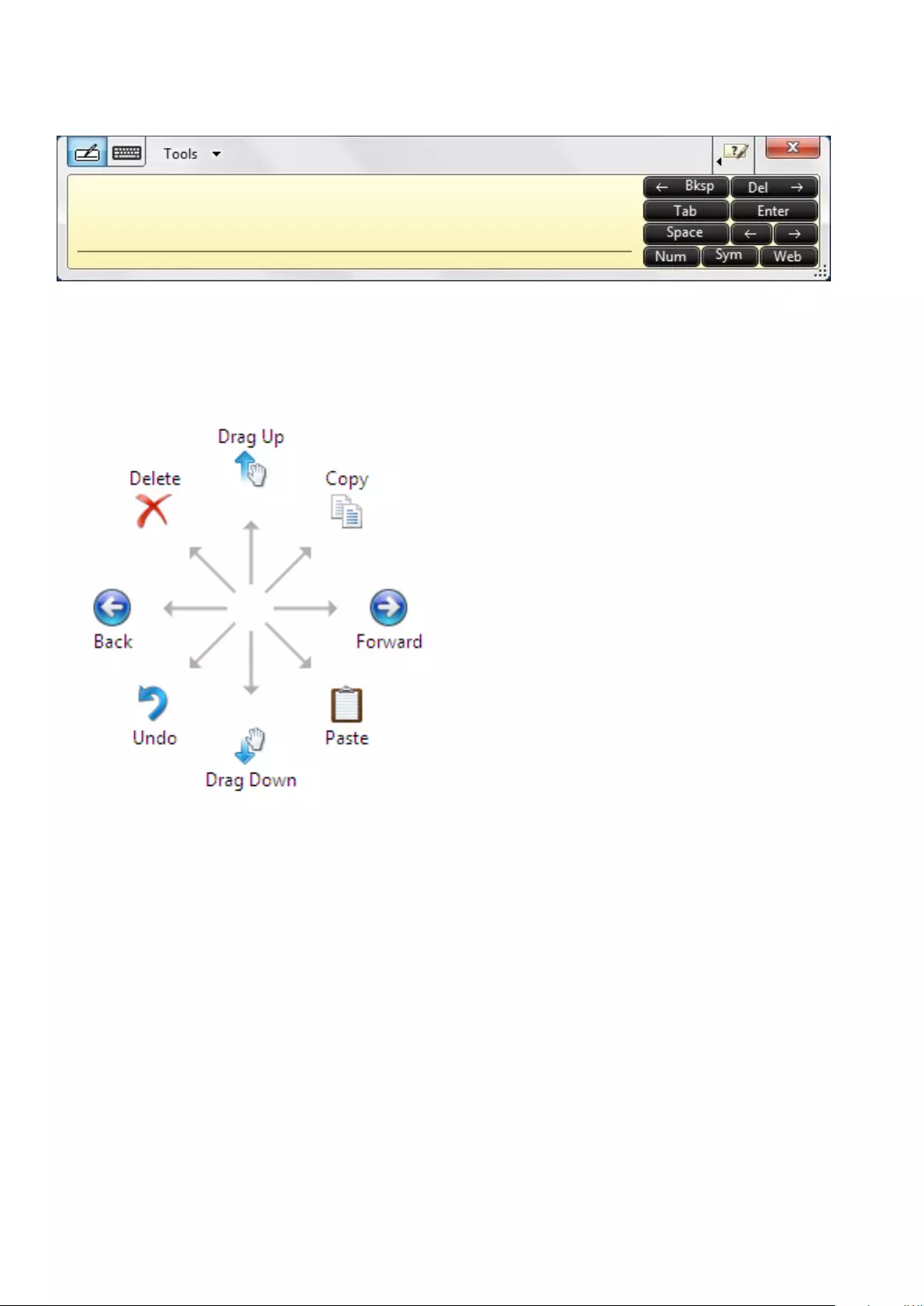
You can move the Input Panel tab by dragging it up or down along the edge of the screen. Then, when you tap it, the Input Panel opens
at the same horizontal location on the screen that the tab appears.
Pen Flicks
Pen flicks enable you to use the pen to perform actions that normally require a keyboard, such as pressing <Page Up> or using the
directional arrow keys. Pen flicks are quick, directional gestures. Draw a short line in one of eight directions. When a pen flick is recognized,
the Tablet PC performs the action assigned.
You can modify the default pen flick settings:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Pen and Touch and click the Flicks tab.
2. Modify the settings and click OK.
32 Technology and components
Media Card Readers
NOTE: The media card reader is integrated into the system board on portable systems. If there is a hardware failure or
the reader malfunctions, replace the system board.
The media card reader expands the usefulness and functionality of portable systems, especially when used with other devices such as
digital cameras, portable MP3 players, and handheld devices. All these devices use a form of media card to store information. Media card
readers allows for easy transfer of data between these devices.
Several different types of media or memory cards are available today. Below is a list of the different types of cards that work in the media
card reader.
SD Card Reader
Technology and components 33

1. Memory Stick
2. Secure Digital (SD)
3. Secure Digital High Capacity (SDHC)
4. Secure Digital eXtended Capacity(SDXC)
UEFI BIOS
UEFI is an acronym for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. The UEFI specification defines a new model for the interface between
personal computer operating systems and platform firmware. The interface consists of data tables that contain platform related
information, plus boot and runtime service calls that are available to the operating system and its loader. Together, these provide a
standard environment for booting an operating system and running pre-boot applications. One of the main differences between BIOS and
UEFI is the way applications are coded. Assembler was used if functions or applications had to be coded for the BIOS while a higher level
language code will be used to program the UEFI.
Dell UEFI BIOS implementation will supersede the existing two different sets of BIOS in the portables and desktop products into one single
UEFI BIOS moving forward.
Important Information
There is no difference in between the conventional BIOS and the UEFI BIOS unless the UEFI option is checked in the 'Boot List Option'
setting in the BIOS page. This will allow the user to create a UEFI boot option list manually without affecting the existing boot priority list.
With the implementation of UEFI BIOS, the changes are more related to the manufacturing tools and functionalities with very minimal
impact to the customer's usages.
Few things to remember are:
• If customers have a UEFI boot media and ONLY if they have UEFI boot media (either in the optical media or via USB storage), the
one-time boot menu will show an additional section listing the UEFI boot options. If they don't have UEFI boot media attached, they
will never see this option. Almost all will never get to see this option unless the UEFI boot option is specified manually through the
'Boot Sequence' settings.
• How to change Service Tag/Owner Tag?
When the service technician replaces a system board, he's required to set the service tag upon the system starts up at one time off
basis. Failure to set a service tag may result system battery not being able to charge. Therefore, it is very important that the service
technician set the correct system service tag. If a wrong service tag is set, there's no way to reset it and the technician will have to
place order for another system board replacement.
• How to change Asset tag information?
To change the Asset tag information, we can use one of the following software utilities.
Portables Technology Dell Command Configure toolkit
Customers may also report that after a motherboard replacement, the asset field is already populated in the system BIOS, and needs to be
cleared or set. For older systems and all newer systems with the UEFI BIOS platform, customers can download the Dell Command
Configure Toolkit (DCC) to customize the BIOS options or even change the ownership or asset tag from within Windows. This technology
is described in Software and Troubleshooting section.
Systems management - From on-premises to the
cloud
Dell Client Command Suite - a free toolkit available for download, for all OptiPlex and Latitude PCs at https://dell.com/command,
automates and streamlines systems management tasks, saving time, money, and resources. It consists of the following modules that can
be used independently, or with a variety of systems management consoles such as SCCM.
Dell Command | Deploy enables easy operating system (OS) deployment across all major OS deployment methodologies and provides
numerous system-specific drivers that have been extracted and reduced to an OS-consumable state.
Dell Command l Configure is a graphical user interface (GUI) admin tool for configuring and deploying hardware settings in a pre-OS or
post-OS environment, and it operates seamlessly with SCCM and Airwatch and can be self-integrated into LANDesk and KACE. Simply,
this is all about the BIOS. Command l Configure allows you to remotely automate and configure over 150+ BIOS settings for a personalized
user experience.
34 Technology and components

Dell Command l PowerShell Provider can do the same things as Command l Configure, but with a different method. PowerShell is a
scripting language that allows customers to create a customized and dynamic configuration process.
Dell Command l Monitor is a Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) agent that provides IT admins with an extensive inventory
of the hardware and health-state data. Admins can also configure hardware remotely by using command line and scripting.
Dell Command | Update (end-user tool) is factory-installed and allows admins to individually manage and automatically present and
install Dell updates to the BIOS, drivers, and software. Command l Update eliminates the time-consuming hunting and pecking process of
update installation.
Dell Command l Update Catalog provides searchable metadata that allows the management console to retrieve the latest system-
specific updates (driver, firmware or BIOS). The updates are then delivered seamlessly to end-users using the customer's systems
management infrastructure that is consuming the catalog (like SCCM).
Dell Command | vPro Out of Band console extends hardware management to systems that are offline or have an un-reachable OS
(Dell exclusive features).
Dell Command | Integration Suite for System Center - This suite integrates all the key components of the Client Command Suite into
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager 2012 and Current Branch versions.
Dell Client Command Suite's integration with VMware Workspace ONE Powered by AirWatch, now allows customers to manage their Dell
client hardware from the cloud, using a single Workspace ONE console.
Out-of-Band Systems Management- Intel vPro and Intel
Standard Manageability
Intel vPro and Intel Standard Manageability must be configured in the Dell factory at the time of purchase, as they are NOT field
ungradable. They offer out-of-band management and DASH compliance.
Intel vPro
Available with Intel Core i5 and i7 processors and offers the most complete set of out-of-band management features including KVM, IPv6
support, graceful shutdown, and all the features from previous versions of vPro. It uses the latest version of Intel's Active Management
Technology (AMT).
To learn more about vPro, visit Intel's website at https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/vpro/vpro-
platform-general.html.
A unique and new Dell Remote Provisioning feature for Intel vPro quickly activates vPro capabilities on a PC, reducing vPro set-up time
from months to less than an hour. The Dell Remote Provisioning feature for Intel vPro is available as a part of the module: Dell Command
| Integration Suite for Systems Center
Intel Standard Manageability (ISM)
ISM offers a limited set of out-of-band features like remote power on/off, Serial-over-LAN redirect, Wake-on-LAN, etc.
To learn more about Intel ISM, visit Intel's website at: https://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2009/03/27/what-is-standard-
manageability.
Trusted Platform Module
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a dedicated cryptoprocessor designed to secure hardware by integrating cryptographic keys into
devices. A software can use a Trusted Platform Module to authenticate hardware devices. As each TPM chip has a unique and secret
RSA key burned in as it is produced, it can perform the platform authentication.
NOTE: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is part of the system board. In an event of system board replacement, the
encryption needs to be suspended in the OS and re-enabled on new system board's BIOS prior to resuming the
encryption.
CAUTION: Attempt to replace the system board without prior suspending the encryption, will cause operating system
corruption and may eventually lead to No-Boot scenario.
Technology and components 35

Fingerprint Reader
This topic explains the software used in fingerprint reader
The Portables Technology has an integrated fingerprint reader located on the palm rest to the right of the touch pad. The fingerprint
reader is an option, so not all systems have it. Included with the driver for the fingerprint reader is a software package from Dell
ControlVault, that provides functionality for the device. Dell provides all support for the software, same as on the Latitude systems.
Dell ControlVault Software
The software package for the fingerprint reader is ControlVault by Dell. It provides the following functionality to the fingerprint reader:
• Uses the fingerprint reader for Windows® logon and system start-up password authentication
• Registers websites and Windows applications for password replacement
• Launches a favorite application with a finger swipe
• Stores confidential information in an encrypted folder
To gain any of this functionality, a user must first enroll fingerprints. An easy-to-follow wizard guides the user through the enrollment
process. The user can choose to save fingerprints to the hard drive or the fingerprint reader
NOTE: A user should enroll more than one finger's print.
USB features
Universal Serial Bus, or USB, was introduced in 1996. It dramatically simplified the connection between host computers and peripheral
devices like mice, keyboards, external drivers, and printers.
Let's take a quick look on the USB evolution referencing to the table below.
Table 19. USB evolution
Type Data Transfer Rate Category Introduction Year
USB 2.0 480 Mbps High Speed 2000
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 5 Gbps Super Speed 2010
USB 3.1 Gen 2 10 Gbps Super Speed 2013
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 (SuperSpeed USB)
For years, the USB 2.0 has been firmly entrenched as the de facto interface standard in the PC world with about 6 billion devices sold, and
yet the need for more speed grows by ever faster computing hardware and ever greater bandwidth demands. The USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1
finally has the answer to the consumers' demands with a theoretically 10 times faster than its predecessor. In a nutshell, USB 3.1 Gen 1
features are as follows:
• Higher transfer rates (up to 5 Gbps)
• Increased maximum bus power and increased device current draw to better accommodate power-hungry devices
• New power management features
• Full-duplex data transfers and support for new transfer types
• Backward USB 2.0 compatibility
• New connectors and cable
The topics below cover some of the most commonly asked questions regarding USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1.
36 Technology and components

Speed
Currently, there are 3 speed modes defined by the latest USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 specification. They are Super-Speed, Hi-Speed and Full-
Speed. The new SuperSpeed mode has a transfer rate of 4.8Gbps. While the specification retains Hi-Speed, and Full-Speed USB mode,
commonly known as USB 2.0 and 1.1 respectively, the slower modes still operate at 480Mbps and 12Mbps respectively and are kept to
maintain backward compatibility.
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 achieves the much higher performance by the technical changes below:
• An additional physical bus that is added in parallel with the existing USB 2.0 bus (refer to the picture below).
• USB 2.0 previously had four wires (power, ground, and a pair for differential data); USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 adds four more for two
pairs of differential signals (receive and transmit) for a combined total of eight connections in the connectors and cabling.
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 utilizes the bidirectional data interface, rather than USB 2.0's half-duplex arrangement. This gives a 10-fold
increase in theoretical bandwidth.
With today's ever increasing demands placed on data transfers with high-definition video content, terabyte storage devices, high
megapixel count digital cameras etc., USB 2.0 may not be fast enough. Furthermore, no USB 2.0 connection could ever come close to the
480Mbps theoretical maximum throughput, making data transfer at around 320Mbps (40MB/s) — the actual real-world maximum.
Similarly, USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 connections will never achieve 4.8Gbps. We will likely see a real-world maximum rate of 400MB/s with
overheads. At this speed, USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 is a 10x improvement over USB 2.0.
Applications
USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 opens up the laneways and provides more headroom for devices to deliver a better overall experience. Where USB
video was barely tolerable previously (both from a maximum resolution, latency, and video compression perspective), it's easy to imagine
that with 5-10 times the bandwidth available, USB video solutions should work that much better. Single-link DVI requires almost 2Gbps
throughput. Where 480Mbps was limiting, 5Gbps is more than promising. With its promised 4.8Gbps speed, the standard will find its way
into some products that previously weren't USB territory, like external RAID storage systems.
Listed below are some of the available SuperSpeed USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 products:
• External Desktop USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• Portable USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Hard Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Drive Docks & Adapters
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Flash Drives & Readers
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Solid-state Drives
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 RAIDs
• Optical Media Drives
• Multimedia Devices
• Networking
• USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 Adapter Cards & Hubs
Technology and components 37
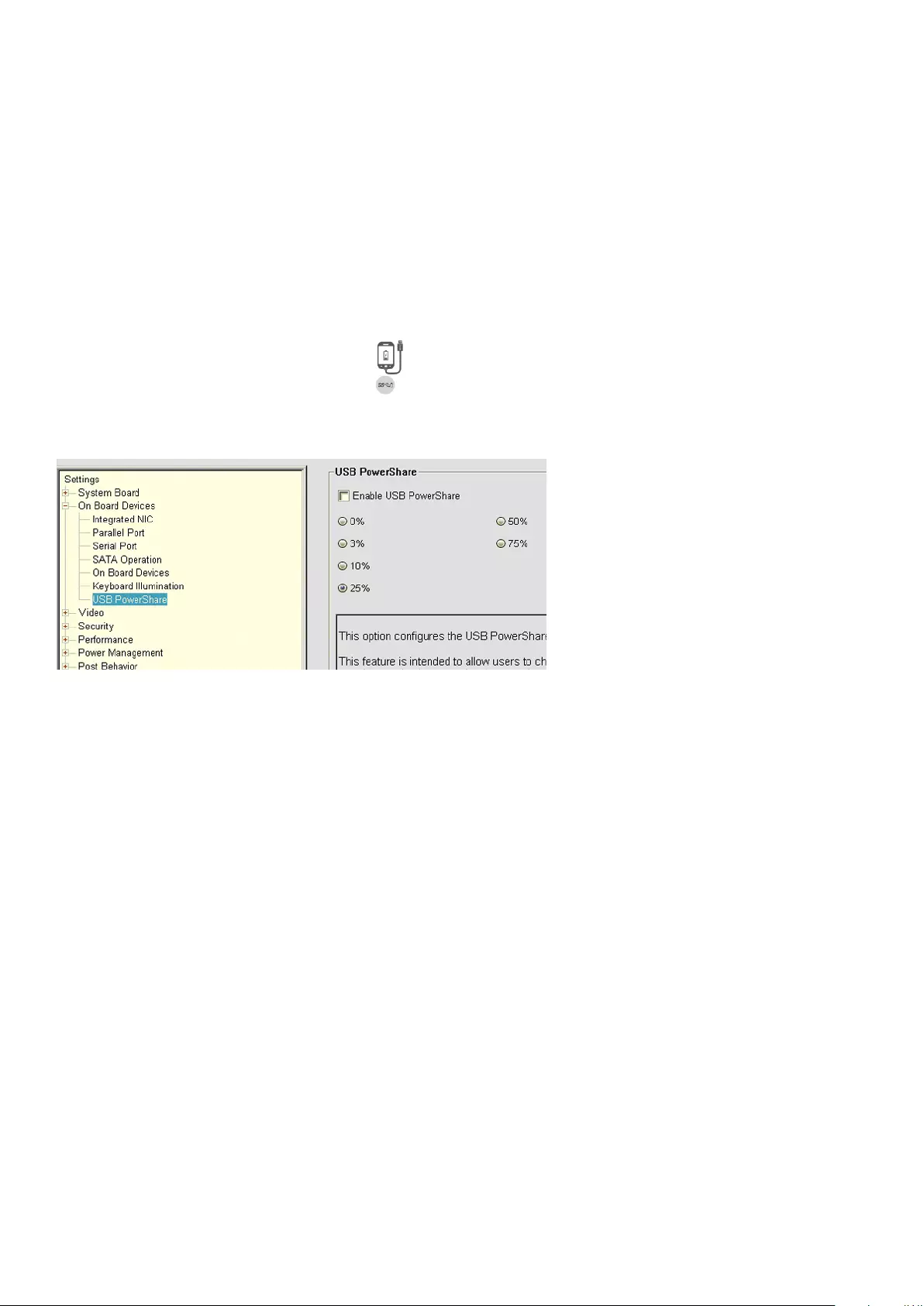
Compatibility
The good news is that USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 has been carefully planned from the start to peacefully co-exist with USB 2.0. First of all,
while USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 specifies new physical connections and thus new cables to take advantage of the higher speed capability of
the new protocol, the connector itself remains the same rectangular shape with the four USB 2.0 contacts in the exact same location as
before. Five new connections to carry receive and transmitted data independently are present on USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1 cables and only
come into contact when connected to a proper SuperSpeed USB connection.
USB Powershare
USB PowerShare is a feature which allows for external USB devices (i.e. cellular phones, portable music players, etc.) to charge using the
portable system's battery.
Only the USB connector with a SS+USB+Battery--> icon, can be used.
This functionality is enabled in the system setup under the On Board Devices heading. You can select how much of the battery's charge
can be used as well (pictured below). If you set the USB PowerShare to 25%, the external device is allowed to charge until the battery
reaches 25% of full capacity (e.g. 75% of the portable's battery charge is used up).
USB Type-C
USB Type-C is a new, tiny physical connector. The connector itself can support various exciting new USB standards like USB 3.1 and USB
power delivery (USB PD).
Alternate Mode
USB Type-C is a new connector standard that is very small. It is about a third the size of an old USB Type-A plug. This is a single
connector standard that every device should be able to use. USB Type-C ports can support a variety of different protocols using
“alternate modes,” which allows you to have adapters that can output HDMI, VGA, DisplayPort, or other types of connections from that
single USB port
USB Power Delivery
The USB PD specification is also closely intertwined with USB Type-C. Currently, smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices often
use a USB connection to charge. A USB 2.0 connection provides up to 2.5 watts of power — that'll charge your phone, but that's about
it. A laptop might require up to 60 watts, for example. The USB Power Delivery specification ups this power delivery to 100 watts. It's bi-
directional, so a device can either send or receive power. And this power can be transferred at the same time the device is transmitting
data across the connection.
This could spell the end of all those proprietary laptop charging cables, with everything charging via a standard USB connection. You could
charge your laptop from one of those portable battery packs you charge your smartphones and other portable devices from today. You
could plug your laptop into an external display connected to a power cable, and that external display would charge your laptop as you used
it as an external display — all via the one little USB Type-C connection. To use this, the device and the cable have to support USB Power
Delivery. Just having a USB Type-C connection doesn't necessarily mean they do.
38 Technology and components

USB Type-C and USB 3.1
USB 3.1 is a new USB standard. USB 3's theoretical bandwidth is 5 Gbps, while USB 3.1's is 10 Gbps. That's double the bandwidth, as fast
as a first-generation Thunderbolt connector. USB Type-C isn't the same thing as USB 3.1. USB Type-C is just a connector shape, and the
underlying technology could just be USB 2 or USB 3.0. In fact, Nokia's N1 Android tablet uses a USB Type-C connector, but underneath
it's all USB 2.0 — not even USB 3.0. However, these technologies are closely related.
Ethernet
The Intel I219LM Jacksonville WGI219LM family of Gigabit Ethernet controllers provides compact, single-port integrated physical layer
devices that connect to the Intel Skylake chipsets.
The Intel WGI219LM supports the latest Ethernet security standard known as MACsec3 (IEEE standard 802.1ae). The Intel WGI219LM is
the corporate LAN product with support for Intel vPro; technology, Intel AMT2, Energy Efficient Ethernet (802.3az), MACsec (802.1ae),
Intel SIPP, iSCSI Boot, Server OS support.
Product Features
General
• 10 BASE-T IEEE 802.3 specification conformance
• 100 BASE-TX IEEE 802.3 specification conformance
• 1000 BASE-T IEEE 802.3 specification conformance
• Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE)
• IEEE 802.3az support [Low Power Idle (LPI) mode]
• IEEE 802.3u autonegotiation conformance
• Supports carrier extension (half duplex)
• Loopback modes for diagnostics
• Advanced digital baseline wander correction
• Automatic MDI/MDIX crossover at all speeds of operation
• Automatic polarity correction
• MDC/MDIO management interface
• Flexible filters in PHY to reduce integrated LAN controller power
• Smart speed operation for automatic speed reduction on faulty cable plants
• PMA loopback capable (no echo cancel)
• 802.1as/1588 conformance
• Power Optimizer Support
• Intel Stable Image Platform Program (SIPP)
• iSCSI Boot
• Network proxy/ARP Offload support
• Up to 32 programmable filters
• No support for Gb/s half-duplex operation
Security and Manageability
• Intel vPro support with appropriate Intel chipset components
Performance
• Jumbo Frames (up to 9 Kb)
• 802.1Q & 802.1p
• Receive Side Scaling (RSS)
• Two Queues (Tx & Rx)
Technology and components 39

Power
• Ultra Low Power at cable disconnect (<1 mW) enables platform support for connected standby
• Reduced power consumption during normal operation and power down modes
• Integrated Intel Auto Connect Battery Saver (ACBS)
• Single-pin LAN disable for easier BIOS implementation
• Fully integrated Switching Voltage Regulator (iSVR)
• Low Power LinkUp(LPLU)
MAC/PHY Interconnect
• PCIe-based interface for active state operation (S0 state)
• SMBus-based interface for host and management traffic (Sx low power state)
Package/Design
• 48-pin package, 6x6mm with a 0.4 mm lead pitch and an Exposed Pad for ground
• Three configurable LED outputs
• Integrated MDI interface termination resistors to reduce BOM costs
• Reduced BOM cost by sharing SPI flash with PCH
HDMI 2.0
This topic explains the HDMI 2.0 and its features along with the advantages.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is an industry-supported, uncompressed, all-digital audio/video interface. HDMI provides an
interface between any compatible digital audio/video source, such as a DVD player, or A/V receiver and a compatible digital audio and/or
video monitor, such as a digital TV (DTV). The intended applications for HDMI TVs, and DVD players. The primary advantage is cable
reduction and content protection provisions. HDMI supports standard, enhanced, or high-definition video, plus multichannel digital audio
on a single cable.
HDMI 2.0 Features
•HDMI Ethernet Channel - Adds high-speed networking to an HDMI link, allowing users to take full advantage of their IP-enabled
devices without a separate Ethernet cable
40 Technology and components
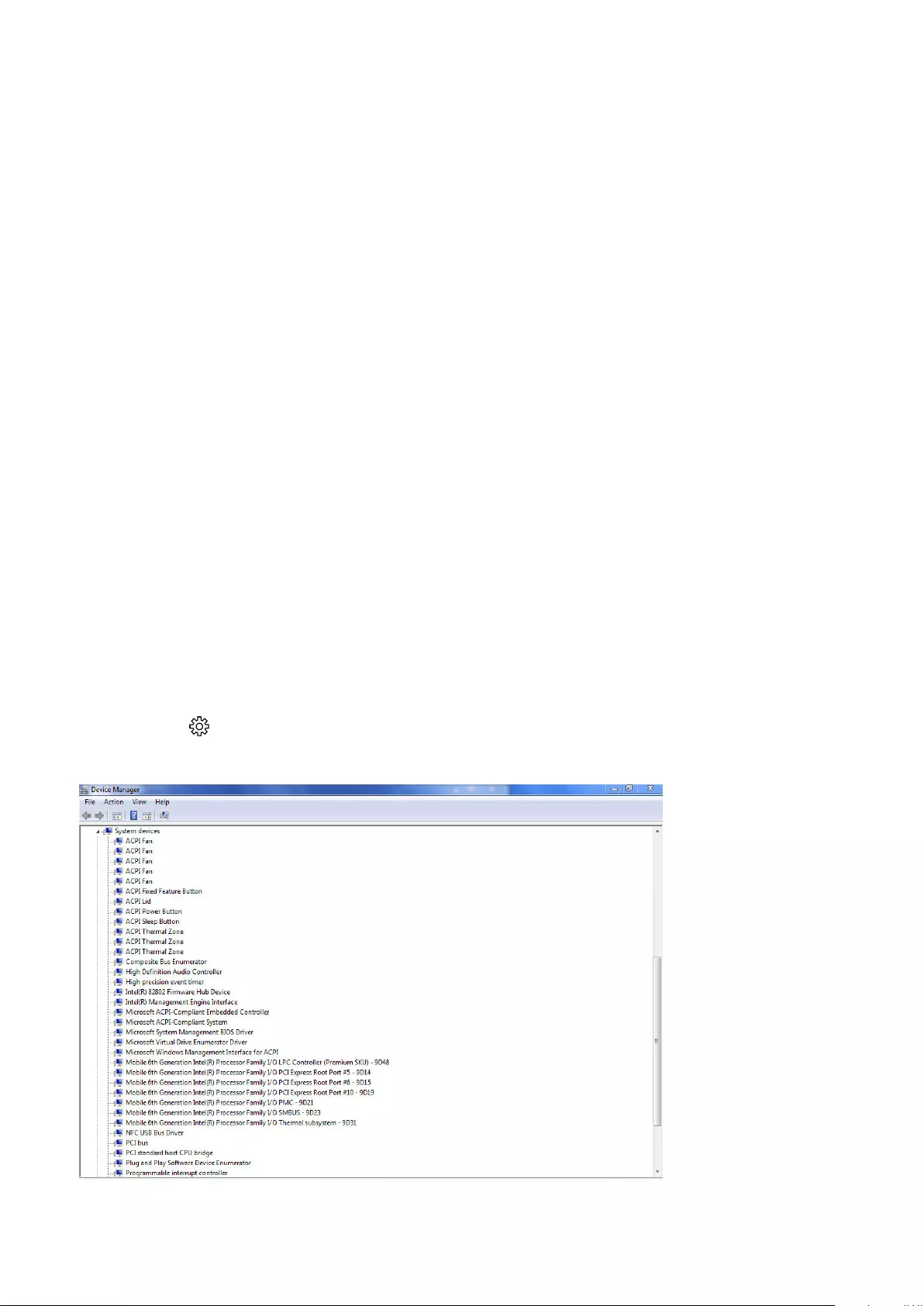
•Audio Return Channel - Allows an HDMI-connected TV with a built-in tuner to send audio data "upstream" to a surround audio
system, eliminating the need for a separate audio cable
•3D - Defines input/output protocols for major 3D video formats, paving the way for true 3D gaming and 3D home theater applications
•Content Type - Real-time signaling of content types between display and source devices, enabling a TV to optimize picture settings
based on content type
•Additional Color Spaces - Adds support for additional color models used in digital photography and computer graphics
•4K Support - Enables video resolutions far beyond 1080p, supporting next-generation displays that will rival the Digital Cinema
systems used in many commercial movie theaters
•HDMI Micro Connector - A new, smaller connector for phones and other portable devices, supporting video resolutions up to 1080p
•Automotive Connection System - New cables and connectors for automotive video systems, designed to meet the unique
demands of the motoring environment while delivering true HD quality
Advantages of HDMI
• Quality HDMI transfers uncompressed digital audio and video for the highest, crispest image quality.
• Low -cost HDMI provides the quality and functionality of a digital interface while also supporting uncompressed video formats in a
simple, cost-effective manner
• Audio HDMI supports multiple audio formats from standard stereo to multichannel surround sound
• HDMI combines video and multichannel audio into a single cable, eliminating the cost, complexity, and confusion of multiple cables
currently used in A/V systems
• HDMI supports communication between the video source (such as a DVD player) and the DTV, enabling new functionality
Software and Troubleshooting
Chipsets
All laptops or notebook communicate with the CPU through the chipset. This laptop is shipped with the Intel Sky Lake or Kaby Lake
chipset.
Identifying the chipset in Device Manager on Windows 10
1. Click All Settings on the Windows 10 Charms Bar.
2. From the Control Panel, select Device Manager.
3. Expand System Devices and search for the chipset.
Technology and components 41

Identifying chipset in Device Manager on Windows 7
1. Click Start → Control Panel → Device Manager.
2. Expand System Devices and search for the chipset.
Intel chipset drivers
Verify if the Intel chipset drivers are already installed in the laptop.
Table 20. Intel chipset drivers
Before installation After installation
Downloading the chipset driver
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Go to Dell.com/support.
3. Click Product Support, enter the Service Tag of your computer, and then click Submit.
NOTE: If you do not have the Service Tag, use the autodetect feature or manually browse for your computer model.
4. Click Drivers and Downloads.
5. Select the operating system installed in your computer.
6. Scroll down the page, expand Chipset, and select your chipset driver.
7. Click Download File to download the latest version of the chipset driver for your computer.
42 Technology and components

8. After the download is complete, navigate to the folder where you saved the driver file.
9. Double-click the chipset driver file icon and follow the instructions on the screen.
Processor
Identifying processors in Windows 10
1. Tap Search the Web and Windows.
2. Type Device Manager.
3. Tap Processor.
The basic information of the processor is displayed.
Identifying processors in Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Device Manager.
2. Select Processor.
The basic information of the processor is displayed.
Verifying the processor usage in Task Manager
1. Press and hold the taskbar.
2. Select Start Task Manager.
The Windows Task Manager window is displayed.
3. Click the Performance tab in the Windows Task Manager window. The processor performance details are displayed.
Verifying the processor usage in Resource Monitor
1. Press and hold the taskbar.
2. Select Start Task Manager.
The Windows Task Manager window is displayed.
3. Click the Performance tab in the Windows Task Manager window.
The processor performance details are displayed.
4. Click Open Resource Monitor.
Technology and components 43
Verifying system memory
Windows 10
1. Tap the Windows button and select All Settings > System .
2. Under System, tap About.
Windows 10
1. From your desktop, start the Charms Bar.
2. Select Control Panel and then select System.
Windows 7
• Click Start → Control Panel → System.
Verifying system memory in system setup BIOS
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Perform the following actions after the Dell logo is displayed
• With keyboard — Tap F2 until the Entering BIOS setup message appears. To enter the Boot selection menu, tap F12.
3. On the left pane, select Settings > General > System Information,
The memory information is displayed on the right pane.
Testing memory using ePSA
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. Perform one of the following actions after the Dell logo is displayed:
• With keyboard press F12.
• The system displays one time boot menu and uses up and down arrow key to go to diagnostics and press enter to launch ePSA.
The Pre Boot System Assessment (PSA) starts on your system.
NOTE: If you wait too long and the operating system logo be displayed, continue to wait until you see the desktop.
Turn off the laptop and try again.
NOTE: ePSA can alternatively be launched by pressing and holding Fn+ Press Power button.
44 Technology and components
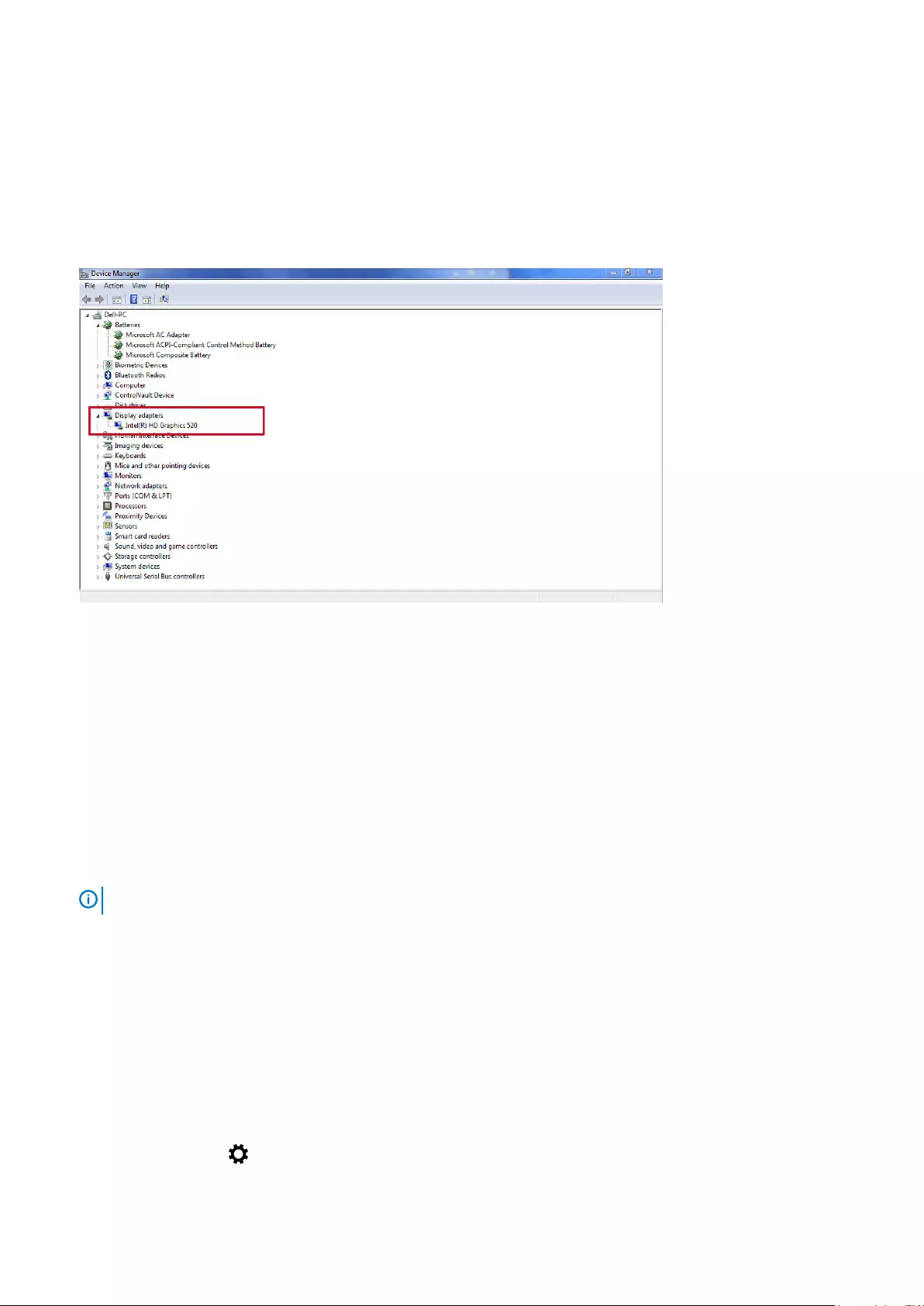
Display
Identifying the display adapter
1. Start the Search Charm and select Settings.
2. Type Device Manager in the search box and tap Device Manager from the left pane.
3. Expand Display adapters.
The display adapters are displayed.
Identifying the display adapter
1. On the taskbar, click or tap the search box, and then type Device Manger.
2. Click or tap Device Manager.
The Device Manager window is displayed.
3. Expand Display adapters.
Figure 7. Display adapters
Downloading drivers
1. Turn on the laptop.
2. Go to Dell.com/support.
3. Click Product Support, enter the Service Tag of your laptop, and then click Submit.
NOTE: If you do not have the Service Tag, use the auto detect feature or manually browse for your laptop model.
4. Click Drivers and Downloads.
5. Select the operating system installed on your laptop.
6. Scroll down the page and select the driver to install.
7. Click Download File to download the driver for your laptop.
8. After the download is complete, navigate to the folder where you saved the driver file.
9. Double-click the driver file icon and follow the instructions on the screen.
Adjusting brightness in Windows 10
To enable or disable automatic screen brightness adjustment:
1. Swipe-in from the right edge of the display to access the Action Center.
2. Tap or click All Settings > System > Display.
3. Use the Adjust my screen brightness automatically slider to enable or disable automatic-brightness adjustment.
Technology and components 45

NOTE: You can also use the Brightness level slider to adjust the brightness manually.
Adjusting brightness in Windows 7
To enable or disable automatic screen brightness adjustment:
1. Click Start → Control Panel → Display.
2. Use the Adjust brightness slider to enable or disable automatic-brightness adjustment.
NOTE: You can also use the Brightness level slider to adjust the brightness manually.
Changing the screen resolution
1. Press and hold the desktop screen and select Display Settings.
2. Tap or click Advanced display settings.
3. Select the required resolution from the drop-down list and tap Apply.
Connecting to external display devices
Follow these steps to connect your laptop to an external display device:
1. Ensure that the external display device is turned on and plug the external display device cable into a video port on your laptop.
2. Press the Windows logo+P key.
3. Select one of the following modes:
• PC screen only
• Duplicate
• Extend
• Second Screen only
NOTE: For more information, see the document that shipped with your display device.
Changing the display settings in Intel HD Graphics Control Panel
1. Right-click your desktop and select Graphics Properties to launch the Intel HD Graphics Control Panel.
46 Technology and components

2. Click Display.
3. Change the display settings as required.
Using touch screen in Windows 8/ Windows 10
Follow these steps to enable or disable the touch screen:
1. Go to the Charms Bar and tap All Settings .
2. Tap Control Panel.
3. Tap Pen and Input Devices in the Control Panel.
4. Tap the Touch tab.
5. Select Use your finger as an input device to enable the touch screen. Clear the box to disable the touch screen.
Touchscreen Troubleshooting
If the touchscreen is not able to access items along the edges of the LCD, it may need to be calibrated. To calibrate the touchscreen,
complete the following steps:
Touchscreen Calibration
Start > Control Panel > Tablet PC Settings > choose Calibrate...You can choose to calibrate Pen input or Touch input.
Perform the point calibrations that appear on the screen to correct the linearity problems.
Touchscreen Sensitivity
The touch screen may start to lose its sensitivity due to foreign particles (such as sticky notes) that are blocking the touch sensors. To
remove these particles:
• Turn off the computer.
• Disconnect the AC adapter cable from the wall outlet.
NOTE: Do not use water or a cleaning liquid to wipe the touch screen.
• Use a clean, lint-free cloth (you may spray mild, non-abrasive cleaner or water on the cloth if needed, but not on the screen) and wipe
the surface and sides of the touch screen to remove any dirt or fingerprints.
Application Promise
Consistent experience across form factors is what's necessary - a user can download any application from the Windows Store and it runs
great on their machine. There is no application that runs great on one device but not on another. This means developers can target all
Windows 8 and this version of Windows touch devices without worrying about the quality of touch devices depending on the type of form
factor. For example, all Windows 8 touch devices require supporting a minimum of five simultaneous touches. All touch points require
meeting requirements of 25 ms initial touch-down hardware latency and 15 ms subsequent contacts hardware latency. Game developers
can design features based on fast and responsive five simultaneous touch points support across all Windows 8 touch devices.
Technology and components 47

Cleaning the display
1. Check for any smudges or areas that must be cleaned.
2. Use a microfiber cloth to remove any obvious dust and gently brush off any dust particles.
3. Proper cleaning kits should be used to clean and keep your display in a crisp clear pristine condition.
NOTE: Never spray any cleaning solutions directly on the screen; spray it to the cleaning cloth.
4. Gently wipe the screen in a circular motion. Do not press hard on the cloth.
NOTE: Do not press hard or touch the screen with your fingers or you may leave oily prints and smears.
NOTE: Do not leave any liquid on the screen.
5. Remove all excess moisture as it may damage your screen.
6. Let the display dry thoroughly before you turn it on.
7. For stains that are hard to remove, repeat this procedure till the display is clean.
Troubleshooting Touchpad
Most touch pad issues are erratic movement or no movement at all. Since erratic movement is the more common problem, it is covered
first.
Erratic Pointer Movement
Here are some easy steps to take to determine the problem with a touch pad demonstrating erratic pointer movement:
1. Get the latest driver from Dell support site - Most problems can be corrected with a simple driver download. This should always be one
of the first steps when diagnosing any touch pad problem.
2. Check for hand and finger placement - The most common cause of random pointer movement is that the touch pad senses a finger or
part of the hand near the surface of the device.
• Have the customer attempt to use the touch pad normally but to pay attention to the location of his or her hands and fingers. Are
any straying too close to the touch pad?
• Adjust the Touch Sensitivity and Touch and check settings in the Touch Pad Settings section of the Dell Touchpad Properties.
3. Try an external mouse - Does this problem happen with an external mouse attached?
• The Device Select section of the Dell Touchpad Properties has options to enable or disable the touch pad or external mouse. Try
several combinations of these settings.
• If the problems only occur when the touch pad is enabled and do not occur any time a mouse or other external device is used, then
the issue is related to the touch pad.
4. Check for mechanical problems - If the problem cannot be corrected by adjusting the settings mentioned above and only occurs with
the touch pad enabled and then this could indicate a mechanical problem.
• Press down on the palm rest on first the left side of the touch pad and then the right. See if the cursor starts moving on its own.
• Run ePSA Diagnostics and try to recreate the problems there. If either of these situations occurs, replace the palm rest.
No Pointer Movement
No pointer movement from the touch pad (or track stick, if available) usually is the result of one of two things: The touch pad has been
disabled in the driver interface, or the touch pad cable is damaged or disconnected. Follow the steps below to determine the problem.
1. Connect an external mouse - In either situation, an external mouse should still function. If it does not, try booting into Safe Mode and
testing both devices again.
2. Enable the touch pad in the driver settings - Using the external mouse (or key strokes if no mouse is available), go into the Dell
Touchpad Properties. Go to the Device Select section and enable the touch pad. If already enabled, get the latest driver from Dell
support site.
3. Test the device in Dell ePSA Diagnostics - To eliminate a potential software problem, run the Dell ePSA Diagnostics and test the
device here.
4. Check for mechanical problems - As a last resort, press down on the palm rest where the touch pad connector is located on the
system board. If the pointer reacts in some way, then the cable may just need to be reseated. Otherwise, replace the palm rest.
48 Technology and components

Troubleshooting Your Pen
The stylus is the first component to be investigated in the event of a suspected problem with the digitizer.
Ensure that you perform the following steps:
1. Verify the pen tip is in good shape (free of chips, excessive wear, etc.).
2. Replace the pen tip with a new one or the one that is in good condition.
3. Verify that the touch capabilities are not affected.
4. Switch to touch mode and see if the problem still exists.
5. If no symptoms persist in touch mode, the pen tip is the most likely suspect.
6. If the problem does persist in touch mode, run diagnostics and take the necessary steps depending on the results.
Realtek HD audio drivers
Verify if the Realtek audio drivers are already installed in the computer.
Table 21. Realtek HD audio drivers
Before installation After installation
Troubleshooting audio issues
This topics details the troubleshooting steps in resolving audio related issues specific to IDT92HD87 audio chip
No Audio
Determine if the problem is only on the internal or external speakers or both.
1. If the problem is external only, try reseating the speakers or headphones. Also try another set of speakers or headphones if available.
Check the speaker connector for damage. If the problem does not happen with different speakers, then the problem is related to the
external device. If it persists, then there is a problem with either the audio connector or the audio controller. Confirm this by running
Dell Diagnostics.
2. If the problem is internal only, try shaking the unit and see if the sound returns or plays intermittently. If it does, then a connection for
the speakers is loose and the unit needs service. If there is still no sound at all, then try deleting the hardware profile (if possible) and
recreating it. Test the speakers using Dell Diagnostics both internally and externally. If the problem only happens on the internal
speakers, then the speakers and possibly the system board need to be replaced.
If there is no audio from either internal or external speakers, then check the following:
1. Adjust the volume controls. Some systems also have an external volume control in addition to the one in the Windows® operating
system.
2. Check Device Manager and ensure the audio driver is installed correctly. Any problems indicated here can normally be resolved by
reinstalling the audio driver from the ResourceDVD or from dell.com/support.
3. If the audio is installed correctly in Windows but there still is no sound, run Dell Diagnostics on the audio controller. If these fail or no
sound is heard, then replace the system board. If audio does play during this test, then the problem is most likely software related.
Poor Sound Quality
1. Determine if the problem is related to a specific application or program. If so, the software may not be fully compatible with the audio
controller on the system. Check the software manufacturer´s website for any updates.
2. Update to the latest BIOS and driver from dell.com/support
3. Some problems can be caused by issues with the DirectX® API. Try downloading the latest version from Microsoft.
4. See if the problem occurs on both internal and external speakers. If isolated to only one of the two, follow the troubleshooting
mentioned above. Otherwise, run Dell Diagnostics to test the audio.
5. If the problem fails during the audio test, this is a hardware problem and the system needs service. If it does not, then a software
problem exists.
Technology and components 49

Sound from Only One Channel
1. The majority of the time, this problem happens only on external speakers. Reseating the speaker connection usually corrects the
problem.
2. Check the volume control in Windows and make sure the balance slider is not set all the way to one side.
3. If this problem is happening only on internal speakers, try shaking the unit to see if sound comes back or if it comes and goes
intermittently. If either of these occurs, a loose speaker connection most likely is the problem and the system needs service.
4. If this issue is happening only on external speakers and the previous steps did not help, then examine the audio connector for damage.
Test the system with Dell Diagnostics. If the problem persists there, then the audio connector needs to be replaced.
Camera features
This laptop comes with front-facing camera with the image resolution of 1280 x 720 (maximum).
NOTE: The camera is at the top center of the LCD.
Identifying the camera in Device Manager on Windows 10
1. In the Search box, type device manager, and tap to start it.
2. Under Device Manager, expand Imaging devices.
Identifying the camera in Device Manager on Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Device Manager.
2. Expand Imaging devices.
Starting the camera
To start the camera, open an application that uses the camera. For instance, if you tap the Skype software that is shipped with the laptop,
the camera turns on. Similarly, if you are chatting on the internet and the application requests to access the webcam, the webcam turns
on.
Starting the camera application
1. Tap or click the Windows button and select All apps.
50 Technology and components
2. Select Camera from the apps list.
3. If the Camera App is not available in the apps list, search for it.
Hard drive options
This laptop supports M.2 SATA drives.
Identifying the hard drive in Windows 10
1. Tap or click All Settings on the Windows 10 Charms Bar.
Technology and components 51

2. Tap or click Control Panel, select Device Manager , and expand Disk drives.
The hard drive is listed under Disk drives.
Identifying the hard drive in Windows 7
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Device Manager.
The hard drive is listed under Disk drives.
2. Expand Disk drives.
Identifying the hard drive in the BIOS
1. Turn on or restart your system.
2. When the Dell logo appears, perform the following action to enter the BIOS setup program:
• With keyboard — Tap F2 until the Entering BIOS setup message appears. To enter the Boot selection menu, tap F12.
The hard drive is listed under the System Information under the General group.
Intel Rapid Storage Technology
Overview
Intel® Rapid Storage Technology provides new levels of protection, performance, and expandability for desktop and mobile platforms.
Whether using one or multiple hard drives, users can take advantage of enhanced performance and lower power consumption. When
using more than one drive, the user can have additional protection against data loss in the event of a hard drive failure.
Intel Rapid Storage Technology was formerly known as Intel® Matrix Storage Manager. Starting with version 9.5, a brand new user
interface makes creating and managing your storage simple and intuitive. Combined with Intel Rapid Recover Technology, setting up data
protection can be accomplished easily with an external drive.
52 Technology and components

Valuable digital memories are protected against a hard drive failure when the system is configured for any one of three fault-tolerant RAID
levels: RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10. By seamlessly storing copies of data on one or more additional hard drives, any hard drive can fail
without data loss or system downtime. When the failed drive is removed and a replacement hard drive is installed, data fault tolerance is
easily restored.
Intel Rapid Storage Technology can also improve the performance of disk intensive retrieval applications such as editing home video. By
combining from two to six drives in a RAID 0 configuration, data can be accessed on each drive simultaneously, speeding up response time
on data-intensive applications. Also, due to drive load balancing, even systems with RAID 1 can take advantage of faster boot times and
data reads.
Intel Rapid Storage Technology provides benefits to users of a single drive as well. Through AHCI, storage performance is improved
through Native Command Queuing (NCQ). AHCI also delivers longer battery life with Link Power Management (LPM), which can reduce
the power consumption of the chipset and Serial ATA (SATA) hard drive.
Installation Instructions
The Intel Rapid Storage Technology software can be install through the Resource DVD provided with the system. When you first launch
the installation file, you'll get the first screen as below:
Please remember to check on the "Install Intel® Control Center" otherwise the user graphical interface RAID management software would
not be install. Click 'Next' to continue the installation. Once the installation completes, user will get the "Intel Rapid Storage Technology"
icon on the Windows task bar:
Technology and components 53
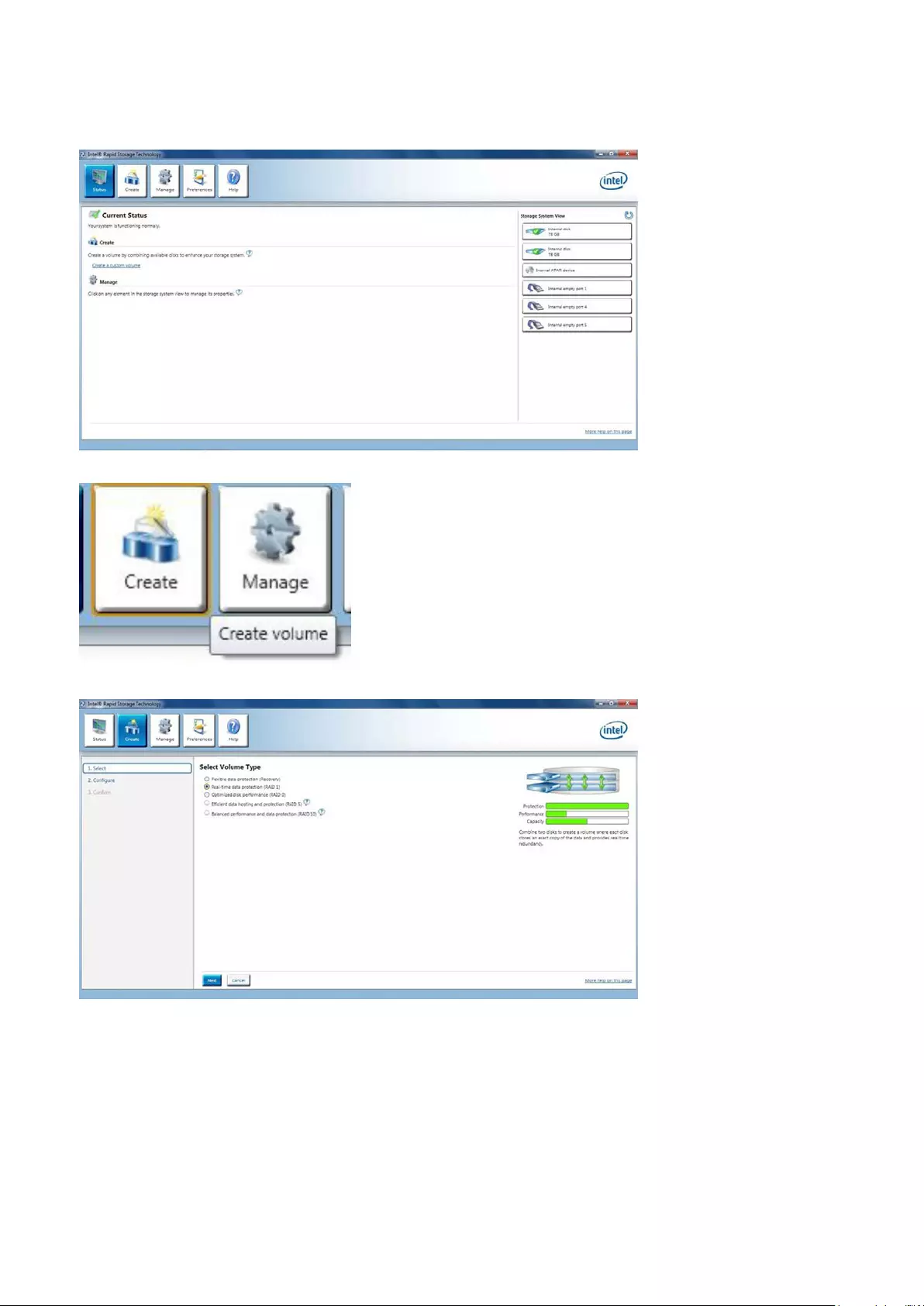
Create a RAID Array
1. Double-click "Intel Rapid Storage Technology" icon, then below main screen appears.
2. Click the "Create" icon to create a RAID array. Here we take RAID 1 for example.
3. In "Select Volume Type", click "Real-time data protection (RAID 1)". Click "Next".
4. In "Configure Volume", you need to key-in the Volume Name with 1-16 letters, select the RAID disks, and then specify the volume size.
Click "Next"
54 Technology and components

5. In "Confirm Volume Creation", you may review the selected configuration. Then click "Create Volume".
6. The volume is created successfully. But you still need to partition your new volume by using Windows Desk Management before
adding any data. Click "OK".
7. You will see the current status.
Technology and components 55

8. In Windows Desk Management, you need to initialize a disk before Logical Disk Management can access it. Click "OK".
9. Right-click on Disk 0, click "New Simple Volume".
10. Then follow the instructions on the New Simple Volume Wizard.
56 Technology and components

11. Finally you can start to use RAID 1 function.
Dell Command Configure
Dell Command | Configure (Command | Configure) is a packaged software offering that provides configuration capability to business
client platforms. This product consists of a Command Line Interface (CLI) and Graphical User Interface (GUI) to configure various BIOS
features. You can use Command | Configure on Microsoft Windows Pre-installation Environment (Windows PE), Windows 7, Windows 8,
and Windows 8.1, Windows 10 operating systems, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments.
What’s new with Dell Command | Configure
The new features for the Dell Command | Configure includes:
• Dell Client Configuration Toolkit (CCTK) is re-branded as Dell Command | Configure (DCC).
• New User Interface.
• Support for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0 Client version (64-bit) operating system.
• Support for x6 client platforms
• Support for Advanced System Management (ASM) 2.0 on Dell Precision™ Workstations for setting the non-critical upper threshold
values for cooling probes.
• Support for additional arguments: medium_high and medium_low for configuring the fan speed using --fanspeed option.
• Support for the following BIOS options:
• --backcamera.
• --fnlock
• --fnlockmode
• --gpsradio
Technology and components 57

• --keyboardbacklightonacpower
• --rearusb
• --sideusb
• --unmanagednic
Platforms Supported
These are the business clients platforms supported:
• Latitude™
• OptiPlex™
• Dell Precision Workstation Mobile
• Dell Precision Workstation
NOTE: Dell Command | Configure will not be pre-loaded for the customer upon purchase. Customers will be able to
download the software from the Dell support website.
Command | Configure Graphical User Interface
The Dell™ Command | Configure Graphical User Interface (Command | Configure GUI) displays all Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
configurations supported by Command | Configure. Using the GUI, you can perform the following tasks:
• Create BIOS configuration for client systems
• Validate the BIOS configuration against the BIOS configuration of the host system
• Export the customized BIOS configurations as a configuration file (.ini/.cctk), Self-Contained Executable (SCE), shell script, or report
NOTE: To apply the configuration using Command Line Interface (CLI), run the required file (.ini , .cctk, or sce).
Accessing Command | Configure From a Windows System
Click Start > All Programs > Dell > Command | Configure > Command Configure Command Wizard.
Accessing Command | Configure From a Linux System
Navigate to the /opt/Dell/toolkit/bin directory.
58 Technology and components

Files And Folders of Command | Configure
The following table displays the files and folders of Command | Configure on a Windows system.
Table 22. Files And Folders configuration
Files/Folders Description
Command | Configure Command
Prompt
Allows access to the Command | Configure command prompt.
Configuration Wizard Allows access to the Command | Configure GUI.
Command | Configure WINPE Allows access to the Windows PE scripts to create a bootable image. For more details, see the Dell
Command | Configure Installation Guide.
Uninstall Uninstalls Command | Configure.
User’s Guide Online Provides access to the Command | Configure online documentation.
Launching The Command | Configure GUI
NOTE: The Command | Configure GUI is supported only on systems running the Microsoft® Windows operating system.
To launch the GUI, click Start > All Programs > Dell > Command Configure > Configuration Wizard or double-click the Dell
Configuration Wizard on the desktop. The screen below appears:
Command Line Interface
This chapter provides a general overview of the Command Line Interface (CLI) utility. It explains how to run the commands and the syntax
details of the command line options used to configure BIOS settings for the client systems.
Running Command | Configure Commands
You can run the Command | Configure commands in two ways:
• Using Command Prompt
Technology and components 59

• Using Bootable Image
Command Prompt
To run Command | Configure commands:
1. Click Start → All Program → Dell → Command Configure → Command Configure Command Prompt.
NOTE: If you are using Microsoft Windows Vista operating system or later, right-click Command | Configure
Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
2. Navigate to the x86 or x86_64 directory depending on the architecture of the operating system.
3. Run the Command | Configure commands.
Bootable Image
To run Command | Configure commands:
1. Copy Dell Command | Configure with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) image to a Compact disc (CD). For
more information, see Dell Command | Configure Installation Guide available at https://Dell.com/Command .
2. Boot the system that you want to configure from the CD.
3. Navigate to the Command Configure\x86 or Command Configure\x86_64 directory.
4. Run the Command | Configure commands.
Intel HD Graphics drivers
Verify if the Intel HD Graphics drivers are already installed in the laptop.
Table 23. Intel HD Graphics drivers
Before installation After installation
60 Technology and components

Removing and installing components
Safety instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to protect your computer from potential damage and to ensure your personal safety. Unless otherwise
noted, each procedure included in this document assumes that the following conditions exist:
• You have read the safety information that shipped with your computer.
• A component can be replaced or, if purchased separately, installed by performing the removal procedure in reverse order.
NOTE: Disconnect all power sources before opening the computer cover or panels. After you finish working inside the
computer, replace all covers, panels, and screws before connecting to the power source.
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For
additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage
CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You should only perform troubleshooting and
simple repairs as authorized in your product documentation, or as directed by the online or telephone service and
support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty. Read and follow
the safety instructions that came with the product.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching
an unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
CAUTION: Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a card. Hold a card by
its edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as a processor by its edges, not by its pins.
CAUTION: When you disconnect a cable, pull on its connector or on its pull-tab, not on the cable itself. Some cables
have connectors with locking tabs; if you are disconnecting this type of cable, press in on the locking tabs before you
disconnect the cable. As you pull connectors apart, keep them evenly aligned to avoid bending any connector pins. Also,
before you connect a cable, ensure that both connectors are correctly oriented and aligned.
NOTE: The color of your computer and certain components may appear differently than shown in this document.
Before working inside your computer
1. Ensure that your work surface is flat and clean to prevent the computer cover from being scratched.
2. Turn off your computer.
3. If the computer is connected to a docking device (docked), undock it.
4. Disconnect all network cables from the computer (if available).
CAUTION: If your computer has an RJ45 port, disconnect the network cable by first unplugging the cable from your
computer.
5. Disconnect your computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
6. Open the display.
7. Press and hold the power button for few seconds, to ground the system board.
CAUTION: To guard against electrical shock unplug your computer from the electrical outlet before performing Step
# 8.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically
touching an unpainted metal surface at the same time as touching a connector on the back of the computer.
8. Remove any installed ExpressCards or Smart Cards from the appropriate slots.
3
Removing and installing components 61

Safety Precautions
Follow the safety precautions described in the following sections when you perform an installation or a disassembly/reassembly procedure:
• Turn off the system and all attached peripherals.
• Disconnect the system and all attached peripherals from AC power, and then remove the battery.
• Disconnect all network cables, telephone or telecommunications lines from the system.
• Use a wrist grounding strap and mat when working inside any computer system to avoid electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage.
• After removing a system component, carefully place the removed component on an anti-static mat.
• Wear shoes with non-conductive rubber soles to help reduce the risk of being shocked or seriously injured in an electrical accident.
Standby Power
Dell products with standby power must be completely unplugged before the case is opened. Systems that incorporate standby power are
essentially powered while turned off. The internal power enables the system to be remotely turned on (wake on LAN), suspended into a
sleep mode, and have other advanced power management features.
After you unplug a system and before you remove components, wait approximately 30 to 45 seconds to allow the charge to drain from
the circuits.
Bonding
Bonding is a method for connecting two or more grounding conductors to the same electrical potential. This is done through the use of a
Field Service ESD kit. When connecting a bonding wire, always ensure that it is connected to bare metal and never to a painted or non-
metal surface. The wrist strap should be secure and in full contact with your skin, and be sure to always remove all jewelry such as
watches, bracelets, or rings prior to bonding yourself and the equipment.
Figure 8. Bonding Properly
Electrostatic Discharge Protection
ESD is a major concern when you handle electronic components, especially sensitive components such as expansion cards, processors,
memory DIMMs, and system boards. Very slight charges can damage circuits in ways that may not be obvious, such as intermittent
problems or a shortened product life span. As the industry pushes for lower power requirements and increased density, ESD protection is
an increasing concern.
Due to the increased density of semiconductors used in recent Dell products, the sensitivity to static damage is now higher than in earlier
Dell products. For this reason some previously approved methods of handling parts are no longer applicable.
There are two recognized types of ESD damage: catastrophic and intermittent failures.
•Catastrophic —The damage causes an immediate and complete loss of device functionality. An example of catastrophic failure is a
memory DIMM that has received a static shock and immediately generates a "No POST/No Video" symptom with a beep code
emitted for missing or nonfunctional memory.
NOTE: Catastrophic failures represent approximately 20 percent of ESD-related failures.
•Intermittent —The DIMM receives a static shock, but the tracing is merely weakened and does not immediately produce outward
symptoms related to the damage. The weakened trace may take weeks or months to melt, and in the meantime may cause
degradation of memory integrity, intermittent memory errors, etc.
NOTE: Intermittent failures represent approximately 80 percent of ESD-related failures. The high rate of
intermittent failures means that most of the time when damage occurs, it is not immediately recognizable.
62 Removing and installing components
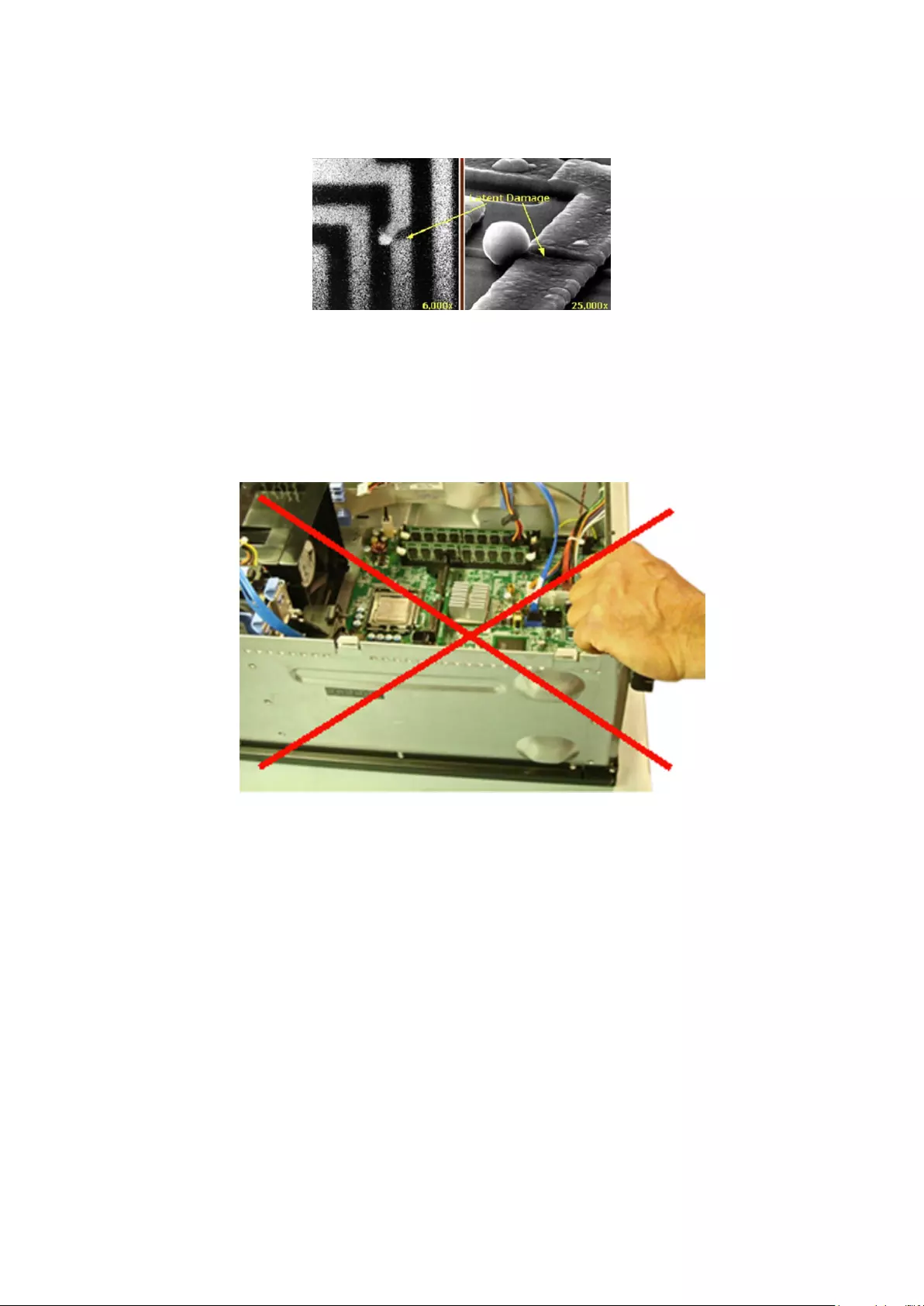
The more difficult type of damage to recognize and troubleshoot is the intermittent (also called latent or “walking wounded”) failure. The
following image shows an example of intermittent damage to a memory DIMM trace. Although the damage is done, the symptoms may
not become an issue or cause permanent failure symptoms for some time after the damage occurs.
Figure 9. Intermittent (Latent) Damage to a Wiring Trace
Do the following to prevent ESD damage:
• Use a wired ESD wrist strap that is properly grounded.
The use of wireless anti-static straps is no longer allowed; they do not provide adequate protection.
Touching the chassis before handling parts does not ensure adequate ESD protection on parts with increased sensitivity to ESD
damage.
Figure 10. Chassis "Bare Metal" Grounding (Unacceptable)
• Handle all static-sensitive components in a static-safe area. If possible, use anti-static floor pads and workbench pads.
• When handling static-sensitive components, grasp them by the sides, not the top. Avoid touching pins and circuit boards.
• When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the component from the anti-static packing
material until you are ready to install the component. Before unwrapping the anti-static packaging, be sure to discharge static
electricity from your body.
• Before transporting a static-sensitive component, place it in an anti-static container or packaging.
The ESD Field Service Kit
The unmonitored Field Service kit is the most commonly used. Each Field Service kit includes three main components: anti-static mat,
wrist strap, and bonding wire.
Removing and installing components 63

Figure 11. ESD Field Service Kit
The anti-static mat is dissipative and should be used to safely place parts on during service procedures. When using an anti-static mat,
your wrist strap should be snug and the bonding wire should be connected to the mat and to bare-metal on the system being worked on.
Once deployed properly, service parts can be removed from the ESD bag and placed directly on the mat. Remember, the only safe place
for ESD-sensitive items are in your hand, on the ESD mat, in the system, or inside a bag.
Figure 12. Anti-Static Mat
The wrist strap and bonding wire can be either directly connected between your wrist and bare metal on the hardware if the ESD mat is
not required, or connected to the anti-static mat to protect hardware that is temporarily placed on the mat. The physical connection of
the wrist strap and bonding wire between your skin, the ESD mat, and the hardware is known as bonding. Use only Field Service kits with
a wrist strap, mat, and bonding wire. Never use wireless wrist straps.
Always be aware that the internal wires of a wrist strap are prone to damage from normal wear and tear, and must be checked regularly
with a wrist strap tester in order to avoid accidental ESD hardware damage. It is recommended to test the wrist strap and bonding wire a
minimum of once per week.
64 Removing and installing components

Table 24. Wrist Straps
Wrist Strap and Bonding Wire Wireless ESD Strap (Unacceptable)
ESD Wrist Strap Tester
The wires inside of an ESD strap are prone to damage over time. When using an unmonitored kit, it is best practice to regularly test the
strap prior to each service call, and at a minimum, test once per week. A wrist strap tester is the best method for doing this test. If you do
not have your own wrist strap tester, check with your regional office to find out if they have one. To perform the test, plug the wrist-
strap’s bonding-wire into the tester while it is strapped to your wrist and push the button to test. A green LED is lit if the test is
successful; a red LED is lit and an alarm sounds if the test fails.
Figure 13. Wrist Strap Tester
Insulator Elements
It is critical to keep ESD sensitive devices, such as plastic heat sink casings, away from internal parts that are insulators and often highly
charged.
Removing and installing components 65

Table 25. Placement of Insulator Elements
Unacceptable — DIMM lying on an insulator part (plastic
heat sink shroud)
Acceptable — DIMM separated from the insulator part
Consider the Working Environment
Before deploying the ESD Field Service kit, assess the situation at the customer location. For example, deploying the kit for a server
environment is different than for a desktop or portable environment. Servers are typically installed in a rack within a data center; desktops
or portables are typically placed on office desks or cubicles.
Always look for a large open flat work area that is free of clutter and large enough to deploy the ESD kit with additional space to
accommodate the type of system that is being repaired. The workspace should also be free of insulators that can cause an ESD event. On
the work area, insulators such as Styrofoam and other plastics should always be moved at least 12 inches or 30 centimeters away from
sensitive parts before physically handling any hardware components.
ESD Packaging
All ESD-sensitive devices must be shipped and received in static-safe packaging. Metal, static-shielded bags are preferred. However, you
should always return the damaged part using the same ESD bag and packaging that the new part arrived in. The ESD bag should be folded
over and taped shut and all the same foam packing material should be used in the original box that the new part arrived in.
ESD-sensitive devices should be removed from packaging only at an ESD-protected work surface, and parts should never be placed on
top of the ESD bag because only the inside of the bag is shielded. Always place parts in your hand, on the ESD mat, in the system, or
inside an anti-static bag.
66 Removing and installing components

Figure 14. ESD Packaging
Transporting Sensitive Components
When transporting ESD-sensitive components such as replacement parts or parts to be returned to Dell, it is critical to place these parts in
anti-static bags for safe transport.
ESD Protection Summary
It is strongly suggested that all field service engineers use the traditional wired ESD grounding wrist strap and protective anti-static mat at
all times when servicing Dell products. In addition, it is critical that engineers keep sensitive parts separate from all insulator parts while
performing service and that they use anti-static bags for transporting sensitive components.
Lifting Equipment
NOTE: Do not lift greater than 50 pounds. Always obtain assistance from another person or persons, or use a
mechanical lifting device.
Adhere to the following guidelines when lifting equipment:
1. Get a firm balanced footing. Keep your feet apart for a stable base, and point your toes out.
2. Bend your knees. Do not bend at the waist.
3. Tighten stomach muscles. Abdominal muscles support your spine when you lift, offsetting the force of the load.
4. Lift with your legs, not your back.
5. Keep the load close. The closer it is to your spine, the less force it exerts on your back.
6. Keep your back upright, whether lifting or setting down the load. Do not add the weight of your body to the load. Avoid twisting your
body and back.
7. Follow the same techniques in reverse to set the load down.
Removing and installing components 67

After working inside your computer
After you complete any replacement procedure, ensure that you connect external devices, cards, and cables before turning on your
computer.
CAUTION: To avoid damage to the computer, use only the battery designed for this particular Dell computer. Do not use
batteries designed for other Dell computers.
1. Connect any external devices, such as a port replicator or media base, and replace any cards, such as an ExpressCard.
2. Connect any telephone or network cables to your computer.
CAUTION: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network device and then plug it into the
computer.
3. Connect your computer and all attached devices to their electrical outlets.
4. Turn on your computer.
Recommended tools
The procedures in this document require the following tools:
• Phillips #0 screwdriver
• Phillips #1 screwdriver
• Plastic scribe
• 5.5 mm Socket wrench
• A pair of tweezers
NOTE: The #0 screw driver is for screws 0-1 and the #1 screw driver is for screws 2-4.
Stylus
Removing the stylus
1. Press the latch [1] and open the right I/O door [2].
68 Removing and installing components

2. Withdraw the stylus out of the slot.
Installing the stylus
1. Insert the stylus in the slot.
Removing and installing components 69

2. Close the I/O door [1] and press the door until it latches [2].
SIM card
Removing the SIM card
1. Remove the SIM card out of the slot on the system board.
70 Removing and installing components

Latch Doors
Removing the latch doors
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Open the I/O door.
3. Remove the screws [1] securing door hinges to the computer and lift the I/O door [2] away from the computer.
Installing the latch doors
1. Install the door on the computer [1].
2. Install the screws securing door hinges to the computer [2].
Removing and installing components 75

3. Lock the I/O door.
4. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
NOTE: Depending on its location each door may have one, two, or three screws.
Battery
Removing the Battery
1. NOTE: This laptop can accommodate two hot-swap capable batteries(primary and optional), both the batteries
follows the same installation and removal procedure.
Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Unlock the battery [1] and slide the latch along the groove to disengage locking mechanism.
3. Pry on the recess point [2] and slide the battery forward [3] to remove it from the computer.
76 Removing and installing components

Installing the Batteries
1. Slide in the battery in battery bay to align the battery contacts[1], with one on the computer.
2. Press the edge of the battery [2] to engage the latch mechanism and lock the battery [3].
3. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
NOTE: This laptop can accommodate two hot-swap capable batteries(primary and optional), both the batteries
follows the same installation and removal procedure.
Removing and installing components 77

Primary SSD carrier
Removing the Primary SSD carrier
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
CAUTION: Attempt to retrieve the primary SSD carrier from an operational computer can cause operating system
crash and potential data loss.
2. Remove the: Batteries.
3. Press the latch [1] and open the right I/O door [2].
4. Release the SSD carrier by sliding the blue hard drive release latch [1] towards right.
5. Slide the SSD carrier out of the computer using the blue pull tab [2] out of the computer.
78 Removing and installing components

Installing the Primary SSD carrier
1. Insert the primary SSD carrier in to the computer.
2. Push the carrier into the slot until the blue tab clicks.
3. Close the right I/O door [1] and press the door until the latch [2] clicks up in locking position.
Removing and installing components 79

4. Install the: Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
SSD
Removing the SSD from carrier
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries.
b) SSD(Primary ).
3. Remove the two 'M2*5' screws [1] and flip over the SSD carrier [2].
4. Remove the single 'M2*5' screw [3] and separate the cover from the SSD carrier [4].
5. Separate the SSD and interposer [1] from the SSD carrier tray.
6. Flip over the assembly [2] and disconnect the SSD from the interposer [3].
80 Removing and installing components

Installing the SSD in carrier
1. Connect the SSD to the interposer [1], flip over [2].
2. Install the SSD with interposer on the SSD carrier tray preassembled with new thermal pad [3].
3. Install the cover [1] on the SSD carrier and install the single 'M2*5' screw [2].
4. Flip over the SSD carrier [3] and tighten the two 'M2*5' screws [4] securing the cover to the SSD carrier.
5. Install the:
a) SSD(Primary ).
b) Batteries
6. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Bottom Chassis Cover
Removing the Bottom Chassis Cover
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries.
3. Open the left and rear I/O door[1] and loosen the two 'M2.5*6' screws [2] in the rear I/O space.
Removing and installing components 81

4. Remove the 17 'M2.5*5' screws on the bottom chassis cover [1] and remove the bottom chassis cover [2] from the computer.
Installing the Bottom Chassis Cover
1. Install the bottom chassis cover over the bottom base [1] of the computer.
2. Install the 17 'M2.5*5' screws on the bottom chassis cover.
82 Removing and installing components

Keyboard
Removing the Keyboard
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the: Batteries.
3. Remove the six 'M2.5*5' screws on the keyboard [1] and pry at the bottom edge of the keyboard [2].
4. Slide the keyboard slightly [1] towards touch pad and flip it over inclined over the LCD panel [2].
5. Remove the four 'M2*3' screws [1] on the keyboard cover and remove it from the computer [2].
84 Removing and installing components

6. Peel-off the tape on the keyboard and back-light FPC [1] and disconnect it from the system board [2].
NOTE: Tweezers might be required to access the keyboard and back-light FPC connectors on the system board.
7. Separate the keyboard from the system [3].
Installing the Keyboard
1. Install the keyboard [1] and connect the keyboard and back-light FPC to the system board [2].
2. Secure keyboard and back-light FPC connections using an insulation tape [3].
Removing and installing components 85

3. Install the keyboard cover [1] and tighten the four 'M2*3' screws [2] to secure it to the chassis.
4. Flip the keyboard [3] over on the chassis [3].
5. Slide the keyboard towards LCD [1] to align it to screw holes [2].
86 Removing and installing components

6. Install the six 'M2.5*5' screws on the keyboard to secure it to the computer.
7. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WWAN card
Removing the WWAN card
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
3. Remove the single 'M2*3' screw [1], remove the metal bracket [2] on the WWAN card.
Removing and installing components 87

4. Disconnect the antennae cables [3] and remove the WWAN card [4] out of the M.2 slot on the system board.
Installing the WWAN card
1. Install the WWAN card in the M.2 slot [1] on the system board and connect the antennae cables [2].
2. Secure the WWAN card using the metal bracket [3] and tighten the single M2.3 screw [4] securing the WWAN card to the system
board.
3. Install the:
88 Removing and installing components

a) Bottom chassis cover
b) Batteries
4. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
WLAN card
Removing the WLAN card
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
3. Remove the single 'M2*3' screw [1] and remove the metal bracket [2] on the WLAN card.
4. Disconnect the antennae cables [3] and remove the WLAN card out from the M.2 slot [4] on the system board.
Installing the WLAN card
1. Install the WLAN card into the M.2 slot [1] on the system board and connect the antennae cables [2].
2. Place the metal bracket on the WLAN card [3] and secure it using the single 'M2*3' screw [4].
Removing and installing components 89

3. Install the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
4. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Removing the GPS module
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Rear I/O board
3. Unroute the aux cables [1] for WLAN and WWAN and disconnect the antennae cable [2] on GPS module.
4. Unroute the main antennae cables [3] and loosen the single 'M2.5*5' screw [4] to separate the RF bracket [5] from the system board.
90 Removing and installing components

5. Peel off the inductive tape on the GPS FPC connector [1] and disconnect the GPS FPC connector [2] from GPS module.
6. Remove the two 'M2.5*5' screws [3] and separate the GPS module [4] from the system board.
Installing the GPS module
1. Align and place the GPS module on the system board and tighten the two 'M2.5*5' screws on GPS module [2].
2. Connect the GPS FPC(system board side first) [3] and secure it using a piece of tape [4].
Removing and installing components 91

3. Install the RF bracket [1] on the system board and secure it using the single 'M2.5*5' screw [2].
4. Route the aux cables for WLAN and WWAN cards through the RF bracket [3].
5. Connect the antennae cable [4] on GPS module and route the main antennae cables [5] through the RF bracket.
6. Install the:
a) Rear I/O board
b) Bottom Chassis Cover
c) Batteries
7. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
92 Removing and installing components

Memory modules
Removing the Memory
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
3. Pull the clips securing the memory module [1] until the socket disengages and remove the memory module from the memory socket
[2] on the system board.
Installing the Memory
1. Align and insert the memory module along the keyed notch [1] at an acute angle and press the memory module [2] until securing clips
engages.
Removing and installing components 93

2. Install the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom Chassis Cover
3. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Coin-cell battery
Removing the Coin cell
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Bottom chassis cover
b) Batteries
3. NOTE: Removing or Disconnecting the coin cell may reset systemboard / BIOS / system time to defaults or engage
bit locker or other similar security protocol devices.
Disconnect the coin cell connector from the system board [1] and remove it from the system [2].
94 Removing and installing components

PCIe Heatsink Fan Assembly
Removing the PCIe Heatsink fan assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
3. Disconnect the fan cable [1], loosen the four 'M2*3' screws from fan case [2].
4. Loosen the seven 'M2.5*5' screws [1] from heat sink pipe and remove the PCIe heatsink assembly from the computer [2].
5. Remove the four M2*3 screws [1] to separate the heatsink from the fan [2].
96 Removing and installing components

Installing the PCIe heatsink fan assembly
1. Replace the fan to th heatsink assembly [1] and secure it using four M2*3 screws [2] .
Removing and installing components 97

2. Install the PCIe heatsink assembly [1] in the computer and install the seven 'M2.5*5' screws on heat sink pipe [2].
3. Tighten the three 'M2*3' screws on the fan case [1] and connect the fan cable [2].
98 Removing and installing components

4. Install the:
a) Bottom chassis cover
b) Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Primary SSD Rail
Removing the Primary SSD rail
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) SSD
c) Bottom chassis cover
d) PCIe heatsink assembly
3. Peel off the inductive tape on the SSD FPC connector [1] on system board and disconnect it [2].
4. Remove the 4 'M2*3' screws [3] and remove it from the computer [4].
Removing and installing components 99

Installing the Primary SSD rail
1. Install the primary SSD rail on the system board [1] and connect the SSD FPC connector to the system board [2].
2. Secure the FPC connection using a piece of tape [3] and install the four 'M2*3' screws [4] securing it to the system board.
3. Install the:
a) PCIe heatsink fan assembly
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) SSD
d) Batteries
4. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
100 Removing and installing components

Docking Port Assembly
Removing the Docking port assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe Heatsink assembly
3. Peel off the tape securing the dock FPC [1] and disconnect the dock FPC [2].
4. Disconnect the antennae cables from RF passthrough connectors [1] and unroute the antennae cables [2] from the routing channels
on the dock assembly.
Removing and installing components 101
5. Remove the two 'M2.5*5' screws [1] and separate the docking board assembly from the chassis [2].
Installing the Docking Port Assembly
1. Install the docking port assembly [1] and install the two 'M2.5*5' screws [2] securing it to the system board.
2. Connect the dock FPC [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
102 Removing and installing components

3. Secure the antennae cables along the routing channels [1] and connect the antennae cables on RF passthrough connectors [2].
4. Install the:
a) PCIe Heatsink assembly
b) Batteries
c) Bottom chassis cover
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Heatsink Assembly
Removing the Heatsink assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
Removing and installing components 103

2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) WLAN card
d) WWAN card
e) PCIe Heatsink fan assembly
f) Docking port assembly
3. NOTE: Depending on the order configuration details the system may have either of the heatsink assembly.
DSC Heatsink
assembly
Unroute the antennae cables from the tabs on the heatsink pipe.
4. Remove the five 'M2.5*5' screws [1] and two 'M1.6*5' [2] screw from the thermal module.
5. Lift and the heat sink assembly from the computer [3].
104 Removing and installing components

NOTE: Discreet and UMA bases have different types of heatsink assembly.
Installing the Heatsink assembly
1. Install the heatsink assembly [1] in the computer and tighten the two 'M1.6*5' [2] cap screw near the CPU.
2. Install the five 'M2.5*5' captive screws [3] on the thermal module securing the thermal module to the system board.
3. Route the antennae cables along the routing channel on the heatsink pipe.
Removing and installing components 105

4. Install the:
a) Docking port assembly
b) PCIe Heatsink assembly
c) WWAN card
d) WLAN card
e) Bottom chassis cover
f) Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Rear Input-Output Board
Removing the Rear I-O board
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
NOTE: A 5 mm socket wrench should be used to remove/install the caps screws located in rear I/O space.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) WLAN card
c) WWAN card
d) PCIe heatsink fan assembly
e) Docking port assembly
f) Bottom chassis Cover
3. Loosen the two cap screws on the serial port in the rear I/O space [1].
4. Peel off the inductive tape on the I/O board FPC connector [2] and disconnect it [3] from the system board.
106 Removing and installing components

5. Loosen the three 'M2.5*5' screws [1] and lift the I/O board away from the system [2].
Installing the Rear I-O board
1. Install the rear I/O board on the system board and slide the serial port through the face plate [1].
2. Secure the I/O board using three 'M2.5*5' screws [2].
Removing and installing components 107

3. Tighten the two cap screws on the serial port [1] in the rear I/O space.
4. Connect the I/O board FPC [2] to the system board and then to I/O board itself [3] and secure it using a piece of tape [3].
5. Install the:
a) Docking port assembly
b) PCIe heatsink fan assembly
c) WWAN card
d) WLAN card
108 Removing and installing components

e) Bottom chassis cover
f) Batteries
6. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Hinge Covers
Removing the Hinge Covers
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Heatsink
3. Remove the two 'M2.5*5' on either sides [1] and lift to remove the brackets [2] from the computer.
4. Press the latch [1] and open the LCD lid [2].
Removing and installing components 109

5. Hold the LCD lid at an obtuse angle and push the hinge covers from the rear end to remove it from the computer.
Installing the Hinge Covers
1. Press the latch [1] and open the LCD lid [2].
110 Removing and installing components

2. Keep LCD lid open at an obtuse angle and insert the hinge covers from front until it clicks in its place.
3. Place the brackets[1] and secure it using two 'M2.5*5' on either sides [2].
Removing and installing components 111

4. Install the:
a) Heatsink
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Display assembly
Removing the Display assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe heatsink assembly
d) Docking port assembly
e) WLAN card
f) WWAN card
g) GPS module
h) Heatsink assembly
i) Hinge covers
3. Remove the two 'M2*3' screws [1] on the EDP bracket, and turn it up side down [2].
4. Pull and disconnect the EDP cable from the system board [3] and remove the two 'M2*3' screws [4] securing the hinges to base
assembly [5].
112 Removing and installing components

5. Open the LCD lid.
6. Loosen the two screws on hinges [1] and to separate the LCD assembly from the computer [2].
Removing and installing components 113

Installing the Display Assembly
1. Install the display assembly along the hinges at an obtuse angle [1] and install the two screws on left [2] and the right side [3].
114 Removing and installing components

2. Install the two 'M2*3' securing the hinges to base assembly [1] and rethread the antennae cables [2].
3. Connect the EDP cable [3] to the system board and place the EDP bracket over the cable [4].
4. Install the two 'M2*3' screws [5] and secure the EDP bracket to the system board.
5. Install the:
a) Hinge covers
Removing and installing components 115

b) Heatsink
c) GPS card
d) WLAN card
e) WWAN card
f) PCIe heatsink assembly
g) Docking port assembly
h) Bottom chassis cover
i) Batteries
6. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
LCD Bezel and Back Cover Assembly
Removing the LCD with bezel and the display back cover
assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) WLAN card
d) WWAN card
e) PCIe heatsink assembly
f) Docking port assembly
g) Heatsink
h) Hinge covers
i) Display assembly
3. Loosen the 12 'M2.5' screws from the back cover.
4. Remove the four 'M2.5' epoxy screws securing the bezel to the back cover [1] and pry at bottom edge to separate the two
subassemblies [2].
116 Removing and installing components

5. Peel off the tape on the LCD connections [1] and open the connector [2] to disconnect the EDP cable [3] from the LCD.
6. Peel off the reflective tape [4] on the LCD panel and the touch connector [5] and disconnect the cable from the board [6].
Installing the LCD with bezel and the display back cover
assembly
1. Replace the EDP cable [1] on the LCD connector and close the actuator [2].
2. Secure the connector using a piece of tape [3] and adhere the reflective tape on the display panel [4] .
3. Connect the touch controller cable [5] and use insulation tape on the connector [6].
Removing and installing components 117

4. Align and place the bezel on the back cover [1] and secure it using the four M2.5 epoxy screws [2].
5. Install the 12 'M2.5' screws to secure the back cover to the LCD with bezel assembly.
118 Removing and installing components

6. Install the:
a) Display assembly.
b) Hinge covers
c) Heatsink
d) PCIe heatsink assembly
e) Docking port assembly
f) WWAN card
g) WLAN card
h) Bottom chassis cover
i) Batteries
7. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Microphone
Removing the Microphone
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Memory
d) WLAN card
e) WWAN card
f) PCIe heatsink assembly
g) Docking port assembly
h) Heatsink
i) Hinge covers
j) Display assembly.
k) LCD bezel and back cover assembly.
3. Peel off the tape securing the microphone daughterboard[1] and remove the two 'M2*3' screws [2] to turn the daughterboard [3] up
side down.
Removing and installing components 119
4. Peel off the insulation tape [1] and disconnect the EDP cable connectors [2].
Installing the Microphone
1. Connect the EDP cable to the microphone daughterboard [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
120 Removing and installing components

2. Turn over the microphone daughterboard on the back cover [1] and tighten the two 'M2*3' screws [2].
3. Secure the microphone daughterboard using a piece of reflective tape on either sides [3] to the LCD back cover.
4. Install the:
a) LCD with bezel assembly.
b) Display assembly.
c) Hinge covers
d) Heatsink
e) PCIe heatsink assembly
f) Docking port assembly
g) WWAN card
h) WLAN card
i) Bottom chassis cover
j) Batteries
Removing and installing components 121

5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Camera
Removing the Camera
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Memory
d) WLAN card
e) WWAN card
f) PCIe heatsink assembly
g) Docking port assembly
h) Heatsink
i) Hinge covers
j) Display assembly.
k) LCD Bezel and back cover assembly.
3. Peel off the reflective tape[1] on camera module and the insulation tape securing the EDP cable[2] to camera module.
4. Disconnect the EDP cable from the camera module [3] and remove the two 'M2*3' screws [4].
5. Lift the camera module away from the back cover [5] to remove it from the computer.
CAUTION: Do not touch the Camera Lens fused to the LCD with bezel assembly.
Installing the Camera
1. Install the camera module [1] on the back cover and install the two 'M2*3'. screws [2]
2. Connect the EDP cable to the camera module [3], stick a piece of insulation tape [4] on the EDP connectors.
3. Secure the camera module on the back cover using a piece of reflective tape [5].
122 Removing and installing components

4. Install the:
a) LCD with bezel assembly
b) Display assembly.
c) Hinge covers
d) Heatsink
e) PCIe heatsink assembly
f) Docking port assembly
g) WWAN card
h) WLAN card
i) Bottom chassis cover
j) Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Battery Bay
Removing the Battery bay
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe Heatsink assembly
3. CAUTION: Use extreme caution when removing cable due to the very limited space cable could be easily pinched or
bent leading to cable damage.
Disconnect both the battery connections from the system board.
Removing and installing components 123

4. Remove the five 'M2.5*5' [1] and nine 'M2.5*3' [2] screws securing the battery bay to chassis and lift to separate the battery bay [3]
from the computer.
Installing the Battery bay
1. Install the battery bay [1] on the computer and tighten the five 'M2.5*5' [2] and nine 'M2.5*3' [3] securing it to the chassis.
124 Removing and installing components

2. Connect the battery cables to the system board.
3. Install the:
a) PCIe Heatsink assembly
b) Batteries
c) Bottom chassis cover
4. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Left I/O board
Removing the Left I/O daughterboard
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
Removing and installing components 125

2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe Heatsink fan assembly
d) Battery bay
3. Peel off the tape [1], disconnect the left I/O daughterboard FPC connector [2] from the system board.
4. Disconnect the speaker cable from the left I/O daughterboard [3].
5. Loosen the two 'M2*5' screws [1] and lift the Left I/O daughterboard from the computer [2].
Installing the Left I/O Board
1. Install the left I/O daughterboard [1] and secure it using the two 'M2*3' screws [2] to the computer.
126 Removing and installing components

2. Connect the FPC to the system board [1] and secure it using a piece of insulation tape [2].
3. Connect the speaker cable to the left I/O daughterboard [3].
4. Install the:
a) Battery bay
b) PCIe Heatsink fan assembly
c) Bottom chassis cover
d) Batteries
5. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Removing and installing components 127

Smart Card
Removing the Smart Card Reader
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe heatsink assembly
d) Battery bay
3. Remove the tape from the smart card reader connector[1] and disconnect it [2] from the USH board.
4. Remove the tape from the fingerprint reader connector [3] and disconnect it from the USH board [4].
5. Remove the two 'M2*3' screws [1] securing the USH board to the bottom base and turn it up side down [2].
128 Removing and installing components
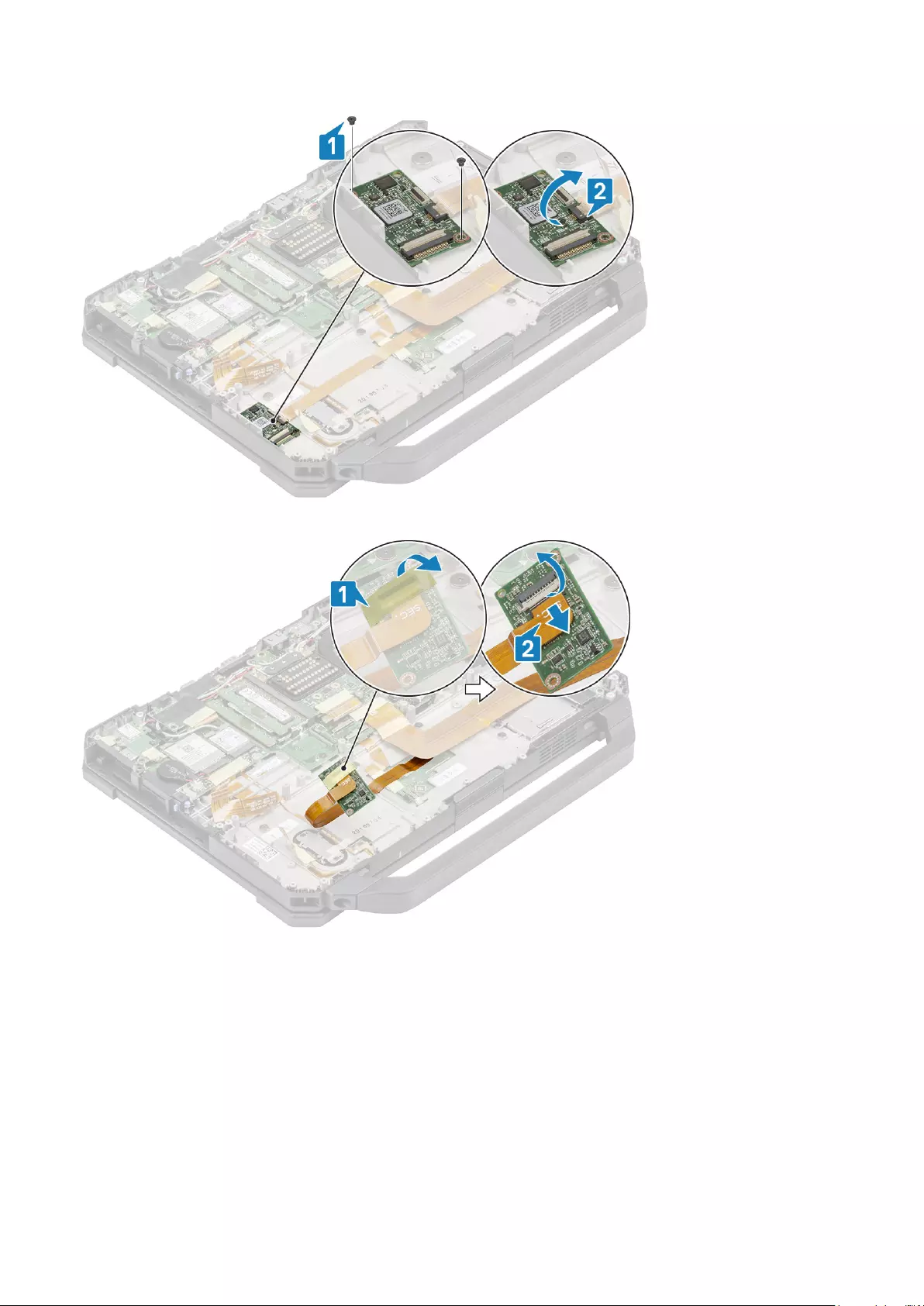
6. Remove the tape [1] and disconnect the Smartcard Reader FPC connector [2] from the USH board.
7. Loosen the four 'M2*3' screws [1] and remove the smart card [2] reader from the computer.
Removing and installing components 129

Installing the Smart Card Reader
1. Insert the smart card reader through the I/O face plate [1] and install the four 'M2*3' screws to secure it to the bottom chassis [2].
2. Connect the Smart Card FPC on the underside of the USH board [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
130 Removing and installing components

3. Install the two 'M2*3' screws [1] and turn over the USH board to secure it to the chassis [2].
4. Connect the finger print reader connector [1] and secure it with a piece of tape [2].
5. Connect the smart card reader connector [3] to the USH board and secure it using a piece of tape [4].
Removing and installing components 131

6. Install the:
a) Battery bay
b) PCIe Heatsink assembly
c) Bottom chassis cover
d) Batteries
7. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Speaker
Removing the Speaker
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) PCIe heatsink assembly
d) Left I/O daughterboard
e) Battery bay
3. Remove the two 'M2.5*7' screws [1] and remove the speaker from the computer [2].
132 Removing and installing components

Installing the Speaker
1. Align and place the speakers [1] on the computer and install the two 'M2.5*7' screws to secure the speaker to the base [2].
2. Install the:
a) Battery Bay
b) Left I/O daughterboard
c) PCIe Heatsink assembly
d) Docking port assembly
e) Bottom Chassis Cover
f) Batteries
3. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Removing and installing components 133

System board
Removing the System board
NOTE: This system cannot be disassembled further. To access underlying components, replace the base assembly as
per order details.
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. Remove the:
a) Batteries
b) Bottom chassis cover
c) Keyboard
d) PCIe heatsink assembly
e) Docking port assembly
f) Primary SSD
g) Heat Sink
h) Memory
i) WLAN card
j) WWAN card
k) GPS module
l) Primary SSD rail
m) Battery bay
n) Rear I/O board
3. Peel off the tape [1] and disconnect the touch pad connector from the system board [2].
4. Peel off the tape [1] and remove the rear I/O board FPC cable [2] from the system board.
5. Peel off the tape [3] and remove the battery indicator LED cable [4] from the system board.
6. Peel off the tape [5] and remove the docking board FPC connector [6] from the system board.
134 Removing and installing components

7. Peel off the tape [1] and disconnect the left I/O board FPC connector [2] from the system board.
8. Peel off the tape [1] and disconnect the power button cable [2].
9. Peel off the tape [3] to disconnect the USH board and touch pad cable [4] from the system board.
Removing and installing components 135

10. Remove the two 'M2*3' screws [1] and remove the EDP bracket [2] from the system board.
11. Remove the EDP cable using the black pull tag [3] and disconnect the DC-in cable [4] from the system board.
12. Remove the two cap screws in the rear I/O space [1].
13. Remove the two 'M2.5*5' screws and two 'M1.6*3.0' screws [2] to remove the USB Type-C bracket [3] from the system board.
136 Removing and installing components

14. Remove the eight 'M2.5*5' screws [1] and single 'M2*3' screw [2] on the system board and remove the system board from the
chassis [3].
Installing the System board
1. Install the system board inserting the serial port on the system board through chassis [1] and install the eight 'M2.5*5' screws [2] and
single 'M2*3' screw [3] on the system board.
Removing and installing components 137

2. Install the two cap screws on the serial port of the system board [1].
3. NOTE: When installing the System Board, technicians must ensure that both the battery cables (1st & 2nd Battery)
and FPC cables (Left I/O FPC and Express Card reader FPC) are not pinched under the System Board.
Install the USB Type-C bracket [2] and secure it with two 'M2.5*5' screws and two 'M1.6*3.0' screws on the system board [3].
4. Install the EDP cable [1] and place the metal bracket [2] over the EDP connector on the system board.
5. Install the two 'M2*3' screws [3] securing it to the system board and connect the DC-in cable [4] to the system board.
138 Removing and installing components

6. Connect the power button cable [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
7. Connect the USH board and touch pad cables [3] to the system board and secure it using a piece of tape [4].
8. Connect the left I/O board FPC cable [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
Removing and installing components 139

9. Connect the rear I/O board FPC cable [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
10. Connect the battery indicator LED cable [3] and secure it using a piece of tape [4].
11. Connect the dock FPC connector [5] and secure it using a piece of tape [6].
12. Connect the touch pad connectors to the system board [1] and secure it using a piece of tape [2].
140 Removing and installing components

13. Install the:
a) Rear I/O board
b) Battery bay
c) Primary SSD rail
d) GPS module
e) WWAN card
f) WLAN card
g) Memory
h) Heatsink
i) Primary SSD
j) Docking port assembly
k) PCIe heatsink assembly
l) Keyboard
m) Bottom chassis cover
n) Batteries
14. Follow the procedure in After working inside your computer.
Bottom Base Assembly
1. Follow the procedure in Before working inside your computer.
2. To replace the bottom base assembly, remove the following components from old base:
a) SIM card
b) SD card
c) Handle
d) Latched Doors
e) Batteries
f) Primary SSD
g) Bottom chassis cover
h) Keyboard
i) WWAN card
j) WLAN card
k) GPS module
Removing and installing components 141

l) Memory
m) Coin cell
n) PCIe heatsink assembly
o) Primary SSD rail
p) Docking port assembly
q) Heatsink assembly
r) Rear I/O board
s) Display assembly
t) Primary SSD rail
u) Battery bay
v) Left I/O board
w) Smart card
x) Speaker
y) System board
3. Reconnect the:
• Power Button
• Speakers
• DC-In cable
• USH Board
• Touchpad
NOTE: See the order details to determine the exact specifics of subcomponents defined in the Bottom Chassis
Assembly.
4. Install the following components to the new base:
a) System board
b) Rear I/O board
c) Battery Bay
d) Primary SSD rail
e) GPS module
f) WWAN card
g) WLAN card
h) Memory
i) Heatsink assembly
j) Primary SSD
k) Docking port assembly
l) PCIe heatsink assembly
m) Keyboard
n) Bottom chassis cover
o) Batteries
142 Removing and installing components

Diagnostics
This chapter details the built in troubleshooting features to diagnose the Dell systems. It also lists the invoking instructions along with
related information for each diagnostics method.
Topics:
•ePSA Diagnostics
•LCD Built-in Self Test
•Battery Status Lights
•Diagnostic LED
•Wi-Fi power cycle
•BIOS recovery
•Self-Heal
ePSA Diagnostics
The ePSA diagnostics (also known as system diagnostics) performs a complete check of your hardware. The ePSA is embedded with the
BIOS and is launched by the BIOS internally. The embedded system diagnostics provides a set of options for particular devices or device
groups allowing you to:
• Run tests automatically or in an interactive mode
• Repeat tests
• Display or save test results
• Run thorough tests to introduce additional test options to provide extra information about the failed device(s)
• View status messages that inform you if tests are completed successfully
• View error messages that inform you of problems encountered during testing
NOTE: The Enhanced Pre-boot System Assessment window displays, listing all devices detected in the computer. The
diagnostics starts running the tests on all the detected devices.
Running ePSA diagnostics
Invoke diagnostics by either of the methods that are suggested below:
•Tap F12 key on keyboard, as the Dell splash screen appears, until you get message Diagnostic Boot Selected.
• On the one time boot menu screen, use Up/Down arrow key to select the Diagnostics option and then press <Return>.
• Press and Hold Function(Fn) key on the keyboard and Press the Power button to power on the system.
ePSA User Interface
This section contains information on ePSA 3.0’s Basic and Advanced Screen.
ePSA opens basic screen on start. You can switch to advanced screen using the arrow icon on the bottom. Advanced screen shows
detected devices on the left column. Specific test can be included or excluded only in the interactive mode.
ePSA Basic Screen
The Basic Screen has minimal controls which allows easy navigation for user to start or stop the diagnostic.
4
144 Diagnostics

ePSA Advanced Screen
The advanced screen allows more directed testing and contains more detail information about the overall health of the system. The user
can get to this screen by simply swiping your finger to the left on touchscreen systems or clicking the next page button on the lower right
hand side of the basic screen.
Diagnostics 145
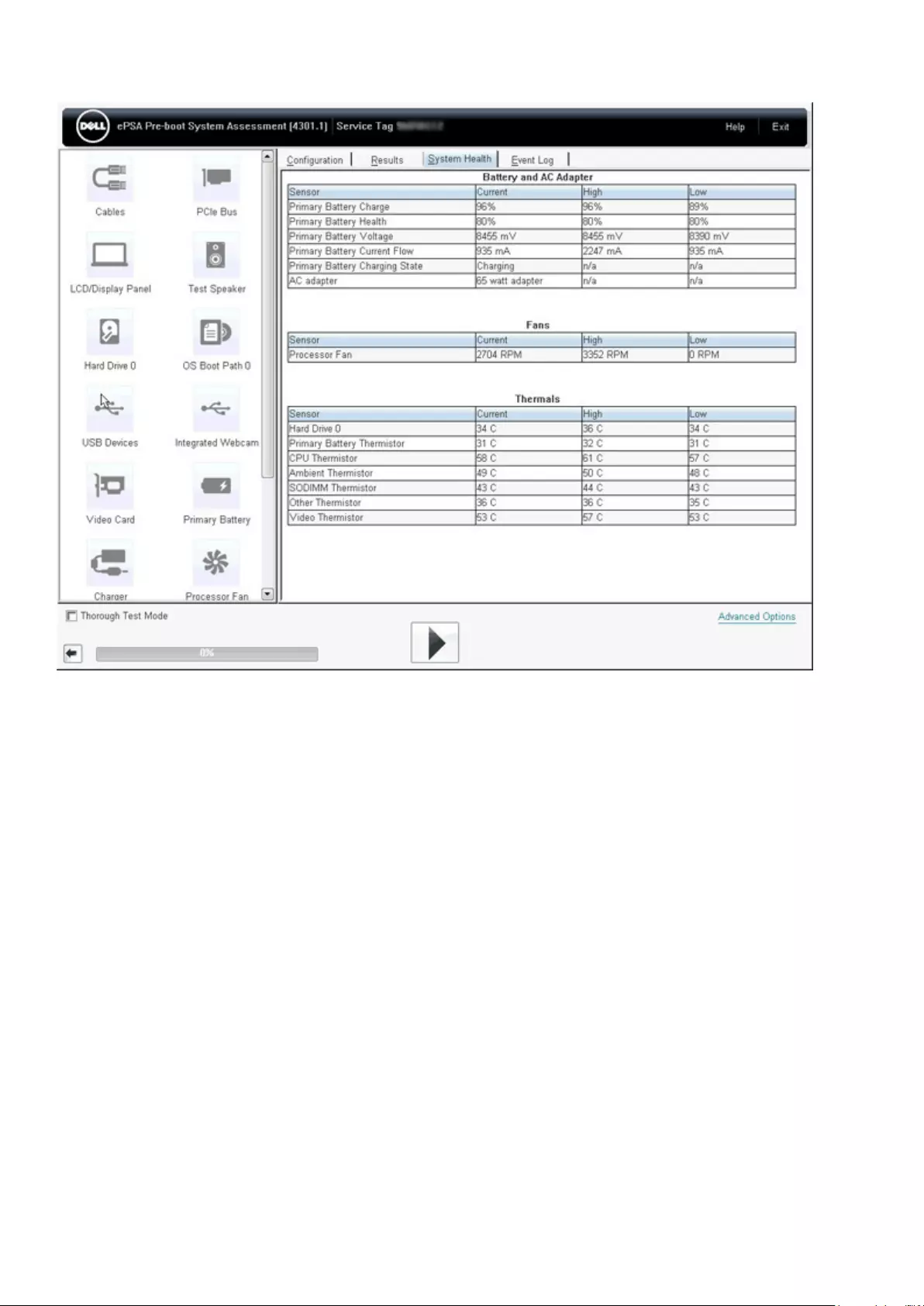
To run test on specific device or run a specific test
1. To run a diagnostic test on a specific device, press Esc and click Yes to stop the diagnostic test.
2. Select the device from the left pane and click Run Tests or use Advanced Option to include or exclude any Test.
ePSA Error Messages
When the Dell ePSA Diagnostic detects an error while running, it will pause the test and then popup a window as shown below :
146 Diagnostics

• By responding to Yes, the diagnostic will continue testing the next device and the error details will be available in the summary report.
• By responding to No, the diagnostic will stop testing the remaining untested device.
• By responding to Retry, the diagnostic will ignore the error and rerun the last test.
Capture the error code with Validation code or Scan QR code and Contact Dell
NOTE: As part of the new feature, user can now mute the beeping sound code when there is an error , by pressing on
at the bottom right side of the error window.
NOTE: Some tests for specific devices require user interaction. Always ensure that you are present at the computer
terminal when the diagnostic tests are performed.
Validation Tools
This section contains information on how to validate the ePSA error code.
Error code verification can be done using below two methods :
•Online Enhanced Preboot System Assessment Validation Tool.
•QR scanning using QR APP on Smart Phone.
Online ePSA Validation Tool
Usage Guide
1. User to obtain information from ePSA error windows.
Diagnostics 147
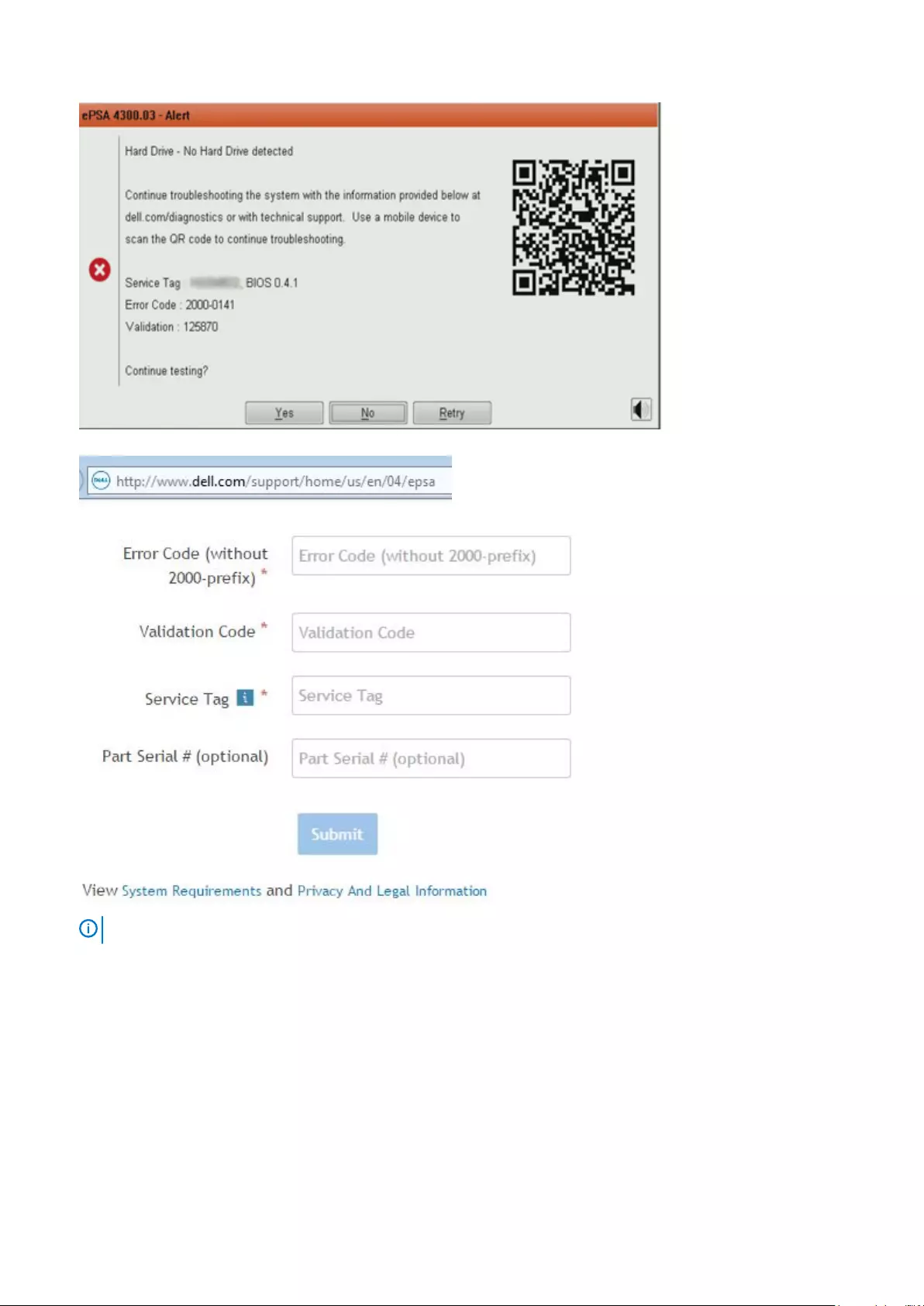
2. Navigate to Online ePSA Validation Tool.
3. Enter error code, validation code, and service tag. Part serial number is optional.
NOTE: For error code, use only the last 3 or 4 digits of the code. (user can enter 0142 or 142 instead of 2000–0142.)
4. Click on Submit once all the necessary information is entered.
148 Diagnostics

Valid Error Code Example
After entering the correct information, the online tools will direct user to above screen which contains information of :
• Confirmation of the error code and result outcome.
• Suggested Part Replacement.
Diagnostics 149
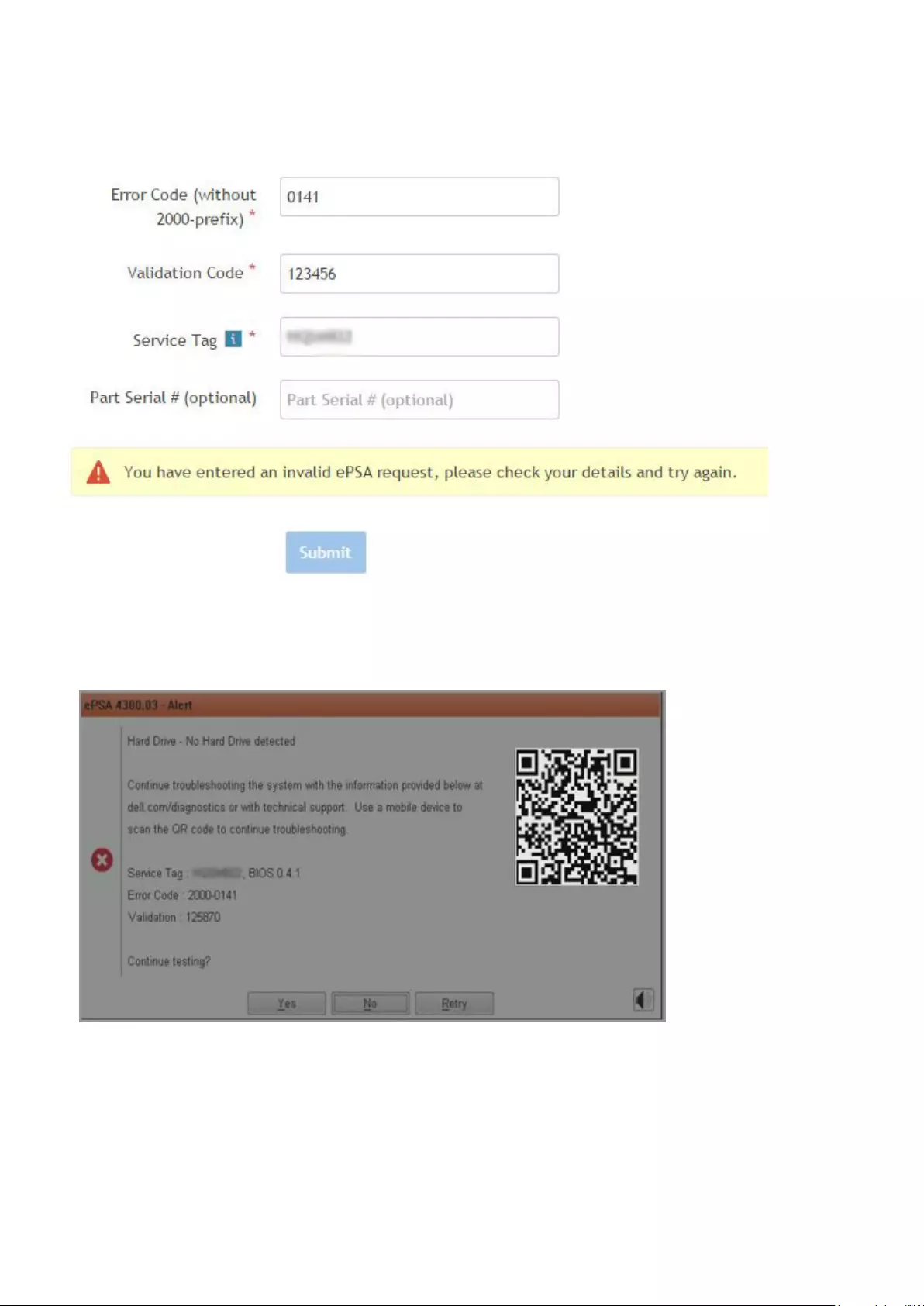
• If customer is still covered under Dell Warranty.
• Case reference number if there is an open case under the service tag .
Invalid Error Code Example
QR APP Validation Tool
Besides using the online tool, customer can also validate the error code by scanning the QR code with a QR APP on smart phone.
1. User to obtain the QR code from ePSA error Windows.
2. User can use any QR code scanner application via smart phone to scan the QR code.
150 Diagnostics

3. QR code scanner application will scan the code and automatically generate the link out. Click on the link to proceed.
Diagnostics 151

The link generated will navigate customer to Dell Support website which contains information of :
• Confirmation of the error code and result outcome.
• Suggested Part Replacement.
• If customer is still covered under Dell Warranty.
• Case reference number if there is an open case under the service tag.
152 Diagnostics

LCD Built-in Self Test
Overview : LCD Built-in Self Test (BIST)
Dell laptop PCs have a built-in diagnostic tool that helps you determine if the screen abnormality you are experiencing is an inherent
problem with the LCD (screen) of the Dell laptop PC or with the video card (GPU) and PC settings .
When you notice screen abnormalities like flickering, distortion, clarity issues, fuzzy or blurry image, horizontal or vertical lines, color fade
etc., it is always a good practice to isolate the LCD (screen) by running the built-in self test (BIST).
How to invoke LCD BIST Test
1. Power off the Dell laptop PC.
2. Disconnect any peripherals connected to the PC. Connect only the AC adapter (charger) to the PC.
3. Make sure that the LCD (screen) is clean (no dust particles on the surface of the screen).
4. Press and hold D key and Power on the PC to enter LCD built-in self test (BIST) mode. Continue to hold the D key, until you see color
bars on the LCD (screen).
5. The screen will display multiple color bars and change colors on the entire screen to red, green and blue.
6. Carefully inspect the screen for abnormalities.
7. Press Esc key to exit.
NOTE: Dell ePSA upon launch, initiates a LCD BIST first, expecting an user intervention confirm functionality of the
LCD.
Diagnostics 153

Battery Status Lights
If the computer is connected to an electrical outlet, the battery light operates as follows:
Alternately
blinking amber
light and green
light
An unauthenticated or unsupported non-Dell AC adapter is attached to your laptop.
Alternately
blinking amber
light with steady
green light
Temporary battery failure with AC adapter present.
Constantly
blinking amber
light
Fatal battery failure with AC adapter present.
Light off Battery in full charge mode with AC adapter present.
green light on Battery in charge mode with AC adapter present.
Diagnostic LED
This section details the diagnostic features of the battery LED in a laptop.
Instead of beep codes errors are indicated via the bicolor Battery Charge LED. A specific blink pattern is followed by flashing a pattern of
flashes in green, followed by white. The pattern then repeats.
NOTE: The diagnostic pattern will consist of a two digit number being represented by a first group of LED blinks (1
through 9) in green, followed by a 1.5 second pause with the LED off, and then a second group of LED blinks (1 through
9) in white. This is then followed by a 3 second pause, with the LED off, before repeating over again. Each LED blink
takes 0.5 seconds.
The system will not shutdown when displaying the Diagnostic Error Codes. Diagnostic Error Codes will always supersede any other use of
the LED. For instance, on laptops, battery codes for Low Battery or Battery Failure situations will not be displayed when Diagnostic Error
Codes are being displayed:
Table 26. LED pattern
Blinking pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
Green White
2 1 processor Processor failure
2 2 system board, BIOS ROM System board, covers BIOS
corruption or ROM error
2 3 memory No memory/no RAM
detected
2 4 memory Memory failure/RAM failure
2 5 memory Invalid memory installed
2 6 system board; chipset System board/ chipset error
2 7 display Display failure
3 1 RTC power failure Coin-cell battery failure
3 2 PCI/Video PCI/Video card/chip failure
3 3 BIOS recovery 1 Recovery image not found
3 4 BIOS recovery 2 Recovery image found but
invalid
3 5 Power Rail Failure EC ran into power
sequencing failure
154 Diagnostics

Blinking pattern Problem Description Suggested Resolution
Green White
3 6 SBIOS Flash Corruption Flash corruption detected by
SBIOS
3 7 ME Error Timeout waiting on ME to
reply to HECI message
Wi-Fi power cycle
If your computer is unable to access the Internet due to Wi-Fi connectivity issues a Wi-Fi power cycle procedure may be performed. The
following procedure provides the instructions on how to conduct a Wi-Fi power cycle:
NOTE: Some ISPs (Internet Service Providers) provide a modem/router combo device.
1. Turn off your computer.
2. Turn off the modem.
3. Turn off the wireless router.
4. Wait for 30 seconds.
5. Turn on the wireless router.
6. Turn on the modem.
7. Turn on your computer.
BIOS recovery
The BIOS recovery is designed to fix the main BIOS, and cannot work if the boot is damaged. The BIOS recovery will not work in the event
of EC corruption, ME corruption, or a hardware related issue. The BIOS recovery image should be available on the unencrypted partition
on the drive for BIOS recovery feature.
Rollback BIOS feature
Two versions of the BIOS recovery image are saved on the hard drive:
• Current running BIOS (old)
• To-be-updated BIOS (new)
The old version is already stored on the hard drive. The BIOS adds new version to the hard drive, maintains the old version, and deletes
other existing versions. For example, A00 and A02 versions are already on the hard drive, A02 is the running BIOS. The BIOS adds A04,
maintains A02, and deletes A00. Having two BIOS version enables the Rollback BIOS feature.
If the recovery file cannot be stored (hard drive is out of space), the BIOS sets a flag to indicate this condition. The flag is reset in the
event it later becomes possible to store the recovery file. The BIOS notifies the user during POST and in BIOS Setup, the BIOS recovery is
degraded. BIOS recovery through hard drive may not be possible, however BIOS recovery through USB flash drive is still possible.
For USB key: root directory or "\"
BIOS_IMG.rcv: the recovery image stored on the USB key.
BIOS recovery using hard drive
NOTE: Ensure that you have the previous version and the latest version of the BIOS from the Dell support site available
to use.
NOTE: Ensure that you have the file type extensions visible in the operating system (OS).
1. Browse to the location of the BIOS update executable (.exe) files.
2. Rename the BIOS executable files to BIOS_PRE.rcv for the earlier version of the BIOS and BIOS_CUR.rcv for the latest version of
the BIOS.
For example, if the latest version’s file name is PowerEdge_T30_1.0.0.exe, rename it to BIOS_CUR.rcv and if the previous
version’s file name is PowerEdge_T30_0.0.9.exe, rename it to BIOS_PRE.rcv
Diagnostics 155

NOTE:
a. If the hard drive is new, there will be no OS installed.
b. If the hard drive has been partitioned at the Dell factory, there will be a Recovery Partition available.
3. Disconnect the hard drive and install the hard drive into another system that has a full operational OS.
4. Start up the system and in the Microsoft Windows OS environment follow these steps to copy the BIOS recovery file to the
Recovery Partition.
a) Open a Windows Command Prompt window.
b) At the prompt, type diskpart to start the Microsoft DiskPart.
c) At the prompt, type list disk to list out the available hard drives.
Select the hard drive that was installed in Step 3.
d) At the prompt, type list partition to view the available partitions on this hard drive.
e) Select Partition 1 which is the Recovery Partition. The size of the partition will be 39 MB.
f) At the prompt, type set id=07 to set the partition ID.
NOTE: The partition will be visible to the OS as Local Disk (E) to read and write data.
g) Create the following folders in Local Disk (E), E:\EFI\Dell\BIOS\Recovery.
h) Copy both the BIOS files BIOS_CUR.rcv and BIOS_PRE.rcv to the recovery folder on Local Disk (E).
i) In the Command Prompt window, at the DISKPART prompt, type set id=DE.
After the executing this command, the partition Local Disk (E) will not be accessible by the OS.
5. Shut the system down and remove the hard drive and install the hard drive into the original system.
6. Start the system up and boot to System Setup, in the Maintenance section ensure that BIOS Recovery from Hard Drive is
enabled in the BIOS Recovery section of the setup.
7. Press the power button to shut the system down.
8. Holding the Ctrl and Esc keys, press the power button to start the system up. Keep holding the Ctrl and Esc keys until the BIOS
Recovery Menu page is displayed.
Ensure that the Recover BIOS radio button is selected and click Continue to start the BIOS recovery.
BIOS recovery using USB key
NOTE: Ensure that you have the file type extensions visible in the operating system.
NOTE: Ensure that you have downloaded the latest BIOS from the Dell support site and save it on your system.
1. Browse to the location of the downloaded BIOS update executable (.exe) file.
2. Rename the file to BIOS_IMG.rcv.
For example, if the file name is PowerEdge_T30_0.0.5.exe, rename it to BIOS_IMG.rcv
3. Copy the BIOS_IMG.rcv file to the root directory of the USB key.
4. If not plugged in, plug in the USB key, restart the system, press F2 to enter the System Setup, and then press power button to shut
down the system.
5. Start the system.
6. While the system is starting up, press the Ctrl+Esc keys while holding the power button until the BIOS Recovery Menu dialog box is
displayed.
7. Click Continue to start the BIOS recovery process.
NOTE: Ensure that the Recovery BIOS option is selected in the BIOS Recovery Menu dialog box.
8. Select the path on the USB drive where BIOS recovery file is stored( root directory or "\") and follow the on-screen instructions.
Self-Heal
Course Introduction
Self-Heal is an option that helps recover a Dell Latitude system from a No Post, No Power, No Video situation.
156 Diagnostics

Self-Heal Instruction
1. Remove the primary battery and the AC adapter.
2. Disconnect the CMOS battery.
3. Release the flea power. Press and hold the power button down for 10 seconds or leave the system idle for 45 seconds.
4. Make sure the CMOS and primary battery are not plugged into the system.
5. Plug in the AC adapter. The system will auto power-on when the AC adapter inserted.
6. The system will start with a blank screen for a while and will shut down automatically. Watch for the LED lights (power, Wi-Fi, and
HDD). It will turn on.
7. The system will try to restart twice and will boot on the third attempt.
8. Place the CMOS battery and the AC adapter back in the system.
9. If self-heal recovers the failure, update the system with the latest BIOS, and perform ePSA to ensure proper functionality of the
system.
NOTE:
• During installation or removal of any hardware, always ensure all data is backed up properly.
• For instructions on how to remove or replace parts, visit the Assembly Disassembly.
• Before beginning to work on the computer, follow the Safety Instructions.
Supported Latitude Models
NOTE:
• Before replacing the system board, perform self-heal as a mandatory step.
• Latitude Self-Heal can be avoided when complete system tear-down is required to access the coin-cell battery.
• For the Latitude E7 Series (XX70), BIOS Recovery 2.0 should be performed as the primary step.
• In order to reduce troubleshooting time associated with Self-Heal, there is no mandatory requirement to reassemble
the system. Technicians can initiate Self-Heal even with the system board exposed.
• Do not touch any of the exposed components or the system board to avoid shorting and static.
• If Self-Heal is unable to recover the failure, proceed with replacing the system board.
NOTE:
Front-line Agent Action: Front-line agents must encourage the customer to perform this step before isolating the issue
as a motherboard failure. If the customer is not comfortable performing the Self-Heal procedure, then please document
the dispatch being created in 5GL. Advise the onsite engineers to perform the Self-Heal procedure as one of the
mandatory initial steps. Advise them that if the Self-Heal procedure is unsuccessful, to continue with the regular
troubleshooting before part replacement.
Onsite Engineer Action: The Latitude Self-Heal procedure has to be a mandatory initial step. If the Self-Heal procedure
is unsuccessful, continue with the regular troubleshooting before part replacement. Document Self-Heal results in the
call closure log (Self-Heal Pass or Fail).
Diagnostics 157

Getting help
Topics:
•Contacting Dell
Contacting Dell
NOTE: If you do not have an active Internet connection, you can find contact information on your purchase invoice,
packing slip, bill, or Dell product catalog.
Dell provides several online and telephone-based support and service options. Availability varies by country and product, and some services
may not be available in your area. To contact Dell for sales, technical support, or customer service issues:
1. Go to Dell.com/support.
2. Select your support category.
3. Verify your country or region in the Choose a Country/Region drop-down list at the bottom of the page.
4. Select the appropriate service or support link based on your need.
5
158 Getting help






