Table of Contents
- Dell EMC SmartFabric Services User Guide Release 1.0
- About this guide
- SFS fundamentals
- Setting up SFS
- Deploying and managing a fabric
- Access fabric setup options
- Update default fabric, switch names, and descriptions
- Create uplink for external network connectivity
- Breakout switch ports
- Configure jump host
- Update network configuration
- Onboard a server onto the fabric
- Edit default fabric settings
- Restore fabric configuration
- Manage network profiles
- Manage routing profiles
- Access fabric setup options
- SFS with VxRail
- SFS with PowerEdge MX
- SFS for Isilon/PowerScale back-end fabric
- SFS commands
- smartfabric l3fabric enable
- smartfabric vlti
- show logging smartfabric
- show smartfabric cluster
- show smartfabric cluster member
- show smartfabric configured-server
- show smartfabric configured-server configured-server-interface
- show smartfabric details
- show smartfabric discovered-server
- show smartfabric discovered-server discovered-server-interface
- show smartfabric networks
- show smartfabric nodes
- show smartfabric personality
- show smartfabric uplinks
- show smartfabric upgrade-status
- show smartfabric validation-errors
- show switch-operating-mode
- Appendix
DELL S5248F-ON User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for S5248F-ON by DELL which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Dell EMC SmartFabric Services User Guide
Release 1.0
March 2021
Rev. A00

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your product.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data and tells you how to avoid
the problem.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
© 2020 -2021 Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Dell, EMC, and other trademarks are trademarks of Dell Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Other trademarks may be trademarks of their respective owners.

Chapter 1: About this guide........................................................................................................... 5
Text and Syntax Conventions.......................................................................................................................................... 5
Related Documents.............................................................................................................................................................5
Documentation Feedback..................................................................................................................................................6
Acronyms............................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Chapter 2: SFS fundamentals........................................................................................................ 7
SFS overview........................................................................................................................................................................ 7
SFS GUI............................................................................................................................................................................8
Supported network topologies......................................................................................................................................... 8
SFS supported platforms...................................................................................................................................................8
Creating a network fabric..................................................................................................................................................8
Server discovery and onboarding.................................................................................................................................... 8
Dynamic server onboarding.........................................................................................................................................9
Static server onboarding..............................................................................................................................................9
Server profile and server interface profile............................................................................................................. 10
Fabric back up and restore.............................................................................................................................................. 10
Chapter 3: Setting up SFS............................................................................................................11
Prerequisites........................................................................................................................................................................ 11
SFS configuration notes....................................................................................................................................................11
Configure SFS.....................................................................................................................................................................12
Enable SFS on PowerSwitches.................................................................................................................................12
Verify the switch operating mode............................................................................................................................15
Disable SFS using CLI..................................................................................................................................................16
Complete the fabric setup......................................................................................................................................... 16
Chapter 4: Deploying and managing a fabric.................................................................................17
Access fabric setup options............................................................................................................................................ 17
Update default fabric, switch names, and descriptions......................................................................................18
Create uplink for external network connectivity.................................................................................................. 19
Breakout switch ports................................................................................................................................................ 26
Configure jump host....................................................................................................................................................27
Update network configuration..................................................................................................................................27
Onboard a server onto the fabric............................................................................................................................29
Edit default fabric settings........................................................................................................................................33
Restore fabric configuration..................................................................................................................................... 33
Manage network profiles........................................................................................................................................... 34
Manage routing profiles............................................................................................................................................. 35
Chapter 5: SFS with VxRail..........................................................................................................37
Supported network topologies....................................................................................................................................... 37
Hardware and software requirements..........................................................................................................................37
Supported switches.................................................................................................................................................... 38
Contents
Contents 3

SFS personalities............................................................................................................................................................... 38
Support matrix................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Fabric operations and life cycle management............................................................................................................ 39
Chapter 6: SFS with PowerEdge MX............................................................................................40
Chapter 7: SFS for Isilon/PowerScale back-end fabric................................................................. 41
Supported network topologies........................................................................................................................................41
Hardware and software requirements.......................................................................................................................... 41
Supported switches.....................................................................................................................................................41
PowerScale requirements............................................................................................................................................... 42
Support matrix................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Chapter 8: SFS commands.......................................................................................................... 43
smartfabric l3fabric enable............................................................................................................................................. 43
smartfabric vlti................................................................................................................................................................... 43
show logging smartfabric ............................................................................................................................................... 44
show smartfabric cluster.................................................................................................................................................44
show smartfabric cluster member................................................................................................................................ 45
show smartfabric configured-server............................................................................................................................ 46
show smartfabric configured-server configured-server-interface....................................................................... 47
show smartfabric details................................................................................................................................................. 48
show smartfabric discovered-server............................................................................................................................48
show smartfabric discovered-server discovered-server-interface...................................................................... 49
show smartfabric networks............................................................................................................................................ 49
show smartfabric nodes.................................................................................................................................................. 50
show smartfabric personality.......................................................................................................................................... 51
show smartfabric uplinks.................................................................................................................................................52
show smartfabric upgrade-status................................................................................................................................. 53
show smartfabric validation-errors...............................................................................................................................54
show switch-operating-mode........................................................................................................................................ 55
Chapter 9: Appendix....................................................................................................................56
Internal fabric components and networks.................................................................................................................. 56
MSTP Support on L3 personality.................................................................................................................................. 57
Networks.............................................................................................................................................................................58
Uplinks..................................................................................................................................................................................59
Routing profiles............................................................................................................................................................59
Uplink bonding options...............................................................................................................................................60
4Contents
About this guide
This guide provides information regarding the integration of SmartFabric Services (SFS) with Dell EMC VxRail, Dell EMC
PowerEdge MX, and Dell EMC Isilon/Dell EMC PowerScale devices. It covers the following details:
●SFS concepts and its components for leaf and spine deployment
●Description, configuration information, limitations, and restrictions of SFS for each solution
●Command reference for all the SFS commands
To use this guide, you must have a good knowledge of Layer 2 (L2) and Layer 3 (L3) networking technologies, and data center
deployments.
This document may contain language that is not consistent with current guidelines of Dell Technologies. There are plans to
update this document over subsequent releases to revise the language accordingly.
Text and Syntax Conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to describe text and command syntax.
Bold text UI elements that you click or select
> (right angle
bracket)
Hierarchy of menu selections
Keyword Keywords are in Courier (a monospaced font) and must be entered in the CLI as listed
parameter Parameters are in italics and require a number or word to be entered in the CLI
{X} Keywords and parameters within braces must be entered in the CLI
[X] Keywords and parameters within brackets are optional
x|y Keywords and parameters separated by a bar require you to choose one option
Related Documents
Use the following documentation set in addition to this guide to get complete information about the SmartFabric Services
capabilities:
Table 1. Related Documents
Related Documentation Link
●Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 User Guide
●Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 Installation, Upgrade, and
Downgrade Guide
SmartFabric OS10 Documentation
Dell Technologies VxRail Documentation Dell Technologies VxRail Networking Solutions
Networking Solutions Support Matrix Support Matrix
PowerEdge MX Documentation PowerEdge MX Manuals and Documents
PowerScale/Isilon Documentation PowerScale OneFS Info Hub
OpenManage Network Integration Documentation OMNI Documentation
1
About this guide 5
Dell EMC Demo Center
The Dell EMC Demo Center is a highly scalable, cloud-based service that provides 24/7 self-service access to virtual labs,
hardware labs, and interactive product simulations. Several interactive demos are available on the Demo Center. Contact Dell
Support to get access to the Demo Center.
Documentation Feedback
Dell Technologies strives to provide accurate and comprehensive documentation and welcomes your suggestions and
comments. You can provide feedback in the following ways:
●Online feedback form—Rate the documentation or provide your feedback on any of product documentation pages at
www.dell.com/support.
●Email—Send your feedback to networkingpub.feedback@dell.com. Include the document title, release number, chapter title,
and section title of the text corresponding to the feedback.
To get answers to your questions related to Dell Networking Solutions through email, chat, or call, go to Dell Technologies
Technical Support page.
Acronyms
The following acronyms are used throughout this guide:
Table 2. Acronyms
Acronym Expansion
API Application Programmable Interface
BGP Border Gateway Protocol
CLI Command-Line interface
GUI Graphical User Interface
ICL Intercluster link
ISL Interswitch link
IOM Input/Output Module
LACP Link Aggregation Control Protocol
LAG Link aggregation group
L2 Layer 2
L3 Layer 3
RPVST+ Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning-Tree Plus
SFS SmartFabric Services
STP Spanning-Tree Protocol
VLAN Virtual LAN
VLT Virtual Link Trunking
VXLAN Virtual extensible LAN
VTEP VXLAN tunnel endpoint
6 About this guide
SFS fundamentals
This chapter provides information about the fundamentals of SFS including overview, supported topologies and platforms,
network fabric formation, and its supported solutions.
SFS overview
SFS is a SmartFabric OS10 feature that provides network fabric automation and API-based programming capabilities. SFS
has different personalities that can be integrated with systems including VxRail, PowerScale, generic PowerEdge servers,
PowerStore, storage, and MX servers. SFS integrated with these solution-specific deployments delivers autonomous fabric
deployment, expansion, and life cycle management.
SFS has two types: SFS for PowerEdge MX and SFS for leaf and spine. The following sections focus on concepts that are
related to SFS for leaf and spine:
SFS for leaf and spine is supported on S-series and Z-series Dell EMC PowerSwitches. See Supported platforms for a complete
list of supported platforms. SFS for leaf and spine has two personalities:
L2 single rack personality
NOTE: This personality is not available for deployments after OS10.5.0.5 release. All single rack and multirack deployments
from 10.5.0.5 release and later uses the L3 personality.
SFS deployments on OS10 releases from 10.4.1.4 to OS10.5.0.5 support only L2 single rack.
●Provide fabric automation for a single pair of leaf switches.
●SFS deployment is limited to a single rack and cannot be expanded to a multirack deployment.
NOTE: When you upgrade switches with this personality enabled, they operate in the L2 single rack personality only.
●SFS L2 single rack personality is enabled by running a Python script in the OS10 Linux shell. See Enable L2 personality for
more information.
L3 multi rack personality
All SFS deployments using OS10.5.0.5 and later releases support SFS L3 personality and the capabilities are as follows:
●Provides fabric automation for leaf and spine.
●Allows SFS deployment in a single rack and expand to multirack as required.
●Allows you to enable SFS using CLI, API, or GUI.
NOTE: In an MX-based deployment, the fabric is configured using OpenManage Enterprise-Modular (OME-M) UI, see Dell
EMC OpenManage Enterprise-Modular Editions User Guide available in PowerEdge MX Documentation.
See the Solutions Support Matrix for a complete list of solutions that can be onboarded onto the fabric.
2
SFS fundamentals 7

This guide covers the following SFS qualified solutions:
●SFS deployment with VxRail
●SFS deployment with PowerEdge MX
●SFS deployment with Isilon/PowerScale
SFS GUI
OS10 has support for SFS GUI to set up the initial SFS configurations in a L3 leaf and spine topology. You access the SFS GUI
using the latest version of the following browsers:
●Google Chrome
●Mozilla Firefox
●Microsoft Edge
For more information about SFS GUI, see Access fabric setup configuration.
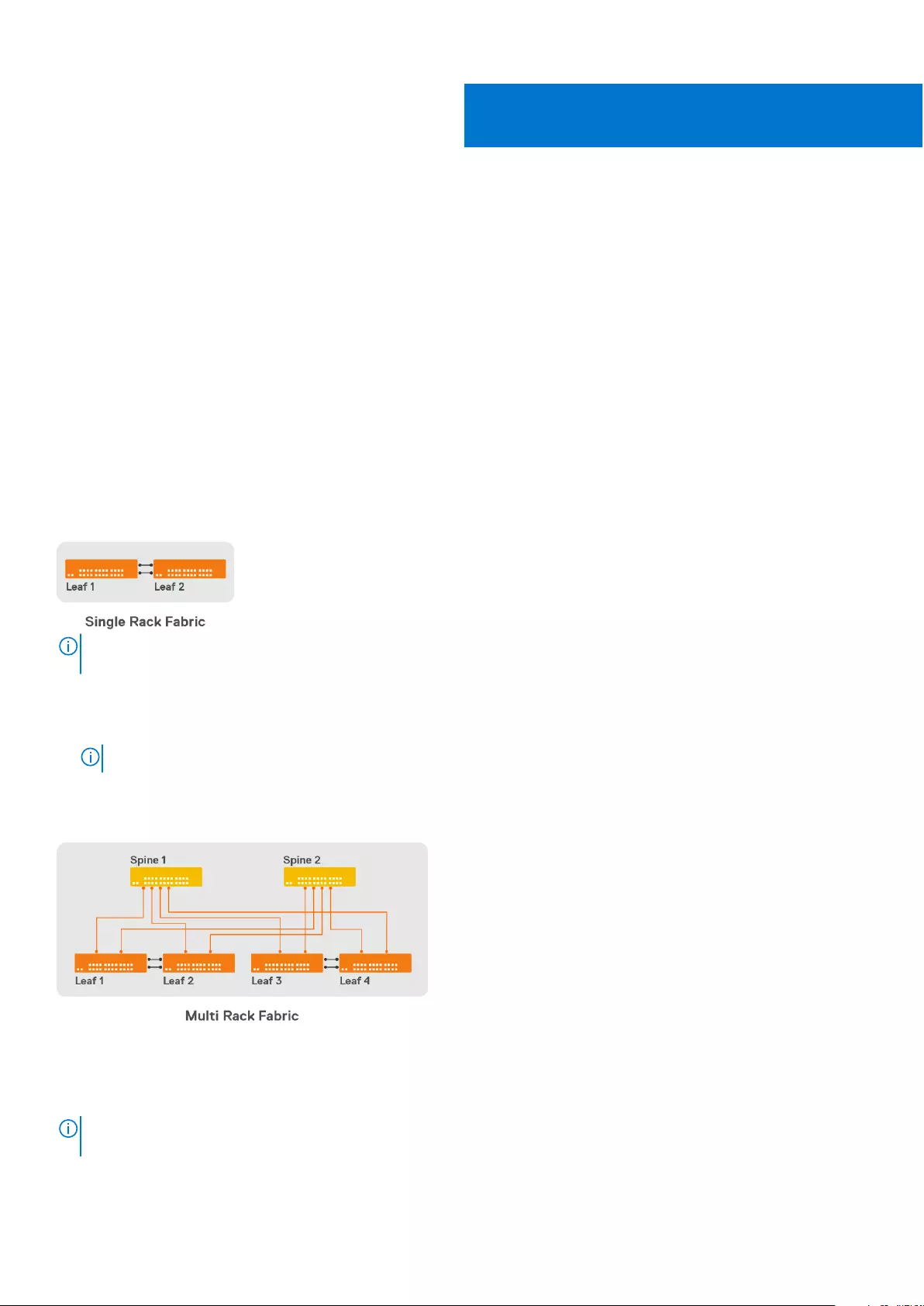
Supported network topologies
Following are the supported network topologies for SFS L3 multirack deployment:
●One leaf switch pair without spine switch
●Multiple leaf switch pairs with a two or more spine switches
SFS supported platforms
SFS is supported on the selected S-series and Z-series PowerSwitches for leaf and spine deployments. The platform support
varies depending on the solutions such as VxRail, PowerScale, and so on. The supported platforms are listed in Supported
Switches section under respective solution chapters.
Creating a network fabric
When you enable SFS on the switches in leaf and spine architecture, a single network fabric is built with all the discovered
switches using industry-standard L2 and L3 protocols. SFS supports the following automation capabilities in a leaf and spine
topology:
●Elects one leaf switch from the fabric as the master switch.
●Creates the infrastructure VLANs on the nodes.
●Allocates all the necessary internal IP addresses for leaf and spine configurations.
●Autoconfigures necessary BGP for all the relevant leaf and spine switches.
●Enables leaf and spine for underlay and overlay.
●Provides workload orchestration of server discovery and binding server profiles to networks.
See Internal components and entities for more information about infrastructure networks and fabrics that are created by SFS.
Also, you can use SFS show commands to view and verify fabric-related configuration.
After the fabric is created, you can configure uplinks, jumphost, and onboard servers to the fabric using the SFS GUI.
Server discovery and onboarding
SFS discovers and onboards a server based on the LLDP from the server when connected to the fabric.
Onboarding a server involves creating a server profile and assigning the networks (VLANs) to a specific server NIC port
connected to the switch port.
You can onboard a server in the following ways:
●Dynamic onboarding
●Static onboarding
8SFS fundamentals

Dynamic server onboarding
When the servers are connected to the fabric, SFS discovers the servers automatically.
SFS discovers a host as known servers based on the specific custom originator TLVs in LLDPDUs sent through the connected
ports. Following are the list of known servers discovered by SFS :
●VxRail
NOTE: SFS discovers and onboards the VxRail server automatically.
●PowerStore X
●PowerStore T
When a known server is discovered on the server-facing port, SFS applies the server profile configuration. When a known server
is disconnected, the stale entry is removed from the LLDP neighbor table.
Dynamic discovery of unknown servers
With OS10.5.2.2 and later releases, SFS dynamically discovers unknown servers using the standard LLDPDUs sent out through
the connected ports. Unknown server is a host that does not send a valid originator in custom TLVs in LLDP frame. Upon
discovery, the client management network is configured by default.
NOTE: If the LLDP TLVs are advertised with both bridge and routing capabilities, SFS considers that the interface is
connected to a switch or router. Hence, the client management network is not configured on that interface.
For onboarding an unknown server, the Port-id TLV in LLDP packet is mandatory. SFS matches the Port-id TLV value in the
LLDP packet against the Interface field in the server interface profile to onboard the unknown server. After the server
interface profile is configured, the onboard criteria for unknown server is same as onboarding a known server.
●If both known and unknown LLDP neighbors exist on the same interface, SFS discovers these servers as known and
unknown servers. During onboarding, if the server profile matches with both the known and unknown discovered servers on
the same physical interface or with the same server interface profile, the order of onboarding is as follows:
○Known discovered server
○Unknown discovered server
If you offboard the known server, SFS checks for the unknown server and onboards it if available.
●If both known and unknown LLDP neighbors exist with the same port ID, SFS discovers both the known and unknown
servers. During the onboard process, the order of onboarding is as follows:
○Known discovered server
○Unknown discovered server
If you offboard the known server, SFS checks for the unknown server and onboards the server if available.
●If there is a static onboarding server profile that is configured on an interface where the known and unknown LLDP
neighbors exist, SFS discovers both the LLDP neighbors. During onboarding if there are conflicts on the physical interface or
server interface profiles, the priority order of onboarding is as follows:
○Static onboarding
○Known discovered server
○Unknown discovered server
If you offboard the statically onboarded server, SFS checks the known servers list first and then the unknown server list to
onboard the device based on the priority order.
Static server onboarding
SFS supports static onboarding of server on assigned ports instead of LLDP-based discovery. This option is used for onboarding
servers that are not discovered by SFS.
To statically onboard a server, you must assign an interface of the leaf switch to which the server is onboarded. See Onboard
nondiscovered server interfaces section in Onboard a Server for more information about static onboarding using GUI.
Configuration notes:
●STP is disabled on the server-connected ports.
SFS fundamentals 9
●The bonding can be static or LACP.
●All existing bonding modes are supported on a statically onboarded server.
●VXLAN does not support STP on access ports and it is not applicable for L3 Fabric. For the VXLAN type of network, you
cannot configure STP; the network topology must remain loop free.
●All existing network types are allowed to be onboarded on statically onboarded servers.
●Since onboarding is static, when server is moved there is no support for moving the configurations along with the server.
●The port-role for the statically onboarded server is EndHost or GenericEndHost.
●When the server profile or server interface profile is deleted, all the impacted interfaces are brought to default configuration.
Server profile and server interface profile
Server profile and server interface profiles are logical entities of SFS. You configure these entities when onboarding a server to
the fabric.
Server interface profile represents the server NIC ports that are connected to the leaf switches. For a server interface profile,
a server interface ID must be configured using the MAC address of the server NIC port. SFS uses the server interface ID to
identify the server NIC port and configure the required networks on the server NIC ports.
Server profile is a list of server interface profiles with a common bonding type. Supported bonding types are AutoDetect and
LACP. You can configure a server profile using SFS UI, see Server onboarding. To view the server profiles available on the SFS,
see Manage server profiles.
Fabric back up and restore
You can backup the SFS configuration to an external device, and restore the fabric to a good state using the backed-up
configuration during a failure or error.
The backup functionality allows you to backup all the user configuration to a text file in JSON format. The REST endpoints are
available that returns a text file containing all the user configuration that was done through the REST interfaces.
The restore functionality allows you to restore the fabric to a last known good configuration. The REST endpoint is available that
enables you to stream the backed-up configuration. The restore action wipes the data completely and restores the configuration
on the switches from the backup file. The restore functionality is followed by mastership switchover. For the successful restore
operation to occur, the restore activity should be applied to the same set of switches in the fabric. Also, the SFS personality
should be the same when the backup was performed.
The backup and restore endpoints are accessible only for the users with sysadmin role. The REST payload is encrypted using
the SSL protocol.
You can also restore the configuration for a fabric from SFS UI, see Restore.
Table 3. HTTP Methods
Functionality HTTP Method URL Payload
Backup GET https://<ip-address>/
redfish/v1/Dnv/Backup
Output is a text as stream and
Content-Type is application or
octet-stream.
Restore POST https://<ip-address>/
redfish/v1/Dnv/Restore
Content-Type: application or
octet-stream and payload
contains the backup file.
10 SFS fundamentals

Setting up SFS
This chapter explains the workflow to setup SFS including initializing SFS and enabling it on leaf and spine switches.
Prerequisites
Ensure that the following are met before enabling SFS on the switches:
●Configure the Out-of-band (OOB) management configuration on the leaf switches. OOB management network enables
connections to the SFS GUI. Dell EMC PowerSwitch S3048-ON can function as an OOB management switch with the
OS10 factory default configuration. For more information about OOB management topology and connection details, see the
respective Solution Deployment Guides
●Verify the SmartFabric OS10 version on the switches and update them with recommended version listed in the Support
Matrix.
SFS configuration notes
This section lists important behaviors, considerations, and recommendations you must know before deploying SFS:
Recommendations
See Internal components and networks for more information about the SFS components and networks that are created by SFS.
Recommendations and notes regarding the SFS components are:
●Dell Technologies recommends that you do not change or disable the STP settings on switches in SmartFabric mode. Any
change to the STP settings results in reboot of all the switches in the fabric and disabling STP settings cause loops.
●Dell Technologies recommends using uplinks from a leaf pair as a best practice. Uplinks from leaf switches to external
switches can be L2 or L3. All uplinks from spine switches to external switches must be L3.
●Except for Isilon/PowerScale deployment, breakout feature is not supported on the leaf switches for the ICL (VLTi) or ISL
(leaf and spine) connections. Use the default speed cables of the leaf switch when creating the ISL or ICL connections in a
L3 fabric.
○ISL example—If the default speed on the leaf switch port is 100G and spine switch port is 400G, use 100G cable for ISL
connection. Since autobreakout feature is enabled on the spine switch, the port speed of the spine switch is set to 100G
automatically.
○ICL example—If the default speed of the leaf switches is 100G, use 100G cable for the ICL connection.
●Ensure that the leaf switches in the existing fabric are set as the Preferred Master before expanding the fabric to prevent
the configuration loss. Preferred Master flag is automatically set when you create an uplink for the leaf switches using SFS
GUI. Once a master is elected, it initiates all applications to automatically build the network fabric, and master virtual IP
address is advertised for applications to automatically discover the fabric through inband networks.
●If you want to breakout the ports to configure uplinks or jump hosts, ensure that the breakout ports are configured on the
switch before creating and configuring these entities. You can configure breakout ports using SFS GUI.
Default settings
●SFS creates VLANs from 4000 to 4094 for internal use. Do not use these VLANs for general use.
●SFS creates 172.16.0.0/16 and 172.30.0.0/16 networks for the leaf and spine network configuration.
●By default, autobreakout feature is enabled on the leaf switches in SmartFabric mode. Autobreakout works only on DAC and
AOC cables.
3
Setting up SFS 11
SFS behavior
SFS elects one switch from the fabric as a master switch and designates the remaining leaf switches as the backup switches.
In the event of a master failover, a new master is elected from the backup switches using the keepalive information. The
switches that are configured as Preferred Master have a higher priority to become the master switch. If none of the switches
are configured as the preferred master, any leaf switch can become the master.
When you expand the fabric, the newly added switches may come up and form a fabric among themselves, and elect a master
before they are connected to the existing fabric. When the new fabric merges with the existing fabric, SFS elects a new master
switch for the combined fabric. If one of the new leaf switches becomes the master, it may overwrite the configuration in the
existing fabric.
Spanning tree considerations
●To avoid loops, SFS does not allow you to configure the same network on multiple uplinks.
●SFS supports RPVST+ and MSTP. The default spanning tree mode in SFS is RPVST+. Once the fabric is created, you can
change the STP mode using SFS GUI, see Edit default settings.
NOTE: When you change the mode using GUI, the whole fabric goes through a reboot and the new mode is set to
MSTP. The reboot action impacts the traffic flow in the cluster.
●By default, RPVST+ is enabled on the uplink interfaces for L3 VLAN networks. When RPVST+ is enabled on the uplink, the
total number of Port VLANs (PV) supported is 400.
Configure SFS
By default, PowerSwitches boot in Full Switch mode when you power them up with SmartFabric OS10. This information explains
how to setup a fabric.
1. Enable SFS and set roles on the switches.
2. Connect to SFS GUI and complete the relevant fabric configurations to setup the fabric. See SFS GUI for more information
regarding login procedure and fabric configurations.
For SFS with Isilon/PowerScale deployment, you only have to enable SFS with roles on all the switches using CLI. All other SFS
initial deployment operations using UI are not required. For more information regarding PowerScale deployments, see the related
documents available in PowerScale Info Hubs.
Enable SFS on PowerSwitches
You can enable SFS on PowerSwitches through CLI, GUI, or REST API from OS10.5.0.5 and later versions. This option is
applicable only for SFS L3 leaf and spine personality.
After you enable SFS on all the switches in a leaf and spine deployment, a network fabric is created automatically with the
default fabric settings. See Internal fabric component and networks for more information about the default settings.
Enable SFS using CLI
To enable SFS on a switch using CLI, run the smartfabric l3fabric enable command and set a role. For more
information, see smartfabric l3fabric enable.
After you enable SFS on the switches and set a role, the system prompts for a confirmation to reload and boots in the
SmartFabric mode. Enter Yes to continue. In SmartFabric mode, the CLI is restricted to global switch management features and
monitoring. Using this command, enable SFS on all the switches with the corresponding role to create a fabric.
The following example shows how you can enable SFS on switches and set roles:
Spine:
OS10(config)# smartfabric l3fabric enable role SPINE
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
12 Setting up SFS
Leaf:
In SFS, the two leaf switches are automatically configured as a VLT pair.
OS10(config)# smartfabric l3fabric enable role LEAF vlti ethernet 1/1/4-1/1/5
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
In the above example, the Ethernet interfaces 1/1/4 and 1/1/5 are the VLTi interfaces.
In Isilon or PowerScale back-end deployments, when enabling SFS in a leaf and spine topology, no VLTi configuration is required
for the leaf switch. To set the leaf role for a switch, use the smartfabric l3fabric enable role LEAF command
without the VLTi parameters.
Enable SFS using RESTCONF API
You can enable SFS on OS10 switches using the RESTCONF API. For more information regarding general RESTCONF API
operations, see Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 User Guide.
Description Enables SFS on the switches with leaf and spine roles.
RESTCONF
endpoint
/restconf/data/dell-smart-fabric:config-personality
JSON content
(spine) {
"dell-smart-fabric:config-personality": {
"service-enable":true,
"role": "SPINE",
}
}
Example curl -k -u admin:admin -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -i -X POST
-d \
'{"dell-smart-fabric:config-personality":
{"service-enable":true,
"role":"SPINE"}
}'
https://100.104.26.104/restconf/data/dell-smart-fabric:config-personality
The following example shows how to enable SFS on a leaf switch with an IP address (100.104.26.104) and ICL interfaces as
1/1/5 and 1/1/6.
JSON content
(leaf) {
"dell-smart-fabric:config-personality": {
"service-enable":true,
"mode": "L3 Fabric",
"role": "LEAF",
"icl": [
"ethernet1/1/5",
"ethernet1/1/6"
]
}
}
Example curl -k -u admin:admin -H 'Content-Type:
application/json' -i -X POST -d \
'{"dell-smart-fabric:config-personality":{"service-
enable":true,"role":"LEAF",
"icl": [
"ethernet1/1/5",
"ethernet1/1/6"
]
}
}'
https://100.104.26.104/restconf/data/dell-smart-fabric:config-personality
Setting up SFS 13
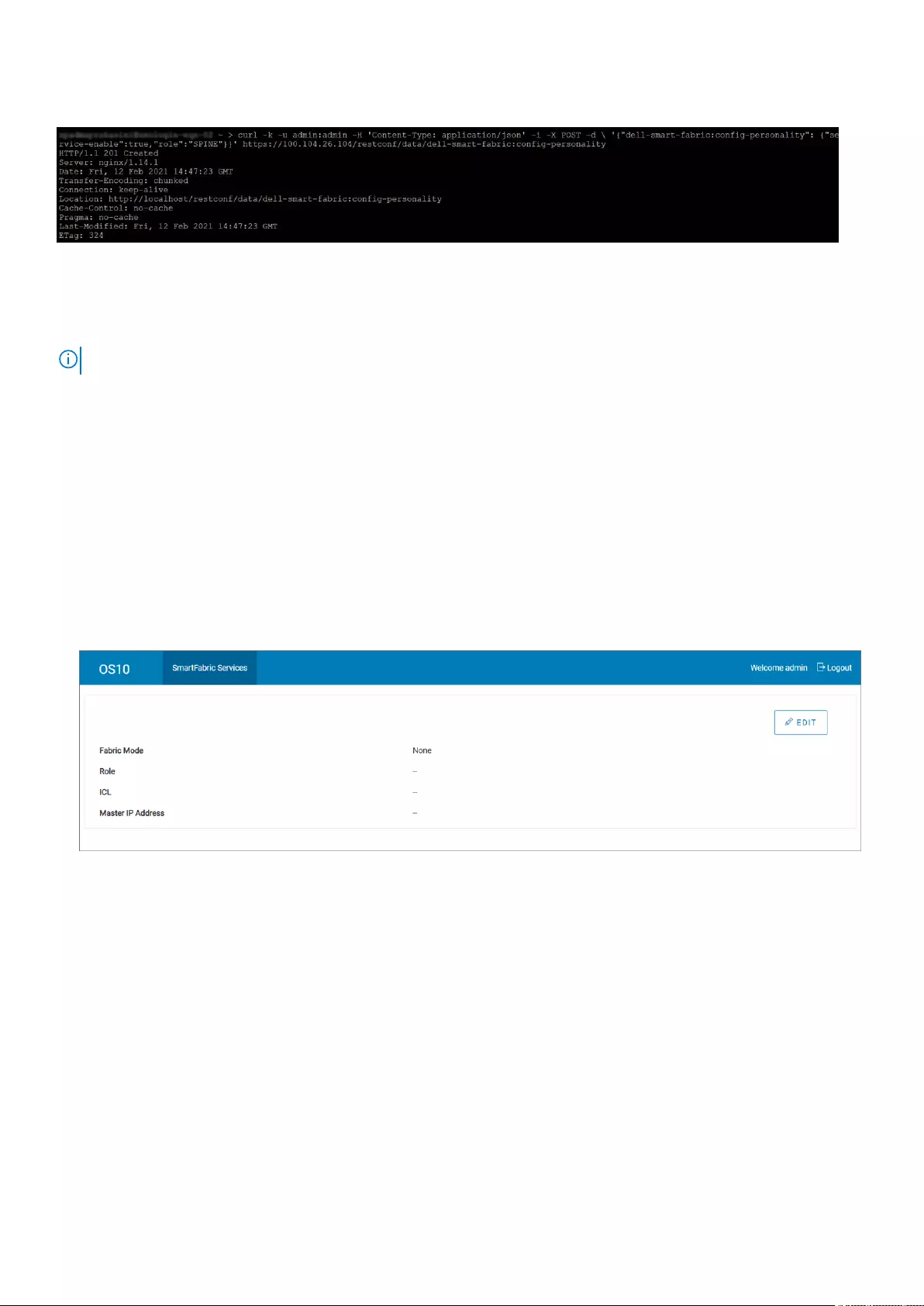
Example—Usage of curl command on a linux server is as shown:
Enable SmartFabric Services L2 personality using script
In SFS L2 personality, you can enable SFS only using API. All deployments from SmartFabric OS10.4.1.4 to OS10.5.0.x version
support only the single rack network fabric.
NOTE: The L2 personality is not available for new deployments after 10.5.0.5 release.
A python script is used to enable SFS. For more information about L2 personality commands and information, see VMware
Integration for VxRail Fabric Automation SmartFabric User Guide, Release 1.1 available in OMNI Documentation page.
Enable SFS using GUI
To enable SFS using the GUI, following the instructions:
1. Enable RESTCONF API on the switch using the OS10 CLI.
To enable RESTCONF API, use rest api restconf command in CONFIGURATION mode. See Dell EMC SmartFabric
OS10 User Guide for more information about RESTCONF API.
2. Open a browser session, go to https://
switch-mgmt-ip-address
.
3. Log in to a switch using the credentials that are created to access an OS10 switch. The default username and password is
admin.
4. Enable SFS on the switch using the Edit option that appears in the upper-right side of the page.
5. Enter the role of the switch and click OK to enable SFS.
14 Setting up SFS
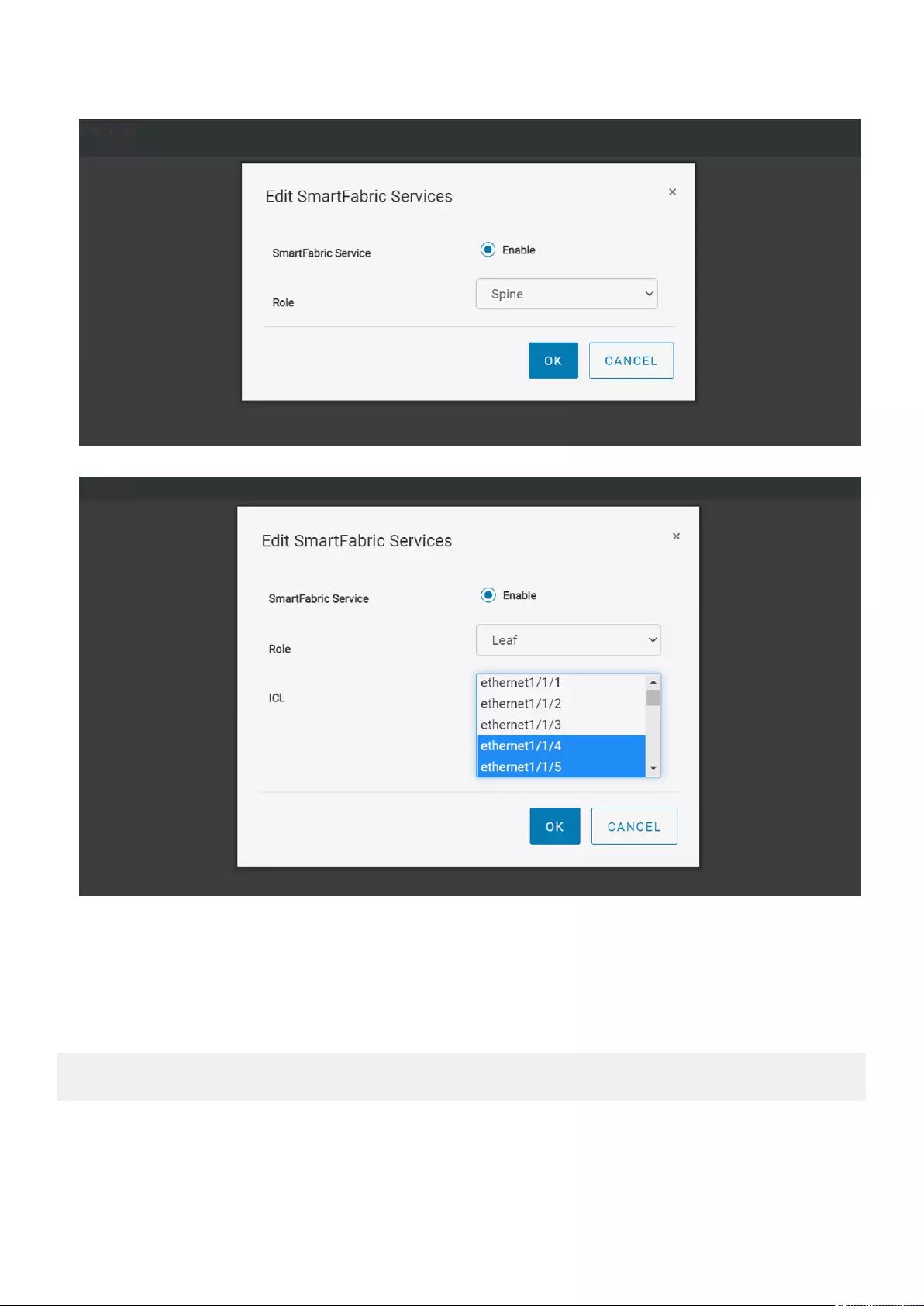
Spine:
Leaf:
After you enable SFS on a switch, the system reloads to apply the configuration.
6. Repeat the steps 1 to 4 on all the remaining switches to enable SFS and set role. All switches reload and forms a fabric.
Verify the switch operating mode
To verify that the switches are in SmartFabric mode, run the show switch-operating-mode command on each switch.
OS10# show switch-operating-mode
Switch-Operating-Mode : SmartFabric Mode
For more information regarding the CLI, see the show switch-operating-mode command.
Setting up SFS 15

Disable SFS using CLI
To delete the existing switch configuration and go back to Full Switch mode, run the no smartfabric l3fabric command
on each switch.
The no smartfabric l3fabric command disables the L3 fabric personality. After you disable the L3 fabric in the switch,
the system prompts for confirmation and reboots in Full Switch mode.
OS10(config)# no smartfabric l3fabric
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
Complete the fabric setup
After enabling SFS, you must configure logical entities to complete the SFS setup.
1. Log in to SFS GUI. For more information, see SFS GUI.
2. Configure unique names for SFS components. For more information, see Update fabric names and descriptions.
3. (Optional) Configure breakout switch ports based on the deployment requirements. For more information, see Breakout
ports.
4. Configure uplinks for connectivity. For more information, see Create uplinks.
5. Configure Jump host for client management based on the requirement. For more information, see Configure Jump host.
6. Onboarding a server by applying server interface profile. For more information, see Server onboarding.
16 Setting up SFS
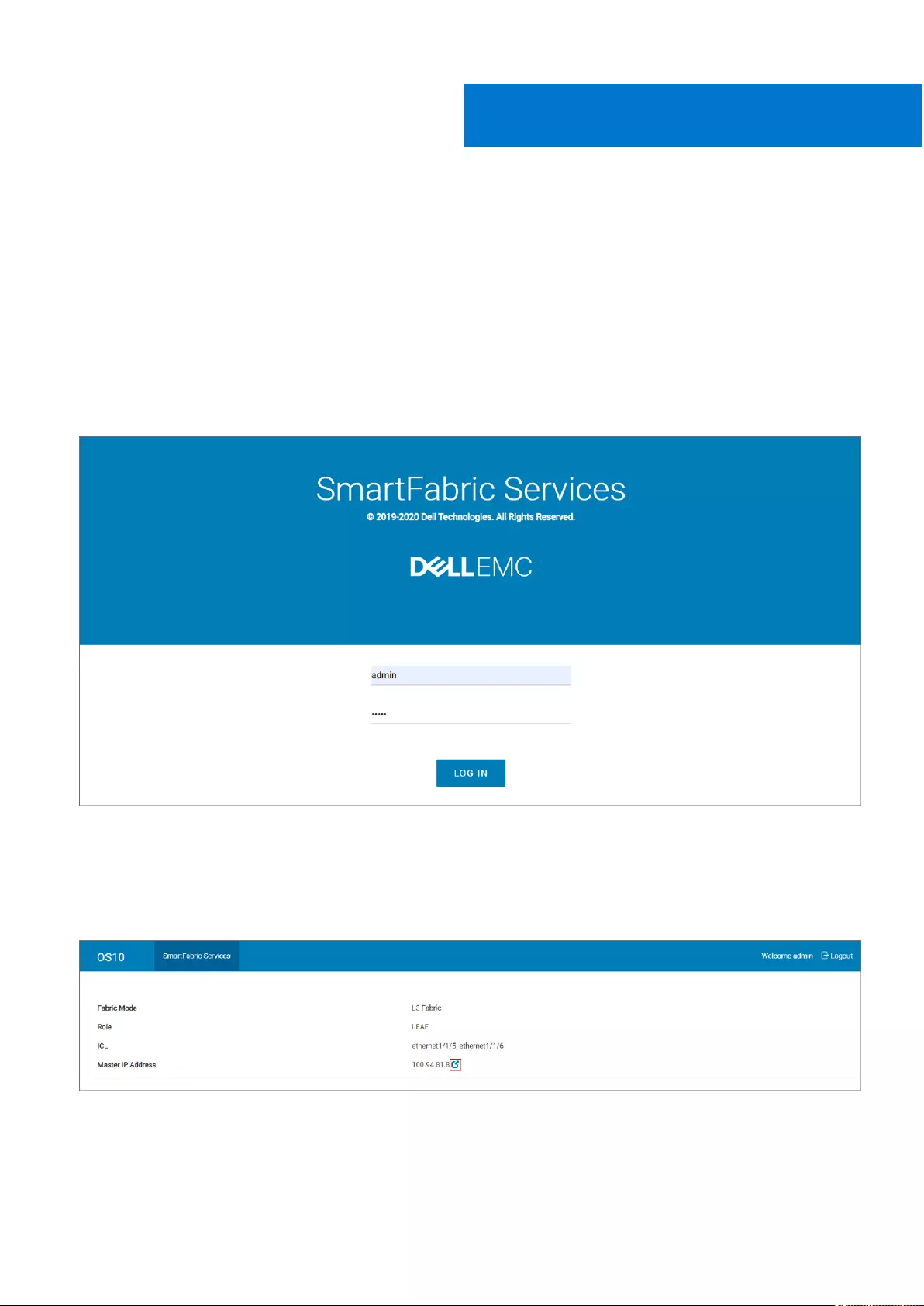
Deploying and managing a fabric
You can use SFS GUI to set up initial SFS configuration in a leaf and spine topology. The SFS GUI helps you with the initial SFS
deployment operations and management of the switches in a fabric.
Access fabric setup options
Follow the instructions to access fabric setup options:
1. Log in to SmartFabric Services GUI using the management IP address of any switch.
2. Enter the credentials that are created to access an OS10 switch from the console or through a network connection. The
default username and password is admin. You can also use any user-configured accounts as credentials.
If you logged in to a switch in a fabric that is not the master, the page displays only the fabric mode of switch and the IP
address of the master along with the link to the master switch. All fabric configuration can be performed only from the SFS
master switch.
You can also launch the SFS GUI directly using the master IP address. To get the IP address of the master switch in the L3
fabric, use the show smartfabric cluster command. For more information, see SFS commands.
3. Click the link to log in to the master switch.
Upon successful login, the GUI appears with the following options on the Home page:
●Links to wizards that enable you to complete the fabric setup. Click the relevant link to set up the fabric.
●The L3 leaf and spine topology view that is created after you enable SFS. The topology view displays the switch icons
with the hostname and the service tag information under each node and the link connectivity between the switches.
4
Deploying and managing a fabric 17
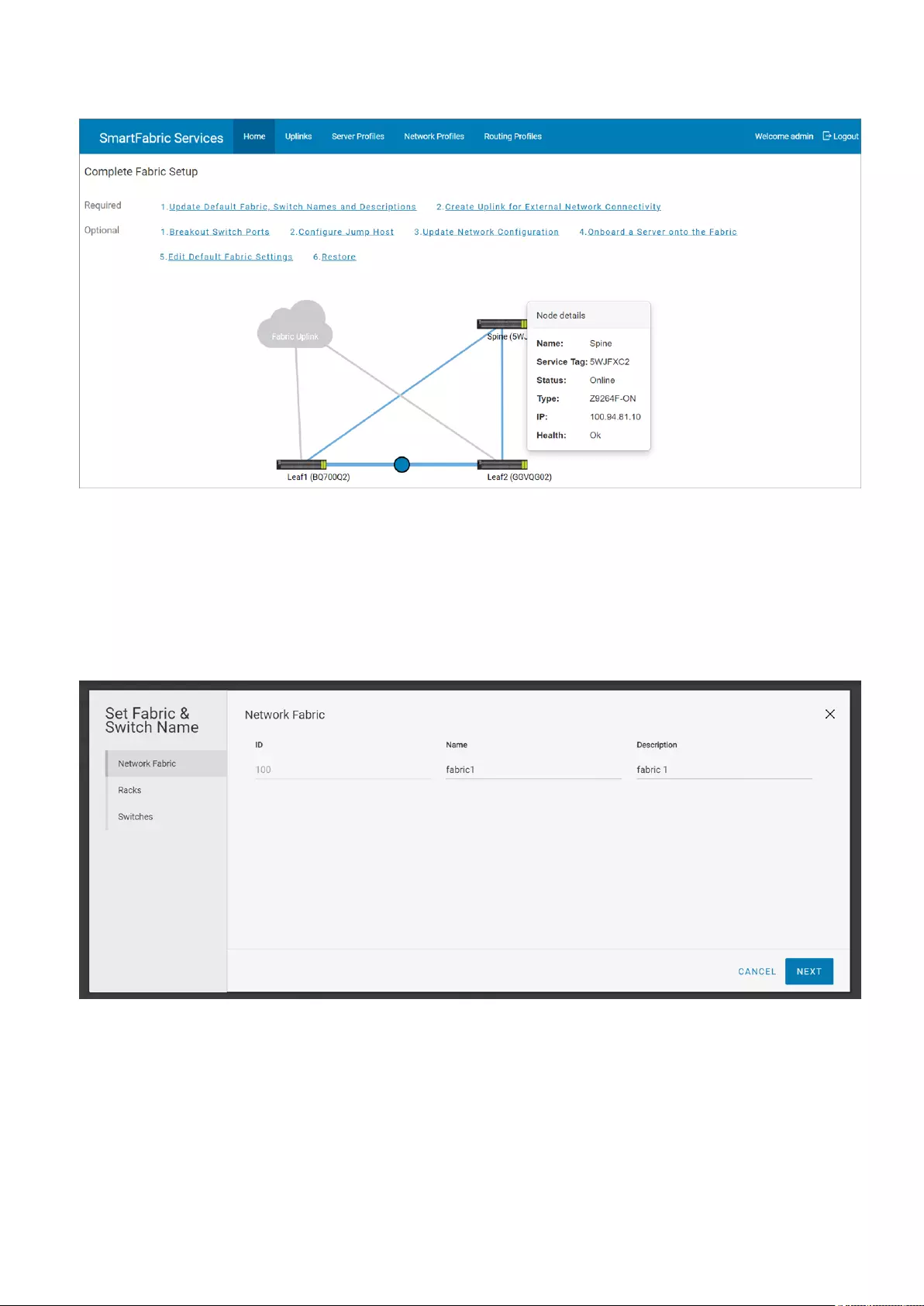
Mouse over a fabric to see the detailed information about the leaf and spine switches, and the link connectivity.
The session is controlled through token-based authentication. The default token timeout value is 120 minutes. You are
automatically logged out, after the token time expires with a warning message.
Update default fabric, switch names, and descriptions
SFS assigns unique names for the network fabric, racks, and switches automatically. Use the following instructions to change
the names and descriptions of the network fabric, racks, and switches:
1. Click Home > Update Default Fabric, Switch Names and Descriptions.
2. Change the name and description of the network fabric, and click Next.
18 Deploying and managing a fabric
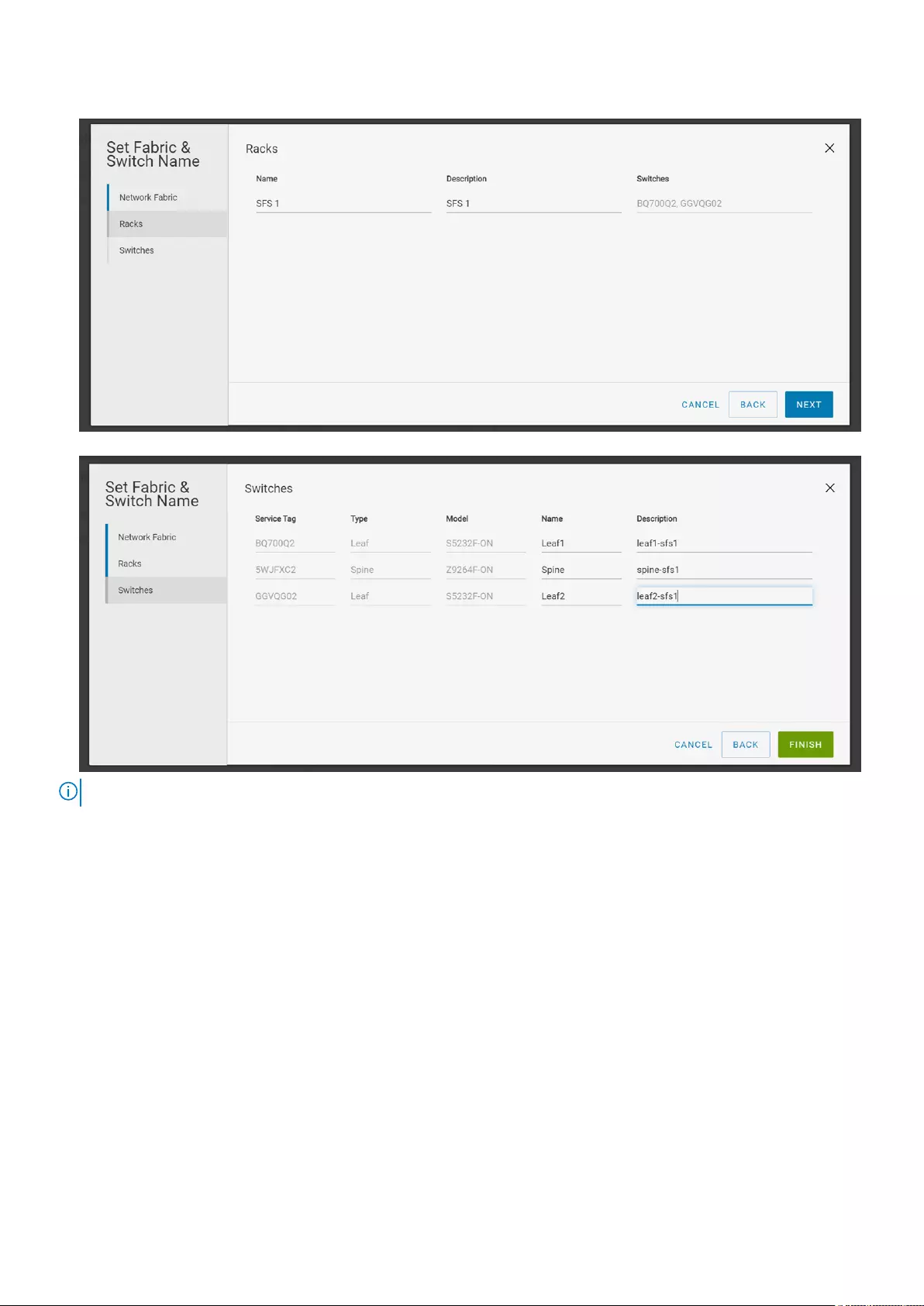
3. Change the name and description of the rack or VLT fabric, and click Next.
4. Change the name and description of the switches, and click Finish.
NOTE: If you change the switch name in the GUI, the hostname on the switch CLI is also updated.
Create uplink for external network connectivity
Uplinks enable the network fabric to communicate with the external network. Before creating an uplink, ensure that the external
network is configured with the L2 or L3 setup. Any ports available on the leaf switches may be used as uplinks, provided they
are compatible with the corresponding ports on the external switches.
SFS supports eBGP and static routes profiles and LACP and static for uplink bonding. For more information, see Uplinks section.
From SmartFabric Services page, click Uplinks tab to view the list of the uplinks that are configured in the SFS. For more
information, see Manage uplinks. The Uplinks page does not display the network and route profiles that are associated with the
uplinks. View these details by running the show smartfabric uplinks command on the switch.
Configure L2 uplink
Follow the instructions to create a L2 uplink:
1. Click Home > Create Uplink for External Network Connectivity.
Deploying and managing a fabric 19
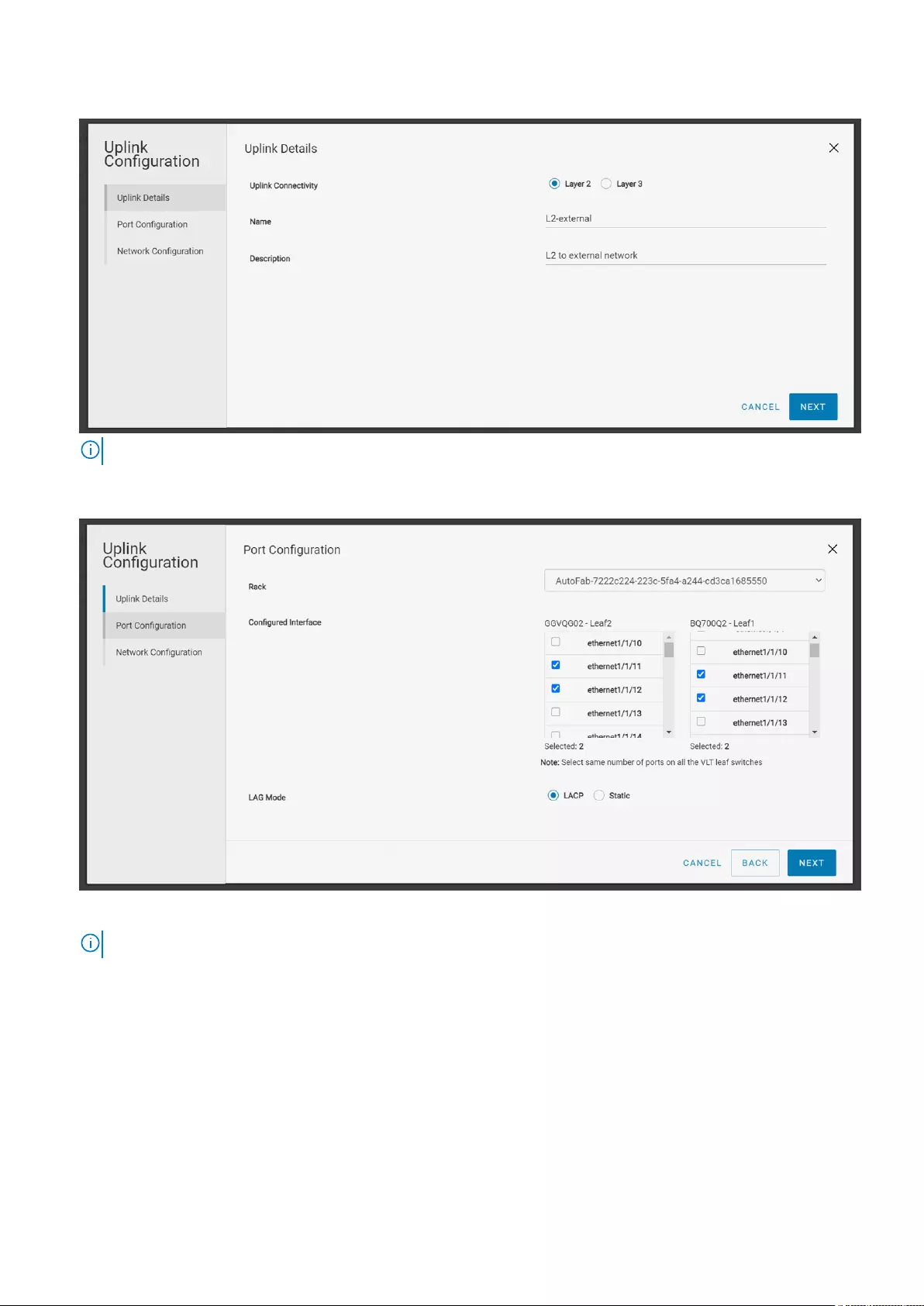
2. Select the Uplink Connectivity as Layer 2, enter the name and description, and click Next.
NOTE: You can create L2 uplinks only on leaf switches.
3. Select a rack and one or more interfaces from the leaf switches to associate to the uplinks.
If you want to split a port speed, breakout the interface first before associating the interface
to the uplinks. See Breakout Switch Ports to configure breakout the ports from SFS GUI.
4. Select the LAG mode based on the configuration setup in the external network, and click Next. To form a LAG on the leaf
switches, select an interface or interfaces that are of the same speed.
NOTE: Ensure that the corresponding ports on the external switches are configured with the same LAG mode.
5. Associate the networks with the selected interfaces:
●Add single or multiple tagged networks.
●Add the network from the displayed list or create a general-purpose network using the Add Network. To add a network,
enter the name, description, and VLAN ID. Networks that are created using this wizard are created on the fabric as
general purpose networks. For more information about different types of network in SFS, see Networks.
20 Deploying and managing a fabric
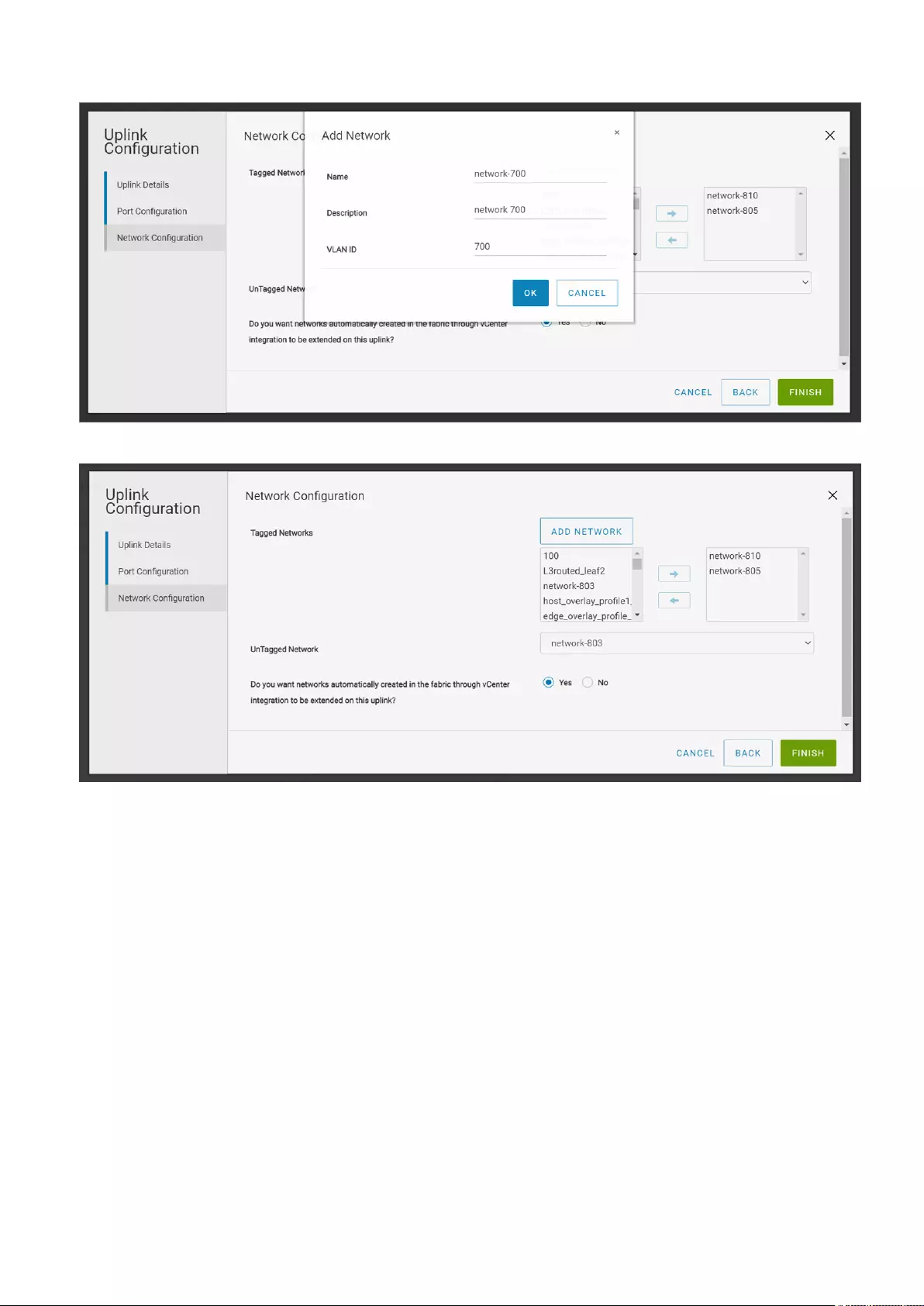
6. Select Yes or No appropriately to integrate the networks that are created automatically in the fabric through vCenter on this
uplink.
When you select Yes, the uplink is created with the type Default and the networks from the vCenter are automatically
appended to the L2 uplink during vCenter integration. For more information, see OpenManage Network Integration for
SmartFabric Services User Guide, Release 2.0.
7. Click Finish.
Configure L3 VLAN uplink
Use the following procedure to create a L3 VLAN uplink:
1. Click Home > Create Uplink for External Network Connectivity.
2. Select the Uplink Connectivity as Layer 3 and Network type as L3 VLAN.
Deploying and managing a fabric 21
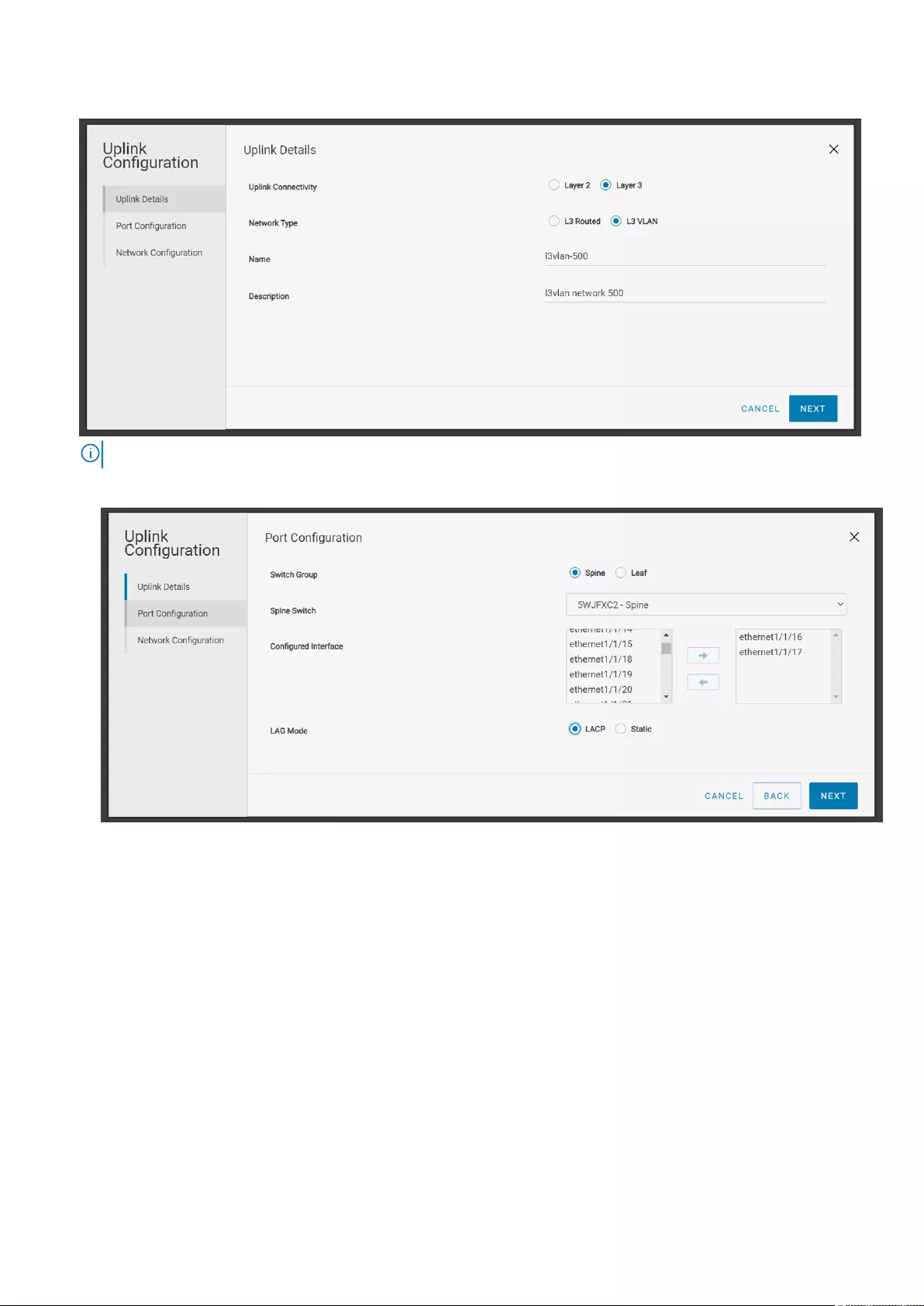
3. Create a L3 VLAN uplink by providing the name and description, and click Next.
NOTE: You can create L3 uplinks on both leaf and spine switches.
4. Associate the interfaces of the spine or leaf switches with the L3 uplink.
●Spine—Select a spine switch and an interface or multiple interfaces of the spine switch to be associated with the uplink.
22 Deploying and managing a fabric
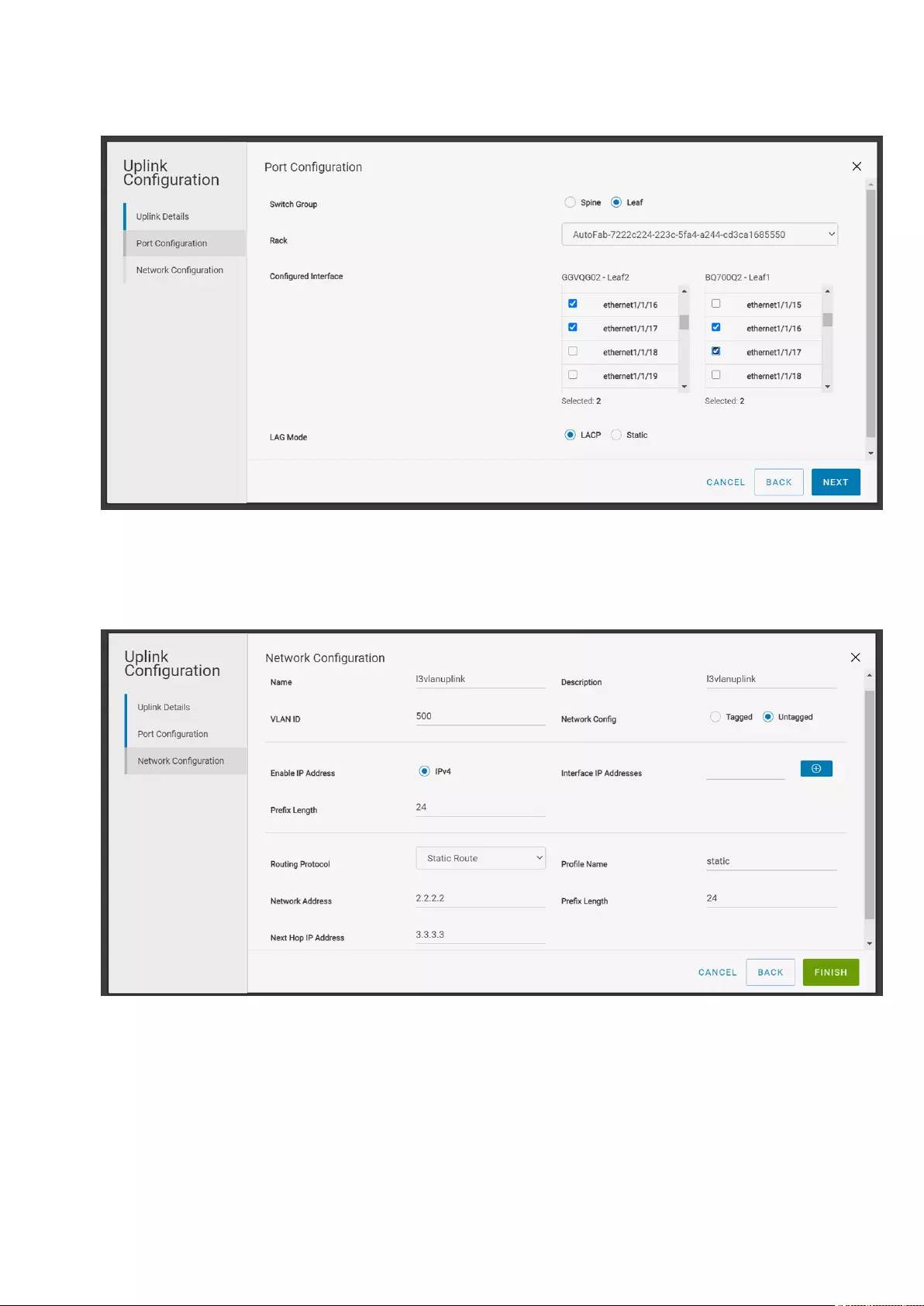
●Leaf—Select a leaf switch from the rack, and an interface or multiple interfaces of the leaf switch to be associated with
the uplink.
5. Select the static or dynamic LAG based on the configuration setup in the external network, and click Next.
6. Create a L3 VLAN network by providing name, description, and VLAN ID, and associate to the selected interfaces.
7. Select if the network is a tagged or an untagged network.
8. Enter the IP address for the network. You can use the + symbol to add more IP addresses.
9. Define a routing policy to associate with the uplink based on the external network connectivity setup.
●Static Route—A route policy template that contains a network prefix and the next hop IP address.
Deploying and managing a fabric 23
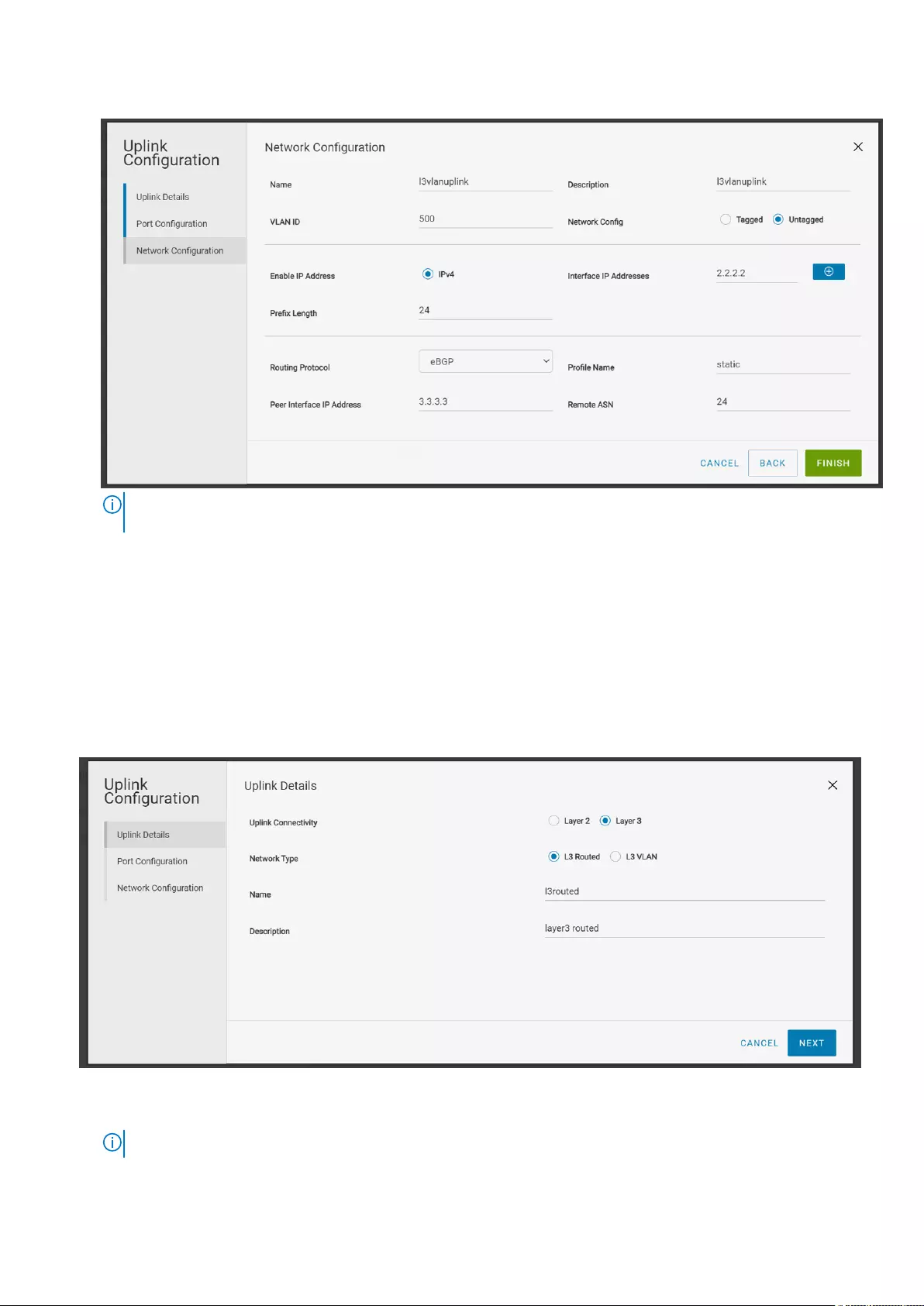
●eBGP—A routing policy template that contains BGP peer IP address and the remote AS number.
NOTE: The network configurations reflect in the switch only after associating the network with an uplink or server
profile.
10. Click Finish.
Click Routing Profiles tab to view the list of all the routing profiles that are configured in the SFS. For more information, see
Manage routing profiles.
Configure L3 Routed uplink
Use the following procedure to create a L3 routed uplink:
1. Click Home >Create Uplink for External Network Connectivity.
2. Select the Uplink Connectivity as Layer 3.
3. Select the Network Type as L3 Routed.
4. Create a L3 Routed uplink by providing the name and description and click Next.
5. Associate an interface from the spine or leaf switch with the L3 Routed uplink.
●Spine—Select a spine switch and an interface from the spine to associate with the uplink.
●Leaf—Select a leaf switch from the rack, and an interface from the leaf switch to associate with the uplink.
NOTE: You can select only one interface from the spine or leaf switch for L3 Routed uplink.
6. Create a L3 Routed network to associate by providing a name, description, interface IP address, and prefix length.
24 Deploying and managing a fabric
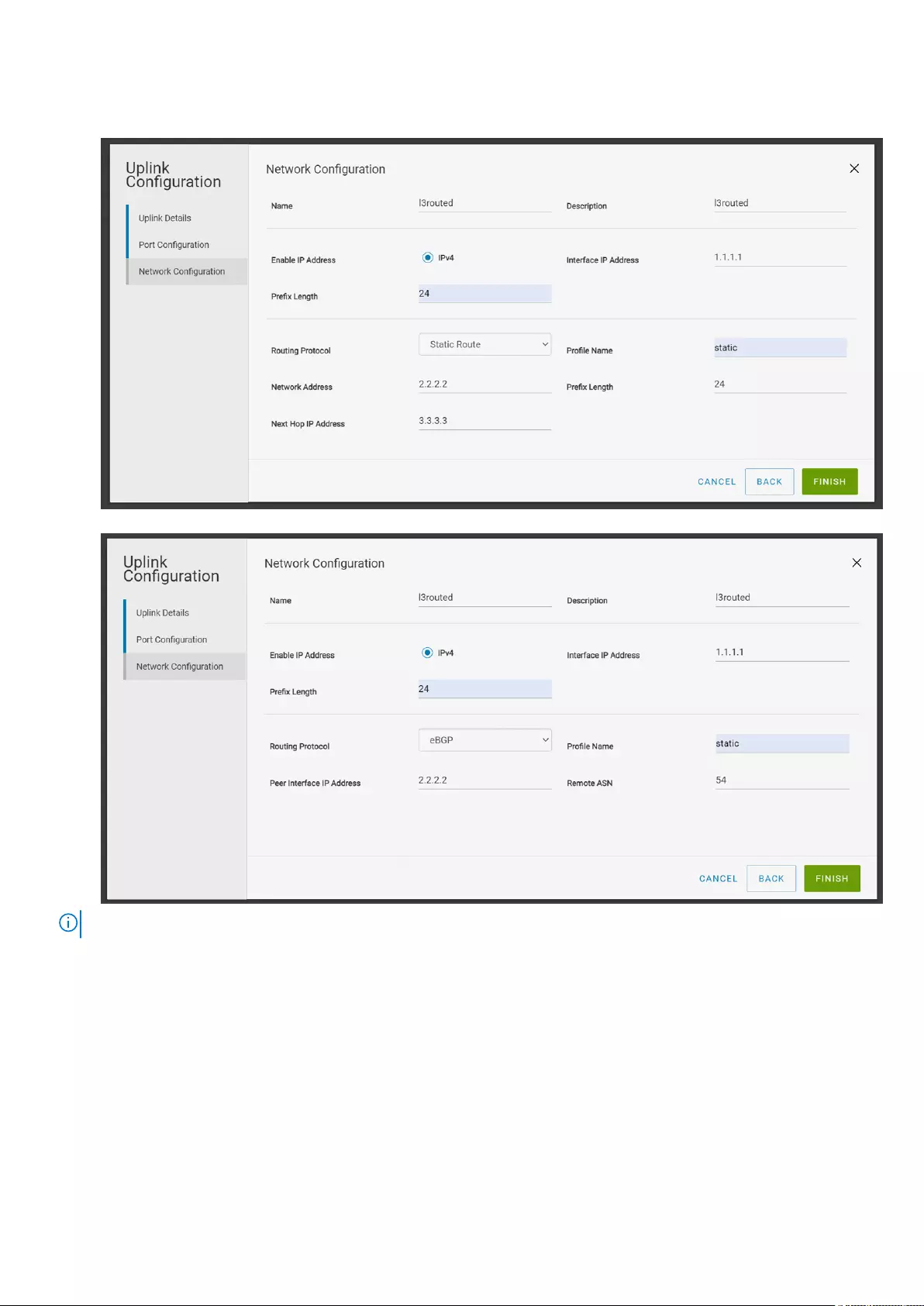
7. Define a routing policy to associate with the uplink based on the external network connectivity setup.
●Static Route—A route policy template that contains a network prefix and the next hop IP address.
●eBGP—A routing policy template that contains BGP peer IP address and the remote AS number.
NOTE: You cannot associate a L3 Routed network with more than one uplink or server profile.
You can view or delete the routing profiles that are created as part of the uplink configuration from the Routing Profiles tab.
For more information, see Manage routing profiles.
Manage uplinks
You can manage the uplinks that are created in the fabric.
From the SmartFabric Services page, click Uplinks tab to view the list of the uplinks that are configured in the SFS.
Deploying and managing a fabric 25
To delete an uplink:
1. Select an uplink from the list and click Delete.
2. Click Ok to confirm deletion.
NOTE: When you delete an uplink, the network and route profile that are associated with the uplink are not deleted.
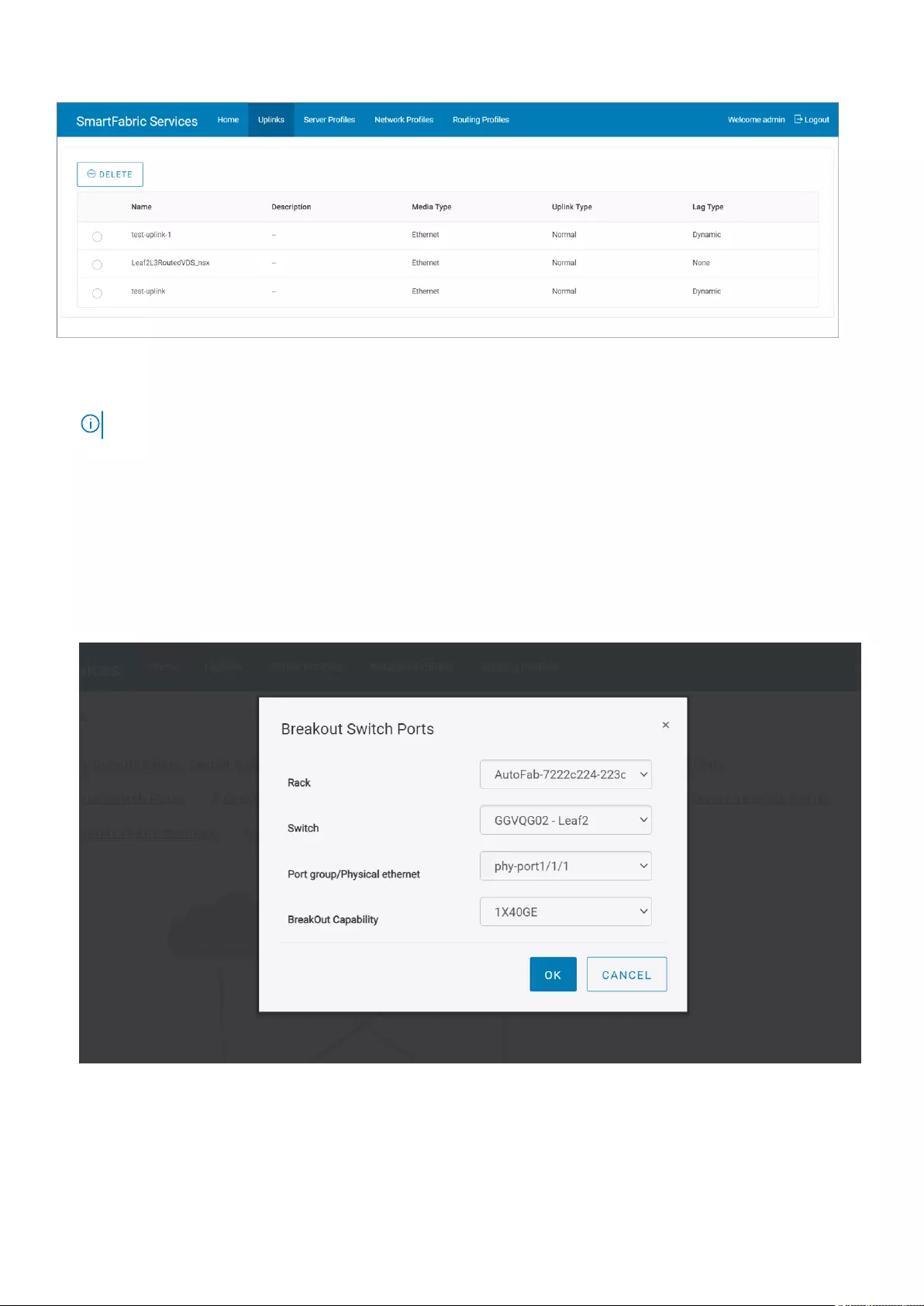
Breakout switch ports
You can configure breakouts for the Ethernet ports or port-group only on the leaf switches to connect to the external device or
jump host. Use the following procedure to breakout switch ports:
1. Click Home > Breakout Switch Ports.
2. Select the rack from the list.
3. Select the leaf switch in the rack.
4. Select a port-group or a physical Ethernet port of the leaf switch to breakout.
5. Select the appropriate breakout option from the list and click Ok.
26 Deploying and managing a fabric
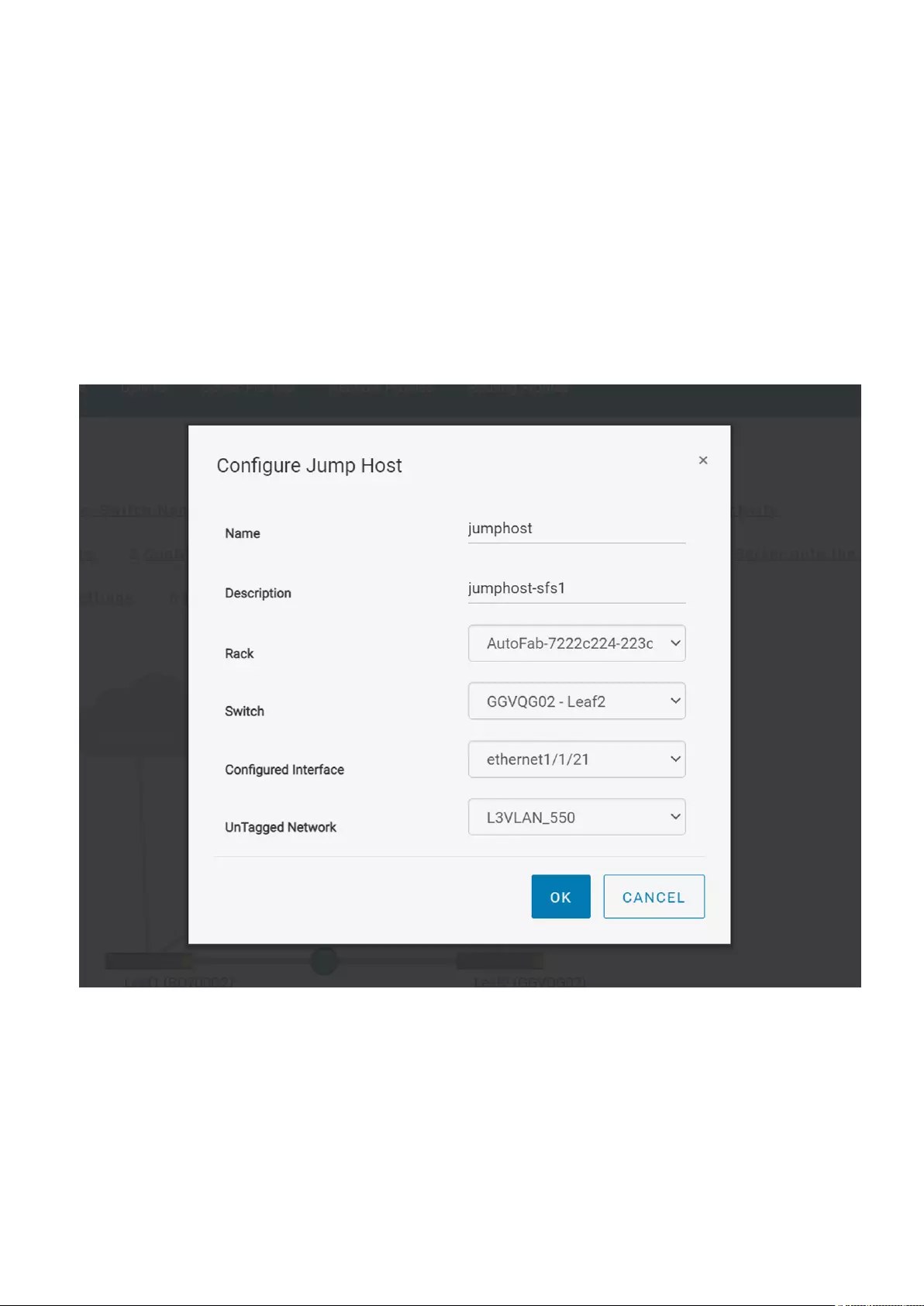
Configure jump host
A jump host is a designated port to which an external device such as a laptop can be connected. You can configure only one
port in a leaf switch port as a jump host for the external device to connect to L3 fabric. Select any available port that is not part
of an uplink, ICL, and port connected to a server in fabric.
In VxRail deployment, a jump host is primarily used to bring up a VxRail cluster. By default, all VxRail nodes are placed in the
client control and client management networks. In VxRail deployment, the jump host port is placed in the client management
network in order to reach the default VxRail Manager VM.
Use the following procedure to configure jump host:
1. Click Home > Configure Jump Host.
2. Assign a user-understandable name and description for the jump host.
3. Select a leaf switch from the rack.
4. Select an interface of the leaf switch as the jump host.
5. Associate an untagged network with the jump host and click Ok.
Click Uplinks tab to view the configured jump host. You can also delete any created jump host from this tab. Select the jump
host from the list and click Delete.
Update network configuration
You can edit the network configuration that is applied on the uplink and server profiles in the fabric anytime. Use the following
procedure to update the existing network configuration or create a network:
1. Click Home > Update Network Configuration.
2. Select a network that you want to update the configuration.
Deploying and managing a fabric 27
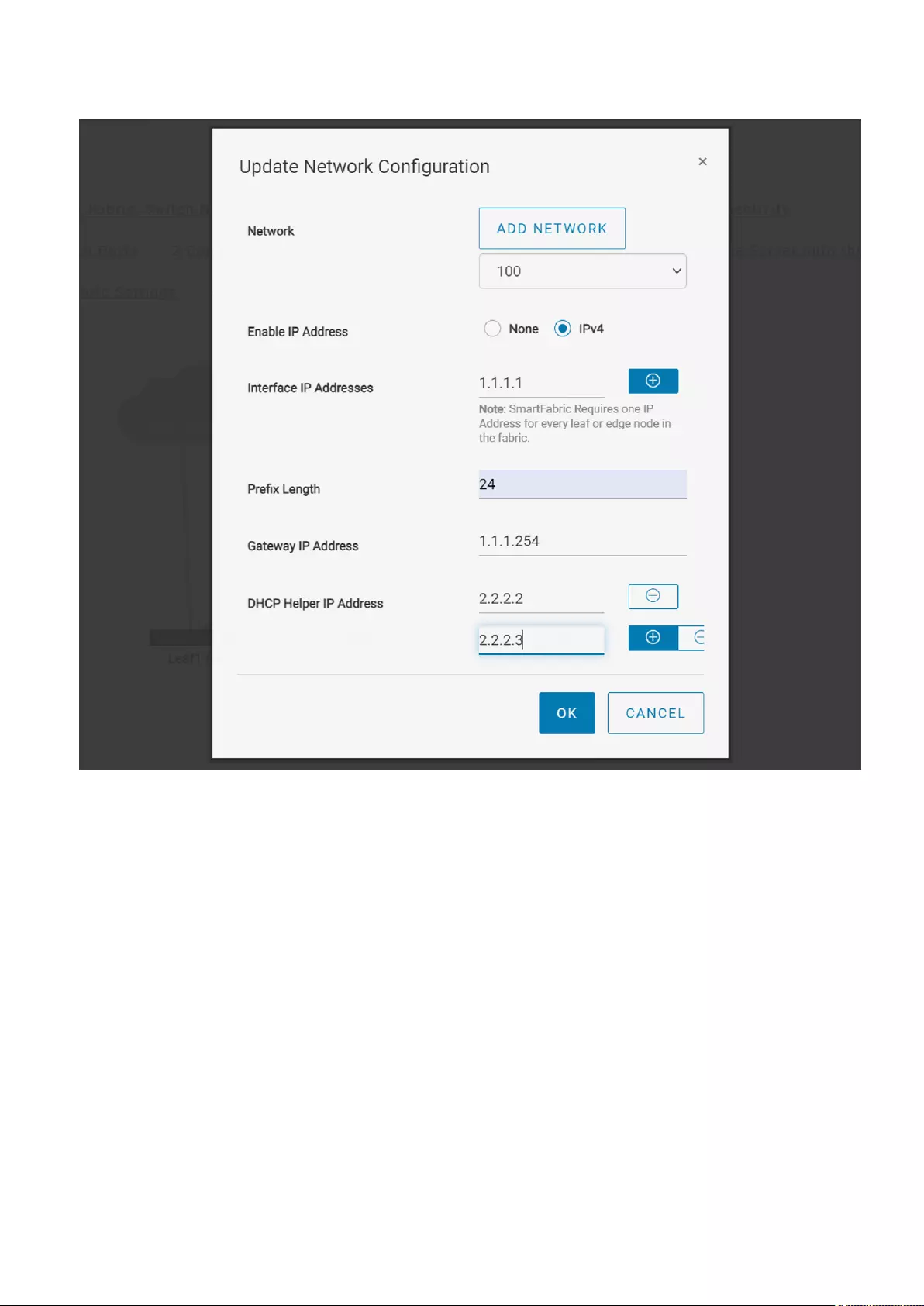
3. Enter interface IP address, gateway, and DHCP helper IP address to change a L2 network to a L3.
4. Click Ok to complete the configuration.
Create a network
You can create the following type of networks:
●General purpose networks
●VXLAN networks
●L3 VLAN networks
●L3 Routed networks
For detailed information about these network types, see Networks. You can create these networks using the Update Network
Configuration option available in the SFS GUI. As part of uplink creation and server onboarding process, you can associate
these networks with the servers profiles, uplinks, or interfaces for communication between the entities.
Use the following procedure to create a network:
1. Click Update Network Configuration link.
2. Click Add Network.
28 Deploying and managing a fabric
3. Enter the required details to create any network of general purpose, VXLAN, L3 VLAN, or L3 Routed type.
Click Network Profiles tab to view the list of networks that are created in the fabric. For more information, see Network
profiles.
Onboard a server onto the fabric
See Server discovery and onboarding for more information about server onboarding and its types. You can onboard a server
statically or dynamically.
Onboard discovered interfaces
Use the following procedure to dynamically onboard a discovered server:
1. Click Home > Onboard a Server onto the Fabric.
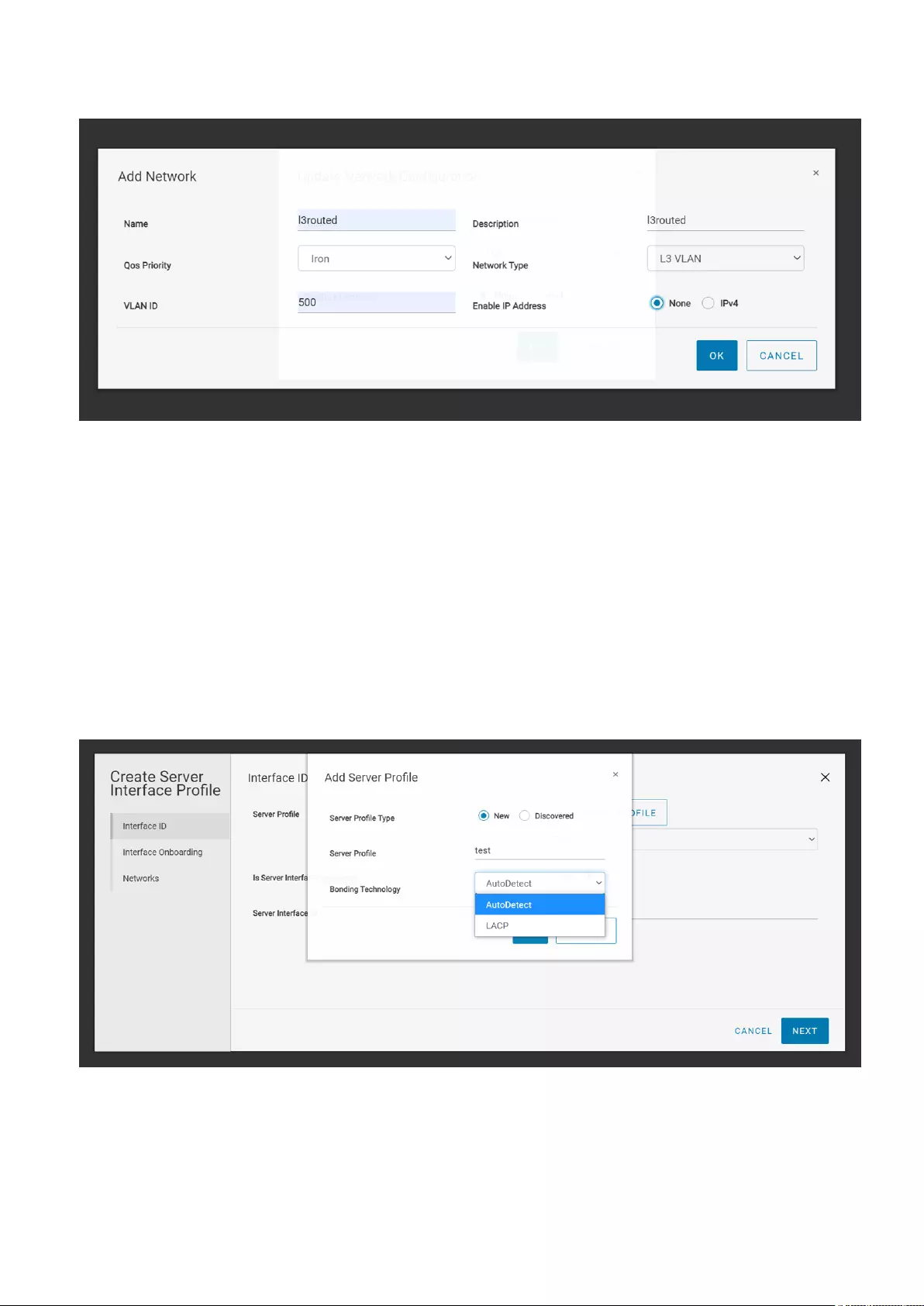
2. Select the server profile from the list or create a profile for the interface using Add Server Profile.
Add Server Profile—Create a server profile by providing the server profile type, name, and bonding technology.
Deploying and managing a fabric 29
3. Select an interface ID from the list and click Next. SFS discovers some of the servers dynamically and
if you are onboarding a discovered interface, the server interface ID lists all the discovered interface.
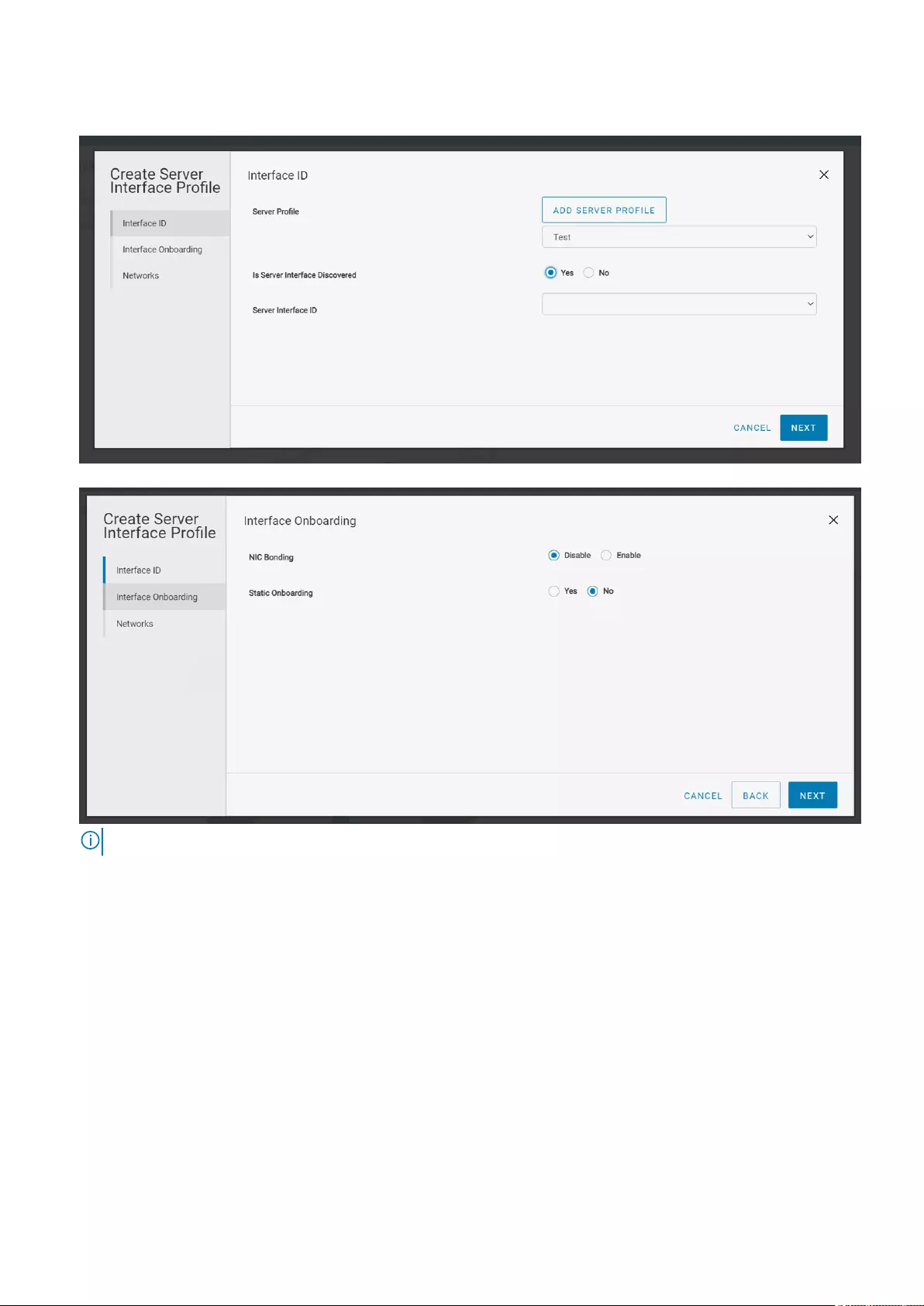
4. Select No for Static Onboarding and click Next.
NOTE: Dell Technologies recommends that you use dynamic onboarding for the discovered interfaces.
5. Associate the networks to the server interface profile from the list or create a network or virtual network according to the
network connectivity. For more information, see Networks.
●Add Network—A template to create a general-purpose, L3 VLAN, VXLAN, and L3 Routed networks. Enter the required
details to create a network.
●Add Virtual Network—A template to create a VXLAN network. Enter the required details to create a virtual network.
30 Deploying and managing a fabric
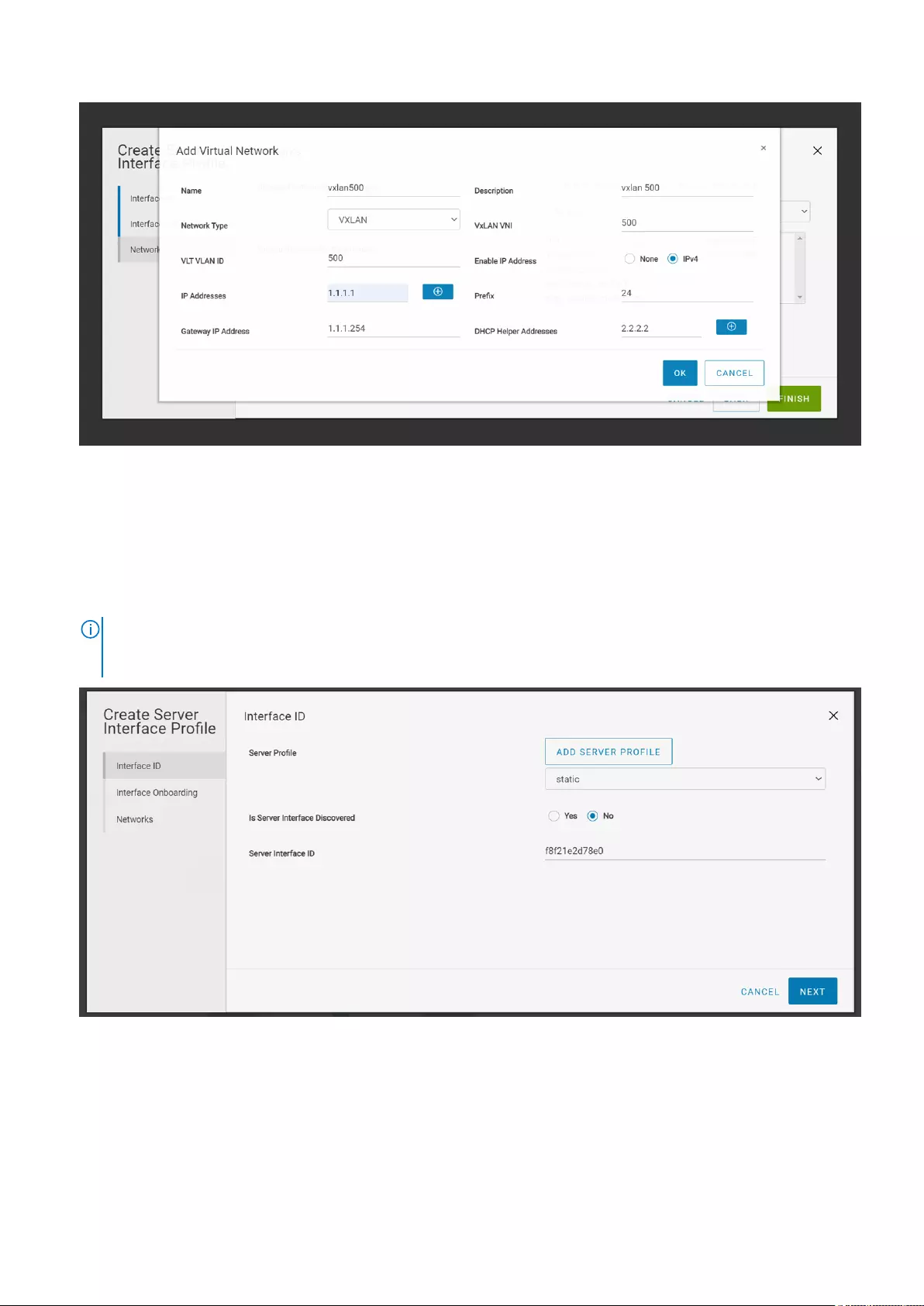
Onboard nondiscovered server interfaces
Use the following procedure to onboard the server statically for nondiscovered server interfaces:
1. Click Onboard a Server onto the Fabric.
2. Select the server profile from the list or create a profile for the interface using Add Server Profile.
3. This option is used for onboarding servers that are not discovered by SFS. Select No for discovered server interface and
enter the Server Interface ID and click Next.
NOTE: You cannot configure duplicate server interface ID. Dell Technologies recommends using MAC address to
onboard server interface without ":". For onboarding ESXi host interfaces for zero touch automation, use the ESXi host
VM NIC physical adapter MAC address without ":", for example, f8f21e2d78e0.
4. Select Yes for static onboarding.
Deploying and managing a fabric 31
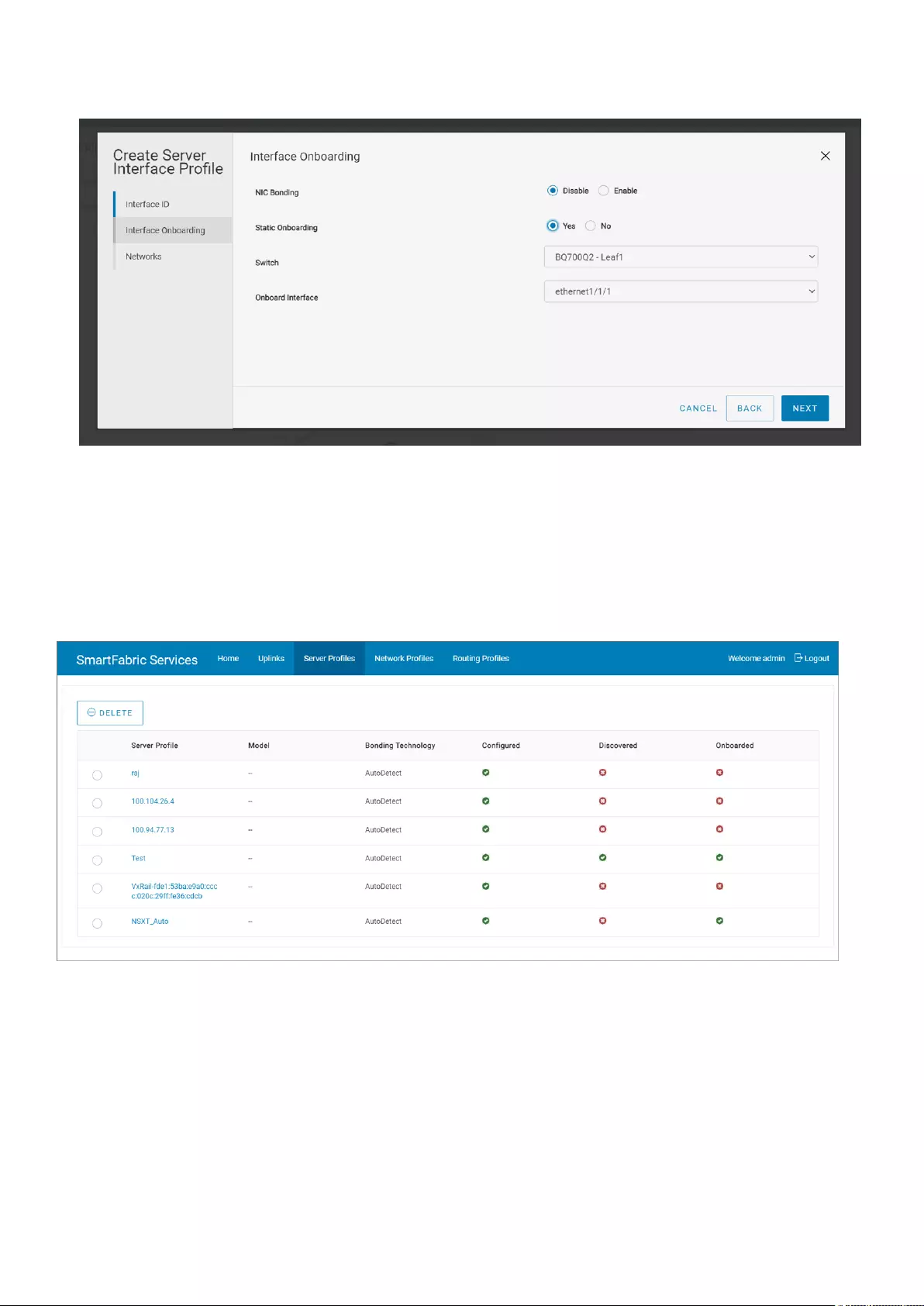
5. Assign an interface of the leaf switch and click Next.
6. Associate the networks with the server interface profile from the list or create a network or virtual network according to the
network connectivity. For more information, see Networks. This step has options to create network and virtual networks.
Manage server profiles
Manage all the server profiles configured in the fabric:
View server profile details
Click Server Profiles tab to view the list of all server profiles that are configured in the SFS. The page
displays the details of server profiles such as bonding technology, discovery of the server, and onboarding status.
Click the server profile for which you want to see the server interface profile details. The page lists all server interface IDs and
the server interface status.
To delete a server profile:
1. Select a server profile from the list and click Delete.
2. Click Ok to confirm.
32 Deploying and managing a fabric
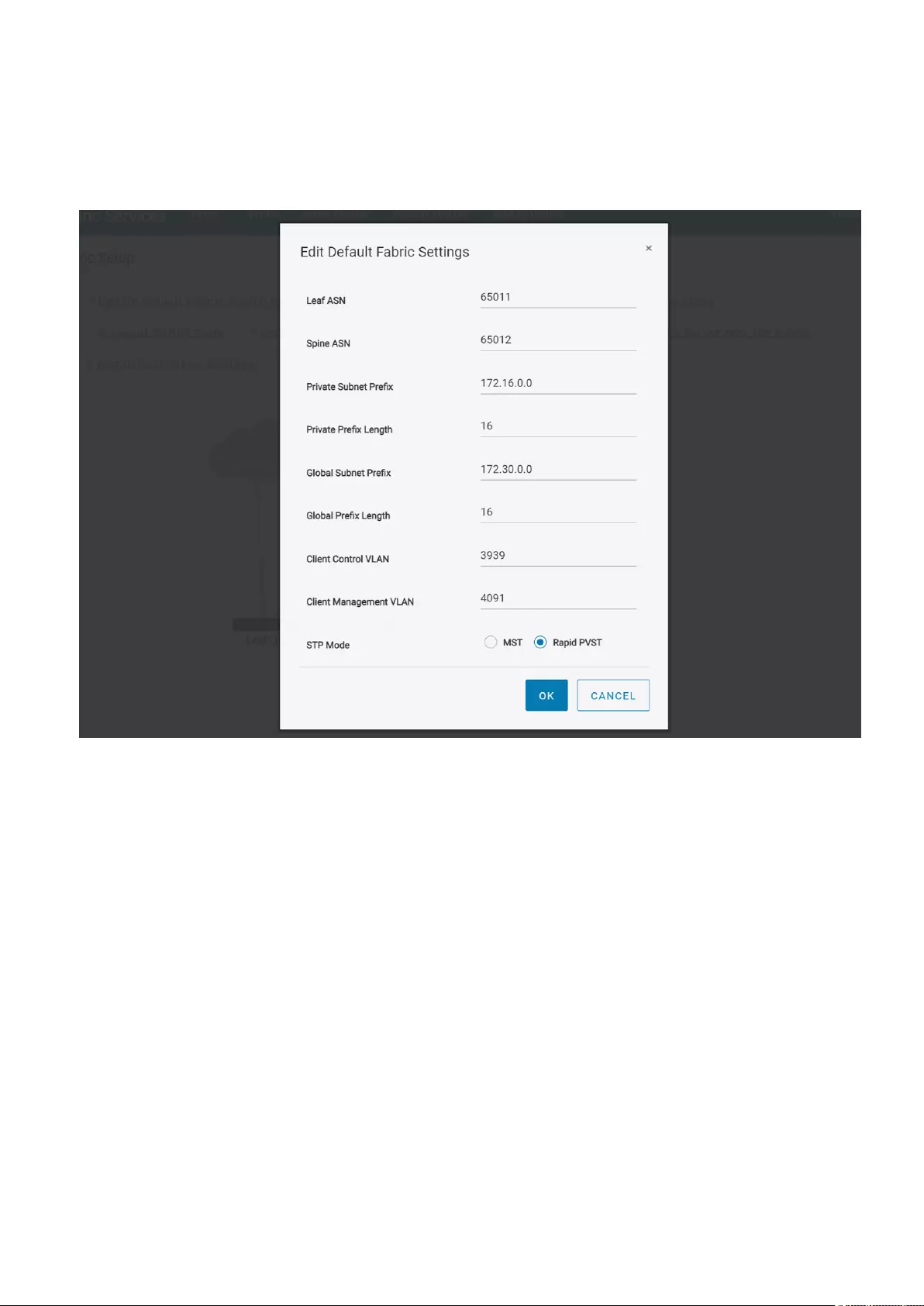
Edit default fabric settings
Use the following procedure to edit the default fabric settings:
1. Click Home > Edit Default Fabric Settings.
2. Change the values of the default settings as required.
3. Click OK. The changed settings are applied only after a reboot. The system prompts for confirmation to continue. After you
click OK, all the switches in the network fabric reload to apply the fabric setting changes.
Restore fabric configuration
Restore the SFS configurations on a fabric to a known good configuration with the backup configuration file stored on your
external device. Use the following procedure to restore:
1. Click Home > Restore.
Deploying and managing a fabric 33
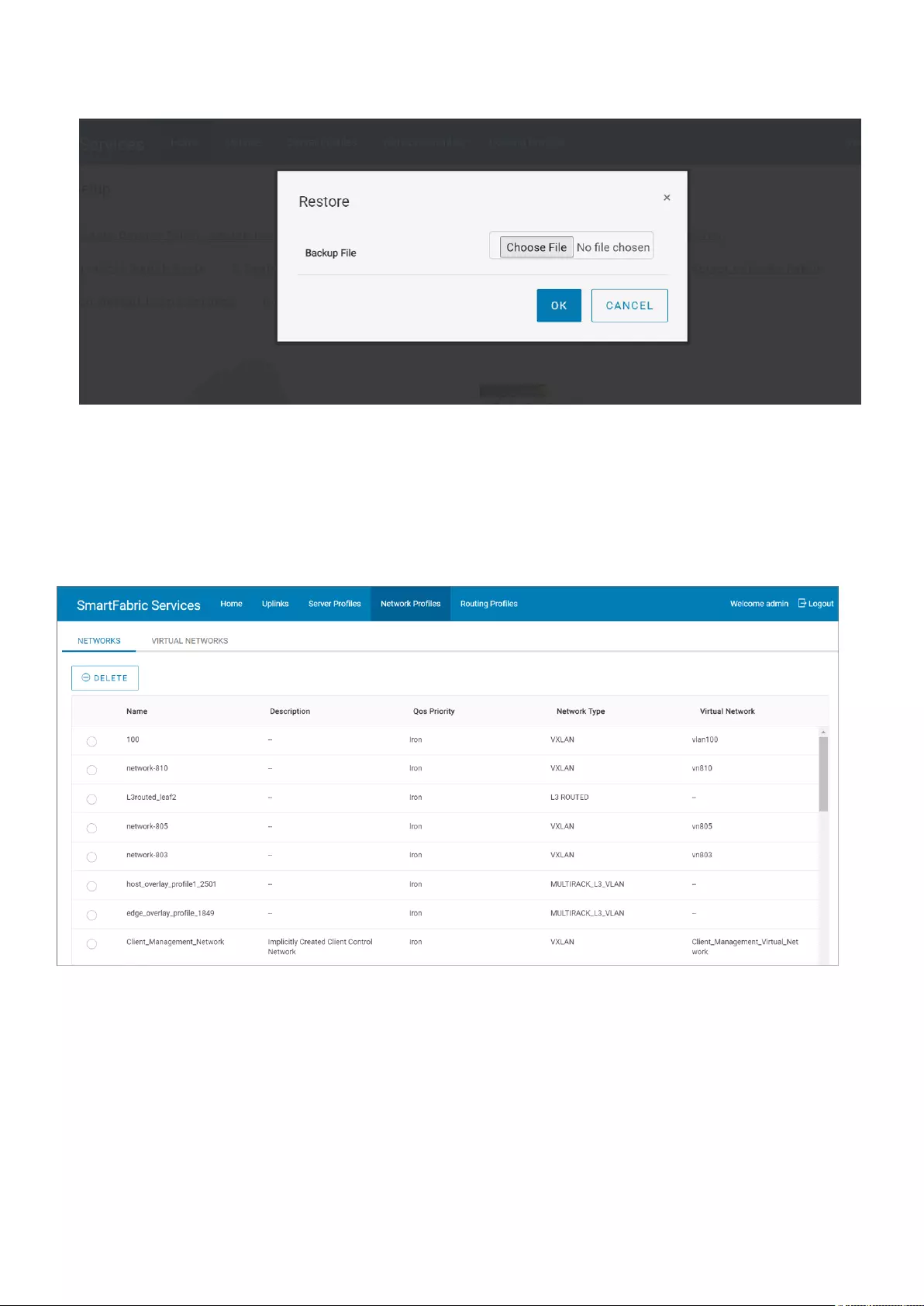
2. Click Choose File and select the backup configuration file that is stored externally, and click Ok.
3. Select the check box to agree and click OK to confirm. All switches in the fabric reboot to apply the new configurations.
Manage network profiles
You can view and manage the network profiles that are created in a fabric.
Click the Network Profiles tab to view a list of all networks and virtual networks that are configured in the SFS. You can also
delete a network profile from this tab. For more information about the network types, see Networks.
Networks—Displays all the networks and virtual networks created in the fabric.
34 Deploying and managing a fabric
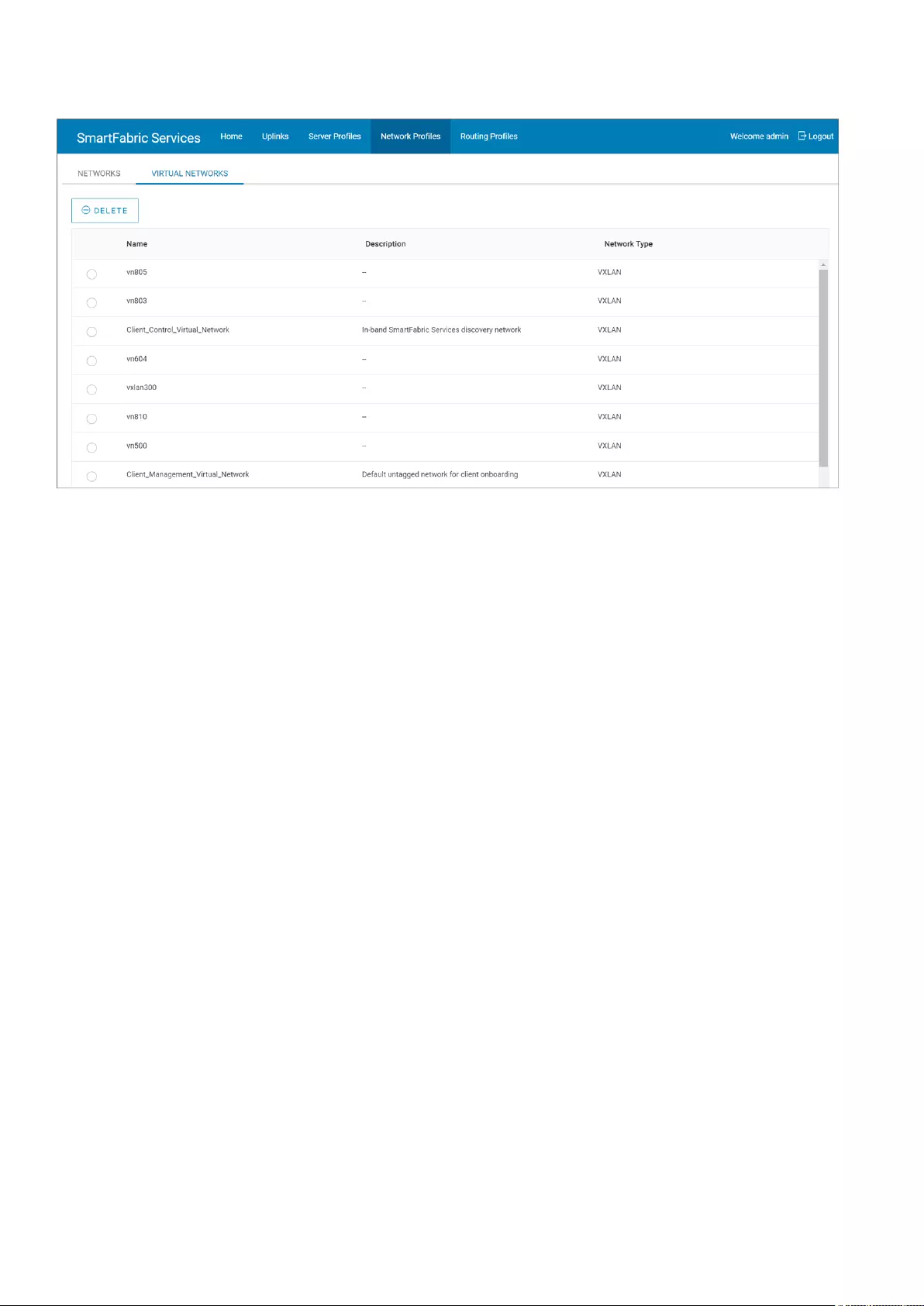
Virtual Networks—Displays only the virtual networks available in the fabric.
Delete a network profile
You can delete a network profile:
1. Click the Networks or Virtual Networks tab and select a profile from the list.
2. Click Delete.
3. Click Ok to confirm.
Manage routing profiles
You can view and manage the routing profiles that are configured in SFS. You can delete a routing profile from this tab. The
routing profiles are created as part of uplink configuration workflow. The routing profile name is configured as policy ID and you
cannot apply a routing profile to multiple uplinks with the same profile name. You can apply the same routing configuration for
multiple uplinks by providing different profile names.
Click the Routing Profiles tab to view the list of all routing profiles that are configured in a fabric. The routing profiles listing in
this page are user-configured profiles and you cannot edit the automated internal routing configurations. For more information,
see Routing profiles.
Deploying and managing a fabric 35
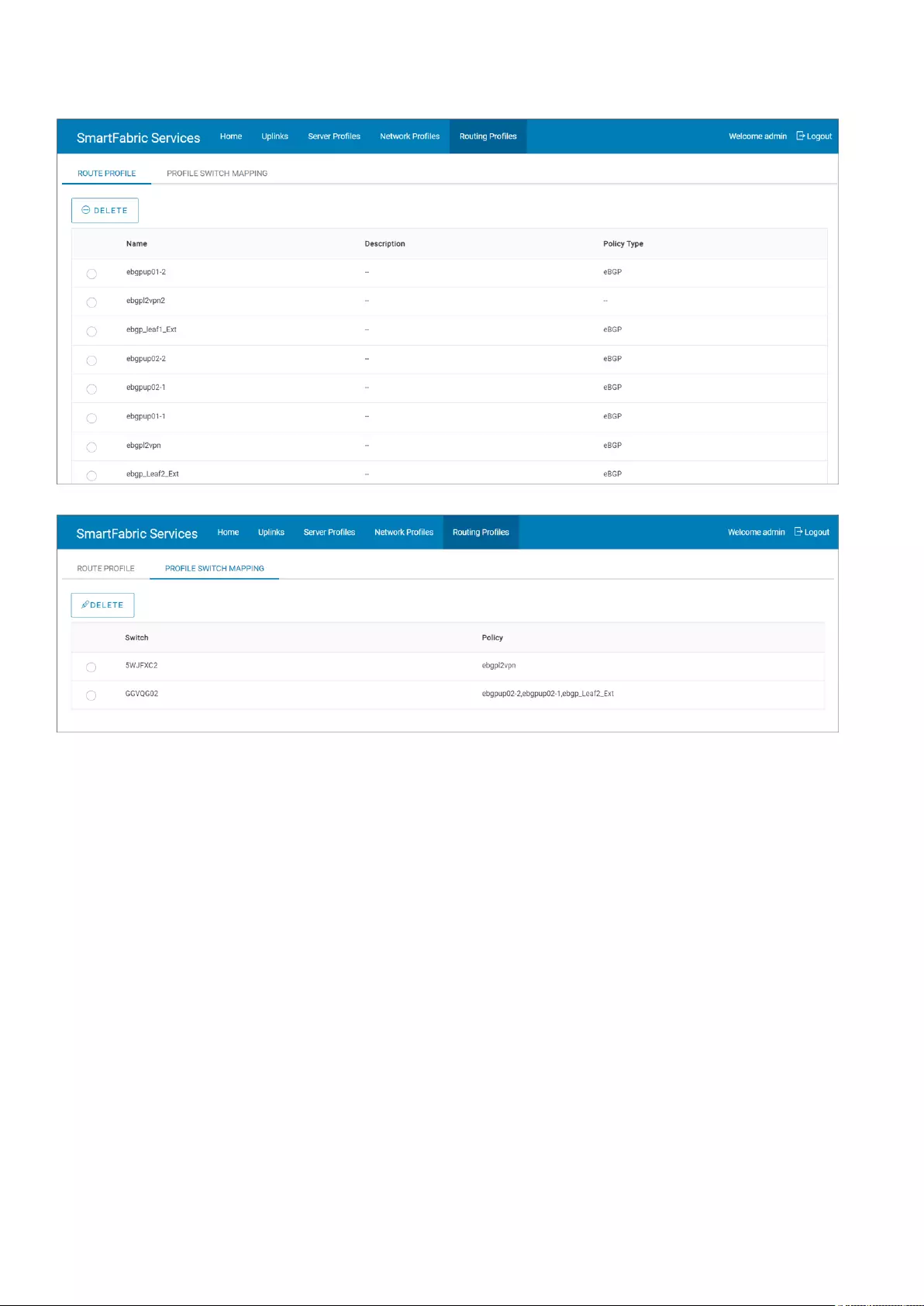
Route Profile—Displays detailed routing profile information.
Profile Switch Mapping—Displays the list of profiles that are mapped to the switch.
Delete a routing profile
You can delete a routing profile or profile switch mapping:
1. Click Routing Profiles > Route Profile or Profile Switch Mapping.
2. Select a routing profile from the list and click Delete.
3. Click Ok to confirm deletion.
36 Deploying and managing a fabric
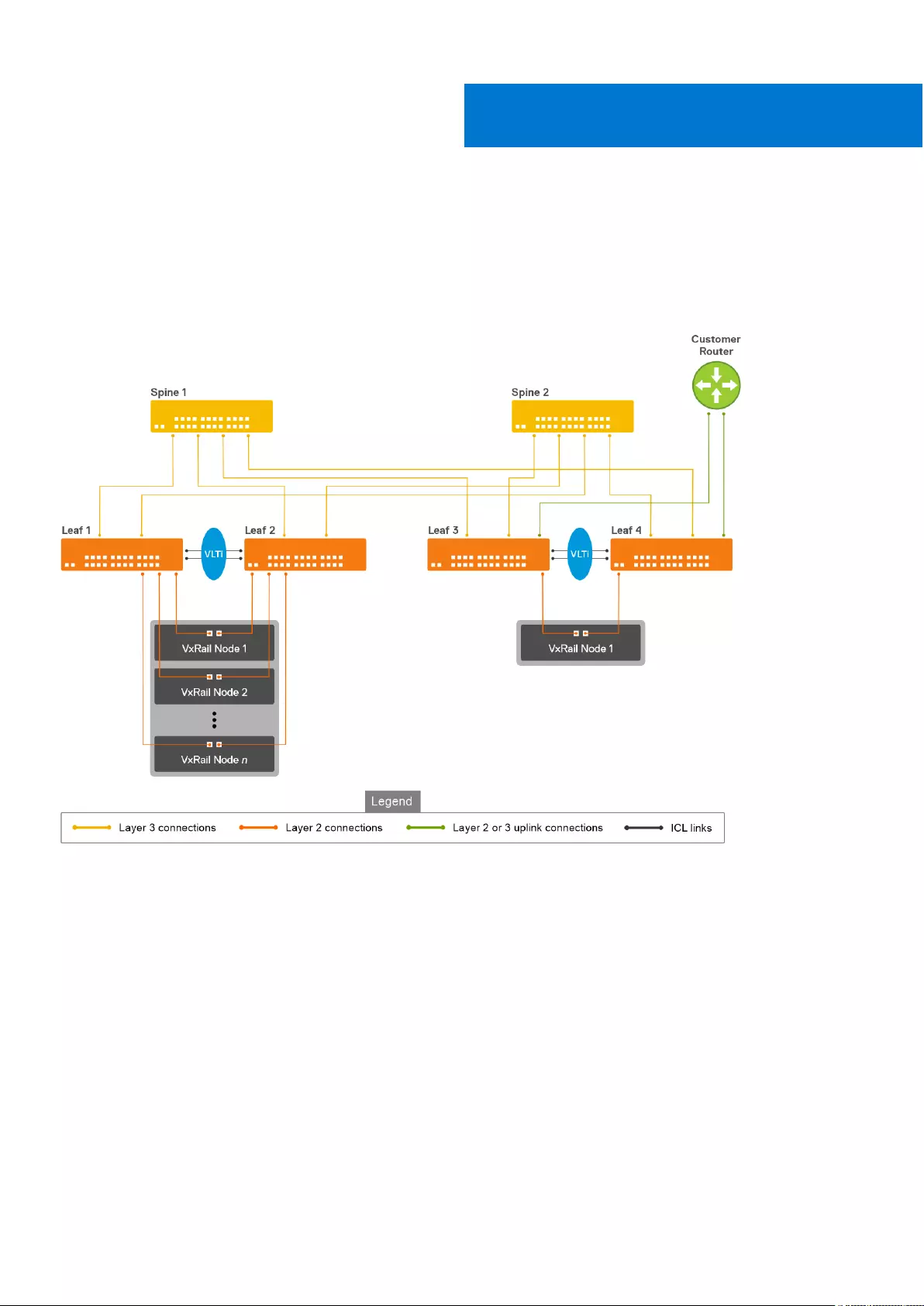
SFS with VxRail
SFS, used in leaf and spine network, creates a fully integrated solution between the fabric and a hyperconverged domain
infrastructure such as VxRail. When integrated with VxRail, SFS automates network setup, simplifying and accelerating the
deployment. Switches are automatically configured. When additional VxRail nodes are connected, the fabric identifies them as
VxRail nodes and automatically onboards the nodes to the required networks.
For more information regarding VxRail deployment-related documents, see Dell Technologies VxRail Networking Solutions.
Supported network topologies
See Supported topologies section for information regarding the topologies of SFS with VxRail deployments.
Hardware and software requirements
The requirements to deploy VxRail with SFS are as follows:
Hardware components
●VxRail nodes
●Dell EMC PowerSwitches
Software components
5
SFS with VxRail 37
●SmartFabric OS10
●OMNI
●VxRail Manager
●VMware vCenter
For more information regarding detailed deployment requirements, see the Deployment Guides for respective releases.
Supported switches
Following is the Dell EMC PowerSwitch typical roles in SFS with VxRail deployment.
Table 4. Switch roles in SFS
SmartFabric
Switches
Switch type (leaf or spine) VxRail node connectivity options
●S4112F-ON
●S4112T-ON
●S4128F-ON
●S4128T-ON
●S4148F-ON
●S4148T-ON
Leaf 10GbE
●S5212F-ON
●S5224F-ON
●S5248F-ON
●S5296F-ON
Leaf 10GbE or 25GbE
S5232F-ON Spine Can be used as a leaf switch with ports that are
connected to VxRail nodes broken out to 10GbE
or 25GbE
Z9264F-ON Spine —
Z9432F-ON Spine —
In VxRail deployment, any combination of the leaf and spine switches is possible with the exception that you must deploy
leaf switches in pairs. Each leaf switch in the pair must be the same model due to VLT requirements. SFS supports up to 20
switches and eight racks in the fabric.
SFS personalities
In SFS-enabled network, VxRail deployment option include L2 single rack or L3 multirack personalities. The table lists the
comparison between L2 and L3 fabric personalities:
Table 5. SFS personalities in VxRail deployment
L2 Single Rack personality L3 multi rack personality
Single rack network fabric is supported for VxRail clusters.
For new SFS deployments, use the L3 leaf and spine fabric
personality as the SFS L2 personality is deprecated.
Multi rack data center network fabric is supported that starts
with a L3 single rack (L3 fabric profile) and which you can
expand to a multi rack solution based on the demand.
Network fabric has two leaf switches in a single rack which
you cannot expand.
Network fabric has up to 20 switches in a leaf and spine
design that starts with a single rack which you can expand up
to eight racks.
All VxRail with SFS deployments from SmartFabric release
OS10.4.1.4 to OS10.5.0.5 support configuration with a single
pair of leaf switches for VxRail clusters.
All SmartFabric deployments with SmartFabric OS10.5.0.5 or
later.
Default uplink and jump host port are created as part of a
fabric initialization, which you cannot modify after enabling
SFS.
You can create uplinks and jump host port through SFS GUI or
OMNI after initial deployment.
38 SFS with VxRail

Table 5. SFS personalities in VxRail deployment
L2 Single Rack personality L3 multi rack personality
Enabled SFS by running a Python script in the OS10 Linux
shell.
Enable SFS using CLI, API, or UI.
Existing deployments when upgraded to SmartFabric
OS10.5.0.5 continue to run in the L2 fabric profile and L3
fabric capabilities are not available. If you upgrade switches
with L2 personality to OS10.5.0.5, SFS operates with the
VxRail L2 single rack personality.
Dell Technologies recommends that you enable all new
deployments with L3 leaf and spine fabric personality. You
cannot upgrade VxRail with SFS deployments to the new L3
leaf and spine fabric personality automatically.
Support matrix
See Networking Solutions Support Matrix regarding support matrices for SFS with VxRail across various releases.
Fabric operations and life cycle management
Dell EMC OpenManage Network Integration (OMNI) enables you to configure and manage SFS-enabled PowerSwitches in
different deployments. You can use OMNI application to manage and operate one or more SFS instances either directly using
the OMNI UI through a web browser or through a vCenter plug-in. After initial deployments, Dell Technologies recommends that
you use OMNI UI to perform all fabric management and life cycle management activities.
For more information about OMNI, see OMNI Documentation.
SFS with VxRail 39

SFS with PowerEdge MX
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX is a unified, high-performance data center infrastructure providing the agility, resiliency, and efficiency
to optimize a wide variety of traditional and new emerging data center workloads and applications. In a Dell EMC PowerEdge
MX7000 infrastructure, the MX9116n fabric engine and MX5108n Ethernet switch support SFS.
For more information about the SFS and PowerEdge MX including architecture, deployment, configuration, operations and
troubleshooting, see the Dell EMC PowerEdge MX Networking Deployment Guide.
6
40 SFS with PowerEdge MX
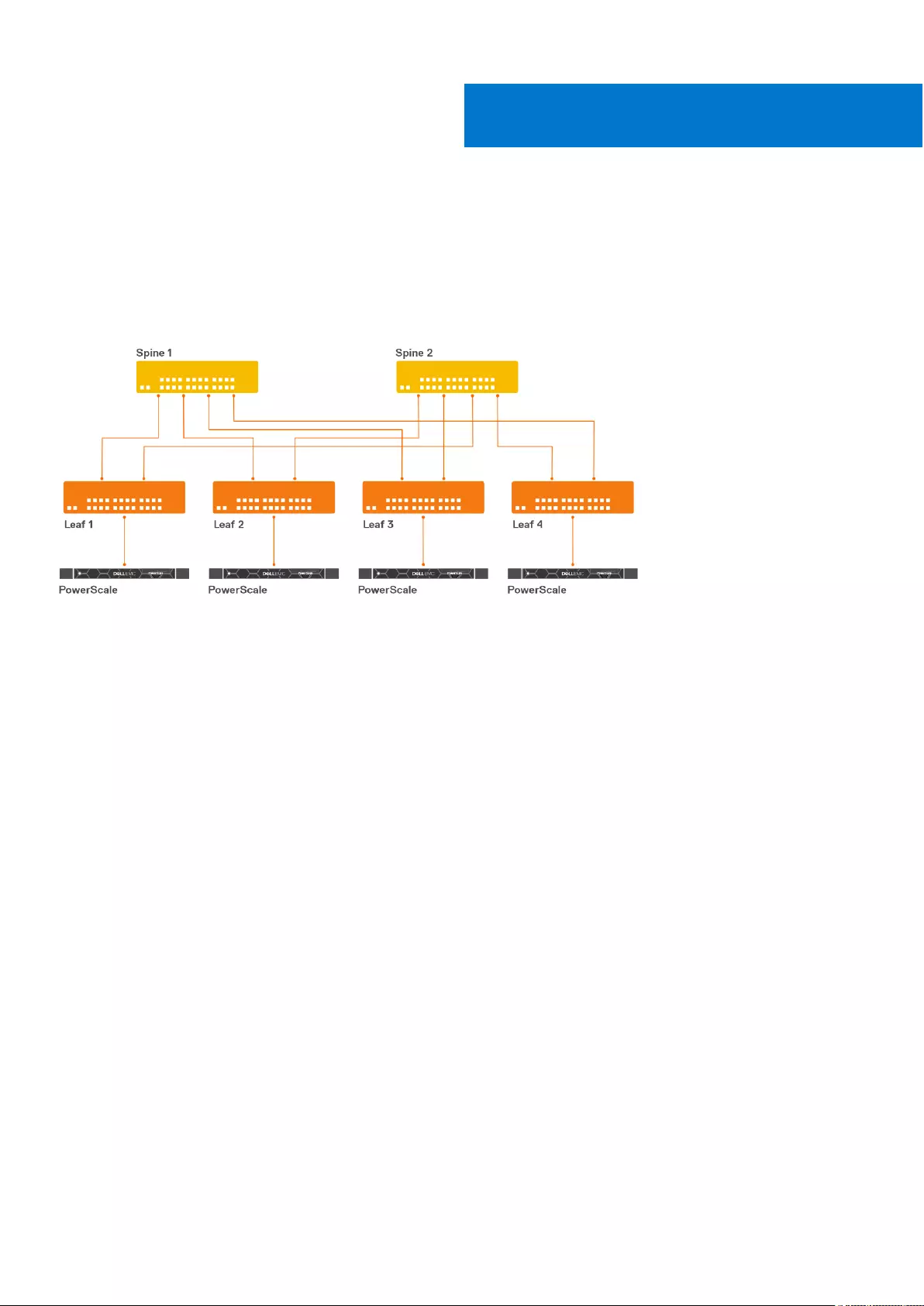
SFS for Isilon/PowerScale back-end fabric
Dell EMC PowerScale is a scale-out network-attached storage (NAS) platform that supports unstructured data workloads.
All PowerScale models are powered by the OneFS operating system. PowerScale uses Dell EMC PowerSwitches to provide
the network. SmartFabric OS10 with SFS, for PowerScale back-end fabric automates onboarding and network configuration
of PowerScale devices on a L3 leaf and spine fabric. Isilon OneFS interacts with back-end fabric formed by SFS. For more
information, see PowerScale Info Hub.
Supported network topologies
See Supported topologies section for information regarding the topologies of SFS. Only L3 personality is supported when
deploying SFS with PowerScale nodes.
Hardware and software requirements
The requirements to deploy PowerScale with SFS are as follows:
Hardware components
●PowerScale devices
●Dell EMC PowerSwitches
Software components
●Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10
●Isilon OneFS
Supported switches
The following PowerSwitches are supported in PowerScale deployment:
●S4112F-ON
●S4148F-ON
●S5232F-ON
●Z9264F-ON
●Z9100-ON
7
SFS for Isilon/PowerScale back-end fabric 41
PowerScale requirements
Requirements specific to SFS with PowerScale deployment are as follows :
●By default, all PowerSwitches for PowerScale deployment are shipped with factory-loaded OS10.
NOTE: Dell EMC PowerSwitches must be running SmartFabric OS10.5.0.5 or later software releases that support the
PowerScale with SFS deployment.
●In SFS with PowerScale deployment, the leaf nodes are not connected as a VLT pair. On the leaf switch, no ICL
configuration is required while enabling SFS. For more information, see Enable SFS using CLI.
●You only have to enable SFS on the switches to setup a fabric. All other fabric operations are managed by Isilon OneFS.
●The switches are connected in a leaf and spine topology with BGP EVPN setup between the leaf switches.
●Leaf and spine switches belong to different autonomous systems (AS).
●PowerScale data traffic is forwarded on an untagged VXLAN network 4091.
●PowerScale appliances are detected through LLDP.
●All ports on which the PowerScale appliance is detected are added as untagged VXLAN access interfaces.
●All load balancing is achieved through BGP ECMP.
●By default, autobreakout feature is enabled on the leaf and spine switches.
Support matrix
See Networking Solutions Support Matrix regarding support matrices for SFS with PowerScale across various releases.
42 SFS for Isilon/PowerScale back-end fabric

SFS commands
You can run show commands specific to SFS from the CLI to view fabric configuration information. The command output varies
depending on the SFS deployment.
smartfabric l3fabric enable
Enables SFS on the switches and creates a L3 network fabric.
Syntax smartfabric l3fabric enable role {LEAF [vlti ethernet node/slot/port] |
SPINE}
Parameters role—Enter the role of the switch in the L3 fabric:
●LEAF [vlti ethernet node/slot/port]—Specify the role as LEAF for top of rack switches
and specify the VLTi ports that interconnect the leaf switches.
NOTE: Option to specify VLTi ports are not applicable for PowerScale deployment.
●SPINE—Specify the role as SPINE for the switch that connects the leaf switches.
Default None
Command Mode CONFIGURATION
Usage
Information
After you enable the L3 fabric and set a role, the system prompts for confirmation of mode change. If
you type Yes, the switch reboots in SmartFabric mode and a network fabric is created automatically with
default fabric settings.
The no smartfabric l3fabric command disables the L3 fabric personality. After you disable the L3
fabric in the switch, the system reboots to change the personality after confirmation.
Example (Spine) OS10(config)# smartfabric l3fabric enable role SPINE
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
Example (Leaf) OS10(config)# smartfabric l3fabric enable role LEAF vlti
ethernet 1/1/4-1/1/5
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
Example (disable
SFS on both leaf
and spine)
OS10(config)# no smartfabric l3fabric
Reboot to change the personality? [yes/no]: yes
Supported
Releases
10.5.0.3 or later
smartfabric vlti
Updates the VLTi ports after SFS is enabled.
Syntax smartfabric vlti ethernet ports
Parameters ethernet ports—Specify the VLTi Ethernet ports which must be updated.
Default None
8
SFS commands 43

Command Mode CONFIGURATION
Usage
Information
Use this command to configure or update the VLTi information after SFS is enabled on the switch. The
system reloads with the configured VLTi ports.
This command can be used only if the switch should already be in L3 fabric mode. If not, enable the L3
fabric personality first and run this command.
If you use any of the existing ports for the VLTi, those ports should also be specified as part of the VLTi
configuration using the SmartFabric Services commands.
Example OS10(config)#smartfabric vlti ethernet 1/1/31-1/1/32
Warning:The system will be reloaded now, for the personality changes to
take effect
Supported
Releases
10.5.0.3 or later
show logging smartfabric
Displays important logs that are related to SFS modules.
NOTE: You must have access to sysadmin, secadmin, or netadmin roles to run this command.
Syntax show logging smartfabric
Parameters <1-65535>—Number of recent messages to be displayed.
Default Not applicable
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
You can run this command on all switches in SmartFabric mode and are provided with a high-level view
of the events happening in the SFS module. When you run this command on an active switch, the system
displays complete cluster-related logs. The logs include events that are related to cluster formation and
update, configuration changes, and on boarding events along with switch-specific information. When you
run this command on a backup switch, the system displays only the switch-specific logs.
Example MX9116N-B2# show logging smartfabric 100 | grep CAGT
2020-03-29 10:09:35.334 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT] [chassis.get_lead_chassis]
lead chassis not in chassis_data
2020-03-29 10:09:35.335 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT] [chassis.get_lead_chassis]
not receive mdns from lead MSM yet
2020-03-29 10:09:56.881 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT]
[app.process_cps_cluster_sync_event] received sync state 2
2020-03-29 10:09:56.881 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT] [ka.clr_priority]
2020-03-29 10:09:56.885 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT] [ka.set_priority] new 100
old 0
2020-03-29 10:09:58.014 MX9116N-B2 [DNV-CAGT] [ka.soft_reload_ka]
reloading ka...
Supported
Releases
10.5.2.1 or later
show smartfabric cluster
Displays the basic cluster information of the switch or IOM.
Syntax show smartfabric cluster
Parameters None
44 SFS commands

Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric cluster
----------------------------------------------------------
CLUSTER DOMAIN ID : 119
VIP : fde1:53ba:e9a0:de14:0:5eff:fe00:1119
ROLE : BACKUP
SERVICE-TAG : 3GB1XC2
MASTER-IPV4 : 10.11.105.15
----------------------------------------------------------
Example (VxRail -
L2 fabric) OS10# show smartfabric cluster
----------------------------------------------------------
CLUSTER DOMAIN ID : 100
VIP : fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:0:5eff:fe00:1100
ROLE : MASTER
SERVICE-TAG : B37HXC2
MASTER-IPV4 : 10.11.106.27
PREFERRED-MASTER :
----------------------------------------------------------
Example (VxRail -
L3 fabric) OS10# show smartfabric cluster
----------------------------------------------------------
CLUSTER DOMAIN ID : 100
VIP : fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:0:5eff:fe00:1100
ROLE : MASTER
SERVICE-TAG : B37HXC2
MASTER-IPV4 : 10.11.106.27
PREFERRED-MASTER : true
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric cluster member
Displays information about the switch in a cluster. Information includes service tag, IP address, status, role, switch type and
chassis model, and chassis service tag where the switch is connected.
Syntax show smartfabric cluster member
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
When you run this command on a switch, the output that is displayed varies depending on the switch
role. For example, if you run this command on the master switch, the output shows both the master
and backup switch information. If you run this command on a backup switch, the output shows only the
master switch information.
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SFS modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric cluster member
Service-tag IP Address Status
Role Type Chassis-Service-Tag Chassis-Slot
SFS commands 45

-------------------------------------------------------------
9GB1XC3 fde1:53ba:e9a0:de14:e6f0:4ff:fe3e:45dd ONLINE
MASTER MX9116n SKY002L B1
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric cluster member
Service-tag IP Address Status
Role Type Chassis-Service-Tag Chassis-Slot
-----------------------------------------------------------
3Z4ZZP2 fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:54bf:64ff:fee6:e462 ONLINE
BACKUP
3Z4ZZP1 fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:54bf:64ff:fee6:e463 ONLINE
BACKUP
BR2ZZP2 fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:3c2c:30ff:fe49:2585 ONLINE
BACKUP
B37HXC2 fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:e4f0:4ff:feb6:fdc3 ONLINE
MASTER
G17HXC2 fde2:53ba:e9a0:cccc:e4f0:4ff:feb6:e1c3 ONLINE
BACKUP
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric configured-server
Displays list of all configured servers information in a fabric. Information includes ID, model type, slot, chassis model and service
tag, bonding technology, list of existing bond members, and server status.
Syntax show smartfabric configured-server
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SFS modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-B1# show smartfabric configured-server
----------------------------------------------------------
Service-Tag : 00FWX20
Server-Model : PowerEdge MX740c
Chassis-Slot : 1
Chassis-Model : POWEREDGE MX7000
Chassis-Service-Tag : SKY002L
Is-Discovered : TRUE
Is-Onboarded : TRUE
Is-Configured : TRUE
**********************************************************
Bonding Technology : LACP
BondMembers:
Nic-Id : Switch-Interface
----------------------------------------------------------
NIC.Mezzanine.1A-1-1 3GB1XC2:ethernet1/1/1
NIC.Mezzanine.1A-2-1 9A2HEM3:port-channel1
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
10.5.1.0 or later
46 SFS commands

show smartfabric configured-server configured-
server-interface
Displays interface-level information of the configured servers. Information includes server ID, port ID, onboarded interface,
server status, fabric ID, native VLAN, network profiles, and bandwidth partition details.
Syntax show smartfabric configured-server configured-server-interface server-id
Parameters server-id—Enter a configured server ID information.
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example MX5108N-B1# show smartfabric configured-server configured-server-
interface 004YX20 | no-more
----------------------------------------------------------
Server-Id : 004YX20
----------------------------------------------------------
Port-Id : NIC.Mezzanine.1B-2-1
Onboard-Interface :
Fabric-id :
Is-Discovered : FALSE
Is-Onboarded : FALSE
Is-Configured : TRUE
NicBonded : FALSE
Native-vlan : 0
Networks : c56d6202-0ec1-4fcd-b119-6abc761a1268
----------------------------------------------------------
Port-Id : NIC.Mezzanine.1A-2-1
Onboard-Interface : 1G86XC2:ethernet1/1/3
Fabric-id :
Is-Discovered : TRUE
Is-Onboarded : FALSE
Is-Configured : TRUE
NicBonded : FALSE
Native-vlan : 0
Networks : c56d6202-0ec1-4fcd-b119-6abc761a1268
----------------------------------------------------------
Port-Id : NIC.Mezzanine.1B-1-1
Onboard-Interface : 2J86XC2:ethernet1/1/3
Fabric-id :
Is-Discovered : TRUE
Is-Onboarded : FALSE
Is-Configured : TRUE
NicBonded : FALSE
Native-vlan : 0
Networks : c56d6202-0ec1-4fcd-b119-6abc761a1268
----------------------------------------------------------
Port-Id : NIC.Mezzanine.1A-1-1
Onboard-Interface :
Fabric-id :
Is-Discovered : FALSE
Is-Onboarded : FALSE
Is-Configured : TRUE
NicBonded : FALSE
Native-vlan : 0
Networks : c56d6202-0ec1-4fcd-b119-6abc761a1268
Supported
Releases
10.5.1.0 or later
SFS commands 47

show smartfabric details
Displays all details specific to the fabric. Details include name, description, ID, nodes that are part of the fabric, design type
associated with the fabric, and status detail of a fabric.
Syntax show smartfabric details
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SFS modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric details
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : A1-A2
Description :
ID : fc6c9051-f499-4816-a54a-25ef6fef2e33
DesignType : 2xMX9116n_Fabric_Switching_Engines_in_same_chassis
Validation Status: VALID
VLTi Status : VALID
Placement Status : VALID
Nodes : 3GB1XC2, 9A2HEM3
----------------------------------------------------------
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric details
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : AutoFab-08ee685b-d6d6-5d0c-99d2-ae78f800d4b7
Description : Auto-Fabric Generator
ID : 08ee685b-d6d6-5d0c-99d2-ae78f800d4b7
DesignType : AutoFabricDesign--1
Validation Status: VALID
VLTi Status : VALID
Placement Status : VALID
Nodes : CAC00N2, AZY1234
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : AutoFab-100
Description : Auto-Fabric Generator
ID : 100
DesignType :
Validation Status: VALID
VLTi Status : VALID
Placement Status : VALID
Nodes : AZY1234, CAC00N2, 9GTWNK2, FHTWNK2
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric discovered-server
Displays information about all the discovered servers. Information includes server tag, model, slot, chassis model, and chassis
service tag.
Syntax show smartfabric discovered-server
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
48 SFS commands

Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example MX5108N-B1# show smartfabric discovered-server
----------------------------------------------------------
Server-Tag : 004YX20
Server-Model : PowerEdge MX740c
Server-Slot : 1
Chassis-Model : POWEREDGE MX7000
Chassis-Service-Tag : SKY002R
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Server-Tag : 0002X20
Server-Model : PowerEdge MX740c
Server-Slot : 1
Chassis-Model : POWEREDGE MX7000
Chassis-Service-Tag : SKY0044
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
10.5.1.0 or later
show smartfabric discovered-server discovered-
server-interface
Displays interface-level information of all the discovered servers. Information includes port ID and switch interfaces on which
the server is onboarded.
Syntax show smartfabric discovered-server discovered-server-interface server-id
Parameters server-id—Enter a discovered server ID information.
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example MX9116N-B1# show smartfabric discovered-server discovered-server-
interface 00FWX
20
Nic-Id : Switch-Interface
------------------------------------------------------
NIC.Mezzanine.1A-1-1 3GB1XC2:ethernet1/1/1
NIC.Mezzanine.1A-2-1 9A2HEM3:ethernet1/1/1
Supported
Releases
10.5.1.0 or later
show smartfabric networks
Displays detailed description of the configured network profiles. Description includes network name, type, network ID, QoS
priority type, and VLAN.
Syntax show smartfabric networks
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
SFS commands 49

Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric networks
Name Type QosPriority
NetworkId Vlan
---------------------------------------------------
v5 GENERAL_PURPOSE BRONZE
8f018a8c-c355-4d81-9bee-85cfedcf8d2a 5
network100-105 GENERAL_PURPOSE BRONZE
deb0886c-4a9b-47f2-8220-55afcb1f1756 100 - 105
fcor STORAGE_FCOE PLATINUM
d1de8f16-ebd0-4b1a-9689-a802d23b2b26 777
VLAN 1 GENERAL_PURPOSE SILVER
4bb446a3-702c-4a0f-abdd-07dd0c14775a 1
v1 GENERAL_PURPOSE BRONZE
9f2bed94-9148-46d8-9df6-3b606c83a472 500
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric networks
Name Type QosPriority
NetworkId Vlan
--------------------------------------------
Client_Control_Network VXLAN IRON
Client_Control_Network 3939
Client_Management_Network VXLAN IRON
Client_Management_Network 4091
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric nodes
Displays detailed inventory information about all the nodes in the fabric. Information includes service tag, type, status, mode,
fabric ID associated with the node, chassis service-tag, and chassis-slot.
Syntax show smartfabric nodes node-id node-id
Parameters node-id node-id—Specify the service tag of a switch to view detailed information of that switch.
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric nodes
Service-Tag Type Status Mode
Chassis-Service-Tag Chassis-Slot FabricId
---------------------------------------------------
3GB1XC2 MX9116n ONLINE FABRIC
SKY002L A1
9GB1XC3 MX9116n ONLINE FULL-SWITCH
SKY002L B1
9A2HEM3 MX9116n ONLINE FABRIC
SKY002L A2
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric nodes
Service-Tag Type Status Mode
Chassis-Service-Tag Chassis-Slot FabricId
-------------------------------------------------
GGVQG02 S5232F-ON ONLINE FABRIC
7222c224-223c-5fa4-a244-
cd3ca1685550 (Name-Rack)
AZY1234 S5232F-ON ONLINE FABRIC
50 SFS commands

7222c224-223c-5fa4-a244-
cd3ca1685550 (Name-Rack)
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric nodes node-id GGVQG02
----------------------------------------------------------
Node Name : Name-Leaf-2
Node Id : GGVQG02
Node Type : S5232F-ON
Node Status : ONLINE
Node Mode : FABRIC
Node Ready : true
Node Model : S5232F-ON
Replacement Node Id :
Chassis service tag :
Chassis slot :
Fabric : 7222c224-223c-5fa4-a244-cd3ca1685550 (Name-Rack)
Fabric node status : OPERATIONAL
Software Version : 10.5.2.xMRDEV
Hardware Version : X01
Serial Number : CN01WJVTCES0085G0037
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric personality
Displays the personality of the SFS cluster.
Syntax show smartfabric personality
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
Use this command to identify the fabric personality of the SFS cluster. The output varies depending on
the mode and roles of the switch, and personality. When this command is run on a switch, the system
displays the personality and the roles of the switch. In VxRail deployment, if vxrail is displayed as
personality it means a L2 fabric.
This command is supported in both Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric personality
Personality :None
Role :
ICL :
Example (VxRail) Full Switch mode:
OS10# show smartfabric personality
Personality :None
Role :
ICL :
SmartFabric Services mode:
TOR1# show smartfabric personality
Personality :vxrail
SFS commands 51

Role :
ICL :ethernet1/1/29, ethernet1/1/30
OS10# show smartfabric personality
Personality :L3 Fabric
Role :LEAF
ICL :ethernet1/1/5, ethernet1/1/6
Leaf1#
OS10# show smartfabric personality
Personality :L3 Fabric
Role :SPINE
ICL :
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric uplinks
Displays all uplink-related information in the SFS. Information includes uplink name, description, ID, media type, native VLAN,
configured interfaces, and the network profile associated with the uplink.
Syntax show smartfabric uplinks
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
This command is supported both in Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example (IOM) MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric uplinks
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : uplink to b1
Description :
ID : 2725707d-886a-41c6-9d0d-38c4115788ff
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 1
Untagged-network :
Networks : deb0886c-4a9b-47f2-8220-55afcb1f1756,
9f2bed94-9148-46d8-9df6-3b606c83a472
Configured-Interfaces : 9A2HEM3:ethernet1/1/42, 3GB1XC2:ethernet1/1/42
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : u1
Description :
ID : e1c8169e-00dd-4a72-9e42-54485c049591
Media Type : FC
Native Vlan : 0
Untagged-network :
Networks : d1de8f16-ebd0-4b1a-9689-a802d23b2b26
Configured-Interfaces : 3GB1XC2:fibrechannel1/1/44:1
----------------------------------------------------------
Example (VxRail) OS10# show smartfabric uplinks
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : FABRICUPLINKNew
Description : L3VxLAN780 Uplink
ID : L3VxLANUplink-780
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 0
52 SFS commands

Untagged-network :
Networks : Network780
Configured-Interfaces : CAC00N2:ethernet1/1/22:2
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : L3VLANUplink
Description : Uplink On L3VLAN Network800
ID : L3VLANUplink-800
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 0
Untagged-network :
Networks : Network800
Configured-Interfaces : CAC00N2:ethernet1/1/22:1
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : L2VxLANUplink
Description : Uplink On L2VxLAN Network770
ID : L2VxLANUplink-770
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 0
Untagged-network :
Networks : Network770
Configured-Interfaces : CAC00N2:ethernet1/1/22:3
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : L2VxLANUplink
Description : Uplink On L2VxLAN Network771
ID : L2VxLANUplink-771
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 0
Untagged-network : Network771
Networks :
Configured-Interfaces : CAC00N2:ethernet1/1/22:4
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
Name : L3Uplink
Description : Uplink On L3 Network600
ID : L3RUplink-600
Media Type : ETHERNET
Native Vlan : 0
Untagged-network : Network600
Networks :
Configured-Interfaces : AZY1234:ethernet1/1/21:2
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show smartfabric upgrade-status
Displays all the information about the upgrade status.
Syntax show smartfabric upgrade-status
NOTE: This command is accessible to users with sysadmin, secadmin, or netadmin roles.
Parameters None
Default Not applicable
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
You can run this command on all the switches in the fabric. The output remains the same on all the switches.
Example MX9116N-A1# show smartfabric upgrade-status
Opaque-id : ea89b7c4-de00-4fc9-ad54-9ed5bf61e300
SFS commands 53

Upgrade Protocol : PUSH
Upgrade start time : 2021-02-12 01:51:29.261000
Status : SUCCESS
Nodes to Upgrade : SVC009F, SVC009A, 7H92Q03, SVC009C, 8PQXV23, 34HQXC2,
8PTXV23, D6RRNK2, BWGQXC2, 9KK1W23, 9J45W23, 8Q52W23
Reboot Sequence : 7H92Q03,SVC009C,9KK1W23,SVC009F,8Q52W23,8PTXV23,D6RRNK2,
BWGQXC2,SVC009A,34HQXC2,5WQQXC2,9J45W23,8PQXV23
Node Current Curent Status-Message
-Action -Status
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SVC009C DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node SVC009C since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
SVC009F DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node SVC009F since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
SVC009A DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node SVC009A since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
8Q52W23 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 8Q52W23 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
34HQXC2 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 34HQXC2 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
BWGQXC2 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node BWGQXC2 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
9J45W23 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 9J45W23 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
7H92Q03 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 7H92Q03 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
9KK1W23 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 9KK1W23 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
8PQXV23 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 8PQXV23 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
D6RRNK2 ONIE-INSTALL SUCCESS [Action: REBOOT] Successfully rebooted.
8PTXV23 DOWNLOAD SUCCESS Skipping ONIE update for the node 8PTXV23 since
ONIE is already installed with latest firmware.
Supported
Releases
10.5.2.1 or Later
show smartfabric validation-errors
Displays validation-error information of the topology. Information includes error category, subcategory, description,
recommended action, severity, timestamp, EEMI, problem, and recommendation for each error.
Syntax show smartfabric validation-errors
Parameters None
Default None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
Use this command to view a list of topology validation errors with detailed description about each error.
This command can be run on any IOM deployed in the same cluster.
This command is supported both in Full Switch and SmartFabric modes.
Example OS10# show smartfabric validation-errors
----------------------------------------------------------
ErrorKey : d77d0133-f8c8-4cd7-82b5-83266e5361eb-ISL-
[ICL-3_REVERSE]-NotFound-Issue
MessageID :
Description : Unable to validate the SmartFabric because
the VLTi cable for link ICL-3_REVERSE is not connected as per
fabric design 2xMX9116n_Fabric_Switching_Engines_in_same_chassis.
EEMI : NFAB0012
Category : FABRIC_ERROR
Subcategory : ISL_ERROR
Severity : SEVERITY_1
54 SFS commands
Recommended Action:Make sure that the VLTi cables are connected
to the correct ports as per the selected fabric design.
Timestamp : 1587488570
Problem Link
SourceNode :HRA0028
SourceInterface :HRA0028:ethernet1/1/38
DestinatioNode :HRA0027
DestinationInterface:
Recommended Link
SourceNode :HRA0028
SourceInterface :HRA0028:ethernet1/1/38
DestinatioNode :HRA0027
DestinationInterface:HRA0027:ethernet1/1/38
----------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
ErrorKey : 8ca24343-c819-4d0b-ab12-2b9d99a36079-ISL-
[ICL-2_REVERSE]-NotFound-Issue
MessageID :
Description : Unable to validate the SmartFabric because
the VLTi cable for link ICL-2_REVERSE is not connected as per
fabric design 2xMX5108n_Ethernet_Switches_in_same_chassis.
EEMI : NFAB0012
Category : FABRIC_ERROR
Subcategory : ISL_ERROR
Severity : SEVERITY_1
Recommended Action:Make sure that the VLTi cables are connected
to the correct ports as per the selected fabric design.
Timestamp : 1587490907
Problem Link
SourceNode :HRA0038
SourceInterface :HRA0038:ethernet1/1/9
DestinatioNode :HRA0037
DestinationInterface:
Recommended Link
SourceNode :HRA0038
SourceInterface :HRA0038:ethernet1/1/9
DestinatioNode :HRA0037
DestinationInterface:HRA0037:ethernet1/1/9
----------------------------------------------------------
Supported
Releases
●MX9116n and MX5108n—10.5.0.1 or later
●SFS-supported OS10 switches—10.5.0.3 or later
show switch-operating-mode
Displays the current operating mode of a switch.
Syntax show switch-operating-mode
Parameters None
Command Mode EXEC
Usage
Information
Some OS10 switches operate in both Full Switch and SFS modes. Use this command to view or verify the
operating mode of a switch that is deployed in the SFS environment.
Example OS10# show switch-operating-mode
Switch-Operating-Mode : SmartFabric Mode
Supported
Releases
10.4.0E(R3S) or later
SFS commands 55

Appendix
This chapter covers additional information that can support you with the fabric configuration tasks.
Internal fabric components and networks
SFS automatically creates the following components and networks:
Internal SFS components
SFS creates a VLT fabric automatically in the leaf and spine environment. VLT fabric is autoassigned with a fabric-ID, a
universally unique identifier (UUID). When a VLT fabric is created, the management IP addresses of the VLT peers are used
automatically to set up the VLT backup link. If the management IP address of the peers is changed after the fabric is created,
the VLT backup link is updated automatically.
SFS creates a network fabric with the leaf and spine switches automatically. The network fabric is autoassigned with a
fabric-ID, a name, and description. The fabric name and description are automatically assigned, but can be changed through the
SFS GUI. For more information, see Update fabric name and description.
Fabric links create a connection between the switches in a network fabric. ISL is a link formed between a leaf and spine switch.
All parallel links with same connectivity are grouped to form a LAG interface. ICL or VLT interconnect (VLTi) is a link formed
between the two leaf switches in a same rack.
Internal virtual networks
The internal virtual networks created by SFS are:
VLAN 4000 for
SFS cluster
control
SFS automatically configures VLAN 4000 on all the switches that are discovered in a fabric, and uses the
network for all internal fabric operations. When a leaf or spine switch is discovered, the ICL or ISL ports
are automatically added as tagged members.
VLAN 4001
to 4079 for
leaf and spine
connections
SFS automatically configures the leaf and spine network using eBGP as the underlay routing protocol.
SFS uses the reserved VLAN range from 4001 to 4079 with automatic IP addressing to set up the peer
connections. When SFS detects an ISL connection on either a leaf or spine switch, it assigns the ISL to
the untagged member of this VLAN. IP address from reserved range is used for this VLAN, and an eBGP
session is started on the VLAN interface.
VLAN 4080 for
Global untagged
VXLAN
SFS automatically configures VXLAN overlay networks with EVPN to extend networks between racks in
a multirack deployment. VLAN 4080 with automatic IP addresses from the reserved range is used for ICL
links. VXLAN requires one VLAN to be assigned globally for untagged port-scoped VLAN (Port, VLAN)
pairs.
VLAN 4089—
OS10 internal use
In SmartFabric mode, VLAN 4089 is the default VLAN and is reserved for OS10 internal use.
VLAN 4090—
iBGP peering
between leaf
switches
SFS automatically configures iBGP peering between a pair of leaf switches directly connected over ICL
links. VLAN 4090 is created automatically with IP addresses from reserved range for enabling iBGP
sessions between the VLT peer switches.
VLAN 4094—VLT
control VLAN
SFS automatically creates VLAN 4094 on all leaf switches. This VLAN is used for all VLT control traffic
between two VLT peer switches and is added on the VLT ICL ports on leaf switches.
VLAN 4091—
Default client
management
network
SFS automatically configures an overlay network that is called a client_Management_Network.
When a device is automatically onboarded on to the network fabric, the device uses the VLAN mapped to
this overlay network. This network is a native VLAN unless there is a policy specifying a different native
VLAN. VLAN 4091 is used as the default client management VLAN for the VXLAN network.
9
56 Appendix

NOTE: You can change this VLAN to a specified VLAN through SFS GUI.
VLAN 3939—
Default client
control network
SFS configures a second overlay network that is called Client_Control_Network for SFS-integrated
solutions. When a device such as VxRail is discovered, it is automatically added as a tagged
member of this network. SFS enables master advertisement and fabric discovery by integrated
solutions. The SFS master virtual IP address for VXLAN network is advertised. The VIP address
fde1:53ba:e9a0:cccc:0:5eff:fe00:1100 is fixed and not user configurable.
VLAN 3939 is used as the default client control VLAN for this VXLAN network for SFS-integrated
solutions including VxRail and PowerScale solutions. Although you can change the VLAN associated with
the default client management and control networks, Dell Technologies recommends not to change the
VLANs for VxRail deployments.
NOTE: For more information about other internal general networks created by SFS, see Networks.
To check the networks that are created in SFS-integrated deployment, use show virtual-network command. Following is
the example output :
OS10# show virtual-network
Codes: DP - MAC-learn Dataplane, CP - MAC-learn Controlplane, UUD - Unknown-Unicast-Drop
Un-tagged VLAN: 4080
Virtual Network: 3939
Description: In-band SmartFabric Services discovery network
VLTi-VLAN: 3939
Members:
VLAN 3939: port-channel1000, ethernet1/1/12, ethernet1/1/13
VxLAN Virtual Network Identifier: 3939
Source Interface: loopback2(172.30.0.0)
Remote-VTEPs (flood-list): 172.30.0.1(CP)
Virtual Network: 4091
Description: Default untagged network for client onboarding
VLTi-VLAN: 4091
Members:
Untagged: ethernet1/1/12, ethernet1/1/13
VLAN 4091: port-channel1000
VxLAN Virtual Network Identifier: 4091
Source Interface: loopback2(172.30.0.0)
Remote-VTEPs (flood-list): 172.30.0.1(CP)
Reserved networks
SFS uses the 172.16.0.0/16 and 172.30.0.0/16 networks internally for the leaf and spine network configuration. If these networks
conflict with any networks in the existing deployment, change the default networks using the instructions that are provided in
Edit Default Fabric Settings.
MSTP Support on L3 personality
The default spanning tree mode in SFS is RPVST+. On Dell EMC PowerSwitches in SFS mode, RPVST+ is enabled globally and
automatically configured.
In L3 personality, SFS is enabled on:
●SFS cluster control VLAN (VLAN 4000). The spine switches are configured to take over the STP root role.
●All user created VLANs.
In L3 personality, SFS is disabled on:
●All inter leaf-spine VLANs and leaf-leaf VLANs (4001-4091).
●All server facing ports.
NOTE: Do not modify STP settings on switches in SFS L3 personality.
If you must interoperate switches that are controlled by SFS to external switches which are running RSTP or MSTP, SFS has an
API to change the global fabric STP mode to MSTP. SFS creates 2 reserved MSTIs:
●MST with instance id 63: Cluster control VLAN 4000 is part of this instance. Spine switches are configured to take over as
STP root for this MSTI.
Appendix 57

●MST with instance id 62: All the SFS reserved VLANs (4001-4091) are part of this configuration. On this MSTI, spanning tree
is disabled.
●All user created VLANs are part of CST (default MST instance), which interoperates with RSTP. STP is enabled for this
MSTI.
You can change the mode to MSTP once the fabric is created. When you change the mode, the whole fabric goes through a
reboot cycle and the new mode is set to MSTP.
NOTE: Changing the STP mode impact the traffic flow in the cluster.
When the mode is changed, MSTI is created and VLANS are assigned to the MSTI. The CST is configured with STP priority such
that SFS-controlled switches have lower priority to become a root bridge.
There is no change on existing STP behavior for SFS-controlled entities because of this change. All other STP behaviors such as
disabling STP on server facing ports still holds good.
You can enable MSTP or revert to RPVST using the Edit Default Fabric Settings option available in the SFS UI. Select STP
Mode as MST or Rapid PVST For more information, see Edit Default Fabric Settings.
NOTE: The default spanning-tree priority value that is configured on a SFS-enabled switch for VLANs or instance 0 is:
default priority for RPVST is 32769 and instance 0 priority for MSTP is 61440.
Networks
This section describes the following type of networks that you can create and associate these networks with the entities
present in a fabric:
●General purpose networks
●VXLAN networks
●L3 VLAN networks
●L3 Routed networks
●Multirack L3 VLAN network
NOTE: You cannot configure this network using SFS GUI. This network template is applicable for NSX-T deployment
and you can configure this network using OMNI UI. For more information about this network type, see OpenManage
Network Integration for SmartFabric Services User Guide, Release 2.0.
You can create these networks using SFS GUI and then associated these networks with servers profiles, uplinks, or interfaces
for traffic flow. For more information, see Create a network.
General purpose networks
General purpose networks can be categorized as L2 VLAN networks in SFS L2 personality and L2 VXLAN networks in SFS L3
personality. In L3 personality, when you create a general purpose network, SFS automatically creates a virtual network (VXLAN)
corresponding to a VLAN network. This virtual network has one-to-one mapping with the network, for each VLAN there exists
a virtual network with VNI same as the VLAN ID. If you delete a VLAN network, it automatically deletes the associated VXLAN
network.
For example, if you create a general purpose network with VLAN ID 50, SFS creates a VLAN 50 and associated VXLAN network
with VNI 50.
VXLAN networks
VXLAN network extends L2 connectivity over an underlay L3 connected network. Association of VXLAN network to interface
creates a binding and associates this interface to VXLAN bridge. L3 VXLAN network supports asymmetric-IRB. Create a virtual
network template and a network template, and associate the virtual network template to network template.
●The virtual network template defines the VNET-ID.
●Network template defines the VLAN ID.
L3 VXLAN network is a VXLAN type of network that contains a list of IP addresses and an anycast IP address. Optionally,
you can specify DHCP relay addresses. L3 VXLAN network can be configured over a leaf switch. L3 VXLAN network can be
attached to an uplink. Each VLTi uplink interface contains an IP address that is allocated from the list of IP addresses that are
configured on the L3 VXLAN network.
L3 VLAN network
L3 VLAN network is used for L3 VLAN underlay. Specify:
●VLAN ID
58 Appendix

●Pair of IP addresses to be assigned to the VLT pair
●VRRP gateway IP address for VIP
L3 VLAN network contains a list of IP addresses and a gateway IP address. Optionally, you can specify DHCP relay addresses.
You can configure and attach a L3 VLAN network to an uplink. Each VLTi uplink interface contains an IP address that is
allocated from the list of IP addresses that are configured on the L3 VLAN network.
L3 Routed network
L3 routed network is used to assign IP address on a single interface. L3 routed network contains a list of IP addresses and a
gateway IP address. Optionally, you can specify DHCP relay addresses. L3 routed network can be configured on a leaf or a spine
switch. L3 routed network can be attached to an uplink. Each uplink interface contains an IP address that is allocated from the
list of IP addresses that are configured on the L3 routed network. An LACP port channel cannot be the remote end for these
uplinks. If gateway IP address is specified, then VRRP is enabled and the switches configure this IP address as the gateway IP
address. Attach this network to any uplink that has a single interface. This network can only be attached to a single entity.
Multirack L3 VLAN network
Multirack L3 VLAN network is a template that contains rack-specific IP configurations for a L3 VLAN. You can configure IPv4
attributes for each rack in an NSX-T deployment consisting of multirack leaf and spine topology. A rack holds a pair of switches
that are configured with VLT. The rack identifier is the same as the fabric ID. A rack containing a single switch without VLT does
not support multirack L3 VLAN network.
In an NSX-T topology that is connected to an SFS cluster, you can create a multi rack L3 VLAN network. Specify the network
identifier, L3 VLAN ID, and list of rack-specific IPv4 configurations for this network. Attach the created network as untagged or
tagged on any uplink or server interface of the rack. After you attach the network, SFS automatically creates a L3 VLAN and
applies the rack-specific IP configurations to the respective rack within the topology. You can modify the IPv4 configuration for
a specific rack in the multi rack L3 VLAN network.
NOTE: For faster traffic convergence, Dell Technologies recommends setting the BGP keepalive timer to 1 second and
hold-time to 3 seconds on the NSX-T tier-0 node.
Uplinks
This information explains the types of uplinks that you can create in a fabric.
L2 uplinks
You can configure L2 uplinks only on the leaf switches in a fabric. L2 uplinks are a set of user-selected ports that belong to same
VLT leaf switches in which the L2 network is applied. The L2 uplink from the leaf switches is either an LACP or a static LAG.
SFS creates a VLT LAG for connected ports. If the ports are from a single device, the VLT LAG is a single armed VLT LAG. In
case these ports exist on multiple switches, a VLT or LAG is formed across these ports. This LAG can be made as an access
point for a VXLAN L2 network.
L3 uplinks
You can configure L3 uplinks on a leaf or spine switch. SFS supports L3 routed or L3 VLAN uplinks.
With L3 routed uplinks, point-to-point links are required between the switches with L3 uplinks and the external switches. With
L3 VLAN, all uplinks are in a LAG, and an IP address is assigned to the VLAN containing the LAG. Point-to-point IP networks
and addresses must be planned for each physical link in the L3 uplink. Each leaf switch in the fabric needs an IP address on the
external Management VLAN, and an anycast gateway address on the same VLAN. The virtual router or anycast gateway address
is shared by all leaf switches in the fabric.
Routing profiles
SFS supports eBGP and static routing profiles.
Static route profile—A static route profile is a routing template that contains a network prefix and the next hop IP address.
During uplink configuration, you can associate this profile to the uplinks created on one or more switches in the fabric. When this
profile is created, a route with the specified prefix and next hop IP address is configured on the switch.
Appendix 59

eBGP peer routing profile—An eBGP peer routing profile is a routing template that contains BGP remote addresses and
the remote AS number. A remote address can be an interface address or a loopback address. During uplink creation, you can
associate this policy to uplink created on one or more switches in a fabric. When this policy is created, a BGP session is
configured on the switch.
Uplink bonding options
Following are the uplink bonding types supported:
●LACP
●Static bonding
LACP
In LACP uplink bonding, SFS configure the LACP LAG for the uplink using the LACP PDUs received from the remote device.
Networks that are attached to the uplink are associated with the LACP LAG that is created.
Static bonding
In static bonding, SFS configures a static LAG for the uplink and the networks that are attached on the uplink are associated
with the LAG that is created.
60 Appendix