Table of Contents
- Contents
- 1. Overview
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. System Settings
- 4. Privilege Settings
- Users
- User Groups
- Shared Folders
- Quota
- Domain Security
- Domain Controller
- 5. Services
- 6. File Station
- Overview
- File Operations
- Uploading a File
- Downloading a File
- Opening a File
- Opening Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint Files Using the Chrome Extension
- Opening a Text File Using Text Editor
- Viewing a File in Google Docs
- Viewing a File in Microsoft Office Online
- Opening Image Files Using Image2PDF
- Viewing File Properties
- Modifying File Permissions
- Sorting Files
- Copying a File
- Moving a File
- Renaming a File
- Deleting a File
- Restoring a Deleted File
- Mounting an ISO File
- Unmounting an ISO File
- Compressing a File
- Extracting Compressed Files or Folders
- Sharing a File or Folder by Email
- Sharing a File or Folder on a Social Network
- Sharing a File or Folder Using Share Links
- Sharing a File or Folder with a NAS User
- Playing an Audio File
- Playing a Video File
- Playing a Video File Using CAYIN MediaSign Player
- Opening a 360-degree Image or Video File
- Streaming to a Network Media Player
- Adding a File to the Transcoding Folder
- Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
- Viewing Transcode Information
- Folder Operations
- Uploading a Folder
- Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop
- Viewing Folder Properties
- Viewing Storage Information
- Modifying Folder Permissions
- Viewing Qsync Folders
- Managing Share Links
- Viewing Files and Folders Shared with Me
- Creating a Folder
- Copying a Folder
- Creating a Desktop Shortcut
- Adding a Folder to Favorites
- Removing a Folder from Favorites
- Compressing a Folder
- Deleting a Folder
- Creating a Shared Folder
- Creating a Snapshot Shared Folder
- Sharing Space with a New User
- Adding a Folder to the Transcoding Folder
- Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
- Locking or Unlocking an Encrypted Shared Folder
- Keeping a Folder or a File in Reserved Cache
- Removing a Folder from Reserved Cache
- 7. Storage & Snapshots
- QTS Flexible Volume Architecture
- Global Settings
- Storage
- Disks
- Volumes
- Storage Pools
- RAID
- Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs)
- Expansion Units
- Qtier
- Snapshots
- Cache Acceleration
- External Storage
- Remote Disk
- VJBOD (Virtual JBOD)
- VJBOD Cloud
- 8. iSCSI & Fibre Channel
- 9. SSD Profiling Tool
- 10. Network & Virtual Switch
- About Network & Virtual Switch
- Parts of the User Interface
- Basic Network Adapter Configuration
- IP Addressing Services Configuration
- LAN Switching Configuration
- Virtual Switch Configuration
- Network Policies Configuration
- Wireless Network Configuration
- USB QuickAccess Configuration
- Thunderbolt Interface Configuration
- 11. Network & File Services
- About Network & File Services
- QNAP Service Ports
- Configuring Network Access Settings
- Configuring Network Protocol Settings
- Configuring File Sharing Protocol Settings
- Enabling Service Discovery Settings
- Network Recycle Bin Management
- 12. myQNAPcloud
- 13. App Center
- 14. Licenses
- 15. Multimedia
- 16. QuLog Center
- Monitoring System Logs
- Local Logs
- QuLog Service
- Configuring Log Sender Settings
- Configuring Log Reciever Settings
- Viewing and Managing Remote Logs
- Managing System Event Logs on the Log Receiver
- Managing System Access Logs on the Log Receiver
- Logging in a Sender Device
- Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log on a Sender Device
- Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Access Log on a Sender Device
- Configuring Event Indicators on the Sender Device
- Notification Settings
- 17. Notification Center
- 18. Malware Remover
- 19. Helpdesk
- 20. Console Management
QNAP TS-251D User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for TS-251D by QNAP which is a product in the NAS & Storage Servers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

QTS 5.0.x
User Guide
Document Version: 2
28/09/2021

Contents
1. Overview
About QTS................................................................................................................................................................. 11
What's New in QTS...................................................................................................................................................12
NAS Access................................................................................................................................................................13
Accessing the NAS Using a Browser................................................................................................................. 14
Accessing the NAS Using Qnder Pro.............................................................................................................. 14
Accessing the NAS Using Qmanager................................................................................................................14
QTS Navigation.........................................................................................................................................................15
Task Bar................................................................................................................................................................ 15
Main Menu........................................................................................................................................................... 23
Desktop................................................................................................................................................................ 24
Qboost..................................................................................................................................................................26
2-step Verication....................................................................................................................................................28
Enabling 2-step Verication............................................................................................................................... 28
Logging in to QTS Using 2-step Verication.................................................................................................... 29
Disabling 2-step Verication..............................................................................................................................29
Support and Other Resources................................................................................................................................30
2. Getting Started
Storing Data..............................................................................................................................................................31
Accessing Data......................................................................................................................................................... 31
Backing Up Data...................................................................................................................................................... 32
Conguring Privilege Settings................................................................................................................................32
Setting Up Remote Access...................................................................................................................................... 33
Acquiring Apps and Licenses..................................................................................................................................33
Securing the NAS..................................................................................................................................................... 34
3. System Settings
General Settings.......................................................................................................................................................36
Conguring System Administration Settings.................................................................................................. 36
Conguring Time Settings................................................................................................................................. 38
Conguring Daylight Saving Time.................................................................................................................... 39
Conguring Codepage Settings........................................................................................................................ 39
Conguring Region Settings..............................................................................................................................39
Conguring the Login Screen............................................................................................................................40
Enabling or Disabling Console Management.................................................................................................. 40
Security..................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Conguring the Allow/Deny List....................................................................................................................... 41
Conguring IP Access Protection......................................................................................................................41
Conguring Account Access Protection........................................................................................................... 42
SSL Certicate & Private Key..............................................................................................................................42
Conguring the Password Policy...................................................................................................................... 44
Hardware.................................................................................................................................................................. 45
Conguring General Hardware Settings.......................................................................................................... 45
Conguring Audio Alert Settings...................................................................................................................... 46
Conguring Smart Fan Settings........................................................................................................................ 47
Conguring Hardware Resource Settings........................................................................................................47
Power........................................................................................................................................................................ 49
Conguring EuP Mode....................................................................................................................................... 49
Enabling or Disabling Wake-on-LAN (WOL)..................................................................................................... 50
Conguring the Power Recovery Settings....................................................................................................... 50
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
1

Conguring the Power Schedule...................................................................................................................... 50
External Device.........................................................................................................................................................51
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS).................................................................................................................51
Firmware Update..................................................................................................................................................... 53
Firmware Update Requirements.......................................................................................................................54
Checking for Live Updates................................................................................................................................. 55
Updating the Firmware Automatically............................................................................................................. 55
Updating the Firmware Manually..................................................................................................................... 56
Updating the Firmware Using Qnder Pro...................................................................................................... 57
Backup/Restore........................................................................................................................................................58
Backing Up System Settings.............................................................................................................................. 58
Restoring System Settings................................................................................................................................. 59
System Reset and Restore to Factory Default................................................................................................. 59
Monitoring System Status and Resource Monitor...............................................................................................63
System Status...................................................................................................................................................... 63
Resource Monitor................................................................................................................................................63
4. Privilege Settings
Users..........................................................................................................................................................................65
Default Administrator Account..........................................................................................................................65
Creating a Local User..........................................................................................................................................67
Creating Multiple Users......................................................................................................................................69
User Account Lists...............................................................................................................................................70
Importing Users.................................................................................................................................................. 71
Exporting Users...................................................................................................................................................72
Modifying User Account Information...............................................................................................................73
Deleting Users..................................................................................................................................................... 74
Home Folders...................................................................................................................................................... 74
User Groups..............................................................................................................................................................75
Default User Groups........................................................................................................................................... 75
Creating a User Group........................................................................................................................................75
Modifying User Group Information.................................................................................................................. 76
Deleting User Groups......................................................................................................................................... 77
Shared Folders......................................................................................................................................................... 78
Default Shared Folders.......................................................................................................................................78
Creating a Shared Folder....................................................................................................................................78
Editing Shared Folder Properties...................................................................................................................... 81
Refreshing a Shared Folder................................................................................................................................84
Removing Shared Folders.................................................................................................................................. 84
Enabling Daily Updates for Shared Folders..................................................................................................... 84
Snapshot Shared Folders................................................................................................................................... 84
ISO Shared Folders..............................................................................................................................................87
Shared Folder Permissions................................................................................................................................ 89
Folder Aggregation.............................................................................................................................................92
Shared Folder Encryption...................................................................................................................................95
Shared Folder Access..........................................................................................................................................97
Quota...................................................................................................................................................................... 102
Enabling Quotas................................................................................................................................................103
Editing Quota Settings..................................................................................................................................... 103
Exporting Quota Settings.................................................................................................................................104
Quota Conicts..................................................................................................................................................104
Domain Security.....................................................................................................................................................104
Active Directory (AD) Authentication.............................................................................................................. 105
Azure Active Directory Single Sign-On (SSO)................................................................................................. 108
LDAP Authentication.........................................................................................................................................109
AD and LDAP Management............................................................................................................................. 111
Domain Controller................................................................................................................................................. 112
2

Enabling a Domain Controller......................................................................................................................... 113
Resetting a Domain Controller........................................................................................................................114
Default Domain User Accounts....................................................................................................................... 114
Creating a Domain User...................................................................................................................................114
Creating Multiple Domain Users.....................................................................................................................115
Domain User Account Lists..............................................................................................................................116
Modifying Domain User Account Information.............................................................................................. 118
Deleting Domain Users.................................................................................................................................... 119
Domain User Groups........................................................................................................................................119
Computers......................................................................................................................................................... 121
DNS..................................................................................................................................................................... 123
Back Up/Restore................................................................................................................................................125
5. Services
Antivirus..................................................................................................................................................................127
Enabling Antivirus.............................................................................................................................................127
Scanning Shared Folders..................................................................................................................................127
Managing Scan Jobs..........................................................................................................................................129
Managing Reported Scan Jobs........................................................................................................................ 129
Managing Quarantined Files........................................................................................................................... 130
Servers.................................................................................................................................................................... 131
Web Server.........................................................................................................................................................131
Enabling the LDAP Server................................................................................................................................ 134
MariaDB Server................................................................................................................................................. 134
Syslog Server..................................................................................................................................................... 140
RADIUS Server................................................................................................................................................... 143
Enabling the TFTP Server................................................................................................................................. 145
Enabling the NTP Server.................................................................................................................................. 146
6. File Station
Overview................................................................................................................................................................. 147
About File Station..............................................................................................................................................147
System Requirements.......................................................................................................................................147
Supported File Formats....................................................................................................................................147
Parts of the User Interface...............................................................................................................................148
Settings.............................................................................................................................................................. 151
File Operations.......................................................................................................................................................154
Uploading a File.................................................................................................................................................155
Downloading a File........................................................................................................................................... 156
Opening a File....................................................................................................................................................156
Opening Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint Files Using the Chrome Extension..............................157
Opening a Text File Using Text Editor.............................................................................................................157
Viewing a File in Google Docs..........................................................................................................................158
Viewing a File in Microsoft Oce Online....................................................................................................... 158
Opening Image Files Using Image2PDF........................................................................................................ 159
Viewing File Properties.....................................................................................................................................159
Modifying File Permissions..............................................................................................................................160
Sorting Files....................................................................................................................................................... 161
Copying a File.................................................................................................................................................... 161
Moving a File......................................................................................................................................................162
Renaming a File.................................................................................................................................................164
Deleting a File....................................................................................................................................................164
Restoring a Deleted File................................................................................................................................... 165
Mounting an ISO File........................................................................................................................................ 165
Unmounting an ISO File...................................................................................................................................166
Compressing a File............................................................................................................................................166
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
3

Extracting Compressed Files or Folders.........................................................................................................167
Sharing a File or Folder by Email.....................................................................................................................167
Sharing a File or Folder on a Social Network.................................................................................................170
Sharing a File or Folder Using Share Links.................................................................................................... 171
Sharing a File or Folder with a NAS User........................................................................................................173
Playing an Audio File........................................................................................................................................ 175
Playing a Video File........................................................................................................................................... 175
Playing a Video File Using CAYIN MediaSign Player..................................................................................... 176
Opening a 360-degree Image or Video File...................................................................................................176
Streaming to a Network Media Player........................................................................................................... 177
Adding a File to the Transcoding Folder.........................................................................................................177
Canceling or Deleting Transcoding.................................................................................................................178
Viewing Transcode Information......................................................................................................................179
Folder Operations..................................................................................................................................................179
Uploading a Folder........................................................................................................................................... 180
Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop......................................................................................................180
Viewing Folder Properties................................................................................................................................181
Viewing Storage Information.......................................................................................................................... 182
Modifying Folder Permissions.........................................................................................................................182
Viewing Qsync Folders..................................................................................................................................... 183
Managing Share Links......................................................................................................................................184
Viewing Files and Folders Shared with Me.....................................................................................................184
Creating a Folder...............................................................................................................................................184
Copying a Folder............................................................................................................................................... 185
Creating a Desktop Shortcut........................................................................................................................... 185
Adding a Folder to Favorites............................................................................................................................186
Removing a Folder from Favorites..................................................................................................................186
Compressing a Folder.......................................................................................................................................187
Deleting a Folder...............................................................................................................................................188
Creating a Shared Folder................................................................................................................................. 188
Creating a Snapshot Shared Folder................................................................................................................ 190
Sharing Space with a New User...................................................................................................................... 192
Adding a Folder to the Transcoding Folder................................................................................................... 193
Canceling or Deleting Transcoding.................................................................................................................193
Locking or Unlocking an Encrypted Shared Folder.......................................................................................194
Keeping a Folder or a File in Reserved Cache................................................................................................194
Removing a Folder from Reserved Cache......................................................................................................196
7. Storage & Snapshots
QTS Flexible Volume Architecture........................................................................................................................197
Global Settings....................................................................................................................................................... 198
Storage Global Settings....................................................................................................................................198
Disk / Device Global Settings........................................................................................................................... 199
Snapshot Global Settings.................................................................................................................................200
Storage....................................................................................................................................................................201
Disks................................................................................................................................................................... 201
Volumes..............................................................................................................................................................207
Storage Pools.....................................................................................................................................................223
RAID....................................................................................................................................................................231
Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs)...........................................................................................................................240
Expansion Units..................................................................................................................................................... 246
Expansion Unit Actions.....................................................................................................................................246
Expansion Unit Recovery..................................................................................................................................247
QNAP External RAID Devices........................................................................................................................... 247
QNAP JBOD Enclosures.....................................................................................................................................260
Qtier.........................................................................................................................................................................262
Qtier Benets.....................................................................................................................................................262
4

Qtier Requirements.......................................................................................................................................... 264
Qtier Creation....................................................................................................................................................264
Qtier Management........................................................................................................................................... 267
Snapshots............................................................................................................................................................... 270
Snapshot Storage Limitations......................................................................................................................... 270
Snapshot Creation............................................................................................................................................ 271
Snapshot Management....................................................................................................................................272
Snapshot Data Recovery.................................................................................................................................. 275
Snapshot Clone................................................................................................................................................. 278
Snapshot Replica...............................................................................................................................................279
Cache Acceleration................................................................................................................................................ 289
Cache Acceleration Requirements.................................................................................................................. 289
Creating the SSD Cache....................................................................................................................................289
Expanding the SSD Cache................................................................................................................................ 291
Conguring SSD Cache Settings..................................................................................................................... 292
Cache Missing....................................................................................................................................................292
Removing the SSD Cache................................................................................................................................. 293
External Storage.................................................................................................................................................... 293
External Storage Device Actions..................................................................................................................... 293
External Storage Disk Actions..........................................................................................................................294
External Storage Partition Actions..................................................................................................................294
Formatting an External Storage Partition......................................................................................................294
Remote Disk........................................................................................................................................................... 295
Remote Disk Limitations.................................................................................................................................. 296
Adding a Remote Disk...................................................................................................................................... 296
Remote Disk Actions.........................................................................................................................................297
VJBOD (Virtual JBOD)............................................................................................................................................. 298
VJBOD Requirements........................................................................................................................................298
VJBOD Limitations.............................................................................................................................................299
VJBOD Automatic Reconnection......................................................................................................................299
VJBOD Creation..................................................................................................................................................299
VJBOD Management.........................................................................................................................................303
VJBOD Cloud........................................................................................................................................................... 306
Installing VJBOD Cloud..................................................................................................................................... 306
VJBOD Cloud Volume and LUN Creation........................................................................................................ 307
VJBOD Cloud Management..............................................................................................................................319
Transfer Resources........................................................................................................................................... 321
Event Logs..........................................................................................................................................................323
Licenses..............................................................................................................................................................323
8. iSCSI & Fibre Channel
Storage Limits........................................................................................................................................................ 325
iSCSI Storage Limits..........................................................................................................................................325
Fibre Channel Storage Limits...........................................................................................................................325
iSCSI & Fibre Channel Global Settings.................................................................................................................325
LUNs........................................................................................................................................................................ 325
QTS LUN Types.................................................................................................................................................. 326
Creating a Block-Based LUN............................................................................................................................ 326
Creating a File-Based LUN................................................................................................................................328
LUN Import/Export........................................................................................................................................... 329
iSCSI.........................................................................................................................................................................332
Getting Started with iSCSI................................................................................................................................332
iSCSI Performance Optimization.....................................................................................................................333
iSCSI Targets...................................................................................................................................................... 333
iSCSI LUN Management................................................................................................................................... 337
iSCSI Access Control List...................................................................................................................................339
iSCSI Target Authorization............................................................................................................................... 341
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
5

QNAP Snapshot Agent......................................................................................................................................342
Fibre Channel......................................................................................................................................................... 343
Fibre Channel Ports.......................................................................................................................................... 343
Fibre Channel Storage......................................................................................................................................346
Fibre Channel WWPN Aliases...........................................................................................................................347
9. SSD Proling Tool
Installing SSD Proling Tool................................................................................................................................. 351
SSD Over-Provisioning.......................................................................................................................................... 351
SSD Extra Over-Provisioning............................................................................................................................351
Creating an SSD Over-Provisioning Test............................................................................................................. 351
Test Reports............................................................................................................................................................353
Test Report Information...................................................................................................................................353
Test Report Actions........................................................................................................................................... 353
Settings................................................................................................................................................................... 353
10. Network & Virtual Switch
About Network & Virtual Switch.......................................................................................................................... 355
Parts of the User Interface................................................................................................................................... 355
Basic Network Adapter Conguration................................................................................................................ 356
Conguring IPv4 Settings................................................................................................................................ 357
Conguring IPv6 Settings................................................................................................................................ 358
Conguring the System Default Gateway......................................................................................................358
Conguring Static Route Settings...................................................................................................................359
IP Addressing Services Conguration................................................................................................................. 360
Conguring DNS Server Settings.................................................................................................................... 361
Conguring DHCP Server Settings .................................................................................................................361
Adding DHCP Clients to a DHCP Server..........................................................................................................364
Conguring RADVD Server Settings............................................................................................................... 365
Conguring DDNS Service Settings................................................................................................................ 367
LAN Switching Conguration............................................................................................................................... 367
Conguring VLAN Settings.............................................................................................................................. 368
Conguring Port Trunking Settings................................................................................................................369
Virtual Switch Conguration................................................................................................................................ 370
Creating a Virtual Switch in Basic Mode.........................................................................................................370
Creating a Virtual Switch in Advanced Mode.................................................................................................371
Creating a Virtual Switch in Software-dened Switch Mode....................................................................... 374
Network Policies Conguration........................................................................................................................... 374
Conguring Forward Error Correction (FEC) Settings...................................................................................374
Wireless Network Conguration..........................................................................................................................375
Adding a Wireless Network..............................................................................................................................375
Enabling Wi-Fi....................................................................................................................................................377
Connecting to a Wireless Network .................................................................................................................377
Understanding the Wireless Connection Messages.....................................................................................384
Accessing the Wireless Access Point (AP) Settings........................................................................................385
USB QuickAccess Conguration...........................................................................................................................385
Enabling USB QuickAccess ..............................................................................................................................386
Conguring the USB QuickAccess IP address .............................................................................................. 386
Conguring USB QuickAccess Authentication ............................................................................................. 387
Thunderbolt Interface Conguration..................................................................................................................387
Enabling T2E with Qnder Pro........................................................................................................................ 388
Enabling T2E on macOS................................................................................................................................... 388
11. Network & File Services
About Network & File Services............................................................................................................................. 389
QNAP Service Ports................................................................................................................................................389
6

Conguring Network Access Settings.................................................................................................................390
Conguring Service Binding Settings ............................................................................................................391
Conguring Proxy Server Settings..................................................................................................................391
Conguring Reverse Proxy Rule Settings.......................................................................................................392
Modifying Reverse Proxy Rules.......................................................................................................................393
Conguring Network Protocol Settings..............................................................................................................394
Conguring Telnet Connections......................................................................................................................394
Conguring SSH Connections......................................................................................................................... 395
Editing SSH Access Permissions......................................................................................................................395
Conguring SNMP Settings............................................................................................................................. 396
Downloading the SNMP MIB........................................................................................................................... 397
Conguring File Sharing Protocol Settings.........................................................................................................398
Conguring Samba (Microsoft Networking) Settings...................................................................................398
Conguring AFP (Apple Networking) Settings.............................................................................................. 400
Conguring NFS Service Settings....................................................................................................................401
Accessing FTP (QuFTP Service) Settings......................................................................................................... 402
Conguring WebDAV Settings.........................................................................................................................402
Enabling Service Discovery Settings....................................................................................................................405
Enabling the UPnP Discovery Service.............................................................................................................405
Enabling the Bonjour Discovery Service........................................................................................................ 405
Network Recycle Bin Management..................................................................................................................... 405
Conguring the Network Recycle Bin.............................................................................................................405
Deleting All Files in the Network Recycle Bin................................................................................................ 406
Restricting Access to the Network Recycle Bin..............................................................................................406
12. myQNAPcloud
Getting Started.......................................................................................................................................................407
Account Setup........................................................................................................................................................ 407
Creating a QNAP ID With Email or Phone Number.......................................................................................407
Registering a Device to myQNAPcloud.......................................................................................................... 408
Installing myQNAPcloud Link..........................................................................................................................409
Overview................................................................................................................................................................. 409
Conguring UPnP Port Forwarding.....................................................................................................................410
Conguring DDNS Settings.................................................................................................................................. 411
Restarting DDNS Service.......................................................................................................................................411
Conguring Published Services........................................................................................................................... 412
Enabling myQNAPcloud Link................................................................................................................................412
Conguring Device Access Controls....................................................................................................................412
Installing an SSL Certicate..................................................................................................................................413
13. App Center
Navigation.............................................................................................................................................................. 415
Left Panel........................................................................................................................................................... 415
Toolbar............................................................................................................................................................... 415
App Management.................................................................................................................................................. 416
Viewing App Information.................................................................................................................................416
Buying an App License..................................................................................................................................... 417
Installing an App from App Center................................................................................................................. 417
Installing an App Manually.............................................................................................................................. 418
Updating an App............................................................................................................................................... 419
Batch Updating Multiple Apps.........................................................................................................................419
Enabling or Disabling an App.......................................................................................................................... 419
Migrating an App.............................................................................................................................................. 420
Granting or Denying User Access to an App................................................................................................. 420
Uninstalling an App.......................................................................................................................................... 420
App Center Settings...............................................................................................................................................421
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
7

Adding an App Repository............................................................................................................................... 421
Conguring App Update Settings................................................................................................................... 421
Digital Signatures..............................................................................................................................................422
Enabling Installation of Apps without Digital Signatures............................................................................ 422
14. Licenses
About QNAP Licenses............................................................................................................................................424
License Types and Plans...................................................................................................................................424
Validity Period....................................................................................................................................................424
License Portals and Utility.................................................................................................................................... 425
Software Store...................................................................................................................................................425
License Center...................................................................................................................................................425
License Manager...............................................................................................................................................425
Buying a License Using QNAP ID.........................................................................................................................426
License Activation.................................................................................................................................................. 427
Activating a License Using QNAP ID............................................................................................................... 427
Activating a License Using a License Key....................................................................................................... 429
Activating a License Using a Product Key or PAK..........................................................................................430
Activating a License Oine..............................................................................................................................431
License Deactivation..............................................................................................................................................432
Deactivating a License Using QNAP ID...........................................................................................................432
Deactivating a License Oine......................................................................................................................... 433
License Extension.................................................................................................................................................. 434
Extending a License Using QNAP ID...............................................................................................................434
Extending a License Oine Using an Unused License.................................................................................435
Extending a License Oine Using a Product Key......................................................................................... 436
Upgrading a License..............................................................................................................................................438
Viewing License Information................................................................................................................................439
Recovering Licenses.............................................................................................................................................. 440
Transferring a License to the New QNAP License Server................................................................................. 440
Deleting a License..................................................................................................................................................441
15. Multimedia
HybridDesk Station (HD Station)..........................................................................................................................442
Installing HD Station.........................................................................................................................................443
Conguring HD Station.................................................................................................................................... 443
HD Station Applications....................................................................................................................................444
Using HD Player in HD Station........................................................................................................................ 444
HDMI Local Display and DLNA Media Server..................................................................................................... 445
Enabling HDMI Display Applications.............................................................................................................. 445
Enabling DLNA Media Server...........................................................................................................................445
Conguring DLNA Media Server..................................................................................................................... 446
Media Streaming Add-on......................................................................................................................................446
Conguring General Settings..........................................................................................................................447
Conguring Browsing Settings....................................................................................................................... 448
Conguring Media Receivers...........................................................................................................................448
Multimedia Console...............................................................................................................................................449
Overview............................................................................................................................................................ 449
Editing Content Sources...................................................................................................................................449
Indexing Multimedia Content......................................................................................................................... 450
Generating Thumbnails for Multimedia Files................................................................................................450
Transcoding....................................................................................................................................................... 452
Multimedia App Suite....................................................................................................................................... 455
Installing and Managing AI Engines ..............................................................................................................457
16. QuLog Center
8

Monitoring System Logs.......................................................................................................................................459
System Event Log..............................................................................................................................................459
System Access Logs.......................................................................................................................................... 459
Local Logs............................................................................................................................................................... 460
Local System Event Logs.................................................................................................................................. 460
Local System Access Logs................................................................................................................................ 463
Online Users...................................................................................................................................................... 465
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for Local Device System Logs........................................................................ 466
Local Log Settings............................................................................................................................................. 469
QuLog Service........................................................................................................................................................ 473
Conguring Log Sender Settings....................................................................................................................473
Conguring Log Reciever Settings..................................................................................................................475
Viewing and Managing Remote Logs.............................................................................................................478
Notication Settings..............................................................................................................................................486
Conguring Notication Rule Settings...........................................................................................................486
Adding a Log Filter............................................................................................................................................487
Editing a Log Filter............................................................................................................................................ 488
Removing a Log Filter.......................................................................................................................................488
17. Notication Center
Overview................................................................................................................................................................. 490
Managing Notication Queue and History.........................................................................................................490
Queue.................................................................................................................................................................491
History................................................................................................................................................................ 491
Service Account and Device Pairing.................................................................................................................... 492
Email Notications............................................................................................................................................492
SMS Notications.............................................................................................................................................. 495
Instant Messaging Notications..................................................................................................................... 497
Push Notications.............................................................................................................................................498
System Notication Rules.....................................................................................................................................499
Managing Event Notication Rules.................................................................................................................499
Alert Notications............................................................................................................................................. 503
Settings................................................................................................................................................................... 507
Enabling Send Notication Data to QNAP..................................................................................................... 507
Disabling Send Notication Data to QNAP.................................................................................................... 507
Global Notication Settings..................................................................................................................................508
System Logs............................................................................................................................................................508
18. Malware Remover
About Malware Remover...................................................................................................................................... 510
Overview................................................................................................................................................................. 510
Running a Malware Scan...................................................................................................................................... 510
Running a Scheduled Scan................................................................................................................................... 511
Conguring Malware Remover............................................................................................................................511
19. Helpdesk
Overview................................................................................................................................................................. 513
Conguring Settings.........................................................................................................................................513
Help Request.......................................................................................................................................................... 513
Submitting a Ticket........................................................................................................................................... 514
Remote Support.....................................................................................................................................................515
Enabling Remote Support................................................................................................................................515
Extending Remote Support............................................................................................................................. 515
Disabling Remote Support...............................................................................................................................515
Diagnostic Tool.......................................................................................................................................................516
Downloading Logs............................................................................................................................................ 516
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
9

Performing an HDD Standby Test................................................................................................................... 516
Performing an HDD Stress Test.......................................................................................................................516
20. Console Management
Enabling Secure Shell (SSH)..................................................................................................................................517
Enabling SSH on the NAS................................................................................................................................. 517
Enabling SSH on the NAS Using Qnder Pro.................................................................................................517
Accessing Console Management.........................................................................................................................517
Accessing Console Management from Windows..........................................................................................517
Accessing Console Management from Mac...................................................................................................518
Logging In to Console Management...................................................................................................................518
Managing Existing Applications...........................................................................................................................518
Activating or Deactivating a License................................................................................................................... 519
Sorting and Filtering System Logs.......................................................................................................................520
Showing Network Settings................................................................................................................................... 522
Restoring or Reinitializing the Device................................................................................................................. 522
Rebooting the NAS................................................................................................................................................ 522
Rebooting the Device Into Rescue Mode.......................................................................................................522
Rebooting the Device Into Maintenance Mode.............................................................................................523
10

1. Overview
About QTS
QTS is a Linux-based operating system that runs applications for le management, virtualization,
surveillance, multimedia, and other purposes. The optimized kernel and various services eciently manage
system resources, support applications, and protect your data. QTS also has built-in utilities that extend the
functionality and improve the performance of the NAS.
The multi-window, multitasking user interface helps you to manage the NAS, user accounts, data, and apps.
Out of the box, QTS provides built-in features that allow you to easily store and share les. QTS also contains
App Center, which oers additional downloadable applications for customizing the NAS and improving user
workows.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 11
What's New in QTS
Version Major New Features and Enhancements
QTS 5.0.0 • QTS now supports Desktop Notice Board, which provides notications for
various events and announcements.
• QTS administrators can now purchase app licenses in the App Center.
• QuLog Center now displays computer names, total connection time of
online users, and accessed resources in System Access Log and Online
Users.
• iSCSI target service binding now supports all types of network portals.
• Users can now import custom root certicates to certify the SSL certicate
of a server that the NAS needs to access.
• Users can now manually specify the time interval and the maximum
number of failed login attempts in Control Panel to further enhance NAS
security.
• Users can now use exFAT on x86 NAS models without purchasing an exFAT
license.
• Users can now use port 443 for Let's Encrypt domain validation challenges.
• Users can now congure reverse proxy rules to hide sensitive information
on the server from clients and to enhance the security of data transmission
over the network.
• Users can now choose to keep le attributes for les uploaded to File
Station via SMB.
• Users in the administrator group now have read/write access permissions
for default shared folders, except the "homes" shared folder.
• Improved SSD cache design to enhance storage performance.
• Added support for QuFTP Service, which allows users to congure and
manage various FTP settings.
• Added an option to choose whether to redirect users to the NAS login
screen when connecting to the NAS IP address without the system port.
• Utilization charts in Storage & Snapshots are now located in Pool/
Volume/LUN Management for better usability.
• A RAID group now only supports a maximum of 16 disks to enhance storage
performance and data security.
• Replaced SQL Server with MariaDB 5/MariaDB 10, which can be installed in
the App Center.
• Added support for Forward Error Correction (FEC) for error detection
and error correction in data transmission over unreliable or noisy
communication channels.
• Added support for ULINK DA Drive Analyzer for disk health monitoring and
disk failure prediction.
• Added support for setting user/group storage space quota up to 128TB.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 12
For details on new features and enhancements, go to https://www.qnap.com/en/release-notes/.
NAS Access
Method Description Requirements
Web browser You can access the NAS using any
computer on the same network if you
have the following information:
• NAS name (Example: http://
example123/) or IP address
• Logon credentials of a valid user
account
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using a
Browser.
• Computer that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Web browser
Qnder Pro Qnder Pro is a desktop utility that
enables you to locate and access QNAP
NAS devices on a specic network. The
utility supports Windows, macOS, Linux,
and Chrome OS.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using
Qnder Pro.
• Computer that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Web browser
•Qnder Pro
Qmanager Qmanager is a mobile application that
enables administrators to manage and
monitor NAS devices on the same
network.
You can download Qmanager from the
Apple App Store and the Google Play
Store.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using
Qmanager.
• Mobile device that is connected to the
same network as the NAS
• Qmanager
Explorer (Windows) You can map a NAS shared folder as a
network drive to easily access les using
Explorer.
For details, see the following topics.
•Mapping a Shared Folder on a
Windows Computer
•Mounting a Shared Folder using
WebDAV on Windows
• Windows computer that is connected
to the same network as the NAS
•Qnder Pro
Finder (macOS) You can mount a NAS shared folder as a
network drive to easily access les using
Finder.
For details, see the following topics.
•Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac
Computer
•Mounting a Shared Folder Using
WebDAV on Mac
• Mac computer that is connected to
the same network as the NAS
•Qnder Pro
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 13

Accessing the NAS Using a Browser
1. Verify that your computer is connected to the same network as the NAS.
2. Open a web browser on your computer.
3. Type the IP address of the NAS in the address bar.
Tip
If you do not know the IP address of the NAS, you can locate it using Qnder Pro.
For details, see Accessing the NAS Using Qnder Pro.
The QTS login screen appears.
4. Optional: Log in QTS using HTTPS.
a. Select Secure login.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click OK.
You will be redirected to the QTS HTTPS login page.
5. Specify your username and password.
6. Click Login.
The QTS desktop appears.
Accessing the NAS Using Qnder Pro
1. Install Qnder Pro on a computer that is connected to the same network as the NAS.
Tip
To download Qnder Pro, go to https://www.qnap.com/en/utilities.
2. Open Qnder Pro.
Qnder Pro automatically searches for all QNAP NAS devices on the network.
3. Locate the NAS in the list, and then double-click the name or IP address.
The QTS login screen opens in the default web browser.
4. Specify your username and password.
5. Click Login.
The QTS desktop appears.
Accessing the NAS Using Qmanager
1. Install Qmanager on an Android or iOS device.
Tip
To download Qmanager, go to the Apple App Store or the Google Play Store.
2. Open Qmanager.
3. Tap Add NAS.
Qmanager automatically searches for all QNAP NAS devices on the network.
4. Locate the NAS in the list, and then tap the name or IP address.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 14
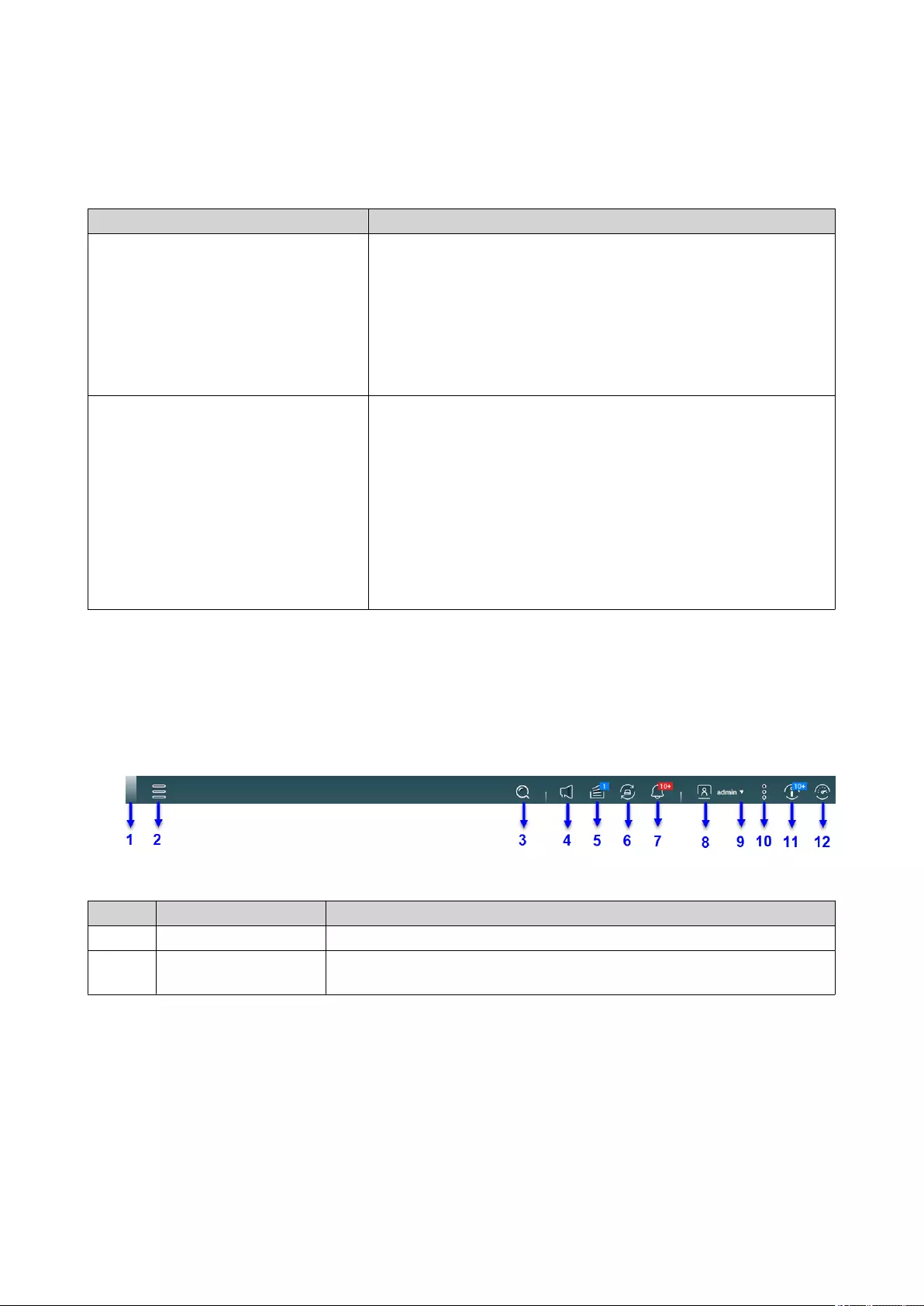
5. Specify your username and password.
6. Optional: If your mobile device and NAS are not connected to the same subnet, perform one of the
following actions.
Action Steps
Add NAS manually a. Tap Add NAS manually.
b. Specify the following information.
• Host name or IP address of the NAS
• Password of the admin account
c. Tap Save.
Sign in using QID a. Tap Sign in QID.
b. Specify the following information.
• Email address that you used to create your QNAP account
• Password of your QNAP account
c. Tap Sign in.
d. Locate the NAS in the list, and then tap the name or IP
address.
QTS Navigation
There are several methods for navigating QTS. You can navigate the operating system using the task bar, left
panel, main menu, and through the desktop.
Task Bar
No. Element Possible User Actions
1Show Desktop Click the button to minimize or restore all open windows.
2Main Menu Click the button to open the Main Menu panel on the left side of the
desktop.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 15
No. Element Possible User Actions
3Search • Type key words to locate settings, applications, and help content.
• Click an entry in the search results to open the application, system
utility, or Help Center window.
If the application is not yet installed, QTS opens the corresponding
download screen in the App Center window.
Tip
App or utility search results are classied into Systems,
Application, and Help.
4Volume Control Important
This feature is only available on models with certain
hardware specications.
Click the button to view the following:
• Media Volume: Click and drag the slider thumb to adjust the audio
volume for applications that use the built-in speaker or line-out jack.
• HD Station
• Music Station
• OceanKTV
• Audio Alert Volume: Click and drag the slider thumb to adjust the
volume of system audio alerts.
5Background Tasks • Hover the mouse pointer over the button to see the number of
background tasks that are running. Examples of background tasks
include le backup and multimedia conversion.
• Click the button to see the following details for each background
task:
• Task name
• Task description
• Progress (percentage of completion)
• Click to stop a task.
6External Devices • Hover the mouse pointer over the button to view the number of
external storage devices and printers that are connected to the USB
and SATA ports on the NAS.
• Click the button to view the details for each connected device.
• Click a listed device to open File Station and view the contents of the
device.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 16
No. Element Possible User Actions
7Event Notications • Hover the mouse pointer over the button to see the number of
recent errors and warnings.
• Click the button to view the following details for each event:
• Event type
• Description
• Timestamp
• Number of instances
• Click a list entry to view the related utility or application screen.
Clicking a warning or error log entry opens the System Event Log
window.
• Click More>> to open the System Event Log window.
• Click Clear All to delete all list entries.
8Options Click your prole picture to open the Options screen.
9[USER_NAME] Click the button to view the last login time and the following menu
items:
•Options: Opens the Options window
•Sleep: Keeps the NAS powered on but signicantly reduces power
consumption
Note
This feature is only available on models with certain
hardware specications.
•Restart: Restarts the NAS
•Shutdown: Shuts down QTS and then powers o the NAS
Tip
You can also power o the NAS using one of the
following methods:
• Press and hold the power button for 1.5 seconds.
• Open Qnder Pro, locate the device in the list. Right click on the
device and select Shut down Device.
• Open Qmanager, and then go to Menu > System Tools >
System . Tap Shutdown.
•Logout: Logs the user out of the current session
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 17
No. Element Possible User Actions
10 More Click the button to view the following menu items:
•What's New: Opens the What's New window, which displays
information on the new features and enhancements available in the
installed QTS version
•Help: Displays links to the Quick Start Guide, Virtualization Guide,
Help Center, and online tutorials page
•Language: Opens a list of supported languages and allows you to
change the language of the operating system
•Desktop Preferences: Opens a list of display modes and allows you
to select the mode based on your device type
•Help Request: Opens the Helpdesk window
•Data & Privacy: Opens the QNAP Privacy Policy page
•About: Displays the following information:
• Operating system
• Hardware model
• Operating system version
• Number of installed drives
• Number of empty drive bays
• System volume name
11 Notication Board Display all system notications and getting started guide during
initialization.
12 Dashboard Click the button to display the dashboard.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 18
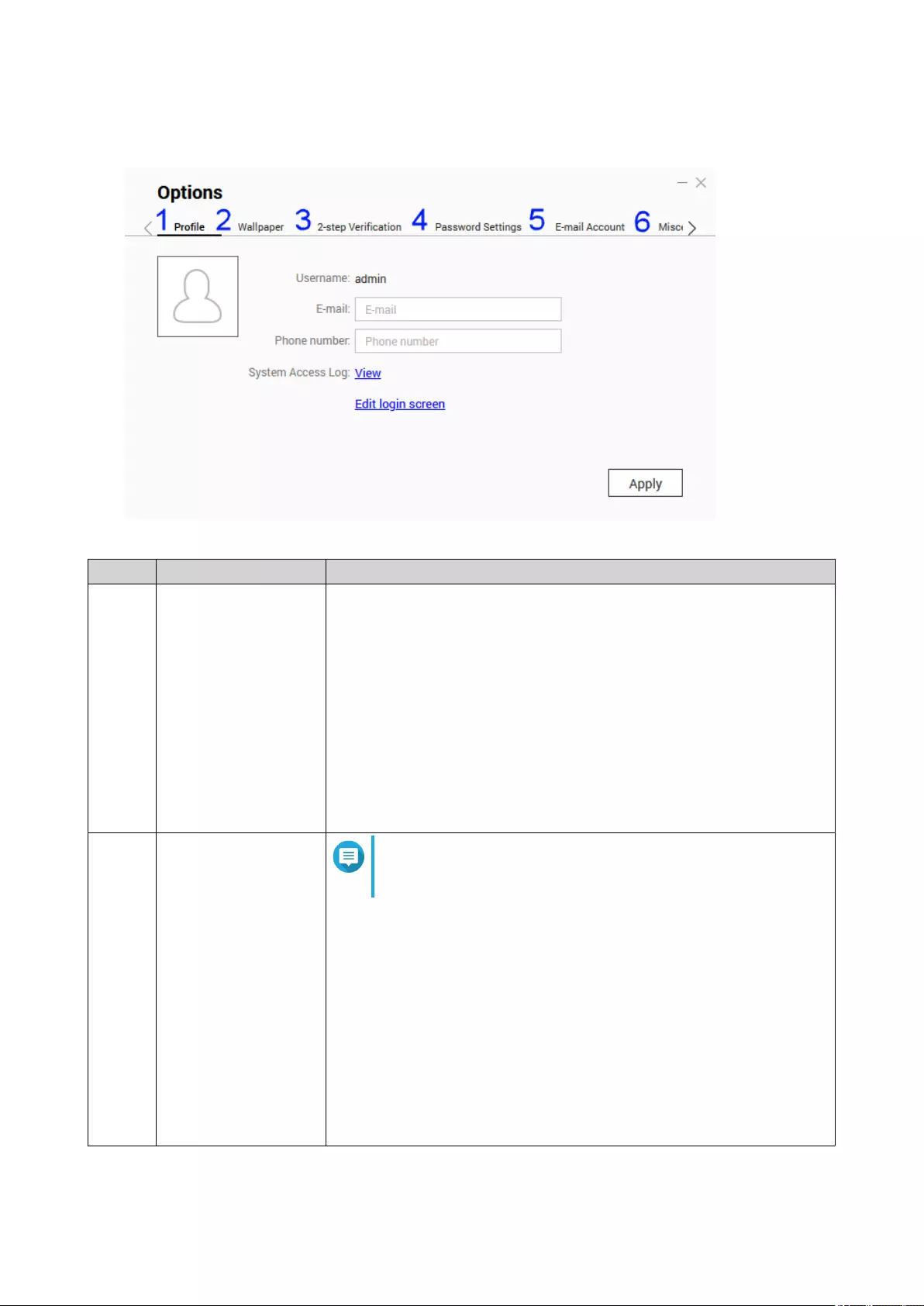
Options
No. Tab Possible User Actions
1Prole • Specify the following optional information:
•Prole picture
• Email address
• Phone number
• Click View to display the System Access Log screen.
• Click Edit login screen to open the Login Screen conguration
screen in the Control Panel window.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
2Wallpaper Note
The nighttime mode dynamic wallpaper is set as the
default wallpaper.
• Perform any of the following actions:
• Dynamic wallpaper: Specify the daytime and nighttime, then
select a wallpaper pairing. The system automatically switches
the wallpaper between daytime and nighttime modes at the
specied time.
• Picture: Select from the default images or upload an image,
then specify the image ll mode.
• Color: Select a color from the default settings or specify a color.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 19
No. Tab Possible User Actions
32-step Verication Click Get Started to open the conguration wizard. For details, see
Enabling 2-step Verication.
4Change Password • Specify the following information to change your password.
•Old password
•New password: Specify a password with a maximum of 64
characters. QNAP recommends using passwords with at least 6
characters.
• Specify an email address to receive a notication email to recover
your password if you forgot the password.
You need to congure SMTP settings in Notication Center to use
this feature.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
5E-mail Account • Add, edit, and delete email accounts to use when sharing les.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
6Miscellaneous • Enable the following settings as necessary.
•Auto logout after an idle period: Specify the duration of
inactivity after which the user is automatically logged out.
•Warn me when leaving QTS: When enabled, QTS prompts
users for conrmation whenever they try to leave the desktop
(by clicking the Back button or closing the browser). QNAP
recommends enabling this setting.
•Reopen windows when logging back into NAS: When
enabled, the current desktop settings (including all open
windows) are retained until the next session.
•Show the desktop switching button: When enabled, QTS
displays the desktop switching buttons < > on the left and right
sides of the desktop.
•Show the link bar on the desktop: When enabled, QTS
displays the link bar on the bottom of the desktop.
•Show the Dashboard button: When enabled, QTS displays the
button to show the dashboard on the taskbar.
•Show the NAS time on the desktop: When enabled, QTS
displays the current NAS time, day, and date at the bottom-right
of the desktop.
•Keep Main Menu open after selection: When enabled, QTS
keeps the main menu pinned to the desktop after you open it.
•Show a list of actions when external storage devices are
detected: When enabled, QTS displays an Autoplay dialog box
whenever an external storage device is inserted into a USB or
SATA port.
• Click Apply to save all changes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 20
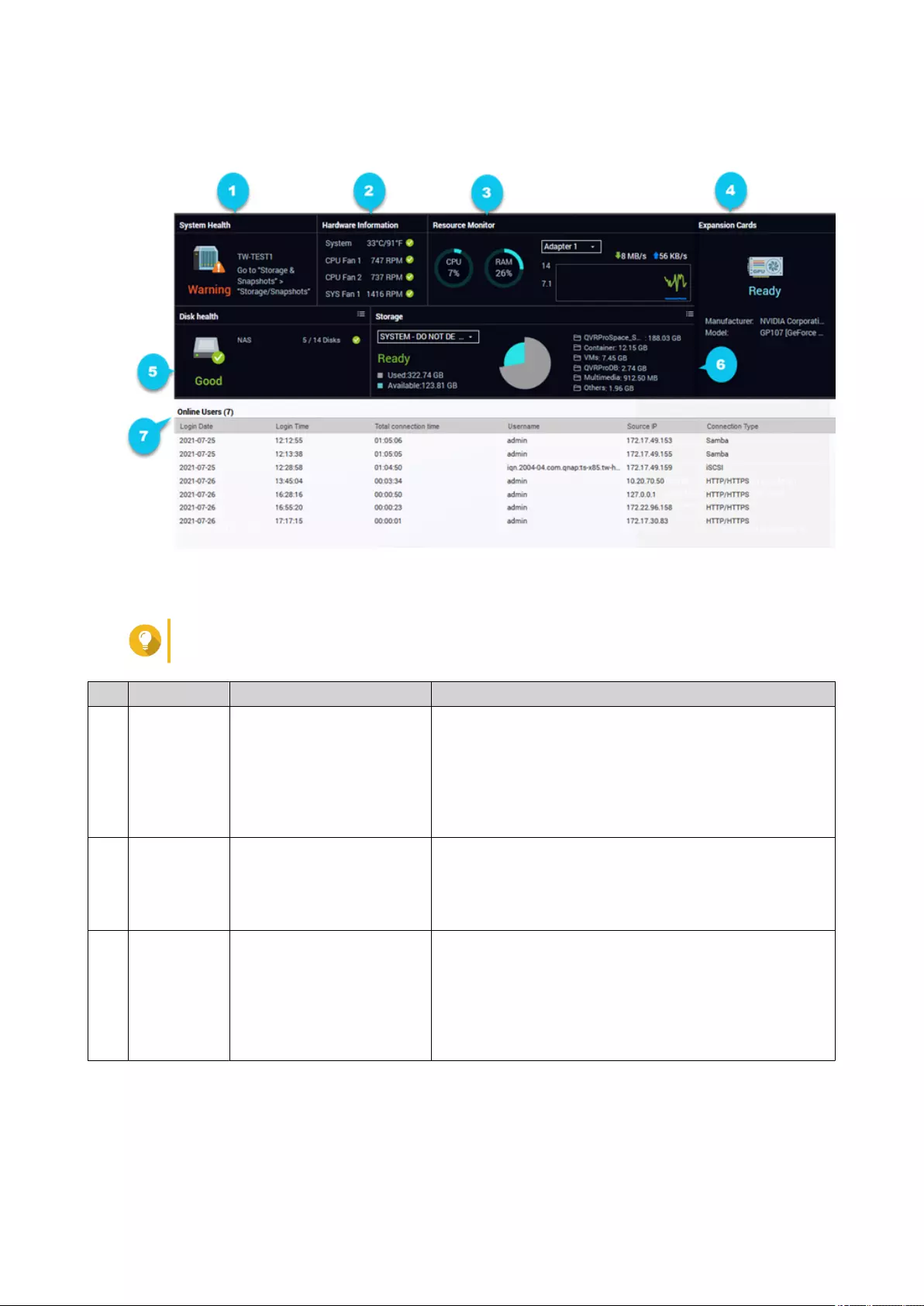
Dashboard
The dashboard opens in the lower right corner of the desktop.
Tip
You can click and drag a section onto any area of the desktop.
No. Section Displayed Information User Actions
1 System
Health
• NAS name
• Uptime (number of
days, hours, minutes
and seconds)
• Health status
Click the heading to open Control Panel > System >
System Status > System Information .
If disk-related issues occur, click the heading to open
Storage & Snapshots.
2 Hardware
Information
• System temperature
• CPU fan speed
• System fan speed
Click the heading to open Control Panel > System >
System Status > Hardware Information .
3 Resource
Monitor
• CPU usage in %
• Memory usage in %
• Network upload and
download speeds for
each adapter.
Click the heading to open Control Panel > System >
Resource Monitor > Overview .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 21
No. Section Displayed Information User Actions
4 Expansion
Cards
For each expansion card:
• Assignment (or "Ready"
if unassigned)
• Manufacturer
• Model
• Memory usage
• GPU usage
• Fan speed
• Temperature
Click the heading to open Control Panel > System >
Hardware > Expansion Cards .
5 Disk Health • Number of installed
disks
• Health status of
installed disks
• Number of VJBOD disks
• Health status of VJBOD
disks
• Click the heading to open the Disk Health screen in
Storage & Snapshots.
•Click to switch between disk and NAS information.
• Click a disk name to view the following information
for each installed disk:
• Capacity/size
• Temperature
• Health status
• Click Details to open Storage & Snapshots >
Overview .
6 Storage For each volume:
• Status
• Used space
• Available space
• Folder size
For each storage pool:
• Status
• Used space
• Available space
• Volume size
• Click the heading to open the Storage Resource
screen in the Resource Monitor window.
•Click to switch between volume and storage pool
information.
7 Online Users • Username
• Total connection time
• IP address
• Connection type
Click the heading to open Control Panel > System >
QuLog Center > Online Users .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 22
Main Menu
No. Section Description Possible User Actions
1 NAS
Information
Displays the NAS name and model
number.
N/A
2 System Displays a list of system utilities and other
programs that enable you to manage the
NAS.
The following are the default system
utilities:
• Control Panel
• Storage & Snapshots
• iSCSI & Fibre Channel
• Users
• Network & Virtual Switch
• myQNAPcloud
• Resource Monitor
• App Center
• Help Center
• Qboost
• HDMI Display Applications
Note
This menu item only appears on
models with certain hardware
specications.
• Open a system utility or application in
the QTS desktop
• Click a menu item.
• Right-click a menu item and then
select Open.
• Open an application in a new browser
tab (only for certain apps)
• Right-click a menu item and then
select Open in new browser tab.
• Create a shortcut on the desktop
• Right-click a menu item and then
select Create shortcut.
• Click and drag a menu item to the
desktop.
3 Applications Displays a list of applications developed by
QNAP or third-party developers.
When an app is installed, it is
automatically added to the applications
list.
The following are the default applications:
• Hybrid Backup Sync 3
• File Station
• Helpdesk
• License Center
• Multimedia Console
•Notication Center
• QTS SSL Certicate
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 23
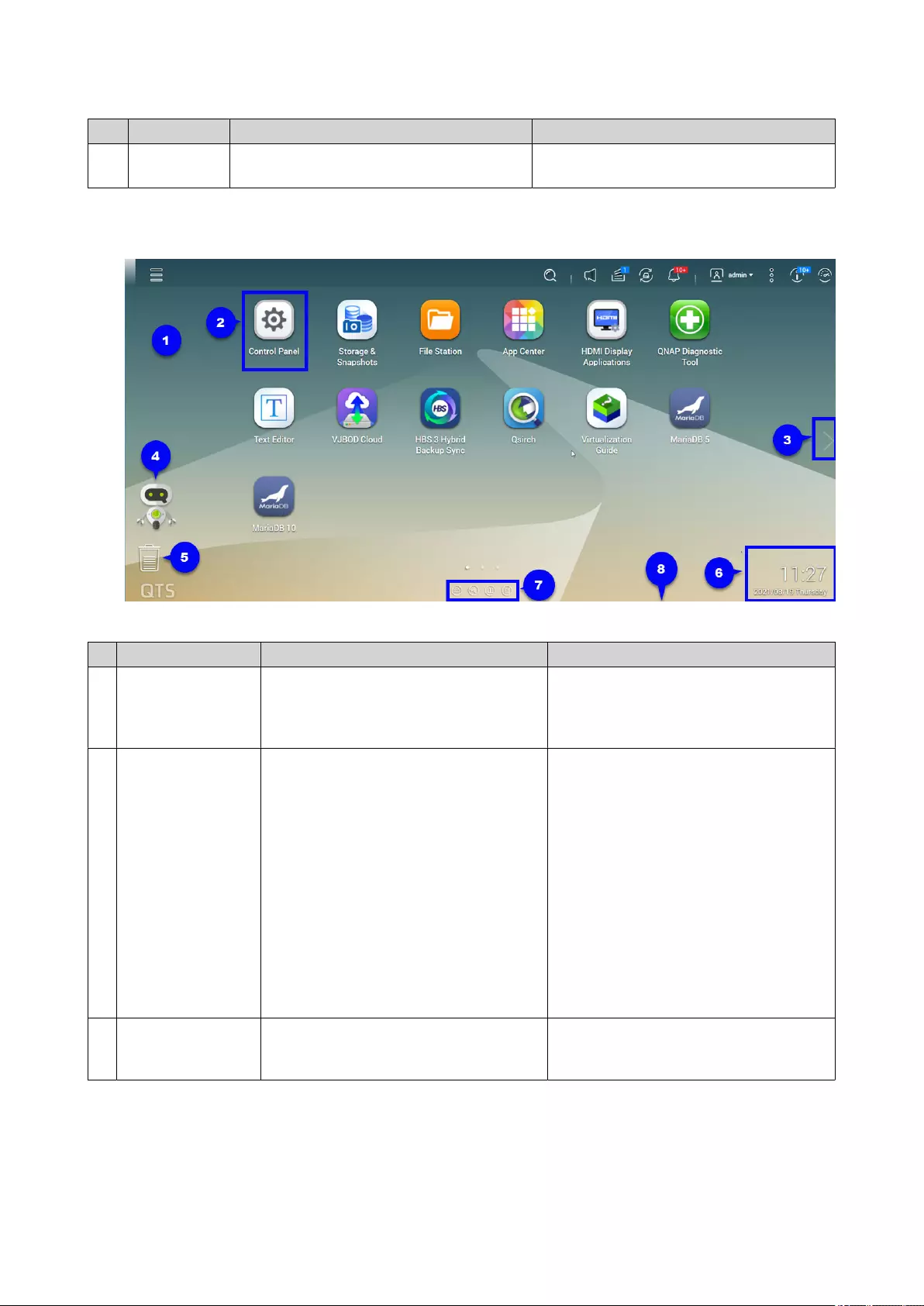
No. Section Description Possible User Actions
4 Search Displays apps that meet your search
criteria.
Enter keywords.
Desktop
# Element Description Possible User Actions
1 Wallpaper This is a digital image that is used as a
background for the QTS desktop.
Users can either select from one of the
provided wallpapers or upload an image
Change the wallpaper in the Options
window.
2 Shortcut icons Each icon opens an app or a utility.
When you install an application,
QTS automatically creates a desktop
shortcut. The following are the default
shortcuts:
• Control Panel
• File Station
• Storage & Snapshots
• App Center
• Help Center
• Click an icon to open the application
window.
• Right-click an icon and then select
one of the following:
•Open: Opens the application
window
•Remove: Deletes the icon from
the desktop
• Click and drag an icon to another
desktop.
3 Desktop This area contains open system utilities
and applications. The desktop consists
of three separate screens.
Click < or > to move to another desktop.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 24
# Element Description Possible User Actions
4 Qboost This enables you to manage and
monitor memory consumption.
•Click or to display the
memory status and open the
Qboost panel.
•Click or to hide the memory
status and close the Qboost panel.
5 Recycle bin This displays the list of les that the
currently active user moved to the
Recycle Bin.
The following applications provide users
a choice between permanently deleting
les and moving les to the Recycle Bin.
• File Station
• Music Station
• Photo Station
• Video Station
•Click to open the Recycle Bin
screen in the File Station window.
•Right-click and then select one
of the following:
•Open: Opens the Recycle Bin
screen in the File Station
window
•Empty All: Permanently
deletes les in the Recycle Bin
•Settings: Opens the Network
Recycle Bin screen in the
Control Panel window
6 Date and time This displays the date and time that
the user congured during system
installation.
N/A
7 Link bar This displays shortcut links to
myQNAPcloud, utility and app
download pages, feedback channels,
and the Helpdesk.
Click any of the following buttons:
•: Opens the myQNAPcloud
website in another browser tab
•: Opens the download page for
mobile applications and utilities
•: Provides links to the QNAP
Wiki, QNAP Forum, and Customer
Service portal
•: Opens the Helpdesk utility
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 25
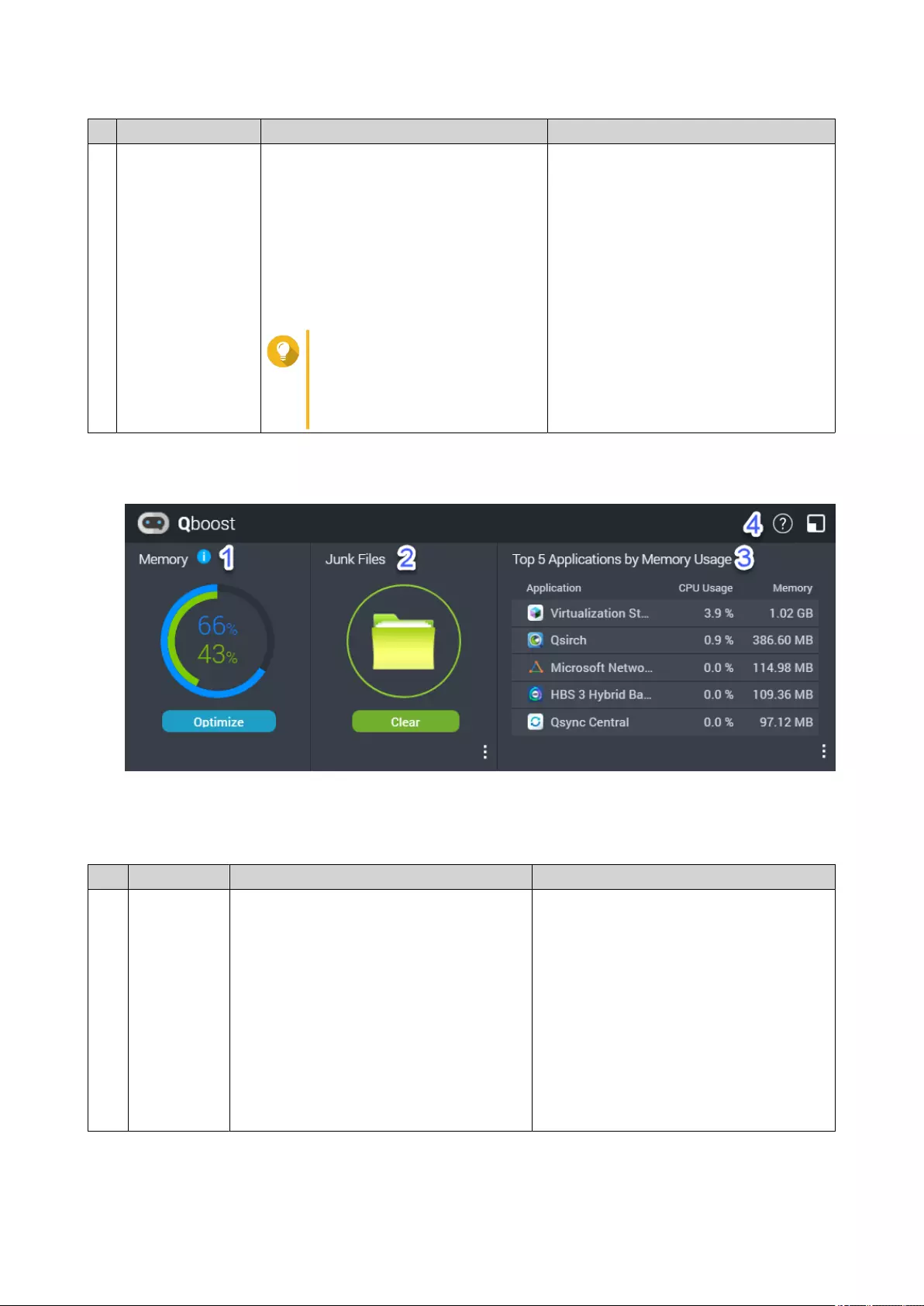
# Element Description Possible User Actions
8Notications This noties the user about important
system events that may or may not
require user action. When there is
more than one group of notications,
the notices will be arranged according
to the notication type on a notice
board. You can also view notications in
Notications Board.
For details, see Task Bar.
Tip
When you initialize QTS, the
Getting Started guide will
appear in notications after
installation.
Click the notication to open the
corresponding utility or app.
Qboost
Qboost is a system utility that monitors and enables you to manage memory consumption. You can
download the utility from App Center. It provides the following information:
# Section Description User Actions
1 Memory A graphic showing memory usage on the
NAS.
• Blue: Available memory, expressed as
a percentage. Available memory is the
sum of free memory, buer memory,
cache memory, and other reclaimable
memory.
• Green: Free memory, expressed
as a percentage. Free memory is
memory that is currently unused and
unallocated.
Click Optimize to clear the buer memory
(block level) and cache memory (le level).
Hover the pointer over the memory
widget to see the amount of available
memory and free memory in MB, GB, or
TB.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 26
# Section Description User Actions
2 Junk Files Junk les are unnecessary system les and
les in the Recycle Bin, which consume
disk space and memory.
• Click Clear to permanently delete junk
les.
By default, clicking Clear only deletes
unnecessary system les, such as
les that the operating system and
applications create while performing
certain tasks.
•Click to select other types of les
to delete.
Select Empty Recycle Bin to include
les that were moved to the Recycle
Bin by the currently active user.
3 Top 5
Applications
by Memory
Usage
Top ve applications and services that
consume the most memory Click to display all applications and
services that can be enabled and disabled
from either the Control Panel or the App
Center.
For details, see Application Management.
4 Qboost
taskbar
Taskbar for the Qboost widget
Click to view the Qboost help.
Click to close the Qboost widget.
Application Management
Application Management displays the following information.
Item Description
Application Displays the application name
CPU Usage Displays the percentage of consumed processing power
Memory Displays the amount of memory consumed
CPU Time Displays the amount of time the CPU requires to process an
application request
Status Displays one of the following statuses:
• Always Enabled
• Always Disabled
• Scheduled
Action Displays icons for the possible actions
You can perform the following actions.
Objective Action
Enable or disable an application or
service.
•Click to change the status to Always Enabled.
•Click to change the status to Always Disabled.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 27
Objective Action
Create a schedule for enabling
and disabling an application or
service.
Warning
Setting a schedule may force an application to stop in
the middle of a task.
1. Click to open the scheduling screen.
2. Select Enable Schedule.
The calendar is activated. All days and hours are enabled by
default.
3. Select the hours during which the application or service should be
enabled or disabled.
Hours are lled with one of the following colors or patterns.
• Blue: The application or service is enabled.
• Gray: The application or service is disabled.
• Striped: The NAS is scheduled to sleep or shut down.
4. Optional: If you want to enable the app at a certain time, specify
the number of minutes after the hour when the application is
enabled or disabled.
Example: To enable an application only after half an hour, type 30.
5. Perform one of the following actions.
• Click Apply: Applies the schedule to the selected application
or service
• Select Auto-apply: Applies the schedule to all applications and
services
Delete a schedule. Click to delete the schedule and disable an application or service.
Remove an application. Click .
This function applies only to applications that are available in App
Center.
2-step Verication
2-step verication enhances the security of user accounts. When the feature is enabled, users are required
to specify a six-digit security code in addition to the account credentials during the login process.
To use 2-step verication, you must install an authenticator application on your mobile device. The
application must implement verication services using the Time-based One-time Password Algorithm
(TOTP). QTS supports Google Authenticator (for Android, iOS, and BlackBerry) and Authenticator (for
Windows Phone).
Enabling 2-step Verication
1. Install an authenticator application on your mobile device.
QTS supports the following applications:
• Google Authenticator: Android, iOS, and BlackBerry
• Authenticator: Windows Phone
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 28
2. Verify that the system times of the NAS and mobile device are synchronized.
Tip
QNAP recommends connecting to an NTP server to ensure that your NAS follows the
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) standard.
3. In QTS, go to Options > 2-step Verication .
4. Click Get Started.
The 2-step Verication window opens.
5. Open the authenticator application on your mobile phone.
6. Congure the application by scanning the QR code or specifying the security key displayed in the
2-step Verication window.
7. In the 2-step Verication window, click Next.
The Conrm your 2-step verication settings screen appears.
8. Specify the security code generated by the authenticator application.
9. Select an alternative verication method that will be used whenever your mobile device is inaccessible.
Method Steps
Answer a security question. Select one of the options or provide your own security question.
Email a security code. a. Go to Control Panel > Notication Center > Service
Account and Device Pairing > Email .
b. Verify that the SMTP server is correctly congured.
10. Click Finish.
Logging in to QTS Using 2-step Verication
1. Specify your username and password.
2. Specify the security code generated by the authenticator application installed on your mobile device.
3. Optional: If your mobile device is inaccessible, click Verify another way.
4. Specify the answer to the security question.
5. Click Login.
Disabling 2-step Verication
Situation User Action Steps
Users are locked out of their
accounts.
Administrators can disable
2-step verication from the
Control Panel.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege >
Users .
2. Identify a locked out user, and then click
.
3. Deselect 2-step Verication.
4. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 29
Situation User Action Steps
An administrator is locked
out and no other
administrators can access
the account.
An administrator must
restore the factory settings.
Press the RESET button on the back of the
NAS for three seconds.
The NAS restores the default administrator
password and network settings.
Note
For information on the default
admin password, see Backup/
Restore.
Warning
Pressing the RESET button for 10
seconds resets all settings and
deletes all data on the NAS.
Support and Other Resources
QNAP provides the following resources:
Resource URL
Documentation https://download.qnap.com
Compatibility List https://www.qnap.com/compatibility
NAS Migration Compatibility https://www.qnap.com/go/nas-migration
Expansion Unit Compatibility https://www.qnap.com/go/compatibility-expansion
Service Portal https://service.qnap.com
Product Support Status https://www.qnap.com/go/product/eol.php
Downloads https://download.qnap.com
Community Forum https://forum.qnap.com
QNAP Accessories Store https://shop.qnap.com
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Overview 30

2. Getting Started
After completing hardware setup and rmware installation, you can start creating storage pools and
volumes to store your data and then congure user accounts to control access to your data. To access
and manage your les via the Internet, you can set up remote access and enable the myQNAPcloud service
for your device. To ensure data availability, you can back up your NAS data to multiple destinations using
various backup solutions.
In addition to built-in features, you can also install applications and purchase software licenses to add
functionality to your device. To protect your data from security threats, you should take action to prevent
unauthorized access, update your software regularly, and use security utilities to secure your QNAP device.
Storing Data
To store data on the NAS, you must create storage pools, volumes, and shared folders, which are features
designed to help you facilitate data storage and management. You can congure storage settings in Storage
& Snapshots, a powerful built-in utility for storage and snapshot management in QTS.
1. Create a storage pool.
A storage pool combines multiple physical disks into one large storage space and may contain one or
more RAID groups. You need to create at least one storage pool. You can also choose a RAID type that
meets your needs for data redundancy and storage performance.
For details, see Creating a Storage Pool.
2. Create a volume.
A volume is a storage space created from a storage pool or a RAID group, allowing you to divide and
manage available storage capacity. QTS provides several volume types for dierent combinations of
performance and exibility. You need to create at least one volume to start storing data on the NAS.
For details, see Volume Creation.
3. Create a shared folder.
A shared folder is created on a volume, allowing you to access, manage, and share your les. QTS
automatically creates several default shared folders for various purposes. You can create more shared
folders and congure their access permission settings to better manage your les.
For details, see Creating a Shared Folder.
Accessing Data
QTS provides several simple ways to access your data on the NAS when your NAS and computer are on the
same local network. With a web browser, you can access and manage your les using File Station in QTS. You
can also access mounted shared folders directly via the le manager on your Windows or macOS computer.
• Access les via File Station.
a. Access the NAS.
You can directly access the NAS via its IP address using a web browser. You can also discover and
access your NAS on the local network using Qnder Pro.
For details, see:
•Accessing the NAS Using a Browser
•Accessing the NAS Using Qnder Pro
b. Open File Station.
File Station is the le manager in QTS, allowing you to browse, manage, and share les on
the NAS. You can also create and congure shared folders in File Station to facilitate le
management.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Getting Started 31

For details, see File Station.
• Access les via shared folders mounted on your computer.
You can mount a shared folder as a network drive on your computer. This allows you to directly access
mounted shared folders using the le manager on your Windows or macOS computer.
For details, see:
•Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer
•Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac Computer
Backing Up Data
Regular backup is crucial for data protection. QNAP provides various backup solutions to ensure the
availability of your data. You can start backup up your les with the following tools designed to meet your
essential backup needs.
Hybrid Backup Sync allows you to back up, restore, and synchronize the data on your local NAS to remote
NAS, external devices, cloud storage services, and vice versa. You can also take snapshots for the volumes
on your local NAS and then use Snapshot Replica to back up these snapshots to a remote NAS.
• Use Hybrid Backup Sync to back up your NAS data.
a. Install Hybrid Backup Sync on the NAS.
b. Create a backup job or a sync job.
Hybrid Backup Sync is a comprehensive solution for data backup and disaster recovery. You can
create several types of backup and sync jobs between the local NAS and multiple destinations
(including remote NAS, external devices, and cloud storage services). Hybrid Backup Sync enhances
data deduplication and encryption for your backup data. This essential tool also provides various
features to facilitate job conguration and management.
For details, see Hybrid Backup Sync Help.
• Take and back up snapshots for your NAS data.
a. Take snapshots for volumes.
b. Use Snapshot Replica to back up snapshots.
An essential feature for data protection, a snapshot records the state of a volume at a specic point in
time. Using a snapshot, you can restore a volume to a previous state or restore the previous versions of
les or folders. You can view and manage your snapshots in Storage & Snapshots.
To further protect your data, you can use Snapshot Replica to back up your snapshots to another
storage pool on the local NAS or to a remote NAS. In the event of a disaster, you can choose to recover
your data on the source NAS or on the destination NAS.
For details, see:
•Taking a Snapshot
•Creating a Snapshot Replica Job
Conguring Privilege Settings
QTS allows you to create user accounts and user groups, specify user privileges, and congure shared folder
permissions. These features are essential for data security and management.
The admin account is the default administrator account in QTS. To enhance your data and device security,
we recommend creating another administrator account and then disabling the admin account.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Getting Started 32

1. Create an administrator account.
You can create a new user account to replace the admin account. To grant administrator privileges to
this new user, you must add this new user to the administrator group. You should also grant shared
folder access permissions to this user.
For details, see Creating an Administrator Account.
2. Disable the admin account.
After creating a new administrator, you should disable the default admin account and then start
managing the NAS with this new administrator account.
For details, see Disabling a Default Administrator Account.
3. Create more users or user groups.
You can create other users or user groups and grant them dierent levels of privileges to control
access to your data on the NAS.
For details, see:
•Creating a Local User
•Creating a User Group
Setting Up Remote Access
myQNAPcloud is a QNAP service that allows you to connect to the NAS via the Internet. With this service,
you can remotely access your data on the NAS and use a wide variety of mobile applications designed for
the QNAP NAS wherever you go. To use the myQNAPcloud service, you must rst create a QNAP ID and then
register your NAS to your QNAP ID.
1. Create a QNAP ID.
QNAP ID is your QNAP account that allows you to access various QNAP services. To create a QNAP ID,
go to https://account.qnap.com/.
For details, see Creating a QNAP ID With Email or Phone Number.
2. Register the NAS to your QNAP ID.
After creating a QNAP ID, you need to enable the myQNAPcloud service on your NAS and then
associate your device with your QNAP ID. You can also congure various remote access settings in
myQNAPcloud.
For details, see Registering a Device to myQNAPcloud.
3. Remotely access the NAS via myQNAPcloud.
After setting up myQNAPcloud on your NAS, you can remotely access and manage the NAS via the
myQNAPcloud website or via the SmartURL generated for your NAS.
4. Remotely access the NAS on your mobile device.
QNAP provides a wide range of mobile applications that enable you to access, manage, monitor, and
back up your NAS wherever you go. After installing theseQNAP applications on your mobile devices,
you must sign in to them with your QNAP ID.
For details, go to https://www.qnap.com/en/mobile-apps.
Acquiring Apps and Licenses
QTS provides various essential applications to help manage your NAS. In addition to these built-in features,
QTS also allows you to install more applications from the App Center to further enhance the functionality
of your device. To gain access to certain advanced features and premium products, you must purchase and
activate licenses for your device.
1. Install applications in the App Center.
App Center provides a wide variety of applications and utilities. You can also manage and update your
installed applications in the App Center.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Getting Started 33

For details, see App Center.
2. Purchase licenses in the QNAP Software Store.
QNAP Software Store is an online store where you can purchase licenses and manage your orders.
QNAP provides various types of licenses and subscription plans to meet dierent needs and usage
environments.
For details, see Licenses.
3. Activate licenses in the License Center or License Manager.
Some licenses are automatically activated after being purchased. However, sometimes you must
manually activate a license.
License Center allows you to manage licenses on your local device. License Manager allows you and
your organization to manage licenses under your QNAP ID.
For details, see Licenses.
Securing the NAS
All networked devices face constant security threats. To reduce the risk of your data being attacked, we
strongly recommend following the best practices to secure your NAS. In essence, you should prevent
unauthorized access, update your device software regularly, and install security utilities to protect your
device.
1. Prevent unauthorized access to your device.
a. Create a new administrator account and disable the admin account.
The admin account is the default administrator account. Nevertheless, to enhance the security of
your device, we strongly recommend creating another administrator account and then disabling
the admin account.
For details, see Default Administrator Account.
b. Enhance user password strength.
We recommend enhancing your password strength and changing your passwords regularly to
prevent brute-force attacks.
For details, see Modifying User Account Information.
c. Set up 2-step verication.
2-step verication further enhances the security of user accounts by requiring users to specify a
security code in addition to their account credentials during the login process.
For details, see 2-step Verication.
d. Remove unknown or suspicious accounts.
We recommend verifying user accounts regularly and deleting any unknown or suspicious
accounts.
For details, see Deleting Users.
e. Remove unnecessary permissions from general users.
We recommend restricting the permissions of non-administrator users to limit their access to
system operations and sensitive data. This helps mitigate the impact of a compromised user
account.
For details, see Modifying User Account Information.
f. Remove unknown or suspicious applications.
We recommend only installing applications and utilities that have digital signatures, which
validate software developed by QNAP and other QNAP-trusted developers.
You should regularly check your installed applications and remove any unknown or suspicious
applications from the App Center.
For details, see Digital Signatures and Uninstalling an App.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Getting Started 34

g. Congure access settings in myQNAPcloud.
To ensure your data security, UPnP is disabled by default. We recommend manually conguring
port forwarding settings on your router.
We also recommend conguring access control and only publishing necessary services in
myQNAPcloud.
For details, see:
•Conguring UPnP Port Forwarding
•Conguring Device Access Controls
•Conguring Published Services
2. Update your rmware and applications to the latest versions.
a. Update the rmware to the latest version.
We strongly recommend regularly updating the rmware of your device to the latest version
to benet from the latest features, enhancements, and security xes. You can also choose to
automatically check for and install available updates.
For details, see Firmware Update.
b. Update applications to the latest versions.
You should regularly update your installed applications to their latest versions for better
performance, functionality, and security. App Center allows you to check for all available updates
and then install updates for multiple applications at the same time.
For details, see:
•Updating an App
•Batch Updating Multiple Apps
3. Install and run security utilities on the NAS.
a. Run Malware Remover.
Malware Remover is a built-in utility designed to protect QNAP devices against malicious
software. You can run instant or scheduled scans to remove malicious software from your device.
For details, see Malware Remover.
b. Install and run Security Counselor.
Security Counselor is the security portal that allows you to centrally congure security settings
and manage security components on your QNAP device. You can choose security policies,
scan the device, and check for potential security weaknesses on the device. Security Counselor
identies potential risks and provides suggestions to help you enhance device security. You
can also subscribe to QNAP security advisories to stay informed of the latest security xes and
solutions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Getting Started 35
3. System Settings
General Settings
Settings Description
System Administration This screen allows you to specify the server name and ports and
congure secure connection settings.
Time Time settings aect event logs and scheduled tasks. This screen
allows you to specify the time zone and format and congure the
system date and time.
Daylight Saving Time (DST) Daylight saving time (DST) settings apply only to regions that use
DST. This screen allows you to either automatically adjust the
system clock or manually congure the settings.
Codepage This screen allows you to select the language that the NAS uses to
display le and directory information.
Region This screen allows you to select a region for your NAS. System
and application content and services are localized according to the
selected region.
Login Screen This screen allows you to customize the NAS login screen.
Console Management This screen allows you to enable console management.
Conguring System Administration Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > System Administration .
2. Specify the following information.
Field User Action
Server name Specify a name containing up to 14 characters from any of the following
groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Dashes (-)
Important
• The server name must contain one or more letters.
• The server name cannot consist of numbers only.
• The server name cannot start with a dash.
• The host name must contain one or more letters.
• The host name cannot consist of numbers only.
• The host name cannot start with a dash.
System port Specify the port used to access the web interface.
The default port is 8080.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 36
Field User Action
Enable HTTP compression Select this option to improve transfer speeds and bandwidth utilization.
This setting is enabled by default.
Warning
Enabling this option may lead to security risks.
Enable secure connection
(HTTPS)
Select this option to allow HTTPS connections.
a. Select Enable secure connection (HTTPS).
b. Select a TLS version.
The default TLS version is 1.2.
Warning
Selecting the latest TLS version may decrease
compatibility for other clients in your system.
c. Enable strong cipher suites.
d. Specify a port number.
e. Optional:
Select Force secure connection (HTTPS) only to require all users to
connect to the NAS using only HTTPS.
Custom "Server" HTTP
header
Select this option to specify a server HTTP header.
Do not allow QTS embedding
in IFrames
a. Select this option to prevent websites from embedding QTS using
IFrames.
b. Click Allowed Websites to allow a specic website to embed QTS in
IFrames.
c. The Allowed Websites window appears.
d. Optional:
Click Add to add a website to the list.
The Add Host Name window appears.
e. Specify a host name.
f. Click Add.
The host name is added to the allowed websites list.
g. Optional:
Select a website, and then click Delete to delete a website from the
list.
h. Click Apply.
Enable X-Content-Type-
Options HTTP header
Select this option to protect your device from attacks that exploit MIME
sning vulnerabilities.
Enable Content Security
Policy HTTP header
Select this option to protect your device from attacks that exploit Cross
Site Scripting (XSS) and data injection vulnerabilities.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 37
Field User Action
Redirect URL to NAS login
page Important
• QNAP recommends disabling this feature to prevent
your NAS system from being exposed to the public.
• If you have disabled the Web Server and entered the
NAS IP address without the system port, the URL will
be redirected to the NAS login page.
Tip
You can check the web server settings by going to
Control Panel > Applications > Web Server .
Select this option to enable redirecting the URL to the NAS login page.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring Time Settings
Important
You must congure the system time correctly to avoid the following issues.
• When using a web browser to connect to the NAS or save a le, the displayed time of
the action is incorrect.
• Event logs do not reect the exact time that events occurred.
• Scheduled tasks run at the wrong time.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Time .
2. Select a time zone.
3. Specify the date and time format.
4. Select the time setting.
Option User Action
Manual setting Specify the date and time.
Synchronize with a time server automatically Ensure that your NAS is connected to the Internet,
and then specify the following information:
•Server: Name of the Network Time Protocol
(NTP) server
Examples: time.nist.gov, time.windows.com
• Optional: Click Test Connection.
The system will test if a connection can be
established with the congured time server.
•Time interval: Number of hours or days
between each time synchronization task
Set the server time the same as your computer
time
Click Update.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 38
5. Click Apply.
Conguring Daylight Saving Time
These settings are available for NAS users in regions that use Daylight Saving Time (DST). Users outside
these regions can disregard these settings.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Daylight Saving Time .
2. Select Adjust system clock automatically for daylight saving time.
3. Optional: Select Enable customized daylight saving time table.
4. Optional: Perform any of the following actions.
Action Steps
Add DST data a. Click Add Daylight Saving Time Data.
The Add Daylight Saving Time Data window appears.
b. Specify a time period and the number of minutes to oset.
c. Click Apply.
Edit DST data a. Select a DST schedule from the table.
b. Click .
c. Specify a time period and the number of minutes to oset.
d. Click Apply.
Delete DST data a. Select a DST schedule from the table.
b. Click Delete.
c. Click OK.
5. Optional: Select a DST schedule from the table.
6. Click Apply.
Conguring Codepage Settings
All les and directories on the NAS use Unicode encoding. If your operating system or FTP client does not
support Unicode, you must congure the following settings to properly view les and directories on the NAS.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Codepage .
2. Select the language of your operating system.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring Region Settings
Important
The NAS region settings aect device connectivity and the functionality, content, and
validity of some applications, utilities, licenses, and certicates. Ensure that you select the
correct region to avoid errors.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 39
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Region .
2. Select a region.
Region Description
Global Select this region if the NAS is located outside of China.
China Select this region if the NAS is located in China.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring the Login Screen
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Login Screen .
2. Congure the following settings.
Field User Action
Login screen template Select a template for the login screen.
Show rmware version Select this option to display the QTS rmware version.
Show the link bar Select this option to display links to myQNAPCloud, QNAP Utilities, and
Feedback.
Background Select a background image or ll color.
Logo Select a logo.
Message Specify a message that will appear on the login screen. You can enter a
maximum of 120 ASCII characters.
You can also select the font color and size.
3. Click Preview to view the changes.
4. Click Apply.
Enabling or Disabling Console Management
Console Management is a text-based tool that helps the admin account perform basic conguration or
maintenance tasks.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > General Settings > Console Management .
2. Optional: Select Enable Console Management.
Note
Enable Console Management is enabled by default.
3. Deselect Enable Console Management to disable the feature.
4. Click Apply.
Security
To protect your NAS from unauthorized access, you can congure allow or deny lists, enable IP access
protection, upload SSL certicates and custom root certicates. Additionally, you can use account access
protection or create a unique password policy for your NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 40
Conguring the Allow/Deny List
Important
If you have installed QuFirewall on your device, go to QuFirewall to congure the allow or
deny list.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > Allow/Deny List .
2. Select an option.
Option Description User Action
Allow all connections The NAS can connect to all IP addresses
and network domains.
Select Allow all connections.
Use IP deny list The NAS cannot connect to any IP
address or network domains included in
the IP deny list.
a. Select Deny connections from the
list.
b. Click Add.
The IP conguration window
appears.
c. Specify an IP address, netmask, or
IP range.
d. Click Create.
Tip
To remove an IP address,
netmask, or IP range, select
an entry from the table, and
then click Remove.
Use IP allow list The NAS can only connect to the IP
addresses or network domains included
in the IP allow list.
a. Select Allow connections from the
list only.
b. Click Add.
The IP conguration window
appears.
c. Specify an IP address, netmask, or
IP range.
d. Click Create.
Tip
To remove an IP address,
netmask, or IP range, select
an entry from the table, and
then click Remove.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring IP Access Protection
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > IP Access Protection .
2. Select the connection methods you want to protect.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 41

Note
SSH, Telnet, and HTTP(S) are enabled by default.
3. Optional: Specify the following information.
• Time period
• Maximum number of unsuccessful login attempts within the time period
• Amount of time the IP will be blocked
4. Click Apply.
Conguring Account Access Protection
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > Account Access Protection .
2. Specify the user type.
3. Select the connection methods you want to protect.
4. Optional: Specify the following information.
• Time period
• Maximum number of unsuccessful login attempts within the time period
5. Click Apply.
SSL Certicate & Private Key
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a protocol used for secure data transfers and encrypted communication
between web servers and browsers. To avoid receiving alerts or error messages when accessing the web
interface, upload a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certicate from a trusted provider through Server Certicate
or import a custom root certicate to your QNAP device. QNAP recommends you purchase a valid SSL
certicate from myQNAPcloud SSL Web Service Certicate. For details, see myQNAPcloud website.
Replacing the Server Certicate
Warning
The NAS supports only X.509 PEM certicates and private keys. Uploading an invalid
security certicate may prevent you from logging in to the NAS through SSL. To resolve the
issue, you must restore the default security certicate and private key.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > SSL Certicate & Private Key .
2. Go to Server Certicate.
3. Click Replace Certicate.
The Replace Certicate window appears.
4. Select an option.
Option Description
Import certicate This option allows you to import an SSL certicate and private key
from your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 42
Option Description
Get from Let's Encrypt This option uses the Let's Encrypt service to validate and issue a
certicate for your specied domain.
Note
QNAP recommends you use port 80 or 443
for authorizing the SSL certicate domain and
accessing the Internet.
Create self-signed certicate This option allows you to create a self-signed certicate.
5. Click Next.
A conguration window appears.
6. Perform any of the following actions:
Option User Action
Import certicate a. Click Browse to upload a valid certicate.
b. Click Browse to upload a valid private key.
c. Optional:
Click Browse to upload an intermediate certicate.
Get from Let's Encrypt a. Specify a domain name containing a maximum of 63 ASCII
characters, without spaces.
b. Specify a valid email address.
c. Optional:
Specify an alternative name.
Tip
Use "," to separate multiple aliases.
Example: 123.web.com,789.web.com
Create self-signed certicate Congure the following information:
•Private key length
•Common name
•Email
•Country
•State/Province/Region
•City
•Organization
•Department
7. Click Apply.
Downloading the Server Certicate
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > SSL Certicate & Private Key .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 43
2. Click Download Certicate.
A dialog box appears.
3. Select Certicate, Private Key, or both.
4. Click OK.
QTS downloads the selected les to your computer.
Managing a Root Certicate
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > SSL Certicate & Private Key .
2. Go to Custom Root Certicate.
3. Select one of the following actions:
Action
Import a root certicate a. Click Import.
The Import Certicate window appears.
b. Click Browse.
The le upload window appears.
c. Select a le.
Important
The root certicate le cannot be larger than 1 MB.
The following le formats are supported: *.PFX, *.P12,
*.PEM, *.crt, *.cert
d. Click Next.
The certicate description page appears.
e. Click Import.
The imported root certicate is displayed in the client certicate
table.
Edit a root certicate a.
Click .
The Edit Root Certicate window appears.
b. Edit the certicate description.
c. Click Apply.
Delete a root certicate a. Select a root certicate.
b. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Yes.
Conguring the Password Policy
Important
The following password policy is congured by default:
• English letters: No restrictions
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 44
• Digits: Enabled
• Minimum length: 8
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Security > Password Policy .
2. Optional: Under Password Strength, congure any of the following password criteria.
Criteria Description
English letters Passwords must contain at least one letter.
Select At least 1 uppercase and 1 lowercase to
require at least one uppercase and one lowercase
letter.
Digits Passwords must contain at least one number.
Special characters Passwords must contain at least one special
character.
Must not include characters repeated three or more
times consecutively
Repeating characters are not allowed. For example,
AAA.
Must not be the same as the associated username,
or the username reversed.
The password must not be the same as the
username or the reversed username. For example,
username: user1 and password: 1resu.
Minimum length The password length must be greater than or equal
to the specied number. The maximum length of a
password is 64 characters.
3. Optional: Require NAS users to periodically change their passwords.
Important
Enabling this option disables Disallow the user to change password under user account
settings.
a. Select Require users to change passwords periodically.
b. Specify the maximum number of days that each user password is valid.
c. Optional: Select Send a notication email to users a week in advance before their password
expires.
4. Click Apply.
Hardware
You can congure general hardware settings, audio alerts, smart fan settings, and view all Single Root I/O
Virtualization (SR-IOV) settings.
Conguring General Hardware Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > General .
2. Congure the following settings.
Settings User Action
Enable conguration reset switch Select this option to enable the reset button.
For details, see System Reset and Restore to Factory Default.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 45
Settings User Action
Enable disk standby mode Select this option to allow the NAS drives to enter standby
mode if there is no disk access within the specied period. Disk
status LED remains on during standby mode.
Important
Some QNAP NAS models that use NVMe solid-
state drives do not support disk standby mode.
Enable light signal alert Select this option to allow the status LED to ash when free
space on the NAS is less than the set value.
Enable write cache (EXT4 delay
allocation)
If the NAS disk volume uses EXT4, select this option for higher
write performance.
If the NAS is set as a shared storage in a virtualized or clustered
environment, disable this option.
Warning
When this option is enabled, an unexpected
system shutdown may lead to data loss.
Enable redundant power supply mode Select this option to enable the redundant power supply.
Run user-dened processes during
startup
Select this option to run user-dened processes during startup.
Turn on LED Select this option to turn on the LED, set its brightness level,
and set a schedule for brightness setting.
Note
This function is only applicable for some models.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring Audio Alert Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > Audio Alert .
2. Congure any of the following settings.
Setting Description
System operations Select this option to trigger an audio alert every time the NAS
starts, shuts down, or upgrades rmware.
System events Select this option to trigger an audio alert when errors or
warnings occur.
Enable speech notication Select this option to replace some audio alerts with speech. You
can select a language and modify the volume.
Tip
Click Test to check the modied speech settings. If
there is no sound, another app may be using the
speaker.
3. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 46
Conguring Smart Fan Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > Smart Fan .
2. Select fan rotation speed settings.
Note
Some NAS models allow users to separately adjust system and CPU smart fans.
Setting User Action
Automatically adjust fan speed
(recommended)
Select from the two automatic fan speed adjustment options.
a. QTS monitors the temperatures of the system, disks, and CPU
and automatically adjusts the fan speed.
b. QTS adjusts the fan speed according to user-specied
temperatures.
Note
Modes are only available for system fans.
•Quiet mode: Fans run on low speed to decrease noise.
•Normal mode: Fans run on normal speed. This is the
default setting.
•Performance mode: Fans run on high speed to lower
the system temperature. This mode is suitable for high
loading systems.
Manually set fan speed Move the slider to set the fan speed.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring Hardware Resource Settings
You can congure and allocate expansion card resources for dierent software QTS applications in
Hardware Resource Settings. You can also congure Thunderbolt expansion cards, TPU modules, or network
expansion cards that support SR-IOV.
For details, see Viewing Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > Hardware Resource .
QTS lists the available expansion cards.
2. Identify the expansion cards you want to congure.
3. Under Resource Use, select an OS or an application.
Note
Some functions are only applicable for certain models and expansion cards.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 47
OS or Application Description
QTS QTS applications share expansion card resources for transcoding.
• Select Hardware Transcoding to allow QTS software to use
expansion card resources to speed up transcoding tasks. Only one
card can be assigned to hardware transcoding.
• Select Output to use expansion card resources for video output
of HD Station or Linux Station. Only one card can be assigned to
output.
Virtualization Station Virtualization Station has exclusive use of all expansion card resources.
Container Station Container Station has exclusive use of all expansion card resources.
4. Click Apply.
Conguring TPU Settings
You can congure the priority level and maximum number of Tensor Processing Units (TPU) allocated to an
app.
Important
• The system will not run apps with lower TPU priority levels until the TPU resource is
released from running higher priority apps.
• The maximum number of TPUs you can allocate to an app is 4.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > Hardware Resource .
2. Locate the TPU device from the list.
3. Click on the TPU device.
The Priority window appears.
4. Select an app.
5. Select a TPU priority level.
6. Select the maximum number of TPUs.
7. Click Apply.
Viewing Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) Settings
You can view all Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) devices mapped to your virtual machines on the
Hardware Resource page. The SR-IOV interface is a hardware specication that allows a single PCIe device,
such as a network adapter, to appear as multiple physical devices to the hypervisor. Because each device is
directly assigned to an instance, it can bypass the hypervisor and virtual switch layer to achieve low latency
and performance matching in nonvirtualized environments. SR-IOV achieves this through the following
types of functions:
• Physical Function (PF): These are PCIe devices that have SR-IOV capabilities. PFs are managed and
congured in the same way as PCIe devices.
• Virtual Function (VF): These are lightweight PCIe functions that only process I/O. Because each VF is
derived from a PF, the device hardware limits the number of VFs a device can have. A VF shares one or
more hardware resources of the device, such as a memory or network port.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 48
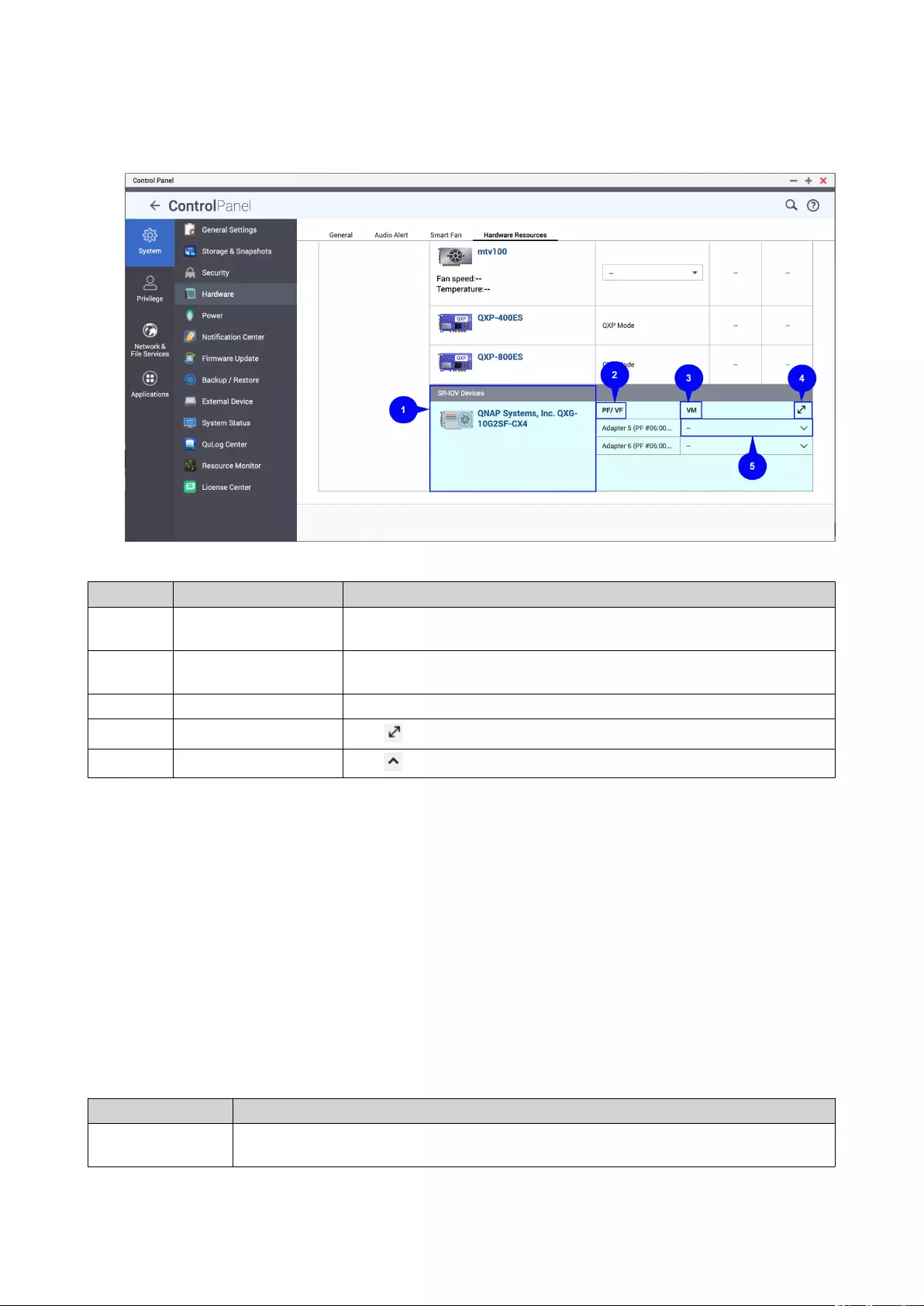
The following table lists all SR-IOV functions you can view in Hardware Resource:
No. Settings Description
1 SR-IOV Devices Lists all the SR-IOV devices that are mapped to your virtual machine
(VM).
2 PF/VF Displays the physical function (PF) or virtual function (VF) congured
to the SR-IOV device.
3 VM Shows the virtual machines that are mapped to the PF or VF.
4 Resize Click to enlarge or minimize the SR-IOV device panel window.
5 Show or Hide Click to show or hide the list of SR-IOV device details.
For details on how to congure an SR-IOV device to a VM, see the Virtualization Station user guide.
Power
You can congure Energy-using Products (EuP) and Wake-on-LAN (WOL) modes, select a NAS behavior after
power outage, and specify power schedules.
Conguring EuP Mode
Energy-using Products (EuP) is a directive designed to improve energy eciency of electrical devices, reduce
use of hazardous substances, and improve environment-friendliness of the product.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Power > EuP Mode Conguration .
2. Select a mode.
Mode Description
Enable When enabled, Wake-on-LAN, power recovery, and power schedule settings are
disabled. The NAS keeps power consumption below 1W when powered o.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 49

Mode Description
Disable When disabled, power consumption of the NAS is slightly higher than 1W when
powered o. EuP mode is disabled by default.
3. Click Apply.
Enabling or Disabling Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
You can power on the NAS remotely using the Wake-on-LAN (WOL) protocol in Qnder. This feature is
enabled by default.
Important
If the power cable is disconnected when the NAS is powered o, WOL will not work until
the NAS has been manually powered on.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Power > Wake-on-LAN (WOL) .
2. Select Enable or Disable.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring the Power Recovery Settings
This feature allows you to congure the power on and o status of the NAS after a power outage.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Power > Power Recovery .
2. Select a power recovery setting.
• Restore the previous NAS power state.
• Turn on the NAS automatically.
• Keep the NAS turned o.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring the Power Schedule
This feature allows you to schedule automatic system power on, power o, and restarts at specied times.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Power > Power Schedule .
2. Select Enable schedule.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 50
Task User Action
Add a scheduled action Note
One schedule is shown by default.
a. Click Add.
b. Select the following.
•Action: Select whether you want to shut down, restart, or turn
on the NAS.
•Schedule Type: Select the frequency of the action.
•Hour and Minute: Select the time of day to perform the action.
Remove a scheduled action a. Select one or mutliple schedules.
b. Click Remove.
4. Optional: Select Postpone scheduled restart/shutdown when a replication job is in progress.
5. Click Apply.
External Device
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
The NAS supports connecting to uninterruptible power supply (UPS) devices to protect the NAS from
abnormal system shutdowns caused by power disruptions.
NAS Behavior During a Power Outage
The following table describes the possible scenarios during a power outage and the corresponding NAS
behavior.
Phase Scenario NAS Behavior
Phase 1: From the start of the
power outage until the end of the
specied waiting time
The power outage occurs. The NAS detects the remaining
UPS power.
The UPS power is greater than
15%.
Depending on your UPS settings,
the NAS powers o or switches
to auto-protection mode after the
specied waiting time elapses.
The UPS power is less than 15%. After 30 seconds, the NAS
automatically powers o or
switches to auto-protection mode
regardless of the specied waiting
time.
The power is restored. The NAS remains functional.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 51
Phase Scenario NAS Behavior
Phase 2: From the end of the
specied waiting time until the
UPS runs out of power
The power is not restored, and the
NAS is in auto-protection mode.
The NAS stops all running
services. All shared folders and
iSCSI LUNs become inaccessible.
The power is not restored, and the
NAS is powered o.
The NAS remains powered o.
The power is restored, and the
NAS is in auto-protection mode.
The NAS restarts and resumes its
previous state.
The power is restored, and the
NAS is powered o.
The NAS remains powered o.
Phase 3: From the moment the
UPS runs out power until the
power is restored
The power is not restored, and the
NAS is in auto-protection mode.
The NAS powers o.
The power is not restored, and the
NAS is powered o.
The NAS remains powered o.
The power is restored. The NAS applies the specied
power recovery settings.
UPS Events and Corresponding NAS Behavior
The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) events handled by the NAS during power disruptions include
OnLine (OL), OnBattery (OB), OnSmartBoost (OSB), OFF (OFF), and OnBatteryTest (OBT). The NAS performs
auto-protection or shutdown mode depending on the detected UPS status and your congured power
failure settings. The following table describes the events and the corresponding NAS behavior.
UPS Event Denition NAS Status NAS Action
OnLine (OL) The UPS is operating normally. Normal None
OnSmartBoost
(OSB)
The UPS is operating on smart
boost mode.
Normal None
OnBatteryTest
(OBT)
The UPS is in battery test mode. Normal None
OnBattery (OB) The UPS is operating on the
backup battery.
Abnormal The NAS enters auto-protection or
shuts down.
OFF (OFF) The UPS is not operating. Abnormal The NAS powers o.
Conguring the UPS Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > External Device > UPS .
2. Select one of the following options and congure the settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 52
Mode User Actions
USB connection a. Connect the UPS to the NAS using a USB cable.
b. Select USB connection.
c. Choose one of the following options.
• Power o the server after the power fails for a specied time period
• Allow the NAS to enter auto-protection mode after the power fails for a
specied time period
Note
In auto-protection mode, the NAS stops all services and
unmounts all volumes to protect your data. After the power
is restored, the NAS restarts and resumes normal operation.
d. (Optional) Select Enable network UPS master and then specify the IP
addresses to which QTS sends notications in the event of power failure.
Note
This option can only be selected when the UPS is connected to
the NAS via USB.
SNMP connection a. Connect the UPS to the same network as the NAS.
b. Select SNMP connection.
c. Specify the IP address of the UPS.
d. Congure the SNMP community.
e. Choose one of the following options.
• Power o the server after the power fails for a specied time period
• Allow the NAS to enter auto-protection mode after the power fails for a
specied time period
Network standby UPS a. Connect the UPS to the same network as the NAS.
b. Select Network UPS slave.
c. Specify the IP address of the UPS server.
d. Choose one of the following options.
• Power o the server after the power fails for a specied time period
• Allow the NAS to enter auto-protection mode after the power fails for a
specied time period
3. Click Apply.
Firmware Update
Important
If the SQL server is enabled during the rmware update in QTS 5.0 or later versions, the
system will automatically download the MariaDB 5 app and migrate the SQL server data to
MariaDB.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 53
For details, see Conguring the MariaDB Database.
QNAP recommends keeping your NAS rmware up to date. By default, QTS will check for updates
automatically every day. This ensures that your NAS can benet from new QTS software features, security
updates, enhancements, and bug xes.
You can update the NAS rmware using one of the following methods:
Update Method Description
Using Live Update Firmware updates are immediately and automatically detected by QTS.
For details, see Checking for Live Updates.
Using Auto Update You can congure QTS to periodically check for rmware updates
and automatically download and install the specied rmware update
version.
For details, see Updating the Firmware Automatically.
Using Manual Update You can check for latest device rmware updates on the QNAP
website, download the rmware update to a computer, and manually
install the rmware update onto your device.
For details, see Updating the Firmware Manually.
Using Qnder Pro If your device is connected to the local area network, you can use
Qnder Pro to check and install the latest rmware updates.
For details, see Updating the Firmware Using Qnder Pro.
Firmware Update Requirements
Your device must meet the following requirements to perform a rmware update:
Settings Requirements
Hardware settings • A computer
Important
A computer is required for updating the rmware
manually or through Qnder Pro.
• Ethernet cables
Important
QNAP recommends updating the rmware using
wired Ethernet connections to ensure your network
connection is reliable during rmware updates.
System reboot QNAP recommends rebooting the NAS system before the rmware
backup.
Administrator privileges You must be a NAS administrator or have admin priveleges to update
rmware.
Stop NAS operations QNAP recommends stopping all other NAS operations before the
rmware update. The NAS must be restarted for the rmware update
to take eect and may disrupt ongoing NAS services or operations.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 54
Settings Requirements
Device model name Ensure you have the correct NAS model name. You can nd the NAS
model name using the following methods:
• Locate the model name on a sticker on the bottom or rear of your
device.
• Log on to your device to nd the model name.
Firmware version If you are updating the rmware using Manual Update or Qnder
Pro, ensure the selected rmware version is correct for your device
model.
Checking for Live Updates
Warning
• To prevent data loss, QNAP recommends backing up all data on your device before
updating the rmware. For details about data backup, see Backup/Restore.
• Do not power o your device during the rmware update process.
Important
• Make sure you read through the Firmware Update Requirements before updating the
rmware.
• The update may require several minutes or longer, depending on your hardware
conguration and network connection.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Firmware Update > Live Update .
2. Click Check for Update.
QTS checks for available rmware updates. You can choose to update QTS if there is an available
update.
3. Click Apply.
4. Optional: Select one or more of the following options.
• Automatically check if a newer version is available when logging into the NAS web administration
interface.
• Join the QTS Beta program to receive beta update notications.
Note
Joining the QTS Beta program allows you to use the latest QTS features and applications before
they are ocially released.
5. Click Apply.
Updating the Firmware Automatically
When you enable auto update, it ensures the operating system automatically downloads the most stable
and comprehensive version of the rmware. QNAP recommends enabling this feature for optimal rmware
stability and security.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 55
Warning
• To prevent data loss, QNAP recommends backing up all data on your device before
updating the rmware. For details about data backup, see Backup/Restore.
• Do not power o your device during the rmware update process.
Important
• Make sure you read through the Firmware Update Requirements before updating the
rmware.
• The update may require several minutes or longer, depending on your hardware
conguration and network connection.
• All ongoing tasks will be suspended during the auto update.
• QNAP recommends enabling this feature after testing the Checking for Live Updates
feature on your device.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Firmware Update > Auto Update .
2. Specify the auto update time.
3. Select the auto update rmware version.
Note
QNAP recommends selecting the recommended version, which includes bug xes from
multiple releases for rmware auto update.
4. Click Apply.
• You will receive email notications about available rmware updates.
• QTS automatically downloads the available stable version rmware during the specied update
time.
Updating the Firmware Manually
Warning
• To prevent data loss, QNAP recommends backing up all data on your device before
updating the rmware. For details about data backup, see Backup/Restore.
• Do not power o your device during the rmware update process.
Important
• Make sure you read through the Firmware Update Requirements before updating the
rmware.
• The update may require several minutes or longer, depending on your hardware
conguration and network connection.
1. Download the NAS rmware.
a. Go to http://www.qnap.com/download.
b. Select the number of drive bays on your NAS model.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 56
c. Select your NAS model.
d. Read the release notes and conrm the following:
• The NAS model matches the rmware version.
• Updating the rmware is necessary.
• Check for any additional rmware update setup instructions.
e. Ensure that the product model and rmware are correct.
f. Select the download server based on your location.
g. Download the rmware package.
h. Click Browse.
i. Select a folder.
j. Save the downloaded rmware package.
k. Extract the rmware package le.
2. Go to Control Panel > System > Firmware Update > Update System .
3. Click Browse and then select the extracted rmware package le.
4. Click Update System.
A conrmation message window appears.
5. Click OK.
The device is immediately restarted.
Note
You can go to Control Panel > QuLog Center > Local Device > System Event Logs to check if
the rmware installation was successful.
Updating the Firmware Using Qnder Pro
Warning
• To prevent data loss, QNAP recommends backing up all data on your device before
updating the rmware. For details about data backup, see Backup/Restore.
• Do not power o your device during the rmware update process.
Important
• Make sure you read through the Firmware Update Requirements before updating QTS.
• The update may require several minutes or longer, depending on your hardware
conguration and network connection. Do not power o the NAS during the update.
1. Download the NAS rmware.
a. Go to http://www.qnap.com/download.
b. Select the number of drive bays on your NAS model.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 57
c. Select your NAS model.
d. Read the release notes and conrm the following:
• The NAS model matches the rmware version.
• Updating the rmware is necessary.
• Check for any additional rmware update setup instructions.
e. Ensure that the product model and rmware version are correct.
f. Download the rmware package.
g. Extract the rmware package le.
2. Open Qnder Pro.
Qnder Pro displays a list of NAS devices on your network.
3. Select a NAS model from the list.
4. Right click the device model on the list and then select Update Firmware .
The Firmware Update window appears.
5. Specify your QTS username and password.
Qnder Pro displays the Update Firmware screen.
6. Select one of the following rmware update methods:
Methods Steps
Update rmware manually a. Click Path of rmware package le.
b. Click Browse.
c. Locate the downloaded rmware package le.
d. Click OK.
Update rmware automatically a. Click Automatically update the rmware to the latest version.
b. Qnder Pro searches for the latest rmware update.
7. Click Start.
Backup/Restore
QTS provides system backup and restore features to help protect your data in the event of data loss or
system failure.
Backing Up System Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Backup/Restore > Backup/Restore Settings .
2. Click Backup.
QTS exports the system settings as a BIN le and downloads the le to your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 58

Restoring System Settings
Warning
If the selected backup le contains user or user group information that already exists on
the NAS, QTS will overwrite the duplicate information.
1. Go to Control Panel > System > Backup/Restore > Backup/Restore Settings .
2. Click Browse.
3. Select a valid BIN le that contains the QTS system settings.
4. Click Restore.
System Reset and Restore to Factory Default
QTS provides several options for resetting or restoring the NAS to its default state.
Important
• QNAP recommends backing up your data before performing this task.
• To protect your device from attacks, QNAP recommends disabling the default "admin"
account after a system reset. To disable the account, change the default admin
password, log out of QTS, and then log in to QTS with another admin account.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 59
Option Description Steps
Basic system reset This resets the following settings
to the default values without
deleting the user data stored on
the disks.
• System administrator
password: MAC address of
adapter 1 without special
characters (all letters must be
uppercase). For example, if
the MAC address of adapter 1
is 11:22:33:AA:BB:CC, then the
default admin password will
be 112233AABBCC.
Tip
You can nd the MAC
address of adapter 1
using Qnder Pro. It is
also printed on a sticker
on the device as "MAC1".
• TCP/IP conguration:
• Obtain IP address
settings automatically via
DHCP
• Disable jumbo frames
• System port: 8080 (system
service port)
• Security level: Low (Allow all
connections)
• LCD panel password: (blank)
• VLAN: Disabled
• Service binding: All NAS
services can run on all
available network interfaces.
1. Power on the NAS.
2. Press and hold the reset
button for 3 seconds.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 60
Option Description Steps
Advanced system reset This performs a basic system
reset and then restores the QTS
default settings, deleting all users,
user groups, and shared folders
previously created. The user data
stored on the disks is retained.
Note
To retrieve old data
after an advanced system
reset, re-create the
previous folder structure
on the NAS.
Perform an advanced system
reset using one of the following
methods.
• Using QTS:
a. Go to Control Panel
> System > Backup/
Restore > Restore to
Factory Default .
b. Click Reset Settings.
c. Choose to restart or shut
down the NAS after the
system is reset.
d. Click OK.
• Using the reset button:
a. Power on the NAS.
b. Press and hold the reset
button for 10 seconds.
Restore factory default settings
and format all volumes
This restores the default system
settings and formats all disk
volumes.
1. Go to Control Panel > System
> Backup/Restore > Restore
to Factory Default .
2. Click Restore Factory
Defaults & Format All
Volumes.
Important
Selecting Restore
Factory Defaults &
Format All Volumes will
delete all data on the
NAS. To retain all les
and data on the hard
drive, see Reset to default
settings.
3. Choose to restart or shut
down the NAS after the
system is reset.
4. Click OK.
Reset to default settings This restores the default system
settings without deleting the user
data.
1. Go to Control Panel > System
> Backup/Restore > Restore
to Factory Default .
2. Click Reset Settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 61
Option Description Steps
Reinitialize the NAS This deletes all data on the disks
and reinstalls QTS.
1. Go to Control Panel > System
> Backup/Restore > Restore
to Factory Default .
2. Click Reinitialize NAS.
3. Choose to restart or shut
down the NAS after the NAS is
reinitialized.
4. Click OK.
Restoring the Settings of a Default Shared Folder
Shared folders are returned to default settings after resetting a NAS to factory default. You must manually
restore the settings of default shared folders.
Important
You must select Reset Settings when restoring the device to retain all les and data on
your drive.
1. Go to Control Panel > General Settings .
2. Select the following options:
•Enable HTTP compression
•Enable secure connection (HTTPS)
•Do not allow QTS embedding in IFrames
3. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders .
4. Go to Others > Restore Default Shared Folders .
All restored shared folders are listed in the Shared Folders table.
Restoring the Settings of a Non-Default Shared Folder
Non-default shared folders are manually created shared folders. Settings of all shared folders are restored to
default settings after resetting the NAS to factory default and must be manually restored.
Important
You must select Reset Settings when restoring the device to retain all les and data on
your drive.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders .
2. Select Create > Shared Folder .
3. Enter the Folder Name.
4. Select Enter path manually.
5. Select the folder path.
6. Select Create.
The non-default shared folders are restored to File Station.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 62
Monitoring System Status and Resource Monitor
You can monitor the system statuses and consumed resources respectively in System Status and Resource
Monitor.
System Status
You can check the status of your NAS in Control Panel > System > System Status .
Section Description
System Information This screen displays basic system information, including the server name,
model name, CPU, Intel QuickAssist Technology (Intel QAT) support, serial
number, BIOS version, memory, dual-channel memory support, rmware
version, system up time, time zone, and lename encoding.
Note
• Intel QuickAssist Technology support only appears
when it is detected by QTS.
• Dual-channel memory support only appears in NAS
models with this feature.
Network Status This screen displays the current network settings of each network interface.
System Service This screen displays the current status of system services, such as antivirus,
networking services, DDNS services, domain controllers, multimedia
management, data backup management, surveillance management,
remote servers, and VPN servers.
Hardware Information This screen displays NAS hardware information, such as CPU usage,
memory, disk temperature, power supply unit (PSU) status, and system fan
speed.
Resource Monitor
You can monitor the status of your NAS in Control Panel > System > Resource Monitor .
Resource Monitor displays information and statistics about hardware usage and system resources.
Section Description
Overview This screen provides a general summary of CPU usage, memory usage,
network usage, and ongoing processes on the NAS.
System Resource This screen uses line charts to display CPU usage, memory usage,
network usage, and graphics card usage (if supported and installed) over
time.
You can hover the mouse pointer over a line chart to view the hardware
usage at a specic point in time.
Tip
You can click More ( ) and then select Settings to
specify the time interval on the line charts.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 63
Section Description
Storage Resource This screen uses line charts to display the activities of volumes, LUNs,
storage pools, RAID groups, and disks on the NAS over time. This screen
also summarizes the storage usage of each volume.
You can hover the mouse pointer over a line chart to view the storage
activity at a specic point in time.
Processes This screen displays all ongoing background processes and provides
information about each process, such as its current status, CPU usage,
and memory usage.
Tip
You can enable Group by Applications to group related
processes together (for example, all the processes
related to an application or a system feature). You can
also sort information in ascending or descending order,
column category, show or hide columns, and choose to
Collapse All or Expand All running processes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
System Settings 64
4. Privilege Settings
Go to Control Panel > Privilege to congure privilege settings, disk quotas, and domain security on the
NAS.
Users
Default Administrator Account
The admin user account is the default administrator account. It can congure settings, create users, and
install applications. You cannot delete this account. To prevent malicious actors from compromising your
system due to easy passwords, QNAP strongly recommends changing the default admin password, creating
another administrator account or logging in with an existing admin account, and disabling the default
admin account. A new administrator account can perform the same actions as the default administrator
account.
The default admin account must be enabled in two specic scenarios. First, if you want to access the QNAP
turbo NAS via Secure Shell (SSH) or Telnet, and second, if you're going to access Console Management.
Creating an Administrator Account
Note
Create another administrator account before disabling the default admin account.
1. Log in as admin.
2. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
3. Click Create > Create a User .
The Create a User window appears.
4. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Prole photo Optional: Upload a prole photo for the user.
User Description (optional) Specify a user description that contains a maximum of 50 characters.
Username Specify a username that contains 1 to 32 characters from any of the
following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Multi-byte characters: Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian
• Special characters: . - _ ~ ! @ # $ % ^ & ( ) { }
Password Specify a password that contains a maximum of 64 ASCII characters.
Phone number (optional) Specify a phone number that will receive SMS notications from QTS.
Note
Other NAS users might be able to see this information.
If you do not want to share this information, leave the
eld blank.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 65
Field Description
Email (optional) Specify an email address that will receive notications from QTS.
For details, see Email Notications.
Note
Other NAS users might be able to see this information.
If you do not want to share this information, leave the
eld blank.
Send a notication mail to the
newly created user (optional)
When selected, QTS sends a message that contains the following
information to the specied email address:
• URLs for connecting to the NAS
Tip
You can edit the notication message.
5. Add the user to one or more user groups.
a. Under User Group, click Edit.
b. Select administrators.
6. Optional: Specify shared folder permissions for the user.
a. Under Shared Folder Permission, click Edit.
b. Select the shared folder permissions for the user.
c. Optional: Select Apply changes to subfolders.
7. Optional: Specify application privileges for the user.
a. Under Edit Application Privilege, click Edit.
b. Select application permissions for the user.
By default, administrator accounts can access to all applications.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to applications and network services that the user does not
require. Users without privileges to specic applications will not see it on their main menu.
8. Optional: Set a quota for the user.
Note
This option is only available when quotas are enabled.
a. Under Quota, click Edit.
b. Set the quota.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user.
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user.
•Use group quotas: Group quota settings apply to the user.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 66
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas. For details, see Quota Conicts.
9. Click Create.
Disabling a Default Administrator Account
1. Log in as an administrator.
Note
Do not use the "admin" account.
2. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
3. Click .
The Edit Account Prole window opens.
4. Select Disable this account.
5. Optional: Select one of the following options.
Option Description
Now Disables the account immediately.
Expiry date Disables the account on the specied date.
6. Click OK.
Creating a Local User
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Click Create > Create a User .
The Create a User window appears.
3. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Prole photo Optional: Upload a prole photo for the user.
User Description (optional) Specify a user description that contains a maximum of 50 characters.
Username Specify a username that contains 1 to 32 characters from any of the
following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Multi-byte characters: Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian
• Special characters: . - _ ~ ! @ # $ % ^ & ( ) { }
Password Specify a password that contains a maximum of 64 ASCII characters.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 67
Field Description
Phone number (optional) Specify a phone number that will receive SMS notications from QTS.
Note
Other NAS users might be able to see this information.
If you do not want to share this information, leave the
eld blank.
Email (optional) Specify an email address that will receive notications from QTS.
For details, see Email Notications.
Note
Other NAS users might be able to see this information.
If you do not want to share this information, leave the
eld blank.
Send a notication mail to the
newly created user (optional)
When selected, QTS sends a message that contains the following
information to the specied email address:
• URLs for connecting to the NAS
Tip
You can edit the notication message.
4. Optional: Add the user to one or more user groups.
a. Under User Group, click Edit.
b. Select one or more user groups.
5. Optional: Specify shared folder permissions for the user.
a. Under Shared Folder Permission, click Edit.
b. Select the shared folder permissions for the user.
c. Optional: Select Apply changes to subfolders.
6. Optional: Specify application privileges for the user.
a. Under Edit Application Privilege, click Edit.
b. Select application permissions for the user.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to applications and network services that the user does not
require. Users without privileges to specic applications will not see it on their main menu.
7. Optional: Set a quota for the user.
Note
This option is only available when quotas are enabled.
a. Under Quota, click Edit.
b. Set the quota.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 68
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user.
•Use group quotas: Group quota settings apply to the user.
Note
Individual quotas may override group quotas. For details, see Quota Conicts.
8. Click Create.
Creating Multiple Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Click Create > Create Multiple Users .
The Multiple Users Creation Wizard appears.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify the following information.
Field Description
User Name Prex Specify a username that contains a maximum of 23 ASCII characters
and that does not:
• Contain a space
• Begin with the following characters: - # @
• Contain the following characters: @ " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '
This prex will be included before all usernames.
Example: test
User Name Start No Specify a start number with a maximum of 8 digits.
Example: 1
Note
QTS removes leading zeros in starting numbers. For
example, 001 becomes 1.
Number of Users Specify the number of users (1–4095).
Example: 5
Password Specify a password that contains a maximum of 64 ASCII characters.
Note
The username format is [username prefix][user number]. The specied start number
and number of users determine the user number.
Using the examples, the users created will have the following usernames: test1, test2,
test3, test4, and test5.
5. Click Next.
The Create Private Network Share screen appears.
6. Optional: Create a private network share for each user.
a. Select Yes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 69
b. Click Next.
c. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Hide network drive Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who know the
specic path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows le locking mechanism that facilitates
caching and access control to improve performance. This feature is enabled
by default and should only be disabled in networks where multiple users
simultaneously access the same les.
Disk Volume Select the data volume where the private network share will be created.
To continue without creating a private network share, select No.
7. Click Next.
QTS creates the user accounts and adds them to the displayed user list.
8. Click Finish.
User Account Lists
The NAS supports importing user accounts from TXT, CSV, and BIN les. The les contain user account
information including usernames, passwords, user groups, and quota settings.
File Format Description
TXT Create user account lists using a text editor. For details, see Creating a TXT User
File.
CSV Create user account lists using a spreadsheet editor. For details, see Creating a
CSV User File.
BIN QNAP NAS devices can export user account information, including quota
settings, to BIN les. For details, see Exporting Users.
Creating a TXT User File
1. Create a new le in a text editor.
2. Specify user information in the following format.
Username,Password,Quota (MB),Group Name
Important
• Separate values using commas.
• Specify a quota between 100 MB and 2048 GB (2048000 MB).
Note
The system only accepts quotas in MB. GB values must be expressed in MB.
• Specify information for only one user on each line.
Example:
John,s8fk4b,100,Sales
Jane,9fjwbx,150,Marketing
Mary,f9xn3ns,390,RD
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 70
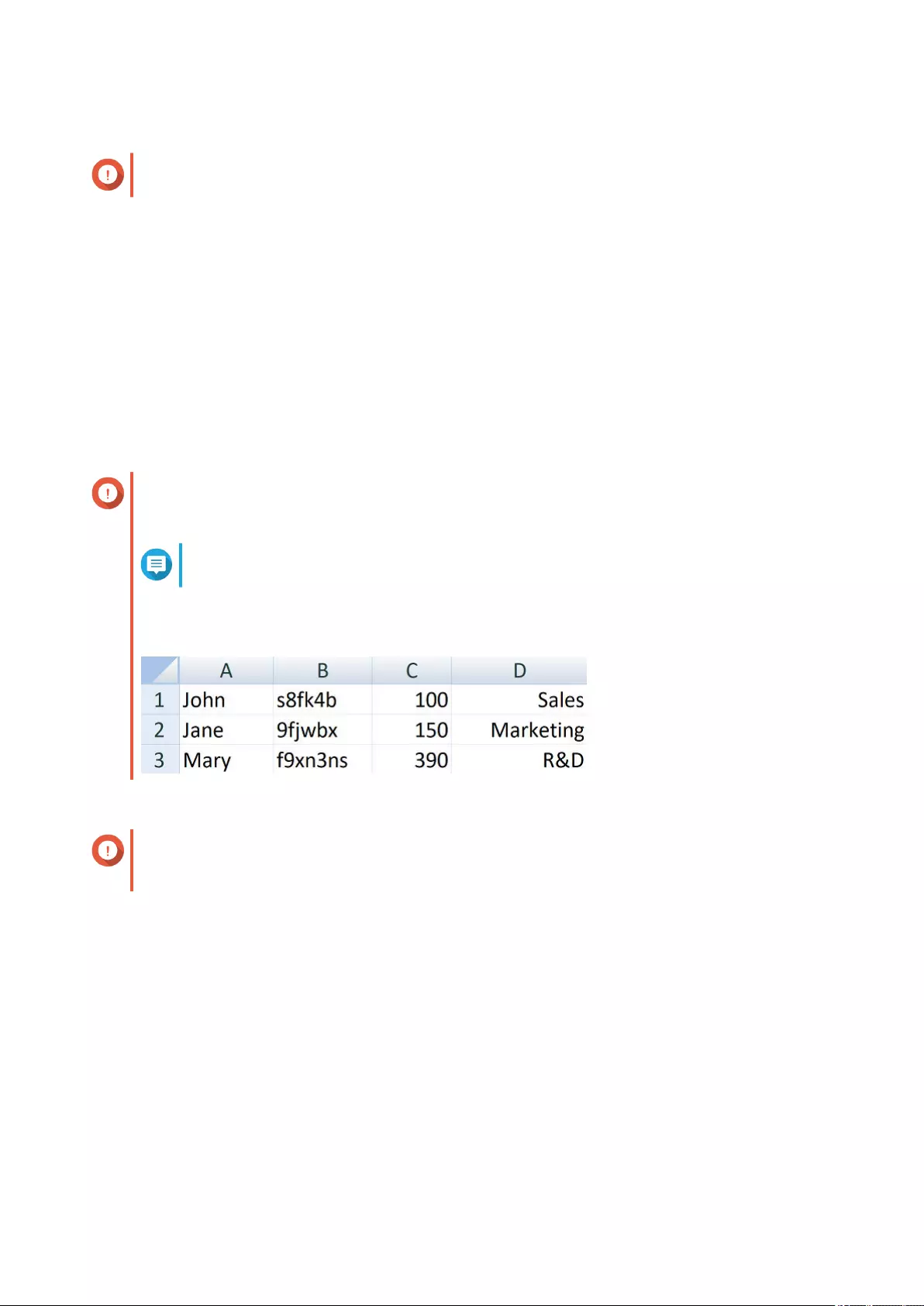
3. Save the list as a TXT le.
Important
If the list contains multi-byte characters, save the le with UTF-8 encoding.
Creating a CSV User File
1. Create a new workbook in a spreadsheet editor.
2. Specify user information in the following format.
• column A: Username
• column B: Password
• column C: Quota (MB)
• column D: Group name
Important
• Specify a quota between 100 MB and 2048 GB (2048000 MB).
Note
The system only accepts quotas in MB. GB values must be expressed in MB.
• Specify information for only one user in each row.
Example:
3. Save the workbook as a CSV le.
Important
If the list contains multi-byte characters, open the le using a text editor and then save with
UTF-8 encoding.
Importing Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Click Create > Import/Export Users .
The Import/Export Users window appears.
3. Select Import user and user group settings.
4. Optional: Select any of the following options.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 71
Field Description
Send a notication mail to
the newly created user
When selected, QTS sends a message that contains the following
information to the specied email address of the user.
• Username and password
• URLs for connecting to the NAS
Important
To send email notications, ensure that you have
congured an SMTP server. For details, see Conguring an
Email Notication Server.
Overwrite duplicate users When selected, QTS overwrites existing user accounts that have duplicates
on the imported user account list.
5. Click Browse, and then select the le that contains the user account list.
Important
Ensure that you are importing a valid QTS user account list le to avoid parsing errors.
For details, see User Account Lists.
6. Click Next.
File Type User Action
TXT or CSV The Import User Preview screen appears.
Check the status of the user account list.
Important
The Status indicates whether any information is invalid. If
any information is invalid, the user account list will not be
imported successfully.
BIN The following screen describes the Overwrite duplicate users feature.
7. Click Next.
QTS imports the user account list.
8. Click Finish.
Exporting Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Click Create > Import/Export Users .
The Import/Export Users window appears.
3. Select Export user and user group settings.
4. Click Next.
QTS exports the user account list to your computer as a BIN le.
Tip
You can use this le to import users to another NAS running QTS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 72
Modifying User Account Information
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Locate a user.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Change password a. Under Action, click .
The Change Password window appears.
b. Specify a password that contains a maximum of 64 ASCII characters.
c. Verify the password.
d. Click Apply.
Edit account prole a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Account Prole window appears.
b. Edit the settings.
The Edit Account Prole window provides the following settings not
included in the Create a User window:
•Description (optional): Specify a user description that contains a
maximum of 50 characters.
•Disallow the user to change password: When selected, QTS
prevents the user from changing the password.
•Disable this account: Select this option to disable the user
account. You can either select to disable the account Now or
specify an Expiry Date.
Note
QNAP recommends users to create a new administrator
account and disable the "admin" account. To create an
administrator account, see Creating an Administrator
Account.
c. Modify the quota for the user.
Note
This option is only available when quotas are enabled.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user.
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user.
•Use group quotas: Group quota settings apply to the user.
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas.
d. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 73
Task User Action
Edit user group membership a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User's Groups window appears.
b. Select or deselect user groups.
c. Click Apply.
Edit shared folder
permissions
a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permission window appears.
b. Edit the user's permissions for each shared folder.
c. Optional: Select Apply changes to subfolders.
d. Click Apply.
Edit application privileges a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Application Privileges window appears.
b. Select the applications that the user is allowed to access.
c. Click Apply.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to applications and
network services that the user does not require.
By default, administrator accounts have access to all
applications.
Deleting Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Select the users to delete.
Note
Default user accounts cannot be deleted.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
4. Optional: Select Also delete the selected user(s)' home folders and data.
5. Click Yes.
Home Folders
Enabling home folders creates a personal folder for each local and domain user on the NAS. When a home
folder is created, the user's home folder appears as a shared folder called home. Users can access their
home folder through Microsoft networking, FTP, and File Station.
All user home folders are located in the homes shared folder. By default, only the administrator can access
this folder. If home folders are disabled, home folders become inaccessible to users. However, the folders
and les they contain are not deleted from the NAS. The administrator can still access the homes folder and
each user's home folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 74
Enabling Home Folders
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
2. Click Home Folder.
The Home Folder window appears.
3. Select Enable home folder for all users.
4. Select a volume.
Home folders are stored on the selected volume.
5. Click Apply.
User Groups
A user group is a collection of users with the same access rights to les or folders. Administrators can create
user groups to manage folder permissions for multiple users.
Default User Groups
User Group Description
administrators Users in this group can congure settings, create users, and install applications.
You cannot delete this group.
everyone Users in this group can only view and modify les. This group contains all local
user accounts and can be used to grant shared folder permissions to all local
user accounts. You cannot delete this group.
Creating a User Group
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups .
2. Click Create.
The Create a User Group window appears.
3. Specify the User group name.
The user group name can contain 1 to 128 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Multi-byte characters: Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian
• Dashes (-)
4. Optional: Specify a description that contains a maxiumum of 128 characters.
5. Optional: Add users to the user group.
a. Under Assign users to this group, click Edit.
b. Select one or more users.
6. Optional: Specify shared folder permissions for the user group.
a. Under Edit shared folder permissions, click Edit.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 75
b. Select the permissions for each shared folder.
For details, see Conicts in Shared Folder Permissions.
7. Optional: Set a quota for the user group.
Note
This option is only available when quotas are enabled.
For details, see Enabling Quotas.
a. Under Quota, click Edit.
b. Set the quota.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user group.
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user group.
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas.
For details, see Quota Conicts.
8. Click Create.
A dialog box appears.
9. Choose whether group quotas will be applied to users in the group.
Option Description
Yes Applies group quota settings to each user in the group.
No Retains individual quota settings for users in the group.
For details on group quota settings, see Quota Conicts.
Modifying User Group Information
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups .
2. Locate a user group.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 76
Task User Action
Edit user group details a. Under Action, click .
The View Group Details window appears.
b. Modify the description.
c. Modify the quota.
Note
• You cannot modify the quota in the default user group.
• This option is only available when quotas are enabled.
For details, see Enabling Quotas.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user group.
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user group.
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas.
For details, see Quota Conicts.
d. Click OK.
Edit user group members a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User Group window appears.
b. Select or deselect users.
c. Click Apply.
Edit shared folder
permissions
a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permissions window appears.
b. Edit the user group's permissions for each shared folder.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
c. Click Apply.
Important
Group-level permissions may override user-level
permissions. For details, see Conicts in Shared Folder
Permissions.
Deleting User Groups
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups .
2. Select the user groups to delete.
Note
Default user groups cannot be deleted.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 77
4. Click OK.
Shared Folders
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders to congure settings and permissions for shared folders.
Default Shared Folders
QTS automatically creates the following shared folders to help you organize data on your NAS.
Important
You cannot delete or modify certain properties of default shared folders.
Folder Description
Download This is the default folder for Download Station. The folder stores
content downloaded in QTS. You can assign a dierent path for
downloads in Download Station.
Multimedia This is the default folder for multimedia apps. The folder stores
multimedia content such as photos, videos, and music. You can
manage this folder in the Multimedia Console utility in Control Panel >
Applications .
Public This folder can be used by any user account. The default permission of
this folder is Read Only. For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
Web This folder stores content from the Web Server utility, which you can
manage in Control Panel > Applications > Web Server .
Note
You must enable Web Server automatically to create
this default shared folder.
Restoring Default Shared Folders
You can restore default shared folders that were deleted.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder > Others .
2. Click Restore Default Shared Folders.
A warning message appears.
3. Click OK.
QTS restores the default shared folders.
Creating a Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Click Create, and then select Shared Folder.
The Create A Shared Folder window opens.
3. Specify the following information:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 78
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
The information is for your reference and is not used by QTS.
Disk Volume Specify the volume on which the shared folder will be created.
Qtier Auto Tiering When enabled, Qtier performs auto-tiering on data in the folder.
For details, see Qtier.
This setting is only available if you select a Qtier-enabled storage pool.
Tip
You can also enable auto-tiering from the Shared
Folders screen.
Path •Specify path automatically: Creates a new root folder on the
selected volume using the specied shared folder name.
•Enter path manually: Select an existing folder as the root folder.
4. Optional: Enable folder encryption.
a. Under Folder Encryption, select Encryption.
Folder encryption protects folder content against unauthorized data access when the drives are
physically stolen.
b. Specify the following information.
Field/Option Description
Input Password Specify a password that contains 8 to 32 characters except the
following: " $ : = \
This eld does not support multibyte characters.
Verify Password The password must match the previously specied password.
Save encryption key When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
When disabled, the administrator must unlock the folder after the NAS
restarts.
For details, see Unlocking a Shared Folder.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can
result in unauthorized data access if unauthorized
personnel are able to physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, all data will
become inaccessible.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 79
5. Click Next.
6. Optional: Specify the access permissions for users.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Congure properties.
Option Description
Guest Access Right Select the permission level assigned to users without a NAS
account.
Hide network drive Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users
who know the specic path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows le locking
mechanism that facilitates caching and access control to improve
performance. This feature is enabled by default and should only
be disabled in networks where multiple users simultaneously
access the same les.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled. Selecting this
option encrypts all Microsoft network communication using the
SMB3 protocol.
Enable Windows Previous Versions When enabled, the Previous Versions feature in Windows can be
used with the shared folder.
Enable Network Recycle Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle Bin to
administrators only for now
Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from
recovering or deleting les in the Recycle Bin.
Note
This option is available only when Enable
Network Recycle Bin is selected.
Enable sync on this shared folder Selecting this option allows this shared folder to be used with
Qsync. This option is only available if Qsync Central is installed on
the NAS.
Enable access-based share
enumeration (ABSE)
When enabled, users can only see the shared folders that they
have permission to mount and access. Guest account users must
enter a username and password to view shared folders.
Enable access-based enumeration
(ABE)
When enabled, users can only see the les and folders that they
have permission to access.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 80
Option Description
Set this folder as the Time Machine
backup folder (macOS)
When enabled, the shared folder becomes the destination folder
for Time Machine in macOS.
Important
• If space in the folder is insucient when
starting a new Time Machine backup, QTS
automatically deletes the oldest Time Machine
backup in the folder to free up space.
• You should disable Enable Network Recycle
Bin when Set this folder as the Time
Machine backup folder (macOS) is selected
to prevent automatically deleted Time
Machine backups from lling the recycle bin.
9. Click Finish.
Tip
Hovering your mouse underneath the columns Size, Folders, and Files displays the shared
folder's size, number of folders, number of les, and last update time.
Editing Shared Folder Properties
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate a shared folder.
3. Under Action, click .
The Edit Properties window appears.
4. Modify any of the following settings.
Important
A HybridMount shared folder can only modify comments, set the shared folder as a backup
folder, and enable access-based share enumeration and access-based enumeration.
Setting Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
The information is for your reference and is not used by QTS.
Disk Volume Specify the volume on which the shared folder will be created.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 81
Setting Description
Qtier Auto Tiering When enabled, Qtier performs auto-tiering on data in the folder.
For details, see Qtier.
This setting is only available if you select a Qtier-enabled storage pool.
Tip
You can also enable auto-tiering from the Shared
Folders screen.
Path Modify the folder path.
Hide network drive Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who
know the specic path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows le locking mechanism that
facilitates caching and access control to improve performance. This
feature is enabled by default and should only be disabled in networks
where multiple users simultaneously access the same les.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled. Selecting this
option encrypts all Microsoft network communication using the SMB3
protocol.
Enable Windows Previous
Versions
When enabled, the Previous Versions feature in Windows can be used
with the shared folder.
Enable Network Recycle Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle
Bin to administrators only for
now
Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from
recovering or deleting les in the Recycle Bin.
Note
This option is available only when Enable Network
Recycle Bin is selected.
Enable write-only access on FTP
connection
When enabled, only the admin has read and write access to the shared
folder. Other users will only be able to write to the folder.
Only allows applications to
access les using the long le
name format
When selected, applications can only use the long le name (LFN)
format to access les in the shared folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 82
Setting Description
Encrypt this folder Folder encryption protects folder content against unauthorized data
access when the drives are physically stolen.
Specify the following information.
a. Input Password
Specify a password that contains 8 to 32 characters except the
following: " $ : = \
This eld does not support multibyte characters.
b. Verify Password
The password must match the previously specied password.
c. Save encryption key
When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after
the NAS restarts.
When disabled, the administrator must unlock the folder after the
NAS restarts.
For details, see Unlocking a Shared Folder.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can
result in unauthorized data access if unauthorized
personnel are able to physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, all data will
become inaccessible.
Enable sync on this shared
folder
Selecting this option allows this shared folder to be used with Qsync.
This option is only available if Qsync Central is installed on the NAS.
Enable access-based share
enumeration (ABSE)
When enabled, users can only see the shared folders that they have
permission to mount and access. Guest account users must enter a
username and password to view shared folders.
Enable access-based
enumeration (ABE)
When enabled, users can only see the les and folders that they have
permission to access.
Set this folder as the Time
Machine backup folder (macOS)
When enabled, the shared folder becomes the destination folder for
Time Machine in macOS.
Important
• If space in the folder is insucient when starting
a new Time Machine backup, QTS automatically
deletes the oldest Time Machine backup in the
folder to free up space.
• You should disable Enable Network Recycle Bin
when Set this folder as the Time Machine
backup folder (macOS) is selected to prevent
automatically deleted Time Machine backups from
lling the recycle bin.
Migrate to Snapshot Shared
Folder
Migrate the shared folder to a snapshot shared folder.
For details, see Migrating to a Snapshot Shared Folder.
5. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 83

Refreshing a Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate a shared folder.
3. Under Action, click .
Removing Shared Folders
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Select the shared folders to remove.
Note
Default shared folders cannot be removed.
3. Click Remove.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Optional: Select Also delete the data.
5. Click Yes.
Enabling Daily Updates for Shared Folders
You can set a time for QTS to check the size and the number of folders and les for all of your shared folders.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder > Others .
2. Click Settings.
The Settings window opens.
3. Select Enable daily updates for shared folder size and the number of folders and les.
4. Select a time.
5. Click Apply.
Snapshot Shared Folders
A snapshot shared folder is a shared folder created on a dedicated volume and allows users to quickly
recover data by restoring a folder or reverting a volume from a snapshot. Users can also set folder quotas
for snapshot shared folders.
For details on snapshots, see Storage & Snapshots.
The snapshot shared folder feature requires a NAS that supports snapshots and contains at least 1 GB of
memory. For details on compatible models, see www.qnap.com/solution/snapshots.
Creating a Snapshot Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Click Create, and then select Snapshot shared folder.
The Create a Snapshot Shared Folder window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 84
3. Specify the following information:
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
Storage Pool Specify the storage pool where the shared folder will be created.
Space Allocation Select one of the following space allocation options:
•Thick provisioning
•Thin provisioning
Qtier Auto Tiering When enabled, Qtier performs auto-tiering on data in the folder.
This setting is only available if you select a Qtier-enabled storage pool.
Tip
You can also enable auto-tiering from the Shared
Folders screen.
Allocate folder quota You can allocate a folder quota for the snapshot shared folder.
4. Click Next.
5. Optional: Specify the access permissions for users.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
6. Optional: Congure properties.
For details, see Creating a Shared Folder.
7. Click Finish.
Migrating to a Snapshot Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Select the folder you want to migrate to a snapshot shared folder.
3. Click Migrate to Snapshot Shared Folder.
The Migrating shared folder to a snapshot shared folder wizard appears.
4. Select the location for the snapshot shared folder.
5. Click Next.
6. Optional: Free up storage pool space on the volume.
Note
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 85
If there is not enough storage space in the storage pool for the snapshot shared folder, the
Free Storage Pool Space screen appears.
Option User Action
Release unused guaranteed
snapshot space Note
This option is only available if guaranteed snapshot
space has been allocated to the storage pool.
a. Click Set up now.
The Snapshot Settings window appears.
b. Congure the snapshot settings to release space.
For details, see Storage & Snapshots.
c. Click OK.
Run a space reclaim to release
used space on thin volumes Note
This option is only available if the storage pool
contains a thin volume with reclaimable space.
a. Click Run now.
A dialog box appears.
b. Click OK to reclaim the available storage space.
QTS reclaims the used space.
A dialog box appears.
c. Click OK.
Convert a thick volume to a thin
volume to release unallocated
space
Note
This option is only available if the storage pool
contains a thick volume.
a. Select a volume to convert.
b. Click Run now.
The Convert to Thin Volume window appears.
Warning
Converting a volume deletes all existing snapshots on
the volume.
c. Click Apply.
QTS converts the volume.
7. Congure the snapshot shared folder.
Field Description
Qtier Auto Tiering When enabled, Qtier performs auto-tiering on data in the folder.
This setting is only available if you select a Qtier-enabled storage pool.
Tip
You can also enable auto-tiering from the Shared
Folders screen.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 86
Field Description
Space Allocation Select one of the following space allocation options:
•Thick provisioning
•Thin provisioning
Allocated space quota Specify a quota for the snapshot shared folder.
Tip
Click Set to Max to allocate all remaining storage pool
space to the volume.
8. Click Next.
9. Review the settings.
10. Click OK.
ISO Shared Folders
Users can mount ISO image les on the NAS as ISO shared folders and access them without having to burn
discs. By default, most NAS models support up to 256 ISO shared folders.
ISO Shared Folder Requirements
By default, most NAS models can support up to 256 ISO shared folders. However, some NAS models support
fewer than 256 ISO image les, depending on the number of Network Recycle Bin folders: Number of
supported ISO image les = 256 − 6 (default shared folders) − (number of Network Recycle Bin folders).
The following NAS models support fewer than 256 ISO image les.
NAS Model
TS-1x:
• TS-110
• TS-112
• TS-119
• TS-119P+
• TS-120
• TS-121
TS-2x:
• TS-210
• TS-212
• TS-219
• TS-219P
• TS-219P+
• TS-220
• TS-221
Other models:
• TS-410
Mounting an ISO File as a Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Click Create, and then select Create an ISO Share.
The Create an ISO Share window opens.
3. Select the source ISO image le to be mounted.
4. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 87
5. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• End with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '
Note
For ARM-based NAS models, ISO shared subfolder
names do not support Cyrillic characters. If a subfolder
name includes Cyrillic characters, it will not be
displayed correctly on the NAS.
Shared folders on macOS that include the character
"#" in their names cannot be mounted.
Hidden Folder Selecting Yes hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who know
the specic path can still access the folder.
Description Specify a description that contains a maximum of 128 ASCII characters.
6. Click Next.
7. Congure user access permissions and guest access rights to the ISO shared folder.
Type Option Description User Action
User access
permissions
Grant read-only
access right for
administrators only
Selecting this
option grants
administrator
accounts read-only
access to the ISO
shared folder.
a. Click Next.
b. Review the settings.
By User Selecting this
option allows you
to congure access
permissions to the
ISO shared folder at
the user level.
a. Click Next.
b. Congure the user account access
rights for the ISO shared folder.
c. Click Next.
d. Review the settings.
By User Group Selecting this
option allows you
to congure access
permissions to the
ISO shared folder
at the user group
level.
a. Click Next.
b. Congure the user group access
rights for the ISO shared folder.
c. Click Next.
d. Review the settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 88
Type Option Description User Action
Guest access
rights
Deny Access Selecting this
option denies
access to guest
accounts.
N/A
Read only Selecting this
option grants read-
only access to guest
accounts.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
8. Click Next.
QTS mounts the ISO le as a shared folder and then adds it to the Shared Folder screen.
9. Click Finish.
Shared Folder Permissions
Permission Description
Read Only (RO) The user or user group can read les in the shared folder, but not write
them.
Read/Write (RW) The user or user group can read and write les in the shared folder.
Note
If a user creates a shared link to a folder they no
longer have RW permissions to, anyone with that
shared link cannot access the folder.
Deny The user or user group cannot read or write les in the shared folder.
Editing Shared Folder Permissions
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate a shared folder.
3. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permission window appears.
4. Under Select permission type, select a permission type to edit.
5. Perform any of the following tasks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 89
Permission Type Description User Action
Users and groups
permission
Edit user and user
group permissions for
shared folders that can
be accessed through
Windows, macOS, FTP, and
File Station.
a. Specify permissions for each user and user group.
b. Optional: Add a user to the list of users with
permissions for the shared folder.
1. Click Add.
The Select users and groups window
appears.
2. Select the type of user or user group from the
drop-down menu in the upper left.
3. Specify the permissions for the users you want
to add.
4. Click Add.
QTS adds the users and their corresponding
permissions to the list.
c. Optional: Remove a user from the list of users with
permissions for the shared folder.
1. Click the user you want to remove.
2. Click Remove.
QTS removes the user from the list.
d. Optional: Modify guest access rights.
Under Guest Access Right, select the permission
type for guest accounts.
NFS host access Edit NFS host access rights
for shared folders.
a. Select Access right to enable NFS access rights.
Note
You can't select this for folders mounted
by HybridMount using SMB le protocol.
These folders do not support NFS host
access. However, you can still access the
NFS host access page.
b. Under Host / IP / Network, enter an IP address or
domain name.
c. Optional: Add an NFS host.
Under Allowed IP Address or Domain Name, click
Add.
QTS adds an entry to the list.
d. Optional: Delete an NFS host.
1. Select an NFS host from the list.
2. Click Delete.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 90
Permission Type Description User Action
Microsoft
Networking host
access
Specify which computers
can access shared
folders through Microsoft
Networking.
a. Add a Microsoft Networking host.
1. Click Add.
QTS adds an entry to the list.
2. Under Host / IP / Network, enter an IP
address or domain name.
b. Optional: Delete a Microsoft Networking host.
1. Select a Microsoft Networking host from the
list.
2. Click Delete.
6. Click Apply.
Conguring Advanced Folder Permissions
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Advanced Permissions .
2. Select any of the following options.
Option Description
Enable Advanced Folder
Permissions
When enabled, users can assign folder and subfolder permissions
to individual users and user groups.
Note
SMB/NFS mounted shared folders do not support
advanced folder permissions.
Enable Windows ACL support When enabled, users can only congure folder and subfolder
permissions from Windows File Explorer.
3. Click Apply.
Conicts in Shared Folder Permissions
When a user is assigned dierent permissions for a shared folder, QTS uses the following hierarchy to
resolve conicts.
1. No Access/Deny
2. Read/Write (RW)
3. Read Only (RO)
User Permission User Group Permission Actual Permission
No Access No Access No Access
Read Only No Access
Read/Write No Access
Not Specied No Access
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 91
User Permission User Group Permission Actual Permission
No Access Read Only No Access
Read Only Read Only
Read/Write Read/Write
Not Specied Read Only
No Access Read/Write No Access
Read Only Read/Write
Read/Write Read/Write
• Shared folders through
Samba/AFP: Read/Write
• Shared folders through NFS:
Read Only
Not Specied Read/Write
No Access Not Specied No Access
Read Only Read Only
Read/Write Read/Write
Not Specied No Access
Folder Aggregation
Users can aggregate shared folders on a Windows network and link them to a portal folder accessible on the
NAS. You can link up to 10 folders to a single portal folder.
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation to enable folder aggregation.
Note
• Folder aggregation is supported in Samba networks only. QNAP recommends folder
aggregation for a Windows Active Directory (AD) environment.
• If access permissions are assigned to portal folders, the NAS and remote servers must
be joined to the same AD domain.
Creating a Portal Folder
Note
Ensure that folder aggregation is enabled before performing the following steps. For
details, see Folder Aggregation.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation .
2. Under Folder Aggregation List, click Create a Portal Folder.
The Create a Portal Folder window appears.
3. Specify the following information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 92
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '
Hidden Folder Selecting Yes hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who know
the specic path can still access the folder.
Comment Specify a comment between 1 and 128 ASCII characters.
Users must login before
accessing the portal folder.
When selected, users must log in to the NAS with their username and
password before accessing the portal folder.
This prevents guest accounts from accessing the portal folder and
other user permission issues.
4. Click Apply.
Modifying Portal Folder Information
Note
Ensure that folder aggregation is enabled before performing the following steps. For
details, see Folder Aggregation.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation .
2. Locate a portal folder.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Edit portal folder properties a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Portal Folder window appears.
b. Edit the folder properties.
For details, see Creating a Portal Folder.
Congure the remote folder
link
a. Under Action, click .
The Remote Folder Link window appears.
b. Specify the Name, Host Name, and Remote Shared Folder for any
remote folder link.
4. Click Apply.
Deleting Portal Folders
Note
Ensure that folder aggregation is enabled before performing the following steps. For
details, see Folder Aggregation.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 93

1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation .
2. Select the portal folders that you want to delete.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
4. Click Yes.
Importing Folder Trees
Note
Ensure that folder aggregation is enabled before performing the following steps. For
details, see Folder Aggregation.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation .
2. Click Import/Export Folder Tree.
The Import/Export Folder Tree window appears.
3. Under Import Folder Tree, click Browse.
4. Select the le that contains the folder tree.
Important
Ensure that you are importing a valid QTS folder tree le to avoid parsing errors.
5. Click Import.
A warning message appears.
6. Click OK.
QTS imports the folder tree.
7. Click OK.
8. Click Finish.
Exporting Folder Trees
Note
Ensure that folder aggregation is enabled before performing the following steps. For
details, see Folder Aggregation.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Folder Aggregation .
2. Click Import/Export Folder Tree.
The Import/Export Folder Tree window appears.
3. Under Export Folder Tree, click Export.
QTS exports the folder tree to your computer as a BIN le.
Tip
You can use this le to import folder trees to another NAS running QTS.
4. Click Finish.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 94
Shared Folder Encryption
Shared folders on the NAS can be encrypted with 256-bit AES encryption to protect data. Encrypted shared
folders can be mounted with normal read/write permissions but can only be accessed using the authorized
password. Encrypting shared folders protects sensitive data from unauthorized access if the drives are
physically stolen.
Encrypting a Shared Folder
Note
• Default shared folders cannot be encrypted.
• The volume or path of an encrypted folder cannot be changed.
• Encrypted folders cannot be accessed through NFS.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate a shared folder.
3. Under Action, click .
The Edit Properties window appears.
4. Select Encrypt this folder.
5. Specify the following information.
Field/Option Description
Input Password Specify a password that contains 8 to 32 characters except the
following: " $ : = \
This eld does not support multibyte characters.
Verify Password The password must match the previously specied password.
Save encryption key When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
When disabled, users must unlock the folder after restarting the NAS.
For details, see Unlocking a Shared Folder.
Note
QNAP strongly recommends exporting and saving the
encryption key. For details, see Conguring Encryption
Settings.
The Folder Encryption window appears.
6. Review the information.
7. Click Yes.
Conguring Encryption Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate an encrypted shared folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 95
3.
Under Action, click .
The Encryption Management window appears.
Note
If the encrypted folder is locked, you must unlock it before conguring encryption settings. For
details, see Unlocking a Shared Folder.
4. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Download the encryption key
le
a. Go to Download.
b. Enter the encryption password.
c. Click OK.
QTS exports the encryption key le to your computer as a TXT.
Save the encryption key a. Go to Save.
b. Select Mount automatically on start up.
When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
c. Enter the encryption password.
d. Click OK.
QTS saves the encryption key.
Lock the shared folder a. Go to Lock.
b. Optional: Select Forget the saved key.
Note
When selected, users must unlock the folder after
restarting the NAS.
This setting is only available if Save encryption key
was enabled when the folder was encrypted or Mount
automatically on start up was enabled after the folder
was encrypted.
c. Click OK.
QTS locks the folder.
Note
• Locked folders do not appear in File Station. A folder
will only reappear after it is unlocked.
• Users cannot edit the properties or permissions of a
locked shared folder.
Unlocking a Shared Folder
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Shared Folder .
2. Locate a locked shared folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 96
3. Under Action, click .
The Unlock Folder window appears.
4. Select one of the following options.
Option User Action
Input Encryption Password a. Enter the encryption password.
b. Optional: Select Save encryption key.
When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
Note
This option is selected by default.
Upload Encryption Key File a. Click Browse.
b. Select the encryption key le.
5. Click OK.
Shared Folder Access
You can map or mount a NAS shared folder as a network drive, allowing you to easily access and manage
les from your Windows, Mac, or Linux computer.
For Windows and Mac, you can use Qnder Pro to map or mount your NAS shared folders. Qnder Pro is a
desktop utility that enables you to locate and access the QNAP NAS devices in your local area network.
To download Qnder Pro, go to https://www.qnap.com/utilities.
Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer
Before mapping a shared folder, ensure that you have Qnder Pro installed on your Windows computer.
1. Power on the NAS.
2. Connect the NAS to your local area network.
3. Open Qnder Pro.
Qnder Pro displays all QNAP NAS devices in your local area network.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 97
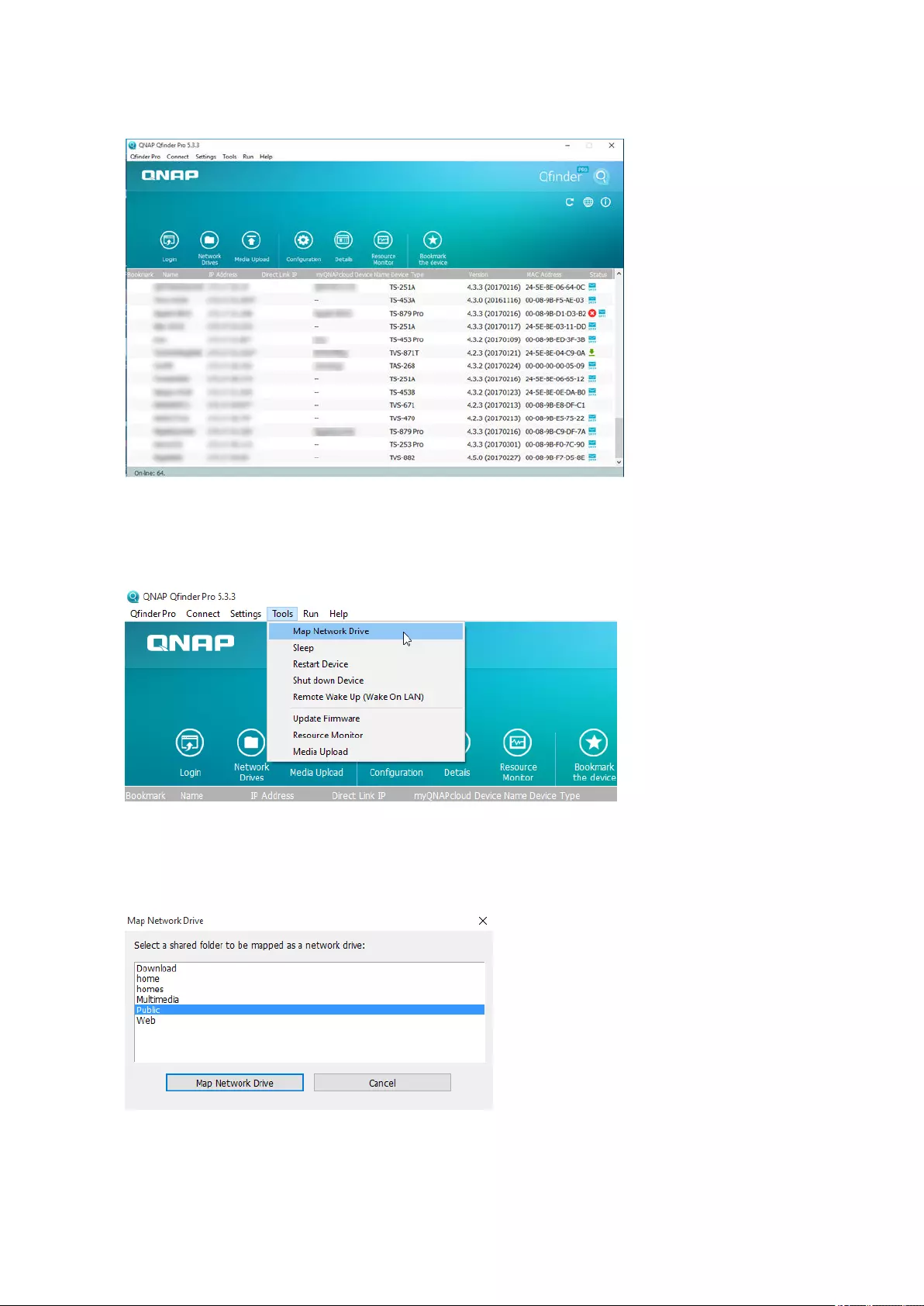
4. Select the NAS where the shared folder is located.
5. Click Tools > Map Network Drive .
6. Select a shared folder.
7. Click Map Network Drive.
8. Specify your QTS username and password.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 98
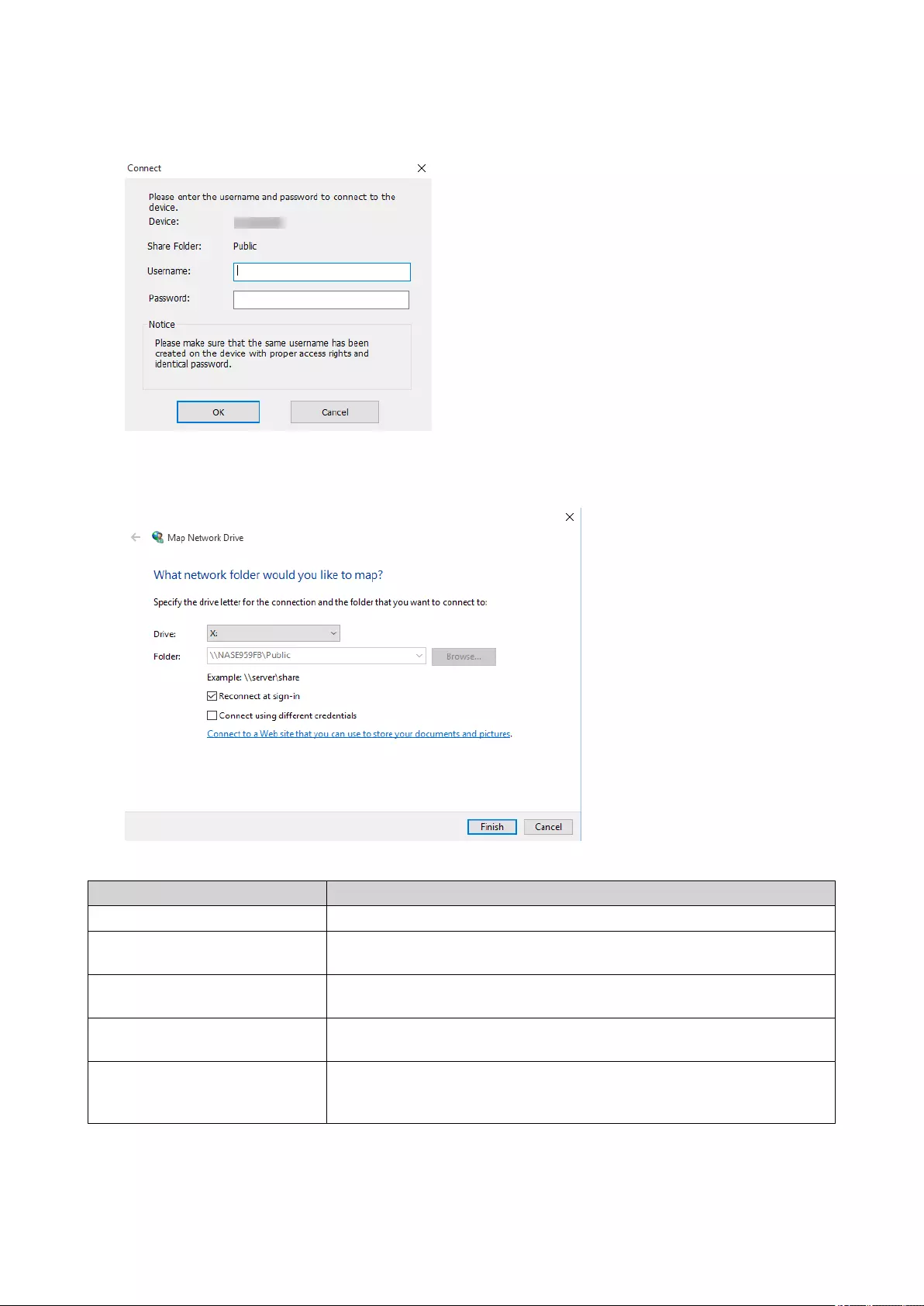
9. Click OK.
10. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Drive Specify the drive letter for the shared folder.
Folder This eld is uneditable because you have already selected the shared
folder. This is for your reference.
Reconnect at sign-in When selected, the shared folder will automatically be connected the
next time the user signs in.
Connect using dierent
credentials
When selected, the user will have the option to sign into the NAS with a
dierent account after mapping the shared folder.
Connect to a Web site that
you can use to store your
documents and pictures.
When clicked, the Add Network Location Wizard appears.
You can use this wizard to create a shortcut to your mapped shared
folder.
11. Click Finish.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 99
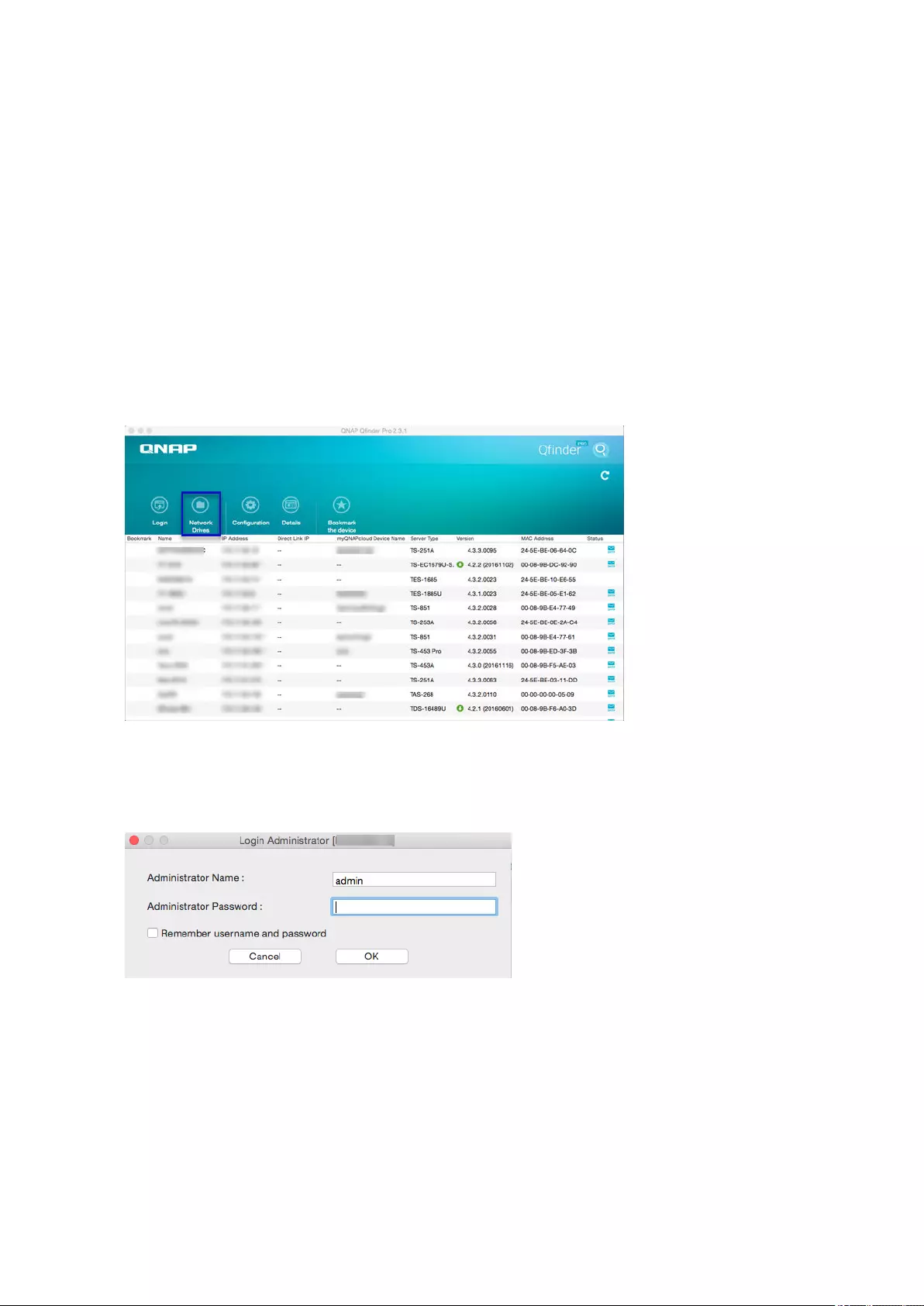
The shared folder is mapped as a network drive and can be accessed using Windows Explorer.
Mounting a Shared Folder on a Mac Computer
Before mounting a shared folder, ensure that you have Qnder Pro installed on your Mac computer.
1. Power on the NAS.
2. Connect the NAS to your local area network.
3. Open Qnder Pro.
Qnder Pro displays all QNAP NAS devices in your local area network.
4. Select the NAS where the shared folder is located.
5. Click Network Drives.
6. Specify your QTS username and password.
7. Click OK.
The Mount Network Drives window opens.
8. Select Add mounted folders to "Favorites" in Finder.
9. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 100
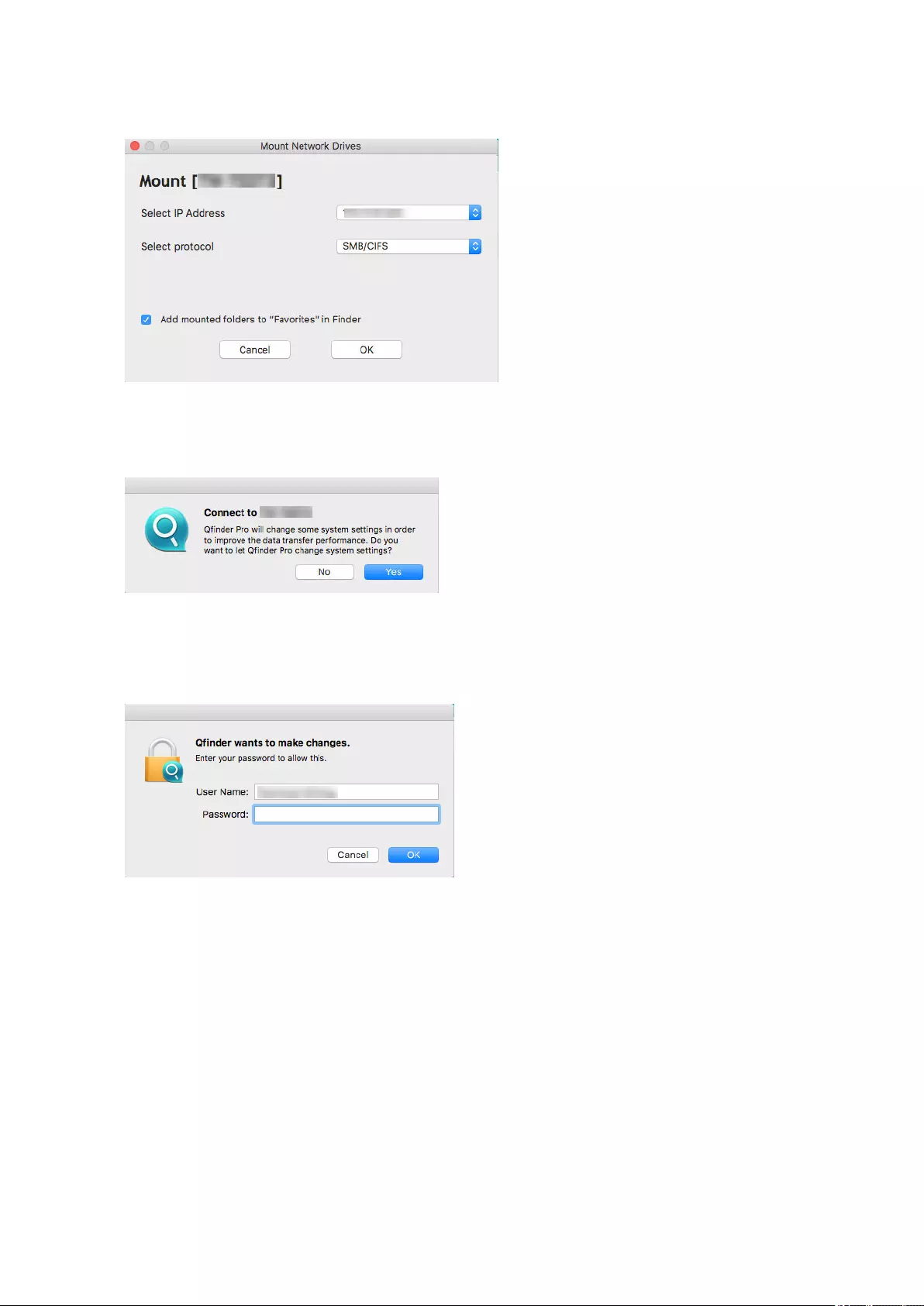
A conrmation message appears.
10. Click Yes.
11. Specify your Mac username and password.
12. Click OK.
13. Select the shared folder.
14. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 101
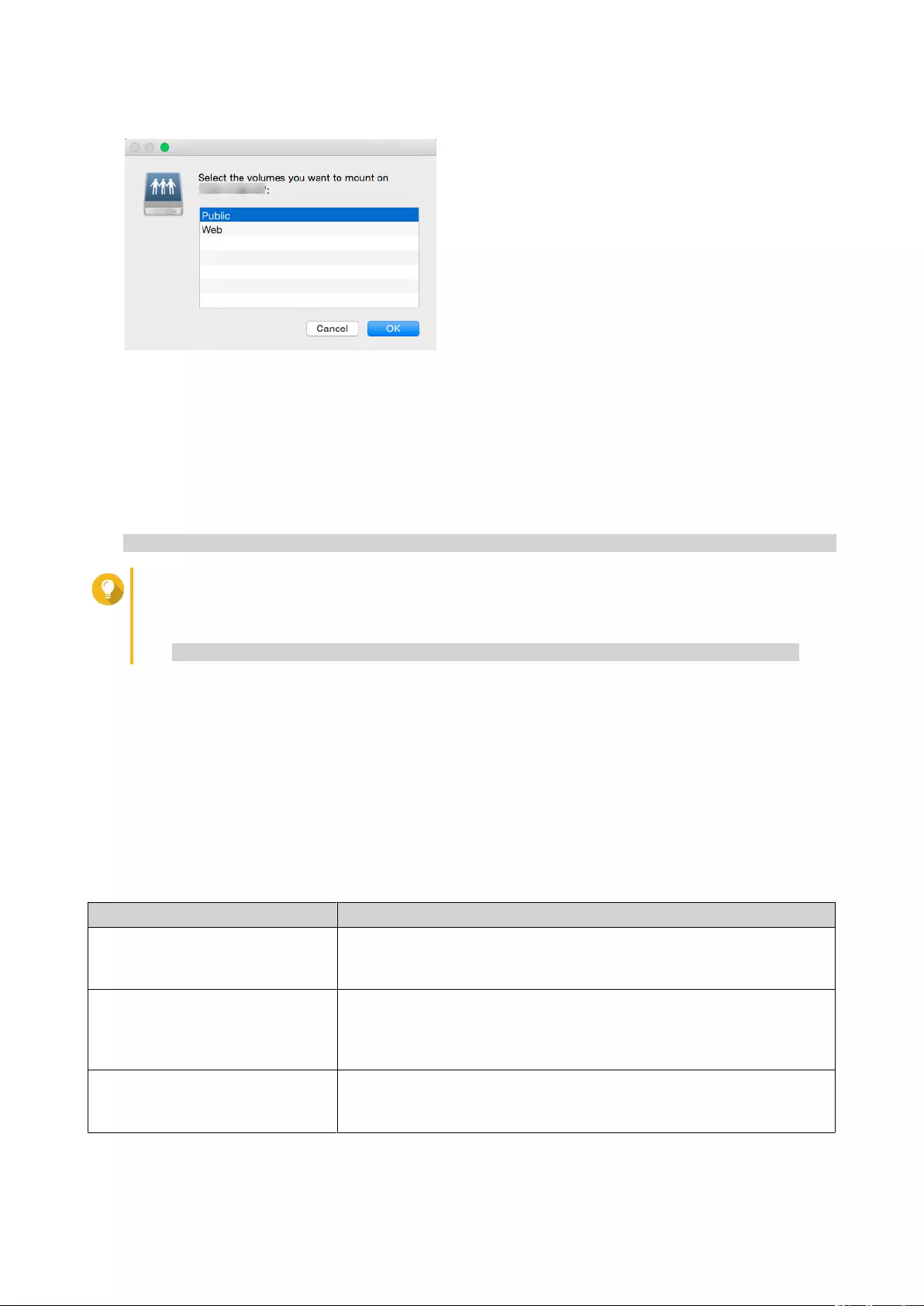
The shared folder is mounted as a network drive and can be accessed using Qnder Pro.
Mounting a Shared Folder on a Linux Computer
1. Open a terminal with root privileges.
2. Run the following command:
mount <NAS Ethernet Interface IP>:/share/<Shared Folder Name> <Directory to Mount>
Tip
If the NAS ethernet interface IP address is 192.168.0.42 and you want to connect to a shared
folder "public" under the /mnt/pub directory, run the following command:
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.42:/share/public/mnt/pub
3. Specify your NAS username and password.
You can connect to the shared folder using the mounted directory.
Quota
You can enable quotas (in MB or GB) for users and user groups to help manage storage space. When quotas
are enabled, QTS prevents users from saving data to the NAS after the quota is reached. By default, quotas
are not enabled for users.
QTS provides three types of quota settings.
Type Description
Individual Set quotas for individual users.
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Users to edit user quotas.
For details, see Modifying User Account Information.
Group Set quotas at the group level. Setting a group quota applies the quota
to each user in the group.
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups to edit group quotas.
For details, see Modifying User Group Information.
All users When enabled, the quota is applied to both new and existing users.
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Quota to enable quotas.
For details, see Enabling Quotas.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 102

Note
Quotas are applied per volume and are not shared across volumes.
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas.
For details, see Quota Conicts.
Tip
You can export quota settings to a CSV le to use as a reference.
For details, see Exporting Quota Settings.
Enabling Quotas
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Quota .
2. Select Enable quota for all users.
3. Specify the all users quota.
Note
The all users quota must be between 100 MB and 128 TB.
4. Click Apply.
QTS displays the quota settings for Local Users.
Editing Quota Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Quota .
2. Select the type of user or group.
•Local Users
•Domain Users
•Local Groups
•Domain Groups
Tip
By default, the Quota screen displays Local Users.
3. Select a user or group.
4. Click Edit.
The Quota window appears.
5. Set a quota for the user or group.
•No Limit: Quota settings do not apply to the user or group.
•Limit disk space to: Specify a quota for the user or group.
Note
The quota must be between 100 MB and 128 TB.
•Use group quotas: Group quota settings apply to the user.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 103
Important
Individual quotas may override group quotas.
For details, see Quota Conicts.
6. Click OK.
Exporting Quota Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Quota .
2. Click Generate.
3. Click Download.
QTS exports the quota settings as a CSV le.
Quota Conicts
QTS uses the following hierarchy to resolve quota conicts.
1. Individual quota
2. Group quota
3. All users quota
The following table describes the possible scenarios for dierent combinations of user quotas and group
quotas.
• The User Quota column shows the quota setting that is applied to the user individually.
• The Group Quota column shows whether the user belongs to any groups.
• The Actual Quota column shows the actual quota setting that is applied to the user.
User Quota Group Quota Actual Quota
No limit Yes No limit
No No limit
Individual Yes Individual quota
No Individual quota
Use group quotas Yes Group quota
No All users quota
Note
If a user belongs to multiple groups with group quotas, the highest group quota applies to
the user.
Domain Security
The NAS supports user authentication through local access rights management, the Microsoft Active
Directory (AD), and the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory.
Joining the NAS to an AD domain or an LDAP directory allows AD or LDAP users to access the NAS using their
own accounts without having to congure user accounts on the NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 104
Note
QTS supports AD running on Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, and 2019.
Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Security to congure domain security settings.
Option Description
No domain security (Local users
only)
Only local users can access the NAS.
Active Directory authentication
(Domain member)
Users can join the NAS to an AD, allowing domain users to be
authenticated by the NAS. Local and AD users can access the NAS
using Samba, AFP, FTP, and File Station. For details, see Active
Directory (AD) Authentication.
LDAP authentication Users can connect the NAS to an LDAP directory, allowing LDAP
users to be authenticated by the NAS. Local and LDAP users can
access the NAS using Samba, AFP, FTP, and File Station. For details,
see LDAP Authentication.
Set this NAS as a domain controller Clicking this directs the user to the Domain Controller screen. For
details, see Domain Controller.
Active Directory (AD) Authentication
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft directory service that stores information for users, user groups, and
computers for authenticating and managing domain access. Windows environments use AD to store, share,
and manage a network's information and resources.
When a NAS is joined to an AD domain, the NAS automatically imports all of the user accounts on the AD
server. AD users can then use the same login details to access the NAS.
Conguring AD Authentication Using the Quick Conguration Wizard
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Security .
2. Select Active Directory authentication (Domain member).
3. Click Quick Conguration Wizard.
The Active Directory Wizard appears.
4. Click Next.
5. Specify the fully qualied domain name (FQDN) of the AD DNS server.
QTS automatically generates the NetBIOS domain name.
6. Specify the IP address of the AD DNS server.
7. Optional: Select Obtain DNS server address automatically by DHCP server.
8. Click Next.
9. Select a domain controller.
10. Select the server signature rule for the domain.
Option Description
Auto SMB signing is oered but not enforced. Clients can choose whether to
use SMB signing or not.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 105
Option Description
Mandatory SMB signing is required.
Disabled SMB signing is disabled for SMB 1. For SMB 2 and above, this option
behaves the same as Auto.
11. Specify the domain administrator username and password.
12. Click Join.
The NAS joins the domain.
13. Click Finish.
Conguring AD Authentication Manually
Verify the following before starting this task:
• The time settings of the NAS and the AD server are identical. The maximum time disparity tolerated is 5
minutes.
• The AD server is congured as the primary DNS server. If you use an external DNS server, you will not
be able to join the domain.
• You have specied the IP address of the WINS server that you use for name resolution.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Security .
2. Select Active Directory authentication (Domain member).
3. Click Manual Conguration.
The Active Directory window appears.
4. Specify the following information.
•Domain NetBIOS Name
•AD Server Name
•Domain
•Domain Administrator Username
Note
The specied user must have administrator access rights to the AD domain.
•Domain Administrator Password
•Organizational Unit (Optional)
•Server description (Optional)
Note
The NAS Samba service replicates this in the server's Comment eld. This description appears
when connecting to a NAS Samba shared folder using the command line interface.
5. Select the server signature rule for the domain.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 106
Option Description
Auto SMB signing is oered but not enforced. Clients can choose whether to
use SMB signing or not.
Mandatory SMB signing is required.
Disabled SMB signing is disabled for SMB 1. For SMB 2 and above, this option
behaves the same as Auto.
6. Click Join.
AD Server and Domain Names
After joining the NAS to the AD domain, you can use the following username formats to log in to the NAS
and access shared folders:
• Local users: NASname\NASusername
• AD users: Domain\DomainUsername
The location of AD server and domain names depends on the version of Windows Server.
Windows Server Version Location
2003 Go to System Properties in Windows.
Example: If the computer name is "node1.qnap-test.com", the AD
server name is "node1" and the domain name is "qnap-test.com".
2008 Go to Control Panel > System in Windows.
The AD server name will appear as the computer name, and the
domain name can be found in the domain eld.
2012, 2016
Right-click , and then click System.
The AD server name will appear as the computer name, and the
domain name can be found in the domain eld.
Enabling Trusted Domain Authentication
A trusted domain is a domain that AD trusts to authenticate users. If you join the NAS to an AD domain, all
users from trusted domains can log in and access shared folders.
Trusted domains are congured in AD. You can only enable trusted domains on the NAS. By default, this
feature is disabled in QTS.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS > Microsoft Networking .
2. Click Advanced Options.
The Advanced Options window appears.
3. Select Enable trusted domains.
Note
This setting is only available if the NAS is joined to a domain.
4. Click Apply.
The Advanced Options window closes.
5. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 107
Azure Active Directory Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a holistic approach to authenticate users when signing on to applications in Azure
Active Directory. If you enable SSO, a user only needs one login credential to access multiple applications,
irrespective of the platform, domain, or technology used. Without SSO, a user needs a separate credential
to access each application. The NAS supports SSO. Depending on which domain service the NAS joins, the
device will synchronize the domain account information with the appropriate service.
Enabling Azure AD Single-Sign-On
Before starting this task, ensure that you create an application registration. For details, see https://
docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/howto-create-service-principal-portal. The user
interface on Microsoft Azure is subject to change without notice.
Important
You must rst complete the following steps before enabling SSO.
• Ensure that your NAS has an x86 (Intel or AMD) processor.
•Congure Azure site-to-site VPN. For details, visit https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/
azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-howto-site-to-site-resource-manager-portal.
You can also add a custom domain name using the Azure AD portal for the
on-premise Windows AD. For details, visit https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/
vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-howto-site-to-site-resource-manager-portal and https://
docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/add-custom-domain.
•Congure Azure AD Domain service. For details, see the following:
•Conguring AD Authentication Using the Quick Conguration Wizard
•Conguring AD Authentication Manually
Note
If you want to enable SSO on more than one NAS, you must repeat all of these steps on
each NAS.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Security > SSO .
2. Select Enable Azure SSO Service.
3. Specify Client ID.
For details, visit https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/howto-create-service-
principal-portal.
Note
The Client ID is also known as an Application ID.
4. Specify Tenant ID.
For details, visit https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/howto-create-service-
principal-portal.
5. Specify Reply URLs.
a. Sign in as an administrator at https://portal.azure.com/#home.
b. Click Azure Active Directory, and then click App registrations > Your app > All settings >
Reply URLS .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 108

c. Add :8080/cgi-bin to the end of the IP address.
d. Copy and paste the URL into the Reply URLs eld label on the NAS.
6. Specify the Public key.
Note
• The public key must be a PEM le.
• You can convert a CA certicate to a public key using a Linux environment or an OpenSSL.
7. Click Apply.
Note
Your NAS login screen changes to include an Azure SSO login option.
LDAP Authentication
A Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory contains user and user group information stored
on an LDAP server. Administrators can use LDAP to manage users in the LDAP directory and connect
to multiple NAS devices with the same login details. This feature requires a running LDAP server and
knowledge of Linux servers, LDAP servers, and Samba.
Conguring LDAP Authentication
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Security .
2. Select LDAP authentication.
3. Select the type of LDAP server.
4. Specify the following information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 109
LDAP Server Type Fields User Action
Remote LDAP server LDAP Server Host Specify the host name or IP address of the LDAP
server.
LDAP Security Select the method that the NAS uses to communicate
with the LDAP server.
•ldap://: Use a standard LDAP connection. The
default port is 389.
•ldap:// (ldap + TLS): Use an encrypted
connection with TLS. The default port is 389.
Newer versions of LDAP servers normally use
this port.
•ldap:// (ldap + SSL): Use an encrypted
connection with SSL. The default port is 686.
Older versions of LDAP servers normally use
this port.
Base DN Specify the LDAP domain.
Example: dc=mydomain,dc=local
Root DN Specify the LDAP root user.
Example: cn=admin, dc=mydomain,dc=local
Password Specify the root user password.
Users Base DN Specify the Organizational unit (OU) where users are
stored.
Example: ou=people,dc=mydomain,dc=local
Group Base DN Specify the OU where groups are stored.
Example: ou=group,dc=mydomain,dc=local
Current Samba ID N/A
LDAP server of the
remote NAS
IP address or NAS name Specify the server IP address or the name of the NAS.
LDAP domain Specify the LDAP domain name.
Password Specify the NAS administrator password.
LDAP server of the
local NAS
N/A N/A
IBM Lotus Domino This server type includes the same elds as Remote LDAP server, in addition to
the following:
uidNumber Specify the uid number.
Select HASH.
gidNumber Specify the gid number.
Select HASH.
5. Click Apply.
The LDAP authentication options window appears.
6. Select which users are allowed to access the NAS.
Note
LDAP authentication options vary depending on when Microsoft Networking is enabled. For
details, see LDAP Authentication Options.
7. Click Finish.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 110
LDAP Authentication Options
The LDAP authentication options vary depending on when Microsoft Networking is enabled.
Scenario Options
Microsoft Networking is enabled before LDAP
settings are applied.
•Local users only: Only local users can access the NAS
using Microsoft Networking.
•LDAP users only: Only LDAP users can access the
NAS using Microsoft Networking.
Microsoft Networking is enabled after the NAS
is connected to the LDAP server.
•Standalone Server: Only local users can access the
NAS using Microsoft Networking.
•LDAP Domain Authentication: Only LDAP users can
access the NAS using Microsoft Networking.
AD and LDAP Management
The administrator can modify domain user accounts and user groups when the NAS joins an AD domain or
connects to an LDAP server.
Managing AD and LDAP Users
1. Go to Privilege > Users .
2. Select Domain Users.
QTS displays the list of domain users.
3. Locate a user.
4. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Edit an account prole a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Account Prole window appears.
b. Edit the user quota.
Note
User quotas must be enabled for this option to appear. For
details, see Enabling Quotas.
Edit shared folder
permissions
a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permission window appears.
b. Edit the user's permissions for each shared folder.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 111
Task User Action
Edit application privileges a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Application Privileges window appears.
b. Select the applications that the user is allowed to access.
Tip
QNAP recommends denying access to applications and
network services that the user does not require.
By default, administrator accounts have access to all
applications.
Tip
Click to display newly created users on the AD or LDAP server. Permission settings are
automatically synchronized with the domain controller.
5. Click Apply.
Managing AD and LDAP User Groups
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > User Groups .
2. Select Domain Groups.
QTS displays the list of domain user groups.
3. Locate a user group.
4. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
View group details Under Action, click .
The View Group Details window appears.
QTS displays the group name and group users.
Edit shared folder
permissions
a. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permission window appears.
b. Edit the user group's permissions for each shared folder.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
Tip
Click to display newly created groups on the AD or LDAP server. Permission settings are
automatically synchronized with the domain controller.
5. Click Apply.
Domain Controller
You can congure your QNAP NAS as a domain controller for Microsoft Windows environments. By
conguring the NAS as a domain controller, you can store user account information, manage user
authentication, and enforce security for a Windows domain.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 112
Enabling a Domain Controller
Important
When the NAS is congured as a domain controller, only domain users can access shared
folders through CIFS/SMB (Microsoft Networking). All local NAS users are denied access.
To enable Domain Controller, you must rst enable Advanced Folder Permissions by
going to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Advanced Permissions .
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller .
2. Select Enable Domain Controller.
Important
The domain controller cannot be enabled if an LDAP server is already running on the NAS.
3. Select the domain controller mode.
Mode Description
Domain Controller Only a domain controller can create a domain. The rst NAS that
creates the domain must be a domain controller. In this mode, the NAS
can create and authenticate users.
Additional Domain Controller If more than one domain controller is needed, you can add additional
domain controllers. When the NAS is set as an additional domain
controller, it can create and authenticate users.
Read-Only Domain Controller This congures the NAS as a read-only domain controller to accelerate
the user authentication process for specied websites. Read-only
domain controllers can authenticate users, but not create domain user
accounts.
4. Specify the following information.
Domain Controller Mode Field Description
Domain Controller Domain Specify the domain.
Administrator Password Specify an administrator password between 8
and 127 characters that contains at least one of
each of the following:
• Uppercase characters (A through Z)
• Lowercase characters (a through z)
• Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
• Nonalphanumeric characters: ~!@#$
%^&*_-+=`|\(){}[]:;"'<>,.?/
Verify Password Verify the administrator password.
•Additional Domain
Controller
•Read-Only Domain
Controller
Domain Specify the domain.
Domain DNS IP Specify the domain DNS IP.
Administrator Account Specify the administrator account name.
Administrator Password Specify the administrator password.
5. Select the server signature rule for the domain.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 113
Option Description
Auto SMB signing is oered but not enforced. Clients can choose whether
to use SMB signing or not.
Mandatory SMB signing is required.
Disabled SMB signing is disabled for SMB 1. For SMB 2 and above, this option
behaves the same as Auto.
6. Click Apply.
Resetting a Domain Controller
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller .
2. Click Reset.
A dialog box appears.
3. Enter the administrator password.
4. Click OK.
Default Domain User Accounts
Domain User Account Description
Administrator This account is used to congure settings, create users, and manage the
domain. This account cannot be deleted.
Guest Users without dedicated accounts can use this account to view and modify les.
krbtgt This is the Key Distribution Center (KDC) service account. The KDC is a domain
service that uses the Active Directory (AD) as the account database and the
Global Catalog for directing referrals to KDCs in other domains.
Creating a Domain User
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Users .
2. Click Create > Create a User .
The Create a User wizard appears.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Username Specify a username between 1 and 20 characters that does not:
• Begin with a space
• Begin with the following characters: - # @
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 114
Field Description
Password Specify a password between 8 and 127 characters that contains at least
three of the following:
• Uppercase characters (A through Z)
• Lowercase characters (a through z)
• Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
• Nonalphanumeric characters: ~!@#$%^&*_-+=`|\(){}[]:;"'<>,.?/
Description (optional) Specify a user description that contains a maximum of 1024 ASCII
characters.
Email (optional) Specify an email address that will receive notications from QTS.
For details, see Email Notications.
5. Click Next.
6. Specify the following information.
Setting Description
User must change the password at
rst logon
The user must change the password after logging in for the
rst time.
Account expiration Set an expiration date for the account.
•Now: The account expires upon creation.
•Expiry date: Specify an expiration date for the account.
7. Click Next.
8. Assign the account to existing Windows user groups.
9. Click Next.
10. Review the summary, and then click Finish.
Creating Multiple Domain Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Users .
2. Click Create > Create Multiple Users .
The Create Multiple Users wizard appears.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify the following information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 115
Field Description
User Name Prex Specify a username prex between 1 and 16 ASCII characters that
does not:
• Begin with a space
• Begin with the following characters: - # @
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '
This prex will be included before all usernames.
User Name Start No Specify a starting number up to 8 digits in length.
Note
QTS removes leading zeros in starting numbers.
For example, 001 becomes 1.
Number of Users Specify a number between 1 and 4095.
This number signies the number of accounts that will be created.
Password Specify a password between 8 and 127 characters that contains at
least three of the following:
• Uppercase characters (A through Z)
• Lowercase characters (a through z)
• Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
• Nonalphanumeric characters: ~!@#$%^&*_-+=`|\(){}[]:;"'<>,.?/
User must change the password at
rst logon
The user must change the password after logging in for the rst
time.
Account expiration Set an expiration date for the account.
•Now: The account expires upon creation.
•Expiry date: Specify an expiration date for the account.
5. Click Create.
QTS creates the accounts and adds them to the list of domain users.
6. Click Finish.
Domain User Account Lists
User accounts can also be imported directly from TXT or CSV les. The les contain user account information
including usernames, passwords, descriptions, and email addresses.
File Format Description
TXT Create domain user account lists using a text editor. For details, see Creating a
TXT Domain User File.
CSV Create domain user account lists using a spreadsheet editor. For details, see
Creating a CSV Domain User File.
Creating a TXT Domain User File
1. Create a new le in a text editor.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 116

2. Specify domain user information in the following format.
Username,Password,Description,Email
Important
• Separate values using commas.
• Ensure that the password meets the requirements for domain user accounts.
For details, see Creating a Domain User.
• Specify information for only one user on each line.
Example:
John,s8fK4br*,John's account,john@qnap.com
Jane,9fjwbXy#,Jane's account,jane@qnap.com
Mary,f9xn3nS%,Mary's account,mary@qnap.com
3. Save the list as a TXT le.
Important
If the list contains multi-byte characters, save the le with UTF-8 encoding.
Creating a CSV Domain User File
1. Create a new workbook in a spreadsheet editor.
2. Specify domain user information in the following format.
• column A: Username
• column B: Password
• column C: Description
• column D: Email
Important
• Ensure that the password meets the requirements for domain user accounts.
For details, see Creating a Domain User.
• Specify information for only one user in each row.
Example:
3. Save the workbook as a CSV le.
Important
If the list contains multi-byte characters, open the le using a text editor and then save with
UTF-8 encoding.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 117
Batch Importing Domain Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Users .
2. Click Create > Batch Import Users .
The Batch Import Users wizard appears.
3. Optional: Select Overwrite existing users.
Important
When selected, QTS overwrites existing domain user accounts that have duplicates on the
imported domain user account list.
4. Click Browse, and then select the le that contains the domain user account list.
Important
Ensure that you are importing a valid QTS domain user account list le to avoid parsing errors.
For details, see Domain User Account Lists.
5. Click Next.
The File content preview screen appears.
Important
Ensure that the le contents are valid. If any information is invalid, the domain user account list
cannot be imported.
6. Click Import.
QTS imports the domain user account list.
7. Click Finish.
Modifying Domain User Account Information
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Users .
2. Locate a user.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Change password a. Under Action, click .
The Change Password window appears.
b. Specify a password that meets the requirements.
c. Verify the password.
d. Click Change.
Edit user properties a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User Properties window appears.
b. Edit the user properties.
For details, see Creating a Domain User.
c. Click Finish.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 118
Task User Action
Edit user group membership a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User Groups wizard appears.
b. Select or deselect user groups.
For details, see Domain User Groups.
c. Click Next.
d. Review the summary, and then click Finish.
Edit user prole a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User Prole window appears.
b. Specify the following:
•Prole path
Specify the shared folder where the roaming proles are stored.
•Login script
Specify the login script that executes when a domain user logs in
from a computer member of the domain.
To directly specify the script lename, connect to \NAS\netlogon
using the domain administrator account and copy the script to the
\sysvol shared folder in the \scripts folder of your domain.
•Home Folder
Specify the drive and shared folder that is mapped to the drive
when the domain user logs in to the domain.
• Click Finish.
Tip
You can also edit quota settings for domain users. For details, see Editing Quota Settings.
Deleting Domain Users
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Users .
2. Select the domain users to delete.
Note
The administrator account cannot be deleted.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
4. Click Yes.
Domain User Groups
A domain user group is a collection of domain users with the same access rights to les and folders. Domain
administrators can create domain user groups to improve security for domain users.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 119

Default Domain User Groups
• Allowed RODC Password Replication Group
•Certicate Service DCOM Access
• Denied RODC Password Replication Group
• Enterprise Read-Only Domain Controllers
• Incoming Forest Trust Builders
• Network Conguration Operators
• Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access
• Read-Only Domain Controllers
• Terminal Server License Servers
• Windows Authorization Access Group
Creating a Domain User Group
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Groups .
2. Click Create a User Group.
The Create a User Group wizard appears.
3. Specify a user group name between 1 and 128 ASCII characters that does not begin with:
• Spaces
• The following characters: - # @
4. Click Next.
5. Optional: Add users to the group.
a. Select Yes.
b. Click Next.
c. Select the users you want to add to the group.
d. Click Next.
6. Review the summary, and then click Finish.
Editing Domain User Groups
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Groups .
2. Locate a domain user group.
3. Under Action, click .
The Edit Group Users wizard appears.
4. Select or deselect user groups.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 120
5. Click Next.
6. Review the summary, and then click Finish.
Deleting Domain User Groups
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Groups .
2. Select the user groups to delete.
Note
Some default user groups cannot be deleted.
Important
Do not delete the default group of the domain.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
4. Click Yes.
Computers
The Computers screen displays the computer accounts for computers or NAS devices that have joined the
domain. Computer accounts are created automatically when a computer or NAS joins the domain.
Creating a Computer Account
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Computers .
2. Click Create a Computer.
The Create a Computer wizard appears.
3. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Computer name Specify a computer name between 1 and 15 ASCII characters that
include any of the following:
• Uppercase characters (A through Z)
• Lowercase characters (a through z)
• Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
• Dashes (-)
Description Specify a user description that contains a maximum of 1024 ASCII
characters.
Location Specify the location of the computer using a maximum of 1024 ASCII
characters.
4. Click Next.
5. Assign the account to existing Windows user groups.
6. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 121
7. Review the summary, and then click Create.
Modifying Computer Account Information
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Computers .
2. Locate a computer account.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Edit computer properties a. Under Action, click .
The Edit computer properties window appears.
b. Edit the Description or Location.
For details, see Creating a Computer Account.
Edit user group membership a. Under Action, click .
The Edit User Groups window appears.
b. Select or deselect user groups.
For details, see Domain User Groups.
c. Click Next.
4. Click Finish.
Editing Computer Account Shared Folder Permissions
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Computers .
2. Locate a computer account.
3. Under Action, click .
The Edit Shared Folder Permission window appears.
4. Edit the computer account's permissions for each shared folder.
For details, see Shared Folder Permissions.
5. Click Apply.
Deleting Computer Accounts
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Computers .
2. Select the accounts to delete.
Note
The host computer account cannot be deleted.
3. Click Delete.
A warning message appears.
4. Click Yes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 122
DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) helps the domain controller locate services and devices within the domain
using service and resource records. Two DNS zones are created by default: the domain created when setting
up the NAS as a domain controller, and a zone called "_msdcs". System administrators can modify DNS
settings and add or delete domains and records.
Modifying DNS Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > DNS .
2. Log in under the domain administrator account.
Note
This is the account created when enabling the domain controller.
a. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Account Enter administrator.
Password Enter the password specied when the account was created.
b. Click Login.
3. Under DNS Settings, select a domain.
A list of records appears.
4. Select a record.
The properties panel appears.
5. Modify any of the following.
Field Description
Name Edit the name of the record.
Type Select the type of record.
6. Modify the values.
Task User Action
Add a value a. Specify a value.
b.
Click .
The value is added to the list.
Move a value up a. Select a value from the list.
b. Click .
The value moves up in the list.
Move a value down a. Select a value from the list.
b. Click .
The value moves down in the list.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 123
Task User Action
Remove a value a. Select a value from the list.
b. Click .
The value is removed from the list.
7. Click Apply.
Adding Domains
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > DNS .
2. Log in under the domain administrator account.
Note
This is the account created when enabling the domain controller.
a. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Account Enter administrator.
Password Enter the password specied when the account was created.
b. Click Login.
3. Click Action > Add Domain .
The Add New Domain window appears.
4. Enter the domain name.
5. Click Create.
Adding Records
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > DNS .
2. Log in under the domain administrator account.
Note
This is the account created when enabling the domain controller.
a. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Account Enter administrator.
Password Enter the password specied when the account was created.
b. Click Login.
3. Select a domain or record.
4. Click Action > Add Record .
The Add New Record window appears.
5. Specify the following information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 124
Field Description
Record Name Specify the name of the record.
Type Select the type of record.
Value Specify the value.
6. Click Create.
Deleting Domains or Records
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > DNS .
2. Log in under the domain administrator account.
Note
This is the account created when enabling the domain controller.
a. Specify the following information.
Field Description
Account Enter administrator.
Password Enter the password specied when the account was created.
b. Click Login.
3. Select a domain or record to delete.
4. Click Action > Delete .
A warning message appears.
5. Click Yes.
Back Up/Restore
Users can back up or restore domain controller settings. Only the primary domain controller needs to be
backed up; backing up the primary domain controller also backs up any additional or read-only domain
controllers. When restoring a domain controller, there are some restrictions and limitations if the domain
controller is in an AD environment with more than one domain controller. For details, see Restoring Domain
Controllers.
Backing Up Domain Controllers
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Backup/Restore .
2. Under Back up ADDC Database, select Back up Database.
3. Specify the following information.
Option Description
Backup frequency Select how often the Active Directory Domain Controller (ADDC)
database is backed up.
Start Time Select when the backup will begin.
Destination folder Select the NAS folder where the backup will be stored.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 125
Option Description
Backup Options Select one of the following:
•Overwrite existing backup le (dc_backup.exp)
•Create a new le for each backup and append the date to the
lename (dc_backupyyyy_mm_dd_exp)
4. Click Apply.
Restoring Domain Controllers
Important
Restoring a domain controller overwrites all user, user group, and domain controller
settings. Any changes made after the backup le was created will be lost.
Warning
Restoring a domain controller in a multiple-controller environment from a backup le will
corrupt the domain controller database. Instead, re-add the NAS as a domain controller,
and it will synchronize with the existing controller.
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain Controller > Backup/Restore .
2. Under Restore ADDC Database, click Browse.
3. Locate a domain controller backup le.
4. Click Import.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Privilege Settings 126
5. Services
QTS provides various services to facilitate your work and device management. You can congure these
settings according to your needs.
Antivirus
To ensure your NAS is protected from malicious attacks, you can scan the NAS manually or on recurring
schedules. Antivirus will delete, quarantine, or report les infected by viruses, malware, trojans, or other
threats.
Enabling Antivirus
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Antivirus > Overview .
3. Select Enable antivirus.
4. Optional: Update the antivirus with one of the following methods.
Option User Action
Update now Click Update now.
The system immediately updates the antivirus.
Update automatically a. Select Check and update automatically.
b. Specify the frequency.
The system automatically checks for antivirus updates on the
specied date.
Update manually a. Click Browse.
An upload window appears.
b. Select a virus database le (.cvd) to upload.
Tip
You can download the latest ClamAV virus database
le from http://www.clamav.net/.
c. Click Import.
5. Click Apply.
QTS enables the antivirus.
Scanning Shared Folders
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Antivirus > Scan Jobs .
3. Click Add a Scan Job.
The Scan Job Creation window opens.
4. Enter a name for this task.
5. Select one of the following options.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 127
Option User Action
All folders Click All folders.
Specic folders a. Click Specic folders.
b. Select a shared folder from the drop-down menu.
c. Click Add.
Tip
To remove a shared folder, click .
6. Click Next.
The Schedule screen appears.
7. Select a scan frequency option and congure the settings if required.
8. Click Next.
The File Filter screen appears.
9. Select one of the following le lter options:
Option Description
Scan all les Scans all les on the NAS for viruses.
Quick scan (Only potentially
dangerous le types listed
below)
Only le types in the list are scanned for viruses. You can modify the
list.
10. Optional: Exclude les and folders from the virus scan.
a. Select Exclude les or folders.
b. Specify the les, le types, and folders to exclude from the scan.
11. Click Next.
The Scan Options screen appears.
12. Enter the maximum le size for the virus scan.
13. Optional: Select at least one of the following options.
Option Description
Scan compressed les content Scans compressed les.
Note
You can specify the maximum compressed le size
that Antivirus will scan.
Deep scan for document les Scans Microsoft Oce, iWork, RTF, PDF, and HTML les.
14. Click Next.
The Action to take when infected les are found screen appears.
15. Select an option on what to do with infected les.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 128
Option Description
Only report the virus QTS only reports detected viruses and does not take any further
action. The detections will appear in Reports.
Move infected les to
quarantine
QTS quarantines the infected les. You cannot access these les from
shared folders. You can review the virus scan report in Reports and
delete or restore infected les in Quarantine.
Delete infected les
automatically
QTS deletes the infected les.
Important
These les are permanently deleted.
16. Click Finish.
The scan job appears in the Job Name list.
Managing Scan Jobs
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Antivirus > Scan Jobs .
3. Locate a scan job you would like to modify.
4. Select one of the following options.
Option User Action
Run now Select .
QTS starts the scan job.
Edit a. Select .
The Details window opens.
b. Modify the settings.
c. Click OK.
QTS modies the scan job's settings.
View last run log a. Select .
The Last run log window opens.
b. Optional: Click the text box to modify the run log.
c. Click Close.
Delete a. Select .
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Yes.
QTS deletes the scan job.
Managing Reported Scan Jobs
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Antivirus > Reports .
3. Optional: Specify the log retention period.
a. Go to Number of days to keep the logs.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 129
b. Enter the number of days.
Tip
Enter a number between 1 to 999.
c. Click Apply.
4. Optional: Archive expired logs.
a. Select Archive logs after expiration.
b. Specify the archive folder.
c. Click Apply.
5. Locate the scan job you want to manage.
6. Select one of the following options.
Option User Action
Download Select .
QTS downloads the scan job as a text document to your computer.
Tip
To download all job logs, click Download All Logs.
Delete a. Select .
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Yes.
QTS deletes the scan job.
Managing Quarantined Files
Warning
You cannot recover deleted quarantined les.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Antivirus > Quarantine .
3. Locate the le or les you want to manage.
4. Perform one of the following options.
Option User Action
Delete Click .
QTS permanently deletes the selected le.
Delete Selected Files a. Select les.
b. Click Delete Selected Files.
Only selected les in the list are permanently deleted.
Delete All Files Click Delete All Files.
All les in the list are permanently deleted.
Restore Click .
QTS restores the le to its shared folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 130
Option User Action
Restore Selected Files a. Select les.
b. Click Restore Selected Files.
Only selected les in the list are restored to their shared folders.
Exclude List Click .
QTS restores the le to its shared folder and adds the le to the
exclude list.
Servers
Depending on your needs, you can congure the NAS to host websites, create VPN connections for secure
data transmission, and more.
Web Server
You can use the NAS to host websites and establish an interactive website.
Enabling the Web Server
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Web Server > Web Server .
3. Select Enable Web Server.
4. Optional: Congure the following settings.
Setting User Action
Port number Specify a port number.
Note
The default port is 80.
Enable HTTP compression Select this option to improve transfer speeds and bandwidth
utilization. This setting is enabled by default.
Warning
Enabling this option may lead to security risks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 131
Setting User Action
Enable secure connection
(HTTPS)
Select this option to allow HTTPS connections.
a. Select Enable secure connection (HTTPS).
b. Select a TLS version.
The default TLS version is 1.2.
Warning
Selecting the latest TLS version may decrease
compatibility for other clients in your system.
c. Enable strong cipher suites.
d. Specify a port number.
Note
The default port is 8081.
e. Optional:
Select Force secure connection (HTTPS) only to require all users
to connect to the NAS using only HTTPS.
Maximum number of clients Enter a maximum client number.
Note
A client number is the number of users that are
allowed to connect to the server.
Do not allow QTS embedding in
IFrames
a. Select this option to prevent websites from embedding QTS using
IFrames.
b. Click Allowed Websites to allow a specic website to embed QTS
in IFrames.
c. The Allowed Websites window appears.
d. Optional:
Click Add to add a website to the list.
The Add Host Name window appears.
e. Specify a host name.
f. Click Add.
The host name is added to the allowed websites list.
g. Optional:
Select a website, and then click Delete to delete a website from
the list.
h. Click Apply.
Enable X-Content-Type-Options
HTTP header
Select this option to protect your device from attacks that exploit MIME
sning vulnerabilities.
Enable Content Security Policy
HTTP header
Select this option to protect your device from attacks that exploit Cross
Site Scripting (XSS) and data injection vulnerabilities.
5. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 132
Tip
To restore the default conguration settings at any time, click Restore.
QTS enables the web server.
Modifying the php.ini Maintenance File
The php.ini le is the default PHP conguration le. To optimize your website performance, you can modify
and congure the default settings in the php.ini le, such as execution time, memory limit, and maximum
le upload size.
Important
This task requires that you enable the Web Server.
For details, see Web Server.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Web Server > Web Server .
3. Below php.ini Maintenance, select one of the following options.
Option User Action
Upload a. Click Upload.
The Upload php.ini window opens.
b. Click Browse.
The Open window opens.
c. Select a php.ini le.
d. Click Upload.
QTS uploads the le.
Edit a. Click Edit.
The Edit php.ini window opens.
b. Edit the php.ini le.
c. Click Apply.
QTS saves the changes.
Restore a. Click Restore.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click OK.
QTS restores the default php.ini le.
Enabling and Creating a Virtual Host
Virtual hosting allows you to use your NAS to host multiple websites.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Web Server > Virtual Host .
3. Select Enable Virtual Host.
4. Click Apply.
You can now create a virtual host.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 133
5. Click Create a Virtual Host.
The Advanced Options window opens.
6. Enter a host name.
7. Select a root directory.
8. Select a protocol.
9. Enter a port number.
10. Click Apply.
The virtual host appears in the Host Name list.
Enabling the LDAP Server
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open and cross-platform protocol used for accessing and
managing a directory service. Enabling the LDAP server will allow users to access and share your directory
service.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > LDAP Server .
3. Select Enable LDAP Server.
4. Enter a domain name.
5. Specify a password.
6. Verify the password.
7. Select a TLS version.
8. Optional: Click Initialize.
Warning
Initializing the LDAP database will delete all users and groups from the LDAP server.
9. Click Apply.
MariaDB Server
MariaDB is an open-source relational database management system compatible with MySQL. You can use
MariaDB for hosting your website database on the NAS. QTS allows you to congure and migrate a MariaDB
database to your NAS or to a server through the MariaDB 5 or MariaDB 10 app. The app is not pre-installed
in QTS.
MariaDB Server Requirements
Software requirements Description
Operating system QTS 5.0.0 or later
App MariaDB 5 or MariaDB 10 app
Download and install the app version that meets your database
requirements from App Center.
For details, see Installing an App from App Center.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 134
Conguring the MariaDB Database
Important
• If the SQL server was enabled in QTS 4.5.4 (or earlier) before you updated to QTS
5.0.0 (or later), after the update the system will have automatically downloaded and
installed the MariaDB 5 app and migrated the SQL server data to MariaDB.
• You can install either the MariaDB 5 or MariaDB 10 app. If you install both app versions
on your NAS, MariaDB 5 will be set as the default database server.
You can congure the MariaDB database using the following methods during setup:
Methods Description
Creating a MariaDB database Create a new MariaDB version 5 or Maria DB version 10 database
by conguring the TCP/IP network congurations and database
password.
For details, see Creating a MariaDB Database.
Restoring a MariaDB Database Restore an existing MariaDB version 5 or MariaDB version 10 database
by conguring the TCP/IP network congurations.
For details, see Restoring a MariaDB Database
Migrating a MariaDB 5 Database
to MariaDB 10
If the MariaDB 10 app is installed on your NAS, you can migrate
an existing MariaDB version 5 database to a MariaDB version 10
database.
For details, see Migrating a MariaDB 5 Database to MariaDB 10
Creating a MariaDB Database
Warning
Creating a new MariaDB database will overwrite an existing MariaDB database.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > MariaDB .
The MariaDB Setup Wizard window opens.
Note
The MariaDB setup wizard only appears during app initialization. To congure more advanced
database features and settings, use the php.ini maintenance le.
3. Click Start.
The Database Actions screen appears.
4. Select Create a new database.
5. Click Next.
The Default Instance Properties screen appears.
6. Specify a root password.
Important
• The password must contain 8 to 64 bytes of UTF-8 characters.
• The password cannot be "admin" or blank.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 135

• If the system detects a weak password, the MariaDB server will be automatically disabled
until a stronger password is congured.
7. Conrm the password.
8. Optional: Enable TCP/IP networking.
a. Select Enable TCP/IP networking.
b. Specify the port number.
Tip
• MariaDB 5: The default port number is 3306.
• MariaDB 10: The default port number is 3307.
9. Click Apply.
QTS creates the MariaDB database. The Finish screen appears.
Note
It may take a few minutes for the system to set up the database.
10. Click Finish.
QTS enables the MariaDB server.
Restoring a MariaDB Database
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > MariaDB .
The MariaDB Setup Wizard window opens.
Note
The MariaDB setup wizard only appears during app initialization. To congure more advanced
database features and settings, use the php.ini maintenance le.
3. Click Start.
The Database Actions screen appears.
4. Select Restore the existing database.
5. Click Next.
The Default Instance Properties screen appears.
6. Optional: Congure TCP/IP networking.
a. Select Enable TCP/IP networking.
Note
This option is enabled by default.
b. Specify the port number for TCP/IP networking.
Note
The default port is 3307.
7. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 136

QTS restores the MariaDB database. The Finish screen appears.
Note
It may take a few minutes for the system to restore the database.
8. Click Finish.
QTS enables the MariaDB server.
Migrating a MariaDB 5 Database to MariaDB 10
This feature is only available in the MariaDB 10 app.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Install the MariaDB 10 app.
Note
For details, see Installing an App from App Center.
3. Open the MariaDB 10 app.
The MariaDB Setup Wizard window opens.
Note
The MariaDB setup wizard only appears during app initialization. To congure more advanced
database features and settings, edit the php.ini maintenance le. For details, see Modifying the
php.ini Maintenance File.
4. Click Start.
The Database Actions screen appears.
5. Select Migrate a MariaDB 5 to a MariaDB 10 database.
6. Click Next.
The Default Instance Properties screen appears.
7. Optional: Congure TCP/IP networking.
a. Select Enable TCP/IP networking.
Note
This option is enabled by default.
b. Specify the TCP/IP networking port.
Note
The default port is 3307.
8. Click Apply.
QTS migrates the existing MariaDB 5 database to MariaDB 10. The Finish screen appears.
Note
The data migration may take a few minutes to complete.
9. Click Finish.
QTS enables the MariaDB server.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 137
Enabling or Disabling the MariaDB Server
Important
If the SQL server was enabled in QTS 4.5.4 (or earlier) before you updated to QTS 5.0.0 (or
later), after the update the system will have automatically downloaded and installed the
MariaDB 5 app and migrated the SQL server data to MariaDB.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > MariaDB .
The MariaDB app opens.
3. Perform one of the following operations:
Options User Actions
Enable the MariaDB server Click .
Disable the MariaDB server Click .
Managing the MariaDB Account and Database
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > MariaDB .
The MariaDB app opens.
3. Click Account and Database.
4. Perform any of the following:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 138
Option User Action
Reset the root password Warning
Resetting the root password will restart the MariaDB
database.
Important
To protect your NAS, the system will automatically
detect weak MariaDB server root passwords and
require you to change the password. Follow the on-
screen instructions to change the root password.
a. Click Reset.
The Reset Root Password screen appears.
b. Specify a new password.
Note
• The password must contain 8 to 64 bytes of UTF-8
characters.
• The password cannot be "admin" or blank.
c. Conrm the password.
d. Click Next.
A conrmation message appears.
e. Click Yes.
The root password is changed.
Reset user passwords a. Click Reset.
The Reset User Passwords screen appears.
b. Enter the root password.
c. Click Next.
d. Select a user account.
e. Specify a new password.
Note
• The password must contain 8 to 64 bytes of UTF-8
characters.
• The password cannot be "admin" or blank.
f. Conrm the password.
g. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 139
Option User Action
Reinitialize the database Warning
Reinitializing the database will delete all data in the
database.
a. Click Reinitialize.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Yes.
The MariaDB Setup Wizard screen appears.
Modifying the TCP/IP Network Settings
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > MariaDB .
The MariaDB app opens.
3. Click Information.
4. Select Enable TCP/IP networking.
5. Specify a port number.
Note
• MariaDB 5: The default port number is 3306.
• MariaDB 10: The default port number is 3307.
6. Click Apply.
The TCP/IP networking settings are updated.
Syslog Server
You can congure the NAS as a syslog server. This allows you to collect log messages from dierent devices
in one location.
Enabling the Syslog Server
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Syslog Server > Server Settings .
3. Select Enable Syslog Server.
4. Select at least one of the following options.
Option User Action
Enable TCP a. Select Enable TCP.
b. Enter a TCP port.
Enable UDP a. Select Enable UDP.
b. Enter a UDP port.
5. Optional: Congure the log settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 140
a. Specify the maximum log size.
Tip
The log size range is 1 to 100.
b. Select the log destination folder.
c. Enter the log le name.
6. Optional: Enable the email notication settings.
Note
The NAS sends an email to up to 2 email addresses when the severity of the received syslog
message matches the specied level.
a. Select Enable the email notication.
b. Select a severity level.
Level Severity Description
0Emerg The system is unusable.
1Alert The system requires immediate attention.
2Crit The system has critical conditions.
3Err The system has error conditions.
4Warning The system has warning conditions.
c. Click Congure Notication Rule.
The Create event notication rule window opens.
For details, see Creating an Event Notication Rule.
Adding a Syslog Server Filter
This task allows the NAS to only receive syslog messages that match a specied lter.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Syslog Server > Filter Settings .
3. Click Add a Filter.
The Add a Filter window opens.
4. Congure the lter.
a. Select the lter type.
•Facility
•Severity
•Hostname
•Application
•Message
•IP
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 141

b. Select a lter option.
•greater than or equal to
•less than or equal to
•equals
•starts with
•contains
•not equals
•does not start with
•does not contain
c. Enter the lter condition.
d. Click Add.
Tip
To remove an existing lter, click Remove.
5. Optional: Manually congure a lter.
a. Select Manual Edit.
b. Type the lter conditions.
6. Click Apply.
QTS adds the syslog lter.
Managing Syslog Filters
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > Syslog Server > Filter Settings .
3. Locate the lter you want to modify.
4. Perform one of the following options.
Option User Action
Enable Click .
QTS enables the lter.
Disable Click .
QTS disables the lter.
Edit a. Click .
The Filter window opens.
b. Modify the lter.
c. Click Apply.
QTS saves the lter information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 142
Option User Action
Delete a. Select one or more lters.
b. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Yes.
QTS deletes the selected lters.
Tip
To view syslog messages, go to Control Panel > Applications > Syslog Server > Syslog
Viewer .
RADIUS Server
You can congure the NAS to become a remote authentication dial-in user service (RADIUS) server. The
RADIUS server provides centralized authentication, authorization, and account management for computers
to connect and use as a network service.
Enabling the RADIUS Server
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > RADIUS Server > Server Settings .
3. Select Enable RADIUS Server.
4. Optional: Select Grant dial-in access to system user accounts.
Note
This option allows local NAS users to access network services using the login credentials for
RADIUS clients.
5. Click Apply.
Creating a RADIUS Client
A RADIUS client is a client device, client program, or a client software utility. You can create up to 10 clients.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > RADIUS Server > RADIUS Clients .
3. Click Create a Client.
The Create a Client window opens.
4. Enter the following information.
•Name
•IP Address
•Prex Length
•Secret Key
5. Click Apply.
QTS creates the RADIUS client.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 143
Managing RADIUS Clients
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > RADIUS Server > RADIUS Clients .
3. Locate the client you want to modify.
4. Perform one of the following options.
Option User Action
Enable Click .
QTS enables the client.
Disable Click .
QTS disables the client.
Edit a. Click .
The Edit Client window opens.
b. Congure the client information.
c. Click Apply.
QTS saves the client information.
Delete a. Select one or more clients.
b. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Yes.
QTS deletes the selected clients.
Creating a RADIUS User
A RADIUS user is the account used for RADIUS authentication. You can create as many users as the NAS
supports.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > RADIUS Server > RADIUS Users .
3. Click Create a User.
The Create a User window opens.
4. Enter the following information.
•Name
•Password
•Verify Password
5. Click Apply.
QTS creates the RADIUS user.
Managing RADIUS Users
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 144
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > RADIUS Server > RADIUS Users .
3. Select one of the following options.
Option User Action
Enable Click .
QTS enables the user.
Disable Click .
QTS disables the user.
Change Password a. Click .
The Edit User window opens.
b. Modify the settings.
c. Click Apply.
QTS saves the new password.
Delete a. Select one or more users.
b. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Yes.
QTS deletes the selected users.
Enabling the TFTP Server
Enabling the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Server allows you to congure network devices and boot
computers on a remote network for system imaging or recovery. TFTP does not provide user authentication
and you cannot connect to it using a standard FTP client.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > TFTP Server .
3. Select Enable TFTP Server.
4. Specify a UDP port.
Note
The default UDP port is 69. Change this port only if necessary.
5. Specify the root directory.
6. Optional: Enable TFTP logging.
Note
This option saves the TFTP logs as les. QNAP recommends viewing the log les using
Microsoft Excel or WordPad on Windows, or TextEdit on macOS.
a. Select Enable TFTP logging.
b. Specify the folder for saving log les.
c. Specify the access right.
7. Congure TFTP access.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 145
Option Description
Anywhere Allows TFTP access from any IP address.
Certain IP range only Allows TFTP access from IP addresses in the specied IP range only.
Enter the start and end IP addresses of the IP range.
8. Click Apply.
QTS enables the TFTP server.
Enabling the NTP Server
The NTP server allows other network devices to synchronize their time with the NAS.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > NTP Server .
3. Select Enable NTP Server (NTP server is Ready).
4. Optional: Select at least one operating mode.
Operating Mode Description
Broadcast Allows the NTP server to periodically send broadcast packets with the IP
address 255.255.255.255.
You can use this to synchronize your time.
Multicast Allows the NTP server to periodically send multicast packets. Enter a multicast
IP after selecting this option.
Manycast Allows the NTP server to listen for manycast requests from NTP clients and reply
to received client requests. Enter a multicast IP after selecting this option.
5. Click Apply.
QTS enables the NTP server.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Services 146
6. File Station
Overview
About File Station
File Station is a QTS le management application that allows you to access les on the NAS. You can quickly
locate les and folders, manage access permissions, play media les, and share data with other users.
System Requirements
Category Detail
Web browser • Microsoft Edge
• Mozilla Firefox 3.6 or later
• Apple Safari 5 or later
• Google Chrome
Java program Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 7 or later
Flash player Adobe Flash Player 9 or later is required for viewing media les.
Supported File Formats
Category File Extension
Image • BMP
• JPG
• JPE
• PNG
• TGA
• GIF
• HEIC
• HEIF
Music • MP3
• FLAC
• OGG
• WAV
• AIF
• AIFF
Video • AVI
• MP4
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 147
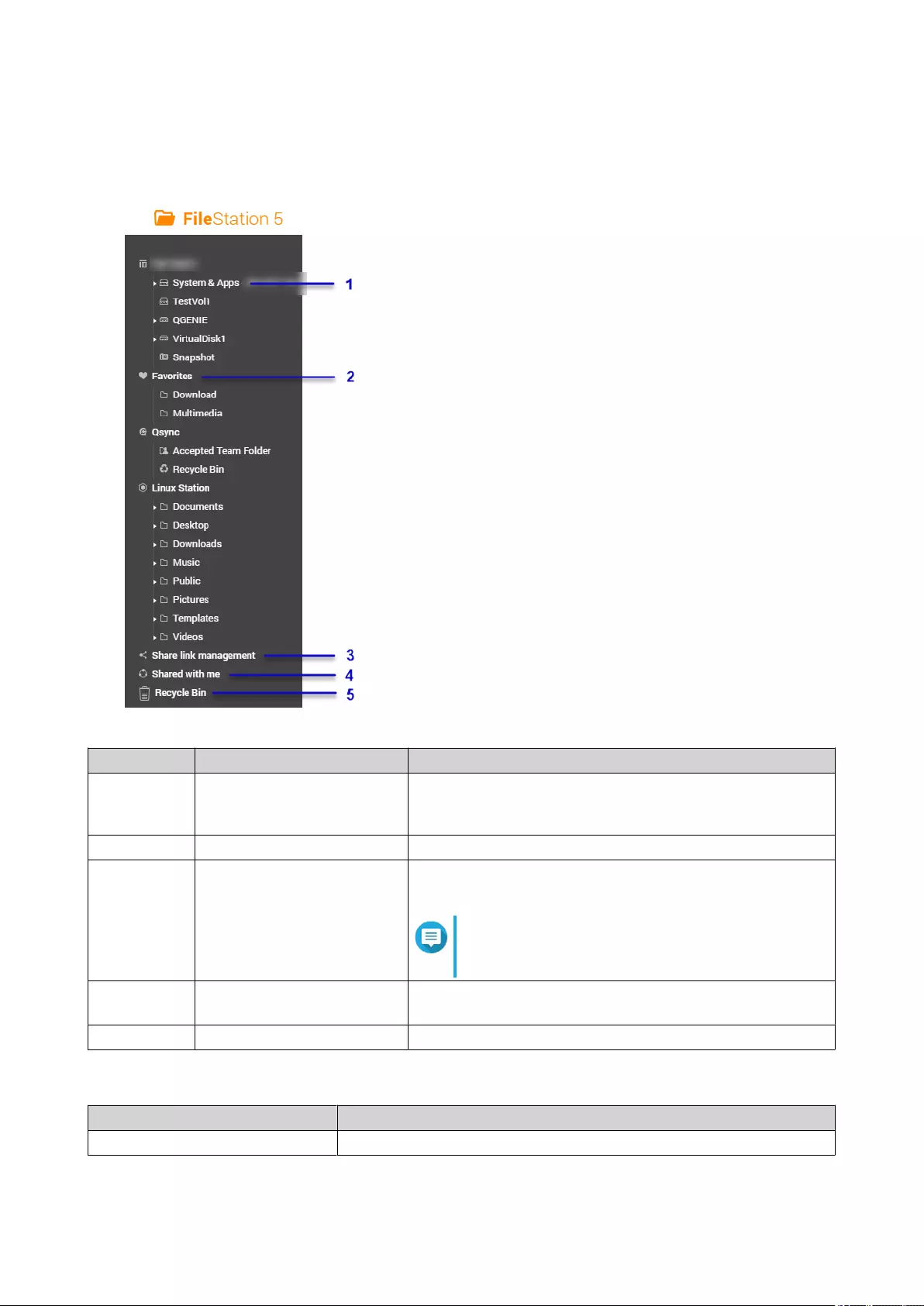
Parts of the User Interface
Left Panel
Label UI Element Description
1 Volume Displays all the folders on the volume, including shared
folders. Default shared folders vary depending on the NAS
model.
2 Favorites Displays bookmarked folders.
3 Share link management Displays links to NAS les shared by the current user
account.
Note
Users in the administrator group can see links
shared by all NAS users.
4 Shared with me Displays les and folders shared with the current user
account.
5 Recycle Bin Displays deleted les and folders.
Depending on your setup, the following folders may also appear on the list.
Folder Description
Snapshot Displays the saved snapshots.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 148
Folder Description
Local folders Displays the local folders on a Windows computer.
Important
To view local folders from File Station, you must rst
install Java Runtime Environment.
Qsync Displays les, folders, and team folders from Qsync.
SMB shared folder Displays les and folders from a shared folder mounted through SMB
protocol.
Note
To view the folder name, connection name, and the le
protocol, hover your cursor over an SMB shared folder.
NFS shared folder Displays les and folders from a shared folder mounted through NFS
protocol.
Note
To view the folder name, connection name, and the le
protocol, hover your cursor over an NFS shared folder.
File Cloud Gateway shared folder Displays les and folders from a shared folder mounted through a File
Cloud Gateway connection via HybridMount.
Depending on your setup, the following mounts created in HybridMount may also appear on the list.
Mount Description
CIFS/SMB Displays a list of connections mounted through CIFS/SMB protocol.
NFS Displays a list of connections mounted through NFS protocol.
FTP Displays a list of connections mounted through FTP protocol.
WevDAV Displays a list of connections mounted through a local network or over
the internet.
Cloud services Displays a list of connections mounted through a cloud service.
Note
To view the folder name, connection name, and the
cloud provider, hover your cursor over the cloud
mount.
Left Panel Tasks
You can perform the following tasks for a volume on the left panel.
Tip
To see the task options, hover the mouse point over a volume and then click .
Task Description
Create a shared folder Click to create a shared folder.
For details, see Creating a Shared Folder.
Open Snapshot Manager Click to open Snapshot Manager.
For details, see the Snapshots section of the QTS User Guide.
Lock/Unlock the volume Click to lock or unlock an encrypted volume in Storage & Snapshots.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 149
Volume Icons
Depending on your NAS model and environment, the following icons may appear beside each available
volume.
Icon Name Description
On Demand Tiering This icon appears when auto tiering is enabled on
the volume.
Snapshots This icon appears when snapshots are available for
the volume.
For details, go to the Snapshot section of the QTS
User Guide.
Cache Acceleration This icon appears when acceleration is enabled on
the volume.
Volume Encryption This icon appears when the volume is encrypted.
Volume Synchronization This icon appears when the cloud volume is
synchronizing data.
Toolbar
Label Item Description
1 Search Search les and folders by their name or type.
Tip
You can select Advanced Search to specify more
criteria.
2 Network Media Player Stream videos, photos, and music to compatible devices on your
network.
3 Refresh Refresh the current page.
4 Smart Filter Filter les and folders based on the specied criteria.
5 More Settings Congure File Station settings, open the Help guide, or view
application information.
6 Remote Mount Manage les across local, external, remote, and cloud storage
resources on a single interface.
To use this feature, install HybridMount from App Center. For more
information on HybridMount, go to the QNAP website.
7 Browsing Mode Select a browsing mode.
8 Create folder Create a folder, shared folder, snapshot shared folder, or share a space
with another NAS user.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 150
Label Item Description
9 Copy Copy the selected les and folders.
Note
This button only appears when a le or folder is
selected.
10 Upload Upload les or folders to the selected shared folder.
11 More Actions Perform dierent tasks.
Note
Some task options only appear when you select
certain types of les.
12 Share Share the selected les and folders.
Note
This button only appears when a le or folder is
selected.
13 Snapshot Open Snapshot Manager or view the Snapshot Manager quick tutorial.
Settings
Modifying General Settings
1. Click on the top-right corner.
2. Select Settings.
The Options window appears.
3. Select General.
4. Modify the following settings.
Option Description
Show hidden les on NAS File Station displays les and folders.
Allow all users to create shared links All users can share data from the NAS using shared
links.
Show Network Recycle Bin(s) File Station displays the @Recycle folder in all user
folders.
Only allow the admin and administrators group
to use "Share to NAS user"
File Station prevents non-administrators from
sharing les with other NAS users.
Only allow the admin and administrators group
to permanently delete les
File Station prevents non-administrators from
permanently deleting les.
Only allow the admin and administrators group
to use on-the-y transcode
File Station prevents non-administrators from using
on-the-y transcoding.
Track le and folder access File Station allows users to track le or folder access
and view information in System Access Logs.
5. Click Close.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 151
Modifying File Transfer Settings
1. Click on the top-right corner.
2. Select Settings.
The Options window appears.
3. Select File Transfer.
4. Under Duplicate File Name Policy, specify policies for handling duplicate les.
Scenario Policy
When uploading les •Always ask me
•Rename duplicate les
•Skip duplicate les
•Overwrite duplicate les
When copying or moving les •Always ask me
•Rename duplicate les
•Skip duplicate les
•Overwrite duplicate les
5. Optional: Select Always merge all le transfer processes into one task.
6. Under Google Drive File Transfer Policy, specify policies for handling Google Drive les.
Scenario Policy
When downloading or moving
Google Drive les
• Always ask me
• Download as Microsoft Oce le formats (.docx, .pptx, .xlsx)
• Keep Google Drive le formats
When downloading a single
Google Drive le to my PC
• Always ask me
• Download as Microsoft Oce le formats (.docx, .pptx, .xlsx)
• Keep Google Drive le formats
7. Click Apply.
8. Click Close.
Modifying Multimedia Settings
1. Open File Station.
2. Click on the toolbar.
3. Select Settings.
The Options window appears.
4. Select Multimedia.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 152
5. Modify the following settings.
Option Description
Support multimedia playback and thumbnail
display
File Station allows multimedia playback and displays
thumbnails for media les.
Note
To enable this feature, you must install
and start Multimedia Console from the
App Center.
Always display the 360° panoramic view button
on the viewer
File Station permanently displays the 360°
panoramic view button without checking the le
metadata.
6. Click Close.
Modifying Document Settings
1. Click on the top-right corner.
2. Select Settings.
The Options window appears.
3. Select Documents.
4. Optional: Select Support PDF thumbnail display.
Note
This feature requires Qsirch. You can install it from the App Center.
5. Under Microsoft Oce File Policy, specify policies for handling Microsoft Oce les.
File Format Policy
For .doc, .ppt, .xls les • Always ask me
• View in Google Docs
• Open with Chrome Extension
• Open with web browser
For .docx, .pptx, .xlsx les • Always ask me
• Edit with Oce Online
• View in Google Docs
• Open with Chrome Extension
• Open with web browser
6. Specify commercial or individual use for Oce Online.
Note
For commercial use, you need to sign up for Oce 365. You will be redirected to the Oce 365
interface when opening a le with Oce Online.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 153
7. Click Apply.
8. Click Close.
Modifying Third-party Service Settings
You can convert Apple iWork le formats to Microsoft Oce le formats using CloudConvert. The converted
les will be stored in the same folder with source les.
1. Click on the top-right corner.
2. Select Settings.
The Options window appears.
3. Select Third-party Service.
4. Acquire your CloudConvert API key.
Tip
For details, see the tutorial: https://www.qnap.com/en/how-to/faq/article/how-to-get-an-api-
key-from-cloudconvert
5. Paste your CloudConvert API key.
6. Click Apply.
File Operations
File Station enables you to perform the following tasks.
Operation Task
Store • Uploading a File
Access • Downloading a File
•Opening a File
•Opening Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint Files Using the
Chrome Extension
•Opening a Text File Using Text Editor
•Viewing a File in Google Docs
•Viewing a File in Microsoft Oce Online
•Opening Image Files Using Image2PDF
•Viewing File Properties
•Modifying File Permissions
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 154
Operation Task
Organize • Sorting Files
•Copying a File
•Moving a File
•Renaming a File
•Deleting a File
•Restoring a Deleted File
•Mounting an ISO File
•Unmounting an ISO File
•Compressing a File
•Extracting Compressed Files or Folders
Share • Sharing a File or Folder by Email
•Sharing a File or Folder on a Social Network
•Sharing a File or Folder Using Share Links
•Sharing a File or Folder with a NAS User
Play • Playing an Audio File
•Playing a Video File
•Playing a Video File Using CAYIN MediaSign Player
•Opening a 360-degree Image or Video File
•Streaming to a Network Media Player
Transcode • Adding a File to the Transcoding Folder
•Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
•Viewing Transcode Information
Uploading a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Click and then select File.
The File Upload window opens.
b. Select the le and then click Open.
Using drag and drop a. Locate the le on your computer.
b. Drag and drop the le to the File Station window.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 155
A conrmation message appears.
3. Select one of the following policies for handling duplicate les.
Option Description
Rename duplicate les Upload and rename a le if another le with the same name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Skip duplicate les Do not upload a le if another le with the same le name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Overwrite duplicate les Upload the le and then overwrite an existing le with the same name
and extension in the destination folder.
Tip
You can set the selected option as the default policy. File Station will not ask again after
remembering the setting. You can still change the policy in File Station > More Settings >
Settings > File Transfer .
4. Click OK.
File Station uploads the le.
Downloading a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Download.
d. Click OK.
Using the context menu Right-click the le and then click Download.
Depending on your browser, a conrmation message appears before the le is downloaded to your
computer.
Opening a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 156
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Open.
Using the context menu Right-click and then select Open.
Open the le directly Double-click the le.
Note
• File Station performs various actions depending on
the type of the selected le.
• For document les, you can choose an action from
the following options.
•Edit with Oce Online
•View in Google Docs
•Open with Chrome Extension
•Open with web browser
File Station opens the selected le.
Opening Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint Files Using the Chrome Extension
This task requires that you use the Google Chrome browser and install the Oce Editing for Docs, Sheets &
Slides extension.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Open with Chrome Extension.
Using the context menu Right-click the le and then select Open with Chrome Extension.
File Station opens an editable le on Google Docs, Sheets, or Slides.
Opening a Text File Using Text Editor
This task requires that you install Text Editor from the App Center.
1. Open File Station.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 157
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Open with Text Editor.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Open with Text Editor.
File Station opens the selected text le using Text Editor.
Viewing a File in Google Docs
This task requires that you use the Google Chrome browser and enable myQNAPcloud Link.
You can open and view les in Google Docs. To use this feature, your web browser must allow pop-up
windows.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select View in Google docs.
Using the context menu Right-click and then select View in Google docs.
File Station opens a preview of the le in Google Docs.
Viewing a File in Microsoft Oce Online
This task requires that you enable myQNAPcloud Link.
You can open and edit Microsoft Word, Excel, and Powerpoint les using Oce Online. To use this feature,
your web browser must allow pop-up windows.
Note
Editing a le in Microsoft Oce Online overwrites the le saved on the NAS.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 158
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Edit with Oce Online.
Using the context menu Right-click the le and then select Edit with Oce Online.
File Station opens the le in Microsoft Oce Online.
Opening Image Files Using Image2PDF
You must to install Image2PDF from the App Center before starting this task.
1. Opening File Station
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Use the menu bar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Open with Image2PDF.
Use the context menu Right-click and then select Open with Image2PDF.
File Station opens the selected image le with the Image2PDF wizard.
Follow the wizard's on-screen instructions to convert the image le into a PDF le.
Viewing File Properties
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Properties.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Properties.
The Properties window opens and displays the following information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 159
Field Description
Type Displays the le type.
Size Displays the le size.
File Path Displays the folder location.
Modied Date Displays the date that the le was last modied.
Owner Displays name of the NAS user who uploaded the le.
Group Displays the name of the NAS group that can access the le.
Storage Pool Displays the name of the storage pool on which the le is located.
Volume Displays the name of the volume on which the le is stored.
View Access Logs Keeps track of access to the le.
Tip
You can view access logs in QuLog Center.
• Open QuLog Center.
• Go to Local Device > System Access Logs .
• Specify File Station in the search eld.
4. Click Close.
Modifying File Permissions
This task requires that you enable advanced folder permissions in Control Panel > Privilege > Shared
Folders > Advanced Permissions .
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Properties.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Properties.
The Properties window opens.
4. Click .
5. Enable or disable the following permissions for the owner, group, or other users on the list.
Permission Description
Read Only Allows a user to view the le.
Read/Write Allows a user to view and make changes to the le.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 160

Deny Denies any access to the le.
Tip
You can click + to add users to the list and click - to remove users from the list.
6. Optional: Select the access rights for guest users.
7. Optional: Specify the ownership of the le.
a. Click .
b. Select a user.
c. Click Set.
8. Click Apply.
Sorting Files
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Click .
4. Select List.
File Station displays les in a list view.
5. Click a column title.
File Station sorts les in an ascending or descending order based on the selected column.
Tip
You can manually adjust column widths, except for Name. To manually adjust the column
width, click and drag the end of the column name.
Copying a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Copy to/Move to and then select Copy to.
d. Select the destination folder.
e. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 161
Method Steps
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Copy.
c. Go to the destination folder.
d. Right-click inside the folder and then select Paste.
Using keyboard shortcuts a. Select the le.
b. Press CTRL + C or Command-C.
c. Go to the destination folder.
d. Press CTRL + V or Command-V.
Using drag and drop a. Select the le.
b. Drag and drop to the destination folder.
Step result: A context menu appears.
c. Select one of the following actions.
• Copy and skip
• Copy and overwrite
• Copy and rename automatically
File Station creates a copy of the selected le.
Moving a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 162
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Copy to/Move to and then select Move to.
d. Select the destination folder.
e. Click OK.
a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Cut.
d. Select the destination folder.
e.
Click .
f. Select Paste.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le and then select Copy to/Move to and Move to.
b. Select the destination folder.
c. Click OK.
a. Right-click the le and then select Cut.
b. Select the destination folder.
c. Right-click inside the folder and then select Paste.
Using keyboard shortcuts a. Select the le.
b. Press CTRL + X or Command-X.
c. Go to the destination folder.
d. Press CTRL + V or Command-V.
Using drag and drop a. Select the le.
b. Drag and drop to the destination folder.
c. Step result: A context menu appears.
d. Select one of the following actions.
• Move and skip
• Move and overwrite
• Move (and rename if a le exists with the same name)
File Station moves the selected le to the specied folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 163
Renaming a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Rename.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Rename.
Use a keyboard shortcut Press F2.
4. Specify the le name and then click OK.
File Station renames the le.
Deleting a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Delete.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Delete.
Use the keyboard Press Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Specify how to delete the le.
• Move to Network Recycle Bin
• Delete permanently
5. Click OK.
File Station either moves the selected le to the Recycle Bin or deletes it permanently.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 164
Restoring a Deleted File
1. Open File Station.
2. Go to Recycle Bin.
3. Locate the le.
4. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Recover.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Recover.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click Yes.
File Station restores the selected le.
Mounting an ISO File
1. Open File Station.
2. Upload an ISO le.
For details, see Uploading a File.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Mount ISO.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Mount ISO.
The Mount ISO window appears.
4. Specify the shared folder name.
5. Click OK.
File Station mounts the ISO le as a shared folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 165
Unmounting an ISO File
1. Open File Station.
2. On the left panel, locate the mounted ISO le.
3. Right-click the le and then select Unmount.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click Yes.
File Station unmounts the ISO le and displays a conrmation message.
5. Click OK.
Compressing a File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le or folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le or folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Compress(Zip).
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le or folder.
b. Select Compress(Zip).
4. Congure the le compression settings.
Option Task
Archive name Specify a name for the compressed le.
Compression level Select the type of compression method.
•Normal - Standard compression
•Maximum compression - Prioritizes compression quality
•Fast compression - Prioritizes compression speed
Archive format Select the format of le compression.
•zip
•7z
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 166
Option Task
Update mode Specify how the les should be updated.
•Add and replace les
•Update and add les
•Update existing les
•Synchronize les
5. Optional: Specify a password to encrypt the le.
6. Click OK.
File Station compresses the selected le and creates a archive le.
Extracting Compressed Files or Folders
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the compressed archive le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Extract.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Extract.
4. Select one of the following le extraction options.
Option Description
Extract les Select specic les to extract.
Extract here Extracts all les in the current folder.
Extract to /<new folder>/ Extract all les in a new folder.
The new folder uses the le name of the compressed le.
File Station extracts the compressed les to the specied folder.
Sharing a File or Folder by Email
Before starting this task, you must congure the QTS email settings in Desktop > > E-mail Account .
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le or folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 167
Method User Action
Using the toolbar a. Select the le or folder.
b. Click Share.
c. Select Via Email.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le or folder.
b. Select Share.
c. Select Via Email.
The Share window appears.
4. Congure the following settings.
Field User Action
Send from Select the email delivery method.
• Use NAS to mail the links.
• Use local computer to mail the links.
Sender Select an email account.
To Specify the email address of the recipient.
Tip
You can select a recipient from your contact list if
Qcontactz is installed on the NAS.
Subject Specify the email subject line.
Message Enter a new message or use the default message.
5. Optional: Click More settings and congure additional settings.
Field User Action
Link Name Enter a name for the link or use the current name of the le or folder.
Note
A link name cannot contain the following characters: /
| \ : ? < > * "
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 168
Field User Action
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Tip
The following domains and IP addresses are
supported:
•myQNAPcloud: Provides a link to the shared
le or folder using the DDNS address set in
myQNAPcloud.
•WAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using a dierent network.
•LAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using the same local network.
•SmartShare: Provides a SmartURL via
myQNAPcloud Link to the shared le or folder.
•All available links: Provides links to the shared
le or folder using all of the available domains and
IPs.
Note
The recipients get direct read access.
Show SSL in URL Use an HTTPS URL.
On-the-y transcoding Allow users to transcode videos on the y.
Note
• This setting only appears when sharing les.
• To use on-the-y transcoding, you must install and
enable Video Station 5.2.0 (or later).
File upload Allow users to upload les to this folder.
Note
This setting only appears when sharing folders.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Note
You cannot access the shared le or folder after the
expiration date.
Password Require a password to access the link.
Tip
To include the password in the email, select Show the
password in the email.
6. Click Share Now.
File Station sends an email to the recipient.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 169
Sharing a File or Folder on a Social Network
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le or folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method User Action
Using the toolbar a. Select the le or folder.
b. Click Share.
c. Select To Social Network.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le or folder.
b. Select Share and then select To Social Network.
The Share window appears.
4. Congure the following settings.
Field User Action
Social Network Select the social network website.
Message Enter a new message or use the default message.
5. Optional: Click More settings and congure additional settings.
Field User Action
Link Name Enter a name for the link or use the current name of the le or folder.
Note
A link name cannot contain the following characters: /
| \ : ? < > * "
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 170
Field User Action
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Tip
The following domains and IP addresses are
supported:
•myQNAPcloud: Provides a link to the shared
le or folder using the DDNS address set in
myQNAPcloud.
•WAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using a dierent network.
•LAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using the same local network.
•SmartShare: Provides a SmartURL via
myQNAPcloud Link to the shared le or folder.
•All available links: Provides links to the shared
le or folder using all of the available domains and
IPs.
Note
The recipients get direct read access.
Show SSL in URL Use an HTTPS URL.
On-the-y transcoding Allow users to transcode videos on the y.
Note
• This setting only appears when sharing les.
• To use on-the-y transcoding, you must install and
enable Video Station 5.2.0 (or later).
File upload Allow users to upload les to this folder.
Note
This setting only appears when sharing folders.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Note
You cannot access the shared le or folder after the
expiration date.
Password Require a password to access the link.
6. Click Share Now.
File Station connects to the specied social network website.
Sharing a File or Folder Using Share Links
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le or folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 171
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method User Action
Using the toolbar a. Select the le or folder.
b. Click Share.
c. Select Create share link only.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le or folder.
b. Select Share and then select Create share link only.
The Share window appears.
Note
You can share a maximum number of 100,000 les and folders. If a link shares one le or
folder, you can create 100,000 share links. However, if a link shares 500 les or folders, you can
only create 200 share links.
4. Congure the following settings.
Field User Action
Link Name Enter a name for the link or use the current name of the le or folder.
Note
A link name cannot contain the following characters: /
| \ : ? < > * "
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Tip
The following domains and IP addresses are
supported:
•myQNAPcloud: Provides a link to the shared
le or folder using the DDNS address set in
myQNAPcloud.
•WAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using a dierent network.
•LAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using the same local network.
•SmartShare: Provides a SmartURL via
myQNAPcloud Link to the shared le or folder.
•All available links: Provides links to the shared
le or folder using all of the available domains and
IPs.
Note
The recipients get direct read access.
Show SSL in URL Use an HTTPS URL.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 172
Field User Action
On-the-y transcoding Allow users to transcode videos on the y.
Note
• This setting only appears when sharing les.
• To use on-the-y transcoding, you must install and
enable Video Station 5.2.0 (or later).
File upload Allow users to upload les to this folder.
Note
This setting only appears when sharing folders.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Note
This setting only appears when you share a folder.
Password Require a password to access the link.
5. Click Create Now.
File Station generates a link.
Sharing a File or Folder with a NAS User
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le or folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method User Action
Using the toolbar a. Select the le or folder.
b. Click Share.
c. Select To NAS user.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le or folder.
b. Select Share and then select To NAS user.
The Share window appears.
4. Select the user to share the le or folder with.
Option User Action
Existing user Select a user from the list.
Optional: Select Send a notication email to the user and then
specify the email subject and message. Only users who have provided
email information will receive notications.
Note
You can specify the email information for each user in
Control Panel > Privilege > Users .
New user Create a new user account.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 173
5. Optional: Click More settings and congure additional settings.
Field User Action
Link Name Enter a name for the link or use the current name of the le or folder.
Note
A link name cannot contain the following characters: /
| \ : ? < > * "
Domain name/IP Select the domain name or IP address.
Tip
The following domains and IP addresses are
supported:
•myQNAPcloud: Provides a link to the shared
le or folder using the DDNS address set in
myQNAPcloud.
•WAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using a dierent network.
•LAN: Provides a link to the shared le or folder to
other computers using the same local network.
•SmartShare: Provides a SmartURL via
myQNAPcloud Link to the shared le or folder.
•All available links: Provides links to the shared
le or folder using all of the available domains and
IPs.
Note
The recipients get direct read access.
Show SSL in URL Use an HTTPS URL.
On-the-y transcoding Allow users to transcode videos on the y.
Note
• This setting only appears when sharing les.
• To use on-the-y transcoding, you must install and
enable Video Station 5.2.0 (or later).
File upload Allow users to upload les to this folder.
Note
This setting only appears when sharing folders.
Expire in Specify the expiration date.
Note
You cannot access the shared le or folder after the
expiration date.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 174
Field User Action
Password Require a password to access the link.
Tip
• If you enable this option, this eld cannot be
empty.
• To include the password in the email, select Show
the password in the email.
6. Click Share Now.
File Station shares the le with the specied user.
Playing an Audio File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Play.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Play.
File Station plays the selected audio le using Media Viewer.
Playing a Video File
You must install Video Station from App Center to play certain video formats.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Play.
d. Select a resolution.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 175
b. Select Play.
c. Select a resolution.
File Station plays the selected le using Media Viewer.
Playing a Video File Using CAYIN MediaSign Player
CAYIN MediaSign Player is a third-party web media player. You must install CAYIN MediaSign Player from
App Center and have an activated license to play video les.
Note
CAYIN MediaSign Player can be enabled and disabled using Multimedia Services.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Click Play with CAYIN MediaSign Player.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Click Play with CAYIN MediaSign Player
File Station plays the selected le using CAYIN MediaSign Player.
Opening a 360-degree Image or Video File
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Play.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Play.
4. Optional: Select the resolution.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 176
File Station opens the selected le using the Media Viewer. You can click 360 Panorama Mode ( ) on
Media Viewer to view the photo or video in Panorama Mode.
Streaming to a Network Media Player
This task requires that you install Media Streaming Add-on from App Center.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b. Click on the toolbar.
c. Select a media player.
The Media Viewer window appears.
d. Select Play the selected item on this player.
e. Click OK.
a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Hover the mouse pointer over Streaming to.
d. Under Network Media Player, select a media player.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Hover the mouse pointer over Streaming to.
c. Under Network Media Player, select a media player.
File Station plays the selected le using the specied network media player.
Adding a File to the Transcoding Folder
Important
• Video les cannot be converted to a resolution higher than the original. If a higher
resolution is selected, File Station automatically transcodes the le in its original
resolution.
• This task requires transcoding to be enabled on the Multimedia Console.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 177
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Add to Transcode.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Add to Transcode.
The Add to Transcode window opens.
4. Select the transcoding video resolution.
• 240p
• 360p
• 480p SD
• 720p HD
• 1080p FULL HD
• Original resolution
• Only audio
5. Optional: Rotate the video.
•Click to rotate the video clockwise.
•Click to rotate the video counterclockwise.
6. Click OK.
File Station adds the transcoded le to the @Transcode folder.
Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Cancel/Delete Transcoding.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Cancel/Delete Transcoding.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 178
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
File Station removes the selected le from the Transcode folder and cancels the transcoding process.
Viewing Transcode Information
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the le.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the le.
b.
Click .
c. Select Transcode Information.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Transcode Information.
Multimedia Console opens. You can view transcoding tasks and congure related settings.
Folder Operations
File Station enables you to perform the following tasks.
Operation Task
Store • Uploading a Folder
•Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop
Access • Viewing Folder Properties
•Viewing Storage Information
•Modifying Folder Permissions
•Viewing Qsync Folders
•Managing Share Links
•Viewing Files and Folders Shared with Me
Organize • Creating a Folder
•Copying a Folder
•Creating a Desktop Shortcut
•Adding a Folder to Favorites
•Removing a Folder from Favorites
•Compressing a Folder
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 179
Operation Task
Share • Creating a Shared Folder
•Creating a Snapshot Shared Folder
•Sharing Space with a New User
Transcoding • Adding a Folder to the Transcoding Folder
•Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
Uploading a Folder
Note
This feature is only available on Google Chrome browsers.
1. Open File Station.
2. Open the destination folder.
3. Click and then select Folder.
The Browse for Folder window opens.
4. Select the folder to upload.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Select one of the following policies for handling duplicate les.
Option Description
Rename duplicate les Upload and rename a le if another le with the same name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Skip duplicate les Do not upload a le if another le with the same le name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Overwrite duplicate les Upload the le and then overwrite an existing le with the same
name and extension in the destination folder.
Tip
You can set the selected option as the default policy. File Station will not ask again after
remembering the setting. You can change the policy later in File Station > More Settings >
Settings > File Transfer .
6. Click OK.
File Station uploads the selected folder.
Uploading a Folder Using Drag and Drop
Note
This feature is only available on Google Chrome browsers.
1. Open File Station.
2. Drag and drop the local folder to File Station.
3. Select one of the following policies for handling duplicate les.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 180
Option Description
Rename duplicate les Upload and rename a le if another le with the same name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Skip duplicate les Do not upload a le if another le with the same le name and
extension already exists in the destination folder.
Overwrite duplicate les Upload the le and then overwrite an existing le with the same
name and extension in the destination folder.
4. Click OK.
File Station uploads the selected folder.
Viewing Folder Properties
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Properties.
Use the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Properties.
Use the left panel a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Properties.
The Properties window opens and displays the following information.
Field Description
Type Displays the folder type.
Size Click to display the folder size and total le count.
File Path Displays the folder location.
Modied Date Displays the date that the folder was last modied.
Owner Displays name of the NAS user who uploaded the folder.
Group Displays the name of the NAS group that can access the folder.
Storage Pool Displays the name of the storage pool on which the folder is stored.
Volume Displays the name of the volume on which the folder is stored.
Transfer to Dedicated Volume Migrates this shared folder to a snapshot shared folder.
View Access Logs Keeps track of access to the folder.
Tip
To enable this feature, select Track le and folder
access in File Station > Options .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 181
Field Description
Multimedia Console Opens Multimedia Console. This allows you to manage multimedia
content sources.
Shared Folder Edits folder properties.
4. Click Close.
Viewing Storage Information
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Storage Info.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Storage Info.
The Storage Info window opens and displays the following information.
Information Description
Shared folder Displays the names of shared folders.
Used size Displays the total storage size currently in use.
Volume Displays the volume name.
Capacity Displays the total storage capacity of the shared folder.
Free size Displays the total available storage space in the shared folder.
Volume status Displays the volume status.
4. Click Close.
Modifying Folder Permissions
This task requires that you enable advanced folder permissions in Control Panel > Privilege > Shared
Folders > Advanced Permissions .
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 182

b.
Click .
c. Select Properties.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Properties.
The Properties window opens.
4. Click .
5. Enable or disable the following permissions for the owner, group, and other users on the list.
Permission Description
Read Only Allows a user to view the folder.
Read/Write Allows a user to view and make changes to the folder.
Deny Denies a user any access to the folder
Tip
You can click + to add users to the list and - to remove users from the list.
6. Optional: Select the access right for guest users.
7. Optional: Specify the ownership of the folder.
a. Click .
b. Select a user.
c. Click Set.
8. Optional: Enable one or more of the following settings.
• Only the owner can delete the contents
• Only admin can create les and folders
• Apply changes to les and subfolders
• Apply and replace all existing permissions
9. Click Apply.
Viewing Qsync Folders
1. Open File Station.
2. On the left panel, click Qsync.
File Station displays the list of team folders shared by other NAS users.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 183
Managing Share Links
Share link management allows you to view, manage, and share previously created shared links easily and
quickly.
1. Open File Station.
2. On the left panel, click Share link management.
File Station displays the list of shared les and folders.
Note
• File Station automatically checks and deletes expired links.
• You can share a maximum number of 100,000 shared les and folders. If each link shares
one le or folder, you can create 100,000 share links. However, if each link shares 500 les
or folders, you can only create 200 share links.
3. Select an item from the list and then perform one of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Re-share Click and then select one of the following share methods.
• Share By Email.
• Share on a social network
• Use share links
• Share with a NAS user
Stop sharing Click .
Copy the link to the clipboard Click .
File Station performs the specied task.
Viewing Files and Folders Shared with Me
1. Open File Station.
2. On the left panel, click Shared with me.
File Station lists the les and folders shared with the current account. You can copy, open, or download a
selected le or folder.
Creating a Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the destination folder.
3. Perform one of the following tasks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 184
Task Steps
Using the toolbar a. Click
b. Select Folder.
The Create folder window opens.
c. Specify the folder name.
d. Click OK.
Using the context menu a. Right-click inside the folder and then select Create folder.
b. Specify the folder name.
c. Click OK.
File Station creates a new folder.
Copying a Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Copy to/Move to and then select Copy to.
d. Select the destination folder.
e. Click OK.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Copy.
c. Go to the destination folder.
d. Right-click inside the folder and then select Paste.
File Station creates a copy of the selected folder.
Creating a Desktop Shortcut
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 185
b.
Click .
c. Select Create Shortcut to Desktop.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Create Shortcut to Desktop.
Drag and Drop a. Select the folder.
b. Drag and drop the folder to the desktop.
File Station creates a desktop shortcut for the selected folder.
Tip
Hovering the mouse pointer over a desktop shortcut displays the path of the original folder.
Adding a Folder to Favorites
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Add to Favorites.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Add to Favorites.
Use the Favorites button a. Select the folder.
b. Click .
File Station adds the selected folder to the Favorites folder.
Removing a Folder from Favorites
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 186
c. Select Remove from Favorites.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Remove from Favorites.
Use the Favorites button a. Select the folder.
b. Click .
File Station removes the selected folder from the Favorites folder.
Compressing a Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Compress(Zip).
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Compress(Zip).
4. Congure the folder compression settings.
Option Task
Archive name Specify a name for the compressed le.
Compression level Select the type of compression method.
• Normal - Standard compression
• Maximum compression - Prioritizes compression quality
• Fast compression - Prioritizes compression speed
Archive format Select the format of le compression.
• zip
• 7z
Update mode Specify how the les should be updated.
• Add and replace les - Add and replace the specied les.
• Update and add les - Update old les and add new les.
• Update existing les - Update older versions of existing les.
• Synchronize les - Update old les, add new les, and remove
les that are no longer in the folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 187
5. Optional: Specify a password to encrypt the le.
6. Click OK.
File Station compresses the selected folder and creates an archive le.
Deleting a Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Delete.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Delete.
Use the keyboard Press Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Specify how to delete the folder.
• Move to Network Recycle Bin
• Delete permanently
5. Click OK.
File Station either moves the selected folder to the Recycle Bin or deletes it permanently.
Creating a Shared Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. On the menu bar, click .
3. Select Shared Folder.
The Create A Shared Folder window opens.
4. Congure the folder settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 188
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• End with "."
• Begin with "_sn_" or "_sn_bk"
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
Disk Volume Specify the volume on which the shared folder will be created.
Qtier auto Tiering Select this option to enable auto-tiering for this folder.
Note
To use this feature, you must enable Qtier on the
storage pool.
Path •Specify path automatically: Creates a new root folder on the
selected volume using the specied shared folder name.
•Enter path manually: Select an existing folder as the root folder.
5. Optional: Congure user access permissions.
a. Under Congure access privileges for users, click Edit.
b. Specify access permissions for each user.
6. Optional: Enable folder encryption.
a. Under Folder Encryption, click Edit.
b. Select Encryption.
c. Specify the following information.
Field/Option Description
Input Password Specify a password that contains 8 to 32 characters except the
following: " $ : = \
Verify Password The password must match the previously specied password.
Save encryption key When enabled, QTS automatically unlocks the shared folder after the
NAS restarts.
When disabled, the administrator must unlock the folder after the NAS
restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can
result in unauthorized data access if unauthorized
personnel are able to physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, all data will
become inaccessible.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 189
7. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
a. Under Advanced Settings, click Edit.
b. Congure the following settings.
Option Description
Guest Access Right Select the permission level assigned to users without a NAS account.
Hide network drive Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who
know the specic path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows le locking mechanism that
facilitates caching and access control to improve performance. This
feature is enabled by default and should only be disabled in networks
where multiple users simultaneously access the same les.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled. Selecting this
option encrypts all Microsoft network communication using the SMB3
protocol.
Enable Windows Previous
Versions
When enabled, the Previous Versions feature in Windows can be used
with the shared folder.
Enable Network Recycle Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle
Bin to administrators only for
now
Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from
recovering or deleting les in the Recycle Bin.
Note
This option is available only when Enable Network
Recycle Bin is selected.
Enable sync on this shared
folder
Selecting this option allows this shared folder to be used with Qsync.
This option is only available if Qsync Central is installed on the NAS.
Enable access-based share
enumeration (ABSE)
When enabled, users can only see the shared folders that they have
permission to mount and access. Guest account users must enter a
username and password to view shared folders.
Enable access-based
enumeration (ABE)
When enabled, users can only see the les and folders that they have
permission to access.
Set this folder as the Time
Machine backup folder (macOS)
When enabled, the shared folder becomes the destination folder for
Time Machine in macOS.
8. Click OK.
File Station creates a shared folder.
Creating a Snapshot Shared Folder
1. Open File Station.
2. On the menu bar, click .
3. Select Snapshot shared folder.
The Create a Snapshot Shared Folder window opens.
4. Congure the folder settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 190
Field Description
Folder Name Specify a folder name that contains 1 to 64 characters and that does
not:
• Begin or end with a space
• Contain consecutive spaces
• Contain the following characters: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % ` '.
Comment (optional) Specify a comment that contains 1 to 128 ASCII characters.
Storage Pool Specify the storage pool where this shared folder will be created.
Space Allocation Select one of the following space allocation options:
• Thick provisioning
• Thin provisioning
Qtier Auto Tiering Select this option to enable auto-tiering for this folder.
Note
To use this feature, you must enable Qtier on the
storage pool.
Allocate Folder Quota Specify a data quota for the folder.
5. Optional: Congure user access permissions.
a. Under Congure access privileges for users, click Edit.
b. Specify access permissions for each user.
6. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
a. Under Advanced Settings, click Edit.
b. Congure the following settings.
Option Description
Guest Access Right Select the permission level assigned to users without a NAS account.
Hide network drive Selecting this option hides the folder in Windows networks. Users who
know the specic path can still access the folder.
Lock File (Oplocks) Opportunistic lock (Oplocks) is a Windows le locking mechanism that
facilitates caching and access control to improve performance. This
feature is enabled by default and should only be disabled in networks
where multiple users simultaneously access the same les.
SMB Encryption This option is available only when SMB3 is enabled. Selecting this
option encrypts all Microsoft network communication using the SMB3
protocol.
Enable Windows Previous
Versions
Selecting this option allows users to use the Previous Versions feature
on Windows to restore the previous versions of this shared folder.
Enable Network Recycle Bin Selecting this option creates a Recycle Bin for this shared folder.
Restrict the access of Recycle
Bin to administrators only for
now
Selecting this option prevents non-administrator users from
recovering or deleting les in the Recycle Bin.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 191
Option Description
Enable access-based share
enumeration (ABSE)
When this option is enabled, users can only see the shared folders that
they have permissions to mount and access. Guests must specify a
username and password to view shared folders.
Enable access-based
enumeration (ABE)
When this option is enabled, users can only see the shared folders that
they have permissions to mount and access.
Set this folder as the Time
Machine backup folder (macOS)
Selecting this option allows users to back up the data on the Mac to
this shared folder via Time Machine.
7. Click Create.
File Station creates a snapshot shared folder.
Sharing Space with a New User
1. Open File Station.
2. On the menu bar, click .
3. Select Share space with a user.
The Create a User window opens.
4. Specify the following information:
Field Description
Username Specify a username that contains 1 to 32 characters from any of
the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: ~ ! @ # $ ^ & ( ) - _ . { }
Password Specify a password that contains 1 to 64 ASCII characters.
Quota Specify the storage capacity available to the user.
Phone number (optional) The information is for your reference and is not used by QTS.
Email (optional) QTS sends a notication to this email address when the account
password is about to expire.
Note
• You must congure the related settings in SMTP
Server and Change Password. Otherwise, QTS would
not send notications to the specied email address.
•SMTP Server: Go to Control Panel > System >
Notication > E-mail .
•Change Password: Go to Control Panel > System >
Security > Password Policy .
(Optional) Send a notication
mail to the newly created user
When selected, QTS sends a message that contains the following
information to the specied email address.
• Username and password
• URLs for connecting to the NAS
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 192
5. Click Create.
File Station creates a new user account and allocates the specied storage space.
Adding a Folder to the Transcoding Folder
Important
Video les cannot be converted to a resolution higher than the original resolution. If a
higher resolution is selected, File Station automatically transcodes the le in its original
resolution.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Add to Transcode.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the le.
b. Select Add to Transcode.
The Add to Transcode window opens.
4. Select the transcoding video resolution.
• 240p
• 360p
• 480p SD
• 720p HD
• 1080p FULL HD
• Original resolution
• Only audio
5. Click OK.
File Station adds the transcoded les to the @Transcode folder.
Canceling or Deleting Transcoding
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate the folder.
3. Perform one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 193
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select the folder.
b.
Click .
c. Select Cancel/Delete Transcoding.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the folder.
b. Select Cancel/Delete Transcoding.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
File Station removes the selected folder from the Transcode folder and cancels the transcoding
process.
Locking or Unlocking an Encrypted Shared Folder
After creating an encrypted shared folder, you can lock or unlock this folder to control user access. For
details on how to create an encrypted shared folder, see Creating a Shared Folder.
1. Open File Station.
2. Locate an encrypted folder on the left panel.
Tip
File Station displays the following icons beside an encrypted shared folder.
Icon Status
The encrypted folder is locked.
The encrypted folder is unlocked.
3. Perform one of the following tasks.
Tasks Steps
Lock the shared folder a. Right-click the shared folder.
b. Select Lock.
Unlock the shared folder a. Click the shared folder.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Unlock.
c. Specify the password.
d. Click OK.
Keeping a Folder or a File in Reserved Cache
You can keep the most important or the most frequently used data in the reserved cache to enhance access
performance. HybridMount is required for this task.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 194
Important
You can only perform this operation for folders in the shared folders mounted via
HybridMount. For details on how to use HybridMount and how to mount cloud services,
see HybridMount Help.
1. Open File Station.
2. Select a mounted shared folder.
3. Select a folder or le.
4. Choose one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a.
Click .
b. Select Always Keep in Reserved Cache.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click OK.
Using the context menu a. Right-click the selected item.
b. Select Always Keep in Reserved Cache.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click OK.
File Station keeps the selected folder or le in the reserved cache.
Folders or les in the reserved cache can have one of the following statuses.
Status Icon Description
This le or folder is only stored in the cloud
File Station is downloading this le or folder.
File Station has encountered an error when downloading this le or
folder.
File Station has cached and is uploading this le or folder.
File Station has cached and placed this le or folder in the upload
queue.
File Station has encountered an error when uploading this le or
folder.
This le or folder has been cached and synced and will always be kept
in the reserved cache.
This le or folder has been cached and synced.
This le or folder has been cached and synced but marked as low
priority. When the cache space is insucient, File Station will remove
les or folders that are the least recently accessed.
This le or folder is ignored and not uploaded to the cloud. File Station
ignores and skips temporary system les during the sync process.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 195
Removing a Folder from Reserved Cache
You can remove folders from the reserved cache.
Important
You can only perform this operation for folders in the shared folders mounted via
HybridMount. For details on how to use HybridMount and how to mount cloud services,
see HybridMount Help.
1. Open File Station.
2. Select a mounted shared folder.
3. Locate one or more folders.
4. Choose one of the following methods.
Method Steps
Using the toolbar a. Select one or more folders.
b.
Click .
c. Select Do Not Keep in Reserved Cache.
A conrmation message appears.
d. Click OK.
Using the context menu a. Select one or more folders.
b. Right-click the folder.
c. Select Do Not Keep in Reserved Cache.
A conrmation message appears.
d. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
File Station 196
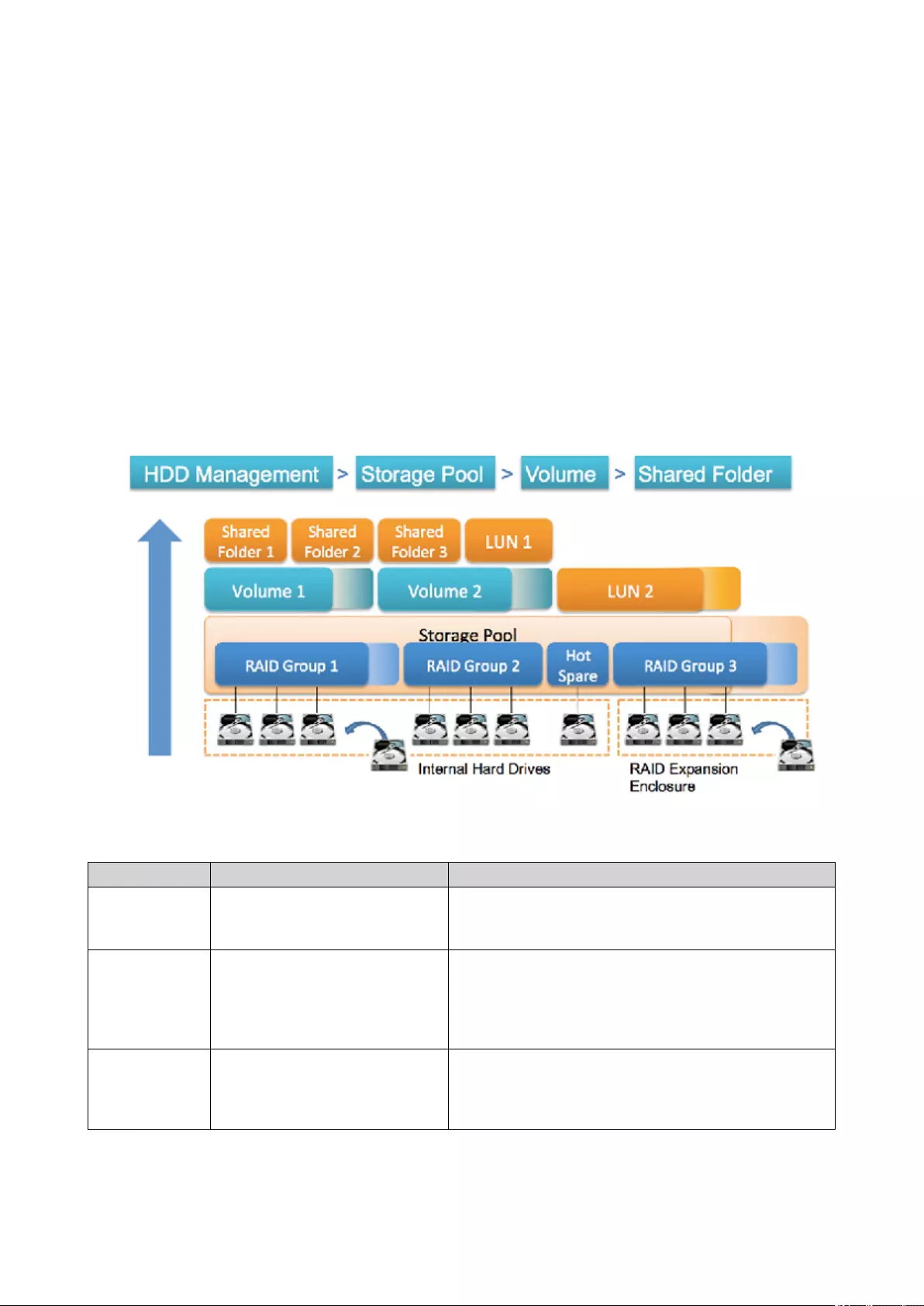
7. Storage & Snapshots
Storage & Snapshots is a QTS utility that helps you create, manage, and monitor storage on your NAS. With
Storage & Snapshots you can perform the following tasks:
• Create RAID groups, storage pools, and shared folders.
• Monitor storage usage and access speeds.
• Back up data using snapshots.
• Accelerate the performance of your NAS by creating an SSD cache.
• Specify which hosts (computers, servers, other NAS devices) are allowed to access the NAS.
QTS Flexible Volume Architecture
QTS Flexible Volume Architecture
Object Description Details
Disk A physical device that stores and
retrieves data.
QTS restricts which type of disk can be used for SSD
cache and storage space (static volumes and storage
pools). For details, see Disk Types.
RAID group A group of one or more disks
combined into one logical disk.
RAID groups usually contain
disks that are of the same type
and capacity.
Data is distributed across the disks in a RAID group.
Each RAID type oers a dierent combination of
reliability, performance, and capacity.
For details, see RAID.
Storage pool A pool of storage space
consisting of one or more RAID
groups.
Storage pools can aggregate RAID groups that consist
of disks of dierent types and capacities. Storage
pools enable easier storage space management and
features such as snapshots.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 197
Object Description Details
Volume A portion of storage space that
is used to divide up and manage
space on the NAS.
You can create volumes by dividing up storage pool
space, or using the space of a RAID group. QTS
oers three dierent volume types, with dierent
combinations of performance and exibility.
Important
You must create at least one volume
before the NAS can start storing data.
iSCSI LUN
(logical unit
number)
A portion of storage space that
can be used by other NAS
devices, servers and desktop
computers using the iSCSI
protocol.
QTS oers two LUN types.
• Block-based LUN: Created from a storage pool. It
is similar to a volume, except that it has no le
system and must be linked to an iSCSI host.
• File-based LUN: Created on a volume. It is similar
to an ISO image le.
Shared folder A folder that is used for storing
and sharing les.
Shared folders are created on volumes. QTS
automatically creates a set of default shared folders.
You can create more shared folders and congure
permissions for each.
Global Settings
You can access global settings by clicking in the Storage & Snapshots window.
Storage Global Settings
Setting Description
RAID Resync Priority Specify the minimum speed of the following RAID operations:
• Rebuild
• Migration
• Scrubbing
• Sync
You can select one of the following priorities:
•Service First: QTS performs RAID operations at lower speeds in order
to maintain NAS storage performance.
•Default: QTS performs RAID operations at the default speed.
•Resync First: QTS performs RAID operations at higher speeds. Users
may notice a decrease in NAS storage performance while RAID
operations are in progress.
Important
This setting only aects RAID operation speeds when the
NAS is in use. When the NAS is idle, all RAID operations are
performed at the highest possible speeds.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 198
Setting Description
RAID Scrubbing Schedule Enable this feature to periodically scan for and x bad sectors on RAID 5
and RAID 6 groups.
Auto Reclaim and SSD Trim
Schedule
Enable this feature to periodically run the following operations on all thin
volumes and SSDs:
• Auto Reclaim: QTS returns unused storage space to the parent storage
pool when les are deleted from thin volumes.
• SSD Trim: QTS tells the SSD rmware which data blocks it is safe to
erase when performing garbage collection. This helps maintain the
SSD's write performance and lifespan.
By default, the operations are scheduled to run daily at 2:00 AM. SSD Trim
is only performed on solid state drives that belong to a RAID 0, RAID 1, or
RAID 10 group.
Tip
You should enable this feature if you have one or more of
the following storage items:
• Thin volumes
• SSD RAID groups of type: Single, RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID
10
Note
To reclaim space on a thin LUN, the reclaim must be run on
the iSCSI client.
Scheduled File System Check Enable this feature to scan and automatically x all volumes that have le
system errors at a later date.
Disk / Device Global Settings
Setting Description
Activate Predictive S.M.A.R.T.
Migration
Enable this feature to regularly monitor disk health. If S.M.A.R.T. errors are
detected on a disk, QTS displays a warning and then begins migrating data
from the faulty disk to a spare disk. After the migration is nished, the
healthy disk is used in place of the faulty disk.
This process is safer than manually initiating a full RAID rebuild after a disk
has failed.
Use SSD estimated remaining
life with S.M.A.R.T. disk
migration
Enable this feature to migrate data from an SSD to a spare disk and rebuild
the RAID group when the SSD's estimated remaining life falls below 5%.
S.M.A.R.T. polling time Specify how often QTS checks disks for S.M.A.R.T. errors in minutes.
Disk Temperature Alarm Enable this feature to monitor the disk temperatures. QTS displays a
warning when the disk temperature is equal to or above the specied
threshold. You can set separate thresholds for hard disk drives and solid
state drives.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 199
Setting Description
TLER/ERC Timer Enable this feature to specify a maximum response time of all disks in
seconds.
When a disk encounters a read or write error, it may become unresponsive
while the disk rmware attempts to correct the error. QTS might interpret
this unresponsiveness as a disk failure. Enabling this feature ensures that
a disk has sucient time to recover from a read or write error before QTS
marks it as failed and initiates a RAID group rebuild.
Tip
• This setting is also known as Error recovery control
(ERC), Time-limited error recovery (TLER) or Command
completion time limit (CCTL).
• When this feature is disabled, QTS uses the default
TLER/ERC settings specied by the disk manufacturer.
Check for expansion unit
rmware updates at login
Enable this feature to automatically check online for newer rmware for
each expansion unit connected to the NAS. If QTS detects newer rmware, it
will ask whether you want to install it.
Share my disk analysis data
with QNAP
Enable this feature to send de-identied disk analysis data and NAS system
information to QNAP to improve future products. QNAP does not collect any
user data. You can opt out of this program at any time.
If the app DA Drive Analyzer is installed, enabling this setting sends disk
analysis data that is linked to your QID to QNAP.
Note
Disabling this setting causes the app DA Drive Analyzer to
stop working.
SSD Estimated Life Warning Enable this feature to change the disk status of an SSD to "Warning" when
its estimated life is lower than the specied threshold.
Snapshot Global Settings
Setting Description
Smart Snapshot Space
Management
Enable this feature to automatically delete the oldest snapshots when the
available snapshot storage space (guaranteed snapshot space plus free
storage pool space) is less than 32GB. You can also choose to automatically
delete the most recent snapshots.
When this feature is enabled and the snapshot retention policy is set to
"Smart Versioning", the system will retain the latest snapshot of each time
interval when deleting snapshots. For details, see Conguring a Snapshot
Retention Policy.
Important
If QTS is unable to create 32GB of free snapshot space, it
will not create any new snapshots.
Enable File Station Snapshot
Directory for administrators
Enable this feature to consolidate all available snapshots into a centralized
folder in File Station. You can restore les and folders from the snapshot
directory by copying them into another folder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 200
Setting Description
Make snapshot directory
(@Recently-Snapshot) visible
in shared folder root
Enable this feature to show a read-only folder @Recently-Snapshot at
the root level of each shared folder, containing all of the shared folder's
snapshots. You can restore les and folders from @Recently-Snapshot
by copying them into another folder.
When the number of
snapshots reaches maximum
Specify the default QTS behavior after a volume, LUN, or NAS reaches
its maximum number of snapshots. You can choose one of the following
behaviors:
• Overwrite the oldest snapshot when taking a new one.
• Stop taking snapshots.
Note
This setting does not apply to Snapshot Vault. For
Snapshot Vault, you can set the maximum number of
snapshots when conguring a Snapshot Replica job. For
details, see Creating a Snapshot Replica Job.
Use timezone GMT+0 for all
new snapshots
Enable this feature to use the GMT+0 time zone in the le names of new
snapshots. This le naming convention can simplify snapshot management
especially when working with snapshots from NAS devices located in
dierent time zones.
This setting only applies to new snapshots. Existing snapshots are not
renamed.
Show hidden les in
Snapshot Manager
Enable this feature to display hidden les in Snapshot Manager. This setting
does not aect les inside the File Station Snapshot Directory.
Enable Windows Previous
Versions
When enabled, Windows users can view and restore les from snapshots
using the Previous Versions feature in Windows. You can disable this feature
for individual folders by modifying the folder's properties.
Storage
QTS provides a exible storage architecture that enables you to easily manage, store, and share les.
Disks
Disk Types
QTS restricts which type of disk can be used to create SSD cache, storage pools, and static volumes.
Important
• For compatibility reasons, PCIe form-factor SSDs and PCIe M.2 SSDs installed in third-
party adapter cards cannot be used to create storage pools and static volumes.
• If you are already using NVMe PCIe SSDs for data storage, then your existing storage
conguration will not be aected after upgrading to the latest version of QTS.
Disk Type Installation Method SSD Cache Storage Pools/
Static Volumes
SATA/SAS/NL-SAS 3.5” HDD NAS drive bay No Yes
SATA/SAS 2.5” HDD NAS drive bay No Yes
SATA/SAS 2.5” SSD NAS drive bay Yes Yes
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 201
Disk Type Installation Method SSD Cache Storage Pools/
Static Volumes
PCIe NVMe M.2 SSD QM2 card Yes Yes
PCIe NVMe M.2 SSD Third-party M.2 to PCIe
adapter card
Yes No
SATA M.2 SSD QM2 card Yes Yes
SATA M.2 SSD NAS internal M.2 slot Yes Yes
PCIe form-factor SSD PCIe slot Yes No
Disk Management
You can manage disks at Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD . Select a disk to view its status
and hardware details.
Disk Status
Status Description
Data The disk is being used for data storage.
Spare The disk is congured as a hot spare.
Free The disk is not in use.
Cache The disk is being used in the SSD cache.
None There is no disk in the drive bay.
Warning QTS has detected S.M.A.R.T. errors. Run a full S.M.A.R.T. test and a disk scan.
Error QTS has detected I/O errors. You must replace the disk immediately.
Safely Detached The disk's storage pool or expansion unit was safely detached from the NAS.
Disk Information
Information Description
Disk Health Status The general health status of the disk
• Good: The disk is healthy.
• Warning: QTS has detected an error. Run a full S.M.A.R.T. test and a disk
scan.
• Error: QTS has detected a critical error. You must replace the disk
immediately.
Manufacturer The manufacturer of the disk
Model The disk model
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 202
Information Description
Disk Capacity The capacity of the disk, in both binary and decimal formats
Note
• Binary format assumes that 1 GB = 1,073,741,824
bytes. This is the true capacity of the disk and is used
by computers and operating systems such as QTS.
• Decimal format assumes that 1 GB = 1,000,000,000
bytes. This format is used by disk manufacturers and
appears in advertising, on the disk's box, and in the
disk's hardware specications.
• Due to dierences in the number of bytes per
gigabyte, a disk's binary capacity will be slightly
lower than its decimal capacity. For example, a disk
advertised as 500 GB (decimal) has a true capacity of
456 GB (binary).
Bus Type The interface that the disk uses
Supported Bus Types The disk types the drive bay supports. For example, an internal M.2 SSD slot
might support SATA and NVMe SSDs.
Status The hardware status of the disk
Current Speed The speed at which the disk is connected to the enclosure
Maximum Speed The maximum transfer speed supported by the drive bay or slot that the
disk is installed in
Temperature The current temperature of the disk
Disk temperature is retrieved from the disk's rmware using S.M.A.R.T.
Disk Access History (I/O) • Good: QTS has not detected any I/O errors on the disk.
• Error: QTS has detected one or more I/O errors on the disk.
Disk SMART Information Important
If any of the S.M.A.R.T. attribute values reach the threshold
set by the disk manufacturer or a predened threshold
determined by QTS, this eld will change to Warning.
Estimated Life Remaining The remaining life of the disk, as calculated by the disk's rmware. When
the value reaches 0, you should replace the disk.
This information is only available for solid-state drives (SSDs).
Disk Actions
Action Description
Disk Info Displays disk details, including the disk manufacturer, model, serial
number, disk capacity, bus type, rmware version, ATA version, and ATA
standard.
Disk Health Displays disk S.M.A.R.T. information.
For details, see Disk Health Information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 203
Action Description
Scan for Bad Blocks Scan the disk for bad blocks.
Tip
Run this scan if the disk's status changes to Warning or
Error. If QTS does not detect any bad blocks, the status
changes back to Ready.
To view the number of bad blocks, see Disk Health > Summary .
Locate Prompt the drive LEDs to blink so that you can locate the drive in a NAS or
expansion unit.
Detach Remove the disk from its RAID group. The group must be of type: RAID 1,
RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10.
Set as Enclosure Spare Assign the disk as a global hot spare for all RAID groups within the same
enclosure (NAS or expansion unit).
For details, see Conguring an Enclosure Spare Disk.
Disable Spare Unassign the disk as a global hot spare.
New Volume Create a new volume.
For details, see Volume Creation.
Secure Erase Permanently erase all data on a disk.
For details, see Securely Erasing a Disk.
RAID Group Select a RAID group to view its RAID type, capacity, and member disks.
Disk Health Information
Tab Description Actions
Summary Displays an overview of S.M.A.R.T.
disk information and the results
from the most recent disk scan and
S.M.A.R.T. test.
-
IronWolf Health
Management
IronWolf Health Management (IHM)
monitors environment and usage
conditions, such as temperature,
shock, and vibration, and suggests
preventative actions to ensure
optimal performance for Seagate
IronWolf disks. Run an IHM test to
view the disk's IHM status.
Click one of the following buttons:
•Test: Run an IHM test now.
Note
The IHM test is only available for
HDDs.
•Set Schedule: Run the IHM test
periodically on a schedule.
•Statistics: View IHM data read/write
statistics.
SSD Features List Displays all supported SSD ATA
features.
-
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 204
Tab Description Actions
SMART Information Displays S.M.A.R.T. disk information
and supported attributes.
Important
If the value of a S.M.A.R.T.
attribute reaches the
threshold set by the
disk manufacturer or
a predened threshold
determined by QTS, the
SMART attribute’s status
will change to Warning.
-
Test Run a S.M.A.R.T. disk self-test. Select one of the following options:
•Rapid Test: Tests the electrical and
mechanical properties of the disk, and a
small portion of the disk surface. The test
takes approximately one minute.
•Complete Test: Tests the electrical and
mechanical properties of the disk, and the
full disk surface. This test duration varies
depending on the storage environment.
Settings Disk settings can be applied
individually, or to multiple disks at
once.
Congure the following settings:
•Enable temperature alarm: QTS displays
a warning when the disk temperature is
equal to or above the specied threshold.
•S.M.A.R.T. Test schedule: Schedule
periodic rapid and complete S.M.A.R.T. disk
tests. The results are displayed on the
Summary screen.
•IronWolf Health Management: Schedule
a daily IHM test for the disk. The results
are saved in the selected shared folder,
and are displayed on the IronWolf Health
Management screen.
Tip
You can apply these settings to the
current disk, all disks, or to disks
with the same type as the current
disk (HDD or SSD).
Disk Performance Tests
QTS can test the sequential and random read speeds of your disks.
Important
• The results provided by these tests are specic to the NAS being tested.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 205
• For accurate results, do not use any resource-intensive applications while the tests are
running.
Testing Disk Performance Manually
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Click Performance Test.
The Performance Test screen appears.
3. Select one or more disks.
4. Click Performance Test and then select a test type.
Test Type Description Test Results Format
Sequential read Test sequential read speed. MB/s
IOPS read Test random read speed. IOPS
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click OK.
QTS runs the test and then displays the results on the Performance Test screen. To see detailed results for
the IOPS read test, select one or more disks and then select Result > IOPS read result .
Testing Disk Performance on a Schedule
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Click Performance Test.
The Performance Test screen appears.
3. Set Weekly Test to On.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
QTS runs a sequential read test for all disks every Monday at 6.30am, and then displays the results on the
Performance Test screen.
Securely Erasing a Disk
Secure erase permanently deletes all data on a disk, ensuring that the data is unrecoverable. Using secure
erase on an SSD also restores the disk's performance to its original factory state. Only administrators can
perform this task.
Important
Do not disconnect any disks or power o the NAS while secure erase is running.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Select a free disk.
3. Click Action, and then select Secure Erase.
The Secure Erase window opens.
4. Optional: Select additional disks to erase.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 206
5. Click Next.
6. Select an erase mode.
Mode Description
Complete QTS writes over all blocks on the disk with zeros or ones. This mode is the most secure
but can take a long time to nish.
Select Customized to congure the following the erase settings.
• Number of rounds: QTS writes over all blocks on the disk the specied number of
times.
• Overwrite with: Overwrite all blocks with zeros, ones, or a random zero or one.
SSD QTS issues a solid state drive (SSD) secure erase ATA command. The SSD rmware then
erases all data and restores the disk to its original factory performance.
Important
This feature is only supported on specic SSD models.
Fast QTS overwrites the partition and RAID conguration data on the disk with zeros. This
mode is the quickest but is less secure than the other modes.
7. Click Next.
8. Enter your password.
Note
You must be logged in as an administrator.
9. Click Apply.
QTS starts erasing the disk. You can monitor the progress in Background Tasks.
Volumes
A volume is a storage space created from a storage pool or RAID group. Volumes are used to divide and
manage your NAS storage space.
Tip
• QTS supports the creation of three types of volume. For more information, see Thick,
Thin, and Static Volumes.
• When organizing your storage space, you can either create one large volume or
multiple smaller volumes. For more information, see Volume Conguration.
Volume Types
Thick, Thin, and Static Volumes
Volume Type
Static Thick Thin
Summary Best overall read/write
performance, but does
not support most
advanced features
Good balance between
performance and
exibility
Enables you to allocate
storage space more
eciently
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 207
Volume Type
Static Thick Thin
Read/write speed Fastest for random writes Good Good
Flexibility Inexible
A volume can only be
expanded by adding
extra drives to the NAS.
Flexible
A volume can easily be
resized.
Very exible
A volume can be resized.
Also unused space can
be reclaimed and added
back into the parent
storage pool.
Parent storage space RAID group Storage pool Storage pool
Volumes allowed in
parent storage space
One One or more One or more
Initial size Size of the parent RAID
group
User-specied Zero
Storage pool space is
allocated on-demand, as
data is written to the
volume. This is called thin
provisioning.
Maximum size Size of the parent RAID
group
Size of the parent storage
pool
Twenty times the amount
of free space in the
parent storage pool
The size of a thin volume
can be greater than that
of its parent storage
pool. This is called over-
allocation.
Eect of data deletion Space is freed in the
volume
Space is freed in the
volume
QTS can reclaim the
space and add it back
into the parent storage
pool.
Method of adding
storage space
• Add disks to the NAS
• Replace existing
disks with higher
capacity disks
Allocate more space from
the parent storage pool
Allocate more space from
the parent storage pool
Snapshot support (fast
backup and recovery)
No Yes Yes
Qtier (automatic data
tiering) support
No Yes Yes
Legacy Volumes
A legacy volume is a volume created in QTS 3.x or earlier, before QTS had storage pools. A NAS will contain
legacy volumes in the following situations:
• A volume was created on a NAS running QTS 3.x or earlier, and then the NAS was updated to QTS 4.0 or
later.
• A volume was created on a NAS running QTS 3.x or earlier, and then the disks containing the volume
were moved to a dierent NAS running QTS 4.0 or later.
You can use legacy volumes for data storage, but their behavior and status will not be consistent with other
volume types. They also cannot use newer QTS features such as snapshots.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 208
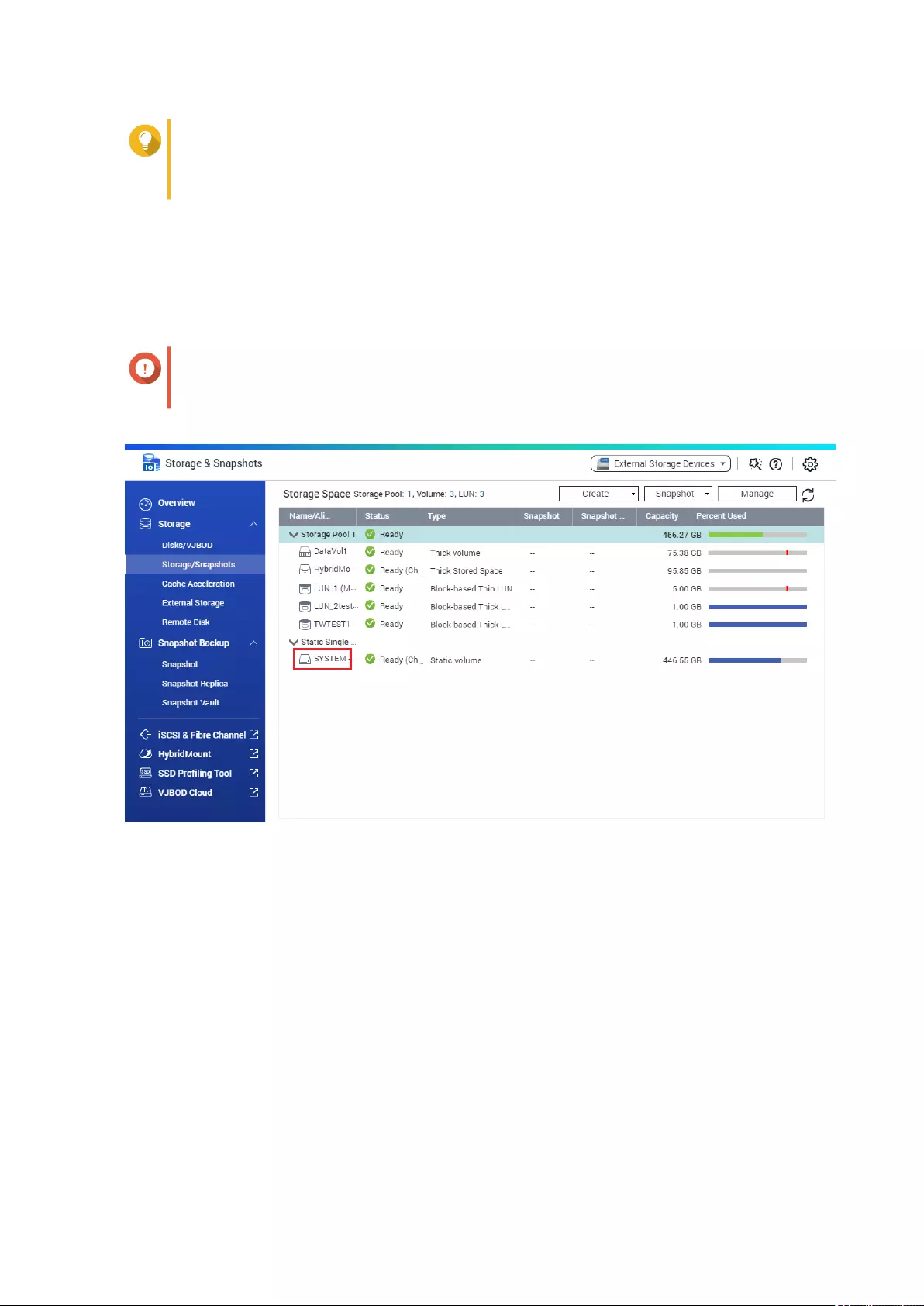
Tip
QNAP recommends replacing legacy volumes with newer volumes. To replace a legacy
volume, back up all data, create a new thick, thin, or static volume, and then restore the
data to the new volume.
The System Volume
The system volume is a regular static or thick volume that QTS uses to store system data such as logs,
metadata, and thumbnails. By default, applications are installed to the system volume. If no system volume
exists, either because the NAS has recently been initialized or the system volume was deleted, QTS will
assign the next static or thick volume that you create as the system volume.
Important
QNAP recommends creating a system volume of at least 10 GB. This is to prevent errors
caused by insucient system volume space
Volume Conguration
Volumes divide the NAS storage space into separate areas. You can create one large volume or multiple
smaller volumes. Each volume can contain one or more shared folders, which are used to store and share
les.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 209
Volume Conguration Examples
Conguration Advantage Description
Single Volume
Example:
• Volume 1
• Shared Folder 1
• Shared Folder 2
• Shared Folder 3
• Shared Folder 4
Simplicity Creating one volume is quick and easy. After the initial
setup, you do not have to worry about changing volume
sizes or creating new volumes.
Speed Single static volumes are faster because they do not
require a storage pool.
Multiple Volumes
Example:
• Volume 1
• Shared Folder 1
• Volume 2
• Shared Folder 2
• Volume 3
• Shared Folder 3
• Shared Folder 4
Storage space
limits
Each volume functions like a separate container. If
a user or an app writes a large amount of les to
a volume, only the specied volume is lled. Other
volumes remain unaected.
Multiple
snapshot
schedules
Snapshots protect les from accidental deletion or
modication. Snapshot creation requires time, memory
resources, and storage space.
QTS takes snapshots of individual volumes. Using
multiple volumes means you can have dierent
snapshot schedules for dierent le types. For example,
you can take hourly snapshots of the volume containing
important documents, and weekly snapshots of the
volume contain photos and movies.
Faster le system
repair
In certain circumstances such as after a power
outage, QTS may encounter errors in the le system
of a volume. While QTS can scan the volume and
automatically repair errors, this process can take a long
time. The required time depends on the volume size.
Files on the volume cannot be accessed during the
scanning process.
Volume Conguration Scenarios
Users often purchase NAS devices to store a combination of documents, media, and backups.
The following table compares the advantages and disadvantages of creating a single large volume or
multiple smaller volumes.
Requirement User Goal Single Volume Multiple Volumes
Simplicity Store les Users create one large thin
volume if they want to use
snapshots, or one large static
volume if they do not. They
then create three shared folders
on the volume, for documents,
movies, and backups.
Users create three separate
volumes for documents, movies,
and backups. Users must decide
how much space to initially
allocate to each volume.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 210
Requirement User Goal Single Volume Multiple Volumes
Speed Edit video and
audio les
Users create one large single
static volume on the NAS. The
les are backed up daily to
another NAS, or to an external
disk.
Users create a thick volume to
store the movie les. Random-
write performance is slightly
lower than a single static
volume.
Containerizing
storage space
Copy a large
number of movie
les to the NAS
Users copy the movie les to the
movies shared folder. However,
they must pay attention to
how much data they have in
the movies folder. If they copy
too many les, the volume will
become full.
Users copy the movie les to
the movies volume. When the
volume becomes full, they can
increase the volume size.
Multiple snapshot
schedules
Protect document
les using
snapshots
Users create a daily snapshot
schedule for a single volume.
The snapshots record all
changes made to document
les. However, the snapshots
also record changes to movie
and backup les which wastes
resources and storage space.
Users create a daily snapshot
schedule for the document
volume only.
File system repair Fix le system
errors
QTS must scan the entire single
volume, which can take a long
time. The volume cannot be
accessed during the scanning
process, making the entire NAS
unusable.
QTS only needs to scan the
volume that has an error. Each
volume is small, so scanning is
relatively quick. Users can still
access les on other volumes
while the scan is in progress.
Volume Creation
You can create a maximum of 128 volumes. QNAP recommends keeping the total number of volumes low
for optimal performance.
Creating a Static Volume
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Select the volume type.
a. Click Change Type.
The Change volume type window opens.
b. Select Static Volume.
c. Click OK.
The Change volume type window closes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 211
4. Click Next.
5. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
6. Select one or more disks.
Important
• For data safety, you cannot select disks that have the status Warning.
• The status In Use means that a disk is currently formatted as an external disk, and may
contain current user data.
• If you select a disk with the status In Use, QTS will temporarily stop all disk storage
services on the NAS in order to unmount the disk, and then delete all data and partitions on
the disk.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
7. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10
Important
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50 RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
For details, see RAID Types.
8. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For details, see RAID Disk Failure Protection.
9. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 subgroups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specied number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 212
• A higher number of subgroups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of subgroups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 subgroups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of storage
capacity.
10. Click Next.
11. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
12. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
13. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
14. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication
when the percentage of used
volume space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
Specify a value.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 213
Setting Description User Actions
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on
the volume with 256-bit AES
encryption.
• Specify an encryption password containing
8 to 32 characters, with any combination
of letters, numbers and special characters.
Spaces are not allowed.
• Select Save encryption key to save a local
copy of the encryption key on the NAS.
This enables QTS to automatically unlock
and mount the encrypted volume when
the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is
not saved, you must specify the encryption
password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key
on the NAS can result in
unauthorized data access if
unauthorized personnel are
able to physically access the
NAS.
• If you forget the encryption
password, all data will become
inaccessible.
Accelerate
performance with SSD
cache
QTS adds data from this volume to
the SSD cache to improve read or
write performance.
-
Create a shared folder
on the volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume is
ready. Only the user account that
creates the shared folder will have
read/write access to the folder.
Note
This setting is only
available when logged in
as "admin".
• Specify a folder name.
• Select Create this folder as a snapshot
shared folder.
A snapshot shared folder enables faster
snapshot creation and restoration.
15. Click Next.
16. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Creating a Thick or Thin Volume
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 214
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Select the volume type.
a. Click Change Type.
The Change volume type window opens.
b. Select a volume type.
• Thick Volume
• Thin Volume
c. Click OK.
The Change volume type window closes.
4. Select a storage pool.
You can select an existing storage pool or create a new storage pool immediately.
5. Optional: Create a new storage pool.
a. Click .
The Create Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
b. Click Next.
c. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
d. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
e. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 215
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50
Note
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
For details, see RAID Types.
f. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For RAID 50 or RAID 60, a spare disk must be congured later. You should congure a global
spare disk so that all subgroups share the same spare disk.
g. Click Next.
h. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
i. Optional: Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
j. Click Next.
k. Verify the storage pool information.
l. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
m. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool. The Create Storage Pool Wizard window closes.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
8. Specify the capacity of the volume.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 216
The volume type determines the maximum volume capacity.
Volume Type Maximum Size
Thick Amount of free space in the parent storage pool.
Thin Twenty times the amount of free space in the parent storage pool
Setting the maximum size of a thin volume to a value that is greater than the amount of free space in
the storage pool is called over-allocation.
9. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
10. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication
when the percentage of used
volume space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
Specify a value.
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on
the volume with 256-bit AES
encryption.
• Specify an encryption password containing
8 to 32 characters, with any combination
of letters, numbers and special characters.
Spaces are not allowed.
• Select Save encryption key to save a local
copy of the encryption key on the NAS.
This enables QTS to automatically unlock
and mount the encrypted volume when
the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is
not saved, you must specify the encryption
password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS
can result in unauthorized data access
if unauthorized personnel are able to
physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, all
data will become inaccessible.
Accelerate
performance with SSD
cache
QTS adds data from this volume to
the SSD cache to improve read or
write performance.
-
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 217
Setting Description User Actions
Create a shared folder
on the volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume is
ready. Only the user account that
creates the shared folder will have
read/write access to the folder.
Note
This setting is only
available when logged in
as "admin".
• Specify a folder name.
• Select Create this folder as a snapshot
shared folder.
A snapshot shared folder enables faster
snapshot creation and restoration.
Enable snapshot
schedule and
snapshot retention
QTS creates a default snapshot
schedule and snapshot retention
policy. You can congure these
settings later in Snapshot
Manager.
For details, see the following:
•Conguring a Snapshot
Schedule
•Conguring a Snapshot
Retention Policy
-
11. Click Next.
12. Click Finish.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Volume Management
Deleting a Volume
Note
• To delete a VJBOD Cloud volume, use the VJBOD Cloud app.
• To delete a HybridMount volume, use the HybridMount app.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a volume.
Warning
All data on the selected volume will be deleted.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select Remove > Remove Volume .
The Volume Removal Wizard window opens.
5. Click Apply.
Conguring a Volume Space Alert
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 218
2. Select a volume.
3. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
4. Click Actions, and then select Set Threshold.
The Alert Threshold window opens.
5. Enable space alerts.
6. Specify an alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used space is greater than or equal to the
specied threshold.
7. Click Apply.
Volume File System Check
A le system check scans for and automatically repairs errors in the le system of a thick, thin, or static
volume. QTS will prompt you to start a le system check if it detects le system errors on one or more
volumes. You can also run a le system check manually or schedule a one-time check.
Running a File System Check Manually
Warning
• A volume is unmounted and becomes inaccessible while its le system is being
checked.
• This process might take a long time, depending on the size of the volume.
Important
QTS will scan the specied volume, even if QTS has not detected any errors on the
volume's le system.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a volume.
3. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
4. Click Actions, and then select Check File System.
The Check File System window opens.
5. Click OK.
QTS creates a background task for the le system check. The status of the volume changes to
Checking....
Running a One-Time File System Check on a Schedule
Warning
• A volume is unmounted and becomes inaccessible while its le system is being
checked.
• This process might take a long time, depending on the size of the volume.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 219
Important
QTS will only scan the specied volume if it has detected errors on the volume's le
system.
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click .
The Global Settings window appears.
3. Click Storage.
4. Enable Scheduled File System Check.
5. Specify a date and time.
6. Click Apply.
Volume Expansion
Expanding a volume increases its maximum capacity so that it can store more data.
Resizing a Thick or Thin Volume
The maximum capacity of thick and thin volumes can be increased or decreased.
Operation Details
Expand Volume • The operation can be performed while the volume is online and accessible to
users.
• For a thick volume, additional space is allocated from the volume's parent storage
pool.
Shrink Volume • Users and applications will be unable to access the volume until the operation is
nished.
• For a thick volume, the freed space is returned to the volume's parent storage
pool.
Volume Type Maximum Allowed Capacity
Thick Amount of free space in the parent storage pool.
Thin Twenty times the amount of free space in the parent storage pool.
Important
Setting the maximum size of a thin volume to a value that is
greater than the amount of free space in the storage pool is called
over-allocation.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Click Resize Volume.
The Volume Resizing Wizard opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 220

5. Specify a new capacity for the volume.
Capacity can be specied in megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB).
6. Optional: Click Set to Max.
Sets the new volume capacity to the maximum available size. This option is only available for thick
volumes.
7. Click Apply.
If you are shrinking the volume, a conrmation message appears.
8. Click OK.
The Volume Resizing Wizard closes. The volume status changes to Expanding... or
Shrinking....
After expansion is complete, the volume status changes back to Ready.
Expanding a Static Volume by Adding Disks to a RAID Group
The total storage capacity of a static volume can be expanded by adding one or more additional disks to a
RAID group in the static volume. This extra capacity can be added online, without any interruption to data
access.
Important
• Adding disks to a RAID 1 group changes the RAID type of the group to RAID 5.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 group, every sub-group must be expanded with the
same number of disks.
1. Verify the following:
• The storage pool you want to expand contains at least one RAID group of type: RAID 1, RAID 5,
RAID 6, RAID 50 or RAID 60.
• The NAS contains one or more free disks. Each free disk must be the same type as the other disks
in the RAID group (either HDD or SSD), and have a capacity that is equal to or greater than the
smallest disk in the group.
• The status of the RAID group that you want to expand is Ready.
2. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
3. Select a static volume.
4. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
5. Click Expand.
The Expand Static Volume Wizard window opens.
6. Select Add new disk(s) to an existing RAID group.
7. Select a RAID group.
The group must be of type: RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 50, RAID 60.
8. Click Next.
9. Select one or more disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 221
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
10. Click Next.
11. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
12. Click Next.
13. Click Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
14. Click OK.
15. Optional: For a RAID 50 or RAID 60 volume, repeat these steps for each sub-group.
QTS starts rebuilding the RAID group. The storage capacity of the volume increases after RAID rebuilding is
nished.
Expanding a Single Static Volume By Adding a New RAID Group
The storage capacity of a static volume can be expanded by creating a new RAID group and then adding it to
the volume. This operation can be performed while the volume is online and accessible to users. QTS writes
data linearly to storage pools containing multiple RAID groups. This means that QTS writes data to a RAID
group until the group is full before writing data to the next RAID group.
Warning
• If a static volume contains multiple RAID groups and one RAID group fails, all data on
the volume will be lost. Ensure that you have a complete data backup plan.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, you must create a new RAID 50 or 60 group with
the same number of disks and sub-groups as the original pool. It is not possible to add
additional sub-groups.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a static volume.
3. Click Manage.
The Volume Management window opens.
4. Click Expand.
The Expanding Static Volume Wizard window opens.
5. Select Create and add a new RAID group.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 222

Important
If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible until
it is reconnected.
8. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
9. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Important
• If the storage pool contains a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10 group, the new RAID group
must also have one of the mentioned RAID types.
• For RAID 50 or RAID 60, you cannot select a dierent RAID type.
10. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
For details, see Conguring a RAID Group Hot Spare.
11. Click Next.
12. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
13. Click Next.
14. Click Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
15. Click OK.
QTS creates the new RAID group and then starts rebuilding the volume. The capacity of the volume
increases after RAID rebuilding is nished.
Storage Pools
A storage pool combines many physical disks into one large pool of storage space. Disks in the storage pool
are joined together using RAID technology to form RAID groups. Storage pools may contain more than one
RAID group.
Using storage pools provides the following benets:
• Multiple volumes can be created in a storage pool, enabling you to divide the storage space among
dierent users and applications.
• Disks of dierent sizes and types can be mixed into one large storage space.
• Disks from connected expansion units can be mixed with disks installed in the NAS to form a storage
pool.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 223
• Extra disks can be added while the storage pool is in use, increasing storage capacity without
interrupting services.
• Qtier provides auto-tiering when a storage pool contains a mix of SATA, SAS, and SSD disks. Qtier
automatically moves frequently accessed hot data to the faster SSDs, and infrequently accessed cold
data to the slower disks.
• Snapshots can be used with storage pools. Snapshots record the state of the data on a volume or
LUN at a specic point in time. Data can then be restored to that time if it is accidentally modied or
deleted.
• Multiple RAID 5 or RAID 6 groups can be striped together using RAID 0 to form a RAID 50 or RAID 60
storage pool.
Creating a Storage Pool
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Storage Pool.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create, and then select New Storage Pool.
The Create Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
5. Select one or more disks.
Important
• For data safety, you cannot select disks that have the status Warning.
• The status In Use means that a disk is currently formatted as an external disk, and may
contain current user data.
• If you select a disk with the status In Use, QTS will temporarily stop all disk storage
services on the NAS in order to unmount the disk, and then delete all data and partitions on
the disk.
• If you select RAID 5, 6, 50, or 60 for the RAID type, you cannot select more than 16 disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 224
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50
Note
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
For details, see RAID Types.
7. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For RAID 50 or RAID 60, a spare disk must be congured later. You should congure a global spare disk
so that all subgroups share the same spare disk.
8. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 subgroups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specied number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
• A higher number of subgroups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of subgroups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 subgroups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of storage
capacity.
9. Click Next.
10. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
11. Optional: Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
12. Optional: Congure pool guaranteed snapshot space.
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling
this feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
13. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 225

14. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
15. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool and then displays the information on the Storage/Snapshots screen.
Storage Pool Management
Deleting a Storage Pool
Only administrators can perform this task.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
4. Click Remove, and then select Remove Pool.
A notication window opens.
5. Select Conrm the removal of every volume/iSCSi LUN/Snapshot Vault on this storage pool.
Warning
All data in the storage pool will be deleted.
6. Click OK.
The Remove Pool window opens.
7. Enter your password.
Note
You must be logged in as an administrator.
8. Click OK.
Conguring a Storage Pool Space Alert
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Click Actions, and then select Set Threshold.
The Alert Threshold window opens.
5. Enable space alerts.
6. Specify an alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used space is greater than or equal to the
specied threshold.
7. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 226
Storage Pool Status
Status Description
Ready The storage pool is working normally. All RAID groups in the pool have the
status Ready.
Warning (Degraded) One or more RAID groups in the storage pool have the status Degraded.
There are not enough spare disks available to QTS to rebuild all of the RAID
groups.
Warning (Rebuilding) One or more RAID groups in the storage pool have the status Degraded
(Rebuilding). QTS is currently rebuilding them due to disk failure.
Warning (Read-Only) One or more RAID groups in the storage pool have the status Not Active.
Note
It might be possible to recover some data from volumes and
LUNs.
Storage Pool Expansion
Expanding a Storage Pool By Adding a New RAID Group
The storage capacity of a storage pool can be expanded by creating a new RAID group and then adding it to
the pool. This operation can be performed while the pool is online and accessible to users. QTS writes data
linearly to storage pools containing multiple RAID groups. This means that QTS writes data to a RAID group
until a group is full before writing data to the next RAID group.
Warning
• If a storage pool contains multiple RAID groups and one RAID group fails, all data in
the storage pool will be lost. Ensure that you have a complete data backup plan.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, you must create a new RAID 50 or 60 group with
the same number of disks and sub-groups as the original pool. It is not possible to add
additional sub-groups.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Select Expand Pool > Expand Pool .
The Expand Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
5. Select Create and add a new RAID group.
6. Click Next.
7. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
• You cannot use the disks from a QNAP JBOD enclosure to expand a storage pool which is
located on a dierent enclosure.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 227

• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
8. Select one or more disks.
Important
If you select RAID 5, 6, 50, or 60 for the RAID type, you cannot select more than 16 disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
9. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Important
• If the storage pool contains a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10 group, the new RAID group
must also have one of the mentioned RAID types.
• For RAID 50 or RAID 60, you cannot select a dierent RAID type.
10. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
11. Click Next.
12. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
13. Click Next.
14. Click Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
15. Click OK.
QTS creates the new RAID group and then starts rebuilding the storage pool. The capacity of the pool
increases after RAID rebuilding is nished.
Expanding a Storage Pool by Adding Disks to a RAID Group
The total storage capacity of a storage pool can be expanded by adding one or more additional disks to a
RAID group. This operation can be performed while the pool is online and accessible to users.
Important
• Adding disks to a RAID 1 group changes the RAID type of the group to RAID 5.
• To expand a RAID 50 or RAID 60 group, every sub-group must be expanded with the
same number of disks.
1. Verify the following:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 228

• The storage pool you want to expand contains at least one RAID group of type: RAID 1, RAID 5,
RAID 6, RAID 50 or RAID 60.
• The NAS contains one or more free disks. Each free disk must be the same type as the other disks
in the RAID group (either HDD or SSD), and have a capacity that is equal to or greater than the
smallest disk in the group.
• The status of the RAID group that you want to expand is Ready.
2. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
3. Select a storage pool.
4. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
5. Select Expand Pool > Expand Pool .
The Expanding Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
6. Select Add new disk(s) to an existing RAID group.
7. Select a RAID group.
The group must be of type: RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 50, RAID 60.
8. Click Next.
9. Select one or more disks.
Important
If you select RAID 5, 6, 50, or 60 for the RAID type, you cannot select more than 16 disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
10. Click Next.
11. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
12. Click Next.
13. Click Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
14. Click OK.
15. Optional: For a RAID 50 or RAID 60 pool, repeat these steps for each sub-group.
QTS starts rebuilding the RAID group. The storage capacity of the pool increases after RAID rebuilding is
nished.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 229

Storage Pool Migration
Storage pool migration enables you to safely remove a storage pool and move it to another QNAP NAS. The
following data is retained:
• Files and folders
• Storage conguration
• Snapshots
Storage Pool Migration Requirements
The following requirements apply when migrating a storage pool to a new NAS.
• The two NAS devices must both be running QTS, or both be running QuTS hero. QTS to QuTS hero
migration is not possible.
• The version of QTS or QuTS hero running on the new NAS must be the same or newer than the version
running on the original NAS.
Migrating a Storage Pool to a New NAS
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Click Action, and then select Safely Detach Pool.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click Yes.
The storage pool status changes to Safely Detaching.... After QTS has nished detaching the
pool, it disappears from Storage & Snapshots.
6. Remove the drives containing the storage pool from the NAS.
7. Install the drives in the new NAS.
8. On the new NAS, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
9. Click Recover, and then select Attach and Recover Storage Pool.
A conrmation message appears.
10. Optional: Enter the SED password.
You must enter this password if you were using self-encrypted drives (SEDs) with encryption enabled.
11. Click Attach.
QTS scans the disks and detects the storage pool.
12. Click Apply.
The storage pool appears in Storage & Snapshots on the new NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 230
RAID
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) combines multiple physical disks into a single storage unit,
and then distributes data across the disks in one of several predened methods.
The following features make RAID ideal for use with data storage and NAS applications.
RAID Feature Description Advantages Disadvantages
Grouping Disks that are combined
using RAID form a
RAID group, which QTS
considers one large
logical disk.
Managing the storage space
of one large disk is simpler
and more ecient than multiple
small disks.
Initial conguration can be
more complicated.
Striping Data is split into smaller
pieces. Each piece is
stored on a dierent
disk in the RAID group.
QTS can then access that
data by reading from
or writing to multiple
disks simultaneously,
increasing read and write
speeds.
• Greater read/write speeds,
compared to a single disk
• Speeds can be increased
further by adding disks
If one disk in the RAID
group fails, and the RAID
group has no redundancy,
all data will be lost.
Redundancy Each disk in the RAID
group can store the
following:
• Complete copy of the
stored data
• Metadata that allows
reconstruction of lost
data
• Disks can fail or be removed
from the RAID group without
any loss of data
• Users can access data
while failed disks are being
replaced
Total storage capacity of
the RAID group is reduced.
RAID Types
QTS supports several RAID types. Each type provides a dierent combination of performance and
redundancy.
Important
• If disks with dierent capacities are combined in one RAID group, all disks function
according to the capacity of the smallest disk. For example, if a RAID group contains
ve 2 TB disks and one 1 TB disk, QTS detects six 1 TB disks.
QNAP recommends the following when mixing disks of dierent capacities.
a. Create a separate RAID group for each capacity.
b. Combine the RAID groups using storage pools.
• If dierent types of disk (HDD, SSD, SAS) are combined in one RAID group, the RAID
group will function according to the speed of the slowest disk.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 231
RAID Type Number of
Disks
Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
Single 1 0 Total disk
capacity
• Uses a single disk for storage.
• Provides no disk failure protection
or performance benets.
• Suitable for single disk
congurations that have a data
backup plan in place.
JBOD (just a
bunch of
disks)
≥ 2 0 Total combined
disk capacity
• Combines disks together in a
linear fashion. QTS writes data to
a disk until it is full before writing
to the next disk.
• Uses the total capacity of all the
disks.
• Not a real RAID type. It provides
no disk failure protection or
performance benets.
• Unless you have a specic reason
to use JBOD, you should use RAID
0 instead.
RAID 0 ≥ 2 0 Total combined
disk capacity
• Disks are combined together using
striping.
• RAID 0 oers the fastest read and
write speeds, and uses the total
capacity of all the disks.
• Provides no disk failure protection.
This RAID type must be paired with
a data backup plan.
• Recommended for high-
performance applications such as
video editing.
RAID 1 2 1 Half of the total
combined disk
capacity
• An identical copy of data is stored
on each disk.
• Half of the total disk capacity is
lost, in return for a high level of
data protection.
• Recommended for NAS devices
with two disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 232
RAID Type Number of
Disks
Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
RAID 5 ≥ 3 1 Total combined
disk capacity
minus 1 disk
• Data and parity information are
striped across all disks.
• The capacity of one disk is lost to
store parity information.
• Striping means read speeds are
increased with each additional disk
in the group.
• Recommended for a good balance
between data protection, capacity,
and speed.
RAID 6 ≥ 4 2 Total combined
disk capacity
minus 2 disks
• Data and parity information are
striped across all disks.
• The capacity of two disks are lost
to store parity information.
• Recommended for critical data
protection, business and general
storage use. It provides high
disk failure protection and read
performance.
RAID 10 ≥ 4
(Must be an
even number)
1 per pair of
disks
Half of the total
combined disk
capacity
• Every two disks are paired using
RAID 1 for failure protection. Then
all pairs are striped together using
RAID 0.
• Excellent random read and write
speeds and high failure protection,
but half the total disk capacity is
lost.
• Recommended for applications
that require high random access
performance and fault tolerance,
such as databases.
RAID 50 ≥ 6 1 per disk
subgroup
Total combined
disk capacity
minus 1 disk per
subgroup
• Multiple small RAID 5 groups are
striped to form one RAID 50 group.
• Better failure protection and faster
rebuild times than RAID 5. More
storage capacity than RAID 10.
• Better random access
performance than RAID 5 if all of
the disks are SSDs.
• Recommended for enterprise
backup with ten or more disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 233
RAID Type Number of
Disks
Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity Overview
RAID 60 ≥ 8 2 per disk
subgroup
Total combined
disk capacity
minus 2 disks per
subgroup
• Multiple small RAID 6 groups are
striped to form one RAID 60 group.
• Better failure protection and faster
rebuild time than RAID 6. More
storage capacity than RAID 10.
• Better random access
performance than RAID 6 if all of
the disks are SSDs.
• Recommended for business
storage and online video editing
with twelve or more disks.
RAID Group Status
Status Description
Ready The RAID group is working normally.
Degraded One or more disks in the RAID group have failed. The number of disk failures
are within the disk failure tolerance of the RAID group. There are not enough
spare disks available to QTS to replace all the failed disks.
Degraded (Rebuilding) One or more disks in the RAID group have failed. The number of disk failures
are within the disk failure tolerance of the RAID group. QTS has replaced the
failed disks with spare disks, and is now rebuilding the RAID group.
Not active One or more disks in the RAID group have failed. The number of disk failures
exceeds the disk failure tolerance of the RAID group.
RAID Disk Failure Protection
All RAID types except for RAID 0 can tolerate a specic number of disk failures without losing data. When a
disk in a RAID group fails, the RAID group status changes to degraded and then QTS performs one of the
following actions.
Spare Disk Available Actions
Yes • QTS automatically replaces the failed disk with a spare disk and then
starts rebuilding the RAID group.
• The status of the RAID group changes to rebuilding, and then
changes back to Ready after rebuilding has nished.
No You must replace the failed disk manually. QTS starts rebuilding the RAID
group after you have installed a working disk.
Conguring a RAID Group Hot Spare
Assigning a hot spare gives extra protection against data loss. In normal conditions, a hot spare disk is
unused and does not store any data. When a disk in the RAID group fails, the hot spare disk automatically
replaces the faulty disk. QTS copies the data to the spare disk in a process called RAID rebuilding.
1. Verify that the NAS contains one or more free disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 234

2. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
4. Click Manage.
5. Select a RAID 1, RAID, 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10 group.
6. Select Manage > Congure Spare Disk .
7. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
8. Click Apply.
A conrmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
The spare disks are added to the RAID group. The disk appears as a green Spare in the disks summary at
Disks/VJBOD.
Conguring an Enclosure Spare Disk
An enclosure space disk acts as a hot spare for all RAID groups within a single enclosure (NAS or expansion
unit). Under normal conditions, the enclosure space disk is unused and does not store any data. When a disk
in any RAID group fails, the hot spare disk automatically replaces the faulty disk.
Important
Storage enclosures (the NAS and expansion units) cannot share enclosure space disks. A
unique spare disk must be assigned to each storage enclosure.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD
2. Optional: Select a connected expansion unit.
3. Select a free disk.
Warning
All data on the selected disk will be deleted.
4. Click Action, and then select Set as Enclosure Spare.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click OK.
The disk appears as a Spare on the Disks/VJBOD screen.
RAID Bitmaps
If a disk is temporarily disconnected from its RAID group and then reconnected, the RAID group must
synchronize all of its data. This process may take a long time. If the RAID group has a bitmap then only
changes that were made after the disk was disconnected need to be synchronized, greatly speeding up the
process.
A disk can become temporarily disconnected in the following situations.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 235
• A disk is accidentally removed from the NAS while the NAS is powered on.
• The NAS unexpectedly shuts down because of a hardware or software error.
• A user presses the power button for 10 seconds or disconnects the power cable while the NAS is
powered on.
Important
• You can only create bitmaps for RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 groups.
• Enabling a RAID bitmap may slightly decrease the read and write performance of the
RAID group.
• A bitmap improves synchronization time only if the same disk is disconnected then
reconnected. Having a bitmap does not improve synchronization time when a new disk
is added to the RAID group.
Creating a RAID Bitmap
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool or single static volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select a RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10 group.
5. Select Manage > Enable Bitmap .
A conrmation message appears.
QTS creates a bitmap for the RAID group.
RAID Management
Expanding a RAID Group by Replacing all Disks
You can increase the maximum storage capacity of a RAID group by replacing all member disks with
higher-capacity disks. This operation can be performed while the RAID group is online and accessible to
users.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool or static volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select a RAID group of type: RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10.
5. Disable all hot spares and global hot spares assigned to the RAID group.
6. Select Manage > Replace Disks One by One .
7. Select a disk to replace.
Ensure that the capacity of the new disk is greater than the capacity of the disk that it is replacing.
8. Click Change.
The disk description changes to Please remove this drive.
9. Remove the disk from the drive bay.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 236
The NAS beeps twice. Then the disk description changes to Please insert the new disk.
10. Insert a new disk into the same bay.
The NAS beeps twice. Then the status of the disk and RAID group change to Rebuilding.
11. Wait for rebuilding to nish.
Warning
Do not remove any disks while the RAID group is rebuilding.
The disks status changes back to Good.
12. Repeat the previous steps until all disks in the RAID group have been replaced.
The Expand Capacity button is enabled after all disks have been replaced and rebuilding has nished.
13. Click Expand Capacity.
A conrmation message appears.
14. Click OK.
The NAS beeps and the RAID group status changes to Synchronizing.
Warning
Do not power o the NAS or remove any disks while synchronization is in progress.
The RAID group status changes to Ready.
Changing the RAID Type of a RAID Group
You can change the RAID type of an existing RAID group online, without losing access to data or any
interruption to NAS services. Changing the RAID type of a RAID group is called RAID migration. QTS allows
the following migrations.
Original RAID Type New RAID Type Additional Disks Required
Single RAID 1 One
RAID 1 RAID 5 One or more
RAID 5 RAID 6 One or more
Tip
Migration from a single disk to RAID 6 is performed in stages. First migrate the group to
RAID 1, then to RAID 5, and then nally to RAID 6.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Verify the following:
• The NAS contains one or more available disks.
• The capacity of each available disk is greater than or equal to the smallest disk in the RAID group.
3. Select a storage pool or static volume.
4. Click Manage.
5. Select a RAID group.
6. Select Manage > Migrate RAID Group .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 237

7. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
8. Click Apply.
A conrmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
The RAID group status changes to Rebuilding....
The RAID type changes to the new type and the RAID group status changes to Ready after migration has
nished.
Recovering a RAID Group with an Error Status
RAID recovery enables you to recover a RAID group in the event of accidental disk removal or SATA
connector failure. When several disks are removed or disconnected from a RAID group:
• The status of the group changes to Error.
• The statuses of all volumes and storage pools using the RAID group change to Inactive.
• All data on the aected volumes and LUNs becomes inaccessible.
Important
RAID recovery only helps when disks are temporarily disconnected and then reconnected.
It does not help in the event of disk failure.
1. Reconnect all disconnected disks.
Important
Ensure that each disk is reinserted into its original drive bay.
2. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume with the status Inactive.
4. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management or Volume Management window opens.
5. Select a RAID group with the status Error.
6. Click Manage, and then select Recover RAID.
QTS starts to rebuild the RAID group.
Recovering a RAID Group with a Degraded Status
If one of more disks fail in a RAID group, but the number of disk failures is within the tolerance of the
group's RAID type,then the following events occur:
• The statuses of the RAID group and its storage pool change to Degraded.
• Data on the RAID group and aected storage pool remains accessible.
1. Ensure you have one or more free disks in the NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 238

2. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
3. Select a storage pool or single static volume with the status Degraded.
4. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management or Volume Management window opens.
5. Select a RAID group with the status Degraded.
6. Click Manage, and then select Rebuild RAID Group.
The Rebuild RAID Group window opens.
7. Click Rebuild.
8. Select one or more disks.
QTS displays the number of disks that you must select, according to the number of disk failures.
9. Click Apply.
QTS starts to rebuild the RAID group.
RAID Scrubbing
RAID scrubbing helps maintain the consistency of data on the NAS. QTS scans the sectors of a RAID 5
or RAID 6 group and automatically attempts to repair any detected errors. You can run RAID scrubbing
manually, or on a schedule.
Tip
QNAP recommends performing RAID scrubbing at least once a month to maintain system
health and prevent data loss.
Running RAID Scrubbing Manually
Warning
The read/write speeds of the RAID group may decrease while RAID scrubbing is in
progress.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool or static volume.
3. Click Manage.
4. Select a RAID 5 or RAID 6 group.
The RAID group status must be Ready.
5. Select Manage > RAID Scrubbing .
The RAID group status changes to Scrubbing.
Running RAID Scrubbing on a Schedule
You can schedule periodic RAID scrubbing of all RAID 5 and RAID 6 groups.
Warning
The read/write speeds of the RAID group may decrease while RAID scrubbing is in
progress.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 239
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Click the Global Settings icon .
The Global Settings menu opens.
3. Enable RAID Scrubbing Schedule.
4. Specify how often data scrubbing will run.
• Daily
• Weekly
• Monthly
5. Specify when data scrubbing will run.
Tip
QNAP recommends specifying a time when the NAS is not in use, such as after business hours
or on weekends.
6. Click Apply.
Data scrubbing will run according to the specied schedule. When data scrubbing is running on a RAID
group, the status of the group changes to Scrubbing.
Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs)
A self-encrypting drive (SED) is a drive with encryption hardware built into the drive controller. An SED
automatically encrypts all data as it is written to the drive and decrypts all data as it is read from the
drive. Data stored on an SED is always fully encrypted by a data encryption key (DEK). The DEK can also be
encrypted by a user-specied authentication key (AK) that allows the SED to be locked and unlocked. Both
encryption keys are stored in the drive's hardware and cannot be accessed by the host operating system or
unauthorized users.
Creating an SED Secure Storage Pool
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Storage Pool.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create, and then select New Storage Pool.
The Create Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 240
• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
5. Select Create SED secure storage pool.
The list of disks only displays SED disks.
6. Select one or more disks.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
7. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50
Note
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
For details, see RAID Types.
8. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For RAID 50 or RAID 60, a spare disk must be congured later. You should congure a global spare disk
so that all subgroups share the same spare disk.
9. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 subgroups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specied number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
• A higher number of subgroups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of subgroups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 subgroups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of storage
capacity.
10. Click Next.
11. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 241
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
12. Optional: Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
13. Optional: Congure pool guaranteed snapshot space.
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling
this feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
14. Specify the SED password.
The SED password must consist of 8 to 32 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Any except for space ( )
Warning
Remember this password. If you forget the password, the pool will become inaccessible and all
data will be unrecoverable.
15. Optional: Save the encryption key to the local NAS
Saving the encryption key enables QTS to automatically unlock and mount the SED pool when the NAS
starts up. If the encryption key is not saved, you must specify the encryption password every time the
NAS restarts.
Warning
Saving the encryption key can result in unauthorized data access if unauthorized personnel are
able to physically access the NAS.
16. Click Next.
17. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
18. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool and then displays the information on the Storage/Snapshots screen.
Creating an SED Secure Static Volume
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Select Static volume.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 242
4. Click Next.
5. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
• If the expansion unit is disconnected from the NAS, the storage pool becomes inaccessible
until it is reconnected.
6. Select Create SED secure static volume.
The list of disks only displays SED disks.
7. Select one or more disks.
8. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
One Single Single
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10
Important
RAID 10 requires an even number of disks.
RAID 5
Five JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6 RAID 6
Six or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50 RAID 6
Eight or more JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 RAID 6
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
For details, see RAID Types.
9. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for this RAID group.
The designated hot spare automatically replaces any disk in the RAID group that fails.
For details, see RAID Disk Failure Protection.
10. Optional: Select the number of RAID 50 or RAID 60 subgroups.
The selected disks are divided evenly into the specied number of RAID 5 or 6 groups.
• A higher number of subgroups results in faster RAID rebuilding, increased disk failure tolerance,
and better performance if all the disks are SSDs.
• A lower number of subgroups results in more storage capacity, and better performance if all the
disks are HDDs.
Warning
If a RAID group is divided unevenly, the excess space becomes unavailable. For example, 10
disks divided into 3 subgroups of 3 disks, 3 disks, and 4 disks will provide only 9 disks of storage
capacity.
11. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 243
12. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
13. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
14. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
15. Specify the SED password.
Warning
Remember this password. If you forget the password, the pool will become inaccessible and all
data will be unrecoverable.
16. Optional: Save the encryption key to the local NAS
Saving the encryption key enables QTS to automatically unlock and mount the SED pool when the NAS
starts up. If the encryption key is not saved, you must specify the encryption password every time the
NAS restarts.
Warning
Saving the encryption key can result in unauthorized data access if unauthorized personnel are
able to physically access the NAS.
17. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication
when the percentage of used
volume space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
Specify a value.
Accelerate performance with SSD
cache
QTS adds data from this volume to
the SSD cache to improve read or
write performance.
-
Create a shared folder on the
volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume is
ready. Only the user account that
creates the shared folder will have
read/write access to the folder.
• Specify a folder name.
• Select Create this folder as a
snapshot shared folder.
A snapshot shared folder enables
faster snapshot creation and
restoration.
18. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 244
19. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
Warning
Clicking OK deletes all data on the selected disks.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
SED Storage Pool and Static Volume Actions
Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots , select a SED pool or volume, click Manage,
then select Actions > SED Settings to perform the following actions.
Action Description
Change SED Pool Password
Change SED Volume Password
Change the SED security password. You can also choose to save the
encryption key to the local NAS.
Warning
Remember this password. If you forget the password,
the pool will become inaccessible and all data will be
unrecoverable.
Saving the encryption key enables QTS to automatically unlock and
mount the SED pool when the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is
not saved, you must specify the encryption password every time the
NAS restarts.
Warning
Saving the encryption key can result in unauthorized
data access if unauthorized personnel are able to
physically access the NAS.
Lock Lock the pool or volume. All volumes, LUNs, snapshots, and data will
become inaccessible until it is unlocked.
Unlock Unlock a locked SED pool or volume. All volumes, LUNs, snapshots,
and data will become accessible.
Disable SED Security Remove user password and disable the ability to lock and unlock the
volume or pool.
Enable SED Security Add user password and enable the ability to lock and unlock the
volume or pool.
Removing a Locked SED Storage Pool or Static Volume
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a locked SED storage pool or static volume.
3. Click Manage, and then select Remove.
The Removal Wizard window opens.
4. Select a removal option.
Option Description
Enter the password of the pool
Enter the password of the volume
QTS unlocks the SED disks in the storage pool or static volume,
and then deletes all data.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 245
Option Description
Forget password QTS removes the storage pool or static volume without
unlocking the disks. The SED disks cannot be used again until
you perform one of the following actions:
• Unlock the disks. Go to Disks/VJBOD, click Recover, and
then select Attach and Recover Storage Pool.
• Erase the disks using SED erase.
5. Click Apply.
Erasing a Disk Using SED Erase
SED Erase erases all of the data on a locked or unlocked SED disk and removes the SED security password.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Select an SED disk.
3. Click Actions, and then select SED Erase.
The SED Erase window opens.
4. Enter the disk's PSID.
Tip
The PSID can usually be found on the front of the disk.
5. Click Apply.
Expansion Units
Expansion units are designed to expand the storage capacity of a QNAP NAS by adding extra drive bays.
Expansion units can be connected to the NAS using USB, Mini-SAS, Thunderbolt, or other cable type.
Tip
Expansion units used to be known as JBODs.
Expansion Unit Actions
Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD and select an expansion unit to perform one of the
following actions.
Action Description
Enclosure Info View full hardware details of the expansion unit, including the model,
serial number, rmware version, BUS type, CPU temperature, system
temperature, power status, and fan speeds.
Action > Locate Prompt the expansion unit chassis LEDs to blink, so that you can locate
the device in a server room or rack.
Action > Safely Detach Stop all activity and safely unmount the enclosure from the host NAS.
Action > Update Firmware Update the expansion unit's rmware.
Action > Rename Enclosure Rename the selected expansion unit.
RAID Group View details about each RAID group on the expansion unit, including
its RAID type, capacity, and member disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 246
Expansion Unit Recovery
If an expansion unit is accidentally disconnected from the NAS, for example by an unscheduled shutdown or
disconnected cable, then the following changes to storage state will occur:
• The status of all storage pools on the expansion unit will change to Error.
• The status of all RAID groups on the expansion unit will change to Not Active.
If you encounter this situation, reconnect the expansion unit to the NAS and QTS will automatically guide
you through the recovery process.
You can also perform recovery manually. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD , select an
expansion unit, and then click Recover to perform one of the following actions.
Action Description
Reinitialize enclosure ID Reset all expansion unit IDs, and then give each unit a new ID number
starting from 1 based on the order that they are physically connected.
Tip
Use this action if the expansion unit IDs appear out of
sequential order in the enclosure list.
Attach and Recover Storage Pool Scan all free disks on the NAS and all connected expansion units for
existing volumes, LUNs, and storage pools.
Tip
Perform this action after moving disks between NAS
devices.
QNAP External RAID Devices
About QNAP External RAID Devices
QNAP External RAID devices are a series of expansion units designed to increase the storage capacity of
your NAS or computer. External RAID devices are dierent from other QNAP expansion units in that they
feature hardware RAID. A host can either access the disks in an external RAID individually, or the external
RAID device can combine the disks using hardware RAID so that the host accesses them as one large disk.
Some external RAID devices have hardware switches for storage conguration, while other models can only
be congured through a software interface.
QNAP External RAID Device Types
Device Type Summary Example Models
External RAID
enclosure
An expansion unit featuring hardware RAID that
connects to a NAS or computer using a connector
cable.
TR-004, TR-002, TR-004U
Drive Adapter A small enclosure featuring hardware RAID that
allows you to install 1-2 smaller drives into a larger
drive bay in a NAS or computer (e.g. two 2.5-inch
SATA drives in a 3.5-inch bay).
QDA-A2AR, QDA-A2MAR, QDA-
U2MP
Note
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 247
When an external RAID enclosure is connected to a QNAP NAS, you can only create one
RAID group on the enclosure. All disks not in the RAID group are automatically assigned as
spare disks, and cannot be used for storage until the RAID group has been deleted.
Storage Modes
QNAP RAID enclosures support two dierent storage modes.
Important
QNAP drive adapters only support NAS storage mode.
Storage Mode Description Supported RAID Types Supported Hosts
NAS Storage Use the RAID enclosure's
storage capacity to create
a new storage pool or
static volume on a QNAP
NAS.
• JBOD
• RAID 0
• RAID 1
• RAID 5
• RAID 10
QNAP NAS running QTS
4.3.6 or later
External Storage Use the RAID enclosure
as an external USB disk.
This mode supports
multiple RAID groups.
Each RAID group appears
as a separate disk
when the enclosure is
connected to a host.
• Individual
• JBOD
• RAID 0
• RAID 1
• RAID 5
• RAID 10
• Windows
• macOS
• Linux
• QNAP NAS
• Other NAS devices
Storage Conguration
Creating a Storage Pool on a RAID Enclosure
Important
• The Mode switch on the RAID enclosure must be set to Software Control mode. For
details, see the enclosure's hardware user guide.
• The RAID enclosure must not contain any existing RAID groups.
Warning
To prevent errors or data loss, do not change the enclosure Mode switch from Software
Control to any other mode while the enclosure is connected to the NAS.
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click External Storage Devices, and then select External Storage Device Management.
The External Storage Device Management window opens.
3. Click Congure.
The External RAID Device Conguration Wizard opens.
4. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 248
5. Select two or more disks.
Warning
• All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
• All unselected disks will be automatically assigned as spare disks, and cannot be used until
the RAID group has been deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 10 RAID 5
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to select.
7. Click Next.
8. Select Create Storage Pool.
9. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
10. Click OK.
• The RAID enclosure creates the RAID group.
• The Create Storage Pool Wizard opens on the Select Disks screen.
• The RAID group you created is automatically selected and the RAID type is set to Single.
11. Click Next.
12. Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
13. Congure pool guaranteed snapshot space.
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling
this feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
14. Click Next.
15. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
16. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool and then displays the information on the Storage/Snapshots screen.
Creating a Storage Pool on a Drive Adapter
1. Set the drive adapter to the RAID mode that you want using the device's hardware Mode switch.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 249

2. Install the drive adapter in the NAS.
For details, see the drive adapter's hardware user guide.
3. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
4. Perform one of the following actions.
• Click New Storage Pool.
• Click Create, and then select New Storage Pool.
The Create Storage Pool Wizard window opens.
5. Click Next.
6. Under Enclosure Unit, select NAS Host.
7. In the list of disks, select the drive adapter.
8. Under RAID Type, select Single.
9. Click Next.
10. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
11. Optional: Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
12. Optional: Congure pool guaranteed snapshot space.
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling
this feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
13. Click Next.
14. Click OK.
• The Create Storage Pool Wizard opens on the Select Disks screen.
• The RAID group created in steps 3-5 is selected as the disk for the storage pool.
• The RAID type is set to Single.
15. Click Next.
16. Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
17. Click Next.
18. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 250
19. Click OK.
QTS creates the storage pool and then displays the information on the Storage/Snapshots screen.
Creating a Static Volume on a RAID Enclosure
Important
• The Mode switch on the RAID enclosure must be set to Software Control mode. For
details, see the enclosure's hardware user guide.
• The RAID enclosure must not contain any existing RAID groups.
Warning
To prevent errors or data loss, do not change the enclosure Mode switch from Software
Control to any other mode while the enclosure is connected to the NAS.
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click External Storage Devices, and then select External Storage Device Management.
The External Storage Device Management window opens.
3. Click Congure.
The External RAID Device Conguration Wizard opens.
4. Click Next.
5. Select two or more disks.
Warning
• All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
• All unselected disks will be automatically assigned as spare disks, and cannot be used until
the RAID group has been deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 10 RAID 5
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to select.
For details on RAID types, see RAID Types.
7. Click Next.
8. Select Create Volume.
9. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
10. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 251
• The RAID enclosure creates the RAID group.
• The Volume Creation Wizard opens on the Select Disks screen.
• The RAID group you created is automatically selected and the RAID type is set to Single.
11. Click Next.
12. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
13. Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
14. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication
when the percentage of used
volume space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
Specify a value.
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on
the volume with 256-bit AES
encryption.
a. Specify an encryption password containing
8 to 32 characters, with any combination
of letters, numbers and special characters.
Spaces are not allowed.
b. Select Save encryption key to save a local
copy of the encryption key on the NAS.
This enables QTS to automatically unlock
and mount the encrypted volume when
the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is
not saved, you must specify the encryption
password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key
on the NAS can result in
unauthorized data access if
unauthorized personnel are
able to physically access the
NAS.
• If you forget the encryption
password, all data will become
inaccessible.
Accelerate
performance with SSD
cache
QTS adds data from this volume to
the SSD cache to improve read or
write performance.
-
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 252
Setting Description User Actions
Create a shared folder
on the volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume is
ready. Only the user account that
creates the shared folder will have
read/write access to the folder.
Note
This setting is only
available when logged in
as "admin".
a. Specify a folder name.
b. Select Create this folder as a snapshot
shared folder.
A snapshot shared folder enables faster
snapshot creation and restoration.
15. Click Next.
16. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
17. Click OK.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Creating a Static Volume on a Drive Adapter
1. Set the drive adapter to the RAID mode that you want using the device's hardware Mode switch.
2. Install the drive adapter in the NAS.
For details, see the drive adapter's hardware user guide.
3. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
4. Perform one of the following actions.
NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Volume.
One or more volumes or storage pools Click Create > New Volume .
The Volume Creation Wizard window opens.
5. Select the volume type.
a. Click Change Type.
The Change volume type window opens.
b. Select Static Volume.
c. Click OK.
The Change volume type window closes.
6. Click Next.
7. Under Enclosure Unit, select NAS Host.
8. In the list of disks, select the drive adapter.
9. Under RAID Type, select Single.
10. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 253
11. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
The alias must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
12. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
13. Optional: Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
14. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication
when the percentage of used
volume space is equal to or above
the specied threshold.
Specify a value.
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on
the volume with 256-bit AES
encryption.
a. Specify an encryption password containing
8 to 32 characters, with any combination
of letters, numbers and special characters.
Spaces are not allowed.
b. Select Save encryption key to save a local
copy of the encryption key on the NAS.
This enables QTS to automatically unlock
and mount the encrypted volume when
the NAS starts up. If the encryption key is
not saved, you must specify the encryption
password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key
on the NAS can result in
unauthorized data access if
unauthorized personnel are
able to physically access the
NAS.
• If you forget the encryption
password, all data will become
inaccessible.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 254
Setting Description User Actions
Accelerate
performance with SSD
cache
QTS adds data from this volume to
the SSD cache to improve read or
write performance.
-
Create a shared folder
on the volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume is
ready. Only the user account that
creates the shared folder will have
read/write access to the folder.
Note
This setting is only
available when logged in
as "admin".
a. Specify a folder name.
b. Select Create this folder as a snapshot
shared folder.
A snapshot shared folder enables faster
snapshot creation and restoration.
15. Click Next.
16. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
17. Click OK.
QTS creates and initializes the volume, and then creates the optional shared folder.
Conguring a RAID Enclosure as an External Storage Device
Important
• The Mode switch on the RAID enclosure must be set to Software Control mode. For
details, see the enclosure's hardware user guide.
• The RAID enclosure must not contain any existing RAID groups.
Warning
To prevent errors or data loss, do not change the enclosure Mode switch from Software
Control to any other mode while the enclosure is connected to the NAS.
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click External Storage Devices, and then select External Storage Device Management.
The External Storage Device Management window opens.
3. Click Congure.
The External RAID Device Conguration Wizard opens.
4. Click Next.
5. Select two or more disks.
Warning
• All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
• All unselected disks will be automatically assigned as spare disks, and cannot be used until
the RAID group has been deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 255
QTS displays all available RAID types and automatically selects the most optimized RAID type.
Number of disks Supported RAID Types Default RAID Type
Two JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 RAID 1
Three JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5 RAID 5
Four JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 5, RAID 10 RAID 5
Tip
Use the default RAID type if you are unsure of which option to choose.
7. Click Next.
8. Select Create External Storage Space.
9. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
10. Click OK.
11. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > External Storage .
12. Select the uninitialized partition on the RAID enclosure.
Tip
Double-click on the RAID enclosure to see all of its partitions.
13. Click Actions, and then select Format.
The Format Partition window opens.
14. Select a le system.
File System Recommended Operating Systems and Devices
NTFS Windows
HTS+ macOS
FAT32 Windows, macOS, NAS devices, most cameras, mobile phones, video game
consoles, tablets
Important
The maximum le size is 4 GB.
exFAT Windows, macOS, some cameras, mobile phones, video game consoles, tablets
Important
Verify that your device is compatible with exFAT before
selecting this option.
EXT3 Linux, NAS devices
EXT4 Linux, NAS devices
15. Specify a disk label.
The label must consist of 1 to 16 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 256
• Special characters: Hyphen "-"
16. Optional: Enable encryption.
a. Select an encryption type.
Select one of the following options:
• AES 128 bits
• AES 192 bits
• AES 256 bits
b. Specify an encryption password.
The password must consist of 8 to 16 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• All special characters (excluding spaces)
c. Conrm the encryption password.
d. Optional: Select Save encryption key.
Select this option to save a local copy of the encryption key on the NAS. This enables QTS to
automatically unlock and mount the encrypted volume when the NAS starts up. If the encryption
key is not saved, you must specify the encryption password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in unauthorized data access if
unauthorized personnel are able to physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will become inaccessible and all data will
be lost.
17. Click Format.
A warning message appears.
18. Click OK.
QTS formats the RAID group on the external RAID enclosure as an external disk. You can view and manage it
at Storage & Snapshots > Storage > External Storage .
QTS External RAID Management
Open Storage & Snapshots, click External Storage Devices, and then select External Storage Device
Management to view, manage, and congure RAID devices connected to the NAS.
Warning
To prevent errors or data loss, do not change a RAID device's Mode switch from Software
Control to any other mode while the device is connected to the NAS.
UI Element Description
External storage device Select a RAID device to manage.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 257
UI Element Description
Safely Detach Disconnect a RAID device from the NAS when the device is in NAS Storage
mode. QTS will stop and then safely remove all storage pools, shared
folders, volumes, and LUNs stored on the device, without deleting any data.
You can then connect it to another NAS or computer.
Tip
To access the storage pools, shared folders, volumes, and
LUNs on another QNAP NAS, connect the RAID device
to the target NAS, go to Storage & Snapshots > Disks/
VJBOD then select Recover > Scan all Free Disks .
Important
This button only appears when the device is in NAS
Storage mode.
Eject Safely disconnect a RAID device from the NAS when the device is in External
Storage mode. You can then connect it to another NAS or computer.
Important
This button only appears when the device is in External
Storage mode.
Congure Create a RAID group on the RAID device and congure the storage mode.
Important
The RAID device's Mode switch must be set to Software
Control mode.
Check for Update Update the RAID device's rmware, either over the internet or from a local
le. For details, see Manually Updating External RAID Device Firmware in
QTS.
Manage > Congure Spare
Disk
Congure a global hot spare disk for the RAID device. If a disk in any RAID
group on the device fails, the hot spare disk will automatically replace the
faulty disk. For details, see Conguring a Spare Disk.
Manage > Remove Delete the RAID group. The member disks will be automatically assigned as
global spare disks if the device contains any other RAID groups.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
Manage > View Disks View the information about the disks installed in the RAID device, including
their status and health information.
Note
Selecting this option takes you to the Disks/VJBOD screen.
Migrating an External RAID Enclosure in NAS Storage Mode
Follow these steps to move a RAID enclosure containing a storage pool or static volume from a QNAP NAS to
a dierent QNAP NAS (which we will call the target NAS).
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
2. Select an enclosure.
3. Select Action > Safely Detach .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 258
The Safely Detaching Enclosure window opens.
4. Click Apply.
Warning
Do not disconnect or power o the RAID enclosure until the enclosure has been detached.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Disconnect the RAID enclosure from the NAS.
6. Connect the RAID enclosure to the target QNAP NAS.
7. On the target NAS, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
8. Click Recover, and then select Attach and Recover Storage Pool.
A conrmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
QTS scans the RAID enclosure for storage pools and static volumes, and then displays them on the
Recover Wizard window.
10. Click Apply.
QTS makes all storage pools, volumes, and LUNs on the RAID enclosure available on the target NAS at
Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
Manually Updating External RAID Device Firmware in QTS
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click External Storage Devices and then select External Storage Device Management.
The External Storage Device Management window opens.
3. Select a RAID device.
4. Click Check for Update.
The Firmware Management window opens. QTS checks online for the latest device rmware.
5. Select a rmware update method.
Firmware Update Method Description
Install the latest rmware version Download and install the latest version of the device rmware.
Note
You can only select this option if QTS has checked
online and found a newer rmware version than the
one currently installed on the device.
Select a local rmware le Update the rmware using a local rmware IMG le on your computer.
Click Browse to select the le.
Tip
You can download rmware updates at https://
download.qnap.com.
6. Click Update.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 259
Warning
Do not power o or disconnect the RAID device unless prompted.
7. Follow the instructions to install the rmware update.
Depending on the model you may be asked to power o then power on the device, or disconnect then
reconnect the device.
QTS re-detects the device and displays a notication message.
8. Wait for conrmation that the rmware update has nished.
9. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
10. Click Recover, and then select Attach and Recover Storage Pool.
Conguring a Spare Disk
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
2. Click External Storage Devices and then select External Storage Device Management.
The External Storage Device Management window opens.
3. Click Manage, and then select Congure Spare Disk.
The Congure Spare Disk window opens.
4. Select one or more free disks.
5. Click Apply.
The selected disks are assigned as spare disks for the RAID group on the external RAID device.
External RAID Device Health
To view the status and health of RAID enclosures connected to the NAS, or drive adapters and the disks
installed in them, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
The Autoplay Menu
The Autoplay menu opens when you connect a RAID enclosure to a NAS. The actions available in this menu
vary depending on the enclosure's current storage mode and RAID conguration.
Action Description
Open and view les Opens the enclosure in File Station.
Use this device for backup Opens HBS.
Congure external storage
partitions
Opens Storage & Snapshots > Storage > External Storage .
For more information, see Conguring a RAID Enclosure as an External
Storage Device.
Create NAS storage space Opens Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
For more information, see Creating a Storage Pool on a RAID
Enclosure.
Edit access permissions Opens the Edit Shared Folder Permissions window to edit access
permissions for this device.
QNAP JBOD Enclosures
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 260
About QNAP JBOD Enclosures
QNAP JBOD enclosures are a series of expansion units designed to increase the storage capacity of your
NAS or computer. JBOD enclosures oer a wide range of storage applications. You can manage drives
independently or group them together in a software RAID conguration using a host NAS or computer.
QNAP oers JBOD enclosures with USB 3.2 Gen 2 Type-C or SFF interface ports to ensure quick and ecient
data transfer between the JBOD enclosure and the host device.
QNAP JBOD Enclosure Types
Enclosure Type Description Supported
Platforms
Example Models
SAS JBOD enclosure A JBOD enclosure that uses SFF
interface ports to connect to a
NAS. These enclosures can only be
connected to a host device that has
a PCIe SAS storage expansion card
installed.
NAS:
• QTS
• QuTS hero
• TL-R1220Sep-RP, TL-
R1620Sep-RP
SATA JBOD
enclosure
A JBOD enclosure that uses SFF
interface ports to connect to a NAS or
computer. These enclosures can only
be connected to a host device that
has a QNAP QXP host bus adapter
installed.
Computer:
• Windows
• Linux
NAS:
• QTS
• QuTS hero
• TL-D400S, TL-D800S,
TL-D1600S
• TL-R400S, TL-
R1200S-RP
USB JBOD
enclosure
A JBOD enclosure that uses USB 3.2
Gen 2 Type-C ports to connect to a
NAS or computer.
Computer:
• Windows
• Linux
• macOS
NAS:
• QTS
• QuTS hero
• TL-D800C
• TL-R1200C-RP
QTS JBOD Management
You can manage JBOD enclosures in QTS from the following locations in the Storage & Snapshots utility.
Location Description
Disks/VJBOD View, manage, and congure storage for attached JBOD enclosures. You can
create storage pools, volumes, and RAID groups using disks installed in the
JBOD enclosure.
External Storage View and manage attached JBOD enclosures and installed disks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 261
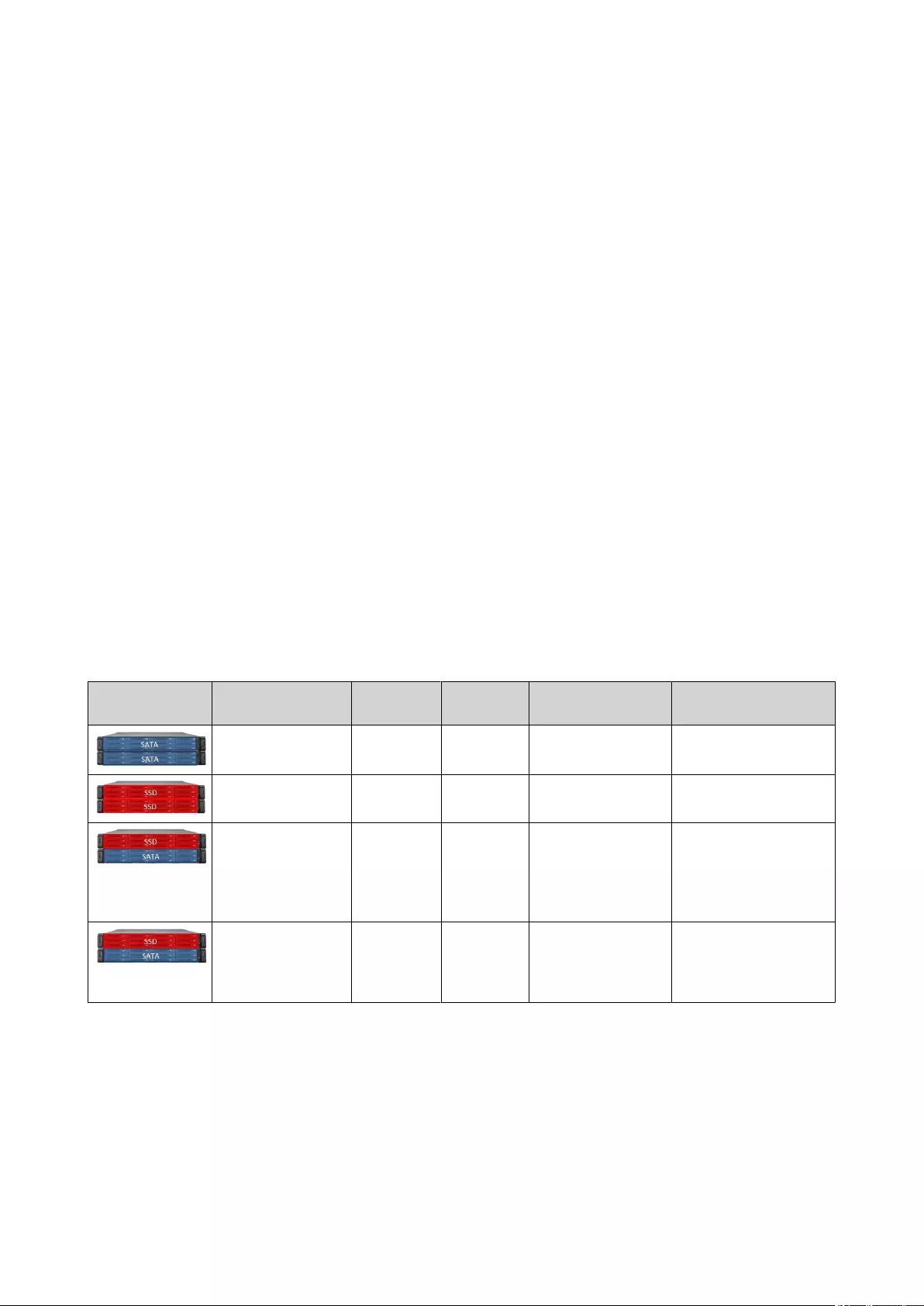
Updating JBOD Enclosure Firmware in QTS
1. Open Storage & Snapshots.
QTS periodically checks for the latest rmware for each connected enclosure on login. If a new
rmware update is available, QTS opens the Start Firmware Update window.
2. Follow the instructions to install the rmware update.
Depending on the model you may be asked to power o then power on the device, or disconnect then
reconnect the device.
QTS re-detects the device and displays a notication message.
3. Wait for conrmation that the rmware update has nished.
4. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
5. Click Recover, and then select Attach and Recover Storage Pool.
Qtier
Qtier is a proprietary automated-tiering technology, designed to increase NAS storage performance and
reduce the total cost of NAS ownership.
With Qtier, a storage pool can contain a mixture of solid-state drives (SSDs), hard disk drives (HDDs), and
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) drives. QTS creates a separate storage tier for each disk type, and then moves
data between the tiers based on access frequency. Frequently accessed data is moved to the fastest disks for
greater read and write performance. Infrequently accessed data is moved to the slower high-capacity disks
for more cost eective data storage.
Qtier Benets
NAS
Conguration
Cost Storage
Capacity
Read/Write
Performance
Management Eort
All HDDs Low High Low Low
All SSDs Very high Low High Low
SSDs and
HDDs manually
separated into two
or more storage
pools
Moderate Medium High for SSD pool,
low for HDD pool
High (admin must
manually move data
between pools)
Qtier with SSDs
and HDDs in
one Qtier-enabled
storage pool
Moderate Medium High for frequently
accessed data
Low (QTS
automatically moves
data between disks)
Qtier 2.0 IO Aware
Qtier 2.0 IO Aware is a feature available in QTS version 4.3.3 or later. With IO Aware, QTS reserves 25% of
the SSD tier capacity in a Qtier storage pool for faster access performance. If data in the capacity or high
speed tiers experiences a high number of read or write requests, QTS immediately moves it to reserved
SSD space instead of waiting to move it using auto-tiering. This improves random I/O performance, oering
performance similar to having an SSD cache.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 262
Qtier and SSD Cache Comparison
Note
Qtier can be used at the same time as SSD cache.
There are three main conguration options when conguring a NAS with a mixture of HDDs and SSDs.
Conguration SSD Usage HDD Usage
Qtier Storage Pool Qtier Storage Pool (combined with
HDDs)
Qtier Storage Pool (combined with SSDs)
SSD Cache SSD cache HDD-only storage pool
All-SSD Storage Pool SSD-only storage pool HDD-only storage pool
Qtier, SSD Cache, and All-SSD Storage Pool Comparison
Qtier Storage Pool SSD Cache All-SSD Storage Pool
Total le storage space High (SSDs + HDDs) Moderate (HDDs only) Low (SSDs only)
Maximum SSD capacity No limit Up to 4 TB depending on
installed memory
No limit
SSD expansion Expand as needed Limited by available
memory
Expand as needed
Applicable storage Thick volumes, thin
volumes and block-based
LUNs in the pool
All volumes and LUNs on
the NAS
Volumes and LUNs
created on the SSDs
Data migration Scheduled or when NAS
load is low
Automatic No migration required
Data migration method QTS writes incoming data
to the SSD tier and
moves data to dierent
tiers based on access
frequency.
• Write cache: QTS
writes incoming data
to the SSD cache
and then ushes
the cache to disk
periodically.
• Read cache: QTS
copies data to the
cache as it is
accessed.
No migration required
Recommended use
cases
• Total SSD capacity is
high
• I/O is predictable
• The storage pool
only occasionally
experiences periods of
intense random I/O
access
• I/O is unpredictable
and frequently
happens in random
bursts
• Home usage, where
the NAS will be used
for a large range of
dierent applications
Applications require
consistent intensive
random read-write
access
Usage examples File server, web server,
email servers, basic
database services (With
Qtier IO Aware)
Video editing,
virtualization
Business critical database
or other application
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 263
Qtier Requirements
NAS Requirements
• The NAS must support Qtier. For a full list of compatible models, see https://www.qnap.com/solution/
qtier-auto-tiering.
• The NAS should have at least 4 GB of installed memory. Using Qtier with less than 4 GB of memory may
cause system instability.
Tier Requirements
A Qtier storage pool can have either two or three tiers.
Important
Each tier must have a total raw storage capacity of at least 144 GB after conguring RAID.
Qtier Pool
Conguration
Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3
Two tiers Ultra-high speed High speed OR capacity N/A
Three tiers Ultra-high speed High speed Capacity
Disk Requirements
Qtier Disk Types
Tier Disk Type
Ultra-High Speed • SATA 2.5" SSD
• SAS 2.5" SSD
• SATA M.2 SSD
• PCIe/NVMe M.2 SSD
High Speed • SAS HDD
Capacity • SATA HDD
• NL-SAS HDD
Qtier Creation
Creating a Qtier Storage Pool
For details on hardware and software requirements, see Qtier Requirements.
Tip
Immediately after creating a Qtier storage pool, QTS starts moving data between tiers.
This data migration may aect system storage performance. You should create the Qtier
storage pool during a period of low NAS activity.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Perform one of the following actions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 264
Current NAS State Action
No volumes or storage pools Click New Storage Pool
One or more volumes or storage pools Select Create > New Storage Pool
The Create Storage Pool Wizard opens.
3. Select Enable Qtier (auto-tiering storage).
4. Click Next.
5. Create the ultra-high speed tier.
a. Click .
b. Optional: Select an expansion unit.
Important
If you create the ultra-high speed tier using disks installed in a TL-series expansion unit, then
the two tiers (high speed, capacity) must consist of disks from the same expansion unit.
c. Select one or more solid-state drives (SSDs).
d. Select a RAID type.
For details, see RAID Types.
e. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for the ultra-high speed tier.
6. Optional: Create the high speed tier.
At least two dierent tiers are required in a Qtier storage pool.
a. Click .
b. Optional: Select an expansion unit.
c. Select one or more SAS hard disk drives (HDDs).
d. Select a RAID type.
For details, see RAID Types.
e. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for the high speed tier.
7. Optional: Create the capacity tier.
At least two dierent tiers are required in a Qtier storage pool.
a. Click .
b. Optional: Select an expansion unit.
c. Select one or more SATA or NL-SAS HDDs.
d. Select a RAID type.
For details, see RAID Types.
e. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for the capacity tier.
8. Click Next.
9. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 265

Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
10. Optional: Congure the alert threshold.
QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used pool space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
11. Optional: Congure pool guaranteed snapshot space.
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling
this feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
12. Click Next.
13. Verify the storage pool information.
14. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
15. Click OK.
QTS creates the Qtier storage pool and starts moving data between tiers. QTS starts automatically tiering
data after it has spent sucient time analyzing data access patterns.
Enabling Qtier in an Existing Storage Pool
You can enable Qtier in an existing storage pool by adding dierent types of disk to the pool. For details on
hardware and software requirements, see Qtier Requirements.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Go to Expand Pool > Upgrade to Qtier .
The Upgrade to Qtier Pool Wizard window opens.
5. Create a second tier.
a. Click , or .
b. Select an expansion unit.
c. Select one or more disks.
d. Select a RAID type.
For details, see RAID Types.
e. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for the tier.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 266

6. Optional: Create a third tier.
a. Click , or .
b. Optional: Select an expansion unit.
c. Select one or more disks.
d. Select a RAID type.
For details, see RAID Types.
e. Optional: Select the disk that will be used as a hot spare for the tier.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
9. Click Next.
10. Verify the storage pool information.
11. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
12. Click OK.
The pool status changes to Upgrading. After Qtier is enabled, the pool status changes back to Ready.
Qtier Management
To manage Qtier on a storage pool, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots . Select a
Qtier storage pool, click Manage, and then click Qtier Auto Tiering.
Item Description
Tiering Schedule Select when QTS moves data between tiers. For details, see
Conguring the Qtier Tiering Schedule.
Tiering on Demand Select which LUNs and shared folders Qtier should perform auto
tiering on. For details, see Conguring Tiering On Demand.
Statistics View detailed on statistics on data movement between tiers. For
details, see Qtier Statistics.
Tiering Status The current status of Qtier. For details, see Qtier Status.
Schedule Setting The current tiering schedule for this pool.
Tier The tier name.
Used Percentage of used space in the tier.
Total Total storage capacity of the tier.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 267

Item Description
Move Down The total amount of data moved to a slower tier.
Move Up The total amount of data moved to a faster tier.
Name/Alias The tier's RAID group.
RAID Type The conguration of the tier's RAID group, including RAID type,
number of disks and number of space disks.
Qtier Status
Qtier Status Message Description
Idle Qtier is analyzing data access patterns but is not currently moving data.
Processing Qtier is moving data between tiers.
Canceling A user stopped the tiering process.
Suspending A user paused the tiering process.
Suspended A user paused the tiering process. Qtier is inactive.
Resuming A user resumed the tiering process from a paused state.
Resumed Qtier is moving data between tiers. This is the same as Processing.
Qtier Statistics
The appearance and functionality of Qtier depends on the current tiering schedule. To view Qtier statistics
on a storage pool, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots . Select a Qtier storage pool,
click Manage, and then click Statistics.
Qtier Schedule Qtier Statistics Screen Description
Automatic data tiering Displays the total amount of data moved between tiers for the
previous day, week, or month.
Manually set tiering schedule Displays the total amount of data moved between tiers for the
previous 20 scheduled tiering runs.
Conguring the Qtier Tiering Schedule
Qtier can move data between tiers on a set schedule. NAS access speeds and system performance may
decrease while Qtier is moving data.
Tip
Schedule Qtier to move data during periods of low usage, such as during the night or on
weekends.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a Qtier storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Go to the Qtier Auto Tiering tab.
5. Click Tiering Schedule.
The Qtier Auto Tiering Schedule Settings window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 268
6. Select a schedule type.
Option Description Recommended usage User Actions
Automatic data
tiering
Qtier moves data
whenever it detects
that the Qtier storage
pool is idle.
The NAS has no regular
usage pattern. Data may be
accessed at any time.
Select Enable exclusion
schedule to specify times
that Qtier should not
perform data tiering.
Manually set tiering
schedule
Qtier only move data
at the times you
specify.
The NAS has a regular known
usage pattern. For example,
if the NAS is primarily used
in an oce environment,
Qtier can be scheduled to
move data at night and on
weekends.
Specify the hours on the
calendar that Qtier should
perform data tiering. You
can congure the following
settings:
•Start minutes: Auto
tiering will start at this
number of minutes past
the hour.
•Run now: Start tiering
data immediately.
7. Click Apply.
Removing the Ultra-High Speed Tier
Removing the ultra-high speed tier converts a Qtier storage pool into a regular storage pool.
Important
You can only remove the ultra-high speed tier if the allocated storage pool space is less
than the remaining storage pool capacity (Total storage pool capacity - Ultra-high speed
tier capacity = Remaining capacity).
Tip
This feature is useful in the following situations:
• You want to use the SSD drives for another purpose.
• You want to increase the amount of SSD over-provisioning in the ultra-high speed tier.
• You want to change the RAID conguration of the ultra-high speed tier.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a Qtier storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Click Remove and then select Remove Ultra-High Speed Tier.
The Ultra-High Speed Tier Removal Wizard window opens.
5. Click Next.
6. Conrm that you want to remove the remove ultra-high speed tier.
7. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 269

Warning
The storage pool will be inaccessible while QTS removes the ultra-high speed tier. This process
might take a long time.
8. Click Finish.
QTS creates a background task. The status of the storage pool changes to Removing SSD Tier....
Conguring Tiering On Demand
Using Tiering On Demand, you can disable auto tiering for specic LUNs and shared folders in a Qtier
storage pool. If auto tiering is disabled, QTS permanently moves all data in the LUN or folder to the slowest
storage tier.
Important
You can only disable auto tiering for user data. Qtier always tiers system and application
data stored in the pool.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a Qtier storage pool.
3. Click Manage.
The Storage Pool Management window opens.
4. Go to the Qtier Auto Tiering tab.
5. Click Tiering On Demand.
6. Congure auto tiering for each LUN and shared folder.
7. Click Apply.
Snapshots
A snapshot protects data by recording the state of a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN at a specic point in
time. With snapshots, you can perform the following:
• Restore a volume or LUN to a previous state.
• Access and restore previous versions of les and folders.
• Create an identical copy of a volume or LUN.
Note
To use snapshots, your NAS model must support snapshots and have at least 1 GB of
memory. For a list of compatible NAS models, see www.qnap.com/solution/snapshots.
Snapshot Storage Limitations
The maximum number of snapshots a NAS can store is determined by the NAS CPU manufacturer or NAS
series, and installed memory.
Tip
For more information on NAS hardware specications, go to https://www.qnap.com.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 270
NAS CPU or Model Installed Memory Maximum Snapshots
per NAS
Maximum Snapshots
per Volume or LUN
• Intel CPU
• AMD CPU
≥ 1 GB 32 16
≥ 2 GB 64 32
≥ 4 GB 1024 256
• Annapurna Labs CPU
• TS-1635AX
• TS-328
• TS-128A, TS-228A
• TS-x51, TS-x51+
≥ 1 GB 32 16
≥ 2 GB 64 32
≥ 4 GB 256 64
Snapshot Creation
Taking a Snapshot
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or block-based LUN.
Tip
To take a snapshot of a le-based LUN, take a snapshot of its parent volume.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Take a Snapshot.
The Take a Snapshot window opens.
4. Optional: Specify a name.
5. Optional: Choose to keep the snapshot permanently.
If selected, QTS retains the snapshot indenitely. If not selected, QTS may delete the snapshot
according to the snapshot retention policy set for the volume or LUN.
For more information, see Conguring a Snapshot Retention Policy.
6. Select the LUN snapshot type.
This setting is only available when taking a snapshot of a block-based LUN.
Type Description
Crash consistent The snapshot records the state of the data on the LUN.
Application consistent The snapshot records the state of data and applications on the LUN.
The iSCSI host ushes data in memory to the LUN before QTS takes a
snapshot. If VMware vCenter is using the LUN, vCenter takes a virtual
machine snapshot.
Important
This option is only available for VMware vCenter, or for
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) aware applications
running on a Windows server. You must install QNAP
Snapshot Agent on the iSCSI initiator.
7. Optional: Specify a description.
The description helps you to identify the snapshot.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 271
8. Click OK.
A conrmation message appears.
9. Click OK.
QTS takes the snapshot. The snapshot appears in Snapshot Manager.
Conguring a Snapshot Schedule
Tip
You can congure a separate snapshot schedule for each volume and LUN.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or block-based LUN.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Click Schedule Snapshot.
The Snapshot Settings window opens.
5. Select Enable schedule.
6. Specify how often QTS will take a snapshot.
7. Select the LUN snapshot type.
This setting is only available when taking a snapshot of a block-based LUN.
Type Description
Crash consistent The snapshot records the state of the data on the LUN.
Application consistent The snapshot records the state of data and applications on the LUN. The
iSCSI host ushes data in memory to the LUN before QTS takes a snapshot.
If VMware vCenter is using the LUN, vCenter takes a virtual machine
snapshot.
Important
This option is only available for VMware vCenter, or for
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) aware applications
running on a Windows server. You must install QNAP
Snapshot Agent on the iSCSI initiator.
8. Optional: Enable smart snapshots.
When enabled, QTS only takes a snapshot if data on the volume or LUN was modied since the last
snapshot was taken.
9. Optional: Specify a description.
The description helps you to identify the snapshot.
10. Click OK.
A conrmation message appears.
11. Click OK.
QTS starts taking snapshots according to the schedule.
Snapshot Management
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 272
Conguring a Snapshot Retention Policy
The snapshot retention policy determines how long QTS keeps each snapshot of a volume or LUN before
deleting it. Each volume and LUN has its own individual snapshot retention policy.
Important
After you create or modify a snapshot retention policy, QTS applies the new policy to
existing snapshots. If the new policy is more restrictive than the previous policy, for
example changing from Keep for: 5 days to Keep for: 2 days, then QTS deletes
existing snapshots to conform with the new policy.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN.
3. Click Snapshot and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Click Schedule Snapshot.
The Snapshot Settings window opens.
5. Click Snapshot Retention.
6. Select a snapshot retention policy.
Snapshot Retention
Policy
UI Label Description
Time-based Keep for Keep each snapshot for the specied length of time.
Fixed number Keep the specied
number of snapshots
Keep a xed maximum number of snapshots on
the NAS. After the maximum number is reached,
QTS deletes the oldest snapshot when taking a new
snapshot.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 273
Snapshot Retention
Policy
UI Label Description
Smart versioning Smart versioning Keep a snapshot created during a time period for a
specied length of time.
Examples:
•Hourly: 24 - At the end of every hour, the earliest
snapshot created that hour becomes the hourly
backup. The snapshot is retained for 24 hours and
then deleted.
•Daily: 14 - At the end of every day, the earliest
snapshot created that day becomes the daily
snapshot. The snapshot is retained for 14 days and
then deleted.
•Weekly: 5 - At the end of every week, the earliest
snapshot created that week becomes the weekly
snapshot. The snapshot is retained for 5 weeks
and then deleted.
•Monthly: 11 - At the end of every month, the
earliest snapshot created that month becomes the
monthly snapshot. The snapshot is retained for 11
months and then deleted.
Important
The maximum number of snapshots for
all time periods combined is 256.
7. Click OK.
Conguring Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space
Pool guaranteed snapshot space is storage pool space that is reserved for storing snapshots. Enabling this
feature ensures that QTS always has sucient space to store new snapshots.
Pool Guaranteed Snapshot
Space Status
Snapshot Storage Location
Disabled Free space in the storage pool
Enabled Pool guaranteed snapshot space until full, then free space in the storage
pool
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or LUN.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
4. Click Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space, and then select Congure.
5. Enable Enable Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space.
6. Select the amount of reserved space.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 274
Option Description
Recommended Reserve a percentage of the total storage pool space.
Tip
The default value is 20%.
Custom Reserve a xed amount of storage pool space.
7. Click OK.
Deleting Snapshots
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick volume, thin volume, or block-based LUN.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Optional: Change the view to list view.
a.
Click .
b. Select List View.
5. Select one or more snapshots.
6.
Click .
Snapshot Data Recovery
Restoring Files and Folders from a Snapshot
Tip
• Use snapshot revert to quickly restore all data on a volume or LUN.
For details, see Reverting a Volume.
• You can restore les and folders from a snapshots in File Station by enabling Enable
File Station Snapshot Directory for administrators.
For details, see Snapshot Global Settings.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
The volume must contain at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Select the les and folders to be restored.
6. Perform one of the following actions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 275
Action Description
Select Restore > Restore Files Restore the les or folders to their original storage location. If the
les or folders still exists on the NAS, then they will be overwritten
with the older versions.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken will
be deleted.
Select Restore > Restore Files to Choose one of the following restoration options.
• Restore the les or folders to a dierent location on the NAS.
• Restore the les or folders to remote mounted storage space.
• Restore a single shared folder as a new shared folder.
In the menu bar, click
Download the les and folders to your computer in a ZIP le.
QTS restores the les and folders then displays a conrmation message.
Reverting a Volume
Reverting restores a volume or LUN to the state at which the snapshot was taken. Restoring data using
snapshot revert is signicantly faster than restoring individual les and folders.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
Important
The volume must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Revert Volume Snapshot.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken will be deleted.
6. Optional: Select Take a new snapshot before reverting.
QTS takes a snapshot before starting the revert. This ensures that changes made on the volume or LUN
are not permanently lost.
7. Click Local Revert.
The status of the volume changes to Reverting. QTS disables access to the volume until the revert process
is nished.
Reverting a LUN
Reverting restores a volume or LUN to the state at which the snapshot was taken. Restoring data using
snapshot revert is signicantly faster than restoring individual les and folders.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 276
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a block-based LUN.
Important
The LUN must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Revert LUN Snapshot.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken will be deleted.
6. Optional: Congure the following settings.
Setting Description
Take a new snapshot before reverting QTS takes a snapshot before starting the revert. This ensures
that changes made to data since the snapshot was taken are not
permanently lost.
Re-map LUN to the same iSCSI target
after revert
If enabled, QTS automatically remaps the LUN to its current target
after reverting. If disabled, you must manually remap the LUN after
reverting.
7. Click Local Revert.
QTS unmaps the LUN from its iSCSI target. The status of the LUN changes to Reverting.
Restoring Files and Folders using Windows Previous Versions
QTS snapshots integrate with the Previous Versions feature, which enables Windows users to restore les
and folders from a snapshot in Windows File Explorer.
Important
• You must be using Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 10.
• The les must be stored on a thick volume or thin volume that has at least one
snapshot.
•Enable Windows Previous Versions must be enabled in the shared folder settings.
•Allow symbolic links between dierent shared folders must be enabled at Control
Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS > Microsoft Networking >
Advanced Options .
1. In Windows, open a NAS shared folder using File Explorer.
For details on mapping a shared folder, see Mapping a Shared Folder on a Windows Computer.
2. Right-click a le or folder, and then select Properties > Previous Versions .
A list of available previous versions appears. Each version corresponds to a snapshot containing the le
or folder.
3. Select a previous version.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 277
4. Select one of the following options.
Button Description
Open Open the previous version of the le or folder.
Restore Overwrite the current version of the le or folder with the previous
version.
Warning
All changes made to the le or folder after the
snapshot was taken will be deleted.
Snapshot Clone
Cloning creates a copy of a volume or LUN from a snapshot. The copy is stored in the same storage pool as
the original volume or LUN.
Cloning a Volume
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
Important
The volume must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
6. Specify a volume alias.
7. Click OK.
QTS clones the volume and shared folders, and then displays a conrmation message.
Cloning a Block-Based LUN
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a block-based LUN.
Important
The LUN must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
6. Specify a LUN name.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 278
7. Optional: Select an iSCSI target.
QTS will map the LUN copy to the target.
8. Click OK.
QTS clones the LUN and then displays a conrmation message.
Snapshot Replica
• Snapshot Replica is a snapshot-based full backup solution for QTS.
• With Snapshot Replica you can back up a volume or block-based LUN to another storage pool, either
on the same NAS or on a dierent QNAP NAS, using snapshots.
• Backing up data with Snapshot Replica reduces storage space and bandwidth requirements, and
simplies data recovery.
Protection Levels
Snapshot Replica can back up your snapshots to another storage pool on the local NAS, or to a remote NAS.
These dierent backup congurations provide dierent levels of data protection.
Protects Against Snapshots only Snapshots + Local
Snapshot Replica
Snapshots + Remote
Snapshot Replica
Accidental modication
or deletion of les
✓ ✓ ✓
Ransomware ✓ ✓ ✓
RAID Group Failure
• Member disks fail
• Member disks are
removed from the
NAS
✓ ✓
Storage Pool Failure
• One or more RAID
groups in the pool
fail
• Pool is deleted
✓ ✓
NAS Hardware Failure
• NAS cannot power on
• QTS encounters an
error and cannot
start
• NAS is stolen
✓
Snapshot Replica Requirements
NAS Requirement
Source and Destination NAS Must be a QNAP NAS that supports snapshots.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 279
NAS Requirement
Source and Destination NAS Both source and destination NAS devices must be running QTS. Replicating
snapshots from QTS to QuTS hero or vice versa is not supported.
Source and Destination NAS Must have at least 1GB of installed memory.
Source and Destination NAS SSH port 22 and TCP data ports 50100-50199 must be open.
Destination NAS The NAS must have at least one storage pool with free space greater than
or equal to the size of the volume or LUN being backed up.
Destination NAS Allow SSH connections must be enabled at Control Panel > Network &
File Services > Telnet / SSH .
Creating a Snapshot Replica Job
Important
When running a Snapshot Replica job for the rst time, all data on the volume or LUN is
transferred to the destination NAS. This may take a long time, depending on the network
connection speed and the read/write speeds of both NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot Replica .
2. Click Create a Replication Job.
The Create a Snapshot Replication Job wizard opens.
3. Select the source volume or LUN.
4. Optional: Specify a job name.
Tip
The default job name is the rst 6 characters of the source volume or LUN name followed by
"_rep".
5. Click Next.
6. Specify the address of the destination NAS.
Perform one of the following actions.
Action Destination NAS Location Description
Manually specify the NAS address LAN, WAN, Internet Allows you to enter an IP address,
hostname, or FQDN
Click Detect and then select a NAS
from the list
LAN Displays a list of all QNAP NAS
devices on the local network
Click Local Host Local NAS Replicates snapshots between
dierent storage pools on the
same NAS
7. Specify an administrator account and password of the destination NAS.
Important
For security reasons, QNAP does not recommend using the "admin" account.
8. Optional: Specify a port.
Tip
The default port is 22.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 280
9. Click Test.
QTS connects to the destination NAS using the specied admin password, and checks that there is
sucient storage space.
10. Click Next.
11. Specify how many replicated snapshots will be kept on the destination NAS.
After the specied number is reached, QTS will delete the oldest snapshot each time it replicates a new
snapshot.
12. Select the destination storage pool.
13. Click Next.
14. Select a backup plan.
Backup Plan Description
Start replication job after taking
a local snapshot
The replica job will run each time QTS creates the specied number of
snapshots. These snapshots may be created manually or on a schedule.
Start replication job on a
schedule
The replica job runs according to the specied schedule, and replicates
all snapshots created since it was last run. If no new snapshots were
created, it will not replicate any data.
Choose one of the following scheduling options, and then click Add.
• Run on a schedule: The job automatically runs daily, weekly, or
monthly. Settings:
• Schedule: How often the job runs
• Day: The day that the job runs on
• Expiration date: The replica job stops running after this date
• Frequency: How often the job runs on the days specied by
"Schedule" and "Day"
• Start at: The time that the job starts running.
• Run once: The job runs once on a specic time and day.
• Manually start: The job does not run unless a user starts it.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 281
Backup Plan Description
Take a new snapshot on a
schedule, then run replication
job
The replica job runs according to the specied schedule. QTS takes a
new snapshot immediately before starting each run of the job. This
ensures that there is always at least one snapshot to replicate.
Choose one of the following scheduling options, and then click Add.
• Run on a schedule: The job automatically runs daily, weekly, or
monthly. Settings:
• Schedule: How often the job runs
• Day: The day that the job runs on
• Expiration date: The replica job stops running after this date
• Frequency: How often the job runs on the days specied by
"Schedule" and "Day"
• Start at: The time that the job starts running.
• Run once: The job runs once on a specic time and day.
• Manually start: The job does not run unless a user starts it.
15. Click Next.
16. Optional: Congure transfer settings.
Setting Description
Encrypt transfer QTS encrypts the snapshot before replicating it.
• SSH connections must be allowed on the destination NAS.
• The job must be run by an administrator account.
• The port used by this job must be the same as the SSH port on the
destination NAS.
Compress transfer QTS compresses snapshots when replicating them. This consumes
more CPU and system memory, but reduces the amount of bandwidth
required.
Tip
Enable this setting in low bandwidth networks, or if the
NAS devices are connected through a WAN.
Maximum transfer speed Limits how much network bandwidth this job uses
17. Optional: Export the source data to an external storage device.
To save time and bandwidth, you can export the source data to a connected external storage device
such as a USB disk. After connecting the external storage device to the destination NAS, QTS will import
the source data when the job is next run.
a. Connect an external storage device to the NAS.
b. Select Export source data to external storage device on rst run.
c. Select the external storage device.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 282
d. Optional: Select Skip the export if you have already exported the source data to the external
storage device.
18. Click Next.
19. Optional: Select Execute backup immediately.
When enabled, the job will run immediately after being created.
20. Review the job information.
21. Click Finish.
QTS creates the job.
22. Optional: If you chose to export source data to an external storage device, disconnect the storage
device from the source NAS and connect it to the destination NAS.
Snapshot Replica Management
To manage snapshot replica jobs and settings, go to Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot
Replica .
Snapshot Replica Job Actions
Icon Description
Enable or disable the schedule
Start
Stop
Edit settings
View logs
Delete
Snapshot Replica Options
Setting Description Default Value
Timeout (seconds) When a job is interrupted, QTS waits the specied
number of seconds before canceling the job and
marking it as failed.
600
Number of retries When a job fails, QTS runs the job again the
specied number of times.
3
Data Recovery on a Source NAS
Restoring Files and Folders from a Remote Snapshot
Important
Restoration time depends on the amount of data being restored and the connection speed
between the two NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 283
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
Important
The volume must be the source volume for a Snapshot Replica job.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Under Select snapshot location, select a remote NAS.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Select the les and folders to be restored.
7. Perform one of the following actions.
Action Description
Select Restore > Restore Files Restore the les or folders to their original storage location.
If the les or folders still exists on the NAS, then they will be
overwritten with the older versions.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken
will be deleted.
Select Restore > Restore Files to Choose one of the following restoration options.
• Restore the les or folders to a dierent location on the
NAS.
• Restore the les or folders to remote mounted storage
space.
• Restore a single shared folder as a new shared folder.
In the menu bar, click
Download the les and folders to your computer in a ZIP le.
QTS restores the les and folders then displays a conrmation message.
Reverting a Volume Using a Remote Snapshot
Reverting restores a volume or LUN to the state at which the snapshot was taken. Restoring data using
snapshot revert is signicantly faster than restoring individual les and folders.
Important
Restoration time depends on the amount of data being restored and the connection speed
between the two NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
Important
The volume must be the source volume for a Snapshot Replica job.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 284
4. Under Select snapshot location, select a remote NAS.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Click Revert Volume Snapshot.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken will be deleted.
7. Optional: Congure the following settings.
Setting Description
Take a new snapshot before reverting QTS takes a snapshot before starting the revert. This ensures
that changes made to data since the snapshot was taken are
not permanently lost.
Enable encryption during transfer QTS encrypts the snapshot before sending it for additional
security.
Warning
If the network connection is interrupted or if the storage conguration of the source or
destination NAS changes while reverting, the volume might become inaccessible. If this
happens, revert the volume again using a local or remote snapshot.
8. Click Remote Revert.
The Remote Revert Warning window opens.
9. Enter the QTS administrator password.
10. Click OK.
The status of the volume changes to Remote Reverting. QTS disables access to the volume until the
revert process is nished.
Reverting a LUN Using a Remote Snapshot
Reverting restores a shared folder or LUN to the state at which the snapshot was taken. Restoring data
using snapshot revert is faster than restoring individual les and folders.
Warning
• While reverting, ensure that data in not being accessed on the LUN. The safest way to
do this is to disconnect all iSCSI initiators. Accessing the LUN during a snapshot revert
might result in data loss.
• Restoration time depends on the amount of data being restored and the connection
speed between the two NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a block-based LUN.
Important
The LUN must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 285
4. Under Select snapshot location, select a remote NAS.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Click Revert LUN Snapshot.
Warning
All changes made after the snapshot was taken will be deleted.
7. Optional: Congure the following settings.
Setting Description
Take a new snapshot before reverting QTS takes a snapshot before starting the revert. This ensures
that changes made to data since the snapshot was taken are not
permanently lost.
Enable encryption during transfer QTS encrypts the snapshot before sending it for additional security.
Re-map LUN to the same iSCSI target
after revert
If enabled, QTS automatically remaps the LUN to its current target
after reverting. If disabled, you must manually remap the LUN after
reverting.
Warning
If the network connection is interrupted or if the storage conguration of the source or
destination NAS changes while reverting, the LUN might become inaccessible. If this happens,
revert the LUN again using a local or remote snapshot.
8. Click Remote Revert.
The Remote Revert Warning window opens.
9. Enter the QTS administrator password.
10. Click OK.
QTS unmaps the LUN from its iSCSI target. The status of the LUN changes to Reverting.
Cloning a Volume from a Remote Snapshot
Important
The time required to clone the volume depends on the amount of data stored on the
volume and the connection speed between the two NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a thick or thin volume.
Important
The volume must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Under Select snapshot location, select a remote NAS.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 286

7. Specify a volume alias.
8. Select a storage pool.
9. Select Enable encryption during transfer.
QTS encrypts the snapshot before sending it for additional security.
10. Click OK.
QTS clones the volume and shared folders, and then displays a conrmation message.
Cloning a Block-Based LUN from a Remote Snapshot
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Select a block-based LUN.
Important
The LUN must have at least one snapshot.
3. Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Manager.
The Snapshot Manager window opens.
4. Under Select snapshot location, select a remote NAS.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
7. Specify a LUN name.
8. Select a storage pool.
9. Optional: Select an iSCSI target.
QTS will map the LUN copy to the target.
10. Select Enable encryption during transfer.
QTS encrypts the snapshot before sending it for additional security.
11. Click OK.
QTS clones the LUN and then displays a conrmation message.
Data Recovery on a Destination NAS
Snapshot Vault
After setting a NAS as the destination for a Snapshot Replica job, the replicated snapshots are stored in
Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot Vault . Each replica job has its own separate vault.
Restoring Files and Folders from a Snapshot Vault
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot Vault .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. On a vault, click .
The Snapshot Vault window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 287

4. Optional: Unlock the vault.
If the original source volume is encrypted, you must unlock the vault with the volume's encryption
password.
a. Click Unlock.
b. Enter the encryption password or upload the encryption key.
c. Click OK.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Select the les and folders to be restored.
7. Click Restore Files To.
8. Specify a restore location.
9. Click OK.
Cloning a Volume from a Snapshot Vault
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot Vault .
2. Select a storage pool.
3. On a vault, click .
The Snapshot Vault window opens.
4. Optional: Unlock the vault.
If the original source volume is encrypted, you must unlock the vault with the volume's encryption
password.
a. Click Unlock.
b. Enter the encryption password or upload the encryption key.
c. Click OK.
5. Select a snapshot.
6. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
7. Specify a volume alias.
8. Click OK.
QTS clones the volume and shared folders, and then displays a conrmation message.
Cloning a Block-Based LUN from a Snapshot Vault
Important
The time required to create the LUN depends on the amount of data stored on the LUN
and the connection speed between the two NAS devices.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Snapshot Backup > Snapshot Vault .
2. Select a storage pool.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 288
3. On a vault, click .
The Snapshot Vault window opens.
4. Select a snapshot.
5. Click Clone.
The Clone Snapshot window opens.
6. Specify a LUN name.
7. Optional: Select an iSCSI target.
QTS will map the LUN copy to the target.
8. Click OK.
QTS clones the LUN and then displays a conrmation message.
Cache Acceleration
Cache Acceleration enables you to create an SSD cache to improve the read and write performance of the
NAS.
Cache Acceleration Requirements
• The NAS model must support Cache Acceleration.
For information about NAS and drive bay compatibility, see https://www.qnap.com/solution/ssd-cache.
• The NAS must have one or more free SSDs installed in a compatible drive bay.
• The NAS must have a suitable amount of installed memory.
The amount of memory required depends on the size of the SSD cache.
SSD Cache Size Required Memory
512GB ≧ 1GB
1TB ≧ 4GB
2TB ≧ 8GB
4TB ≧ 16GB
Creating the SSD Cache
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Cache Acceleration .
2. Click .
The Create SSD Cache window opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Select one or more SSDs.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
5. Select a cache type.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 289
Cache Type Description
Read-only When data is read from a LUN or volume, QTS copies the data to the
SSD cache to speed up future read requests.
Write-only QTS writes incoming data to the SSD cache rst, then ushes the
data to regular storage later. Read access to the new data is also
accelerated while it is in the cache.
Read-write QTS uses the SSD cache for both read and write caching, accelerating
both read and write speeds.
6. Select a RAID type.
Warning
Selecting a RAID type with no disk failure protection (Single, JBOD, RAID 0) when the cache type
is Write-only or Read-write may result in data loss.
Tip
RAID 10 provides the best write cache performance.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Congure SSD over-provisioning.
Over-provisioning reserves a percentage of SSD storage space on each disk in the RAID group to
improve write performance and extend the disk's lifespan. You can decrease the amount of space
reserved for over-provisioning after QTS has created the RAID group.
Tip
To determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning for your SSDs, download and run SSD
Proling Tool from App Center.
For details, see SSD Proling Tool.
9. Select a cache mode.
Cache Mode Description Recommended Use Cases
Random I/O Only small data blocks are added to the SSD cache.
Larger blocks are accessed directly from regular
storage.
Virtualization, databases
All I/O Small and large data blocks are added to the SSD
cache. Both sequential and random I/O requests are
accelerated.
Video streaming, large le
access operations
Tip
An HDD RAID group may outperform a SSD RAID group for sequential I/O if the ratio of HDDs
to SSDs is 3:1 or greater, and the HDD group has a RAID type of RAID 0, 5, 6, or 10. However,
SSDs will always be faster for random I/O. If the NAS contains a RAID group of type RAID 0, 5, 6,
or 10 that contains three times more disks than the SSD cache, you should select Random I/O.
10. Optional: Congure the following advanced settings.
Setting Description
Bypass block size This value determines the maximum size of the data blocks that are
stored in the SSD cache. Selecting a larger size may improve the
cache's hit rate but uses more cache space. The default value is 1 MB.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 290
Setting Description
Cache replacement policy Specify how data is removed from the SSD cache. Choose one of the
following options:
• Least recently used (LRU): Better cache performance but uses
more CPU resources. This is the default option.
• First in rst out (FIFO): Lower CPU usage than LRU but might
cause worse cache performance.
11. Click Next.
12. Select which volumes and LUNs can use the SSD cache.
Important
For data safety, volumes and LUNs created on an external storage device cannot use the SSD
cache if the cache type is Read-write.
13. Click Next.
14. Click Create.
A conrmation message appears.
15. Select I understand and then click OK.
Expanding the SSD Cache
The SSD cache can be expanded by adding a new SSD RAID group.
Important
Expanding the SSD cache clears all cached data.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Cache Acceleration .
2. Click Manage and then select Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click OK.
4. Select one or more SSDs.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
5. Select a RAID type.
Warning
Selecting a RAID type with no disk failure protection (Single, JBOD, RAID 0) when the cache type
is Write-only or Read-write may result in data loss.
Tip
RAID 10 provides the best write cache performance.
6. Click Expand.
A conrmation message appears.
7. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 291
Conguring SSD Cache Settings
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Cache Acceleration .
2. Click Manage and then select Settings.
The Switch SSD Cache window opens.
3. Select which volumes and LUNs can use the SSD cache.
Important
For data safety, volumes and LUNs created on an external storage device cannot use the SSD
cache if the cache type is Read-write.
4. Click Next.
5. Select a cache mode.
Cache Mode Description Recommended Use
Cases
Random I/O Only small data blocks are added to the SSD cache.
Larger blocks are accessed directly from regular
storage.
Virtualization, databases
All I/O Small and large data blocks are added to the SSD
cache. Both sequential and random I/O requests
are accelerated.
Video streaming, large le
access operations
Tip
An HDD RAID group may outperform a SSD RAID group for sequential I/O if the ratio of HDDs
to SSDs is 3:1 or greater, and the HDD group has a RAID type of RAID 0, 5, 6, or 10. However,
SSDs will always be faster for random I/O. If the NAS contains a RAID group of type RAID 0, 5, 6,
or 10 that contains three times more disks than the SSD cache, you should select Random I/O.
6. Optional: Congure bypass block size.
This value determines the maximum size of the data blocks that are stored in the SSD cache. Selecting
a larger size may improve the cache's hit rate but uses more cache space. The default value is 1 MB.
7. Click Finish.
Cache Missing
If the write-only or read-write cache disks become unavailable because of hardware failure or physical
removal from the NAS, all volumes using the write-cache will also become unavailable and will have Cache
Missing as their status. QTS restricts access to these volumes to protect data integrity, as some volume
data may be stored in the write cache without being ushed to disk.
When the SSD cache is missing, restore it using one of the following methods:
• If the SSD cache disks were removed from the NAS, re-insert the disks into the same drive bays.
• Resolve any RAID errors.
• Restart the NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 292

Removing a Missing SSD Cache
Important
You should only delete a missing SSD cache if it is not possible to restore the cache, for
example, because of disk failure.
Warning
Removing a missing SSD write-only or read-write cache will delete all unushed write data.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Cache Acceleration .
2. Select Manage > Remove .
A conrmation message appears.
3. Enter the admin password.
4. Click OK.
5. Restart the NAS.
6. Run a le system check on all volumes that used the SSD cache.
For the details, see Volume File System Check.
Removing the SSD Cache
Warning
Removing an SSD from the SSD cache while write caching is enabled may cause data loss.
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Cache Acceleration .
2. Click Manage and then select Remove.
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click OK.
QTS ushes all data in the cache to disk, then deleted the RAID groups. This process make take a long time.
External Storage
QTS supports external USB and eSATA storage devices, such as ash drives, portable hard drives, and
storage enclosures. After connecting a USB or eSATA external storage device to the NAS, the device and all
of its readable partitions will be displayed in Storage & Snapshots > Storage > External Storage . QTS will
also create a shared folder for each readable partition on the device.
External Storage Device Actions
Action Description
Erase Delete all data and partitions on the device.
Eject Safely unmount the external storage device from the NAS, so that you
can disconnect it.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 293
External Storage Disk Actions
Action Description
Full Disk Format Format the disk.
For details, see Formatting an External Storage Partition.
Secure Erase Permanently erase all data on a disk.
For details, see Securely Erasing a Disk.
External Storage Partition Actions
Action Description
Storage Information Displays details about the selected partition, including partition name,
capacity, used space, and le system type.
Format Formats the partition. For details, see Formatting an External Storage
Partition.
Encryption Management Manages encryption on a previously encrypted device. You can lock or
unlock the device, change the encryption password, or download the
encryption key.
Eject Unmounts the partition. The external storage device and any stored
partitions will continue working.
Formatting an External Storage Partition
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > External Storage .
2. Select a storage partition.
3. Click Action, and then select Format.
The Format Partition window opens.
4. Select a le system.
File System Recommended Operating Systems and Devices
NTFS Windows
HTS+ macOS
FAT32 Windows, macOS, NAS devices, most cameras, mobile phones, video
game consoles, tablets
Important
The maximum le size is 4 GB.
exFAT Windows, macOS, some cameras, mobile phones, video game
consoles, tablets
Important
Verify that your device is compatible with exFAT before
selecting this option.
EXT3 Linux, NAS devices
EXT4 Linux, NAS devices
5. Specify a disk label.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 294

The label must consist of 1 to 16 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Hyphen "-"
6. Optional: Enable encryption.
a. Select an encryption type.
Select one of the following options:
• AES 128 bits
• AES 192 bits
• AES 256 bits
b. Specify an encryption password.
The password must consist of 8 to 16 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• All special characters (excluding spaces)
c. Conrm the encryption password.
d. Optional: Select Save encryption key.
Select this option to save a local copy of the encryption key on the NAS. This enables QTS to
automatically unlock and mount the encrypted volume when the NAS starts up. If the encryption
key is not saved, you must specify the encryption password each time the NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the NAS can result in unauthorized data access if
unauthorized personnel are able to physically access the NAS.
• If you forget the encryption password, the volume will become inaccessible and all data will
be lost.
7. Click Format.
A warning message appears.
8. Click OK.
Remote Disk
Remote disk enables QTS to act as an iSCSI initiator, allowing you to expand NAS storage by adding iSCSI
LUNs from other NAS or storage servers as remote disks. When connected, remote disks are automatically
shared on the Shared Folders screen. If a remote disk is disconnected, the disk will become inaccessible
and QTS will try to reconnect to the target after 2 minutes. If the target cannot be reached, the status of the
remote disk will change to Disconnected.
This feature is only available on NAS models that support iSCSI.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 295
Remote Disk Limitations
Limit Value
Maximum number of remote disks per NAS 8
Supported le systems ext3, ext4, FAT32, NTFS, HFS+
Maximum remote disk size 16 TB
Adding a Remote Disk
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Remote Disk .
2. Click Add Virtual Disk.
3. Specify the IP address or hostname of the remote server.
4. Optional: Specify the iSCSI port of the remote server.
5. Click Get Remote Disk.
QTS connects to the remote server and then lists all available iSCSI targets.
6. Select an iSCSI target.
7. Optional: Specify a CHAP username and password.
This is required if the remote server has CHAP authentication enabled.
8. Optional: Enable CRC checksums.
Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI protocol data units (PDU). The
sending device can send a checksum with each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum to verify
the integrity of the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are two checksum
types, which can be enabled separately.
Checksum Type Description
Data Digest The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of the PDU.
Header Digest The checksum can be used to verify the header portion of the PDU.
9. Click Next.
10. Optional: Specify a disk name.
The name must consist of 1 to 50 characters from the following groups:
• Letters: a to z, A to Z
• Numbers: 0-9
• Special characters: space ( ), hyphen (-), underscore (_), period (.)
The following are not allowed:
• The last character is a space
• The name starts with "_sn_"
11. Select a LUN.
12. Optional: Format the disk.
Select one of the following options.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 296
File System Compatible Operating Systems and Devices
ext4 Linux, NAS devices
ext3 Linux, NAS devices
FAT32 Windows, macOS, NAS devices, most cameras, mobile phones, video
game consoles, tablets
Important
The maximum le size is 4 GB.
NTFS Windows
HTS+ macOS
Warning
All data on the LUN will be deleted.
13. Congure synchronous I/O.
If the remote server is using ZFS, select the ZFS Intent Log I/O mode for the LUN to improve data
consistency or performance.
Mode Description
Synchronous All I/O transactions are treated as synchronous and are always written
and ushed to a non-volatile storage (such as a SSD or HDD). This
option gives the best data consistency, but might have a small impact
on performance.
Asynchronous All I/O transactions are treated as asynchronous. This option gives the
highest performance, but has a higher risk of data loss in the event
of a power outage. Ensure that a UPS (uninterrupted power supply) is
installed when using this option.
14. Click Next.
15. Click Finish.
QTS adds the remote disk and shares it at Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders . By default only the
admin account has access.
Remote Disk Actions
Action Description
Edit Edit the name of the disk.
Delete Disconnect the remote disk and delete its shared folder.
Existing data on the disk will not be deleted.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 297

Action Description
Format Format the remote disk.
Select one of the following le system options:
• ext4
• ext3
• FAT32
• NTFS
• HTS+
Select one of the following I/O options:
• Synchronous
• Asynchronous
VJBOD (Virtual JBOD)
VJBOD (Virtual JBOD) enables you to add storage space from other QNAP NAS devices to your NAS as local
VJBOD disks, to create a virtual expansion enclosure. VJBOD disks can be used to create new local storage
space, expanding local NAS storage capacity. VJBOD is based on iSCSI technology.
VJBOD Requirements
Local NAS requirements:
• The NAS is running QTS 4.2.2 or later, or QuTS hero 4.5.0 or later.
• The NAS model supports VJBOD.
For a list of supported series and models, see https://www.qnap.com/solution/vjbod.
Remote NAS requirements:
• The NAS is running QTS 4.2.1 or later, or QuTS hero.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 298
• The NAS model supports iSCSI and storage pools.
• The NAS has a storage pool with at least 154 GB of free space, or an unused thick LUN with a capacity
of 154 GB or more.
Tip
For a stable VJBOD connection, ensure the following conditions:
• All NAS devices are on the same local network.
• All NAS devices are congured with static IP addresses.
• On a remote NAS, additional LUNs are not mapped to an iSCSI target that is being
used by a VJBOD disk.
VJBOD Limitations
• You can create a maximum of 8 VJBOD disks.
• You can only expand an existing storage pool using VJBOD disks if the pool consists of VJBOD disks
from the same storage pool on the same remote NAS.
• It is not possible to create a system volume using VJBOD disks.
• VJBOD disks only support the RAID type Single.
VJBOD Automatic Reconnection
If a remote NAS gets disconnected, QTS automatically tries to reconnect to the NAS and recover the VJBOD
disk every 30 seconds.
Important
• To allow automatic reconnection, all NAS devices should be congured with static IP
addresses.
• The following things may prevent VJBOD connection or reconnection:
• Use of dynamic IP addresses
• Host IQN binding
• Firewalls of IP blocks
• Incorrect CHAP credentials
VJBOD Creation
Creating a VJBOD Disk from a New LUN
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Click Create, and then select Create Virtual JBOD.
The Create Virtual JBOD Disk Wizard opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify the IP address or hostname of the remote NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 299

Important
The remote NAS must have at least one storage pool containing at least 153 GB of free space.
Tip
Click Detect to view the IP addresses of all QNAP NAS devices on the local network. Click Local
Host to use the IP of the local NAS.
5. Specify an administrator account and password of the remote NAS.
Important
For security reasons, QNAP does not recommend using the "admin" account.
6. Optional: Specify the system administration port of the remote NAS.
Tip
The default port is 8080. If HTTPS is enabled, the default port is 443.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Select the local interface that will be used by VJBOD.
9. Optional: Select the remote interface that will be used by VJBOD.
10. Optional: Enable iSER.
Enabling iSER increases data transfer speeds and reduces CPU and memory load.
a. Ensure that selected local and remote network adapters are iSER-compatible and have iSER
listed under Supported Protocols.
b. Select Use iSER when available.
11. Click Next.
12. Select Create a new iSCSI LUN on the remote NAS.
13. Optional: Select Host Binding.
When selected, only the local NAS will be able to access the VJBOD disk.
Tip
Enable this option if the VJBOD disk will be used to store sensitive information.
14. Click Next.
15. Select a storage pool.
16. Click Next.
17. Specify the capacity of the VJBOD disk.
Important
The size of the VJBOD disk cannot be changed after creation.
18. Optional: Congure advanced settings.
Setting Description
4K bytes sector size Changing the sector size to 4 KB increases LUN performance for
specic applications and disk types.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 300
Setting Description
SSD cache The SSD cache will be used to improve VJBOD disk access
performance.
19. Click Next.
QTS starts creating a dedicated iSCSI target on the remote NAS for the VJBOD disk.
20. Optional: Enable CHAP authentication.
An initiator must authenticate with the target using the specied username and password. This
provides security, as iSCSI initiators do not require a NAS username or password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
21. Optional: Enable CRC checksums.
Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI protocol data units (PDU). The
sending device can send a checksum with each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum to verify
the integrity of the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are two checksum
types, which can be enabled separately.
Checksum Type Description
Data Digest The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of the PDU.
Header Digest The checksum can be used to verify the header portion of the
PDU.
22. Click Next.
23. Review the summary, and then click Next.
QTS creates the iSCSI target and LUN on the remote NAS, and then creates a VJBOD disk using the LUN.
The disk appears at Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
24. Select a follow-up action.
Action Description
Create New Storage Pool Creates a storage pool using the VJBOD disk
Create New Static Volume Creates a static volume using the VJBOD disk
Do nothing Ends the creation process. You can congure the VJBOD disk later.
Tip
To create a storage pool or static volume on a
VJBOD disk later, go through the normal steps of
creating a storage pool or static volume. Then on
the disk selection screen, under Enclosure Unit
select Virtual JBOD.
25. Click Finish.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 301

Creating a VJBOD Disk from an Existing LUN
1. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
2. Click Create, and then select Create Virtual JBOD.
The Create Virtual JBOD Disk Wizard opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify the IP address or hostname of the remote NAS.
Important
The remote NAS must have at least one storage pool containing at least 153 GB of free space.
Tip
Click Detect to view the IP addresses of all QNAP NAS devices on the local network. Click Local
Host to use the IP of the local NAS.
5. Specify an administrator account and password of the remote NAS.
Important
For security reasons, QNAP does not recommend using the "admin" account.
6. Optional: Specify the system administration port of the remote NAS.
Tip
The default port is 8080. If HTTPS is enabled, the default port is 443.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Select the local interface that will be used by VJBOD.
9. Optional: Select the remote interface that will be used by VJBOD.
10. Optional: Enable iSER.
Enabling iSER increases data transfer speeds and reduces CPU and memory load.
a. Ensure that selected local and remote network adapters are iSER-compatible and have iSER
listed under Supported Protocols.
b. Select Use iSER when available.
11. Click Next.
12. Select Choose an existing iSCSI LUN on the selected NAS.
13. Click Next.
14. Select a LUN.
Important
The LUN must be thick and block-based, and must have a capacity of at least 154 GB. Mutual
CHAP must be disabled.
15. Click Next.
16. Optional: Enable CHAP authentication.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 302
An initiator must authenticate with the target using the specied username and password. This
provides security, as iSCSI initiators do not require a NAS username or password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
17. Optional: Enable CRC checksums.
Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI protocol data units (PDU). The
sending device can send a checksum with each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum to verify
the integrity of the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are two checksum
types, which can be enabled separately.
Checksum Type Description
Data Digest The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of the PDU.
Header Digest The checksum can be used to verify the header portion of the
PDU.
18. Click Next.
19. Review the summary, and then click Next.
QTS creates a VJBOD disk using the LUN. The disk appears at Storage & Snapshots > Storage >
Disks/VJBOD .
20. Select a follow-up action.
Action Description
Create New Storage Pool Creates a storage pool using the VJBOD disk
Create New Static Volume Creates a static volume using the VJBOD disk
Recover Existing Data Restores a static volume or storage pool that was previously
created on the VJBOD disk
Do nothing Ends the creation process. You can congure the VJBOD disk later.
Tip
To create a storage pool or static volume on a
VJBOD disk later, go through the normal steps of
creating a storage pool or static volume. Then on
the disk selection screen, under Enclosure Unit
select Virtual JBOD.
21. Click Finish.
VJBOD Management
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 303
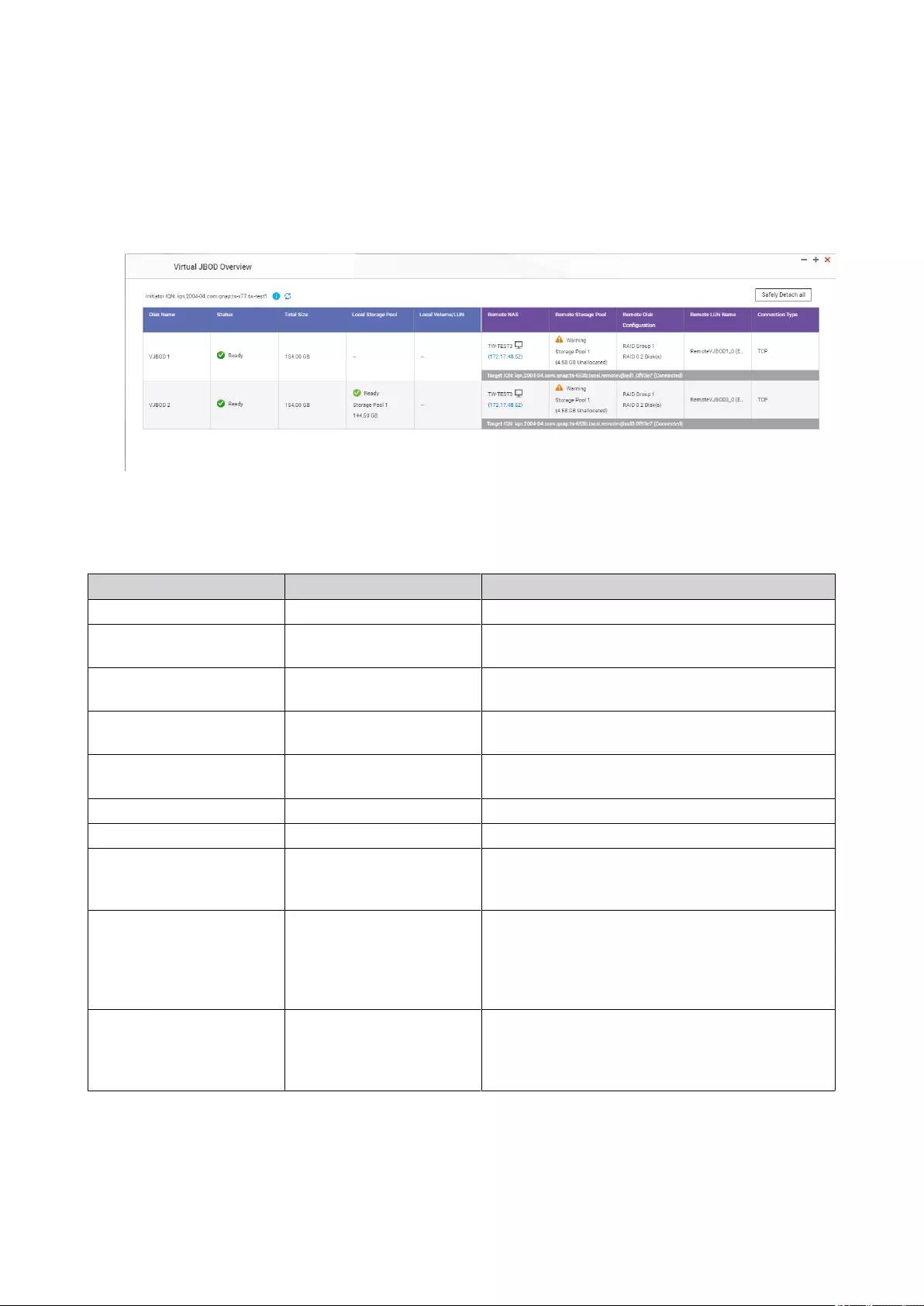
Virtual JBOD Overview
To view an overview of all VJBOD disks including information on their source remote NAS devices, go
to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD , click VJBOD/VJBOD Cloud, and then select VJBOD
Overview.
VJBOD Disk Actions
Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD , select a VJBOD disk, and then click Action.
Action Disk Status Description
New Volume Free Creates a new static volume on the VJBOD disk
NAS Detail Any Displays information about VJBOD disk's remote
NAS
Remote Log Any Displays the event log on the VJBOD disk's remote
NAS
Data Recovery Free Restores a static volume or storage pool that was
previously created on the VJBOD disk
Edit Disk Any Edits the disk name, and congure whether this
disk uses the SSD cache
Disconnect Free Disconnects the VJBOD from its remote NAS
Connect Disconnected Reconnects a disconnected VJBOD disk
Edit Target Disconnected Edits the following iSCSI target settings: port
number, CHAP authentication, and CRC checksum
settings
Detach Data Safely disconnects the VJBOD disk containing a
storage pool or static volume. You can then
connect the LUN to another NAS, create a new
VJBOD disk, and recover the pool or volume using
Action > Data Recovery .
Delete Disconnected Deletes a VJBOD from the local disk. The LUN and
all data will remain on the remote NAS
You can also choose to delete the iSCSI target and
LUN on the remote NAS.
Moving a VJBOD Disk to Another QNAP NAS
1. Note the details of the VJBOD disk's remote LUN.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 304

a. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
b. Click VJBOD/VJBOD Cloud, and then select VJBOD Overview.
The VJBOD Overview window opens.
c. Locate the VJBOD disk that you want to move, and then note the Remote LUN Name and the IP
address under Remote NAS.
2. Detach the VJBOD disk's static volume or storage pool.
a. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots .
b. Select the static volume or storage pool on the VJBOD disk.
c. Click Manage.
The Volume Management or Storage Pool Management window opens.
d. Click Action, and then select Safely Detach.
3. Remove the VJBOD disk from the NAS.
a. Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
b. Select the VJBOD disk.
c. Click Action, and then select Disconnect.
The status of the VJBOD disk changes to Disconnected.
d. Click Action, and then select Delete.
QTS removes the VJBOD disk from the local NAS.
4. Add the VJBOD disk on another QNAP NAS.
a. On the other NAS, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD .
b. Click Create, and then select Create Virtual JBOD.
The Create Virtual JBOD Disk Wizard opens.
c. Click Next.
d. Specify the IP address or hostname of the remote NAS.
e. Specify an administrator account and password of the remote NAS.
Important
For security reasons, QNAP does not recommend using the "admin" account.
f. Optional: Specify the system administration port of the remote NAS.
Tip
The default port is 8080. If HTTPS is enabled, the default port is 443.
g. Click Next.
h. Optional: Select the local interface that will be used by VJBOD.
i. Optional: Select the remote interface that will be used by VJBOD.
j. Optional: Select Use iSER when available.
Enabling iSER increases data transfer speeds and reduces CPU and memory load.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 305

k. Click Next.
l. Select Choose an existing iSCSI LUN on the selected NAS.
m. Click Next.
n. Select the LUN containing the VJBOD disk.
o. Click Next.
p. Optional: Enable CRC checksums.
Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI protocol data units (PDU).
The sending device can send a checksum with each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum
to verify the integrity of the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are
two checksum types, which can be enabled separately.
Checksum Type Description
Data Digest The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of the PDU.
Header Digest The checksum can be used to verify the header portion of the
PDU.
q. Click Next.
r. Review the summary, and then click Next.
QTS creates a VJBOD disk using the LUN. The disk appears at Storage & Snapshots > Storage >
Disks/VJBOD .
s. In the actions list, select Recover Existing Data.
t. Click Finish.
QTS scans for and restores any storage pools, volumes, and LUNs on the VJBOD disk.
VJBOD Cloud
VJBOD Cloud is a block-based storage gateway solution that enables you to create volumes and LUNs on
your NAS using cloud space from cloud services such as Google Cloud and Amazon S3. VJBOD Cloud volumes
and LUNs can utilize local storage space for accelerated read and write speeds, allowing both NAS users and
applications to seamlessly and transparently access cloud storage space.
Installing VJBOD Cloud
Requirements:
• A QNAP NAS running QTS 4.4.1 or later
• A cloud space (bucket or container) with at least 1 GB of free space from a supported cloud service
provider
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Ensure that a system volume is congured on the NAS.
For details, see The System Volume.
3. Open App Center, and then click .
A search box appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 306

4. Type VJBOD Cloud, and then press ENTER.
The VJBOD Cloud application appears in the search results.
5. Click Install.
The installation window appears.
6. Select the volume on which you want to install VJBOD Cloud.
7. Click OK.
QTS installs VJBOD Cloud.
VJBOD Cloud Volume and LUN Creation
Creating a VJBOD Cloud Volume
1. Open the VJBOD Cloud app.
2. Click Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN.
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN window opens.
3. Click Cloud Volume.
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume screen appears.
4. Select a cloud service.
5. Congure the selected cloud service.
Depending on the selected cloud storage provider, you may need to log in, authenticate, or congure
settings through a third-party interface.
For details, see Connecting to a VJBOD Cloud Service.
6. Optional: Select Use system proxy settings.
When enabled, VJBOD Cloud connects to the cloud storage space using the system proxy server
setting, congured at Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Proxy .
7. Click Search.
8. Select a cloud space.
This may be a bucket, container, account name, or something else depending on the cloud service
provider.
Note
If you do not have permission to browse the list of cloud spaces, then you need to enter the
name of the cloud space manually.
9. Optional: Click Performance test.
QTS tests the read and write speeds of the cloud space, and then displays the results with a warning if
speeds are too low.
10. Click Next.
11. Select Create a new volume.
12. Optional: Specify an alias for the volume.
Alias requirements:
• Length: 1–64 characters
• Valid characters: A–Z, a–z, 0–9
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 307
• Valid special characters: Hyphen (-), Underscore (_)
13. Specify the capacity of the volume.
The amount of free space in the cloud storage space determines the maximum capacity.
Important
• The minimum volume capacity is 3 GB.
• Increasing the capacity may increase cloud storage costs. Check with the cloud service
provider for details.
14. Optional: Congure any of the following advanced settings.
Setting Description User Actions
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning
notication when the
percentage of used volume
space is equal to or above the
specied threshold.
Specify a value.
Encryption QTS encrypts all data on
the volume with 256-bit AES
encryption.
• Specify an encryption password containing 8 to
32 characters, with any combination of letters,
numbers and special characters. Spaces are not
allowed.
• Select Save encryption key to save a local
copy of the encryption key on the NAS. This
enables QTS to automatically unlock and mount
the encrypted volume when the NAS starts up.
If the encryption key is not saved, you must
specify the encryption password each time the
NAS restarts.
Warning
• Saving the encryption key on the
NAS can result in unauthorized data
access if unauthorized personnel
are able to physically access the
NAS.
• If you forget the encryption
password, all data will become
inaccessible.
Create a shared
folder on the
volume
QTS automatically creates the
shared folder when the volume
is ready. Only the user account
that creates the shared folder
will have read/write access to
the folder.
Specify a folder name.
15. Optional: Specify the number of bytes per inode.
The number of bytes per inode determines the maximum volume size and the number of les and
folders that the volume can store. Increasing the number of bytes per inode results in a larger
maximum volume size, but a lower maximum number of les and folders.
16. Allocate stored space.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 308

Stored space is space used to store a copy of the volume's data locally on the NAS.
a. Select a storage pool.
b. Specify the capacity of the stored space.
Limit Amount Notes
Minimum stored space capacity 1.25x the volume's capacity Additional space is needed to
store metadata.
Maximum stored space capacity 2x the volume's capacity -
17. Click Next.
18. Review the summary information, and then click Finish.
The VJBOD Cloud volume appears in the Cloud Storage table at VJBOD Cloud > Overview .
Creating a VJBOD Cloud LUN
1. Open the VJBOD Cloud app.
2. Click Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN.
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN window opens.
3. Click Cloud LUN.
The Create VJBOD Cloud LUN screen appears.
4. Select a cloud service.
5. Congure the selected cloud service.
Depending on the selected cloud storage provider, you may need to log in, authenticate, or congure
settings through a third-party interface.
For details, see Connecting to a VJBOD Cloud Service.
6. Optional: Select Use system proxy settings.
When enabled, VJBOD Cloud connects to the cloud storage space using the system proxy server
setting, congured at Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Proxy .
7. Click Search.
8. Select a cloud space.
This may be a bucket, container, account name, or something else depending on the cloud service
provider.
Note
If you do not have permission to browse the list of cloud spaces, then you need to enter the
name of the cloud space manually.
9. Optional: Click Performance test.
QTS tests the read and write speeds of the cloud space, and then displays the results with a warning if
speeds are too low.
10. Click Next.
11. Select Create a new cloud LUN.
12. Specify a LUN name.
Name requirements:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 309
• Length: 1–31 characters
• Valid characters: A–Z, a–z, 0–9
• Valid special characters: Underscore (_)
13. Specify the capacity of the LUN.
The amount of free space in the cloud storage space determines the maximum capacity.
Important
• The minimum LUN capacity is 3 GB.
• Increasing the capacity may increase cloud storage costs. Check with the cloud service
provider for details.
14. Optional: Congure the sector size.
Changing the sector size to 4 KB increases LUN performance for specic applications and disk types.
Important
VMware does not currently support a 4 KB sector size.
15. Allocate stored space.
Stored space is space used to store a copy of the LUN's data locally on the NAS.
a. Select a storage pool.
b. Specify the capacity of the stored space.
Limit Amount Notes
Minimum stored space capacity 1.25x the LUN's capacity Additional space is needed to
store metadata.
Maximum stored space capacity 2x the LUN's capacity -
16. Click Next.
17. Optional: Deselect Do not map it to a target for now.
If deselected, the Edit LUN Mapping wizard appears after QTS has nished creating the LUN.
18. Review the summary information, and then click Finish.
The VJBOD Cloud LUN appears in the Cloud Storage table at VJBOD Cloud > Overview .
Reattaching an Existing VJBOD Cloud Volume
Note
• QTS uses shared folders instead of volumes. For this reason, after creating a VJBOD
Cloud volume QTS automatically creates a shared folder with the same name which is
stored on the volume. You can then write data to the shared folder.
• When transferring a VJBOD Cloud volume from QuTS hero to QTS, ensure that all les
are in subfolders. Files in the shared folder that are not in a subfolder will not be
visible in QTS.
1. Open the VJBOD Cloud app.
2. Click Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 310
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN window opens.
3. Click Cloud Volume.
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume screen appears.
4. Select a cloud service.
5. Congure the selected cloud service.
Depending on the selected cloud storage provider, you may need to log in, authenticate, or congure
settings through a third-party interface.
For details, see Connecting to a VJBOD Cloud Service.
6. Optional: Select Use system proxy settings.
When enabled, VJBOD Cloud connects to the cloud storage space using the system proxy server
setting, congured at Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Proxy .
7. Click Search.
8. Select a cloud space.
This may be a bucket, container, account name, or something else depending on the cloud service
provider.
Note
If you do not have permission to browse the list of cloud spaces, then you need to enter the
name of the cloud space manually.
9. Optional: Click Performance test.
QTS tests the read and write speeds of the cloud space, and then displays the results with a warning if
speeds are too low.
10. Click Next.
11. Select Attach an existing cloud volume.
12. Select an existing volume.
13. Allocate stored space.
Stored space is space used to store a copy of the volume's data locally on the NAS.
a. Select a storage pool.
b. Specify the capacity of the stored space.
Limit Amount Notes
Minimum stored space capacity 1.25x the volume's capacity Additional space is needed to
store metadata.
Maximum stored space capacity 2x the volume's capacity -
14. Click Next.
15. Optional: Forcibly disconnect the volume from its current NAS.
If a volume is connected to another NAS, then the volume's status will be Occupied and Current NAS
will display an IP address other than Localhost.
Warning
Forcibly disconnecting a volume deletes the volume's data from the other NAS, and then
recreates the volume locally from its last restore point. Any changes to data made since the last
restore point will be lost.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 311

a. Specify the admin password of the other NAS.
b. Click OK.
16. Review the summary information, and then click Finish.
The VJBOD Cloud volume appears in the Cloud Storage table at VJBOD Cloud > Overview .
QTS automatically creates a shared folder on the volume. The shared folder has the same name as the
volume.
Reattaching an Existing VJBOD Cloud LUN
1. Open the VJBOD Cloud app.
2. Click Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN.
The Create VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN window opens.
3. Click Cloud LUN.
The Create VJBOD Cloud LUN screen appears.
4. Select a cloud service.
5. Congure the selected cloud service.
Depending on the selected cloud storage provider, you may need to log in, authenticate, or congure
settings through a third-party interface.
For details, see Connecting to a VJBOD Cloud Service.
6. Optional: Select Use system proxy settings.
When enabled, VJBOD Cloud connects to the cloud storage space using the system proxy server
setting, congured at Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Proxy .
7. Click Search.
8. Select a cloud space.
This may be a bucket, container, account name, or something else depending on the cloud service
provider.
Note
If you do not have permission to browse the list of cloud spaces, then you need to enter the
name of the cloud space manually.
9. Optional: Click Performance test.
QTS tests the read and write speeds of the cloud space, and then displays the results with a warning if
speeds are too low.
10. Click Next.
11. Select Attach an existing cloud LUN.
12. Select an existing LUN.
13. Allocate stored space.
Stored space is space used to store a copy of the LUN's data locally on the NAS.
a. Select a storage pool.
b. Specify the capacity of the stored space.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 312
Limit Amount Notes
Minimum stored space capacity 1.25x the LUN's capacity Additional space is needed to
store metadata.
Maximum stored space capacity 2x the LUN's capacity -
14. Click Next.
15. Optional: Forcibly disconnect the LUN from its current NAS.
If a volume is connected to another NAS, then the LUN's status will be Occupied and Current NAS will
display an IP address other than Localhost.
Warning
Forcibly disconnecting a LUN deletes the LUN's data from the other NAS, and then recreates
the LUN locally from its last restore point. Any changes to data made since the last restore
point will be lost.
a. Specify the admin password of the other NAS.
b. Click OK.
16. Optional: Deselect Do not map it to a target for now.
If deselected, the Edit LUN Mapping wizard appears after QTS has nished creating the LUN.
17. Review the summary information, and then click Finish.
The VJBOD Cloud LUN appears in the Cloud Storage table at VJBOD Cloud > Overview .
Connecting to a VJBOD Cloud Service
Refer to this table when conguring a cloud service for a VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN.
Cloud Service Steps
Alibaba Cloud OSS 1. Select AlibabaCloudOSS.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Note
If transfer acceleration is enabled on the
bucket, VJBOD Cloud automatically enables transfer
acceleration on the NAS and displays a conrmation
message.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 313
Cloud Service Steps
Amazon S3 1. Select AmazonS3.
2. Select a cloud service:
•AWS Global
•AWS China
•AWS GovCloud (US): Select either Standard or FIPS
protocol.
•S3 Compatible: Specify the server address.
3. Specify the access key.
4. Specify the secret key.
5. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
6. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Microsoft Azure 1. Select Azure.
2. Specify the storage account.
3. Specify the access key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Backblaze 1. Select Backblaze.
2. Specify the key ID.
3. Specify the application key.
4. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Catalyst 1. Select Catalyst.
2. Specify the user ID.
3. Specify the password.
4. Specify the project name.
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 314
Cloud Service Steps
Cynny Space 1. Select Cynny Space.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
DigitalOcean 1. Select Digital Ocean.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Select a region.
DreamObjects 1. Select DreamObjects.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Google Cloud Storage (P12 Key) 1. Select GoogleCloudStorage.
2. Select P12 key.
3. Specify the project ID.
4. Specify the email address.
5. Click Browse, and then select the P12 key le.
6. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Google Cloud Storage (JSON Key) 1. Select GoogleCloudStorage.
2. Select JSON key.
3. Specify the project ID.
4. Specify the email address.
5. Click Browse, and then select the JSON key le.
6. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 315
Cloud Service Steps
Google Cloud Storage (OAuth) 1. Select GoogleCloudStorage.
2. Select OAuth.
3. Specify the project ID.
4. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
HiCloud 1. Select HiCloud.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
HKT Cloud Storage 1. Select HKT.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Huawei Cloud OBS 1. Select HuaweiCloudOBS.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
IBM Cloud 1. Select IBM Cloud.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 316
Cloud Service Steps
luckycloud S3 1. Select luckycloud S3.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Oracle Cloud 1. Select Oracle Cloud.
2. Specify the name space.
3. Specify the access key.
4. Specify the secret key.
5. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
6. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
7. Select a region.
Qcloud Italy 1. Select Qcloud IT.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Rackspace 1. Select Rackspace.
2. Specify the user ID.
3. Specify the password.
4. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
5. Select a region.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 317
Cloud Service Steps
S3 Compatible 1. Select S3 Compatible.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Specify the authentication service.
5. Select a signature version.
6. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
7. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
8. Optional:
Specify a region.
Swift 1. Select Swift.
2. Optional:
Enable keystone authentication.
a. Select Enable Keystone Auth.
b. Specify a tenant ID or tenant name.
3. Select the large object type.
4. Specify the user ID.
5. Specify the auth service.
6. Specify the API key or password.
7. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
Swift (Keystone v3) 1. Select Swift.
2. Select Enable Keystone Auth.
3. Select V3.
4. Specify a project name or project ID.
5. Specify the domain name.
6. Select the large object type.
7. Specify the user name.
8. Specify the auth service.
9. Specify the password.
10. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
11. Select a region.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 318
Cloud Service Steps
Wasabi 1. Select Wasabi.
2. Specify the access key.
3. Specify the secret key.
4. Optional:
Select Enable secure connection (SSL).
5. Optional:
Select Validate SSL certicate.
VJBOD Cloud Management
You can manage VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs by going to VJBOD Cloud > Overview . Select a volume or
LUN and then click Manage.
Volume Actions
Action Description Steps
Resize volume Increase or decrease the size of the
volume.
1. Click Resize Volume.
2. Specify the new capacity of the volume.
3. Select the unit of storage space.
4. Optional:
Click Set to Max to set the capacity of
the volume equal to all free space in
the cloud space.
5. Click Apply.
Utilization View statistics showing data uploaded,
data downloaded, and cache space
utilization for the volume.
Click Actions, and then select Utilization.
Set Threshold QTS issues a warning notication when
the percentage of used volume space
is equal to or above the specied
threshold.
1. Click Actions, and then select Set
Threshold.
2. Enable Please input the alert
threshold [1-100].
3. Specify the alert threshold.
4. Click Apply.
Check le system A le system check scans for and
automatically repairs errors in the le
system of the volume.
1. Click Actions, and then select Check
File System.
2. Click OK.
Recovery QTS periodically takes snapshots of a
VJBOD Cloud volume. You can use these
recovery point snapshots to restore the
volume to a previous state.
For details, see Recovering a VJBOD Cloud
Volume or LUN.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 319
LUN Actions
Action Description Steps
Expand LUN Increase the capacity of the LUN or its
stored space.
1. Click Expand LUN.
2. Specify the new capacity of the LUN
or its stored space, in GB.
3. Optional:
Click Set to Max to set the capacity
of the LUN equal to all free space in
the cloud space.
4. Click Apply.
Utilization Info View statistics showing data uploaded,
data downloaded, and cache space
utilization for the LUN.
Click Actions, and then select
Utilization.
Recovery QTS periodically takes snapshots of a
VJBOD Cloud LUN. You can use these
recovery point snapshots to restore the
LUN to a previous state.
For details, see Recovering a VJBOD
Cloud Volume or LUN.
Volume/LUN Connection Status
Status Description
Ready The cloud storage space is working normally.
Syncing A volume or LUN is currently syncing with the cloud space.
License Expiring The VJBOD Cloud license attached to this storage space will expire within
one month. You must renew it if you want to continue using volumes and
LUNs in this storage space.
License Expired The license attached to this storage space has expired. All volumes and
LUNs created in this storage space are set to read-only.
Not Ready There is a problem with the connection to this storage space.
Volume/LUN Connection Actions
To perform one of the following actions go to VJBOD Cloud > Overview , select a VJBOD Cloud volume or
LUN, click Manage, and then click Connection.
Action Description
Connect Reconnects the volume or LUN to the cloud space.
Disconnect Disconnects the volume or LUN from the cloud space. The volume or LUN becomes
read-only.
Edit Edits the volume or LUN's cloud space connection details.
Remove Remove the volume or LUN from the NAS and delete all of its data from the cloud
space.
Important
If QTS is unable to connect to the cloud service provider, then the
volume or LUN will be removed from the local NAS but its data
might be left in the cloud space.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 320
Action Description
Safely Detach Removes the volume or LUN from the NAS but do not delete its data from the cloud
space. The volume or LUN can be reattached to this NAS or another NAS later.
Important
• QTS moves all non-uploaded data in the write cache to the
cloud space before removing the volume or LUN. This process
may take a long time to complete.
• If it's not possible to connect to the cloud space, the detach
operation will fail.
Force Detach: QTS removes the volume or LUN from the local NAS and leaves its
data in the cloud space. If it's not possible to connect to the cloud space, QTS will still
delete the volume or LUN from the local NAS.
Warning
If Force Detach is selected, non-uploaded data stored in the
volume or LUN might be deleted.
Recovering a VJBOD Cloud Volume or LUN
QTS periodically takes recovery point snapshots of each VJBOD Cloud volume and LUN to ensure that the
volume or LUN can be recovered if it encounters an error. You can use these recovery points to restore the
volume or LUN to a previous state.
1. Go to VJBOD Cloud > Overview .
2. Under Cloud Storage, select a VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN.
3. Click Manage.
The volume or LUN management window opens.
4. Click Actions, and then select Recovery.
The VJBOD Cloud Volume/LUN Recovery window opens.
5. Select a recovery point.
Warning
All changes to data made after the recovery point will be deleted.
6. Click Recover.
The status of the volume or LUN changes to Recovering, and then changes back to ready when the
recovery process has nished.
Transfer Resources
In VJBOD Cloud, transfer resources correspond to data uploads and downloads. If VJBOD Cloud has 100
total transfer resources, that means the application can create 100 threads for uploading data to and
downloading data from the cloud.
The total transfer resources allocated to VJBOD Cloud is determined by your NAS hardware. You can manage
transfer resources by going to VJBOD Cloud > Transfer Resources .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 321
Transfer Resource Allocation
By default, transfer resources are shared between all VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs. When a volume or
LUN needs to upload to or download data from the cloud, VJBOD Cloud removes transfer resources from the
shared transfer resource pool and temporarily allocates them to the volume or LUN, then returns them to
the pool after the data transfer has nished.
A single volume or LUN may use a large number of shared transfer resources, stopping other volumes and
LUNs from syncing data with the cloud. To prevent this you can reserve transfer resources for a volume or
LUN, guaranteeing that those resources will always be available. You can also set a limit on the maximum
number of transfer resources a volume or LUN can use.
Transfer Resource Usage Guidelines
Problem Solution
VJBOD Cloud is taking a long time to sync data to the
cloud.
Increase the total number of transfer resources
allocated to VJBOD Cloud.
VJBOD Cloud is using too much NAS memory, CPU,
or network bandwidth.
Decrease the total number of transfer resources
allocated to VJBOD Cloud.
• A VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN is taking a long
time to sync data to the cloud.
• A VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN contains
important data, which should always be backed
up before other volumes and LUN data.
Increase the transfer resources reserved for the
volume or LUN.
A VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN is using too many
transfer resources or too much network bandwidth.
Limit the maximum number of transfer resources
the volume or LUN can use.
Conguring Total Transfer Resources
1. Go to VJBOD Cloud > Transfer Resources .
2. Under Total resources, specify the total number of transfer resources available to VJBOD Cloud.
The minimum number is one. The maximum number is determined by your NAS hardware.
Important
Total transfer resources must be greater than current reserved transfer resources.
3. Click Apply.
Conguring Transfer Resources for a Volume or LUN
1. Go to VJBOD Cloud > Transfer Resources .
2. Under Cloud Volume/LUN Resources, locate a VJBOD Cloud volume or LUN.
3. Congure any of the following settings.
Setting Description
Reserved The number of transfer resources reserved for this volume or LUN.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 322
Setting Description
Limit The maximum number of transfer resources this volume or LUN can use.
Note
To set this value, Limitation Rule must be set to Limit.
Limitation Rule Select one of the following rules:
• Limit: The maximum number of transfer resources this volume or LUN
can use is restricted. It can only use the number specied under Limit.
• No Limit: The maximum number of transfer resources this volume or
LUN can use is unrestricted. It can use all of its reserved resources and
all shared transfer resources.
4. Click Apply.
Event Logs
Event logs, error messages, and warnings related to VJBOD Cloud are displayed in VJBOD Cloud > Event
Logs . You can view logs by severity level, search logs using keywords, and congure notication settings.
Licenses
You can go to VJBOD Cloud > Licenses to view how many VJBOD Cloud licenses are registered to the local
NAS, and how many of those licenses are currently being used. You can also purchase additional VJBOD
Cloud licenses.
VJBOD Cloud Licensing Overview
VJBOD Cloud requires a license for each connection to a unique cloud space. A cloud space may be called a
bucket, container, account name, or something else depending on the cloud service provider. For example,
the following VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs require three licenses:
•Amazon S3
→
Bucket1
→
Volume1
•Amazon S3
→
Bucket2
→
Volume2
•Azure
→
Space1
→
LUN1
Each unique cloud space can contain an unlimited number of VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs. For example,
the following VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs require only one license:
•Amazon S3
→
Bucket1
→
Volume1
•Amazon S3
→
Bucket1
→
Volume2
•Amazon S3
→
Bucket1
→
LUN1
If a license expires, all VJBOD Cloud volumes and LUNs created from the cloud space attached to the license
become read-only until the license is renewed.
VJBOD Cloud includes one free license.
Purchasing VJBOD Cloud Licenses
1. Go to VJBOD Cloud > Licenses .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 323

2. Click Purchase License.
The License Center window opens.
3. Click Software Store.
4. Locate VJBOD Cloud, and then click Buy.
5. Follow the onscreen instructions to purchase and activate the VJBOD Cloud licenses.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots 324
8. iSCSI & Fibre Channel
iSCSI & Fibre Channel is a QTS utility that enables you to congure iSCSI and Fibre Channel storage settings
on your NAS.
Storage Limits
iSCSI Storage Limits
iSCSI Storage Limit Maximum
iSCSI LUNs and targets per NAS 255 (combined)
Connections per iSCSI session 8
iSCSI sessions per target The maximum number of sessions is determined by available NAS CPU
resources, memory, and network bandwidth.
iSCSI sessions per NAS The maximum number of sessions is determined by available NAS CPU
resources, memory, and network bandwidth.
Fibre Channel Storage Limits
Fibre Channel Storage Limit Maximum
Fibre Channel ports + port groups 256 (combined)
WWPN aliases 256
LUN masking rules 256
Port binding rules 256
LUNs mapped to 1 Fibre Channel port 256
iSCSI & Fibre Channel Global Settings
You can access global settings by clicking in the iSCSI & Fibre Channel window.
Setting Description
Enable iSCSI and Fibre Channel
services
Enable these services to use iSCSI and Fibre Channel on your NAS.
iSCSI service port View and modify the port that iSCSI initiators connect to.
Tip
The default port is 3260.
Enable iSNS SNS enables the automatic discovery and management of iSCSI
initiators and targets within a TCP/IP network.
iSNS server IP: Specify the IP address of the iSNS server.
LUNs
QNAP NAS devices allow other devices to access their storage space in the form of LUNs over iSCSI and Fibre
Channel networks. The LUNs must rst be created on the NAS, and then mapped to iSCSI targets or Fibre
Channel port groups for access over the network.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 325
QTS LUN Types
QTS supports the following types of LUNs.
Tip
Block-based LUNs support more features and have faster read/write speeds. QNAP
recommends using block-based LUNs over le-based LUNs if possible.
Feature Block-based LUN File-based LUN VJBOD Cloud LUN
Parent storage space Storage pool Thick volume Cloud space
VAAI Full Copy Supported Supported Supported
VAAI Block Zeroing Supported Supported Supported
VAAI Hardware-Assisted
Locking
Supported Supported Supported
VAAI Thin Provisioning
and Space Reclaim
Supported Not supported Supported
Thin provisioning Supported Supported Not supported
QTS space reclamation Supported (when using
VAAI or the host is
Windows Server 2012,
Windows 8 or later)
Not supported Supported (when using
VAAI or the host is
Windows Server 2012,
Windows 8 or later)
Microsoft ODX Supported Not supported Supported
LUN export Supported Supported Supported
LUN snapshots Supported Partially supported (You
can take a snapshot
of the LUN's parent
volume.)
Supported
Read/write speeds High Medium to low High when using caching
(stored space)
Low when not using
caching
Creating a Block-Based LUN
1. Go to one of the following screens.
•iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage
•iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Storage
2. Click Create, and then select New Block-Based LUN.
The Block-Based LUN Creation Wizard opens.
3. Select the storage pool that this LUN will be created in.
4. Select a LUN allocation method.
Allocation Description
Thick instant allocation QTS allocates storage pool space when creating the LUN. This space is
guaranteed to be available later.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 326
Allocation Description
Thin provisioning QTS allocates storage pool space only when needed, such as when
data is being written to the LUN. This ensures ecient use of space but
there is no guarantee that space will be available.
5. Click Next.
6. Congure the following LUN settings.
Setting Description
LUN name • Length: 1 to 32 characters
• Valid characters: 0-9, a-z, A-Z, underscore (_)
LUN capacity Specify the maximum capacity of the LUN. The maximum capacity
depends on the LUN allocation method:
• Thick provisioning: Equal to the amount of free space in the parent
storage pool.
• Thin provisioning: 250 TB
Tip
Select Maximum to allocate all remaining free space
to the LUN.
7. Optional: Congure any of the following advanced settings.
Setting Description
Sector size Changing the sector size to 4 KB increases LUN performance for
specic applications and disk types.
Important
VMware does not currently support a 4 KB sector size.
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used LUN
space is equal to or above the specied threshold.
Accelerate performance with SSD
cache
The SSD cache will be used to improve LUN access performance.
Important
This setting is only available when the SSD cache is
enabled.
Report volatile write cache for
data safety
When enabled, QTS informs iSCSI initiators connected to this LUN that
volatile write-cache is being used on the NAS. As a result, initiators
might frequently tell QTS to ush cached LUN data to disk, which
increases data safety but decreases LUN performance.
FUA bit support When enabled, iSCSI initiators are able to tell QTS to ush important
cached data to disk, instead of the whole read-write cache.
Important
Both the iSCSI initiator and the application using the
LUN must support this feature.
8. Click Next.
9. Optional: Deselect Do not map it to a target for now.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 327
If deselected, the Edit LUN Mapping wizard appears after QTS has nished creating the LUN.
10. Click Finish.
11. Optional: Map the LUN to an iSCSI target or Fibre Channel port group.
For details, see the following topics:
•Mapping a LUN to an iSCSI Target
•Mapping a LUN to a Fibre Channel Port Group
Creating a File-Based LUN
1. Go to one of the following screens.
•iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage
•iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Storage
2. Click Create, and then select New File-Based LUN.
The File-Based LUN Creation Wizard opens.
3. Select the thick volume that this LUN will be created on.
4. Select a LUN allocation method.
Allocation Description
Thick instant allocation QTS allocates storage pool space when creating the LUN. This space is
guaranteed to be available later.
Thin provisioning QTS allocates storage pool space only when needed, such as when
data is being written to the LUN. This ensures ecient use of space but
there is no guarantee that space will be available.
5. Click Next.
6. Congure the following LUN settings.
Setting Description
LUN name • Length: 1 to 32 characters
• Valid characters: 0-9, a-z, A-Z, underscore (_)
LUN capacity Specify the maximum capacity of the LUN. The maximum capacity
depends on the LUN allocation method:
• Thick provisioning: Equal to the amount of free space in the parent
storage pool.
• Thin provisioning: 250 TB
7. Optional: Congure any of the following advanced settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 328
Setting Description
Sector size Changing the sector size to 4 KB increases LUN performance for
specic applications and disk types.
Important
VMware does not currently support a 4 KB sector size.
Alert threshold QTS issues a warning notication when the percentage of used LUN
space is equal to or above the specied threshold.
Report volatile write cache for
data safety
When enabled, QTS informs iSCSI initiators connected to this LUN that
volatile write-cache is being used on the NAS. As a result, initiators
might frequently tell QTS to ush cached LUN data to disk, which
increases data safety but decreases LUN performance.
FUA bit support When enabled, iSCSI initiators are able to tell QTS to ush important
cached data to disk, instead of the whole read-write cache.
Important
Both the iSCSI initiator and the application using the
LUN must support this feature.
8. Click Next.
9. Optional: Deselect Do not map it to a target for now.
If deselected, the Edit LUN Mapping wizard appears after QTS has nished creating the LUN.
10. Click Finish.
11. Optional: Map the LUN to an iSCSI target or Fibre Channel port group.
For details, see the following topics:
•Mapping a LUN to an iSCSI Target
•Mapping a LUN to a Fibre Channel Port Group
LUN Import/Export
With LUN Import/Export, you can back up a LUN as an image le to an SMB or NFS le server, local NAS
folder, or external storage device. You can then import the LUN image le and restore the LUN on any QNAP
NAS.
Creating a LUN Export Job
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > LUN Import/Export .
2. Click Create a Job.
The Create LUN Export Job windows opens.
3. Select Export a LUN.
4. Select a LUN.
5. Optional: Specify a job name.
The name must consist of 1 to 55 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 329
• Special characters: Underscore (_)
6. Click Next.
7. Select the destination folder.
Option Description Required Information
Linux Share (NFS) NFS share on an external server • IP address or host name
• NFS folder or path
Windows Share
(CIFS/SMB)
CIFS/SMB share on an external server • IP address or host name
• Username
• Password
• CIFS/SMB folder or path
Local Host Local NAS shared folder or connected
external storage device
• NAS shared folder or external device
• Sub-folder
8. Click Next.
9. Optional: Specify a LUN image name.
• The name must consist of 1 to 64 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Underscore (_), hyphen (-), space ( )
• The name cannot begin or end with a space.
10. Optional: Select Use Compression to compress the image le.
When enabled, the image le will be smaller but exporting will take longer and will use more processor
resources.
11. Select when the job will run.
Option Description
Now Run the job immediately after the job has been created. After this rst
run, the job will only run when manually started.
• Hourly
• Daily
• Weekly
• Monthly
Run the job periodically according to the specied schedule.
12. Click Next.
13. Click Apply.
QTS creates the job. The job then starts running if Now was selected as the scheduling option.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 330
Importing a LUN from an Image File
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > LUN Import/Export .
2. Click Create a Job.
The Create LUN Export Job windows opens.
3. Select Import a LUN.
4. Optional: Specify a job name.
The name must consist of 1 to 55 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Special characters: Underscore (_)
5. Click Next.
6. Select the source folder.
Option Description Required Information
Linux Share (NFS) NFS share on an external server • IP address or host name
• NFS folder or path
Windows Share
(CIFS/SMB)
CIFS/SMB share on an external server • IP address or host name
• Username
• Password
• CIFS/SMB folder or path
Local Host Local NAS shared folder or connected
external storage device
NAS shared folder or external device
7. Click Next.
8. Select the LUN image le.
9. Click Next.
10. Specify the import destination.
Option Description Required Information
Overwrite existing
LUN
Import the image le data to an existing
LUN.
Warning
All existing data on the LUN will
be overwritten.
An existing LUN with the same type
(block-based or le-based) as the LUN
being imported
Create a new LUN Import the image le as a new LUN. • LUN name
• LUN location. This will be a storage
pool or volume.
11. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 331
12. Click Apply.
QTS creates the job, and then immediately runs it.
LUN Import/Export Job Actions
You can perform various actions on LUN import/export jobs by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > LUN
Import/Export . Select a LUN import/export job and then click Action to select the desired action.
Action Description
Edit Edit the job.
Delete Delete the job.
Start Start the job.
Stop Stop a running job.
View Logs View the job's status, properties, details of its last run, and event logs.
LUN Import/Export Job Status
You can view LUN import/export job statuses by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > LUN Import/Export .
Status Description
-- The job has not run yet.
Initializing The job is preparing to run.
Processing The job is running. The job's progress is displayed a percentage next to
the status.
Finished The job has nished running or was canceled by a user.
Failed The job failed. View the job's event log for details.
iSCSI
iSCSI enables computers, servers, other NAS devices, and virtual machines to access NAS storage in the form
of LUNs over a TCP/IP network. Hosts can partition, format, and use the LUNs as if they were local disks.
Getting Started with iSCSI
1. Create an iSCSI target on the NAS.
For details, see Creating an iSCSI Target.
2. Create a LUN on the NAS.
A LUN is a portion of storage space, similar to a volume. LUNs are created from storage pool space
(block-based) or from space in a thick volume (le-based).
For more information, see:
•QTS LUN Types
•Creating a Block-Based LUN
•Creating a File-Based LUN
3. Map the LUN to the iSCSI target.
Multiple LUNs can be mapped to one target.
For details, see iSCSI LUN Actions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 332

4. Install an iSCSI initiator application or driver on the host.
The host is the service, computer, or NAS device that will access the LUN.
5. Connect the iSCSI initiator to the iSCSI target on the NAS.
Warning
To prevent data corruption, multiple iSCSI initiators should not connect to the same LUN
simultaneously.
The LUNs mapped to the iSCSI target appear as disks on the host.
6. In the host OS, format the disks.
iSCSI Performance Optimization
You can optimize the performance of iSCSI by following one or more of these guidelines:
• Use thick provisioning (instant allocation). Thick provisioning gives slightly better read and write
performance than thin provisioning.
• Create multiple LUNs, one for each processor thread on the NAS. For example, if the NAS has four
processor threads, then you should create four or more LUNs.
Tip
Go to Control Panel > System > System Status > System Information > CPU to view the
number of processor threads.
• Use separate LUNs for dierent applications. For example, when creating two virtual machines which
intensively read and write data, you should create one LUN for each VM to distribute the load.
• You can use iSER (iSCSI Extensions for RDMA) for faster data transfers between QNAP NAS devices
and VMware ESXi servers. Enabling iSER requires a compatible network card and switch. For a list of
compatible network devices, see https://www.qnap.com/solution/iser.
iSCSI Targets
iSCSI targets allow iSCSI initiators from other devices on the network to access mapped LUNs on the NAS.
You can create multiple iSCSI targets and also map multiple LUNs to a single iSCSI target.
Creating an iSCSI Target
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Click Create, and then select New iSCSI Target.
The iSCSI Target Creation Wizard window opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Specify a target name.
QTS appends the specied name to the iSCSI qualied name (IQN). IQNs are unique names used to
identify targets and initiators.
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z
• Length: 1 to 16 characters
5. Optional: Specify a target alias.
An alias enables you to identify the target more easily on the initiator.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 333

• Length: 1 to 32 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, underscore (_), hyphen (-), space ( )
6. Optional: Select Allow clustered access to this target.
When enabled, multiple iSCSI initiators can access this target and its LUNs simultaneously.
Warning
To prevent data corruption, the initiators and LUN lesystems must all be cluster-aware.
7. Optional: Enable CRC checksums.
Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI protocol data units (PDU). The
sending device can send a checksum with each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum to verify
the integrity of the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are two checksum
types, which can be enabled separately.
Checksum Type Description
Data Digest The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of the PDU.
Header Digest The checksum can be used to verify the header portion of the PDU.
8. Click Next.
9. Optional: Enable CHAP authentication.
An initiator must authenticate with the target using the specied username and password. This
provides security, as iSCSI initiators do not require a NAS username or password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
10. Optional: Enable mutual CHAP authentication.
Both the initiator and the target must authenticate with each other for additional security. First, the
initiator authenticates with the target using the CHAP authentication username and password. Next,
the target authenticates with the initiator using the mutual CHAP username and password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
11. Click Next.
12. Optional: Select Create a LUN and map it to this target.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 334
If selected, QTS opens the Block-Based LUN Creation Wizard immediately after nishing this wizard.
The new LUN will then be automatically mapped to this target.
13. Click Apply.
QTS creates the iSCSI target, and then opens the Block-Based LUN Creation Wizard window if Create an
iSCSI LUN and map it to this target was enabled.
Editing iSCSI Target Settings
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select an iSCSI target.
3. Click Action, and then select Modify.
The Modify iSCSI Target window opens.
4. Modify any of the following settings.
Setting Description
Target Alias An alias enables you to identify the target more easily on the initiator.
• Length: 1 to 32 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, underscore (_), hyphen (-), space
( )
Enable clustered access to
the iSCSI target from multiple
initiators
When enabled, multiple iSCSI initiators can access this target and its LUNs
simultaneously.
Warning
To prevent data corruption, the initiators and LUN
lesystems must all be cluster-aware.
CRC/Checksum Initiators and targets communicate over TCP connections using iSCSI
protocol data units (PDU). The sending device can send a checksum with
each PDU. The receiving device uses this checksum to verify the integrity of
the PDU, which is useful in unreliable network environments. There are two
checksum types, which can be enabled separately.
• Data Digest: The checksum can be used to verify the data portion of
the PDU.
• Header Digest: The checksum can be used to verify the header portion
of the PDU.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 335
Setting Description
Use CHAP authentication An initiator must authenticate with the target using the specied
username and password. This provides security, as iSCSI initiators do not
require a NAS username or password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
Mutual CHAP Both the initiator and the target must authenticate with each other
for additional security. First, the initiator authenticates with the target
using the CHAP authentication username and password. Next, the target
authenticates with the initiator using the mutual CHAP username and
password.
• Username
• Length: 1 to 127 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, colon (:), period (.), hyphen (-)
• Password
• Length: 12 to 16 characters
• Valid characters: 0 to 9, a to z, A to Z, all special characters
5. Click Apply.
Binding an iSCSI Target to a Network Interface
You can bind an iSCSI target to one or more network interfaces so that the iSCSI target can only be accessed
via specic IP addresses.
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select an iSCSI target.
3. Click Action, and then select Modify.
The Modify an iSCSI Target window opens.
4. Select Network Portal.
5. Optional: Select one or more network interfaces you want to bind to the iSCSI target.
6. Optional: Deselect one or more network interfaces you want to remove from the iSCSI target.
7. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 336
iSCSI Target Actions
You can perform various actions on iSCSI targets by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage . Select
a target and then click Action to select the desired action.
Action Description
Disable Disable an active target and disconnect all connected iSCSI initiators.
Enable Enable a disabled target.
Modify Edit the target's settings.
For details, see the following topics:
•Editing iSCSI Target Settings
•iSCSI Target Authorization
View Connections View the IP addresses and IQN information of all iSCSI initiators
connected to this target.
Delete Disconnect all connected iSCSI initiators and delete the target. Any
LUNs mapped to the target will be unmapped and then added to the
unmapped LUN list.
iSCSI Target Status
You can view iSCSI target statuses by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
Status Description
Ready The target is accepting connections but no initiators are currently
connected.
Connected An initiator is connected to the target.
Oine The target is not accepting connections.
iSCSI LUN Management
Mapping a LUN to an iSCSI Target
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select a LUN.
Tip
Double-click an iSCSI target to view all of its mapped LUNs.
3. Optional: If the LUN is already mapped to a target, disable the LUN.
a. Click Action, and then select Disable .
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click OK.
QTS disables the LUN.
4. Click Action, and then select Edit LUN Mapping.
The Edit LUN Mapping window opens.
5. Select Map to iSCSI target.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 337
6. Select an iSCSI target.
7. Optional: Select Enable LUN.
If selected, QTS will enable the LUN after mapping it to the target.
8. Click OK.
Changing the Target of an iSCSI LUN
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select a mapped LUN.
Tip
Double-click an iSCSI target to view all of its mapped LUNs.
3. Click Action, and then select Disable .
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
QTS disables the LUN.
5. Click Action, and then select Edit LUN Mapping.
The Edit LUN Mapping window opens.
6. Select Map to iSCSI target.
7. Select an iSCSI target.
8. Optional: Select Enable LUN.
If selected, QTS will enable the LUN after mapping it to the target.
9. Click OK.
iSCSI LUN Actions
You can perform various actions on iSCSI LUNs by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage . Expand
a target to view its mapped LUNs, then select a LUN and click Action to select the desired action.
LUN Action Description
Disable Disable the LUN. The LUN will become inaccessible to connected iSCSI
initiators.
Enable Enable the LUN if it is currently disabled.
Modify Edit the LUN settings.
Delete Delete the LUN and all data stored on it.
Important
• This action is only available if the LUN is
unmapped.
• To delete a VJBOD Cloud LUN, use the VJBOD Cloud
app.
Utilization View LUN utilization percentages over a specied period of time.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 338
LUN Action Description
Edit LUN Mapping Unmap the LUN, or map it to a dierent iSCSI target or Fibre Channel
Port group.
For details, see the following topics:
•Mapping a LUN to a Fibre Channel Port Group
•Mapping a LUN to an iSCSI Target
Show in Storage & Snapshots Manage the LUN at Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/
Snapshots .
LUN Import/Export Export the LUN to another server, a local NAS folder, or an external
storage device.
For details, see LUN Import/Export.
iSCSI LUN Status
You can view iSCSI LUN statuses by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage . Expand a target to
view its mapped LUNs.
Status Description
Enabled The LUN is active and visible to connected initiators.
Disabled The LUN is inactive and invisible to connected initiators.
iSCSI Access Control List
The iSCSI access control list (ACL) allows you to congure a LUN masking policy for each connected iSCSI
initiator. A LUN masking policy determines which LUNs the initiator is able to see and access. If no policy is
specied for an iSCSI initiator, then QTS applies the default policy to it.
Tip
• The default policy gives all iSCSI initiators full read/write access to all LUNs.
• You can edit the default policy so that all LUNs are either read-only or not visible to all
iSCSI initiators, except for initiators with specic permissions from a policy.
Adding an iSCSI LUN Masking Policy
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Click iSCSI ACL.
The iSCSI ACL window opens.
3. Click Add a Policy.
The Add a Policy window opens.
4. Specify the policy name.
The name must consist of 1 to 32 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: a-z, A-Z
• Numbers: 0-9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), space ( ), underscore (_)
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 339

5. Specify the initiator IQN.
6. Congure the access permissions for each LUN.
Permission Description
Read Only The iSCSI initiator can read data on the LUN, but cannot write, modify,
or delete data.
Read/Write The iSCSI initiator can read, write, modify, and delete data on the LUN.
Deny Access The LUN is invisible to the iSCSI initiator.
Tip
Click the values in the columns to change the permissions.
7. Click Apply.
Editing an iSCSI LUN Masking Policy
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Click iSCSI ACL.
The iSCSI ACL window opens.
3. Select a policy.
4. Click Edit.
The Modiy a Policy window opens.
5. Optional: Edit the policy name.
The name must consist of 1 to 32 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: a-z, A-Z
• Numbers: 0-9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), space ( ), underscore (_)
6. Optional: Congure the access permissions for each LUN.
Permission Description
Read Only The iSCSI initiator can read data on the LUN, but cannot write, modify,
or delete data.
Read/Write The iSCSI initiator can read, write, modify, and delete data on the LUN.
Deny Access The LUN is invisible to the iSCSI initiator.
Tip
Click the values in the columns to change the permissions.
7. Click Apply.
Deleting an iSCSI LUN Masking Policy
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Click iSCSI ACL.
The iSCSI ACL window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 340

3. Select a policy.
4. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click OK.
iSCSI Target Authorization
Each iSCSI target can be congured either to allow connections from all iSCSI initiators, or to only allow
connections from a list of authorized initiators.
Important
By default, iSCSI target authorization is disabled.
Conguring an iSCSI Target's Authorized Initiators List
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select an iSCSI target.
3. Click Action, and then select Modify.
The Modify an iSCSI Target window opens.
4. Click Initiators.
5. Select Allow connections from the list only.
6. Optional: Add one or more iSCSI initiators to the authorized iSCSI initiators list.
a. Click Add.
b. Specify the initiator IQN.
c. Click Conrm.
d. Repeat the previous steps for each additional iSCSI initiator that you want to add.
7. Optional: Delete one or more iSCSI initiators from the authorized iSCSI initiators list.
a. Select an initiator IQN.
b. Click Delete.
c. Repeat the previous steps for each additional iSCSI initiator that you want to delete.
8. Click Apply.
Enabling iSCSI Target Authorization
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select an iSCSI target.
3. Click Action, and then select Modify.
The Modify an iSCSI Target window opens.
4. Click Initiators.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 341

5. Select Allow connections from the list only.
6. Add one or more iSCSI initiators to the authorized iSCSI initiators list.
a. Click Add.
b. Specify the initiator IQN.
c. Click Conrm.
7. Repeat the previous step for each additional iSCSI initiator that you want to add.
8. Click Apply.
Disabling iSCSI Target Authorization
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > iSCSI Storage .
2. Select an iSCSI target.
3. Click Action, and then select Modify.
The Modify an iSCSI Target window opens.
4. Click Initiators.
5. Select Allow all connections.
6. Click Apply.
QNAP Snapshot Agent
QNAP Snapshot Agent enables QTS to take application-consistent snapshots of iSCSI LUNs on VMware
or Microsoft servers. Application-consistent snapshots record the state of running applications, virtual
machines, and data. When QTS takes a LUN snapshot, QNAP Snapshot Agent triggers the following actions:
• Windows: The server ushes data in memory, logs, and pending I/O transactions to the LUN before the
snapshot is created.
• VMware: The server takes a virtual machine snapshot.
Tip
To download QNAP Snapshot Agent, go to https://www.qnap.com/utilities and then click
Enterprise.
Snapshot Agent Server List
To view a list of all iSCSI initiators that are using QNAP Snapshot Agent with this NAS, go to iSCSI & Fibre
Channel > iSCSI Storage . Click Snapshot, and then select Snapshot Agent.
Tip
To unregister an iSCSI initiator, select it in the list and then click Remove.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 342
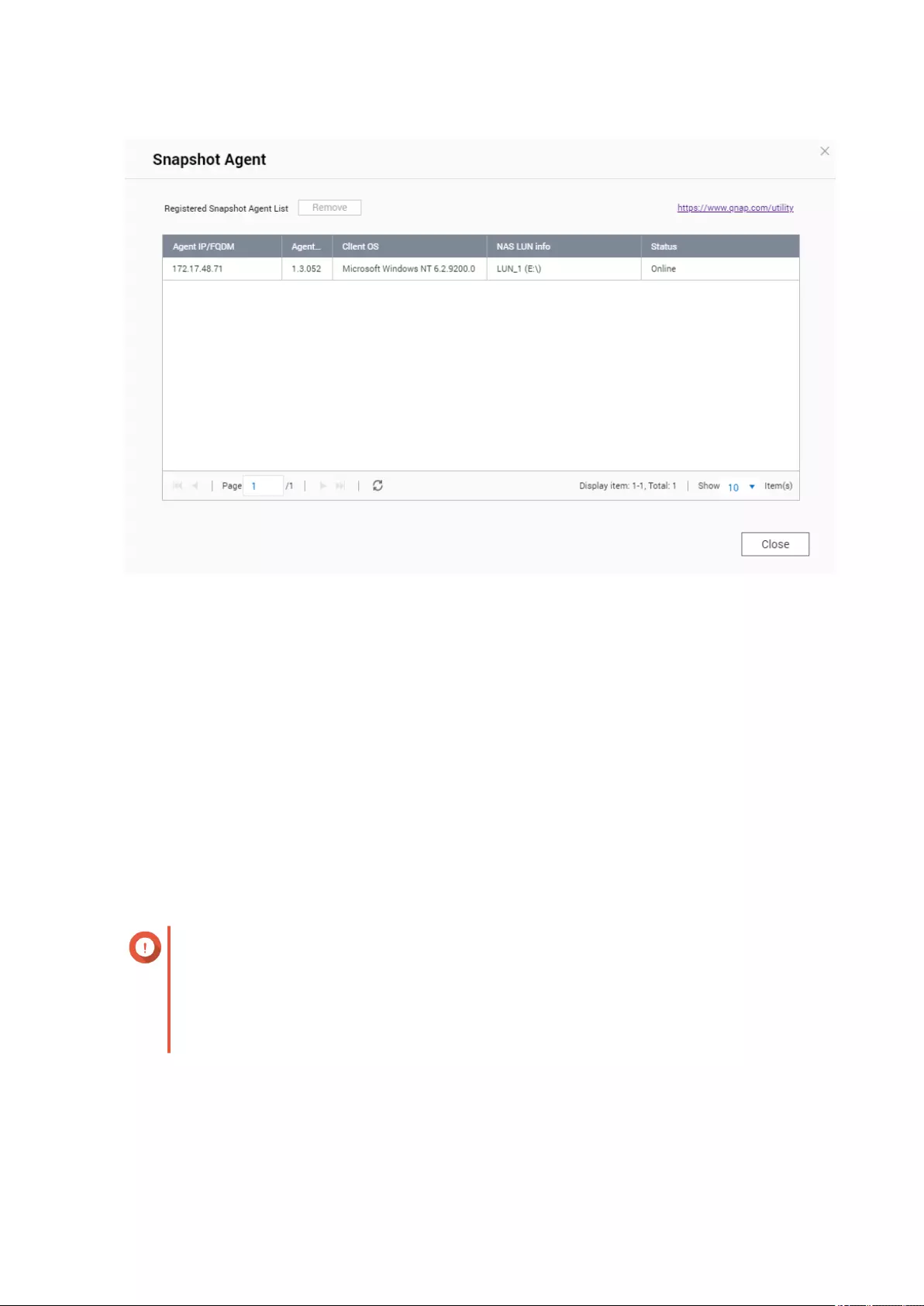
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel enables computers, servers, other NAS devices, and virtual machines to access NAS storage
in the form of LUNs over a Fibre Channel network. Hosts can partition, format, and use the LUNs as if they
were local disks.
Fibre Channel Ports
You can view and congure Fibre Channel ports and port groups on the NAS by going to iSCSI & Fibre
Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Ports .
Fibre Channel Port Groups
A Fibre Channel port group is a group of one or more Fibre Channel ports. Fibre Channel port groups help
you organize and manage LUN mappings more easily. When a LUN is mapped to a Fibre Channel port group,
QTS automatically maps the LUN to every Fibre Channel port in the group.
Important
• Each Fibre Channel port can be in one or more Fibre Channel port groups.
• Each LUN can only be mapped to one Fibre Chanel group.
• There is a default port group that contains all Fibre Channel ports.
Creating a Fibre Channel Port Group
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Ports .
2. Click Create Port Group.
The Create Port Group window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 343
3. Specify a group name.
Name requirements:
• Length: 1–20 characters
• Valid characters: A–Z, a–z, 0–9
4. Select one or more Fibre Channel ports.
5. Click Create.
Mapping a LUN to a Fibre Channel Port Group
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Storage .
2. Select a LUN.
3. Click Action, and then select Edit LUN Mapping.
The Edit LUN Mapping window opens.
4. Select Map to FC port group.
5. Select a Fibre Channel port group.
Tip
The default group contains all Fibre Channel ports.
6. Choose whether you want to congure LUN masking.
Option Description
Enable LUN and do not congure
LUN masking
Do not congure LUN masking. Any initiator that is able to connect to
a Fibre Channel port in the port group will be able to see the LUN.
Keep LUN disabled and congure
LUN masking in the next step
Congure LUN masking. You can restrict which initiators can see the
LUN.
7. Click OK.
8. Optional: Congure LUN masking.
a. Add one or more initiator WWPNs to the LUN's authorized initiators list.
Method Steps
Add from WWPN list 1. Select one or more initiator WWPNs in the WWPN list.
2. Click Add.
Add WWPNs as text 1. Specify one WWPN per line using any of the following formats:
•XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
•XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
2. Click Add.
b. Optional: Select Add unknown WWPNs to the FC WWPN Aliases List.
When selected, QTS will add any unknown WWPNs to the list of known aliases. To view the list, go
to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
c. Optional: Select Enable LUN.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 344
If selected, QTS will enable the LUN after mapping it to the target.
d. Click OK.
Conguring Fibre Channel Port Binding
Port binding is a Fibre Channel security method that enables you to restrict which initiator WWPNs are
allowed to connect through a Fibre Channel port. It is similar to iSCSI target authorization.
Tip
By default, port binding is disabled on all Fibre Channel ports.
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Ports .
2. Select a Fibre Channel port.
3. Click Action, and then select Edit Port Binding.
The Fibre Channel Port Binding window opens.
4. Add one or more initiator WWPNs to the LUN's authorized initiators list.
Method Steps
Add from WWPN list a. Select one or more initiator WWPNs in the WWPN list.
b. Click Add.
Add WWPNs as text a. Specify one WWPN per line using any of the following formats:
•XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
•XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
b. Click Add.
5. Optional: Select Add unknown WWPNs to the FC WWPN Aliases List.
When selected, QTS will add any unknown WWPNs to the list of known aliases. To view the list, go to
iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
6. Click OK.
Fibre Channel Port Actions
You can perform various actions on Fibre Channel ports by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel
> FC Ports . Select a port and then click Action to select the desired action.
Action Description
Edit Alias Edit the alias for the Fibre Channel port.
The alias must consist of 1 to 20 characters from any of the following
groups:
• Letters: A-Z, a-z
• Numbers: 0-9
• Special characters: Hyphen (-), underscore (_)
View initiators View a list of all Fibre Channel initiators currently logged into the port.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 345
Action Description
Edit port binding Modify the port binding for the port. Port binding allows you to restrict
which initiators are allowed to connect to the port.
For more information, see Conguring Fibre Channel Port Binding.
Fibre Channel Port Status
You can view Fibre Channel port statuses by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Ports .
Status Description
Connected The port has an active network connection.
Disconnected The port does not have an active network connection.
Fibre Channel Storage
You can manage and monitor Fibre Channel LUNs by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC
Storage .
Masking a LUN from Fibre Channel Initiators
LUN masking is a security feature that enables you to make a LUN visible to some Fibre Channel initiators
and invisible to other initiators.
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Storage .
2. Select a LUN.
Important
The LUN must be disabled.
3. Click LUN Masking.
The LUN Masking window opens.
4. Add one or more initiator WWPNs to the LUN's authorized initiators list.
Method Steps
Add from WWPN list a. Select one or more initiator WWPNs in the WWPN list.
b. Click Add.
Add WWPNs as text a. Specify one WWPN per line using any of the following formats:
•XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
•XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
b. Click Add.
5. Optional: Select Add unknown WWPNs to the FC WWPN Aliases List.
When selected, QTS will add any unknown WWPNs to the list of known aliases. To view the list, go to
iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
6. Select Enable LUN.
If selected, QTS will enable the LUN after mapping it to the target.
7. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 346
Fibre Channel LUN Actions
You can perform various actions on Fibre Channel LUNs by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel
> FC Storage . Expand a port group to view its LUNs, then select a LUN and click Action to select the desired
action.
LUN Action Description
Edit LUN Mapping Edit the LUN's mapping conguration.
Unmap the LUN, or map it to a dierent iSCSI target or Fibre Channel
Port group.
For details, see the following topics:
•Mapping a LUN to a Fibre Channel Port Group
•Mapping a LUN to an iSCSI Target
Edit LUN Masking Edit the LUN's masking conguration.
LUN masking is an authorization method that makes a Logical
Unit Number (LUN) visible to some initiators and invisible to other
initiators.
For details, see Masking a LUN from Fibre Channel Initiators.
Show in Storage & Snapshots Manage the LUN at Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/
Snapshots .
Modify Edit the LUN settings.
Enable Enable the LUN if it is currently disabled.
Disable Disable the LUN. The LUN will become inaccessible to connected iSCSI
initiators.
Delete Delete the LUN and all data stored on it.
Important
This action is only available if the LUN is unmapped.
LUN Import/Export Export the LUN to another server, a local NAS folder, or an external
storage device.
For details, see Creating a LUN Export Job.
Fibre Channel LUN Status
You can view Fibre Channel LUN statuses by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC Storage .
Expand a port group to view its LUNs.
Status Description
Enabled The LUN is active and visible to connected initiators.
Disabled The LUN is inactive and invisible to connected initiators.
Fibre Channel WWPN Aliases
A WWPN (World Wide Port Name) is a unique identier for Fibre Channel ports. A WWPN alias is a unique
human-readable name for a Fibre Channel port that makes it easier to identify it.
You can view, edit, and add WWPNs and WWPN aliases by going to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel >
FC WWPN Aliases .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 347
Adding WWPNs
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
2. Click Add.
The Add WWPN window appears.
3. Add one or more WWPNs to the list of known WWPNs using any of the following methods.
Method Steps
Add WWPNs from logged-in Fibre
Channel initiators.
Select Add WWPNs from all logged-in FC initiators.
Add WWPNs as text Specify one WWPN per line using any of the following formats:
•XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
•XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
4. Click Add.
Conguring a WWPN Alias
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
2. Locate a WWPN.
3. Under Alias, specify an alias for the WWPN.
The alias must consist of 1 to 20 characters from any of the following groups:
• Letters: A-Z, a-z
• Numbers: 0-9
• Special Characters: Underscore (_), hyphen (-)
4. Click Save.
Removing a WWPN Alias
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
2. Locate a WWPN.
3. Clear the Alias eld.
4. Click Save.
Exporting a List of WWPN Aliases
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
2. Click Export.
The le browser window opens.
3. In the le browser window, navigate to the folder where you want to save the le.
4. Specify a lename.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 348

5. Click Save.
The list of WWPN aliases is saved to your local computer as a CSV le, in the format:
• Field 1: WWPN
• Field 2: Alias
Example CSV Output
Importing a List of WWPN Aliases
You can import a list of WWPNs and aliases from a CSV le in the following format:
• Field 1: WWPN
• Field 2: Alias
Example CSV File
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 349

Important
• Identical aliases will be overwritten from the CSV le.
• Lines not formatted correctly will be ignored.
1. Go to iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Fibre Channel > FC WWPN Aliases .
2. Click Import.
The le browser window opens.
3. Locate and open the CSV le.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
iSCSI & Fibre Channel 350
9. SSD Proling Tool
SSD Proling Tool controls the creation and execution of SSD over-provisioning tests. These tests help
determine the optimum amount of SSD over-provisioning to set when creating an SSD RAID group.
Installing SSD Proling Tool
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Open App Center, and then click .
A search box appears.
3. Type SSD Profiling Tool, and then press ENTER.
The SSD Proling Tool application appears in the search results.
4. Click Install.
A conrmation window appears.
5. Click OK.
QTS installs SSD Proling Tool.
SSD Over-Provisioning
When an SSD is full, the disk's rmware frees up space in a process called garbage collection. Garbage
collection results in an eect called write amplication, which reduces the lifespan and random write
performance of the SSD. Write amplication can be reduced by over-provisioning, which means reserving
space on the disk for garbage collection. Most SSDs are manufactured with 7% or more of their capacity
reserved for over-provisioning.
SSD Extra Over-Provisioning
SSD Extra Over-Provisioning enables you to reserve additional space for over-provisioning at the RAID level
when creating an SSD RAID group in QTS. Reserving extra space can increase the consistent random write
performance and lifespan of the SSD group.
Important
• Space reserved for SSD Extra Over-Provisioning cannot be used for data storage. The
total storage capacity of the SSD RAID group will be reduced by the specied amount.
• SSD Extra Over-Provisioning can only be enabled during RAID group creation.
• After creating a RAID group with SSD Extra Over-Provisioning enabled, you can disable
the feature or decrease the amount of reserved space. It is not possible to increase
reserved space.
• Results will vary depending on the SSD model. Enabling SSD Extra Over-Provisioning
may have no eect on some SSDs.
Creating an SSD Over-Provisioning Test
During an SSD over-provisioning test, SSD Proling Tool rst lls the SSDs with random data. It then tests
the random write performance of the SSDs over several test phases, each using a dierent amount of
over-provisioning.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
SSD Proling Tool 351
For example, if a test is created with a test range of 0-20% and a test interval of 5%, SSD Proling Tool will
test SSD write performance in 5 phases, with over-provisioning set to 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%. If the
random write performance of the disk is very low during any phase, SSD Proling Tool will end the phase
early and move to the next one.
1. Go to SSD Proling Tool > Review .
2. Click + Create Test.
The Create SSD Test wizard opens.
3. Click Next.
4. Optional: Select an expansion unit from the Enclosure Unit list.
Important
• You cannot select disks from multiple expansion units.
5. Select one or more disks.
Selecting a single SSD determines the optimum amount of over-provisioning for all SSDs of the same
model and capacity. Selecting multiple SSDs determines the optimum amount of over-provisioning for
that specic combination of disks and RAID type. Testing multiple disks gives more accurate results,
but takes signicantly longer than testing a single disk.
Warning
All data on the selected disks will be deleted.
6. Select a RAID type.
7. Click Next.
8. Optional: Congure the test settings.
Setting Description
Test data size SSD Proling Tool writes the specied amount of test data to the SSD
during each test phase. Decreasing the test data size decreases test
time but gives less accurate results.
Over-provisioning test range Specify the minimum and maximum amount of over-provisioning to
test.
Test interval Specify the over-provisioning increments to test.
End a test phase early if consistent
performance is too low
SSD Proling Tool will end a test phase after 5 minutes of testing if
the random write speeds during the phase are lower than a system-
dened threshold.
Tip
Enabling this avoids wasting time testing disks when
the specied amount of over-provisioning is producing
no measurable benets.
9. Review the estimated time required.
For multiple SSDs, the test may take more than 24 hours.
Tip
If the estimated test time is too long, reduce the test range, test interval or the test data size.
10. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
SSD Proling Tool 352
11. Verify the test information.
12. Click Finish.
A conrmation message appears.
13. Click OK.
SSD Proling Tool creates and starts running the test. The test appears as a background task in QTS.
Test Reports
Test reports provide information to help you determine the optimal amount of over-provisioning. You can
view, export, and delete test results in SSD Proling Tool > Test Reports .
Test Report Information
Section Description
Test Information View information about the NAS, the disks being tested, and the
settings used in this test.
Test Result View the test results as a graph. Choose from the following views:
• IOPS / Time
• IOPS / Data Written
• Data Written / Time
Tip
Use these graphs to compare what eect dierent
amounts of over-provisioning had on random write
speeds (IOPS).
Over-Provisioning Evaluation
Results
Enter an IOPS value in Target write performance. SSD Proling
Tool will recommend the amount of over-provisioning needed to
consistently achieve the target random write performance.
Temperature View the temperature of the SSDs during each test phase.
Test RAID Group View information about the test SSD RAID group. Details include the
RAID type, number of disks, model and capacity of each disk, and disk
read/write performance.
Test Report Actions
Icon Description
Open the report in a new window.
Download a copy of the report in XLSX format.
Delete the report.
Settings
You can congure settings in SSD Proling Tool > Settings .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
SSD Proling Tool 353

Setting Description
Maximum number of reports SSD Proling Tool retains the specied number of reports. Creating
additional reports deletes the oldest ones.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
SSD Proling Tool 354
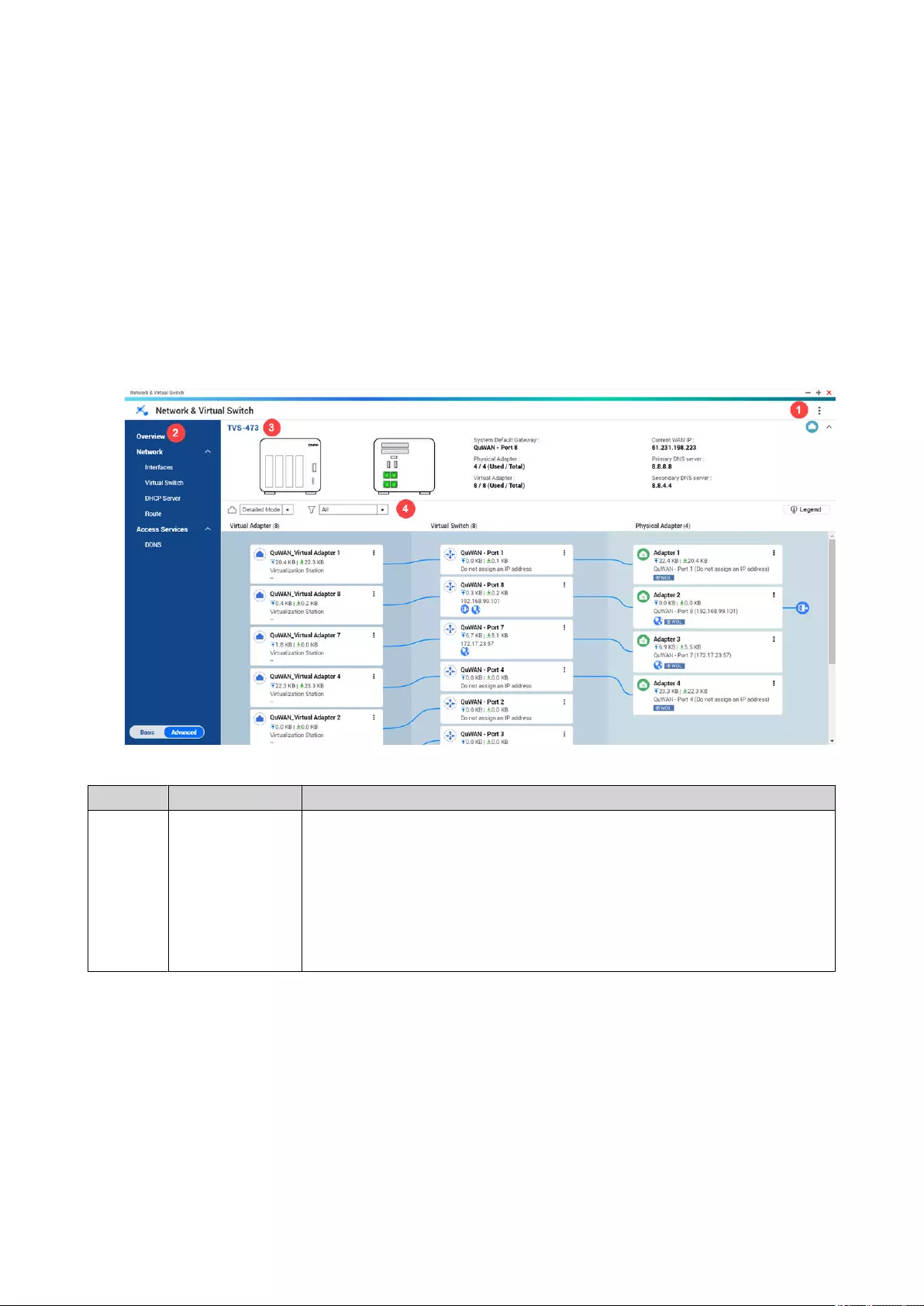
10. Network & Virtual Switch
About Network & Virtual Switch
Network & Virtual Switch is a QTS utility that centralizes the creation, conguration, and control of network
connections. Network & Virtual Switch also manages physical network interfaces, virtual adapters, Wi-Fi, and
Thunderbolt connections in addition to controlling DHCP, DDNS,and gateway services.
Parts of the User Interface
The Network & Virtual Switch user interface has four main areas.
Label Area Description
1 Toolbar The toolbar displays the following buttons:
•More: Click and then select one of the following.
•Quick Start: Opens the Network & Virtual Switch guide.
•Help: Opens the Network & Virtual Switch Help panel.
•About: Displays the Container Station version.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 355
Label Area Description
2 Menu Network & Virtual Switch features two separate usage modes in the menu
pane. Switch between these modes by clicking Basic or Advanced.
•Basic: This mode is well-suited for most users, and requires minimal
conguration of network settings. The following functions are disabled:
• Static route
• Virtual switch
•Advanced: This mode is best-suited for power-users who need more
control over the conguration of network settings. The following
functions are enabled:
• Static route
• Virtual switch
3 Main panel The main panel displays the device network information.
You can perform the following tasks on the main panel.
•
: Click to view the MAC address of the network adapters.
•
: Click to collapse the main panel.
4 Network topology The network topology provides a visual representation of the connected
physical and virtual network adapters.
You can perform the following tasks on the network topology panel.
•
Click the drop-down list beside to view the topology in simple or
detailed mode.
•
Click the drop-down list beside to lter and view specic network
topology components.
• Click Legend to view the dierent icons and their descriptions.
•Physical adapters: Click and select one of the following.
•Locate: Click to identify the network port on the main panel.
•Setting: Click to congure the physical adapter settings.
•Virtual switches: Click and then click Settings to open the virtual
switch conguration page.
•Virtual adapters: Click and then click Execute to view the virtual
adapter information on Virtualization Station
Basic Network Adapter Conguration
Network & Virtual Switch allows QTS users to congure and manage the basic network adapter settings
including dierent IP addressing methods, routing protocols, and system default gateway.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 356
Conguring IPv4 Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3.
Identify the adapter that you want to congure, then click > Congure .
The Congure window opens.
4. Congure the IPv4 settings.
Setting Description
Obtain IP address settings
automatically via DHCP
If the network supports DHCP, the adapter automatically obtains the IP
address and network settings.
Use static IP address Manually assign a static IP address. You must specify the following
information:
• Fixed IP Address
• Subnet Mask
• Default Gateway
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frames are Ethernet frames that are larger than 1500 bytes.
They are designed to enhance Ethernet networking throughput, and
to reduce CPU usage when transferring large les. QTS supports the
following MTU sizes:
• 1500 bytes (default)
• 4074 bytes
• 7418 bytes
• 9000 bytes
Important
• All connected network devices must enable Jumbo
Frames and use the same MTU size.
• Only certain NAS models support Jumbo Frames.
• Using Jumbo Frames requires a network speed of
1000 Mbps or faster.
Network Speed Select the network transfer rate allowed by the network environment.
Tip
Selecting Auto-negotiation will automatically detect
and set the transfer rate.
Important
The Network Speed eld is automatically set to Auto-
negotiation and hidden when conguring 10GbE &
40GbE adapters.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 357
5. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch updates the IPv4 settings.
Conguring IPv6 Settings
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Identify the adapter that you want to congure and then click > Congure .
The Congure window opens.
4. Go to the IPv6 tab.
5. Congure the IPv6 settings.
Setting Description
Disable Do not assign an IPv6 address.
IPv6 Auto-Conguration (Stateful) The adapter automatically acquires an IPv6 address and DNS settings
from the DHCPv6-enabled server.
Important
This option requires an available DHCPv6-enabled
server on the network.
IPv6 Auto-Conguration
(Stateless)
The adapter automatically acquires an IPv6 address and DNS settings
from the router.
Important
This option requires an available IPv6 RA(router
advertisement)-enabled router on the network.
Use static IP address Manually assign a static IP address to the adapter. You must specify
the following information:
• Fixed IP Address
•Prex length
Tip
Obtain the prex length information from your
network administrator.
• Default Gateway
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch updates the IPv6 settings.
Conguring the System Default Gateway
The system default gateway serves as the network access point for the NAS. By default, all external network
trac will pass through the gateway. You must congure a network interface rst prior to assigning the
default gateway.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 358
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Click System Default Gateway.
The System Default Gateway window opens.
4. Congure the system default gateway.
Setting User Action
Auto-select system default
gateway
Select to allow QTS automatically detect all adapter, virtual switch,
PPPoE, and VPN connections that can be used to connect to the
internet. It selects one of these connections and then sets it as the
default gateway.
Select the system default gateway Manually assign an adapter to serve as the system default gateway.
Optionally, set a backup failover gateway. The failover default gateway
eld is only available when multiple interfaces are connected.
Tip
When assigning a PPPoE or VPN connection as the
default gateway, ensure a stable physical connection is
also set as the failover default gateway.
5. Optional: Disable the NCSI service.
Tip
The QTS Network Connectivity Status Indicator (NCSI) periodically performs tests to check the
speed and status of NAS network connections.
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch updates the system default gateway.
Conguring Static Route Settings
You can create and manage IPv4 and IPv6 static routes in the Route section of Network & Virtual Switch.
Under normal circumstances, QTS automatically obtains routing information after it has been congured for
Internet access. Static routes are only required in special circumstances, such as having multiple IP subnets
located on your network.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Route .
3. Select a method for adding the IP static route.
• IPv4 static route
• IPv6 static route
4. Congure the IPv4 static route settings.
a. Beside Main Routing Table, select IPv4 from the drop-down menu.
b. Click Add.
The Static Route (IPv4) window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 359
c. Congure the IP address settings.
Setting Description
Destination Specify a static IP address where connections are routed to.
Netmask Specify the IP address of the destination's netmask.
Gateway Specify the IP address of the destination's gateway.
Metric Specify the number of nodes that the route will pass through.
Note
Metrics are cost values used by routers to determine
the best path to a destination network.
Interface Select the interface that connections should be routed through.
d. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the IPv4 static route.
5. Congure the IPv6 static route settings.
a. Beside Main Routing Table, select IPv6 from the drop-down menu.
b. Click Add.
The Static Route (IPv6) window opens.
c. Congure the IP address settings.
Setting Description
Destination Specify a static IPv6 address where connections are routed to.
Prex Length Select the destination prex length for the IPv6 static route.
Next Hop Specify the next hop IP address in IPv6 format.
Tip
IPv6 next hop format: 2001:db8::1
Metric Specify the number of nodes that the route will pass through.
Note
Metrics are cost values used by routers to determine
the best path to a destination network.
Interface Select the interface that connections should be routed through.
d. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the IPv6 static route.
IP Addressing Services Conguration
QNAP provides IP addressing services for network adaptability and scalability. You can deploy dynamic
address allocation and resolution techniques such as DNS, DDNS, DHCP server, and RADVR settings to meet
evolving network requirements.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 360
Conguring DNS Server Settings
A Domain Name System (DNS) server translates a domain name into an IP address. You can either
automatically obtain a public DNS server IP address or manually assign an IP address for the DNS server.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3.
Identify the adapter that you want to congure, then click > Congure .
The Congure window opens.
4. Go to the DNS tab.
5. Select one of the following options:
Setting User Action
Obtain DNS server address
automatically
Automatically obtain the IP address using DHCP.
Use the following DNS server
address
Manually assign the IP address for the primary and secondary DNS
servers.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch updates the DNS server settings.
Conguring DHCP Server Settings
The Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol (DHCP) allows devices in a TCP/UDP network to be automatically
congured for the network as the device is booted. The DHCP service uses a client-server mechanism,
wherein a DHCP server stores and manages network conguration information for clients and oers
necessary data when a client requests the information. The information includes the IP address and subnet
mask, the IP address of the default gateway, the DNS server IP address, and the IP lease information.
Important
Do not create a new DHCP server if one already exists on the network. Enabling multiple
DHCP servers on the same network can cause IP address conicts or network access
errors.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > DHCP Server .
3. Click Add.
The DHCP Server window opens.
4. Select an interface.
5. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 361
6. Select the network environment for the DHCP server.
Option Description
Enable DHCP server on the current
network.
• The adapter keeps the existing IP address and subnet mask.
• The DHCP server shares the subnet mask with the adapter and is
assigned the next available IP address.
Reassign an IP address to the
adapter and enable a DHCP server
on a new subnet.
• The adapter is assigned a new IP address and subnet mask.
• The DHCP server uses a dierent subnet mask and IP address.
Enable DHCP server for another
subnet.
• The adapter keeps the existing IP address and subnet mask.
• The DHCP server uses a dierent subnet mask and IP address.
7. Click Next.
8. Congure a static IP address for the adapter.
Important
A static IP address must be congured when creating a DHCP server.
a. Click Yes.
b. Congure IP address settings.
Setting Description
Fixed IP Address Specify a xed IP address.
Tip
Examine your network setup for guidance on how to
best congure these settings.
Subnet Mask Specify the subnet mask used to subdivide your IP address.
Default Gateway Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the adapter.
Jumbo Frame Jumbo Frames are Ethernet frames that are larger than 1500 bytes.
They are designed to enhance Ethernet networking throughput, and
to reduce CPU usage when transferring large les. QTS supports the
following Jumbo Frame sizes:
• 1500 bytes (default)
• 4074 bytes
• 7418 bytes
• 9000 bytes
Important
• Jumbo Frames are only supported by certain NAS
models.
• Using Jumbo Frames requires a network speed
of 1000 Mbps or faster. All connected network
devices must enable Jumbo Frames and use the
same MTU size.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 362
Setting Description
Network Speed Specify the speed at which the adapter will operate.
Tip
Auto-negotiation will automatically detect and set
the transfer rate.
Primary DNS Server Assign an IP address for the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS server Assign an IP address for the secondary DNS server.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
c. Click Next.
9. Congure DHCP settings.
Setting Description
Start IP Address Specify the starting IP address in a range allocated to DHCP clients.
End IP Address Specify the ending IP addresses in a range allocated to DHCP clients.
Subnet Mask Specify the subnet mask used to subdivide your IP address.
Lease Time Specify the length of time that an IP address is reserved for a DHCP
client. The IP address is made available to other clients when the lease
expires.
Default Gateway Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the DHCP server.
Primary DNS Server Specify a DNS server for the DHCP server.
Secondary DNS Server Specify a secondary DNS server for the DHCP server.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
WINS Server Specify the WINS server IP address.
Tip
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) converts
computer names (NetBIOS names) to IP addresses,
allowing Windows computers on a network to easily
nd and communicate with each other.
DNS Sux Specify the DNS sux.
Tip
The DNS sux is used for resolving unqualied or
incomplete host names.
TFTP Server Specify the public IP address for the TFTP server.
Tip
QTS supports both PXE and remote booting of devices.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 363
Setting Description
Boot File Specify location and le name of the TFTP server boot le.
Tip
QTS supports both PXE and remote booting of devices.
10. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the DHCP server.
Adding DHCP Clients to a DHCP Server
A DHCP client is a network device using DHCP service to obtain network coguration parameters such as an
IP address from a DHCP server. When a DHCP client sends a broadcast message to locate a DHCP server, the
DHCP server provides conguration parameters (IP address, MAC address, domain name, and a lease for the
IP address) to the client.
The following table describes the two types of DHCP clients employed in Network & Virtual Switch.
DHCP Client Description
Physical Adapter DHCP
Client
Enabling a DHCP IPv4 address allows the device to automatically acquire an
IPv4 address for a specic physical adapter from a DHCP server. The physical
adapter is assigned an IP address by the DHCP server for a predened lease
time.
Note
For details on obtaining a DHCP provided IP address, see
Conguring IPv4 Settings.
Virtual Switch DHCP Client Virtual switches allow virtual machines to obtain IP-related congurations
automatically from an external DHCP server. The virtual switch obtains the
IP address from the DHCP server through the connected physical adapter on
the device.
Note
1. A virtual switch congured with an automatic DHCP
IP address cannot utilize the NAT and DHCP server
functions.
2. Virtual switches cannot automatically acquire the IP
address of the physical adapter unless the virtual switch
has been congured to connect to a physical adapter in
Network > Virtual Switch .
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > DHCP Server .
3. Identify a DHCP server.
4.
Under Actions, click .
The DHCP Client Table window appears.
5. Click Add Reserved IP.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 364
The Add Reserved IP window appears.
6. Congure the DHCP client information.
Setting User Action
Device Name Specify a device name for the DHCP client.
IP Address Specify the IP address of the DHCP client.
MAC Address Specify the MAC address of the DHCP client.
7. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the DHCP client.
Conguring RADVD Server Settings
This RADVD screen controls the creation and management of Router Advertisement Daemon (RADVD)
servers. This service sends messages required for IPv6 stateless auto-conguration. This service periodically
sends router advertisement (RA) messages to devices on the local network, and can also send a router
solicitation messages when requested from a connected node.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > DHCP Server .
3. Go to the RADVD tab.
4. Click Add.
The RADVD - Outgoing Interface window opens.
5. Select the outgoing interface.
6. Click Next.
7. Congure a static IP address for the adapter.
Important
A static IP address must be congured when creating a RADVD server.
a. Click Yes.
b. Optional: Congure Static IP address settings.
Setting Description
Fixed IP Address Specify a xed IP address.
Tip
Examine your network setup for guidance on how to
best congure these settings.
Prex Length Specify the prex length for the adapter.
Tip
Obtain the prex and the prex length information
from your ISP.
Default Gateway Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the DHCP server.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 365
Setting Description
Primary DNS Server Assign an IP address for the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS server Assign an IP address for the secondary DNS server.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
c. Click Next.
8. Select a second adapter for the RADVD service interface.
9. Click Next.
10. Optional: Congure a static IP address for the second RADVD adapter.
Important
Creating an RADVD interface requires that the adapter use a static IP address. If the adapter
already uses a static IP address, skip this step.
a. Click Yes.
b. Congure Static IP address settings.
Setting Description
Fixed IP Address Specify a xed IP address.
Tip
Examine your network setup for guidance on how to
best congure these settings.
Prex Length Specify the prex length for the adapter.
Tip
Obtain the prex and the prex length information
from your ISP.
Default Gateway Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the adapter.
Primary DNS Server Specify the DNS server address.
Secondary DNS server Specify the DNS server address.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
c. Click Apply.
11. Congure the RADVD server settings.
Setting Description
Prex Specify the routing prex for the adapter.
Tip
Examine your network setup for guidance on how to
best congure these settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 366
Setting Description
Prex Length Specify the prex length for the adapter.
Tip
Obtain the prex and the prex length information
from your ISP.
Lease Time Specify the length of time that an IP address is reserved for a DHCP
client. The IP address is made available to other clients when the lease
expires.
Primary DNS Server Specify the DNS server address.
Secondary DNS server Specify the DNS server address.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
12. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the RADVD server.
Conguring DDNS Service Settings
This DDNSscreen controls the management of Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) services. DDNS allows
access to the NAS from the internet using a domain name rather than an IP address.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Access Services > DDNS .
3. Click Add.
The DDNS (Add) window opens.
4. Congure the DDNS settings.
Setting Description
Select DDNS server Select the DDNS service provider.
Username Specify the username for the DDNS service.
Password Specify the password for the DDNS service.
Hostname Specify the hostname or domain name for the DDNS service.
Check the External IP Address Specify how often to update the DDNS record.
5. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the DDNS server service.
LAN Switching Conguration
LAN switching enables users to resolve bandwidth issues by increasing the eciency of LANs using VLAN
and port trunking technologies.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 367
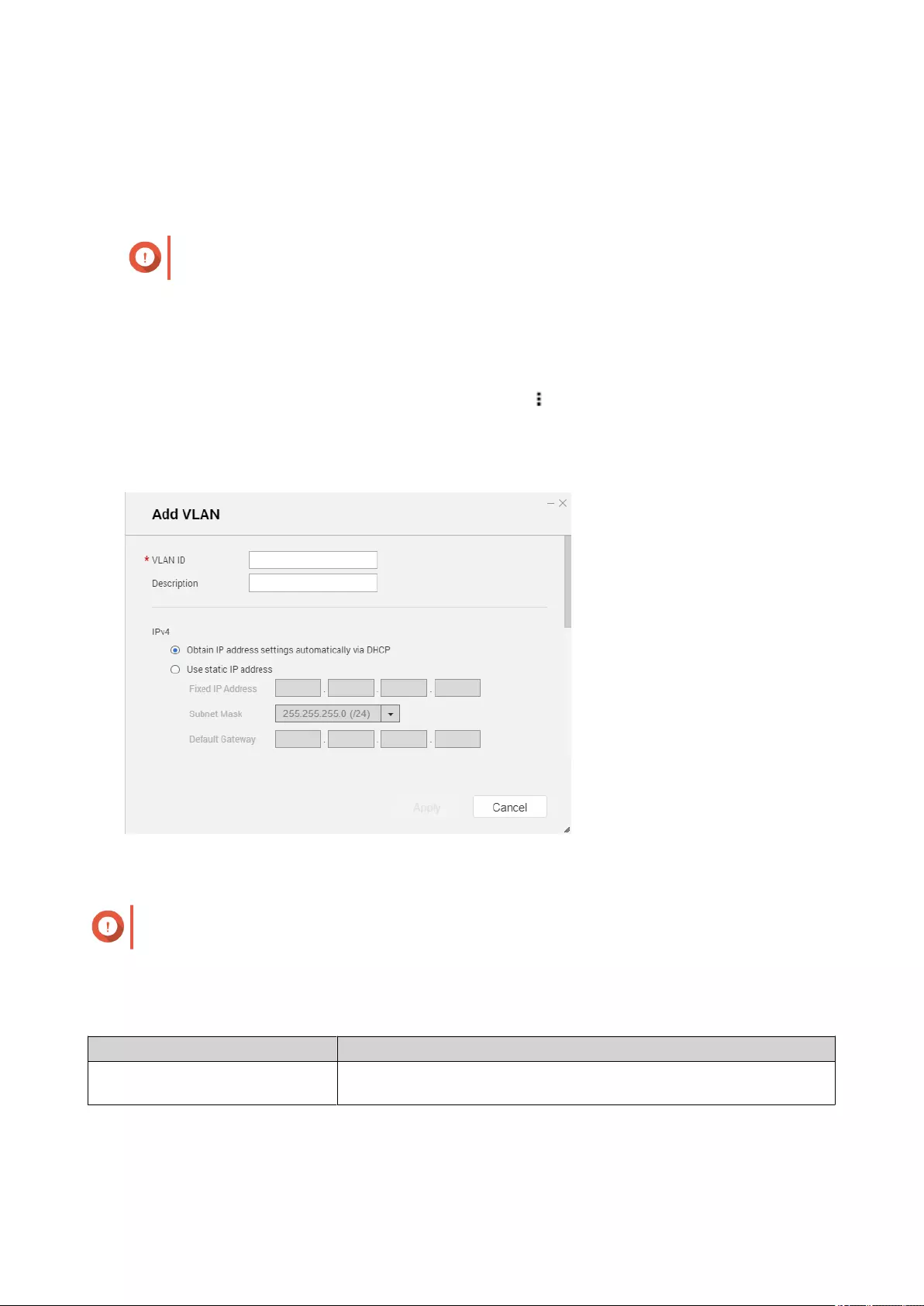
Conguring VLAN Settings
A virtual LAN (VLAN) groups multiple network devices together and limits the broadcast domain. Members
of a VLAN are isolated and network trac is only sent between the group members. You can use VLANs to
increase security and exibility while also decreasing network latency and load.
Important
When using both port trunking and a VLAN, port trunking must be congured rst.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3.
Identify the adapter that you want to congure, then click .
4. Select Add VLAN.
The Add VLAN window opens.
5. Specify a VLAN ID.
Important
The VLAN ID must be between 1 and 4094.
6. Specify a description for the VLAN.
7. Select one of the following options.
Option Steps
Automatically obtain the IP
address using DHCP
Select Obtain IP address settings automatically via DHCP.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 368
Option Steps
Use a static IP address a. Select Use static IP address
b. Specify a xed IP address.
c. Select a subnet mask.
d. Specify the default gateway.
8. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the VLAN.
Conguring Port Trunking Settings
Port trunking combines two or more Ethernet interfaces for increased bandwidth, load balancing and fault
tolerance (failover). Load balancing is a feature that distributes workloads evenly across multiple Ethernet
interfaces for higher redundancy. Failover ensures that a network connection remains available even if a
port fails.
Important
Before conguring port trunking settings, ensure at least two network interfaces are
connected to the same switch.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Click Port Trunking.
The Port Trunking window opens.
4. Click Add.
The Port Trunking (Add) window opens.
5. Select two or more network interfaces to add to the trunking group.
6. Click Next.
7. Select a switch type.
8. Click Next.
9. Select a trunking mode.
Important
Some port trunking modes must be supported by your network switches. Selecting an
unsupported mode may aect network performance or cause the network interface to freeze.
Mode Description
Fault Tolerance (Failover)
Active-Backup All trac is sent and received using the interface that was rst added
to the trunking group. If this primary interface becomes unavailable,
the secondary interface will become active.
Broadcast Transmits the same network packets to all the network interface cards.
Load balancing & Failover
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 369
Mode Description
Balance-tlb Incoming trac is received by the current interface. If the interface
fails, a secondary interface takes over the MAC address of the failed
interface. Outgoing trac is distributed based on the current load for
each interface relative to the interface's maximum speed.
Balance-alb Similar to Balance-tlb, but oers additional load balancing for
incoming IPv4 trac.
Balance-rr Transmits network packets sequentially to each network interface card
in order to distribute the internet trac among all the NICs.
Balance-xor Transmits network packets using the Hash algorithm, which selects the
same NIC slave for each destination MAC address.
802.3ad dynamic Uses a complex algorithm to aggregate NICs and congure speed and
duplex settings.
10. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch applies the pork trunking settings.
Virtual Switch Conguration
The Virtual Switch screen controls the conguration and management of virtual switches running on the
NAS. Virtual Switches allow physical interfaces and virtual adapters to communicate with each other.
QTS supports three dierent virtual switch modes.
Mode Description
Basic This mode is well-suited for most users, and requires minimal conguration of
network settings.
Advanced This mode is best-suited for power-users who need more control over the
conguration of network settings.
Software-Dened
Switch
This mode is suited for power-users who need to simulate an L2 physical switch.
Important
Packet forwarding rates are limited when using this mode.
Tip
To access this page, Network & Virtual Switch must be operating in Advanced Mode.
Creating a Virtual Switch in Basic Mode
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Virtual Switch .
3. Click Add.
The Create a Virtual Switch window opens.
4. Select Basic Mode.
5. Select one or more adapters.
6. Optional: Select Enable the Spanning Tree Protocol.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 370
Tip
Enabling this setting prevents bridge loops.
7. Click Apply.
Creating a Virtual Switch in Advanced Mode
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Virtual Switch .
3. Click Add.
The Create a Virtual Switch window opens.
4. Select Advanced Mode.
5. Select one or more adapters.
6. Optional: Select Enable the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Tip
Enabling this setting prevents bridge loops.
7. Click Next.
8. Congure the virtual switch IP address.
Address Type Description
DHCP Client Assigns a dynamic IP address to the virtual switch.
Static IP Assigns a static IP address to the virtual switch.
Tip
Examine your network setup for guidance on how to
best congure these settings.
Do not assign IP Addresses Does not assign an IP address to the virtual switch after creation.
Tip
This setting should be used when creating a virtual
switch for special purposes, such as when building an
external or isolated network.
9. Click Next.
10. Congure the virtual switch services.
a. Enable the NAT service.
Important
• The virtual switch must be congured with a static IP address. The IP address cannot be
within the subnet of an interface that is currently in use.
• The IP address of the virtual switch cannot be in a reserved range that doesn't support
forwarding:
• 127.xxx.xxx.xxx
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 371
• 169.254.xxx.xxx
• 192.0.2.xxx
• 198.51.100.xxx
• 203.0.113.xxx
b. Optional: Enable the DHCP Server.
Important
• The virtual switch must be congured with a static IP address. The IP address cannot be
within the subnet of an interface that is currently in use.
• To avoid IP address conicts, do not enable DHCP server if there is another DHCP server
running on the local network.
Setting Description
Start IP Address Specify the starting IP address in a range allocated to DHCP clients.
End IP Address Specify the ending IP addresses in a range allocated to DHCP clients.
Subnet Mask Specify the subnet mask used to subdivide your IP address.
Lease Time Specify the length of time that an IP address is reserved for a DHCP
client. The IP address is made available to other clients when the lease
expires.
Default Gateway Specify the IP address of the default gateway for the DHCP server.
Primary DNS Server Specify a DNS server for the DHCP server.
Secondary DNS Server Specify a secondary DNS server for the DHCP server.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
WINS Server Specify the WINS server IP address.
Tip
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS ) converts
computer names (NetBIOS names) to IP addresses,
allowing Windows computers on a network to easily
nd and communicate with each other.
DNS Sux Specify the DNS sux.
Tip
The DNS sux is used for resolving unqualied or
incomplete host names.
TFTP Server Specify the public IP address for the TFTP server.
Tip
QTS supports both PXE and remote booting of devices
Boot File Specify location and le name of the TFTP server boot le.
Tip
QTS supports both PXE and remote booting of devices
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 372
11. Click Next.
12. Congure the virtual switch IPv6 address.
Setting Description
Disable Do not assign an IPv6 address.
IPv6 Auto-Conguration (Stateful) The adapter automatically acquires an IPv6 address and DNS settings
from the DHCPv6-enabled server.
Important
This option requires an available DHCPv6-enabled
server on the network.
IPv6 Auto-Conguration
(Stateless)
The adapter automatically acquires an IPv6 address and DNS settings
from the router.
Important
This option requires an available IPv6 RA(router
advertisement)-enabled router on the network.
Use static IP address Manually assign a static IP address. You must specify the following
information:
• Fixed IP Address
•Prex length
Tip
Obtain the prex length information from your
network administrator.
• Default Gateway
13. Click Next.
14. Congure the DNS settings.
Setting Description
Obtain DNS server address
automatically
Automatically obtain the DNS server address using DHCP.
Use the following DNS server
address
Manually assign the IP address for the primary and secondary DNS
servers.
Important
QNAP recommends specifying at least one DNS server
to allow URL lookups.
15. Click Next.
16. Conrm the virtual switch settings.
17. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 373
Creating a Virtual Switch in Software-dened Switch Mode
Important
To avoid bridge loops, please ensure any Ethernet cables are connected to the same
switch before conguring a Software-dened Switch.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Virtual Switch .
3. Click Add.
The Create a Virtual Switch window opens.
4. Select Software-dened Switch Mode.
5. Select one or more adapters.
6. Optional: Select Enable the Spanning Tree Protocol.
Tip
Enabling this setting prevents bridge loops.
7. Click Apply.
Network Policies Conguration
Network policies allow QTS users to manage data trac by implementing data reliability policies on the
network adapters of the device.
Conguring Forward Error Correction (FEC) Settings
Forward Error Correction (FEC) is a digital signal processing technique to recover lost packets on a link by
sending extra parity packets. Enabling FEC enhances data reliability by introduces redundant data or error
correcting data before the system stores or transmits data.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3.
Identify the adapter that you want to congure, then click > Congure .
The Congure window opens.
4. Click FEC Settings.
5. Click Enable forward error correction (FEC).
6. Select an FEC mode.
Setting Description
Auto-negotiation The device automatically selects the best FEC mode.
BASE-R FEC BASE-R FEC (also known as Fire Code FEC or IEEE 802.3 Clause 74) oers simple,
low latency (less than 100 nanoseconds) protection against bursty errors. This mode
oers a weaker error correction but with lower latency.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 374
Setting Description
RS-FEC RS-FEC (also known as Reed Solomon FEC or IEEE 802.3 Clause 91) oers better error
protection but adds latency (approximately 250 nanoseconds).
Important
The same FEC mode should be selected on both ends of the network link.
7. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch applies the FEC settings.
Wireless Network Conguration
The Network & Virtual Switch Wi-Fi service provides all the functions of a wired network, while also providing
location exibility to QTS users within the wireless signal range. The Wi-Fi screen controls the conguration
and management of Wi-Fi connections accessible from the device.
Important
• A USB or PCIe Wi-Fi device must be installed to access wireless features.
• For a list of compatible USB Wi-Fi dongles, visit http://www.qnap.com/
compatibility, then select Search by Devices > USB Wi-Fi .
• For a list of compatible PCIe Wi-Fi cards, visit http://www.qnap.com/compatibility,
then select Search by Devices > Expansion Card > QNAP .
• QTS supports the simultaneous use of multiple PCIe Wi-Fi cards, but only one USB
Wi-Fi dongle can be in used at a time.
Adding a Wireless Network
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the Wi-Fi tab.
4. Click Add Wi-Fi.
The Connect to a Wi-Fi network window opens.
5. Congure connection settings.
Setting User Action
Network Name Enter the name of the wireless network.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 375
Setting User Action
Security Type Select the encryption used by the wireless network.
•No Authentication (Open):Any wireless device can connect to the
network. This is the default setting.
•WEP: Use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) if the wireless device does not
support WPA or WPA2.
•WPA- Personal: Use Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)- Personal as an
intermediate security measure if the wireless device does not support
WPA2.
•WPA2-Personal: Uses Advanced Security Encryption (AES) for data
encryption. This is the suggested security mechanism if the wireless device
supports WPA2.
•WPA- & WPA2- Enterprise: Use this security mechanism if the wireless
device supports transition from WPA-Enterprise to WPA2-Enterprise. The
network automatically chooses the encryption method used by the
wireless device.
Password Enter the password provided by the network administrator.
Tip
Click to make the password visible.
Automatically connect
when the
Automatically connect to this network whenever it is in range.
Connect even if hidden Attempt to connect to this network even if the SSID is hidden.
6. Optional: Congure WPA- & WPA2 Enterprise settings.
Setting User Action
Authentication Authentication is specic to WPA- and WPA2- Enterprise encryption. Select a
method based on the authentication supported by your device.
•Protected EAP (PEAP): Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol
(PEAP) provides a more secure authentication to 802.11 WLANs.
•EAP-TTLS: EAP Tunneled Transport Layer Security (EAP-TTLS) supports
legacy authentication mechanisms.
Certicate Authority (CA)
File
A data le that contains identication credentials to help authenticate the
WPA-WPA2 public key ownership.
Note
Select CA le is not required if you do not have access to a
digital certicate.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 376
Setting User Action
Inner Authentication Select an inner authentication method based on PEAP or EAP-TTLS
authentication.
MS-CHAPv2 is the default inner authentication method for PEAP.
The following inner authentication methods are available if the authentication
method is set to EAP-TTLS:
•PAP
•CHAP
•MS-CHAP
•MS-CHAPv2
Username Enter the username provided by the network administrator.
Password Enter the password provided by the network administrator.
Tip
Click to make the password visible.
7. Click Connect.
Network & Virtual Switch adds the wireless network.
Enabling Wi-Fi
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the Wi-Fi tab.
4.
Click .
Network & Virtual Switch enables the Wi-Fi function.
Connecting to a Wireless Network
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the Wi-Fi tab.
4. Optional: Click Scan to search for accessible networks.
5. Select a wireless network from the list.
Icon Description
The Wi-Fi network requires a password.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 377
Icon Description
Connect to a Wi-Fi network without a password.
• The Wi-Fi connection cannot access the internet.
• The Wi-Fi connection requires an additional login.
Tip
QTS does not support networks that require an additional login.
The settings panel expands.
6. Click Connect.
7. Optional: Congure connection settings.
Setting User Action
Password Enter the password provided by the network administrator.
Tip
Click to make the password visible.
Connect automatically Automatically connect to this network whenever it is in range.
Connect even if hidden Attempt to connect to this network even if the SSID is hidden.
8. Click Apply
The device connects to the wireless network.
Connecting to a Captive-Portal-Enabled Wireless Network Using Browser Station
A captive portal allows organizations to easily share their network environment with customers, employees,
and other guests.
QTS supports the captive portal function that connects to the internet through an access point in the
wireless network.
Note
Download and install Browser Station from App Center to access the captive portal
functions.
Alternatively, QNAP recommends installing Qnder Pro (6.9.2 or later) to utilize the captive
portal function on a wireless network.
For details, see Connecting to a Captive-Portal-Enabled Wireless Network Using Qnder
Pro.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the Wi-Fi tab.
4. Optional: Click Scan to search for accessible wireless networks with a captive portal.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 378
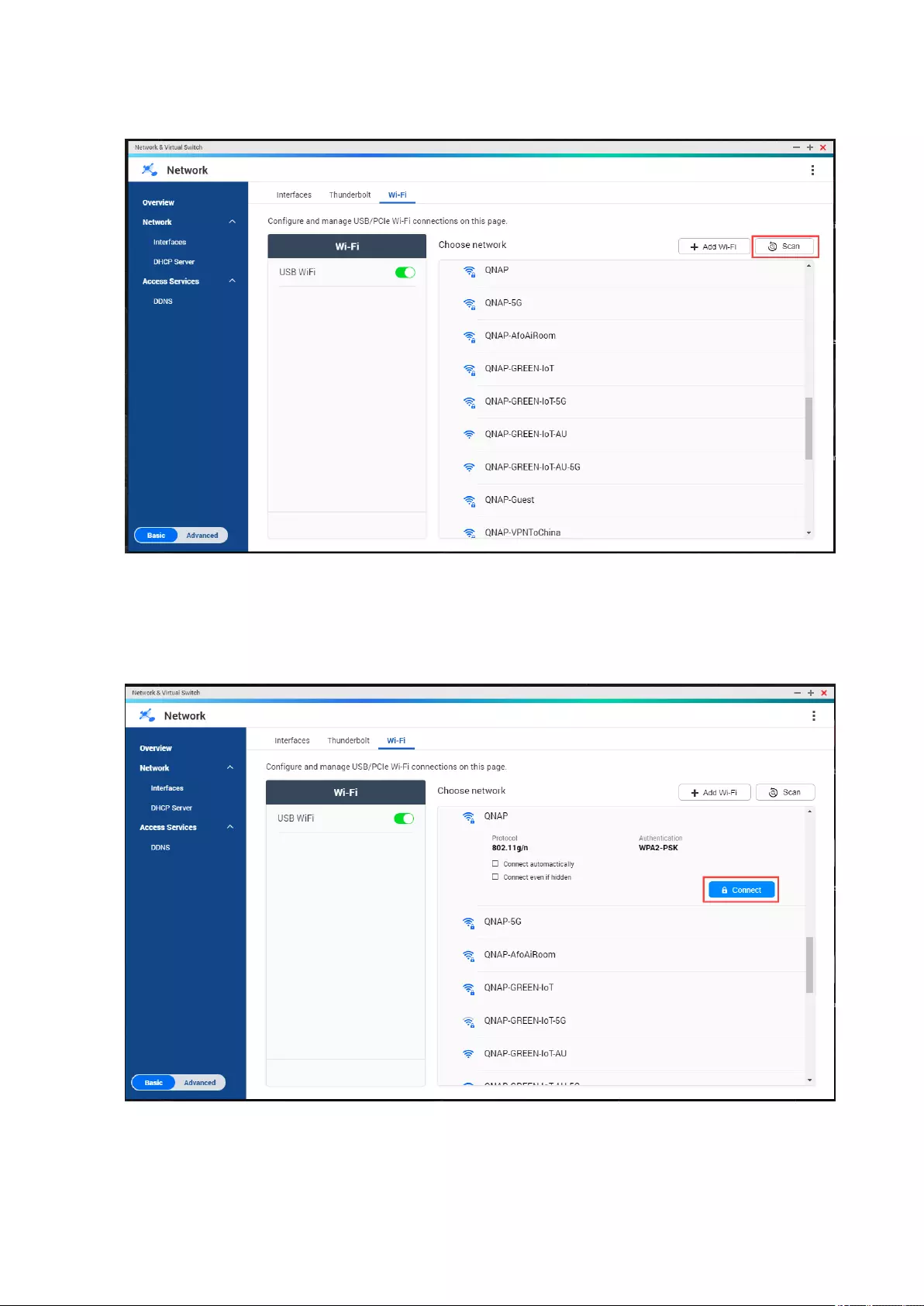
5. Select the captive-portal-enabled wireless network from the list.
The settings panel expands.
6. Click Connect.
7. Optional: Congure connection settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 379
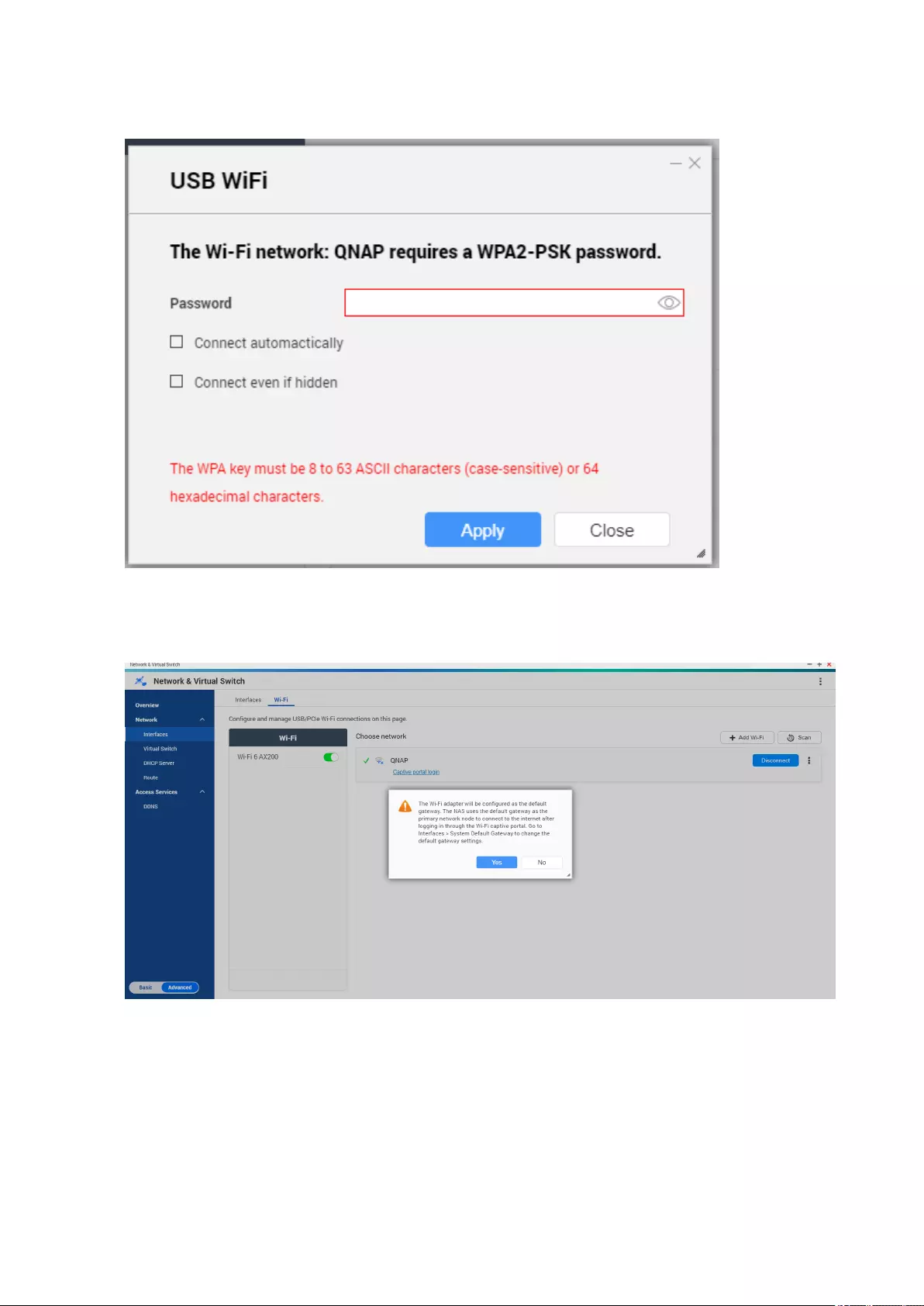
For conguration details and wireless icon descriptions, see Connecting to a Wireless Network.
8. Click Apply.
A pop-up window opens specifying the change in the default network gateway.
9. Click Yes.
10. Optional: Go to Interfaces > System Default Gateway to change the default network gateway
settings.
11. Click Captive portal login.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 380
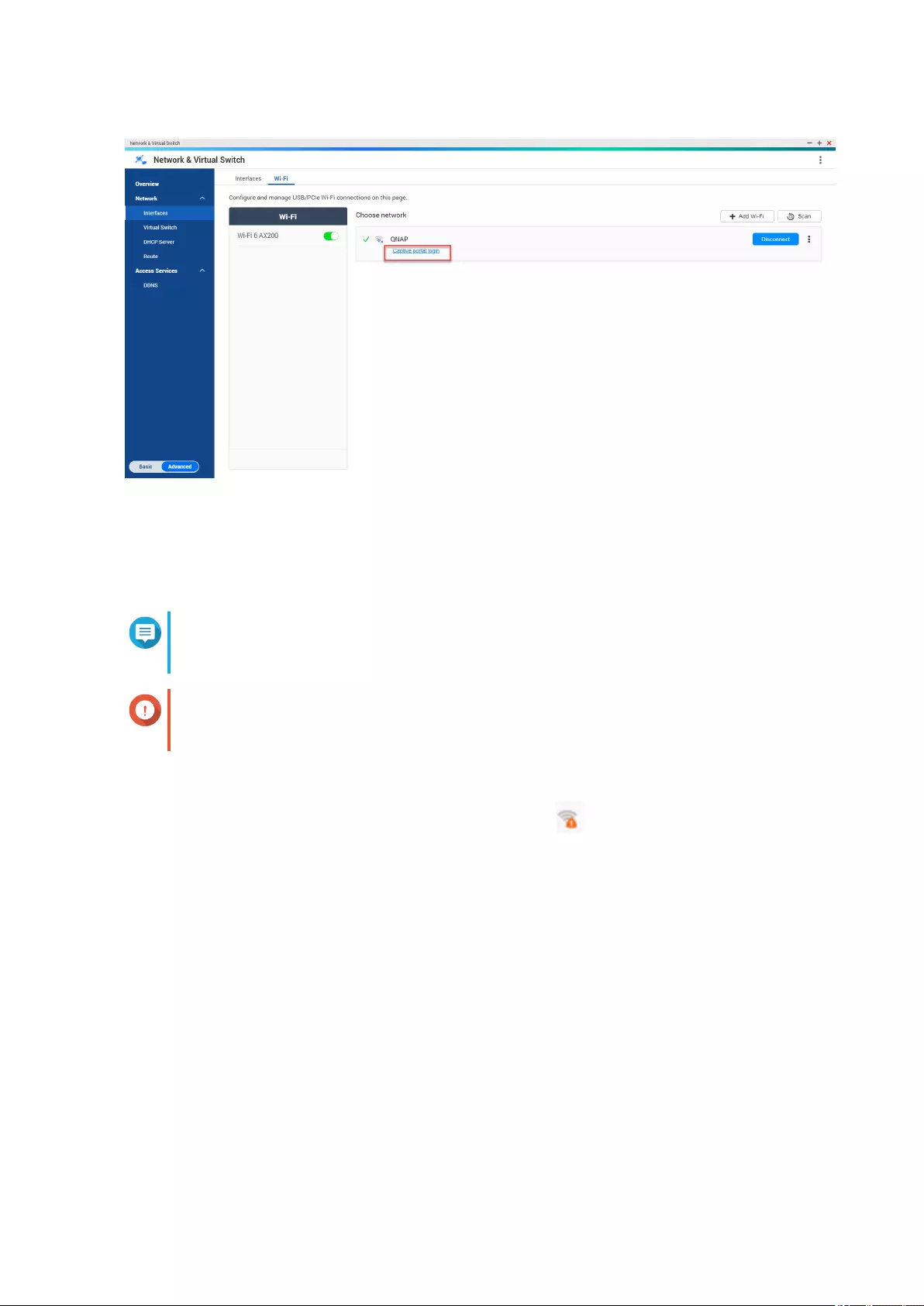
Browser Station automatically redirects you to the captive portal landing page.
12. Enter the username and password to connect to the wireless network.
Connecting to a Captive-Portal-Enabled Wireless Network Using Qnder Pro
Note
QNAP recommends installing Qnder Pro (Windows 6.9.2 or later and MacOS/Linux 7.3.2
or later) to utilize the captive portal function on a wireless network.
Important
Connect the NAS directly to the PC using an ethernet cable in order to connect to a
wireless network enabled with captive portal.
1. Open Qnder Pro.
2.
Locate the NAS in the list and click the uncongured Wi-Fi icon located under the Status table
header.
3. Optional: Alternatively, select the NAS and go to Settings > Wi-Fi Settings .
The Login page opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 381
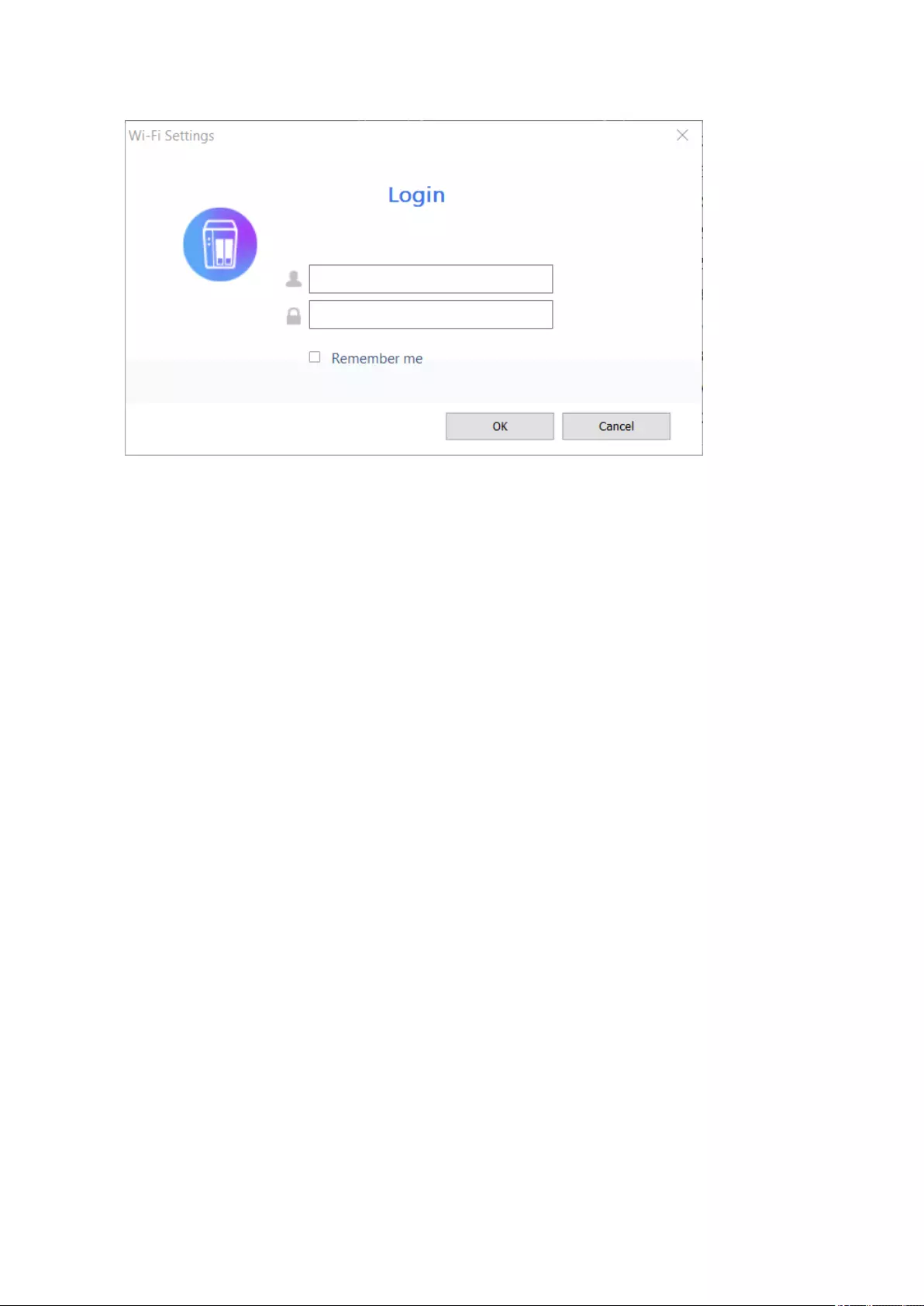
4. Enter the username and password.
5. Click OK.
The Wi-Fi Connection Settings page opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 382
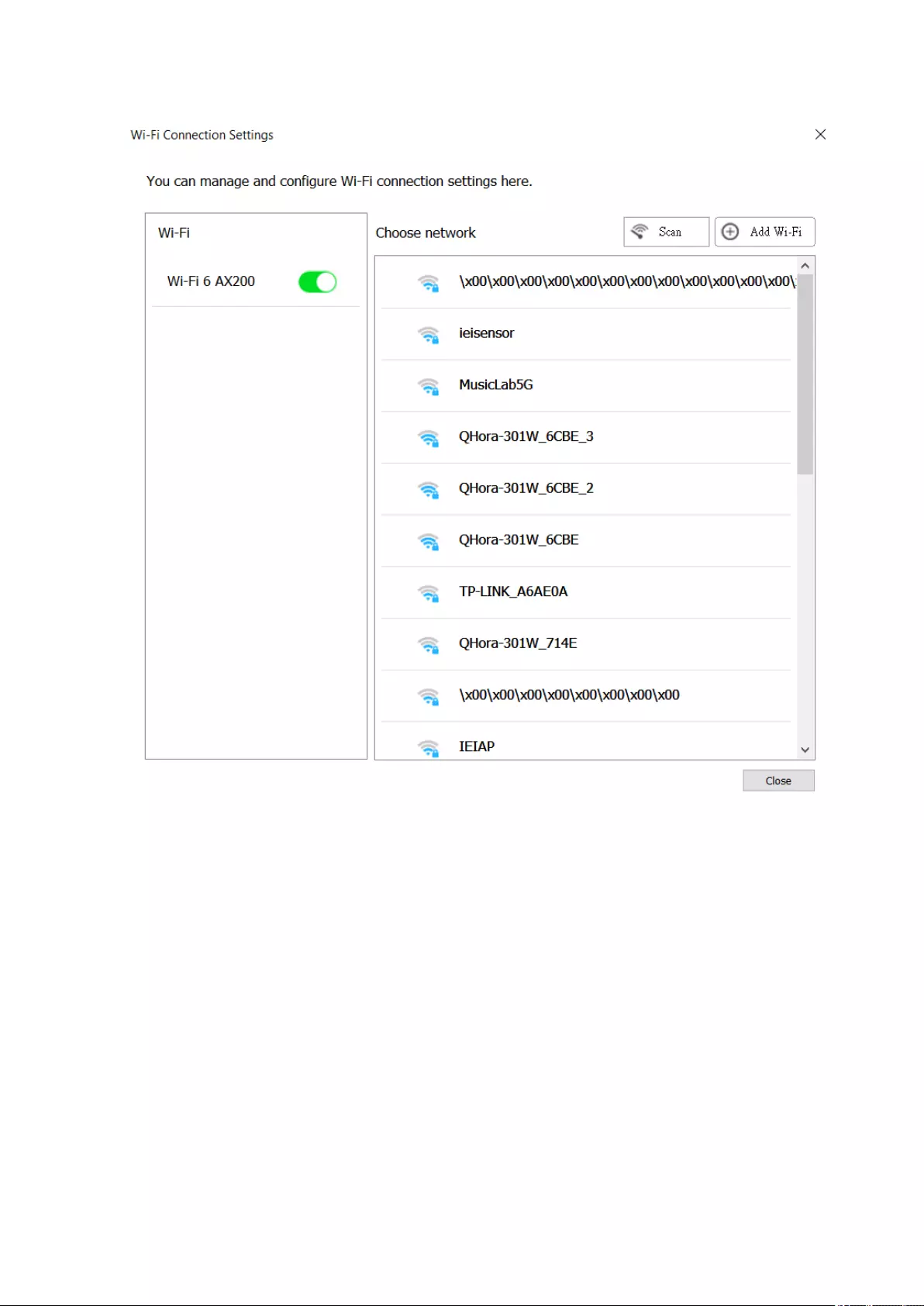
6. Select the wireless network from the list.
The settings panel expands.
7. Click Connect.
8. Congure connection settings.
9. Click Apply.
A pop-up window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 383
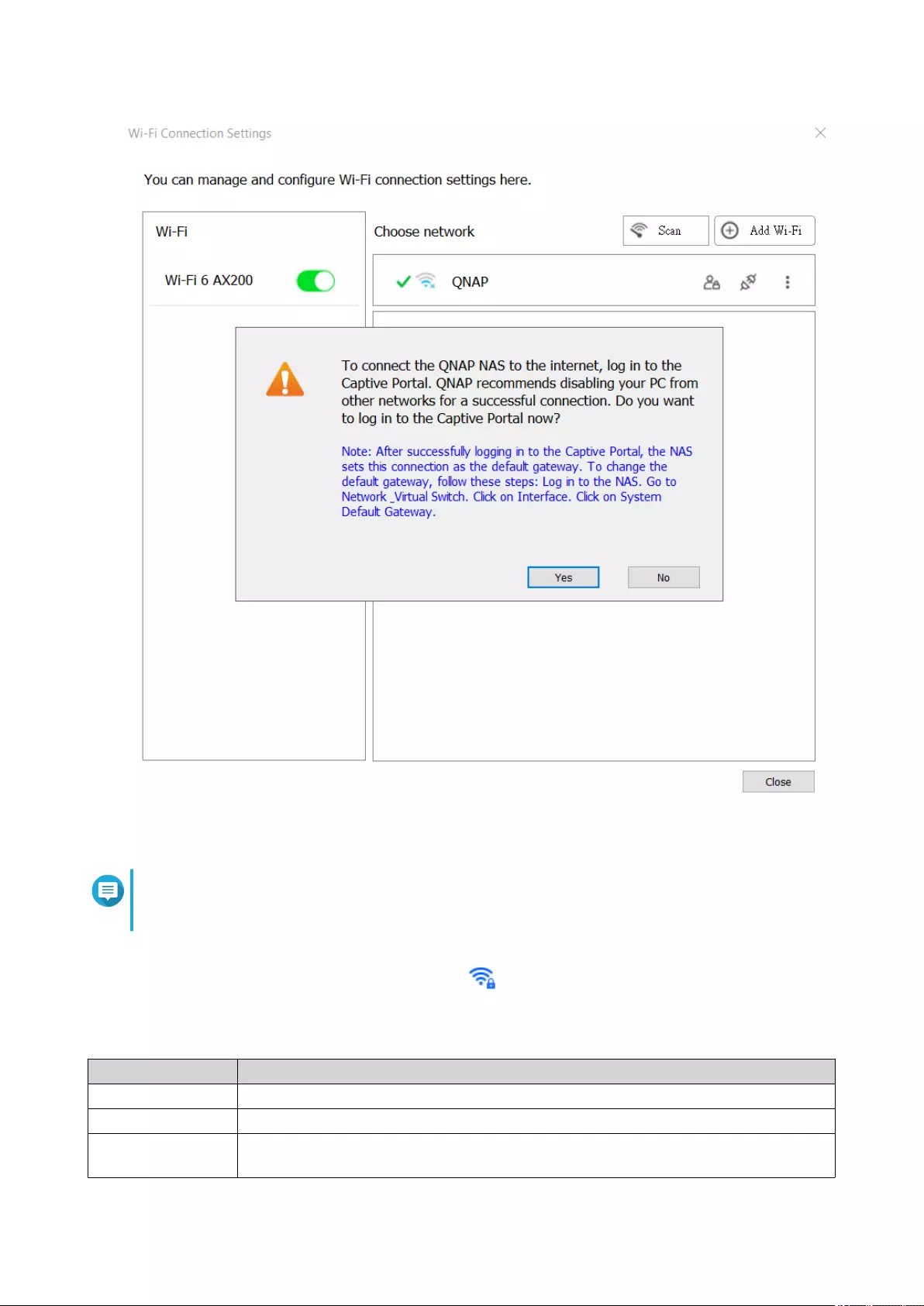
10. Click Yes.
The default browser automatically opens and redirects you to the captive portal landing page.
Note
Network & Virtual Switch automatically enables NAT and DHCP on the Wi-Fi adapter in the
background.
11. Enter the username and password to connect to the wireless network.
Qnder Pro displays the wireless connection icon in the Qnder Pro NAS status panel.
Understanding the Wireless Connection Messages
Message Description
Connected The NAS is currently connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Connecting The NAS is trying to connect to the Wi-Fi network.
Out of range or
hidden SSID
The wireless signal is not available or the SSID is not being broadcast.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 384
Message Description
Failed to get IP The NAS is connected to the Wi-Fi network but could not get an IP address from the
DHCP server. Check the router settings.
Association failed The NAS cannot connect to the Wi-Fi network. Check the router settings.
Incorrect key The entered password is incorrect.
Auto connect Automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network. This is not supported if the SSID of the
Wi-Fi network is hidden.
Accessing the Wireless Access Point (AP) Settings
The Network & Virtual Switch utility enables users to congure and manage wireless access points through
the WirelessAP Station utility.
Note
The WirelessAP Station is not a built-in application on QTS 5.0.0. To install the application,
go to App Center > All Apps , and then install the WirelessAP Station application.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Click the WirelessAP Station tab.
QTS opens the WirelessAP Station application.
For details on conguring the access point settings, click on the application taskbar.
USB QuickAccess Conguration
The USB QuickAccess screen controls the conguration and management of USB QuickAccess services on
the NAS. USB QuickAccess allows a computer to connect to the NAS using a USB cable and the Common
Internet File System (CIFS).
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 385
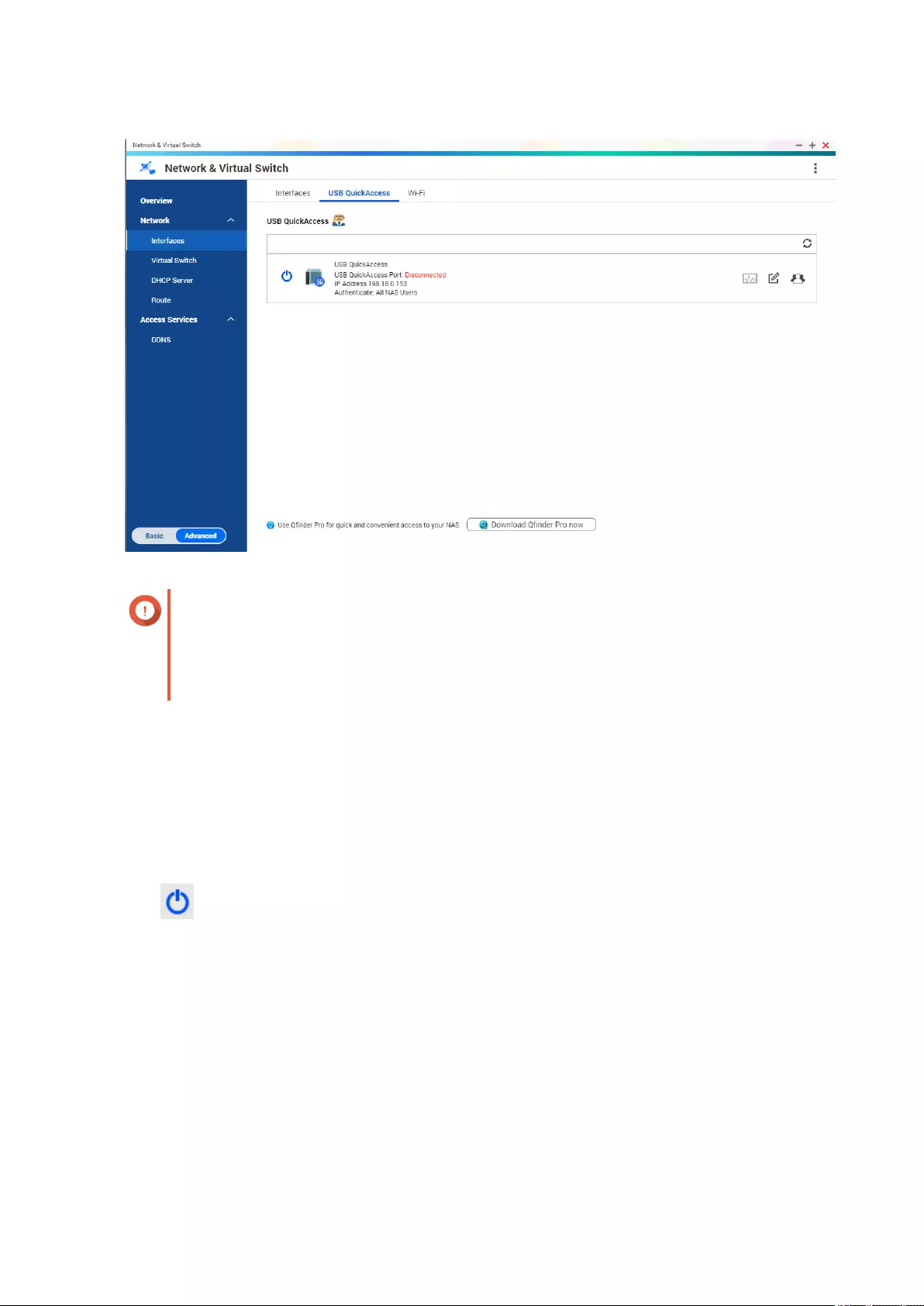
Important
• USB QuickAccess is only available on certain models.
• It is not possible to congure, delete, or disable DHCP servers created with USB
QuickAccess.
Enabling USB QuickAccess
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the USB QuickAccess tab.
4.
Click .
Network & Virtual Switch enables USB QuickAccess.
Conguring the USB QuickAccess IP address
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the USB Quick Access tab.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 386
4.
Click .
The Congure window opens.
5. Enter a xed IP Address.
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch applies the IP address settings.
Conguring USB QuickAccess Authentication
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network & Virtual Switch .
The Network & Virtual Switch window opens.
2. Go to Network > Interfaces .
3. Go to the USB Quick Access tab.
4.
Click .
The Conguration window opens.
5. Select an authentication method:
Authentication Method Description
All NAS Users A QTS username and password is required to access les.
Everyone No username or password is required to access les.
Selected Users/Groups Administrators can grant access to specic QTS users or groups. A QTS
username and password is required to access les.
Tip
To grant access to domain users, rst set up Domain
Security. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Domain
Security .
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch applies the USB QuickAccess authentication settings.
Thunderbolt Interface Conguration
The Thunderbolt screen displays port and connection information related to any Thunderbolt interfaces on
the NAS.
Thunderbolt to Ethernet (T2E)
Thunderbolt to Ethernet functionality allows the Thunderbolt port to act as an Ethernet interface.
Tip
QNAP recommends using Qnder Pro when conguring Thunderbolt to Ethernet.
Important
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 387
Due to Thunderbolt driver issues, T2E connections using Thunderbolt port 2 may have
connectivity problems when connecting to Windows. Thunderbolt port 3 connections are
unaected.
Enabling T2E with Qnder Pro
Qnder Pro is a utility for Windows, Mac, and Linux that allows you to quickly nd and access a QNAP NAS
over a LAN.
For the current version of Qnder Pro, please visit https://www.qnap.com/utilities.
Tip
Qnder Pro automatically congures the /etc/sysctl.conf settings le on macOS.
1. Open Qnder Pro.
2. Locate the NAS using Qnder Pro.
3. Click the Thunderbolt icon.
The T2E window opens.
4. Select Enable T2E.
5. Click Apply.
Enabling T2E on macOS
1. Open the Terminal.
2. Run the command.
Command Notes
sudosysctlnet.inet.tcp.path_mtu_discovery=0 &&
sudosysctlnet.inet.tcp.tso=0
This command will only temporarily enable T2E.
Restarting the Mac will delete the connection.
sudo bash –c ‘printf
“#QNAP\nnet.inet.tcp.path_mtu_discovery=0\nnet.in
et.tcp.tso=0\n#QNAP\n” >> /etc/sysctl.conf’
This command will permanently apply these
settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & Virtual Switch 388
11. Network & File Services
About Network & File Services
The Network & File Services utility allows QTS users to congure and control network and le protocols over
a LAN or WAN connection. You can access shared resources over le sharing services and also handle data
transfer using various le transfer protocols.
Network administrators can enable multiple protocols for clients to perform remote le editing functions
over a web server and allow clients to automatically create a network of devices without manual
conguration using service discovery protocols.
QNAP Service Ports
QNAP uses designated ports for communication. These ports are assigned to a specic service and users
must manually open the required ports by adding the port number.
Note
For these services to operate correctly, their ports should remain open. This may require
additional conguration of your rewall or router.
Backup Service
Service Default Port Protocol
Rsync 873 TCP
RTRR 8899 TCP
Download
Service Default Port Protocol
BitTorrent 6681-6999 TCP/UDP
File Transfers
Service Default Port Protocol
AFP 548 TCP
Netbios/SAMBA 137, 138, 139, 445 139, 445(TCP/UDP), 137, 138(UDP)
FTP/FTPES 20 and 21 TCP
NFS 2049, 111, dynamic ports TCP/UDP
TFTP 69 UDP
Multimedia
Service Default Port Protocol
Twonkymedia 9000 TCP/UDP
UPnP Internet Gateway Device
daemon
49152 TCP/UDP
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 389
Q'center
Service Default Port Protocol
Q’center Server 6600, 6606 TCP/UDP
Q'center Client NAS 6600, 6621, 6623 TCP/UDP
Qsync
Service Default Port Protocol
NAS Web 8080 TCP
NAS Web (HTTPS) 443 TCP
System Management
Service Default Port Protocol
LDAP Server 389 TCP
MySQL 3306 TCP
SNMP 161 TCP/UDP
SMTP 25 TCP
Syslog 514 TCP/UDP
Telnet 13131 TCP
SSH/SFTP Server 22 TCP
Virtualization Station
Service Default Port Protocol
Virtualization Station 8088 TCP
Virtualization Station (HTTPS) 8089 TCP
VPN
Service Default Port Protocol
QVPN (OpenVPN) 1194 UDP
QVPN (PPTP Server) 1723 TCP
QVPN (L2TP/IPSec Server) 500, 4500, 1701 UDP
QVPN (QBelt Server) 443 UDP
Web
Service Default Port Protocol
NAS Web 8080 TCP
NAS Web (HTTPS) 443 TCP
Web Server (HTTP, HTTPS) 80, 8081 TCP
Conguring Network Access Settings
QTS users can use network access settings to connect applications to supported services using service
binding and securely route trac between networks using proxy and reverse proxy servers.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 390
Conguring Service Binding Settings
NAS services run on all available network interfaces by default. Service binding enables you to bind services
to specic network interfaces to increase security. You can bind services to one or more specic wired or
wireless network interfaces.
Important
Conguring service binding does not aect users currently connected to the NAS. When
users reconnect they will only be able to access the congured services using the specied
network interfaces.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Service Binding .
2. Select Enable Service Binding.
A list of available services and interfaces is displayed.
3. Bind services to interfaces.
Important
• By default, QTS services are available on all network interfaces.
• Services must be bound to at least one interface.
Tip
Click Use Default Value to bind all services.
a. Identify a service.
b. Deselect interfaces not bound to the service.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the service binding settings.
Conguring Proxy Server Settings
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between the NAS and the internet. When enabled, QTS will route
internet requests through the specied proxy server.
Important
Prior to enabling the proxy server, ensure that Web Server is enabled in Control Panel >
Services > Applications > Web Server .
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access > Proxy .
2. Select Use a proxy server.
3. Specify the proxy server URL or IP address.
4. Specify a port number.
5. Optional: Congure proxy authentication.
a. Select Authentication.
b. Specify a username.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 391
c. Specify a password.
6. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the proxy server settings.
Conguring Reverse Proxy Rule Settings
Reverse proxy settings allow users to congure a control point closer to web resources, enabling ecient
and secure data distribution between users and websites.
Note
You can add up to 64 reverse proxy rules.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access .
2. Click the Reverse Proxy tab.
3. Click Add.
The Add Reverse Proxy Rule window appears.
4. Congure the rule settings.
Setting User Action
Rule name Specify a name for the reverse proxy rule.
Source
Protocol Select a connection protocol from the following:
•HTTP: Select to establish an unencrypted connection with the website.
•HTTPS: Select to establish an encrypted connection with the website.
Select Enable HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) to advertise to
clients that the device accepts only HTTPS requests.
Domain name Specify the domain name of the website. Example: www.example.com
Note
You can only specify one domain name for a reverse proxy
rule.
Port number Specify a port number for the reverse proxy port for recording the HTTP or
HTTPS trac.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 392
Setting User Action
Access control prole Select from the following:
•Allow all connections
•Use existing prole: Select from congured access control prole
•Create a new prole: Select to create a new access control rule.
1. Specify the access control permission.
2. Click Add.
The Add Access Control Rule window appears.
3. Select the IP address type.
•Single IP address
•CIDR: Specify an IP address with the subnet mask. Example:
192.0. 1.0/24
4. Click Add.
Destination
Protocol Select the destination protocol.
•HTTP
•HTTPS
•WebSocket
•WebSocket Secure
Hostname Specify the destination hostname.
Port number Specify the destination port number.
5. Congure the advanced settings.
a. Click Edit.
b. Specify the proxy connection timeout in seconds.
c. Specify a custom header name containing a custom response to generated server responses.
Warning
You cannot repeat header names.
d. Specify the custom header macro value to dene the custom response.
6. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the reverse proxy settings.
Modifying Reverse Proxy Rules
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Access .
2. Click the Reverse Proxy tab.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 393

3. Perform the following tasks on congured reverse proxy rules.
Task User Action
Delete a reverse proxy
rule
a. Beside the reverse proxy rule name, select the checkbox.
Tip
You can select multiple rules.
b. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click OK.
Edit a reverse proxy rule a. Identify a reverse proxy rule.
b.
User Action, select .
The Edit Reverse Proxy Rule window appears.
c. Congure the rule settings.
Note
For details, see Conguring Reverse Proxy Rule Settings
d. Click Apply.
Enable a reverse proxy
rule
a. Beside the reverse proxy rule name, select the checkbox.
Tip
You can select multiple rules.
b. Click Enable.
Disable a reverse proxy
rule
a. Beside the reverse proxy rule name, select the checkbox.
Tip
You can select multiple rules.
b. Click Disable.
Conguring Network Protocol Settings
Network protocols enable QTS users to remotely access network devices over the internet or a TCP/IP
network. These protocols can be used to map, manage, and monitor network performance and notify users
during events of network warnings, failures, bottlenecks, and other events.
Conguring Telnet Connections
Telnet is a network protocol used to provide a command line interface for communicating with the NAS.
Important
Only administrator accounts can access the NAS through Telnet.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Telnet/SSH .
2. Select Allow Telnet connection.
3. Specify a port number.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 394

Port numbers range from 1 to 65535.
Tip
The default Telnet port is 13131.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the Telnet settings.
Conguring SSH Connections
Secure Shell (SSH) is a network protocol used for securely accessing network services over an unsecured
network. Enabling SSH allows users to connect to the NAS using an SSH-encrypted connection or a SSH client
such as PuTTY.
SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a secure network protocol that works with SSH connections to transfer
les and navigate through the QTS lesystem. SFTP can be enabled after allowing SSH connections on the
NAS.
Important
Only administrator accounts can access the NAS through SSH.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Telnet/SSH .
2. Select Allow SSH connection.
3. Specify a port number.
Port numbers range from 1 to 65535.
Tip
The default SSH port is 22.
4. Optional: Select Enable SFTP.
5. Click Apply.
Network & File Services updates the SSH connection settings.
Editing SSH Access Permissions
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Telnet/SSH .
2. Click Edit Access Permission.
The Edit Access Permission window opens.
3. Select user accounts to give access permissions.
Important
Only administrator accounts can log in using an SSH connection.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services updates the SSH access permissions.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 395
Conguring SNMP Settings
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to collect and organize information about
managed devices on a network. Enabling the QTS SNMP service allows for the immediate reporting of
NAS events, such as warnings or errors, to a Network Management Station (NMS).
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > SNMP .
2. Select Enable SNMP Service.
3. Congure the SNMP settings.
Setting User Action
Port number Specify the port that the Network Management Station (NMS) will use to
connect to QTS.
SNMP Trap Level Select the type of alert messages that the NAS will send to the NMS.
•Information: QTS sends information regarding ongoing or scheduled NAS
operations.
•Warning: QTS sends alerts when NAS resources are critically low or the
hardware behaves abnormally.
•Error: QTS sends alerts when NAS features or applications fail to be
enabled or updated.
Trap Address Specify the IP addresses of the NMS. You can specify a maximum of 3 trap
addresses.
4. Select the SNMP version that the NMS uses.
Option User Action
SNMP V1/V2 Specify an SNMP community name that contains 1 to 64 characters from any of the
following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
The SNMP community string functions as a password that is used to authenticate
messages sent between the NMS and the NAS. Every packet that is transmitted
between the NMS and the SNMP agent includes the community string.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 396
Option User Action
SNMP V3 Specify the username, authentication protocol and password, and privacy protocol
and password.
a. Specify a username.
Note
The username should contain 1 to 32 characters from any of the
following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Multi-byte characters: Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian
• Special characters: All except " ' / \
b. Optional:
Select Use Authentication.
1. Specify the authentication protocol.
Tip
You can select either HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA. If you are unsure
about this setting, QNAP recommends selecting HMAC-SHA.
2. Specify an authentication password that contains 8 to 64 ASCII characters.
c. Optional:
Select Use Privacy.
1. Specify a privacy password that contains 8 to 64 ASCII characters.
5. Click Apply.
QTS saves the SNMP settings.
Downloading the SNMP MIB
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a type of database in ASCII text format that is used to manage
the NAS in the SNMP network. The SNMP manager uses the MIB to determine the NAS status or understand
the messages that the NAS sends within the network. You can download the MIB and then view the contents
using any word processor or text editor.
MIBs describe the structure of the management data of a device subsystem. They use a hierarchical
namespace containing object identiers (OID). Each OID identies a variable that you can read or set using
SNMP. You must assign the correct OID to retrieve the NAS information. The default OID for QNAP NAS
devices is 1.3.6.1.4.1.24681.2.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > SNMP .
2. Under SNMP MIB, click Download.
QTS downloads the NAS.mib le to your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 397
Conguring File Sharing Protocol Settings
File sharing protocols allows users to access shared resources on a server that supports the le sharing
protocol of each client. Shared le access is implemented over local area network (LAN) service and
implements automatic synchronization of folder information whenever a folder is changed on the server.
Conguring Samba (Microsoft Networking) Settings
Microsoft Networking refers to Samba, a network protocol that allows data to be accessed over a computer
network and provides le and print services to Windows clients.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV > Microsoft Networking .
2. Select Enable le service for Microsoft networking.
3. Congure Microsoft networking settings.
Setting User Action
Server description (Optional) Specify a description that contains a maximum of 256 characters.
The description should enable users to easily identify the NAS on a
Microsoft network.
Workgroup Specify a workgroup name that contains 1 to 15 characters from any of
the following groups:
• Letters: A to Z, a to z
• Numbers: 0 to 9
• Multi-byte characters: Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Russian
• Special characters: ~ ! @ # $ ^ & ( ) - _ { } . '
4. Select an authentication method.
Option Description
Standalone server QTS uses the local user account information for authentication.
AD domain member QTS uses Microsoft Active Directory (AD) for authentication.
LDAP domain authentication QTS uses an LDAP directory for authentication.
5. Congure the advanced settings.
a. Click Advanced Options.
The Advanced Options window opens.
b. Congure the advanced settings.
c. Congure any of the following settings.
Option User Action
Enable WINS server Select to run a WINS server on the NAS.
Use the specied WINS server Select to specify a WINS server IP address that QTS will use for name
resolution.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 398
Option User Action
Local master browser Select to use the NAS as a local master browser. A local master
browser is responsible for maintaining the list of devices in a specic
workgroup on a Microsoft network.
Important
To use the NAS as local master browser, specify
the workgroup name when conguring Microsoft
networking. The default workgroup in Windows is
"workgroup".
Allow only NTLMSSP
authentication
Select to authenticate clients using only NT LAN Manager Security
Support Provider.
When this option is deselected, QTS uses NT LAN Manager (NTLM).
Name resolve priority Select a name service to use for name resolution.
The default service is DNS only.
If a WINS server is specied, Try WINS then DNS is selected by
default.
Alternative login style Select to change how usernames are structured when accessing FTP,
AFP, or File Station services.
After selecting this option, users can access NAS services using
Domain\Username, instead of Domain+Username.
Automatically register in DNS Select to register the NAS on the DNS server. If the NAS IP address
changes, the NAS automatically updates the IP address on the DNS
server.
This option is only available if AD authentication is enabled.
Enable trusted domains Select to join users from trusted AD domains.
This option is only available if AD authentication is enabled.
Enable Asynchronous I/O Select to improve the Samba performance using asynchronous I/O.
Asynchronous I/O refers to the I/O behavior on the CIFS protocol layer.
This is dierent from the synchronous I/O feature found in the shared
folder settings, which only applies to specic shared folders on the le
system level.
Tip
To prevent power interruption, use a UPS when
asynchronous I/O is enabled.
Enable WS-Discovery to help
SMB clients discover the NAS
Select to enable Web Services Dynamic Discovery (WS-Discovery). WS-
Discovery makes the NAS visible in File Explorer on Windows 10
computers.
Highest SMB version Select the highest SMB protocol version used in your networking
operation.
Use the default SMB version if you are unsure about this setting.
Note
Selecting SMB3 will also include SMB 3.1 and SMB
3.1.1.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 399
Option User Action
Lowest SMB version Select the lowest SMB protocol version used in your networking
operation.
Use the default SMB version if you are unsure about this setting.
Note
Selecting SMB 3 will also include SMB 3.1 and SMB
3.1.1.
Allow Symbolic links within a
shared folder
Select to allow symbolic links within shared folders.
Important
You must enable this setting in order to restore les
from snapshots on Windows using Windows Previous
Versions. For details, see Snapshot Data Recovery.
Allow Symbolic links between
dierent shared folders
Select to allow symbolic links between shared folders.
Note
This setting requires Allow Symbolic links within a
shared folder to be selected rst.
Restrict anonymous users from
accessing SMB shared folders
Select to enable user login before accessing SMB shared folders.
Note
This setting will be locked to Enabled (strict) if ABSE is
enabled on any shared folder.
Veto les Enable to hide les from users accessing the NAS via SMB. Files are
hidden if their lename matches a pattern in the veto criteria le.
Veto criteria Specify lename criteria for hiding les from SMB NAS users.
Note
This option is only available when Veto les is
selected.
d. Click Apply.
The Advanced Options window closes.
6. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the Samba settings.
Conguring AFP (Apple Networking) Settings
The Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) is a le service protocol that allows data to be accessed from a macOS device
and supports many unique macOS attributes that are not supported by other protocols.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV > Apple Networking .
2. Select Enable AFP (Apple Filing Protocol).
3. Optional: Select DHX2 authentication support.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the AFP settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 400
Conguring NFS Service Settings
Network File System (NFS) is a le system protocol that allows data to be accessed over a computer network.
Enabling the NFS service allows Linux and FreeBSD users to connect to the NAS.
The NFS service supports the following permissions in the NFS host access settings. You can apply these
permissions to shared folders in Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Edit Shared Folder
Permissions , and then selecting NFS host access as the permission type.
Permission Status Description
sync Disabled Disabling sync allows the NFS server to override the NFS protocol
and reply to requests before any changes made by that request have
been committed to stable storage. Using this option usually improves
performance, but could result in an unclean server restart (e.g., a
server crash), data loss, or corruption.
Enabled • wdelay: Causes the NFS server to delay writing to the disk to
accommodate requests committed to stable storage.
•no wdelay: The NFS server normally delays committing a write
request to disc if it suspects another related write request is in
progress or arriving soon. This allows multiple write requests to be
committed to the disc with the one operation which can improve
performance. no wdelay is available to turn o the delay behavior
if an NFS server received mainly small unrelated requests. The
default can be explicitly requested with the wdelay option.
secure Disabled Disabling secure requires that requests originate on TCP/IP ports
above 1024.
Enabled Enabling secure requires that requests originate on TCP/IP ports
between 1-1024.
Security Enabled The transparent le sharing system oered by NFS exposes the data
to several security vulnerabilities. The security mechanism allows safe
network transmission over trusted networks. NFS protocol provides
the following security options to enable secure data transfer between
the server and the client.
•sys: sys or AUTH_SYS is the default unencrypted NFS version 3
security mechanism
•krb5: Use Kerberos for authentication only.
•krb5i: Use Kerberos for authentication, and include a hash with
each transaction to ensure data integrity. Trac can still be
intercepted and examined, but modications to the trac are
made apparent.
•krb5p: Use Kerberos for authentication, and encrypt all trac
between the client and server. This authentication is the most
secure mechanism but also incurs the most load.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 401
Permission Status Description
Squash Enabled Remote root users can change any le on the shared le system
and expose other users to executable Trojan-infected applications. The
squash permission enables the NFS server to transfer the client root
role and prevent possible security threats.
•Squash root users: Maps the remote root user identity to a single
anonymous identity and denies the user special access rights on
the specied host.
•Squash all users: Maps all the client requests to a single
anonymous identity on the NFS server.
•Squash no users: The default option does not transfer the client
root role.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV > NFS Service .
2. Enable NFS Service.
a. Optional: Click Enable NFS v2/v3 Service.
b. Optional: Click Enable NFS v4 Service.
3. Click Enable manage-gids.
Tip
Enable to increase the default maximum number of groups a user can belong to. This option
replaces the list of group IDs (GIDs) received from the client with a list of GIDs mapped to the
user ID (UID) that can access NFS share if the appropriate client UID also exists in the NAS.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services saves the NFS service settings.
Accessing FTP (QuFTP Service) Settings
QuFTP Service is the QTS File Transfer Protocol (FTP) application that you can access through Network & File
Services.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services .
2. Click QuFTP Service.
QTS opens the QuFTP Service application.
Note
To use this feature, install QuFTP Service from App Center. For more information on QuFTP
Service, go to the QNAP website.
Conguring WebDAV Settings
The Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) protocol allows you to share, copy, move and edit
remote content on the web.
1. Log on to QTS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/MAC/NFS/WebDAV > WebDAV .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 402
3. Select Enable WebDAV.
4. Select one of the following options.
•Shared folder permission
•WebDAV permission
5. Optional: Congure the WebDAV port number settings.
Setting User Action
Dedicated port number Manually specify the port numbers for unencrypted (HTTP) and
encrypted (HTTPS) connections.
•HTTP port number
•HTTPS port number
Web server port number Select to use the default WebDAV port numbers.
6. Click Apply.
Network & Virtual Switch enables WebDAV and saves the settings.
Mounting a Shared Folder using WebDAV on Windows
Important
Before beginning this task, ensure that you have enabled WebDAV in the Control Panel.
For details, see Conguring WebDAV Settings.
WebDAV allows users to access and manage les on remote servers. You can mount a shared folder on your
Windows computer as a network drive via WebDAV.
1. On your Windows computer, open File Explorer.
2. Right-click This PC and select Map network drive.
Map Network Drive window appears.
3. Specify the path of the shared folder that you want to access.
Tip
The shared folder path uses the following format: http://NAS-IP-address: port number/shared-
folder-name. For example: http://172.17.45.155:80/Public
4. Enable Reconnect at sign-in and Connect using dierent credentials.
5. Click Finish.
Windows Security window appears.
6. Specify your NAS login credentials.
7. Click Connect.
Tip
If you cannot connect to the NAS shared folders using WebDAV, see Troubleshooting WebDAV
Connectivity Issues on Windows.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 403

The NAS shared folder is mounted as a network drive via WebDAV. You can now access and manage the les
in this shared folder using Windows File Explorer.
Troubleshooting WebDAV Connectivity Issues on Windows
If you are unable to connect to the NAS shared folders using WebDAV protocol on a Windows computer,
follow the instructions below to modify the basic authentication level.
1. Right click Start.
2. Select Run.
3. Type regedit.
4. Click OK.
5. Open Registry Editor.
6. Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Services > WebClient >
Parameters .
7. Open BasicAuthLevel.
8. Set the value data to 2.
9. Restart your computer.
10. Try using WebDAV to connect your computer to the NAS shared folder again.
Mounting a Shared Folder Using WebDAV on Mac
Important
Before beginning this task, ensure that you have enabled WebDAV in the Control Panel.
For details, see Conguring WebDAV Settings.
WebDAV allows users to access and manage les on remote servers. You can mount a shared folder on your
Mac as a network drive via WebDAV.
1. On your Mac, go to Finder > Go > Connect to Server .
The Connect to Server window appears.
2. Specify the path of the shared folder that you want to access.
Tip
The shared folder path uses the following format: http://NAS-IP-address: port number/shared-
folder-name. For example: http://172.17.45.155:80/Public
3. Click Connect.
4. Specify your NAS login credentials.
5. Click Connect.
The NAS shared folder is mounted as a network drive via WebDAV. You can now access and manage the les
in this shared folder using macOS Finder.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 404

Enabling Service Discovery Settings
Service discovery enables QTS users to automatically detect and locate services on the network. Service
discovery uses zero-conguration networking (zeroconf) to create a usable network based on the Internet
Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) when devices are interconnected.
Enabling the UPnP Discovery Service
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a networking technology that enables the discovery of networked devices
connected to the same network. After enabling this service, devices supporting UPnP can discover the NAS.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Service Discovery > UPnP Discovery Service .
2. Select Enable UPnP Discovery Service.
3. Click Apply.
Network & File Services enables UPnP discovery service.
Enabling the Bonjour Discovery Service
Bonjour is a networking technology developed by Apple that enables devices on the same local area network
to discover and communicate with each other.
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Service Discovery > Bonjour .
2. Select Enable Bonjour Service.
3. Select the services to be advertised by Bonjour.
Important
You must enable the services in QTS before advertising them with Bonjour.
4. Click Apply.
Network & File Services enables Bonjour discovery service.
Network Recycle Bin Management
The Network Recycle Bin contains les deleted from the device through File Station, FTP settings, or by
clients connected using Samba (Microsoft networking).
Conguring the Network Recycle Bin
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Recycle Bin .
2. Select Enable Network Recycle Bin.
3. Optional: Congure the Network Recycle Bin settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 405

Setting Description
File retention time Specify the number of days les are retained.
The Daily check time controls when recycled les are checked against
the retention time.
Tip
This eld supports a maximum of 9999 days. The
default is 180 days.
Exclude these le extensions Specify which le extensions are excluded from the Network Recycle
Bin.
Important
File types are case insensitive and must be separated
by a comma.
4. Click Apply.
Deleting All Files in the Network Recycle Bin
1. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Network Recycle Bin .
2. Click Empty All Network Recycle Bin.
A warning message appears.
3. Click OK.
QTS deletes all les from the Network Recycle Bin.
Restricting Access to the Network Recycle Bin
1. Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders .
2. Identify a shared folder.
3.
Under Actions, click .
The Edit Properties window appears.
4. Select Enable Network Recycle Bin.
5. Select Restrict the access to Recycle Bin to administrators only for now.
6. Click OK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Network & File Services 406
12. myQNAPcloud
myQNAPcloud is a service that allows you to access, manage, and share les stored on your QNAP devices
remotely through the internet.
Getting Started
1. Create a QNAP ID.
For details, see Creating a QNAP ID With Email or Phone Number.
2. Register the device to myQNAPcloud.
For details, see Registering a Device to myQNAPcloud.
3. Optional: Congure any of the following settings.
Settings Description
Port forwarding Port forwarding allows you to access your device on the internet through a
UPnP router.
For details, see Conguring UPnP Port Forwarding.
My DDNS My DDNS allows you to specify a dedicated myQNAPcloud subdomain name
that you can use to access your device on the internet.
For details, see Conguring DDNS Settings.
Published services You can publish QNAP services on your device, such as the QNAP desktop and
File Station, so they can be accessible on myQNAPcloud.
For details, Conguring Published Services.
myQNAPcloud Link myQNAPcloud Link allows you to access your device on the myQNAPcloud
website or through mobile apps and client utilities without changing your
router settings. Using shared links, you can also simultaneously download and
sync les to a remote NAS without needing to rst save them to client device.
For details, see Enabling myQNAPcloud Link.
Access controls Access controls allow you to congure device access permissions for
myQNAPcloud users.
For details, see Conguring Device Access Controls.
SSL certicates myQNAPcloud allows you to add SSL certicates to help secure your network
communication. You can either download and install a myQNAPcloud or Let's
Encrypt certicate.
For details, see Installing an SSL Certicate.
Account Setup
Before using myQNAPcloud services, you must rst create a QNAP ID and then congure required settings
using your QNAP ID.
Creating a QNAP ID With Email or Phone Number
1. Go to https://account.qnap.com/.
The QNAP Account login page displays.
2. Click Create Account.
The Create Account screen appears.
3. Specify a nickname, a valid email address or phone number, and a password.
4. Read and acknowledge the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 407
5. Click Sign Up.
The Data Privacy Notice box appears.
6. Read the notice, and then click I Agree.
myQNAPcloud sends a verication email or message.
7. Conrm the registration.
Your QNAP ID is activated.
Tip
The registration link automatically expires in 15 days. You can go to QNAP Account to send a
new activation email.
Registering a Device to myQNAPcloud
1. Log in as administrator.
2. Go to myQNAPcloud > Overview .
3. Click Get Started.
The myQNAPcloud wizard appears.
4. Click Start.
5. Specify your QNAP ID and password.
6. Click Next.
7. Specify a device name containing up to 30 alphanumeric characters.
You may reuse an existing device name. The device currently using this name will be deregistered from
myQNAPcloud.
8. Click Next.
9. Select the services you want to enable.
Service Description
Auto Router
Conguration
This allows you to congure port forwarding.
DDNS This allows you to access your device on the internet using a dedicated address.
Published Services This allows you to select which services you want to publish on the
myQNAPcloud website.
myQNAPcloud Link myQNAPcloud Link allows you to access your device on the myQNAPcloud
website or through mobile apps and client utilities without changing your
router settings. Using shared links, you can also simultaneously download and
sync les to a remote NAS without needing to rst save them to a client device.
If you enable this option and your device does not have myQNAPcloud Link,
myQNAPcloud Link will automatically be downloaded and installed after you
click Next.
10. Select an access control option.
Option Description
Public All users can search for your device and view the published services on the
myQNAPcloud website. They can also access your device with a SmartURL.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 408
Option Description
Private Your device will not appear in the search results. Only you can access your
device on the myQNAPcloud website.
Customized Your device will only be visible to you and invited users. Other users will not be
able to access your device even with a SmartURL.
11. Click Next.
myQNAPcloud applies your settings.
The Summary screen appears.
12. Review the details, and then click Finish.
Installing myQNAPcloud Link
Only perform this task if you did not enable myQNAPcloud Link when registering your device to your
myQNAPcloud account.
1. Log in to QNAP as administrator.
2. Open App Center.
3. Click .
A search box appears.
4. Type myQNAPcloud Link and then press ENTER.
The myQNAPcloud Link application appears in the search results list.
5. Click Install.
App Center installs myQNAPcloud Link on your device.
Overview
The Overview screen displays your basic myQNAPcloud settings, as well as the device network connectivity
and DDNS status.
Status Icon Description
The item is enabled and functioning properly.
The item is disabled.
One or more settings need to be congured for the item to function properly.
There is no network connectivity.
Button Description
Click this to view your QNAP ID details.
Click this to sign out of myQNAPcloud.
Click this to modify your device name.
Click this to copy the SmartURL to your clipboard.
Click this to open the myQNAPcloud FAQ page on your browser.
Click this to diagnose connection problems.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 409
Button Description
Test Click this to test the internet connectivity.
Conguring UPnP Port Forwarding
UPnP allows your devices to automatically congure port forwarding settings and discover other devices on
the network. Port forwarding is only available if your router supports UPnP.
Warning
Despite its convenience, UPnP may expose your device to public networks. This may allow
malicious attackers to access your sensitive data, scan your private networks, and use
your devices for DDoS attacks. To ensure your device and data security, we recommend
disabling UPnP and manually conguring port forwarding settings on your router.
1. Go to Auto Router Conguration.
2. Enable UPnP Port Forwarding.
A conrmation message appears.
3. Read the instructions carefully and understand the risks of enabling UPnP.
4. Select Enable.
Your device scans for UPnP routers on the network.
Tip
• You can go to Overview to verify that there are no connectivity errors.
• If your device cannot locate the router, click Rescan. If the issue persists, click Diagnostics,
and then verify your network conguration or contact QNAP support through Helpdesk.
5. Optional: Add a new service to the Forwarded Services table.
a. Click Add NAS Service.
The Add NAS Service window appears.
b. Specify a NAS service name that contains 1 to 64 ASCII characters.
c. Specify a port number.
d. Select an external port setting.
•Automatic: myQNAPcloud automatically selects an available external port.
•Manual: You can specify a new port if the current service port is being used by other
services.
e. Select a protocol.
If you are unsure about this setting, select TCP.
f. Click OK.
6. In the Forwarded Services table, select the services you want to forward.
7. Click Apply to Router.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 410
Conguring DDNS Settings
1. Open myQNAPcloud.
2. Go to My DDNS.
3. Enable My DDNS.
4. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Change the
myQNAPcloud DDNS
domain name
a. Click here.
The Change Device Name Wizard appears.
b. Specify a device name containing up to 30 alphanumeric characters.
c. Click Apply.
Update myQNAPcloud Click Update.
Manually congure the
DDNS IP address
a. Click Manually congure your DDNS IP address.
The Public IP Address window appears.
b. Select an option.
•Assign static IP addresses: myQNAPcloud binds the DDNS to the
specied static IP address regardless of changes to the network
environment.
•Automatically obtain IP address: myQNAPcloud automatically
detects the WAN IP.
c. Click Apply.
Restarting DDNS Service
DDNS service may sometimes be disabled or suspended due to security concerns. You can restart the DDNS
service in myQNAPcloud to regain access to the service.
1. Clear the cache on your web browser.
2. Log on to QTS as administrator.
3. Open myQNAPcloud.
4. Go to My DDNS.
5. Disable My DDNS.
6. Enable My DDNS.
myQNAPcloud DDNS service is restarted and resumed.
Tip
If you still cannot connect to the NAS via myQNAPcloud DDNS, the service may be
temporarily blocked by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Wait at least two hours before
attempting to restart the DDNS service.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 411
Conguring Published Services
1. Open myQNAPcloud.
2. Go to Published Services.
3. In the Publish column, select all the services you want published.
Published services are accessible through the myQNAPcloud website.
4. Optional: In the Private column, select all the services you want publish privately.
Private services are only available to specied users with the access code.
a. Specify an access code containing 6 to 16 alphanumeric characters.
b. In the User Management table, select the users you want to grant access to.
You can select a maximum of 9 users.
Tip
Click Add Users to add users to the list.
Click Delete to remove users from the list.
c. Optional: Modify user access privileges.
Option Description
myQNAPcloud Connect (VPN) Select this option to grant users access to private NAS services
when they use the myQNAPcloud Connect utility.
Users can download myQNAPcloud Connect from the QNAP
Utilities page (https://www.qnap.com/en/utilities/essentials).
myQNAPcloud Website Select this option to grant users access to private NAS
services published in the myQNAPcloud website (https://
www.myqnapcloud.com/).
5. Click Apply.
Enabling myQNAPcloud Link
1. Open myQNAPcloud.
2. Go to myQNAPcloud Link.
3. Enable myQNAPcloud Link.
Tip
If there are issues with the connection, click Reconnect.
Conguring Device Access Controls
1. Open myQNAPcloud.
2. Go to Access Control.
3. Select an access control option.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 412
Option Description User Action
Public All users can search for your device
and view the published services on the
myQNAPcloud website.
Select Public.
Private Your device will not appear in the search
results. Only you can access your device on
the myQNAPcloud website.
Select Private.
Customized Your device will only be visible to you and
invited users. Other users will not be able
to access your device even with a SmartURL
a. Select Customized.
b. Optional: Add a user.
1. Click Add.
2. Specify the user's email address or
phone number.
3.
Click .
c. Optional: Remove a user.
• From the list of users, identify a
user you want to remove.
• Click .
4. Click Apply.
Installing an SSL Certicate
Important
myQNAPcloud SSL web service and Let's Encrypt certicates can only be used with the
myqnapcloud domain.
1. Open myQNAPcloud.
2. Go to SSL Certicate.
3. Download and install a certicate.
Type Description User Action
myQNAPcloud
SSL web service
certicate
This certicate provides a secure
environment for exchanging condential
information online and conrms the
identity of your site to employees, business
partners, and other users.
You can purchase certicates on the
myQNAPcloud website.
a. Under myQNAPcloud SSL Certicate,
click Download and install.
The Download & Install SSL
Certicate window appears.
b. Select a license from the list.
A notication appears if you have
not yet purchased a myQNAPcloud
certicate.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 413

Type Description User Action
Let's Encrypt
certicate
Let's Encrypt is a free, automated, and
open certicate authority that issues
domain-validated security certicates. You
can install Let's Encrypt certicates with
the myQNAPcloud DDNS service. You
can choose to automatically renew this
certicate before it expires.
a. Under Let's Encrypt, click Download
and install.
The Download & Install SSL
Certicate window appears.
b. Specify a valid email address.
This address is required for the Let's
Encrypt account registration.
c. Optional: Select Automatically renew
domain before expiration.
4. Click Conrm.
myQNAPcloud applies the certicate and displays the details.
Tip
To delete the certicate from the device, click Release and then Conrm.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
myQNAPcloud 414
13. App Center
App Center is a digital distribution and management platform in QTS where you can browse, download, and
manage applications and utilities developed for the QNAP NAS.
Navigation
You can view all App Center apps in the left panel or congure a number of settings using the toolbar.
Left Panel
The left panel allows you to browse available apps in various categories. You can go to the My Apps section
to view all your installed apps. App Center displays a badge count to indicate the number of available
updates.
Toolbar
Left side
No. Elements Possible User Actions
1 View mode • Click the icon to switch between two view modes.
•Click and select a view mode.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 415
No. Elements Possible User Actions
2 App sorting Click and select an app sorting method.
3 Volume information View the basic volume information and the installation
locations of your apps.
For more volume information, click Details.
Right side
No. Elements Possible User Actions
1 Search Specify keywords to search for apps.
App Center instantly displays search results based on
specied keywords.
2 Refresh Reload the data in App Center to view the current status of
your apps.
3 Manual installation Manually install an app by uploading an installation
package.
For details, see Installing an App Manually.
4 Settings Congure various App Center settings.
For details, see App Center Settings.
5 More View the Quick Start or the Help document for more
information about App Center.
App Management
The App Center allows you to enable or disable an app, assign CPU resources to load-intensive apps, update
apps, and congure app update settings.
Viewing App Information
You can browse apps and view their descriptions in the App Center. This helps you decide whether to install
or update an app.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
3. Click the app icon.
App Center displays the app information in a new window.
4. Perform one of the following actions.
• View the app description
• View the digital signature details
• View the app changelog
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 416
• Go to the QNAP forum
• View the app tutorial
• Download the app installation package
Buying an App License
Important
• Some apps require you to purchase an app license or subscription. You can purchase
app licenses or subscriptions in Software Store.
• You must activate a purchased app license to operate a paid app.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
3. Click Buy License.
The Buy License window opens in a new web page.
Important
For details about license subscription or purchasing a license from Software Store, see
Licenses.
4. Click Activate License.
The License Center window appears.
5. Activate the license.
For details, see License Activation.
6. Click Next.
• The App Center window appears.
• App installation will automatically start in App Center.
Installing an App from App Center
Warning
QNAP recommends only installing apps from the App Center or from the QNAP website.
QNAP shall not be held liable for any damages, data loss, or security vulnerabilities
resulting from the installation and use of unauthorized apps from untrusted sources.
Important
• Certain apps require activating a subscription or license before app installation. For
details, see Licenses.
• Based on the app you choose to install, App Center may display a conrmation
message that provides more information and asks for your approval for installation.
Certain apps also require you to specify the installation location. Read the message
carefully before installing the app.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 417
3. Optional: Click the app icon to view the app information.
4. Select the app update frequency.
5. Click Install.
The app is installed.
Installing an App Manually
Warning
• QNAP recommends only installing apps from the App Center or from the QNAP
website. QNAP shall not be held liable for any damages, data loss, or security
vulnerabilities resulting from the installation and use of unauthorized apps from
untrusted sources.
• App Center does not allow the installation of invalid apps, including apps with invalid
digital signatures, apps not approved by App Center, or from the Software Store.
If App Center detects the app installed is invalid, it will immediately terminate app
installation and request you to remove the app.
Important
Certain apps require activating a subscription or license before app installation. You can
go to the Software Store to purchase an app license or subscription. For details about
activating an app license, see Licenses.
1. Open App Center.
2. Click on the toolbar.
The Install Manually window appears.
3. Click Browse.
4. Locate and select the installation package.
5. Click Install.
A message appears.
6. Depending on the scenario, perform one of the following actions.
Scenario Actions
The app has a valid digital signature. a. Read the conrmation message.
b. Click OK.
The app does not have a valid digital signature, and
you enabled the installation of apps without valid
digital signatures.
a. Read the conrmation message.
b. Click OK.
The app does not have a valid digital signature, and
you did not enable the installation of apps without
valid digital signatures.
a. Read the warning message.
b. Select I understand the risks and want to
install this application.
c. Click Install.
Tip
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 418
For more information on this setting, see Enabling Installation of Apps without Digital
Signatures.
App Center installs the app.
Updating an App
When updates are available for an installed app, App Center moves the app to the Update or Required
Update section based on the importance of updates. You must perform required updates to ensure the
functionality, compatibility, and data security of your apps.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app in the Update or Required Update section.
3. Click Update or Required Update.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click OK.
Batch Updating Multiple Apps
1. Open App Center.
2. Perform one of the following updates.
Updates Action
Only required updates Below the toolbar, click Required Update.
All available updates Below the toolbar, click All.
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click OK.
Enabling or Disabling an App
You can enable or disable non-built-in apps in App Center.
Note
• Disabling an app may aect the functionality of other apps.
• Disabling an app does not remove or uninstall the app.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
3. Perform one of the following actions.
Action Steps
Enable the app Click Start.
Disable the app a. Click .
b. Select Stop.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 419
• After an app is enabled, its action button displays Open.
• After an app is disabled, its action button displays Start.
Migrating an App
You can migrate an installed app to another volume to better allocate system resources.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
3. Click .
4. Select Migrate to.
The App Migration window appears.
5. Select the destination volume.
6. Click Migrate.
A conrmation message appears.
7. Click OK.
Granting or Denying User Access to an App
QTS administrators can grant or deny user access to apps. The main menu of non-administrator users only
display the apps that they have access to.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
3. Click .
4. Hover the mouse pointer over Display on.
5. Select one of the following options:
• Administrator's main menu
Note
This is the only available option for many built-in system utilities, which non-administrators
cannot be granted access to.
• Every user's main menu
• Every user's main menu and as an app shortcut on the login screen
Uninstalling an App
Warning
Uninstalling an app also deletes the related user data.
1. Open App Center.
2. Locate an app.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 420
3. Click .
4. Select Remove.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Click OK.
App Center Settings
You can congure the app respository, update settings, and enable installation of apps without digital
signatures.
Adding an App Repository
You can add an app repository to enrich the content in App Center. This allows you to download and install
apps from third-party sources.
1. Open App Center.
2. Click on the toolbar.
3. Go to App Repository.
4. Click Add.
The Add window appears.
5. Specify the following connection information.
• Name
• URL
6. Optional: Specify the login credentials.
• Username
• Password
7. Click Add.
App Center adds the repository to the list. You can select the repository and then click Edit to modify its
settings or click Delete to remove this repository from App Center.
Conguring App Update Settings
1. Open App Center.
2. Click .
3. Go to Update.
4. Select When updates are available and then select one of the following options.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 421
Option Description
Send a notication QTS sends notication messages when updates are available for your
apps.
You can click Congure Notication Rule to create rules in
Notication Center. For details, see Notication Center.
Note
If you select this option, the system will skip the check
for updates frequency step.
Install all updates
automatically
App Center automatically installs all available updates for your apps.
You can select how often App Center should check for available
updates.
Install all required updates
automatically
App Center automatically installs all required updates for your apps to
ensure their functionality, compatibility, and data security.
You can select how often App Center should check for required
updates.
5. Select an automatic update detection frequency.
6. Click Apply.
Digital Signatures
QNAP uses digital signatures to validate apps created by QNAP or QNAP-trusted publishers. The use of
digital signatures prevent the unauthorized tampering of apps that may lead to security risks.
A digital signature is considered valid if it meets the following criteria.
• The digital signature has not been tampered with.
• The digital signature has not expired.
• The digital signature is certied by QNAP.
Enabling Installation of Apps without Digital Signatures
Warning
• A valid digital signature ensures that an application was created by QNAP or a QNAP-
trusted publisher. It also ensures that the app has not been maliciously tampered with.
Installing apps without valid digital signatures may expose your NAS to security risks.
QNAP shall not be held liable for any damages, data loss, or security vulnerabilities
resulting from the installation and use of such apps.
• App Center does not allow the installation of invalid apps, including apps with invalid
digital signatures, apps unapproved by App Center, or from Software Store. If App
Center detects the app installed is invalid, it will immediately terminate app installation
and request you to remove the app.
1. Open App Center.
2. Click on the toolbar.
The Settings window appears.
3. Go to General.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 422

4. Select Allow installation and execution of applications without a digital signature.
Important
App Center does not allow the installation of apps with tampered digital signatures even when
this setting is enabled.
5. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
App Center 423
14. Licenses
QNAP licenses enable users to gain access to certain advanced features or premium products. This chapter
introduces important concepts and demonstrate essential tasks to help you start using QNAP licenses.
About QNAP Licenses
QNAP oers a wide variety of licenses. Some basic licenses are provided free of charge. You can purchase
premium licenses to further enhance the functionality of your QNAP products. QNAP also provides multiple
management portals, exible subscription plans, and various activation options to meet your dierent
needs.
License Types and Plans
The licensing mechanisms and available plans of QNAP licenses vary depending on corresponding software
products. They can be divided into the following categories.
License Types
License Types Description
Device-based • Allows users to use a software product installed on hardware devices,
such as applications.
• Multi-seat licenses can be activated and used on multiple devices.
Floating • Allows users to use a software product in the cloud or on a virtual
platform, such as QuTScloud and applications in QuTScloud.
• Can be activated and used on a limited number of devices at a time
User-based • Allows a limited number of authorized users to access a web-based
service, such as Qmiix.
License Plans
License Plans Description
Subscription Authorizes users to use a software product with a recurring monthly or
annual fee
Perpetual Authorizes users to use a software product indenitely
One-time Authorizes users to use a software product within a predened period of
time
Validity Period
The validity period of a QNAP subscription-based license starts from the date of purchase, not from the date
of activation.
For example, if a user starts the subscription of an annual license on January 1, 2020, the next billing date
will be January 1, 2021, regardless of the date of activation. If the user cancels the subscription, the license
will still remain valid until January 1, 2021.
If the user unsubscribes from a license but subscribes to the same product later, the validity period and
billing cycle will begin from the date of the new subscription.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 424
License Portals and Utility
Portal Description URL
QNAP Software Store The QNAP Software Store is a one-stop shop
where you can purchase licenses for QNAP and
QNAP-aliated software.
https://software.qnap.com
QNAP License Center The QNAP License Center allows you to monitor
and manage licenses of applications running on
your local device.
-
QNAP License
Manager
QNAP License Manager is a portal that allows
you and your organizations to remotely activate
and manage licenses under your QNAP ID.
https://license.qnap.com
Old QNAP License
Store
Users of QTS 4.3.4 (or earlier) can purchase
licenses from this online store.
https://license2.qnap.com
Software Store
Software Store allows you to purchase licenses for applications. Through Software Store, you can perform
the following actions.
• Purchase or upgrade licenses
• Manage your account information
• View purchased subscriptions
• Cancel your subscriptions
• Request a refund for your orders
License Center
License Center allows you to monitor and manage the licenses of your applications running on your local
device. Through License Center, you can perform the following actions.
• Activate and deactivate licenses either online or oine
• Remove licenses from the local device
• Recover licenses if your device is reset, reinitialized, or restored to factory default
• Transfer licenses purchased from the old QNAP License Store to the new QNAP License Manager
License Manager
License Manager is a portal that allows you to manage all licenses under QNAP IDs and organizations.
Through License Manager, you can perform the following actions.
• View details of your licenses
• Activate and deactivate licenses
• Assign a user-based license to a QNAP ID
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 425
Important
To remotely activate or deactivate licenses, you must enable myQNAPcloud Link on your
QNAP device.
Buying a License Using QNAP ID
Before buying a license, ensure the following.
• The application is already installed on your device.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
1. Go to https://software.qnap.com/.
2. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
3. Locate the product on the list, and then click Buy or Subscribe Now.
The license details appear.
4. Select the item you want to buy, and then review the price.
5. Click Checkout Now.
Tip
You can also click Add to Cart and then continue shopping.
The purchase summary page appears in your web browser.
6. Select a payment method.
Payment Method User Action
Credit card a. Specify your card information.
b. Verify the items and the price on the order.
c. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
d. Click Place Order.
PayPal a. Verify the items and the price on the order.
b. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
c. Click Pay with PayPal
PayPal authentication window appears.
d. Specify your PayPal login credentials.
e. Click Next.
f. Follow PayPal instructions to complete the payment.
Google Pay a. Verify the items and the price on the order.
b. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
c. Click Buy with Google Pay.
Google Pay authentication window appears.
d. Follow Google Pay instructions to complete the payment.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 426
After the payment, you can view order details in My Orders and manage your subscriptions in My
Subscriptions.
You can activate your license right after the purchase or at a later time.
For details, see License Activation.
License Activation
You need to activate purchased licenses to access features provided by the license. You can activate QNAP or
QNAP-aliated licenses using the following methods.
Activation Method Description
Using QNAP ID Licenses purchased through Software Store are stored in your
QNAP ID account. They can be accessed through both License
Center and the QNAP License Manager website.
Using a license key You can generate the 25-character license key after purchasing
licenses through the QNAP Software Store. For details, see
Generating a License Key.
You can use license keys to activate licenses in License Center. For
details, see Activating a License Using a License Key.
Using a product key The 25-character product key is purchased together with the
product from either QNAP or an authorized reseller. The product
key is normally printed on the product package.
You can use product keys to activate licenses in License Center.
For details, see Activating a License Using a Product Key or PAK.
Using a product authorization key
(PAK)
The 24-character PAK is purchased together with the product from
either QNAP or an authorized reseller. The product key is normally
printed on the product package.
If you are using NAS devices running QTS version 4.3.4 or older,
use PAKs to activate licenses through License Center.
If you are using NAS devices running QTS version 4.3.4 or later,
you can transfer PAKs purchased from the Old QNAP License
Store to NAS devices. For details, see Activating a License Using
a Product Key or PAK.
Oine Use this method when the NAS is not connected to the internet.
For details, see Activating a License Oine.
Activating a License Using QNAP ID
Before activating your license, ensure the following.
• Your device is connected to the internet.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
Users can activate their licenses using QNAP ID in either Qnder Pro, License Center, or License Manager.
• Activate your license using one of the following methods.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 427
Method Steps
Qnder Pro Qnder Pro allows you to discover QNAP devices on your local network.
a. Open Qnder Pro on your computer.
Tip
You can download Qnder Pro from the QNAP website.
b. Select your device form the list.
c. Right-click the device and select License Activation.
d. Specify your device username and password.
The License Activation windows appears.
e. Select Activate with QNAP ID.
f. Click Select License.
g. Specify your QNAP ID and password.
h. Click Select License.
i. Select a license from the list.
j. Click Activate.
License Server activates the license.
A conrmation message appears.
k. Click Close.
The license is activated for the device.
License Center a. Open License Center.
b. Go to My Licenses.
c. Click Activate License.
The License Activation window appears.
d. Select Activate with QNAP ID.
e. Click Select License.
f. Select a license from the list.
Tip
If you select a multi-seat license, you can specify the
number of seats that you want to activate.
g. Click Add.
License Center activates the license.
A conrmation message appears.
h. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 428
Method Steps
License Manager a. Open your web browser.
b. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
c. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
d. Locate a license from the license list.
e. Click .
The Activate License window appears.
f. Select Online Activation.
g. Select a device.
h. Specify your credentials on the device.
i. Click Allow.
A conrmation message appears.
j. Click OK.
License Manager activates the license.
k. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
Activating a License Using a License Key
Before activating your license, ensure that your device is connected to the internet and you have signed in
with your QNAP ID.
You can activate a license using a license key. After purchasing a license from QNAP Software Store, you can
generate a license key from the License Manager website and apply the key in License Center. A license key
contains 25 characters and always starts with the letter L.
For details, see Generating a License Key.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Click Activate License.
The License Activation window appears.
4. Select Activate with a License Key.
5. Specify the key.
6. Read and agree to the terms of service.
7. Click Verify Key.
8. Verify the license information.
9. Optional: Specify the number of seats to activate.
Note
This option is only available for licenses that support multiple seats.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 429

10. Click Activate.
The license is activated.
A conrmation message appears.
11. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
Generating a License Key
1. Open your web browser.
2. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
3. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
4. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to generate a key for.
5. Click .
The Activate License window appears.
6. Select License Key.
License Manager generates the license key.
Tip
Click Renew License Key to generate a new key.
This renews your license key and protects you from any unauthorized access to your existing
license key.
7. Hover the mouse pointer over the license key and click .
Your system copies the license.
8. Click Done.
The copied license key can be pasted later for license activation.
Activating a License Using a Product Key or PAK
Before activating a license using a product key or a product authorization key (PAK), ensure the following.
• Your NAS is connected to the internet.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
You can activate a license with a product key or PAK. You may nd a product key printed on a physical copy
of your product. A product key contains 25 characters and always starts with the letter P.
On the other hand, you may obtain a product authorization key (PAK) if you purchase a license from the old
QNAP License Store. A PAK contains 24 digits of random numbers.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Click Activate License.
4. The License Activation window appears.
5. Select Activate with a Product Key or PAK.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 430
6. Specify the key.
7. Read and agree to the terms of service.
8. Click Verify Key.
9. Verify the license information.
10. Click Activate.
The license is activated.
A conrmation message appears.
11. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
Activating a License Oine
You can activate your license oine if your QNAP device is not connected to the Internet. You rst need to
generate a device identity le (DIF) from Qnder Pro or from License Center on your device and then upload
the DIF to License Manager in exchange for the license install le (LIF). You can then activate the license
using the LIF in Qnder Pro or in License Center on your device.
1. Choose one of the following methods.
Methods User Action
Oine activation using Qnder Pro Qnder Pro allows you to discover QNAP devices on
your local network.
a. Open Qnder Pro on your computer.
Tip
You can download Qnder Pro from the
QNAP website.
b. Select your device from the list.
c. Right-click the device and then select License
Activation.
d. Specify your username and password.
The License Activation window appears.
e. Select Oine Activation.
Oine activation using License Center a. Log in to your QNAP device.
b. Open License Center.
c. Go to My Licenses.
d. Click Activate License.
The License Activation window appears.
e. Select Oine Activation.
2. Read and agree to the Terms of Service.
3. Click Generate Device Identity File.
Qnder Pro or License Center downloads the device identity le (DIF) to your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 431
4. Read the instructions and click Go to License Manager.
Your web browser opens the QNAP License Manager website.
5. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
6. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to activate.
7. Click (Upload Device Identity File).
The Activate License window appears.
8. Click Browse.
The le browser appears.
9. Locate and select the DIF from your computer.
10. Click Upload.
A conrmation message appears.
11. Click Download.
QNAP License Manager downloads the license install le (LIF) to your computer.
12. Click Done.
13. Go back to Qnder Pro or License Center.
14. In the License Activation window, click Upload License File.
15. Click Browse.
The le browser appears.
16. Locate and select the LIF from your computer.
17. Click Import.
Qnder Pro or License Center uploads the LIF and displays the license summary.
18. Click Activate.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
License Deactivation
You can deactivate QNAP or QNAP-aliated licenses using the following methods.
Activation Method Description
Using QNAP ID Licenses purchased through Software Store are stored in your
QNAP ID account, and can be accessed through both License
Center and the QNAP License Manager website
To deactivate this type of license, see Deactivating a License Using
QNAP ID.
Oine Use this method when the NAS is not connected to the internet.
For details, see Deactivating a License Oine.
Deactivating a License Using QNAP ID
Before deactivating your license, ensure the following.
• Your device is connected to the internet.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 432
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
Users can deactivate their licenses using QNAP ID in either License Center or License Manager.
• Deactivate your license using one of the following methods.
Method Steps
License Center a. Open License Center.
b. Go to My Licenses.
c. Identify the license you want to deactivate, and then click .
The License Deactivation window appears.
d. Select Use QNAP ID.
e. Read and acknowledge the warning.
f. Click Deactivate.
A conrmation message appears.
g. Click Close.
License Center deactivates the license and removes the license from the
list of active licenses.
License Manager a. Open your web browser.
b. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
c. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
d. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to deactivate.
e. Click .
The Deactivate License window appears.
f. Read and acknowledge the warning.
g. Click Deactivate.
License Center deactivates the license.
A conrmation message appears.
h. Click Close.
License Center removes the license from the list of active licenses.
Deactivating a License Oine
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Identify the license you want to deactivate, and then click .
The License Deactivation window appears.
4. Select Oine Deactivation.
5. Read and acknowledge the warning.
6. Read the instructions, and then click Generate License Uninstall File.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 433
License Center downloads the license uninstall le (LUF) to your computer.
7. Open your web browser.
8. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
9. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
10. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to deactivate.
11. Under Advanced Options, click .
The Deactivate License window appears.
12. Read and agree to the terms.
13. Click Oine Deactivation.
14. Click Browse.
The le browser appears.
15. Locate and select the LUF from your computer.
16. Click Upload.
QNAP License Manager deactivates the license.
A conrmation message appears.
17. Click Done.
License Extension
License Center will notify you soon before any of your subscription-based licenses expire. The exact dates
vary depending on the type of your licenses (ranging from one week to one month before the expiration
date). You can extend your QNAP or QNAP-aliated licenses using the following methods.
Activation Method Description
Using QNAP ID Licenses purchased through License Center or Software Store are
stored in your QNAP ID account, and can be accessed through
both License Center and the QNAP License Manager website.
If you have an existing valid, unused subscription-based license in
License Center, you can use this to extend your expiring license.
For details, see Extending a License Using QNAP ID.
Oine using an unused license If you have a valid, unused subscription-based license and your
NAS is not connected to the internet, you can use this method to
extend your expiring license. For details, see Extending a License
Oine Using an Unused License.
Oine using a product key The 25-character product key is purchased together with the
product from either QNAP or an authorized reseller. The product
key is normally printed on the product package.
If you have a valid, unused product key for a subscription-based
license, and your NAS is not connected to the internet, you can
use this method to extend your expiring license. For details, see
Extending a License Oine Using a Product Key.
Extending a License Using QNAP ID
Before extending licenses, ensure the following.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 434

• Your device is connected to the internet.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
• You have an existing valid, unused license.
Note
Subscription-based licenses will be automatically renewed in License Manager. You cannot
manually extend a subscription-based license.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Identify the license you want to extend, and then click .
Tip
If a license is expiring in 30 days or less, its status is Expires soon.
The License Extension window appears.
4. Select an unused license.
Warning
License Center will use this license to extend your expiring license. This process is irreversible.
Once this license is used for extension, you cannot use it for anything else.
5. Click Extend.
License Center extends the license.
A conrmation message appears.
6. Click Close.
Extending a License Oine Using an Unused License
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Identify the license you want to extend, and then click .
Tip
If a license is about to expire, its status is Expires soon.
The License Extension window appears.
4. Select manually extend a license.
5. Select Extend oine.
6. Click Next.
7. Read the instructions, and then click Download.
License Center downloads the device identity le (DIF) le to your computer.
8. Read and agree to the terms of service.
9. Click Next.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 435

10. Read the instructions, and then click Go to License Manager.
Your web browser opens the QNAP License Manager website.
11. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
12. Go to My Licenses.
13. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to activate.
14. In the table below, click Activation and Installation.
The license activation details appear.
15. Click Extend.
The Extend License window appears.
16. Select Use an unused license, and then click Next.
The list of unused licenses appears.
17. Select an unused license.
Warning
License Center will use this license to extend your expiring license. This process is irreversible.
Once this license is used for extension, you cannot use it for anything else.
18. Click Next.
19. Click Browse.
The le browser appears.
20. Locate and select the DIF from your computer.
21. Click Upload.
A conrmation message appears.
22. Click Download.
QNAP License Manager downloads the license install le (LIF) to your computer.
23. Click Done.
24. Go back to License Center.
25. In the License Extension window, click Next.
26. Click Browse Files.
The le browser appears.
27. Locate and select the LIF from your computer.
28. Click Next.
License Center uploads the LIF and displays the license summary.
29. Click Extend.
A conrmation message appears.
30. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
Extending a License Oine Using a Product Key
1. Open License Center.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 436

2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Identify the license you want to extend, and then click .
Tip
If a license is about to expire, its status is Expires soon.
The License Extension window appears.
4. Click manually extend a license.
5. Select Extend oine.
6. Click Next.
7. Read the instructions, and then click Download.
A notication message appears.
8. Click Download.
License Center downloads the device identity le (DIF) le to your computer.
9. Read and agree to the terms of service.
10. Click Next.
11. Read the instructions, and then click Go to License Manager.
Your web browser opens the QNAP License Manager website.
12. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
13. Go to My Licenses.
14. From the list of licenses, select the license you want to activate.
15. In the table below, click Activation and Installation.
The license activation details appear.
16. Click Extend.
The Extend License window appears.
17. Select Use a product key, and then click Next.
18. Specify the product key.
19. Click Next.
A conrmation message appears.
20. Click Download.
QNAP License Manager downloads the license install le (LIF) to your computer.
21. Click Done.
22. Go back to License Center.
23. In the License Extension window, click Next.
24. Click Browse Files.
The le browser appears.
25. Locate and select the LIF from your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 437
26. Click Next.
License Center uploads the LIF and displays the license summary.
27. Click Extend.
A conrmation message appears.
28. Click Close.
The license appears on the list of active licenses.
Upgrading a License
Before upgrading a license, ensure the following.
• The application is already installed on your device.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
Users can upgrade their existing basic licenses to premium licenses to gain access to advanced features.
1. Open your web browser.
2. Go to https://software.qnap.com.
3. Click your account name and select MY ACCOUNT.
4. Click Upgrade Plans.
A list of upgradable subscriptions is displayed.
5. From the list of subscriptions, nd the license you want to upgrade and click Upgrade.
The Current Plan window appears.
6. From the list of upgrade plans, select an upgrade and click Add to Cart.
7.
Click .
8. Click GO TO CHECKOUT.
9. Select a payment method.
Payment Method User Action
Credit card a. Specify your card information.
b. Verify the items and the price on the order.
c. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
d. Click Place Order.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 438
Payment Method User Action
PayPal a. Verify the items and the price on the order.
b. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
c. Click Pay with PayPal
PayPal authentication window appears.
d. Specify your PayPal login credentials.
e. Click Next.
f. Follow PayPal instructions to complete the payment.
Google Pay a. Verify the items and the price on the order.
b. Agree to QNAP terms and conditions.
c. Click Buy with Google Pay.
Google Pay authentication window appears.
d. Follow Google Pay instructions to complete the payment.
10. Apply the license upgrade to your QNAP device.
a. Open your web browser.
b. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
c. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
d. Locate the license from the license list.
e. Click .
The Activate Upgraded License window appears.
f. Select Online Activation
g. Click Next.
h. Specify your credentials on the device.
i. Click Allow.
A conrmation message appears.
j. Click Close.
The upgraded license is activated.
Viewing License Information
1. Open your web browser.
2. Go to https://license.qnap.com.
3. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
4. View the license information using one of the following modes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 439
Viewing Mode User Actions
List by Device This mode displays all the activated licenses on each device. This allows
you to quickly view and manage your licenses on a specic device.
• Click a device and then click Device Details to view the details of the
selected device.
• Click a device and then click Activation and Installation to view the
details of your licenses. You can also activate or deactivate licenses.
List by License This mode displays your purchased licenses and their details, including
available seats, license types, validity period, and status.
• Click a license and then click License Details to view the details.
• Click a license and then click Activation and Installation to view the
details. You can also activate licenses, deactivate licenses, download
the license le, or upload the device identity le.
• Click a license and then click Usage Record to view the history of the
selected license.
List by Product This mode displays your purchased licenses for each product. This allows
you to view and manage all related licenses designed for the same
product.
• Click a product to view the details of your licenses. You can also
activate licenses, deactivate licenses, download the license le, or
upload the device identity le.
Recovering Licenses
Before recovering licenses, ensure that your device is connected to the internet.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to Recover Licenses.
3. Click Get Started.
The License Recovery dialog box appears.
4. Read and agree to the terms of service.
5. Click Recovery.
License Center automatically recovers all available licenses for applications installed on your devices.
Transferring a License to the New QNAP License Server
This task only applies to existing licenses that have been activated using PAK.
Before transferring licenses, ensure the following.
• Your NAS is connected to the internet.
• You are signed in to myQNAPcloud.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 440

3. Identify the license you want to transfer, and then click .
A conrmation message appears.
4. Read the terms of service, and then click Transfer & Activate.
Warning
After you register a license with your current QNAP ID, it will no longer be transferable.
License Center transfers the license.
A conrmation message appears.
5. Optional: Click QNAP License Manager to review the license details.
6. Click Close.
Deleting a License
Before deleting a license, ensure that you have deactivated this license.
1. Open License Center.
2. Go to My Licenses.
3. Identify the license you want to delete, and then click .
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click Yes.
License Center deletes the license.
Tip
If the license has not yet expired, the license will still be listed in the License Activation table.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Licenses 441
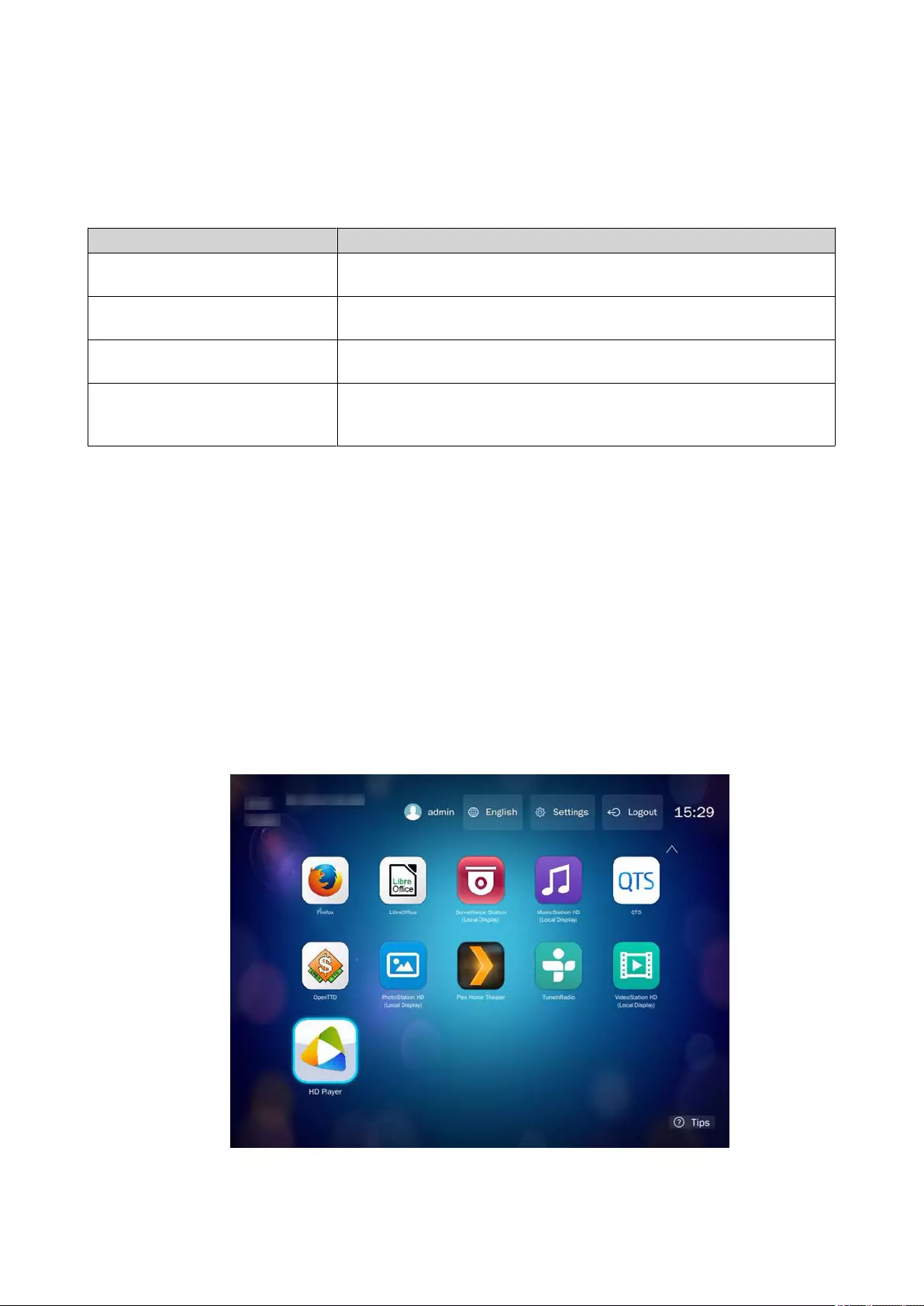
15. Multimedia
QTS provides a range of applications and utilities for viewing, playing, and streaming multimedia les stored
on the NAS.
Application/Utility Description
HybridDesk Station (HD Station) Connect to an HDMI display to access multimedia content on your
NAS.
DLNA Media Server Congure your NAS as a Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) server
to access media les on your NAS from devices on your home network.
Media Streaming Add-on Stream media from your NAS to DLNA, Chromecast, and HDMI-
connected devices.
Multimedia Console Manage multimedia apps and content on the NAS.
You can index les, transcode videos, and generate thumbnails for
multimedia content.
HybridDesk Station (HD Station)
HybridDesk Station (HD Station) allows you to connect to an HDMI display and directly access multimedia
content and use other applications on your NAS. You can use your NAS as a home theater, multimedia
player, or desktop substitute. After installing HD Station and connecting the NAS to an HDMI display, you can
navigate your NAS using HD Station.
HD Station requires:
• A TV or monitor with an HDMI port
• A mouse, keyboard, or remote control for navigation
• A graphics card (some NAS models only). Go to https://www.qnap.com to check the software
specications for your NAS and verify that it is compatible with HD Station.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 442
Installing HD Station
1. Go to Control Panel > Applications > HDMI Display Applications .
2. Choose one of the following installation methods.
Installation Method Steps
Guided installation a. Click Get Started Now.
The HybridDesk Station window appears.
b. Review the list of selected applications.
Tip
All applications are selected by default. You can
deselect applications that you do not want to install.
c. Click Apply.
Manual installation a. Under Install Manually, click Browse.
b. Select HD Station.
c. Click Install.
QTS installs HD Station and the selected applications.
Note
Multimedia Services must be enabled to play multimedia content in HD Station. Go to
Main Menu > Applications > Multimedia Console to enable Multimedia Services.
HD Player, Photo Station, Music Station, and Video Station must also be installed on the
NAS to play multimedia content from the respective applications.
Conguring HD Station
1. Go to Control Panel > Applications > HDMI Display Applications > Local Display settings .
2. Perform any of the following actions.
Action Steps
Enable HD Station Click Enable.
Note
HD Station must be disabled to perform this action.
Disable HD Station Click Disable.
Note
HD Station must be enabled to perform this action.
Install all HD Station applications a. Click Install All Apps.
A dialog box appears.
b. Click OK.
Update installed apps Click Update.
Restart HD Station Click Restart.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 443
Action Steps
Remove HD Station and related
applications
a. Click Remove.
A dialog box appears.
b. Click OK.
Edit HD Station settings a. Click Settings.
The Settings window appears.
b. Modify any of the following settings:
•Output resolution: Change the resolution of HD Station.
•Overscan: Reduce the visible area of a video displayed in
HD Station.
•Enable Remote Desktop: View the NAS HDMI output
using your web browser.
Note
• Enabling Remote Desktop may aect the
playback quality of local videos.
• You must restart Remote Desktop after
changing the output resolution.
Tip
You can also open and restart Remote Desktop from
this screen.
Install HD Station apps a. Under Install Manually, click Browse.
b. Select the application.
c. Click Install.
HD Station Applications
Go to App Center > HybridDesk Station to install or congure applications used with HD Station.
Using HD Player in HD Station
You can use HD Player to browse and play multimedia content in Photo Station, Music Station, and Video
Station.
1. Connect an HDMI display to the NAS.
2. Select your NAS account.
3. Specify your password.
4. Start HD Player.
5. Select your NAS account.
6. Specify your password.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 444
HDMI Local Display and DLNA Media Server
You can stream multimedia content to High-Denition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) display applications or
Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) devices. These services require you to enable Multimedia Services. To
enable Multimedia Services, go to Control Panel > Applications > Multimedia Console > Overview .
Enabling HDMI Display Applications
1. Log in as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Applications > HDMI Display Applications .
3. Locate the application you want to enable.
4. Optional: Congure the following settings.
a. Click Settings.
b. Congure the application settings.
Note
You may be required to update an application, connect a monitor, display to the NAS before
successfully applying the settings.
c. Click Apply.
5. Click Enable.
A conrmation window appears.
Note
A conrmation window only appears if you have another application enabled.
6. Click OK.
QTS enables the application.
Enabling DLNA Media Server
You can congure your NAS as a DLNA server, allowing you to access media les on your NAS through your
home network using DLNA devices such as TVs, smartphones, and computers.
The contents displayed in DLNA Media Server are based on user account permissions and Multimedia
Console settings.
Important
The rst time you enable DLNA Media Server, QTS automatically installs the Media
Streaming Add-on if it is not already installed on the NAS. For details, see Media Streaming
Add-on.
1. Go to Control Panel > Applications > DLNA Media Server .
2. Select Enable DLNA Media Server.
3. Optional: Specify the following information.
Field Description
Service Name Specify a name for the DLNA Media Server.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 445
Field Description
Select default user account Select the user account that will be the directory for the DLNA Media
Server.
4. Click Apply.
Conguring DLNA Media Server
1. Go to Control Panel > Applications > DLNA Media Server .
2. Perform any of the following actions.
Action Steps
Scan for multimedia content Click Scan now.
Restart DLNA Media Server Click Restart.
Congure advanced settings a. Click Advanced Settings.
The Media Streaming Add-on portal opens in a new browser
window.
b. Congure the settings.
Note
Media Streaming Add-on must be installed to
congure advanced settings. For details, see Media
Streaming Add-on.
Media Streaming Add-on
Media Streaming Add-on allows you to stream media from your NAS to dierent DLNA, Chromecast, and
HDMI-connected devices simultaneously using the following QTS multimedia applications:
• File Station
• Photo Station
• Music Station
• Video Station
Go to App Center to install Media Streaming Add-on.
Tip
You can restart Media Streaming Add-on anytime by clicking Restart on the home screen.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 446
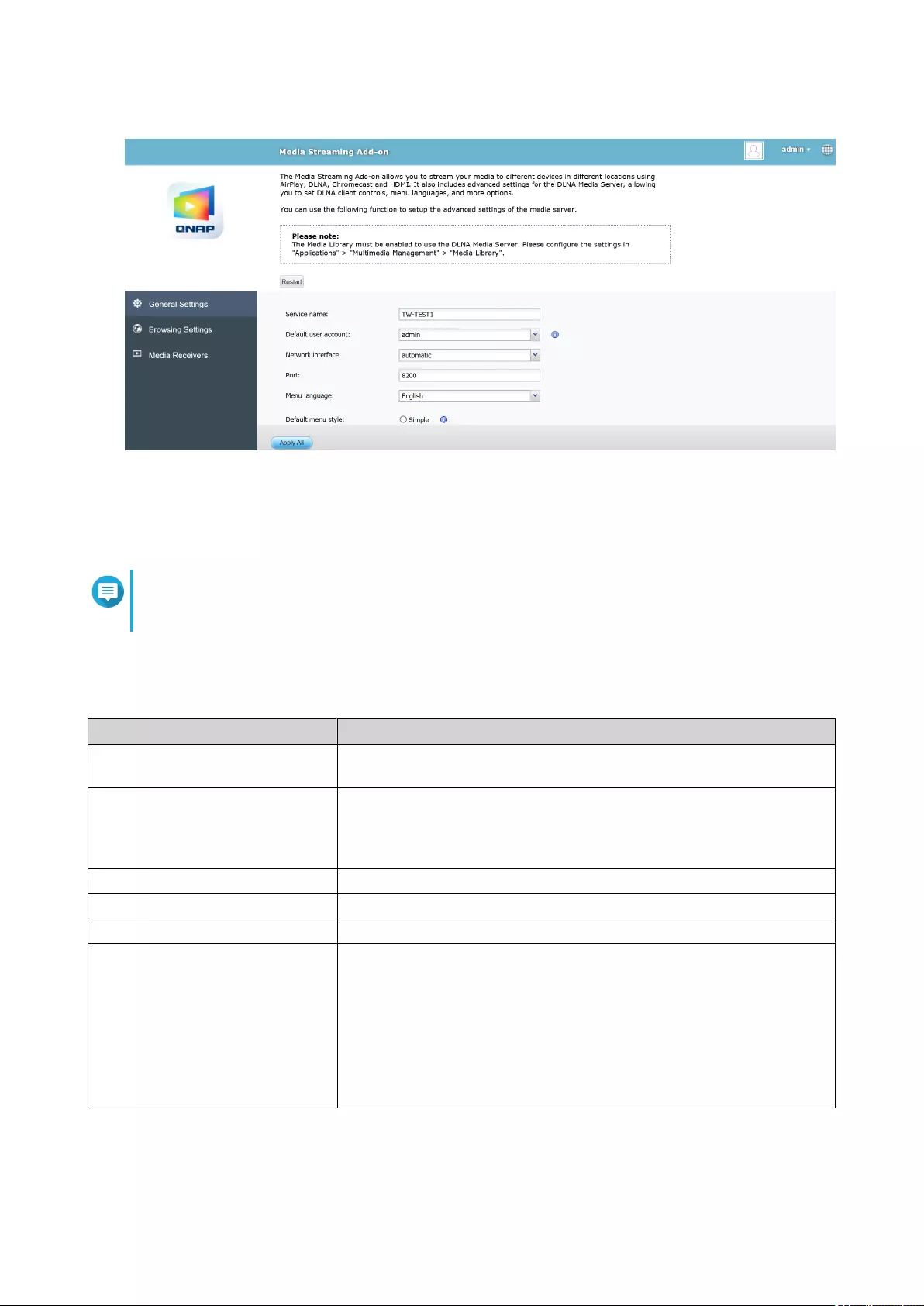
Conguring General Settings
1. Open Media Streaming Add-on.
Media Streaming Add-on opens in a new tab.
Note
Media Streaming Add-on logs you in based on your QTS user credentials. If a login screen
appears, you will need to specify your username and password to log in.
2. Go to General Settings.
3. Modify any of the following settings.
Setting Description
Service name This is the name that devices on the local network will see when
connecting to the NAS.
Default user account Select the user account that media devices receive content from.
To connect using a dierent user account, you must specify the
account's username and password in the connection settings of the
media receiver.
Network interface Select the network interface.
Port Specify the port number.
Menu language Select the language displayed for menu items.
Default menu style Select the type of menu style.
•Simple
•All categories
•Custom
Select one of the Custom options and click Customize to
congure the display options for the menu.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 447
Setting Description
Always stream videos to Apple
TV and Chromecast in original
le formats
When selected, the NAS streams videos to these devices without
transcoding or embedding subtitles.
Important
Ensure that Apple TV and Chromecast support the le
formats of videos on your NAS when selecting this
option.
4. Click Apply All.
Conguring Browsing Settings
1. Open Media Streaming Add-on.
Media Streaming Add-on opens in a new tab.
Note
Media Streaming Add-on logs you in based on your QTS user credentials. If you see a login
screen, you will need to specify your username and password and log in.
2. Go to Browsing Settings.
3. Modify any of the following settings.
Setting Description
Display Photo Select the display size of the thumbnail for photo albums.
Music title display style Select the type of information that is displayed for music les.
Video title display style Select whether video titles display the le name of the video or the
embedded information.
4. Click Apply All.
Conguring Media Receivers
1. Open Media Streaming Add-on.
Media Streaming Add-on opens in a new tab.
Note
Media Streaming Add-on logs you in based on your QTS user credentials. If you see a login
screen, you will need to specify your username and password and log in.
2. Go to Media Receivers.
3. Perform any of the following actions.
Action Steps
Enable device sharing Select Enable sharing for new media receivers automatically.
When enabled, newly discovered devices will automatically be
allowed to connect to DLNA Media Server.
Scan for new devices Click Scan for devices
Media Streaming Add-on searches for new media devices
connected to the NAS.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 448
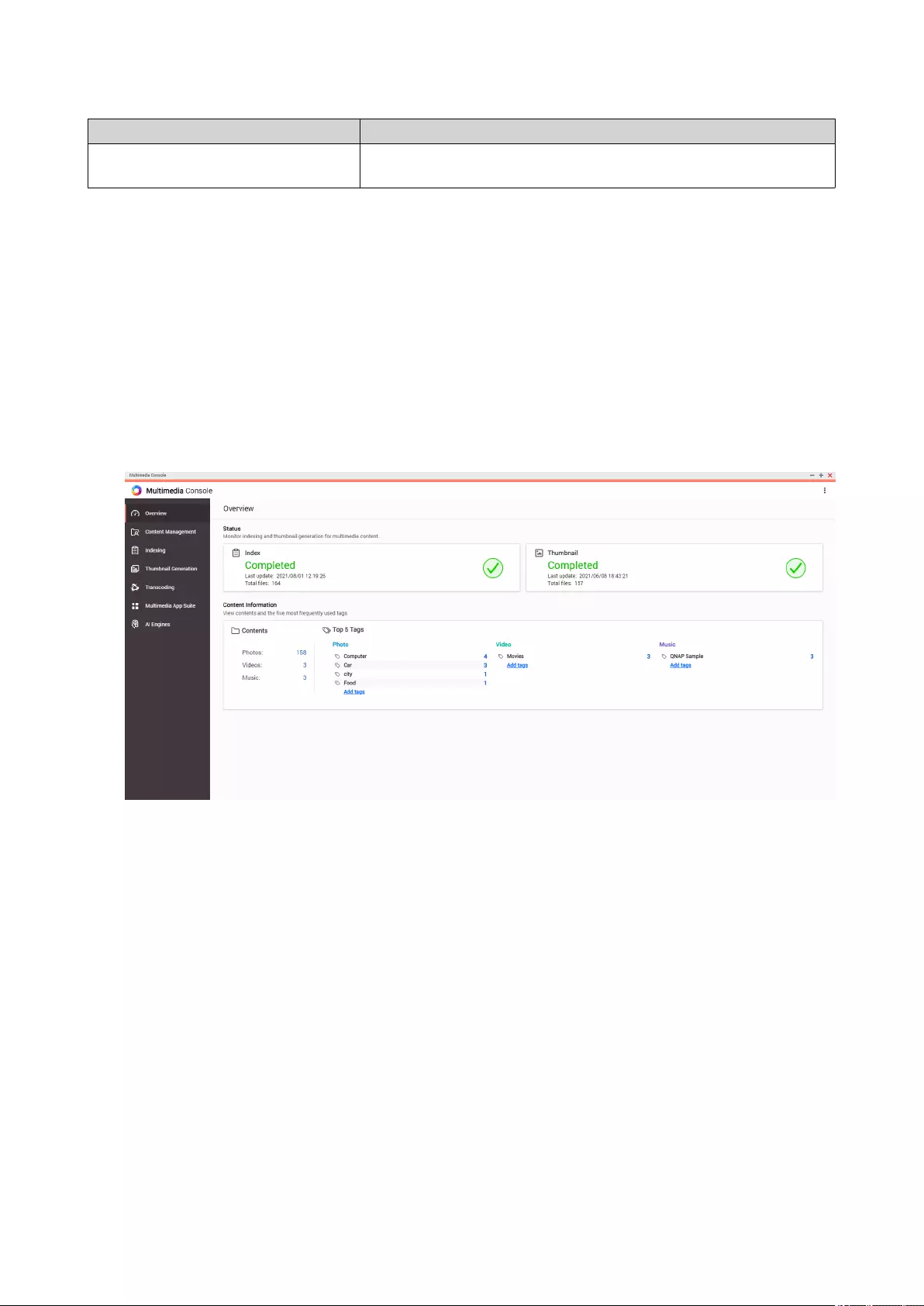
Action Steps
Modify device connections Select or deselect media devices.
Only selected devices can connect to DLNA Media Server.
4. Click Apply All.
Multimedia Console
Multimedia Console helps you manage installed multimedia apps and content stored on the NAS.
Multimedia Console can index les, transcode videos, and generate thumbnails for apps and system services
such as Photo Station, Video Station, Music Station, and DLNA Server.
Overview
The Overview screen displays the indexing and thumbnail generation status for multimedia les as well as
the total number of photos, videos, and music les on your NAS
Editing Content Sources
The Content Management screen displays the content source folders for multimedia apps installed on the
NAS. You can view and edit the content source folders for apps and system services such as Photo Station,
Video Station, Music Station, and DLNA Media Server.
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Content Management.
3. Select an app or service.
4. Click Edit.
The Edit Content Sources window appears.
5. Select or deselect content source folders.
The Selected Folder Paths list updates.
6. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 449

Tip
Click Excluded System Sources on the Content Management screen to view system folder
paths that are excluded from Multimedia Services.
Indexing Multimedia Content
Multimedia Console improves content management, browsing, and playback when accessing les in various
multimedia apps by scanning and indexing multimedia les on your NAS.
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Indexing.
3. Select the Priority.
•Low (Default)
•Normal
The Priority determines the amount of system resources allocated to the indexing process.
4. Select the type of Text encoding.
The type of Text encoding determines the character encoding scheme that Multimedia Console uses
to index text and data in your multimedia les. The default encoding scheme is Unicode.
5. Click Apply.
Tip
Click Re-index to rebuild the multimedia content database and revert dependent databases to
their default settings.
Generating Thumbnails for Multimedia Files
Multimedia Console generates thumbnails for multimedia les to improve browsing.
Note
• Thumbnail generation is enabled by default if Multimedia Services is enabled.
• You can disable thumbnail generation in the upper right of the screen.
• Generating thumbnails may aect system performance.
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Perform any of the following tasks.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 450
Task Steps
Pause thumbnail generation a. Go to Thumbnail Generation > Status .
b. Next to Progress, click Pause.
The Pause window opens.
c. Select Pause.
d. Click OK.
Tip
Click Resume when thumbnail generation is paused to
resume thumbnail generation.
Postpone thumbnail generation a. Go to Thumbnail Generation > Status .
b. Next to Progress, click Pause.
The Pause window opens.
c. Select Postpone.
1. Select the duration.
d. Click OK.
Tip
Click Resume when thumbnail generation is
postponed to resume thumbnail generation.
Remove thumbnails a. Go to Thumbnail Generation > Status .
b. Under Used, click Remove All Thumbnails.
A dialog box appears.
c. Click OK.
Regenerate thumbnails a. Go to Thumbnail Generation > Status .
b. Under Used, click Regenerate All Thumbnails.
A dialog box appears.
c. Click OK.
Option Description
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Schedule .
b. Select Generate in real time.
Multimedia Console generates thumbnails for new les as soon as
they are detected.
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Schedule .
b. Select Generate using
schedule.
Multimedia Console generates thumbnails according to a specied
schedule.
Note
When selected, you must specify a thumbnail
generation schedule.
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Schedule .
b. Select Generate manually.
Multimedia Console generates thumbnails only after clicking
Generate Now.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 451
Tip
Click Generate Now to force Multimedia Console to start generating thumbnails immediately.
Setting Description
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Advanced Settings .
b. Select Large thumbnails.
When selected, Multimedia Console generates high-resolution
thumbnails (2160 pixels) for media les.
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Advanced Settings .
b. Select Image quality.
Select High or Low.
Tip
Click See the dierence to view a side-by-side
comparison of high- and low-quality thumbnails.
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Advanced Settings .
b. Select Excluded le sizes.
Multimedia Console only generates thumbnails for images that are
larger than the specied resolution.
a. Go to Thumbnail Generation
> Advanced Settings .
b. Select Excluded le types.
Multimedia Console will not generate thumbnails for the selected le
types.
Transcoding
The transcoding feature in Multimedia Console converts video les to MPEG-4 format for improved
compatibility with media players on mobile devices, smart TVs, and web browsers. Transcoding can also
scale down the resolution of video les to prevent buering in slower network environments.
You can create and manage transcoding tasks and congure settings from the Transcoding screen in
Multmedia Console.
Managing Transcoding Tasks
You can manage Background Transcoding and On-the-Fly Transcoding tasks from the Overview tab on the
Transcoding screen.
Note
• Transcoding is only available for certain NAS models. Go to https://www.qnap.com/en/
compatibility to view specications for your NAS and verify that it is compatible.
• Transcoding uses additional NAS storage space to store transcoded les.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 452
Type Description
Background Transcoding Background Transcoding converts videos asynchronously to minimize
consumption of system resources if the video is accessed by multiple
users simultaneously.
The Background Transcoding tab displays the overall background
transcoding status as well as additional information about specic
background transcoding tasks. You can view and manage background
transcoding tasks from this tab.
You can manually add videos to background transcoding folders using
File Station, Photo Station, or Video Station.
For details on managing background transcoding folders, see
Conguring Background Transcoding Folders.
On-the-Fly Transcoding On-the-Fly Transcoding converts videos in real time as you watch
them.
The On-the-Fly Transcoding tab displays information about on-the-y
transcoding tasks. You can view and manage on-the-y transcoding
tasks from this tab.
Note
• You cannot specify the output format for On-the-
Fly Transcoding.
• On-the-Fly Transcoding uses more system
resources than Background Transcoding and may
aect the performance of your NAS.
Tip
You can install CodexPack to increase transcoding
speed and reduce system resource consumption.
You can check whether your NAS supports GPU-
acclerated transcoding on the Transcoding Settings
screen. For details, see Conguring Transcoding
Resources.
Conguring Transcoding Resources
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Transcoding > Settings > Transcoding Resources .
3. Optional: Enable GPU-accelerated transcoding.
a. Click GPU Management.
The System > Hardware > Graphics Card screen appears.
b. Congure graphics card settings.
4. Specify the Maximum CPU usage allocated to transcoding tasks.
5. Click Apply.
Conguring Background Transcoding Settings
1. Open Multimedia Console.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 453
2. Go to Transcoding > Settings > Background Transcoding .
3. Congure any of the following settings.
Setting Description
Transcode manually-added videos rst Videos in File Station, Video Station, and Photo Station
that are manually added will be transcoded rst.
Embed subtitles when transcoding Multimedia Console automatically embeds subtitles to
videos when transcoding them.
4. Click Apply.
Conguring Background Transcoding Folders
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Transcoding > Settings > Background Transcoding Folders .
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Congure the scanning schedule
for background transcoding
folders
Select one of the following options:
•Scan in real time: Multimedia Console scans background
transcoding folders for new les and adds the les as
background transcoding tasks as soon as they are detected.
•Scan using schedule: Multimedia Console scans background
transcoding folders for les according to a specied schedule.
Note
When selected, you must specify the time of day that
Multimedia Console generates thumbnails.
•Scan manually: Multimedia Console scans background
transcoding folders only when you click Scan Now.
Add a background transcoding
folder
a. Click Add.
The Add Background Transcoding Folders window appears.
b. Select a folder.
c. Specify the output format.
d. Click Apply.
Remove a background
transcoding folder
a. Select a background transcoding folder.
b. Click Delete.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 454
Task User Action
Congure transcoding output
format
a. Locate a background transcoding folder on the list.
b. Select the output format.
Note
Multimedia Console upscales the video if the selected
resolution is higher than the original resolution of the
video.
c. Click Apply.
Multimedia App Suite
You can view statuses and congure user and group access permissions for installed multimedia apps and
services from the Multimedia App Suite screen.
Conguring Multimedia Apps and Services
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Multimedia App Suite.
3. Perform any of the following tasks.
Task User Action
Install an app or service a. Locate an app or service with the status Not Installed under the
app or service name.
b. Click Not Installed.
The App Center and app installation windows open.
c. Click .
Enable an app or service a. Locate an app or service with the status Disabled under the app or
service name.
b. Click Disabled.
c. The app or service opens in a new window.
d. Enable the app or service.
Disable an app or service a. Locate an app or service with the status Enabled under the app or
service name.
b. Click Enabled.
c. The app or service opens in a new window.
d. Disable the app or service.
Conguring Multimedia App Permissions
1. Open Multimedia Console.
2. Go to Multimedia App Suite.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 455
3. Locate an app with access permissions.
4. Under Permissions, click the permission status.
The Permission Settings window opens.
5. Select a permission type.
Permission Type Description
All Users All users can access the app.
Local Administrator Group Only Only users in the local administrator group can access the app.
Custom Specied users and user groups can access the app.
A dialog box appears.
6. Click OK.
7. Perform any of the following actions.
Permission Type User Action
All Users Click Close.
Local Administrator Group Only Click Close.
Custom a. Select a user or user group type:
•Local
•Domain
b. Choose to deny or allow access to selected users or groups.
A dialog box appears.
1. Click OK.
c. Filter the list by users or groups.
Tip
Use the Search eld to quickly nd users or groups.
d. Select a user or group.
e. Click Add.
The user or group is added to the Selected Users/Groups list.
Tip
• Select a user or group and click Delete to remove
the user or group from the list.
• Click Delete All to remove all users or groups from
the list.
f. Click Save.
g. Click Close.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 456
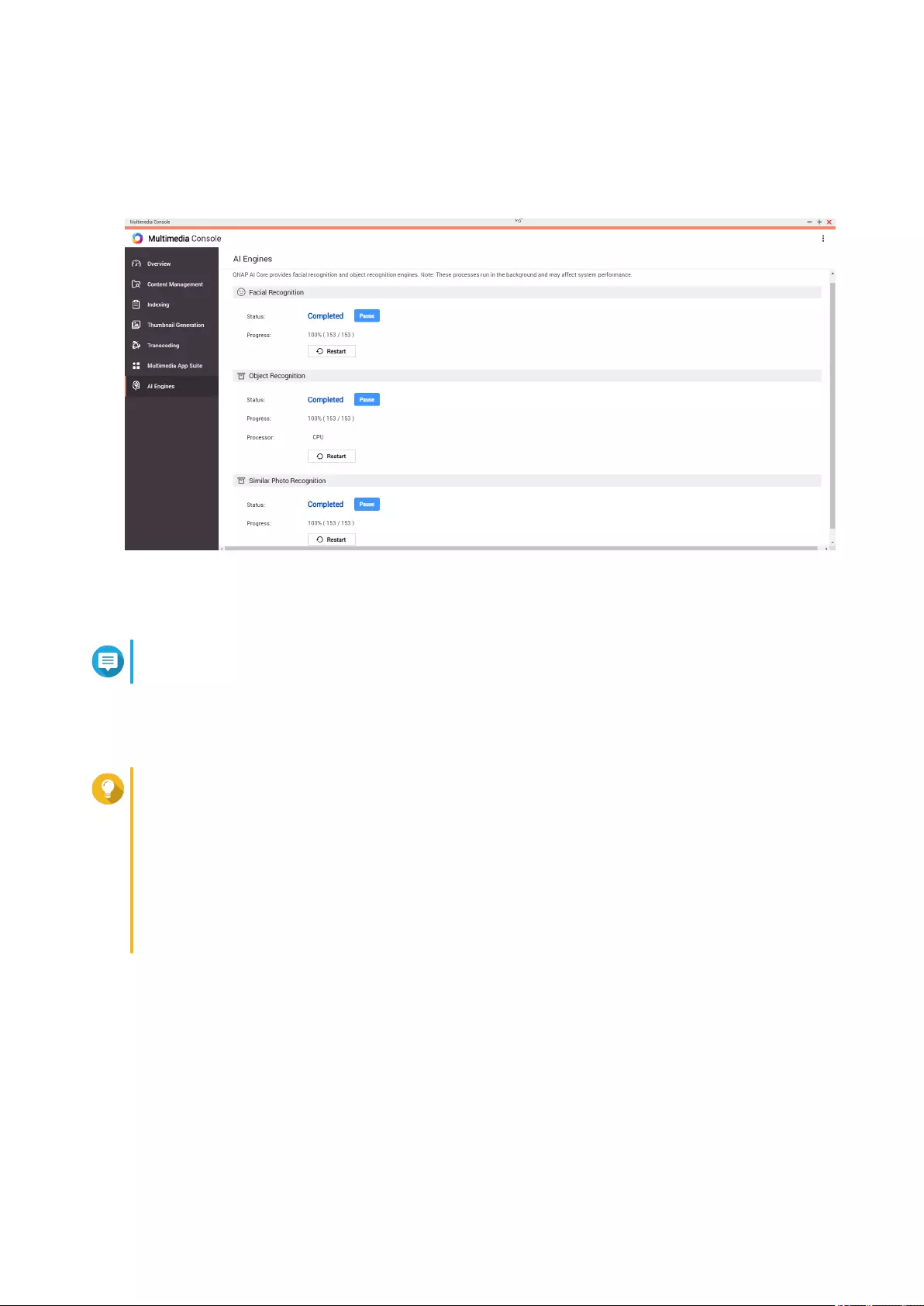
Installing and Managing AI Engines
QNAP AI Core provides facial and object recognition engines.
1. Install QNAP AI Core.
For details, see Installing an App from App Center.
Note
This process can take a while.
2. Open Multimedia Console.
3. Select AI Engines.
Tip
• QNAP AI Core supports Google TPU devices. To check if the Google TPU device is
successfully running on the NAS, go to Control Panel > System > Hardware > Hardware
Resources .
• You can check the status of the Google TPU device on the top right corner of the screen.
If QNAP AI Core is running the Google TPU device, the status changes to Google TPU:
Running. If the Google TPU device is not running, the status changes to Google TPU:
Stopped.
4. Locate an AI engine you want to manage and select one of the following options.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 457
Option User Action
Pause a. Click Pause.
The Pause window opens.
b. Select one of the following options.
•Pause: Pauses the engine now.
•Postpone: Pauses the engine after a specic time period.
Note
You can postpone by 1, 2, or 5 hours.
c. Click OK.
Restart a. Click Restart.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click OK.
QNAP AI Core pauses or restarts the AI engine.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Multimedia 458
16. QuLog Center
QuLog Center allows you to centrally manage and monitor logs from local devices and remote devices. You
can specify log lters, create notication rules, and congure log settings to stay informed of your device
status and important events. You can view and manage system logs in Control Panel > System > QuLog
Center .
Monitoring System Logs
The Overview screen provides statistical graphics to help you visualize system log data and monitor device
status.
System Event Log
The System Event Log tab provides the following widgets to visualize the statistical data of the system
event logs from your devices.
Important
You must congure a log destination to enable the system event log feature.
For details, see Conguring Event Log Settings.
Tip
The System Event Log page allows you to view log data from local devices or sender
devices. You can view data from all sender devices or view each device's information
separately. You can also specify the displayed statistics period.
Widget Description
Logs Over Time This widget displays a line chart to visualize the number of
log entries over time.
Tip
•Click to specify the event types that
you want to include in the line chart.
• Hover the mouse pointer over the line
chart to see the number of logs at a
particular point in time.
Top 5 Applications for Error Logs This widget displays the ve applications that have the
largest numbers of error log entries.
Top 5 Applications for Warning Logs This widget displays the ve applications that have the
largest numbers of warning log entries.
System Access Logs
The System Access Log tab provides the following widgets to visualize the statistical data of the system
access logs from your devices.
Tip
The System Access Log page allows you to view log data from local devices or sender
devices. You can view data from all sender devices or view each device's information
separately. You can also specify the displayed statistics period.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 459
Section Description
Logs Over Time This widget displays a line chart to visualize the number of log entries over time.
Tip
•Click to specify the event types that you want to include
in the line chart.
• Hover the mouse pointer over the line chart to see the
number of logs at a particular point in time.
Currently Online This widget lists the current online users and provides the information of their
user sessions.
Connection Types This widget displays a pie chart to visualize the numbers of user sessions for each
communication protocol.
Logged in This widget displays a pie chart to visualize the numbers of successful logins using
each IP address or user account.
Failed to log in This widget displays a pie chart to visualize the numbers of failed login attempts
using each IP address or user account.
Local Logs
Local Device Logs allows you to monitor system event logs, system access logs, and online user status on
one local device. You can also congure log lters, log settings, and remove event indicators.
Local System Event Logs
You can monitor and manage system event logs from local devices in Local Device > System Event Log .
Important
• You must congure a log destination to enable the local system event log feature.
For details, see Conguring Event Log Settings.
• QuLog Center can download or export a maximum of 10,000 log entries. You can use
log lters to specify the maximum number of log entries per le for download or
export.
For details, see Adding a Log Filter.
On the System Event Log screen, you can perform the following tasks:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 460
Task Steps
Select a group mode 1. Click .
2. Select one of the following grouping modes.
•No grouping: this mode displays and lists all log entries.
•By app: this mode groups log entries by app name.
•By date: this mode groups log entries by date.
•By content: this mode groups log entries by log content.
•By user: this mode groups log entries by users.
•By source IP: this mode groups log entries by source IP
address.
Select a display style 1. Click .
2. Select a display style.
Tip
You can also click Add Style to create a display style.
For details, see Conguring a Display Style.
Export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Export.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le formats.
4. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
5. Specify the destination shared folder for exporting logs.
a. Click Browse.
The Select a shared folder window appears.
b. Select a shared folder.
6. Click Export.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 461
Task Steps
Download export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Download.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le formats.
4. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
5. Click Download.
The log le is downloaded to your computer.
Perform a search 1. Specify keywords in the search eld.
2. Press Enter.
3. Optional:
Click Add as Customized Tab and specify a tab name.
This allows you to create a custom tab using the keywords and
criteria that you have specied. For details, see Creating a Custom
Filter Tab for System Event Log.
Select display items 1. Click .
2. Select the item category to display.
Create an event notication rule You can quickly create an event notication rule using a log entry. This
allows you to receive notications for events similar to the selected log
entry.
1. Locate a log entry.
2. Click .
3. Select Create event notication rule.
Notication Center opens and the Create event notication rule
windows appears.
For details, see Creating an Event Notication Rule.
Create an event ag rule 1. Locate a log entry.
2. Click .
3. Select Create Event Flag Rule.
The Create Event Flag Rule window appears.
4. Click Create.
The event is agged.
Go to Log Settings > Event Indicators to view all event ags.
Select all log entries 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Select all.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 462
Task Steps
Invert selection 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Invert selection.
Copy one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
The content of the selected log entries is copied to the clipboard
and can be pasted elsewhere.
Delete one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click Yes.
Local System Access Logs
You can monitor and manage system access logs from local devices in Local Device > System Access Log .
Important
• You must congure a log destination to enable the system access logs feature.
For details, see Conguring Access Log Settings.
• QuLog Center can download or export a maximum of 10,000 log entries. You can use
log lters to specify the maximum number of log entries per le for download or
export.
For details, see Adding a Log Filter.
On the System Access Log screen, you can perform the following tasks:
Task Steps
Select a group mode 1. Click .
2. Select one of the following grouping modes.
•No grouping: this mode displays and lists all log
entries.
•By date: this mode groups log entries by date.
•By user: this mode groups log entries by user.
•By source IP: this mode groups log entries by source IP
address.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 463
Task Steps
Select a display style 1. Click .
2. Select a display style.
Tip
You can also click Add Style to create a display
style.
For details, see Conguring a Display Style.
Export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Export.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le
formats.
4. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
5. Specify the destination shared folder for exporting logs.
a. Click Browse.
The Select a shared folder window appears.
b. Select a shared folder.
6. Click Export.
Download export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Download.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le
formats.
4. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
5. Click Download.
The log le is downloaded to your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 464
Task Steps
Perform a search 1. Specify keywords in the search eld.
2. Press Enter.
3. Optional:
Click Add as Customized Tab and specify a tab name.
This allows you to create a custom tab using the keywords
and criteria that you have specied.
For details, see Creating a Custom Filter Tab for Local
System Access Log.
Select display items 1. Click .
2. Select the item category to display.
Select all log entries 1. Select one log entry.
2. Click Select multiple entries.
The Select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
3. Click Select all .
All log entries are selected.
Invert selection 1. Select one log entry.
2. Click Select multiple entries.
The Select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
3. Click Invert selection.
Copy one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
The content of the selected log entries is copied to the
clipboard and can be pasted elsewhere.
Delete one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click Yes.
Add one or more log entry to the block
list
1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click Add to block list.
The Add to block list drop-down menu appears.
3. Select a block period option.
Online Users
On the Online Users screen, you can see the list of online users and their detailed information, such as login
date, login time, username, source IP address, computer name, connection type, and accessed resources.
You can perform the following tasks:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 465
Tasks Steps
Remove a connection 1. Locate a user from the list.
2. Right-click the user.
3. Select Disconnect.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Click Yes.
Block a user 1. Locate a user from the list.
2. Right-click the user.
3. Select Add to block list.
4. Select a block period option.
Remove the connection and block the
user
1. Locate a user from the list.
2. Right-click the user.
3. Select Disconnect and add to a block list.
A conrmation message appears.
4. Select a block period option.
Select the items to display on the list 1. Click .
2. Select the item category to display.
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for Local Device System Logs
You can create custom lter tabs for Local System Event Logs and Local System Access Logs. The customized
lter tabs can lter logs or user information based on specied keywords or criteria. For details, see the
following topics:
•Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log
•Creating a Custom Filter Tab for Local System Access Log
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Local Device > System Event Log .
3. Go to the search bar.
4. Click .
The Advanced Search window appears.
5. Specify the following lter elds:
Fields Steps
Severity Level a. Click .
The severity level drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a severity level option.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 466
Fields Steps
Application a. Click .
The application drop-down menu appears.
b. Select an application.
The Category option appears.
Note
The Category option only appears when you specify the
application.
c. Specify the application Category.
Date a. Click .
The date drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a date option.
Content a. Click .
The content condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the content keywords.
User a. Click .
The user condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Source IP a. Click .
The source IP address condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the source IP address.
6. Optional: Click Reset to clear all search lters.
Respecify search lters as many times as required.
7. Click Search.
The list of ltered results is displayed.
8. Click Add as Customized Tab.
The Add as Customized Tab window appears.
9. Enter a tab name.
10. Click Apply.
• The custom lter tab is created.
• The custom lter tab is displayed next to the Main tab.
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for Local System Access Log
1. Open QuLog Center.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 467
2. Go to Local Device > System Access Log .
3. Go to the search bar.
4. Click .
The Advanced Search window appears.
5. Specify the following lter elds:
Fields Steps
Severity Level a. Click .
The severity level drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a severity level option.
Accessed Resources a. Click .
The content condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Date a. Click .
The date drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a date option.
Connection type a. Click .
The connection type option appears.
b. Select a connection type.
User a. Click .
The user condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Action a. Click .
The action drop-down menu appears.
b. Select an action option.
Source IP a. Click .
The source IP address condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the source IP address.
6. Optional: Click Reset to clear all search lters.
Respecify search lters as many times as required.
7. Click Search.
The list of ltered results is displayed.
8. Click Add as Customized Tab.
The Add as Customized Tab window appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 468
9. Enter a tab name.
10. Click Apply.
• The custom lter tab is created.
• The custom lter tab is displayed next to the Main tab.
Local Log Settings
Log Settings allows you to congure the following types of settings: event logs, access logs, display styles,
and event indicators.
Conguring Event Log Settings
You can specify the database size and the log language or delete all the log entries for system event logs.
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Local Device > Log Settings > Event Log Settings .
3. Specify the following settings:
Settings Steps
Destination a. Click .
The log destination option drop-down menu
appears.
b. Select a log destination.
Important
• You must congure a log
destination to enable event logging
features.
• You cannot select a volume that is
encrypted or has less than 10% of
free volume space.
Maximum number of entries a. Click .
The maximum number of entries option drop-
down menu appears.
b. Select the maximum number of entries allowed.
The log database size is specied.
Log retention time a. Click .
The log retention time drop-down menu
appears.
b. Select the log retention time.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 469
Settings Steps
Archive overow log entries to a standby log
destination
a. Click Archive and move log entries to
the specied location after reaching the
database limit.
The destination folder option is activated.
b. Click Browse.
The Select a shared folder window appears.
c. Select a shared folder.
d. Click OK.
The shared folder is selected as the standby log
destination.
4. Optional: Delete all event logs.
a. Click Delete All Event Logs.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Yes.
Warning
You cannot restore deleted logs.
5. Select the log language.
a. Click .
The log language drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a language.
6. Click Apply.
Conguring Access Log Settings
You can specify the database size, log retention time, connection type or delete all system access log entries.
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Local Device > Log Settings > Access Log Settings .
3. Specify the following settings:
Settings Steps
Destination a. Click .
The log destination option drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a log destination.
Important
• You must congure a log destination to enable
event logging features.
• You cannot select a volume that is encrypted or
has less than 10% of free volume space.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 470
Settings Steps
Maximum number of entries a. Click .
The maximum number of entries option drop-down menu
appears.
b. Select the maximum number of entries allowed.
Log retention time a. Click .
The log retention time drop-down menu appears.
b. Select the log retention time.
Connection Types Select the connection types you want to log.
Tip
You can select multiple connection types.
4. Optional: Delete all event logs.
a. Click Delete All Access Logs.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Yes.
Warning
You cannot restore deleted logs.
5. Click Apply.
Conguring a Display Style
You can customize your log display style to enhance readability or to highlight certain entries.
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Open Display Settings through one of the following methods:
Accessing Display Setting Method Steps
System Event Log Go to Local Device > System Event Log > Display style .
System Access Log Go to Local Device > System Access Log > Display style .
3. Click .
The display style drop-down menu appears.
4. Click Settings.
The Display Style Settings window appears.
5. Perform one or more of the following tasks:
Task Steps
Add a display style a. Click Add Style.
The Add Style window appears.
b. Specify a name for the style.
c. Click Apply.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 471
Task Steps
Delete a style a. Select a display style.
b. Click Delete Style.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Yes.
Add a rule to a display style a. Select a display style.
b. Click Add Rule.
The Style Rule window appears.
c. Select a eld.
d. Select a keyword.
e. Select one or more formatting eects.
Tip
You can instantly preview the results of the selected
formatting eects.
f. Click Apply.
Edit a rule a. Select a display style.
b. Select a rule from the list.
c. Click Edit.
The Style Rule window appears.
d. Select a eld.
e. Specify the condition.
f. Select one or more formatting eects.
Tip
You can instantly preview the results of selected
formatting eects.
g. Click Apply.
Remove a rule a. Select a display style.
b. Select a rule from the list.
c. Click Delete.
A conrmation message appears.
d. Click Yes.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 472
Task Steps
Specify the priority of rules a. Select a display style.
b. Select a rule from the list.
c. Beside Priority, click or to change its priority.
Note
The formatting results of rules with a higher priority
overwrite those with a lower priority.
Removing Event Indicators
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Local device > Log Settings > Event Indicators .
3. Select an event ag rule.
Tip
Click the box in the top left column to select all event ag rules.
4. Click Remove or .
The event ag rule is removed.
QuLog Service
QuLog Service allows you to centrally manage logs from multiple remote devices. You can congure a single
device as a Log Receiver to manage and monitor all incoming system logs from other devices, or congure
the device as a Log Sender that sends all system logs to a remote QuLog Center.
Conguring Log Sender Settings
The Log Sender allows you to send system event logs and system access logs on the local device to a remote
QuLog Center or Syslog Server.
Adding a Destination IP Address
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Select one of the following options:
Options User Actions
Send to QuLog Center a. Go to QuLog Service > Log Sender > Send to QuLog
Center .
b. Enable Send logs to a remote QuLog Center.
System event logs and access logs from the local device are
sent to a remote QuLog Center.
Send to Syslog Server a. Go to QuLog Service > Log Sender > Send to Syslog
Server .
b. Enable Send logs to a remote syslog server.
System event logs and access logs from the local device are
sent to a remote syslog server.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 473
3. Click Add Destination.
The Add Destination window appears.
4. Specify the following IP address information:
•Destination IP
Tip
You can enter the destination IP address manually or click Search to automatically select a
device from your local network. This option is only available for sending logs to a remote
QuLog Center.
•Port
•Transfer protocol
•Log type
•Format
Note
You can click Send a Test Message to test the connection. This option is only available for
sending logs to a remote QuLog Center.
5. Click Apply.
Editing a Destination IP Address
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Log Sender.
3. Select Send to QuLog Center or Send to Syslog Server.
4. Select a destination IP address.
5. Click .
The Edit Destination window appears.
6. Edit the IP address information.
For details, see Adding a Destination IP Address.
7. Click Apply.
Sending a Test Message
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Select one of the following options:
Methods Actions
Add Destination IP Address Add a destination IP address.
For details, see Adding a Destination IP Address
Send a Test Message a. Select a destination IP address.
b. Click Send a Test Message.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 474

Methods Actions
Click .
A test message is sent to the destination IP address to test the network connection.
Removing a Destination IP Address
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Sender .
3. Select Send to QuLog Center or Send to Syslog Server.
4. Select one or multiple destination IP addresses.
5. Click Remove or .
A conrmation message window appears.
6. Click Yes.
The destination IP address is removed.
Conguring Log Reciever Settings
The Log Reciever allows you to congure a local device as the recipient of remote device logs. You can
centrally manage and monitor system event logs and access logs from remote QNAP devices. Additionally,
you can congure customized lters to search for logs eciently.
Conguring Log Receiver General Settings
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Receiver > General Settings .
3. Select Receive logs from a remote QuLog Center.
4. Select transfer protocols and then specify the port number.
Note
QuLog Center supports TCP and UDP protocols.
5. Optional: Click Enable Transport Layer Security (TLS).
6. Select System Event Log or System Access Log.
7. Specify the following settings:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 475
Settings Steps
Destination a. Click .
The log destination option drop-down menu
appears.
b. Select a log destination.
Important
You cannot select a volume that is
encrypted or has less than 10% of free
volume space.
Maximum number of entries a. Click .
The maximum number of entries option drop-
down menu appears.
b. Select the maximum number of entries allowed.
The log database size is specied.
Log retention time a. Click .
The log retention time drop-down menu
appears.
b. Select the log retention time.
Archive overow log entries to a standby log
destination
a. Click Archive and move log entries to
the specied location after reaching the
database limit.
The destination folder option is activated.
b. Click Browse.
The Select a shared folder window appears.
c. Select a shared folder.
d. Click OK.
The shared folder is selected as the standby log
destination.
Delete all event logs a. Click Delete All Event Logs.
A conrmation window appears.
Warning
You cannot restore deleted logs.
b. Click Yes.
8. Click Apply.
Log Filter Congurations
You can specify log lter conditions for system logs received from multiple sender devices on the Log
Receiver to simplify locating specic types of logs and monitoring large volume of logs.
Conguring a Log Filter Criterion
You can specify log lter criteria to choose the types of log entries that will be received by Log Receiver.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 476
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Receiver > Filter Criteria .
3. Select System Event Log or System Access Log.
4. Click Add Filter Criteria.
The lter criteria window appears.
5. Specify the following information:
Log Type Settings
System Event Log • Severity level
• User
• Source IP
• Application
• Category
• Content
• Hostname
System Access Log • Severity level
• User
• Source IP
• Accessed resources
• Hostname
• Connection type
• Action
6. Click Apply.
QuLog Center adds the specied log lter criteria.
Editing a Log Filter Criterion
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Receiver > Filter Criteria .
3. Go to System Event Log or System Access Log.
4. Select a lter criteria.
5. Optional: Click Reset to clear all lter criteria settings.
6. Click .
The Filter Criteria window appears.
7. Edit the log lter elds.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 477

For details, see Conguring a Log Filter Criterion.
8. Click Apply.
All changes are applied.
Deleting a Log Filter Criterion
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Receiver > Filter Criteria .
3. Select System Event Log or System Access Log.
4. Select a lter criteria.
5. Click .
A conrmation window appears.
6. Click Yes.
Importing a Custom Filter Criterion
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Log Receiver > Filter Criteria .
3. Click System Event Log or System Access Log.
4. Click Add Filter Criteria.
5. Go to Import custom lter criteria from the selected tab.
6. Click .
The custom lter criteria drop-down menu appears.
7. Select the custom lter tab from the drop-down menu.
Note
For details on how to create a custom lter tab, see the following topics:
•Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log on a Sender Device
•Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Access Log on a Sender Device
The selected custom lter criteria are applied to the log.
Viewing and Managing Remote Logs
You can view and manage remote logs under the Sender Devices section in QuLog Center. This section lists
all remote devices that send their logs to the QuLog Center on the local device. You can monitor logs from all
sender devices or from individual sender devices. QuLog Center can manage up to 500 sender devices on a
log receiver.
Managing System Event Logs on the Log Receiver
You can monitor and manage system event logs received by the Log Reciever in QuLog Service > All
Devices > System Event Log . You can also monitor system event logs from individual sender devices.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 478
Important
You must congure the log destination of the log receiver to enable this feature. For
details, see Conguring Log Receiver General Settings.
On the System Event Log screen, you can perform the following tasks:
Task Steps
Select a group mode 1. Click .
2. Select one of the following grouping modes.
•No grouping: this mode displays and lists all log entries.
•By app: this mode groups log entries by app name.
•By date: this mode groups log entries by date.
•By content: this mode groups log entries by log content.
•By user: this mode groups log entries by users.
•By source IP: this mode groups log entries by source IP
address.
•By Host Name: this mode groups log entries by the host
name.
Select a display style 1. Click .
2. Select a display style.
Tip
You can also click Add Style to create a display style.
For details, see Conguring a Display Style.
Create an event ag rule You can quickly create an event ag rule using a log entry. This allows
you to set event indicators for malware detection.
1. Locate a log entry.
2. Click .
3. Select Create event ag rule.
The Create Event Flag Rule window appears.
4. Click Create.
The log ag rule is created.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 479
Task Steps
Export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Export.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le formats.
4. Select the maximum number of log entries per le.
5. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
6. Specify the destination shared folder for exporting logs.
a. Click Browse.
The Select a shared folder window appears.
b. Select a shared folder.
7. Click Export.
Download export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Download.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le formats.
4. Select the maximum number of log entries per le.
5. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
6. Click Download.
The log le is downloaded to your computer.
Perform a search 1. Specify keywords in the search eld.
2. Press Enter.
3. Optional:
Click Add as Customized Tab and specify a tab name.
This allows you to create a custom tab using the keywords and
criteria that you have specied.
For details, see Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log on
the Sender Device.
Select display items 1. Click .
2. Select the items to display.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 480
Task Steps
Select all log entries 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Select all.
Invert selection 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Invert selection.
Copy one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
The content of the selected log entries is copied to the clipboard
and can be pasted elsewhere.
Delete one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click Yes.
Managing System Access Logs on the Log Receiver
You can monitor and manage system access logs received by the Log Receiver in QuLog Service > All
Devices > System Access Log . You can also monitor system access logs from individual sender devices by
clicking on the device.
Important
You must congure the log destination of the log receiver to enable this feature.
For details, see Conguring Log Receiver General Settings.
On the System Access Log tab, you can perform the following tasks:
Task Steps
Select a group mode 1. Click .
2. Select one of the following grouping modes.
•No grouping: this mode displays and lists all log entries.
•By date: this mode groups log entries by date.
•By user: this mode groups log entries by user.
•By source IP: this mode groups log entries by source IP.
•By Host Name: this mode groups log entries by host name.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 481
Task Steps
Select a display style 1. Click .
2. Select a display style.
Tip
You can also click and select Create a Style to create a
display style.
For details, see Conguring a Display Style.
Export logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs window appears.
2. Select an export le format.
3. Specify the maximum number of log entries per le.
4. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
5. Click Export.
Download exported logs 1. Click .
The Export Logs drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Download.
3. Select an export le format.
Note
QuLog Center supports CSV and HTML log le formats.
4. Select the maximum number of log entries per le.
5. Optional:
Compress the export le and specify a password.
6. Click Download.
The log le is downloaded to your computer.
Perform a search 1. Specify keywords in the search eld.
2. Press Enter.
3. Optional:
Click Add as Customized Tab and specify a tab name.
This allows you to create a custom tab using the keywords and criteria
that you have specied.
For details, see Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Access Log on
the Sender Device.
Select display items 1. Click .
2. Select the items to display.
Select all log entries 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Select all.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 482
Task Steps
Invert selection 1. Click Select multiple entries.
The select multiple entries drop-down menu appears.
2. Click Invert selection.
Copy one or more log entries 1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
The content of the selected log entries is copied to the clipboard and
can be pasted elsewhere.
Delete one or more log
entries
1. Select one or more log entries.
2. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
3. Click Yes.
Logging in a Sender Device
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Sender Devices .
3. Select a device.
4. Click Settings.
5. Specify the following:
•Host IP address
•Port
•Username
•Password
6. Optional: Select Secure login (HTTPS).
7. Click Sign in.
• You are logged into the sender device.
• All destination IP addresses of the sender device are listed.
• You can congure the destination for sender device logs.
For details, see Conguring Log Sender Settings.
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Event Log on a Sender Device
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Sender Devices .
3. Click on a sender device.
4. Go to System Event Log .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 483
5. Go to the search bar.
6. Click .
7. Specify the following lter elds:
Fields Steps
Severity Level a. Click .
The severity level drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a severity level option.
Application a. Click .
The application drop-down menu appears.
b. Select an application.
The Category option appears.
Note
The Category option does not appear if you select any
applications or do not specify the application.
c. Specify the application Category.
Date a. Click .
The date drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a date option.
Content a. Click .
The content condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the content keywords.
User a. Click .
The user condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Source IP a. Click .
The source IP address condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the source IP address.
8. Optional: Click Reset to clear all search lters.
Respecify search lters as many times as required.
9. Click Search.
The list of ltered results is displayed.
10. Click Add as Customized Tab.
The Add as Customized Tab window appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 484
11. Enter a tab name.
12. Click Apply.
• The custom lter tab is created.
• The custom lter tab is displayed next to the Main tab.
Creating a Custom Filter Tab for System Access Log on a Sender Device
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Sender Devices .
3. Click on a sender device.
4. Go to System Access Log .
5. Go to the search bar.
6. Click .
7. Specify the following lter elds:
Fields Steps
Severity Level a. Click .
The severity level drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a severity level option.
Accessed Resources a. Click .
The content condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Date a. Click .
The date drop-down menu appears.
b. Select a date option.
Connection type a. Click .
The connection type option appears.
b. Select a connection type.
User a. Click .
The user condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the keywords.
Action a. Click .
The action drop-down menu appears.
b. Select an action option.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 485

Fields Steps
Source IP a. Click .
The source IP address condition option appears.
b. Select a condition.
c. Specify the source IP address.
8. Optional: Click Reset to clear all search lters.
Respecify search lters as many times as required.
9. Click Search.
The list of ltered results is displayed.
10. Click Add as Customized Tab.
The Add as Customized Tab window appears.
11. Enter a tab name.
12. Click Apply.
• The custom lter tab is created.
• The custom lter tab is displayed next to the Main tab.
Conguring Event Indicators on the Sender Device
The event severity indicators on the device list are displayed according to the event severity level
(information, warning, and error) that occurs over a specied period. Only the highest severity level icon
is displayed when multiple events occur.
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Sender Devices .
3. Select a device.
4. Click Event Indicators.
5. Click .
The event period drop-down menu appears.
6. Select the event period.
Events that meet the specied criteria are listed in the Event Flag Rules table below.
Tip
You can remove event ag rules from the list.
Notication Settings
You can congure notication rules in Notication Center. You can also create lters for sending local NAS
system access logs, QuLog Service system event logs, and QuLog Service system access logs.
Conguring Notication Rule Settings
QuLog Center can send notications to recipients when the Log Receiver receives system event logs or
system access logs from the Log Sender.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 486
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Notication Settings.
3. Select the log types.
4. You can perform any of the following actions:
Setting Steps
Create a notication rule a. Click Congure Notication Rule.
Notication Center opens. Follow the instructions on the
Create event notication rule wizard to add an event
notication rule for QuLog Center.
For details, see Creating an Event Notication Rule.
Important
You must select the Log lter criteria option
in System Notication Rules when creating
QuLog Center notication rules for receiving
local device logs, QuLog Service system event
logs, and QuLog Service system access logs.
To enable the Log lter criteria option, go
to Notication Center > System Notication
Rules > QuLog Center > Log Filter Criteria .
b. Click Apply.
The notication rule is created.
Edit a notication rule Click .
Enable or disable a notication rule Click toggle.
Delete a notication rule a. Click .
A conrmation message window appears.
b. Click Yes.
The notication rule is deleted.
View notication history Click View notication history.
Notication Center opens and displays the QuLog Center
notication history page.
Adding a Log Filter
You can add lter criteria to local NAS system access logs, QuLog Service system event logs, and QuLog
Service system access logs. The ltered log results are sent to Notication Center.
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to Notication Settings.
3. Select a system log type.
4. Click Add Filter Criteria.
The lter criteria window appears.
5. Specify the following information:
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 487
Log Type Settings
System Event Log • Severity level
• User
• Source IP
• Application
• Category
• Content
• Hostname
System Access Log • Severity level
• User
• Source IP
• Accessed resources
• Hostname
Note
This option is only available for QuLog Service devices.
• Connection type
• Action
6. Click Apply.
The lter is applied to logs sent to Notication Center.
Editing a Log Filter
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Notication Settings .
3. Select a lter criteria.
4. Optional: Click Reset to clear all lter criteria settings.
5. Click .
The Filter Criteria window appears.
6. Edit the log lter criteria.
For details, see Adding a Log Filter.
7. Click Apply.
All changes are applied.
Removing a Log Filter
1. Open QuLog Center.
2. Go to QuLog Service > Notication Settings .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 488

3. Select a lter criteria.
4. Click .
A conrmation message window appears.
5. Click Yes.
The lter criteria is removed.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
QuLog Center 489
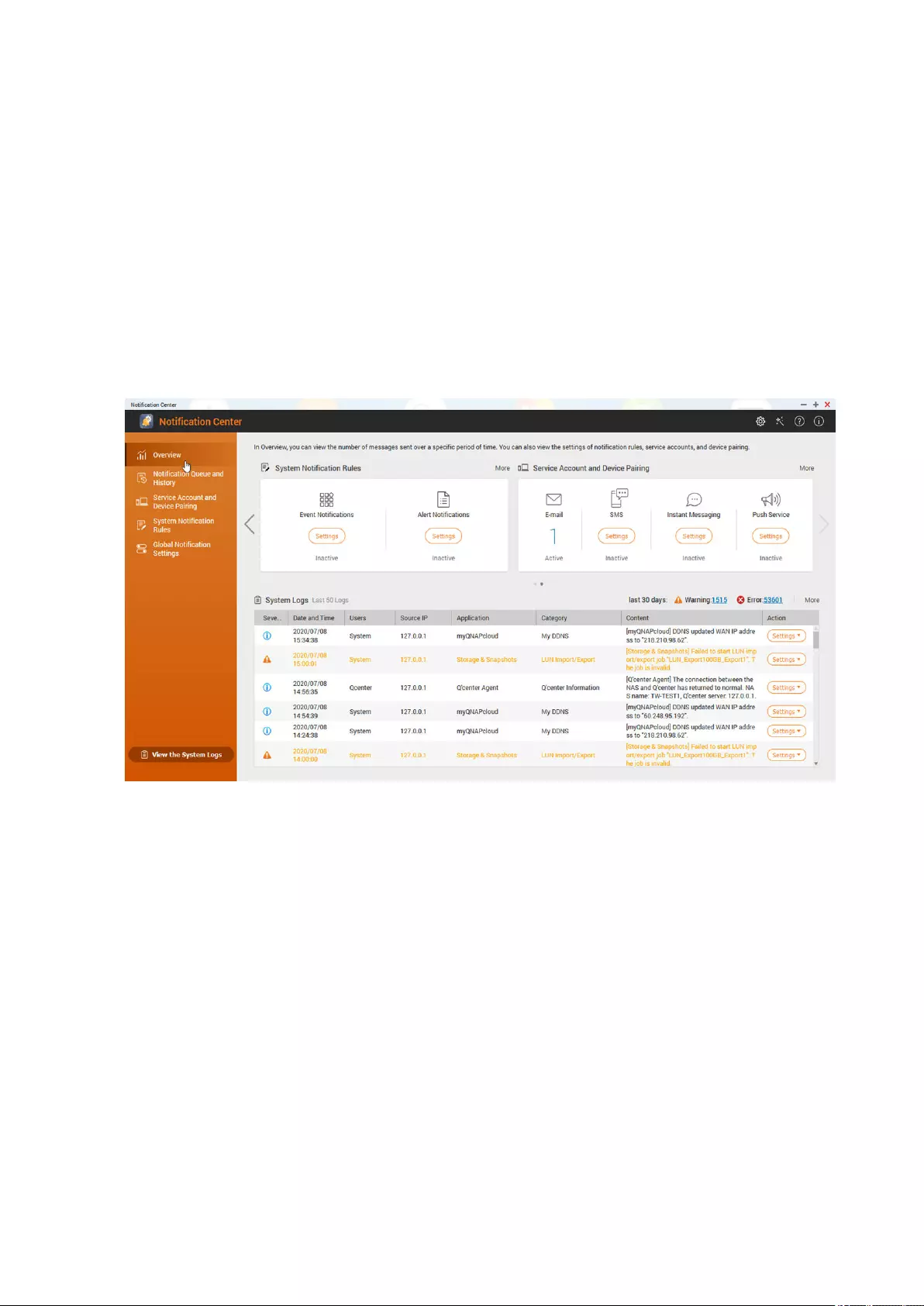
17. Notication Center
Notication Center consolidates all QTS notications to help you monitor the status of your NAS and its
applications and address potential issues more closely and promptly. You can send notications to recipients
through dierent channels including emails, SMS, instant messaging, and other push services. Notication
Center also lets you create custom notication rules and criteria, ensuring that you receive notications that
are most relevant to your needs.
Overview
The Overview screen displays the number of notications delivered over a specic period of time. It also
displays the number of notication rules, service accounts, and paired devices you congured.
Managing Notication Queue and History
Notication Center allows you to view notication queues and notication history. You can view pending
notication messages that Notication Center will send on the Queue screen, or go to the History screen to
view all delivered notication messages.
Queue
The Queue screen displays the messages that Notication Center is going to send. The required
transmission time depends on the current status of your device. You can remove a message from the queue
before it is sent. Messages removed from the queue will not appear in the History screen.
History
The History screen displays the messages that Notication Center has sent. You can view details, resend
messages, congure settings, and export the history as a CSV le. You can also specify how long notication
records are retained and where they are stored in Settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 490
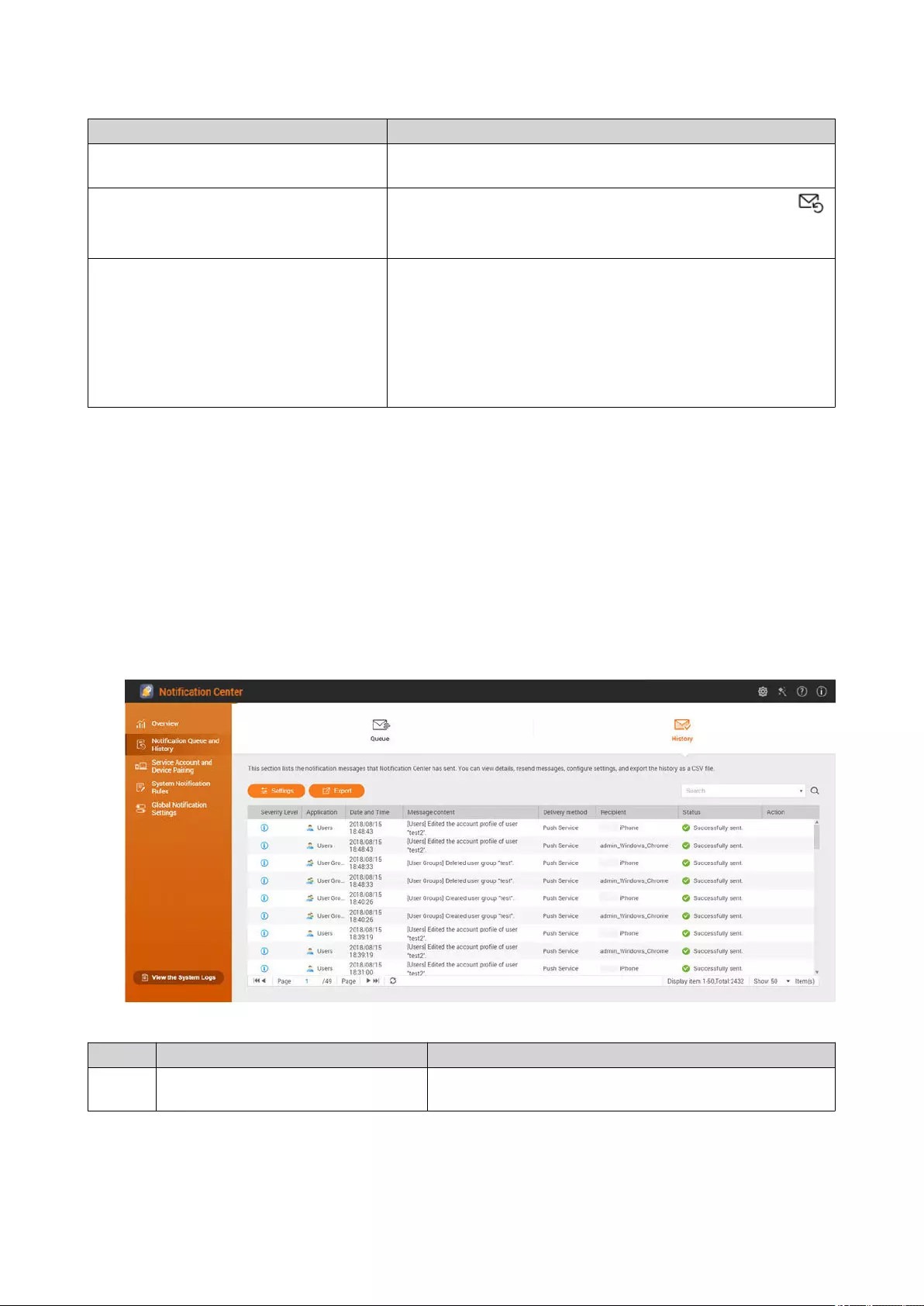
Tasks User Actions
Export the notication message history. Click Export.
Notication Center saves the CSV le on your computer.
Resend the notication. Identify the notication you want to resend, and then click .
This button only appears when Notication Center is unable to
send the notication to the recipient.
Congure the history settings. 1. Click Settings.
The Settings window appears.
2. Specify the maximum number of days Notication Center
retains notication records before deleting them.
3. Click Conrm.
Notication Center saves your settings.
Queue
The Queue screen displays the messages that Notication Center is going to send. The required
transmission time depends on the current status of your NAS. You can remove a message from the queue
before it is sent. Messages removed from the queue will not appear in the History screen.
History
The History screen displays the messages that Notication Center has sent. You can view details, resend
messages, congure settings, and export the history as a CSV le. In the settings, you can specify how long
your notication records are retained and where they are stored.
No. Task User Action
1 Export the notication message
history.
Click Export.
Notication Center saves the CSV le on your computer.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 491
No. Task User Action
2 Resend the notication. Identify the notication you want to resend, and then
click .
This button only appears when Notication Center is
unable to send the notication to the recipient.
Conguring History Settings
1. Open Notication Center.
2. Go to Notication Queue and History > History .
3. Click Settings.
The Settings window appears.
4. Congure the following information.
• Retention period: Specify the maximum number of days Notication Center retains notication
records before deleting them.
•Notication record storage: Select whether or not you want to keep notication records in a
specied local folder.
5. Click Conrm.
Notication Center saves your settings.
Service Account and Device Pairing
Service Account and Device Pairing allows you to congure the simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) and
short message service center (SMSC) settings so you can receive notications through email and SMS. You
can also pair your instant messaging accounts and devices with your NAS to receive notications through
instant messaging or push services.
Email Notications
The Email screen allows you to add and view email notication recipients and congure your simple mail
transfer protocol (SMTP) service settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 492
Button Task User Action
Send a test message to a specied
recipient.
1. Click .
2. Specify an email address.
3. Click Send.
Edit the congurations of an existing
email server.
1. Click .
The Edit SMTP Service Account
window appears.
2. Edit the email account settings.
3. Optional:
Click Re-authorization.
The congured email account is
authorized again.
4. Optional:
Click Authenticate with Browser
Station.
For details, see Pairing Notication
Center with a Web Browser.
5. Optional:
Click Set as the default SMTP
service account.
6. Click Conrm.
Remove an email server. 1. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
2. Click Conrm.
Conguring an Email Notication Server
1. Go to Service Account and Device Pairing > E-mail .
2. Click Add SMTP Service.
The Add SMTP Service window appears.
3. Select an email account.
4. Congure the following.
Service Providers User Actions
Outlook a. Click Add account.
The email account window appears.
b. Specify the email address that will act as the sender for QTS notications.
A conrmation message appears.
c. Click Allow.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 493
Service Providers User Actions
Gmail a. Click Add account.
The email account window appears.
b. Specify the email address that will act as the sender for QTS notications.
A warning notication appears.
c. Click Allow.
Yahoo Important
Before conguring the Yahoo Mail settings, do the following.
a. Log in to your Yahoo Mail account.
b. Go to Help > Account Info > Account Security .
c. Enable Allow apps that use less secure sign in.
Return to Notication Center and specify a valid Yahoo mail address and
password.
Custom a. Specify the domain name or the IP address of your SMTP service such as
smtp.gmail.com.
b. Specify the port number for the SMTP server. If you specied an SMTP port
when you congured the port forwarding settings, use this port number.
c. Specify the email address that will act as the sender for QTS notications.
d. Specify a username that contains a maximum of 128 ASCII characters.
e. Specify a password that contains a maximum of 128 ASCII characters.
f. Select one of the following secure connection options.
•SSL: Use SSL to secure the connection.
•TLS: Use TLS to secure the connection.
•None: Do not use a secure connection.
QNAP recommends enabling a secure connection if the SMTP server supports it.
Others Specify a valid email address and its account password.
Tip
To congure multiple email servers, click Add SMTP Service, and then perform the previous
steps.
5. Optional: Select Set as default SMTP service account.
6. Optional: Click .
The SMTP server sends a test email.
7. Click Create.
Notication Center adds the SMTP service to the list.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 494
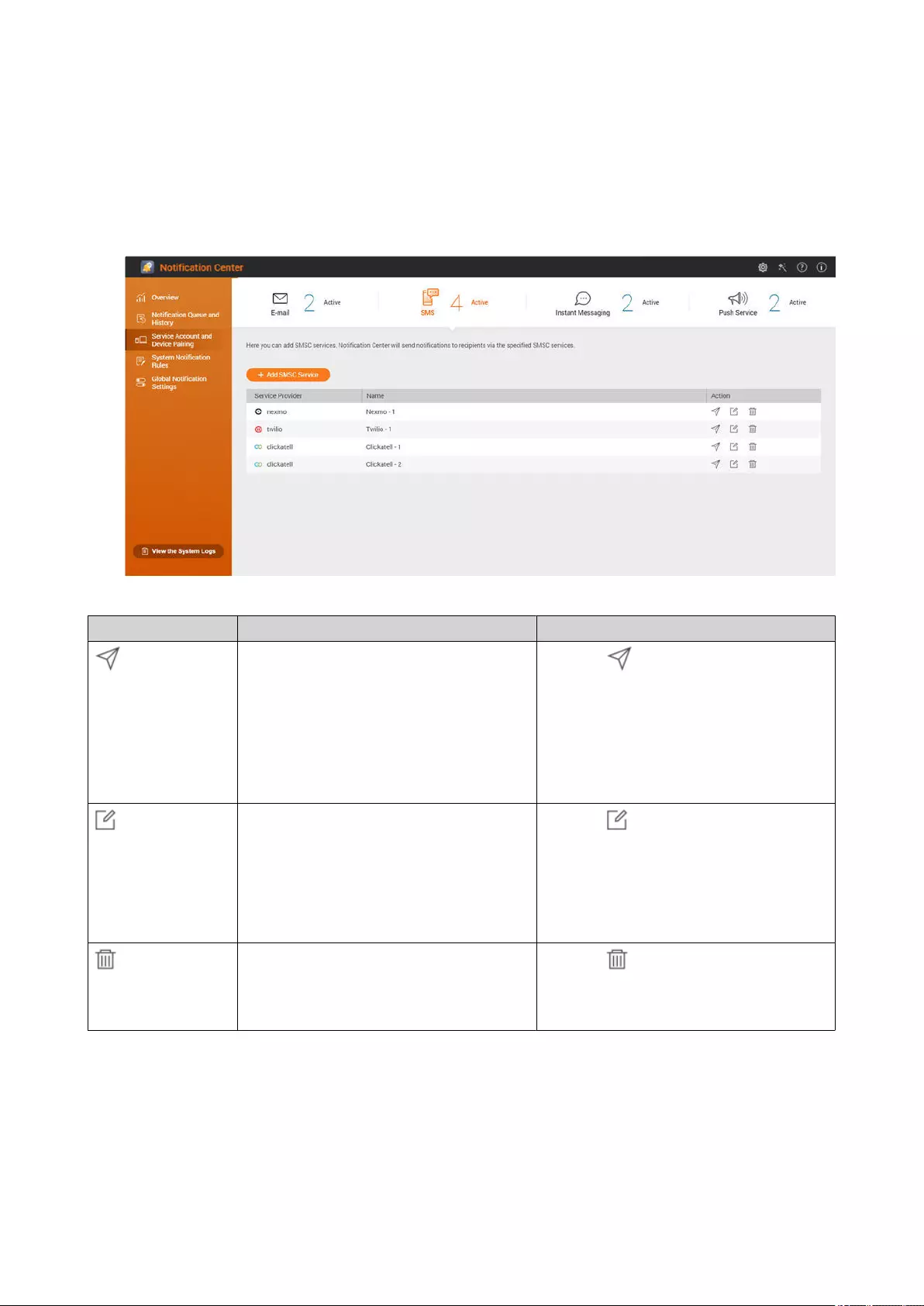
SMS Notications
The SMS screen allows you to view and congure your short message service center (SMSC) settings. You
can either congure a custom SMSC or use any of the currently supported SMS service providers: Clickatell,
Nexmo, and Twilio.
Button Task User Action
Send a test message to a specied
recipient.
1. Click .
The Send test message window
appears.
2. Specify a country code and phone
number.
3. Click Send.
Edit the congurations of an existing SMS
server.
1. Click .
The Edit SMSC Service Account
window appears.
2. Edit the settings.
3. Click Conrm.
Remove an email server. 1. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
2. Click Conrm.
Conguring an SMS Notication
1. Go to Service Account and Device Pairing > SMS .
2. Click Add SMSC Service.
The Add SMSC Service window appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 495
3. Select a service provider.
4. Specify an alias.
5. Specify the following information.
SMS Service Provider Information
Clickatell - Communicator/Central Clickatell username, password, and API ID
Clickatell - SMS Platform Clickatell API key
Nexmo Nexmo API key and secret question, and a sender name
The sender name can contain a maximum of 32 characters.
Twilio Your Twilio account SID, access token, and the Twilio-provided
phone number linked to your account
Custom • URL template text formatted according to the format specied
by your SMS service provider.
Use the following replaceable URL template parameters.
•@@UserName@@: Specify the username for this
connection.
•@@Password@@: Specify the password for this
connection.
•@@PhoneNumber@@: Specify the phone number where
the SMS messages are sent. This parameter is required.
•@@Text@@: Specify the text content of the SMS message.
This parameter is required.
Important
You will not be able to receive SMS messages if the
template text does not match the format used by
your SMS service provider.
• The name of the service provider. The name can contain a
maximum of 32 ASCII characters.
• A password. The password can contain a maximum of 32
ASCII characters.
Tip
To congure multiple SMS servers, click Add SMSC Service, and then perform the previous
steps.
6. Click .
The SMS server sends a test message.
7. Click Create.
Notication Center adds the SMTP service to the list.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 496
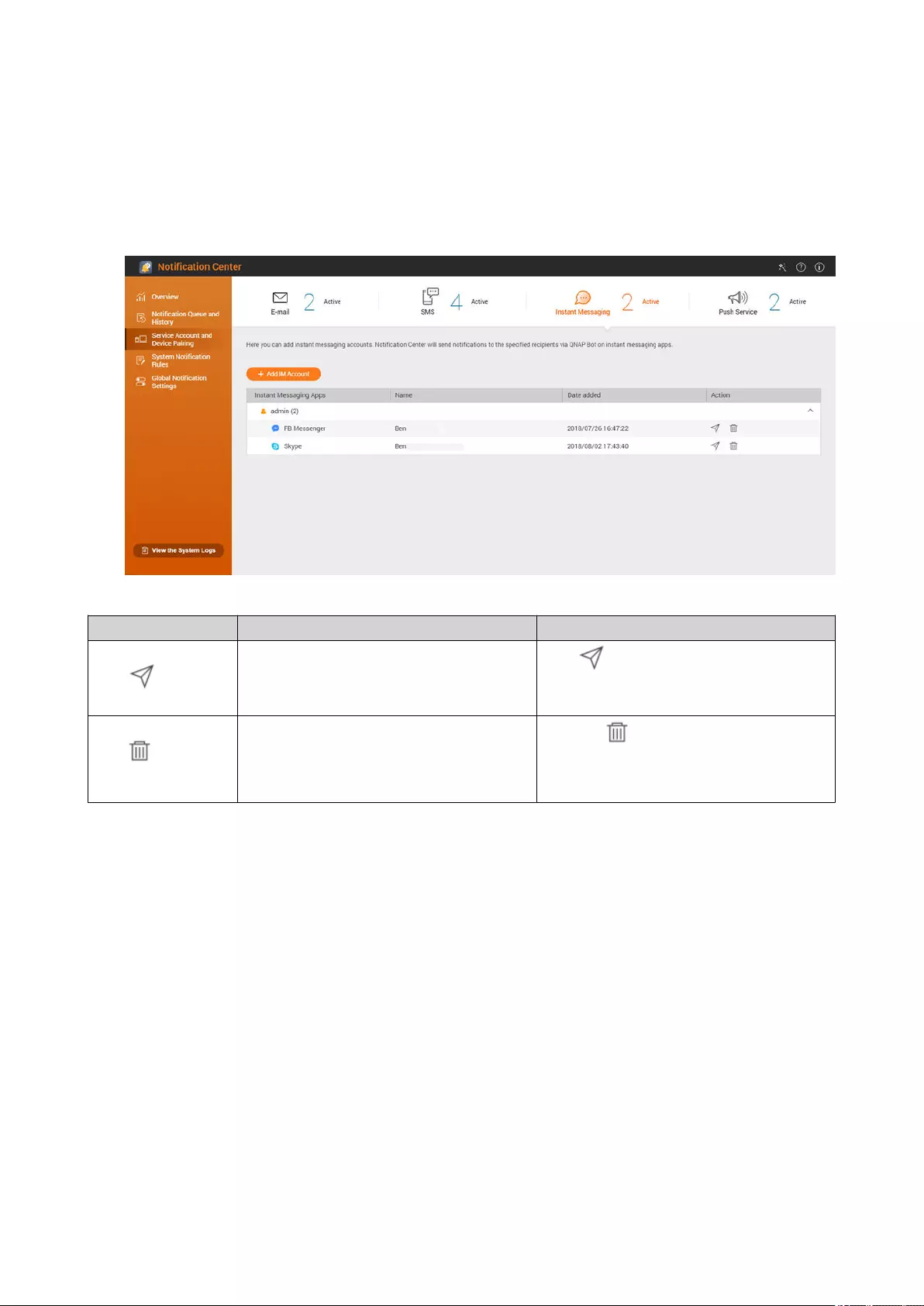
Instant Messaging Notications
The Instant Messaging screen allows you to pair Notication Center with instant messaging accounts
such as Skype and Facebook Messenger. Notication Center sends notications to the specied recipients
through QBot, the QNAP instant messaging bot account.
Button Task User Action
Send a test message. Click .
Unpair from and remove the instant
messaging account.
1. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
2. Click Conrm.
Pairing Notication Center with Skype
Before conguring Skype notications, ensure the following.
• Your NAS is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
• You have an active Skype account.
• Skype is installed on your device.
1. Go to Service Account and Device Pairing > Instant Messaging .
2. Click Add IM Account.
The Notication IM Wizard appears.
3. Select Skype.
The Add Bot to Contacts window appears.
4. Log in to the Skype account you want to pair.
Skype adds QNAP Bot as a contact.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 497

5. Close the Add Bot to Contacts window.
6. Click Next.
A verication code appears.
7. On Skype, enter the verication code.
Notication Center veries and pairs with the Skype account.
8. Click Finish.
Notication Center adds the Skype account to the list.
Pairing Notication Center with Facebook Messenger
Before conguring instant messaging (IM) notications, ensure the following.
• Your NAS is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
• You have an active Facebook Messenger account.
1. Go to Service Account and Device Pairing > Instant Messaging .
2. Click Add IM Account.
The Notication IM Wizard appears.
3. Select Facebook Messenger.
The Add Bot to Contacts window appears.
4. Log in to the Facebook Messenger account you want to pair.
Facebook Messenger adds QNAP Bot as a contact.
5. Click Get Started.
A verication code appears on the Notication IM Wizard.
6. On Facebook Messenger, enter the verication code.
Notication Center veries and pairs with the Facebook Messenger account.
7. Click Finish.
Notication Center adds the Facebook Messenger account to the list.
Push Notications
The Push Service screen allows you to congure push services for web browsers and mobile devices.
Notication Center supports pairing the application with multiple third-party push notication services.
Pairing Notication Center with a Mobile Device
Before starting pairing, ensure that the following requirements are met.
• Your NAS is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
• Qmanager iOS 1.8.0 or Qmanager Android 2.1.0 (or later versions) is installed on your mobile device.
• Your NAS is added to Qmanager.
1. Open Qmanager on the mobile device.
2. Perform one of the following.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 498
Pairing Option User Action
Automatic pairing a. From the device list, click the NAS you want to pair.
A conrmation message appears.
b. Click Conrm.
Manual pairing a. Identify your NAS from the device list, and then click .
The device settings screen appears.
b. Select Push notications.
c. Click Save.
A conrmation message appears.
d. Click Conrm.
Notication Center pairs with the mobile device.
3. In Notication Center, go to Service Account and Device Pairing > Push Service .
4. Verify that the mobile device appears in the list of paired devices.
Pairing Notication Center with a Web Browser
Before starting pairing, ensure that the following requirements are met.
• Your device is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
• You are using one of the following web browsers:
• Chrome 42 (or later versions)
• Firefox 50 (or later versions)
1. Go to Service Account and Device Pairing > Push Service .
2. Under Browser, click Pair.
Notication Center pairs with your current browser.
The browser appears in the list of paired devices.
3. Change your browser name.
a. Beside your browser name, click .
b. Specify a browser name.
The eld accepts a maximum of 127 ASCII characters.
c. Press ENTER.
Notication Center saves your browser name.
System Notication Rules
You can create and manage event notication rules to receive event notications promptly.
Managing Event Notication Rules
You can create custom rules and select applications and features that you want to receive event notications
from. You can also specify the message type, keywords, and time range to further dene notication types
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 499
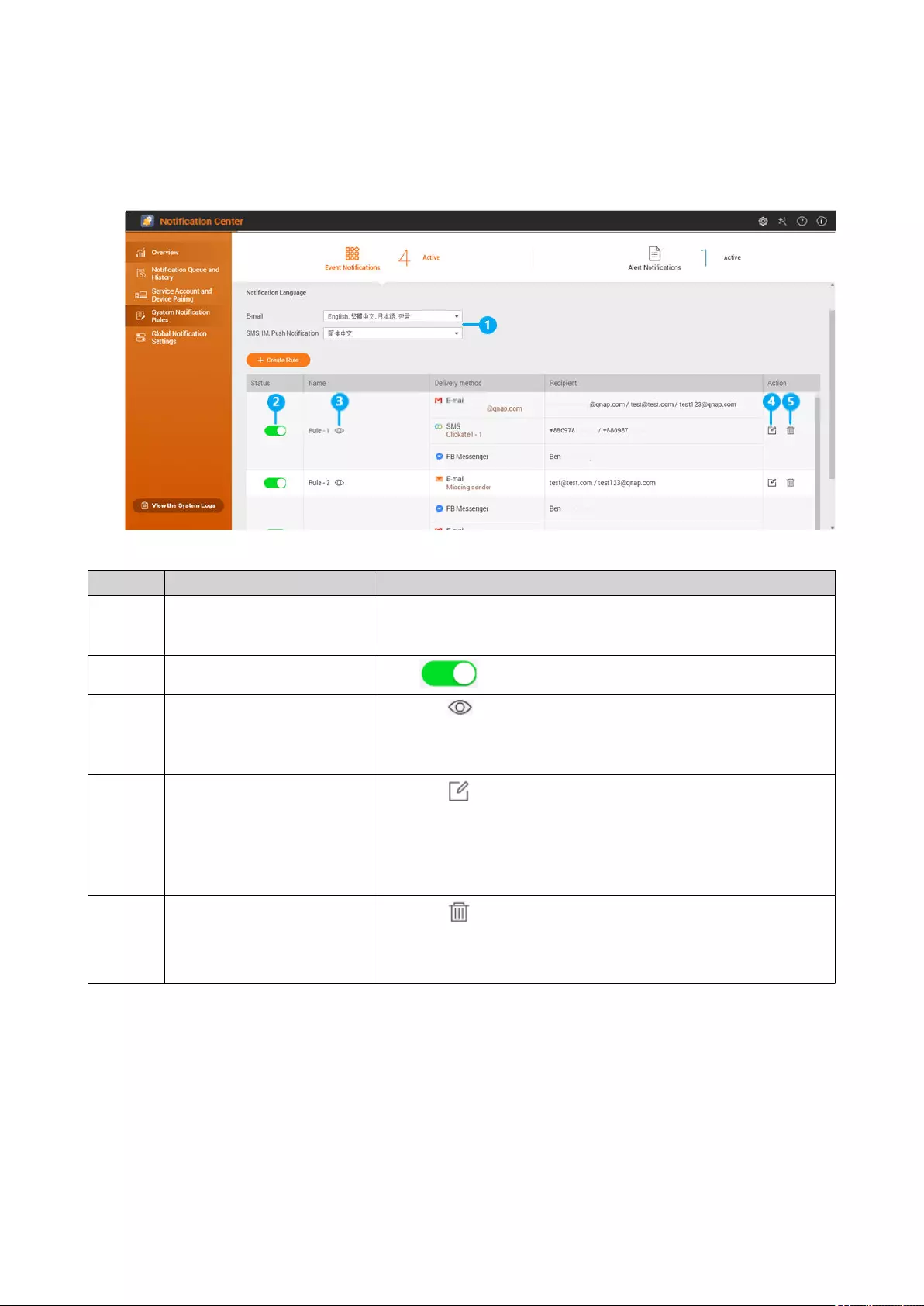
or narrow the scope. Notication Center supports sending event notications in multiple languages and
provides four delivery methods to meet your dierent needs, including emails, SMS, instant messaging, and
push services.
No. Tasks User Actions
1 Specify a notication
language.
1. Select one or more languages for email notications.
2. Select a language for SMS, IM, and push notications.
2 Enable or disable the rule. Click .
3 Preview the rule settings. 1. Click .
The Event Notications window appears.
2. Review the settings, and then click Close.
4 Edit the rule. 1. Click .
The Edit Rule for Event Notications window appears.
2. Edit the settings.
3. Click Conrm.
5 Delete the rule. 1. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
2. Click Conrm.
Creating an Event Notication Rule
Before creating a notication rule, ensure that your NAS is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
1. Go to System Notication Rules > Event Notications .
2. Click Create Rule.
The Create event notication rule window appears.
3. Specify a rule name.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 500
4. Select the events you want recipients to be notied of.
Tip
To select all events, select Select all.
To display only the events for a specic application or service, select the item from the
Displayed Items drop-down menu.
5. Click Next.
6. Select a severity level.
Severity Level Description
Information Information messages inform users of changes in the NAS settings or its
applications.
Warning Warning messages inform users of events when NAS resources, such as
storage space and memory, are critically low, or when the hardware behaves
abnormally.
Error Error messages inform users of problems that occur when the system tries to
update or run applications or processes or when it fails to enable or disable NAS
features.
7. Specify a keyword lter.
Filter Description
All messages Notication Center sends all notications that are classied under the types you
selected.
Includes Notication Center sends only the notications that are classied under the
types you selected and includes the keywords you specify.
To add keyword lters, click , and then specify one or more keywords.
Excludes Notication Center sends only the notications that are classied under the
types you selected and excludes the keywords you specify.
To add keyword lters, click , and then specify one or more keywords.
Important
The event notication lter only accepts keywords that are in English or in any of the languages
specied on the Event Notications screen.
8. Specify a time range when you want to receive notications.
9. Click Next.
10. Select a delivery method.
11. Congure the sender information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 501
Method User Action
Email a. Select an SMTP server.
Tip
To add an SMTP server, see Conguring an Email Notication
Server.
b. Optional: Specify a custom subject line.
This text replaces the original email subject line. Use this to help recipients
better understand the notications they receive.
c. Optional: Select Send email as plain text.
SMS Select an SMSC server.
Note
To add an SMSC server, see Conguring an SMS Notication
Server.
Instant Messaging or
Push Service
Notication Center automatically assigns Qbot.
12. Congure the recipient information.
Method User Action
Email a. Click Select NAS User.
The Select NAS User window appears.
b. Select one or more NAS users.
c. Click Finish.
The Select NAS User window closes.
Tip
• To add a recipient, click Add, and then specify their email
address.
•To delete a recipient, click .
SMS a. Click Select NAS User.
The Select NAS User window appears.
b. Select one or more NAS users.
c. Click Finish.
The Select NAS User window closes.
d. Select a country code for each recipient.
Tip
• To add a recipient, click Add, and then specify their cell
phone number.
•To delete a recipient, click .
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 502
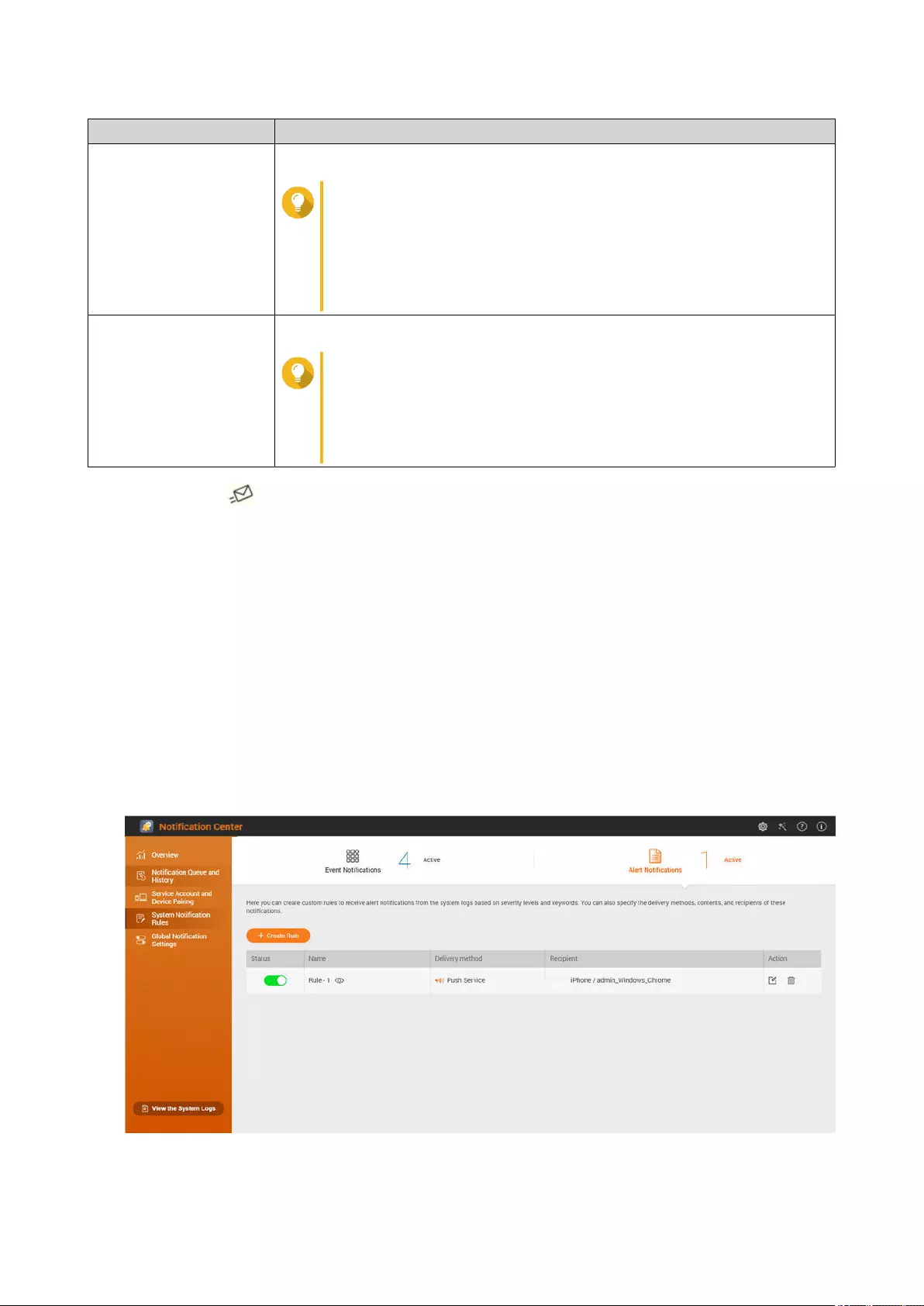
Method User Action
Instant Messaging Select one or more recipients.
Tip
To add instant messaging notication recipients, see the
following topics:
•Pairing Notication Center with Skype
•Pairing Notication Center with Facebook Messenger
Push Service Select one or more recipients.
Tip
To add push notication recipients, see the following topics:
•Pairing Notication Center with a Mobile Device
•Pairing Notication Center with a Web Browser
13. Optional: Click to send a test message.
14. Optional: Click Add Pair to create a new pair.
15. Click Next.
16. Verify the rule settings.
17. Click Finish.
Notication Center displays the new rule on the Event Notications screen.
Alert Notications
You can create custom rules to receive alert notications from the System Logs based on the notication
type and keywords. You can also specify the delivery methods, contents, and recipients of these
notications.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 503
Button Task User Action
Enable or disable the rule. Click .
Preview the rule settings. 1. Click .
The Alert Notications window appears.
2. Review the settings, and then click Close.
Edit the rule. 1. Click .
The Edit Rule for Alert Notications window
appears.
2. Edit the settings.
3. Click Conrm.
Unpair from and remove the device
or browser.
1. Click .
A conrmation message appears.
2. Click Conrm.
Creating an Alert Notication Rule
Before creating a notication rule, ensure that your NAS is registered to an active myQNAPcloud account.
1. Go to System Notication Rules > Alert Notications .
2. Click Create Rule.
The Create alert notication rule window appears.
3. Specify a rule name.
4. Select the events you want recipients to be notied of.
a. Select a severity level.
Severity Level Description
Information Information messages inform users of changes in the NAS settings or its
applications.
Warning Warning messages inform users of events when NAS resources, such as storage
space and memory, are critically low, or when the hardware behaves abnormally.
Error Error messages inform users of problems that occur when the system tries to
update or run applications or processes or when it fails to enable or disable NAS
features.
b. Optional: Specify a keyword lter.
Filter Description
All messages Notication Center sends all notications that are classied under the types you
selected.
Includes Notication Center sends only the notications that are classied under the types
you selected and includes the keywords you specify.
To add keyword lters, click , and then specify one or more keywords.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 504
Filter Description
Excludes Notication Center sends only the notications that are classied under the types
you selected and excludes the keywords you specify.
To add keyword lters, click , and then specify one or more keywords.
Important
The alert notication lter only accepts keywords that are in English.
5. Optional: Specify a time range when you want to receive notications.
6. Optional: Specify a notication message threshold.
7. Click Next.
8. Select a delivery method.
9. Congure the sender information.
Method User Action
Email a. Select an SMTP server.
Tip
To add an SMTP server, see Conguring an Email Notication
Server.
b. Optional: Specify a custom subject line.
This text replaces the original email subject line. Use this to help recipients
better understand the notications they receive.
c. Optional: Select Send email as plain text.
SMS Select an SMSC server.
Note
To add an SMSC server, see Conguring an SMS Notication
Server.
Instant Messaging or
Push Service
Notication Center automatically assigns Qbot.
10. Congure the recipient information.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 505
Method User Action
Email a. Click Select NAS User.
The Select NAS User window appears.
b. Select one or more NAS users.
c. Click Finish.
The Select NAS User window closes.
Tip
• To add a recipient, click Add, and then specify their email
address.
•To delete a recipient, click .
SMS a. Click Select NAS User.
The Select NAS User window appears.
b. Select one or more NAS users.
c. Click Finish.
The Select NAS User window closes.
d. Select a country code for each recipient.
Tip
• To add a recipient, click Add, and then specify their cell phone
number.
•To delete a recipient, click .
Instant Messaging Select one or more recipients.
Tip
To add instant messaging notication recipients, see the
following topics:
•Pairing Notication Center with Skype
•Pairing Notication Center with Facebook Messenger
Push Service Select one or more recipients.
Tip
To add push notication recipients, see the following topics:
•Pairing Notication Center with a Mobile Device
•Pairing Notication Center with a Web Browser
11. Optional: Click to send a test message.
12. Optional: Click Add Pair to create a new pair.
13. Click Next.
14. Verify the rule settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 506
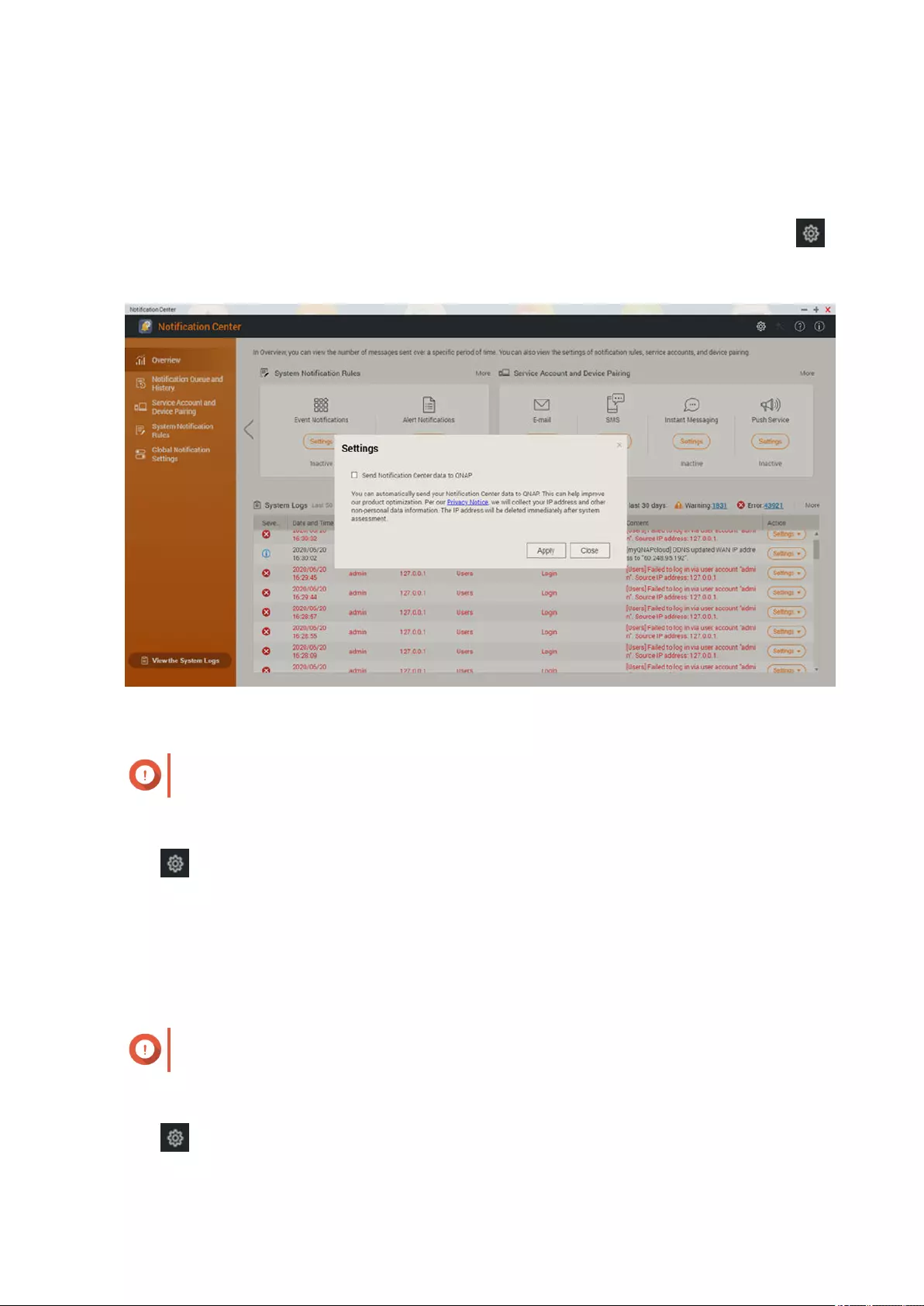
15. Click Finish.
Notication Center displays the new rule on the Alert Notications screen.
Settings
The Settings screen allows you to enable or disable submitting Notication Center data to QNAP. Click
to open the Settings window.
Enabling Send Notication Data to QNAP
Important
QNAP does not collect your personal data or information.
1. Open Notication Center.
2. Click .
The Send Notication data to QNAP window appears.
3. Select Send Notication data to QNAP.
4. Click Apply.
Disabling Send Notication Data to QNAP
Important
QNAP does not collect your personal data or information.
1. Open Notication Center.
2. Click .
The Send Notication data to QNAP window appears.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 507
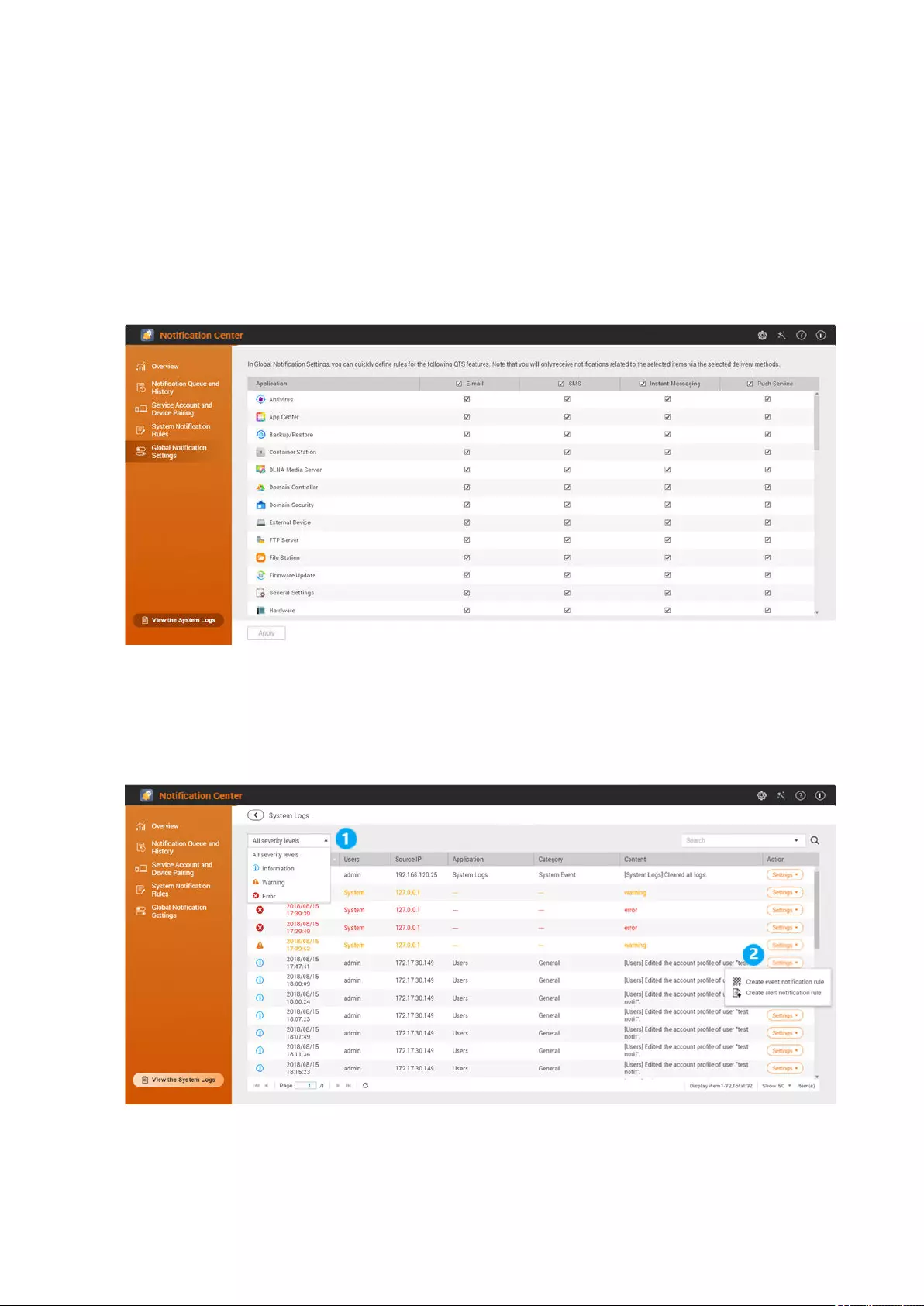
3. Deselect Send Notication data to QNAP.
4. Click Apply.
Global Notication Settings
The Global Notication Settings screen allows you to quickly dene global notication rules. From the list,
you can select or deselect, and then apply the delivery methods for each QTS feature or application. Users
only receive notications related to the selected features through their selected delivery methods.
System Logs
The System Logs screen displays all system events on the NAS. On this screen, you can sort and lter the
logs or create notication rules based on existing logs.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 508
No. Task User Action
1 Filter system logs Select a severity level.
2 Search system logs Search for logs by keywords or through advanced search. To
use advanced search follow the instructions below:
1. Click in the search bar.
The advanced search option drop down menu appears.
2. Specify the following parameters where applicable:
• Keyword
• Severity Level
• Date
• Users
• Source IP
• Application
• Category
3. Click Search.
Lists all log entries that meet the specied conditions.
3 Create a notication rule 1. Click Settings.
2. Select one of the following options.
•Create event notication rule
•Create alert notication rule
The Create notication rule window appears.
3. Select one of the following options.
•Add as a new rule
•Add to an existing rule
4. Click Conrm.
Tip
To add or edit notication rules, see the
following topics:
•Creating an Event Notication Rule
•Creating an Alert Notication Rule
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Notication Center 509
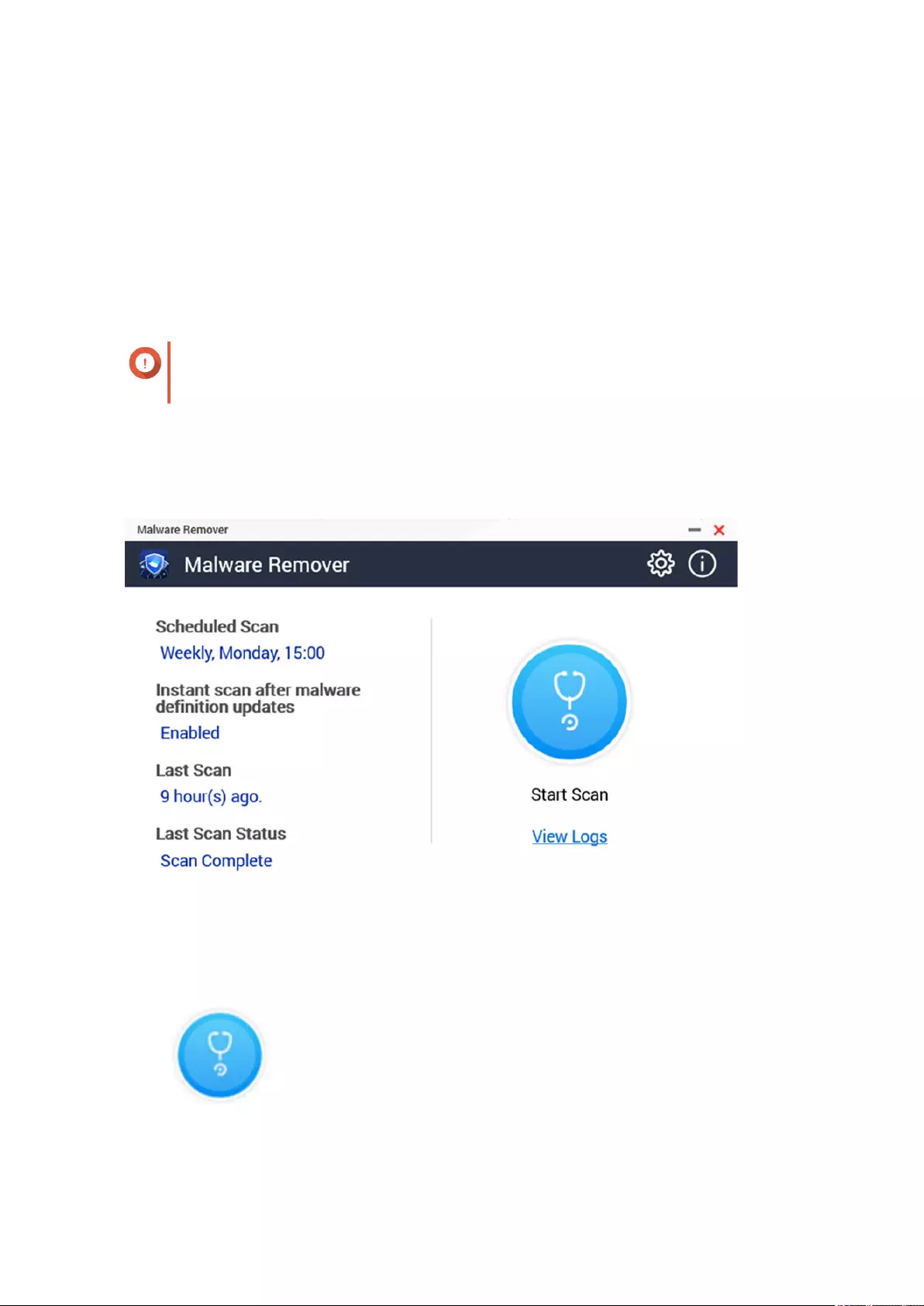
18. Malware Remover
About Malware Remover
Malware Remover is a built-in utility designed to protect QNAP devices against harmful software. Malware
programs are often disguised as or embedded in nonmalicious les and software. They often attempt to
gain access to sensitive user information and may negatively impact device performance.
Implementing several layers of protection, Malware Remover allows you to perform instant and scheduled
scans on your QNAP device and prevents malicious software from putting your data at risk.
Important
QNAP strongly recommends running routine scans to prevent malware infections and
protect the system from advanced risks, threats, and vulnerabilities.
Overview
This screen displays information and controls connected to Malware Remover.
Running a Malware Scan
1. Open Malware Remover.
2.
Click .
Malware Remover begins the scan.
3. Optional: After the scan nishes, click View Logs to view the results.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Malware Remover 510
Running a Scheduled Scan
Scheduled scans periodically look for security threats on your QNAP device.
Note
The Enable scheduled scan checkbox is enabled by default.
1. Open Malware Remover.
2.
Click .
3. Choose from the scheduled scan drop-down menu to congure the settings.
Setting Description
Daily The scheduled scan runs daily at the specied time.
Weekly The schedules scan runs once a week on the specied day and time.
Monthly The scheduled scan runs once a month on the specied date and time.
4. Click Apply.
Conguring Malware Remover
1. Open Malware Remover.
2.
Click .
The Settings window opens.
3. Congure the settings.
Note
All settings are enabled by default to prevent malware threats from infecting the system.
Tip
QNAP recommends running scans during o-peak hours.
Setting Description
Enable scheduled scan Enable to scan all applications and les at the user-congured
frequency and time.
For details, see Running a Scheduled Scan.
Note
Enabling this setting ensures Malware Remover
performs routine scans of your device.
Instant scan after malware
denition updates
Enable this option to run instant scans once Malware Remover updates
the malware denitions.
Note
Malware Remover automatically updates malware
signatures and security patches to have the most up-
to-date security content.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Malware Remover 511
Setting Description
Send Malware Remover scan
results to QNAP
Enable this option to submit the scan results for malware analysis.
QNAP collects the following data:
• NAS model
• NAS IP address (The IP address is immediately deleted after
analyzing the malware scan results.)
• Scan status
• Scan errors
• Malware detection date and time
• Malware ID
Note
Disabling this option prevents Malware Remover from
sending any data to QNAP.
4. Click Apply.
Malware Remover saves the settings.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Malware Remover 512
19. Helpdesk
Helpdesk is a built-in application that allows you to quickly nd solutions or contact the QNAP support team
when you encounter any issues while using QTS and related applications.
Overview
On the Overview screen, you can contact the QNAP support team, browse frequently asked questions
and application notes, download QNAP user manuals, nd out how to use a QNAP NAS, search the QNAP
knowledge base, and nd compatible devices. This screen also displays Helpdesk message logs.
Title Description
Help Request Contact the QNAP support team by submitting your issues or questions.
QNAP Online
Tutorial & FAQ
Browse frequently asked questions and application notes for QNAP NAS and
applications.
NAS User Manual View or download QNAP NAS user manuals.
Help Center Find how to use a QNAP NAS.
QNAP Helpdesk
Knowledge Base
Search the QNAP knowledge base for answers from the support team for dierent
issues.
Compatibility List Find drives and devices that are compatible with QNAP NAS.
My Tickets View your submitted tickets status.
Conguring Settings
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Overview.
3. Click .
The Settings window appears.
4. Specify the message retention time.
5. Optional: Click Retain all messages.
6. Optional: Click I am allowing QNAP Support to access my system logs.
7. Optional: Click Sign In.
The Settings window appears.
8. Specify your QNAP ID.
9. Specify the password.
10. Click Sign In.
11. Click Apply.
Help Request
Help Request allows users to directly submit requests to QNAP from your NAS. Helpdesk automatically
collects and attaches NAS system information and system logs to your request to help the QNAP technical
support team identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Helpdesk 513
Submitting a Ticket
You can submit a Helpdesk ticket to receive support from QNAP. Helpdesk automatically collects and
attaches device system information and system logs to your request to help the QNAP technical support
team identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Help Request.
3. Sign in with your QNAP ID.
4. Specify the ticket details.
Fields User Actions
Subject Specify the subject.
Issue Category Select an issue category, and then select an issue.
Issue Type Select an issue type.
Operating System Select an operating system.
Description Specify a short description for each issue.
5. Upload the attachments.
a. Optional: Select I am allowing QNAP Support to access my system logs.
b. Upload screenshots or other related les.
Note
• You can upload up to 8 attachments, including system logs.
• Each le must be less than 5 MB.
6. Specify the following information.
Fields User Actions
Your Email Address Specify your email address.
Phone number Specify your phone number.
Customer type Select a customer type.
Company name Specify your company name.
Note
This eld only appears when you select Business User
as the Customer type.
Your timezone Select a timezone.
Apply the changes to my prole
in QNAP Account
Click to apply your prole changes in QNAP Account.
First name Specify your rst name.
Last name Specify your last name.
Your location Select a location.
7. Optional: Select Apply the changes to my prole in QNAP Account.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Helpdesk 514

8. Click Submit.
Remote Support
Remote Support allows the QNAP support team to access your NAS directly to assist you with your issues.
Enabling Remote Support
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Remote Support.
3. Specify your ticket ID.
4. Specify your email address.
5. Click Enable Remote Support.
The QNAP Helpdesk Terms of Service window appears.
6. Accept the terms of service.
a. Click I agree to these Terms of Service.
b. Click Agree.
The Enable Remote Support window appears.
Note
Enable Remote Support is only required when you enable the feature for the rst time.
7. Click Conrm.
Helpdesk creates a private key and temporary account.
Extending Remote Support
Extending Remote Support allows the users to extend the remote session by a week in case users want to
have the remote session at a specic time. QNAP will also notify the user to extend the session if the issue is
unsolved.
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Remote Support.
3. Click Extend.
Note
The Extend button only appears after Remote Support is enabled.
Disabling Remote Support
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Remote Support.
3. Click Disable.
Note
The Disable button only appears after Remote Support is enabled.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Helpdesk 515

4. Click Finish.
Note
Remote Support will also be disabled when the support team has completed the remote
session, or when the private key has expired.
Diagnostic Tool
The Diagnostic Tool provides several features for checking the stability of the NAS. Users can export system
kernel records to quickly check whether abnormal operations have recently occurred. In addition, users can
send the records to QNAP technical support for further investigation. The Diagnostic Tool also provides
features for checking the le system, hard drives, and RAM.
Downloading Logs
The Diagnostic Tool provides download log features for checking the device stability. You can export the
system kernel records to quickly check for exceptions or errors that have occurred. In addition, you can send
the records to QNAP technical support for further investigation.
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Diagnostic Tool > Download Logs .
3. Click Download.
Helpdesk generates a ZIP le.
4. Download the ZIP le.
5. Optional: Send the le to QNAP through Help Request for further investigation.
Performing an HDD Standby Test
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Diagnostic Tool > HDD Standby Test .
3. Select an enclosure to analyze.
4. Click Start.
Helpdesk performs an HDD standby test.
5. Optional: Click Download to download the test reports.
Performing an HDD Stress Test
1. Open Helpdesk.
2. Go to Diagnostic Tool > HDD Stress Test .
3. Click Start.
Helpdesk performs an HDD stress test.
4. Optional: Click Download to download the test reports.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Helpdesk 516

20. Console Management
Console Management is a text-based tool that helps system administrators perform basic conguration or
maintenance tasks, and provide technical support to the NAS users. The program is accessible only after the
operating system has nished initialization. Console Management is enabled by default, but you can disable
it in the Control Panel. For details, go to the System Settings section of the QTS User Guide. Currently,
disabling Console Management only applies to QTS.
Only users in the administrator group can use Console Management, which launches automatically when
administrators log in using SSH login, a serial console, or an HDMI monitor and a USB keyboard.
Enabling Secure Shell (SSH)
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol that can access Console Management. If you want to
access Console Management using SSH, you must rst enable SSH on the NAS.
Enabling SSH on the NAS
1. Log in to the NAS as administrator.
2. Go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Telnet / SSH .
3. Select Allow SSH connection (Only administrators can login remotely.).
4. Optional: Change the port number.
5. Click Apply.
Enabling SSH on the NAS Using Qnder Pro
1. Open Qnder Pro, and then locate the NAS you want to access.
2. Click Settings.
3. Select Connect via SSH.
The Connect via SSH screen appears.
4. Log in to the NAS as administrator.
Accessing Console Management
Before you can access Console Management, you must rst enable SSH using the NAS or Qnder Pro. A
third-party software is also required on Windows platforms but not on Mac platforms.
Accessing Console Management from Windows
1. Download PuTTY from https://www.putty.org/, and then follow the on-screen instructions to install the
software.
2. Open PuTTY, and type the device's IP address underneath Host Name (or IP address).
3. Select SSH as the connection type.
Note
This option is selected by default.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 517
4. Click Open.
The PuTTY Security Alert window appears.
Note
This window only appears when you rst run the application.
5. Click Yes.
A login screen appears.
Accessing Console Management from Mac
1. Open Terminal.
2. Enter ssh USERNAME@NAS_IP.
Note
Replace NAS_IP with the device's IP address.
Tip
If you encounter an error, enter ssh-keygen -R NAS_IP. Replace NAS_IP with the device's
IP address.
3. Press ENTER.
A login screen appears.
Logging In to Console Management
Important
Before performing this task, you must rst complete the following tasks:
• Enable Secure Shell (SSH).
• Download the third-party software for your platform if it is required. For details, see
the following topics:
•Accessing Console Management from Windows
•Accessing Console Management from Mac
1. Log in as administrator.
a. Enter the username.
b. Enter the password.
Note
For security purposes, the password does not show.
Tip
Do not copy and paste the password to the program.
The Console Management - Main menu screen appears.
Managing Existing Applications
1. Log in to Console Management, and then enter 5.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 518
The App window and three options appear.
2. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the action you want to perform.
Tip
To browse your applications, enter n or p to go to the next or previous page.
Option User Action
List installed apps Enter 1.
Console Management displays a list of all installed applications on the
operating system.
List enabled apps Enter 2.
Console Management displays a list of all enabled applications on the
operating system.
List disabled apps Enter 3.
Console Management displays a list of all disabled applications on the
operating system.
Return Enter r.
Console Management returns to Main menu.
A list of applications appear.
3. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the application you want to perform an action
on.
Five options appear.
4. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the action you want to perform.
Option User Action
Start Enter 1.
The application starts.
Stop Enter 2.
The application stops.
Restart Enter 3.
The application restarts.
Remove Enter 4.
The application is removed.
Note
If an application can't be removed, Console
Management tells you that this function is currently
unavailable.
Return Enter r.
Console Management returns to Main menu.
The system performs the specied action and tells you whether the action has succeeded or not.
Activating or Deactivating a License
1. Log in to Console Management, and then enter 4.
Two options appear.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 519
2. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the action you want to perform.
Option User Action
Activate a License a. Enter 1.
b. Enter a license activation key.
Deactivate a License a. Enter 2.
b. Enter a license activation key.
Return Enter r.
Console Management returns to Main menu.
The system performs the specied action.
Sorting and Filtering System Logs
1. Log in to Console Management, and then enter 2.
Eleven options appear.
2. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the action you want to perform.
Note
System logs are displayed in the following format: record_id, date, time, user, app_id,
application, category_id, category, msg_id, message.
Option User Action
date in ascending order Enter 1.
Console Management displays all system logs in ascending order
according to the date.
date in descending order
(default)
Enter 2.
Console Management displays all system logs in descending order
according to the date.
user in ascending order Enter 3.
Console Management displays all system logs in ascending order
according to the username.
user in descending order Enter 4.
Console Management displays all system logs in descending order
according to the username.
IP in ascending order Enter 5.
Console Management displays all system logs in ascending order
according to the IP address.
IP in descending order Enter 6.
Console Management displays all system logs in descending order
according to the IP address.
app name in ascending order Enter 7.
Console Management displays all system logs in ascending order
according to the application name.
app name in descending order Enter 8.
Console Management displays all system logs in descending order
according to the application name.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 520
Option User Action
category in ascending order Enter 9.
Console Management displays all system logs in ascending order
according to the application category.
category in descending order Enter 10.
Console Management displays all system logs in descending order
according to the application category.
The lter screen appears.
3. Optional: Enter a lter query.
Note
• Ensure all lter conditions follow the relevant on-screen format. For example, ltering by an
application name should follow this format: A={myQNAPcloud}.
• To lter by multiple conditions, use '&' in between lters. For example, ltering by severity
level and an application name should follow this format: T={0}&A={myQNAPcloud}.
Filter User Action
Severity level a. Enter one of the following options.
•T={0}
Note
This lter only includes system logs classied as information.
This type of system log is indicated as in QuLog Center.
•T={1}
Note
This lter only includes system logs classied as warnings.
This type of system log is indicated as in QuLog Center.
•T={2}
Note
This lter only includes system logs classied as errors. This
type of system log is indicated as in QuLog Center.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied severity
level.
Keyword Enter a keyword.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied keyword.
Username Type an username.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied
username.
Source IP Enter a source IP.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied source IP.
Application name Enter an application name.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied
application name.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 521
Filter User Action
Category name Enter an application category.
Console Management lters all system logs according to the specied category.
A list of system logs appear.
Tip
To browse your applications, enter n or p to go to the next or previous page.
Showing Network Settings
1. Log in to Console Management as administrator, and then enter 1.
Note
Network settings appear in the following format: adapter, virtual switch, status, IP, MAC
address.
The Network settings window appears.
Restoring or Reinitializing the Device
1. Log in to Console Management as administrator, and then enter 3.
The Reset window and ve options appear.
2. Enter the alphanumeric character corresponding with the action you want to perform.
Note
The admin password is required to reset the settings or reinitialize the device.
Option User Action
Reset network settings Enter 1.
Console Management resets the network settings.
Reset system settings Enter 2.
Console Management restores system settings to default without
erasing user data.
Restore factory defaults &
format all volumes
Enter 3.
Console Management restores the system settings to default and
formats all disk volumes.
Reboot to reinitialize the device Enter 4.
Console Management erases all data and reinitializes the device.
Return Enter r.
Console Management returns to Main menu.
Rebooting the NAS
You can reboot the NAS into rescue or maintenance mode from Console Management.
Rebooting the Device Into Rescue Mode
1. Log in to Console Management as administrator, and then type 6 and press ENTER.
The Reboot in rescue mode window opens.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 522
2. Type y, and then press ENTER.
Note
Press escape or type n and press to go to the Main Menu.
Console Management reboots the device.
Rebooting the Device Into Maintenance Mode
1. Log in to Console Management as administrator, and then type 7 and press ENTER.
The Reboot in maintenance mode window opens.
2. Type y, and then press ENTER.
Press escape or type n and press to go to the Main Menu.
Console Management reboots the device.
QTS 5.0.x User Guide
Console Management 523