Table of Contents
Zyxel Nebula User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for Nebula by Zyxel which is a product in the Software Licenses/Upgrades category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Default Login Details
User’s Guide
NCC
Nebula Control Center
Copyright © 2016 Zyxel Communications Corporation
NCC URL http://nebula.zyxel.com
myZyXEL.com URL https://portal.myzyxel.com
Version 1.10 Edition 1, 10/2016

NCC User’s Guide
2
IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a User’s Guide for a system managing a series of products. Not all products support all features.
Menushots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from what you see due to differences in release
versions or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the information
in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the managed device, such as the Nebula AP, switch or
security gateway.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the NCC.

Table of Contents
NCC User’s Guide
3
Table of Contents
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................3
Part I: User’s Guide............................................................................................6
Chapter 1
Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................7
1.1 NCC Overview .................................................................................................................................. 7
1.1.1 Relationship between Organizations, Sites and Accounts ................................................ 7
1.2 Getting Started ................................................................................................................................ 9
1.2.1 Create MyZyXEL.com Account ............................................................................................. 9
1.2.2 Connect Nebula Managed Devices ................................................................................... 9
1.2.3 Access the NCC Portal ........................................................................................................... 9
1.3 NCC Portal Overview .................................................................................................................... 10
1.3.1 Title Bar ................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3.2 Navigation Panel ................................................................................................................. 13
Part II: Technical Reference...........................................................................17
Chapter 2
Site-Wide.............................................................................................................................................18
2.1 Monitor Menus ............................................................................................................................... 18
2.1.1 Dashboard ............................................................................................................................. 18
2.1.2 Summary Report .................................................................................................................... 19
2.1.3 Map & Floor Plan ................................................................................................................... 22
2.1.4 Topology ................................................................................................................................ 24
2.2 Configure Menus ............................................................................................................................ 25
2.2.1 General Setting ..................................................................................................................... 25
2.2.2 Alert Setting ........................................................................................................................... 28
2.2.3 Add Device ........................................................................................................................... 29
Chapter 3
AP ........................................................................................................................................................31
3.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 31
3.2 Monitor ............................................................................................................................................. 31
3.2.1 Access Point .......................................................................................................................... 31
3.2.2 Client ...................................................................................................................................... 35

Table of Contents
NCC User’s Guide
4
3.2.3 Event Log ............................................................................................................................... 38
3.2.4 Summary Report .................................................................................................................... 39
3.3 Configure ......................................................................................................................................... 41
3.3.1 SSIDs ........................................................................................................................................ 41
3.3.2 Authentication ...................................................................................................................... 43
3.3.3 Captive Portal ....................................................................................................................... 46
3.3.4 Radio Setting ......................................................................................................................... 49
3.3.5 Load Balancing ..................................................................................................................... 51
Chapter 4
Switch..................................................................................................................................................53
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 53
4.2 Monitor ............................................................................................................................................. 53
4.2.1 Switch ..................................................................................................................................... 53
4.2.2 Client ...................................................................................................................................... 62
4.2.3 Event Log ............................................................................................................................... 63
4.2.4 Summary Report .................................................................................................................... 64
4.3 Configure ......................................................................................................................................... 67
4.3.1 Switch Ports ............................................................................................................................ 68
4.3.2 IP Filtering ............................................................................................................................... 71
4.3.3 RADIUS Policy ......................................................................................................................... 72
4.3.4 PoE Schedule ......................................................................................................................... 73
4.3.5 Switch Configuration ............................................................................................................ 74
Chapter 5
Gateway.............................................................................................................................................78
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 78
5.2 Monitor ............................................................................................................................................. 78
5.2.1 Security Gateway ................................................................................................................. 78
5.2.2 Client ...................................................................................................................................... 81
5.2.3 Event Log ............................................................................................................................... 84
5.2.4 VPN Connection ................................................................................................................... 84
5.2.5 Summary Report .................................................................................................................... 85
5.3 Configure ......................................................................................................................................... 88
5.3.1 Interfaces Addressing .......................................................................................................... 88
5.3.2 Firewall ................................................................................................................................... 97
5.3.3 Site-to-Site VPN .................................................................................................................... 103
5.3.4 L2TP over IPSec Client ......................................................................................................... 108
5.3.5 Captive portal ..................................................................................................................... 109
5.3.6 Network Access Method ....................................................................................................113
5.3.7 Traffic Shaping ..................................................................................................................... 115
5.3.8 Security Filtering ................................................................................................................... 116
5.3.9 My Authentication Server ................................................................................................. 116

Table of Contents
NCC User’s Guide
5
Chapter 6
Organization.....................................................................................................................................119
6.1 Organization Overview ................................................................................................................ 119
6.1.1 Sites ....................................................................................................................................... 119
6.1.2 Site tags ................................................................................................................................ 120
6.1.3 Devices ................................................................................................................................. 121
6.2 Create Organization .................................................................................................................... 123
6.3 Create Site .................................................................................................................................... 123
6.4 Inventory ........................................................................................................................................ 124
6.5 License Management .................................................................................................................. 125
6.6 Change Log .................................................................................................................................. 127
6.7 Organization Setting .................................................................................................................... 128
6.8 Administrator ................................................................................................................................. 130
6.8.1 Create/Update Administrator ........................................................................................... 131
6.9 Cloud Authentication .................................................................................................................. 132
6.9.1 Create/Update User ........................................................................................................... 134
Chapter 7
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................136
7.1 Getting More Troubleshooting Help ........................................................................................... 137
Appendix A Customer Support ..................................................................................................... 138
Appendix B Legal Information ....................................................................................................... 144

6
PART I
User’s Guide

NCC User’s Guide
7
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
1.1 NCC Overview
The Zyxel Nebula Control Center (NCC) is a cloud-based network management system that allows you
to remotely manage and monitor Zyxel Nebula APs, Ethernet switches and security gateways. Being a
SaaS (Software as a Service) solution, it provides access to the licensed software and applications on a
subscription basis over the Internet.
Each Nebula managed device needs to have a management license. To extend the license before it
expires, contact your vendor for further information. At the time of writing, the supported Nebula
devices are NAP102, NAP203, NAP303, NAP353, NSW100-28P, NSW200-28P and NSG100.
Feature support includes:
• System accounts with different privilege levels
• Site Administrator: manage one site
• Organization Administrator: manage one or multiple organizations
• Multi-tenant management
• Inventory and license management
• Alerts to view events, such as when a device goes down
• Graphically monitoring individual devices
• Securely managing Nebula devices by using the Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) over TLS
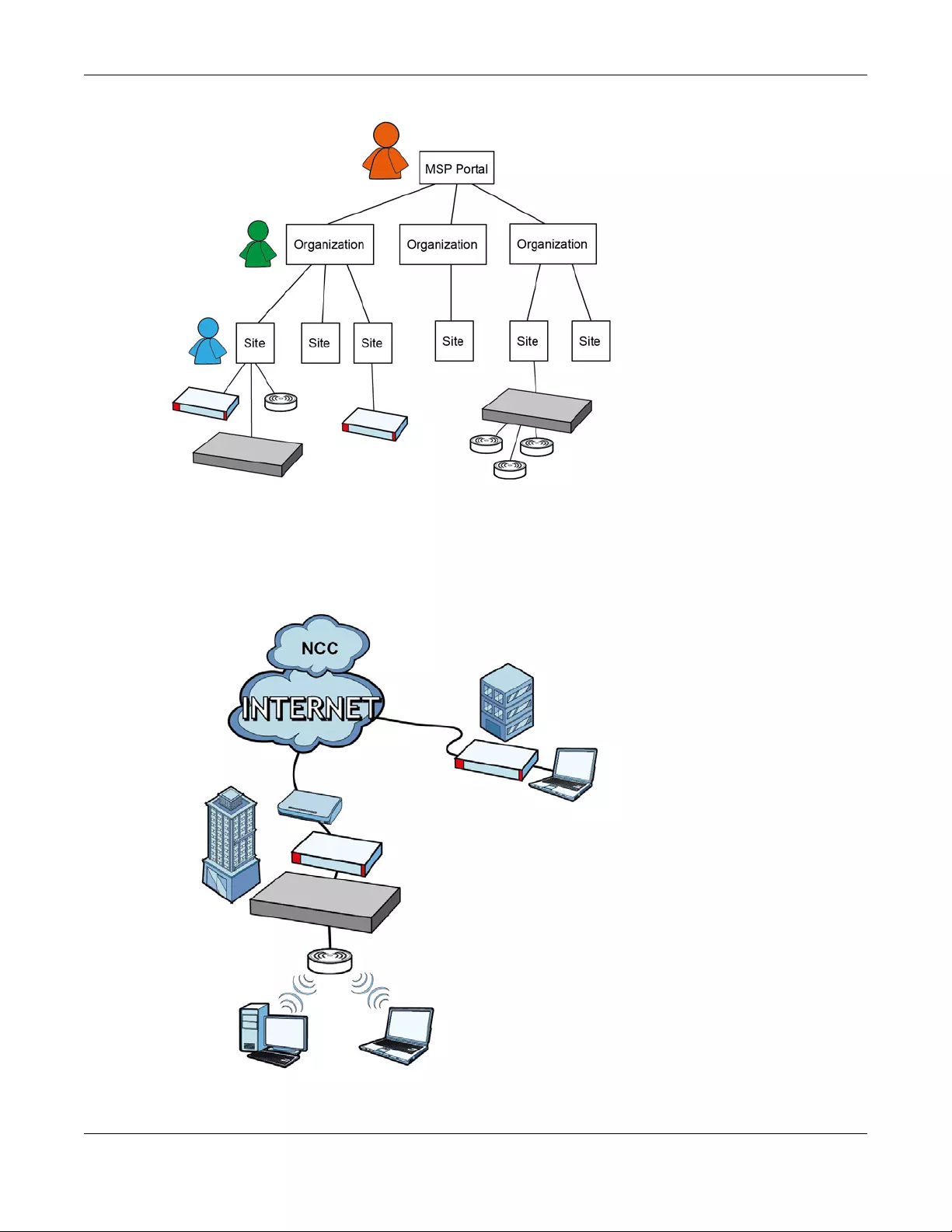
1.1.1 Relationship between Organizations, Sites and Accounts
In the NCC, a site is a group of devices and an organization is a group of sites. To use the NCC to
manage your Nebula devices, each device should be assigned to a site and the site must belong to an
organization.
• A site can have multiple Nebula devices, but can only belong to one organization.
• A site can be managed by more than one site/organization administrator.
• An organization can contain multiple sites and can be managed by more than one organization
administrator.
• A myZyXEL.com account can be an organization administrator and/or site administrator in the NCC
(see Section 6.8 on page 130).
• An organization administrator can manage more than one organization. The organization
administrator that manages multiple organizations can see a MSP portal page (see MSP Portal on
page 11).
• A site administrator can manage more than one site.
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
8
In the following example, Nebula managed devices, such as the NAP102 or the NSW100-28P, are
deployed in two separate networks (Site A and Site B). With the NCC organization administrator
account, you can remotely manage and monitor all devices even when they are located at different
places.
Figure 1 NCC Example Network Topology
Site A
Site B
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
9
1.2 Getting Started
You can perform network management by the NCC using an Internet browser. Browsers supported are:
• Firefox 36.0.1 or later
• Chrome 41.0 or later
• IE 10 or later
1.2.1 Create MyZyXEL.com Account
First, use myZyXEL.com to create an account in order to log into NCC and manage Nebula devices over
networks.
1Open your web browser and go to https://portal.myzyxel.com.
2Sign in with your email and password. Click Not a Membe r Yet if you don't have a myZyXEL.com account
and create an account.
1.2.2 Connect Nebula Managed Devices
Connect your Nebula managed devices (such as the NAP102 or the NSW100-28P) to your local network.
Your local network must have Internet access. See the corresponding Quick Start Guides for hardware
connections.
1.2.3 Access the NCC Portal
Go to the NCC portal website.
1Type http://nebula.zyxel.com in a supported web browser. Log into the NCC with your myZyXEL.com
account.
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
10
2If this is the first time you have logged into NCC, you need to create your organization and site(s),
register Nebula devices and associate them with a site. See Chapter 6 on page 119 for detailed
information.
1.3 NCC Portal Overview
The NCC portal screen is divided into these parts:
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
11
Figure 2 NCC Overview
•A - Title Bar
•B - Navigation Panel
• C - Main Screen
1.3.1 Title Bar
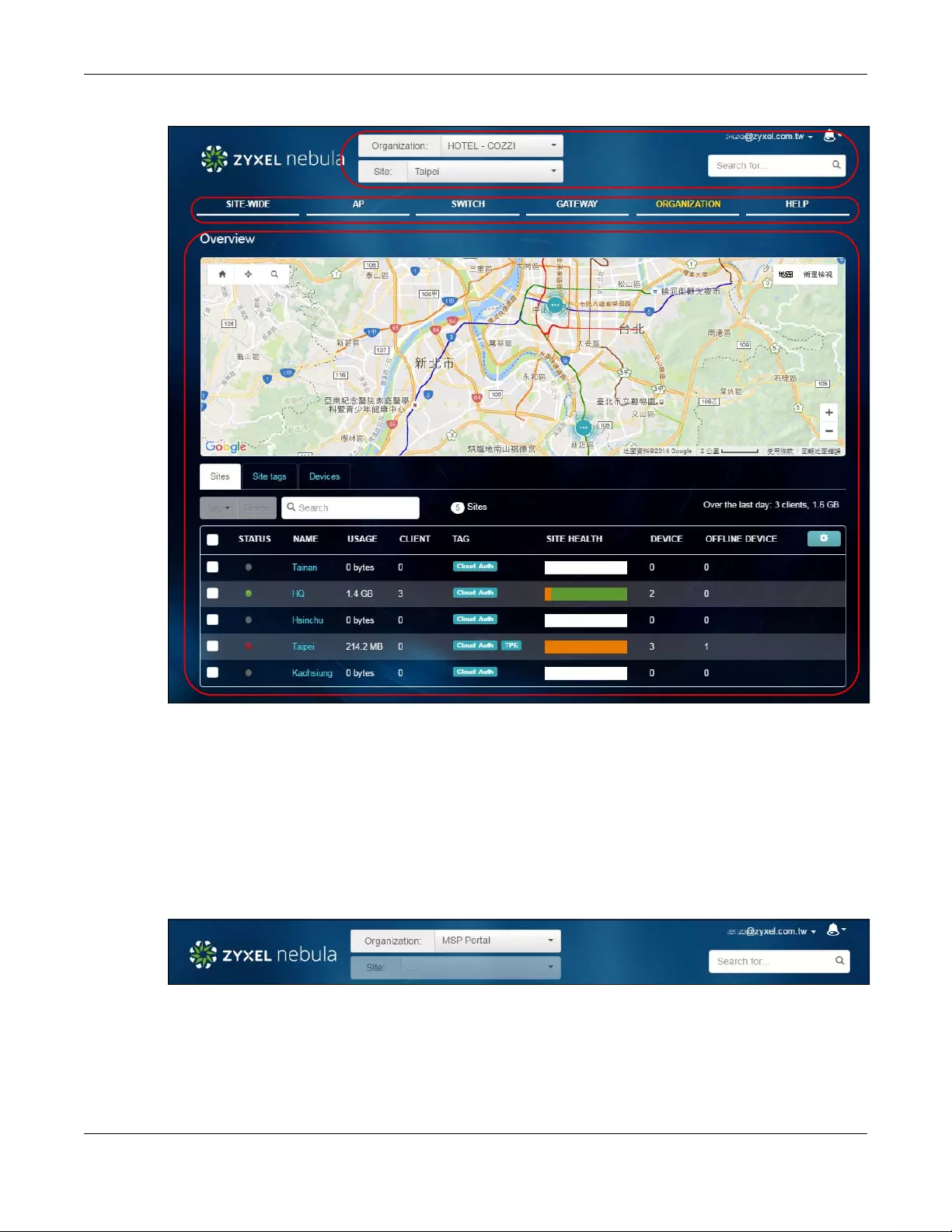
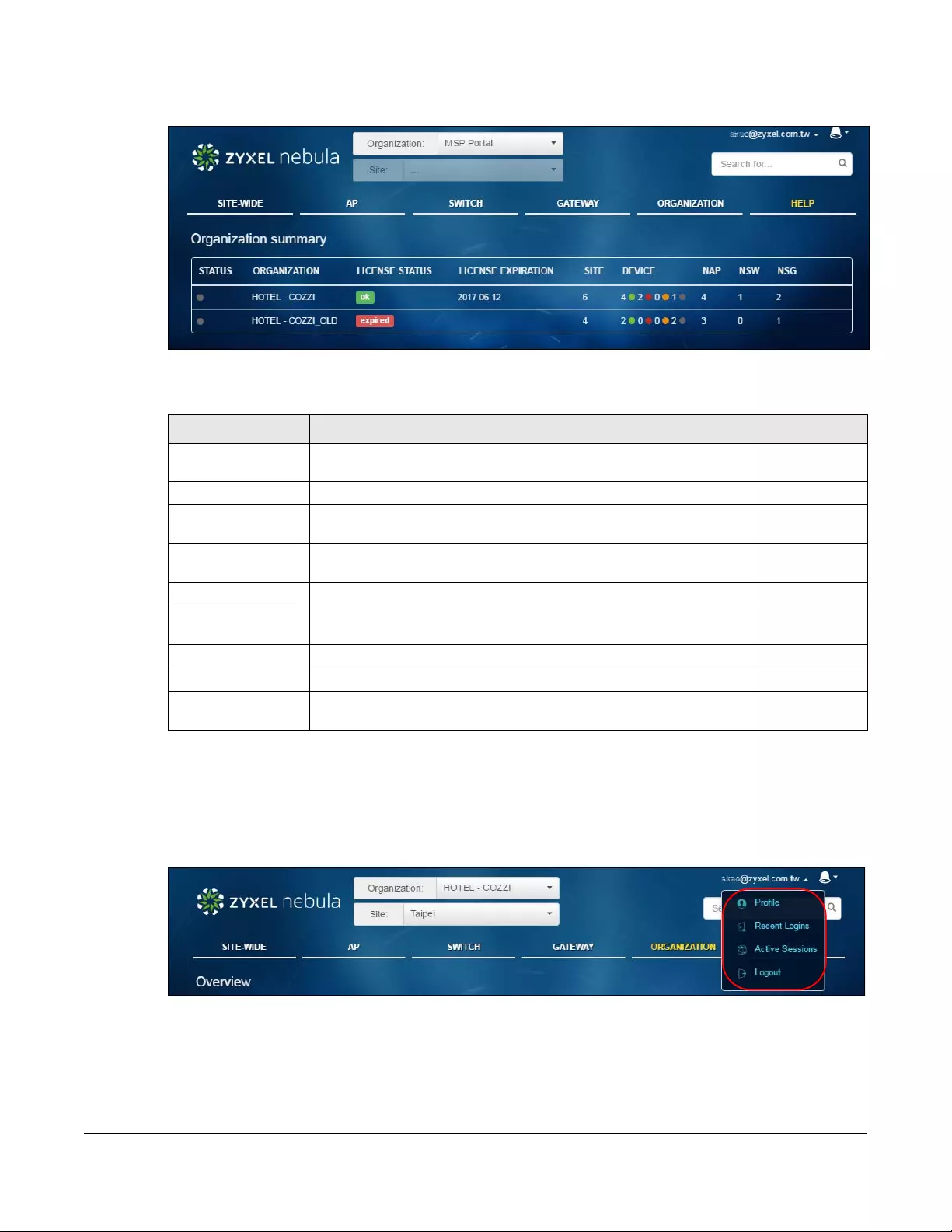
Select the organization and site you want to manage. If you create multiple organizations, select MSP
Portal from the Organization drop-down list box to view your organization summary.
Figure 3 NCC Title Bar
MSP Portal
The MSP (Managed Services Provider) Portal option is available only for an organization administrator
account which manages more than one organization. Click the organization entry you want to
manage and go to its SITE WIDE > Dashboard screen.
A
B
C
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
12
Figure 4 NCC MSP Portal
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Login Account
Click your login account at the top right hand corner of the screen to display a menu, where you can
click a link to view your account profile settings, login history, active sessions or log out of the NCC portal.
Figure 5 NCC Login Account
Alert
Click the alert icon to view log messages for the selected organization and site. You can click the
message record to go to the Dashboard or Event Log page.
Table 1 NCC MSP Portal
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This shows whether the organization is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), goes
off-line (red) or has been off-line for at least six days (gray).
Organization This shows the descriptive name of the organization.
License Status This shows whether the license is valid (ok), will expire soon or has expired. It shows Warning
if the license should be renewed within one month.
License expiration This shows the date when the license will expire, or N/A when there is no Nebula device in
the organization.
Site This shows the number of sites belonging to this organization.
Device This shows the number of Nebula devices in this organization which are online (green), have
generated alerts (yellow), go off-line (red) or have been off-line for at least six days (gray).
NAP This shows the number of Nebula APs connecting to the sites in this organization.
NSW This shows the number of Nebula switches connecting to the sites in this organization.
NSG This shows the number of Nebula security gateways connecting to the sites in this
organization.

Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
13
Figure 6 NCC Alert
1.3.2 Navigation Panel
Use the NCC menu items to configure network management for each site, organization and/or Nebula
device.
Table 2 NCC Menu Summary
LEVEL 1 LEVEL2/LEVEL3 FUNCTION
SITE-WIDE Use these menus to view information on all Nebula managed devices that
are deployed in the selected site.
Monitor
Dashboard Use this menu to view device connection status and traffic summary.
Summary
Report
Use this menu to view network statistics for a site, such as bandwidth
usage, power usage, top devices, top clients and/or top SSIDs.
Map & Floor
Plan
Use this menu to locate devices on the world map and even on a floor
plan.
Topology Use this menu to view the site’s network topology.
Configure
General Setting Use this menu to change the general settings for the site, such as the site
name, device login password and firmware upgrade schedule.
Alert Setting Use this menu to set which alerts are created and emailed. You can also
set the email address(es) to which an alert is sent.
Add Device Use this menu to register a device and add it to the site.
AP Use these menus to monitor and configure the managed AP(s) by the
NCC.
The settings are applied when a Nebula AP is registered and attached to
the selected site.
Monitor
Access Point Use this menu to view the list of APs added to the site.
Client Use this menu to view Wi-Fi clients which are connecting to the APs in the
site.
Event Log Use this menu to view all events on the AP. An event is a log of something
that has happened to a managed device.
Summary
Report
Use this menu to view network statistics specific to APs in the site.
Configure
SSIDs Use this menu to enable and configure basic settings for SSID profiles.
Authentication Use this menu to configure Wi-Fi security, L2 isolation, intra-BSS and walled
garden settings for SSID profiles.
Captive Portal Use this menu to configure captive portal settings for SSID profiles.
Radio Setting Use this menu to configure global radio settings for all APs in the site.
Load
Balancing
Use this menu to configure load balancing settings for all APs in the site.
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
14
SWITCH Use these menus to monitor and configure the managed switch(es) by
the NCC.
The settings are applied when a Nebula switch is registered and attached
to the selected site.
Monitor
Switch Use this menu to view the list of switches added to the site.
Client Use this menu to view detailed information about the clients which are
connecting to the switches in the site.
Event Log Use this menu to view all events on the switch. An event is a log of
something that has happened to a managed device.
Summary
Report
Use this menu to view network statistics specific to switches in the site.
Configure
Switch Ports Use this menu to view the switch port statistics and configure switch
settings for the ports.
IP filtering Use this menu to configure the access control list in order to control
access to the switches.
RADIUS Policy Use this menu to configure port authentication.
PoE Schedule Use this menu to set the schedule for switches in distributing power to
powered devices.
Switch
Configuration
Use this menu to configure global switch settings, such as (R)STP, QoS,
IGMP snooping, port mirroring, authentication servers, voice VLAN and
DHCP white list.
Table 2 NCC Menu Summary (continued)
LEVEL 1 LEVEL2/LEVEL3 FUNCTION
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
15
Gateway Use these menus to monitor and configure the managed security
gateway(s) by the NCC.
The settings are applied when a Nebula gateway is registered and
attached to the selected site.
Monitor
Security
Gateway
Use this menu to view the detailed information about a security gateway
in the selected site.
Client Use this menu to view the connection status and detailed information
about a client in the selected site.
Event Log Use this menu to view all events on the gateway. An event is a log of
something that has happened to a managed device.
VPN
Connection
Use this menu to view status of the site-to-site VPN connections.
Summary
Report
Use this menu to view network statistics specific to the gateway in the site.
Configure
Interfaces
Addressing
Use this menu to configure network mode, port grouping, interface
address, static route and DDNS settings on the gateway.
Firewall Use this menu to configure firewall rules for outbound traffic, application
patrol, schedule profiles and port forwarding rules for inbound traffic.
Site-to-Site VPN Use this menu to configure VPN rules.
L2TP over IPSec
client
Use this menu to enable and configure L2TP VPN settings.
Captive Portal Use this menu to configure captive portal settings for each gateway
interface.
Network
Access
Method
Use this menu to enable or disable web authentication on an interface.
Traffic Shaping Use this menu to configure the maximum bandwidth and load balancing.
Security
Filtering
Use this menu to enable or disable Intrusion Detection and Prevention
(IDP) on the security gateway.
My
Authentication
Server
Use this menu to configure external AD (Active Directory) server or RADIUS
server that the security gateway can use in authenticating users.
Table 2 NCC Menu Summary (continued)
LEVEL 1 LEVEL2/LEVEL3 FUNCTION
Chapter 1 Introduction
NCC User’s Guide
16
ORGANIZATION Overview Use this menu to view a list of sites belonging to the selected organization
and detailed information about the devices connected to the sites.
Create
Organization
Use this menu to create a new organization.
Create Site Use this menu to create a new site.
Inventory Use this menu to view the summary of devices which have been
registered and assigned to the sites in the selected organization.
License
Management
Use this menu to view and manage your licenses.
Change Log Use this menu to view log messages about configuration changes in this
organization.
Setting Use this menu to configure the security and notification settings.
Administrator Use this menu to view, remove or create a new administrator account for
this organization.
Cloud
Authentication
Use this menu to create or remove user accounts which are allowed
access to the Nebula devices via different authentication methods, such
as the MAC-based authentication, captive portal or the IEEE 802.1x
authentication method.
HELP Online Doc Use this menu to view the documentation for the NCC and Nebula
devices.
Support Request Use this menu to view or submit a new eITS ticket.
Security Policy
Information
Use this menu to view information required for firewall rules to allow
management traffic between the NCC and Nebula devices, such as the
port number and protocol type.
Table 2 NCC Menu Summary (continued)
LEVEL 1 LEVEL2/LEVEL3 FUNCTION

17
PART II
Technical Reference

NCC User’s Guide
18
CHAPTER 2
Site-Wide
2.1 Monitor Menus
Use the Monitor menus to check the dashboard, summary report, map and floor plan, network topology
and client list of the Nebula devices for the selected site.
2.1.1 Dashboard
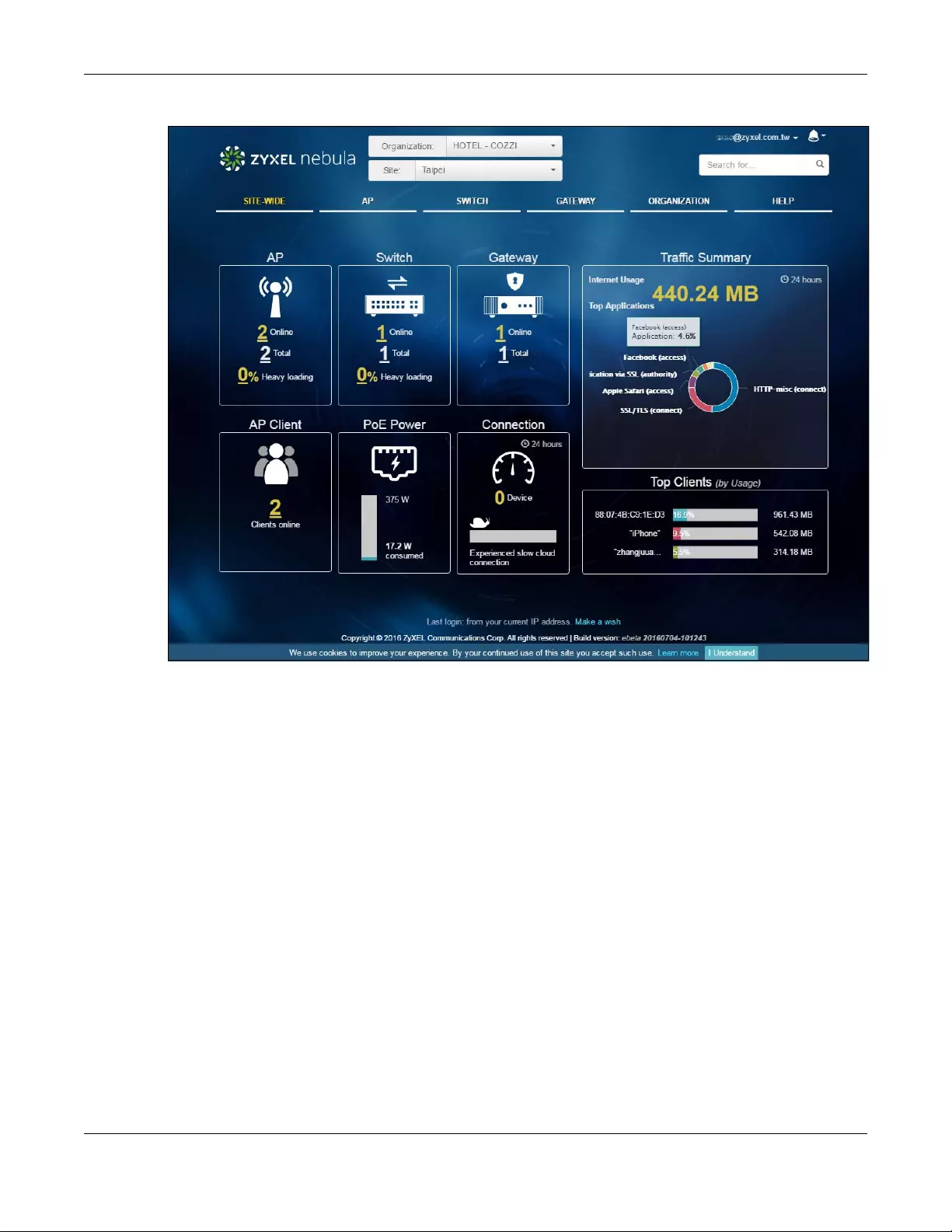
If a site is created and selected, the Dashboard is always the first menu you see when you log into the
NCC. You can also click SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Dashboard to access this screen. It shows:
•AP: how many Nebula APs are assigned and connected, and what percentage of the APs become
overloaded, that is, the number of online APs that exceed the maximum client device number (in AP
> Configure > Load Balancing) by total number of online APs in the site,
•AP Client: how many Wi-Fi clients are currently connecting to the managed AP(s),
•Switch: how many Nebula switches are assigned and connected, and what percentage of the
switches become overloaded, that is, the number of online Nebula switches that exceed 70% of their
upstream bandwidth by total number of online Nebula switches in the site,
•PoE Power: the total PoE power budget on the switch and the current amount of power consumed by
the powered devices,
•Gateway: how many Nebula security gateways are assigned and connected, and what percentage
of the gateway’s processing capability is currently being used if the CPU goes over 93% usage,
•Connection: the number of devices that are experiencing slow connection speeds,
•Traffic Summary: the Internet usage and top ten applications in the past 24 hours,
•Top Clients: the top three clients with the highest percentage of bandwidth usage in the past week.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
19
Figure 7 SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Dashboard
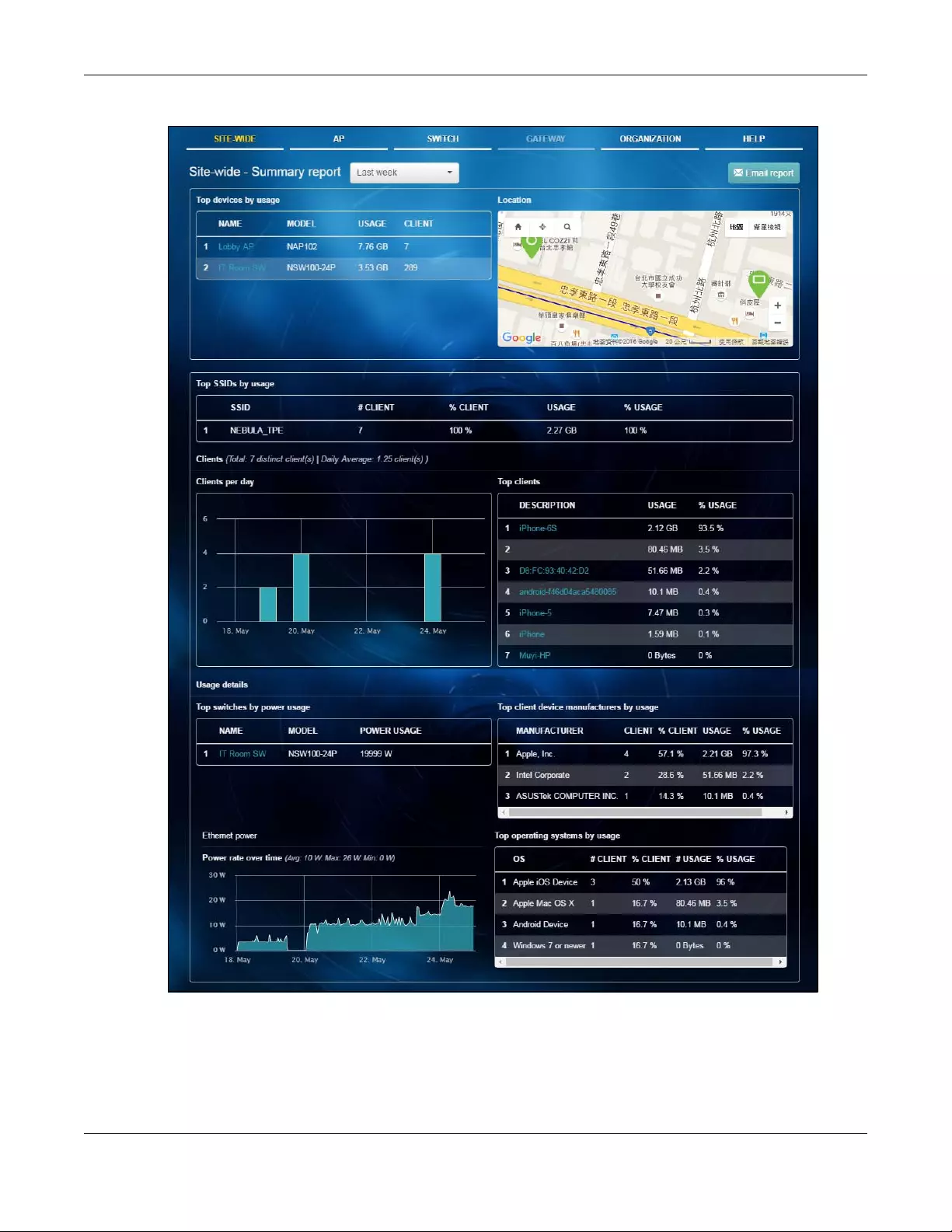
2.1.2 Summary Report
This screen displays network statistics for the selected site, such as bandwidth usage, power usage, top
devices, top clients and/or top SSIDs.
Click SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Summary Report to access this screen.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
20
Figure 8 SITE-Wide > Monitor > Summary Report
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
21
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 3 SITE-Wide > Monitor > Summary Report
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the report for the past day, week or month. Alternatively, select Select
range... to specify a time period the report will span. You can also select the number of
results you want to view in a table.
Email report Click this button to send summary reports by email, change the logo and set email
schedules.
Top devices by usage
#This shows the index number of the Nebula device.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula device.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula device.
Usage This shows the amount of date transmitted or received by the Nebula device.
Client This shows how many clients are currently connecting to the Nebula device.
Location This shows the location of the top Nebula devices on the map.
Top SSIDs by usage
#This shows the index number of the SSID.
SSID This shows the SSID network name.
# Clients This shows how many Wi-Fi clients are connecting to this SSID.
% Clients This shows what percentage of associated Wi-Fi clients are connecting to this SSID.
Usage This shows the total amount of data transmitted or received by clients connecting to this
SSID.
% Usage This shows what percentage of the transmitted data is for this SSID.
Clients
Total This shows the total number of clients connected to the Nebula device within the specified
time period.
Daily Average This shows the average daily number of clients within the specified time period.
Clients per day
The y-axis represents the number of clients.
The x-axis represents the date.
Top clients
#This shows the index number of the client.
Description This shows the descriptive name or MAC address of the client.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the client.
% Usage This shows what percentage of the transmitted data is for the client.
Usage details
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
22
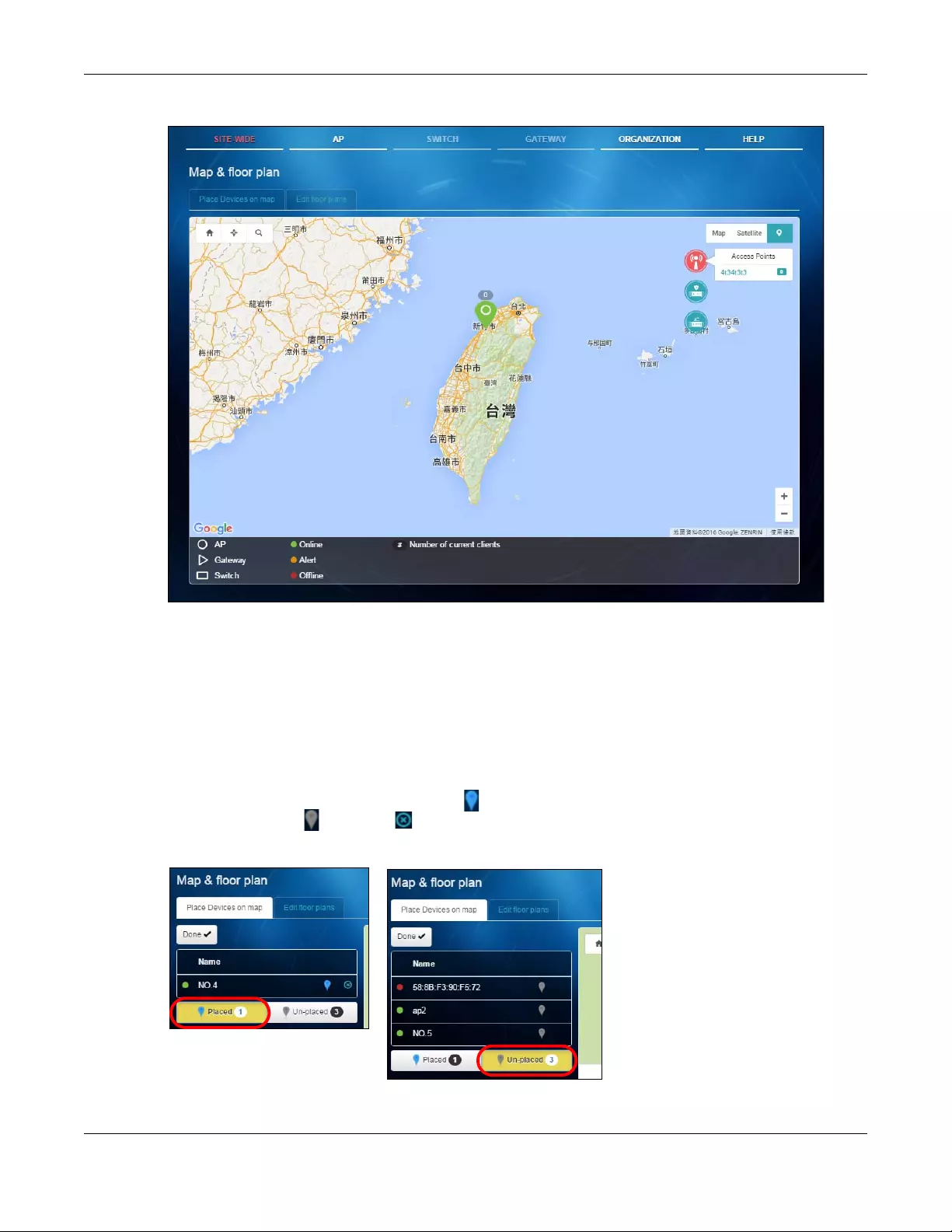
2.1.3 Map & Floor Plan
This screen allows you to locate a device on the world map and use a floor plan to show the space and
relationship between the Nebula devices. Click SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Map & floor plan to access this
screen.
Top switches by power usage
#This shows the index number of the switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the switch.
Model This shows the model number of the switch.
Power usage This shows what percentage of the power is used by the switch.
Ethernet power
Power rate over time This shows the average, maximum and minimum power consumption of the switches.
The y-axis shows how much power is used in Watts.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the power consumption is recorded.
Top client device manufacturer by usage
Manufacturer This shows the manufacturer name of the client device.
# Clients This shows how many client devices are made by the manufacturer.
% Clients This shows the percentage of top client devices which are made by the manufacturer.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the client device.
% Usage This shows what percentage of the transmitted data is for the client device.
Top operating systems by usage
OS This shows the operating system of the client device.
# Clients This shows how many client devices use this operating system.
% Clients This shows the percentage of top client devices which use this operating system.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the client device on which this operating
system is running.
% Usage This shows what percentage of top client devices use this operating system.
Table 3 SITE-Wide > Monitor > Summary Report (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
23
Figure 9 SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Map & Floor Plan
Place devices on map
You can mark spots on the map, that is, the places where the devices are located. Click the Place
devices on map tab to display the device list for the selected site. Click Done to hide the device list.
Click the Placed button to show the devices that you have pined on the map and/or the floor plan.
Click the Un-placed button to show the devices that remain to be pined on the map. To pin a device,
select the device from the Un-placed list, then drag and drop it on to the map.
The pin icon next to a device name is blue ( ) if you have marked the device on the map. Otherwise,
the pin icon is gray ( ). Click the icon to remove a device from the map.
Figure 10 SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Map & Floor Plan: Place devices on map
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
24
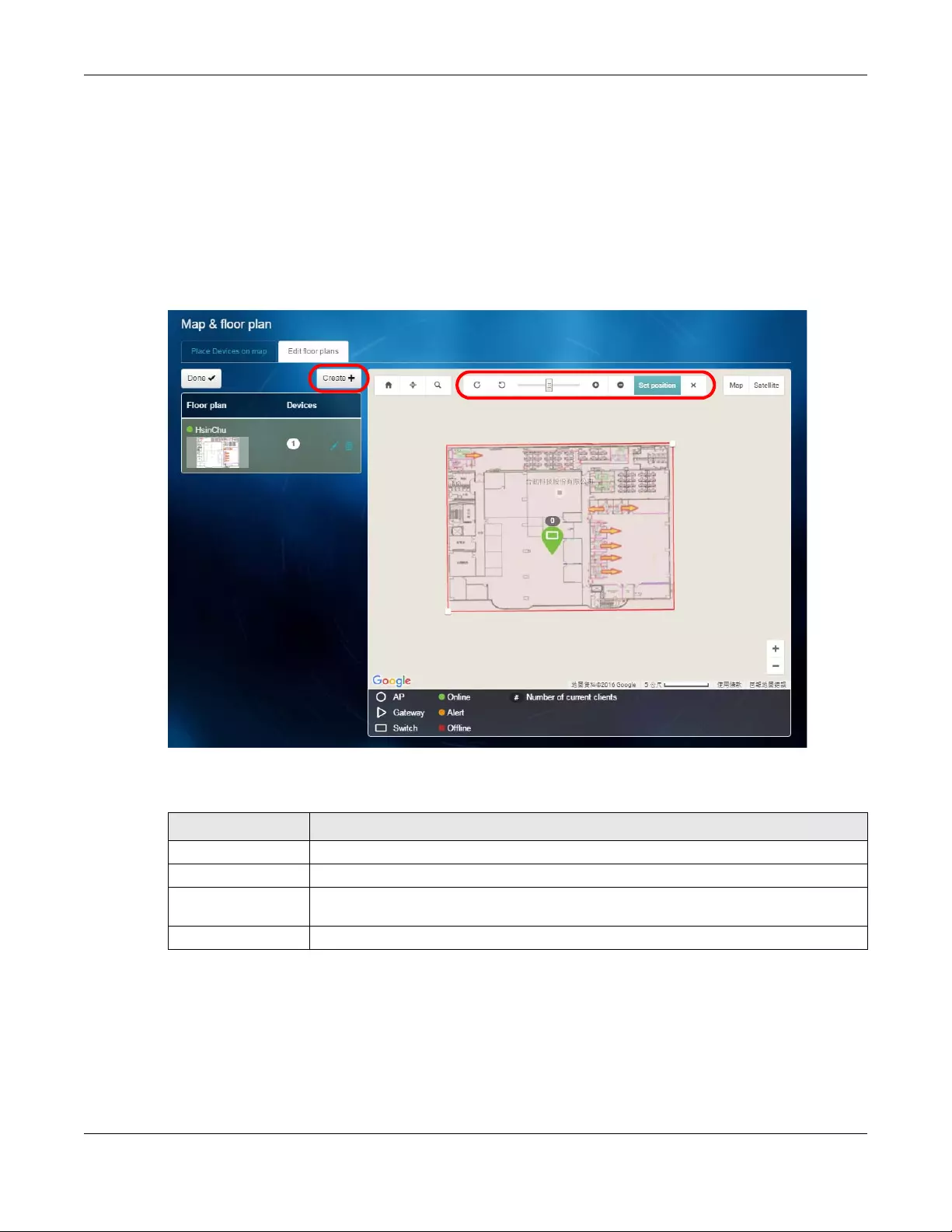
Edit floor plans
Click the Edit floor plans tab to display the list of existing floor plan, a drawing that shows the rooms
scaled and viewed from above. Click Done to hide the list. Use the Create+ button to upload new floor
plans.
Select a floor plan from the list. The floor plan then shows on the Google map at the right side of the
screen. Use your mouse to move the floor plan, and use the icons at the top of the map to rotate,
change the transparency, resize or hide the floor plan. Click Set position to apply your changes.
Figure 11 SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Map & Floor Plan: Edit floor plans
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
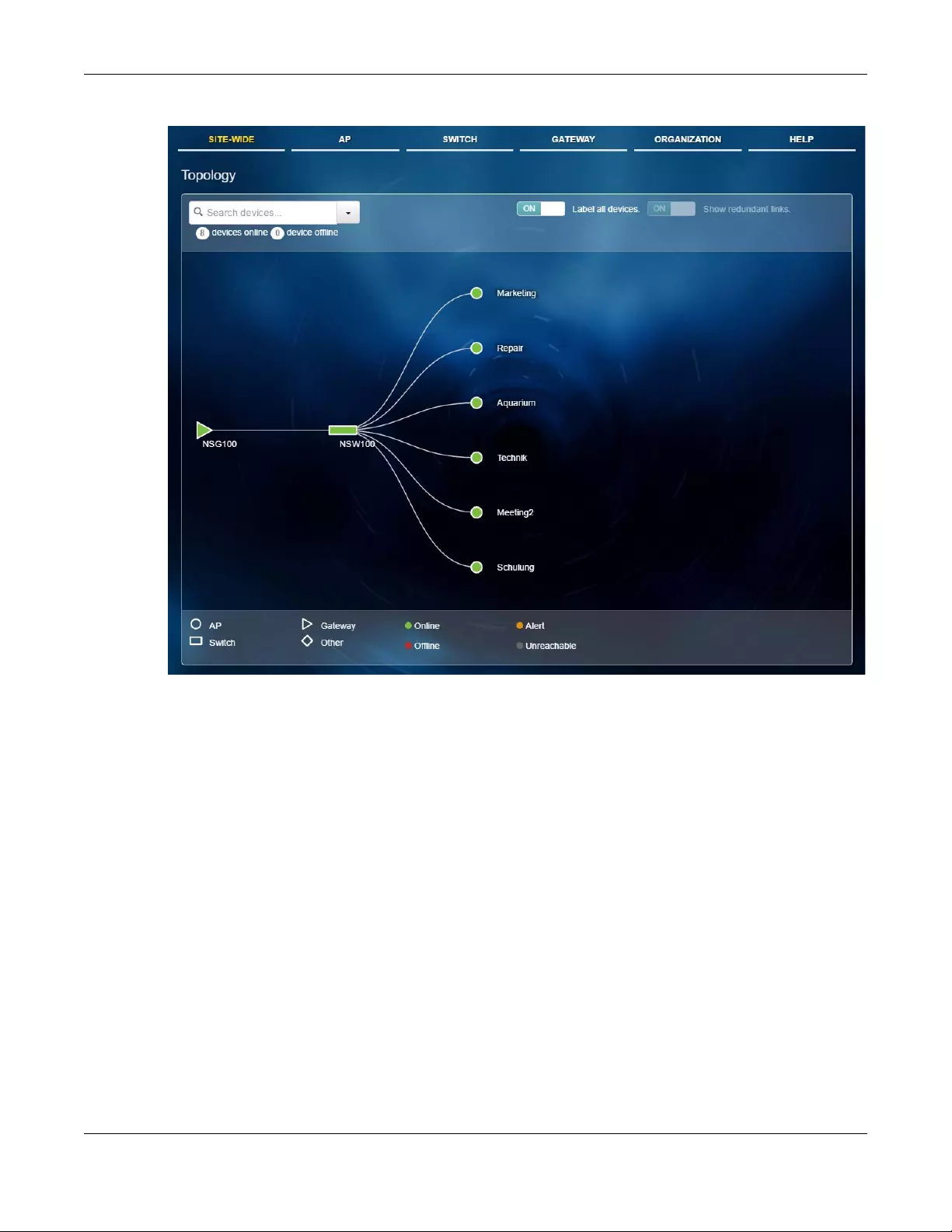
2.1.4 Topology
Use this screen to view the network topology of the site. Click SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Topology to access
this screen.
Table 4 SITE-Wide > Monitor > Map & Floor Plan: Edit floor plans
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Floor plan This shows the descriptive name of the floor plan.
Devices This shows the number of the device(s) marked on this floor plan.
Edit Click this icon to open a screen, where you can modify the name, address and/or
dimension of the floor plan.
Remove Click this icon to delete the floor plan.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
25
Figure 12 SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Topology
2.2 Configure Menus
Use the Configure menus to set the general and email alert settings for the selected site, or register a
new Nebula device and assign it to the site.
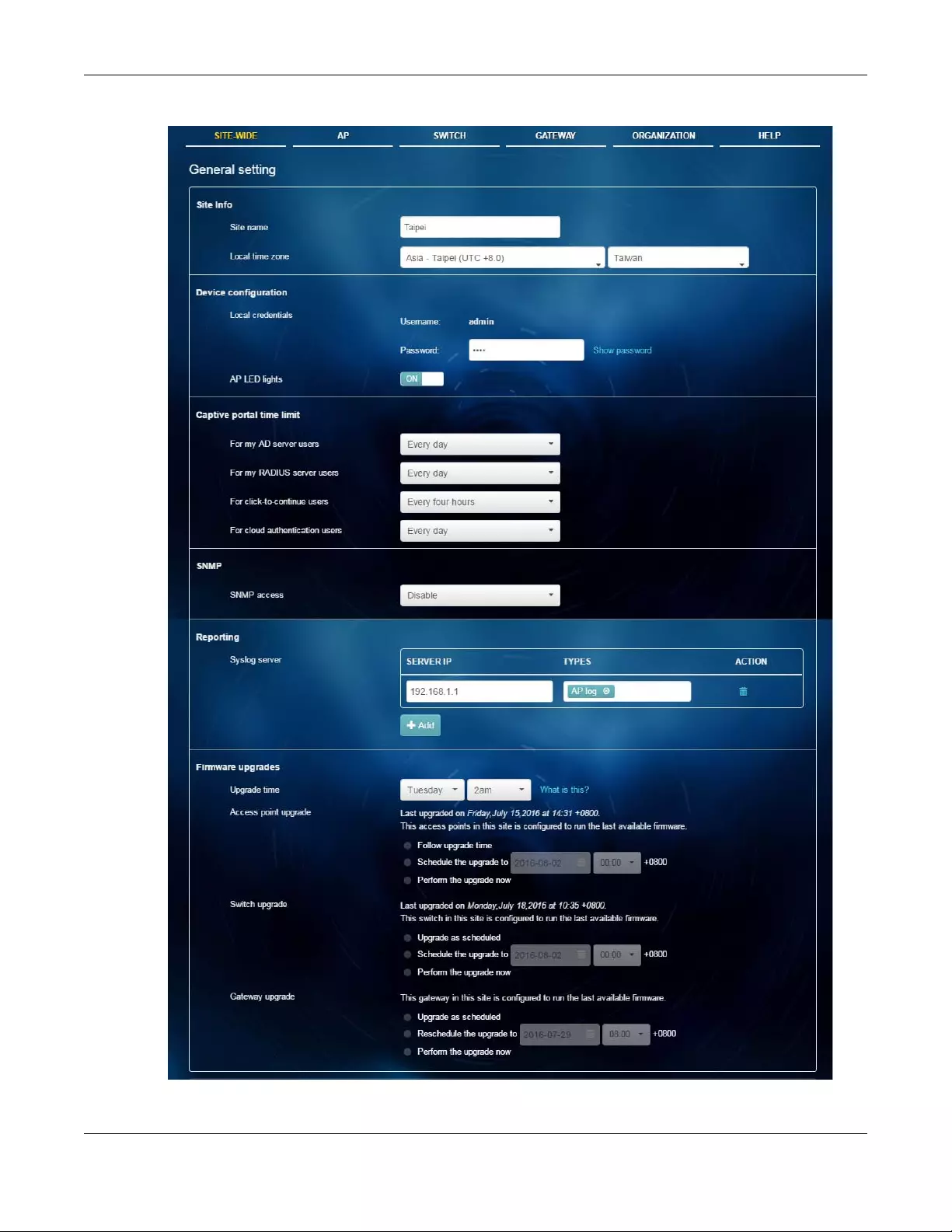
2.2.1 General Setting
Use this screen to change the general settings for the site, such as the site name, device login password
and firmware upgrade schedule. Click SITE-WIDE > Configure > General Setting to access this screen.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
26
Figure 13 SITE-WIDE > Configure > General setting
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
27
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 SITE-Wide > Configure > General setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Site Info
Site Name Enter a descriptive name for the site.
Local time zone Choose the time zone of the site’s location.
Device configuration
Local credentials The default password is generated automatically by the NCC when the site is created. You
can specify a new password to access the status page of the device’s built-in web-based
configurator. The settings here apply to all Nebula devices in this site.
AP LED lights Click to turn on or off the LED(s) on the APs.
Captive portal time
limit
For my AD server
users
Select how often the user (authenticated by an AD server) has to log in again.
For my RADIUS
server users
Select how often the user (authenticated by an RADIUS server) has to log in again.
For click-to-
continue users
Select how often the user (authenticated via the captive portal) has to log in again.
For cloud
authentication
users
Select how often the user (authenticated using the NCC user database) has to log in
again.
SNMP
SNMP access Select V1/V2c to allow SNMP managers using SNMP to access the devices in this site.
Otherwise, select Disable.
SNMP community
string
This field is available when you select V1/V2c.
Enter the password for the incoming SNMP requests from the management station.
Reporting
Syslog server Click Add to create a new entry.
Server IP Enter the IP address of the server.
Types Select the type of logs the server is for.
Action Click the Delete icon to remove the entry.
Firmware upgrades
Upgrade time Select the day of the week and time of the day to install the firmware.
Access point
upgrade
This section is grayed out if there is no AP in this site. It shows if there is a new version of the
firmware available for the APs, and the date and time of the last firmware upgrade.
Select Follow upgrade time to install the firmware at the time you choose in the Upgrade
time field.
Select Schedule the upgrade to xx at xx to set a new schedule for the firmware upgrade.
Select Perform the upgrade now to install the firmware immediately.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
28
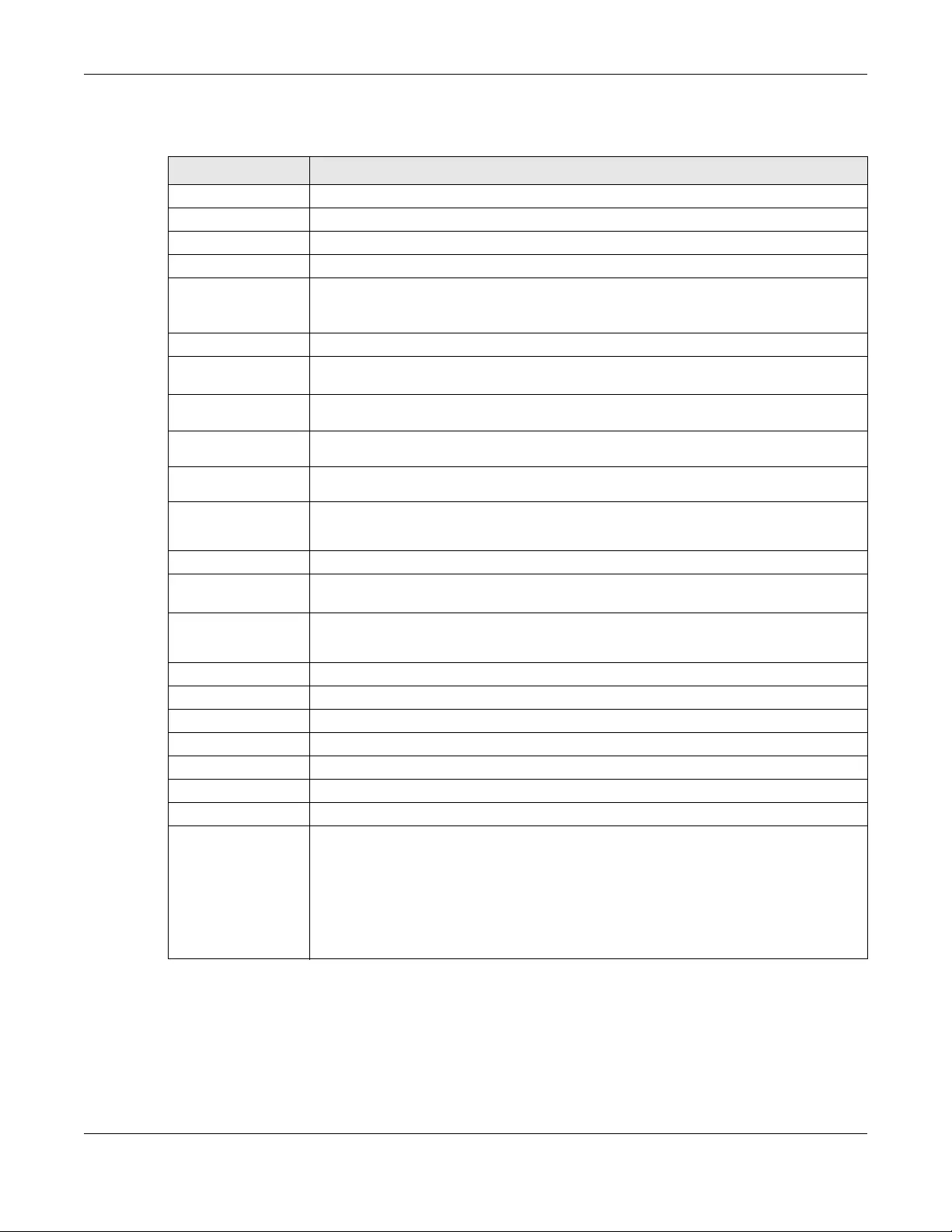
2.2.2 Alert Setting
Use this screen to set which alerts are created and emailed. You can also set the email address(es) to
which an alert is sent. Click SITE-WIDE > Configure > Alert Setting to access this screen.
Figure 14 SITE-WIDE > Configure > Alert setting
Switch upgrade This section is grayed out if there is no switch in this site. It shows if there is a new version of
the firmware available for the switches, and the date and time of the last firmware
upgrade.
Select Upgr ade as scheduled to install the firmware at the time you choose in the Upgrade
time field.
Select Schedule the upgrade to xx at xx to set a new schedule for the firmware upgrade.
Select Perform the upgrade now to install the firmware immediately.
Gateway upgrade This section is grayed out if there is no gateway in this site. It shows if there is a new version of
the firmware available for the gateways, and the date and time of the last firmware
upgrade.
Select Upgr ade as scheduled to install the firmware at the time you choose in the Upgrade
time field.
Select Schedule the upgrade to xx at xx to set a new schedule for the firmware upgrade.
Select Perform the upgrade now to install the firmware immediately.
Table 5 SITE-Wide > Configure > General setting (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
29
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
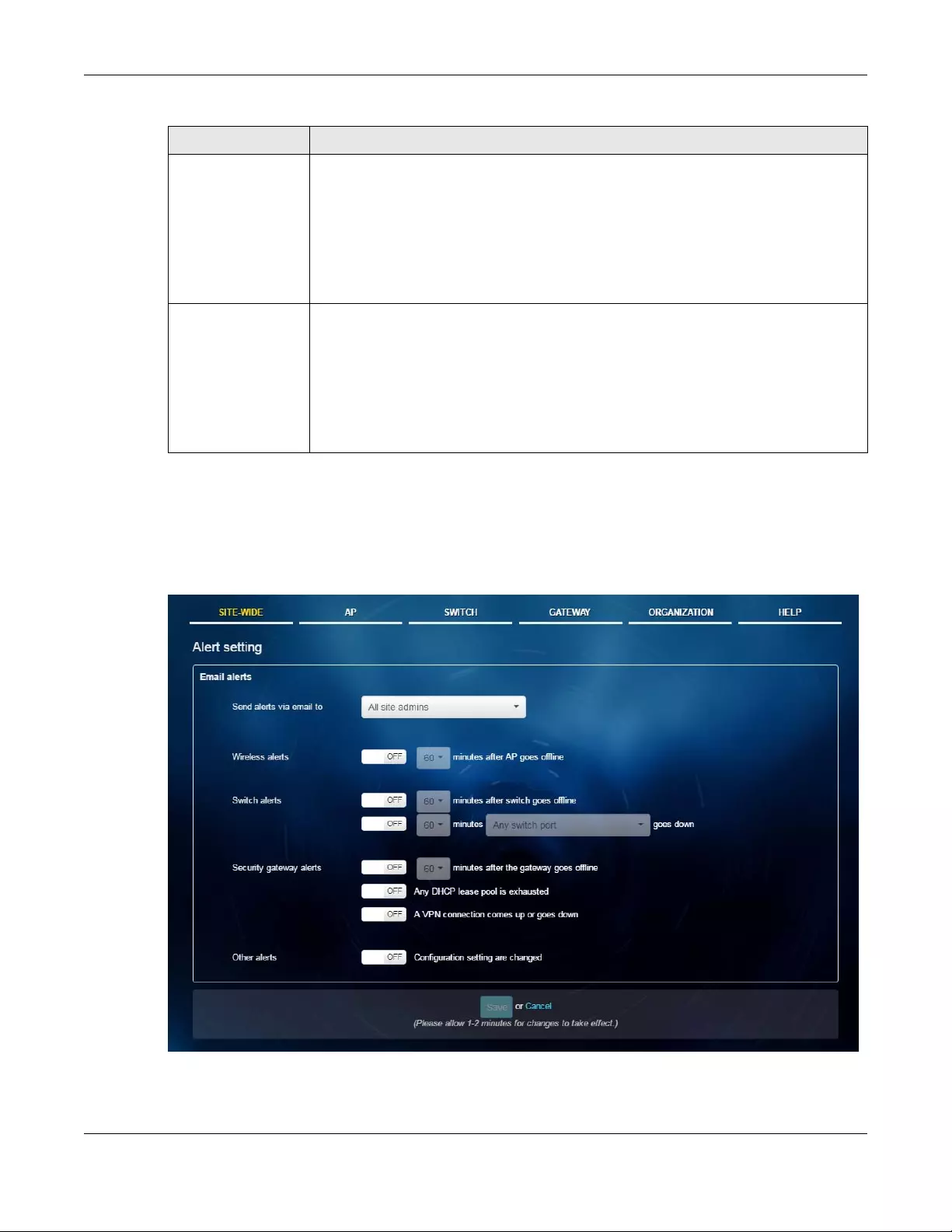
2.2.3 Add Device
Use this screen to register a device and add it to the site. Click SITE-WIDE > Configure > Add device to
access this screen.
Figure 15 SITE-WIDE > Configure > Add device
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 6 SITE-Wide > Configure > Alert setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Send alerts via email
to
Select Other email addresses to enter the email address(es) to which you want to send
alerts. Otherwise, select All site domains.
Wireless alerts Click On to have the NCC generate and send an alert when the event occurs.
You can also specify how long in minutes the NCC waits before generating and sending an
alert when an AP becomes off-line.
Switch alerts Click On to have the NCC generate and send an alert when the event occurs.
You can also specify how long in minutes the NCC waits before generating and sending an
alert when a port or a switch goes down.
Security gateway
alerts
Click On to have the NCC generate and send an alert when the event occurs.
You can also specify how long in minutes the NCC waits before generating and sending an
alert when a gateway becomes off-line.
Other alerts Click On to have the NCC generate and send an alert when the event occurs.
Table 7 SITE-Wide > Configure > Add device
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add to this site Click this button to assign the selected device(s) to the site.
Unused devices This shows the number of registered devices which have not been assigned to a site.
Chapter 2 Site-Wide
NCC User’s Guide
30
+ Register This button is available only for an organization administrator or site administrator that has
full access.
Click this button to pup up a window where you can enter a device’s serial number and
MAC address to register it at the NCC.
Select the check box of the device that you want to add to the selected site.
Device Name This shows the descriptive name of the device.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the device.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the device.
Model This shows the model name of the device.
Table 7 SITE-Wide > Configure > Add device (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
NCC User’s Guide
31
CHAPTER 3
AP
3.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the menus that you can use to monitor the Nebula managed APs in your network
and configure settings even before an AP is deployed and added to the site.
3.2 Monitor
Use the Monitor menus to check the AP information, client information, event log messages and
summary report for APs in the selected site.
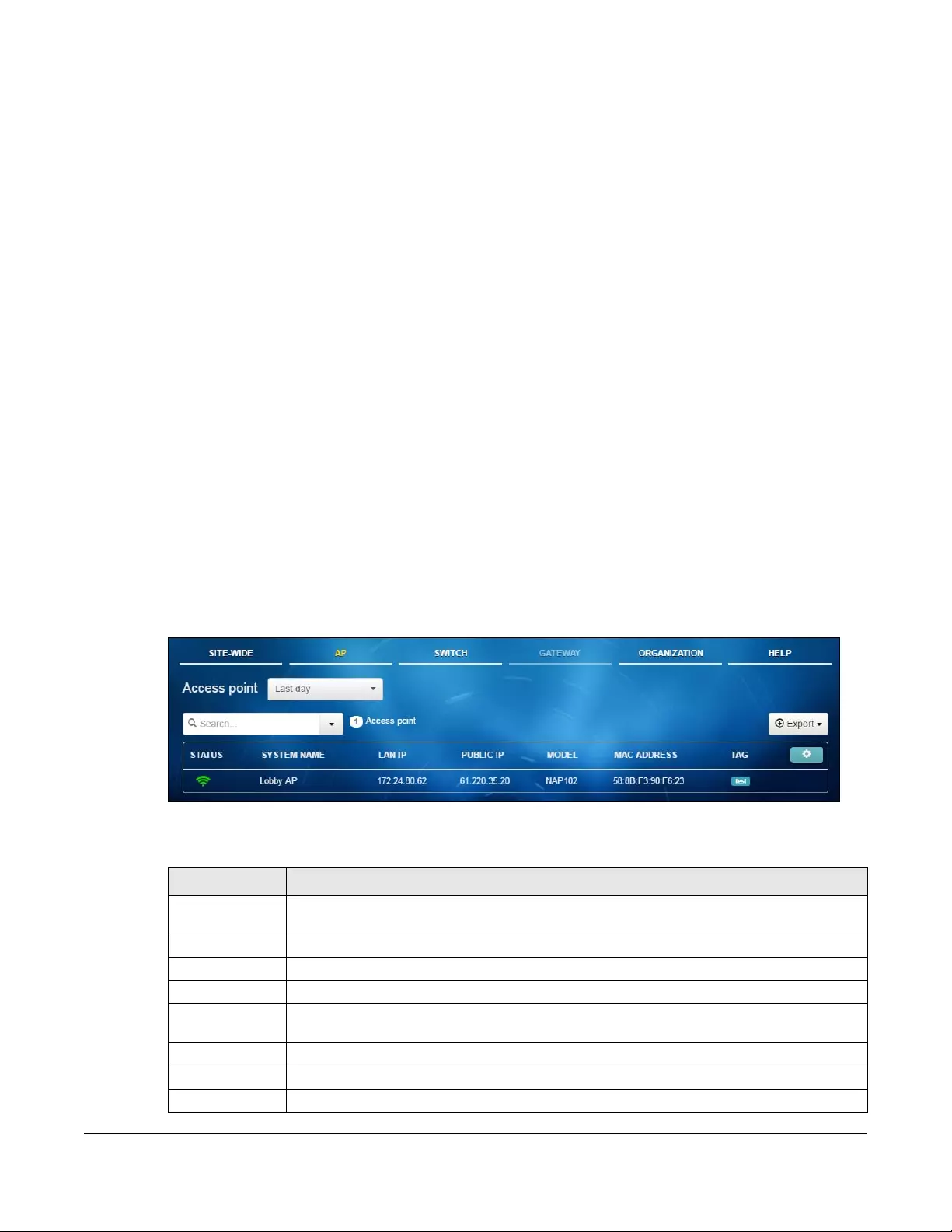
3.2.1 Access Point
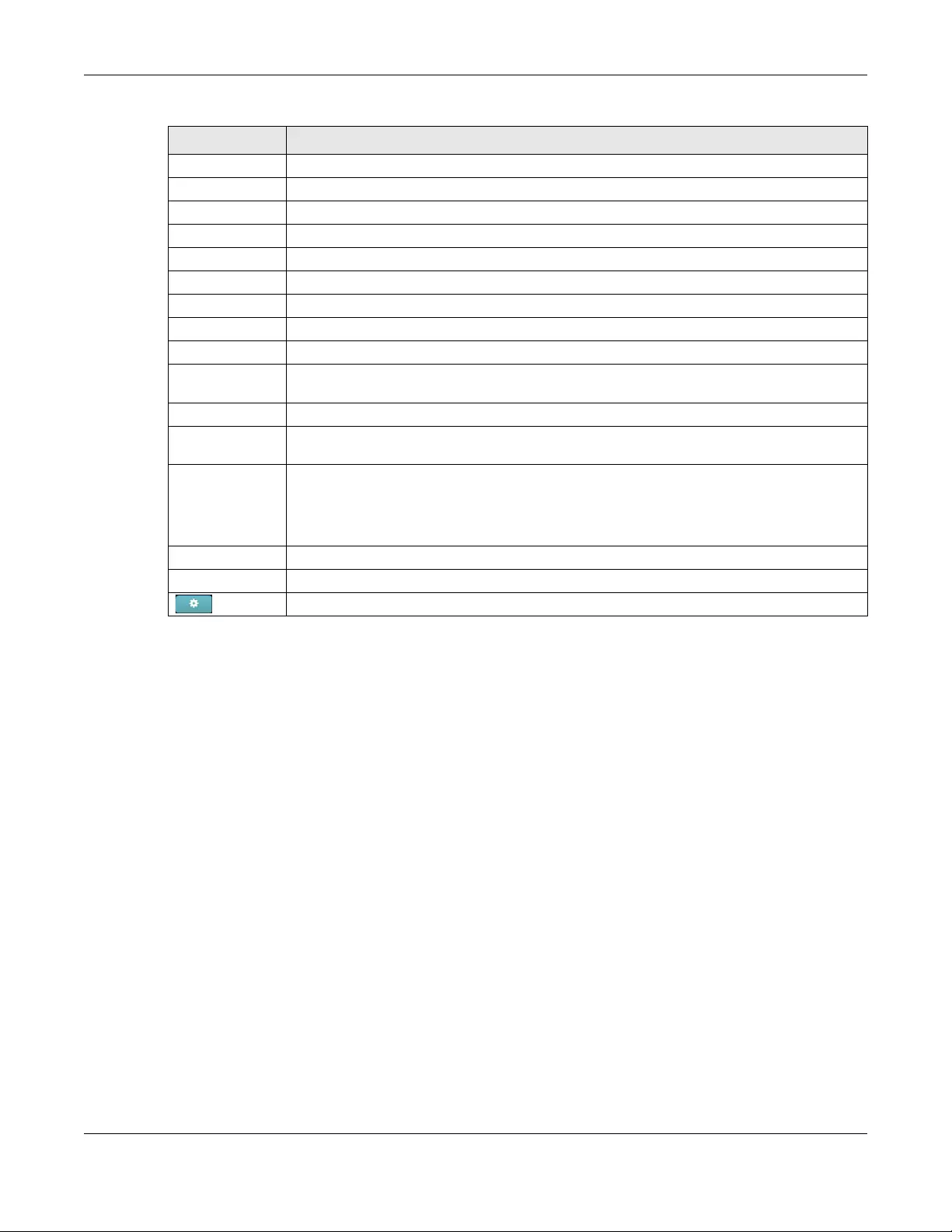
This screen allows you to view the detailed information about an AP in the selected site. Click AP >
Monitor > Access Point to access this screen.
Figure 16 AP > Monitor > Access Point
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 AP > Monitor > Access Point
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of APs.
Access points This shows the number of APs connected to the site network.
Export Click this button to save the AP list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Status This shows whether the AP is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), goes off-line (red) or
has been off-line for at least six days (gray).
System Name This shows the descriptive name of the AP.
LAN IP This shows the local (LAN) IP address of the AP.
Public IP This shows the global (WAN) IP address of the AP.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
32
3.2.1.1 AP Details
Click an AP entry in the AP > Monitor > Access Point screen to display individual AP statistics.
Model This shows the model number of the AP.
Client This shows how many clients connected to the AP within the specified time period.
Current Clients This shows how many clients are currently connecting to the AP.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the AP.
Channel This shows the channel number(s) the AP is using.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the AP’s clients.
% Usage This shows the percentage of the AP’s data usage.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag for the AP.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the AP.
Production
Information
This shows the production information of the AP.
Description This shows the user-specified description for the AP.
Configuration
Status
This shows whether the configuration on the AP is up-to-date.
Connectivity This shows the AP connection status. Nothing displays if the AP is off-line.
The gray time slot indicates the connection to the NCC is down, and the green time slot
indicates the connection is up. Move the cursor over a time slot to see the actual date and
time when an AP is connected or disconnected.
Ethernet 1 This shows the speed and duplex mode of the Ethernet connection on the AP’s port.
Ethernet 1 LLDP This shows the LLDP information received on the up-link port.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 8 AP > Monitor > Access Point (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
33
Figure 17 AP > Monitor > Access Point: AP Details
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 AP > Monitor > Access Point: AP Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Click the edit icon to change the device name, description, tags and address. You can also move the device to
another site.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the AP.

Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
34
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the AP.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the AP.
Description This shows the user-specified description for the AP.
Address This shows the user-specified address for the AP.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag for the AP.
Status
LAN IP 1 This shows the local (LAN) IP address of the AP. It also shows the IP addresses of the
gateway and DNS server.
Click the edit icon to open a screen where you can change the IP addresses, VLAN ID
number and tagging setting.
Public IP This shows the global (WAN) IP address of the AP.
Usage This shows the number of the AP’s clients and the amount of data consumed by the clients.
Topology Click Show to go to the SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Topology screen. See Section 2.1.4 on page
24.
Channel (Band) This shows the channel number(s) and Wi-Fi frequency band currently being used by the
AP.
Ethernet 1 This shows the speed and duplex mode of the Ethernet connection on the AP’s port.
History Click Event log to go to the AP > Monitor > Event log screen.
Firmware This shows whether there is firmware update available for the AP.
Configuration status This shows whether the configuration on the AP is up-to-date.
Map This shows the location of the AP on the Google map.
Photo This shows the photo of the AP.
Live tools
Traffic This shows the AP traffic statistics.
Ping Enter the domain name or IP address of a computer that you want to perform ping from
the AP in order to test a connection and click Ping.
This can be used to determine if the AP and the computer are able to communicate with
each other.
Table 9 AP > Monitor > Access Point: AP Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
35
3.2.2 Client
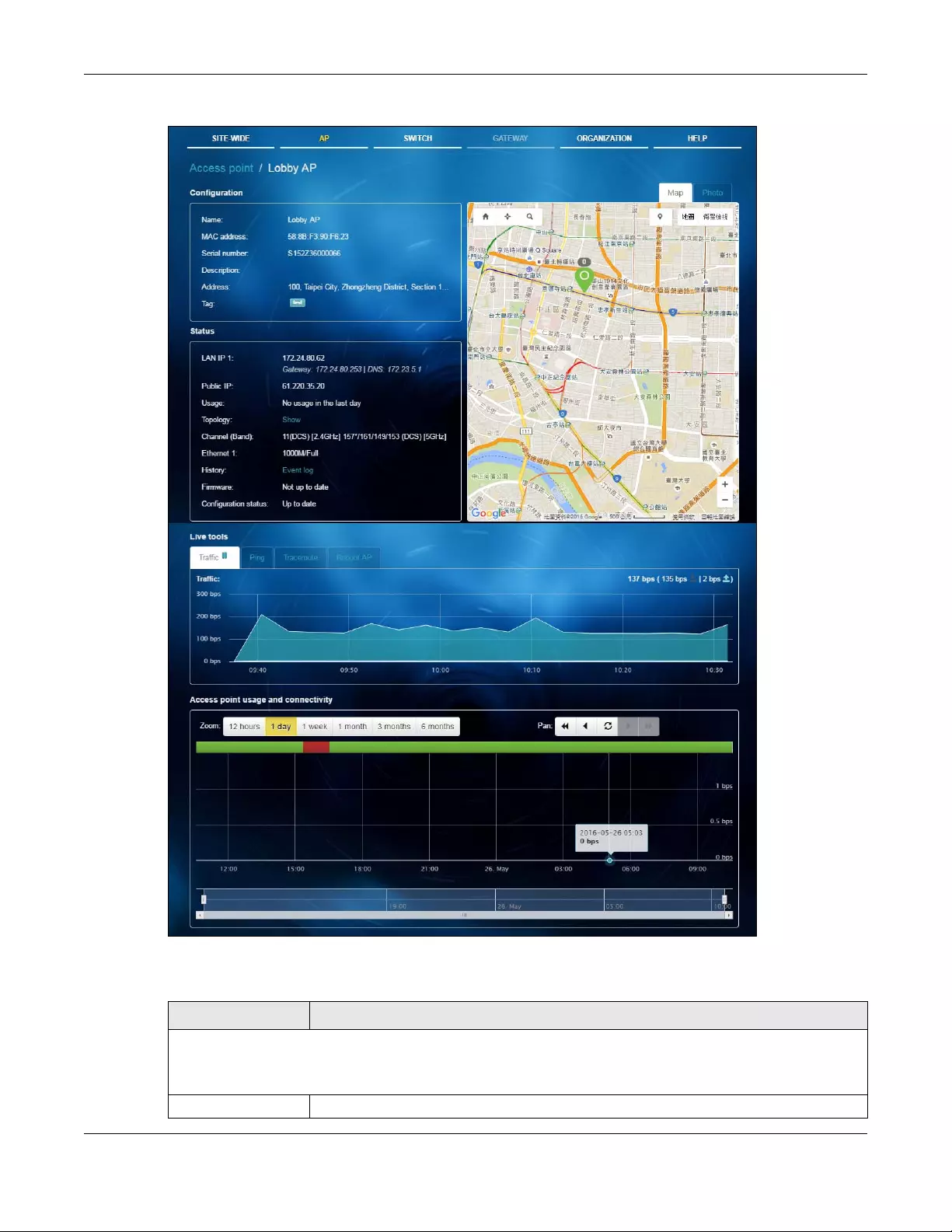
This screen allows you to view the connection status and detailed information about a client in the
selected site. Click AP > Monitor > Client to access this screen.
Figure 18 AP > Monitor > Client
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Traceroute Enter the domain name or IP address of a computer that you want to perform traceroute
from the AP and click Run. This determines the path a packet takes to the specified
computer.
Reboot AP Click the Reboot button to restart the AP.
Access point usage and connectivity
Move the cursor over the chart to see the transmission rate at a specific time.
Zoom Select to view the statistics in the past twelve hours, day, week, month, three months or six
months.
Pan Click to move backward or forward by one day or week.
Table 9 AP > Monitor > Access Point: AP Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 10 AP > Monitor > Client
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
The y-axis shows the transmission speed of data sent or received by the client in kilobits per
second (Kbps).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Policy Select the client(s) from the table below, and then choose the policy that you want to apply to
the selected client(s).
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of clients.
Clients This shows the number of clients connected to the site network.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
36
3.2.2.1 Client Details
Click a client entry in the AP > Monitor > Client screen to display individual client statistics.
Add client Click this button to open a window where you can specify a client’s name and MAC address
to apply a policy before it is connected to the AP’s network.
Export Click this button to save the client list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red).
Description This shows the descriptive name of the client.
Click the name to display the individual client statistics. See Section 3.2.2.1 on page 36.
Connected to This shows the name of the Nebula managed AP to which the client is connected.
Click the name to display the individual AP statistics. See Section 3.2.1.1 on page 32.
SSID Name This shows the name of the AP’s wireless network to which the client is connected.
Security Mode This shows which secure encryption method is being used by the client to connect to the
Nebula device.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Channel This shows the channel number the client is using.
Band This shows the Wi-Fi frequency band currently being used by the client.
Signal Strength This shows the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the client’s wireless connection.
IPv4 Address This shows the IP address of the client.
Tx Rate This shows maximum transmission rate of the client.
Rx Rate This shows maximum reception rate of the client.
Tx This shows the amount of data (in bytes) transmitted from the client since it was last connected.
Rx This shows the amount of data (in bytes) received by the client since it was last connected.
Association time This shows the date and time the client associated with the Nebula device.
First seen This shows the first date and time the client was discovered.
Last seen This shows the last date and time the client was discovered.
Manufacturer This shows the manufacturer of the client device.
Auth type This shows the authentication method used by the client to access the network.
User This shows the number of users currently connected to the network through the client device.
OS This shows the operating system running on the client device.
Policy This shows the security policy applied to the client.
LLDP This shows the LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) information received from the remote
device.
VLAN This shows the ID number of the VLAN to which the client belongs.
Note This shows additional information for the client.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 10 AP > Monitor > Client (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
37
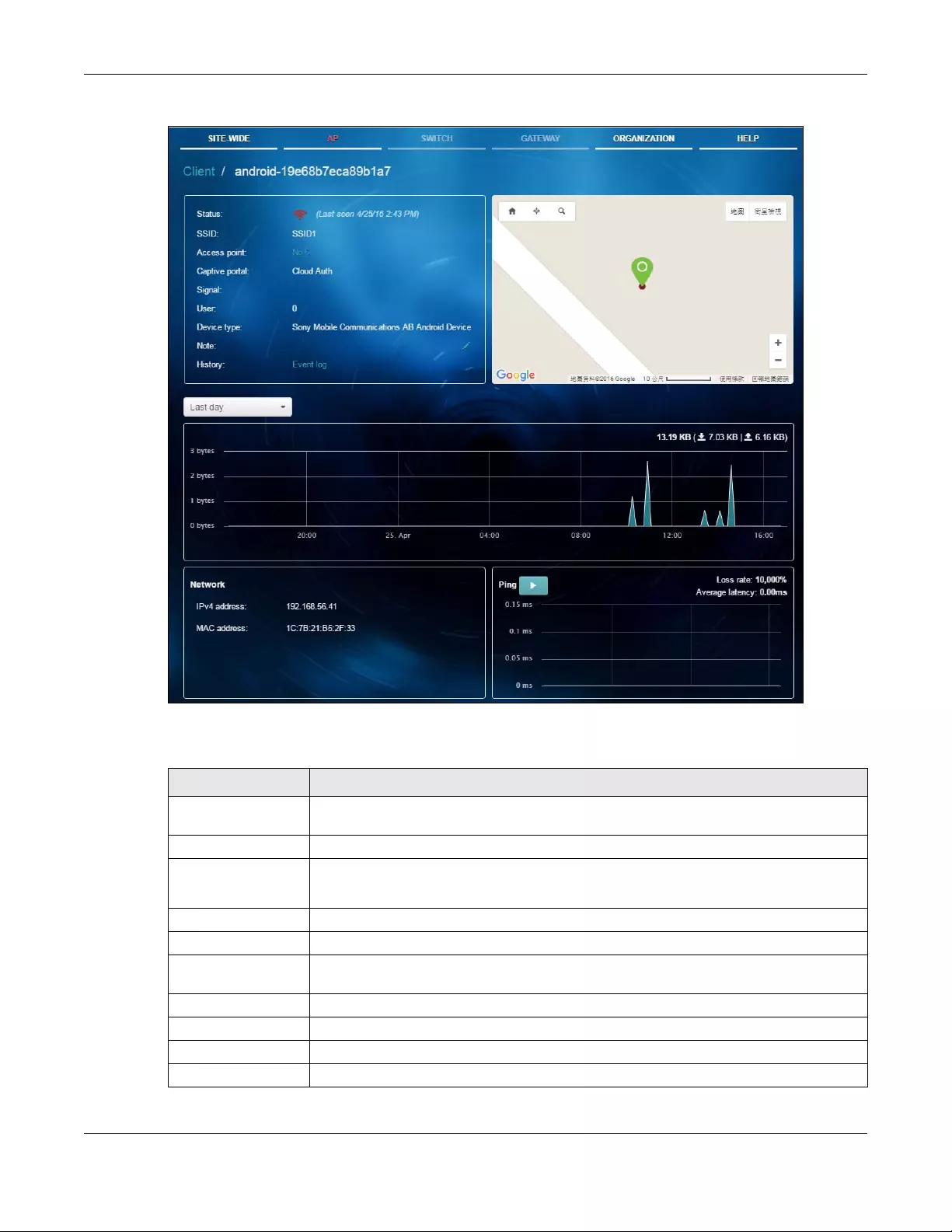
Figure 19 AP > Monitor > Client: Client Details
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 AP > Monitor > Client: Client Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red). It also shows the last
date and time the client was discovered.
SSID This shows the name of the AP’s wireless network to which the client is connected.
Access Point This shows the name of the Nebula managed AP to which the client is connected.
Click the name to display the individual AP statistics. See Section 3.2.1.1 on page 32.
Captive portal This shows the web authentication method used by the client to access the network.
Signal This shows the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the client’s wireless connection.
User This shows the number of users currently connected to the network through the client
device.
Device type This shows the manufacturer of the client device.
Note This shows additional information for the client. Click the edit icon to change it.
History Click Event log to go to the AP > Monitor > Event log screen.
Map This shows the location of the client on the Google map.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
38
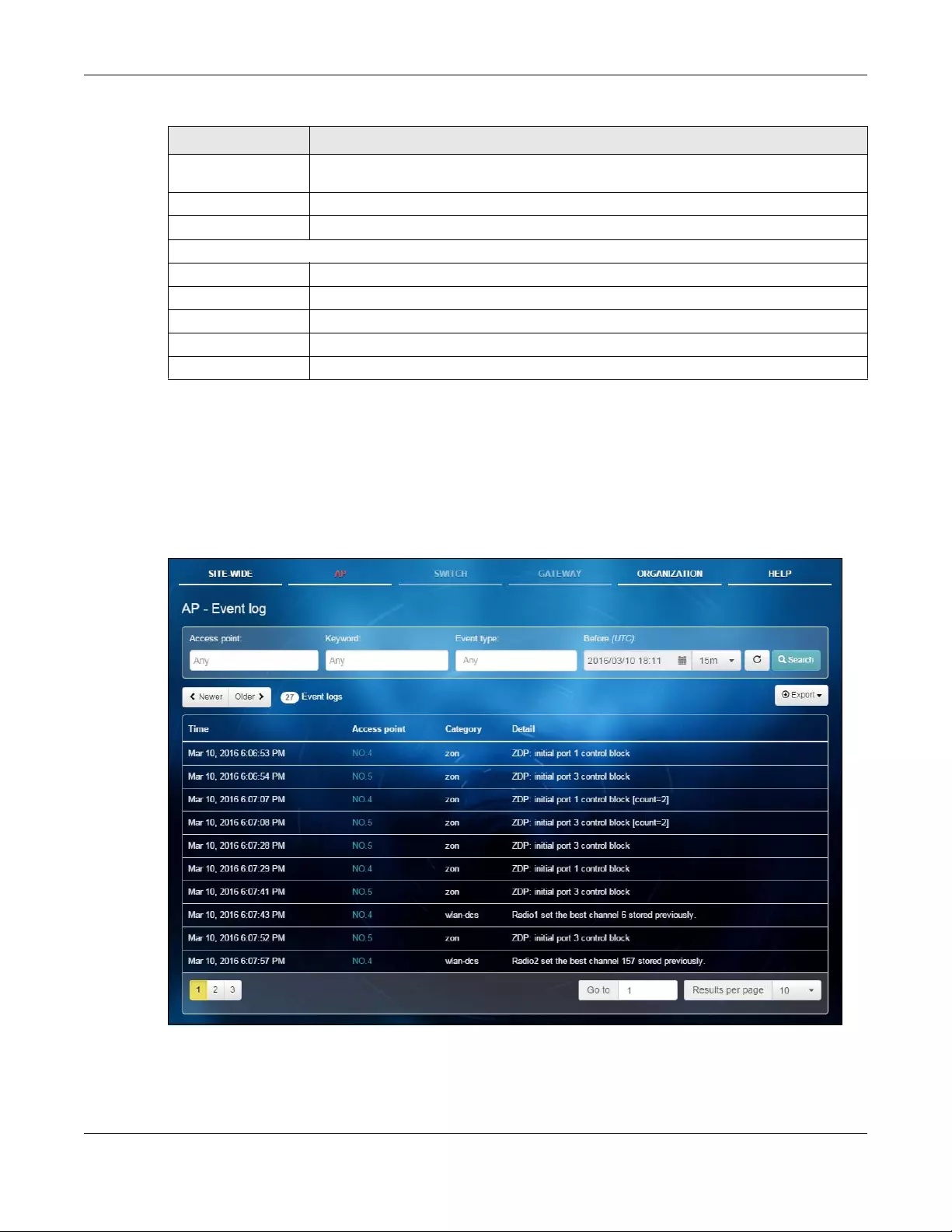
3.2.3 Event Log
Use this screen to view wireless AP log messages. You can enter the AP name, a key word, select one or
multiple event types, or specify a date/time to display only the log messages related to it.
Click AP > Monitor > Event Log to access this screen.
Figure 20 AP > Monitor > Event log
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day,
week or month.
The y-axis shows the amount of data sent or received by the client in kilobytes (KB).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Network
IPv4 address This shows the IP address of the client.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Ping Click the button to ping the client’s IP address from the Nebula AP to test connectivity.
Loss rate This shows the rate of packet loss when you perform ping.
Average latency This shows the average latency in ms when you perform ping.
Table 11 AP > Monitor > Client: Client Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
39
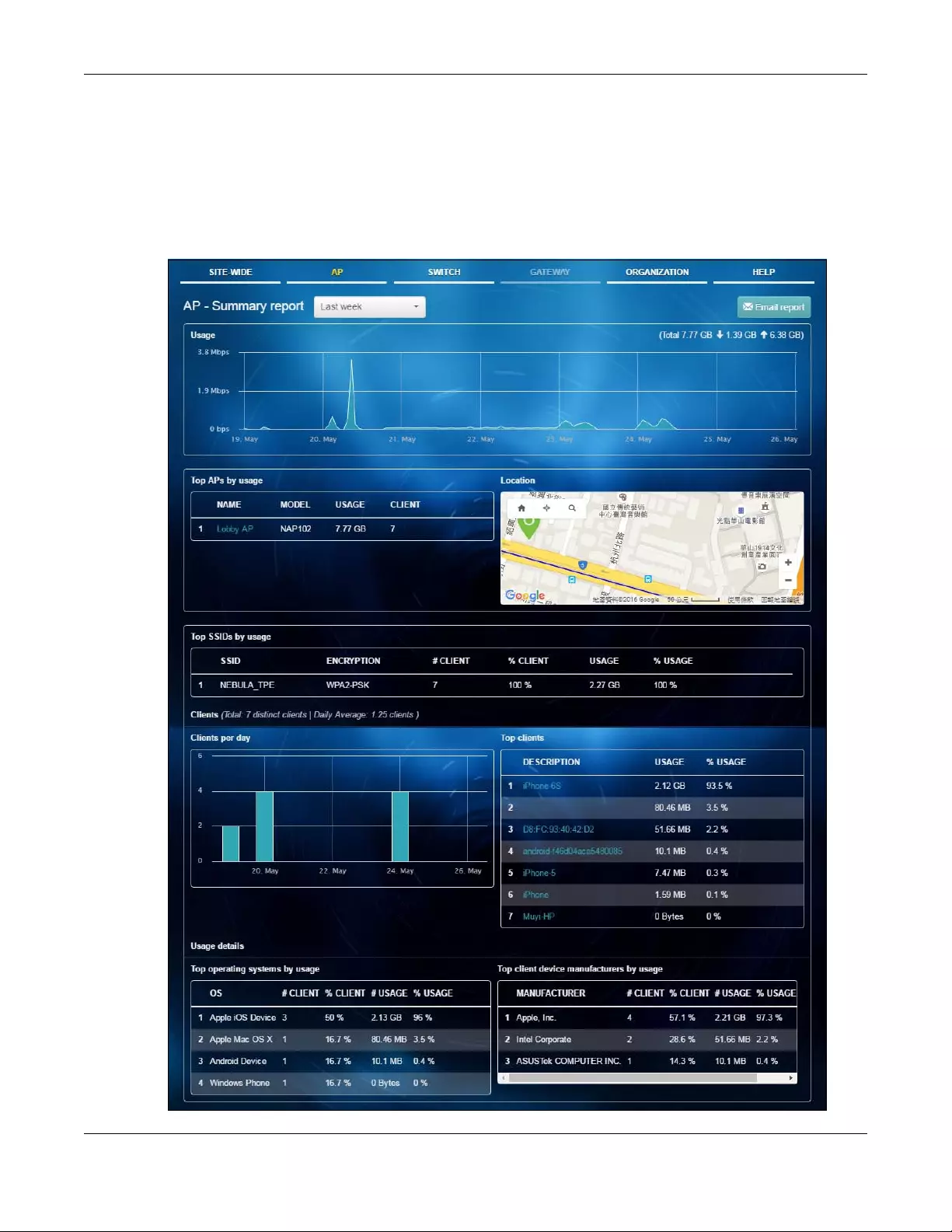
3.2.4 Summary Report
This screen displays network statistics for APs of the selected site, such as bandwidth usage, top clients
and/or top SSIDs.
Click AP > Monitor > Summary Report to access this screen.
Figure 21 AP > Monitor > Summary Report
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
40
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 AP > Monitor > Summary Report
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the report for the past day, week or month. Alternatively, select Select
range... to specify a time period the report will span. You can also select the number of
results you want to view in a table.
Email report Click this button to send summary reports by email, change the logo and set email
schedules.
Usage
The y-axis shows the transmission speed of data sent on this port in megabits per second
(Mbps).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Top APs by usage
This shows the index number of the Nebula AP.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula AP.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula AP.
Usage This shows the amount of date transmitted or received by the Nebula AP.
Clients This shows how many clients are currently connecting to the Nebula AP.
Location
This shows the location of the Nebula APs on the map.
Top SSID by usage
This shows the index number of the SSID.
SSID This shows the SSID network name.
Encryption This shows the encryption method use by the SSID network.
# Clients This shows how many Wi-Fi clients are connecting to this SSID.
% Clients This shows what percentage of associated Wi-Fi clients are connecting to this SSID.
Usage This shows the total amount of data transmitted or received by clients connecting to this
SSID.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the clients connecting to this SSID.
Clients
Total This shows the total number of clients connected to the Nebula device within the specified
time period.
Daily Average This shows the average daily number of clients within the specified time period.
Clients per day
The y-axis represents the number of clients.
The x-axis represents the date.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
41
3.3 Configure
Use the Configure menus to set the wireless and Wi-Fi security settings for APs of the selected site.
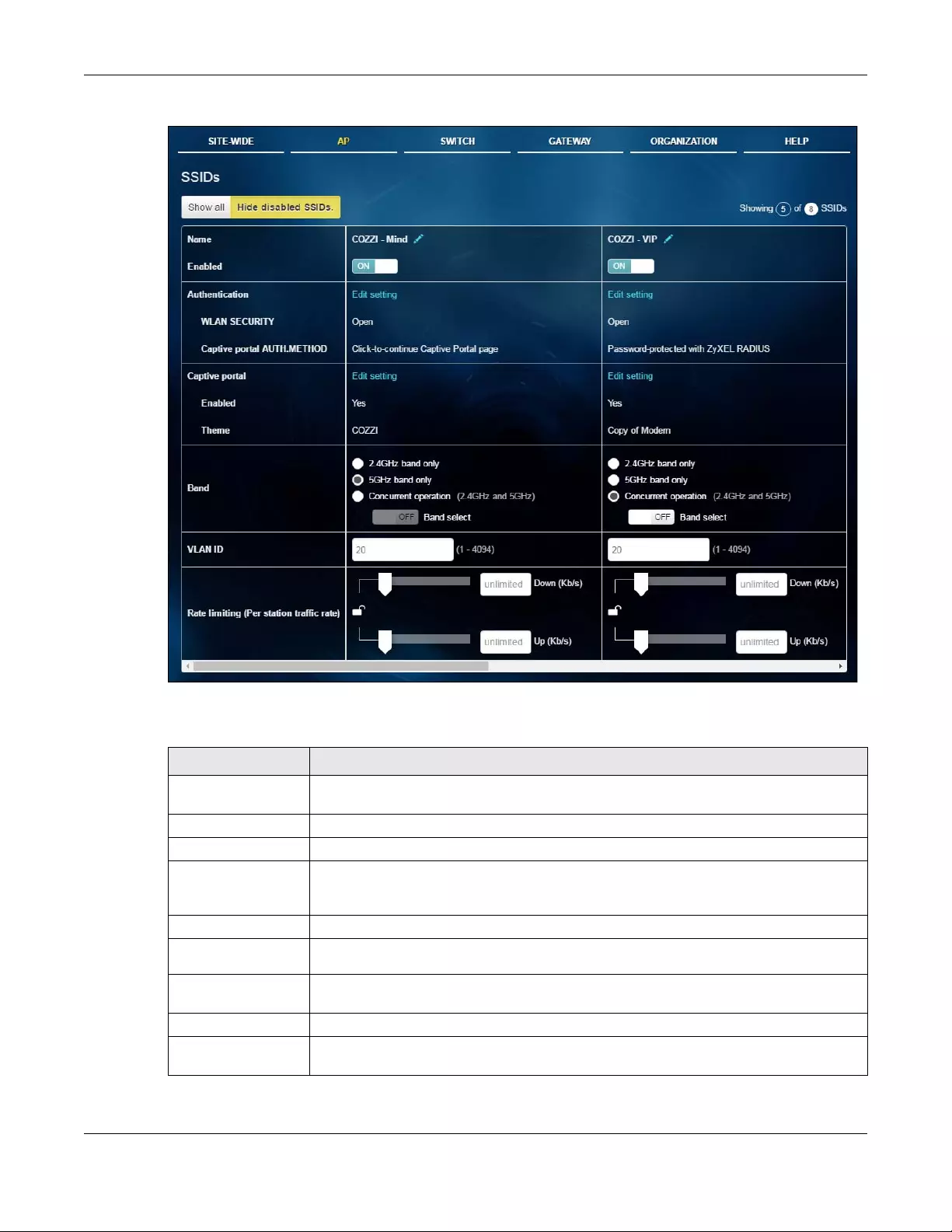
3.3.1 SSIDs
This screen allows you to configure up to eight different SSID profiles for your APs. An SSID, or Service Set
IDentifier, is basically the name of the wireless network to which a wireless client can connect. The SSID
appears as readable text to any device capable of scanning for wireless frequencies (such as the Wi-Fi
adapter in a laptop), and is displayed as the wireless network name when a person makes a
connection to it.
Click AP > Configure > SSIDs to access this screen.
Top client
This shows the index number of the client.
Description This shows the descriptive name or MAC address of the client.
Usage This shows the total amount of data transmitted and received by the client.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the client.
Usage details
Top operating systems by usage
This shows the index number of the operating system.
OS This shows the operating system of the client device.
# Clients This shows how many client devices use this operating system.
% Clients This shows the percentage of top client devices which use this operating system.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the client device on which this operating
system is running.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for top client devices which use this operating system.
Top client device manufacturers by usage
This shows the index number of the manufacturer.
Manufacturer This shows the manufacturer name of the client device.
# Clients This shows how many client devices are made by the manufacturer.
% Clients This shows the percentage of top client devices which are made by the manufacturer.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the client device.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the client device.
Table 12 AP > Monitor > Summary Report (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
42
Figure 22 AP > Configure > SSIDs
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 AP > Configure > SSIDs
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show all/Hide
disabled SSIDs
Select to display all SSID profiles or the active SSID profiles only.
Name This shows the SSID name for this profile. Click the edit icon to change it.
Enabled Click to turn on or off this profile.
Authentication Click Edit setting to go to the Authentication screen and configure the Wi-Fi security, L2
isolation, intra-BSS traffic blocking and walled garden settings. See Section 3.3.2 on page
43.
WLAN security This shows the encryption method used in this profile.
Captive portal
auth. method
This shows the authentication method used in this profile.
Captive portal Click Edit setting to go to the Captive portal screen and configure the captive portal page.
See Section 3.3.3 on page 46.
Enabled This shows whether captive portal is enabled for the SSID profile.
Theme If captive portal is enabled, this shows the name of the captive portal page used in this
profile.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
43
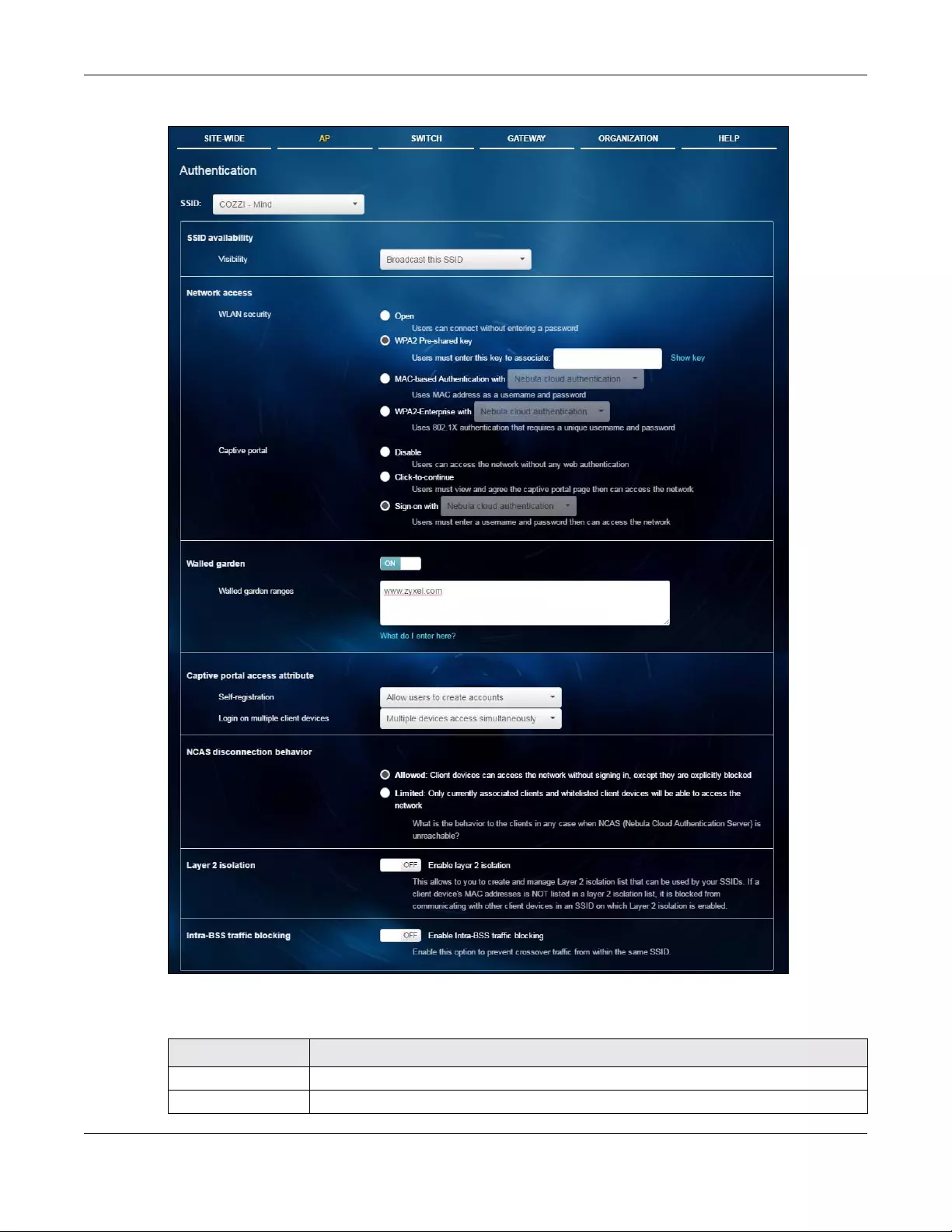
3.3.2 Authentication
Use this screen to configure the Wi-Fi security, L2 isolation, intra-BSS traffic blocking and walled garden
settings for the SSID profiles.
Click AP > Configure > Authentication to access this screen.
Band Select to have the SSID use either 2.4 GHz band or the 5 GHz band only.
If you select Concurrent operation, the SSID uses both frequency bands. You can then turn
on Band Select to have the dual-band AP steer the wireless clients to the 5 GHz band.
VLAN ID Enter the ID number of the VLAN to which the SSID belongs.
Rate limiting Set the maximum incoming/outgoing transmission data rate (in kbps) on a per-station basis.
Table 13 AP > Configure > SSIDs (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
44
Figure 23 AP > Configure > Authentication
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 AP > Configure > Authentication
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Select the SSID profile to which the settings you configure here is applied.
SSID availability
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
45
Visibility Select Hide this SSID if you want to hide your SSID from wireless clients. This tells any wireless
clients in the vicinity of the AP using this SSID profile not to display its SSID name as a
potential connection. Not all wireless clients respect this flag and display it anyway.
Otherwise, select Broadcast this SSID.
When an SSID is “hidden” and a wireless client cannot see it, the only way you can connect
to the SSID is by manually entering the SSID name in your wireless connection setup
screen(s) (these vary by client, client connectivity software, and operating system).
Network access Note: You cannot enable MAC authentication, 802.1X authentication and web
authentication at the same time.
Note: User accounts can be created and authenticated using the NCC user
database. See Section 6.9 on page 132.
WLAN security Select Open to allow any client to associate this network without any data encryption or
authentication.
Select WPA2 Pr e-shared key and enter a pre-shared key from 8 to 64 case-sensitive
keyboard characters to enable WPA2-PSK data encryption.
Select MAC-based Authentication with to authenticate wireless clients by their MAC
addresses. You can select My RADIUS server to use an external RADIUS server or select
Nebula Cloud authentication to use the NCC for MAC authentication.
Select WPA2-Enterprise with to enable 802.1X secure authentication. You can select My
RADIUS server to use an external RADIUS server or select Nebula Cloud authentication to
use the NCC for 802.1X authentication.
Captive portal Select Disable to turn off web authentication.
Select Click-to-continue to block network traffic until a client agrees to the policy of user
agreement.
Select Sign-on with to block network traffic until a client authenticates with the NCC
(Nebula Cloud authentication) or an external RADIUS server (My RADIUS server) through the
specifically designated web portal page.
RADIUS server This field is available only when you select to use MAC-based Authentication with My
RADIUS serv er or WPA2-Enterprise with My RADIUS server in the WLAN security field, or when
you select Sign-on with My RADIUS server in the Captive portal field.
Click Add a server to specify the IP address, port number and shared secret password of
the RADIUS server to be used for authentication.
RADIUS
accounting
This field is available only when you select to use MAC-based Authentication with My
RADIUS server or WPA2-Enterprise with My RADIUS server in the WLAN security field.
Select RADIUS accounting enabled to enable user accounting through an external RADIUS
server.
Select RADIUS accounting disabled to disable user accounting through an external RADIUS
server.
Click Add a server to specify the IP address, port number and shared secret password of
the RADIUS server to be used for accounting.
Walled garden Select to turn on or off the walled garden feature.
With a walled garden, you can define one or more web site addresses that all users can
access without logging in. These can be used for advertisements for example.
Walled garden
ranges
Specify walled garden web site links, which use a (wildcard) domain name or an IP address
for web sites that all users are allowed to access without logging in. The web site link(s)
displays in the user login screen by default.
Table 14 AP > Configure > Authentication (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
46
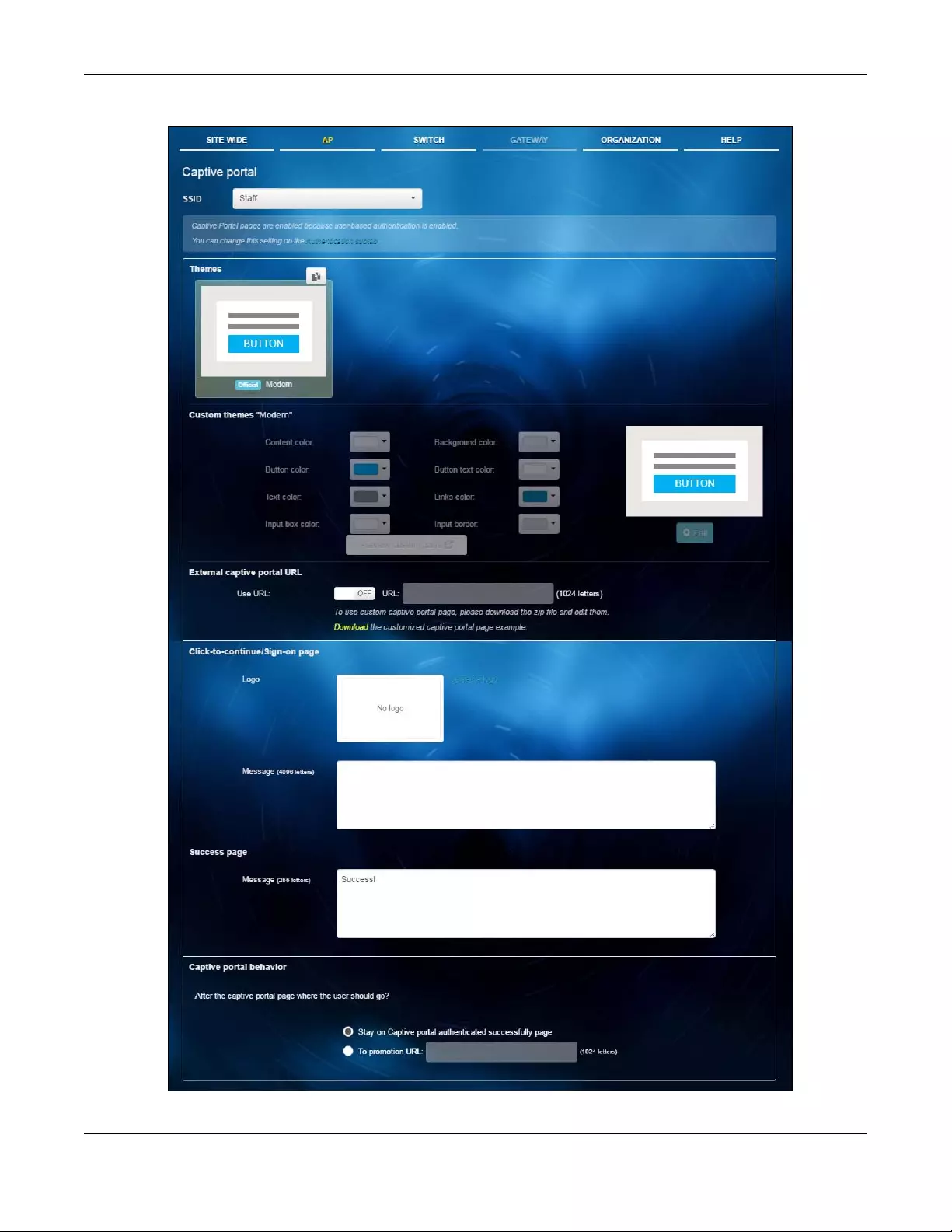
3.3.3 Captive Portal
Use this screen to configure captive portal settings for SSID profiles. A captive portal can intercepts
network traffic until the user authenticates his or her connection, usually through a specifically
designated login web page.
Click AP > Configure > Captive portal to access this screen.
Captive portal
access attribute
Self-registration This field is available only when you select Sign-on with Nebula Cloud authentication in the
Captive portal field.
Select Allow users to create accounts to display a link in the captive portal login page. The
link directs users to a page where they can create an account before they authenticate
with the NCC. After the account is authorized, the user can log in using it.
Select Don’t allow users to create accounts to not display a link for account creation in the
captive portal login page.
Login on multiple
client devices
This field is available only when you select Sign-on with My RADIUS server or Sign-on with
Nebula Cloud authentication in the Captive portal field.
Select Multiple devices access simultaneously if you allow users to log in as many times as
they want as long as they use different IP addresses.
Select One device at a time if you don’t allow users to have simultaneous logins.
NCAS disconnection
behavior
This field is available only when you select Click-to-continue or Sign-on with in the Captive
portal field.
Select Allowed to allow any users to access the network without authentication when the
NCAS (Nebula Cloud Authentication Server) is not reachable.
Select Limited to allow only the currently connected users or the users in the white list to
access the network.
Layer 2 isolation
Enable layer 2
isolation
Select to turn on or off layer-2 isolation. If a device’s MAC addresses is NOT listed, it is
blocked from communicating with other devices in an SSID on which layer-2 isolation is
enabled.
Click Add to enter the MAC address of each device that you want to allow to be accessed
by other devices in the SSID on which layer-2 isolation is enabled.
Intra-BSS traffic
blocking
Enable Intra-BSS
traffic blocking
This field is not configurable if you enable Layer 2 isolation.
Select On to prevent crossover traffic from within the same SSID. Select Off to allow intra-BSS
traffic.
Table 14 AP > Configure > Authentication (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
47
Figure 24 AP > Configure > Captive portal

Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
48
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 AP > Configure > Captive portal
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID Select the SSID profile to which the settings you configure here is applied.
Themes Click the Copy icon at the upper right corner of the default theme image to create a new
custom theme (login page).
Click the Remove icon to delete a custom theme page.
Custom themes
"Modern"
Select a custom theme page and customize the colors on the selected login page, such as
the color of the button, text, window’s background, links, borders, and etc.
Select a color that you want to use in the Saved Colors tab. If the color you want is not
listed, click the Advanced tab to define a new one.
Preview custom
page
Click this button to update the theme image that displays at the right side of the screen
Edit Click this button to go to a screen where you can view and configure the details of the
custom login page. See Section 3.3.3.1 on page 49.
External captive
portal URL
Use URL Select On to use a custom login page from an external web portal instead of the one built
into the NCC. You can configure the look and feel of the web portal page.
Specify the login page’s URL; for example, http://IIS server IP Address/login.asp. The Internet
Information Server (IIS) is the web server on which the web portal files are installed.
Click-to-continue/
Sign-on page
Logo This shows the logo image that you uploaded for the customized login page.
Click Upload a logo and specify the location and file name of the logo graphic or click
Browse to locate it. You can use the following image file formats: GIF, PNG, or JPG.
Message Enter a note to display below the title. Use up to 1024 printable ASCII characters. Spaces
are allowed.
Success page
Message Enter a note to display on the page that displays when a user logs in successfully. Use up to
1024 printable ASCII characters. Spaces are allowed.
Captive portal
behavior
After the captive
portal page
where the user
should go?
Select To promotion URL and specify the URL of the web site/page to which the user is
redirected after a successful login. Otherwise, select Stay on Captive portal authenticated
successfully page.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
49
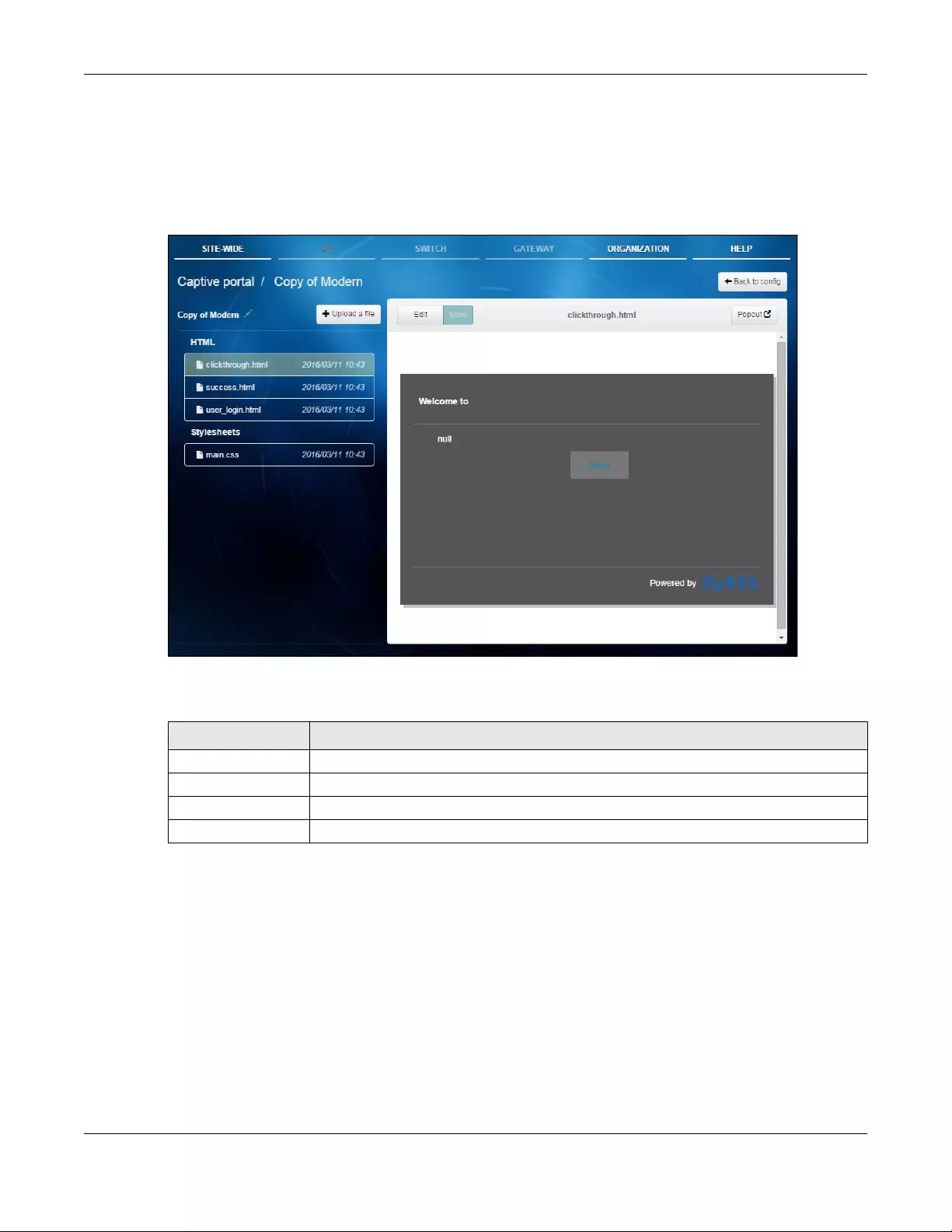
3.3.3.1 Custom Login Page Edit
Use this screen to check what the custom portal pages look like. You can also view and modify the CSS
values of the selected HTML file. Click a custom login page’s Edit button in the AP > Configure > Captive
portal screen to access this screen.
Figure 25 AP > Configure > Captive portal: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
3.3.4 Radio Setting
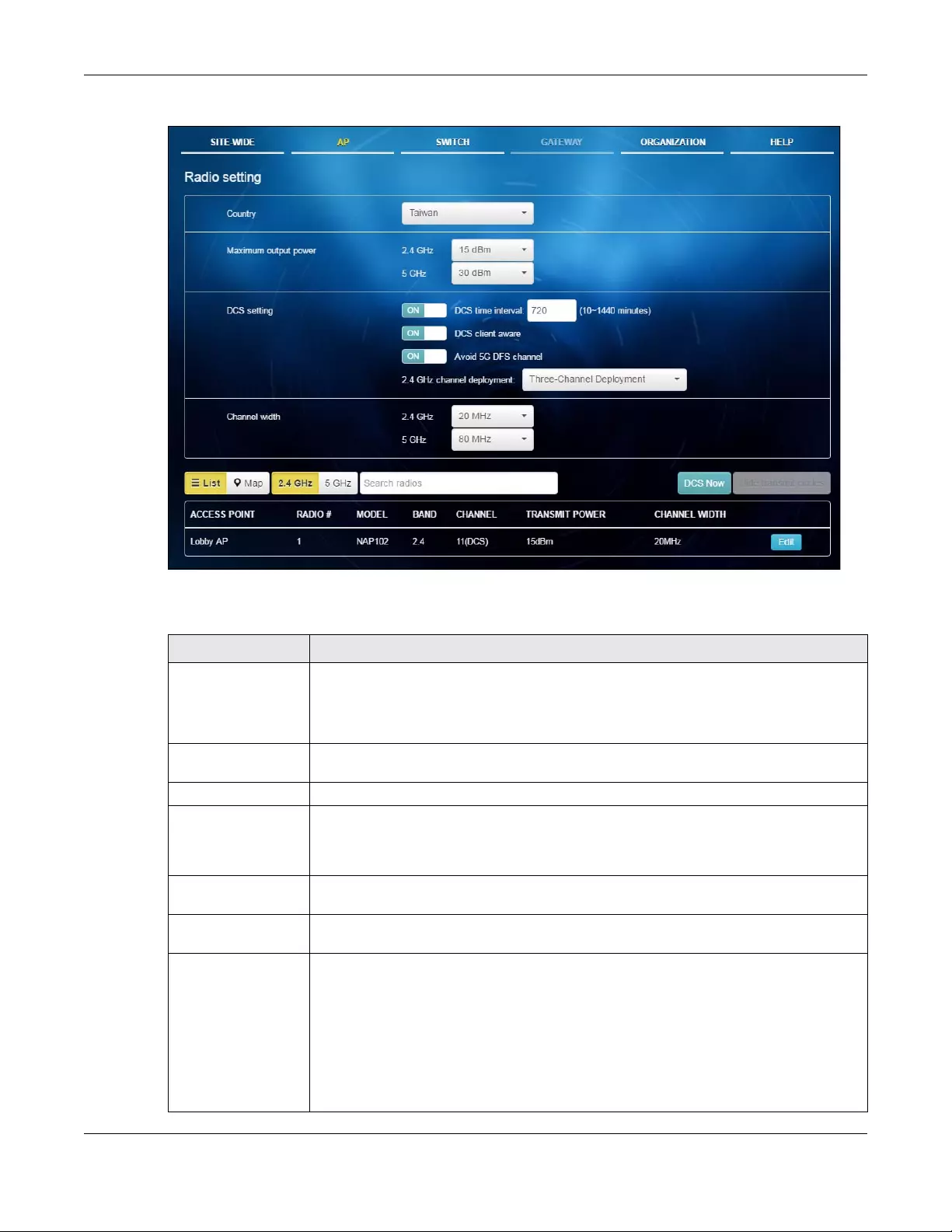
Use this screen to configure global radio settings for all APs in the site. Click AP > Configure > Radio
setting to access this screen.
Table 16 AP > Configure > Captive portal: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Back to config Click this button to return to the Captive portal screen.
Copy of Modern This shows the name of the theme. Click the edit icon the change it.
Upload a file Click this button to upload a web portal file with custom html pages to the NCC.
Popout Click this button to display the corresponding portal page in a popup window.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
50
Figure 26 AP > Configure > Radio setting
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 AP > Configure > Radio setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Country Select the country where the AP is located/installed.
The available channels vary depending on the country you selected. Be sure to select the
correct/same country for both radios on an AP and all connected APs, in order to prevent
roaming failure and interference to other systems.
Maximum output
power
Set the maximum target output power of the radio (in dBm).
DCS setting
DCS time interval Select ON to set the DCS time interval (in minutes) to regulate how often the AP surveys the
other APs within its broadcast radius. If the channel on which it is currently broadcasting
suddenly comes into use by another AP, the AP will then dynamically select the next
available clean channel or a channel with lower interference.
DCS client aware Select ON to have the AP wait until all connected clients have disconnected before
switching channels.
Avoid 5G DFS
channel
Select ON to force the AP to select a non-DFS channel if your APs are operating in an area
known to have RADAR devices.
2.4 GHz channel
deployment
Select Three-Channel Deployment to limit channel switching to channels 1,6, and 11, the
three channels that are sufficiently attenuated to have almost no impact on one another.
In other words, this allows you to minimize channel interference by limiting channel-hopping
to these three “safe” channels.
Select Four-Channel Deployment to limit channel switching to four channels. Depending
on the country domain, if the only allowable channels are 1-11 then the AP uses channels 1,
4, 7, 11 in this configuration; otherwise, the AP uses channels 1, 5, 9, 13 in this configuration.
Four channel deployment expands your pool of possible channels while keeping the
channel interference to a minimum.
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
51
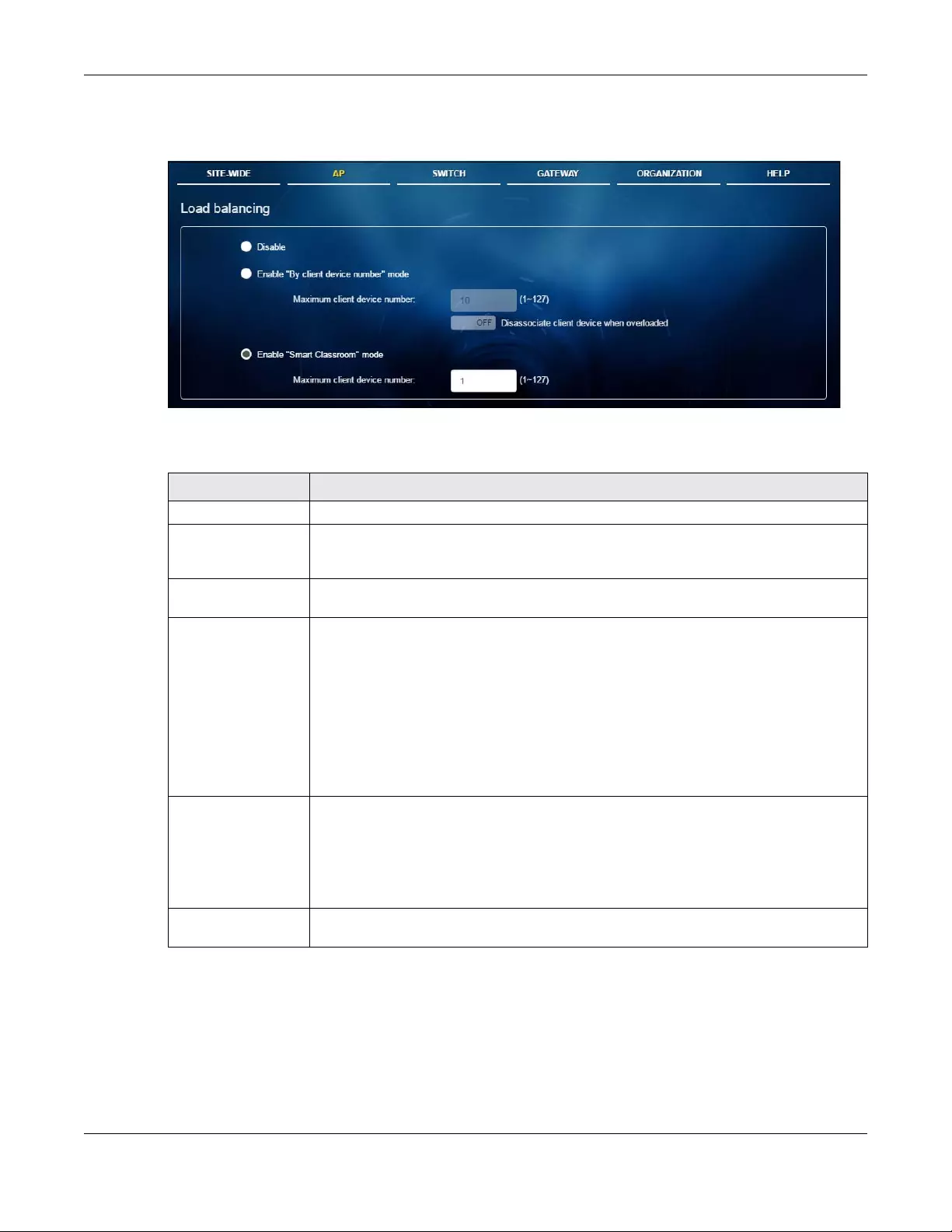
3.3.5 Load Balancing
Use this screen to configure network traffic load balancing between the APs.
Channel width Select the wireless channel bandwidth you want the AP to use.
A standard 20 MHz channel offers transfer speeds of up to 144Mbps (2.4GHz) or 217Mbps
(5GHZ) whereas a 40MHz channel uses two standard channels and offers speeds of up to
300Mbps (2.4GHz) or 450Mbps (5GHZ). An IEEE 802.11ac-specific 80MHz channel offers
speeds of up to 1.3Gbps.
40 MHz (channel bonding or dual channel) bonds two adjacent radio channels to increase
throughput. A 80 MHz channel consists of two adjacent 40 MHz channels. The wireless
clients must also support 40 MHz or 80 MHz. It is often better to use the 20 MHz setting in a
location where the environment hinders the wireless signal.
Note: It is suggested that you select 20 MHz when there is more than one 2.4GHz
AP in the network.
List Click this to display a list of all connected APs.
Map Click this to display the locations of all connected APs on the Google map.
2.4 GHz Click this to display the connected APs using the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
5 GHz Click this to display the connected APs using the 5 GHz frequency band.
DCS Now Click this button to have the APs immediately scan for and select a channel that has least
interference.
Hide transmit circles Click this button to not show the transmission range on the Map.
Access point This displays the descriptive name or MAC address of the connected AP.
Radio # This displays the number of the connected AP’s radio.
Model This displays the model name of the connected AP.
Band This displays the frequency band used by the connected AP’s radio.
Channel This displays the number of channel currently used by the connected AP’s radio.
Transmit power This displays the transmitting power of the connected AP’s radio.
Channel width This displays the wireless channel bandwidth the connected AP’s radio is set to use.
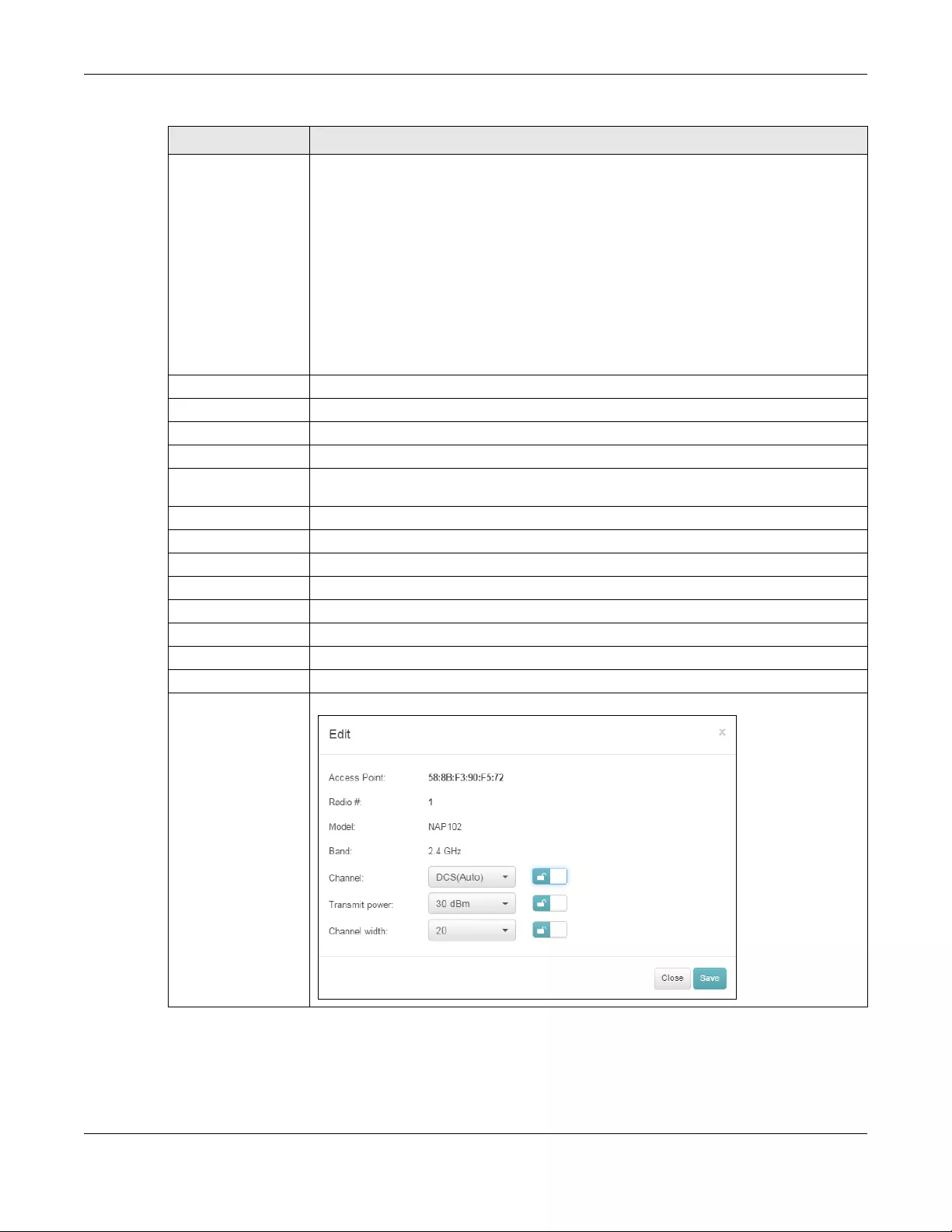
Edit Click this button to modify the AP’s channel, output power and channel width settings.
Table 17 AP > Configure > Radio setting (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 3 AP
NCC User’s Guide
52
Click AP > Configure > Load balancing to access this screen.
Figure 27 AP > Configure > Load balancing
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 AP > Configure > Load balancing
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Disable Select this option to disable load balancing on the AP.
Enable "By client
device number"
mode
Select this option to balance network traffic based on the number of specified client
devices connected to the AP.
Max client
device number
Enter the threshold number of client devices at which the AP begins load balancing its
connections.
Disassociate
client device
when
overloaded
Select ON to disassociate wireless clients connected to the AP when it becomes
overloaded.
Select OFF to disable this option, then the AP simply delays the connection until it can
afford the bandwidth it requires, or it transfers the connection to another AP within its
broadcast radius.
The disassociation priority is determined automatically by the AP and is as follows:
•Idle Time - Devices that have been idle the longest will be kicked first. If none of the
connected devices are idle, then the priority shifts to Signal Strength.
•Signal Strength - Devices with the weakest signal strength will be kicked first.
Enable "Smart
Classroom" mode
Select this option to balance network traffic based on the number of specified client
devices connected to the AP. The AP ignores association request and authentication
request packets from any new client device when the maximum number of client devices
is reached.
The Disassociate client device when overloaded function is enabled by default and the
disassociation priority is always Signal Strength when you select this option.
Max client
device number
Enter the threshold number of client devices at which the AP begins load balancing its
connections.

NCC User’s Guide
53
CHAPTER 4
Switch
4.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the menus that you can use to monitor the Nebula managed switches in your
network and configure settings even before a switch is deployed and added to the site.
4.2 Monitor
Use the Monitor menus to check the switch information, client information, event log messages and
summary report for switches in the selected site.
4.2.1 Switch
This screen allows you to view the detailed information about a switch in the selected site. Click Switch >
Monitor > Switch to access this screen.
Figure 28 Switch > Monitor > Switch
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Switch > Monitor > Switch
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of switches.
Switch(es) This shows the number of switches connected to the site network.
Export Click this button to save the switch list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Status This shows whether the switch is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), goes off-line (red)
or has been off-line for at least six days (gray).
System Name This shows the descriptive name of the switch.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag for the switch.
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
54
4.2.1.1 Switch Details
Click a switch entry in the Switch > Monitor > Switch screen to display individual switch statistics.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the switch.
LAN IP This shows the local (LAN) IP address of the switch.
Public IP This shows the global (WAN) IP address of the switch.
Model This shows the model number of the switch.
# Port This shows the number of the switch port which is connected to the NCC.
Configuration
status
This shows whether the configuration on the switch is up-to-date.
Bandwidth
Utilization
This shows what percentage of the upstream/downstream bandwidth is currently being used
by the switch’s uplink port.
Production
Information
This shows the production information of the switch.
Connectivity This shows the switch connection status. Nothing displays if the switch is off-line.
The gray time slot indicates the connection to the NCC is down, and the green time slot
indicates the connection is up. Move the cursor over a time slot to see the actual date and
time when a switch is connected or disconnected.
Description This shows the user-specified description for the switch.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the switch.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 19 Switch > Monitor > Switch (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
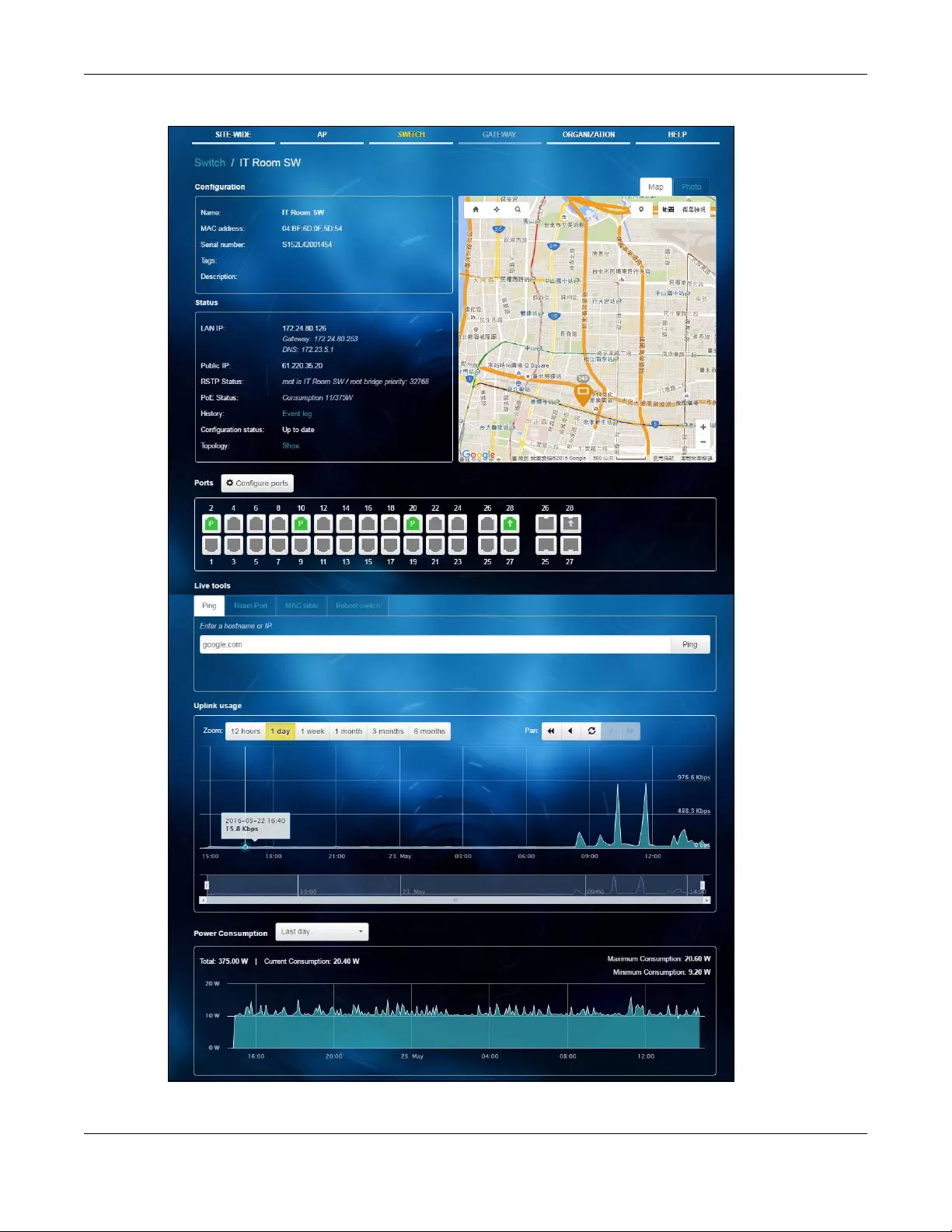
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
55
Figure 29 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details
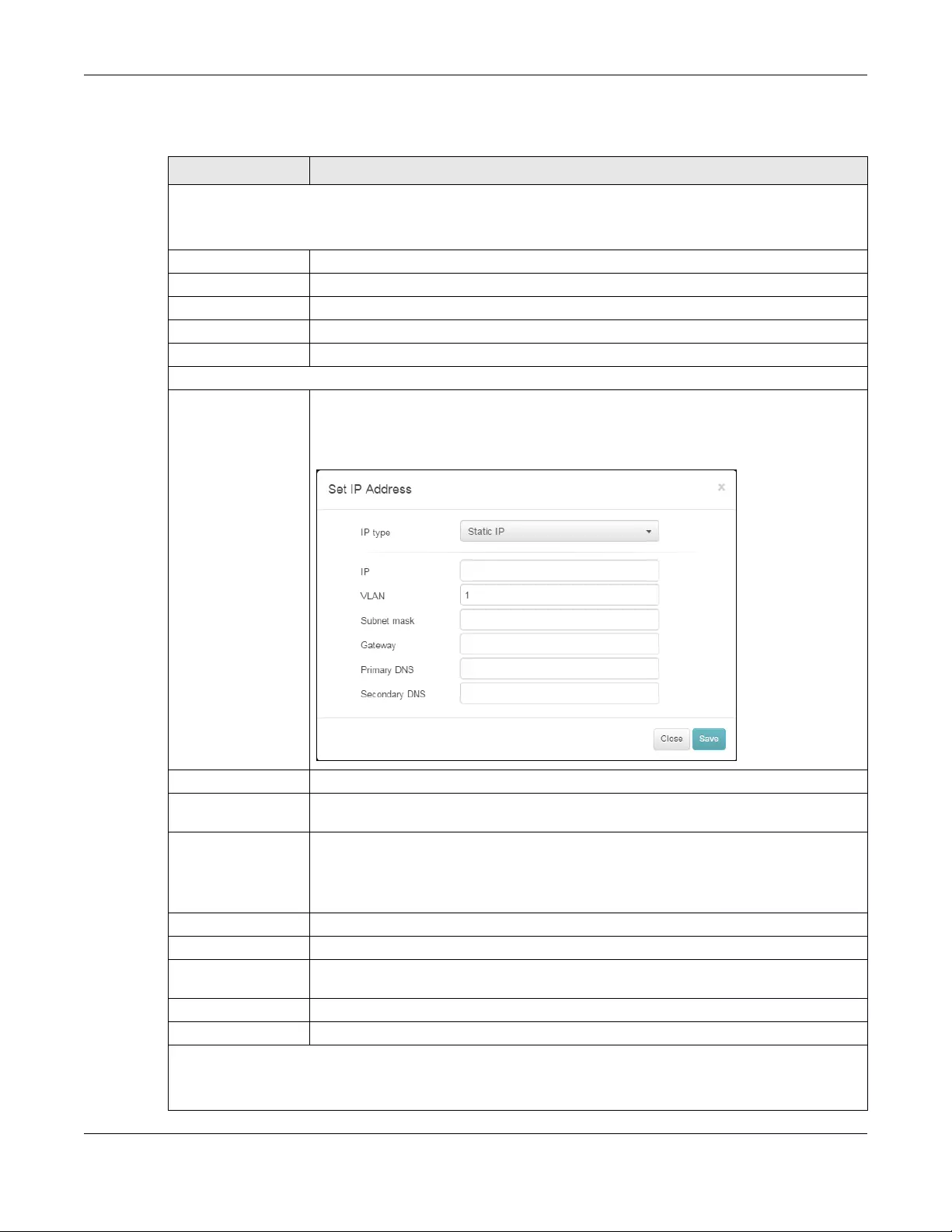
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
56
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Click the edit icon to change the device name, description, tags and address. You can also move the device to
another site.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the switch.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the switch.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the switch.
Tags This shows the user-specified tag for the switch.
Description This shows the user-specified description for the switch.
Status
LAN IP This shows the local (LAN) IP address of the switch. It also shows the IP addresses of the
gateway and DNS servers.
Click the edit icon to open a screen where you can change the IP address, VLAN ID
number and DNS server settings.
Public IP This shows the global (WAN) IP address of the switch.
RSTP Status This shows Disabled when RSTP is disabled on the switch. Otherwise, it shows the name or
MAC address of the switch that is the root bridge of the spanning tree.
PoE Status This shows the amount of power the switch is currently supplying to the connected PoE-
enabled devices and the total power the switch can provide to the connected PoE-
enabled devices on the PoE ports.
Click the edit icon to open the PoE Configuration screen. See Section 4.2.1.2 on page 57.
History Click Event log to go to the SWITCH > Monitor > Event log screen.
Configuration status This shows whether the configuration on the switch is up-to-date.
Topology Click Show to go to the SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Topology screen. See Section 2.1.4 on page
24.
Map This shows the location of the switch on the Google map.
Photo This shows the photo of the switch.
Ports
This shows the ports on the switch. You can click a port to see the individual port statistics. See Section 4.2.1.3 on
page 59.
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
57
4.2.1.2 PoE Configuration
Use this screen to set the PoE mode, priority levels and power-up mode for the switch in distributing
power to PDs. To access this screen, click the edit icon next to PoE Status in the Switch > Monitor > Switch:
Switch Details screen.
Configure ports Click this button to go to the Switch > Configure > Switch ports screen, where you can view
port summary. See Section 4.3.1 on page 68.
Live tools
Ping Enter the host name or IP address of a computer that you want to perform ping in order to
test a connection and click Ping.
Reset port Enter the number of the port(s) and click the Reset button to disable and enable the port(s)
again.
MAC table This shows what device MAC address, belonging to what VLAN group (if any) is forwarded
to which port(s).
You can define how it displays and arranges the data in the summary table below.
Reboot switch Click the Reboot button to restart the switch.
Uplink usage
Move the cursor over the chart to see the transmission rate at a specific time.
Zoom Select to view the statistics in the past twelve hours, day, week, month, three months or six
months.
Pan Click to move backward or forward by one day or week.
Power Consumption
Select to view the switch power consumption in the past two hours, day, week or month.
This shows the current, total, maximum and minimum power consumption of the switch.
Table 20 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
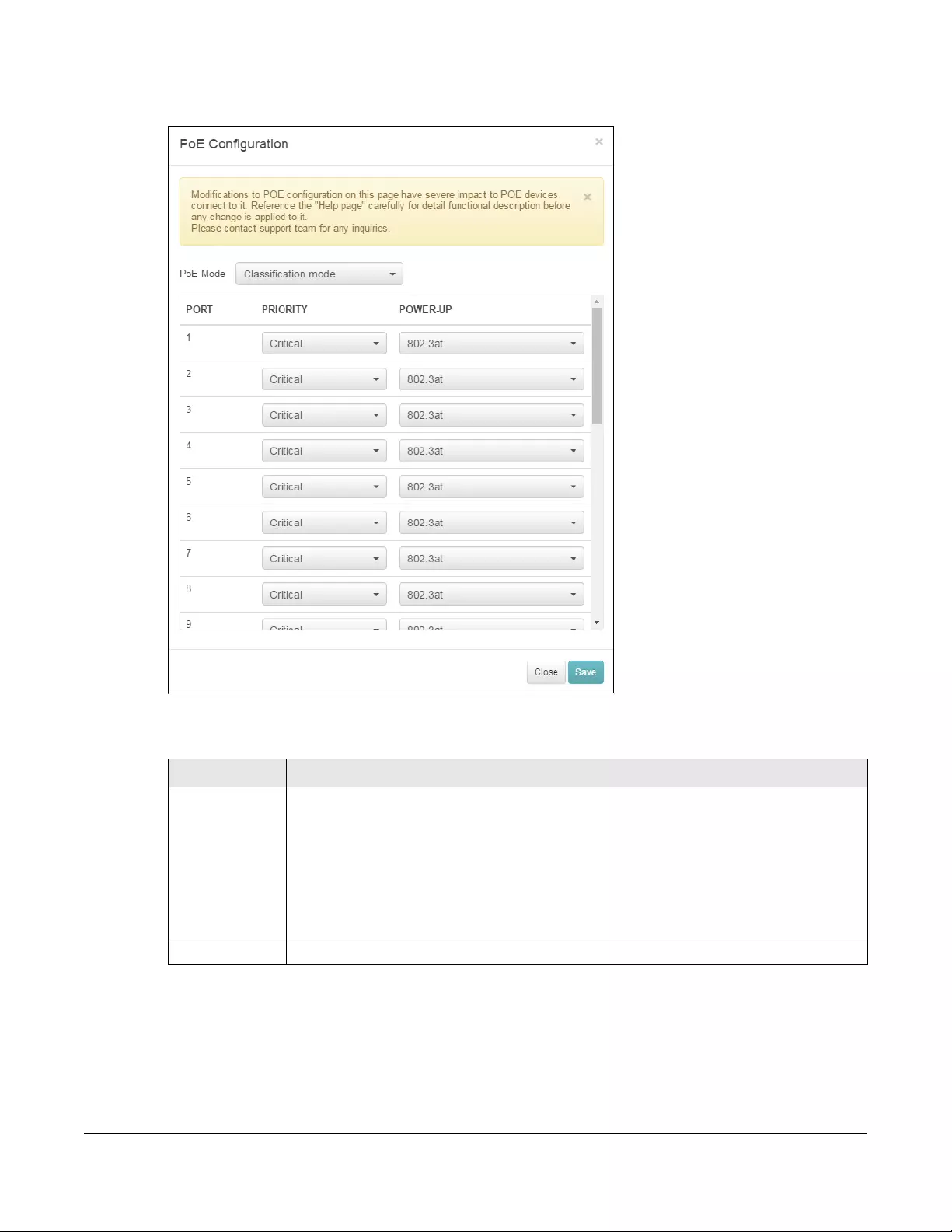
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
58
Figure 30 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: PoE Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: PoE Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PoE Mode Select the power management mode you want the switch to use.
Classification mode - Select this if you want the switch to reserve the Max Power (mW) to each
powered device (PD) according to the priority level. If the total power supply runs out, PDs with
lower priority do not get power to function.
Consumption mode - Select this if you want the switch to manage the total power supply so
that each connected PD gets a resource. However, the power allocated by the switch may be
less than the Max Power (mW) of the PD. PDs with higher priority also get more power than
those with lower priority levels.
Port This is the port index number.

Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
59
4.2.1.3 Switch Port Details
Use this to view individual switch port statistics. To access this screen, click a port in the Ports section of
the Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details screen or click the details link next to a port in the Switch >
Configure > Switch ports screen.
Priority When the total power requested by the PDs exceeds the total PoE power budget on the
switch, you can set the PD priority to allow the switch to provide power to ports with higher
priority.
Select Critical to give the highest PD priority on the port.
Select High to set the switch to assign the remaining power to the port after all critical priority
ports are served.
Select Low to set the switch to assign the remaining power to the port after all critical and high
priority ports are served.
Power-up Set how the switch provides power to a connected PD at power-up.
802.3af - the switch follows the IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet standard to supply power to
the connected PDs during power-up.
Legacy - the switch can provide power to the connected PDs that require high inrush currents
at power-up. Inrush current is the maximum, instantaneous input current drawn by the PD when
first turned on.
Pre-802.3at - the switch initially offers power on the port according to the IEEE 802.3af standard,
and then switches to support the IEEE 802.3at standard within 75 milliseconds after a PD is
connected to the port. Select this option if the switch is performing 2-event Layer-1
classification (PoE+ hardware classification) or the connected PD is NOT performing Layer 2
power classification using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP).
802.3at - the switch supports the IEEE 802.3at High Power over Ethernet standard and can
supply power of up to 30W per Ethernet port. IEEE 802.3at is also known as PoE+ or PoE Plus. An
IEEE 802.3at compatible device is referred to as Type 2. Power Class 4 (High Power) can only be
used by Type 2 devices. If the connected PD requires a Class 4 current when it is turned on, it
will be powered up in this mode.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Save Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
Table 21 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: PoE Configuration (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
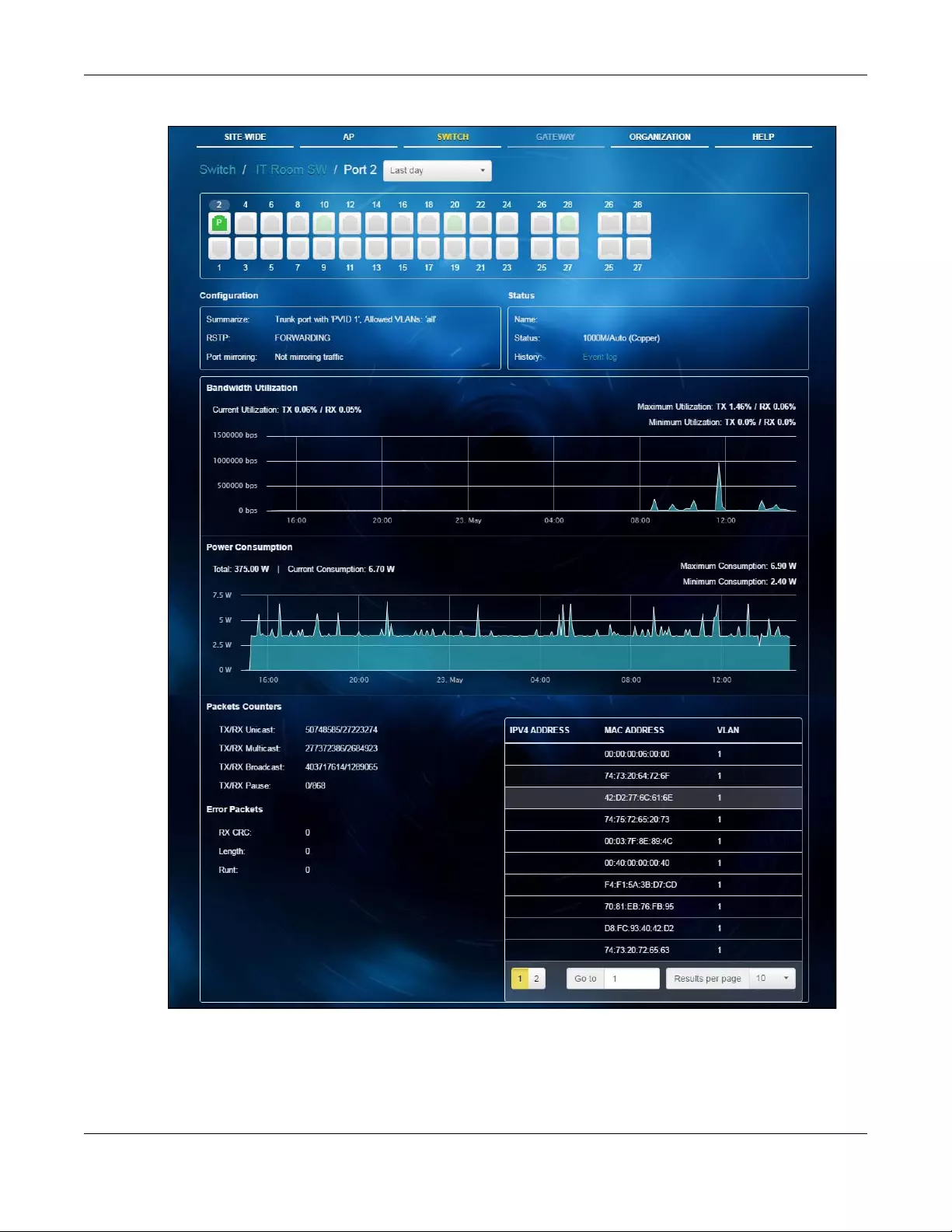
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
60
Figure 31 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: Port Details
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
61
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: Port Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the port information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
This drawing shows the ports on the switch.
Click a port to go to the corresponding port details screen. The selected port is highlighted
in green color.
Configuration
Click the edit icon to open the Switch ports screen and show the port(s) that match the filter criteria (the selected
port number). See Section 4.3.1 on page 68.
Summarize This shows the port’s VLAN settings.
RSTP This shows whether RSTP is disabled or enabled on the port.
Port mirroring This shows whether traffic is mirrored on the port.
Status
Name This shows the name of the port.
Status This shows the status of the port.
History Click Event log to go to the SWITCH > Monitor > Event log screen.
Bandwidth Utilization
Current Utilization This shows what percentage of the upstream/downstream bandwidth is currently being
used by the port.
Maximum Utilization This shows the maximum upstream/downstream bandwidth utilization (in percentage).
Minimum Utilization This shows the minimum upstream/downstream bandwidth utilization (in percentage).
The y-axis represents the transmission rate in bps (bits per second).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Power Consumption
Total This shows the total power consumption of the port.
Current Consumption This shows the current power consumption of the port.
Maximum
Consumption
This shows the maximum power consumption of the port.
Minimum
Consumption
This shows the minimum power consumption of the port.
The y-axis shows how much power is used in Watts.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the power consumption is recorded.
Packets Counters
TX/RX Unicast This shows the number of good unicast packets transmitted/received on the port.
TX/RX Multicast This shows the number of good multicast packets transmitted/received on the port.
TX/RX Broadcast This shows the number of good broadcast packets transmitted/received on the port.
TX/RX Pause This shows the number of 802.3x Pause packets transmitted/received on the port.
Error Packets
RX CRC This shows the number of packets received with CRC (Cyclic Redundant Check) error(s).
Length This shows the number of packets received with a length that was out of range.
Runt This shows the number of packets received that were too short (shorter than 64 octets),
including the ones with CRC errors.
IPv4 Address This shows the IP address of the incoming frame which is forwarded on the port.
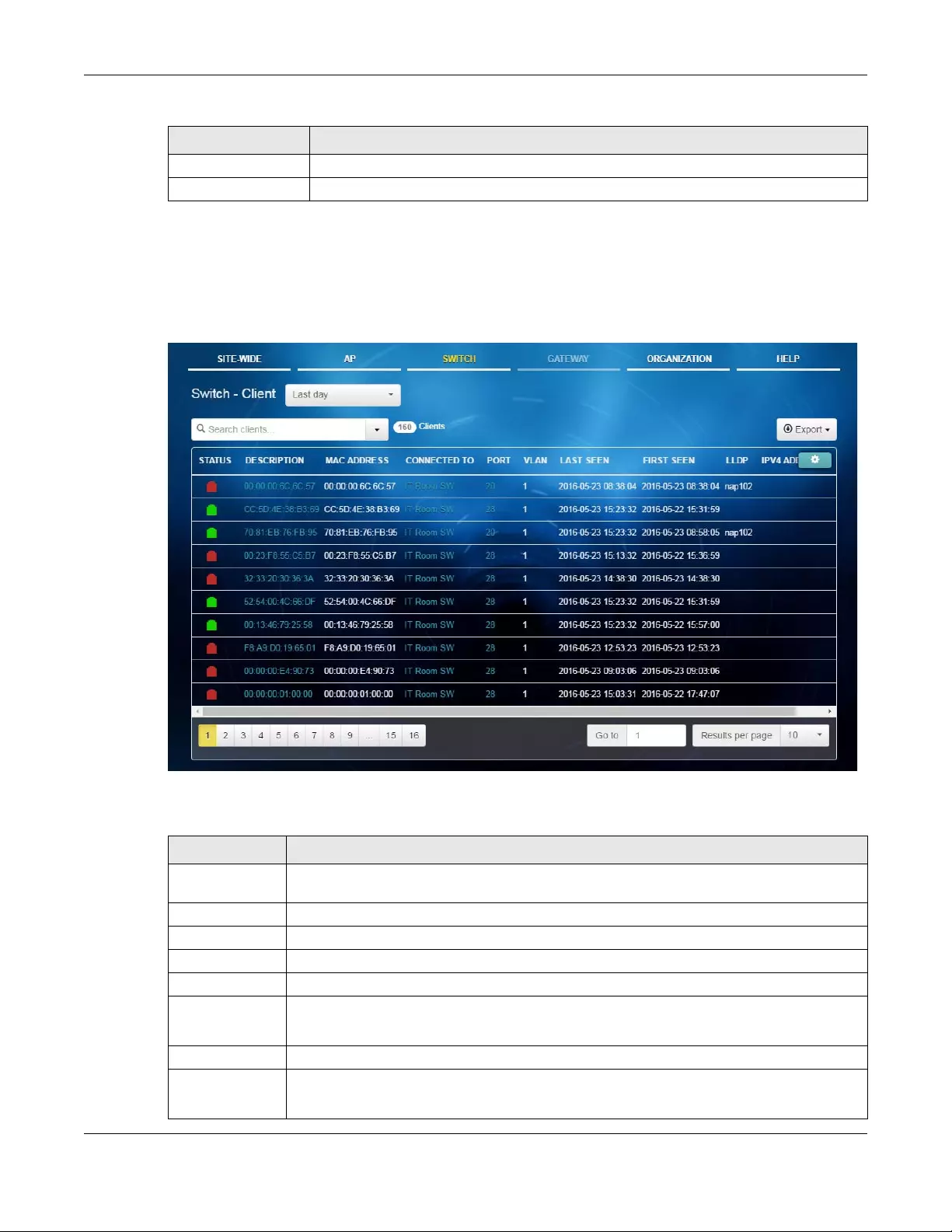
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
62
4.2.2 Client
This screen allows you to view the connection status and detailed information about a client in the
selected site. Click Switch > Monitor > Client to access this screen.
Figure 32 Switch > Monitor > Client
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the incoming frame which is forwarded on the port.
VLAN This shows the VLAN group to which the incoming frame belongs.
Table 22 Switch > Monitor > Switch: Switch Details: Port Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 23 Switch > Monitor > Client
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of clients.
Clients This shows the number of clients connected to the site network.
Export Click this button to save the client list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red).
Description This shows the descriptive name of the client.
Click the name to display the individual client statistics. See Section 4.2.2.1 on page 63.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Connected to This shows the name of the Nebula managed switch to which the client is connected.
Click the name to display the individual switch statistics. See Section 4.2.1.1 on page 54.

Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
63
4.2.2.1 Client Details
Click a client entry in the Switch > Monitor > Client screen to display individual client statistics.
Figure 33 Switch > Monitor > Client: Client Details
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
4.2.3 Event Log
Use this screen to view switch log messages. You can enter the switch name, a key word, select one or
multiple event types, or specify a date/time to display only the log messages related to it.
Click Switch > Monitor > Event Log to access this screen.
Port This shows the number of the switch port to which the client is connected.
VLAN This shows the ID number of the VLAN to which the client belongs.
Last seen This shows the last date and time the client was discovered.
First seen This shows the first date and time the client was discovered.
LLDP This shows the LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) information received from the remote
device.
IPv4 address This shows the IP address of the client.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 23 Switch > Monitor > Client (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 24 Switch > Monitor > Client: Client Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Basic Information
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red). It also shows the last
date and time the client was discovered.
LLDP information This shows the LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) information received from the remote
device.
Manufacturer This shows the manufacturer of the client device.
Network
IP address This shows the IP address of the client.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
64
Figure 34 Switch > Monitor > Event log
4.2.4 Summary Report
This screen displays network statistics for switches of the selected site, such as bandwidth usage, top
ports and/or top switches.
Click Switch > Monitor > Summary Report to access this screen.
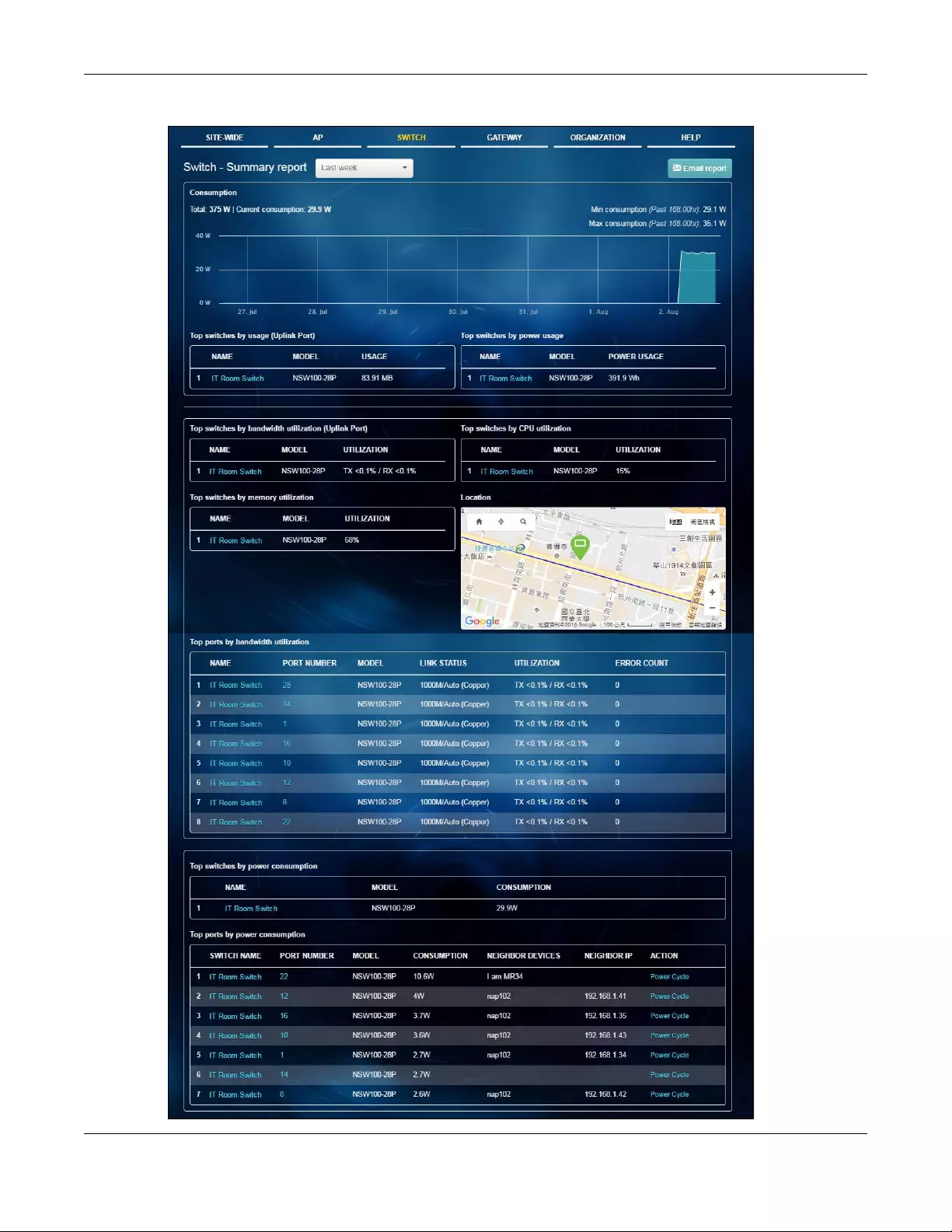
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
65
Figure 35 Switch > Monitor > Summary Report
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
66
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Switch > Monitor > Summary Report
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the report for the past day, week or month. Alternatively, select Select
range... to specify a time period the report will span. You can also select the number of
results you want to view in a table.
Email report Click this button to send summary reports by email, change the logo and set email
schedules.
Consumption
Total This shows the total power consumption of the switch ports.
Current Consumption This shows the current power consumption of the switch ports.
Min Consumption This shows the minimum power consumption of the switch ports.
Max Consumption This shows the maximum power consumption of the switch ports.
The y-axis shows how much power is used in Watts.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the power consumption is recorded.
Top switches by usage (Uplink Port)
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Usage This shows the amount of data that has been transmitted through the switch’s uplink port.
Top switches by power usage
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Power Usage This shows the amount of power consumed by the Nebula switch.
Top switches by bandwidth utilization
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Utilization This shows what percentage of the NCC’s upstream/downstream bandwidth is currently
being used by the switch.
Top switches by memory utilization
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
67
4.3 Configure
Use the Configure menus to configure port setting, IP filtering, RADIUS policies, PoE schedules, and other
switch settings for switches of the selected site.
Utilization This shows what percentage of the NCC’s RAM is currently being used by the switch.
Top switches by CPU utilization
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Utilization This shows what percentage of the NCC’s processing capability is currently being used by
the switch.
Location
This shows the location of the Nebula switches on the map.
Top ports by bandwidth utilization
This shows the index number of the entry.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Port number This shows the port number on the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Link status This shows the speed of the Ethernet connection on the port. This also shows whether it is a
fiber-optic or copper connection.
Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate with a peer port automatically to
obtain the connection speed and duplex mode that both ends support.
Utilization This shows what percentage of the upstream/downstream bandwidth is currently being
used by the port.
Error count This shows the number of received CRC (Cyclic Redundant Check) errors on the port.
Top switches by power consumption
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Consumption This shows how much power (in watts) is currently being consumed by the switch.
Top ports by power consumption
This shows the index number of the Nebula switch.
Switch Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula switch.
Port Number This shows the port number on the Nebula switch.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula switch.
Consumption This shows how much power (in watts) is currently being consumed by the port.
Neighbor Devices The shows the model name of the powered device that is connected to this port.
Neighbor IP The shows the IP address of the powered device that is connected to this port.
Action Click Power cycle to turn off the connected device and then turn it on again.
Table 25 Switch > Monitor > Summary Report (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
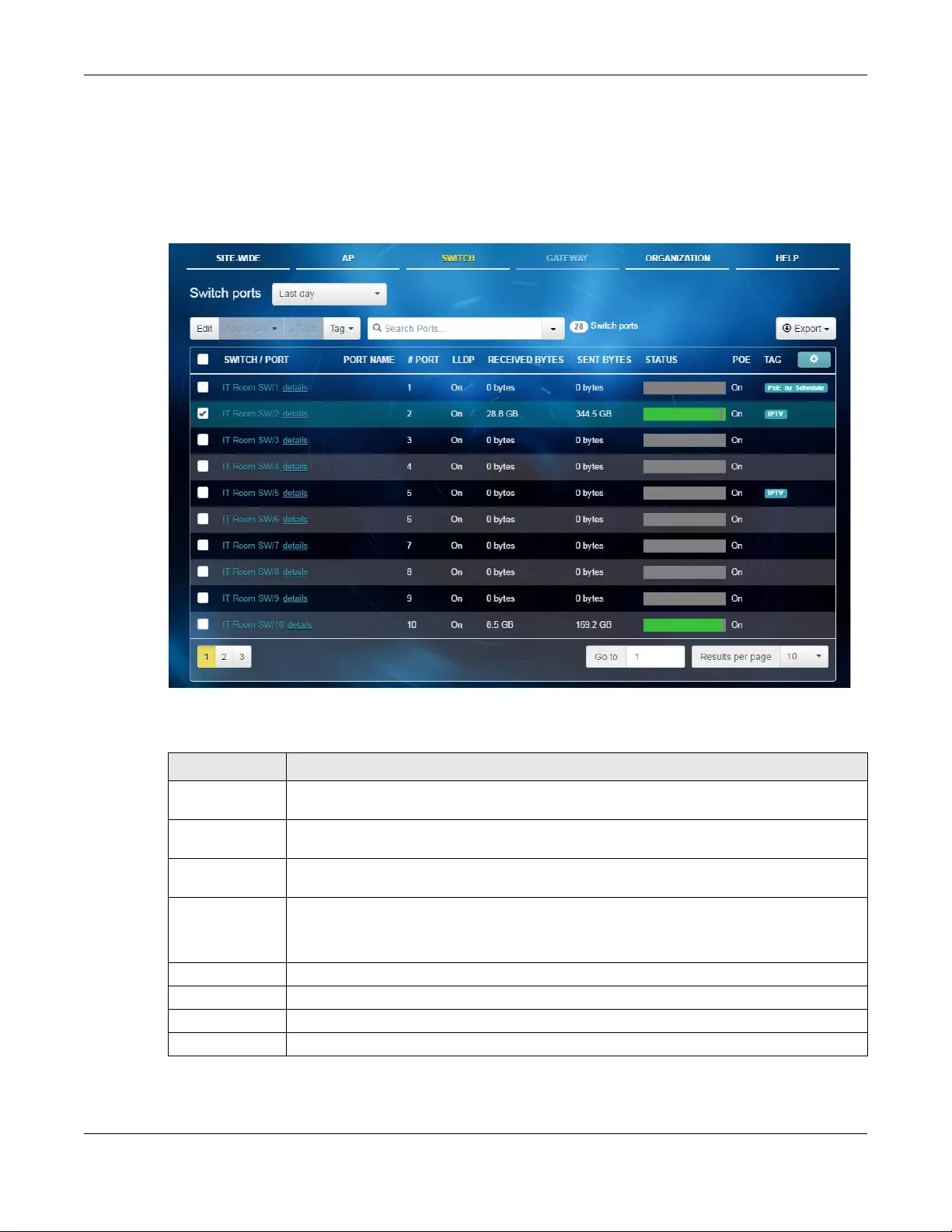
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
68
4.3.1 Switch Ports
Use this screen to view port summary and configure switch settings for the ports. To access this screen,
click Switch > Configure > Switch ports or click the Configure ports button in the Switch > Monitor >
Switch: Switch Details screen.
Figure 36 Switch > Configure > Switch ports
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Switch > Configure > Switch ports
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the detailed information and connection status of the switch port in the past two
hours, day, week or month.
Edit Select the port(s) you want to configure and click this button to configure switch settings on the
port(s), such as link aggregation, PoE schedule, LLDP and STP.
Aggregate Select more than one port and click this button to group the physical ports into one logical
higher-capacity link.
Split Select a trunk group and click this button to delete the trunk group. The ports in this group then
are not aggregated.
A trunk group is one logical link containing multiple ports.
Tag Click this button to create a new tag or delete an existing tag.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of switch ports.
Switch ports This shows the number of ports on the switch.
Export Click this button to save the switch port list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
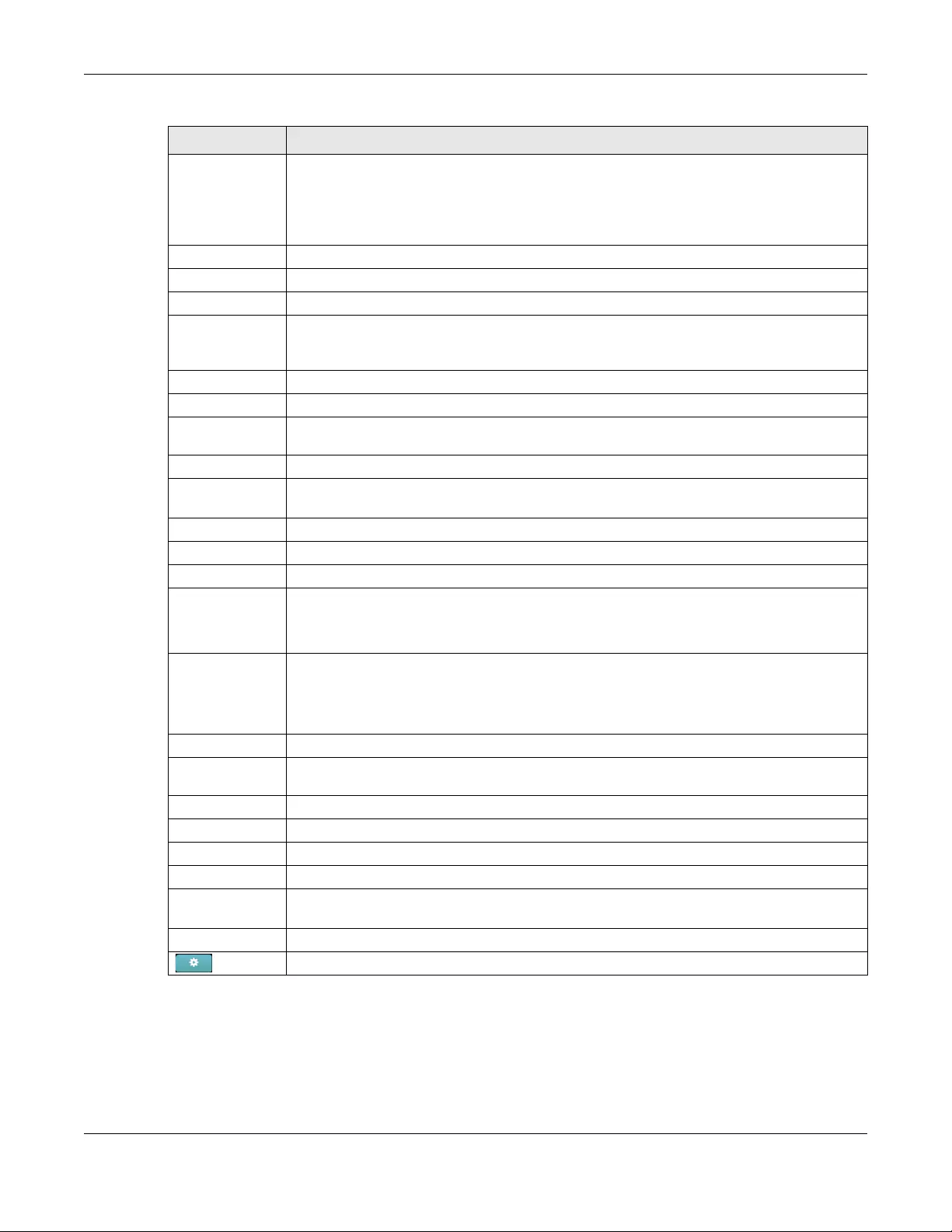
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
69
4.3.1.1 Update ports
Select the port(s) you want to configure and click the Edit button in the Switch > Configure > Switch ports
screen.
Switch/port This shows the switch name and port number.
If the port is added to a trunk group, this also shows whether it is configured as a static member
of the trunk group (Static) or configured to join the trunk group via LACP (LACP).
Click details to display the port details screen. See Section 4.2.1.3 on page 59.
Port Name This shows the descriptive name of the port.
#Port This shows the port number.
LLDP This shows whether Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is supported on the port.
Received
broadcast
packets
This shows the number of good broadcast packets received.
Received bytes This shows the number of bytes received on this port.
Received packet This shows the number of received frames on this port.
Sent broadcast
packets
This shows the number of good broadcast packets transmitted.
Sent bytes This shows the number of bytes transmitted on this port.
Sent multicast
packet
This shows the number of good multicast packets transmitted.
Sent packet This shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
Total bytes This shows the total number of bytes transmitted or received on this port.
Enabled This shows whether the port is enabled or disabled.
Link This shows the speed of the Ethernet connection on this port.
Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate with a peer port automatically to obtain
the connection speed and duplex mode that both ends support.
Status This shows the connection status of the port.
The gray time slot indicates the connection to an Ethernet device is down, and the green time
slot indicates the connection is up. Move the cursor over a time slot to see the actual date and
time when a port is connected or disconnected.
RADIUS policy This shows the name of RADIUS authentication policy applied to the port.
Allowed VLAN This shows the VLANs from which the traffic comes is allowed to be transmitted or received on
the port
PoE This shows whether PoE is enabled on the port.
RSTP This shows whether RSTP is enabled on the port
Schedule This shows the name of the PoE schedule applied to the port.
Type This shows the port type (Trunk or Access).
PVID This shows the port VLAN ID. It is a tag that adds to incoming untagged frames received on the
port so that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag that the switch adds to the outbound traffic on this port.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 26 Switch > Configure > Switch ports (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
70
Figure 37 Switch > Configure > Switch ports: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Switch > Configure > Switch ports: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Switch ports This shows the switch name and port number for the port(s) you are configuring in this
screen.
Name Enter a descriptive name for the port(s).
Tags Select or create a new tag for outgoing traffic on the port(s).
Enabled Select to enable or disable the port(s). A port must be enabled for data transmission to
occur.
RSTP Select to enable or disable RSTP on the port(s).
STP guard Select Root guard to prevent the switch(es) attached to the port(s) from becoming the root
bridge.
Select BPDU guard to have the switch shut down the port(s) if there is any BPDU received on
the port(s).
Otherwise, select Disable.
LLDP Select to enable or disable LLDP on the port(s).
PoE Select Enable to provide power to a PD connected to the port(s).
Link Select the speed and the duplex mode of the Ethernet connection on the port(s). Choices
are Auto-1000M, 10M/Half Duplex, 10M/Full Duplex, 100M/Half Duplex, 100M/Full Duplex
and 1000M/Full Duplex (Gigabit connections only).
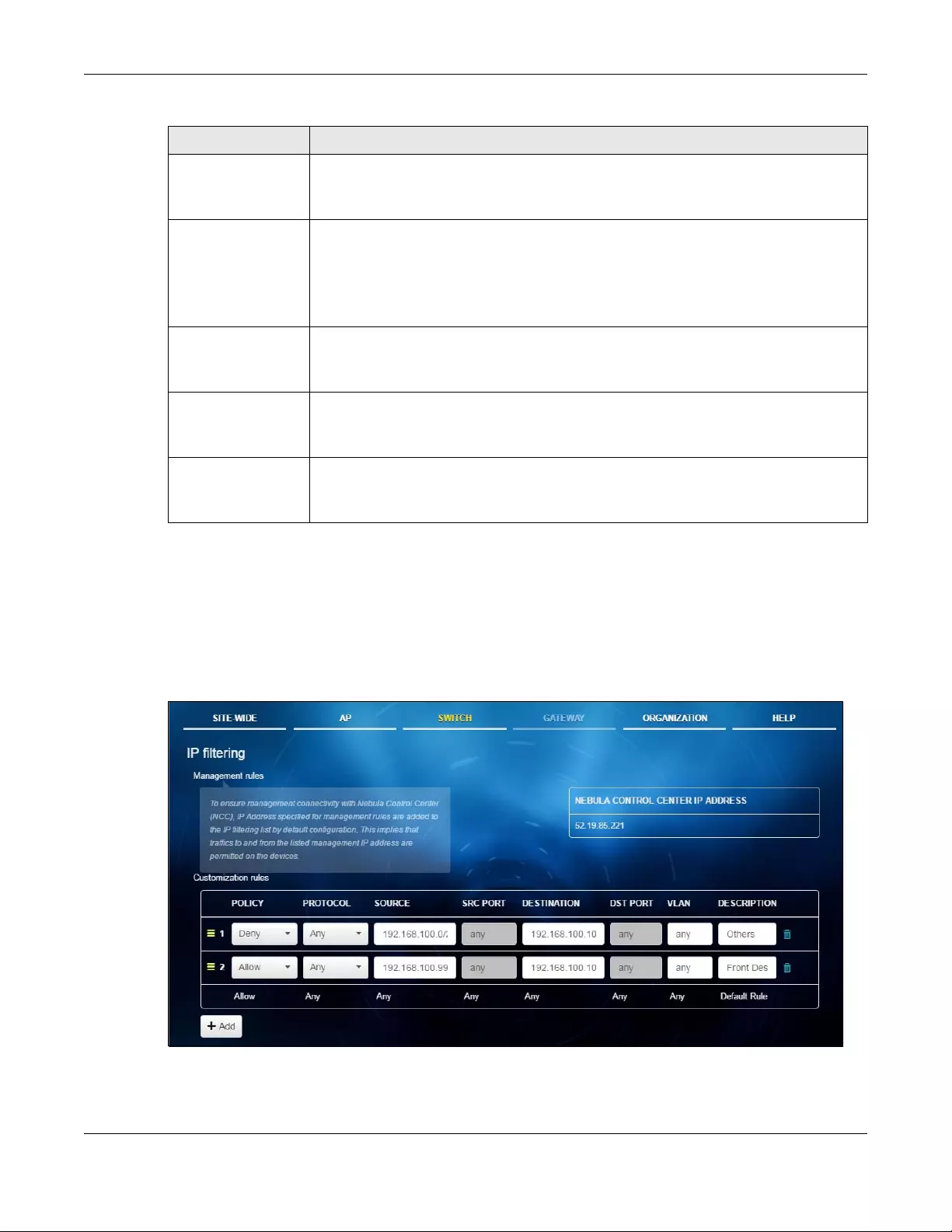
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
71
4.3.2 IP Filtering
IP filtering lets you allow or block traffic according to the rule settings. Use this screen to configure IP
filtering rules on the switches.
Click Switch > Configure > IP filtering to access this screen.
Figure 38 Switch > Configure > IP filtering
PoE schedule Select a pre-defined schedule (created using the Switch > Configure > PoE schedule
screen) to control when the switch enables PoE to provide power on the port(s).
If you select Unschedule, PoE is disabled on the port(s).
Type Set the type of the port.
Select Access to configure the port as an access port which can carry traffic for just one
single VLAN. Frames received on the port are tagged with the port VLAN ID.
Select Trunk to configure the port as a trunk port which can carry traffic for multiple VLANs
over a link. A trunk port is always connected to a switch or router.
PVID A PVID (Port VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to incoming untagged frames received on a port
so that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
Enter a number between 1and 4094 as the port VLAN ID.
RADIUS policy This field is available only when you select Access in the Type field.
Select the name of the pre-configured RADIUS policy that you want to apply to the port(s).
Select Open if you don’t want to enable port authentication on the port(s).
Allowed VLANs This field is available only when you select Trunk in the Type field.
Specify the VLANs from which the traffic comes is allowed to be transmitted or received on
the port(s).
Table 27 Switch > Configure > Switch ports: Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
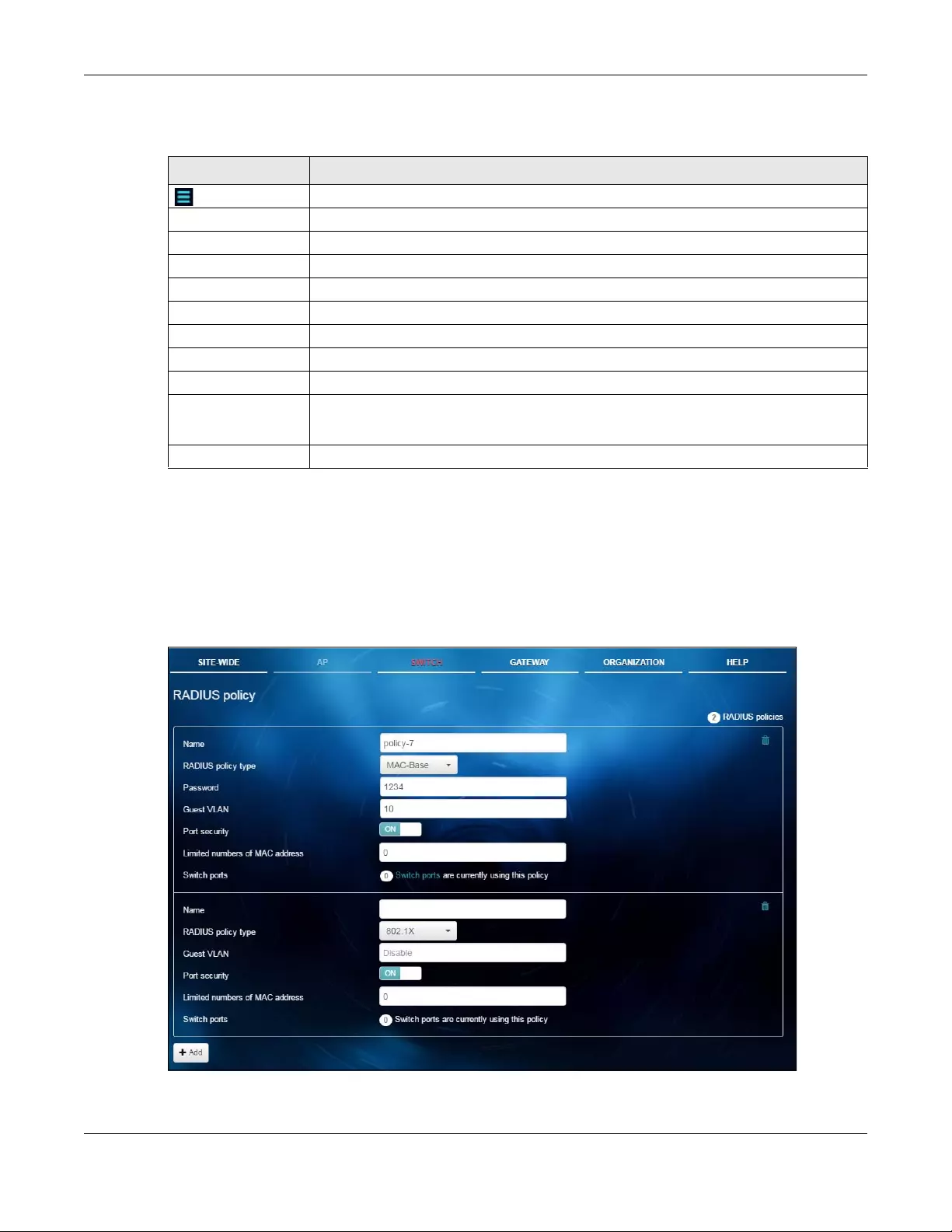
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
72
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
4.3.3 RADIUS Policy
Use this screen to configure port authentication to validate access to ports on the switch using an
external RADIUS server.
Click Switch > Configure > RADIUS policy to access this screen.
Figure 39 Switch > Configure > RADIUS policy
Table 28 Switch > Configure > IP filtering
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Click the icon of a rule and drag the rule up or down to change the order.
Policy Select to allow or deny traffic that matches the filtering criteria in the rule.
Protocol Select the type of IP protocol used to transport the traffic to which the rule is applied.
Source Enter the source IP address of the packets that you want to filter.
Src port Enter the source port number(s) that defines the traffic type.
Destination Enter the destination IP address of the packets that you want to filter
Dst port Enter the destination port number(s) that defines the traffic type.
VLAN Enter the ID number of the VLAN group to which the matched traffic belongs.
Description Enter a descriptive name for the rule.
Click the up or down arrow icon to change the order of the rule in the list.
Click the delete icon to remove the rule.
Add Click this button to create a new rule.

Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
73
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
4.3.4 PoE Schedule
Use this screen to view and configure the schedules which can be applied to the ports. PoE is enabled
at the specified time/date. Click Switch > Configure > PoE schedule to access this screen.
The table shows the name of the existing schedules and the number of ports to which a schedule is
applied. Click a schedule’s edit icon to modify the schedule settings or click the Add button to create a
new schedule. See Section 4.3.4.1 on page 73.
Figure 40 Switch > Configure > PoE schedule
4.3.4.1 Create new schedule
Click the Add button in the Switch > Configure > PoE schedule screen to access this screen.
Table 29 Switch > Configure > RADIUS policy
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for the policy.
RADIUS policy type Select MAC-Base if you want to validate access to the port(s) based on the MAC address
and password of the client.
Select 802.1x if you want to validate access to the port(s) based on the user name and
password provided by the client.
Password Type the password the switch sends along with the MAC address of a client for
authentication with the RADIUS server. You can enter up to 32 printable ASCII characters.
Guest VLAN A guest VLAN is a pre-configured VLAN on the switch that allows non-authenticated users
to access limited network resources through the switch.
Enter the number that identifies the guest VLAN.
Port security Click On to enable port security on the port(s). Otherwise, select Off to disable port security
on the port(s).
Limited numbers of
MAC address
This field is configurable only when you enable port security.
Specify the maximum number of MAC addresses that may be learned on a port.
Switch ports This shows the number of the switch ports to which this policy is applied.
Add Click this button to create a new policy.
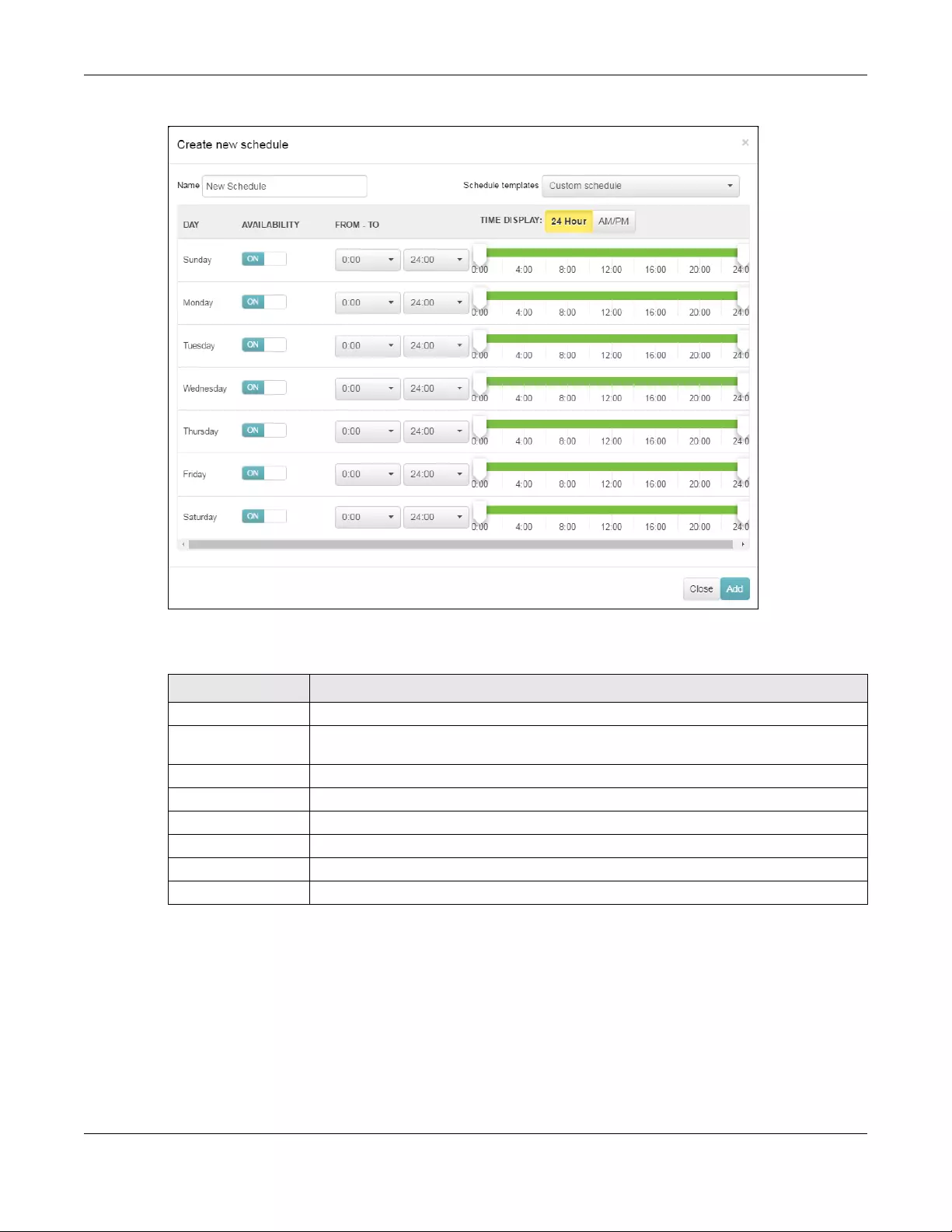
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
74
Figure 41 Switch > Configure > PoE schedule: Add
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
4.3.5 Switch Configuration
Use this screen to configure global switch settings, such as (R)STP, QoS, IGMP snooping, port mirroring,
authentication servers, voice VLAN and DHCP white list.
Click Switch > Configure > Switch configuration to access this screen.
Table 30 Switch > Configure > PoE schedule: Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for this schedule for identifying purposes.
Schedule templates Select a pre-defined schedule template or select Custom schedule and manually
configure the day and time at which PoE is enabled.
Day This shows the day of the week.
Availability Click On to enable PoE on this day. Otherwise, select Off to turn PoE off.
From - To Specify the hour and minute when the schedule begins and ends each day
Time display Select the time format in which the time is displayed.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Add Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
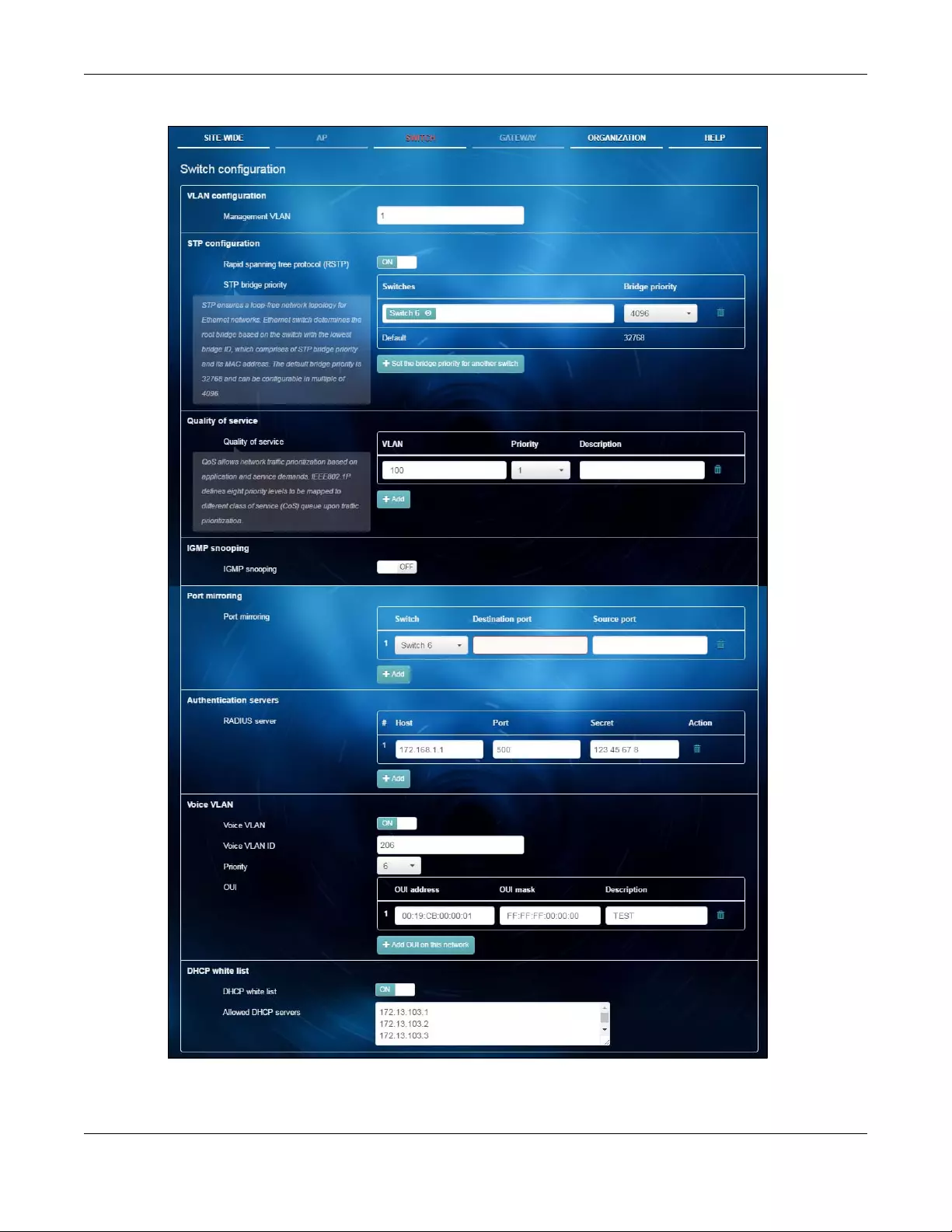
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
75
Figure 42 Switch > Configure > Switch configuration
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
76
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Switch > Configure > Switch configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN configuration
Management VLAN Enter the VLAN identification number associated with the switch IP address. This is the VLAN
ID of the CPU and is used for management only. The default is "1". All ports, by default, are
fixed members of this "management VLAN" in order to manage the device from any port. If
a port is not a member of this VLAN, then users on that port cannot access the device. To
access the switch make sure the port that you are connected to is a member of
Management VLAN.
STP configuration
Rapid spanning tree
protocol (RSTP)
Select On to enable RSTP on the switch. Otherwise, select Off.
STP bridge priority Bridge priority is used in determining the root switch, root port and designated port. The
switch with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) becomes the STP root switch. If all
switches have the same priority, the switch with the lowest MAC address will then become
the root switch.
The lower the numeric value you assign, the higher the priority for this bridge.
Click the button to create a new entry. Select the switch(es) for which you want to
configure the bridge priority, and select a value from the drop-down list box.
Quality of service
Quality of service Enter a VLAN ID and select the priority level that the switch assigns to frames belonging to
this VLAN.
Click Add to create a new entry.
IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping Select On to enable IGMP snooping on the switch. Otherwise, select Off.
Port mirroring
Port mirroring Click Add to create a new entry.
Select the switch for which you want to configure port mirroring, specify the destination
port you copy the traffic to in order to examine it in more detail without interfering with the
traffic flow on the original port(s), and also enter the source port on which you mirror the
traffic.
Authentication servers
RADIUS server Click Add to create a new RADIUS server entry.
Enter the IP address of an external RADIUS server, the port of the RADIUS server for
authentication (default 1812), and a password (up to 32 alphanumeric characters) as the
key to be shared between the external RADIUS server and the switch.
Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN Select On to enable the Voice VLAN feature on the switch. Otherwise, select Off.
It groups the voice traffic with defined priority into an assigned VLAN which enables the
separation of voice and data traffic coming onto the switch port.
Voice VLAN ID Enter a VLAN ID number.
Priority Select the priority level of the Voice VLAN from 0 to 7.
OUI Click the button to add MAC address of IP phones from specific manufacturers by using its
ID from the Organizationally Unique Identifiers (OUI). You also need to type the mask for the
specified MAC address to determine which bits a packet’s MAC address should match.
Enter “f” for each bit of the specified MAC address that the IP phone’s MAC address should
match. Enter “0” for the bit(s) of the IP phone’s MAC address, which can be of any
hexadecimal character(s).
Chapter 4 Switch
NCC User’s Guide
77
DHCP white list
DHCP white list Select On to enable the DHCP white list on the switch. Otherwise, select Off.
Allowed DHCP
servers
Enter the IP address of your DHCP server. Traffic from the DHCP server which is not in the list
will be blocked.
Table 31 Switch > Configure > Switch configuration (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

NCC User’s Guide
78
CHAPTER 5
Gateway
5.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the menus that you can use to monitor the Nebula managed security gateways in
your network and configure settings even before a gateway is deployed and added to the site.
5.2 Monitor
Use the Monitor menus to check the security gateway information, client information, event log
messages and summary report for the gateway in the selected site.
5.2.1 Security Gateway
This screen allows you to view the detailed information about a security gateway in the selected site.
Click Gateway > Monitor > Security Gateway to access this screen.
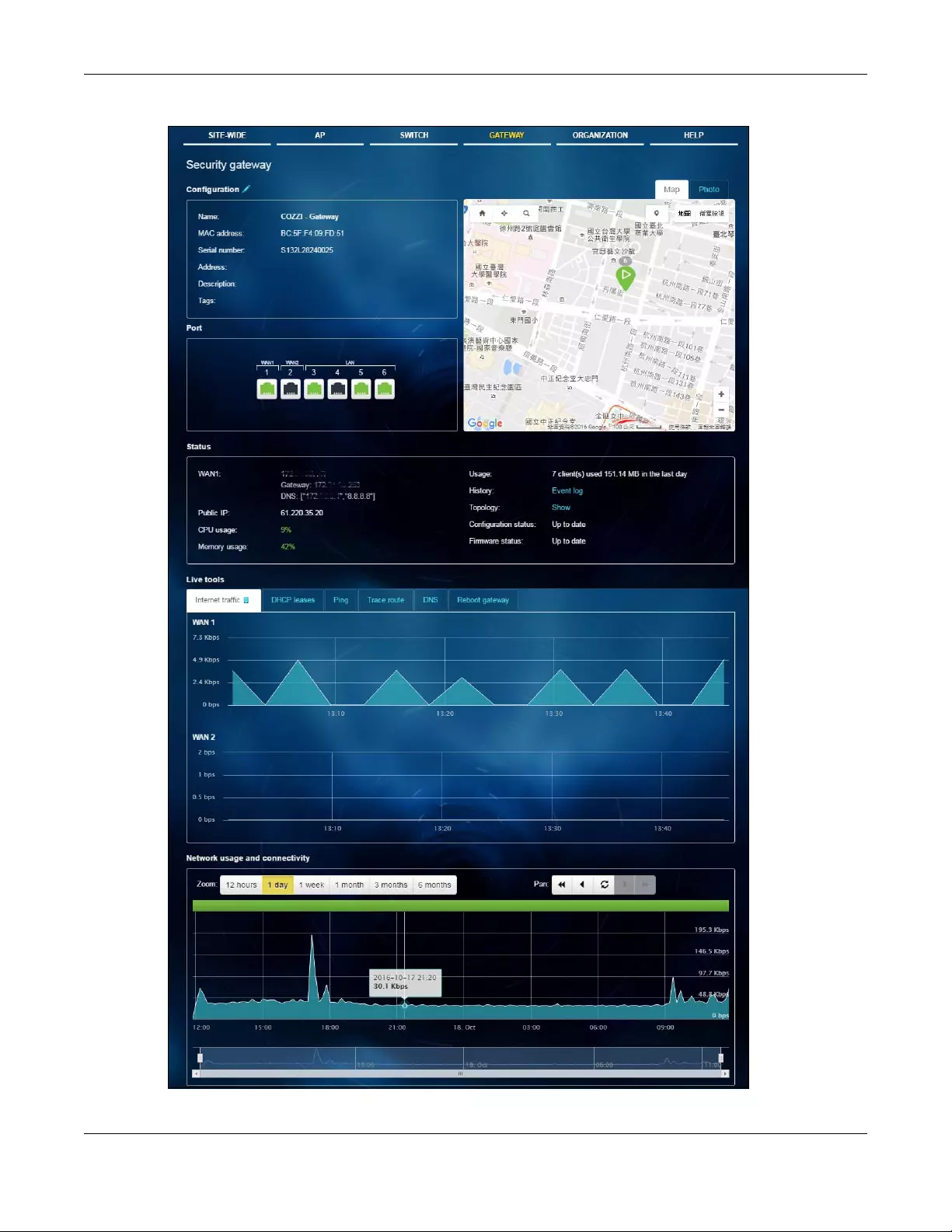
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
79
Figure 43 Gateway > Monitor > Security Gateway
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
80
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 32 Gateway > Monitor > Security Gateway
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Click the edit icon to change the device name, description, tags and address. You can also move the device to
another site.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the gateway.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the gateway.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the gateway.
Address This shows the user-specified address for the gateway.
Description This shows the user-specified description for the gateway.
Tags This shows the user-specified tag for the gateway.
Port This shows the ports on the gateway.
The port is highlighted in green color when it is connected and the link is up.
Map This shows the location of the gateway on the Google map.
Photo This shows the photo of the gateway.
Status
WAN1/WAN2 This shows the IP address, gateway and DNS information for the active WAN connection.
Public IP This shows the global (WAN) IP address of the gateway.
CPU usage This shows what percentage of the gateway’s processing capability is currently being used.
Memory usage This shows what percentage of the gateway’s RAM is currently being used.
Usage This shows the amount of data that has been transmitted or received by the gateway’s
clients.
History Click Event log to go to the Gateway > Monitor > Event log screen.
Topology Click Show to go to the SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Topology screen. See Section 2.1.4 on page
24.
Configuration status This shows whether the configuration on the gateway is up-to-date.
Firmware status This shows whether the firmware installed on the gateway is up-to-date.
Live tools
Internet traffic This shows the WAN port statistics.
The y-axis represents the transmission rate in bps (bits per second).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
DHCP leases This shows the IP addresses currently assigned to DHCP clients.
Ping Enter the host name or IP address of a computer that you want to perform ping in order to
test a connection and click Ping.
Trace route Enter the host name or IP address of a computer that you want to perform the traceroute
function. This determines the path a packet takes to the specified computer.
DNS Enter a host name and click Run to resolve the IP address for the specified domain name.
Reboot gateway Click the Reboot button to restart the gateway.
Network usage and connectivity
Move the cursor over the chart to see the transmission rate at a specific time.
Zoom Select to view the statistics in the past twelve hours, day, week, month, three months or six
months.
Pan Click to move backward or forward by one day or week.
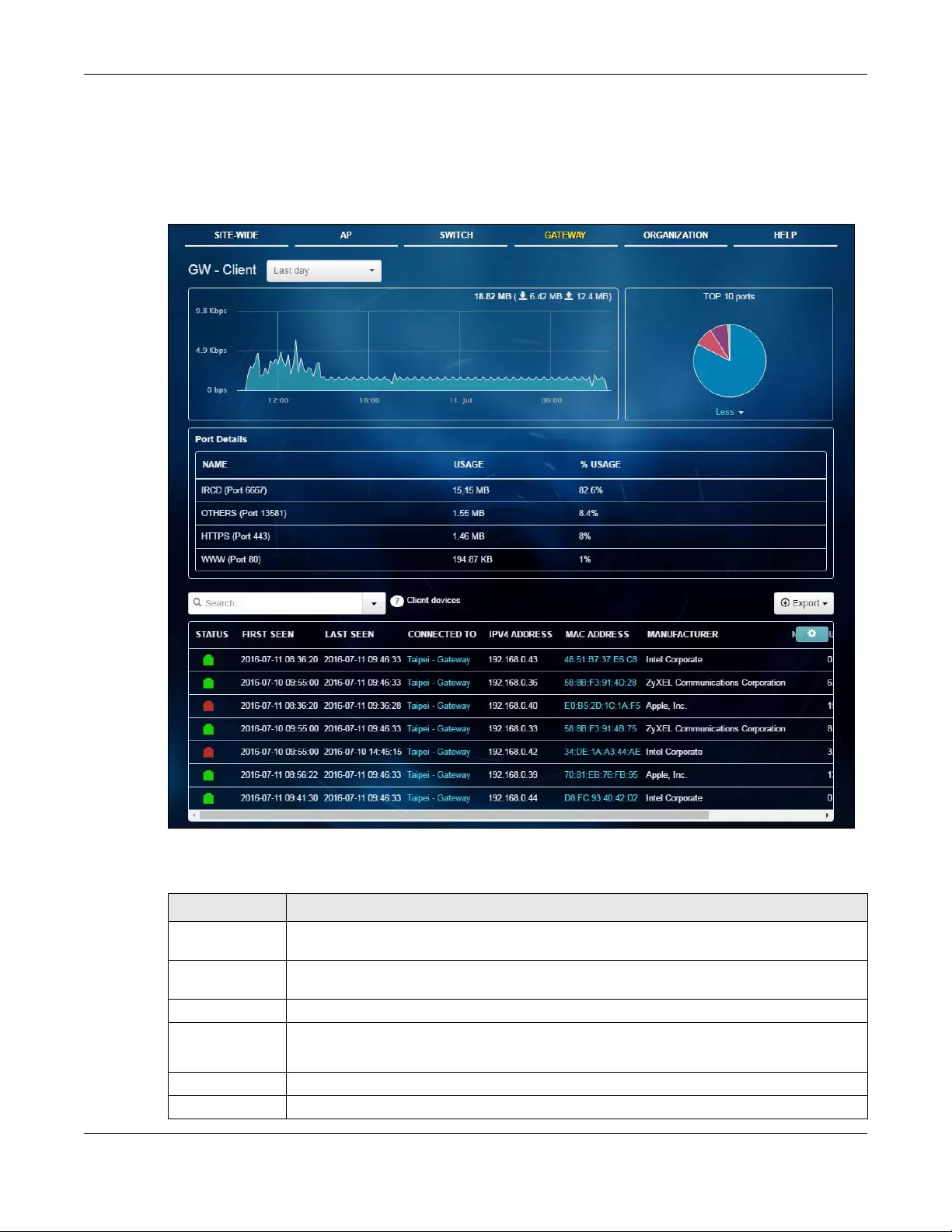
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
81
5.2.2 Client
This screen allows you to view the connection status and detailed information about a client in the
selected site. Click Gateway > Monitor > Client to access this screen.
Figure 44 Gateway > Monitor > Client
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 33 Gateway > Monitor > Client
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the device information and connection status in the past two hours, day, week
or month.
The y-axis shows the transmission speed of data sent or received by the client in bits per second
(bps).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Top 10 Ports This shows top ten applications/services and the ports that identify a service.
Click More to display port details. Click Less to hide them.
Port Details
Name This shows the service name and the associated port number(s).
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
82
5.2.2.1 Client Details
Click a client’s MAC address in the Gateway > Monitor > Client screen to display individual client
statistics.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the service.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the service.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of clients.
Client devices This shows the number of clients connected to the site network.
Export Click this button to save the client list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red).
Description This shows the descriptive name of the client.
Click the name to display the individual client statistics. See Section 5.2.2.1 on page 82.
First seen This shows the first date and time the client was discovered over the specified period of time.
Last seen This shows the last date and time the client was discovered over the specified period of time.
Connected to This shows the name of the Nebula device to which the client is connected in this site.
Click the device name to display the screen where you can view detailed information about
the Nebula device.
IPv4 address This shows the IP address of the client.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Click the MAC address to display the individual client statistics. See Section 5.2.2.1 on page 82.
Manufacturer This shows the manufacturer of the client device.
Note This shows additional information for the client.
Usage This shows the amount of data transmitted by the client.
User This shows the number of users currently connected to the network through the client device.
Interface This shows the interface on the security gateway to which the client belongs.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 33 Gateway > Monitor > Client (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
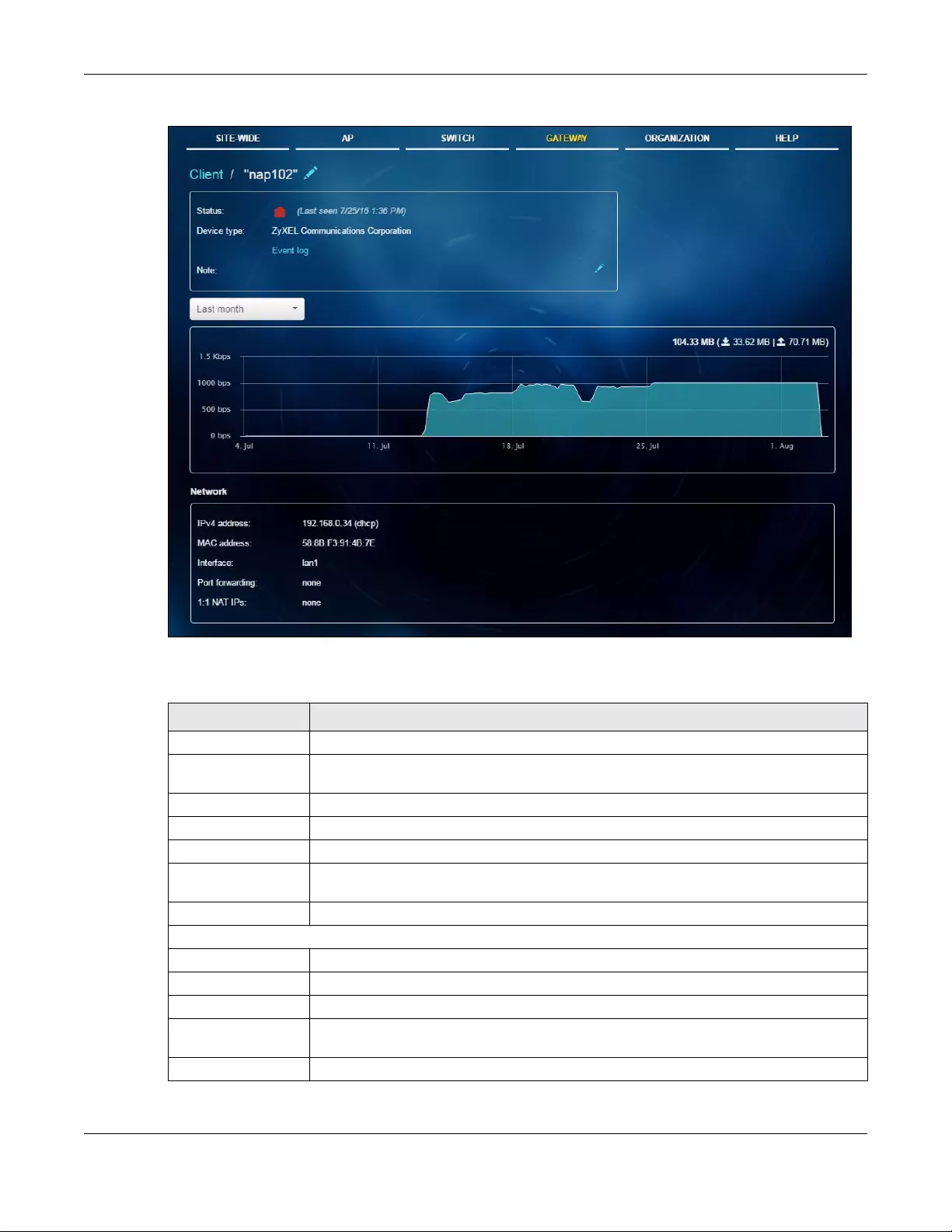
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
83
Figure 45 Gateway > Monitor > Client: Client Details
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 Gateway > Monitor > Client: Client Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Client Click the edit icon to change the client name.
Status This shows whether the client is online (green), or goes off-line (red). It also shows the last
date and time the client was discovered.
Device type This shows the manufacturer of the client device.
Note This shows additional information for the client. Click the edit icon to modify it.
Select to view the client connection status in the past two hours, day, week or month.
The y-axis shows the transmission speed of data sent or received by the client in bits per
second (bps).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Network
IPv4 address This shows the IP address of the client.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the client.
Interface This shows the interface on the security gateway to which the client belongs.
Port forwarding This shows the public IP address or DDNS host name and port mapping information if there is
a virtual server rule configured for this client.
1:1 NAT IPs This shows the public IP address information if there is a 1:1 NAT rule configured for this client.
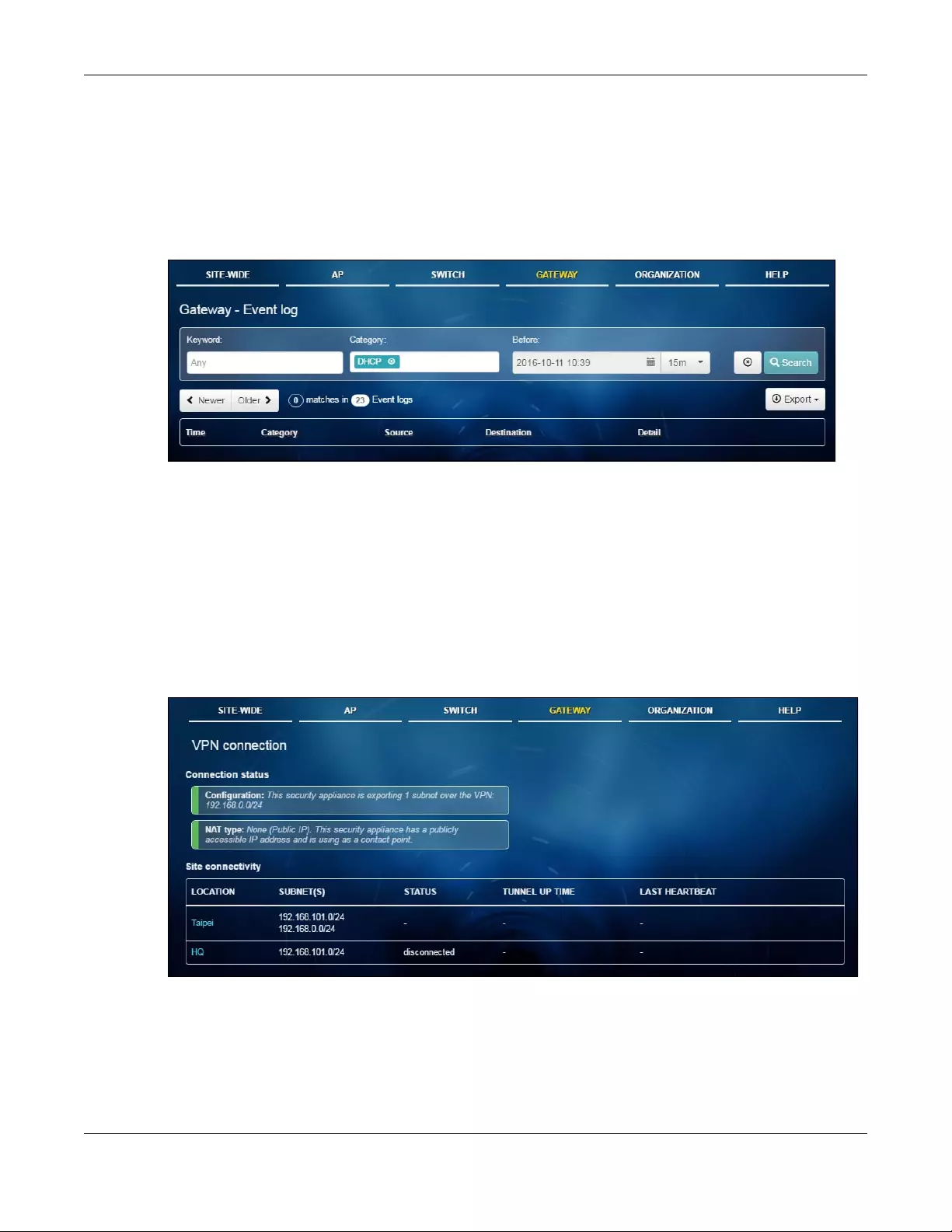
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
84
5.2.3 Event Log
Use this screen to view gateway log messages. You can enter a key word, select one or multiple event
types, or specify a date/time to display only the log messages related to it.
Click Gateway > Monitor > Event Log to access this screen.
Figure 46 Gateway > Monitor > Event log
5.2.4 VPN Connection
Use this screen to view status of the site-to-site IPSec VPN connections.
Note: If the peer gateway is not a Nebula device, go to the Gateway > Configure > Site-to-
Site VPN screen to view and configure a VPN rule. See Section 5.3.3 on page 103 for
more information.
Click Gateway > Monitor > VPN Connection to access this screen.
Figure 47 Gateway > Monitor > VPN Connection

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
85
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
5.2.5 Summary Report
This screen displays network statistics for the gateway of the selected site, such as WAN usage, top
applications and/or top clients.
Click Gateway > Monitor > Summary Report to access this screen.
Table 35 Gateway > Monitor > VPN Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Site Connectivity
Location This shows the name of the site to which the peer gateway is assigned.
Click the name to go to the Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN screen, where you can
modify the VPN settings.
Subnet(s) This shows the address(es) of the local network behind the gateway.
Status This shows whether the VPN tunnel is connected or disconnected.
Tunnel up time This shows how many seconds the VPN tunnel has been active.
Last heartbeat This shows the last date and time a heartbeat packet is sent to determine if the VPN tunnel
is up or down,
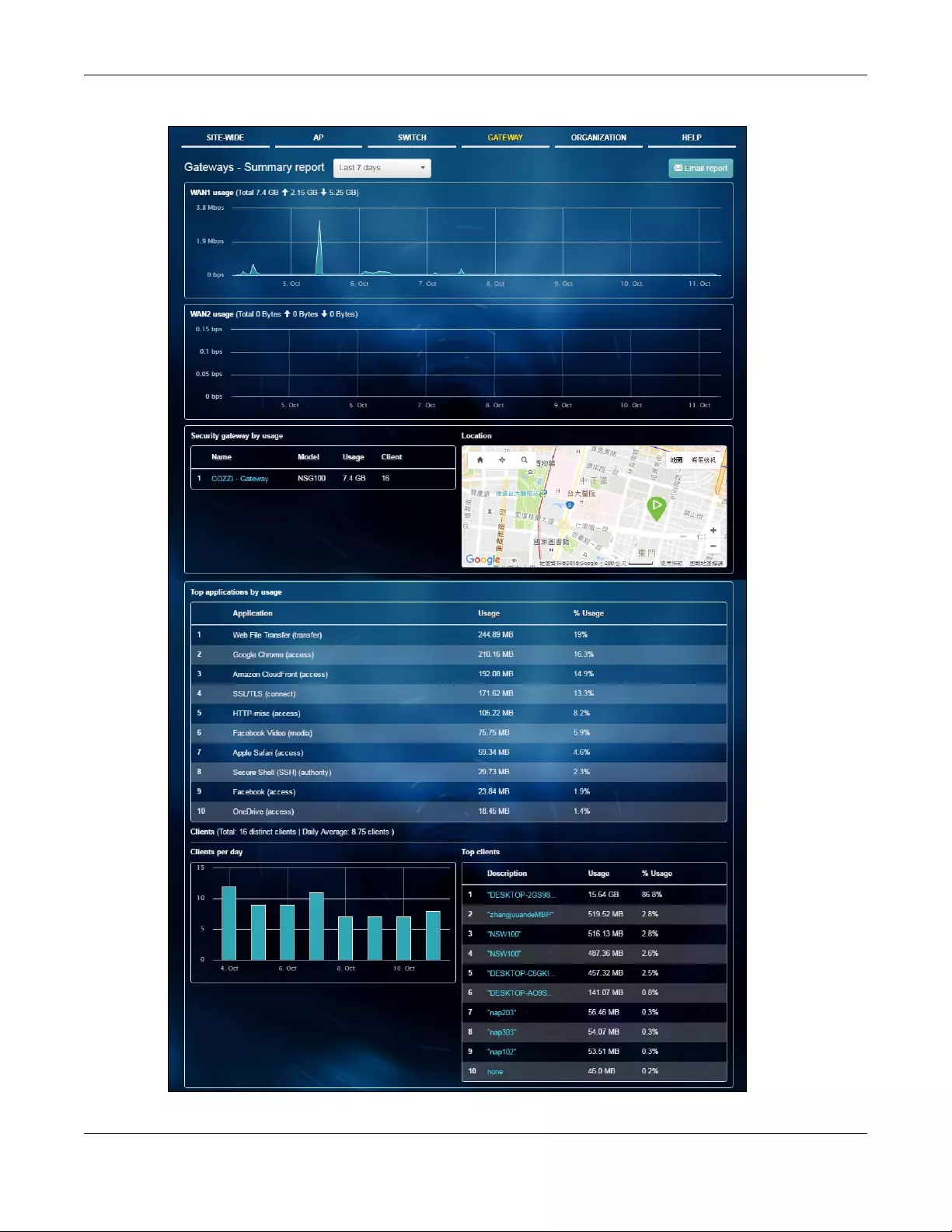
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
86
Figure 48 Gateway > Monitor > Summary Report
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
87
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 36 Gateway > Monitor > Summary Report
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select to view the report for the past day, week or month. Alternatively, select Select
range... to specify a time period the report will span. You can also select the number of
results you want to view in a table.
Email report Click this button to send summary reports by email, change the logo and set email
schedules.
WAN1/WAN2 usage
The y-axis shows the transmission speed of data sent or received through the WAN
connection in bits per second (bps).
The x-axis shows the time period over which the traffic flow occurred.
Security gateway by usage
This shows the index number of the Nebula gateway.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the Nebula gateway.
Model This shows the model number of the Nebula gateway.
Usage This shows the amount of data that has been transmitted through the gateway’s WAN port.
Client This shows the number of clients currently connected to the gateway.
Location
This shows the location of the Nebula gateways on the map.
Top applications by usage
This shows the index number of the application.
Application This shows the application name.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the application.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the application.
Clients
Total This shows the total number of clients connected to the Nebula device within the specified
time period.
Daily Average This shows the average daily number of clients within the specified time period.
Clients per day
The y-axis represents the number of clients.
The x-axis represents the date.
Usage details
Top clients
This shows the index number of the client.
Description This shows the descriptive name or MAC address of the client.

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
88
5.3 Configure
Use the Configure menus to configure interface addressing, firewall, site-to-site VPN, captive portal,
traffic shaping, authentication server and other gateway settings for gateway of the selected site.
5.3.1 Interfaces Addressing
Use this screen to configure network mode, port grouping, interface address, static route and DDNS
settings on the gateway. To access this screen, click Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing.
Usage This shows the total amount of data transmitted and received by the client.
% Usage This shows the percentage of usage for the client.
Table 36 Gateway > Monitor > Summary Report (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
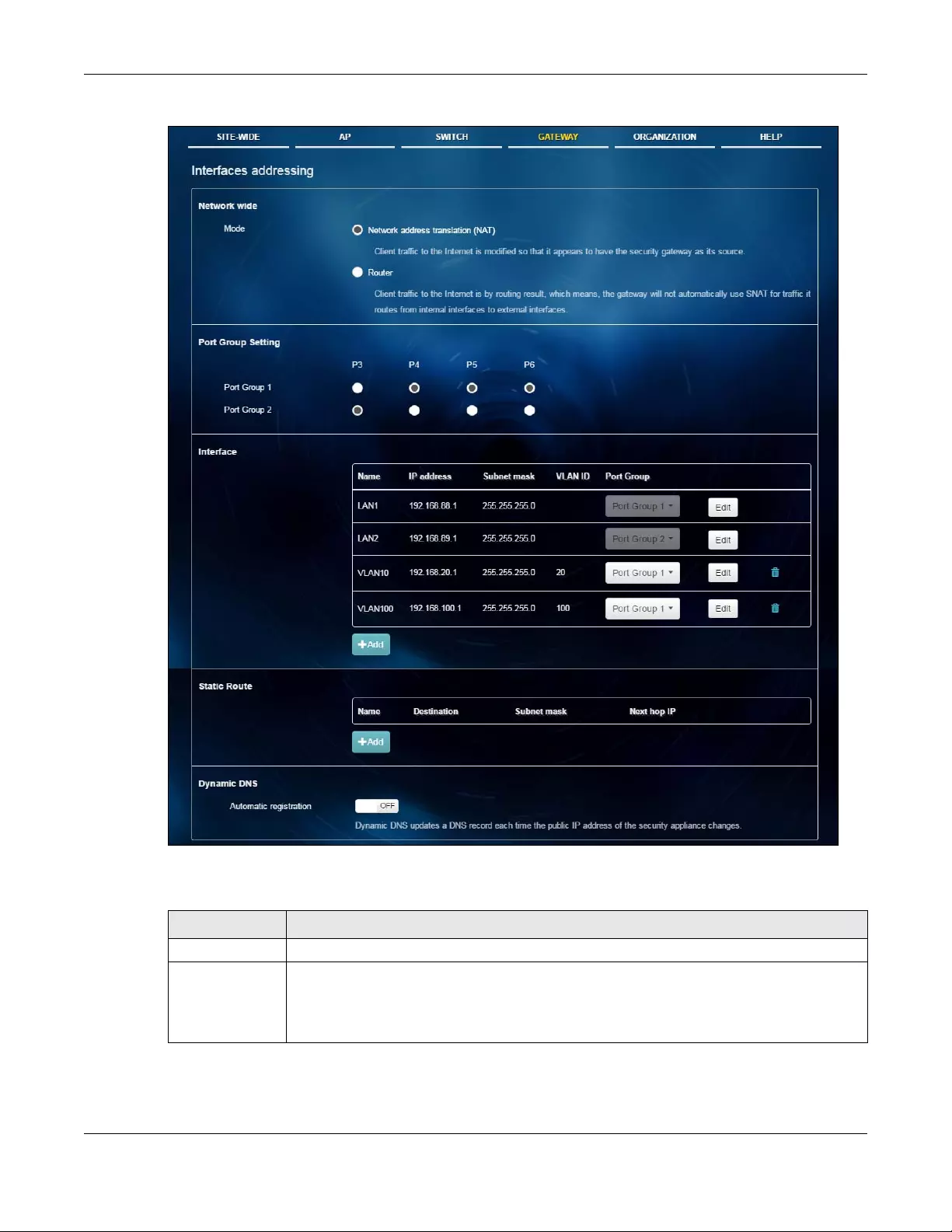
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
89
Figure 49 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 37 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network wide
Mode Select Network address translation (NAT) to have the gateway automatically use SNAT for
traffic it routes from internal interfaces to external interfaces.
Select Router to have the gateway forward packets according to the routing policies. The
gateway don’t convert a packet’s source IP address automatically.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
90
Port Group
Setting
Port groups create a hardware connection between physical ports at the layer-2 (data link,
MAC address) level.
The physical Ethernet ports are shown at the top and the port groups are shown at the bottom
of the screen. Use the radio buttons to select for which port group (network) you want to use
each physical port.
For example, select a port’s Port Group 1 radio button to use the port as part of the first port
group. The port will use the first group’s IP address.
Interface By default, LAN1 is created on top of port group 1 and LAN2 is on top of port group 2.
Name This shows the name of the interface (network) on the gateway.
IP Address This shows the IP address of the interface (network).
Subnet Mask This shows the subnet mask of the interface (network).
VLAN ID This shows the ID number of the VLAN with which the interface (network) is associated.
Port Group This shows the name of the port group to which the interface (network) belongs.
Edit Click this button to modify the network settings. See Section 5.3.1.1 on page 92 for detailed
information.
Click this icon to remove a VLAN entry.
Add Click this button to create a VLAN, which is then associated with one Ethernet interface
(network). See Section 5.3.1.1 on page 92 for detailed information.
Static Route
Name This shows the name of the static route.
Destination This shows the destination IP address.
Subnet Mask This shows the IP subnet mask.
Next Hop IP This shows the IP address of the next-hop gateway or the interface through which the traffic is
routed. The gateway is a router or switch on the same segment as your security gateway's
interface(s). It helps forward packets to their destinations.
Click this icon to remove a static route.
Add Click this button to create a new static route. See Section 5.3.1.3 on page 96 for detailed
information
Dynamic DNS
Automatic
registration
Click On to use dynamic DNS. Otherwise, select Off to disable it.
General Settings
DDNS provider Select your Dynamic DNS service provider from the drop-down list box.
If you select User custom, create your own DDNS service
DDNS type Select the type of DDNS service you are using.
Select User custom to create your own DDNS service and configure the DYNDNS Server, URL,
and Additional DDNS Options fields below.
DDNS account
Username Enter the user name used when you registered your domain name.
Password Enter the password provided by the DDNS provider.
Confirm
password
Enter the password again to confirm it.
DDNS settings
Domain name Enter the domain name you registered.
Table 37 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
91
Primary binding
address
Use these fields to set how the security gateway determines the IP address that is mapped to
your domain name in the DDNS server. The security gateway uses the Backup binding address
if the interface specified by these settings is not available.
Interface Select the interface to use for updating the IP address mapped to the domain name.
IP address Select Auto if the interface has a dynamic IP address. The DDNS server checks the source IP
address of the packets from the gateway for the IP address to use for the domain name. You
may want to use this if there are one or more NAT routers between the gateway and the DDNS
server.
Note: The gateway may not determine the proper IP address if there is an HTTP proxy
server between the gateway and the DDNS server.
Select Custom if you have a static IP address. Enter the IP address to use it for the domain
name.
Select Interface to have the security gateway use the IP address of the specified interface.
Backup binding
address
Use these fields to set an alternate interface to map the domain name to when the interface
specified by the Primary binding address settings is not available.
Interface Select the interface to use for updating the IP address mapped to the domain name.
IP address Select Auto if the interface has a dynamic IP address. The DDNS server checks the source IP
address of the packets from the gateway for the IP address to use for the domain name. You
may want to use this if there are one or more NAT routers between the gateway and the DDNS
server.
Note: The gateway may not determine the proper IP address if there is an HTTP proxy
server between the gateway and the DDNS server.
Select Custom if you have a static IP address. Enter the IP address to use it for the domain
name.
Select Interface to have the security gateway use the IP address of the specified interface.
Enable wildcard This option is only available with a DynDNS account.
Enable the wildcard feature to alias subdomains to be aliased to the same IP address as your
(dynamic) domain name. This feature is useful if you want to be able to use, for example,
www.yourhost.dyndns.org and still reach your hostname.
Mail exchanger This option is only available with a DynDNS account.
DynDNS can route e-mail for your domain name to a mail server (called a mail exchanger). For
example, DynDNS routes e-mail for john-doe@yourhost.dyndns.org to the host record specified
as the mail exchanger.
If you are using this service, type the host record of your mail server here. Otherwise, leave the
field blank.
Backup mail
exchanger
This option is only available with a DynDNS account.
Select this check box if you are using DynDNS’s backup service for e-mail. With this service,
DynDNS holds onto your e-mail if your mail server is not available. Once your mail server is
available again, the DynDNS server delivers the mail to you. See www.dyndns.org for more
information about this service.
DYNDNS Server This field displays when you select User custom from the DDNS provider field above.
Type the IP address of the server that will host the DDSN service.
Table 37 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
92
5.3.1.1 Local LAN
Click the Add a local VLAN button or click the Edit button in the Gateway > Configure > Interfaces
addressing screen.
URL This field displays when you select User custom from the DDNS provider field above.
Type the URL that can be used to access the server that will host the DDSN service.
Additional DDNS
Options
This field displays when you select User custom from the DDNS provider field above.
These are the options supported at the time of writing:
• dyndns_system to specify the DYNDNS Server type - for example, dyndns@dyndns.org
• ip_server_name which should be the URL to get the server’s public IP address - for example,
http://myip.easylife.tw/
Table 37 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
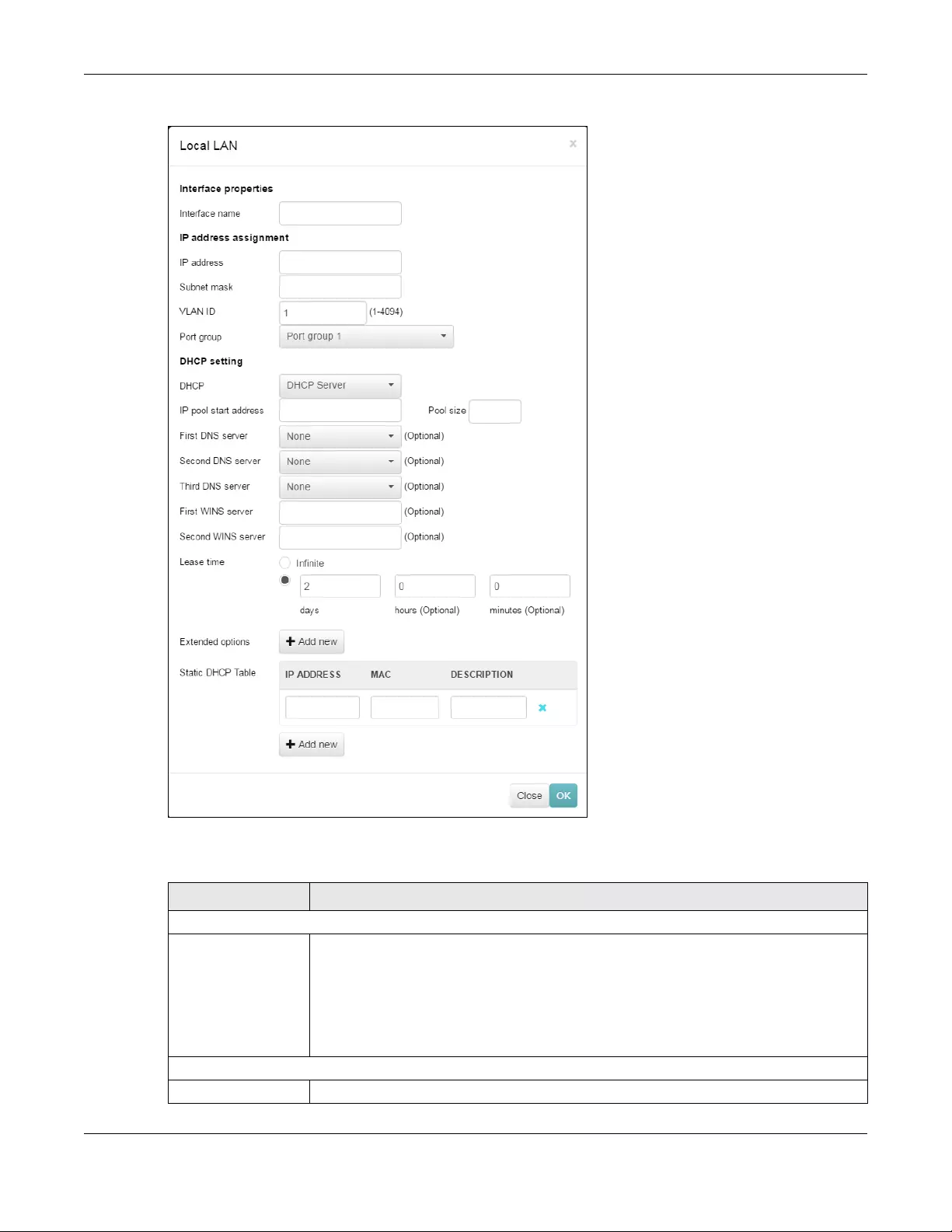
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
93
Figure 50 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 38 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface properties
Interface name This field is read-only if you are editing an existing interface.
Specify a name for the interface.
The format of interface names is strict. Each name consists of 2-4 letters (interface type),
followed by a number (x). For most interfaces, x is limited by the maximum number of the
type of interface. For VLAN interfaces, x is defined by the number you enter in the VLAN
name field. For example, VLAN interfaces are vlan0, vlan1, vlan2, ...; and so on.
IP address assignment
IP address Enter the IP address for this interface.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
94
Subnet mask Enter the subnet mask of this interface in dot decimal notation. The subnet mask indicates
what part of the IP address is the same for all computers in the network.
VLAN ID Enter the VLAN ID. This 12-bit number uniquely identifies each VLAN. Allowed values are 1 -
4094. (0 and 4095 are reserved.)
Port group Select the name of the port group to which you want the interface to (network) belong.
DHCP setting
DHCP Select what type of DHCP service the security gateway provides to the network. Choices
are:
None - the security gateway does not provide any DHCP services. There is already a DHCP
server on the network.
DHCP Relay - the security gateway routes DHCP requests to one or more DHCP servers you
specify. The DHCP server(s) may be on another network.
DHCP Serve r - the security gateway assigns IP addresses and provides subnet mask,
gateway, and DNS server information to the network. The security gateway is the DHCP
server for the network.
These fields appear if the security gateway is a DHCP Relay.
Relay server 1 Enter the IP address of a DHCP server for the network.
Relay server 2 This field is optional. Enter the IP address of another DHCP server for the network.
These fields appear if the security gateway is a DHCP Server.
IP pool start address Enter the IP address from which the security gateway begins allocating IP addresses. If you
want to assign a static IP address to a specific computer, click Add new under Static DHCP
Table.
Pool size Enter the number of IP addresses to allocate. This number must be at least one and is
limited by the interface’s Subnet mask. For example, if the Subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 and
IP pool start address is 10.10.10.10, the security gateway can allocate 10.10.10.10 to
10.10.10.254, or 245 IP addresses.
First DNS server
Second DNS server
Third DNS server
Specify the IP addresses up to three DNS servers for the DHCP clients to use. Use one of the
following ways to specify these IP addresses.
Custom Defined - enter a static IP address.
From ISP - select the DNS server that another interface received from its DHCP server.
NSG - the DHCP clients use the IP address of this interface and the security gateway works
as a DNS relay.
First WINS server
Second WINS server
Type the IP address of the WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) server that you want to
send to the DHCP clients. The WINS server keeps a mapping table of the computer names
on your network and the IP addresses that they are currently using.
Lease time Specify how long each computer can use the information (especially the IP address)
before it has to request the information again. Choices are:
infinite - select this if IP addresses never expire
days, hours, minutes - select this to enter how long IP addresses are valid.
Extended options This table is available if you selected DHCP server.
Configure this table if you want to send more information to DHCP clients through DHCP
packets.
Click Add new to create an entry in this table. See Section 5.3.1.2 on page 95 for detailed
information
Name This is the option’s name.
Code This is the option’s code number.
Table 38 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
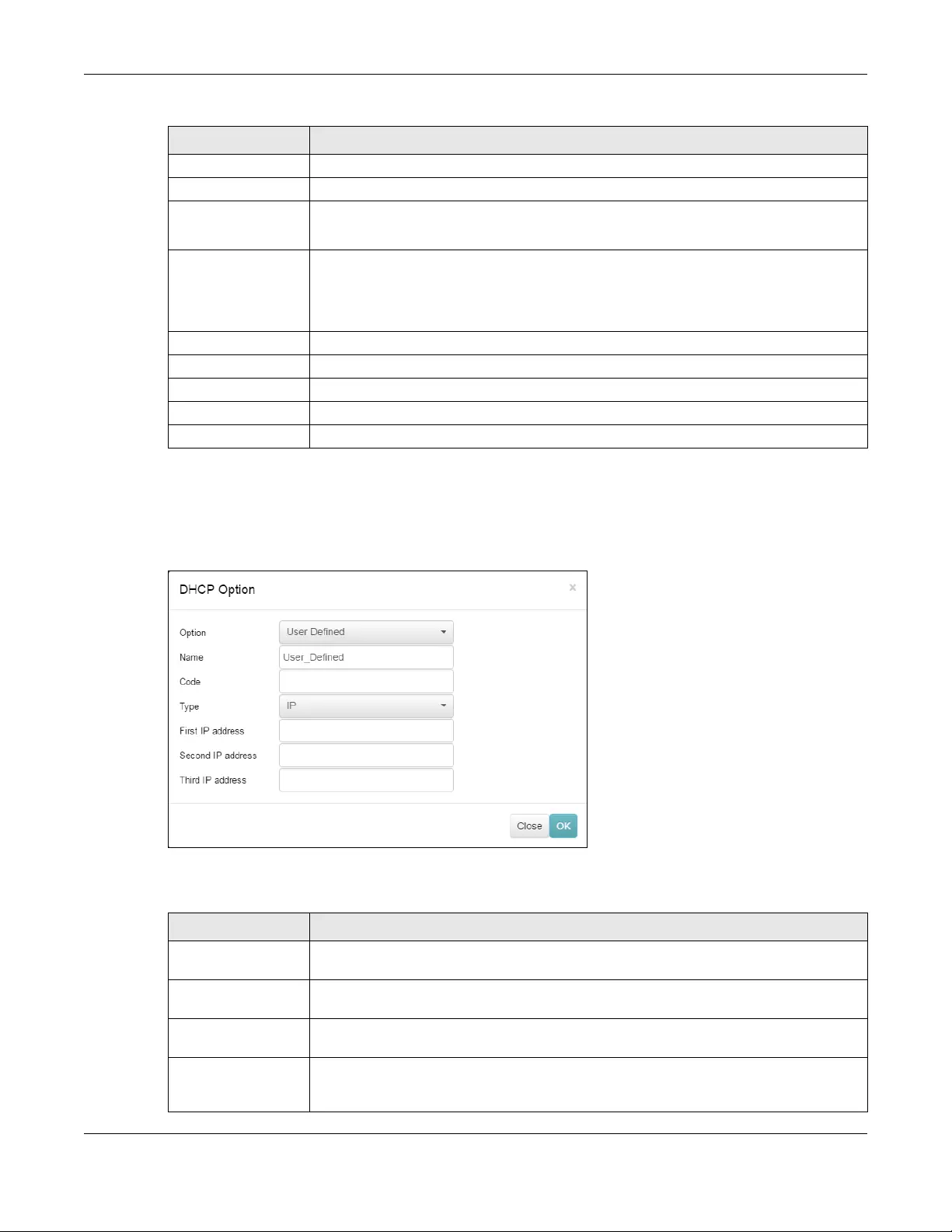
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
95
5.3.1.2 DHCP Option
Click the Add new button under Extended options in the Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing:
Local LAN screen.
Figure 51 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN: DHCP Option
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Type This is the option’s type.
Value This is the option’s value.
Click the edit icon to modify it.
Click the remove icon to delete it.
Static DHCP Table Configure a list of static IP addresses the security gateway assigns to computers connected
to the interface. Otherwise, the security gateway assigns an IP address dynamically using
the interface’s IP pool start address and Pool size.
Click Add new to create an entry in this table.
IP address Enter the IP address to assign to a device with this entry’s MAC address.
MAC Enter the MAC address to which to assign this entry’s IP address.
Description Enter a description to help identify this static DHCP entry.
Close Click Close to exit this screen without saving.
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Table 38 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 39 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN: DHCP Option
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Option Select which DHCP option that you want to add in the DHCP packets sent through the
interface.
Name This field displays the name of the selected DHCP option. If you selected User_Defined in the
Option field, enter a descriptive name to identify the DHCP option.
Code This field displays the code number of the selected DHCP option. If you selected
User_Defined in the Option field, enter a number for the option. This field is mandatory.
Type This is the type of the selected DHCP option. If you selected User_Defined in the Option field,
select an appropriate type for the value that you will enter in the next field.
Misconfiguration could result in interface lockout.

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
96
5.3.1.3 Static Route
Click the Add a static route button in the Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing screen.
Figure 52 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Static Route
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Value Enter the value for the selected DHCP option. For example, if you selected TFTP Server
Name (66) and the type is TEXT, enter the DNS domain name of a TFTP server here. This field
is mandatory.
First IP address
Second IP address
Third IP address
If you selected Time Server (4), NTP Server (41), SIP Server (120), CAPWAP AC (138), or TFTP
Server (150) , you have to enter at least one IP address of the corresponding servers in these
fields. The servers should be listed in order of your preference.
First enterprise ID
Second enterprise ID
If you selected VIVC (124) or VIVS (125), you have to enter at least one vendor’s 32-bit
enterprise number in these fields. An enterprise number is a unique number that identifies a
company.
First class
Second class
If you selected VIVC (124), enter the details of the hardware configuration of the host on
which the client is running, or of industry consortium compliance.
First information
Second information
If you selected VIVS (125), enter additional information for the corresponding enterprise
number in these fields.
First FQDN
Second FQDN
Third FQDN
If the Type is FQDN, you have to enter at least one domain name of the corresponding
servers in these fields. The servers should be listed in order of your preference.
Close Click Close to exit this screen without saving.
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Table 39 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Local LAN: DHCP Option (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 40 Gateway > Configure > Interfaces addressing: Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for this route.
Destination Specifies the IP network address of the final destination. Routing is always based on network
number.
Subnet mask Enter the IP subnet mask.
Next hop IP Enter the IP address of the next-hop gateway.
Close Click Close to exit this screen without saving.
OK Click OK to save your changes.

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
97
5.3.2 Firewall
By default, a LAN user can initiate a session from within the LAN zone and the security gateway allows
the response. However, the security gateway blocks incoming traffic initiated from the WAN zone and
destined for the LAN zone. Use this screen to configure firewall rules for outbound traffic, application
patrol, schedule profiles and port forwarding rules for inbound traffic.
Click Gateway > Configure > Firewall to access this screen.
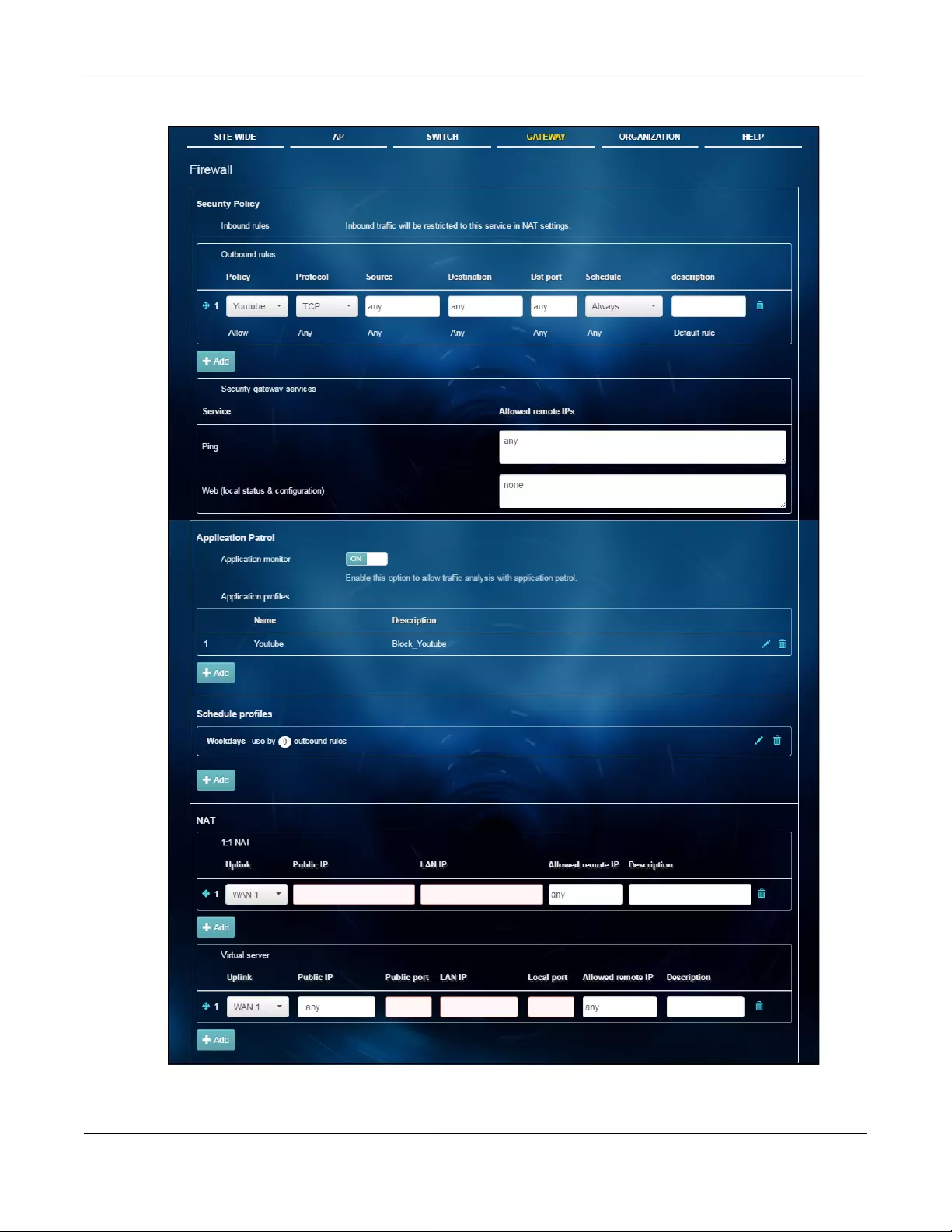
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
98
Figure 53 Gateway > Configure > Firewall
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
99
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 41 Gateway > Configure > Firewall
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Policy
Outbound rules
Click the icon of a rule and drag the rule up or down to change the order.
Policy Select what the firewall is to do with packets that match this rule.
Select Deny to silently discard the packets without sending a TCP reset packet or an ICMP
destination-unreachable message to the sender.
Select Allow to permit the passage of the packets.
Protocol Select the IP protocol to which this rule applies. Choices are: TCP, UDP, and Any.
Source Specify the source IP address(es) to which this rule applies. You can specify multiple IP
addresses or subnets in the field separated by a comma (","). Enter any to apply the rule to
all IP addresses.
Destination Specify the destination IP address(es) or subnet to which this rule applies. You can specify
multiple IP addresses or subnets in the field separated by a comma (","). Enter any to apply
the rule to all IP addresses.
Dst Port Specify the destination port(s) to which this rule applies. You can specify multiple ports
separated by a comma (","). Enter any to apply the rule to all ports.
Schedule Select the name of the schedule profile that the rule uses. Unschedules means the rule is
active at all times if enabled.
Description Enter a descriptive name of up to 60 printable ASCII characters for the rule.
Click this icon to remove the rule.
Add Click this button to create a new rule.
Security appliance services
Service This shows the name of the service.
Allowed remote IPs Specify the IP address with which the computer is allowed to access the security gateway
using the service. You can specify a range of IP addresses.
any means any IP address.
Application Patrol
Application monitor Click On to enable traffic analysis for all applications and display information about top 10
applications in the SITE-WIDE > Monitor > Dashboard: Traffic Summary screen. Otherwise,
select Off to disable traffic analysis for applications.
Application profiles
Name This shows the name of the application patrol profile.
Description This shows the description of the application patrol profile.
Click this icon to change the profile settings.
Click this icon to remove the profile.
Add Click this button to create a new application patrol profile. See Section 5.3.2.1 on page 100
for more information.
Schedule profiles
This shows the name of the schedule profile and the number of the outbound rules that are
using this schedule profile.
Click the edit icon to modify it.
Click the remove icon to delete it.
Click this icon to change the profile settings.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
100
5.3.2.1 Add application patrol profile
Click the Add button in the Application Patrol section of the Gateway > Configure > Firewall screen to
access this screen. Use the application patrol profile screens to customize action and log settings for a
group of application patrol signatures.
Add Click this button to create a new schedule profile. See Section 5.3.2.3 on page 102 for more
information.
NAT
1:1 NAT
Click the icon of a rule and drag the rule up or down to change the order.
Uplink Select the interface of the security gateway on which packets for the NAT rule must be
received.
Public IP Specify to which translated destination IP address this NAT rule forwards packets.
LAN IP Specify the destination IP address of the packets received by this NAT rule’s specified
interface.
Allowed remote IP Specify the remote IP address with which the computer is allowed to use the public IP
address to access the private network server. You can specify a range of IP addresses.
any means any IP address.
Description Enter a description for the rule.
Click this icon to remove the rule.
Add Click this button to create a new 1:1 NAT mapping rule.
Virtual server
Click the icon of a rule and drag the rule up or down to change the order.
Uplink Select the interface of the security gateway on which packets for the NAT rule must be
received.
Public IP Specify to which translated destination IP address this NAT rule forwards packets.
Public port Enter the translated destination port if this NAT rule forwards the packet.
LAN IP Specify the destination IP address of the packets received by this NAT rule’s specified
interface.
Local port Enter the original destination port this NAT rule supports.
Allowed remote IP Specify the remote IP address with which the computer is allowed to use the public IP
address to access the private network server. You can specify a range of IP addresses.
any means any IP address.
Description Enter a description for the rule.
Click this icon to remove the rule.
Add Click this button to create a new virtual server mapping rule.
Table 41 Gateway > Configure > Firewall (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
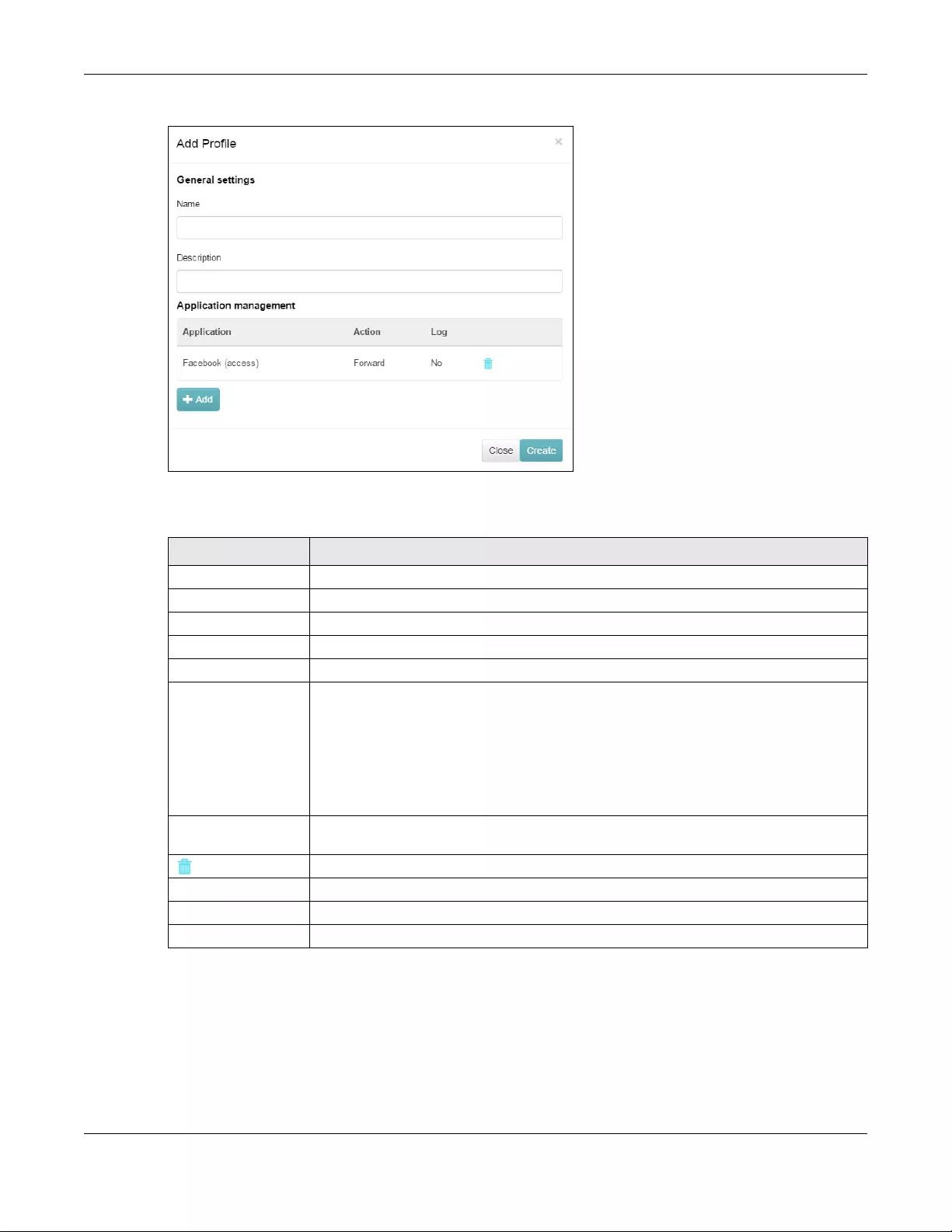
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
101
Figure 54 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add an application profile
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
5.3.2.2 Add application
Click the Add button in the Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add Profile screen to access this screen. Use
this screen to set actions for application categories and for specific applications within the category.
Table 42 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add an application profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General settings
Name Enter a name for this profile for identifying purposes.
Description Enter a description for this profile.
Profile management
Application This field displays the application name of the policy.
Action This shows the default action for all signatures in this category.
Forward - the security gateway routes packets that matches these signatures.
Drop - the security gateway silently drops packets that matches these signatures without
notification.
Reject - the security gateway drops packets that matches these signatures and sends
notification.
Log This shows whether the security gateway generates a log (Log), log and alert (Log Alert) or
neither (No) by default when traffic matches a signature in this category.
Click this icon to remove the entry.
Add Click this button to create a new application category.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Create Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
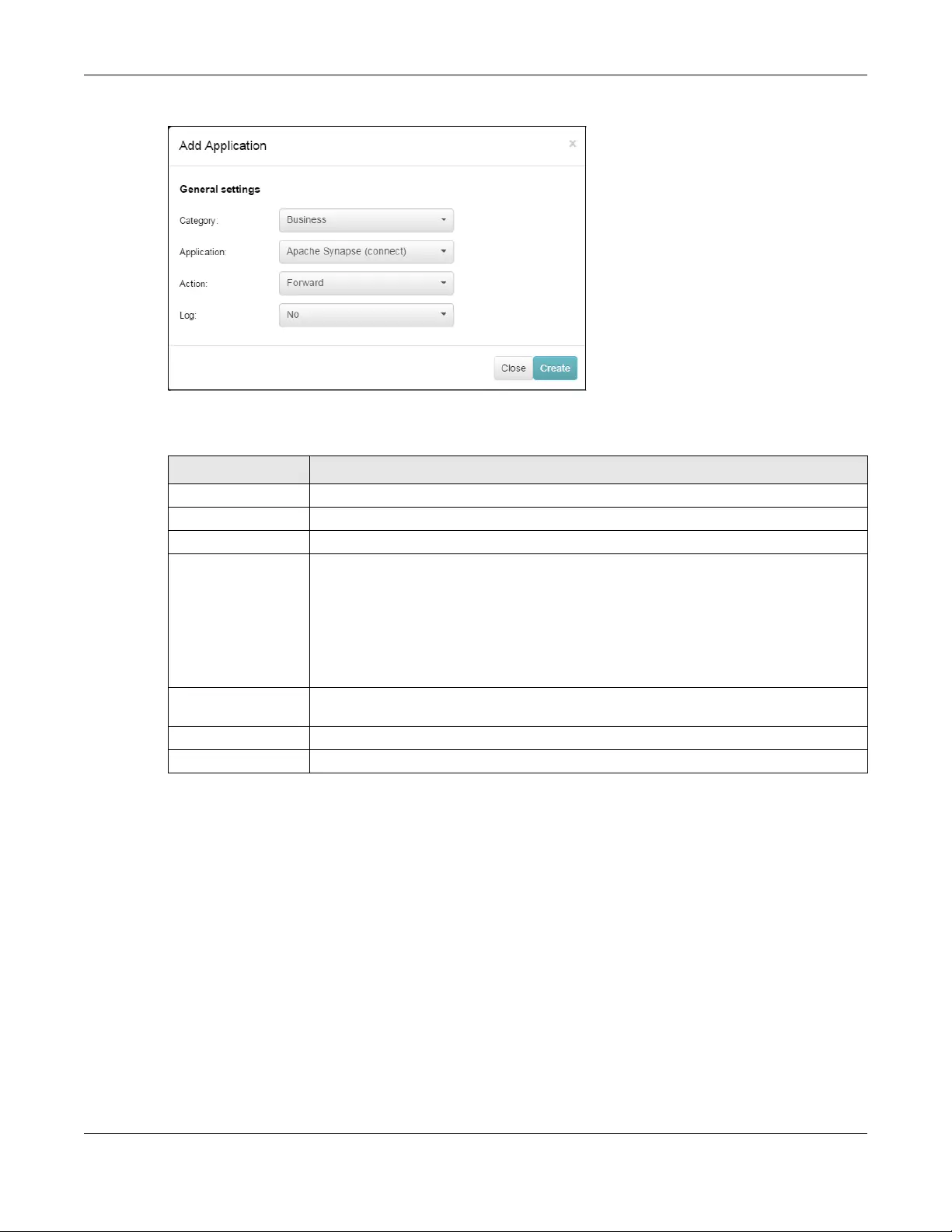
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
102
Figure 55 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add an application profile: Add application
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
5.3.2.3 Create new schedule
Click the Add button in the Schedule Profiles section of the Gateway > Configure > Firewall screen to
access this screen.
Table 43 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add an application profile: Add application
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General settings
Category Select an application category.
Application Select an application to apply the policy.
Action Select the default action for all signatures in this category.
Forward - the security gateway routes packets that matches these signatures.
Drop - the security gateway silently drops packets that matches these signatures without
notification.
Reject - the security gateway drops packets that matches these signatures and sends
notification.
Log Select whether to have the security gateway generate a log (Log), log and alert (Log Alert)
or neither (No) by default when traffic matches a signature in this category.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Create Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
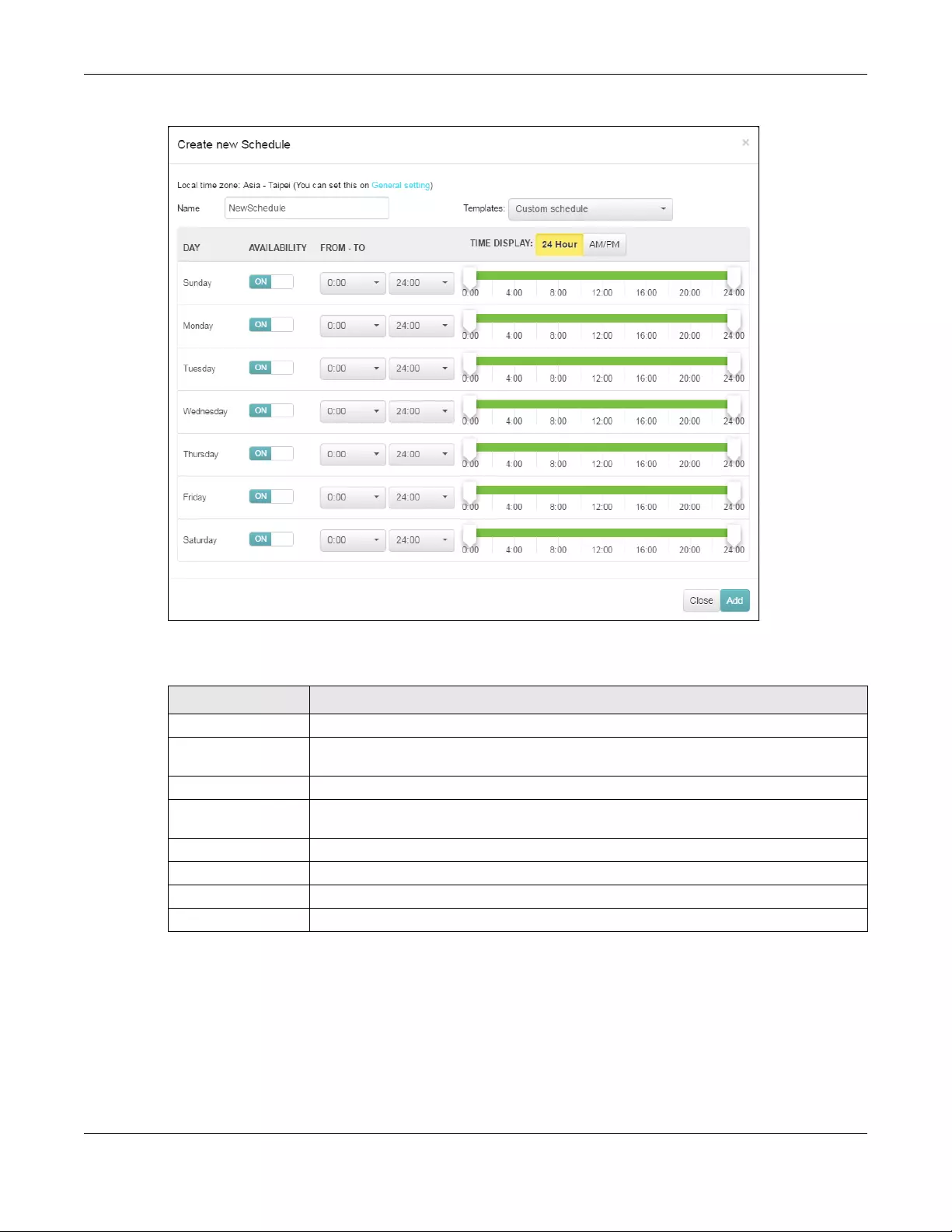
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
103
Figure 56 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add a schedule profile
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
5.3.3 Site-to-Site VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) provides secure communications between sites without the expense of
leased site-to-site lines. Use this screen to configure a VPN rule.
Click Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN to access this screen.
Table 44 Gateway > Configure > Firewall: Add a schedule profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for this schedule for identifying purposes.
Templates Select a pre-defined schedule template or select Cust om schedule and manually
configure the day and time at which the associated firewall outbound rule is enabled.
Day This shows the day of the week.
Availability Click On to enable the associated rule on this day. Otherwise, select Off to turn the
associated rule off.
From - To Specify the hour and minute when the schedule begins and ends each day
Time display Select the time format in which the time is displayed.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Add Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
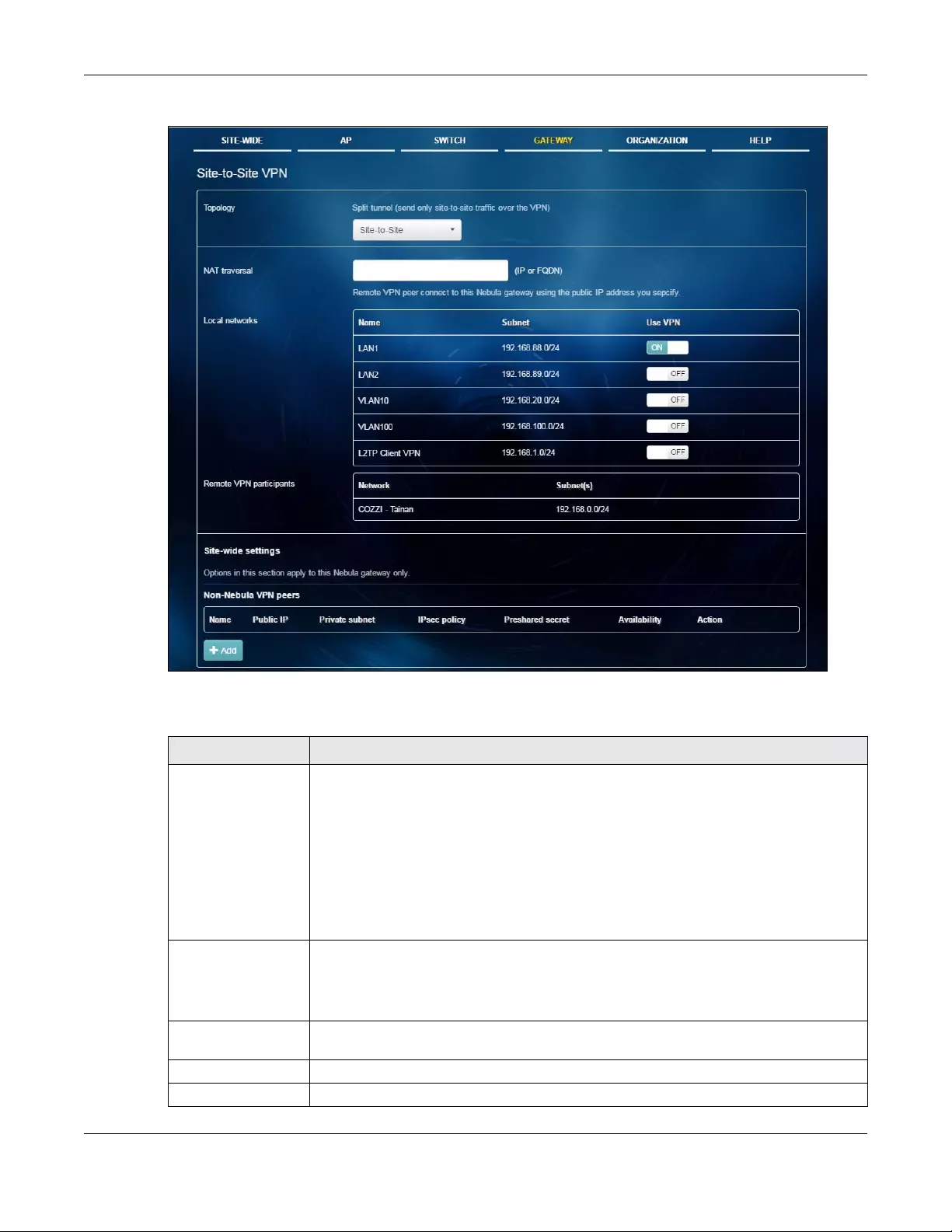
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
104
Figure 57 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 45 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Topology This shows the VPN mode supported by the security gateway.
Select a VPN topology.
Select Disable to not set a VPN connection.
In the Site-to-Site VPN topology. the remote IPSec device has a static IP address or a
domain name. This security gateway can initiate the VPN tunnel.
In the Hubs-and-Spoke VPN topology, there is a VPN connection between each spoke
router and the hub router, which uses the VPN concentrator. The VPN concentrator routes
VPN traffic between the spoke routers and itself.
Hubs (peers to
connect to)
This field is available when you set Topology to Hubs-and-Spoke. The field is configurable
only when the security gateway of the selected site is the hub router.
You can select another site’s name to have the gateway of that site act as the hub router
in the Hubs-and Spoke VPN topology.
NAT traversal If the security gateway is behind a NAT router, enter the public IP address or the domain
name that is configured and mapped to the security gateway on the NAT router.
Local networks This shows the local networks behind the security gateway.
Name This shows the network name.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
105
5.3.3.1 Custom IPSec Policy
Click the IPSec Policy column in the Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN screen to access this
screen.
Subnet This shows the IP address and subnet mask of the computer on the network.
Use VPN Select Yes to allow the computers on the network to use the VPN tunnel. Otherwise, select
No.
Remote VPN
participants
This shows the remote (peer) Nebula gateway’s network name and address.
Non-Nebula VPN
peers
If the remote VPN gateway is not a Nebula device, use this section to set up a VPN
connection between it and the Nebula security gateway.
Name Enter the name of the peer gateway.
Public IP Enter the public IP address of the peer gateway.
Private Subnet Enter the local network address or subnet behind the peer gateway.
IPSec Policy Click to select a pre-defined policy or have a custom one. See Section 5.3.3.1 on page 105
for detailed information.
Preshared Secret Enter a pre-shared key (password). The Nebula security gateway and peer gateway use
the key to identify each other when they negotiate the IKE SA.
Availability Select All Network to allow the peer gateway to connect to any Nebula security gateway
in the organization via a VPN tunnel.
Select This site and the peer gateway can only connect to the Nebula security gateway in
this site via a VPN tunnel.
Action Click the remove icon to delete the entry.
Add Click this button to add a peer VPN gateway to the list.
Table 45 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
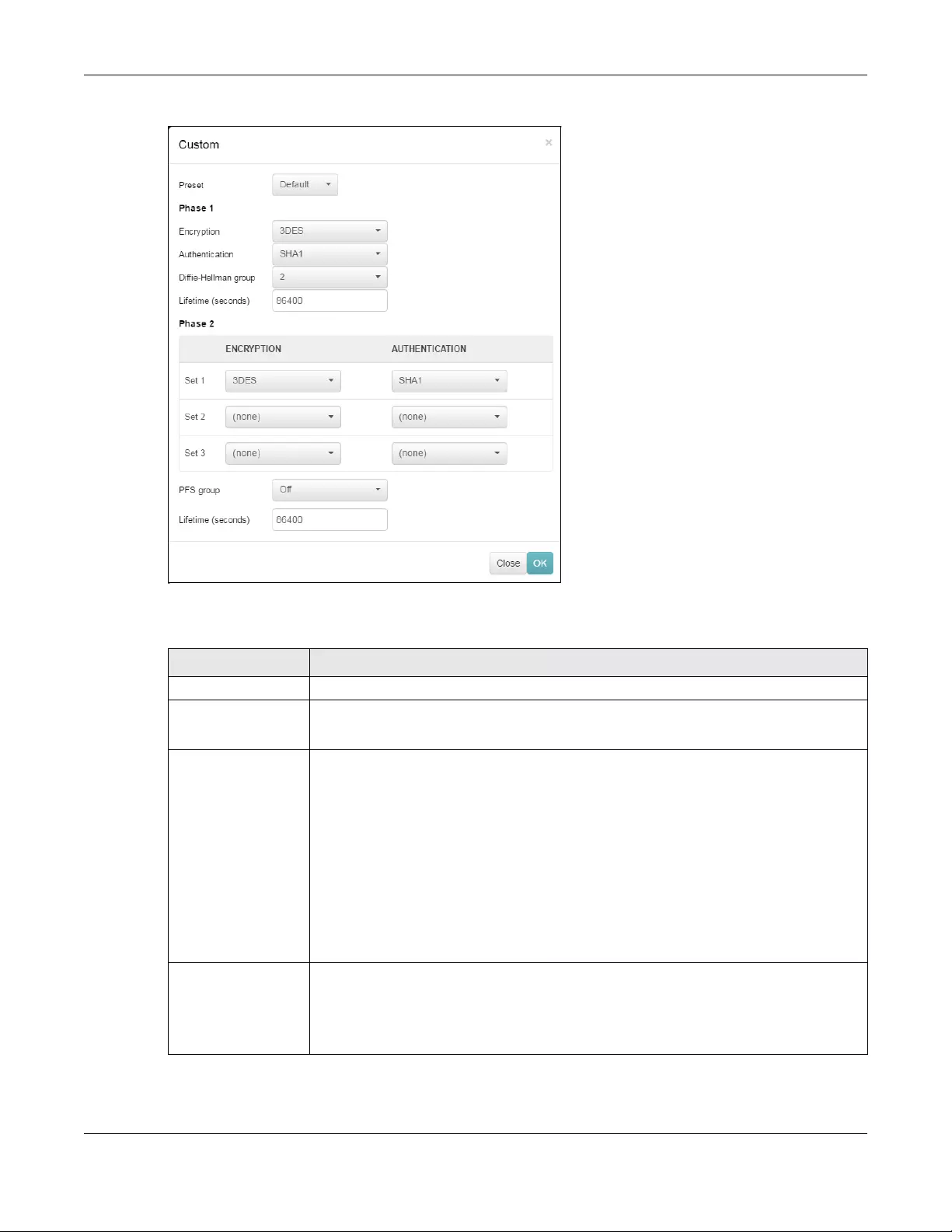
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
106
Figure 58 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN: Custom IPSec Policy
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 46 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN: Custom IPSec Policy
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Preset Select a pre-defined IPSec policy, or select Custom to configure the policy settings yourself.
Phase 1 IPSec VPN consists of two phases: Phase 1 (Authentication) and Phase 2 (Key Exchange).
A phase 1 exchange establishes an IKE SA (Security Association).
Encryption Select which key size and encryption algorithm to use in the IKE SA. Choices are:
DES - a 56-bit key with the DES encryption algorithm
3DES - a 168-bit key with the DES encryption algorithm
AES128 - a 128-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
AES192 - a 192-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
AES256 - a 256-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
The security gateway and the remote IPSec router must use the same key size and
encryption algorithm. Longer keys require more processing power, resulting in increased
latency and decreased throughput.
Authentication Select which hash algorithm to use to authenticate packet data in the IKE SA.
Choices are SHA1, SHA256, SHA512 and MD5. SHA is generally considered stronger than
MD5, but it is also slower.
The remote IPSec router must use the same authentication algorithm.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
107
Diffie-Hellman group Select which Diffie-Hellman key group (DHx) you want to use for encryption keys. Choices
are:
1 - use a 768-bit random number
2 - use a 1024-bit random number
5 - use a 1536-bit random number
14 - use a 2048-bit random number
The longer the key, the more secure the encryption, but also the longer it takes to encrypt
and decrypt information. Both routers must use the same DH key group.
Lifetime (seconds) Type the maximum number of seconds the IKE SA can last. When this time has passed, the
security gateway and remote IPSec router have to update the encryption and
authentication keys and re-negotiate the IKE SA. This does not affect any existing IPSec SAs,
however.
Phase 2 Phase 2 uses the SA that was established in phase 1 to negotiate SAs for IPSec.
Encryption Select which key size and encryption algorithm to use in the IPSec SA. Choices are:
none - no encryption key or algorithm
DES - a 56-bit key with the DES encryption algorithm
3DES - a 168-bit key with the DES encryption algorithm
AES128 - a 128-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
AES192 - a 192-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
AES256 - a 256-bit key with the AES encryption algorithm
The security gateway and the remote IPSec router must both have at least one proposal
that uses use the same encryption and the same key.
Longer keys are more secure, but require more processing power, resulting in increased
latency and decreased throughput.
Authentication Select which hash algorithm to use to authenticate packet data in the IPSec SA.
Choices are none, MD5, SHA1, SHA256, and SHA512. SHA is generally considered stronger
than MD5, but it is also slower.
The security gateway and the remote IPSec router must both have a proposal that uses the
same authentication algorithm.
PFS group Select whether or not you want to enable Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) and, if you do,
which Diffie-Hellman key group to use for encryption. Choices are:
Off - disable PFS
1 - enable PFS and use a 768-bit random number
2 - enable PFS and use a 1024-bit random number
5 - enable PFS and use a 1536-bit random number
14 - enable PFS and use a 2048-bit random number
PFS changes the root key that is used to generate encryption keys for each IPSec SA. The
longer the key, the more secure the encryption, but also the longer it takes to encrypt and
decrypt information. Both routers must use the same DH key group.
PFS is ignored in initial IKEv2 authentication but is used when reauthenticating.
Lifetime (seconds) Type the maximum number of seconds the IPSec SA can last. Shorter life times provide
better security. The security gateway automatically negotiates a new IPSec SA before the
current one expires, if there are users who are accessing remote resources.
Table 46 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN: Custom IPSec Policy (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
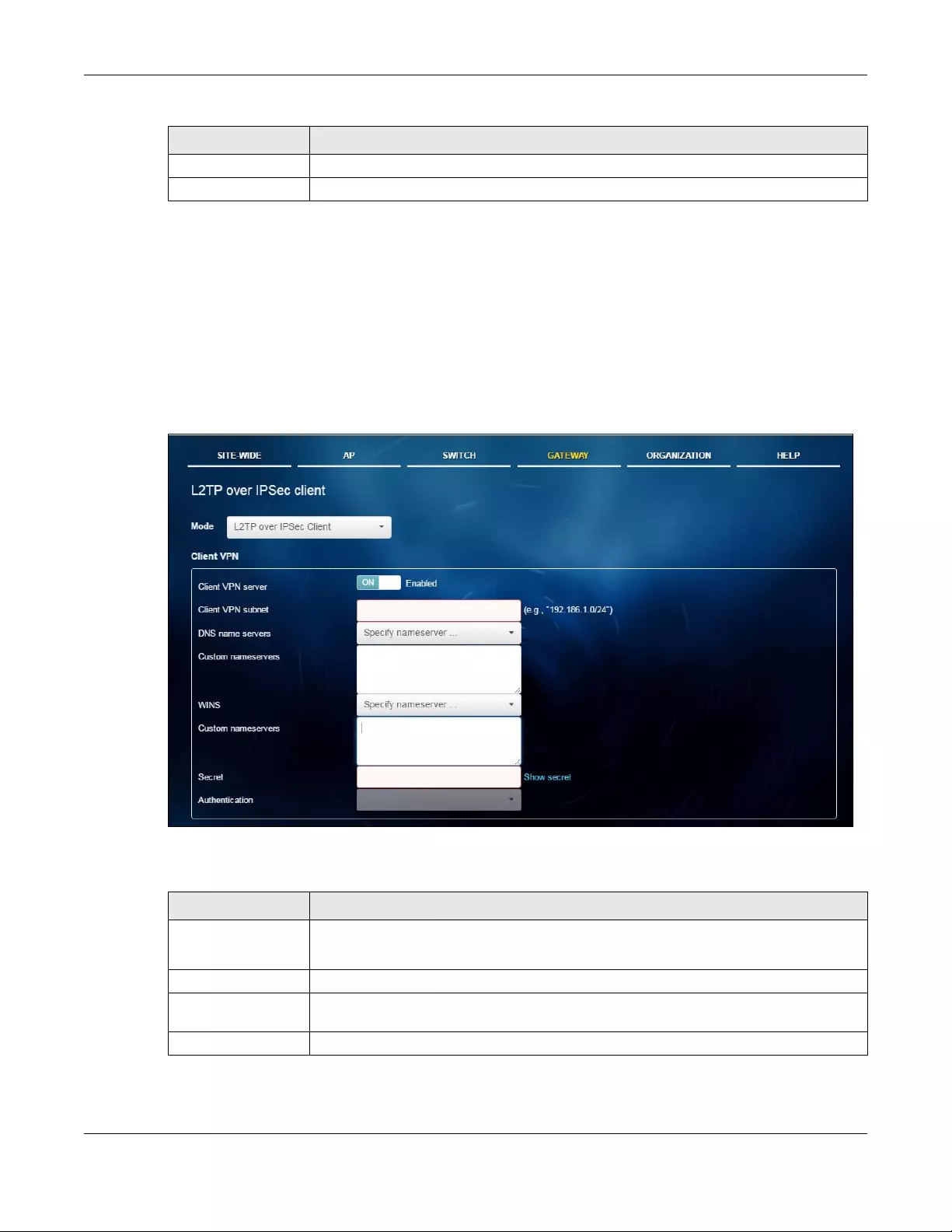
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
108
5.3.4 L2TP over IPSec Client
Use this screen to configure the L2TP VPN settings.
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) works at layer 2 (the data link layer) to tunnel network traffic
between two peers over another network (like the Internet). In L2TP VPN, an IPSec VPN tunnel is
established first and then an L2TP tunnel is built inside it.
Click Gateway > Configure > L2TP over IPSec client to access this screen.
Figure 59 Gateway > Configure > L2TP over IPSec client
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
OK Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
Table 46 Gateway > Configure > Site-to-Site VPN: Custom IPSec Policy (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 47 Gateway > Configure > L2TP over IPSec client
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Mode Select L2TP over IPSec Client to enable the L2TP VPN function on the security gateway.
Other wise, select Disabled to turn it off.
Client VPN The following fields display when you enable the L2TP VPN function.
Client VPN server Click ON to enable the L2TP/IPSec VPN server feature on the security gateway. Otherwise,
click OFF to disable it.
Client VPN subnet Specify the IP addresses that the security gateway uses to assign to the L2TP VPN clients.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
109
5.3.5 Captive portal
Use this screen to configure captive portal settings for each interface. A captive portal can intercepts
network traffic until the user authenticates his or her connection, usually through a specifically
designated login web page.
Click Gateway > Configure > Captive portal to access this screen.
DNS name servers Specify the IP addresses of DNS servers to assign to the remote users.
Select Use Google Public DNS to use the DNS service offered by Google. Otherwise, select
Specify nameserver to enter a static IP address.
Custom nameservers If you select Specify nameserver, manually enter the DNS server IP address(es).
WINS The WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) server keeps a mapping table of the
computer names on your network and the IP addresses that they are currently using.
Select No WINS Servers to not send WINS server addresses to the users. Otherwise, select
Specify nameserver to type the IP addresses of WINS servers to assign to the remote users.
Custom nameservers If you select Specify nameserver, manually enter the WINS server IP address(es).
Secret Enter the pre-shared key (password) which is used to set up the IPSec VPN tunnel.
Authentication Select how the security gateway authenticates a remote user before allowing access to
the L2TP VPN tunnel.
Table 47 Gateway > Configure > L2TP over IPSec client (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
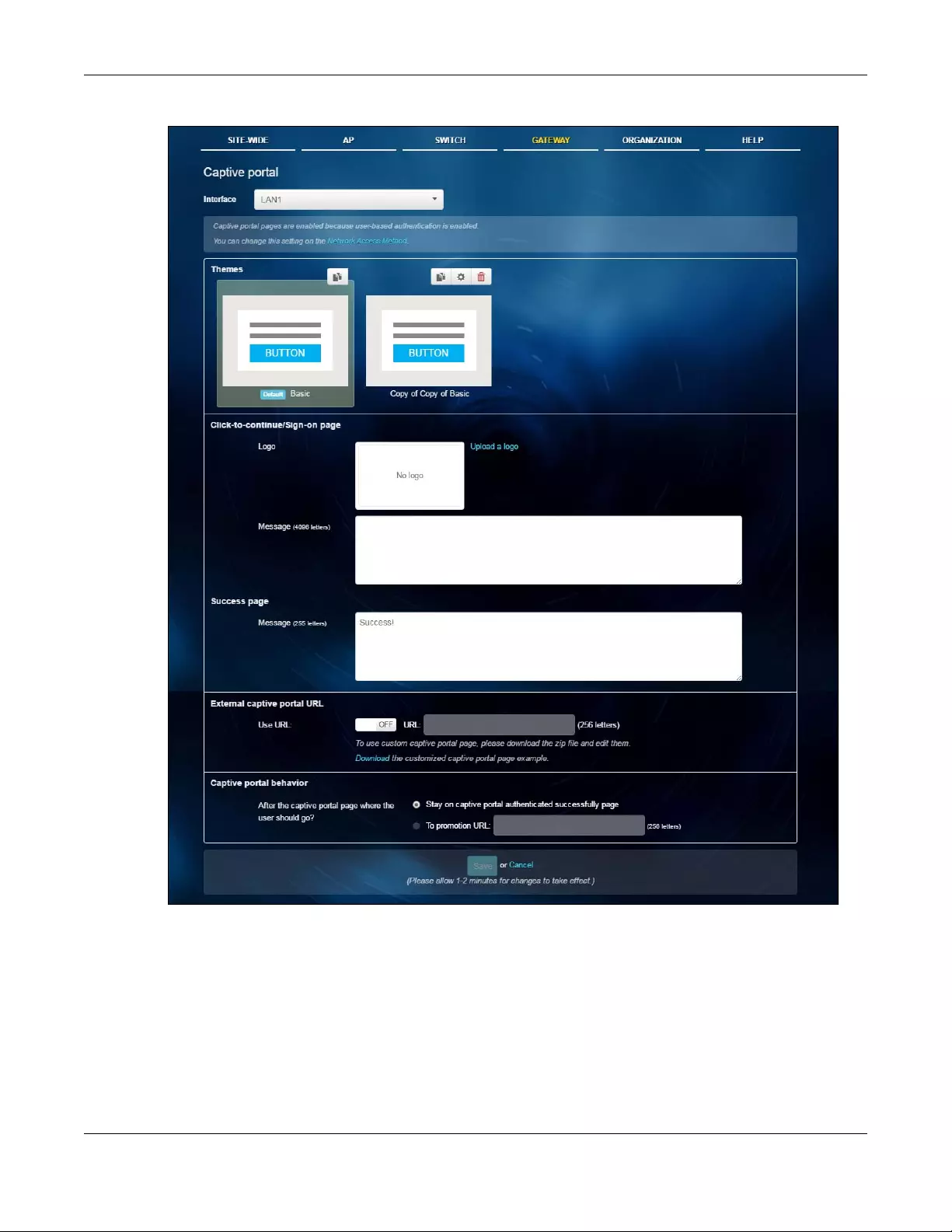
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
110
Figure 60 Gateway > Configure > Captive portal

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
111
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 48 Gateway > Configure > Captive portal
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface Select the gateway’s interface (network) to which the settings you configure here is
applied.
Themes Click the Copy icon at the upper right corner of the default theme image to create a new
custom theme (portal page).
Click the Edit icon of a custom theme to go to a screen, where you can view and configure
the details of the custom portal page(s). See Section 5.3.5.1 on page 112.
Click the Remove icon to delete a custom theme.
Custom themes
"Modern"
Select a custom theme page and customize the colors on the selected login page, such as
the color of the button, text, window’s background, links, borders, and etc.
Select a color that you want to use in the Saved Colors tab. If the color you want is not
listed, click the Advanced tab to define a new one.
Click-to-continue/
Sign-on page
Logo This shows the logo image that you uploaded for the customized login page.
Click Upload a logo and specify the location and file name of the logo graphic or click
Browse to locate it. You can use the following image file formats: GIF, PNG, or JPG.
Message Enter a note to display below the title. Use up to 1024 printable ASCII characters. Spaces
are allowed.
Success page
Message Enter a note to display on the page that displays when a user logs in successfully. Use up to
1024 printable ASCII characters. Spaces are allowed.
External captive
portal URL
Use URL Select On to use a custom login page from an external web portal instead of the one built
into the NCC. You can configure the look and feel of the web portal page.
Specify the login page’s URL; for example, http://IIS server IP Address/login.asp. The Internet
Information Server (IIS) is the web server on which the web portal files are installed.
Captive portal
behavior
After the captive
portal page
where the user
should go?
Select To promotion URL and specify the URL of the web site/page to which the user is
redirected after a successful login. Otherwise, select Stay on Captive portal authenticated
successfully page.
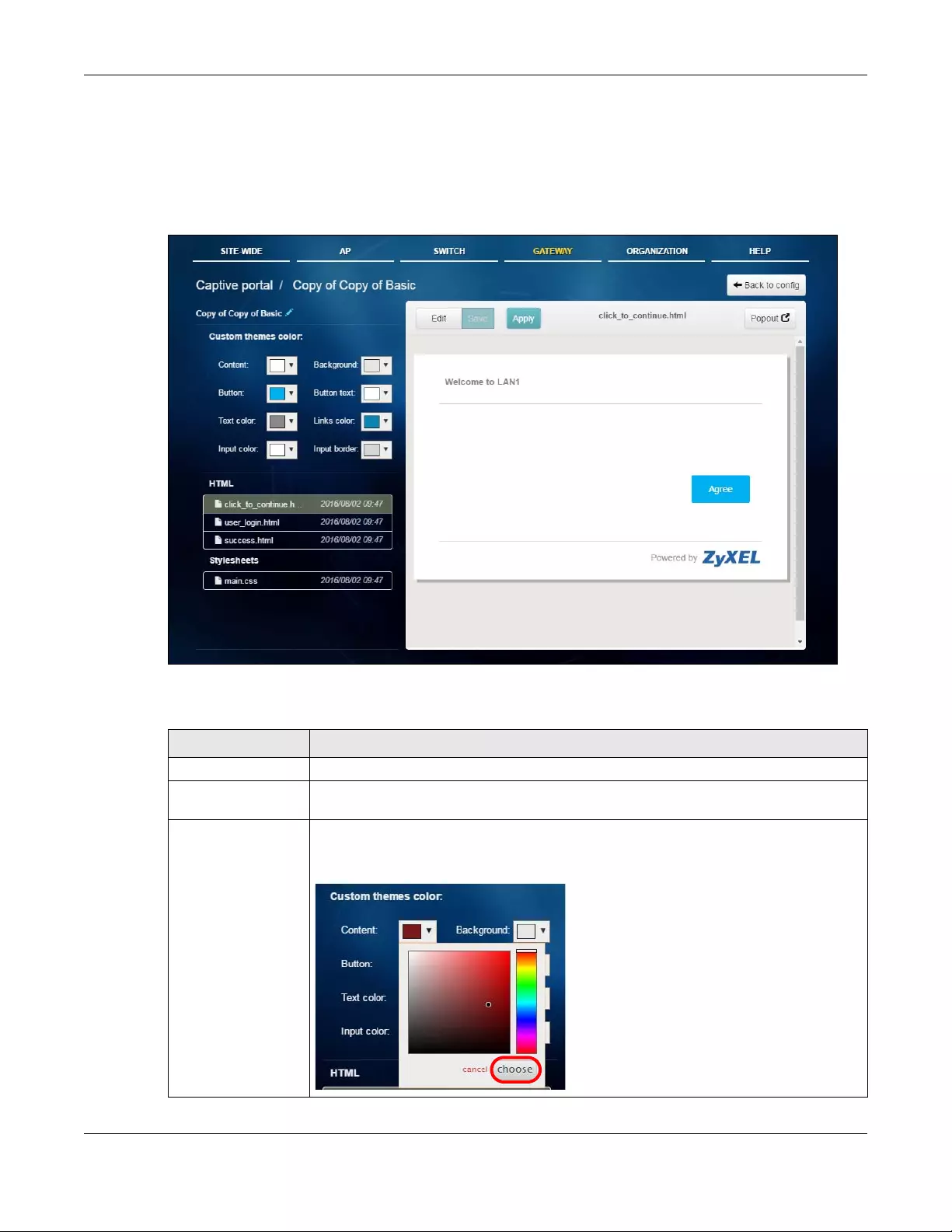
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
112
5.3.5.1 Custom Theme Edit
Use this screen to check what the custom portal pages look like. You can also view and modify the CSS
values of the selected HTML file. Click a custom login page’s Edit button in the Gateway > Configure >
Captive portal screen to access this screen.
Figure 61 Gateway > Configure > Captive portal: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 49 Gateway > Configure > Captive portal: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Back to config Click this button to return to the Captive portal screen.
Copy of Copy of
Basic
This shows the name of the theme. Click the edit icon the change it.
Custom themes color Customize the colors on the selected custom portal page (HTML file), such as the color of
the button, text, window’s background, links, borders, and etc.
Select a color that you want to use and click the Choose button.
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
113
5.3.6 Network Access Method
Use this screen to enable or disable web authentication on an interface.
Click Gateway > Configure > Network access method to access this screen.
HTML This shows the name and when the HTML file of the portal page is created for the selected
custom theme.
Click a HTML file to display the portal page on the right side of the screen. You can also
change colors and modify the CSS values of the selected HTML file.
Stylesheets This shows the name and when the main CSS file is created for the selected custom theme.
Edit/Preview Click Edit to view and modify the CSS values of the selected HTML file.
Click Preview to display the corresponding portal page.
Save Click this button to save your color settings for the selected HTML file.
Apply Click this button to apply your color settings to the selected HTML file.
Popout Click this button to display the corresponding portal page in a popup window.
Table 49 Gateway > Configure > Captive portal: Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
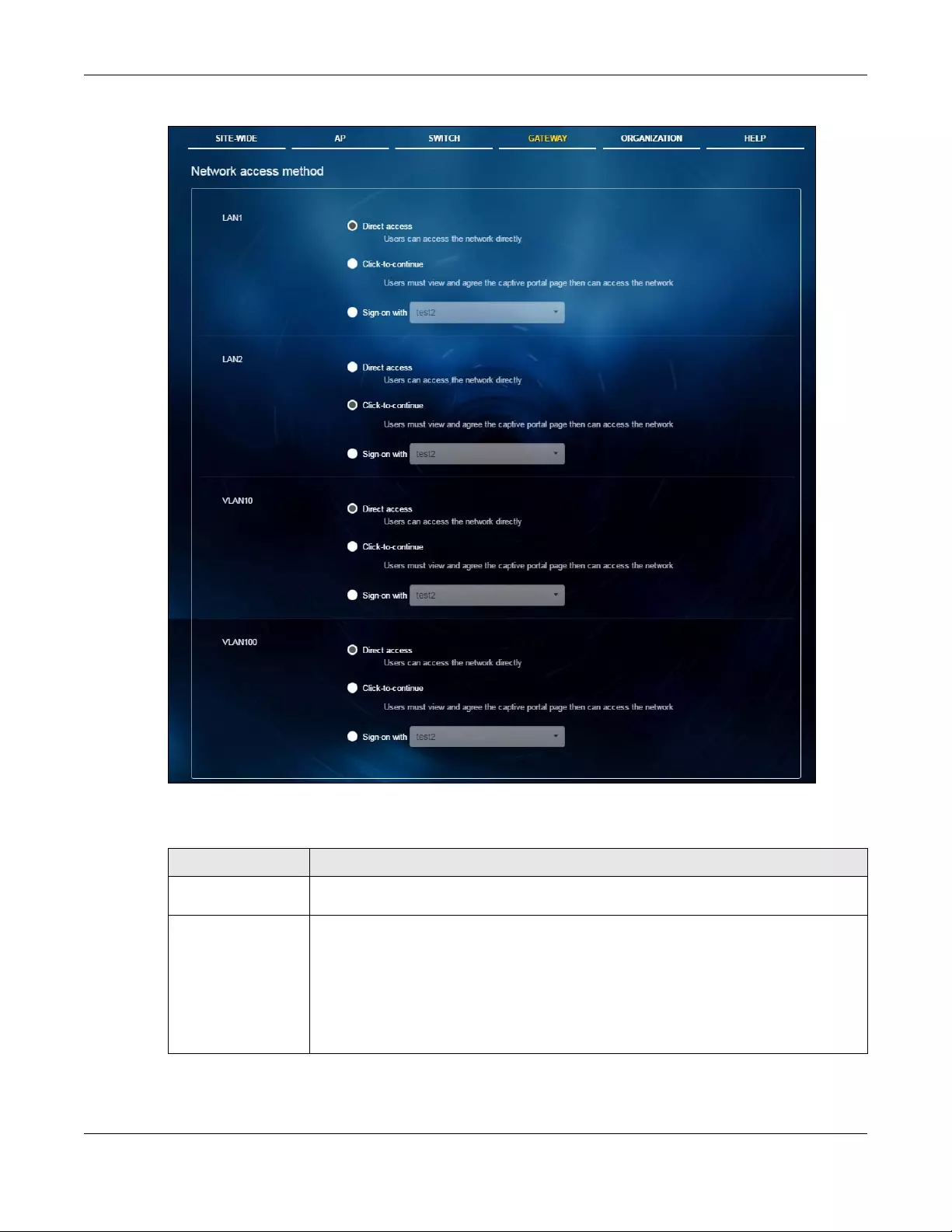
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
114
Figure 62 Gateway > Configure > Network access method
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 50 Gateway > Configure > Network access method
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAN1/LAN2/VLANx This shows the gateway’s interface (network) to which the settings you configure here is
applied.
Select Direct access to turn off web authentication.
Select Click-to-continue to block network traffic until a client agrees to the policy of user
agreement.
Select Sign-on with to block network traffic until a client authenticates with an external
RADIUS or AD server through the specifically designated web portal page. Select an
authentication server that you have configured in the Gateway > Configure > My
authentication server screen (see Section 5.3.9 on page 116),
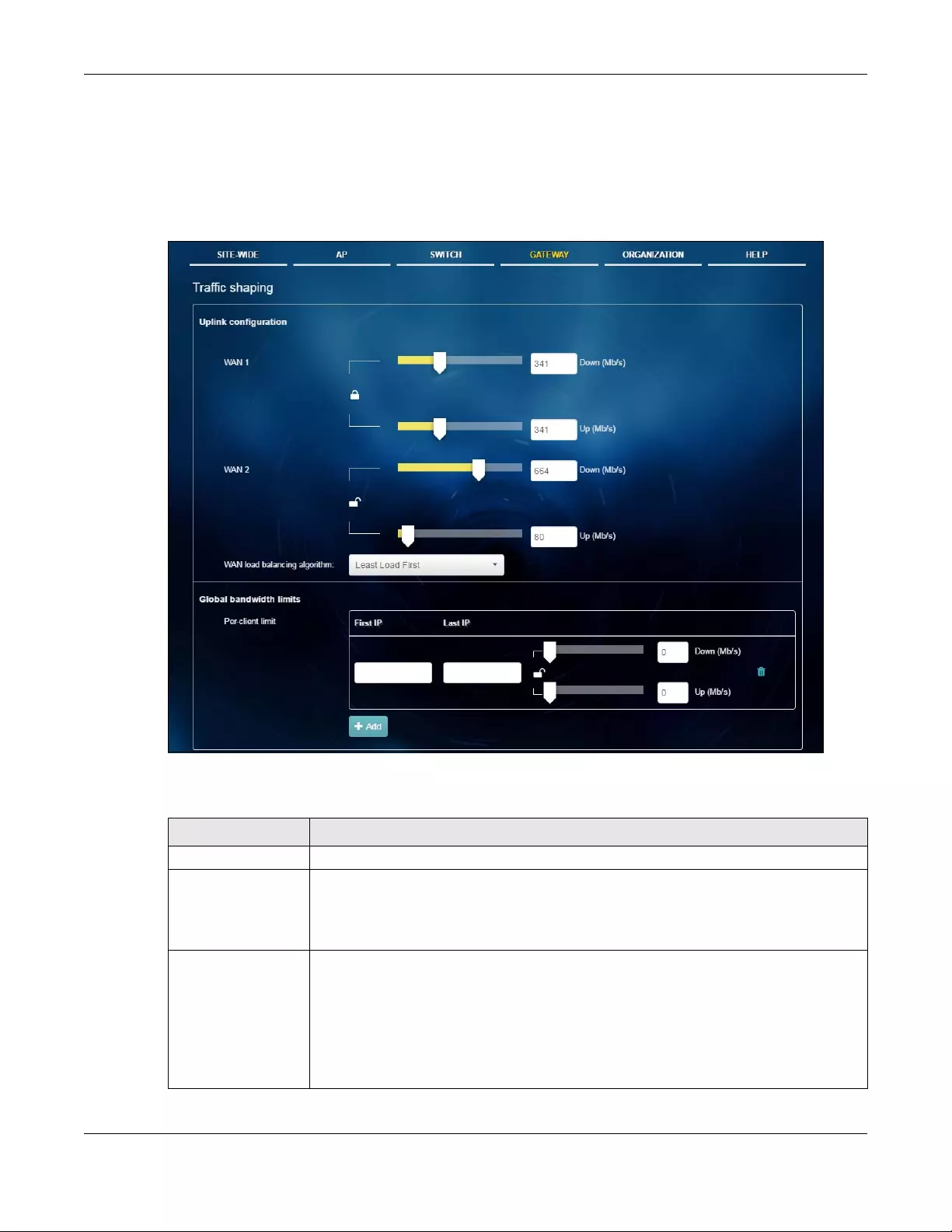
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
115
5.3.7 Traffic Shaping
Use this screen to configure the maximum bandwidth and load balancing.
Click Gateway > Configure > Traffic shaping to access this screen.
Figure 63 Gateway > Configure > Traffic shaping
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 51 Gateway > Configure > Traffic shaping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Uplink configuration
WAN 1
WAN 2
Set the amount of upstream/downstream bandwidth for the WAN interface.
Click a lock icon to change the lock state. If the lock icon for a WAN interface is locked, the
bandwidth limit you set applies to both inbound and outbound traffic. If the lock is
unlocked, you can set inbound and outbound traffic to have different transmission speeds.
Wan load balancing
algorithm
Select a load balancing method to use from the drop-down list box.
Select Least Load First to send new session traffic through the least utilized WAN interface.
Select Weighted Round Robin to balance the traffic load between interfaces based on
their respective weights (bandwidth). An interface with a larger weight gets more chances
to transmit traffic than an interface with a smaller weight. For example, if the weight ratio of
WAN 1 and WAN 2 interfaces is 2:1, the security gateway chooses WAN 1 for 2 sessions’
traffic and WAN 2 for 1 session’s traffic in each round of 3 new sessions.

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
116
5.3.8 Security Filtering
Use this screen to enable or disable Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP) on the security gateway,
which can detect malicious or suspicious packets used in network-based intrusions and respond
instantaneously.
Click Gateway > Configure > Security Filtering to access this screen.
Note: Packet inspection signatures examine packet content for malicious data. Packet
inspection applies to OSI (Open System Interconnection) layer-4 to layer-7 contents.
You need to subscribe for IDP service in order to be able to download new signatures.
Figure 64 Gateway > Configure > Security Filtering
5.3.9 My Authentication Server
Use this screen to configure external AD (Active Directory) server or RADIUS server that the security
gateway can use in authenticating users.
AD (Active Directory) is a directory service that is both a directory and a protocol for controlling access
to a network. The directory consists of a database specialized for fast information retrieval and filtering
activities. You create and store user profile and login information on the external server.
Click Gateway > Configure > My authentication server to access this screen.
Global bandwidth
limits
Per-client limit You can limit a client’s outbound or inbound bandwidth.
First IP Enter the first IP address in a range of IP addresses for which the security gateway applies
the rule.
Last IP Enter the last IP address in a range of IP addresses for which the security gateway applies
the rule.
Down/Up Set the maximum upstream/downstream bandwidth for traffic from an individual source IP
address.
Click a lock icon to change the lock state. If the lock icon is locked, the bandwidth limit you
set applies to both inbound and outbound traffic. If the lock is unlocked, you can set
inbound and outbound traffic to have different transmission speeds.
Click this icon to remove the rule.
Add Click this button to create a new rule.
Table 51 Gateway > Configure > Traffic shaping (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
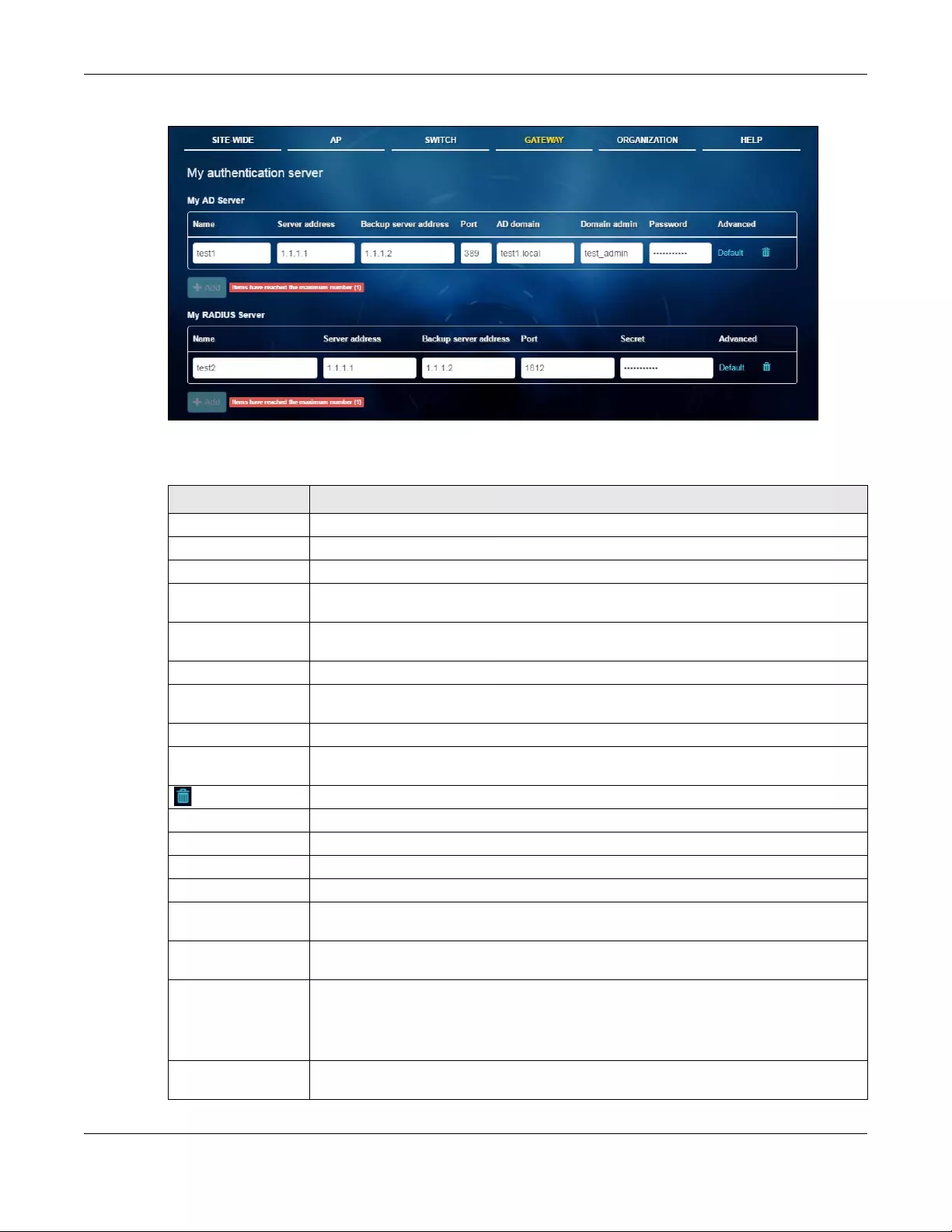
Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
117
Figure 65 Gateway > Configure > My authentication server
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 52 Gateway > Configure > My authentication server
LABEL DESCRIPTION
My AD Server
Name Enter a descriptive name for the server.
Server Address Enter the address of the AD server.
Backup Server
Address
If the AD server has a backup server, enter its address here.
Port Specify the port number on the AD server to which the security gateway sends
authentication requests. Enter a number between 1 and 65535.
AD Domain Specify the Active Directory forest root domain name.
Domain Admin Enter the name of the user that is located in the container for Active Directory Users, who is
a member of the Domain Admin group.
Password Enter the password of the Domain Admin user account.
Advanced Click to open a screen where you can select to use Default or Custom advanced settings.
See Section 5.3.9.1 on page 118.
Click this icon to remove the server.
Add Click this button to create a new server.
My RADIUS Server
Name Enter a descriptive name for the server.
Server Address Enter the address of the RADIUS server.
Backup Server
Address
If the RADIUS server has a backup server, enter its address here.
Port Specify the port number on the RADIUS server to which the security gateway sends
authentication requests. Enter a number between 1 and 65535.
Secret Enter a password (up to 15 alphanumeric characters) as the key to be shared between the
external authentication server and the security gateway.
The key is not sent over the network. This key must be the same on the external
authentication server and the security gateway.
Advanced Click to open a screen where you can select to use Default or Custom advanced settings.
See Section 5.3.9.1 on page 118.

Chapter 5 Gateway
NCC User’s Guide
118
5.3.9.1 Advanced Settings
Click the Advanced column in the Gateway > Configure > My authentication server screen to access
this screen.
Figure 66 Gateway > Configure > My authentication server: Advanced
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Click this icon to remove the server.
Add Click this button to create a new server.
Table 52 Gateway > Configure > My authentication server (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 53 Gateway > Configure > My authentication server: Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Preset Select Default to use the pre-defined settings, or select Custom to configure your own
settings.
Timeout Specify the timeout period (between 1 and 300 seconds) before the security gateway
disconnects from the server. In this case, user authentication fails.
Search timeout occurs when either the user information is not in the server(s) or the AD or
server(s) is down.
Case-Sensitive User
Name
Click ON if the server checks the case of the user name. Otherwise, click OFF to not
configure your user name as case-sensitive.
NAS IP Address This field is only for RADIUS.
Type the IP address of the NAS (Network Access Server).
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
OK Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
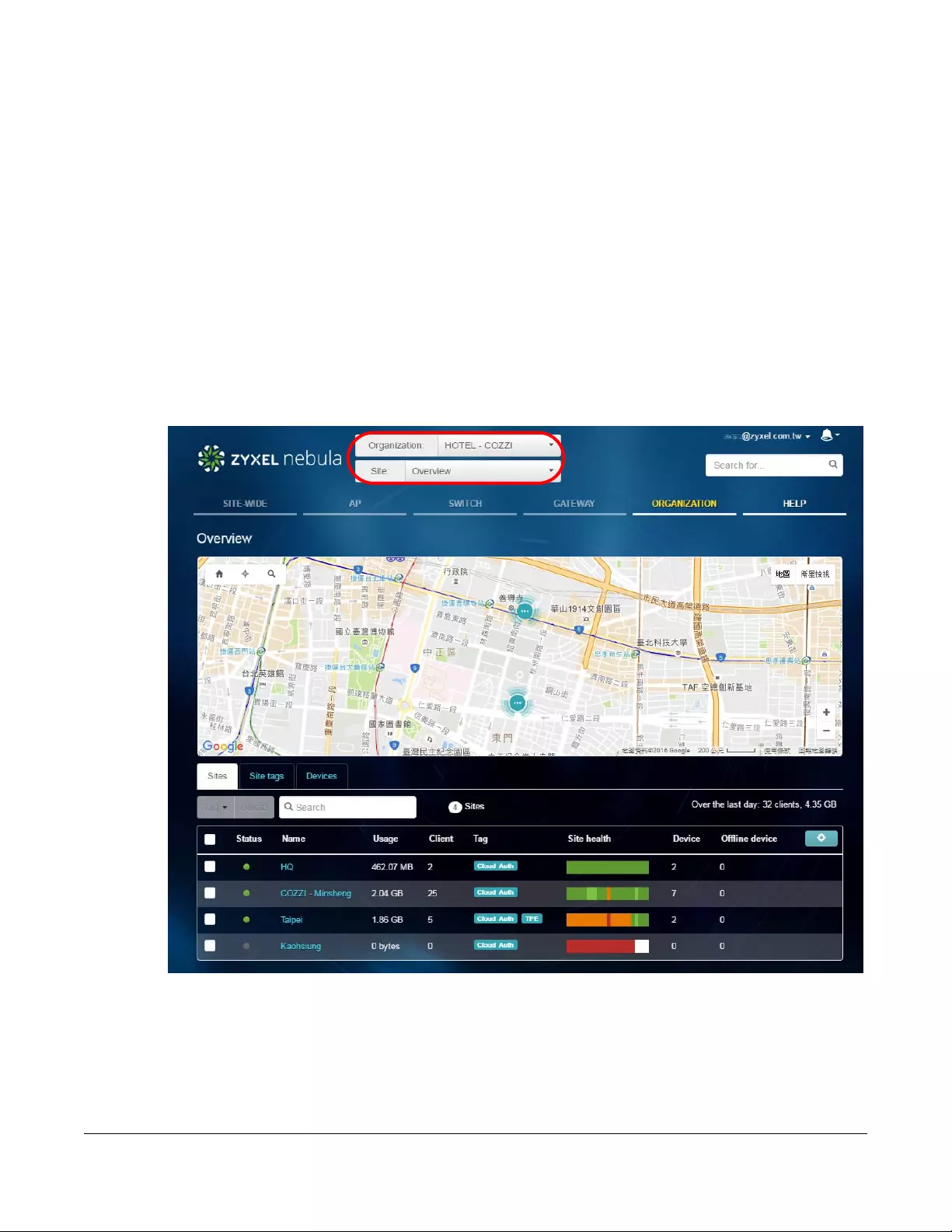
NCC User’s Guide
119
CHAPTER 6
Organization
6.1 Organization Overview
This menu shows you the site locations on the Google map and the summary of sites, site tags and
connected devices for the selected organization.
Click Organization > Overview to access this screen.
Figure 67 Organization > Overview: Sites
6.1.1 Sites
Click the Sites tab in the Overview screen to view detailed information of the sites which are associated
with the selected organization.
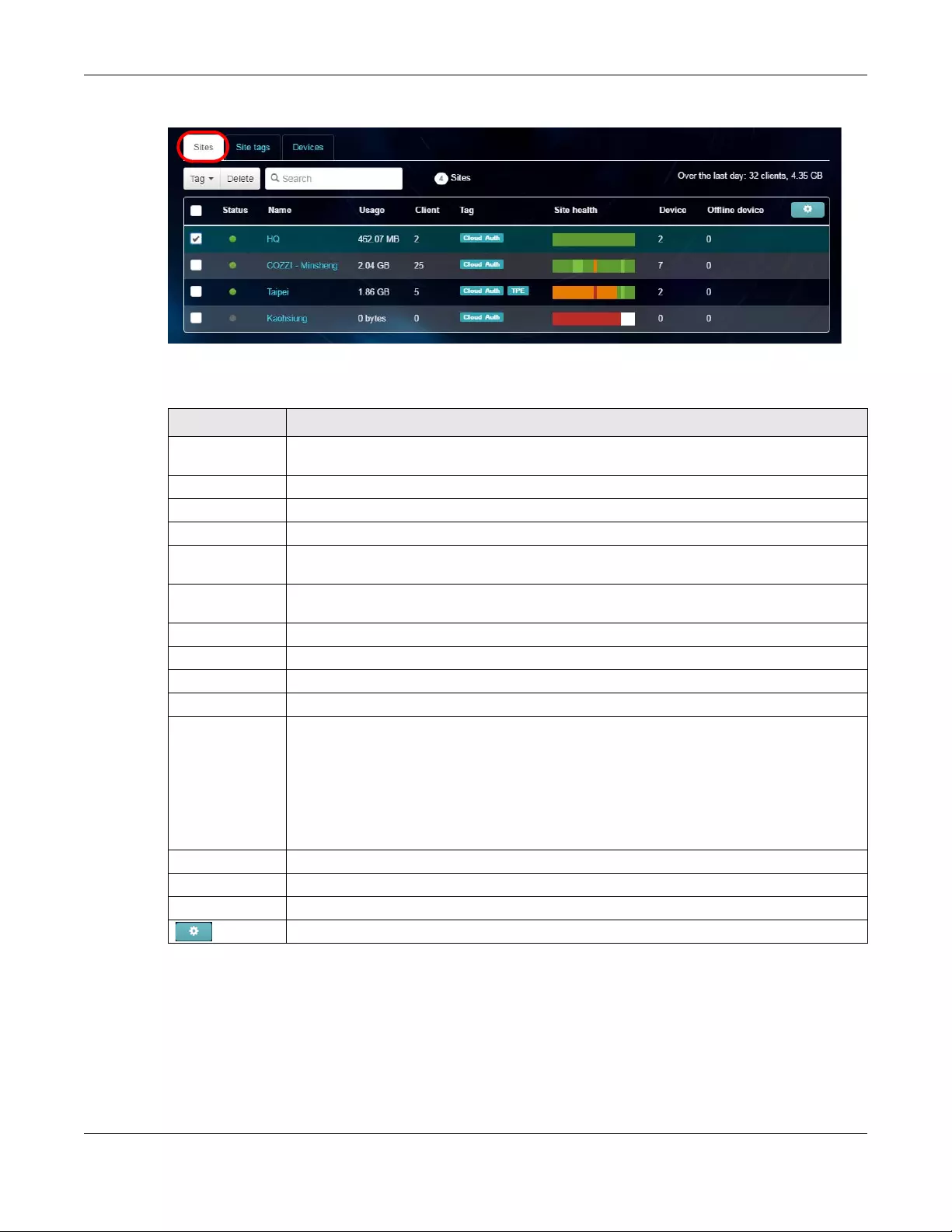
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
120
Figure 68 Organization > Overview: Sites
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
6.1.2 Site tags
Click the Site tags tab in the Overview screen to view the tags created and added to the sites for
monitoring or management purposes.
Table 54 Organization > Overview: Sites
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Tag Select one or multiple sites and click this button to create a new tag for the site(s) or delete an
existing tag.
Delete Select the site(s) and click this button to remove it.
Enter a key word as the filter criteria to filter the list of sites.
Site This shows the number of sites in this organization.
Over the last day This shows how many clients associated with the sites in this organization and the total amount
of data transmitted or received by the clients in the past day.
Status This shows whether the site is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), or goes off-line (red)
during the past day or has been off-line for at least one week (gray).
Name This shows the descriptive name of the site.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the site.
Client This shows the number of clients associated with the site.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag that is added to the site.
Site Health This shows the percentage of uptime in a given time interval to indicate the site’s network
availability.
• Green: 95-100% Network uptime
• Dark green: 75-95% Network uptime
• Brown: 50-75% Network uptime
• Red: <50% Network uptime
•Grey: No uptime data
Device This shows the total number of Nebula devices deployed in the site.
Offline device This shows the number of off-line Nebula devices deployed in the site.
% offline This shows what percentage of the connected clients are currently off-line.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.

Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
121
Figure 69 Organization > Overview: Site tags
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
6.1.3 Devices
Click the Devices tab in the Overview screen to view the detailed information about devices which are
connected to the sites in the selected organization.
Table 55 Organization > Overview: Site tags
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of tags.
Site This shows the number of site tags created and added to the sites in this organization.
Over the last day This shows how many clients associated with the sites in this organization and the total amount
of data transmitted or received by the clients in the past day.
Status This shows whether the device is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), or goes off-line
(red) during the past day or has been off-line for at least one week (gray).
Tag This shows the tag created and added to the site.
Site This shows the name of the site to which the tag is added.
Offline device This shows the number of off-line Nebula devices deployed in the site.
Client This shows the number of clients associated with the site.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the site.
Device This shows the total number of Nebula devices deployed in the site.
Offline site This shows the number of off-line sites to which the tag is added.
% offline This shows what percentage of the sites are currently off-line.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
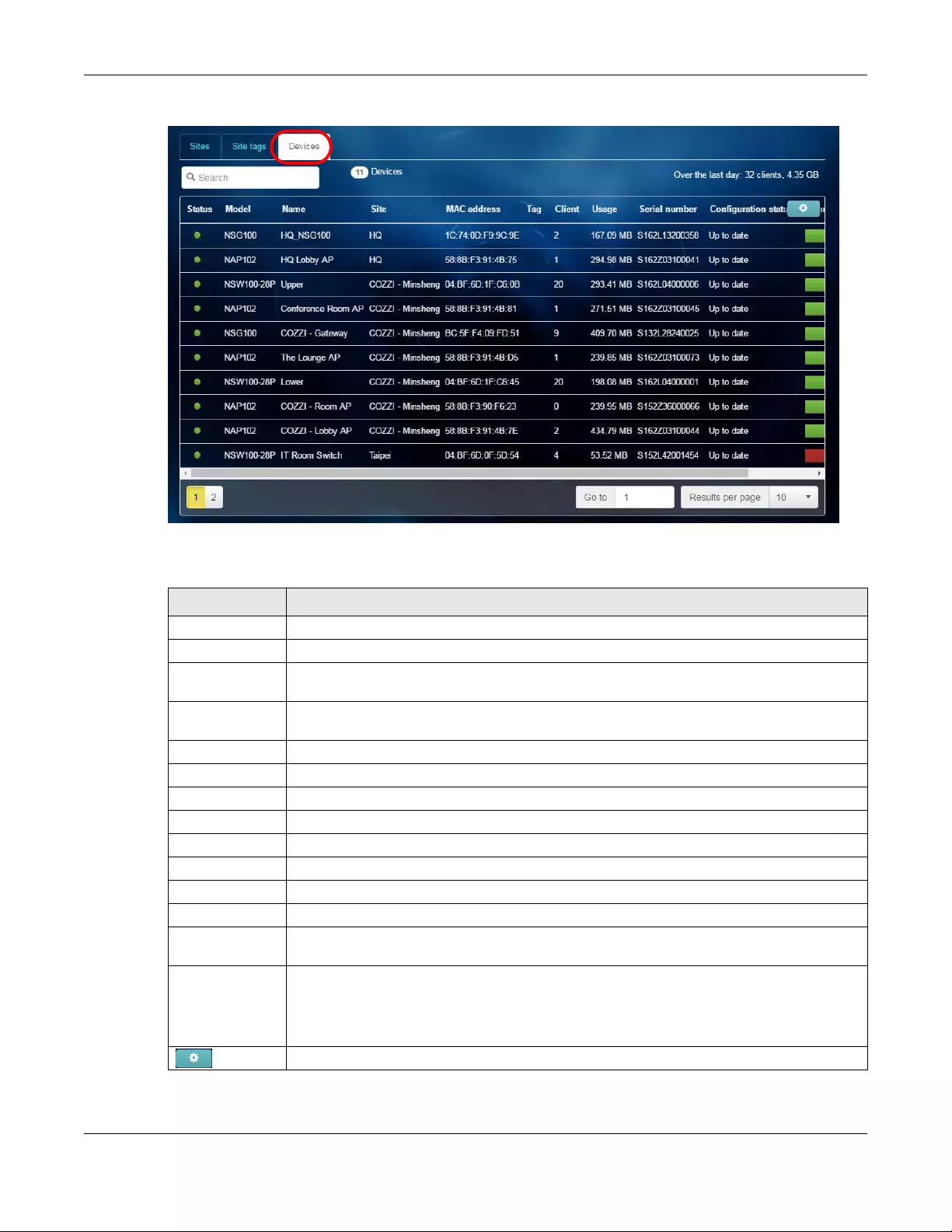
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
122
Figure 70 Organization > Overview: Devices
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 56 Organization > Overview: Devices
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of connected devices.
Devices This shows the number of Nebula devices assigned to the sites in this organization.
Over the last day This shows how many clients associated with the sites in this organization and the total amount
of data transmitted or received by the clients in the past day.
Status This shows whether the device is online (green), has generated alerts (yellow), or goes off-line
(red) during the past day or has been off-line for at least one week (gray).
Model This shows the model number of the device.
Name This shows the descriptive name of the device.
Site This shows the name of the site to which the device is connected.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the device.
Tag This shows the user-specified tag for the device.
Client This shows the number of the clients which are currently connected to the device.
Usage This shows the amount of data consumed by the device.
Serial Number This shows the serial number of the device.
Configuration
status
This shows whether the configuration on the device is up-to-date.
Connectivity This shows the device connection status. Nothing displays if the device is off-line.
The gray time slot indicates the connection to the NCC is down, and the green time slot
indicates the connection is up. Move the cursor over a time slot to see the actual date and
time when a device is connected or disconnected.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
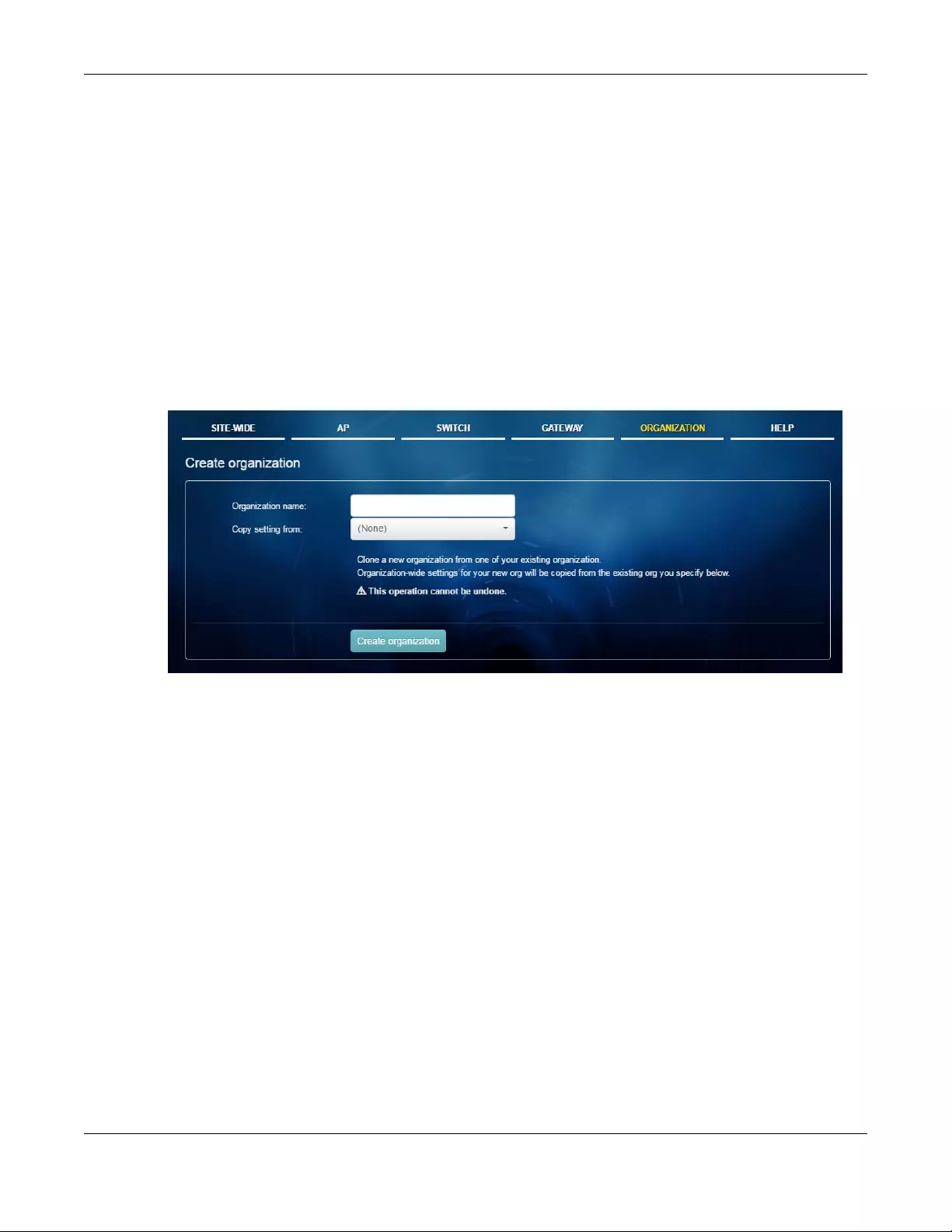
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
123
6.2 Create Organization
Use this screen to create an organization before you can create a site (network) in the organization and
add devices to the network in order to manage them via the NCC.
1Click Organization > Create Organization to access this screen.
2Enter a name for your organization.
3If you already have one or more than one organizations under your account and you want to copy the
organization settings of an existing one, select the organization name from the Copy setting from field
before clicking the Create organization button.
4Click the Create organization button to add a new organization.
Figure 71 Organization > Create Organization
6.3 Create Site
After an organization is created, click Organization > Create Site to add a site (network) to your
organization.
1Enter a descriptive name for the site.
2If you already have one or more than one sites in the organization and you want to copy the site settings
of an existing one, select the Clone from checkbox and then the site name.
3Enter the name of the registered device that is to be added to this site. If there is no registered Nebula
devices in the organization, you can click Register to claim one.
4Click Create site to add the new site to your organization.
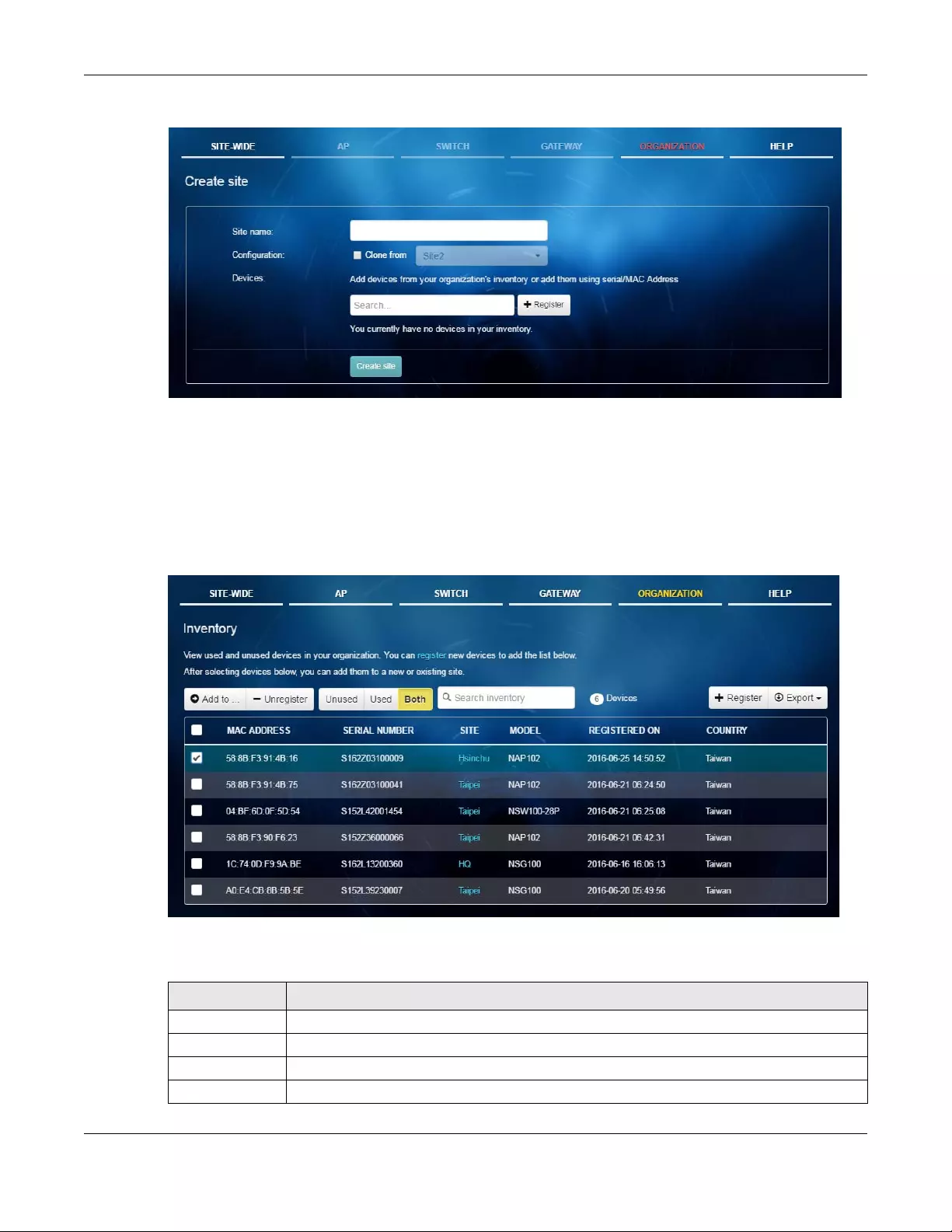
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
124
Figure 72 Organization > Create Site
6.4 Inventory
Use this screen to view and manage the Nebula devices you registered for the selected organization.
Click Organization > Inventory to access this screen.
Figure 73 Organization > Inventory
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 57 Organization > Inventory
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add to ... Click this button to assign the selected device(s) to an existing site.
Unregister Click this button to remove the selected device(s) from the organization.
Unused Click this button to show the Nebula device(s) which is not assigned to a site yet.
Used Click this button to show the Nebula device(s) which has been assigned to a site.
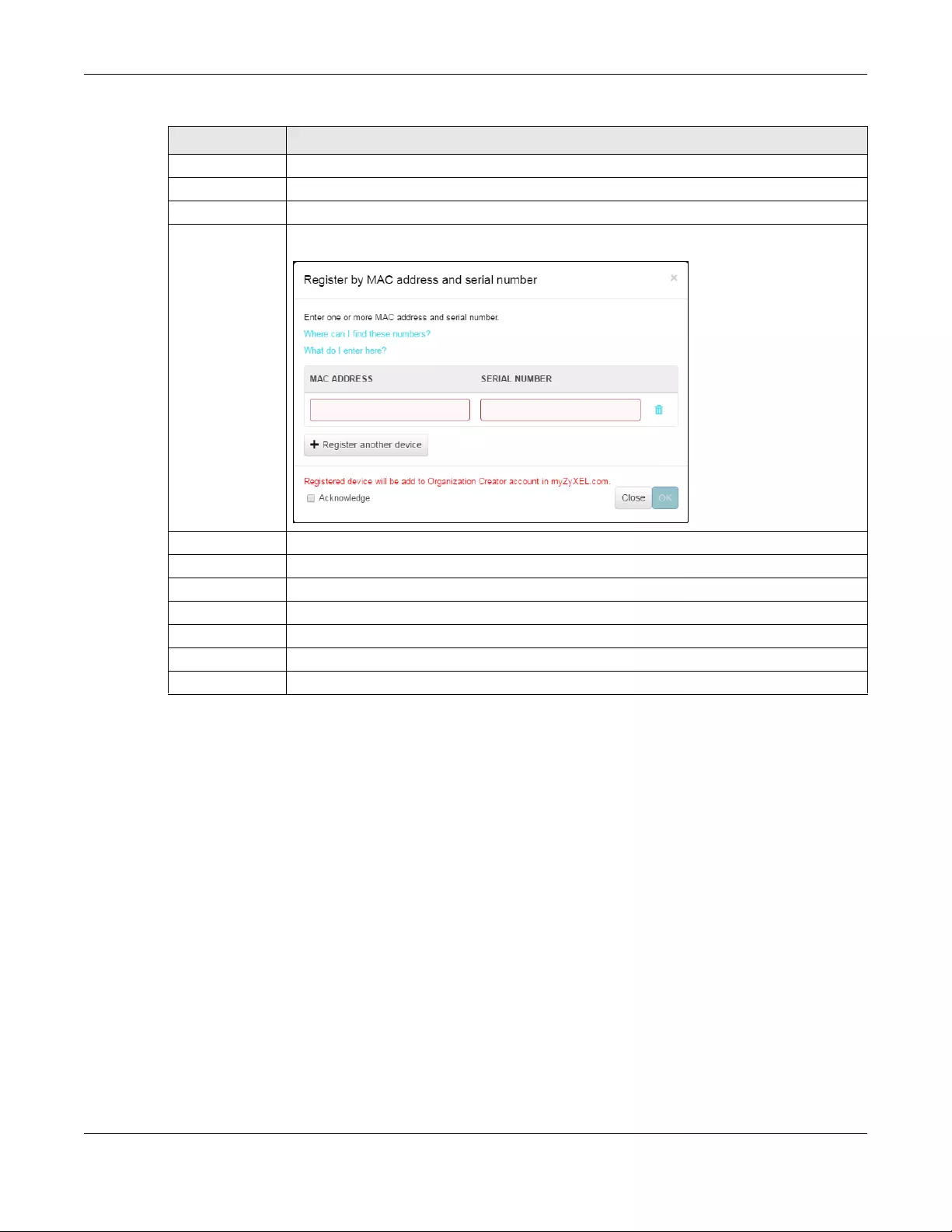
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
125
6.5 License Management
Use this screen to view and manage the licenses for Nebula devices in the organization. Click
Organization > License management to access this screen.
Note: Licenses for different Nebula devices in the same organization are re-calculated and
set to expire on the same day.
The license credit (device points) varies depending on the type and number of Nebula devices you are
managing and for how long you want to manage the devices using the NCC service.
Both Click this button to show all Nebula devices which are registered for the organization.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of connected devices.
Devices This shows the number of the devices in the list.
Register Click this button to display a screen where you can register a device by entering its MAC
address and serial number even before the device is connected to a site.
Export Click this button to save the device list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
MAC address This shows the MAC address of the device.
Serial number This shows the serial number of the device.
Site This shows the name of the site to which the device is connected.
Model This shows the model number of the device.
Registered on This shows the date and time that the device was registered at the NCC.
Country This shows the country where the device is located.
Table 57 Organization > Inventory (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
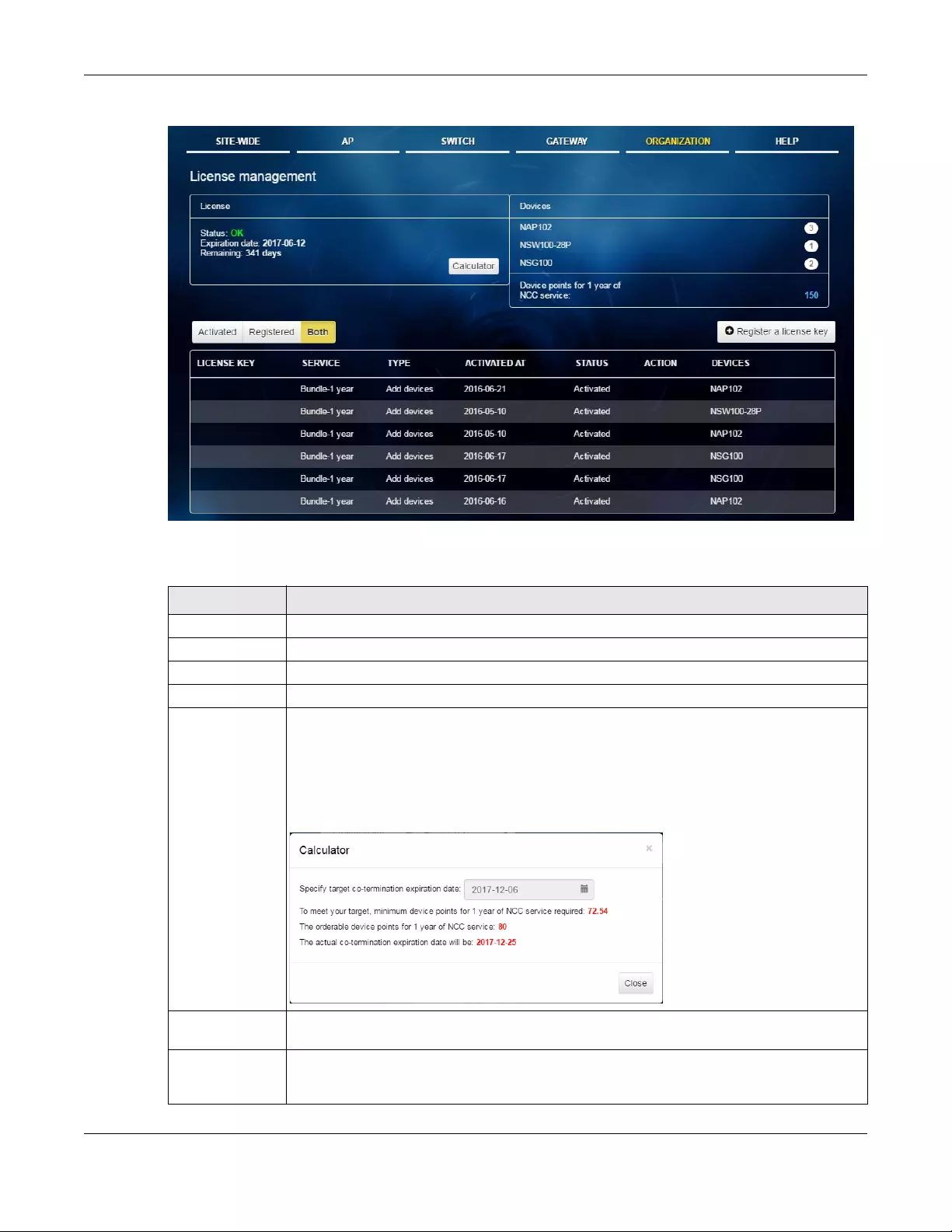
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
126
Figure 74 Organization > License management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 58 Organization > License management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
License
Status This shows whether the license is active.
Expiration date This shows the date the license expires.
Remaining This shows the number of days remaining before the license expires.
Calculator Click the button to open a screen where you can determine the additional license credit
(device points) you should get to allow more time for the service.
Select a date to which you want to extend the expiration date for the current license. You
should purchase the device points in increments of 10. Therefore, the required minimum device
points (based on the date you specified) might be different to the actual device points you
can purchase. The screen also shows the actual date the license will expire after you get the
device points.
Devices This shows the model name and the number of Nebula devices that you can manage with the
current license.
Device points for
1 year of NCC
service
This shows the number of device points (license credit) you need to have one-year NCC service
for the Nebula devices listed above in the Devices section.
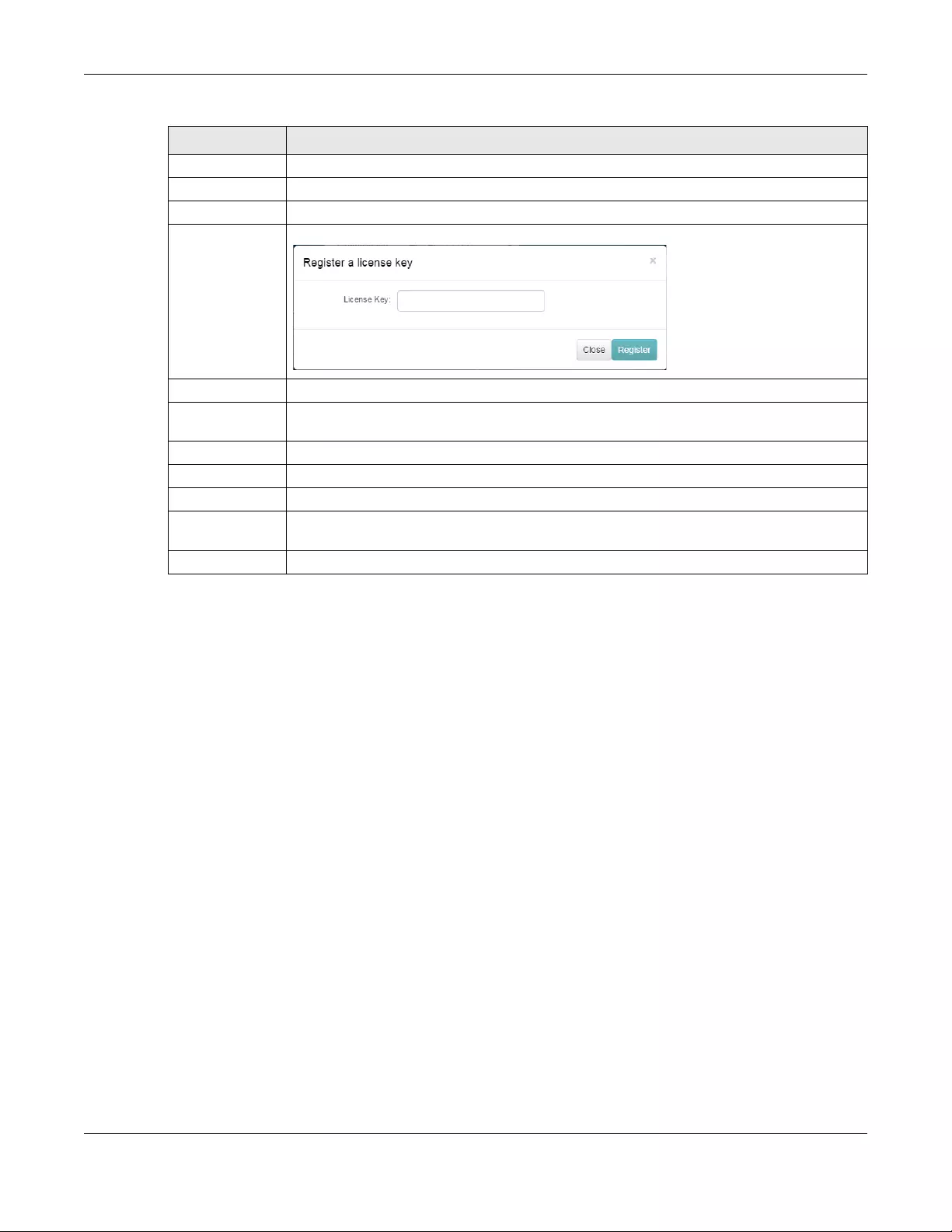
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
127
6.6 Change Log
Use this screen to view the logged messages for changes in the specified organization. Click
Organization > Change log to access this screen.
When the log is full, it deletes older entries one by one to make room for new ones.
Activated Click this button to show the service that has been activated.
Registered Click this button to show the service that has been registered.
Both Click this button to show the service that has been registered and also activated
Register a license
key
Click this button and enter your license key to register a new service.
License Key This shows the license key for the service.
Service This shows the type of the service. Each Nebula managed device is offered one-year NCC
service by default.
Type This shows how the service is registered.
Activated at This shows when the service is activated.
Status This shows whether the service is registered (and activated).
Action Click the Activate button to activate or extend the service with the license key. You can renew
the license’s expiration date.
Devices This shows the model name of the Nebula device which you can manage with the license.
Table 58 Organization > License management (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
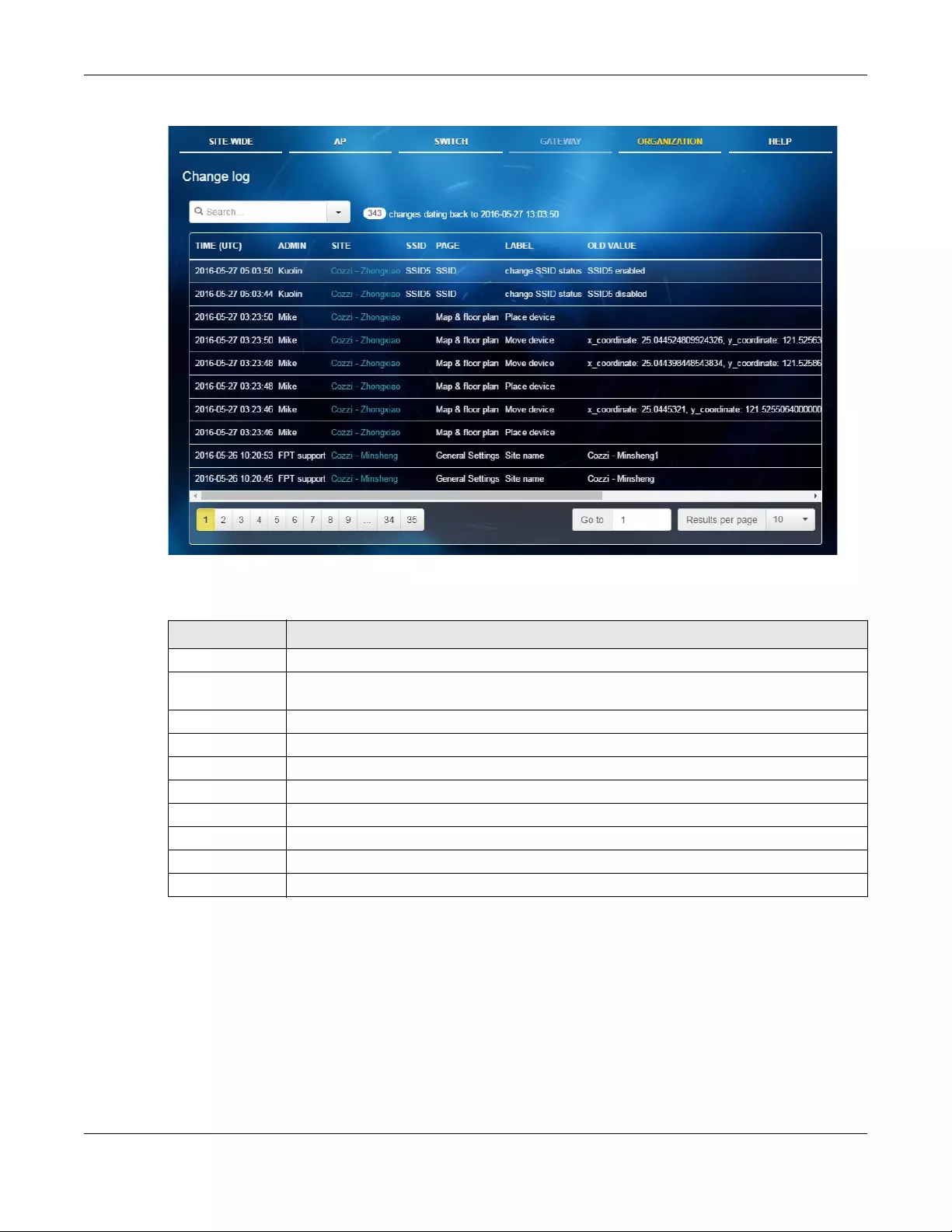
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
128
Figure 75 Organization > Change log
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
6.7 Organization Setting
Use this screen to change your general organization settings, such as the organization name and
security. Click Organization > Organization Setting to access this screen.
Table 59 Organization > Change log
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of logs.
This shows the date the last log was recorded and the total number of the log messages in the
list.
Time (UTC) This shows the date and time the log was recorded.
Admin This shows the name of the administrator who made the changes.
Site This shows the name of the site to which the change was applied.
SSID This shows the SSID name to which the change was applied.
Page This shows the name of the NCC menu in which the change was made.
Label This shows the reason for the log.
Old value This shows the old setting that was discarded and overwritten with the new attribute value.
New value This shows the new setting that was adopted.
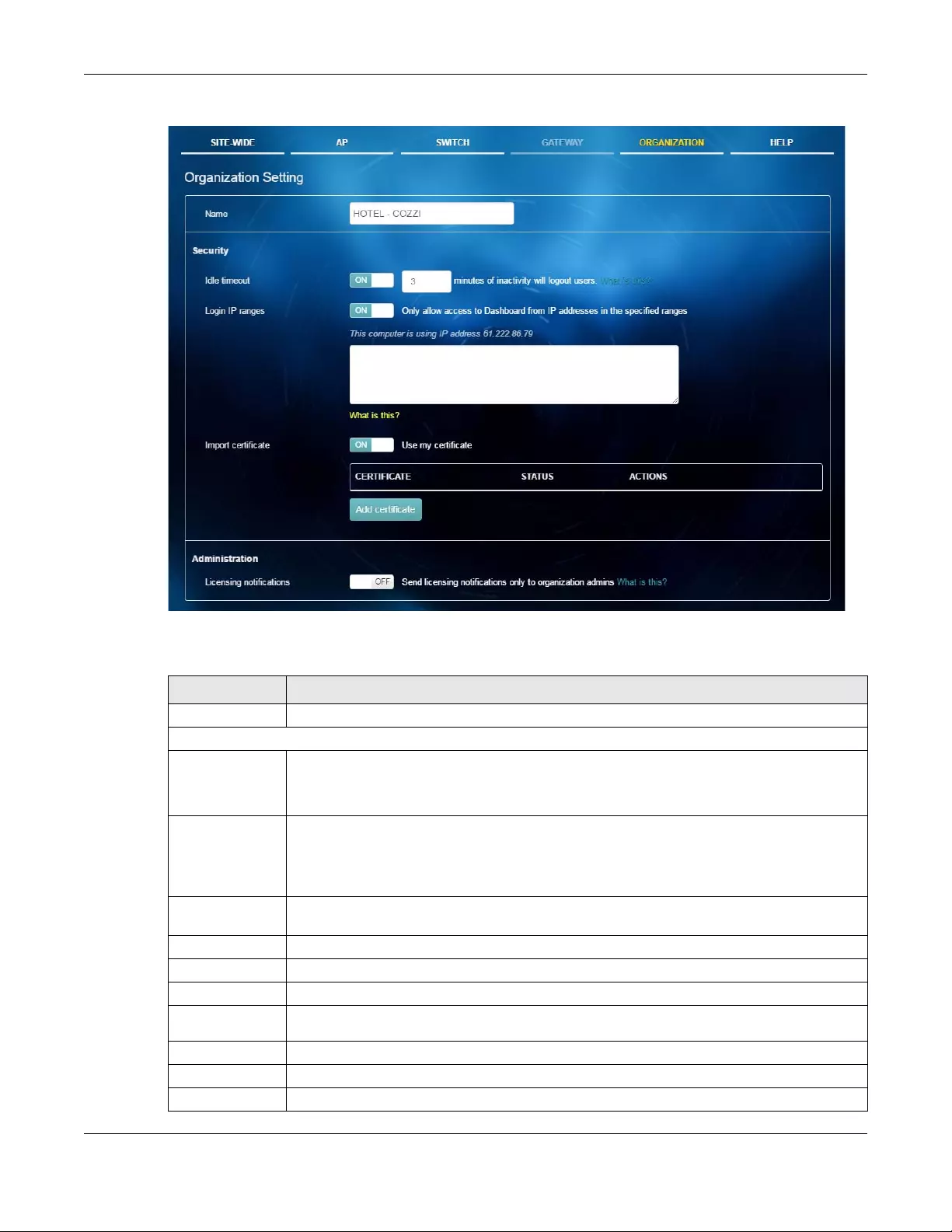
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
129
Figure 76 Organization > Organization Setting
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 60 Organization > Organization Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for the organization.
Security
Idle timeout Select ON and enter the number of minutes each user can be logged in and idle before the
NCC automatically logs out the user.
Select OFF if you don’t want the NCC to log out users.
Login IP ranges Select ON and specify the IP address range of the computers from which an administrator is
allowed to log into the NCC.
Select OFF to allow any IP address of the computer from which an administrator can log into
the NCC.
Import certificate Select ON to import a certificate that can be used by connected Nebula APs in WPA2
authentication.
Certificate This shows the name used to identify the certificate.
Status This shows whether the certificate is active.
Actions Click Edit to change the certificate name or password or replace the certificate.
Add
certificate
Click this button to save a certificate to the NCC.
Name Enter a name for the certificate.
File Path Click to find the certificate file you want to upload.
Password Enter the certificate file’s password.
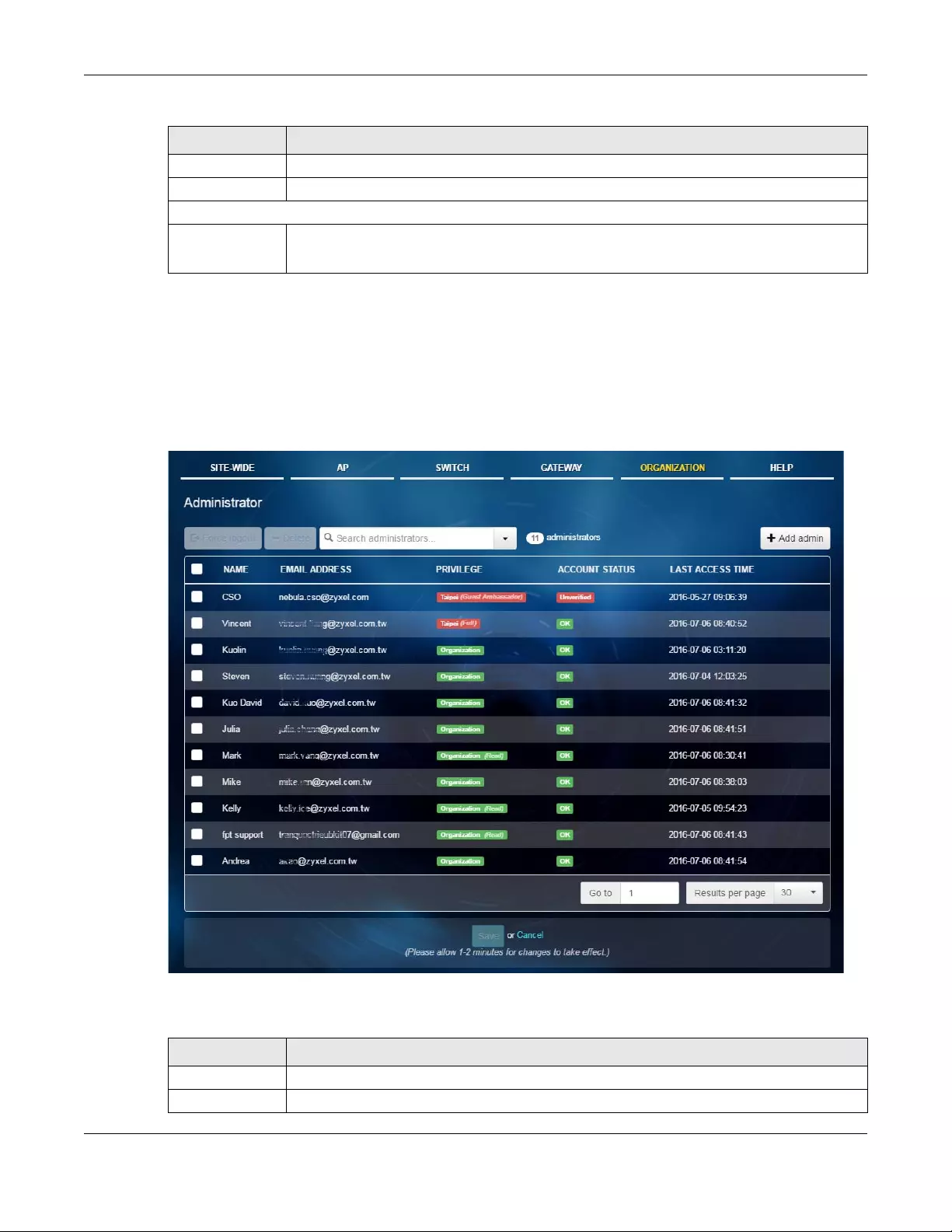
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
130
6.8 Administrator
Use this screen to view, manage and create administrator accounts for the specified organization. Click
Organization > Administrator to access this screen.
Figure 77 Organization > Administrator
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Update Click this button to save your changes.
Cancel Click this button to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
Administration
Licensing
notifications
Select ON to send license notifications to organization administrators of this organization.
Select OFF to send license notifications to both organization and site administrators.
Table 60 Organization > Organization Setting (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 61 Organization > Administrator
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Force logout Click this button to force the selected account(s) to log out the NCC.
Delete Click this button to remove the selected account(s).

Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
131
6.8.1 Create/Update Administrator
In the Organization > Administrator screen, click the Add admin button to create a new administrator
account or double-click an existing account entry to modify the account settings.
Figure 78 Organization > Administrator: Create/Update administrator
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Select your desired filter criteria to filter the list of administrator accounts.
This shows the number of administrator accounts in the list.
Add admin Click this button to create a new administrator account.
Name This shows the name of the administrator account.
Email address This shows the email address of the administrator account.
Privilege This shows whether the administrator account has read-only, monitor-only, guest ambassador,
or read and write (full) access to the organization and sites.
Account status This shows whether the administrator account has been validated.
Last access time This shows the last date and time traffic was sent from the administrator account.
Table 61 Organization > Administrator (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 62 Organization > Administrator: Create/Update administrator
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter a descriptive name for the administrator account.
Email Enter the email address of the administrator account, which is used to log into the NCC.
This field is read-only if you are editing an existing account.

Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
132
6.9 Cloud Authentication
Use this screen to view and manage the user accounts which are authenticated using the NCC user
database. Click Organization > Cloud Authentication to access this screen.
Organization
access
Set the administrator account’s access to the organization.
When an administrator account has read and write (Full) access, the administrator can create
or delete other administrator accounts, create or delete a site, and add or renew licenses for
Nebula devices in the organization.
Note: The account you use to create an organization is the administrator account
the has full access to that organization.
If you select Read-only, the administrator account can be the organization administrator (that
has no write access to the organization) and also be a site administrator.
If you select None, the administrator account can only be a site administrator.
Site This field is available only when you set the account’s organization access to Read-only or
None.
Select the site to which you want to set the account’s access.
Privilege This field is available only when you set the account’s organization access to Read-only or
None.
Set the administrator account’s access to the site.
You can select from Read-only, Monitor-only, Guest Ambassador, and Full (read and write).
An administrator account that has Guest Ambassador access can create, remove or mange
guest accounts using the Cloud Authentication screen (see Section 6.9 on page 132).
Add Click this button to create a new entry in order to configure the account’s access to another
site.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Create admin Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
Table 62 Organization > Administrator: Create/Update administrator (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
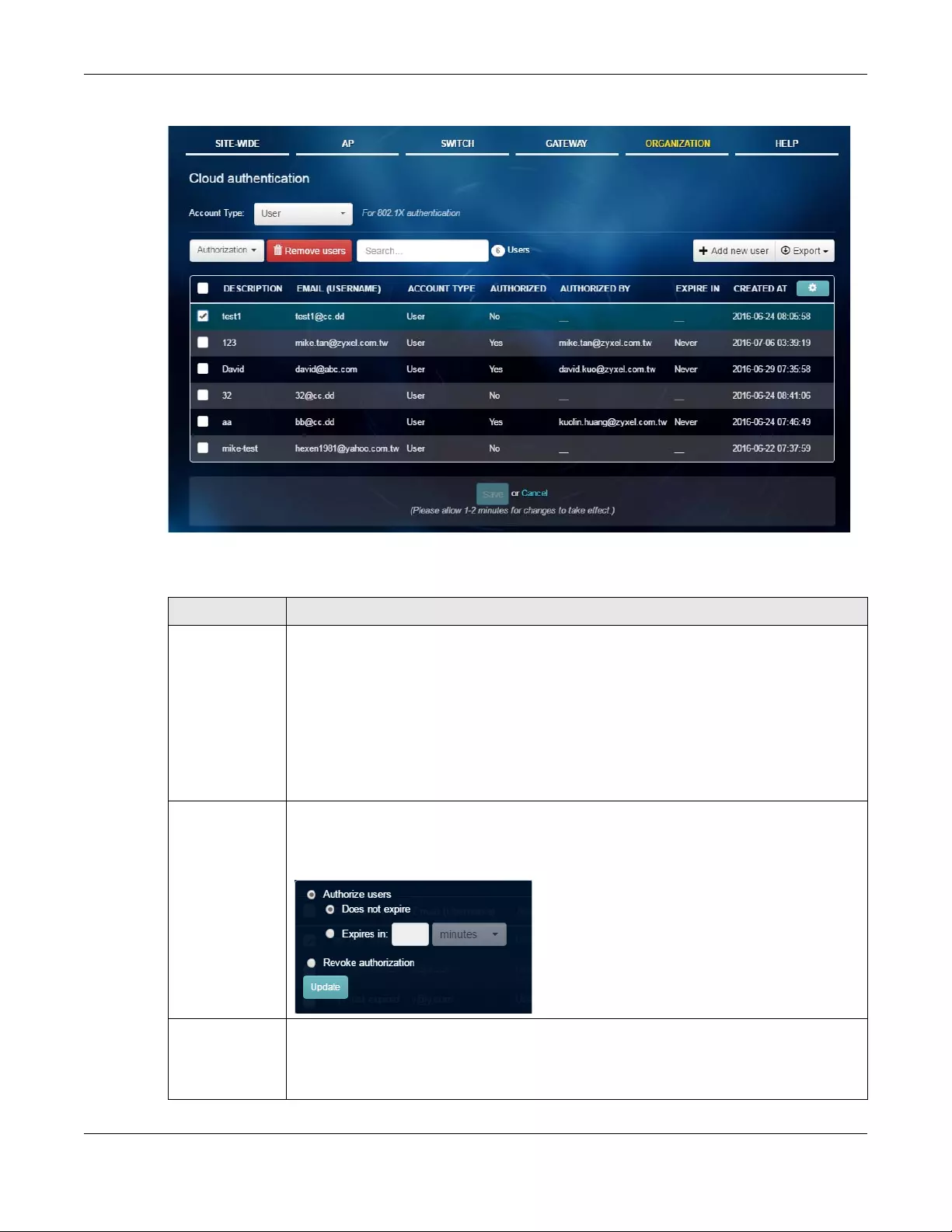
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
133
Figure 79 Organization > Cloud Authentication
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 63 Organization > Cloud Authentication
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Account Type Select the type of user accounts that you want to display or create.
User - an internal user that can gain access to the networks by authenticating with a RADIUS
server via the IEEE 802.1x or WPA2 authentication method or the captive portal.
MAC - an internal user that can gain access to the networks by authenticating with a RADIUS
server via the MAC-based authentication method.
Guest - a guest that can gain access to the networks via the captive portal.
VPN User - a L2TP VPN client that can gain access to the networks by authenticating with an AD
or RADIUS server.
Authorization This button is available only when your administrator account has full access to the
organization.
Select one or more than one user account and click this button to configure the authorization
settings for the selected user account(s).
Remove users This button is available only when your administrator account has full access to the
organization.
Select one or more than one user accounts and click this button to remove the selected user
account(s).

Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
134
6.9.1 Create/Update User
In the Organization > Cloud Authentication screen, click the Add user button to create a new user
account or double-click an existing account entry to modify the account settings.
Figure 80 Organization > Administrator: Create/Update user
Enter a key word as the filter criteria to filter the list of user accounts.
This shows how many user accounts of the selected type displayed in the list and how many
user accounts match the filter criteria.
Add new user Click this button to create a new user account.
Export Click this button to save the account list as a CSV or XML file to your computer.
Description This shows the descriptive name of the user account.
Email (Username) This field is available only when the account type is set to User, Guest or VPN User.
This shows the email address of the user account.
MAC address This field is available only when the account type is set to MAC.
This shows the MAC address of the user account.
Account type This shows the type of the user account.
Authorized This shows whether the user has been authorized or not.
Authorized by This shows the email address of the administrator account that authorized the user.
Expire in This shows the date and time that the account expires.
This shows - if authentication is disabled for this account.
This shows Never if the account never expires.
Created at This shows the date and time that the account was created.
Click this icon to display a greater or lesser number of configuration fields.
Table 63 Organization > Cloud Authentication (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 6 Organization
NCC User’s Guide
135
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 64 Organization > Administrator: Create/Update user
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Account type This is the type of the user account.
Description Enter a descriptive name for the account.
Email (Username) Enter the email address of the user account, which is used to log into the networks.
Password Enter the password of this user account. It can consist of 4 - 31 alphanumeric characters.
You can click Generate to have the NCC create a password for the account automatically,
and select the checkbox to send the password to the user via email.
Authorized Set whether you want to authorize the user of this account.
Expire in This field is available only when the user is authorized.
Click Change to specify the number of minutes/hours/days/weeks the user can be logged into
the network in one session before the user of this account has to log in again.
Otherwise, select Never and the user of this account will never be logged out.
Close Click this button to exit this screen without saving.
Print Click this button to print the account information.
Create user Click this button to save your changes and close the screen.
NCC User’s Guide
136
CHAPTER 7
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter with NCC and Nebula
devices.
None of the Nebula device LEDs turn on.
• Make sure that you have the power cord connected to the Nebula device and plugged in to an
appropriate power source. Make sure you have the Nebula device turned on. Check all cable
connections. See the related Quick Start Guide.
• If the LEDs still do not turn on, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you should contact
your local customer support.
The Nebula device PWR LED is red.
• The Nebula device has a power-related error. Disconnect and reconnect the power cord. Make sure
that you are using the included power cord for the Nebula device and it is plugged into an
appropriate power source. See the related Quick Start Guide.
• If the LED is still red, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you should contact your local
customer support.
I cannot access myZyXEL.com or the NCC portal.
• Check that you are using the correct URLs:
• MyZyXEL.COM: https://portal.myzyxel.com
• NCC: https://nebula.zyxel.com/
• Make sure your computer’s Ethernet card is installed and functioning properly.
• Check that you have Internet access. In your computer, click Start, (All) Programs, Accessories and
then Command Prompt. In the Command Prompt window, type ‘ping’ followed by a website such as
‘zyxel.com’. If you get a reply try to ping ‘nebula.zyxel.com’.
• Make sure you are using the correct web browser. Browsers supported are:
• Firefox 36.0.1 or later
• Chrome 41.0 or later
• IE 10 or later

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
NCC User’s Guide
137
I cannot log into myZyXEL.com or the NCC portal.
• Open your web browser and go to https://portal.myzyxel.com. Sign in with the correct email and
password. Click Not a Member Yet if you don't have a myZyXEL.com account and create an
account.
• Then go to https://nebula.zyxel.com using a supported web browser.
I cannot see my devices in the NCC Dashboard or the corresponding device monitor page.
• At the time of writing, you can only manage Zyxel Nebula APs, switches or security gateways via the
NCC.
• Make sure that you have registered your Nebula devices with the NCC. See Section 6.4 on page 124.
• Make sure that you have created an organization and site and add the devices to the site. See
Section 6.2 on page 123 and Section 6.3 on page 123.
• Check that the license has not expired.
7.1 Getting More Troubleshooting Help
Go to support.zyxel.com at the Zyxel website for other technical information on the CNA100 and NCC.

NCC User’s Guide
138
APPENDIX A
Customer Support
In the event of problems that cannot be solved by using this manual, you should contact your vendor. If
you cannot contact your vendor, then contact a Zyxel office for the region in which you bought the
device.
See http://www.zyxel.com/homepage.shtml and also
http://www.zyxel.com/about_zyxel/zyxel_worldwide.shtml for the latest information.
Please have the following information ready when you contact an office.
Required Information
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
Corporate Headquarters (Worldwide)
Taiwan
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com
Asia
China
• Zyxel Communications (Shanghai) Corp.
Zyxel Communications (Beijing) Corp.
Zyxel Communications (Tianjin) Corp.
• http://www.zyxel.cn
India
•Zyxel Technology India Pvt Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.in
Kazakhstan
•Zyxel Kazakhstan
• http://www.zyxel.kz

Appendix A Customer Support
NCC User’s Guide
139
Korea
• Zyxel Korea Corp.
• http://www.zyxel.kr
Malaysia
• Zyxel Malaysia Sdn Bhd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.my
Pakistan
• Zyxel Pakistan (Pvt.) Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.pk
Philippines
• Zyxel Philippines
• http://www.zyxel.com.ph
Singapore
• Zyxel Singapore Pte Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.sg
Taiwan
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/tw/zh/
Thailand
• Zyxel Thailand Co., Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.co.th
Vietnam
• Zyxel Communications Corporation-Vietnam Office
• http://www.zyxel.com/vn/vi
Europe
Austria
•Zyxel Deutschland GmbH
• http://www.zyxel.de
Belarus
•Zyxel BY
• http://www.zyxel.by

Appendix A Customer Support
NCC User’s Guide
140
Belgium
• Zyxel Communications B.V.
• http://www.zyxel.com/be/nl/
• http://www.zyxel.com/be/fr/
Bulgaria
•Zyxel България
• http://www.zyxel.com/bg/bg/
Czech Republic
• Zyxel Communications Czech s.r.o
• http://www.zyxel.cz
Denmark
• Zyxel Communications A/S
• http://www.zyxel.dk
Estonia
• Zyxel Estonia
• http://www.zyxel.com/ee/et/
Finland
• Zyxel Communications
• http://www.zyxel.fi
France
•Zyxel France
• http://www.zyxel.fr
Germany
•Zyxel Deutschland GmbH
• http://www.zyxel.de
Hungary
• Zyxel Hungary & SEE
• http://www.zyxel.hu
Italy
• Zyxel Communications Italy
• http://www.zyxel.it/

Appendix A Customer Support
NCC User’s Guide
141
Latvia
•Zyxel Latvia
• http://www.zyxel.com/lv/lv/homepage.shtml
Lithuania
•Zyxel Lithuania
• http://www.zyxel.com/lt/lt/homepage.shtml
Netherlands
• Zyxel Benelux
• http://www.zyxel.nl
Norway
• Zyxel Communications
• http://www.zyxel.no
Poland
• Zyxel Communications Poland
• http://www.zyxel.pl
Romania
• Zyxel Romania
• http://www.zyxel.com/ro/ro
Russia
• Zyxel Russia
• http://www.zyxel.ru
Slovakia
• Zyxel Communications Czech s.r.o. organizacna zlozka
• http://www.zyxel.sk
Spain
• Zyxel Communications ES Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.es
Sweden
• Zyxel Communications
• http://www.zyxel.se
Switzerland
•Studerus AG

Appendix A Customer Support
NCC User’s Guide
142
• http://www.zyxel.ch/
Turkey
• Zyxel Turkey A.S.
• http://www.zyxel.com.tr
UK
• Zyxel Communications UK Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.co.uk
Ukraine
•Zyxel Ukraine
• http://www.ua.zyxel.com
Latin America
Argentina
• Zyxel Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/ec/es/
Brazil
• Zyxel Communications Brasil Ltda.
• https://www.zyxel.com/br/pt/
Ecuador
• Zyxel Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/ec/es/
Middle East
Israel
• Zyxel Communication Corporation
• http://il.zyxel.com/homepage.shtml
Middle East
• Zyxel Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/me/en/

Appendix A Customer Support
NCC User’s Guide
143
North America
USA
• Zyxel Communications, Inc. - North America Headquarters
• http://www.zyxel.com/us/en/
Oceania
Australia
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/au/en/
Africa
South Africa
• Nology (Pty) Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.co.za

NCC User’s Guide
144
APPENDIX B
Legal Information
Copyright
Copyright © 2016 by Zyxel Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any
language, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of Zyxel Communications Corporation.
Published by Zyxel Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
Zyxel does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software described herein. Neither does it convey any
license under its patent rights nor the patent rights of others. Zyxel further reserves the right to make changes in any products described herein
without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Viewing Certifications
Go to http://www.zyxel.com to view this product’s documentation and certifications.
Zyxel Limited Warranty
Zyxel warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects in material or workmanship for a specific period (the
Warranty Period) from the date of purchase. The Warranty Period varies by region. Check with your vendor and/or the authorized Zyxel local
distributor for details about the Warranty Period of this product. During the warranty period, and upon proof of purchase, should the product
have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship and/or materials, Zyxel will, at its discretion, repair or replace the defective products or
components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product or components to
proper operating condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent product of equal or higher value,
and will be solely at the discretion of Zyxel. This warranty shall not apply if the product has been modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by
an act of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions.
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties,
express or implied, including any implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. Zyxel shall in no event be held
liable for indirect or consequential damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact your vendor. You may also refer to the warranty policy for the region in which you bought the
device at http://www.zyxel.com/web/support_warranty_info.php.
Registration
Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and information at www.zyxel.com for global products, or at
www.us.zyxel.com for North American products.
Open Source Licenses
This product contains in part some free software distributed under GPL license terms and/or GPL like licenses. Open source licenses are provided
with the firmware package. You can download the latest firmware at www.zyxel.com. If you cannot find it there, contact your vendor or Zyxel
Technical Support at support@zyxel.com.tw.
To obtain the source code covered under those Licenses, please contact your vendor or Zyxel Technical Support at support@zyxel.com.