Table of Contents
- Contents
- 1. Overview
- 2. Storage & Snapshots
- 3. Privilege
- 4. File Station
QNAP TS-251A User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for TS-251A by QNAP which is a product in the NAS & Storage Servers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

QTS 4.3.4
Getting Started Guide
Document Version: 2
06/02/2018

Contents
1. Overview
NAS Access..................................................................................................................................................3
Accessing the NAS Using a Browser....................................................................................................... 3
Accessing the NAS Using Qfinder Pro..................................................................................................... 4
Accessing the NAS Using Qmanager.......................................................................................................4
2-step Verification.....................................................................................................................................5
About QTS.................................................................................................................................................... 6
QTS Navigation............................................................................................................................................ 7
Task Bar....................................................................................................................................................7
Main Menu..............................................................................................................................................15
Desktop.................................................................................................................................................. 16
Getting Started............................................................................................................................................20
2. Storage & Snapshots
Storage....................................................................................................................................................... 21
Storage Creation.................................................................................................................................... 22
Storage Management.............................................................................................................................36
Snapshots...................................................................................................................................................46
Snapshot Creation..................................................................................................................................46
Snapshot Management.......................................................................................................................... 48
Global Settings........................................................................................................................................... 50
Storage Settings.....................................................................................................................................51
Disk Health Settings............................................................................................................................... 51
Snapshot Settings.................................................................................................................................. 52
3. Privilege
Users...........................................................................................................................................................53
Creating a Local User.............................................................................................................................53
User Account Settings............................................................................................................................55
User Groups................................................................................................................................................57
Creating a User Group........................................................................................................................... 57
Shared Folders........................................................................................................................................... 57
Creating a Shared Folder....................................................................................................................... 57
Editing Shared Folder Properties........................................................................................................... 59
Conflicts in Shared Folder Permissions..................................................................................................60
Drive Mapping.............................................................................................................................................60
Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer...............................................................................61
Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac Computer..................................................................................... 63
4. File Station
Overview.....................................................................................................................................................66
About File Station................................................................................................................................... 66
Supported File Formats..........................................................................................................................66
System Requirements............................................................................................................................ 66
Parts of the User Interface......................................................................................................................66
Settings...................................................................................................................................................68
File Operations........................................................................................................................................... 69
Uploading a File......................................................................................................................................70
Downloading a File.................................................................................................................................70
Opening a File........................................................................................................................................ 71
Playing a Media File............................................................................................................................... 71
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
1

Sharing a File By Email.......................................................................................................................... 72
Sharing a File on a Social Network........................................................................................................ 72
Sharing a File Using Share Links........................................................................................................... 73
Sharing a File with a NAS User..............................................................................................................74
Folder Operations....................................................................................................................................... 75
Uploading a Folder................................................................................................................................. 75
Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop.............................................................................................. 75
Creating a Folder....................................................................................................................................76
Creating a Desktop Shortcut.................................................................................................................. 76
Creating a Shared Folder....................................................................................................................... 77
2
1. Overview
NAS Access
Method Description Requirements
Web browser You can access the NAS using any
computer on the same network if you
have the following information:
• NAS name (Example: http://
example123/) or IP address
• Logon credentials of a valid user
account
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using
a Browser.
• Computer that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Web browser
Qfinder Pro Qfinder Pro is a desktop utility that
supports Windows, macOS, Linux, and
Chrome OS.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using
Qfinder Pro.
• Computer that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Web browser
• Qfinder Pro
Qmanager Qmanager is a mobile application that
enables administrators to manage and
monitor NAS devices on the same
network.
You can download Qmanager from the
Apple App Store and the Google Play
Store.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using
Qmanager.
• Mobile device that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Qmanager
Explorer (Windows) You can map a NAS shared folder as a
network drive to easily access files using
Explorer.
For details on mapping shared folders,
see Mapping a Shared Folder on a
Windows Computer.
• Windows computer that is connected
to the same network as the NAS
• Qfinder Pro (during mapping)
Finder (macOS) You can map a NAS shared folder as a
network drive to easily access files using
Finder.
For details on mounting shared folders,
see Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac
Computer.
• Mac computer that is connected to
the same network as the NAS
• Qfinder Pro (during mapping)
Accessing the NAS Using a Browser
You can access the NAS using any computer on the network if you know its IP address and the logon
credentials of a valid user account.
Note
If you do not know the IP address of the NAS, you can locate it using Qfinder Pro.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using Qfinder Pro.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 3

1. Verify that your computer is connected to the same network as the NAS.
2. Open a web browser on your computer.
3. Type the IP address of the NAS in the address bar.
The QTS login screen appears.
4. Specify your user name and password.
The default user name and password is admin.
5. Click Login.
The QTS desktop appears.
Accessing the NAS Using Qfinder Pro
Qfinder Pro is a desktop utility that enables you locate and access QNAP NAS devices on a specific
network. The utility supports Windows, macOS, Linux, and Chrome OS.
1. Install Qfinder Pro on a computer that is connected to the same network as the NAS.
To download Qfinder Pro, go to https://www.qnap.com/en/utilities.
2. Open Qfinder Pro.
Qfinder Pro automatically searches for all QNAP NAS devices on the network.
3. Locate the NAS in the list and then double-click the name or IP address.
The QTS login screen opens in the default web browser.
4. Specify your user name and password.
The default user name and password is admin.
5. Click Login.
The QTS desktop appears.
Accessing the NAS Using Qmanager
Qmanager is a mobile application that enables administrators to manage and monitor NAS devices on the
same network.
Administrators can perform the following actions with Qmanager.
• View system information such as CPU usage, memory usage, connection status, and system events
• Manage download and backup tasks
• Enable and disable application services
• Restart or shut down the NAS
1. Install Qmanager on an Android or iOS device.
To download Qmanager, go to the Apple App Store or the Google Play Store.
2. Open Qmanager.
3. Tap Add NAS.
Qmanager automatically searches for all QNAP NAS devices on the network.
4. Locate the NAS in the list, and then tap the name or IP address.
5. Specify your user name and password.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 4
The default user name and password is admin.
6. Optional: If your mobile device and NAS are not connected to the same subnet, perform one of the
following actions.
Action Steps
Tap Add NAS manually.a. Specify the following information.
• Host name or IP address of the NAS
• Password of the admin account
b. Tap Save.
Tap Sign in QID.a. Specify the following information.
• Email address that you used to create
your QNAP account
• Password of your QNAP account
b. Tap Sign in.
c. Locate the NAS in the list, and then tap the
name or IP address.
2-step Verification
2-step verification enhances the security of user accounts. When the feature is enabled, users are required
to specify a six-digit security code in addition to the account credentials during the login process.
To use 2-step verification, you must install an authenticator application on your mobile device. The
application must implement verification services using the Time-based One-time Password Algorithm
(TOTP). QTS supports Google Authenticator (for Android, iOS, and BlackBerry) and Authenticator (for
Windows Phone).
Enabling 2-step Verification
1. Install an authenticator application on your mobile device.
QTS supports the following applications:
• Google Authenticator: Android, iOS, and BlackBerry
• Authenticator: Windows Phone
2. Verify that the system times of the NAS and mobile device are synchronized.
Tip
QNAP recommends connecting to an NTP server to ensure that your NAS follows the
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) standard.
3. In QTS, go to Options > 2-step Verification .
4. Click Get Started.
The 2-step Verification window opens.
5. Open the authenticator application on your mobile phone.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 5
6. Configure the application by scanning the QR code or specifying the security key displayed in the 2-
step Verification window.
7. In the 2-step Verification window, click Next.
The Confirm your 2-step verification settings screen appears.
8. Specify the security code generated by the authenticator application.
9. Select an alternative verification method that will be used whenever your mobile device is inaccessible.
• Answer a security question: Select one of the options or provide your own security question.
• Email a security code: To use this method, go to Control Panel > Notification > Email and then
verify that the SMTP server is correctly configured.
10. Click Finish.
Logging into QTS with 2-step Verification
1. Specify your user name and password.
2. Specify the security code generated by the authenticator application installed on your mobile device.
3. Optional: If your mobile device is inaccessible, click Verify another way.
4. Specify the answer to the security question.
5. Click Login.
Disabling 2-step Verification
Situation User Action Steps
Users are locked out of their
accounts.
Administrators can disable 2-
step verification from the
Control Panel.
Go to Control Panel > Users > Edit
Account Profile .
An administrator is locked out
and no other administrators
can access the account.
An administrator must restore
the factory settings.
Press the RESET button at the back of the
NAS for three seconds.
The NAS restores the default administrator
password and network settings.
Warning
Pressing the RESET button for 10
seconds resets all settings and
deletes all data on the NAS.
About QTS
QTS is a Linux-based operating system that runs applications for file management, virtualization,
surveillance, multimedia, and other purposes. The optimized kernel and various services efficiently manage
system resources, support the applications, and protect your data. QTS also has built-in utilities that extend
the functionality and improve the performance of the NAS.
The multi-window, multitasking user interface enables you to manage the NAS, user accounts, data, and
applications. Out of the box, QTS provides built-in features that allow you to easily store and share files. QTS
also links to the App Center, which offers plenty of options for customizing the NAS and improving user
workflows.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 6
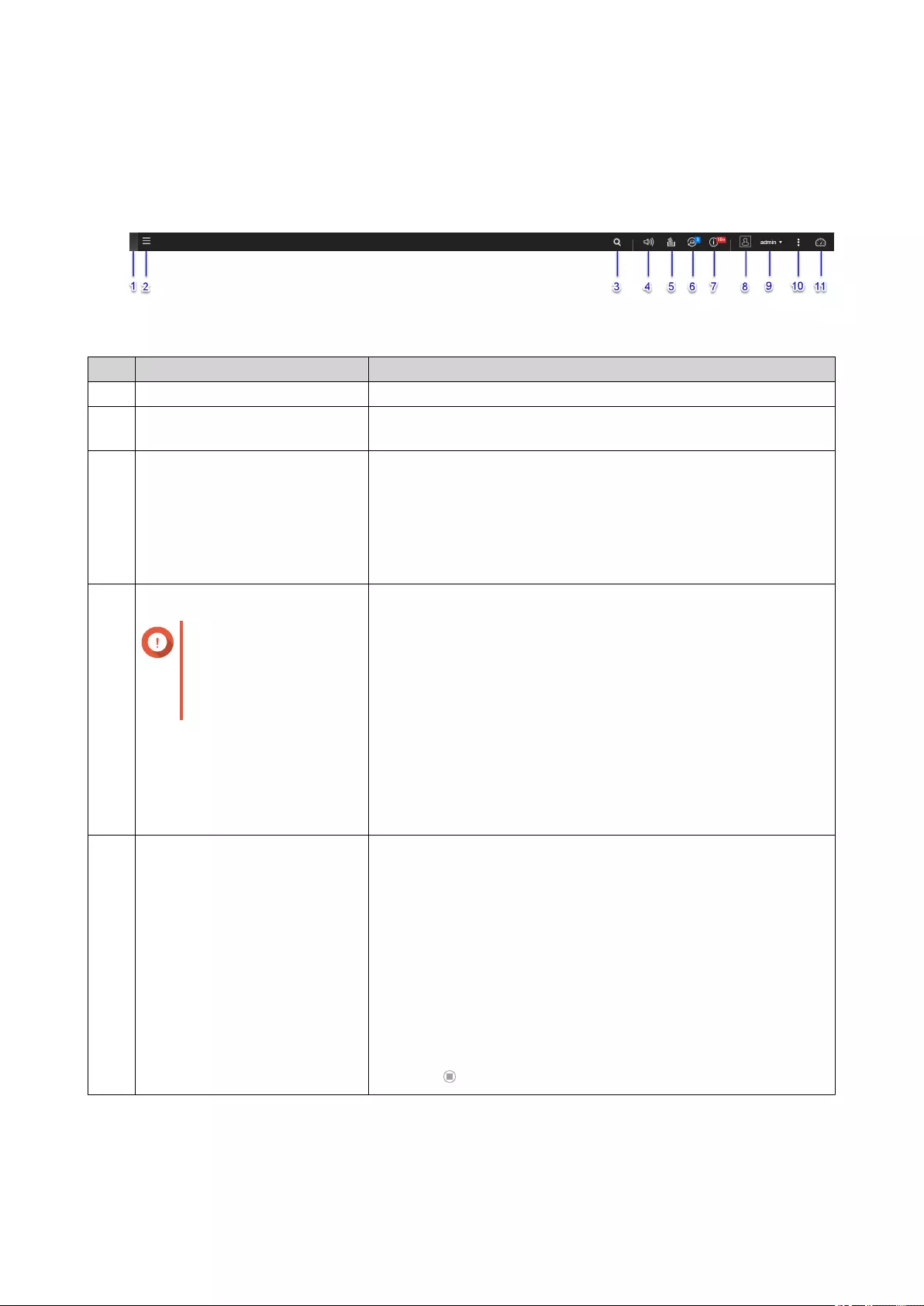
QTS Navigation
Task Bar
# Element Possible User Actions
1Show Desktop Click the button to minimize or restore all open windows.
2Main Menu Click the button to open the Main Menu panel on the left side of
the desktop.
3Search • Type key words to locate settings, applications, and help
content.
• Click an entry in the search results to open the application,
system utility, or Help Center window.
If the application is not yet installed, QTS opens the
corresponding download screen in the App Center window.
4Volume Control
Important
The feature is available
only in models with
certain hardware
specifications.
Click the button to view the following:
• Media Volume: Click and drag the slider thumb to adjust the
volume of audio from applications that use the built-in speaker
or line out port.
• HD Station
• Music Station
• OceanKTV
• Audio Alert Volume: Click and drag the slider thumb to adjust
the volume of system audio alerts.
5Background Tasks • Position the mouse pointer over the button to see the number
of background tasks that are running. Examples of
background tasks are file backup and multimedia conversion.
• Click the button to see the following details for each
background task:
• Task type
• Affected settings
• Progress (percentage of completion)
•Click to stop a task.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 7
# Element Possible User Actions
6External Devices • Position the mouse pointer over the button to view the number
of external storage devices and printers that are connected to
the USB and SATA ports of the NAS.
• Click the button to view the following details for each
connected device.
• Click a listed device to open File Station and view the contents
of the device.
7Event Notifications • Position the mouse pointer over the button to see the number
of recent errors, warnings, and notices.
• Click the button to view the following details for each event:
• Event type
• Description
• Timestamp
• Number of instances
• Click a list entry to view the related utility or application
screen.
Clicking a warning or error log entry opens the System Logs
window.
• Click More>> to open the System Logs window.
• Click Clear All to delete all list entries.
8Options Click your profile picture to open the Options screen.
For details, see Options.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 8
# Element Possible User Actions
9[USER_NAME] Click the button to view the last login time and the following menu
items:
•Options: Opens the Options window.
For details, see Options.
•Sleep: Keeps the NAS powered on but significantly reduces
power consumption.
This feature is available only in models with certain
specifications.
•Restart: Restarts the NAS
•Shutdown: Shuts down QTS and then powers off the NAS
Note
You can also power off the NAS using one of the
following methods:
• Press and hold the power button for 1.5
seconds.
• Run Qfinder Pro and go to Tools > Shut down
Server .
• Open Qmanager and go to Menu > System
Tools > System . Tap Shutdown.
•Logout: Logs the user off the current session
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 9
# Element Possible User Actions
10 More Click the button to view the following menu items:
•What's New: Opens the What's New window, which displays
information on the new features and enhancements avaiilable
in the installed QTS version
•Help: Displays links to the Quick Start Guide, Virtualization
Guide, Help Center, and online tutorials page
•Language: Opens a list of supported languages and allows
you to change the language of the operating system
•Desktop Preferences: Opens a list of display modes and
allows you to select your preferred mode of displaying the
QTS desktop based on your device type
•Help Request: Opens the Helpdesk window
•About: Displays the following information:
• Operating system
• Hardware model
• Operating system version
• Number of installed drives
• Number of empty drive bays
• System volume name
• Used disk space
• Available disk space
11 Dashboard Click the button to display the dashboard.
For details, see Dashboard.
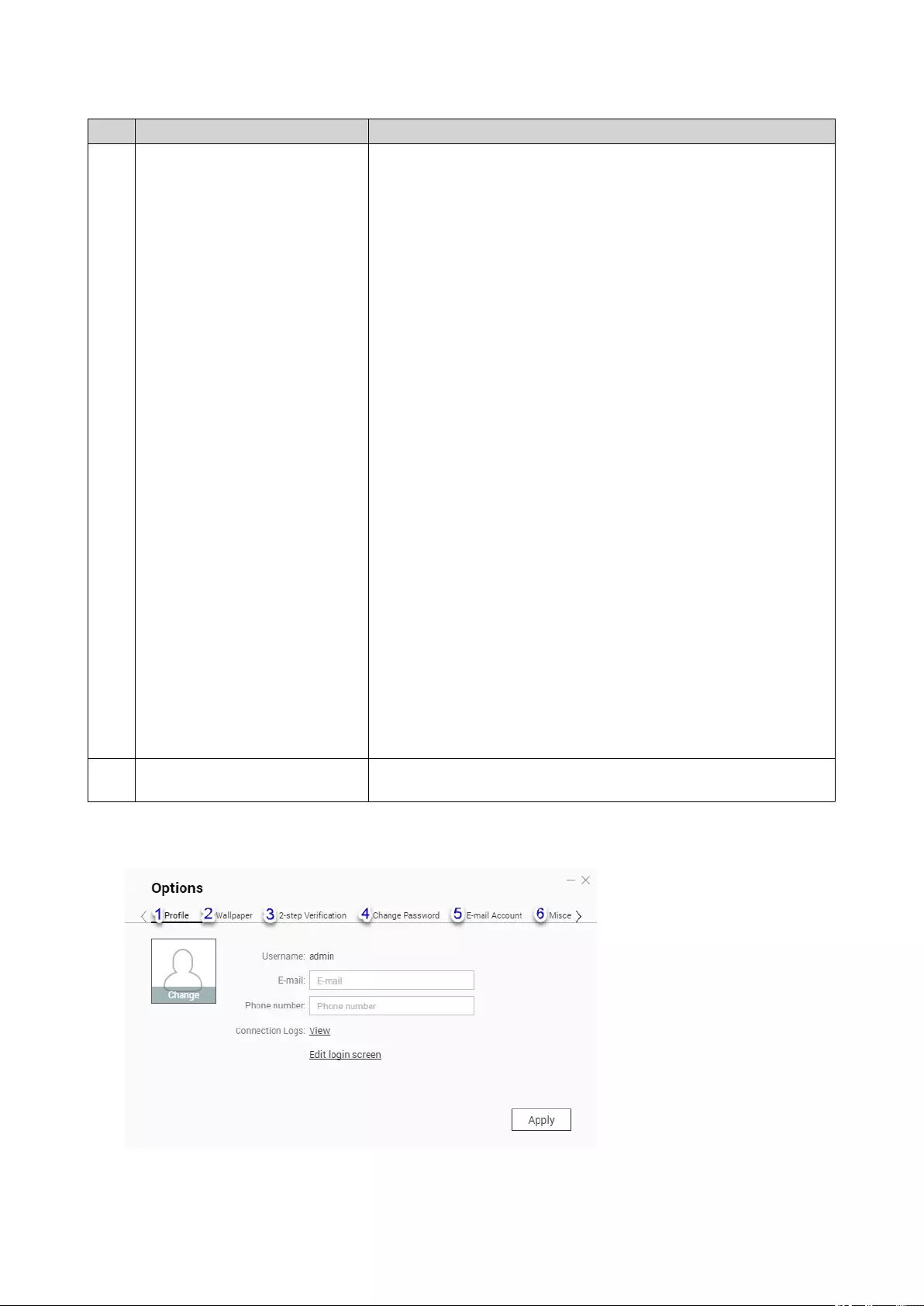
Options
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 10
# Tab Possible User Actions
1Profile • Specify the following optional information:
• Profile picture
• Email address
• Phone number
• Click View to open the System Connection Logs screen.
• Click Edit login screen to open the Login Screen
configuration screen in the Control Panel window.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
2Wallpaper • Select a wallpaper from the built-in options or upload a photo.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
32-step Verification Click Get Started to open the configuration wizard. For details,
see Enabling 2-step Verification.
4Change Password • Specify the following information:
•Old password
•New password: Specify a password with a maximum of
64 characters. QNAP recommends using passwords with
at least 6 characters.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
5E-mail Account • Add, edit, and delete email accounts that you intend to use to
share files.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 11
# Tab Possible User Actions
6Miscellaneous • Enable the following settings as necessary.
•Auto logout after an idle period: Specify the duration of
inactivity after which the user is automatically logged out.
•Warn me when leaving QTS: When enabled, QTS
prompts users for confirmation whenever they try to leave
the desktop (by clicking the Back button or closing the
browser). QNAP recommends enabling this setting.
•Reopen windows when logging back into NAS: When
enabled, the current desktop settings (including all open
windows) are retained until the next session.
•Show the desktop switching button: When enabled,
QTS displays the desktop switching buttons < > on the
left and right sides of the desktop.
•Show the link bar on the desktop: When enabled, QTS
displays the link bar on the bottom of the desktop.
•Keep Main Menu open after selection: When enabled,
QTS keeps the main menu pinned to the desktop after
you open it.
•Show a list of actions when external storage devices
are detected: When enabled, QTS displays an Autoplay
dialog box whenever an external storage device is
inserted into a USB or SATA port.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 12
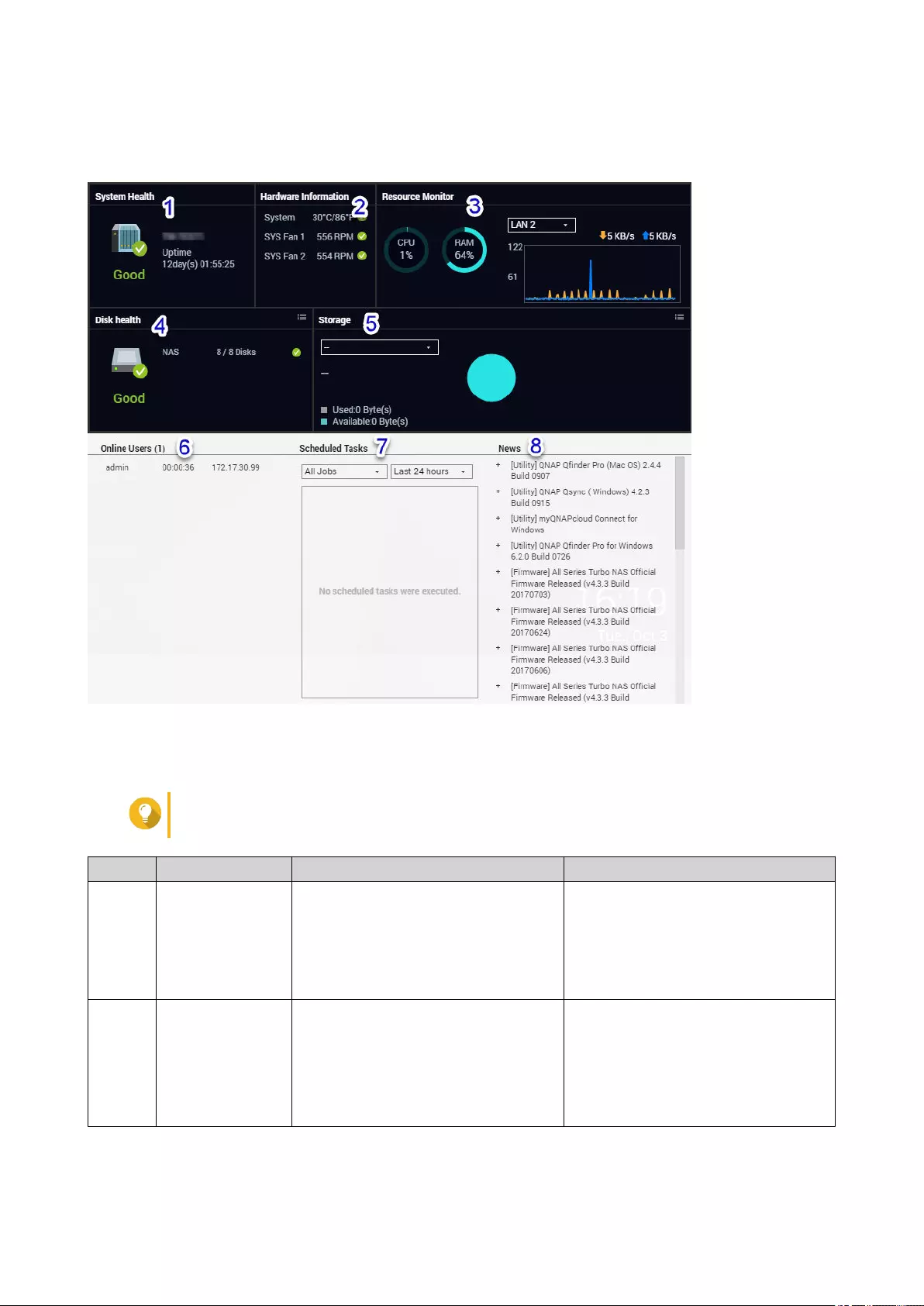
Dashboard
The dashboard opens in the lower right corner of the desktop.
Tip
You can click and drag a section onto any area of the desktop.
# Section Displayed Information User Actions
1 System Health • NAS name
• Uptime (number of days, hours,
minutes and seconds)
• Health status
Click the heading to open the System
Information screen in the System
Status window.
If disk-related issues occur, clicking
the heading opens the Storage &
Snapshots window.
2 Hardware
Information
• System temperature
• CPU fan speed
• System fan speed
• System fan speed
Click the heading to open the
Hardware Information screen in the
System Status window.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 13
# Section Displayed Information User Actions
3 Resource Monitor • CPU usage in %
• Memory usage in %
• Network upload and download
speeds/rates
Click the heading to open the
Overview screen in the Resource
Monitor window.
4 Disk Health • Number of installed disks
• Health status of installed disks
• Click the heading to open the
Disk Health screen in the
Storage & Snapshots window.
•Click to view the following
information for each installed
disk:
• Capacity/size
• Temperature
• Health status
• Click Details to open the
Overview screen in the Storage
& Snapshots window.
5 Storage For each volume:
• Status
• Used space
• Available space
• Folder size
For each storage pool:
• Status
• Used space
• Available space
• Volume size
• Click the heading to open the
Storage Resource screen in the
Resource Monitor window.
•Click to switch between
volume and storage pool
information.
6 Online Users • User name
• Session duration
• IP address
Click the heading to open the Online
Users screen in the System Logs
window.
7 Scheduled Tasks • Task type
• Task summary
• Task name
• Timestamp
• Status
Use the filters to view tasks that were
executed within a specific period.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 14
# Section Displayed Information User Actions
8 News Links to QNAP announcements Click the heading to open the relevant
pages in the QNAP website.
Main Menu
# Section Description Possible User Actions
1 NAS Information NAS name and model number N/A
2 Systems System utilities and other programs that
enable you to manage the NAS
The following are the default system
utilities:
• Control Panel
• Storage & Snapshots
• Users
• Network & Virtual Switch
• myQNAPcloud
• Resource Monitor
• App Center
• Help Center
• Open a system utility or application
in the QTS desktop
• Click a menu item.
• Right-click a menu item and
then select Open.
• Open an application in a new
browser tab (only for certain apps)
• Right-click a menu item and
then select Open in new
browser tab.
• Create a shortcut on the desktop
• Right-click a menu item and
then select Create shortcut.
• Click and drag a menu item to
the desktop.
3 Applications Applications developed by QNAP or
third-party developers
When an app is installed, it is
automatically added to the applications
list.
The following are the default
applications:
• Backup Station
• File Station
• Helpdesk
• HybridDesk Station
This application is only available in
models with certain specifications.
• QTS SSL Certificate
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 15
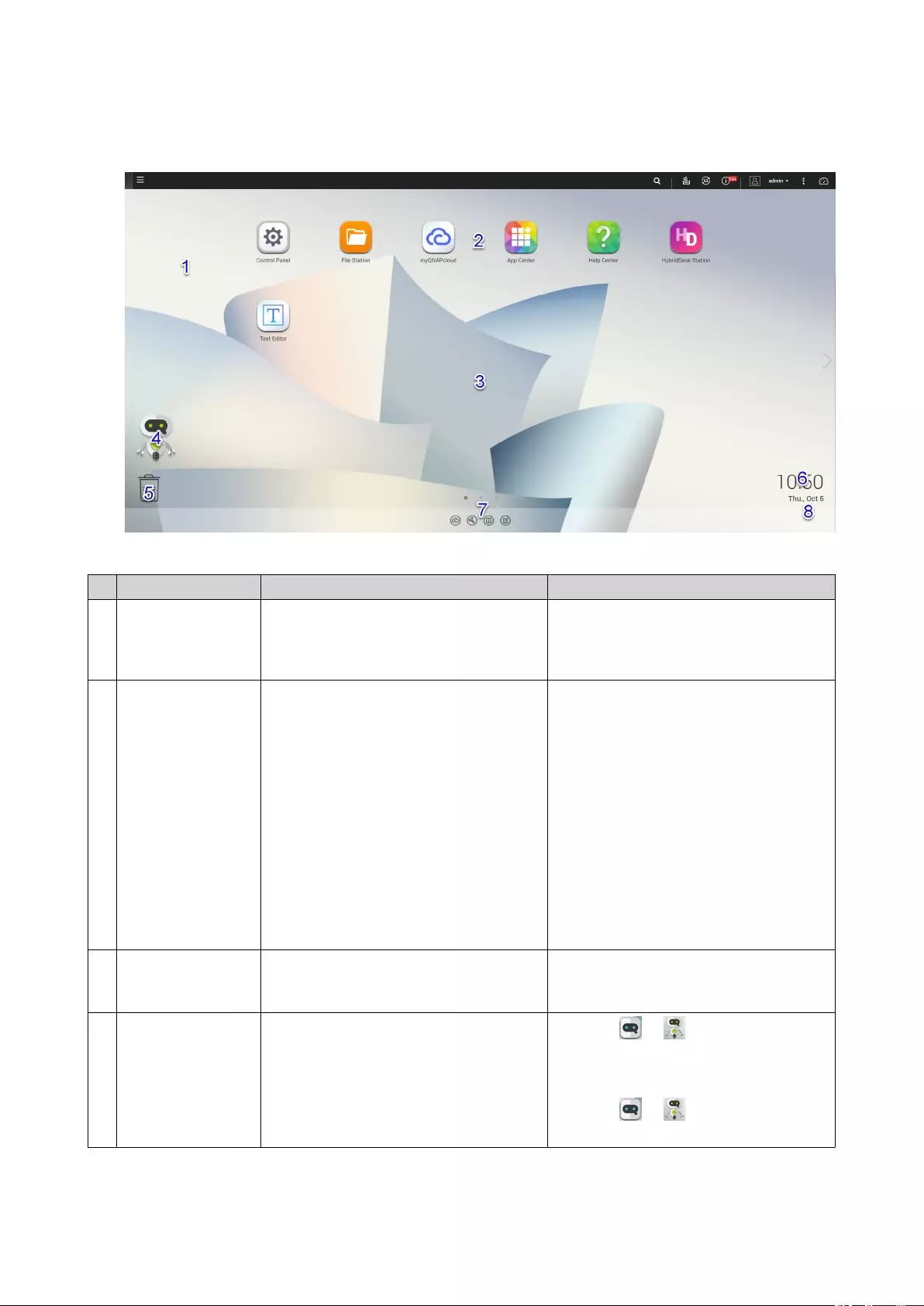
Desktop
# Element Description Possible User Actions
1 Wallpaper This is a digital image that is used as a
background for the QTS desktop.
Users can either select from one of the
provided wallpapers or upload an image
Change the wallpaper in the Options
window.
2 Shortcut icons This opens an app or a utility.
When you install an application, QTS
automatically creates a shortcut on the
desktop. The following are the default
shortcuts:
• Control Panel
• File Station
• Storage & Snapshots
• App Center
• Help Center
• Click an icon to open the application
window.
• Right-click an icon and then select
one of the following:
•Open: Opens the application
window
•Remove: Deletes the icon from
the desktop
• Click and drag an icon to another
desktop.
3 Desktop This area contains open system utilities
and applications. The desktop consists
of three separate screens.
Click < or > to move to another desktop.
4 Qboost This enables you to manage and
monitor memory consumption.
•Click or to display the
memory status and open the
Qboost panel.
•Click or to hide the memory
status and close the Qboost panel.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 16
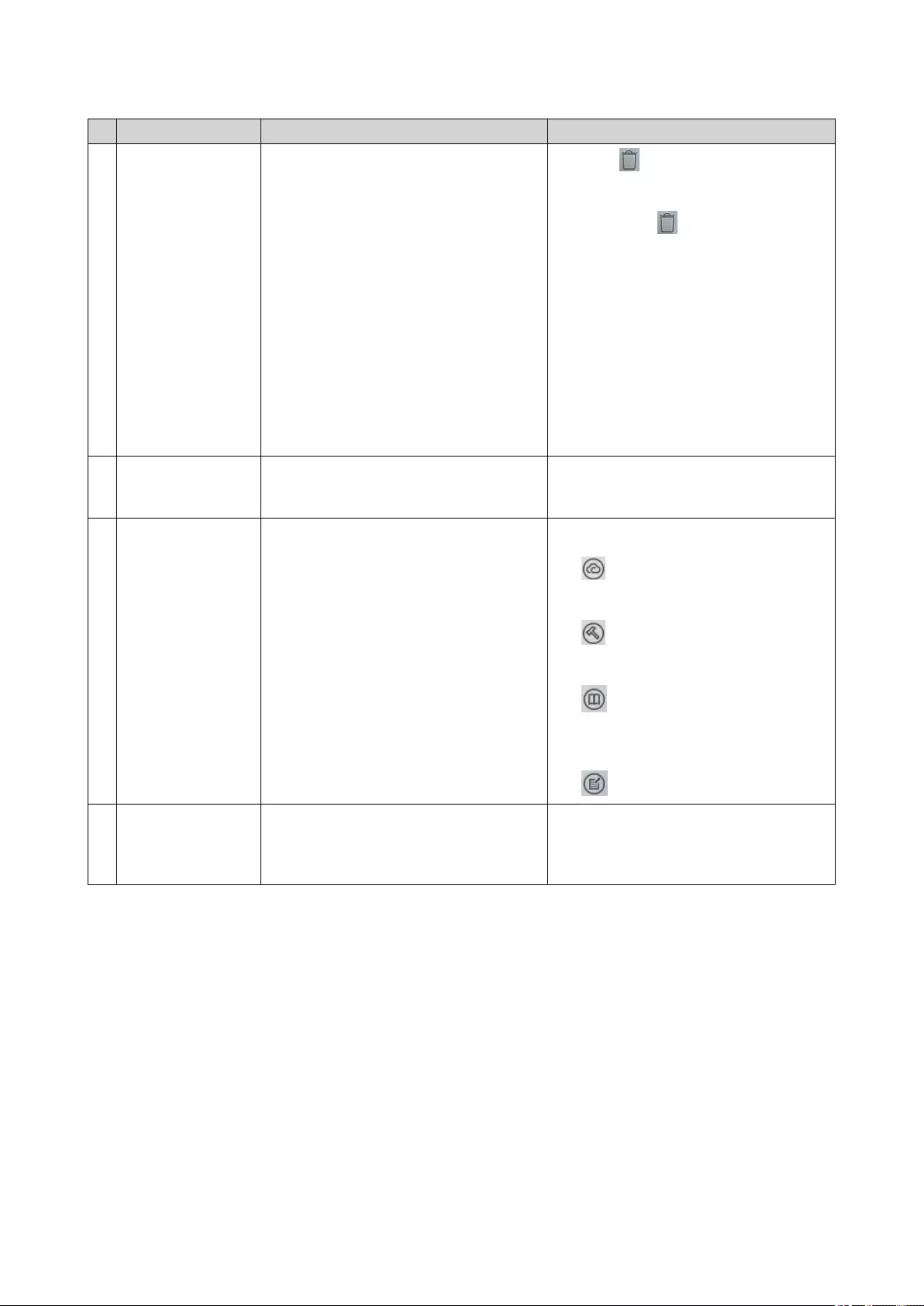
# Element Description Possible User Actions
5 Recycle Bin This displays the list of files that the
currently active user moved to the
Recycle Bin.
The following applications provide users
a choice between permanently deleting
files and moving files to the Recycle Bin.
• File Station
• Music Station
• Photo Station
• Video Station
•Click to open the Recycle Bin
screen in the File Station window.
•Right-click and then select one
of the following:
•Open: Opens the Recycle Bin
screen in the File Station
window
•Empty All: Permanently
deletes files in the Recycle Bin
• Settings: Opens the Network
Recycle Bin screen in the
Control Panel window
6 Date and time This displays the date and time that the
user configured during installation of the
operating system.
N/A
7 Link bar This displays shortcut links to
myQNAPcloud, utility and app download
pages, feedback channels, and the
Helpdesk.
Click any of the following buttons:
•: Opens the myQNAPcloud
website in another browser tab
•: Opens the download page for
mobile applications and utilities
•: Provides links to theQNAP
Wiki, QNAP Forum, and Customer
Service portal
•: Opens the Helpdesk utility
8 Notifications This notifies the user about important
system events that may or may not
require user action. Notifications appear
in the lower right corner of the desktop.
Click the notification to open the
corresponding utility or app.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 17
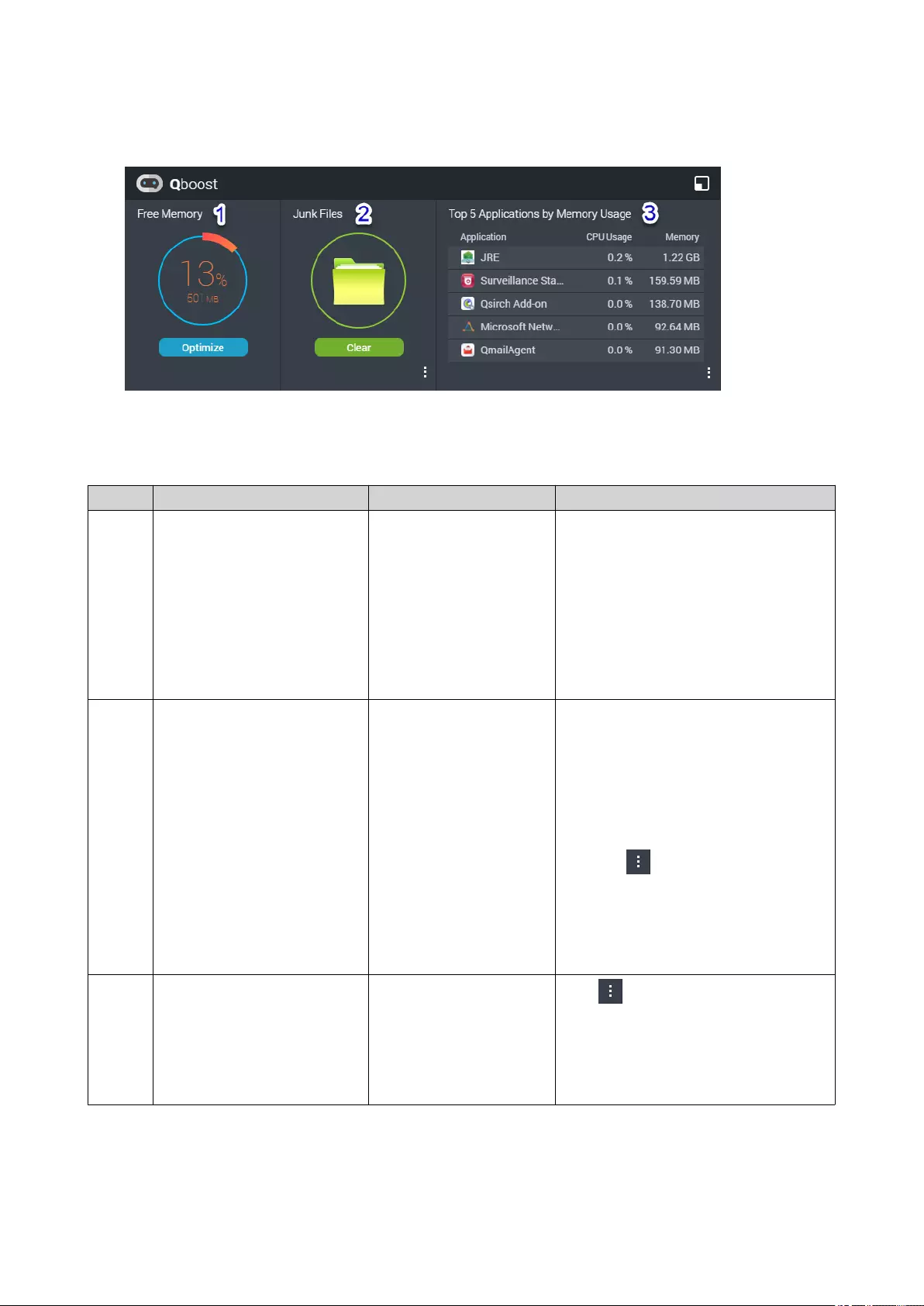
Qboost
Qboost is a system utility that monitors and enables you to manage memory consumption. It provides the
following information:
# Section Description User Actions
1 Free Memory • Memory that has not
been allocated, is
currently unused,
and does not contain
useful information
• Expressed as a
percentage of the
total memory and the
number of bytes
Click Optimize to clear the buffer
memory (block level) and cache
memory (file level).
2 Junk Files • Unnecessary system
files and files in the
Recycle Bin
• Consume disk space
and memory because
they are not
automatically deleted
when no longer
needed
• Click Clear to permanently delete
the specified files.
By default, clicking Clear only
deletes unnecessary system files,
such as files that the operating
system and applications create
while performing certain tasks
•Click to select other types of
files to delete.
Select Empty Recycle Bin to
include files that were moved to
the Recycle Bin by the currently
active user.
3 Top 5 Applications by
Memory Usage
Top five applications and
services that consume
the most memory
Click to display all applications and
services that can be enabled and
disabled from either the Control Panel
or the App Center.
For details, see Application
Management.
Application Management
Application Management displays the following information.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 18
Item Description
Application Displays the application name
CPU Usage Displays the percentage of consumed processing power
Memory Displays the amount of memory consumed
CPU Time Displays the amount of time the CPU requires to process an
application request
Status Displays one of the following statuses:
• Always Enabled
• Always Disabled
• Scheduled
Action Displays icons for the possible actions
You can perform the following actions.
Objective Action
Enable or disable an application or
service.
•Click to change the status to Always Enabled.
•Click to change the status to Always Disabled.
Create a schedule for enabling
and disabling an application or
service.
Warning
Setting a schedule may
force an application to
stop in the middle of a
task.
1. Click to open the scheduling screen.
2. Select Enable Schedule.
Step result: The calendar is activated. All days and hours are
enabled by default.
3. Select the hours during which the application or service should be
enabled or disabled.
Hours are filled with one of the following colors or patterrns.
• Blue: The application or service is enabled.
• Gray: The application or service is disabled.
• Striped: The NAS is scheduled to sleep or shut down.
4. Optional: If you want to enable the app at a certain time, specify
the number of minutes after the hour when the application is
enabled or disabled.
Example: To enable an application only after half an hour, type 30.
5. Perform one of the following actions.
• Click Apply: Applies the schedule to the selected application
or service
• Select Auto-apply: Applies the schedule to all applications
and services
Delete a schedule. Click to delete the schedule and disable an application or service.
Remove an application. Click .
This function applies only to applications that are available on the App
Center.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 19

Getting Started
1. Plan how you want to combine or divide the available storage space.
For details, see Volume Configuration.
2. Optional: Create one or more storage pools.
Creating multiple volumes requires a storage pool. For details, see Storage Pools.
3. Create one or more volumes.
The NAS can store files only if at least one volume is created. For details, see Volumes.
4. Create user accounts.
QNAP recommends creating a user account for each person that requires access to the NAS. For
details, see Users.
5. Optional: Create user groups.
User groups enable you easily manage user accounts. For details, see User Groups.
6. Optional: Create shared folders.
QTS creates four default shared folders. For details, see Shared Folders.
7. Edit the shared folders permissions.
Permissions enable you to control who can view and modify files in a shared folder. For details, see
Editing Shared Folder Properties.
8. Map the shared folders as network drives on your computer.
For details, see Drive Mapping.
9. Store and manage files.
For details, see File Station.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Overview 20
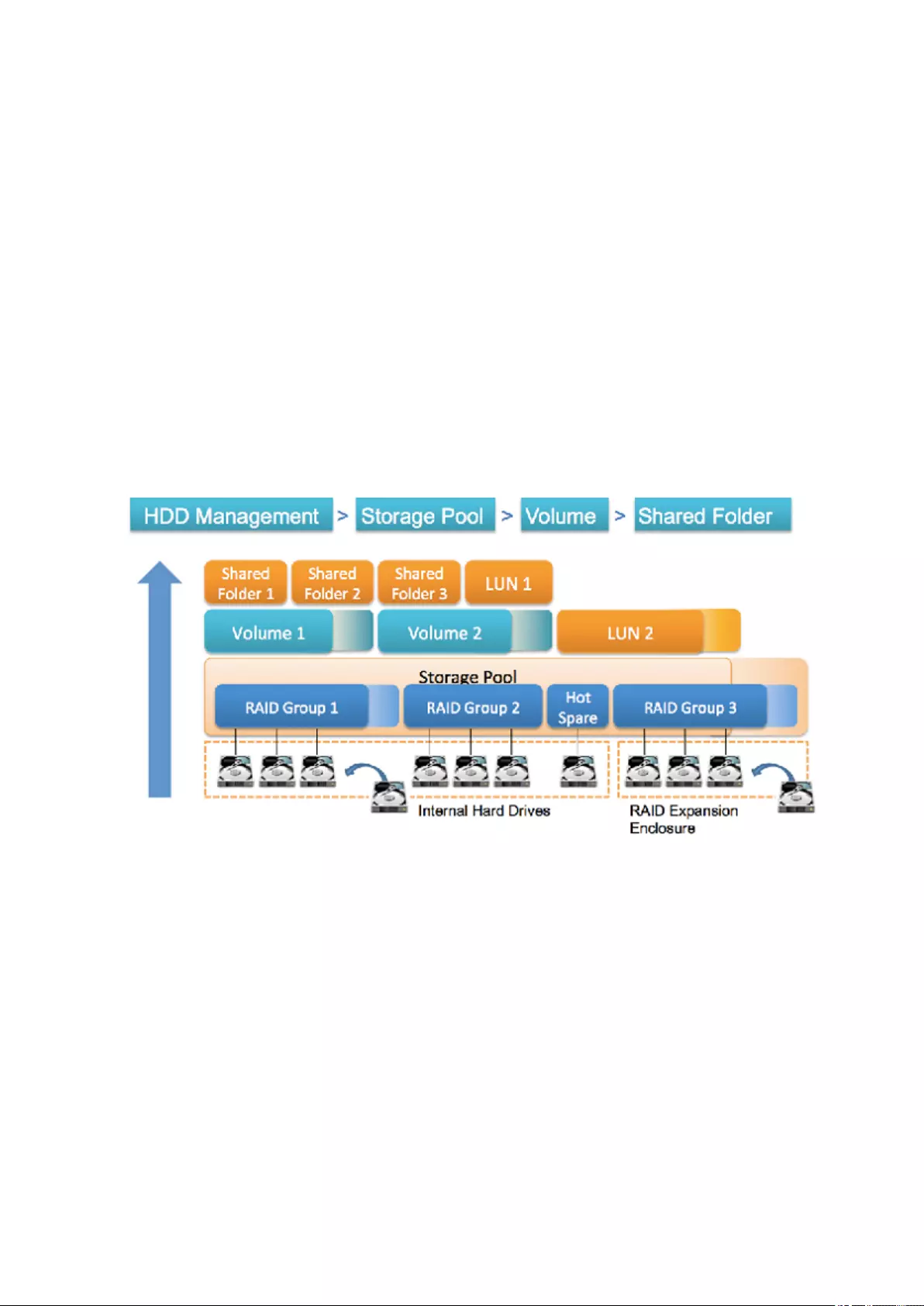
2. Storage & Snapshots
Storage & Snapshots is a system utility that enables you to manage storage space. You can perform the
following tasks with Storage & Snapshots.
• Create and configure storage pools, volumes, LUNs, and shared folders.
• View the amount of free storage space.
• Check the health of installed disks.
• Back up data using snapshots.
• Manage external storage devices connected to the NAS, such as USB drives and expansion units.
Storage
QTS provides a flexible volume architecture that enables you to easily manage, store, and share files.
QTS Flexible Volume Architecture
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 21
Object Description Details
Disk Physical device that stores
and retrieves data
QNAP NAS devices support the following disk sizes and
types:
Size.
• 3.5-inch, 2.5-inch
• Specific models: M.2
Type:
• SATA, SSD
• Specific models: SAS, NL-SAS, NVMe PCIe SSD, NVMe
M.2 PCIe SSD
Note
All of the above disk types can be used to
create storage pools and static volumes. Only
SSDs, NVMe PCIe SSDs, and NVMe M.2
SSDs can be used in the SSD cache.
RAID group Logical disk that consists of
one or more disks. RAID
groups usually contain disks
that are of the same type and
capacity.
Data is distributed across the disks in a RAID group. Each
RAID type offers a different combination of reliability,
performance, and capacity. For details, see RAID.
Storage
pool
Pool of storage space that
consists of RAID groups
Storage pools can aggregate RAID groups that consist of
disks of different types and capacities. Storage pools enable
easier storage space management and features such as
snapshots.
Volume Portion of storage space that
is used to divide and manage
storage capacity
You can create volumes by dividing storage pool space, or
using the space of a RAID group. QTS offers three different
volume types, with different combinations of performance and
flexibility. At least one volume must be created before the
NAS can start storing data.
iSCSI LUN
(logical unit
number)
Portion of storage space that
can be used by other NAS
devices through the iSCSI
protocol
QTS offers two LUN types.
• Block-based LUN: Created from a storage pool. It is
similar to a volume, except that it has no file system and
must be linked to an iSCSI host.
• File-based LUN: Created on a volume. It is similar to an
ISO image file.
Shared
folder
Folder that is used for storing
and sharing files
Shared folders are created on volumes. QTS automatically
creates default shared folders for multimedia, public
documents, and downloads. You can create more shared
folders and configure permissions for each.
Storage Creation
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 22
Volumes
A volume is a portion of storage space within the NAS. Each volume is created from the storage space of a
storage pool, or of a RAID group. Volumes are used to divide and manage your storage space. QNAP NAS
devices support three different types of volume.
Volume Type
Single Static Thick Multiple Thin Multiple
Summary Best overall read/write
performance, but does
not support most
advanced features
Good balance between
performance and
flexibility
Enables you to allocate
storage space more
efficiently
Read/write speed Fastest for random writes Good Good
Flexibility Inflexible
A volume can only be
expanded by adding
extra drives to the NAS.
Flexible
A volume can easily grow
in size.
Very flexible
A volume can easily grow
in size, and unused
space can be reclaimed
and added back to the
parent storage pool.
Parent storage space RAID group Storage pool Storage pool
Number of volumes that
can be created in the
parent storage space
One One or more One or more
Initial size Size of the parent RAID
group
User-specified Zero
Storage pool space is
allocated on-demand,
data is written to the
volume. This is called
thin provisioning.
Maximum size Size of the parent RAID
group
Size of the parent
storage pool
Twenty times the amount
of free space in the
parent storage pool
The size of a thin volume
can be greater than that
of its parent storage pool.
This is called over-
allocation.
Effect of data deletion Space is freed in the
volume
Space is freed in the
volume
QTS can reclaim the
space and add it back
into the parent storage
pool.
Method of adding storage
space
• Add disks to the NAS
• Replace existing
disks with higher
capacity disks
Allocate more space from
the parent storage pool
Allocate more space from
the parent storage pool
Snapshot support (fast
backup and recovery)
No Yes Yes
Qtier (automatic data
tiering) support
No Yes Yes
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 23
Volume Configuration
Volumes divide your storage space into separate areas. You can have one large volume or several smaller
volumes. Shared folders are then created on the volumes to store and share files.
Configuration Advantage Description
Single Volume
Example:
• Volume 1
• Shared Folder 1
• Shared Folder 2
• Shared Folder 3
• Shared Folder 4
Simplicity Creating one volume is quick and easy. You do
not have to worry about changing volume sizes
or creating new volumes after the initial NAS
setup.
Speed Single static volumes are faster because they do
not require a storage pool.
Multiple Volumes
Example:
• Volume 1
• Shared Folder 1
• Volume 2
• Shared Folder 2
• Volume 3
• Shared Folder 3
• Shared Folder 4
Limiting of storage space
usage
Each volume functions like a separate container.
If a user or an app writes a large amount of files
to a volume, only the specified volume is filled.
Other volumes remain unaffected.
Multiple snapshot
schedules
Snapshots protect files from accidental deletion
or modification. Snapshot creation requires time,
memory resources, and storage space.
QTS takes snapshots of individual volumes.
QNAP recommends storing important files on
dedicated volumes, so that QTS only creates
snapshots of important files to save system
resources.
Faster file system repair QTS occasionally encounters errors in the file
system of a volume. While QTS can scan the
volume and automatically repair errors, this
process can take a long time. The required time
depends on the volume size. Files on the volume
cannot be accessed during the scanning
process.
Volume Configuration Examples
Users often purchase NAS devices to store a combination of documents, media, and backups.
The following table compares the advantages and disadvantages of creating one large volume or multiple
smaller volumes.
Requirement User Goal Single Volume Multiple Volumes
Simplicity Store files Users create one large thin volume
if they want to use snapshots, or
one large static volume if they do
not. They then create three shared
folders on the volume, for
documents, movies, and backups.
Users create three
separate volumes for
documents, movies, and
backups. Users must
decide how much space
to initially allocate to each
volume.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 24
Requirement User Goal Single Volume Multiple Volumes
Speed Edit video and audio
files
Users create one large single static
volume on the NAS. The files are
backed up daily to another NAS, or
to an external disk.
Users create a thick
volume to store the
movies files. Random-
write performance is
sightly lower than a
single static volume.
Containerizing
storage space
Copy a large number
of movie files to the
NAS
Users copy the movie files to the
movies shared folder. However,
they must pay attention to how
large the movies folder is. If they
copy too many files, the NAS
becomes full and unable save any
more files.
Users copy the movie
files to the movies
volume. When the
volume becomes full,
they can increase the
volume size.
Multiple snapshot
schedules
Protect document files
using snapshots
Users create a daily snapshot
schedule for a single volume. The
snapshots record all changes made
to document files. However, the
snapshots also record changes to
movie and backup files which
wastes resources and storage
space.
Users create a daily
snapshot schedule for
the document volume
only.
File system repair Fix file system errors QTS must scan the entire single
volume, which takes a long time.
The volume is not readable while
the scan is in progress, making the
entire NAS unusable.
QTS only needs to scan
the volume that has an
error. Each volume is
small, so scanning is
relatively quick. Users
can still access files on
other volumes while the
scan is in progress.
Creating a Single Static Volume
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Select Static Single Volume.
4. Click Next.
5. Optional: If you want to use disks in a connected expansion unit, select the expansion unit from the
Enclosure Unit list.
You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
6. Select one or more disks.
7. Select a RAID type.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 25
Storage & Snapshots displays all RAID types that match the number of selected disks and
automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10
Important
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50 RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50,
RAID 60
RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unfamiliar with the technology.
For details, see RAID Types.
8. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For details, see RAID Spare Disks.
9. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 sub-groups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specified number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
• A higher number of sub-groups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of sub-groups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 sub-groups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of
storage capacity.
10. Click Next.
11. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen "-" and underscore "_"
12. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size, and the number of files and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of files and folders.
13. Configure advanced settings.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 26
Setting Description
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notification when the percentage of used disk space on the
volume reaches the specified value.
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on the volume with 256-bit AES encryption.
• Specify an encryption password containing 8 to 32 characters, with any
combination of letters, numbers and special characters. Spaces are not
allowed.
• Select Save encryption key to save a local copy of the encryption key on the
NAS. This enables QTS to automatically unlock and mount the encrypted
volume when the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is not saved, you must
specify the encryption password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in
unauthorized access to data if the entire NAS is stolen.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will
become inaccessible and all data will be lost.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in
unauthorized access to data if the entire NAS is stolen.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will
become inaccessible and all data will be lost.
Create a shared
folder on the volume
QTS automatically creates the shared folder when the volume is ready. Only the
NAS admin account can access the new folder.
14. Click Next.
15. Click Finish.
A confirmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Creating a Thick or Thin Multiple Volume
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Select the volume type.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 27
• Thick Multiple Volume
• Thin Multiple Volume
For details, see Volumes.
4. Select the storage pool that will be used to create the volume.
You can select an existing storage pool or create a new storage pool immediately.
5. Optional: Create a new storage pool.
a.
Click the Create Storage Pool icon .
The Create Storage Pool Wizard opens.
b. Click Next.
c. Optional: If you want to use disks in a connected expansion unit, select the expansion unit from
the Enclosure Unit list.
You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
d. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
e. Select a RAID type.
Storage & Snapshots displays all RAID types that match the number of selected disks and
automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50
Note
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unfamiliar with the technology.
For details, see RAID Types.
f. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
g. Click Next.
The Pool Creation Summary window opens.
h. Click Create.
A confirmation message appears.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 28
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
i. Click OK.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen "-" and underscore "_"
8. Specify the capacity of the volume.
The volume type determines the maximum volume capacity.
Volume Type Maximum Size
Thick Amount of free space in the parent storage pool.
Thin Twenty times the amount of free space in the parent
storage pool
Setting the maximum size of a thin volume to a value that is greater than the amount of free space in
the storage pool is called over-allocation.
9. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size, and the number of files and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of files and folders.
10. Configure advanced settings.
Setting Description
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notification when the percentage of used disk space on the
volume reaches the specified value.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 29
Setting Description
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on the volume with 256-bit AES encryption.
• Specify an encryption password containing 8 to 32 characters, with any
combination of letters, numbers and special characters. Spaces are not
allowed.
• Select Save encryption key to save a local copy of the encryption key on the
NAS. This enables QTS to automatically unlock and mount the encrypted
volume when the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is not saved, you must
specify the encryption password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in
unauthorized access to data if the entire NAS is stolen.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will
become inaccessible and all data will be lost.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in
unauthorized access to data if the entire NAS is stolen.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will
become inaccessible and all data will be lost.
Create a shared
folder on the volume
.
QTS automatically creates the shared folder when the volume is ready. Only the
NAS admin account can access the new folder.
11. Click Next.
12. Click Finish.
A confirmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Storage Pools
A storage pool aggregates many physical disks into one large storage space. Disks are joined together using
RAID technology to form a RAID group. Storage pools may contain more than one RAID group. Using a
storage pool provides the following benefits:
• Multiple volumes can be created on a storage pool, enabling you to divide the storage space among
different users and applications.
• Disks of different sizes and types can be mixed into one large storage space.
• Disks from connected expansion units can be mixed with disks in the NAS to form a storage pool.
• Extra disks can be added while the storage pool is in use, increasing storage capacity without
interrupting services.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 30
• Qtier provides auto-tiering when a storage pool contains a mix of SATA, SAS, and SSD disks. Qtier
automatically moves frequently accessed hot data to the faster SSDs, and infrequently accessed cold
data to the slower disks.
• Snapshots can only be used with storage pools. Snapshots record the state of the data on a volume or
LUN at a specific point in time. Data can then be restored to that time if it is accidentally modified or
deleted.
• Multiple RAID 5 or RAID 6 can be striped together to form a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool.
Creating a Storage Pool
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Storage Pool
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Storage Pool
The Create Storage Pool Wizard opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Optional: If you want to use disks in a connected expansion unit, select the expansion unit from the
Enclosure Unit list.
You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
5. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
Storage & Snapshots displays all RAID types that match the number of selected disks and
automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50
Note
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unfamiliar with the technology.
For details, see RAID Types.
7. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 31
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For RAID 50 or RAID 60, a spare disk must be configured later. You should configure a global spare
disk so that all sub-groups share the same spare disk. For details, see Configuring a Global Hot Spare.
8. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 sub-groups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specified number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
• A higher number of sub-groups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of sub-groups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 sub-groups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of
storage capacity.
9. Click Next.
The Pool Creation Summary window opens.
10. Click Create.
A confirmation message appears.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
11. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool and then displays the information on the Storage/Snapshot screen.
RAID
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) combines multiple physical disks into a single storage unit,
and then distributes data across the disks in one of several predefined methods.
The following features make RAID ideal for use with data storage and NAS applications.
RAID Feature Description Advantages Disadvantages
Grouping Disks that are combined
using RAID form a RAID
group, which QTS
considers one large
logical disk.
Managing the storage space of
one large disk is simpler and
more efficient than multiple small
disks.
Initial configuration can be
more complicated.
Striping Data is split into smaller
pieces. Each piece is
stored on a different disk
in the RAID group. QTS
can then access that
data by reading from or
writing to multiple disks
simultaneously,
increasing read and write
speeds.
• Greater read/write speeds,
compared to a single disk
• Speeds can be increased
further by adding disks
If one disk in the RAID
group fails, and the RAID
group has no redundancy,
all data will be lost.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 32
RAID Feature Description Advantages Disadvantages
Redundancy Each disk in the RAID
group can store the
following:
• Complete copy of the
stored data
• Metadata that allows
reconstruction of lost
data
• Disks can fail or be removed
from the RAID group without
any loss of data
• Users can access data while
failed disks are being
replaced
Total storage capacity of
the RAID group is reduced.
RAID Types
QNAP NAS devices support several RAID types. Each type provides a different combination of striping and
redundancy.
Important
• If disks with different capacities are combined in one RAID group, all disks function
according to the capacity of the smallest disk. For example, if a RAID group contains
five 2 TB disks and one 1 TB disk, QTS detects six 1 TB disks.
QNAP recommends the following.
• Create a RAID group for each capacity.
• Combine the RAID groups using storage pools.
• Using only one disk type (HDD, SSD, SAS) in a RAID group is recommended. If
different types of disk are combined in one RAID group, the RAID group will function
according to the speed of the slowest disk.
RAID Type Count Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
Single 1 0 Size of the one disk • A single disk is used for storage.
• It does not provide any disk
failure protection and
performance benefits.
• It should be selected if only one
disk is available and if a data
backup plan is in place.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 33
RAID Type Count Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
JBOD (just
a bunch of
disks)
1 or more 0 Combined disk
capacity
• JBOD appends disks together in
a linear fashion. QTS writes data
to a disk until it is full, and then
writes to the next disk.
• JBOD allows all of the disks
capacity to be used.
• JBOD Single is not real RAID. It
does not provide any disk failure
protection or performance
benefits.
• JBOD is generally not
recommended. RAID 0 should be
used instead.
RAID 0 2 or more 0 Combined disk
capacity
• Disks are combined together
using striping.
• RAID 0 offers the fastest read/
write speeds and allows all disk
capacity to be used
• No disk failure protection. This
type should be paired with a data
backup plan.
RAID 1 2 1 Disk size divided by
2
• An identical copy of data is
stored on two disks.
• If either disk fails, data can still
be read from the other disk.
• Half of the total disk capacity is
lost, in return for a high level of
data protection.
• Recommended for NAS devices
with two disks.
RAID 5 3 or more 1 Total number of
disks minus 1 disk
• Data and parity information are
striped across all disks.
• The capacity of one disk is lost
for parity. This means that if any
one disk fails, it can be replaced
and the data on it can be
restored.
• Striping means read speeds are
increased with each additional
disk.
• Recommended for a good
balance between data protection
and speed.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 34
RAID Type Count Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
RAID 6 4 or more 2 Total number of
disks minus 2 disks
• Data and parity information are
striped across all disks.
• Same as RAID 5, but two disks
are used for parity. This means
that it protects against two disk
failures, but the capacity of two
disks are lost.
• Recommended for business and
general storage use. It provides
high disk failure protection and
read performance.
RAID 10 4 or more
(even number
required)
1 per pair of
disks
Total number of
disks divided by 2
• Every two disks are paired using
RAID 1 for failure protection.
Then all pairs are striped
together using RAID 0.
• Excellent read/write speeds and
high failure protection, but half
the disk capacity is lost.
• Recommended for application or
database storage.
RAID 50 6 or more 1 per disk sub-
group
Total number of
disks minus 1 disk
per sub-group
• Multiple small RAID 5 groups are
striped to form one RAID 50
group.
• Better failure protection and
faster rebuild times than RAID 5.
More storage capacity than RAID
10.
• Better random access
performance than RAID 5 if all of
the disks are SSDs.
• Recommended for enterprise
backup with ten or more disks.
RAID 60 8 or more 2 per disk sub-
group
Total number of
disks minus 2 disks
per sub-group
• Multiple small RAID 6 groups are
striped to form one RAID 60
group.
• Better failure protection and
faster rebuild time than RAID 6.
More storage capacity than RAID
10.
• Better random access
performance than RAID 6 if all of
the disks are SSDs.
• Recommended for business
storage and online video editing
with twelve or more disks.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 35

Storage Management
Storage Pool Management
Expanding a Storage Pool by Adding Disks to a RAID Group
You can add one or more disks to a RAID group in the storage pool.
Important
• Adding disks to a RAID 1 group changes the RAID type of the group to RAID 5.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, every sub-group must be expanded with the
same number of disks.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Verify that the NAS contains one or more free disks.
3. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
4. Verify the following:
• The storage pool contains at least one RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 group.
• The status of the RAID group that you want to expand is Ready.
5. Select the storage pool that you want to expand.
6. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
7. Click Expand Pool.
The Expanding Storage Pool window opens.
8. Select Add new disk(s) to an existing RAID group.
9. Select a RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 group.
10. Click Next.
11. Select the disks that will be used to expand the storage pool.
12. Click Expand.
A confirmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
13. Click OK.
14. Optional: For a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, repeat these steps for each sub-group.
QTS starts rebuilding the RAID groups. The capacity of the new disks appears as free space after RAID
rebuilding is completed.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 36
Expanding a Storage Pool By Adding a New RAID Group
You can create a new RAID group and then add it to the storage pool. The total capacity of the new RAID
group appears as additional free space.
QTS writes data to a storage pool that contains multiple RAID groups in a linear manner. This means that
QTS writes data to a RAID group until is it full before writing data to the next RAID group.
Warning
• If a storage pool contains multiple RAID groups and one RAID group fails, all data in
the storage pool will be lost. Ensure that you have a complete data backup plan.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, you must create a new RAID 50 or 60 group
with the same number of disks and sub-groups as the original pool. It is not possible to
just add additional sub-groups.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select the storage pool that you want to expand.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Click Expand Pool.
The Expanding Storage Pool window opens.
5. Select Create and add a new RAID group.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: If you want to use disks in a connected expansion unit, select the expansion unit from the
Enclosure Unit list.
Warning
If the selected expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, all data in the storage pool will
become inaccessible.
8. Select one or more disks.
Important
For RAID 50 or RAID 60 pools, the number of selected disks must be equal to or greater than
the number of disks initially used to create the pool.
9. Select a RAID type.
Important
• If the storage pool contains a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10 group, the new RAID
group must also have one of the mentioned RAID types.
• For RAID 50 or RAID 60 you cannot select a different RAID type.
10. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
For details, see Configuring a RAID Group Hot Spare.
11. Click Next.
12. Click Expand.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 37
A confirmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
13. Click OK.
QTS creates the new RAID group and then the RAID group starts rebuilding. The capacity of the new RAID
group appears as free space in the storage pool after RAID rebuilding is completed.
Volume Management
Expanding a volume increases its maximum size, also known as its capacity, enabling it to store more data.
Expansion should be performed when free space is low, to prevent users suddenly discovering that they are
unable to save files to the volume.
Expanding a Thick or Thin Volume
Thick and thin volumes can be expanded online, meaning that space can be added to the volume while it is
still being accessed. The extra space is allocated from the volumes parent storage pool.
Volume Type Maximum Allowed Expansion
Thick Amount of free space in the parent storage pool.
Thin Twenty times the amount of free space in the parent storage pool
Important
Setting the maximum size of a thin volume to a value that
is greater than the amount of free space in the storage
pool is called over-allocation.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Click Expand Volume.
The Volume Resizing Wizard opens.
5. Specify a new capacity for the volume.
Capacity can be specified in megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). The new capacity
must be greater than the current volume capacity.
6. Optional: Click Set to Max.
Sets the new volume capacity to the maximum available size. This option is only available for thick
volumes.
7. Click Apply.
The Volume Resizing Wizard closes. The volume status changes to Resizing....
After expansion is complete, the volume status changes back to Ready.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 38
Expanding a Single Static Volume by Adding Disks to a RAID Group
The total storage capacity of a single static volume can be expanded by adding one or more additional disks
to a RAID group in the static volume. This extra capacity can be added online, without any interruption to
data access.
Important
• Adding disks to a RAID 1 group changes the RAID type of the group to RAID 5.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, every sub-group must be expanded with the
same number of disks.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Verify the following:
• The NAS contains one or more free disks.
• The storage pool contains at least one RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 group.
• The status of the RAID group that will be expanded is Ready.
3. Select the single static volume that you want to expand.
4. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
5. Click Expand Volume.
The Volume Resizing Wizard window opens.
6. Select Add new disk(s) to an existing RAID group.
7. Select a RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6 group.
8. Click Next.
9. Select one or more disks.
10. Click Next.
11. Click Expand.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
A confirmation message appears.
12. Click OK.
13. Optional: For a RAID 50 or RAID 60 volume, repeat these steps for each sub-group.
QTS starts rebuilding the RAID groups. The capacity of the new disks appears as free space after RAID
rebuilding is completed.
Expanding a Single Static Volume By Adding a New RAID Group
A new RAID group is created and appended to the single static volume. The total capacity of this new RAID
group is then appears as additional storage pool free space.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 39

Warning
• If a storage pool contains multiple RAID groups and one RAID group fails, all data in
the storage pool will be lost. Ensure that you have a complete data backup plan.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, you must create a new RAID 50 or 60 group
with the same number of disks and sub-groups as the original pool. It is not possible to
just add additional sub-groups.
QTS writes data to a single static volume that contains multiple RAID groups in a linear manner. This means
that QTS writes data to a RAID group until is it full before it writes data to the next RAID group.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select the single static volume that you want to expand.
3. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
4. Click Expand Volume.
The Expanding Volume Wizard window opens.
5. Select Create and add a new RAID group.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: If you want to use disks in a connected expansion unit, select the expansion unit from the
Enclosure Unit list.
Warning
If the selected expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, all data on the volume will become
inaccessible.
8. Select one or more disks.
Important
For RAID 50 or RAID 60 volumes, the number of selected disks must be equal to or greater
than the number of disks initially used to create the volume.
9. Select a RAID type.
Important
For RAID 50 or RAID 60 you cannot select a different RAID type.
10. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as the hot spare for this RAID group.
Note
For details, see Configuring a RAID Group Hot Spare
11. Click Next.
12. Click Expand.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
A confirmation message appears.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 40

13. Click OK.
QTS creates the new RAID group, and the RAID group starts rebuilding. The volumes status changes
to Rebuilding...
After expansion is complete, the volume status changes back to Ready.
RAID Management
RAID Spare Disks
Configuring a RAID Group Hot Spare
Assigning a hot spare gives extra protection against data loss. In normal conditions, a hot spare disk is
unused and does not store any data. When a disk in the RAID group fails, the hot spare disk automatically
replaces the faulty disk. QTS copies the data to the spare disk in a process called RAID rebuilding.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Verify that the NAS contains one or more available disks.
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
4. Click Manage.
5. Select a RAID 1, RAID, 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10 group.
6. Select Manage > Configure Spare Drive .
7. Select one or more disks that will be used as spare disks.
8. Click Apply.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
A confirmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
The spare disks are added to the RAID group. The disk appears as a green Spare in the disks summary at
Disks/VJBOD.
Configuring a Global Hot Spare
A global spare disk acts as a hot spare for all RAID groups in a storage device such as a NAS or a
connected expansion unit. In normal conditions, the disk is unused and does not store any data. When a disk
in any RAID group fails, the hot spare disk automatically replaces the faulty disk. QTS copies the data to the
spare disk in a process called RAID rebuilding.
Important
Storage enclosures (the NAS and connected expansion units) cannot share global spare
disks. A unique global hot spare disk must be assigned to each storage enclosure.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Verify that the NAS contains one or more available disks.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 41

3. Optional: Select a connected expansion unit.
4. Select a free disk.
5. Select Action > Set as Enclosure Spare .
Warning
All data on the selected disk will be deleted.
A confirmation message appears.
6. Click OK.
The disk appears as a green Spare on the Disks/VJBOD screen.
Expanding a RAID Group by Replacing all Disks
You can increase the maximum storage capacity of a RAID group by replacing all member disks with higher-
capacity disks. This can be done online, without losing access to data or any interruption to NAS services.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Verify that all hot spares and global hot spares assigned to this RAID group are disabled.
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
4. Click Manage.
5. Select a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10 group.
6. Select Manage > Replace Disks One by One .
7. Select a disk to replace.
Ensure that the capacity of the new disk is greater than the capacity of the disk that it is replacing.
8. Click Change.
The disk description changes to Please remove this drive.
9. Remove the disk from the bay.
The NAS beeps twice. Then the disk description changes to Please insert the new disk.
10. Insert a new disk into the same bay.
The NAS beeps twice. Then the status of the disk and RAID group change to Rebuilding.
11. Wait for rebuilding to finish.
Warning
Do not remove any disks while the RAID group is rebuilding.
The disks status changes back to Good.
12. Repeat the previous steps until all disks in the RAID group have been replaced.
The Expand Capacity button is enabled after all disks have been replaced and rebuilding has
completed.
13. Click Expand Capacity.
A confirmation message appears.
14. Click OK.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 42

The NAS beeps and then the RAID group status changes to Synchronizing.
Warning
Do not power off the NAS or remove any disks while hard drive synchronization is in progress.
The RAID group status changes to Ready.
Changing the RAID Type of a RAID Group
You can change the RAID type of an existing RAID group online, without losing access to data or any
interruption to NAS services. Changing the RAID type of a RAID group is called RAID migration. QTS allows
the following migrations:
Original RAID Type New RAID Type Extra Disks Required
Single RAID 1 One
RAID 1 RAID 5 One or more
RAID 5 RAID 6 One or more
Tip
Migration from a single disk to RAID 6 is performed in stages. First migrate the group to
RAID 1, then to RAID 5, and then finally to RAID 6.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Verify the following:
• The NAS contains one or more available disks.
• The capacity of each available disk is equal to or greater than the smallest disk in the RAID group.
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
4. Click Manage.
5. Select a RAID group.
6. Select Manage > Migrate .
7. Select one or more disks.
8. Click Apply.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
A confirmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
The RAID group status changes to Migrating.
The RAID type changes and then the RAID group status changes back to Ready when migration is
completed.
Creating a RAID Bitmap
If a disk is temporarily disconnected from its RAID group and then reconnected, the RAID group must
resynchronize all of its data. This process may take a long time. If the RAID group has a bitmap, only
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 43
changes that were made after the disk was removed need to be synchronized, greatly speeding up the
process.
A disk can become temporarily disconnected in the following situations.
• A disk is accidentally removed from the NAS while the NAS is powered on.
• The NAS unexpectedly shuts down because of a hardware or software error.
• A user presses the power button for 10 seconds or disconnects the power cable while the NAS is
powered on.
Important
• You can only create bitmaps for RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 groups.
• Enabling a RAID bitmap causes the RAID groups performance to decrease slightly.
• A bitmap improves resynchronization time only if the same disk is added back to the
RAID group. If a new disk is added to a RAID group, the bitmap makes no difference.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10 group.
5. Click Manage and then select Enable Bitmap.
A confirmation message appears.
QTS creates a bitmap for the RAID group.
Recovering a RAID Group
RAID recovery enables you to recover a RAID group in the event of accidental disk removal or SATA
connector failure. When several disks are removed or disconnected from a RAID group:
• The status of the group changes to Error.
• The statuses of all volumes and storage pools using the RAID group change to Inactive.
• All data on the affected volumes and LUNs becomes inaccessible.
Important
RAID recovery only helps when disks are temporarily disconnected and then reconnected.
It does not help in the event of disk failure.
1. Reconnect all disconnected disks.
Important
Ensure that each disk is reinserted into its original drive bay.
2. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume with the status Inactive.
4. Click Manage.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 44

5. Select a RAID group with the status Error.
6. Click Manage and then select Recover.
The RAID group starts to rebuild.
RAID Scrubbing
RAID scrubbing helps maintain the consistency of data on the NAS. QTS scans the sectors of a RAID 5 or
RAID 6 group and automatically attempts to repair any detected errors. You can run RAID scrubbing
manually, or on a schedule.
Tip
QNAP recommends performing RAID scrubbing at least once a month to maintain system
health and prevent data loss.
Running RAID Scrubbing Manually
Warning
The read/write speeds of the RAID group may decrease while RAID scrubbing is in
progress.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
Verify that the RAID status is Ready.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select a RAID 5 or RAID 6 group.
5. Click Manage and then select RAID Scrubbing.
The RAID group status changes to Scrubbing.
Running RAID Scrubbing on a Schedule
You can schedule periodic RAID scrubbing of all RAID 5 and RAID 6 groups.
Warning
The read/write speeds of the RAID group may decrease while RAID scrubbing is in
progress.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots .
2.
Click the Global Settings icon .
The Global Settings menu opens.
3. Enable RAID Scrubbing Schedule.
4. Specify how often data scrubbing will run.
• Daily
• Weekly
• Monthly
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 45

5. Specify when data scrubbing will run.
Tip
QNAP recommends specifying a time when the NAS is not in use, such as after business hours
or on weekends.
6. Click Apply.
Data scrubbing will run according to the specified schedule. When data scrubbing is running on a RAID
groups, the status of the group changes to Scrubbing.
Snapshots
Snapshots help protect stored data by recording the state of thick volumes, thin volumes, and LUNs at a
specific time. You can restore data to a previous state if the data is unintentionally modified or deleted. Single
static volumes and legacy volumes do not support snapshots.
To use snapshots, your NAS model must support snapshots and must contain at least 1 GB of memory. For
details on compatible models, see www.qnap.com/solution/snapshots.
Snapshot Creation
Taking a Snapshot
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or block-based LUN.
To take a snapshot of a file-based LUN, select the volume that it is stored on.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Take a Snapshot.
A confirmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
The Take a Snapshot window opens.
5. Specify a name.
6. Specify a retention time.
Option Description
Keep For Specify the number of days, weeks, or months that QTS
retains the snapshot before it is automatically deleted.
Keep this snapshot permanently When selected, QTS retains the snapshot indefinitely, even
when storage space is low.
7. Optional: Specify a description that will help you identify the snapshot.
8. Click OK.
A confirmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
QTS takes the snapshot, then the snapshot appears in Snapshot Manager.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 46

Configuring a Snapshot Schedule
Configure a snapshot schedule to ensure that snapshots are taken at regular intervals. You can configure a
separate schedule for each volume and LUN.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Snapshot Manager. The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Click Snapshot Settings.
The Snapshot Settings window opens.
5. Enable scheduling.
6. Specify the snapshot frequency.
7. Optional: Specify a retention time.
a. Select Keep for.
b. Specify the number of days, weeks, or months that QTS keeps the snapshot before it is deleted.
If this option is not selected, QTS retains the snapshot indefinitely.
8. Optional: Select Enable smart snapshots.
When selected, QTS takes a snapshot only if the data was modified after the last snapshot was taken.
This reduces the number of snapshots and saves storage space.
9. Optional: Specify a description that will help you identify the snapshot.
10. Click OK.
A confirmation message appears.
11. Click OK.
QTS takes snapshots according to the specified schedule.
Configuring Guaranteed Snapshot Space
Guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling this
feature ensures that QTS always has sufficient space for taking new snapshots.
Setting Space Available for Storing Snapshots
Disabled Free space in the storage pool
Enabled Guaranteed snapshot space until full, then free space in the storage pool
When all space available for snapshots is full, QTS deletes the oldest snapshots to create free space for new
snapshots. If creating free space is not possible, new snapshots are not created.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Guaranteed Snapshot Space and then select Configure.
4. Select Actions > Set Snapshot Reserved .
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 47
5. Enable Guaranteed Snapshot Space
6. Select a method for specifying the amount of space that will be reserved for snapshots.
Option Description
Recommended Select a percentage of the total storage pool space. The default value is
20%.
Custom Specify a fixed amount of storage pool space in gigabytes (GB).
7. Click OK.
Guaranteed Snapshot Space appears in the Space Allocation section of the Snapshot screen.
Snapshot Storage Limitations
The maximum number of snapshots a NAS can store is determined by the NAS series, CPU type, and
installed memory.
QNAP NAS Processor Type
You can determine your CPU type by looking for a sticker on the NAS or on the retail packing, or by
searching for the NAS specifications at https://www.qnap.com.
CPU Type CPU Manufacturer
x86 Intel, AMD
ARM Annapurna Labs, Realtek
Maximum Number of Snapshots
Installed Memory NAS Maximum Snapshots
per NAS
Maximum Snapshots
per Volume/LUN
< 1GB Unsupported Unsupported Unsupported
≥ 1 GB All 32 16
≥ 2 GB All 64 32
≥ 4 GB x86 CPU 1024 256
X51/X51+ series 256 64
ARM CPU 256 64
Snapshot Management
Restoring Files and Folders from a Snapshot
You can restore individual files or entire folders to a previous state using snapshots. The number of files and
the total file size affect the duration of the restoration process.
Tip
• Use snapshot revert to quickly restore all files and folders on a volume. For details, see
Reverting to a Volume or LUN Snapshot.
• You can restore files and folders from a snapshots in File Station by enabling Enable
File Station Snapshot Directory for administrators. For details, see Snapshot
Settings.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 48
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN.
The volume or LUN must contain at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Select the files and folders that you want to restore.
6. Click Restore and then select one of the following.
Option Description
Restore File When selected, QTS restores the files and folders to their original locations.
Warning
Restoring files to their original locations overwrites all changes that were
made to the files after the snapshot was taken.
Restore File to When selected, you must specify a storage location for the restored files and
folders.
You can restore the files to a local or remote folder. If you are restoring a folder, you
can restore it as a new NAS shared folder.
7. Click OK.
QTS restores the files and folders to the specified location and then displays a message.
Reverting to a Volume or LUN Snapshot
You can restore all the data on a volume or LUN to a previous state using snapshot revert. Reverting a
volume or LUN takes significantly less time than restoring individual files and folders.
Tip
Create a snapshot shared folder to take a snapshot of a single folder. Snapshot shared
folders have their own dedicated volume and can be restored faster than a larger volume
containing multiple folders.
1. Go to Main Menu > Storage & Snapshots > Storage/Snapshot .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN.
The volume or LUN must contain at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Revert Volume Snapshot.
Warning
Reverting a snapshot overwrites all changes made to files and folders on the selected volume
or LUN after the snapshot was taken.
A confirmation message appears.
6. Optional: Select Take a new snapshot before reverting
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 49

7. Click Local Revert.
The volume or LUNs status changes to Reverting.QTS disables access to the volume or LUN until the
process is completed.
Restoring Files and Folders using Windows Previous Versions
• You must be using Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 10.
• The files to be restored must be stored on a NAS shared folder that can be accessed in Windows.
• The files must be stored on a thick volume, thin volume or LUN that supports snapshots. The volume or
LUN must have at least one snapshot.
QTS snapshots integrate with the Previous Versions feature, which enables Windows users to restore files
and folders from a snapshot in Windows File Explorer.
1. Open a NAS shared folder in Windows File Explorer.
For details on mapping a shared folder, see Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer.
2. Right-click the file or folder, and then select Properties > Previous Versions
A list of available versions appears. Each version corresponds to a snapshot of this NAS shared folder.
3. Optional: Preview the file or folder to be restored.
a. Click Open.
The file or folder opens.
b. Verify that the version of the file or folder is correct.
4. Click Restore.
QTS restores the file or folder to the specified previous version.
Global Settings
You can access global settings by clicking at the top-right of the Storage & Snapshots window.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 50
Storage Settings
Setting Description
RAID Resync Priority Specify the priority level for the following RAID operations when the NAS is
in use:
• Rebuild
• Scrubbing
• Sync
You can select one of the following priorities.
•Service: When selected, QTS performs RAID operations at lower
speeds to maintain NAS performance.
•Default: When selected, QTS performs RAID operations at medium
speeds.
•Resync First: When selected, QTS performs RAID operations at higher
speeds. Users may notice a decrease in NAS performance.
Important
When the NAS is idle, all RAID operations are performed
at the highest possible speeds.
RAID Scrubbing Schedule Enable this feature to periodically scan for and automatically fix bad sectors
on RAID 5 and RAID 6 groups. For details, see Running RAID Scrubbing on
a Schedule.
Auto Reclaim and SSD Trim
Schedule
Enable this feature to periodically run the following tasks on all thin volumes
and SSDs:
• Auto Reclaim: QTS returns unused storage space to the parent storage
pool. The unused storage space is derived from files deleted from thin
volumes.
• SSD Trim: QTS cleans deleted data blocks to maintain SSD read and
write performance.
By default, the operations are scheduled to run daily at 2:00 AM. SSD Trim
is only performed on solid state drives if they are in a RAID 0, RAID 1 or
RAID 10 group.
Disk Health Settings
Setting Description
Activate Predictive
S.M.A.R.T. Migration:
Enable this feature to regularly monitor disk health. If S.M.A.R.T. errors are
detected on a disk, QTS displays a warning and then begins migrating data
from the faulty disk to a healthy spare disk. After migration is completed, the
healthy disk is used in place of the faulty disk.
This process is faster and safer than waiting for a disk to fail, and then
initiating a full RAID rebuild.
Disk S.M.A.R.T. polling time
(minutes)
QTS will check periodically for S.M.A.R.T. errors. You can specify the
frequency in minutes or hours.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 51
Setting Description
Disk Temperature Alarm Enable this feature to monitor the disk temperatures. QTS displays a
warning when the disk temperature reaches the specified value. You can set
separate alerts for hard disk drives and solid state drives.
TLER/ERC timer (seconds): Enable this feature to specify how long before QTS flags a disk as
unresponsive.
A disk temporarily becomes unresponsive when it encounters a read or
write error, which it tries to fix. QTS might interpret this unresponsiveness as
disk failure, and automatically initiate a rebuild of the disks in the RAID
group. Enabling this feature ensures that a disk has sufficient time to
recover from a read or write error.
Tip
This setting is usually known as Error recovery control
(ERC), Time-limited error recovery (TLER) or Command
completion time limit (CCTL), depending on the
manufacturer.
Snapshot Settings
Setting Description
Smart snapshot space
management
Enable this feature to delete the oldest snapshots when the space available
for storing snapshots (guaranteed snapshot space plus free storage pool
space) is less than 32GB. QTS excludes the last snapshot taken, or
snapshots that are set to be kept permanently. If QTS is unable to create
32GB of free snapshot space, then it does not take any new snapshots.
Enable File Station Snapshot
Directory for administrators
Enable this feature to consolidate the available snapshots into one folder on
File Station. You can restore files and folders from the snapshot directory by
copying and then pasting into a NAS shared folder.
Make snapshot directory
(@Recently-Snapshot)
visible in shared folder root
Enable this feature to show a special read-only folder at the root level of
each shared folder. Making the folder visible allows users to browse its
contents and restore previous versions of files using copy and paste.
When the number of
snapshots reaches maximum
Specify the default QTS behavior after the maximum number of snapshots
for any volume, LUN or NAS is reached. You can choose to overwrite the
oldest available snapshots or to stop taking snapshots.
The maximum number of snapshots depends on your NAS model. For
details, see Snapshot Storage Limitations.
Use timezone GMT+0 for all
new snapshots
Enable this feature to use the GMT+0 time zone in the file names of new
snapshots. This file naming convention can simplify snapshot management
especially when working with snapshots from NAS devices on different time
zones.
This setting only applies to new snapshots. Existing snapshots are not
renamed.
Show hidden files in
Snapshot Manager
Enable this feature to display hidden files in Snapshot Manager.
The setting does not affect files inside the File Station Snapshot Directory.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Storage & Snapshots 52
3. Privilege
Users
The following user types are supported:
User Type Description
Local user • User accounts created in QTS are synced to Storage & Snapshots.
• User accounts created in Storage & Snapshots are synced to QTS.
• Both QTS and Storage & Snapshots store the account data.
• Storage & Snapshots authenticates users and assigns the
surveillance privileges.
Domain user • User accounts created on a domain controller are synced to
Storage & Snapshots.
• Storage & Snapshots authenticates users and assigns the
surveillance privileges.
Creating a Local User
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
The Users screen appears.
2. Click Create, and then select Create a User.
The Create a User window opens.
3. Specify the following information:
Field Description
Username Specify a username that contains 1 to 32
characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: ~ ! @ # $ ^ & ( ) - _ . { }
Password Specify a password that contains 1 to 64 ASCII
characters.
Phone number (optional) The information is for your reference and is not
used by QTS.
Email (optional) QTS sends a notfication to this email address
when the account password is about to expire.
Note
•SMTP Server: Go to Control Panel >
System > Notification > E-mail .
•Change Password: Go to Control
Panel > System > Security .
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 53
• If the SMTP Server and Change
Password are not configured, QTS
does not use the information.
• For details, see the QTS User Guide.
Send a notification mail to the newly created
user (optional)
When selected, QTS sends a message that
contains the following information to the specified
email address.
• Username and password
• URLs for connecting to the NAS
4. Optional: Add the user to one or more user groups.
a. Under User Groups, click Edit.
b. Select one or more user groups.
QTS provides two default user groups.
User Group Description
Administrators Users in this group can configure settings, create users, and install
applications.
Everyone Users in this group can only view and modify files.
This group contains all local user accounts and can be used to grant
shared folder permissions to all local user accounts.
c. Optional: Select Create a User Group.
For details, see Creating a User Group.
5. Optional: Specify shared folder permissions for the user.
a. Under Shared Folder Permission, click Edit.
b. Specify the actions the user can perform in shared folders.
For details, see Editing Shared Folder Properties.
Permission Description
RO (read-only) The user can read but not write files in the shared folder.
RW (read/write) The user can read and write files in the shared folder.
Deny The user cannot read or write files in the shared folder.
6. Optional: Specify the applications the user can access.
a. Under Edit Application Privilege, click Edit.
b. Select the applications the user can use.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to applications and network services that the user does not
require.
7. Click Create.
QTS creates the user account and then adds it to the Users screen.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 54
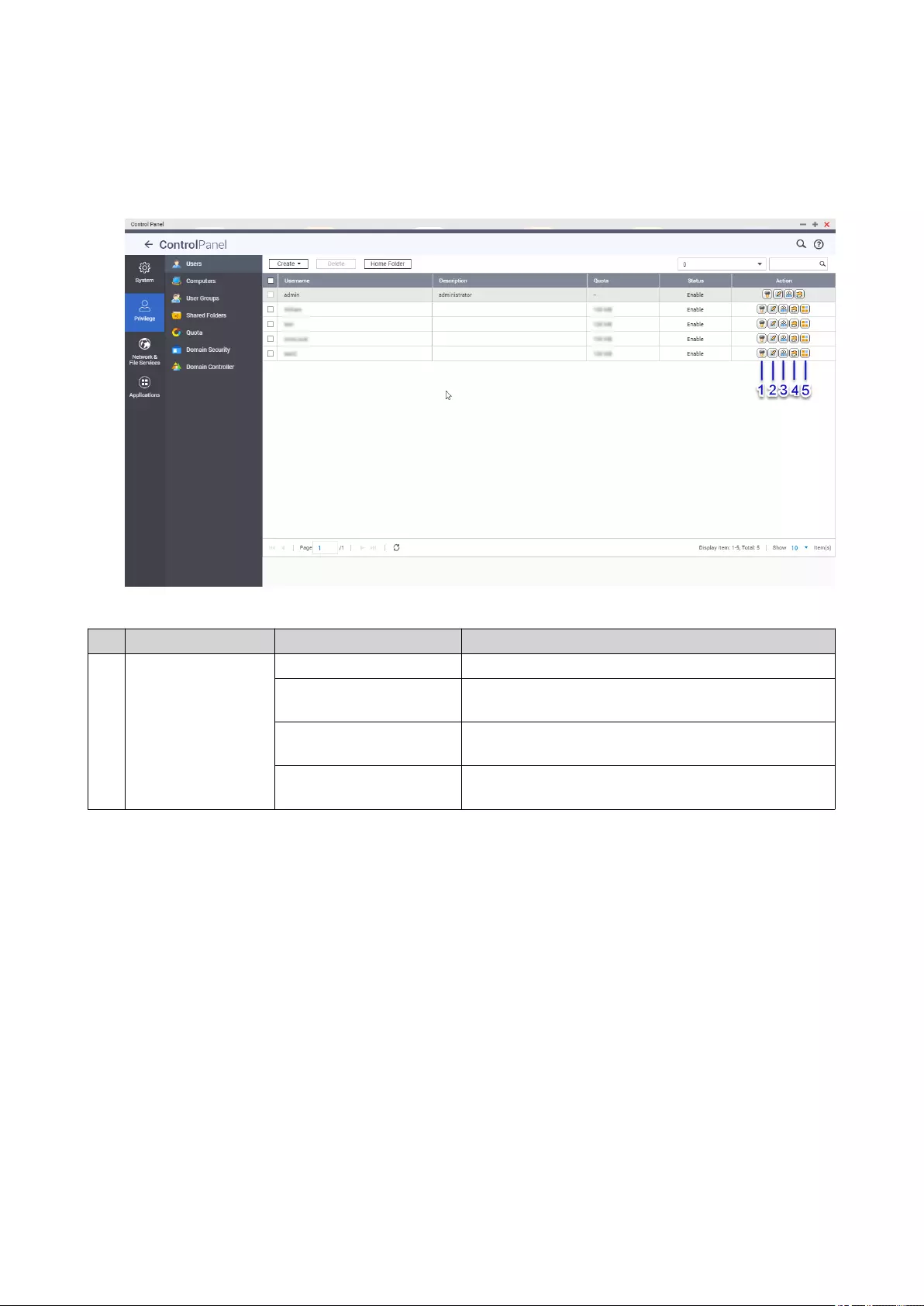
User Account Settings
Administrators can configure user account settings.
# Action Field/Option Description
1Change password Old Password This field is only available to admin accounts.
Password The password must contain 1 to 64 ASCII
characters.
Verify Password The password must match the previously specified
password.
Show Password When selected, QTS displays the specified
password.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 55
# Action Field/Option Description
2Edit Account
Profile
Email (optional) QTS sends a notfication to this email address when
the account password is about to expire.
You must configure the following settings:
•SMTP Server: Go to Control Panel > System >
Notification > E-mail .
•Change Password: Go to Control Panel >
System > Security .
If the SMTP Server and Change Password are not
configured, QTS does not use the information.
For details, see the QTS User Guide.
Phone number
(optional)
The information is for your reference and is not used
by QTS.
Description (optional): The information is for your reference and is not used
by QTS.
Disallow the user to
change password
When selected, QTS prevents the user from
changing the password.
Disable this account When selected, the account can be disabled
immediately or on a specified date.
Quota When selected, QTS limits the amount of data that
each user can store on the NAS.
To enable this feature, go to Main Menu > Control
Panel > Privilege > Quota .
3Edit User Group N/A User groups, along with user-level shared folder
permissions, determine which shared folders the
user will have access to.
QTS provides two default user groups.
• Administrators: Users in this group can configure
settings, create users, and install applications.
• Everyone: Users in this group can only view or
modify files.
4Edit Shared Folder
Permission
N/A A shared folder can have any of the following access
permissions.
•RO (read-only): The user can read but not write
files in the shared folder.
•RW (read/write): The user can read and write
files in the shared folder.
•Deny: The user cannot read or write files in the
shared folder.
Important
Group-level permissions may override
user-level permissions. For details, go
to Conflicts in Shared Folder
Permissions.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 56
# Action Field/Option Description
5Edit Application
Privilege
N/A This button is not available to admin accounts
because they have access to all applications.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to
applications and network services that
the user does not require.
User Groups
Administrators can create user groups to manage permissions for multiple users.
Creating a User Group
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups .
The User Groups screen appears.
2. Click Create.
The Create a User Group window opens.
3. Specify the following information:
•User group name: The name must contain 1 to 128 characters, and cannot include the following
characters: ` * @ = + [ ] \ | ; : " , < > / ? % ' SPACE.
•Description: The description must contain 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
4. Optional: Add users to the user group.
a. Under Assign users to this group, click Edit.
b. Select one or more users.
5. Optional: Edit Shared Folder Permissions
A shared folder can have any of the following access permissions.
•RO (read-only): The group can read but not write files in the shared folder.
•RW (read/write): The group can read and write files in the shared folder.
•Deny: The group cannot read or write files in the shared folder.
Important
Group-level permissions may override user-level permissions. For details, go to Conflicts in
Shared Folder Permissions.
6. Click Create.
Storage & Snapshots creates the user group and then adds it to the User Groups screen.
Shared Folders
Creating a Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 57
The Shared Folder screen appears.
2. Click Create, and then select Shared Folder.
The Create A Shared Folder window opens.
3. Specify the following information:
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin with a space or "_sn_"
• Contain consecutive spaces
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
Disk Volume Specify the volume on which the shared folder will be created.
Path You can specify a path or allow the operating system to automatically
create one.
4. Optional: Configure user access permissions.
a. Under Configure access privileges for users, click Edit.
b. Specify the access permissions for users.
User Group Description
Administrators Users in this group can configure settings, create
users, and install applications.
Everyone Users in this group can only access files.
This group contains all local user accounts and can
be used to grant shared folder permissions to all
local user accounts.
5. Optional: Enable folder encryption.
a. Under Folder Encryption, click Edit.
b. Select Encryption.
Folder encryption protects folder content against unauthorized data access when the drives are
physically stolen.
c. Specify the following information:
Field/Option Description
Input Password Specify a password that contains 8 to 32 characters except the
following: " $ : = \
Verify Password The password must match the previously specified password.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 58
Field/Option Description
Save encryption key When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
When disabled, the admin must perform the following steps:
a. Restart the NAS.
b. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared
Folder .
c. Click the unlock icon.
Warning
The data will be inaccessible if the encryption
password is lost.
6. Optional: Configure advanced settings.
Option Description
Guest Access Right Select the permission level that is assigned to users
without a NAS account.
Media Folder Selecting this option allows media applications to
scan this folder for media files.
Hide Network Drives Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows
networks. Users that know the specific path can still
access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows file
locking mechanism that facilitates caching and
access control to improve performance. This feature
is enabled by default and should only be disabled in
networks where multiple users simultaneously
access the same files.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled.
Selecting this option encrypts all Microsoft network
communication on the SMB3 protocol.
Enable Network Recycle Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this
shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle Bin to
administrators only for now
This option is available only when Enable Network
Recycle Bin is selected. Selecting this option
prevents non-administrator users from recovering
and deleting files in the Recycle Bin.
Enable sync on this shared folder Selecting this option allows this shared folder to be
used with Qsync.
7. Click Create.
QTS creates the shared folder and then adds it to the Shared Folders screen.
Editing Shared Folder Properties
1. Go to Main Menu > Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Select Action > Edit Properties .
The Edit Properties window appears.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 59
3. Configure the following settings.
Option Description
Comment Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters. The
information is for your reference and is not used by QTS.
Hide Network Drives Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users that
know the specific path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows file locking mechanism that
facilitates caching and access control to improve performance. This
feature is enabled by default and should only be disabled in networks
where multiple users simultaneously access the same files.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled. Selecting this
option encrypts all Microsoft network communication on the SMB3
protocol.
Enable Network Recycling Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle
Bin to administrators only for
now
This option is available only when Enable Network Recycle Bin is
selected. Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from
recovering and deleting files in the Recycle Bin.
Enable write-only access on
FTP connection
Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from viewing
and downloading the content of this folder with an FTP connection.
Encrypt this folder Selecting this option enables folder encryption, which protects folder
content against unauthorized data access when the drives are
physically stolen.
Enable sync on this shared
folder
Selecting this option allows this shared folder to be used with Qsync.
4. Click OK.
Conflicts in Shared Folder Permissions
When a user is assigned different permissions for a shared folder, QTS uses the following hierarchy to
resolve conflicts.
1. No Access (Deny)
2. Read/Write (RW)
3. Read Only (RO)
User Permission User Group Permission Actual Permission
Read Only Read/Write Read/Write
Read/Write Read Only Read/Write
Read Only User group 1: No Access
User group 2: Read/Write
User group 3: Read Only
No Access
Drive Mapping
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 60
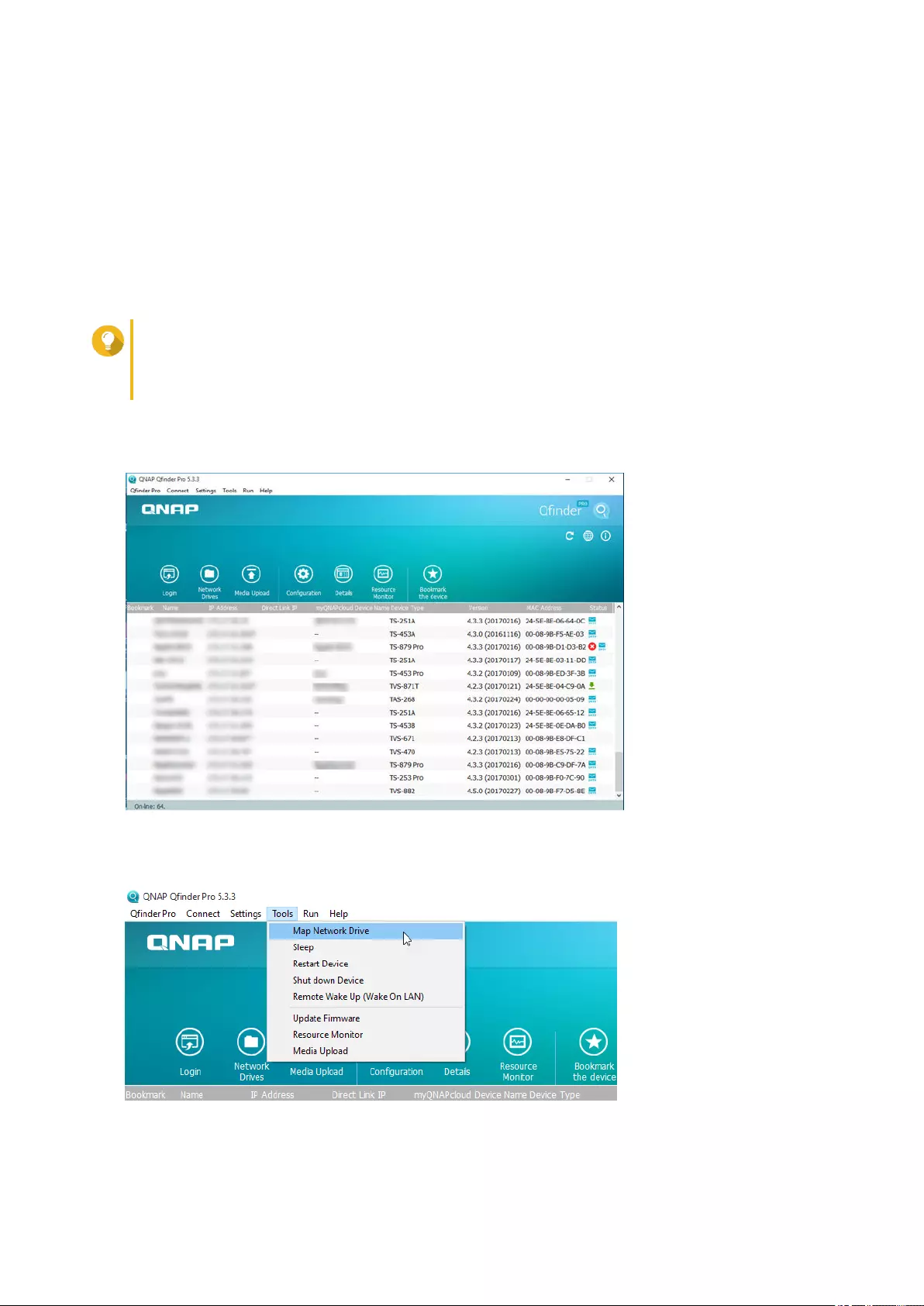
Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer
Mapping a NAS shared folder as a network drive lets you easily access and manage files from your
Windows computer.
1. Power on the NAS.
2. Connect the NAS to your local area network.
3. Install Qfinder Pro on a Windows computer that is connected to the same local area network.
Tip
Qfinder Pro is a desktop utility that enables you to locate and access the QNAP NAS devices in
your local area network.
To download Qfinder Pro, go to https://www.qnap.com/utilities.
4. Open Qfinder Pro.
Qfinder Pro displays all QNAP NAS devices in your local area network.
5. Select the NAS, and then go to Tools > Map Network Drive .
6. Select a shared folder, and then click Map Network Drive.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 61
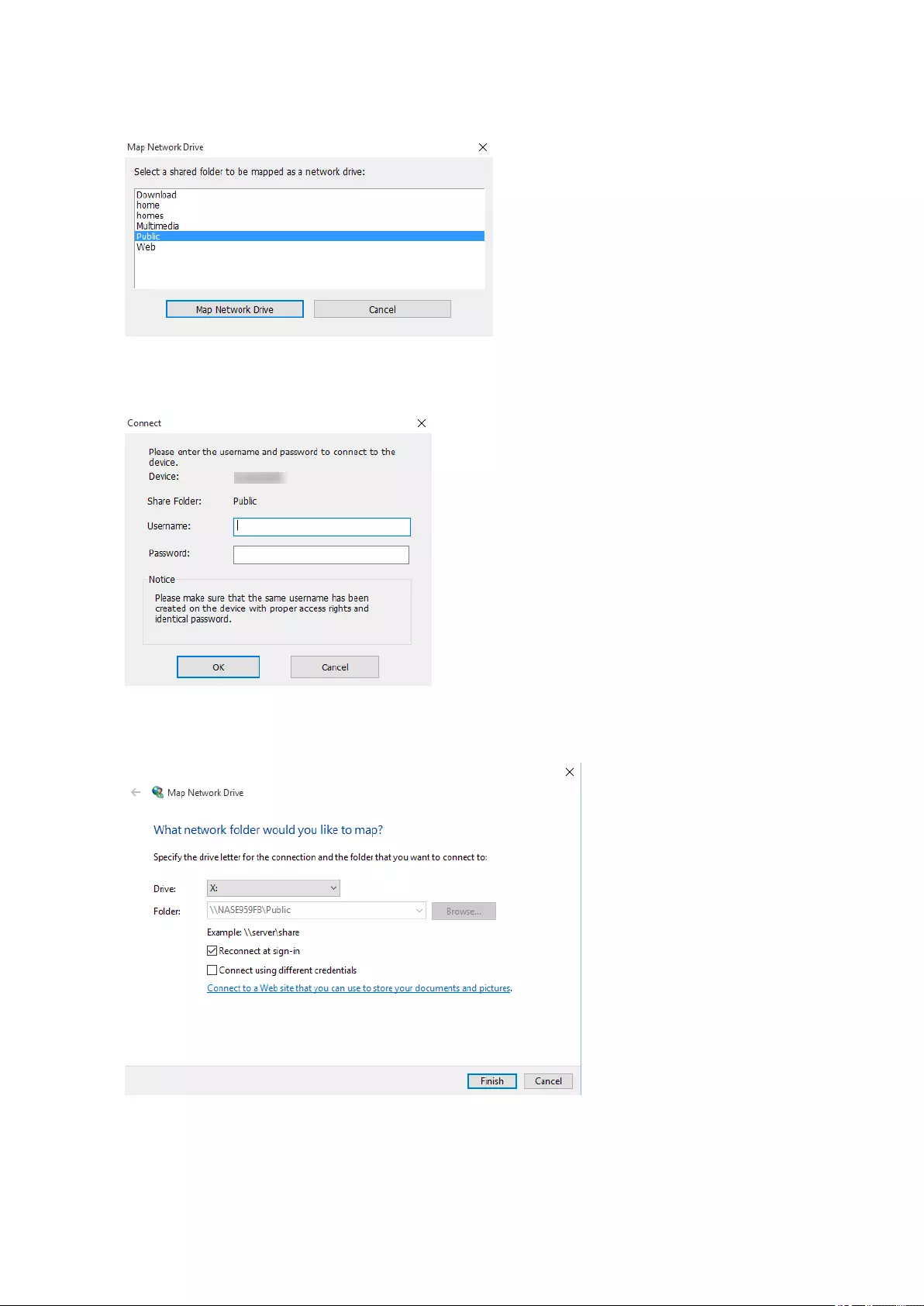
7. Specify your QTS username and password.
8. Specify a drive letter.
9. Click Finish.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 62
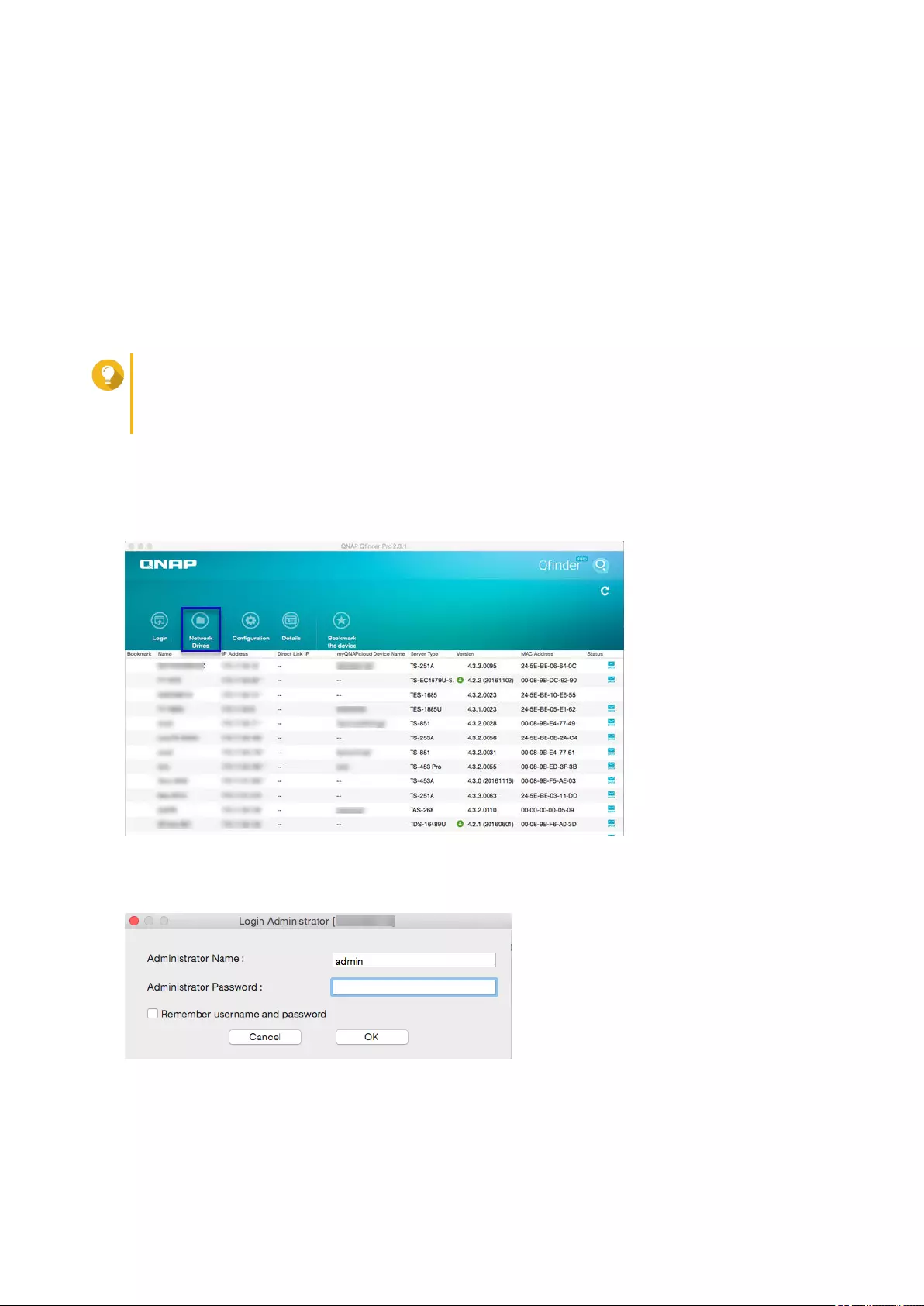
The shared folder is mapped as a network drive and can be accessed using Windows Explorer.
Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac Computer
With Qfinder Pro, you can find all the available QNAP NAS devices on your network. Mapping a NAS shared
folder as a network drive lets you quickly access and manage files from your Mac device.
1. Power on the NAS.
2. Connect the NAS to your local area network.
3. Install Qfinder Pro on a Mac computer that is connected to the same local area network.
Tip
Qfinder Pro is a desktop utility that enables you to locate and access the QNAP NAS devices in
your local area network.
To download Qfinder Pro, go to https://www.qnap.com/utilities.
4. Open Qfinder Pro.
Qfinder Pro displays all QNAP NAS devices in your local area network.
5. Select the NAS, and then click Network Drives.
6. Specify your QTS user name and password, and then click OK.
The Mount Network Drives window opens.
7. Select Add mounted folders to "Favorites" in Finder, and then click OK.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 63
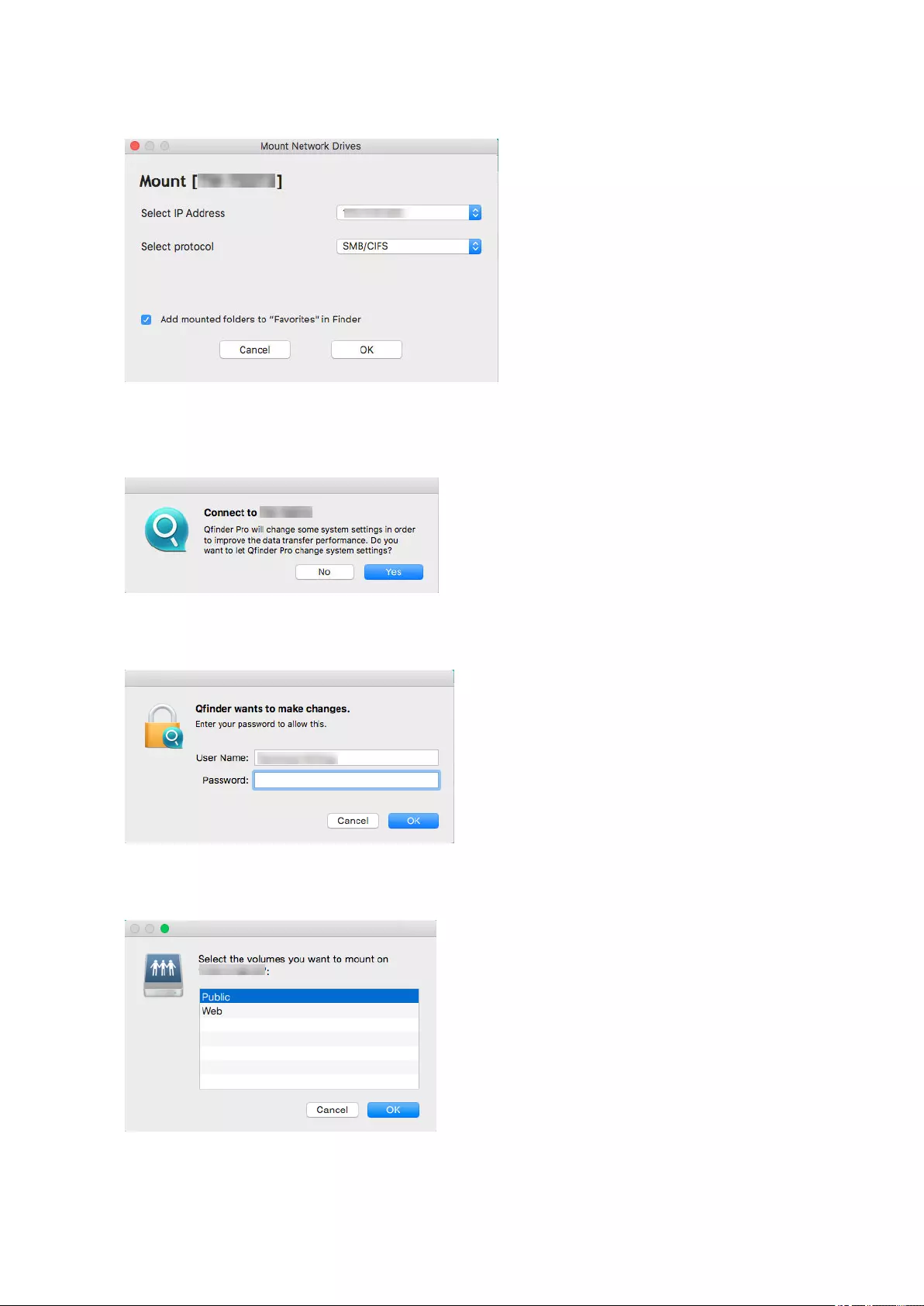
A confirmation message appears.
8. Click Yes.
9. Specify your Mac user name and password, and then click OK.
10. Select the shared folder, and then click OK.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 64

The shared folder is mapped as a network drive and can be accessed using Qfinder.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
Privilege 65
4. File Station
Overview
About File Station
File Station is a QTS file management application that allows you to access your NAS files. You can quickly
find files, manage file and folder permissions, play media files, and share files and folders.
Supported File Formats
Category File Extension
Image • BMP
• JPG
• JPE
• PNG
• TGA
• GIF
Music • MP3
• FLAC
• OGG
• WAV
• AIF
• AIFF
Video • AVI
• MP4
System Requirements
Category Detail
Web browser • Microsoft Internet Explorer 9 or later
• Mozilla Firefox 3.6 or later
• Apple Safari 5 or later
• Google Chrome
Java program Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 7 or later
Flash player Adobe Flash Player 9 or later
Parts of the User Interface
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 66
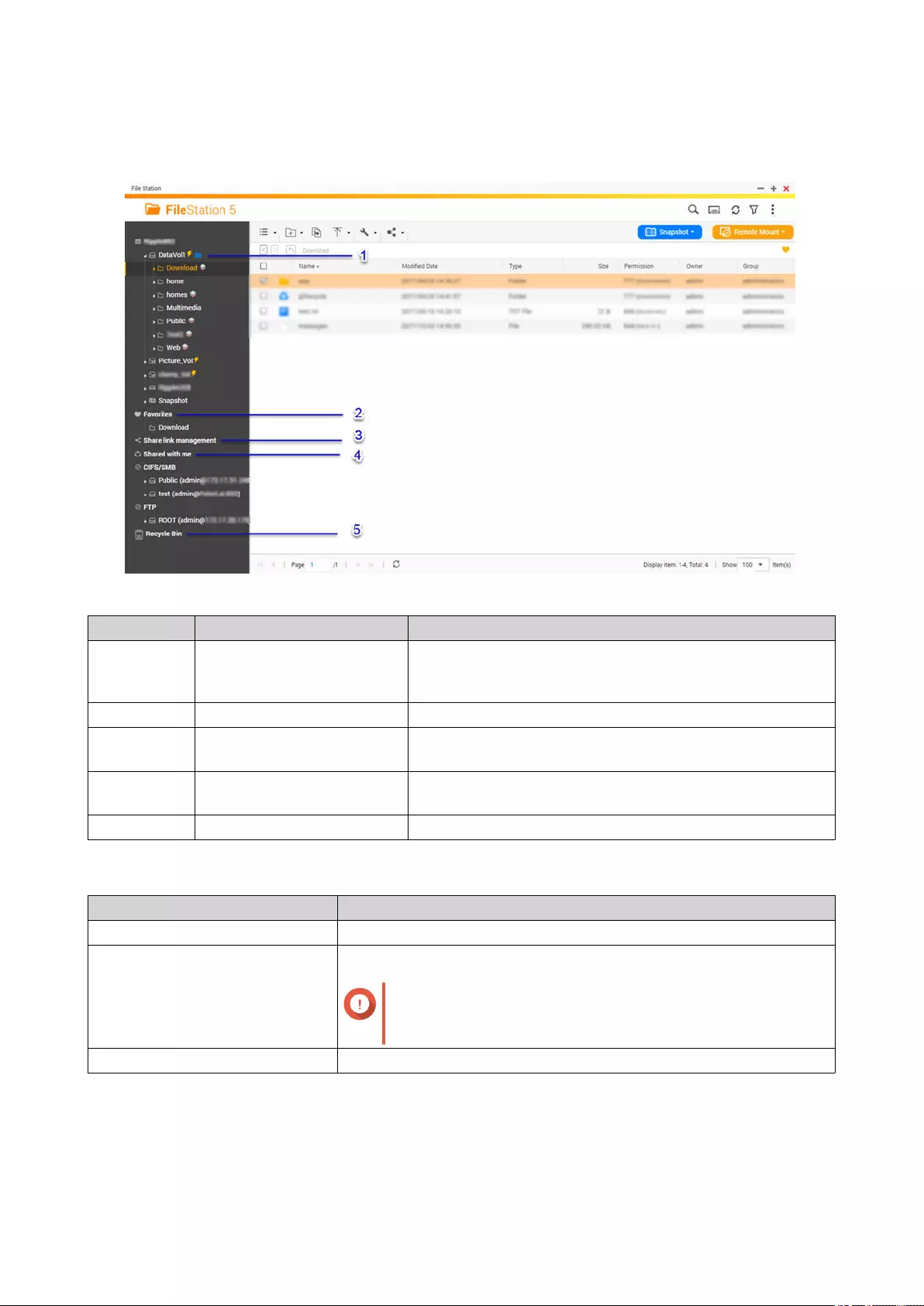
Left Panel
Label UI Element Description
1 Volume Displays all the folders in the volume, including shared
folders. The default shared folders vary depending on the
NAS model.
2 Favorites Displays bookmarked folders.
3 Share link management Displays links of NAS files shared by the logged on user.
Administrators see links shared by all NAS users.
4 Share with me Displays files and folders shared by other NAS users with
the logged on user.
5 Recycle Bin Displays deleted files and folders.
Depending on your setup, the following folders may also appear on the list.
Folder Description
Snapshot Displays the saved snapshots from enabled volumes.
Local folders Displays the local folders on a Windows computer.
Important
To view local folders from File Station, you must first
install Java Runtime Environment.
Qsync Displays files, folders, and team folders from Qsync.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 67
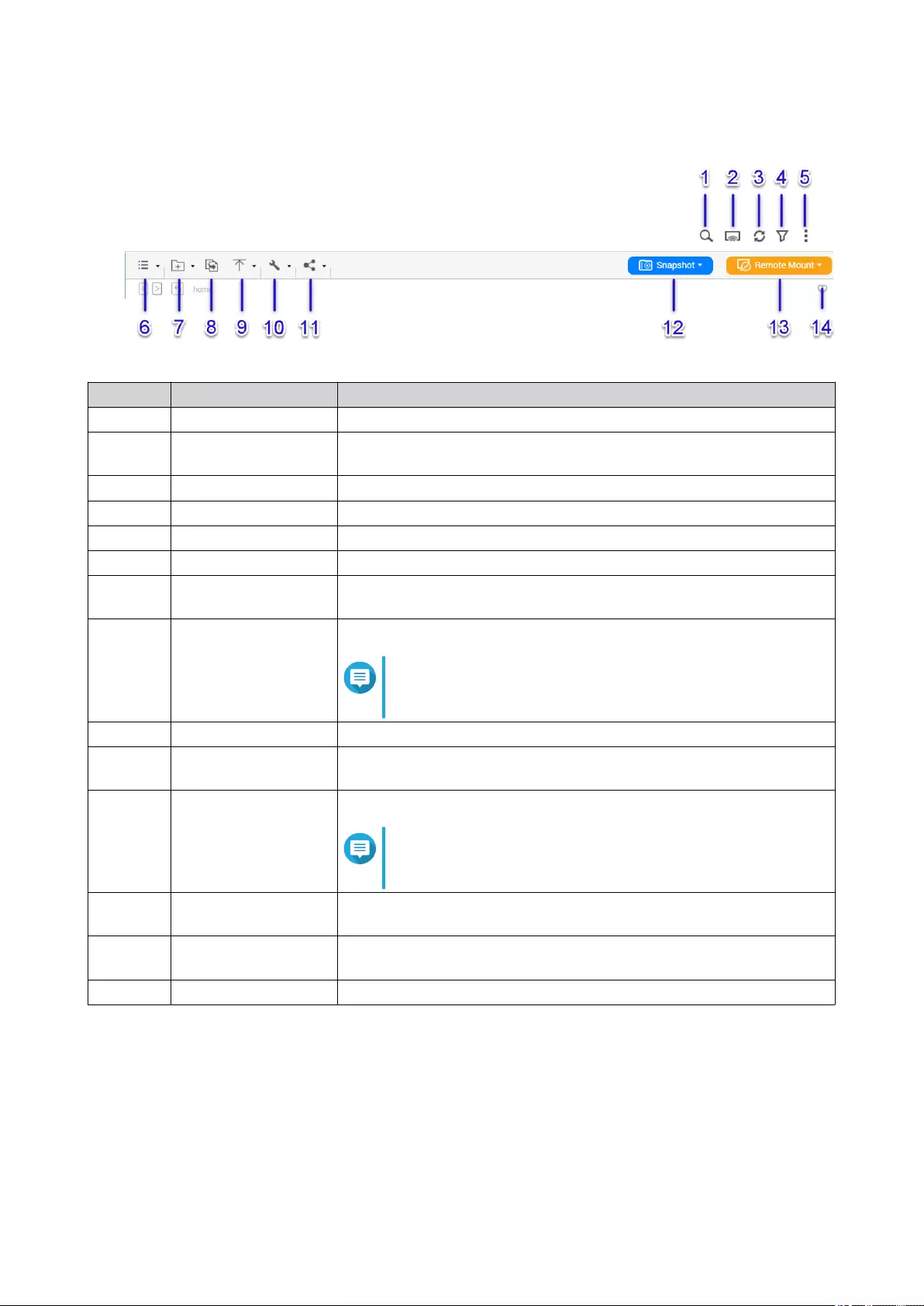
Menu Bar
Label Item Description
1 Search Search files by their name or file type, or using advanced search.
2 Network Media Player Stream videos, photos, and music to compatible devices in different
rooms over your home network.
3 Refresh Refresh the current page.
4 Smart File Filter Filter files based on the specified conditions.
5 More Settings Modify the settings, or view the Help or app information.
6 Browsing Mode Select a browsing mode.
7 Create folder Create a folder, shared folder, snapshot shared folder, or share a
space with another NAS user.
8 Copy Copy the selected files and folders.
Note
This button only appears when a file or folder is
selected.
9 Upload Upload files or folders to the selected shared folder.
10 More Action Perform different tasks.
The list of available actions changes after selecting a file or folder.
11 Share Share the selected files and folders.
Note
This button only appears when a file or folder is
selected.
12 Snapshot Open the Snapshot Manager or view the Snapshot Manager quick
tutorial.
13 Remote Mount Manage files across local devices, external devices, cloud services,
and remote devices from a single interface
14 Add to Favorites Add the current folder to your list of favorite folders
Settings
Modifying the General Settings
1. Go to More settings > Settings .
The Options window appears.
2. Under General, modify the following as needed.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 68
Option Description
Show files and folders of my PC When enabled, File Station displays the local files
and folders on the computer.
This feature only supports Windows computers
and requires the installation of Java Runtime
Environment.
Show hidden files on NAS When enabled, File Station displays files and
folders with the hidden attribute.
Allow all users to create shared links When enabled, File Station allows all users to
share NAS files using shared links.
Support multimedia playback and thumbnail
display
When enabled, File Station allows on-the-fly
transcoding and displays thumbnail previews of
multimedia files.
Always display the 360º panoramic view button on
the viewer
When enabled, File Station permanently displays
the 360º panoramic view button and allows users
to manually switch between the panorama and
general modes.
Show Network Recycle Bin(s) When enabled, File Station displays the
@Recycle folder in all user folders.
Only allow the admin and administrators group to
use "Share to NAS user"
When enabled, File Station prevents non-
administrators from sharing files with other NAS
users.
Only allow the admin and administrators group to
permanently delete files
When enabled, File Station prevents non-
administrators from permanently deleting files.
Only allow the admin and administrators group to
use on-the-fly transcoding
When enabled, File Station prevents non-
administrators from using on-the-fly transcoding.
Always play videos using VLC media player Videos opened in File Station will be played in
VLC media player rather than Video Station.
To use this feature, you must install QVHelper and
VLC Player on your computer.
3. Click Close.
Modifying the Remote Mount Settings
1. Go to More settings > Settings .
The Options window appears.
2. Under Remote Mount, select one of the following.
• admin only
• administrators group only
• specific users
3. Click Apply.
File Operations
File Station enables you to perform the following basic tasks.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 69
Operation Task
Store • Uploading a File
Access • Downloading a File
•Opening a File
•Playing a Media File
Share • Sharing a File By Email
•Sharing a File on a Social Network
•Sharing a File Using Share Links
•Sharing a File with a NAS User
Uploading a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Click Upload and then select File.
The File Upload window opens.
b. Select the file and then click Open.
Use drag and drop a. Locate the file on your computer.
b. Drag and drop the file to the File Station window.
A confirmation message appears.
3. Select one of the following.
Option Description
Skip the files Do not upload a file if another file with the same file name and
extension already exists on File Station.
Overwrite the files Upload the file and then overwrite an existing file with the same
name and extension.
Rename if a file exists with the
same name
Upload and rename a file if another file with the same name and
extension already exists on File Station.
4. Click OK.
File Station uploads the file.
Downloading a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 70
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click More Action.
c. Select Download.
d. Click OK.
Use the context menu Right-click the file and then click Download.
Depending on your browser, a confirmation message appears before the file is downloaded to your
computer.
Opening a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click More Action.
c. Select Open.
Use the context menu Right-click and then select Open.
File Station opens the selected file.
Playing a Media File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click More Action.
c. Select Play.
d. Under Online streaming, select the resolution.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the file.
b. Select Play.
c. Under Online streaming, select the resolution.
File Station plays the selected file using Media Viewer.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 71
Sharing a File By Email
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click Share.
c. Select Via Email.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the file.
b. Select Share and Via Email.
The Share window appears.
4. Specify the following.
Field Description
Send from Select one of the following.
• Use NAS to mail the link(s).
• Use local computer to mail the link(s).
Sender Select an email account or click Add email account.
To Specify the email address of the recipient.
Subject Specify the email subject.
Message Use the default message or type a new one.
5. Optional: Click More settings and then specify the following.
Field Task
Link Name Type a name for the link or use the current file name.
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Show SSL in URL Select to use HTTPS.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Password Move the switch to the right and then type a password.
6. Click Share Now.
File Station sends an email to the recipient.
Sharing a File on a Social Network
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 72
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click Share.
c. Select To Social Network.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the file.
b. Select Share and then select To Social Network.
The Share window appears.
4. Specify the following.
Field Description
Social Network Select the social media website.
Message Use the default message or type a new one.
5. Optional: Click More settings and then specify the following.
Field Task
Link Name Type a name for the link or use the current file name.
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Show SSL in URL Select to use HTTPS.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Password Move the switch to the right and then type a password.
6. Click Share Now.
File Station connects to the specified social media website.
Sharing a File Using Share Links
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click Share.
c. Select Create share link only.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the file.
b. Select Share and then select Create share link only.
The Share window appears.
4. Specify the following.
Field Task
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 73
Link Name Type a name for the link or use the current file name.
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Show SSL in URL Select to use HTTPS.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Password Move the switch to the right and then type a password.
5. Click Create Now.
File Station generates a link.
Sharing a File with a NAS User
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the file.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the file.
b. Click Share.
c. Select To NAS user.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the file.
b. Select Share and then select To NAS user.
The Share window appears.
4. Select one of the following options.
Option Description
Existing user Select a user from the list.
Optional: Select Send a notification email to the user and then
specify the email subject and message.
New user Specify the following information.
• User name
• Password
• Phone number (Optional)
• Email (Optional)
5. Optional: Click More settings and then specify the following.
Field Task
Link Name Type a name for the link or use the current file name.
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Show SSL in URL Select to use HTTPS.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Password Move the switch to the right and then type a password.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 74
6. Click Share Now.
File Station shares the file with the specified user.
Folder Operations
File Station enables you to perform the following basic tasks.
Operation Task
Store • Uploading a Folder
•Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop
Organize • Creating a Folder
•Creating a Desktop Shortcut
Share • Creating a Shared Folder
Uploading a Folder
Note
This feature is only available on Google Chrome browsers.
1. Open File Station.
2. Click Upload and then select Folder.
The Browse for Folder window opens.
3. Perfom one of the following tasks.
Task Steps
Upload an existing folder Select the folder.
Upload a new folder Click Make New Folder and then specify a folder name.
A confirmation message appears.
4. Select one of the following.
Option Description
Skip the files Do not upload a folder if the folder name already exists on Storage
& Snapshots.
Overwrite the files Upload the folder and then overwrite an existing folder with the
same name.
Rename if a file exists with the
same name
Upload and rename the folder if another folder with the same name
already exists on Storage & Snapshots.
5. Click OK.
File Station uploads the selected folder.
Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop
Note
This feature is only available on Google Chrome browsers.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 75
1. Open File Station.
2. Drag and drop the local folder to Storage & Snapshots.
3. Select one of the following.
Option Description
Skip the files Do not upload a folder with a folder name that already exists on
Storage & Snapshots.
Overwrite the files Upload the folder and then overwrite a folder with the same name
already exists on Storage & Snapshots.
Rename if a file exists with the
same name
Upload and rename a folder if another folder with the same name
already exists on Storage & Snapshots.
4. Click OK.
File Station uploads the selected folder.
Creating a Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. Perfom one of the following tasks.
Task Steps
Use the menu bar a. Click More Action.
b. Click Create folder and then select Folder.
The Create folder window opens.
c. Specify the folder name.
d. Click OK.
Use the context menu a. Right-click inside the folder and then select
Create folder.
b. Specify the folder name.
c. Click OK.
File Station creates a new folder.
Creating a Desktop Shortcut
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the folder.
b. Click More Action.
c. Select Create Shortcut to Desktop.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 76
Use the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Create Shortcut to Desktop.
File Station creates a desktop shortcut for the selected folder.
Creating a Shared Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. On the menu bar, click Create folder and then select Shared Folder.
The Create A Shared Folder window opens.
3. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin with a space or "_sn_"
• Contain consecutive spaces
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
Disk Volume Specify the volume on which the shared folder will be created.
Path You can specify a path or allow the operating system to automatically
create one.
4. Click OK.
File Station creates a new folder.
QTS 4.3.4 Getting Started Guide
File Station 77