Table of Contents
ASUS ROG STRIX Z390-I GAMING User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for ROG STRIX Z390-I GAMING by ASUS which is a product in the Motherboards category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals
RAID
Conguration
Guide
Motherboard

ii
E14794
Revised Edition V4
August 2018
Copyright © 2018 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form or by
any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express
written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modied or altered, unless
such repair, modication of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2) the serial number of the
product is defaced or missing.
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS
DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS,
LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE),
EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM
ANY DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR PRODUCT.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR
INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE,
AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO
RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MAY APPEAR IN
THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or
copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identication or explanation and to the
owners’ benet, without intent to infringe.
Offer to Provide Source Code of Certain Software
This product contains copyrighted software that is licensed under the General Public License (“GPL”),
under the Lesser General Public License Version (“LGPL”) and/or other Free Open Source Software
Licenses. Such software in this product is distributed without any warranty to the extent permitted by the
applicable law. Copies of these licenses are included in this product.
Where the applicable license entitles you to the source code of such software and/or other additional
data, you may obtain it for a period of three years after our last shipment of the product, either
(1) for free by downloading it from https://www.asus.com/support/
or
(2) for the cost of reproduction and shipment, which is dependent on the preferred carrier and the location
where you want to have it shipped to, by sending a request to:
ASUSTeK Computer Inc.
Legal Compliance Dept.
15 Li Te Rd.,
Beitou, Taipei 112
Taiwan
In your request please provide the name, model number and version, as stated in the About Box of the
product for which you wish to obtain the corresponding source code and your contact details so that we
can coordinate the terms and cost of shipment with you.
The source code will be distributed WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY and licensed under the same license as
the corresponding binary/object code.
This offer is valid to anyone in receipt of this information.
ASUSTeK is eager to duly provide complete source code as required under various Free Open Source
Software licenses. If however you encounter any problems in obtaining the full corresponding source
code we would be much obliged if you give us a notication to the email address gpl@asus.com, stating
the product and describing the problem (please DO NOT send large attachments such as source code
archives, etc. to this email address).

iii
Contents
About this guide ......................................................................................................... iv
Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Configuration
1.1 Intel® RAID configurations ........................................................................1-5
1.1.1 RAID denitions .......................................................................... 1-5
1.1.2 Installing storage devices ............................................................ 1-5
1.1.3 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology in UEFI BIOS .......................... 1-6
1.1.4 Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU in UEFI BIOS .................................. 1-10
1.1.5 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Option ROM utility ................ 1-14
1.2 Installing the RAID controller driver during
Windows® 10 OS installation ..................................................................1-19
Chapter 2: AMD RAID Configuration
2.1 RAID configurations ..................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 RAID denitions .......................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 Installing storage devices ............................................................ 2-2
2.1.3 RaidXpert2 Conguration Utility in UEFI BIOS ........................... 2-2
2.2 Installing the RAID controller driver during
Windows® 10 OS installation ....................................................................2-6

iv
About this guide
This guide contains information that you need to create RAID congurations. You can create
different RAID congurations based on your motherboard chipset and software.
The screenshots in this guide are for reference only. The screenshots may vary with
models, but the congurations steps are similar.
How this guide is organized
This guide contains the following parts:
• Chapter1:Intel® RAID Configuration
This chapter describes the Intel® RAID congurations and lists the setup procedures
to create Intel® RAID congurations.
• Chapter2:AMDRAIDConfiguration
This chapter describes the AMD RAID congurations and lists the setup procedures to
create AMD RAID congurations.
Where to find more information
The ASUS website (www.asus.com) provides updated information on ASUS hardware and
software products.
RAID Conguration Guide 1-5
Intel® RAID Conguration
Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
1
1.1 Intel® RAID configurations
If your motherboard supports Intel® Rapid Storage Technology, you can create RAID 0,
RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 10 congurations.
Please refer to your motherboard’s user manual for details on the actual supported RAID
congurations.
If you want to install a Windows® operating system to a hard disk drive included in a RAID
set, you have to create a RAID driver disk and load the RAID driver during OS installation.
Refer to section 1.2 Creating a RAID driver disk for details.
1.1.1 RAID definitions
RAID 0 (Data striping) optimizes two identical hard disk drives to read and write data in
parallel, interleaved stacks. Two hard disks perform the same work as a single drive but at a
sustained data transfer rate, double that of a single disk alone, thus improving data access
and storage. Use of two new identical hard disk drives is required for this setup.
RAID 1 (Data mirroring) copies and maintains an identical image of data from one drive to
a second drive. If one drive fails, the disk array management software directs all applications
to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive. This RAID
conguration provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system.
Use two new drives or use an existing drive and a new drive for this setup. The new drive
must be of the same size or larger than the existing drive.
RAID 5 stripes both data and parity information across three or more hard disk drives.
Among the advantages of RAID 5 conguration include better HDD performance, fault
tolerance, and higher storage capacity. The RAID 5 conguration is best suited for
transaction processing, relational database applications, enterprise resource planning, and
other business systems. Use a minimum of three identical hard disk drives for this setup.
RAID 10 is data striping and data mirroring combined without parity (redundancy data)
having to be calculated and written. With the RAID 10 conguration you get all the benets
of both RAID 0 and RAID 1 congurations. Use four new hard disk drives or use an existing
drive and three new drives for this setup.
1.1.2 Installing storage devices
The motherboard supports Serial ATA hard disk drives and PCIE SSD storage devices. For
optimal performance, install identical drives of the same model and capacity when creating
a disk array.
Refer to Chapter 2 in your motherboard’s user manual for details on installing storage
devices to your motherboard.

1-6 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
1.1.3 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology in UEFI BIOS
To enter the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology in UEFI BIOS:
1. Enter the BIOS Setup during POST.
Refer to Chapter 3 in your motherboard’s user manual for details on entering and
navigating through the BIOS Setup.
2. Go to Advanced > PCH Storage Configuration, then set SATA Mode Selection to
[Intel RST Premium With Intel Optane System Acceleration (RAID)].
Due to chipset limitation, when SATA ports are set to RAID mode, all SATA ports run at
RAID mode together.
3. Congure additional settings for your storage device and RAID conguration:
• If you are using SATA storage devices, no additional settings are required.
Please proceed to next step.
• If you are using onboard M.2 cards, go to Advanced > PCH Storage
Configuration, then set all the corresponding M.2 PCIE Storage RAID Support
to [Enabled].
• If you are using Hyper M.2 cards or PCIE SSDs, go to Advanced > CPU
Storage Configuration, then set all the corresponding PCIE slots to [Hyper M.2
X16] or [PCIE X4 SSD Card] accordingly.
The Hyper M.2 card is purchased separately.
4. Go to Boot > CSM (Compatibility Support Module), then set Launch CSM to
[Disabled].
5. Save your changes and exit the BIOS Setup, then enter the BIOS Setup again.
6. Go to the Advanced > Intel(R) Rapid Storage Technology to display the Intel®
Rapid Storage Technology menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 1-7
Creating a RAID set
To create a RAID set:
1. From the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology menu, select Create RAID Volume and
press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
2. When the Name item is selected, enter a name for the RAID set and press <Enter>.
3. When the RAID Level item is selected, press <Enter> to select the RAID level to
create, and then press <Enter>.
4. Under Select Disks, press <Enter> and select X for the disks you want to include in
the RAID set.

1-8 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
5. When the Strip Size item is selected, press <Enter> to select strip size for the RAID
array (for RAID 0, 10 and 5 only), and then press <Enter>. The available strip size
values range from 4 KB to 128 KB. The following are typical values:
- RAID 0: 128 KB
- RAID 10: 64 KB
- RAID 5: 64 KB
We recommend a lower strip size for server systems, and a higher strip size for
multimedia computer systems used mainly for audio and video editing.
6. When the Capacity (MB) item is selected, enter the RAID volume capacity that you
want and press <Enter>. The default value indicates the maximum allowed capacity.
7. When the Create Volume item is selected, press <Enter> to create the RAID volume
and return to the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 1-9
Deleting a RAID set
Be cautious when deleting a RAID set. You will lose all data on the hard disk drives when
you delete a RAID set.
To delete a RAID set:
1. From the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology menu, select the RAID volume you want to
delete and press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
2. When the Delete item is selected, press <Enter>, then select Yes to delete the RAID
volume and return to the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology menu, or select No to
cancel.

1-10 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
1.1.4 Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU in UEFI BIOS
Some motherboards support Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU with RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and
RAID 10 solution. RAID 0 can be created without a KEY module, while RAID 1, RAID 5, and
RAID 10 requires a KEY module.
• The KEY module is purchased separately.
• The Hyper M.2 x16 card is purchased separately.
• Due to CPU behavior, CPU RAID functions with Intel® CPU RSTe only supports Intel®
Core™ X-series Processors (6-core or above) and Intel® SSD modules.
• Refer to section Internal connectors in your motherboard’s user manual for the
location of the VROC_HW_KEY connector.
If you plan on using the CPU RAID conguration spanned across different PCIE slots
as OS drives, please install the Hyper M.2 x16 cards into supported PCIE slots. Refer to
section Expansion slots in your motherboard’s user manual for more information on the
PCIE slots.
To enter the Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU in UEFI BIOS:
1. Enter the BIOS Setup during POST.
Refer to Chapter 3 in your motherboard’s user manual for details on entering and
navigating through the BIOS Setup.
2. Go to Boot > CSM (Compatibility Support Module), then set Launch CSM to
[Disabled].
3. Go to the Advanced > CPU Storage Configuration, then set the PCIE slot(s) that
you have installed the Hyper M.2 x16 card(s) or PCIE X4 SSD card(s) to [Hyper M.2
X16] or [PCIE X4 SSD Card] accordingly.
4. Save your changes and exit the BIOS Setup, then enter the BIOS Setup again.
5. Go to the Advanced > Intel(R) Virtual Raid on CPU to display the Intel® Virtual Raid
on CPU menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 1-11
Creating a RAID set
To create a RAID set:
1. From the Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU menu, select Create RAID Volume and press
<Enter>. The following screen appears:
2. When the Name item is selected, enter a name for the RAID set and press <Enter>.
3. When the RAID Level item is selected, press <Enter> to select the RAID level to
create, and then press <Enter>.
4. When the Enable RAID spanned over VMD Controllers item is selected, press
<Enter> and select X to enable this function.
5. Under Select Disks, press <Enter> and select X for the disks you want to include in
the RAID set.

1-12 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
6. When the Strip Size item is selected, press <Enter> to select strip size for the RAID
array (for RAID 0, 10 and 5 only), and then press <Enter>. The available strip size
values range from 4 KB to 128 KB. The following are typical values:
- RAID 0: 128 KB
- RAID 10: 64 KB
- RAID 5: 64 KB
We recommend a lower strip size for server systems, and a higher strip size for
multimedia computer systems used mainly for audio and video editing.
7. When the Capacity (MB) item is selected, enter the RAID volume capacity that you
want and press <Enter>. The default value indicates the maximum allowed capacity.
8. When the Create Volume item is selected, press <Enter> to create the RAID volume
and return to the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 1-13
Deleting a RAID set
Be cautious when deleting a RAID set. You will lose all data on the hard disk drives when
you delete a RAID set.
To delete a RAID set:
1. From the Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU menu, select the RAID volume you want to delete
and press <Enter>. The following screen appears:
2. When the Delete item is selected, press <Enter>, then select Yes to delete the RAID
volume and return to the Intel® Virtual Raid on CPU menu, or select No to cancel.
1-14 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
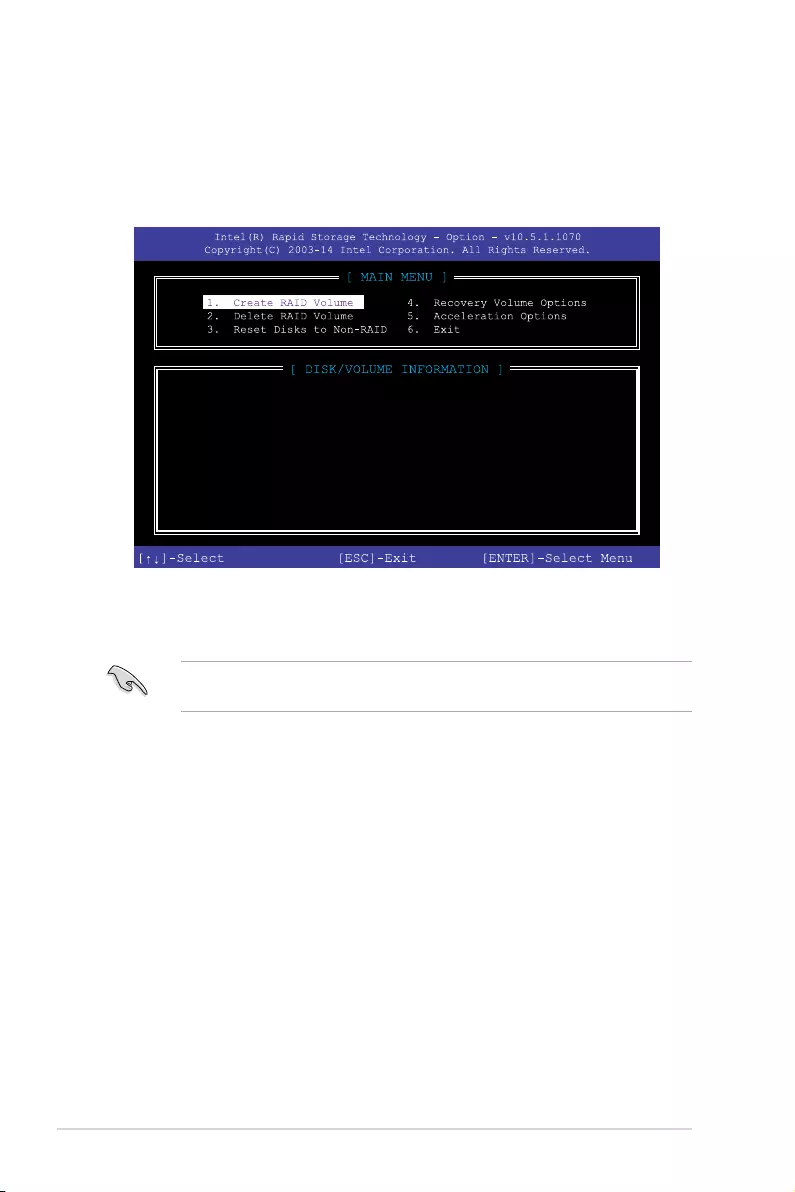
1.1.5 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Option ROM utility
To enter the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Option ROM utility:
1. Turn on the system.
2. During POST, press <Ctrl> + <I> to display the utility main menu.
The navigation keys at the bottom of the screen allow you to move through the menus
and select the menu options.
The RAID BIOS setup screens shown in this section are for reference only and may not
exactly match the items on your screen.
RAID Volumes:
None defined.
Physical Devices:
Port Device Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 ST3160812AS 9LS0HJA4 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
1 ST3160812AS 9LS0F4HL 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
2 ST3160812AS 3LS0JYL8 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
3 ST3160812AS 9LS0BJ5H 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk

RAID Conguration Guide 1-15
Creating a RAID set
To create a RAID set:
1. From the utility main menu, select 1. Create RAID Volume and press <Enter>. The
following screen appears:
2. Enter a name for the RAID set and press <Enter>.
3. When the RAID Level item is selected, press the up/down arrow key to select a RAID
level to create, and then press <Enter>.
4. When the Disks item is selected, press <Enter> to select the hard disk drives you
want to include in the RAID set. The SELECT DISKS screen appears:
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters
and is 16 characters or less.
[HELP]
Name: Volume 0
RAID Level: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Disks: dssdsdsds
Strip Size:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Capacity:aaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Sync:aaaaaaaaaa
Create volume
[SELECT DISKS]
Port Device Model Serial # Size Status
0 ST3160812AS 9LS0HJA4 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
1 ST3160812AS 9LS0F4HL 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
2 ST3160812AS 3LS0JYL8 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
3 ST3160812AS 9LS0BJ5H 149.0GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 to use in creating the volume.
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [ENTER]-Done

1-16 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
5. Use the up/down arrow key to select a drive, and then press <Space> to select. A
small triangle marks the selected drive. Press <Enter> after completing your selection.
6. Use the up/down arrow key to select the strip size for the RAID array (for RAID 0, 10
and 5 only), and then press <Enter>. The available strip size values range from 4 KB
to 128 KB. The following are typical values:
- RAID 0: 128 KB
- RAID 10: 64 KB
- RAID 5: 64 KB
We recommend a lower strip size for server systems, and a higher strip size for
multimedia computer systems used mainly for audio and video editing.
7. When the Capacity item is selected, enter the RAID volume capacity that you want
and press <Enter>. The default value indicates the maximum allowed capacity.
8. When the Create Volume item is selected, press <Enter>. The following warning
message appears:
9. Press <Y> to create the RAID volume and return to the main menu, or <N> to go back
to the CREATE VOLUME menu.
WARNING: ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST.
Are you sure you want to create this volume? (Y/N)

RAID Conguration Guide 1-17
Deleting a RAID set
Be cautious when deleting a RAID set. You will lose all data on the hard disk drives when
you delete a RAID set.
To delete a RAID set:
1. From the utility main menu, select 2. Delete RAID Volume and press <Enter>. The
following screen appears:
2. Use the up/down arrow key to select the RAID set you want to delete, and then press
<Delete>. The following warning message appears:
3. Press <Y> to delete the RAID set and return to the utility main menu, or press <N> to
return to the DELETE VOLUME menu.
Deleting a volume will reset the disks to non-RAID.
WARNING: ALL DISK DATA WILL BE DELETED.
(This does not apply to Recovery volumes)
[HELP]
[DELETE VOLUME MENU]
Name Level Drives Capacity Status Bootable
Volume0 RAID0 (Stripe) 2 298.0GB Normal Yes
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Previous Menu [DEL]-Delete Volume
ALL DATA IN THE VOLUME WILL BE LOST!
(This does not apply to Recovery volumes)
Are you sure you want to delete “Volume0”? (Y/N):
[DELETE VOLUME VERIFICATION]

1-18 Chapter 1: Intel® RAID Conguration
Exiting the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Option ROM utility
To exit the utility:
1. From the utility main menu, select 6. Exit, then press <Enter>. The following warning
message appears:
2. Press <Y> to exit or press <N> to return to the utility main menu.
Are you sure you want to exit? (Y/N):
[CONFIRM EXIT]
RAID Conguration Guide 1-19
1.2 Installing the RAID controller driver during
Windows® 10 OS installation
After creating the RAID sets, you are now ready to install an operating system to the
independent drives or bootable array. This part provides the instructions on how to install the
RAID controller drivers during OS installation.
If you plan on using the CPU RAID conguration spanned across different PCIE slots as
OS drives, please install the Hyper M.2 x16 cards to the supported PCIE slots. Refer to
section Expansion slots in your motherboard’s user manual for more information on the
PCIE slots.
To install the RAID controller driver when installing Windows® 10 OS:
1. Boot the computer using the Windows® 10 OS installation disc. Follow the screen
instructions to start installing Windows® 10.
2. When prompted to choose a type of installation, click Custom: Install Windows only
(advanced).
3. Click Load Driver.
1-20 Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration
4. A message appears, reminding you to insert the installation media containing the
driver of the RAID controller driver. Click Browse to continue.
• If you have only one optical drive installed in your system, eject the Windows OS
installation disc and replace it with the motherboard Support DVD.
• If you do not have an optical drive, you can use another computer with an optical
drive to copy the RAID driver from the support DVD to a USB ash drive.
5. Locate the driver in the corresponding folder of the Support DVD or the USB ash
drive with RAID driver, then click OK to continue.
6. Select the RAID controller driver you need from the list and click Next.
7. When the system nishes loading the RAID driver, select the drive to install Windows
and click Next.
If you have ejected the Windows OS installation disc in a previous step, ensure to replace
the motherboard Support DVD with the Windows OS installation disc.
8. Setup then proceeds with the OS installation. Follow screen instructions to complete.
RAID Conguration Guide 2-1
AMD RAID Conguration
Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration
2
2.1 RAID configurations
If your motherboard supports RaidXpert2 Conguration Utility, you can create Volume,
RAIDABLE, RAID 0, RAID 1, or RAID 10 (depends on system licensing) congurations.
Please refer to your motherboard’s user manual for details on the actual supported RAID
congurations.
If you want to install a Windows® operating system to a hard disk drive included in a RAID
set, you have to create a RAID driver disk and load the RAID driver during OS installation.
Refer to section 1.2 Creating a RAID driver disk for details.
2.1.1 RAID definitions
Volume provides the ability to link-together storage from one or several disks, regardless
of the size of the space on those disks. This conguration is useful in scavenging space on
disks unused by other disks in the array. This conguration does not provide performance
benets or data redundancy, disk failure will result in data loss.
RAIDABLE arrays (also known as RAID Ready) are a special type of Volume (JBOD) that
allows the user to add more storage space or create a redundant array after a system is
installed. RAIDABLE arrays are created using Option ROM, UEFI, or rcadm.
The ability to create RAIDABLE arrays may vary per system.
RAID 0 (Data striping) optimizes two identical hard disk drives to read and write data in
parallel, interleaved stacks. Two hard disks perform the same work as a single drive but at a
sustained data transfer rate, double that of a single disk alone, thus improving data access
and storage. Use of two new identical hard disk drives is required for this setup.
RAID 1 (Data mirroring) copies and maintains an identical image of data from one drive to
a second drive. If one drive fails, the disk array management software directs all applications
to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive. This RAID
conguration provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system.
Use two new drives or use an existing drive and a new drive for this setup. The new drive
must be of the same size or larger than the existing drive.
RAID 10 is data striping and data mirroring combined without parity (redundancy data)
having to be calculated and written. With the RAID 10 conguration you get all the benets
of both RAID 0 and RAID 1 congurations. Use four new hard disk drives or use an existing
drive and three new drives for this setup.

2-2 Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration
2.1.2 Installing storage devices
The motherboard supports Serial ATA hard disk drives and PCIE SSD storage devices. For
optimal performance, install identical drives of the same model and capacity when creating
a disk array.
Refer to Chapter 2 in your motherboard’s user manual for details on installing storage
devices to your motherboard.
2.1.3 RaidXpert2 Configuration Utility in UEFI BIOS
To enter the RaidXpert2 Conguration Utility in UEFI BIOS:
1. Enter the BIOS Setup during POST.
Refer to Chapter 3 in your motherboard’s user manual for details on entering and
navigating through the BIOS Setup.
2. Go to Advanced > SATA Configuration, then set SATA Mode to [RAID].
Due to chipset limitation, when SATA ports are set to RAID mode, all SATA ports run at
RAID mode together.
3. Congure additional settings for your storage device and RAID conguration:
• If you are using SATA storage devices, no additional settings are required.
Please proceed to next step.
• If you are setting up an NVMe RAID set, go to Advanced > SATA Configuration
(or Advanced > AMD PBS), then set NVMe RAID mode to [Enabled].
• If you are using Hyper M.2 x16 card(s), go to Advanced > Onboard Devices
Configuration, then set the corresponding PCIE slot(s) to [PCIe RAID Mode].
The Hyper M.2 x16 card is purchased separately.
4. Go to Boot > CSM (Compatibility Support Module), then set Launch CSM to
[Disabled].
5. Save your changes and exit the BIOS Setup, then enter the BIOS Setup again.
6. Go to Advanced > RaidXpert2 Configuration Utility to display the RaidXpert2
Conguration Utility menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 2-3
Creating a RAID set
To create a RAID set:
1. From the RaidXpert2 Conguration Utility menu, go to Array Management > Create
Array to enter the Create Array menu. The following screen appears:
2. When the Select RAID Level item is selected, press <Enter> to select the RAID level
to create, and then press <Enter>.
3. When the Select Physical Disks item is selected, press <Enter> to enter the Select
Physical Disks menu. The following screen appears:
4. Toggle the physical disks that you want to include in the RAID set to On, then select
Apply Changes and press <Enter> to complete selection.

2-4 Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration
5. When the Array Size: item is selected, enter the RAID volume capacity that you want
and press <Enter>. The default value indicates the maximum allowed capacity.
6. When the Array Size Unit: item is selected, press <Enter> to select the size unit for
the RAID array, and then press <Enter>.
7. When the Read Cache Policy: item is selected, press <Enter> to select the read
policy for the RAID array, and then press <Enter>.
8. When the Write Cache Policy: item is selected, press <Enter> to select the write
policy for the RAID array, and then press <Enter>.
9. When the Create Array item is selected, press <Enter> to create the RAID volume
and return to the Array Management menu.

RAID Conguration Guide 2-5
Deleting a RAID set
Be cautious when deleting a RAID set. You will lose all data on the hard disk drives when
you delete a RAID set.
To delete a RAID set:
1. From the RaidXpert2 Conguration Utility menu, go to Array Management > Delete
Array to enter the Delete Array menu. The following screen appears:
2. Toggle the array(s) that you want to delete to On.
3. When the Delete Array(s) item is selected, press <Enter>, toggle the Confirm item to
On, then select YES to delete the RAID volume, or select NO to cancel.
2-6 Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration
2.2 Installing the RAID controller driver during
Windows® 10 OS installation
After creating the RAID sets, you are now ready to install an operating system to the
independent drives or bootable array. This part provides the instructions on how to install the
RAID controller drivers during OS installation.
To install the RAID controller driver when installing Windows® 10 OS:
1. Boot the computer using the Windows® 10 OS installation disc. Follow the screen
instructions to start installing Windows® 10.
2. When prompted to choose a type of installation, click Custom: Install Windows only
(advanced).
3. Click Load Driver.
DO NOT delete any of the partitions or format the NVMe devices. Doing so will delete the
AMD-RAID metadata and the desired RAID level will be deleted.
RAID Conguration Guide 2-7
4. A message appears, reminding you to insert the installation media containing the
driver of the RAID controller driver. Click Browse to continue.
• If you have only one optical drive installed in your system, eject the Windows OS
installation disc and replace it with the motherboard Support DVD.
• If you do not have an optical drive, you can use another computer with an optical
drive to copy the RAID driver from the support DVD to a USB ash drive.
5. Locate the driver in the corresponding folder of the Support DVD or the USB ash
drive with RAID driver, then click OK to continue.
6. Select the RAID controller driver (rcbottom.inf) from the list and click Next. The available
drives will temporary disappear.
7. Repeat steps 3 to 5 and select the RAID controller driver (rcraid.inf) from the list and
click Next. The available drives will reappear.
8. Repeat steps 3 to 5 and select the RAID controller driver (rccfg.inf) from the list and click
Next. The AMD-RAID Virtual Disk will appear.
9. Select the drive to install Windows and click Next.
If you have ejected the Windows OS installation disc in a previous step, ensure to replace
the motherboard Support DVD with the Windows OS installation disc.
10. Setup then proceeds with the OS installation. Follow screen instructions to complete.

2-8 Chapter 2: AMD RAID Conguration