Table of Contents
- GS1900 Series
- User’s Guide
- Technical Reference
- Monitor: System
- Monitor: Port
- Monitor: VLAN
- Monitor: MAC Table
- Monitor: Link Aggregation
- Monitor: Loop Guard
- Monitor: Multicast
- Monitor: Spanning Tree
- Monitor: LLDP
- Monitor: Security
- Monitor: Management
- Configuration: System
- Configuration: Port
- Configuration: VLAN
- Configuration: MAC Table
- Configuration: Link Aggregation
- Configuration: Loop Guard
- Configuration: Mirror
- Configuration: Multicast
- Configuration: Spanning Tree
- Configuration: LLDP
- Configuration: QoS
- Configuration: Security
- Configuration: AAA
- Configuration: Management
- 31.1 Overview
- 31.2 Syslog
- 31.3 SNMP
- 31.3.1 The Global Screen
- 31.3.2 The Community Screen
- 31.3.3 The Community Add/Modify Screen
- 31.3.4 The Group Screen
- 31.3.5 The Group Add/Modify Screen
- 31.3.6 The User Screen
- 31.3.7 The User Add/Modify Screen
- 31.3.8 The Trap Screen
- 31.3.9 The Trap Destination Screen
- 31.3.10 The Trap Destination Add/Modify Screen
- 31.4 Error Disable
- 31.5 HTTP/HTTPS
- 31.6 Users
- 31.7 Remote Access Control
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Customer Support
- Legal Information
Zyxel GS1900-48HP User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for GS1900-48HP by Zyxel which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Quick Start Guide
www.zyxel.com
GS1900 Series
GbE Smart Managed Switch
Ve rsion 2.10
Edition 2, 04/2016
Copyright © 2016 ZyXEL Communications Corporation
User’s Guide
Default Login Details
IP Address http://192.168.1.1 (In-band ports)
User Name admin
Password 1234

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
2
IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Note: This guide is a reference for a series of products. Therefore so me features or
options in this guide may not be available in your product.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in
your product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure
that the information in this manual is accurate.
Note: It is recommended you use the Web Configurator to configure the Switch.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Click the help icon in any screen for help in configuring that screen and supplementary
information.
•More Inforamtion
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the Switch.

Contents Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
3
Contents Overview
User’s Guide .................................................................... ...................................................................14
Getting to Know Your Switch ...................................................................................................................15
Hardware Installation and Connection ....................................................................................................19
Hardware Overview .................................................................................................................................24
ZON Utility ...............................................................................................................................................32
The Web Configurator .............................................................................................................................33
Getting Start ............................................................................................................................................41
Technical Reference ..........................................................................................................................51
Monitor: System ......................................................................................................................................52
Monitor: Port ............................................................................................................................................55
Monitor: VLAN .........................................................................................................................................62
Monitor: MAC Table .................................................................................................................................68
Monitor: Link Aggregation .......................................................................................................................70
Monitor: Loop Guard ...............................................................................................................................72
Monitor: Multicast ....................................................................................................................................75
Monitor: Spanning Tree ...........................................................................................................................79
Monitor: LLDP .........................................................................................................................................85
Monitor: Security .....................................................................................................................................88
Monitor: Management .............................................................................................................................91
Configuration: System .............................................................................................................................94
Configuration: Port ..................................................................................................................................99
Configuration: VLAN ............................................................................................................................. 112
Configuration: MAC Table .....................................................................................................................125
Configuration: Link Aggregation ............................................................................................................129
Configuration: Loop Guard ....................................................................................................................136
Configuration: Mirror .............................................................................................................................139
Configuration: Multicast .........................................................................................................................141
Configuration: Spanning Tree ...............................................................................................................149
Configuration: LLDP ..............................................................................................................................159
Configuration: QoS ................................................................................................................................172
Configuration: Security ..........................................................................................................................181
Configuration: AAA ................................................................................................................................191
Configuration: Management ..................................................................................................................196
Maintenance ..........................................................................................................................................213
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................................224

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
4
Table of Contents
Contents Overview ..............................................................................................................................3
Table of Contents .................................................................................................................................4
Part I: User’s Guide .........................................................................................14
Chapter 1
Getting to Know Your Switch.............................................................................................................15
1.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................15
1.1.1 Bridging Example ....................................................................................................................15
1.1.2 Gigabit Ethernet to the Desktop ..............................................................................................16
1.1.3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Example ................................................................................16
1.1.4 IPv6 Support ............................................................................................................................17
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch ..............................................................................................................18
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch ...............................................................................................18
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation and Connection .............................................................................................19
2.1 Freestanding Installation ..................................................................................................................19
2.2 Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................................20
2.2.1 Wall Mounting ..........................................................................................................................20
2.2.2 Rack Mounting .........................................................................................................................21
Chapter 3
Hardware Overview ............................................................................................................................24
3.1 Front Panel Connections ..................................................................................................................24
3.1.1 Ethernet Ports ..........................................................................................................................25
3.1.2 SFP Slots ................................................................................................................................26
3.2 Rear Panel ........................................................................................................................................27
3.2.1 Power Connection ...................................................................................................................29
3.3 LEDs .............................................................................................................................................30
Chapter 4
ZON Utility ...........................................................................................................................................32
4.1 ZyXEL One Network (ZON) Utility Screen .......................................................................................32
Chapter 5
The Web Configurator........................................................................................................................33

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
5
5.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................33
5.2 Access ...............................................................................................................................................33
5.3 Navigating the Web Configurator ......................................................................................................34
5.3.1 Title Bar ...................................................................................................................................34
5.3.2 Navigation Panel .....................................................................................................................35
Chapter 6
Getting Start ........................................................................................................................................41
6.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................41
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................41
6.2 Getting Start ......................................................................................................................................41
6.2.1 Wizard .....................................................................................................................................42
Part II: Technical Reference............................................................................51
Chapter 7
Monitor: System..................................................................................................................................52
7.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................52
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................52
7.2 IP .......................................................................................................................................................52
7.2.1 IPv4 ........................................................................................................................................52
7.2.2 IPv6 ........................................................................................................................................53
7.3 Information ........................................................................................................................................54
Chapter 8
Monitor: Port .......................................................................................................................................55
8.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................55
8.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................55
8.2 Port ....................................................................................................................................................55
8.2.1 Status .......................................................................................................................................55
8.2.2 Port Counters ..........................................................................................................................56
8.2.3 Bandwidth Utilization ...............................................................................................................58
8.3 PoE ...................................................................................................................................................59
8.4 Bandwidth Management ...................................................................................................................60
8.4.1 Bandwidth Control ...................................................................................................................60
8.5 Storm Control ....................................................................................................................................61
Chapter 9
Monitor: VLAN.....................................................................................................................................62
9.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................62
9.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................62

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
6
9.2 VLAN .................................................................................................................................................62
9.2.1 VLAN .......................................................................................................................................62
9.2.2 Port ..........................................................................................................................................63
9.2.3 VLAN Port ................................................................................................................................64
9.3 Guest VLAN ......................................................................................................................................65
9.4 Voice VLAN .......................................................................................................................................66
Chapter 10
Monitor: MAC Table............................................................................................................................68
10.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................68
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................69
10.2 MAC Table .......................................................................................................................................69
Chapter 11
Monitor: Link Aggregation.................................................................................................................70
11.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................70
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................70
11.2 Link Aggregation .............................................................................................................................70
Chapter 12
Monitor: Loop Guard..........................................................................................................................72
12.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................72
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................73
12.2 Loop Guard .....................................................................................................................................73
Chapter 13
Monitor: Multicast...............................................................................................................................75
13.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................75
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................75
13.2 IGMP ...............................................................................................................................................75
13.2.1 Vlan .......................................................................................................................................75
13.2.2 Statistics ................................................................................................................................76
13.2.3 Group .....................................................................................................................................77
13.2.4 Router ....................................................................................................................................78
Chapter 14
Monitor: Spanning Tree......................................................................................................................79
14.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................79
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................79
14.2 Spanning Tree .................................................................................................................................79
14.2.1 CIST ......................................................................................................................................79
14.2.2 CIST Port ...............................................................................................................................80
14.2.3 MST .......................................................................................................................................81

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
7
14.2.4 MST Port ...............................................................................................................................82
14.2.5 STP Statistics ........................................................................................................................83
Chapter 15
Monitor: LLDP.....................................................................................................................................85
15.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................85
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................85
15.2 LLDP ...............................................................................................................................................85
15.2.1 Statistics ................................................................................................................................85
15.2.2 Remote Information ...............................................................................................................86
15.2.3 Overloading ...........................................................................................................................87
Chapter 16
Monitor: Security ................................................................................................................................88
16.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................88
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................88
16.2 Port Security ....................................................................................................................................88
16.3 802.1X .............................................................................................................................................89
16.3.1 Port ........................................................................................................................................89
16.3.2 Authenticated Hosts ..............................................................................................................90
Chapter 17
Monitor: Management ........................................................................................................................91
17.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................91
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................91
17.2 Syslog .............................................................................................................................................91
17.3 Error Disable ...................................................................................................................................92
Chapter 18
Configuration: System .......................................................................................................................94
18.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................94
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................94
18.2 IP .....................................................................................................................................................94
18.2.1 The IPv4 Screen ....................................................................................................................94
18.2.2 The IPv6 Screen ....................................................................................................................95
18.3 Time ................................................................................................................................................96
18.3.1 The System Time Screen ......................................................................................................96
18.3.2 The SNTP Server Screen .....................................................................................................97
18.4 Information ......................................................................................................................................97
18.4.1 The System Information Screen ...........................................................................................97
Chapter 19
Configuration: Port.............................................................................................................................99

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
8
19.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................99
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................99
19.2 Port .................................................................................................................................................99
19.2.1 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................100
19.3 EEE ...............................................................................................................................................101
19.3.1 The EEE Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................102
19.4 PoE ..............................................................................................................................................102
19.4.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................103
19.4.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................103
19.4.3 The PoE Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................105
19.5 Bandwidth Management ...............................................................................................................108
19.5.1 The Bandwidth Control Screen ...........................................................................................108
19.5.2 The Port Rate Edit Screen ..................................................................................................109
19.6 Storm Control ................................................................................................................................ 110
19.6.1 The Port Screen ................................................................................................................. 110
19.6.2 The Port Edit Screen .......................................................................................................... 111
Chapter 20
Configuration: VLAN ........................................................................................................................112
20.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 112
20.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................ 112
20.2 VLAN ............................................................................................................................................. 113
20.2.1 The VLAN Screen ................................................................................................................ 113
20.2.2 The VLAN Add Screen ....................................................................................................... 113
20.2.3 The Port Screen ................................................................................................................. 114
20.2.4 The Port Edit Screen .......................................................................................................... 115
20.2.5 The VLAN Port Screen ....................................................................................................... 116
20.3 Guest VLAN .................................................................................................................................. 118
20.3.1 The Global Screen .............................................................................................................. 118
20.3.2 The Port Screen ................................................................................................................. 119
20.3.3 The Port Edit Screen .......................................................................................................... 119
20.4 Voice VLAN ...................................................................................................................................120
20.4.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................120
20.4.2 The OUI Screen ...................................................................................................................121
20.4.3 The OUI Add/Edit Screen ....................................................................................................122
20.4.4 The Port Screen .................................................................................................................123
20.4.5 The Port Edit Screen ..........................................................................................................124
Chapter 21
Configuration: MAC Table................................................................................................................125
21.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................125
21.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................125
21.2 MAC Table .....................................................................................................................................125

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
9
21.2.1 The Static MAC Screen .......................................................................................................125
21.2.2 The Static MAC Add Screen ................................................................................................126
21.2.3 The Filtering MAC Screen ...................................................................................................126
21.2.4 The Filtering MAC Add Screen ...........................................................................................127
21.2.5 The Dynamic Age Screen ....................................................................................................127
Chapter 22
Configuration: Link Aggregation ....................................................................................................129
22.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................129
22.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................129
22.2 Link Aggregation ...........................................................................................................................129
22.2.1 The Global Screen ..............................................................................................................129
22.2.2 The LAG Management Screen ...........................................................................................130
22.2.3 The LAG Add Screen ..........................................................................................................131
22.2.4 The LAG Port Screen .........................................................................................................132
22.2.5 The LAG Port Edit Screen ...................................................................................................133
22.2.6 The LACP Port Screen .......................................................................................................133
22.2.7 The LACP Port Edit Screen .................................................................................................134
Chapter 23
Configuration: Loop Guard..............................................................................................................136
23.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................136
23.2 Loop Guard ...................................................................................................................................136
23.2.1 The Global Screen ..............................................................................................................136
23.2.2 The Loop Guard Port ...........................................................................................................137
23.2.3 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................137
Chapter 24
Configuration: Mirror........................................................................................................................139
24.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................139
24.2 Mirror .............................................................................................................................................139
24.2.1 The Mirror Screen ...............................................................................................................139
Chapter 25
Configuration: Multicast ..................................................................................................................141
25.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................141
25.2 IGMP .............................................................................................................................................141
25.2.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................141
25.2.2 The VLAN Screen ................................................................................................................142
25.2.3 The Edit IGMP Screen ........................................................................................................143
25.2.4 The Router Port Screen .......................................................................................................144
25.2.5 The Add/Edit Router Port Screen ........................................................................................144
25.2.6 The Profile Screen ...............................................................................................................145

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
10
25.2.7 The Add/Edit Profile Screen ................................................................................................146
25.2.8 The Throttling Screen ..........................................................................................................147
25.2.9 The Add/Edit Throttling Screen ...........................................................................................147
Chapter 26
Configuration: Spanning Tree .........................................................................................................149
26.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................149
26.2 Spanning Tree ...............................................................................................................................149
26.2.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................149
26.2.2 The STP Port Screen ..........................................................................................................150
26.2.3 The STP Port Edit Screen ...................................................................................................151
26.2.4 The CIST Screen .................................................................................................................152
26.2.5 The CIST Port Screen .........................................................................................................154
26.2.6 The CIST Port Edit Screen ..................................................................................................154
26.2.7 The MST Screen .................................................................................................................155
26.2.8 The Add/Modify MST Screen ..............................................................................................156
26.2.9 The MST Port Screen ..........................................................................................................156
26.2.10 The MST Port Edit Screen .................................................................................................157
Chapter 27
Configuration: LLDP.........................................................................................................................159
27.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................159
27.2 LLDP .............................................................................................................................................159
27.2.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................159
27.2.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................160
27.2.3 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................161
27.2.4 The Local Information Screen .............................................................................................162
27.2.5 The Local Information Edit Screen ......................................................................................164
27.2.6 The MED Network Policy Screen ........................................................................................167
27.2.7 The MED Network Policy Add/Edit Screen ..........................................................................167
27.2.8 The MED Port Screen .........................................................................................................169
27.2.9 The MED Port Add/Edit Screen ..........................................................................................170
Chapter 28
Configuration: QoS...........................................................................................................................172
28.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................172
28.2 General .........................................................................................................................................172
28.2.1 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................172
28.2.2 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................173
28.2.3 The Queue Screen ..............................................................................................................174
28.2.4 The CoS Mapping Screen ...................................................................................................174
28.2.5 The DSCP Mapping Screen ................................................................................................176
28.2.6 The IP Precedence Mapping Screen ...................................................................................177

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
11
28.3 Trust Mode ....................................................................................................................................178
28.3.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................178
28.3.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................178
28.3.3 The Trust Mode Edit Screen ...............................................................................................179
Chapter 29
Configuration: Security....................................................................................................................181
29.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................181
29.2 Port Security ..................................................................................................................................181
29.2.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................181
29.2.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................181
29.2.3 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................182
29.3 Protected Port ...............................................................................................................................183
29.3.1 The Protected Port Screen ..................................................................................................183
29.3.2 The Protected Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................184
29.4 802.1X ...........................................................................................................................................185
29.4.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................185
29.4.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................185
29.4.3 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................186
29.5 DoS ...............................................................................................................................................187
29.5.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................188
29.5.2 The Port Screen ..................................................................................................................188
29.5.3 The Port Edit Screen ...........................................................................................................189
29.5.4 DoS Attack Types ................................................................................................................190
Chapter 30
Configuration: AAA ..........................................................................................................................191
30.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................191
30.2 Auth Method ..................................................................................................................................191
30.2.1 The Auth Method Screen .....................................................................................................191
30.2.2 The Auth Method Add/Modify Screen ..................................................................................192
30.3 RADIUS .........................................................................................................................................192
30.3.1 The RADIUS Screen ...........................................................................................................192
30.3.2 The RADIUS Add/Modify Screen .......................................................................................193
30.4 TACACS+ ......................................................................................................................................194
30.4.1 The TACACS+ Screen .........................................................................................................194
30.4.2 The TACACS+ Add/Modify Screen .....................................................................................195
Chapter 31
Configuration: Management............................................................................................................196
31.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................196
31.2 Syslog ...........................................................................................................................................196
31.2.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................196

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
12
31.2.2 The Local Screen ................................................................................................................197
31.2.3 The Local Add/Modify Screen ............................................................................................197
31.2.4 The Remote Screen ............................................................................................................198
31.2.5 The Remote Add/Modify Screen .........................................................................................198
31.3 SNMP ............................................................................................................................................199
31.3.1 The Global Screen ...............................................................................................................199
31.3.2 The Community Screen .......................................................................................................200
31.3.3 The Community Add/Modify Screen ...................................................................................200
31.3.4 The Group Screen ...............................................................................................................201
31.3.5 The Group Add/Modify Screen ...........................................................................................202
31.3.6 The User Screen .................................................................................................................202
31.3.7 The User Add/Modify Screen .............................................................................................203
31.3.8 The Trap Screen ..................................................................................................................204
31.3.9 The Trap Destination Screen ...............................................................................................205
31.3.10 The Trap Destination Add/Modify Screen .........................................................................206
31.4 Error Disable .................................................................................................................................206
31.4.1 The Error Disabled Screen .................................................................................................206
31.5 HTTP/HTTPS ................................................................................................................................207
31.5.1 The HTTP Screen ...............................................................................................................207
31.5.2 The HTTPS Screen .............................................................................................................208
31.6 Users .............................................................................................................................................209
31.6.1 The Users Screen ...............................................................................................................209
31.6.2 The Users Add/Modify Screen ............................................................................................210
31.7 Remote Access Control ................................................................................................................210
31.7.1 The Global Screen ..............................................................................................................210
31.7.2 The Profile Add/Modify Screen ........................................................................................... 211
Chapter 32
Maintenance......................................................................................................................................213
32.1 Firmware Upgrade ........................................................................................................................213
32.1.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................213
32.1.2 Upgrade the firmware from a file on your computer ............................................................214
32.2 Firmware Management .................................................................................................................214
32.2.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................214
32.2.2 Activate the Backup Image ..................................................................................................215
32.3 Backup a Configuration File ..........................................................................................................215
32.3.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................215
32.3.2 Back up configuration or log files to a server .......................................................................216
32.3.3 Back up configuration or log files to your computer .............................................................216
32.4 Restore a Configuration File .........................................................................................................217
32.4.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................217
32.4.2 Restore the configuration from a file on a server .................................................................217
32.4.3 Restore the configuration from a file on your computer .......................................................218

Table of Contents
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
13
32.5 Manage Configuration Files ..........................................................................................................218
32.5.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................218
32.6 Reset to Factory Defaults ..............................................................................................................219
32.6.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................219
32.6.2 Reset the Switch to Factory Defaults ...................................................................................219
32.7 Network Diagnostics .....................................................................................................................219
32.7.1 Port Test ..............................................................................................................................219
32.7.2 IPv4 Ping Test ......................................................................................................................220
32.7.3 IPv6 Ping Test ......................................................................................................................221
32.7.4 Trace Route .........................................................................................................................222
32.8 Reboot ...........................................................................................................................................223
32.8.1 Overview ..............................................................................................................................223
32.8.2 Reboot the Switch ...............................................................................................................223
Chapter 33
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................224
33.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ....................................................................................224
33.2 Switch Access and Login ..............................................................................................................225
33.3 Switch Configuration .....................................................................................................................227
Appendix A Customer Support ........................................................................................................228
Appendix B Legal Information..........................................................................................................234
Index ..................................................................................................................................................243

14
PART I
User’s Guide
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
15
CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know Your Switch
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the Switch.
1.1 Introduction
The GS1900 series is a new generation Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) Web-Managed Switch.
This User’s Guide covers the following models:
See the datasheet for a full list of firmware features av ailable on the Sw itch.
1.1.1 Bridging Example
In this example the Switch connects different company departments (RD and Sales) to the
corporate backbone. It can alleviate bandwidth contention and eliminate server and network
bottlenecks. All users that need high bandwidth can connect to high-speed department servers via
the Switch.
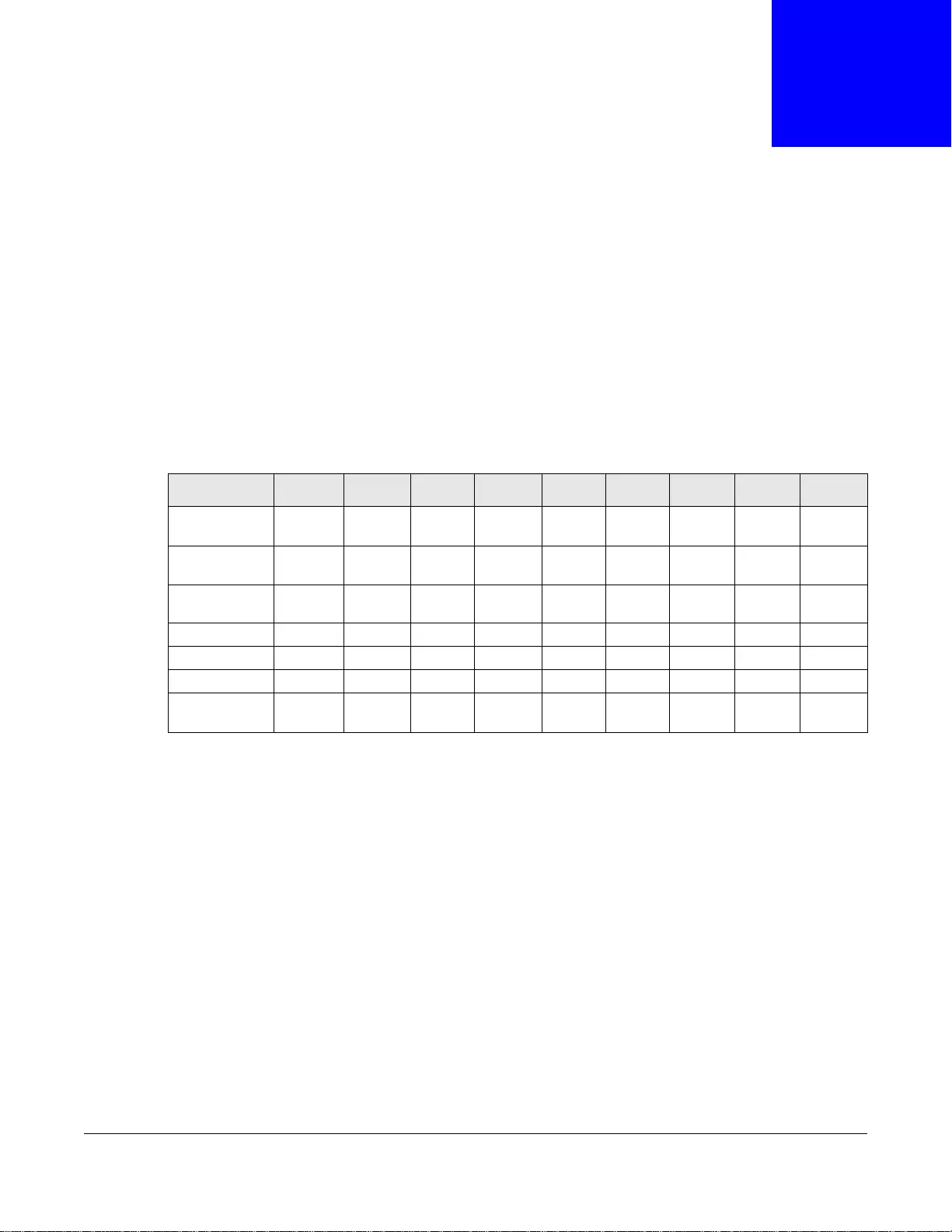
Table 1 GS1900 Series Comparison Table
MODEL GS1900-8 GS1900-
8HP GS1900-
10HP GS1900-
16 GS1900-
24E GS1900-
24 GS1900-
24HP GS1900-
48 GS1900-
48HP
100/1000
Mbps Port 8--162424-4824
100/1000
Mbps PoE Port -88---24-24
1G SFP Slots
Fiber --2--2222
Desktop v v v v v
Wall-mount v v v v v
Rack-mount v v v v v v
Power ON/OFF
Switch vvvvv
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
16
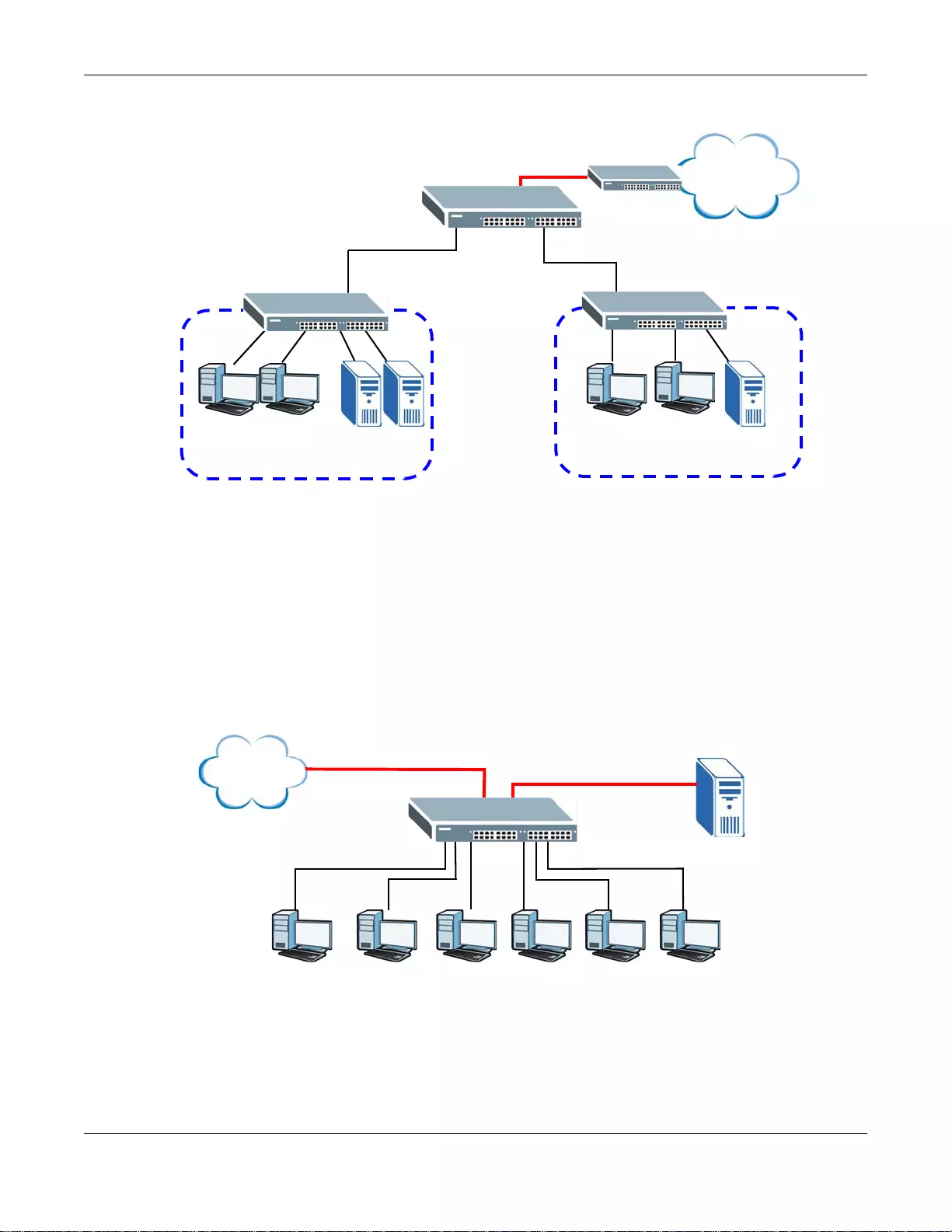
Figure 1 Bridging Application
1.1.2 Gigabit Ethernet to the Desktop
The Switch is an ideal solution for small networks which demand high bandwidth for a group of
heavy tr affic users. You can connect computers and servers directly to the Switch’s port or connect
other switches to the Switch.
In this example, all computers can share high-speed applications on the server and access the
Internet. To expand the network, simply add more networking devices such as switches, routers,
computers, print servers and so on.
Figure 2 Gigabit to the Desktop
1.1.3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Example
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a ph ysical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Stations on a logical network belong to one or more groups. With VLAN, a station cannot
Backbone
RD Sales
Internet
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
17
directly talk to or hear from stations that are not in the same group(s) unless such traffic first goes
through a router.
For more information on VLANs, refer to Chapter 9 on page 62.
1.1.3.1 Tag-based VLAN Example
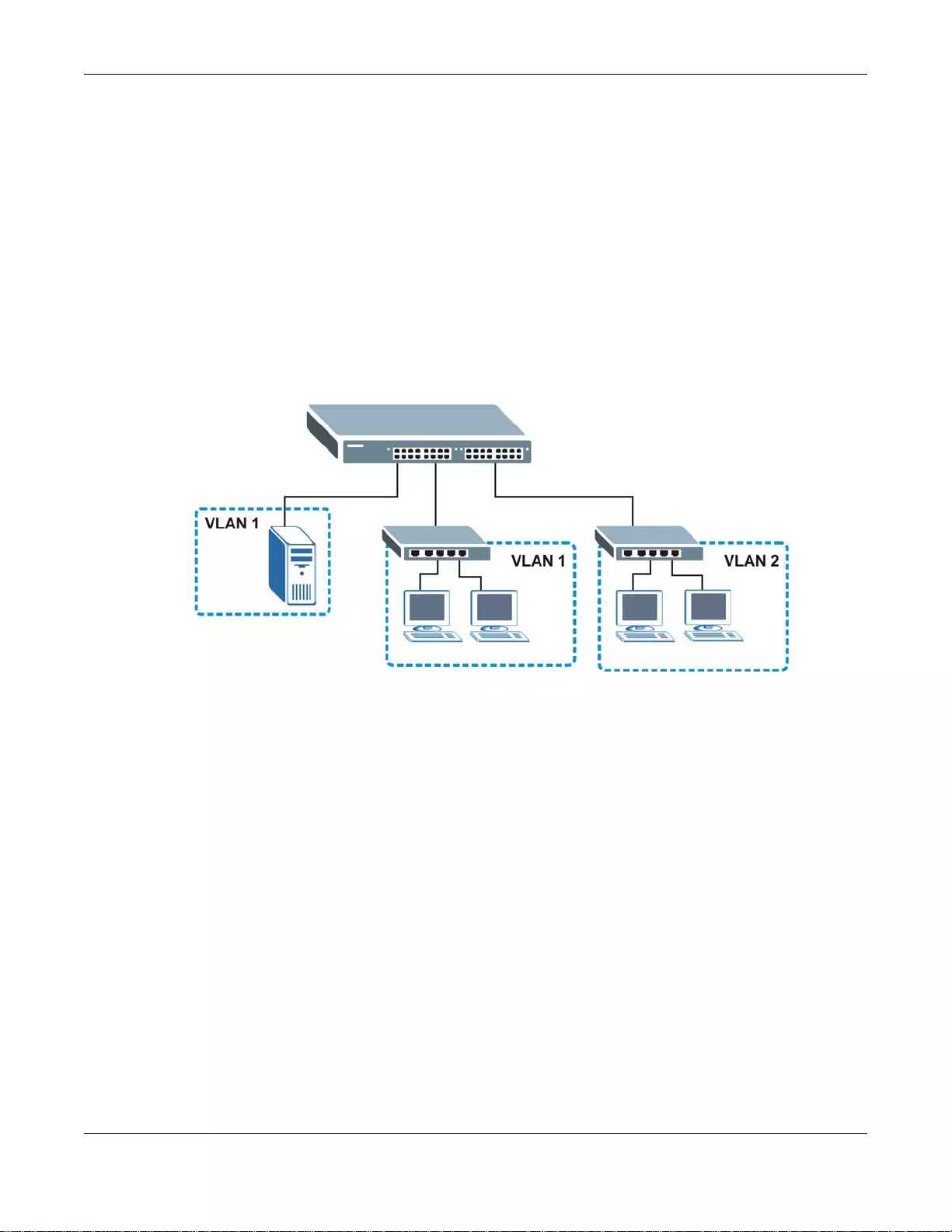
Ports in the same VLAN group share the same frame broadcast domain, thus increasing network
performance by reducing broadcast traffic. VLAN groups can be modified at any time by adding,
moving or changing ports without any re-cabling.
Shared resources such as a server can be used by all ports in the same VLAN as the server. In the
following figure only ports that need access to the server need to be part of VLAN 1. Ports can
belong to other VLAN groups too.
Figure 3 Shared Server Using VLAN Example
1.1.4 IPv6 Support
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and features. The
increase in IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4 address) allows up to 3.4 x 1038 IP
addresses. At the time of writing, the Switch supports the following features.
• Static address assignment and stateless auto-configuration
• Neighbor Discovery Protocol (a protocol used to discover other IPv6 devices in a network)
• Remote Management using PING, SNMP, HTTP and TFTP services
• ICMPv6 to report errors encountered in packet processing and perform diagnostic functions, such
as "PING”
• IPv4/IPv6 dual stack; the Switch can run IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time
•DHCPv6 client

Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
18
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch
Use any of the following methods to manage the Switch.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the Switch using a
(supported) web browser. See Chapter 5 on page 33.
• TFTP. Use Trivial File Transfer Protocol for firmware upgrades and configuration backup/restore.
See Section 32.1 on page 213, Section 32. 3 on page 215, and Section 32.4 on page 217
• SNMP. The device can be configured by a SNMP manager. See Section 31.3 on page 199.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch
Do the following things regularly to make the Switch more secure and to manage the Switch more
effectively.
• Change the password . Use a pass w ord that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier
working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you
forget your password, you will have to reset the Switch to its factory default settings. If you
backed up an earlier configur ation file, you would not have to totally re-configure the S witch. You
could simply restore your last configuration.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
19
CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation and Connection
This chapter shows you how to install and connect the Switch.
2.1 Freestanding Installation
1Make sure the Switch is clean and dry.
2Set the Switch on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of the Switch and
the connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
3Make sure there is enough clearance around the Switch to allow air circulation and the attachment
of cables and the power cord.
4Remo ve the adhesiv e backing from the rubber feet.
5Attach the rubber feet to each corner on the bottom of the Switch. These rubber feet help protect
the Switch from shock or vibration and ensure space between devices when stacking.
Figure 4 Attaching Rubber Feet
Note: Do NOT block the ventilation holes. Leave space between devices when stacking.
Note: For proper ventilation, allow at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance at the front and
3.4 inches (8 cm) at the back of the Switch. This is espec ial l y important for
enclosed rack installations.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
20
2.2 Hardware Installation
See Table 1 on page 15 for a comparison of the hardware installation methods of each model:
Note: Ask an authorized technician to attach the Switch to the r ack/wall.
Refer to Section 2.2.2 on page 21 for rack-mounting instructions. Take note of the following:
• The Switch should have a minimum 25 mm space around it for ventilation.
• The Switch should be placed on a desk that has a level surface and that is able to support the
weight of the Switch.
To start using it, simply connect the power cables and turn on the Switch.
2.2.1 Wall Mounting
Do the following to attach your Switch to a wall.
See the following table for how far apart to place the screws.
Screw the two screws provided with your S witch into the wall (see the figure in step 2). Use screws
with 6 mm ~ 8 mm (0.24" ~ 0.31") wide heads. Do not screw the screws all the wa y in to the wall;
leave a small gap between the head of the screw and the wall.
The gap must be big enough for the screw heads to slide into the screw slots and the connection
cables to run down the back of the Switch.
Note: Make sure the screws are securely fixed to the wall and strong enough to hold the
weight of the Switch with the connection cables.
Align the holes on the back of the Switch with the screws on the wall. Hang the Switch on the
screws.
Table 2 Distance bet ween the centers of the holes for wall mounting
GS1900-8 GS1900-8HP GS1900-10HP GS1900-16 GS1900-24E
176 mm 176 mm 176 mm 148 mm 207 mm
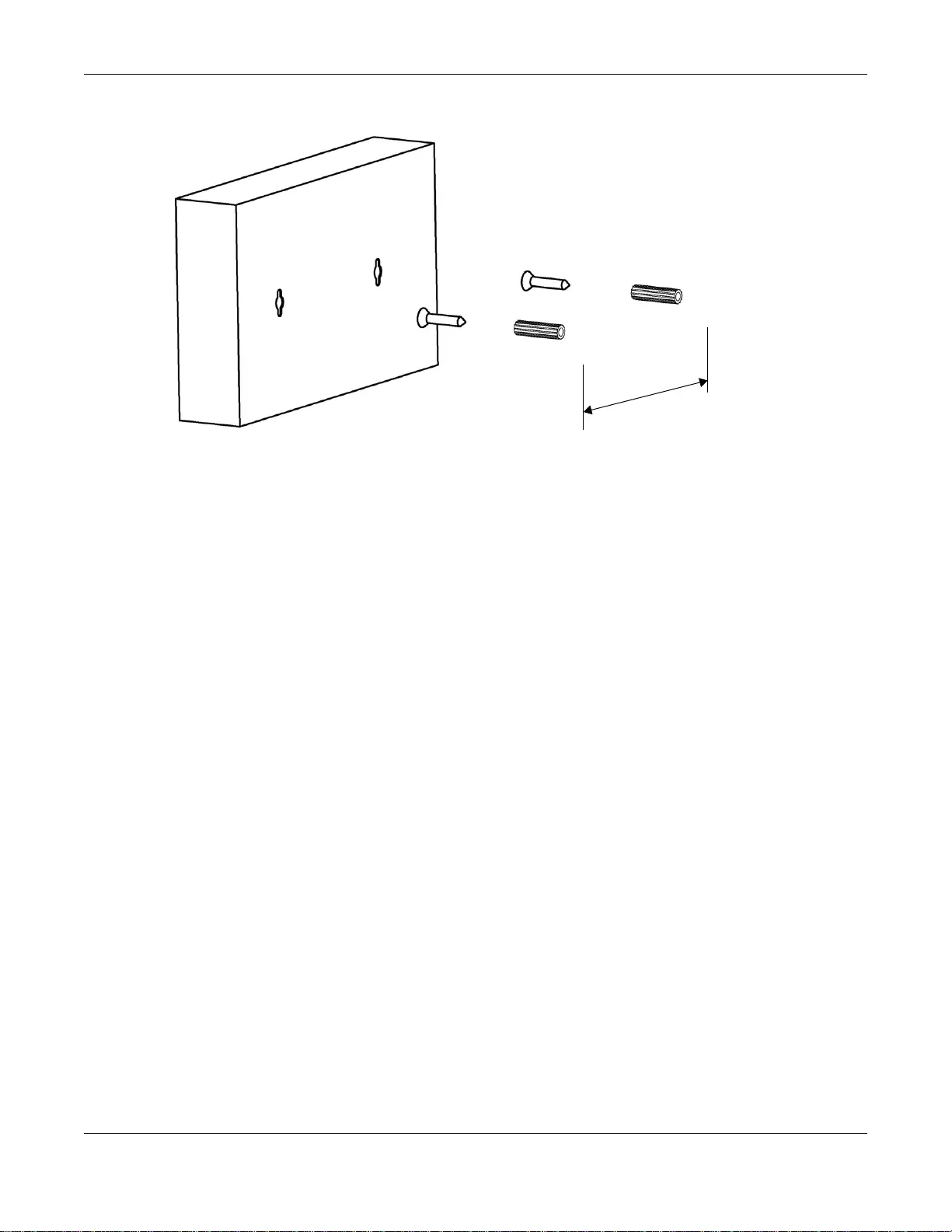
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
21
The Switch should be wall-mounted horizontally. The Switch's side
panels with ventilation slots should not be facing up or down as this
position is less safe.
2.2.2 Rack Mounting
The Switch can be mounted on an EIA standard size, 19-inch rack or in a wiring closet with other
equipment. Follow the steps below to mount your Switch on a standard EIA rack using a ra ck-
mounting kit.
Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
• Two mounting brackets.
• Eight M3 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
• Four M5 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
Precautions
• Make sure the rack will safely support the combined weight of all the equipment it contains.
• Make sure the position of the Switch does not make the rack unstable or top-heavy. Take all
necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before installing the unit.
Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch
1Po sition a mounting bracket on one side of the Switch, lining up the four screw holes on the brack et
with the screw holes on the side of the Switch.
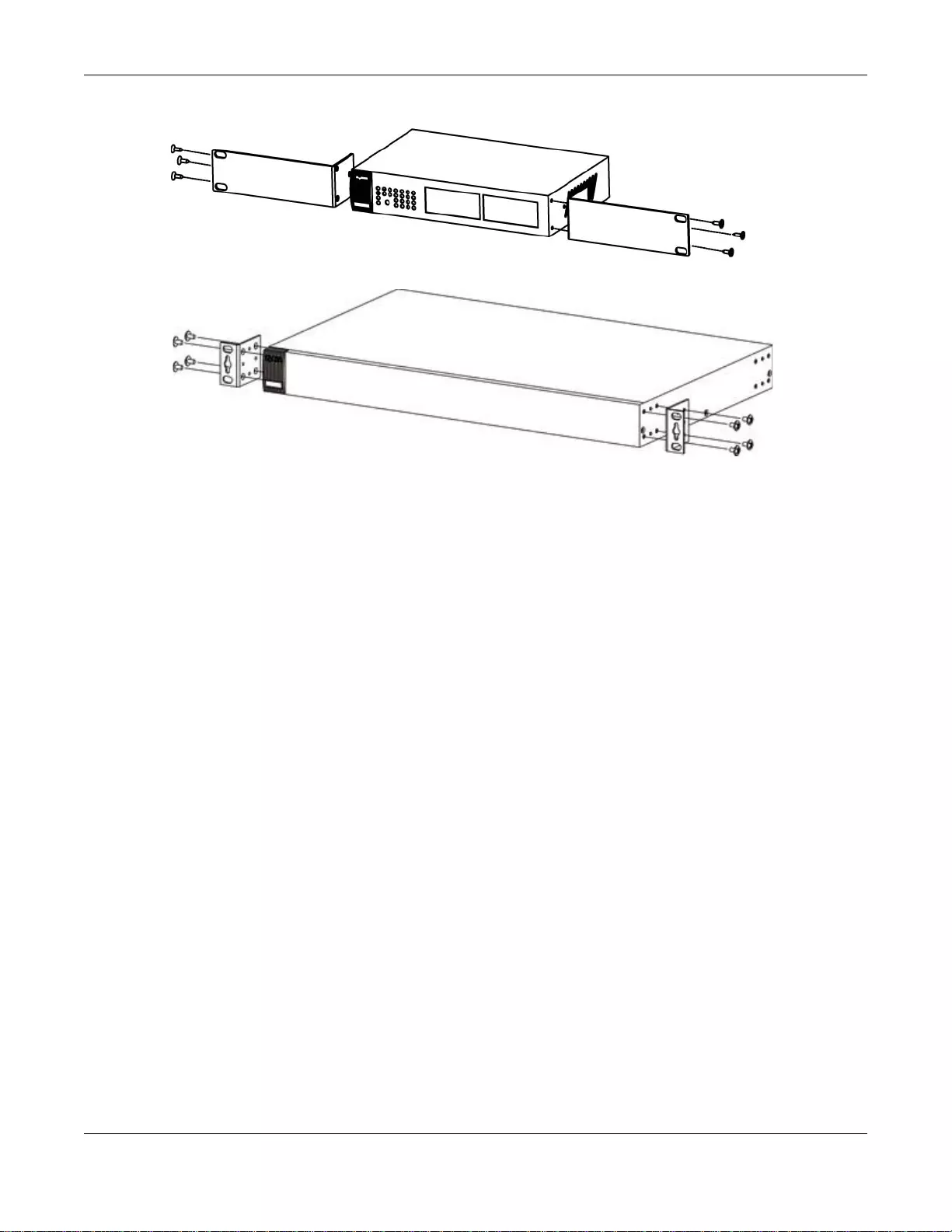
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
22
Figure 5 Attaching the Mounting Brackets (GS1900-16 and GS1900-24E)
Figure 6 Attaching the Mounting Brackets (GS1900-24, GS1 900-24HP, GS1900-48, GS1900-48HP)
2Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M3 flat head screws through the mounting bracket holes
into the Switch.
3Repeat steps 1 and 2 to install the second mounting bracket on the other side of the Switch.
4You may now mount the Switch on a rack. Proceed to the next section.
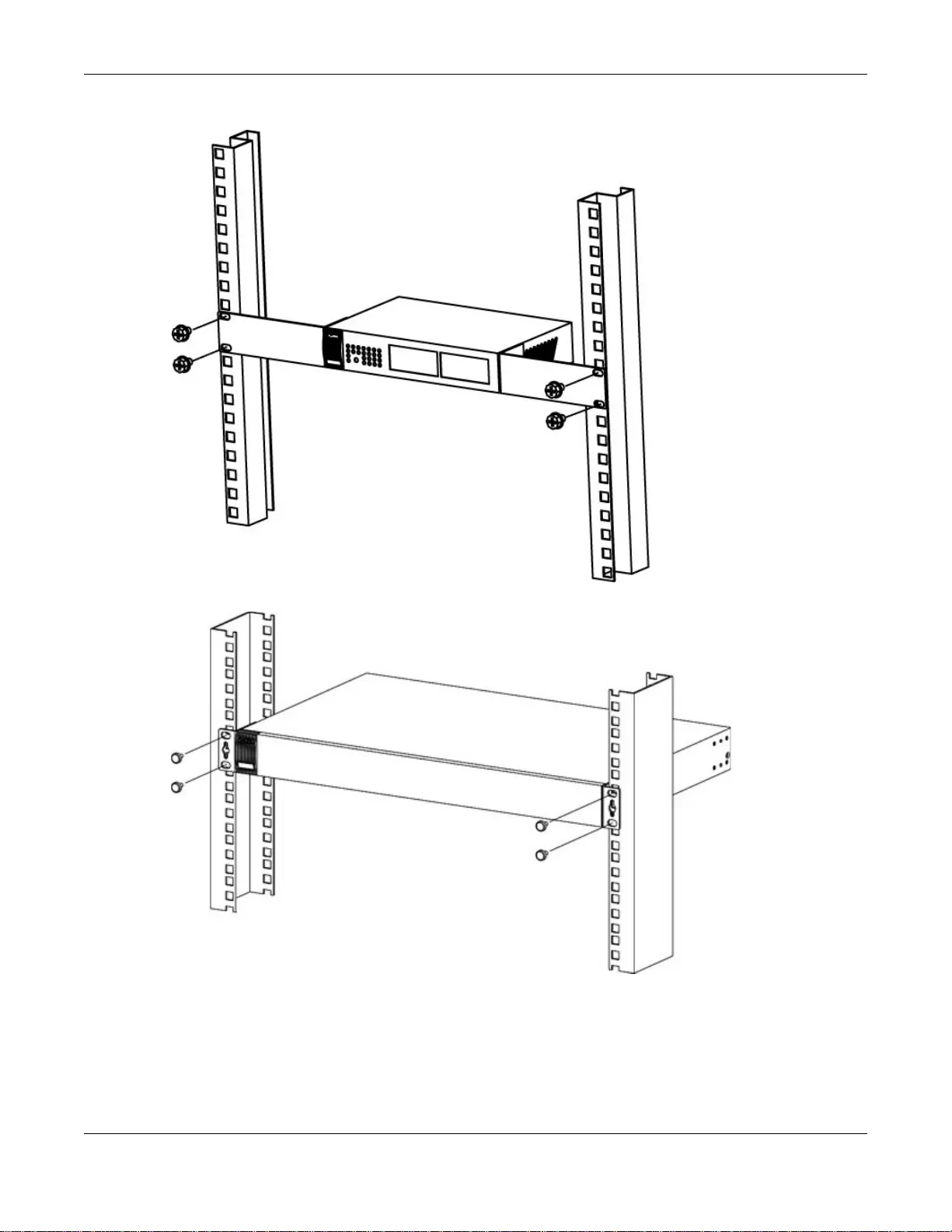
2.2.2.1 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
1Position a mounting bracket (that is already attached to the Switch) on one side of the rack, lining
up the two screw holes on the bracket with the screw holes on the side of the rack.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
23
Figure 7 Mounting the Switch on a Rack (GS1900-16 and GS1900-24E)
Figure 8 Mounting the Switch on a Rack (GS1900-24, GS1900-24HP, GS1900-48, GS1900-48HP)
2Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M5 flat head screws through the mounting bracket holes
into the rack.
3Repeat steps 1 and 2 to attach the second mounting bracket on the other side of the rack.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
24
CHAPTER 3
Hardware Overview
This chapter describes the front panel and rear panel of the Switch and shows you how to make the
hardware connections.
3.1 Front Panel Connections
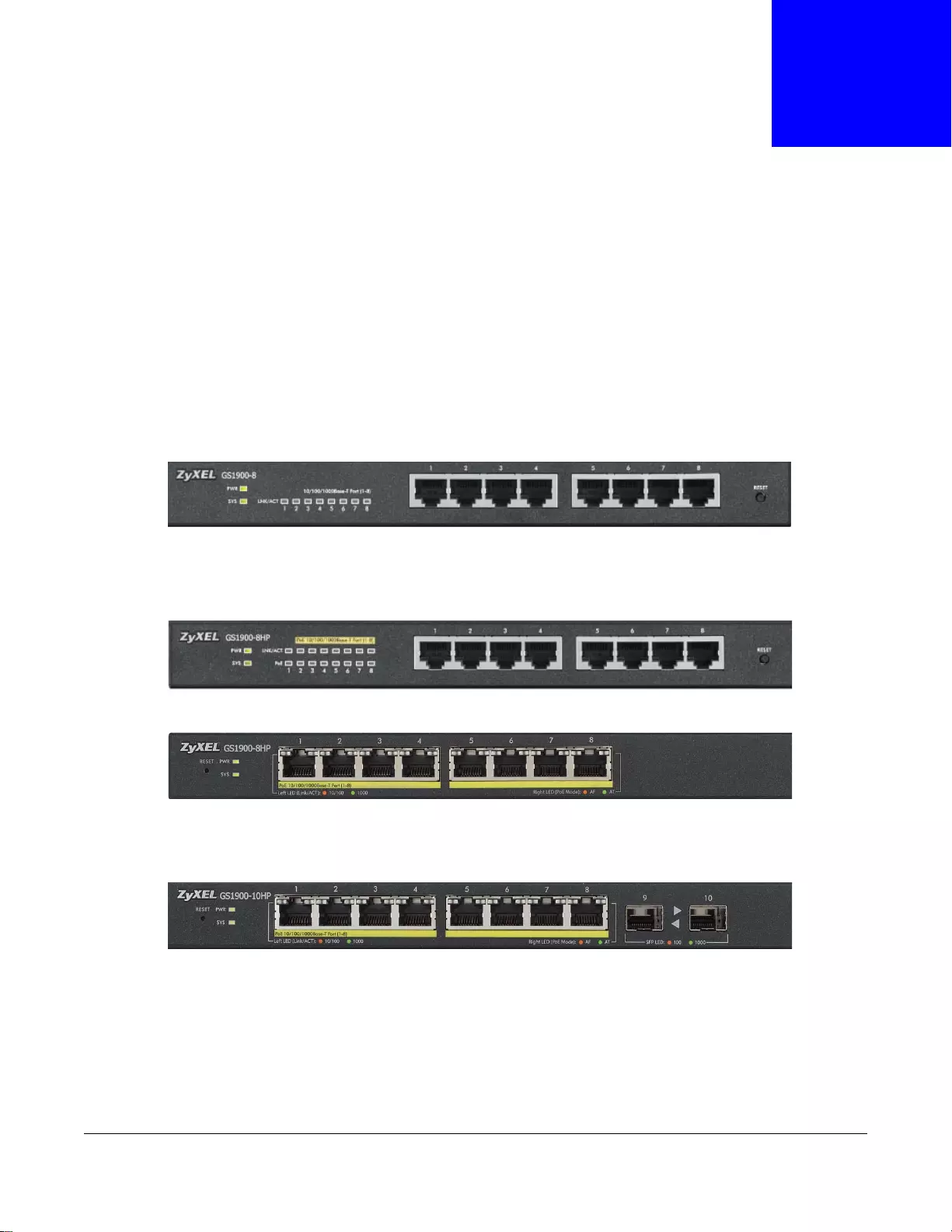
The following figures show the front panels of the Switch.
Figure 9 Front Panel: GS1900-8
Figure 10 Front Panel: GS1900-8HP
Figure 11 Front Panel: GS1900-10HP
Revision A1
Revision B1

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
25
Figure 12 Front Panel: GS1900-16
Figure 13 Front Panel: GS1900-24E
Figure 14 Front Panel: GS1900-24
Figure 15 Front Panel: GS1900-24HP
Figure 16 Front Panel: GS1900-48
Figure 17 Front Panel: GS1900-48HP
3.1.1 Ethernet Ports
The Switch has 1000Base-T auto-negotiating, auto-crossover Ethernet ports. In 10/100/1000 Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet, the speed can be 10Mbps, 100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps. The duplex mode can be both
half or full duplex at 100 Mbps and full duplex only at 1000 Mbps.
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
26
An auto-negotiating port can detect and adjust to the optimum Ethernet speed (10/100/1000
Mbps) and duplex mode (full duplex or half duplex) of the connected device.
An auto-crossover (auto-MDI/MDI - X) port automatically works with a str aight-through or crossover
Ethernet cable.
3.1.1.1 Default Ethernet Settings
The factory default negotiation settings for the Ethernet ports on the Switch are:
• Speed: Auto
•Duplex: Auto
• Flow control: Off
3.1.2 SFP Slots
These are slots for Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers. A transceiver is a single unit
that houses a transmitter and a receiver. Use a transceiver to connect a fiber-optic cable to the
Switch. The Switch does not come with transceivers. You must use transceivers that comply with
the Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver MultiSource Agreement (MSA). See the SFF
committee’s INF-8074i specification Rev 1.0 for details.
You can change transceivers while the Switch is operating. You can use different transceivers to
connect to Ethernet switches with different types of fiber-optic connectors.
• Type: SFP connection interface
• Connection speed: 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps)
To avoid possible eye injury, do not look into an operating fiber-optic
module’s connectors.
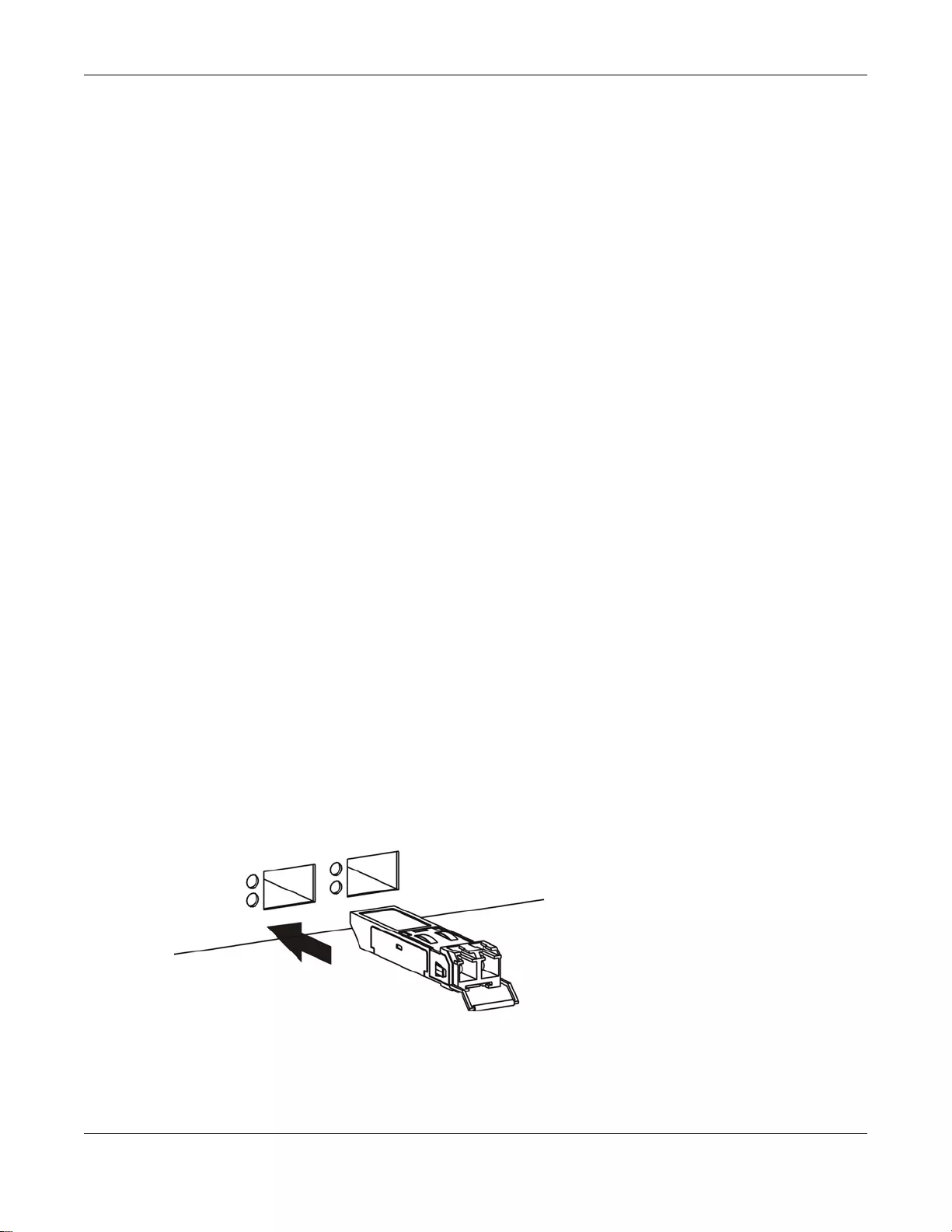
3.1.2.1 Transceiver Installation
Use the following steps to install a transceiver.
1Insert the transceiver into the slot with the exposed section of PCB board facing down.
Figure 18 Transceiver Installation Example
2Press the transceiver firmly until it clicks into place.
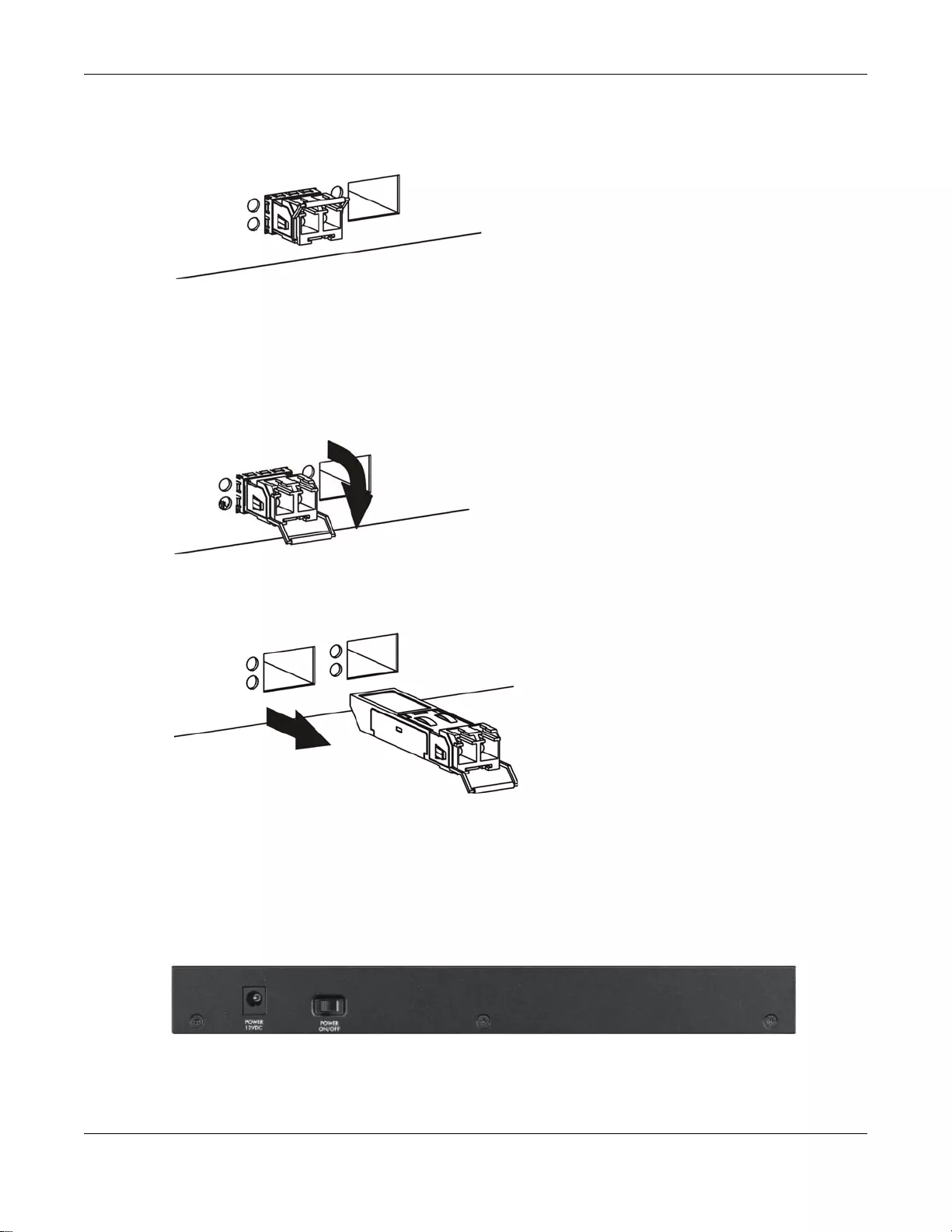
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
27
3The Switch automatically detects the installed transceiver. Check the LEDs to verify that it is
functioning properly.
Figure 19 Installed Transceiver
3.1.2.2 Transceiver Removal
Use the following steps to remove a transceiver.
1Open the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
Figure 20 Opening the Transceiver’s Latch Example
2Pull the transceiver out of the slot.
Figure 21 Transceiver Removal Example
3.2 Rear Panel
The following figures show the rear panels of the Switch.
Figure 22 Rear Panel: GS1900-8

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
28
Figure 23 Rear Panel: GS1900-8HP
Figure 24 Rear Panel: GS1900-10HP
Figure 25 Rear Panel: GS1900-16
Figure 26 Rear Panel: GS1900-24E
Figure 27 Rear Panel: GS1900-24
Figure 28 Rear Panel: GS1900-24HP
Revision B1
Revision A1

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
29
Figure 29 Rear Panel: GS1900-48
Figure 30 Rear Panel: GS1900-48HP
3.2.1 Power Connection
Make sure you are using the correct power source and that no objects obstruct the airflow of the
fans.
The Switch uses two power supply modules, one of which is redundant, so if one power module fails
the system can operate on the remaining module.
Rear Panel Power Connection
Connect one end of the supplied power cord or power adaptor to the power receptacle on the back
of the Switch and the other end to the appropriate power source.
For Switches with a power switch (see Table 1 on page 15), use the POWER ON/OFF switch to
have the Switch power on or off.
Connecting the Power
Use the following procedures to connect the Switch to a power source after you have installed it in
a rack.
Note: Use the included power cord for the AC power connection.
1Connect the female end of the power cord to the AC power socket.
2Connect the other end of the cord to a power outlet.
Disconnecting the Power
The power input connectors can be disconnected from the power source individually.
1Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet.
2Disconnect the power cord from the AC power socket.
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
30
3.3 LEDs
After you connect the power to the Switch, view the LEDs to ensure proper functioning of the
Switch and as an aid in troubleshooting.
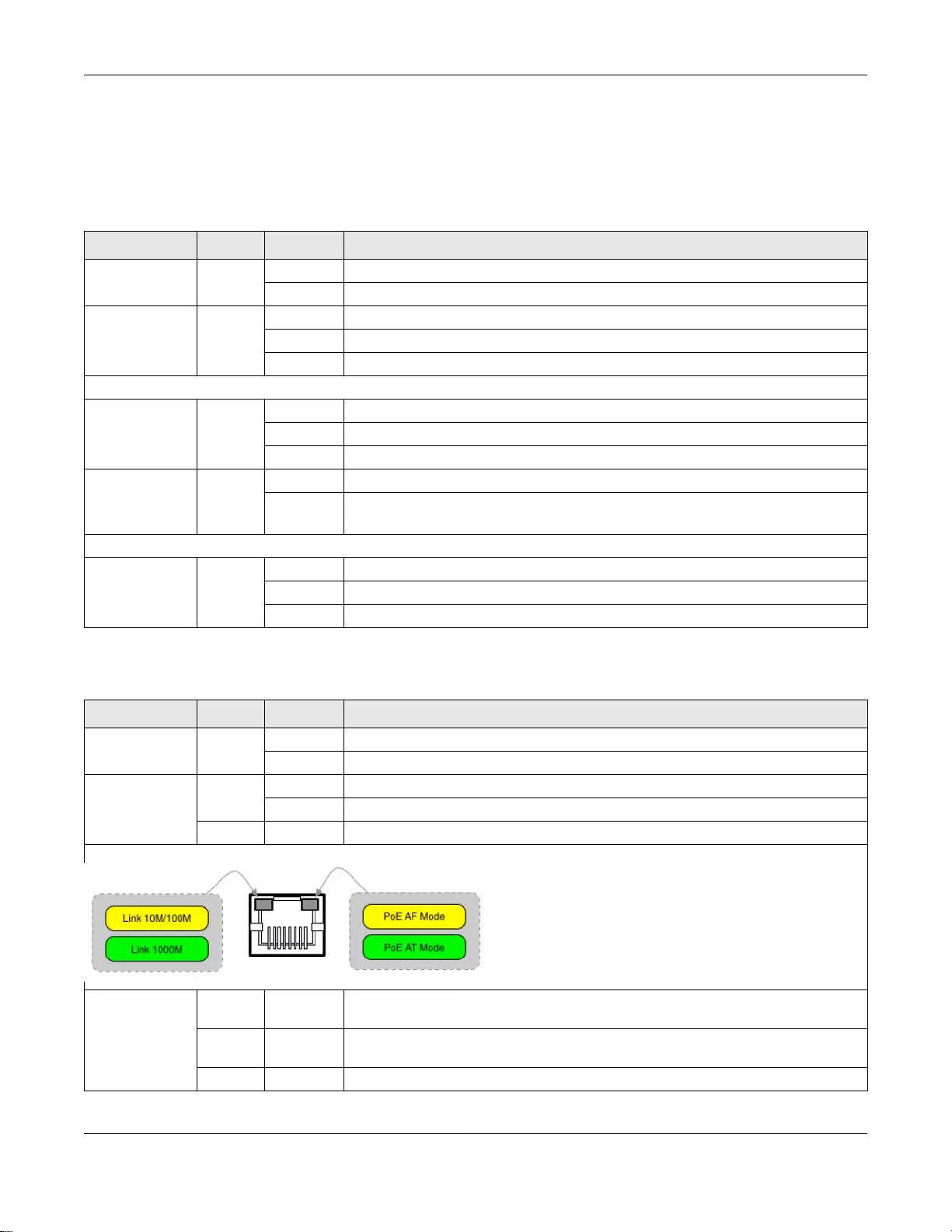
Table 3 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The system is turned on.
Off The system is off or has failed.
SYS Green On The system is on and functioning properly.
Blinking The system is rebooting and performing self-diagnostic tests.
Off The power is off or the system is not ready/malfunctioning.
Ethernet Ports
LNK/ACT Green Blinking The syst e m is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100/1 000 Mbps Et hernet network.
On The link to a 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Off The link to an Ethernet network is down.
PoE
(see Section
1.1 on page 15)
Green On Power is supplied to all PoE Ethernet ports.
Off There is no power supply.
1G SFP Slots (Fiber Ports - see Section 1.1 on page 15)
LNK/ACT Green Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100/1000 Mbps Fiber network.
On The link to a 100/1000 Mbps Fiber network is up.
Off The link to a Fiber network is down.
Table 4 LED Descriptions (GS1900-8HP (Revison B1) and GS1900-10HP Only)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The system is turned on.
Off The system is off or has failed.
SYS Green On The system is on and functioning properly.
Blinking The system is rebooting.
Red On There is a system error.
PoE 10/100/1000Base-T Ports (1-8), 2 LEDs per port
Right Amber On The port is in PoE AF mode. That is , the Switch is following the IEEE 802.3af
standard to supply power to this port.
Green On The port is in PoE AT mode. That is, the Switch is following the IEEE 802.3at
standard to supply power to this port.
Off Power is not supplied to this port.
RightLeft

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
31
Left Amber On The link to a 10/100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100/1000 Mbps Fiber network.
Green On The link to a 1 Gbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from 1 Gbps Mbps Ethernet network.
Table 4 LED Descriptions (continued)(GS1900-8HP (Revison B1) and GS1900-10HP Only)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Table 5 LED Descriptions for SFP Port (GS1100-10HP and GS1900-10HP Only)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Two arrow LEDs for 1G SFP Slots (Fiber Ports)
right/left
arrows Amber On The link to a 100 Mbps Fiber network is up.
Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100 Mbps Fiber network.
Green On The link to a 1 Gbps Fiber network is up.
Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from 1 Gbps Mbps Fiber network.
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
32
CHAPTER 4
ZON Utility
This chapter describes the screens for ZON Utility.
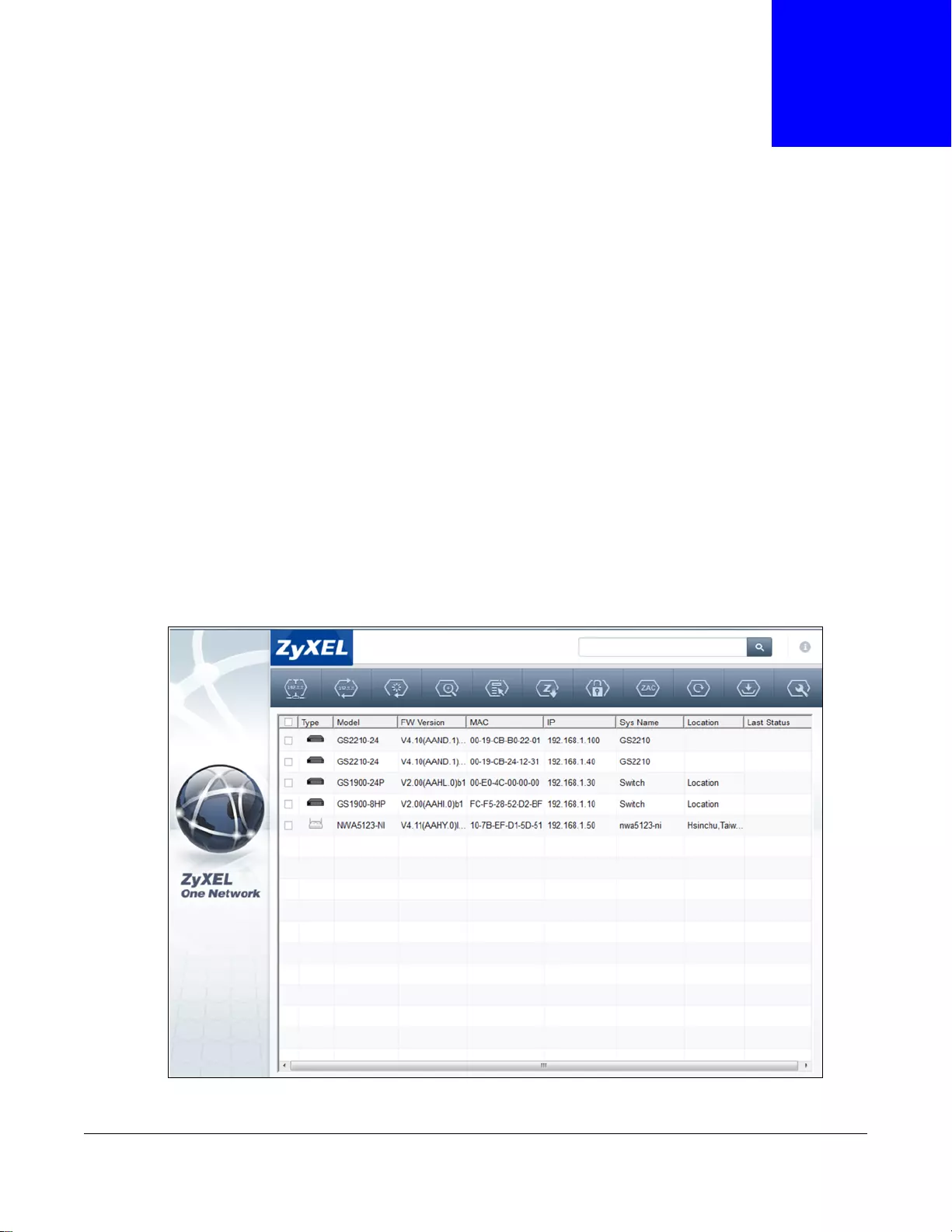
4.1 ZyXEL One Network (ZON) Utility Screen
ZON Utility is a program designed to help you deploy and manage a network more efficiently. It
detects devices automatically and allows you to do basic settings on devices in the network without
having to be near it.
The ZON Utility issues requests via ZyXEL Discovery Protocol (ZDP) and in response to the query,
the device responds back with basic information including IP address, firmware version, location,
system and model name in the same broadcast domain. The information is then displayed in the
ZON Utility screen and you can perform tasks like basic configuration of the devices and batch
firmware upgrade in it. You can download the ZON Utility at www.zyxel.com and install it on a PC.
The following figure shows the ZON Utility screen.
Figure 31 ZON Utility Screen
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
33
CHAPTER 5
The Web Configurator
5.1 Overview
The Switch Web Configurator allows easy management using an Internet browser.
In order to use the Web Configurator, you must:
• Use Internet Explorer 7.0 and later or Firefox 1.5 and later
• Allow pop-up windows
• Enable JavaScript (enabled by default)
• Enable Java permissions (enabled by default)
• Enable cookies
The recommended screen resolution is 1024 x 768 pixels and higher.
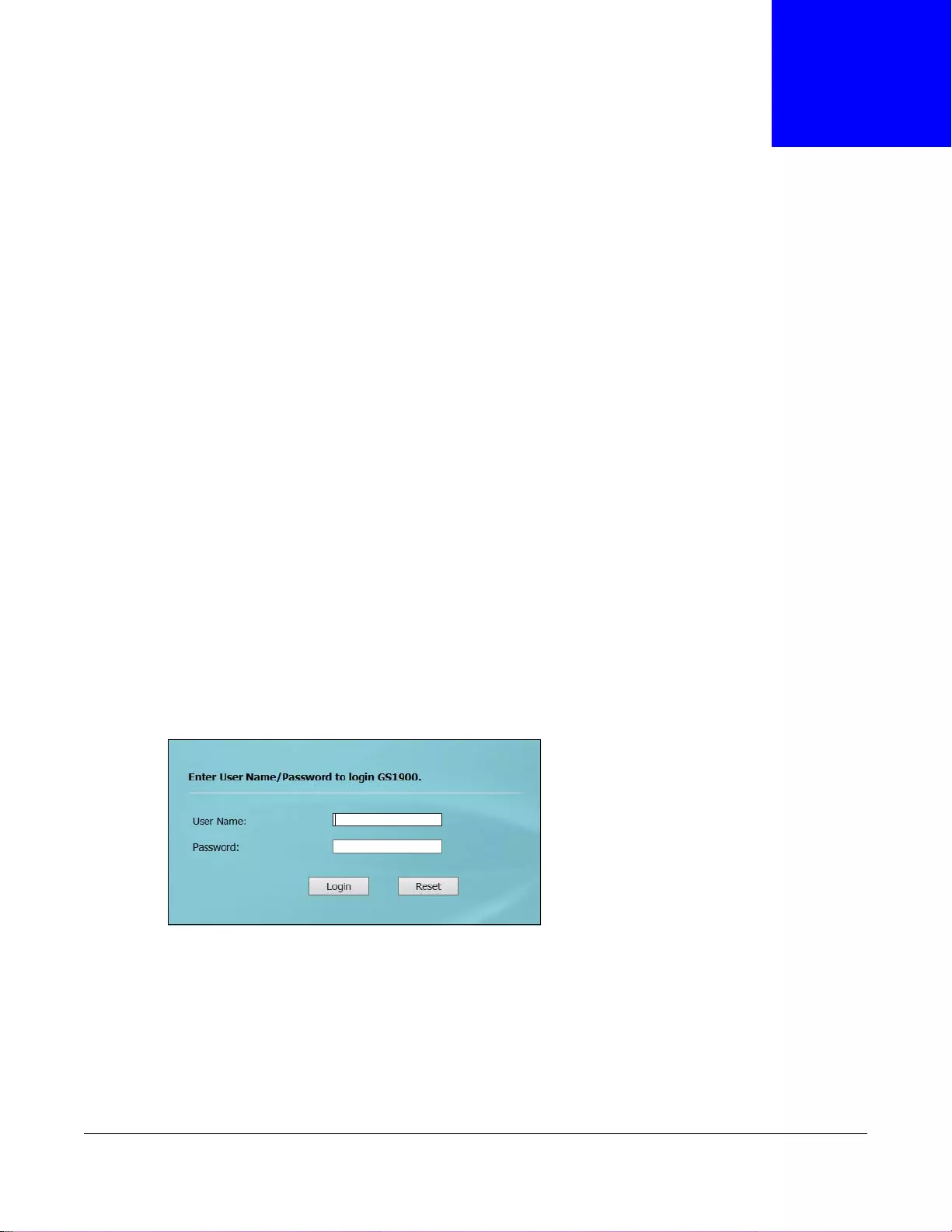
5.2 Access
1Make sure your Switch hardware is properly connected. See the Quick Start Guide.
2Browse to https://192.168.1.1. The Login screen appears.
Figure 32 The Login Screen
3Enter the user name (default: “admin”) and password (default: “1234”).
4Click Login. If y ou logged in using the default user name and password, getting start appears. The
Getting Start screen appe ars every time you log in using the default user name and default
password.

Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
34
5.3 Navigating the Web Configurator
The following summarizes how to navigate the web configurator from the Getting Start screen.
This guide uses the GS1900-10HP screens as an example. The screens may vary slightly for
different models.
Figure 33 The Web Configurator’s Main Screen
The Web Configurator’s main screen is divided into these parts:
•A - Title Bar
•B - Navigation Panel
•C - Main Window
5.3.1 Title Bar
The title bar provides some useful links that always appear over the screens below, regardless of
how deep into the Web Configurator y ou na vigate.
Figure 34 Title Bar
The icons provide the following functions.
Click Logout in a screen to exit the web configurator. You have to log in with your password again
after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session for security reasons.
A
BC
Table 6 Title Bar: Web Configurator Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this to log out of the Web Configurator.
OK Click OK to apply the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Save Click this to apply your changes to the Switch’s run-time memory. The Swit ch loses these
changes if it is turned off or loses power, so use the Save link on the top navigation panel
to save your changes to the non-volatile memory when you are done configuring.
About Click this to display basic information about the Switch.
Help Click this to open the help page for the current screen.
Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
35
Click OK and confirm at the pop-up screen to complete the task. Click Cancel and confirm at the
pop-up screen to discard the changes.
Figure 17 Web Configurator: Logout Screen
5.3.2 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens to configure Switch features. The
following sections introduce the Switch’s navigation panel menus and their screens.
Figure 35 Navigation Panel
Getting Start
Getting Start displays general device information, system status, system resource usage, and
interface status.
For details on Getting Start features, see Chapter 6 on page 41.
Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
36
Monitor Menu
The monitor menu screens display status and statistics information.
Table 7 Monitor Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
System This link takes you to a screen where you can see general
identification information for the Switch.
IP IPv4 This link takes you to a screen where you can see an IPv4 interface
and the IPv4 settings on the Switch.
IPv6 This link takes you to a screen where you can see an IPv6 interface
and the IPv6 settings on the Switch.
Information This link takes you to a screen that displays general system
information: system name, system location, and system contact.
Port This link takes you to screens where you can see speed, flow control
and priority settings for individual Switch ports.
Port Status Displays status settings for individual Switch ports.
Port Counters Displays interface, port 1 interface mib counters, port 1 etherlike mi b
counters, port 1 RMON mib counters settings for individual Switch
ports.
Bandwidth
Utilization Displays port bandwidth utilization settings for individual Switch
ports.
PoE Displays PoE status.
Bandwidth
Management Bandwidth
Control Displays egress global burst and port rate for individual Switch ports.
Storm Control This link takes you to a screen that displays broadcast filters.
VLAN This link takes you to screens where you can see port-based or
802.1Q VLAN (depending on what you configured in the Switch Setup
menu). Yo u can also see a protocol based VLAN or a subnet based
VLAN in these screens.
VLAN VLAN Displays VLAN settings.
Port Displays port settings.
VLAN Port Displays VLAN port settings.
Guest VLAN Displays global and port settings.
Voice VLAN Displays global and port settings.
MAC Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC address
and VLAN ID of a device attach to a port. Y ou can also view what kind
of MAC address it is.
Link Aggregation LAG This link takes you to screen where you can view aggregate physical
links to form one logical, higher-bandwidth link.
Loop Guard This link takes you to a screen where you can view protection against
network loops that occur on the edge of your network.
Multicast This link takes you to screen where you can view various multicast
features, IGMP s nooping and create multicast VLANs.
IGMP VLAN Displays VLAN settings.
Statistics Displays statisti cs settings.
Group Displays group settings.
Router Displays router settings.
Spanning Tree This link takes you to screens where you can view CIST, MST, STP
preventing network loops.

Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
37
Configuration Menu
Use the configuration menu screens to configure the Switch’s features.
CIST Displays CIST instance status.
CIST Port Displays CIST port status.
MST Displays MST instance status.
MST Port Displays MST port status.
STP Statistics Displays STP statistics.
LLDP Displays statistics, remote information, and overloading.
Statistics Displays LLDP global and port statistics.
Remote
Information Displays remote device information.
Overloading Displays port overloading information.
Security Displays port security and 802.1X settings.
Port Security Displays global and port settings.
802.1X Port Displays 802.1X port settings.
Authenticated
Hosts Displays authenticated hosts table.
Management Displays syslog and error disable.
Syslog Displays logging filter select and show system log.
Error Disable Displays global and port settings.
Table 8 Configuration Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
System This link takes you to a screen where you can configur e general
identification informat ion and time settings for the Switch.
IP IPv4 This link takes you to a screen where you can enable an IPv4
interface and configure the IPv4 settings on the Switch.
IPv6 This link takes you to a screen where you can enable an IPv6
interface and configure the IPv6 settings on the Switch.
Time System Time Configure time of system.
SNTP Server Configure SNTP server settings .
Information System
Information This link takes you to a screen that configures general system
information: syste m name, system location, and system contact.
Port This link takes y ou to screens wher e you can con figure speed, f low
control and priority settings for individual Switch ports.
Port Configure port settings for individual Switch ports.
EEE Configure EEE settings for individual Switch ports.
PoE Global This link tak es you to a s cr een where y o u can co nfig ure th e glob al
settings for the Switch to supply power over Ethernet (PoE).
Port This link takes you to a screen where you can configure port PoE
settings.
Bandwidth
Management Bandwidth Control Configure egress global burst and port rate.
Storm Control Port Configure port setting s.
Table 7 Monitor Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
38
VLAN This link takes you to screens where you can configure VLAN,
guest VLAN, and voice VLAN settings.
VLAN VLAN Configure VLAN settings.
Port Configure port settings.
VLAN Port Configure VLAN port settings.
Guest VLAN Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
Voice VLAN Global Configure global settings.
OUI Configure OUI settin gs.
Port Configure port settings.
MAC Table This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the MAC
address and VLAN ID of a device attach to a port. You can also
configure what k ind of MAC address it is.
Static MAC This link tak e s y o u t o sc re ens where you can configure static MAC
addresses for a port. These static MAC addresses do not age out.
Filtering MAC This link takes you to a screen to set up filtering rules.
Dynamic Age Configure dynamic learned and MAC address information.
Link Aggregation This link takes you to screen where you can logically aggregate
physical links to form one logical, higher-bandwidth link.
Global Configure global settings.
LAG Management Configure LAG management settings.
LAG Port Configure LAG port settings.
LACP Port Configure LACP port settings.
Loop Guard This link takes you to a screen where you can configure protection
against network loops that occur on the edge of your network.
Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
Mirror This link takes you to screens where you can copy traffic from one
port or ports to another port. Thus, allowing you to examine the
traffic from the first port without interference.
Multicast This link takes you to screen where you can configure various
multicast features, IGMP snooping and create multicast VLANs.
IGMP Global Configure global settings.
VLAN Configure Vlan settings.
Router Port Configure router port settings.
Profile Configure profile settings.
Throttling Configure throttling settings.
Spanning Tree This link takes you to screens where you can configure the RSTP/
MRSTP/MSTP to prevent network loops.
Global Configure global settings.
STP Port Configure STP port settings.
CIST Configure CIST settings.
CIST Port Configure CIST port settings.
MST Configure MST settings.
Table 8 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
39
MST Port Configure MST port settings.
LLDP Configure global, port, local information, MED network policy, and
MED port settings.
Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
Local Information Configure local information settings.
MED Network
Policy Configure MED network policy settings.
MED Port Configure MED port settings.
QoS Configure general and trust mode settings.
General Port Configure port settings.
Queue This link takes you to a screen where you can configure queuing
with associated queue weights for each port.
CoS Mapping Configure CoS mapping settings.
DSCP Mapping Configure DSCP mapping settings.
IP Precedence
Mapping Configure IP precedence mapping settings.
Trust Mode Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
Security Configure port security, protected port, 802.1X and DoS settings.
Port Security Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
Protected Port Configure protected port settings.
802.1X Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
DoS Global Configure global settings.
Port Configure port settings.
AAA This link takes you to a screen where you can view authentication,
authorization and accounting services via external servers. The
external servers can be either RADIUS (Remote Authentication
Dial-In User Service) or TACA CS+ (Terminal Access Controller
Access-Control System Plus).
Auth Me thod Configure auth method settings .
RADIUS Configure RADIUS settings.
TACACS+ Configure TACACS+ settings.
Management Configure syslog, SNMP, error disable, HTTP/HTTPS, users and
remote access control.
Syslog Global Configure global settings.
Local Configure local settings.
Remote Configure remote settings.
SNMP Global Configure global settings.
Community Configure community settings.
Group Configure group settings.
User Configure users settings.
Table 8 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Web Configurator
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
40
Maintenance Menu
Use the maintenance menu screens to manage configuration and firmware files, run diagnostics,
and reboot or shut down the Switch.
Trap Configure trap settings.
Trap Destination Configure trap destination settings.
Error Disable This link takes you to a screen where you can configure CPU
protection and error disable recovery.
HTTP/HTTPS HTTP Configure HTTP settings.
HTTPS Configure HTTPS sett ings.
Users Configure users settings.
Remote Access
Control This link takes you to a screen where you can configure global and
profile settings.
Table 9 Maintenance Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Firmware Upload Manage upload settings.
Management Manage dual image and images information.
Configuration Backup Manage backup configuration.
Restore Manage restore configuration.
Management Manage configuration settings.
Factory Default Restore factory defaults.
Diagnostics This link takes you to screens where you can view system logs and
can test port(s).
Port Test Cable Diag Manage cable diag a n d test results.
PING IPv4 Manage ping test settings.
IPv6 Manage IPv6 ping test settings.
Trace Trace Route Manage trace route settings.
Reboot Reset the system.
Table 8 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
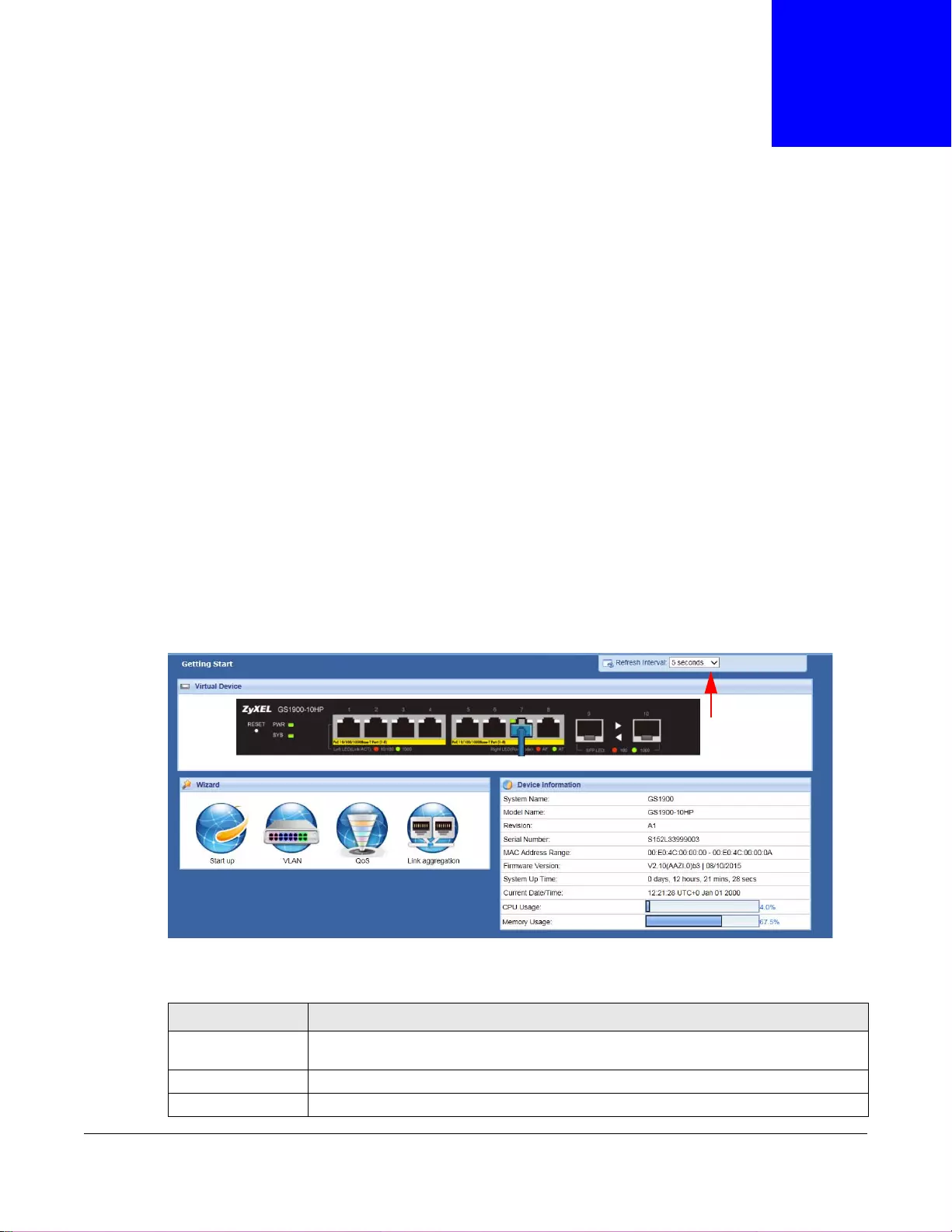
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
41
CHAPTER 6
Getting Start
6.1 Overview
Use the Getting Start screens to check status information about the Switch.
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The main Getting Start screen (Section 6.2 on page 41) displays the Switch’s general device
information, system status, system resource usage, and interface status. You can also display
other status screens for more information.
6.2 Getting Start
This screen is the first thing you see when you log into the Switch. It also appears every time you
click the Getting Start icon in the navigation panel. The Getting Start displays general device
information, system status, system resource usage, and interface status in widgets.
Figure 36 Getting Start
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 10 Getting Start
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interv al (A) Use the drop-box to select: None, 5 seconds, 10 seconds, 15 seconds, 20 seconds, 25
seconds, or 30 seconds.
Virtual Device Displays an image of the Switch.
Wizard Displays the following links: Start up, VLAN, QoS, and link aggregation.
A

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
42
6.2.1 Wizard
Wizard displays start up, VLAN, QoS, and link aggregation.
For details on Wizard features, see system Chapter 7 on page 52, VLAN Chapter 9 on page 62, QoS
Chapter 28 on page 172, and link aggregation Chapter 11 on page 70.
Star t up
In start up, you can set up IP/DNS, set up your username/password, and view finished results.
In order to set up your IP/DNS, please do the following. Click Getting Start > Start up > 1 Step
1 Set up IP to access this screen.
Device Information
System Name This field displays the name used to identify the Switch on any network.
Model Name This field displays the model name of this Switch.
Revision This field displays the hardware revision number of this Switch.
Serial Number This field displays the serial number of this Switch.
MAC Address
Range This field displays the MAC addresses used by the Switch. Each phys ical port or wireless
radio has one MAC address. The first MAC address is assigned to the Ethernet LAN port,
the second MAC address is assigned to the first radio, and so on.
Firmware
Version This field displays the version number and date of the firmware the Switch is currently
running.
System Up Time This field displays how long the Switch has been running since it last restarted or was
turned on.
Current Date/
Time This field displays the current date and time in the Switch. The format is hh:mm:ss
yyyy-mm-dd .
CPU Usage This field displays the Switch’s recent CPU usage.
Memory Usage This field displays the Switch’s recent memory usage.
Ta ble 10 Getting Start (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
43
Figure 37 Getting Start > Start up > 1 Step 1 Set up IP
Each field is described in the following table.
After clicking Next, the set up your user name screen appears.
Table 1 1 Getting Start > Start up > 1 Step 1 Set up IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Host Name This field displays a host name.
IP Address The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory
default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies t he network number portion of an IP address.
The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Gateway Type the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted deci mal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254.
DNS DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa. Enter a domain name server IP address in order to be able to
use a domain name instead of an IP address.
NTP(Network Time
Protocol) This field displays the NTP time servers from which the Switch gets the time and date.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.
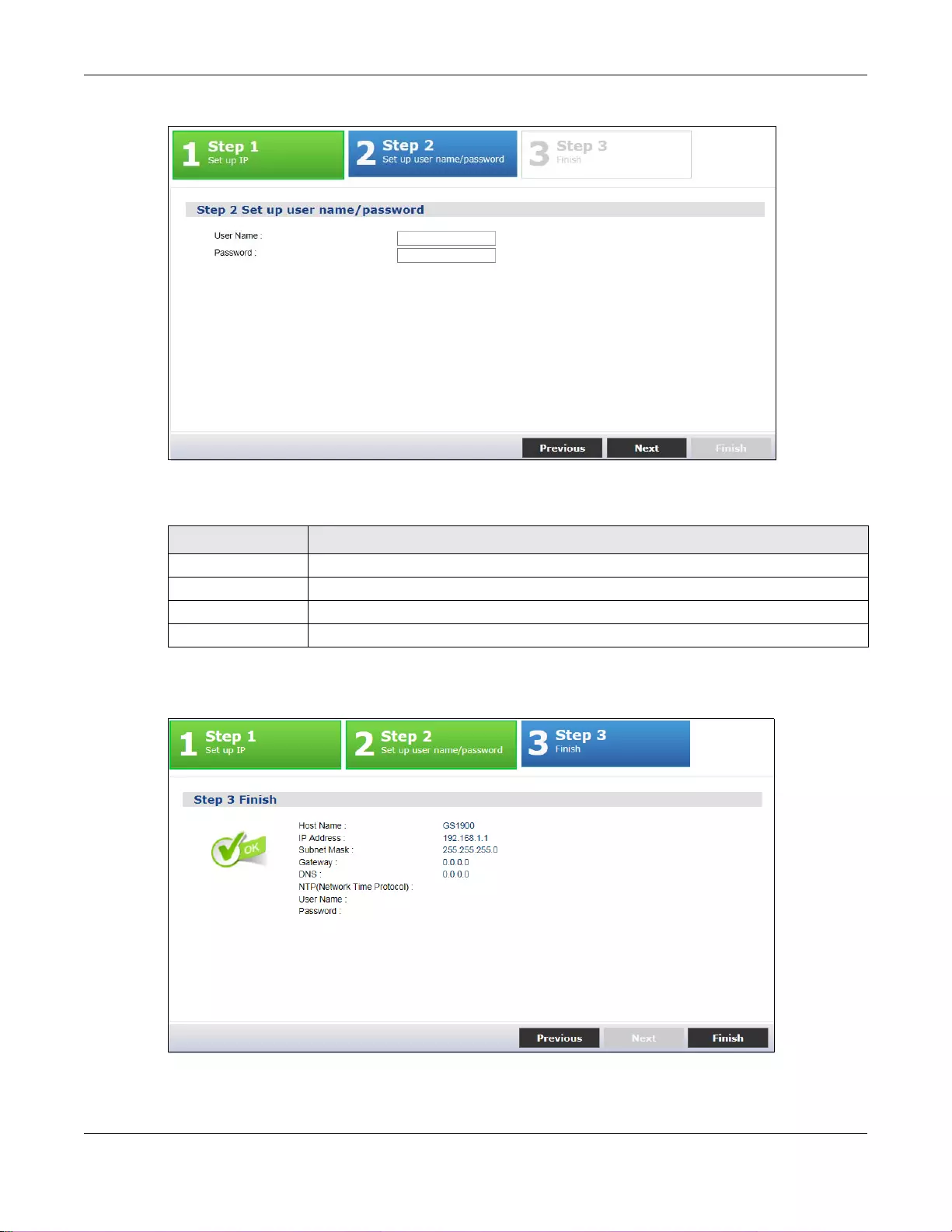
Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
44
Figure 38 Getting Start > Start up > 2 Step 2 Set up user name/password
Each field is described in the following table.
After clicking Next, the finish screen appears.
Figure 39 Getting Start > Start up > 3 Step 3 Finish
Ta ble 12 Getting Start > Start up > 2 Step 2 Set up user name/password
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username The default username is admin and associated default password is 1234.
Password The default username is admin and associated default password is 1234.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
45
Each field is described in the following table.
VLAN
In VLAN, you can create VLAN, tag VLAN setting, and view finished results.
In order to create VLAN, please do the following. Click Getting Start > VLA N > 1 St ep 1 Cr eate
VLAN to access this screen.
Figure 40 Getting Start > VLAN > 1 Step 1 Cre a te VLAN
Ta ble 13 Getting Start > Start up > 3 Step 3 Finish
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Host Name This field displays a host name.
IP Address The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory
default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies t he network number portion of an IP address.
The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Gateway Type the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted deci mal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254.
DNS DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa. Enter a domain name server IP address in order to be able to
use a domain name instead of an IP address.
NTP(Network Time
Protocol) This field displays the NTP time servers from which the Switch gets the time and date.
Username The default username is admin and associated default password is 1234.
Password The default username is admin and associated default password is 1234.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Finish Review the information and click Finish to create the task.
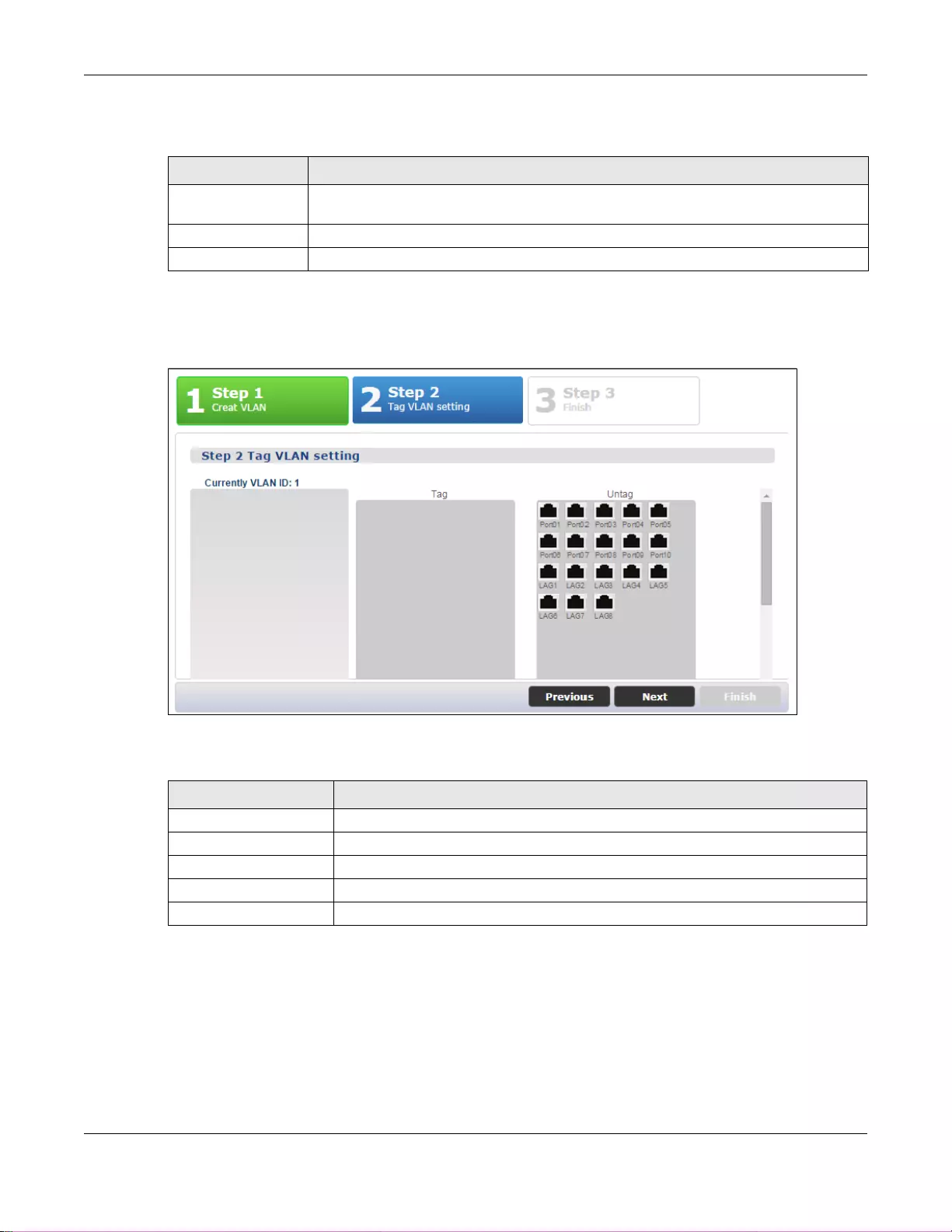
Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
46
Each field is described in the following table.
After clicking Next, the tag VLAN setting screen appears.
Figure 41 Getting Start > VLAN > 2 Step 2 Tag VLAN Setting
Each field is described in the following table.
After clicking Next, the finish screen appears.
Ta ble 14 Getting Start > VLAN > 1 Step 1 Create VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Create VLAN ID (1-
4094) Type a number between 1 and 4094 to create a VLAN ID.
Edit VLAN ID Select from the drop-box a VLAN ID.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.
Ta ble 15 Getting Start > VLAN > 2 Step 2 Tag VLAN Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Currently VLAN ID This field displays the VLAN identification number.
Tag Ports belonging to the specified VLAN tag all outgoing frames transmitted.
Untag Ports belonging to the specified VLAN don't tag all outgo ing frames transmitted.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
47
Figure 42 Getting Start > VLAN> 3 Step 3 Finish
Each field is described in the following table.
QoS
In QoS, you can create QoS settings, and view finished results.
In order to create QoS settings, please do the following. Click Getting Start > QoS > 1 Step 1
QoS (Quality ofOf Service) to access this screen.
Ta ble 16 Getting Start > VLAN > 3 Step 3 Finish
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Currently VLAN ID This field displays the VLAN identification number.
Tag Ports belonging to the spe cified VLAN tag all outgoing frames transmitted.
Untag Ports belonging to the specified VLAN don't tag all outgoing frames transmitted.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Finish Review the information and click Finish to create the task.

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
48
Figure 43 Getting Start > QoS > 1 Step 1 QoS (Quality of Service)
Each field is described in the following table.
After clicking Next, the finish screen appears.
Figure 44 Getting Start > QoS > 2 Step 2 Finish
Ta ble 17 Getting Start > QoS > 1 Step 1 QoS (Quality ofOf Service)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Highest Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Medium Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Low Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
49
Each field is described in the following table.
Link aggregation
In link aggregation, you can link aggregation and view finished results.
In order to create link aggregation settings, please do the following. Click Getting Start > Link
aggregation > 1 Step 1 Link aggregation to access this screen.
Figure 45 Getting Start > Link aggregation > 1 Step 1 Link aggregation
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 18 Getting Start > QoS > 2 Step 2 Finish
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Highest Displays summary results.
Medium Displays summary results.
Low Displays summary results.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Finish Review the information and click Finish to create the task.
Ta ble 19 Getting Start > Link aggregation > 1 Step 1 Link aggregation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Group 1 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 2 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 3 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 4 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 5 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 6 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Group 7 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.

Chapter 6 Getting Start
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
50
After clicking Next, the finish screen appears.
Figure 46 Getting Start > Link aggregation > 2 Step 2 Finish
Each field is described in the following table.
Group 8 Click and drag icons located on the left to desired preference.
Next Click Next to show the next screen.
Ta ble 20 Getting Start > Link aggregation > 2 Step 2 Finish
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Group 1 Displays summary results.
Group 2 Displays summary results.
Group 3 Displays summary results.
Group 4 Displays summary results.
Group 5 Displays summary results.
Group 6 Displays summary results.
Group 7 Displays summary results.
Group 8 Displays summary results.
Previous Click Previous to show the previous screen.
Finish Review the information and click Finish to create the task.
Ta ble 19 Getting Start > Link aggregation > 1 Step 1 Link aggregation
LABEL DESCRIPTION

51
PART II
Technical Reference
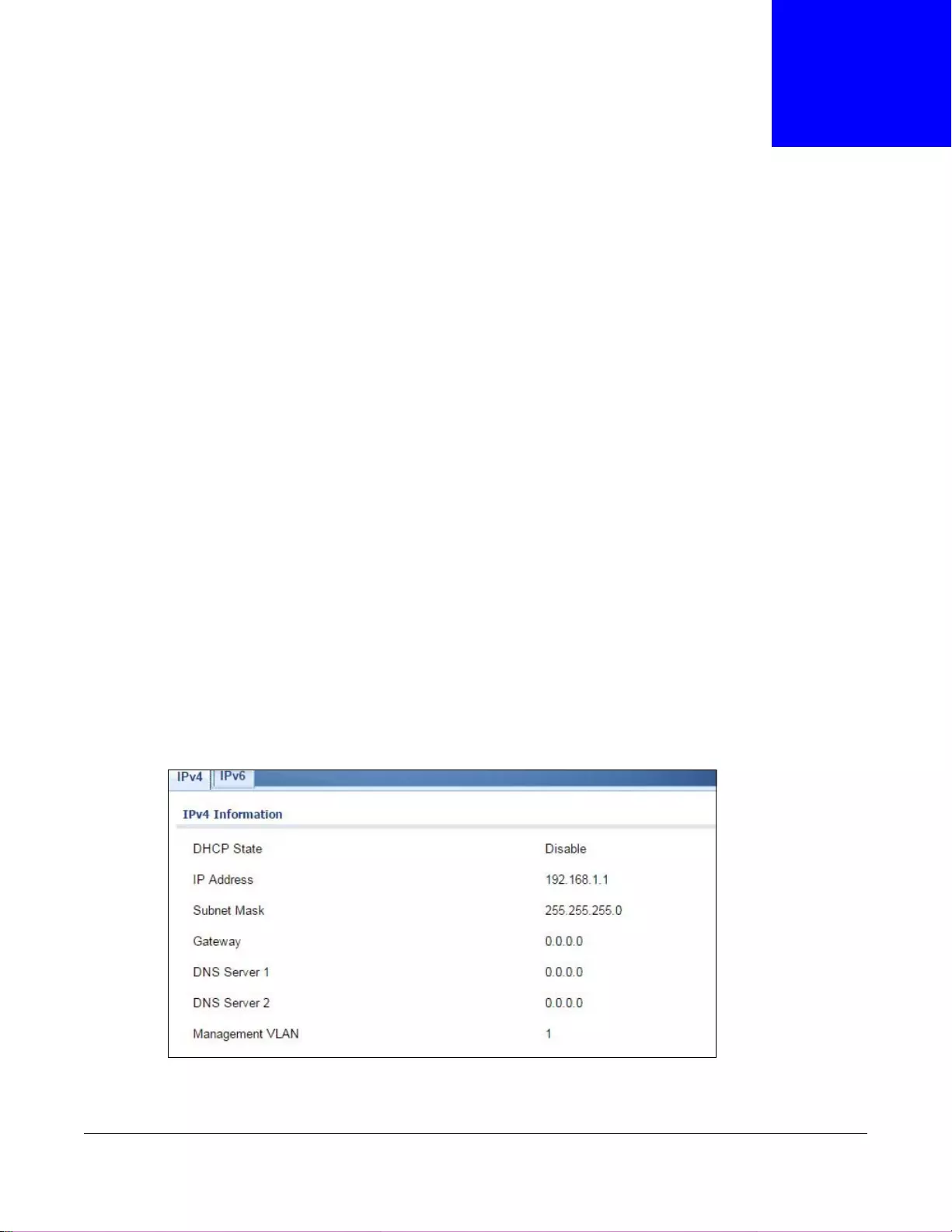
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
52
CHAPTER 7
Monitor: System
7.1 Overview
This section provides information for System in Monitor. Use the System screens to view general
Switch settings.
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The IP screen (Section 7.2 on page 52) displays IPv4 and IPv6.
•The Information screen (Section 7.3 on page 54) displays the system information.
7.2 IP
The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default IP
address is 192.168.1.1. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address.
The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
7.2.1 IPv4
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IPv4 information. Click Monitor > System > IP > IPv4 to
open this screen.
Figure 47 Monitor > System > IP > IPv4

Chapter 7 Monitor: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
53
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
7.2.2 IPv6
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IPv6 information. Click Monitor > System > IP > IPv6 to
open this screen.
Figure 48 Monitor > System > IP > IPv6
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 21 Monitor > System > IP > IPv4
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DHCP State This field displa ys the state of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol RFC 2131 and RFC 2132
(DHCP).
IP Address This field displays IP address of the Switch in the IP domain.
Subnet Mask This field displays the subnet mask of the Switch in the IP domain.
Gateway This field displays the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal
notation, for example 192.168.1.254.
DNS Server 1 DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address
and vice versa. This field displays a domain name server IP address, enabling the use of a
domain.
DNS Server 2 DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address
and vice versa. This field displays a domain name server IP address, enabling the use of a
domain.
Management
VLAN This field displays the management VLAN.
Ta ble 22 Monitor > System > IP > IPv6
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Auto
Configuration This field displays auto configuration.
IPv6 Address This field displays IP address of the Switch in the IP domain.
IPv6 Gateway This field displays the IP address of the default outgoing gateway.
DHCPv6 Client This field displays the Switch’s DHCP settings when it is acting as a DHCPv6 client.
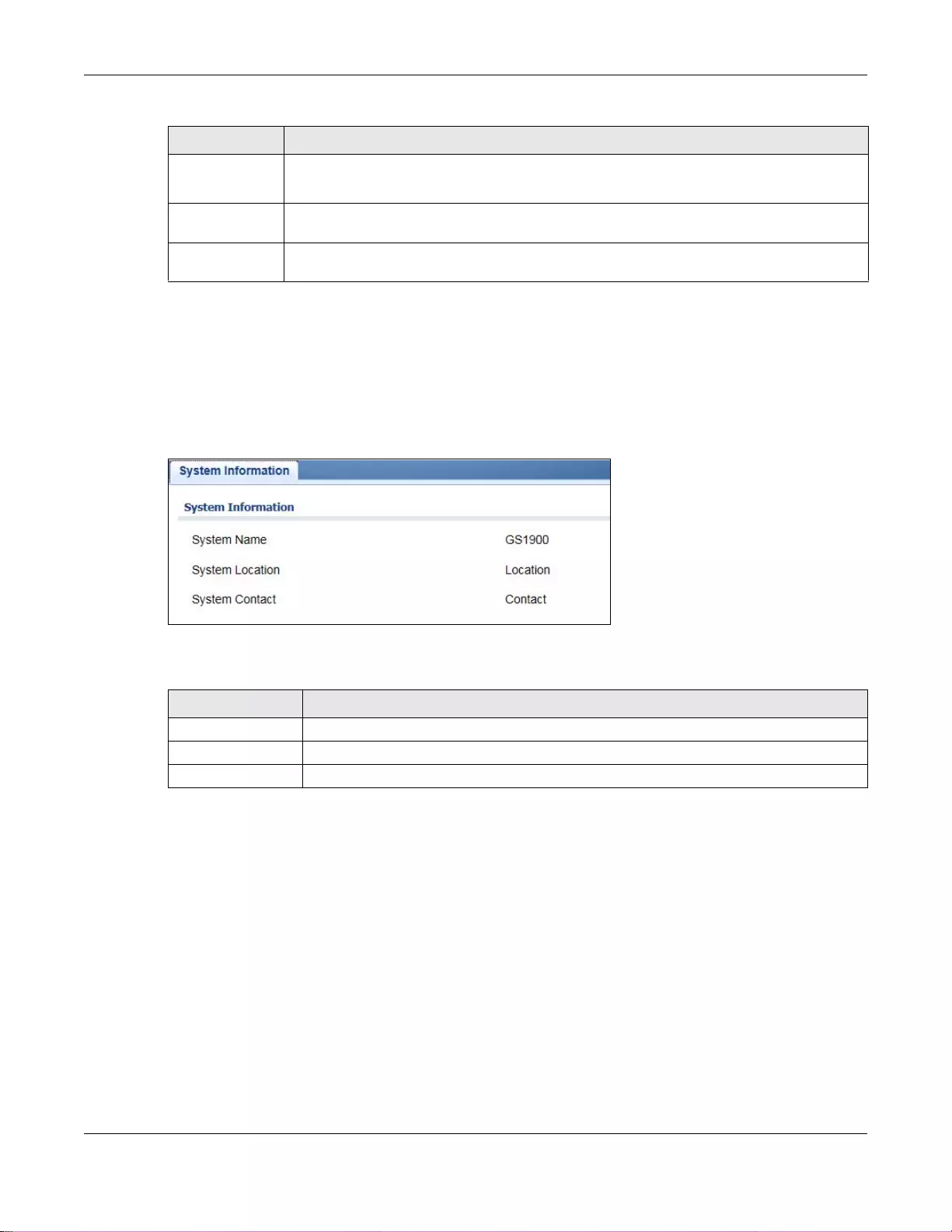
Chapter 7 Monitor: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
54
7.3 Information
In the navigation panel, click Monitor > System > Information > System Information to
display the screen as shown. You can view system information.
Figure 49 Monitor > System > Information > System Information
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
DHCPv6 DUID DUID(DHCP Unique Identifier).
The DHCP server will provide the IP address based on the DUID information from client.
DHCPv6 DNS
server 1 Primary DNS server IPv6 address form DHCP.
DHCPv6 DNS
server 2 Secondary DNS server IPv6 address from DHCP.
Ta ble 22 Monitor > System > IP > IPv6 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 23 Monitor > System > Information > System Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Name This field displays the descriptive name of the Switch for identification purposes.
System Location This field displays the geographic location of the Switch for identification purposes.
System Contact This field displays the person in charge of the Switch for identification purposes.
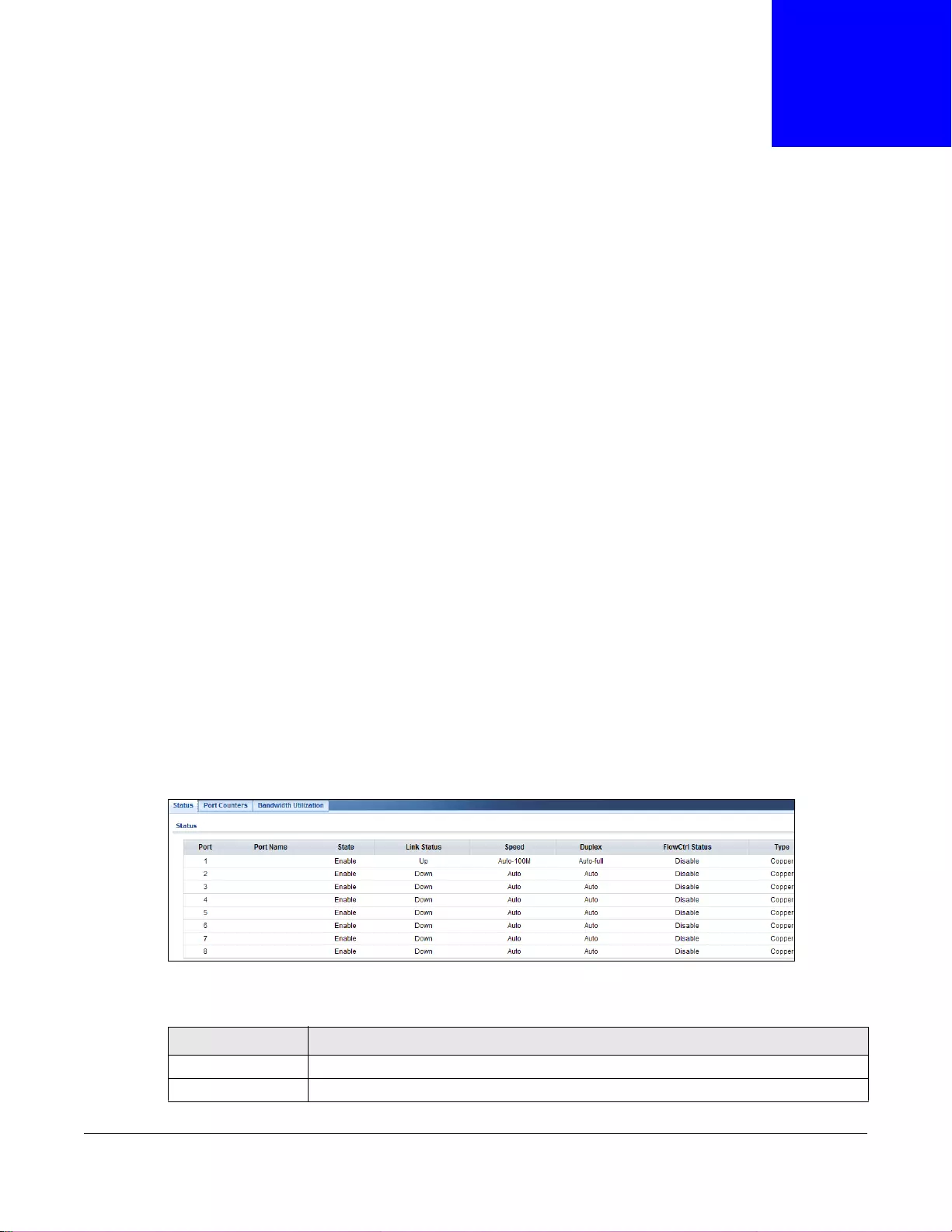
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
55
CHAPTER 8
Monitor: Port
8.1 Overview
This section provides information for Port in Monitor. Use the Port screens to view general S witch
port settings.
8.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Port screen (Section 8.2 on page 55) displays status, port counters, and bandwidth
utilization.
•The PoE screen (Section 8.3 on page 59) displays PoE.
•The Bandwidth Management screen (Section 8.4 on page 60) displays bandwidth control.
•The Storm Control screen (Section 8.5 on page 61) displays port settings of the Switch.
8.2 Port
Use this screen to view Switch port settings.
8.2.1 Status
Use this screen to view the Switch’s port statistics. Click Monitor > Port > Port > Status to
access this screen.
Figure 50 Monitor > Port > Port > Status
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 24 Monitor > Port > Port > Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This is the port index number.
Port Name A descriptive name that identifies this port.
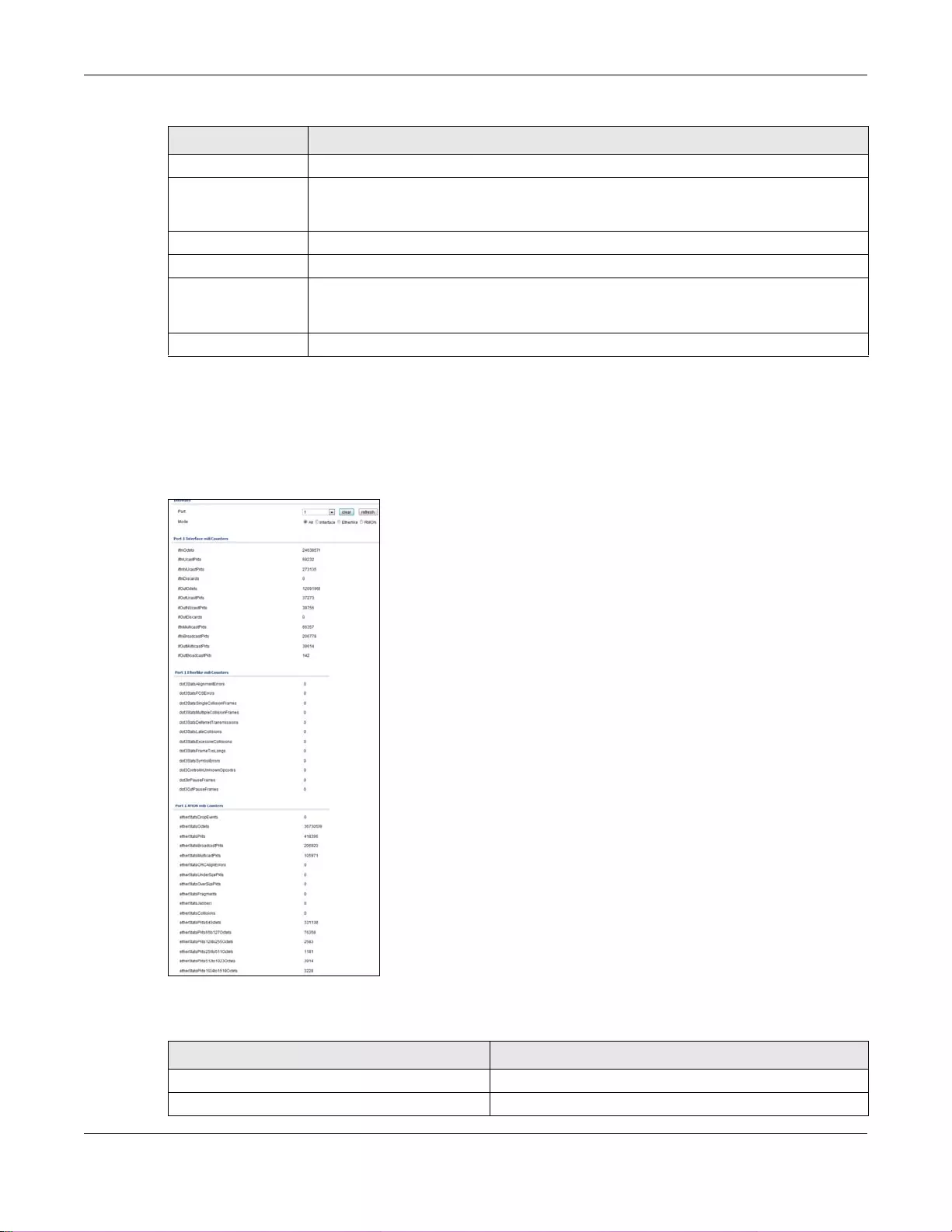
Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
56
8.2.2 Port Counters
Use this screen to view the Switch’s port counters settings. Click Monitor > Port > Port > Port
Counters to access this screen.
Figure 51 Monitor > Port > Port > Port Counters
Each field is described in the following table.
State This is port admin setting state.
Link Status This field displays Up, Down or NotPresent. It di spla ys Up when the port is linked up
or Down when it is not. When no any physical port is binding with this group, it
displays NotPresent.
Speed View the speed of the Et hernet connection on this port.
Duplex View the duplex mode of the Ethernet connection on this port.
FlowCtrl Status A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and overflows buffer
memory causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow Control is used to regulate
transmission of signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port.
Type View the type on this port.
Ta ble 24 Monitor > Port > Port > Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 25 Monitor > Port > Port > Port Counters
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface
Port This field displays the port.
Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
57
Mode This field displays the mode.
Port 1 Interface mib Counters
iflnOctet s This field displays the iflnOctets.
iflnUcastPk ts This field dis plays the iflnUcastPkts.
iflnNUca stPkts This field dis plays the iflnNUcastPkts..
ifInDiscards This field displays the ifInD iscards.
ifOutOctets This field dis plays the ifOutOctets.
ifOutUcast Pkts This field disp lays the ifOutUcastPkts.
ifOutNUcastPkts This field displays the ifOutNUcastPkts.
ifOutDiscards This field displays the ifOutDiscards.
ifInMulticastPkts This field displays the ifInMulticastPkts.
ifInBroadcastPkts This field displays the ifInBroadcastPkts.
ifOutMulticastP kts This field displays t he ifOutMulticastP k ts.
ifOutBroadcastPkts This field displays the ifOutB roadcastPkts.
Port 1 Etherlike mib Counters
dot3StatsAlignmentErrors This field displays the dot3StatsAlignmentErrors.
dot3StatsFCSErrors This field displays the dot3StatsFCSErrors.
dot3StatsSingleCollisionFrames This field displays the dot3StatsSingleCollisionFrames.
dot3StatsMultipleCollisionFrames This field displays the dot3StatsMultipleCollisionFrames.
dot3StatsDeferredTransmissions This field displays the dot3StatsDeferredTransmissions.
dot3StatsLateCollisions This field displays the dot3StatsLateCollisions.
dot3StatsExcessiveCollisions This field displays the dot3StatsExcessiveCollisions.
dot3StatsFrameTooLongs This field displays the dot3StatsFrameTooLongs.
dot3StatsSymbolErrors This field displays the dot3StatsSymbolErrors.
dot3ControlInUnkownOpcodes This field displays the dot3ControlInUnkownOpcodes.
dot3lInPauseFrames This field displays the dot3lInPauseFrames.
dot3lOutPauseFrames This field displays the dot3lOutPauseFrames.
Port 1 RMON mib Counters
etherStatsDropEvents This field displays the etherStatsDropEvents.
etherStatsOctets This field displays the etherStatsOctets.
etherStatsPkts This field displays the etherStatsPkts.
etherStatsBroadcastPkts This field displays the etherStatsBroadcastPkts.
etherStats MulticastPkts This field dis plays the etherStatsMultic astPkts.
etherStatsCRCAlignErrors This field displays the etherStatsCRCAlignErrors.
etherStatsUnderSizePkts This field displays the etherStatsUnderSizePkts.
etherStatsOverSizePkts This field displays the etherStatsOverSizePkts.
etherStatsFragments This field displays the etherStatsFragments.
etherStatsJabbers This field displays the etherStatsJabbers.
etherStats Collisions This field disp lays the etherStatsCollisions.
etherStatsPkts64Octets This field displays the etherStatsPkts64Octets.
etherStatsPkts65to127Octets This field displays the etherStatsPkts65to127Octets.
Ta ble 25 Monitor > Port > Port > Port Counters (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
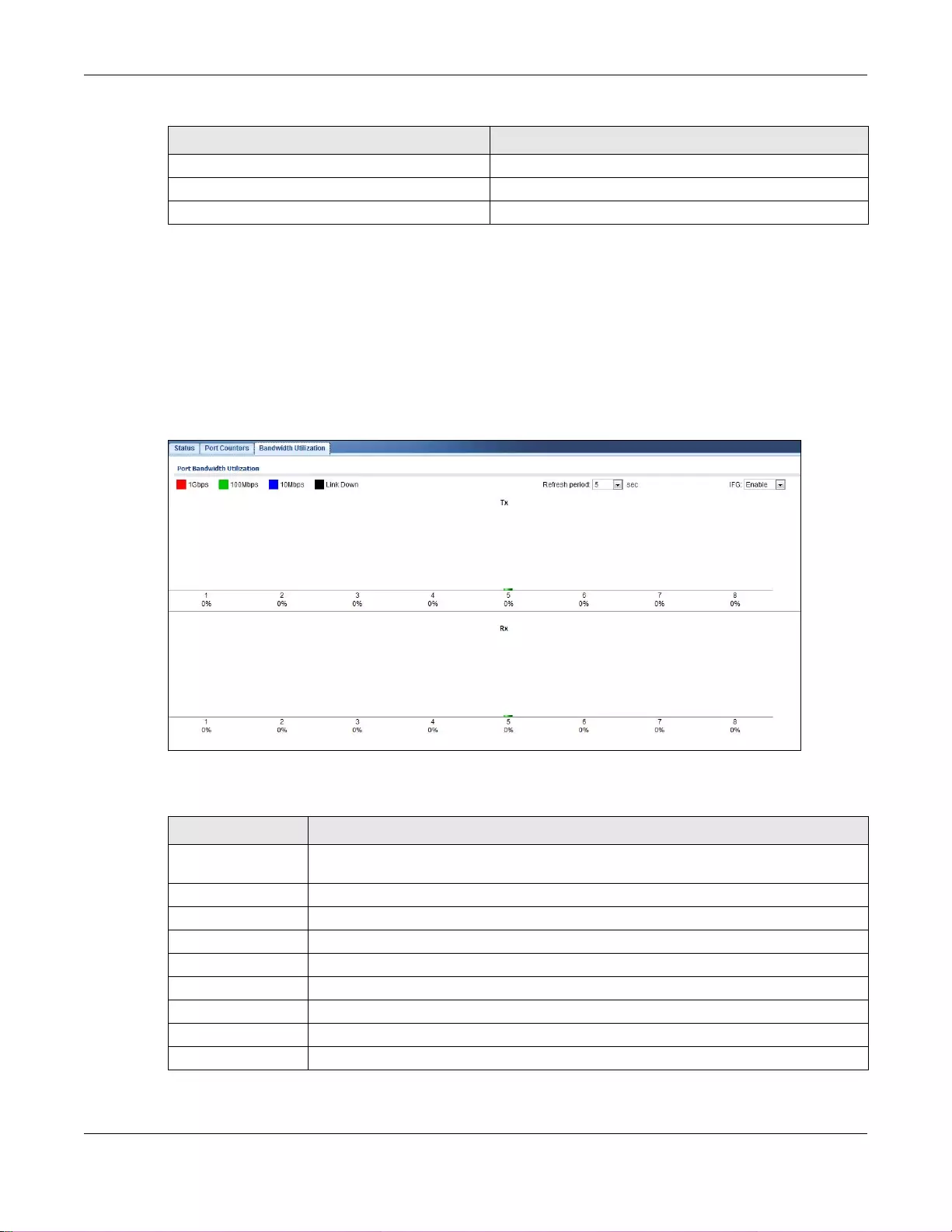
Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
58
8.2.3 Bandwidth Utilization
Utilization is the percentage of a network's bandwidth that is currently being consumed by network
traffic. Each vertical bar represents the highest utilization on a port, and can be either transmitted
(Tx) traffic or received (Rx) traffic during the last time interval in seconds.
Use this screen to view the Switch’s bandwidth utilization settings. Click Monitor > Port > Port >
Bandwidth Utilization to access this screen.
Figure 52 Monitor > Port > Port > Bandwidth Utilization
Each field is described in the following table.
etherStatsPkts128to255Octets This field displays the etherStatsPkts128to255Octets.
etherStatsPkts256to511Octets This field displays the etherStatsPkts256to511Octets.
etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets This field displays the etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets.
Ta ble 25 Monitor > Port > Port > Port Counters (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 26 Monitor > Port > Port > Bandwidth Utilization
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Bandwidth
Utilization
1Gbps This field displays the 1Gbps.
100Mbps This field displays the 100Mbps.
10Mbps This field displays the 10Mbps.
Link down This field displays the link down.
Refresh period This field displays the refresh period.
IFG This field displays the IFG.
Tx Transmitted (Tx) traffic during t he last time interval in seconds.
Rx Received (Rx) traffic during thetime interval in seconds.

Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
59
8.3 PoE
Note: The PoE function and the following screens are available for models ending in “HP”
only.
The Switch supports both the IEEE 802.3af P ower over Ethernet (PoE) and IEEE 802.3at High Power
over Ethernet (PoE) standards. The Switch is Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) because it provides
a source of power via its Ethernet ports, and each device that receives power through an Ethernet
port is a Powered Device (PD).
In the figure below, the IP camer a and IP phone get their power directly from the Switch. Aside
from minimizing the need for cables and wires, PoE removes the hassle of trying to find a nearby
electric outlet to power up devices.
Figure 53 Powered Device Examples
You can also set priorities so that the Switch is able to reserve and allocate power to certain PDs.
Note: The PoE devices t h at su pp l y or receive power and their connected Ethernet cables
must all be completely indoors.
To view the current amount of power that PDs are receiving from the Switch, click Monitor > Port
> PoE.
Figure 54 Monitor > Port > PoE
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 27 Monitor > Port > PoE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PoE Mode This field displays the power management mode used by the Switch, whether it is in
Classification or Consumption mode.
Total Power(W) This field displays the total power the Switch can provide to the connected PoE-enabled
devices on the PoE ports. The total power of GS1900-10HP is 77W and GS1900-8HP is
70W.
Consuming
Power(W) This field displays the total amount of power the Switch is currently supplying to the
connected PoE-enabled devices.
PSE
PD PD
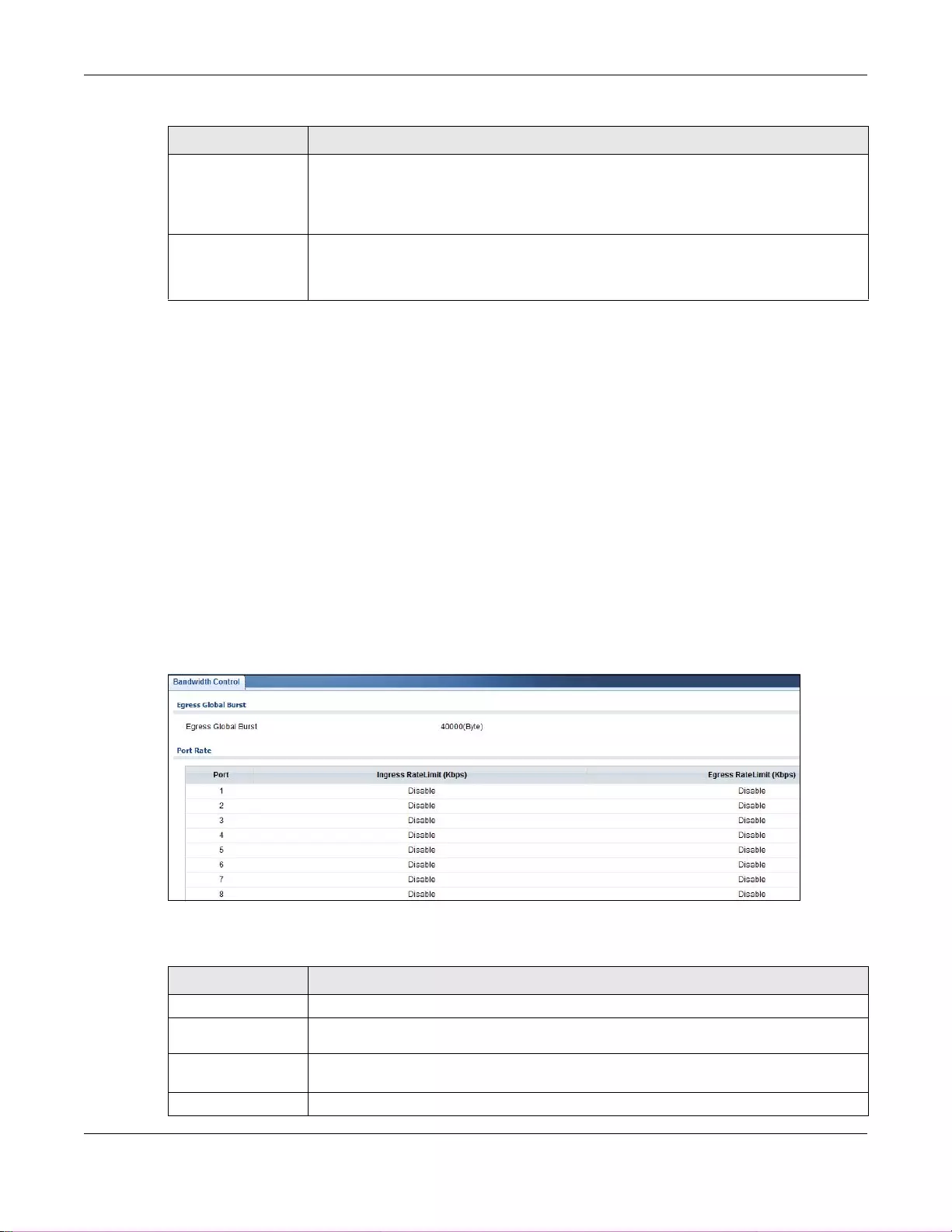
Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
60
8.4 Bandwidth Management
This section shows you the maximum bandwidth using the Bandwidth Management screen.
Bandwidth m a nagement shows th emaximum allowable bandwidth for incoming and/or out-going
traffic flows on a port.
8.4.1 Bandwidth Control
Use this screen to view the Switch’s bandwidth control in egress global burst and port rate.
An egress port is an outgoing port, that is, a port through which a data packet leaves for both ports.
An ingress port is an incoming port, that is, a port through which a data packet enters.
Click Monitor > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control to access this screen.
Figure 55 Monitor > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control
Each field is described in the following table.
Allocated Power(W) This field displays the total amount of power the Switch has reserved for PoE after
negotiating with the connected PoE device(s).
Consumi n g Power (W) can be less than or equal but not more than the Allocated
Power (W).
Remaining
Power(W) This field displays the amount of power the Switch can still provide for PoE.
Note: The Swit ch mus t hav e at l east 16 W of remaining power in order to supply power
to a PoE device, even if the PoE device needs less than 16 W.
Ta ble 27 Monitor > Port > PoE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 28 Monitor > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Egress Global Burst
Egress Global
Burst This field specifies the current egress burst size in bytes all ports.
Port Rate View the maximum bandwidth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the traffic flow
on a port.
Port This field displays the port number.

Chapter 8 Monitor: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
61
8.5 Storm Control
This section shows you the storm control feature.
Storm control limits the number of broadcast, multicast and unicast packets the S witch receives per
second on the ports. When the maximum number of allowable broadcast, multicast and/or unicast
packets is reached per second, the subsequent packets are discarded. Enabling this feature reduces
broadcast, multicast and/or unicast packets in your network. You can specify limits for each packet
type on each port.
Click Monito r > P or t > Storm Control to access this screen.
Figure 56 Monitor > Port > Storm Control
Each field is described in the following table.
Ingress
Rat e Limit (Kbps) View the maximum bandwidth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the incoming
traffic flow on a port.
Egress RateLimit
(Kbps) View the maximum bandwidth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the out-going
traffic flow on a port.
Ta ble 28 Monitor > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 29 Monitor > Port > Storm Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port This field displays the port number.
State This field displays the state.
Broadcast (pps) Displays how many broadcast packets the port receives (in pps).
Unknown
Multicast (pps) Displays how many unknown multicast packets the port receives (in pps).
Unknown
Unicast (pps) Displays how many unknown unicast packets the port re ceives (in pps).
Action Displays the action the de vice takes when a limit is reached. The following options are
available:
• Drop - drop the packet.
• Shutdown - shutdown the connection.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
62
CHAPTER 9
Monitor: VLAN
9.1 Overview
This section provides information for VLAN in Monitor.
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a ph ysical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one
group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same
group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
In MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security among the
subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from accessing the network
resources of another on the same LAN, thus a user will not see the printers and hard disks of
another user on the same network.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets
go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast
domain.
9.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The VLAN screen (Section 9.2 on page 62) displays VLAN, port, and VLAN port settings.
•The Guest VLAN screen (Section 9.3 on page 65) displays the global and port settings of the
Switch.
•The Voice VLAN screen (Sectio n 9. 4 on pa g e 66) displays the global and port settings of the
Switch.
9.2 VLAN
Use this screen to view Switch VLAN settings.
9.2.1 VLAN
Use this screen to view the Switch’s VLAN settings. Click Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN to
access this screen.
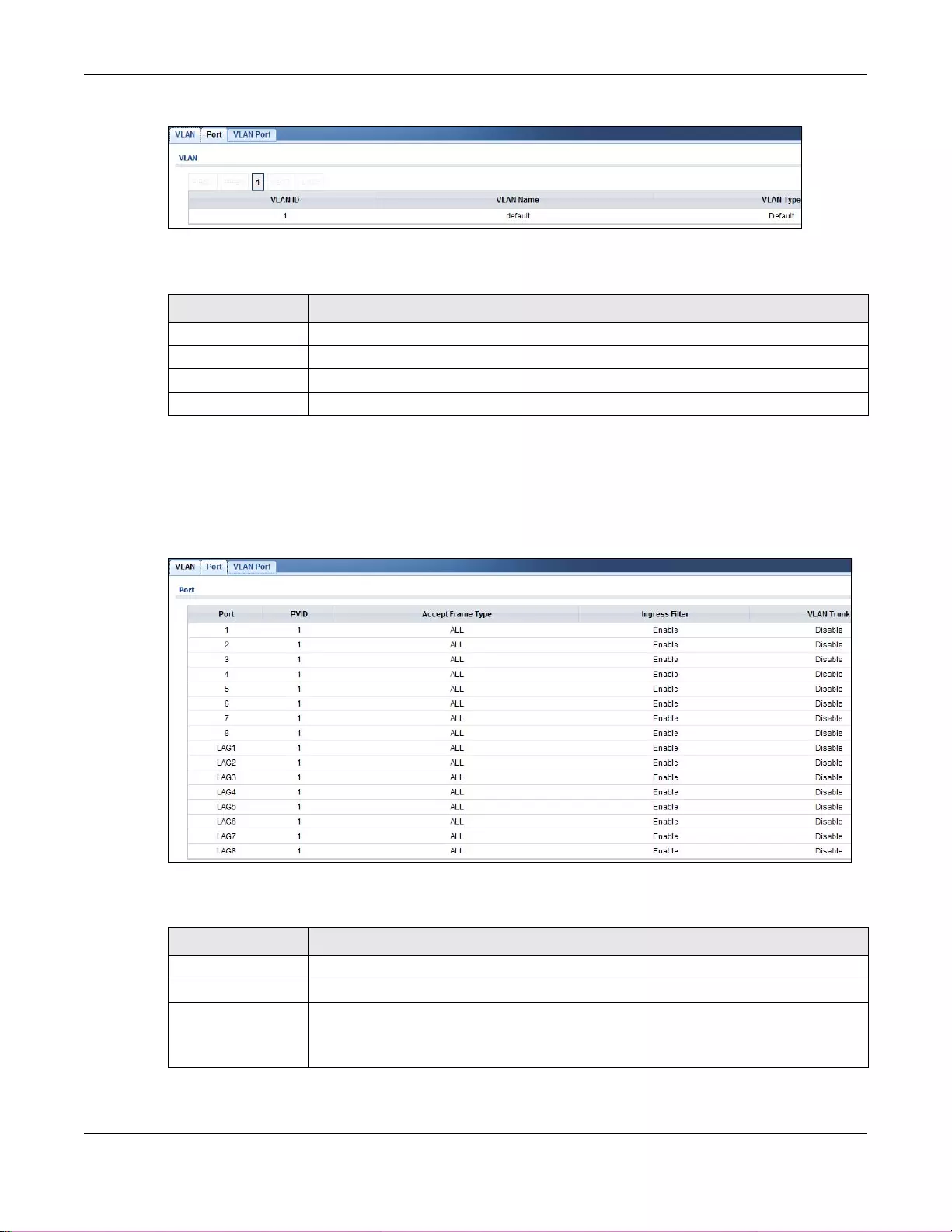
Chapter 9 Monitor: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
63
Figure 57 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN
Each field is described in the following table.
9.2.2 Port
Use this screen to view the Switch’ s port setting in VLAN. Click Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > Port to
access this screen.
Figure 58 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > Port
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 30 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN
VLAN ID This is the VLAN identification number.
VLAN Name Displays a descriptive name for the VLAN for identification purposes.
VLAN Type Displays a type for the VLAN for identification purposes.
Ta ble 31 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port This field displays the port number.
PVID This is the port VLAN identification number.
A PVID (Port VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to incoming untagged frames received on a
port so that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
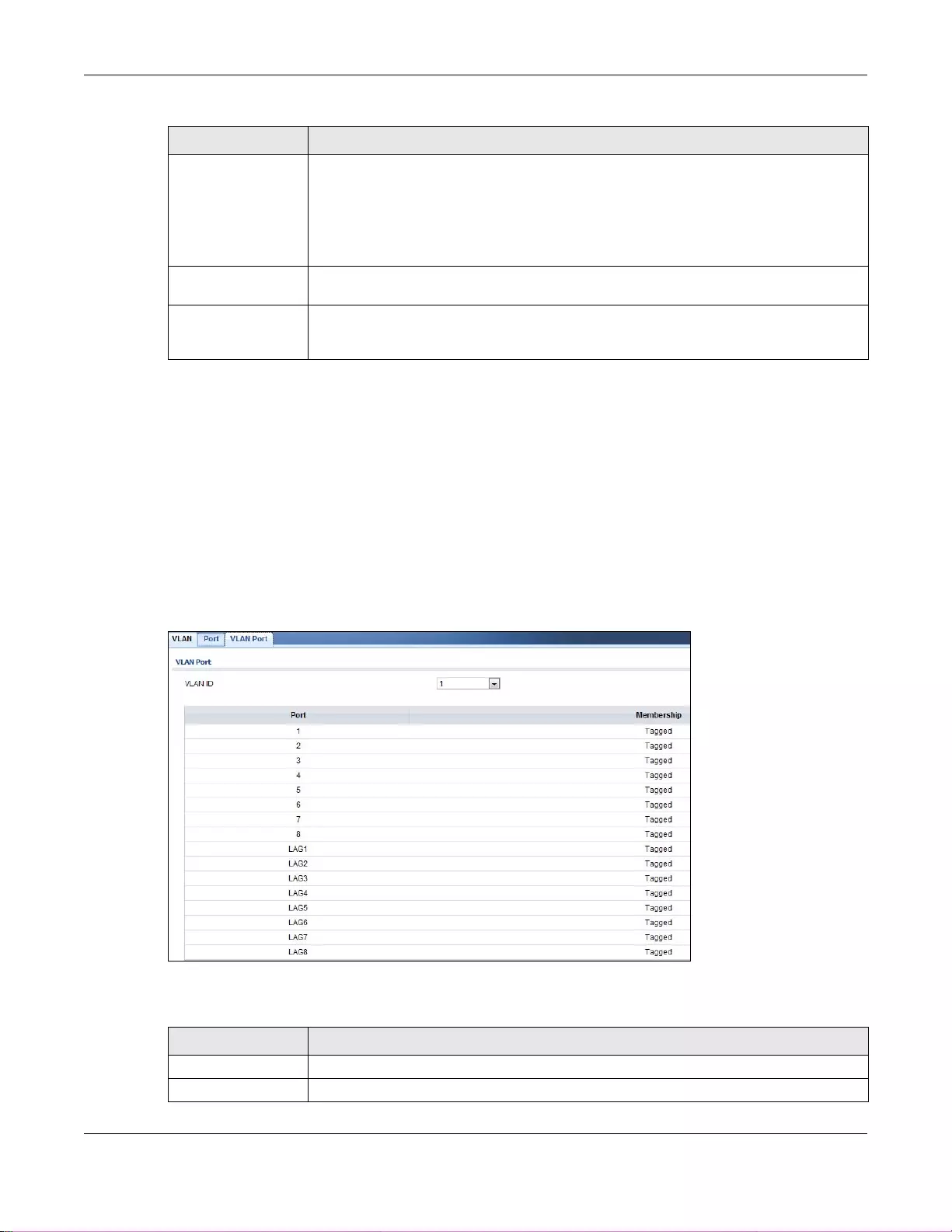
Chapter 9 Monitor: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
64
9.2.3 VLAN Port
Port -based VLANs are VLANs where the packet forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC
address and its associated port. Po rt-based VLANs require allowed outgoing ports to be defined for
each port. Therefore, if you wish to allow two subscriber ports to talk to each other, for example,
between conference rooms in a hotel, you must define the egress (an egress port is an outgoing
port, that is, a port through which a data packet leaves) for both ports. Port-based VLANs are
specific only to the Switch on which they were created.
Use this screen to view the Switch’s VLAN port settings. Click Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN
Port to access this screen.
Figure 59 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Port
Each field is described in the following table.
Accept Frame
Type This field displays the type that is accepted by the frame.
Specifes the type of frames allowed on a port. Choices are All, Tag Only and Untag
Only. All accepts all untagged or tagged frames on this port. This is the default
setting. Tag Only accepts only tagged frames on this port. All untagged fr ames wi ll be
dropped. Untag Only accepts only untagged frames on this port. All tagged frames will
be dropped.
Ingress Filter If set, the Switch discards incoming frames for VLANs that do not have this port as a
member.
VLAN Trunks Enable VLAN Trunking on ports connected to other switches or routers (but not ports
directly connected to end users) to allow frames belonging to unknown VLAN groups to
pass through the Switch.
Ta ble 31 Monitor > VLAN > VLA N > Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 32 Monitor > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Port
VLAN ID This is the VLAN identification number.

Chapter 9 Monitor: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
65
9.3 Guest VLAN
When 802.1x port authentication is enabled on the Switch and its ports, clients that do not have the
correct credentials are blocked from using the port(s). You can configure your Switch to have one
VLAN that acts as a guest VLAN. If you enable the guest VLAN (102 in the example) on a port (2 in
the example), the user (A in the example) that is not IEEE 802.1x capable or fails to enter the
correct username and password can still access the port, but traffic from the user is forwarded to
the guest VLAN. That is, unauthenticated users can ha ve access to limited network resources in the
same guest VLAN, such as the Internet. The rights gr anted to the Gu est VLAN depends on how the
network administrator configures switches or routers with the guest network feature.
Figure 60 Guest VLAN Example
Use this screen to view the Switch’s guest VLAN. Click Monitor > VLAN > Guest VLAN to access
this screen.
Figure 61 Monitor > VLAN > Guest VLAN
Port Displays the port index value.
Membership Displays the status of the VLAN group: Forbidden, Excluded, Tagged or Untagged.
Ta ble 32 Monitor > VLAN > VLA N > VLAN Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Internet
2
VLAN 100
A
VLAN 102
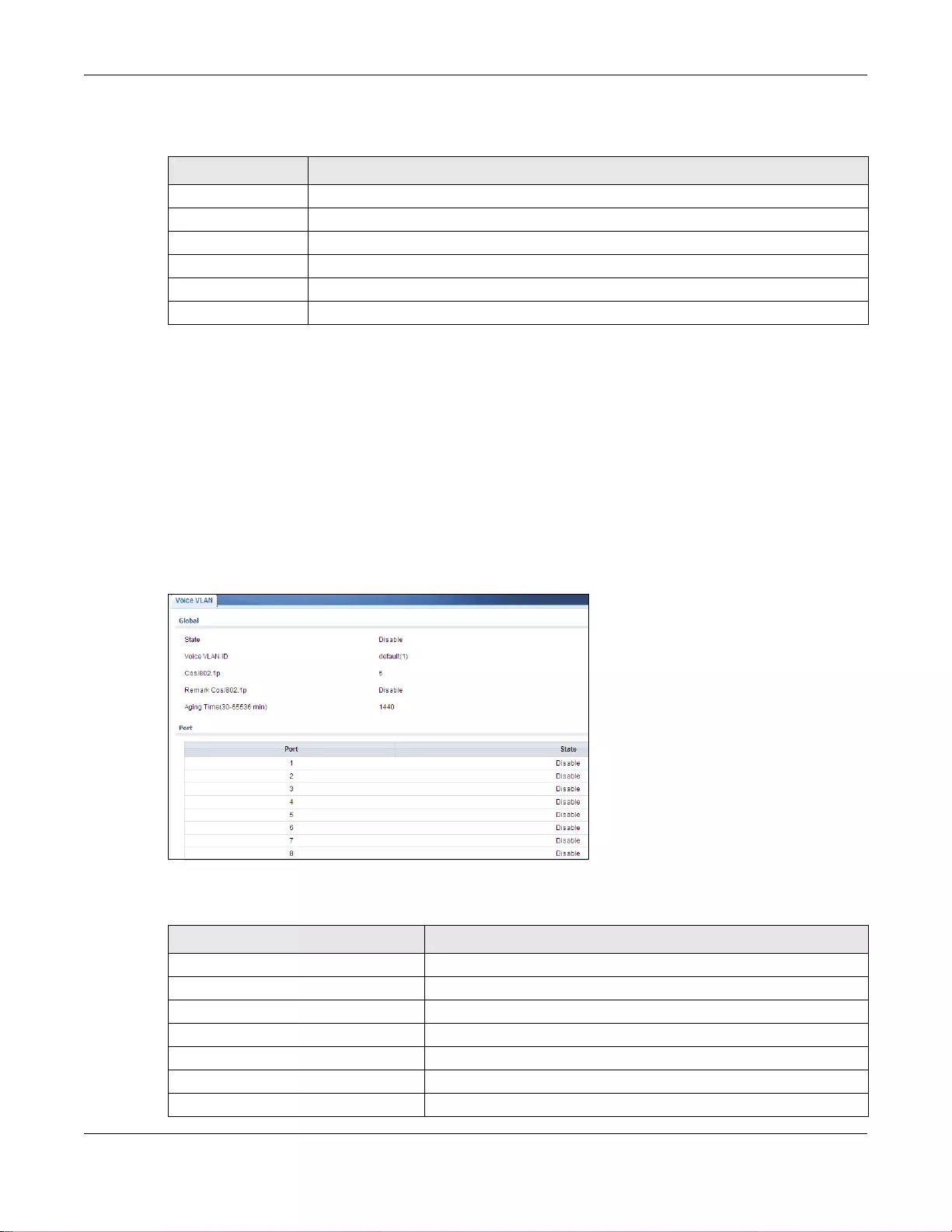
Chapter 9 Monitor: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
66
Each field is described in the following table.
9.4 Voice VLAN
Voice VLANs are VLANs configured specially for voice traffic. By adding the ports connected with
voice devices to voice VLANs, you can have voice traffic transmitted within voice VLANs and
perform QoS-related configuration for voice tr aff ic as required, thus ensuring the transmission
priority of voice traffic and voice quality.
Use this screen to view Switch global and port voice VLAN settings for voice traffic. Click Monitor
> VLAN > Voice VLAN to access this screen.
Figure 62 Monitor > VLAN > Voice VLAN
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 33 Monitor > VLAN > Guest VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State This field displays the state of global guest VLAN.
Port
Port This field displays a port number.
State This field displays the state of a port.
In Guest VLAN This field displays the status of the port, is the port is in guest VLAN or not.
Ta ble 34 Monitor > VLAN > Voice VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State This field displays the state of a port.
Voice VLAN ID This is the voice VLAN identification number.
Cos/802.1p This displays the packet’s 802.1p priority field.
Remark Cos/802.1p This field displays the state of the cos/802.1p.
Aging Time (30-65536 min) Displays the time interval (from 30 to 65536) in minutes.
Port

Chapter 9 Monitor: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
67
Port This field displays a port number.
State This field displays the state of a port.
Ta ble 34 Monitor > VLAN > Voice VL AN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
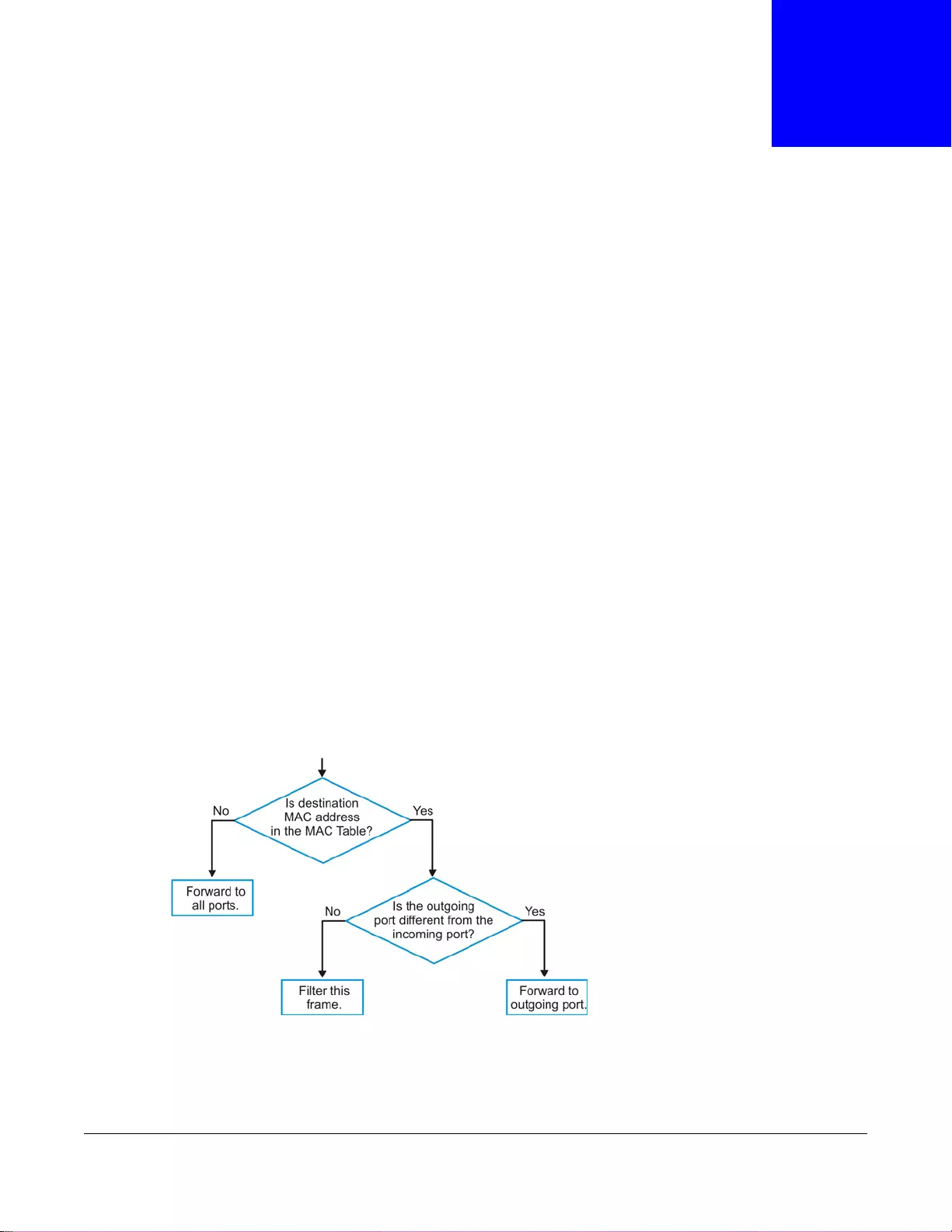
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
68
CHAPTER 10
Monitor: MAC Table
10.1 Overview
This section provides information for MAC Table in Monitor.
The MAC Table screen (a MAC table is also known as a filtering database) shows how frames are
forwarded or filtered across the Switch’ s ports. When a device (which may belong to a VLAN group)
sends a packet which is forw arded to a port on th e S witch, the MAC address of the device is shown
on the Switch’s MAC Table. It also shows whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the
Switch) or static (manually entered in the Static MAC Forwarding screen).
The Switch uses the MAC Table to determine how to forward frames. See the following figure.
1The Switch examines a received frame and learns the port from which this source MAC address
came.
2The Switch checks to see if the frame's destination MAC address matches a source MAC address
already learned in the MAC Table.
• If the Switch has already learned the port for this MAC address, then it forwards the frame to
that port.
• If the Switch has not already learned the port for this MAC address, then the frame is flooded to
all ports. Too much port flooding leads to network congestion.
• If the Switch has already learned the port for this MAC address, but the destination port is the
same as the port it came in on, then it filters the frame.
Figure 63 MAC Table Flowchart
This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC address and VLAN ID of a device attach
to a port. You can also view what kind of MAC address it is.
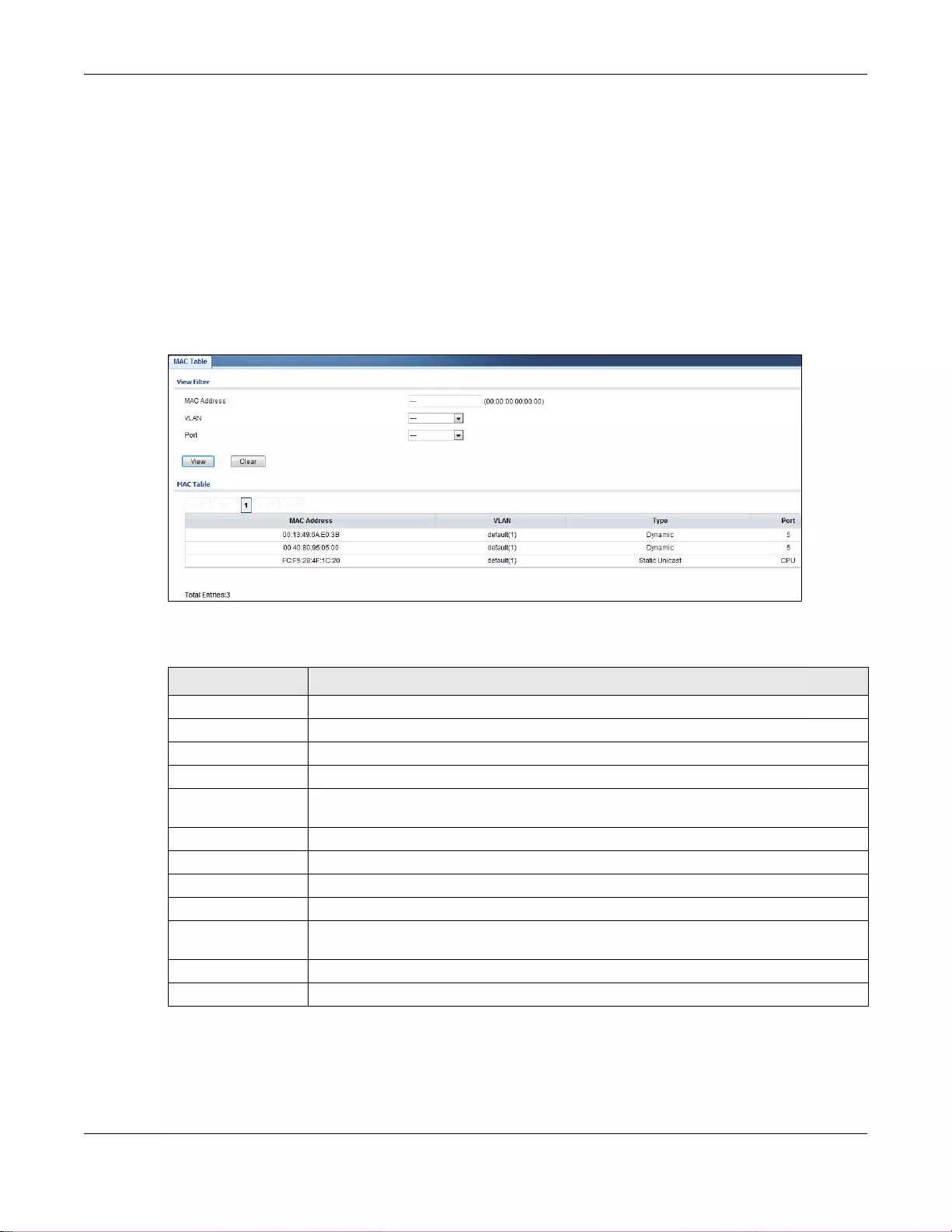
Chapter 10 Monitor: MAC Table
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
69
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The MAC Table screen (Section 10.2 on page 69) displays view filter and MAC table of the
Switch.
10.2 MAC Table
Use this screen to view filter static and MAC table settings. Click Monitor > MAC Table to access
this screen.
Figure 64 Monitor > MAC Table
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 35 Monitor > MAC Tab l e
LABEL DESCRIPTION
View filter
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the device from which this incoming frame came.
VLAN Displays a type for the VLAN for identification purposes.
Port This is the port from which the above MAC address was learned.
View This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC address and VLAN ID of a
device attach to a port. You can also view what kind of MAC address it is.
Clear Click Clear to return the fields to the factory defaults.
MAC Table
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the device from which this incoming frame came.
VLAN Displays a type for the VLAN for identification purposes.
Type This shows whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the Switch) or static
(manually entered in the Static MAC Forwarding screen).
Port This is the port from which the above MAC address was learned.
Total Entries Displays the number of total entries.
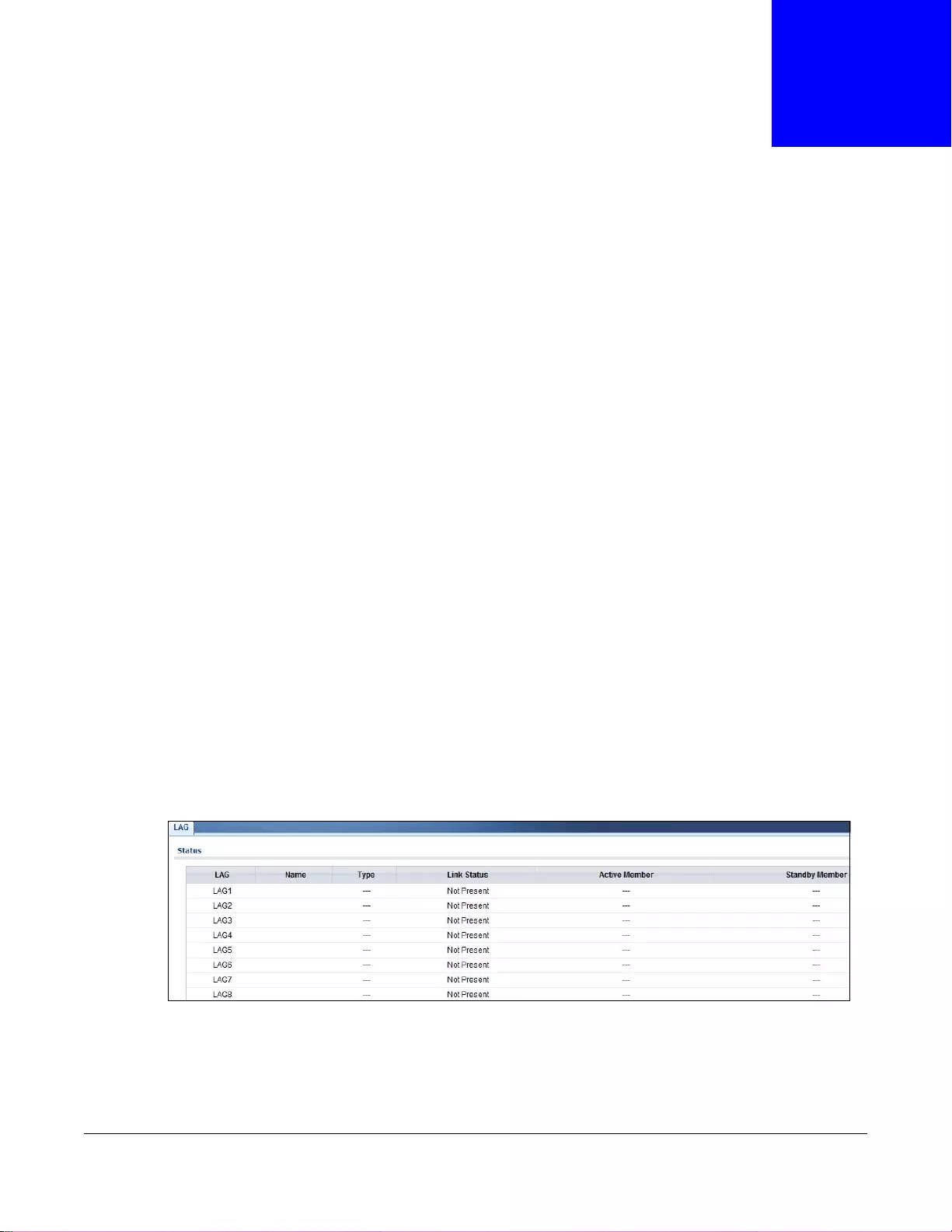
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
70
CHAPTER 11
Monitor: Link Aggregation
11.1 Overview
This section provides information for Link Aggreg ation in Monitor.
Link aggregation (trunking) is the grouping of physical ports into one logical higher-capacity link.
You may want to trunk ports if for example, it is cheaper to use multiple lower-speed links than to
under-utilize a high-speed, but more costly, single-port link. However, the more ports you
aggregate then the fewer available ports you have. A trunk group is one logical link containing
multiple ports.
The Switch supports both static and dynamic link aggregation.
Note: In a properly planned network, it is recommended to implement static link
aggregation only. This ensures increased network stability and control over the
trunk groups on your Switch.
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Link Aggregation screen (Section 11.2 on page 70) displays link aggregation status.
11.2 Link Aggregation
Use the Link Aggregation screens to view Switch link aggregation status. Click Monitor > Link
Aggregation > LAG to access this screen.
Figure 65 Monitor > Link Aggregation > LAG
Chapter 11 Monitor: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
71
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 36 Moni tor > Link Aggregation > LAG
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAG Displays the link aggregation status index value.
Name This field displays the name.
Type This field displays the type.
Link Status This field displays the status of the link. It displays Up when the port is linked up or
Down when it is not. When no any physical port is binding with this group, it displays
NotPresent.
Active Member Displays if this member is an active member of a trunk.
Standby Member Displays if this member is an standby member of a trunk.
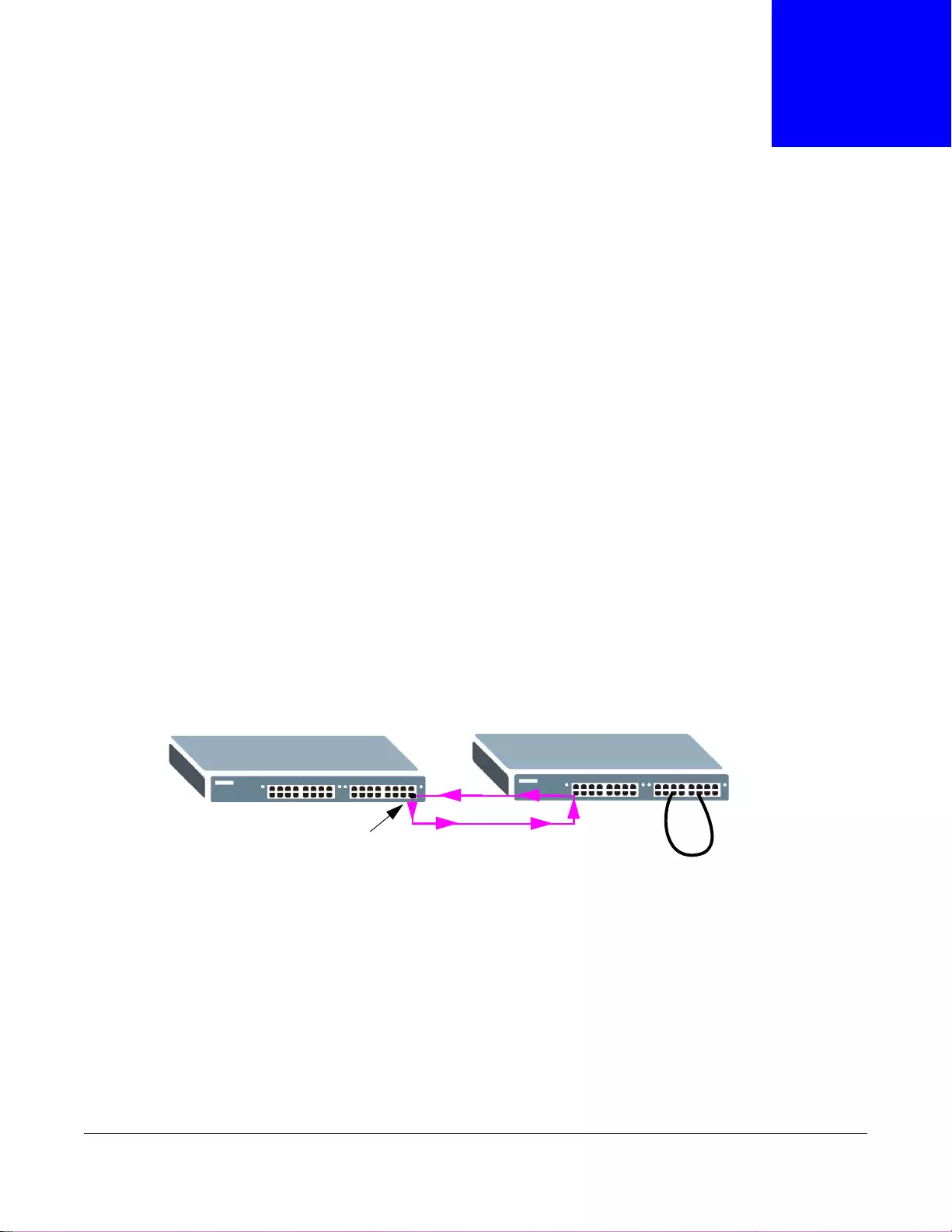
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
72
CHAPTER 12
Monitor: Loop Guard
12.1 Overview
This section provides information for Loop Guard in Monitor.
Loop guard is designed to handle loop problems on the edge of your network. This can occur when
a port is connected to a Switch that is in a loop state. Loop state occurs as a result of human error.
It happens when two ports on a switch are connected with the same cable. When a switch in loop
state sends out broadcast messages the messages loop back to the switch and are re-broadcast
again and again causing a broadcast storm.
If a switch (not in loop state) connects to a switch in loop state, then it will be affected by the
switch in loop state in the following way:
• It will receive broadcast messages sent out from the switch in loop state.
• It will receive its own broadcast messages that it sends out as they loop back. It will then re-
broadcast those messages again.
The following figure shows port N on switch A connected to switch B. Switch B is in loop state.
When broadcast or multicast packets leave port N and reach switch B, they are sent back to port N
on A as they are rebroadcast from B.
Figure 66 Switch in Loop State
The loop guard feature checks to see if a loop guard enabled port is connected to a switch in loop
state. This is accomplished by periodically sending a probe packet and seeing if the packet returns
on the same port. If this is the case, the Switch will shut down the port connected to the switch in
loop state.
The following figure shows a loop guard enabled port N on switch A sending a probe packet P to
switch B. Since switch B is in loop state, the probe packet P returns to port N on A. The Switch
then shuts down port N to ensure that the rest of the network is not affected by the switch in loop
state.
AB
N
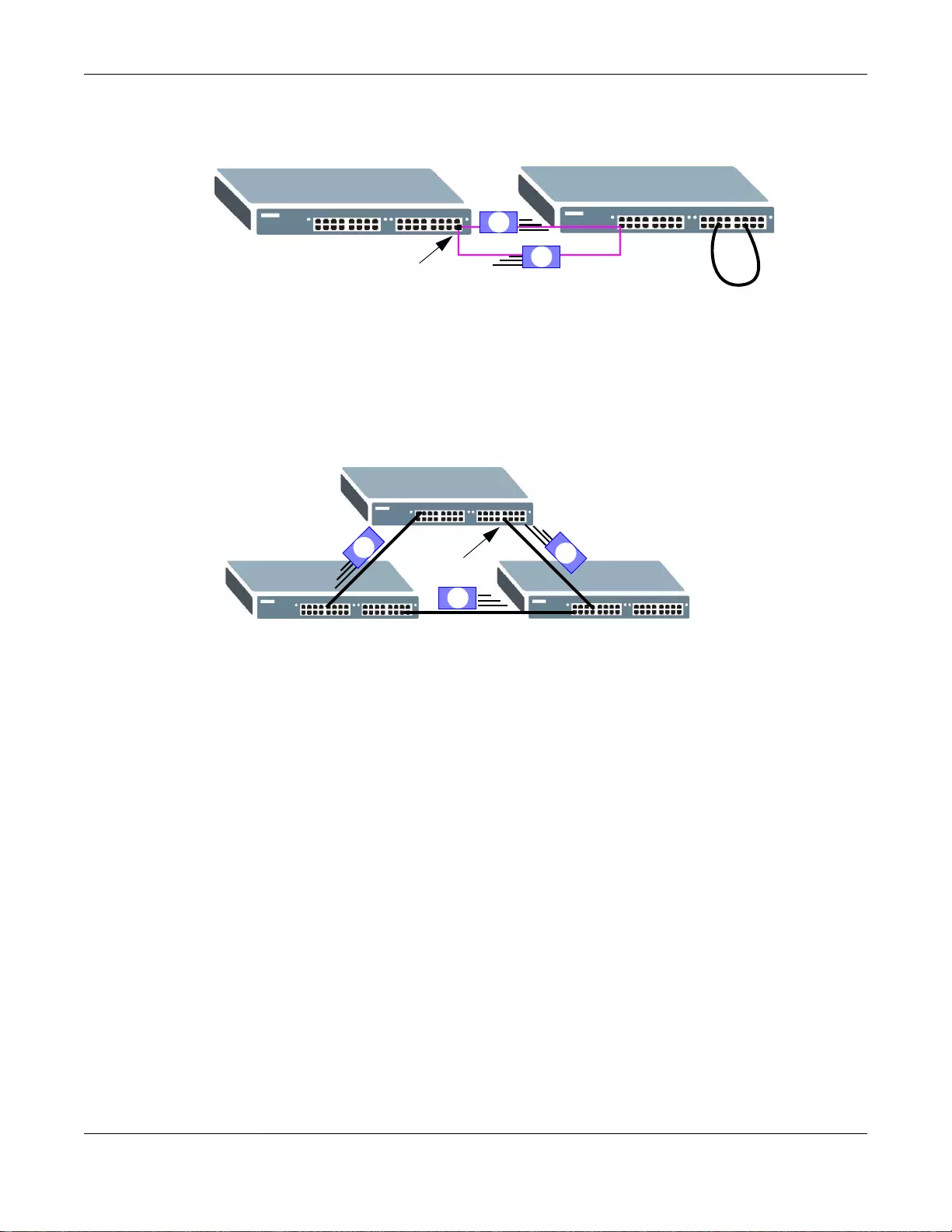
Chapter 12 Monitor: Loop Guard
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
73
Figure 67 Loop Guard - Probe Packet
The Switch also shuts down port N if the probe packet returns to switch A on any other port. In
other words loop guard also protects against standard network loops. The following figure
illustrates three switches forming a loop. A sample path of the loop guard probe packet is also
shown. In this example, the probe packet is sent from port N and returns on another port. As long
as loop guard is enabled on port N. The Switch will shut down port N if it detects that the probe
packet has returned to the Switch.
Figure 68 Loop Guard - Network Loop
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Loop Guard screen (Section 12.2 on page 73) displays loop guard status.
12.2 Loop Guard
Use the Loop Guard screen to view Switch loop guard status. Click Monitor > Loop Guard to
access this screen.
AB
P
P
N
A
P
P
N
P

Chapter 12 Monitor: Loop Guard
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
74
Figure 69 Monitor > Loop Guard
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 37 Monitor > Loop Guard
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Loop Guard Status
Port This field displays a port number.
Status This field displays the status.
Time Left (sec) This field displays the amount of time left in seconds.
Action This field displays the ac tion.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
75
CHAPTER 13
Monitor: Multicast
13.1 Overview
This section provides information for Multicast in Monitor.
Traditionally , IP packets are tr ansmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender to 1 recipient)
or Broadcast (1 sender to everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to just a group
of hosts on the network.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in an IPv4 multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. Refer to RFC 1112, RFC
2236 and RFC 3376 for information on IGMP versions 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The IGMP screen (Section 13.2 on pag e 75) displays Vlan, statistics, group, and router.
13.2 IGMP
Use this screen to view Switch various multicast features.
13.2.1 Vlan
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IGMP vlan. Click Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Vlan to
access this screen.
Figure 70 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Vlan
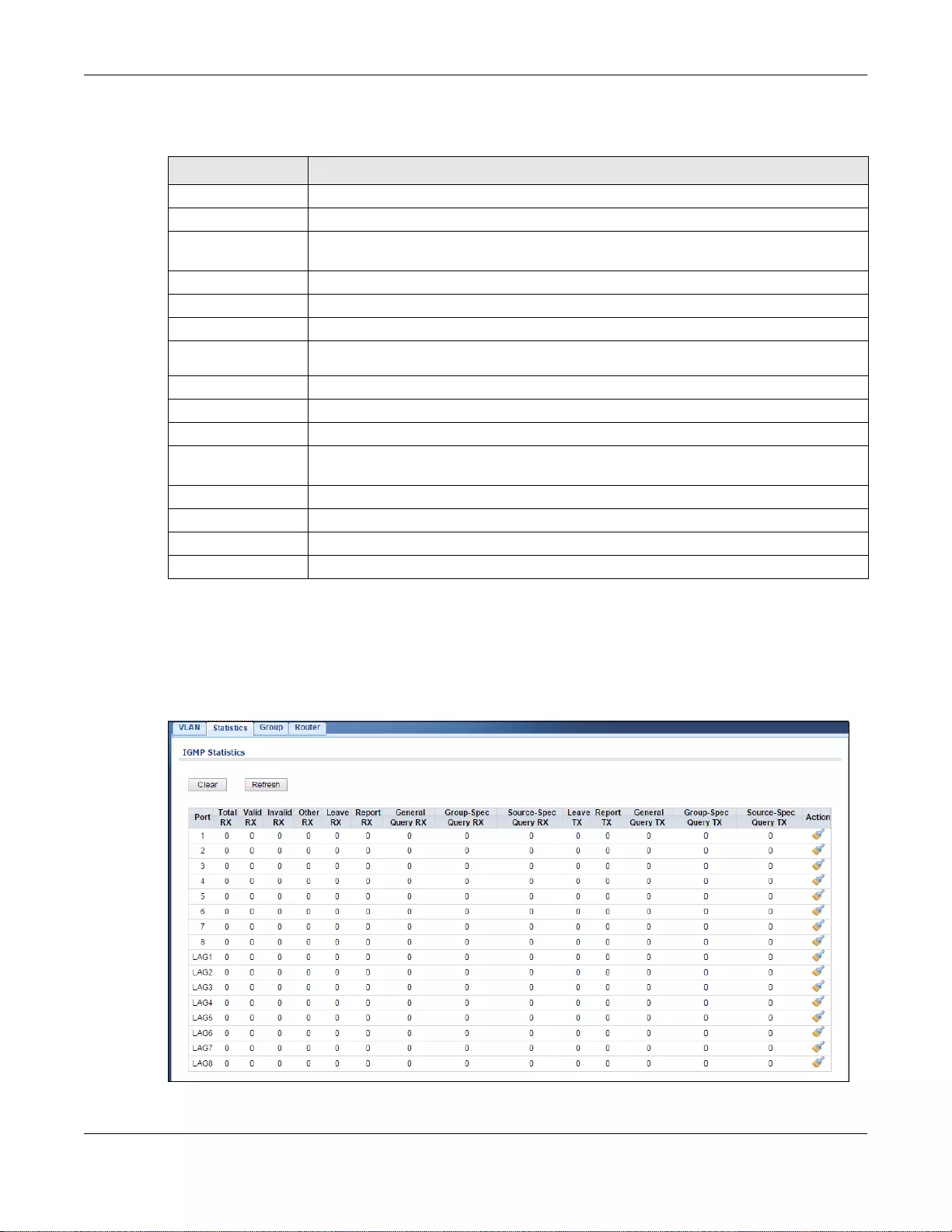
Chapter 13 Monitor: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
76
Each field is described in the following table.
13.2.2 Statistics
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IGMP statistics. Click Monitor > Multicast > IGMP >
Statistics to access this screen.
Figure 71 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Statistics
Ta ble 38 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Vlan
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN ID Displays the identification for the VLAN.
Operate Status Displays the status of the operation.
Router Ports Auto
Learn Displays whether the router ports are auto learn or not.
Query
Retry Displays the number of retry.
Interval Displays the number (in seconds) for the time interval.
Max. Reponse
Interval(sec) Displays the maximum reponse (in seconds) for the time interval.
Last Member Query
Count Displays the number of count.
Interval(sec) Displays the in seconds for the time interval.
Querier Allow sthe Switch to send IG MP General Query messages to the VLANs with the
multicast hosts attached.
Status This field displays the entry as querier or non-querier.
Version This field displays the entry querier version.
IP This field displays the the entry querier IP address.
Total Entri es This field displays the nu mber of total entries.
Chapter 13 Monitor: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
77
Each field is described in the following table.
In the Action column, the Action option allows you to clear the statistics.
Click OK and confirm at the pop-up screen to complete the task. Click Cancel and confirm at the
pop-up screen to discard the changes.
Figure 72 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Statistics > Action
13.2.3 Group
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IGMP group. Click Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Group to
access this screen.
Ta ble 39 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Clear Click Clear to reset the fields to the factory defaults.
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the page.
Port This field displays a port number.
Total RX This field displays the total amount of RX.
Valid RX This field displays the total amount of valid RX.
Invalid RX This field displays the total amount of invalid RX.
Other RX This field displays the total amount of other RX.
Leave RX This field displays the total amount of leave RX.
Report RX This field displays the total amount of report RX.
General Query RX This field displays the total amount of general query RX.
Group-Spec Query RX This field displays the total amount of group-spec query RX.
Source-Spec Query RX This field displays the total amount of source-spec query RX.
Leave TX This field displays the total amount of leave TX.
Report TX This field displays the total amount of report TX.
General Query TX This field displays the total amount of general query TX.
Group-Spec Query TX This field displays the total amount of group-spec query TX.
Source-Spec Query TX This field displays the total amount of source-spec query TX.
Action Click Action to reset the statistics of the specific field back to zero .
OK Click OK to apply the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 13 Monitor: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
78
Figure 73 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Group
Each field is described in the following table.
13.2.4 Router
Use this screen to view the Switch’s IGMP router. Click Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Router to
access this screen.
Figure 74 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Router
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 40 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Group
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Clear Click Clear to delete the dynamic groups.
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the page.
VLAN ID Displays the identification for the VLAN.
Group IP Address This field displays the group IP address.
Member Ports This field displays the member ports.
Life(sec) Displays life in seconds for the time interval.
Total Entri es This field displays the nu mber of total entries.
Ta ble 41 Monitor > Multicast > IGMP > Router
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the page.
VLAN ID Displays the identification for the VLAN.
Dynamic Router Ports This field displays the dynamic router ports.
Static Router Ports This field displays the static router ports.
Forbidden Router Ports This field displays the forbidden router ports.
Total Entries This field displays the number of total entries.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
79
CHAPTER 14
Monitor: Spanning Tree
14.1 Overview
This section provides information for Spanning Tree in Monitor.
The Switch supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST),
and Multiple Spanning Tree (MST).
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Spanning Tree screen (Section 14.2 on page 79) displays CIST, CIST port, MST, MST port,
STP statistics.
14.2 Spanning Tree
Use this screen to view Switch spanning tree settings.
14.2.1 CIST
Use this screen to view the Switch’ s spanning tree CIST instance. Click Monitor > Spanning Tree
> CIST to access this screen.
Figure 75 Monitor > Spanning Tree > CIST
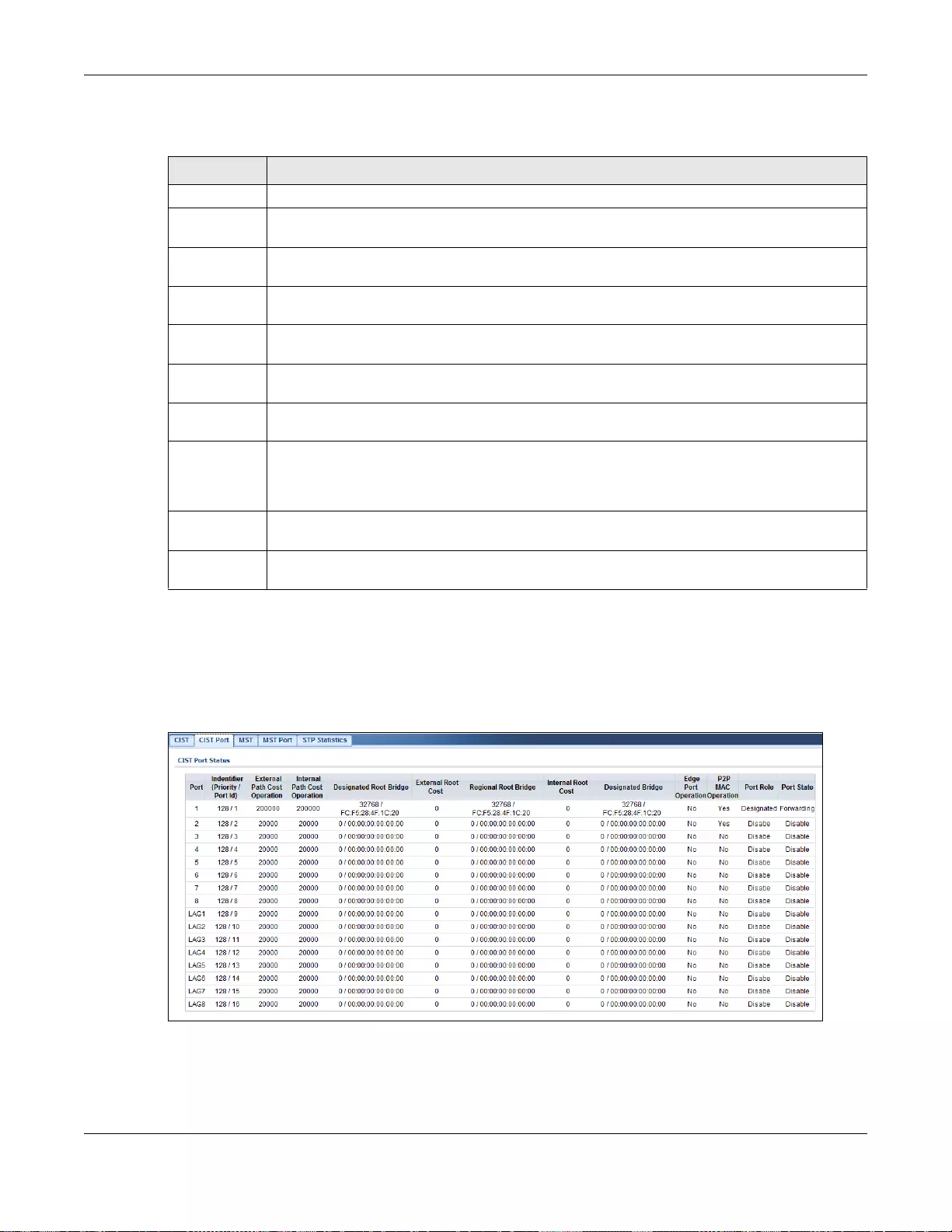
Chapter 14 Monitor: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
80
Each field is described in the following table.
14.2.2 CIST Port
Use this screen to view the Switch’s spanning tree CIST port status. Click Monitor > Spanning
Tree > CIST Port to access this screen.
Figure 76 Monitor > Spanning Tr ee > CIST Port
Ta ble 42 Monitor > Spanning Tree > CIST
LABEL DESCRIPTION
State This field displays the state.
Bridge
Indentifier This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of the bridge priority plus the MAC
address.
Designate
Root Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tree.
External Root
Path Cost The cost of the path from this bridge to the cist Root Bridge.
Regional Root
Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tree.
Internal Root
Path Cost The cost of the path from this bridge to the internal Regional Root Bridge.
Designated
Bridge For each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowest cost to the
root among the bridges connected to the LAN.
Root Port On each bridge, the bridge communicates with the root through the root port. The root port i s
the port on this Switch with the lowest path cost to the root (the root path cost). If there is
no root port, then this Switch has been accepted as the root bridge of the spanning tree
network.
Remanining
Hops This field displays the number of remanining hops.
Last T opology
Change Topology change information is directly propagated throughout the network from the device
that generates the topology change.
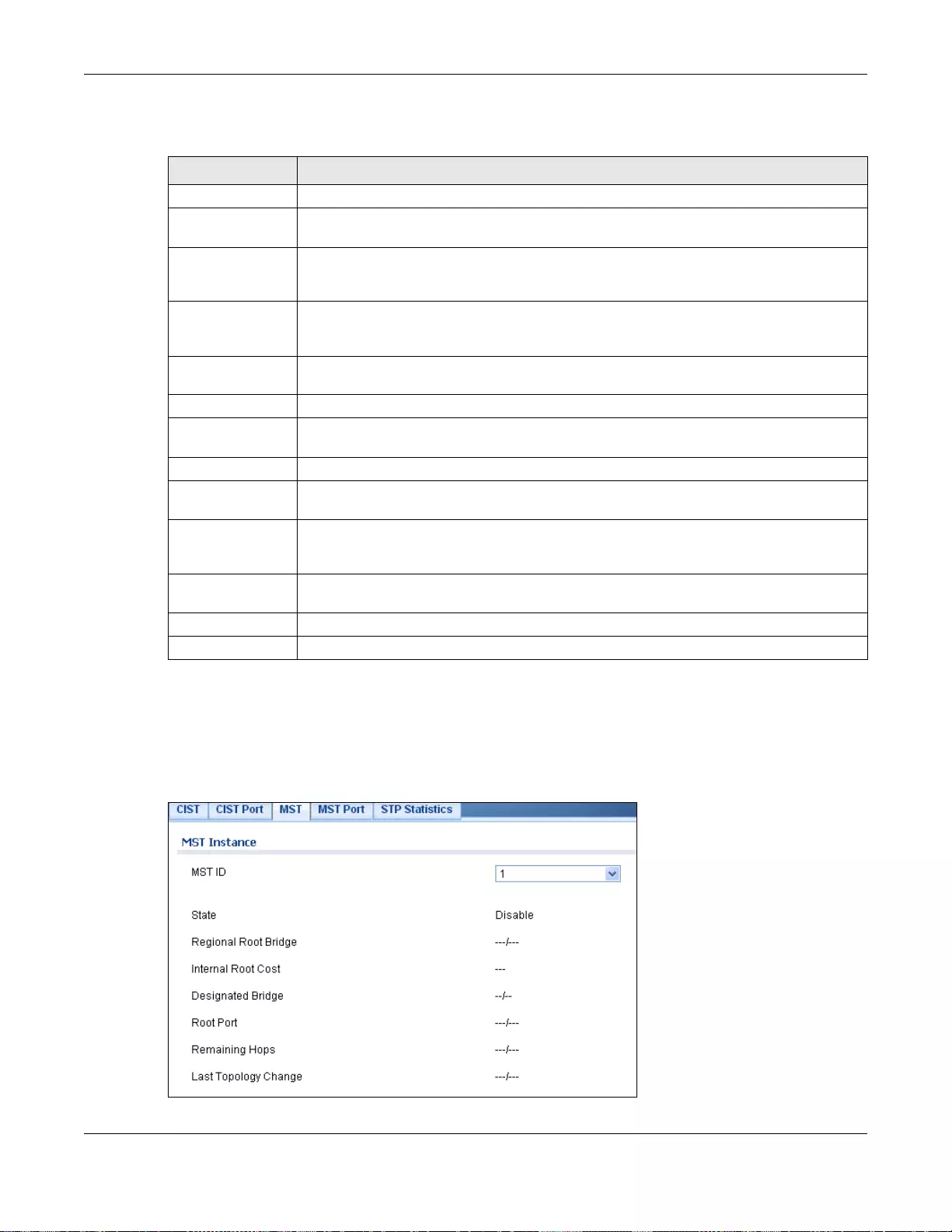
Chapter 14 Monitor: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
81
Each field is described in the following table.
14.2.3 MST
Use this screen to view the Switch’s spanning tree MST instance. Click Monitor > Spanning Tree
> MST to access this screen.
Figure 77 Monitor > Spanning Tr ee > MST
Ta ble 43 Monitor > Spanning Tree > CIST Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This field displays the port number.
Indentifier
(Priority / Port Id) This field displays the identifier (in priority / port number).
External P ath Cost
Operation Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN through that port. It is
recommended to assign this value according to the speed of the bridge. The slower the
media, the higher the cost.
Internal Path Cost
Operation Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN through that port. It is
recommended to assign this value according to the speed of the bridge. The slower the
media, the higher the cost.
Designated Root
Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tre e.
External Root Cost This field displays the external root cost.
Regional Root
Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tre e.
Internal Root Cost This field displays the internal root cost.
Designated Bridge For each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowes t cost
to the root among the bridges connected to the LAN.
Edge Port
Operation An edge port changes its initial STP port state from blocking state to forwarding state
immediately without going through listenin g and learning states right after the port is
configured as an edge port or when its link status changes.
P2P MAC
Operation This field displays t he state of the P2P MAC operation.
Port Role This field displays the state of the port role.
Port State This field displays the state of the port.
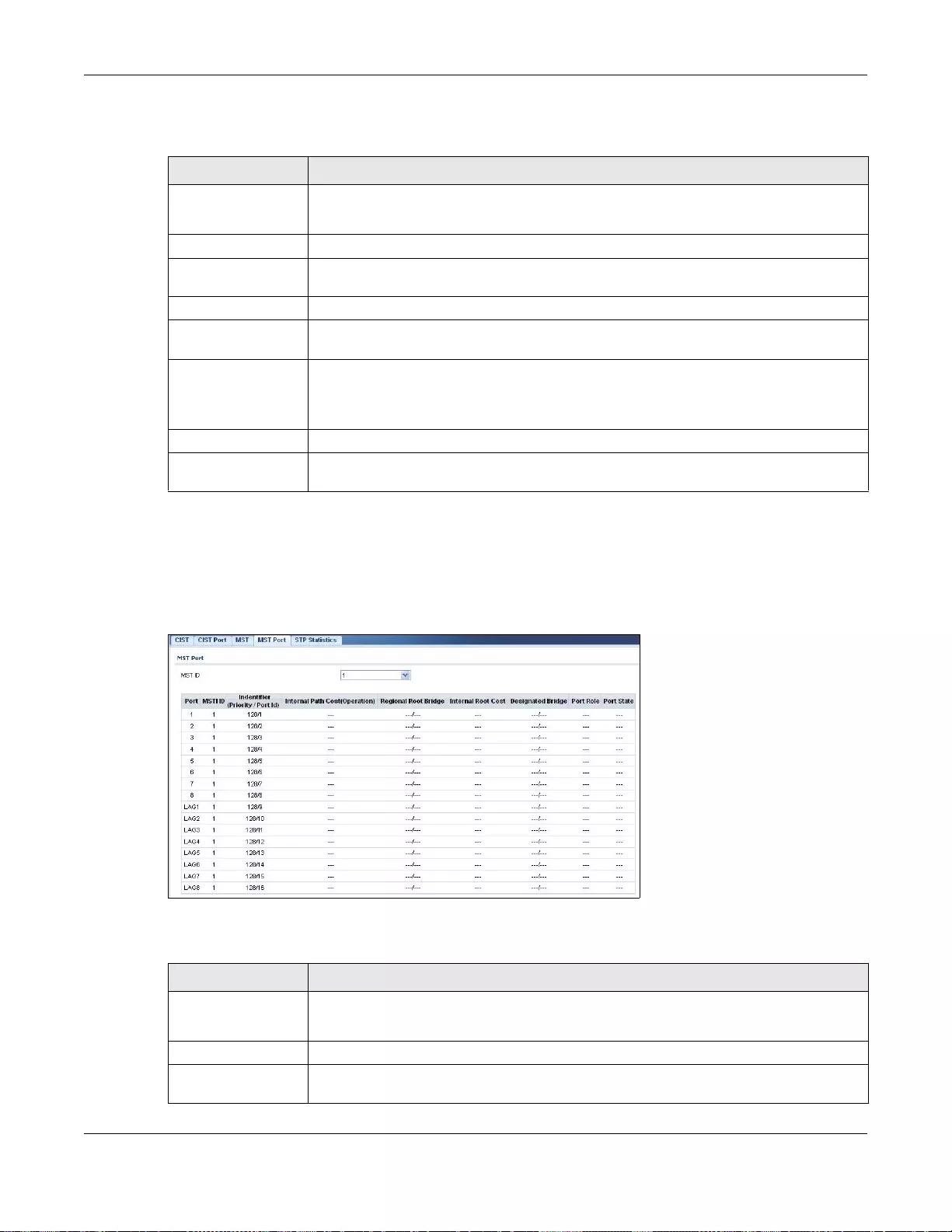
Chapter 14 Monitor: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
82
Each field is described in the following table.
14.2.4 MST Port
Use this screen to view the Switch’s spanning tree MST port status. Click Monitor > Spanning
Tree > MST Port to access this screen.
Figure 78 Monitor > Spanning Tree > MST Port
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 44 Monitor > Spanning Tree > MST
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MST ID This is the unique identifier for this MST.
Select a number from the drop-down menu to display results.
State This field displays the state.
Regional Root
Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tree.
Internal Root Cost This field displays the internal root cost.
Designated Bridge F or each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowest cost
to the root among the bridges connected to the LAN.
Root Port On each bridge, the bridge communicates with the root through the root port. The root
port is the port on this Switc h with the lowest path cost to the root (th e root path cost).
If there is no root port, then this Switch has been accepted as the root bridge of the
spanning tree network.
Remanining Hops This field displays the number of remanining hops.
Last Topology
Change Topology change information is directly propagated throughout the network from the
device that generates the topology change.
Ta ble 45 Monitor > Spanning Tree > MST Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MST ID This is the unique identifier for this MST.
Select a number from the drop-down menu to display results.
Port This field displays the port number.
MSTI ID A VLAN can be mapped to a specific Multiple Spanning Tree Instance (MSTI). MSTI
allows multip le VLANs to use the same spanning tree.

Chapter 14 Monitor: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
83
14.2.5 STP Statistics
(R)STP detects and breaks netw ork loops and provides backup links between switches, bridges or
routers. It allows a Switch to interact with other (R)STP-compliant switches in your network to
ensure that only one path exists between any two stations on the network.
The Switch uses IEEE 802.1w RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) that allows faster convergence
of the spanning tree than STP (while also being backwards compatible with STP-only aware
bridges). In RSTP, topology change information is directly propagated throughout the network from
the device that generates the topology ch ange. In STP, a longer delay is required as the device that
causes a topology change first notifies the root bridge and then the root bridge notifies the
network. Both RSTP and STP flush unwanted learned addresses from the filtering database. In
RSTP, the port states are Discarding, Learning, and Forwarding.
Note: In this user’s guide, “STP” refers to both STP and RSTP.
Use this screen to view the Switch’s spanning tree STP statistics. Click Monitor > Span ning Tree
> STP Statistics to access this screen.
Figure 79 Monitor > Spanning Tree > STP Statistics
Indentifier (Priority
/ Port Id) This field displays the identifier (in priority / port number).
Internal Path
Cost(Operation) Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN through that port. It is
recommended to assi gn this v a lue ac cording to the speed of the bridge. The slower the
media, the higher the cost.
Regional Root
Bridge Root bridge refers to the base of the spanning tree.
Internal Root Cost This field displays the internal root cost.
Designated Bridge F or each LAN segment, a designated bridge is selected. This bridge has the lowest cost
to the root among the bridges connected to the LAN.
Port Role This field displays the state of the port role.
Port State This field displays the state of the port.
Ta ble 45 Monitor > Spanning Tree > MST Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Chapter 14 Monitor: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
84
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 46 Monitor > Spanning Tree > STP Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This field displays the port number.
Configuration
BDPUs Received This field displays the configuration BDPUs received.
TCN BDPUs
Received This field displays the TCN BDPUs received.
MSTP BDPUs
Received This field displays the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) BDPUs re ceived.
Configuration
BDPUs Transmitted This field displays the configuration BDPUs transmitted.
TCN BDPUs
Transmitted This field displays the TCN BDPUs transmitted.
MSTP BDPUs
Transmitted This field displays the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) BDPUs transmitted.
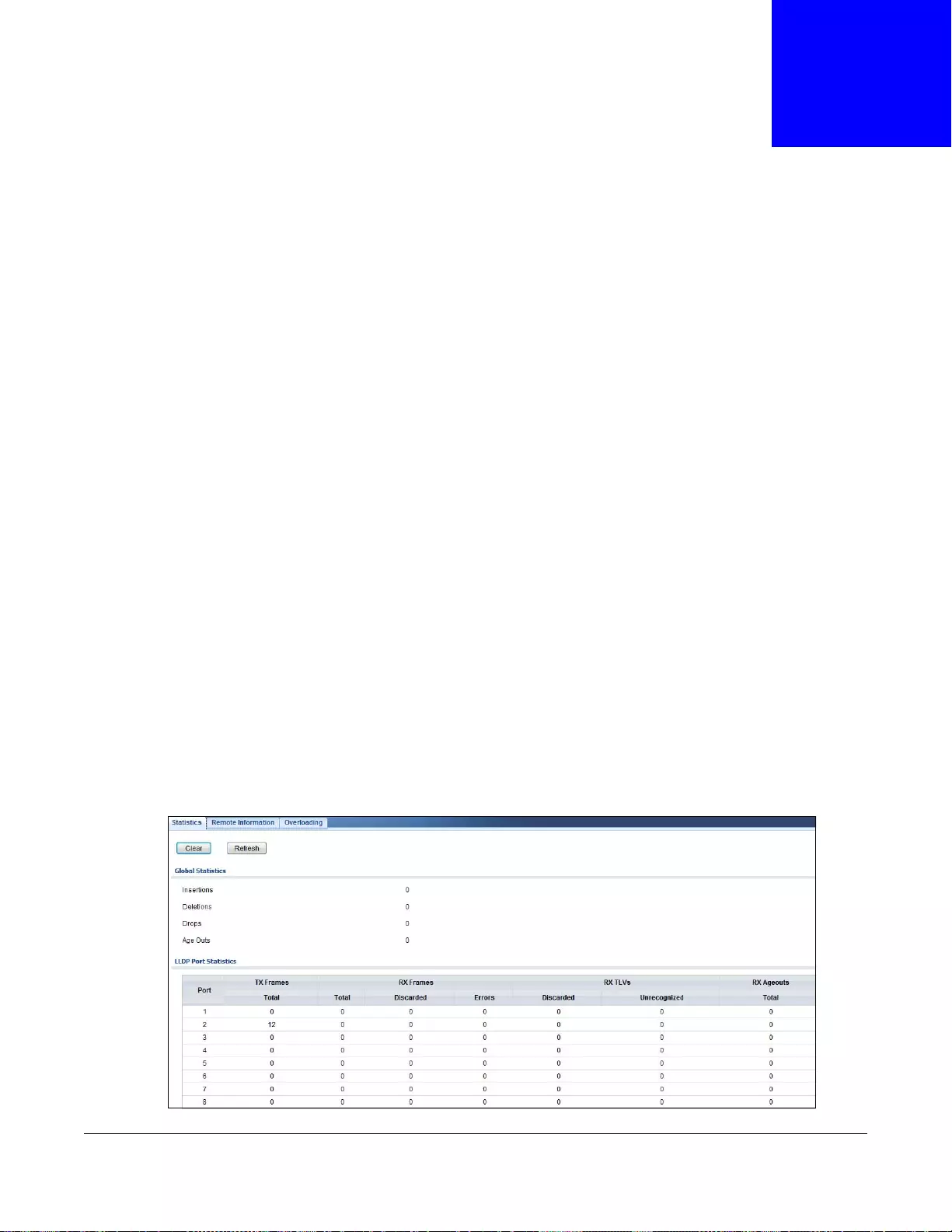
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
85
CHAPTER 15
Monitor: LLDP
15.1 Overview
This section provides information for LLDP in Monitor.
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), defined as IEEE 802.1ab, enables LAN devices that support
LLDP to exchange their configured settings. This helps eliminate configuration mismatch issues.
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The LLDP screen (Section 15.2 on page 85) displays statistics, remote information, and
overloading.
15.2 LLDP
This link takes you to a screen where you can view LLDP on the Switch. LLDP allows a network
device to advertise its identity and capabilities on the local network. It also allows the device to
maintain and store information from adjacent devices which are directly connected to the network
device.
15.2.1 Statistics
Use this screen to view the Switch’s LLDP global and port statistics. Click Monitor > LLDP >
Statistics to access this screen.
Figure 80 Monitor > LLDP > Statistics

Chapter 15 Monitor: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
86
Each field is described in the following table.
15.2.2 Remote Information
Use this screen to view the Switch’s LLDP remote device information. Click Monitor > LLDP >
Remote Information to access this screen.
Figure 81 Monitor > LLDP > Remote Information
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 47 Monitor > LLDP > Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Clear Click Clear to clear statistics.
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the page.
Global Statistics
Insertions This field displays the number of insert ions.
Deletions This fie ld displays the number of deletions.
Drops This field displays the number of drops.
Age Outs This field displays the number of age outs.
LLDP Port Statistics
Port This field displays the port number.
TX Frames Total This field displays the total number of TX LLDP frames.
RX Frames Total This field displays the total number of RX LLDP frames.
RX Frames
Discarded This field displays the number of discarded RX LLDP frames.
RX Frames
Errors This field displays the number of RX LLDP frames errors.
RX TLVs
Discarded This field displays the number of discarded RX LLDP TLVs.
RX TLVs
Unrecognized This field displays the number of unrecognized RX LLDP TLVs.
RX Ageouts
Total This field displays the total number of RX LLDP ageouts.
Ta ble 48 Monitor > LLDP > Remote Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local Port This field displays the local port.
Chassis ID Subtype This field displays the chassis ID subtype.
Chassis ID This field displays the chassis ID.
Port ID Subtype This field displays the port ID subtype.
Port ID This field displays the port ID.
System Name This field displays the descriptive name of the Switch for identification purposes.
Time to Live This field displays the live time of this entry.

Chapter 15 Monitor: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
87
15.2.3 Overloading
Use this screen to view the Switch’ s LLDP port overloading. Click Monitor > LLDP > Overloading
to access this screen.
Figure 82 Monitor > LLDP > Overloading
Each field is described in the following table.
Action
Detail Click Detail to show more information about this entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
Ta ble 48 Monitor > LLDP > Remote Information (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 49 Monitor > LLDP > Overloading
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This label shows the port you are viewing.
Total (Bytes) This field displays the total in bytes.
Left to Send (Bytes) This field displays what is left to send in bytes.
Status This field displays whether the Switch is overloading or not.
Bytes Details This field displays how many bytes used by TLVs
Mandatory TLVs This field displays how many bytes used by mandatory TLVs.
MED Capabilities This field displays how many bytes used by MED capabilities.
MED Location This field displays how many bytes used by MED location.
MED Network
Policy This field displays how many bytes used by MED network policy.
MED Extended
Power vi a MDI This field displays how many bytes used by MED extended power via MDI.
802.3 TLVs This field displays how many bytes used by 802.3 TLVs.
Optional TLVs This field displays how many bytes used by optional TLVs.
MED Inventory This field displays how many bytes used by MED inventory.
802.1 TLVs This field displays how many bytes used by 802.1 TLVs.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
88
CHAPTER 16
Monitor: Security
16.1 Overview
This section provides information for Security in Monitor.
This link takes you to a screen where you can view the settings or traffic statistics which contain
detailed information about specific activities.
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Port Security screen (Section 16.2 on page 88) displays global and port.
•The 802.1X screen (Section 16.3 on page 89) displays port and authenticated hosts.
16.2 Port Security
Port security allows only packets with dynamically learned MAC addresses and/or configured static
MAC addresses to pass through a port on the Switch. The Switch can learn up to 8K MAC addresses
in total with no limit on individual ports; system total MAC address entry is 8K. Static MAC address
still can be configured when port security is enabled; the function of port security is concerned with
dynamic mac address learn action. When total MAC address entry is 8k, static MAC can't be
configured.
Use this screen to view Switch port security settings. Click Monitor > Security > Port Security
to access this screen.
Figure 83 Monitor > Security > Port Security
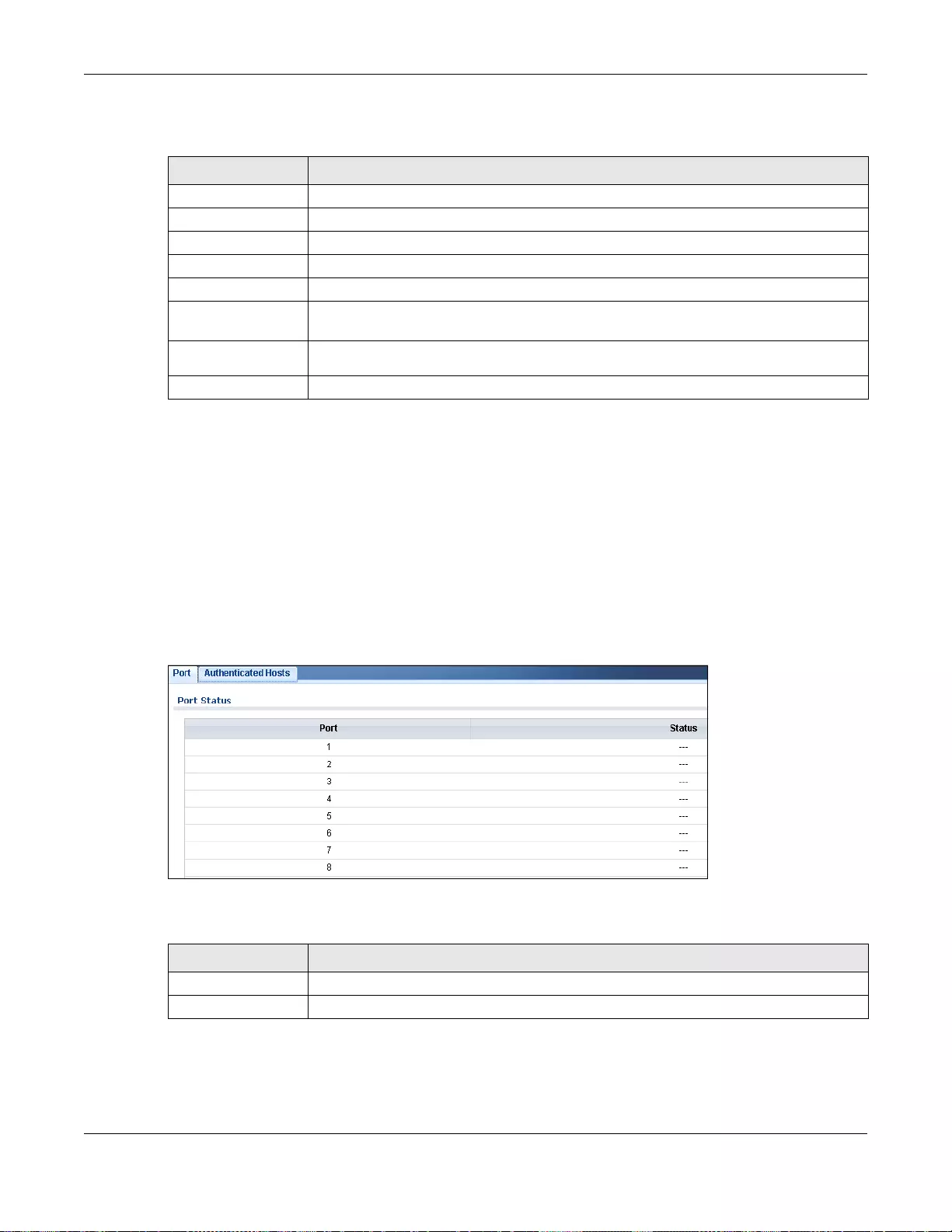
Chapter 16 Monitor: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
89
Each field is described in the following table.
16.3 802.1X
Use this screen to view Switch 802.1x security settings.
16.3.1 Port
Use this screen to view the Switch’s 802. 1x port status. Click Monitor > Security > 802.1X >
Port to access this screen.
Figure 84 Monitor > Security > 802.1X > Port
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 50 Monitor > Security > Port Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
Status This field displays the status of global control information.
Port
Port This field displays a port number.
Status This field displays the status of port based control information.
Max MAC Entry
Number Displays the designated maximum number of allowed MAC entries. The maxi mum MAC
entry number can be learned for individual ports.
Current Addr
Number This field displays the number of the current addr.
Action This field displays the action(s) the Switch takes on the associated classified traffic flow .
Ta ble 51 Monitor > Security > 802.1X > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This label shows the port you are viewing.
Status This field displays status of the port.

Chapter 16 Monitor: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
90
16.3.2 Authenticated Hosts
Use this screen to view the Switch’s 802. 1x security authenticated host status. Click Monitor >
Security > 802.1X > Authenticated Hosts to access this screen.
Figure 85 Monitor > Security > 802.1X> Authenticated Hosts
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 52 Monitor > Security > 802.1X > Authenticated Hosts
LABEL DESCRIPTION
User Name This field displays the name of a user.
Port This label shows the port you are viewing.
Session Time This label shows th e session time.
Authentication
Method This label shows the authentication method.
MAC Address This field displays the source MAC address in the binding.
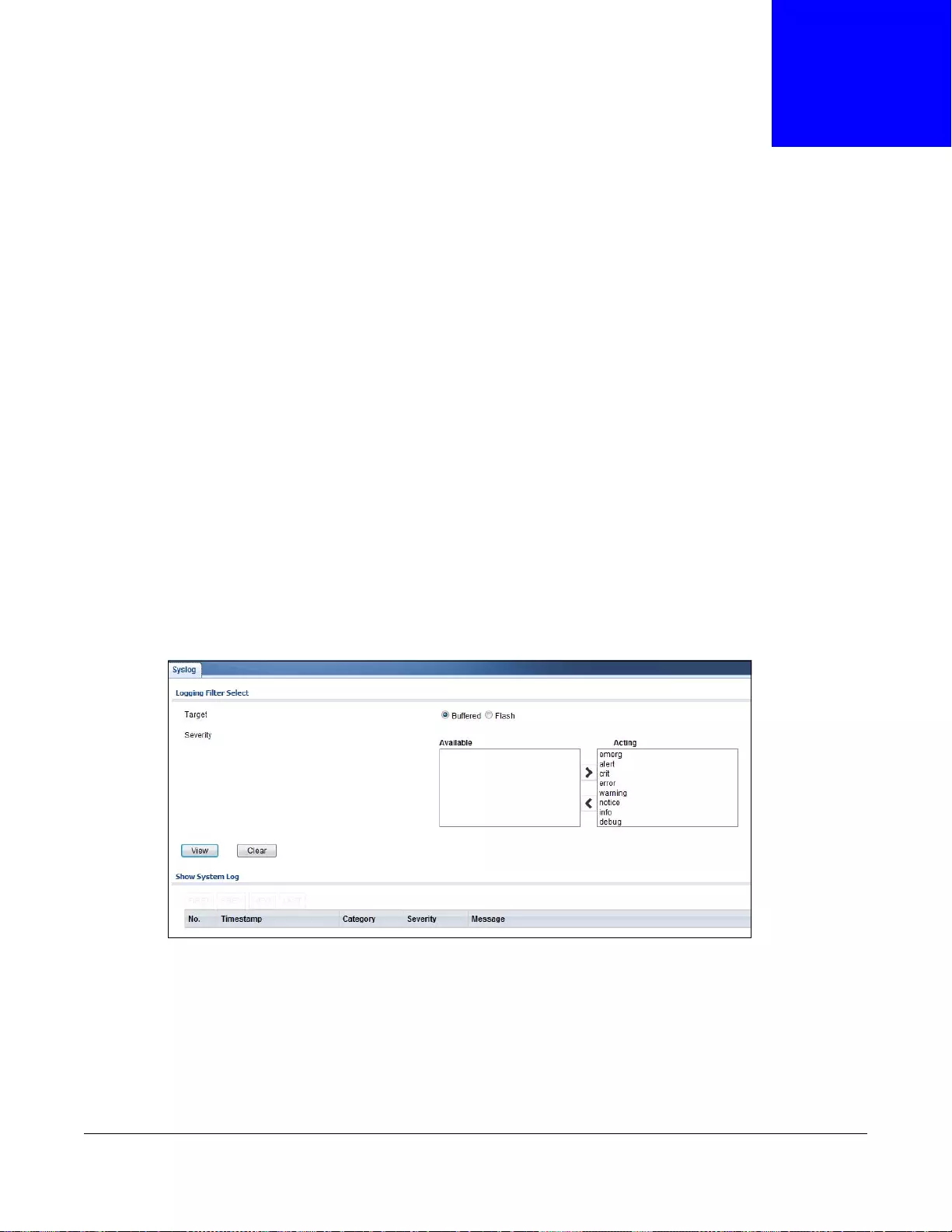
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
91
CHAPTER 17
Monitor: Management
17.1 Overview
This section provides information for Management in Monitor.
This chapter describes how to view management settings on the Switch.
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Syslog screen (Section 17.2 on page 91) displays logging filter select and shows system log.
•The Error Disable screen (Section 17.3 on page 92) displa ys global and port.
17.2 Syslog
Use this screen to view Switch syslog management. Click Monitor > Management > Syslog to
access this screen.
Figure 86 Monitor > Management > Syslog
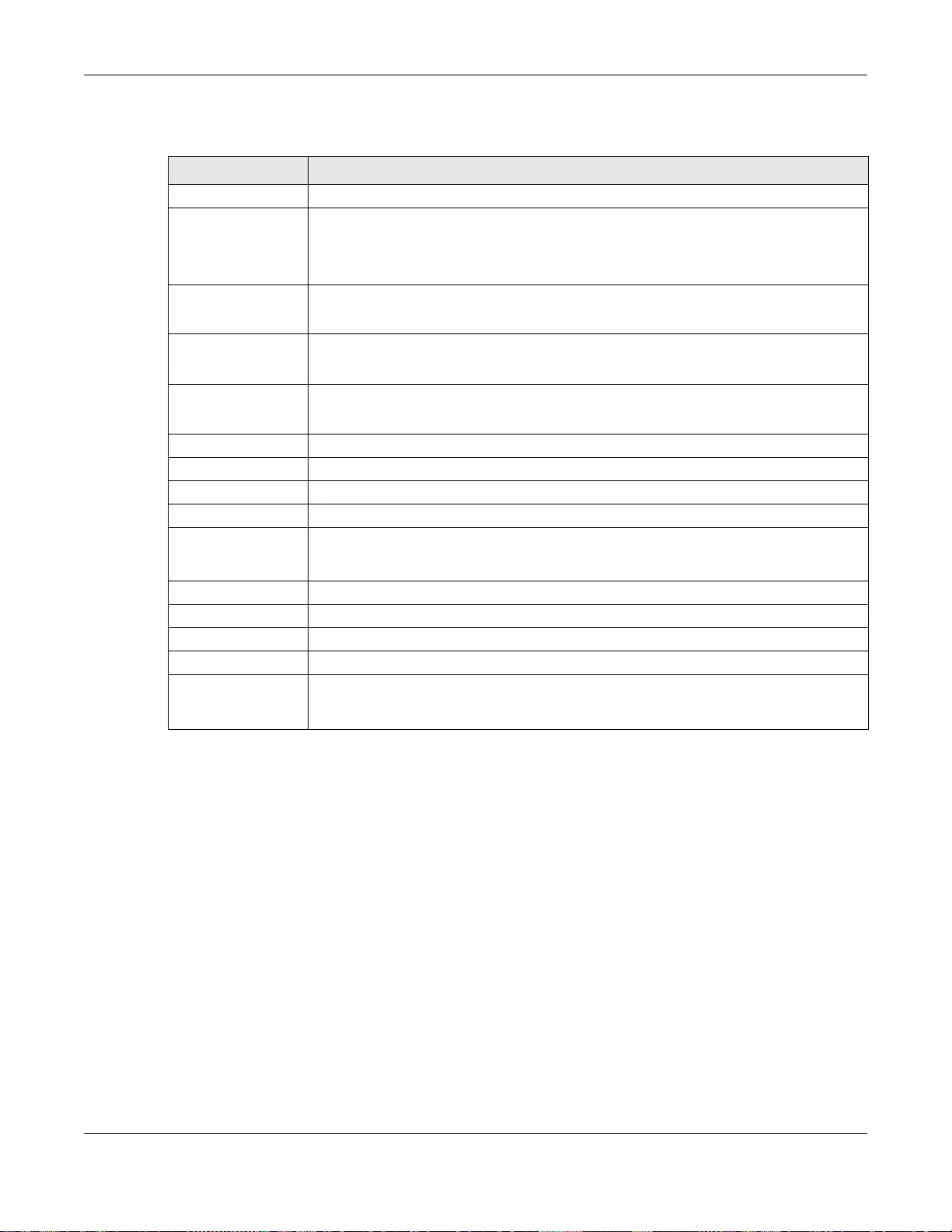
Chapter 17 Monitor: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
92
Each field is described in the following table.
17.3 Error Disable
This link takes you to a screen where you can view CPU protection and error disable recovery.
Use this screen to view Switch global and port error disable management. Click Monitor >
Management > Error Disable to access this screen.
Ta ble 53 Monitor > Management > Syslog
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logging Filter Select
Target Select Buffered or Flash.
Buffered: Login saved to temporary memory.
Flash: Login saved to permanent memory.
Severity This field displays two options: Available and Acting.
Severity type: crit, emerg, alert, error, warning, notice, info, and debug.
Available Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
Acting Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
>Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
<Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
View Click View to display results.
Clear Click Clear to clear results.
Show System Log The syslog protocol allows devices to send event notification messages across an IP
network to syslog servers that collect the event messages. A syslog-enabled device can
generate a syslog message and send it to a syslog server
No. This field displays the nu mber you are viewing.
Timestamp This field displays the timestamp.
Category This field displays the category.
Severity This field displays the severity.
Message The syslog protocol allows devices to send event notification messages across an IP
network to syslog servers that collect the event messages. A syslog-enabled device can
generate a syslog message and send it to a syslog server.

Chapter 17 Monitor: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
93
Figure 87 Monitor > Management > Error Disable
Each field is described in the following table.
Ta ble 54 Monitor > Management > Error Disable
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
Recovery
Interval View the number of sec onds (from 3 0 to 2592 000) for t he time interval of the recovery.
Error Disabled
Reason This field displays the supported features that allow the Switch to shut down a port or
discard packets on a port according to the feature requirements and what action you
configure.
Timer Status Select this option to allow the Switch to wait for the specified time interval to activate a
port or allow specific packets on a port, after the error was gone. Deselect this opti on to
turn off this rule.
Port
Port This field displays the port number.
Error Disabled
Reason This field displays the supported features that allow the Switch to shut down a port or
discard packets on a port according to the feature requirements and what action you
configure.
Time Left (sec) This field displays the time left in seconds.
Action This field displays the ac tion.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
94
CHAPTER 18
Configuration: System
18.1 Overview
This section provides information for System in Configuration.
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The IP screen (Section 18.2 on page 94) displays IPv4 and IPv6 settings.
• The Time screen (Section 18.3 on page 96) displays the system time and SNTP settings.
• The Information screen (Section 18.4 on page 97) displays the system information.
18.2 IP
The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default IP
address is 192.168.1.1. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address.
The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
18.2.1 The IPv4 Screen
Use this screen to view the IPv4 interface status and Switch’s management IPv4 addresses. Click
Configuration > System > IP > IPv4 to open this screen.
Figure 88 Configuration > System > IP > IPv4
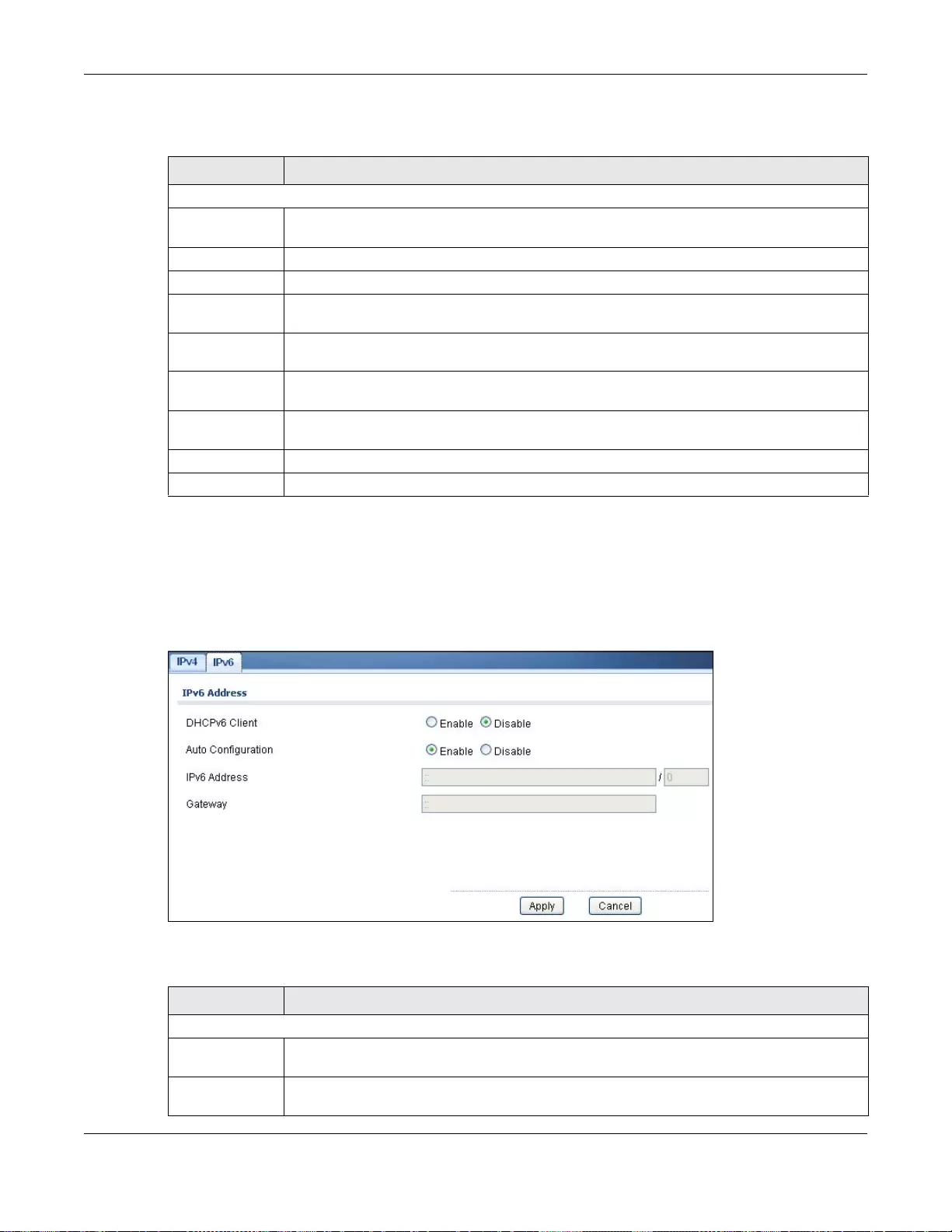
Chapter 18 Configuration: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
95
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
18.2.2 The IPv6 Screen
Use this screen to view the IPv6 interface status and Switch’s management IPv6 addresses.
Click Configuration > System > IP > IPv6 to open this screen.
Figure 89 Configuration > Sy stem > IP > IPv6
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 55 Configuration > System > I P > IPv4
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv4 Address
Mode Select Static to define the IPv4 network properties or DHCP to allow the device to define
the properties.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the Switch in the IP domain.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask of the Switch in the IP domain.
Gateway Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254.
DNS Server 1 Enter the IP address for the primary domain name server. DNS (Domain Name System) is
for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice versa.
DNS Server 2 Enter the IP address for the secondary domain name server. DNS (Domain Name System)
is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice versa.
Management
VLAN Enter the port number of the management VLAN.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 56 Co nfiguration > System > IP > IPv6
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Address
DHCPv6 Client Select Enable to allow the device to act as a DHCPv6 client or Disable to disallow it. This
field displays the Switch’s DHCP settings when it is acting as a DHCPv6 client.
Auto
Configuration Select Enable to allow the device to auto-configure the IPv6 properties or Disable to
manually enter the properties.
Chapter 18 Configuration: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
96
18.3 Time
The Time option is used to setup the system time and SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) server
settings.
18.3.1 The System Time Screen
In the navigation panel, click Configuration > System > Time > System Time to display the
screen as shown.
Figure 90 Configuration > System > Time > System Time
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
IPv6 Address Enter the IPv6 address of the Switch in the IP domain.
Gateway Enter the IPv6 address of the default outgoing gateway.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 56 Configuration > System > IP > IPv6 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 57 Co nfiguration > System > Time
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Time
Enable SNTP Select Enable to enable using a simple network time protocol (SNTP) server to manage the
system time or Disable to manually manage system time.
Manual Time Select the system date and time values from the dropdown li st s.
Time Zone Select the time zone from the dropdown list.
Daylight Saving
Time Select Enable to use Daylight Saving Time to offset the system time or Disable not adjust
system time.

Chapter 18 Configuration: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
97
18.3.2 The SNTP Server Screen
In the navigation panel, click Configuration > System > Time > SNTP Server to display the
screen as shown.
Figure 91 Configuration > Sy stem > Time > SNTP Server
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
18.4 Information
The information option is used to set the following system information properties: system name,
system location, and system contact information.
18.4.1 The System Information Screen
In the navigation panel, click Configuration > System > System Information to display the
screen as shown. You can set the system name, system location, and system contact.
Daylight Saving
Time Offset Enter the daylight saving time offset value in minutes.
Start Date Select the start date of the daylight saving time period from the dropdown lists.
End Date Select the end date of the daylight saving time period from the dropdown lists.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 57 Configuration > System > Time (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 58 Configuration > System > Time > SNTP Server
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNTP Server
Server Enter the address of the simple network time protocol (SNTP) server as an IP address
(192.168.0.1) or as a URL (www.zyxel.com).
Server Port Enter the port number of the SNTP s erv er. The numeric v a lue can be be tween 1 and 65535.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
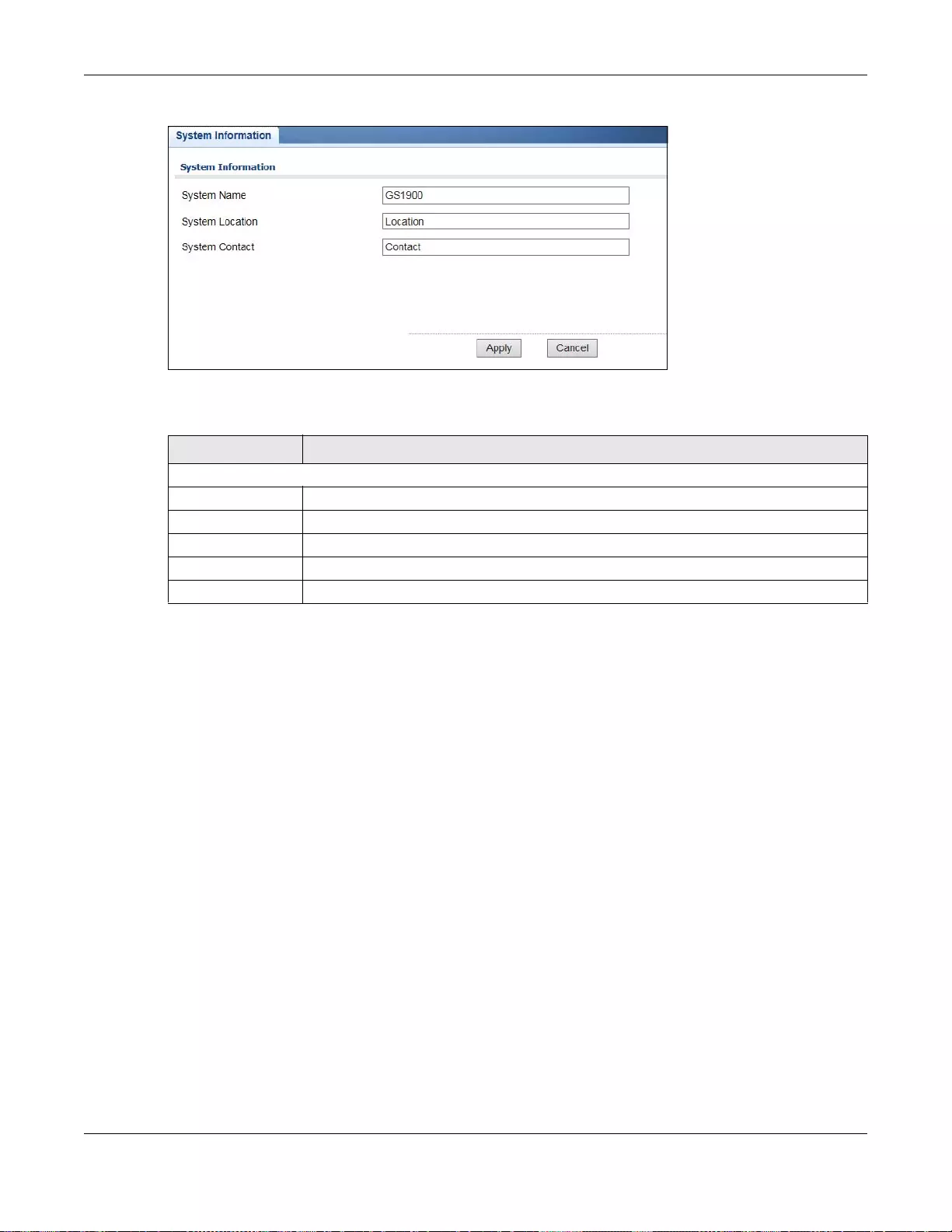
Chapter 18 Configuration: System
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
98
Figure 92 Configuration > System > System Information
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 59 Configuration > System > System Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Information
System Name Enter the descriptive name of the Switch for identification purposes.
System Location Enter the geographic location of the Switch for identification purposes.
System Contact Enter the person in charge of the Switch for identification purposes.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
99
CHAPTER 19
Configuration: Port
19.1 Overview
This section provides information for Port in Configuration.
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The Port screen (Section 19.2 on page 99) displays gener al port settings.
• The EEE screen (Section 19.3 on page 101) displays the port EEE settings.
• The PoE screen (Section 19.4 on page 102) displays the port PoE settings.
• The Bandwidth Management screen (Section 19.5 on page 108) displays the port ingress and
egress settings.
• The Storm Control screen (Section 19. 6 on pag e 110) displays the port storm control settings.
19.2 Port
Use this screen to view Switch port settings and select ports for configuration. Click Configuration
> Port > Port > Port to open this screen.
Figure 93 Configuration > Port > Port > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 60 Configuration > Port > Port > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
100
19.2.1 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure Switch port settings. Click Configuration > Port > Port > Edit to
open this screen.
Figure 94 Configuration > Port > Port > Edit
Port N ame Displays a descriptive name that identifies this port. The length of the name can be up to
32 alpha-numerical characters.
Note: Due to space limitations, the port name may be truncated in some web configurator
screens.
State Displays the port status as enabled or disabled.
Link Status Displays the link status as up or down.
Speed Displays the speed of the Ethernet connection on this port. The choices are Auto, 10M,
100M, and 1000M.
Duplex Displays the duplex mode of the Ethernet connection on this port. The choices are auto,
full, or half.
FlowCtrl State Displays the flow control state as enabled or disabled. A concentration of traffic on a port
decreases port bandwidth and overflows buffer memory causing pack et discards and frame
losses. Flow Control is used to regulate transmission of signals to match the bandwidth of
the receiving port.
Ta ble 60 Configuration > Port > Port > Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
101
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
19.3 EEE
Use this screen to view Switch port Energy-Efficient Ethernet (EEE) settings and select ports for
configuration. Click Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE to open this screen.
Figure 95 Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE
Ta ble 61 Configuration > Port > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Edit
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
Port N ame Enter a descriptive name that identifies this port. The length of the name can be up to 32
alpha-numerical characters.
Note: Due to space limitations, the port name may be truncated in some web configurator
screens.
State Select Enable to enable the ports or Disable to disable them.
Speed Select the spee d of the Ethernet connection on thi s port. The choices are Auto, 10M,
100M, and 1000M.
Duplex Select the duplex mode of the Ethern et connection on this port. The choices are Auto, Full,
or Half.
FlowCtrl State Select Enable to allow the device to manage data flow or Disable to have no data flow
management. A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and overflows
buffer memory causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow Control is used to regulate
transmission of signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
102
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
19.3.1 The EEE Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure Switch port EEE settings. Click Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE >
Edit to open this screen.
Figure 96 Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
19.4 PoE
The Switch supports both the IEEE 802.3af P ower over Ethernet (PoE) and IEEE 802.3at High Power
over Ethernet (PoE) standards. The Switch is Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) because it provides
a source of power via its Ethernet ports, and each device that receives power through an Ethernet
port is a Powered Device (PD).
Ta ble 62 Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
EEE
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
State Displays the port status as enabled or disabled.
Ta ble 63 Configuration > Port > EEE > EEE > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
EEE
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
State Select Enable to designate the ports as EEE or Disable to not designate them as EEE.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
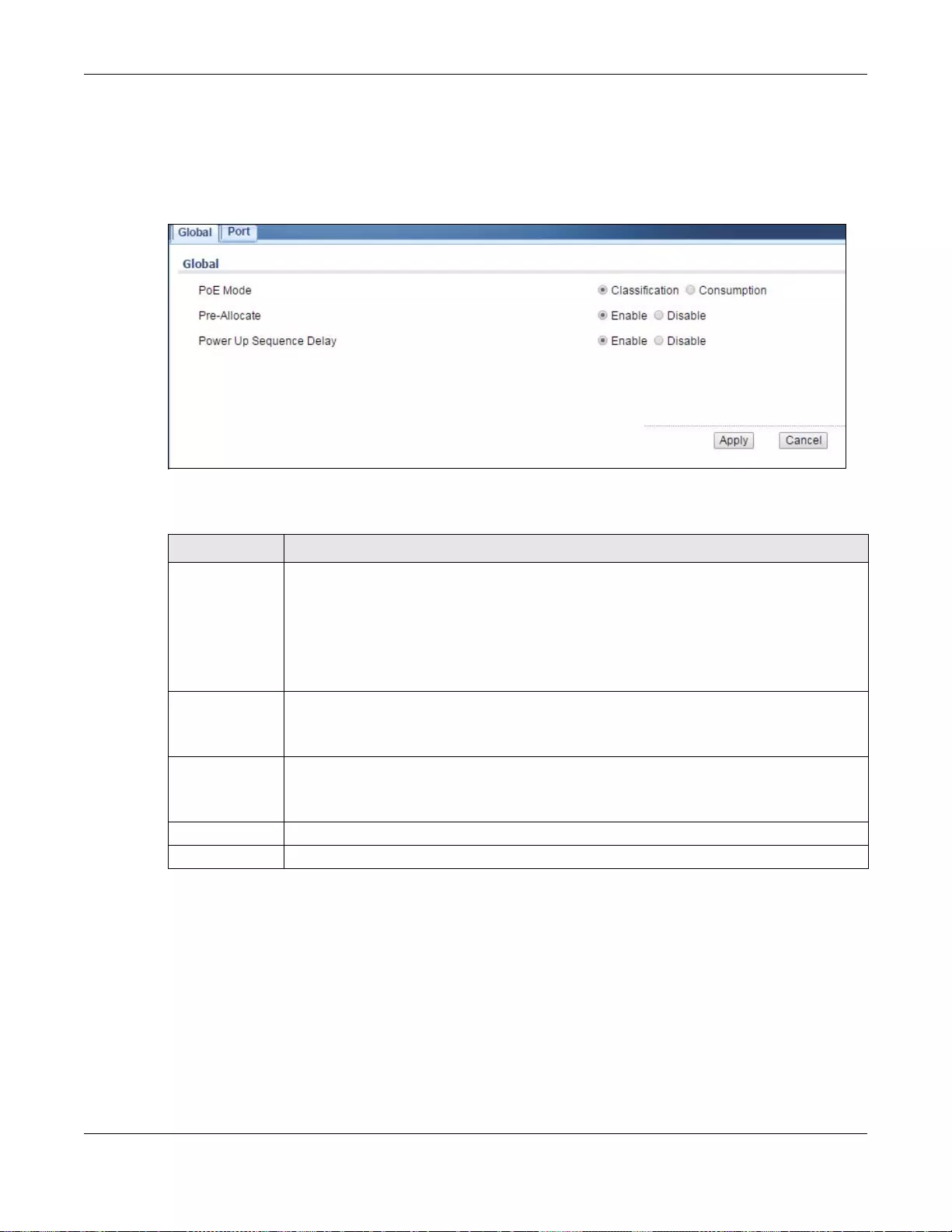
Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
103
19.4.1 The Global Screen
In the navigation panel, click Configuration > Port > PoE > Global to display the screen as
shown. Use this screen to configure Power over Ethernet (PoE) global settings.
Figure 97 Configuration > Port > PoE > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
19.4.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view Switch port PoE settings and select ports for configuration. Click
Configuration > Port > PoE > Port to open this screen.
Ta ble 64 Configuration > Port > PoE > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PoE Mode Select the power management mode you want the Switch to use.
•Classification - Select this if you want the Switch to reserve the Max Power (mW) to
each PD according to the priority level. If the total power supply runs out, PDs with
lower priority do not get power to function.
•Consumption - Select this if you w ant the S witc h to manage the total power supply so
that each conne cted PD gets a resource. However, the power allocated by the Switch
may be less than the Max Power (mW) of the PD. PDs with higher priority also get more
power than those with lower priority levels.
Pre-Allocate This field is only available on GS1900-8HP (Revision B1) and GS1900-10HP only.
Select Enable to have the Switch pre-allocate power to each port based on the
classification of the PD device. Otherwise, select Disable.
Power Up
Sequence Delay This field is only available on GS1900-8HP (Revision B1) and GS1900-10HP only.
Select Enable to allow PoE ports to be powered up one-by-one randomly or Disable to
allow them all to be powered up at the same time.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
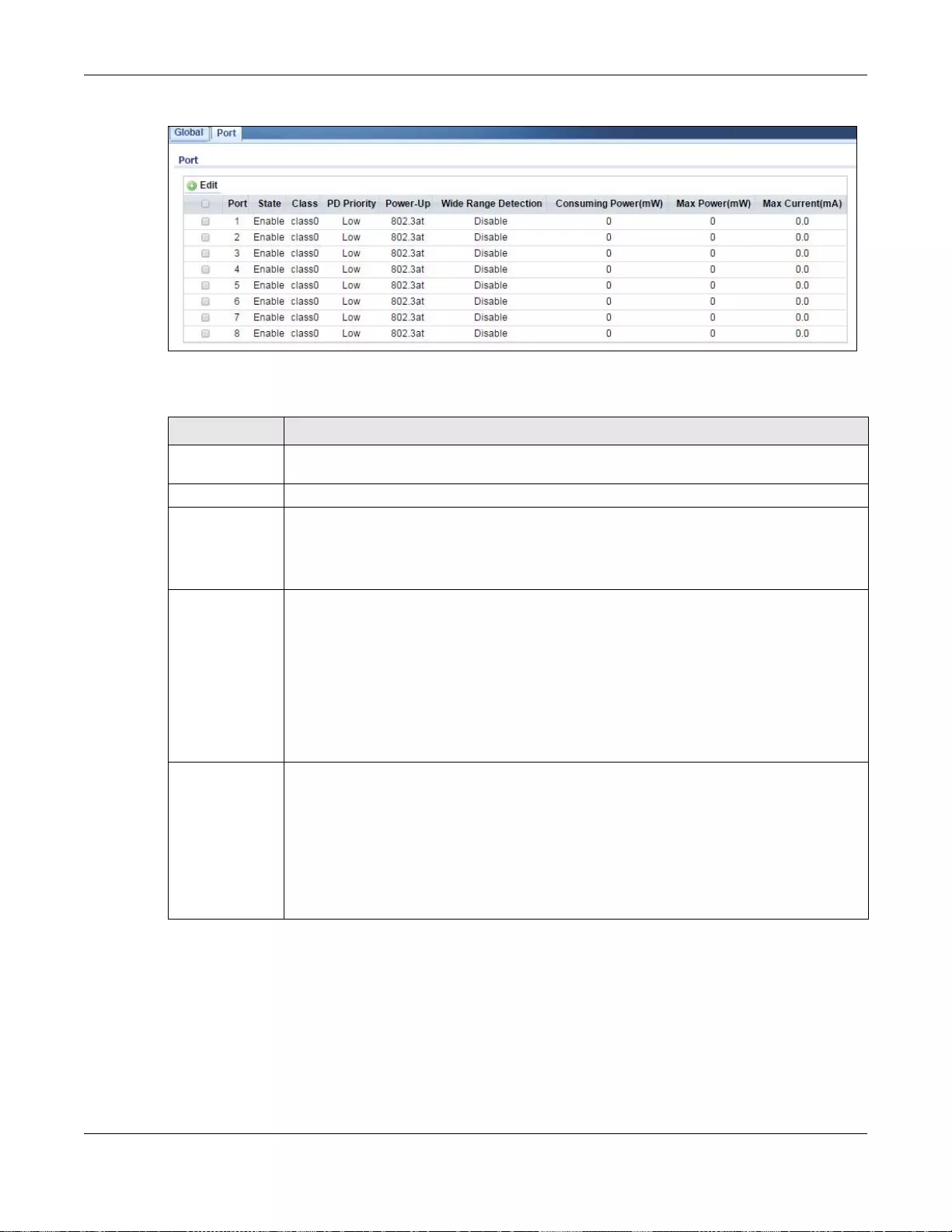
Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
104
Figure 98 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 65 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Edit Select one or more ports in the first column of the table and click this to configure PoE
settings for the ports.
Port Displays the port index number.
State Displays which ports can receive power from the Switch. You can set this in the
Configuration > Port > PoE Edit screen.
•Disable - The powered device (PD) connected to this port cannot get power.
•Enable - The PD con nected to this port can receive power.
Class This shows the power classification of the PD.
This is a number from 0 to 4, where each value represents a range of power (W) and
current (mA) that the PD requires to function. The ranges are as follows.
•Class 0 - Default, 0.44 to 12.94
•Class 1 - Optional, 0.44 to 3.84
•Class 2 - Optional, 3.84 to 6.49
•Class 3 - Optional, 6.49 to 12.95
•Class 4 - Reserved (PSEs classify as Class 0) in a switch that supports IEEE 802.3af
only. Optional, 12.95 to 25.50 in a switch that supports IEEE 802.3at.
PD Priority When the total power requested by the PDs exceeds the total PoE power budget on the
Switch, you can set the PD priority to allow the Switch to provide power to ports with higher
priority first.
•Critical has the highest priority.
•High has the Switch assign power to the port after all critical priority ports are served.
•Medium has the Switch assign power to the port after all critical and high prior ity ports
are served.
•Low has the Switch assign power to the port after all critical, high and medium priority
ports are served.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
105
19.4.3 The PoE Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure Switch port PoE settings. Click Configuration > Port > PoE > Port >
Edit to open this screen.
Power-Up This shows how the Switch provides power to the connected PD at power-up.
802.3af - the Switch follows the IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet standard to supply
power to the connected PDs during power-up.
Legacy - the Switch can provide power to the connected PDs that require high inrush
currents at power-up.
Pre-802.3at - the Switch initially offers power on the port according to the IEEE 802.3af
standard, and then switches to support the IEEE 802.3at standard within 75 milliseconds
after a PD is connected to the port. Select this option if the Switch is performing 2-event
Layer-1 classification (PoE+ hardware classification) or the connected PD is NOT performing
Layer 2 power classification using Link Layer Discover y Protocol (LLDP).
802.3at - the Switch supports the IEEE 802.3 at High Power over Ethernet standard and
can supply power of up to 30W per Ethernet port. IEEE 802.3at is also known as PoE + or
PoE Plus. An IEEE 802.3at compatible device is referred to as Type 2. Power Class 4 (High
Power) can only be used by Type 2 devices. If the connected PD requires a Class 4 current
when it is turned on, it will be powered up in this mode.
Wide Range
Detection This field is available on GS1900-8HP (Revision B1) and GS1900-10HP only.
This shows whether the Switch enables a wider detection range for the PD or not.
The Switch de tects whether a connected device is a powered device or not before supplying
power to the port. For the PD detection, the Switch applies a fixed voltage to the device and
then receives returned current. If the returned current is within the IEEE 802.3AF/AT
standard range, the device will be considered as a valid PD by the Switch.
However, in real cases, environmental interferences might easily cause the returned current
out of the standard r ange. This field displ ays Enable if the Switch applies a wider range for
PD detection. Otherwise, it displays Disable.
Consuming
Power (mW) Displays the current amount of power consumed by the PD from the Switch on this port.
Max Power
(mW) Displa ys the maximum amou nt of power the PD could use from the Swit ch on this port. The
maximum power the Switch can supply to a port is 30W.
Max Current
(mA) Displays the maximum amount of current drawn by the PD from the Switch on this port.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 65 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
106
Figure 99 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port > E dit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 66 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
PD State Select Enable to provide power to a PD connected to the port or Disable so the po rt
cannot receive power from the Switch.
PD Priority This field is not available for the SFP or SFP+ ports.
When the total power requested by the PDs exceeds the total PoE power budget on the
Switch, you can set the PD priority to allow the Switch to provide power to ports with higher
priority.
Select Critical to give the PD connected to this port the highest priority.
Select High to set the Switch to assign the remaining power to the port after all critical
priority ports are served.
Select Medium to set the S witc h to assi gn the rema ining powe r to the port aft er all cri tical
and high priority ports are served.
Select Low to set the Switch to assign the remaining power to the port after all critical,
high and medium priority ports are served.
Power-Up Set how the Switch provides power to a connected PD at power-up.
802.3af - the Switch follows the IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet standard to supply
power to the connected PDs during power-up.
Legacy - the Switch can provide power to the connected PDs that require high inrush
currents at power-up.
Pre-802.3at - the Switch initially offers power on the port according to the IEEE 802.3af
standard, and then switches to support the IEEE 802.3at standard within 75 milliseconds
after a PD is connected to the port. Select this option if the Switch is performing 2-event
Layer-1 classification (PoE+ hardware classification) or the connected PD is NOT performing
Layer 2 power classification using Link Layer Discover y Protocol (LLDP).
802.3at - the Switch supports the IEEE 802.3 at High Power over Ethernet standard and
can supply power of up to 30W per Ethernet port. IEEE 802.3at is also known as PoE + or
PoE Plus. An IEEE 802.3at compatible device is referred to as Type 2. Power Class 4 (High
Power) can only be used by Type 2 devices. If the connected PD requires a Class 4 current
when it is turned on, it will be powered up in this mode.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
107
Wide Range
Detection This field is available on GS1900-8HP (Revision B1) and GS1900-10HP only.
Select whether to enable a wider detection range for the PD or not.
The Switch de tects whether a connected device is a powered device or not before supplying
power to the port. For the PD detection, the Switch applies a fixed voltage to the device and
then receives returned current. If the returned current is within the IEEE 802.3AF/AT
standard range, the device will be considered as a valid PD by the Switch.
However, in real cases, environmental interferences might easily cause the returned current
out of the standard r ange. This field displ ays Enable if the Switch applies a wider range for
PD detection. Otherwise, it displays Disable.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 66 Configuration > Port > PoE > Port > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
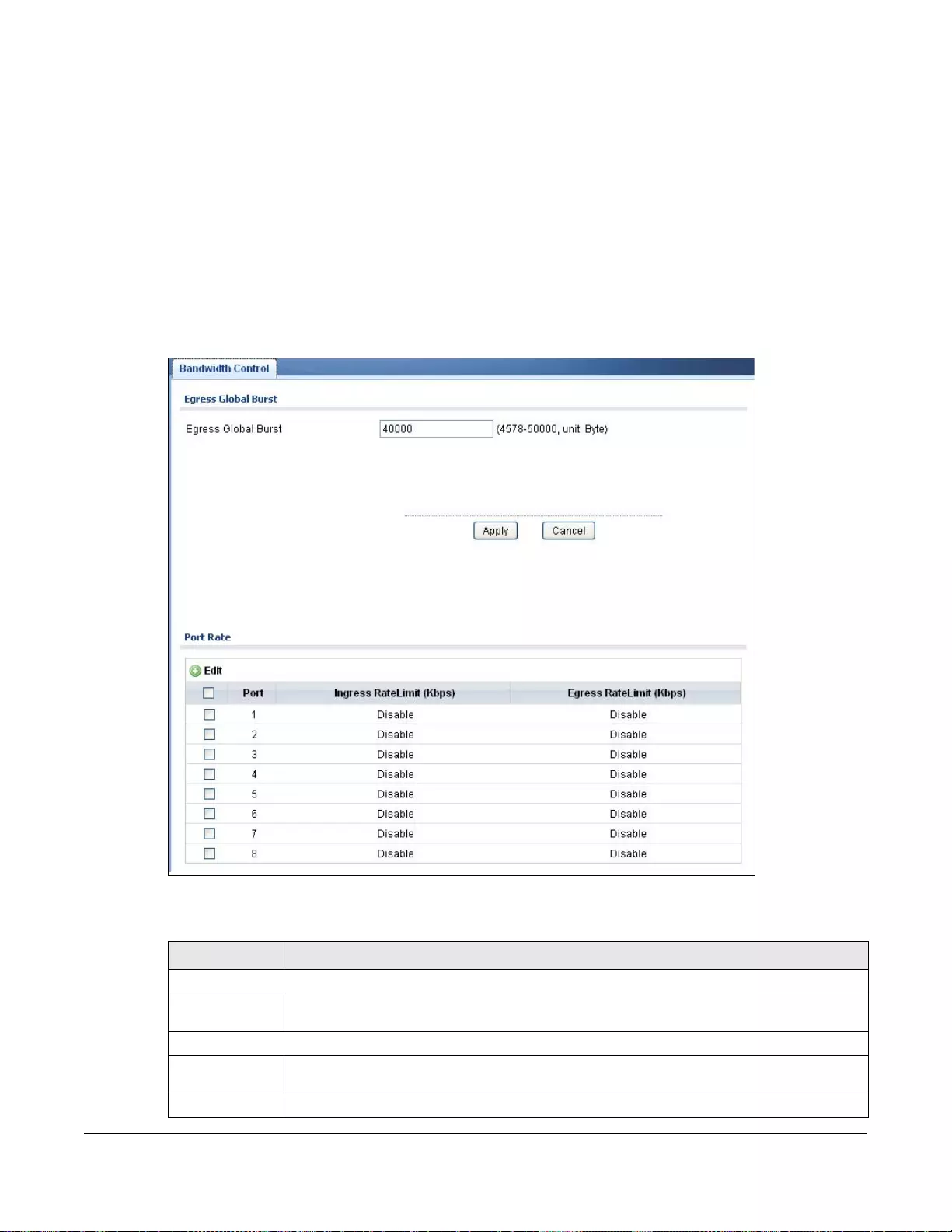
Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
108
19.5 Bandwidth Management
Bandwidth management means defining a maximum allowable bandwidth for incoming and/or out-
going traffic flows on a port.
19.5.1 The Bandwidth Control Screen
Use this screen to view Egress Bandwidth Management settings and select ports for configuration.
Click Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control to open this
screen.
Figure 100 Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 67 Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Egress Global Burst
Egress Global
Burst Specify the current egress burst size in bytes for all ports.
Por t Ra te
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
109
19.5.2 The Port Rate Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure port rate Bandwidth Management settings. Click Configuration >
Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control > Edit to open this screen.
Figure 101 Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ingress Rate
Limit (Kbps) Displays the maximum bandwidth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the incoming
traffic flow on a port.
Egress Rate
Limit (Kbps) Displays the maximum bandwidth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the outgoing
traffic flow on a port.
Ta ble 67 Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 68 Configuration > Port > Bandwidth Management > Bandwidth Control > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Por t Ra te
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
Ingress State Select Enable to activate ingress peak rate limits on the port(s).
Ingress
Bandwidth
(Kbps)
Enter the maximum bandwi dth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the outgoing tr affic
flow on a port.
Egress State Select Enable to activate egress peak rate limits on the port(s).
Egress
Bandwidth
(Kbps)
Enter the maximum bandwi dth allowed in kilobits per second (Kbps) for the outgoing tr affic
flow on a port.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
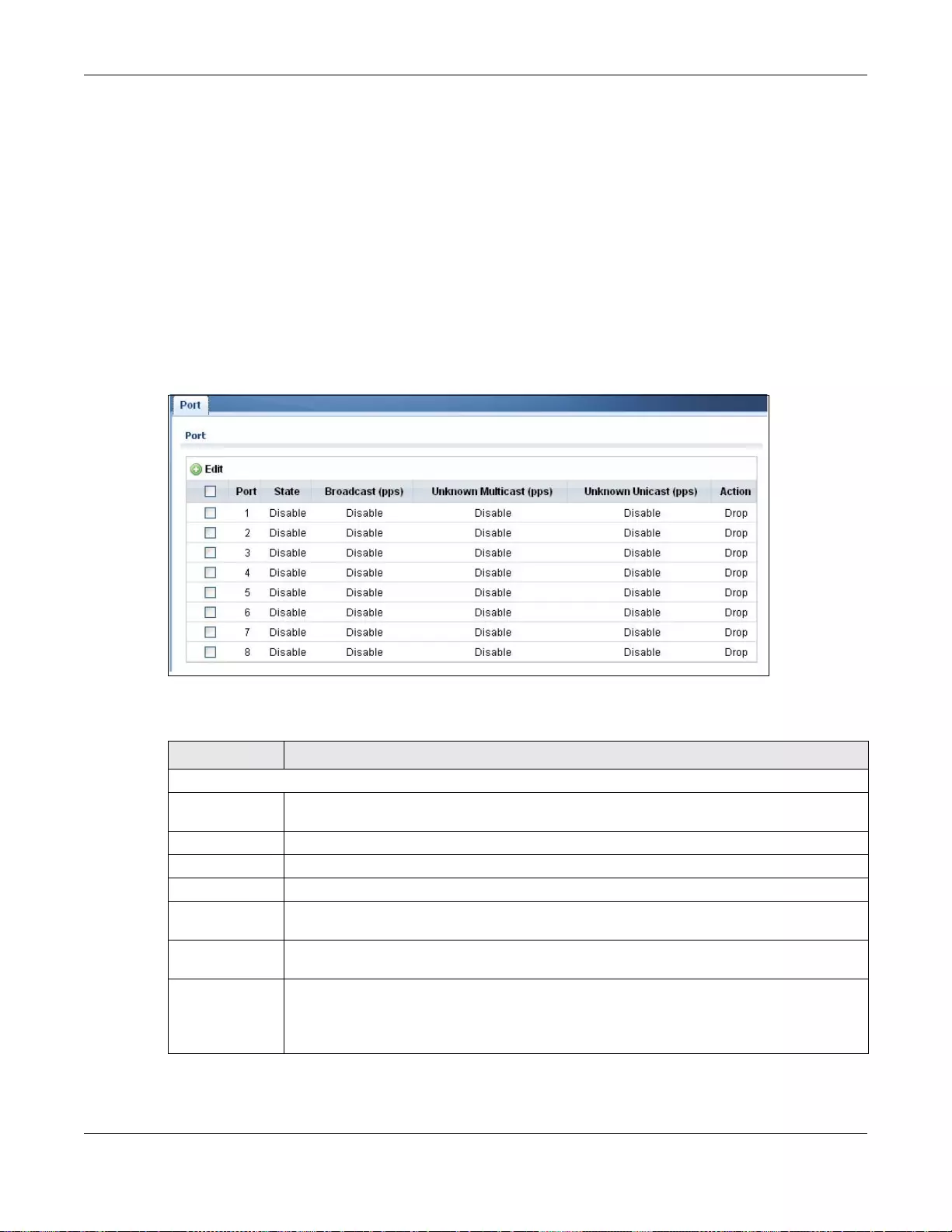
Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
110
19.6 Storm Control
Broadcast storm control limits the number of broadcast, multicast and destination lookup failure
(DLF) packets the Switch receives per second on the ports. When the maximum number of
allowable broadcast, multicast and/or DLF packets is reached per second, the subsequent packets
are discarded. Enable this feature to reduce broadcast, multicast and/or DLF packets in your
network. You can specify limits for each packet type on each port.
19.6.1 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view Storm Control settings for individual ports. Click Configuration > Port >
Storm Control > Port to open this screen.
Figure 102 Configuration > Port > Storm Control > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 69 Configuration > Port > Storm Control > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
State Displays whether the traffic storm control on the Switch is enabled or disabled.
Broadcast (pps) Displays how many broadcast packets the port receives per second.
Unknown
Multicast (pps) Displays how many multicast packets the port receives per second.
Unknown
Unicast (pps) Displays how many unicast packets the port receives per second.
Action Displays the action the device takes when a limit is reached. The following options are
available:
•Drop - drop the packet.
•Shutdown - shutdown the connection.

Chapter 19 Configuration: Port
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
111
19.6.2 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure Storm Control settings for individual ports. Click Configuration >
Port > Storm Control > Port > Edit to open this screen.
Figure 103 Configuration > Port > Storm Control > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 70 Configuration > Port > Storm Control > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port List Displays the port list index number(s).
State Select Enable to activate traffic storm control on the port(s).
Action Determines the action the dev ice takes when a limit is reached. The following options are
available:
•Drop - drop the packet when limit is reached.
•Shutdown - shutdown the connection when a limit is reached.
Broadcast (pps) Click the Enable checkbox to active the feature.
Enter the maximum number of broadcast packets the port can receive per seco nd.
Unknown
Multicast (pps) Click the Enable checkbox to active the feature.
Enter the maximum number of multicast packets the port can receive per second.
Unknown
Unicast (pps) Click the Enable checkbox to active the feature.
Enter the maximum number of unicast packets the port can rece ive per second.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
112
CHAPTER 20
Configuration: VLAN
20.1 Overview
This section provides information for VLAN in Configuration.
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a ph ysical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one
group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same
group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
In MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security among the
subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from accessing the network
resources of another on the same LAN, thus a user will not see the printers and hard disks of
another user on the same network.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets
go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast
domain.
20.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
• The VLAN screen (Section 20.2 on page 113) displays VLAN, port, and VLAN port settings.
• The Guest VLAN screen (Section 20.3 on page 118) displa ys the global and port settings of the
Switch.
• The Voice VLAN screen (Section 20.4 on page 120) displays the global, OUI, and port settings
of the Switch.

Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
113
20.2 VLAN
Use this screen to view and configure VLAN settings.
20.2.1 The VLAN Screen
Use this screen to view VLAN settings. Click Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN to open this
screen.
Figure 104 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.2.2 The VLAN Add Screen
Use this screen to add a VLAN. Click Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN > Add to open this
screen.
Figure 105 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN > Add
Ta ble 71 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Create VLAN
Add Click Add to create a new VLAN entry.
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN ID number.
VLAN Name Displays a descriptive name for the VLAN group for identification purposes. This name
consists of up to 64 printable characters; spaces are allowed.
VLAN Type Displays Default or Static.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
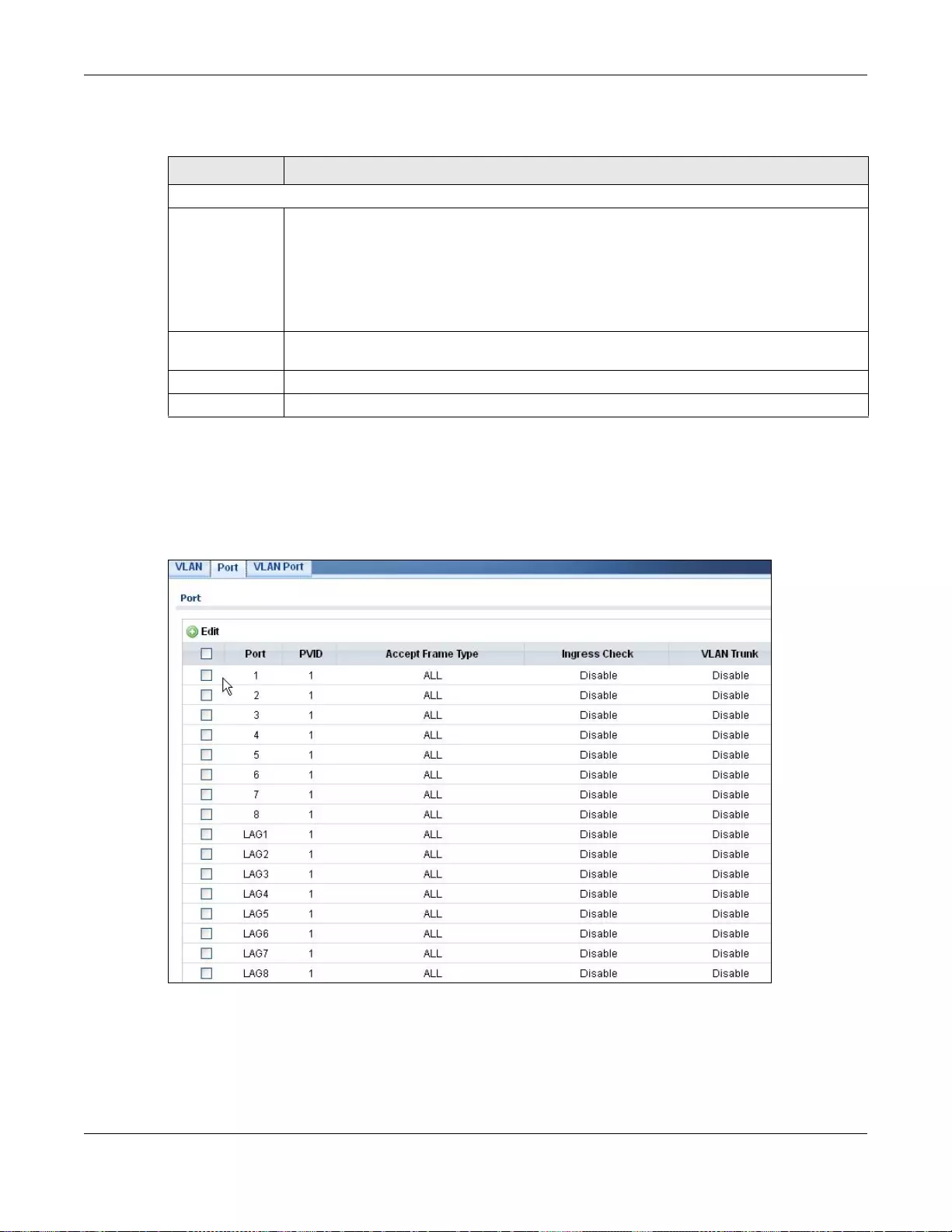
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
114
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.2.3 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view port settings and select VLANs for configuration. Click Configuration >
VLAN > VLAN > Port to open this screen.
Figure 106 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port
Ta ble 72 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN > Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN
VLAN List Primary privat e VLANs can ass ociate with sev er al (sec ondary ) Community private VLANs
and up to one (secondary) Isolated private VLAN.
You only configur e VL AN Asso ciation List for Primary private VLANs. Use a dash to
associate consecutive VLANs and a comma (no spaces) to associate non-cons ecutive
VLANs. For example, 51-53 includes 51, 52 and 53, but 51,53 does not include 52.
Secondary private VLANs can only be associated with one primary private VLAN.
VLAN Name
Prefix Enter a prefix for the VLAN name.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
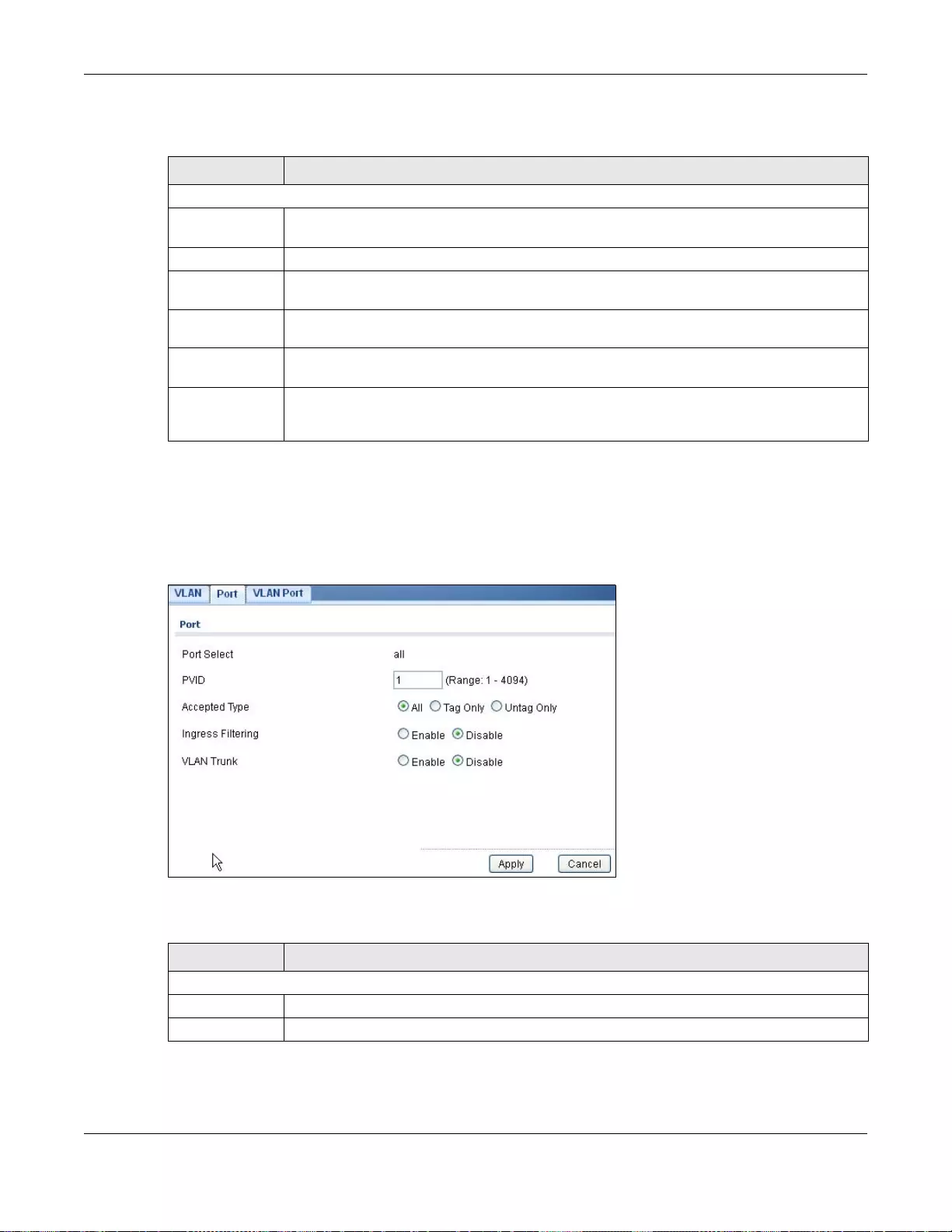
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
115
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.2.4 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure port settings. Click Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port > Edit to
open this screen.
Figure 107 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 73 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
PVID A PVID (P ort VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to in coming untagged frames received on a port so
that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
Accept Frame
Type Specify the type of frames allowed on a port. Choices are All, Tag Only and Untag Only.
Ingress Check If this check bo x is selected for a port, the Switch discards incoming frames for VLANs that
do not include this port in its member set.
VLAN Trunk Enable VLAN Trunking on ports connected to other switches or routers (but not ports
directly connected to end users) to allow frames belonging to unknown VLAN groups to
pass throug h the Switch.
Ta ble 74 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port Select Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
PVID Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the port VLAN ID.
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
116
20.2.5 The VLAN Port Screen
Port -based VLANs are VLANs where the packet forwarding decision is based on the destination MAC
address and its associated port. Port-based VLANs require allowed outgoing ports to be defined for
each port. Therefore, if you wish to allow two subscriber ports to talk to each other, for example,
between conference rooms in a hotel, you must define the egress (an egress port is an outgoing
port, that is, a port through which a data packet leaves) for both ports. Port-based VLANs are
specific only to the Switch on which they were created.
Use this screen to view VLAN port settings. Click Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Port to
open this screen.
Accepted Type Select All from the drop-down list box to accept all untagged or tagged fr ames on this port.
This is the default setting.
Select Tag Only to accept only tagged frames on this port. All untagged frames will be
dropped.
Select Untag Only to accept only untagged frames on this port. All tagged frames will be
dropped.
Ingress Filtering If this check box is selected for a port, the Switch discards incoming frames for VLANs that
do not include this port in its member set.
Clear this check box to disable ingress filtering.
VLAN Trunk Enable VLAN Trunking on ports connected to other switches or routers (but not ports
directly connected to end users) to allow frames belonging to unknown VLAN groups to
pass throug h the Switch.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 74 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > Port > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
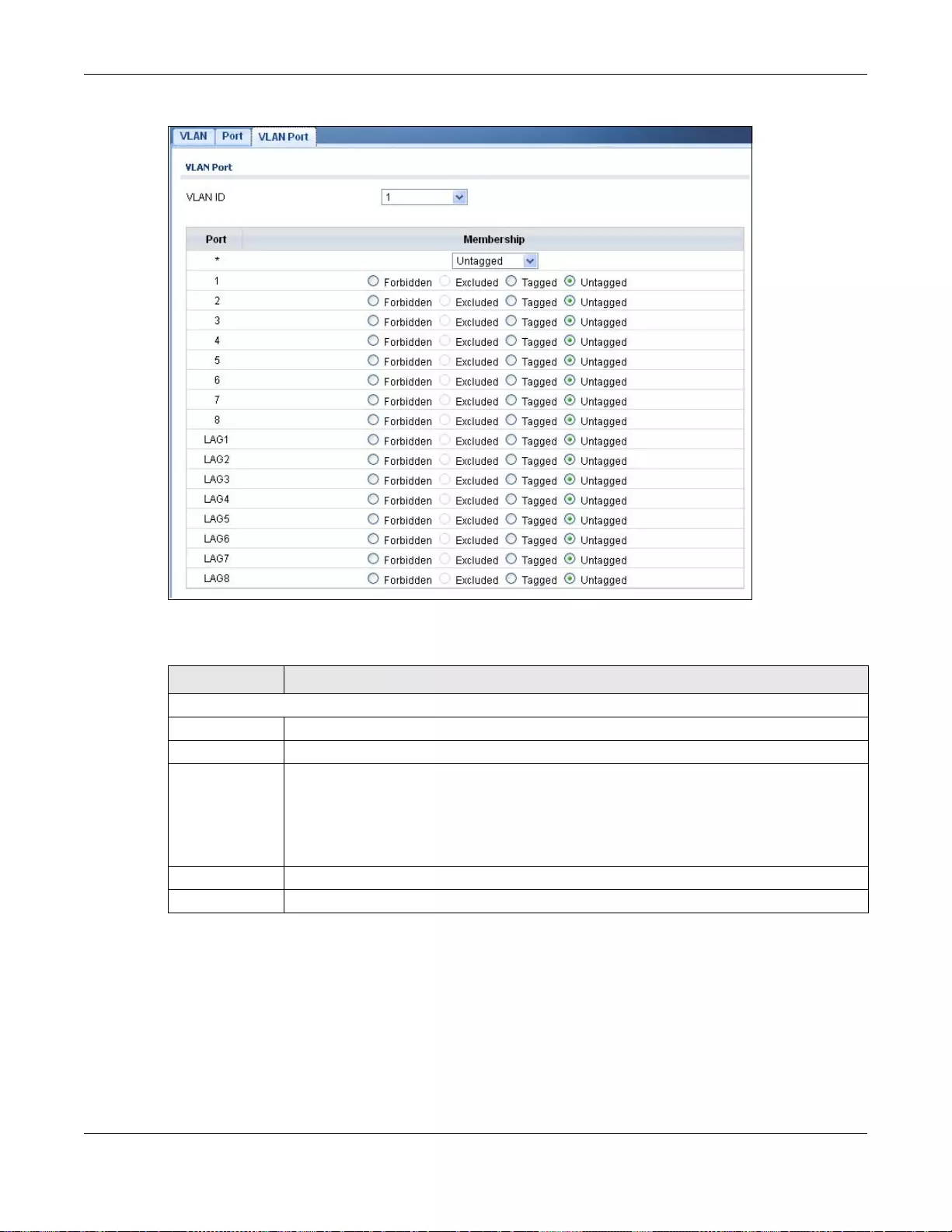
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
117
Figure 108 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 75 Configuration > VLAN > VLAN > VLAN Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Port
VLAN ID Select the ID of the VLAN you want to configure.
Port Displays the port index value.
Membership Select Forbidden if you want to prohibit the port from joining this VLAN group.
Select Excluded to remove the port from the VLAN.
Select Tagged to set the port TX tag status to tagged in the VLAN.
Select Untagged to set the port TX tag status to untagged in the VLAN.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
118
20.3 Guest VLAN
When 802.1x port authentication is enabled on the Switch and its ports, clients that do not have the
correct credentials are blocked from using the port(s). You can configure your Switch to have one
VLAN that acts as a guest VLAN. If you enable the guest VLAN (102 in the example) on a port (2 in
the example), the user (A in the example) that is not IEEE 802.1x capable or fails to enter the
correct username and password can still access the port, but traffic from the user is forwarded to
the guest VLAN. That is, unauthenticated users can ha ve access to limited network resources in the
same guest VLAN, such as the Internet. The rights gr anted to the Gu est VLAN depends on how the
network administrator configures switches or routers with the guest network feature.
Figure 109 Guest VLAN Example
Use this screen to view and configure guest VLAN settings.
20.3.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure the global Guest VLAN settings. Click Configuration > VLAN > Guest
VLAN to open this screen.
Figure 110 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 76 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select to enable the global Guest VLAN feature.

Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
119
20.3.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Guest VLAN port settings and select VLAN port(s) for configuration.
Click Configuration > VLAN > Gu est VLAN > Port to open this screen.
Figure 111 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.3.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the guest VLAN port EEE settings. Click Configuration > VLAN >
Guest VLAN > Port > Edit to open this screen.
Guest VLAN ID Enter the global guest VLAN ID.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 76 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Global (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 77 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
State Display the state of the selected port.
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
120
Figure 112 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.4 Voice VLAN
The Voice VLAN feature enables voice traffic forwarding on the Voice VLAN, then the switch can
classify and schedule network traffic. It is recommended that there be two VLANs on a port - one
for voice, one for data. Before connecting the IP device to the switch, the IP phone should configure
the voice VLAN ID correctly. It should be configured through its own GUI.
Use this screen to view and configure voice VLAN settings.
20.4.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure the global V oice VLAN settings. Click Configuration > VLAN > Voice
VLAN > Global to open this screen.
Ta ble 78 Configuration > VLAN > Guest VLAN > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers that are being configured.
State Enable/Disable the guest VLAN feature.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
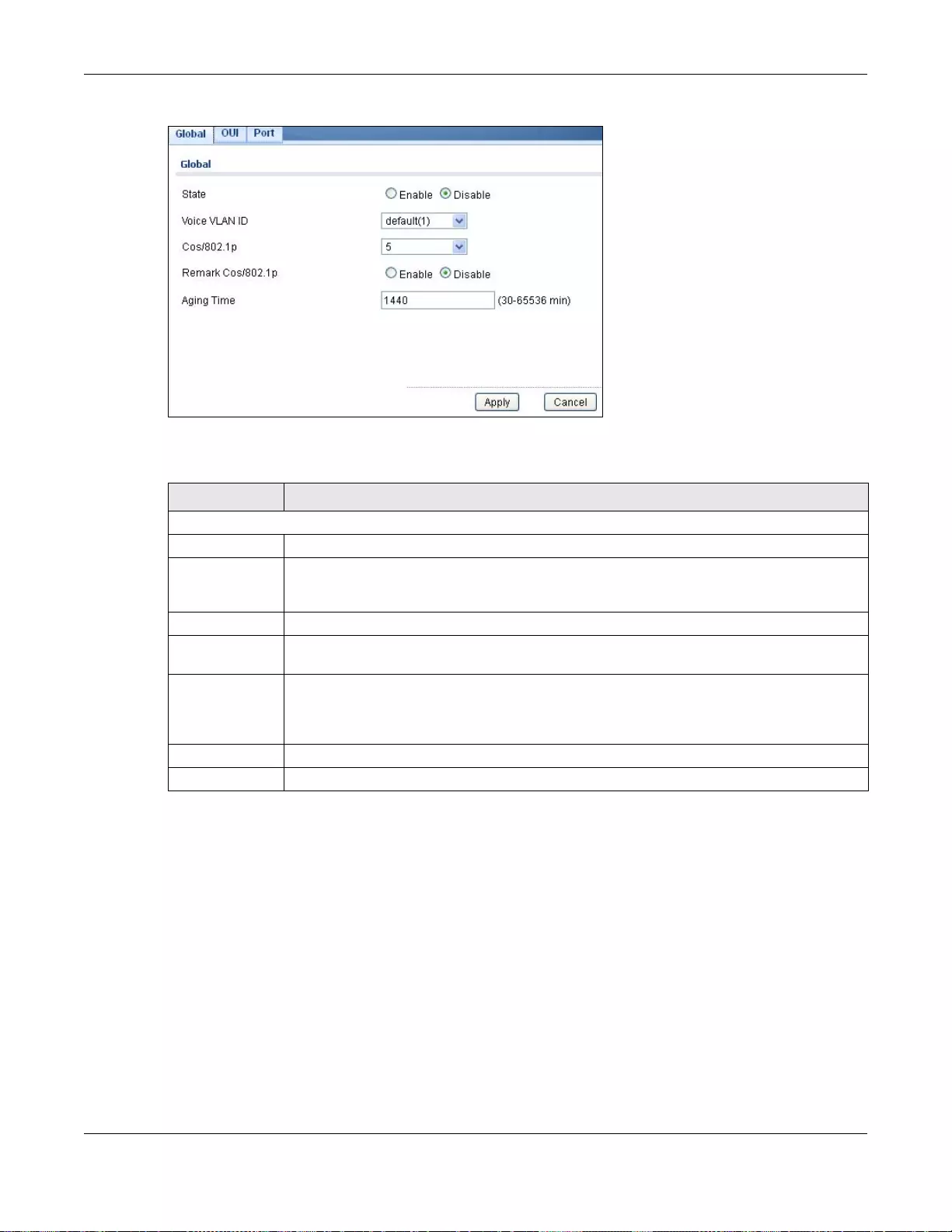
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
121
Figure 113 Conf iguration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.4.2 The OUI Screen
Use this screen to view the OUI settings. The maximum number of entries is 16. Modifying the OUI
table will restart auto detection of OUI process. Click Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN >
OUI to open this screen.
Ta ble 79 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select Enable to activate the global voice VLAN feature.
Voice VLAN ID Enter the global voice VLAN ID. It should be a unique VLAN ID in the system and cannot
equal each port PVID. It is a conflict in configuration if the value equals manageme nt VID,
MVR VID, PVID etc. The allowed range is 1 to 4095.
Cos/802.1p Displays the 802.1p packet priority field.
Remark Cos/
802.1p Select to Enable the priority remark function for cos/802.1p.
Aging Ti me Enter the voice VLAN secure learning aging time. The allowed range is 10 to 10000000
seconds. It is used when security mode or auto detect mode is enabled. In other cases, it
will be based on hardware aging time. The actual aging time will be situated between the
[age_time; 2 * age_time] interval.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
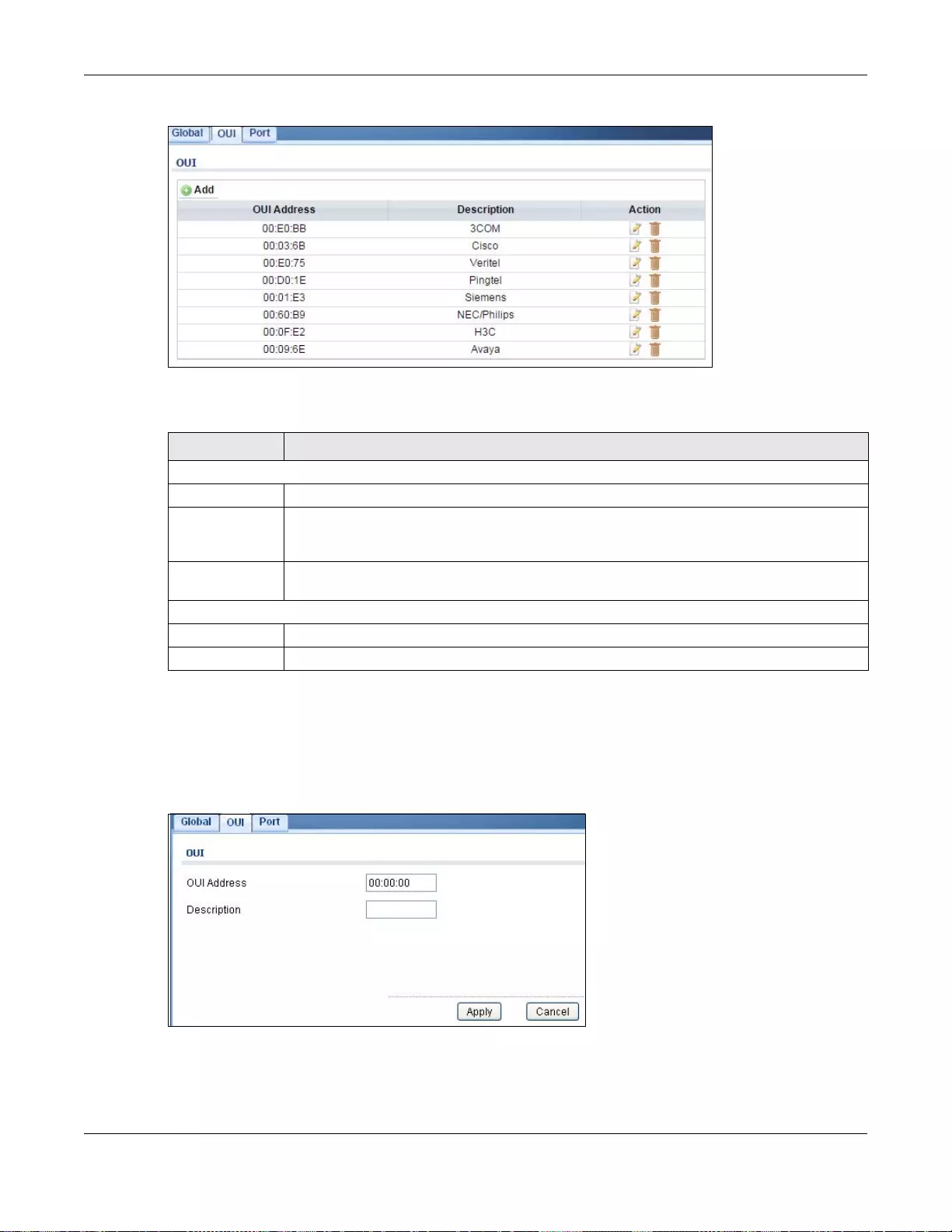
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
122
Figure 114 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > OUI
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.4.3 The OUI Add/Edit Screen
Use this screen to add/edit an OUI address. Click Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > OUI >
Add/Edit to open this screen.
Figure 115 Conf iguration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > OUI > Add/Edit
Ta ble 80 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > OUI
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OUI
Add Click Add to create a new OUI entry.
OUI Address Displays an OUI address. A telephony OUI address is a globally unique identifier assigned to
a vendor by IEEE. It must be 6 characters long and the input format is "xx-xx-xx" (x is a
hexadecimal digit).
Description Displays a description of the OUI address. Normally, it describes which vendor telephony
device it belongs to. The allowed string length is 0 to 32.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
123
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
20.4.4 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Voice VLAN port settings and select a port for configuration. Click
Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port to open this screen.
Figure 116 Conf iguration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 81 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > OUI > Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OUI
OUI Address Enter an OUI address. A telephony OUI address is a globally unique identifier assigned to a
vendor by IEEE. It must be 6 characters long and the input format is "xx-xx-xx" (x is a
hexadecimal digit).
Description Enter a description of the OUI address. Normally, it describes which vendor telephony
device it belongs to. The allowed string length is 0 to 32.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 82 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Chapter 20 Configuration: VLAN
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
124
20.4.5 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to edit the port(s) security state. Click Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN >
Port > Add/Edit to open this screen.
Figure 117 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port > Add/Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Port Displays the port index value.
State Displays the Voice VLAN port security mode state. When the function is enabled, all non-
telephonic MAC addresses in the Voice VLAN will be blocked for 10 seconds. Possible port
modes are:
•Enabled: Enable Voice VLAN security mode operation.
•Disabled: Disable Voice VLAN security mode operation.
Ta ble 82 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 83 Configuration > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Port > Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port Displays the port(s) index value.
State Select the Voice VLAN port security mode state. When the function is enabled, all non-
telephonic MAC addresses in the Voice VLAN will be blocked for 10 seconds. Possible port
modes are:
•Enabled: Enable Voice VLAN security mode operation.
•Disabled: Disable Voice VLAN security mode operation.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
125
CHAPTER 21
Configuration: MAC Table
21.1 Overview
This section provides information for MAC Table in Configuration.
The MAC Table screen (a MAC table is also known as a filtering database) shows how frames are
forwarded or filtered across the Switch’ s ports. When a device (which may belong to a VLAN group)
sends a packet which is forw arded to a port on th e S witch, the MAC address of the device is shown
on the Switch’s MAC Table. It also shows whether the MAC address is dynamic (learned by the
Switch) or static (manually entered in the Static MAC Forwarding screen).
21.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
The MAC Table screen (Section 21.2 on page 125) displays Static MAC, Filtering MAC, and Dynamic
MAC settings.
21.2 MAC Table
21.2.1 The Static MAC Screen
Use this screen to view Static MAC addresses settings. Click Configuration > MAC Table > Static
MAC to open this screen.
Figure 118 Configuration > MAC Table > Static MAC
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 84 Configuration > MAC Table > Static MAC
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static MAC
Add Click Add to create a new Static MAC entry.
MAC Address Displays the object MAC address from which this incoming frame came.

Chapter 21 Configuration: MAC Table
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
126
21.2.2 The Static MAC Add Screen
Use this screen to add new Static MAC addresses. Click Configuration > MAC Table > Static
MAC > Add to open this screen.
Figure 119 Configuration > MAC Table > Static MAC > Add
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
21.2.3 The Filtering MAC Screen
Use this screen to view Filtering MAC addresses. Click Configuration > MAC Table > Filtering
MAC to open this screen.
Figure 120 Configuration > MAC Table > Filtering MAC
VLAN Displays the VLAN group to which this frame belongs.
Port Displays the port from which the above MAC address was learned.
Action Click Delete to remove the MAC address.
Ta ble 84 Configuration > MAC Table > Static MAC (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 85 Configuration > MAC Table > Static MAC > Ad d
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static MAC
MAC Address Enter the object MAC address.
VLAN Select the VLAN group which to associate the MA C address.
Port Select the port which to a ssociate the above MAC address.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 21 Configuration: MAC Table
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
127
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
21.2.4 The Filtering MAC Add Screen
Use this screen to add new Filtering MAC addresses. Click Configuration > MAC Table >
Filtering MAC > Add to open this screen.
Figure 121 Configuration > MAC Table > Filtering MAC > Add
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
21.2.5 The Dynamic Age Screen
Use this screen to enter the Dynamic MAC Age. The dynamic MAC age is how long all dynamically
learned MAC addresses remain in the MAC address table before they age out (and must be
relearned). Click Configuration > MAC Table > Dynamic Age to open this screen.
Ta ble 86 Configuration > MAC Table > Filtering MAC
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Filtering
Add Click Add to create a new Filtering MAC entry.
MAC Address Displays the filtering object MAC address from which this incoming frame came.
VLAN Displays the VLAN group to which this frame belongs.
Action
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
Ta ble 87 Configuration > MAC Table > Filtering MAC > Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Filtering MAC
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the device.
VLAN Select the VLAN group to associate the filtering object MAC address.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Chapter 21 Configuration: MAC Table
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
128
Figure 122 Configuration > MAC Table > Dynamic Age
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 88 Configuration > Dynamic Age
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic MAC Age
Aging Ti me Enter the aging time of the MAC address. The value can be between 10 and 630 seconds.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
129
CHAPTER 22
Configuration: Link Aggregation
22.1 Overview
This section provides information for Link Aggreg ation in Configuration.
This chapter shows you how to logically aggregate physical links to form one logical, higher
bandwidth link.
22.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
The Link Aggregation screen (Section 22.2 on page 129) displays global, LAG management, LAG
port, and LACP port settings.
22.2 Link Aggregation
Link aggregation (trunking) is the grouping of physical ports into one logical higher-capacity link.
You may want to trunk ports if for example, it is cheaper to use multiple lower-speed links than to
under-utilize a high-speed, but more costly, single-port link.
However, the more ports you aggregate then the fewer available ports you have. A trunk group is
one logical link containing multiple ports.
The Switch supports both static and dynamic link aggregation.
Note: In a properly planned network, it is recommended to implement static link
aggregation only. This ensures increased network stability and control over the
trunk groups on your Switch.
22.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure global Link Aggregation settings. Click Configuration > Link
Aggregation > Global to open this screen.

Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
130
Figure 123 Configuration > Link Aggregation > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
22.2.2 The LAG Management Screen
Use this screen to view LAG management settings. Click Configuration > Link Aggregation >
LAG Management to open this screen.
Figure 124 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Management
Ta ble 89 Configuration > Link Aggrega tion > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
LACP State Select Enable to activate the link aggregation control protocol.
LACP System
Priority LACP system priority is a number between 1 and 65,535. The switch with the lowest system
priority (and lowest port number if system priority is the same) becomes the LACP “server”.
The LACP “server” controls the operation of LACP setup. Enter a number to set the priority
of an active port using Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). The smaller the number,
the higher the priority level.
Load Balance
Algorithm Select the outgoing traffic distribution type. Packets from the same source and/or to the
same destinati on are sent over the same link within the trunk. B y default, the Switch uses
the IP/MAC Address distribution type. If the Switch is behind a router, the packet’s
destination or source MAC address will be changed. In this case, set the Switc h to distribute
traffic based on its IP address to make sure port trunking can work properly.
Select MAC Address to distribute traffic based on a combination of the packet’s source and
destination MAC addresses.
Select IP/MAC Address to distribute traffic based on a combination of the packet’ s source
and destination IP addresses.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
131
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
22.2.3 The LAG Add Screen
Use this screen to add a LAG. Click Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Management >
Add to open this screen.
Figure 125 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Management > Add
Ta ble 90 Configuration > L ink Aggregatio n > LAG Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAG Management
Add Click Add to create a new LAG Management entry.
LAG Displays the link aggregation group (LAG), that is, one logical link contai ning multiple ports.
Name Displays the name of the link aggregation group.
Type This field displays how these ports were added to the trunk group. It displays:
Static - if the ports are configured as static members of a trunk group.
LACP - if the ports are configured to join a trunk group via LACP.
Link Status Displays link status as either Link up or Link down.
Active Member Displays if this member is an active member of a trunk.
Standby
Member Displays if this member is an standby member of a tr unk.
Modify
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
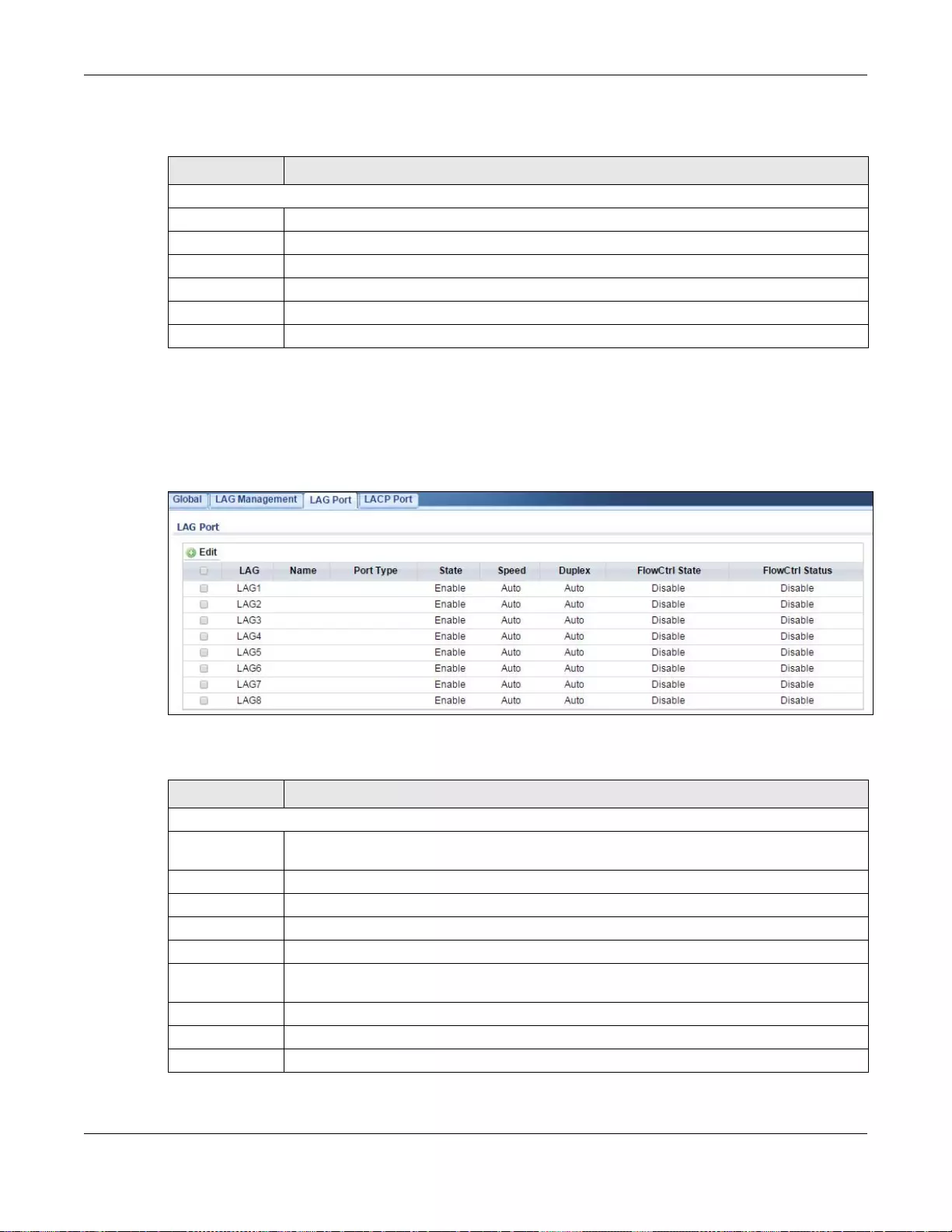
Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
132
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
22.2.4 The LAG Port Screen
Use this screen to view LAG port settings. Click Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Port
to open this screen.
Figure 126 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 91 Configuration > L ink Aggregatio n > LAG Management > Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAG Management
LAG Select the link aggregation group (LAG).
Name Enter the name of this entry.
Type Select Static or LACP.
Member Ports Select the member ports to be part of the LAG.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 92 Configuration > L ink Aggregatio n > LAG Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAG Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
LAG Displays the LAG index value.
Name Displays the LAG name.
Port Type Displays the port type.
State Displays the state as Enable/Disable.
Speed Displays the speed value as Auto, Auto-10M, Auto-100M, Auto-1000M, Auto-10/
100M, 10M, 100M, or 1000M.
Duplex Displays the duplex value as Full, Half, or Auto.
FlowCtrl State Displays whether flow control is Enable/Disable.
FlowCtrl Status Displays whether flow control is in use (Enable) or not (Disable).
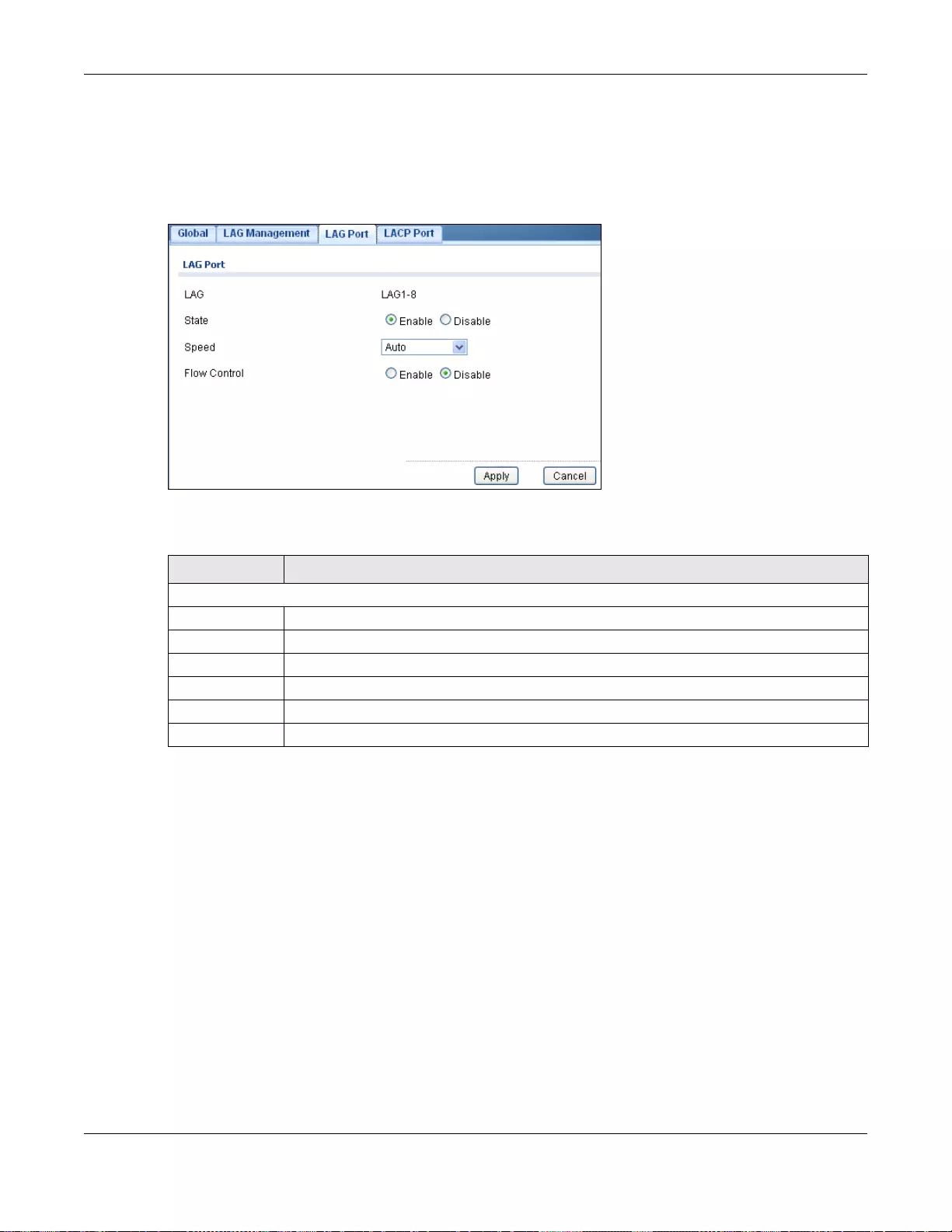
Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
133
22.2.5 The LAG Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to edit a LAG port. Click Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Port > Edit
to open this screen.
Figure 127 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
22.2.6 The LACP Port Screen
Use this screen to view LACP Port settings. Click Configuration > Link Agg regation > LACP Port
to open this screen.
Ta ble 93 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LAG Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LAG Port Edit
LAG Displays the LAG index values.
State Select the state to be Enable or Disable.
Speed Displays the speed value as Auto, 10M, 100M, or 1000M.
Flow Control Select Enable to use the flow control feature.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
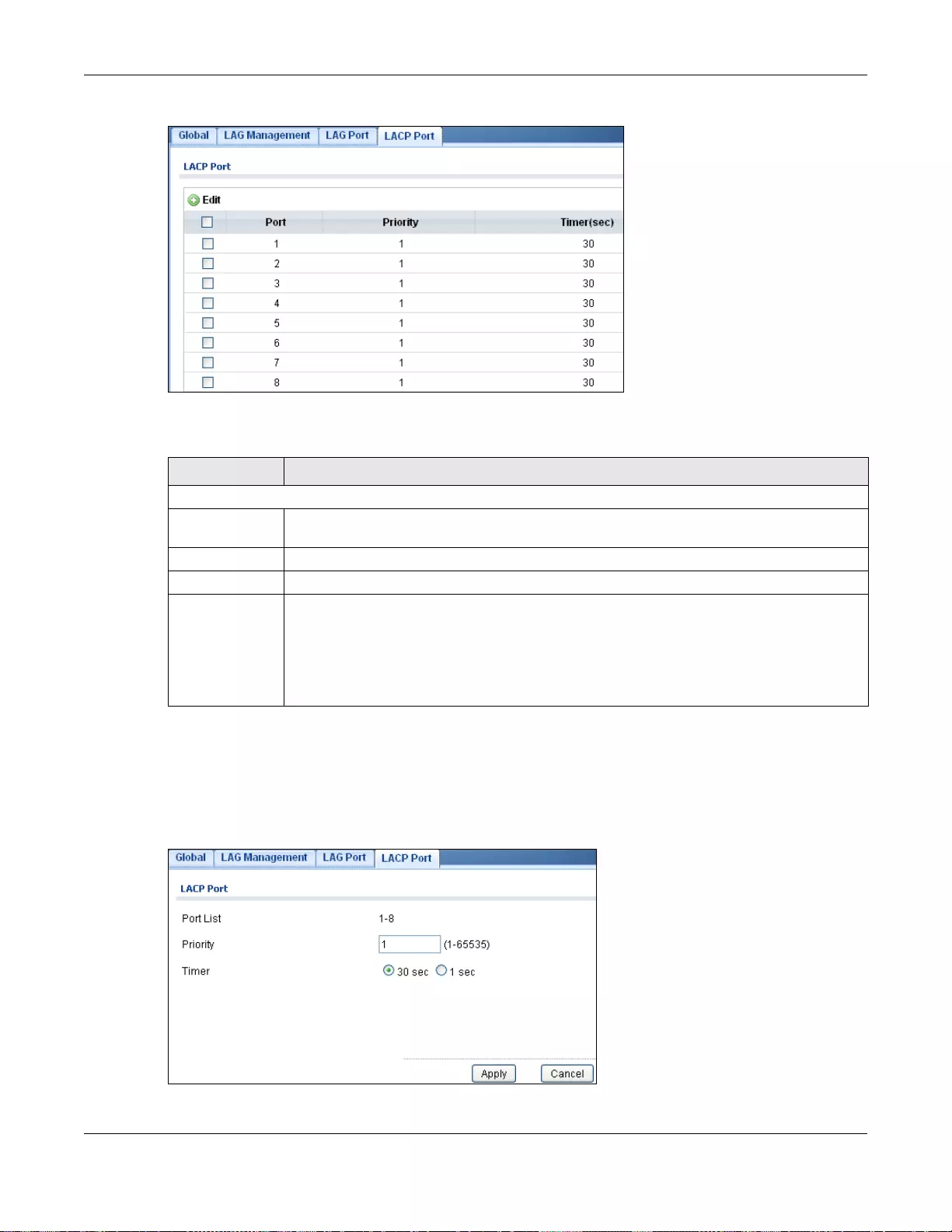
Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
134
Figure 128 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
22.2.7 The LACP Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to edit a LACP Port. Click Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port > Edit
to open this screen.
Figure 129 Configuration > Link Aggregation > LACP Port > Edit
Ta ble 94 Configuration > Link Aggregat ion > LACP Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LACP Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
Priority Displays the priority value.
Timer (sec) Displays the Timer value in seconds.
Timeout is the time interval between the individual port exchanges of LACP packets in order
to check that the peer port in the trunk group is still up. If a port does not respond after
three tries, then it is deemed to be “down” and is removed from the trunk. Set a short
timeout (one second) for busy trunked links to ensure that disabled ports are removed from
the trunk group as soon as possible.

Chapter 22 Configuration: Link Aggregation
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
135
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 95 Configuration > L ink Aggregatio n > LACP Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LACP Port
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers to be confi gure d .
Priority Enter a value for the port priority. The nu mber can be between 1 and 65,535.
Timer Select a timer value of either 1 second or 30 seconds.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
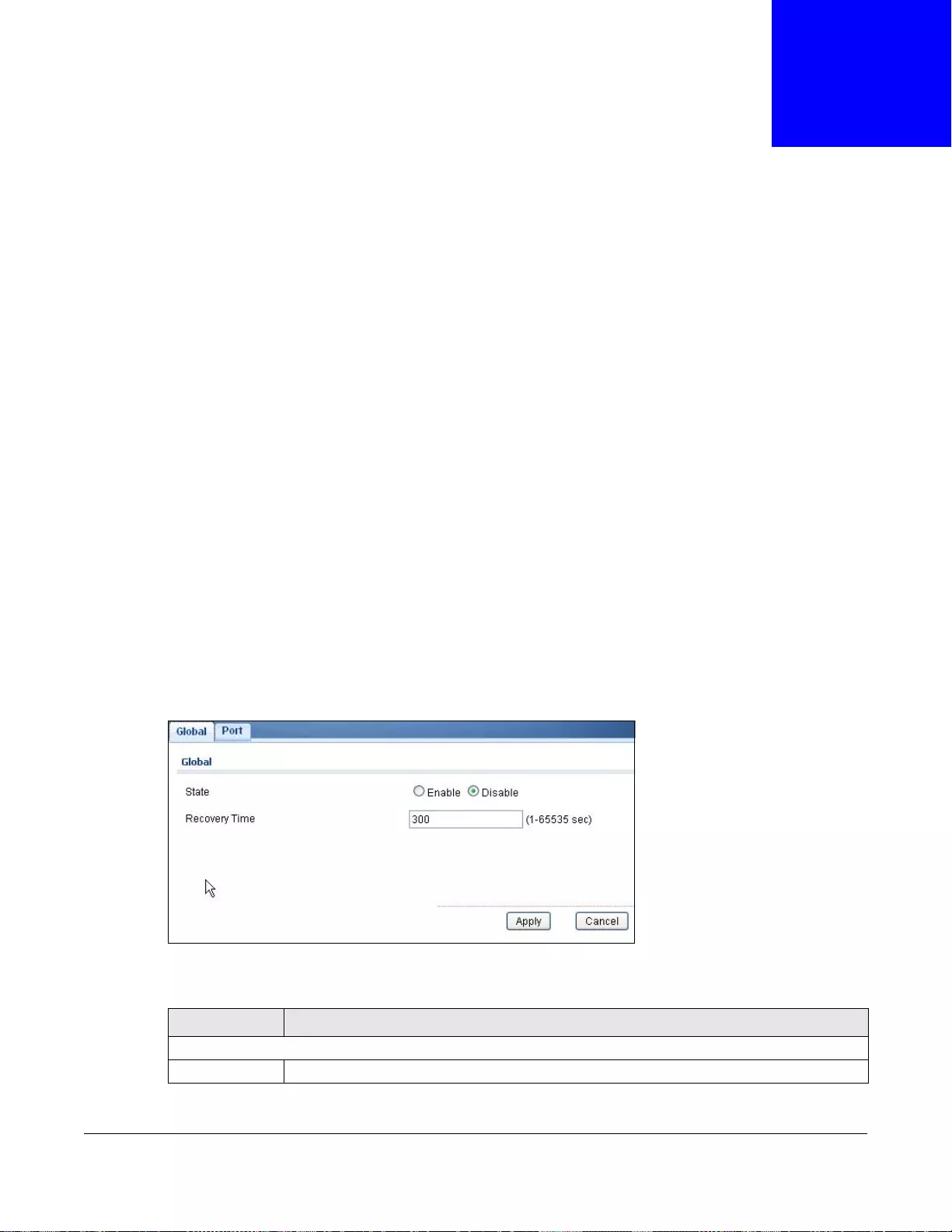
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
136
CHAPTER 23
Configuration: Loop Guard
23.1 Overview
This section provides information for Loop Guard in Configuration.
This chapter shows you how to configure the Switch to guard against loops on the edge of your
network.
23.2 Loop Guard
Loop guard allows you to configure the Switch to shut down a port if it detects that packets sent out
on that port loop back to the Switch. While you can use Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent
loops in the core of your network. STP cannot prevent loops that occur on the edge of your
network.
23.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure the global Loop Guard. Click Configuration > Loop Guard to open
this screen.
Figure 130 Configuration > Loop Guard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 96 Co nfiguration > Loop Guard
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select Enable to activate loop protection on this switch.
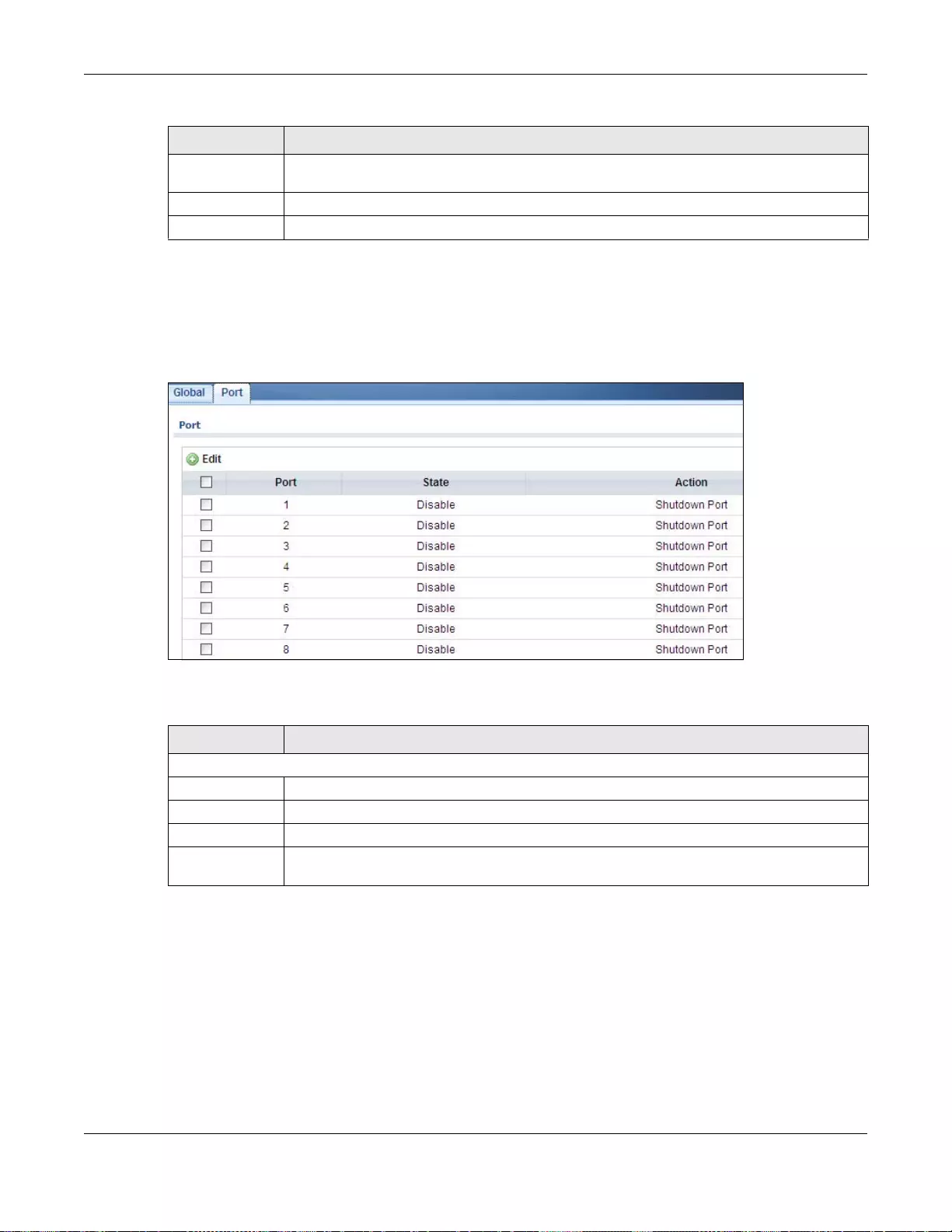
Chapter 23 Configuration: Loop Guard
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
137
23.2.2 The Loop Guard Port
Use this screen to view the Loop Guard Port. Click Configuration > Loop Guard > Port to open
this screen.
Figure 131 Configuration > Loop Guard > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
23.2.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure a Loop Guard port. Click Configuration > Loop Guard > Port > Edit
to open this screen.
Recovery Time Enter the period (in seconds) for which a port will be kept di sabled in the ev ent of a loop is
detected (and the port action shuts down the port).
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 96 Configuration > Loop Guard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 97 Configuration > Loop Gua rd > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Click Edit to change the properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index number.
State Displays whether the port state is Enable or Disable.
Action Displays the action to take by the Switch. The options are Log, Shutdown Port, and
Shutdown and Log.
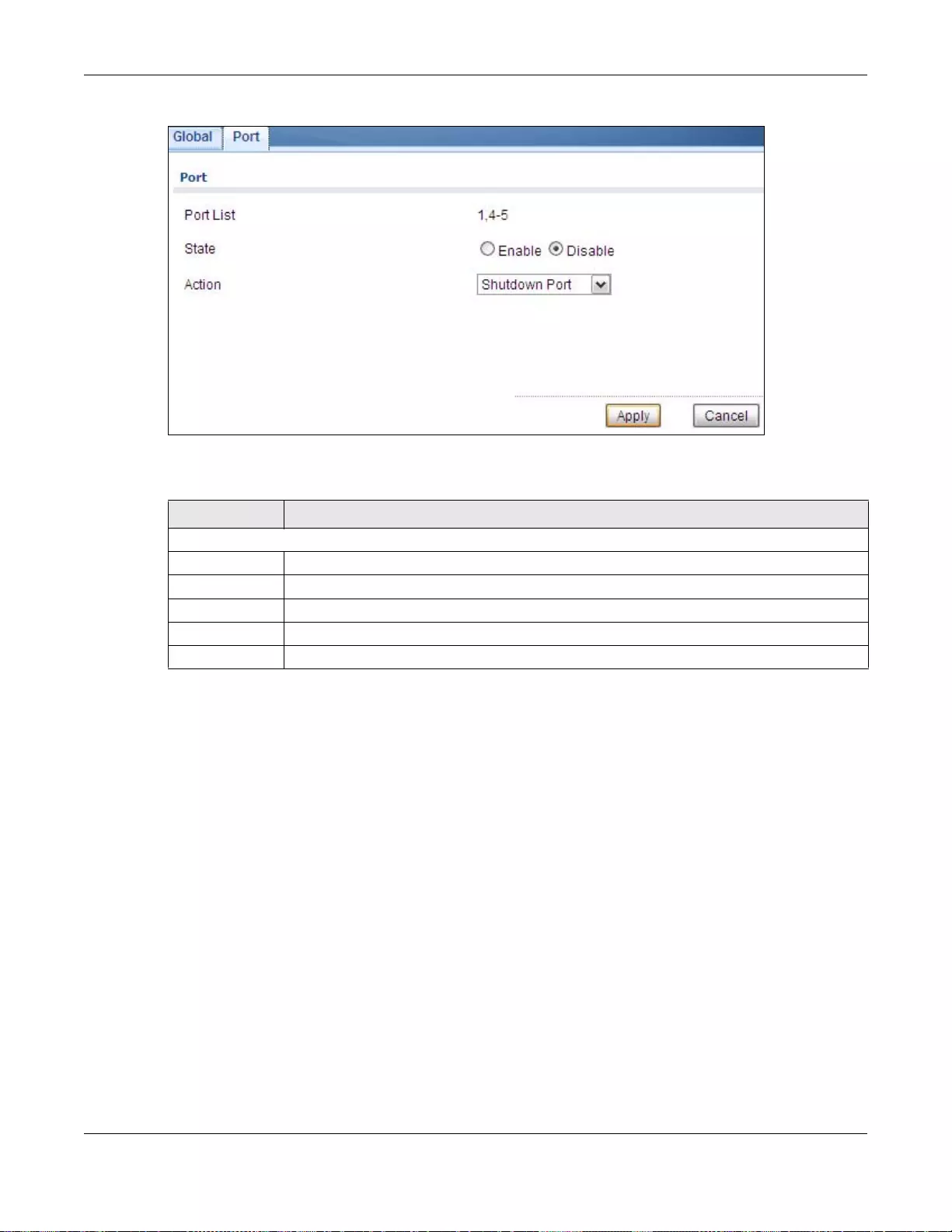
Chapter 23 Configuration: Loop Guard
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
138
Figure 132 Configuration > Loop Guard > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 98 Configuration > Loop Guard > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port List Displays the list of port index numbers to be confi gure d .
State Select Enable to use the Admin Enabled feature.
Action Select the action to take by the Switch.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
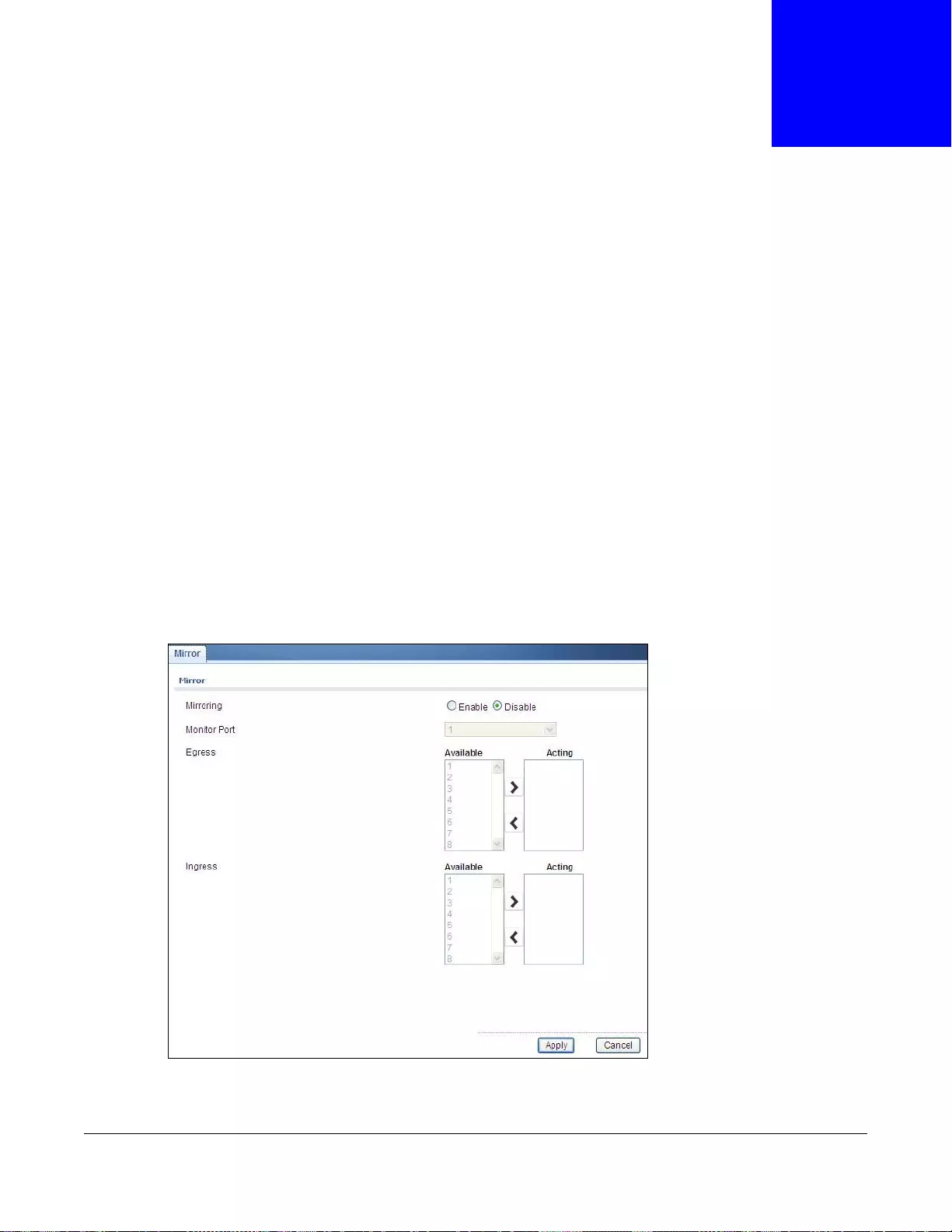
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
139
CHAPTER 24
Configuration: Mirror
24.1 Overview
This section provides information for Mirror in Configuration.
24.2 Mirror
Po rt mirroring allows you to copy a tr affic flow to a monitor port (the port y ou copy the tr affic to) in
order that you can examine the traffic from the monitor port without interference.
The Switch supports local port mirroring.
24.2.1 The Mirror Screen
Use this screen to configure Mirroring. Click Configuration > Mirror to open this screen.
Figure 133 Configuration > Mirror
Chapter 24 Configuration: Mirror
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
140
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 99 Configuration > Mirr or
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Mirror
Mirroring Select Enable to activate port mirroring on the Switch or Disable to disable the feature.
Monitor Port The monitor port is the port you copy the traffic to in order to examine it in more detail
without interfering with the traffic flow on t he original port(s). Type the port number of the
monitor port.
Egress Specify the ports to mirror outgoing traffic.
Available Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
Acting Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
>Click > to move a severity type to th e acting box from the available box.
<Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Ingress Specify the ports to mirror incoming traffic.
Available Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
Acting Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Click > to move a severity type to the acting box from the available box.
>Click > to move a severity type to th e acting box from the available box.
<Click < to move a severity type from the acting box to the available box.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
141
CHAPTER 25
Configuration: Multicast
25.1 Overview
This section provides information for Multicast in Configuration.
Traditionally , IP packets are tr ansmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender to 1 recipient)
or Broadcast (1 sender to everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to just a group
of hosts on the network.
25.2 IGMP
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in an IPv4 multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. Refer to RFC 1112, RFC
2236 and RFC 3376 for information on IGMP versions 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
25.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the IGMP Global settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP to
open this screen.
Figure 134 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 100 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Glo b a l
Snooping Status Select Enable to turn on IGMP packet snooping or Disable to turn snooping off.
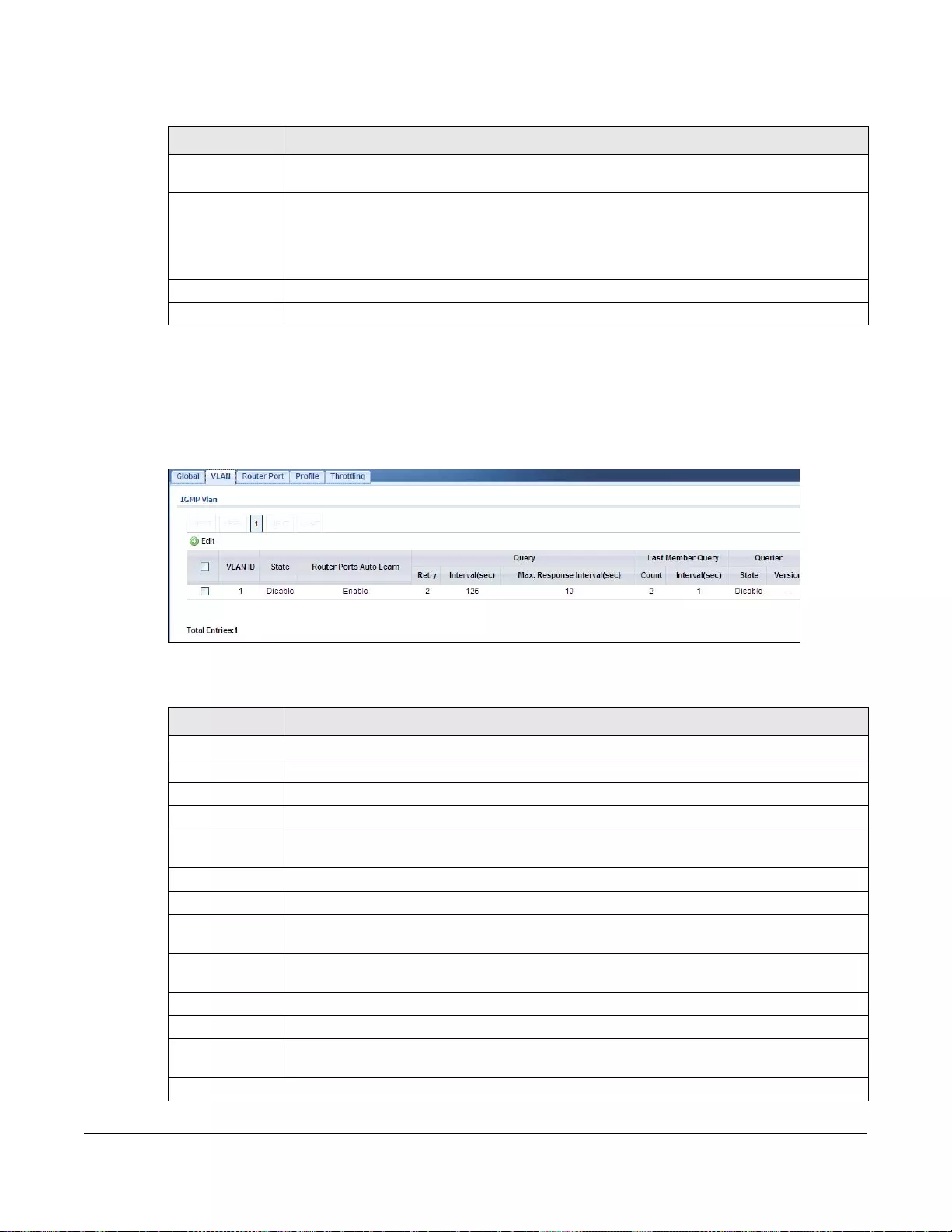
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
142
25.2.2 The VLAN Screen
Use this screen to view the IGMP VLAN settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP >
VLAN to open this screen.
Figure 135 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Snooping
Version Select v2 or v3 depending on the snooping version you require.
Unknown
Multicast Action Select to send the IPv4 unknown multicast frame to the router port. The following options
are available:
•Flood - select to send the frame(s) to all ports.
•Drop - select to discard the frame(s).
•Router Port - select to send the frame to router port.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 100 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 101 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP VLA N
Edit Click Edit to change the properties of the IGMP VLAN entry.
VLAN ID Displays the ID of a static VLAN; the valid range is between 1 and 4094.
Status Display the status of the VLAN as enabled or disabled.
Router Ports
Auto Learn Displays the Switch learn multicast router port member status of any VLANs as enabled or
disabled.
Query
Retry Displays the number of query retry times.
Interval (sec) Displays the amount of time (in seconds) between general query messages sent by the
router connected to the upstream port.
Max. Response
Interval (sec) Displays the amount of time (in seconds) the rout er connected to the upstream port waits
for a response to an IGMP general query message.
Last Member Query
Count Displays the number of queries.
Interval (sec) Displays the amount of time (in milliseconds) between the IGMP group-specific queries sent
by an upstream port when an IGMP Done message is receive d.
Querier
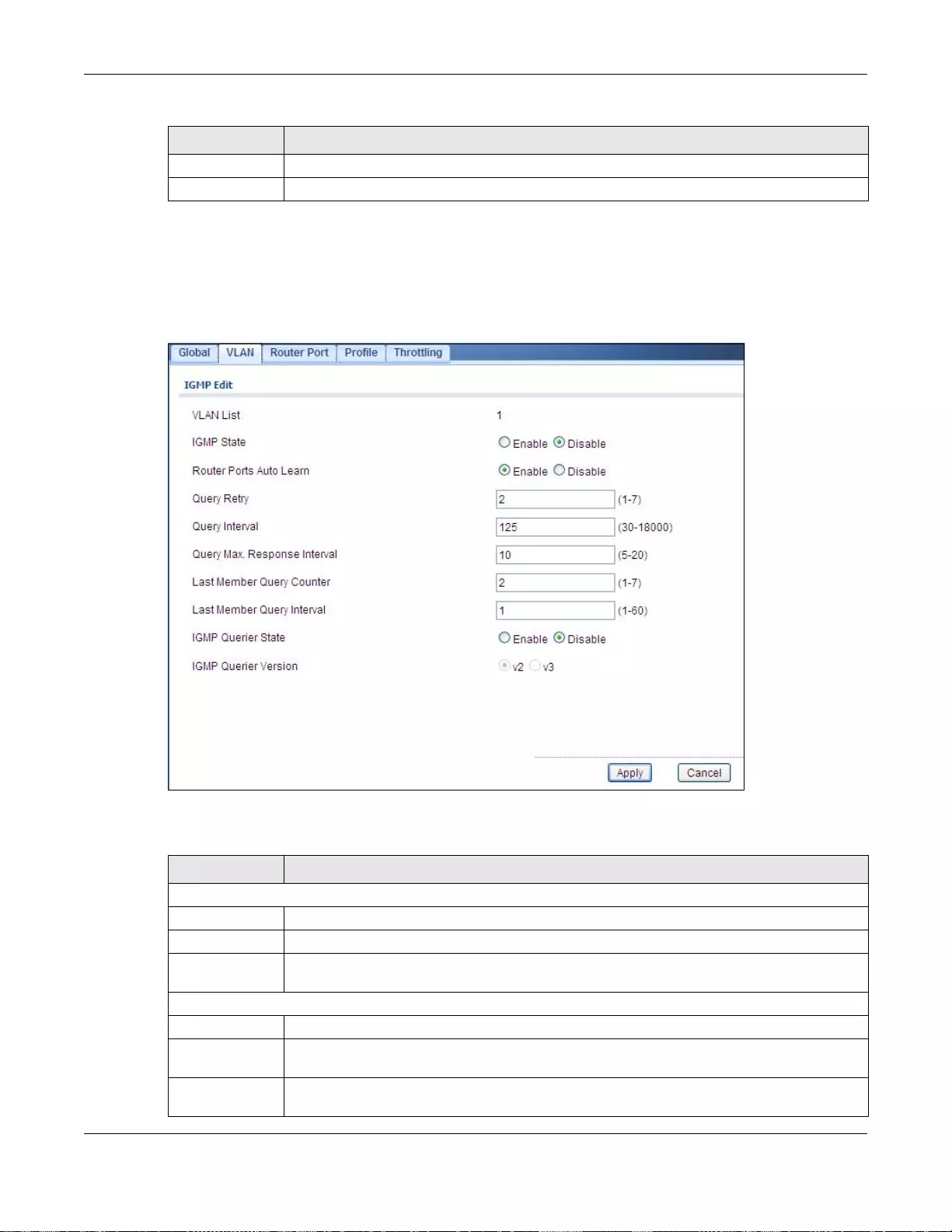
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
143
25.2.3 The Edit IGMP Screen
Use this screen to configure the IGMP VLAN settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP
> VLAN > Edit to open this screen.
Figure 136 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
State Displays the switch current VLAN querier entry as Enable or Disable.
Version Displays the switch cur rent VLAN querier entry version.
Table 101 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 102 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN > Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Edi t
VLAN List Enter the ID of a static VLAN; the valid range is between 1 and 4094.
IGMP State Select the status of the VLAN to Enable or Disable the function.
Router Ports
Auto Learn Select Enabled to have the Switch learn multicast router membership information of any
VLANs automatically.
Query
Retry Enter the number of query retry ti mes. The value can be between 1 and 7.
Interval (sec) Enter the amount of time (in seconds) between general query messages sent by the router
connected to the upstream port. The value can be between 30 and 18000.
Max. Response
Interval (sec) Enter the amount of time (in seconds) the router connected to the upstream port waits for
a response to an IGMP general query message.
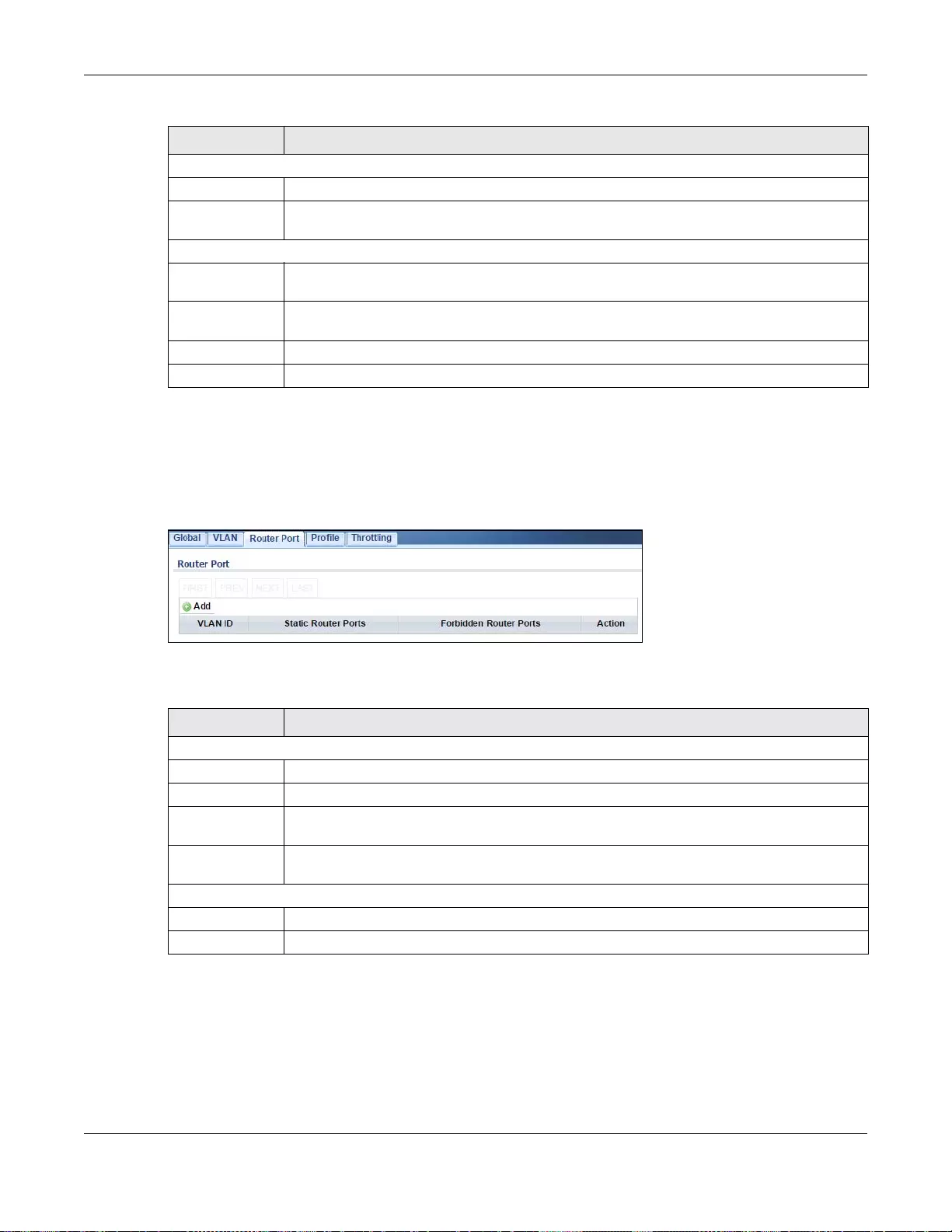
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
144
25.2.4 The Router Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Router Port settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP >
Router Port to open this screen.
Figure 137 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Router Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
25.2.5 The Add/Edit Router Port Screen
Use this screen to configure the Router Port settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP
> Router Port > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Last Member Query
Count Enter the number of queries.
Interval (sec) Enter the amount of time (in seconds) between the IGMP group-specific queries sent by an
upstream port when an IGMP Done message is received.
Querier
IGMP Querie r
State Select the IGMP querier status to Enable or Disable the function.
IGMP Querie r
Version Select the IGMP Querier version to v2 or v3.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 102 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > VLAN > Modify (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 103 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Router Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Router Port
Add Click Add to create a new Router Port entry.
VLAN ID Displays the ID of a static VLAN; the valid range is between 1 and 4094.
Static Router
Ports Displays the ports that are defined as static router ports.
Forbidden
Router Ports Displays the ports that are defined as forbidden router ports.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
145
Figure 138 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Router Port > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
25.2.6 The Profile Screen
Use this screen to view the IGMP Profile settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP >
Profile to open this screen.
Table 104 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Router Port > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Router Edit
VLAN List Enter the static VLAN IDs (valid range for each ID value is between 1 and 4094).
Static Router
Ports Selects Select the port(s) to be static router ports.
Forbidden
Router Ports
Selects
Select the port(s) to be forbidden router ports.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
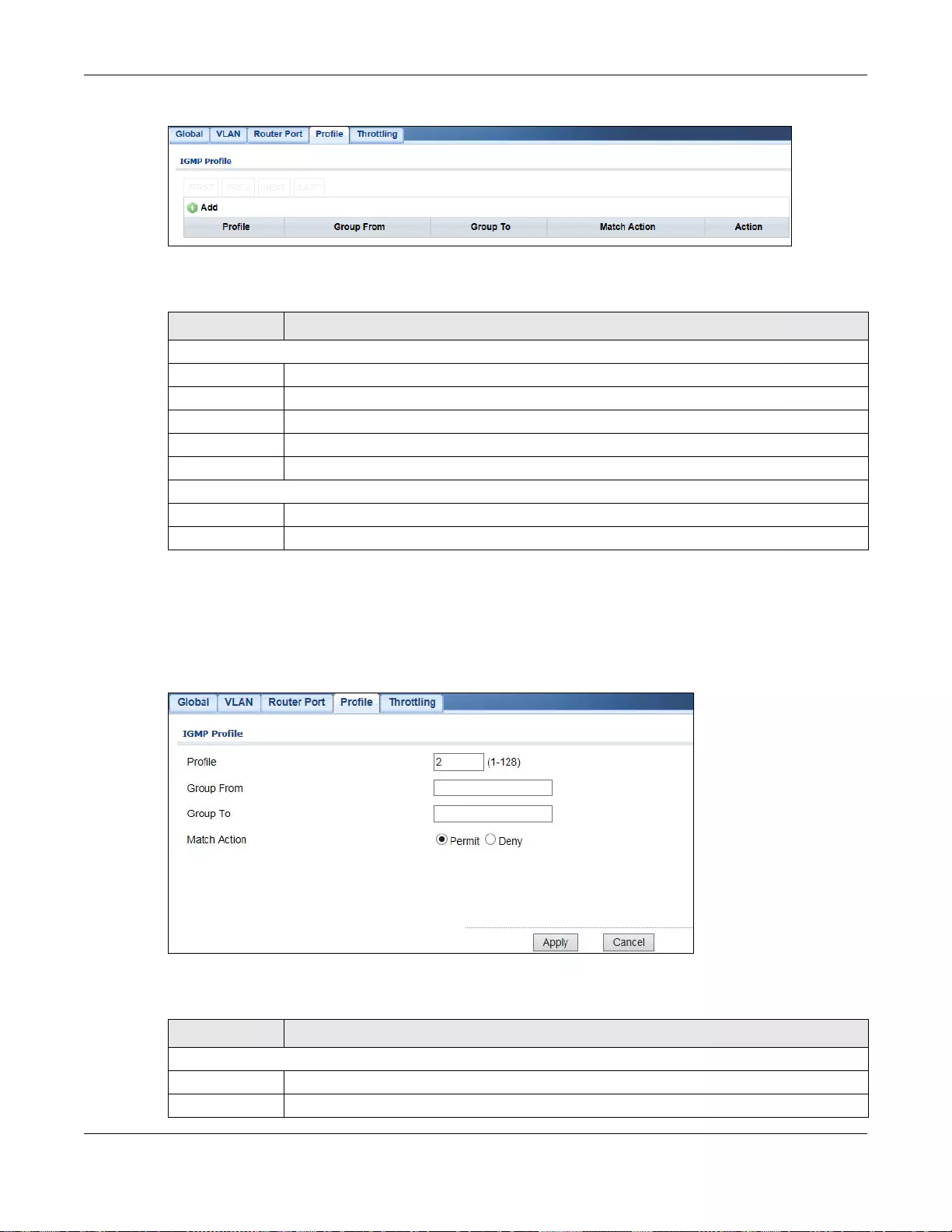
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
146
Figure 139 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Profile
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
25.2.7 The Add/Edit Profile Screen
Use this screen to configure the IGMP Profile settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP
> Profile > Add/Edit to open this screen.
Figure 140 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Profile > Add/Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 105 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Prof i l e
Add Click Add to create a new IGMP Profile entry.
Profile Displays the Profile index number.
Group From Displays the profile start group IP address.
Group To Displa ys the profile end group IP address.
Match Action Displays the action of the profile as Permit or Deny.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
Table 106 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Profile > Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Prof i l e
Profile Enter the Profile index number.
Group From Enter the profile start group IP address.
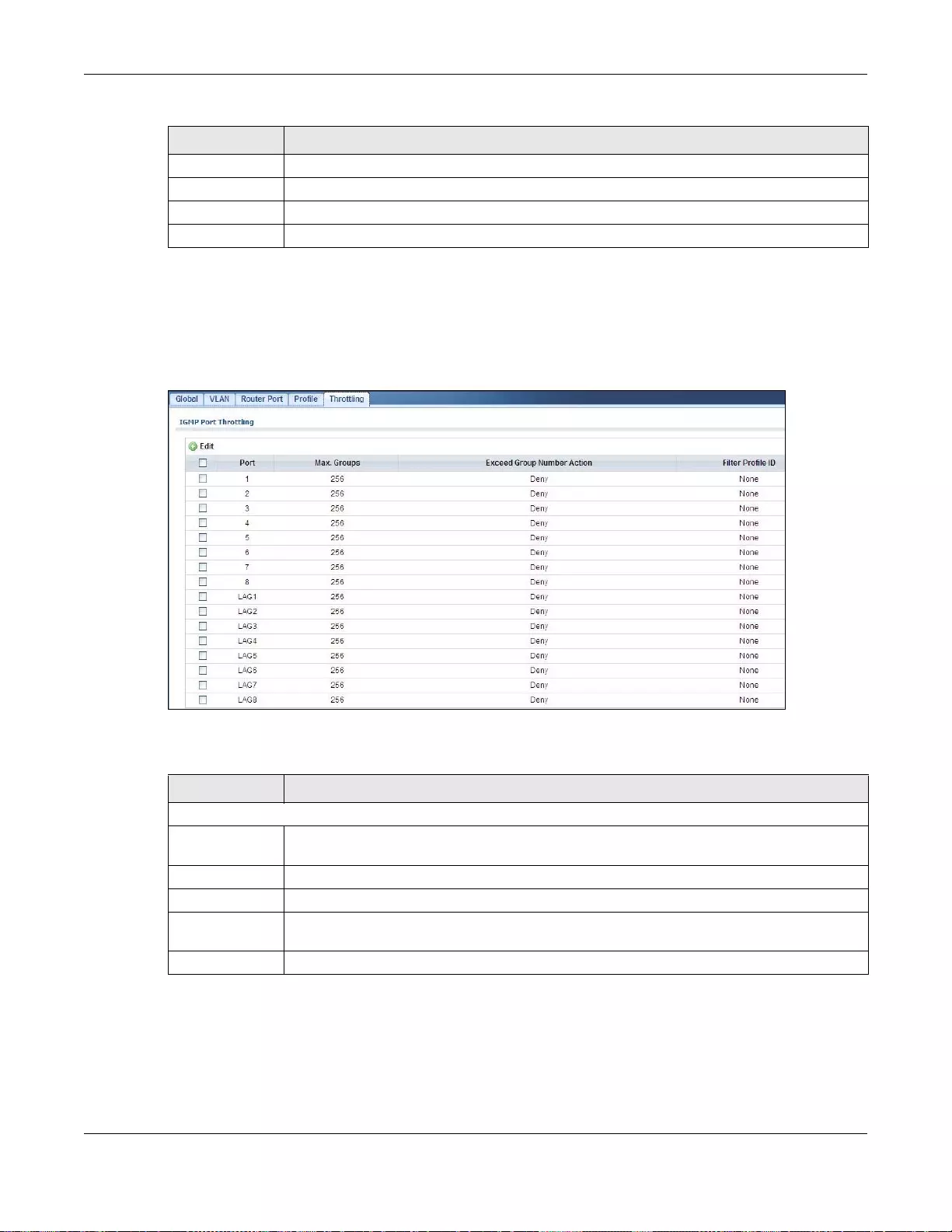
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
147
25.2.8 The Throttling Screen
Use this screen to view the Throttling settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP >
Throttling to open this screen.
Figure 141 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Throttling
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
25.2.9 The Add/Edit Throttling Screen
Use this screen to configure the Throttling settings. Click Configuration > Multicast > IGMP >
Throttling > Add/Edit to open this screen.
Group To Enter the profile end group IP address.
Match Action Select the action of the profile as to be Permit or Deny.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 106 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Profile > Add/Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 107 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Throttling
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Port Throttling
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
Max. Groups Displays the maximum number of groups.
Exceed Grou p
Number Action Displays the action taken by the groups as Permit or Deny.
Filter Profile ID Displays the throttling filter pro file ID.
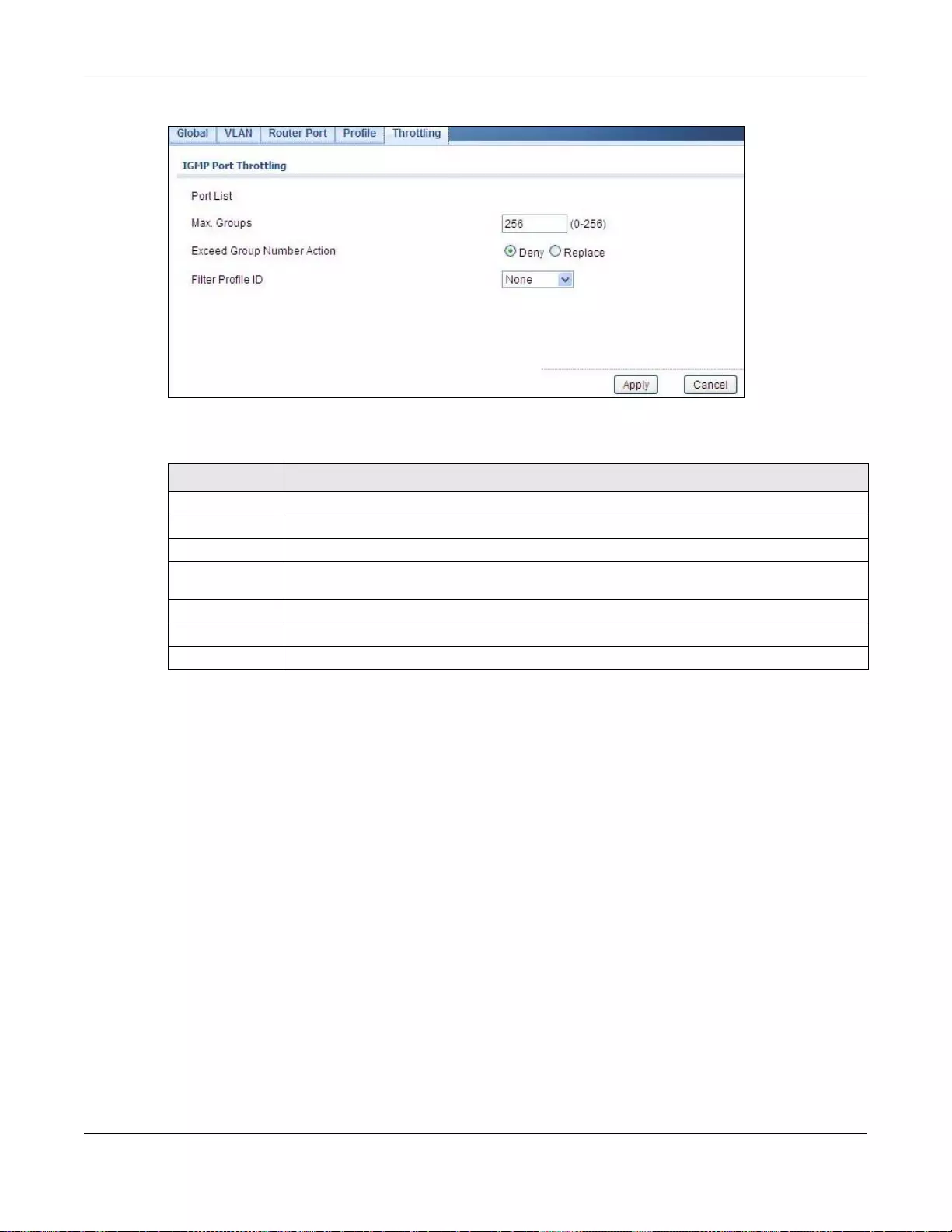
Chapter 25 Configuration: Multicast
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
148
Figure 142 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Throttling > Add/Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 108 Configuration > Multicast > IGMP > Throttling > Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Port Throttling
Port List Enter the port index value(s).
Max. Groups Enter the maximum number of groups. Enter a value between 0 and 256.
Exceed Grou p
Number Action Select the action taken by the groups to be Deny or Replace.
Filter Profile ID Select the throttling filter profile ID from the dropdown list.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
149
CHAPTER 26
Configuration: Spanning Tree
26.1 Overview
This section provides information for Spanning Tree in Configuration.
The Switch supports Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) as defined in the following standards.
• IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
• IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
• IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
The Switch also allows you to set up multiple STP configurations (or trees). Ports can then be
assigned to the trees.
26.2 Spanning Tree
(R)STP detects and breaks netw ork loops and provides backup links between switches, bridges or
routers. It allows a Switch to interact with other (R)STP-compliant switches in your network to
ensure that only one path exists between any two stations on the network.
26.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree to open this
screen.
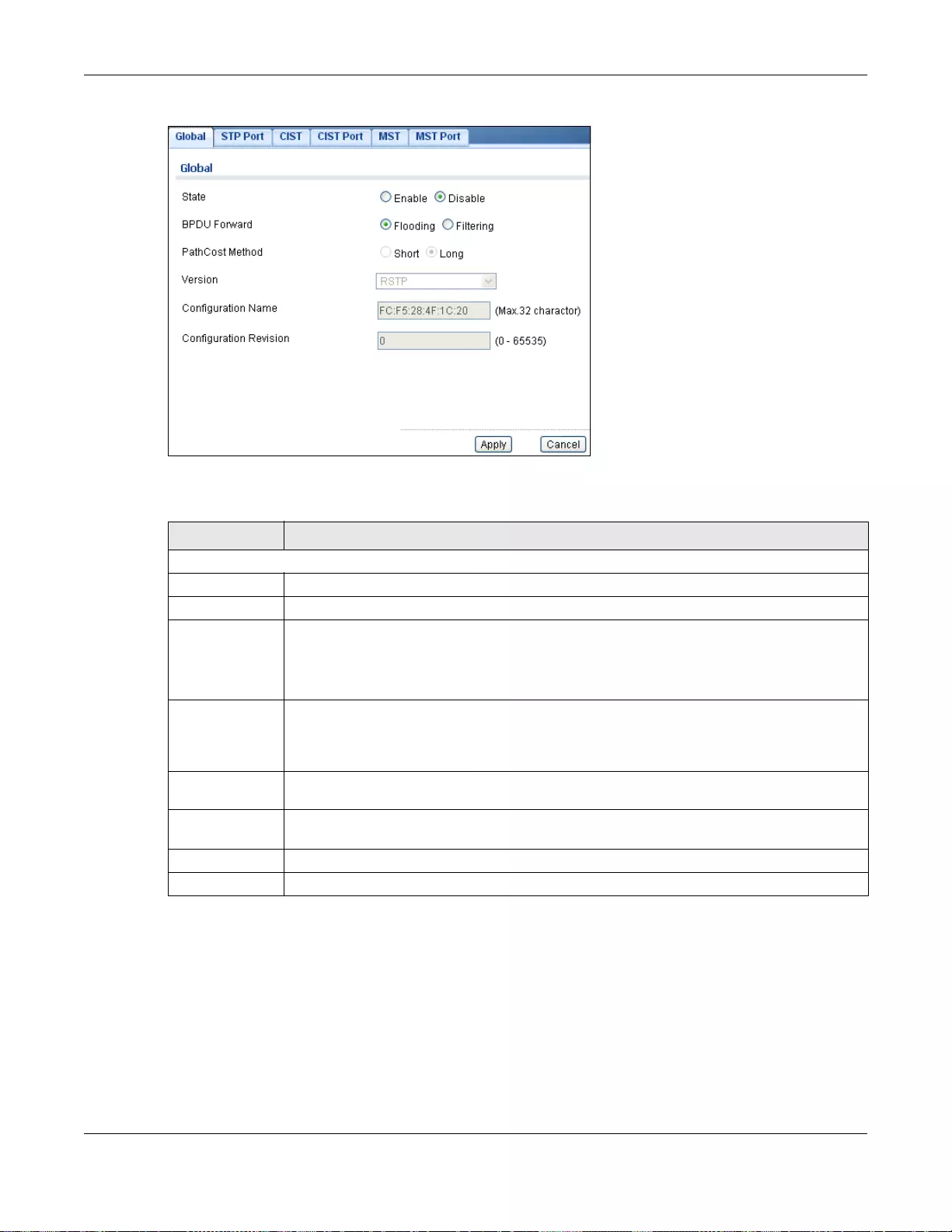
Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
150
Figure 143 Configuration > Spanning Tree
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.2 The STP Port Screen
Use this screen to view the STP Port settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port
to open this screen.
Table 109 Configuration > Spanning Tree
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select to Enable or Disable the Spanning-Tree function.
BPDU Forward Select the bridge protocol data units forward (BPDU) option to be Flooding or Filtering.
Path Cost
Method Select Short or Long as a Path Cost method.
Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN through that port. It is
recommended that you assign this value according to the speed of the bridge. The slower
the media, the higher the cost - see Table 40 on page 112 for more information.
Version Sel ect the type of spanning tree protocol to use. The followin g options are available:
•STP
•RSTP
•MSTP
Configuration
Name Enter the name of the configuration in hexadecimal. The maximum number characters is
32.
Configuration
Revision Enter the revision number of configuration. The number can be between 0 and 65535.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
151
Figure 144 Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.3 The STP Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the STP Port Edit settings. Click Conf iguration > Spanning Tree >
STP Port > Edit to open this screen.
Ta ble 110 Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
STP Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the index number of the STP port.
State Display the status of the STP port as enabled or disabled.
External Cost Displays the external path cost.
Edge Port Displays the edge port status as Yes or No.
BPDU Filter Displays the BPDU fil te r statu s as Yes or No.
P2P MAC Displays the P2P MAC status as Yes or No.
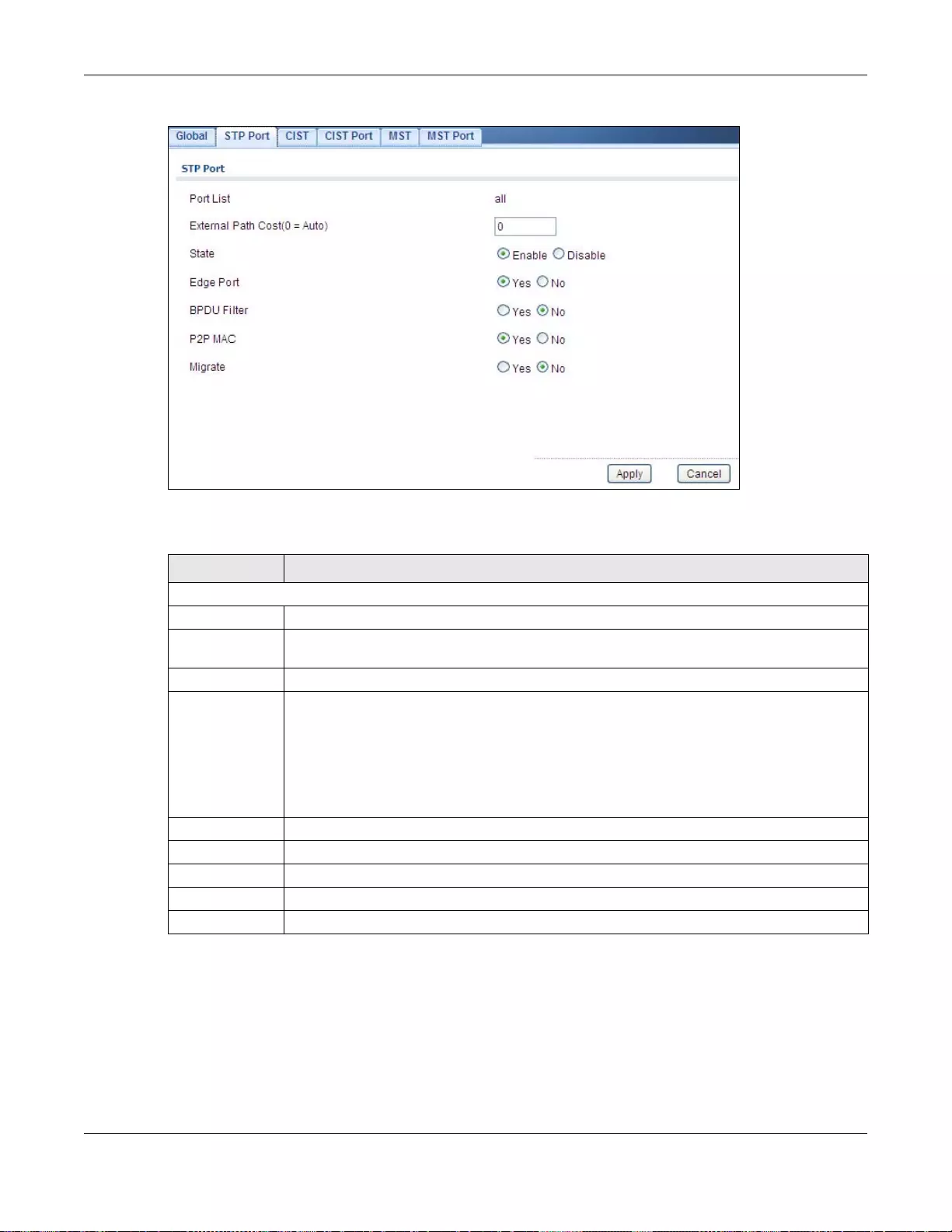
Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
152
Figure 145 Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.4 The CIST Screen
Use this screen to view the CIST settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST to open
this screen.
Table 111 Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
STP Port
Port List Enter the index number of the STP port(s).
External Path
Cost (0=Auto) Enter the external path cost. Enter 0 for Auto.
State Select the state of the STP port as e nabled or disabled.
Edge Port Select this check box to configure a port as an edge port when it is directly attached to a
computer. An edge port changes its initial STP port state from blocking state to forwarding
state immediately without going through listening and learning states right after the port is
configured as an edge port or when its link status changes.
Note: An edge port becomes a non-edge port as soon as it receives a
Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU).
BPDU Filter Select Yes to activate BPDU filter or No to deacti vate it.
P2P MAC Sel ect Yes to activate P2P MAC or No to deactivate it.
Migrate Select Yes to activate Migrate or No to deactivate it.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
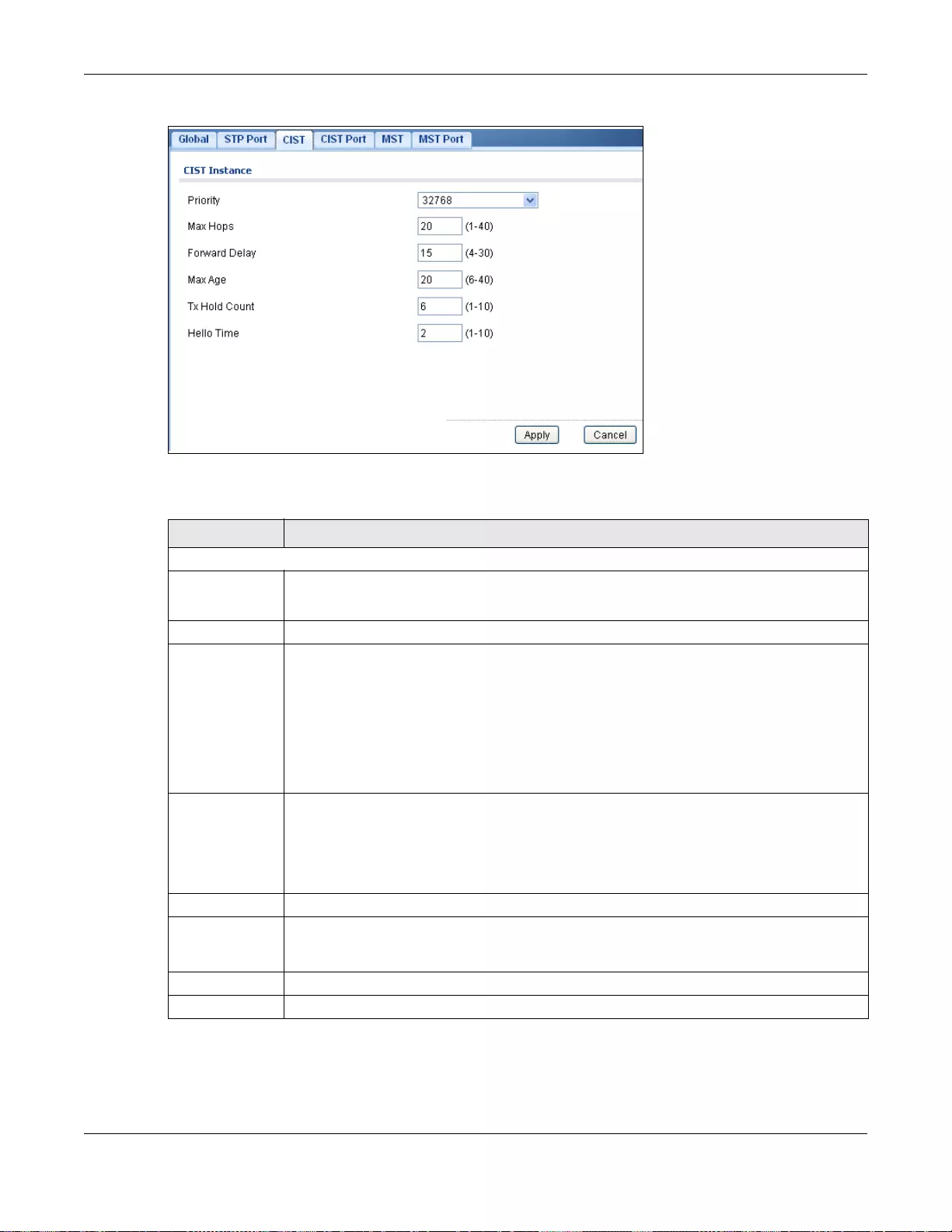
Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
153
Figure 146 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 112 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST
LABEL DESCRIPTION
CIST Instance
Priority Configure priority of CIST bridge ID.
Priority is part of bridge ID, used for CIST root bridge selection.
Max Hops Enter a maximum number of hops value. The value can be between 1 and 40.
Forward Delay This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch will wait before changing states. This delay
is required because every switch must receive information about topology changes before it
starts to forward frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen for conflicting
information that would make it return to a blocking state; otherwise, temporary data loops
might result. The allowed range is 4 to 30 seconds.
As a general rule:
Note: 2 * (Forward Delay - 1) >= Max Age >= 2 * (Hello Time + 1)
Max Age This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch can wait without receiving a BPDU before
attempting to reconfigure. All switch ports (except for designated ports) should receive
BPDUs at regular intervals. Any port that ages out STP information (provided in the last
BPDU) becomes the designated port for the attached LAN. If it is a root port, a new root
port is selected from among the switch ports attached to the network. The allowed r ange is
6 to 40 seconds.
Tx Hold Count Enter a transmission hold count value. The value can be between 1 and 10.
Hello Time This is the time interval in seconds between BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Units)
configuration message generations by the root switch. The allowed range is 1 to 10
seconds.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
154
26.2.5 The CIST Port Screen
Use this screen to view the CIST Port settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST
Port to open this screen.
Figure 147 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.6 The CIST Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the CIST Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree >
CIST Port > Edit to open this screen.
Ta ble 113 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
CIST Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the index number of the STP port.
Priority Displays the priority for each port here.
External Path
Cost Displays the external pat h cost.
Internal Path
Cost Displays the internal path cost.
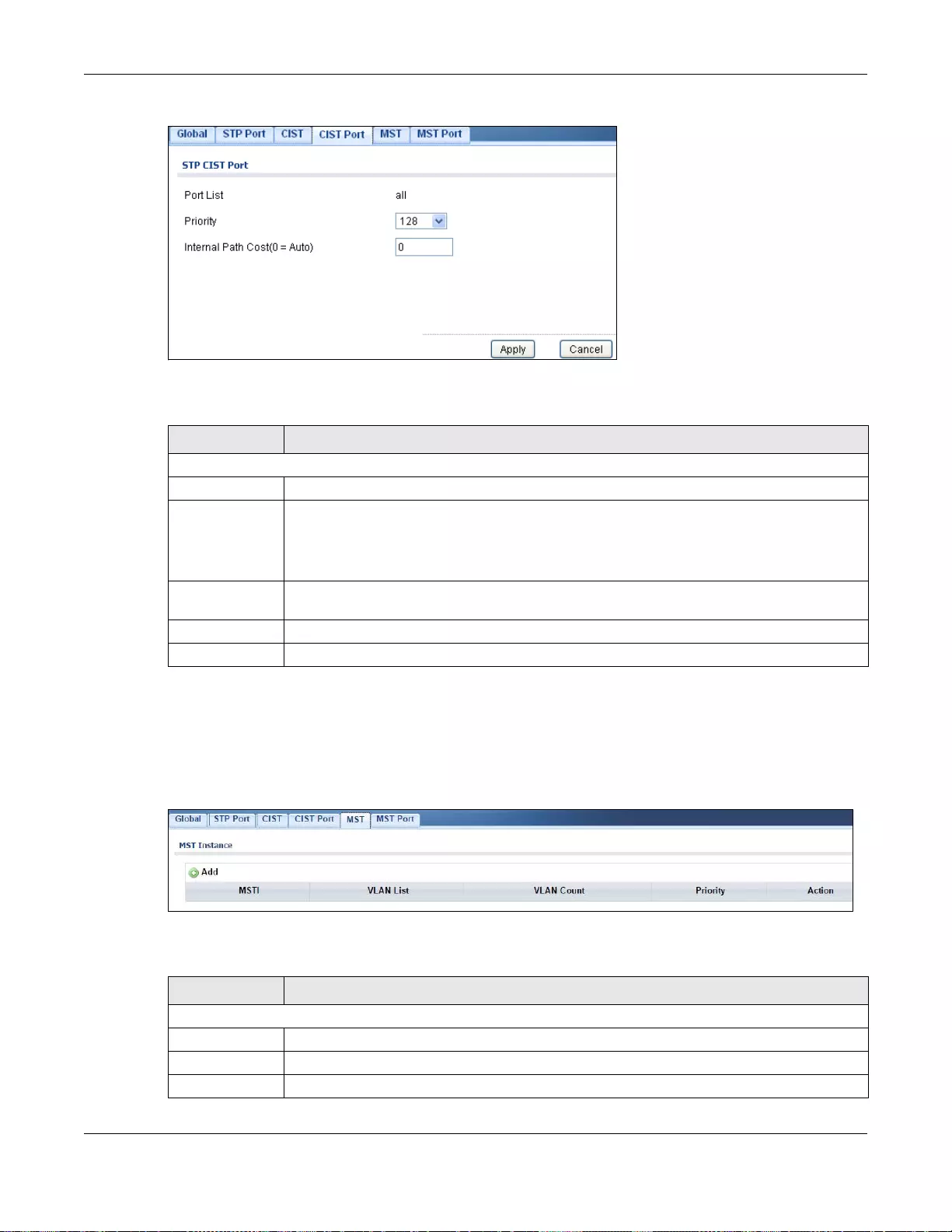
Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
155
Figure 148 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.7 The MST Screen
Use this screen to view the MST settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST to open
this screen.
Figure 149 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 114 Configuration > Spanning Tree > CIST Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
STP CIST Port
Port List Enter the index number of the STP port(s).
Priority Configure the priority for each port here.
Priority decides which port should be disabled when more than one port forms a loop in a
switch. Ports with a higher priority numeric value are disabled first. The allowed range is
between 0 and 255 and the default value is 128.
Internal Path
Cost (0=Auto) Enter the internal path cost. Enter 0 or Auto.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 115 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MST Instance
Add Click Add to create a new MST Instance entry.
MSTI Displays the Multiple Spanning Tree Instance(s) (MSTI).
VLAN List Display a list of MSTI VLANs.

Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
156
26.2.8 The Add/Modify MST Screen
Use this screen to configure the MST settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST >
Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 150 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.9 The MST Port Screen
Use this screen to view the MST Port settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST
Port to open this screen.
VLAN Count Displays the VLAN count.
Priority Displays the priority for each port here.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
Ta ble 115 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ta ble 116 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MST Instance
MST ID Displays the Multiple Spanning Tree Instance (MSTI) ID(s).
VLAN List Display a list of MSTI VLANs.
Priority Displays MSTI bridge ID priority value.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
157
Figure 151 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
26.2.10 The MST Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the MST Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > Spanning Tree >
MST Port > Edit to open this screen.
Ta ble 117 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MST Port
MST ID Select the MST port ID number from the dropdown list.
Edit Select this check box to configure the properties of MST ID. Click the Edit button change
the properties of the MST ID.
Port Displays the index number of the MST port.
MSTI ID Displays the index value of the MSTI.
Priority Displays the priority for each port.
Internal Path
Cost Displays the internal path cost.
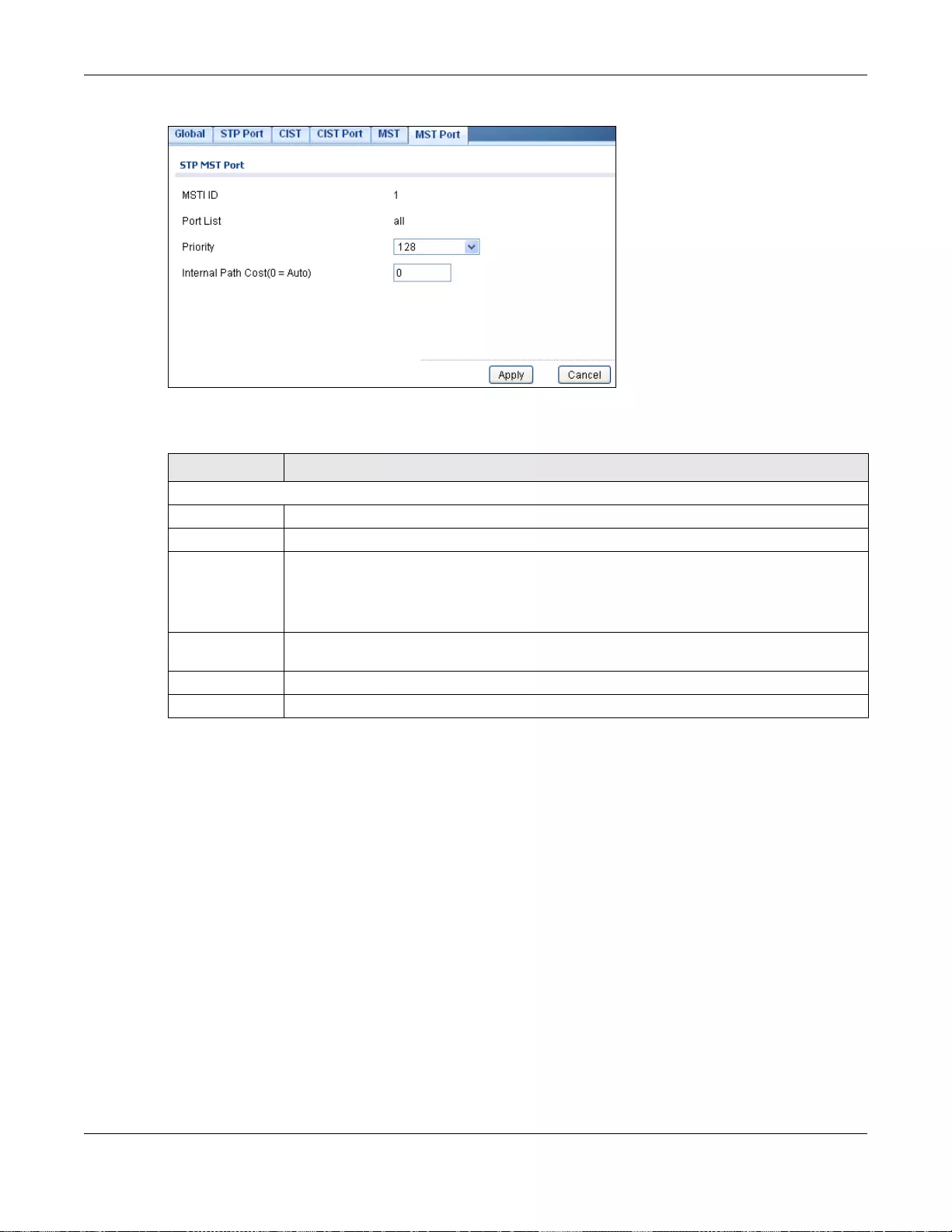
Chapter 26 Configuration: Spanning Tree
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
158
Figure 152 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 118 Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
STP MST Port
MST ID Displays the MST ID number.
Port List Enter the index number of the MTP port(s).
Priority Configure the priority for each port here.
Priority decides which port should be disabled when more than one port forms a loop in a
switch. Ports with a higher priority numeric value are disabled first. The allowed range is
between 0 and 255 and the default value is 128.
Internal Path
Cost (0=Auto) Enter the internal path cost. Enter 0 for Auto.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
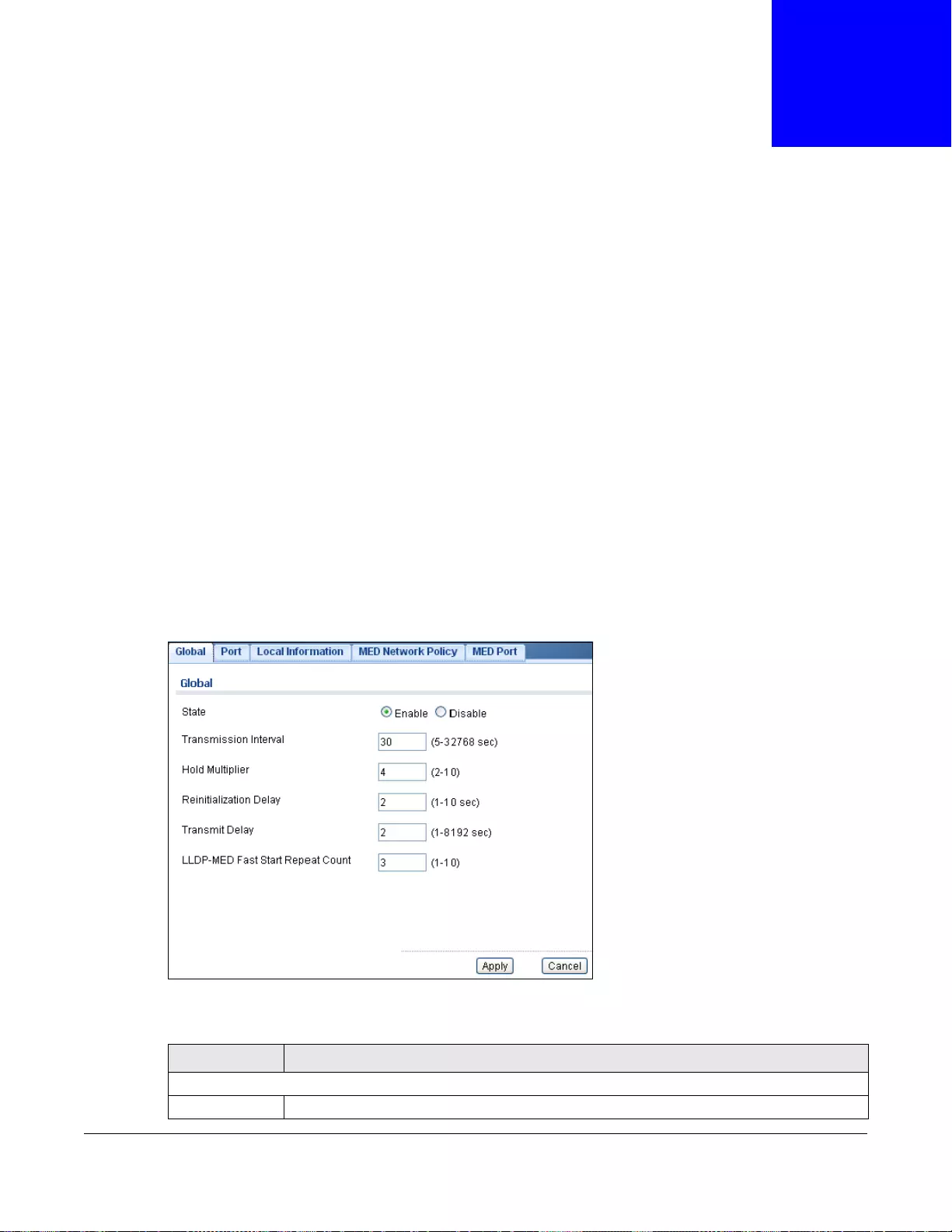
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
159
CHAPTER 27
Configuration: LLDP
27.1 Overview
This section provides information for LLDP in Configuration.
Use the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) screens to configure LLDP Switch settings.
27.2 LLDP
This page allows the user to inspect and configure the current LLDP port settings.
27.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure the Global settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > Global to open
this screen.
Figure 153 Configuration > LLDP > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Ta ble 119 Configuration > LLDP > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select Enable to activate the global LLDP.
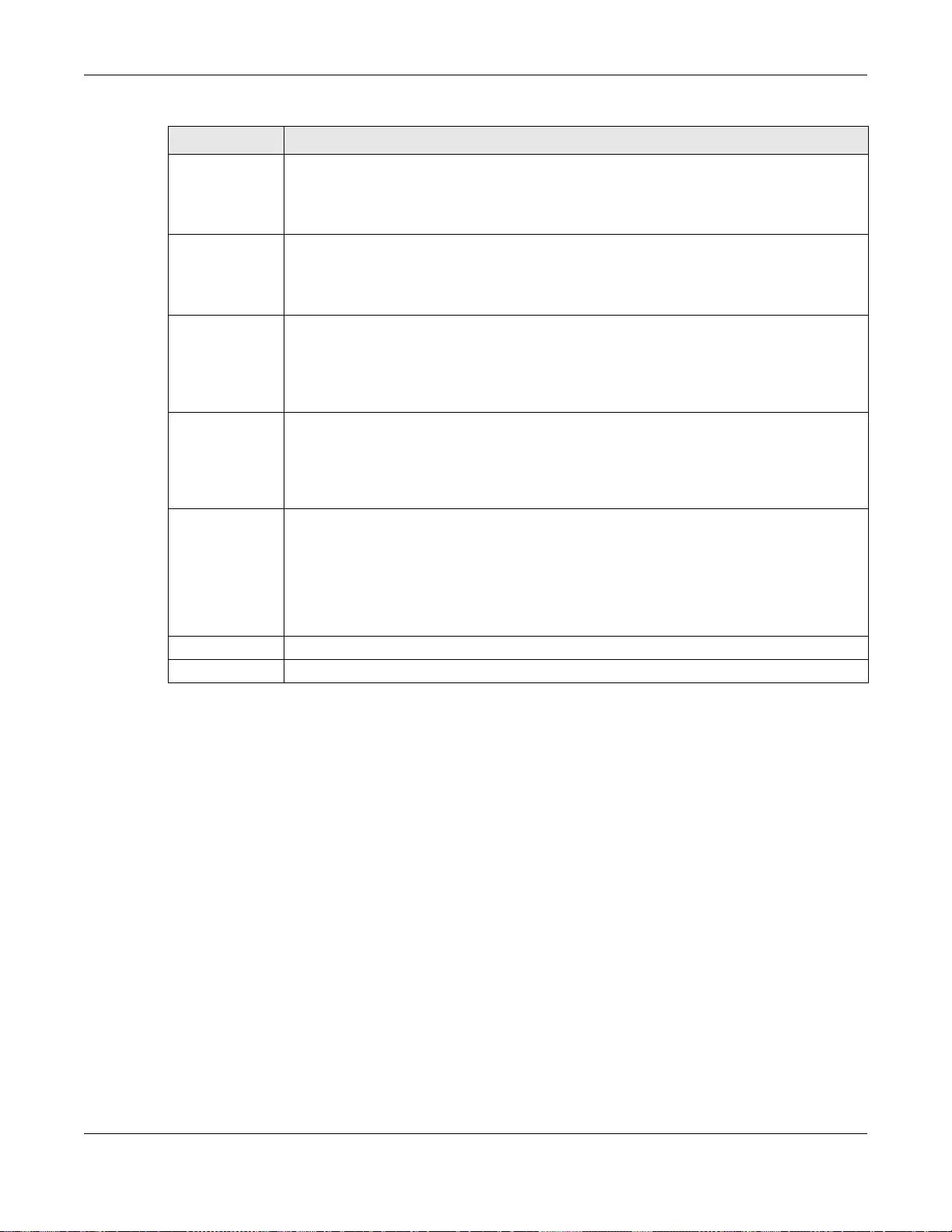
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
160
27.2.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > Port to open this screen.
Transmission
Interval Enter the transmission interval value.
The switch periodically transmits LLDP frames to its neighbors for having the network
discovery information up-to-date. The interval between each LLDP frame is determined by
the Tx Interval value. Valid values are restricted to 5 - 32768 seconds.
Hold Multiplier Enter the hold multiplier value.
Each LLDP frame contains information about how long the information in the LLDP frame
shall be considered valid. The LLDP information valid period is set to Tx Hold multiplied by
Tx Interval seconds. Valid values are restricted to 2 - 10 times.
Reinitialization
Delay Enter the reinitialization delay value.
When a port is disabled, LLDP is disabled or the switch is rebooted, an LLDP shutdown
frame is transmitted to the neighboring units, signalling that the LLDP information isn't
valid anymore. Tx Reinit con trols the amount of seconds between the shutdown frame and
a new LLDP initial ization. Valid values are restricted to 1 - 10 seconds.
Transmit Delay Enter the transmission del ay value.
If some configurat ion is changed (e.g. the IP address) a new LLDP frame is tr ansmitted, but
the time between the LLDP frames will always be at least the value of Tx Delay seconds. Tx
Delay cannot be larger than 1/4 of the Tx Interval value. Valid values are restricted to 1 -
8192 seconds.
LLDP-MED Fast
Start Repeat
Count
Enter the LLDP-MED fast start repeat count value.
Because there is a risk of an LLDP frame being lost during transmission between neighbors,
it is recommended to repeat the fast start transmission multiple times to increase the
possibility of the neighbors receiving the LLDP frame. With Fast start repeat count it is
possible to specify the number of times the fast start transmission would be repeated. The
recommended value is 4 times, given that 4 LLDP frames with a 1 second interval will be
transmitted, when an LLDP frame with new i nformation is received.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Ta ble 119 Configuration > LLDP > Global (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
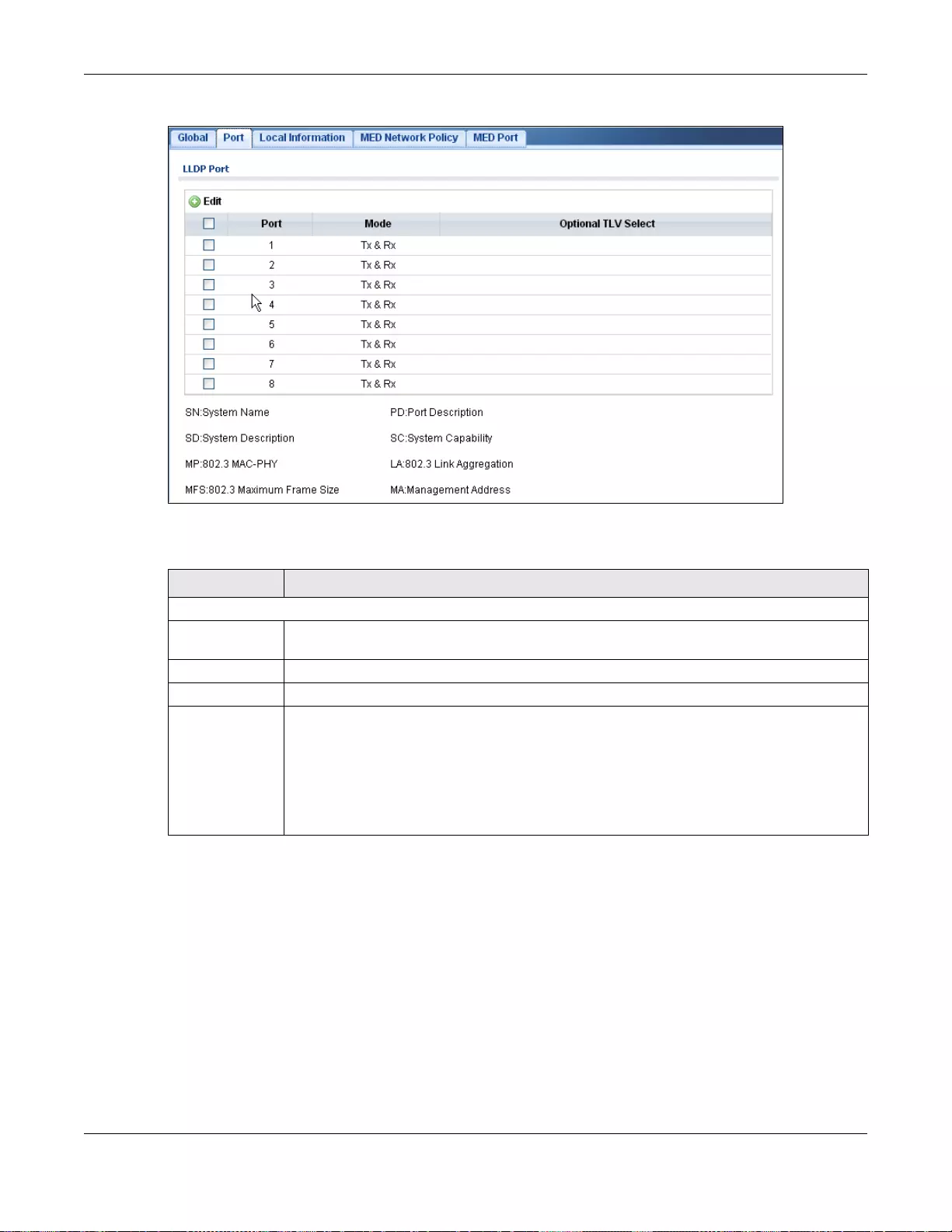
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
161
Figure 154 Configuration > LLDP > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
27.2.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > Port > Edit to
open this screen.
Table 120 Configuration > LLDP > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LLDP VLAN
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the index number of the LLDP port.
Mode Displays the mode of the LLDP port as Disable, Tx Only, Rx Only, or Tx & Rx.
Optional TLV
Select Displays the TLV as one or more of the following options:
•SN - System Name
• PD - Port Description
• SD - System Description
• SC - System Capability
• MP - 802.3 MAC-PHY
• LA - 802.3 Link Aggregation
• MFS - 802.3 Maximum Frame Size
• MA - Management Address
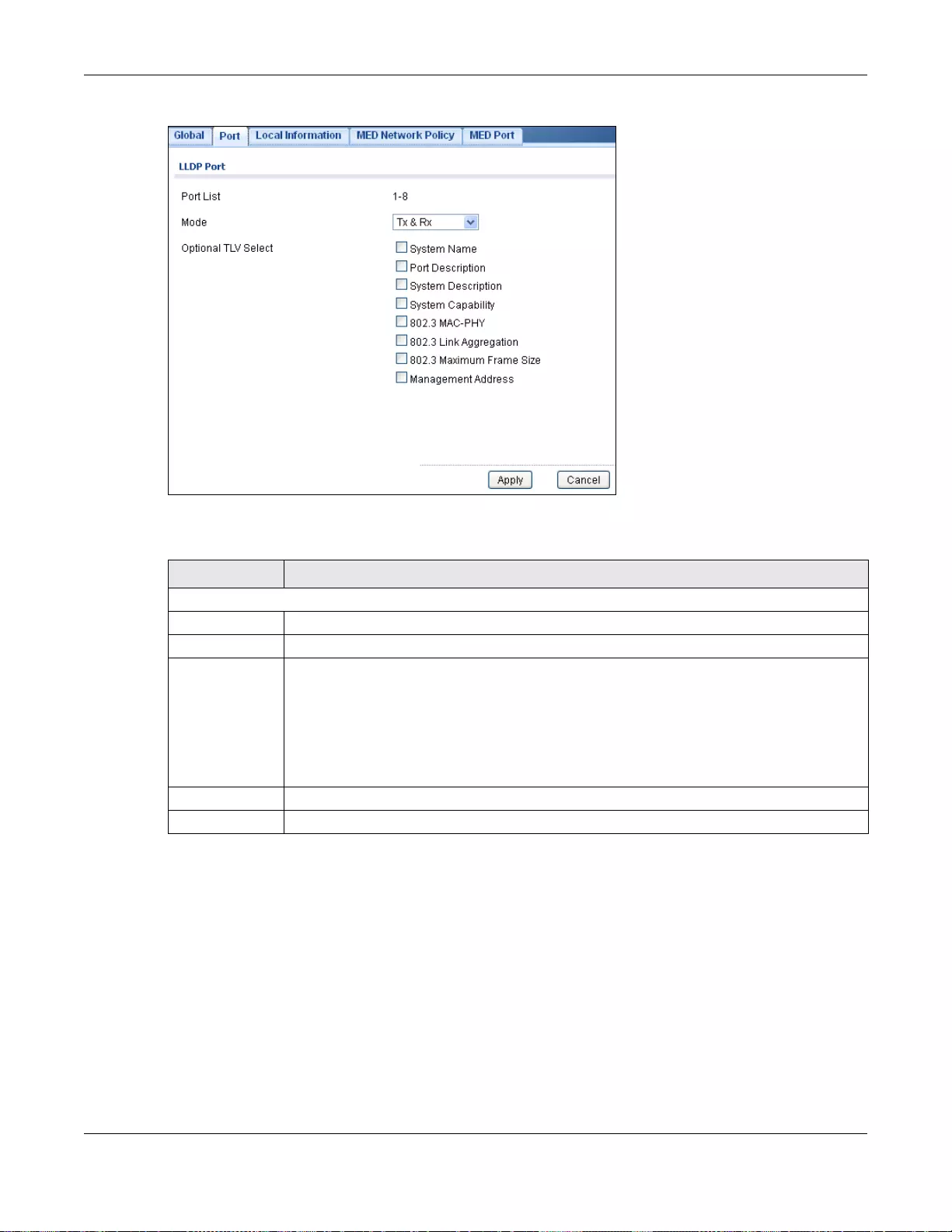
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
162
Figure 155 Configuration > LLDP > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
27.2.4 The Local Information Screen
Use this screen to view the Local Information settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > Local
Information to open this screen.
Table 121 Configuration > LLDP > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LLDP Port
Port List Displays the index number of the LLDP port(s).
Mode Select the mode of the LLDP port as Disable, Tx Only, Rx Only, or Tx & Rx.
Optional TLV
Select Select the TLV as one or more of the following options:
•SN - System Name
•PD - Port Description
•SD - System Description
•SC - System Capability
•MP - 802.3 MAC-PHY
•LA - 802.3 Link Aggregation
•MFS - 802.3 Maximum Frame Size
•MA - Management Address
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
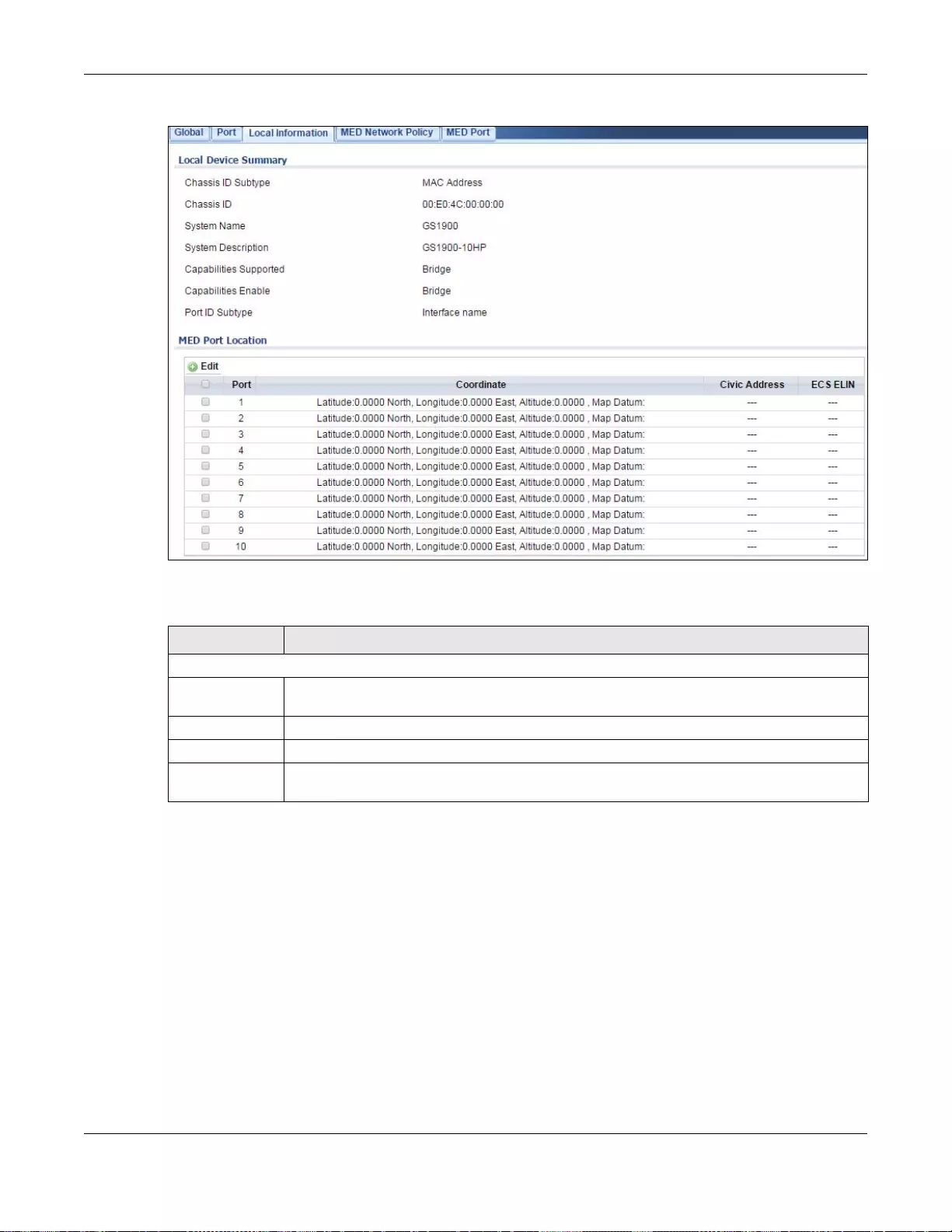
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
163
Figure 156 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 122 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local Device Summary
Chassis ID
Subtype Displays the chassis ID subtype.
Chassis ID The Chassis ID is the identification of the neighbor's LLDP frames.
System Name Sy stem Name is the name advertised by the neighbor unit.
System
Description Displays the System Description.

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
164
27.2.5 The Local Information Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > Local
Information > Edit to open this screen.
Capabilities
Supported Capabilities Supported describes the neighbor unit's capabilities. The possible
capabilities are:
1. Other
2. Repeater
3. Bridge
4. WLAN Access Point
5. Router
6. Telephone
7. DOCSIS cable device
8. Station only
9. Reserved
When a capability is enabled, the capability is followed by (+). If the capability is disabled,
the capability is followed by (-).
Capabilities
Enable Displays which capability is enabled.
Port ID Subtype Displays the Port ID Subtype.
MED Port Location
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the index number of the LLDP port(s).
Coordinate Displays the location coordinate of the LLDP port(s).
Civic Address Displays the location of the civic address(es) in hexadecimal.
ECS ELIN Emergency Call Service (e.g. E911 and others), such as defined by TIA or NENA.
Emergency Call Service ELIN ident ifier data format is def ined to carry the ELIN identifier as
used during emergency call setup to a traditional CAMA or ISDN trunk-based PSAP. This
format consists of a numerical digit string, corresponding to the ELIN to be used for
emergency calling.
Table 122 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
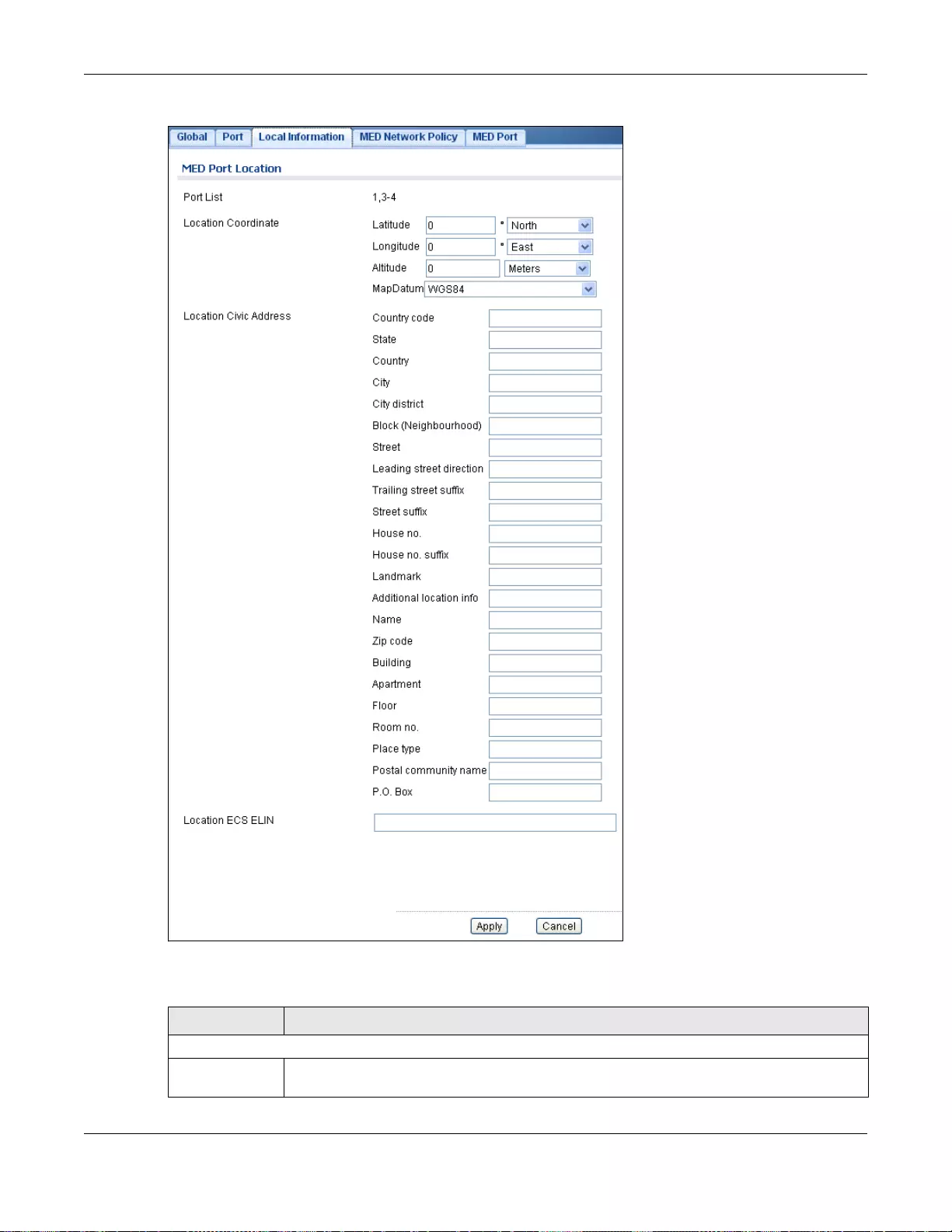
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
165
Figure 157 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 123 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MED Port Location
Port List Displays the index number of the LLDP port(s). The value is made of 16 pairs of
hexadecimal characters.

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
166
Location Coordinates
Latitude Latitude SHOULD be normalized to within 0-90 degrees with a maximum of 4 digits.
It is possible to specify the direction to either North of the equator or South of the
equator.
Longitude Longitude SHOULD be normalized to within 0-180 degrees with a maximum of 4 digits.
It is possible to specify the direction to either East of the prime meridian or West of the
prime meridian.
Altitude Altitude SHOULD be normalized to within -32767 to 32767 with a maximum of 4 digits.
It is possible to select between two altitude types (floors or meters).
Meters: Representing meters of Altitude defined by the vertical datum specified.
Floors: Representing altitude in a form more relevant in buildings which have different
floor-to-floor dimensions. An altitude = 0.0 is meaningful even outside a building, and
represents grou nd level at the given latitude and longitude. Inside a building, 0.0
represents the floor level associated with ground level at the main ent rance.
Map Datum The Map Datum is used for the coordinates given in these options:
WGS84: (Geographical 3D) - World Geodesic System 1984, CRS Code 4327, Prime
Meridian Name: Greenwich.
NAD83/NAVD88: North American Datum 1983, CRS Code 4269, Prime Meridian Name:
Greenwich; The associate d vertical datum is the North American Vertical Datum of 1988
(NAVD88). This datum pair is to be used when referencing locations on land, not near tidal
water (which would use Datum = NAD83/MLLW).
NAD83/MLLW: North American Datum 1983, CRS Code 4269, Prime Meridian Name:
Greenwich; The associated vertical datum is Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW). This datum
pair is to be used when referencing locations on water/sea/ocean.
Location Civic
Address IETF Geopriv Civic Address based Location Configuration Information (Civic Address LCI).
•Country code: The two-letter ISO 3166 country code in capital ASCII letters -
Example: DK, DE or US.
•State: National subdivisions (state, canton, region, province, prefecture).
•County: County, parish, gun (Japan), district.
•City: City, township, shi (Japan) - Example: Copenhagen.
•City district: City division, borough, city district, ward, chou (J apan).
•Block (Neighborhood): Neighborhood, block.
•Street: Street - Example: Poppelvej.
•Leading street direction: Leading street direction - Example: N.
•Trailing street suffix: Trailing street suffix - Example: SW.
•Street suffix: Street suffix - Example: Ave, Platz.
•House no.: House number - Example: 21.
•House no. suffix: House number suffix - Example: A, 1/2.
•Landmark: Landmark or vanity address - Example: Columbia University.
•Additional location info: Additional location info - Example: South Wing.
•Name: Name (residence and office occupant) - Example: Fle mming Jahn.
•Zip code: Postal/zip code - Example: 2791.
•Building: Building (structure) - Example: Low Library.
•Apartment: Unit (Apartment, suite) - Example: Apt 42.
•Floor: Floor - Example: 4.
•Room no.: Room number - Example: 450F.
•Place type: Place type - Example: Office.
•Postal community name: Postal community name - Example: Leonia.
•P.O. Box: Post office box (P.O. BOX) - Example: 12345.
Table 123 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
167
27.2.6 The MED Network Policy Screen
Use this screen to view the MED Network Policy settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > MED
Network Policy to open this screen.
Figure 158 Configuration > LLDP > MED Network Policy
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
27.2.7 The MED Network Policy Add/Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > MED Network
Policy > Add/Edit to open this screen.
Location ECS
ELIN Emergency Call Service (e.g. E911 and others), such as defined by TIA or NENA.
Emergency Call Service ELIN ident ifier data format is def ined to carry the ELIN identifier as
used during emergency call setup to a traditional CAMA or ISDN trunk-based PSAP. This
format consists of a numerical digit string, corresponding to the ELIN to be used for
emergency calling.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 123 Configuration > LLDP > Local Information > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 124 Configuration > LLDP > MED Network Policy
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network Policy Configuration
Add Click Add to create a new Network Policy Configuration entry.
No. Displays index of network policy.
Application Displays the Application type indicating the primary function of the application(s).
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN ID (VID) for the port as defined in IEEE 802.1Q-2003.
VLAN Tag Displays the VLAN Tag value as Tagged or Untagged.
L2 Priority Displays the L2 priority layer value.
DSCP Value Displays the DSCP Value.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
168
Figure 159 Configuration > LLDP > MED Network Policy > Add/Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 125 Configuration > LLDP > MED Network Policy > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MED Port Location Edit
No. Select the index of network policy
Application Select the Application type indicating the primary function of the application(s) defined for
this network policy , adv ertised by an Endpoint or Network Connectivity Device. The possible
application types are shown below.
1. Voice - for use by dedicated IP Telephony handsets and other similar appli-
ances supporting interactive voice services. These devices are typically
deployed on a separate VLAN for ease of deployment and enhanced security
by isolation from data applications.
2. Voice Signalling - for use in network topologies that require a different pol-
icy for the voice signalling than for the voice media.
3. Guest Voice - to support a separate limited feature-set voice service for
guest users and visitors with their own IP Telephony handsets and other sim-
ilar appliances supporting interactive voice services.
4. Guest Voice Signalling - for use in network topologies that require a differ-
ent policy for the guest voice signalling than for the guest voice media.
5. Softphone Voice - for use by softphone applications on typical data centric
devices, such as PCs or laptops.
6. Video Conferencing - for use by dedicated Video Conferencing equipment
and other similar appliances supporting real-time interactive video/audio ser-
vices.
7. Streaming Video - for use by broadcast or multicast based video content
distribution and other similar applications supporting streaming video ser-
vices that require specific network policy treatment. Video applications rely-
ing on TCP with buffering would not be an intended use of this application
type.
8. Video Signalling - for use in network topologies that require a separ ate pol-
icy for the video signalling than for the video media.

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
169
27.2.8 The MED Port Screen
Use this screen to view the MED Port settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > MED Port to open
this screen.
Figure 160 Configuration > LLDP > MED Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
VLAN ID Enter the VLAN ID (VID) for the port as defined in IEEE 802.1Q-2003. A value of 1 through
4094 is used to define a valid VLAN ID . A value of 0 (Priority Tagged) is used if the device is
using priority tagged frames as defined by IEEE 802.1Q-2003, meaning that only the IEEE
802.1D priority level is significant and the default PVID of the ingress port is used instead.
VLAN Tag TAG is indicative of whether the specified application type is using a tagged or an untagged
VLAN. Select Tagged or Untagged.
Untagged: The device is using an untagged frame format and as such does not include a
tag header as defined by IEEE 802.1Q-2003.
Tagged: The device is using the IEEE 802.1Q tagged frame format.
L2 Priority Priority is the Layer 2 priority to be used for the specified application type. One of the
eight priority levels (0 through 7).
DSCP Value DSCP is the DSCP value to be used to provide Diffserv node behavior for the specified
application type as defined in IETF RFC 2474. Contain one of 64 code point values (0
through 63).
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 125 Configuration > LLDP > MED Network Policy > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 126 Configuration > LLDP > MED Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MED Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the MED Port val ue.
State Displays the state of the MED port as Enable or Disable.
Network Policy Displays the Network Policy value.
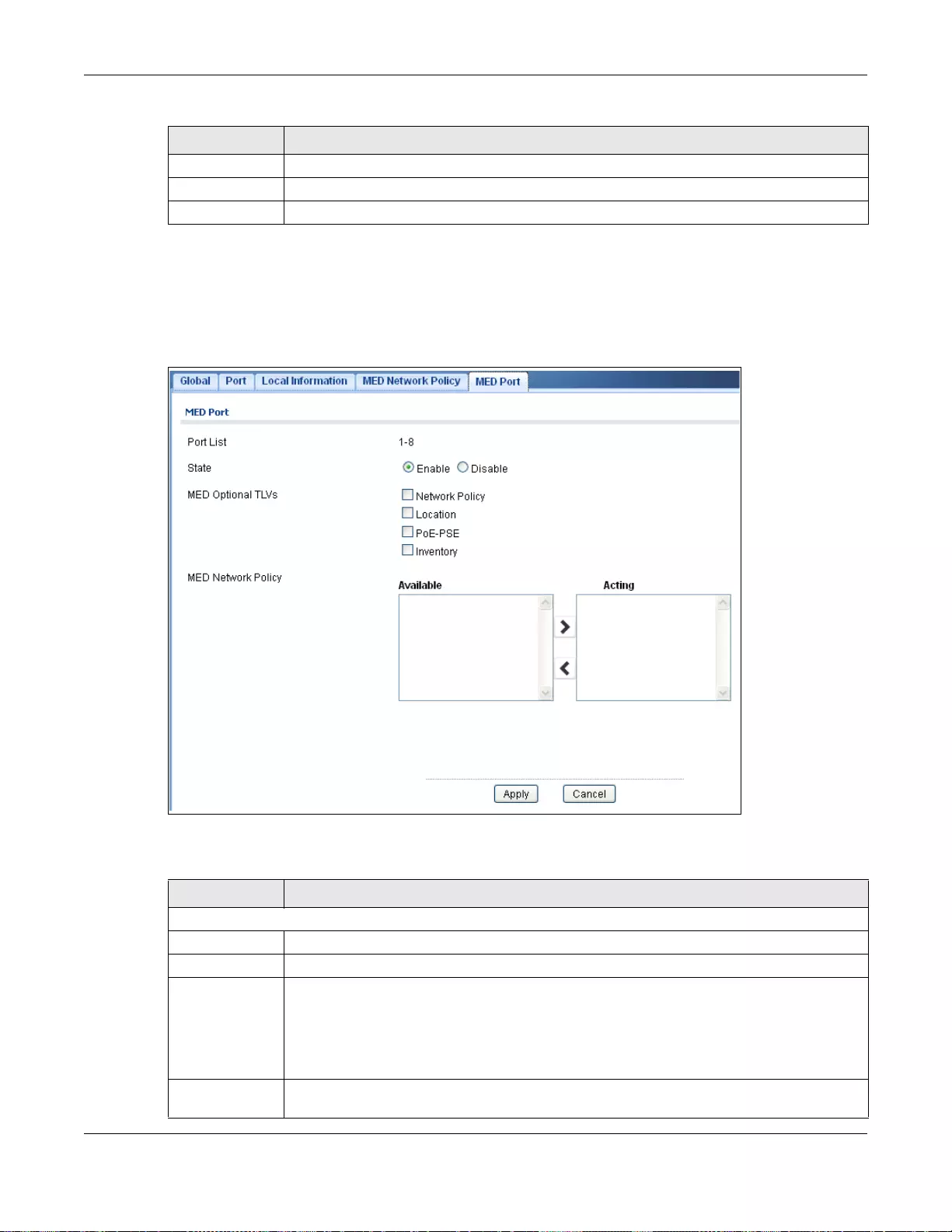
Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
170
27.2.9 The MED Port Add/Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the MED Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > LLDP > MED Port
> Edit to open this screen.
Figure 161 Configuration > LLDP > MED Po rt > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Location Displays the Location value.
PoE Displays the PoE value.
Inventory Displays the Inventory value.
Table 126 Configuration > LLDP > MED Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 127 Configuration > LLDP > MED Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MED Port
Port List Displays the Port List.
State Select Enable to activate the MED Port feature.
MED Optional
TLVs Select one or more of the MED Optional TLVs:
• Network Policy
•Location
•PoE PSE
•Inventory
MED Network
Policy Select one or more of the MED Network Policies in Available and move them to Acting
to activate.

Chapter 27 Configuration: LLDP
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
171
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 127 Configuration > LLDP > MED Port > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
172
CHAPTER 28
Configuration: QoS
28.1 Overview
This section provides information for QoS (Quality of Service) in Configuration.
28.2 General
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and
the networking methods used to control the use of bandwidth. Without QoS, all traffic data is
equally likely to be dropped when the network is congested. This can cause a reduction in network
performance and make the network inadequate for time-critical application such as video-on-
demand.
28.2.1 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > QoS > General to open this
screen.
Figure 162 Configuration > QoS > General
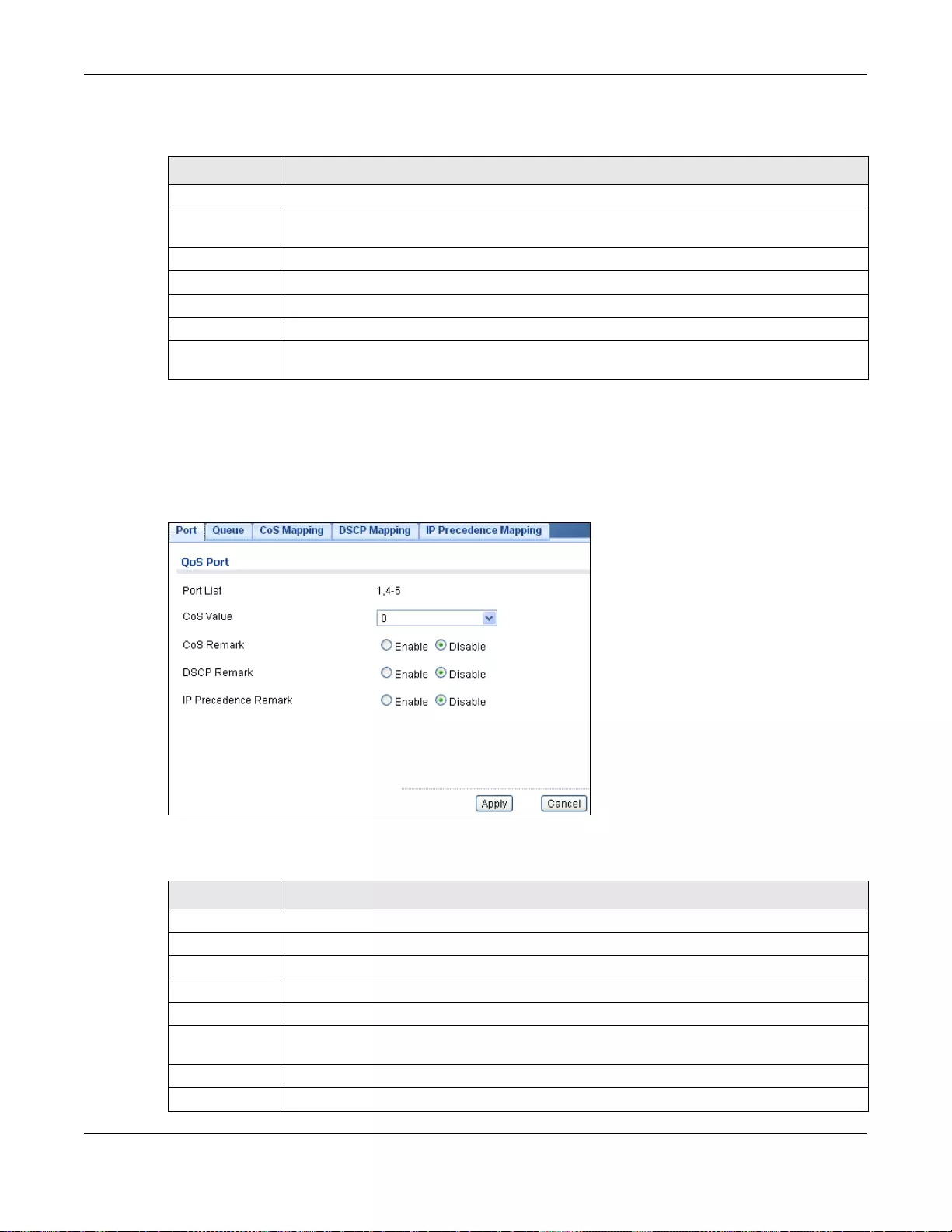
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
173
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
28.2.2 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port Edit settings. Click Configuration > QoS > General > Port
> Edit to open this screen.
Figure 163 Configuration > QoS > General > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 128 Configuration > QoS > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the QoS port list.
CoS Value Displays the CoS value, range: 0 - 7.
Remark CoS Displays if this function is disabled or enabled.
Remark DSCP Displays if this function is disabled or enabled.
Remark IP
Precedence Displays if this function is disabled or enabled.
Table 129 Configuration > QoS > General > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Port
Port List Displays the index number of the QoS port(s).
CoS Value Select the CoS Value from the dropdown list.
CoS Remark Select Enable to acti vate CoS Remark.
DSCP Remark Select En able to activate DSCP Remark.
IP Precedence
Remark Select Enable to activate IP Precedence Remark.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
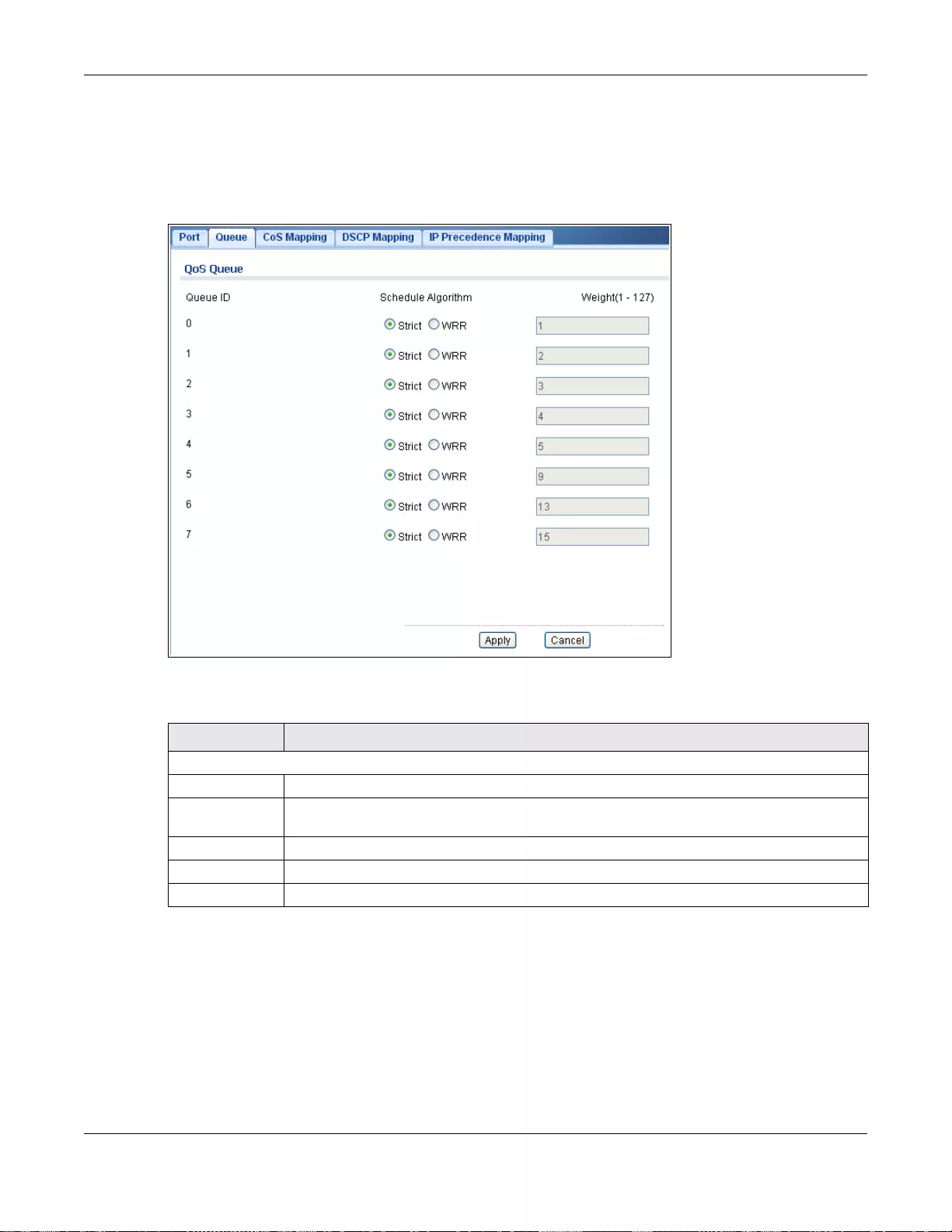
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
174
28.2.3 The Queue Screen
Use this screen to view the Queue settings. Click Configuration > QoS > General > Queue to
open this screen.
Figure 164 Configuration > QoS > General > Queue
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
28.2.4 The CoS Mapping Screen
Use this screen to configure the Cos Mapping settings. Click Configuration > QoS > General >
CoS Mapping to open this screen.
Table 130 Configuration > QoS > General > Queue
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Queue
Queue ID Displays the Queue ID value.
Schedule
Algorithm Select the Schedule Algorithm as Strict or WRR.
Weight (1-127) Enter the weight of the QoS item.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
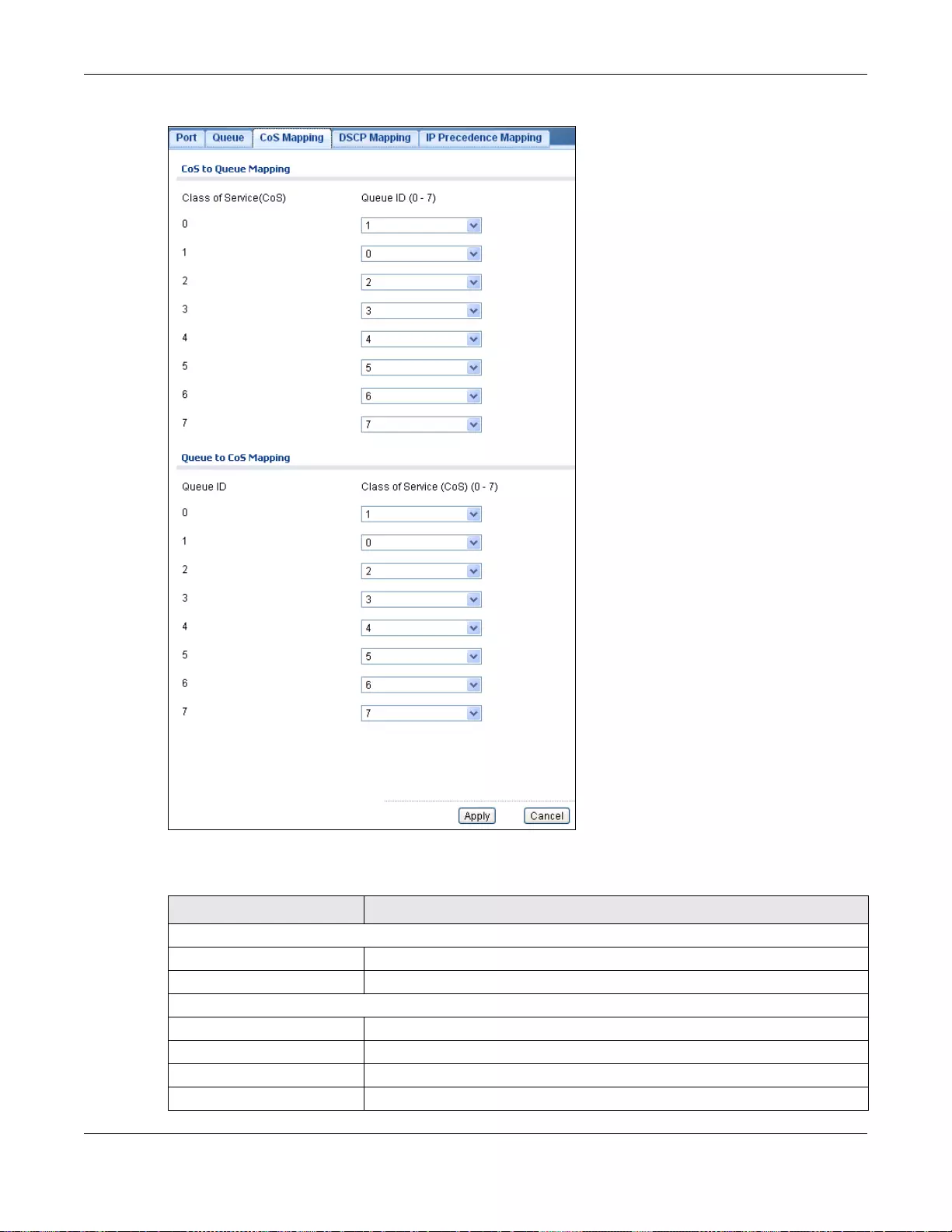
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
175
Figure 165 Configuration > QoS > General > CoS Mapping
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 131 Configuration > QoS > General > CoS Mapping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
CoS to Queue Mapping
Class of Service (CoS) Displays a listing of the CoS, range: 0 - 7.
Queue ID (0-7) Click the drop-down menu to map the CoS to a specific Queue ID.
Queue to CoS Mapping
Queue ID Displays a listing of the Queue ID, range: 0 - 7.
Class of Service (CoS) (0-7) Click the drop-down menu to map the Queue ID to a specific CoS.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
176
28.2.5 The DSCP Mapping Screen
Use this screen to configure the DSCP Mapping settings. Click Configuration > QoS > General
> DSCP Mapping to open this screen.
Figure 166 Configuration > QoS > General > DSCP Mapping
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 132 Configuration > QoS > General > DSCP Mapping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DSCP to Queue Mapping
Queue ID Displays the DSCP Queue ID value.
Queue to DSCP Mapping
DSCP (0-63) Select the DSCP mapping value from the dropdown list.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
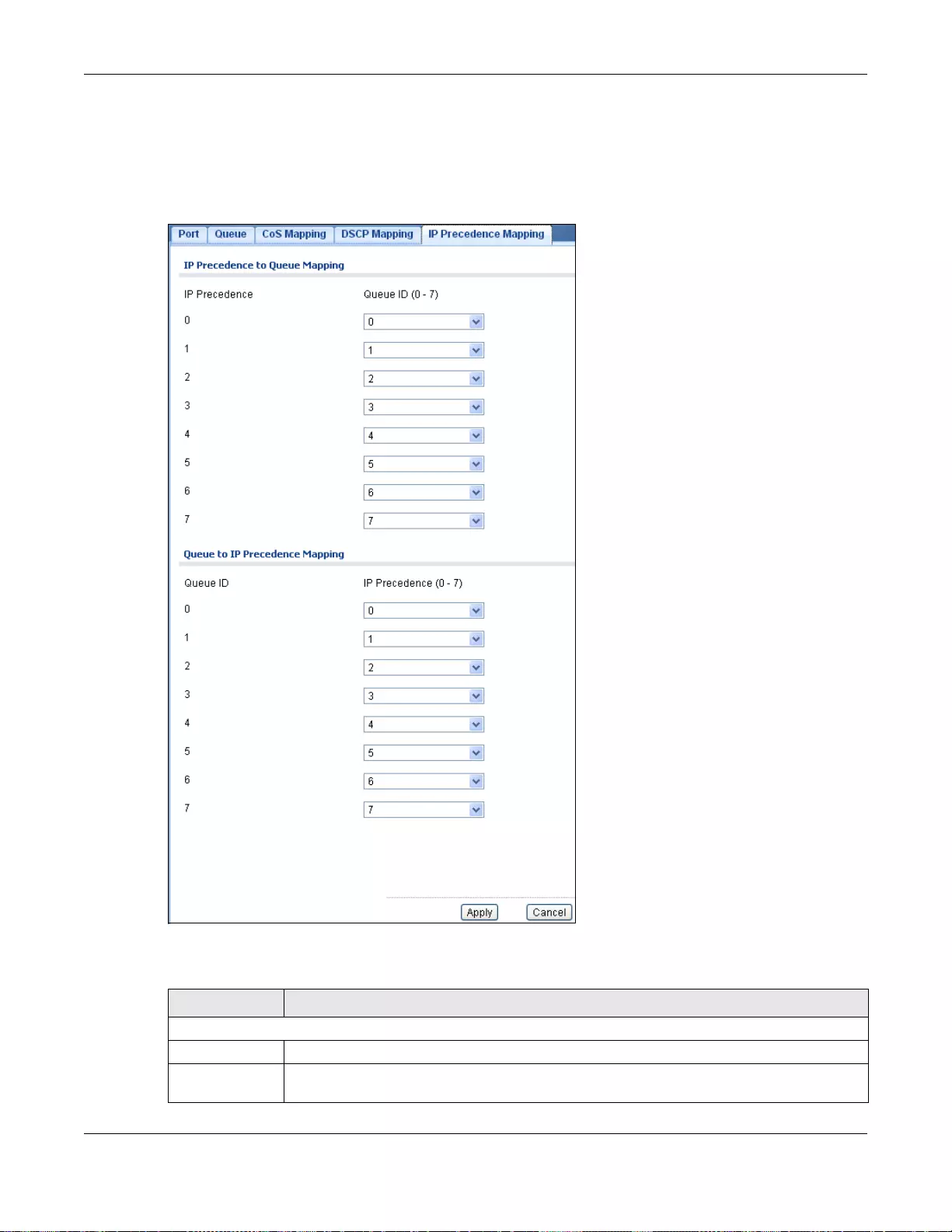
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
177
28.2.6 The IP Precedence Mapping Screen
Use this screen to configure the IP Precedence Mapping settings. Click Configuration > QoS >
General > IP Precedence Mapping to open this screen.
Figure 167 Configuration > QoS > General > IP Precedence Mapping
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 133 Configuration > QoS > General > IP Precedence Mapping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Precedence to Queue Mapping
IP Precedence Displays a listing of IP Precedence, range: 0 - 7.
Queue ID (0-7) Click the drop-down menu to map an IP Precedence designation to a spec ific Queue ID (0 -
7).

Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
178
28.3 Trust Mode
28.3.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode to open
this screen.
Figure 168 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
28.3.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode > Port to
open this screen.
Queue to IP Precedence Mapping
Queue ID Displays a listing of Queue ID, range: 0 - 7.
IP Precedence
(0-7) Click the drop-down menu to map a Queue ID to a specific IP precedence.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 133 Configuration > QoS > General > IP Precedence Mapping (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 134 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
Trust Mode Select the Trust Mode from the dropdown list.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
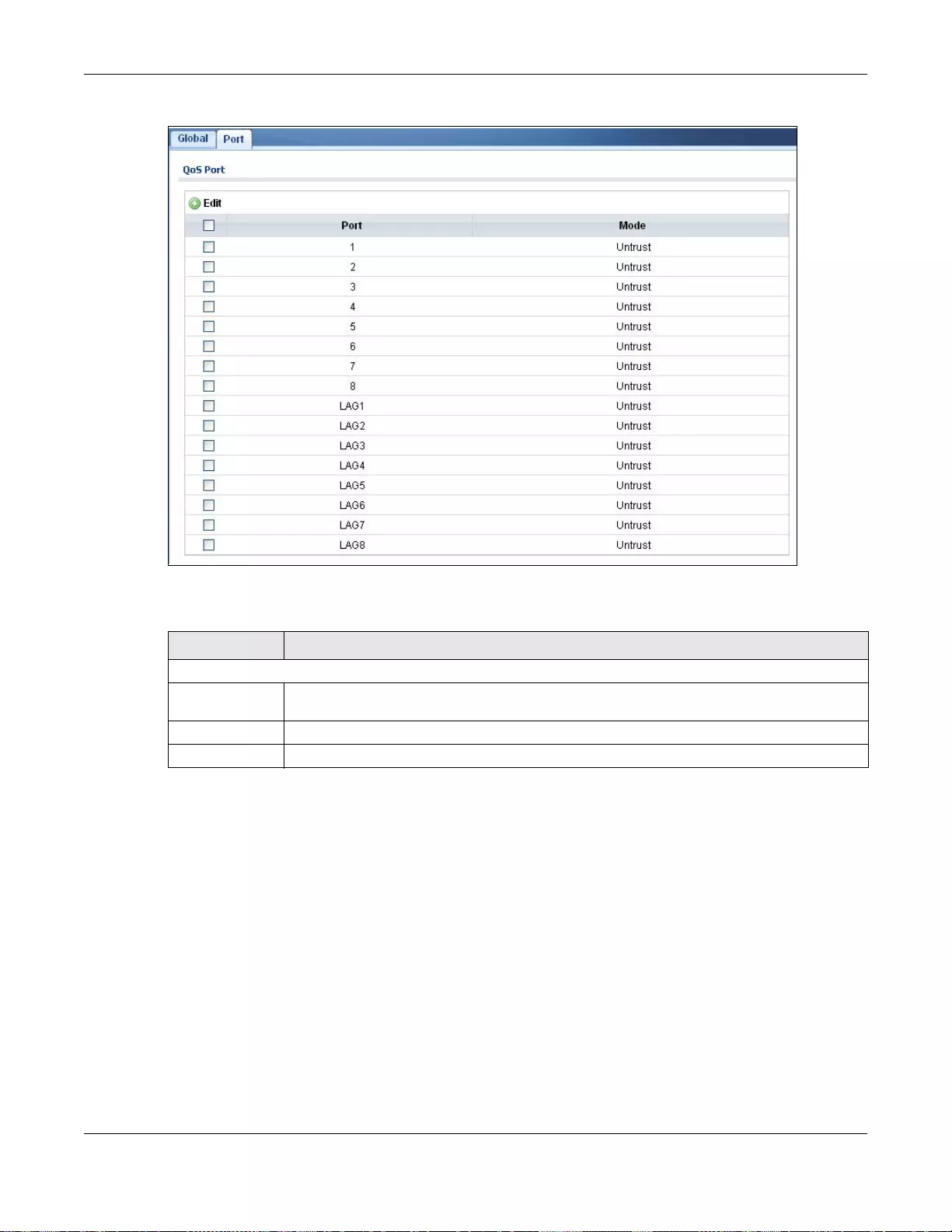
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
179
Figure 169 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
28.3.3 The Trust Mode Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Trust Mode settings. Click Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode
> Port > Edit to open this screen.
Table 135 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Port
Edit Select t his check bo x to confi gure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
Mode Displays the Trust status as Trust or Untrust.
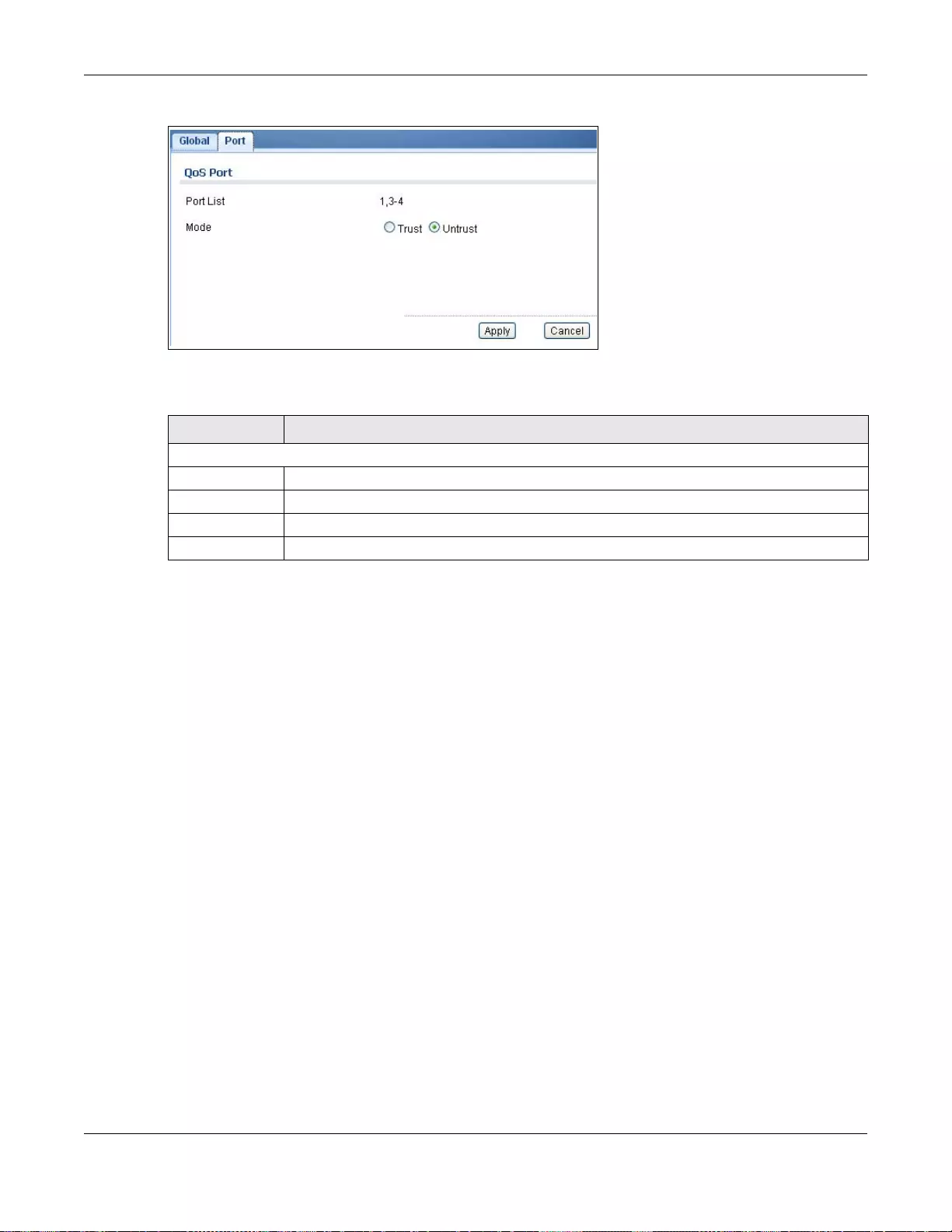
Chapter 28 Configuration: QoS
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
180
Figure 170 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 136 Configuration > QoS > Trust Mode > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Port Trust Edit
Port List Displays the port index value(s).
Mode Select the Trust Mode for the QoS port list as Trust or Untrust.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
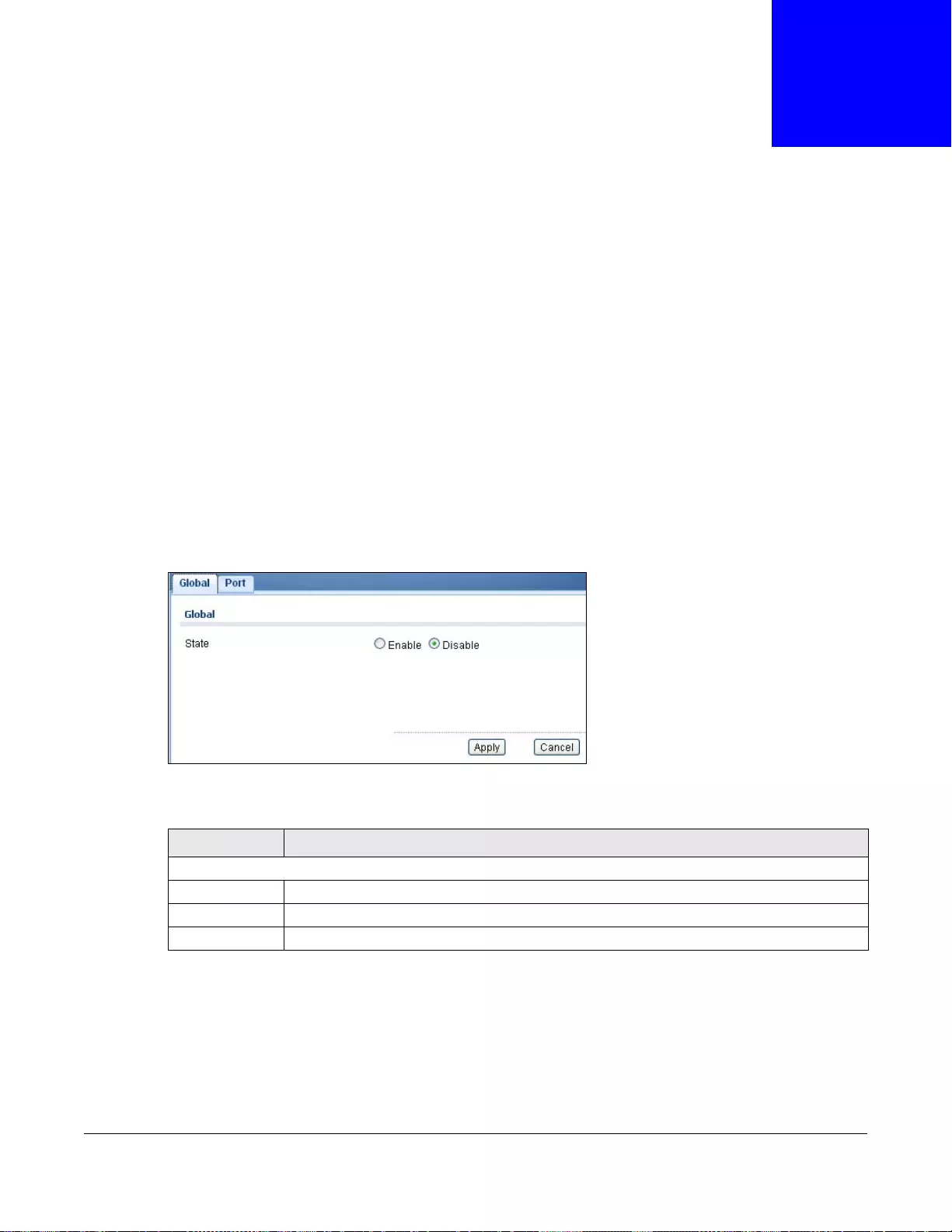
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
181
CHAPTER 29
Configuration: Security
29.1 Overview
This section provides information for Security in Configuration.
29.2 Port Security
29.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Security > Port Security to
open this screen.
Figure 171 Configuration > Security > Port Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.2.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > Port Security >
Port to open this screen.
Table 137 Configuration > Security > Port Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the global security setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
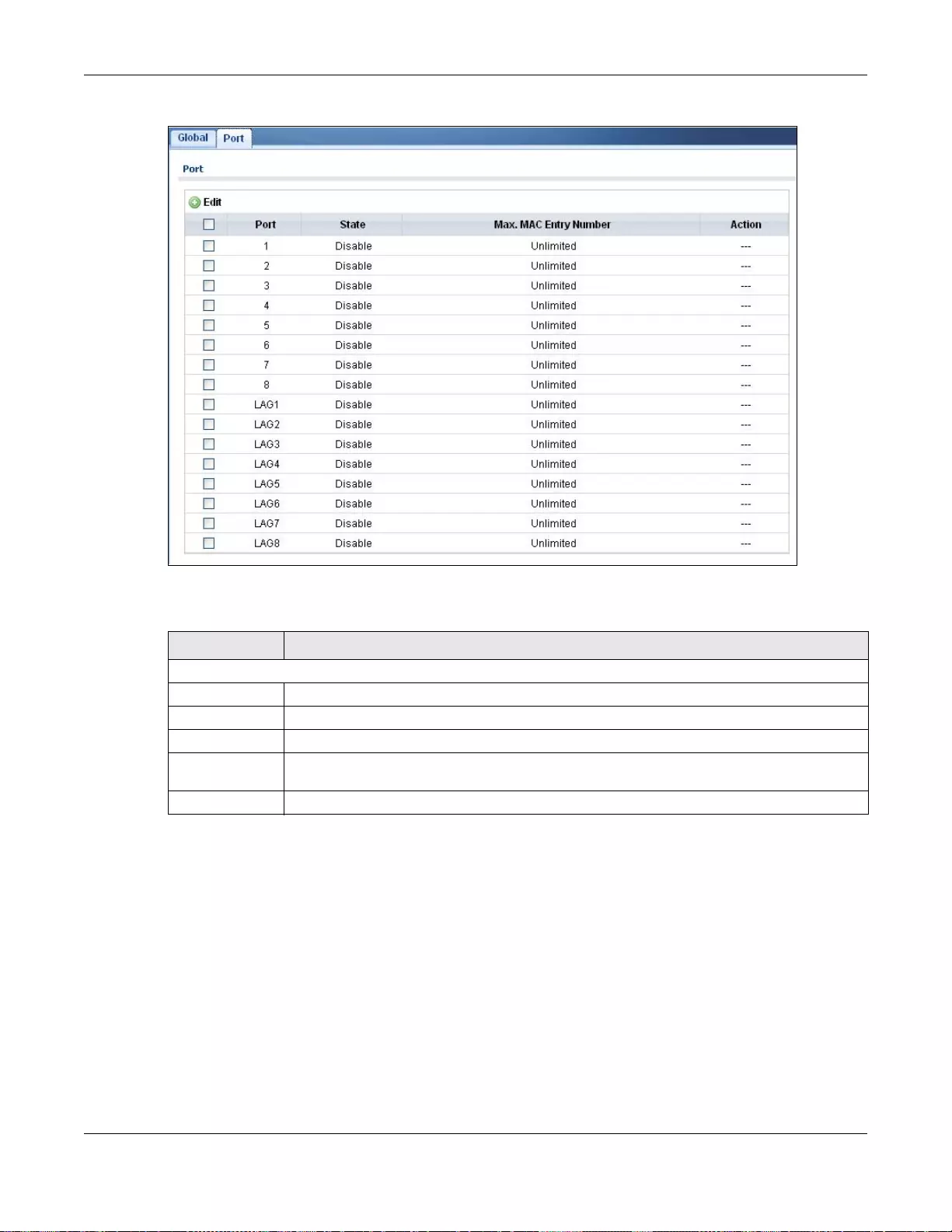
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
182
Figure 172 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.2.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port settings. Select the port(s) you want to configure and then
click Edit in the Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port screen to open this screen.
Table 138 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Click Edit to change the properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
State Displays the Trust status as Enable/Disable.
Max. MAC Entr y
Number Displays the designated maximum number of allowed MAC entries. The maximum MAC
entry number can be learned for individual ports.
Action Displays the Action as Discard or Shutdown.
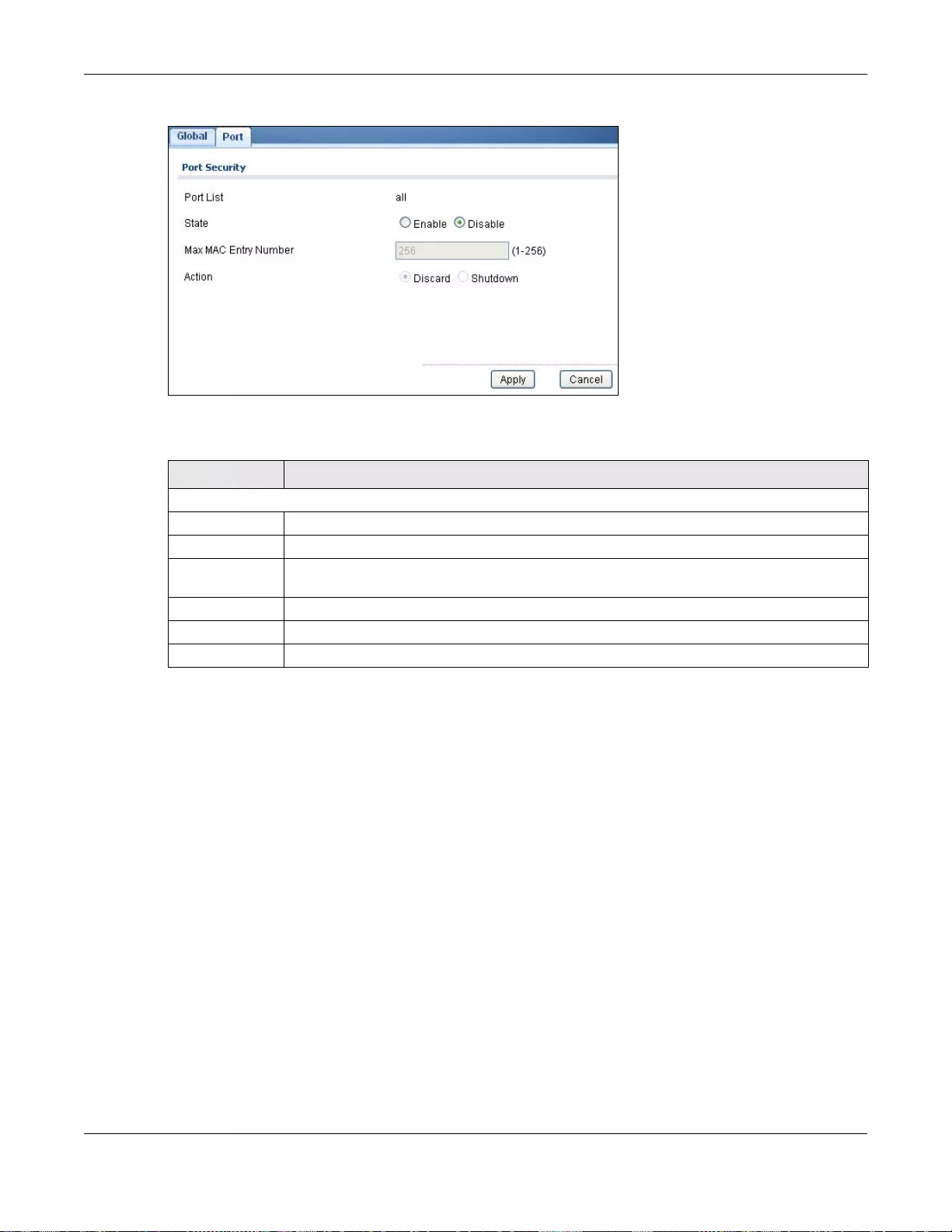
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
183
Figure 173 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.3 Protected Port
29.3.1 The Protected Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > Protected Port to
open this screen.
Table 139 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Security Edit
Port List Displays the port index value.
State Select Enable or Disable for the Trust status.
Max MAC Entry
Number Enter the maximum MAC entry number (maximum MAC entry number can be learned for
individual ports).
Action Select the Action as Discard or Shutdown.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
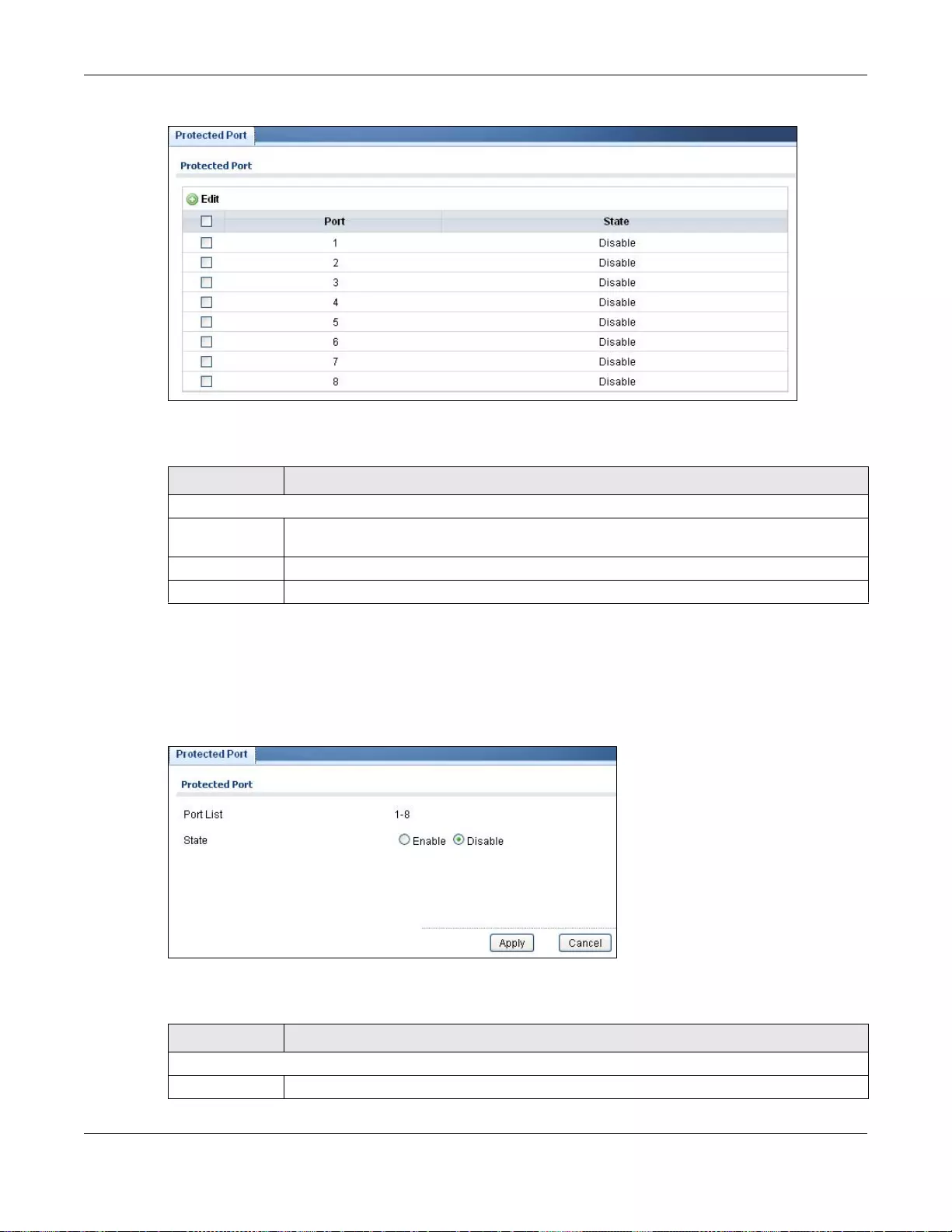
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
184
Figure 174 Configuration > Security > Protected Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.3.2 The Protected Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > Port Security >
Port > Edit to open this screen.
Figure 175 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 140 Configuration > Security > Protected Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Protected Port
Edit Select this chec k box to c onfigure th e properties of a port. Click th e Edit button change the
properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
State Displays the Trust status as Enable/Disable.
Table 141 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Protected Port
Port List Displays the port list index value(s).

Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
185
29.4 802.1X
29.4.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Global
to open this screen.
Figure 176 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.4.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port to
open this screen.
State Select Enable or Disable for the Protected Port status.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 141 Configuration > Security > Port Security > Port > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 142 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the 802.1X security setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
186
Figure 177 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.4.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port
> Edit to open this screen.
Table 143 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select this check box to configure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change
the properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
State Displays the Trust status as enabled or disabled.
Reauthentication Displays if Reauthentication function is enabled. If enabled, the subscriber has to
periodically re-enter his or her username and password to stay connected to the port.
Reauthentication
Period Displays the Reauthentication period for the function: t he period of time ften a client has
to re-enter his or her username and password to stay connected to the port.
Quiet Period Display the time out period to transmit request after receiving a rejection from the sever.
Supplicant Time
out Displ ay the time out period to transmit a request when the client does not responsed.
Max EAP
Requests Enter the maximum number of request retries.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
187
Figure 178 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.5 DoS
The Switch protects against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, such as Scan attack and Ping of Death.
The goal of DoS attacks is not to steal information, but to disable a device or network on the
Internet.
By default, the DoS feature is disabled. You need to enable it on the Switch and its port(s). See
Table 148 on page 190 for the types of DoS attacks that the Switch prevents when you turn on this
feature. You cannot set the Switch to block a specific type of DoS attacks.
Note: DoS protection doesn’t work on LACP-enabled ports.
Table 144 Configuration > Security > 802.1X > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
802.1X Port Edit
Port List Displays the port index value.
State Displays the Trust stat us as enabled or disabled.
Reauthentication
State Specify if a subscriber has to periodically re-enter his or her username and pa ssword to
stay connected to t he port. Select Enable to activate feature.
Reauthentication
Period Specify how often a client has to re-enter his or her username and password to stay
connected to the port.
Quiet Period Display the time out period to transmit request after receiving a rejection from the sever.
Supplicant Period Display the time out p eriod to transmit a request when the client does not responsed.
Maximum
Request Retries Enter the maximum number of request retries.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
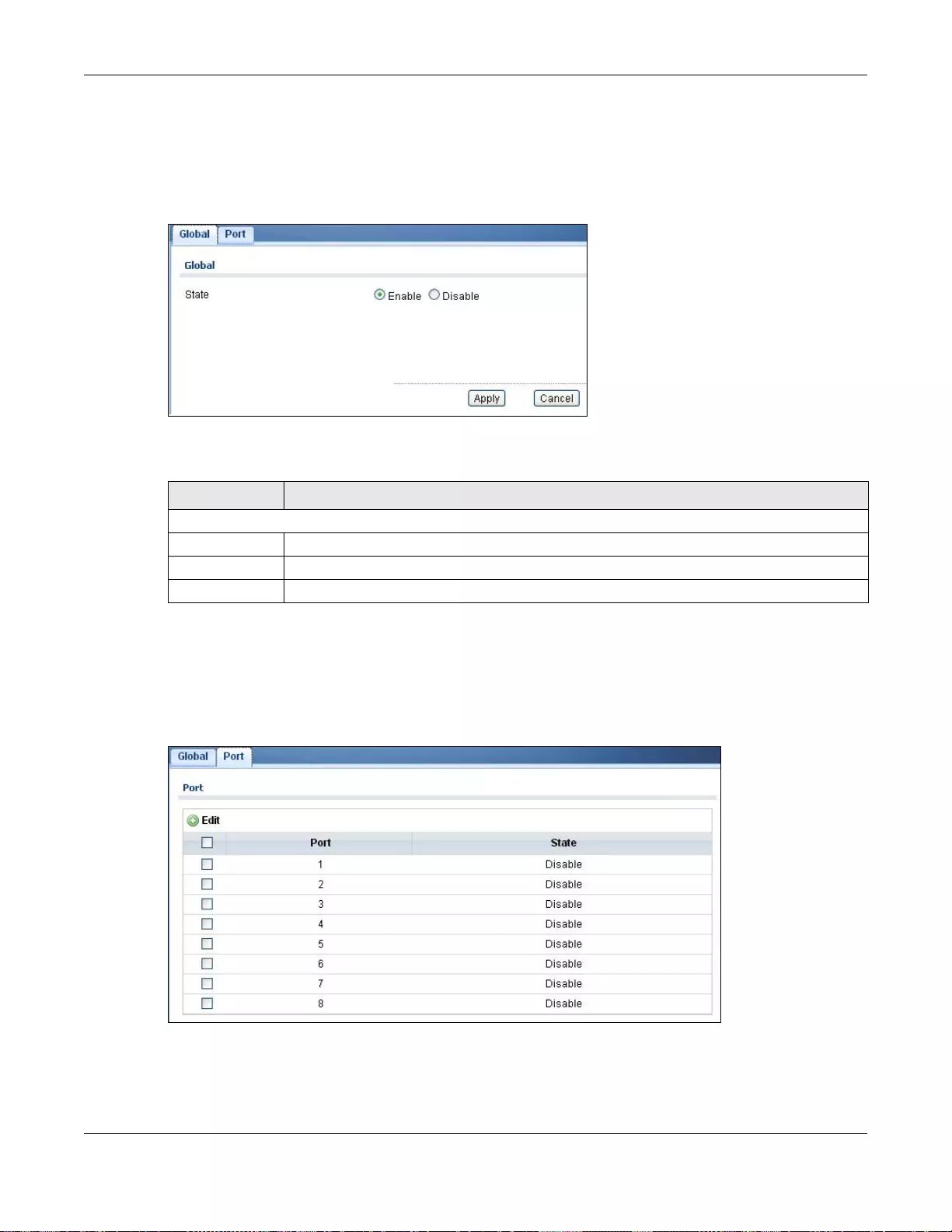
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
188
29.5.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Security > DoS > Global to
open this screen.
Figure 179 Configuration > Security > DoS > Global
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.5.2 The Port Screen
Use this screen to view the Port settings. Click Configuration > Security > DoS > Port to open
this screen.
Figure 180 Configuration > Security > DoS > Port
Table 145 Configuration > Security > DoS > Global
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the DoS security setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
189
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
29.5.3 The Port Edit Screen
Use this screen to configure the Port settings.
Click Configuration > Security > DoS > Port > Edit to open this screen.
Figure 181 Configuration > Security > DoS > Port > Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 146 Configuration > Security > DoS > Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Edit Select this check box to configure the properties of a port. Click the Edit button change
the properties of the port.
Port Displays the port index value.
State Displays the port’s DoS feature as Enable or Disable.
Table 147 Configuration > Security > DoS > Port > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port
Port List Displays the port index value.
State Select Enable to activate the port’s DoS feature.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Chapter 29 Configuration: Security
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
190
29.5.4 DoS Attack Types
The following table describes the types of DoS attacks that the Sw itch can prevent when you enable
the DoS feature on the Switch and the port(s).
Table 148 DoS Attack Types
TYPE PACKET TYPE DESCRIPTION
DA_EQUAL_SA Layer 2 These attacks result from sending a speci a lly crafted packet
to a machine where the source MAC address is the same as
the destination MAC address. The system attempts to reply
to itself, resulting in system lockup.
LAND Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 These attacks result from sending a specially crafted packet
to a machine where the source host IPv4/IPv6 address is the
same as the destination host IPv4/IPv6 address. The system
attempts to reply to itself, resulting in syst em lockup.
UDP_BLAT / TCP_BLAT
(Blat Attack) Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 These attacks result from sending a specially crafted packet
to a machine where the source host UDP/TCP port is the
same as the destination host UDP/TCP port. The system
attempts to reply to itself, resulting in syst em lockup.
PoD (Ping of Death) Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 Ping of Death uses a "ping" utility to create and send an IP
packet that exceeds th e maximum 65,536 bytes of data
allowed by the IP specification. This may cause systems t o
crash, hang or reboot.
IPv6_FRAG_LEN_MIN Layer 3 IPv6 This attack uses IPv6 fragmented packets (excluding the last
one) whose payload length is less than 1240 bytes.
ICMP_FRAG_PKT Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 This attack uses many small fragmented ICMP p a ckets.
ICMPv4_PING_MAX /
ICMPv6_PING_MAX Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 This attack uses Ping packets whose length is larger than
512 bytes.
SMURF Layer 3 IPv4 This attack uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
echo requests packets (pings) to cause network congestion
or outages.
SYNchronization (SYN), ACKnowledgment (ACK) and FINish (FIN) packets are used to initiate, acknowledge
and conclude TCP/IP communication sessi o ns. The following scans exploit weaknesses in the TCP/IP
specification and try to illicit a response from a host to identify ports for an attack:
TCP_HDR_LEN_MIN Layer 3 IPv4 TCP packets with header length less than 20 bytes.
SYN_SPORT_LESS_1024 Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 TCP SYN packets with source port less than 1024.
NULL_SCAN (Scan
Attack) Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 TCP sequence number is zero and all control bits are zeroes.
XMAS (Scan Attack) Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 TCP sequence number is zero and the FIN, URG and PSH bits
are set.
SYN_FIN Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 SYN and FIN bits are set in the TCP packet.
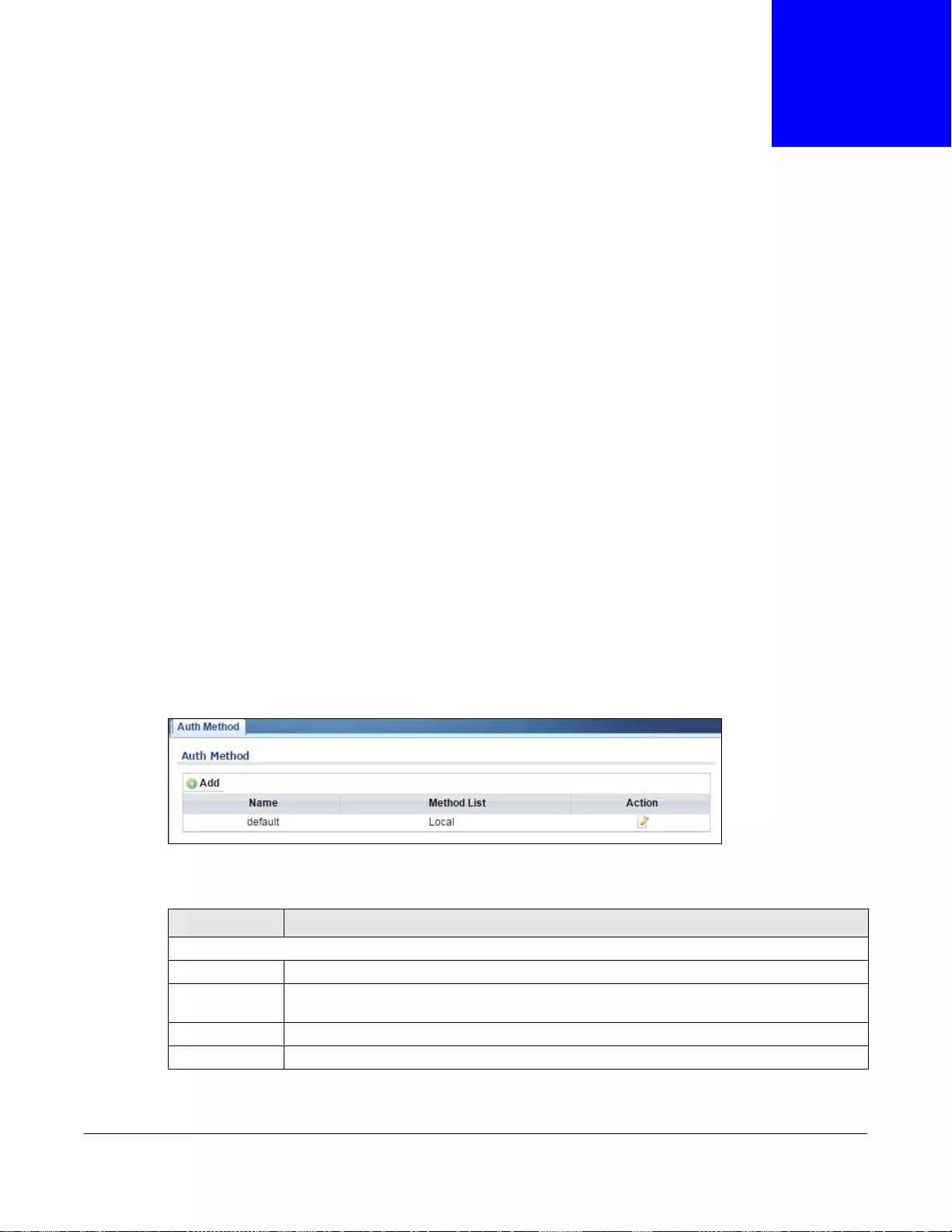
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
191
CHAPTER 30
Configuration: AAA
30.1 Overview
This section provides information for AAA in Configuration.
Use the AAA screens to configure authentication, authorization and accounting settings on the
Switch.
30.2 Auth Method
Authentication is the process of determining who a user is and v alidating access to the Sw itch. The
Switch can authenticate users who try to log in based on user accounts configured on the Switch
itself. The Switch can also use an external authentication server to authenticate a large number of
users.
30.2.1 The Auth Method Screen
Use this screen to view the Auth Method settings. Click Configuration > AAA > Auth Method to
open this screen.
Figure 182 Configuration > AAA > Auth Method
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 149 Configuration > AAA > Auth Method
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Auth Method
Add Click Add to create a new Auth Method entry.
Name Displays the authentication method name. The name can be between 1 and 31 ASCII
Alphanumeric Characters.
Method List Displays the list of authentication methods as being Local or Radius or TACACS+.
Action Click the Action button to change the configuration settings for a VLAN entry.
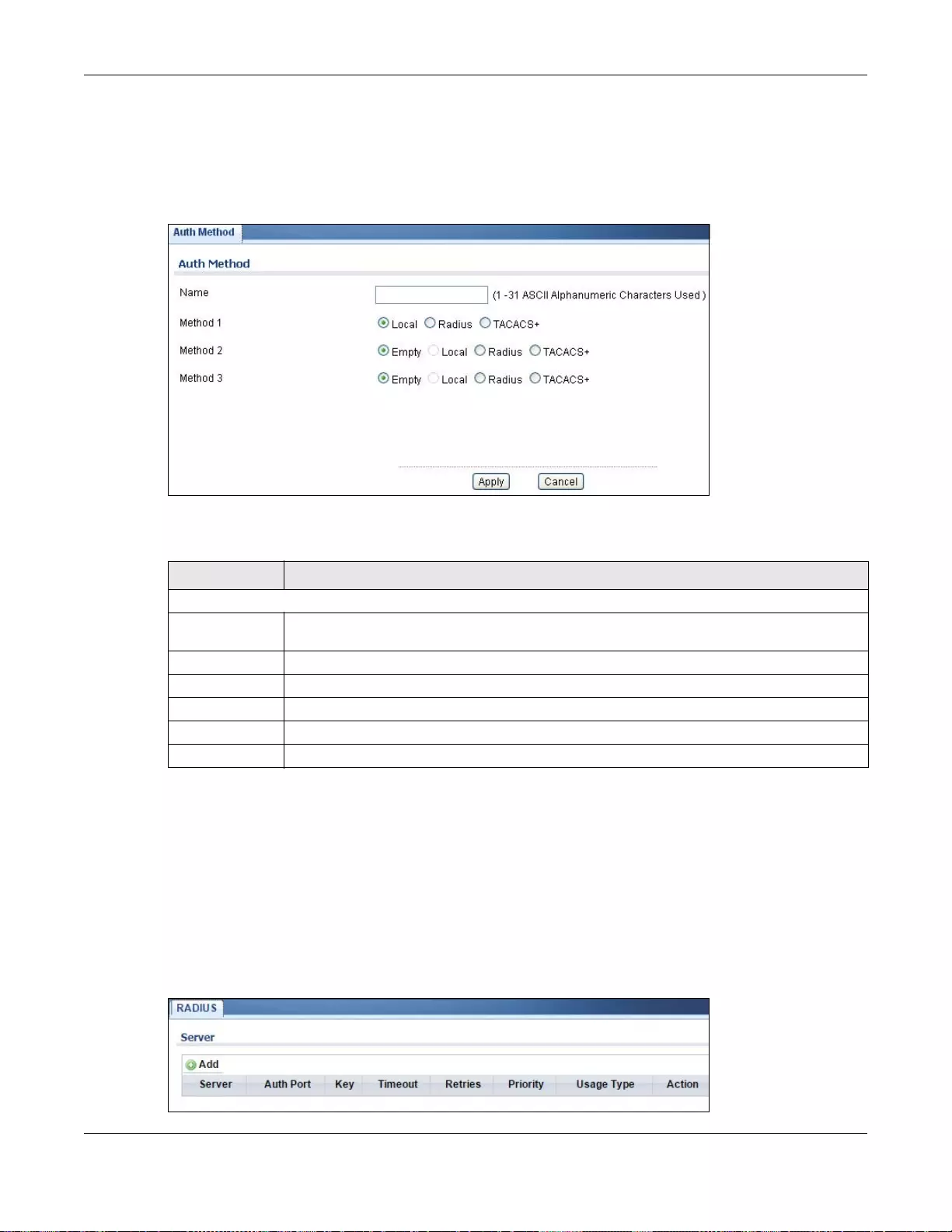
Chapter 30 Configuration: AAA
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
192
30.2.2 The Auth Method Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Auth Method settings. Click Configuration > AAA > Auth
Method > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 183 Configuration > AAA > Auth Method > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
30.3 RADIUS
30.3.1 The RADIUS Screen
Use this screen to configure the RADIUS settings. Click Configuration > AAA > RADIUS to open
this screen.
Figure 184 Configuration > AAA > RADIUS
Table 150 Configuration > AAA > Auth Method > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Auth Method
Name Enter the authentication method name. The name can be between 1 and 31 ASCII
Alphanumeric Characters.
Method 1 Select the first authentication method as being Local, Radius, or TACACS+.
Method 2 Select the second authentication method as being Empty, Local, Radius, or TACACS+.
Method 3 Select the third authentication method as being Empty, Local, Radius, or TACACS+.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 30 Configuration: AAA
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
193
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
30.3.2 The RADIUS Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the RADIUS settings. Click Configuration > AAA > RADIUS > Add/
Modify to open this screen.
Figure 185 Configuration > AAA > RADIUS > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 151 Configuration > AAA > RADIUS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server
Add Click Add to create a new Server entry.
Server Displays the server name(s) as an IP address or a domain name.
Auth Port Displays the authentication port number(s) as a value between 0 and 65535.
Key Displays the authentication key.
Time out Displays the number of time outs for replies. The value can be between 1 and 30 seconds.
Retries Displays the number of retries. The value can be between 1 and 30.
Priority Displays the server priority as High or Low.
Usage Type Displays the server usage type as Login, 802.1X, or All.
Action
Edit Click to Edit modify the en try.
Modify Click Delete to delete the entry.
Table 152 Configuration > AAA > RADIUS > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RADIUS
Server Enter the server name(s) as an IP address or a domain name.
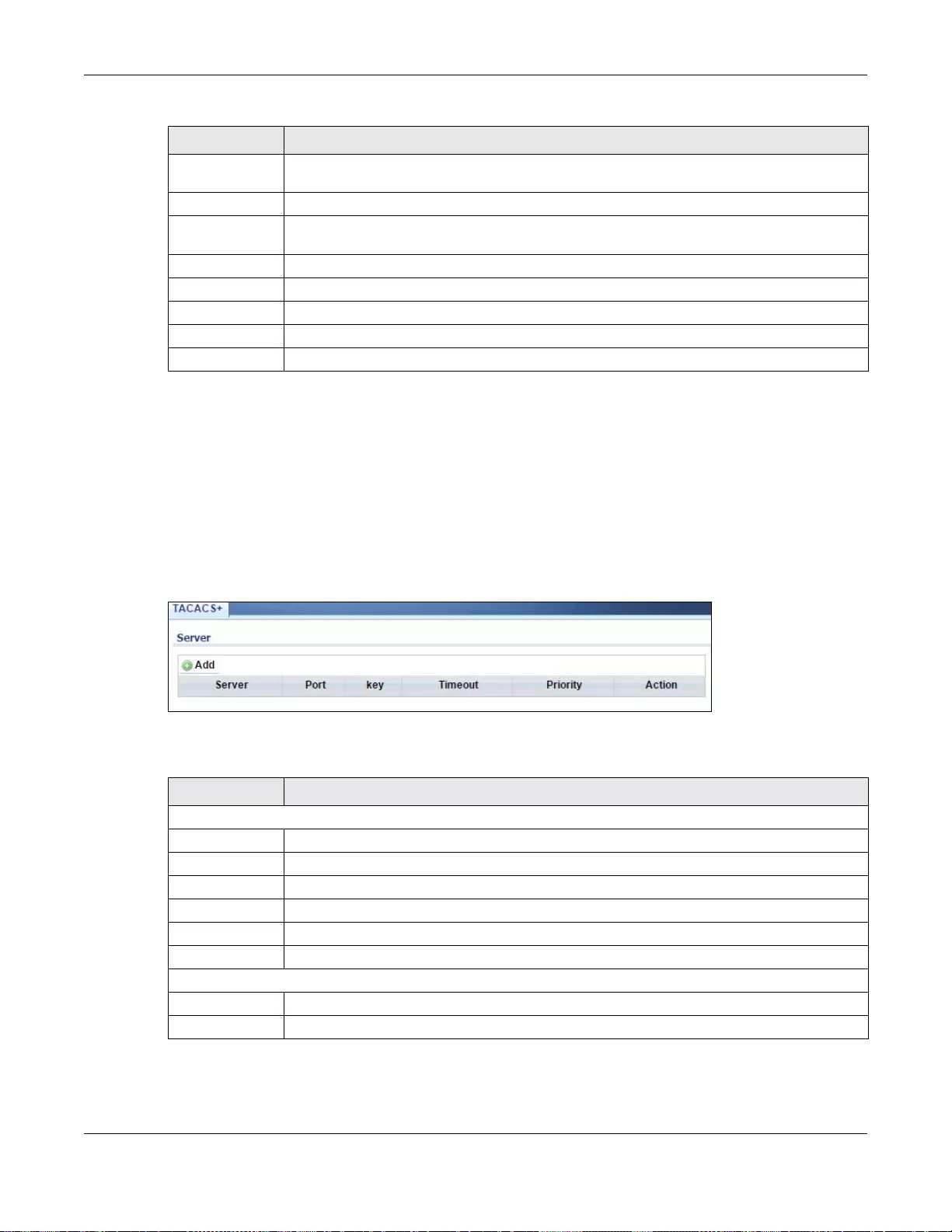
Chapter 30 Configuration: AAA
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
194
30.4 TACACS+
30.4.1 The TACACS+ Screen
Use this screen to configure the TACACS+ settings. Click Configuration > AAA > TACACS+ to
open this screen.
Figure 186 Configuration > AAA > TACACS+
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Authentication
Port Enter the authentication port number(s) as a value between 0 and 65535.
Key String Enter the authentication key string: 0 - 63 ASCII Alphanumeric Characters.
Timeout for
Reply Enter the number of time outs for replies. The value can be between 1 and 30 seconds.
Retries Enter the number of retries. The value can be between 1 a nd 30.
Server Priority Select the server priority as High or Low.
Usage Select the server usage type as Login, 802.1X, or All.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 152 Configuration > AAA > RADIUS > Add/Modify (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 153 Configuration > AAA > TACACS+
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server
Add Click Add to create a new Server entry.
Server Displays the server name(s) as an IP address or a domain name.
Port Displays the port number(s) as a value between 0 and 65535.
Key Displays the authentication key.
Timeout Displays the number of time outs for replies. The value can be between 1 and 30 seconds.
Priority Displays the priority as High or Low.
Action
Edit Click to Edit modify the en try.
Modify Click Delete to delete the entry.

Chapter 30 Configuration: AAA
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
195
30.4.2 The TACACS+ Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the TACACS+ settings. Click Configuration > AAA > TACACS+ >
Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 187 Configuration > AAA > TACACS+ > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 154 Configuration > AAA > TACACS+ > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
TACACS+
Server Enter the server name(s) as an IP address or a domain name.
Port Enter the port number(s) as a value between 0 and 65535.
Key String Enter the authentication key string: 0 - 63 ASCII alphanumeric characters.
Timeout for
Reply Enter the number of time outs for replies. The value can be between 1 and 30 seconds.
Priority Select the server priority as High or Low.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
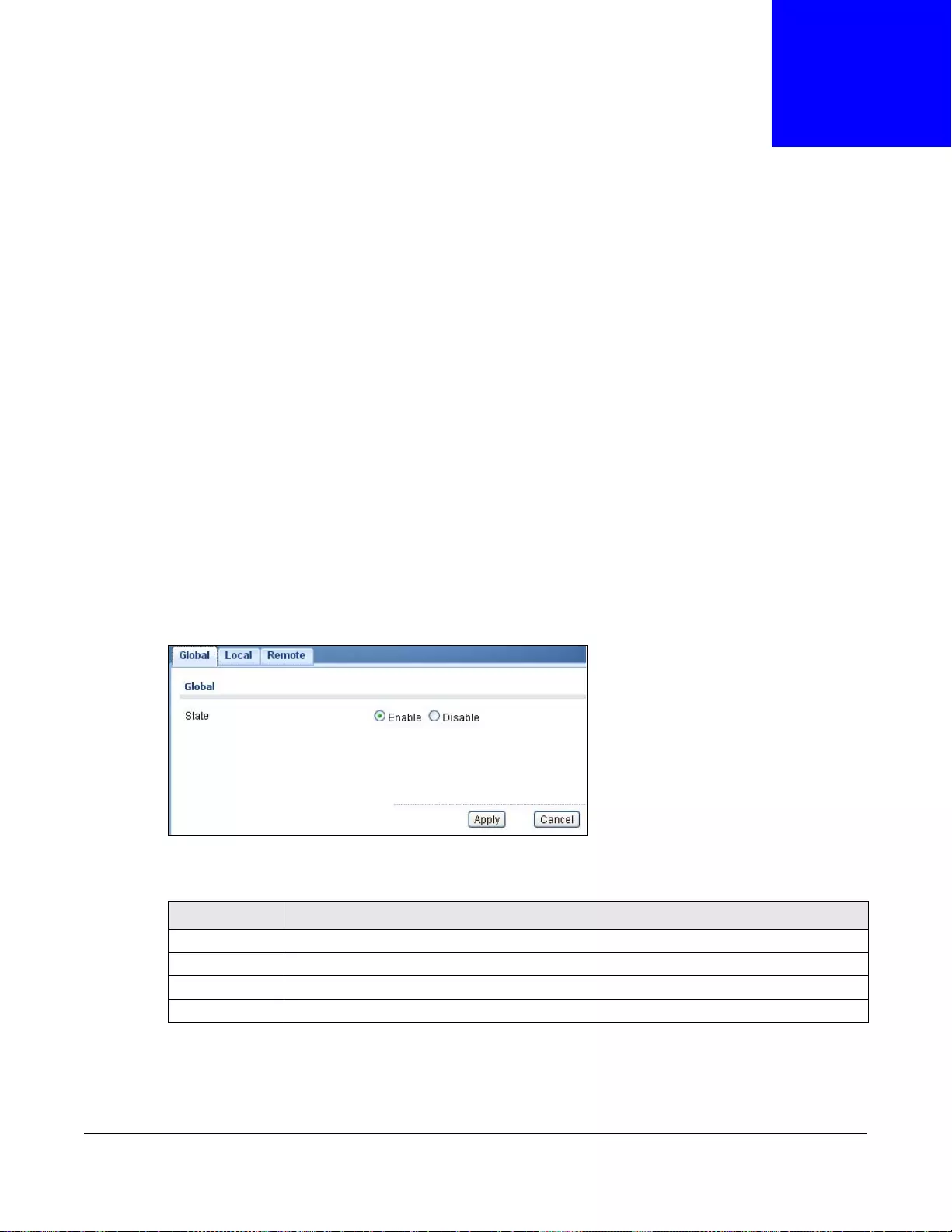
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
196
CHAPTER 31
Configuration: Management
31.1 Overview
This section provides information for Management in Configuration.
Use the Management screens to configure settings on the Switch. The following submenus are
accessed from this section: Syslog, SNMP, Error Disable, HTTP/HTTPS, Users, Remote
Access Control.
31.2 Syslog
31.2.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Management > Syslog to
open this screen.
Figure 188 Configuration > Management > Syslog
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 155 Configuration > Management > Syslog
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the global logging setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
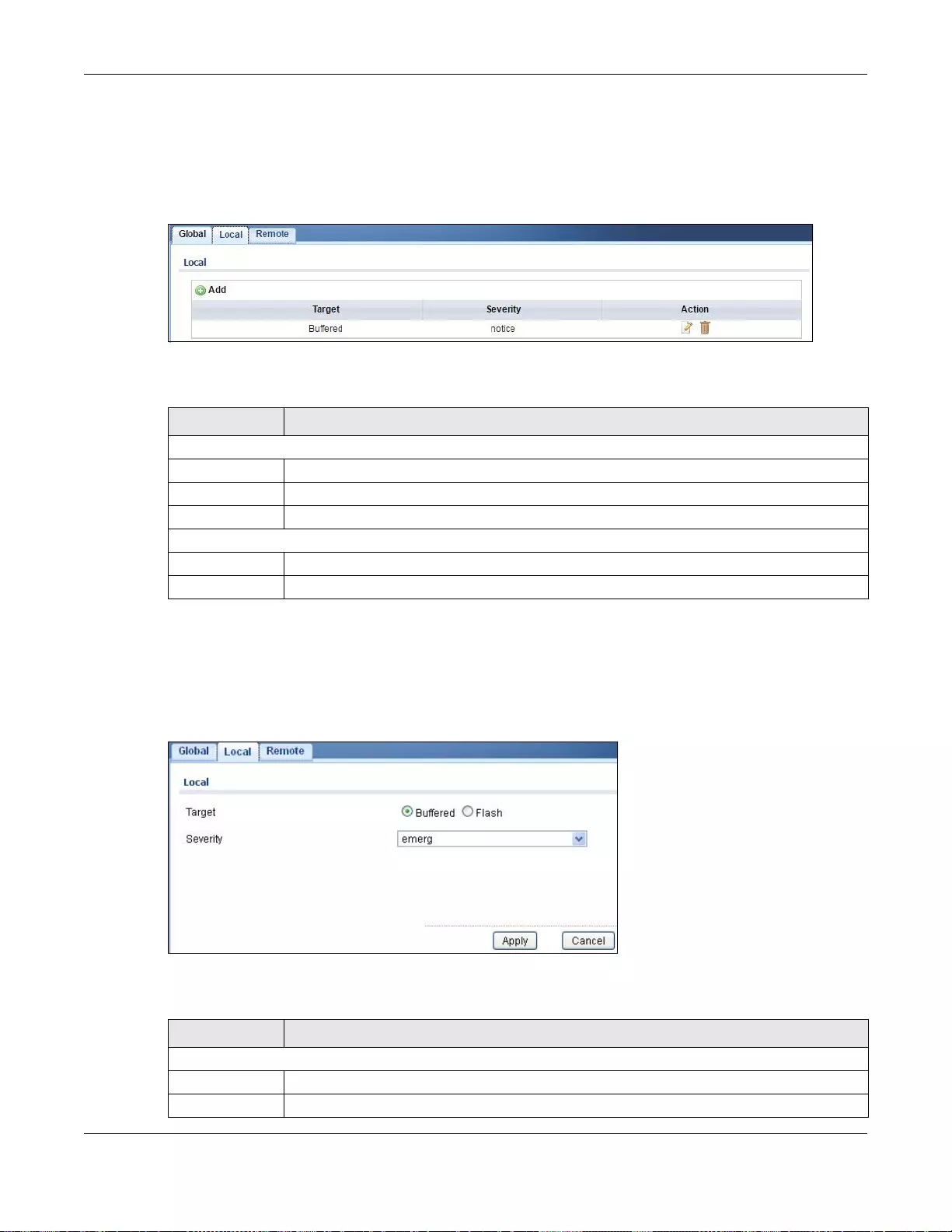
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
197
31.2.2 The Local Screen
Use this screen to view the Local settings. Click Configuration > Management > Syslog >
Local to open this screen.
Figure 189 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Local
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.2.3 The Local Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Local settings. Click Configuration > Management > Syslog >
Local > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 190 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Local > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 156 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Local
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local
Add Click Add to create a new Local entry.
Target Displays the local storage target for logging messages. The options are Buffered or Flash.
Severity Displays the severity level of messages to be written to logs.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
Table 157 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Local > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local Add
Target Select the local storage target for logging messages. The options are Buffered or Flash.
Severity Select the severity level of messages to be written to logs.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
198
31.2.4 The Remote Screen
Use this screen to view the Remote settings. Click Configuration > Management > Syslog >
Remote to open this screen.
Figure 191 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Remote
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.2.5 The Remote Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Remote settings. Click Configuration > Management > Syslog
> Remote > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 192 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Remote > Add/Modify
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 157 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Local > Add/Modify (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Table 158 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Remote
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Local
Add Click Add to create a new Remote entry.
Server Displays the server information which includes the server IP address and port number.
Severity Displays the severity level of messages to be written to logs.
Facility Displays the facility designation of the rem ote entry.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
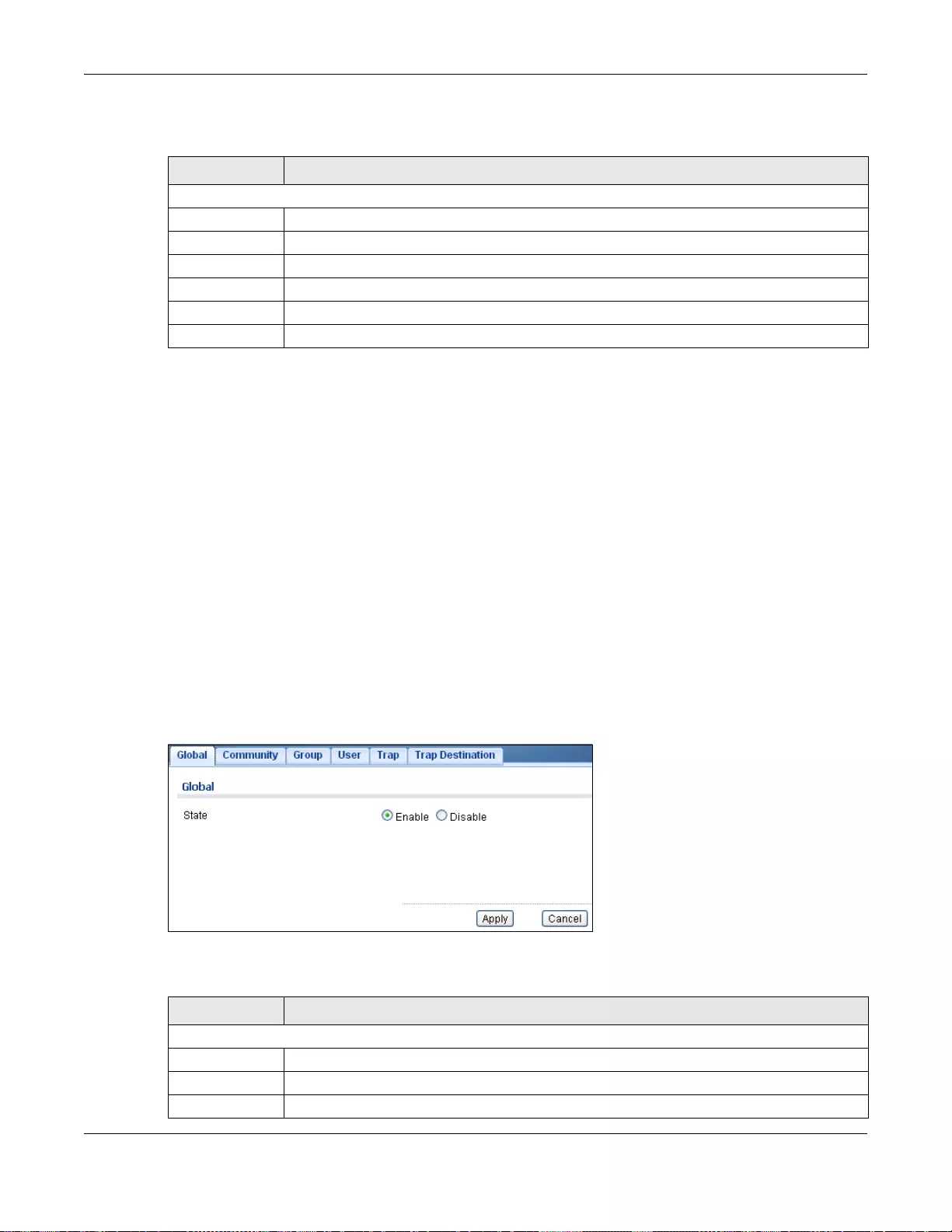
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
199
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3 SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol used to manage and
monitor TCP/IP-based devices. SNMP is used to exchange management information between the
network management system (NMS) and a network element (NE). A manager station can manage
and monitor the Switch through the network via SNMP version 1 (SNMPv1), SNMP version 2c or
Table 170 Access Control Overview Console Port SSH Telnet FTP W eb SNMP One session Share up to
nine sessions One session Up to five accounts No limit Chapter 42 Access Control 338 GS3700/
XGS3700 Series User’s Guide SNMP version 3. The next figure illustrates an SNMP management
operation. SNMP is only available if TCP/IP is configured.
31.3.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to view the Global settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP to
open this screen.
Figure 193 Configuration > Management > SNMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 159 Configuration > Management > Syslog > Remote > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Remote
Server Enter a server IP address or domain name.
Server Port Enter a server port number.
Severity Select the severity level of messages to be written to logs.
Facility Select the facility from the dropdown list.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 160 Configuration > Management > SNMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the global SNMP setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
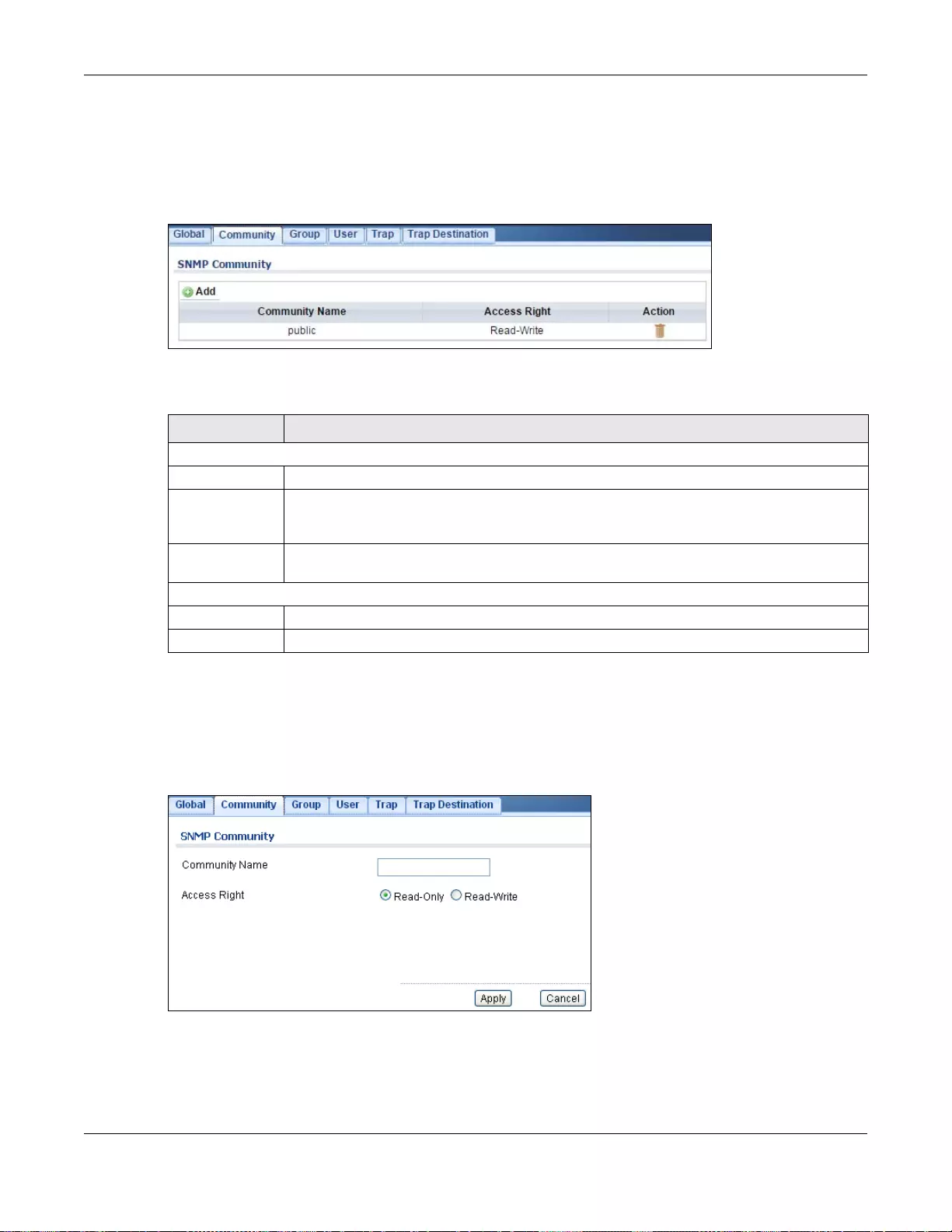
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
200
31.3.2 The Community Screen
Use this screen to view the Community settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP >
Community to open this screen.
Figure 194 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Community
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.3 The Community Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Community settings. Click Configuration > Management >
SNMP > Community > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 195 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Community > Add/Modify
Table 161 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Community
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP community
Add Click Add to create a new SNMP Community entry.
Community
Name Displays a string identifying the community name that this entry should belong to. The
allowed string length is 1 to 20, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to
126.
Access Right Displays the acce ss mode for this entry. The possible values are Read-Only and Read-
Write.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
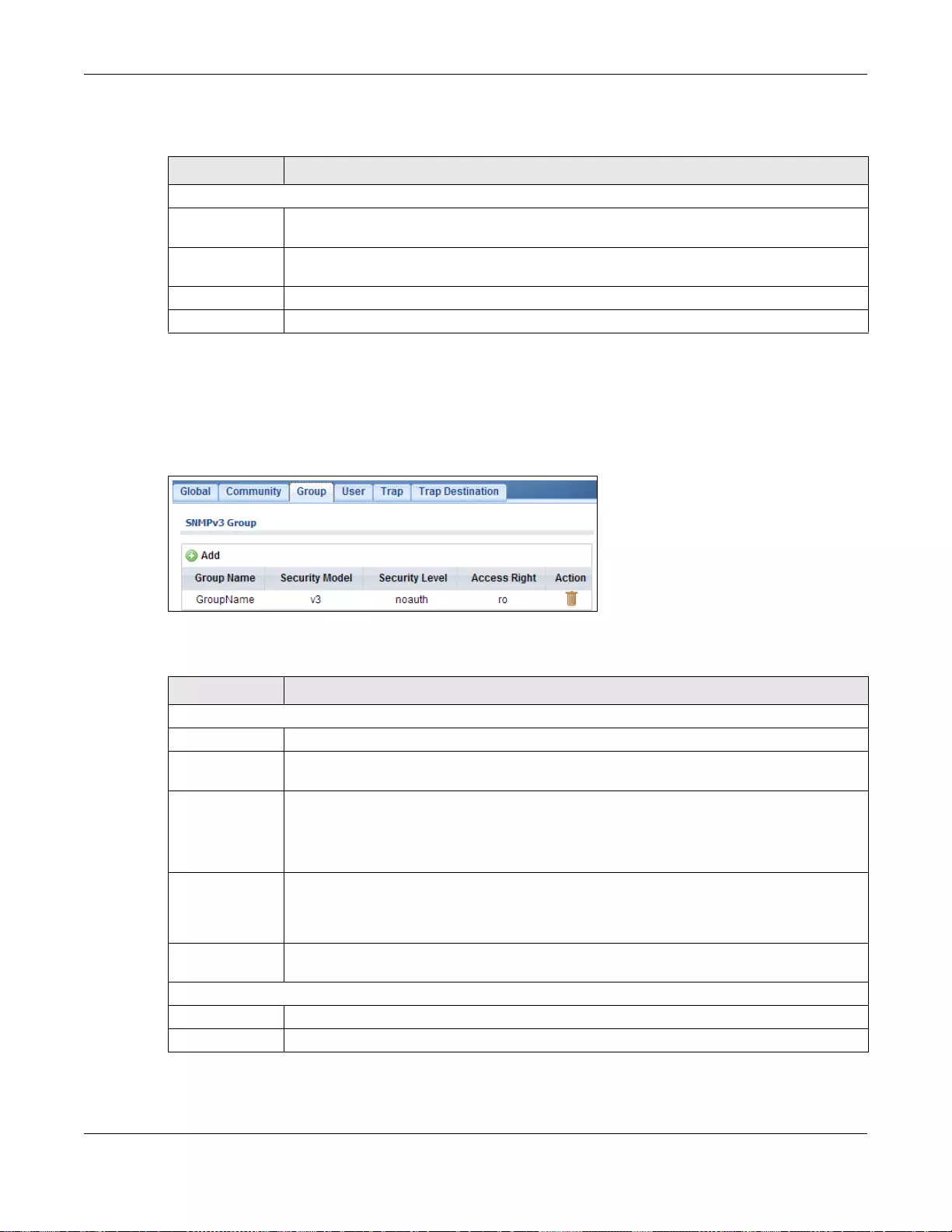
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
201
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.4 The Group Screen
Use this screen to view the Group settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP >
Group to open this screen.
Figure 196 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Group
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 162 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Community > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP Community
Community
Name Enter a string identifying the community name that this entry should be long to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 20, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Access Right Select the access mode for this entry. The possible values are Read-Only and Read-
Write.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 163 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Group
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMPv3 Group
Add Click Add to create a new SNMPv3 Group entry.
Group Name Displays a string identifying the group name that this entry sh ould belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Security Model Displays the security model that this entry belongs to. Possible security models are:
•any: Any security model accepted(v1|v2c|usm).
•v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
•v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
•usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
Security Level Displays the security model that this entr y belongs to. Possible security models are:
•NoAuth, NoPriv: No authentication and no privacy.
•Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and no privacy.
•Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
Access Right Displays the acce ss mode for this entry. The possible values are Read Only and Read-
Write.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.
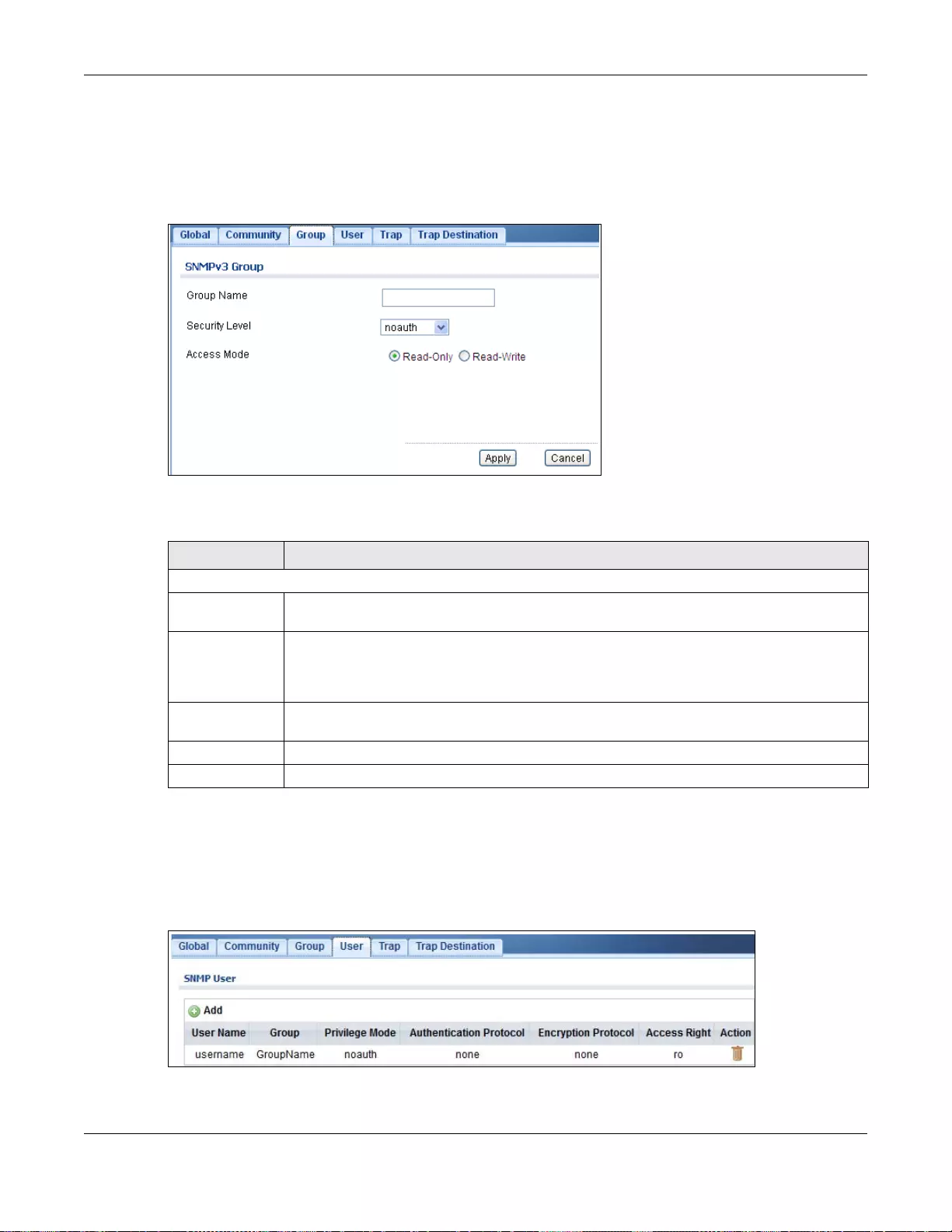
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
202
31.3.5 The Group Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Group settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP >
Group > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 197 Configuration > M anagement > SNM P > Group > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.6 The User Screen
Use this screen to view the User settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP > User
to open this screen.
Figure 198 Configuration > Management > SNMP > User
Table 164 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Group > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMPv3 Group Edit
Group Name Enter a string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Security Level Select the security model that this entry belongs to. Possible security models are:
•NoAuth, NoPriv: No authentication and no privacy.
•Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and no privacy.
•Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
Access Right Select the access mode for this entry. The possible values are Read-Only and Read-
Write.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
203
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.7 The User Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the User settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP >
User > Add/Modif y to open this screen.
Figure 199 Configuration > Ma nagement > SNMP > User > Add/Modi fy
Table 165 Configuration > Management > SNMP > User
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP User
Add Click Add to create a new SNMP user.
User Name Displays a string identifying the user name that this entry belongs to. The allowed string
length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Group Displays a string identifying the group name that this entry belongs to. Th e allowed string
length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Privilege Mode Displays the privilege mode that this entry belongs to.
Authentication
Protocol Displays the authentication protocol that this entry belongs to. Possible authentication
protocols are:
•None: No authentication protocol.
•MD5: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses MD5 authentication protocol.
•SHA: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses SHA authentication protocol.
The value of the secu rity level cannot be m odified if the entry already exists. That means
you must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
Encryption
Protocol Displays the encryption protocol that this entry belongs to.
Access Right Displays the acce ss mode for this entry. The possible values are Read-Only and Read-
Write.
Action
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
204
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.8 The Trap Screen
Use this screen to configure the Trap settings. Click Configuration > Management > SNMP >
Trap to open this screen.
Figure 200 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap
Table 166 Configuration > Management > SNMP > User > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP User
User Name Enter a string identifying the user name that this entry belongs to. The allowed string
length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Group Name Enter a string identifying the group name that this entry belongs to. The allowed string
length is 1 to 30, and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Auth Protocol Select the authentication protocol that this entry belongs to. Possible authentication
protocols are:
•MD5: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses MD5 authentication protocol.
•SHA: An optional flag to indicate that this user uses SHA authentication protocol.
The value of the secu rity level cannot be m odified if the entry already exists. That means
you must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
Auth Password Enter a string identifying the authentication password phrase. For MD5 authentication
protocol, the allowed string length is 8 to 32. For SHA authentication protocol, the allowed
string length is 8 to 32. The allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Priv password Enter a string identifying the privacy password phrase. The allowed string length is 8 to 64
and the allowed content is ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
205
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.3.9 The Trap Destination Screen
Use this screen to view the Trap Destination settings. Click Configuration > Management >
SNMP > Trap Destination to open this screen.
Figure 201 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap Destination
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 167 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP Trap
SNMP Authfailure
Trap State Sel ect the SNMP entity is permitted to generate authentication failure traps. Possible
modes are:
•Enabled: Enable SNMP trap authentication failure.
•Disabled: Disable SNMP trap authentication failure.
SNMP LinkupDown
Trap State Select th e SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation. Possible modes are:
•Enabled: Enable SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation.
•Disabled: Disable SNMP trap link-up and link-down mode operation.
SNMP Warm-Start
Trap State Reboot using software or hardware button reboot.
SNMP Cold-Start
Trap State Reboot though power off.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 168 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap Destination
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP Trap Host
Add Click Add to create a new SNMP Trap Host entry.
Server Displays a string identifying the server address that this entry belongs to.
Version Indicates the SNMP trap supported version. Possible versions are:
•SNMP v1: Set SNMP trap supported version 1.
•SNMP v2c: Set SNMP trap supported versi on 2c.
•SNMP v3: Set SNMP trap supported version 3.
Community/
User Name Displays the community / user name that this entry belongs to.
UDP Port Displays the trap use destination for the UDP port.
Action
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
206
31.3.10 The Trap Destination Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Trap Destination settings. Click Configuration > Management
> SNMP > Trap Destination > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 202 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap Destination > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.4 Error Disable
31.4.1 The Error Disabled Screen
Use this screen to configure the Error Disabled settings. Click Configuration > Management >
Error Disable to open this screen.
Table 169 Configuration > Management > SNMP > Trap Destination > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SNMP Trap Destination
Server Enter the IP address of the server or a string identifying the server address that this entry
belongs to.
Version S elect the SNMP trap supported version. Possible versions are:
•SNMP v1: Set SNMP trap supported version 1.
•SNMP v2c: Set SNMP trap supported version 2c.
•SNMP v3: Set SNMP trap supported version 3.
Community
Name Displays the community name that this entry belongs to.
User Name Displays the user name that this entry belongs to.
UDP Port Enter a UDP port for this entry.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
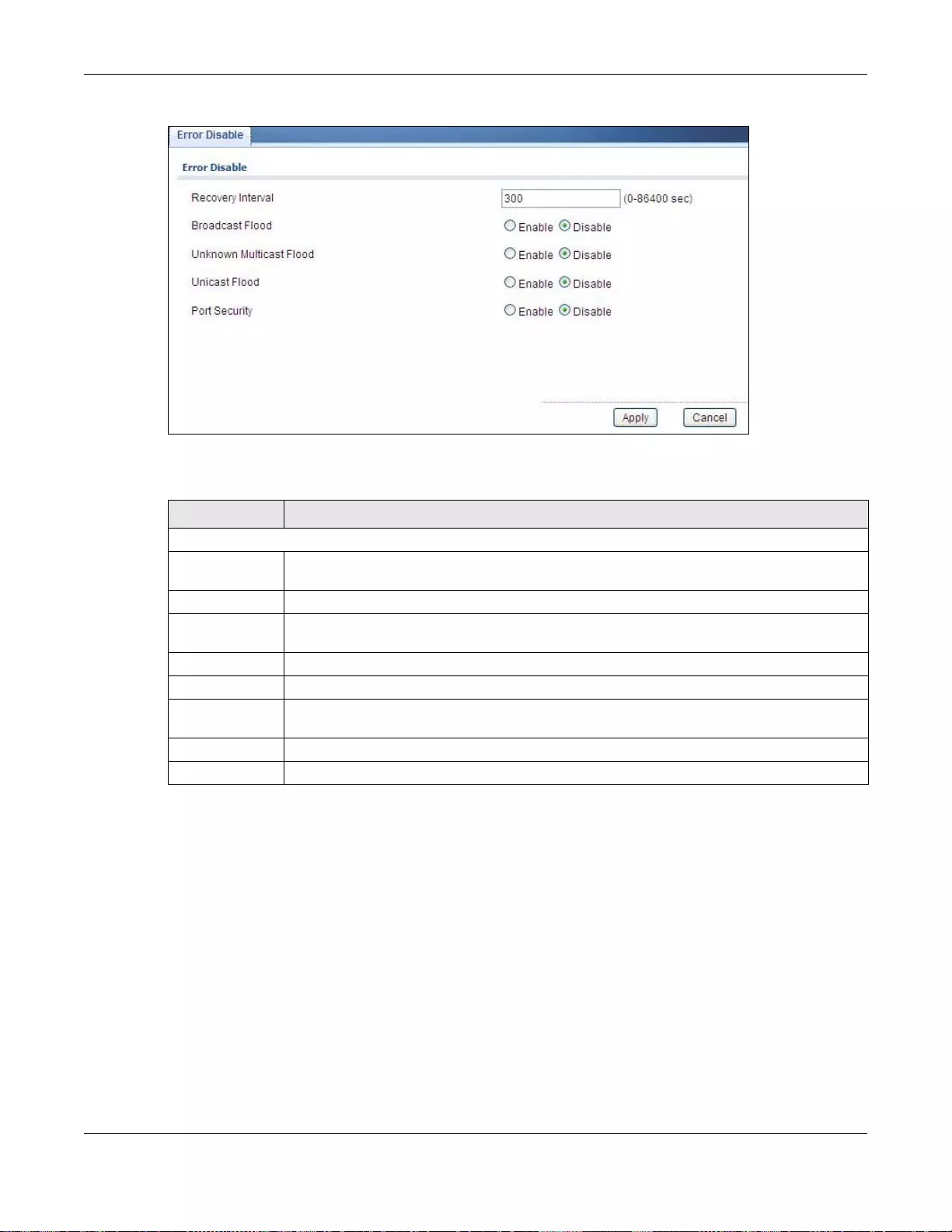
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
207
Figure 203 Configuration > Management > Error Disable
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.5 HTTP/HTTPS
31.5.1 The HTTP Screen
Use this screen to configure the HTTP settings. Click Configuration > Management > HTTP/
HTTPS to open this screen.
Table 170 Configuration > Management > Error Disable
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Error Disabled Settings
Recovery
Interval Enter the recovery interval value.
Broadcast Flood Select an option to Enable or Disable the Broadcast Flood.
Unknown
Multicast Flood Select an option to Enable or Disable the Unknown Multicast Flood.
Unicast Flood Select an option to Enable or Disable the Unicast Flood.
Port Security Select an option to Enable or Disable the Port Security.
POE Inline
Power Select an option to Enable or Disable the POE Inline Power.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
208
Figure 204 Configuration > Management > HTTP/HTTPS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.5.2 The HTTPS Screen
Use this screen to configure the HTTPS settings. Click Configuration > Management > HTTP/
HTTPS > HTTPS to open this screen.
Figure 205 Configuration > Management > HTTP/HTTPS > HTTPS
Table 171 Configuration > Management > HTTP/HTTPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
HTTP
State Select the HTTP mode operation.
Possible modes are:
•Enabled: Enable HTTP mode operation.
•Disabled: Disable HTTP mode operation.
Authentication
Method Select the authentication method from the dropdown list.
Session Timeout Enter the session timeout value. The timeout can be between 0 and 86400 minutes.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
209
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.6 Users
31.6.1 The Users Screen
Use this screen to configure the Users settings. Click Configuration > Management > Users to
open this screen.
Figure 206 Configuration > Management > Users
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 172 Configuration > Management > HTTP/HTTPS > HTTPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
HTTPS
State Select the HTTPS mode operation.
Possible modes are:
•Enabled: Enable HTTPS mode operation.
Authentication
Method Select the authentication method from the dropdown list.
Session Timeout Enter the session timeout value. The timeout can be between 0 and 86400 minutes.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Table 173 Configuration > Management > Users
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Users
Add Click Add to create a new User entry.
User A string identifying the user name that this entry should belong to. The allowed string
length is 1 to 32. The valid user name is a com b ination of letter s, numbers and
underscores.
Encryption Displays the encryption status. The va lues can be Clear Text, Encrypted, and No
Password.
Password D ispl ays the password of the user. The a ll o wed string length is 0 to 32.
Privilege Level Displays the privilege level of the user, range: admin and user.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
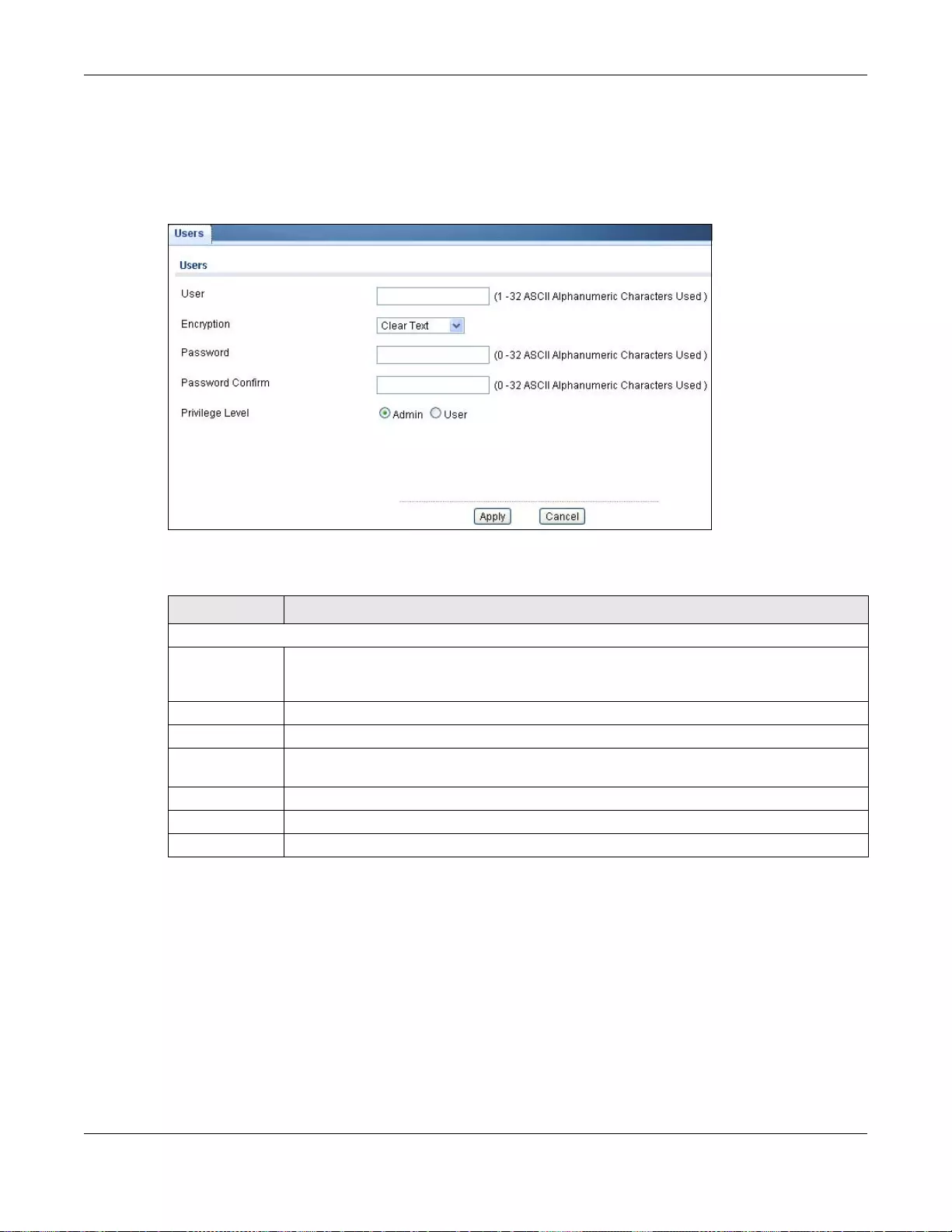
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
210
31.6.2 The Users Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Users settings. Click Configuration > Management > Users >
Add/Modify to open this screen.
Figure 207 Configuration > Ma nagement > User s > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.7 Remote Access Control
31.7.1 The Global Screen
Use this screen to configure the Global settings. Click Configuration > Management > Remote
Access Control to open this screen.
Table 174 Configuration > Management > Users > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add New Local User
User Enter a string identifying the user name that this entry should belong to. The allowed string
length is 1 to 32. The valid user name is a com b ination of letter s, numbers and
underscores.
Encryption Select the encryption type. The v alues can be Clear Text, Encrypted, an d No Password.
Password Enter a password for the user. The allowed string length is 0 to 32.
Password
Confirm Enter the same password again to confirm.
Privilege Level Select the pri vilege level of the user range: admin and user.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
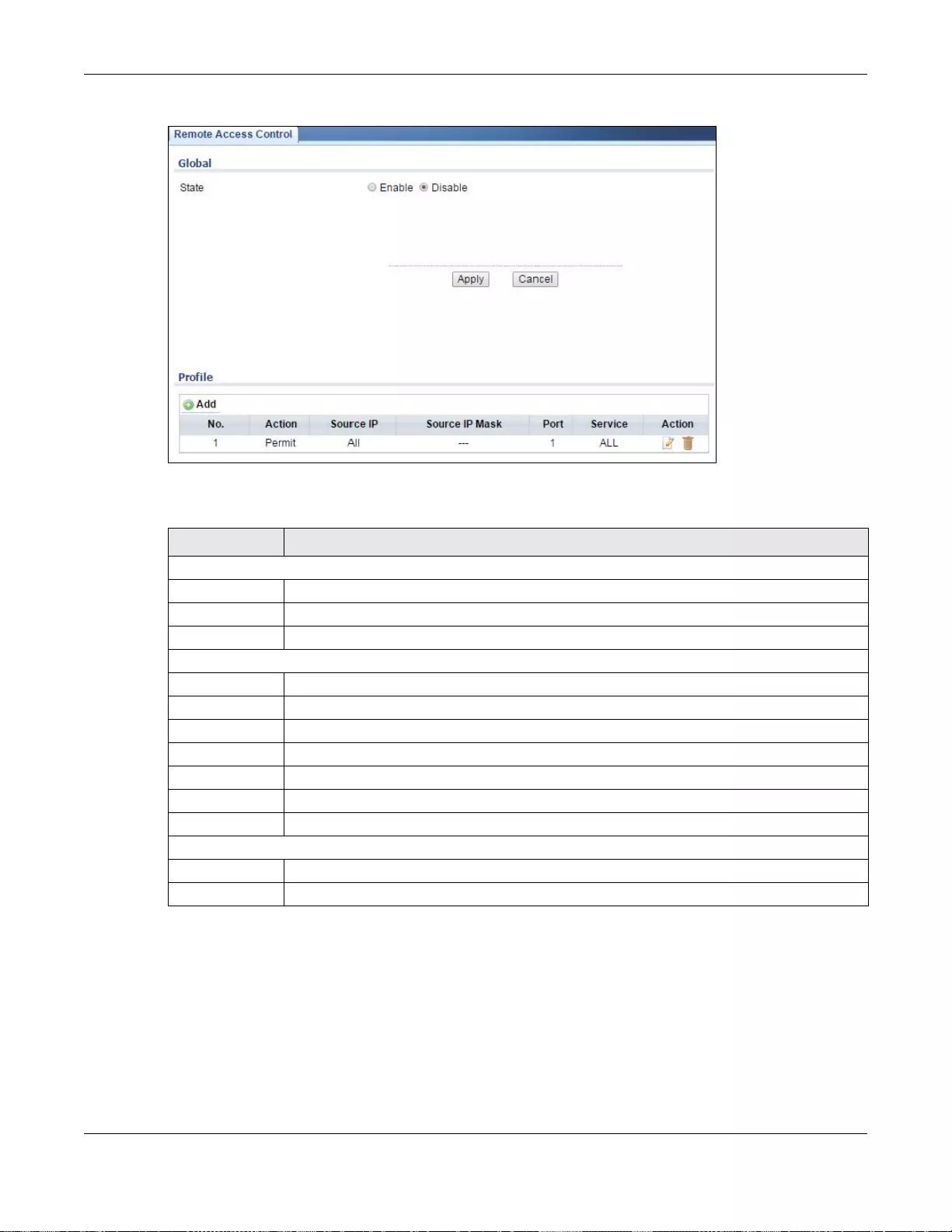
Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
211
Figure 208 Configuration > Management > Remote Access Control
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
31.7.2 The Profile Add/Modify Screen
Use this screen to configure the Profile settings. Click Configuration > Management > Remote
Access Control > Profile > Add/Modify to open this screen.
Table 175 Configuration > Management > Remote Access Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Global
State Select the global remote access setting to be enabled or disabled.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Profile
Add Click Add to create a new profile entry.
No. Displays the priority level of the entry. The value can be between 1 and 16.
Action Displays the action value . The values are Permit or Deny.
Source IP Display the source IP value.
Source IP Mask Displays the source IP wildcard.
Port Display the port value.
Service Display the service used for remote access. The values are ALL, HTTP, HTTPS, or SNMP.
Action
Edit Click Edit to make changes to the entry.
Delete Click Delete to remove the entry.

Chapter 31 Configuration: Management
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
212
Figure 209 Configuration > Management > Remote Access Control > Profile > Add/Modify
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 176 Configuration > Management > Remote Access Control > Profile > Add/Modify
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Management Access List Add
No. Enter the priority level of the entry. Th e value can be between 1 and 16.
Action Select the action value. The values are Permit or Deny.
Port Select a value in Available and click the Add (>) icon to transfer to the Acting column.
Select a v alue in Acting and click the Remove (<) icon to tr ansfe r to the A v ailabl e column .
Source Select the source IP value. The options are ALL or IPv4/Wildcard.
IPv4/Wildcard Select and enter the IPv4/Wildcard source.
Service Select the service to use for remote access. The values are ALL, HTTP, HTTPS, or SNMP.
Apply Click Apply to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
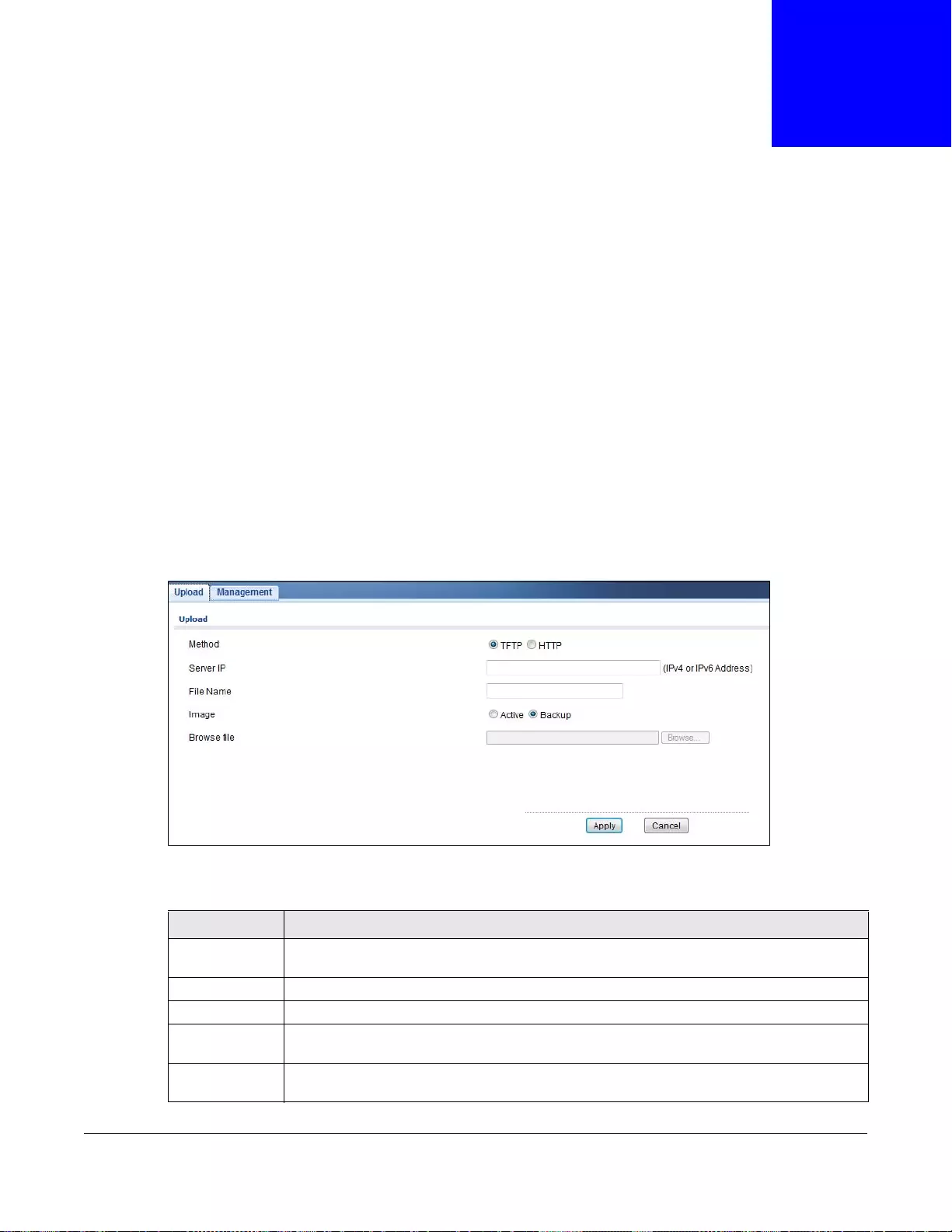
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
213
CHAPTER 32
Maintenance
32.1 Firmware Upgrade
32.1.1 Overview
Firmware updates contain bug fixes and fix es for security vulnerabilities. It is recommended to ke ep
the Switch’s firmware up to date. You can upgrade the Switch’s firmware manually using a file
downloaded on your computer or through the online web configu rator.
Note: Be sure to upload the correct model firmware as uploading the wrong model
firmware may damage your device.
From the Maintenance screen, display the Upload screen as shown next. Use this screen to
upgrade the Switch firmware.
Figure 210 Maintenance > Firmware > Upload
The following table describes the labels under Upload.
Table 177 Maintenance > Firmware > Upload
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Method Choose HTTP to use the web configurator for the firmware upload. Alternatively, choose
TFTP to download the firmware from a TFTP server.
Server IP To download from a TFTP server, enter the TFTP server IP address.
File Name Enter the name of the firmware file on the TFTP server.
Image Choose Backup to upload the firmware file as the backup image. Alternatively, choose
Active to upload the firmware file as the active image.
Browse File Browse to the path on your computer where the firmware you want to upload to be the
active image is kept.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
214
Upgrade the firmware from a file on a server
Follow the steps below to upgrade the firmware from a TFTP server.
1. In Method, choose TFTP.
2. In Serv er IP, enter the TFTP server IP address.
3. In File Name, enter the name of the firmware file on the TFTP server.
4. In Image, choose Backup to upload the firmware file as the backup image.
OR
Choose Active to upload the firmware file as the active image.
5. Click Apply to upgrade the chosen image.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
After the firmware upgrade process is complete, see the System Info screen to verify your current
firmware version number.
32.1.2 Upgrade the firmware from a file on your computer
Note: For manual upgrade, make sure you have downloaded (and unzipped) the correct
model firmware and version to your computer before uploading it to the device.
The file name should have a .bin extension.
F ol lo w the s tep s bel ow to upgrade the firmware from a file on your computer.
1. In Method, choose HTTP.
2. In Image, choose Active to upload the firmware file on the active partition image.
OR
Choose Backup to upload the firmware file on the Backup partition image.
3. Click Browse to display the Choose File screen from which you can locate the firmware file in
the bin format on your computer.
4. Click Apply to upload the chosen file.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
After the firmware upgrade process is complete, see the System Info screen to verify your current
firmware version number.
32.2 Firmware Management
32.2.1 Overview
The Firmware Management screen provides instant access to the firmware versions installed on
your Switch. Active and backup firmware versions are saved as images on flash partitions. The
backup image is used when the active partition has problems during boot.
From the Maintenance screen, display the Firmware Management screen as shown next. Use
this screen to view image information and activate an image.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
215
Figure 211 Maintenance > Firmware > Management
The following table describes the labels shown under Images Information.
32.2.2 Activate the Backup Image
The current active partition is shown under Image Select.
Follow the steps below to choose the backup image if you are facing problems with the active
partition during boot.
1. In Acti ve Image, choose Partition0 (Backup).
2. Click Apply to activate the backup image.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
32.3 Backup a Configuration File
32.3.1 Overview
You can save various “snapshots” of your device to the server or your computer and restore them
at a later date, if required.
Table 178 Maintenance > Firmware > Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Flash Part it ion Displays the partition number.
Firmware
Version Displays the name given to the partition image, if any.
This field also displays the imagine type: Active or Backup.
Image Size Displays the size of the partition image in bytes.
Created Time Displays the dat e and t im e wh en t he im age was created in the Coordinated Uni versal Time
(UTC) format.
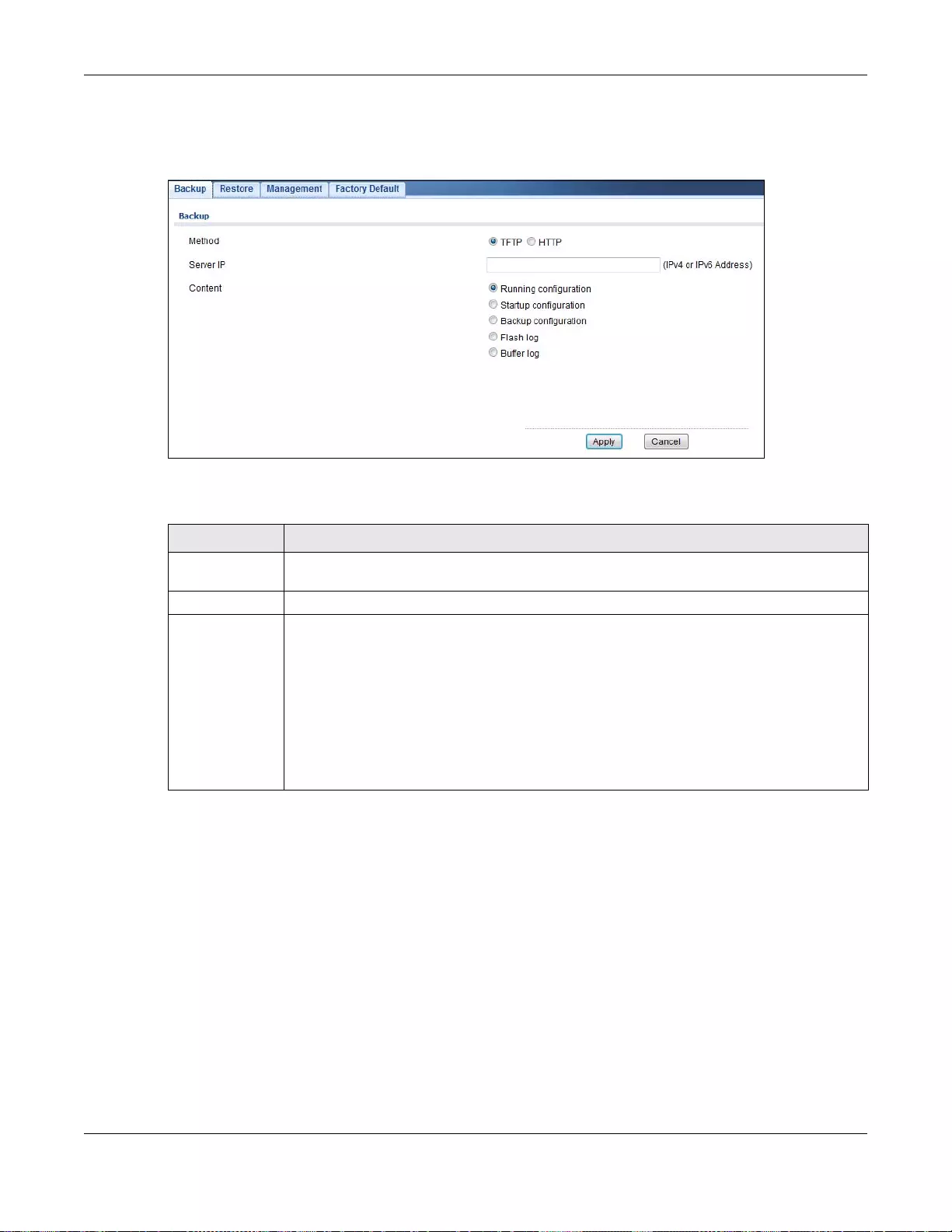
Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
216
From the Maintenance screen, display the Backup screen as shown next. Use this screen to back
up your current Switch configuration and log files to a server or as local files to your computer.
Figure 212 Maintenance > Configuration > Backup
The following table describes the labels under Backup.
32.3.2 Back up configuration or log files to a server
Follow the steps below to backup configuration or log files to a TFTP server.
1. In Method, choose TFTP.
2. In Serv er IP, enter the TFTP server IP address.
3. In Content, choose any one file type.
4. Click Apply to save a snapshot of your current configuration to the TFTP server.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
32.3.3 Back up configuration or log files to your computer
Follow the steps below to backup configuration or log files to your computer.
Table 179 Maintenance > Configuration > Backup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Method Choose HTTP to use the web configurator to backup the configuration. Alternatively,
choose TFTP to upload the snapshot to a TFTP server.
Server IP To upload the backup to a TFTP server, en ter the TFTP server IP address.
Content Choose the type of file for backup . You can back up configuration files (running, startup, or
backup) or log files (flash or buffer).
There are three different types of configuration files:
Startup - this is the configuration used when the switch is booting up.
Running - this is the configuration when the switch is running.
Backup - this is sa ved in th e Swit ch. If yo u make chan ges to the current configur ation , and
there are pr oblems , y ou can rev ert t o th e Bac ku p confi guration without ha vi ng to res tore a
new file.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
217
1. In Method, choose HTTP.
2. In Content, choose any one file type.
3. Click Apply to display the Save File screen from which you can save the configuration file in
the cfg format or the log file in the log format to your computer.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
32.4 Restore a Configuration File
32.4.1 Overview
You can restore a previously saved device configuration from the server or your computer.
From the Maintenance screen, display the Restore screen as shown next. Use this screen to
restore a previously saved configuration from a server or your computer.
Figure 213 Maintenance > Configuration > Restore
The following table describes the labels under Configuration Restore.
32.4.2 Restore the configuration from a file on a server
Follow the steps below to restore the configuration from a server.
1. In Method, choose TFTP.
2. In Serv er IP, enter the TFTP server IP address.
3. In File Name, enter the name of the configuration file on the TFTP server.
Table 180 Maintenance > Configuration > Restore
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Method Choose HTTP to use the web confi gurator for restoring the configur ati on file. Alt ernat iv ely,
choose TFTP to download the snapshot from a TFTP server.
Server IP To download from a TFTP server, enter the TFTP server IP address.
File Name Enter the name of the configuration file on the TFTP server.
Browse File Browse to the path on your computer where the configur ation you w ant to up load to be the
active image is kept.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
218
4. Click Apply to restore to the chosen file as the running configuration.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
32.4.3 Restore the configuration from a file on your computer
Follow the steps below to restore the configuration from a file on your computer.
1. In Method, choose HTTP.
2. Click Browse to display the Choose File screen from which you can locate the configuration
file in the cfg format on your computer.
3. Click Apply to restore to the chosen file as the running configuration.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
32.5 Manage Configuration Files
32.5.1 Overview
The Configuration Management screen provides instant access to the configuration files of your
Switch. You can overwrite the startup and backup configurations with the current run ning, startup,
or backup configuration file.
From the Maintenance screen, display the Management screen as shown next. Use this screen to
replace startup and backup configuration files.
Figure 214 Maintenance > Configuration > Management
Follow the steps to overwrite the startup or backup configuration file.
1. In Source File, select the file to be used as a reference.
2. In Destination File, select the file to be overwritten.
3. Click Apply to restore to overwrite the destination file with the source file.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
219
32.6 Reset to Factory Defaults
32.6.1 Overview
You can reset the Switch to it’s original settings.
From the Maintenance screen, display the Factory Default screen as shown next. Use this screen
to reset the Switch back to factory defaults.
Table 181 Maintenance > Configuration > Factory Default
32.6.2 Reset the Switch to Factory Defaults
Follow the steps below to reset the Switch back to factory defaults.
1. Click Restore.
2. Click OK to reset all Switch configurations to the factory defaults. W ait for the Switch to restart.
This takes up to two minutes.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
Note: If you want to access the Switch web configurator again, you may need to change
the IP address of your computer to be in the same subnet as that of the default
Switch IP address (192.168.1.1).
32.7 Network Diagnostics
Use the network utilities to perform diagnostics.
32.7.1 Port Test
Click Maintenance > Diagnostics > Port Test in the navigation panel to open this screen. Use
this screen to perform an internal loopback test on an ethernet port.

Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
220
Figure 215 Maintenance > Diagnostics > Port Test
Follow the steps to perform the port test.
1. In Port Test, select the port number from the Port drop-down list.
2. Click Test to start the port test.
The test results are displayed in Test Results.
32.7.2 IPv4 Ping Test
Click Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv4 in the navigation panel to open this screen.
Use this screen to ping an IPv4 server.
Figure 216 Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv4
The following table describes the labels under Ping Test.
Table 182 Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv4
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address Enter the address of the target host server.
Count Ente r the number of ping pac ke ts to s end. The range is 1 to 5 packets; the de fault count is
4.
Interval Enter the time in seconds between sending ping packets. The range is 1 to 5 seconds; the
default is 1 second.
Size Enter the individual packet size in bytes. The range is 8 to 5120 bytes; the default is 56
bytes.
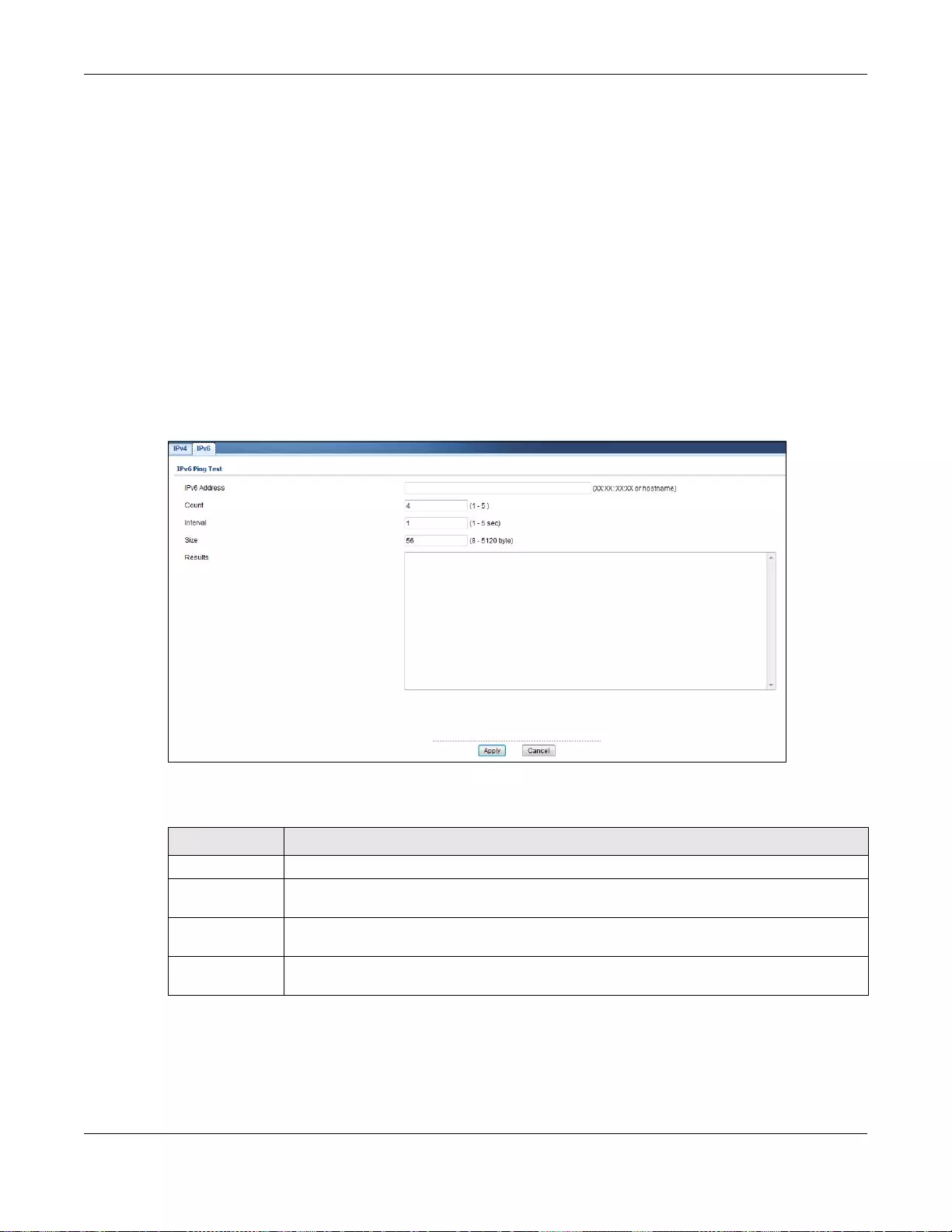
Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
221
Follow the steps to perform a ping test.
1. In IP Address, enter the IPv4 address.
2. In Count, enter the number of ping packets.
3. In Interval, enter the time interval in seconds.
4. In Size, enter the packet size in bytes
5. Click Apply to perform the ping test.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The test results are displayed in Results.
32.7.3 IPv6 Ping Test
Click Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv6 in the navigation panel to open this screen.
Use this screen to ping an IPv6 server.
Figure 217 Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv6
The following table describes the labels in IPv6 Ping Test.
Follow the steps to perform a ping test.
1. In IP Address, enter the IPv6 address.
2. In Count, enter the number of ping packets.
3. In Interval, enter the time interval in seconds.
4. In Size, enter the packet size in bytes
Table 183 Maintenance > Diagnostics > PING > IPv6
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Address Enter the address of the target host server.
Count Ente r the number of ping pac ke ts to s end. The range is 1 to 5 packets; the de fault count is
4.
Interval Enter the time in seconds between sending ping packets. The range is 1 to 5 seconds; the
default is 1 second.
Size Enter the individual packet size in bytes. The range is 8 to 5120 bytes; the default is 56
bytes.
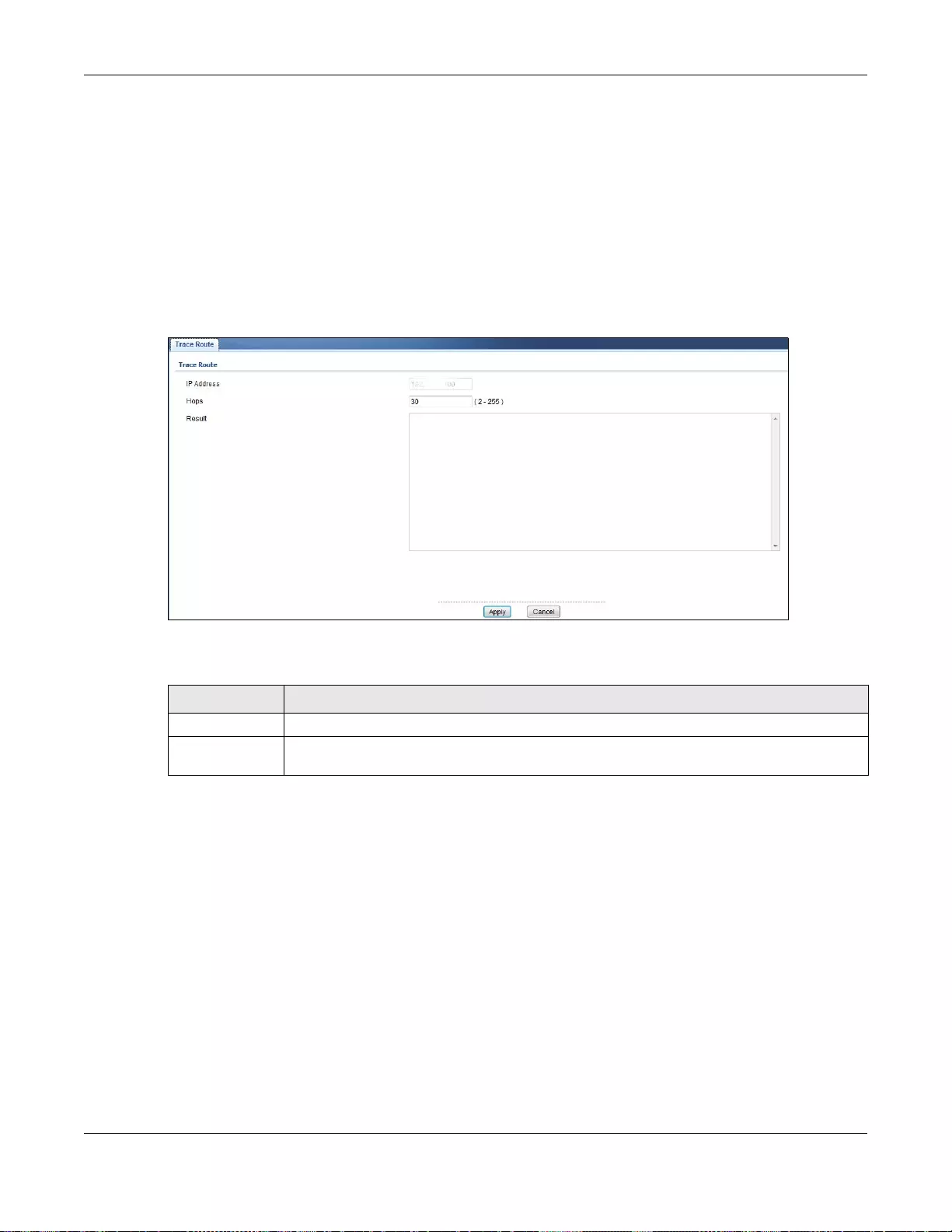
Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
222
5. Click Apply to perform the ping test.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The test results are displayed in Results.
32.7.4 Trace Route
Click Maintenance > Diagnostics > Trace in the navigation panel to open this screen. Use this
screen to print the route that IP packets take to a network host.
Figure 218 Maintenance > Diagnostics > Trace
The following table describes the labels in Trace Ro ute.
Follow the steps to perform a trace route.
1. In IP Address, enter the IPv6 address.
2. In Hops, enter the number of hops.
3. Click Apply to perform the test.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
The test results are displayed in Result.
Table 184 Maintenance > Diagnostics > Trace
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Addres Enter the address of the target host server.
Hops Enter the maximum number of time-to-live or hops used in outgoing probe packets. The
range is 2 to 255 packets; the default is 30 hops.
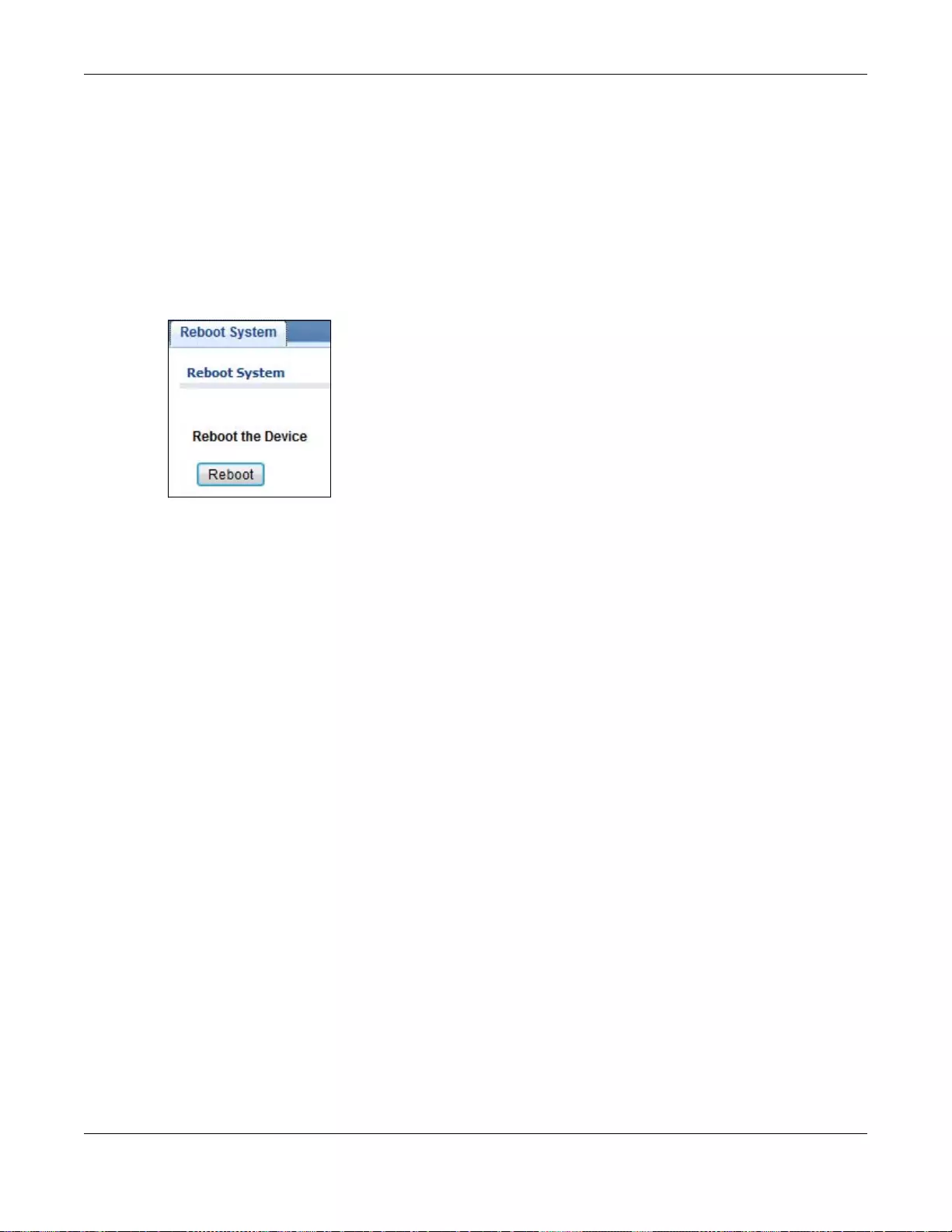
Chapter 32 Maintenance
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
223
32.8 Reboot
32.8.1 Overview
You can reboot the Switch from the web configurator.
Click Maintenance > Reboot in the navigation panel to open this screen. Use this screen to
restart the Switch without physically turning the power off.
Figure 219 Maintenance > Reboot
32.8.2 Reboot the Switch
F ollow the steps below to restart the Switch.
1. Click Reboot.
2. Click OK and then wait for the Sw itch to restart. This process takes up to two minutes and does
not affect the Switch’s configuration.
OR
Click Cancel to discard the changes.
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
224
CHAPTER 33
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The potential
problems are divided into the following categories.
•Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
•Switch Access and Login
•Switch Configuration
33.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
The Switch does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1Make sure the Switch is turned on (in DC models or if the DC power supply is connected in AC/DC
models).
2Make sure you are using the power adaptor or cord included with the Switch.
3Make sure the power adaptor or cord is connected to the Switch and plugged in to an appropriate
power source. Make sure the power source is turned on.
4Turn the Switch off and on (in DC models or if the DC power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
5Disconnect and re-connect the power adaptor or cord to the Switch (in AC models or if the AC
power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
6If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
The ALM LED is on.
1Turn the Switch off and on (in DC models or if the DC power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
2Disconnect and re-connect the power adaptor or cord to the Switch (in AC models or if the AC
power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
3If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
Chapter 33 Troubleshooting
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
225
One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. See Section 3.3 on page 30.
2Check the hardware connections. See Chapter 2 on page 19.
3Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged cables.
4Turn the Switch off and on (in DC models or if the DC power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
5Disconnect and re-connect the power adaptor or cord to the Switch (in AC models or if the AC
power supply is connected in AC/DC models).
6If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
33.2 Switch Access and Login
I forgot the IP address for the Switch.
1The default in-band IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2Use the console port to log in to the Switch.
3Use the MGMT port to log in to the Switch, the default IP addr ess of the MGMT port is 192.168.0.1.
4If this does not work, you have to reset th e device to its factory defaults. See Section 32.6 on page
219.
I forgot the username and/or password.
1The default username is admin and the default password is 1234.
2If this does not work, you have to reset th e device to its factory defaults. See Section 32.6 on page
219.
I cannot see or access th e Login screen in the web configurator.
1Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
• The default in-band IP address is 192.168.1.1.

Chapter 33 Troubleshooting
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
226
• If you changed the IP address, use the new IP address.
• If you changed the IP address and hav e forgotten it, see the troubleshooting su ggestions for I
forgot the IP address for the Switch.
2Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See Section
on page 19.
3Make sure your Internet browser does not block pop-up windows and has JavaScripts and Java
enabled.
4Make sure your computer is in the same subnet as the Switch. (If you know that there are routers
between your computer and the Switch, skip this step.)
5Reset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the Switch with the default IP address.
See Section 32.6 on page 219.
6If the problem continues, contact the vendor, or try one of the advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Try to access the Switch using another service, such as Telnet. If you can access the Switch,
check the remote management settings to find out why the Switch does not respond to HTTP.
I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the Switch.
1Make sure you have entered the user name and password correctly. The default user name is
admin, and the default password is 1234. These fields are case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps
Lock] is not on.
2You may have exceeded the maximum number of concurrent Telnet sessions. Close other Telnet
session(s) or try connecting again later.
Check that you have enabled logins for HTTP or Telnet. If you have configured a secured client IP
address, your computer’s IP address must match it. Refer to the chapter on access control for
details.
3Disconnect and re-connect the cord to the Switch.
4If this does not work, you have to reset th e device to its factory defaults. See Section 32.6 on page
219.
Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
• JavaScripts (enabled by default).
• Jav a pe rmission s (enabled by default).
Chapter 33 Troubleshooting
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
227
I cannot see some of Advanced Application submenus at the bottom of the navigation
panel.
The recommended screen resolution is 1024 by 768 pixels. Adjust the value in your computer and
then you should see the rest of Advanced Application submenus at the bottom of the navigation
panel.
There is unauthorized access to my Switch via telnet, HTTP and SSH.
Click the Maintenance > Diagnostics screen to check for unauthorized access to you r Switch. To
avoid unauthorized access, configure the secured client setting in the Configuration >
Management > Remote Access Control screen for telnet, HTTP and SSH (see Section 31.7 on
page 210). Computers not belonging to the secured client set cannot get permission to access the
Switch.
33.3 Switch Configuration
I lost my configuration settings after I restart the Switch.
Make sure you save your configuration into the Switch’s
nonvolatile memory each time you make changes. Click
Save at the top right corner of the web configurator to save the configuration permanently. See
also Section 5.3.1 on page 34 for more information about how to save your configuration.

GS1900 Series User’s Guide
228
APPENDIX A
Customer Support
In the event of problems that cannot be solved by using this manual, you should contact your
vendor. If you cannot contact your vendor, then contact a ZyXEL office for the region in which you
bought the device.
See http://www.zyxel.com/homepage.shtml and also
http://www.zyxel.com/about_zyxel/zyxel_worldwide.shtml for the latest information.
Please have the following information ready when you contact an office.
Required Information
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
Corporate Headquarters (Worldwide)
Taiwan
• ZyXEL Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com
Asia
China
• ZyXEL Communications (Shanghai) Corp.
ZyXEL Communications (Beijing) Corp.
ZyXEL Communications (Tianjin) Corp.
• http://www.zyxel.cn
India
• ZyXEL Technology Ind ia Pvt Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.in
Kazakhstan
•ZyXEL Kazakhstan
• http://www.zyxel.kz

Appendix A Customer Support
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
229
Korea
• ZyXEL Korea Corp.
• http://www.zyxel.kr
Malaysia
• ZyXEL Malaysia Sdn Bhd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.my
Pakistan
• ZyXEL Pa kistan (Pvt.) Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.pk
Philippines
• ZyXEL Philippines
• http://www.zyxel.com.ph
Singapore
• ZyXEL Singapore Pte Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.sg
Taiwan
• ZyXEL Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/tw/zh/
Thailand
• ZyXEL Thailand Co., Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.co.th
Vietnam
• ZyXEL Communications Corporation-Vietnam Office
• http://www.zyxel.com/vn/vi
Europe
Austria
• ZyXEL Deutschland GmbH
• http://www.zyxel.de
Belarus
•ZyXEL BY
• http://www.zyxel.by

Appendix A Customer Support
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
230
Belgium
• ZyXEL Communications B.V.
• http://www.zyxel.com/be/nl/
• http://www.zyxel.com/be/fr/
Bulgaria
•ZyXEL България
• http://www.zyxel.com/bg/bg/
Czech Republic
• ZyXEL Communications Czech s.r.o
• http://www.zyxel.cz
Denmark
• ZyXEL Communications A/S
• http://www.zyxel.dk
Estonia
•ZyXEL Estonia
• http://www.zyxel.com/ee/et/
Finland
• ZyXEL Communications
• http://www.zyxel.fi
France
•ZyXEL France
• http://www.zyxel.fr
Germany
• ZyXEL Deutschland GmbH
• http://www.zyxel.de
Hungary
• ZyXEL Hungary & SEE
• http://www.zyxel.hu
Italy
• ZyXEL Communications Italy
• http://www.zyxel.it/

Appendix A Customer Support
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
231
Latvia
•ZyXEL Latvia
• http://www.zyxel.com/lv/lv/homepage.shtml
Lithuania
• ZyXEL Lithuania
• http://www.zyxel.com/lt/lt/homepage.shtml
Netherlands
•ZyXEL Benelux
• http://www.zyxel.nl
Norway
• ZyXEL Communications
• http://www.zyxel.no
Poland
• ZyXEL Communications Poland
• http://www.zyxel.pl
Romania
•ZyXEL Romania
• http://www.zyxel.com/ro/ro
Russia
• ZyXEL Russia
• http://www.zyxel.ru
Slovakia
• ZyXEL Communications Czech s.r.o. organizacna zlozka
• http://www.zyxel.sk
Spain
• ZyXEL Communications ES Ltd
• http://www.zyxel.es
Sweden
• ZyXEL Communications
• http://www.zyxel.se
Switzerland
•Studerus AG

Appendix A Customer Support
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
232
• http://www.zyxel.ch/
Turkey
•ZyXEL Turkey A.S.
• http://www.zyxel.com.tr
UK
• ZyXEL Communications UK Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.co.uk
Ukraine
•ZyXEL Ukraine
• http://www.ua.zyxel.com
Latin America
Argentina
• ZyXEL Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/ec/es/
Brazil
• ZyXEL Communications Brasil Ltda.
• https://www.zyxel.com/br/pt/
Ecuador
• ZyXEL Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/ec/es/
Middle East
Israel
• ZyXEL Communication Corporation
• http://il.zyxel.com/homepage.shtml
Middle East
• ZyXEL Communication Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/me/en/

Appendix A Customer Support
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
233
North America
USA
• ZyXEL Communications, Inc. - North America Headquarters
• http://www.zyxel.com/us/en/
Oceania
Australia
• ZyXEL Communications Corporation
• http://www.zyxel.com/au/en/
Africa
South Africa
• Nology (Pty) Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.co.za
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
234
APPENDIX B
Legal Information
Copyright
Copyright © 2016 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into
any language, or tr ansmitted in any form or by an y means, elec tronic, mec hanical, mag netic, o ptical, che mical, phot ocopying , manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software described herein. Neither does it
convey any license under its patent rights nor the patent rights of others. ZyXEL further reserves the right to make changes in any
products described herein without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Regulatory Notice and Statement (Class A)
Model List: GS1900-8HP (Revision A1), GS1900-24, GS1900-24HP, GS1900-48, GS1900-48HP
United States of America
The following information applies if you use the product within USA area.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) EMC Statement
• This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operations.
• Changes or modif ications not expressly app roved by th e party resp onsible for co mpliance co uld void th e user’s aut hority to op erate the
equipment.
• This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Ru le s.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Canada The following information applies if you use the product within Canada area
Industry Canada ICES statement
CAN ICES-3 (A)/NMB-3(A)
European Union
The following information applies if you use the product within the European Union.
CE EMC statement
This is Clas s A Product. I n domestic en vironment t his product may cause r adio inte rference in wh ich case the us er may be re quired to take
adequate measures.
Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
235
List of National Codes
Safety Warnings
• Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
• Do not expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do not store things on the device.
• Do not install, use, or s ervice this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk of electric shock from ligh tning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do not open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks. Only
qualified service personnel should service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Do not remove the plug and connect it to a power outlet by itself; alwa ys attach the plug to the power adaptor first before connecting
it to a power outlet.
• Do not allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the product where anyone can walk on the p ower adaptor
or cord.
• Please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/ adaptors. Connect it to the right supply voltage (for example,
110V AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe). If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, it might cause electrocution. Remove it
from the de vice an d the pow er sou rce, re pairin g the po wer adap ter or c ord is pr ohibit ed. Co ntact y our loc al ve ndor t o order a n ew one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Caution: Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type, dispose of used batteries according to the instruction. Dispose
them at the applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic device. For detailed information about recycling of
this prod uct, pl ease co ntact y our l ocal cit y offi ce, yo ur hou sehold was te dis posal se rvice o r the st ore wher e you purch ased th e product.
• Use ONLY power wires of the appropriate wire gauge for your device. Connect it to a power supply of the correct voltage.
• Fuse Warning! Replace a fuse only with a fuse of the same type and rating.
• The POE (Power over Ethernet) devices that supply or receive power and their connected Ethernet cables must all be completely
indoors.
• Do not obstruct the device ventillation slots as insufficient airflow may harm your device.
• The followin g wa rnin g st atem ents appl y, where the disc onnec t devi ce i s not inc orpo r ated i n th e devi ce o r wher e th e pl ug on the power
supply cord is intended to serve as the disconnect device,
- For permanently connected devices, a readily accessible disconnect device shall be incorporated external to the device;
- For pluggable devices, the socket-outlet shall be installed near the device and shall be easily accessible.
• This device must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the device in the absence of a suitably installed ground
conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is
available.
• When connecting or disconnecting power to hot-pluggable power supplies, if offered with your system, observe the following
guidelines:
- Install the power supply before connecting the power cable to the power supply.
- Unplug the power cable before removing the power supply.
- If the system has multiple sources of power, disconnect power from the system by unplugging all power cables from the power
supply.
COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE
Austria AT Liechtenstein LI
Belgium BE Lithuania LT
Bulgaria BG Luxembourg LU
Croatia HR Malta MT
Cyprus CY Netherlands NL
Czech Republic CR Norway NO
Denmark DK Poland PL
Estonia EE Portugal PT
Finland FI Romania RO
France FR Serbia RS
Germany DE Slovakia SK
Greece GR Slovenia SI
Hungary HU Spain ES
Iceland IS Sweden SE
Ireland IE Switzerland CH
Italy IT Turkey TR
Latvia LV United Kingdom GB
Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
236
Environment Statment
European Union - Disposal and Recycling Information
The symbol belo w means that ac cording to local regulat ions y our product and/or its battery shall be disposed of separately from domestic
waste. If this product is end of life, take it to a recycling station designated by local authorities. At the time of disposal, the separate
collection of your product and/or its battery will help save natural resources and ensure that the environment is sustainable development .
Die folgende Symbol bedeutet, dass Ihr Produkt und/oder seine Batterie gemäß den örtlichen Bestimmungen getrennt vom Hausmüll
entsorgt werden muss. Wenden Sie sich an eine Recyclingstation, wenn dieses Produkt das Ende seiner Lebensdauer erreicht hat. Zum
Zeitpunkt der Entsorgung wird die getrennte Sammlung von Produkt und/oder seiner Batterie dazu beitragen, natürliche Ressourcen zu
sparen und die Umwelt und die menschliche Gesundheit zu schützen.
El símbolo de abajo indica que según las regulaciones locales, su producto y/o su batería deberán depositarse como basura separada de la
doméstica. Cuando este producto alcance el final de su vida útil, llévelo a un punto limpi o. Cuando llegue el momento de desechar el
producto, la recogida por separado éste y/o su batería ayudará a salvar los recursos naturales y a proteger la salud humana y
medioambiental.
Le symbole ci-dessous signifie que selon les réglementations locales votre produit et/ou sa batterie doivent être éliminés séparément des
ordures ménagères. Lorsque ce produit atteint sa fin de vie, amenez-le à un centre de recyclage. Au moment de la mise au rebut, la
collecte sép arée de votre produit et/ou de sa batterie aidera à économiser les ressources naturelles et protéger l'environnement et la
santé humaine.
Il simbolo sotto significa che secondo i regolamenti locali il vostro prodotto e/o batteria deve essere smaltito separatamente dai rifiuti
domestici. Quando questo prodotto raggiunge la fine della vita di servizio portarlo a una stazione di ri ciclaggio. Al momento dello
smaltimento, la raccolta separata del vostro prodotto e/o della sua batteria aiuta a risparmiare risorse naturali e a proteggere l'ambiente
e la salute umana.
Symbolen innebär att enligt lokal lagstiftning ska produkten och/eller dess batteri kastas separat från hushållsavfallet. När den här
produkten når slutet av sin livslängd ska du ta den till en återvinningsstation. Vid tiden för kasseringen bidrar du till en bättre miljö och
mänsklig hälsa genom att göra dig av med den på ett återvinningsställe.
Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
237
Environmental Product Declaration

Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
238
台灣
警告使用者:
這是甲類的資訊產品,在居住的環境中使用時,可能會造成射頻干擾,在這種情況下,使用者會被要求採取某些適當的對策。」
安全警告
為了您的安全,請先閱讀以下警告及指示 :
• 請勿將此產品接近水、火焰或放置在高溫的環境。
• 避免設備接觸
任何液體 - 切勿讓設備接觸水、雨水、高濕度、污水腐蝕性的液體或其他水份。
灰塵及污物 - 切勿接觸灰塵、污物、沙土、食物或其他不合適的材料。
• 雷雨天氣時,不要安裝,使用或維修此設備。有遭受電擊的風險。
• 切勿重摔或撞擊設備,並勿使用不正確的電源變壓器。
• 若接上不正確的電源變壓器會有爆炸的風險。。
• 請勿隨意更換產品內的電池。
• 如果更換不正確之電池型式,會有爆炸的風險,請依製造商說明書處理使用過之電池。
• 請將廢電池丟棄在適當的電器或電子設備回收處。
• 請勿將設備解體。
• 請勿阻礙設備的散熱孔,空氣對流不足將會造成設備損害。
• 請插在正確的電壓供給插座 ( 如 : 北美 / 台灣電壓 110V AC,歐洲是 230V AC)。
• 假若電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線損壞,請從插座拔除,若您還繼續插電使用,會有觸電死亡的風險。
• 請勿試圖修理電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線,若有毀損,請直接聯絡您購買的店家,購買一個新的電源變壓器。
• 請勿將此設備安裝於室外,此設備僅適合放置於室內。
• 請勿隨一般垃圾丟棄。
• 請參閱產品背貼上的設備額定功率。
• 請參考產品型錄或是彩盒上的作業溫度。
• 設備必須接地,接地導線不允許被破壞或沒有適當安裝接地導線,如果不確定接地方式是否符合要求可聯繫相應的電氣檢驗機構檢驗。
• 如果您提供的系統中有提供熱插拔電源,連接或斷開電源請遵循以下指導原則
- 先連接電源線至設備連,再連接電源。
- 先斷開電源再拔除連接至設備的電源線。
- 如果系統有多個電源,需拔除所有連接至電源的電源線再關閉設備電源。
• 產品沒有斷電裝置或者採用電源線的插頭視為斷電裝置的一部分,以下警語將適用 :
- 對永久連接之設備, 在設備外部須安裝可觸及之斷電裝置;
- 對插接式之設備, 插座必須接近安裝之地點而且是易於觸及的。
Regulatory Notice and Statement (Class B)
Model List: GS1900-8, GS1900-8HP (Revision B1), GS1900-10HP, GS1900-16, GS1900-24E
UNITED STATES of AMERICA
The following information applies if you use the product within USA area.
FCC EMC St atement
• The device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
• Changes or modif ications not expressly app roved by th e party resp onsible for co mpliance co uld void th e user’s aut hority to op erate the
device.
• This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This device
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation.
• If this device does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the device off and on, the us er
is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance

Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
239
CANADA
The following information applies if you use the product within Canada area
Industry Canada ICES statement
ICAN ICES-3 (B)/NMB-3(B)
EUROPEAN UNION
The following information applies if you use the product within the European Union.
List of national codes
Safety Warnings
• Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
• Do not expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do not store things on the device.
• Do not install, use, or s ervice this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk of electric shock from ligh tning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do not open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY
qualified service personnel should service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Do not remove the plug and connect it to a power outlet by itself; alwa ys attach the plug to the power adaptor first before connecting
it to a power outlet.
• Do not allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the product where anyone can walk on the p ower adaptor
or cord.
• Please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/ adaptors. Connect it to the right supply voltage (for example,
110V AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe). If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, it might cause electrocution. Remove it
from the de vice an d the pow er sou rce, re pairin g the po wer adap ter or c ord is pr ohibit ed. Co ntact y our loc al ve ndor t o order a n ew one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• CAUTION: Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type, dispose of used batteries according to the instruction. Dispose
them at the applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic devices. For detailed information about recycling of
this prod uct, pl ease co ntact y our l ocal cit y offi ce, yo ur hou sehold was te dis posal se rvice o r the st ore wher e you purch ased th e product.
• Do not obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your device.
• The followin g wa rnin g st atem ents appl y, where the disc onnec t devi ce i s not inc orpo r ated i n th e devi ce o r wher e th e pl ug on the power
supply cord is intended to serve as the disconnect device,
• For permanently connected devices, a readily accessible disconnect device shall be incorporated external to the device;
COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE
Austria AT Liechtenstein LI
Belgium BE Lithuania LT
Bulgaria BG Luxembourg LU
Croatia HR Malta MT
Cyprus CY Netherlands NL
Czech Republic CZ Norway NO
Denmark DK Poland PL
Estonia EE Portugal PT
Finland FI Romania RO
France FR Serbia RS
Germany DE Slovakia SK
Greece GR Slovenia SI
Hungary HU Spain ES
Iceland IS Switzerland CH
Ireland IE Sweden SE
Italy IT Turkey TR
Latvia LV United Kingdom GB
Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
240
• For pluggable devices, the socket-outlet shall be installed near the device and shall be easily accessible.
Environment Statement
ErP (Energy-related Products)
ZyXEL products put on the EU market in compliance with the requirement of the European Parliament and the Council published Directive
2009/125/EC establishing a framework for the setting of ecodesign requirements for ener gy-related products (recast), so called as "ErP
Directive (Energy-related Products directive) as well as ecodesign requirement laid down in applicable implementing measures, power
consumption has satisfied regulation requirements which are:
Network standby power consumption < 12W, and/or
Off mode power consumption < 0.5W, and/or
Standby mode power consumption < 0.5W.
Wireless setting, please refer to "Wireless" chapter for more detail.
European Union - Disposal and Recycling Information
The symbol belo w means that ac cording to local regulat ions y our product and/or its battery shall be disposed of separately from domestic
waste. If this product is end of life, take it to a recycling station designated by local authorities. At the time of disposal, the separate
collection o f y o ur p r oduc t and / or its battery w il l help save n a tu ral resourc e s and e nsur e t hat th e environment is s ustainable development.
Die folgende Symbol bedeutet, dass Ihr Produkt und/oder seine Batterie gemäß den örtlichen Bestimmungen getrennt vom Hausmüll
entsorgt werden muss. Wenden Sie sich an eine Recyclingstation, wenn dieses Produkt das Ende seiner Lebensdauer erreicht hat. Zum
Zeitpunkt der Entsorgung wird die getrennte Sammlung von Produkt und/oder seiner Batterie dazu beitragen, natürliche Ressourcen zu
sparen und die Umwelt und die menschliche Gesundheit zu schützen.
El símbolo de abajo indica que según las regulaciones locales, su producto y/o su batería deberán depositarse como basura separada de la
doméstica. Cuando este producto alcance el final de su vida útil, llévelo a un punto limpi o. Cuando llegue el momento de desechar el
producto, la recogida por separado éste y/o su batería ayudará a salvar los recursos naturales y a proteger la salud humana y
medioambiental.
Le symbole ci-dessous signifie que selon les réglementations locales votre produit et/ou sa batterie doivent être éliminés séparément des
ordures ménagères. Lorsque ce produit atteint sa fin de vie, amenez-le à un centre de recyclage. Au moment de la mise au rebut, la
collecte sép arée de votre produit et/ou de sa batterie aidera à économiser les ressources naturelles et protéger l'environnement et la
santé humaine.
Il simbolo sotto significa che secondo i regolamenti locali il vostro prodotto e/o batteria deve essere smaltito separatamente dai rifiuti
domestici. Quando questo prodotto raggiunge la fine della vita di servizio portarlo a una stazione di ri ciclaggio. Al momento dello
smaltimento, la raccolta separata del vostro prodotto e/o della sua batteria aiuta a risparmiare risorse naturali e a proteggere l'ambiente
e la salute umana.
Symbolen innebär att enligt lokal lagstiftning ska produkten och/eller dess batteri kastas separat från hushållsavfallet. När den här
produkten når slutet av sin livslängd ska du ta den till en återvinningsstation. Vid tiden för kasseringen bidrar du till en bättre miljö och
mänsklig hälsa genom att göra dig av med den på ett återvinningsställe.

Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
241
Environmental Product Declaration

Appendix B Legal Information
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
242
台灣
安全警告
為了您的安全,請先閱讀以下警告及指示 :
• 請勿將此產品接近水、火焰或放置在高溫的環境。
• 避免設備接觸任何液體 - 切勿讓設備接觸水、雨水、高濕度、污水腐蝕性的液體或其他水份。
• 灰塵及污物 - 切勿接觸灰塵、污物、沙土、食物或其他不合適的材料。
• 雷雨天氣時,不要安裝,使用或維修此設備。有遭受電擊的風險。
• 切勿重摔或撞擊設備,並勿使用不正確的電源變壓器。
• 若接上不正確的電源變壓器會有爆炸的風險。
• 請勿隨意更換產品內的電池。
• 如果更換不正確之電池型式,會有爆炸的風險,請依製造商說明書處理使用過之電池。
• 請將廢電池丟棄在適當的電器或電子設備回收處。
• 請勿將設備解體。
• 請勿阻礙設備的散熱孔,空氣對流不足將會造成設備損害。
• 請插在正確的電壓供給插座 ( 如 : 北美 / 台灣電壓 110V AC,歐洲是 230V AC)。
• 假若電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線損壞,請從插座拔除,若您還繼續插電使用,會有觸電死亡的風險。
• 請勿試圖修理電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線,若有毀損,請直接聯絡您購買的店家,購買一個新的電源變壓器。
• 請勿將此設備安裝於室外,此設備僅適合放置於室內。
• 請勿隨一般垃圾丟棄。
• 請參閱產品背貼上的設備額定功率。
• 請參考產品型錄或是彩盒上的作業溫度。
• 產品沒有斷電裝置或者採用電源線的插頭視為斷電裝置的一部分,以下警語將適用 :
- 對永久連接之設備, 在設備外部須安裝可觸及之斷電裝置;
- 對插接式之設備, 插座必須接近安裝之地點而且是易於觸及的。
Viewing Certifications
Go to http://www.zyxel.com to view this product’s documentation and certifi cations.
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects in material or workmanship for a specific
period (the Warranty Period) from the date o f purchase. The Warranty Period varies by region. Check with your vendor and/or the
authorized ZyXEL local distributor for details about the Warranty Period of this product. During the warranty period, and upon proof of
purchase , should the prod uct have indi cations of failu re due to faulty workmanshi p and/or material s, Zy XEL will, at its disc retion, repair or
replace the defective products or components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to
restore the product or components to proper operating condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally
equivalent product of equal or higher value, and will be solely at the discretion of ZyXEL. This warranty shall not apply if the product has
been modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by an act of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions.
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other
warranties, express or implied, including any implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. Z yXEL shall in
no event be held liable for indirect or consequential damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact your vendor. You may also refer to the warranty policy for the region in which you bought
the device at http://www.zyxel.com/web/support_warranty_info.php.
Registration
Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and information at www.zyxel.com for global products, or at
www.us.zyxel.com for North American products.
Trademarks
ZyNOS (ZyXEL Network Operating System) and ZON (ZyXEL One Network) are registered trademarks of ZyXEL Communications, Inc.
Other tr ademar ks men tioned i n thi s public ation ar e used for ide ntific ation p urposes only an d ma y be p roperti es of their r espect iv e owners.
Open Source Licenses
This product contains in part some free software distributed under GPL license terms and/or GPL like licenses. Open source licenses are
provided with the firmware package. You can download the latest firmware at www.zyxel.com. To obtain the source code covered under
those Licenses, please contact support@zyxel.com.tw to get it.

Index
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
243
Index
A
access 33
applications
bridging 15
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN 16
C
certifications 239
viewing 242
Chapter 31 on page 227 18
contact information 228
cookies 33
copyright 234
current date/time 42
customer support 228
D
DHCP
and domain name 53, 95, 96, 99, 101, 102, 104,
106, 108, 120
disclaimer 234
domain name 53, 95, 96, 99, 101, 102, 104, 106, 108,
120
E
Ethernet ports
default settings 26
F
FCC interference statement 234
Firefox 33
firmware
current version 42
front panel 24
FTP 18
H
hardware installation 19
hardware overview 24
I
installation
freestanding 19
precautions 21
interfaces
as DHCP servers 53, 95, 96, 99, 101, 102, 104, 106,
108, 120
Internet Explorer 33
Internet Protocol version 6, see IPv6
introduction 15
IPv6 17
Neighbor Discovery Protocol 17
ping 17
J
Java
permissions 33
JavaScripts 33
L
LEDs 30

Index
GS1900 Series User’s Guide
244
logout
Web Configurator 34
loop guard
how it works 72
probe packet 72, 73
M
MAC address
range 42
managing the device
good habits 18
using FTP. See FTP.
using SNMP. See SNMP.
using the web configurator. See web configurator.
mini GBIC ports 26
connection speed 26
connector type 26
transceiver installation 26
transceiver removal 27
model name 42
mounting brackets 21
MSA (MultiSource Ag reeme nt) 26
MSTP 79
MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol) 79
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol, See MSTP. 79
N
Netscape Navigator 33
P
packet
statistics 94, 95, 125, 136, 137, 139, 141, 142, 149,
150, 159, 160, 172, 174, 178, 191, 192, 194, 196,
199, 206, 207, 209, 210
physical ports
packet statistics 94, 95, 125, 136, 137, 139, 141,
142, 149, 150, 159, 160, 172, 174, 178, 191, 192,
194, 196, 199, 206, 207, 209, 210
PoE
power management mode 103
pop-up windows 33
power module
disconnecting 29
product registration 242
protocol based VLAN 67
and IEEE 802.1Q tagging 67
isolate traffic 67
R
rack mounting 21
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, See RSTP. 79
registration
product 242
RSTP 79
rubber feet 19
S
screen resolution 33
serial number 42
SNMP 18
Spanning Tree Protocol, See STP. 79
status 41
LED 30
STP 79
supported browsers 33
system name 42, 53, 95, 125, 126, 127, 128
system uptime 42
T
trademarks 242
transceiver
installation 26
removal 27
U
users
