Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Product Family Overview
- 3 System Storage and Peripheral Drive Bay Overview
- 4 Power Subsystem
- 4.1 Power Distribution Board (PDB)
- 4.2 Mechanical Overview
- 4.3 Power Connectors
- 4.4 Power Supply Module Efficiency
- 4.5 AC Power Cord Specification Requirements
- 4.6 AC Input Specifications
- 4.6.1 Power Factor
- 4.6.2 AC Input Voltage Specification
- 4.6.3 AC Line Isolation Requirements
- 4.6.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
- 4.6.5 AC Line Fuse
- 4.6.6 AC Inrush
- 4.6.7 AC Line Transient Specification
- 4.6.8 Susceptibility Requirements
- 4.6.9 Electrostatic Discharge Susceptibility
- 4.6.10 Fast Transient/Burst
- 4.6.11 Radiated Immunity
- 4.6.12 Surge Immunity
- 4.6.13 Voltage Interruptions
- 4.6.14 Protection Circuits
- 4.6.15 Over Current Protection (OCP)
- 4.6.16 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
- 4.6.17 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
- 4.7 Power Supply Status LED
- 5 Thermal Management
- 6 JBOD2000S3SP Internal Connection Overview
- 7 JBOD2000S3SP External SAS Connection Mode Overview
- Appendix A. Qualified External Mini-SAS Cable List
- Appendix B. Reference Documents
Intel Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP by Intel which is a product in the Disk Arrays category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP
Hardware Guide
A document providing a system level overview of product features, functions,
architecture, and support specifications
Revision 1.3
Mar 2016
Intel® Server Boards and Systems

<This page is intentionally left blank.>

JBOD2000S3SP Hardware Guide
ii
Revision History
Date
Revision
Number
Modifications
November 2014
0.9
Pre-production release.
December 2014
1.0
Production version release.
May 2015
1.1
Removed references to PSU Cold Redundancy support.
October 2015
1.2
Added optional PSU and power cable references in the Power Subsystem
section.
March 2016
1.3
Converted to the new format.

JBOD2000S3SP Hardware Guide
iii
Disclaimers
No license (express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise) to any intellectual property rights is granted by this
document.
Intel disclaims all express and implied warranties, including without limitation, the implied warranties of
merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement, as well as any warranty arising from
course of performance, course of dealing, or usage in trade.
This document contains information on products, services and/or processes in development. All information
provided here is subject to change without notice. Contact your Intel representative to obtain the latest
Hardware Guide.
The products and services described may contain defects or errors known as errata which may cause
deviations from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others
© 2016 Intel Corporation.

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
iv
Table of Contents
1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 Server Product Use Disclaimer ............................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Product Errata ............................................................................................................................................................................... 1
2 Product Family Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 2
2.1 Chassis Dimensions .................................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.2 System Level Environmental Limits ...................................................................................................................................... 4
2.3 System Features and Options Overview ............................................................................................................................. 5
2.3.1 Hot Swap Hard Drive Bay .................................................................................................................................................. 5
2.3.2 Front Control Panel .............................................................................................................................................................. 6
2.3.3 Back Panel Features ............................................................................................................................................................ 7
3 System Storage and Peripheral Drive Bay Overview ........................................................................................... 8
3.1 3.5” Hard Disk Drive Support .................................................................................................................................................. 8
3.2 3.5” Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview ........................................................................................................................ 9
3.2.1 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller ............................................................................... 10
4 Power Subsystem ..................................................................................................................................................... 11
4.1 Power Distribution Board (PDB) .......................................................................................................................................... 12
4.2 Mechanical Overview .............................................................................................................................................................. 14
4.3 Power Connectors ..................................................................................................................................................................... 16
4.3.1 Power Supply Module Card Edge Connector ........................................................................................................ 16
4.3.2 Hot-Swap Backplane Power Connector ................................................................................................................... 16
4.4 Power Supply Module Efficiency ......................................................................................................................................... 17
4.5 AC Power Cord Specification Requirements ................................................................................................................... 17
4.6 AC Input Specifications........................................................................................................................................................... 17
4.6.1 Power Factor ....................................................................................................................................................................... 17
4.6.2 AC Input Voltage Specification .................................................................................................................................... 18
4.6.3 AC Line Isolation Requirements .................................................................................................................................. 18
4.6.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup ............................................................................................................................................... 18
4.6.5 AC Line Fuse ........................................................................................................................................................................ 19
4.6.6 AC Inrush............................................................................................................................................................................... 19
4.6.7 AC Line Transient Specification ................................................................................................................................... 19
4.6.8 Susceptibility Requirements ......................................................................................................................................... 20
4.6.9 Electrostatic Discharge Susceptibility ...................................................................................................................... 20
4.6.10 Fast Transient/Burst ....................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.6.11 Radiated Immunity.......................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.6.12 Surge Immunity ................................................................................................................................................................ 20
4.6.13 Voltage Interruptions ..................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.6.14 Protection Circuits ........................................................................................................................................................... 21
4.6.15 Over Current Protection (OCP) .................................................................................................................................. 21
4.6.16 Over Voltage Protection (OVP) .................................................................................................................................. 21

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
v
4.6.17 Over Temperature Protection (OTP) ........................................................................................................................ 21
4.7 Power Supply Status LED ...................................................................................................................................................... 21
5 Thermal Management ............................................................................................................................................. 23
5.1 Thermal Operation and Configuration Requirements ............................................................................................... 23
5.2 Thermal Management Overview ........................................................................................................................................ 23
5.3 Thermal Sensor Input for Fan Speed Control ................................................................................................................ 23
5.4 System Fans ................................................................................................................................................................................ 24
5.5 Fan Speed Control .................................................................................................................................................................... 26
5.6 Power Supply Module Fan ..................................................................................................................................................... 26
6 JBOD2000S3SP Internal Connection Overview ................................................................................................ 27
6.1 Expander Board ......................................................................................................................................................................... 27
6.1.1 JBOD SAS Expander Port Numbering ...................................................................................................................... 29
6.1.2 JBOD2312S3SP Interconnection ............................................................................................................................... 30
7 JBOD2000S3SP External SAS Connection Mode Overview ........................................................................... 31
7.1 External SAS Controller Support ........................................................................................................................................ 31
7.2 External SAS Cable .................................................................................................................................................................. 31
7.3 Hard Drive Type ......................................................................................................................................................................... 32
7.4 JBOD Cascade ............................................................................................................................................................................ 32
7.5 Single-port JBOD2000S3SP External Connection Mode ......................................................................................... 32
7.5.1 Single JBOD2000S3SP Connection .......................................................................................................................... 32
7.5.2 Two JBOD2000S3SP Cascade ..................................................................................................................................... 33
7.5.3 Dual-path Connection ..................................................................................................................................................... 34
7.5.4 Dual-path with Cascaded JBOD2000S3SP ............................................................................................................ 35

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
vi
List of Figures
Figure 1. 12 x 3.5” Drive JBOD2000S3 Product Drawing ....................................................................................2
Figure 2. Chassis Dimensions ................................................................................................................................3
Figure 3. System Components Overview..............................................................................................................5
Figure 4. 12 x 3.5" Drive JBOD2000S3SP Front View ..........................................................................................5
Figure 5. Front Panel Options ................................................................................................................................6
Figure 6. JBOD2312S3SP Back View ....................................................................................................................7
Figure 7. 3.5” Hard Drive Bay – 12-Drive Configuration ......................................................................................8
Figure 8. 3.5” Drive Tray Assembly .......................................................................................................................8
Figure 9. Status and Activity LED on 3.5” Drive Tray ...........................................................................................8
Figure 10. 3.5” Hot-Swap Backplane and Drive Bay Assembly ..........................................................................9
Figure 11. SFF-8482 Connector on 3.5” HSBP .....................................................................................................9
Figure 12. Components on 3.5” HSBP ................................................................................................................ 10
Figure 13. Power Supply Assembly .................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 14. Power Distribution Board (PDB) ........................................................................................................ 12
Figure 15. PDB Component Placement ............................................................................................................... 13
Figure 16. Fan Fault LED Block Diagram ............................................................................................................. 14
Figure 17. Power Supply Module Mechanical Drawing ..................................................................................... 15
Figure 18. Power Supply Module ........................................................................................................................ 15
Figure 19. AC Power Supply – Connector View .................................................................................................. 15
Figure 20. AC Power Cord .................................................................................................................................... 17
Figure 21. System Fan Identification .................................................................................................................. 24
Figure 22. System Fan Assembly ......................................................................................................................... 25
Figure 23. Internal SAS Expander Location ........................................................................................................ 28
Figure 24: SAS Expander Port Numbering ......................................................................................................... 29
Figure 25. 12x3.5” Single-port JBOD2000S3SP Interconnection Diagram..................................................... 30
Figure 26. SFF-8644 mini-SAS Cable .................................................................................................................. 31
Figure 27. Single JBOD2000S3SP Connection .................................................................................................. 32
Figure 28. Two Single-port JBOD2000S3SP Cascade ....................................................................................... 33
Figure 29. Two Groups of Cascaded Single-port JBOD2000S3SP ................................................................... 33
Figure 30. Dual-path Connection ........................................................................................................................ 34
Figure 31. Dual-path with Cascaded JBOD2000S3SP ....................................................................................... 35

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
vii
List of Tables
Table 1. System Environmental Limits Summary ................................................................................................4
Table 2. Power LED Functional States ..................................................................................................................6
Table 3. System Status LED State Definitions ......................................................................................................6
Table 4. Status LED Status .....................................................................................................................................9
Table 5. Activity LED Status ...................................................................................................................................9
Table 6: Auto Power On Jumper Options ........................................................................................................... 13
Table 7. Power Supply Module Output Power Connector Pin-out ................................................................... 16
Table 8. Hot-swap Backplane Power Connector Pin-out (“HSBP PWR”) ......................................................... 17
Table 9. 460 Watt Power Supply Efficiency ....................................................................................................... 17
Table 10. AC Power Cord Specifications ............................................................................................................. 17
Table 11. Power Factor ......................................................................................................................................... 18
Table 12. AC Input Voltage Range ....................................................................................................................... 18
Table 13. AC Line Dropout/Holdup ..................................................................................................................... 18
Table 14. AC Line Sag Transient Performance ................................................................................................... 19
Table 15. AC Line Surge Transient Performance ................................................................................................ 19
Table 16. Performance Criteria............................................................................................................................ 20
Table 17. 460 Watt Power Supply Over Current Protection ............................................................................. 21
Table 18. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits ................................................................................................ 21
Table 19. LED Indicators ...................................................................................................................................... 22
Table 20. System Fan Connector Pin-out ........................................................................................................... 25
Table 21: PWM Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 26
Table 22: Temperature Notification Thresholds ................................................................................................ 26
Table 23: External Cable List ............................................................................................................................... 36

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
viii
< This page intentionally left blank. >

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
1
1 Introduction
This Hardware Guide provides system-level information for the Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP.
This document describes the functions and features of this JBOD product and includes the chassis layout,
system boards, power subsystem, cooling subsystem, storage subsystem options, and available installable
options.
This document is divided into the following chapters:
Chapter 1 – Introduction
Chapter 2 –Product Family Overview
Chapter 3 – System Storage and Peripheral Drive Bay Overview
Chapter 4 – Power Subsystem
Chapter 5 – Thermal Management
Chapter 6 – JBOD2000S3SP Internal Connection Overview
Chapter 7 – JBOD2000S3SP External SAS Connection Mode Overview
Appendix A – Qualified External Mini-SAS Cable List
Reference Documents
1.1 Server Product Use Disclaimer
It is the responsibility of the system integrator who chooses not to use Intel-developed server building
blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of airflow required
for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible if
components fail to operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating
limits.
1.2 Product Errata
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may
cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Product Errata are documented in the Intel®
Storage System JBOD2312S3SP Monthly Specification Update which can be downloaded from
http://www.Intel.com/support.

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
2
2 Product Family Overview
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP offers the flexibility of adding additional storage to an existing
server system with support for 12Gb/s SAS or SATA hard disk drives or SSDs, redundant fan power and
power options, and SES communication with the server to monitor the health of the JBOD subsystems.
This chapter provides a high-level overview of the detail for each major system components and features
provided in the following sections.
Figure 1. 12 x 3.5” Drive JBOD2000S3 Product Drawing
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
3
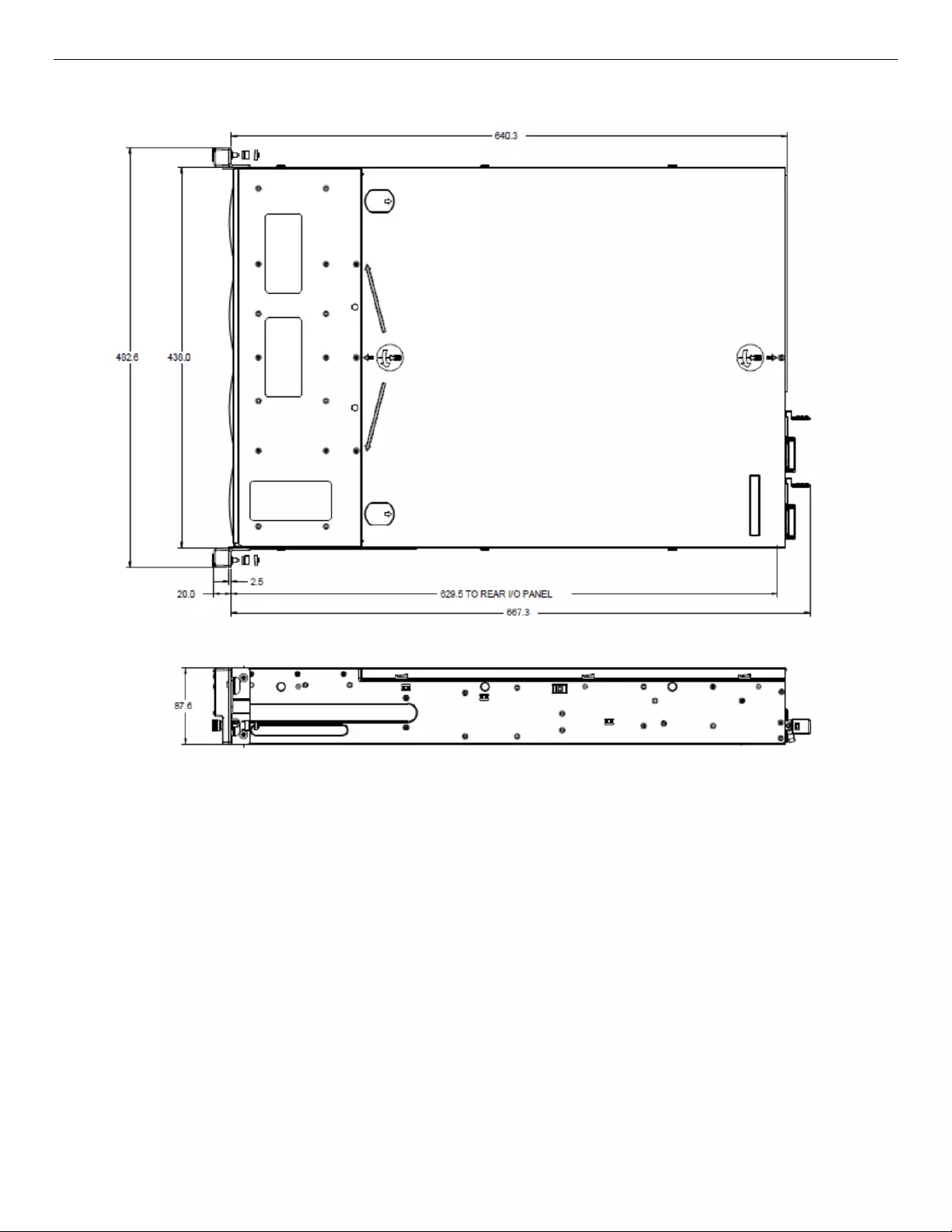
2.1 Chassis Dimensions
Figure 2. Chassis Dimensions
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
4
2.2 System Level Environmental Limits
The following table defines the system level operating and non-operating environmental limits.
Table 1. System Environmental Limits Summary
Parameter
Limits
Temperature Operating
ASHRAE Class A2 – Continuous Operation. 10ºC to 35ºC1
1
(50ºF to 95ºF) with the
maximum rate of change not to exceed 10ºC per hour.
ASHRAE Class A3 – Includes operation up to 40ºC for up to 900 hrs per year.
ASHRAE Class A4 – Includes operation up to 45ºC for up to 90 hrs per year.
Shipping
-40ºC to 70ºC (-40ºF to 158ºF)
Altitude
Operating
Support operation up to 3050m with ASHRAE class deratings.
Humidity Shipping
50% to 90%, non-condensing with a maximum wet bulb of 28ºC (at temperatures from
25ºC to 35ºC)
Shock
Operating
Half sine, 2g, 11 mSec
Unpackaged
Trapezoidal, 25g, velocity change is based on packaged weight
Packaged
Product Weight: ≥ 40 to < 80
Non-palletized Free Fall Height = 18 inches
Palletized (single product) Free Fall Height = NA
Vibration
Unpackaged
5 Hz to 500 Hz 2.20 g RMS random
Packaged
5 Hz to 500 Hz 1.09 g RMS random
AC-DC
Voltage
90 V AC to 132 V AC and 180 V AC to 264 V AC
Frequency
47 Hz to 63 Hz
Source Interrupt
No loss of data for power line drop-out of 12 mSec
Surge Non-
operating and
operating
Unidirectional
Line to earth Only
AC Leads 2.0 kV
I/O Leads 1.0 kV
DC Leads 0.5 kV
ESD
Air Discharged
12.0 kV
Contact Discharge
8.0 kV
Acoustics Sound
Power Measured
Power in Watts
<300 W ≥300 W ≥600 W ≥1000 W
Servers/Rack
Mount BA
7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0
System 460W Redundant Power Supplies (CRPS) operate in spread-core flow conditions (positive pressure
to the power supply’s inlet) and incorporate a 40mm fan for its own thermal management. To ensure PS
thermal protection under all operating conditions the fan speed control has a closed loop algorithm based
on both the critical component temperature and the ambient temperature (inlet temperature). The PS over
Temperature Protection (OTP) protects against over temperature conditions created by the loss of fan
cooling or excessive ambient temperature. In an OTP condition the PS will shut down and restore power
1 Intel Corporation server boards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery components that need adequate airflow to
cool. Intel ensures through its own chassis development and testing that when Intel server building blocks are used together, the fully
integrated system will meet the intended thermal requirements of these components. It is the responsibility of the system integrator who
chooses not to use Intel developed server building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the
amount of airflow required for their specific application and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible if
components fail or the server board does not operate correctly when used outside any of its published operating or non-operating limits.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
5
when the temperature drops to within specified limits. The OTP trip level for inlet temperature is 65ºC with a
minimum of 4ºC margin to prevent on and off oscillation.
Disclaimer Note: Intel ensures the unpackaged JBOD system meets the shock requirement mentioned above
through its own chassis development and system configuration. It is the responsibility of the system
integrator to determine the proper shock level of the JBOD system if the system integrator chooses a different
system configuration or different chassis. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible, if components fail or
the system boards do not operate correctly when used outside any of its published operating or non-
operating limits.
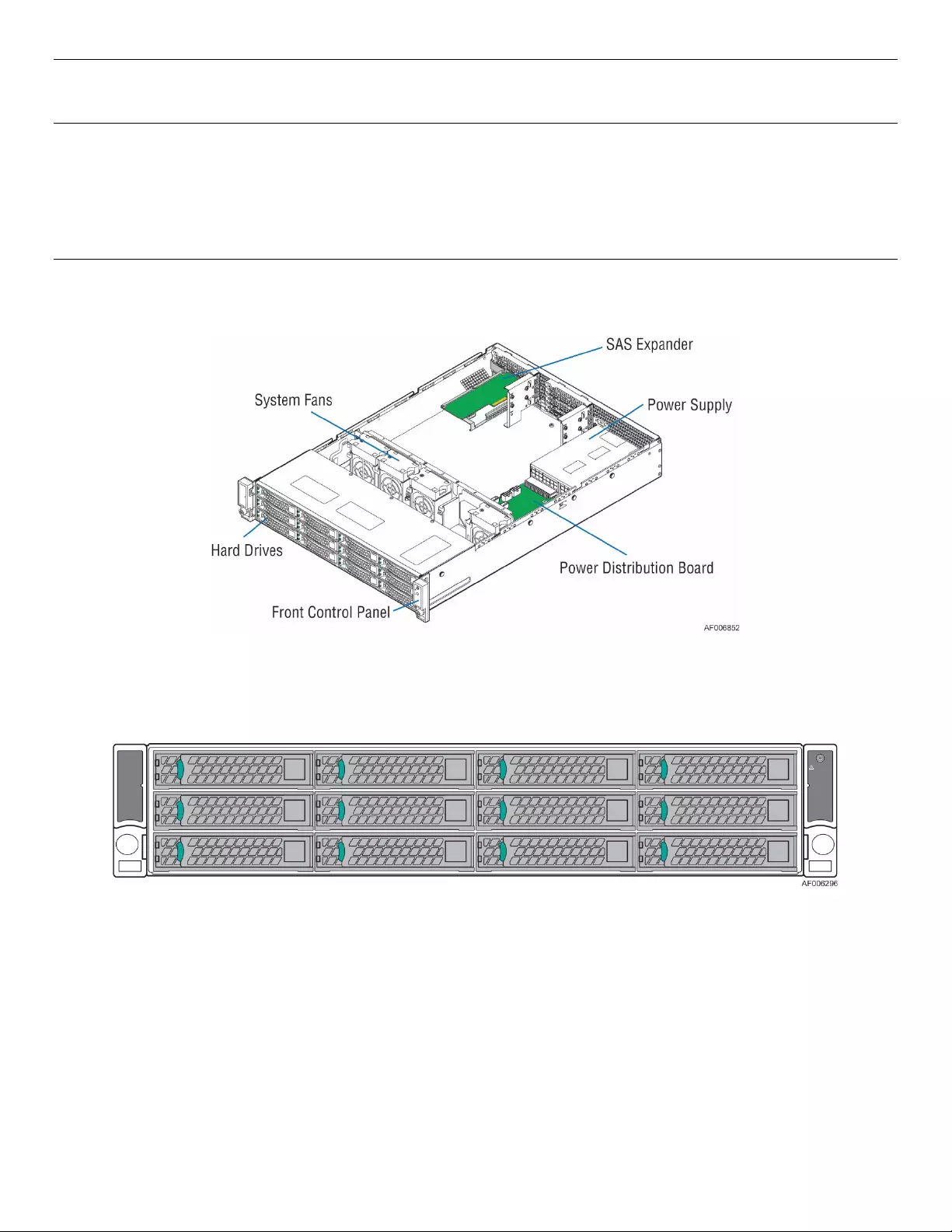
2.3 System Features and Options Overview
Figure 3. System Components Overview
2.3.1 Hot Swap Hard Drive Bay
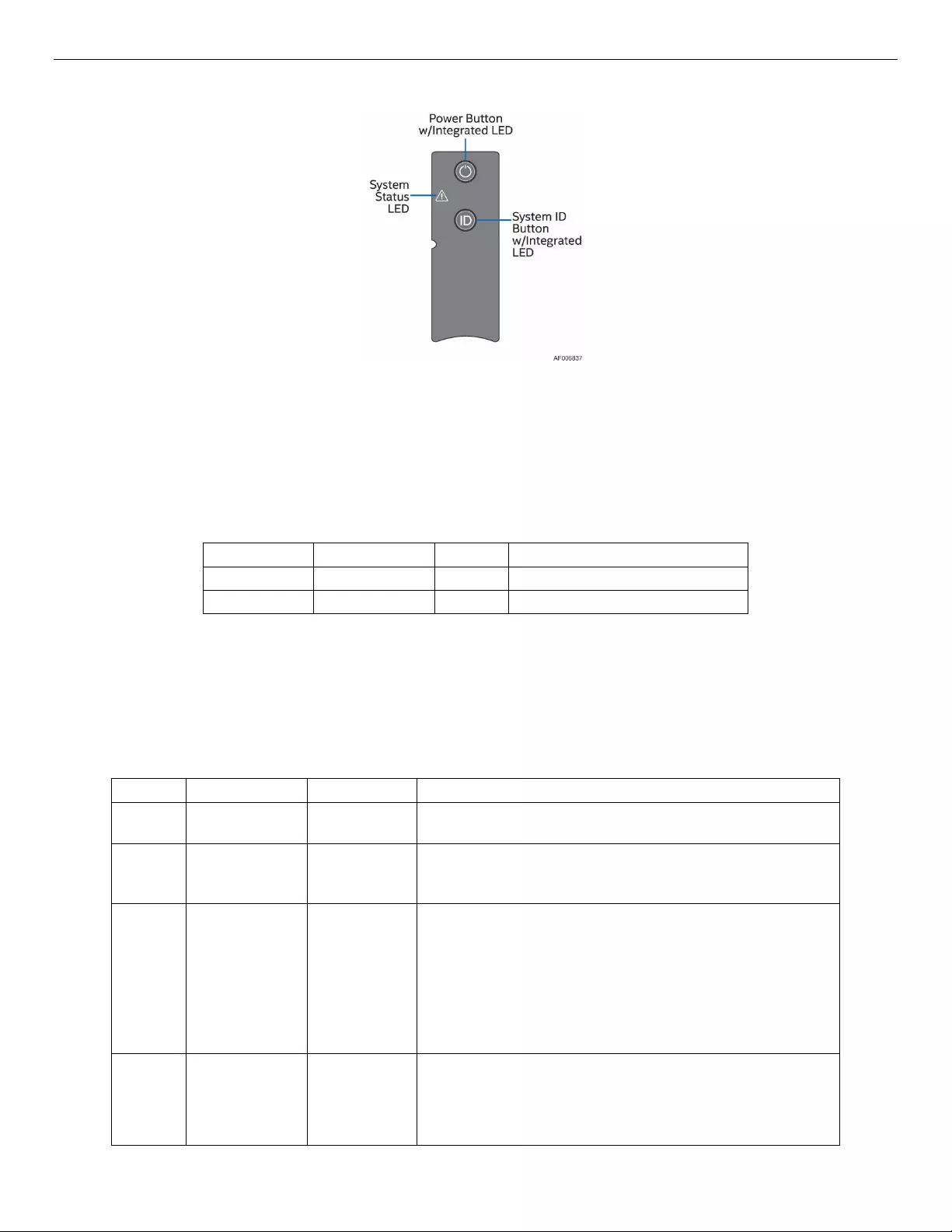
Figure 4. 12 x 3.5" Drive JBOD2000S3SP Front View
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
6
2.3.2 Front Control Panel
Figure 5. Front Panel Options
The Power Button toggles the system power on and off. Pressing this button sends a signal to the integrated
PDB board, which either powers on or powers off the system. The integrated LED is a single-color (Green)
indicator that supports different states as defined in the following table.
Table 2. Power LED Functional States
State
Power Mode
LED
Description
Power-off
Non-ACPI
Off
System power is off.
Power-on
Non-ACPI
On
System power is on.
The ID button has no function in this system.
The System Status LED is a bi-color (Green/Amber) indicator that shows the current health of the JBOD
system. The System Status LED states are driven by the platform management subsystem. The following
table provides a description of each supported LED state.
Table 3. System Status LED State Definitions
Color
State
Criticality
Description
Off
System is not
operating
Not ready
The system is powered off (AC and/or DC).
Green
Solid on
Ok
Indicates that the system status is “healthy”. The system is not
exhibiting any errors. AC power is present and has been
powered on.
Amber
Solid on
Warning
Threshold
Alert Event
Encountered
P12V has exceeded the warning threshold.
P5V has exceeded the warning threshold.
P3.3V has exceeded the warning threshold.
One of the power supply modules is in a degraded state
(No AC or failed).
Temperature has exceeded the warning threshold. Event
has been detected.
Amber
Blinking
Critical
Threshold
Alert Event
Encountered
P12V has exceeded the critical threshold.
P5V has exceeded the critical threshold.
P3.3V has exceeded the critical threshold.
A fan failure has been detected.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
7
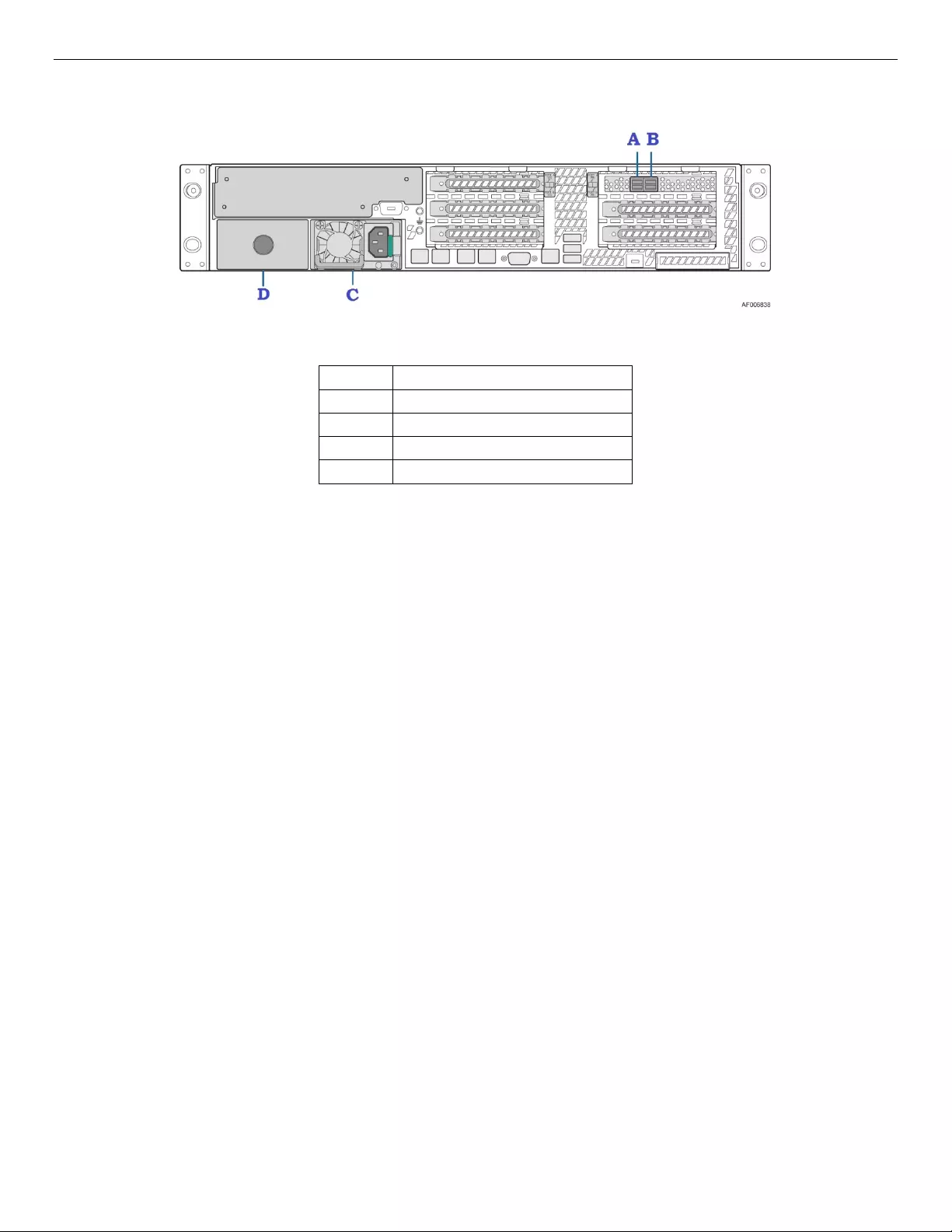
2.3.3 Back Panel Features
Figure 6. JBOD2312S3SP Back View
Label
Description
A
SFF-8644 receptacle (label: A PRI)
B
SFF-8644 receptacle (label: B PRI)
C
PSU
D
Optional second power module

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
8
3 System Storage and Peripheral Drive Bay Overview
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2000S3SP product supports 12 Hot-swap 3.5” hard disk drives.
3.1 3.5” Hard Disk Drive Support
The server is available as a 3.5” hard disk configuration of 12 drives as illustrated below.
Figure 7. 3.5” Hard Drive Bay – 12-Drive Configuration
The drive bay can support either SATA or SAS hard disk drives. Mixing of drive types within the hard drive
bay is not supported. Hard disk drive type is dependent on the type of host bus controller used, SATA only
or SAS. Each 3.5” hard disk drive is mounted to a drive tray, allowing for hot-swap extraction and insertion.
Drive trays have a latching mechanism that is used to extract and insert the drives from the chassis, and lock
the tray in place.
Figure 8. 3.5” Drive Tray Assembly
Light pipes integrated into the drive tray assembly direct the light emitted from Amber drive status and
Green activity LEDs located next to each drive connector on the backplane, to the drive tray faceplate,
making them visible from the front of the system.
Figure 9. Status and Activity LED on 3.5” Drive Tray
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
9
Table 4. Status LED Status
Amber
Off
No access and no fault.
Solid on
Hard drive fault has occurred.
Blink
RAID rebuild in progress (1 Hz);
Identify (2 Hz). (Dependent on
which RAID controller is used
and attached to the JBOD)
Table 5. Activity LED Status
Green
Condition
Drive Type
Behavior
Power on with no drive
activity
SAS
LED stays on.
SATA
LED stays off.
Power on with drive
activity
SAS
LED blinks off when processing a command.
SATA
LED blinks on when processing a command.
Power on and drive
spun down
SAS
LED stays off.
SATA
LED stays off.
Power on and drive
spinning up
SAS
LED blinks.
SATA
LED stays off.
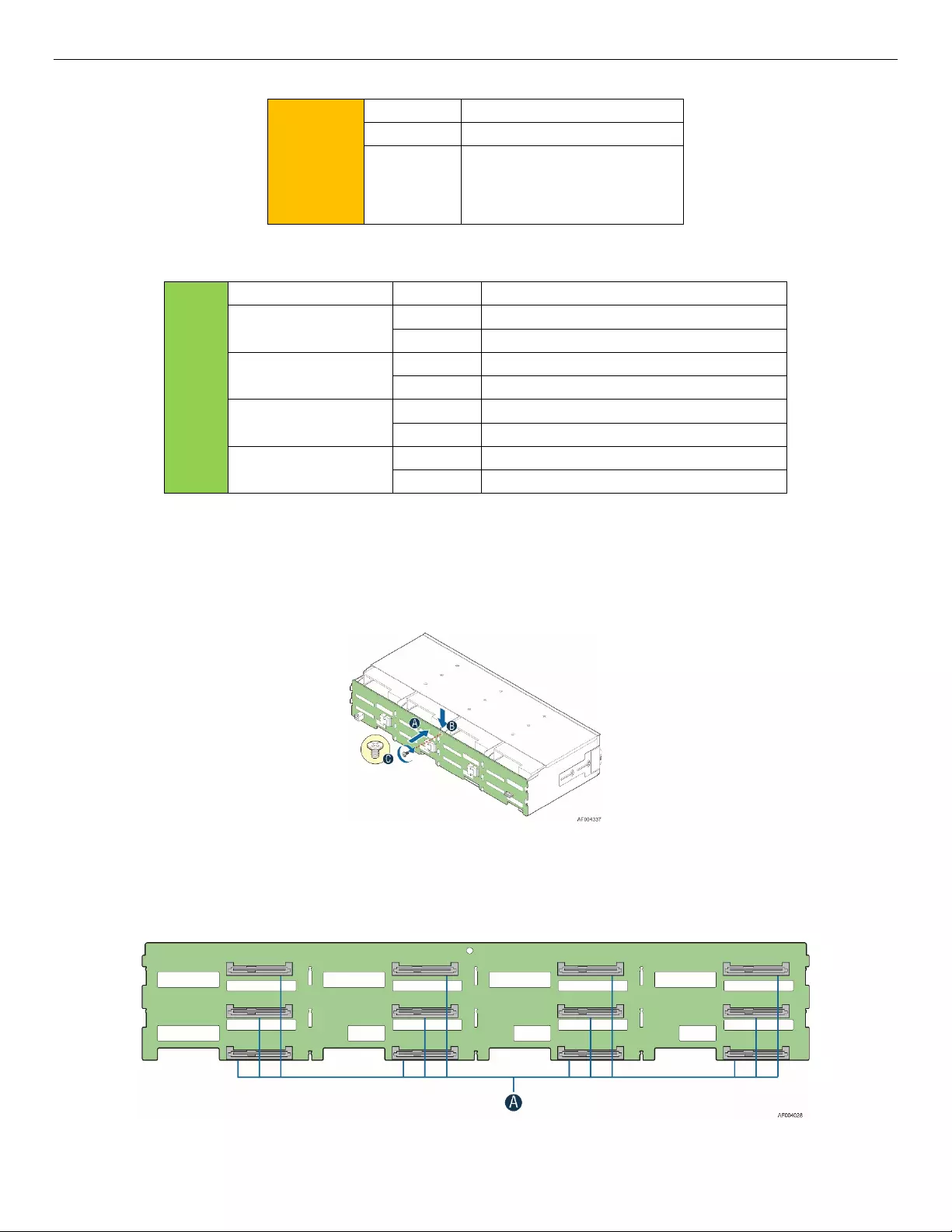
3.2 3.5” Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview
Systems with 12-drive configurations have their own unique backplane. The backplanes mount to the back
of the drive bay assembly.
Figure 10. 3.5” Hot-Swap Backplane and Drive Bay Assembly
There are 12 hard disk drive interface connectors mounted on the front side of each backplane, each
providing both power and I/O signals to the attached hard disk drives.
Figure 11. SFF-8482 Connector on 3.5” HSBP
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
10
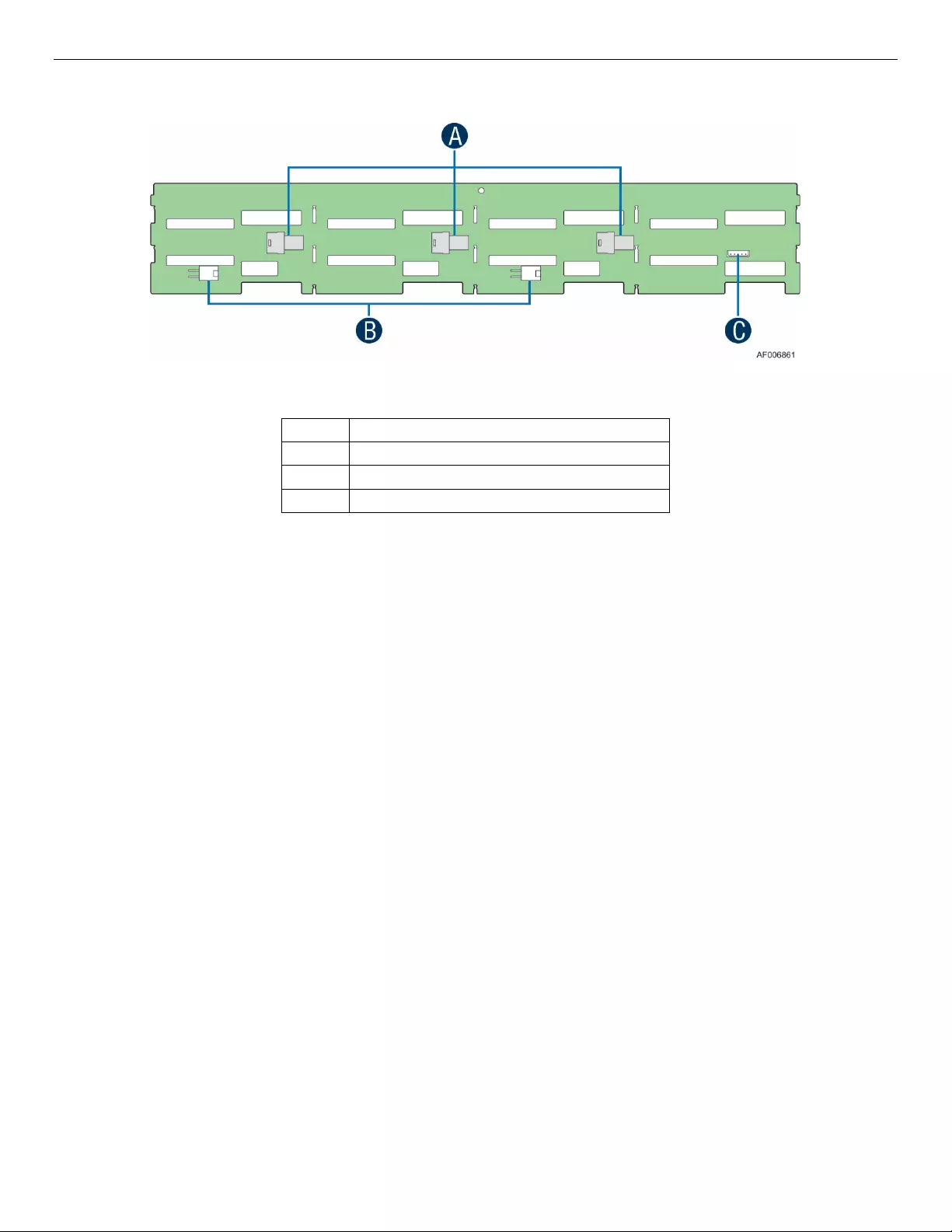
On the back side of each backplane, there are several connectors, each of which is identified in the following
illustration.
Figure 12. Components on 3.5” HSBP
Label
Description
A
4-port mini-SAS HD SFF8643 connectors
B
Power connectors
C
SMBus connector (not used)
A – 4-port Mini-SAS HD SFF8643 Connectors – The backplane includes two or three multi-port mini-SAS
cable connectors, each providing SGPIO and I/O signals for four SAS/SATA hard drives on the backplane.
Cables can be routed from matching connectors on the Expander card. Each mini-SAS HD connector
includes a silk-screen identifying which drives the connector supports: Drives 0-3, Drives 4-7, and Drives 8-
11.
B – Power Harness Connector – The backplane includes a 2x2 connector supplying power to the backplane.
Power is routed to the backplane via a power cable harness from the power distribution board (PDB).
3.2.1 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller
The backplanes support enclosure management using a Cypress* CY8C22545 Programmable System-on-
Chip (PSoC*) device. The CY8C22545 drives the hard drive activity/fault LED, hard drive present signal, and
controls hard drive power-up during system power-on.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
11
4 Power Subsystem
This section provides a high-level overview of the power management features and specification data for the
power supply options available for the Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP. Specification variations are
identified for each supported power supply.
Although the Intel® Storage System JBOD2000S3SP ships with only one power supply, a second one can be
installed and have up to two power supply modules installed, supporting the following power supply
configurations: 1+0 (single power supply), 1+1 Redundant Power, and 2+0 Combined Power non-redundant
(Although this system cannot be loaded high enough to hit this mode). The 1+1 redundant power and 2+0
combined power configurations are automatically configured depending on the total power draw of the
system. If the total system power draw exceeds the power capacity of a single power supply module, then
power from the second power supply module will be utilized. If this occurs, power redundancy is lost. In a
2+0 power configuration, total power available may be less than twice the rated power of the installed power
supply modules due to the amount of heat produced with both supplies providing peak power. If system
thermals exceed programmed limits, platform management will attempt to keep the system operational.
Thermal support is open loop based on ambient temp sensor on the front panel.
The only power supply option validated for the Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP is the 460W AC PS.
The 750 W AC PS will fit and operate, but will not be validated in the JBOD or plan of record.
NOTE: The power cord is not included with the spare power supply and must be ordered separately. Please
refer to the Intel® Storage System JBOD2000S3 Product Family Configuration Guide for ordering information
in support.intel.com
The power supplies are modular, allowing for tool-less insertion and extraction from a bay in the back of the
chassis. When inserted, the card edge connector of the power supply mates blindly to a matching slot
connector on the PDB board.
In the event of a power supply failure, redundant 1+1 power supply configurations have support for hot-
swap extraction and insertion.
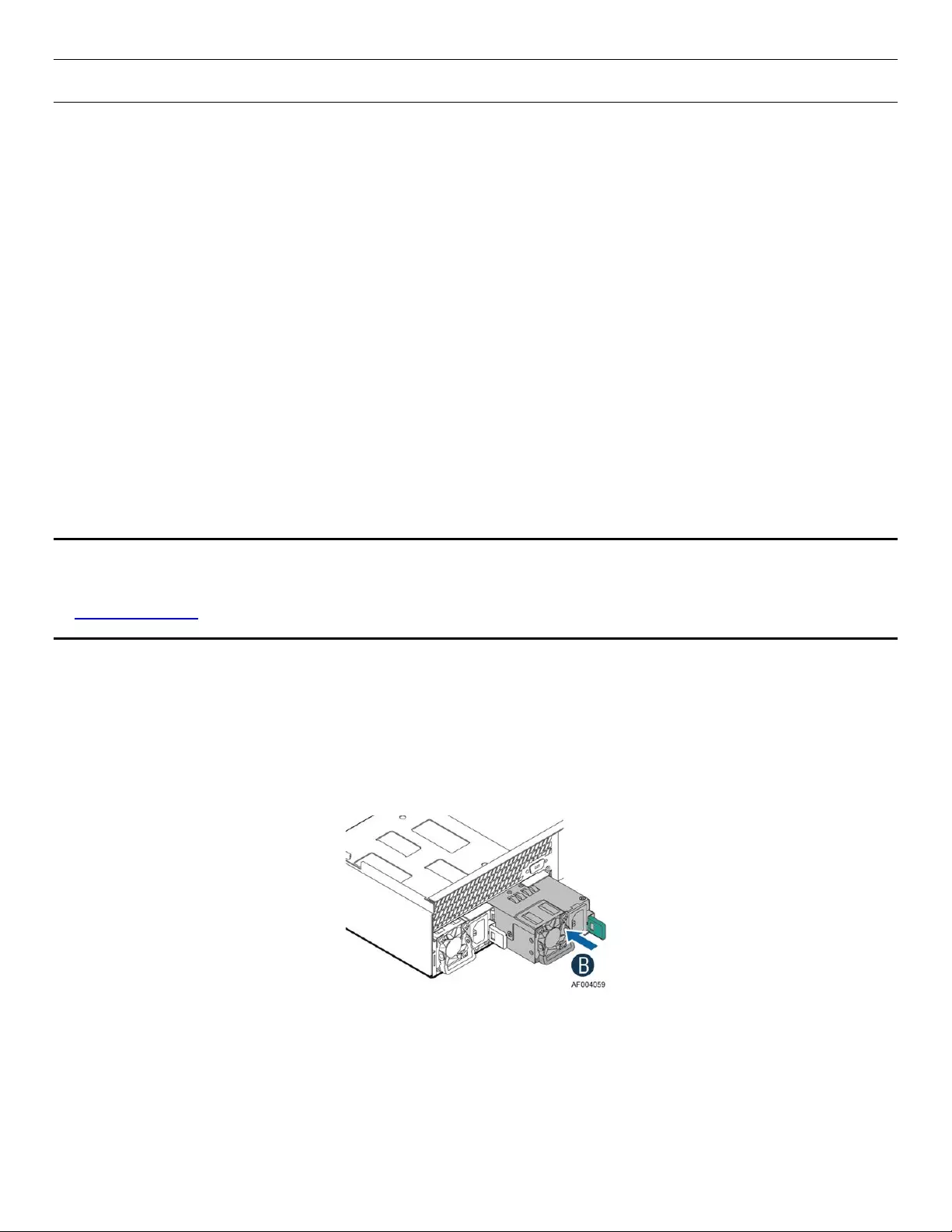
Figure 13. Power Supply Assembly
The AC input is auto-ranging and power factor corrected.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
12
4.1 Power Distribution Board (PDB)
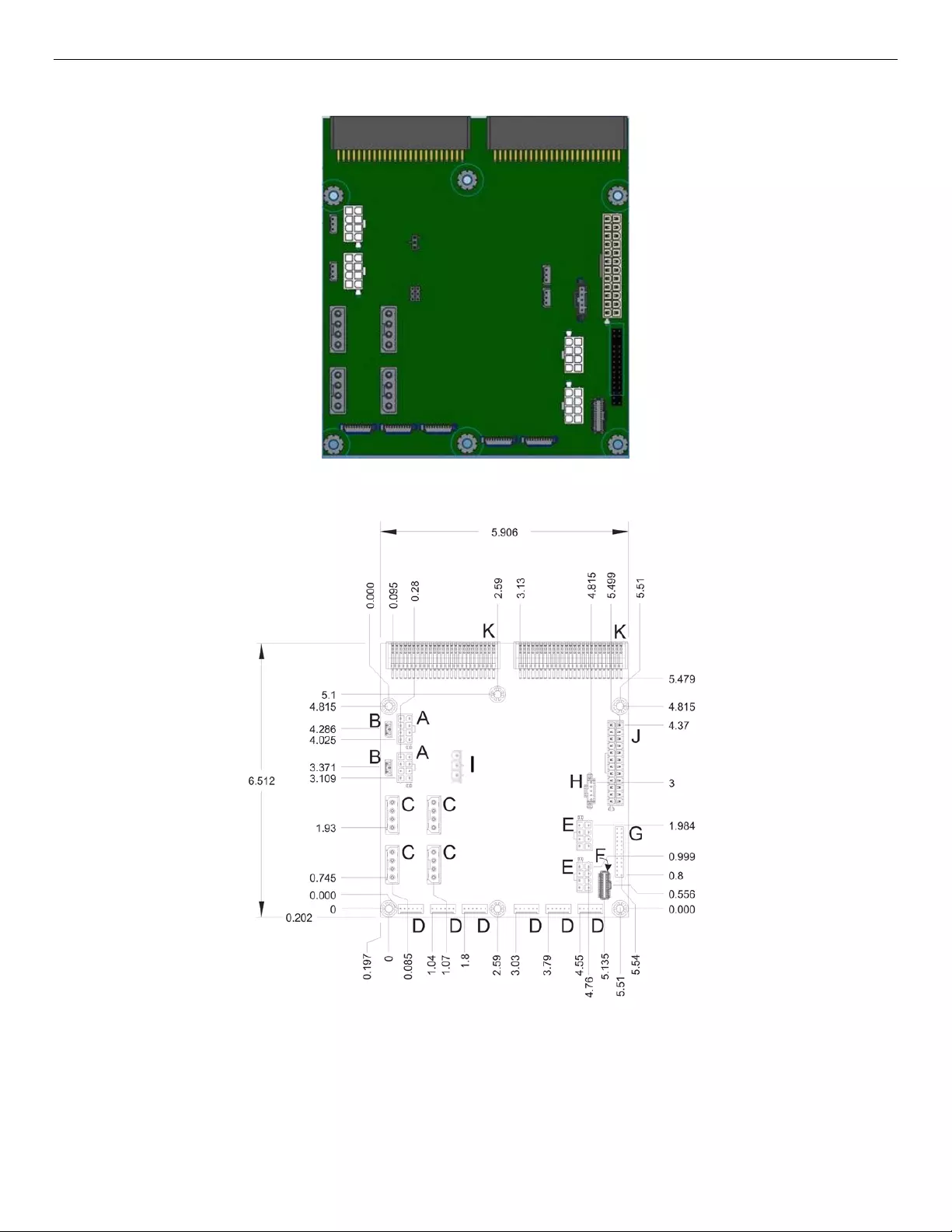
Figure 14. Power Distribution Board (PDB)
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
13
Figure 15. PDB Component Placement
Label
Description
Label
Description
A
HSBP power header
G
2x12-pin front panel header
B
Expander SES-2 header
H
1x5 aux header
C
Expander power header
I
2x3 Auto Power Jumper
D
FAN header
J
2x12 SSI power connector
E
HSBP power header
K
power supply connector
F
2x15-pin storage mini front
panel header
The PDB provides power from the power supply modules to the JBOD components, and provides thermal
monitoring and fan control, and includes the following features:
The PDB connects to the power supply canister through two CRPS card edge connectors.
Optional 2x12-pin SSI and 1x5-pin SSI power control headers (for potential future use)
Power for up to two internal 36-port SAS expander cards (RES3FV288) with additional connectors for
future use
Two 2x4-pin 12V power headers and an additional two 2x4-pin 12V power headers for future use,
each cable is used to connect power to a single 12x 3.5” HSBP or up to three 8x 2.5” HSBPs.
Support for hot-swap redundant fan speed control solutions up to four system fans and identification
of fan failures at front panel fault LED indicator with communication over SES2 interface to host PC
SMB interface for communicating enclosure status through the expander board to the host system
external host controller via SES interface. Monitoring capabilities include:
- Fan tachs.
- 12V voltage out from PSU.
- Temperature sensor on front panel.
- Ambient overtemp protection: Reported to host system and fan boost only. No shutdown.
- Degraded (PSU, FAN) state reportable to host system and on JBOD status LED.
A 3-pin jumper (J2C1) allows setting the Auto Power Enable/Disable setting. The auto power-on jumper
setting determines whether the JBOD power-on status will resume automatically if system power is removed
and then reapplied. When Auto-Power-On is enabled, the JBOD will power on automatically with application
of AC power. When Auto-Power-On is disabled, the JBOD is powered on using the Front Panel push-button
switch. The jumper options are described in the table below.
Table 6: Auto Power on Jumper Options
Jumper Status
Auto Power-on Status
System Behavior after a system
power interruption
No Jumper
JBOD Auto-Power-On enabled
JBOD Auto-Powers-On when power
is applied to the power supply
Jumper pins 1 + 2
JBOD Auto-Power-On disabled
JBOD powers on from front panel
push-button only when power is
applied to the power supply
Jumper pins 2 + 3
JBOD Auto-Power-On enabled
JBOD Auto-Powers-On when power
is applied to the power supply
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
14
The ADT7476 thermal controller on the PDB can measure and control the speed of up to four fans. The
controller provides acoustic enhancements to ensure the fans run at the lowest possible speed for the given
temperature. The controller interfaces with two remote temp sensors and a local temp sensor built into the
chip.
The thermal controller on the PDB is programmed using the SAS expander that comes with the Intel® Storage
System JBOD2312S3SP. The SAS expander in the Intel® Storage System JBOD2000S3SP uses firmware that
programs the thermal controller when the system is turned on. If the SAS expander is not plugged into the
PDB using the I2C cable, the fans will run at 100% and the thermal controller will not be programmed
correctly.
The cable must be connected to the I2C port B (Port C will not program the PDB) on the expander board and
then either of the I2C connectors on the PDB before the system is turned on.
If the fan runs at 100% at room temperature, there is an issue with the SMBUS connection, the SAS expander
is not getting power, or the incorrect firmware is on the expander.
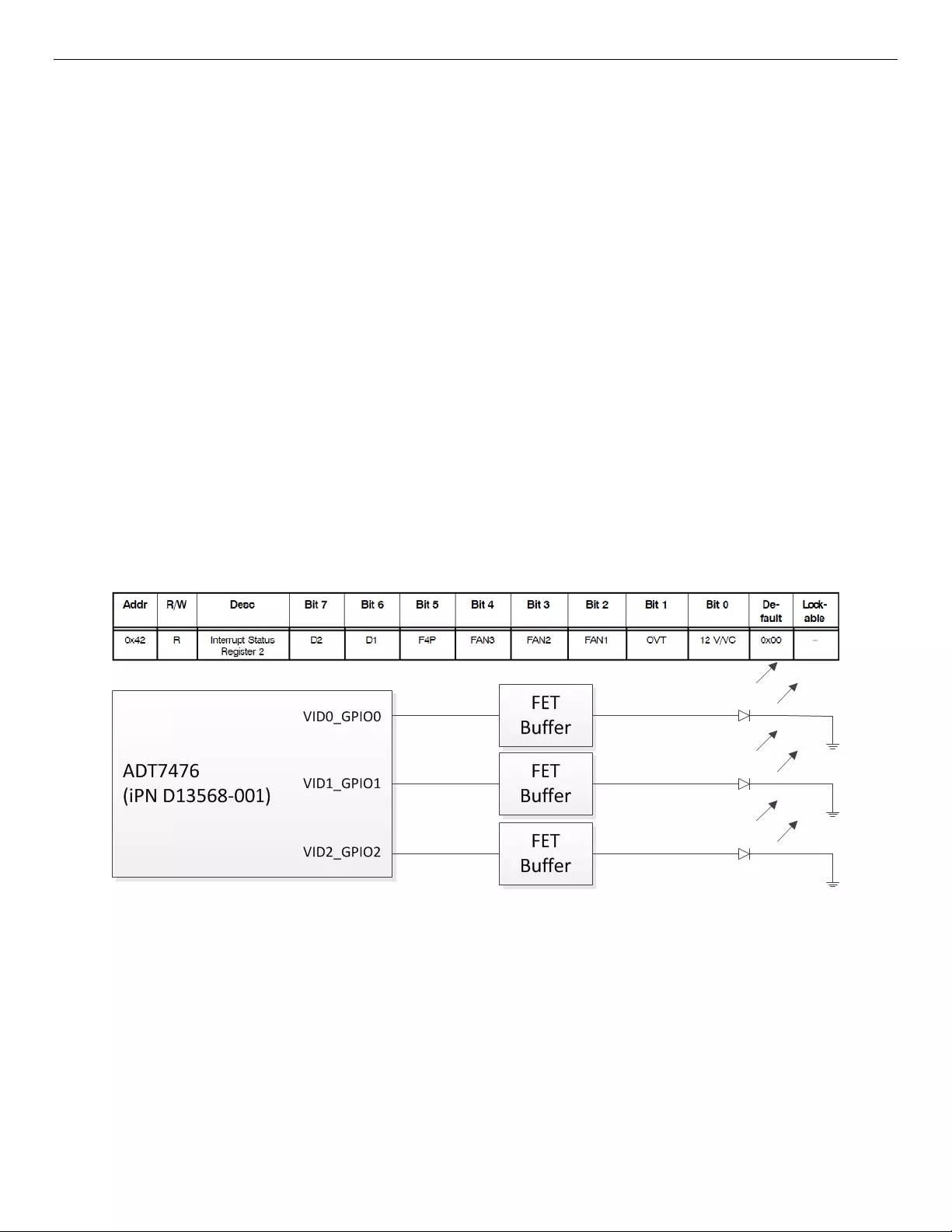
When a fan fails in the Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP, an interrupt register bit is set in the ADT7476
Thermal Controller that signals the fan fault (register shown below). The PMC expander chip on the SAS
expander monitors this register, and when a fan fault bit is set in the interrupt register, this information is
sent to the host system through SES. The ADT7476 controller also sends a signal out of its GPIOs to light the
LED on the failed fan’s hot-swap housing which makes replacing/diagnosing the failed fan much easier.
Interrupt Register 2 for ADT7476 (Bits 2, 3, and 4 used for fan faults):
Figure 16. Fan Fault LED Block Diagram
4.2 Mechanical Overview
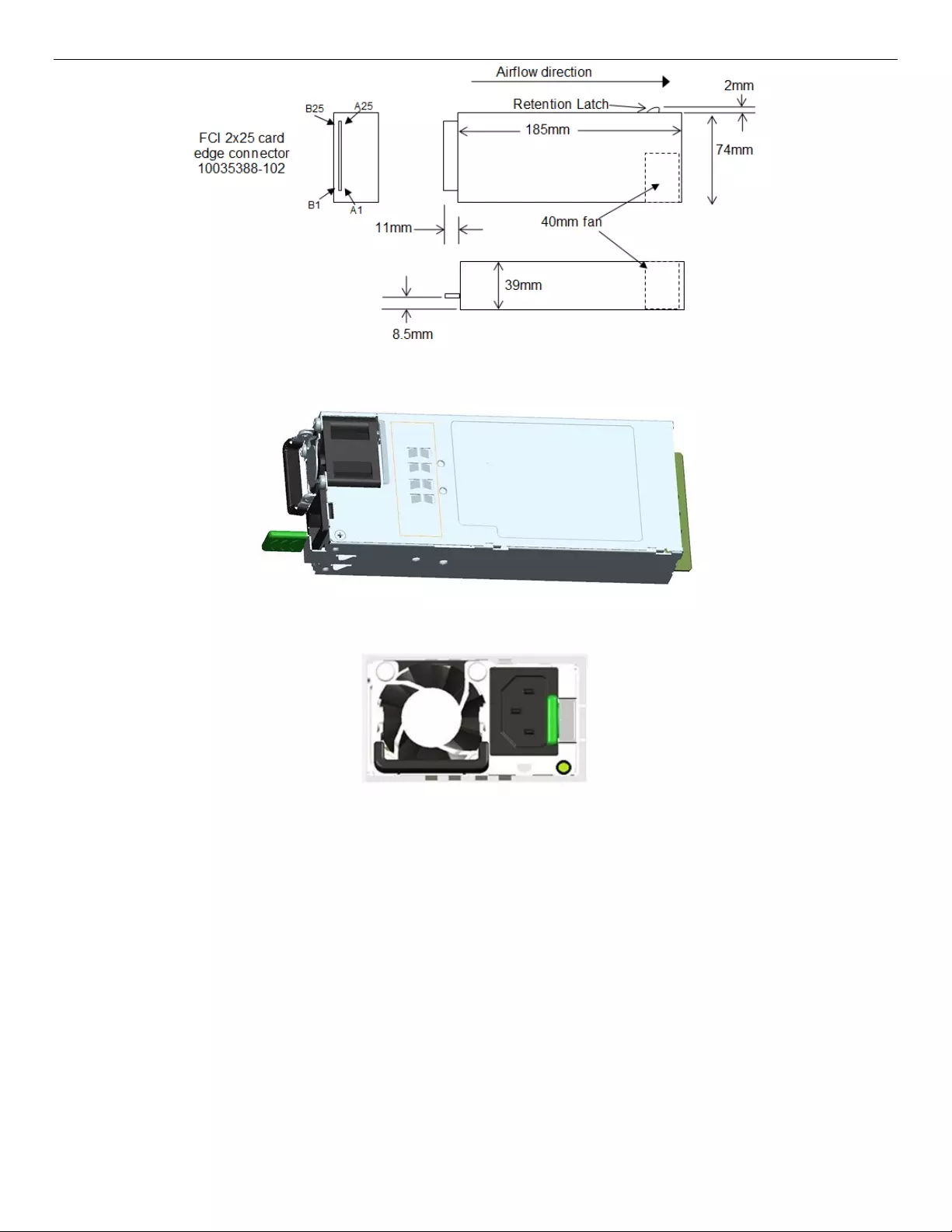
The physical size of the power supply enclosure is 39/40mm x 74mm x 185mm. The power supply contains
a single 40mm fan. The power supply has a card edge output that interfaces with a 2x25 card edge
connector in the system. The AC plugs directly into the external face of the power supply.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
15
Figure 17. Power Supply Module Mechanical Drawing
Figure 18. Power Supply Module
Figure 19. AC Power Supply – Connector View
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
16
4.3 Power Connectors
4.3.1 Power Supply Module Card Edge Connector
Each power supply module has a single 2x25 card edge output connection that plugs directly into a matching
slot connector on the server board. The connector provides both power and communication signals to the
server board. The following table defines the connector pin-out.
Table 7. Power Supply Module Output Power Connector Pin-out
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A1
GND
B1
GND
A2
GND
B2
GND
A3
GND
B3
GND
A4
GND
B4
GND
A5
GND
B5
GND
A6
GND
B6
GND
A7
GND
B7
GND
A8
GND
B8
GND
A9
GND
B9
GND
A10
+12V
B10
+12V
A11
+12V
B11
+12V
A12
+12V
B12
+12V
A13
+12V
B13
+12V
A14
+12V
B14
+12V
A15
+12V
B15
+12V
A16
+12V
B16
+12V
A17
+12V
B17
+12V
A18
+12V
B18
+12V
A19
PMBus SDA
B19
A0 (SMBus address)
A20
PMBus SCL
B20
A1 (SMBus address)
A21
PSON
B21
12V stby
A22
SMBAlert#
B22
Cold Redundancy Bus
A23
Return Sense
B23
12V Load Share Bus
A24
+12V Remote Sense
B24
No Connect
A25
PWOK
B25
Compatibility Check pin*
The JBOD’s PDB provides several connectors to provide power to various system options. The following sub-
sections identify the location, provide the pin-out definition, and provide a brief usage description for each.
4.3.2 Hot-Swap Backplane Power Connector
The JBOD’s PDB board includes four white 2x4-pin power connectors, used to provide power to the hot-
swap backplanes. On the JBOD PDB, this connector is labeled as “HSBP PWR”. The following table provides
the pin-out for this connector.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
17
Table 8. Hot-swap Backplane Power Connector Pin-out (“HSBP PWR”)
Pin
Signal Description
Pin
Signal Description
1
Ground
5
P12V_240VA
2
Ground
6
P12V_240VA
3
Ground
7
P12V_240VA
4
Ground
8
P12V_240VA
4.4 Power Supply Module Efficiency
The following table provides the required minimum efficiency level at various loading conditions. These are
provided at four different load levels: 100%, 50%, 20%, and 10%. Efficiency is tested over an AC input
voltage range of 115 VAC to 220 VAC.
Table 9. 460 Watt Power Supply Efficiency
Loading
100% of Maximum
50% of Maximum
20% of Maximum
10% of Maximum
Minimum efficiency
88%
92%
88%
80%
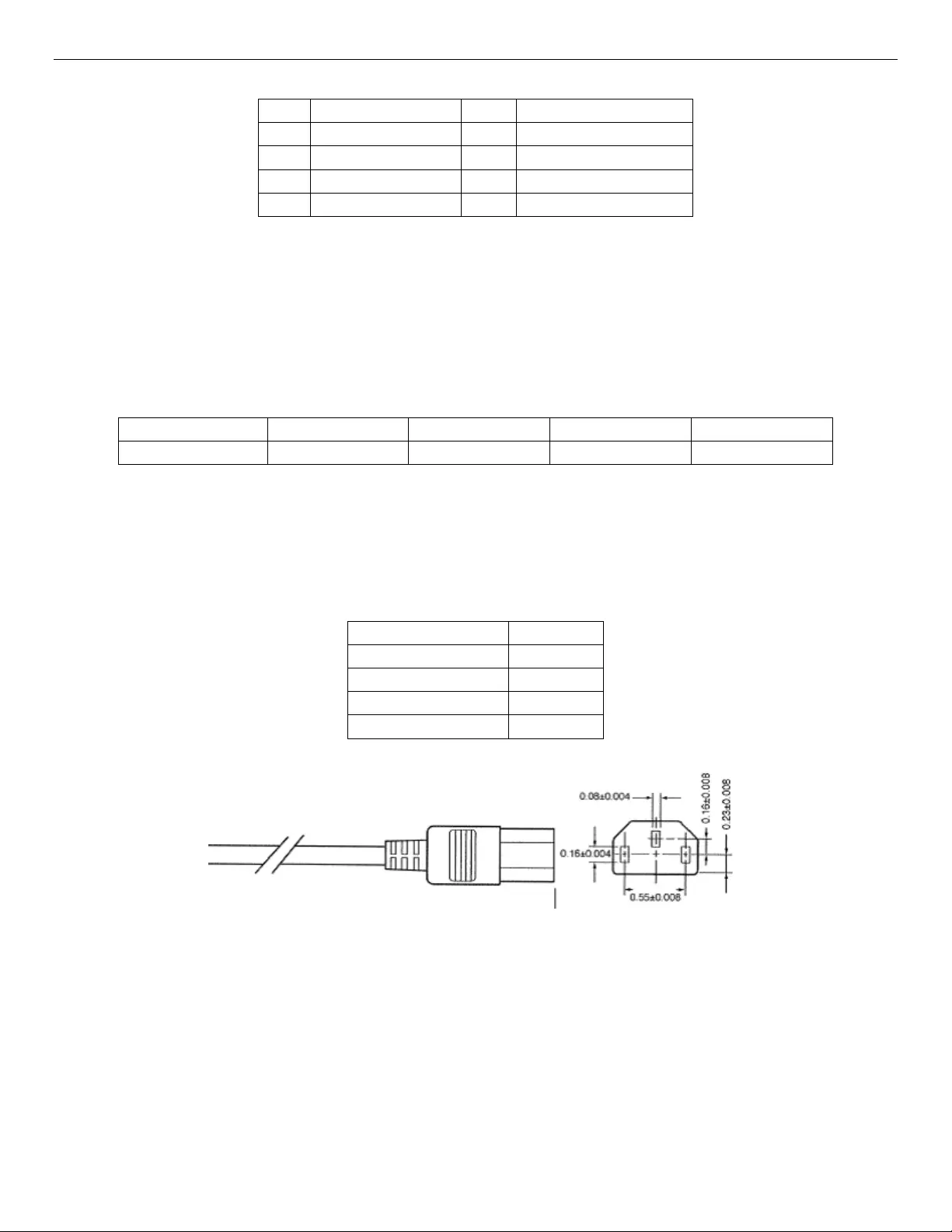
4.5 AC Power Cord Specification Requirements
The AC power cord used meets the specification requirements listed in the following table.
Table 10. AC Power Cord Specifications
Cable Type
SJT
Wire Size
16 AWG
Temperature Rating
105ºC
Amperage Rating
13 A
Voltage Rating
125 V
Figure 20. AC Power Cord
4.6 AC Input Specifications
4.6.1 Power Factor
The power supply meets the power factor requirements stated in the Energy Star Program Requirements for
Computer Servers. These requirements are stated below.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
18
Table 11. Power Factor
Output Power
10% Load
20% Load
50% Load
100% Load
Power factor
> 0.65
> 0.80
> 0.90
> 0.95
Note: Tested at 230VAC, 50Hz and 60Hz and 115VAC, 60Hz
4.6.2 AC Input Voltage Specification
The power supply operates within all specified limits over the following input voltage range. Harmonic
distortion of up to 10% of the rated line voltage does not cause the power supply to go out of specified
limits. Application of an input voltage below 85VAC does not cause damage to the power supply, including a
blown fuse.
Table 12. AC Input Voltage Range
Parameter
Min
Rated
Vmax
Start-up VAC
Power-off VAC
Voltage (110)
90 Vrms
100-127 Vrms
140 Vrms
85VAC +/-4VAC
70VAC +/-5VAC
Voltage (220)
180 Vrms
200-240 Vrms
264 Vrms
Frequency
47 Hz
50/60 Hz
63 Hz
1. The maximum input current at low input voltage range is measured at 90VAC, at max load.
2. The maximum input current at high input voltage range is measured at 180VAC, at max load.
3. This requirement is not to be used for determining agency input current markings.
4.6.3 AC Line Isolation Requirements
The power supply meets all safety agency requirements for dielectric strength. Transformers’ isolation
between primary and secondary windings complies with the 3000VAC (4242VDC) dielectric strength criteria.
If the working voltage between primary and secondary dictates a higher dielectric strength test voltage, the
highest test voltage will be used. In addition the insulation system complies with reinforced insulation per
safety standard IEC 950. Separation between the primary and secondary circuits, and primary to ground
circuits, complies with the IEC 950 spacing requirements.
4.6.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
An AC line dropout is defined to be when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC line for any
length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply meets dynamic voltage regulation requirements. An
AC line dropout of any duration does not cause tripping of control signals or protection circuits. If the AC
dropout lasts longer than the holdup time, the power supply will recover and meet all turn-on requirements.
The power supply meets the AC dropout requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of
the AC line for any duration does not cause damage to the power supply.
Table 13. AC Line Dropout/Holdup
Loading
Holdup Time
70%
12msec
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
19
4.6.4.1 AC Line 12VSB Holdup
The 12VSB output voltage stays in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during an AC dropout of
70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF state (PSON asserted or de-
asserted).
4.6.5 AC Line Fuse
The power supply has one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the AC input. The line
fusing is acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input fuse is a slow blow type. The AC inrush
current does not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any conditions. All protection circuits in the power
supply will not cause the AC fuse to blow unless a component in the power supply has failed. This includes
DC output load short conditions.
4.6.6 AC Inrush
The AC line inrush current does not exceed 55A peak, for up to one-quarter of the AC cycle, after which, the
input current is no more than the specified maximum input current. The peak inrush current is less than the
ratings of its critical components (including input fuse, bulk rectifiers, and surge limiting device).
The power supply meets the inrush requirements for any rated AC voltage, during turn-on at any phase of
AC voltage, during a single cycle AC dropout condition as well as upon recovery after AC dropout of any
duration, and over the specified temperature range (Top).
4.6.7 AC Line Transient Specification
The AC line transient conditions are defined as sag and surge conditions. Sag conditions are also commonly
referred to as “brownout”; these conditions are defined as the conditions when the AC line voltage drops
below nominal voltage. Surge conditions are defined as the conditions when the AC line voltage rises above
nominal voltage.
The power supply meets the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge conditions.
Table 14. AC Line Sag Transient Performance
AC Line Sag (10sec interval between each sagging)
Duration
Sag
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
0 to 1/2 AC cycle
95%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60 Hz
No loss of function or performance
> 1 AC cycle
> 30%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60 Hz
Loss of function acceptable, self
recoverable
Table 15. AC Line Surge Transient Performance
AC Line Surge
Duration
Surge
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
Continuous
10%
Nominal AC Voltages
50/60 Hz
No loss of function or performance
0 to ½ AC cycle
30%
Mid-point of nominal AC
Voltages
50/60 Hz
No loss of function or performance

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
20
4.6.8 Susceptibility Requirements
The power supply meets the following electrical immunity requirements when connected to a cage with an
external EMI filter that meets the criteria defined in the SSI document EPS Power Supply Specification. For
further information on Intel standards, request a copy of the Intel Environmental Standards Handbook.
Table 16. Performance Criteria
Level
Description
A
The apparatus continues to operate as intended. No degradation of performance.
B
The apparatus continues to operate as intended. No degradation of performance beyond spec limits.
C
Temporary loss of function is allowed provided that the function is self-recoverable or can be
restored by the operation of the controls.
4.6.9 Electrostatic Discharge Susceptibility
The power supply complies with the limits defined in EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003 using the IEC
61000-4-2: Edition 1.2: 2001-04 test standard and performance criteria B defined in Annex B of CISPR 24.
4.6.10 Fast Transient/Burst
The power supply complies with the limits defined in EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003 using the IEC
61000-4-4: Second edition: 2004-07 test standard and performance criteria B defined in Annex B of CISPR
24.
4.6.11 Radiated Immunity
The power supply complies with the limits defined in EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003 using the IEC
61000-4-3: Edition 2.1: 2002-09 test standard and performance criteria A defined in Annex B of CISPR 24.
4.6.12 Surge Immunity
The power supply is tested with the system for immunity to AC unidirectional wave, 2kV line to ground and
1kV line to line, per EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003, EN 61000-4-5: Edition 1.1:2001-04.
The pass criteria include: no unsafe operation is allowed under any condition; all power supply output
voltage levels to stay within proper spec levels; no change in operating state or loss of data during and after
the test profile; no component damage under any condition.
The power supply complies with the limits defined in EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003 using the IEC
61000-4-5: Edition 1.1:2001-04 test standard and performance criteria B defined in Annex B of CISPR 24.
4.6.13 Voltage Interruptions
The power supply complies with the limits defined in EN 55024: 1998/A1: 2001/A2: 2003 using the IEC
61000-4-11: Second Edition: 2004-03 test standard and performance criteria C defined in Annex B of CISPR
24.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
21
4.6.14 Protection Circuits
The protection circuits inside the power supply cause only the power supply’s main outputs to shut down. If
the power supply latches off due to a protection circuit tripping, an AC cycle OFF for 15 seconds and a
PSON# cycle HIGH for one second reset the power supply.
4.6.15 Over Current Protection (OCP)
The power supply has a current limit to prevent the outputs from exceeding the values shown in the table
below. If the current limit is exceeded, the power supply will shut down and latch off. The latch will be
cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption. The power supply will not be damaged
from repeated power cycling in this condition. 12VSB will be auto-recovered after removing the OCP limit.
Table 17. 460 Watt Power Supply Over Current Protection
Output Voltage
Input Voltage Range
Over Current Limit
+12V
90–264VAC
47A min; 55A max
12VSB
90–264VAC
2A min; 2.5A max
4.6.16 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
The power supply over voltage protection is locally sensed. The power supply will shut down and latch off
after an over voltage condition occurs. This latch will be cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC
power interruption. The values are measured at the output of the power supply’s connectors. The voltage
never exceeds the maximum levels when measured at the power connectors of the power supply connector
during any single point of fail. The voltage never trips any lower than the minimum levels when measured at
the power connector. 12VSB will be auto-recovered after removing the OVP limit.
Table 18. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits
Output Voltage
Min (V)
Max (V)
+12V
13.3
14.5
12VSB
13.3
14.5
4.6.17 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
The power supply is protected against over temperature conditions caused by loss of fan cooling or
excessive ambient temperature. In an OTP condition the PSU will shut down. When the power supply
temperature drops to within specified limits, the power supply will restore power automatically, while the
12VSB remains always on. The OTP circuit has a built-in margin so that the power supply will not oscillate on
and off due to temperature recovering conditions. The OTP trip level has a minimum of 4ºC of ambient
temperature margin.
4.7 Power Supply Status LED
There is a single bi-color LED to indicate power supply status. The LED operation is defined in the following
table.

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
22
Table 19. LED Indicators
Power Supply Condition
LED State
Output ON and OK
Green
No AC power to all power supplies
Off
AC present / Only 12VSB on (PS off)
1 Hz Blink Green
AC cord unplugged or AC power lost, with a second
power supply in parallel still with AC input power
Amber
Power supply warning events where the power
supply continues to operate; high temp, high power,
high current, slow fan
1 Hz Blink Amber
Power supply critical events causing a shutdown;
failure, OCP, OVP, fan fail
Amber

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
23
5 Thermal Management
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP is designed to operate at external ambient temperatures of
between 10ºC and 35ºC with limited excursion-based operation up to 45ºC and limited performance impact.
Working with integrated platform management, several features within the system are designed to move air
in a front-to-back direction, through the system and over critical components to prevent them from
overheating and allow the system to operate with best performance.
The installation and functionality of several JBOD components are used to maintain system thermals. They
include up to three managed 60-mm system fans and one integrated 40-mm fan for each installed power
supply module. Hard drive carriers can be populated with a hard drive or supplied drive blank.
5.1 Thermal Operation and Configuration Requirements
To keep the system operating within supported maximum thermal limits, the system must meet the
following operating and configuration guidelines:
The system operating ambient is designed for sustained operation up to 35ºC (ASHRAE Class A2)
with short-term excursion-based operation up to 45ºC (ASHRAE Class A4).
- The system can operate up to 40ºC (ASHRAE Class A3) for up to 900 hours per year.
- The system can operate up to 45ºC (ASHRAE Class A4) for up to 90 hours per year.
- System performance may be impacted when operating within the extended operating
temperature range.
- There is no long-term system reliability impact when operating at the extended temperature
range within the approved limits.
All hard drive bays must be populated. Hard drive carriers can be populated with a hard drive or
supplied drive blank.
In single power supply configurations, the second power supply bay must have the supplied filler
blank installed at all times.
The system must be configured with dual power supplies for the system to support fan redundancy.
The system top cover must be installed at all times when the system is in operation. The only
exception to this requirement is to hot replace a failed system fan, in which case the top cover can be
removed for no more than three minutes at a time.
5.2 Thermal Management Overview
In order to maintain the necessary airflow within the system, all of the previously listed components and top
cover need to be properly installed. For best system performance, the external ambient temperature should
remain below 35ºC and all system fans should be operational. The system is designed for fan redundancy
when the system is configured with two power supplies.
5.3 Thermal Sensor Input for Fan Speed Control
The power distribution board uses various sensors as inputs to fan speed control. Some of the sensors are
actual physical sensors and some are virtual sensors derived from calculations. The Front Panel
Temperature Sensor is used as an input to fan speed control.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
24
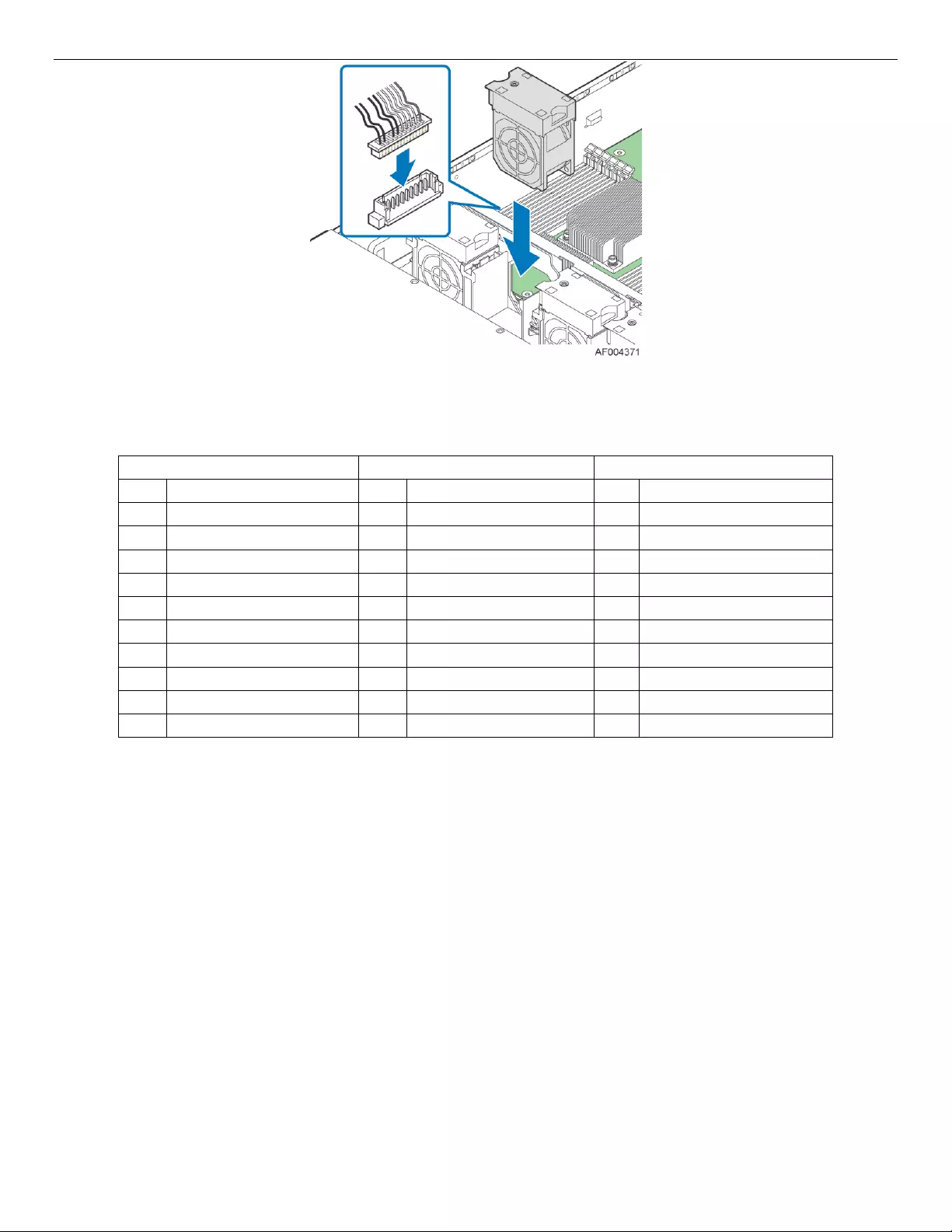
5.4 System Fans
Four 60x38-mm fans and an embedded fan for each installed power supply, provide the primary airflow for
the system. The system is designed for fan redundancy when configured with two power supply modules. If a
single fan fails (system fan or power supply fan), platform management will adjust the airflow of the
remaining fans and manage other platform features to maintain system thermals. Fan redundancy is lost if
more than one fan is in a failed state.
Figure 21. System Fan Identification
The system fan assembly is designed for ease of use and supports several features:
Each fan is hot-swappable.
Each fan is designed for tool-less insertion and extraction from the fan assembly. For instructions on
installing or removing a fan module, see the Intel® JBOD2000S3SP Service Guide.
Fan speed for each fan is controlled by integrated platform management controlled by the PDB.
When system thermals fluctuate high and low, the PDB firmware will increase or decrease the speeds
of specific fans within the fan assembly to regulate system thermals.
Each fan has a tachometer signal that allows the PDB to monitor its status.
On top of each fan is an integrated fan fault LED, which will turn on when a fan failure occurs.
Each fan has a 10-pin wire harness that connects to a matching connector on the PDB.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
25
Figure 22. System Fan Assembly
Table 20. System Fan Connector Pin-out
SYS_FAN 1
SYS_FAN 2
SYS_FAN 3
Pin#
Signal Description
Pin#
Signal Description
Pin#
Signal Description
1
FAN_TACH1_IN
1
FAN_TACH3_IN
1
FAN_TACH5_IN
2
FAN_BMC_PWM0_R_BUF
2
FAN_BMC_PWM1_R_BUF
2
FAN_BMC_PWM2_R_BUF
3
P12V_FAN
3
P12V_FAN
3
P12V_FAN
4
P12V_FAN
4
P12V_FAN
4
P12V_FAN
5
FAN_TACH0_IN
5
FAN_TACH2_IN
5
FAN_TACH4_IN
6
GROUND
6
GROUND
6
GROUND
7
GROUND
7
GROUND
7
GROUND
8
FAN_SYS0_PRSNT_N
8
FAN_SYS1_PRSNT_N
8
FAN_SYS2_PRSNT_N
9
LED_FAN_FAULT0_R
9
LED_FAN_FAULT1_R
9
LED_FAN_FAULT2_R
10
LED_FAN0
10
LED_FAN1
10
LED_FAN2
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
26
5.5 Fan Speed Control
Fan speed control for this system is driven primarily by the front panel temp sensor which is representative
of system ambient Temperature (Tsa). Fan speed override is driven by thermal sensors located on the
expander board.
The thermal solution in this 2U system utilizes four 60mm x 38mm fans.
Table 21: PWM Settings
Altitude
Up to 3000M
Tsa[C]
PWM
Fan Failed
11C
45%
100%
25C
45%
28C
50%
30C
55%
33C
60%
35C
65%
40C
80%
43C
100%
The FSC algorithm includes a 4 data point rolling average to assert the threshold value and 2ºC hysteresis to
prevent fan speed oscillations.
Table 22: Temperature Notification Thresholds
Limit
Sensor1
Front Panel
Sensor 3 – Expander
Processor Internal
High Critical
56C
125
High Warning
54C
120
Low Warning
27C
25
Low Critical
22C
20
Actual sensor temperature is -20ºC – SES protocol uses a 20ºC offset.
Front Panel Sensor 1 has a 2ºC offset due to self-heating.
Fan control overrides:
If Temperature Sensor 3 exceeds its High Warning threshold -> set Fans to 80%.
If Temperature Sensor 3 exceeds its High Critical threshold -> set Fans to 100%.
5.6 Power Supply Module Fan
Each installed power supply module includes one embedded (non-removable) 40-mm fan. It is responsible
for airflow through the power supply module. If this fan fails, the power supply will continue to operate until
its internal temperature reaches an upper critical limit. The power supply will be protected against over
temperature conditions caused by loss of fan cooling or excessive ambient temperature. In an over-
temperature protection condition, the power supply module will shut down.

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
27
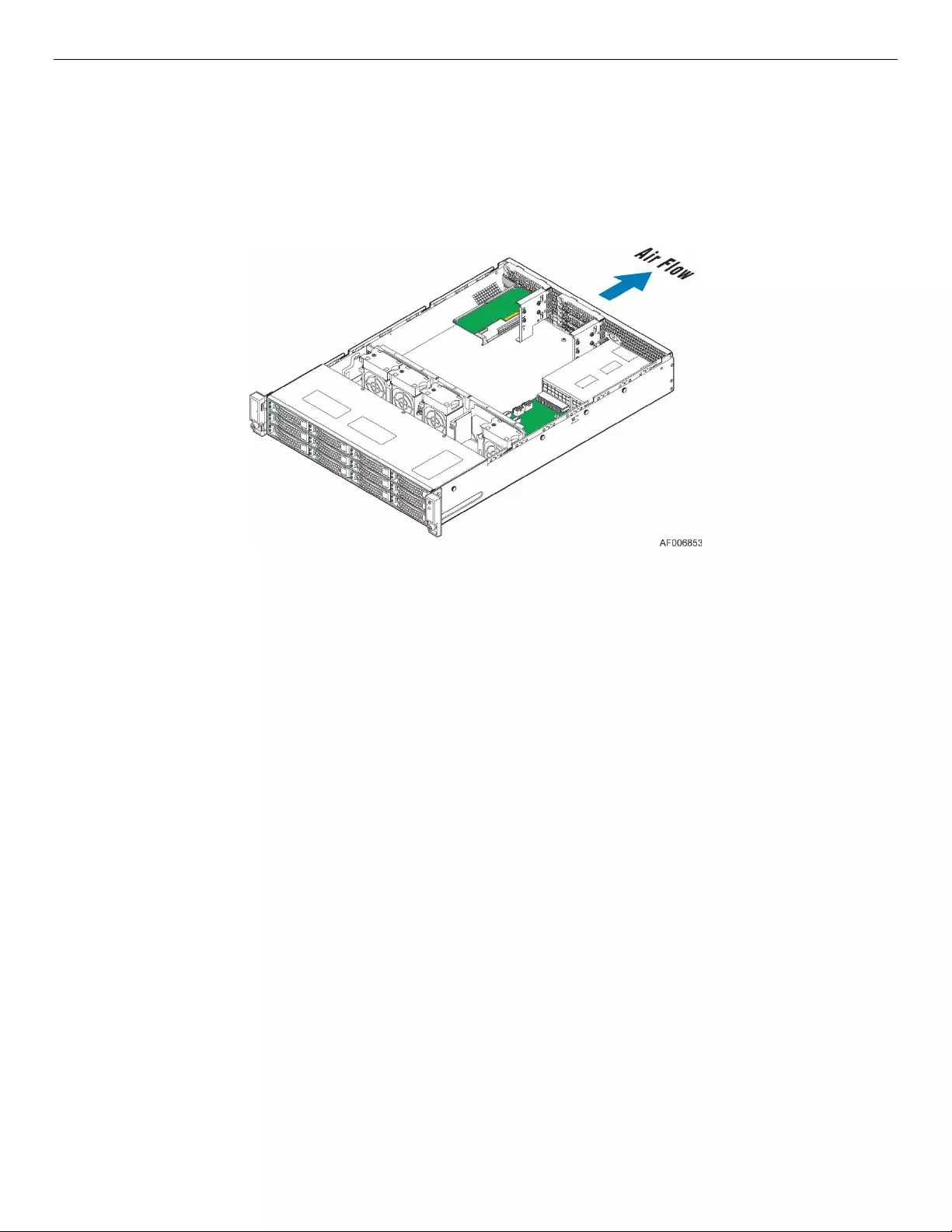
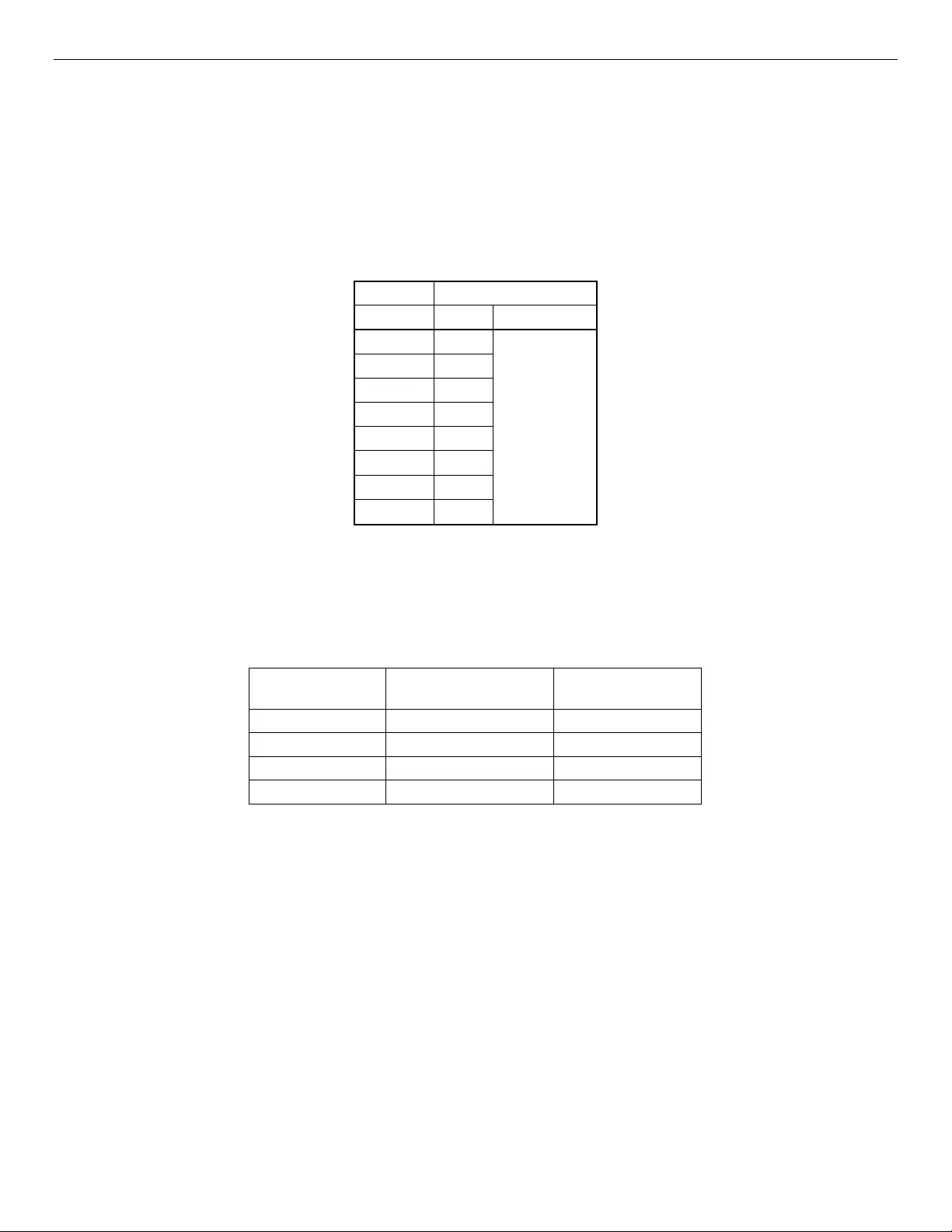
6 JBOD2000S3SP Internal Connection Overview
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2000S3SP contains one or two SAS expander board(s), power distribution
board, HSBP, and fans in its chassis. This section provides specification of the SAS expander board and SAS
converter, and interconnection between those components.
6.1 Expander Board
The Intel 36-port expander (RES3FV288) is mounted in a retention mechanism at the rear of the chassis that
provides access to the external facing SAS ports, and is designed on PMC’s 12Gb/s expander technology.
The expander has seven SFF8643 mini-SAS HD connectors that connect internally to the backplane and two
externally facing SFF8644 connectors. The dual-port backplane of the JBOD contains two 36-port
expanders, while the single-port backplane contains one 36-port expander.
Features of the Intel® RAID Expander are as follows:
SAS protocol, described in the Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) Standard, version 3.0
Serial SCSI Protocol (SSP) to enable communication with other SAS devices
Serial Tunneling Protocol (STP) support for SATA II through expander interfaces
Serial Management Protocol (SMP) to share topology management information with expanders
Supports SES for enclosure management
Output mini-SAS HD connectors support sideband SGPIO as per SFF-8448 specification
Supports both Serial Attached SCSI and Serial ATA device targets
12Gb/s, 6Gb/s, 3Gb/s, and 1.5 Gb/s data transfer rates
SFF-8643 and SFF-8644 mini-SAS HD connectors
Provides a low-latency connection to create and maintain transparent access to each connected
SAS/SATA physical drive
Staggered spin-up
Hot-plug
Native Command Queuing
Allows multiple initiators to address a single target (in a fail-over configuration)
SAS Expander Major Components:
36-Port 12 Gb/s SAS-3 Expander Chip
- Provides 36 PHYs
Any PHYs may be combined into wide port(s)
Any PHY can be SAS or SATA attached
- Supports multiple data rates and auto-negotiation between the following:
3 Gb/s, 6.0 Gb/s, and 12.0 Gb/s SAS
1.5 Gb/s, 3 Gb/s, and 6.0 Gb/s SATA
- Supports SSP, STP, and SMP
- Supports the SAS protocol described in the Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) Standard, version 3.0r5
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
28
- Provides a low-latency connection router to efficiently create and maintain connections
- Supports T10-Based and Phy-Based Zoning for storage partitioning
- Allows any number of phys to be included in a wide port
- Provides up to 12 I2C interfaces
Flash ROM – A 128-Mbit Quad SPI flash ROM is used to accommodate expander card firmware.
Heartbeat LED – A green LED provides a heartbeat with a 1 second blink rate to indicate the expander
has booted properly.
All JBOD SKUs use the 36-port SAS expander card. Single-port JBOD2000S3SP SKU has one 36-port SAS
expander card.
See the Intel® RAID Expander RES3FV288 User Guide at www.intel.com.
Figure 23. Internal SAS Expander Location
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
29
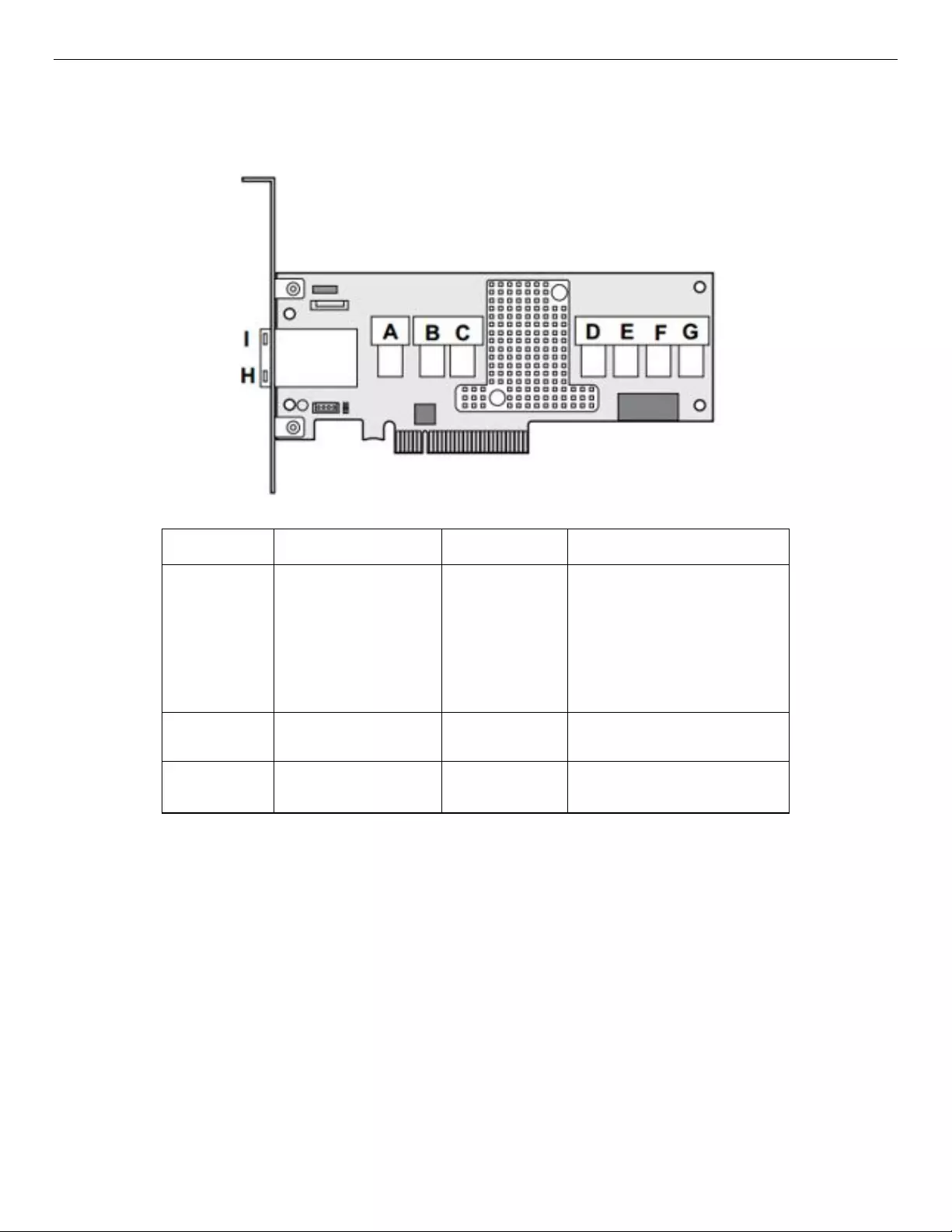
6.1.1 JBOD SAS Expander Port Numbering
Following is a suggestion for the JBOD SAS expander port numbering for internal and external connections.
Connector
Description
Type
Comment
A, B, C, D, E Internal Output
connectors
(to backpla ne) SFF-8643 A– SAS Output ports (0-3)
B – SAS Output ports (4-7)
C – SAS Output ports (8-11)
D– SAS Outp ut ports (12-15)
E – SAS Output ports ( 16-19)
F, G Internal Input
connectors
(from RAID controller/HBA) SFF-8643 F – SAS Input ports (0-3)
G – SAS
Input
ports (4-7)
H, I External Output connectors
(to JBOD)
SFF-8644 H – S A S Output ports (20-23)
I – SAS Out put ports (24-27)
Figure 24: SAS Expander Port Numbering
The Intel® RAID Expander RES3FV288 is transparent to users in RAID configurations. Refer to the technical
specification or user guide of the RAID controller connected to this expander card to know how to configure
a RAID system.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
30
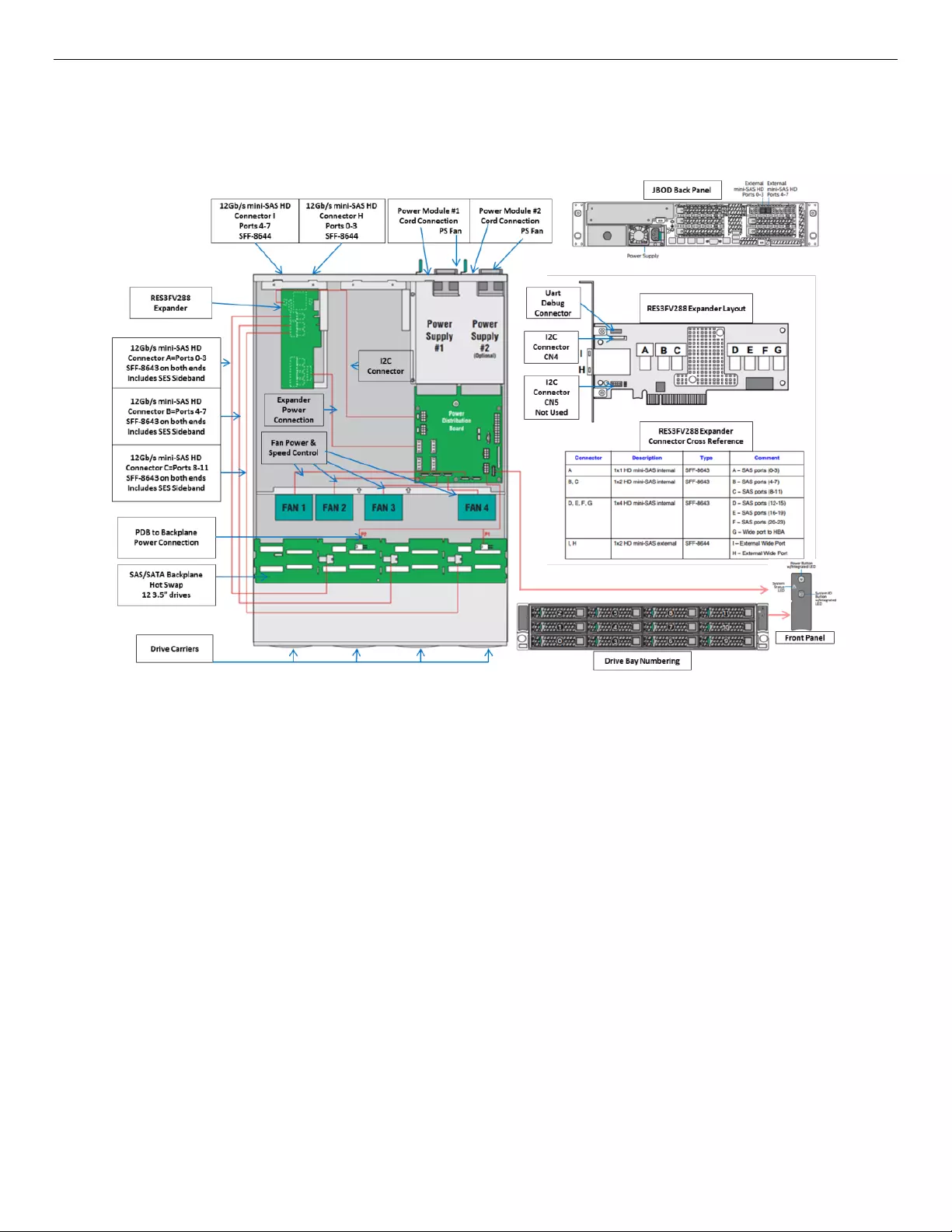
6.1.2 JBOD2312S3SP Interconnection
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP has a 12x3.5” single-port HSBP, a primary SAS expander, a dual-
port SAS interface board, a PDB, a PSU, and four fans in its chassis.
Figure 25. 12x3.5” Single-port JBOD2000S3SP Interconnection Diagram

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
31
7 JBOD2000S3SP External SAS Connection Mode
Overview
The Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP supports connection to many different external SAS HBA and
SAS RAID controller solutions, to achieve single JBOD connection, multiple JBODs daisy chain connection,
and failover connections. This section provides an overview of the different options available.
7.1 External SAS Controller Support
Our current and future supported controllers are referenced via our JBOD2000S3SP THOL or SCT.
SAS connectivity is via the external SAS connectors (SFF8644); both native SAS HBAs and RAID HBAs are
supported.
7.2 External SAS Cable
JBOD2000S3SP system uses SFF-8644 mini-SAS receptacle, so SFF-8644 mini-SAS cable is needed when
connecting the JBOD2000S3SP to host or cascading to other JBOD2000. The following figure is an
illustration of SFF-8644 mini-SAS cable.
Figure 26. SFF-8644 mini-SAS Cable
According to SAS 3.0 specification, the length of mini-SAS cable has the following rules:
The 12Gb/s SAS cables work up to 10 meters with DFE (decision feedback equalization).
The 12Gb/s SAS cables run at less than 6 meters without DFE.
The 6Gb/s SAS deployments are limited to cable length of 6 meters.
The 3Gb/s SAS deployments are limited to cable length 6 meters.
The standard package of JBOD2000S3SP system doesn’t contain external cables (you need to order the
cable from other vendors). Intel has tested some models of the mini-SAS HD cable (see Appendix A for the
list). However, the mini-SAS HD cables that JBOD2000S3SP can support are not limited to that list; users can
qualify new cables by themselves.
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
32
7.3 Hard Drive Type
JBOD2000S3SP can support 12Gb/s, 6Gb/s, and 3Gb/s SAS hard drives and 3Gb/s and 6Gb/s SATA hard
drives. SATA hard drives do not support some configurations, which need to take advantage of the dual-port
SAS hard drives, such as dual-domain SAS or failover clustering.
Refer to the Intel server configurator tool to a list of tested hard drives at https://serverconfigurator.intel.com.
7.4 JBOD Cascade
JBOD cascading is also called daisy-chaining, which means connecting multiple JBOD units to constitute
deeper storage pool. How many JBOD2000S3SP can be cascaded depends on the property of the SAS HBA
or RAID adapter that connects to JBOD2000SP3. However, only two layers of cascaded JBOD2000S3SP
system have been fully validated by Intel. Only cascading the same type of JBOD2000S3SP is
recommended.
7.5 Single-port JBOD2000S3SP External Connection Mode
The following sections provide the external connection modes supported by the Intel® Storage System
JBOD2000S3SP single-port backplane SKU.
7.5.1 Single JBOD2000S3SP Connection
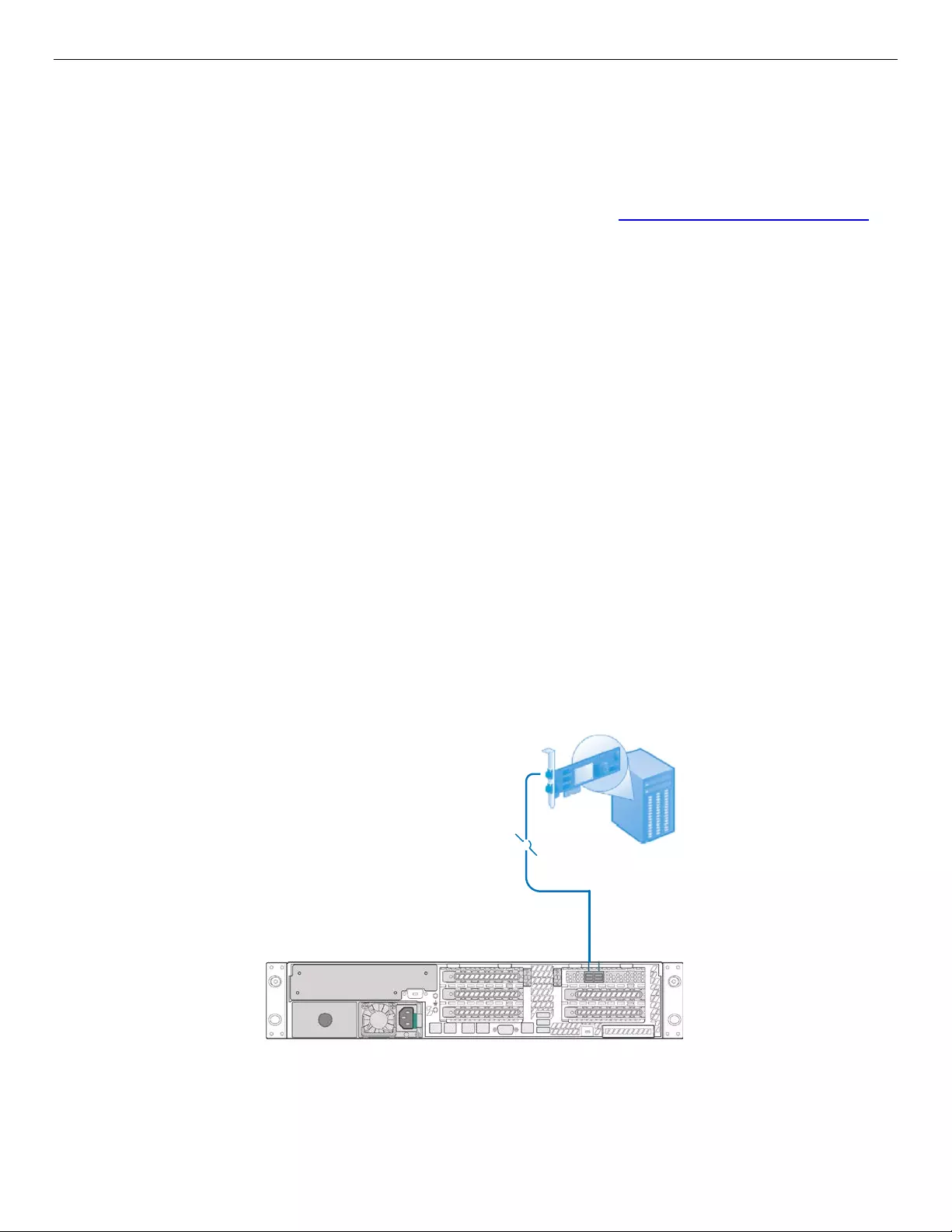
Figure 27 below shows the SAS HBA or RAID adapter connecting to one single-port JBOD2000S3SP with
one mini-SAS HD cable. The single controller port incorporates four SAS lanes for a total maximum
throughput of 4800MB/s with SAS 3.0 technology. In the figure, the “4\” notation indicates a 4-lane bundled
path. Either A PRI or B PRI SAS port on JBOD2000S3SP can be connected in this scenario. SATA or SAS hard
drives can be supported.
4
Figure 27. Single JBOD2000S3SP Connection
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
33
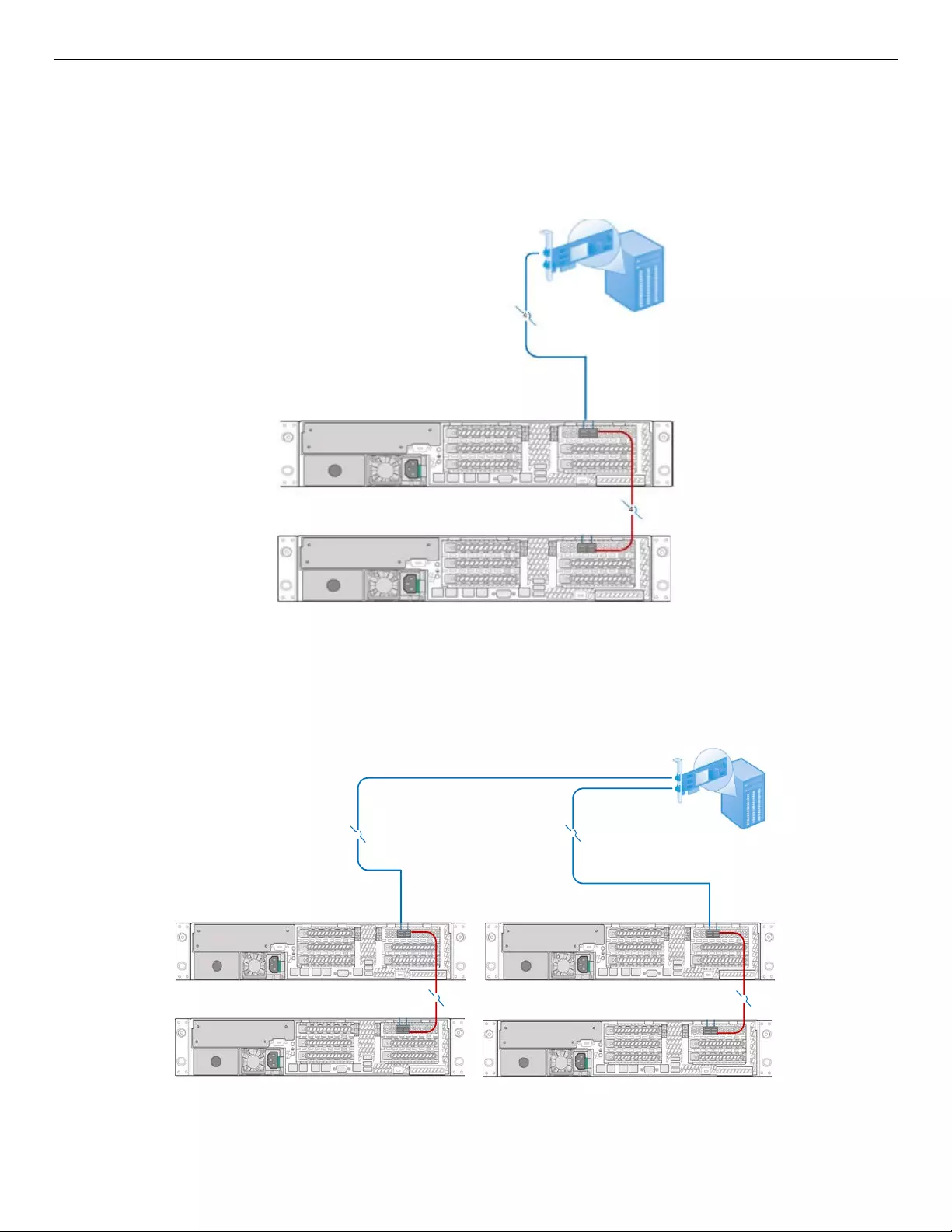
7.5.2 Two JBOD2000S3SP Cascade
Figure 28 below shows two cascaded single-port JBOD2000S3SP connecting to the SAS HBA or RAID
adapter with one mini-SAS cable. The function of SAS port “A PRI” and “B PRI” on JBOD2000S3SP are
equivalent. Either “A PRI” or “B PRI” SAS port can be connected to the SAS adapter or cascaded with other
JBOD2000S3SP in this scenario. SATA or SAS hard drive can be supported.
Figure 28. Two Single-port JBOD2000S3SP Cascade
Figure 29 below shows another connection scenario in which the SAS HBA or RAID adapter has two external
mini-SAS connectors. Other group of two cascaded single-port JBOD2000S3SP can be connected to the
host adapter with one mini-SAS cable. Users can get more storage space with this kind of connection mode.
4
44
4
Figure 29. Two Groups of Cascaded Single-port JBOD2000S3SP
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
34
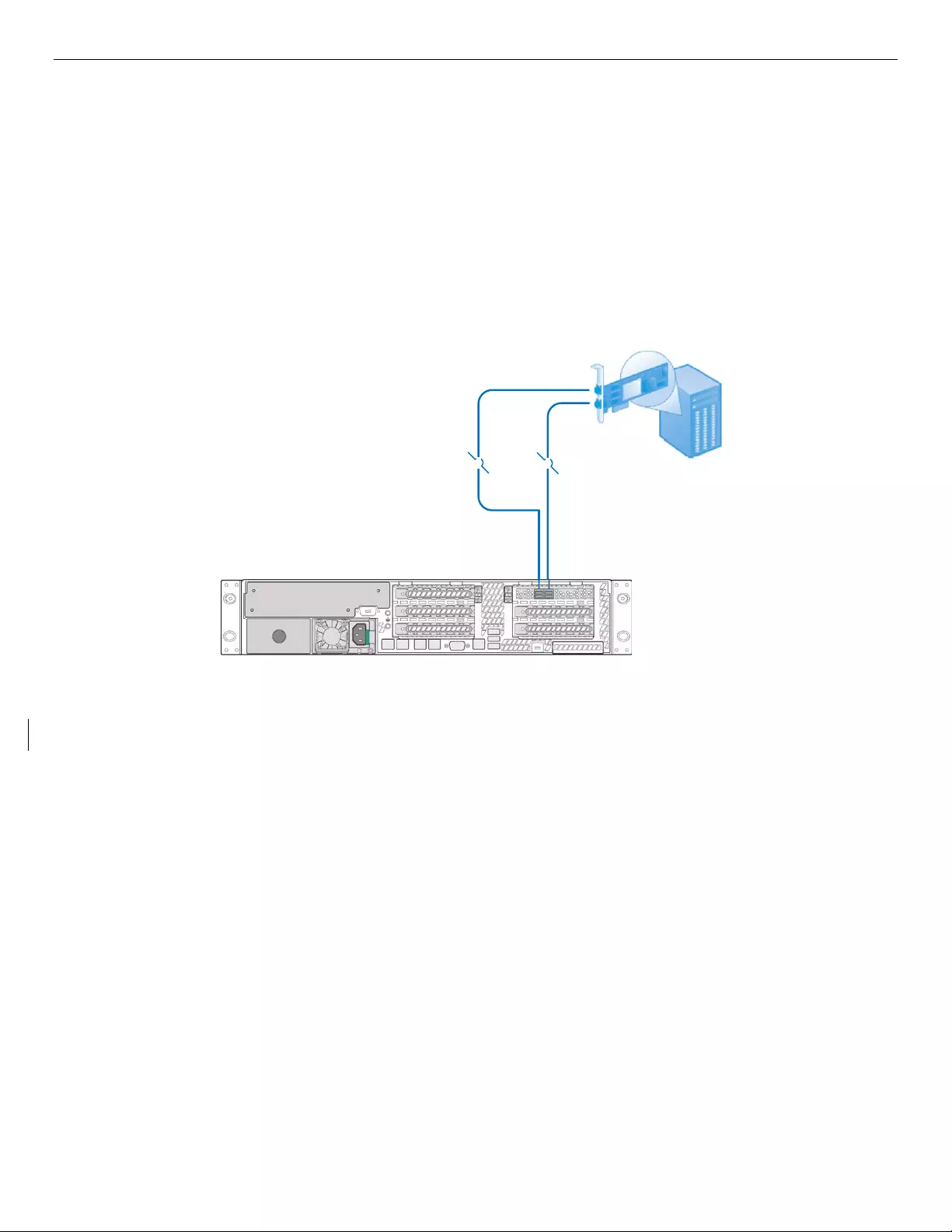
7.5.3 Dual-path Connection
Dual-path means a host has redundant pathways to the storage device. When any part of the data pathway
to a SAS domain fails, data transfer will not stop. This is one advantage of dual-path connection. Dual-path
implementations cost less than dual-domain SAS implementations but do not provide the full redundancy
like a dual-domain SAS solution.
Figure 30 below shows the dual external mini-SAS HD connectors of the SAS HBA or RAID adapter
connecting to JBOD2000S3SP with two mini-SAS HD cables. Each single controller port incorporates four
SAS lanes for a total maximum throughput of 4800MB/s with SAS 3.0 technology. SATA or SAS hard drive
can be supported. The SAS HBA or RAID adapter can handle either mini-SAS cable disconnection and
maintain the data transfer between the host and JBOD2000S3SP.
44
Figure 30. Dual-path Connection
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
35
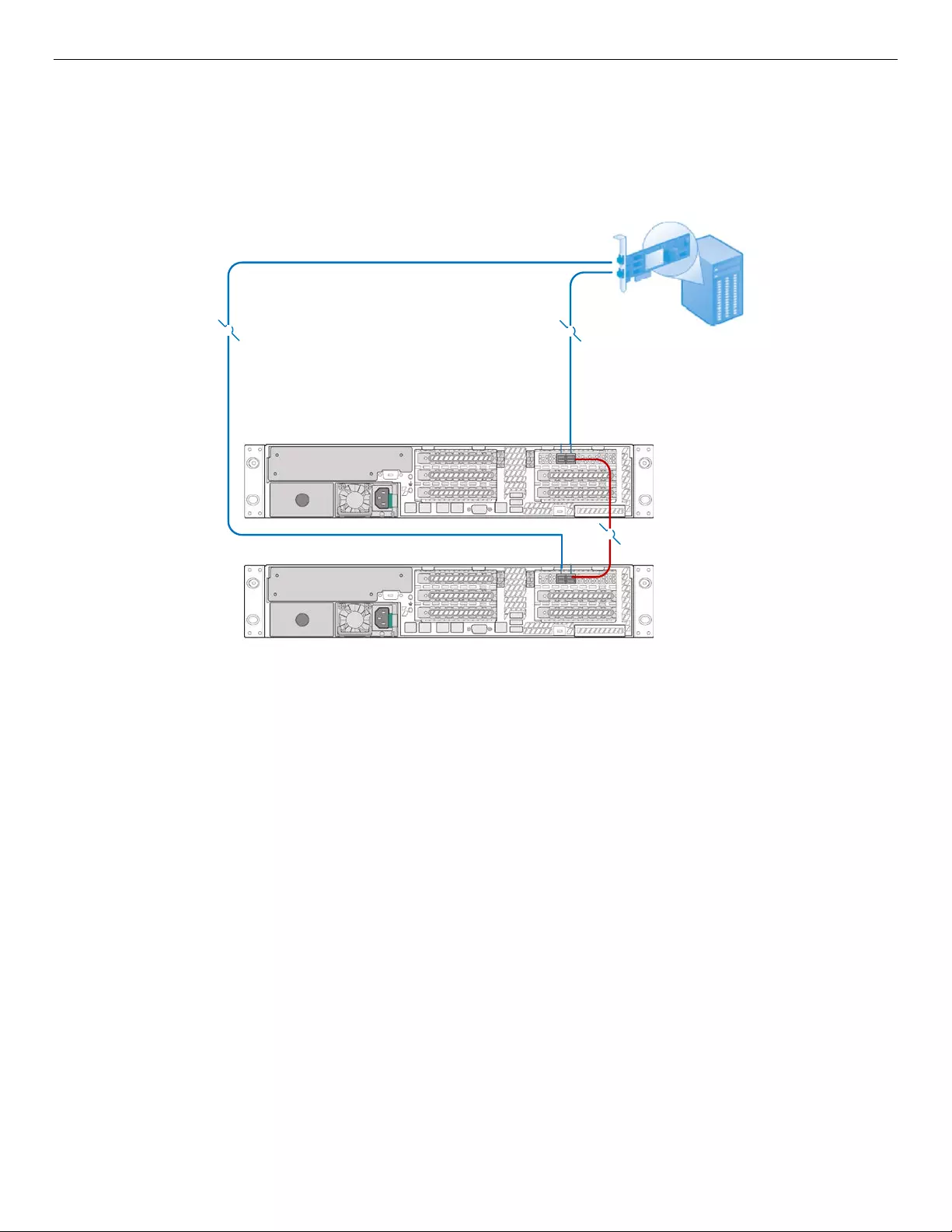
7.5.4 Dual-path with Cascaded JBOD2000S3SP
Dual-path to a single-domain provides tolerance of cable failure. Two single-port JBOD2000S3SP systems
are cascaded with a mini-SAS cable between each “B PRI” SAS port, and a controller connects to each “A PRI”
SAS port with two mini-SAS HD cables. Any mini-SAS HD cable failure will not stop the data transfer between
the host and two JBOD2000S3SP. Both SAS and SATA drives support this configuration.
44
4
Figure 31. Dual-path with Cascaded JBOD2000S3SP
Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
36
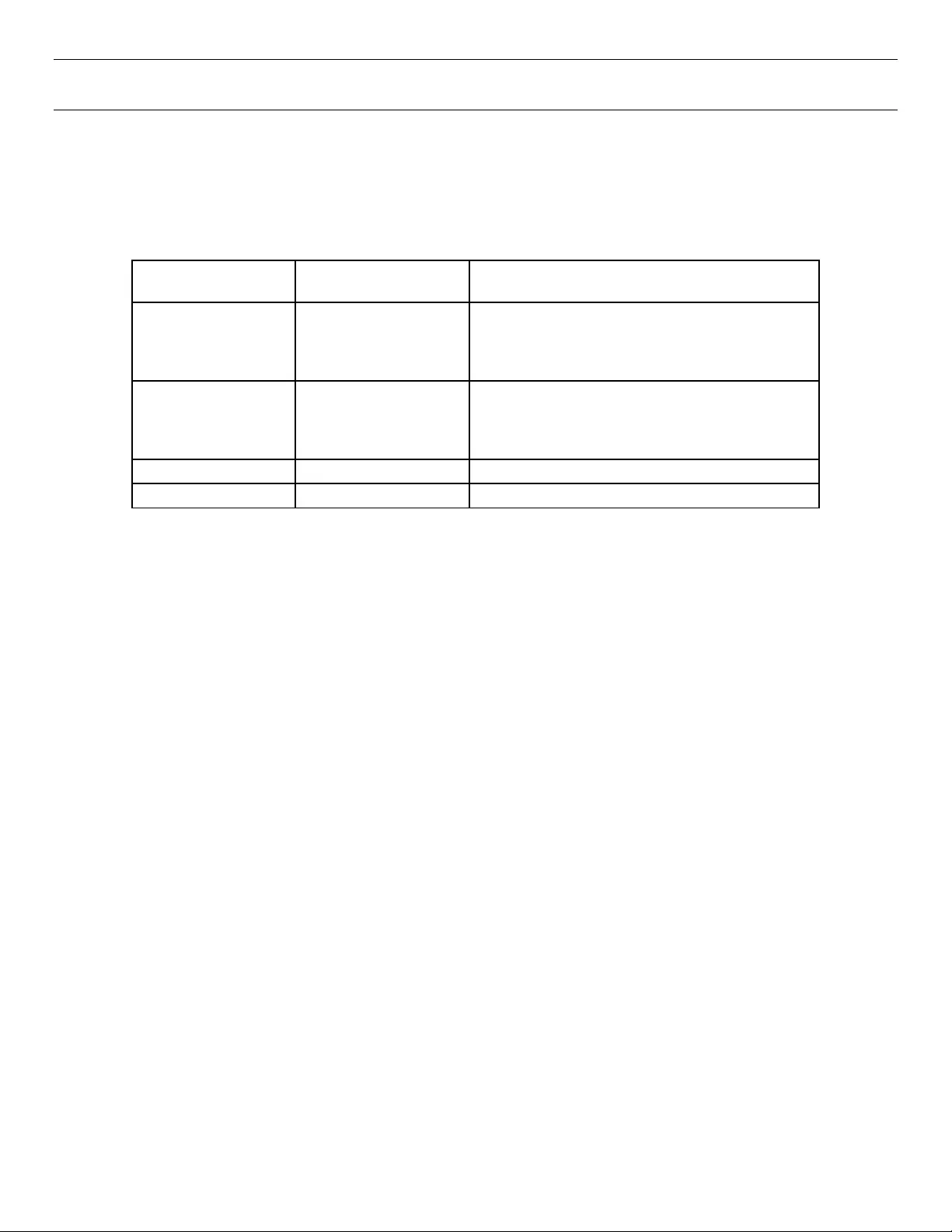
Appendix A. Qualified External Mini-SAS Cable List
HD MiniSAS external cables are available from a variety of vendors. For reference, the list of external cables
below used during Intel testing is provided. Customers should perform their own qualification testing of the
cables they select for use.
Table 23: External Cable List
Vendor
Manufactures Part
Number
Description
Amphenol
Cables on Demand CS-SASMINIHD2-001
1m (3.3') External 4x HD Mini-SAS Cable - 4x Mini-
SAS HD (SFF-8644) to 4x Mini-SAS HD (SFF-8644)
Passive Copper Cable Assembly [30 AWG] - 12 Gbps
SAS 3.0 & iPass+™ HD Compliant
Amphenol
Cables on Demand CS-SASMINIHD2-003
3m (9.8') External 4x HD Mini-SAS Cable - 4x Mini-
SAS HD (SFF-8644) to 4x Mini-SAS HD (SFF-8644)
Passive Copper Cable Assembly [28 AWG] - 12 Gbps
SAS 3.0 & iPass+™ HD Compliant
Data Storage Cables
C5555-.5M
HD Mini SAS 4X - HD Mini SAS 4X, .5M
Data Storage Cables
C5555-6M
HD Mini SAS 4X - HD Mini SAS 4X, 6M

Intel® Storage Server System JBOD2312S3SP Hardware Guide
37
Appendix B. Reference Documents
Refer to the following documents for additional information:
Intel® Storage System JBOD2312S3SP Service Guide
Intel® High Availability Storage User Guide
Intel® RAID Expander RES3FV288 User Guide