Table of Contents
Zyxel XGS1250-12 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for XGS1250-12 by Zyxel which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

Default Login Details
User’s Guide
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12
Copyright © 2021 Zyxel and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Management IP Address http://192.168.1.3
Password 1234
Version 1.00 Edition 2, 08/2021

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
2
IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in your
product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the Switch and access the Web Configurator.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the Switch.
Document Conventions
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
3
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may need to
configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The XGS1210-12 and XGS1250-12 may be referred to as the “Switch” in this guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example, QoS > Port-
Based QoS means you first click QoS in the navigation panel, then the Port-Based QoS sub menu to
get to that screen.
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this user guide may use the following generic icons. The Switch icon is not an exact
representation of your device.
Switch Generic Switch Generic Router
IP Camera Firewall Cell Tower
Printer Server

Contents Overview
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
4
Contents Overview
User’s Guide ........................................................................................................................................8
Getting to Know Your Switch ................................................................................................................ 9
Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................................... 14
Hardware Panels .................................................................................................................................. 17
Web Configurator ................................................................................................................................. 21
Initial Setup Example ............................................................................................................................ 30
Tutorials .................................................................................................................................................. 33
Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................37
System .................................................................................................................................................... 38
Port ......................................................................................................................................................... 41
VLAN ...................................................................................................................................................... 45
Link Aggregation .................................................................................................................................. 48
Mirroring ................................................................................................................................................. 50
QoS ......................................................................................................................................................... 52
IGMP Snooping ..................................................................................................................................... 56
Management ........................................................................................................................................ 58
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................... 63

Table of Contents
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
5
Table of Contents
Document Conventions ....... .... ... .... .......................... ... .......................... .......................... .... ...............3
Contents Overview ..............................................................................................................................4
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide............................................................................................8
Chapter 1
Getting to Know Your Switch ..............................................................................................................9
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 9
1.1.1 Model Feature Differences .................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Applications ...................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.1 Multi-Gigabit .......................................................................................................................... 10
1.2.2 Backbone Application ......................................................................................................... 11
1.2.3 Bridging Application ............................................................................................................. 11
1.2.4 VLAN Application Example .................................................................................................. 12
1.3 Way to Manage the Switch .......................................................................................................... 12
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the Switch ........................................................................................12
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation ........................................................................................................................14
2.1 Installation Scenarios ...................................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Safety Precautions .......................................................................................................................... 14
2.2.1 Freestanding Installation Procedure ................................................................................... 14
2.2.2 Wall Mounting ....................................................................................................................... 15
Chapter 3
Hardware Panels................................................................................................................................17
3.1 Hardware Overview ....................................................................................................................... 17
3.2 Front Panel ...................................................................................................................................... 17
3.3 Rear Panel ....................................................................................................................................... 17
3.3.1 Power Connector ................................................................................................................. 18
3.3.2 Smart Fan (for XGS1250-12) .................................................................................................. 18
3.4 LEDs .................................................................................................................................................. 19
Chapter 4
Web Configurator...............................................................................................................................21

Table of Contents
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
6
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 21
4.2 System Login .................................................................................................................................... 21
4.3 Zyxel One Network (ZON) Utility .................................................................................................... 22
4.3.1 Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 22
4.3.2 Run the ZON Utility ................................................................................................................. 23
4.4 Web Configurator Layout .............................................................................................................. 26
4.4.1 Change Your Password ........................................................................................................ 28
4.5 Switch Lockout/Resetting the Switch ........................................................................................... 29
4.6 Logging Out of the Web Configurator ........................................................................................29
Chapter 5
Initial Setup Example.........................................................................................................................30
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 30
5.1.1 Change the IP Address ........................................................................................................ 30
5.1.2 Change the Password .......................................................................................................... 31
Chapter 6
Tutorials ...............................................................................................................................................33
6.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 33
6.2 Creating a VLAN ............................................................................................................................. 33
6.3 Setting Port VID ............................................................................................................................... 35
Part II: Technical Reference...........................................................................37
Chapter 7
System.................................................................................................................................................38
7.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 38
7.2 System Settings ................................................................................................................................ 38
Chapter 8
Port ......................................................................................................................................................41
8.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 41
8.1.1 What You Need to Know ..................................................................................................... 41
8.2 Port Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 42
Chapter 9
VLAN....................................................................................................................................................45
9.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 45
9.1.1 What You Need to Know ..................................................................................................... 45
9.2 VLAN Settings .................................................................................................................................. 46

Table of Contents
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
7
Chapter 10
Link Aggregation .......... .... .... .... ......................... .......................... .......................... ............................48
10.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 48
10.2 Link Aggregation .......................................................................................................................... 48
Chapter 11
Mirroring..............................................................................................................................................50
11.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 50
11.2 Mirroring Settings ........................................................................................................................... 50
Chapter 12
QoS......................................................................................................................................................52
12.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 52
12.2 What You Need to Know ............................................................................................................. 52
12.2.1 Port-Based QoS ................................................................................................................... 52
12.2.2 IEEE 802.1p QoS ................................................................................................................... 52
12.2.3 Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) ...................................................................... 53
12.3 Port-Based QoS ............................................................................................................................. 53
12.4 IEEE 802.1p QoS ............................................................................................................................. 54
Chapter 13
IGMP Snooping ..................................................................................................................................56
13.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 56
13.2 IGMP Snooping Settings ............................................................................................................... 56
Chapter 14
Management .....................................................................................................................................58
14.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 58
14.1.1 What You Need to Know ...................................................................................................58
14.2 Management Settings ................................................................................................................. 59
14.2.1 Firmware Upgrade .............................................................................................................. 61
Chapter 15
Troubleshooting..................................................................................................................................63
15.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ................................................................................. 63
15.2 Switch Access and Login ............................................................................................................. 64
15.3 Switch Configuration .................................................................................................................... 65
Appendix A Customer Support ....................................................................................................... 66
Appendix B Legal Information......................................................................................................... 72
Index ...................................................................................................................................................76

8
PART I
User’s Guide
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
9
CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know Your Switch
1.1 Overview
Switch refers to these models as outlined below.
• XGS1210-12
• XGS1250-12
1.1.1 Model Feature Differences
Note the following differences between the Switch models:
1.2 Applications
This section shows a few examples of using the Switch in various network environments.
Table 1 Model Feature Comparison
FEATURE/MODEL XGS1210-12 XGS1250-12
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) YES YES
QoS (Quality of Service) YES YES
Switch Management YES YES
Link Aggregation YES YES
Port Mirroring YES YES
IGMP Snooping YES YES
IEEE 802.3az (Energy Efficient Ethernet Standard) YES YES
Management VLAN YES YES
HTTP or HTTPS enable YES YES
Save configuration YES YES
Upload stored device configuration file YES YES
1G, 10G SFP+ interface 2 1
100M, 1000M, 2.5G Ethernet Ports 2 NO
100M, 1000M, 2.5G, 5G, 10G Ethernet Ports NO 3
10M, 100M, 1000M Ethernet Ports 8 8
Multi-Gigabit Ethernet Up to 2.5G Up to 10G
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
10
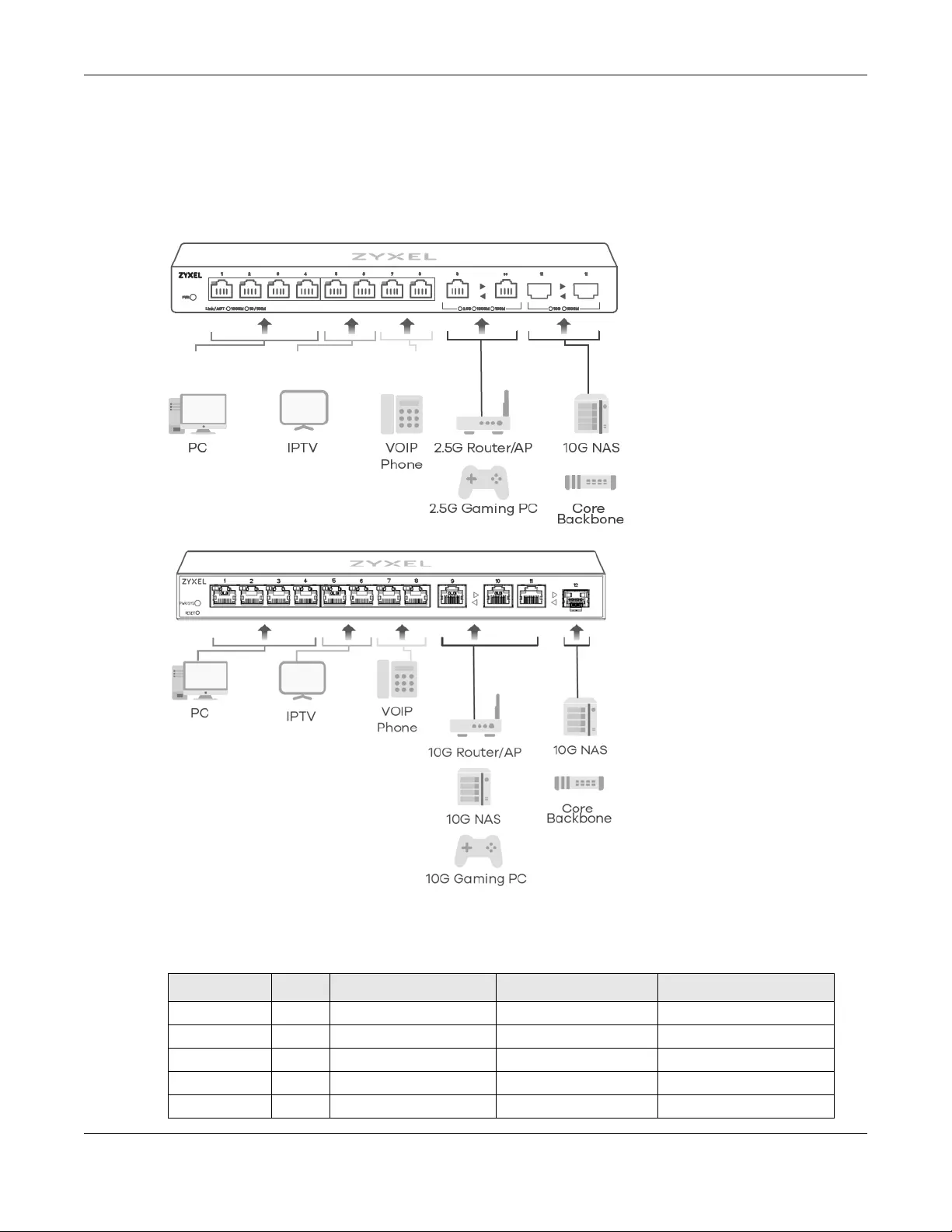
1.2.1 Multi-Gigabit
Multi-Gigabit Ethernet ports automatically allow connections up to the speed of the connected network
device (100M, 1G, 2.5G, 5G, or 10G), and you just need to use a CAT 5e or CAT 6 Ethernet cable. You
must use CAT 6A or better Ethernet cables to achieve 10G speeds.
Figure 1 Multi-Gigabit Application (XGS1210-12)
Figure 2 Multi-Gigabit Application (XGS1250-12)
See the following table for the cables required and distance limitation to attain the corresponding
speed.
Table 2 Cable Types
CABLE PORT TRANSMISSION SPEED MAXIMUM DISTANCE BANDWIDTH CAPACITY
Category 5 1 – 11 100M 100 m 100 MHz
Category 5e 1 – 11 1G / 2.5G / 5G 100 m 100 MHz
Category 6 9 – 11 5G / 10G 50 m 250 MHz
Category 6a 9 – 11 10G 100 m 500 MHz
Category 7 9 – 11 10G 100 m 650 MHz
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
11
Make sure to select the correct speed for the port in Port > Port Setting.
1.2.2 Backbone Application
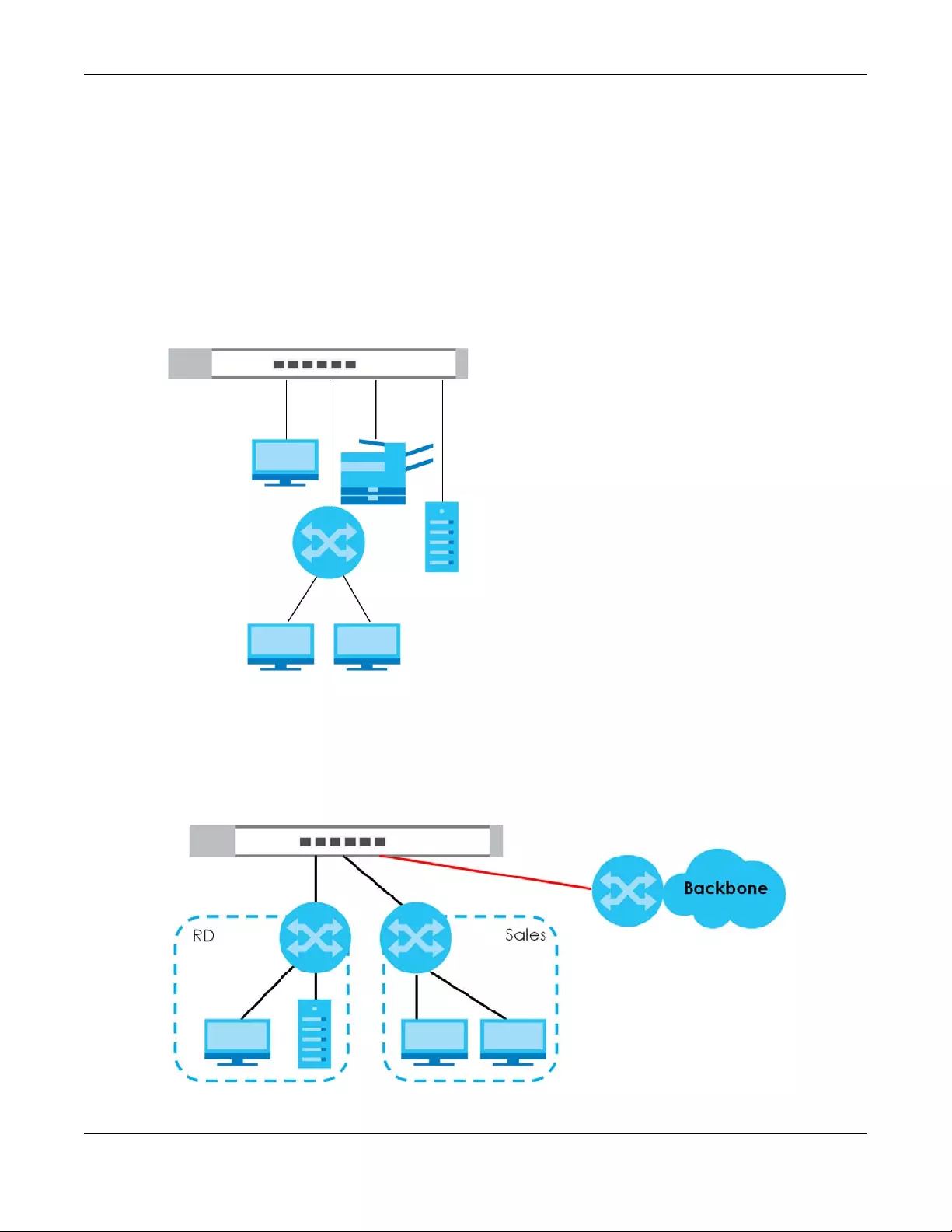
The Switch is an ideal solution for small networks where rapid growth can be expected in the near future.
The Switch can be used standalone for a group of heavy traffic users. You can connect computers and
servers directly to the Switch’s port or connect other switches to the Switch.
In this example, all computers can share high-speed applications on the server. To expand the network,
simply add more networking devices such as switches, routers, computers, print servers, and so on.
Figure 3 Backbone Application
1.2.3 Bridging Application
In this example the Switch connects different company departments (RD and Sales) to the corporate
backbone. It can alleviate bandwidth contention and eliminate server and network bottlenecks. All
users that need high bandwidth can connect to high-speed department servers via the Switch.
Figure 4 Bridging Application
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
12
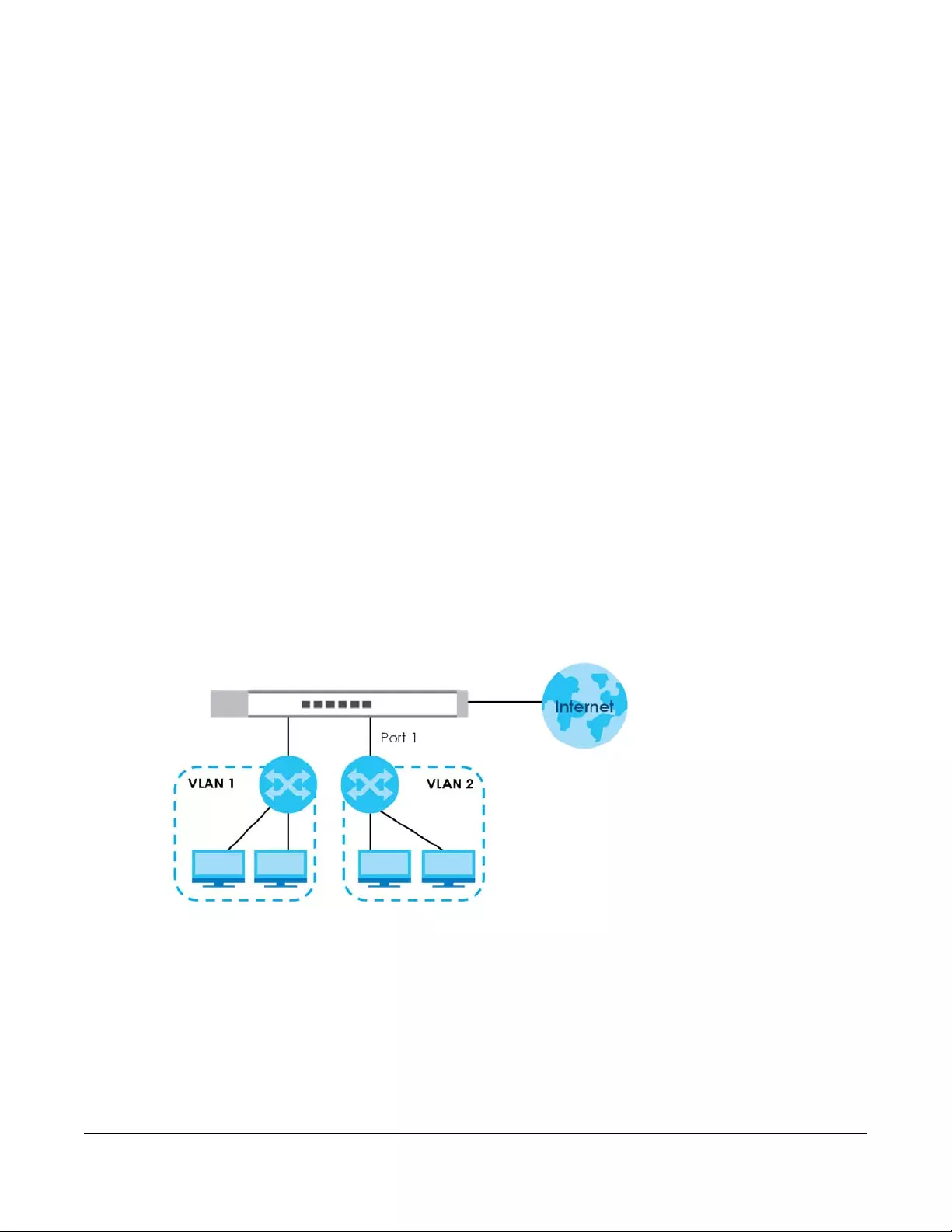
1.2.4 VLAN Application Example
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Stations on a logical network belong to one or more groups. With VLAN, a station cannot
directly talk to or hear from stations that are not in the same groups unless such traffic first goes through
a router.
1.2.4.1 Tag-based VLAN Example
Ports in the same VLAN group share the same frame broadcast domain, thus increasing network
performance by reducing broadcast traffic. VLAN groups can be modified at any time by adding,
moving or changing ports without any re-cabling.
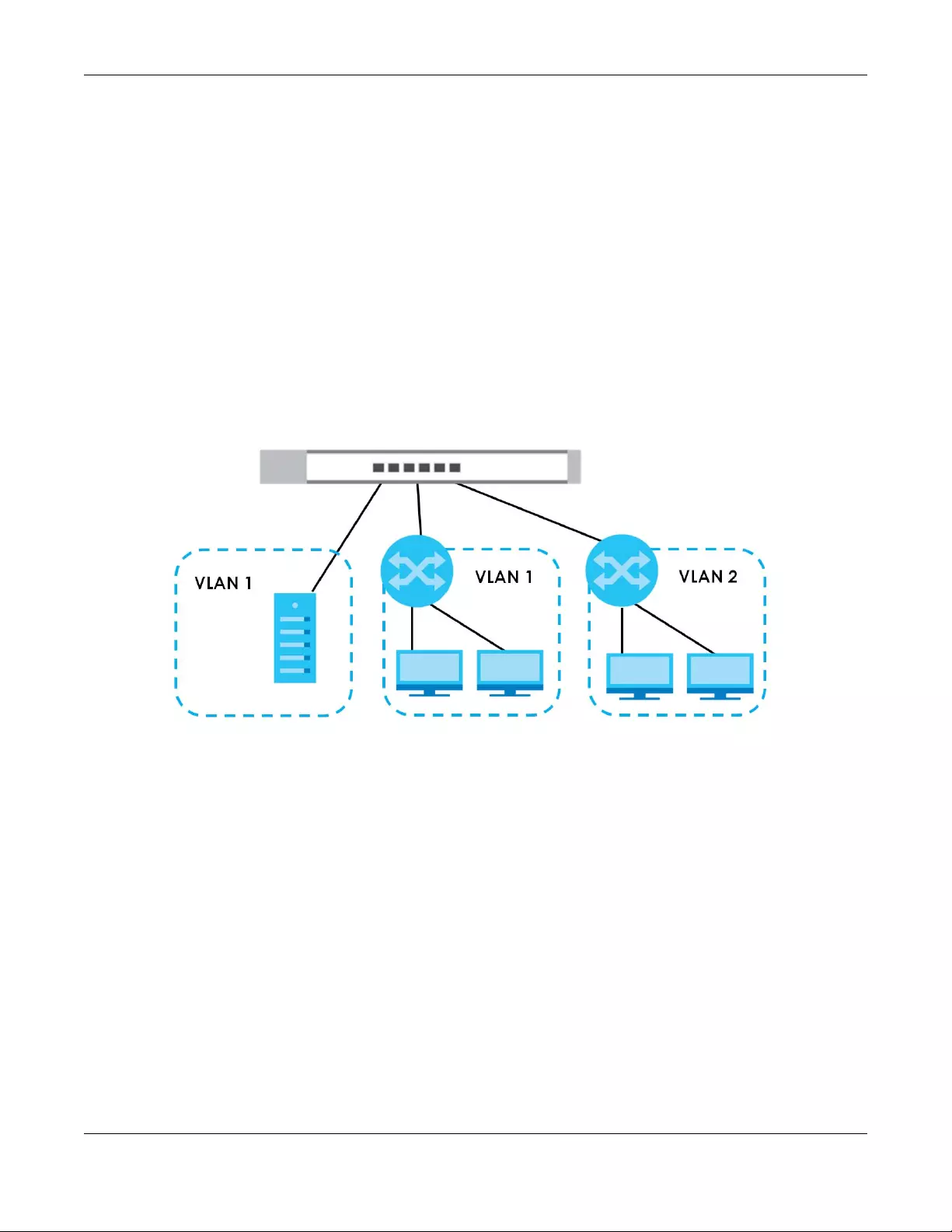
Shared resources such as a server can be used by all ports in the same VLAN as the server. In the
following figure only ports that need access to the server need to be part of VLAN1. Ports can belong to
other VLAN groups too.
Figure 5 Shared Server Using VLAN Example
1.3 Way to Manage the Switch
Use the Web Configurator to manage the Switch. This allows easy Switch setup and management using
a (supported) web browser. See Chapter 4 on page 21.
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the Switch
Do the following things regularly to make the Switch more secure and to manage the Switch more
effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that is not easy to guess and that consists of different types of
characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.

Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
13
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier working
configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you forget your
password, you will have to reset the Switch to its factory default settings. If you backed up an earlier
configuration file, you would not have to totally re-configure the Switch. You could simply restore your
last configuration.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
14
CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation
2.1 Installation Scenarios
This chapter shows you how to install and connect the Switch.
2.2 Safety Precautions
Please observe the following before using the Switch:
• Do NOT stack Switches with fans (for XGS1250-12).
• It is recommended to ask an authorized technician to attach the Switch on a desk or to the rack or
wall. Use the proper screws to prevent damage to the Switch. See the Screw Specifications figures in
this chapter to know the types of screws and screw drivers for each model.
• Make sure there is at least 2 cm of clearance on the top and bottom of the Switch, and at least 5 cm
of clearance on all four sides of the Switch. This allows air circulation for cooling.
• Do NOT block the ventilation holes nor store cables or power cords on the Switch. Allow clearance for
the ventilation holes to prevent your Switch from overheating. This is especially crucial when your
Switch does not have fans. Overheating could affect the performance of your Switch, or even
damage it.
• The surface of the Switch could be hot when it is functioning. Do NOT put your hands on it. You may
get burned. This could happen especially when you are using a fanless Switch.
• The Switches with fans are not suitable for use in locations where children are likely to be present.
To start using the Switch, simply connect the power cables and turn it on.
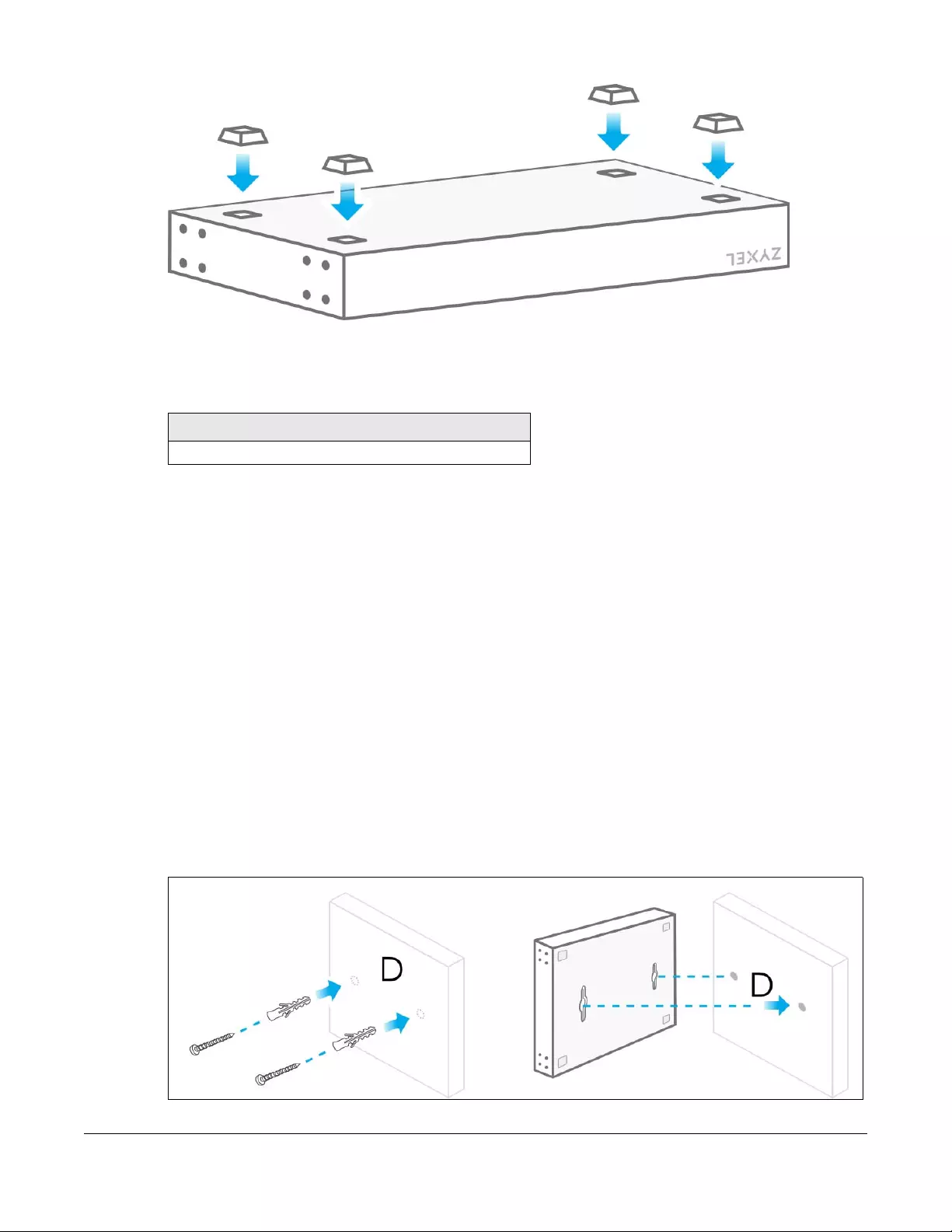
2.2.1 Freestanding Installation Procedure
1Make sure the Switch is clean and dry.
2Attach the rubber feet as shown if they are not already attached – see Figure 6 on page 15.
3Set the Switch on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of the Switch and the
connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
4Make sure there is enough space around the Switch to allow the attachment of cables and the power
cord, and sufficient air circulation.
Note: Make sure you are using the correct type of Ethernet cable (CAT 5e, 6UTP/STP, or better
Ethernet cable). See Table 2 on page 10 for more information.
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
15
Figure 6 Attach Rubber Feet
2.2.2 Wall Mounting
Do the following to mount your Switch on a wall.
1Drill two holes on the wall at the distance of ‘D’ – see Figure 7 on page 15.
2Insert screw anchors and screws (not provided) into the holes. Leave a small gap between the head of
the screw and the wall.
3The gap must be big enough for the screws to slide into the wall mount holes and the power cord to run
down the back of the Switch.
Note: Make sure the screws are securely fixed to the wall and strong enough to hold the
weight of the Switch with the connection cables.
4Place the Switch so the wall mount holes line up with the screws. Slide the Switch down gently to fix it into
place.
Wall-mount the Switch with the Ethernet ports facing down and the
ventilation holes on the side.
Figure 7 Wall Mounting
Table 3 Wall Mounting Distance
DISTANCE ‘D’ BETWEEN MOUNTING HOLES
180 mm / 7.09 in
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
16
Figure 8 Screw Specifications (XGS1210-12)
Figure 9 Screw Specifications (XGS1250-12)

Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
17
CHAPTER 3
Hardware Panels
3.1 Hardware Overview
This section describes the front and rear panels for each model.
The following table summarizes the port features of the Switch by model.
3.2 Front Panel
The following figure shows the front panel of the Switch.
Figure 10 Front Panel (XGS1210-12)
Figure 11 Front Panel (XGS1250-12)
3.3 Rear Panel
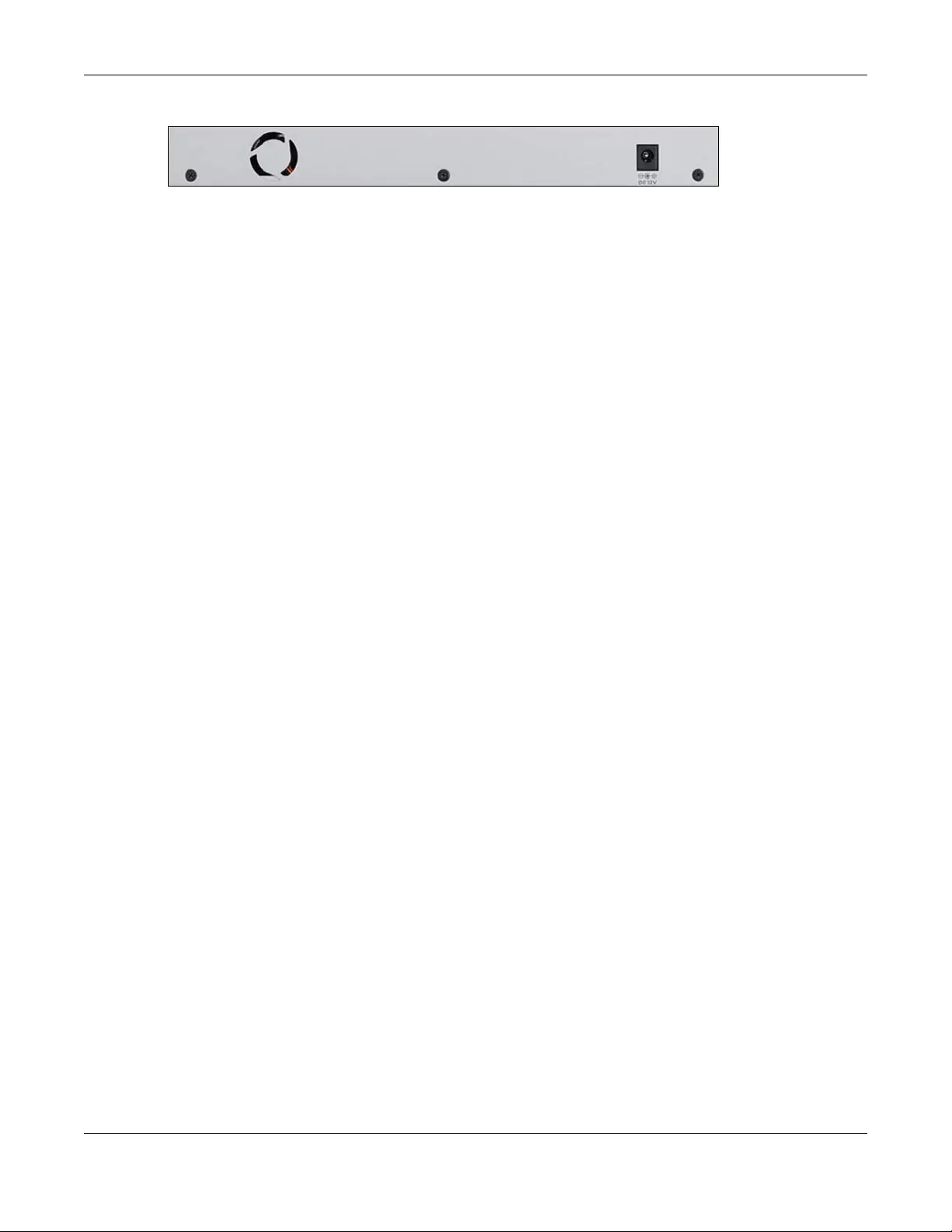
The following figure shows the rear panel of the Switch.
Figure 12 Rear Panel (XGS1210-12)
Table 4 Port Comparison Table
MODELS XGS1210-12 XGS1250-12
10M / 100M / 1000M Ethernet Ports 8 8
100M / 1000M / 2.5G Ethernet Ports 2 –
100M / 1000M / 2.5G / 5G / 10G Ethernet Ports – 3
10G SFP+ interface 2 1
Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
18
Figure 13 Rear Panel (XGS1250-12)
3.3.1 Power Connector
Note: Make sure you are using the correct power source as shown on the panel.
To connect power to the Switch, insert the female end of the power cord to the AC power receptacle
on the rear panel. Connect the other end of the supplied power cord to a power outlet. Make sure that
no objects obstruct the airflow.
3.3.2 Smart Fan (for XGS1250-12)
A properly functioning fan is essential, along with a sufficiently ventilated and cool operating
environment, to prevent the Switch from overheating.
With Smart Fan, the fan in the Switch automatically adjust its speed according to the internal
temperature. This prevents overheating, minimizes noise, and reduces power consumption.
Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
19
3.4 LEDs
After you connect the power to the Switch, view the LEDs to ensure proper functioning of the Switch
and as an aid in troubleshooting.
Table 5 LED Descriptions (XGS1210-12)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Green On The Switch power is on.
Blinking The Switch is starting up.
Off The Switch power is off.
Ports 1–8
LINK/ACT
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Amber On The port has a successful 10M / 100M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
If you enable Loop Prevention in the Port screen, and a loop
happens on two ports, the higher-numbered port will be off.
Port 9
(Left LED)
Port 10
(Right LED)
Sky Blue On The port has a successful 2.5G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Amber On The port has a successful 100M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
Port 11
(Left LED)
Port 12
(Right LED)
Blue On The port has a successful 10G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
Table 6 LED Descriptions (XGS1250-12)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Green On The Switch power is on.
Blinking The Switch is starting up.
Off The Switch power is off.
Ports 1–8
LINK/ACT
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Amber On The port has a successful 10M / 100M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
If you enable Loop Prevention in the Port screen, and a loop
happens on two ports, the higher-numbered port will be off.
Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
20
Port 9
(Left LED)
Port 10
(Right LED)
Port 11
(Left LED)
Blue On The port has a successful 10G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Purple On The port has a successful 5G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Sky Blue On The port has a successful 2.5G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Amber On The port has a successful 100M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
Port 12
(Right LED)
Blue On The port has a successful 10G connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Green On The port has a successful 1000M connection.
Blinking The Switch is transmitting data through the port.
Off The port is disconnected or disabled.
Table 6 LED Descriptions (XGS1250-12) (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
21
CHAPTER 4
Web Configurator
4.1 Overview
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web Configurator.
The Web Configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy system setup and
management through Internet browser. Use a browser that supports HTML5, such as Microsoft Edge,
Internet Explorer 11, Mozilla Firefox, or Google Chrome. The recommended minimum screen resolution is
1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the Web Configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
4.2 System Login
1Start your web browser.
2Type “http://” and the IP address of the Switch (for example, the default management IP address is
192.168.1.3) in the Location or Address field. Press [ENTER]. Your computer must be in the same subnet in
order to access this website address.
3The login screen appears. The default password is 1234.
Figure 14 Web Configurator: Log In
4The following screen displays if you log into the Switch for the first time. Enter a new password using the
keyboard characters ("a – z", "A – Z", "0 – 9", ~!@#$%^&*()_+`–={}[]:;<>./\). The password must be 8 to 15
characters long. Retype it to confirm and click Apply to view the first Web Configurator screen.

Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
22
Figure 15 Web Configurator: Change Password
Note: Make sure to log out of the Switch from a computer before logging in again on another
computer. The Web Configurator automatically logs out after 5 minutes of inactivity.
4.3 Zyxel One Network (ZON) Utility
ZON Utility is a program designed to help you deploy and manage a network more efficiently. It detects
devices automatically and allows you to do basic settings on devices in the network without having to
be near it.
The ZON Utility issues requests through Zyxel Discovery Protocol (ZDP) and in response to the query, the
device responds back with basic information including IP address, firmware version, location, system
and model name in the same broadcast domain. The information is then displayed in the ZON Utility
screen and you can perform tasks like basic configuration of the devices and batch firmware upgrade
in it. You can download the ZON Utility at www.zyxel.com and install it in a computer (Windows
operating system).
4.3.1 Requirements
Before installing the ZON Utility in your computer, please make sure it meets the requirements listed
below.
Operating System
At the time of writing, the ZON Utility is compatible with:
• Windows 7 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Windows 8 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Windows 8.1 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Windows 10 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
Note: To check for your Windows operating system version, right-click on My Computer >
Properties. You should see this information in the General tab.
Hardware
Here are the minimum hardware requirements to use the ZON Utility on your computer.
Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
23
• Core i3 processor
•2 GB RAM
• 100 MB free hard disk
• WXGA (Wide XGA 1280 by 800)
4.3.2 Run the ZON Utility
1Double-click the ZON Utility to run it.
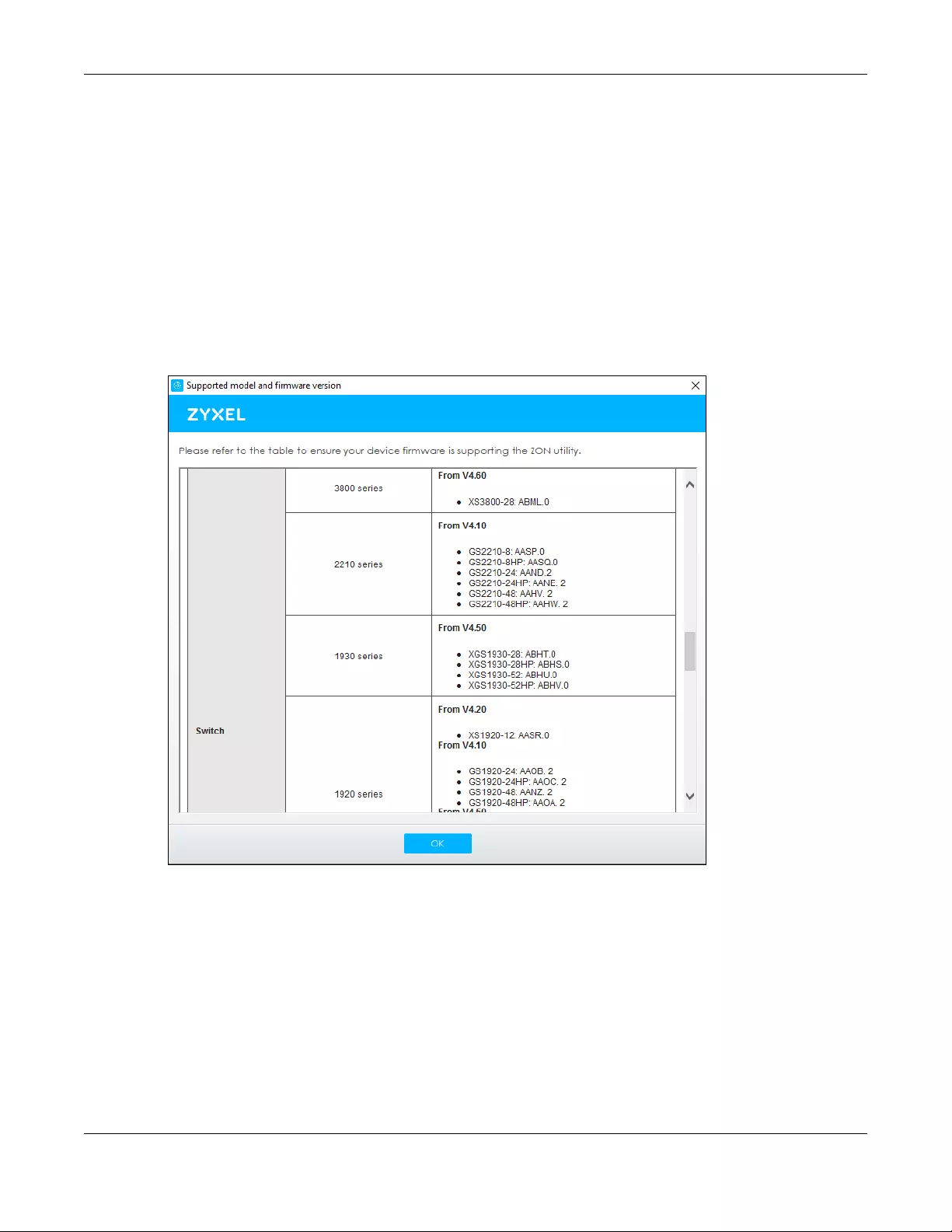
2The first time you run the ZON Utility, you will see if your device and firmware version support the ZON
Utility. Click the OK button to close this screen.
Figure 16 Supported Devices and Versions
If you want to check the supported models and firmware versions later, you can click the Show
information about ZON icon in the upper right hand corner of the screen. Then select the Supported
model and firmware version link. If your device is not listed here, see the device release notes for ZON
Utility support. The release notes are in the firmware zip file on the Zyxel web site.
Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
24
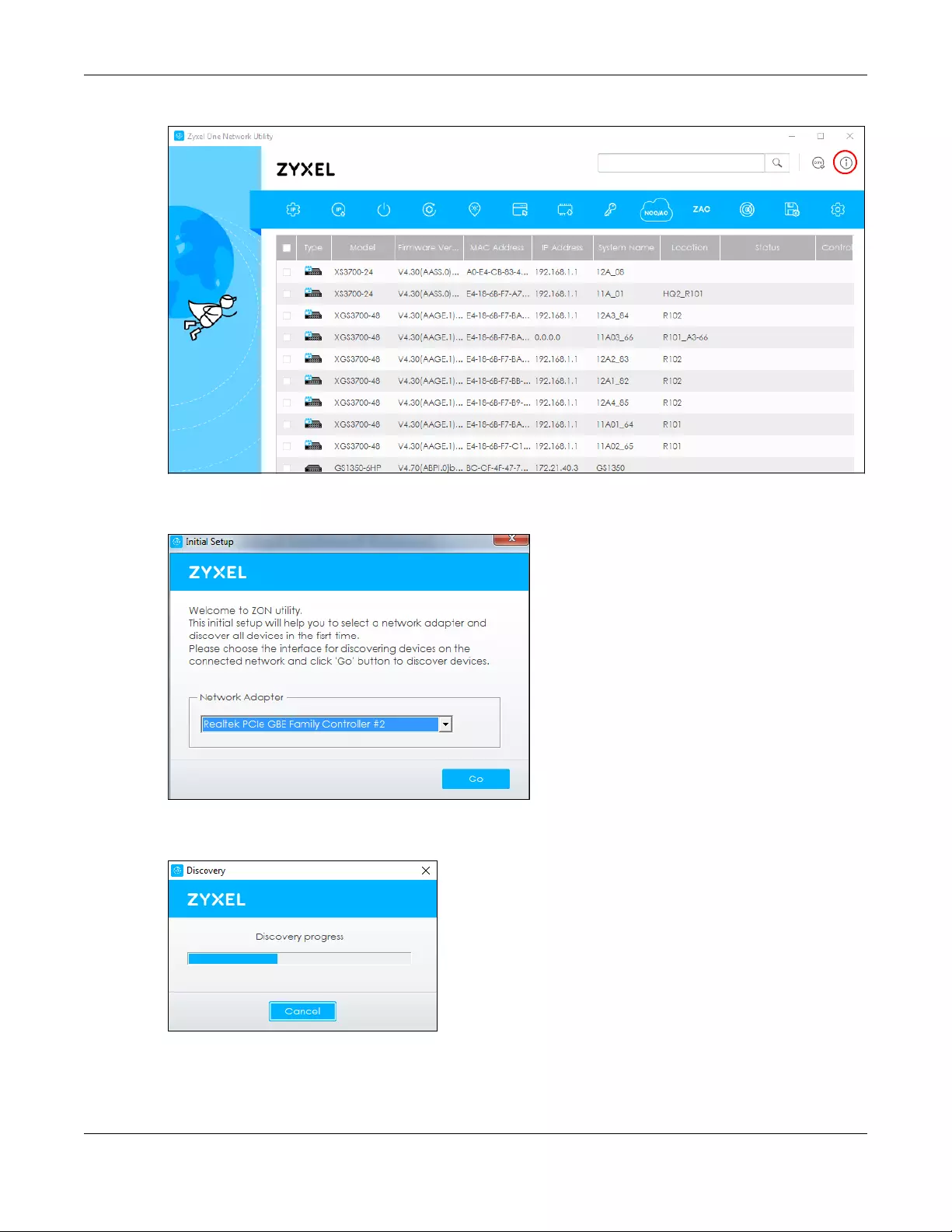
Figure 17 ZON Utility Screen
3Select a network adapter to which your supported devices are connected.
Figure 18 Network Adapter
4Click the Go button for the ZON Utility to discover all supported devices in your network.
Figure 19 Discovery
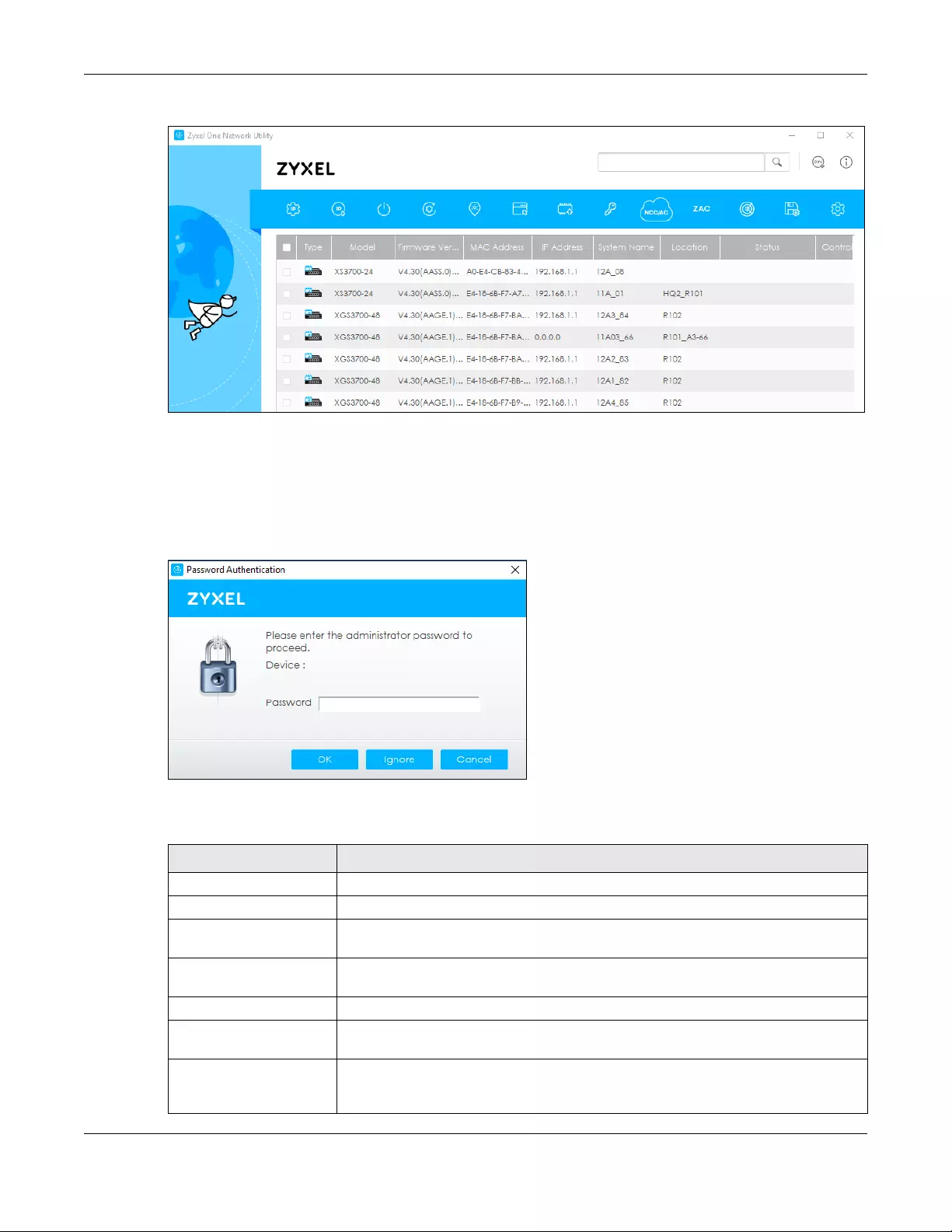
5The ZON Utility screen shows the devices discovered.
Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
25
Figure 20 ZON Utility Screen
6Select a device and then use the icons to perform actions. Some functions may not be available for
your devices.
Note: You must know the selected device admin password before taking actions on the
device using the ZON Utility icons.
Figure 21 Password Prompt
The following table describes the icons numbered from left to right in the ZON Utility screen.
12345678910 11 12 13
Table 7 ZON Utility Icons
ICON DESCRIPTION
1 IP Configuration Change the selected device’s IP address.
2 Renew IP Address Update a DHCP-assigned dynamic IP address.
3 Reboot Device Use this icon to restart the selected devices. This may be useful when troubleshooting
or upgrading new firmware.
4 Reset Configuration to
Default
Use this icon to reload the factory-default configuration file. This means that you will
lose all previous configurations.
5 Locator LED Use this icon to locate the selected device by causing its Locator LED to blink.
6 Web GUI Use this to access the selected device Web Configurator from your browser. You will
need a user name and password to log in.
7 Firmware Upgrade Use this icon to upgrade new firmware to selected devices of the same model. Make
sure you have downloaded the firmware from the Zyxel website to your computer and
unzipped it in advance.
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
26
The following table describes the fields in the ZON Utility main screen.
4.4 Web Configurator Layout
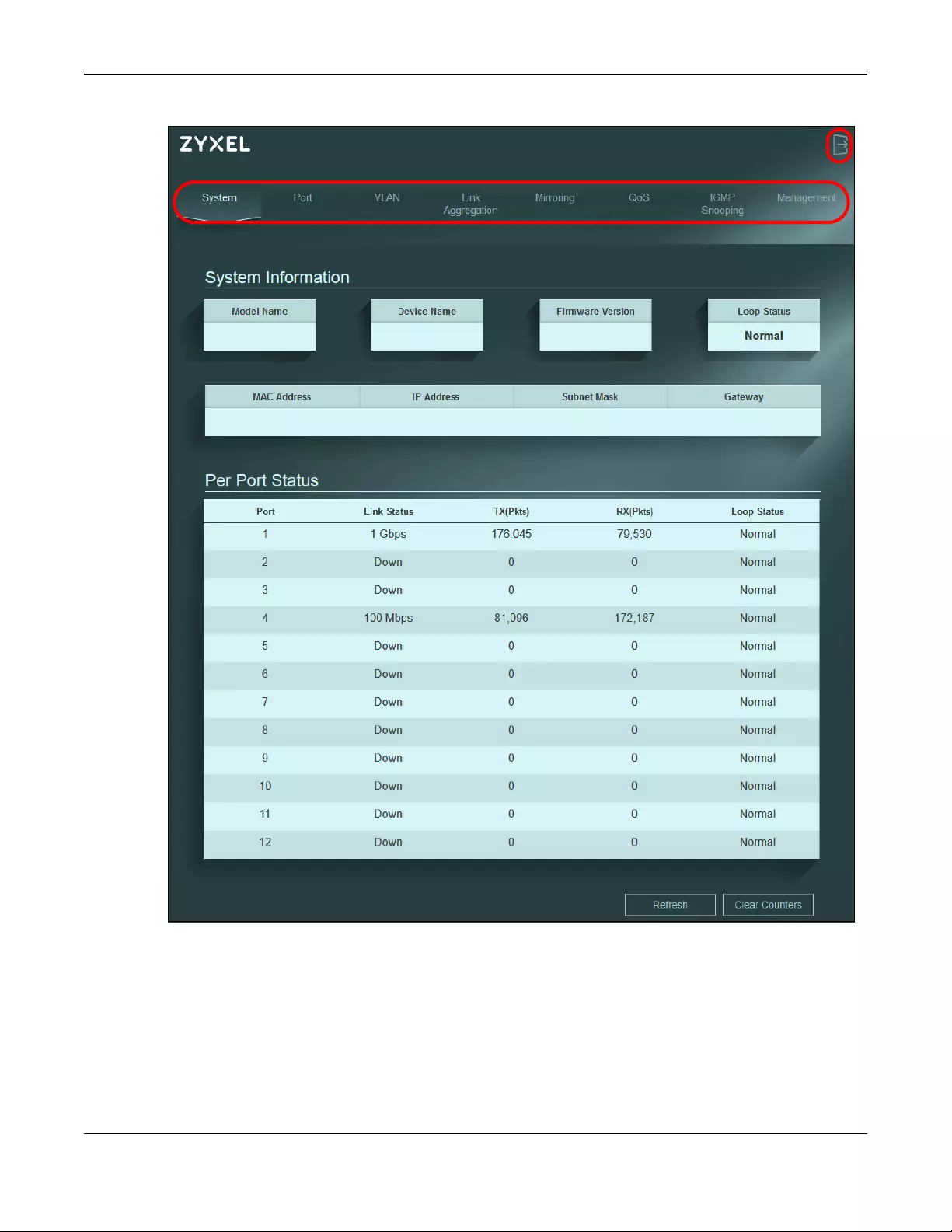
The System screen is the first screen that displays when you access the Web Configurator.
The following figure shows the navigating components of the Web Configurator screen.
8 Change Password Use this icon to change the admin password of the selected device. You must know
the current admin password before changing to a new one.
9 Configure NCC
Discovery
You must have Internet access to use this feature. Use this icon to enable or disable the
Nebula Control Center (NCC) discovery feature on the selected device. If it is
enabled, the selected device will try to connect to the NCC. Once the selected
device is connected to and has registered in the NCC, it will go into the Nebula cloud
management mode.
10 ZAC Use this icon to run the Zyxel AP Configurator of the selected AP.
11 Clear and Rescan Use this icon to clear the list and discover all devices on the connected network again.
12 Save Configuration Use this icon to save configuration changes to permanent memory on a selected
device.
13 Settings Use this icon to select a network adapter for the computer on which the ZON utility is
installed, and the utility language.
Table 8 ZON Utility Fields
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Type This field displays an icon of the kind of device discovered.
Model This field displays the model name of the discovered device.
Firmware Version This field displays the firmware version of the discovered device.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the discovered device.
IP Address This field displays the IP address of an internal interface on the discovered device that
first received a ZDP discovery request from the ZON Utility.
System Name This field displays the system name of the discovered device.
Location This field displays where the discovered device is.
Status This field displays whether changes to the discovered device have been done
successfully. As the Switch does not support IP Config uration, Renew IP address and
Flash Locator LED, this field displays “Update failed”, “Not support Renew IP address”
and “Not support Flash Locator LED” respectively.
Controller Discovery This field displays if the discovered device supports the Nebula Control Center (NCC)
discovery feature. If it is enabled, the selected device will try to connect to the NCC.
Once the selected device is connected to and has registered in the NCC, it will go
into the Nebula cloud management mode.
Serial Number Enter the admin password of the discovered device to display its serial number.
Hardware Version This field displays the hardware version of the discovered device.
Table 7 ZON Utility Icons (continued)
ICON DESCRIPTION
Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
27
Figure 22 Web Configurator Layout
A – Click the menu items to open the screen in the main window.
B – Click this link to log out of the Web Configurator.
AB

Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
28
The following table describes the links in the navigation panel.
4.4.1 Change Your Password
After you log in for the first time, you must enter a new password using the keyboard characters ("a – z",
"A – Z", "0 – 9", ~!@#$%^&*()_+`–={}[]:;<>./\). The password must be 8 to 15 characters long. To change it,
click Management to display the next screen to change your login password.
Figure 23 Change Administrator Login Password
Table 9 Navigation Panel Links
LINK DESCRIPTION
System This link takes you to a screen that displays general system information, loop status, and
individual port statistics.
Port This link takes you to a screen to enable Broadcast Storm Control and Loop Detection/Loop
Prevention. You can also configure advanced settings, such as transmission speed and flow
control on a port.
VLAN This link takes you to a screen where you can set the PVID (Port VLAN ID) on a port and create/
modify/delete IEEE 802.1Q VLAN for the Switch.
Link Aggregation This link takes you to screens where you can logically aggregate physical links to form one
logical and higher-bandwidth link.
Mirroring This link takes you to a screen where you can copy traffic from one port or ports to another port
so that you can examine the traffic from the first port without interference.
QoS This link takes you to a screen where you can configure port-based or IEEE 802.1p QoS. The
Switch can put packets into the queues according to the port on which the packet is received
or the priority tag in the packet.
IGMP Snooping This link takes you to a screen where you can configure IGMP snooping. You must enable IGMP
snooping to use the IPTV service. It checks the IGMP packets passing through it, picks out the
group registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly.
Management This link takes you to screens where you can change the system login password, perform
firmware upgrade and configuration file maintenance as well as reset/reboot the system. You
can also configure the IP address and subnet mask, set management VID, and enable HTTP/
HTTPS and IEEE 802.3az EEE.

Chapter 4 Web Configurator
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
29
4.5 Switch Lockout/Resetting the Switch
You could block yourself (and all others) from managing the Switch if you remove all ports from VLAN1
and you do not configure other VLAN groups.
Note: Be careful not to lock yourself and others out of the Switch.
Make sure to log out of the Switch from a computer before logging in again on another
computer.
If you forget the administrator password or cannot access the Web Configurator, you will need to use
the RESET button at the front panel of the Switch to reset it back to the factory defaults.
This means that you will lose all configurations that you had previously and the password will be reset to
“1234”. IP address will also be reset to 192.168.1.3.
1Make sure the PWR/SYS LED is on (not blinking).
2To set the device back to the factory default settings, press the RESET button for more than 6 seconds or
until the PWR/SYS LED begins to blink and then release it. When the PWR/SYS LED begins to blink, the
defaults have been restored and the device restarts.
4.6 Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Click the logout icon in a screen to exit the Web Configurator. You have to log in with your password
again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session for security reasons.
Note: You are automatically logged out of the Web Configurator after 5 minutes of inactivity.

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
30
CHAPTER 5
Initial Setup Example
5.1 Overview
This chapter shows how to set up the Switch for use.
The following lists the configuration steps for the initial setup:
•Change the IP Address
•Change the Password
5.1.1 Change the IP Address
If you do not wish to set your Switch as a DHCP client (DHCP client field is Disable), assign an IP address
for the Switch. The IP address makes it accessible from an outside network. It is used by the Switch to
communicate with other devices in other networks.
In this example, you want to change the IP address to 192.168.1.5.
1Click Management in the navigation panel to open the following screen.
Figure 24 Change the IP Address
2Enter the new IP address 192.168.1.5 in the IP Address field.
3Click Apply.
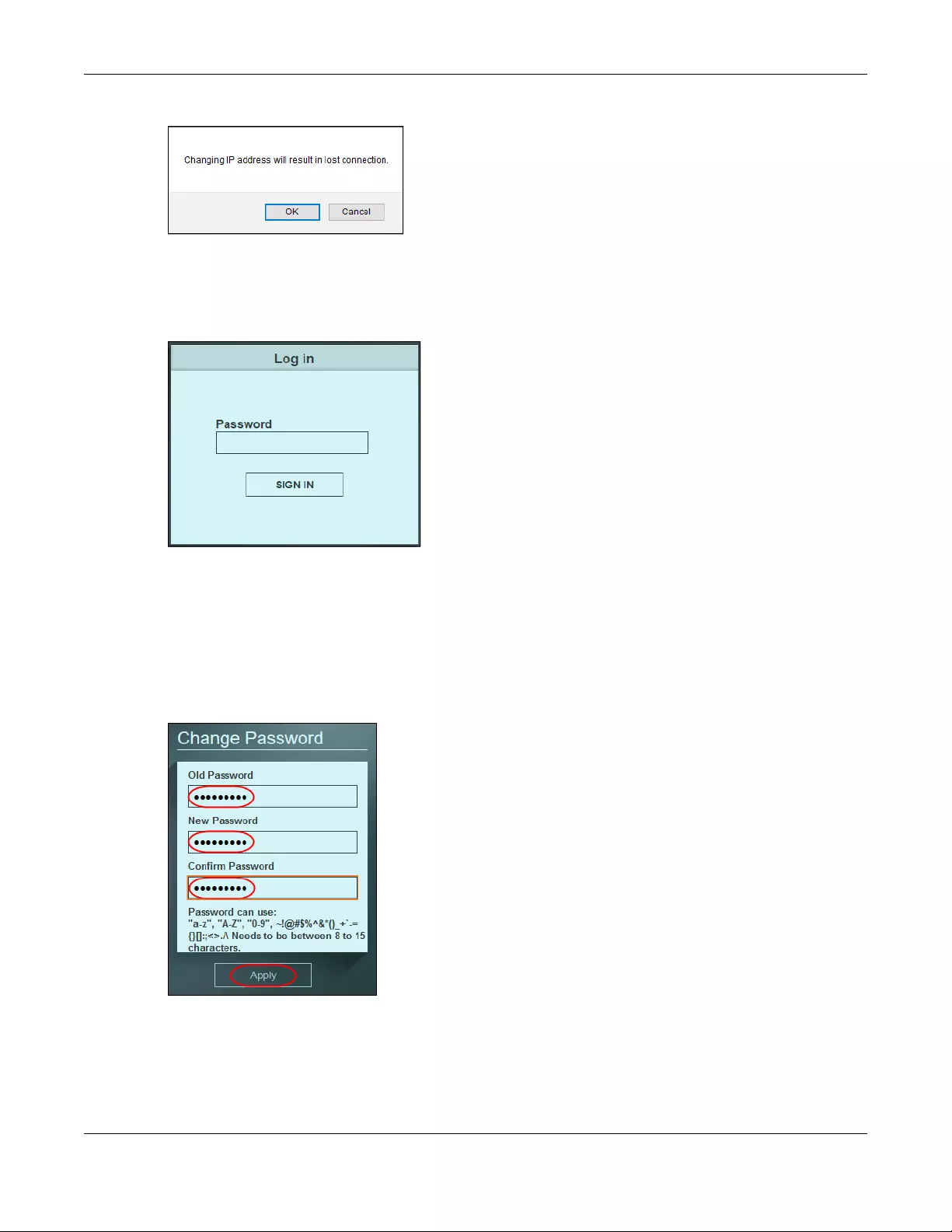
4The following screen appears. Click OK to save the setting. Connection to the Web Configurator will be
lost.
Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
31
Figure 25 Lost Connection Warning
5On your web browser, go to http://192.168.1.5.
6A Log in screen appears. Enter the existing password and click SIGN IN to log in through the new IP
address.
5.1.2 Change the Password
The first time you log in to the Web Configurator, you will be asked to change the default password
1234. If you wish to change the password again, perform the following steps:
1Click Management in the navigation panel to open the following screen.
Figure 26 Change the Password
2Enter the existing password in the Old Password field.
3Enter the new system password in the New Password field using the keyboard characters (a – z, A – Z, 0 –
9, and ~!@#$%^&*()_+`–={}[]:;<>./\). The password must be 8 to 15 characters long.

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
32
4Enter the new password again to in the Confirm Password field for confirmation.
5Click Apply. You will automatically be logged out of the Web Configurator.
6A Log in screen appears. Enter the new password and click SIGN IN to log in using the new password.
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
33
CHAPTER 6
Tutorials
6.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to use the Switch’s various features.
•Creating a VLAN, see page 33
•Setting Port VID, see page 35
6.2 Creating a VLAN
By default, all ports on the Switch are in VLAN 1.
VLANs confine broadcast frames to the VLAN group in which the ports belongs. You can create a VLAN
group with fixed port members to do this.
If you want to have a port (for example port 1) belong to another VLAN as well, say VLAN 2, you need to
create a VLAN first, and then add the port to the VLAN.
Figure 27 Initial Setup Network Example: VLAN
1Click VLAN in the navigation panel and click Create New VLAN.
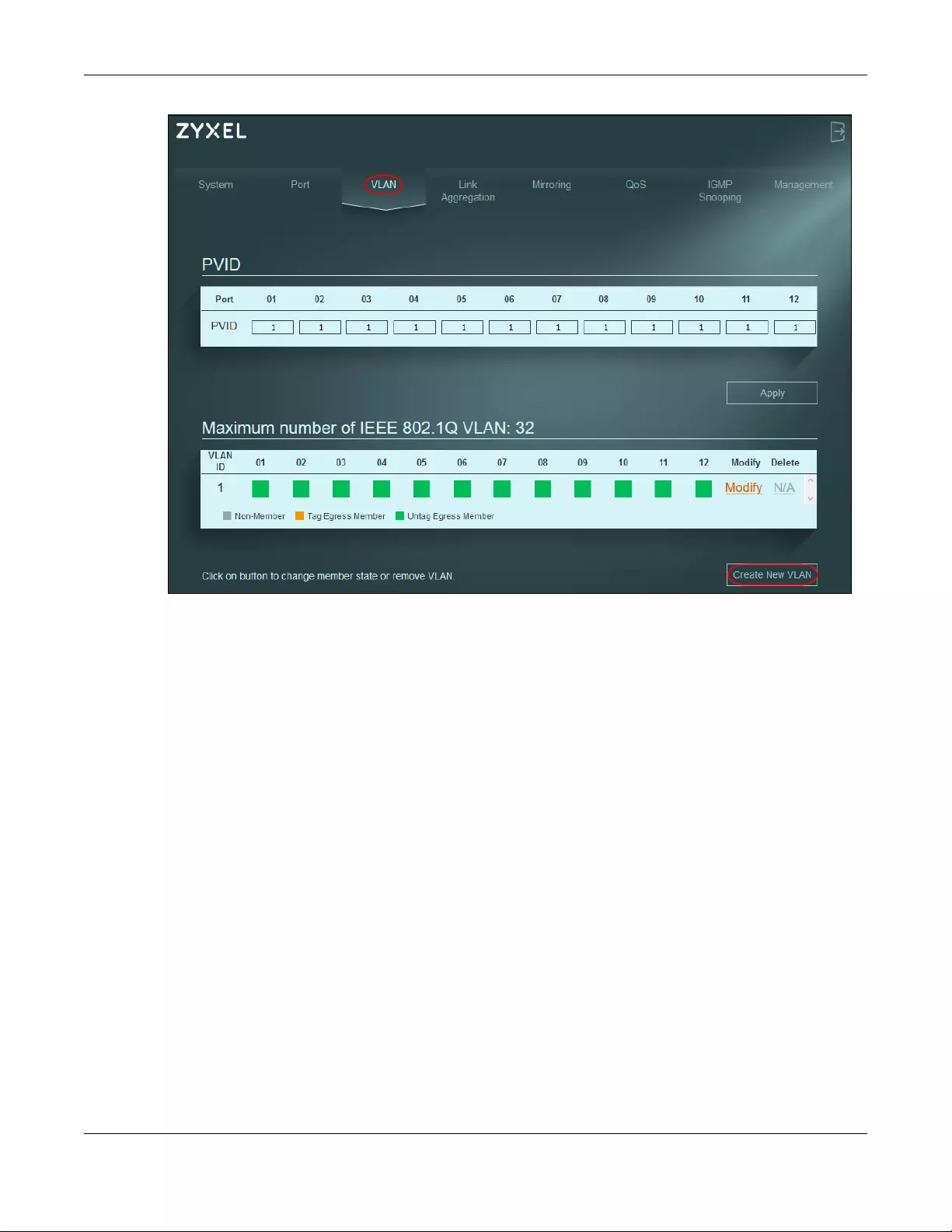
Chapter 6 Tutorials
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
34
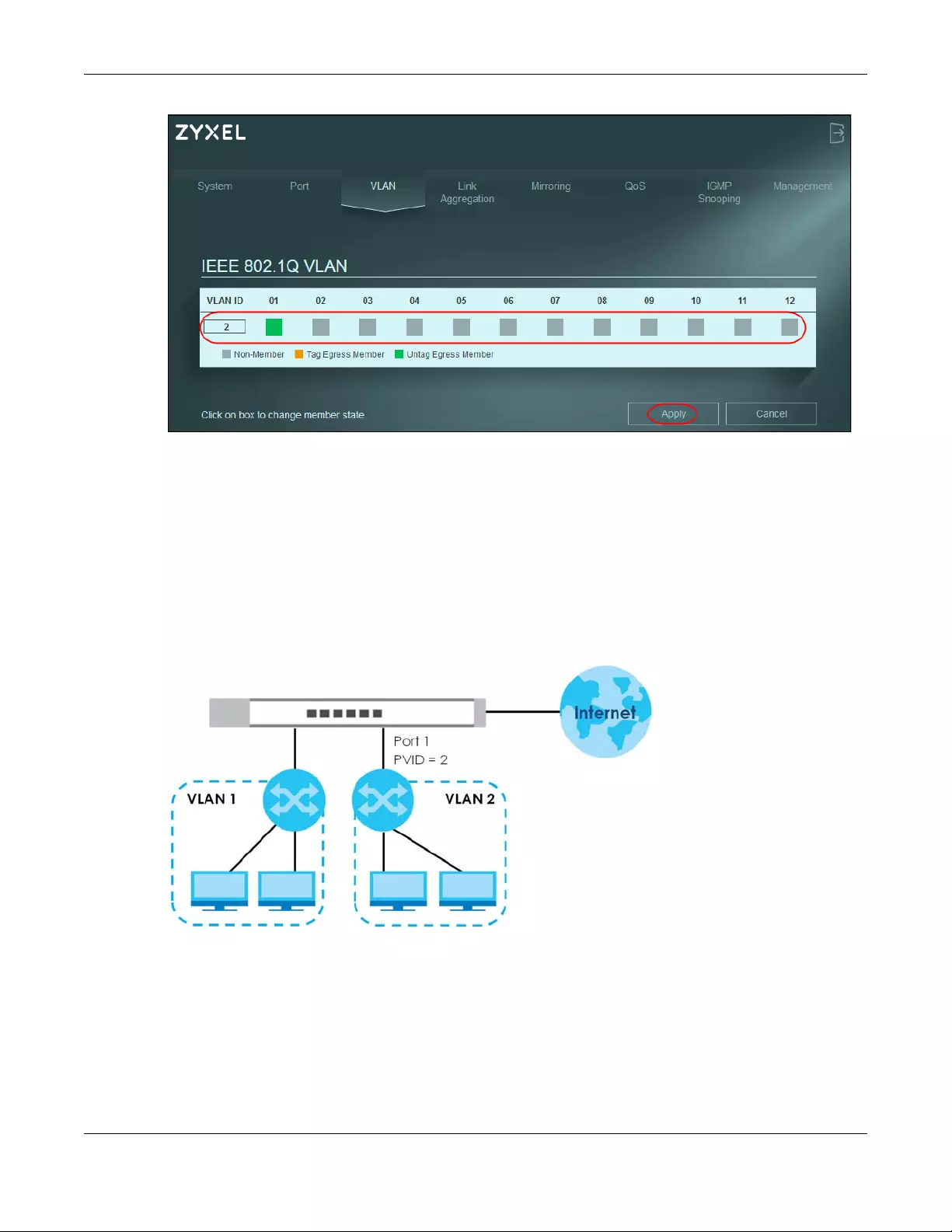
2Enter 2 in the VLAN ID field for the VLAN2 network.
3Since the VLAN2 network is connected to port 1 on the Switch, configure port 1 to be a permanent
member of the VLAN. To ensure that VLAN-unaware devices (such as computers and hubs) can receive
frames properly, click the port’s box color to green to set the Switch to remove VLAN tags before
sending. Clicking the port’s check box loops between untagging, non-member, and tagging.
4Change the box color of other ports not a member of the VLAN group to gray.
5Click Apply to save the settings.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
35
6.3 Setting Port VID
Use PVID to add a tag to incoming untagged frames received on that port so that the frames are
forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
In the example network, configure 2 as the port VID on port 1 so that any untagged frames received on
that port get sent to VLAN 2.
Figure 28 Initial Setup Network Example: Port VID
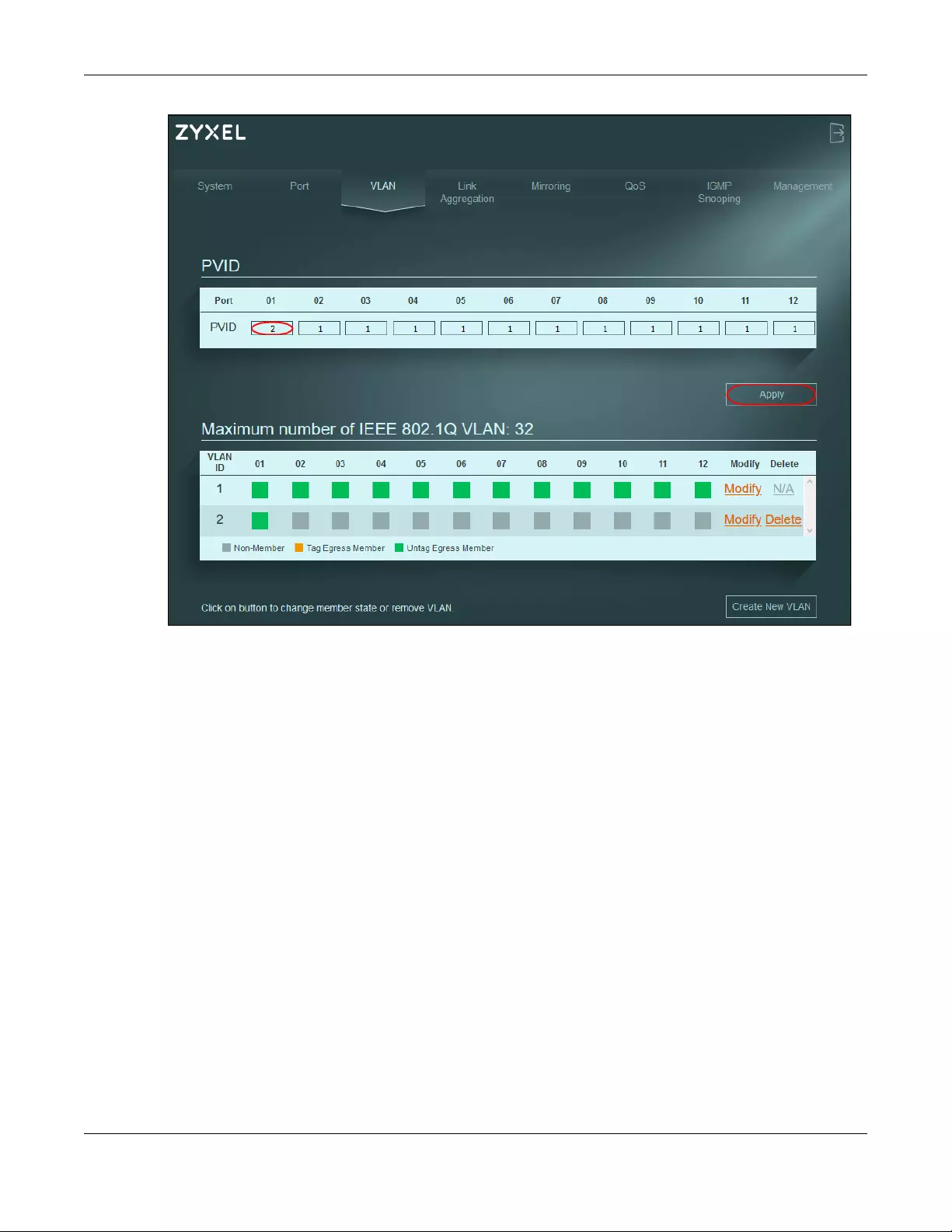
1Click VLAN in the navigation panel.
2Enter 2 in the PVID field for port 2 and click Apply to save your changes back to the Switch.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
36

37
PART II
Technical Reference

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
38
CHAPTER 7
System
7.1 Overview
This chapter describes the screens for system status, and port details.
7.2 System Settings
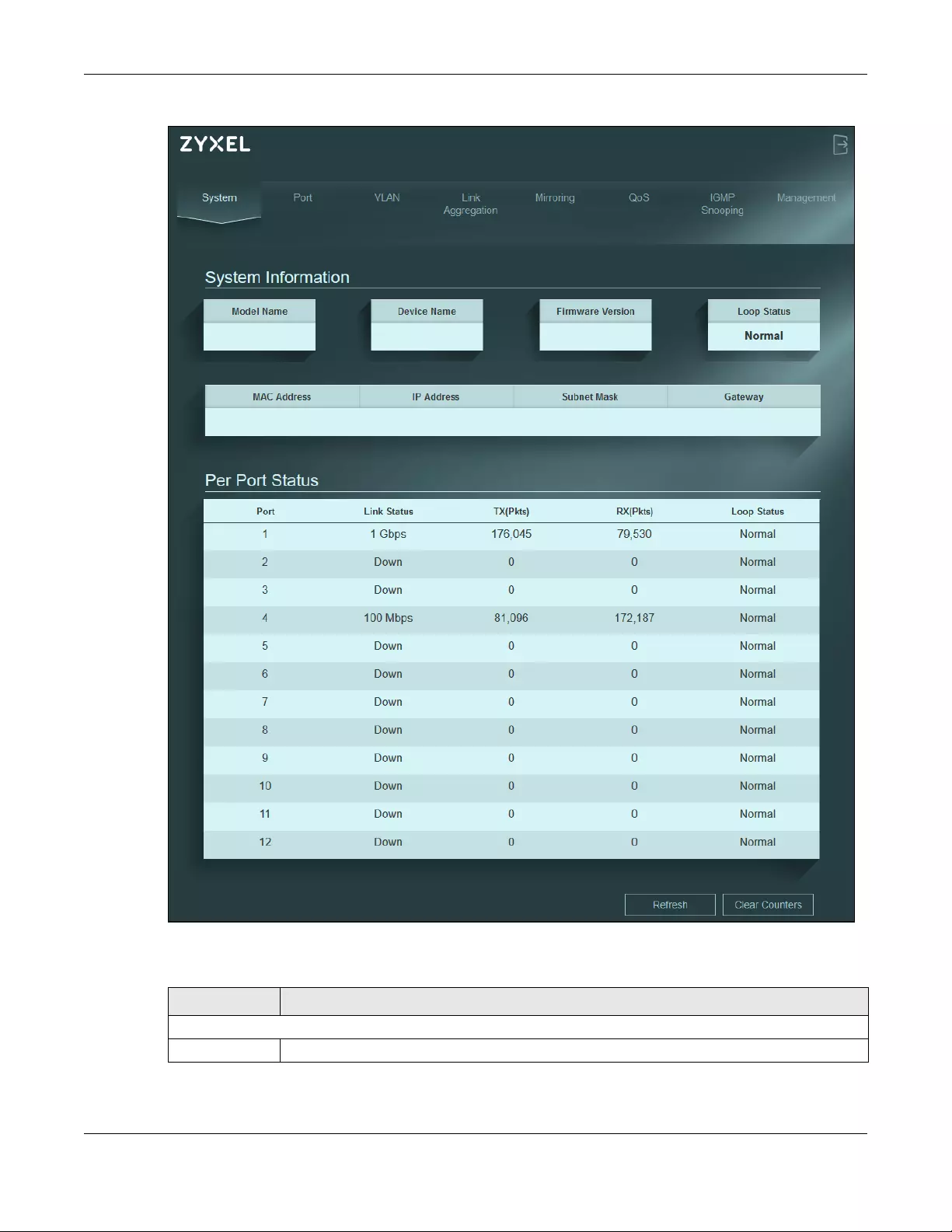
The System screen displays when you log into the Switch or click System at the top of the Web
Configurator. The System screen displays the Switch’s general device information, and the port statistics.
Chapter 7 System
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
39
Figure 29 System
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 System
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Information
Model Name This field displays the model name of this Switch.

Chapter 7 System
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
40
Device Name This field displays the name used to identify the Switch on any network.
The device name is a link that you can click to open a screen where you can change the
name. Enter a descriptive name of up to 14 characters. Also, spaces and the following special
characters listed in the brackets ["`<>^$|&;\/:*?’] are not allowed.
Note: You must enter a descriptive name to identify the Switch.
Firmware
Version
This field displays the version number and date of the firmware the Switch is currently running.
Loop Status This field displays whether the Switch is in a loop state. It displays Loop when the Switch detects a
loop on one of the ports. Otherwise, it displays Normal.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the Switch.
IP Address The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default IP
address is 192.168.1.3.
This field displays the Switch’s current IPv4 address.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. The factory default
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
This field displays the Switch’s subnet mask.
Gateway The field displays the gateway that allows you to send or receive data traffic to or from a
different network than the one the Switch is on.
Per Port Status
Port This identifies the Ethernet port on the Switch.
Link status This field displays the current status or speed of each port. Otherwise, it displays Down.
For XGS1210-12:
• either 10M, 100M, 1000M for ports 1 – 8
• either 100M, 1000M, 2.5G for ports 9 – 10
• either 1000M or 10G for port 11 – 12
For XGS1250-12:
• either 10M, 100M, 1000M for ports 1 – 8
• either 100M, 1000M, 2.5G, 5G, 10G for ports 9 – 11
• either 1000M or 10G for port 12
TX(Pkts) This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RX(Pkts) This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Loop Status It displays Loop when the Switch detects a loop on the port. Otherwise, it displays Normal.
Refresh Click this button to update the information in this screen.
Clear Counters Click this button to clear the statistics in the TX(Pkts) and RX(Pkts) fields.
Table 10 System (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
41
CHAPTER 8
Port
8.1 Overview
This chapter introduces and shows you how to configure the broadcast storm control feature and use
loop prevention or loop detection to prevent loops in your network. In addition, you can configure the
transmission speed and flow control on a port.
8.1.1 What You Need to Know
Read this section to know more about Loop Detection, Loop Prevention, and Broadcast Storm Control.
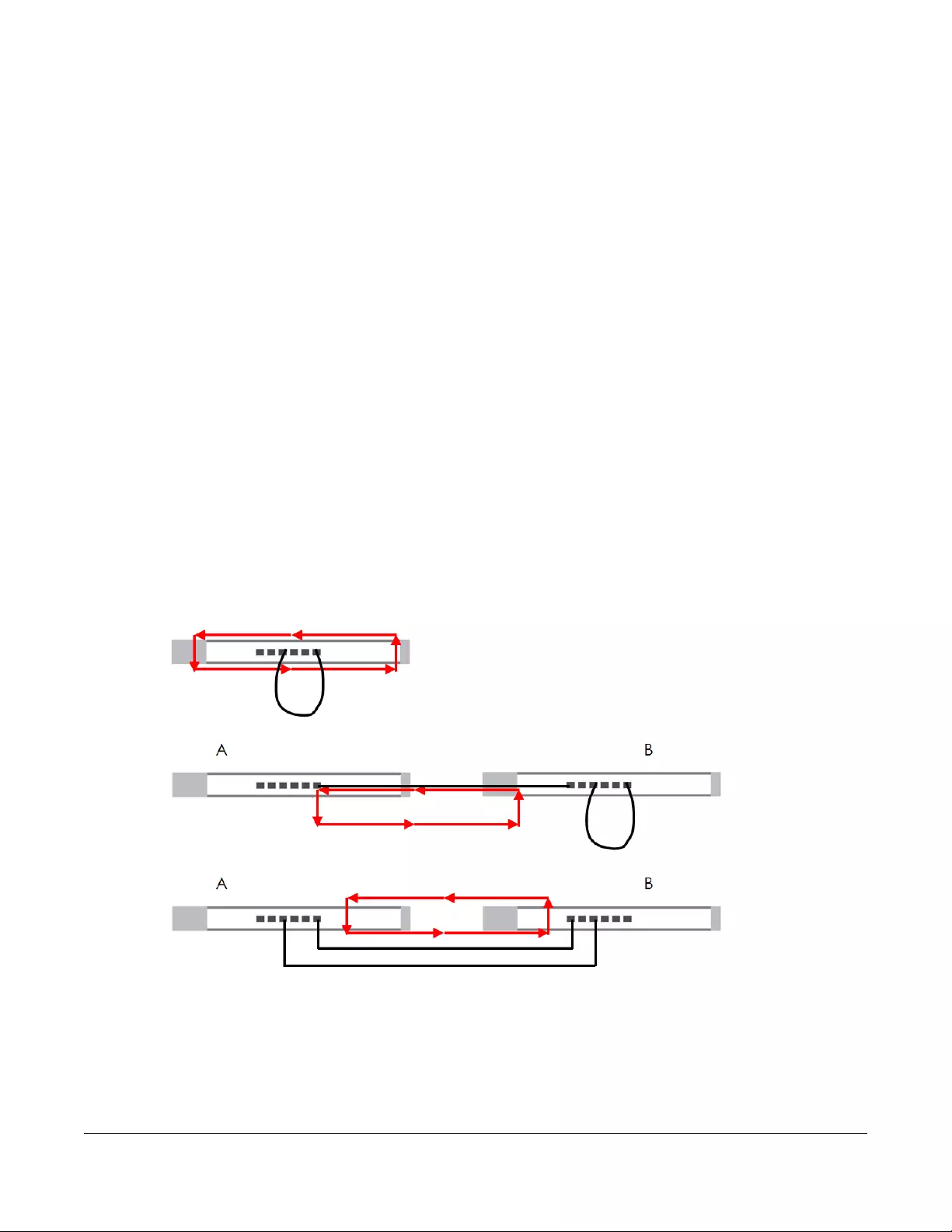
8.1.1.1 Loop Detection and Loop Prevention
A switch loop happens if there is more than one connection between two ports on the same switch or
between two switches connected together. If this happens, broadcasts are continually rebroadcast
and could flood the network. You must break the loop by stopping multiple paths between two switch
ports.
Figure 30 The Switch has Two Ports Connected with the Same Cable
Figure 31 The Connected Switch has Two Ports Connected with the Same Cable
Figure 32 Two Connections between Switches Without Using the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Loop Detection allows the Switch to discover a loop if it happens, and create a log. Loop Prevention
allows the Switch to shut down a port automatically if it discover a loop on that port. See Section 3.4 on
page 19 for more information about LEDs.
8.1.1.2 Broadcast Storm Control
Broadcast storm control limits the number of broadcast packets the Switch receives per second on the
Chapter 8 Port
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
42
ports. When the maximum number of allowable broadcast packets is reached per second, the
subsequent packets are discarded. Enable this feature to reduce broadcast packets in your network.
You can specify limits on each port.
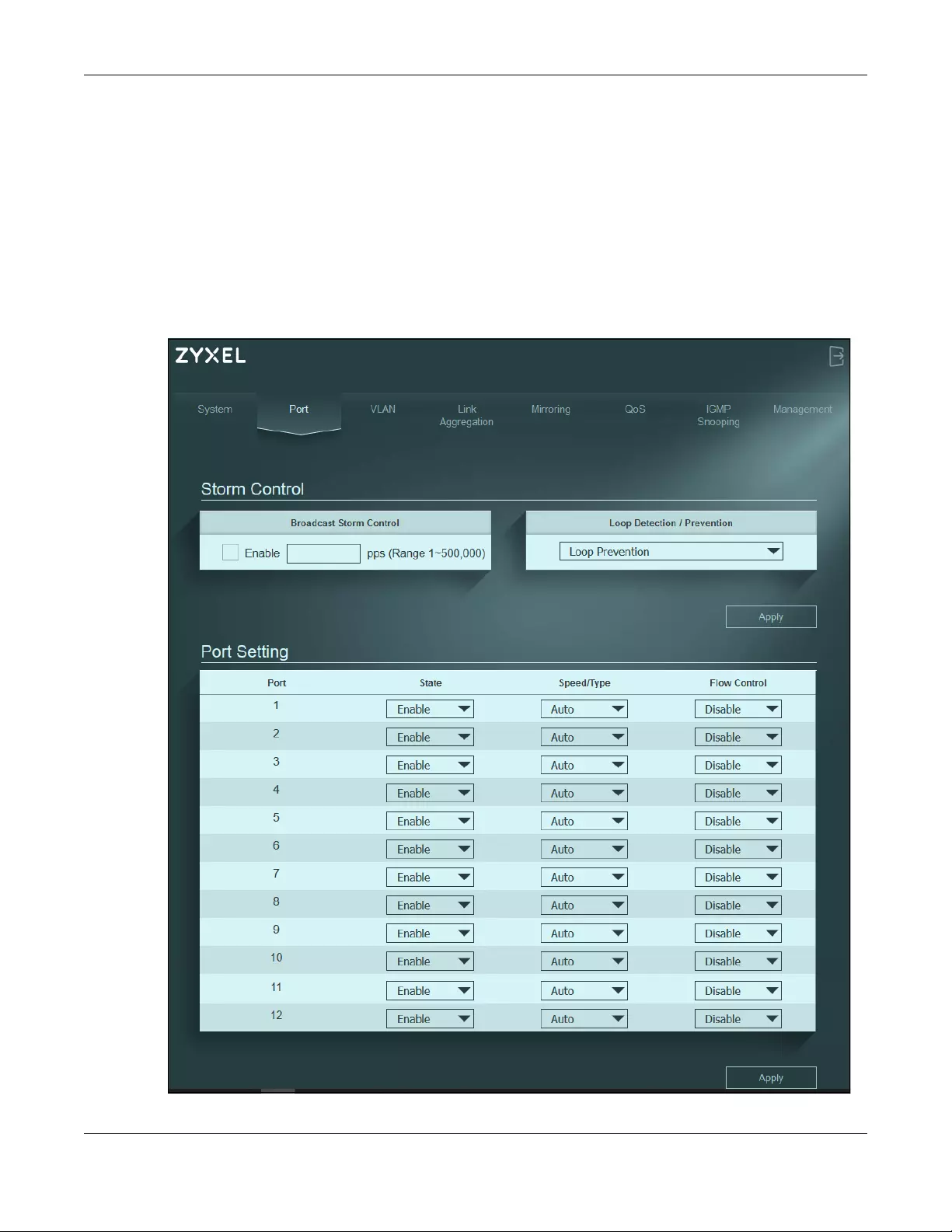
8.2 Port Settings
Click Port in the navigation panel to open the following screen. See Section 1.2.1 on page 10 for
information on Multi-Gigabit.
Figure 33 Port

Chapter 8 Port
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
43
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Storm Control
Broadcast Storm
Control
Enable traffic storm control on the Switch by specifying how many broadcast packets a port
receives per second.
Loop Detection /
Prevention
Select Loop Detection to allow the Switch to detect a loop on the port. The port becomes
active when the loop disappears.
Select Loop Prevention to allow the Switch to shut down a port automatically when it detects a
loop on the port. The port becomes active when the loop disappears.
Select Off to disable this feature.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.
Port Setting
Port This identifies the Ethernet port on the Switch.
State Select Enable to enable the port or Disable to disable it.
Speed/Type Select the speed of the Ethernet connection on this port.
The choices for XGS1210-12 are:
•Auto for all ports
•10 Mbps for ports 1 – 8
•100 Mbps for ports 1 – 10
•1000 Mbps for all ports
•2.5 G for ports 9 – 10
•DAC for ports 11 – 12, when using the DAC (Direct Attach Copper) cable
•SFP 1000M for ports 11 – 12
•SFP+ 10G for ports 11 – 12
The choices for XGS1250-12 are:
•Auto for all ports
•10 Mbps for ports 1 – 8
•100 Mbps for ports 1 – 11
•1000 Mbps for all ports
•2.5 G for ports 9 – 11
•5 G for ports 9 – 11
•10 G for ports 9 – 11
•DAC for port 12, when using the DAC (Direct Attach Copper) cable
•SFP 1000M for port 12
•SFP+ 10G for port 12
Select Auto to have the Switch obtain the following speeds (XGS1210-12):
• ports 1 – 8 connection speed of up to 1000M
• ports 9 – 10 connection speed of up to 2.5G, and ports 11-12 connection speed of up to
10G
Select Auto to have the Switch obtain the following speeds (XGS1250-12):
• ports 1 – 8 connection speed of up to 1000M
• ports 9 – 12 connection speed of up to 10G

Chapter 8 Port
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
44
Flow Control A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and overflows buffer memory
causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow Control is used to regulate transmission of
signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port.
The Switch uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full duplex mode and back pressure flow control in
half duplex mode.
IEEE802.3x flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal to the sending port,
causing it to temporarily stop sending signals when the receiving port memory buffers fill.
Back pressure flow control is typically used in half duplex mode to send a “collision” signal to
the sending port (mimicking a state of packet collision) causing the sending port to temporarily
stop sending signals and resend later. Select the check box to enable it.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.
Table 11 Port (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
45
CHAPTER 9
VLAN
9.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure VLAN settings.
9.1.1 What You Need to Know
Read this section to know more about VLAN and how to configure the screens.
9.1.1.1 IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLANs
A tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identify the VLAN membership of a
frame across bridges – they are not confined to the switch on which they were created. The VLANs can
be created statically by hand or dynamically through GVRP. The VLAN ID associates a frame with a
specific VLAN and provides the information that switches need to process the frame across the network.
A tagged frame is 4 bytes longer than an untagged frame and contains 2 bytes of TPID (Tag Protocol
IDentifier, residing within the type or length field of the Ethernet frame) and 2 bytes of TCI (Tag Control
Information, starts after the source address field of the Ethernet frame).
The CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) is a single-bit flag, always set to zero for Ethernet switches. If a
frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not be forwarded as it is to
an untagged port. The remaining 12 bits define the VLAN ID, giving a possible maximum number of 4,096
VLANs. Note that user priority and VLAN ID are independent of each other. A frame with VID (VLAN
Identifier) of null (0) is called a priority frame, meaning that only the priority level is significant and the
default VID of the ingress port is given as the VID of the frame. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is
used to identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN
configurations are 4,094.
Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames
Each port on the Switch is capable of passing tagged or untagged frames. To forward a frame from an
802.1Q VLAN-aware switch to an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware switch, the Switch first decides where to
forward the frame and then strips off the VLAN tag. To forward a frame from an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware
switch to an 802.1Q VLAN-aware switch, the Switch first decides where to forward the frame, and then
inserts a VLAN tag reflecting the ingress port's default VID. The default PVID is VLAN 1 for all ports, but this
can be changed.
A broadcast frame (or a multicast frame for a multicast group that is known by the system) is duplicated
only on ports that are members of the VID (except the ingress port itself), thus confining the broadcast to
a specific domain.
TPID
2 Bytes
User Priority
3 Bits
CFI
1 Bit
VLAN ID
12 bits
Chapter 9 VLAN
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
46
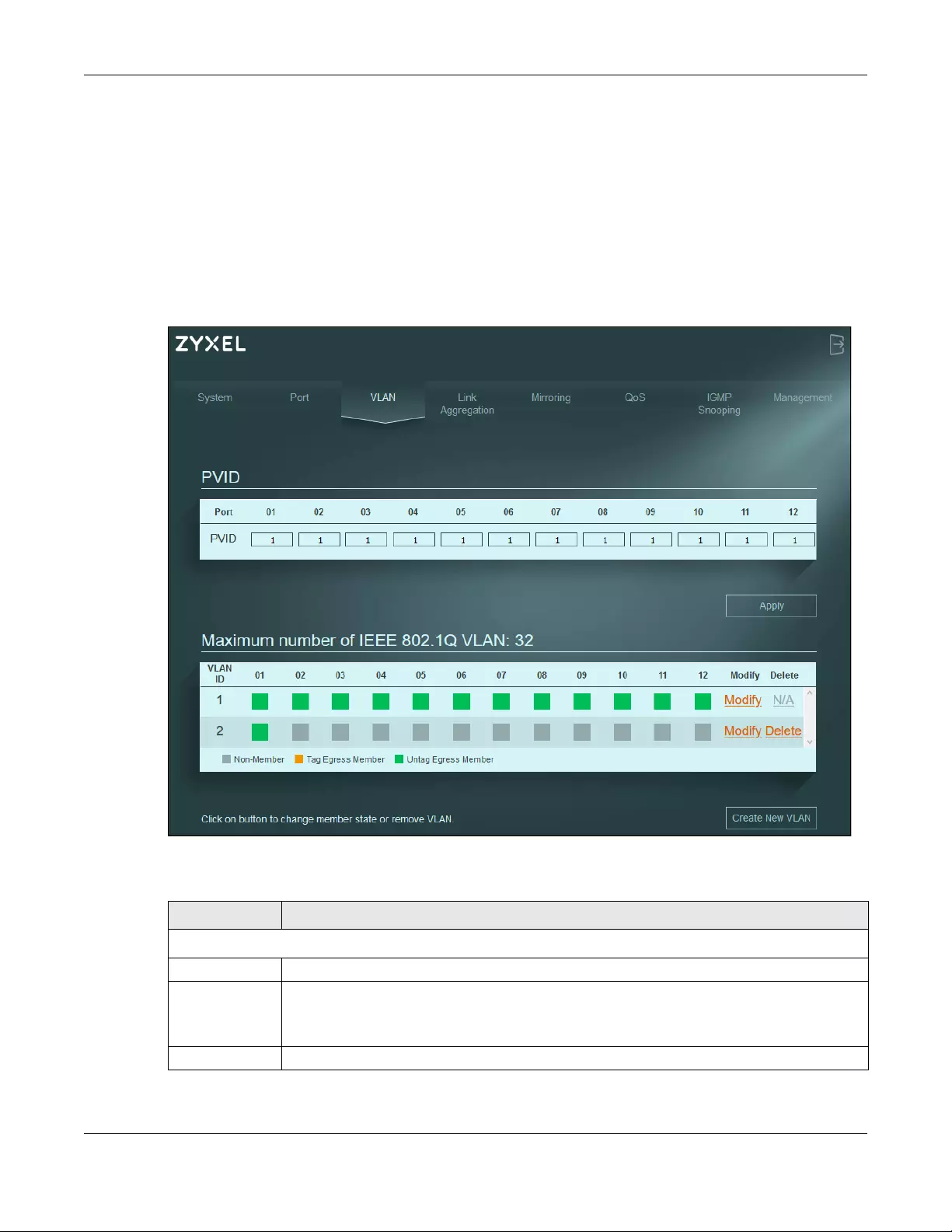
9.2 VLAN Settings
Use this screen to view and configure VLAN settings for the Switch. Click VLAN in the navigation panel to
open the following screen.
Note: You could block yourself (and all others) from managing the Switch if you remove all
ports from VLAN1 and you do not configure other VLAN groups. In case this happens,
reset the Switch to the default settings (see Section 4.5 on page 29 for more
information).
Figure 34 VLAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 VLAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PVID
Port This field displays the port number.
PVID A PVID (Port VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to incoming untagged frames received on a port so
that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the port VLAN ID.
Apply Click this button to save your PVID settings to the Switch.
Chapter 9 VLAN
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
47
Maximum
number of IEEE
802.1Q VLAN
This shows the maximum number of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs you can have on the Switch.
VLAN ID This is the ID number of the VLAN group.
Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the VLAN ID.
01 – 12 This displays the ports that are participating in a VLAN. A tagged port is orange, an untagged
port is green and ports not participating in a VLAN are gray. Multiple ports in a VLAN can be
configured as tagged or untagged or not participating.
A port is a ‘tagged port’ when the interface is expecting frames containing VLAN tags. An
example of this is when two switches are connected, and pass tagged traffic.
Modify Click Modify to edit the VLAN settings.
Delete Click Delete to remove the VLAN group. You cannot delete the default VLAN.
Create New
VLAN
Click this button to configure a new IEEE 802.1Q VLAN for the Switch.
Table 12 VLAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
48
CHAPTER 10
Link Aggregation
10.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to logically aggregate physical links to form one logical and higher
bandwidth link.
Link aggregation is the grouping of physical ports into one logical higher-capacity link. You may want to
trunk ports if for example, it is cheaper to use multiple lower-speed links than to under-utilize a high-
speed, but more costly, single-port link.
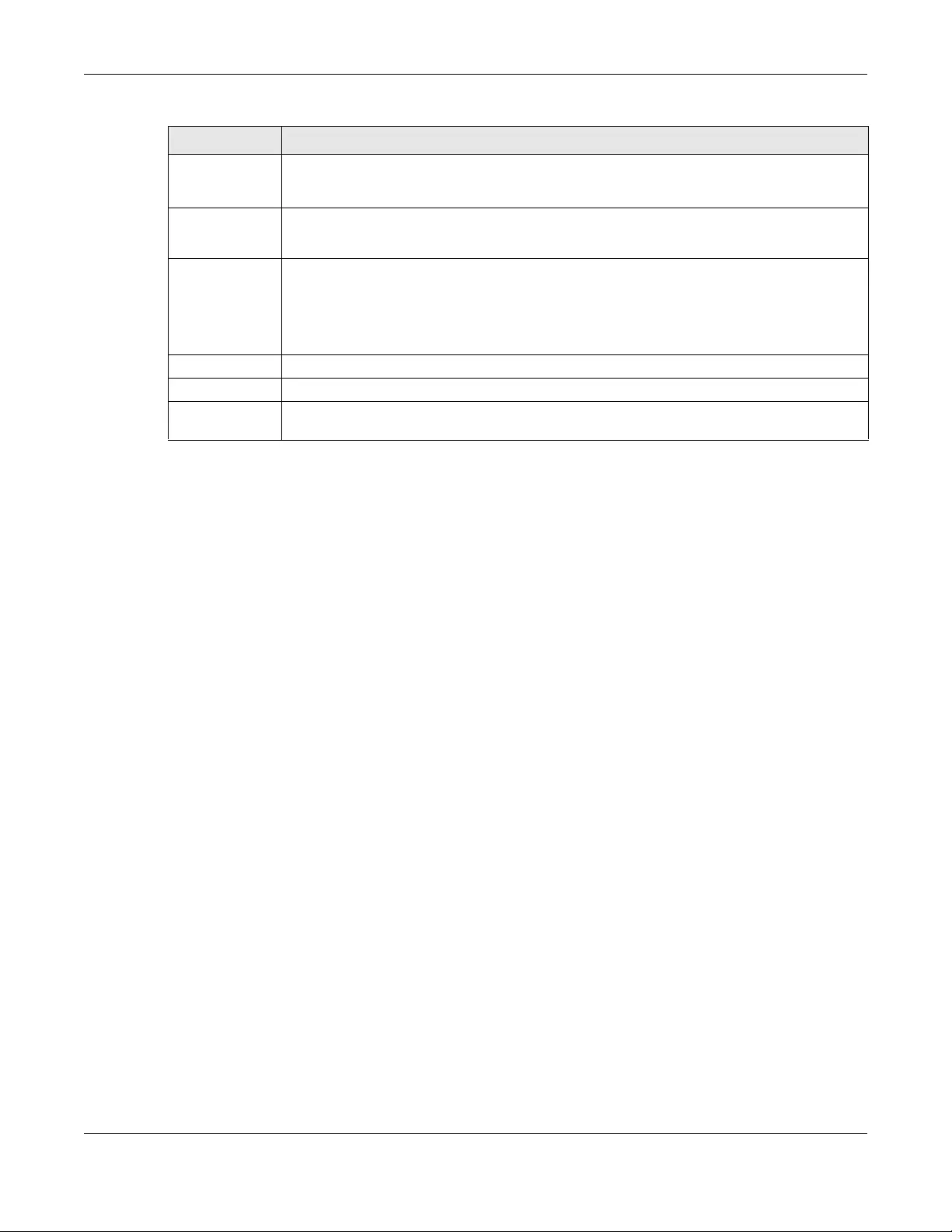
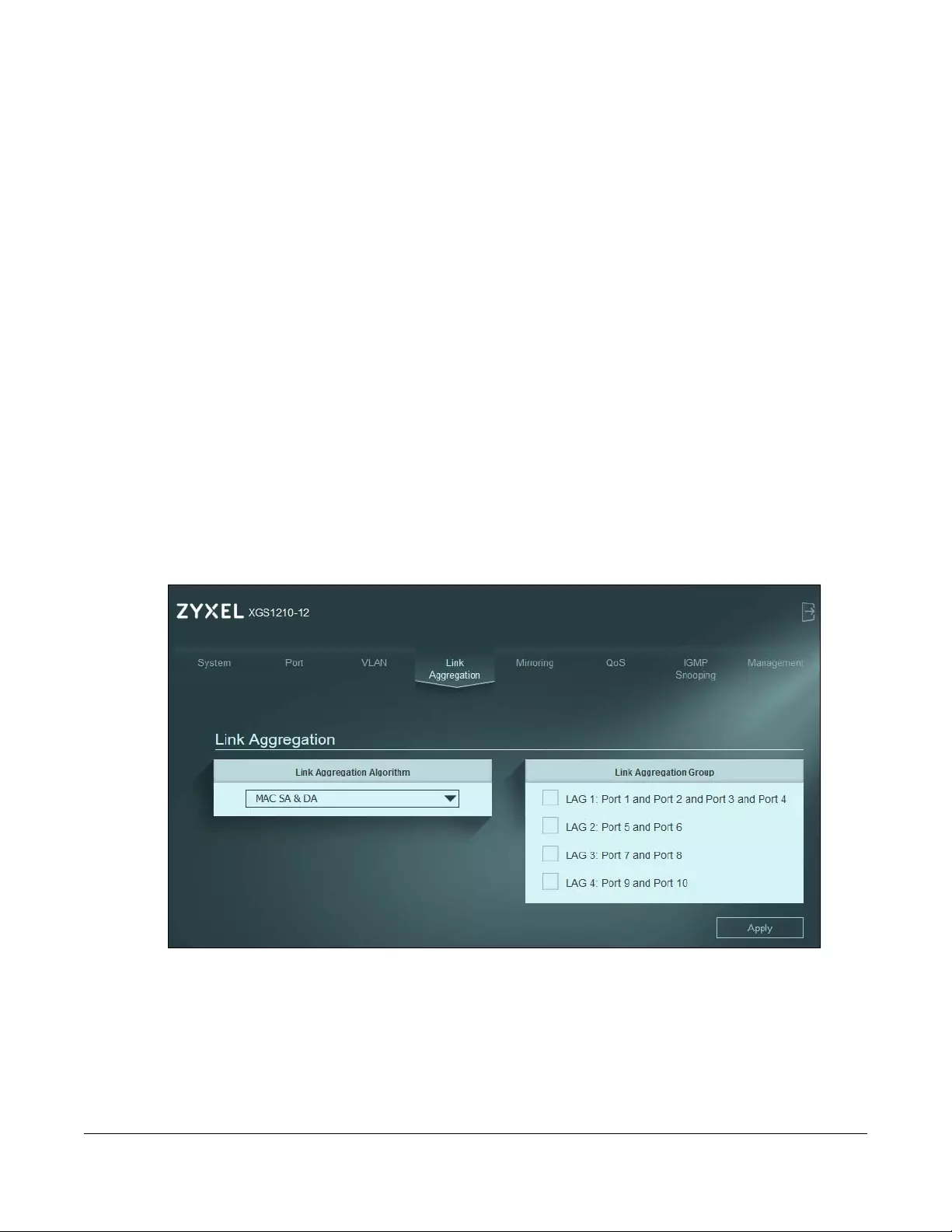
10.2 Link Aggregation
Use this screen to configure static link aggregation.
Figure 35 Link Aggregation (XGS1210-12)
Chapter 10 Link Aggregation
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
49
Figure 36 Link Aggregation (XGS1250-12)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Link Aggregation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Link Aggregation
Link Aggregation
Algorithm
Select the outgoing traffic distribution type. Packets from the same source and/or to the same
destination are sent over the same link within the trunk. By default, the Switch uses the MAC SA
& DA distribution type. If the Switch is behind a router, the packet’s destination or source MAC
address will be changed. In this case, set the Switch to distribute traffic based on its IP address
to make sure port trunking can work properly.
Select MAC SA to distribute traffic based on the packet’s source MAC address.
Select MAC DA to distribute traffic based on the packet’s destination MAC address.
Select MAC SA & DA to distribute traffic based on a combination of the packet’s source and
destination MAC addresses.
Link Aggregation
Group
The field identifies the default link aggregation groups the Switch supports. Select which link
aggregation group supports your choice in the previous field Link Aggregation Algorithm. For
example, enabling LAG 1: Port 1 and Port 2 and Port 3 and Port 4 will allow packets from the
same source and/or to the same destination to go through ports 1 – 4 for a maximum
throughput of 8G. This allows for faster speed compared to passing packets through ports 1 – 4
individually (maximum 2G).
Note: The Switch has a link aggregation group containing ports 1 – 4, ports 5 and 6,
ports 7 and 8, and the other contains ports 9 – 10 (XGS1210-12) / 9 – 11
(XGS1250-12).
Note: Make sure the ports in a link aggregation group have the same PVID and
VLAN ID.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
50
CHAPTER 11
Mirroring
11.1 Overview
This chapter discusses the port mirroring setup screens.
Port mirroring allows you to copy a traffic flow to a monitor port (the port you copy the traffic to) to
examine the traffic from the monitor port without interference.
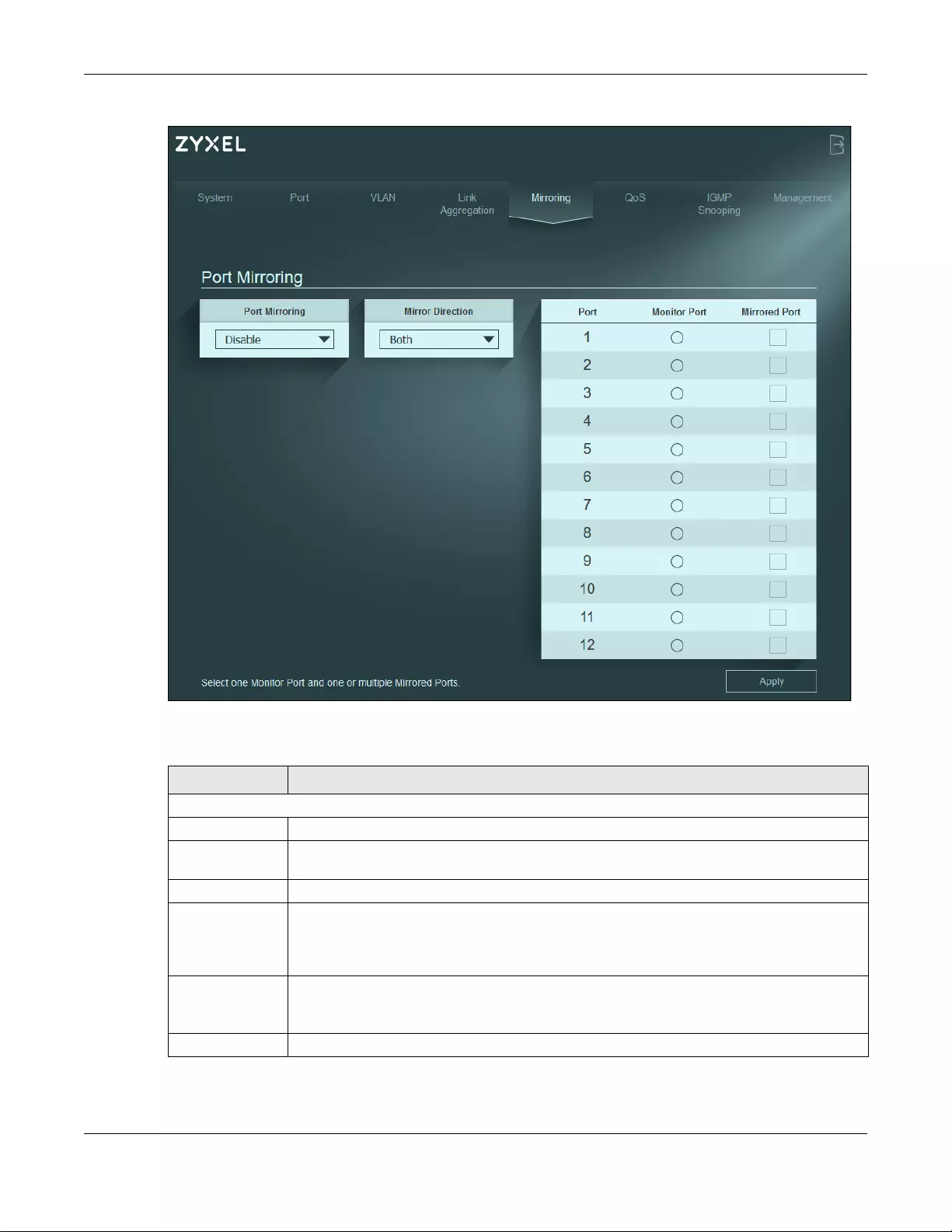
11.2 Mirroring Settings
Use this screen to select a monitor port and specify the traffic flow to be copied to the monitor port.
Note: A port cannot be the monitor port and the mirrored port at the same time.
Chapter 11 Mirroring
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
51
Figure 37 Mirroring
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Mirroring
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring Select Enable to activate port mirroring on the Switch, or Disable to disable the feature.
Mirror Direction Specify the direction of the traffic to mirror by selecting from the drop-down list box. Choices
are Egress (outgoing), Ingress (incoming) and Both.
Port This displays the port number.
Monitor Port The monitor port is the port you copy the traffic to in order to examine it in more detail without
interfering with the traffic flow on the original ports.
Note: Select one monitor port.
Mirrored Port Select this option to mirror the traffic on a port.
Note: Select one or multiple mirrored ports.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
52
CHAPTER 12
QoS
12.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the configuration and functions of the QoS (Quality of Service) screen.
The QoS (Quality of Service) feature allows you to prioritize the flow of data passing through the Switch.
Occasionally, data might be delayed, depending on the volume of traffic and the capacity of the
equipment. Numeric and text data are usually not affected by delays, because they are reassembled
at the destination. However, when VoIP and streaming videos are reassembled, they might have some
troublesome gaps. Without QoS, all traffic data is equally likely to be dropped when the network is
congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and make the network inadequate for
time-critical applications such as VOD (Video on Demand).
You can enable QoS to have the Switch assign each packet a priority and then queues the packet
accordingly. Packets assigned a high priority are processed more quickly than those with low priority if
there is congestion, allowing time-sensitive applications to flow more smoothly. Time-sensitive
applications include both those that require a low level of latency (delay) and a low level of jitter
(variations in delay) such as Voice over IP (VoIP) or Internet gaming, and those for which jitter alone is a
problem such as Internet radio or streaming video.
12.2 What You Need to Know
The Switch can put packets into the queues according to the port on which the packet is received or
the priority tag in the packet.
12.2.1 Port-Based QoS
The Port-Based QoS feature assigns priority to data transmitted through a particular port. When the data
arrives to a port it begins a queue. Therefore, the Switch has a queue for each port. If data arrives at the
same time to all ports, ports with higher priority will be first to transmit the data received. The higher the
priority of the port, the less delays the data passing through will have.
12.2.2 IEEE 802.1p QoS
IEEE 802.1p defines a 3-bit field called PCP (Priority Code Point) within the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tag, which is
also referred to as a CoS (Class of Service) value and indicates the frame priority level. IEEE 802.1p QoS
uses the priority value (from 0 to 7) to define up to 8 traffic types. That is, each priority level defines a
class of service. The table below shows the IEEE recommendations for traffic types, these may vary or be
Chapter 12 QoS
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
53
reassigned.
Note: Frames without an explicit priority tag are treated as system traffic and assigned to
Queue0.
12.2.3 Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR)
Round Robin Scheduling services queues on a rotating basis and is activated only when a port has more
traffic than it can handle. A queue is a given amount of bandwidth irrespective of the incoming traffic
on that port. This queue then moves to the back of the list. The next queue is given an equal amount of
bandwidth, and then moves to the end of the list; and so on, depending on the number of queues
being used. This works in a looping fashion until a queue is empty.
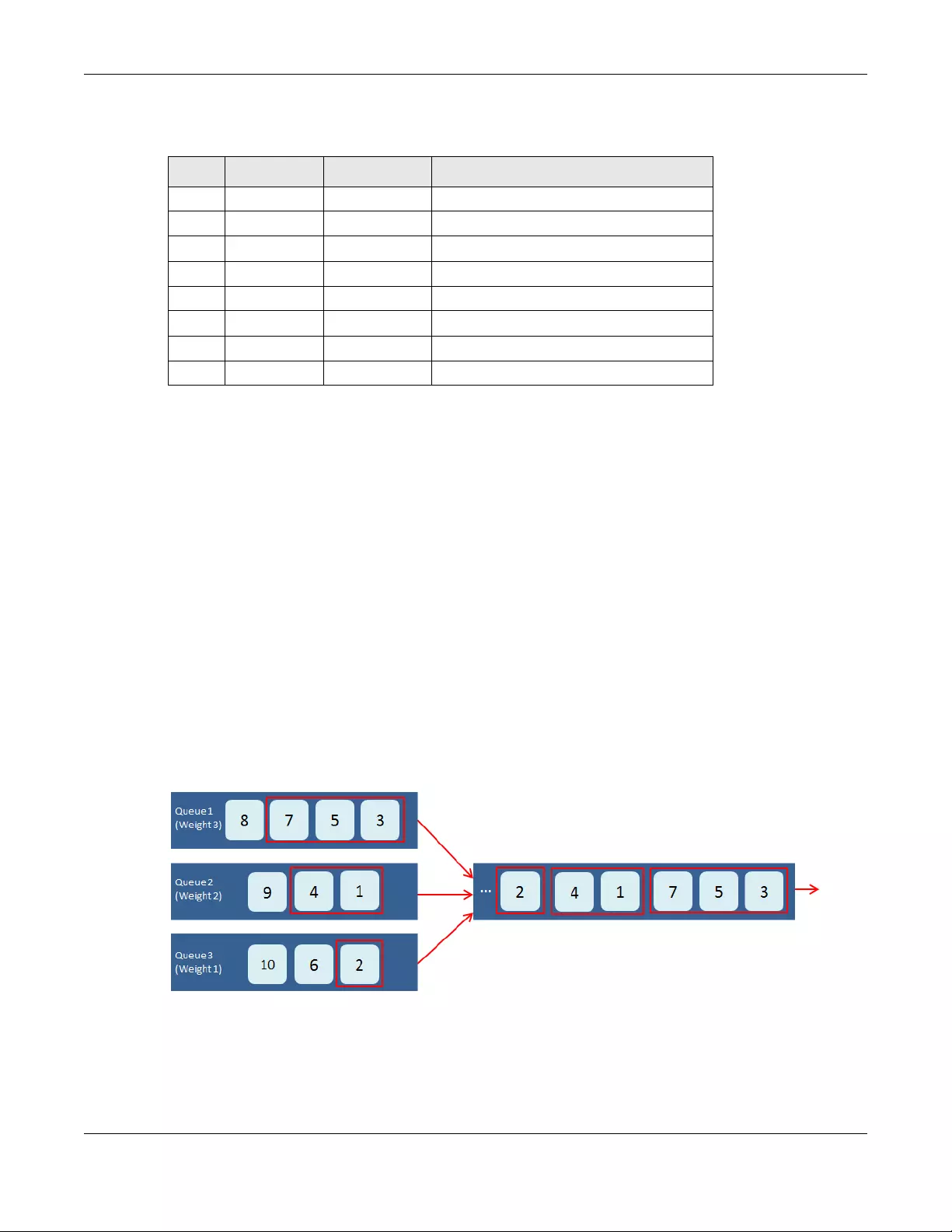
Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) uses the same algorithm as round robin scheduling, but
services queues based on their priority and queue weight (the number you select in the queue Weight
field) rather than a fixed amount of bandwidth. WRR is activated only when a port has more traffic than
it can handle. The bandwidth is divided across the different traffic queues according to their weights.
Queues with larger weights get more service than queues with smaller weights. This queuing mechanism
is highly efficient in that it divides any available bandwidth across the different traffic queues and returns
to queues that have not yet emptied.
Figure 38 WRR Application Example
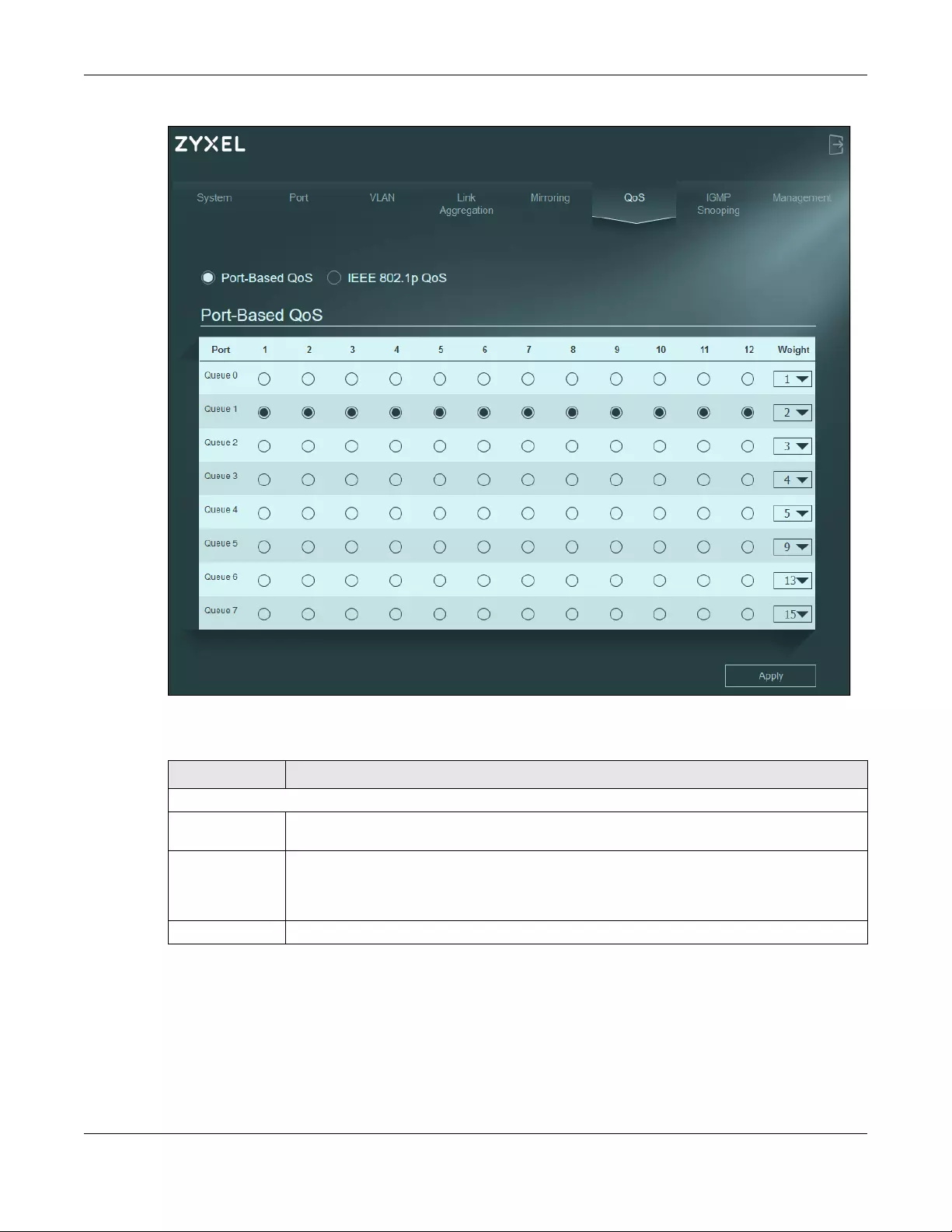
12.3 Port-Based QoS
The Switch’s default settings for Port-Based QoS are shown in the next figure.
Table 15 IEEE Priority to Traffic Type Mapping Recommendations
PCP PRIORITY ACRONYM TRAFFIC TYPES
1 0 (lowest) BK Background
0 1 (default) BE Best Effort
2 2 EE Excellent Effort
3 3 CA Critical Applications
4 4 VI Video, <100 ms latency and jitter
5 5 VO Voice, <10 ms latency and jitter
6 6 IC Internetwork Control
7 7 (highest) NC Network Control
Chapter 12 QoS
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
54
Figure 39 QoS > Port-Based QoS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
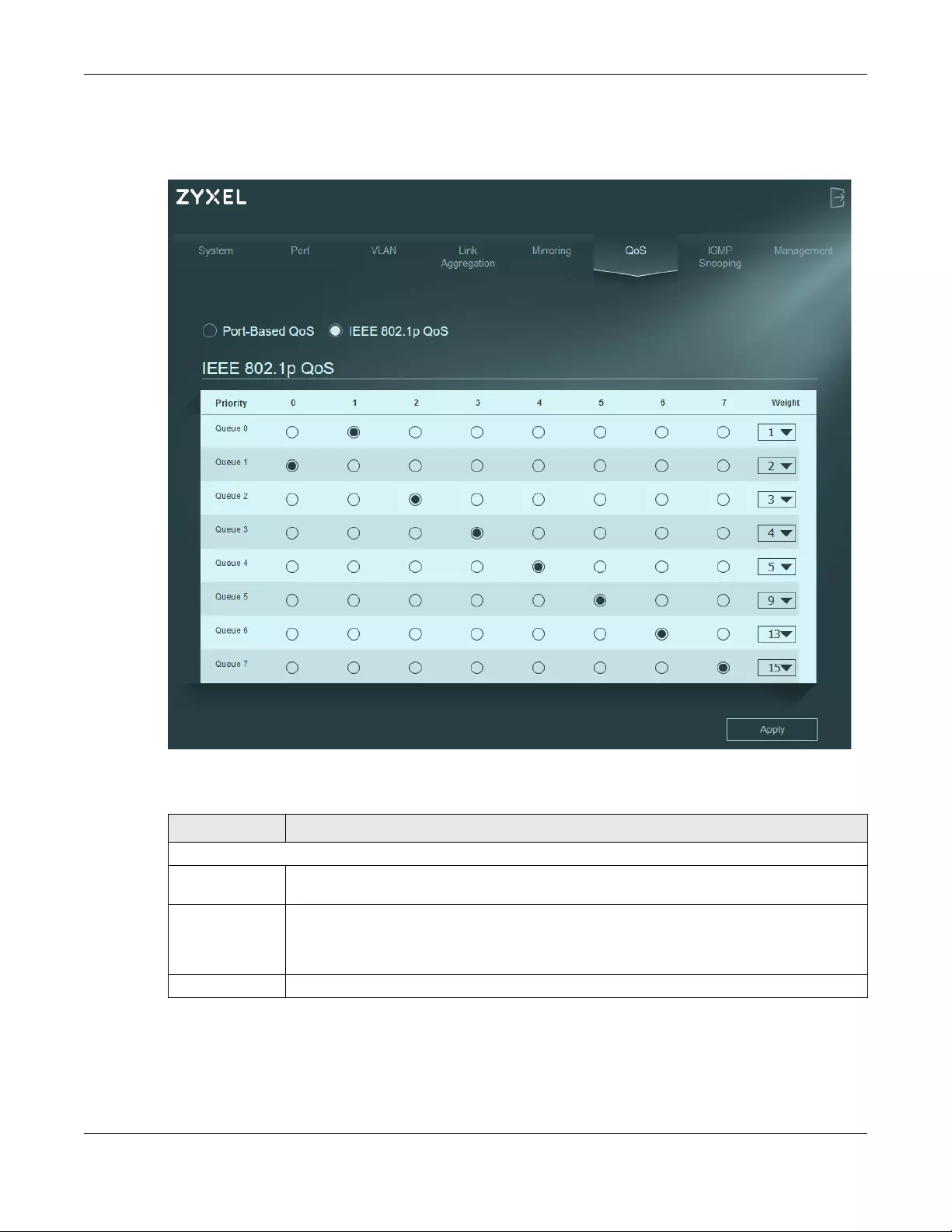
12.4 IEEE 802.1p QoS
Both Port-Based QoS and IEEE 802.1p QoS use the same priority queuing levels. Remember the
difference amongst both features relies on how the priority queuing is assigned. Let us recap, Port-Based
QoS assigns priority queuing by port, whereas IEEE 802.1p QoS assigns queuing by PCP priority tags.
Table 16 QoS > Port-Based QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port-Based QoS
Port 1 – 12 Select which ports will carry the sensitive data, using the priority queuing levels given. Click on
each port’s radio button to assign a priority queue.
Weight Assign the weight (the number you select in the queue Weight field) to each priority.
Remember the weight is based on WRR Scheduling, explained in Section 12.2.3 on page 53.
Bandwidth is divided across the different traffic queues according to their weights. Queues with
larger weights get more service than queues with smaller weights.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Chapter 12 QoS
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
55
The Switch’s default settings for IEEE 802.1p QoS are shown in the next figure. The numbers from 0 to 7
refer to the priority tags for each traffic type. Refer to Table 15 on page 53.
Figure 40 QoS > IEEE 802.1p QoS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 QoS > IEEE 802.1p QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IEEE 802.1p QoS
Priority 0 – 7 Select which priority tags will carry the sensitive data, using the priority queuing levels given.
Click each priority tag’s radio button to assign a priority queue.
Weight Assign the weight (the number you select in the queue Weight field) to each priority.
Remember the weight is based on WRR Scheduling, explained in Section 12.2.3 on page 53.
Bandwidth is divided across the different traffic queues according to their weights. Queues with
larger weights get more service than queues with smaller weights.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
56
CHAPTER 13
IGMP Snooping
13.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure the various multicast features.
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways – Unicast (one sender to one recipient)
or Broadcast (one sender to everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to just a group of
hosts on the network.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership
in a multicast group – it is not used to carry user data. Refer to RFC 1112, RFC 2236 and RFC 3376 for
information on IGMP versions 1, 2, and 3 respectively.
Note: You must enable IGMP snooping to use the IPTV service.
IGMP snooping is enabled, and the IGMP Static Router Port is set to Auto by default. The
port can be used as an IGMP router port.
IGMP Snooping
The Switch can passively snoop on IGMP packets transferred between IP multicast routers or switches
and IP multicast hosts to learn the IP multicast group membership. It checks the IGMP packets passing
through it, picks out the group registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly. IGMP
snooping allows the Switch to learn multicast groups without you having to manually configure them.
The Switch forwards multicast traffic destined for multicast groups (that it has learned from IGMP
snooping or that you have manually configured) to ports that are members of that group. IGMP
snooping generates no additional network traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce multicast traffic
passing through your Switch.
13.2 IGMP Snooping Settings
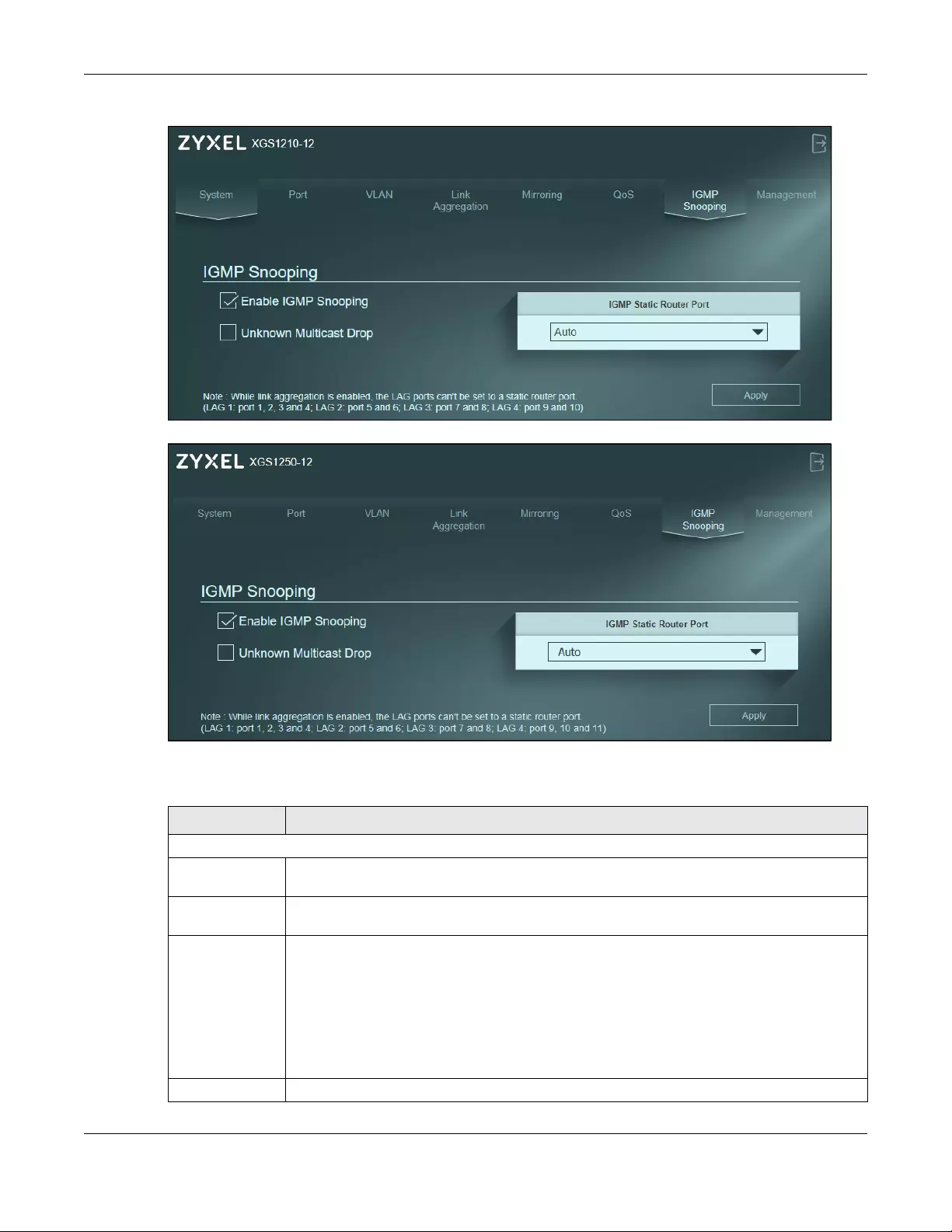
Click IGMP Snooping in the navigation panel to display the screen as shown next.
Chapter 13 IGMP Snooping
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
57
Figure 41 IGMP Snooping (XGS1210-12)
Figure 42 IGMP Snooping (XGS1250-12)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 IGMP Snooping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IGMP Snooping
Enable IGMP
Snooping
Select this option to enable IGMP Snooping to forward group multicast traffic only to ports that
are members of that group.
Unknown
Multicast Drop
Select this option to discard the frame when the Switch receives an unknown multicast frame.
Otherwise, the Switch sends the frame to all ports.
IGMP Static
Router Port
Select a port (Port 1 – 12) to be used as an IGMP router port.
Select Auto to allow any port to be used as an IGMP router port upon receiving an IGMP query.
The Switch treats an IGMP query port as being connected to an IGMP multicast router (or
server). The Switch forwards IGMP join or leave packets to an IGMP router port.
Note: If link aggregation is enabled, the ports in a link aggregation group will not be
available in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
58
CHAPTER 14
Management
14.1 Overview
This chapter explains how to use the Management screens to configure settings on the Switch, such as
login password change, firmware upgrade, system reset or reboot, IP address change, and so on.
14.1.1 What You Need to Know
Read this section to know more about IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) and HTTPS (HyperText
Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL).
14.1.1.1 IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE)
If EEE is enabled, both sides of a link support EEE and there is no traffic, the port enters Low Power Idle
(LPI) mode. LPI mode turns off some functions of the physical layer (becomes quiet) to save power.
Periodically the port transmits a REFRESH signal to allow the link partner to keep the link alive. When there
is traffic to be sent, a WAKE signal is sent to the link partner to return the link to active mode.
14.1.1.2 Introduction to HTTPS
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL) is a web protocol that
encrypts and decrypts web pages. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is an application-level protocol that
enables secure transactions of data by ensuring confidentiality (an unauthorized party cannot read the
transferred data), authentication (one party can identify the other party) and data integrity (you know if
data has been changed).
It relies upon certificates, public keys, and private keys.
HTTPS on the Switch is used so that you may securely access the Switch using the Web Configurator. The
SSL protocol specifies that the SSL server (the Switch) must always authenticate itself to the SSL client (the
computer which requests the HTTPS connection with the Switch), whereas the SSL client only should
authenticate itself when the SSL server requires it to do so. Authenticating client certificates is optional
and if selected means the SSL-client must send the Switch a certificate. You must apply for a certificate
for the browser from a Certificate Authority (CA) that is a trusted CA on the Switch.
Please refer to the following figure.
1HTTPS connection requests from an SSL-aware web browser go to port 443 (by default) on the Switch’s
WS (web server).
2HTTP connection requests from a web browser go to port 80 (by default) on the Switch’s WS (web
server).
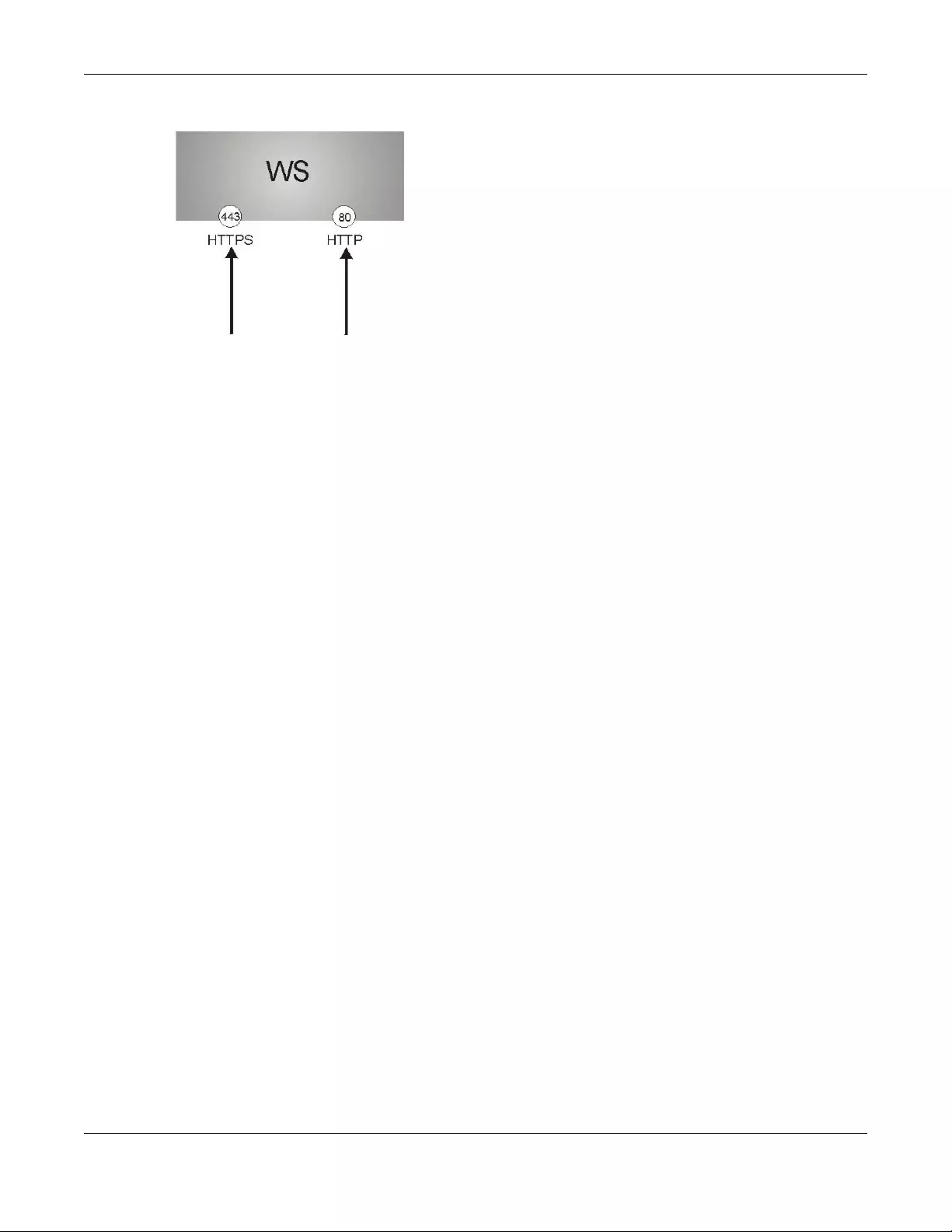
Chapter 14 Management
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
59
Figure 43 HTTPS Implementation
Note: If you disable HTTP in the Management screen, then the Switch blocks all HTTP
connection attempts.
14.2 Management Settings
An administrator is someone who can both view and configure Switch changes. The default
administrator password is 1234.
Note: It is highly recommended that you change the default administrator password (1234).
Click Management in the navigation panel to open the following screen.
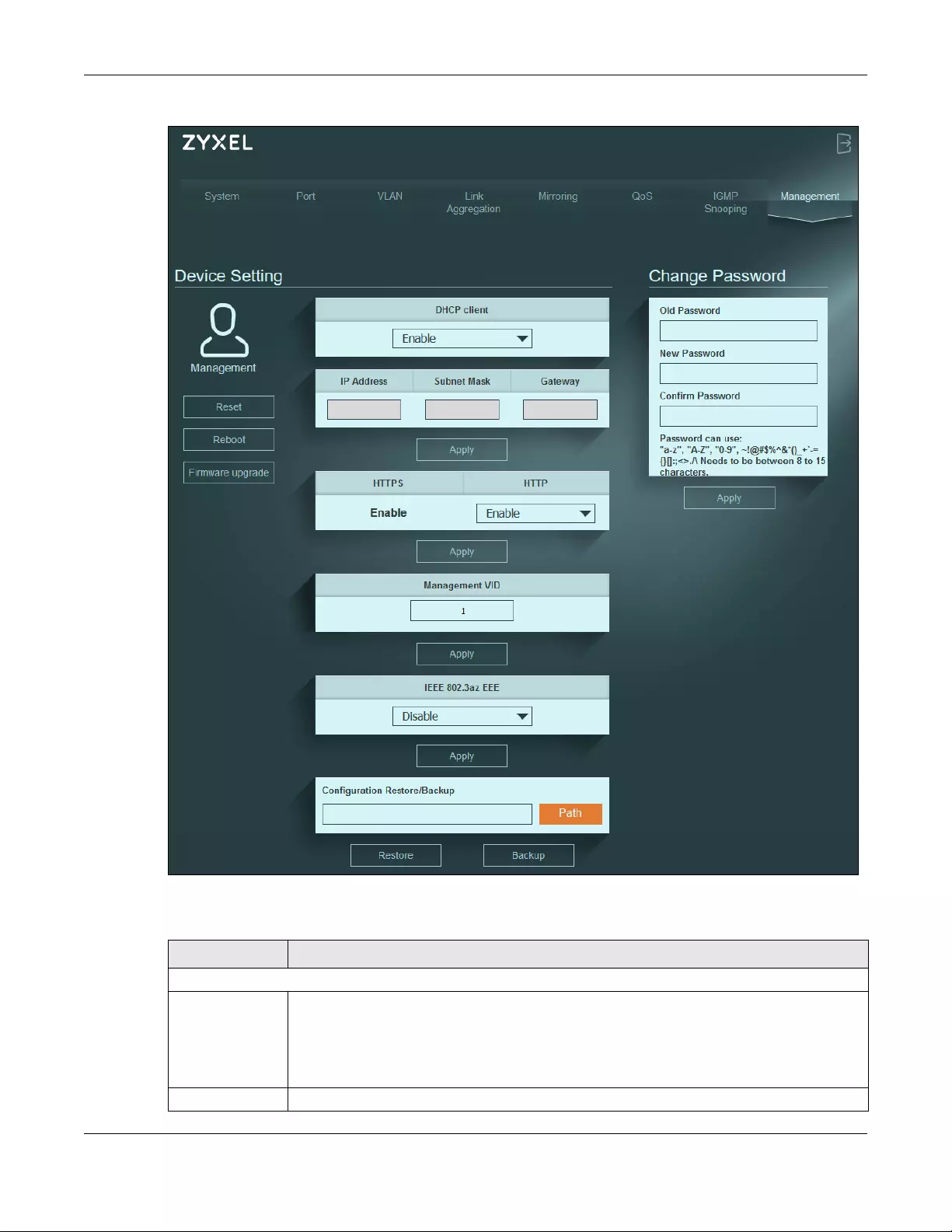
Chapter 14 Management
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
60
Figure 44 Switch Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Switch Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Setting
Reset Click this button to clear all Switch configuration information you configured and return to the
factory defaults.
If you want to access the Switch Web Configurator again, you may need to change the IP
address of your computer to be in the same subnet as that of the default Switch IP address
(192.168.1.3).
Reboot Click this button to restart the Switch without physically turning the power off.
Chapter 14 Management
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
61
14.2.1 Firmware Upgrade
Firmware upgrades contain bug fixes and fixes for security vulnerabilities. It is recommended to keep the
Switch’s firmware up to date.
Make sure you have downloaded (and unzipped) the correct model firmware and version to your
computer before uploading to the Switch.
Firmware
upgrade
Click this button to upgrade the Switch to the latest firmware.
DHCP Client Select Enable if you have a DHCP server that can assign the Switch an IP address, subnet mask,
a default gateway IP address and a domain name server IP address automatically. Otherwise,
select Disable.
IP Address Enter the IP address of your Switch in dotted decimal notation, for example, 192.168.1.3. This is
the IP address of the Switch in an IP routing domain.
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask of an IP routing domain in dotted decimal notation, for example,
255.255.255.0.
Gateway Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation, for example,
192.168.1.254.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.
HTTPS / HTTP Select Enable to allow for HTTP or HTTPS services that may be used for managing the Switch
from the specified trusted computers.
Select Disable to allow for HTTPS service only. This ensures that connection request to the Web
Configurator is from an SSL-aware web browser only.
Management
VID
This is the ID number of the management VLAN. Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the
management VLAN ID.
Any ports assigned to this VLAN are considered management ports and should be secured to
control which devices can connect to these ports. See Section 9.2 on page 46 for details on
creating VLANs.
Note: Changing the Management VID may cause the Switch to loose its network
connection.
IEEE 802.3az EEE Select Enable to activate Energy Efficient Ethernet globally. Otherwise, select Disable.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.
Configuration
Restore/Backup
Type the path and file name of the configuration file you wish to restore in the text box or click
path to locate it.
Restore Click Restore to restore a previously saved configuration from your computer to the Switch.
Note: “config” is the name of the configuration file on the Switch, so your backup
configuration file is automatically renamed when you restore using this screen.
Backup Click Backup to save and store your current device settings.
Change Password
Old Password Type the existing system password.
New Password Enter your new system password using the keyboard characters (a – z, A – Z, 0 – 9, and
~!@#$%^&*()_+`–={}[]:;<>./\). The password must be 8 to 15 characters long.
Confirm Password Retype your new system password for confirmation.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the Switch.
Table 19 Switch Management (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
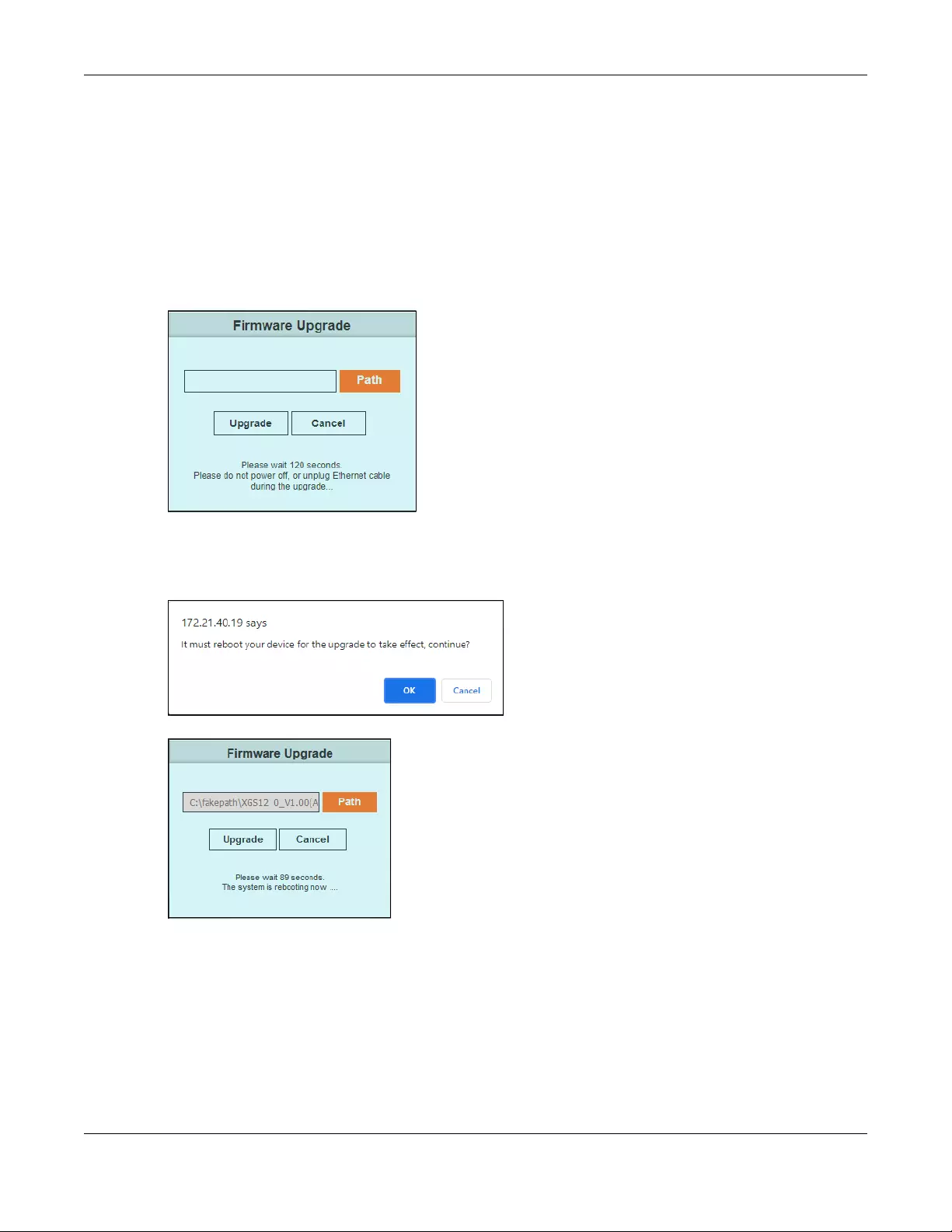
Chapter 14 Management
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
62
Be sure to upload the correct model firmware as uploading the wrong
model firmware may damage your device.
Do NOT disconnect power to the Switch while firmware upload is in
progress!
The following screen will appear after you click the Firmware Upgrade button. You will not be able to
configure other settings during the firmware upgrade process to avoid system crashes on the Switch.
Figure 45 Firmware Upgrade Path
Type the path and file name of the firmware file you wish to upload to the Switch in the text box or click
Path to locate it. After you select the firmware file, click the Upgrade button to load the new firmware.
Figure 46 Firmware Upgrade Confirmation
Figure 47 Firmware Uploading
After a successful upload, the system will reboot, and you will need to log into the Switch again.
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
63
CHAPTER 15
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The potential problems are
divided into the following categories.
•Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
•Switch Access and Login
•Switch Configuration
15.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
The Switch does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1Make sure you are using the power adapter or cord included with the Switch.
2Make sure the power adapter or cord is connected to the Switch and plugged in to an appropriate
power source. Make sure the power source is turned on.
3Disconnect and re-connect the power adapter or cord to the Switch.
4If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. See Section 3.4 on page 19.
2Check the hardware connections. See Section 1.2.1 on page 10 on using the correct cable type.
3Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged cables.
4Disconnect and re-connect the power adapter or cord to the Switch.
5If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
A loop is detected.
Chapter 15 Troubleshooting
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
64
1To restore a port in a loop state, disconnect it, check the network connections, and reconnect it.
2You can log into the Web Configurator. Go to System in the Web Configurator to check your port status.
Note that you can do this when you enable Loop Prevention (default) in the Port screen. If Loop
Detection is enabled, you cannot log into the Switch.
15.2 Switch Access and Login
I forgot the IP address for the Switch.
1The default IP address is 192.168.1.3.
2If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 4.5 on page 29.
I forgot the password.
1The default password is 1234.
2If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 4.5 on page 29.
I cannot see or access the Login screen in the Web Configurator.
1Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
• The default IP address is 192.168.1.3.
• If you changed the IP address, use the new IP address.
• If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, see the troubleshooting suggestions for I
forgot the IP address for the Switch.
2Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See Section 3.4
on page 19.
3Make sure your Internet browser does not block pop-up windows and has JavaScripts and Java
enabled.
4Make sure your computer is in the same subnet as the Switch. (If you know that there are routers
between your computer and the Switch, skip this step.)
5Reset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the Switch with the default IP address. See
Section 4.5 on page 29.
6If the problem continues, contact the vendor.

Chapter 15 Troubleshooting
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
65
I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the Switch.
1Make sure you have entered the password correctly. The default password is 1234.
2Disconnect and re-connect the cord to the Switch.
3If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 4.5 on page 29.
Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
In order to use the Web Configurator you need to allow the following:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
• JavaScripts (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
15.3 Switch Configuration
After upgrading the firmware on the Switch, the login screen does not display.
When any of the following should happen during the firmware upgrade process, a failure may occur.
During the firmware upgrade process:
• The Switch loses power.
• The computer from where you upload the firmware file to the Switch is turned off.
• The Ethernet cable connecting the Switch and the computer comes loose. This is the computer from
where you uploaded the firmware file to the Switch.
When any of the above occurs, and you are directed to the Firmware Upgrade screen, follow the steps
below:
1Make sure the power supply is sufficient in your environment.
2Make sure your computer’s Ethernet cable is securely connected to the Switch.
3Select the firmware file that you tried to upload to the Switch before and try upgrading the firmware
again in the Firmware Upgrade screen.
4Wait for the firmware upgrade process to complete. After a successful upload, the system will reboot,
and you will need to log into the Switch again.

XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
66
APPENDIX A
Customer Support
In the event of problems that cannot be solved by using this manual, you should contact your vendor. If
you cannot contact your vendor, then contact a Zyxel office for the region in which you bought the
device.
See https://www.zyxel.com/homepage.shtml and also
https://www.zyxel.com/about_zyxel/zyxel_worldwide.shtml for the latest information.
Please have the following information ready when you contact an office.
Required Information
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
Corporate Headquarters (Worldwide)
Taiwan
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com
Asia
China
• Zyxel Communications (Shanghai) Corp.
Zyxel Communications (Beijing) Corp.
Zyxel Communications (Tianjin) Corp.
• https://www.zyxel.com/cn/zh/
India
•Zyxel Technology India Pvt Ltd.
• https://www.zyxel.com/in/en/
Kazakhstan
•Zyxel Kazakhstan
• https://www.zyxel.kz

Appendix A Customer Support
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
67
Korea
• Zyxel Korea Corp.
• http://www.zyxel.kr
Malaysia
• Zyxel Malaysia Sdn Bhd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.my
Pakistan
• Zyxel Pakistan (Pvt.) Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.pk
Philippines
• Zyxel Philippines
• http://www.zyxel.com.ph
Singapore
• Zyxel Singapore Pte Ltd.
• http://www.zyxel.com.sg
Taiwan
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/tw/zh/
Thailand
• Zyxel Thailand Co., Ltd.
• https://www.zyxel.com/th/th/
Vietnam
• Zyxel Communications Corporation – Vietnam Office
• https://www.zyxel.com/vn/vi
Europe
Belarus
•Zyxel BY
• https://www.zyxel.by
Belgium
• Zyxel Communications B.V.
• https://www.zyxel.com/be/nl/

Appendix A Customer Support
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
68
• https://www.zyxel.com/be/fr/
Bulgaria
•Zyxel България
• https://www.zyxel.com/bg/bg/
Czech Republic
• Zyxel Communications Czech s.r.o
• https://www.zyxel.com/cz/cs/
Denmark
• Zyxel Communications A/S
• https://www.zyxel.com/dk/da/
Estonia
• Zyxel Estonia
• https://www.zyxel.com/ee/et/
Finland
• Zyxel Communications
• https://www.zyxel.com/fi/fi/
France
•Zyxel France
• https://www.zyxel.fr
Germany
•Zyxel Deutschland GmbH
• https://www.zyxel.com/de/de/
Hungary
• Zyxel Hungary & SEE
• https://www.zyxel.com/hu/hu/
Italy
• Zyxel Communications Italy
• https://www.zyxel.com/it/it/
Latvia
•Zyxel Latvia
• https://www.zyxel.com/lv/lv/

Appendix A Customer Support
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
69
Lithuania
•Zyxel Lithuania
• https://www.zyxel.com/lt/lt/
Netherlands
• Zyxel Benelux
• https://www.zyxel.com/nl/nl/
Norway
• Zyxel Communications
• https://www.zyxel.com/no/no/
Poland
• Zyxel Communications Poland
• https://www.zyxel.com/pl/pl/
Romania
• Zyxel Romania
• https://www.zyxel.com/ro/ro
Russia
• Zyxel Russia
• https://www.zyxel.com/ru/ru/
Slovakia
• Zyxel Communications Czech s.r.o. organizacna zlozka
• https://www.zyxel.com/sk/sk/
Spain
• Zyxel Communications ES Ltd.
• https://www.zyxel.com/es/es/
Sweden
• Zyxel Communications
• https://www.zyxel.com/se/sv/
Switzerland
•Studerus AG
• https://www.zyxel.ch/de
• https://www.zyxel.ch/fr

Appendix A Customer Support
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
70
Turkey
• Zyxel Turkey A.S.
• https://www.zyxel.com/tr/tr/
UK
• Zyxel Communications UK Ltd.
• https://www.zyxel.com/uk/en/
Ukraine
•Zyxel Ukraine
• http://www.ua.zyxel.com
South America
Argentina
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/co/es/
Brazil
• Zyxel Communications Brasil Ltda.
• https://www.zyxel.com/br/pt/
Colombia
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/co/es/
Ecuador
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/co/es/
South America
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/co/es/
Middle East
Israel
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• http://il.zyxel.com/

Appendix A Customer Support
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
71
Middle East
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/me/en/
North America
USA
• Zyxel Communications, Inc. – North America Headquarters
• https://www.zyxel.com/us/en/
Oceania
Australia
• Zyxel Communications Corporation
• https://www.zyxel.com/au/en/
Africa
South Africa
• Nology (Pty) Ltd.
• https://www.zyxel.com/za/en/
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
72
APPENDIX B
Legal Information
Copyright
Copyright © 2021 by Zyxel and/or its affiliates.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any
language, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of Zyxel and/or its affiliates.
Published by Zyxel and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
Zyxel does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software described herein. Neither does it convey any
license under its patent rights nor the patent rights of others. Zyxel further reserves the right to make changes in any products described herein
without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Regulatory Notice and Statement
UNITED STATES of AMERICA
The following information applies if you use the product within USA area.
US Importer: Zyxel Communications, Inc, 1130 North Miller Street Anaheim, CA92806-2001, https://www.zyxel.com/us/en/
FCC EMC Statement
• The device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
• Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
device.
• This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This device generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
• If this device does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the device off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
EUROPEAN UNION and UNITED KINGDOM
The following information applies if you use the product within the European Union and United Kingdom.
Appendix B Legal Information
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
73
List of national codes
Safety Warnings
• Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
• Do not expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do not store things on the device.
• Do not obstruct the device ventilation slots as insufficient airflow may harm your device. For example, do not place the device in an
enclosed space such as a box or on a very soft surface such as a bed or sofa.
• Do not install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do not open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to dangerous high voltage points or other risks.
• Only qualified service personnel should service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Do not remove the plug and connect it to a power outlet by itself; always attach the plug to the power adaptor first before connecting it to
a power outlet.
• Do not allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the product where anyone can walk on the power adaptor
or cord.
• Please use the provided or designated connection cables/power cables/adaptors. Connect it to the right supply voltage (for example, 110V
AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe). If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, it might cause electrocution. Remove it from the
device and the power source, repairing the power adapter or cord is prohibited. Contact your local vendor to order a new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• CAUTION: Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type, dispose of used batteries according to the instruction. Dispose them at
the applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic devices. For detailed information about recycling of this
product, please contact your local city office, your household waste disposal service or the store where you purchased the product.
• The following warning statements apply, where the disconnect device is not incorporated in the device or where the plug on the power
supply cord is intended to serve as the disconnect device,
– For permanently connected devices, a readily accessible disconnect device shall be incorporated external to the device;
– For pluggable devices, the socket-outlet shall be installed near the device and shall be easily accessible.
• CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
• APPAREIL À LASER DE CLASS 1
• PRODUCT COMPLIES WITH 21 CFR 1040.10 AND 1040.11.
• PRODUIT CONFORME SELON 21 CFR 1040.10 ET 1040.11.
Environment Statement
ErP (Energy-related Products) (for XGS1210-12)
Zyxel products put on the EU and United Kingdom market in compliance with the requirement of the European Parliament and the Council
published Directive 2009/125/EC and UK regulation establishing a framework for the setting of ecodesign requirements for energy-related
products (recast), so called as "ErP Directive (Energy-related Products directive) as well as ecodesign requirement laid down in applicable
implementing measures, power consumption has satisfied regulation requirements which are:
• Network standby power consumption < 8W, and/or
• Off mode power consumption < 0.5W, and/or
• Standby mode power consumption < 0.5W.
COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE COUNTRY ISO 3166 2 LETTER CODE
Austria AT Liechtenstein LI
Belgium BE Lithuania LT
Bulgaria BG Luxembourg LU
Croatia HR Malta MT
Cyprus CY Netherlands NL
Czech Republic CZ Norway NO
Denmark DK Poland PL
Estonia EE Portugal PT
Finland FI Romania RO
France FR Serbia RS
Germany DE Slovakia SK
Greece GR Slovenia SI
Hungary HU Spain ES
Iceland IS Switzerland CH
Ireland IE Sweden SE
Italy IT Turkey TR
Latvia LV United Kingdom GB
Appendix B Legal Information
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
74
Disposal and Recycling Information
The symbol below means that according to local regulations your product and/or its battery shall be disposed of separately from domestic
waste. If this product is end of life, take it to a recycling station designated by local authorities. At the time of disposal, the separate collection of
your product and/or its battery will help save natural resources and ensure that the environment is sustainable development.
Die folgende Symbol bedeutet, dass Ihr Produkt und/oder seine Batterie gemäß den örtlichen Bestimmungen getrennt vom Hausmüll entsorgt
werden muss. Wenden Sie sich an eine Recyclingstation, wenn dieses Produkt das Ende seiner Lebensdauer erreicht hat. Zum Zeitpunkt der
Entsorgung wird die getrennte Sammlung von Produkt und/oder seiner Batterie dazu beitragen, natürliche Ressourcen zu sparen und die Umwelt
und die menschliche Gesundheit zu schützen.
El símbolo de abajo indica que según las regulaciones locales, su producto y/o su batería deberán depositarse como basura separada de la
doméstica. Cuando este producto alcance el final de su vida útil, llévelo a un punto limpio. Cuando llegue el momento de desechar el
producto, la recogida por separado éste y/o su batería ayudará a salvar los recursos naturales y a proteger la salud humana y
medioambiental.
Le symbole ci-dessous signifie que selon les réglementations locales votre produit et/ou sa batterie doivent être éliminés séparément des ordures
ménagères. Lorsque ce produit atteint sa fin de vie, amenez-le à un centre de recyclage. Au moment de la mise au rebut, la collecte séparée
de votre produit et/ou de sa batterie aidera à économiser les ressources naturelles et protéger l'environnement et la santé humaine.
Il simbolo sotto significa che secondo i regolamenti locali il vostro prodotto e/o batteria deve essere smaltito separatamente dai rifiuti domestici.
Quando questo prodotto raggiunge la fine della vita di servizio portarlo a una stazione di riciclaggio. Al momento dello smaltimento, la raccolta
separata del vostro prodotto e/o della sua batteria aiuta a risparmiare risorse naturali e a proteggere l'ambiente e la salute umana.
Symbolen innebär att enligt lokal lagstiftning ska produkten och/eller dess batteri kastas separat från hushållsavfallet. När den här produkten når
slutet av sin livslängd ska du ta den till en återvinningsstation. Vid tiden för kasseringen bidrar du till en bättre miljö och mänsklig hälsa genom att
göra dig av med den på ett återvinningsställe.
台灣
安全警告 – 為了您的安全,請先閱讀以下警告及指示 :
• 請勿將此產品接近水、火焰或放置在高溫的環境。
• 避免設備接觸
– 任何液體 – 切勿讓設備接觸水、雨水、高濕度、污水腐蝕性的液體或其他水份。
– 灰塵及污物 – 切勿接觸灰塵、污物、沙土、食物或其他不合適的材料。
• 雷雨天氣時,不要安裝,使用或維修此設備。有遭受電擊的風險。
• 切勿重摔或撞擊設備,並勿使用不正確的電源變壓器。
• 若接上不正確的電源變壓器會有爆炸的風險。
• 請勿隨意更換產品內的電池。
• 如果更換不正確之電池型式,會有爆炸的風險,請依製造商說明書處理使用過之電池。
• 請將廢電池丟棄在適當的電器或電子設備回收處。
• 請勿將設備解體。
• 請勿阻礙設備的散熱孔,空氣對流不足將會造成設備損害。
• 請插在正確的電壓供給插座 ( 如 : 北美 / 台灣電壓 110V AC,歐洲是 230V AC)。
• 假若電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線損壞,請從插座拔除,若您還繼續插電使用,會有觸電死亡的風險。
• 請勿試圖修理電源變壓器或電源變壓器的纜線,若有毀損,請直接聯絡您購買的店家,購買⼀個新的電源變壓器。
• 請勿將此設備安裝於室外,此設備僅適合放置於室內。
• 請勿隨⼀般垃圾丟棄。
• 請參閱產品背貼上的設備額定功率。
• 請參考產品型錄或是彩盒上的作業溫度。
• 產品沒有斷電裝置或者採用電源線的插頭視為斷電裝置的⼀部分,以下警語將適用 :
– 對永久連接之設備, 在設備外部須安裝可觸及之斷電裝置;
– 對插接式之設備, 插座必須接近安裝之地點而且是易於觸及的。
About the Symbols
Various symbols are used in this product to ensure correct usage, to prevent danger to the user and others, and to prevent property damage.
The meaning of these symbols are described below. It is important that you read these descriptions thoroughly and fully understand the
contents.
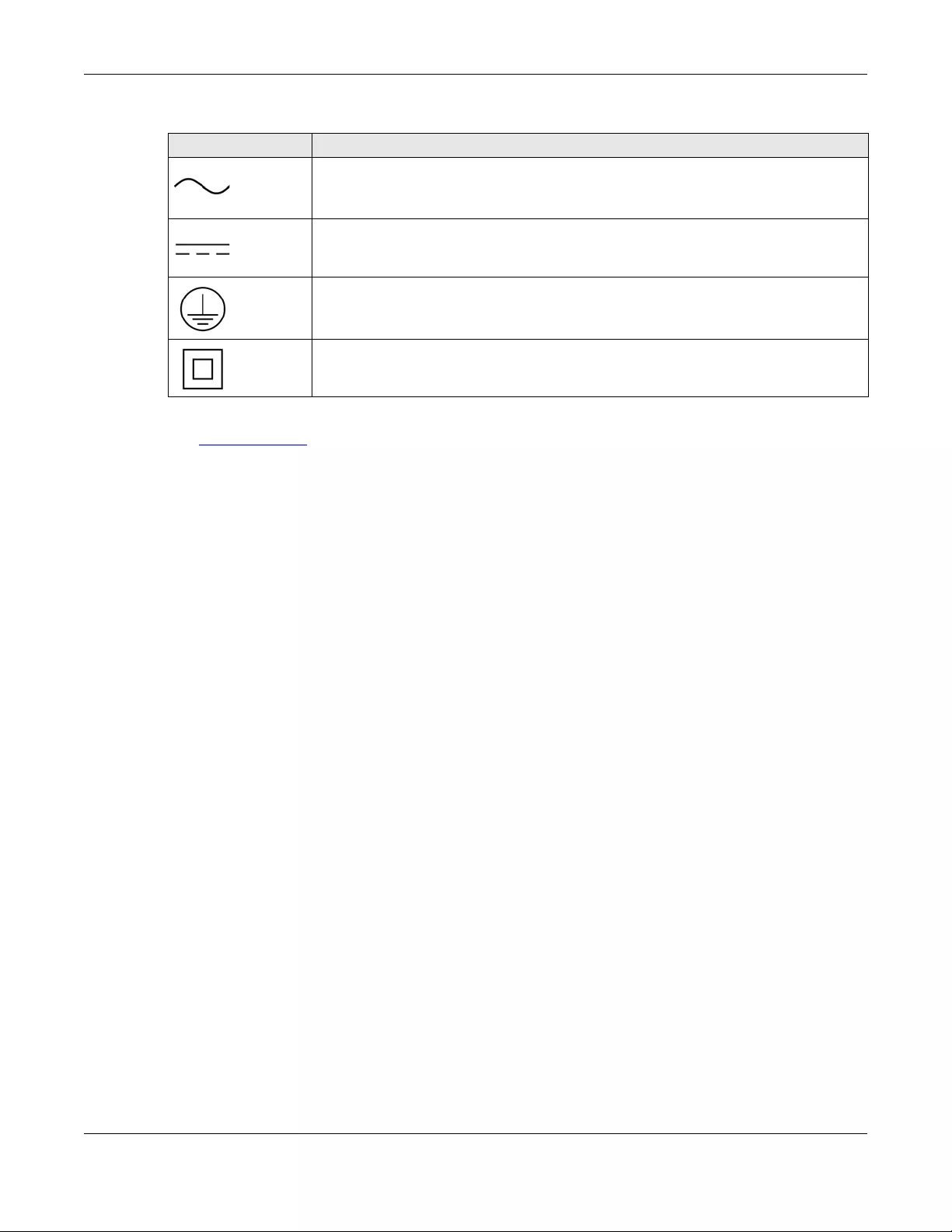
Appendix B Legal Information
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
75
Explanation of the Symbols
Viewing Certifications
Go to http://www.zyxel.com to view this product’s documentation and certifications.
Zyxel Limited Warranty
Zyxel warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects in material or workmanship for a specific period (the
Warranty Period) from the date of purchase. The Warranty Period varies by region. Check with your vendor and/or the authorized Zyxel local
distributor for details about the Warranty Period of this product. During the warranty period, and upon proof of purchase, should the product
have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship and/or materials, Zyxel will, at its discretion, repair or replace the defective products or
components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product or components to
proper operating condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent product of equal or higher value,
and will be solely at the discretion of Zyxel. This warranty shall not apply if the product has been modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by
an act of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions.
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties,
express or implied, including any implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. Zyxel shall in no event be held
liable for indirect or consequential damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact your vendor. You may also refer to the warranty policy for the region in which you bought the
device at http://www.zyxel.com/web/support_warranty_info.php.
Registration
Register your product online at www.zyxel.com to receive email notices of firmware upgrades and related information.
Trademarks
The trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for identification purposes only and may be properties of their respective owners.
Open Source Licenses
This product contains in part some free software distributed under GPL license terms and/or GPL like licenses. To request the source code
covered under these licenses, please go to: https://www.zyxel.com/form/gpl_oss_software_notice.shtml.
SYMBOL EXPLANATION
Alternating current (AC):
AC is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction.
Direct current (DC):
DC if the unidirectional flow or movement of electric charge carriers.
Earth; ground:
A wiring terminal intended for connection of a Protective Earthing Conductor.
Class II equipment:
The method of protection against electric shock in the case of class II equipment is either double insulation or
reinforced insulation.

Index
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
76
Index
Numerics
1 Gbps 10
10 Gbps 10
100 Mbps 10
2.5 Gbps 10
5 Gbps 10
802.1Q VLAN-aware 45
802.1Q VLAN-unaware 45
A
aggregate physical link 48
air circulation
for cooling 14
airflow 18
application
backbone 11
bridging 11
authorized technician
install the Switch 14
B
back pressure flow control 44
bandwidth capacity
cable types 10
bandwidth link 48
bridging application 11
broadcast 56
broadcast frame 45
broadcast packets 41
broadcast storm control 41
button
RESET 29
C
cable types 10
CAT 5 cable 10
CAT 5e cable 10
CAT 6 cable 10
CAT 6a cable 10
CAT 7 cable 10
Certificate Authority (CA) 58
certifications 73
viewing 75
CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) 45
changing the password 28
clear counters 40
clearance
Switch installation 14
collision signal 44
contact information 66
copyright 72
CoS (Class of Service) 52
counters
clear 40
customer support 66
D
default IP 21
device name
configuration 40
DHCP server 61
disclaimer 72
disposal information 74
distance limitation
cable types 10
distribution type 49

Index
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
77
E
Energy Efficient Ethernet Standard 9
ErP (Energy-related Products) 73
Ethernet
connection speed 43
Ethernet cable
type 14
F
FCC EMC statement 72
firmware upgrade 61
process 61
firmware version 40
flow control 44
frames
received 40
tagged 45
transmitted 40
untagged 35, 45, 46
front panel 17
full duplex mode 44
G
gateway 40, 61
H
half duplex mode 44
hardware installation 14
hardware overview 17
higher-capacity link 48
HTTP service
enable 61
HTTPS
certificates 58
implementation 58
public keys, private keys 58
HTTPS introduction 58
HTTPS service
enable 61
I
icon
logout 29
IEEE 9
IEEE 802.1p QoS
apply 55
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN 52
add ports 33
maximum number 47
IEEE 802.3az EEE
enable 61
IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) 58
IEEE priority 53
IEEE802.3x flow control 44
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) 56
IGMP join packet 57
IGMP leave packet 57
IGMP query port 57
IGMP snooping 56
overview 56
settings 56
IGMP Snooping screen 56
IGMP static router port 57
inactivity timeout
Web Configurator 22
ingress port 45
initial setup
example 30
installation
air circulation 14
desktop 14
installation scenarios 14
Internet browser
pop-up window 21
supported 21
IP address 40
change 30
default management 21
manage 61
IP packet

Index
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
78
transmission method 56
IPTV service 56
J
Java permissions 21
JavaScript 21
jitter (variations in delay) 52
L
latency (delay) 52
LED
left 19, 20
LINK/ACT 19
PWR/SYS 19, 29
right 19, 20
LEDs 19
behavior 19
link aggregation 48, 57
algorithm 49
group 49
link status 40
login 21
password 28
login account
administrator 59
logout icon 29
loop detection 41
loop prevention 41
LED 19
loop state 40
loop status 40
Low Power Idle (LPI) mode 58
lower-speed link 48
M
MAC address 40
Management screen 30, 31, 59
Management settings 59
management VLAN
enable 61
managing the Switch
good habits 12
maximum distance
cable types 10
mirrored port 50, 51
model name 39
monitor port 50, 51
mounting
wall 15
mounting holes
distance 15
multicast 56
multicast drop 57
multicast frame 45
multicast group 45
Multi-Gigabit 10
Multi-Gigabit application 10
N
network applications 9
network flooded 41
O
open source licenses 75
overheating
prevention 14
P
packet collision 44
password 28
administrator 59
change 28, 61
default 21
default administrator 28
set 31
PCP (Priority Code Point) 52

Index
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
79
port
untagged 47
port mirroring
direction 51
overview 50
port number 46, 51
Port screen 42
port settings 43
port statistics 38
Port VID
set 35
port VLAN ID, see PVID 46
power connector 18
product registration 75
PVID 35, 45
PVID (Port VLAN ID) 46
Q
QoS
IEEE 802.1p 52
port-based 52
QoS (Quality of Service) 52
QoS screen 52
queue
weight 54
R
rear panel 17
rear panel connections 18
reboot the Switch 60
recycling information 74
registration
product 75
RESET button 29
reset the Switch 60
resetting 29
restart the Switch 60
restoring configuration 29
rubber feet
attach 14
S
safety warnings 73
screen resolution
recommended 21
screw specifications
wall mount 16
single-port link 48
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) 41
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) 58
status 26
subnet mask 40, 61
Switch
fanless-type usage precaution 14
fan-type usage precaution 14
general information 38
IPv4 address 40
lock 29
managing 12
model name 39
reset 29
Switch lockout 29
System screen 38
T
tagged VLAN 45
TCI (Tag Control Information) 45
TPID (Tag Protocol IDentifier) 45
trademarks 75
traffic distribution 49
traffic type mapping 53
transmission speed
cable types 10
Troubleshooting 63
U
unicast 56

Index
XGS1210-12 / XGS1250-12 User’s Guide
80
V
ventilation holes 14
VID 47
number of possible VIDs 45
priority frame 45
VID (VLAN IDentifier) 45
VLAN
creation 33
ID 45
introduction 45
PVID 46
settings 45
shared server example 12
tag-based example 12
tagged 45
VLAN application
example 12
VLAN ID 45, 47
VLAN tags 34
VLAN-unaware devices 34
VOD (Video on Demand) 52
Voice over IP (VoIP) 52
W
wall-mounting 15
warranty
note 75
Web Configurator
home 26
inactivity timeout 22
layout 26
log out link 27
login 21
logout 29
main window 27
overview 21
Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) 53
Windows OS version
check 22
WRR application
example 53
WRR scheduling 54
WS (web server) 58
Z
ZDP 22
ZON Utility 22
compatible OS 22
fields description 26
icon description 25
installation requirements 22
introduction 22
minimum hardware requirements 22
network adapter select 24
password prompt 25
run 23
supported firmware version 23
supported models 23
Zyxel AP Configurator (ZAC) 26
Zyxel Discovery Protocol (ZDP) 22
Zyxel limited warranty 75
Zyxel One Network (ZON) Utility 22