Table of Contents
- Notice
- Getting Started
- QTS Basics and Desktop
- System Settings
- Privilege Settings
- Network & File Services
- Applications
- QNAP Applications
- Mobile Apps
- Computer Utilities
- NAS Add-ons
- Use the LCD Panel
- GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
QNAP TVS-1282 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for TVS-1282 by QNAP which is a product in the NAS & Storage Servers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

QNAP Turbo NAS
Software User Manual
(Version: 4.3.x)
This manual is applicable to the following Turbo NAS models: TS-112, TS-112P, TS-120,
TS-121, TS-212, TS-212-E, TS-212P, TS-220, TS-221, HS-210, TS-420, TS-420U, TS-421,
TS-421U.
*Unless otherwise specified, the content of this manual applies to all the above NAS models.
*For user manuals of other NAS models and firmware versions, please visit
http://docs.qnap.com

Table of Contents
Notice ................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
Legal Notice and Disclaimer .......................................................................................................................................... 7
Regulatory Notice ......................................................................................................................................................... 9
Document Annotation ................................................................................................................................................ 11
Safety Information and Precautions ........................................................................................................................... 12
Getting Started ................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Hardware Installation ................................................................................................................................................. 14
Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List ........................................................................................................................... 15
Checking System Status .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Software Installation ................................................................................................................................................... 19
Smart Installation Guide ......................................................................................................................................... 20
Cloud Installation .................................................................................................................................................... 21
HDMI Installation .................................................................................................................................................... 22
Getting Utilities ........................................................................................................................................................... 23
Connecting to NAS Shared Folders ............................................................................................................................. 24
Windows ................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Mac or Linux ............................................................................................................................................................ 26
Connecting to NAS by Web Browser ........................................................................................................................... 27
Migrating NAS ............................................................................................................................................................. 28
QTS Basics and Desktop .................................................................................................................................................. 32
Introducing QTS .......................................................................................................................................................... 33
Using QTS Desktop ...................................................................................................................................................... 35
System Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 41
General Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 42
Storage Manager ......................................................................................................................................................... 45
Volume Management ............................................................................................................................................. 46
RAID Management .................................................................................................................................................. 48

Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T ................................................................................................................................................ 60
Encrypted File System ............................................................................................................................................. 61
iSCSI ......................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Virtual Disk .............................................................................................................................................................. 79
Security ....................................................................................................................................................................... 81
Hardware .................................................................................................................................................................... 82
Power .......................................................................................................................................................................... 86
Notification ................................................................................................................................................................. 88
Firmware Update ........................................................................................................................................................ 91
Backup/Restore ........................................................................................................................................................... 93
External Device ........................................................................................................................................................... 95
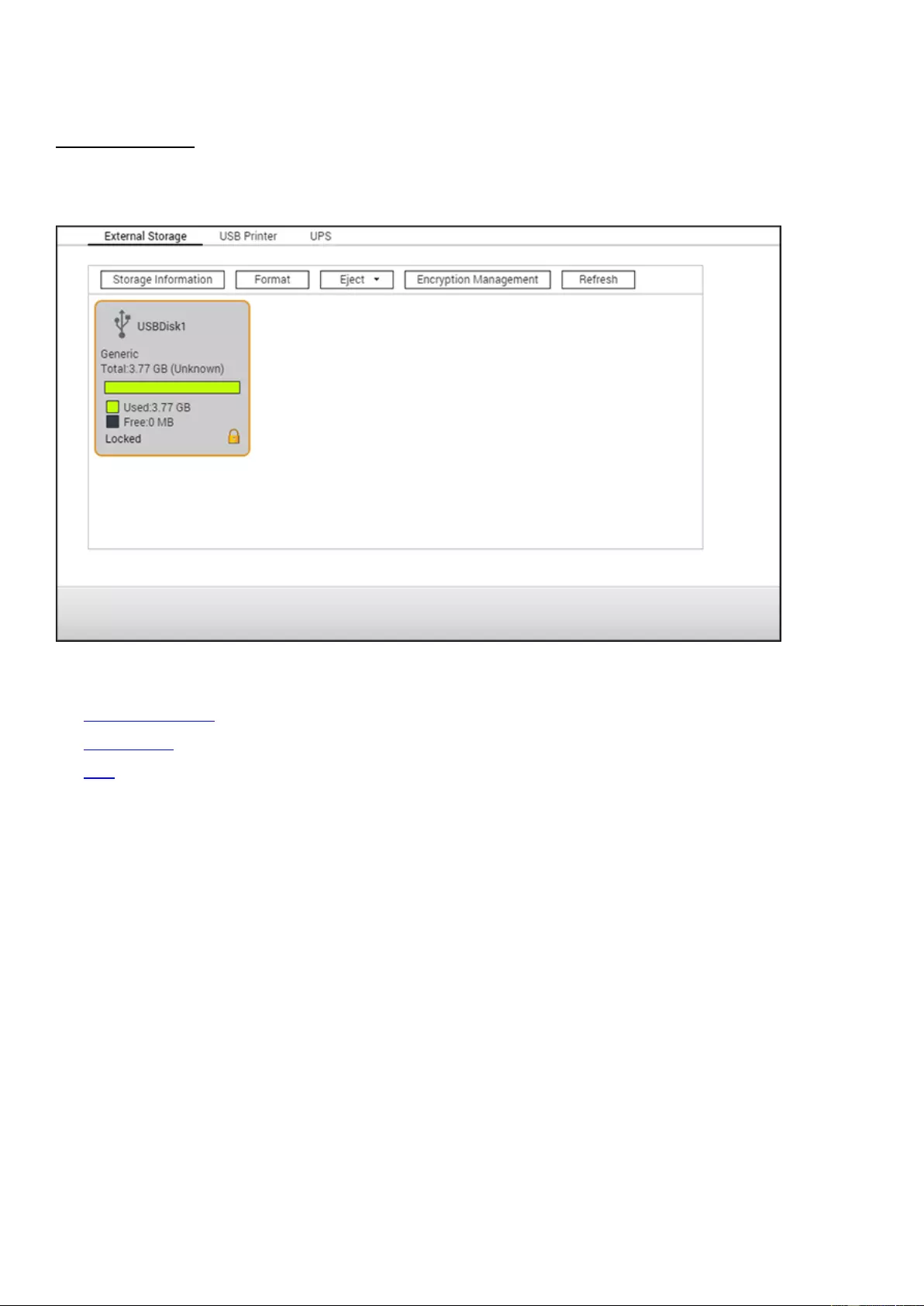
External Storage ...................................................................................................................................................... 96
USB Printer .............................................................................................................................................................. 99
UPS ........................................................................................................................................................................ 106
System Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 109
System Logs ............................................................................................................................................................... 111
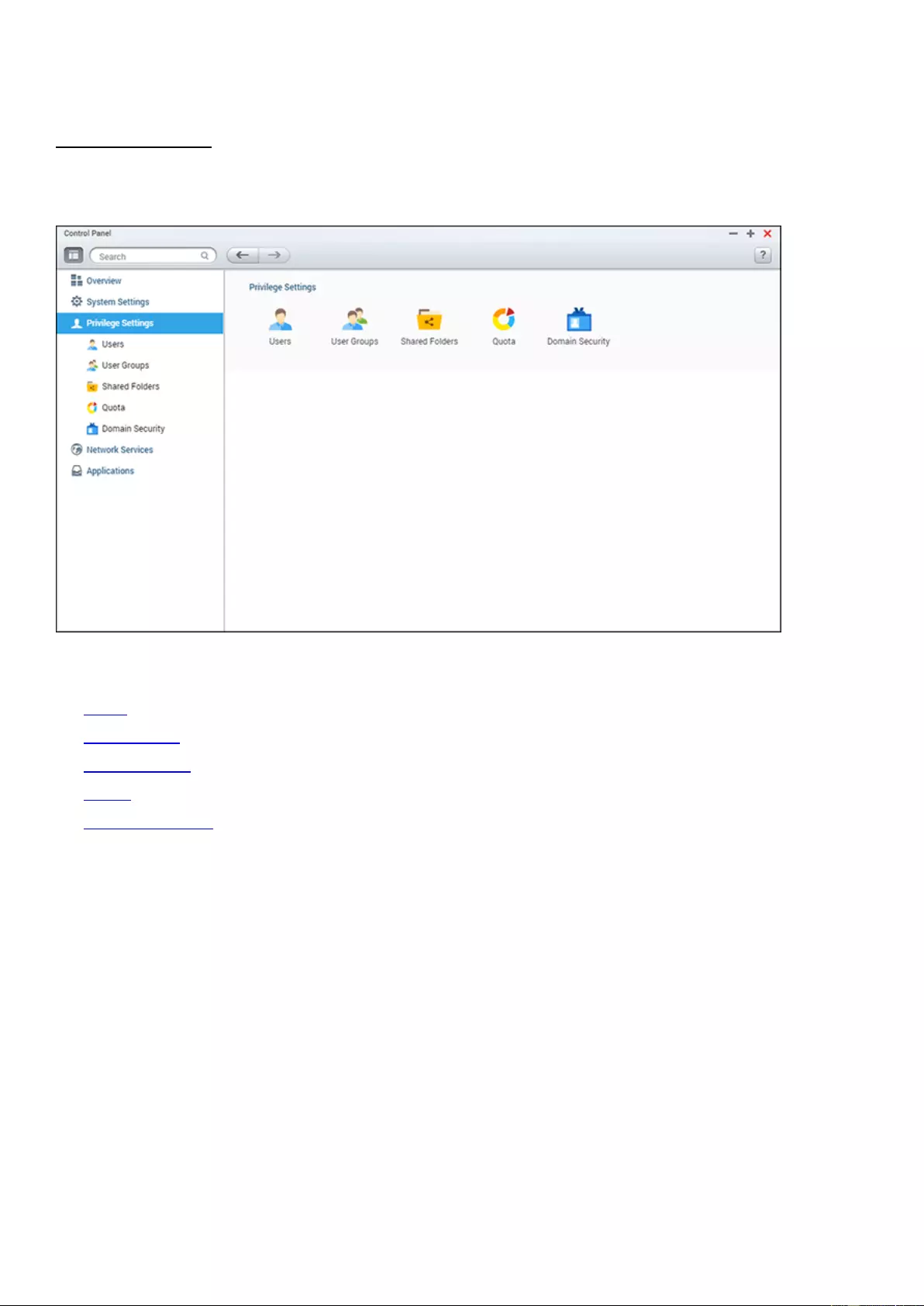
Privilege Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 114
Users ......................................................................................................................................................................... 115
User Groups .............................................................................................................................................................. 119
Shared Folders .......................................................................................................................................................... 121
Quota ........................................................................................................................................................................ 130
Domain Security ........................................................................................................................................................ 131
Joining NAS to Active Directory (Windows Server 2003/2008/2012) .................................................................. 132
Connecting NAS to an LDAP Directory .................................................................................................................. 135
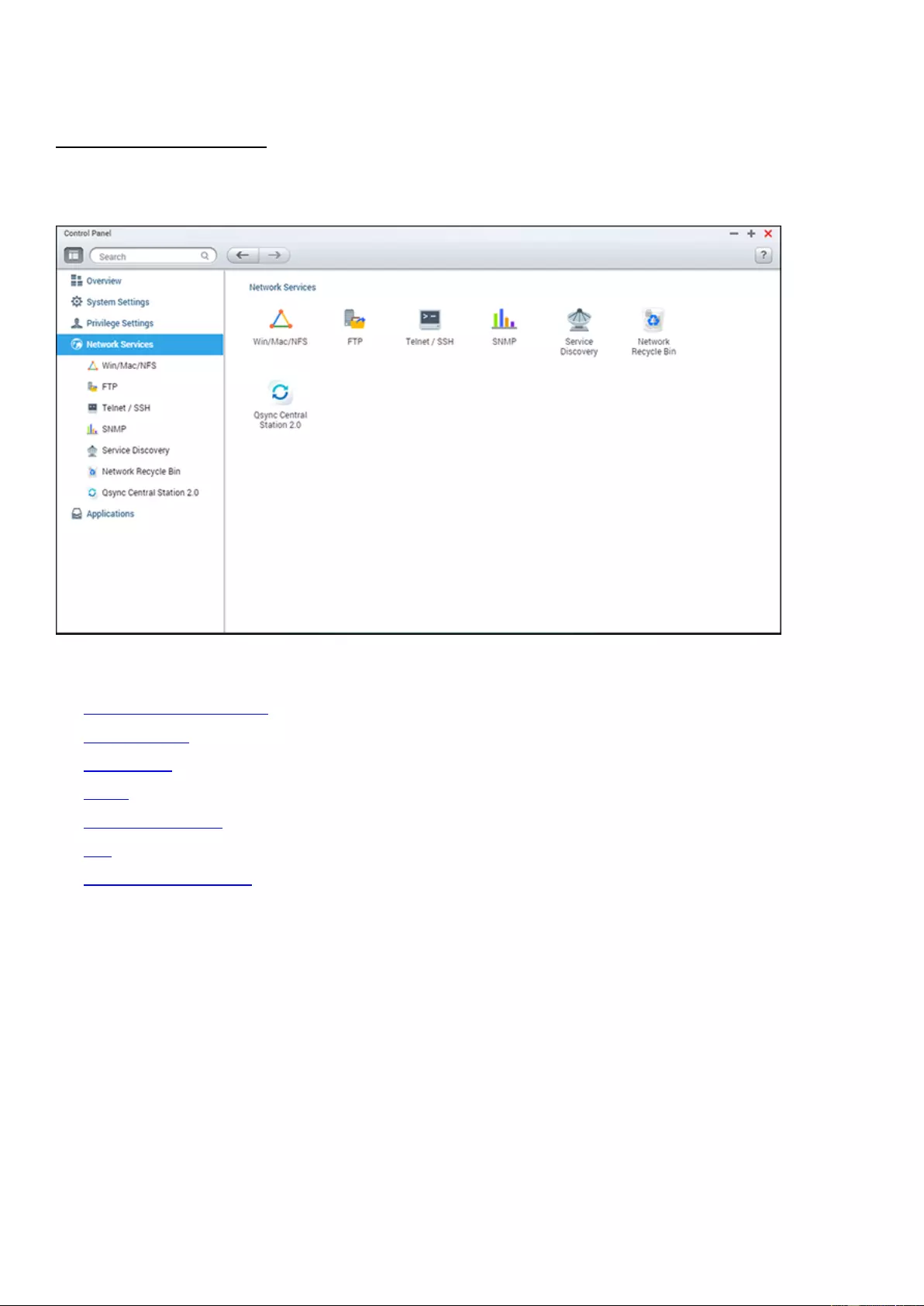
Network & File Services ................................................................................................................................................ 138
Network & Virtual Switch ......................................................................................................................................... 139
Win/Mac/NFS ............................................................................................................................................................ 149
FTP ............................................................................................................................................................................. 153
Telnet/SSH................................................................................................................................................................. 155

SNMP ......................................................................................................................................................................... 156
Service Discovery ...................................................................................................................................................... 158
Network Recycle Bin ................................................................................................................................................. 159
Applications ................................................................................................................................................................... 161
iTunes Server ............................................................................................................................................................. 162
DLNA Media Server ................................................................................................................................................... 163
Multimedia Management ......................................................................................................................................... 163
Web Server ................................................................................................................................................................ 168
Virtual Host ........................................................................................................................................................... 171
LDAP Server ............................................................................................................................................................... 173
QVPN Service ............................................................................................................................................................ 175
Qsync Central Station ................................................................................................................................................ 190
SQL Server ................................................................................................................................................................. 201
Syslog Server ............................................................................................................................................................. 203
Antivirus .................................................................................................................................................................... 206
RADIUS Server ........................................................................................................................................................... 210
TFTP Server ............................................................................................................................................................... 212
QNAP Applications ........................................................................................................................................................ 214
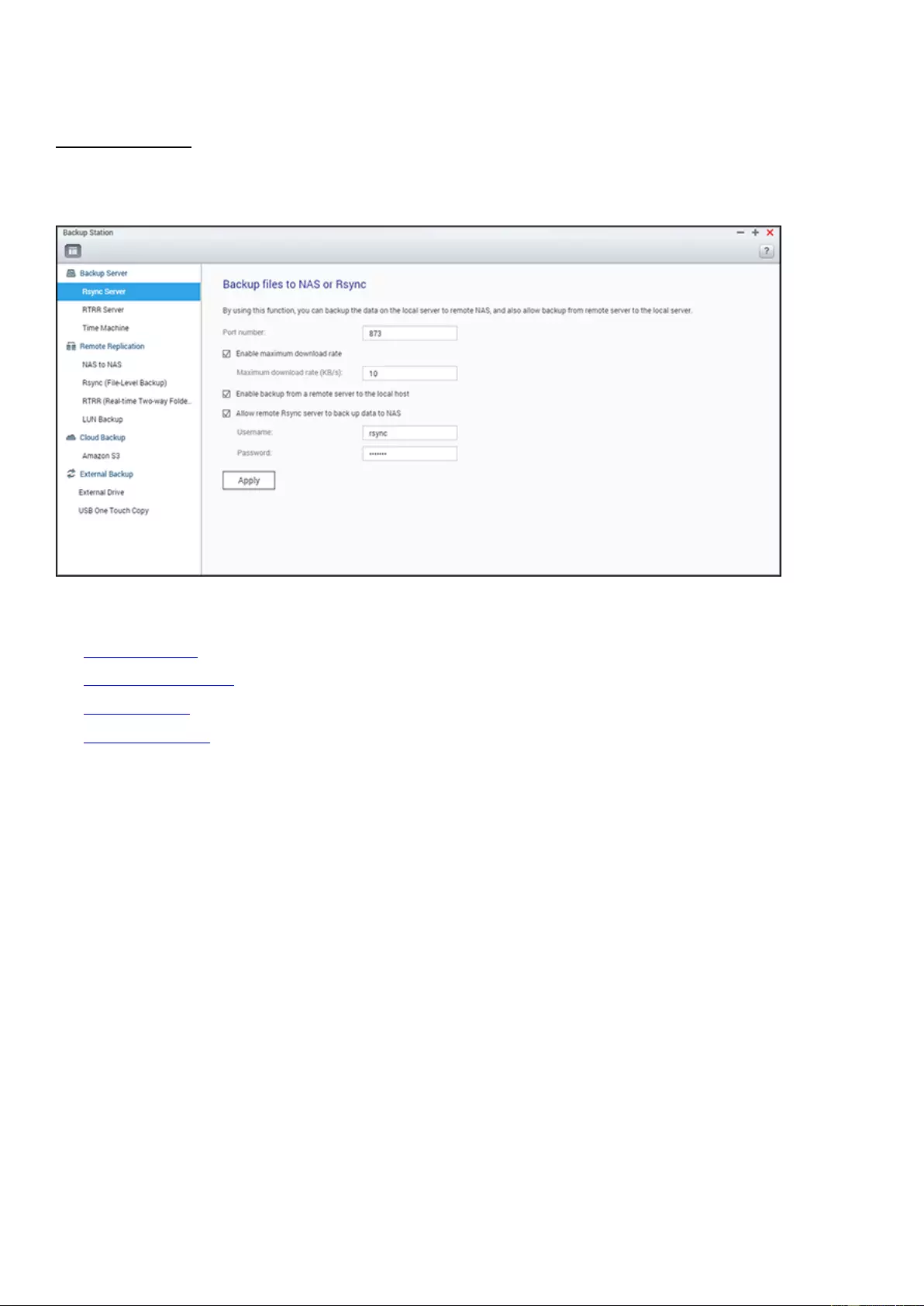
Backup Station .......................................................................................................................................................... 215
Backup Server ....................................................................................................................................................... 216
Remote Replication ............................................................................................................................................... 220
Cloud Backup......................................................................................................................................................... 227
External Backup ..................................................................................................................................................... 228
myQNAPcloud Service .............................................................................................................................................. 234
File Station ................................................................................................................................................................ 242
Video Station ............................................................................................................................................................. 256
Photo Station ............................................................................................................................................................ 266
Music Station ............................................................................................................................................................ 280
Download Station ...................................................................................................................................................... 287

HybridDesk Station ................................................................................................................................................... 295
App Center ................................................................................................................................................................ 298
Mobile Apps .................................................................................................................................................................. 301
Computer Utilities ......................................................................................................................................................... 306
NAS Add-ons ................................................................................................................................................................. 308
Use the LCD Panel ......................................................................................................................................................... 314
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE .................................................................................................................................... 319

Legal Notice and Disclaimer
Thank you for choosing QNAP products! This user manual provides detailed instructions of using the
Turbo NAS (network-attached storage). Please read carefully and start to enjoy the powerful functions
of the Turbo NAS!
The Turbo NAS is hereafter referred to as the NAS.
This manual provides the description of all the functions of the NAS. The product you purchased
may not support certain functions dedicated to specific models.
Legal Notices
All the features, functionality, and other product specifications are subject to change without prior
notice or obligation. Information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
QNAP and the QNAP logo are trademarks of QNAP Systems, Inc. All other brands and product names
referred to are trademarks of their respective holders.
Further, the ® or ™ symbols are not used in the text.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is provided in connection with QNAP products. No license, express or
implied, by estoppels or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document.
Except as provided in QNAP's terms and conditions of sale for such products, QNAP Assumes no liability
whatsoever, and QNAP disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of QNAP
products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right.
QNAP products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety
systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
In no event shall QNAP Systems, Inc. (QNAP) liability exceed the price paid for the product from direct,
indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages resulting from the use of the product, its
accompanying software, or its documentation. QNAP makes no warranty or representation, expressed,
implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all
accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness
for any particular purpose. QNAP reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or
documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity.

Back up the system periodically to avoid any potential data loss. QNAP disclaims any responsibility of
all sorts of data loss or recovery.
Should you return any components of the NAS package for refund or maintenance, make sure they are
carefully packed for shipping. Any form of damages due to improper packaging will not be
compensated.
QNAP, QNAP logo, QTS, myQNAPcloud and VioStor are trademarks or registered trademarks of QNAP
Systems, Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.

Regulatory Notice
FCC Notice
QNAP NAS comply with different FCC compliance classes. Please refer the Appendix for details. Once
the class of the device is determined, refer to the following corresponding statement.
FCC Class A Notice
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Modifications: Any modifications made to this device that are not approved by QNAP Systems, Inc.
may void the authority granted to the user by the FCC to operate this equipment.
FCC Class B Notice
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.

Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Modifications: Any modifications made to this device that are not approved by QNAP Systems, Inc.
may void the authority granted to the user by the FCC to operate this equipment.
CE Notice
QNAP Turbo NAS models comply with different CE compliance classes. Please refer to the table for
details.
FCC
CE
NAS Models
Class A
Class A
TS-EC1679U-RP, TS-EC1279U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP, TS-1679U-RP,
TS-1279U-RP, TS-1270U-RP, TS-1263U-RP, TS-1263U,TS-1253U-RP,
TS-1253U, TS-879U-RP, TS-870U-RP, TS-863U-RP, TS-853U-RP,
TS-453U-RP, TS-1079 Pro, TS-879 Pro, TS-863U, TS-853U, TS-463U,
TS-463U-RP, TS-453U-RP, TS-453U, TS-451U, TS-431U, TVS-871U-RP,
TVS-1271U-RP
Class B
Class B
TS-853S Pro, TS-453S Pro, TS-870 Pro, TS-853 Pro, TS-670 Pro, TS-653
Pro, TS-470 Pro, TS-453 Pro, TS-253 Pro, TS-431+, TS-231+, TS-451S,
TS-870, TS-851, TS-670, TS-651, TS-470, TVS-863+, TVS-863, TVS-663,
TVS-463, TVS-471, TVS-671, TVS-871,TS-451, TS-451+, TS-431, TS-251,
TS-251+, TS-251C, TS-231, TS-131, TS-269H, TS-212P, TS-112P, HS-251,
HS-251+, HS-210, TS-453mini, TS-563, IS-453S, TS-531P, TS-253A,
TS-453A, TS-653A, TS-853A, TS-128, TS-228, TAS-168, TAS-268,
TS-831X, TVS-682T, TVS-882T, TVS-1282T, TVS-682, TVS-882, TVS-1282

Document Annotation
Annotations in this document
Warning: This indicates the instructions must be strictly followed. Failure to do so could result in
injury to human body or death.
Caution: This indicates the action may lead to disk clearance or loss OR failure to follow the
instructions could result in data damage, disk damage, or product damage.
Important: This indicates the information provided is important or related to legal regulations.

Safety Information and Precautions
1. The NAS can operate normally in the temperature of 0ºC–40ºC and relative humidity of 0%–95%.
Ensure the environment is well-ventilated.
2. The power cord and devices connected to the NAS must provide correct supply voltage (100W,
90–264V).
3. Do not place the NAS in direct sunlight or near chemicals. Ensure the usage environment's
temperature and humidity is suited for using electronics.
4. Unplug the power cord and all connected cables before cleaning. Wipe the NAS with a dry towel.
Do not use chemicals or aerosols to clean the NAS.
5. Do not place any objects on the NAS during normal system operations and to avoid overheating.
6. Use the flat head screws in the product package to lock the hard disk drives in the NAS when
installing the hard drives for proper operation.
7. Do not place the NAS near any liquid.
8. Do not place the NAS on any uneven surface to avoid falling off and damage.
9. Make sure the voltage is correct in your location when using the NAS. If unsure, contact your
distributor or the local power company.
10. Do not place any object on the power cord.
11. Never attempt to repair the NAS. Improper disassembly of the product may expose you to
electric shock or other risks. For repair-related enquiries, please contact your distributor.
12. Rackmount NAS models should only be installed in server rooms and maintained by authorized
server managers or IT administrators. The server room should be sufficiently locked and only
certified staff allowed to enter.
Warning:
There is the danger of explosion if a battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries
according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
To avoid serious injuries do NOT touch the fan inside the system.

Getting Started
New NAS users are advised to follow the below steps to complete their NAS installation. For users who
already own a QNAP NAS and would like to move the data to a new QNAP NAS, refer to Migrating NAS
for detailed instructions.
For New NAS Users:
1. Hardware Installation
2. Software Installation
3. Getting Utilities
4. Connecting to the Shared Folders
5. Connecting to the NAS by Web Browser
For Existing NAS Users:
Migrating NAS

Hardware Installation
After unpacking the NAS, first follow these instructions to install your hardware:
1. Install the hard drives. Before doing so, ensure the hard drives (HDDs) that you use are
compatible with the NAS. Go to the Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List section for more details.
2. Connect the QNAP NAS to the same network as your PC and power it on. During your installation
process, pay attention to LEDs and alarm buzzers to make sure that the NAS functions properly.
Go to the Checking System Status section for more details.
Note:
The steps above are also illustrated in the Quick Installation Guide (QIG) that can
be found in the product package or QNAP website (http://start.qnap.com).

Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List
This product works with 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch SATA hard disk drives and/or solid-state drives (SSD)
from major hard drive brands. For a full list of compatible drives, check the compatibility list on the
QNAP website (http://www.qnap.com/compatibility).
Note:
If you encounter a "Device not found" message, ensure that:
1.
Your NAS has been powered on;
2.
The network cable is connected to the NAS and the orange and green indicator lights
on its LAN port(s) are blinking; and
3.
The cloud key is correct.
Important:
QNAP disclaims any responsibility for product damage/malfunction or data
loss/recovery due to misuse or improper installation of hard disks in any occasions for any
reasons.
Caution:
Note that
if you install a hard drive (new or used) which has never been
installed on the NAS before, the hard drive will be formatted and partitioned
automatically and all the disk data will be cleared.

Checking System Status
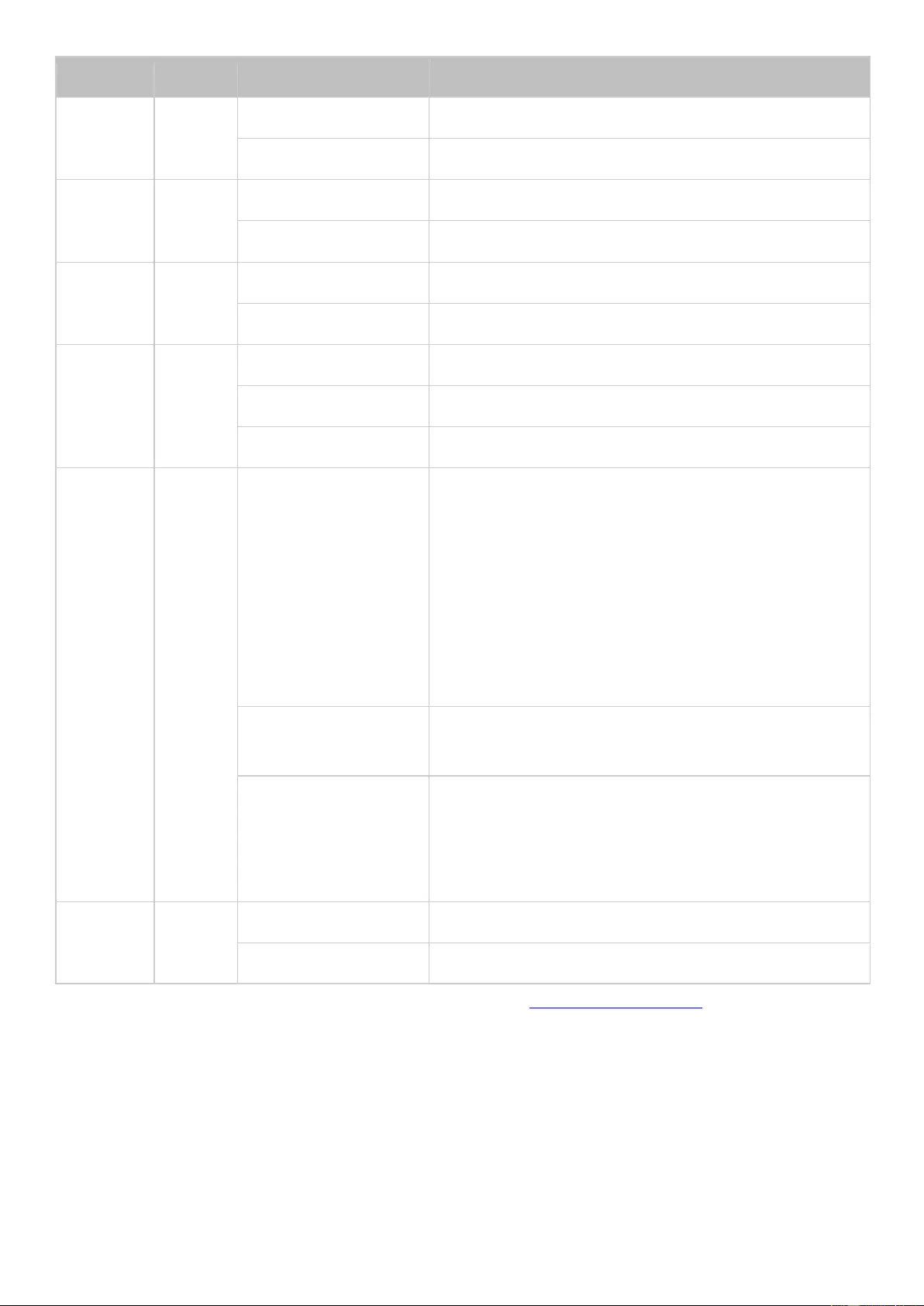
LED Display & System Status Overview
LED
Color
LED Status
Description
System
Status
Red/Gr
een
Flashes green and
red alternately every
0.5 sec
1) The hard disk drive on the NAS is being
formatted.
2) The NAS is being initialized.
3) The system firmware is being updated.
4) RAID rebuilding is in process.
5) Online RAID capacity expansion is in process.
6) Online RAID level migration is in process.
Red
1) The hard disk drive is invalid.
2) The disk volume has reached its full capacity.
3) The disk volume is going to be full.
4) The system fan is out of function (TS-119 does
not support smart fan.)
5) An error occurs when accessing (read/write) the
disk data.
6) A bad sector is detected on the hard disk drive.
7) The NAS is in degraded read-only mode (2
member hard drives fail in a RAID 5 or RAID 6
configuration, the disk data can still be read.)
8) Hardware self-test error.
Flashes red every
0.5 sec
The NAS is in degraded mode (one member hard
drive fails in RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6
configuration.)
Flashes green every
0.5 sec
1) The NAS is starting up.
2) The NAS is not configured.
3) The hard disk drive is not formatted.
Flashes green every
2 sec
The NAS is in S3 Sleep Mode1.
Green
The NAS is ready.
Off
All the hard disk drives on the NAS are in standby
mode.
LED
Color
LED Status
Description
Power1
Green
Flashes green
The NAS is booting up.
Green
The NAS is on and ready.
LAN
Orange
Orange
The disk data is being accessed from the network.
Flashes orange
The NAS is connected to the network.
10 GbE
Green
Green
The 10GbE network expansion card is installed.
Off
No 10GbE network expansion card is installed.
HDD
Red/Gre
en
Red
A hard drive read/write error occurs.
Flashes green
The disk data is being accessed.
Green
The hard drive can be accessed.
USB
Blue
Flashes blue every
0.5 sec
1) A USB device (connected to front USB port) is
being detected.
2) A USB device (connected to front USB port) is
being removed from the NAS.
3) The USB device (connected to the front USB
port) is being accessed.
4) The data is being copied to or from the external
USB or eSATA device.
Blue
A front USB device is detected (after the device is
mounted.)
Off
1) No USB device is detected.
2) The NAS has finished copying the data to or from
the USB device connected to the front USB port
of the NAS.
eSATA
Orange
Flashes
The eSATA device is being accessed.
Off
No eSATA device can be detected.
1This feature is only supported by certain NAS models. Visit http://www.qnap.com for more details.
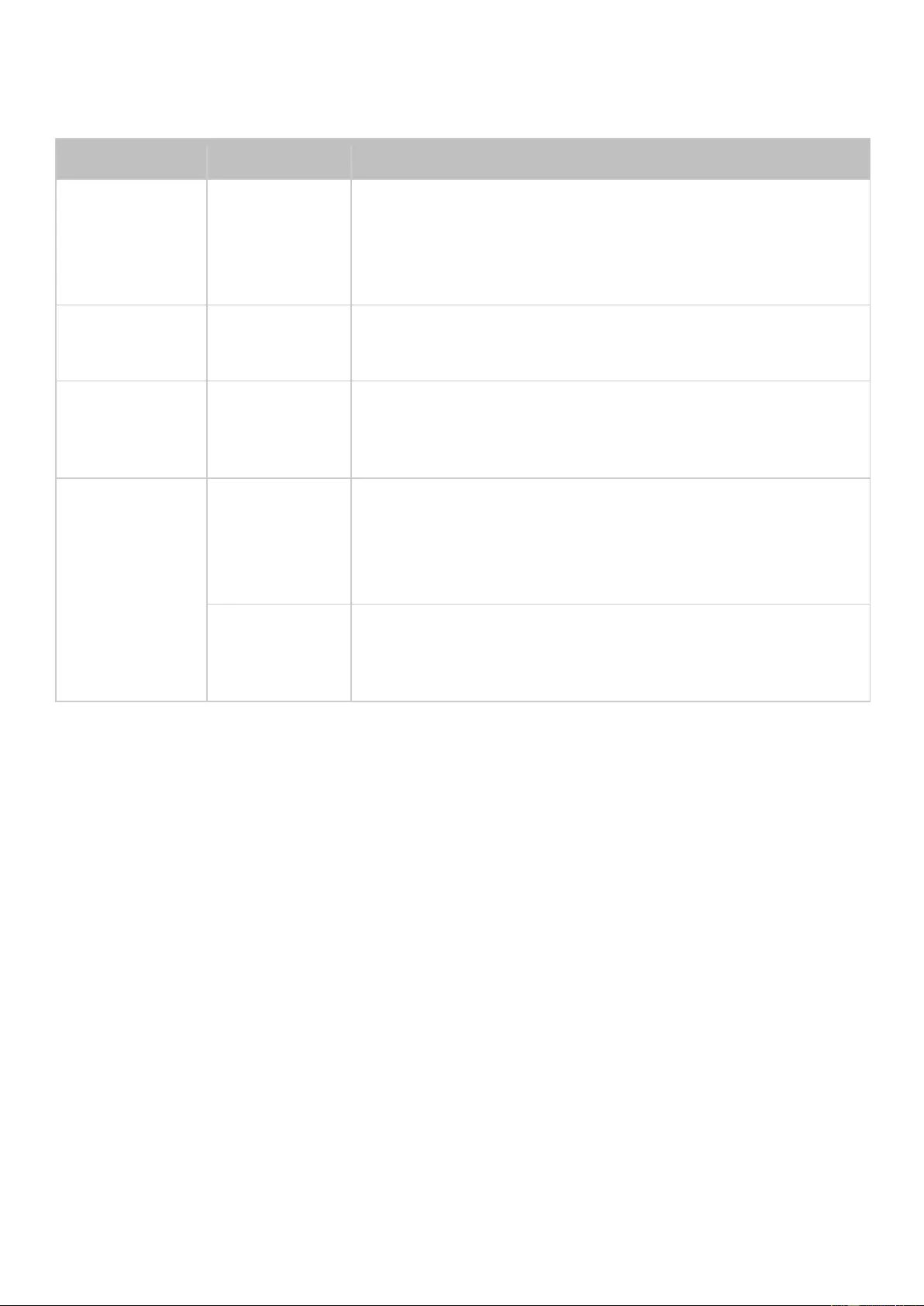
Alarm Buzzer
The alarm buzzer can be disabled in "Control Panel" >
"
System Settings
"
> "Hardware
"
>
"
Buzzer
".
Beep sound
No. of Times
Description
Short beep
(0.5 sec)
1
1) The NAS is starting up.
2) The NAS is being shut down (software shutdown).
3) The user presses the reset button to reset the NAS.
4) The system firmware has been updated.
Short beep
(0.5 sec)
3
The NAS data cannot be copied to the external storage device
from the front USB port.
Short beep
(0.5 sec), long
beep (1.5 sec)
3, every 5 min
The system fan is out of function (TS-119 does not support
smart fan.)
Long beep
(1.5 sec)
2
1) The disk volume is going to be full.
2) The disk volume has reached its full capacity.
3) The hard disk drives on the NAS are in degraded mode.
4) The user starts hard drive rebuilding.
1
1) The NAS is turned off by force shutdown (hardware
shutdown).
2) The NAS has been turned on and is ready.

Software Installation
After installing the NAS hardware, proceed to software installation. There are three approaches for
software installation:
1. Smart Installation Guide
2. Cloud Installation
3. HDMI Installation
Online installation and cloud installation are available for all new NAS models. All users are
encouraged to use cloud and online installation if possible. Contact our technical support
department if any problem arises during the installation process
(http://www.qnap.com/support.)

Smart Installation Guide
Follow the steps in this section to complete online installation for your NAS:
1. Go to http://start.qnap.com.
2. Choose the number of HDD bays and the model of your NAS and click "Start Now".
3. Click "Hardware" and follow the on-screen instructions to get hardware ready.
4. Scroll down to "Install firmware" and click "Local Installation".
5. Choose your operating system to download, install and run Qfinder Pro.
6. After installing Qfinder Pro, launch it to search for your NAS. Double click on your NAS in Qfinder
Pro to start the Smart Installation Guide. Follow the on-screen instructions to the built-in Qfinder
Pro Setup Wizard will guide you along the way to complete the firmware installation.
7. Proceed to log into QTS with your account username and password to log in (QTS is the operating
system for the Turbo NAS.)

Cloud Installation
Follow the steps in this section to complete cloud installation for your NAS:
1. Connect your NAS to the Internet, and on your PC, go to "install.qnap.com”.
2. Enter the cloud key (cloud key can be found from the sticker on top of your QNAP NAS) and click
"Enter".
3. Login to or register for myQNAPclould account. An activation email will be sent for new accounts.
Click Confirm Registration in email to activate account.
4. Enter a name for your QNAP NAS. This name will be used to remotely access your device. Click
Next.
5. Install hard drives on your Turbo NAS if you have not already done so.
6. On the Welcome page, click Start Smart Installation Guide to start the NAS installation process.
7. On the Name / Password page, enter your NAS name and admin password. Click Next.
8. On the Date / Time page, select your preferred time and date settings. Click Next.
9. On the Network page, enter your network settings. Click Next.
10. On the Services page, select which OS features you would like enabled. Multiple selections are
allowed. Click Next.
11. On the Multimedia page, select if you would like to enable multimedia functions immediately
after set up. Multiple selections are allowed. Click Next.
12. On the Disk page, select if you would like to configure disks now or later. Click Next.
13. On the Summary page, review your settings. Click Next if settings are correct. Click Back to
make changes.
Note:
If you encounter a "Device not found" message, ensure that:
1. Your NAS has been powered on;
2. the network cable is connected to the NAS and the orange and green indicator lights on its LAN
port(s) are blinking; and
3. The cloud key is correct.

HDMI Installation
Follow the steps in this section to complete the HDMI installation for your NAS:
1. Connect the NAS to an HDMI display.
2. Follow the onscreen instructions to complete the firmware installation.
3. Choose to install HD Station or log into QTS with QTS account username and password (QTS is
the operating system for the NAS.)
Note:
This installation is restricted to NAS models with an HDMI port.
The default login ID and password of the NAS are both "admin".

Getting Utilities
Visit http://www.qnap.com/ and go to "Support" > "Download" > "Utilities" and choose to
download and install the utilities on your PC.

Windows
There are two methods for connecting to shared folders of the NAS when using Windows:
Method 1: Connect to the shared folders of the NAS by using QNAP Qfinder Pro
1. Launch QNAP Qfinder Pro. Select your NAS and then click "Tool" > "Map Network Drive".
2. Select a shared folder on the NAS to be mapped as a network drive and click "Map Network
Drive".
3. Enter the username and password to connect to the NAS and click "OK".
4. Select a drive in the OS to map the folder chosen in Step 2 and click "Finish".
5. The mapped folder will appear when opening the File Explorer in Windows.
Note:
Alternatively, you can use the Storage Plug & Connect Wizard to connect to NAS
shared folders. The steps:
1.
Launch QNAP
Qfinder Pro
;
2.
Select "Storage Plug & Connect" under "Connect";
3.
Check "Login with username and password
"
and enter the username and password;
4.
Click a NAS shared folder;
5.
Click
"Map the Network Drive"
.
Method 2: Connect to the shared folders of the NAS by using File Explorer or Run
1. Open the Windows File Explorer, click on "Network" on the left and find the workgroup of the NAS.
If the NAS cannot be found, browse the whole network to search for the NAS. Double click the
name of the NAS to connect to it, or use the Run function in Windows (Windows key + R). Enter
\\NAS_name or \\NAS_IP.
2. Enter the default administrator name and password (the default login ID and password are both
"admin".).
3. Upload files to the shared folders.

Mac or Linux
Mac Users
There are two methods to connect shared folders on a NAS:
Method 1: Using QNAP Qfinder Pro
1. Launch QNAP Qfinder Pro, select your NAS, and go to "Connect" > "Open in File Explorer".
2. Enter your login ID and password.
3. Select the folder you want to mount and click "OK".
4. The folder is mounted.
Method 2: Connecting to Server
1. Choose "Go" > "Connect to Server".
2. Enter the NAS IP address.
3. Enter your login ID and password.
4. Select the folder you want to mount and click "OK".
5. The folder is mounted.
Linux Users
On Linux, run the following command:
mount -t nfs <NAS IP>:/<Shared Folder Name> <Directory to Mount>
For example, if the IP address of the NAS is 192.168.0.1, to connect to the shared folder "public"
under the /mnt/pub directory, use the following command:
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.1:/public /mnt/pub
Log into the NAS with the specified user ID, use the mounted directory to connect to the shared
folders.
Note: You must login as the "root" user to initiate the above command.
Connecting to NAS by Web Browser
To connect to the NAS by a web browser, follow these steps:
1. Enter http://NAS IP:8080 in the web browser. Or if using QNAP Qfinder Pro, simply double click
on the NAS to open the login page.
Note: The default NAS IP is 169.254.100.100:8080. If the NAS has been configured to use DHCP,
you can use QNAP Qfinder Pro to check the IP address of the NAS. Make sure the NAS and the
computer that runs QNAP Qfinder Pro are connected to the same subnet. If the NAS cannot be
found, connect the NAS to the computer directly and run QNAP Qfinder Pro again.
2. Enter the administrator's login id and password. Enable "Secure login" (Secure Sockets Layer login)
to allow a secure connection to the NAS. If a user without administration rights logs into the NAS,
the user can only change the login password (the default login ID and password of the NAS are
both "admin".)
Note: If the NAS is behind a NAT gateway, to connect to the NAS by secure login on the Internet,
port 443 must be opened on the NAT router and forwarded to the LAN IP of the NAS.
3. The NAS Desktop will be displayed.
Migrating NAS
Users can migrate their existing NAS to another NAS model with all data and configuration retained by
simply installing the hard drives from the original (source) NAS to the new (destination) NAS and
restarting the destination NAS. To determine which NAS models support system migration, see the
NAS Migration Compatibility Table below.
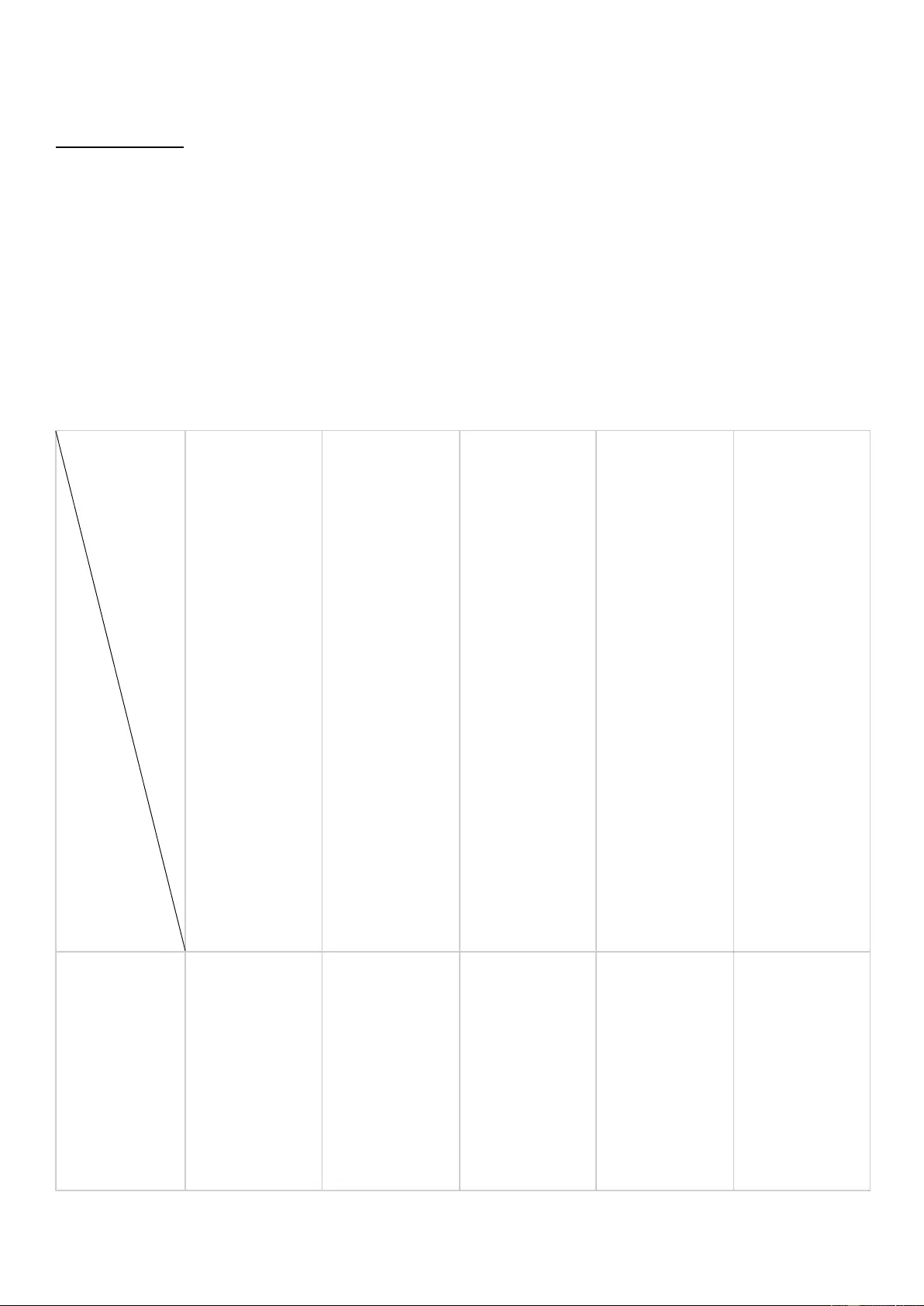
NAS Migration Compatibility Table
The series listed in this table include all models in the series. For example, TS-x51 includes the models TS-251,
TS251+, TS-251C, TS-251A, TS-451, TS-451+, TS-451C, TS-451A, TS-651, TS-851. Note that x31, x31+, x31X,
x31P, and x35 are listed individually.
Destination
Source
HS-210,
TS-x09,
TS-x10,
TS-x12,
TS-x19,
TS-x20,
TS-x21,
TS-x39,
TS-x59
TS-x31
TS-x69
TS-x31+,
TS-x31X,
TS-x31P,
TS-1635
IS-400,
TS-x51,
TBS-x53,
IS-x53,
TS-x53,
TS-x63,
TVS-x63,
TS-x70,
TVS-x70,
TVS-x71,
TVS-x73,
TS-x79,
TS-ECx79,
SS-ECx79,
TS-ECx80,
TVS-ECx82,
TS-x85,
TDS-x89
HS-210,
TS-x09,
TS-x10,
TS-x12,
TS-x19,
TS-x20,
TS-x21,
TS-x39,

TS-x59
TS-x31
TS-x69
TS-x31+,
TS-x31X,
TS-x31P,
TS-1635
IS-400,
TS-x51,
TBS-x53,
IS-x53,
TS-x53,
TS-x63,
TVS-x63,
TS-x70,
TVS-x70,
TVS-x71,
TVS-x73,
TS-x79,
TS-ECx79,
SS-ECx79,
TS-ECx80,
TVS-ECx82,
TS-x85,
TDS-x89
Note:
TS-109, TS-209, and TS-409 do not support system migration
.
Using System Migration
Note:
Users are encouraged to use drives that are compatible with the NAS. Non-compatible drives
may lead to system migration failure. For the compatibility list, go to
http://www.qnap.com/compatibility.
The destination NAS must have the drive slots to enclose all of the drives from the source NAS.
It is recommended that drive ordering of the source NAS is maintained in the destination NAS.
The myQNAPcloud account of the source NAS will need to be updated manually to the
destination NAS after system migration.
The McAfee License cannot be migrated to the new NAS. A new license will need to be
purchased.
The myQNAPCloud SSL certification will have to be manually migrated to the destination NAS.
The camera licenses for QVR Pro will not be migrated automatically. Contact technical support
to migrate the licenses to the new NAS after the migration.
Caution:
For rack mount NAS, the system migration procedure should be performed by an
authorized server manager or IT administrator to avoid system damage or serious injury.
1. Check that the source and destination NAS support system migration using the NAS Migration
Compatibility table.
2. Connect the power supply and network cable(s) to the destination NAS.
3. Boot up the destination NAS.
4. Download the source and destination NAS firmware from
https://www.qnap.com/en/product_x_down/. Make sure that both firmware are the same version
and build (QTS 4.2.0 or later).
5. Upgrading the firmware on the NAS.
a. Update the source firmware on NAS.
i. Reboot the NAS.
ii. Log into to QTS as an administrator. The default username/password is admin/admin.
iii. Go to “Control Panel” > “Firmware Update” > “Firmware Update”.
iv. Click "Browse" and locate source firmware.
v. Click "Update System".
b. Update the destination firmware on the NAS (use Qfinder Pro if not any hard drives are
installed).
If the destination NAS has not been initialized:
i. Download Qfinder Pro at https://www.qnap.com/en/utility/ and install.
ii. Launch Qfinder Pro.
iii. Right-click the destination NAS in Qfinder Pro and select "Update Firmware".
iv. Enter username and password of an administrator account. The default
username/password is admin/admin.
v. Click "Browse" and locate source firmware.
vi. Click "Update System".
If the destination NAS already has hard drives installed and has been initialized, the user may use
the steps in either 5a or 5b to upgrade the firmware of the NAS.
6. Shut down both NAS.

7. Remove the hard drives from the source NAS and any hard drives from the destination NAS. Install
drives from the source NAS to destination NAS. It is recommended that drive order is maintained.
Refer to hardware user guides for drive slot numbering.
8. Boot up the destination NAS.
9. If prompted to update the firmware, follow the firmware update instructions to install the newest
firmware.
10. If the volumes do not appear after the firmware update, reinstalled the firmware using the
steps in 5a and the volumes will be accessible.
11. Optional: Check your NAS settings to determine if all settings were migrated by logging into
QTS as an administrator.
Due to the different specifications of different models, there is a slight chance that the settings may
not be imported to the destination NAS. In this event, manual configuration will be required.
Some new features that are available on the destination NAS, but not on the source NAS, may only be
available on newly created storage pools.

QTS Basics and Desktop
QTS is a user-friendly NAS operating system designed to enhance every aspect of your NAS experience.
With basic methods such as drag-and-drop or point and click, you can complete most NAS operations.
Check the following links to learn more about QTS:
Introducing QTS
Using QTS Desktop

Introducing QTS
Built on a Linux foundation, QTS is shaped from an optimized kernel to deliver
high-performance services that satisfy needs for file storage, management, backup,
multimedia applications, surveillance, and more. The intuitive, multi-window and
multi-tasking QTS GUI make it incredibly easy to manage your NAS, use its rich home
applications, enjoy multimedia, and install more applications from an integrated App Center.
QTS also adds value to business applications and effectively increase business efficiency with
abundant features, including file sharing, iSCSI, virtualization, backup, privilege settings, and
more. Coupled with various utilities and smart mobile apps, QTS is the ultimate platform for
building a personal or private cloud, synchronizing data and sharing files.
NAS for Home - Easily enrich home entertainment and content sharing
Tons of photos, music, videos and documents are often scattered across multiple computers
in modern homes. QNAP NAS feature plenty of handy applications to let you smartly connect
and manage your data and enjoy a truly digital life in a well-secured home network. No
boundaries for multimedia sharing at home, and no boundaries for sharing content with
family, and friends. Learn more about the exciting features that a QNAP NAS offers you:

Intuitive GUI with Multi-Windows, Multi-Tasking, Multi-Application, Multi-Device access support
Cross platform data storage, backup and sharing center
Revolutionary music, photo and home video center
Personal cloud storage
Free and large capacity for Dropbox-style data sync
Hundreds of install-on-demand applications from the App Center
Energy-efficient & eco-friendly
NAS for Business - Efficiently optimize business IT infrastructure
IT efficiency, coupled with low total cost of ownership (TCO) is an essential factor for business
competitiveness. QNAP NAS features advanced capabilities for keeping businesses running at
maximum efficiency including business-critical applications, seamless file sharing, easy integration into
existing networks, flexible virtualized IT environments, and more. Learn more about the compelling
features that a QNAP NAS offers your business:
Large data storage, backup and file sharing center
Supports both scale-up and scale-out solutions for growing data needs
Advanced storage management with dynamic thin-provisioning, SSD caching and JBOD expansion
functions
Trustworthy data security and data encryption
Reliable IP SAN storage (iSCSI) as primary and secondary storage for virtualization environments
Private cloud storage
Free and large capacity for Dropbox-style data sync
Hundreds of install-on-demand applications from the App Center
Development Center for third-party partners to build apps for the NAS
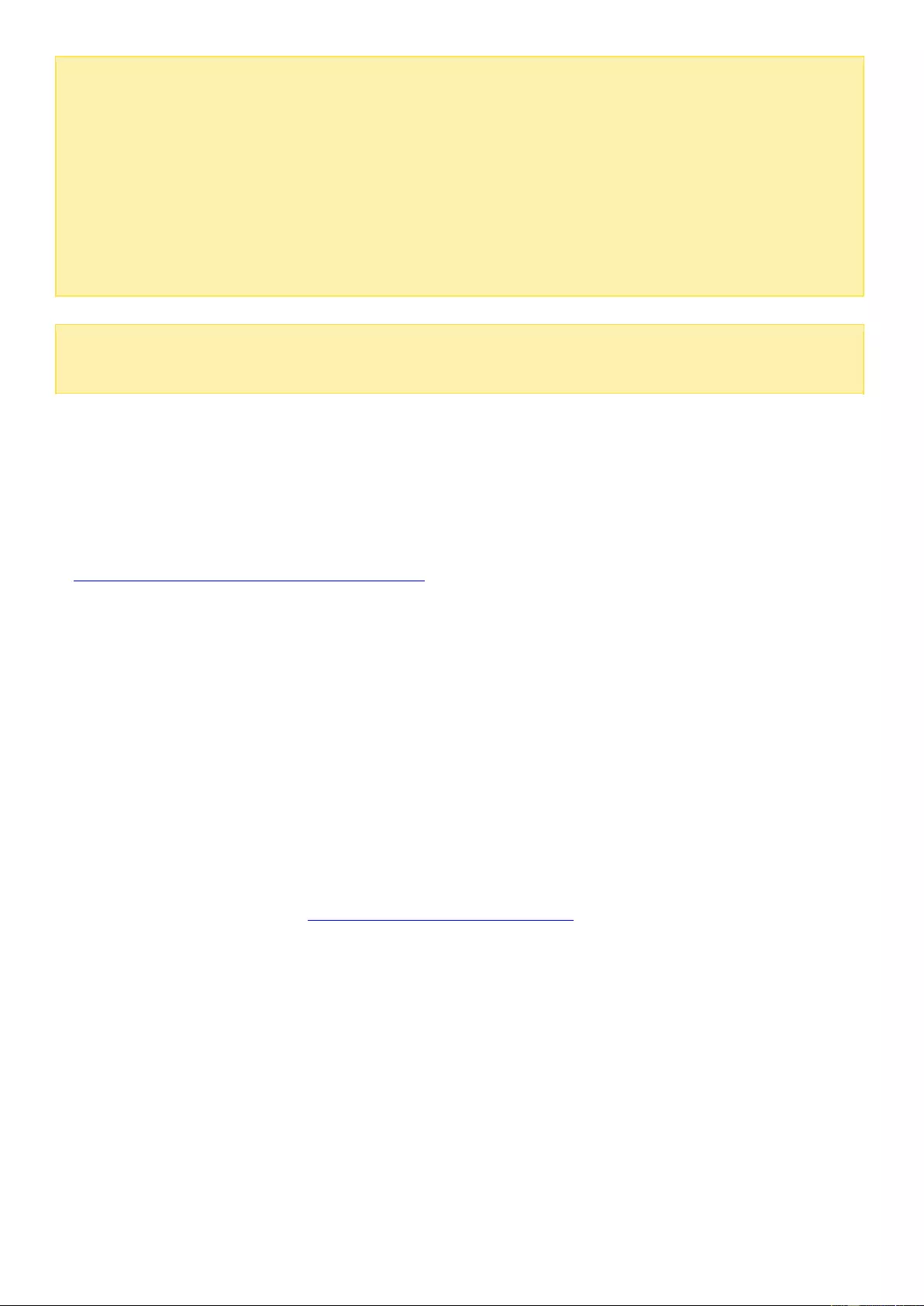
Using QTS Desktop
After you finish the basic setup and login to the NAS, the desktop will appear. Each main desktop
feature is introduced in the following sections.
Topics covered in this chapter:
QTS Desktop
2-step Verification
QTS Desktop
No.
Name
Description
1
Show Desktop
Minimize or restore all open windows.
2
Main Menu
Show the Main Menu. It includes two parts:
1) SYSTEMS: Key system features and options designed to help you manage
or optimize your NAS.
2) APPLICATIONS: Applications developed by QNAP to enhance your NAS

experience.
Please note that the default Internet browser, instead of a new window on
the NAS Desktop, will be launched once you click a third-party application.
3
Search
Enter keywords in the search bar to find an application or function and
related instructions. Click the search result to launch an application or
function or consult its online QTS help.
4
Background
Task
Review or control (such as pause or postpone) all the tasks running in the
background. For example, HDD S.M.A.R.T. scanning, anti-virus scanning, file
backup, or multimedia conversion.
5
External
Device
List all external storage devices and USB printers that are connected to the
NAS via its USB or SATA ports. Click a listed device to open File Station to
view this device. Click "More>>" to open the External Device page for
relevant settings and operations (for more information about File Station,
refer to the File Station chapter). Click the eject icon (up-arrow icon) to eject
the external device.
6
Notification
and Alert
You can check recent errors, warnings, and notifications here. Click “Clear
All” to clear the list. To view all historical events, click “More>>” to open
System Logs. For more information about System Logs, refer to the System
Logs chapter.
7
Options
Profile: Specify your email address and change your profile picture. You
can also check System Logs and edit the Login Screen here.
Wallpaper: Change the default wallpaper or upload your own photo and
set it as the wallpaper.
2-step Verification: Enable 2-step Verification to enhance the security of
user accounts. For more information, refer to the 2-step Verification
section.
Change Password: Change your login password.
E-mail Account: Set up the email address you use when sharing files via
email in Music Station, Photo Station, Video Station, or File Station.
Miscellaneous:
o Auto log-out after an idle period of: Specify the idle period after which
the user will be automatically logged out.
o Warn me when leaving QTS: Users will be prompted for confirmation
every time they try to leave the QTS Desktop (such as closing the
browser or clicking the “back” button of the browser). It is
recommended to enable this option.
o Reopen windows when logging back into QTS: If you enable this

option, all the current desktop settings (such as “the windows opened
when your log out") will be retained until your next login.
o Show the desktop switching button: Check this option to hide the next
desktop button (No. 12) and only display them when you move your
mouse cursor close to the buttons.
o Show the desktop switching button: Enable this option to show the
“next desktop” button (No. 12). If you disable this option, the “next
desktop” button will only appear when you move the mouse cursor
near it.
o Show the link bar on the desktop: Enable this option to show the link
bar (No. 13, No. 14, No. 15, and no.16).
o Show the Dashboard button: Enable this option to show the
Dashboard button (NO. 10).
o Show the NAS time on the desktop: Enable this option to display the
NAS time in the bottom-right corner of the desktop.
o Keep Main Menu open after selection: Keep the Main Menu
pinned/unpinned on the desktop.
o Show a list of actions when external storage devices are detected:
Enable this option and the Autoplay dialog box will appear after you
plug in an external device.
8
Admin Options
Configure user-specific settings, change your user password, restart/shut
down the NAS or log out.
Last login time: The last time when you logged in to the system.
Options: Refer to the previous section.
Sleep: Put your NAS into sleep. There are three ways to wake up the
NAS: 1) Press the power button until you hear a beep; 2) Use the
Wake-on-LAN (WOL) feature with QNAP Qfinder Pro or Qmanager. Note
that to use this method, WOL must be enabled in "Control Panel" >
"Power" > "Wake-on-LAN(WOL)"; 3) Press the power button on a
RM-IR002 or MCE remote control.
o Note: This feature is only available on certain models.
Restart: Restart your NAS.
Shutdown: Shut down your NAS.
o Note: To power off a NAS, you can also:
Press and hold the power button on your NAS for 1.5
seconds.
Run Qfinder Pro and click "Tools" > "Shut down Server".
Logout: Log yourself out

9
More
Help: Show NAS references, including Quick Start, Virtualization Guide,
Help Center, and Tutorials.
Language: Choose your preferred language.
Desktop Preference: Applications can be opened in Tab Mode, Window
Mode, or Frameless Mode. Only Tab Mode is available if you log in to the
NAS using a mobile device.
o Tab Mode: In this mode, the application window will be expanded to
fit the entire NAS Desktop, and only one application window can be
displayed at a time.
o Window mode: In this mode, the application window can be resized to
your preferred shape.
o Frameless Mode: In this mode, applications will be opened without
their frames.
Help Request: Send a help request to QNAP.
About: Check the NAS model, firmware version, numbers of hard drives
already installed and empty bays, used and unused storage space.
10
Dashboard
Check important NAS statistics, including system and hard drive health,
resources, storage usage, online users, scheduled tasks, etc. Click the
header in each widget to open its own page.
11
Desktop Area
Arrange or remove the applications on the desktop.
12
Next Desktop/
Last Desktop
Switch between different desktop pages.
13
myQNAPcloud
Go to the myQNAPcloud website.
14
QNAP Utility
Check and download NAS utilities and mobile apps.
15
Feedback
Go to QNAP Wiki or QNAP Forum, or seek Customer Service.
16
Help Request
Send a help request to QNAP.
17
Network
Recycle Bin
All of the deleted items can be found here. Right click on this icon to open
the Network Recycle Bin, empty it (delete files permanently), or configure it
(refer to the Network Recycle Bin chapter for more information.)

2-step Verification
2-step Verification enhances the security of user accounts. After enabling it, you will need to enter a
one-time security code (6 digits) in addition to your password whenever you sign in to the NAS. 2-step
verification requires a mobile device with an authenticator app which supports the Time-based
One-Time Password (TOTP) protocol. Supported apps include Google Authenticator
(Android/iPhone/BlackBerry) or Authenticator (Windows Phone).
Start 2-step verification
1. Install the authenticator App on your mobile device: For Android and iOS devices, install the
Google Authenticator App from their respective App stores. For Windows Phone, install the
Authenticator from its Store.
2. The system times of your mobile device and NAS must be synchronized. It is recommended to use
the time provided from the Internet.
3. Go to "Options" > "2-step Verification" and click "Get Started". Complete the steps in the wizard
to set up the NAS and your mobile device.
4. Configure your authenticator App by scanning the QR code or by entering the Secret Key into the
App.
5. Enter the code generated from the app to the NAS to verify the correct configuration.
6. Select an alternative verification method by emailing you a security code or by answering a
security question if you cannot use your mobile device. To email a security code, the SMTP server
must be properly configured in "Control Panel" > "Notification" > "E-mail".
Sign in QTS with 2-step verification
After your username and password are verified, you will be promoted to enter a security code. Enter
the code currently provided from the authenticator app to sign in to QTS. If you cannot use your
mobile device or your device is lost, you can select "Verify another way" to sign in with your chosen
alternative verification method.
Stop 2-step verification
If you want to disable 2-step verification, go to "Options" > "2-step Verification" and click "Stop".
Administrators can disable 2-step verification for other NAS account users, if they are locked out, by
going to "Control Panel" > "Users" > "Edit Account Profile".
If an administrator cannot use a mobile device to sign in to QTS and no other administrators are
available to disable 2-step verification for the locked-out administrator, the NAS must be restored to
factory settings by physically pressing the "RESET" button on the NAS.
Tip:
All of the Dashboard widgets can be dragged onto the desktop for monitoring specific details.

The Dashboard will be presented differently on different screen resolutions.
The color of the Dashboard button will change based on the status of system health for quick
recognition.
Note:
The recommended minimum screen resolution for QTS 4.x is 1024x768.
The sleep function will automatically be disabled if the NAS has QNAP expansion
enclosure(s) connected to it.
System Settings
Go to
"Control Panel" > "System Settings" to set up your NAS.
For details on the settings, refer to the following links:
General Settings
Storage Manager
Network
Security
Hardware
Power
Notification
Firmware Update
Backup/Restore
External Device
System Status
System Logs
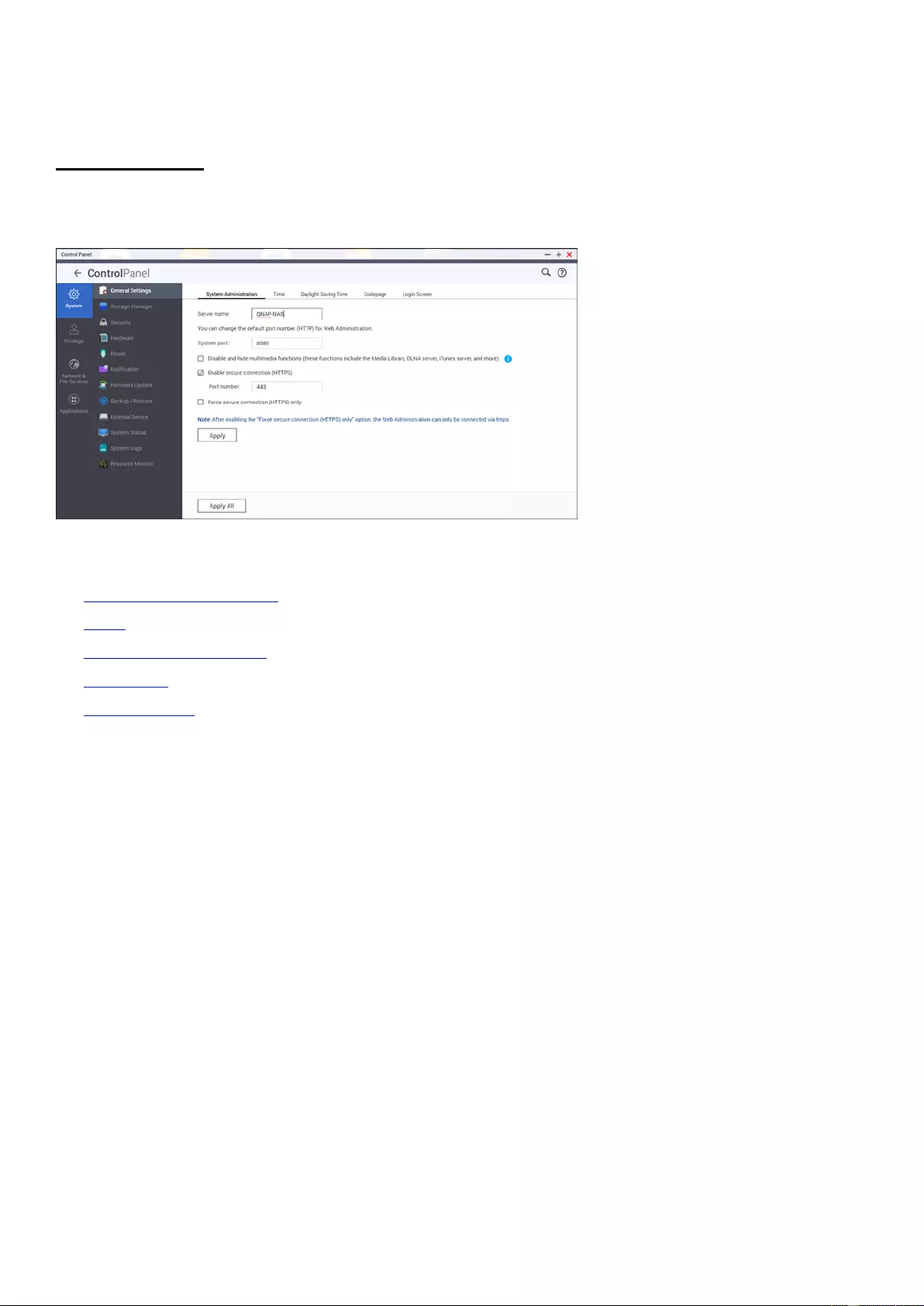
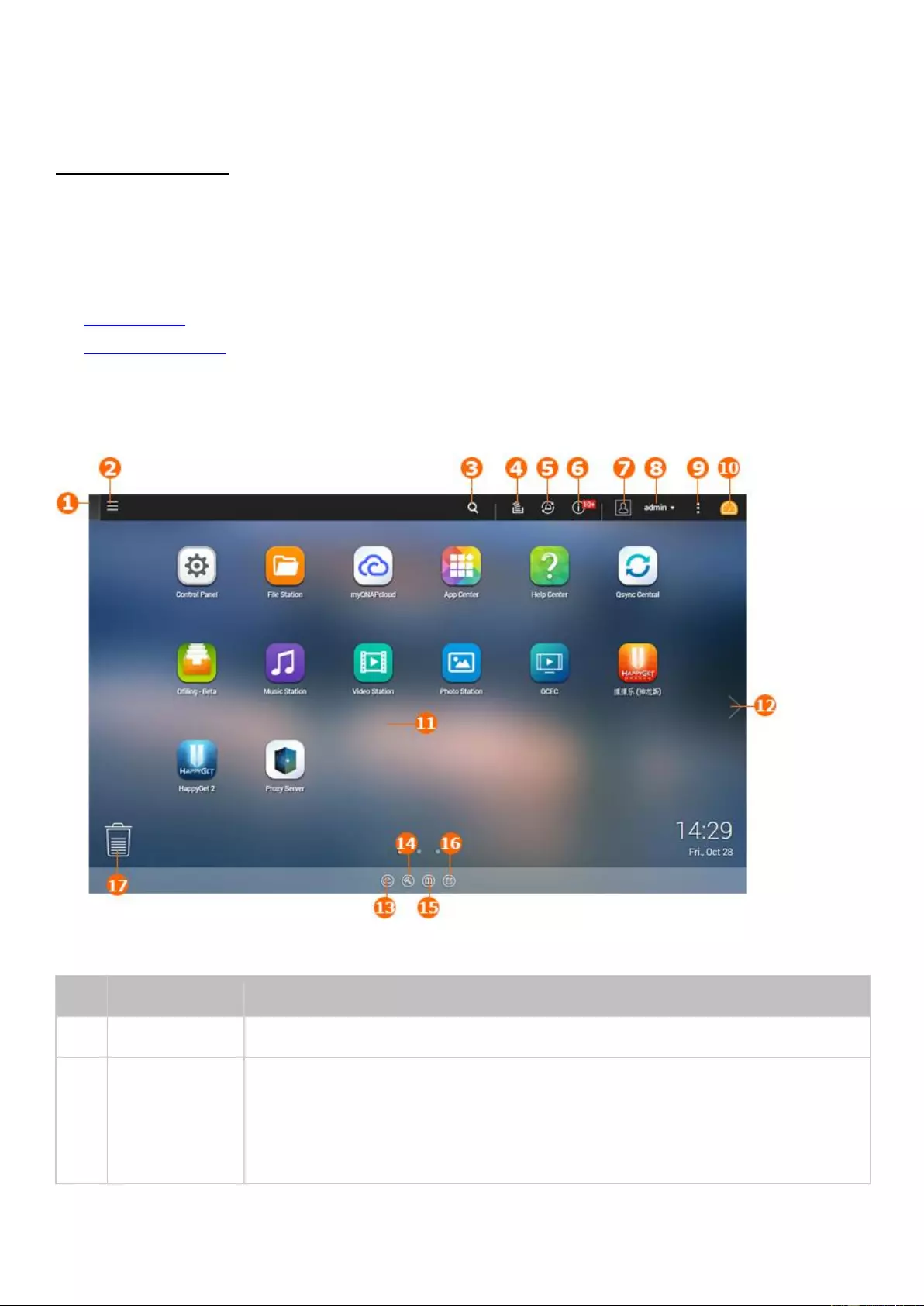
General Settings
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "General Settings" to configure basic settings of
the NAS.
Topics covered in this chapter:
System Administration
Time
Daylight Saving Time
Codepage
Login Screen
System Administration
Basic Settings:
Enter the name of the NAS. The NAS name supports maximum 14
characters and can be a combination of letters (a-z, A-Z), numbers (0-9), and dash (-),
Space ( ), period (.), or pure numbers are not allowed. Enter a port number for system
management. The default port is 8080. The services which use this port include: System
Management, Photo Station, Music Station, File Station and Download Station. If you are
not sure about this setting, use the default port number.
Enable Secure Connection (HTTPS):
Allows users to connect to the NAS by HTTPS.
Enable secure connection (HTTPS) and enter the port number. If the option "Force secure
connection (HTTPS) only" is enabled, users can only connect to the web administration
page by HTTPS.
Force Secure Connection (HTTPS):
After enabling this option, you can only connect
and log into the NAS using HTTPS.
Disable and hide the home/multimedia features such as Photo Station, Music
Station, Surveillance Station, Download Station, iTunes server, and DLNA media

server:
Multimedia features, including Photo Station, Music Station, Video Station (both
2.0 and 1.0.5), Surveillance Station, Download Station, DJ Station, iTunes server, Media
Library and DLNA media server, may be hidden or disabled by default on the following
NAS models: x70U, x79 Pro, x79U, TS-x51,TS-x31+, TS-x31,TS-269H and HS-210. To
enable the multimedia features for those models, uncheck this option.
Time
Basic time settings:
Adjust the date and time format and time zone according to the
location of the NAS. If the settings are incorrect, the following problems may occur:
o
When using a web browser to connect to the NAS or save a file, the displayed time of
the action will be incorrect.
o
The time of event logs will be inconsistent with the actual time when an action occurs.
o
All scheduled jobs will be run at an incorrect time.
Manual Setting:
Select this option to manually set the time of the NAS.
Synchronize with an Internet time server automatically:
Enable this option to
automatically synchronize the date and time of the NAS with an NTP (Network Time
Protocol) server. Enter the IP address/domain name of the NTP server (for example:
time.nist.gov, time.windows.com) then enter the time interval for synchronization. This
option can only be used when the NAS is connected to the Internet.
Set the server time the same as your computer time:
To synchronize the time of
the NAS with your computer's time, click "Update" next to this option.
Note:
First time synchronization may take several minutes to complete.
Daylight Saving Time
If your region uses daylight saving time (DST), enable "Adjust system clock automatically for
daylight saving time" and click "Apply". The latest DST schedule of the time zone specified in
the "Time" section will be shown. The system time will be adjusted automatically according to
the DST. Note that if your region does not adopt DST, the options on this page will not be
available. To manually enter the DST table, select the option "Enable customized daylight
saving time table". Click "Add Daylight Saving Time Data", enter the daylight saving time
schedule, and click "Apply" to save the settings.
Codepage
Select the language the NAS uses to display files and directories.

Note:
All of the files and directories on the NAS use Unicode encoding. If your FTP clients
or PC OS does not support Unicode, select the language which is the same as the OS
language in order to properly view files and directories on the NAS.
Login Screen
The administrator can customize the login screen by going to “Control Panel” > “General
Settings” > “Login Screen”. There are two templates to choose from: classic and photo wall.
Classic login page settings:
Show firmware version: Display QTS firmware verion on bottom right of login page.
Show the link bar: Display links to myQNAPCloud, QNAP Utility, and Feedback links to the
bottom of the login page.
Background: Select a photo to use as login screen background, then select center, fill, fit,
stretch, or tile as the display mode. Click remove to set background to default image.
Logo: Select image to use as a logo on login screen. Click remove to remove logo.
Message: Enter a personal login message. You may select font color and size.
Photo Wall page settings:
Show firmware version: Display QTS firmware verion on bottom right of login page.
Show the link bar: Display links to myQNAPCloud, QNAP Utility, and Feedback links at the
bottom of the login page.
Message Title: Enter a personal message title for the login page.
Message: Enter a personal message for the login page.
Randomly select 100 photos: Use 100 random photos stores on the NAS for login page
background.
Display the most recently shared 100 photos: Use 100 most recently shared photos on
NAS for login page background.
Change Picture: Select an image to use as a logo on login screen. Click remove to
remove logo.
Use my profile picture: Use user account profile picture as login screen logo.
After you finish the above settings, click "Preview" to preview your settings or "Apply" to save
changes.
Storage Manager
Manage volumes and RAID systems, monitor hard drive health, encrypt/decrypt file systems, and
configure iSCSI systems and virtual disks with Storage Manager.
For storage management features, refer to the following links:
Volume Management
RAID Management
Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T
Encrypted File System
iSCSI
Virtual Disk

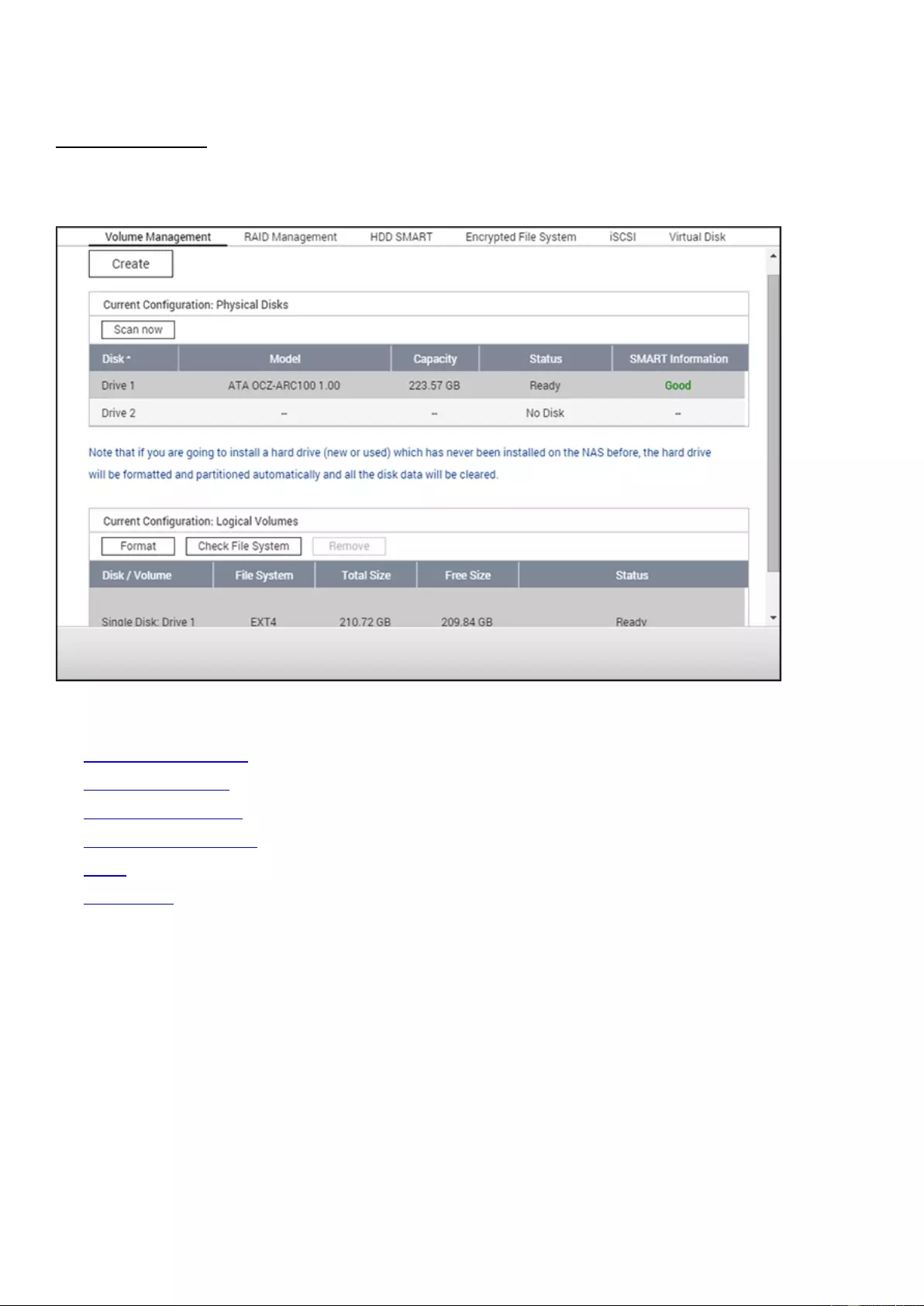
Volume Management
This page shows the model, size, and current status of the hard drives on the NAS. You can format,
check, and scan for bad blocks on the hard drives.
Topics covered in this chapter:
Default Shared Folders
Overview on RAID Systems
Disk Configuration and NAS Models
Default Shared Folders
When the hard drives are formatted, the NAS will create the following default share folders:
home: The user's home folder.
Public: The default shared folder for file sharing by everyone.
Qdownload/Download: The shared folder for Download Station.
Qmultimedia/Multimedia: The shared folder for Multimedia Station.
Qusb/Usb: The shared folder for data copy function using USB ports.
Qweb/Web: The shared folder for Web Server.
Qrecordings/Recordings: The shared folder for Surveillance Station.
Note:
The default shared folders of the NAS are created on the first disk volume and the
directory cannot be changed.
Depending on the NAS model, some of the above shared folders may not be created by
default by the NAS.
We recommend formatting disk volumes larger than 2TB using the EXT4 file system.
Overview on RAID Systems
Single Disk Volume: Every hard drive is used as a standalone disk. If a hard drive is damaged,
all the data will be lost.
JBOD (Just a bunch of disks): A collection of hard drives that does not offer any RAID
protection. The data is written to the physical disks sequentially. The total storage capacity is
equal to the sum of the capacity of all member hard drives.
RAID 0 Striping Disk Volume: RAID 0 (striping disk) combines 2 or more hard drives into one
larger volume. The data is written to the hard drive without any parity information and no

redundancy is offered. The total storage capacity of a RAID 0 disk volume is equal to the sum of
the capacity of all member hard drives.
RAID 1 Mirroring Disk Volume: RAID 1 duplicates the data between two hard drives to provide
disk mirroring. To create a RAID 1 array, a minimum of 2 hard drives are required. The storage
capacity of a RAID 1 disk volume is equal to the size of the smallest hard drive.
RAID 5 Disk Volume: The data is striped across all the hard drives in a RAID 5 array. The parity
information is distributed and stored across each hard drive. If a member hard drive fails, the
array enters degraded mode. After installing a new hard drive to replace the failed one, the data
can be rebuilt from other member drives that contain the parity information. To create a RAID 5
disk volume, a minimum of 3 hard drives are required. The storage capacity of a RAID 5 array is
equal to (N-1) * (size of smallest hard drive.) N is the number of hard drives in the array.
RAID 6 Disk Volume: The data is striped across all of the hard drives in a RAID 6 array. RAID 6
differs from RAID 5 that a second set of parity information is stored across the member drives in
the array. It tolerates the failure of two hard drives. To create a RAID 6 disk volume, a minimum
of 4 hard drives are required. The storage capacity of a RAID 6 array is equal to (N-2) * (size of
smallest hard drive.) N is the number of hard drives in the array.
RAID 10 Disk Volume: RAID 10 combines four or more disks in a way that protects data against
loss of non-adjacent disks. It provides security by mirroring all data on a secondary set of disks
while using striping across each set of disks to speed up data transfers. RAID 10 requires an even
number of hard drives (a minimum of 4.) The storage capacity of a RAID 10 disk volume is equal
to (size of the smallest capacity disk in the array) * N/2. N is the number of hard drives in the
volume.
Disk Configuration and NAS Models
For disk configuration and applied NAS models, please refer to the table below:
Disk Configuration
Applied NAS Models
Single disk volume
All models
RAID 1, JBOD (just a bunch of disks)
2-drive models or above
RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 5+hot spare
4-drive models or above
RAID 6+hot spare
5-drive models or above
RAID 10
4-drive models or above
RAID 10+hot spare
5-drive models or above
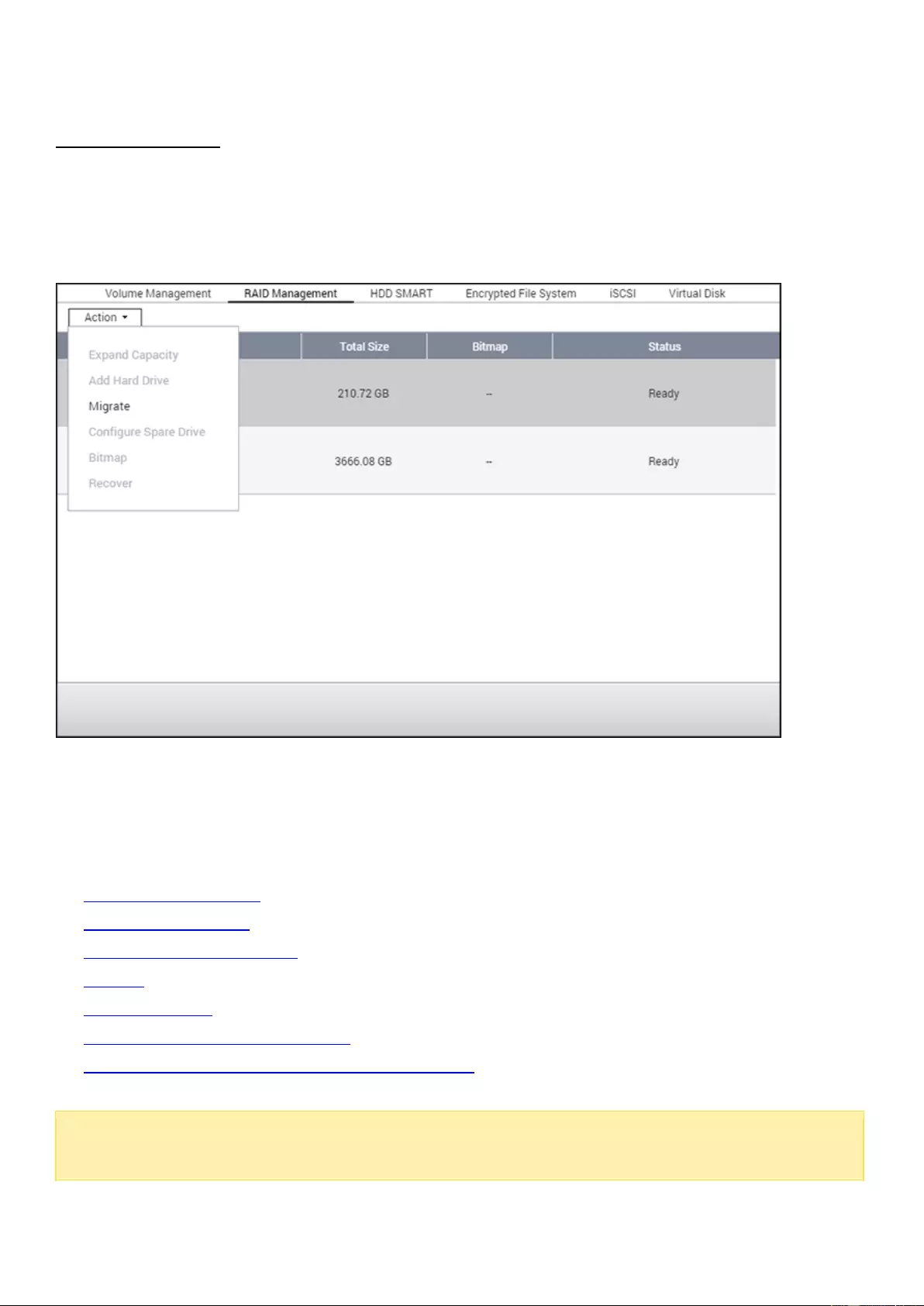
RAID Management
On this page, you can perform online RAID capacity expansion (RAID 1, 5, 6, 10) and online
RAID level migration (single disk, RAID 1, 5, 10), add a hard drive member to a RAID 5, 6, or
10 configuration, configure a spare hard drive (RAID 5, 6, 10) with the data retained, enable
Bitmap, recover a RAID configuration, and set a global spare.
To expand the storage capacity of a RAID 10 volume, you can perform online RAID capacity
expansion or add an even number of hard disk drives to the volume.
Topics covered in this chapter:
Expanding Capacity
Adding Hard Drives
Configuring Spare Drives
Bitmap
RAID Recovery
Setting/Canceling Global Spare
Further Information about RAID Management
Note: Online RAID capacity expansion, online RAID level migration, and RAID recovery are not
supported by one-bay NAS models, the TS-210, and TS-212.

Expanding Capacity (Online RAID Capacity Expansion)
Scenario
You bought three 250GB hard drives for initial setup of a TS-509 Pro NAS and configured
RAID 5 disk configuration with the three hard drives.
A half year later, the data size of the department has largely increased to 1.5TB. In other
words, the storage capacity of the NAS is running out of use. At the same time, the price of
1TB hard drives has dropped to a large extent.
Operation procedure
In "Storage Manager" > "RAID Management", select the disk volume for expansion and click
"Action" > "Expand Capacity".
Click "Change" for the first hard drive to be replaced. Follow the instructions to proceed.
1.
When the description displays "Please remove this drive", remove the hard drive from
the NAS. Wait for the NAS to beep twice after removing the hard drive.
2.
When the description displays "Please insert the new drive", plug in the new hard drive to
the drive slot.
3.
After plugging in the hard drive, wait for the NAS to beep. The system will start
rebuilding.
4.
After rebuilding has completed, repeat the steps above to replace other hard drives.
5.
After changing the hard drives and disk rebuilding has completed, click "Expand
Capacity" to execute RAID capacity expansion.
6.
Click "OK" to proceed.
7.
The NAS beeps and starts to expand the capacity.
Tip:
After replacing the hard drive, the description field shows "You can replace this drive". This
means you can replace the hard drive to a larger one or skip this step if the hard drives have been
replaced already.
Caution:
When the hard drive synchronization is in process, Do NOT turn off the NAS or plug
in or unplug the hard disk drives.
The process may take from hours to tens of hours to finish depending on the drive size. Do
NOT turn off the NAS during this process.
After RAID capacity expansion has finished, the new capacity is shown and the status is
"Ready". You can start to use the NAS. (In the example you have 1.8TB logical volume.)
Tip:
If the description still shows "You can replace this hard drive" and the status of the

drive volume says "Ready", it means the RAID volume is still expandable.
Note:
If you have a hot spare drive set up in a RAID configuration, remember to manually remove
that drive before expanding a RAID Volume or adding a drive to that volume.
Starting with QTS 4.1.1, the maximum volume capacity supported for online RAID capacity
expansion in ARM-based NAS models is 16TB. For previous versions, the maximum volume
capacity supported is 8TB.
Online RAID Level Migration
During the initial setup of the TS-509 Pro, you bought a 250GB hard drive and configured it
as a single disk. The TS-509 Pro is used as a file server for data sharing across departments.
After six months an increasing amount of data is being saved on the TS-509 Pro. There are
growing concerns regarding the hard drive capacity and health. Therefore, you planned to
upgrade the disk configuration to RAID 5. You can install one hard drive for setting up the
TS-509 Pro and upgrade the RAID level of the NAS with online RAID level migration in the
future. The migration process can be done without turning off the NAS. All of the data will be
retained.
You can do the following with online RAID level migration:
Migrate the system from single disk to RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10
Migrate the system from RAID 1 to RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10
Migrate the system from RAID 5 with 3 hard drives to RAID 6
You need to:
Prepare a hard drive of the same or larger capacity as an existing drive in the RAID
configuration.
Execute RAID level migration (migrate the system from single disk mode to RAID 5 with 4
hard drives.)
1.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "Volume Management". The current disk volume
configuration displayed on the page is single disk (the capacity is 250GB.)
2.
Plug in the new hard drives to drive slots 2 and 3 of NAS. The NAS will detect the new
hard drives. The status of the new hard drives is "Unmounted".
3.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "RAID Management", click "Action" > "Migrate".
4.
Select one or more available drives and the migration method. The drive capacity after
migration is shown. Click "Migrate".
5.
Note that all the data on the selected hard drive will be cleared. Click "OK" to confirm.

6.
When migration is in process, the required time and total drive capacity after migration
are shown in the description field.
7.
The NAS will enter "Read only" mode when migration is in process during 11%–49% to
assure the data of the RAID configuration will be consistent after RAID migration
completes.
8.
After migration completes, the new drive configuration (RAID 5) is shown and the status
is Ready. You can start to use the new drive configuration.
The process may take from hours to tens of hours to finish depending on the hard drive size.
You can connect to the web page of the NAS to check the status later.
Online RAID Capacity Expansion
Scenario
You had a tight schedule to set up a file server and an FTP server. However, you had only one
250GB hard drive. Therefore, you set up the TS-509 Pro with a single disk configuration. The
original plan was to set up a 3TB RAID 5 network data center with the TS-509 Pro. You now
plan to upgrade the disk configuration of the TS-509 Pro to RAID 5 and expand the total
storage capacity to 3TB with all the original data retained after the hard drives are purchased.
Using online RAID level migration to migrate the system from single disk to RAID 5 the total
storage capacity will be 750GB (with one 250GB hard drive and three 1TB hard drives, the
disk usage will be 250GB*4 for RAID 5.) You can refer to the previous step for the operation
procedure.
Use online RAID capacity expansion to replace the 250GB hard drive with a new 1TB hard
drive, and then expand the logical volume from 750GB to 3TB of RAID 5. You can refer to the
previous step for the operation procedure.
Adding Hard Drives
Follow the steps below to add a hard drive member to a RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk configuration.
1. Make sure the status of the RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration is "Ready".
2. Install a hard drive on the NAS. If you have a hard drive which has already been formatted as
single disk volume on the NAS, you can add this hard drive to the RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration.
It is recommended to use hard disk drives with the same capacity for the RAID configuration.
3. Select the RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration on the "RAID Management" page and click "Add Hard
Drive".
4. Select the new hard drive. The total drive capacity after adding the drive will be shown. Click "Add
Hard Drive."
5. All the data on the new hard drive will be deleted during this process. The data on the original
RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration will be retained. Click "OK". The NAS will beep twice.

To add hard drives to a RAID 10 disk volume, repeat the above steps. Note that you need to add an
even number of hard disk drives to a RAID 10 volume. The storage capacity of the RAID 10 volume will
increase upon successful configuration.
This process may take a few hours to tens of hours to complete depending on the number
and the size of the hard drive. Do NOT turn off the NAS during this process. You can use a
RAID configuration of larger capacity after the process.
Configuring Spare Drives
You can add a spare drive to or remove a spare drive from a RAID 5, 6, or 10 configuration.
Follow these steps to use this feature.
1. Make sure the status of the RAID 5, 6, 10 configuration is "Ready".
2. Install a hard drive in the NAS. If you have a hard drive which has already been formatted as
single disk volume on the NAS, you can configure this hard drive as the spare drive. It is
recommended to use hard disk drives with the same storage capacity for RAID configuration.
3. Select the RAID volume and click "Configure Spare Drive."
4. To add a spare drive to the selected configuration, select the hard drive and click "Configure
Spare Drive." To remove a spare drive, unselect the spare drive and click "Configure Spare Drive."
5. All the data on the selected hard drive will be deleted. Click "OK" to proceed.
The original data on the RAID 5, 6, or 10 disk volume will be retained. After the configuration
completes, the status of the disk volume will become "Ready".
Note:
A hot spare drive must be removed from the disk volume before executing the
following action:
Online RAID capacity expansion
Online RAID level migration
Adding a hard drive member to a RAID 5, RAID 6 or RAID 10 volume
Bitmap
Bitmap improves the time for RAID rebuilding after an unexpected error, or removing or
re-adding a hard drive from/to a RAID configuration. If an array has a bitmap, the member
hard drive can be removed and re-added and only block changes since the removal (as
recorded in the bitmap) will be re-synchronized. To use this feature, select a RAID volume
and click "Action" > "Bitmap".
Note:
Bitmap support is only available for RAID 1, 5, 6, and 10.
RAID Recovery
RAID Recovery: If the NAS is configured as RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 6 hard drives are
accidentally unplugged from the NAS, you can plug in the same hard drives into the same
drive slots and click "Recover" to recover the volume status from "Not active" to "Degraded
mode".
If the disk volume is configured as RAID 0 or JBOD and one or more of the hard drive
members are disconnected or unplugged, you can plug in the same hard drives into the same
drive slots and use this function to recover the volume status from "Not active" to "Normal".
The disk volume can be used normally after successful recovery.
Disk volume
Supports RAID
recovery
Maximum number of disk removal allowed
Single
No
-
JBOD
Yes
1 or more
RAID 0
Yes
1 or more
RAID 1
Yes
1 or 2
RAID 5
Yes
2 or more
RAID 6
Yes
3 or more
RAID 10
No
-
Note:
After recovering a RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6 disk volume from not active to degraded
mode by the RAID recovery, you can read or write the volume normally. The volume
status will be recovered to normal after synchronization.
If the disconnected drive is damaged, the RAID recovery function will not work.
Standard
RAID 5
QNAP RAID 5
Standard
RAID 6
QNAP RAID 6
Degraded
mode
N-1
N-1
N-1 & N-2
N-1 & N-2
Read Only
N/A
N-1, bad blocks
N/A
N-2, bad blocks

Protection (for
immediate data
backup & hard
drive
replacement)
found in the
surviving hard
drives of the array.
found in the
surviving hard
drives of the array.
RAID Recovery
(RAID Status:
Not Active)
N/A
If re-plugging in all
original hard drive
to the NAS and
they can be spun
up, identified,
accessed, and the
hard drive
superblock is not
damaged.
N/A
If re- plugging in all
original hard drives
to the NAS and
they can be spun
up, identified,
accessed, and the
hard drive
superblock is not
damaged.)
RAID Crash
N-2
N-2 failed hard
drives and any of
the remaining hard
drives cannot be
spun
up/identified/access
ed.
N-3
N-3 and any of the
remaining hard
drives cannot be
spun
up/identified/acces
sed.
N = Number of hard disk drives in the array
Setting/Canceling Global Spare
A global spare drive replaces a failed hard drive in any RAID 1, 5, 6, 10 disk volumes on the
NAS automatically. When the same global spare drive is shared by multiple RAID volumes on
the NAS, the spare drive will replace the first failed drive in a RAID volume.
To set a disk drive as a global spare drive, select the single disk volume and click "Action" >
"Set Global Spare".
All the disk data will be cleared on the hard drive.
Note:
The capacity of the global spare drive must be equal to or larger than that of a
member drive of a RAID disk volume.
To cancel a global spare drive, select the drive and click "Action" > "Cancel Spare Drive".
Further Information about RAID Management of the NAS
The NAS supports the following actions according to the number of hard disk drives and disk
configurations supported. Refer to the following table for details.
Original Disk
Configuration * No.
of Hard Disk Drives
No. of New
Hard Disk
Drives
Action
New Disk Configuration *
No. of Hard Disk Drives
RAID 5 * 3
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 5 * 3
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 3
3
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 3
4
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 3
5
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 4
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 4
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 4
3
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 4
4
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 5
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 5
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 5
3
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 6
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 6
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 5 * 7
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 6 * 4
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 6 * 4
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 6 * 4
3
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 4
4
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 6 * 5
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 6 * 5
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 5
3
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 8

RAID 6 * 6
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 6
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 6 * 7
1
Add hard drive member
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 10 * 4
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 10 * 4
4
Add hard drive member
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 10 * 6
2
Add hard drive member
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 1 * 2
RAID 5 * 3
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 3
RAID 5 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 5 * 5
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 5 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 5 * 7
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 5 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 6 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 4
RAID 6 * 5
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 6 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 6 * 7
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 6 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 10 * 4
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 4
RAID 10 * 6
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 10 * 8
1
Online RAID capacity
expansion
RAID 10 * 8
Single * 1
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 1 * 2
Single * 1
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 3
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 4
Single * 1
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 5
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 6
Single * 1
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 7
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 8
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 4
Single * 1
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
Single * 1
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8
Single * 1
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 4
Single * 1
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 6
Single * 1
7
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 3
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 5
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 7
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 5 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8
RAID 1 * 2
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 4
RAID 1 * 2
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 6
RAID 1 * 2
6
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 10 * 8
RAID 5 * 3
1
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 4
RAID 5 * 3
2
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 5
RAID 5 * 3
3
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 6
RAID 5 * 3
4
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 7
RAID 5 * 3
5
Online RAID level
migration
RAID 6 * 8

Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T
Monitor the hard disk drives (HDD) health, temperature, and the usage status by HDD
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology.)
The following information of each hard drive on the NAS is available.
Field
Description
Summary
Displays the hard drive S.M.A.R.T. summary and the latest test result.
Hard disk
information
Displays the hard drive details (model, serial number, HDD capacity, etc.)
SMART
information
Displays the hard drive S.M.A.R.T. information. Any drives with values lower than
the threshold are regarded as abnormal.
Test
Perform quick or complete hard drive S.M.A.R.T. tests.
Settings
Configures the temperature alarm. When a hard drive temperature exceeds the
preset values, the NAS records the error logs.
You can also set quick and complete test schedules. The latest test result is
shown on the Summary page.

Encrypted File System
On this page, you can manage encrypted disk volumes on the NAS. Each encrypted disk
volume is locked by a particular key. The encrypted volume can be unlocked by the following
methods:
Encryption Password: Enter the encryption password to unlock the disk volume. The default
password is "admin". The password must be 8-16 characters long. Symbols (! @ # $ % ^ & *
( )_+ = ?) are supported.
Encryption Key File: Upload the encryption file to the NAS to unlock the disk volume. The key can
be downloaded from the "Encryption Key Management" page after the disk volume has been
unlocked successfully.
Data encryption functions may be unavailable in accordance with legislative restrictions of some
countries (Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, etc.)
Topics covered in this chapter:
Data Encryption on the NAS
Before you Start
Creating New Encrypted Disk Volumes
Encryption Verification
Behavior of Encrypted Volumes upon System Reboot
Encryption Key Management
Unlocking Disk Volumes Manually
Data Encryption on the NAS
NAS disk volumes can be encrypted using 256-bit AES encryption to provide data breach protection.
Encrypted disk volumes can only be mounted for normal read/write access with the authorized
password. Encryption protects confidential data from unauthorized access even if the hard drives or the
entire NAS were stolen.
About AES encryption:
In cryptography, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is an encryption standard adopted by the
U.S. government. The standard comprises three block ciphers, AES-128, AES-192 and AES-256 […].
Each AES cipher has a 128-bit block size, with key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits, respectively. The
AES ciphers have been analyzed extensively and are now used worldwide. (Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard)

AES volume-based encryption is applicable only to specific NAS models. Refer to the comparison table
at: http://www.qnap.com/images/products/comparison/Comparison_NAS.html
Before you Start
Please be aware of the following before using data encryption on the NAS.
NAS encryption is volume-based. A volume can be a single disk, a JBOD configuration, or a RAID
array.
Select whether or not to encrypt a disk volume before it is created on the NAS. You will not be able
to encrypt a volume after it has been created unless the disk volume is initialized. Note that
initializing a disk volume will clear all the disk data.
Disk volume encryption cannot be removed without initialization. To remove the encryption on the
disk volume, you have to initialize the disk volume and all of the data will be cleared.
Keep the encryption password or key safe. If you forget the password or lose the encryption key,
you will not be able to access the data.
Before you start, read the instructions carefully and strictly adhere to the instructions.
Creating New Encrypted Disk Volumes
If the NAS has been installed, follow these steps to create a new encrypted disk volume by installing
new hard drives in the NAS:
1. Install the new hard drive(s) in the NAS.
2. Login to the NAS as an administrator. Go to Storage Manager" > "Volume Management".
3. Click "Create".
4. Select the disk volume you want to configure according to the number of new hard drives.
5. Check the drive for the intended volume.
6. Select "Yes" for the "Encryption" option and enter the encryption settings. Then click "Create" to
create the new encrypted volume.
All of the data on the selected drives will be DELETED! Back up your data before creating an encrypted
volume.
You have created an encrypted disk volume on the NAS.
Encryption Verification
To verify the disk volume is encrypted, login to the NAS as an administrator. Go to
"Storage
Manager" > "Volume Management".
You will be able to see the encrypted disk volume, with a lock
icon in the Status column. The lock will be open if the encrypted volume has been unlocked. A disk
volume without the lock icon in the Status column is not encrypted.

Behavior of Encrypted Volumes upon System Reboot
In this example, we have two encrypted disk volumes on the NAS.
The first volume (Single Disk Drive 1) has been created with the option "Save Encryption
Key" disabled.
The second volume (Single Disk Drive 4) has been created with the option "Save Encryption
Key" enabled.
After restarting the NAS, check the volume status. The first drive has been unlocked and
mounted but the second drive is locked. Since the encryption key is not saved on the second
disk volume, you have to manually enter the encryption password to unlock it.
Saving the key on the NAS will protect you only if your hard drives are stolen. However,
there is a risk of data breach if the entire NAS is stolen as the data is accessible after
restarting the NAS.
If you do not save the encryption key on the NAS, your NAS will be protected against
data breach even if the entire NAS were stolen. The disadvantage is that you have to
unlock the disk volume manually on each system restart.
Encryption Key Management
To manage encryption key settings, login to the NAS as an administrator and go to
Storage Manager
"
> "Encrypted File System".
There are four options to manage the encryption key:
Change the encryption key: Input your old encryption password and input the new
password. (After the password is changed, any previously exported keys will not work.
You must download the new encryption key if necessary.)
Download Encryption Key File: Input the encryption password to download the encryption
key file. Downloading the encryption key file will allow you to save the encryption key in
a file. The file is also encrypted and can be used to unlock a volume, without knowing the
real password (see "unlock a disk volume manually" below.) Save the encryption key file
in a secure place!
Remove Saved Key: Remove saved keys with this option.
Save Encryption Key: Save the encryption key on the NAS for automatic unlocking and
mounting the encrypted disk volume when the NAS restarts.
Unlocking Disk Volumes Manually
Login to the NAS as an administrator and go to "Storage Manager" > "Encrypted File System". You will
see your encrypted volumes and their status: locked or unlocked. To unlock your volume, first click
"Unlock this device". Choose to either input the encryption password, or use the encryption key file. If
the encryption password or the key file is correct, the volume will be unlocked and accessible.
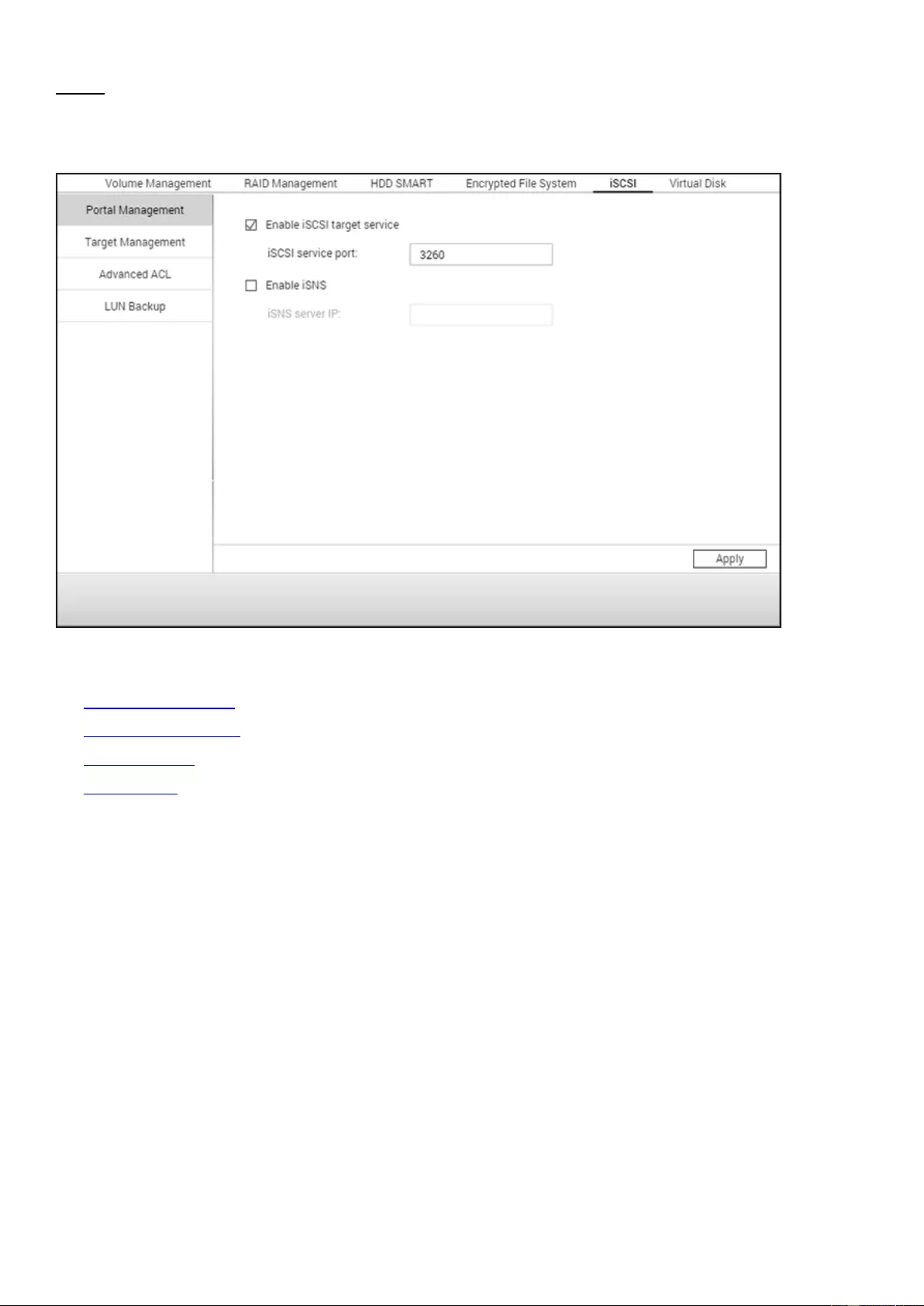
iSCSI
Go to
"Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Storage Manager" to m
anage the iSCSI target
service, create iSCSI target lists and the advanced ACL and back up LUNs.
For setting up relevant features, refer to the following links:
Portal Management
Target Management
Advanced ACL
LUN Backup

Portal Management
The NAS supports a built-in iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) service for server
clustering and virtualized environments.
Topics covered in this chapter:
Manual iSCSI Configuration
iSCSI Quick Configuration Wizard
Creating iSCSI LUNs
Manual iSCSI Configuration
The NAS supports built-in iSCSI service. To use this function, follow the steps below:
1. Install an iSCSI initiator on the computer (Windows PC, Mac, or Linux).
2. Enable iSCSI Target Service on the NAS and create an iSCSI target.
3. Run the iSCSI initiator and connect to the iSCSI target (NAS).
4. After logging in, format the iSCSI target (disk volume.) You can start using the disk volume on
the NAS as a virtual drive on the computer.
When referring to your computer and the storage device, the computer is called an initiator because
it initiates the connection to the device, which is called a target.
Note: It is NOT recommended to connect to the same iSCSI target with two different clients
(iSCSI initiators) at the same time, as it may lead to data loss or disk damage.
iSCSI Quick Configuration Wizard
A maximum of 256 iSCSI targets and LUNs can be created. For example, if you create 100
targets on the NAS, the maximum number of LUNs you can create is 156. Multiple LUNs can
be created for each target. However, the maximum number of concurrent connections to the
iSCSI targets supported by the NAS varies depending on network infrastructure and
application performance. Excessive concurrent connections may impact NAS performance.
Follow these steps to configure the iSCSI target service on the NAS.
1.
Under "Portal Management" enable iSCSI target service. Apply the settings.
2.
Go to "Target Management" and create iSCSI targets on the NAS. If you have not
created any iSCSI targets, the Quick Installation Wizard will automatically be launched
and prompt users to create iSCSI targets and LUNs. Click "OK".
3.
Select to create an iSCSI target with a mapped LUN, an iSCSI target only, or an iSCSI
LUN only. Click "Next."
4.
Create iSCSI target with a mapped LUN.
5.
Click "Next."
6.
Enter the target name and target alias. You can check the options "Data Digest" and/or
"Header Digest" (optional). These are the parameters that the iSCSI initiator will be
verified when it attempts to connect to the iSCSI target.
7.
Enter the CHAP authentication settings. If you enter the username and password settings
under "Use CHAP authentication" only, only the iSCSI target authenticates the initiator,
i.e. the initiators have to enter the username and password settings here to access the
target.
Mutual CHAP: Enable this option for two-way authentication between the iSCSI target and
the initiator. The target authenticates the initiator using the first set of username and
password. The initiator authenticates the target using the "Mutual CHAP" settings.
Field
Username limitation
Password limitation
Use CHAP
authentication
The only valid characters are
0-9, a-z, A-Z
Maximum length: 256
characters
The only valid characters are
0-9, a-z, A-Z
Maximum length: 12-16
characters
Mutual CHAP
The only valid characters are
0-9, a-z, A-Z, : (colon), . (dot),
and - (dash)
Maximum length: 12-16
characters
The only valid characters are
0-9, a-z, A-Z, : (colon), . (dot),
and - (dash)
Maximum length: 12-16
characters
Creating iSCSI LUNs
An iSCSI LUN is a logical volume mapped to the iSCSI target. Select one of the following modes to
allocate disk space to the LUN:
Thin Provisioning: Allocate disk space in a flexible manner. You can allocate disk space to the
target anytime regardless of the current storage capacity available on the NAS. Over-allocation is
allowed as the storage capacity of the NAS can be expanded by online RAID capacity expansion.
Instant Allocation: Allocate the disk space to the LUN instantly. This option guarantees the disk
space assigned to the LUN but may take more time to create the LUN.
1. Enter the name of the LUN and specify the LUN location (disk volume on the NAS.) Enter the
capacity for the LUN. Click "Next".
2. Confirm the settings and click "Next".

3. When the target and the LUN have been created, click "Finish".
4. The target and LUN are shown on the list under the "Target Management" tab.

Target Management
You can create multiple LUNs for an iSCSI target. In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Creating iSCSI Targets
Switching LUN Mapping
iSCSI LUN Capacity Expansion
Optimizing iSCSI Performance
Creating iSCSI Targets
Note: The following information only applies to ARM-based NAS models with firmware version
3.3.0 or later and x86-based NAS models running firmware version 3.2.0 or later.
You can create multiple LUNs for an iSCSI target. Follow the steps below to create more LUNs for an
iSCSI target.
1. Click "Quick Configuration Wizard" under "Target Management".
2. Select "iSCSI LUN only" and click "Next".
3. Select the allocation method. Enter the name of the LUN, select the LUN directory, and specify the
capacity for the LUN. Click "Next."
4. Select the target to map the LUN to (optional).
5. Confirm the settings and click "Next."
6. When the LUN has been created, click "Finish" to exit the wizard.
7. The LUNs can be mapped to and unmapped from the iSCSI target anytime. You can also unmap
the LUN from a target and map it to another target.
Item
Status
Description
iSCSI target
Ready
The iSCSI target is ready but no initiator
has connected to it yet.
Connected
The iSCSI target has been connected by an
initiator.
Disconnected
The iSCSI target has been disconnected.
Offline
The iSCSI target has been deactivated and
cannot be connected by the initiator.
LUN
Enabled
The LUN is active for connection and is
visible to authenticated initiators.
Disabled
The LUN is inactive and is invisible to the
initiators.
Button
Name
Description
Deactivate
Deactivate a ready or connected target. Note that the connection from
the initiators will be removed.
Activate
Activate an offline target.
Modify
Modify the target settings: target alias, CHAP information, and checksum
settings.
Modify the LUN settings: LUN allocation, name, disk volume directory,
etc.
Delete
Delete an iSCSI target. All the connections will be removed.
Disable
Disable an LUN. All the connections will be removed.
Enable
Enable an LUN.
Unmap
Unmap the LUN from the target. You must disable the LUN before
unmapping it. When you click this button, the LUN will be moved to
"Un-Mapped iSCSI LUN List".
Map
Map the LUN to an iSCSI target. This option is only available on the
"Un-Mapped iSCSI LUN List".
View
View the connection status of an iSCSI target.
Switching LUN Mapping
Note: The following information only applies to ARM-based NAS models with firmware version
3.3.0 or later and x86-based NAS models running firmware version 3.2.0 or later.
Follow the steps below to switch the mapping of an iSCSI LUN.
1.
Select an iSCSI LUN to unmap from an iSCSI target and click "Disable".
2.
Click "Unmap" and the LUN will appear on the Un-Mapped iSCSI LUN List. Click "Map" to
map the LUN to another target.
3.
Select the target to map the LUN to and click "Apply"
4.
The LUN is mapped to the target.
After creating the iSCSI targets and LUN on the NAS, you can use the iSCSI initiator
installed on your computer (Windows PC, Mac, or Linux) to connect to the iSCSI targets and
LUN and use the disk volumes as the virtual drives on your computer.

iSCSI LUN Capacity Expansion
The NAS supports expanding the capacity of an iSCSI LUN. To do so, follow the steps below.
1.
Locate an iSCSI LUN on the iSCSI target list in "iSCSI" > "Target Management". Click
"Modify".
2.
Specify the capacity of the LUN. Note that the LUN capacity can be increased many times
up to the maximum limit but cannot be decreased.
3.
Click "Apply" to save the settings.
Note:
An iSCSI LUN must be mapped to an iSCSI target before increasing the capacity.
For the type of LUN allocation, the maximum LUN capacity for thin provisioning is 32TB, while
for instant allocation, the maximum LUN capacity is limited by the available free space on the
disk volume.
Optimizing iSCSI Performance
In the environments that require high performance storage, such as virtualization, users are
recommended to do the following to optimize the iSCSI and NAS hard disks performance:
Use instant allocation
: When creating an iSCSI LUN, select "Instant Allocation" to
achieve slightly higher iSCSI performance. However, the benefits of thin provisioning will
be lost.
Create multiple LUNs
: Create multiple LUNs according to the number of processors on
the NAS (this can be found in "System Status" > "Resource Monitor".) If the NAS has
four processors, it is recommended to create four or more LUNs to optimize iSCSI
performance.
Use different LUNs for heavy load applications
: Spread applications such as
databases and virtual machines that need high read/write performance to different LUNs.
For example, if there are two virtual machines which intensively read and write data on
LUNs, it is recommended to create two LUNs so that the VM workloads can be efficiently
distributed.

Connecting to iSCSI Targets using Microsoft iSCSI Initiator on Windows
Before you start to use the iSCSI target service, make sure you have created an iSCSI target
with a LUN on the NAS and installed the correct iSCSI initiator for your OS.
ISCSI initiator on Windows:
Microsoft iSCSI Software Initiator is an official application for Windows that allow users to
implement an external iSCSI storage array over the network.
Using iSCSI initiator:
Start the iSCSI initiator from "Control Panel" > "Administrative Tools". Under the "Discovery"
tab click "Add Portal" (or "Discover Portal".) Enter the NAS IP and the port number for the
iSCSI service. The available iSCSI targets and their status will then be shown under the
"Targets" tab. Select the target you want to connect to and click "Connect". You can click
"Advanced" to specify login information if you have configured the authentication otherwise
simply click "OK" to continue. Upon logging in, the status of the target will show "Connected".
After the target has been connected Windows will detect its presence and treat it as if a new
hard disk drive has been added which needs to be initialized and formatted before we can use
it. Go to "Control Panel" > "Administrative Tools" > "Computer Management" > "Disk
Management" and you should be prompted to initialize the newly-found hard drive. Click "OK"
then format this drive as you normally would when adding a new disk. After disk initialization
and formatting, the new drive is attached to your PC. You can now use this iSCSI target as a
regular disk partition.

Connecting to iSCSI Targets by Xtend SAN iSCSI Initiator on Mac OS
This section shows you how to use Xtend SAN iSCSI Initiator on Mac OS to add the iSCSI
target (QNAP NAS) as an extra partition. Before you start to use the iSCSI target service,
make sure you have created an iSCSI target with a LUN on the NAS and installed the correct
iSCSI initiator for your OS.
About Xtend SAN iSCSI initiator:
ATTO's Xtend SAN iSCSI Initiator for Mac OS X allows Mac users to utilize and benefit from
iSCSI. It is compatible with Mac OS X 10.4.x to 10.6.x. For more information, visit:
http://www.attotech.com/products/product.php?sku=INIT-MAC0-001
Using
Xtend SAN iSCSI initiator:
Follow the steps below:
1.
After installing the Xtend SAN iSCSI initiator, you can find it in "Applications".
2.
Click the "Discover Targets" tab and choose "Discover by DNS/IP" or "Discover by iSNS"
according to the network topology. In this example, we will use the IP address to
discover the iSCSI targets.
3.
Follow the instructions and enter the server address, iSCSI target port number (default:
3260), and CHAP information (if applicable). Click "Finish" to retrieve the target list.
4.
The available iSCSI targets on the NAS will be shown. Select the target you want to
connect to and click "Add".
You can configure the connection properties of selected iSCSI target in the "Setup" tab. Click
the "Status" tab, select the target to connect to. Then click "Login" to proceed. The first time
you login to the iSCSI target, a message will remind you the disk is not initialized. Click
"Initialize…" to format the disk. You can also open "Disk Utilities" to initialize the disk. You can
now use the iSCSI target as an external drive on your Mac.

Connecting to iSCSI Targets by Open-iSCSI Initiator on Ubuntu Linux
This section shows you how to use the Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator on Ubuntu to add the iSCSI target as
an extra partition. Before you start using the iSCSI target service, make sure you have created an
iSCSI target with a LUN on the NAS and installed the correct iSCSI initiator for your OS.
About Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator:
The Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator is a built-in package in Ubuntu 8.04 LTS (and later). You can connect to
an iSCSI volume at a shell prompt with just a few commands. More information about Ubuntu is
available at http://www.ubuntu.com and for information and download location of Open-iSCSI, visit:
http://www.open-iscsi.org
Note: Snapshot LUNs are not supported by the Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator.
Using Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator:
Install the open-iscsi package. The package is also known as the Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator.
# sudo apt-get install open-iscsi
Follow these steps to connect to an iSCSI target with Linux Open-iSCSI Initiator:
You may need to modify the iscsid.conf for CHAP logon information, such as
node.session.auth.username & node.session.auth.password.
# vi /etc/iscsi/iscsid.conf
Save and close the file, then restart the open-iscsi service.
# /etc/init.d/open-iscsi restart
Discover the iSCSI targets on a specific host, for example, 10.8.12.31 with default port 3260.
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p 10.8.12.31:3260
Check the available iSCSI nodes to connect.
# iscsiadm -m node
** You can delete the nodes you do not want to connect to when the service is on with the following
command:
# iscsiadm -m node --op delete --targetname THE_TARGET_IQN
Restart open-iscsi to login all the available nodes.
# /etc/init.d/open-iscsi restart

You should be able to see the login message as below:
Login session [iface: default, target: iqn.2004-04.com:NAS:iSCSI.ForUbuntu.B9281B, portal:
10.8.12.31,3260] [ OK ]
Check the device status with dmesg.
# dmesg | tail
Enter the following command to create a partition, /dev/sdb is the device name.
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Format the partition.
# mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
Mount the file system.
# mkdir /mnt/iscsi
# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/iscsi/
You can test the I/O speed using the following command.
# hdparm -tT /dev/sdb1
Below are some "iscsiadm" related commands.
Discover the targets on the host:
# iscsiadm -m discovery --type sendtargets --portal HOST_IP
Login a target:
# iscsiadm –m node --targetname THE_TARGET_IQN --login
Logout a target:
# iscsiadm –m node --targetname THE_TARGET_IQN --logout
Delete a Target:
# iscsiadm –m node --op delete --targetname THE_TARGET_IQN
Advanced ACL
Note: The following information only applies to ARM-based NAS models with firmware version
3.3.0 or later and x86-based NAS models running firmware version 3.2.0 or later.
You can create a LUN masking policy to configure permissions of iSCSI initiators which
attempt to access the LUN mapped to the iSCSI targets on the NAS. To use this feature, click
"Add a Policy" under "Advanced ACL".
Enter the policy name, the initiator IQN, and assign access rights for each LUN on the NAS.
Read-only: The connected initiator can only read the data from the LUN.
Read/Write: The connected initiator has read and write access right to the LUN.
Deny Access: The LUN is invisible to the connected initiator.
If no LUN masking policy is specified for a connected iSCSI initiator, the default policy
(Read/Write) will be applied. You can click "Edit" to edit the default policy.
Note:
Make sure you have created at least one LUN on the NAS before editing the default
LUN policy.
Hint: How do I find the initiator IQN?
Start the Microsoft iSCSI initiator and click "General". You will find the IQN of the initiator.

LUN Backup
The NAS supports backing up iSCSI LUNs to different storage locations (Windows, Linux, or
local shared folders), restoring the LUNs to the NAS, or creating a LUN snapshot and mapping
it to an iSCSI target.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Backing up iSCSI LUNs
Restoring iSCSI LUNs
Creating iSCSI LUN Snapshots
Managing LUN Backup/Restore/Snapshot by Command Line
Backing up iSCSI LUNs
Before backing up an iSCSI LUN, make sure at least one iSCSI LUN has been created on the
NAS. To create iSCSI targets and LUN, follow these steps.
1.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "iSCSI" > "LUN Backup". Click "Create a new job".
2.
Select "Back up an iSCSI LUN" and click "Next".
3.
Select the source LUN for backup. If an online LUN is selected, the NAS will automatically
create a point-in-time snapshot for the LUN.
4.
Specify the destination where the LUN will be backed up to. The NAS supports LUN
backup to a Linux share (NFS), a Windows share (CIFS/SMB), and a local folder on the
NAS. Click "Test" to test the connection to the specified path. Then click "Next".
5.
Enter a name of the backup LUN image or use the one generated by the NAS. Select the
subfolder where the image file will be stored. Select to use compression or not and click
"Next". (More system resources will be used for compression, but the backup LUN size
can be reduced. The backup time may vary depending on the size of the iSCSI LUN.)
6.
Specify the backup schedule, choose the backup period (Now, Hourly, Daily, Weekly, or
Monthly) and click "Next".
7.
The settings will be shown. Enter a name for the job or use the one generated by the
NAS. Click "Next."
8.
Click "Finish" to exit.
9.
The backup job will be shown on the list.
Button
Name
Description
Start
Start the job immediately.
Stop
Stop the running job.
Edit
Edit the job settings.
View
View the job status and logs.
Restoring iSCSI LUNs
To restore an iSCSI LUN to the NAS, follow the steps below:
1.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "iSCSI" > "LUN Backup". Click "Create a job".
2.
Select "Restore an iSCSI LUN" and click "Next."
3.
Specify the protocol, IP address/host name, and folder/path of the restore source. Click
"Test" to test the connection. Then click "Next".
4.
Browse and select the LUN image file and click "Next."
5.
Select the destination and click "Next".
6.
The settings will be shown. Enter a name for the job or use the one generated by the
NAS. Click "Next".
7.
Click "Finish" to exit.
The restore job will be executed immediately.
Button
Name
Description
Stop
Stop the running job.
Edit
Edit the job settings.
View
View the job status and logs.
Note:
For Step 5 above:
Overwrite existing LUN: Restore the iSCSI LUN and overwrite the existing LUN on the
NAS. All the data on the original LUN will be overwritten.
Create a new LUN: Restore the iSCSI LUN to the NAS as a new LUN. Enter the name
and select the location of the new LUN. Make sure you have created at least one LUN
on the NAS before editing the default LUN policy.
Creating iSCSI LUN Snapshots
Before creating an iSCSI LUN snapshot, make sure at least one iSCSI LUN and one iSCSI
target has been created on the NAS. To create iSCSI targets and LUN, go to "Storage
Manager" > "iSCSI" > "Target Management".
To create an iSCSI LUN snapshot, follow these steps:

1.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "iSCSI" > "LUN Backup". Click "Create a job".
2.
Select "Create a LUN Snapshot" and click "Next".
3.
Select an iSCSI LUN on the NAS. Only one snapshot can be created for each iSCSI LUN.
Click "Next".
4.
Enter a name for the LUN snapshot or use the one generated by the NAS. Select an iSCSI
target where the LUN snapshot is mapped to. Click "Next". The LUN snapshot must be
mapped to another iSCSI target different from the original one.
5.
Specify the snapshot schedule and the snapshot duration. The snapshot will be removed
automatically when the snapshot duration is reached.
6.
The settings will be shown. Enter a name for the job or use the one generated by the NAS.
Click "Next".
7.
Click "Finish" to exit.
8.
The snapshot will be created immediately. The status and duration will be shown on the
list.
9.
Go to "iSCSI" > "Target Management", the snapshot LUN will be shown in the iSCSI Target
List. Use iSCSI initiator software to connect to the iSCSI target and access the
point-in-time data on the snapshot LUN.
Note:
The source LUN and snapshot LUN cannot be mounted on the same NAS in certain
operating systems such as Windows 7 and Windows 2008 R2. In such case, mount the LUN
to a different NAS.
Managing LUN Backup/Restore/Snapshot by Command Line
NAS users can start or stop the iSCSI LUN backup, restore, or snapshot jobs by command line.
Follow these instructions to use this feature.
Note:
The following instructions should only be operated by IT administrators who are
familiar with command line interfaces.
1.
First make sure the iSCSI LUN backup, restore, or snapshot jobs have been created on
the NAS in "Storage Manager" > "iSCSI" > "LUN Backup".
2.
Connect to the NAS using an SSH utility such as Pietty.
3.
Login to the NAS as an administrator.
4.
Input the command "lunbackup". The command usage description will be shown.
5.
Use the lunbackup command to start or stop an iSCSI LUN backup, restore, or snapshot
job on the NAS.

Virtual Disk
You can use this function to add iSCSI targets of other NAS or storage servers to the NAS as
virtual disks for storage capacity expansion. The NAS supports up to 8 virtual disks.
Note:
The NAS supports a virtual disk with a maximum size of 16TB.
When a virtual disk (iSCSI target) is disconnected, the virtual disk will disappear from
the interface and the NAS will try to connect to the target in 2 minutes. If the target
cannot be connected to after 2 minutes, the status of the virtual disk will become
"Disconnected".
To add a virtual disk to the NAS, make sure an iSCSI target has been created and follow
these steps:
1.
Click "Add Virtual Disk".
2.
Enter the target server IP and port number (default: 3260.) Click "Get Remote Disk".
Select a target from the list. If authentication is required, enter the login details. You can
select the options "Data Digest" and/or "Header Digest" (optional.) These are the
parameters that the iSCSI initiator will verify when it attempts to connect to the iSCSI
target. Then, click "Next".
3.
Enter a name for the virtual disk. If the target is mapped with multiple LUNs, select a
LUN from the list. Make sure only this NAS can connect to the LUN. The NAS supports
mounting EXT3, EXT4, FAT32, NTFS, HFS+ file systems. If the file system of the LUN is
"Unknown", select "Format virtual disk now" and the file system. You can format virtual
disks as EXT3, EXT4, FAT 32, NTFS, or HFS+. By selecting "Format virtual disk now", the
data on the LUN will be removed.
4.
Click "Finish" to exit the wizard.
5.
The storage capacity of your NAS has been expanded by the virtual disk. You can go to
"Privilege Settings" > "Share Folders" to create new shared folders on the virtual disk.
Icon
Name
Description
Edit
Edit a virtual disk name or the authentication information of an iSCSI
target.
Connect
Connect to an iSCSI target.
Disconne
ct
Disconnect an iSCSI target.

Format
Format a virtual disk as EXT3, EXT 4, FAT 32, NTFS, or HFS+.
Delete
Delete a virtual disk or iSCSI target.
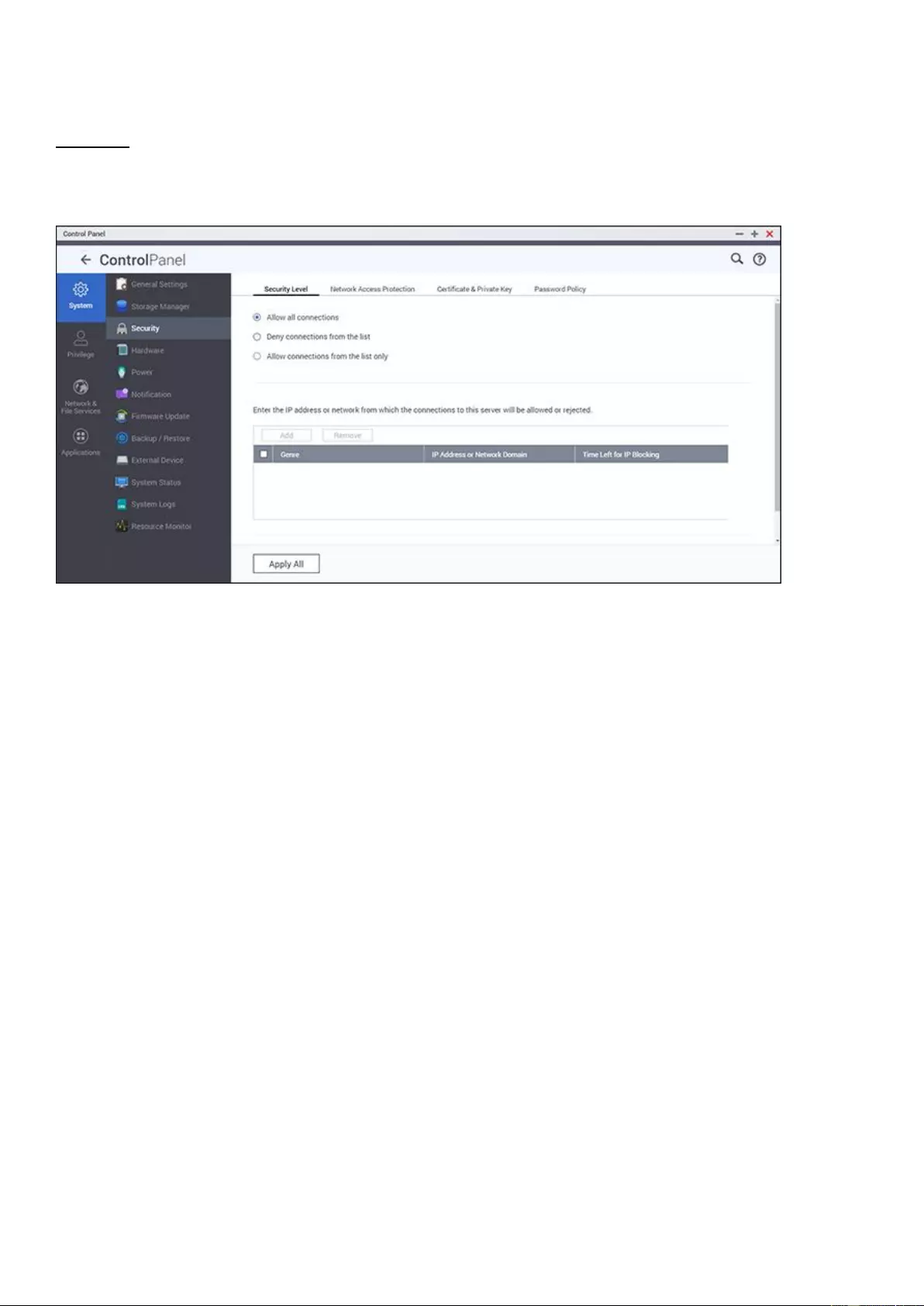
Security
Go to "Control Panel" > "System" > "Security" to configure relevant security settings for your
NAS.
Security Level
Specify the IP address or network domain from which connections to the NAS are allowed or
denied. When the connection of a host server is denied, all the protocols of that server are
not allowed to connect to the NAS. After changing the settings, click "Apply" to save the
changes. Network services will be restarted and current connections to the NAS will be
terminated.
Network Access Protection
Network access protection enhances system security and prevents unwanted intrusion. You
can block an IP address for a certain period of time or indefinitely if the IP address fails to
login to the NAS using a particular connection method (e.g. SSH, Telnet, HTTPS, FTP, SAMBA,
or AFP).
Certificate & Private Key
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a protocol for encrypted communication between web servers
and browsers for secure data transfer. You can upload an SSL certificate issued by trusted
providers. After uploading an SSL certificate, users can connect to the administration
interface of the NAS by SSL and there will not be any alert or error message. The NAS only
supports X.509 certificates and private keys.
Replace Certificate: Upload a new certificate from a trusted provider, create a self-signed
certificate, or get one from the open certificate authority “Let’s Encrypt”.
Download Certificate: Download the secure certificate which is currently in use.
Download Private Key: Download the private key which is currently in use.
Restore Default Certificate & Private Key: Restores the secure certificate and private key
to system default. The secure certificate and private key in use will be overwritten.
Note:
This option is only available after the default certificate has been replaced.
Password Policy
Password policy allows the administrator to set the minimum password strength of user
passwords and to force users to change their passwords periodically.
Password Strength
Specify the password rules. After applying the setting, the NAS will automatically check the
validity of the password.
A new password must contain characters from at least three of the following types of
characters: lowercase letters, uppercase letters, digits, and special characters.
No character in the new password may be repeated more than three consecutive times.
The new password must be different than the username and must not be the username
reversed.
Force Password Change
The administrator may force users to change their passwords periodically by setting the
number of days before a password expires. There is also an option to email users a week in
advance of their password expiring.
Hardware
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Hardware" to configure the NAS hardware
functions.
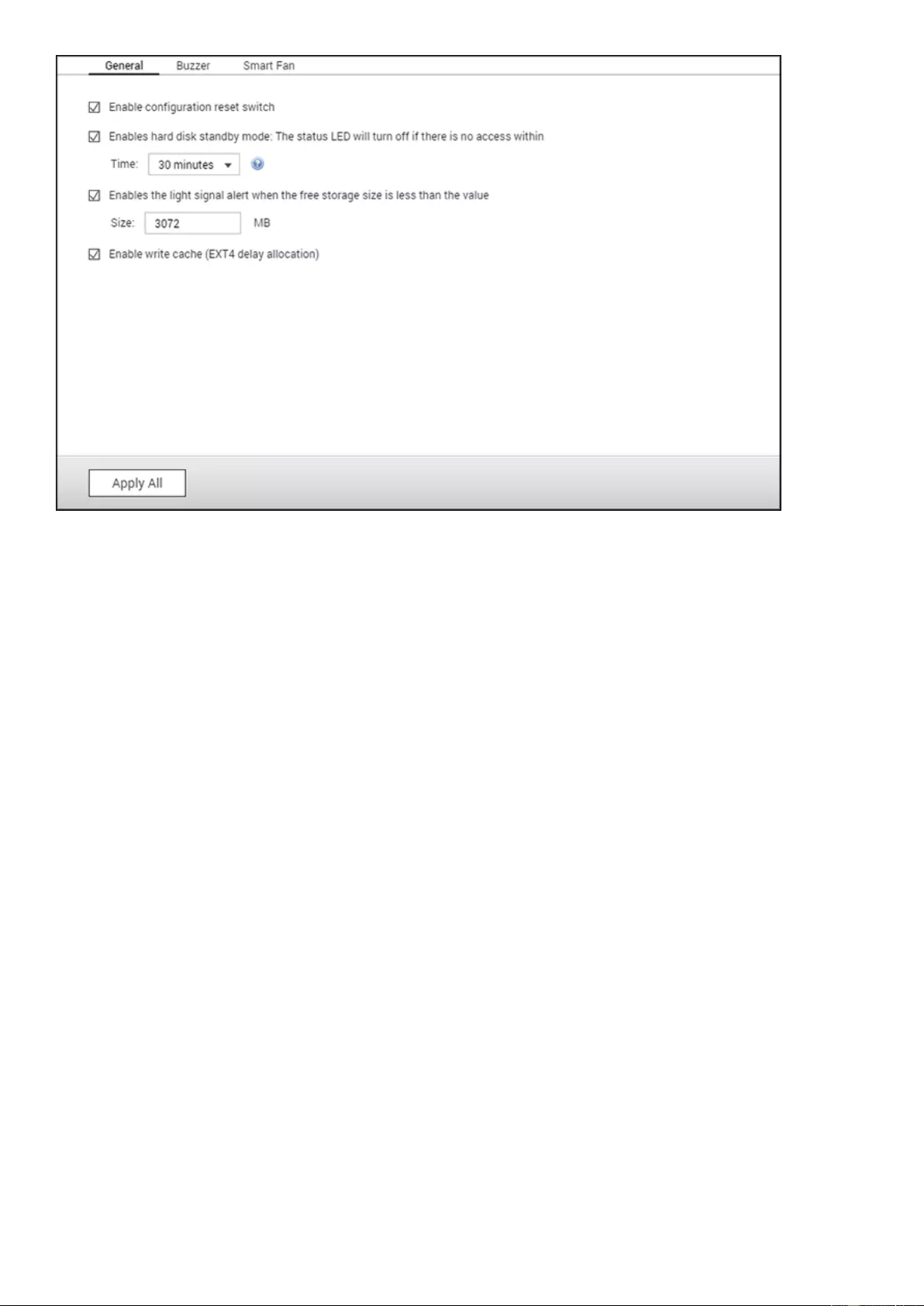
General
Enable configuration reset switch:
When this is enabled, you can press the reset
button for 3 seconds to reset the administrator password and the system settings to
default (NAS data will be retained) or 10 seconds for advanced system reset.
o
Basic system reset:
You will hear a beep after pressing and holding the reset button.
The following settings will be reset to default:
System administration password: admin.
TCP/IP configuration: Obtain IP address settings automatically via DHCP.
TCP/IP configuration: Disables Jumbo Frames.
TCP/IP configuration: If port trunking is enabled, the port trunking mode will be
reset to "Active Backup (Failover)".
System port: 8080 (system service port.)
Security level: Low (Allows all connections.)
LCD panel password: (blank); this feature is only for NAS models with LCD panels.
VLAN will be disabled.
Service binding: All NAS services will be run on all available network interfaces.
o
Advanced system reset:
You will hear two beeps after continuously pressing the
reset button. The NAS will reset all system settings to default (similar to the system
reset in "Administration" > "Restore to Factory Default") except all the NAS data will
be reserved. Settings such as users, user groups, and shared folders will be cleared.
To retrieve old data after an advanced system reset, create the same shared folders
on the NAS and the data will be accessible again.

Enable hard disk standby mode:
This option allows the NAS drives to enter standby
mode if there is no disk access within the specified period. Note that during standby
mode, the system LED on the NAS will be off but the HDD status LED will remain steady.
Enable light signal alert when the free size of SATA disk is less than the value:
The status LED will flash red and green if this option is enabled and the free space of the
SATA hard drive is less than the set value.
Enable write cache (EXT4 only):
If the NAS disk volume uses EXT4, enable this option
for higher write performance. Note that an unexpected system shutdown may lead to
data loss. It is recommended to disable this option if the NAS is set as shared storage in
a virtualized or clustered environment.
Enable warning alert for redundant power supply on the web-based interface:
If
two power supply units (PSU) are installed on the NAS and connected to the power
sockets, both PSU will supply the power to the NAS (applied to 1U and 2U models.) Turn
on the redundant power supply mode in "System Settings" > "Hardware" to receive
warnings for the redundant power supply. The NAS will sound and record error messages
in "System Logs" if the PSU is plugged out or does not respond correctly. If only one PSU
is installed on the NAS, DO NOT enable this option. This function is disabled by default.
Turn on LED light:
If your NAS has a LED indicator (ex. TS-453mini), you can choose to
turn on its LED indicator, set the LED brightness level and configure a schedule for the
brightness setting. This function is only applicable on some models.
Buzzer
Enable alarm buzzer:
Enable this option to allow the alarm buzzer to beep when certain
system operations (startup, shutdown, or firmware upgrade) are executed or system events
(error or warning) occur.
Write Cache
Better write performance can be obtained when this option is enabled. Please note that an
unexpected system shutdown may cause data loss. This option is disabled when the
Download Station or SQL service is enabled.
Smart Fan
Smart Fan Configuration:
Enable smart fan (recommended):
Select to use the default smart fan settings or to
manually define the settings. When the system default settings are selected, the fan
rotation speed will be automatically adjusted when the NAS temperature, CPU
temperature, and hard drive temperature meet the criteria. It is recommended to enable
this option.

Set fan rotation speed manually:
By manually setting the fan rotation speed, the fan
will continually rotate at this speed.
Note:
The NAS will automatically shut down to protect itself if a temperature threshold is
exceeded. The threshold values vary depending on NAS models.
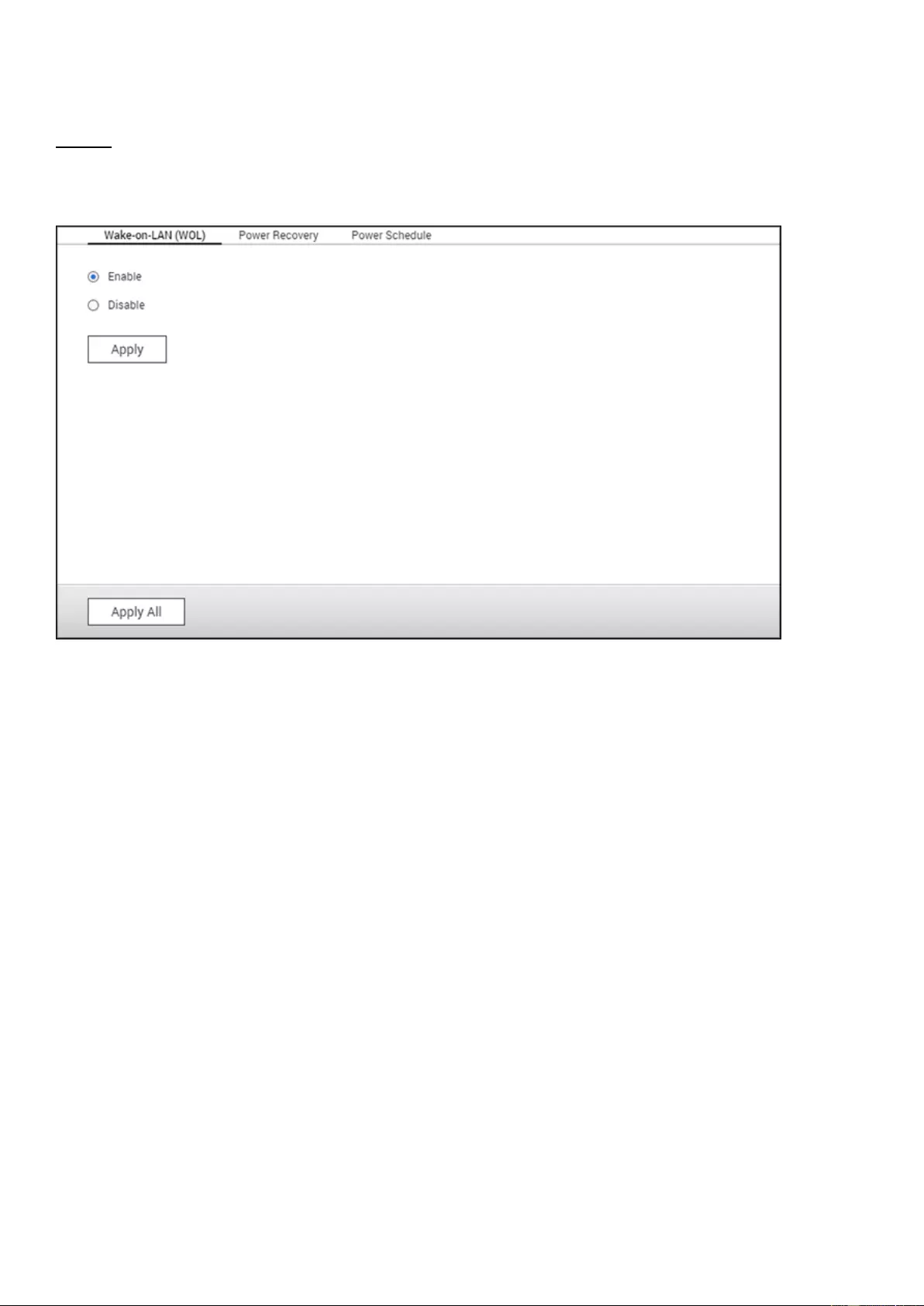
Power
You can restart or shut down the NAS, specify the behavior of the NAS after a power recovery,
and set the schedule for automatic system power on/off/restart on this page.
EuP Mode Configuration
EuP (also Energy-using Products) is a European Union (EU) directive designed to improve the
energy efficiency of electrical devices, reduce the use of hazardous substances, increase ease
of product recycling, and to improve environment-friendliness of products.
When EuP is enabled, the following settings will be affected so that the NAS maintains low
power consumption (less than 1W) when the NAS is powered off:
Wake on LAN: Disabled.
AC power resumption: The NAS will remain off after the power restores from an outage.
Scheduled power on, off, restart settings: Disabled.
When EuP is disabled, the power consumption of the NAS is slightly higher than 1W when the
NAS is powered off. EuP is disabled by default so that you can use the functions Wake on LAN,
AC power resumption, and power schedule settings properly.
This feature is only supported by certain NAS models.
Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
Enable this option to allow users to power on the NAS remotely by Wake on LAN. If the power
cable is unplugged when the NAS is turned off, Wake on LAN will not function even if the
power supply is reconnected afterwards. To wake up the NAS when it is in sleep mode or
powered down, press the NAS power button or use the WOL feature in
Qfinder Pro
or
Qmanager. The wake-up function on the NAS is only available after the WOL option is enabled
in "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "General Settings" > "Power" > "Wake-on-LAN
(WOL)".
For
Qfinder Pro
, select a NAS and click "Tools" > "Remote Wake Up (Wake on LAN)".
For Qmanager, click ">" next to the NAS to be selected on the login page, scroll down to
the bottom of the screen and click "Wake on LAN (WOL)".
This feature is only supported by certain NAS models.
Power Recovery
Configure the NAS to resume to the previous power-on or power-off status, turn on, or
remain off when the AC power resumes after a power outage.
Note:
Only x86-based NAS models can be turned on automatically after power recovery.
To set it up, select "Turn on the server automatically" in "Control Panel" > "System
Settings" > "Power" > "Power Recovery".
Power Schedule
Specify the schedule for automatic system power on/off, restart, or sleep mode. Weekdays
are Monday to Friday, weekends are Saturday and Sunday. Up to 15 schedules can be set.
Enable "Postpone the sleep/restart/shutdown schedule when replication job is in process" to
allow scheduled system restart/shutdown to be carried out after a running replication job
completes. Otherwise, the NAS will ignore the running replication job and execute scheduled
system restart or shutdown.
Note:
The system cannot be shut down or restarted in sleep mode.
If there are other QNAP storage expansion enclosures connected to the NAS, the sleep
mode will be disabled automatically and system will not go into sleep mode.
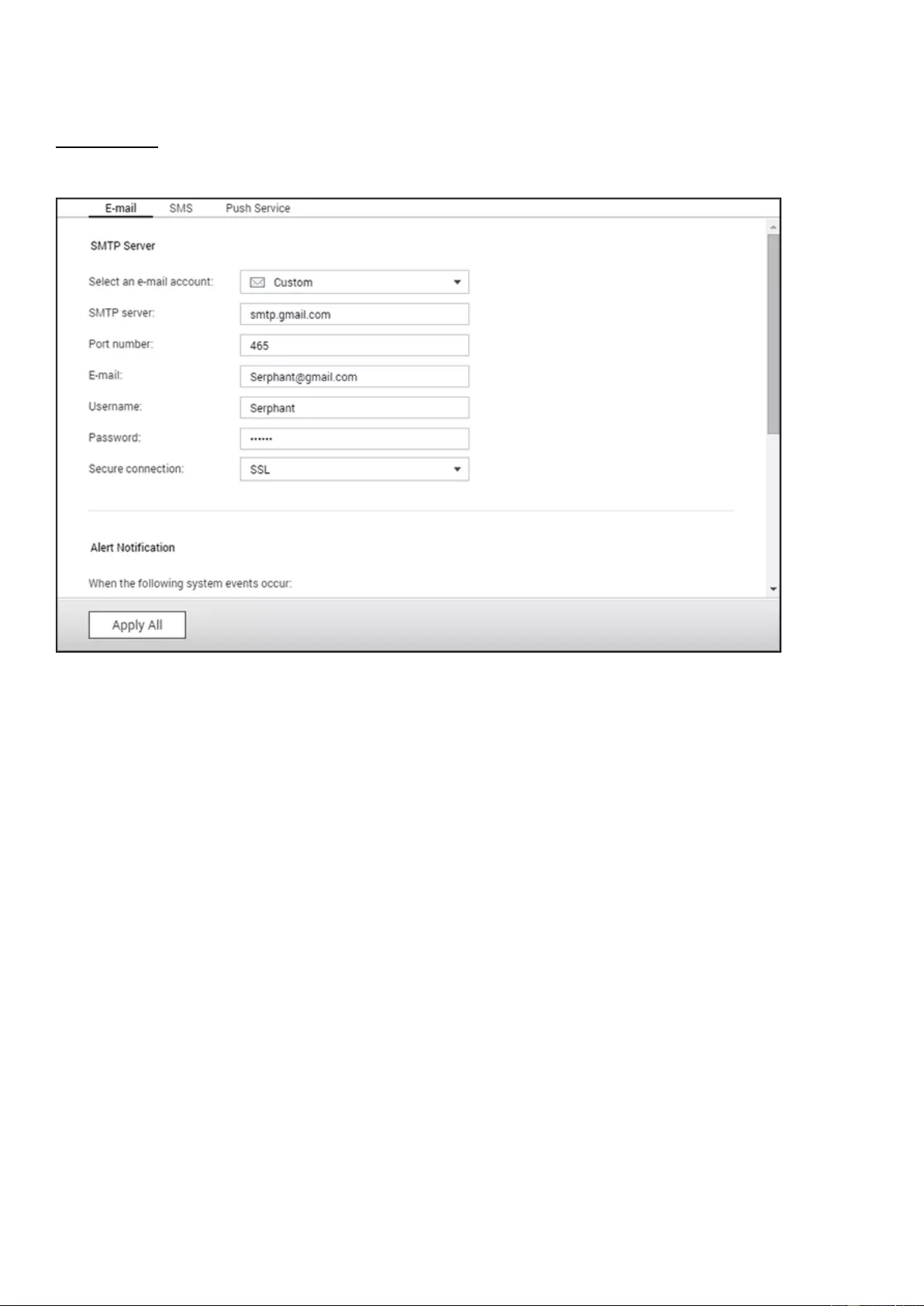
Notification
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Notification" to configure NAS notifications.
E-mail
The NAS supports email alerts to inform the administrator of system errors and warnings. To
receive alerts by email, configure the SMTP server.
Select an email account: specify the type of email account you would like to use for email
alerts.
SMTP Server: Enter the SMTP server name (for example: smtp.gmail.com.)
Port Number: Enter the port number for the SMTP server. The default port number is 25.
E-mail: Enter the email address of the alert recipient.
Username and Password: Enter the email account's login information.
Secure connection: Choose SSL or TLS to ensure a secure connection between the NAS
and SMTP server or None. It is recommended to use this if the SMTP server supports it.
Alert Notification: Select the type of instant alerts the NAS will send if system events
(warnings/errors/firmware update) occur.
SMS
Configure the SMSC server settings to send SMS messages to specified phone numbers from
the NAS. Follow these steps to set up a SMSC server:
1.
Choose an SMS service provider. The default SMS service provider is Clickatell. You can
add your own SMS service provider by selecting "Add SMS Provider" from the drop-down
menu. When "Add SMS service provider" is selected, enter the name of the SMS provider
and the URL template text.
2.
Specify to enable SSL connection to the SMS service provider and fill out the server
details, including the login name, login password and server API_ID.
3.
Enable the alert notification by ticking the checkbox "When a system error event occurs,
send a SMS notification to the following phone number". Up to two phone numbers can
be specified to receive instant system alerts from the NAS.
Note:
The URL template text must follow the standard of the SMS service provider to
receive the SMS alert properly.
Push Service
The push service lets you receive notification messages on your mobile devices if a warning or
error event occurs - allowing you to quickly receive first-hand information from your NAS and
instantly react to keep your data safe. You must have "Qmanager" installed on your mobile
devices to receive notifications.
Note:
You must have firmware QTS 4.2.0 with Qmanager iOS 1.8.0 / Qmanager Android
2.1.0 or above.
Follow these steps to set up the push service:
1.
Log into myQNAPcloud using your QID.
2.
Choose the notification types that you want to receive (warnings or errors.)
3.
Install Qmanager on your mobile device (Qmanager iOS 1.8.0 / Android 2.1.0 or above.)
4.
Log into the NAS using Qmanager and confirm to receive push notifications (you can also
disable this service in Qmanager > click ">" next to a NAS connection > "server settings"
page > change push service properties.)
5.
The NAS will send alert notifications to paired mobile devices when a warning or error
event occurs.
The paired devices will be listed in the "Manage Paired Devices" table. You can disable or
delete a paired device from the table.

Note:
On occasion you may not receive system notifications instantly due to iOS and
Android server mechanisms.
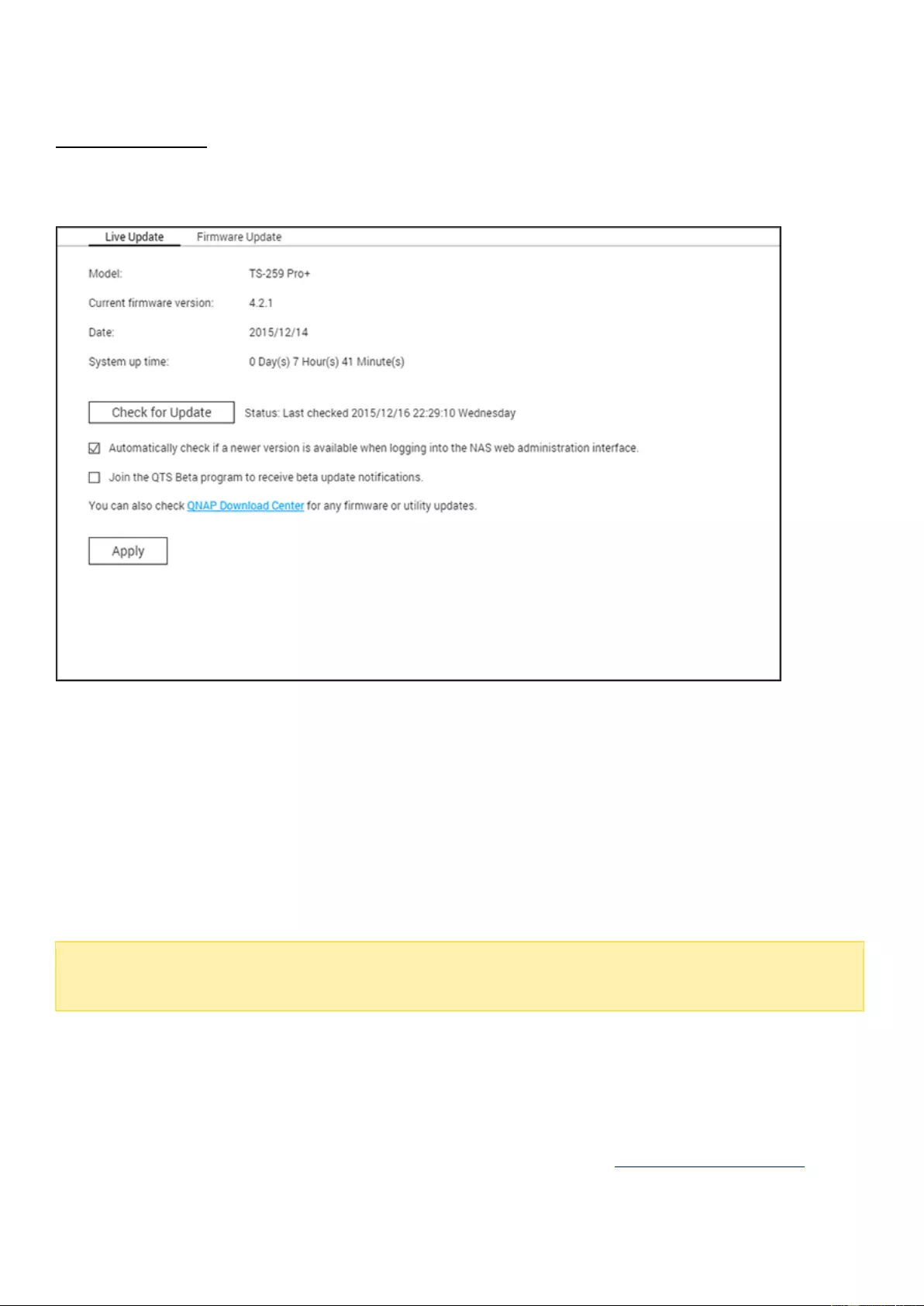
Firmware Update
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Firmware Update" to update the firmware
version of the NAS.
Live Update
Select "Automatically check if a newer version is available when logging into the NAS web
administration interface" to allow the NAS to automatically check if a new firmware version is
available. If a new firmware is found, you will be notified after logging in the NAS as an
administrator. Click "Check for Update" to check if any firmware update is available. Note that
the NAS must be connected to the Internet for these features to work.
Note:
Experience the latest apps and features for QNAP NAS by joining our beta programs.
You can join by checking "Join the QTS Beta program to receive beta update notifications".
Firmware Update
Before updating the system firmware, make sure the product model and firmware version are
correct. Follow these steps to update the firmware:
1.
Download the firmware release notes from the QNAP website http://www.qnap.com.
Read the release notes carefully to make sure it is necessary to update the firmware.
2.
Download the NAS firmware and unzip the IMG file to the computer.
3.
Before updating the system firmware, back up all the NAS data to avoid any potential
data loss from unforeseen issues arising during the system update.
4.
Click "Browse" to select the firmware image for the system update. Click "Update
System" to update the firmware.
The system update may take seconds, minutes or longer to complete depending on the
network connection status. The NAS will inform you when the system update has completed.
Note:
If the system is running properly, you do not need to update the firmware.
QTS does not support downgrading the firmware. However, if you choose to apply an
older firmware version, please back up all of your important data before downgrading.
QNAP is not responsible for any damage to the NAS or its contents after downgrading.
Update Firmware by QNAP Qfinder Pro
The NAS firmware can be updated using
Qfinder Pro
by following these steps:
1.
Select a NAS model and choose "Update Firmware" from the "Tools" menu.
2.
Login to the NAS as an administrator.
3.
Browse and select the firmware for the NAS. Click "Start" to update the system.
Note:
If you have multiple identical NAS on the same LAN, they can be updated at the
same time with
Qfinder Pro
. Administrator access is required.
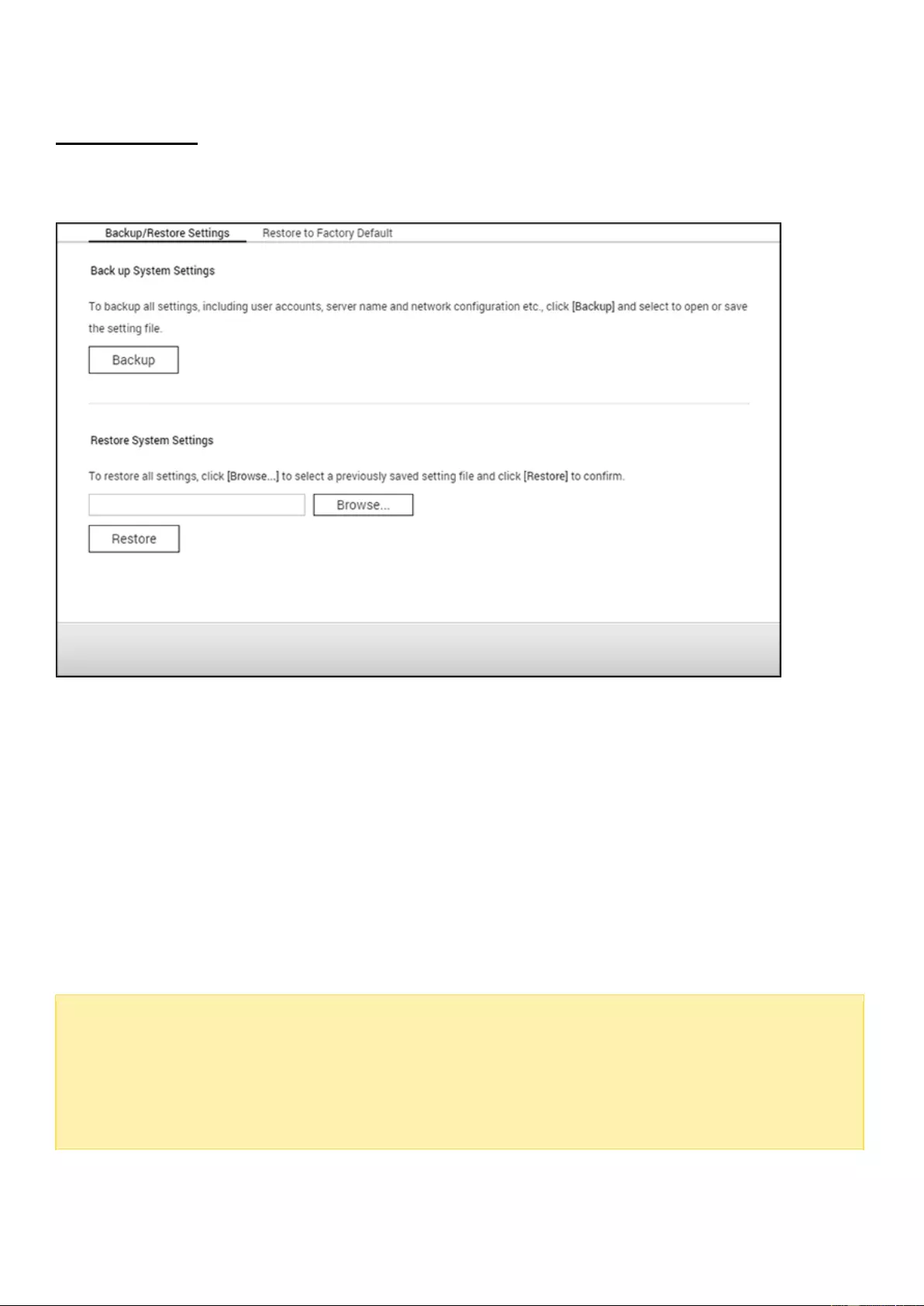
Backup/Restore
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Backup/Restore" to back up, restore your NAS
or restore your NAS to factory default settings.
Backup/Restore Settings
Back up System Settings:
To back up all the settings, including the user accounts,
server name, network configuration and so on, click "Backup" and select to open or save
the setting file. Settings will be backed up include: User, Group, Shared Folder,
Workgroup, Domain, and LDAP, Windows File Service, Mac File Service, NFS, FTP,
WebDAV, Network Backup, User Home, Password Settings, SNMP, and Backup Service.
Restore System Settings:
To restore all the settings, click "Browse" to select a
previously saved setting file and click "Restore".
Note:
User Home includes basic service settings (excluding user data in the user home
folder.)
If the users or groups you try to restore from the backup file already exist in the
current system, the users and groups in the current system will be overwritten.
Restore to Factory Default
Restore Factory Defaults & Format all Volumes:
Restore system settings to default
and
formats all disk volumes
.
Reset Settings:
Restore system settings to default without erasing user data.
Reinitialize NAS: Erases all data
and reinitializes the NAS.
Caution:
The administrator's password and system settings will be reset to default if you
press and hold the reset button on the back of the NAS for 3 seconds (data and files on
the NAS will be unaffected.) However, if you press and hold the Reset button for 10
seconds, all settings including users, user groups, and shared folders will be cleared (but
user data will be unaffected.)
Note:
For the above "Reset Settings" and "Reset Factory Default & Format Volume"
buttons, only one of them is available on the page (depending on the NAS model.)

External Storage
The NAS supports USB and eSATA storage devices for backup and data storage. Connect the
external storage device to a USB or an eSATA port of the NAS and its details will be shown on
this page.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Storage Information
Format
Eject
Encryption Management
Data Sharing
Storage Information
Select a storage device and click "Storage Information" to check its details. The number of
USB and eSATA interfaces supported varies by model. It may take a few seconds for the NAS
to detect external USB/eSATA devices.
Format
External storage devices can be formatted as EXT3, EXT4, FAT32, NTFS, or HFS+ (Mac only).
Click "Format" and select the option from the drop-down menu.
Note:
Starting with QTS 4.1, labeling is supported for external USB devices. To edit a
USB drive's label, click "Storage Information" to edit its label. The label will become the
shared folder name of this USB device in File Station.
The NAS supports encrypting external drives. To encrypt an external storage device, click
"Encryption". Select the encryption method: AES 128-, 192- or 256-bit and enter the
password (8-16 characters.) Select "Save encryption key" to save the password in a hidden
location on a hard drive in the NAS. The NAS will automatically unlock the encrypted external
storage device when the device is connected. Click "Format" to proceed. Click "OK" and all the
data will be cleared. The device will be "Ready" after disk initialization.
Note:
We recommend formatting disk volumes larger than 2TB using EXT4, NTFS, or
HFS+.
Eject
"Eject" offers two different options. "Disconnect disk partition" allows you to remove a single
disk partition or a disk drive in a multi-drive enclosure. "Remove device" allows you to
disconnect external storage devices without the risk of losing any data when the device is
removed. First choose a device to eject, click "Eject" and then disconnect the disk partition or
remove the device.
Note: To avoid potential data loss, always use the hardware removal function before removing your
external storage device (for a Windows PC, use the "Safely Remove Hardware"; for a Mac, use the
"Eject" icon; for QTS, use the "Eject" button.)
Encryption Management
If an external storage device is encrypted by the NAS, the button "Encryption Management"
will appear. Click this button to manage the encryption password/key, or to lock/unlock the
device.
Locking the device
1.
To lock an encrypted external storage device, click "Encryption Management".
2.
Select "Lock this device" and click "Next".
3.
Click "Next" to lock the device.
Note:
Before you encrypt an external storage device, you must format that device and select
an encryption standard from the "Encryption" drop-down list in the "Format External
Storage Drive" dialog.
External storage devices cannot be locked if a real-time or scheduled backup job is
running on it. To disable the backup job, go to "Control Panel" > "Applications" >
"Backup Station" > "External Drive".
Unlocking the device
1.
To unlock an encrypted external storage device, click "Encryption Management".
2.
Select "Unlock this device". Click "Next".
3.
Enter the encryption password or upload the key file. Select "Save encryption key" to save
the password in a hidden location on a hard drive of the NAS. The NAS will automatically
unlock the encrypted external storage device every time the device is connected.

Managing the encryption key
1.
To change the encryption password or download an encryption key file, click "Encryption
Management".
2.
Select "Manage encryption key". Click "Next".
3.
Select to change the encryption password or download the encryption key file to the local
PC.
Data Sharing
Select one of the following settings for an external storage device connected to a 1-bay NAS:
Data sharing: Use the external drive for storage expansion of the NAS.
Q-RAID 1: Configure the external drive and a local hard drive on the NAS as Q-RAID 1.
Q-RAID 1 enables one-way data synchronization from the NAS to the external storage
device but does not offer any RAID redundancy.
Note that the external drive will be
formatted when Q-RAID 1 is executed.
After Q-RAID 1 has been executed once, the NAS data will be automatically copied to the
external storage device whenever it is connected to the NAS.
Note:
Only one external drive can be set as Q-RAID 1 at one time.
The maximum capacity supported by Q-RAID 1 is 2TB.
It is recommended to use an external storage device with the same capacity as the
internal NAS drive. If the storage capacity of the external storage device is too small to
synchronize with the internal hard drive, the device can only be used for data sharing.
HD Station will reboot when external devices are unmounted.

USB Printer
The NAS supports network printing sharing service over local networks and the Internet in
Windows, Mac, and Linux (Ubuntu) environments. Up to 3 USB printers are supported.
To share a USB printer, connect the printer to a USB port on the NAS. The printer will be
automatically detected and its information displayed.
Printer Info
Click on a connected USB printer and then "Printer Info" to review its details.
Note:
Connect a USB printer to the NAS after the software configuration is completed.
The NAS does not support multifunction printers.
The file name display for the printer job table is only available for printer jobs sent via
IPP (Internet Printing Protocol).
For a list of supported USB printers, visit http://www.qnap.com.
Printer Log
Click on a connected USB printer and then "Printer Log" to view its print job history. You can
pause or cancel ongoing/pending jobs, resume paused jobs, or delete completed or pending
jobs. To clear the history, click "Clear".
Note:
Do NOT restart the NAS or update the system firmware when printing is in process
or there are queued jobs. Otherwise all the queued jobs will be cancelled and removed.
Clean Up Spool Space
Click "Clean Up Spool Space" to clean up the data saved in the printer spool.
Settings
Click "Settings" to configure basic settings of the printer.
Stop printer sharing and clear print spool:
Select this option to temporarily disable
the selected printer for print sharing. All of the data in the printer spool will be cleared.

Bonjour printer support:
Select this option to broadcast printing service to Mac users
via Bonjour. When naming your printer, the name can only contain "a-z", "A-Z", "0-9",
dot (.), comma (,) and dash (-).
Maximum Printer Jobs and Blacklist
Maximum printer jobs per printer:
Specify the maximum number of printer jobs for a
printer. A printer supports up to 1,000 printer jobs. The oldest printer job will be
overwritten by the newest one if the printer has reached the maximum number of printer
jobs.
Enter IP addresses or domain names to allow or deny printing access:
To allow or
deny particular IP addresses or domain names from using the NAS printing service,
select "Allow printing" or "Deny printing" and enter the IP addresses or domain names.
An asterisk (*) denotes all connections. To allow all users to use the printer, select "No
limit". Click "Apply" to save the settings.
Note:
This feature only works for printing service via IPP and Bonjour, but not Samba.

Windows 7
Follow these steps to set up your printer connection:
1.
Go to Devices and Printers.
2.
Click "Add a printer".
3.
In the Add printer wizard, click "Add a network, wireless or Bluetooth printer".
4.
While Windows is searching for available network printers, click "The printer that I want
isn't listed".
5.
Click "Select a shared printer by name", and then enter the address of the network
printer. The address is in the following format –
http://NAS_IP:631/printers/ServernamePR, where the NAS_IP can also be a domain
name address if you want to print remotely. For example,
http://10.8.13.59:631/printers/NASPR3
6.
The wizard will prompt you for the correct printer driver. You can also download the
latest printer driver from the manufacturer’s website if it is not built-into Windows
operating system.
7.
After installing the correct printer driver, the wizard shows the address and driver of the
new network printer.
8.
You can also set the network printer as the default printer or print a test page. Click
"Finish" to exit the wizard.
9.
The new network printer is now available for printing.

Mac OS 10.6
If you are using Mac OS 10.6, follow these steps to configure the NAS printer function:
1.
First make sure that Bonjour is enabled on the NAS in "External Device" > "USB Printer"
> "Settings". You can change the Service Name to better represent the printer.
2.
On your Mac, go to "System Preferences", and then click "Print & Fax".
3.
In the Print & Fax window, click + to add a printer.
4.
The USB network printer will be listed via Bonjour. Select the default printer driver or
download and install the latest one from the printer manufacturer’s website. Click "Add"
to add this printer.
5.
Additional options may be available for your printer. Click "Continue".
6.
The new network printer is now available for printing.

Mac OS 10.5
If you are using Mac OS X 10.5, follow these steps to configure the NAS printer function:
1.
Go to "Network Services" > "Win/Mac/MFS" > "Microsoft Networking". Enter a workgroup
name for the NAS. You will need this information later.
2.
Go to "Print & Fax" on your Mac.
3.
Click + to add a printer.
4.
Select the NAS workgroup and find the printer name.
5.
Enter the username and password to login the printer server on the NAS.
6.
Select the printer driver.
7.
After installing the printer driver correctly, you can start using the printer.

Mac OS 10.4
If you are using Mac OS 10.4, follow these steps to configure the NAS printer function:
1.
On the toolbar, click "Go/Utilities".
2.
Click "Printer Setup Utility".
3.
Click "Add".
4.
Hold the "alt" key and click "More Printers".
5.
In the pop up window, select "Advanced" and "Windows Printer with SAMBA", enter the
printer name and the printer URI (the format is smb://NAS IP/printer name. The printer
name is found on the "Device Configuration" > "USB Printer page"), select "Generic" for
Printer Model and click "Add".
6.
The printer appears on the printer list and is ready to use.
Note:
For "Advanced" in Step 5 above, you must hold the "alt" key and click "More Printers"
at the same time to view the Advanced printer settings.
The network printer service of the NAS supports Postscript printer on Mac OS only.

Linux (Ubuntu 10.10)
If you are using Linux (Ubuntu 10.10), follow these steps to configure the NAS printer
function:
1.
Click the "System" tab, choose "Administration". Then select "Printing".
2.
Click "Add".
3.
Click "Network Printer", and then select "Internet Printing Protocol (ipp)". Enter the NAS
IP address in "Host". "/printers" is already present. Enter the printer name after
"printers/" in the field "Queue".
4.
Before you continue, click "Verify" to test the printer connection.
5.
The operating system starts to search for the possible drivers.
6.
Select the printer driver from the built-in database, or search online.
7.
Choose the correct printer model and driver. Depending on the printer, some additional
printer options may be available in the next step.
8.
You can rename this printer or enter additional information. Click "Apply" to exit and
finish.
9.
The network printer is now available for printing.

UPS
By enabling UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) support, you can protect your NAS from
abnormal system shutdown caused by power disruption. There are two options provided on
the "UPS" page for the NAS during a power failure: 1) turn off the server after the AC power
fails, or 2) enter the auto-protection mode after the AC power fails. For option 1, the NAS will
shut itself down after the specified time. For option 2, the NAS will stop all running services
and unmount all volumes to protect your data after the specified time. For details on NAS
behavior during a power failure, refer to the "Behavior of the UPS Feature of the NAS" section.
Please note that to protect your data, once the power outage starts, the NAS will
automatically turn itself off or enter auto-protection mode (depending on your settings) after
30 seconds regardless of the specified time for either of the above options if the remaining
UPS battery charge is < 15%.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
USB Modes
o
Standalone Mode – USB
o
Standalone Mode – SNMP
o
Network Master Mode
o
Network Slave Mode
Behavior of the UPS Feature of the NAS
USB Modes
Standalone Mode – USB
To operate under USB standalone mode, follow the steps below:
1.
Plug in the USB cable on the UPS to the NAS.
2.
Choose between whether the NAS will shut down or enter auto-protection mode after the
AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NAS should wait before executing the
option you have selected. After the NAS enters auto-protection mode, the NAS resumes
the previous operation status when the power restores.
3.
Click "Apply All" to confirm.
Standalone Mode – SNMP
To operate under SNMP standalone mode, follow the steps below:
1.
Make sure the NAS is connected to the same physical network as the SNMP-based UPS.
2.
Enter the IP address of the SNMP-based UPS.

3.
Choose between whether the NAS should shut down or enter auto-protection mode after
the AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NAS should wait before executing
the option you have selected. After the NAS enters auto-protection mode, the NAS
resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
4.
Click "Apply All" to confirm.
Network Master Mode
A network UPS master is responsible for communicating with network UPS slaves on the same
physical network regarding critical power status. To set your NAS with UPS as network master
mode, plug in the USB cable on the UPS to the NAS and follow these steps:
1.
Make sure the NAS (the "UPS master") is connected to the same physical network as the
network UPS slaves.
2.
Click "Enable network UPS Support". This option only appears when your NAS is
connected to the UPS by a USB cable.
3.
Choose between whether the NAS should shut down or enter auto-protection mode after
the AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NAS should wait before
executing the option you have selected. After the NAS enters auto-protection mode, the
NAS resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
4.
Enter the "IP address" of other network UPS slaves to be notified in the event of power
failure.
5.
Click "Apply All" to confirm and continue the setup for the NAS systems which operate in
network slave mode below.
Network Slave Mode
A network UPS slave communicates with network UPS master to receive the UPS status. To
set up your NAS with UPS as network slave mode, follow these steps:
1.
Make sure the NAS is connected to the same physical network as the network UPS
master.
2.
Select "Network UPS slave" from the "Protocol" drop down menu.
3.
Enter the IP address of the network UPS server.
4.
Choose between whether the NAS should shut down or enter auto-protection mode after
AC power fails. Specify the time in minutes that the NAS should wait before executing
the option you have selected. After the NAS enters auto-protection mode, the NAS
resumes the previous operation status when the power restores.
5.
Click "Apply All" to confirm.
Note:
To allow the UPS device to send SNMP alerts to the NAS in the event of power loss,
you may have to enter the NAS IP address in the UPS configuration page.

Behavior of the UPS Feature of the NAS
There are three phases during a power outage:
Phase 1: Power loss starts until the end of the waiting time.
Phase 2: From the end of the waiting time to the point when the UPS device runs out of
its battery.
Phase 3: After the UPS device runs out of its battery and until the power restores.
Phase 1:
As soon as the power loss starts, the NAS will detect the UPS device’s battery. If the
remaining UPS battery charge is < 15%, the system will automatically turn itself off or enter
auto-protection mode (depending on your settings) after 30 seconds regardless the time you
specified for either of the settings (turn off the NAS or enter auto protection mode.) If the
UPS battery charge is > 15%, the NAS will wait for the specified time you entered in the
"UPS" page.
If the power resumes during this phase, the NAS will remain in operation.
Phase 2:
Depending on your setting on the "UPS" page:
If in auto-protection mode, the NAS will stop all running services and unmount all
volumes. The NAS at this moment will become inaccessible.
If the NAS is powered off, it will remain off.
If the power resumes during this phase:
If in auto-protection mode, the NAS will reboot and resume its previous state.
If the NAS is powered off, it will remain off.
Phase 3:
Depending on your setting on the "UPS" page:
If in auto-protection mode, the NAS will lose its power and shut down.
If the NAS is powered off, it will remain off.
After the power resumes during this phase, the NAS will react according to your settings in
"System Settings" > "Power Recovery".

System Status
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "System Status" to check the status of your
NAS.
System Information
View the summary of system information such as the server name, CPU, memory, firmware
and system up time on this page.
Note:
CPU and memory information is only available on certain NAS models.
Network Status
View the current network settings and statistics on this page. They are displayed based on
network interface. Click the up arrow in the top right to collapse the interface page and the
down arrow to expand it.
System Service
View the current settings of system services provided by the NAS.
Hardware Information
View basic hardware information of the NAS.
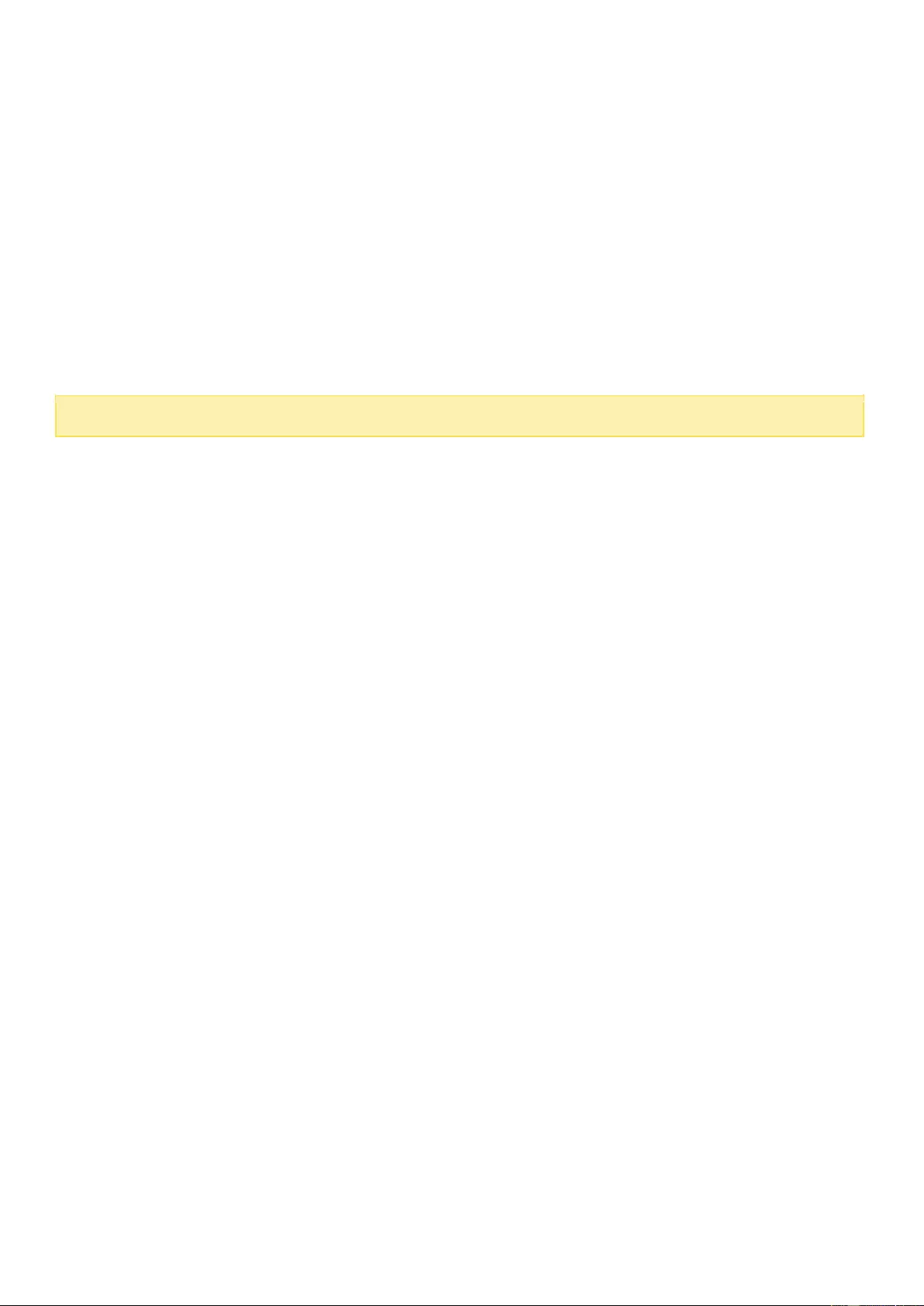
Resource Monitor
You can view the CPU usage, disk usage, and bandwidth transfer statistics of the NAS.
CPU Usage: Shows the CPU usage of the NAS.
Memory Usage: Shows the memory usage of the NAS by real-time dynamic graph.
Disk Usage: Shows the disk space usage of each disk volume and its shared folders.
Bandwidth Usage: Provides bandwidth transfer information of each available NAS LAN
port.
Process: Shows information about the processes running on the NAS.
Disk Performance: Shows IOPS and latency of the selected volume.
Note:
Disk Performance is only available on certain NAS models.
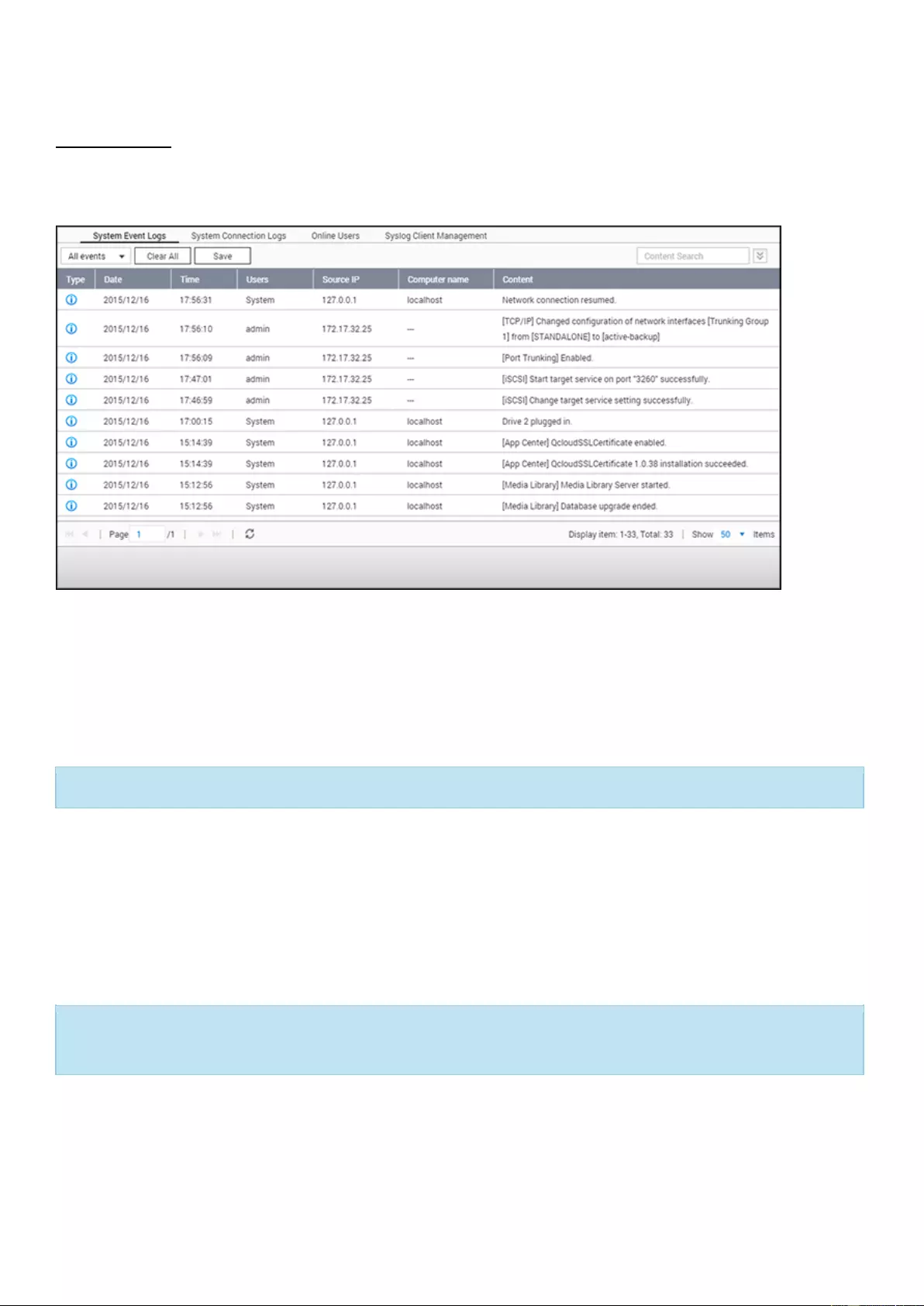
System Logs
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "System Logs" to configure the logs settings of
your NAS.
System Event Logs
The NAS can store 10,000 recent event logs, including warnings, errors, and information. If
the NAS does not function correctly, refer to the event logs for troubleshooting.
Tip:
Right click on a record to delete it. To clear every log, click "Clear All".
System Connection Logs
The NAS can record HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SSH, AFP, SAMBA, and iSCSI connections. Click
"Options" to select the connection type to be logged. File transfer performance may be
slightly impacted when this feature is enabled.
Tip:
Right click on a record and select to delete the record or to block the IP and select
how long the IP should be blocked. To clear every log, click "Clear All".
Start Logging: Enable this option to archive connection logs. When the number of logs
reaches the upper limit the NAS will automatically generate a CSV file and save it to a
specified folder. File-level access logs are available on this page. The NAS will record logs

when users access, create, delete, move, or rename any files/folders via the connection type
specified in "Options". To disable this feature, click "Stop logging".
Note:
For AFP and SSH connections, the system can only record login and logout events.
Online Users
The information of online users connected to the NAS by networking services is shown here.
Tip:
Right click on a record to disconnect the IP connection and block the IP.
Syslog Client Management
Syslog is a standard for forwarding log messages on an IP network. Enable this option to save
event and connection logs to a remote Syslog server. When converting connection logs into a
CSV file, the connection type and action will be number coded. Refer to the table for code
meanings.
Connection type codes
Action codes
0 - UNKNOWN
1 - SAMBA
2 - FTP
3 - HTTP
4 - NFS
5 - AFP
6 - TELNET
7 - SSH
8 - ISCSI
0 - UNKNOWN
1 - DEL
2 - READ
3 - WRITE
4 - OPEN
5 - MKDIR
6 - NFSMOUNT_SUCC
7 - NFSMOUNT_FAIL
8 - RENAME
9 - LOGIN_FAIL
10 - LOGIN_SUCC
11 - LOGOUT
12 - NFSUMOUNT
13 - COPY
14 - MOVE
15 - ADD
Advanced Log Search
Advanced log search is provided to search for system event logs, system connection logs and
online users based on user preferences. First, specify the log type, users, computer name,

date range and source IP and click "Search" to search for desired logs or reset to list all logs.
Please note that for online users, only the source IP and Computer name can be specified.
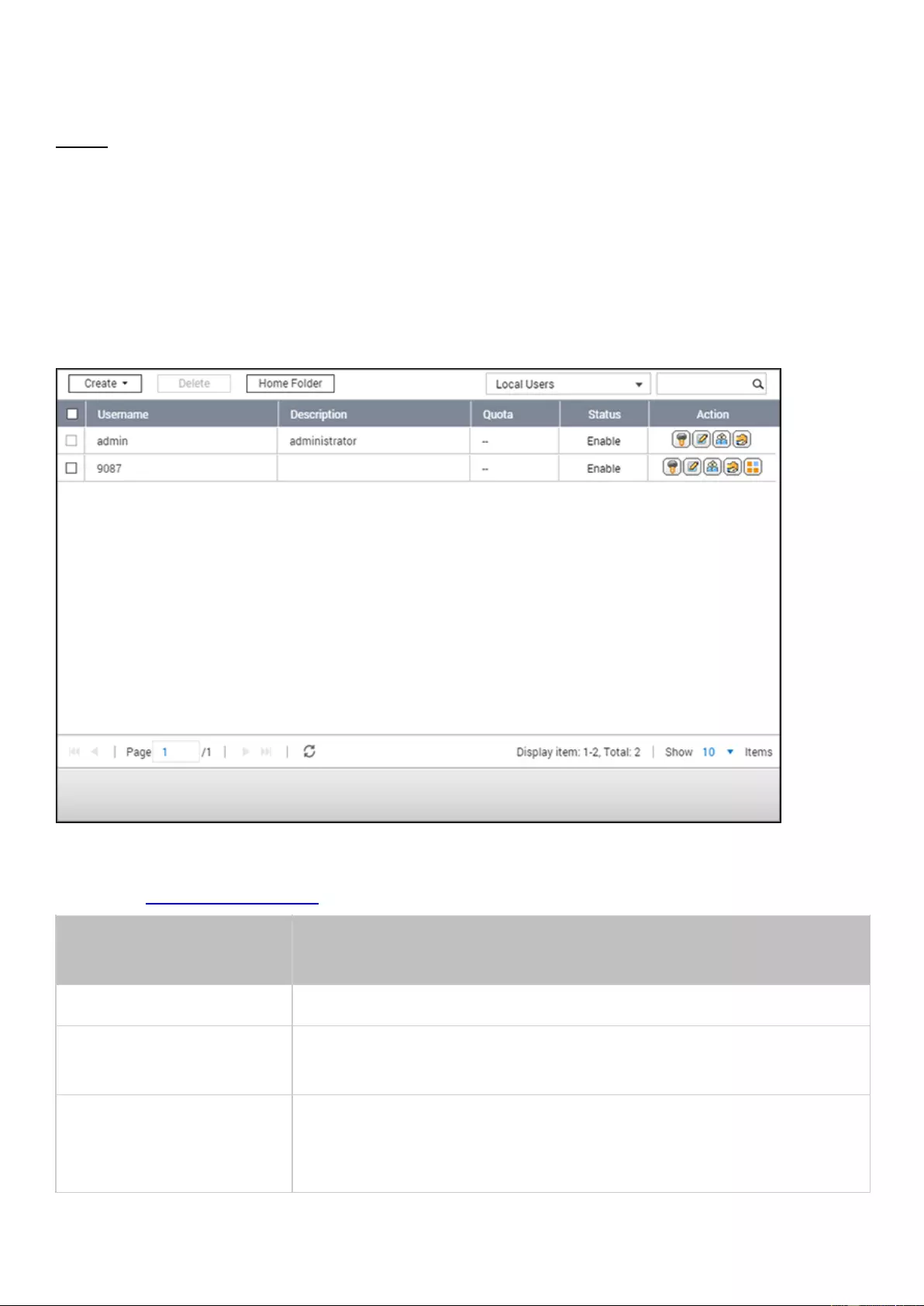
Users
The NAS creates the following users by default:
admin: The administrator "admin" has full access to system administration and all shared folders.
It cannot be deleted.
guest: This is a built-in user and will not be displayed on the "User Management" page. A guest
does not belong to any user group. The login password is "guest".
anonymous: This is a built-in user and will not be shown on the "User Management" page. When
you connect to a NAS by FTP, you can use this name to login.
The number of users you can create on the NAS varies by NAS models. If your NAS models are not
listed, visit http://www.qnap.com for more details.
Maximum number of
users
NAS models
1,024
TS-110, TS-210
2,048
TS-112, TS-119, TS-119P+, TS-212, TS-219P+, TS-410,
TS-239 Pro II+, TS-259 Pro+
4,096
TS-412, TS-419P+, TS-410U, TS-419U, TS-412U, TS-419U+,
SS-439 Pro, SS-839 Pro, TS-439 Pro II+, TS-459U-RP/SP,
TS-459U-RP+/SP+, TS-459 Pro+, TS-459 Pro II, TS-559 Pro+,

TS-559 Pro II, TS-659 Pro+, TS-659 Pro II, TS-859 Pro+,
TS-859U-RP, TS-859U-RP+, TS-809 Pro, TS-809U-RP, TS-879
Pro, TS-1079 Pro, TS-879U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP, TS-1279U-RP,
TS-EC1279U-RP, TS-269 Pro, TS-269L, TS-469 Pro, TS-469L,
TS-569 Pro, TS-569L, TS-669 Pro, TS-669L, TS-869 Pro,
TS-869L, TS-251, TS-451, TS-651, TS-851, TS-253 Pro,
TS-453 Pro, TS-653 Pro, TS-853 Pro, SS-453 Pro, SS-853 Pro.
The following information is required to create new users:
Username: The username is case-insensitive and supports multi-byte characters, such as Chinese,
Japanese, Korean, and Russian. The maximum length is 32 characters. Invalid characters are: " /
\ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < > ` '
Password: The password is case-sensitive. It is recommended to use a password of at least 6
characters. The maximum length is 64 characters.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Creating a User
Creating Multiple Users
Importing/Exporting Users
Home Folders
Creating a User
To create a user on the NAS, follow the steps below:
1.
Go to
"Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Users".
2.
Click
"Create" >
"Create a User".
3.
Follow the wizard instructions to complete the details.
Creating Multiple Users
To create multiple users on the NAS, follow the steps below:
1.
Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Users".
2.
Click "Create" > "Create Multiple Users".
3.
Click "Next".
4.
Enter the name prefix (for example: "test".) Enter the start number for the username,
e.g. 0001 and the number of users to be created (for example: 10.) The NAS will then
create ten users named: test0001, test0002, test0003 ... test0010. The password
entered here is the same for all the new users.

5.
Select to create a private shared folder for each user or not. The shared folder will be
named after the username. If a shared folder of the same name has already existed, the
NAS will not create the folder.
6.
Specify the folder settings.
7.
You can view the new users created in the last step. Click "Finish" to exit the wizard.
8.
Check that the users have been created.
9.
Check that the shared folders have been created for the users.
Importing/Exporting Users
You can import users to or export users from the NAS with this function.
Exporting users
Follow the steps below to export users from the NAS:
1.
Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Users".
2.
Click "Create" > "Import/Export Users".
3.
Select the option "Export user and user group settings".
4.
Click "Next" to download and save the account setting file (*.bin.) This file can be
imported to another NAS for account setup.
Importing users
Before importing users to the NAS, make sure you have backed up the original users' settings
by exporting the users. Follow these steps to import users to the NAS:
1.
Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Users".
2.
Click "Create" > "Import/Export Users".
3.
Select "Import user and user group settings". Select the option "Overwrite duplicate
users" to overwrite existing users on the NAS. Click "Browse", select the file (*.txt, *.csv,
*.bin) which contains the users' information and click "Next" to import the users.
4.
Click "Finish" after the users have been created.
5.
The imported user accounts will be displayed.
Note:
The password rules (if applicable) will not be applied when importing users.
The quota settings can be only exported when the quota function is enabled in
"Privilege Settings" > "Quota".
The NAS supports importing user accounts from TXT, CSV or BIN files. To create a list of user
accounts with these file types, follow these steps:

TXT
1.
Open a new file with a text editor.
2.
Enter a user's information in the following order and separate them by ",": Username,
Password, Quota (MB), Group Name
3.
Go to the next line and repeat the previous step to create another user account. Each line
indicates one user's information.
4.
Save the file with UTF-8 encoding if it contains double-byte characters.
Note that if the quota is left empty, the user will have no limit in using the disk space of the
NAS.
CSV (Excel)
1.
Open a new file with Excel.
2.
Enter a user's information in the same row in the following order:
o
Column A: Username
o
Column B: Password
o
Column C: Quota (MB)
o
Column D: Group name
3.
Go to the next row and repeat the previous step to create another user account. Each
row indicates one user's information. Save it as a CSV file.
4.
Open the CSV file with Notepad and save it in UTF-8 encoding if it contains double-byte
characters.
BIN (Exported from the NAS)
The BIN file is exported from a QNAP NAS. It contains information including username,
password, quota, and user group. The quota setting can only be exported when the quota
function is enabled in "Privilege Settings" > "Quota".
Home Folders
Enable Home Folders to create a personal folder to each local and domain user on the NAS.
Users can access their home folders via Microsoft networking, FTP, AFP, and File Station. All
the home folders are located in the shared folder "Homes", which can only be accessed by
"admin" by default.
To use this feature, click "Home Folders". Select "Enable home folder for all users" and the
disk volume where the home folders will be created in. Click "Apply".
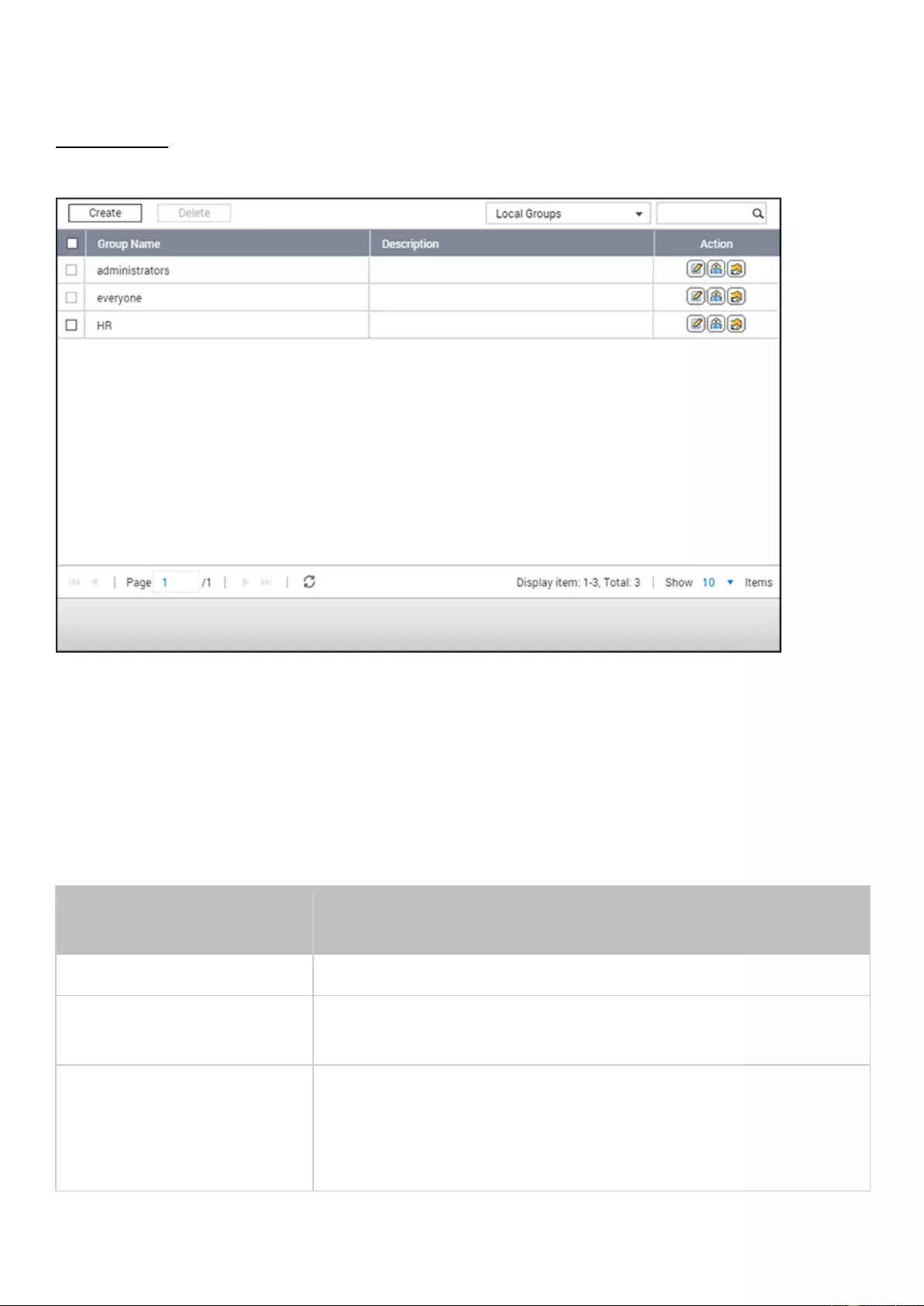
User Groups
A user group is a collection of users with the same access rights to files or folders.
The NAS creates the following user groups by default:
administrators: All the members in this group have administration rights of the NAS. This group
cannot be deleted.
everyone: All the registered users belong to this group. This group cannot be deleted.
The number of user groups you can create on the NAS varies by NAS model. If your NAS is not listed,
visit http://www.qnap.com for more details.
Maximum number of user
groups
NAS models
128
TS-110, TS-210
256
TS-112, TS-119, TS-119P+, TS-212, TS-219P+, TS-410,
TS-239 Pro II+, TS-259 Pro+
512
TS-412, TS-419P+, TS-410U, TS-419U, TS-412U,
TS-419U+, SS-439 Pro, SS-839 Pro, TS-439 Pro II+,
TS-459U-RP/SP, TS-459U-RP+/SP+, TS-459 Pro+, TS-459
Pro II, TS-559 Pro+, TS-559 Pro II, TS-659 Pro+, TS-659
Pro II, TS-859 Pro+, TS-859U-RP, TS-859U-RP+, TS-809
Pro, TS-809U-RP, TS-879 Pro, TS-1079 Pro, TS-879U-RP,
TS-EC879U-RP, TS-1279U-RP, TS-EC1279U-RP, TS-269 Pro,
TS-269L, TS-469 Pro, TS-469L, TS-569 Pro, TS-569L,
TS-669 Pro, TS-669L, TS-869 Pro, TS-869L, TS-251, TS-451,
TS-651, TS-851, TS-253 Pro, TS-453 Pro, TS-653 Pro,
TS-853 Pro, SS-453 Pro, SS-853 Pro.
A group name cannot exceed 256 characters. It is case-insensitive and supports double-byte
characters, such as Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, except the following ones: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ?
< > ` '
Creating a User Group
Follow these steps to create a user group on the NAS:
1. Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "User Groups".
2. Click "Create", enter the group name and description, assign users to the group, and edit shared
folder permissions (Read Only, Read/Write, and Deny) for the group.
3. Click "Create".
Deleting a User Group
Follow these steps to delete a user group on the NAS:
1. Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "User Groups".
2. Select the user group(s) to be deleted.
3. Click "Delete".
Tip: You can use the buttons under "Action" to view group details, edit group users, or edit shared
folder permissions for a particular user group.
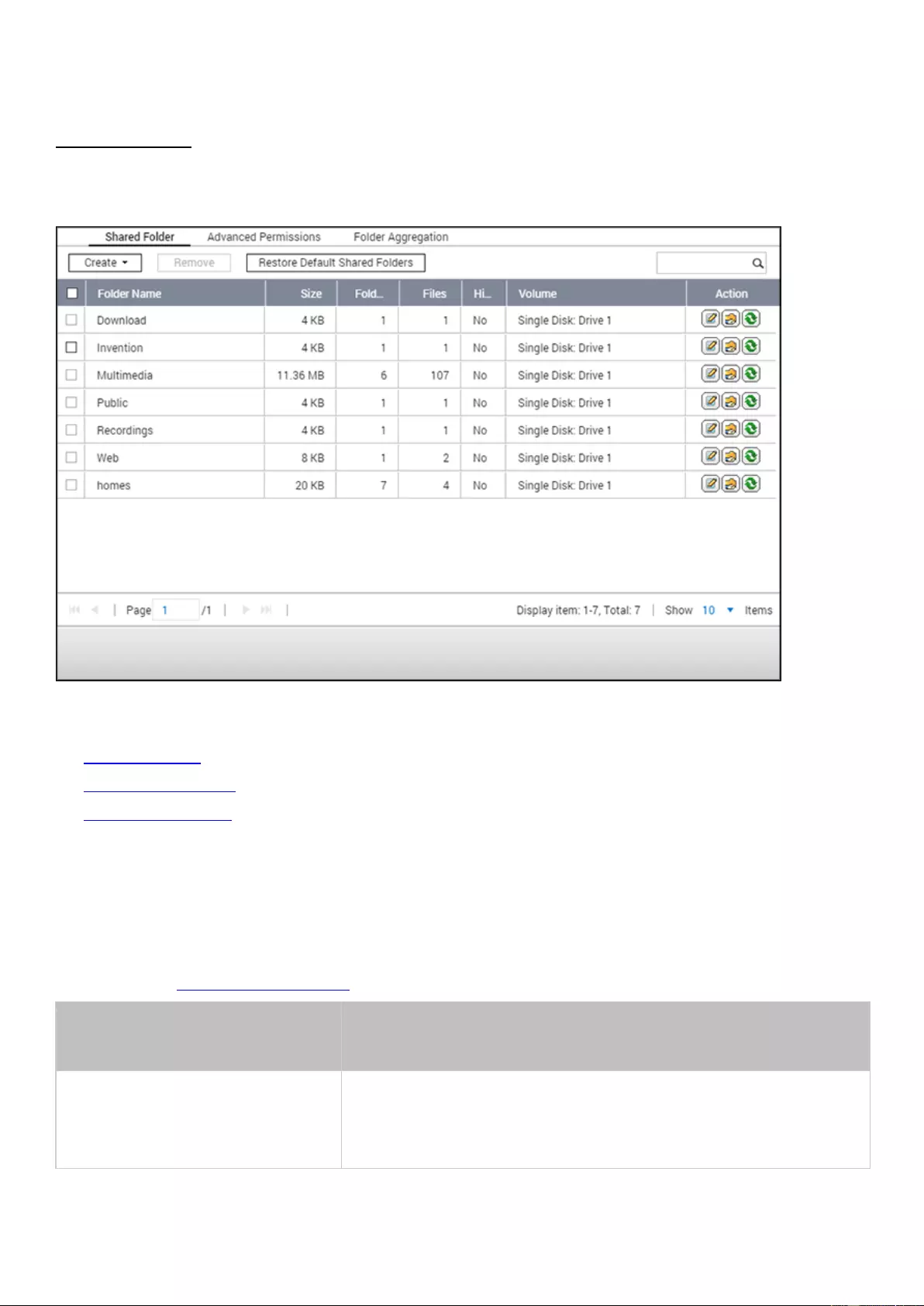
Shared Folders
Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders" to configure shared folders of
your NAS.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Shared Folders
ISO Shared Folders
Folder Aggregation
Shared Folders
You can create multiple shared folders on the NAS and specify access rights for users and user groups.
The number of shared folders you can create on the NAS varies by NAS model. If your NAS model is
not listed, visit http://www.qnap.com for more details.
Maximum number of shared
folders
NAS models
256
TS-110, TS-210, TS-112, TS-119, TS-119P+, TS-212,
TS-219P+, TS-x20, TS-x21, TS-410, TS-239 Pro II+, TS-259
Pro+
512
TS-412, TS-419P+, TS-410U, TS-419U, TS-412U, TS-419U+,
SS-439 Pro, SS-839 Pro, TS-439 Pro II+, TS-459U-RP/SP,
TS-459U-RP+/SP+, TS-459 Pro+, TS-459 Pro II, TS-559 Pro+,
TS-559 Pro II, TS-659 Pro+, TS-659 Pro II, TS-859 Pro+,
TS-859U-RP, TS-859U-RP+, TS-809 Pro, TS-809U-RP, TS-x70,
TS-879 Pro, TS-1079 Pro, TS-879U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP,
TS-1279U-RP, TS-EC1279U-RP
On the folder list, you can view the current data size, number of sub-folders and files created in the
shared folder, and the folder status (hidden or not.)
To create a shared folder, follow these steps:
1.
Click "Create" > "Shared Folder".
2.
Enter the folder settings.
o
Folder name: Enter the name. The name does not support " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >
` '
o
Comment: Enter an optional description of the shared folder.
o
Disk Volume: Select which disk volume on which to create the folder.
o
Path: Specify the path of the shared folder or choose to let the NAS specify the path
automatically.
3.
Configure Access privileges for users: Select the way you want to specify the access
rights to the folder. If you select to specify the access right by user or user group, you
can select to grant read only, read/write, or deny access to the users or user groups.
4.
Advanced settings:
o
Guest Access Right: Specify the guest access right.
o
Media Folder: Set this folder as a media folder (refer to the Media Folder chapter for
details.)
o
Hide Network Drive: Select to hide the shared folder or not in Microsoft Networking.
When a shared folder is hidden, you have to enter the complete directory
\\NAS_IP\share_name to access the share.
o
Lock file (oplocks): Opportunistic locking is a Windows mechanism for the client to
place an opportunistic lock (oplock) on a file residing on a server in order to cache the
data locally for improved performance. Oplocks is enabled by default for everyday
usage and should be disabled on networks that require multiple users concurrently
accessing the same files.
o
Enable Network Recycle Bin: Enable the Network Recycle Bin for created shared
folders. The option "Restrict the access of Recycle Bin to administrators only for now"
will ensure that files deleted and moved to the Network Recycle Bin can only be
recovered by administrators.
o
Enable sync on this shared folder: Enable this option if you want to sync the contents
in this shared folder.
5.
Confirm the settings and click "Next".
6.
Click "Finish" to complete the setup.
To delete a shared folder, select the folder checkbox and click "Remove". You can select the
option "Also delete the data. (Mounted ISO image files will not be deleted)" to delete the
folder and the files in it. If you do not select to delete the folder data, the data will be
retained in the NAS. You can create a shared folder of the same name again to access the
data.
Icon
Name
Description
Folder
Property
Edit the folder property. Select to hide or show the network
drive, enable/disable oplocks, folder path, comment, restrict the
access of Recycle Bin to administrators (files can only be
recovered by administrators from the Network Recycle Bin) and
enable or disable write-only access on FTP connection.
Folder
Permissions
Edit folder permissions and subfolder permissions.
Refresh
Refresh the shared folder details.
Tip: In the event that default shared folders are removed due to human error (such as accidental
hard drive removal), you can attempt to restore them using the "Restore Default Shared Folders"
button once the errors have been fixed.
Folder Permissions
Configure folder and subfolder permissions on the NAS. To edit basic folder permissions,
locate a folder name in "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders" and click "Folder Permissions"
in the "Action" column. The folder name will be shown on the left and the users with
configured access rights are shown in the panel. You can also specify guest access rights on
the bottom of the panel. Click "Add" to select more users and user groups and specify their
access rights to the folder. Click "Add" to confirm. Click "Remove" to remove any configured
permissions. You can select multiple items by holding the Ctrl key and left clicking the mouse.
Click "Apply" to save the settings.
Subfolder Permissions
The NAS supports subfolder permissions for secure management of folders and subfolders.
You can specify read, read/write, and deny access to individual users for each folder and
subfolder.
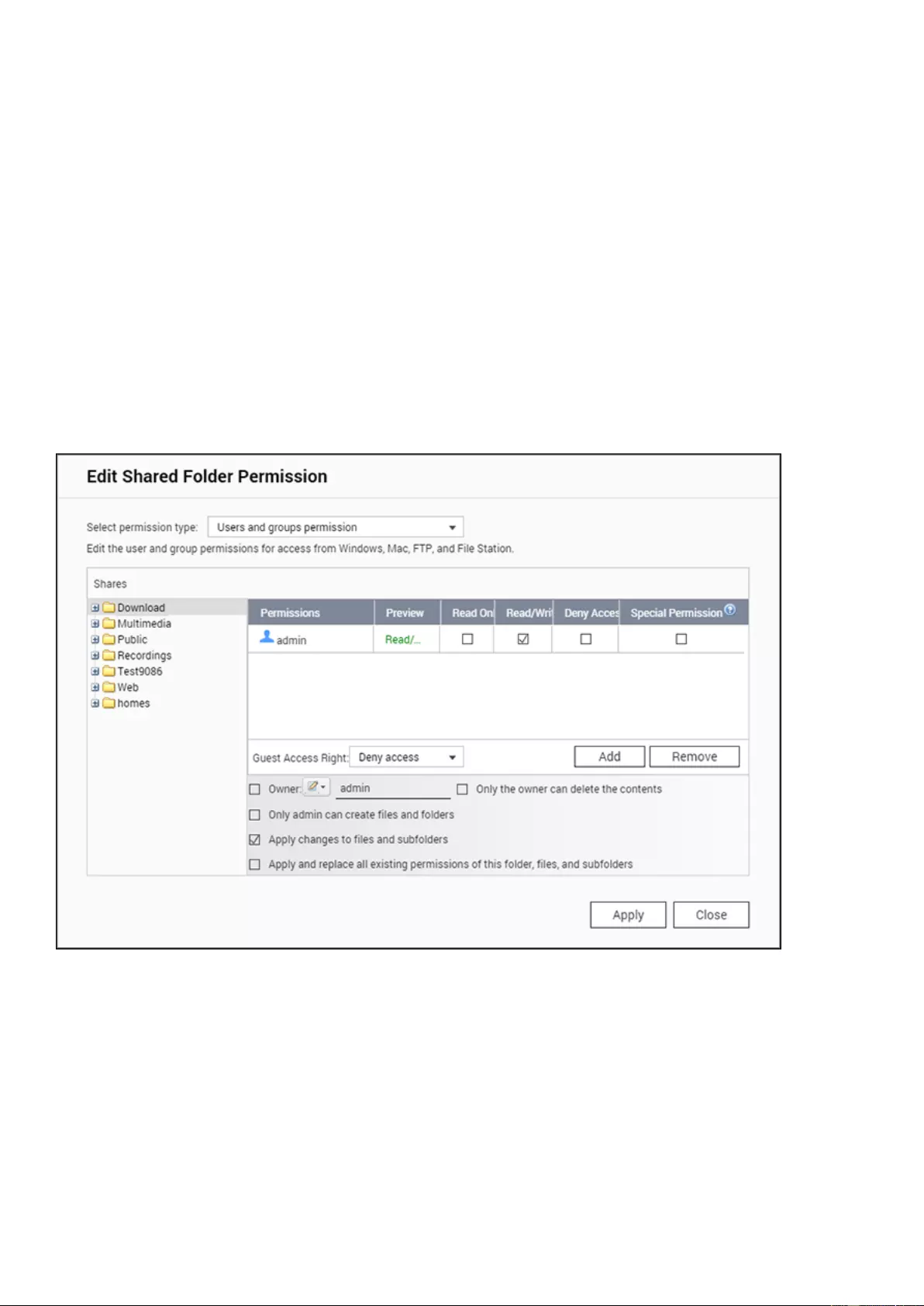
To configure subfolder permissions, follow these steps:
1.
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders" > "Advanced Permissions" tab. Select
"Enable Advanced Folder Permissions" and click "Apply All".
2.
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders" > "Shared Folder" tab. Select a root folder
(for example, "Dept") and click "Folder Permissions". The shared folder name and its
first-level subfolders are shown on the left. The users with configured access rights are
shown in the panel, with special permission below. Double click on first-level subfolders
to view the second-level subfolders. Select the root folder (Dept). Click "+ Add" to
specify read only, read/write, or deny access for users and user groups.
3.
Click "Add" when you have finished the settings.
4.
Specify other permissions below the folder permissions panel.
o
Guest Access Right: Specify to grant full or read only access or deny guest access.
o
Owner: Specify the owner of the folder. By default, the folder owner is the creator.
5.
To change the folder owner, click the "Folder Property" button next to the owner field.
6.
Select a user from the list or search a username. Then click "Set".
o
Only the owner can delete the contents: When you apply this option to a folder (for
example, "Dept"), only the folder owner can delete the first-level subfolders and files.
Users who are not the owner but possess read/write permission to the folder cannot
delete the folders Admin, HR, Production, Sales, and test in this example. This option
does not apply to the subfolders of the selected folder even if the options "Apply
changes to files and subfolders" and "Apply and replace all existing permissions of this
folder, files, and subfolders" are selected.

o
Only admin can create files and folders: This option is only available for root folders.
Select this option to allow admin to create first-level subfolders and files in the
selected folder only. For example, in the folder "Dept", only the admin can create files
and subfolders Admin, HR, Production, and so on. Other users with read/write access
to Dept can only create files and folders in the second and lower-level subfolders such
as Admin01, Admin02, HR1, and HR2.
o
Apply changes to files and subfolders: Apply permissions settings except owner
protection and root folder write protection settings to all the files and subfolders within
the selected folder. These settings include new users, deleted users, modified
permissions, and folder owner. The options "Only the owner can delete the contents"
and "Only admin can create files and folders" will not be applied to subfolders.
o
Apply and replace all existing permissions of this folder, files, and subfolders: Select
this option to override all previously configured permissions of the selected folder and
its files and subfolders except owner protection and root folder write protection
settings. The options "Only the owner can delete the contents" and "Only admin can
create files and folders" will not be applied to subfolders.
o
Special Permission: This option is only available for root folders. Select this option and
choose between "Read only" or "Read/Write" to allow a user to access to all the
contents of a folder irrespectively of the pre-configured permissions. A user with
special permission will be identified as "admin" when he/she connects to the folder via
Microsoft Networking. If you have granted special permission with "Read/Write" access
to the user, the user will have full access and is able to configure the folder
permissions on Windows. Note that all the files created by this user belong to "admin".
Since "admin" does not have quota limit on the NAS, the number and size of the files
created by users with special permission will not be limited by their pre-configured
quota settings. This option should only be used for administrative and backup tasks.
7.
After changing the permissions, click "Apply" and then "YES" to confirm.
Note:
You can create up to 230 permission entries for each folder when Advanced Folder
Permission is enabled.
If you have specified "deny access" for a user on the root folder, the user will not be
allowed to access the folder and subfolders even if you select read/write access to the
subfolders.
If you have specified "read only access" for a user on the root folder, the user will have
read only access to all the subfolders even if you select read/write access to the
subfolders.
To specify read only permission on the root folder and read/write permission on the
subfolders, you must set read/write permission on the root folder and use the option
"Only admin can create files and folders" (to be explained later).

If an unidentified account ID (such as 500) is shown for a subfolder on the permission
assignment page after you click the "Access Permissions" button next to a shared folder
in "Control Panel">"Privilege Settings">"Shared Folders">"Shared Folder", it is likely
that the permission of that subfolder has been granted to a user account that no longer
exists. In this case, select the unidentified account ID and click "Remove" to delete it.
Microsoft Networking Host Access Control
NAS folders can be accessed via Samba (Windows) by default. You can specify authorized IP
addresses and hosts by following these steps:
1.
Click "Folder Permissions".
2.
Select "Microsoft Networking host access" from the drop-down menu at the top of the
page.
3.
Specify authorized IP addresses and host names. The following IP address and host name
are used as an example:
o
IP address: 192.168.12.12 or 192.168.*.*
o
Host name: dnsname.domain.local or *.domain.local
4.
Click "Add" to enter the IP address and host name and then "Apply".
Notifications on characters used:
Wildcard characters: You can enter wildcard characters in an IP address or host name
entry to represent unknown characters.
Asterisk (*): Use an asterisk (*) as a substitute for zero or more characters. For example,
if you enter *.domain.local, the following items are included: a.domain.local,
cde.domain.local, or test.domain.local
Question mark (?): Use a question mark (?) as a substitute for only one character. For
example, test?.domain.local includes the following: test1.domain.local, test2.domain.local,
or testa.domain.local
When you use wildcard characters in a valid host name, dot (.) is included in wildcard
characters. For example, when you enter *.example.com, "one.example.com" and
"one.two.example.com" are included.
ISO Shared Folders
You can mount ISO image files on the NAS as ISO shares. The NAS supports mounting up to
256 ISO shares.
TS-110, TS-119, TS-120, TS-121, TS-210, TS-219, TS-219P, TS-220, TS-221, TS-410, ,
TS-119P+, TS-219P+, TS-112, TS-212 support up to 256 network shares only (including 6

default network shares.) The maximum number of ISO image files supported by these models
is less than 256 (256 minus 6 default shares minus number of network recycle bin folders.)
Follow these steps to mount an ISO file on the NAS:
1.
Log in to the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Share Folders" > "Create". Click "Create an
ISO Share".
2.
Select an ISO image file on the NAS. Click "Next".
3.
The image file will be mounted as a shared folder of the NAS. Enter the folder name.
4.
Specify the access rights of NAS users or user groups to the shared folder. You can also
select "Deny Access" or "Read only" for the guest access right. Click "Next".
5.
Confirm the settings and click "Next".
6.
Click "Finish".
7.
After mounting the image file, you can specify access rights for the users over different
network protocols such as SMB, AFP, NFS, and WebDAV by clicking the Access
Permission icon in the "Action" column.
The NAS supports mounting ISO image files and you can preview them using File Station.
Refer to the File Station chapter for more details.
Note:
ARM-based NAS models do not support using Cyrillic characters for the name of a
subfolder in an ISO shared folder (the name will be incorrectly displayed if a subfolder
is created with a Cyrillic name.) Please name the subfolder with a different language
before an ISO file is created.
For Mac OSX, mounting a folder that contains the # character in the folder name
through WebDAV is not supported. Please rename the folder before mounting it if
necessary.
Folder Aggregation
You can aggregate the shared folders on Microsoft network as a portal folder on the NAS and
let NAS users access the folders through your NAS. Up to 10 folders can be linked to a portal
folder. To use this function, follow these steps:
1.
Enable folder aggregation.
2.
Click "Create A Portal Folder".
3.
Enter the portal folder name. Select to hide the folder or not, and enter an optional
comment for the portal folder.
4.
Click the "Link Configuration" button under "Action" and enter the remote folder settings.
Make sure the folders are open for public access.
5.
Upon successful connection, you can connect to the remote folders through the NAS.
Note:
Folder Aggregation is only supported in Microsoft networking service and is
recommended for a Windows AD environment.
If there is permission control on the folders, you need to join the NAS and the remote
servers to the same AD domain.
Advanced Permissions
"Advanced Folder Permissions" and "Windows ACL" provide subfolder and file level
permissions control. They can be enabled independently or together.
Protocols
Permission
Options
How to Configure
Advanced Folder
Permissions
FTP, AFP, File
Station, Samba
3 (Read, Read &
Write, Deny)
NAS web UI
Windows ACL
Samba
13 (NTFS
permissions)
Windows File
Explorer
Both
FTP, AFP, File
Station, Samba
Please see the
application note
(https://www.qnap.
com/i/en/trade_tea
ch/con_show.php?o
p=showone&cid=6)
for more details.
Windows File
Explorer
Advanced Folder Permissions
Use "Advanced Folder Permissions" to directly configure subfolder permissions on the NAS.
There is no depth limitation for subfolder permission, but it is highly recommended to only
change permissions on the first or second subfolder level. When "Advanced Folder
Permissions" is enabled, click "Folder Permissions" under the "Shared Folders" tab to
configure subfolder permission settings. See Shared Folders" > "Folder Permission of this
section for details.
Windows ACL
Use "Windows ACL" to configure the subfolder and file level permissions from Windows File
Explorer. All Windows Permissions are supported. For detailed Windows ACL behavior, please
refer to standard NTFS permissions: http://www.ntfs.com/ntfs-permissions.htm
To assign subfolder and file permissions to a user or a user group, full control share-level
permissions must be granted to the user or user group.
When Windows ACL is enabled when "Advanced Folder Permissions" is disabled, subfolder
and file permissions will only have effect when accessing the NAS from Windows File
Explorer. Users connecting to the NAS via FTP, AFP, or File Station will only have
share-level permissions.
When Windows ACL and Advanced Folder Permissions are both enabled; users cannot
configure Advanced Folder Permissions from the NAS. Permissions (Read only,
Read/Write, and Deny) of Advanced Folder Permissions for AFP, File Station, and FTP will
automatically follow Windows ACL configuration.
Note:
Only the “List Folders" / "Read Data” and “Create Files" / "Write Data” permissions
will be available when using other file protocols (such as AFP, NFS, FTP, WebDAV, etc)
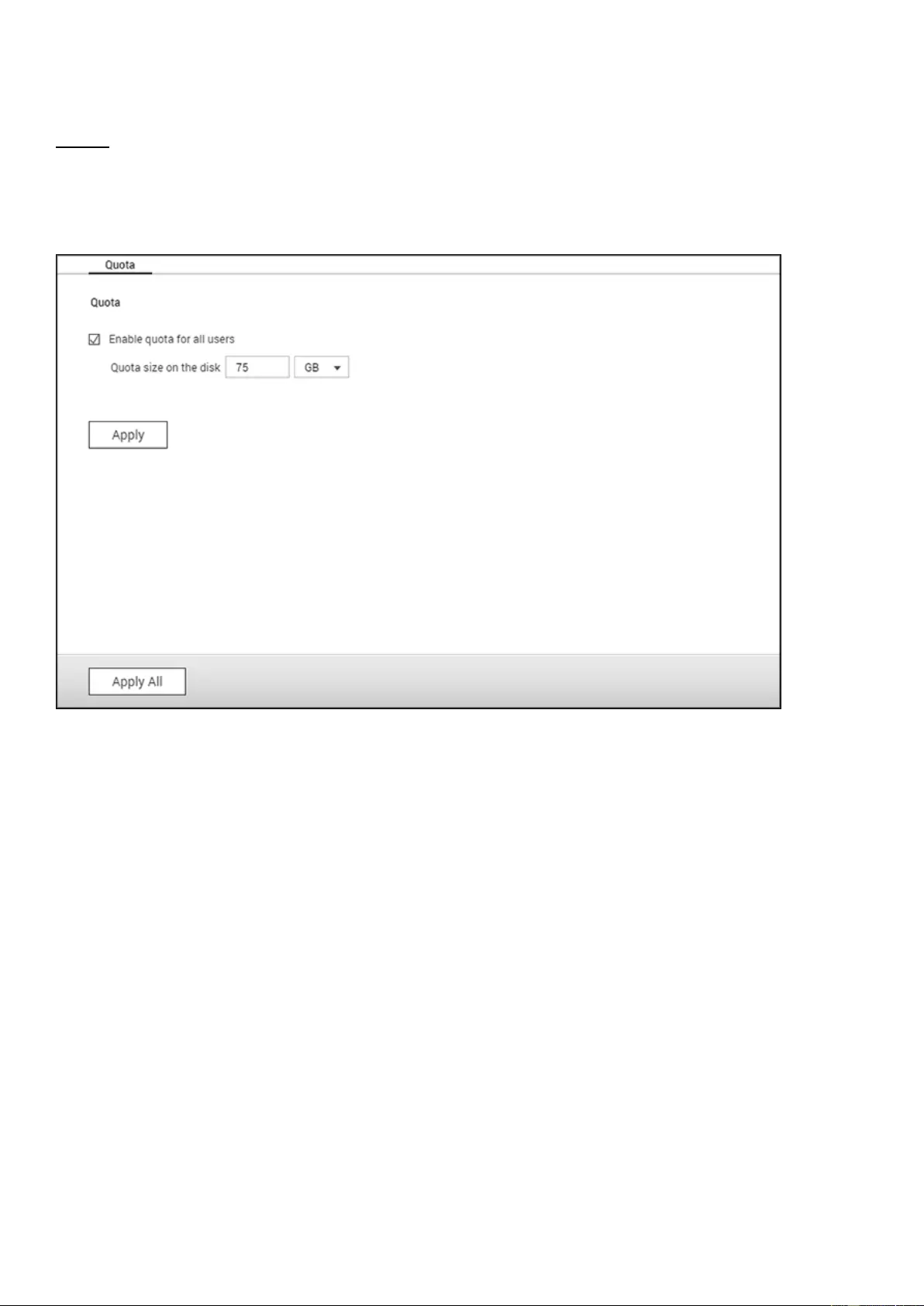
Quota
To efficiently allocate storage space, you can specify a quota value (in megabytes or
gigabytes) that applies to all users and disk volumes. QTS prevents users from uploading data
to the NAS when the feature is enabled and the quota is reached.
After the quota is specified and applied, the screen displays a list of all local and domain users
and the corresponding storage details (quota size, used space, and available space). You can
perform the following actions:
Modify quota settings: Click “Edit” and then specify a new quota value or select “No limit”.
Export quota settings to a CSV file: Click “Generate”.
Download generated CSV files: Click “Download” and then save the file to a preferred location.
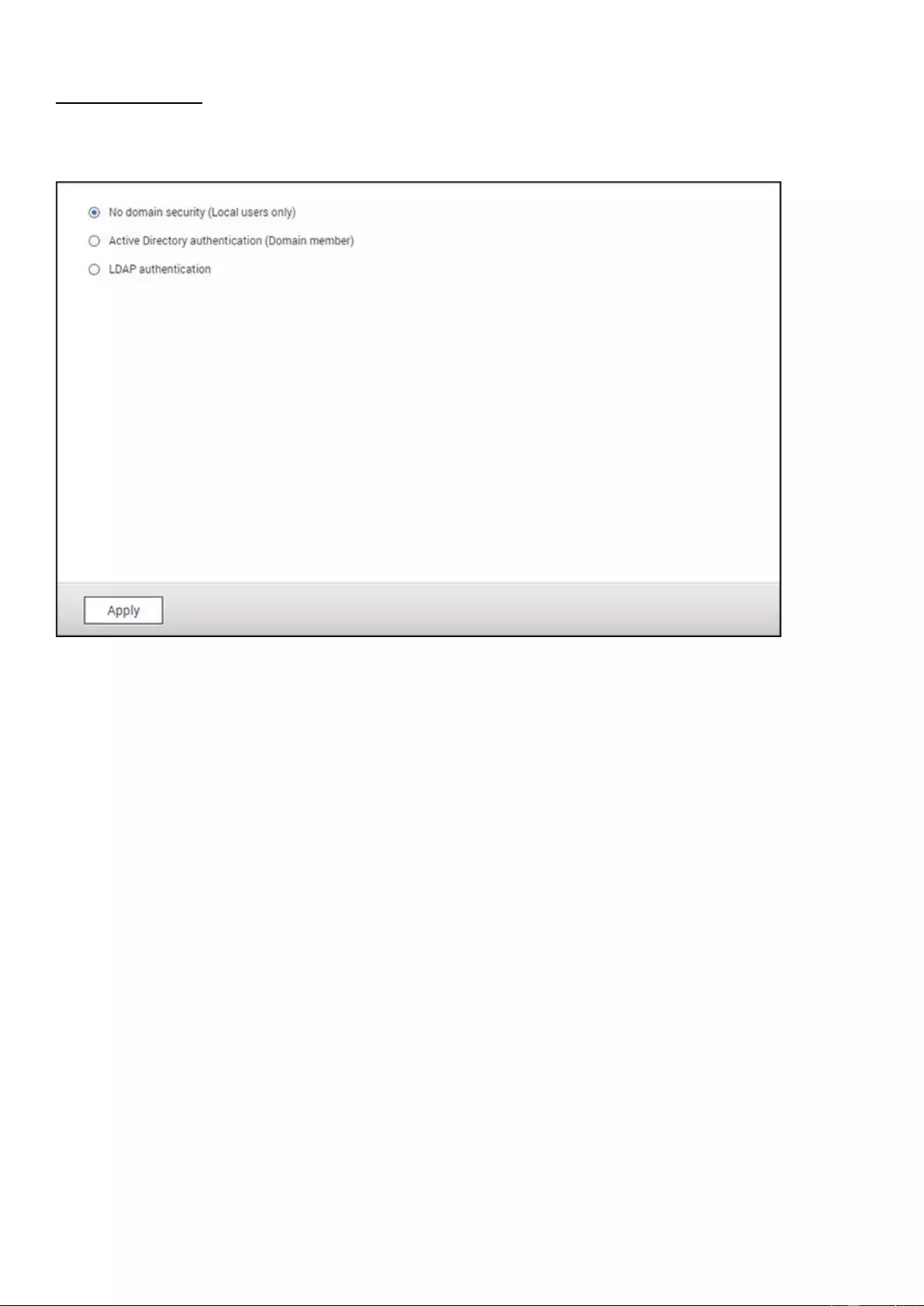
Domain Security
The NAS supports user authentication by local access right management, Microsoft Active Directory
(Windows Server 2003/2008/2012), and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory.
By joining the NAS to an Active Directory or a LDAP directory, the AD or LDAP users can access the
NAS using their own accounts without extra user account setup on the NAS.
No domain security: Only the local users can access the NAS.
Active Directory authentication (domain members): Join the NAS to an Active Directory. The
domain users can be authenticated by the NAS. After joining the NAS to an AD domain, both the
local NAS users and AD users can access the NAS via the following protocols/services:
o Samba (Microsoft Networking)
o AFP
o FTP
o File Station
LDAP authentication: Connect the NAS to an LDAP directory. The LDAP users can be
authenticated by the NAS. After connecting the NAS to an LDAP directory, either the local NAS
users or the LDAP users can be authenticated to access the NAS via Samba (Microsoft
Networking). Both the local NAS users and LDAP users can access the NAS via the following
protocols/services:
o AFP
o FTP
o File Station

Joining NAS to Active Directory (Windows Server 2003/2008/2012)
Active Directory is a directory used in Windows environments to centrally store, share, and
manage a network's information and resources. It is a hierarchical data center which
centrally holds information for users, user groups, and the computers for secure access
management. The NAS supports Active Directory (AD.) By joining the NAS to the Active
Directory, all the user accounts of the AD server will be automatically imported to the NAS.
AD users can use their same login details to access the NAS. If you are using Active
Directory with Windows Server 2008 R2, you must update the NAS firmware to at least
3.2.0 to join the NAS to the AD.
Joining the NAS to Active Directory (AD) by Quick Configuration Wizard (Recommended)
To join the NAS to an AD domain by the Quick Configuration Wizard, follow these steps:
1.
Login to the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Domain Security".
Select "Active Directory authentication (domain member)" and click "Quick Configuration
Wizard".
2.
Read the wizard introduction. Click "Next".
3.
Enter the full domain name of the AD domain (DNS.) The NetBIOS name will be
automatically generated from the domain name but can be changed manually if the
name is different than the generated one. Specify the DNS server IP for domain
resolution. The IP must be the same as the DNS server of your Active Directory. Click
"Next".
4.
Select the domain controller from the multiple selection window. For domain controller
redundancy, select multiple domain controllers and set the order of priority for the
controllers. The domain controller is responsible for time synchronization between the
NAS and the domain server and user authentication. Enter the domain administrator
name and password. Click "Join".
5.
Upon successful login to the domain server, the NAS has joined to the domain. Click
"Finish" to exit the wizard.
6.
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Users" or "User Groups" to load the domain users or user
groups to the NAS.
Joining the NAS to Active Directory (AD) by Quick Configuration Manually
Follow the steps below to join the QNAP NAS to the Windows Active Directory.
1.
Login to the NAS as an administrator. Go to “Control Panel” > “System” > "General
Settings" > "Time". Set the date and time of the NAS to synchronize with you domain
controller time as it must be consistent with the time of the AD server. The maximum
time disparity tolerated is 5 minutes.
2.
Go to “Control Panel” > “Network & File Services”. Click” Network & Virtual Switch” and
go to “Interfaces”. Click “DNS Server” and set the IP of the primary DNS server as the IP
of the Active Directory server that contains the DNS service. The primary DNS server
field must be the IP of the DNS server that is used for your Active Directory. If you use
an external DNS server, you will not be able to join the domain.
3.
Go to “Control Panel" > “Privilege" > "Domain Security". Select "Active Directory
authentication (domain member)", click “Manual Configuration”.
4.
Enter the AD domain information, click “Join”.
Note:
Enter a fully qualified AD domain name, for example, qnap-test.com
The AD user entered here must have administrator access rights to the AD domain.
WINS Support: If you are using a WINS server on the network and the workstation is
configured to use that WINS server for name resolution, you must set up the WINS
server IP on the NAS (use the specified WINS server.)
Windows 2003
The AD server name and AD domain name can be checked in "System Properties" in
Windows. As an example, for Windows 2003 servers, if you see "node1.qnap-test.com" as
the "Full computer name" on the system properties dialog window, the AD server name is
"node1" and NOT "node1.qnap-test.com" and the domain name remains the same as
qnap-test.com.
Windows Server 2008
Check the AD server name and domain name in "Control Panel" > "System" in Windows. In
the system dialog window, the AD server name will appear as the computer name and the
domain name can be found in the domain field.
Note:
After joining the NAS to the Active Directory, the local NAS users who have access
rights to the AD server should use "NASname\username" to login. AD users should use
their own usernames to login to the AD server.
For TS-x09 series NAS, if the AD domain is based on Windows 2008 Server, the NAS
firmware must be at least version 2.1.2.
Windows 7

If you are using a Windows 7 PC that is not a member of an Active Directory, while your
NAS is an AD domain member and its firmware version is earlier than v3.2.0, change your
PC settings as shown below to allow your PC to connect to the NAS:
1.
Go to "Control Panel" > "Administrative Tools".
2.
Click "Local Security Policy".
3.
Go to "Local Policies" > "Security Options". Select "Network security: LAN Manager
authentication level".
4.
In "Local Security Setting" select "Send LM & NTLMv2 – use NTLMv2 session security if
negotiated" from the list. Then click "OK".
Verifying the settings
To verify that the NAS has successfully joined the Active Directory, go to "Privilege Settings"
> "Users" and "User Groups". A list of users and user groups will be shown on the "Domain
Users" and "Domain Groups" lists respectively. If you have created new users or user groups
in the domain, you can click the Refresh button to add users and user group lists from the
Active Directory to the NAS. The user permission settings will be synchronized in real time
with the domain controller.

Connecting NAS to an LDAP Directory
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a directory that can store the information of
every user and group in a centralized server. Administrators can use LDAP to manage users
in the LDAP directory and allow them to connect to multiple NAS with the same login details.
This feature is intended for use by administrators and users who have knowledge of Linux
servers, LDAP servers, and Samba. A running LDAP server is required when using this
feature.
Requirements
Required information/settings:
The LDAP server connection and authentication information
The LDAP structure, where the users and groups are stored
The LDAP server security settings
Connecting QNAP Turbo NAS to LDAP Directory
Follow the steps below to connect the QNAP NAS to an LDAP directory:
1.
Login to the NAS as an administrator.
2.
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Domain Security". By default, "No domain security" is
enabled. This means only local NAS users can connect to the NAS.
3.
Select "LDAP authentication" and complete the settings.
o
LDAP Server Host: The host name or IP address of the LDAP server.
o
LDAP Security: Specify how the NAS will communicate with the LDAP server:
ldap:// = Use a standard LDAP connection (default port: 389.)
ldap:// (ldap + SSL) = Use an encrypted connection with SSL (default port: 686.)
This is normally used by older version of LDAP servers.
Ldap:// (ldap + TLS) = Use an encrypted connection with TLS (default port: 389.)
This is normally used by newer version of LDAP servers
o
BASE DN: The LDAP domain. For example: dc=mydomain,dc=local
o
Root DN: The LDAP root user. For example cn=admin, dc=mydomain,dc=local
o
Password: The root user password.
o
Users Base DN: The organization unit (OU) where users are stored. For example:
ou=people,dc=mydomain,dc=local
o
Groups Base DN: The organization unit (OU) where groups are stored. For example
ou=group,dc=mydomain,dc=local

4.
Click "Apply" to save the settings. Upon successful configuration, the NAS will be able to
connect to the LDAP server.
5.
Configure LDAP authentication options.
o
If Microsoft Networking has been enabled (Network Services > Win/Mac/NFS >
Microsoft Networking) when applying the LDAP settings, specify the users who can
access the NAS via Microsoft Networking (Samba.)
Local users only: Only local NAS users can access the NAS via Microsoft Networking.
LDAP users only: Only LDAP users can access the NAS via Microsoft Networking.
o
If Microsoft Networking is enabled after the NAS has already been connected to the
LDAP server, select the authentication type for Microsoft Networking.
Standalone Server: Only local NAS users can access the NAS via Microsoft
Networking.
LDAP Domain Authentication: Only LDAP users can access the NAS via Microsoft
Networking.
6.
When the NAS is connected to an LDAP server, the administrator can:
o
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Users" and select "Domain Users" from the drop-down
menu. The LDAP users list will be shown.
o
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "User Groups" and select "Domain Groups" from the
drop-down menu. The LDAP groups will be shown.
o
Specify the folder permissions of LDAP domain users or groups in "Privilege Settings"
> "Shared Folders" > click the "Access Permissions" button next to the folder to be
configured.
Note:
Both LDAP users and local NAS users can access the NAS via File Station, FTP, and
AFP.
LDAP Authentication Technical Requirements with Microsoft Networking
Required items to authenticate the LDAP users on Microsoft Networking (Samba):
1.
A third-party software to synchronize the password between LDAP and Samba in the
LDAP server.
2.
Importing the Samba schema to the LDAP directory.
A.
Third-party software
Some software applications are available and allow management of LDAP users, including
Samba password. For example:
LDAP Account Manager (LAM), with a web-based interface, available from:
http://www.ldap-account-manager.org/
smbldap-tools (command line tool)
webmin-ldap-useradmin - LDAP user administration module for Webmin.

B.
Samba schema
To import the a Samba schema to the LDAP server, please refer to the documentation or
FAQ of the LDAP server. A samba.schema file is required and can be found in the directory
examples/LDAP in the Samba source distribution. Example for open-ldap in the Linux server
where the LDAP server is running (it can be different depending on the Linux distribution):
Copy the samba schema:
zcat /usr/share/doc/samba-doc/examples/LDAP/samba.schema.gz >
/etc/ldap/schema/samba.schema
Edit /etc/ldap/slapd.conf (openldap server configuration file) and make sure the following
lines are present in the file:
include /etc/ldap/schema/samba.schema
include /etc/ldap/schema/cosine.schema
include /etc/ldap/schema/inetorgperson.schema
include /etc/ldap/schema/nis.schema
Configuration examples
The following are some configuration examples. They are not mandatory and need to be
adapted to match the LDAP server configuration:
1.
Linux OpenLDAP Server
o
Base DN: dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Root DN: cn=admin,dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Users Base DN: ou=people,dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Groups Base DN: ou=group,dc=qnap,dc=com
2.
Mac Open Directory Server
o
Base DN: dc=macserver,dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Root DN: uid=root,cn=users,dc=macserver,dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Users Base DN: cn=users,dc=macserver,dc=qnap,dc=com
o
Groups Base DN: cn=groups,dc=macserver,dc=qnap,dc=com
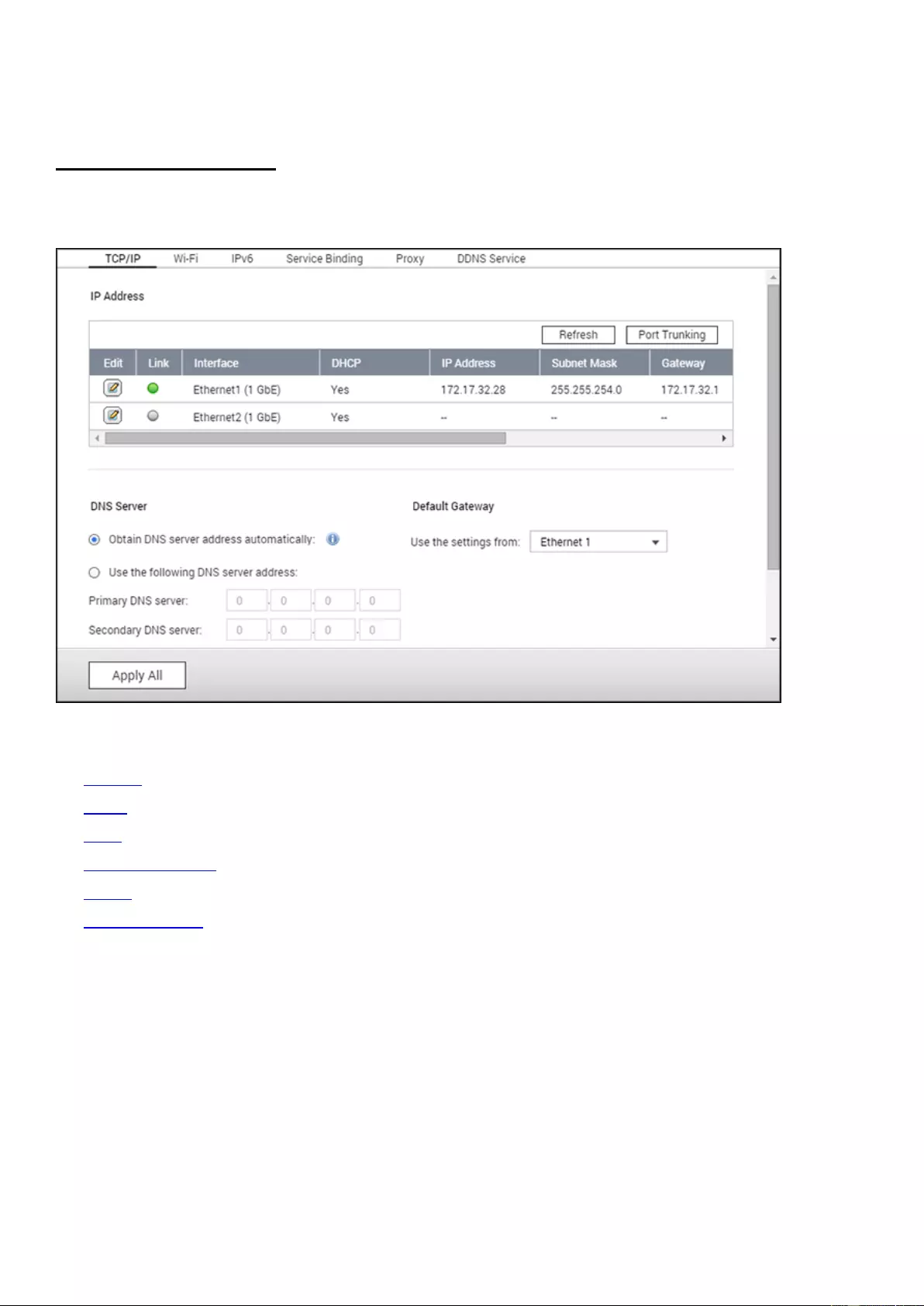
Network & Virtual Switch
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Network & File Services" to configure the NAS
network settings.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
TCP/IP
Wi-Fi
IPv6
Service Binding
Proxy
DDNS Service
TCP/IP
(i) IP Address
Configure the TCP/IP settings, DNS Server and default Gateway of the NAS on this page.
Click the "Edit" button next to an interface to edit the network settings (including "Network
Parameters", "Advanced Options", and "DHCP Server".) For the NAS with two LAN ports,
users can connect both network interfaces to two different switches and configure the TCP/IP
settings. The NAS will acquire two IP addresses which allow access from two different subnets.
This is known as multi-IP settings*. When using
Qfinder Pro
to detect the NAS IP, the IP of
Ethernet 1 will be shown in LAN 1 only and the IP of Ethernet 2 will be shown in LAN 2 only.
To use port trunking for a dual LAN connection, see section (iii).
* TS-110, TS-119, TS-210, TS-219, TS-219P, TS-119P+, TS-219P+, TS-112, and TS-212
only have one LAN port and do not support dual LAN configuration or port trunking.
Network Parameters
Under "Network Parameters" on the TCP/IP Property page, configure the following settings:
Network Speed:
Select the network transfer rate according to the network environment
of the NAS. Select auto negotiation and the NAS will automatically adjust the transfer
rate.
Obtain the IP address settings automatically via DHCP:
If the network supports
DHCP, select this option and the NAS will automatically obtain the IP address and
network settings.
Use static IP address:
To use a static IP address for network connections, enter the IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
Jumbo Frame:
"Jumbo Frames" refers to Ethernet frames that are larger than 1500
bytes. It is designed to enhance Ethernet networking throughput and reduce the CPU
utilization of large file transfers by enabling more efficient larger payloads per packet.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) refers to the size (in bytes) of the largest packet that
a given layer of a communications protocol can transmit. The NAS uses standard
Ethernet frames (1500 bytes) by default. If network appliances support Jumbo Frames,
select the appropriate MTU value for the network environment. The NAS supports 4074,
7418, and 9000 bytes for MTU.
Note:
Jumbo Frames is only valid in Gigabit networks. All of the connected network
appliances must enable Jumbo Frames and use the same MTU value.
Jumbo Frames are only supported by certain NAS models. Refer to the software
specification page on the QNAP website for further details.
Advanced Options
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of hosts which communicate as if they were attached to the
same broadcast domain even if they are located in different physical locations. The NAS can
join a VLAN and be configured as a backup storage of other devices on the same VLAN.
To join a VLAN, select "Enable VLAN" and enter the VLAN ID (a value between 0 and 4094.)
Keep the VLAN ID safe and make sure the client devices are able to join the VLAN. If you

forget the VLAN ID and cannot connect to the NAS, you will need to reset the network
settings by pressing the NAS reset button. Once the NAS is reset, the VLAN feature will be
disabled. If the NAS supports two Gigabit LAN ports and only one network interface is
configured to enable VLAN, you can also connect to the NAS via the other network interface.
Note:
The VLAN feature is only supported by x86-based NAS models.
DHCP Server
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server assigns IP addresses to clients on a
network. Select "Enable DHCP Server" to set the NAS a DHCP server if there are none on the
local network where the NAS is located.
Note:
Do not enable DHCP server if there is one on the local network to avoid IP address
conflicts or network access errors.
The DHCP server option is only available to Ethernet 1 when both LAN ports of a dual
LAN NAS are connected to the network and configured as standalone IP settings.
Start IP, End IP, Lease Time:
Set the range of IP addresses allocated by the NAS to
the DHCP clients and the lease time. The lease time refers to the time that an IP address
is leased to the clients. During that time, the IP will be reserved to the assigned client.
When the lease time expires, the IP can be assigned to another client.
WINS Server (optional):
WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) resolves Windows
network computer names (NetBIOS names) to IP addresses, allowing Windows
computers on a network to easily find and communicate with each other. Enter the IP
address of the WINS server on the network if available.
DNS Suffix (optional):
The DNS suffix is used for resolution of unqualified/incomplete
host names.
TFTP Server & Boot File (optional):
The NAS supports PXE booting of network devices.
Enter the IP address of the TFTP server and the boot file (including directory on the TFTP
server and file name.) For remote booting of devices, enter the public IP address of the
TFTP server.
(ii) DNS Server
A DNS (Domain Name Service) server translates between a domain name (such as
google.com) and an IP address (74.125.31.105.) Configure the NAS to obtain a DNS server
address automatically or to specify the IP address of a DNS server.
Primary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Secondary DNS Server: Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.

Note:
Contact your ISP or network administrator for the IP address of the primary and the
secondary DNS servers. When the NAS plays the role as a terminal and needs to
perform independent connection (BT download, etc) enter at least one DNS server IP
for proper URL connection. Otherwise, the function may not work properly.
If you obtain the IP address by DHCP, there is no need to configure the primary and
secondary DNS servers. In this case, enter "0.0.0.0".
(iii) Default Gateway
Select the gateway settings to use if both LAN ports have been connected to the network
(dual LAN NAS models only.)
(iv) Port Trunking
The NAS supports port trunking that combines two Ethernet interfaces into one to increase
bandwidth and offers load balancing and fault tolerance (also known as failover.) Load
balancing is a feature that distributes workloads evenly across two Ethernet interfaces for
higher redundancy. Failover ensures that the network connection will remain available even if
a port fails.
To use port trunking on the NAS, make sure at least two LAN ports of the NAS have been
connected to the same switch and the settings described in sections (i) and (ii) have been
configured.
Follow these steps to configure port trunking on the NAS:
1.
Click "Port Trunking".
2.
Select the network interfaces for a trunking group (Ethernet 1+2, Ethernet 3+4, Ethernet
5+6, or Ethernet 7+8.) Choose a port trunking mode from the drop-down menu. The
default option is Active Backup (Failover.)
3.
Select a port trunking group to use. Click "Apply".
4.
Click "here" to connect to the login page.
Note:
Make sure the Ethernet interfaces are connected to the correct switch and the switch
has been configured to support the port trunking mode selected on the NAS.
Port Trunking is only available for NAS models with two or more LAN ports.

The port trunking options available on the NAS:
Field
Description
Switch Required
Balance-rr
(Round-Robin
)
Round-Robin mode is good for general purpose
load balancing between two Ethernet interfaces.
This mode transmits packets in sequential order
from the first available slave through the last.
Balance-rr provides load balancing and fault
tolerance.
Supports static
trunking. Make
sure static trunking
is enabled on the
switch.
Active Backup
Active Backup only uses one Ethernet interface. It
switches to the second Ethernet interface if the
first Ethernet interface does not work properly.
Only one interface in the bond is active. The
bond's MAC address is only visible externally on
one port (network adapter) to avoid confusing the
switch. Active Backup mode provides fault
tolerance.
General switches
Balance XOR
Balance XOR balances traffic by splitting up
outgoing packets between the Ethernet interfaces,
using the same one for each specific destination
when possible. It transmits based on the selected
transmit hash policy. The default policy is a
simple slave count operating on Layer 2 where
the source MAC address is coupled with
destination MAC address. Alternate transmit
policies may be selected via the xmit_hash_policy
option. Balance XOR mode provides load
balancing and fault tolerance.
Supports static
trunking. Make
sure static trunking
is enabled on the
switch.
Broadcast
Broadcast sends traffic on both network
interfaces. This mode provides fault tolerance.
Supports static
trunking. Make
sure static trunking
is enabled on the
switch.
IEEE 802.3ad
(Dynamic Link
Aggregation)
Dynamic Link Aggregation uses a complex
algorithm to aggregate adapters by speed and
duplex settings. It utilizes all slaves in the active
aggregator according to the 802.3ad specification.
Dynamic Link Aggregation mode provides load
Supports 802.3ad
LACP

balancing and fault tolerance but requires a
switch that supports IEEE 802.3ad with LACP
mode properly configured.
Balance-tlb
(Adaptive
Transmit Load
Balancing)
Balance-tlb uses channel bonding that does not
require any special switch. The outgoing traffic is
distributed according to the current load on each
Ethernet interface (computed relative to the
speed.) Incoming traffic is received by the current
Ethernet interface. If the receiving Ethernet
interface fails, the other slave takes over the MAC
address of the failed receiving slave. Balance-tlb
mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance.
General switches
Balance-alb
(Adaptive
Load
Balancing)
Balance-alb is similar to balance-tlb but also
attempts to redistribute incoming (receive load
balancing) for IPV4 traffic. This setup does not
require any special switch support or
configuration. The receive load balancing is
achieved by ARP negotiation sent by the local
system on their way out and overwrites the
source hardware address with the unique
hardware address of one of the Ethernet
interfaces in the bond such that different peers
use different hardware address for the server.
This mode provides load balancing and fault
tolerance.
General switches
Wi-Fi
To connect to a Wi-Fi network, plug a USB wireless dongle into the NAS. The NAS will detect a
list of wireless access points. You can connect the NAS to a Wi-Fi network in two ways.
Note:
Wireless connection performance depends on many factors such as the adapter model,
the USB adapter's performance, and the network environment. Wired connections will
always provide greater stability and performance.
The system only supports one USB Wi-Fi dongle at a time.
For a list of compatible USB Wi-Fi dongles, visit http://www.qnap.com/compatibility
and select "USB Wi-Fi".
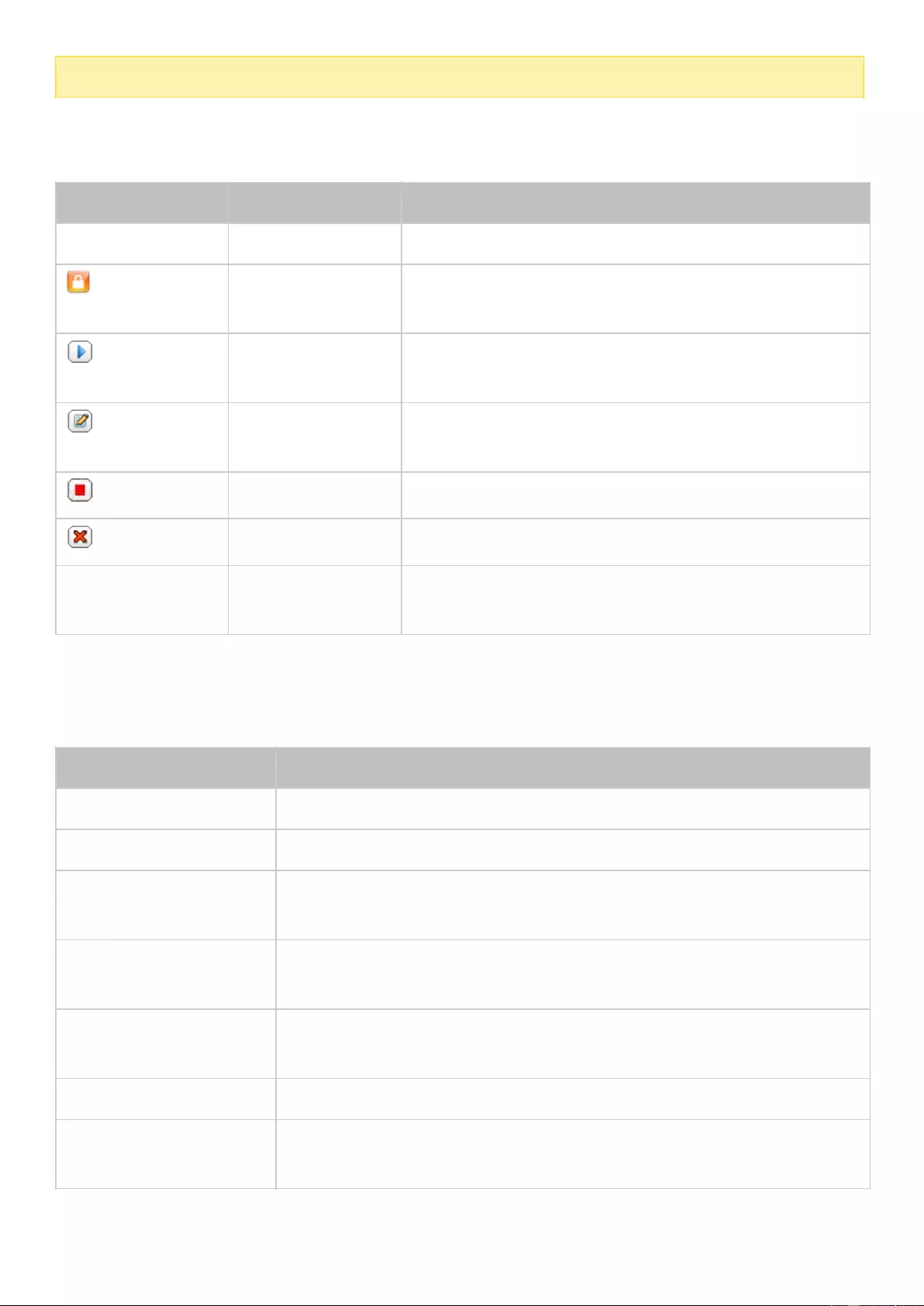
This feature is not supported by the TS-269H.
Method 1: Connecting to an existing Wi-Fi network:
A list of Wi-Fi access points with signal strength are displayed in "Wi-Fi Network Connection".
Icon / Option
Name
Description
Rescan
Rescan
Search for Wi-Fi networks in range.
Secured
network
The Wi-Fi network requires a network key.
Connect
Connect to a Wi-Fi network. If a security key is
required, you will be prompted to enter the key.
Edit
Edit the connection information. You can select to
automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network.
Disconnect
Disconnect from the Wi-Fi network.
Remove
Delete the Wi-Fi network profile.
Show all
Show all
Display all available Wi-Fi networks. Deselect this
option to only show configured network profiles.
Click "Rescan" to search for available Wi-Fi networks. Select a Wi-Fi network to connect to
and click "Connect". Enter the security key if needed. Click "Next" and the NAS will attempt to
connect to the wireless network. You can view the status of the configured network profiles.
Message
Description
Connected
The NAS is currently connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Connecting
The NAS is trying to connect to the Wi-Fi network.
Out of range or
hidden SSID
The wireless signal is not available or the SSID is not broadcast.
Failed to get IP
The NAS is connected to the Wi-Fi network but could not get an
IP address from the DHCP server. Check the router settings.
Association failed
The NAS cannot connect to the Wi-Fi network. Check the router
settings.
Incorrect key
The entered security key is incorrect.
Auto connect
Automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network. This is not supported
if the SSID of the Wi-Fi network is not broadcast.

Method 2: Manually connecting to a Wi-Fi network:
To manually connect to a Wi-Fi network that does not broadcast its SSID (network name),
click "Connect to a Wi-Fi network".
You can choose to connect to an ad hoc network in which you can connect to any wireless
devices without the need for an access point. To set up, follow these steps:
1.
Enter the network name (SSID) of the wireless network and select the security type.
o
No authentication (Open): No security key required.
o
WEP: Enter up to 4 WEP keys and choose 1 key to be used for authentication.
o
WPA-Personal: Choose AES or TKIP encryption and enter the encryption key.
o
WPA2-Personal: Enter a security key.
2.
Type in the security key.
3.
Click "Finish" after the NAS has added the Wi-Fi network.
4.
To edit IP address settings, click "Edit". You can choose to automatically obtain the IP
address by DHCP or to set a fixed IP address.
If the Wi-Fi connection is the only connection between the NAS and the router/AP, you must
select "WLAN1" as the default gateway in "Network" > "TCP/IP" page. Otherwise, the NAS will
be unable to connect to the Internet or communicate with another network.
Note:
The WEP key must be exactly 5 or 13 ASCII characters; or exactly 10 or 26
hexadecimal characters (0-9 and A-F.)
If you have trouble connecting to an encrypted wireless network, check the wireless
router/AP settings and change the transfer rate from "N-only" mode to "B/G/N mixed"
or similar settings.
Windows 7 users with WPA2 encryption cannot establish ad-hoc connection with the
NAS. WEP encryption must be used on Windows 7.
A fixed IP address is required for wireless interfaces to establish an ad-hoc connection.
IPv6
The NAS supports IPv6 connectivity with "stateless" address configurations and RADVD
(Router Advertisement Daemon) for IPv6, RFC 2461 to allow the hosts on the same subnet to
automatically acquire IPv6 addresses from the NAS. NAS services which support IPv6 include:
CIFS/SMB
AFP
NFS
FTP

iSCSI
Web Server
QTS Desktop
RTRR
SSH
Qsync for Windows
Netbak Replicator
To use this function, select the option "Enable IPv6" and click "Apply". The NAS will restart.
After the system restarts, go to the IPv6 page. The settings of the IPv6 interface will be
shown. Click the "Edit" button to edit the settings:
IPv6 Auto Configuration:
If an IPv6 enabled router is available on the network, select
this option to allow the NAS to automatically acquire the IPv6 address and
configurations.
Use static IP address:
To use a static IP address, enter the IP address (e.g.
2001:bc95:1234:5678), prefix length (e.g. 64), and the gateway address for the NAS.
Contact your ISP for the prefix and the prefix length information.
o
Enable Router Advertisement Daemon (radvd): To configure the NAS as an IPv6 host
and distribute IPv6 addresses to the local clients which support IPv6, enable this
option and enter the prefix and prefix length.
IPv6 DNS server:
Enter the preferred DNS server in the upper field and the alternate
DNS server in the lower field. Contact the ISP or network administrator for the
information. If IPv6 auto configuration is selected, leave the fields as "::".
Service Binding
NAS services run on all available network interfaces by default. You can bind services to one
or more specific network interfaces (wired or wireless). Available network interfaces on the
NAS will be shown. Select at least one network interface that each service should be bound to.
Then click "Apply". Users will only be able to connect to services via the specified network
interfaces. If the settings cannot be applied, click "Refresh" to list the current network
interfaces on the NAS and configure service binding again.
Note:
Service binding is only available for NAS models with multiple network interfaces (wired
and wireless.)
After applying service binding settings, the connection of currently online users will be
kept even if they were not connected to services via the specified network interfaces.
The specified network interfaces will be used for the next connected session.

Proxy
Enter the proxy server settings to allow the NAS to access the Internet through a proxy
server to update the firmware, get new virus definitions, and to download Apps.
DDNS Service
To allow remote access to the NAS using a domain name instead of a dynamic IP address,
enable the DDNS service.
The NAS supports the DDNS providers: http://www.dyndns.com, http://update.ods.org,
http://www.dhs.org, http://www.dyns.cx, http://www.3322.org, http://www.no-ip.com,
http://www.Selfhost.de, http://www.oray.com.
Note:
Some of these DDNS services are not free.
Additional Reference:
How to set up proxy server on QNAP Turbo NAS for optimized website access.
Set up DDNS Service for Remote Internet Access to QNAP NAS.
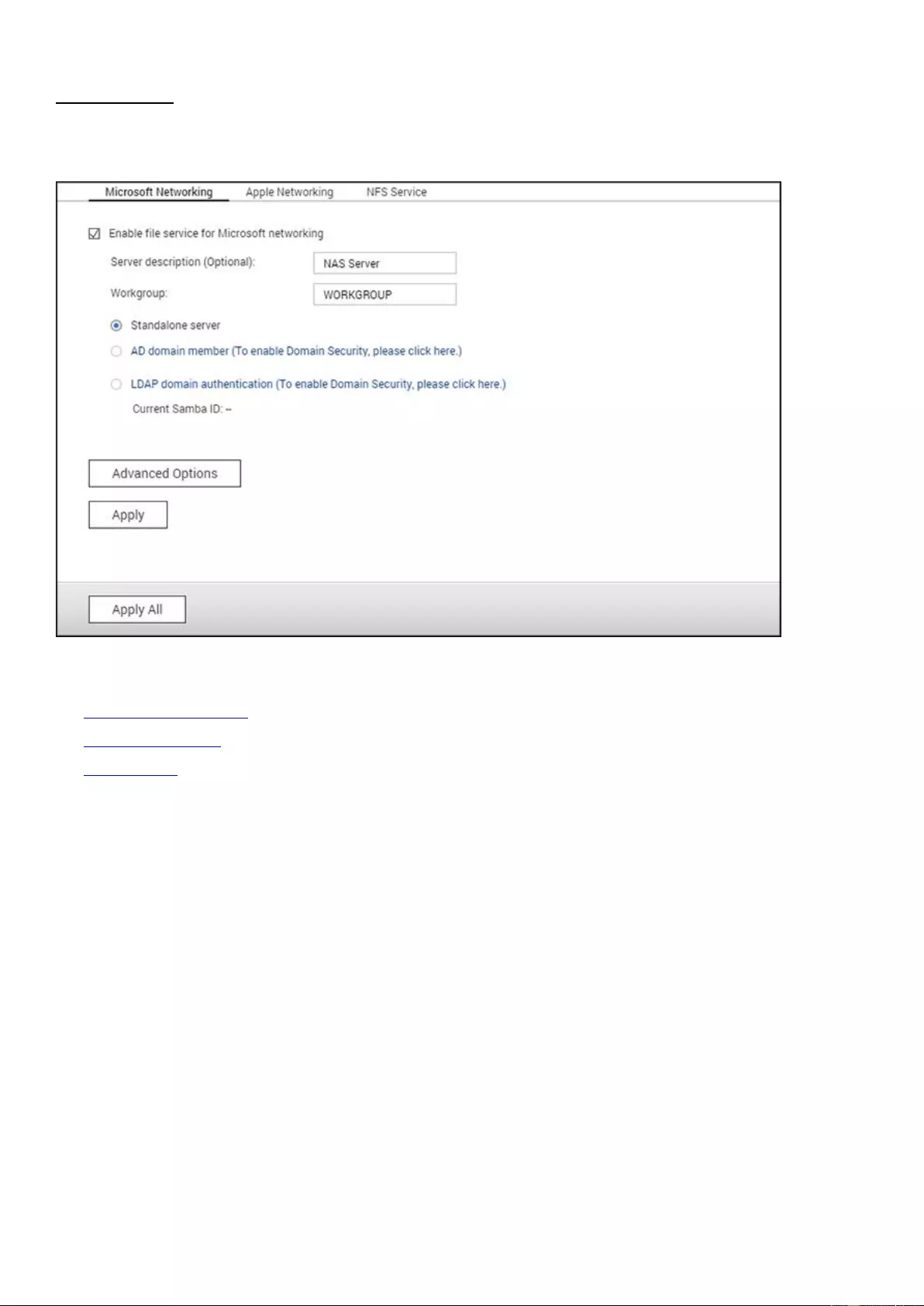
Win/Mac/NFS
Go to "Control Panel" > "Network & File Services" > "Win/Mac/NFS" to configure networking
services.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Microsoft Networking
Apple Networking
NFS Service
Microsoft Networking
To allow access to the NAS on Microsoft Windows Network, enable file service for Microsoft
networking. Also specify how users will be authenticated.
Standalone Server
Use local users for authentication. The NAS will use local user account information (created
in "Privilege Settings" > "Users") to authenticate users who access the NAS.
Server Description (optional): Describe the NAS so that users can easily identify it on a
Microsoft Network.
Workgroup: Specify the workgroup to which the NAS belongs. A workgroup name
supports up to 15 characters but cannot contain: " + = / \ : | * ? < > ; [ ] % , `

AD Domain Member
Use Microsoft Active Directory (AD) to authenticate users. To use this option, enable Active
Directory authentication in "Privilege Settings" > "Domain Security" and join the NAS to an
Active Directory.
LDAP Domain Authentication
Use an LDAP directory to authenticate the users. To use this option, enable LDAP
authentication and specify the settings in "Privilege Settings" > "Domain Security". When
this option is enabled, you need to select either the local NAS users or the LDAP users that
can access the NAS via Microsoft Networking.
Advanced Options
WINS server:
If you have a WINS server on your network and want to use this server,
enter the WINS server IP. The NAS will automatically register its name and IP address
with the WINS service. Do not enable this option if you are unsure about the settings.
Local Domain Master:
A Domain Master Browser is responsible for collecting and
recording resources and services available for each PC on the network or a workgroup of
Windows. When you find the waiting time for loading network resources to be too long, it
may be caused by a failure of an existing master browser or a missing master browser on
the network. If there is no master browser on your network, select the option "Domain
Master" to configure the NAS as the master browser. Do not enable this option if you are
unsure about the settings.
Allow only NTLMv2 authentication:
NTLMv2 stands for NT LAN Manager version 2.
When this option is enabled, login to the shared folders by Microsoft Networking will only
be allowed using NTLMv2 authentication. If the option is disabled, NTLM (NT LAN
Manager) will be used by default and NTLMv2 can be negotiated by the client. The default
setting is disabled.
Name resolution priority:
You can select to use DNS server or WINS server to resolve
client host names from IP addresses. When you set up your NAS to use a WINS server or
to be a WINS server, you can choose to use DNS or WINS first for name resolution.
When WINS is enabled, the default setting is "Try WINS then DNS". Otherwise, DNS will
be used for name resolution by default.
Login style: DOMAIN\USERNAME instead of DOMAIN+USERNAME for FTP, AFP,
and File Station:
In an Active Directory environment, the default login formats for the
domain users are:
o
Windows shares: domain\username
o
FTP: domain+username
o
File Station: domain+username
o
AFP: domain+username

When you enable this option, users can use the same login name format
(domain\username) to connect to the NAS via AFP, FTP, and File Station.
Automatically register in DNS:
When this option is enabled and the NAS is joined to
an Active Directory, the NAS will automatically register itself in the domain DNS server.
This will create a DNS host entry for the NAS in the DNS server. If the NAS IP changes,
the NAS will automatically update the IP in the DNS server.
Enable trusted domains:
Select this option to load users from trusted Active Directory
domains and specify their NAS access permissions in "Privilege Settings" > "Shared
Folders". Domain trusts are only set up in Active Directory, not on the NAS.)
Enable Asynchronous I/O:
Enable this option to increase SAMBA performance. Please
note: we strongly recommend using a UPS when this option is enabled.
Enable Highest SMB version:
Please choose the version of the SMB protocol (Server
Message Block) for your Microsoft Networking operations. If you are unsure, please use
the default option.
Apple Networking
To connect to the NAS from Mac OS X, enable Apple Filing Protocol. If the AppleTalk network
uses extended networks and is assigned with multiple zones, assign a zone name to the NAS.
Enter an asterisk (*) to use default settings. This setting is disabled by default. To allow
access to the NAS from Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, enable "DHX2 authentication support". Click
"Apply" to save the settings. You can use the Finder to connect to a shared folder from Mac.
Go to "Go" > "Connect to Server", or simply use the default keyboard shortcut
"Command+k". Enter the connection information in the "Server Address" field, such as
"afp://YOUR_NAS_IP_OR_HOSTNAME". Here are some examples:
afp://10.8.12.111
afp://NAS-559
smb://192.168.1.159
Note:
Mac OS X supports both Apple Filing Protocol and Microsoft Networking. To connect
to the NAS via Apple Filing Protocol, the server address should start with "afp://". To
connect to the NAS via Microsoft Networking, please use "smb://".

NFS Service
To connect to the NAS from Linux, enable the NFS service under NFS. Select “Enable NFS
v2/v3 Service” for NFS version 2 or 3. Select “Enable NFS v4 Service” for NFS version 4.
Multiple selections can be selected. To configure NFS access rights to shared folders on the
NAS, go to "Privilege Settings" > "Share Folders" and click the Access Permission button on
the "Action" column. Select NFS host access from the drop-down menu on the top of the
page and specify the access rights. For either the "read/write" or "read-only" option, you can
specify the IP address or domains that are allowed to connect to the folder by NFS.
read/write: Allow users to create, read, write, and delete files or folders in the shared
folder and any subdirectories.
read-only: Allow users to read files in the shared folder and any subdirectories but they
are not allowed to write, create, or delete any files.
Connecting to the NAS by NFS
On Linux, run this command:
mount -t nfs <NAS IP>:/<Shared Folder Name> <Directory to Mount>
For example, if the IP address of your NAS is 192.168.0.1 and you want to link the shared
folder "public" under the /mnt/pub directory, use this command:
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.1:/public /mnt/pub
Note:
You must login as the "root" user to use the above command.
Login as the user ID you define, you can use the mounted directory to connect to your
shared files.
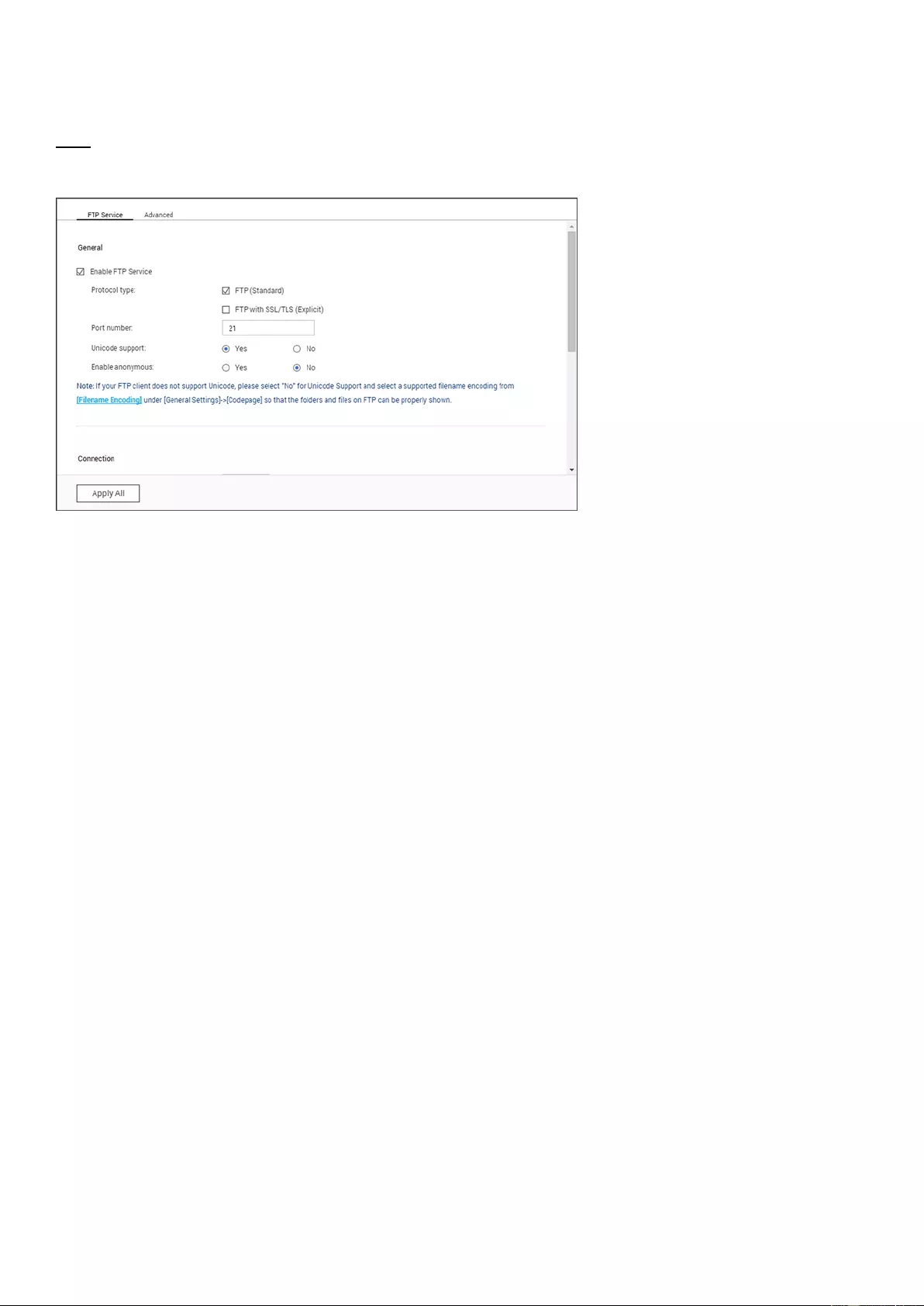
FTP
Go to "Control Panel" > "Network Services" > "FTP" to Configure the FTP server.
FTP Service
When you enable the FTP service, you can specify the port number and the maximum
number of users that are allowed to connect to the NAS by FTP at the same time. To use the
FTP service of the NAS, enable this function. Open an IE browser and enter ftp://NAS IP.
Enter the username and the password to login the FTP service.
Protocol Type:
Select to use standard FTP connection or SSL/TLS encrypted FTP. Select
the correct protocol type in your client FTP software to ensure successful connection.
Port number:
Specify the port number of the FTP service.
Unicode Support:
Toggles Unicode support. The default setting is No. If your FTP client
does not support Unicode, it is recommended to disable this option and select the
specified language in "General Settings" > "Codepage" so that the file and folder names
can be correctly displayed. If your FTP client supports Unicode, enable this option for
both your client and NAS.
Enable Anonymous:
Enable this option to allow anonymous access to the NAS by FTP.
Anonymous users can connect to files and folders which are open for public access. If this
option is disabled, users must enter an authorized username and password to connect to
the NAS.
Connection:
Enter the maximum number of allowed FTP connections for the NAS and a
single account and check "Enable FTP transfer limitation" to specify the maximum upload
and download rates.
Online Users:
Check details of the current FTP connections, including the type of
connection, login date, login time, user account, source IP, and computer name.

Note:
The maximum number of FTP connections varies based on the size of RAM installed
on the NAS:
If the NAS memory =< 1 GB, the maximum is 256.
If the NAS memory = 2 GB, the maximum is 512.
If the NAS memory >= 3 GB, the maximum is 1024.
Advanced
Passive FTP Port Range:
You can use the default port range (55536-56559) or specify
a port range larger than 1023. When using this function, make sure you have opened the
ports on your router or firewall.
Respond with external IP address for passive FTP connection request:
Enable
this function when a passive FTP connection is in use, the FTP server (NAS) is behind a
router, and a remote computer cannot connect to the FTP server over the WAN. When
this is enabled, the NAS replies with the specified IP address or automatically detects an
external IP address so that the remote computer is able to connect to the FTP server.
Set root directory:
After enabling this function and selecting a root directory, only that
directory will be visible to FTP users. Otherwise, all of the shared folders will be visible.
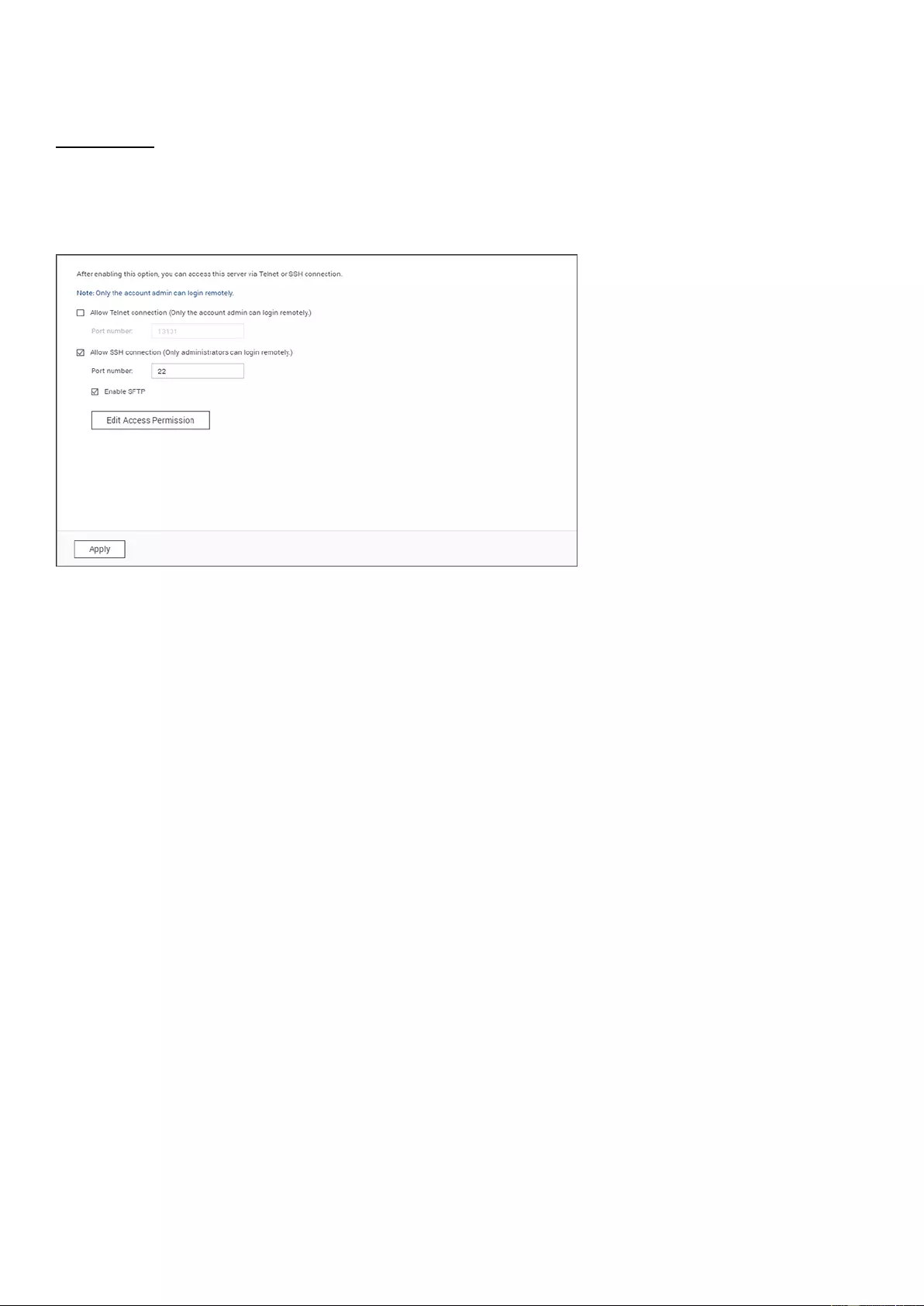
Telnet/SSH
Enable this option to connect to the NAS by Telnet or SSH encrypted connection (only the
"admin" account can remotely log in.) Use Telnet or SSH connection clients such PuTTY to
connect to the NAS. Ensure the specified ports have been opened on the router or firewall.
To use SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol/Secure File Transfer Protocol), ensure that the
option "Allow SSH connection" has been enabled. You can click “Edit Access Permission” to
choose which administrators can access the NAS via SSH connections.
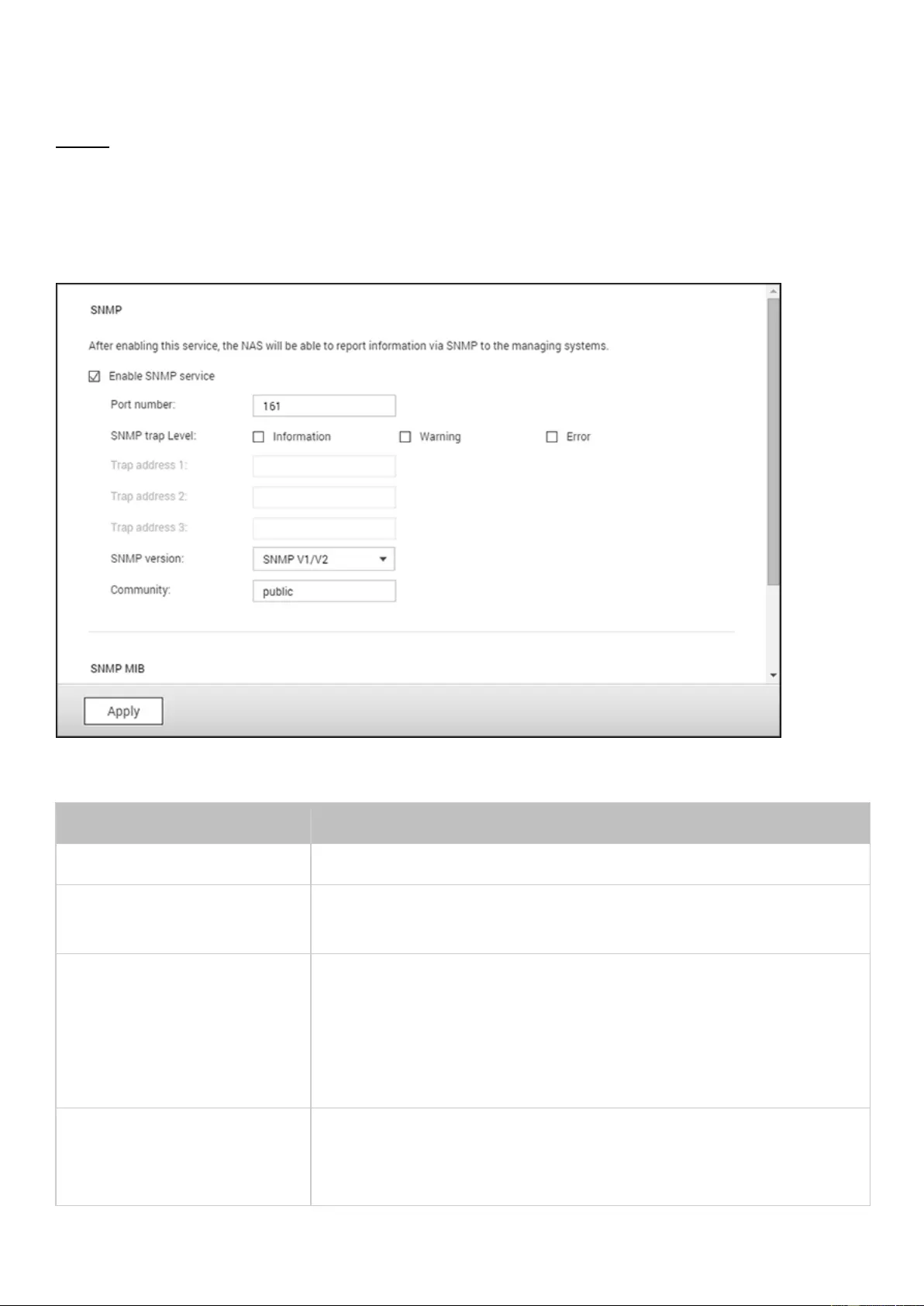
SNMP
Enable SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) on the NAS and enter the trap address
of the SNMP management stations (SNMP manager) - for example, a PC with SNMP software
installed. When an event, warning, or error occurs on the NAS, it will report a real-time alert
to SNMP management stations.
The fields are described as below:
Field
Description
SNMP Trap Level
Select information to be sent to the SNMP management stations.
Trap Address
The IP address of the SNMP manager. Specify up to 3 trap
addresses.
SNMP MIB (Management
Information Base)
The MIB is a type of database in ASCII text format used to manage
the NAS in the SNMP network. The SNMP manager uses the MIB to
determine the values or understand the messages sent from the
agent (NAS) within the network. You can download the MIB and
view it with any word processor or text editor.
Community (SNMP V1/V2)
An SNMP community string is a text string that acts as a password.
It is used to authenticate messages that are sent between the
management station and the NAS. The community string is
included in every packet that is transmitted between the SNMP
manager and the SNMP agent.
SNMP V3
The NAS supports SNMP version 3. Specify the authentication and
privacy settings if available.
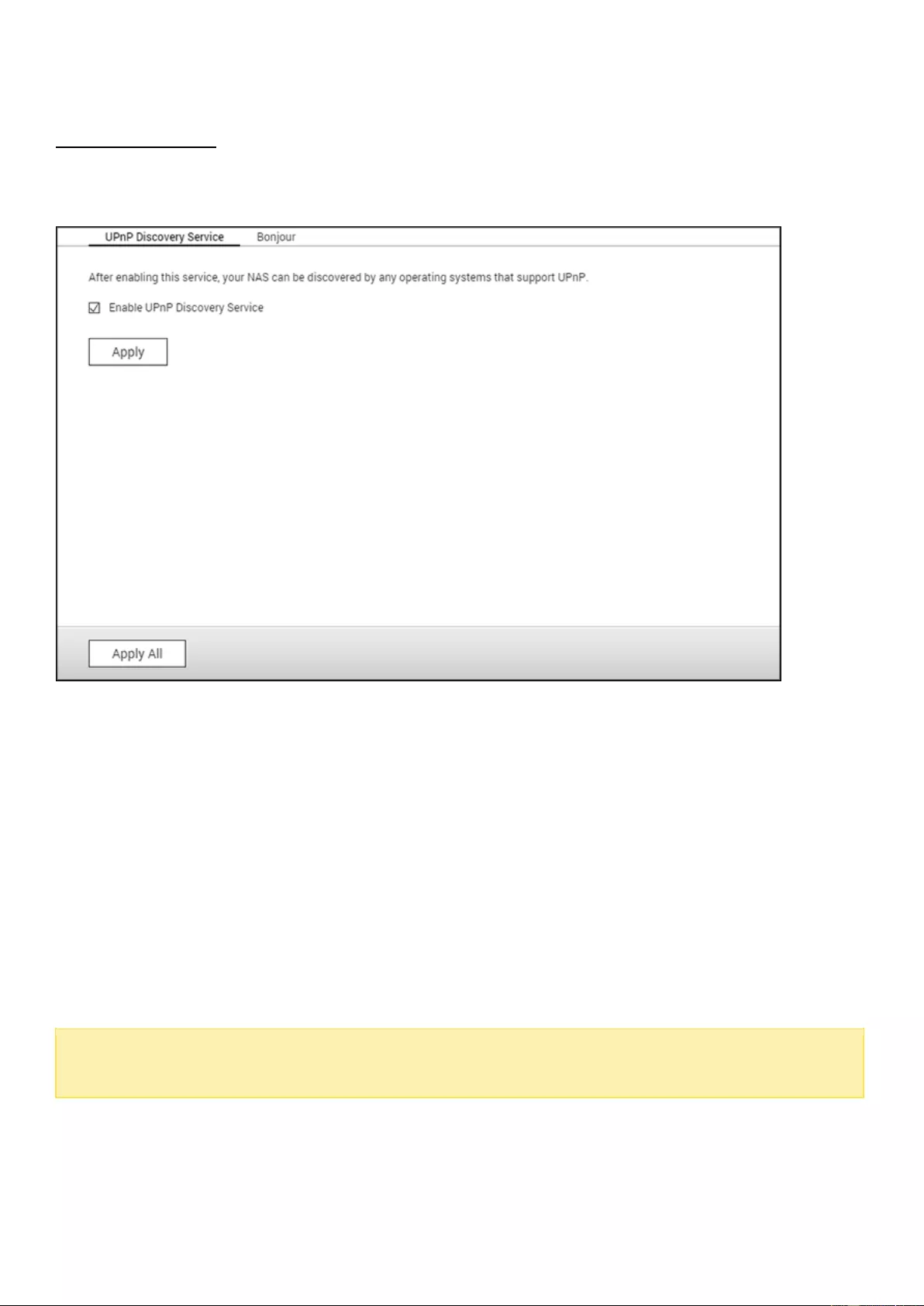
Service Discovery
Go to "Control Panel" > "Network Services" > "Service Discovery" to configure the UPnP
discovery service and Bonjour.
UPnP Discovery Service
When a UPnP device is added to the network, the UPnP discovery protocol allows the device
to advertise its services to the network control points. By enabling UPnP Discovery Service,
the NAS can be discovered by any systems that support UPnP.
Bonjour
By using Bonjour, your Mac will automatically discover network services (such as FTP)
running on the NAS without needing to enter IP addresses or configuring DNS servers.
Note:
You must activate the services on their setup pages and then enable them in this
section so that the NAS can advertise them using Bonjour.
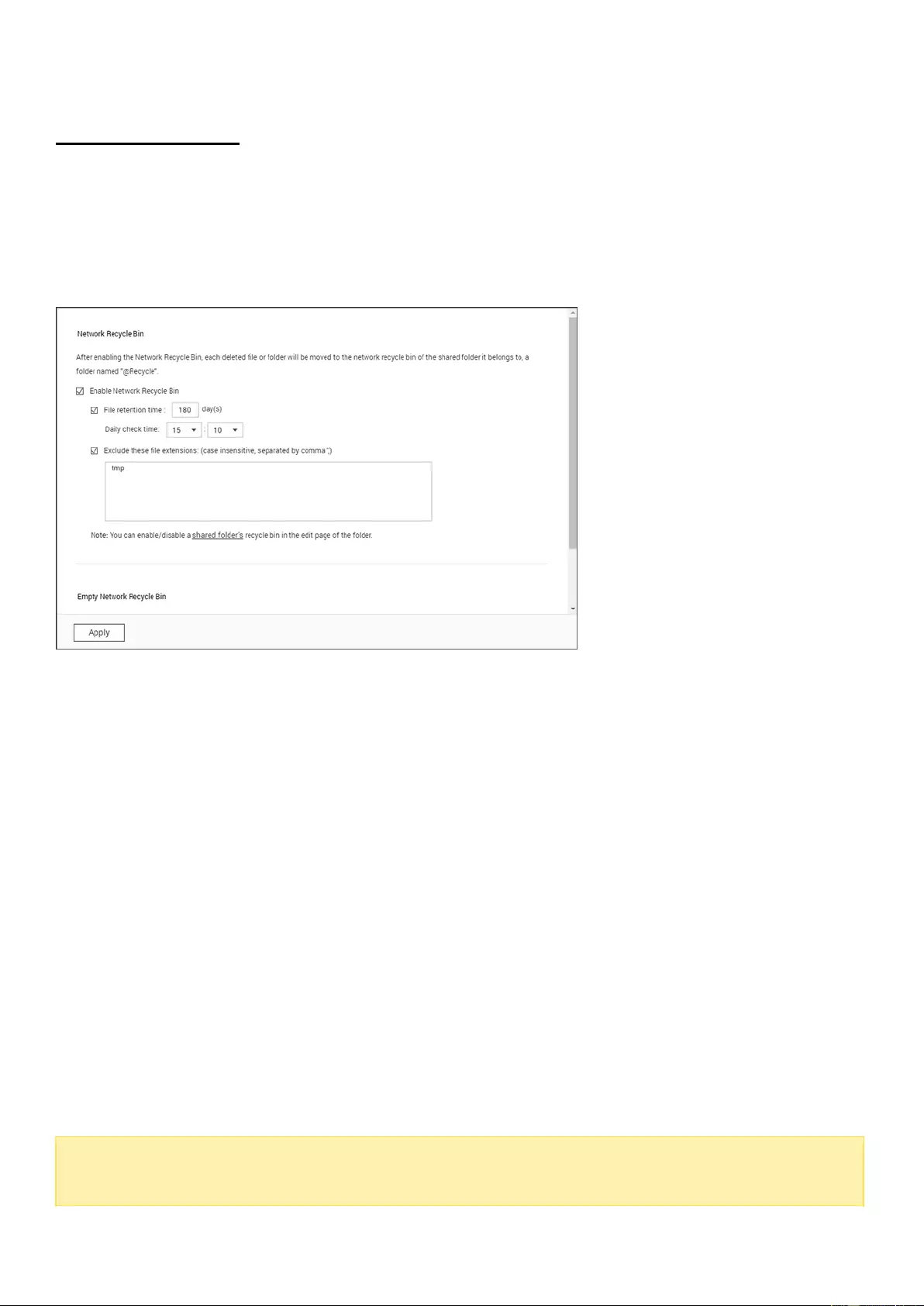
Network Recycle Bin
The Network Recycle Bin retains files deleted on the NAS. Within each shared folder, a
dedicated folder with the name @Recycle is created after the initial QTS installation. Specify
the number of days (1-180) to retain files and the daily time. You can also specify the file
extensions to be excluded from the bin. This feature only supports file deletion via Samba,
AFP, FTP and File Station.
Using Network Recycle Bin
To delete all the files in the bin, click "Empty All Network Recycle Bin".
To recover deleted files from the Network Recycle Bin, right click on the files in the
@Recycle folder and select "RECOVER".
To permanently delete a file in the recycle bin, right click on the file in the @Recycle
folder and select "Del (from recycle)".
To empty the recycle bin for an individual shared folder, right click inside the recycle bin
and select "Empty Recycle Bin".
Restricting Access to Network Recycle Bin
The Network Recycle Bin can be restricted to administrators usage by going to "Control
Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders". Click "Property" under "Action" for the
shared folder to be configured and check "Restrict the access of Recycle Bin to
administrators only for now".
Caution:
All of the files in network recycle bins will be permanently deleted when files
are deleted in "@Recycle" on the network share or when you click "Empty All Network

Recycle Bins". The Network Recycle Bin feature is not supported for USB/eSATA external storage
devices and virtual disks.
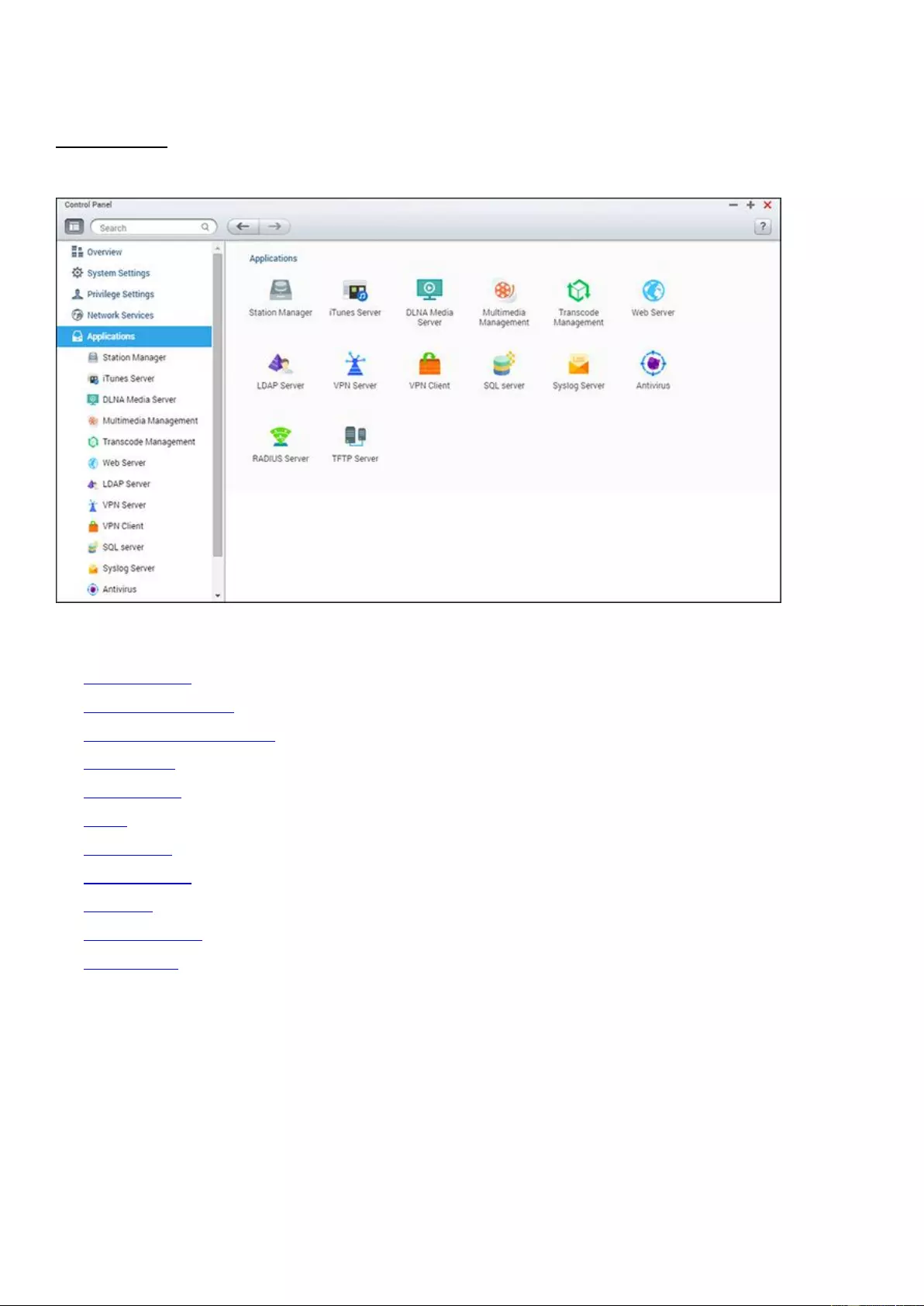
Applications
Go to
"Control Panel" > "Applications" to configure NAS applications.
For setup details, refer to the following links:
iTunes Server
DLNA Media Server
Multimedia Management
Web Server
LDAP Server
QVPN
SQL Server
Syslog Server
Antivirus
RADIUS Server
TFTP Server
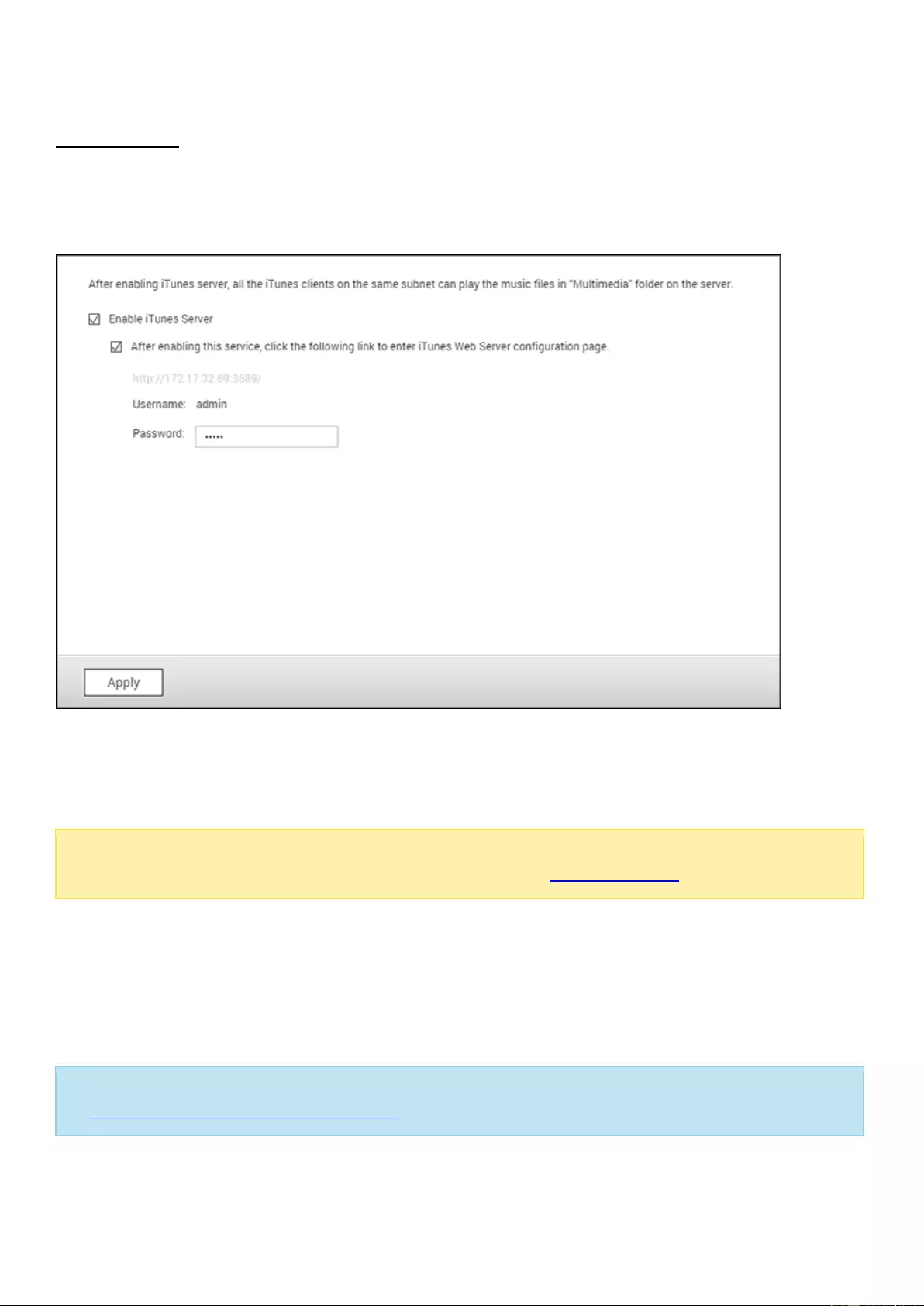
iTunes Server
Using this service MP3 files in the Qmultimedia/Multimedia folder of the NAS can be shared
with iTunes. Computers on the LAN with iTunes installed will be able to find, browse, and
play the shared music files.
To use the iTunes Server, enable this feature and then upload music files to the
Qmultimedia/Multimedia folder of the NAS.
Note: iTunes Server may be disabled or hidden on some Enterprise and SMB models. To enable
iTunes server, please refer to "System Administration" in the General Settings section.
To configure the iTunes server settings and add smart playlists, login to the iTunes server
web page (http://NAS-IP:3689/index.html.) Connect the PC and the NAS to the same LAN
and run iTunes on the PC. Find the NAS name under "SHARED" and music and playlists will
be available.
Additional Reference:
Setup iTunes Music Server on QNAP.
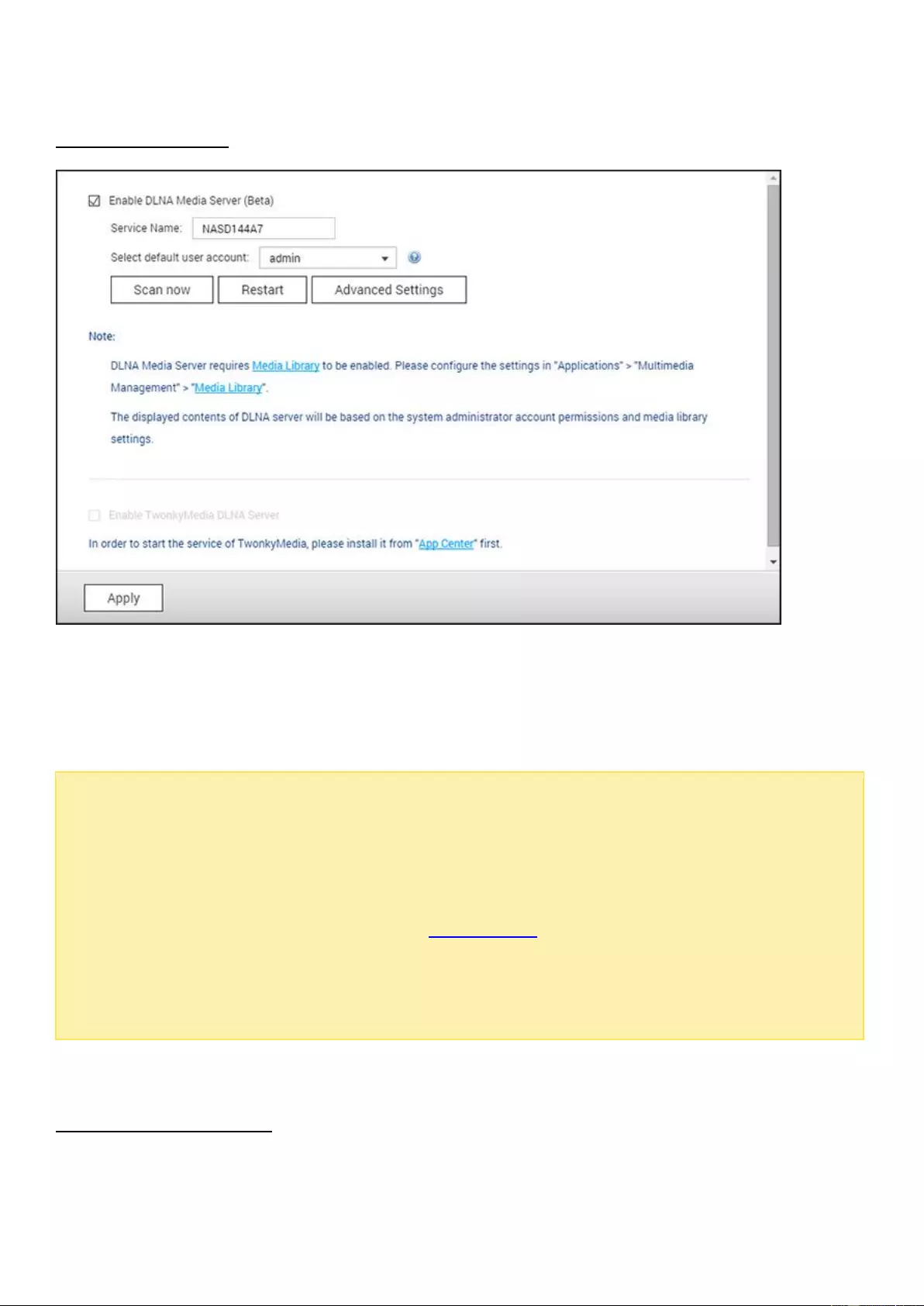
DLNA Media Server
QNAP DLNA Media Server is developed by QNAP. To allow DLNA media players to access and play the
NAS multimedia content via QNAP DLNA Media Server, enable the QNAP DLNA Media Server and
configure the Media Library and the default user account.
Note:
The contents allowed to be browsed on devices connected to the media server are based on the
shared folder permission set for the default user account. Viewers can only watch multimedia
contents from the media folders that the default user account is assigned the permission with.
For media folder setup, please refer to the chapter on Multimedia Management. For permission
assignment, please refer to the chapter on Shared Folder.
If you upload multimedia files to the default folder but the files are not shown in the Media
Player, click "Rescan content directories" or "Restart server" on the DLNA Media Server
configuration page.
Multimedia Management
Media Library scans photos, music, and videos from designated media folders and indexes
them for multimedia applications. Thumbnails for media files will be generated to enhance
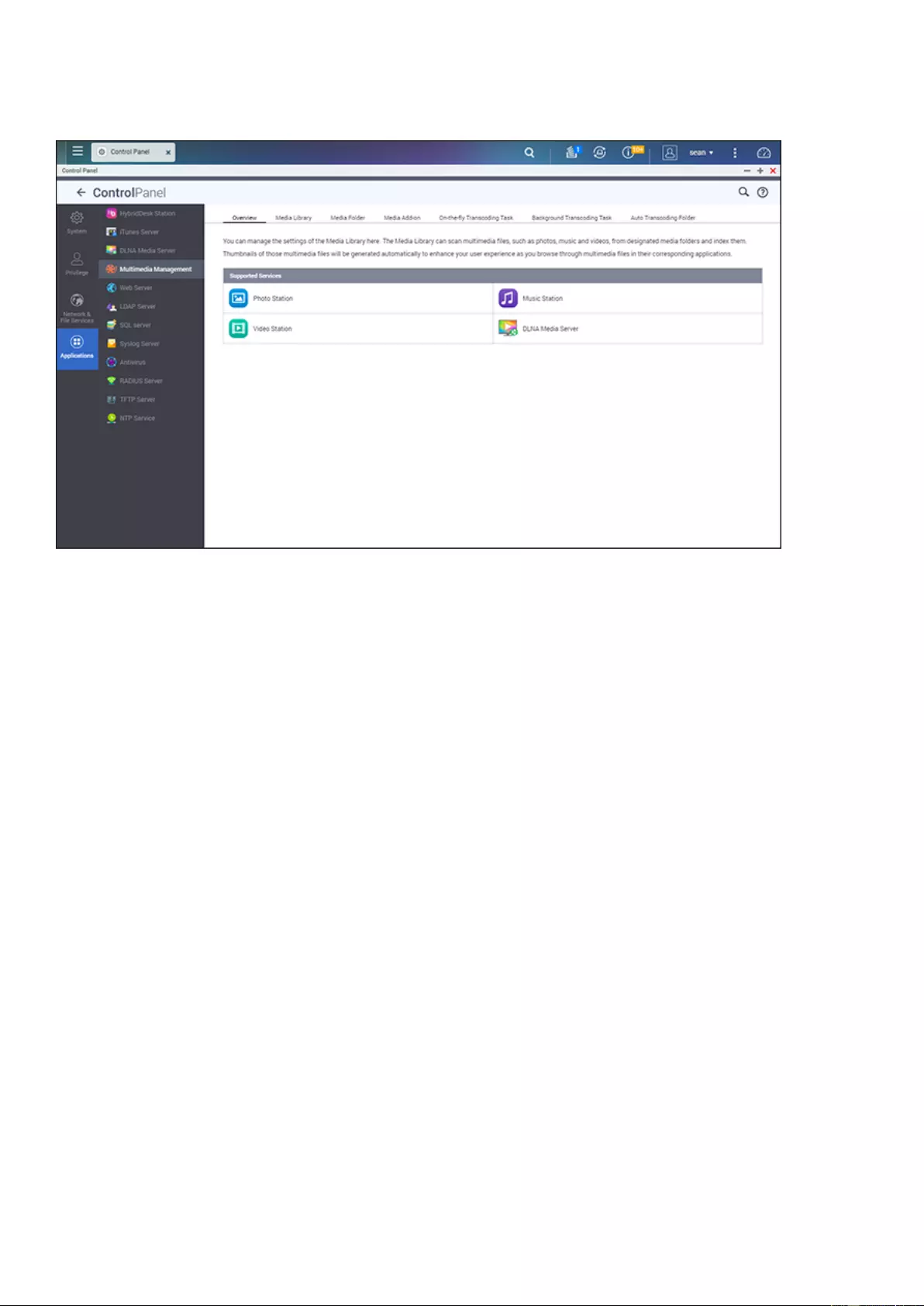
your user experience as you browse through them in their corresponding applications. You
can configure multimedia settings in “Control Panel” > “Applications” > “Multimedia
Management”.
Media Library
Scan Setting: Three options are provided for the media scan:
o
Real-time scan: New files are scanned as soon as they are added to media folders.
o
Scan by schedule: Specify a start and end time for the scan, and it will be
automatically conducted on a daily basis.
o
Manual Scan: You must click "Scan now" to check for new media.
Set media scanning priority to high: The option will allow the Media Library to
immediately process media files in order to quickly generate thumbnails. When the NAS
needs to run scan tasks and transfer files at the same time, it will lower the file transfer
speed and prioritize media scan tasks.
Multimedia code page setting: Change this setting to the corresponding code for non-UTF
media files for fonts and characters in the associated applications to be displayed
correctly.
Rebuild media library indexing: By rebuilding the media library, the NAS will scan the
specified media folders and replace the existing library with a new one.
You can enable or disable Media Library by clicking “Activate Media Library” or “Deactivate Media
Library”. Please note that disabling Media Library will make multimedia applications function
incorrectly. For more information, see the notes below.
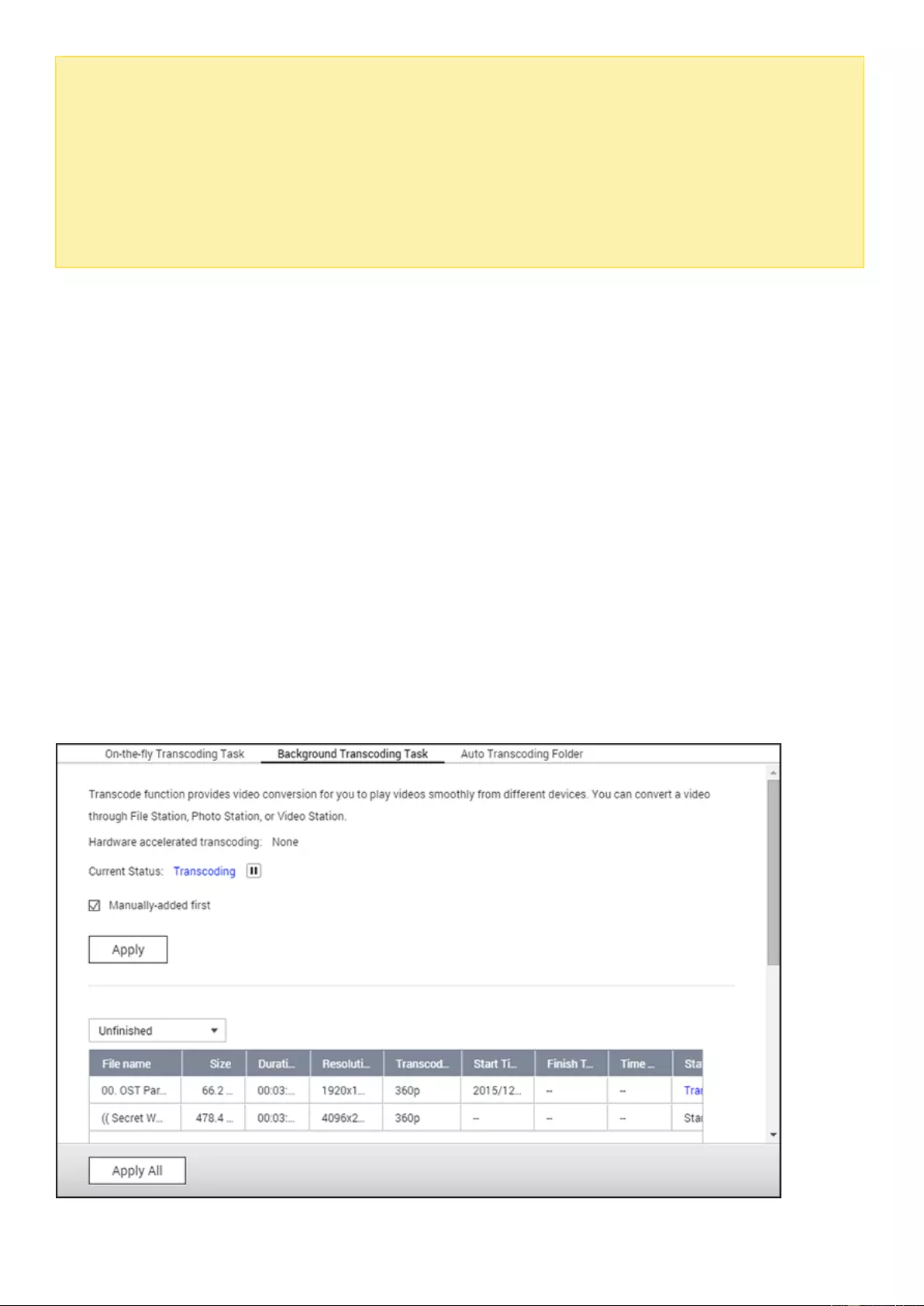
Note:
If Media Library is disabled, multimedia services such as Photo Station, Music Station,
DLNA Media Server, and OceanKTV will function incorrectly.
By default, image files with a width or height less than 400 pixels will not be indexed
and will not have any thumbnails generated. Nevertheless, you can this setting and set
up the minimum image size to index in “Control Panel” > “Applications” > “Multimedia
Management” > “Media Folder” > “Setting”.
Media Folder
Media folders are shared folders on the NAS that are scanned for multimedia files. "/Multimedia" and
"/Home" are the default media folders on the NAS (from QTS 4.1, all default shared folders on the
NAS are identified as media folders for the purpose of multimedia application services.) To add media
folders: click "Add", select media types and folders from the list, and click "Add". To change scanned
file types for the media folders, first uncheck the media file types and click "Apply". To remove media
folders, first select media folders from the list, and then click "Delete" and "Apply".
Transcode Management
Transcoding is the process of converting video files into an universal format (*.MP4) that is
compatible with most media players, including mobile devices and Smart TVs. Converted files with a
range of resolutions can be used across different network environments for better viewing experience.
After transcoding tasks are created, they can be managed here. This service is enabled by default.

On-the-fly Transcoding Task
On-the-fly transcoding will simultaneously convert and stream a video while you watch it. This task
requires some computing resources. If your NAS has hardware transcoding acceleration, it is
recommended to install CodexPack to accelerate transcoding and reduce CPU usage. You can monitor
and manage the use of on-the-fly transcoding services.
Manage transcoding tasks using the following buttons:
Button
Name
Description
Refresh
Refresh
Refresh the list.
Manage each task with the following buttons:
Button
Name
Description
Priority
Adjust the order each task is executed.
Remove
Remove the selected task from the list.
Note: This feature is for the x86 series NAS only. Please check the product page (software
specification) on the QNAP website (www.qnap.com) to see if this feature is available for your
model.
Background Transcoding Task
Background transcoding is when a video file is converted in advance, potentially avoiding high CPU
usage if the video will be simultaneously accessed by many users. You can manually add videos to be
transcoded using File Station, Photo Station, or Video Station. Video files can be converted to 240p,
360p, 480p, 720p and 1080p and will be saved in the "@Transcode" folder that is in the same
directory as the video.
Manage all transcoding tasks using the following buttons:
Button
Name
Description
Stop Transcoding
Stop Transcoding
Suspend all ongoing tasks in the list.
Remove All
Incomplete Tasks
Remove All
Incomplete Tasks
Remove all tasks that are yet to finish from the list.
Remove All
Complete Tasks
Remove All
Complete Tasks
Remove all complete tasks from the list.
Refresh
Refresh
Refresh the list.
Manage each task with the following buttons:
Button
Name
Description
Priority
Adjust the order each task is executed.
Remove
Remove the selected task from the list.
Auto Transcoding Folder
This feature is designed to convert the contents of an entire folder, and within the folder, the
resolution of each subfolder can be specified independently. Click "Add" to add a new folder and
select the video quality (resolution) and the folder to add it to the task list.
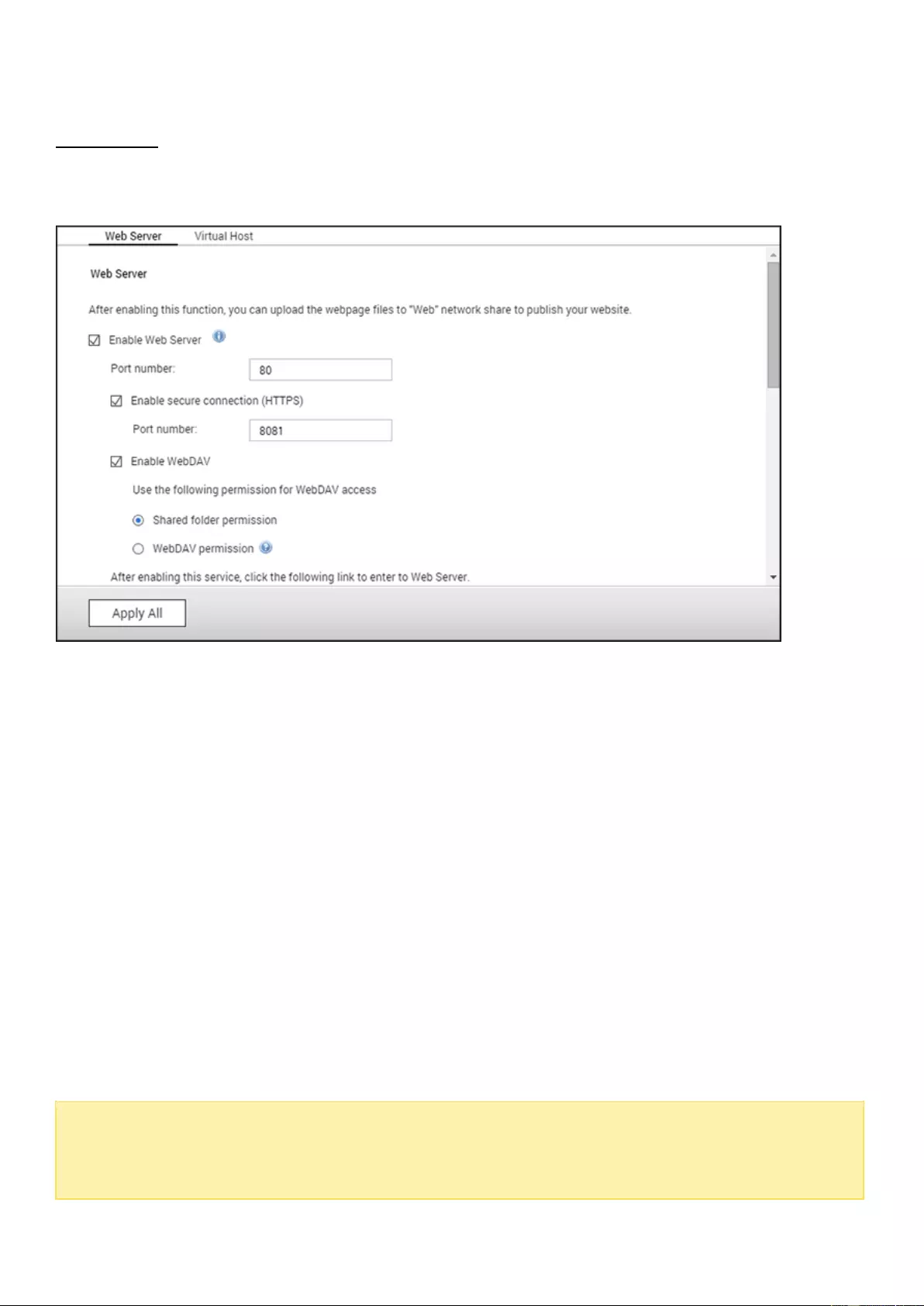
Web Server
Go to "Control Panel" > "Applications" > "Web Server" to configure the web server and
virtual host.
Web Server
The NAS can host web sites including those that use Joomla!, PHP and MySQL/SQLite to
establish an interactive website. To use the Web Server, follow these steps.
1.
Enable the service and enter the port number. The default number is 80.
2.
Configure other settings:
a.
Maintenance: Click "Restore" to restore the web server configuration to default.
b.
php.ini Maintenance: Choose to upload, edit or restore php.ini.
3.
Secure Connection (HTTPS): Enter the port number for SSL connection.
4.
Upload HTML files to the shared folder (Qweb/Web) on the NAS. The file index.html,
index.htm or index.php will be the home path of your web page.
5.
You can access the web page you upload by entering http://NAS IP/ in the web browser.
When the Web Server is enabled, you must enter http://NAS IP:8080 in your web
browser to access the NAS login page.
Note:
If the Web Server is disabled, all relevant applications including Music Station, Photo
Station, Happy Get, or QAirplay will become unavailable.
To use PHP mail(), go to "System Settings" > "Notification" > "SMTP Server" and
configure the SMTP server settings.
WebDAV
WebDAV (Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is a set of extensions to the
HTTP(S) protocol that allows users to edit and manage files collaboratively on remote
servers. After enabling this function, you can map shared folders of your NAS as network
drives of a remote PC over the Internet. To edit the access rights, go to "Privilege Settings"
> "Shared Folders" page.
Note:
WebDAV currently supports NAS user accounts and AD domain user accounts.
LDAP user accounts are not supported.
To map a NAS shared folder as a network drive on your PC, enable WebDAV and follow
these steps.
1.
Go to "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders". Click "Access Permissions" for the
designated folder under the "Action" column.
2.
Select "WebDAV access" from the dropdown menu on the top of the page and specify the
access rights. Choose the authentication level or scroll down to search for the account to
grant its access rights. Click "Apply".
3.
Next, mount the NAS shared folders as the shared folders on your computer using
WebDAV.
Windows Vista
If you are using Windows Vista, you may need to install "Software Update for Web Folders
(KB907306)". This update is only for 32-bit versions of Windows Vista.
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=17c36612-632e-4c04-9382-98
7622ed1d64&displaylang=en
1.
Right click on "Computer" and select "Map Network Drive…"
2.
Click "Connect to a Web site that you can use to store your documents and pictures".
3.
Select "Choose a custom network location".
4.
Enter the NAS URL with the folder name. Format:
http://NAS_IP_or_HOST_NAME/SHARE_FOLDER_NAME
5.
Enter the account login details that have WebDAV access rights to connect to the folder.
6.
Enter a name for this network place.
7.
The Web folder has been successfully created.
8.
You can locate the web folder in the "Network Location" section in "Computer".
9.
You can connect to the folder though this link via HTTP/WebDAV.

Mac OS X
Follow these steps to connect to your NAS via WebDAV on Mac OS X.
Client Operating System: Mac OS X Snow Leopard (10.6.1)
1.
Open "Finder" > "Connect to Server", and enter the URL of the folder. Format:
http://NAS_IP_or_HOST_NAME/SHARE_FOLDER_NAME
2.
Enter the account login details that have WebDAV access rights to connect to the folder.
3.
You can connect to the folder through this link via HTTP/WebDAV.
4.
You can also find the mount point in the "SHARED" category in Finder and make it one of
the login items.
These instructions are based on Mac OS X 10.6, and can be applied to 10.4 or later.
Ubuntu
Follow these steps to connect to your NAS via WebDAV on Ubuntu.
Client Operating System: Ubuntu 9.10 Desktop
1.
Open "Places" > "Connect to Server…"
2.
Select "WebDAV (HTTP)" or "Secure WebDAV (HTTPS)" for the Service type according to
your NAS settings and enter your host information. Enter the account login details that
have WebDAV access rights to connect to the folder. Click "Connect" to initialize the
connection.
3.
The WebDAV connection has been successfully established, a linked folder will be
automatically created on the desktop.
MySQL Management
Install phpMyAdmin and save program files in the Web or Qweb share of the NAS. You can
change the folder name and connect to databases by entering the URL in the browser.
Note:
The default username of MySQL is "root". The password is "admin". Change the
root password
immediately
after logging in to the phpMyAdmin management interface.
SQLite Management
Follow these steps or refer to the INSTALL file in the downloaded SQLiteManager-*.tar.gz?
to install SQLiteManager.
1.
Unpack the downloaded file SQLiteManager-*.tar.gz.
2.
Upload the unpacked folder SQLiteManager-* to \\NAS IP\Web\ or \\NASIP\Qweb.
3.
Open a web browser and go to http://NAS IP/SQLiteManager-*/.?:
o
The symbol "*" refers to the version number of SQLiteManager.
Virtual Host
A virtual host is a web server technique that provides the capability to host more than one
domain (website) on one physical host and offers a cost-effective solution for personal and
small businesses with such need. You can host up to 32 websites on the NAS with this
feature.
Before you Start
In this tutorial we will use the information provided in the below table as a reference guide.
Host name
WAN/LAN IP and
port
Document root
Demo web
application
site1.mysite.com
WAN IP:
111.222.333.444
LAN IP: 10.8.12.45
(NAS)
Port: 80 (NAS)
/Qweb/site1_mysite
Joomla!
site2.mysite.com
/Qweb/site2_mysite
WordPress
www.mysite2.com
/Qweb/www_mysite
2
phpBB3
Before starting, make sure you have checked the following items:
Web Server: Enable Web Server in "Applications" > "Web Server".
DNS records: The host name must point to the NAS WAN IP. You can normally configure
this from your DNS service providers.
Port forwarding: If the web server listens on port 80 you need to configure port
forwarding on your router to allow inbound traffic from port 80 to the LAN IP (10.8.12.45)
of your NAS.
SSL certificate import: If you are going to enable SSL connection for the website and
intend to use your own trusted SSL certificates you can import certificates from within
the administration backend under "System Settings" > "Security" > "Certificate & Private
Key".
Using Virtual Host
Follow these steps to use virtual host:
1.
Select "Enable Virtual Host" and click "Apply".
2.
Click "Create a Virtual Host".
3.
Enter the host name and specify the folder where the web files will be uploaded to.
4.
Specify the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) for connection. If you select HTTPS, make sure the
option "Enable Secure Connection (SSL)" in Web Server has been enabled.
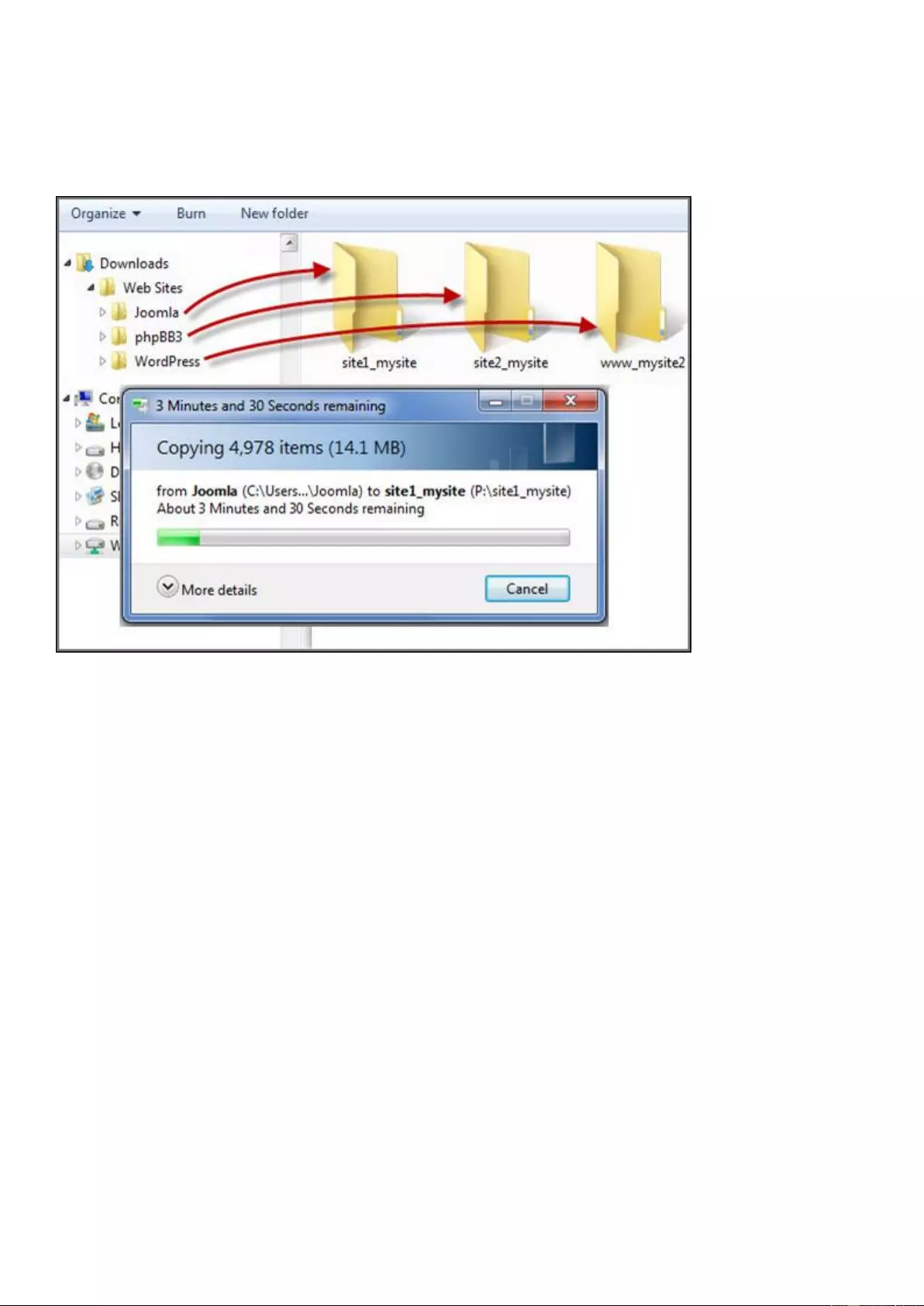
5.
Specify the port number for connection.
6.
Click "Apply".
7.
Continue to enter the information for the rest of the sites you want to host on the NAS.
8.
Create a folder for each website (site1_mysite, site2_mysite, and www_mysite2) and
start transferring the website files to the corresponding folders.
Once the files transfer is complete, point your web browser to the websites by
http://NAS_host_name or https://NAS_host_name according to your settings. In this
example, the URLs are:
http://site1.mysite.com
http://site2.mysite.com
http://www.mysite2.com
Using the above example, you would see the Joomla!, phpBB3, and WordPress sites
respectively.
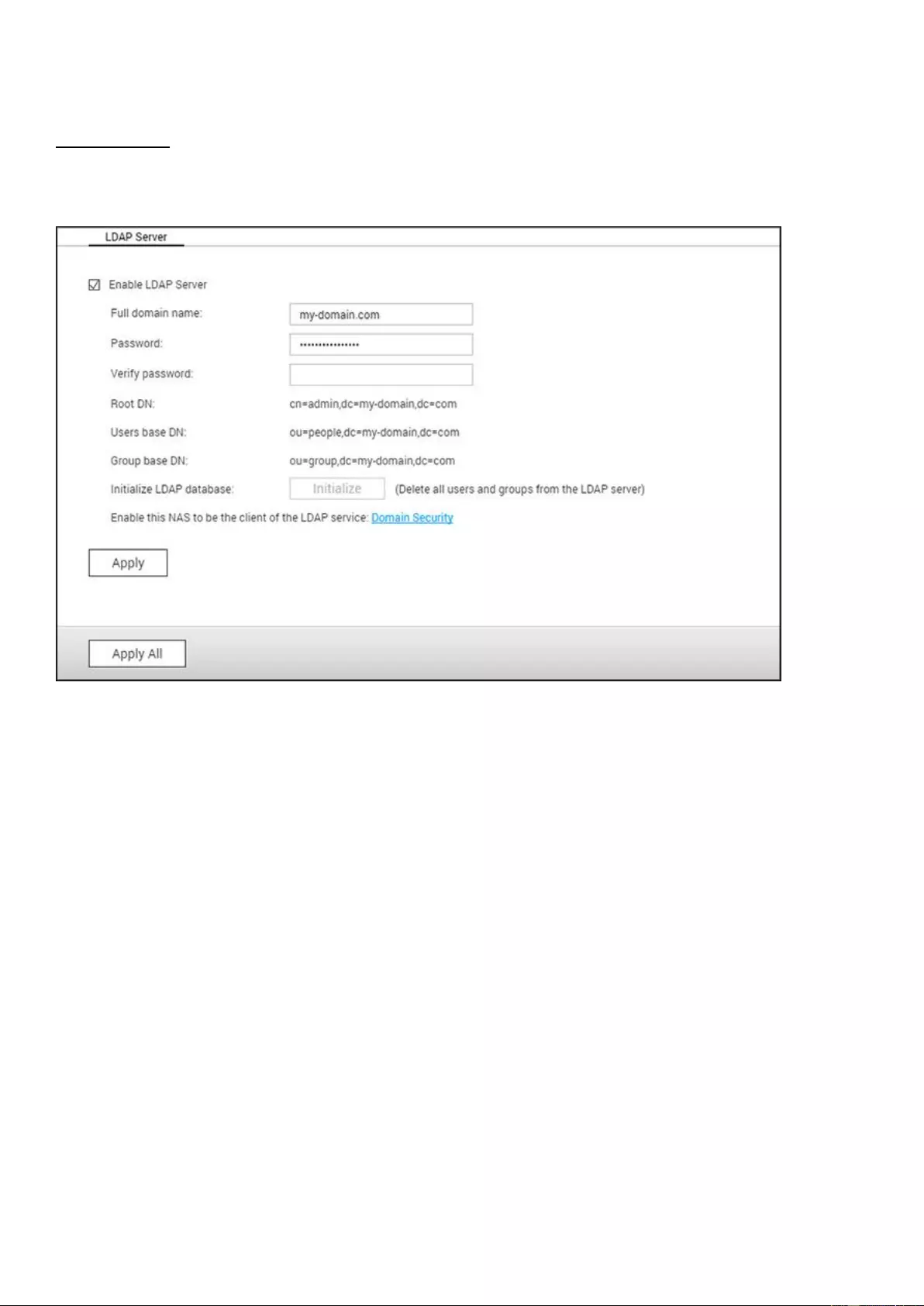
LDAP Server
The LDAP server of the NAS allows the administrator to create users to access multiple NAS
servers with the same username and password.
Configuring LDAP Server
Follow these instructions to configure the LDAP server.
1.
Enable LDAP Server: Log in to the NAS as "admin". Go to “Control Panel” > "Applications"
> "LDAP Server" and enable the LDAP server. Enter the full LDAP domain name and the
password for the LDAP server, then click "Apply".
2.
Create LDAP Users: Under the "Users" tab, click “Create” then click "Create a User" or
"Create Multiple Users" or "Batch Import Users". Follow the wizard instructions to create
LDAP users. Once you have created the LDAP users, the NAS can be joined to the domain.
You can set the permissions of LDAP users and allow them to be authenticated by the
NAS.
3.
Join a NAS to LDAP Domain: To allow LDAP users to connect to the NAS, join the NAS to
the LDAP domain. Go to "Privilege" > "Domain Security". Select "LDAP authentication" and
choose "LDAP server of local NAS" as the server type. Then click "Apply". The NAS is now
a client of the LDAP server. To view the domain users or groups, go to "Privilege Settings"
> "Users" or "User Groups", then select "Domain Users" or "Domain Groups". You can also
set the folder permission for the domain users or groups.
4.
Join a Second NAS to LDAP Domain: You can join multiple NAS to the same LDAP domain
and allow the LDAP users to connect to these NAS using the same login credentials. To
join another NAS to the LDAP domain, login to the NAS and go to "Privilege" > "Domain
Security", select "LDAP authentication" and set "LDAP server of a remote NAS" as the
server type. Enter the DNS name or IP address of the remote NAS, the name of the
previously-created LDAP domain, and enter the LDAP server password. Click "Apply".
Backing up/Restoring LDAP Database
To back up the LDAP database on the NAS, select "Back up Database" and specify the
backup frequency, destination folder on the NAS and other options. To restore an LDAP
database, browse to select the *.exp file and click "Import".
Note:
If the name of a user is changed in a LDAP server, it is necessary to assign the folder
permissions again on the NAS.
To avoid account conflicts, do not create NAS local user accounts that already exist in
the LDAP directory.
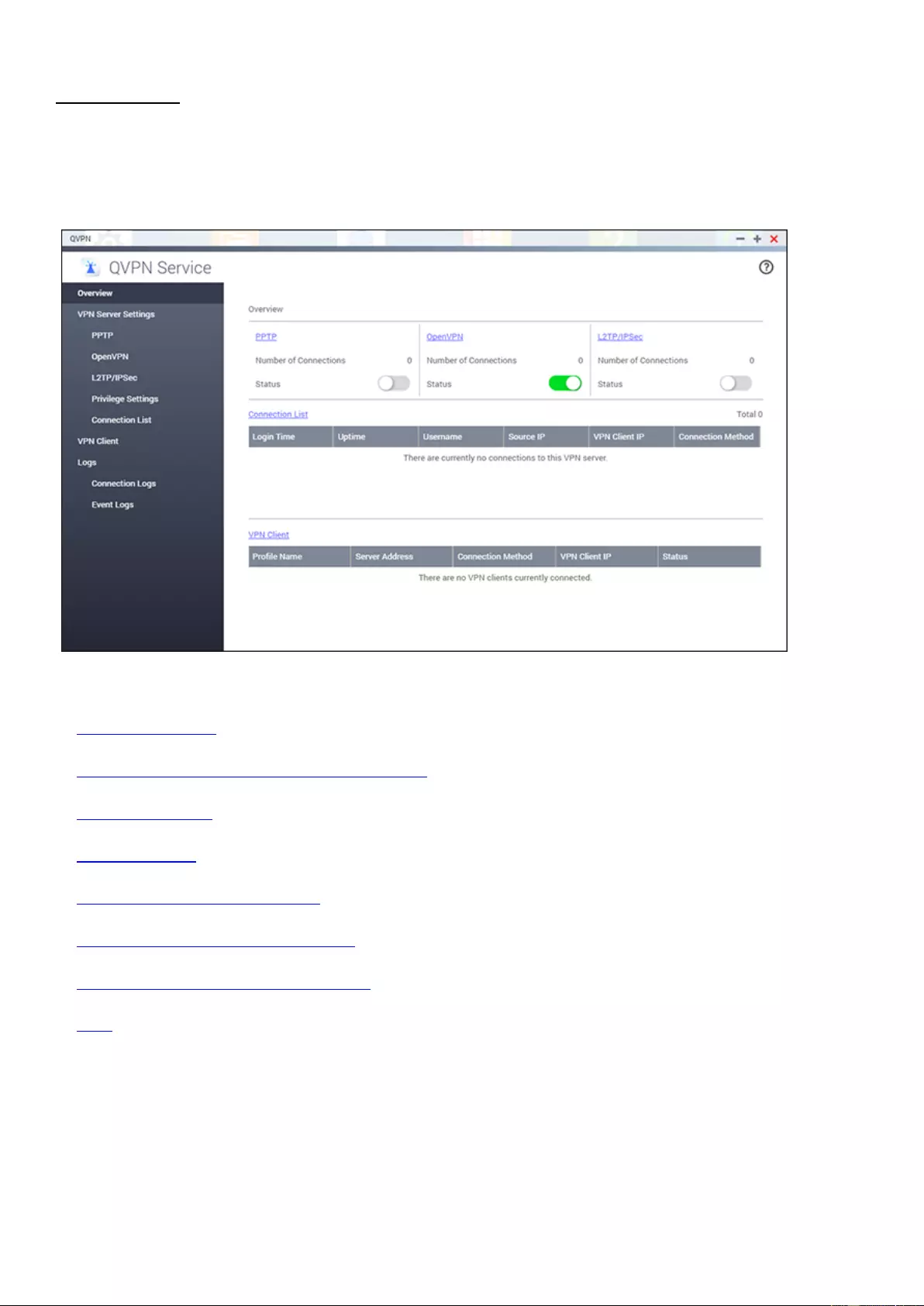
QVPN Service
The NAS supports Virtual Private Network (VPN) service for users to access the NAS and resources on
a private network from the Internet. Use QVPN Service to set up your NAS as a VPN server and
establish a VPN client connection.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
VPN Server Setup
Third Party VPN Client Setup and Connection
Privilege Settings
Connection List
Connect a VPN Server via PPTP
Connect a VPN Server via OpenVPN
Connect a VPN Server via L2TP/IPSec
Logs
VPN Server Setup
1. Enable PPTP, OpenVPN, or L2TP/IPSec: The NAS supports PPTP, OpenVPN or L2TP/IPSec for VPN
connection. Select one of the following options and configure the settings.

o PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is one of the most commonly used methods for VPN
connection. It is natively supported by Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, and iPhone. You can also
specify the VPN client IP pool and advanced settings (including the maximum number of clients,
authentication protocol, encryption method, network interface and DNS server).
o OpenVPN: OpenVPN is an open source VPN solution which utilizes SSL encryption for secure
connection. To connect to the OpenVPN server, the OpenVPN client must be installed on your PC.
Click "Download Configuration File" to download the VPN client settings, certificate/key and
installation guide from the NAS and upload the files to the OpenVPN client. You can also specify the
VPN client IP pool and advanced settings (including the VPN server port, maximum number of clients,
encryption method, network interface, DNS server, and whether to use the redirect-gateway and
compressed data before their transfer via VPN).
o L2TP/IPSec: L2TP (Layer Two Tunneling Protocol) is a combination of the Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol (PPTP) and Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F). Compared to PPTP, which only establishes a single
tunnel between the two end points, L2TP supports the use of multiple tunnels. IPSec is often used to
secure L2TP packets by providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity checks. The
combination of these two protocols provides a high-security VPN solution which is known as
L2TP/IPSec. L2TP/IPSec is supported by most clients, including Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile
devices.
2. Configure port forwarding by auto router configuration: The NAS supports auto port forwarding for
UPnP (Universal Plug-and-Play network protocol) routers. Go to "myQNAPcloud" > "Auto Router
Configuration" to enable UPnP port forwarding and open the ports of the PPTP, OpenVPN or
L2TP/IPSec service on the router.
3. Register myQNAPcloud service: You can connect to the NAS by WAN IP or myQNAPcloud name. To
configure myQNAPcloud service, check the chapter on myQNAPcloud Service or visit myQNAPcloud
(https://www.myqnapcloud.com).
4. Add VPN users: Go to "QVPN Service" > "Privilege Settings", click "Add VPN Users". The local NAS
users will be listed. Select the users who are allowed to use the VPN service and their connection
method (PPTP, OpenVPN or L2TP/IPSec, multiple methods are also allowed). Click "Add".
5. Connect to the private network by a VPN client device: Now you can use your VPN client device to
connect to the NAS via the VPN service.
Notes:
The default NAS IP is 10.0.0.1 under PPTP VPN connection.
Upload the configuration file to the OpenVPN client every time the OpenVPN settings,
myQNAPcloud name, or the secure certificate is changed.
To connect to the PPTP or L2TP/IPSec server on the Internet, the PPTP or L2TP/IPSec
passthrough options on some routers have to be opened. PPTP uses only port TCP-1723

and L2TP/IPSec uses UDP 500, 1701 and 4500; forward those ports manually if your
router does not support UPnP.

Third-Party VPN Client Setup and Connection
PPTP on Windows 8
1. Go to "Control Panel" > "Network and Sharing Center".
2. Select "Set up a new connection or network".
3. Select "Connect to a workplace" and click "Next".
4. Select "Use my Internet connection (VPN)".
5. Enter your myQNAPcloud name or IP address in “Internet address”.
6. Enter a name for the connection in “Destination name”.
7. Click "Create".
8. Go to “Control Panel” > “Network and Sharing Center” > “Change adapter settings”.
9. Right-click the VPN connection and then select “Properties”.
10. Enter “Security” page, select the “Type of VPN” as PPTP.
11. Click “OK”.
PPTP on Mac OS X 10.10
1. Go to "Apple menu" > "System Preferences", and click "Network".
2. Click "Add (+)" at the bottom of the list, and choose "VPN" as the interface.
3. Select “Add new service (+)” and choose “VPN” in “Interface”.
4. Select “PPTP” in “VPN Type”.
5. Enter a name for the connection in “Service Name”.
6. Enter your myQNAPcloud name or IP address in “Server Address” and your QNAP NAS user name
in “Account Name”.
7. Click “ Authentication Settings” and then enter the password and preshared key.
8. Click “Connect”.
PPTP on Android 5.0
1. Go to “Settings” > “VPN”. Click “Add VPN profile”.

2. Enter “Name” and select “PPTP”.
3. Click the VPN profile and enter your username and password to start the connection.
OpenVPN on Windows
1. Download OpenVPN from http://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/downloads.html/.
2. Install the OpenVPN client on Windows.
The default installation directory is C:\Program Files\OpenVPN.
3. Download the settings files from your QNAP NAS, including the certification file “ca.crt” and the
configuration file “openvpn.ovpn”.
4. Open “openvpn.ovpn” and replace “OPENVPN_SERVER_IP” with your NAS IP address.
5. Place “ca.crt” and “openvpn.ovpn” in the folder C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config.
6. Use an administrator account to launch OpenVPN and activate the connection.
Note:
If the OpenVPN client is running on Windows 7, add the firewall rules in the
advanced settings of OpenVPN.

OpenVPN on Mac OS X 10.11
1. Download and install Tunnelblick from https://tunnelblick.net/.
2. Launch Tunnelblick.
3. Download the settings files from your QNAP NAS, including the certification file “ca.crt” and the
configuration file “openvpn.ovpn”.
4. Open “openvpn.ovpn” and replace “OPENVPN_SERVER_IP” with your NAS IP address.
5. Double-click the configuration file (or right-click and import the file with Tunnelblick).
The certification file will be imported automatically.
6. Click “Connect”.
7. Enter your NAS username and password.
OpenVPN on iOS 9
1. Install OpenVPN Connect from
https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/openvpn-connect/id590379981?mt=8.
2. Download the settings files from your QNAP NAS, including the certification file “ca.crt” and the
configuration file “openvpn.ovpn”.
3. Open “openvpn.ovpn” and replace “OPENVPN_SERVER_IP” with your NAS IP address.
4. Open the configuration file with OpenVPN Connect.
Tip: You can send the file to your email address and open it on your device, or you can send the file
to the OpenVPN folder via PC with a third-party application such as “iTools for Windows”.
5. Enter your NAS username and password
If you have imported the configuration file to the OpenVPN folder you will see it in OpenVPN Connect.
Note:
Ensure this option on your iOS device is enabled: “Settings” > ”OpenVPN” >
“Advanced Settings” > ”Force AES-CBC cipher suites”.

OpenVPN on Android 5.0
1. Install OpenVPN Connect from
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.openvpn.openvpn&hl=en.
2. Download the settings files from your QNAP NAS, including the certification file “ca.crt” and the
configuration file “openvpn.ovpn”.
3. Open “openvpn.ovpn” and replace “OPENVPN_SERVER_IP” with your NAS IP address.
4. Import your settings files to the folder on your Android device.]
5. Launch OpenVPN Connect and select "Import" in the top-right menu. Find and import the
configuration file, and then follow the instructions for importing the certification file.
6. Enter your NAS username and password.
OpenVPN on Windows
1. Download and install OpenVPN from http://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/downloads.html/.
The default folder for the installation is "C:\Program Files\OpenVPN".
2. Download the settings files from your QNAP NAS, including the certification file “ca.crt” and the
configuration file “openvpn.ovpn”.
3. Open “openvpn.ovpn” and replace “OPENVPN_SERVER_IP” with your NAS IP address.
4. Place “ca.crt” and “openvpn.ovpn” in the folder C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config.
5. Use an administrator's account to launch OpenVPN and activate the connection.
L2TP/IPSec on Windows 8
1. Go to “Control Panel” > “Network and Internet” > “Network and Sharing Center” and select “Set up
a new connection or network”.
2. Select “Connect to a workplace”.
3. Select “Use my Internet connection (VPN)”.
4. Enter your myQNAPcloud name or IP address in “Internet address”.
5. Enter a name for the connection in “Destination name”.
6. Go to “Control Panel” > “Network and Sharing Center” > “Change adapter settings”.

7. Right-click the VPN connection and select “Properties”.
8. Go to “Security”, select the “Type of VPN” as L2TP/IPSec, and then click “Advanced settings”.
9. Select “Use preshared key for authentication” and enter the same key as the server’s settings.
You can now connect to the VPN.
Note:
If your NAS is behind a NAT router, use the following configuration:
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/926179.

L2TP/IPSec on Mac OS X10.10
1. Go to “System Preferences” > “Network”.
2. Select “Add new service (+)” and choose “VPN” in “Interface”.
3. Select “L2TP/IPSec” in “VPN Type”.
4. Enter a name for the connection in “Service Name”.
5. Enter your myQNAPcloud name or IP address in “Server Address” and your QNAP NAS user name in
“Account Name”.
6. Click “Authentication Settings”, and enter the password and preshared key.
7. Click “Connect”.
L2TP/IPSec on Android 5.0
1. Go to “Settings” > “VPN”.
2. Click “Add VPN profile”.
3. Enter “Name” and choose the type as “L2TP/IPSec PSK”.
4. Enter “IPSec Pre-shared key”.
5. Click the VPN profile and enter your username and password.
L2TP/IPSec on iOS 8
1. Go to “Settings” > “General” > “VPN”.
2. Choose “Add VPN Configuration…”.
3. Select “L2TP”.
4. Enter a name for the connection in “Destination”.
5. Enter the myQNAPcloud name or IP address in “Server”.
6. Enter your QNAP NAS username, password and preshared key.
7. Go to “Settings” > “General” > “VPN” to connect to the VPN.
Privilege Settings
Select the VPN users and specify their privileges.
Add VPN users
Click "Add VPN Users" and check the services you want to allow each user to connect with. Both local
users and domain users can be VPN users. You can also search for users in the search bar.
Note:
To connect to a VPN server using domain user accounts, you must enable the
service in Domain Security.

Delete VPN users
Click "Delete" to remove VPN users. The users will be unable to connect to the VPN service after being
deleted.
Connection List
This list shows information about each connection with a server including login time, uptime,
username, source IP, VPN client IP, and connection method.
Click “Disconnect” on the table to disable client connections.
VPN Client
The NAS provides the VPN client service which can connect to a VPN server via PPTP, OpenVPN and
L2TP/IPSec. The NAS also supports saving multiple VPN settings to easily switch between different
connections.
Before you start
Before starting the VPN client service, please ensure that the Internet connection is normal.
Connect a VPN server via PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a commonly-used method for implementing VPN and is
supported by most clients, including Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and mobile devices.
1. Go to "QVPN Service" > "VPN Client".
2. Click "Add" > "PPTP" to connect a VPN server.
3. Enter the connection configuration settings, including the profile name, server address (that you
want to connect to), and the username and password of the VPN server.
4. Choose any of the following authentication mechanisms from the ”Authentication" menu to protect
the VPN client’s password during authentication:
o MS-CHAPv2: The password will be encrypted using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
o MS-CHAP: The password will be encrypted using Microsoft CHAP version 1.
o PAP: The password will not be encrypted.
o CHAP: The password will be encrypted using CHAP.
5. If you choose MS-CHAP or MS-CHAPv2, go to the "Encryption" menu and select an option:
o None: The VPN connection will not be encrypted.
o Medium (AES 40/128 bit): The VPN connection will be encrypted using a 40-bit or 128-bit key.
o High (AES 256 bit): The VPN connection will be encrypted using a 256-bit key (the highest-possible
level.)
6. Specify the subnet mask.
7. Select any of the following options, as required:
o Use the default gateway on remote network: This will allow all packets to be transferred via the VPN
server.
o Allow other network devices to connect to the VPN through the NAS: This will allow network devices
on the same LAN as the NAS to connect to the same VPN.
o Reconnect when the VPN connection is lost: This will automatically reconnect to the VPN server
when the connection is lost.
8. Select "Create" to start.
Note:
To connect to a VPN server using domain user accounts, you must enable the
service in Domain Security.

If you select "Allow other network devices to connect to the VPN through the NAS", the network
device can access the VPN via the NAS. To enable this function, you must change the default gateway
on that other device. Using a Windows PC as an example:
1. Go to "Control Panel" > "Network and Sharing Center" > "Change adapter settings".
2. Right-click the connection icon and choose "Properties".
3. Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IP)" and click "Properties".
4. Choose "Use the following IP address" and change the Default gateway to the IP address of the
NAS that is operating the VPN Client service then click "OK".
Connect a VPN server via OpenVPN
The NAS also supports OpenVPN, which is an open-source solution for VPN services. It protects a
VPN's connection with the SSL/TLS encrypting mechanism. It is also available on Windows, Mac OS X,
Linux, Android and iOS.
To connect to a VPN server via OpenVPN, follow these steps:
1. Go to "QVPN Service" > "VPN Client".
2. Click "Add" > "OpenVPN" to connect to a VPN server.
3. Select the OVPN file (.ovpn) and click “Open”.
4. Enter the connection configuration settings, including the profile name, and the username and
password of the VPN server.
5. Click inside the required text field to import the certificate (ca.crt) exported from the OpenVPN
server.
6. Specify the subnet mask.
7. Select any of the following options, as required:
o Use the default gateway on remote network: This will allow all packets to be transferred via the
VPN server.
o Allow other network devices to connect to the VPN through the NAS: This will allow network devices
on the same LAN as the NAS to connect to the same VPN.
o Reconnect when the VPN connection is lost: This will automatically reconnect to the VPN server
when the connection is lost.
8. Click "Apply" to start.
o If you check "Use the default gateway on remote network", the default gateway on your NAS will
change to the VPN server’s default gateway.
o If you check "Allow other network devices to connect to the VPN through the NAS", the network
device can access the VPN via the NAS.
Connect a VPN server via L2TP/IPSec
1. Go to "QVPN Service" > "VPN Client".
2. Click "Add" > "L2TP/IPSec" to connect a VPN server.
3. Enter the connection configuration settings, including the profile name, server address (that you
want to connect to), and the username and password of the VPN server.
4. Choose any of the following authentication mechanisms from the "Authentication" menu to protect
VPN client’s password during authentication:
o MS-CHAPv2: The password will be encrypted using Microsoft CHAP version 2.
o MS-CHAP: The password will be encrypted using Microsoft CHAP version 1.
o PAP: The password will not be encrypted.
o CHAP: The password will be encrypted using CHAP.
5. If you choose MS-CHAP or MS-CHAPv2, go to the "Encryption" menu and select an option:
o None: The VPN connection will not be encrypted.
o Medium (AES 40/128 bit): The VPN connection will be encrypted using a 40-bit or 128-bit key.
o High (AES 256 bit): The VPN connection will be encrypted using a 256-bit key (the highest-possible
level.)
6. Type the preshared key.
7. Specify the subnet mask.
8. Select any of the following options, as required:
o Use the default gateway on remote network: This will allow all packets to be transferred via the
VPN server.
o Allow other network devices to connect to the VPN through the NAS: This will allow network devices
on the same LAN as the NAS to connect to the same VPN.
o Reconnect when the VPN connection is lost: This will automatically reconnect to the VPN server
when the connection is lost.
9. Select "Create" to start.
Logs
Connection Logs
QVPN Service creates a log entry every time a user accesses a VPN server. The connection logs
include the connection method, date, time, username, source IP, and content.
Note:
QVPN Service only displays the connection logs. To copy or delete a log, or to
export the list, go to “Control Panel” > “System” > “System Logs”.
Enable Connection Logs on QVPN Service
1. Open QVPN Service.
2. Go to “Logs” > “Connection Logs”.
3. Move the slider to the right.
Event Logs
QVPN Service creates a log entry every time a user enables or disables services, changes settings,
and modifies the configuration. The event logs include the date, time, username, and content.
Note:
QVPN Service only displays the event logs. To copy or delete a log, or to export the
list, go to “Control Panel” > “System” > “System Logs”.
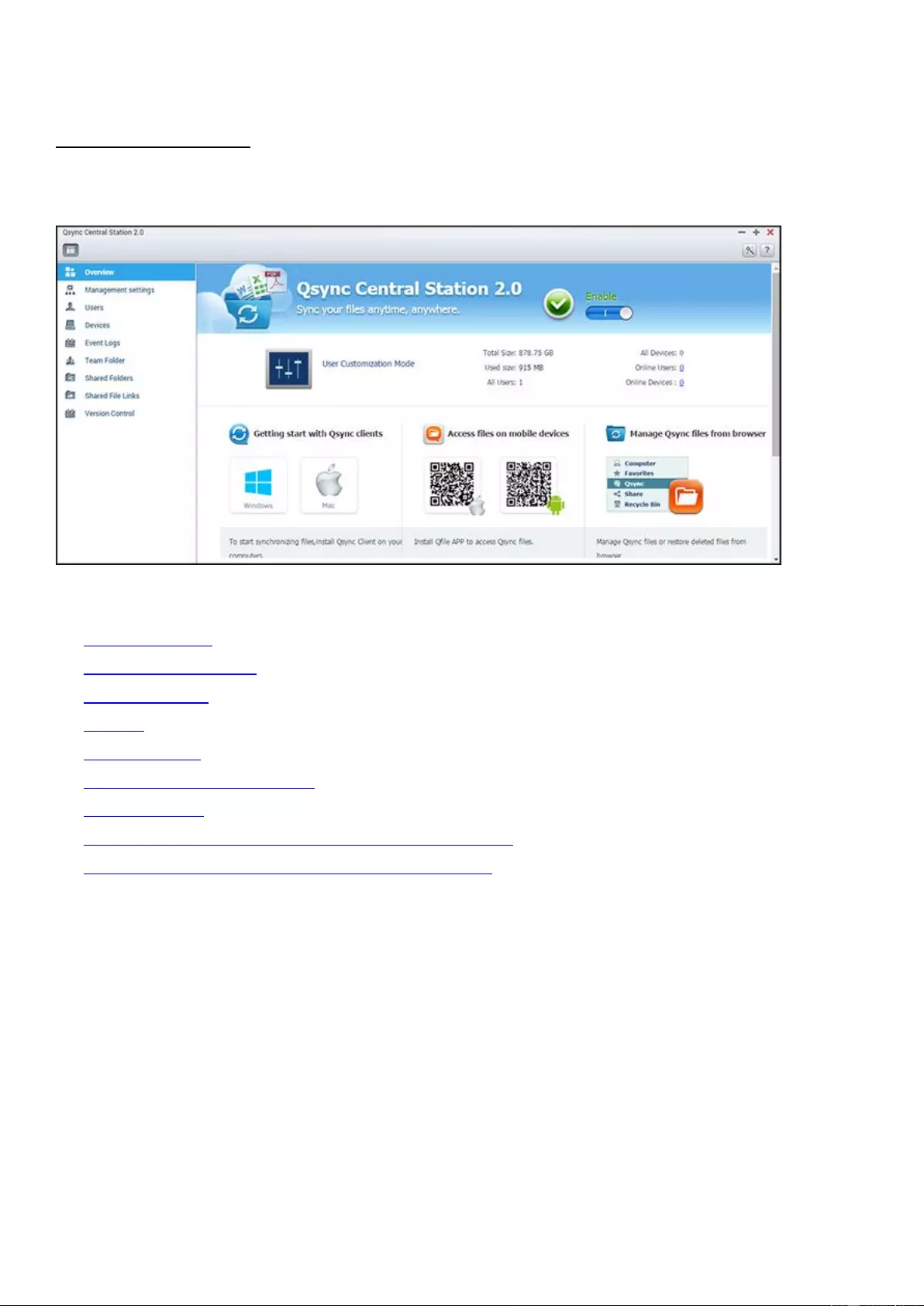
Qsync Central Station
Qsync Central is a cloud-based file synchronization service on the NAS. Simply add files to
your local Qsync folder, and they will be available on your NAS and all its connected devices.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Before you Start
Starting Qsync Client
Synchronization
Sharing
Remote Access
Synchronization Management
Version Control
Managing or Monitoring Qsync Status via Web Browser
Using Centralized Mode for Centralized Management
Before you Start
Follow the 5 steps below before Qsync deployment.
1.
Create user accounts on the NAS,
2.
Downloading Qsync Central on your NAS.
3.
Enable home folders for all users.
4.
Download the Qsync Client utility on your computers and Qfile on your mobile devices.
5.
Log into the NAS (serving as a Qsync server) from your computers or mobile devices
(referred to in this document as "Qsync clients".)

1.
Creating user accounts on the NAS
o
Go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Users" > click "Create" (or go to "Qsync
Central" > "Users" > "Create a User".)
o
Only NAS administrators can create accounts.
2.
Downloading Qsync Central
1. Go to “Main Menu” > “App Center” to launch App Center.
2. In the search field, type “Qsync”.
3. Select “+ Install” under the Qsync Central icon in the search results.
3.
Enable Home Folders for All Users
1. Go to “Control Panel” > “Privilege” > “Users” > “Home Folder”.
2. Select “Enable home folder for all users”, select disk volume to create folders in. Click
“Apply”.
4.
Downloading Qsync Client
Follow the instructions on the "Overview" page to download the utility for your client device
(log into the NAS, click "Qsync Central" on the NAS Desktop > "Overview" page,) or
directly download the utility from the QNAP website: "Support" > "Download" >
"Utilities".
o
For computers, download the Qsync Client utility (only available for Windows.)
o
For mobile devices, download and install Qfile from the iOS or Android app stores.
5.
Setting up Qsync Client
Launch the installer and follow these steps to set up the Qsync Client:
1.
To locate the NAS within a LAN, simply click "Search" or key in its IP address or name
(e.g. IP address: 10.8.1.20 or 192.168.1.100.) To connect to a remote NAS (over the
Internet) use your myQNAPcloud address (e.g. andy@myQNAPcloud.com.)
2.
Enter the NAS login username and password.
3.
Set up the Qsync local folder on your PC.
4.
Assign a name to identify the local PC for the Qsync server.
5.
Click "Apply" .
6.
Pair a local folder with the shared folder on the NAS.
Note:
If the NAS connection ports have been changed, please append the port number to
the IP address; otherwise only enter an IP address. (Default port number: 8080)

Starting Qsync Client
Double click the Qsync shortcut in Windows to open the Qsync local folder. Click the Qsync
Client icon on the taskbar to bring up the menu. If you copy/move files to the local Qsync
folder on one of your devices, the files will be synced with all the other devices (devices with
the Qsync Client installed that are connected to the NAS.) From now on, there is no need to
copy files back-and-forth between your PC and these other devices or worry about the size
of files as you try to attach them to an email.
Synchronization
There are several methods for synchronizing files. Qsync Central will automatically
synchronize the files across your computers and mobile devices that have the Qsync Client
installed, and they will also be synchronized to the Qsync folder on the NAS:
1.
For PCs, drag and drop files to the local Qsync folder.
2.
For mobile devices (Qfile), copy or move files into the local Qsync folder.
3.
For the NAS, copy or move files to the Qsync folder using File Station.
Note:
If files are "dragged and dropped" to the local Qsync folder, they will be moved (and
not copied) to that folder if the files and the local Qsync folder are on the same disk
drive. This behavior is the same as Windows File Explorer.
The maximum size of a single file that Qsync can transmit across a LAN is 50GB.
Qsync does not support SAMBA, FTP or AFP for files access. Please access files using
File Station or a Qsync Client.
Qfile only synchronizes the file list and does not download the files to a mobile device.
Please download the files when you need them.
Offline editing
You can edit your files offline and Qsync Central will automatically synchronize the changes
made once your device is online.
Sharing
Sharing files by download links
You can share files by sending download links to those who have not installed Qsync Client.
For Windows:
1.
Right click on the file that you want to share in the local Qsync folder and click "Share
the link".
2.
Choose to send the link via email or copy the link to directly share it.
3.
Click "Settings" to see more options, including creating a SSL link, the expiration date, or
password.
For the NAS, right click on the file that you want to share in the Qsync folder within File
Station and click "Share".
For mobile devices, launch Qfile to share the file in the local Qsync folder by clicking the icon
to the right and click "Share".
The file recipients can click the link or copy and paste it to a web browser to download the
file.
Sharing folders with a group
You can share a folder with a user group. If any member from the group shares the files in
the folder, other members can receive the file.
1.
Create user accounts in the NAS for each group member.
2.
Ensure that a Qsync Client is installed on each member’s device.
3.
Right click on the folder you want to share in the local Qsync folder and click "Share this
folder as a team folder".
4.
Select users from the list of local or domain users.
All of the members in the group will receive a file sharing invitation. Once accepted, the
group members can start accessing this shared folder.
Note:
The team folder will only take effect after users accept their invitation.
Users cannot share team folders that have been shared with them.
Only the folders under /home on your NAS can be shared as a Team Folder.
Remote Access
Accessing the NAS over the Internet
To connect to a remote NAS (over the Internet), the administrator must first configure the
device name for the NAS in "myQNAPcloud". The administrator can then share the
myQNAPcloud address to allow users to access the remote NAS. (e.g.
andy@myQNAPcloud.com)
Note:
A connection with a NAS over the Internet will be slower compared to a LAN

environment.
As you switch back to a LAN-based NAS, ensure that you reconnect to the NAS via LAN
to get a better connection quality.
To improve file transmission performance, it is recommended that you configure port
forwarding on the router.
Synchronizing photos and videos automatically
Qsync Central can synchronize your photos and videos from mobile devices to the Qsync
folder across all Qsync client devices.
Steps:
1.
Install Qfile on your mobile devices by following instructions outlined on the Qsync
Central Overview page on the NAS or find it from your device’s app store.
2.
Launch Qfile.
3.
Click "Settings" on the bottom-right side of the screen.
4.
Scroll down and look for "Auto upload from photo gallery" and click on "Set up now".
5.
Select a NAS to upload photos and videos to.
6.
Select the folder.
7.
Select "Use default setting" ( /Qsync/Camera Uploads) or select "Set up manually" to set
the path.
8.
Select if you want to upload all photos from the photo gallery immediately.
9.
You can tick the checkbox "Limit to Wi-Fi" to ensure that you only upload files through
Wi-Fi and not your phone’s network.
10.
The uploaded files will be synchronized to the "Camera Uploads" folder under the
Qsync folder on Qsync client devices.
Note:
If files that were previously uploaded are deleted from the "Camera Uploads"
folder, Qfile will not upload those copies in the photo library again.
Synchronization Management
Click the Qsync Client icon on the taskbar to see the management functions:

1.
Add files and view the synchronization result on the NAS:
a.
Open Qsync folder: Open the local Qsync folder to add files.
b.
View files by the web browser: Browse files in the Qsync folder using File Station.
2.
Control synchronization progress:
a.
Pause syncing / Resume syncing: Click to pause or resume syncing.
b.
Sync with NAS now: Force Qsync to scan again and refresh the synchronization list.
3.
Information for syncing and sharing:
a.
Sharing & File Update Center
i.
File Update Center: List the file or folder update logs.
ii.
Sharing Center: List the folders or files shared with others. Users can choose to
accept or decline the team folders. However, users cannot share team folders that
are shared by others.
b.
Recently changed files: Lists the recently updated files.
4.
Preference:
a.
General:
i.
Link Status: Shows the current status. Click "Logout" to change users.
ii.
Network Recycle Bin: Browse or recover files deleted from the Qsync folder.
b.
Sync:
i.
Manage paired folders: Add, delete, or edit folder pair settings.
ii.
Import photos and videos: Import photos and videos when an USB device is
connected. This feature only checks for photos and videos in the "DCIM" folder in
the root directory of USB devices.
iii.
Default folder: choose a folder to import files from external drives or QGenie.

iv.
Do not remove any files on the NAS when synchronizing: You can remove files
within the local Qsync folder, and files deleted from your computer will not be
synchronized with the NAS. The NAS will still retain copies of deleted files.
c.
Policy:
i.
Conflict Policies: The policies for handling the name conflicts between the Qsync
server (NAS) and clients after it is back online from a disconnection:
1)
Rename the local files,
2)
Rename the remote NAS files,
3)
Replace local files with remote NAS files, or
4)
Replace remote NAS files with local files.
ii.
Sharing Policies: The policies of the team folders when other Qsync users share
them to this local computer:
1)
Always reject sharing,
2)
Automatically accept sharing, or
3)
Send a notification message once sharing occurs.
iii.
Filter Settings: During file synchronization, Qsync will skip the file types specified in
filter settings.
d.
E-Mail:
i.
Set up E-mail: Set up an email account for sharing file links. You can use the NAS
SMTP server settings (for administrators only), your PC’s mail server settings, or
configure a new SMTP server.
e.
Proxy:
i.
Set up Proxy: Use a proxy server for the Qsync client device.
f.
Advanced:
i.
Debug log: The system will record all of the synchronization activities between your
computer and the NAS for diagnosing technical problems.
Note:
The "Sync" and "Proxy" tab is not available on Mac.
Version Control
This will retain one copy of a file as a version whenever you add or modify it, allowing you to
retrieve a specific previous version at any time. Or, if you accidently overwritten a previous
version made by others while editing the file in team folder, you can still restore the
previous version. And you can restore the previous versions even if you have deleted the file
from the recycle bin.
Viewing the version history
You can view the version history by using File Station. Right click on a file or folder in the
Qsync folder in File Station and select "Previous Versions" to show the version list (or you

can access it from menu bar "More Action" > "Previous Versions". Or, just click the "Show
Right Panel" > "Version". You can also access it from the Qsync client utility. Right click on a
file of folder in the Qsync folder and select "Previous Versions".
Restoring the previous versions
In the version history page, select the version you want to restore and click "Restore".
Click "Download" to download the version to the local computer.
Click "Delete All" to delete all of the listed versions.
Click "Refresh" to update the status of the version history.
Restoring versions of a deleted file
Version control retains versions in a separate location, so even you delete the file, you can
still restore the previous versions of the file - even if the file has been deleted from the
recycle bin.
To restore the version of a deleted file, click on any folder/file in the Qsync folder, and then
click "More Action" > "Show Deleted Files" in the menu bar. To view the version history,
right click on a file/folder in Qsync folder and select "Previous Versions". Or you can access it
from the menu bar, "More Action" > "Previous Versions". Or just click the "Show Right
Panel" > "version" to show the version list.
Restoring previous versions
In the version history page, select the version you want to restore and click "Restore".
Click "Download" to download the version to the local computer.
Click "Delete All" to delete all of the listed versions.
Click "Refresh" to update the status of the version history.
Note:
If you click "Delete All", then click "Refresh" and the associated files will be
removed from the list.
To exit the view of the deleted file list, right click on any file/folder and select "Hide Deleted
Files". Or access it from menu bar, "More Action" > "Hide Deleted Files".
Managing and setting version control
To access the management and settings of version control, click the Qsync button on the
desktop of the NAS, then click "Version Control" in the right-side menu.
The target folder
"Enable version control" is the main switch of the version control. Disabling this option will
not delete versions that have already been created. "Enable version for my Qsync folder"
allows each user to apply the function to their files.

Target folder for version control
You can apply the version control to the files under specific Qsync folders to save space. To
assign specific folders, select "Assign specific subfolder under the Qsync folder", then click
"Add" to add folders. You can add up to 5 folders. Click "Delete" to remove all versions
under the selected folders and subfolders. This will not take effect until you click "Apply" or
"Apply All".
Advanced
Maximum Number of Versions: You can choose how many versions you want to retain. This
is a control only for administrators. The more versions you keep the more storage space will
be taken up. To know how much space has been used for version control, click "Check" in
the "Disk Used for Version Control" section.
Note:
If you reduce the maximum number of versions, it will impact the versions that have
been created and if the volume of versions exceeds the new settings, the earlier
versions will be dropped. Only the equivalent number of latest versions as of the new
settings will be kept.
The deletion will only take effect after you click "Apply" or "Apply All".
The maximum number of versions supported for Version Control is 64.
Managing or Monitoring Qsync Status via Web Browser
Log into the NAS via web browser and click Qsync Central.
1.
Overview: This page shows the mode of use management (User Customization Mode or
Central Configuration Mode) and the total number of online users and devices. It also
provides links to File Station and for installing Qsync. In addition, you can enable or
disable the Qsync service (for administrators only.)
2.
Management settings: This provides a centralized management for administrators to edit
Qsync Client default settings. For details on the management settings, please refer to the
Using Centralized Mode for Centralized Management section.
3.
Users: Lists the information of online users, and you can manage the users of Qsync
service here (for administrators only.)
4.
Devices: This table lists the status of connected devices. It also provides options for you
to manage each device, allowing you to edit their settings, block them, or to remotely
erase them.
a.
If users log in from their PC, the name of the device will be shown as their computer
name.

b.
If users log in from Qfile, the name of the device will be shown as "Qfile-Android" or
"Qfile-iPhone".
c.
If users move or copy files to the Qsync folder in the File Station, the name of the
device will be shown as "Qsync-File Station".
5.
Event Logs: Lists activity details by user.
6.
Team Folder: Lists information about team folders, including folders that you shared and
folders that are shared with you.
7.
Shared Folder: Administrators can decide which shared folders will be synced with client
devices. If a user has Read/Write or Read-only and synchronization privileges on a
shared folder, it can then be synced with their client device.
8.
Shared File Links: Lists the status of shared links.
9.
Version Control: You can set the maximum number of version for your files and check
the space used for Version Control.
Using Centralized Mode for Centralized Management
Administrators can now apply pre-configured settings to devices that connect to the NAS for
the first time, restrict users’ right on modifications to all or certain preference settings of their
client utilities, edit settings for individual Qsync client devices online, or set a management
password (a master password for all client devices.)
To apply pre-configured settings on connected devices, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the NAS as an administrator > "Qsync Central" > Management settings,
2.
Click "Edit default settings".
3.
Under the "Synchronize" tab, choose whether to remotely remove any files on the NAS
during synchronization.
4.
Under the "Policy" tab, set conflict policies, and filter settings.
5.
Under the "Mails" tab, set up the email option and sender details.
6.
Click "Apply".
To allow all users to configure their own client utility, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the NAS as an administrator > "Qsync Central" > Management settings,
2.
Select "Central Configuration Mode" and tick the preference settings that users are
allowed to modify for their Qsync client device.
3.
Click "Apply".
To edit settings for individual Qsync client devices, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the NAS as an administrator and navigate to the "Devices" page in Qsync
Central.
2.
Click the "Edit settings for Qsync utility" icon under "Action" for the device to be modified
3.
Modify its preference settings (including synchronization, policy and mail settings.)

To set a management password, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the NAS as an administrator and navigate to the "Management Settings" page in
Qsync Central.
2.
Select Central Configuration Mode.
3.
Tick "Enable your management password".
4.
Enter the password and click "Lock".
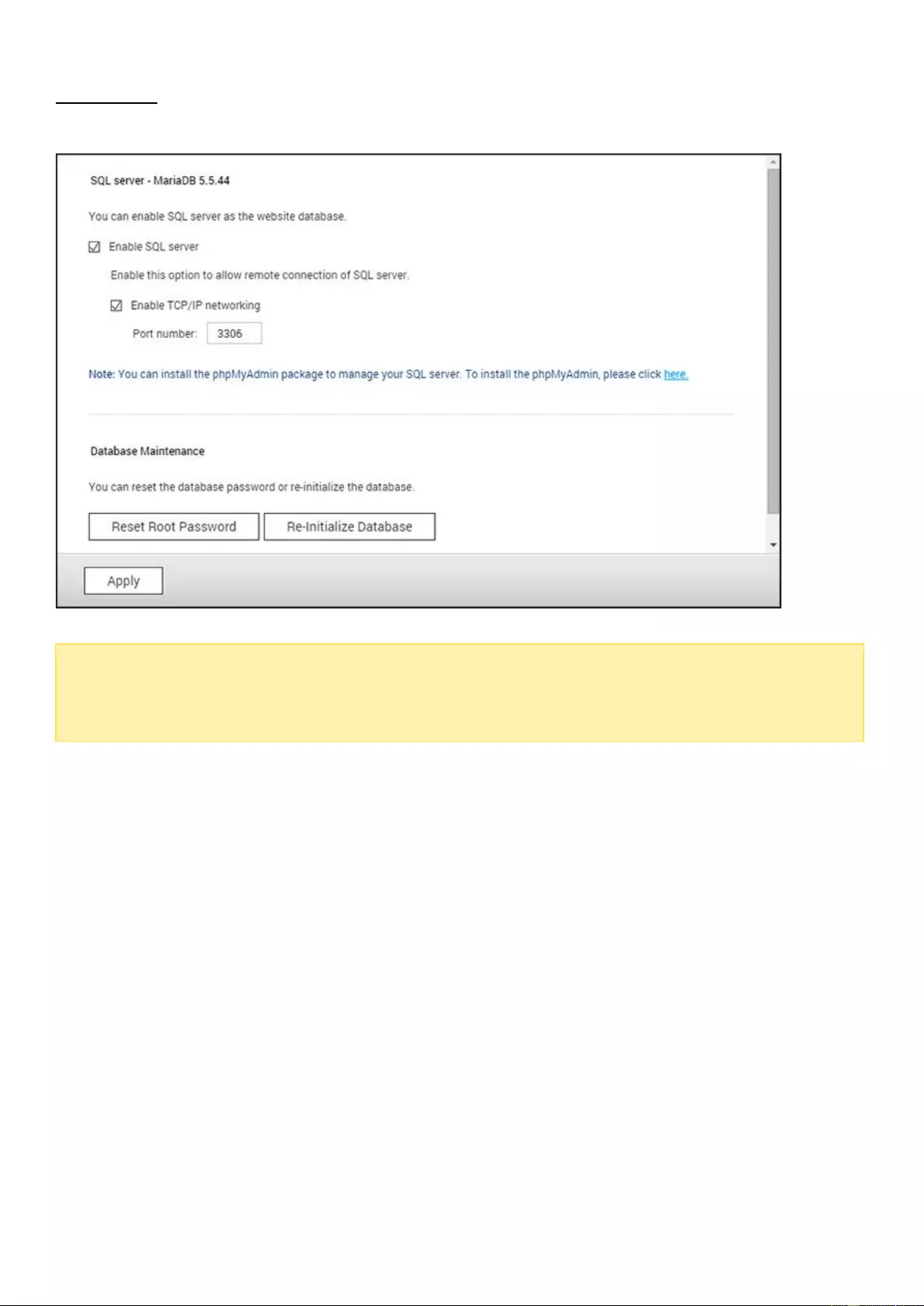
SQL Server
You can enable an SQL Server to be a website database.
Note:
For legacy ARM models (TS-x21, TS-x20, TS-x19, TS-x12 and TS-x10), MySQL will
still be used as the default SQL server. If you are using a legacy ARM model, you can still
install MariaDB from the App Center.
Enable TCP/IP Networking
You can enable this option to configure MySQL server of the NAS as a database server of
another web server in remote site through Internet connection. If this option is disabled,
your MySQL server will only be configured as a local database server for the web server of
the NAS. After enabling remote connection, assign a port for the remote connection service
of the MySQL server. The default port is 3306. After the first-time installation of the NAS, a
phpMyAdmin folder is created in the Qweb/Web network folder. You can enter http://NAS
IP/phpMyAdmin/ in the web browser to enter the phpMyAdmin page and manage the MySQL
database.
Database Maintenance
o
Reset root password: Reset the password of MySQL root as "admin".
o
Re-initialize database: Delete all the data on the MySQL database.

Note:
To use this feature on the TS-x39/509/809 series NAS, please update the system
firmware with the image file enclosed in the product CD or download the latest system
firmware from http://www.qnap.com.
Do not delete the phpMyAdmin folder. You can rename the folder but the link on the
MySQL server page will not be updated. To connect to the renamed folder, you can
enter the link http://NAS IP/renamed folder in the web browser.
The phpMyAdmin folder is created after the first-time installation. When you update the
firmware, the folder will remain unchanged.
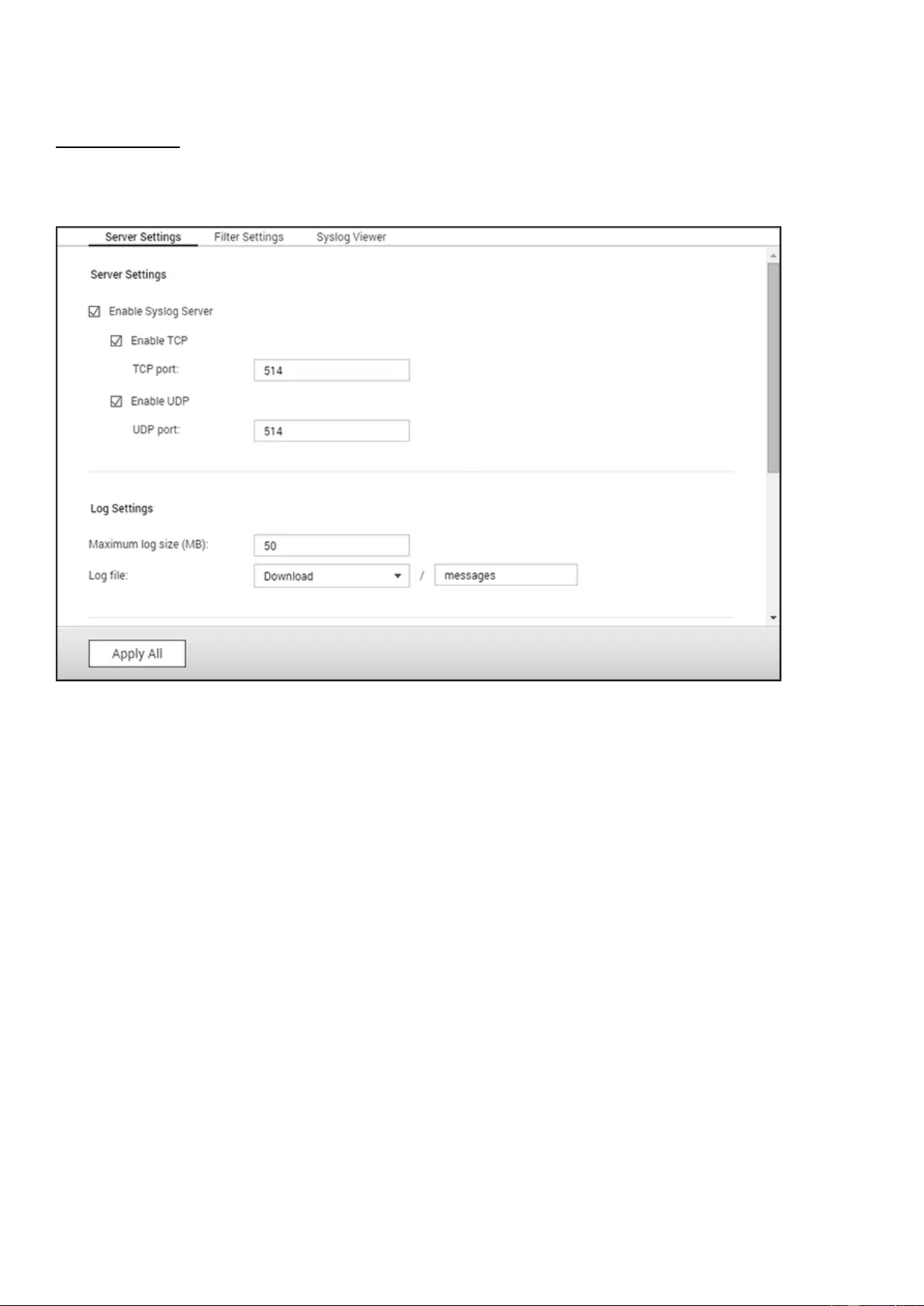
Syslog Server
Configure the NAS as a Syslog server, create Syslog filters and view available Syslog
messages on this page.
Server Settings
Server Settings:
To configure the NAS as a Syslog server and allow it to receive Syslog
messages from clients, enable Syslog Server. Select the protocols (TCP and/or UDP) the
NAS uses to receive Syslog messages. Specify the port numbers if necessary or use the
default port number 514. Click "Apply" to save the settings. After enabling the NAS as a
Syslog server, enter the NAS IP as the Syslog server IP on the Syslog clients to receive
Syslog messages from them.
Log Settings:
Specify the maximum log size (1-100 MB) of Syslog messages, the
location (NAS shared folder) where the logs will be saved, and the file name. Once the
logs have reached their maximum size, the log file will be automatically archived and
renamed with the archive date as MyLogFile_yyyy_mm_dd, for example
MyLogFile_2011_12_31. If multiple log files are archived on the same day, the file will be
named as MyLogFile_yyyy_mm_dd.[number]. For example, MyLogFile_2011_12_31.1,
MyLogFile_2011_12_31.2, and so on. Click "Apply" to save the settings.
Email Notification:
The NAS supports sending email alerts to up to 2 dedicated email
addresses (configured in "System Settings" > "Notification" > "Alert Notification") when
the severity of the received Syslog messages match the specified level. To use this
feature, configure the SMTP server settings in "System Settings" > "Notification" >
"SMTP Server". Next, enable email notification and select the severity level in
"Applications" > "Syslog Server" > "Server Settings". Click "Apply" to save the settings.
Severity
Level
(smallest
number the
highest)
Description
Emerg
0
Emergency: the system is unusable.
Alert emails will be sent when Syslog messages of levels
0-4 are received.
Alert
1
Alert: immediate action required.
Alert emails will be sent when Syslog messages of levels
1-4 are received.
Crit
2
Critical: critical conditions.
Alert emails will be sent when Syslog messages of levels
2-4 are received.
Err
3
Error: error conditions.
Alert emails will be sent when Syslog messages of levels
3-4 are received.
Warning
4
Warning: warning conditions.
Alert emails will be sent when Syslog messages of level 4
are received.
Filter Settings
This feature should only be operated by administrators who are familiar with Syslog filters.
Follow these steps to create Syslog filters for the NAS to receive Syslog messages that
match the criteria:
1.
Click "Add a Filter".
2.
Define the filter settings and click "Add". To edit the filters or to manually add filters,
click "Manual Edit" and modify the contents in the dialog. Click "Apply" to save the filter.
3.
The filters will be shown on the list. The NAS will only receive Syslog messages that
match the filters which are in use.
Button
Name
Description
Enable
Enable a filter
Disable
Disable a filter
Edit
Edit filter settings
Delete
Delete
Delete filters
Syslog Viewer
Use the Syslog viewer to view the available Syslog messages on the NAS. Select to view the
latest logs or the logs in a particular archived file. Log files can be accessed on the directory
configured in "Syslog Server" > "Server Settings" > "Log Settings".
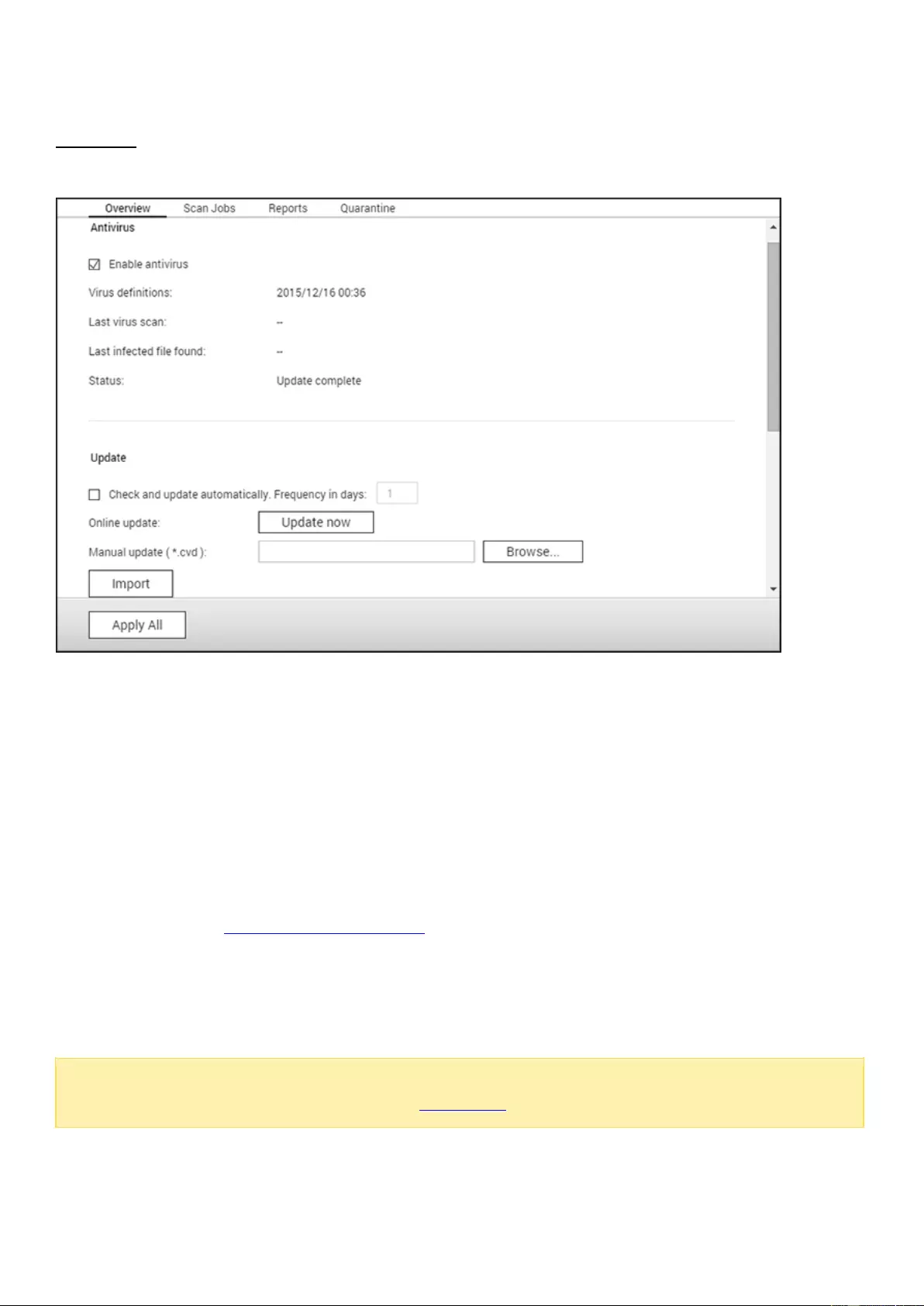
Antivirus
Configure antivirus features on this page.
Overview
Antivirus: Use the antivirus to scan the NAS manually or on recurring schedules. It will
delete, quarantine, or report files infected by viruses, malware, Trojans, and other
malicious threats. To use this feature, select "Enable antivirus" and click "Apply".
Update: Select "Check and update automatically" and specify the intervals in days to
automatically update the antivirus definitions. Click "Update Now" to check for new
antivirus definitions and to update if necessary. Users can also download updated
definitions from http://www.clamav.net and manually update the antivirus definitions.
The NAS must be connected to the Internet to use this feature.
Quarantine: View the quarantine information of the disk volumes on the NAS. For more
details, go to "Applications" > "Antivirus" > "Quarantine".
Note: The antivirus engine selector next to the "Enable antivirus" checkbox is only available after
an antivirus App has been installed from the App Center.

Scan Jobs
The NAS supports manual and scheduled scanning of all or specific shared folders. Up to 64
schedules can be created and up to 5 scan jobs can run concurrently. To create a scan job,
follow these steps.
1.
Go to "Applications" > "Antivirus" > "Scan Jobs". Click "Add a Scan Job".
2.
Enter the job name and select the shared folders to scan. To scan a specific shared folder,
select the share and click "Add".
3.
Multiple shared folders can be selected. To remove a shared folder, click the "Delete (X)"
button next to the share name and click "Next". Define the scan job schedule and click
"Next".
4.
Select to scan all the files in the shared folder(s) or quick scan to scan only potentially
dangerous files. Select "Exclude files or folders" and specify a file, a folder, or a file
extension to be excluded from the virus scan and click "Next". Separate each entry with
a space in the same line or enter one entry per line. For example:
o
/Public/testfile.txt
o
/Download
o
*.log
o
*.exe *.com
o
*.txt; click "Next".
5.
Enable other scan options and click "Next":
o
Specify the maximum file size (1-4096 MB) allowed for scanning.
o
Enable "Scan compressed files" to include these files in shared folders. Specify the
maximum amount of data (1-4096 MB) in a compressed file for scanning (if
applicable).
o
The maximum file size and maximum compressed file size may vary based on the NAS
model and available memory.
o
To scan MS Office and Mac Office files, RTF, PDF, and HTML files, select "Deep scan for
document files".
6.
Specify the actions to take when infected files are discovered and click "Finish" to create
the scan job.
o
Only report the virus: The virus scan reports are recorded under the "Reports" tab. No
actions will be taken for the infected files.
o
Move infected files to quarantine: The infected files will be quarantined and cannot be
accessed from their original shared folders. Users can view the virus scan reports
under the "Reports" tab and delete/restore the infected files under the "Quarantine"
tab.
o
Delete infected files automatically: Infected files will be deleted and cannot be
recovered.
o
To receive an alert email when an infected file is found or after scanning has
completed, configure the SMTP server settings in "System Settings" > "Notification" >
"SMTP Server".
7.
The scan job will run according to its schedule.
Button
Name
Description
Run
Run the scan job now.
Stop
Stop the scan job.
Edit
Edit the scan job settings.
View last
run log
Open the last virus scan summary.
Delete
Delete the scan job.
Reports
View or download the reports of the latest scan jobs on the NAS.
Button
Name
Description
Download
Download the virus scan report. The file can be opened by
any text editor.
Delete
Delete an entry on the list.
DOWNLOAD
Download
All
Download all the virus scan logs on the list as a zip file.
Report options
Specify the number of days (1-999) to retain the logs
Enable the option "Archive logs after expiration" and specify the shared folder to save the
logs to once the retention period has been reached. Click "Apply All" to save the changes.
Quarantine
This page shows the quarantined files on the NAS. Users can manually delete or restore
quarantined files, or restore and add the files to the exclude list.
Button
Name
Description
Delete
Delete an infected file. The file cannot be recovered.
Restore
Restore an infected file to its original shared folder.
Exclude List
Restore an infected file and add the file into the exclude
list (scan filter).
Restore
Selected
Files
Restore Selected
Files
Restore multiple files on the list.
Delete
Selected
Files
Delete Selected
Files
Delete multiple files on the list. The files cannot be
recovered.
Delete All
Files
Delete All Files
Delete all of the files on the list. The files cannot be
recovered.
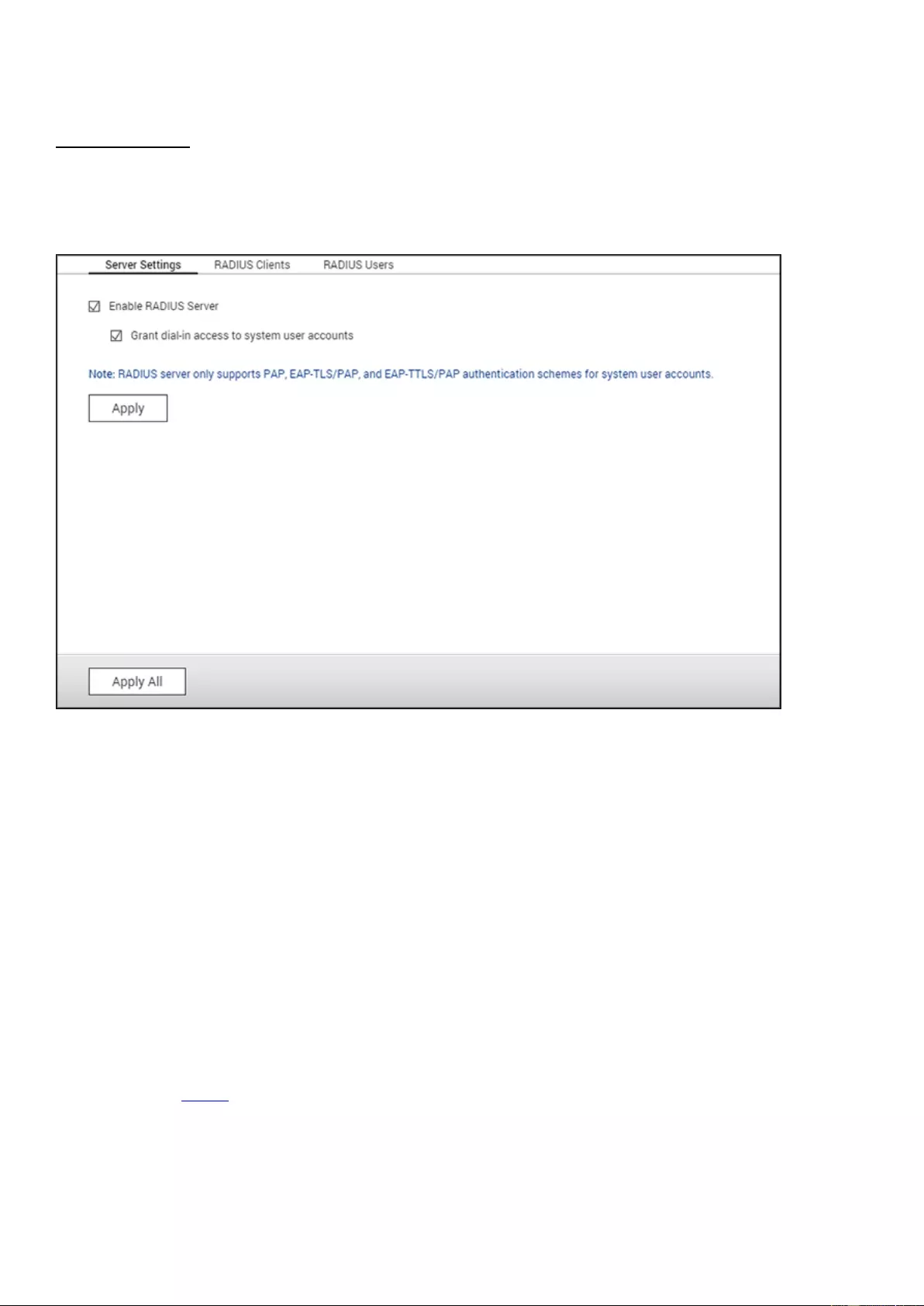
RADIUS Server
The NAS can be configured as a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) server
to provide centralized authentication, authorization, accounting management for computers
to connect and use a network service.
To use this feature, follow these steps:
1.
Enable RADIUS Server on the NAS in "Control Panel" > "Applications" > "RADIUS Server"
> "Server Settings". Click "Apply".
2.
Add RADIUS clients, such as Wi-Fi access points and VPN, on the NAS in "RADIUS
Server" > "RADIUS Clients". Up to 10 RADIUS clients are supported. Click "Create a
Client".
3.
Enter the client information and click "Apply".
4.
The clients are shown on the list.
5.
Create RADIUS users and their password in "Control Panel" > "Applications" > "RADIUS
Server" > "RADIUS Users". The users will be authenticated when trying to access the
network through RADIUS clients. The maximum number of RADIUS users the NAS
supports is the same as the maximum number of local NAS users supported. See the
chapter on Users for details. Click "Create a User".
1.
Enter the username and password. The username only supports letters (a-z and A-Z) and
numbers (0-9). The password must be 8-32 characters in length.

2.
Specify to grant dial-in access to local NAS users. Enable this option to allow local NAS
users to access network services via RADIUS clients using their NAS login name and
password.
Note:
The RADIUS server only supports PAP, EAP-TLS/PAP, and EAP-TTLS/PAP
authentication for local NAS user accounts.
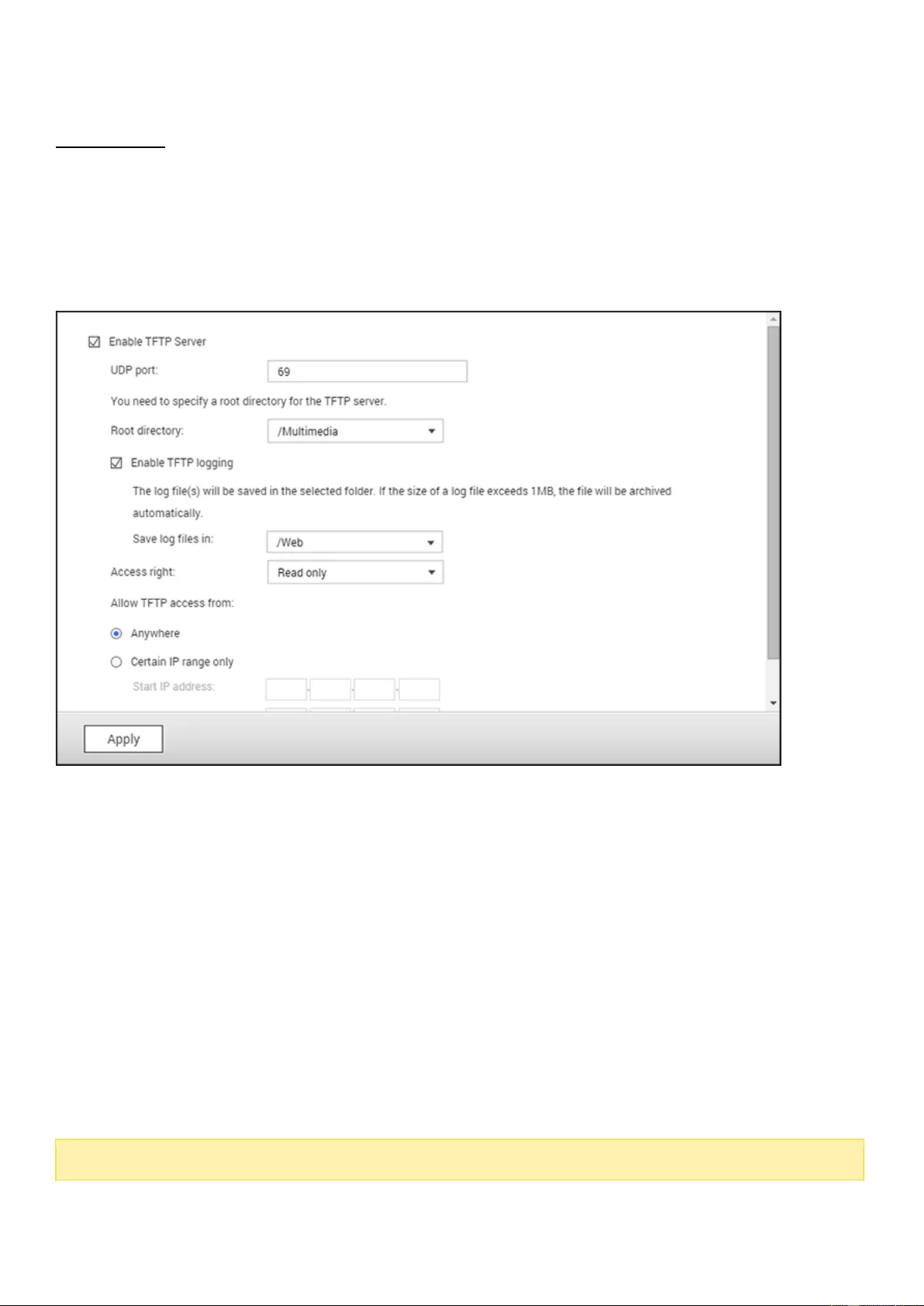
TFTP Server
Configure the NAS as a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server for configuration
management of network devices and remote network booting of computers for system
imaging or recovery. TFTP is a file transfer protocol with the functionality of a very basic
form of FTP. TFTP does not provide user authentication and cannot be connected to using a
standard FTP client.
Follow these steps to use this feature:
1.
Select "Enable TFTP Server".
2.
The default UDP port for file transfer is 69 and you should only change it if necessary.
3.
Specify a folder on the NAS as the root directory of the TFTP server.
4.
Enable TFTP Logging: Enable this option and specify the directory to save the TFTP log
file (opentftpd.log.) It is recommended to view the log file using Microsoft Excel or
WordPad on Windows OS or by TextEdit on Mac OS.
5.
Assign read only or full access to the clients.
6.
Restrict the TFTP client access by specifying the IP address range or select "Anywhere" to
allow any TFTP client access.
7.
Click "Apply".
Note:
To set up PXE with your NAS, please use a static IP for your NAS, enable its DHCP

QNAP Applications
QNAP provides applications to enhance your NAS experiences. For details on these applications, refer
to the following links:
Backup Station
myQNAPcloud_Service
File Station
Video Station
Photo Station
Music Station
Download Station
HybridDesk Station
App_Center
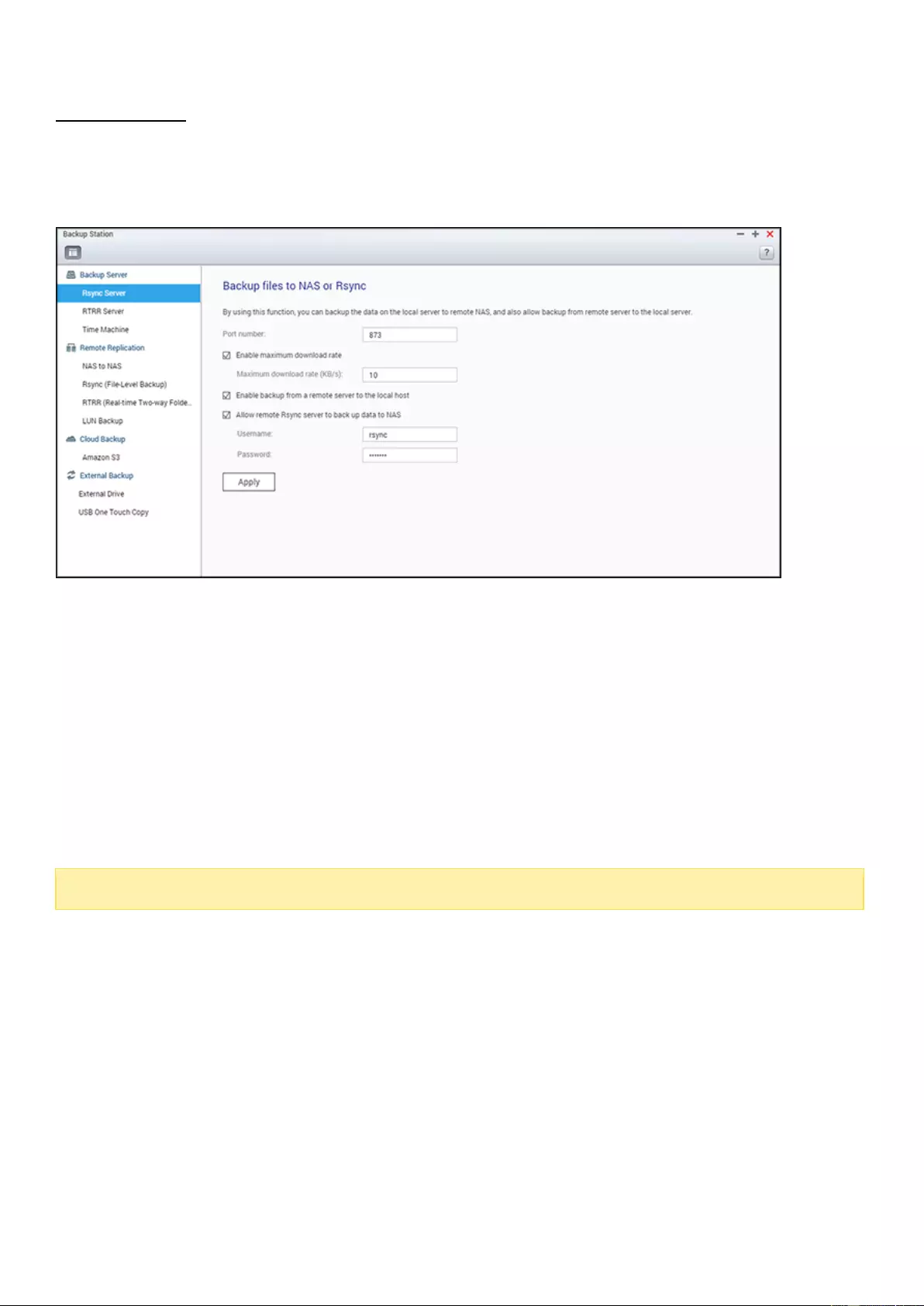
Backup Server
Rsync Server
Enable Rsync server to configure the NAS as a backup server for data backup from a remote
Rsync server or NAS server. The default port number for remote replication via Rsync is 873.
Specify the maximum download rate for bandwidth control. 0 means unlimited.
Enable backup from a remote server to the local host:
Select this option to allow
data backup from a remote server (NAS) to the local server (NAS).
Allow remote Rsync server to back up data to the NAS:
Select this option to allow
data backup from an Rsync server to the local server (NAS). Enter the username and
password to authenticate the Rsync server which attempts to back up data to the NAS.
Note:
You can only create up to 64 rsync jobs on the NAS.
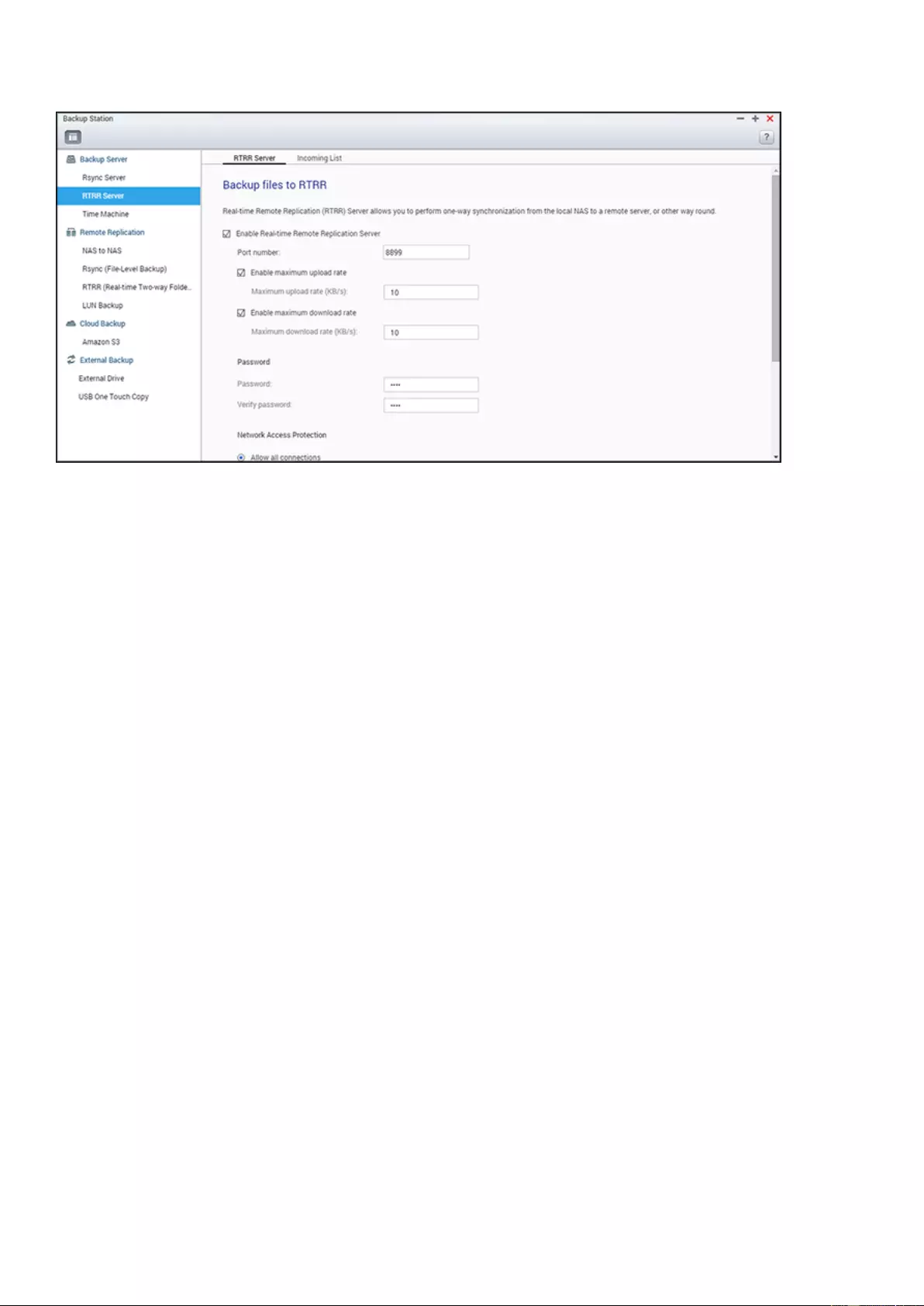
RTRR Server
To allow real-time or schedule data replication from a remote server to a local NAS, select
"Enable Real-time Remote Replication Server". You can specify the port number for remote
replication. The default port number is 8899. Specify the maximum upload and download
rate for bandwidth control. 0 means unlimited. To only allow authenticated access to back
up data to the local NAS, specify the access password. The client server will be prompted to
enter the password to back up data to the NAS via RTRR.
You can specify the IP addresses or host names which are allowed to access the NAS for
remote replication. Up to 10 rules can be configured. To allow all connections, select "Allow
all connections". To specify IP addresses or host names, select "Allow connections from the
list only" and click "Add".
Enter an IP address or specify a range of IP addresses by entering the IP and subnet mask.
Select the access right "Read Only" or "Read/Write". By selecting "Read/Write", the client
server is allowed to delete files on the local NAS. Click "Finish" to exit. After saving the
access rule, click "Apply" and the NAS will restart to apply the settings.
Check backup jobs from other NAS
You can check and manage backup jobs from other NAS that use the current NAS as a
target destination for their backup. To check backup jobs, click the "Incoming List" tab and
the details (including the job name, source NAS, destination NAS, job schedule and job
status) of the backup jobs will be shown in the list. You can also manage backup jobs in this
list. To do so, select backup jobs under "Incoming List" > choose to clear job records, open
the backup folder, or deny access of the backup jobs to your NAS.
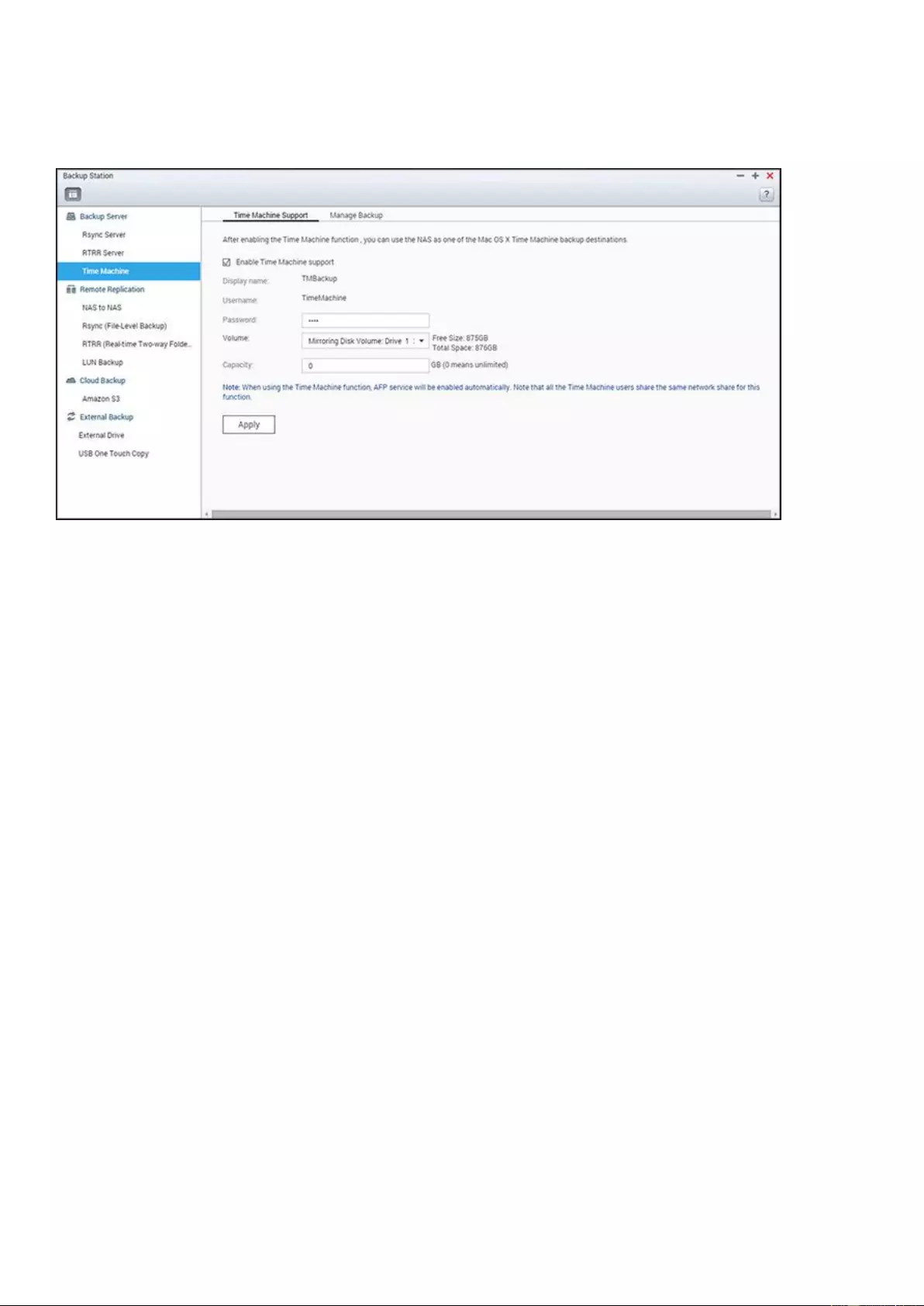
Time Machine
You can enable Time Machine support to use the NAS as a backup destination for Macs by
the Time Machine feature on OS X.
To use this function, follow these steps.
Configure the settings on the NAS:
1.
Go to “Main Menu” > “Backup Station” > “Backup Server” > “Time Machine” > “Time
Machine Support”. Select “Enable Time Machine support”.
2.
Enter the Time Machine password. The password is empty by default.
3.
Select a volume on the NAS as the backup destination.
4.
Enter the storage capacity that Time Machine backup is allowed to use. The maximum
value is 4095GB, 0 means unlimited.
5.
Click "Apply" to save the settings.
6.
Optional: Enable SMB 3.0 on Time Machine.
Note: Mac OS Sierra is required.
i.
Go to “Control Panel” > “Win/Mac/NFS” > “Microsoft Networking” > “Advanced
Options”. The Advanced Options window will launch.
ii.
Select “SMB 3.0” in “Highest SMB version”.
All the Time Machine users share the same shared folder for this function. Configure the
backup settings on Mac:
1.
Open Time Machine on your Mac and click "Select Backup Disk".
2.
Select the TMBackup on your NAS from the list and click "Use for Backup".
3.
Enter the username and password to login to the NAS and click "Connect".
o
Registered username: TimeMachine
o
Password: The password you have configured on the NAS. It is empty by default.

4.
Upon successful connection, the Time Machine is switched "ON". The available space for
backup is shown and the backup will start in 120 seconds.
The first backup may take more time according to the data size on the Mac. To recover data
to the Mac OS, please see a tutorial on http://www.apple.com.
Managing Backup
You can manage existing backups on this page.
Volume (drop down menu on top right side of the screen): Display Time Machine backup
tasks stored in the volume.
Name: The name of the Time Machine backup (the sparse bundle disk image which was
created by Time Machine.)
Size: Size of this Time Machine backup.
Date Modified: Last modified date of this Time Machine backup.
Delete: Delete the selected Time Machine backup.
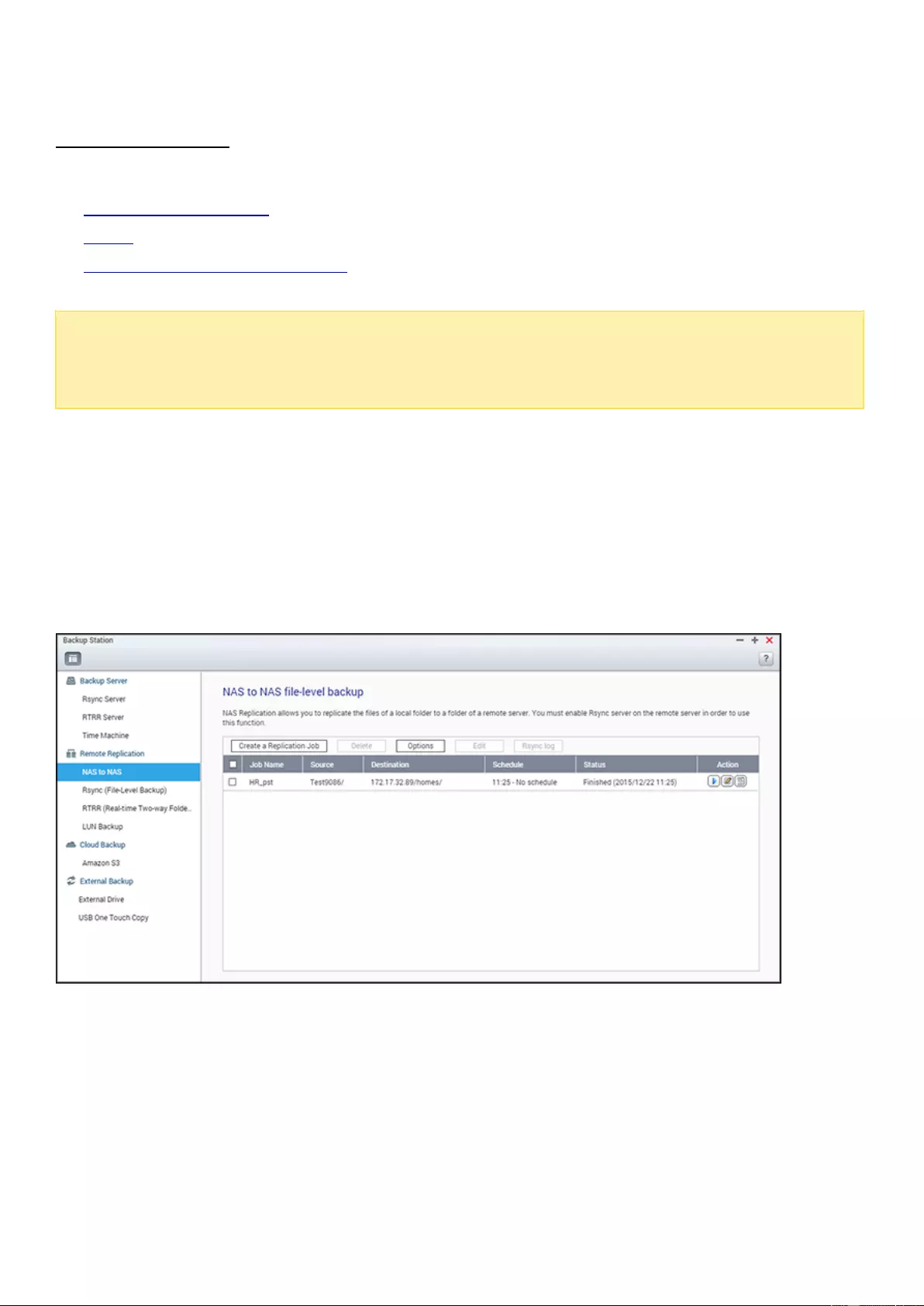
Remote Replication
This chapter covers the following topics:
NAS to NAS and Rsync
RTRR
Downloading Replication Job Logs
Note:
Starting from QTS 4.2, if a source storage pool supports snapshots, a snapshot will
be taken before an Rsync or RTRR backup job starts to ensure data consistency. Please
check that there is enough space reserved for taking snapshots before creating the job.
NAS to NAS and Rsync
The NAS data can be backed up to a remote NAS or Rsync server using Rsync remote replication.
For Rsync and NAS to NAS, there is no limitation for the maximum number of jobs. However, the
actual result will be limited and affected by the size of NAS memory and the file structure. Each job
supports 1 folder pair.
If the backup destination is a NAS, go to "Main Menu" > "Backup Station" > "Rsync Server" and
enable the remote NAS as an Rsync backup server.
1. To create a replication job, click "Create a Replication Job".
2. Click “Settings”.

3. Enter the IP address, port number, username and password to login to the remote server. The
default port number is 873. The login username must have read/write access to the remote
server and a sufficient quota limit on the server. Click "Test" to verify the connection, and then
click "Apply".
4. Specify the local folder by clicking the Source folder box. After expanding and locating the folder,
double click on it to set it as the directory where the data will be replicated from.
5. Specify the destination folder Destination folder box. Locate the folder in the folder tree and
double click on it to set it as the directory where the data will be replicated to. And, click "Add" to
add this pair of replication folders.
6. Click "Backup frequency" to configure the backup frequency. Select to immediately replicate the
data or to specify a backup schedule.
7. Click "Options" and then select one of the following.
o Enable encryption: Executes encrypted remote replication. Note that you must enable "Allow
SSH connection" in "Network Services > "Telnet/SSH" and specify the same port number for
SSH and encrypted remote replication.
o Activate file compression: Allows file compression during the data transfer process. This option
is recommended for low bandwidth environments or remote replication over WAN.
o Only copy files that differ from files at the destination: Reduces the time required for transfers
and minimizes the network traffic.
o Delete extra files on remote destination: Synchronizes the source data with the destination
data (one-way synchronization.) Extra files on the destination will be deleted. Source data
remains unchanged.
o Handle sparse files efficiently: A sparse file is a type of computer file that contains large blocks
of zero-byte data. Turning on this option may reduce the time required for remote replication.
o Replicate ACL and extended attributes: Keeps the information in extended attributes. Please
note that the destination host needs to enable the same ACL functions or join to the same
domain.
o Enable maximum transfer rate: Specifies the maximum transfer rate.
8. Click "Apply". If you selected "Execute backup immediately", the replication task will start at once.
Otherwise it will be performed according to your schedule. Note that the job is recursive. Do not
turn off the local NAS and the remote server when remote replication is running.
Note: For step 5, the order of selecting the source and destination folders can be changed. The
above is just an example.
Icon
Name
Description
Start
Start a replication job immediately.
Stop
Stop a running replication job.
View
View Rsync logs (replication results).
Edit
Edit a replication job.
Disable
Disable replication schedule.
Enable
Enable replication schedule.
To configure the timeout and retry settings of the replications jobs, click "Options".
Timeout (second): Specify a timeout value for each replication job. This is the maximum number
of seconds to wait until a replication job is cancelled if no data has been received.
Number of retries: Specify the number of times the NAS should try to execute a replication job if
it fails.
Retry intervals (second): Specify the number of seconds to wait in between each retry.
For example, if you entered 600 seconds for timeout, 3 retries, and 60 seconds for retry intervals, a
replication job will timeout in 600 seconds if no data is received. The NAS will wait for 60 seconds and
try to execute the job a second time. If the job timed out again, the NAS wait for another 60 seconds
and retry for a third and final time.
RTRR
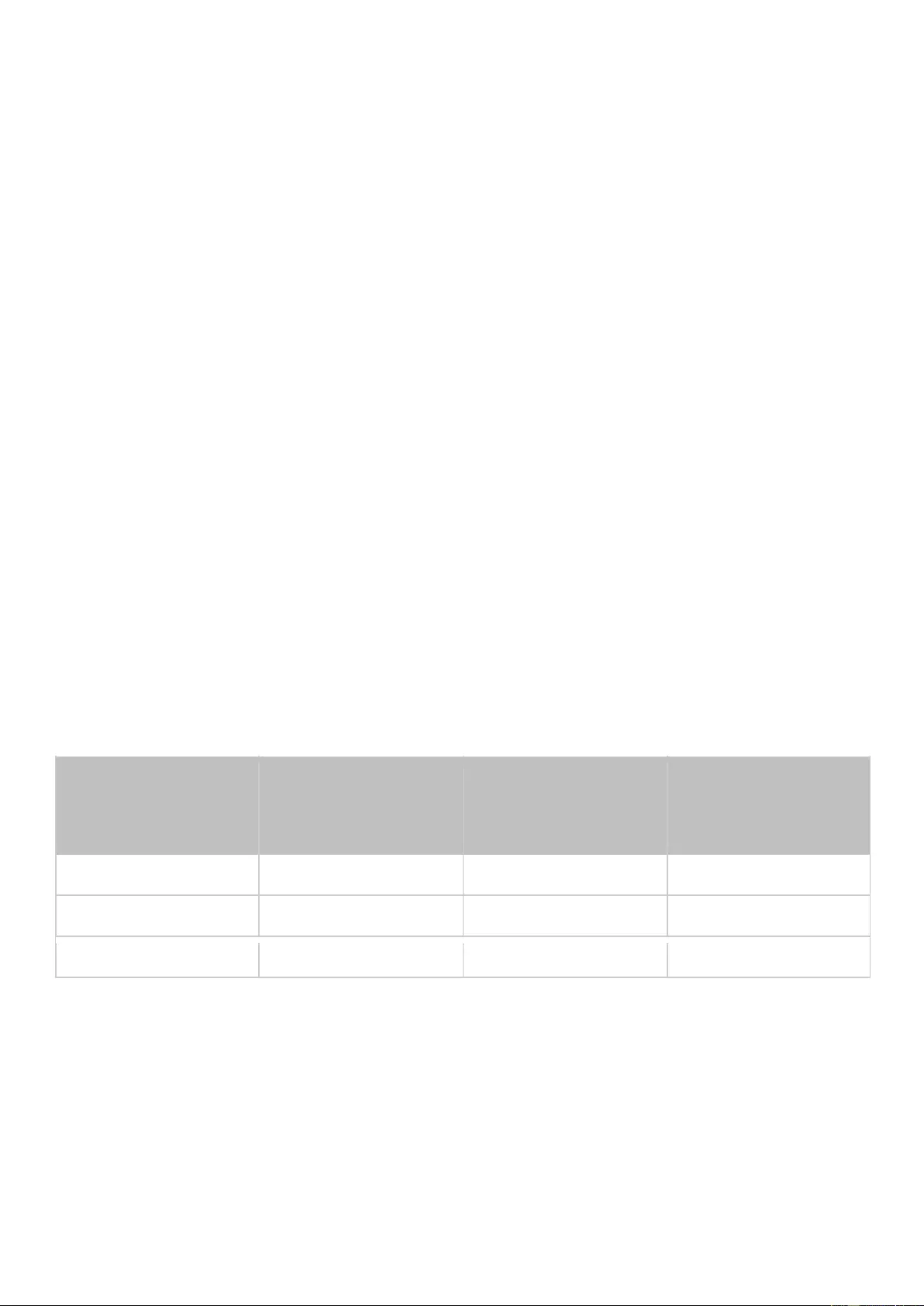
Real-time Remote Replication (RTRR) provides real-time or scheduled data replication and one-way
and two-way data synchronization between two locations (such as a local NAS and a remote NAS,
local NAS and an FTP server, or local NAS and an external drive, or replication between two local
folders.) In real-time mode, the source folder will be monitored and any files that are new, changed,
and renamed will be immediately replicated to the target folder. In scheduled mode, the source folder
will be replicated to the target folder according to the pre-defined schedule.
One way synchronization refers to data synchronization from the source to the destination, while
two-way synchronization means both the source and destination are synchronized after new files are
copied in either side or files stored on either side are changed or deleted.
If the backup destination is a NAS, the RTRR server ("Main Menu" > "Backup Station" > "RTRR
Server") or FTP service must first be enabled ("Main Menu" > "Control Panel" > "Network Services" >
"FTP") on the remote NAS.
For RTRR, the maximum number of jobs is 400. Each job supports up to 16 folder pairs.
Follow these steps to create a replication job.
1. Click "Create a Replication Job".
2. When the wizard shows up, click "Next".
3. Select the synchronization locations and click "Next". Make sure the destination device has been
formatted and folders have been created. Select the action to take (Backup, Synchronize, or
Restore), the synchronization locations, and click "Next". Make sure the destination device has
been formatted and folders have been created. For comparison between available actions and
their folder pairs, refer to the following table:
Direction
Action
Local folder to
remote folder
Local folder to local
folder/external
drive
Remote folder to
local folder
Backup
Synchronization
Restoration
Two synchronization options are available: one-way synchronization and two-way synchronization.
o For one-way synchronization, you can choose to:
Synchronize data from a local folder to a remote folder (NAS or FTP server)
Synchronize data from a remote folder (NAS or FTP server) to a local folder
Synchronize data from a local folder to another local folder or an external drive
o For two-way synchronization, you can choose to:
Synchronize data between the source and destination

4. Enter the IP address or host name. Select the server type (Windows Share (CIFS/SMB), FTP
server or NAS server with RTRR service enabled; For two-way synchronization, only the NAS
server is available.)
o Remote replication to FTP server: Specify the port number and if you want to enable FTP
with SSL/TLS (Explicit) for encrypted data transfer. If the FTP server is behind a firewall,
enable passive mode. Enter the username and password with read/write access to the server.
Click "Next".
o Remote replication to NAS with RTRR service: Enter the IP address of the RTRR
service-enabled server. Specify the connection port and select whether or not to enable secure
connection. The default port number for remote replication via RTRR is 8899. Enter the
password for RTRR connection. Click "Next".
o Remote replication to Windows Share (CIFS/SMB): Enter the IP address of the Windows
server. Specify the destination folder, username and password and click "Next".
5. Select the folder pair for data synchronization.
6. Each sync job supports up to 5 folder pairs. Select more folder pairs and click "Add". Click "Next".
7. Choose between real-time and scheduled synchronization. Real-time synchronization copies files
that are new, changed, and renamed from the source folder to the target folder as soon as the
changes are made after the first-time backup. Scheduled synchronization copies files from the
source folder to the target folder according to the pre-configured schedule. The options are:
o Replicate Now: Replicate data immediately.
o Periodically: Enter the time interval in hours and minutes that the backup should be executed.
The minimum time interval is 5 minutes.
o Hourly: Specify the minute when an hourly backup should be executed (for example, enter
"01" to execute backup on the first minute of every hour.)
o Daily: Specify the time when a daily backup should be executed (for example: 02:02 every
day.)
o Weekly: Select a day of the week and the time when a weekly backup should be executed.
o Monthly: Select a day of the month and the time when a monthly backup should be executed.
o Occurs once at: Specify the date and time the scheduled replication job will once be executed
and this replication job will be executed only once.
Note:
If a folder or its parent folder or child folder has been selected as the source or destination in a
folder pair of a replication job, you cannot select the folder as the source or destination of
another folder pair of the same job.
You can also create a folder as you select the folder pair. To do so, enter the folder name and
click the folder icon from the drop down list.
From QTS 4.1, RTRR can also back up the entire FTP site. To do so, select the root (/) from the
folder drop-down list. Please note that this is only the case when the source is a FTP site.
Two-way synchronization only supports scheduled data replication.
The expiration time setting is not available for "Replicate Now" and "Occurs once at" in Step 7.
Bandwidth Control in both RTRR and Rsync only works if both NAS servers of a replication job
(sender and receiver) are QNAP NAS and use firmware version 3.6 or above.
8. To configure synchronization policy, select "Configure policy and filter" and click "Next". Select
whether or not to enable the following options:
o Delete extra files: Delete extra files in the target folder. Deletions made on the source folder
will be repeated on the target folder. This option is not available for real-time synchronization.
o Detect sparse files: Select this option to ignore files of null data.
o Check file contents: Specify to examine file contents, date, size, and name to determine if two
files are identical. This option is not available for real-time synchronization.
o Compress files during transmissions: Specify whether or not the files should be compressed for
synchronization operations. Note that more CPU resources will be used.
o Ignore symbolic links: Select this option to ignore symbolic links in the pair folder.
o Replicate ACL and extended attributes: Select this option to keep the information in extended
attributes. Please note that the destination host needs to enable the same ACL functions or join
to the same domain.
o Filter system-generated temporary files: Filters temporary files created by system (including
thumbnails and @recycle) will be filtered.
o Timeout and retry settings: Specify the timeout period and retry settings if a synchronization
operation fails.
9. Specify the file size, file types to include/exclude, and file date/time to filter data synchronization.
Enter a job name.
o File size: Specify the minimum and maximum size of the files to be replicated.
o Last modified: Specify the number of days files are last modified for replication.
o Include file types: Specify the file types to be replicated.
o Exclude file types: Specify the file types to be excluded for replication.
o File date/time: Specify the date and time of the files to be replicated.
10. Click "Next".
11. Confirm the settings and click "Next".
12. Click "Finish" to exit the wizard.
Icon
Name
Description
Enable and Start
Enable connection to a remote server.
Start a replication job.
Stop
Stop connection to a remote server or external drive.
Stop
Stop a replication job.
View
View job status and logs; download logs.
Edit
Edit the connection settings of a remote server.
Edit the settings of a replication job.
Delete
Delete connection settings to a remote server.
Delete a replication job.
This button is available only after a replication job is stopped or the
connection to the remote server is stopped.
To edit the replication job properties, click "Options".
Under "Event Logs" you can enable "Download Detailed Logs" and specify the maximum file size of
log files. You can also set up sending email alerts when synchronization fails or completes. SMTP
server settings must be set up on the NAS before using email alerts ("System Settings" >
"Notification".)
Specify the replication policy in "Policy" and filter settings in "Filter". These will become the default
settings for all RTRR replication jobs.
Downloading Replication Job Logs
To view the status and logs of a replication job, click the "View" button under "Action". You can view
job logs or download them by clicking "Download Logs". Log files can be opened by Microsoft Excel or
text editors. This button is only available after you have enabled "Download Detailed Logs" in
"Options" > "Event Logs" and executed at least one replication job.
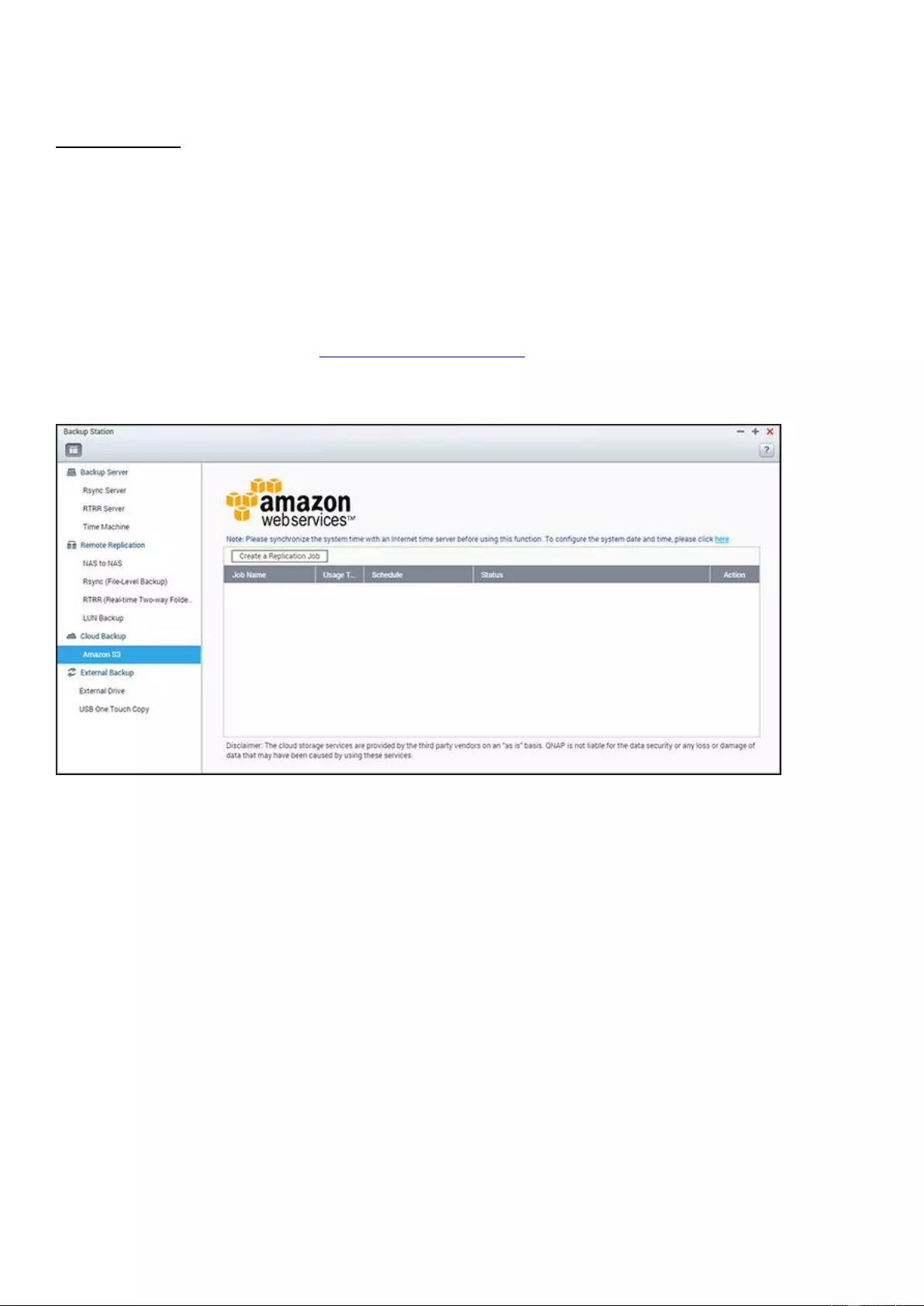
Cloud Backup
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is an online storage web service offered by AWS
(Amazon Web Services.) It provides a simple web service interface that can be used to store
and retrieve data from anywhere on the web. With Amazon S3, you can upload data from
your NAS to Amazon S3 or download the data from Amazon S3 to your NAS. You need to
register an AWS account from http://aws.amazon.com and pay for the service. After signing
up, you need to create at least one bucket (root folder) on Amazon S3 using an Amazon S3
application. We recommend the Mozilla Firefox add-on "S3Fox" for beginners.
After setting up the Amazon S3 account, follow these steps to back up or retrieve data from
Amazon S3 using the NAS.
1.
Click "Create a Replication Job".
2.
Enter the remote replication job name.
3.
Select the usage type: "Upload" or "Download" and enter other settings. A bucket is the
root directory on Amazon S3. You can test the connection to the remote host testing by
clicking "Test". Other settings are optional.
4.
Specify the local directory on the NAS for replication.
5.
Enter the replication schedule.
6.
Click "Finish". The replication job will be executed according to your schedule.
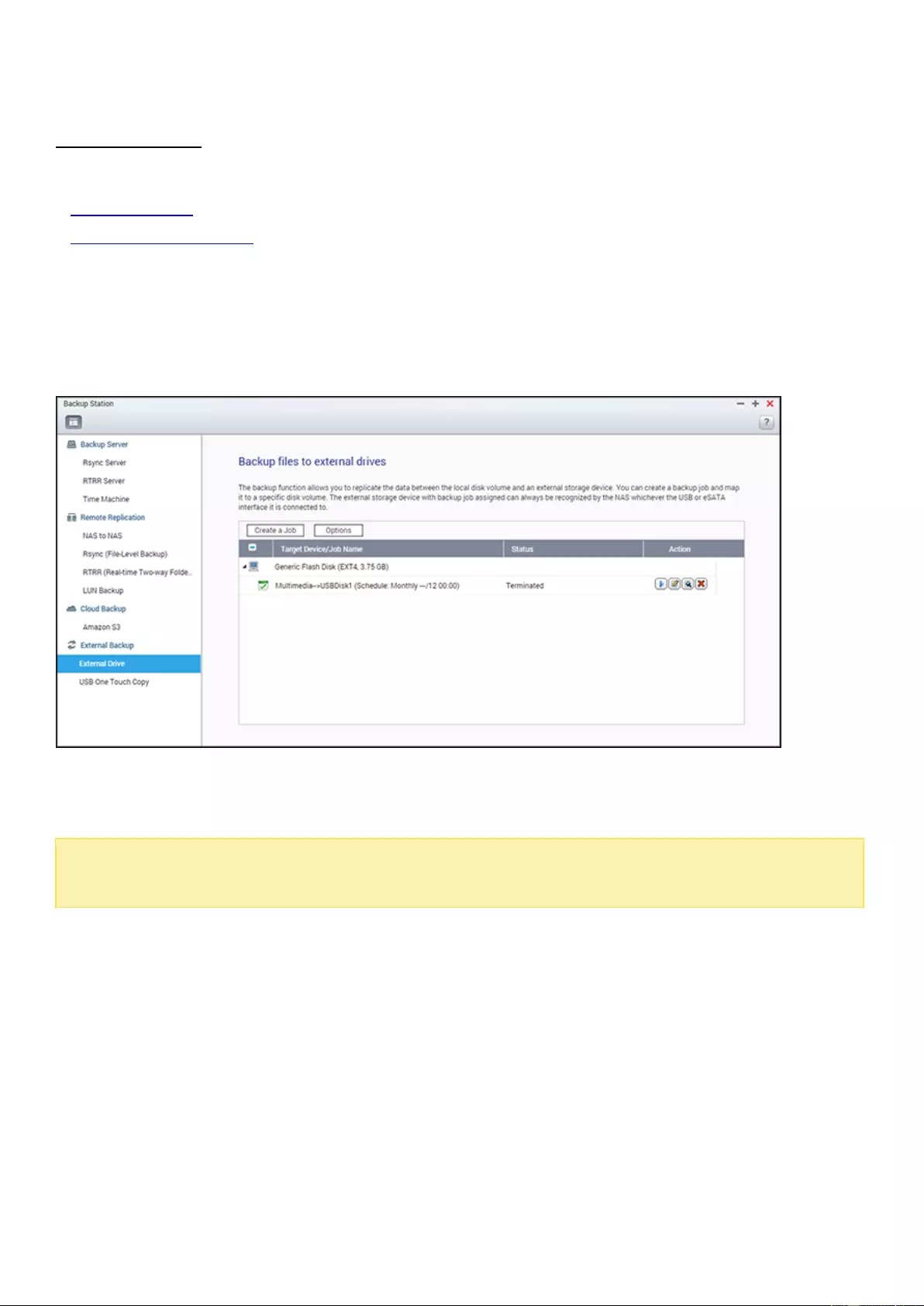
External Backup
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
External Drive
USB One Touch Copy
External Drive
The NAS supports real-time and scheduled data backup between internal disks volumes on
the NAS and external USB/eSATA storage devices.
To use this feature, follow these steps.
Note:
If an external storage device is encrypted by the NAS, make sure it is unlocked in
"External Device" > "External Storage" before creating any backup jobs.
1.
Connect one or more storage devices to the USB or eSATA (if available) interfaces of the
NAS.
2.
Click "Create a new job".
3.
When the wizard is shown, read the instructions carefully and click "Next".
4.
Select the backup locations.
a.
Select an external disk volume from the drop-down menu. The NAS supports EXT3,
EXT4, FAT, NTFS, and HFS+. The storage device's general information will be shown.
b.
Select "Map this backup job to the volume ID only" to map the backup job to this
particular external storage device. The NAS will recognize the device and automatically

execute the backup job according to the settings every time it is connected to the NAS
via any USB/eSATA interface.
c.
Select to back up the data from a local disk volume to the external storage or vice
versa.
d.
Click "Next".
5.
Select the source and destination folders for backup. Then click "Add". Up to 128 folder
pairs can be created. Click "Next".
Note:
Multiple partitions on the external storage device will be recognized as individual disk
volumes.
If a folder or its parent folder or child folder has been selected as the source or
destination in a folder pair of a backup job, the same folder cannot be selected as the
source or destination of another folder pair of the same backup job.
External Drive supports up to 100 jobs and each job supports up to 16 folder pairs.
6.
Choose between real-time and scheduled backup. Real-time backup copies files that are
new, changed, and renamed from the source folder to the target folder as soon as the
changes are made after the first-time backup. Scheduled backup copies files from the
source folder to the target folder according to the schedule. The options are:
o
Replicate Now: Copy the data immediately.
o
Periodically: Enter the time interval in hours and minutes that the backup job should
be executed. The minimum time interval is 5 minutes.
o
Hourly: Specify the minute when an hourly backup should be executed (for example,
enter "01" to execute backup on the first minute of every hour).
o
Daily: Specify the time when a daily backup should be executed (for example: 02:02
every day).
o
Weekly: Select a day of the week and the time when a weekly backup should be
executed.
o
Monthly: Select a day of the month and the time when a monthly backup should be
executed.
o
Auto-Backup: Execute data backup automatically every time the device is connected
and detected by the NAS.
7.
Choose to automatically eject the external drive after the job is finished.
8.
To configure the backup policy and filter settings, select "Configure policy and filter" and
click "Next". Select whether or not to enable the following options:
o
Delete extra files: Deletes extra files in the target folder. Deletions made on the source
folder will be repeated on the target folder. This option is not available for real-time
data backup.
o
Detect sparse files: Select this option to ignore files with null data.
o
Overwrite the file if the source file is newer or the file size is different.
o
Check file contents: Examine the file contents, date, size, and name to determine if
two files are identical. This option is not available for real-time data backup.
o
Ignore symbolic links: Select this option to ignore symbolic links in the pair folder.
9.
Create filters for the backup job.
o
File size: Specify the minimum and maximum sizes of the files to be copied.
o
File date/time: Specify the date and time of the files to be copied.
o
Include file types: Specify the file types to be copied.
o
Exclude file types: Specify the file types to be excluded from the data copy.
10.
Enter a name for the backup job. A job name supports up to 63 characters and cannot
start or end with a space.
11.
Confirm the settings and click "Next".
12.
Click "Finish" to exit the wizard.
13.
The backup job and the status will be shown on the list.
Button
Name
Description
Start
Start a backup job.
Stop
Stop a backup job.
Edit
Edit the backup job.
View /
Download
View the job status and logs.
Download the backup job logs.
Delete
Delete a backup job.
This button is only available after a backup job is stopped.
To disable a backup job's schedule, click "Edit" and select "Disabled" under "Settings" >
"Schedule Type" and click "OK".
Default Backup Job Settings
1.
To edit the default backup job properties, click "Options".
2.
Under "Event Logs" you can select to enable "Download Detailed Logs" and specify the
maximum file size of the log file. Select to send an email alert when a backup job fails or
completes. Note that the SMTP server settings must be properly set up in "System
Settings" > "Notification".
3.
Specify the backup policy in "Policy" and filter settings in "Filter". These will become the
default settings for all the backup jobs.
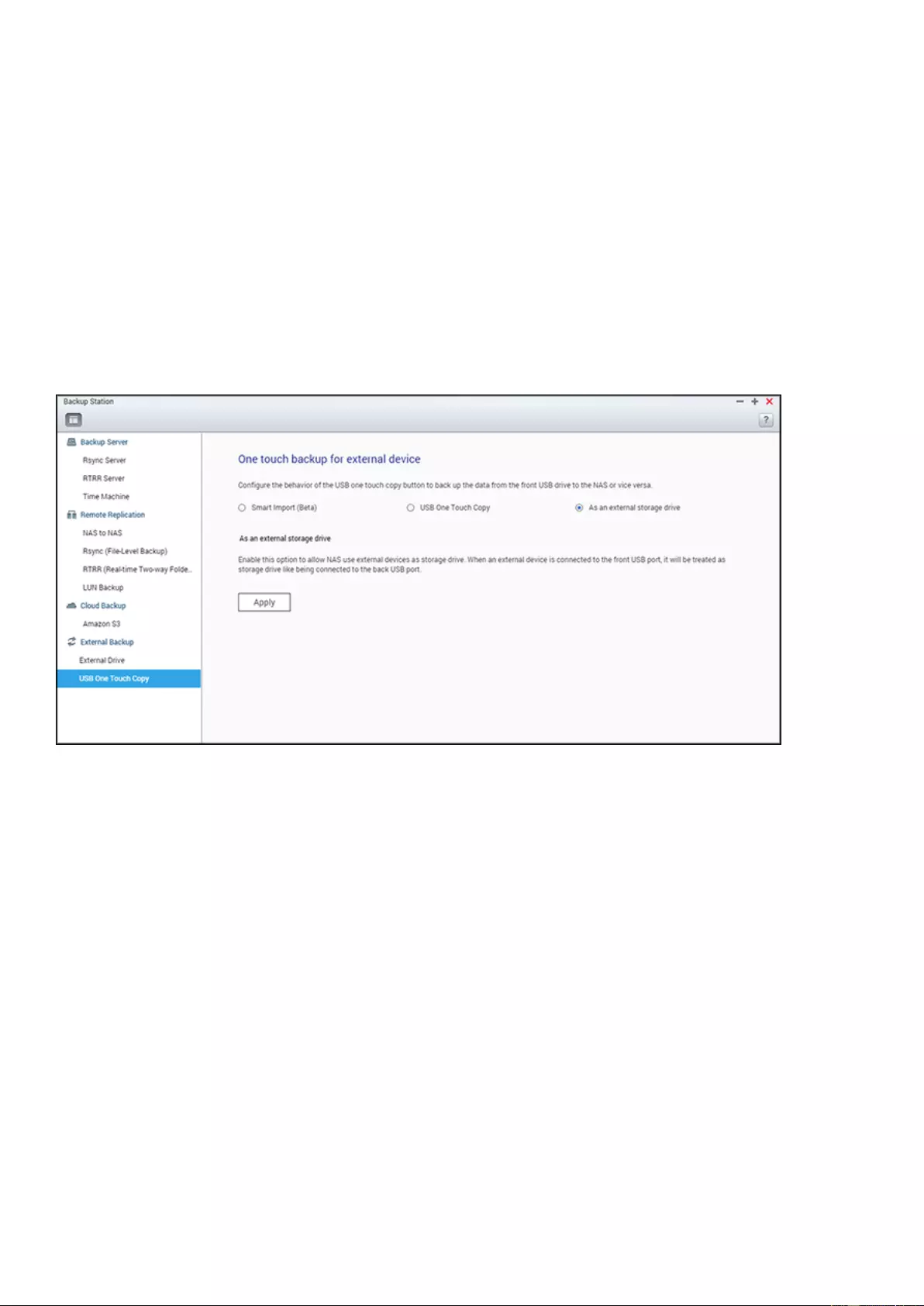
Download Backup Logs
1. To download a backup job's logs, make sure the option "Download Detailed Logs" is
enabled in "Options" > "Event Logs".
2. Click the "View / Download" button in "Action" column of a backup job.
3. Go to "Job Logs" and click "Download Logs". The log file can be opened by Microsoft
Excel or any text editor. This button is only available after you have enabled "Download
Detailed Logs" in "Options" > "Event Logs" and executed a backup job.
USB One Touch Copy
Enable the USB one touch copy button to back up data from USB storage connected to the
front-panel USB port to the NAS or vice versa.
This feature is not supported by the TS-809U-RP, TS-879U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP,
TS-1279U-RP, and TS-EC1279U-RP.
Smart Import (Beta)
When a USB device (such as a camera) is connected to the front USB port, all of the photos
and videos on the device will be automatically imported to the NAS without pressing the
"Copy" button. Imported files will be stored in "SmartImport," a newly-created folder, under
the default backup directory. During each import, only new photos and videos will be
imported to a new folder.
USB One Touch Copy
For customized backup configuration, please select "USB One Touch Copy."
Backup direction: From the front USB drive to the NAS or vice versa.
Backup method:
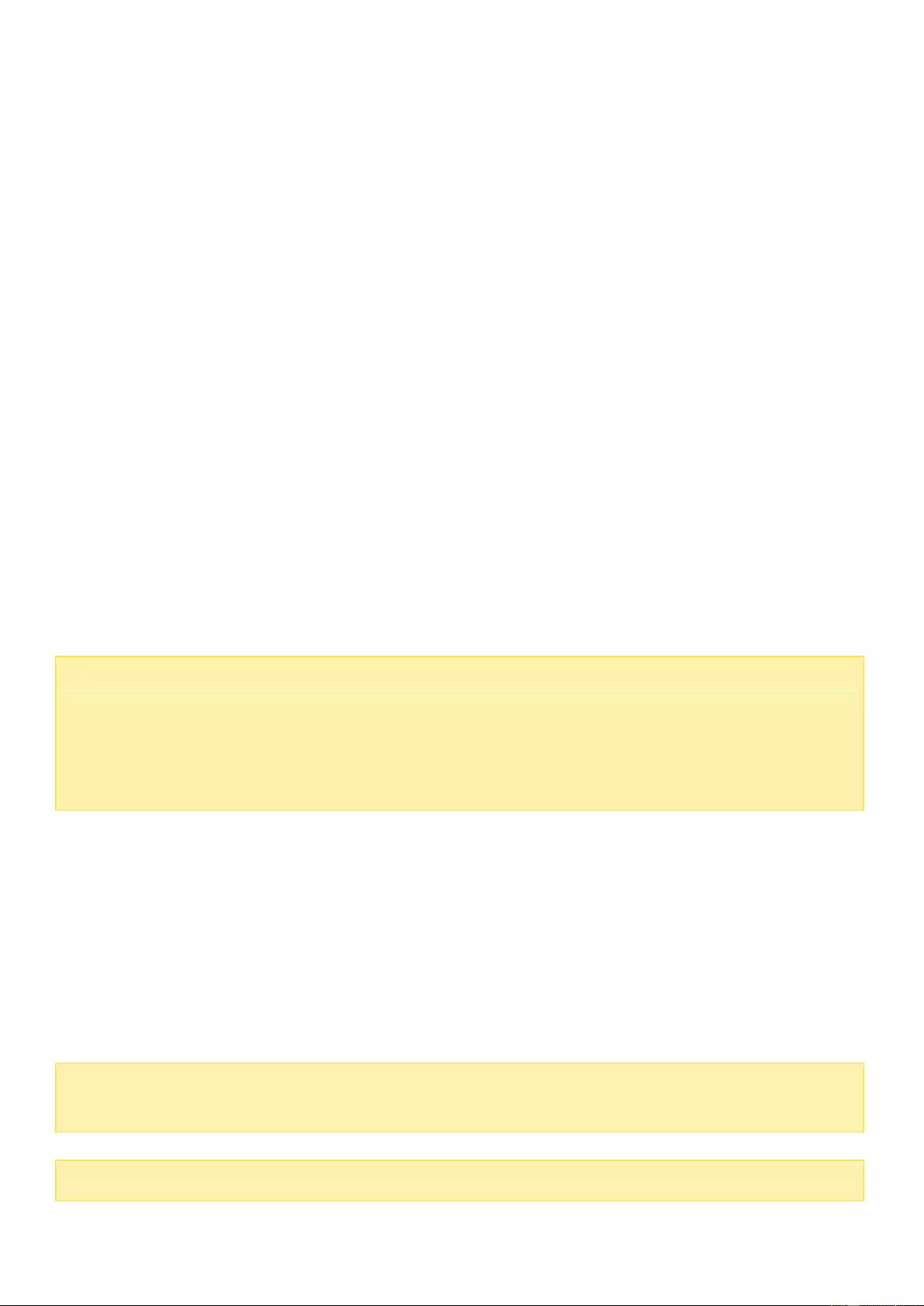
o
Create directory: A new directory will be created on the destination and the source
data will be copied to this directory. The new directory will be named as the backup
date (YYYYMMDD). If there are two or more backups on the same day, the directory
will be named with YYYYMMDD-1, YYYYMMDD-2... and so on.
o
Copy: Back up data to the destination share. If the same file exists, the destination file
will be overwritten.
o
Synchronize: Back up data to the destination share and clear the redundant files. If
the same file exists, the destination file will be overwritten.
Handle sparse files efficiently: A sparse file is a type of computer file that contains large
blocks of zero-byte data. Turn on this option may reduce the time required for backup.
Source and destination folders: Specify the folder pairs for backup and click "Add".
Maximum 9 folder pairs can be added.
Options: Click "Options" to set up notification of the backup jobs by email, SMS, or
instant messaging (IM).
Unmount the front USB drive manually: When enabled, users can press the Copy button
for about 8–10 seconds until the USB LED light turns off and remove the front USB drive
from the NAS.
Enable the alarm buzzer:
o
One short beep: Backup has started.
o
Two short beeps: The front USB drive is being unmounted.
Note:
If there are multiple partitions on the source storage device, a new folder will be
created for each partition on the destination as the backup folder. The backup folder will
be named with the backup date and the partition number (YYYYMMDD-1 for partition 1,
YYYYMMDD-2 for partition 2, etc). If the source storage device only contains one partition,
the backup folder will be named YYYYMMDD.
Data copy using front USB port
The NAS supports instant data copy backup from USB devices to the NAS or vice versa using
the one touch copy button. To use this function, follow these steps:
1.
Make sure a hard drive is installed and formatted on the NAS.
2.
Configure the behavior of the Copy button in "Backup Station" > "USB One Touch Copy".
3.
Connect the USB device to the front USB port of the NAS.
4.
Press the Copy button once. The data will be copied according to your settings.
Note:
Incremental backup is used for this feature. After the first data backup, the NAS
only copies the files changed since the last backup.
Caution:
Files are copied from the source to the destination.
Extra files in the

destination will be deleted. Files with the same names will be overwritten by the
source.
Source data will remain unchanged.
As an external storage drive
When an external device is connected to the front USB port, it will be identified as an
external storage drive connected to the port.
myQNAPcloud Service
To offer users with a better remote access experience, QNAP provides the myQNAPcloud
service, which helps users connect to their QNAP devices via the Internet when they are
outside of their LAN (local area network) environment. When you log in to your QNAP NAS
with your myQNAPcloud ID (QID), all the complex port forwarding settings on the router will
be automatically configured by CloudLink, an innovative remote access feature from QNAP.
CloudLink chooses the best connection for you according to your network environment and
resolves difficult issues such as the needs for the router to support UPnP (Universal Plug and
Play). After enabling CloudLink, you can access the files on your QNAP NAS via
myQNAPcloud website and share these files with your friends and contacts via download
links.
To use the myQNAPcloud service, click the myQNAPcloud shortcut from the NAS Desktop or
Main Menu.
This chapter includes two parts. The first part deals with the myQNAPcloud App you use on
the NAS and covers the following setup:
myQNAPcloud Wizard
Auto Router Configuration
My DDNS
Cloud Portal
CloudLink
Access Control
SSL Certificate
The second part of the chapter focuses on the following topic:

myQNAPcloud Portal (a portal for remote accessing and managing multiple NAS across
the Internet.)
myQNAPcloud Wizard
It is recommended to use the wizard the first time you use myQNAPcloud. Follow these
steps:
1.
Click "Get Started" to use the wizard.
2.
Click "Start".
3.
Fill out your myQNAPcloud ID(QID) and password. Click "Next" (or click "Create
myQNAPcloud account" to sign up a myQNAPcloud account if you don’t already have an
account.)
4.
Enter a name to register your NAS and click "Next".
5.
Select to enable the myQNAPcloud services (Auto Router Configuration, DDNS, Publish
Services and CloudLink) and set the level of access control. Click "Next".
6.
The wizard will configure your router automatically.
7.
Review the summary page and click "Finish" to complete the wizard.
Auto Router Configuration
In "Auto Router Configuration", you can enable/disable UPnP port forwarding. When enabled,
your NAS is accessible from the Internet via the UPnP router.
Note: If there is more than one router on the network, only the one which is set as the default
gateway of the NAS will be detected.
If no UPnP router is found on the local network, click "Rescan" and "Diagnostics" to check
the diagnostic logs. If the UPnP router is incompatible with the NAS, click the tooltip icon (!)
and then click "UPnP Router Compatibility Feedback..."
(http://www.qnap.com/go/compatibility_router.html) to contact technical support. Select
the NAS services to be allowed for remote access and click "Apply to Router". The NAS will
automatically configure the port forwarding on the UPnP router. You will then be able to
access NAS services from the Internet.
Note:
If more than two NAS are connected to one UPnP router, please specify a different port
for each NAS. If the router does not support UPnP, users must manually configure port
forwarding on the router. Please refer to these links:
Application notes: http://www.qnap.com/go/notes.html

FAQ: http://www.qnap.com/faq
UPnP router compatibility list: http://www.qnap.com/UPnP_Router_Compatibility_List
My DDNS
By enabling the myQNAPcloud DDNS service, you can connect to the network services on
your NAS by using your specified internet address. To change your myQNAPcloud DDNS
domain name, click the "here" link on the page. Your recent DDNS information will be shown
here and you can click the "Update" button to refresh the result.
Cloud Portal
With the Cloud Portal, web-based NAS services (including File Station, Web Server, Photo
Station, Music Station, Secure File Station, Secure Web Server, Secure Photo Station and
Secure Music Station) can be published to http://www.myqnapcloud.com. By enabling the
NAS services here, they will be opened for remote access even if they are not published.
Enable the myQNAPcloud DDNS service and the NAS will automatically notify the
myQNAPcloud server if the WAN IP address of the NAS has changed. To use the
myQNAPcloud service, make sure the NAS has been connected to a UPnP router and the
Internet.
Note:
The myQNAPcloud name of each QNAP NAS is unique. One myQNAPcloud name can
only be used for one NAS.
A registered myQNAPcloud name will expire in 120 days if your NAS remains offline
within that period. Once the name is expired, it will be released for registration by
other users.
For My DDNS, if the default port is not used, you will need to specify the port number
when accessing network services.
1.
In "Cloud Portal", web-based NAS services are shown. Select "Publish" to publish the NAS
services to the myQNAPcloud website. Select "Private" to hide published NAS services
from public access. The private services on the myQNAPcloud website are only visible to
specified users with the myQNAPcloud access code. If a disabled NAS service is published,
the service will be inaccessible even if the corresponding icon is shown on the
myQNAPcloud website (http://www.myQNAPcloud.com.)
2.
Set myQNAPcloud Access Code: Enter a 6-16 characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9 only) code that
NAS users will need to enter when they attempt to view private NAS services on the
myQNAPcloud website.
3.
Click "Add Users" and specify up to 9 local NAS users who are allowed to view private
NAS services published on the myQNAPcloud website.
4.
Select the connection method: the myQNAPcloud Connect (VPN) utility and/or
myQNAPcloud website.
5.
To send instructions to use the myQNAPcloud service to users via email, select the users
and click "Send Invitation".
6.
Enter the email address. Click "Send".
Note:
To use this function, the email server settings must be properly configured in
"System Settings" > "Notification" > "SMTP Server".
CloudLink
CloudLink is an innovative service provided by QNAP for remote access to your NAS over the
network without changing router settings - even if UPnP is not supported. After you enable
the service (click the switch on the blue banner to enable/disable the service) the direct
access link will be shown on the page and you can provide this link to your friends for them
to access to your NAS, using their mobile device or computer.
Access Control
This function allows you to control who can search for your device and access published NAS
services on the myQNAPcloud website or with mobile apps remotely via CloudLink. The
following options are available:
Public: Everyone can search for your device on the myQNAPcloud website and access
your public services.
Private: Only you can access your NAS remotely on the myQNAPcloud website or with
mobile apps via CloudLink.
Customized: You can specify who is allowed to access your device on the myQNAPcloud
website or with mobile apps by entering their registered accounts here. Or you can add
email addresses of your friends who are not currently myQNAPcloud members to send
them an invitation. To set access controls, first set the "Device access controls" to
"Customized", then click "Add" to add QID account holders.
SSL Certificate
myQNAPcloud SSL certificates are used to provide secured connections between the NAS
and web browsers, providing authorization and connection encryption. Encrypted
connections secure data and transactions. Before installing a myQNAPcloud certificate, an
error may occur when you try to connect to your NAS using HTTPS (for example:

https://nossl.myqnapcloud.com.) The data transmitted in the connection is not protected
against security threats. Unauthorized users have the potential to intercept data being sent
between a NAS and web browser.
Purchasing and installing a myQNAPcloud SSL certificate will bring you better protection
when connecting your NAS via DDNS.
Note:
A myQNAPcloud SSL certificate can only be used on NAS with QTS 4.2 or above.
Purchasing myQNAPcloud SSL certificates
1.
Sign into the myQNAPcloud website with your myQNAPcloud account and go to "SSL
Certificate" on the left side.
2.
Read and agree to the terms and conditions.
3.
Choose the number of certificates you want to buy (only one certificate can be used on
one device at a time) and complete the purchase and checkout process.
4.
Confirm the order and return to the "SSL Certificate" page on the myQNAPcloud website.
Installing myQNAPcloud SSL certificates
1.
Log into your NAS as an administrator and launch myQNAPcloud.
2.
Select "SSL Certificate" on the left panel > click "Download and install" to install the
certificate.
3.
Choose one of your purchased certificates from the list > click "Confirm".
To install the same certificate on another device, log into the NAS as an administrator, go to
myQNAPcloud > "SSL Certificate" and click "Release" to release the certificate. Then, follow
the same above steps to install that released myQNAPcloud SSL certificate on another
device.
On the myQNAPcloud portal site, you can review the transaction history in "SSL Certificate"
> "Transaction record". There are three transaction types:
Apply: The certificate has been installed.
Release: The certificate has been released from the device.
Reissue: The certificated has been reissued due to a DDNS name change.
Extend: The certificate’s validity has been extended.
The system will remind you of the expiration date within 30 days of expiration. Please renew
your certificate before it expires. To extend your certificate, log into the myQNAPcloud
website and go to "SSL Certificate" > "Certificate License".
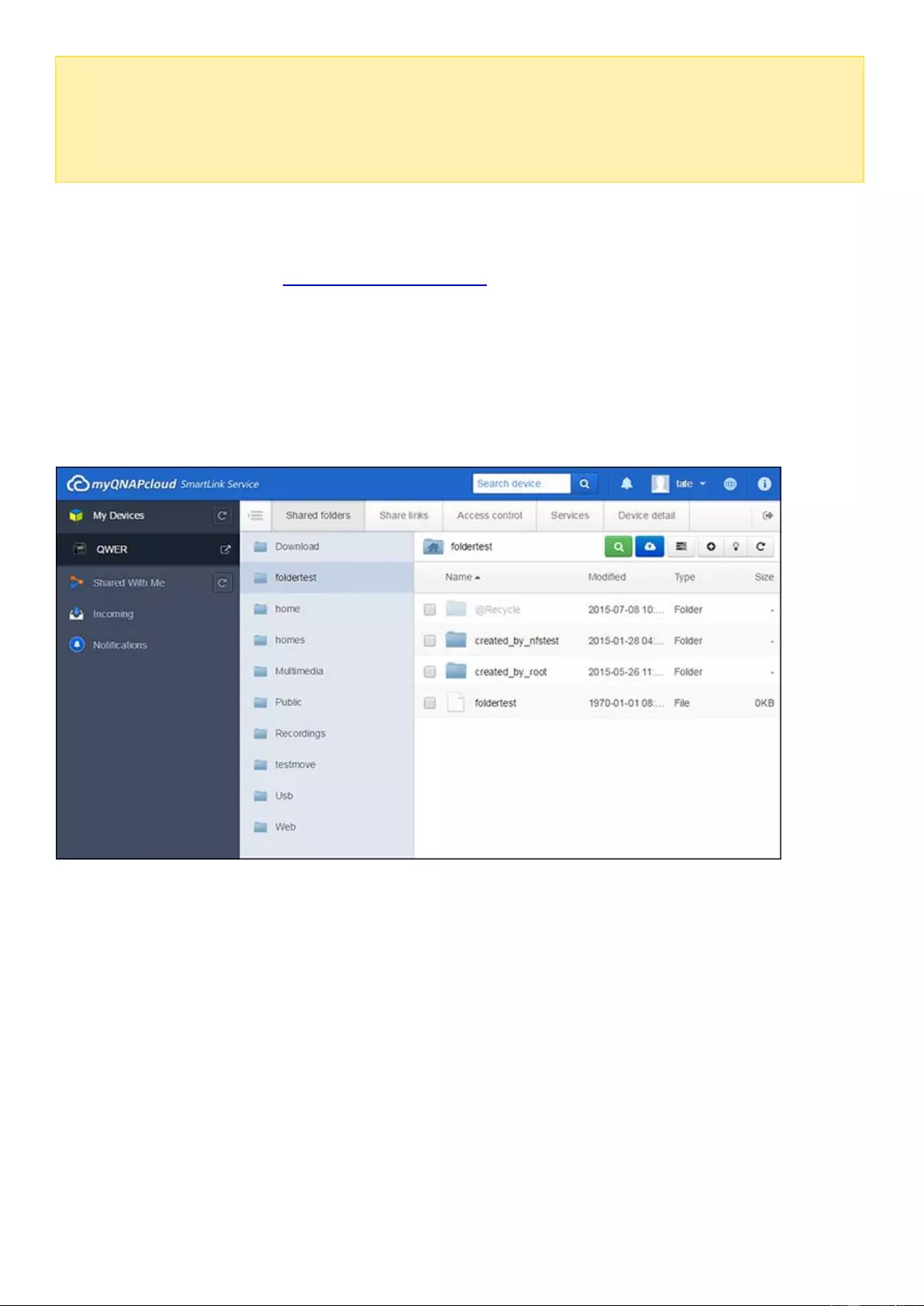
Note:
A myQNAPcloud SSL certificate can only be used on a NAS with QTS 4.2 or above.
To use this service, first download and install the myQNAPcloud SSL Certificate QPKG
from the App Center.
myQNAPcloud Portal
The myQNAPcloud portal (www.myqnapcloud.com) is an integrated web interface that allows
you to:
Manage and configure your myQNAPcloud account
Access NAS servers
Use published services from other NAS
Open links shared with you
Be notified of myQNAPcloud activities
You must configure your myQNAPcloud account using the myQNAPcloud App before logging
into the myQNAPcloud portal.
Managing and Configuring your myQNAPcloud Account
After launching myQNAPcloud or logging into your account on the myQNAPcloud website,
click on your nickname (next to the notification icon in the top-right corner) > "User Profile".
On this page, you can:
Update your profile
Change your myQNAPcloud login password
Add or edit your contact list
Check application logs

Monitor myQNAPcloud activities
Accessing NAS Servers via myQNAPcloud Website
After you log into the myQNAPcloud web portal, you will see a list of NAS servers under "My
Devices" on the left of the screen. Click on any of the NAS and there will be a list of
available actions to perform and you will be able to:
Perform basic file management tasks as in File Station
Manage share links
Configure access controls (check the above Access Control section for more details)
View and access published and private services (for private services, check the above
Cloud Portal section for more details)
Review and refresh device details or unregister the device
Note:
Once you unregister your device from myQNAPcloud, all of the services will be stopped.
You must install the CloudLink QPKG in the App Center before performing basic file
management tasks or managing share links on the myQNAPcloud portal site.
Using published Services from other NAS Servers via myQNAPcloud Website
The "Shared with me" feature allows you to quickly find your friend’s devices and access
their published NAS services. Follow these steps to add a device and access its published
services:
1.
Log into the myQNAPcloud web portal
2.
Type the device name of your friend’s device in the search box in top right corner.
3.
Click the "Add to Shared With Me" button (the gray heart icon)
4.
Click "Shared With Me" to the left of the screen.
5.
Click the newly added device from the list and the service you want to access.
6.
Choose an access method.
Sharing Files and Opening Links Shared with You via myQNAPcloud Website
If you share data to your friends who have registered on myQNAPcloud, they will see these
shared links here.
To share a file on the myQNAPcloud portal site, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the site
2.
Select a device under "My Devices" on the left panel
3.
Log into your device
4.
Choose the folders or files you want to share
5.
Click "Share" and fill out the required fields for the link (link name, domain name/IP,
expiration, and password protection) > "Next" > and finish link recipient and email
details > "Share".
To open a such link, first log into the myQNAPcloud website and click "Incoming" to the left
of the screen and you will see the links you can click to access them.
Note:
Before you use this feature, you must install the CloudLink QPKG in the App
Center.
Be notified for myQNAPcloud activities
The portal will notify you of myQNAPcloud activities. Examples of such activities are:
Your friends have added your device as a favorite
Your friends have created a shared link for you.
Your friends have shared their device with you.
To check myQNAPcloud activities, follow these steps:
1.
Log into the myQNAPcloud portal site
2.
Click "Notifications" on the left of the screen (or the notification icon next to the device
search box.)
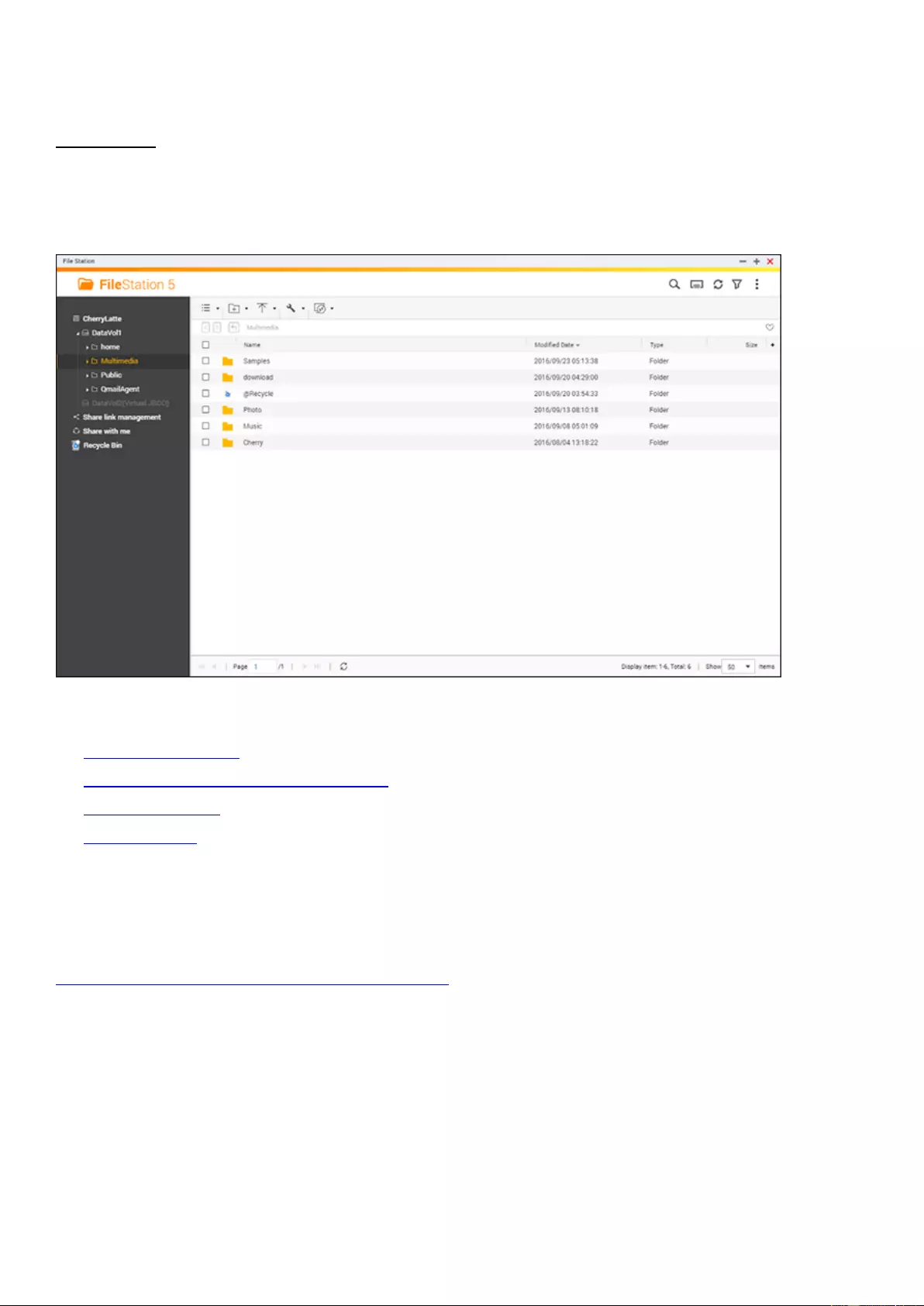
File Station
File Station is an online file management center. With the File Station, you can access the NAS across
the Internet, manage files using a web browser, quickly find files, play media files, set file and folder
permissions, and easily share your files and folders on the NAS.
Topics covered in this chapter:
Starting File Station
Familiarizing yourself with File Station
Using File Station
Remote Mount
Starting File Station
Launch File Station from the Main Menu/Desktop shortcut, or directly log into File Station by going to:
http://NAS_Name_or_IP/cgi-bin/filemanager.html.
Familiarizing yourself with File Station
Menu Bar

No.
Name
Description
1
Search
Search files by their name, file type (music, video, or
photo) or with advanced search.
2
Network Media Player
Stream videos, photos and music to compatible devices
in different rooms over your home network.
3
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
4
Smart File Filter
Filter files based on conditions set by users and the
conditions will apply to all folders.
5
More settings
Click to display the following:
Settings – Select any of the following, as required.
o Show files and folders of my PC: Set to show/hide
files and folders on the local PC. This allows you to
see the contents of your PC in File Station. This
feature is currently only available in Windows and
requires Java to be installed (you can download it
from http://java.com).
o Show hidden files on NAS: Set to show/hide hidden
files.
o Allow all users to create shared links.
o Support multimedia playback and thumbnail
display: If this option is checked, the file icon will
be displayed as thumbnails.
o Show Network Recycle Bin(s): Set to show/hide the
"@Recycle" folder.
o Only allow the admin and administrators group to
use "Share to NAS user".
o Only allow the admin and administrators group to
permanently delete files: Check this option and 1)
only administrators can permanently delete files

from File Station; and 2) files deleted by other
users will be moved to the Trash.
o Remote mount: Configure the groups of users
(administrators, administrators group, or specific
users) that are allowed to use the Remote Mount
feature.
Help – Open the File Station Help.
About – Display information about File Station.
6
Browsing Mode
Select a browsing mode:
List
Large icons
Medium icons
Small icons
7
Create folder
Create a folder/shared folder or share space with a user
(see the below Sharing NAS space section.)
8
Upload
Upload files or folders to the selected shared folder.
9
More Action
Bookmark the selected shared folder (and it will
appear under "Favorites" on the left panel).
Perform file or folder operations including open,
download, rename, copy/move, delete, cut, create
desktop shortcut, compress, transcode files/folders
(these options are only available when files and/or
folders are selected).
Check folder properties.
Review transcode information, background tasks (file
compression, file upload and moving files within the
NAS) or storage information.
10
Remote Mount
Create remote mounts
Check connection records and the current connection
status (see Remote Mount)
Tip:
If you are using Google Chrome, you can drag and drop files from your PC to File
Station. However, some computers may not be able to upload files that are larger than
1GB using this method due to their low performance. When this happens, please consider
uploading using File Station.
Note:
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support On-the-fly
Transcoding. You can consider transcoding them into different media formats if they
are desirable. For details on transcoding, see Transcode Management.
If your NAS supports transcoding, please install the CodexPack App before using this
function. The NAS will try to transcode to a suitable format for your device. If your NAS
does not support transcoding, the NAS will only output the original file format and the
seek function may not work properly. In this case, please make sure that your device is
compatible with the file format used by the video.
Some video formats may experience issues when streaming via DLNA, Apple TV or
Chromecast. If any of these issues arise during video playback, you can consider
transcoding your videos into universally-compatible media formats. For more details on
transcoding, please refer to the Transcode Management chapter.
Some media players do not support pausing during playback. If this happens, playback
will continue even if you use the pause feature.
For multimedia files transcoded using on-the-fly Transcoding, the time displayed on the
media player seek bar will become 00:00 while you forward or rewind the multimedia
files during playback.
The original photo files will be used for streaming if their thumbnails are not available.
Left Panel
Volume: Every shared folder and folder on the NAS is listed here. Depending on your NAS model,
the default shared folders are different and can include "Download", "homes", "Multimedia",
"Public", "Recordings", "USB" and "Web". You can click "+" next to a volume to create a shared
folder on the volume.
Local folders: Folders on your local PC are listed here. The Java JRE must be installed to use this
feature.
Favorites: Bookmarked folders are listed here.
Qsync: Folders or files synchronized from the Qsync service, and team folders are listed here.
Share link management: Links of files shared from the NAS are listed here.
Share with me: Files and folders that have been shared to you from other NAS users are listed
here.
Recycle Bin: Deleted files or folders can be found here. Right-click on deleted items in the recycle
bin to permanently delete or recover them.
Using File Station
Creating shared folders
To create a shared folder, click "Create folder" and select “Shared folder”. Specify the folder name,
folder description, disk volume, user access privileges, and advanced settings in the shared folder
creation dialog window and click "Create".
Subfolder operations
Right-click a subfolder and select one of the following actions:
Action
Description
Sort By
Sort all the subfolders and files within the page by name, modified
date, type, or size.
Create folder
Create a subfolder.
Copy/Paste
Copy a subfolder and paste it into another shared folder.
Share
Share the selected folder via email;
Publish the selected folder on social networks;
Set sharing details
Open
Enter the chosen subfolder.
Download
Compress and download the subfolder.
Rename
Rename the subfolder.
Copy to/Move to
Copy or move the subfolder to another location on the NAS.
Delete
Delete the subfolder.
Cut/Paste
Cut a subfolder and paste it to another shared folder.
Add to Transcode
Create transcode tasks for the files within the subfolder. If you
see certain resolution options disabled in the "Add to Transcode"
window, it means the selected video files have already been
transcoded into these resolutions.
Note: This feature is for the x86 series NAS only.
Cancel/Delete Transcoding
Cancel / Delete transcode tasks created for the subfolder
Transcode Information
Bring up the Transcode Task window for your review on transcode
tasks.
Create Shortcut to Desktop
Create a shortcut icon on the Desktop for the selected folder.
Add to Favorites
Bookmark the subfolder and it will appear under "Favorites" in the
left panel.
Compress(Zip)
Compress the subfolder.
Properties
Display the properties in a new window.
Tip:
For folders and files, the shortcut keys are provided for quick file and folder
operations. Available shortcut keys include:
Ctrl + C: Copy selected files/folders.
Ctrl + V: Paste selected files/folders.
Ctrl + X: Cut selected files/folders.
Ctrl + A: Select all files/folders.
Del: Delete selected files/folders.
F2: Rename the selected file/folder.
F5: Reload the current list.
File operations
Right-click a file and select one of the following actions:
Action
Description
Sort By
Sort all the subfolders and files within the page by name, modified
date, type, or size.
Copy/Paste
Copy a subfolder and paste it into another shared folder.
Share
Share selected files/folders via email, social network, by shared links,
or to other NAS users. Refer to the Sharing files section for more
details.
View in Office Online
Open Office files stored on the NAS using Office Online. The document
will be first uploaded to Office Online and opened in a new browser tab.
You must first install and sign in to the myQNAPcloud App to use this
function.
View in Google Docs
Open Office files stored on the NAS using Google Docs. The document
will be first uploaded to Office Online and opened in a new browser tab.
You must first install and sign in to the myQNAPcloud App to use this
function.
Open with Chrome
Extension
Preview and edit Microsoft Office files offline with a Chrome browser
extension (Chrome only and requires the "Office Editing for Docs,
Sheets & Slides" Chrome extension to be installed.)
Streaming to (Network
Stream multimedia files (videos, music, and photos) to compatible

Media Player)
devices in different rooms over your home network.
Play
Launch the Media Viewer and play the selected item.
Open
Open the file with a corresponding application on your PC. If no such
applications are available, the file will be downloaded instead.
Open with VLC
If the chosen file is a video file, it will be opened in the browser (the
VLC plug-in needs to be installed first.)
Download
Download the file. If the chosen file is a video that has been
transcoded, you can choose its resolution and download the file. If
multiple files are selected for download, they will be compressed before
the download.
Rename
Rename the file.
Copy to/Move to
Copy or move the file to another location on the NAS.
Delete
Delete the file.
Cut/Paste
Cut a file and paste it to another shared folder.
Add to Transcode
Create a transcode task for the file. Create transcode tasks for files
within the subfolder. If you see certain resolution options disabled in
the "Add to Transcode" window, it means the selected video files have
already been transcoded into these resolutions.
Note: This feature is for the x86 series NAS only.
Cancel/Delete
Transcoding
Cancel/Delete transcode task.
Transcode Information
Bring up the Transcode Task window for you to review transcode tasks.
Extract
Extract the compressed file.
Compress(Zip)
Compress the file.
Mount ISO
Mount the iso image as a shared folder on the left panel. After the file
is mounted, you can click that shared folder to access the content of
that iso image. To unmount an iso file, right click on the iso-mounted
shared folder in the left panel and choose "Unmount".
Properties
Display the properties in a new window.
Note:
For IE 8, the maximum size of a file that can be uploaded to the NAS by File Station is

2GB if the Java plug-in is not installed. We recommend using a modern web browser to
access File Station.
Due to limitations with Google Chrome, when using the upload folder function of the
File Station toolbar only folders that contain at least one file can be uploaded. You can
use drag & drop to circumvent this limitation.
For Chrome, multiple files and folders can be dragged & dropped into File Station to
upload them directly.
ARM-based NAS models do not support using Cyrillic characters for the name of a
subfolder in an ISO shared folder (the name will be incorrectly displayed if a subfolder
is created with a Cyrillic name.) Please name the subfolder with a different language
before an ISO file is created.
For Mac OSX, mounting a folder that contains the # character in the folder name
through WebDAV is not supported. Please rename the folder before mounting it if
necessary.
You can preview Microsoft Office files using File Station. To do so on Mac OSX,
mounting a folder that contains the # character in the folder name through WebDAV is
not supported. Please rename the folder before mounting it if necessary.
For "View in Office Online" and "View in Google Docs", please set your browser to allow
pop-ups and you will need a myQNAPcloud account. Supported file
formats: .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, and .pptx.
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. To enable Bonjour, go to
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support On-the-fly
Transcoding. You can consider transcoding them into different media formats if they
are desirable.
Playing media files
To play media files with File Station, double-click a multimedia file (photo, music and video files) and
the Media Viewer (a built-in media player on the NAS) plays the file. Use the following buttons to
control the Media Viewer:
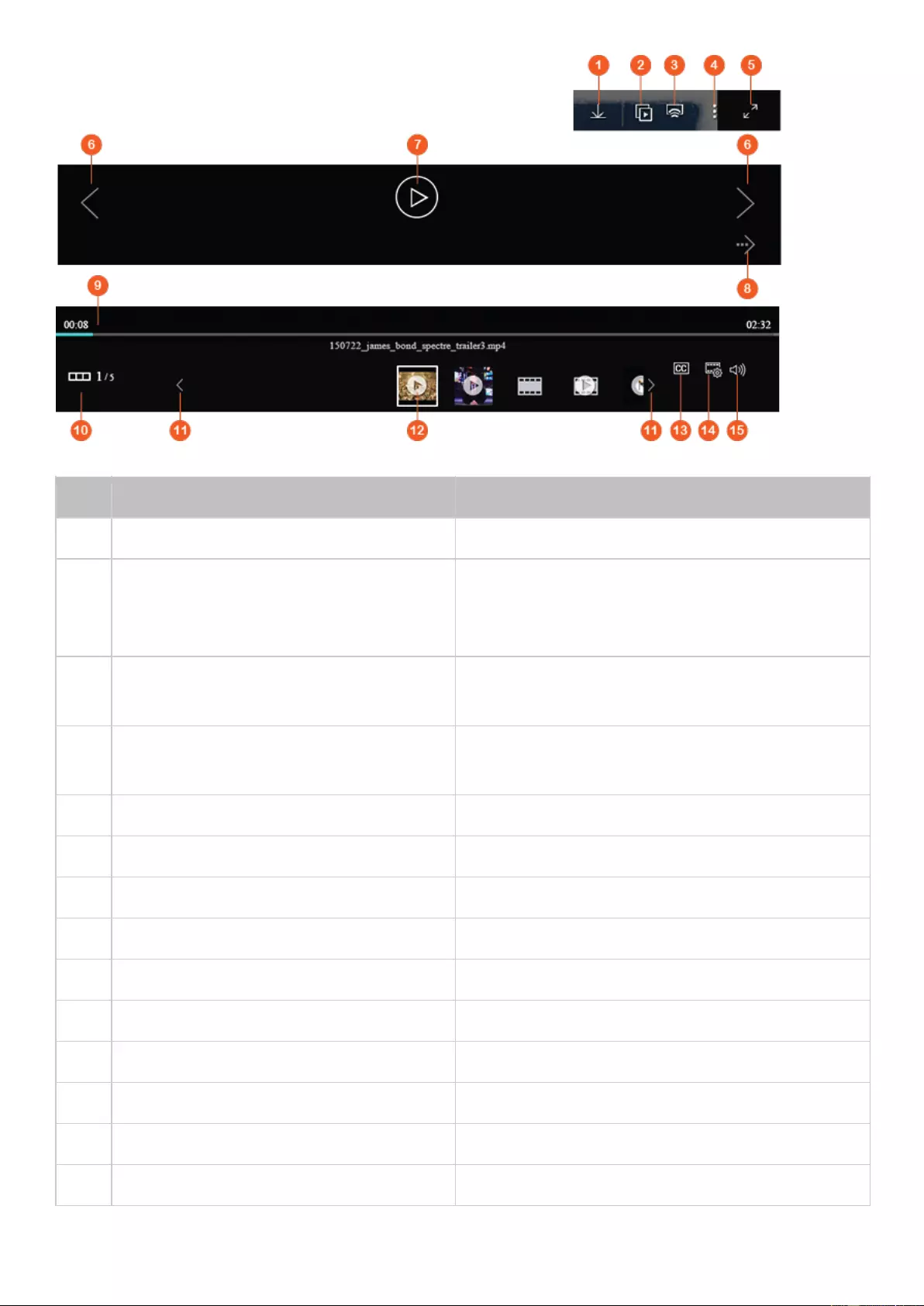
No
Name
Description
1
Download
Download the item.
2
Slideshow
Play all chosen photos as a slideshow. You can
adjust the speed and effect of the slideshow (for
photos only.)
3
Network Media Player
Stream videos to compatible devices in different
rooms over your home network.
4
More Action
Rotate the photo, set the photo as the QTS
wallpaper, or delete the photo/video.
5
Full Screen
Switch to full screen mode.
6
Previous Item/Next Item
Play the previous/next item.
7
Play/Pause (videos)
Play/Pause the video.
8
Play/Pause (photos)
Play/Pause photos as slideshow.
9
Seek Bar
Control the playback progress.
10
Show/Hide Preview Bar
Hide/show the preview bar.
11
Last Item/Next Item
Play the last/next item on the preview bar.
12
Preview Bar
Preview the items in queue.
13
Subtitle
Manage subtitles of the video.
14
Resolution
Change resolution and transcoding settings.

15
Volume
Adjust the volume.
Note:
The media viewer can be used to play photos and music files on all NAS models.
However, the feature to play videos using the media viewer is available on NAS models
that support hardware-accelerated transcoding.
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support On-the-fly
Transcoding. You can consider transcoding them into different media formats if they
are desirable. For details on transcoding, please refer to the Transcode Management
chapter.
Before enabling subtitles, please save the subtitles file (.srt format) in the same folder
as the video file and ensure its name is the same as the video file.
Finding your files/folders quickly
File Station supports smart searching for files, sub-folders, and folders on the NAS. You can search
for files or folders using all or part of the file/folder name, by file type, or by file extension. There are
two additional approaches you can quickly find your files: 1) advanced search and 2) smart file filter.
For the advanced search, first click the magnifier on the search bar and then select "Advanced
Search". Specify the search conditions (including name, size, date files are modified, location,
type and owner/group) and click "Search". The files that match these conditions in the current
folder will be listed.
For the smart file filter, click "Smart File Filter" in the Main Menu. Specify the filtering conditions
(including name, size, date files are modified, type and owner/group) and click "OK". Files that
match the conditions will be listed for the folder. This is the case even if you switch to a different
folder.
Note:
To search across all folders on the NAS, click the drop down list in "Location" and
select "…".
Setting file/folder level permission
You can set file or folder level permissions on the NAS using File Station. Right-click on a file/folder
and select "Properties".

If "Advanced Folder Permissions" is disabled in "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folder" > "Advanced
Permissions", the following settings will be shown. Define the Read, Write, and Execute access rights
for Owner, Group, and Others.
Owner: Owner of file or folder.
Group: Group owner of the file or folder.
Others: Any other (local or domain member) users who are not the owner or a member of the
group owner.
If a folder is selected, you can choose "Apply changes to folder(s), subfolder(s) and file(s)" to apply
the settings to all the files and subfolders within the selected folder. Click "OK" to confirm.
If the "Enable Advanced Folder Permissions" option is enabled in "Privilege Settings" > "Shared
Folder" > "Advanced Permissions", you will be able to specify the file and folder permissions by users
and user groups. Click + to do so.
To select users and user groups and specify the Read and Write permissions, click "Add".
To remove permissions on the list, select the users or user groups and click "–".
You can also define the file and folder owner by clicking the edit button next to the owner field. To do
this, select a user from the list or search for a username, and then, click "Set".
The following options are available for folder permission settings. It is recommended to configure
folder permissions and subfolder permissions in "Privilege Settings" > "Shared Folders".
Only the owner can delete the contents: When you apply this option to a folder, the first-level
subfolders and files can only be deleted by their owner.
Only admin can create files and folders: When you apply this option to a folder, only
administrators can create files or folders.
Apply changes to files and subfolders: Apply changed permissions settings except owner
protection to all the files and subfolders within the selected folder. The option "Only the owner can
delete the contents" will not be applied to subfolders.
Apply and replace all existing permissions of this folder, files, and subfolders: Select this option to
override all previously configured permissions of the selected folder and its files and subfolders
except owner protection. The option "Only the owner can delete the contents" will not be applied
to subfolders.
Sharing files
To share files on the NAS using File Station, right click on the files/folders and select "Share". There
are four sharing methods:
Via email: Enter the required fields (including mail server from NAS or local computer, sender,
recipient, subject, message, domain name/IP and link name), choose to include SSL (https://) in
the URL, and optionally set an expiration time and password in "More settings" . Finally, preview
the settings or directly share the file.
Note: To share files/folders using your own email account, your email account must be
set up in QTS Desktop > "Options" > "E-mail Account".

To social networks: Enter the required fields (including the social network to share the file, post
message, domain name/IP and link name) choose to include SSL (https://) in the URL, and
optionally set an expiration time and password in "More settings".
Create share links only (generate a link to provide on instant messengers or store for later use):
Complete required files (domain name/IP and link name), choose to include SSL (https://) in the
URL, and optionally set an expiration time and password in "More settings".
To NAS users: Choose to share with new or existing NAS users.
o For new NAS users, fill out account details (username and password), choose to allocate the
quote, choose whether to send an email notification (and fill out message subject and content),
set domain name/IP, link name and password for the link, decide whether to include SSL
(https://) in the URL, and optionally set an expiration time and password in "More settings" .
Click "Preview" to preview the message or "Share Now".
o For existing users, select existing user account(s), choose whether to send a notification email
to the user (and fill out message subject and content), set domain name/IP, link name and
password for the link, decide whether to include SSL (https://) in the URL, and optionally set
an expiration time and password in "More settings" . Click "Preview" to preview the message or
"Share Now".
For folders, there will be an option "Allow file upload to this folder" in the dialog window for all four
sharing options. This feature is only for administrators and can allow link recipients to upload files to
the folder pointed to by the link.
For the "To NAS users" option, if you choose to share with new NAS users, the system will create new
user accounts. Also, the email recipients (or users you share files with) can check files shared in File
Station > "Share with me" on the left panel after they log into the NAS.
Sharing NAS space
Administrators can allocate space to NAS users and specify a storage quota in File Station by
following these steps:
1. Click "Create" (the "+" icon) on the Menu Bar > "Share space with a user".
2. Complete the required fields in the "Create a User" page.
3. Enable the quota feature and set the quota size in "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > Quota"
if you have not already done so.
4. Specify the email (optional) and phone number (optional) for the user.
5. Choose to send an email notification to the newly-created user (optional), fill out the message
details (including mail server (from NAS or local computer), sender, recipient, subject, message,
domain name/IP and link name) and choose to include SSL (https://) in the URL.
6. Click "Create".

Remote Mount
The remote connection mount service allows you to easily manage files across local devices, external
devices, cloud services and remote devices from a single interface. You can easily carry out file
management tasks such as copying and moving from remote to local devices or vice versa. The
remote connection mount service supports multiple cloud services (such as Google Drive, Dropbox,
and OneDrive), and remote device network protocols (such as CIFS/SMB, FTP and WebDAV.), and
automatic searches for local devices.
Create remote mounts
1. Click "Remote Mount" > "Create remote mount".
2. Choose to connect to a remote storage via Auto Search, SMB/CIFS, FTP, or WebDAV.
3. Fill out the necessary details (including the protocol, codepage, hostname/IP, port,
username/password, destination folder, and connection name) and choose to enable support for
multimedia playback and thumbnail display (the system will generate thumbnails at the
destination. If the destination is another QNAP NAS, it must have QTS 4.2 or later installed).
4. Click "Create".
Check recent connection records
1. Click "Remote Mount" > "Connection record".
2. Review recent connection records and their details including the connection time, connection
name, protocol, Hostname/IP, port, account username, codepage and source path.
3. To sort the records, click on a header.
Check the current connection status
1. Click "Remote Mount" > "Current connection status".
2. Review the status of the current connections records and their details, including the owner,
connection time, protocol, Hostname/IP, port, source path, status and creation time.
3. To sort records, click on a header.
Notes:
The maximum number of remote mounts that can be created per NAS is 256.
To share links by email, the email server settings must be properly configured in
"System Settings" > "Notification" > "SMTP Server".
Up to 1000 sharing links are supported.
For best performance, use one of the following browsers: IE 9+, Firefox 3.6+, Safari
5+, or Chrome.
Do not close the browser before the file transfer process (upload or download) is
completed or the process will fail.
To use Remote Mount, you must install the Connect to Cloud Drive app from the App

Center before connecting to cloud services.
Using a remote mount is identical to an external device and ongoing tasks will be
terminated if the NAS is restarted or powered off.
Limitations of your cloud service account may affect what files can be transferred.
Please check the account details with your cloud service providers for more information
regarding what files can and cannot be transferred.
When transferring a large amount of files over CIFS/SMB using a remote mount, some
antivirus software may cause the transfer to fail. If you encounter this problem, please
temporarily disable your antivirus software and try again.
Due to performance limitations of web browsers and PCs, you may not be able to
upload a large amount of files in one task. If you encounter this problem, please
separate your upload task into multiple tasks or use another upload method.
Video Station
Video Station (5.0.0) is a video management application for you to organize videos on the NAS and
share them with friends and family on the Internet. With Video Station, you can classify videos into
home videos, movies, TV shows, or music videos for personal collections. You can also use smart
collections to automatically arrange videos that meet your own criteria to manage your files more
effectively. Video Station has many more features for you to explore.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Starting Video Station
Familiarizing yourself with Video Station
Using Video Station
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Starting Video Station
Install and enable Video Station from the App Center (for QTS 4.1 or later) and follow these steps:
1. Upload videos to a shared folder on the NAS: You can upload videos to the NAS in two different
ways: 1) Install Qfinder Pro on your PC or Mac, set up a network drive and upload files to your
preferred shared folders. For details on setting up a network drive, please refer to "Connecting to
NAS Shared Folders"; 2) Click "Upload" on the menu bar to upload videos from your local devices.
An “Upload” window will appear and prompt you to choose the destination folder and decide
whether to copy videos to a collection. If you want to create a new folder, click the “orange
folder” icon beside the destination folder, select a root folder, specify a name for the new folder,
and click the “orange folder with a plus” icon next to the text field. You can now find the new
folder in its root folder.

2. Launch Video Station from the Main Menu/Desktop shortcut, or directly log into Video Station by
going to: http://NAS_Name_or_IP/video/
Note:
Admin login credentials of Video Station is the same as that of the NAS administrator.
Video Station supports MP4 (H.264).
Familiarizing yourself with Video Station
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Viewing Mode
Choose to display items as icons or in a list.
2
Sort
Choose to sort videos by their title, date, duration, size,
rating, color label, and other attributes. You can also choose to
sort videos in ascending or descending order.
3
Filter
Choose to only show videos that meet certain criteria (genre,
year, director, cast). Please note that this button is only
available for “Movies” and “TV Show”.
4
Add to Transcode
Convert the selected video into a compatible file format for
streaming on your devices. You can choose your desired
resolution and sound track. To configure more advanced
transcoding settings, go to “Control Panel” > “Applications” >
“Multimedia Management”. Please note that transcoding
requires more computing resources and may affect the system
performance.
5
Upload
Upload files to an existing media folder or a new folder from
your local devices. You can also decide whether to copy the
uploaded videos to a collection.
6
Download
Download the selected video with or without subtitles.

7
Share
Share the selected collections or videos via email, social
networking websites, or sharing link. For more information,
see the below Sharing Collections section.
8
Multi-select
Select multiple items at the same time.
9
Select/Deselect All
Select or deselect all the items.
10
Create New Collection
Create a new collection. You have to specify its name, select
display mode, and configure its sharing settings.
11
Advanced Search
Search videos by their title, description, classification, source,
date, duration, size, rating, color label, and tag.
12
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
13
Background Task
Show tasks running in the background, such as uploading
tasks.
14
Settings
Configure settings, launch Quick Guide, and show the Help
instructions. For settings, there are four categories:
Classification settings: You can add new classifications, add
new media folders to the existing classifications, and decide
whether to show content in these folders in Video Station.
For movies and TV shows, you can also add more data
sources to enrich their information.
Search subtitles: Decide whether to search for subtitles
using Internet databases and the languages of subtitles. You
can also decide whether to log in to the database when
searching for subtitles.
Privilege: Decide whether to allow NAS users and domain
users to use on-the-fly transcoding and multi-zone
streaming.
Miscellaneous: Choose the default folder for uploading.
15
Multi-zone Streaming
Stream videos to the media devices on your network. You can
drag & drop videos to a device or its playlist to stream them to
this device.
Note:
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when you use multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour
in "Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 (H.264) files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support
on-the-fly transcoding. You may consider transcoding videos into different formats. For
more information about transcoding, please refer to the Transcode Management
chapter.
If your NAS supports transcoding, please install the CodexPack App before using this
function. Your NAS will try to transcode your video into a file format compatible with
your device. If your NAS does not support transcoding, it will only play videos in their
original file formats and the progress bar may not work properly. In this case, please
ensure that your device is compatible with the format of the video.
Some video formats may encounter issues when streamed via DLNA, Apple TV or
Chromecast. If any of these issues arise during video playback, you may consider
transcoding your videos into a universal file format that is compatible with most
devices. For more information about transcoding, please refer to the Transcode
Management chapter.
Some media players do not support pausing during playback. In this case, playback will
continue even if you use “Pause”.
Left Panel
Shared Videos: List all the videos in shared folders on the NAS (except videos in the "/home" and
"Qsync" folders) and all videos are only visible to authorized users.
Private Collection: List all videos located in the "/home" folder, and those multimedia files can
only be viewed by the user.
Qsync: List videos synchronized by the Qsync service.
Video Collection: List all virtual collections. All entries listed under a collection are only links to the
physical files. This can effectively save your NAS storage space, as you can keep only one copy of
videos even though you put videos in several collections of different themes. For more information
about collections, please refer to the Using Video Station section.
Smart Collection: List all smart collections. Smart collections only contain videos that meet your
own criteria, such as Home Videos, Movies, TV Shows and Music Videos. For more information
about smart collections, please refer to the Using Video Station section.
Shared Center: Show the sharing history of your videos. You can check the name, link, expiration
date, and summary of each entry or share these videos again.
Trash Can: All deleted videos can be found here and can be restored or permanently deleted. Only
deleted files (and not virtual links) will appear in the trash can.
Note:
The "/home" folder can only be accessed by its owner and NAS administrators. Private
or personal videos should only be stored in your "/home" folder.
For media folder configuration, refer to the Multimedia Management chapter. For user

setup and configuration, refer to the User section in the Privilege Settings chapter.
If uploaded videos do not appear in Video Station, scan them using Media Library. For
more information, please refer to the Multimedia Management chapter.
Using Video Station
Creating and managing collections and smart collections.
There are two ways to create a collection:
1. Click “Video Collection” on the left panel and then click “Create New Collection” on the menu bar.
2. Right click a video, select Copy to Collection”, specify a name for the new collection in the text
field, and then click the “orange folder with a plus” button next to the field.
When you create a collection, you have to specify its name, choose its display mode, and decide
whether to share it with other users. You can right click a collection to play, download, remove,
rename, share, or configure this collection.
To create a smart collection, click "Smart Collection" on the left panel and then click “Create New
Collection” on the menu bar. You have to specify its name, choose its display mode, decide whether
to share it with other users, and specify the search criteria, including classification, rating, color label,
tag, date, resolution, and duration. You can right click a smart collection to play, download, remove,
rename, share, or configure this smart collection.
Sharing collections
As you create a collection, you can decide whether to share it with other NAS users or with the public,
or even not to share it at all. You can also set the valid period on the collection creation page. If a
collection is shared with the public, you can right click the collection and select "Email" to email it,
"Publish" to publish it on social networking websites, or "Sharing Links" to generate and paste the
sharing link to your blog, forum, or instant messengers. You can still edit the content of the collection
after sharing, and the updated content will be presented when viewers click the link. You can also
share a number of videos as you do with collections. To do so, select multiple videos and either click
“Share” on the menu bar or right click these videos and select “Share”. Your friends can log into
Video Station with the link provided to them to watch videos from shared collections. To check the
sharing history of your shared videos, click “Shared Center”.
Note:
To share files or folders using your own email account, ensure that you set up your
email account in QTS Desktop > "Options" > "E-mail Account".
Video Operations
Right click on a video and choose to perform an action from the table.

Operation
Description
Play
Play the selected video.
Open with Browser
Play the selected video in a new browser tab. Please note that if your
browser does not support the file format, it will download the video
instead.
Streaming To
Stream the selected video to the media devices on your network.
Download
Download the selected video with or without subtitles.
Share
Share the selected video via email, social networking websites, and
sharing link.
Copy to Collection
Copy the video to a collection.
Add to Transcode
Stream videos to the media devices on your network.
Delete
Delete the selected video.
Information
View and modify the detailed information of the selected video,
including title, color label, rating, classification, tag, and description.
For movies and TV shows, you can also see the introduction from
online databases.
Note:
Only videos classified as “Movies” or “TV Shows” can access the information provided
by online databases. You can right click a video to change its classification.
Information about movies or TV shows is retrieved from online databases according to
its English title. If you find the information incorrect, modify the video’s English name
and retrieve the information again.
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 (H.264) video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support
On-the-fly Transcoding. You may consider transcoding them into formats compatible
with your media devices.
Finding your videos quickly
To quickly locate videos, you can rate or classify them. To do so, right click videos and then tag, rate,
or color label them. After videos are tagged, rated, or color labeled, you can find them by their rating,
color label, or tag in “Advanced Search” on the menu bar.
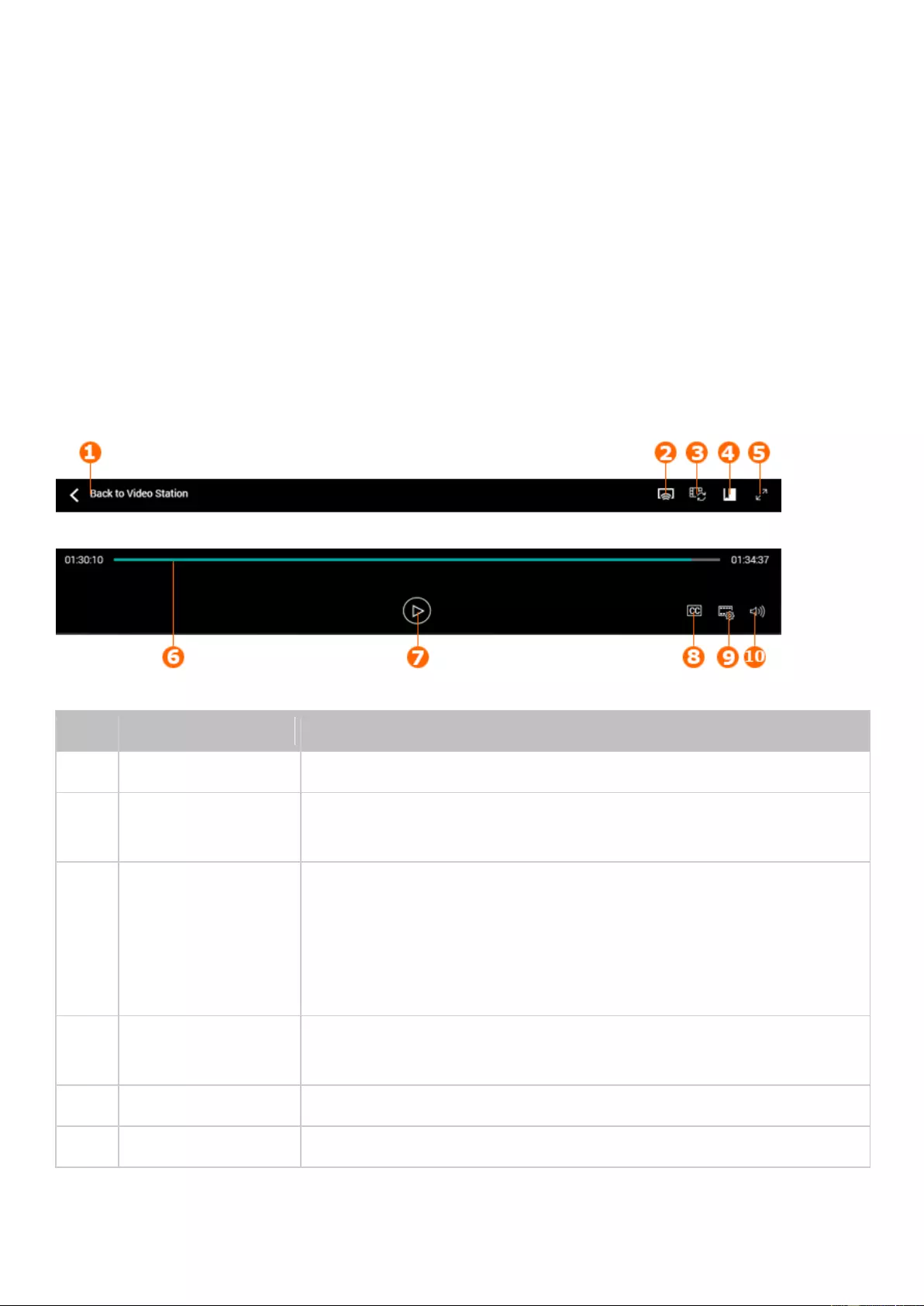
Manage your TV show videos
We recommend organizing your TV show videos properly so that you can manage and access them
more easily. Video Station will display your TV shows by their seasons, episodes, and titles, if you
arrange and name files in a specific order.
1. In your TV show folder, create a subfolder that has the same name as the TV show and place all
the related files here. For example, if the show is called “QNAP Show”, then a recommended path
is“/Multimedia/TV show/QNAP Show”.
2. Name your TV show files according to their seasons and episodes in the format “show
title.SxxExx”. For example, the first episode of the first season of “QNAP Show” should be named
“QNAP Show.S01E01”.
Playing Videos
Double click a video to enter the Viewing Mode:
No
Name
Description
1
Return
Exit the View Mode and go back to Video Station.
2
Multi-zone
Streaming
Stream the video to the compatible media devices on your network.
3
Add to Transcode
Convert the video to a file format compatible with your media
devices for streaming. You can configure related settings in “Control
Panel” > “Applications” > “Multimedia Management”. Please note
that the conversion process requires extra computing resources and
may affect the system performance.
4
Bookmark
Add a bookmark at a particular moment to share your comments on
the video with other people.
5
Full Screen
Switch to the full screen mode.
6
Progress Bar
Control the playback progress of the video.

7
Play/Pause
Play or stop the video.
8
Subtitles
Import subtitles from NAS or from your local devices, search for
subtitles on the internet, and configure subtitle settings. You can
embed the subtitles into videos when converting them to compatible
formats in “Add to Transcode”
9
Video Playing
Settings
You can adjust the resolution of on-the-fly transcoding, choose its
sound track, or play the video in a new browser tab. Please note
that if your browser does not support the file format, it will
download the video instead.
10
Volume
Adjust the volume of the video.
Note:
You can also control the playback and volume with your computer keyboard:
o
Left: Rewind
o
Right: Forward
o
Up: Increase volume (available after launching the volume controller)
o
Down: Decrease volume (available after launching the volume controller)
o
Space: Play / Pause
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Only MP4 (H.264) video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support
On-the-fly Transcoding. You may consider transcoding videos into different formats.
Downloading and searching movie information online
Video Station supports downloading online information (movie poster, year, rating, director, etc) for
movies. To enable this feature, follow these steps:
1. Classify a video as a movie or TV show (right click a video, select "Information", and set its
classification to “Movies”).
2. Switch to the "Movies" or “TV Shows” category on the left panel.
3. Right click a movie, select “Information" to see its information.
4. If the information of the movie is incorrect, click "Edit" in the top-right corner of the "Information"
window and enter its name to search again.
5. If the movie poster is incorrect, you can change it by clicking “change poster” on the movie poster
to upload an image from your local devices or via a URL.
6. The online database for movie or TV show information by default is the IMDb (Internet Movie
Database). To add more dada sources, go to “Control Panel” > “Multimedia Management” >
“Media Add-on” and install a new database. To change the default database, go to “Video Station”

> “Settings” > “Classification settings” and select the data source. Please note that you can only
choose one data source.
Importing, displaying and adjusting subtitles
You can import, display and adjust subtitles files.
To import and display subtitle files:
a. Save the subtitles file and the video file in the same folder and give them with the same
filename (for example, a video with the filename "video.avi" must have subtitle files named
"video.eng.srt" or "video.cht.srt"). The subtitles will be available when you watch the video and
you can switch between multiple languages.
b. In the Viewing Mode, click "Subtitles", select "Import subtitles", and choose a subtitles file from
NAS or from your local device. You can also search for subtitle files on the Internet using
related keywords.
Adjust Subtitles: In the video player, click "Subtitles" and select "Adjust subtitles" to change the
font, font size, and color of subtitles, or enable background effect. You can also shift subtitles to
synchronize with movies.
Note:
"Import subtitles" and "Search for subtitles" are only supported by firmware 4.2.0 or
newer versions.
Supported subtitles file formats: .srt, .ass,and .ssa.
If your subtitles use an incompatible format, we recommend using Aegisub to convert
them.
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Videos in Video Station are listed and displayed according to shared folder privileges and media
folders settings in Multimedia Management. For shared folder privileges, only users with the
permission to access a shared folder can view its content in Video Station. For example, if a user does
not have read/write, or read-only permissions to a certain shared folder, that user cannot see the
videos in the shared folder. You can also configure related folder privilege settings in “Control Panel”
>“Privilege” >“Shared Folders” > “Advanced Permissions” to decide whether to enable advanced
folder permissions and Windows ACL support.
Videos stored in the shared folders are visible only after they are detected and scanned by Media
Library. To set the Media Library to scan for videos manually or by a schedule, go to "Control Panel"
>“Applications” >"Multimedia Management" > "Media Library". For more information about media
folder settings, please refer to the chapter on Multimedia Management.
Note:
As the media folders in Media Library are shared by Photo Station, Music Station,
Video Station, and DLNA Media Server as their content source, contents in those
applications will be affected if new media folders are added or existing media folders are
removed from Media Library.
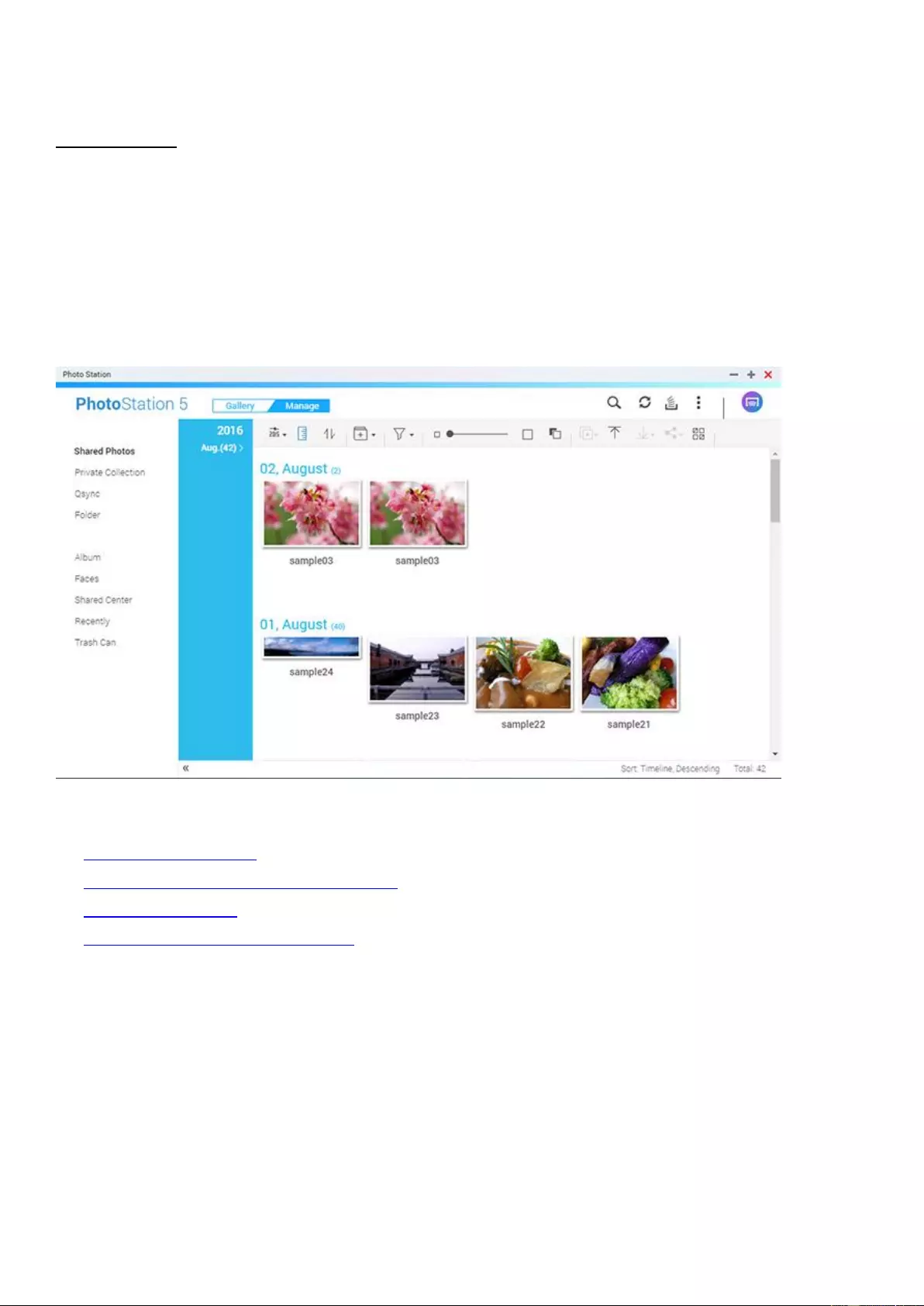
Photo Station
Photo Station (5.3.0) is an application for you to organize photos and videos on the NAS and share
them with friends and family on the Internet. With Photo Station, you can drag & drop photos onto
virtual albums, sparing you from having to tediously move or copy files around and helping you save
storage space because Photo Station only needs one copy of your photos on the NAS even if you put
them in several albums with different themes. You can also use smart albums to automatically
arrange photos that meet your own criteria. Photo Station has many more useful features for you to
explore.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Starting Photo Station
Familiarizing yourself with Photo Station
Using Photo Station
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Starting Photo Station
Photo Station can be enabled by default and can be launched from the Desktop or the Main Menu. If
not, install and enable it in the App Center (for QTS 4.1 or later versions only) and follow these steps:

1. Import photos and videos to a shared folder on the NAS. There are three ways to upload photos
and videos to the NAS: 1) Install Qfinder Pro on your PC or Mac, set up a network drive and
upload files to your preferred shared folders. For details on setting up a network drive, check the
Connecting to NAS Shared Folders chapter; 2) Click "Shared Photos" or "Private Collection" on the
left panel in Manage Mode and click "Import" on the menu bar to import photos or videos from
your local device. You can either upload files to an existing folder or to a new folder (for "Shared
Photos", by default this newly created shared folder is located in the "Multimedia" folder; for
"Private Collection", this shared folder is located in the "/home" folder. You can change the default
folder settings in “Settings” > “Miscellaneous”). A corresponding album will be created under
"Album" as well; and 3) Click “Folder” on the left panel and open a folder where you want to
upload files, and drag & drop photos or videos here.
Photo Station supports the following file formats:
Image
BMP, JPG, JPE, PNG, TGA, and GIF
Video
MP4 (other video formats will be converted to MP4 when you play them online)
Tips on file upload:
The maximum size of an image file is 2GB.
You can only upload up to 500 files at one time.
2. Launch Photo Station from the Main Menu/Desktop shortcut, or directly log into Photo Station by
going to: http://NAS_Name_or_IP/photo/
Note:
The administrator log-in credentials of Photo Station are the same as those of the
NAS administrator.
Familiarizing yourself with Photo Station
In Photo Station, there are two modes you can use: Gallery Mode and Manage Mode. Gallery Mode is
designed for a better viewing experience, while Manage Mode provides easier photo and video
management.
Gallery Mode
Menu Bar

No
Name
Description
1
Mode Switch
Switch between Gallery Mode and Manage Mode.
2
Advanced
Search
Search photos and videos by their title, date, size, resolution, camera
brand, color label, rating, description, or tag.
3
Multi-Select
Select multiple items at the same time. You can also select or deselect
all the items.
4
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
5
Background
Task
Show tasks running in the backgrounds, such as uploading tasks.
6
Settings
Launch Quick Start or Photo Station Help.
7
Display
Switch between Thumbnail View and Wallpaper View. Move your mouse
cursor over this button and click “Display Settings” to configure more
advanced display settings, including gallery view, source, content filter,
and sorting methods. For more information, see Viewing photos and
videos.
8
Music
Play or pause the background music. Move your mouse cursor over this
button and click “Music Settings” to choose the source of music.
9
Slideshow
Show all the photos in an album one by one. Move mouse cursor over
this icon and click “Slideshow Settings” to configure more advanced
settings, including speed, effect, and music. For more information, see
Viewing photos and videos.
10
Show/Hide
Show or hide the previous three buttons (Display, Music, and
Slideshow).
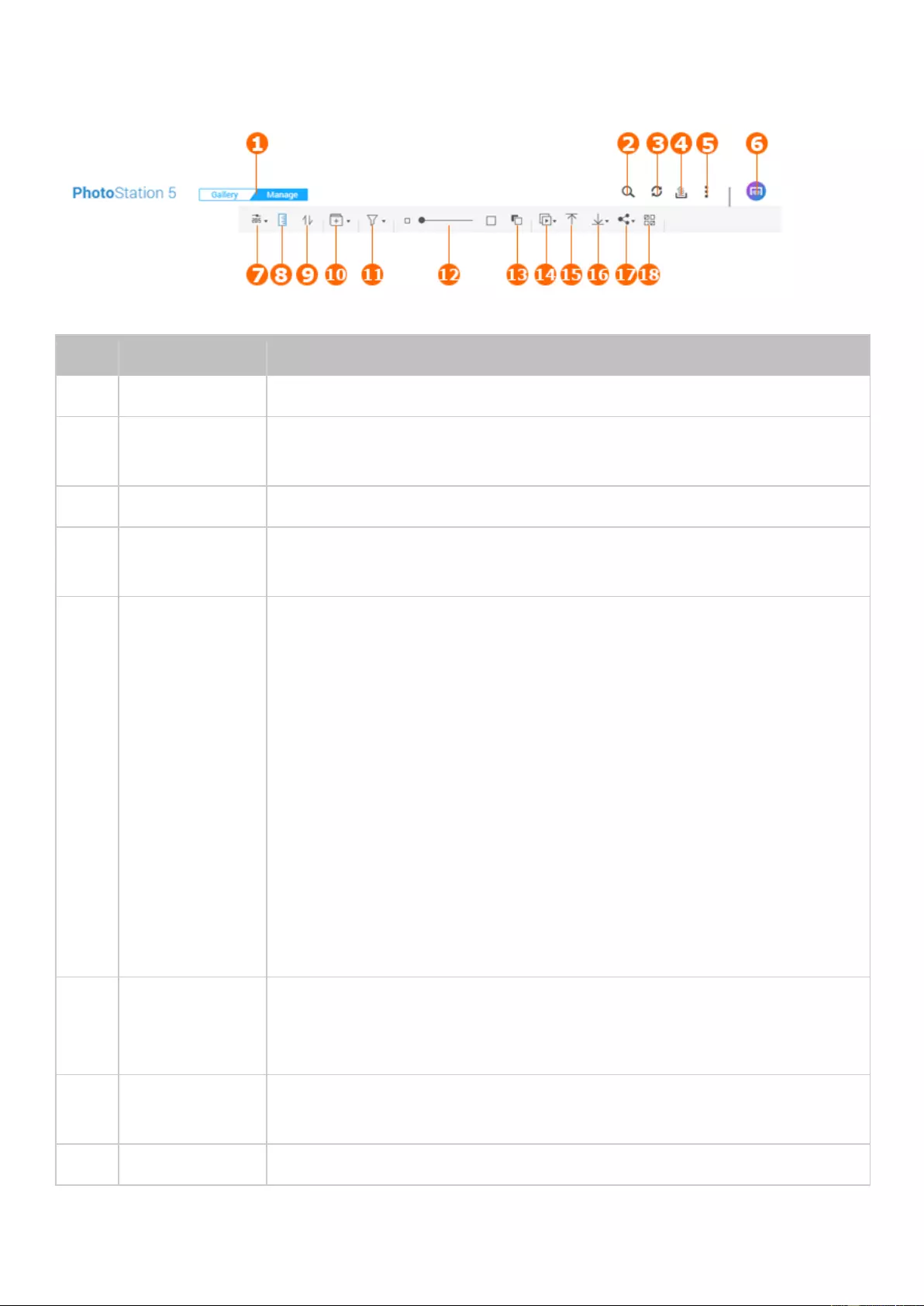
Manage Mode
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Switch Mode
Switch between Gallery Mode or Manage Mode.
2
Advanced
Search
Search photos and videos by title, date, size, resolution, camera brand,
color label, rating, description, or tag.
3
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
4
Background
Task
Show tasks running in the backgrounds, such as uploading tasks.
5
Settings
Launch Quick Start, show Photo Station Help, or download the system
log to report bugs to QNAP custom service if issues arise. You can also
configure advanced settings:
Content Management: Select shared folders and add new folders as
the content source of Photo Station. This setting will be synchronized
with “Multimedia Management” in “Control Panel”.
Backup/Restore: You can export or import a configuration file for
backup or restoration. A configuration file contains the information
about how you arrange photos and videos in Photo Station.
Miscellaneous: You can select a shared folder to store uploaded
photos, set up the display ratio, choose the default viewing mode, and
decide whether guest can download photos and videos, and who can
view the GPS information.
6
Multi-zone
Streaming
You can stream files to the media devices on your network. Click this
button and drag & drop files to any devices on the left (blue) panel to
create its own playlists.
7
Browsing Mode
Choose between three browsing modes: You can show item either as
icons, in a list, or in a timeline.
8
Timeline
Show/Hide the timeline (only available in Timeline Mode).
9
Sort
Sort items chronologically in an ascending or descending order.
10
Add Album
Create an album or smart album.
11
Photo/Video
Filter
Display either photos or videos, or both.
12
Zoom in/Zoom
out
Increase or decrease the thumbnail size.
13
Background
Color
Switch between the white and black background.
14
Slideshow
Display selected items in a slideshow. You can also click the down arrow
to select the slideshow speed, effect, and background music.
15
Import
Upload videos or photos to Photo Station.
16
Download
Download the selected photos or videos. You can also decide the
resolution of downloaded photos (For a video, this is only applicable to
the size of its thumbnail).
17
Share
Choose to share the selected items via email, on social networking
websites, or via sharing link. After you choose a sharing method,
Sharing Cart will appear. For more information about Sharing Cart, see
Sharing photos, videos, albums, or smart albums.
18
Multi-Select
Select multiple items at the same time.
Note:
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, the
Media Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Only MP4 video files can be directly streamed if your NAS does not support On-the-fly
Transcoding. You may consider transcoding them into different media formats. For
more information about transcoding, please refer to the Transcode Management
chapter.
If your NAS supports transcoding, please install the CodexPack App before using this
function. Your NAS will try to choose a suitable file format. If your NAS does not
support transcoding, your NAS will only play files in their formats. In such a case,
please ensure that your devices support the file format of the video you play.
Some video formats may encounter issues when streamed via DLNA, Apple TV or
Chromecast. If any of these issues arise during video playback, you may consider

transcoding your videos into file formats compatible with most devices. For more
information about transcoding, see Transcode Management.
Some media players do not support pausing during playback. If this happens, playback
will continue even if you click “pause”.
Left Panel
Shared Photos: List all photos and videos chronologically by their thumbnails (except photos and
videos in the "/home" and "Qsync" folders) and all photos and videos are only visible to
authorized users.
Private Collection: List all photos and videos located in the "/home" folder, and those multimedia
files can only be viewed by the user.
Qsync: List photos and videos synchronized by the Qsync service.
Folder: Show the media folders on the NAS (except photos and videos in the "/home" and "Qsync"
folders) and all photos and videos are only visible to authorized users.
Album: List all virtual albums and smart albums. Smart albums only contain photos or videos that
meet specific criteria chosen by users. Note that all entries listed under an album or smart albums
are only links to files. This can effectively save your NAS storage space, as you keep only one
copy of every photo even if you put a photo in several albums that have different themes. You
can also right click on "Album" (the category header) to expand/collapse the album list or add an
album or smart album. For more information, see Creating and managing albums and Creating
and managing smart albums.
List albums containing photos with face tags. Please refer to Adding face tags to photos for more
information.
Shared Center: Show the sharing history of your photos and videos. You can check the name, link,
expiration date and summary of each entry or share items again. You can also right click on
"Shared Center" (the category header) to expand / collapse the album list.
Recently: Include photos and videos that were recently imported from local devices or those that
were taken with a camera or recording device within two months.
Trash Can: All deleted photos and videos can be found here and can be restored or permanently
deleted. Only deleted files (and not virtual links) will appear in the trash can.
Note:
The "/home" folder can only be accessed by its owner and NAS administrators. Private
or personal videos should only be stored in your "/home" folder.
For media folder configuration, refer to the Multimedia Management chapter. For user
setup and configuration, refer to the User section in the Privilege Settings chapter.
If uploaded photos or videos do not appear in Photo Station, scan them using Media
Library. For more information, see the Multimedia Management chapter.
Using Photo Station

Creating and managing albums
There are four ways to create an album:
1. In Manage Mode, click “Add Album” on the menu bar and select “Create an Album”..
2. Switch to the folder view in Manage Mode, right click a folder, and select "Create New Album" to
turn that folder into an albumel.
3. Drag and drop photos or videos onto "Album" on the left panel.
4. Right-click "Album" on the left panel and select “Create an Album".
When you create an album, you have to specify its name and configure its privilege settings, and there
are three options:
Only me: Only you can browse and edit this album.
Public: Allow everyone, including guests, to view the content of this album. You can also choose to
show the photos in this album on the QTS log-in page.
NAS users: Share this album with other NAS users and allow them to browse its content. By default,
only the administrator and the creator of this album can edit it. To make changes to this setting, click
“Custom Permissions” and specify the permissions you want to give to individual users, user groups,
and domain users.
When you share an album, you can also decide a valid period for this sharing. You can either make it
always valid or specify a definite period.
To manage albums, right click on an album and choose to download, remove, rename, share, stream,
play as a slideshow, open, or configure its settings.
Creating and managing smart albums
There are two ways to create smart albums:
1. In Manage Mode, click “Add Album” on the menu bar and select “Create a smart album”.
2. Switch to the folder view in Manage Mode, right click a folder, and you will see two smart album
options. Select "Create a Smart Album" to turn that folder into a collective smart album. Select
"Convert subfolder to Smart Album" and all the subfolders in that selected folder will become
individual smart albums listed under "Smart Album" on the left panel.
When you create a smart album, you have to specify its search criteria. You can choose to include
photos taken on a certain day, in a certain period, with a certain tag, or simply select photos
randomly.
To manage smart albums, right click on an album under "Smart Album" in the left panel and choose to
download, remove, rename, share, stream, play in a slideshow, open, or configure its settings.
For privilege settings, refer to the previous section Creating and managing albums.

Sharing photos, videos, albums, or smart albums
You can share photos, videos, albums, or smart albums with your friends via email, social networking
websites, or sharing links using Sharing Cart or configure sharing settings when you create an album
or smart album.
Sharing Cart
Sharing Cart allows you to conveniently collect photos and videos stored in different albums or folders
before sharing them. In Manage Mode, click “Sharing” on the menu bar and select one sharing method
to launch Sharing Cart. You can also drag & drop items onto the dotted rectangle in Sharing Cart to
collect them before sharing. Sharing Cart provides three sharing methods:
Email: Complete the required fields (including sender email, recipient emails, password, valid
period, subject and message (click "More settings") and click "Create". Please note: To share
files/folders using your own email account, set up your account in “Desktop” > "Options" >
"E-mail Account".
Social Network: Complete required fields (including website, message, and domain name,
password, valid period), decide whether to use SSL, set the password and valid period, and click
"Create". You can also upload files to a photo sharing websites.
Sharing link: Choose a link format and domain name. Decide whether to create a secure link
using SSL and set a password and valid period, and click "Create".
Note that when you share albums or smart albums, all the photos/videos in the selected albums will be
loaded to Sharing Cart.
Checking sharing history
To check the sharing history of your photos and videos, click "Shared Center" on the left panel in
Manage Mode. You can view the details of sharing records or re-shared your shared items.
Note:
You can also display photos in public albums on the NAS log-in screen (configure this
setting in "Control Panel" > "General Settings" > "Login Screen").
If an album is set to share with the public, users can click the photo wall on the log-in
page to check the album.
An exclamation mark will appear on the album thumbnail if the sharing period of that
album has expired.
Photo and Video Operations
In Manage Mode, after right clicking a photo or video or clicking the “down arrow”, you can see a
menu that provides more options for you to manage or configure your files.

Operation
Description
Rotation(counter-clockwise
rotation icon)
Rotate the item 90 degrees counter-clockwise.
View (eye icon)
Launch the Media Viewer to view the item. Refer to the Viewing
photos and videos section for more information.
Information (i)
Display the detailed information, properties, and description of the
item.
View
Launch the media viewer to view the photo (photos only.) Refer to
the Viewing photos and videos section for more details.
Rotation(clockwise rotation
icon)
Rotate the item 90 degrees clockwise.
Play
Play the selected video. You can choose to launch on-the-fly
transcoding to convert the video to a universal format that is
compatible with your devices. Please note that on-the-fly
transcoding requires extra system resources.
Open in new browser tab
View the selected video or play photo in a new tab. Please note that
if your browser does not support the file format of the video, it will
download the video instead.
Open with VLC
Play the video in a browser window (videos only; the VLC plug-in
must be installed.)
Streaming to (Network
Media Player)
Stream videos to compatible devices in different rooms over your
home network.
Share
Share the selected photos or videos on social networking sites, via
email or link. Sharing Cart will be launched after you select a sharing
method.
Download
Download the selected photo or video. For photos, there are four
sizes: small, medium, large and original; for videos, you can choose
to download the video file (if you select "Original") or video
thumbnail (as a photo).
Add to Album
Put the selected photos and videos to an existing album or create a
new album and then copy the item to that new album.
Add to Transcode
Convert the video to the following resolutions: 240P, 360P, 480P SD,
720P HD and 1080P Full HD (only for videos).
Note: This feature is for the x86 series NAS only.
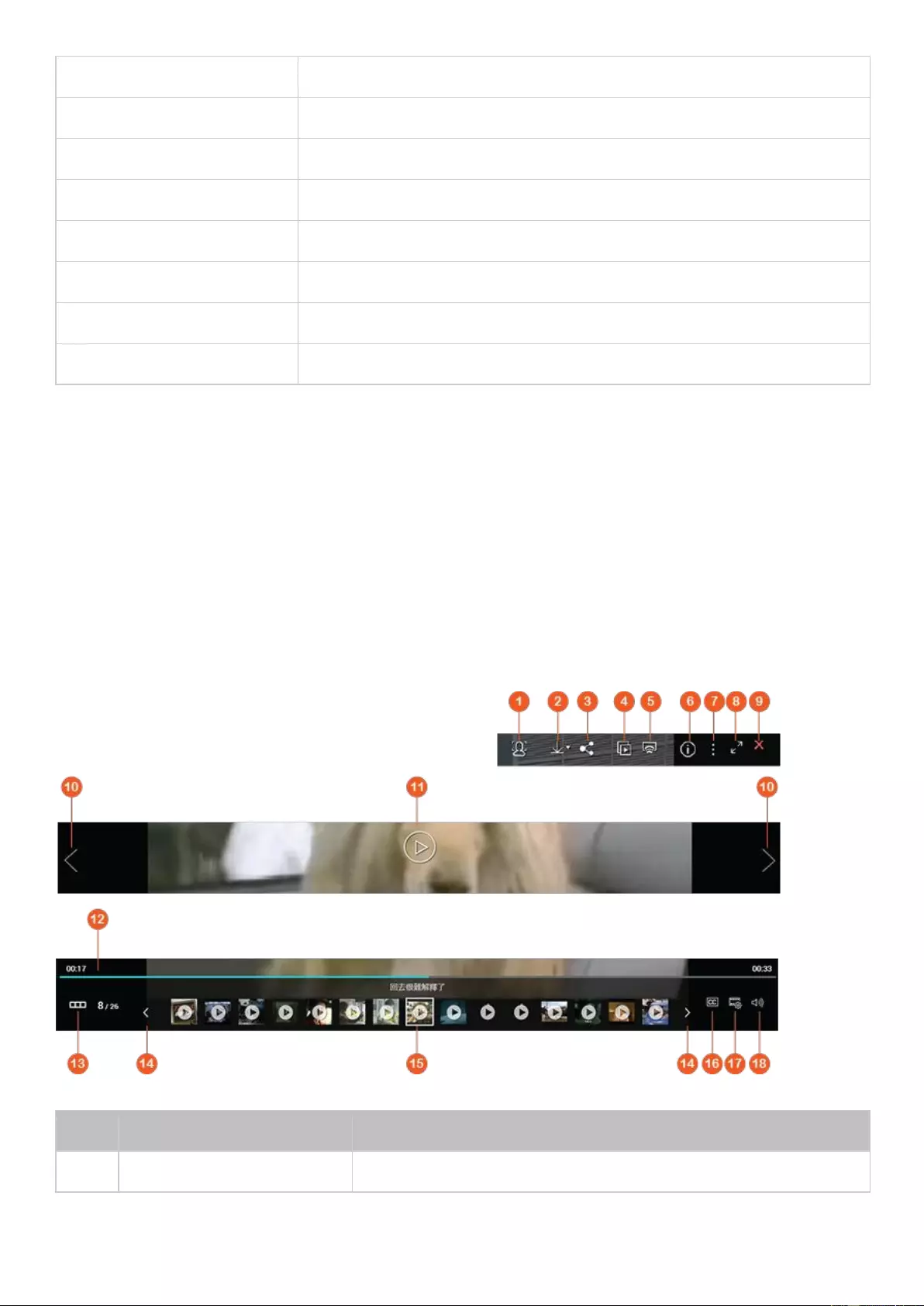
Edit
Edit the photo online using Pixlr Editor or Pixlr Express (photos only.)
Rebuild thumbnail
Rebuild thumbnail for selected photos or videos.
Delete
Delete photos or videos.
Information
Display file details, property and description of the photo/video.
Set Coordinates
Set up GPS information of the photo (photos only).
Add Tag
Add a tag to photos or videos.
Rating
Rate photos or videos.
Color Label
Color-label photos or videos.
Finding your photos and videos quickly
You can rate or classify photos/videos to locate them more efficiently. To do so, right click a photo or
video and then tag, rate or color label them. To mark or classify multiple photos or videos, click
"Multi-select" button on the main menu (or hold the Ctrl key), select photos or videos and right click
them. You can then find your target items by their tags, color-labels, or ratings in Advanced Search.
Viewing photos and videos
In Gallery Mode, double click a photo or video or click "Display" in the Thumbnail View to launch the
Media Viewer for more operations.
No
Name
Description
1
Face Detection
Enable Face Detection to show tagged faces. You can also

manually add a face tag. Please refer to the Adding face tags
to photos section for more information.
2
Download
Download the selected photo or video. For photos, there are
four sizes: small, medium, large and original; for videos, you
can choose to download the video file (if you select "Original")
or video thumbnail (as a photo).
3
Share
Share the photo or video image on social networks, via email
or via link.
4
Slideshow
Display the selected photos or videos in this album in a
slideshow in the full screen mode. Check the Playing photos
and videos as slideshow section for more information.
5
Network Media Player
Stream videos to compatible devices in different rooms over
your home network.
6
Information
Display the detailed information, properties, and description
of the item.
7
Miscellaneous Settings
Set the currently displayed photo/video image as QTS
wallpaper.
8
Full Screen
View the photo or play the video in the full screen mode.
9
Return to Photo Station
Close the photo/video viewer and return to Photo Station.
(Please note that if you launch the Media Viewer in Manage
Mode, this exit will appear in the top-left corner).
10
Previous Item/Next Item
Display the previous/next item.
11
Play/Pause
Play or pause the selected video.
12
Progress Bar
Control the playback progress.
13
Hide/Show Preview Bar
Hide/show the Preview Bar.
14
Rewind/Forward
Rewind/Forward the Preview Bar.
15
Preview Bar
Preview the photo and video thumbnails.
16
CC (only for videos)
Display or configure subtitle settings.
17
Resolution (available when
the item opened is a video)
Change the resolution of on-the-fly transcoding for the
selected video (only available if your NAS model supports
on-the-fly transcoding).
Watch the video in another browser page or with VLC
Media Player (VLC plug-in must be installed).
18
Volume (only or videos)
Adjust the volume of the video.
Viewing photos and videos as slideshow
A slideshow is a presentation of a series of photos in sequential order. To display photos or videos in
a slideshow, click "Slideshow" in the Media Viewer to launch Slideshow Mode.
No
Name
Description
1
Effect
Choose a special effect for slide transitionct.
2
Speed
Choose the speed of the slideshoweed.
3
Music
Choose playlists created in Music Station (from the "Playlist",
personal playlist, and shared playlist on the left panel). Please refer
to the chapter on Music Station for more information.
4
Play/Pause
Play/Pause the slideshow.
5
Previous/Next Slide
Go to the previous/next slide.
6
Background Music
Turn on or off the background music.
7
Title
Show the photo title.
8
Download
Download the current photo or every photo in the slideshow in the
original size or as thumbnails.
9
Full Screen
Switch between the full screen mode and window mode.
Geotagging photos and photo map
To geotag a photo, right click a photo and select "Set Coordinates" to set its coordinates (you can
type the location in the search box in the "View Map" window) and click "Save". To locate photos on a
map, click a photo, select "Information", and click the red pin next to "Coordinates". This feature is
only available for photos with GPS coordinates. For photos with no GPS coordinates, please follow the
above steps to set up their GPS coordinates.
To view the geographical information of photos in an album, select “View Map” on the menu bar to
see the locations of photos on a map. If your photos do not have geographical information, you can
still manually add coordinates to them so that your photos can be presented on the map.
Adding face tags to photos
1. Set up face detection folders in Photo Station > "Manage Mode" > "Settings" > "Face Detection".
2. Open a photo in the Media Viewer and enable Face Detection.
3. Add face tags to the photo or manually change the face area.
To view photos with face tags, switch to Manage Mode and click "Faces" on the left panel.
Browsing PDF files
You can also browse PDF files as photos using Photo Station. To use this feature, right click a PDF file
to create a new album. After clicking that album, you will see all the pages of the PDF file displayed
as individual photos.
Note:
Before using Face Detection and PDF browsing features, the Photo Station Extension
App must first be installed in Control Panel. Please note that Photo Station Extension is
only available on x86-based NAS models.
As Face Detection function can affect system performance, please avoid using it during
peak NAS usage periods.
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Photo and video files in Photo Station are listed and displayed according to shared folder privileges
and media folders settings in Media Library. Only users with permission to access shared folder can
view or edit its content in Photo Station. For example, if a user does not have read/write, or
read-only permissions to a certain shared folder, that user cannot see the photos and videos in the
shared folder.
Note:
For x86-based NAS models, all shared folders except "/recording" and "/web" are
media folders by default. For ARM-based NAS models, only "/multimedia" and "/homes"
are media folders by default. However, users can always add more media folders.
In addition to shared folder privileges, you can also store private videos in your
"/home" shared folder to hide them from other NAS users (except the administrator.)
The content of the "/home" folder can be found under "Private Collection". Anyone
attempting to access this folder in Photo Station will be prompted for a password.
To create a shared folder, go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Shared
Folders".
Photos and videos stored in the shared folders are only visible after they are detected and scanned by
Media Library. To set Media Library to scan for photos and videos manually or by a schedule, go to
"Control Panel" > "Multimedia Management" > "Media Library". You can also set up media folders for
Photo Station in “Photo Station” > “Settings” > “Content Management”. Please note that this setting
will be synchronized with Multimedia Management. For more information about media folder settings,
please refer to the chapter on Multimedia Management.
Note:
As the media folders in Media Library are shared by Photo Station, Music Station,
Video Station and DLNA Media Server as their content source, related content will be
affected in those applications if new media folders are added or existing media folders are
removed from Media Library.
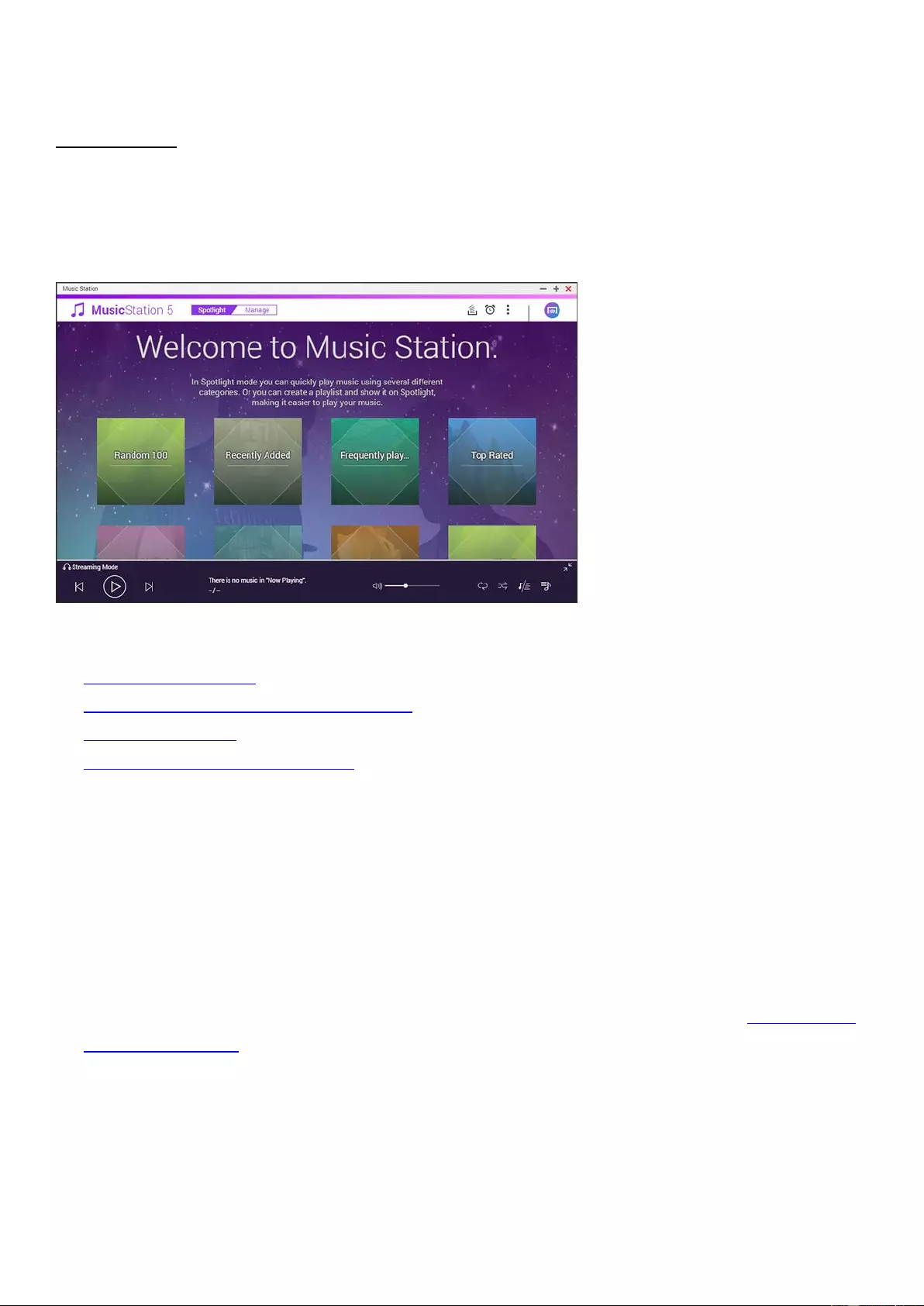
Music Station
Music Station (5.0) helps you create a personal music center on the cloud. This web-based application
is designed for users to play music files on the NAS, listen to thousands of radio stations on the
Internet, and share your music with your friends and family. Your music collection stored on the NAS
is automatically organized into categories for easy access.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Starting Music Station
Familiarizing yourself with Music Station
Using Music Station
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Starting Music Station
Depending on your NAS model, Music Station may be enabled by default and can be launched from
the Desktop or the Main Menu. If not, install and enable it in the App Center (for QTS 4.1 or newer
versions only) and follow these steps:
1. Upload music files to a shared folder on the NAS. There are three ways to upload music files to
the NAS: 1) Install Qfinder Pro on your PC or Mac, set up a network drive and upload files to your
preferred shared folders. For details on setting up a network drive, please check the Connecting to
NAS Shared Folders chapter; 2) In Manage Mode, click “Import Music” (up arrow) on the menu
bar or drag & drop files to the Music Station window. In the “Upload” window, select the
destination folder and then either click “Select the music file to upload” or drag & drop files to the
dotted rectangle to upload files. 3) Click “Folder” on the left panel, open the folder where you
want to upload files, and drag & and drop music files here.

Note:
The admin login credentials of Music Station are the same as that of the NAS
administrator.
If you use Music Station for the first time, it is recommended to upload or copy music
files to media folders and scan them using the Multimedia Management. For more
information about media folders, please refer to the Multimedia Management chapter.
2. Launch Music Station from the Main Menu/Desktop shortcut, or directly log into Music Station by
going to: http://NAS_Name_or_IP/musicstation/
Familiarizing yourself with Music Station
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Spotlight Mode
Provide an intuitive interface for you to view and play songs in default
categories and your own playlists.
2
Manage Mode
Provides a detailed interface for you to manage and share your music
files.
3
Advanced Search
Search songs by their title, artist, rating, and other information.
4
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
5
Background Task
Shows tasks running in the background, such as uploading.
6
Music Alarm
Set music alarms.
7
Settings
Provides more setting options and shows Help, Quick Start, and About.
8
Multi-zone
Control and
Streaming
Streams music to the devices on your network and manage
Now-playing lists on each device.
9
Show/Hide Menu
Bar
Show or hide the lower part of the menu.
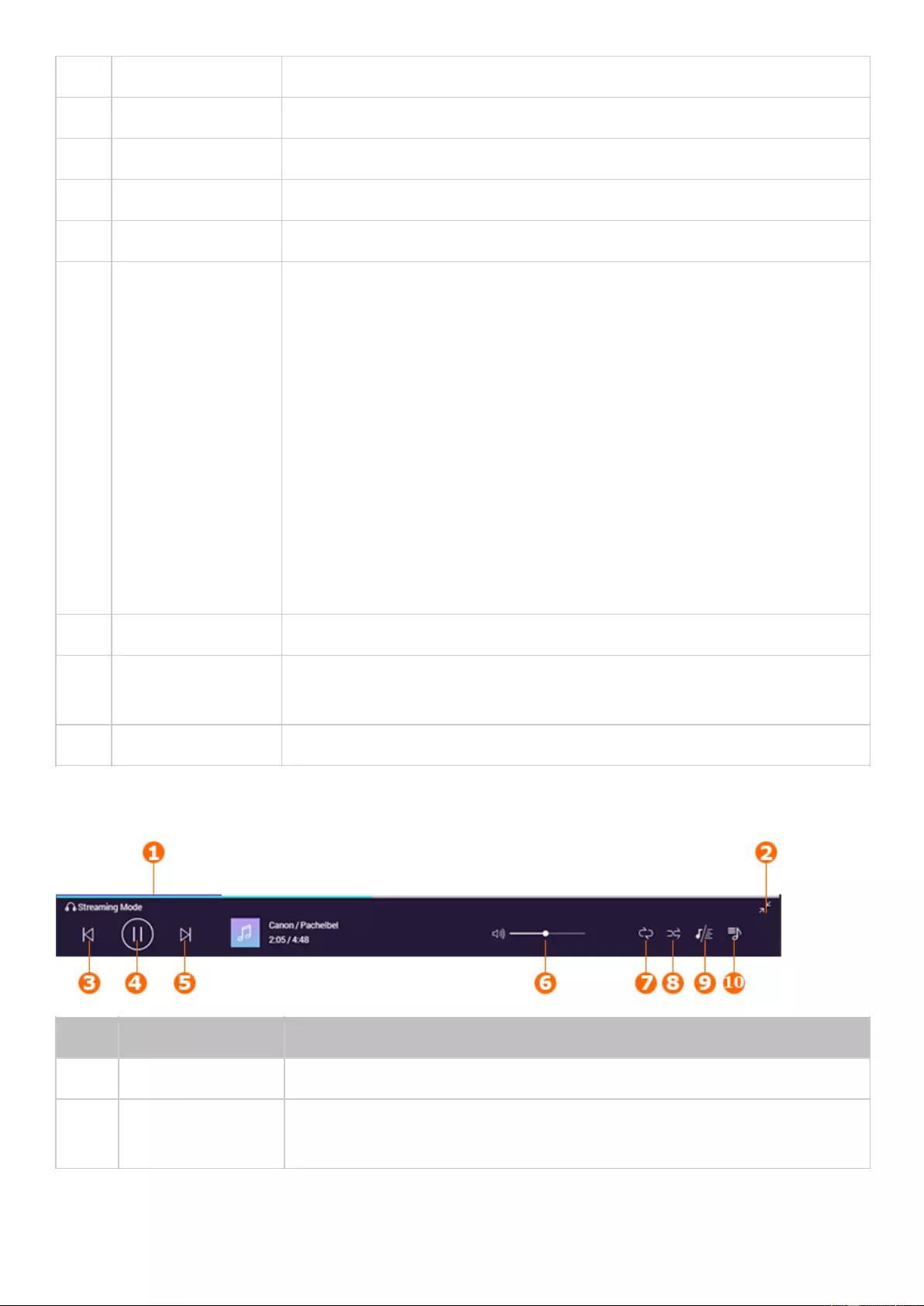
10
Items Viewing
Show items in List Mode or Thumbnail Mode
11
Sort
Sort items by various attributes in ascending or descending order.
12
Add Playlist
Create a playlist or a smart playlist.
13
Import Music
Upload music files from your local device.
14
Download
Download music files to your local device.
15
Share Music
Share link via email: Please ensure that your email settings are
correctly configured. Click your profile icon in the top-right corner of
the desktop and go to “E-mail Account” to set up your account. You
can also specify the subject and add a message to the mail.
Share link on social networking websites: Choose your preferred
website and add a message to supplement your link.
Create link code: Select a domain name and format for the link of
your music files or playlists
For all three methods, you can decide whether to protect files with a
password, allow users to download files, and you can also choose an
expiration date for your sharing. After you share music files, you
can view and re-share them in “Shared Center”.
16
Multi-Select
Select multiple items.
17
Select/Deselect
All
Select or deselect all the items.
18
Information
View and modify the information of the selected item.
Player
No
Name
Description
1
Progress Bar
Control the playback progress.
2
Mini Player
Minimize the player (not available if you choose “Tab Mode” in
“Desktop Preferences”).
3
Previous
Play the previous song.
4
Play/Pause
Play or pause the current song.
5
Next
Play the next song.
6
Volume
Adjust the volume.
7
Repeat
Repeat the current song or repeat all the songs in the playlist.
8
Shuffle
Randomly play songs in the playlist.
9
Lyrics
Show the lyrics of the current song.
10
Now Playing
Show the Now-playing panel. Drag & drop songs to the panel to add
them to the now-playing list.
Note:
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast using the Network Media Player, Media
Streaming Add-On must first be installed in the App Center.
Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Left Panel
Songs, Artist, Album, and Genre: All authorized music files are listed and grouped into these four
categories.
Private Collection: Personal music files in the "/home" folder are listed here. These music files
belong to the user that is currently logged in.
Qsync: Music files synchronized with the Qsync service are listed here.
Folder: You can view and manage the music files in media folders here.
Playlist: You can create, manage, and delete playlists here. Each playlist can include up to 600
items, and Music Station can contain up to 200 playlists.
Smart Playlist: You can create smart playlists that only include songs meeting your own criteria.
Shared Center: Your shared music files are listed here. You can view their sharing history and
share them again.
My Favorite Radio: Enter the radio URL or search TuneIn Radio to add your favorite radio stations
on the Internet (up to 1024 stations). Please note that only the URLs with the MP3 format are
supported.
TuneIn: Users can browse and play on-line radio stations streamed by TuneIn.
Trash Can: All deleted music files can be found here. You can either restore or permanently delete
them.
Note:
"Playlist" names should not include: / | \ : ? <> * " ' $.
Music Station only supports these file formats: MP3, FLAC, OGG, WAV, AIF, and AIFF.
Using Music Station
Import music files
Please refer to the Starting Music Station section.
Creating and managing playlists
To create a playlist, click “Add Playlist” on the menu bar and select “Create a Playlist,” or drag & drop
music files onto “Playlist” on the left panel. You can also create a Smart Playlist that only contains
songs meeting your criteria. To share a playlist, select a playlist and click “Create a new share” on the
menu bar to email it to other people, publish it to social networking sites, or create a link for it. After
you share playlists, you can view the detailed information about your shared lists in “Shared Center”.
You can also right click a playlist and add it to the “Now Playing” list or select “Information” to change
its name or modify its settings.
Sharing playlists
When you create a playlist, you have to decide how to share it with other NAS users. You can choose
to make it open to all the NAS users or just the creator and administrator (and allow them to edit it),
or you can choose not to share it at all by leaving both options unchecked.
You can also share a list of songs as you do with playlists. To do so, click “Songs” on the right panel,
select songs from the list, and click “Create a new share” to choose the way you want to share the
list. Please note that the difference between a playlist and a list of songs is that the former falls into
the “Playlist” category on the left panel, while the latter is a temporary list of songs selected from
different albums.
Multi-zone control and streaming
Music Station works with your NAS Audio output (USB speaker, Soundcard, HDMI), Bluetooth,
SONOS devices, and Network Media Players (DLNA, Chromecast, AirPlay), making it easy for you to
stream music to many types of devices. It can stream different music to all the supported devices in
your home or play the same music at the same time. You can change the output devices by clicking
the purple button in the top-right corner, drag and drop songs to the Now Playing list on your desired
devices, and then double click a song to play it.
Note:
To stream media files to HDMI or Chromecast, Media Streaming Add-on must be
installed in the App Center.

Bonjour must be enabled when using multi-zone streaming. You can enable Bonjour in
"Control Panel" > "Network Service" > "Service Discovery" > "Bonjour".
Please check the QNAP website for supported USB speakers.
Some models with 3.5mm audio output may not support USB audio output.
Radio stations only support playing under streaming mode and Bluetooth.
Changing album covers or artist photos
Music Station automatically searches for an image for your albums and artists. If an appropriate
cover cannot be found, you can also import your own images. To change album covers or artist
photos, follow these steps:
1. Select "Album" or “Artist” on the left panel.
2. Right click an album or an artist and select "Information". In the information window, click the
album cover or artist photo to upload your own images. You can also click “Search” to search for
images on the Internet.
Finding your music files quickly
To quickly locate your music files, you can rate or classify them:
You can either select a file and click “Information” on the menu bar or right click a file and select
“Information”. You can then give it a rating or modify its data in the information window.
To rate or modify music multiple files, click the multi-select button on the Main Menu (or hold the
Ctrl key) and select your desired files to rate and modify them all at once.
After music files are rated or classified, they can be searched by their rating, artist, genre, or other
attributes in Advanced Search.
Media Library and Privacy Settings
Music files in Music Station are listed and displayed according to shared folder privileges (media
folders) and settings in Media Library. For shared folder privileges, only users (including domain users)
with the permission to access a shared folder can view its contents in Music Station. For example, if a
user does not have read/write or read-only permissions to access a shared folder, that user cannot
see the music files in the shared folder. The administrator can give or deny other users permissions
to access various functions in Music Station. To configure privilege settings, click “More settings” in
the top-right corner and go to “Access Permissions”.
Note:
Besides shared folder privileges, you can also import your private music files to your
"/home" shared folder to hide them from other NAS users (except the NAS
administrator.) Your "/home" folder contents can be found under "Private Collection".
To create a shared folder, go to "Control Panel" > "Privilege Settings" > "Shared
Folders".
Music files stored in the shared folders are only visible after they are detected and scanned by Media
Library. To set Media Library to scan for music files manually or by a schedule, go to "Control Panel"
> "Multimedia Management" > "Media Library". For more information about media folder settings,
please refer to the chapter on Multimedia Management.
Note:
Because the media folders in Media Library are shared by Photo Station, Music
Station, Video Station and DLNA Media Server as their content source, content will be
affected in those applications if new media folders are added or existing media folders are
removed from Media Library.
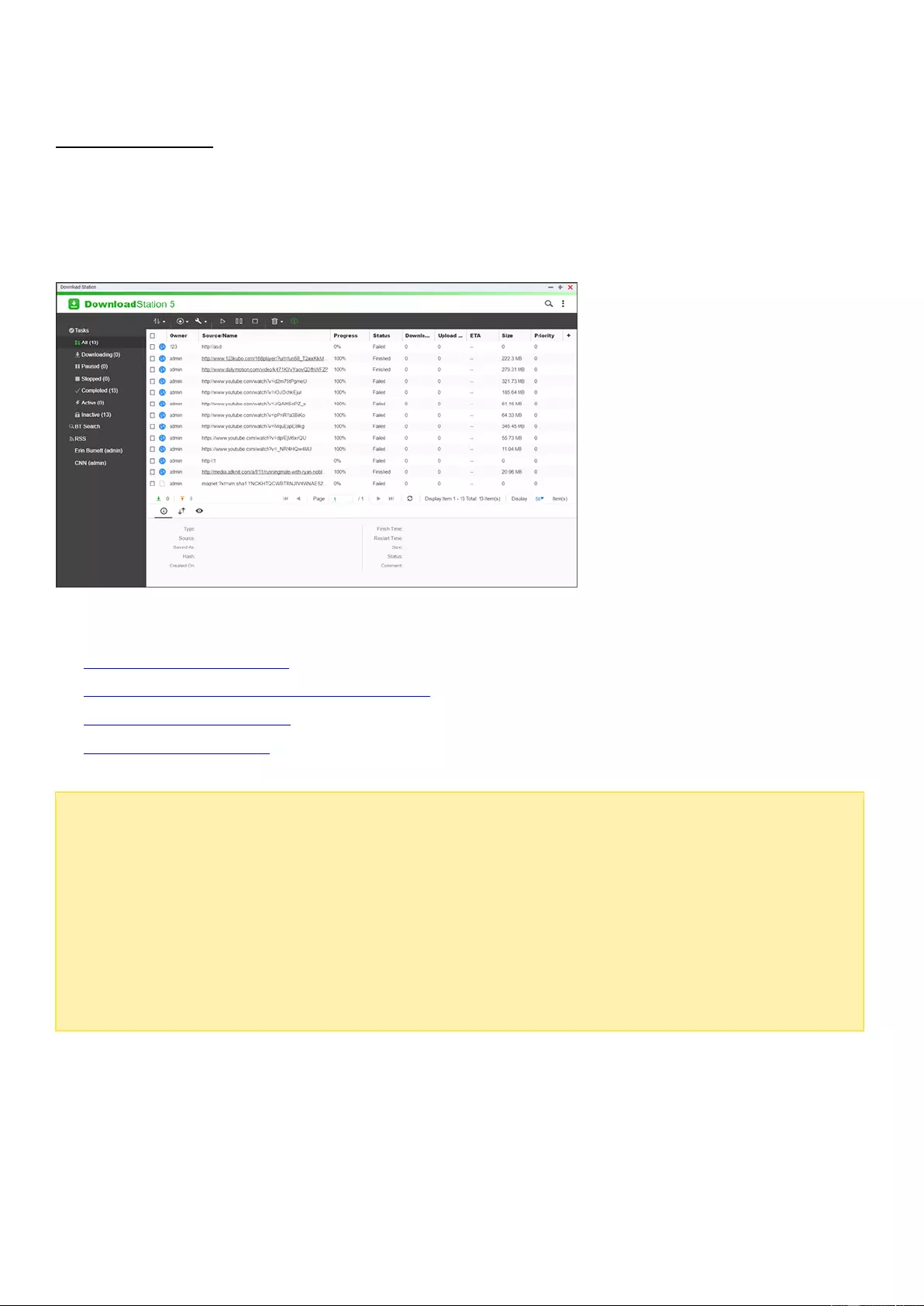
Download Station
Download Station is a web-based download tool that allows you to download files from the Internet
through BT, PT, Magnet Link, HTTP/HTTPS, FTP/FTPS, Xunlei, FlashGet, qqdl, Baidu Cloud downloads
and RSS feed subscriptions. With the BT Search function, you can easily find BT seeds to download
and make your NAS a 24/7 download center.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Starting Download Station
Familiarizing yourself with Download Station
Download Station Settings
Using Download Station
Important: The Download Station is provided for downloading authorized files
only.
Downloading or distributing unauthorized materials is against the law and may
result in severe civil and criminal penalties. Users should be aware that they are subject
to copyright restrictions and they will be held responsible for the consequences of their
actions.
Note:
For PT download, the supported client applications vary based on the PT sites. If
the Download Station (libtorrent) is not in the client application list recommended by your
PT sites, please search for an alternative one in the App Center.
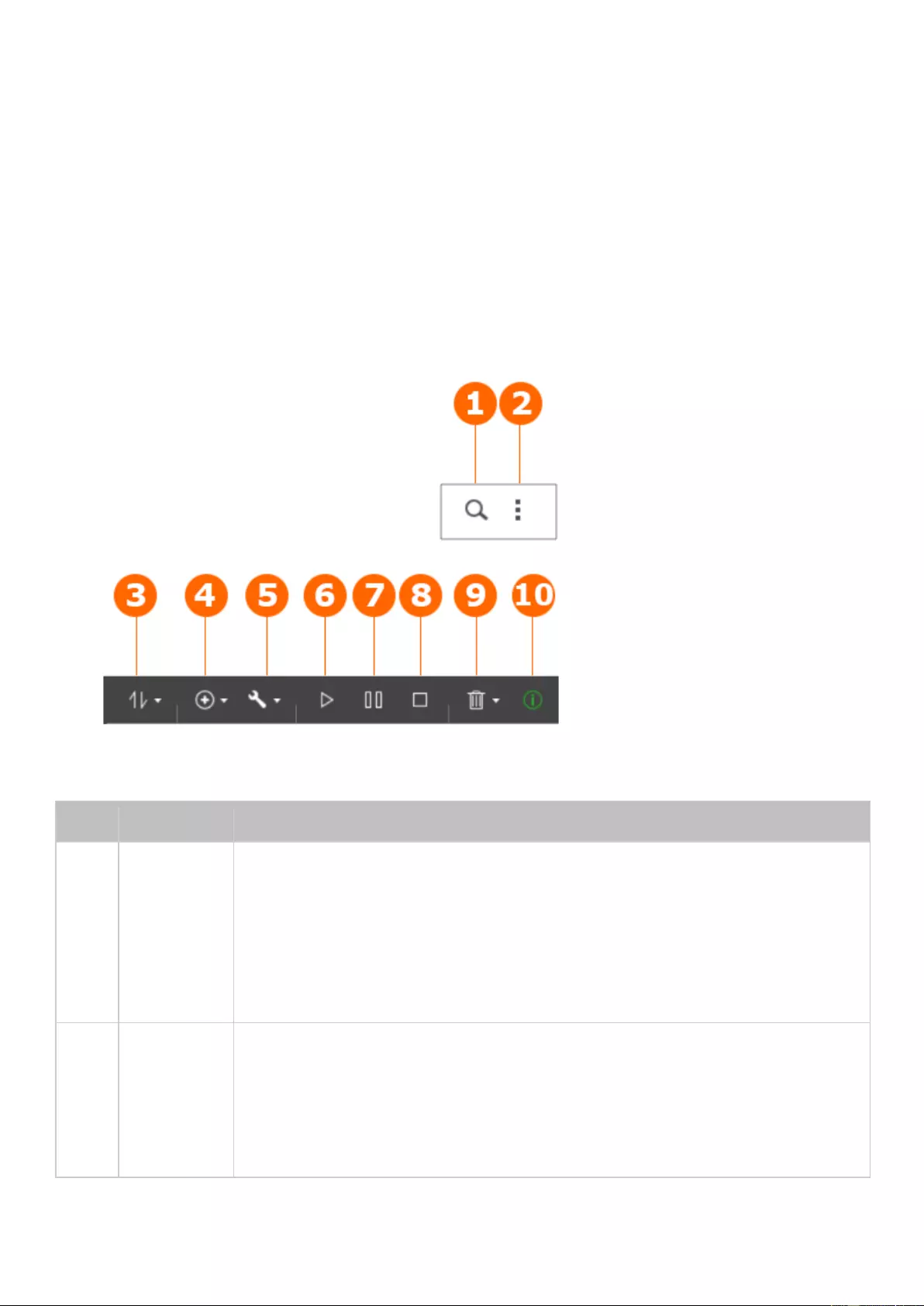
Starting Download Station
Depending on your NAS model, Download Station may be enabled by default and can be launched
from the Desktop or the Main Menu. If not, install and enable it from the App Center (for QTS 4.1 or
later versions only.) Launch Download Station from the Main Menu/Desktop shortcut, or directly log
into Download Station by going to: http://NAS_Name_or_IP/downloadstation/
Familiarizing yourself with Download Station
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Search
Click the magnifier button to show the search bar, type a keyword, and then
click “Add-on” to select the search engine. Press enter to search for BT
seeds.
Note: The BT search feature is only available after you agree to the terms
and conditions. Go to "Settings" > "Global" > " Search".
2
More
Click to display the following:
Settings - Configure BT or RSS settings (refer to the Download Station
Settings section below).
Help - Open the Download Station Help.
About - Display information about Download Station.
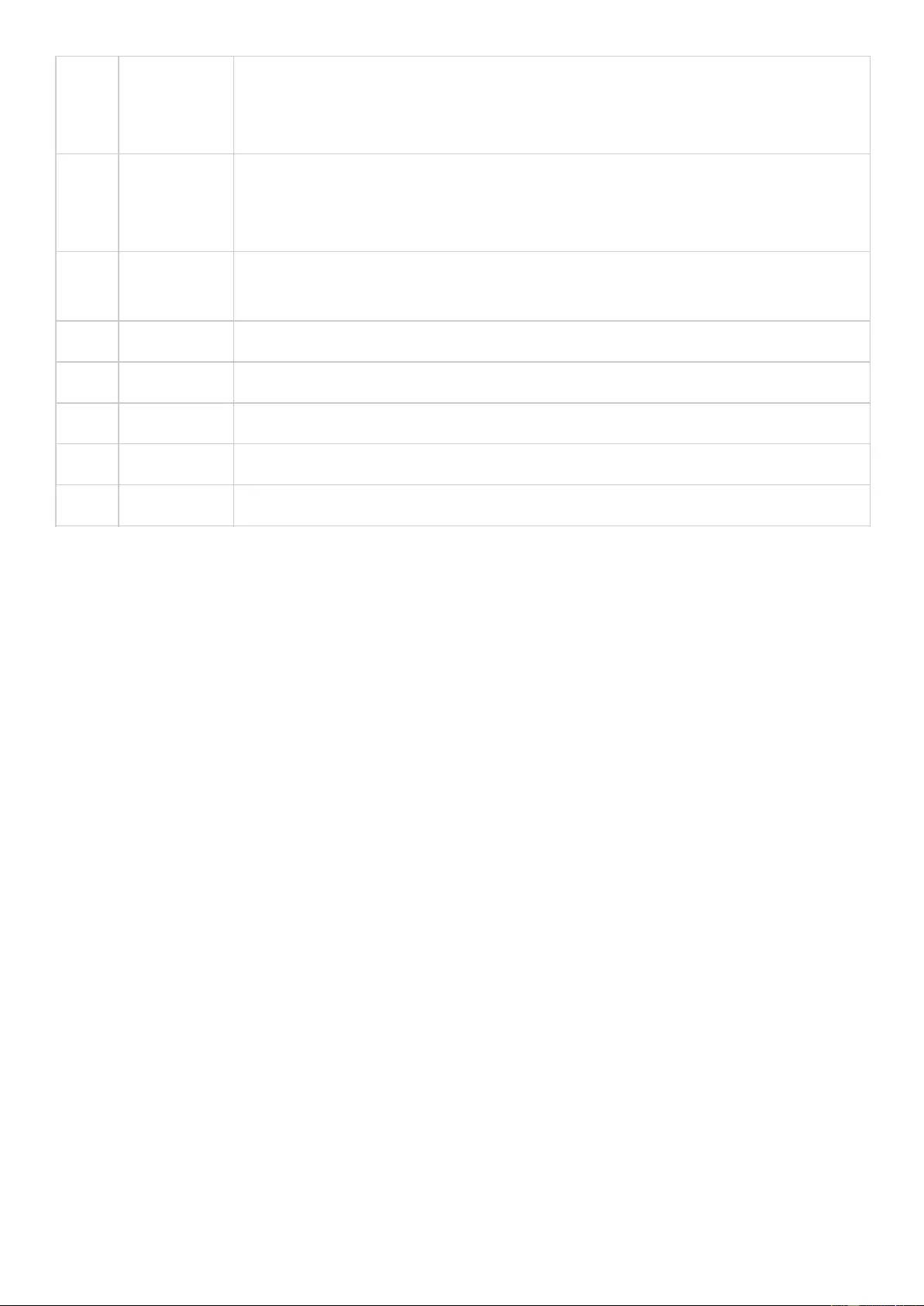
3
View Mode
and Task
Filter
Click to select a view or to filter the task list.
4
Add
download
task(s)
Add a BT seed by entering the URL or upload a torrent file from the local PC.
5
Action
Start all, pause all, or pause all download tasks for a specified time period,
remove all completed tasks, remove all completed tasks and delete data.
6
Start
Start BT tasks.
7
Pause
Pause BT tasks.
8
Stop
Stop BT tasks.
9
Remove
Click to remove BT tasks or to remove BT tasks and delete data.
10
Summary
Summary
Left Panel
Tasks: List all BT tasks based on their download status (All, Downloading, Paused, Stopped,
Completed, Active and Inactive.) Right-click on a task to start, pause, stop, remove, remove and
delete data, or open the File Station folder..
BT Search: Lists all BT seeds searched using the BT Search Bar. Right-click a searched BT seed to
download that seed (create a task), open the link URL, or download the torrent file.
RSS: List, add, edit, delete or update RSS feeds.
Download Station Settings
Go to “More” > "Settings" to configure Download Station.
Global Settings
Download Schedule: Select continuous download or specify the download schedule. When setting
the download schedule, select "Full speed" to use the global speed limit (unlimited) for all the
download tasks. Select "Limited" to apply the speed limit settings of the downloaded services.
Notification: Select to send a notification by email when a download task completes (SMTP
settings must be configured properly in "System Settings" > "Notification".)
Search: Agree to enable the BT search function.
HTTP
Connection: Specify the maximum number of concurrent HTTP downloads.

Bandwidth Limit: Specify the maximum download rate of HTTP download tasks. 0 means
unlimited (the maximum number of concurrent HTTP downloads for x86-based NAS models is 30,
and 10 for ARM-based NAS models.)
FTP
Connection: Specify the maximum number of concurrent FTP downloads.
Bandwidth Limit: Specify the maximum download rate of FTP download tasks. 0 means unlimited
(the maximum number of concurrent FTP downloads for x86-based NAS models is 30, and 10 for
ARM-based NAS models.)
BT
Connection Setting:
o Specify the ports for BT download. The default port numbers are 6881-6889.
o Enable UPnP port mapping: Enable automatic port mapping on the UPnP supported gateway.
o Enable DHT network: To allow the NAS to download the files even if torrent trackers cannot
connect, enable Distributed Hash Table ( DHT) network and specify the UDP port number for
DHT.
o Enable LSD network: To allow the NAS to discover local peers, enable local discovery service
(LSD).
o Enable NAT-PMP network: To automate port mapping and allow peers to easily download your
files, enable NAT port mapping (NAT-PMP).
o Protocol encryption: Enable this option for encrypted data transfer.
Bandwidth Limit: Specify the maximum download rate of BT download tasks.
o Global maximum concurrent downloads: Specify the maximum number of concurrent BT
downloads (the maximum number of concurrent downloads for x86-based NAS models is 30,
and 10 for ARM-based NAS models.)
o Global maximum upload rate (KB/s): Enter the maximum upload rate for BT download. 0
means unlimited.
o Global maximum download rate (KB/s): Enter the maximum download rate for BT download. 0
means unlimited.
o Maximum upload rate per torrent (KB/s): Enter the maximum upload rate per torrent. 0 means
unlimited.
o Global maximum number of connections: The maximum number of allowed connections to the
torrent.
o Maximum number of connected peers per torrent: The maximum number of allowed peers to
connect to a torrent.
Seeding Preferences: Specify the share ratio for seeding a torrent and the sharing time. The share
ratio is calculated by dividing the amount of uploaded data by the amount of downloaded data.

Proxy: Specify the proxy server for BT download. Select the proxy type and enter the host IP and
port, login username and password for the proxy server. For details on the setup of the proxy
server, please refer to its user manual.
BT Search: Select the BT engines to enable for BT search on the Download Station.
RSS
Update: Enable RSS download and specify the time interval to for the NAS to update the RSS feeds
and check if any new contents that match the filters are available.
Add-on
You can enable and disable supported BT sites, torrent search engines and indexers on this page.
New BT sites, search engines and indexers can be added as an Add-on to enrich the possibilities of
Download Station.
Tip: You can click the following link to download the developer guide for creating Download Station
Add-ons: http://download.qnap.com/dev/download-station-addon-developers-guide_v4.pdf
File Hosting Account
You can save the login information for up to 64 HTTP and FTP accounts. To add login information,
click "Add Account". Enter the host name or IP, username and password. To allow the login
information to appear for account selection when configuring HTTP or FTP download, select "Enabled"
next to the newly added account. To edit the settings of an account, select an entry on the list and
click "Edit Account". To delete an account, select an entry on the list and click "Delete Account".
Using Download Station
Adding a download task
There are three ways to add download tasks:
1. Perform one of the following tasks.
a.
Drag and drop BT/PT files from the local PC to Download Station.
b.
Click “Add download task” (+) button and select Input URL or Torrent file.
c.
Search for BT files using the BT search function to add download tasks.
d.
Add an RSS feed and then create a download task.
2. Specify the following:
a.
Location of temporary files
b.
Location of completed downloads
3. Specify if you want to use your account credentials.
4. Click “Apply”.

Note:
The maximum number of concurrent downloads for x86-based NAS models is 60 (30
BT/PT and 30 HTTP/FTP) and 20 for ARM-based NAS models (10 BT/PT and 10
HTTP/FTP.)
Dragging & dropping BT files from PC to Download Station is only supported by Chrome
and Firefox.
Adding HTTP, FTP, Magnet download tasks
1. Click “Add download task” (+) and select Input URL.
2. Enter the HTTP, FTP, or Magnet link. Note: Separate multiple entries by pressing "Enter". There
should only be one URL on each line.
3. Click “Next”.
4. Specify the following:
a.
Location of temporary files
b.
Location of completed downloads
5. Specify if you want to use your account credentials.
6. Click “Apply”.
Note:
You can enter up to 30 entries at one time.
Managing downloads in a BT seed
You can right-click a task and select "Edit Downloads" to only select the files within a BT seed that
you want to download.
Limiting the download/upload speed
To limit the bandwidth usage of the Download Station, configure the settings in "Settings" > "HTTP",
"FTP", or "BT" > "Bandwidth Limit".
Scheduling downloads
To set scheduled downloads, go to "Settings" > "Global" > "Download Schedule". After enabling the
download schedule, select "Full speed", "Turn off", or "Limited" and then click the preferred time
slots.
Sending a notification after a download is completed
Go to "Settings" > "Global"> "Notification" and enable "Email".
Subscribing to and managing RSS feeds
You can subscribe to RSS feeds using the Download Station and download the files.

Adding an RSS subscription
1. Click "+" next to "RSS" on the left panel to add an RSS feed.
2. Enter the label.
3. Enter the feed URL.
4. Specify the following:
a.
Location of temporary files
b.
Location of completed downloads
5. Click “Apply”.
6. Click “Close”.
Downloading an RSS file
1. Select the file.
2. Perform one of the following tasks.
a.
Click ”Add download task(s)”.
b.
Right-click the file and select "Download".
The NAS automatically downloads the file. You can view the download status in the Downloading list.
Managing RSS subscriptions
To manage the RSS subscriptions, right-click on an RSS feed label. You can open the RSS Download
Manager, add, update, edit, or delete an RSS feed.
Downloading torrent files using RSS Download Manager
You can use the RSS Download Manager to create and manage filters to download particular torrent
files for BT Download.
To add a filter, first launch the RSS Download Manager, select a label and click "Add".
Enter the filter name and specify keywords to include and exclude.
Select the RSS feed to apply the filter settings.
You may also specify the quality of the video torrent files (leave it as "All" if you do not need this
function or the torrent file is not a video.)
Episode number: Select this option to specify particular episodes or a series of episodes. For
example, to download episodes 1-26 of season 1 of a TV program, enter 1x1-26. To only
download episode 1 of season 1, enter 1x1.
Select the time interval for automatic update of RSS feeds. The NAS will update the RSS feeds
and check if any new contents that match the filters are available.
Click "Apply" to save the filter or "Cancel" to cancel or exit.
To delete a filter, select the filter from the list and click "Delete".
Shortening BT seeding time
Go to "Settings" > "BT" > "Bandwidth Limit">"Seeding Preferences".
Change the "Share Ratio" to a smaller percentage or modify "Share Time" to shorten BT seeding
time.

Sharing with multiple users
Administrators can grant Download Station access to NAS users, enabling friends and family
members to enjoy the convenience brought by Download Station. Follow these steps to grant access
to NAS users:
1. Go to "Control Panel" >"Privilege" > "Users"
2. Click the "Edit Application Privilege" button under "Action" for the user
3. Select Download Station.
4. Click "Apply".
Tips for
slow BT download rates or download errors
:
1. The torrent file has expired, the peers have stopped sharing this file, or there is error in the file.
2. The NAS has been configured to use a fixed IP but the DNS server is not configured or it has
failed.
3. Set the maximum number of simultaneous downloads as 3-5 for the best download rate.
4. The NAS is located behind a NAT router. The port settings have led to slow BT download rate or
no response. You can try the following means to solve the problem:
a. Manually open the BT port range on NAT router. Forward these ports to the LAN IP of the
NAS.
b. Recent NAS firmware supports UPnP NAT port forwarding. If your NAT router supports UPnP,
enable this function on the NAT. Then enable UPnP NAT port forwarding of the NAS. The BT
download rate should be enhanced.
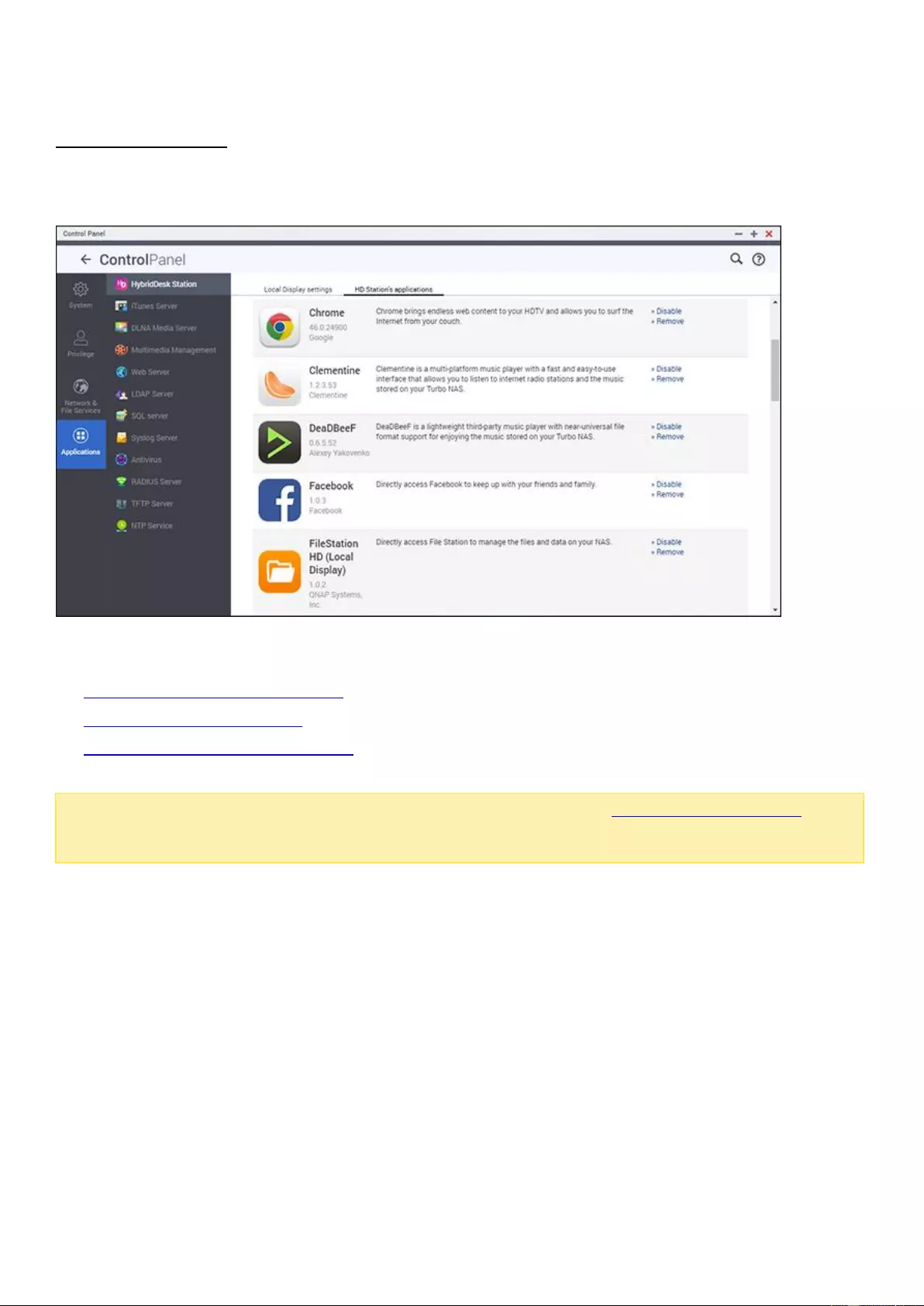
HybridDesk Station
HybridDesk Station is a platform where numerous home and office apps can be installed to
enhance your entertainment and productivity needs.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Setting up HybridDesk Station
Using HybridDesk Station
Configuring HybridDesk Station
Note:
To check whether your model support HD Station, go to http://www.qnap.com and
use “HD station” as a keyword to find the related information.
Setting up HybridDesk Station
Create your lovely media environment by following these steps:
1.
Setting up the environment of the HybridDesk Station: Connect the NAS to the
HDMI TV with a HDMI cable
o
Remote controller: There are 4 different ways to control the HybridDesk Station.
QNAP remote controller
USB keyboard or mouse
Qremote: QNAP remote app, designed exclusively for the HybridDesk Station.

Note:
If you want to use Chrome on HD Station, you must use the Qremote mouse
function or use a USB mouse that is connected to the NAS.
2.
Installing the HybridDesk Station
o
Go to "Applications" > "HybridDesk Station" and click the "Get Started Now" button.
The system will automatically install the HybridDesk Station.
3.
Choosing the applications to install
o
You can choose from a variety of powerful QNAP and third-party applications to
increase your work productivity and enrich your entertainment experience.
Note:
Using Chrome or other applications may affect the hard drive hibernation of the NAS.
Remember to exit the application and return to the HybridDesk Station portal.
To exit an application, press the power button on the remote control for 6 seconds at
any time.
Press the one touch copy button on the NAS for 6 seconds to restart the HybridDesk
Station.
For the best HybridDesk Station experience, we recommend using a NAS with at least
2GB memory.
The HybridDesk Station will restart when formatting an USB external device.
After installation, choose your preferred language on the TV screen, then you will see the
HybridDesk Station portal.
4.
Enjoying HybridDesk Station: On the HybridDesk Station portal, select the
application you want to use and start enjoying the service.
Enjoy the comfort of your living room and play movies, photos, and music directly on your
TV.
Using HybridDesk Station
Taking Pictures with Smart Phone and Watching them on TV
The first part is done by Qfile on your phone:
1.
Use Qfile to browse your NAS.
2.
Choose the multimedia shared folder.
3.
Select the upload function.
4.
Take a picture and upload it to the NAS.

The second part is performed by the HybridDesk Station on your TV:
5.
Turn on your TV and choose HD Player.
6.
Choose "Pictures".
7.
Select the "Multimedia" folder.
8.
Double click the picture you just uploaded.
Viewing Photos on your USB Device or Camera
Steps:
1.
Connect a USB device or camera to the NAS.
2.
Choose "Pictures".
3.
Choose "Options".
4.
Select the photo you want to view.
Configuring HybridDesk Station
Configure the HybridDesk Station by choosing "Settings" at the HybridDesk Station portal
and HybridDesk Station in QTS.
HybridDesk Station portal:
o
App: Applications can be enabled or disabled here.
o
Display: Change the screen resolution and set up to turn off the screen after an
amount of idle time.
o
Preferences: Here you may change the language or type of remote control and audio
output. The default setting is HDMI. If there is an installed USB sound card, you can
choose that option in the NAS Audio Output.
HybridDesk Station in QTS:
o
Output resolution: Change the resolution for the HybridDesk Station portal screen.
Before you change this setting, please make sure that no apps are opened in the
HybridDesk Station portal.
o
Overscan: This setting can reduce the visible area of a video displayed on the
HybridDesk Station portal. The higher the percentage, the more the visible area will be
reduced.
Note:
Only the QNAP remote or MCE remote control is supported. NOT all of the TS-x69
models support the internal remote control and the TS-x70 models only support the
MCE remote control.
HDMI Audio Passthrough is currently not supported by the TS-x69 series.
App Center
The App Center is a platform for the distribution of NAS apps. Users can search for, install, remove
and update apps developed by QNAP and third-party developers to expand services and add new
features to the NAS.
Starting App Center
The App Center can be launched from the App Center shortcut on the Main Menu or the NAS Desktop.
Familiarizing yourself with App Center
Menu Bar
No
Name
Description
1
Search
Search for Apps that are available to install on the NAS.
2
Refresh
Refresh the current page.
3
Settings
Install Manually: Browse to upload and manually install a QPKG add-on.
You can also find information on App add-on developments here.

App Repository: If you have an URL provided by a third-party community
or developer, you can add or modify it here to import applications from
other sources.
QTS Help
4
View Mode
Switch to item mode or list mode for the apps.
5
Sort
Sort apps by category, name, or release date, in an ascending or
descending fashion.
6
Update All
Update all of the Apps that are currently installed on the NAS
Left Panel
My Apps: List Apps that are currently installed on the NAS.
My Licenses: List licenses for all Apps to be installed on the NAS. You can also add and activate
your licenses.
All Apps: List all Apps that can be installed on the NAS.
QNAP Essentials: List Apps developed by QNAP.
Recommended: List Apps recommended by QNAP (they could be either developed by QNAP or
third party developers.)
Beta Lab: Lists Apps that are currently in development.
Partners: List Apps developed by QNAP partners.
Apps by types: From "Backup/Sync" to "Education", those are App categories listed to facilitate
your App searches.
Using App Center
Searching apps
To search for an App, enter the keyword in the search bar.
Installing, updating and removing apps
To install an app, click the "+ Install" button and the installation process will begin. After the
installation process is complete, the "+ Install" button will turn to the "O Open" button and you can
directly click this button to launch this newly installed app. This newly installed app will then show up
in "My Apps".
Note:
Make sure the NAS is connected to the Internet.
QNAP is not responsible for troubleshooting any issues caused by open source
software/add-ons. Users are encouraged to visit the QNAP community forum or contact
the creators of the open source software for solutions.

When installing an add-on that requires a prerequisite app, the prerequisite add-on will
be automatically added to the installation queue prior to the dependent add-on.
If the app update process is canceled before it is finished, please re-install the app from
the App Center.
To update an App, click "Update" and click "OK" to confirm. Alternatively, you can click "Update All"
on the menu bar to install all updates and "Refresh" to check for the latest updates. The button will
turn to "Open" to signify that the update is complete. You can also click the down arrow icon on the
button to open an installed app, stop an app (the button will turn to "Start" after you stop an app and
you can click it to start the app again), remove an app, or set to display the app on the
administrator’s main menu, every user’s main menu, or the login screen as a shortcut.
Note:
Click the on/off button in an App icon to enable or disable an App.
For more apps, please visit the QNAP official site
(http://www.qnap.com/go/qpkg.html).
Offline Installation
To install apps when the NAS is offline or to install beta apps that are not officially available on the
QNAP App Center, users can download the application (*.qpkg) from the QNAP website
(http://www.qnap.com/go/qpkg.html) or forum (http://forum.qnap.com/), unzip the files, and click
"Install Manually" on the menu bar to install the Apps manually.

Mobile Apps
QNAP has introduced a list of mobile apps to help users access their NAS with their mobile devices.
The following are a list of benefits that QNAP mobile apps can bring you:
Automatically update photos from your phones on your trip: When on vacation, photos on your
mobile device can be automatically uploaded to your NAS, allowing you to focus on your photos
instead of worrying about running out of space.
Easily share large files with friends and families: Sharing huge files is extremely easy with QNAP
mobile apps. Share them whenever and wherever you want.
Browse files stored on your NAS: Access your multimedia (photos, videos and music) and office
documents (Word, PDF, or Excel) stored on your NAS using your mobile device.
Manage services on your NAS with ease: Check the status of your NAS or enable/disable NAS
application services remotely using your phone.
Topics covered in this chapter:
Qfile
Qmanager
Qnotes
Qremote
Qmusic
Qvideo
Qphoto
Qget
Vmobile
Vcam
Qfile
Qfile enables you to browse and manage the files on your NAS from your mobile device.
Manage multiple QNAP NAS in different locations conveniently from your mobile device.
A simple and intuitive interface makes management easy. Thumbnails help you identify file types at a
glance and you can move, copy, rename, and delete files on your NAS without needing a PC.
Download
Qmanager
Qmanager is a powerful management platform with a simple to use and intuitive interface that makes
monitoring and managing your NAS from mobile devices amazingly easy.
Monitor system information, such as CPU usage, memory usage, system event info, online users,
backup status, download progress, and file transfers. Use "App Center" to turn application services on
or off with a single click. Restart or shut down your NAS remotely.
Download
Qnotes
Qnotes is a powerful digital notebook and workspace for organizing your to-do lists, shopping lists,
lecture notes, meeting notes, and everything else you want to remember. Synchronize your notes
across your devices so you can access them wherever you go. Add audio recordings or take a picture
and save it to Qnotes to keep it for you. Enjoy peace of mind that your notes are securely stored, and
available from anywhere.
You can easily share your notes with others. Work together with your friends, family, classmates, and
colleagues. Share your notebooks with others for viewing or editing.
Download
Qremote
Qremote is QNAP’s remote control for HD Station. Use Qremote to control HD Station from your
mobile devices.
Download
Qmusic
Qmusic helps you enjoy the music collection on your NAS via your mobile devices at anytime,
anywhere. Create and send links to share your favorite music with friends and family using social
networks, instant messengers or by email.
Download
Qvideo
Qvideo helps you enjoy the videos on your NAS via your mobile devices at anytime, anywhere and
also to share your videos with friends and family.
Download
Qphoto
Qphoto helps you enjoy your personal photo collection on your mobile devices at any time, from
anywhere, without limits. Relive and share your special moments on the go.
Download

Qget
Qget allows you to manage all of the download tasks on your NAS using your mobile devices at
anytime, anywhere. Use Qget to add and monitor your download tasks in Download Station. The Qget
built-in browser helps you to add tasks from direct download links or from magnet links. Qget can
also search across multiple Bit Torrent sites and add the torrent to your download queue.
Download
Vmobile
Vmobile is a mobile video surveillance application provided by QNAP that enables you to connect to
and manage your video surveillance system from your mobile device at anytime from anywhere.
Connect Vmobile to a NAS with Surveillance Station installed and you can monitor IP cameras and
play recordings. Monitor several servers/channels from all of your network cameras of by simply
connecting to any available NAS on the network.
Download
Vcam
Vcam can turn your mobile device into a network camera, allowing you to record any moment around
you to your NAS. Vcam provides a great way to deploy a home surveillance system without
purchasing expensive IP cameras.

Download

Computer Utilities
QNAP constantly develops new ways for users to improve their NAS experience, and provides the
following utilities to improve productivity:
Qfinder Pro
myQNAPcloud connect
Qsync 2.0
NetBak Replicator
Qget
vSphere Client plug-in
Qsnap
Qfinder Pro
Qfinder Pro is a utility, available for Windows, Mac, and Linux, to quickly find and access a NAS on
LAN. Install Qfinder Pro on your computer, open it, double click your NAS, and the login page is ready
for you.
Download
myQNAPcloud connect
myQNAPcloud Connect helps you to quickly and securely access published services of your NAS on
the Internet. myQNAPcloud Connect is designed for Windows users. By installing myQNAPcloud
Connect, you will be able to connect to the NAS and easily manage files by drag & drop within the
Windows File Explorer.
Download
Qsync 2.0
Qsync is a file synchronization service. Simply add files to your designated sync folder(s) and those
folders and files will be available on the NAS and all devices linked to it.
Download
NetBak Replicator
The NetBak Replicator helps you easily back up files from a Windows PC to the NAS, including entire
disk drives, documents, pictures, music, videos, fonts, emails, and more. The operation is very simple.
You can carry out backup tasks in just a few clicks using by setting real-time synchronization,
scheduled backup and auto-backup from multiple PCs to the NAS.
NetBak Replicator also supports backing up to a remote server via FTP and WebDAV through the
Internet.
Download User Manual
Qget
QGet is a powerful utility for download management. The software is available for Windows and Mac
computers, allowing the management of BT, HTTP, and FTP download tasks of Download Station on
multiple NAS.
QGet enables you to add, remove, and monitor BT download jobs from LAN or WAN. You can manage
your download tasks in school or at work. QGet supports intuitive drag & drop of torrent files, HTTP
or FTP URL to the software interface for convenient adding of download tasks.
Download
vSphere Client plug-in
The NAS supports vSphere Client Plug-in that allows managing VMware datastores on the NAS
directly from the vSphere client console. In a large-scale server virtualization environment,
management is centralized and straightforward. Administrators can easily control the status of the
NAS and datastores and create additional datastores to multiple ESXi hosts in just a few clicks.
Download
Qsnap
Qsnap is a handy utility that can assist in quickly capturing screenshots on your PC. They can be
quickly edited, saved and shared allowing quick note-taking and productive communication.
Download

NAS Add-ons
The following NAS Add-ons (QPKG) are recommended to help you explore other NAS possibilities:
Storage and Backup
Backup Versioning – Beta
Gmail Backup -Beta
Hybrid Backup Sync - Beta
Virtualization
Container Station – Beta
Virtualization Station - Beta
Linux Station - Beta
Productivity
Notes Station - Beta
Qsirch – Beta
Qmail Agent– Beta
Entertainment
Media Streaming Add-On
Photo Station Extension - Beta
OceanKTV - Beta
Security
L2TP/IPsec VPN Service
MyQNAPcloud SSL Certificate
Surveillance Station
Proxy Server
Connectivity
CloudLink
Business
Signage Station
Tool
Diagnostic Tool – Beta
Q'center

Note:
Some of the add-ons in this chapter are only supported by certain NAS models. Please
refer to the software specification page on the QNAP website for further details. If a
certain Add-on is not supported by your NAS, that Add-on will not be available when
you search it in the App Center.
For more Apps, please visit the QNAP site (http://www.qnap.com/go/qpkg.html).
Backup Versioning – Beta
Backup Versioning enables version control option in RTRR backup jobs. When creating a RTRR backup
job, the option "version control" is available and allows preserving a certain amount of versions, and
also a smart version recycling to be able to retain backups longer time.
Gmail Backup - Beta
Gmail backup provides Gmail backup and recovery functionality, allowing users to create individual
backup or domain account backup tasks. Gmail can be backed up by schedule and the content
previewed through a web management interface. Backed up mail can be restored to the original mail
account or other accounts: just configure the restore account, enter the account and password and
the user can restore mail to the specified account.
Hybrid Backup Sync - Beta
Hybrid Backup Sync is a comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery solution for files stored on
QNAP NAS. It integrates backup, restoration and synchronization features to provide a variety of
options for data backup and synchronization including USB one-touch backup, Time Machine backup,
RTRR backup and synchronization through RTRR, Rsync, FTP, CIFS/SMB and various cloud services
such as Amazon® S3, Amazon® Glacier, Azure™ Storage, Google Cloud Storage™, S3/OpenStack
Swift/WebDAV compatible services, Google Drive™, Microsoft® OneDrive® and Dropbox®. Hybrid
Backup Sync allows users to create storage, remote and cloud account settings in advance which can
help save time in creating backup jobs.
Container Station – Beta
Container Station integrates both LXC and Docker virtualization technologies. This enables the use of
multiple, isolated Linux systems on the NAS. We have also engineered one-click download, install,
and deployment of thin applications from the built-in Docker Hub Registry to make virtualization
easier than ever.

Virtualization Station - Beta
Virtualization Station turns the NAS into an appliance server, and allows you to install virtual
machines (VMs) on the NAS with Windows, Linux, UNIX and Android operating systems. It can
increase the functionality of the NAS and be eco-friendly by using VMs instead of physical servers.
With an easy-to-use interface, you can centrally manage all of the VMs created on the NAS with
minimal effort. You can also access virtual machines remotely on PCs and mobile devices by using
web browsers at anytime. Virtualization Station allows users to open the data on the NAS directly
through VMs, reducing bandwidth utilization and greatly enhancing data security as all of the actions
are carried out within the NAS and no data is transmitted externally. Running application services on
VMs is also efficient and secure by leveraging the high-performance I/O and the comprehensive data
protection of the NAS.
Linux Station - Beta
Linux Station is a standard Linux desktop platform that allows you to use QTS while simultaneously
using Linux on an HDMI display. Simply connect a keyboard and mouse to the NAS to use the NAS as
a PC. You can also enable the remote desktop connection to use Linux Station with a web browser.
Notes Station - Beta
Notes Station enables you to create digital notebooks on the private cloud provided by the NAS. You
can also easily leverage the files, photos, music and videos stored on the NAS to enrich your notes.
With Notes Station, digital memos are safely kept for instant access. Notes Station provides a
straightforward interface for note taking. You can easily insert all kinds of files stored on the NAS as
part of your notes or as attachment to enhance the content. The Media Library of QTS 4.1 provides
multimedia file preview to help quickly find the correct files to insert.
Qsirch – Beta
With Qsirch you can enhance your productivity with a powerful full-content search. NAS allows you to
store huge amounts of data, files, and information. But it can be very easy for important files to get
lost as increasing amounts of data is stored on it, making productivity suffer as users spend time
searching for files instead of working. Qsirch can help users locate files in the shortest possible time.
Qsirch has advanced file extraction and a near real-time search engine, allowing users to quickly
search through the entire NAS to find desired files as soon as possible. The uniquely crafted QNAP
TF-IDF algorithm actively predicts your results as you type for lightning speed.

Qmail Agent – Beta
Qmail Agent is an online mail client that allows users to access Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo mail, and any
IMAP server. It also works with Gmail Backup to review archived emails. It can easily switch accounts
with its quick launch bar and provides complete functionality for composing, reading and organizing
email messages. Files, photos and documents stored on the NAS can also be attached to emails.
Qmail Agent also supports automatically backing up all of the emails on the server to the NAS upon
logging in. In this article we will walk you through on how to use the Qmail Agent app to manage
your emails on a QNAP NAS.
Media Streaming Add-On - Beta
The Media Streaming Add-On is an add-on for stations in QTS (File Station, Photo Station, Music
Station and Video Station) that allows you to stream your media to different devices in different
locations simultaneously using AirPlay, DLNA, Chromecast, and HDMI-connected devices. With the
advanced management of the DLNA Media Server, you can also set advanced settings, such as DLNA
client control, menu language and more.
Photo Station Extension - Beta
This Photo Station Extension App will enable the face detection* and pdf album import features for
your Photo Station. You will be able to browse the imported pdf files as albums easily on other mobile
devices.
OceanKTV - Beta
OceanKTV transforms your QNAP NAS into a high-quality karaoke machine. Just import your songs to
the OceanKTV folder and start using it. A companion mobile app is also available to remotely control
OceanKTV. Invite your friends to sing together now!
L2TP/IPsec VPN Service
L2TP (Layer Two Tunneling Protocol) is a combination of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
and Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F.) Compared to PPTP, which only establishes a single tunnel between the
two end points, L2TP supports the use of multiple tunnels. IPsec is often used to secure L2TP packets
by providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity checks. The combination of these two
protocols provides a high-security VPN solution which is known as L2TP/IPsec. L2TP/IPsec is
supported by most clients, including Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile devices.

MyQNAPcloud SSL Certificate
After installing the myQNAPcloud SSL Certificate App, you will see the user interface on QTS
myQNAPcloud to download and install your purchased SSL certificates from the myQNAPcloud website
(https://www.myqnapcloud.com.) SSL certificates bring better protection when connecting to your
QNAP NAS via myQNAPcloud DDNS.
Surveillance Station
Surveillance Station is a professional network surveillance system and video management system. As
one of the standard NAS applications, the Surveillance Station can be activated on the App Center to
turn your NAS into a professional network video recorder. When used with compatible IP cameras,
Surveillance Station can perform the following operations: real-time monitoring, recording, playback,
alarm notifications, Intelligent Video Analytics and video management to help you secure your assets
and property.
Proxy Server
The Proxy Server application provides an intuitive interface to simplify proxy server settings on your
NAS, enabling you to operate your own proxy server in just a few clicks. The proxy server provides
cache and connection controls for Internet services. For companies that need a boost to web
response time and security, this application can be leveraged to make your NAS a web proxy server
to protect other devices in your local network from Internet attacks.
CloudLink
CloudLink is the best remote access service provided by myQNAPcloud that allows you to connect to
your device via the Internet using the myQNAPcloud website (www.myqnapcloud.com.) No
complicated port forwarding settings on the router are required: just install CloudLink App on device
App Center and sign in myQNAPcloud ID (QID) on your device. Then you can access files from the
myQNAPcloud website. CloudLink will select the best connection for you according to your network
environment. In addition to the web-based connection, CloudLink also allows you to connect to your
QNAP device with QNAP Mobile Apps Qfile, Qmanager and the PC utility Qsync. CloudLink makes
remote connectivity so easy.
Signage Station
Signage Station provides digital signage display functionalities and allows content to be managed with
access permissions. Users can use iArtist Lite to design the digital signage content and upload to the
NAS, and use Signage Station to display the digital signage media content on the web browser from
the NAS.

Diagnostic Tool – Beta
The diagnostic tool provides a variety of system analysis functions to check the stability of a NAS.
Users can export system kernel records for sending to technical support staff for further investigation
and system kernel log analysis tools can quickly check if abnormal actions have occurred. There are
also tools for checking the file system, hard drives and RAM to provide a simple way to test system
reliability.
Q'center
Q’center is a central management platform that enables you to consolidate the management of
multiple QNAP NAS. The Q’center web interface gives you the ease-of-use, cost-efficiency,
convenience and flexibility to manage multiple NAS, across multiple sites, from any internet browser.
Use the LCD Panel
This feature is only available for NAS models with LCD panels.
You can use the LCD panel to configure system settings and view system information.You can use the
“ENTER” and “SELECT” buttons next to the panel to navigate through the LCD menu.
After starting the NAS, you can see its name and firmware version appear on the panel:
N
A
S
5
F
4
D
E
3
4
.
3
.
0
(
2
0
1
6
0
7
0
3
)
After a few seconds, the panel will be automatically turned off. Then you can begin to configure settings or view
system information.
Viewing system IP address
1. Press“ENTER”or “SELECT”to turn on the panel.
2. Press “SELECT”to browse the NAS model name and the available IP addresses (for each network
interface).
This feature is particularly useful when the NAS is near you.
Viewing and configuring system settings
When the name and firmware version of the NAS appear on the panel, press “ENTER” for two seconds to view the
Main Menu, which will automatically disappearif no further actions are performed in ten seconds.
There are eight options on the Main Menu:
1. TCP/IP
2. Physical disk
3. Volume
4. System
5. Shut down
6. Reboot
7. Password
8. Back
Press “SELECT” to go to the next option and “ENTER” to select an option.
TCP/IP
In TCP/IP, you can see the following information:
1. LAN IP Address
2. LAN Subnet Mask
3. LAN Gateway
4. LAN PRI. DNS
5. LAN SEC. DNS
(You can configure the above settings for every interface.)
6. Enter Network Settings
a. Network Settings – DHCP
i. Set upDHCP on LAN1 and LAN2
Network Settings – Static IP*
ii. Press “SELECT” to switch to the next available option.
iii. Press “ENTER” to configure the selected option.The first digit will begin to blink.
iv. Press “SELECT” to increment the selected digit, press“ENTER” to confirm the value,
and go to the next digit until all digits are set.
v. Repeat this procedure this for every setting you want to change.
c. Network Settings – BACK
7. Back to Main Menu
* In this section, you can only configure IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS of
LAN1 and LAN2.
Physical disk
In Physical disk, you can see the following options:
1. Disk Info
2. Back to Main Menu
Disk Info shows the temperature and the capacity of the hard drives.
D
i
s
k
:
1
T
e
m
p
:
5
0
°
C
S
i
z
e
:
2
3
2
G
B
Volume
This section shows the capacities of volumes and LUNs. You can view the name and capacity of a
volume/LUN. If there are multiple volumes/LUNs, press "Select" to view the information of a specific
volume/LUN.
D
a
t
a
V
o
l
1
7
5
0
G
B
L
U
N
_
0
7
5
0
G
B
System
This section shows the system temperature and the rotation speed of the system fan.
C
P
U
T
e
m
p
:
5
0
°
C
S
y
s
T
e
m
p
:
5
5
°
C
F
a
n
1
:
2
3
2
1
R
P
M
F
a
n
2
:
2
4
0
2
R
P
M
Shut down
You can use this option to turn off the NAS. Press "SELECT", select "Yes", and then press "ENTER" to
confirm.
Reboot
You can use this option to restart the NAS. Press "SELECT", select "Yes", and press "ENTER" to
confirm.
Password
The default password for the LCD panel is empty. If you want to change the password, select "Yes" to
continue.
C
h
a
n
g
e
P
a
s
s
w
o
r
d
Y
e
s
→
N
o
You can enter up to 8 digits for your password.
Press “SELECT” to increment the digit and press “ENTER” to add a new digit.
After inputting your desired password, press “ENTER”.
When the cursor moves next to "OK", press “ENTER” to confirm the password.
N
e
w
P
a
s
s
w
o
r
d
:
2
3
4
→
O
K
V
e
r
i
f
y
P
a
s
s
w
o
r
d
2
3
4
→
O
K
Back
Select this option to return to the Main Menu.
System Messages
When an error occurs, a message will appear on the LCD panel. Press “ENTER” to view the message
and press “ENTER” again to go to the next message.
S
y
s
t
e
m
E
r
r
o
r
!
P
l
s
.
C
h
e
c
k
L
o
g
s
System Message
Description
Sys. Fan Failed
The system fan has failed.
Sys. Overheat
The system has overheated.
HDD Overheat
A hard drive has overheated.
CPU Overheat
The CPU has overheated.
Network Lost
Both LAN 1 and LAN 2 are disconnected in failover or load balancing
mode.
LAN1 Lost
LAN 1 is disconnected.
LAN2 Lost
LAN 2 is disconnected.
HDD Failure
A hard drive has failed.
Vol1 Full
The disk volume (1) is full.
NAS HDD Ejected
A hard drive has been ejected from the NAS.
RX#3 HDD Ejected
A hard drive has been ejected from the expansion unit 3.
M.2 SSD Ejected
A M.2 SSD has been ejected and may be defective as hot-plugging isnot
supported for M.2 drives.
PCIe SSD Ejected
A PCIe SSD has been ejected and may be defective as hot-plugging is
not supported for PCIe devices.
Vol1 Degraded
The disk volume (1) is in degraded mode.
Vol1 Unmounted
The disk volume (1) is unmounted.
Vol1 Nonactivate
The disk volume (1) is inactive.

System startup
S
Y
S
T
E
M
B
O
O
T
I
N
G
>
>
>
There are several phases in the system startup process:
- System Booting: BIOS and hardware initialization, and system booting (no actions need to be
performed)
- Loading Driver: Loading QTS and its drivers (no actions need to be performed)
- Mount Volume: Prepare volumes (no actions need to be performed)
- Starting Service: Starting NAS system services (no actions need to be performed). Note that
applications start only after the system finishes booting

GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 3, 29 June 2007
Copyright © 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <http://fsf.org/>
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license document, but changing
it is not allowed.
Preamble
The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for software and other kinds of works.
The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed to take away your freedom to
share and change the works. By contrast, the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee
your freedom to share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free software
for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the GNU General Public License for most of
our software; it applies also to any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
your programs, too.
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not price. Our General Public Licenses
are designed to make sure that you have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and
charge for them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you want it, that you can
change the software or use pieces of it in new free programs, and that you know you can do these
things.
To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you these rights or asking you to
surrender the rights. Therefore, you have certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the
software, or if you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether gratis or for a fee, you must pass on
to the recipients the same freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive or
can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they know their rights.
Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps: (1) assert copyright on the
software, and (2) offer you this License giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify
it.

For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains that there is no warranty for this
free software. For both users' and authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked
as changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to authors of previous versions.
Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run modified versions of the software
inside them, although the manufacturer can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic pattern of such abuse occurs in the
area of products for individuals to use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore,
we have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those products. If such problems
arise substantially in other domains, we stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in
future versions of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents. States should not allow patents
to restrict development and use of software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we
wish to avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could make it effectively
proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that patents cannot be used to render the program
non-free.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and modification follow.
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
0. Definitions.
'This License' refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
'Copyright' also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of works, such as semiconductor
masks.
'The Program' refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this License. Each licensee is
addressed as 'you'. 'Licensees' and 'recipients' may be individuals or organizations.
To 'modify' a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work in a fashion requiring
copyright permission, other than the making of an exact copy. The resulting work is called a 'modified
version' of the earlier work or a work 'based on' the earlier work.
A 'covered work' means either the unmodified Program or a work based on the Program.
To 'propagate' a work means to do anything with it that, without permission, would make you directly
or secondarily liable for infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying, distribution (with or without
modification), making available to the public, and in some countries other activities as well.

To 'convey' a work means any kind of propagation that enables other parties to make or receive
copies. Mere interaction with a user through a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not
conveying.
An interactive user interface displays 'Appropriate Legal Notices' to the extent that it includes a
convenient and prominently visible feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the extent that warranties are
provided), that licensees may convey the work under this License, and how to view a copy of this
License. If the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a menu, a prominent
item in the list meets this criterion.
1. Source Code.
The 'source code' for a work means the preferred form of the work for making modifications to it.
'Object code' means any non-source form of a work.
'Standard Interface' means an interface that either is an official standard defined by a recognized
standards body, or, in the case of interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one
that is widely used among developers working in that language.
The 'System Libraries' of an executable work include anything, other than the work as a whole, that:
a) is included in the normal form of packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that
Major Component, and
b) serves only to enable use of the work with that Major Component, or to implement a Standard
Interface for which an implementation is available to the public in source code form. A 'Major
Component', in this context, means a major essential component (kernel, window system, and
so on) of the specific operating system (if any) on which the executable work runs, or a
compiler used to produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
The 'Corresponding Source' for a work in object code form means all the source code needed to
generate, install, and (for an executable work) run the object code and to modify the work, including
scripts to control those activities. However, it does not include the work's System Libraries, or
general-purpose tools or generally available free programs which are used unmodified in performing
those activities but which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source includes
interface definition files associated with source files for the work, and the source code for shared
libraries and dynamically linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require, such as
by intimate data communication or control flow between those subprograms and other parts of the
work.
The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users can regenerate automatically from
other parts of the Corresponding Source.

The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that same work.
2. Basic Permissions.
All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of copyright on the Program, and are
irrevocable provided the stated conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a covered work is covered by
this License only if the output, given its content, constitutes a covered work. This License
acknowledges your rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not convey, without conditions so long
as your license otherwise remains in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole
purpose of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you with facilities for
running those works, provided that you comply with the terms of this License in conveying all
material for which you do not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works for
you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction and control, on terms that prohibit
them from making any copies of your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under the conditions stated below.
Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10 makes it unnecessary.
3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological measure under any applicable law
fulfilling obligations under article 11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such measures.
When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid circumvention of technological
measures to the extent such circumvention is effected by exercising rights under this License with
respect to the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or modification of the
work as a means of enforcing, against the work's users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid
circumvention of technological measures.
4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you receive it, in any medium,
provided that you conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright
notice; keep intact all notices stating that this License and any non-permissive terms added in accord
with section 7 apply to the code; keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey, and you may offer support or
warranty protection for a fee.

5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to produce it from the Program,
in the form of source code under the terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these
conditions:
a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified it, and giving a relevant date.
b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is released under this License and any
conditions added under section 7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
'keep intact all notices'.
c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this License to anyone who comes into
possession of a copy. This License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts, regardless of how they are
packaged. This License gives no permission to license the work in any other way, but it does
not invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display Appropriate Legal Notices;
however, if the Program has interactive interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices,
your work need not make them do so.
A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent works, which are not by their
nature extensions of the covered work, and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger
program, in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an 'aggregate' if the
compilation and its resulting copyright are not used to limit the access or legal rights of the
compilation's users beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work in an
aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other parts of the aggregate.
6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms of sections 4 and 5, provided
that you also convey the machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License, in
one of these ways:
a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product (including a physical distribution
medium), accompanied by the Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
customarily used for software interchange.
b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product (including a physical distribution
medium), accompanied by a written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as long as
you offer spare parts or customer support for that product model, to give anyone who
possesses the object code either (1) a copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in
the product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical medium customarily used for
software interchange, for a price no more than your reasonable cost of physically performing
this conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the Corresponding Source from a network
server at no charge.

c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the written offer to provide the
Corresponding Source. This alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord with subsection 6b.
d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated place (gratis or for a charge), and
offer equivalent access to the Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place
at no further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the Corresponding Source along
with the object code. If the place to copy the object code is a network server, the
Corresponding Source may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party) that
supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain clear directions next to the object
code saying where to find the Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is available for as long as needed
to satisfy these requirements.
e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided you inform other peers
where the object code and Corresponding Source of the work are being offered to the general
public at no charge under subsection 6d.
A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded from the Corresponding Source
as a System Library, need not be included in conveying the object code work.
A 'User Product' is either (1) a 'consumer product', which means any tangible personal property which
is normally used for personal, family, or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for
incorporation into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product, doubtful cases
shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular product received by a particular user, 'normally
used' refers to a typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status of the
particular user or of the way in which the particular user actually uses, or expects or is expected to
use, the product. A product is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent the only significant mode of
use of the product.
'Installation Information' for a User Product means any methods, procedures, authorization keys, or
other information required to install and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User
Product from a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must suffice to ensure
that the continued functioning of the modified object code is in no case prevented or interfered with
solely because modification has been made.
If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or specifically for use in, a User
Product, and the conveying occurs as part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of
the User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a fixed term (regardless of how
the transaction is characterized), the Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be
accompanied by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply if neither you nor

any third party retains the ability to install modified object code on the User Product (for example,
the work has been installed in ROM).
The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a requirement to continue to
provide support service, warranty, or updates for a work that has been modified or installed by the
recipient, or for the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a network may
be denied when the modification itself materially and adversely affects the operation of the network
or violates the rules and protocols for communication across the network.
Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided, in accord with this section
must be in a format that is publicly documented (and with an implementation available to the public
in source code form), and must require no special password or key for unpacking, reading or copying.
7. Additional Terms.
'Additional permissions' are terms that supplement the terms of this License by making exceptions
from one or more of its conditions. Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program
shall be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent that they are valid under
applicable law. If additional permissions apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used
separately under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by this License without
regard to the additional permissions.
When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option remove any additional
permissions from that copy, or from any part of it. (Additional permissions may be written to require
their own removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place additional permissions
on material, added by you to a covered work, for which you have or can give appropriate copyright
permission.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you add to a covered work, you may
(if authorized by the copyright holders of that material) supplement the terms of this License with
terms:
a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the terms of sections 15 and 16 of this
License; or
b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or author attributions in that
material or in the Appropriate Legal Notices displayed by works containing it; or
c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or requiring that modified versions
of such material be marked in reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or authors of the material; or
e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some trade names, trademarks, or
service marks; or
f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that material by anyone who conveys the
material (or modified versions of it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient,

for any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on those licensors and
authors.
All other non-permissive additional terms are considered 'further restrictions' within the meaning of
section 10. If the Program as you received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
governed by this License along with a term that is a further restriction, you may remove that term. If
a license document contains a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms of that license document,
provided that the further restriction does not survive such relicensing or conveying.
If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you must place, in the relevant source
files, a statement of the additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating where to find
the applicable terms.
Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the form of a separately written
license, or stated as exceptions; the above requirements apply either way.
8. Termination.
You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly provided under this License.
Any attempt otherwise to propagate or modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights
under this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third paragraph of section 11).
However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your license from a particular copyright holder
is reinstated (a) provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and finally terminates
your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright holder fails to notify you of the violation by some
reasonable means prior to 60 days after the cessation.
Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated permanently if the copyright
holder notifies you of the violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have received
notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that copyright holder, and you cure the
violation prior to 30 days after your receipt of the notice.
Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the licenses of parties who have
received copies or rights from you under this License. If your rights have been terminated and not
permanently reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same material under
section 10.
9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or run a copy of the Program. Ancillary
propagation of a covered work occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However, nothing other than this License

grants you permission to propagate or modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if
you do not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a covered work, you indicate
your acceptance of this License to do so.
10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically receives a license from the original
licensors, to run, modify and propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible for
enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
An 'entity transaction' is a transaction transferring control of an organization, or substantially all
assets of one, or subdividing an organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
work results from an entity transaction, each party to that transaction who receives a copy of the
work also receives whatever licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could give
under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the Corresponding Source of the work
from the predecessor in interest, if the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the rights granted or affirmed under
this License. For example, you may not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation (including a cross-claim or
counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling,
offering for sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
11. Patents.
A 'contributor' is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this License of the Program or a work
on which the Program is based. The work thus licensed is called the contributor's 'contributor
version'.
A contributor's 'essential patent claims' are all patent claims owned or controlled by the contributor,
whether already acquired or hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version, but do not include claims that
would be infringed only as a consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
purposes of this definition, 'control' includes the right to grant patent sublicenses in a manner
consistent with the requirements of this License.
Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free patent license under the
contributor's essential patent claims, to make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run,
modify and propagate the contents of its contributor version.
In the following three paragraphs, a 'patent license' is any express agreement or commitment,
however denominated, not to enforce a patent (such as an express permission to practice a patent or

covenant not to sue for patent infringement). To 'grant' such a patent license to a party means to
make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a patent against the party.
If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license, and the Corresponding Source
of the work is not available for anyone to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License,
through a publicly available network server or other readily accessible means, then you must either
(1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the
benefit of the patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner consistent with the
requirements of this License, to extend the patent license to downstream recipients. 'Knowingly
relying' means you have actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work in a country, would infringe
one or more identifiable patents in that country that you have reason to believe are valid.
If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or arrangement, you convey, or propagate
by procuring conveyance of, a covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify or convey a specific copy of
the covered work, then the patent license you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the
covered work and works based on it.
A patent license is 'discriminatory' if it does not include within the scope of its coverage, prohibits the
exercise of, or is conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are specifically
granted under this License. You may not convey a covered work if you are a party to an arrangement
with a third party that is in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment to
the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying the work, and under which the third
party grants, to any of the parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work conveyed by you (or copies made
from those copies), or (b) primarily for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement, or that patent license was
granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting any implied license or other
defenses to infringement that may otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or otherwise) that contradict
the conditions of this License, they do not excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you
cannot convey a covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this License and
any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may not convey it at all. For example, if
you agree to terms that obligate you to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom
you convey the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this License would be
to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.

13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have permission to link or combine any
covered work with a work licensed under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a
single combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this License will continue to
apply to the part which is the covered work, but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General
Public License, section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the combination as
such.
14. Revised Versions of this License.
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of the GNU General Public
License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program specifies that a certain
numbered version of the GNU General Public License 'or any later version' applies to it, you have the
option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered version or of any later version
published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published by the Free Software
Foundation.
If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future versions of the GNU General Public
License can be used, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes
you to choose that version for the Program.
Later license versions may give you additional or different permissions. However, no additional
obligations are imposed on any author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
later version.
15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW.
EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER
PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM 'AS IS' WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND
PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU
ASSUME THE COST OF ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
16. Limitation of Liability.
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING WILL ANY
COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS THE PROGRAM AS

PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE
PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED
INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM
TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS), EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided above cannot be given local legal
effect according to their terms, reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the Program, unless a warranty or
assumption of liability accompanies a copy of the Program in return for a fee.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS