Table of Contents
- Command Reference for AlliedWare Plus™ Version 5.4.9-0.x
- Contents
- List of Commands
- Part 1: Setup and Troubleshooting
- CLI Navigation Commands
- File and Configuration Management Commands
- Introduction
- autoboot enable
- boot config-file
- boot config-file backup
- boot system
- boot system backup
- cd
- copy (filename)
- copy current-software
- copy debug
- copy running-config
- copy startup-config
- copy zmodem
- create autoboot
- delete
- delete debug
- dir
- edit
- edit (filename)
- erase factory-default
- erase startup-config
- ip tftp source-interface
- ipv6 tftp source-interface
- mkdir
- move
- move debug
- pwd
- rmdir
- show autoboot
- show boot
- show file
- show file systems
- show running-config
- show running-config interface
- show startup-config
- show version
- unmount
- write file
- write memory
- write terminal
- User Access Commands
- Introduction
- aaa authentication enable default local
- aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
- aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
- aaa login fail-delay
- clear aaa local user lockout
- clear line console
- clear line vty
- enable password
- enable secret
- exec-timeout
- flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console)
- length (asyn)
- line
- privilege level
- security-password history
- security-password forced-change
- security-password lifetime
- security-password min-lifetime-enforce
- security-password minimum-categories
- security-password minimum-length
- security-password reject-expired-pwd
- security-password warning
- service advanced-vty
- service password-encryption
- service telnet
- service terminal-length (deleted)
- show aaa local user locked
- show privilege
- show security-password configuration
- show security-password user
- show telnet
- show users
- telnet
- telnet server
- terminal length
- terminal resize
- username
- Feature Licensing Commands
- Subscription Licensing Commands
- GUI Commands
- System Configuration and Monitoring Commands
- Introduction
- banner exec
- banner login (system)
- banner motd
- clock set
- clock summer-time date
- clock summer-time recurring
- clock timezone
- ecofriendly led
- findme
- findme trigger
- hostname
- no debug all
- reboot
- reload
- show clock
- show cpu
- show cpu history
- show debugging
- show ecofriendly
- show interface memory
- show memory
- show memory allocations
- show memory history
- show memory pools
- show memory shared
- show process
- show reboot history
- show router-id
- show system
- show system environment
- show system interrupts
- show system mac
- show system serialnumber
- show tech-support
- speed (asyn)
- system territory (deprecated)
- terminal monitor
- undebug all
- Pluggables and Cabling Commands
- Introduction
- clear fiber-monitoring interface
- clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
- debug fiber-monitoring
- fiber-monitoring action
- fiber-monitoring baseline
- fiber-monitoring enable
- fiber-monitoring interval
- fiber-monitoring sensitivity
- show system fiber-monitoring
- show system pluggable
- show system pluggable detail
- show system pluggable diagnostics
- show test cable-diagnostics tdr
- test cable-diagnostics tdr interface
- Connectivity Fault Management Commands
- Introduction
- cc interval
- cc multicast
- cc unicast
- clear (MEP Attribute)
- clear ethernet cfm errorlog
- clear mep counter
- ethernet cfm domain-name
- ethernet cfm mep
- mep (FNG attributes)
- mep active
- mep ccm-ltm-priority
- mep crosscheck
- service ma-name
- show ethernet cfm details
- show ethernet cfm domain
- show ethernet cfm errorlog
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep
- show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
- show ethernet cfm service
- show mep-alarm status
- Logging Commands
- Introduction
- clear exception log
- clear log
- clear log buffered
- clear log external
- clear log permanent
- copy buffered-log
- copy permanent-log
- default log buffered
- default log console
- default log email
- default log external
- default log host
- default log monitor
- default log permanent
- log buffered
- log buffered (filter)
- log buffered exclude
- log buffered size
- log console
- log console (filter)
- log console exclude
- log email
- log email (filter)
- log email exclude
- log email time
- log external
- log external (filter)
- log external exclude
- log external rotate
- log external size
- log facility
- log host
- log host (filter)
- log host exclude
- log host source
- log host startup-delay
- log host time
- log monitor (filter)
- log monitor exclude
- log permanent
- log permanent (filter)
- log permanent exclude
- log permanent size
- log-rate-limit nsm
- log trustpoint
- show counter log
- show exception log
- show log
- show log config
- show log external
- show log permanent
- show running-config log
- unmount
- Scripting Commands
- Interface Commands
- Port Mirroring and Remote Mirroring Commands
- Alarm Monitoring Commands
- Part 2: Interfaces and Layer 2
- Switching Commands
- Introduction
- backpressure
- clear loop-protection counters
- clear mac address-table dynamic
- clear mac address-table static
- clear port counter
- clear port-security intrusion
- debug loopprot
- debug platform packet
- duplex
- flowcontrol (switch port)
- linkflap action
- loop-protection loop-detect
- loop-protection action
- loop-protection action-delay-time
- loop-protection timeout
- mac address-table acquire
- mac address-table ageing-time
- mac address-table logging
- mac address-table static
- mac address-table thrash-limit
- platform hwfilter-size
- platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
- platform load-balancing
- platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
- platform multicast-ratelimit
- platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
- platform vlan-stacking-tpid
- polarity
- show debugging loopprot
- show debugging platform packet
- show flowcontrol interface
- show interface err-disabled
- show interface switchport
- show loop-protection
- show mac address-table
- show mac address-table thrash-limit
- show platform
- show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
- show platform port
- show port-security interface
- show port-security intrusion
- show storm-control
- speed
- storm-control level
- switchport port-security
- switchport port-security aging
- switchport port-security maximum
- switchport port-security violation
- thrash-limiting
- undebug loopprot
- undebug platform packet
- VLAN Commands
- Introduction
- debug private-vlan ufo
- port-vlan-forwarding-priority
- private-vlan
- private-vlan association
- platform vlan-stacking-tpid
- private-vlan ufo trap
- show debugging private-vlan
- show port-vlan-forwarding-priority
- show vlan
- show vlan access-map
- show vlan filter
- show vlan private-vlan
- show vlan private-vlan ufo
- switchport access vlan
- switchport mode access
- switchport mode private-vlan
- switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous
- switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary
- switchport mode private-vlan ufo
- switchport mode trunk
- switchport private-vlan host-association
- switchport private-vlan mapping
- switchport trunk allowed vlan
- switchport trunk native vlan
- switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging)
- switchport voice dscp
- switchport voice vlan
- switchport voice vlan priority
- vlan
- vlan access-map
- vlan database
- vlan filter
- Spanning Tree Commands
- Introduction
- clear spanning-tree statistics
- clear spanning-tree detected protocols (RSTP and MSTP)
- debug mstp (RSTP and STP)
- instance priority (MSTP)
- instance vlan (MSTP)
- region (MSTP)
- revision (MSTP)
- show debugging mstp
- show spanning-tree
- show spanning-tree brief
- show spanning-tree mst
- show spanning-tree mst config
- show spanning-tree mst detail
- show spanning-tree mst detail interface
- show spanning-tree mst instance
- show spanning-tree mst instance interface
- show spanning-tree mst interface
- show spanning-tree statistics
- show spanning-tree statistics instance
- show spanning-tree statistics instance interface
- show spanning-tree statistics interface
- show spanning-tree vlan range-index
- spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP)
- spanning-tree bpdu
- spanning-tree cisco-interoperability (MSTP)
- spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)
- spanning-tree enable
- spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
- spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval
- spanning-tree force-version
- spanning-tree forward-time
- spanning-tree guard root
- spanning-tree hello-time
- spanning-tree link-type
- spanning-tree max-age
- spanning-tree max-hops (MSTP)
- spanning-tree mode
- spanning-tree mst configuration
- spanning-tree mst instance
- spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
- spanning-tree mst instance priority
- spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
- spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
- spanning-tree path-cost
- spanning-tree portfast (STP)
- spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
- spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
- spanning-tree priority (bridge priority)
- spanning-tree priority (port priority)
- spanning-tree restricted-role
- spanning-tree restricted-tcn
- spanning-tree transmit-holdcount
- undebug mstp
- Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) Commands
- Link Aggregation Commands
- Introduction
- channel-group
- clear lacp counters
- debug lacp
- lacp global-passive-mode enable
- lacp port-priority
- lacp system-priority
- lacp timeout
- platform load-balancing
- show debugging lacp
- show diagnostic channel-group
- show etherchannel
- show etherchannel detail
- show etherchannel summary
- show lacp sys-id
- show lacp-counter
- show port etherchannel
- show static-channel-group
- static-channel-group
- undebug lacp
- Power over Ethernet Commands
- Introduction
- clear power-inline counters interface
- debug power-inline
- power-inline allow-legacy
- power-inline description
- power-inline enable
- power-inline max
- power-inline priority
- power-inline usage-threshold
- service power-inline
- show debugging power-inline
- show power-inline
- show power-inline counters
- show power-inline interface
- show power-inline interface detail
- GVRP Commands
- Switching Commands
- Part 3: Layer 3 Switching
- IP Addressing and Protocol Commands
- Introduction
- arp-aging-timeout
- arp
- arp log
- arp opportunistic-nd
- arp-reply-bc-dmac
- clear arp-cache
- debug ip packet interface
- ip address (IP Addressing and Protocol)
- ip gratuitous-arp-link
- ip redirects
- ip tcp synack-retries
- ip unreachables
- ping
- show arp
- show debugging ip packet
- show ip flooding-nexthops
- show ip interface
- show ip sockets
- show ip traffic
- tcpdump
- traceroute
- undebug ip packet interface
- Domain Name Service (DNS) Commands
- IPv6 Commands
- Introduction
- clear ipv6 neighbors
- ipv6 address
- ipv6 address autoconfig
- ipv6 address suffix
- ipv6 enable
- ipv6 eui64-linklocal
- ipv6 forwarding
- ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet
- ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
- ipv6 nd current-hoplimit
- ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
- ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval
- ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- ipv6 nd prefix
- ipv6 nd ra-interval
- ipv6 nd ra-lifetime
- ipv6 nd raguard
- ipv6 nd reachable-time
- ipv6 nd retransmission-time
- ipv6 nd suppress-ra
- ipv6 neighbor
- ipv6 opportunistic-nd
- ipv6 unreachables
- optimistic-nd
- ping ipv6
- show ipv6 forwarding
- show ipv6 interface brief
- show ipv6 neighbors
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 route summary
- traceroute ipv6
- Routing Commands
- IP Addressing and Protocol Commands
- Part 4: Multicast Applications
- IGMP and IGMP Snooping Commands
- Introduction
- clear ip igmp
- clear ip igmp group
- clear ip igmp interface
- debug igmp
- ip igmp
- ip igmp access-group
- ip igmp flood specific-query
- ip igmp immediate-leave
- ip igmp last-member-query-count
- ip igmp last-member-query-interval
- ip igmp limit
- ip igmp maximum-groups
- ip igmp querier-timeout
- ip igmp query-holdtime
- ip igmp query-interval
- ip igmp query-max-response-time
- ip igmp ra-option
- ip igmp robustness-variable
- ip igmp snooping
- ip igmp snooping fast-leave
- ip igmp snooping mrouter
- ip igmp snooping querier
- ip igmp snooping report-suppression
- ip igmp snooping routermode
- ip igmp snooping source-timeout
- ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
- ip igmp source-address-check
- ip igmp static-group
- ip igmp startup-query-count
- ip igmp startup-query-interval
- ip igmp trusted
- ip igmp version
- show debugging igmp
- show ip igmp groups
- show ip igmp interface
- show ip igmp snooping mrouter
- show ip igmp snooping routermode
- show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
- show ip igmp snooping statistics
- undebug igmp
- MLD Snooping Commands
- Introduction
- clear ipv6 mld
- clear ipv6 mld group
- clear ipv6 mld interface
- debug mld
- ipv6 mld immediate-leave
- ipv6 mld limit
- ipv6 mld snooping
- ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave
- ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
- ipv6 mld snooping querier
- ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
- ipv6 mld static-group
- show debugging mld
- show ipv6 mld groups
- show ipv6 mld interface
- show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
- show ipv6 mld snooping statistics
- IGMP and IGMP Snooping Commands
- Part 5: Access and Security
- IPv4 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands
- Introduction
- access-group
- access-list (numbered hardware ACL for ICMP)
- access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets)
- access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP protocols)
- access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)
- access-list (numbered hardware ACL for TCP or UDP)
- access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
- (named hardware ACL entry for ICMP)
- (named hardware ACL entry for IP packets)
- (named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols)
- (named hardware ACL entry for MAC addresses)
- (named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP)
- commit (IPv4)
- show access-group
- show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
- show interface access-group
- IPv4 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands
- Introduction
- access-list extended (named)
- access-list (extended numbered)
- (access-list extended ICMP filter)
- (access-list extended IP filter)
- (access-list extended IP protocol filter)
- (access-list extended TCP UDP filter)
- access-list standard (named)
- access-list (standard numbered)
- (access-list standard named filter)
- (access-list standard numbered filter)
- maximum-access-list
- show access-list (IPv4 Software ACLs)
- show ip access-list
- vty access-class (numbered)
- IPv6 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands
- IPv6 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands
- QoS Commands
- Introduction
- class
- class-map
- clear mls qos interface policer-counters
- default-action
- description (QoS policy-map)
- egress-rate-limit
- match access-group
- match cos
- match dscp
- match eth-format protocol
- match inner-cos
- match inner-vlan
- match ip-precedence
- match mac-type
- match tcp-flags
- match vlan
- mls qos cos
- mls qos enable
- mls qos map cos-queue
- mls qos map premark-dscp
- no police
- police single-rate action
- police twin-rate action
- policy-map
- priority-queue
- remark-map
- remark new-cos
- service-policy input
- show class-map
- show mls qos
- show mls qos interface
- show mls qos interface policer-counters
- show mls qos interface queue-counters
- show mls qos interface storm-status
- show mls qos maps cos-queue
- show mls qos maps premark-dscp
- show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
- show policy-map
- storm-action
- storm-downtime
- storm-protection
- storm-rate
- storm-window
- trust dscp
- wrr-queue disable queues
- wrr-queue egress-rate-limit queues
- wrr-queue weight queues
- 802.1X Commands
- Introduction
- dot1x accounting
- dot1x authentication
- debug dot1x
- dot1x control-direction
- dot1x eap
- dot1x eapol-version
- dot1x initialize interface
- dot1x initialize supplicant
- dot1x keytransmit
- dot1x max-auth-fail
- dot1x max-reauth-req
- dot1x port-control
- dot1x timeout tx-period
- show debugging dot1x
- show dot1x
- show dot1x diagnostics
- show dot1x interface
- show dot1x sessionstatistics
- show dot1x statistics interface
- show dot1x supplicant
- show dot1x supplicant interface
- undebug dot1x
- Authentication Commands
- Introduction
- auth auth-fail vlan
- auth critical
- auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
- auth dynamic-vlan-creation
- auth guest-vlan
- auth guest-vlan forward
- auth host-mode
- auth log
- auth max-supplicant
- auth multi-vlan-session
- auth profile (Global Configuration)
- auth profile (Interface Configuration)
- auth reauthentication
- auth roaming disconnected
- auth roaming enable
- auth supplicant-ip
- auth supplicant-mac
- auth timeout connect-timeout
- auth timeout quiet-period
- auth timeout reauth-period
- auth timeout server-timeout
- auth timeout supp-timeout
- auth two-step enable
- auth-mac accounting
- auth-mac authentication
- auth-mac enable
- auth-mac method
- auth-mac password
- auth-mac reauth-relearning
- auth-mac static
- auth-mac username
- auth-web accounting
- auth-web authentication
- auth-web enable
- auth-web forward
- auth-web max-auth-fail
- auth-web method
- auth-web-server blocking-mode
- auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress
- auth-web-server dhcp lease
- auth-web-server dhcp-wpad-option
- auth-web-server host-name
- auth-web-server intercept-port
- auth-web-server ipaddress
- auth-web-server page language
- auth-web-server login-url
- auth-web-server page logo
- auth-web-server page sub-title
- auth-web-server page success-message
- auth-web-server page title
- auth-web-server page welcome-message
- auth-web-server ping-poll enable
- auth-web-server ping-poll failcount
- auth-web-server ping-poll interval
- auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh
- auth-web-server ping-poll timeout
- auth-web-server port
- auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
- auth-web-server redirect-url
- auth-web-server session-keep
- auth-web-server ssl
- auth-web-server ssl intercept-port
- copy proxy-autoconfig-file
- copy web-auth-https-file
- description (Authentication Profile)
- erase proxy-autoconfig-file
- erase web-auth-https-file
- platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
- platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
- show auth
- show auth diagnostics
- show auth interface
- show auth sessionstatistics
- show auth statistics interface
- show auth supplicant
- show auth supplicant interface
- show auth two-step supplicant brief
- show auth-web-server
- show auth-web-server page
- show proxy-autoconfig-file
- AAA Commands
- Introduction
- aaa accounting auth-mac
- aaa accounting auth-web
- aaa accounting commands
- aaa accounting dot1x
- aaa accounting login
- aaa accounting update
- aaa authentication auth-mac
- aaa authentication auth-web
- aaa authentication dot1x
- aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+
- aaa authentication enable default local
- aaa authentication login
- aaa authorization commands
- aaa authorization config-commands
- aaa group server
- aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
- aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
- aaa login fail-delay
- accounting login
- authorization commands
- clear aaa local user lockout
- debug aaa
- login authentication
- proxy-port
- radius-secure-proxy aaa
- server (radsecproxy-aaa)
- server mutual-authentication
- server name-check
- server trustpoint
- show aaa local user locked
- show aaa server group
- show debugging aaa
- show radius server group
- undebug aaa
- RADIUS Commands
- Introduction
- auth radius send nas-identifier
- auth radius send service-type
- deadtime (RADIUS server group)
- debug radius
- ip radius source-interface
- radius-server deadtime
- radius-server host
- radius-server key
- radius-server retransmit
- radius-server timeout
- server (server group)
- show debugging radius
- show radius
- show radius statistics
- undebug radius
- Local RADIUS Server Commands
- Introduction
- attribute
- authentication
- client (radsecproxy-srv)
- client mutual-authentication
- client name-check
- client trustpoint
- clear radius local-server statistics
- copy fdb-radius-users (to file)
- copy local-radius-user-db (from file)
- copy local-radius-user-db (to file)
- crypto pki enroll local (deleted)
- crypto pki enroll local local-radius-all-users (deleted)
- crypto pki enroll local user (deleted)
- crypto pki export local pem (deleted)
- crypto pki export local pkcs12 (deleted)
- crypto pki trustpoint local (deleted)
- debug crypto pki (deleted)
- domain-style
- egress-vlan-id
- egress-vlan-name
- group
- nas
- radius-secure-proxy local-server
- radius-server local
- server auth-port
- server enable
- show radius local-server group
- show radius local-server nas
- show radius local-server statistics
- show radius local-server user
- user (RADIUS server)
- vlan (RADIUS server)
- Public Key Infrastructure Commands
- Introduction
- crypto key generate rsa
- crypto key zeroize
- crypto pki authenticate
- crypto pki enroll
- crypto pki enroll user
- crypto pki export pem
- crypto pki export pkcs12
- crypto pki import pem
- crypto pki import pkcs12
- crypto pki trustpoint
- enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode)
- fingerprint (trustpoint configuration mode)
- no crypto pki certificate
- rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode)
- show crypto key mypubkey rsa
- show crypto pki certificates
- show crypto pki enrollment user
- show crypto pki trustpoint
- subject-name (trustpoint configuration)
- TACACS+ Commands
- DHCP Snooping Commands
- Introduction
- arp security
- arp security violation
- clear arp security statistics
- clear ip dhcp snooping binding
- clear ip dhcp snooping statistics
- debug arp security
- debug ip dhcp snooping
- ip dhcp snooping
- ip dhcp snooping agent-option
- ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted
- ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet
- ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
- ip dhcp snooping binding
- ip dhcp snooping database
- ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
- ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
- ip dhcp snooping max-bindings
- ip dhcp snooping trust
- ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
- ip dhcp snooping violation
- ip source binding
- service dhcp-snooping
- show arp security
- show arp security interface
- show arp security statistics
- show debugging arp security
- show debugging ip dhcp snooping
- show ip dhcp snooping
- show ip dhcp snooping acl
- show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
- show ip dhcp snooping binding
- show ip dhcp snooping interface
- show ip dhcp snooping statistics
- show ip source binding
- OpenFlow Commands
- Introduction
- openflow
- openflow controller
- openflow datapath-id
- openflow failmode
- openflow failmode standalone
- openflow inactivity
- openflow native vlan
- openflow ssl peer certificate
- openflow ssl trustpoint
- openflow version
- show openflow config
- show openflow coverage
- show openflow flows
- show openflow rules
- show openflow ssl
- show openflow status
- IPv4 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands
- Part 6: Network Availability
- Ethernet Protection Switched Ring (EPSRing™) Commands
- Introduction
- debug epsr
- epsr
- epsr configuration
- epsr datavlan
- epsr enhancedrecovery enable
- epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
- epsr mode transit controlvlan
- epsr priority
- epsr state
- epsr topology-change
- epsr trap
- show debugging epsr
- show epsr
- show epsr common segments
- show epsr config-check
- show epsr <epsr-instance>
- show epsr <epsr-instance> counters
- show epsr counters
- show epsr summary
- undebug epsr
- G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Commands
- Introduction
- cfm-sf-notify
- clear g8032 erp-instance
- clear g8032 erp-instance statistics
- data-traffic
- debug g8032
- enable (G.8032)
- epsr topology-change
- erp-instance
- g8032 erp-instance
- g8032 forced-switch erp-instance
- g8032 manual-switch erp-instance
- g8032 physical-ring
- g8032 profile
- level (G.8032)
- physical-ring
- profile name
- raps-channel
- rpl role
- show debugging g8032
- show g8032 erp-instance
- show g8032 erp-instance statistics
- show g8032 physical-ring
- show g8032 profile
- sub-ring
- timer (G.8032)
- topology-change
- trap (G.8032)
- undebug g8032
- RRP Snooping Commands
- Ethernet Protection Switched Ring (EPSRing™) Commands
- Part 7: Network Management
- Allied Telesis Management Framework™ (AMF) Commands
- Introduction
- application-proxy whitelist enable
- application-proxy whitelist server
- area-link
- atmf area
- atmf area password
- atmf authorize
- atmf authorize provision
- atmf backup
- atmf backup area-masters delete
- atmf backup area-masters enable
- atmf backup area-masters now
- atmf backup area-masters synchronize
- atmf backup bandwidth
- atmf backup delete
- atmf backup enable
- atmf backup guests delete
- atmf backup guests enable
- atmf backup guests now
- atmf backup guests synchronize
- atmf backup now
- atmf backup redundancy enable
- atmf backup server
- atmf backup stop
- atmf backup synchronize
- atmf cleanup
- atmf container
- atmf container login
- atmf controller
- atmf distribute firmware
- atmf domain vlan
- atmf enable
- atmf group (membership)
- atmf guest-class
- atmf log-verbose
- atmf management subnet
- atmf management vlan
- atmf master
- atmf mtu
- atmf network-name
- atmf provision (interface)
- atmf provision node
- atmf reboot-rolling
- atmf recover
- atmf recover guest
- atmf recover led-off
- atmf recovery-server
- atmf remote-login
- atmf restricted-login
- atmf secure-mode
- atmf secure-mode certificate expire
- atmf secure-mode certificate expiry
- atmf secure-mode certificate renew
- atmf secure-mode enable-all
- atmf select-area
- atmf topology-gui enable
- atmf trustpoint
- atmf virtual-crosslink
- atmf virtual-link
- atmf virtual-link protection
- atmf working-set
- bridge-group
- clear atmf links
- clear atmf links virtual
- clear atmf links statistics
- clear atmf recovery-file
- clear atmf secure-mode certificates
- clear atmf secure-mode statistics
- clone (amf provisioning)
- configure boot config (amf provisioning)
- configure boot system (amf provisioning)
- create (amf provisioning)
- debug atmf
- debug atmf packet
- delete (amf provisioning)
- discovery
- description (amf container)
- erase factory-default
- http-enable
- identity (amf provisioning)
- license-cert (amf provisioning)
- locate (amf provisioning)
- log event-host
- modeltype
- show application-proxy whitelist interface
- show application-proxy whitelist server
- show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
- show atmf
- show atmf area
- show atmf area guests
- show atmf area guests-detail
- show atmf area nodes
- show atmf area nodes-detail
- show atmf area summary
- show atmf authorization
- show atmf backup
- show atmf backup area
- show atmf backup guest
- show atmf container
- show atmf detail
- show atmf group
- show atmf group members
- show atmf guests
- show atmf guests detail
- show atmf links
- show atmf links detail
- show atmf links guest
- show atmf links guest detail
- show atmf links statistics
- show atmf nodes
- show atmf provision nodes
- show atmf recovery-file
- show atmf secure-mode
- show atmf secure-mode audit
- show atmf secure-mode audit link
- show atmf secure-mode certificates
- show atmf secure-mode sa
- show atmf secure-mode statistics
- show atmf tech
- show atmf virtual-links
- show atmf working-set
- show debugging atmf
- show debugging atmf packet
- show running-config atmf
- state
- switchport atmf-agentlink
- switchport atmf-arealink remote-area
- switchport atmf-crosslink
- switchport atmf-guestlink
- switchport atmf-link
- type atmf node
- undebug atmf
- username
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Commands
- Introduction
- bootfile
- clear ip dhcp binding
- default-router
- dns-server
- domain-name
- host (DHCP)
- ip address dhcp
- ip dhcp bootp ignore
- ip dhcp leasequery enable
- ip dhcp option
- ip dhcp pool
- ip dhcp-client default-route distance
- ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific
- ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
- lease
- network (DHCP)
- next-server
- option
- probe enable
- probe packets
- probe timeout
- probe type
- range
- route
- service dhcp-server
- short-lease-threshold
- show counter dhcp-client
- show counter dhcp-server
- show dhcp lease
- show ip dhcp binding
- show ip dhcp pool
- show ip dhcp server statistics
- show ip dhcp server summary
- subnet-mask
- DHCP for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Commands
- NTP Commands
- Introduction
- ntp access-group (deprecated)
- ntp authenticate
- ntp authentication-key
- ntp broadcastdelay
- ntp discard
- ntp master
- ntp peer
- ntp rate-limit
- ntp restrict
- ntp server
- ntp source
- ntp trusted-key (deprecated)
- show counter ntp (deprecated)
- show ntp associations
- show ntp counters
- show ntp counters associations
- show ntp status
- Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Transparent Clock Commands
- SNMP Commands
- Introduction
- alias (interface)
- debug snmp
- show counter snmp-server
- show debugging snmp
- show running-config snmp
- show snmp-server
- show snmp-server community
- show snmp-server group
- show snmp-server user
- show snmp-server view
- snmp trap link-status
- snmp trap link-status suppress
- snmp-server
- snmp-server community
- snmp-server contact
- snmp-server enable trap
- snmp-server engineID local
- snmp-server engineID local reset
- snmp-server group
- snmp-server host
- snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus
- snmp-server location
- snmp-server source-interface
- snmp-server startup-trap-delay
- snmp-server user
- snmp-server view
- undebug snmp
- LLDP Commands
- Introduction
- clear lldp statistics
- clear lldp table
- debug lldp
- lldp faststart-count
- lldp holdtime-multiplier
- lldp management-address
- lldp med-notifications
- lldp med-tlv-select
- lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check
- lldp notification-interval
- lldp notifications
- lldp port-number-type
- lldp reinit
- lldp run
- lldp timer
- lldp tlv-select
- lldp transmit receive
- lldp tx-delay
- location civic-location configuration
- location civic-location identifier
- location civic-location-id
- location coord-location configuration
- location coord-location identifier
- location coord-location-id
- location elin-location
- location elin-location-id
- show debugging lldp
- show lldp
- show lldp interface
- show lldp local-info
- show lldp neighbors
- show lldp neighbors detail
- show lldp statistics
- show lldp statistics interface
- show location
- Mail (SMTP) Commands
- RMON Commands
- Secure Shell (SSH) Commands
- Introduction
- banner login (SSH)
- clear ssh
- crypto key destroy hostkey
- crypto key destroy userkey
- crypto key generate hostkey
- crypto key generate userkey
- crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
- crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
- debug ssh client
- debug ssh server
- service ssh
- show banner login
- show crypto key hostkey
- show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
- show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
- show crypto key userkey
- show running-config ssh
- show ssh
- show ssh client
- show ssh server
- show ssh server allow-users
- show ssh server deny-users
- ssh
- ssh client
- ssh server
- ssh server allow-users
- ssh server authentication
- ssh server deny-users
- ssh server max-auth-tries
- ssh server resolve-host
- ssh server scp
- ssh server sftp
- undebug ssh client
- undebug ssh server
- Trigger Commands
- Introduction
- active (trigger)
- day
- debug trigger
- description (trigger)
- repeat
- script
- show debugging trigger
- show running-config trigger
- show trigger
- test
- time (trigger)
- trap
- trigger
- trigger activate
- type atmf node
- type card
- type cpu
- type interface
- type linkmon-probe
- type log
- type memory
- type periodic
- type ping-poll
- type reboot
- type time
- undebug trigger
- Ping-Polling Commands
- sFlow Commands
- Allied Telesis Management Framework™ (AMF) Commands
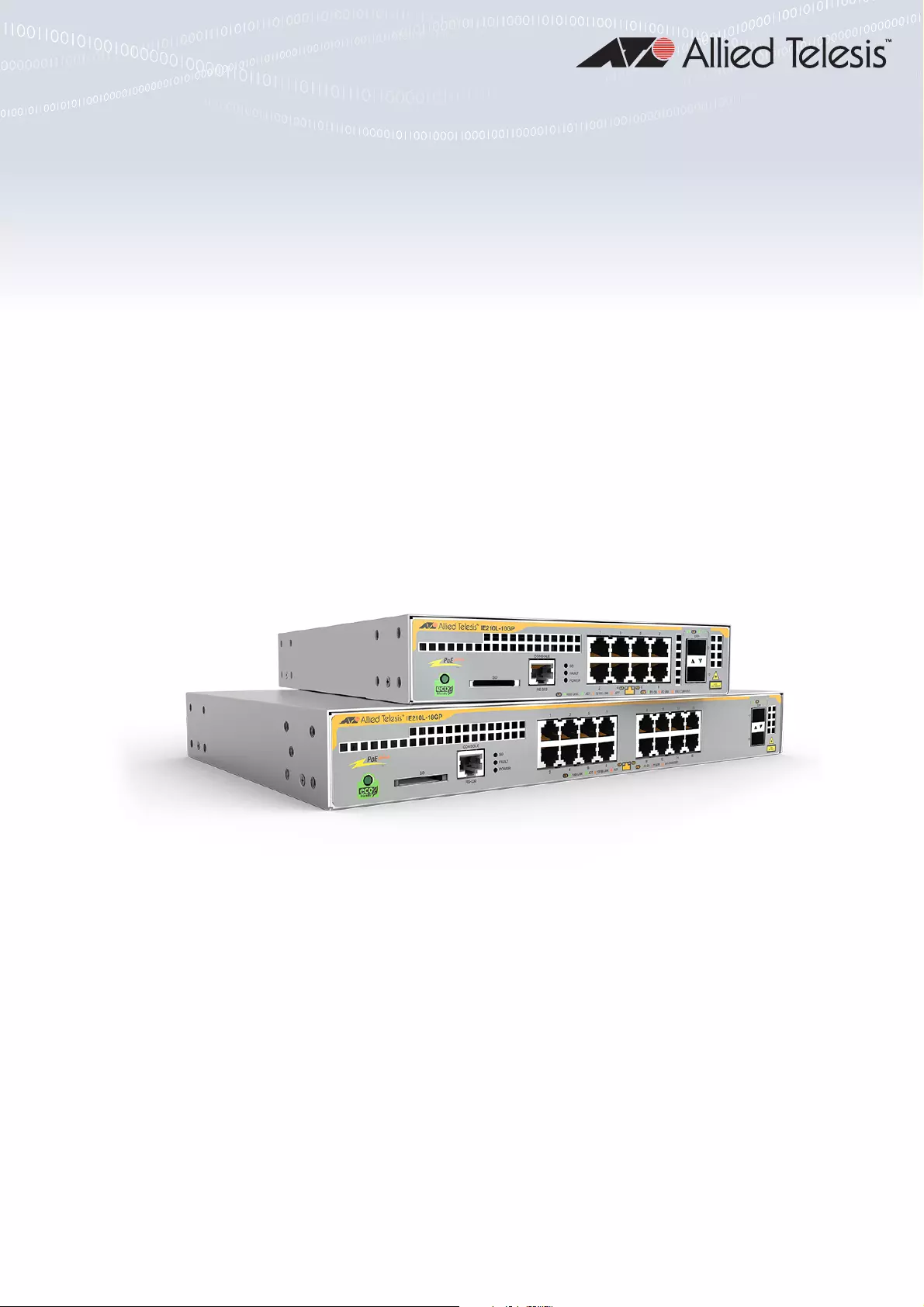
Allied Telesis AT-IE210L-10GP-60 User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for AT-IE210L-10GP-60 by Allied Telesis which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

C613-50292-01 Rev A
IE210L Series
INDUSTRIAL-LITE ETHERNET LAYER 2 SWITCHES
Command Reference for
AlliedWare Plus™ Version 5.4.9-0.x
IE210L-10GP
IE210L-18GP

Acknowledgments
This product includes software developed by the University of California, Berkeley and its contributors.
Copyright ©1982, 1986, 1990, 1991, 1993 The Regents of the University of California.
All rights reserved.
This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit. For information about this see
www.openssl.org/
Copyright ©1998-2008 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved.
This product includes software licensed under v2 and v3 of the GNU General Public License, available from: www.gnu.org/licenses/
gpl2.html and www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html respectively.
Source code for all GPL licensed software in this product can be obtained from the Allied Telesis GPL Code Download Center at:
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/
Allied Telesis is committed to meeting the requirements of the open source licenses including the GNU General Public License (GPL) and
will make all required source code available.
If you would like a copy of the GPL source code contained in Allied Telesis products, please send us a request by registered mail including
a check for US$15 to cover production and shipping costs and a CD with the GPL code will be mailed to you.
GPL Code Request
Allied Telesis Labs (Ltd)
PO Box 8011
Christchurch
New Zealand
Allied Telesis, AlliedWare Plus, Allied Telesis Management Framework, EPSRing, SwitchBlade, VCStack, and VCStack Plus are trademarks or
registered trademarks in the United States and elsewhere of Allied Telesis, Inc.
Microsoft and Internet Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product names, company names, logos or
other designations mentioned herein may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
2019 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior
written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesis, Inc. be liable for any
incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related to this
manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been advised of, known, or should have known, the possibility
of such damages.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 3
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Contents
PART 1: Setup and Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Chapter 1: CLI Navigation Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
configure terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
disable (Privileged Exec mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
do . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
enable (Privileged Exec mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
show history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Chapter 2: File and Configuration Management Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
autoboot enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
boot config-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
boot config-file backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
boot system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
boot system backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
cd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
copy (filename) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
copy current-software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
copy debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
copy running-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
copy startup-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
copy zmodem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
create autoboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
delete debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
dir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
edit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
edit (filename) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 4
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
erase factory-default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
erase startup-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
ip tftp source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
ipv6 tftp source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
mkdir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
move . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
move debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
pwd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
rmdir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
show autoboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
show boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
show file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
show file systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
show running-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
show running-config interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
show startup-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
show version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
unmount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
write file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
write memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
write terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Chapter 3: User Access Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
aaa authentication enable default local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
aaa login fail-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
clear aaa local user lockout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
clear line console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
clear line vty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
enable password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
enable secret . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
exec-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
length (asyn) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
privilege level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
security-password history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
security-password forced-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
security-password lifetime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
security-password min-lifetime-enforce . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
security-password minimum-categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
security-password minimum-length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
security-password reject-expired-pwd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
security-password warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
service advanced-vty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
service password-encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
service telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
service terminal-length (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
show aaa local user locked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
show privilege . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
show security-password configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 5
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show security-password user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
show telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
show users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
telnet server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
terminal length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
terminal resize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Chapter 4: Feature Licensing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
show license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
show license brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Chapter 5: Subscription Licensing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
license update (filename) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
license update online . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
show license external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Chapter 6: GUI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
atmf topology-gui enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
gui-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
http port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
http secure-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
log event-host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
service http . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
show http . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Chapter 7: System Configuration and Monitoring Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
banner exec . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
banner login (system) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
banner motd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
clock set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
clock summer-time date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
clock summer-time recurring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
clock timezone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
ecofriendly led . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
findme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
findme trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
no debug all . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
reload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
show clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
show cpu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
show cpu history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
show debugging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
show ecofriendly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 6
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show interface memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
show memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
show memory allocations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
show memory history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
show memory pools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
show memory shared . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
show process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
show reboot history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
show router-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
show system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
show system environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
show system interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
show system mac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
show system serialnumber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
show tech-support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
speed (asyn) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
system territory (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
terminal monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
undebug all . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
Chapter 8: Pluggables and Cabling Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
clear fiber-monitoring interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
clear test cable-diagnostics tdr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
debug fiber-monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
fiber-monitoring action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
fiber-monitoring baseline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
fiber-monitoring enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
fiber-monitoring interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
fiber-monitoring sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
show system fiber-monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
show system pluggable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
show system pluggable detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
show system pluggable diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
show test cable-diagnostics tdr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
test cable-diagnostics tdr interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Chapter 9: Connectivity Fault Management Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
cc interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
cc multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
cc unicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
clear (MEP Attribute) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
clear ethernet cfm errorlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
clear mep counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
ethernet cfm domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
ethernet cfm mep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
mep (FNG attributes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
mep active . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
mep ccm-ltm-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
mep crosscheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
service ma-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 7
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show ethernet cfm details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 309
show ethernet cfm domain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
show ethernet cfm errorlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
show ethernet cfm service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
show mep-alarm status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
Chapter 10: Logging Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
clear exception log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
clear log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
clear log buffered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
clear log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
clear log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
copy buffered-log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
copy permanent-log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
default log buffered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
default log console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
default log email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
default log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
default log host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
default log monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
default log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
log buffered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
log buffered (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
log buffered exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
log buffered size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
log console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
log console (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
log console exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
log email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
log email (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
log email exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
log email time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
log external (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
log external exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
log external rotate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
log external size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
log facility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
log host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
log host (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
log host exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
log host source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
log host startup-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
log host time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
log monitor (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
log monitor exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
log permanent (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
log permanent exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
log permanent size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 8
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
log-rate-limit nsm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
log trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
show counter log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
show exception log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
show log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
show log config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
show log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
show log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
show running-config log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
unmount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
Chapter 11: Scripting Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
activate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
echo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
wait . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
Chapter 12: Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
description (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
interface (to configure) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
mru . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
mtu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
service statistics interfaces counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
show interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 435
show interface brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
show interface memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
show interface status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
Chapter 13: Port Mirroring and Remote Mirroring Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
mirror interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
remote-mirror interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
show mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
show mirror interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 450
show remote-mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
switchport remote-mirror-egress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
Chapter 14: Alarm Monitoring Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
alarm facility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
debug alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
show alarm settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
show debugging alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
show facility-alarm status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 463
PART 2: Interfaces and Layer 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
Chapter 15: Switching Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 465

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 9
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 465
backpressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
clear loop-protection counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
clear mac address-table dynamic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
clear mac address-table static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 472
clear port counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 473
clear port-security intrusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 474
debug loopprot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
debug platform packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
duplex . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 480
flowcontrol (switch port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
linkflap action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
loop-protection loop-detect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
loop-protection action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
loop-protection action-delay-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
loop-protection timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
mac address-table acquire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 488
mac address-table ageing-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
mac address-table logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
mac address-table static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
mac address-table thrash-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 492
platform hwfilter-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
platform load-balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 496
platform multicast-ratelimit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 498
platform vlan-stacking-tpid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
polarity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 501
show debugging loopprot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 502
show debugging platform packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
show flowcontrol interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
show interface err-disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
show interface switchport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
show loop-protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
show mac address-table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
show mac address-table thrash-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
show platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
show platform classifier statistics utilization brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 515
show platform port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 518
show port-security interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
show port-security intrusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
show storm-control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 522
speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 523
storm-control level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 525
switchport port-security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 526
switchport port-security aging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 527
switchport port-security maximum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 528
switchport port-security violation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 529
thrash-limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 530
undebug loopprot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 532
undebug platform packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 533

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 10
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Chapter 16: VLAN Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 534
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 534
debug private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 536
port-vlan-forwarding-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
private-vlan association . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 542
platform vlan-stacking-tpid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
private-vlan ufo trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 544
show debugging private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
show port-vlan-forwarding-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
show vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
show vlan access-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
show vlan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
show vlan private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 550
show vlan private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
switchport access vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
switchport mode access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
switchport mode private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 554
switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
switchport mode private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
switchport mode trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 561
switchport private-vlan host-association . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 562
switchport private-vlan mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 563
switchport trunk allowed vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 564
switchport trunk native vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 567
switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 568
switchport voice dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 569
switchport voice vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 570
switchport voice vlan priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
vlan access-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 574
vlan database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
vlan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 576
Chapter 17: Spanning Tree Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 577
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 577
clear spanning-tree statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 579
clear spanning-tree detected protocols (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . 580
debug mstp (RSTP and STP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
instance priority (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 585
instance vlan (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 587
region (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 589
revision (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 590
show debugging mstp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 591
show spanning-tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 592
show spanning-tree brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
show spanning-tree mst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 596
show spanning-tree mst config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 597
show spanning-tree mst detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598
show spanning-tree mst detail interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 600
show spanning-tree mst instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 602

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 11
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show spanning-tree mst instance interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 603
show spanning-tree mst interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 604
show spanning-tree statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
show spanning-tree statistics instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
show spanning-tree statistics instance interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 608
show spanning-tree statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610
show spanning-tree vlan range-index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 612
spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
spanning-tree bpdu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 614
spanning-tree cisco-interoperability (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 616
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 617
spanning-tree enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 618
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 620
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 621
spanning-tree force-version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 622
spanning-tree forward-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 623
spanning-tree guard root . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 624
spanning-tree hello-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 625
spanning-tree link-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 626
spanning-tree max-age . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 627
spanning-tree max-hops (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 628
spanning-tree mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 629
spanning-tree mst configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 630
spanning-tree mst instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 631
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 632
spanning-tree mst instance priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 634
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 635
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 637
spanning-tree path-cost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 638
spanning-tree portfast (STP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 639
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 641
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 643
spanning-tree priority (bridge priority) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 645
spanning-tree priority (port priority) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 646
spanning-tree restricted-role . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 647
spanning-tree restricted-tcn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 648
spanning-tree transmit-holdcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 649
undebug mstp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 650
Chapter 18: Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . 651
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 651
debug udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 652
show debugging udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 653
show udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 654
show udld neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 655
show udld port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 656
udld aggressive-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 657
udld enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 658
udld port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 659
udld port aggressive-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 660
udld port disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 661
udld reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 662
udld time disable-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 663

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 12
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
udld time message-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 664
undebug udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 665
Chapter 19: Link Aggregation Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 666
channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 668
clear lacp counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 670
debug lacp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 671
lacp global-passive-mode enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 672
lacp port-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 673
lacp system-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 674
lacp timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 675
platform load-balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 677
show debugging lacp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 678
show diagnostic channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 679
show etherchannel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 681
show etherchannel detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 682
show etherchannel summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 683
show lacp sys-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 684
show lacp-counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 685
show port etherchannel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 686
show static-channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 687
static-channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 688
undebug lacp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 690
Chapter 20: Power over Ethernet Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 691
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 691
clear power-inline counters interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 693
debug power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 694
power-inline allow-legacy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 696
power-inline description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 697
power-inline enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 698
power-inline max . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 699
power-inline priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 701
power-inline usage-threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 703
service power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 704
show debugging power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 705
show power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 706
show power-inline counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 709
show power-inline interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 711
show power-inline interface detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 714
Chapter 21: GVRP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 717
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 717
clear gvrp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 718
debug gvrp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 719
gvrp (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 721
gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 722
gvrp enable (global) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 723
gvrp registration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 724
gvrp timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 725
show debugging gvrp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 726

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 13
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show gvrp configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 727
show gvrp machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 728
show gvrp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 729
show gvrp timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730
PART 3: Layer 3 Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 731
Chapter 22: IP Addressing and Protocol Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 732
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 732
arp-aging-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 734
arp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 735
arp log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 736
arp opportunistic-nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 739
arp-reply-bc-dmac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740
clear arp-cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 741
debug ip packet interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 742
ip address (IP Addressing and Protocol) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 744
ip gratuitous-arp-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 746
ip redirects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 748
ip tcp synack-retries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 749
ip unreachables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 752
show arp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 753
show debugging ip packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 754
show ip flooding-nexthops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 756
show ip interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 757
show ip sockets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 758
show ip traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 761
tcpdump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 763
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 764
undebug ip packet interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 765
Chapter 23: Domain Name Service (DNS) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 766
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 766
ip domain-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 767
ip domain-lookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 768
ip domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 769
ip name-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 770
ip name-server preferred-order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 772
show hosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 773
show ip domain-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 774
show ip domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 775
show ip name-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 776
Chapter 24: IPv6 Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 777
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 777
clear ipv6 neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 779
ipv6 address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 780
ipv6 address autoconfig . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 782
ipv6 address suffix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 784
ipv6 enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 785
ipv6 eui64-linklocal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 787

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 14
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ipv6 forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 788
ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 789
ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 790
ipv6 nd current-hoplimit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 791
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 792
ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 793
ipv6 nd other-config-flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 794
ipv6 nd prefix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 795
ipv6 nd ra-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 797
ipv6 nd ra-lifetime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 798
ipv6 nd raguard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 799
ipv6 nd reachable-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 801
ipv6 nd retransmission-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 802
ipv6 nd suppress-ra . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 803
ipv6 neighbor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 804
ipv6 opportunistic-nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 805
ipv6 unreachables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 806
optimistic-nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 807
ping ipv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 808
show ipv6 forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 810
show ipv6 interface brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 811
show ipv6 neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 812
show ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 813
show ipv6 route summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 815
traceroute ipv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 816
Chapter 25: Routing Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 817
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 817
ip route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 818
ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 820
maximum-paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 821
show ip route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 822
show ip route database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 824
show ip route summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 825
show ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 826
show ipv6 route summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 828
PART 4: Multicast Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 829
Chapter 26: IGMP and IGMP Snooping Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 830
clear ip igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 832
clear ip igmp group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 833
clear ip igmp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 834
debug igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 835
ip igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 836
ip igmp access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 837
ip igmp flood specific-query . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 838
ip igmp immediate-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 839
ip igmp last-member-query-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 840
ip igmp last-member-query-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 841
ip igmp limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 842

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 15
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ip igmp maximum-groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 843
ip igmp querier-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 845
ip igmp query-holdtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 846
ip igmp query-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 848
ip igmp query-max-response-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850
ip igmp ra-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 852
ip igmp robustness-variable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 853
ip igmp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 854
ip igmp snooping fast-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 855
ip igmp snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 856
ip igmp snooping querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 857
ip igmp snooping report-suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 858
ip igmp snooping routermode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 859
ip igmp snooping source-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 861
ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 862
ip igmp source-address-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 864
ip igmp static-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 865
ip igmp startup-query-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 867
ip igmp startup-query-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 868
ip igmp trusted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 869
ip igmp version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 870
show debugging igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 871
show ip igmp groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 872
show ip igmp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 874
show ip igmp snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 876
show ip igmp snooping routermode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 877
show ip igmp snooping source-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 878
show ip igmp snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 879
undebug igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 881
Chapter 27: MLD Snooping Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 882
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 882
clear ipv6 mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 883
clear ipv6 mld group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 884
clear ipv6 mld interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 885
debug mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 886
ipv6 mld immediate-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 887
ipv6 mld limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 888
ipv6 mld snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 890
ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 892
ipv6 mld snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 893
ipv6 mld snooping querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 895
ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 896
ipv6 mld static-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 898
show debugging mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 900
show ipv6 mld groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 901
show ipv6 mld interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 902
show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 903
show ipv6 mld snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 904
PART 5: Access and Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 905

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 16
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Chapter 28: IPv4 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . 906
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 906
access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 909
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for ICMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 911
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 915
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP protocols) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 918
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses) . . . . . . . . . . . 923
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for TCP or UDP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 926
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 930
(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 932
(named hardware ACL entry for IP packets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 936
(named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 940
(named hardware ACL entry for MAC addresses) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 945
(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 948
commit (IPv4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 952
show access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 953
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 954
show interface access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 956
Chapter 29: IPv4 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . 957
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 957
access-list extended (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 959
access-list (extended numbered) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 967
(access-list extended ICMP filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 970
(access-list extended IP filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 972
(access-list extended IP protocol filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 975
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 979
access-list standard (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 981
access-list (standard numbered) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 983
(access-list standard named filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 985
(access-list standard numbered filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 987
maximum-access-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 989
show access-list (IPv4 Software ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 990
show ip access-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 992
vty access-class (numbered) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 993
Chapter 30: IPv6 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . 994
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 994
commit (IPv6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 996
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 997
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 999
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1003
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1006
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1011
ipv6 traffic-filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1015
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1016
Chapter 31: IPv6 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . 1017
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1017
ipv6 access-list standard (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1019
(ipv6 access-list standard filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1021
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1023

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 17
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
vty ipv6 access-class (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1024
Chapter 32: QoS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1025
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1025
class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1027
class-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1028
clear mls qos interface policer-counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1029
default-action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1030
description (QoS policy-map) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1031
egress-rate-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1032
match access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1033
match cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1035
match dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1036
match eth-format protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1037
match inner-cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1040
match inner-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1041
match ip-precedence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1042
match mac-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1043
match tcp-flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1044
match vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1045
mls qos cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1046
mls qos enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1047
mls qos map cos-queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1048
mls qos map premark-dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1049
no police . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1051
police single-rate action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1052
police twin-rate action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1054
policy-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1056
priority-queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1057
remark-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1058
remark new-cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1060
service-policy input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1062
show class-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1063
show mls qos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1064
show mls qos interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1065
show mls qos interface policer-counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1068
show mls qos interface queue-counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1069
show mls qos interface storm-status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1070
show mls qos maps cos-queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1071
show mls qos maps premark-dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1072
show platform classifier statistics utilization brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1073
show policy-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1076
storm-action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1077
storm-downtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1078
storm-protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1079
storm-rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1080
storm-window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1081
trust dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1082
wrr-queue disable queues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1083
wrr-queue egress-rate-limit queues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1084
wrr-queue weight queues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1085

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 18
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Chapter 33: 802.1X Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1086
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1086
dot1x accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1088
dot1x authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1089
debug dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1090
dot1x control-direction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1091
dot1x eap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1093
dot1x eapol-version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1094
dot1x initialize interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1096
dot1x initialize supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1097
dot1x keytransmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1098
dot1x max-auth-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1099
dot1x max-reauth-req . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1101
dot1x port-control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1103
dot1x timeout tx-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1105
show debugging dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1107
show dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1108
show dot1x diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1111
show dot1x interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1113
show dot1x sessionstatistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1118
show dot1x statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1119
show dot1x supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1120
show dot1x supplicant interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1122
undebug dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1125
Chapter 34: Authentication Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1126
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1126
auth auth-fail vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1129
auth critical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1131
auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1132
auth dynamic-vlan-creation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1134
auth guest-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1137
auth guest-vlan forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1139
auth host-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1141
auth log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1143
auth max-supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1145
auth multi-vlan-session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1147
auth profile (Global Configuration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1148
auth profile (Interface Configuration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1149
auth reauthentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1150
auth roaming disconnected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1151
auth roaming enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1153
auth supplicant-ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1155
auth supplicant-mac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1157
auth timeout connect-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1160
auth timeout quiet-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1162
auth timeout reauth-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1163
auth timeout server-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1165
auth timeout supp-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1167
auth two-step enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1169
auth-mac accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1172
auth-mac authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1173

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 19
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
auth-mac enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1174
auth-mac method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1176
auth-mac password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1178
auth-mac reauth-relearning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1179
auth-mac static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1181
auth-mac username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1182
auth-web accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1183
auth-web authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1184
auth-web enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1185
auth-web forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1187
auth-web max-auth-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1190
auth-web method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1192
auth-web-server blocking-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1193
auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1194
auth-web-server dhcp lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1195
auth-web-server dhcp-wpad-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1196
auth-web-server host-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1197
auth-web-server intercept-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1198
auth-web-server ipaddress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1199
auth-web-server page language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1200
auth-web-server login-url . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1201
auth-web-server page logo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1202
auth-web-server page sub-title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1203
auth-web-server page success-message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1204
auth-web-server page title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1205
auth-web-server page welcome-message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1206
auth-web-server ping-poll enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1207
auth-web-server ping-poll failcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1208
auth-web-server ping-poll interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1209
auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1210
auth-web-server ping-poll timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1211
auth-web-server port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1212
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1213
auth-web-server redirect-url . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1214
auth-web-server session-keep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1215
auth-web-server ssl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1216
auth-web-server ssl intercept-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1217
copy proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1218
copy web-auth-https-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1219
description (Authentication Profile) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1220
erase proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1221
erase web-auth-https-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1222
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1223
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1224
show auth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1225
show auth diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1227
show auth interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1229
show auth sessionstatistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1232
show auth statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1233
show auth supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1234
show auth supplicant interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1237
show auth two-step supplicant brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1238
show auth-web-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1239

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 20
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show auth-web-server page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1240
show proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1241
Chapter 35: AAA Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1242
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1242
aaa accounting auth-mac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1244
aaa accounting auth-web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1246
aaa accounting commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1248
aaa accounting dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1250
aaa accounting login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1252
aaa accounting update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1255
aaa authentication auth-mac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1257
aaa authentication auth-web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1259
aaa authentication dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1261
aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1263
aaa authentication enable default local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1265
aaa authentication login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1266
aaa authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1268
aaa authorization config-commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1270
aaa group server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1271
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1273
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1274
aaa login fail-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1275
accounting login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1276
authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1277
clear aaa local user lockout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1279
debug aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1280
login authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1281
proxy-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1282
radius-secure-proxy aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1283
server (radsecproxy-aaa) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1284
server mutual-authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1286
server name-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1287
server trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1288
show aaa local user locked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1290
show aaa server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1291
show debugging aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1292
show radius server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1293
undebug aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1295
Chapter 36: RADIUS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1296
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1296
auth radius send nas-identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1297
auth radius send service-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1298
deadtime (RADIUS server group) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1299
debug radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1300
ip radius source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1301
radius-server deadtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1302
radius-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1303
radius-server key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1306
radius-server retransmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1307
radius-server timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1309

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 21
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
server (server group) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1311
show debugging radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1313
show radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1314
show radius statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1317
undebug radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1318
Chapter 37: Local RADIUS Server Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1319
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1319
attribute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1321
authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1324
client (radsecproxy-srv) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1325
client mutual-authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1327
client name-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1328
client trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1329
clear radius local-server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1330
copy fdb-radius-users (to file) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1331
copy local-radius-user-db (from file) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1333
copy local-radius-user-db (to file) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1334
crypto pki enroll local (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1335
crypto pki enroll local local-radius-all-users (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1336
crypto pki enroll local user (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1337
crypto pki export local pem (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1338
crypto pki export local pkcs12 (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1339
crypto pki trustpoint local (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1340
debug crypto pki (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1341
domain-style . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1342
egress-vlan-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1343
egress-vlan-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1345
group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1347
nas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1348
radius-secure-proxy local-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1349
radius-server local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1350
server auth-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1351
server enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1352
show radius local-server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1353
show radius local-server nas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1354
show radius local-server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1355
show radius local-server user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1356
user (RADIUS server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1358
vlan (RADIUS server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1360
Chapter 38: Public Key Infrastructure Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1361
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1361
crypto key generate rsa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1362
crypto key zeroize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1363
crypto pki authenticate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1364
crypto pki enroll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1365
crypto pki enroll user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1366
crypto pki export pem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1368
crypto pki export pkcs12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1369
crypto pki import pem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1371
crypto pki import pkcs12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1373

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 22
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
crypto pki trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1374
enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1375
fingerprint (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1376
no crypto pki certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1378
rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1379
show crypto key mypubkey rsa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1380
show crypto pki certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1381
show crypto pki enrollment user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1383
show crypto pki trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1384
subject-name (trustpoint configuration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1385
Chapter 39: TACACS+ Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1387
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1387
authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1388
aaa authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1390
aaa authorization config-commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1392
ip tacacs source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1393
show tacacs+ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1394
tacacs-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1396
tacacs-server key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1398
tacacs-server timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1399
Chapter 40: DHCP Snooping Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1400
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1400
arp security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1402
arp security violation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1403
clear arp security statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1405
clear ip dhcp snooping binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1406
clear ip dhcp snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1407
debug arp security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1408
debug ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1409
ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1410
ip dhcp snooping agent-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1411
ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1412
ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1413
ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1414
ip dhcp snooping binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1415
ip dhcp snooping database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1416
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1417
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1418
ip dhcp snooping max-bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1419
ip dhcp snooping trust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1420
ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1421
ip dhcp snooping violation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1422
ip source binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1423
service dhcp-snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1425
show arp security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1427
show arp security interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1428
show arp security statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1430
show debugging arp security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1432
show debugging ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1433
show ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1434

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 23
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show ip dhcp snooping acl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1435
show ip dhcp snooping agent-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1438
show ip dhcp snooping binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1440
show ip dhcp snooping interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1442
show ip dhcp snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1444
show ip source binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1447
Chapter 41: OpenFlow Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1448
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1448
openflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1449
openflow controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1450
openflow datapath-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1452
openflow failmode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1453
openflow failmode standalone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1455
openflow inactivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1456
openflow native vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1457
openflow ssl peer certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1458
openflow ssl trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1459
openflow version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1460
show openflow config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1461
show openflow coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1463
show openflow flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1465
show openflow rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1468
show openflow ssl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1470
show openflow status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1471
PART 6: Network Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1474
Chapter 42: Ethernet Protection Switched Ring (EPSRing™) Commands . . . . . . 1475
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1475
debug epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1477
epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1478
epsr configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1479
epsr datavlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1480
epsr enhancedrecovery enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1481
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1482
epsr mode transit controlvlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1483
epsr priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1484
epsr state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1485
epsr topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1486
epsr trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1487
show debugging epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1488
show epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1489
show epsr common segments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1493
show epsr config-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1494
show epsr <epsr-instance> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1495
show epsr <epsr-instance> counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1496
show epsr counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1497
show epsr summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1498
undebug epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1499
Chapter 43: G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Commands . . . . . . . . 1500

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 24
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500
cfm-sf-notify . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1502
clear g8032 erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1504
clear g8032 erp-instance statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1506
data-traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1507
debug g8032 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1509
enable (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1510
epsr topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1511
erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1512
g8032 erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1513
g8032 forced-switch erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1515
g8032 manual-switch erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1517
g8032 physical-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1518
g8032 profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1520
level (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1521
physical-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1522
profile name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1523
raps-channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1524
rpl role . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1525
show debugging g8032 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1527
show g8032 erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1528
show g8032 erp-instance statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1533
show g8032 physical-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1535
show g8032 profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1537
sub-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1539
timer (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1540
topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1542
trap (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1544
undebug g8032 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1545
Chapter 44: RRP Snooping Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1546
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1546
ip rrp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1547
show ip rrp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1548
PART 7: Network Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1549
Chapter 45: Allied Telesis Management Framework™ (AMF) Commands . . . . . . 1550
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1550
application-proxy whitelist enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1555
application-proxy whitelist server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1556
area-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1558
atmf area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1560
atmf area password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1562
atmf authorize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1564
atmf authorize provision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1566
atmf backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1568
atmf backup area-masters delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1569
atmf backup area-masters enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1570
atmf backup area-masters now . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1571
atmf backup area-masters synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1572
atmf backup bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1573

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 25
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
atmf backup delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1574
atmf backup enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1575
atmf backup guests delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1576
atmf backup guests enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1577
atmf backup guests now . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1578
atmf backup guests synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1579
atmf backup now . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1580
atmf backup redundancy enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1582
atmf backup server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1583
atmf backup stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1585
atmf backup synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1586
atmf cleanup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1587
atmf container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1588
atmf container login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1589
atmf controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1590
atmf distribute firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1591
atmf domain vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1593
atmf enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1596
atmf group (membership) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1597
atmf guest-class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1599
atmf log-verbose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1601
atmf management subnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1602
atmf management vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1605
atmf master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1607
atmf mtu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1608
atmf network-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1609
atmf provision (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1610
atmf provision node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1611
atmf reboot-rolling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1613
atmf recover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1617
atmf recover guest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1619
atmf recover led-off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1620
atmf recovery-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1621
atmf remote-login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1623
atmf restricted-login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1625
atmf secure-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1627
atmf secure-mode certificate expire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1629
atmf secure-mode certificate expiry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1630
atmf secure-mode certificate renew . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1631
atmf secure-mode enable-all . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1632
atmf select-area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1634
atmf topology-gui enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1635
atmf trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1636
atmf virtual-crosslink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1638
atmf virtual-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1640
atmf virtual-link protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1643
atmf working-set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1645
bridge-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1647
clear atmf links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1648
clear atmf links virtual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1649
clear atmf links statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1650
clear atmf recovery-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1651
clear atmf secure-mode certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1652

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 26
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
clear atmf secure-mode statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1653
clone (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1654
configure boot config (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1656
configure boot system (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1658
create (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1660
debug atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1662
debug atmf packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1664
delete (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1667
discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1669
description (amf container) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1671
erase factory-default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1672
http-enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1673
identity (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1675
license-cert (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1677
locate (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1679
log event-host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1680
modeltype . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1681
show application-proxy whitelist interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1682
show application-proxy whitelist server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1684
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1685
show atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1687
show atmf area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1691
show atmf area guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1694
show atmf area guests-detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1696
show atmf area nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1698
show atmf area nodes-detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1700
show atmf area summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1702
show atmf authorization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1703
show atmf backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1706
show atmf backup area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1710
show atmf backup guest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1712
show atmf container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1714
show atmf detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1717
show atmf group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1719
show atmf group members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1721
show atmf guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1723
show atmf guests detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1725
show atmf links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1728
show atmf links detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1730
show atmf links guest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1739
show atmf links guest detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1741
show atmf links statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1745
show atmf nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1748
show atmf provision nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1750
show atmf recovery-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1752
show atmf secure-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1753
show atmf secure-mode audit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1755
show atmf secure-mode audit link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1756
show atmf secure-mode certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1757
show atmf secure-mode sa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1760
show atmf secure-mode statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1763
show atmf tech . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1765
show atmf virtual-links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1768

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 27
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show atmf working-set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1770
show debugging atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1771
show debugging atmf packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1772
show running-config atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1773
state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1774
switchport atmf-agentlink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1776
switchport atmf-arealink remote-area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1777
switchport atmf-crosslink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1779
switchport atmf-guestlink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1781
switchport atmf-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1783
type atmf node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1784
undebug atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1787
username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1788
Chapter 46: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Commands . . . . . . . 1790
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1790
bootfile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1792
clear ip dhcp binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1793
default-router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1794
dns-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1795
domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1796
host (DHCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1797
ip address dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1798
ip dhcp bootp ignore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1800
ip dhcp leasequery enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1801
ip dhcp option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1802
ip dhcp pool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1804
ip dhcp-client default-route distance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1805
ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1807
ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1808
lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1809
network (DHCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1811
next-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1812
option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
probe enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1815
probe packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1816
probe timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1817
probe type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1818
range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1819
route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1820
service dhcp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1821
short-lease-threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1822
show counter dhcp-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1824
show counter dhcp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1825
show dhcp lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1826
show ip dhcp binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1827
show ip dhcp pool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1828
show ip dhcp server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1833
show ip dhcp server summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1835
subnet-mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1836
Chapter 47: DHCP for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1837

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 28
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1837
clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1838
clear ipv6 dhcp client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1839
ipv6 address dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1840
show counter ipv6 dhcp-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1841
show ipv6 dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1843
show ipv6 dhcp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1844
Chapter 48: NTP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1845
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1845
ntp access-group (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1847
ntp authenticate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1848
ntp authentication-key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1849
ntp broadcastdelay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1850
ntp discard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1851
ntp master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1852
ntp peer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1853
ntp rate-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1855
ntp restrict . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1856
ntp server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1858
ntp source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1860
ntp trusted-key (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1862
show counter ntp (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1863
show ntp associations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1864
show ntp counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1866
show ntp counters associations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1867
show ntp status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1868
Chapter 49: Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Transparent Clock Commands . . 1869
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1869
clock-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1870
ptp-clk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1871
ptp global . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1873
show ptp data transparent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1874
show ptp port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1875
Chapter 50: SNMP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1876
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1876
alias (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1878
debug snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1879
show counter snmp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1880
show debugging snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1884
show running-config snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1885
show snmp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1886
show snmp-server community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1887
show snmp-server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1888
show snmp-server user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1889
show snmp-server view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1890
snmp trap link-status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1891
snmp trap link-status suppress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1892
snmp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1894
snmp-server community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1896

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 29
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
snmp-server contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1897
snmp-server enable trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1898
snmp-server engineID local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1901
snmp-server engineID local reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1903
snmp-server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1904
snmp-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1906
snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1908
snmp-server location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1909
snmp-server source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1910
snmp-server startup-trap-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1911
snmp-server user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1912
snmp-server view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1915
undebug snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1916
Chapter 51: LLDP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1917
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1917
clear lldp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1919
clear lldp table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1920
debug lldp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1921
lldp faststart-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1923
lldp holdtime-multiplier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1924
lldp management-address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1925
lldp med-notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1926
lldp med-tlv-select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1927
lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1930
lldp notification-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1931
lldp notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1932
lldp port-number-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1933
lldp reinit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1934
lldp run . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1935
lldp timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1936
lldp tlv-select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1937
lldp transmit receive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1939
lldp tx-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1940
location civic-location configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1941
location civic-location identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1945
location civic-location-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1946
location coord-location configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1947
location coord-location identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1949
location coord-location-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1950
location elin-location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1952
location elin-location-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1953
show debugging lldp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1954
show lldp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1956
show lldp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1958
show lldp local-info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1960
show lldp neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1965
show lldp neighbors detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1967
show lldp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1971
show lldp statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1973
show location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1975

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 30
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Chapter 52: Mail (SMTP) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1977
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1977
debug mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1978
delete mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1979
mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1980
mail from . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1982
mail smtpserver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1983
mail smtpserver authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1984
mail smtpserver port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1986
show counter mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1988
show mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1989
undebug mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1990
Chapter 53: RMON Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1991
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1991
rmon alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1992
rmon collection history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1994
rmon collection stats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1995
rmon event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1996
show rmon alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1997
show rmon event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1998
show rmon history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000
show rmon statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2002
Chapter 54: Secure Shell (SSH) Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2004
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2004
banner login (SSH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2006
clear ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2007
crypto key destroy hostkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2008
crypto key destroy userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2009
crypto key generate hostkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2010
crypto key generate userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2012
crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2013
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2015
debug ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2017
debug ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2018
service ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2019
show banner login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2021
show crypto key hostkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2022
show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2024
show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2025
show crypto key userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2026
show running-config ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2027
show ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2029
show ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2031
show ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2032
show ssh server allow-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2034
show ssh server deny-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2035
ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2036
ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2038
ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2040
ssh server allow-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2042

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 31
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ssh server authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2044
ssh server deny-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2046
ssh server max-auth-tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2048
ssh server resolve-host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2049
ssh server scp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2050
ssh server sftp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2051
undebug ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2052
undebug ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2053
Chapter 55: Trigger Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2054
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2054
active (trigger) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2056
day . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2057
debug trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2059
description (trigger) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2060
repeat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2061
script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2062
show debugging trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2064
show running-config trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2065
show trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2066
test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2071
time (trigger) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2072
trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2074
trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2075
trigger activate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2076
type atmf node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2077
type card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2080
type cpu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2081
type interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2082
type linkmon-probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2083
type log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2085
type memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2086
type periodic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2087
type ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2088
type reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2089
type time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2090
undebug trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2091
Chapter 56: Ping-Polling Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2092
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2092
active (ping-polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2094
clear ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2095
critical-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2096
debug ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2097
description (ping-polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2098
fail-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2099
ip (ping-polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2100
length (ping-poll data) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2101
normal-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2102
ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2103
sample-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2104
show counter ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2106

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 32
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2108
source-ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2112
timeout (ping polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2114
up-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2115
undebug ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2116
Chapter 57: sFlow Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2117
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2117
debug sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2118
debug sflow agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2119
sflow agent (address) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2120
sflow collector (address) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2122
sflow collector max-datagram-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2124
sflow enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2125
sflow max-header-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2126
sflow polling-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2128
sflow sampling-rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2129
show debugging sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2130
show running-config sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2132
show sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2133
show sflow interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2135
undebug sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2136

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 33
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
List of Commands
(access-list extended ICMP filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .970
(access-list extended IP filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .972
(access-list extended IP protocol filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .975
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .979
(access-list standard named filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .985
(access-list standard numbered filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .987
(ipv6 access-list standard filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1021
(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .932
(named hardware ACL entry for IP packets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .936
(named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .940
(named hardware ACL entry for MAC addresses) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .945
(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .948
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .999
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1006
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1003
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1011
aaa accounting auth-mac . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1244
aaa accounting auth-web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1246
aaa accounting commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1248
aaa accounting dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1250
aaa accounting login. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1252
aaa accounting update. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1255
aaa authentication auth-mac. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1257
aaa authentication auth-web. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1259
aaa authentication dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1261

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 34
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1263
aaa authentication enable default local. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1265
aaa authentication enable default local. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
aaa authentication login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1266
aaa authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1268
aaa authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1390
aaa authorization config-commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1270
aaa authorization config-commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1392
aaa group server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1271
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1273
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1274
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
aaa login fail-delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1275
aaa login fail-delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 909
access-list (extended numbered) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 967
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for ICMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 911
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 915
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP protocols). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 918
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 923
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for TCP or UDP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 926
access-list (standard numbered). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 983
access-list extended (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 959
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 930
access-list standard (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 981
accounting login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1276
activate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
active (ping-polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2094
active (trigger). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2056
alarm facility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
alias (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1878
application-proxy whitelist enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1555
application-proxy whitelist server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1556
area-link. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1558

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 35
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
arp log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 736
arp opportunistic-nd. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 739
arp security violation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1403
arp security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1402
arp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 735
arp-aging-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 734
arp-reply-bc-dmac. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740
atmf area password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1562
atmf area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1560
atmf authorize provision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1566
atmf authorize. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1564
atmf backup area-masters delete. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1569
atmf backup area-masters enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1570
atmf backup area-masters now. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1571
atmf backup area-masters synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1572
atmf backup bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1573
atmf backup delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1574
atmf backup enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1575
atmf backup guests delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1576
atmf backup guests enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1577
atmf backup guests now. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1578
atmf backup guests synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1579
atmf backup now. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1580
atmf backup redundancy enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1582
atmf backup server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1583
atmf backup stop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1585
atmf backup synchronize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1586
atmf backup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1568
atmf cleanup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1587
atmf container login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1589
atmf container. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1588
atmf controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1590
atmf distribute firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1591
atmf domain vlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1593
atmf enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1596

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 36
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
atmf group (membership) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1597
atmf guest-class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1599
atmf log-verbose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1601
atmf management subnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1602
atmf management vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1605
atmf master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1607
atmf mtu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1608
atmf network-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1609
atmf provision (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1610
atmf provision node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1611
atmf reboot-rolling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1613
atmf recover guest. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1619
atmf recover led-off. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1620
atmf recover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1617
atmf recovery-server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1621
atmf remote-login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1623
atmf restricted-login. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1625
atmf secure-mode certificate expire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1629
atmf secure-mode certificate expiry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1630
atmf secure-mode certificate renew . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1631
atmf secure-mode enable-all. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1632
atmf secure-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1627
atmf select-area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1634
atmf topology-gui enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1635
atmf topology-gui enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
atmf trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1636
atmf virtual-crosslink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1638
atmf virtual-link protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1643
atmf virtual-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1640
atmf working-set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1645
attribute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1321
auth auth-fail vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1129
auth critical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1131
auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1132
auth dynamic-vlan-creation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1134

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 37
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
auth guest-vlan forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1139
auth guest-vlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1137
auth host-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1141
auth log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1143
auth max-supplicant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1145
auth multi-vlan-session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1147
auth profile (Global Configuration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1148
auth profile (Interface Configuration). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1149
auth radius send nas-identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1297
auth radius send service-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1298
auth reauthentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1150
auth roaming disconnected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1151
auth roaming enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1153
auth supplicant-ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1155
auth supplicant-mac. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1157
auth timeout connect-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1160
auth timeout quiet-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1162
auth timeout reauth-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1163
auth timeout server-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1165
auth timeout supp-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1167
auth two-step enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1169
authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1324
auth-mac accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1172
auth-mac authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1173
auth-mac enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1174
auth-mac method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1176
auth-mac password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1178
auth-mac reauth-relearning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1179
auth-mac static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1181
auth-mac username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1182
authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1277
authorization commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1388
auth-web accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1183
auth-web authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1184
auth-web enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1185

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 38
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
auth-web forward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1187
auth-web max-auth-fail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1190
auth-web method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1192
auth-web-server blocking-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1193
auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1194
auth-web-server dhcp lease. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1195
auth-web-server dhcp-wpad-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1196
auth-web-server host-name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1197
auth-web-server intercept-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1198
auth-web-server ipaddress. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1199
auth-web-server login-url . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1201
auth-web-server page language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1200
auth-web-server page logo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1202
auth-web-server page sub-title. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1203
auth-web-server page success-message. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1204
auth-web-server page title . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1205
auth-web-server page welcome-message . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1206
auth-web-server ping-poll enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1207
auth-web-server ping-poll failcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1208
auth-web-server ping-poll interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1209
auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1210
auth-web-server ping-poll timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1211
auth-web-server port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1212
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1213
auth-web-server redirect-url . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1214
auth-web-server session-keep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1215
auth-web-server ssl intercept-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1217
auth-web-server ssl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1216
autoboot enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
backpressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
banner exec . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
banner login (SSH). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2006
banner login (system). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
banner motd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
boot config-file backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 39
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
boot config-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
boot system backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
boot system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
bootfile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1792
bridge-group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1647
cc interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
cc multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
cc unicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
cd. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
cfm-sf-notify. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1502
channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 668
class. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1027
class-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1028
clear (MEP Attribute). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
clear aaa local user lockout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1279
clear aaa local user lockout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
clear arp security statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1405
clear arp-cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 741
clear atmf links statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1650
clear atmf links virtual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1649
clear atmf links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1648
clear atmf recovery-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1651
clear atmf secure-mode certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1652
clear atmf secure-mode statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1653
clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1838
clear ethernet cfm errorlog. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
clear exception log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
clear fiber-monitoring interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
clear g8032 erp-instance statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1506
clear g8032 erp-instance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1504
clear gvrp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 718
clear ip dhcp binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1793
clear ip dhcp snooping binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1406
clear ip dhcp snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1407
clear ip igmp group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 833

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 40
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
clear ip igmp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 834
clear ip igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 832
clear ipv6 dhcp client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1839
clear ipv6 mld group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 884
clear ipv6 mld interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 885
clear ipv6 mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 883
clear ipv6 neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 779
clear lacp counters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 670
clear line console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
clear line vty. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
clear lldp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1919
clear lldp table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1920
clear log buffered. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
clear log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
clear log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
clear log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
clear loop-protection counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
clear mac address-table dynamic. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
clear mac address-table static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 472
clear mep counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
clear mls qos interface policer-counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1029
clear ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2095
clear port counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 473
clear port-security intrusion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 474
clear power-inline counters interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 693
clear radius local-server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1330
clear spanning-tree detected protocols (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 580
clear spanning-tree statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 579
clear ssh. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2007
clear test cable-diagnostics tdr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
client (radsecproxy-srv) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1325
client mutual-authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1327
client name-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1328
client trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1329
clock set. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 41
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
clock summer-time date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
clock summer-time recurring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
clock timezone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
clock-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1870
clone (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1654
commit (IPv4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 952
commit (IPv6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 996
configure boot config (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1656
configure boot system (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1658
configure terminal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
copy (filename) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
copy buffered-log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
copy current-software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
copy debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
copy fdb-radius-users (to file) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1331
copy local-radius-user-db (from file). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1333
copy local-radius-user-db (to file) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1334
copy permanent-log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
copy proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1218
copy running-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
copy startup-config. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
copy web-auth-https-file. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1219
copy zmodem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
create (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1660
create autoboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
critical-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2096
crypto key destroy hostkey. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2008
crypto key destroy userkey. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2009
crypto key generate hostkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2010
crypto key generate rsa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1362
crypto key generate userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2012
crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2013
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
crypto key zeroize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1363
crypto pki authenticate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1364

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 42
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
crypto pki enroll local (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1335
crypto pki enroll local local-radius-all-users (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1336
crypto pki enroll local user (deleted). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1337
crypto pki enroll user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1366
crypto pki enroll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1365
crypto pki export local pem (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1338
crypto pki export local pkcs12 (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1339
crypto pki export pem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1368
crypto pki export pkcs12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1369
crypto pki import pem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1371
crypto pki import pkcs12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1373
crypto pki trustpoint local (deleted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1340
crypto pki trustpoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1374
data-traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1507
day. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2057
deadtime (RADIUS server group) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1299
debug aaa. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1280
debug alarm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
debug arp security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1408
debug atmf packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1664
debug atmf. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1662
debug crypto pki (deleted). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1341
debug dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1090
debug epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1477
debug fiber-monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
debug g8032 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1509
debug gvrp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 719
debug igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 835
debug ip dhcp snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1409
debug ip packet interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 742
debug lacp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 671
debug lldp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1921
debug loopprot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
debug mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1978
debug mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 886

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 43
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
debug mstp (RSTP and STP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
debug ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2097
debug platform packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
debug power-inline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 694
debug private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 536
debug radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1300
debug sflow agent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2119
debug sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2118
debug snmp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1879
debug ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2017
debug ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2018
debug trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2059
debug udld. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 652
default log buffered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
default log console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
default log email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
default log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
default log host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
default log monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
default log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
default-action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1030
default-router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1794
delete (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1667
delete debug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
delete mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1979
delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
description (amf container) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1671
description (Authentication Profile) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1220
description (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
description (ping-polling). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2098
description (QoS policy-map) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1031
description (trigger) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2060
dir. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
disable (Privileged Exec mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
discovery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1669

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 44
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
dns-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1795
do. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1796
domain-style . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1342
dot1x accounting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1088
dot1x authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1089
dot1x control-direction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1091
dot1x eap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1093
dot1x eapol-version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1094
dot1x initialize interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1096
dot1x initialize supplicant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1097
dot1x keytransmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1098
dot1x max-auth-fail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1099
dot1x max-reauth-req . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1101
dot1x port-control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1103
dot1x timeout tx-period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1105
duplex . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 480
echo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
ecofriendly led . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
edit (filename). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
edit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
egress-rate-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1032
egress-vlan-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1343
egress-vlan-name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1345
enable (G.8032). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1510
enable (Privileged Exec mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
enable password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
enable secret . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1375
epsr configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1479
epsr datavlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1480
epsr enhancedrecovery enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1481
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1482
epsr mode transit controlvlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1483

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 45
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
epsr priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1484
epsr state. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1485
epsr topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1486
epsr topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
epsr trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1487
epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1478
erase factory-default. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
erase factory-default. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1672
erase proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1221
erase startup-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
erase web-auth-https-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1222
erp-instance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1512
ethernet cfm domain-name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
ethernet cfm mep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
exec-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
exit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
fail-count. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2099
fiber-monitoring action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
fiber-monitoring baseline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
fiber-monitoring enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
fiber-monitoring interval. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
fiber-monitoring sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
findme trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
findme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
fingerprint (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1376
flowcontrol (switch port). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
g8032 erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1513
g8032 forced-switch erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1515
g8032 manual-switch erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1517
g8032 physical-ring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1518
g8032 profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1520
group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1347
gui-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
gvrp (interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 721

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 46
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 722
gvrp enable (global) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 723
gvrp registration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 724
gvrp timer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 725
help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
host (DHCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1797
hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
http port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
http secure-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
http-enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1673
identity (amf provisioning). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1675
instance priority (MSTP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 585
instance vlan (MSTP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 587
interface (to configure) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
ip (ping-polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2100
ip address (IP Addressing and Protocol) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 744
ip address dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1798
ip dhcp bootp ignore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1800
ip dhcp leasequery enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1801
ip dhcp option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1802
ip dhcp pool. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1804
ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1412
ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1413
ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1414
ip dhcp snooping agent-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1411
ip dhcp snooping binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1415
ip dhcp snooping database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1416
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1417
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1418
ip dhcp snooping max-bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1419
ip dhcp snooping trust. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1420
ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1421
ip dhcp snooping violation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1422
ip dhcp snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1410
ip dhcp-client default-route distance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1805

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 47
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1807
ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1808
ip domain-list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 767
ip domain-lookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 768
ip domain-name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 769
ip gratuitous-arp-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 746
ip igmp access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 837
ip igmp flood specific-query . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 838
ip igmp immediate-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 839
ip igmp last-member-query-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 840
ip igmp last-member-query-interval. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 841
ip igmp limit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 842
ip igmp maximum-groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 843
ip igmp querier-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 845
ip igmp query-holdtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 846
ip igmp query-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 848
ip igmp query-max-response-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850
ip igmp ra-option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 852
ip igmp robustness-variable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 853
ip igmp snooping fast-leave. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 855
ip igmp snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 856
ip igmp snooping querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 857
ip igmp snooping report-suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 858
ip igmp snooping routermode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 859
ip igmp snooping source-timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 861
ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 862
ip igmp snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 854
ip igmp source-address-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 864
ip igmp startup-query-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 867
ip igmp startup-query-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .868
ip igmp static-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 865
ip igmp trusted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 869
ip igmp version. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 870
ip igmp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 836
ip name-server preferred-order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 772

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 48
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ip name-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 770
ip radius source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1301
ip redirects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 748
ip route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 818
ip rrp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1547
ip source binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1423
ip tacacs source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1393
ip tcp synack-retries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 749
ip tftp source-interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
ip unreachables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 997
ipv6 access-list standard (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1019
ipv6 address autoconfig . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 782
ipv6 address dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1840
ipv6 address suffix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 784
ipv6 address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 780
ipv6 enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 785
ipv6 eui64-linklocal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 787
ipv6 forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 788
ipv6 mld immediate-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 887
ipv6 mld limit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 888
ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 892
ipv6 mld snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 893
ipv6 mld snooping querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 895
ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 896
ipv6 mld snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 890
ipv6 mld static-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 898
ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 789
ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 790
ipv6 nd current-hoplimit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 791
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 792
ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 793
ipv6 nd other-config-flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 794
ipv6 nd prefix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 795
ipv6 nd raguard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 799

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 49
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ipv6 nd ra-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 797
ipv6 nd ra-lifetime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 798
ipv6 nd reachable-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 801
ipv6 nd retransmission-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 802
ipv6 nd suppress-ra. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 803
ipv6 neighbor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 804
ipv6 opportunistic-nd. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 805
ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 820
ipv6 tftp source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
ipv6 traffic-filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1015
ipv6 unreachables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 806
lacp global-passive-mode enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 672
lacp port-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 673
lacp system-priority. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 674
lacp timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 675
lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1809
length (asyn) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
length (ping-poll data). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2101
level (G.8032). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1521
license update (filename) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
license update online . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
license-cert (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1677
line. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
linkflap action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
lldp faststart-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1923
lldp holdtime-multiplier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1924
lldp management-address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1925
lldp med-notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1926
lldp med-tlv-select. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1927
lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1930
lldp notification-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1931
lldp notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1932
lldp port-number-type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1933
lldp reinit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1934

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 50
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
lldp run . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1935
lldp timer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1936
lldp tlv-select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1937
lldp transmit receive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1939
lldp tx-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1940
locate (amf provisioning) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1679
location civic-location configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1941
location civic-location identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1945
location civic-location-id. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1946
location coord-location configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1947
location coord-location identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1949
location coord-location-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1950
location elin-location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1952
location elin-location-id. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1953
log buffered (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
log buffered exclude. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
log buffered size. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
log buffered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
log console (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
log console exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
log console. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
log email (filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
log email exclude. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
log email time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
log email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
log event-host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1680
log event-host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
log external (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
log external exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
log external rotate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
log external size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
log external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
log facility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
log host (filter). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
log host exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 51
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
log host source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
log host startup-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
log host time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
log host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
log monitor (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
log monitor exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
log permanent (filter) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
log permanent exclude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
log permanent size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
log permanent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
log trustpoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
login authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1281
logout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
log-rate-limit nsm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
loop-protection action. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
loop-protection action-delay-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
loop-protection loop-detect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
loop-protection timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
mac address-table acquire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 488
mac address-table ageing-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
mac address-table logging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
mac address-table static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
mac address-table thrash-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 492
mail from. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1982
mail smtpserver authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1984
mail smtpserver port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1986
mail smtpserver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1983
mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1980
match access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1033
match cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1035
match dscp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1036
match eth-format protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1037
match inner-cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1040
match inner-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1041
match ip-precedence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1042

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 52
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
match mac-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1043
match tcp-flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1044
match vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1045
maximum-access-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 989
maximum-paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 821
mep (FNG attributes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
mep active . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
mep ccm-ltm-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
mep crosscheck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
mirror interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
mkdir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
mls qos cos. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1046
mls qos enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1047
mls qos map cos-queue. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1048
mls qos map premark-dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1049
modeltype . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1681
move debug. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
move. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
mru . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
mtu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
nas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1348
network (DHCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1811
next-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1812
no crypto pki certificate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1378
no debug all. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
no police . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1051
normal-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2102
ntp access-group (deprecated). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1847
ntp authenticate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1848
ntp authentication-key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1849
ntp broadcastdelay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1850
ntp discard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1851
ntp master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1852
ntp peer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1853
ntp rate-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1855

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 53
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ntp restrict . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1856
ntp server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1858
ntp source. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1860
ntp trusted-key (deprecated). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1862
openflow controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1450
openflow datapath-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1452
openflow failmode standalone. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1455
openflow failmode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1453
openflow inactivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1456
openflow native vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1457
openflow ssl peer certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1458
openflow ssl trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1459
openflow version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1460
openflow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1449
optimistic-nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 807
option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
physical-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1522
ping ipv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 808
ping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 752
ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2103
platform hwfilter-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1223
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
platform load-balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
platform load-balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 677
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1224
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 496
platform multicast-ratelimit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 498
platform vlan-stacking-tpid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
platform vlan-stacking-tpid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
polarity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 501
police single-rate action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1052
police twin-rate action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1054
policy-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1056

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 54
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
port-vlan-forwarding-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
power-inline allow-legacy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 696
power-inline description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 697
power-inline enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 698
power-inline max. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 699
power-inline priority. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 701
power-inline usage-threshold. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 703
priority-queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1057
private-vlan association. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 542
private-vlan ufo trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 544
private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
privilege level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
probe enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1815
probe packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1816
probe timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1817
probe type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1818
profile name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1523
proxy-port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1282
ptp global . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1873
ptp-clk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1871
pwd. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
radius-secure-proxy aaa. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1283
radius-secure-proxy local-server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1349
radius-server deadtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1302
radius-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1303
radius-server key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1306
radius-server local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1350
radius-server retransmit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1307
radius-server timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1309
range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1819
raps-channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1524
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
region (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 589
reload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
remark new-cos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1060

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 55
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
remark-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1058
remote-mirror interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
repeat. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2061
revision (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 590
rmdir. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
rmon alarm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1992
rmon collection history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1994
rmon collection stats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1995
rmon event. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1996
route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1820
rpl role . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1525
rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1379
sample-size. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2104
script. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2062
security-password forced-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
security-password history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
security-password lifetime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
security-password minimum-categories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
security-password minimum-length. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
security-password min-lifetime-enforce . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
security-password reject-expired-pwd. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
security-password warning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
server (radsecproxy-aaa) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1284
server (server group). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1311
server auth-port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1351
server enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1352
server mutual-authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1286
server name-check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1287
server trustpoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1288
service advanced-vty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
service dhcp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1821
service dhcp-snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1425
service http. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
service ma-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
service password-encryption. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 56
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
service power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 704
service ssh. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2019
service statistics interfaces counter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
service telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
service terminal-length (deleted). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
service-policy input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1062
sflow agent (address) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2120
sflow collector (address) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2122
sflow collector max-datagram-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2124
sflow enable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2125
sflow max-header-size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2126
sflow polling-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2128
sflow sampling-rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2129
short-lease-threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1822
show aaa local user locked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1290
show aaa local user locked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
show aaa server group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1291
show access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 953
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 954
show access-list (IPv4 Software ACLs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 990
show alarm settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
show application-proxy whitelist interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1682
show application-proxy whitelist server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1684
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1685
show arp security interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1428
show arp security statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1430
show arp security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1427
show arp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 753
show atmf area guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1694
show atmf area guests-detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1696
show atmf area nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1698
show atmf area nodes-detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1700
show atmf area summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1702
show atmf area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1691
show atmf authorization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1703

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 57
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show atmf backup area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1710
show atmf backup guest. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1712
show atmf backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1706
show atmf container. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1714
show atmf detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1717
show atmf group members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1721
show atmf group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1719
show atmf guests detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1725
show atmf guests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1723
show atmf links detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1730
show atmf links guest detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1741
show atmf links guest. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1739
show atmf links statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1745
show atmf links. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1728
show atmf nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1748
show atmf provision nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1750
show atmf recovery-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1752
show atmf secure-mode audit link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1756
show atmf secure-mode audit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1755
show atmf secure-mode certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1757
show atmf secure-mode sa. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1760
show atmf secure-mode statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1763
show atmf secure-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1753
show atmf tech . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1765
show atmf virtual-links. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1768
show atmf working-set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1770
show atmf. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1687
show auth diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1227
show auth interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1229
show auth sessionstatistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1232
show auth statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1233
show auth supplicant interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1237
show auth supplicant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1234
show auth two-step supplicant brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1238
show auth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1225

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 58
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show auth-web-server page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1240
show auth-web-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1239
show autoboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
show banner login. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2021
show boot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
show class-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1063
show clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
show counter dhcp-client. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1824
show counter dhcp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1825
show counter ipv6 dhcp-client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1841
show counter log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
show counter mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1988
show counter ntp (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1863
show counter ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2106
show counter snmp-server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1880
show cpu history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
show cpu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
show crypto key hostkey. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2022
show crypto key mypubkey rsa. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1380
show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2024
show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2025
show crypto key userkey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2026
show crypto pki certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1381
show crypto pki enrollment user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1383
show crypto pki trustpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1384
show debugging aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1292
show debugging alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
show debugging arp security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1432
show debugging atmf packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1772
show debugging atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1771
show debugging dot1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1107
show debugging epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1488
show debugging g8032. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1527
show debugging gvrp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 726
show debugging igmp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 871

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 59
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show debugging ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1433
show debugging ip packet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 754
show debugging lacp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 678
show debugging lldp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1954
show debugging loopprot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 502
show debugging mld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 900
show debugging mstp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 591
show debugging platform packet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
show debugging power-inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 705
show debugging private-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
show debugging radius. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1313
show debugging sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2130
show debugging snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1884
show debugging trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2064
show debugging udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 653
show debugging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
show dhcp lease. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1826
show diagnostic channel-group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 679
show dot1x diagnostics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1111
show dot1x interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1113
show dot1x sessionstatistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1118
show dot1x statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1119
show dot1x supplicant interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1122
show dot1x supplicant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1120
show dot1x. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1108
show ecofriendly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
show epsr <epsr-instance> counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1496
show epsr <epsr-instance> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1495
show epsr common segments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1493
show epsr config-check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1494
show epsr counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1497
show epsr summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1498
show epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1489
show etherchannel detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 682
show etherchannel summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 683

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 60
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show etherchannel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 681
show ethernet cfm details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 309
show ethernet cfm domain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
show ethernet cfm errorlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
show ethernet cfm service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
show exception log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
show facility-alarm status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 463
show file systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
show file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
show flowcontrol interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
show g8032 erp-instance statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1533
show g8032 erp-instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1528
show g8032 physical-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1535
show g8032 profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1537
show gvrp configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 727
show gvrp machine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 728
show gvrp statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .729
show gvrp timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730
show history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
show hosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 773
show http . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
show interface access-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 956
show interface brief. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
show interface err-disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
show interface memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
show interface memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
show interface status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
show interface switchport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
show interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 435
show ip access-list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 992
show ip dhcp binding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1827
show ip dhcp pool. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1828
show ip dhcp server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1833

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 61
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show ip dhcp server summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1835
show ip dhcp snooping acl. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1435
show ip dhcp snooping agent-option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1438
show ip dhcp snooping binding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1440
show ip dhcp snooping interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1442
show ip dhcp snooping statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1444
show ip dhcp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1434
show ip domain-list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 774
show ip domain-name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 775
show ip flooding-nexthops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 756
show ip igmp groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 872
show ip igmp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 874
show ip igmp snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 876
show ip igmp snooping routermode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 877
show ip igmp snooping source-timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 878
show ip igmp snooping statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 879
show ip interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 757
show ip name-server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 776
show ip route database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 824
show ip route summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 825
show ip route. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 822
show ip rrp snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1548
show ip sockets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 758
show ip source binding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1447
show ip traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 761
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1016
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1023
show ipv6 dhcp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1844
show ipv6 dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1843
show ipv6 forwarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 810
show ipv6 interface brief. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 811
show ipv6 mld groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 901
show ipv6 mld interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 902
show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 903
show ipv6 mld snooping statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 904

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 62
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show ipv6 neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 812
show ipv6 route summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 815
show ipv6 route summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 828
show ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 813
show ipv6 route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 826
show lacp sys-id . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 684
show lacp-counter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 685
show license brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
show license external . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
show license. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
show lldp interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1958
show lldp local-info. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1960
show lldp neighbors detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1967
show lldp neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1965
show lldp statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1973
show lldp statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1971
show lldp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1956
show location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1975
show log config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
show log external. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
show log permanent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
show log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
show loop-protection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
show mac address-table thrash-limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
show mac address-table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
show mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1989
show memory allocations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
show memory history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
show memory pools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
show memory shared. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
show memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
show mep-alarm status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
show mirror interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 450
show mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
show mls qos interface policer-counters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1068

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 63
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show mls qos interface queue-counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1069
show mls qos interface storm-status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1070
show mls qos interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1065
show mls qos maps cos-queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1071
show mls qos maps premark-dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1072
show mls qos. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1064
show ntp associations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1864
show ntp counters associations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1867
show ntp counters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1866
show ntp status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1868
show openflow config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1461
show openflow coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1463
show openflow flows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1465
show openflow rules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1468
show openflow ssl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1470
show openflow status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1471
show ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2108
show platform classifier statistics utilization brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1073
show platform classifier statistics utilization brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 515
show platform port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 518
show platform. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
show policy-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1076
show port etherchannel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 686
show port-security interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
show port-security intrusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
show port-vlan-forwarding-priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
show power-inline counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 709
show power-inline interface detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 714
show power-inline interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 711
show power-inline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 706
show privilege. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
show process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
show proxy-autoconfig-file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1241
show ptp data transparent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1874
show ptp port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1875

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 64
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show radius local-server group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1353
show radius local-server nas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1354
show radius local-server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1355
show radius local-server user. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1356
show radius server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1293
show radius statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1317
show radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1314
show reboot history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
show remote-mirror . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
show rmon alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1997
show rmon event. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1998
show rmon history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2000
show rmon statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2002
show router-id. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
show running-config atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1773
show running-config interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
show running-config log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
show running-config sflow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2132
show running-config snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1885
show running-config ssh. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2027
show running-config trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2065
show running-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
show security-password configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
show security-password user. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
show sflow interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2135
show sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2133
show snmp-server community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1887
show snmp-server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1888
show snmp-server user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1889
show snmp-server view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1890
show snmp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1886
show spanning-tree brief . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
show spanning-tree mst config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 597
show spanning-tree mst detail interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 600
show spanning-tree mst detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 65
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show spanning-tree mst instance interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 603
show spanning-tree mst instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 602
show spanning-tree mst interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 604
show spanning-tree mst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 596
show spanning-tree statistics instance interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 608
show spanning-tree statistics instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
show spanning-tree statistics interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610
show spanning-tree statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
show spanning-tree vlan range-index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 612
show spanning-tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 592
show ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2031
show ssh server allow-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2034
show ssh server deny-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2035
show ssh server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2032
show ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2029
show startup-config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
show static-channel-group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 687
show storm-control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 522
show system environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
show system fiber-monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
show system interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
show system mac. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
show system pluggable detail. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
show system pluggable diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
show system pluggable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
show system serialnumber. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
show system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
show tacacs+. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1394
show tech-support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
show telnet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
show test cable-diagnostics tdr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
show trigger. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2066
show udld neighbors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 655
show udld port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 656
show udld. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 654

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 66
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
show users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
show version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
show vlan access-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
show vlan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
show vlan private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
show vlan private-vlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 550
show vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
snmp trap link-status suppress . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1892
snmp trap link-status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1891
snmp-server community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1896
snmp-server contact. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1897
snmp-server enable trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1898
snmp-server engineID local reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1903
snmp-server engineID local . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1901
snmp-server group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1904
snmp-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1906
snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1908
snmp-server location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1909
snmp-server source-interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1910
snmp-server startup-trap-delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1911
snmp-server user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1912
snmp-server view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1915
snmp-server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1894
source-ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2112
spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
spanning-tree bpdu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 614
spanning-tree cisco-interoperability (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 616
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 617
spanning-tree enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 618
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 620
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 621
spanning-tree force-version. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 622
spanning-tree forward-time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 623
spanning-tree guard root . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 624

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 67
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
spanning-tree hello-time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 625
spanning-tree link-type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 626
spanning-tree max-age . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 627
spanning-tree max-hops (MSTP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 628
spanning-tree mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 629
spanning-tree mst configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 630
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 632
spanning-tree mst instance priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 634
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 635
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 637
spanning-tree mst instance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 631
spanning-tree path-cost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 638
spanning-tree portfast (STP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 639
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 641
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 643
spanning-tree priority (bridge priority) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 645
spanning-tree priority (port priority). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 646
spanning-tree restricted-role. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 647
spanning-tree restricted-tcn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 648
spanning-tree transmit-holdcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 649
speed (asyn). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 523
ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2038
ssh server allow-users. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2042
ssh server authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2044
ssh server deny-users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2046
ssh server max-auth-tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2048
ssh server resolve-host. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2049
ssh server scp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2050
ssh server sftp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2051
ssh server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2040
ssh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2036
state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1774
static-channel-group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 688
storm-action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1077

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 68
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
storm-control level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 525
storm-downtime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1078
storm-protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1079
storm-rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1080
storm-window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1081
subject-name (trustpoint configuration). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1385
subnet-mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1836
sub-ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1539
switchport access vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 552
switchport atmf-agentlink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1776
switchport atmf-arealink remote-area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1777
switchport atmf-crosslink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1779
switchport atmf-guestlink. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1781
switchport atmf-link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1783
switchport mode access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
switchport mode private-vlan ufo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
switchport mode private-vlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 554
switchport mode trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 561
switchport port-security aging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 527
switchport port-security maximum. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 528
switchport port-security violation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 529
switchport port-security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 526
switchport private-vlan host-association . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 562
switchport private-vlan mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 563
switchport remote-mirror-egress. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
switchport trunk allowed vlan. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 564
switchport trunk native vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 567
switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 568
switchport voice dscp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 569
switchport voice vlan priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
switchport voice vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 570
system territory (deprecated) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
tacacs-server host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1396

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 69
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
tacacs-server key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1398
tacacs-server timeout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1399
tcpdump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 763
telnet server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
terminal length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
terminal monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
terminal resize. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
test cable-diagnostics tdr interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2071
thrash-limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 530
time (trigger) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2072
timeout (ping polling) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2114
timer (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1540
topology-change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1542
traceroute ipv6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 816
traceroute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 764
trap (G.8032) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1544
trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2074
trigger activate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2076
trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2075
trust dscp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1082
type atmf node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1784
type atmf node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2077
type card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2080
type cpu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2081
type interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2082
type linkmon-probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2083
type log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2085
type memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2086
type periodic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2087
type ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2088
type reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2089
type time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2090
udld aggressive-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 657

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 70
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
udld enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 658
udld port aggressive-mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 660
udld port disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 661
udld port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 659
udld reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 662
udld time disable-period. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 663
udld time message-interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 664
undebug aaa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1295
undebug all . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
undebug atmf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1787
undebug dot1x. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1125
undebug epsr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1499
undebug g8032 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1545
undebug igmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 881
undebug ip packet interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 765
undebug lacp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 690
undebug loopprot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 532
undebug mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1990
undebug mstp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 650
undebug ping-poll . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2116
undebug platform packet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 533
undebug radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1318
undebug sflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2136
undebug snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1916
undebug ssh client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2052
undebug ssh server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2053
undebug trigger. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2091
undebug udld . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 665
unmount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
unmount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
up-count . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2115
user (RADIUS server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1358
username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1788
username . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
vlan (RADIUS server) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1360

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 71
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
vlan access-map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 574
vlan database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
vlan filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 576
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
vlan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
vty access-class (numbered) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 993
vty ipv6 access-class (named) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1024
wait . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
write file. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
write memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
write terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
wrr-queue disable queues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1083
wrr-queue egress-rate-limit queues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1084
wrr-queue weight queues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1085

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 72
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 1: Setup and Troubleshooting

1
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 73
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI Navigation
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for the commands used to
navigate between different modes. This chapter also provides a reference for the
help and show commands used to help navigate within the CLI.
Command List •“configure terminal” on page 74
•“disable (Privileged Exec mode)” on page 75
•“do” on page 76
•“enable (Privileged Exec mode)” on page 77
•“end” on page 79
•“exit” on page 80
•“help” on page 81
•“logout” on page 82
•“show history” on page 83

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 74
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
CONFIGURE TERMINAL
configure terminal
Overview This command enters the Global Configuration command mode.
Syntax configure terminal
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enter the Global Configuration command mode (note the change in the
command prompt), enter the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 75
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
DISABLE (PRIVILEGED EXEC MODE)
disable (Privileged Exec mode)
Overview This command exits the Privileged Exec mode, returning the prompt to the User
Exec mode. To end a session, use the exit command.
Syntax disable
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To exit the Privileged Exec mode, enter the command:
awplus# disable
awplus>
Related
Commands
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
end
exit

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 76
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
DO
do
Overview This command lets you to run User Exec and Privileged Exec mode commands
when you are in any configuration mode.
Syntax do <command>
Mode Any configuration mode
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# do ping 192.0.2.23
Parameter Description
<command>Specify the command and its parameters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 77
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
ENABLE (PRIVILEGED EXEC MODE)
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
Overview This command enters the Privileged Exec mode and optionally changes the
privilege level for a session. If a privilege level is not specified then the maximum
privilege level (15) is applied to the session. If the optional privilege level is omitted
then only users with the maximum privilege level can access Privileged Exec mode
without providing the password as specified by the enable password or enable
secret commands. If no password is specified then only users with the maximum
privilege level set with the username command can assess Privileged Exec mode.
Syntax enable [<privilege-level>]
Mode User Exec
Usage Many commands are available from the Privileged Exec mode that configure
operating parameters for the device, so you should apply password protection to
the Privileged Exec mode to prevent unauthorized use. Passwords can be
encrypted but then cannot be recovered. Note that non-encrypted passwords are
shown in plain text in configurations.
The username command sets the privilege level for the user. After login, users are
given access to privilege level 1. Users access higher privilege levels with the
enable (Privileged Exec mode) command. If the privilege level specified is higher
than the users configured privilege level specified by the username command,
then the user is prompted for the password for that level.
Note that a separate password can be configured for each privilege level using the
enable password and the enable secret commands from the Global Configuration
mode. The service password-encryption command encrypts passwords
configured by the enable password and the enable secret commands, so
passwords are not shown in plain text in configurations.
Example The following example shows the use of the enable command to enter the
Privileged Exec mode (note the change in the command prompt).
awplus> enable
awplus#
The following example shows the enable command enabling access the
Privileged Exec mode for users with a privilege level of 7 or greater. Users with a
privilege level of 7 or greater do not need to enter a password to access Privileged
Exec mode. Users with a privilege level 6 or less need to enter a password to access
Parameter Description
<privilege
- level>Specify the privilege level for a CLI session in the range <1-15>, where
15 is the maximum privilege level, 7 is the intermediate privilege level
and 1 is the minimum privilege level. The privilege level for a user must
match or exceed the privilege level set for the CLI session for the user
to access Privileged Exec mode. Privilege level for a user is configured
by username.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 78
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
ENABLE (PRIVILEGED EXEC MODE)
Privilege Exec mode. Use the enable password command or the enable secret
commands to set the password to enable access to Privileged Exec mode.
awplus> enable 7
awplus#
Related
Commands
disable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable password
enable secret
exit
service password-encryption
username

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 79
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
END
end
Overview This command returns the prompt to the Privileged Exec command mode from
any other advanced command mode.
Syntax end
Mode All advanced command modes, including Global Configuration and Interface
Configuration modes.
Example The following example shows the use of the end command to return to the
Privileged Exec mode directly from Interface mode.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# end
awplus#
Related
Commands
disable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
exit

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 80
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
EXIT
exit
Overview This command exits the current mode, and returns the prompt to the mode at the
previous level. When used in User Exec mode, the exit command terminates the
session.
Syntax exit
Mode All command modes, including Global Configuration and Interface Configuration
modes.
Example The following example shows the use of the exit command to exit Interface mode,
and return to Configure mode.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# exit
awplus(config)#
Related
Commands
disable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
end
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 81
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
HELP
help
Overview This command displays a description of the AlliedWare Plus™ OS help system.
Syntax help
Mode All command modes
Example To display a description on how to use the system help, use the command:
awplus# help
Output Figure 1-1: Example output from the help command
When you need help at the command line, press '?'.
If nothing matches, the help list will be empty. Delete
characters until entering a '?' shows the available options.
Enter '?' after a complete parameter to show remaining valid
command parameters (e.g. 'show ?').
Enter '?' after part of a parameter to show parameters that
complete the typed letters (e.g. 'show ip?').

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 82
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
LOGOUT
logout
Overview This command exits the User Exec or Privileged Exec modes and ends the session.
Syntax logout
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To exit the User Exec mode, use the command:
awplus# logout
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 83
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CLI NAVIGATION COMMANDS
SHOW HISTORY
show history
Overview This command lists the commands entered in the current session. The history
buffer is cleared automatically upon reboot.
The output lists all command line entries, including commands that returned an
error.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show history
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the commands entered during the current session, use the command:
awplus# show history
Output Figure 1-2: Example output from the show history command
1 en
2 show ru
3 conf t
4 route-map er deny 3
5 exit
6 ex
7 di

2
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 84
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
File and
Configuration
Management
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of AlliedWare Plus™ OS file and
configuration management commands.
Filename Syntax
and Keyword
Usage
Many of the commands in this chapter use the placeholder “filename” to represent
the name and location of the file that you want to act on. The following table
explains the syntax of the filename for each different type of file location.
When you copy a
file... Use this syntax: Example:
Copying in local
Flash memory flash:[/][<directory>/]<filename>To specify a file in the configs directory
in Flash:
flash:configs/example.cfg
Copying to or from
an SD (or SDHC)
card
card:[/][<directory>/]<filename>To specify a file in the top-level
directory of the SD card:
card:example.cfg
Copying with
HTTP http://[[<username>:<password>]@]
{<hostname>|<host-ip>}[/<filepath
>]/<filename>
To specify a file in the configs directory
on the server:
http://www.company.com/configs/exa
mple.cfg
Copying with TFTP tftp://[[<location>]/<directory>]
/<filename>To specify a file in the top-level
directory of the server:
tftp://172.1.1.1/example.cfg
Copying with SCP scp://<username>@<location>[/<dir
ectory>][/<filename>] To specify a file in the configs directory
on the server, logging on as user “bob”:
e.g.
scp://bob@10.10.0.12/configs/example
.cfg
Copying with SFTP sftp://[[<location>]/<directory>]
/<filename>To specify a file in the top-level
directory of the server:
sftp://10.0.0.5/example.cfg

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 85
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
Valid characters The filename and path can include characters from up to four categories. The
categories are:
1) uppercase letters: A to Z
2) lowercase letters: a to z
3) digits: 0 to 9
4) special symbols: most printable ASCII characters not included in the previous
three categories, including the following characters:
•-
•/
•.
•_
•@
•"
•'
•*
•:
•~
•?
Do not use spaces, parentheses or the + symbol within filenames. Use hyphens or
underscores instead.
Syntax for
directory listings
A leading slash (/) indicates the root of the current filesystem location.
In commands where you need to specify the local filesystem’s Flash base directory,
you may use flash or flash: or flash:/. For example, these commands are all the
same:
•dir flash
•dir flash:
•dir flash:/
Similarly, you can specify the SD (or SDHC) card base directory with card or card:
or card:/
You cannot name a directory or subdirectory flash, nvs, usb, card, tftp, scp, sftp
or http. These keywords are reserved for tab completion when using various file
commands.
Command List •“autoboot enable” on page 87
•“boot config-file” on page 88
•“boot config-file backup” on page 90
•“boot system” on page 91

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 86
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
•“boot system backup” on page 93
•“cd” on page 94
•“copy (filename)” on page 95
•“copy current-software” on page 97
•“copy debug” on page 98
•“copy running-config” on page 99
•“copy startup-config” on page 100
•“copy zmodem” on page 101
•“create autoboot” on page 102
•“delete” on page 103
•“delete debug” on page 104
•“dir” on page 105
•“edit” on page 107
•“edit (filename)” on page 108
•“erase factory-default” on page 109
•“erase startup-config” on page 110
•“ip tftp source-interface” on page 111
•“ipv6 tftp source-interface” on page 112
•“mkdir” on page 113
•“move” on page 114
•“move debug” on page 115
•“pwd” on page 116
•“rmdir” on page 117
•“show autoboot” on page 118
•“show boot” on page 119
•“show file” on page 121
•“show file systems” on page 122
•“show running-config” on page 124
•“show running-config interface” on page 127
•“show startup-config” on page 129
•“show version” on page 130
•“unmount” on page 131
•“write file” on page 132
•“write memory” on page 133
•“write terminal” on page 134

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 87
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
AUTOBOOT ENABLE
autoboot enable
Overview This command enables the device to restore a release file and/or a configuration
file from an SD card.
When the Autoboot feature is enabled, the device looks for a special file called
autoboot.txt on the external media. If this file exists, the device will check the key
and values in the file and recover the device with a new release file and/or
configuration file from the external media. An example of a valid autoboot.txt file
is shown in the following figure.
Figure 2-1: Example autoboot.txt file
Use the no variant of this command to disable the Autoboot feature.
Syntax autoboot enable
no autoboot enable
Default The Autoboot feature operates the first time the device is powered up in the field,
after which the feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the Autoboot feature, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# autoboot enable
Related
Commands
create autoboot
show autoboot
show boot
[AlliedWare Plus]
Copy_from_external_media_enabled=yes
Boot_Release=IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel
Boot_Config=network1.cfg
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 88
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
BOOT CONFIG-FILE
boot config-file
Overview Use this command to set the configuration file to use during the next boot cycle.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configuration file.
Syntax boot config-file <filepath-filename>
no boot config-file
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You can only specify that the configuration file is on an SD card if there is a backup
configuration file already specified in Flash. If you attempt to set the configuration
file on an SD card and a backup configuration file is not specified in Flash, the
following error message is displayed:
In addition, you can only specify that the configuration file is on an SD card if the
card is writable.
For an explanation of the configuration fallback order, see the File Management
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Examples To run the configuration file “branch.cfg” the next time the device boots up, when
“branch.cfg” is stored on the device’s Flash filesystem, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot config-file flash:/branch.cfg
To stop running the configuration file “branch.cfg” when the device boots up,
when “branch.cfg” is stored on the device’s Flash filesystem, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no boot config-file flash:/branch.cfg
To run the configuration file “branch.cfg” the next time the device boots up, when
“branch.cfg” is stored on an SD card, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot config-file card:/branch.cfg
Parameter Description
<filepath-filename> Filepath and name of a configuration file.
The specified configuration file must exist in the
specified filesystem.
Valid configuration files must have a . cfg extension.
% Backup configuration files must be stored in the flash
filesystem

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 89
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
BOOT CONFIG-FILE
To stop running the configuration file “branch.cfg” when the device boots up,
when “branch.cfg” is stored on an SD card, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no boot config-file card:/branch.cfg
Related
Commands
boot config-file backup
boot system
boot system backup
show boot
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 90
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
BOOT CONFIG-FILE BACKUP
boot config-file backup
Overview Use this command to set a backup configuration file to use if the main
configuration file cannot be accessed.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the backup configuration file.
Syntax boot config-file backup <filepath-filename>
no boot config-file backup
Mode Global Configuration
Usage For an explanation of the configuration fallback order, see the File Management
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Examples To set the configuration file backup.cfg as the backup to the main
configuration file, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot config-file backup flash:/backup.cfg
To remove the configuration file backup.cfg as the backup to the main
configuration file, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no boot config-file backup flash:/backup.cfg
Related
Commands
boot config-file
boot system
boot system backup
show boot
Parameter Description
<filepath-filename> Filepath and name of a backup configuration file.
Backup configuration files must be in the Flash filesystem.
Valid backup configuration files must have a . cfg
extension.
backup The specified file is a backup configuration file.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 91
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
BOOT SYSTEM
boot system
Overview Use this command to set the release file to load during the next boot cycle.
Use the no variant of this command to stop specifying a primary release file to boot
from. If the device boots up with no release file set, it will use autoboot or the
backup release file if either of those are configured, or you can use the boot menu
to select a release file source. To access the boot menu, type Ctrl-B at bootup.
Syntax boot system <filepath-filename>
no boot system
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You can only specify that the release file is on an SD card if there is a backup release
file already specified in Flash. If you attempt to set the release file on an SD card and
a backup release file is not specified in Flash, the following error message is
displayed:
In addition, you can only specify that the configuration file is on an SD card if the
card is writable.
Examples To boot up with the release IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel file the next time the device boots
up, when the release file is stored on the device’s Flash filesystem, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot system flash:/IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel
To run the release file IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel the next time the device boots up, when
the release file is stored on an SD card, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot system card:/IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel
Parameter Description
<filepath-filename> Filepath and name of a release file.
The specified release file must exist and must be stored
in the root directory of the specified filesystem.
Valid release files must have a . rel extension.
A backup boot image must be set before setting a current boot
image on card
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 93
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
BOOT SYSTEM BACKUP
boot system backup
Overview Use this command to set a backup release file to load if the main release file cannot
be loaded.
Use the no variant of this command to stop specifying a backup release file.
Syntax boot system backup <filepath-filename>
no boot system backup
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To specify the file IE210-5.4.8-2.1.rel as the backup to the main release file, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# boot system backup flash:/IE210-5.4.8-2.1.rel
To stop specifying a backup to the main release file, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no boot system backup
Related
Commands
boot config-file
boot config-file backup
boot system
show boot
Parameter Description
<filepath-filename> Filepath and name of a backup release file.
Backup release files must be in the Flash filesystem.
Valid release files must have a . rel extension.
backup The specified file is a backup release file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 94
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CD
cd
Overview This command changes the current working directory.
Syntax cd <directory-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To change to the directory called images, use the command:
awplus# cd images
Related
Commands
dir
pwd
show file systems
Parameter Description
<directory-name> Name and path of the directory.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 95
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY (FILENAME)
copy (filename)
Overview This command copies a file. This allows you to:
• copy files from your device to a remote device
• copy files from a remote device to your device
• copy files stored on Flash memory to or from a different memory type, such
as an SD card
• create two copies of the same file on your device
Syntax copy [force] <source-name> <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To use TFTP to copy the file “bob.key” into the current directory from the remote
server at 10.0.0.1, use the command:
awplus# copy tftp://10.0.0.1/bob.key bob.key
To use SFTP to copy the file “new.cfg” into the current directory from a remote
server at 10.0.1.2, use the command:
awplus# copy sftp://10.0.1.2/new.cfg bob.key
To use SCP with the username “beth” to copy the file old.cfg into the directory
config_files on a remote server that is listening on TCP port 2000, use the
command:
awplus# copy scp://beth@serv:2000/config_files/old.cfg old.cfg
To copy the file “newconfig.cfg” onto your device’s Flash from an SD (or SDHC)
Card, use the command:
awplus# copy card:/newconfig.cfg flash:/newconfig.cfg
To copy the file “newconfig.cfg” to an SD (or SDHC) Card from your device’s Flash,
use the command:
awplus# copy flash:/newconfig.cfg card:/newconfig.cfg
Parameter Description
force This parameter forces the copy command to overwrite the
destination file, if it already exists, without prompting the
user for confirmation.
<source-name> The filename and path of the source file. See Introduction
on page 84 for valid syntax.
<destination-name> The filename and path for the destination file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 96
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY (FILENAME)
To copy the file “config.cfg” into the current directory from an SD (or SDHC) Card,
and rename it to “configtest.cfg”, use the command:
awplus# copy card:/config.cfg configtest.cfg
To copy the file “config.cfg” into the current directory from a remote file server, and
rename it to “configtest.cfg”, use the command:
awplus# copy fserver:/config.cfg configtest.cfg
On an AMF network, to copy the file “file.txt” from the node named master to the
Flash memory of the local node, use the commands:
awplus# atmf working-set group all
network-name[80]# copy master.atmf/flash:/file.txt flash:
Related
Commands
copy zmodem
copy buffered-log
copy permanent-log
edit (filename)
show file systems

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 97
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY CURRENT-SOFTWARE
copy current-software
Overview This command copies the AlliedWare Plus™ OS software that the device has
booted from, to a destination file. Specify whether the destination is Flash or card
when saving the software to the local filesystem.
Syntax copy current-software <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To copy the current software as installed in the working directory with the file
name my-release.rel, use the command:
awplus# copy current-software my-release.rel
Related
Commands
boot system backup
show boot
Parameter Description
<destination-name> The filename and path where you would like the current
running-release saved. This command creates a file if no file
exists with the specified filename. If a file already exists,
then the CLI prompts you before overwriting the file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 98
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY DEBUG
copy debug
Overview This command copies a specified debug file to a destination file.
Syntax copy debug {<destination-name>|card|debug|flash|scp|tftp}
{<source-name>|card|debug|flash|scp|tftp}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To copy debug output to a file on flash called “my-debug”, use the following
command:
awplus# copy debug flash:my-debug
To copy debug output to an SD (or SDHC) card with a filename “my-debug”, use
the following command:
awplus# copy debug card:my-debug
Output Figure 2-2: CLI prompt after entering the copy debug command
Related
Commands
delete debug
move debug
Parameter Description
<destination-name> The filename and path where you would like the debug
output saved. See Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.
<source-name> The filename and path where the debug output originates.
See the Introduction to this chapter for valid syntax.
Enter source file name []:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 99
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY RUNNING-CONFIG
copy running-config
Overview This command copies the running-config to a destination file, or copies a source
file into the running-config. Commands entered in the running-config do not
survive a device reboot unless they are saved in a configuration file.
Syntax copy <source-name> running-config
copy running-config [<destination-name>]
copy running-config startup-config
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To copy the running-config into the startup-config, use the command:
awplus# copy running-config startup-config
To copy the file layer3.cfg into the running-config, use the command:
awplus# copy layer3.cfg running-config
To use SCP to copy the running-config as current.cfg to the remote server
listening on TCP port 2000, use the command:
awplus# copy running-config
scp://user@server:2000/config_files/current.cfg
Related
Commands
copy startup-config
write file
write memory
Parameter Description
<source-name>The filename and path of a configuration file. This must be
a valid configuration file with a . cfg filename extension.
Specify this when you want the script in the file to become
the new running-config. See Introduction on page 84 for
valid syntax.
<destination-name>The filename and path where you would like the current
running-config saved. This command creates a file if no file
exists with the specified filename. If a file already exists,
then the CLI prompts you before overwriting the file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax. If you do not
specify a file name, the device saves the running-config to
a file called default.cfg.
startup-config Copies the running-config into the file set as the current
startup-config file.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 100
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY STARTUP-CONFIG
copy startup-config
Overview This command copies the startup-config script into a destination file, or
alternatively copies a configuration script from a source file into the startup-config
file. Specify whether the destination is Flash or card when loading from the local
filesystem.
Syntax copy <source-name> startup-config
copy startup-config <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To copy the file Layer3.cfg to the startup-config, use the command:
awplus# copy Layer3.cfg startup-config
To copy the startup-config as the file oldconfig.cfg in the current
directory, use the command:
awplus# copy startup-config oldconfig.cfg
Related
Commands
copy running-config
Parameter Description
<source-name> The filename and path of a configuration file. This must be
a valid configuration file with a . cfg filename extension.
Specify this to copy the script in the file into the startup-
config file. Note that this does not make the copied file the
new startup file, so any further changes made in the
configuration file are not added to the startup-config file
unless you reuse this command. See Introduction on page
84 for valid syntax.
<destination-name> The destination and filename that you are saving the
startup- config as. This command creates a file if no file
exists with the specified filename. If a file already exists,
then the CLI prompts you before overwriting the file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 101
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
COPY ZMODEM
copy zmodem
Overview This command allows you to copy files using ZMODEM using Minicom. ZMODEM
works over a serial connection and does not need any interfaces configured to do
a file transfer.
Syntax copy <source-name> zmodem
copy zmodem
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To copy the local file asuka.key using ZMODEM, use the command:
awplus# copy asuka.key zmodem
Related
Commands
copy (filename)
show file systems
Parameter Description
<source-name> The filename and path of the source file. See Introduction on
page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 102
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CREATE AUTOBOOT
create autoboot
Overview Use this command to create an autoboot.txt file on an external storage device. This
command will automatically ensure that the keys and values that are expected in
this file are correct. After the file is created the create autoboot command will
copy the current release and configuration files across to the external storage
device. The external storage device is then available to restore a release file and/or
a configuration file to the device.
Syntax create autoboot card
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To create an autoboot.txt file on an SD card, use the command:
awplus# create autoboot card
Related
Commands
autoboot enable
show autoboot
show boot

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 103
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
DELETE
delete
Overview This command deletes files or directories.
Syntax delete [force] [recursive] <filename>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To delete the file temp.cfg from the current directory, use the command:
awplus# delete temp.cfg
To delete the read-only file one.cfg from the current directory, use the
command:
awplus# delete force one.cfg
To delete the directory old_configs, which is not empty, use the command:
awplus# delete recursive old_configs
To delete the directory new_configs, which is not empty, without prompting if
any read-only files are being deleted, use the command:
awplus# delete force recursive new_configs
Related
Commands
erase startup-config
rmdir
Parameter Description
force Ignore nonexistent filenames and never prompt before deletion.
recursive Remove the contents of directories recursively.
<filename>The filename and path of the file to delete. See Introduction on page
84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 104
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
DELETE DEBUG
delete debug
Overview Use this command to delete a specified debug output file.
Syntax delete debug <source-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete debug output, use the following command:
awplus# delete debug
Output Figure 2-3: CLI prompt after entering the delete debug command
Related
Commands
copy debug
move debug
Parameter Description
<source-name> The filename and path where the debug output originates.
See Introduction on page 84 for valid URL syntax.
Enter source file name []:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 105
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
DIR
dir
Overview This command lists the files on a filesystem. If you don’t specify a directory or file,
then this command lists the files in the current directory.
Syntax dir [all] [recursive] [sort [reverse] [name|size|time]]
[<filename>|card|debug|flash|nvs]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To list the files in the current working directory, use the command:
awplus# dir
To list the non-hidden files in the root of the Flash filesystem, use the command:
awplus# dir flash
To list all the files in the root of the Flash filesystem, use the command:
awplus# dir all flash:
To list recursively the files in the Flash filesystem, use the command:
awplus# dir recursive flash:
To list the files in alphabetical order, use the command:
awplus# dir sort name
Parameter Description
all List all files.
recursive List the contents of directories recursively.
sort Sort directory listing.
reverse Sort using reverse order.
name Sort by name.
size Sort by size.
time Sort by modification time (default).
<filename>The name of the directory or file. If you don’t specify a
directory or file, then this command lists the files in the
current directory.
card SD (or SDHC) card root directory
debug Debug root directory
flash Flash memory root directory
nvs NVS memory root directory
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 106
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
DIR
To list the files by size, smallest to largest, use the command:
awplus# dir sort reverse size
To sort the files by modification time, oldest to newest, use the command:
awplus# dir sort reverse time
Output Figure 2-4: Example output from the dir command
Related
Commands
cd
pwd
awplus#dir
630 -rw- May 19 2016 23:36:31 example.cfg
23652123 -rw- May 17 2016 03:41:18
149 -rw- Feb 9 2016 00:40:35 exception.log
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 107
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
EDIT
edit
Overview This command opens a text file in the AlliedWare Plus™ text editor. Once opened
you can use the editor to alter to the file.
If a filename is specified and it already exists, then the editor opens it in the text
editor.
If no filename is specified, the editor prompts you for one when you exit it.
Before starting the editor make sure your terminal, terminal emulation program, or
Telnet client is 100% compatible with a VT100 terminal. The editor uses VT100
control sequences to display text on the terminal.
For more information about using the editor, including control sequences, see the
File Management Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax edit [<filename>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To create and edit a new text file, use the command:
awplus# edit
To edit the existing configuration file myconfig.cfg stored on your device’s
Flash memory, use the command:
awplus# edit myconfig.cfg
Related
Commands
edit (filename)
show file
Parameter Description
<filename> Name of a file in the local Flash filesystem.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 108
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
EDIT (FILENAME)
edit (filename)
Overview This command opens a remote text file as read-only in the AlliedWare Plus™ text
editor.
Before starting the editor make sure your terminal, terminal emulation program, or
Telnet client is 100% compatible with a VT100 terminal. The editor uses VT100
control sequences to display text on the terminal.
Syntax edit <filename>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To view the file bob.key stored in the security directory of a TFTP server, use the
command:
awplus# edit tftp://security/bob.key
Related
Commands
copy (filename)
edit
show file
Parameter Description
<filename> The filename and path of the remote file. See Introduction on
page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 109
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ERASE FACTORY-DEFAULT
erase factory-default
Overview This command erases all data from Flash except the following:
• the boot release file (a .rel file) and its release setting file
• all license files
• the latest GUI release file
The device is then rebooted and returned to its factory default condition. The
device can then be used for AMF automatic node recovery.
Syntax erase factory-default
Mode Privileged Exec.
Usage This command is an alias to the atmf cleanup command.
Example To erase data, use the command:
Node_1# erase factory-default
This command will erase all NVS, all flash contents except for
the boot release, a GUI resource file, and any license files,
and then reboot the switch. Continue? (y/n):y
Related
Commands
atmf cleanup

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 110
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ERASE STARTUP-CONFIG
erase startup-config
Overview This command deletes the file that is set as the startup-config file, which is the
configuration file that the system runs when it boots up.
At the next restart, the device loads the default configuration file, default.cfg. If
default.cfg no longer exists, then the device loads with the factory default
configuration. This provides a mechanism for you to return the device to the
factory default settings.
Syntax erase startup-config
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the file currently set as the startup-config, use the command:
awplus# erase startup-config
Related
Commands
boot config-file backup
copy running-config
copy startup-config
show boot
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 111
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
IP TFTP SOURCE-INTERFACE
ip tftp source-interface
Overview Use this command to manually specify the IP address that all TFTP requests
originate from. This is useful in network configurations where TFTP servers only
accept requests from certain devices, or where the server cannot dynamically
determine the source of the request.
Use the no variant of this command to stop specifying a source.
Syntax ip tftp source-interface [<interface>|<ip-add>]
no ip tftp source-interface
Default There is no default source specified.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command is helpful in network configurations where TFTP traffic needs to
traverse point-to-point links or subnets within your network, and you do not want
to propagate those point-to-point links through your routing tables.
In those circumstances, the TFTP server cannot dynamically determine the source
of the TFTP request, and therefore cannot send the requested data to the correct
device. Specifying a source interface or address enables the TFTP server to send the
data correctly.
Example To specify that TFTP requests originate from the IP address 192.0.2.1, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip tftp source-interface 192.0.2.1
Related
Commands
copy (filename)
Parameter Description
<interface> The VLAN that TFTP requests originate from. The device will use
the IP address of this interface as its source IP address.
<ip-add> The IP address that TFTP requests originate from, in dotted
decimal format
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 112
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
IPV6 TFTP SOURCE-INTERFACE
ipv6 tftp source-interface
Overview Use this command to manually specify the IPv6 address that all TFTP requests
originate from. This is useful in network configurations where TFTP servers only
accept requests from certain devices, or where the server cannot dynamically
determine the source of the request.
Use the no variant of this command to stop specifying a source.
Syntax ipv6 tftp source-interface [<interface>|<ipv6-add>]
no ipv6 tftp source-interface
Default There is no default source specified.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command is helpful in network configurations where TFTP traffic needs to
traverse point-to-point links or subnets within your network, and you do not want
to propagate those point-to-point links through your routing tables.
In those circumstances, the TFTP server cannot dynamically determine the source
of the TFTP request, and therefore cannot send the requested data to the correct
device. Specifying a source interface or address enables the TFTP server to send the
data correctly.
Example To specify that TFTP requests originate from the IPv6 address 2001:db8::8a2e:7334,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 tftp source-interface 2001:db8::8a2e:7334
Related
Commands
copy (filename)
Parameter Description
<interface> The VLAN that TFTP requests originate from. The device will use
the IPv6 address of this interface as its source IPv6 address.
<ipv6-add> The IPv6 address that TFTP requests originate from, in the format
x:x::x:x, for example, 2001:db8::8a2e:7334.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 113
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MKDIR
mkdir
Overview This command makes a new directory.
Syntax mkdir <name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You cannot name a directory or subdirectory flash, nvs, usb, card, tftp, scp, sftp
or http. These keywords are reserved for tab completion when using various file
commands.
Example To make a new directory called images in the current directory, use the
command:
awplus# mkdir images
Related
Commands
cd
dir
pwd
Parameter Description
<name> The name and path of the directory that you are creating.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 114
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MOVE
move
Overview This command renames or moves a file.
Syntax move <source-name> <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To rename the file temp.cfg to startup.cfg, use the command:
awplus# move temp.cfg startup.cfg
To move the file temp.cfg from the root of the Flash filesystem to the directory
myconfigs, use the command:
awplus# move temp.cfg myconfigs/temp.cfg
Related
Commands
delete
edit
show file
show file systems
Parameter Description
<source-name> The filename and path of the source file. See Introduction
on page 84 for valid syntax.
<destination-name> The filename and path of the destination file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 115
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MOVE DEBUG
move debug
Overview This command moves a specified debug file to a destination debug file.
Syntax move debug {<destination-name>|card|debug|flash}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To move debug output into Flash memory with a filename “my-debug”, use the
following command:
awplus# move debug flash:my-debug
To move debug output onto an SD (or SDHC) card with a filename “my-debug”, use
the following command:
awplus# move debug card:my-debug
Output Figure 2-5: CLI prompt after entering the move debug command
Related
Commands
copy debug
delete debug
Parameter Description
<destination-name> The filename and path where you would like the debug
output moved to. See Introduction on page 84 for valid
syntax.
Enter source file name []:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 116
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
PWD
pwd
Overview This command prints the current working directory.
Syntax pwd
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To print the current working directory, use the command:
awplus# pwd
Related
Commands
cd

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 117
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
RMDIR
rmdir
Overview This command removes a directory. This command only works on empty
directories, unless you specify the optional force keyword.
Syntax rmdir [force] <name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To remove the directory “images” from the top level of the Flash filesystem, use the
command:
awplus# rmdir flash:/images
To create a directory called “level1” containing a subdirectory called “level2”, and
then force the removal of both directories, use the commands:
awplus# mkdir level1
awplus# mkdir level1/level2
awplus# rmdir force level1
Related
Commands
cd
dir
mkdir
pwd
Parameter Description
force Optional keyword that allows you to delete directories that
are not empty and contain files or subdirectories.
<name>The name and path of the directory.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 118
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW AUTOBOOT
show autoboot
Overview This command displays the Autoboot configuration and status.
Syntax show autoboot
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show the Autoboot configuration and status, use the command:
awplus# show autoboot
Output Figure 2-6: Example output from the show autoboot command
Figure 2-7: Example output from the show autoboot command when an
external media source is not present
Related
Commands
autoboot enable
create autoboot
show boot
awplus#show autoboot
Autoboot configuration
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Autoboot status : enabled
SD Card file autoboot.txt exists : yes
Restore information on SD card
Autoboot enable in autoboot.txt : yes
Restore release file : IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel (file exists)
Restore configuration file : network_1.cfg (file exists)
awplus#show autoboot
Autoboot configuration
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Autoboot status : enabled
External media source : SD card not found.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 119
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW BOOT
show boot
Overview This command displays the current boot configuration. We recommend that the
currently running release is set as the current boot image.
Syntax show boot
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show the current boot configuration, use the command:
awplus# show boot
Output Figure 2-8: Example output from show boot when the current boot config is
on an SD card
awplus#show boot
Boot configuration
----------------------------------------------------------------
Current software : IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel
Current boot image : card:/IE210-5.4.9-0.1.rel
Backup boot image : flash:/IE210-5.4.8-2.1.rel
Default boot config: flash:/default.cfg
Current boot config: card:/my.cfg (file exists)
Backup boot config: flash:/backup.cfg (file not found)
Autoboot status : enabled
Table 2-1: Parameters in the output from show boot
Parameter Description
Current software The current software release that the device is using.
Current boot image The boot image currently configured for use during the
next boot cycle.
Backup boot image The boot image to use during the next boot cycle if the
device cannot load the main image.
Default boot
config The default startup configuration file. The device loads
this configuration script if no file is set as the startup-
config file.
Current boot
config The configuration file currently configured as the
startup-config file. The device loads this configuration file
during the next boot cycle if this file exists.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 120
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW BOOT
Related
Commands
autoboot enable
boot config-file backup
boot system backup
show autoboot
Backup boot config The configuration file to use during the next boot cycle if
the main configuration file cannot be loaded.
Autoboot status The status of the Autoboot feature; either enabled or
disabled.
Table 2-1: Parameters in the output from show boot (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 121
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW FILE
show file
Overview This command displays the contents of a specified file.
Syntax show file <filename>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the contents of the file oldconfig.cfg, which is in the current
directory, use the command:
awplus# show file oldconfig.cfg
Related
Commands
edit
edit (filename)
show file systems
Parameter Description
<filename> Name of a file on the local Flash filesystem, or name and
directory path of a file.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 122
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW FILE SYSTEMS
show file systems
Overview This command lists the filesystems and their utilization information where
appropriate.
Syntax show file systems
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To display the filesystems, use the command:
awplus# show file systems
Output Figure 2-9: Example output from the show file systems command
awplus#show file systems
Size(b) Free(b) Type Flags Prefixes S/D/V Lcl/Ntwk Avail
-------------------------------------------------------------------
125.9M 118.0M flash rw flash: static local Y
- - system rw system: virtual local -
10.0M 9.9M debug rw debug: static local Y
- - sdcard rw card: dynamic local N
- - fserver rw fserver: dynamic network N
- - tftp rw tftp: - network -
- - scp rw scp: - network -
- - sftp ro sftp: - network -
- - http ro http: - network -
- - rsync rw rsync: - network -
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show file systems command
Parameter Description
Size (B)
Available The total memory available to this filesystem. The units are given
after the value and are M for Megabytes or k for kilobytes.
Free (B) The total memory free within this filesystem. The units are given
after the value and are M for Megabytes or k for kilobytes.
Type The memory type used for this filesystem, such as:
flash
system
sdcard
tftp
scp
sftp
http.
Flags The file setting options: rw (read write), ro (read only).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 123
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW FILE SYSTEMS
Related
Commands
edit
edit (filename)
show file
Prefixes The prefixes used when entering commands to access the
filesystems, such as:
flash
system
card
tftp
scp
sftp
http.
S/V/D The memory type: static, virtual, dynamic.
Lcl / Ntwk Whether the memory is located locally or via a network
connection.
Avail Whether the memory is accessible: Y (yes), N (no), - (not applicable)
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show file systems command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 124
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG
show running-config
Overview This command displays the current configuration of your device. Its output
includes all non-default configuration. The default settings are not displayed.
NOTE: You can control the output by entering | or > at the end of the command:
• To display only lines that contain a particular word, enter:
| include <word>
• To start the display at the first line that contains a particular word, enter:
| begin <word>
• To save the output to a file, enter:
> <filename>
Syntax show running-config [full|<feature>]
Parameter Description
full Display the running-config for all features. This is the default setting, so
it is the same as entering show running-config.
<feature>Display only the configuration for a single feature. The features
available depend on your device and will be some of the following list:
access-list ACL configuration
antivirus Antivirus configuration
application Application configuration
as-path Autonomous system path filter
configuration
as-path access-list Configuration of ACLs for AS path filtering
atmf Allied Telesis Management Framework
configuration
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
configuration
community-list Community-list configuration
crypto Security-specific configuration
dhcp DHCP configuration
dpi Deep Packet Inspection configuration
entity Entity configuration
firewall Firewall configuration
interface Interface configuration. See show
running-config interface for further
options.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 125
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG
ip Internet Protocol (IP) configuration
ip pim dense-mode PIM-DM configuration
ip pim sparse-mode PIM-SM configuration
ip route IP static route configuration
ip-reputation IP Reputation configuration
ips IPS configuration
ipsec Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
configuration
ipv6 Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
configuration
ipv6 access-list IPv6 ACL configuration
ipv6 mroute IPv6 multicast route configuration
ipv6 prefix-list IPv6 prefix list configuration
ipv6 route IPv6 static route configuration
isakmp Internet Security Association Key
Management Protocol (ISAKMP)
configuration
key chain Authentication key management
configuration
l2tp-profile L2TP tunnel profile configuration
lldp LLDP configuration
log Logging utility configuration
malware-protection Malware protection configuration
nat Network Address Translation configuration
power-inline Power over Ethernet (PoE) configuration
policy-based-routing Policy-based routing (PBR) configuration
pppoe-ac PPPoE access concentrator configuration
prefix-list Prefix-list configuration
route-map Route-map configuration
router Router configuration
router-id Configuration of the router identifier for
this system
security-password Strong password security configuration
snmp SNMP configuration
ssh Secure Shell configuration
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 126
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration of your device, use the command:
awplus# show running-config
Output Figure 2-10: Example output from show running-config
Related
Commands
copy running-config
show running-config interface
switch Switch configuration
web-control Web Control configuration
Parameter Description
awplus#show running-config
!
service password-encryption
!
no banner motd
!
username manager privilege 15 password 8 $1$bJoVec4D$JwOJGPr7YqoExA0GVasdE0
!
no service ssh
!
service telnet
!
service http
!
no clock timezone
...
line con 0
line vty 0 4
!
end

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 127
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG INTERFACE
show running-config interface
Overview This command displays the current configuration of one or more interfaces on the
device.
You can optionally limit the command output to display only information for a
given protocol or feature. The features available depend on your device and will be
a subset of the features listed in the table below.
Syntax show running-config interface [<interface-list>] [dot1x|ip
igmp|ip multicast|ip pim dense-mode|ip pim sparse-mode|ipv6
rip|lacp|mstp|ospf|rip|rstp|stp]
Parameter Description
<interface-list>The interfaces or ports to display information about. An
interface-list can be:
•a VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• the loopback interface (lo)
• a continuous range of interfaces separated by a hyphen
(e.g. vlan10-20)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. vlan1,vlan10-20). Do not mix
interface types in a list.
The specified interfaces must exist.
dot1x Displays running configuration for 802.1X port
authentication for the specified interfaces.
lacp Displays running configuration for LACP (Link Aggregation
Control Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
ip igmp Displays running configuration for IGMP (Internet Group
Management Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
ip multicast Displays running configuration for general multicast
settings for the specified interfaces.
ip pim sparse-mode Displays running configuration for PIM-SM (Protocol
Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode) for the specified
interfaces.
ip pim dense-mode Displays running configuration for PIM-DM (Protocol
Independent Multicasting - Dense Mode) for the specified
interfaces.
mstp Displays running configuration for MSTP (Multiple
Spanning Tree Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
ospf Displays running configuration for OSPF (Open Shortest
Path First) for the specified interfaces.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 128
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG INTERFACE
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Default Displays information for all protocols on all interfaces
Examples To display the current running configuration of your device for ports 1 to 4, use the
command:
awplus# show running-config interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
To display the current running configuration of a device for vlan2, use the
command:
awplus# show running-config interface vlan2
Output Figure 2-11: Example output from show running-config interface for a
switchport
Related
Commands
copy running-config
show running-config
rip Displays running configuration for RIP (Routing Information
Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
ipv6 rip Displays running configuration for RIPng (RIP for IPv6) for
the specified interfaces.
rstp Displays running configuration for RSTP (Rapid Spanning
Tree Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
stp Displays running configuration for STP (Spanning Tree
Protocol) for the specified interfaces.
Parameter Description
awplus#show running-config interface port1.0.2
!
interface port1.0.2
switchport
switchport mode access
!
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 129
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW STARTUP-CONFIG
show startup-config
Overview This command displays the contents of the start-up configuration file, which is the
file that the device runs on start-up.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show startup-config
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the contents of the current start-up configuration file, use the
command:
awplus# show startup-config
Output Figure 2-12: Example output from the show startup-config command
Related
Commands
boot config-file backup
copy running-config
copy startup-config
erase startup-config
show boot
awplus#show startup-config
!
service password-encryption
!
no banner motd
!
username manager privilege 15 password 8 $1$bJoVec4D$JwOJGPr7YqoExA0GVasdE0
!
no service ssh
!
service telnet
!
service http
!
no clock timezone
...
line con 0
line vty 0 4
!
end

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 130
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW VERSION
show version
Overview This command displays the version number and copyright details of the current
AlliedWare Plus™ OS your device is running.
Syntax show version
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the version details of your currently installed software, use the
command:
awplus# show version
Related
Commands
boot system backup
show boot
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 131
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
UNMOUNT
unmount
Overview Use this command to unmount an external storage device. We recommend you
unmount storage devices before removing them, to avoid file corruption. This is
especially important if files may be automatically written to the storage device,
such as external log files or AMF backup files.
Syntax unmount card
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To unmount an SD card and safely remove it from the device, use the command:
awplus# unmount card
Related
Commands
clear log external
log external
show file systems
show log config
show log external
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
card Unmount the SD card.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 132
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
WRITE FILE
write file
Overview This command copies the running-config into the file that is set as the current
startup-config file. This command is a synonym of the write memory and copy
running-config startup-config commands.
Syntax write [file]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To write configuration data to the start-up configuration file, use the command:
awplus# write file
Related
Commands
copy running-config
write memory
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 133
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
WRITE MEMORY
write memory
Overview This command copies the running-config into the file that is set as the current
startup-config file. This command is a synonym of the write file and copy
running-config startup-config commands.
Syntax write [memory]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To write configuration data to the start-up configuration file, use the command:
awplus# write memory
Related
Commands
copy running-config
write file
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 134
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FILE AND CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
WRITE TERMINAL
write terminal
Overview This command displays the current configuration of the device. This command is a
synonym of the show running-config command.
Syntax write terminal
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of your device, use the command:
awplus# write terminal
Related
Commands
show running-config

3
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 135
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
User Access
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
user access.
Command List •“aaa authentication enable default local” on page 137
•“aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time” on page 138
•“aaa local authentication attempts max-fail” on page 139
•“aaa login fail-delay” on page 140
•“clear aaa local user lockout” on page 141
•“clear line console” on page 142
•“clear line vty” on page 143
•“enable password” on page 144
•“enable secret” on page 147
•“exec-timeout” on page 150
•“flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console)” on page 152
•“length (asyn)” on page 154
•“line” on page 155
•“privilege level” on page 157
•“security-password history” on page 158
•“security-password forced-change” on page 159
•“security-password lifetime” on page 160
•“security-password min-lifetime-enforce” on page 161
•“security-password minimum-categories” on page 162
•“security-password minimum-length” on page 163

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 136
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
•“security-password reject-expired-pwd” on page 164
•“security-password warning” on page 165
•“service advanced-vty” on page 166
•“service password-encryption” on page 167
•“service telnet” on page 168
•“service terminal-length (deleted)” on page 169
•“show aaa local user locked” on page 170
•“show privilege” on page 171
•“show security-password configuration” on page 172
•“show security-password user” on page 173
•“show telnet” on page 174
•“show users” on page 175
•“telnet” on page 176
•“telnet server” on page 177
•“terminal length” on page 178
•“terminal resize” on page 179
•“username” on page 180

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 137
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION ENABLE DEFAULT LOCAL
aaa authentication enable default local
Overview This command enables local privilege level authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to disable local privilege level authentication.
Syntax aaa authentication enable default local
no aaa authentication enable default
Default Local privilege level authentication is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The privilege level configured for a particular user in the local user database is the
privilege threshold above which the user is prompted for an enable (Privileged
Exec mode) command.
Examples To enable local privilege level authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication enable default local
To disable local privilege level authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication enable default
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable password
enable secret

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 138
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
AAA LOCAL AUTHENTICATION ATTEMPTS LOCKOUT-TIME
aaa local authentication attempts
lockout-time
Overview This command configures the duration of the user lockout period.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the duration of the user lockout
period to its default of 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Syntax aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time <lockout-tiime>
no aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
Mode Global Configuration
Default The default for the lockout-time is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Usage While locked out all attempts to login with the locked account will fail. The lockout
can be manually cleared by another privileged account using the clear aaa local
user lockout command.
Examples To configure the lockout period to 10 minutes (600 seconds), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
600
To restore the default lockout period of 5 minutes (300 seconds), use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa local authentication attempts
lockout-time
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Parameter Description
<lockout-time><0-10000>. Time in seconds to lockout the user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 139
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
AAA LOCAL AUTHENTICATION ATTEMPTS MAX-FAIL
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Overview This command configures the maximum number of failed login attempts before a
user account is locked out. Every time a login attempt fails the failed login counter
is incremented.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the maximum number of failed
login attempts to the default setting (five failed login attempts).
Syntax aaa local authentication attempts max-fail <failed-logins>
no aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Mode Global Configuration
Default The default for the maximum number of failed login attempts is five failed login
attempts.
Usage When the failed login counter reaches the limit configured by this command that
user account is locked out for a specified duration configured by the aaa local
authentication attempts lockout-time command.
When a successful login occurs the failed login counter is reset to 0. When a user
account is locked out all attempts to login using that user account will fail.
Examples To configure the number of login failures that will lock out a user account to two
login attempts, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa local authentication attempts max-fail 2
To restore the number of login failures that will lock out a user account to the
default number of login attempts (five login attempts), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
clear aaa local user lockout
Parameter Description
<failed-logins><1-32>. Number of login failures allowed before locking out a
user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 140
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
AAA LOGIN FAIL-DELAY
aaa login fail-delay
Overview Use this command to configure the minimum time period between failed login
attempts. This setting applies to login attempts via the console, SSH and Telnet.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the minimum time period to its default
value.
Syntax aaa login fail-delay <1-10>
no aaa login fail-delay
Default 1 second
Mode Global configuration
Example To apply a delay of at least 5 seconds between login attempts, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa login fail-delay 5
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
clear aaa local user lockout
Parameter Description
<1-10> The minimum number of seconds required between login
attempts

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 141
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
CLEAR AAA LOCAL USER LOCKOUT
clear aaa local user lockout
Overview Use this command to clear the lockout on a specific user account or all user
accounts.
Syntax clear aaa local user lockout {username <username>|all}
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To unlock the user account ‘bob’ use the following command:
awplus# clear aaa local user lockout username bob
To unlock all user accounts use the following command:
awplus# clear aaa local user lockout all
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
Parameter Description
username Clear lockout for the specified user.
<username> Specifies the user account.
all Clear lockout for all user accounts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 142
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
CLEAR LINE CONSOLE
clear line console
Overview This command resets a console line. If a terminal session exists on the line then the
terminal session is terminated. If console line settings have changed then the new
settings are applied.
Syntax clear line console 0
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To reset the console line (asyn), use the command:
awplus# clear line console 0
awplus# % The new settings for console line 0 have been applied
Related
Commands
clear line vty
flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console)
line
show users

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 143
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
CLEAR LINE VTY
clear line vty
Overview This command resets a VTY line. If a session exists on the line then it is closed.
Syntax clear line vty <0-32>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To reset the first VTY line, use the command:
awplus# clear line vty 1
Related
Commands
privilege level
line
show telnet
show users
Parameter Description
<0-32>Line number

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 144
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE PASSWORD
enable password
Overview To set a local password to control access to various privilege levels, use the enable
password Global Configuration command. Use the enable password command to
modify or create a password to be used, and use the no enable password
command to remove the password.
Note that the enable secret command is an alias for the enable password
command, and the no enable secret command is an alias for the no enable
password command. Issuing a no enable password command removes a password
configured with the enable secret command. The enable password command is
shown in the running and startup configurations. Note that if the enable secret
command is entered then enable password is shown in the configuration.
Syntax enable password [<plain>|8 <hidden>|level <1-15> 8 <hidden>]
no enable password [level <1-15>]
Default The privilege level for enable password is level 15 by default. Previously the default
was level 1.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables the Network Administrator to set a password for entering
the Privileged Exec mode when using the enable (Privileged Exec mode)
command. There are three methods to enable a password. In the examples below,
for each method, note that the configuration is different and the configuration file
output is different, but the password string to be used to enter the Privileged Exec
mode with the enable command is the same (mypasswd).
A user can now have an intermediate CLI security level set with this command for
privilege level 7 to access all the show commands in Privileged Exec mode and all
the commands in User Exec mode, but not any configuration commands in
Privileged Exec mode.
Parameter Description
<plain>Specifies the unencrypted password.
8Specifies a hidden password will follow.
<hidden>Specifies the hidden encrypted password. Use an encrypted
password for better security where a password crosses the network
or is stored on a TFTP server.
level Privilege level <1-15>. Level for which the password applies. You can
specify up to 16 privilege levels, using numbers 1 through 15. Level 1
is normal EXEC-mode user privileges for User Exec mode. If this
argument is not specified in the command or the no variant of the
command, the privilege level defaults to 15 (enable mode privileges)
for Privileged Exec mode. A privilege level of 7 can be set for
intermediate CLI security.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 145
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE PASSWORD
Note that the enable password command is an alias for the enable secret
command and one password per privilege level is allowed using these commands.
Do not assign one password to a privilege level with enable password and another
password to a privilege level with enable secret. Use enable password or enable
secret commands. Do not use both on the same level.
Using plain
passwords
The plain password is a clear text string that appears in the configuration file as
configured.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable password mypasswd
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Using encrypted
passwords
You can configure an encrypted password using the service password-encryption
command. First, use the enable password command to specify the string that you
want to use as a password (mypasswd). Then, use the service
password-encryption command to encrypt the specified string (mypasswd). The
advantage of using an encrypted password is that the configuration file does not
show mypasswd, it will only show the encrypted string fU7zHzuutY2SA.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable password mypasswd
awplus(config)# service password-encryption
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Using hidden
passwords
You can configure an encrypted password using the HIDDEN parameter (8) with
the enable password command. Use this method if you already know the
encrypted string corresponding to the plain text string that you want to use as a
password. It is not required to use the service password-encryption command for
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password mypasswd
!
interface lo
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
service password-encryption
!
interface lo
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 146
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE PASSWORD
this method. The output in the configuration file will show only the encrypted
string, and not the text string.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable password 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Related
Commands
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable secret
service password-encryption
privilege level
show privilege
username
show running-config
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
!
interface lo

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 147
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE SECRET
enable secret
Overview To set a local password to control access to various privilege levels, use the enable
secret Global Configuration command. Use the enable secret command to modify
or create a password to be used, and use the no enable secret command to remove
the password.
Note that the enable secret command is an alias for the enable password
command, and the no enable secret command is an alias for the no enable
password command. Issuing a no enable password command removes a password
configured with the enable secret command. The enable password command is
shown in the running and startup configurations. Note that if the enable secret
command is entered then enable password is shown in the configuration
Syntax enable secret [<plain>|8 <hidden>|level <0-15> 8 <hidden>]
no enable secret [level <1-15>]
Default The privilege level for enable secret is level 15 by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables the Network Administrator to set a password for entering
the Privileged Exec mode when using the enable (Privileged Exec mode)
command. There are three methods to enable a password. In the examples below,
for each method, note that the configuration is different and the configuration file
output is different, but the password string to be used to enter the Privileged Exec
mode with the enable command is the same (mypasswd).
A user can have an intermediate CLI security level set with this command for
privilege level 7 to access all the show commands in Privileged Exec mode and all
the commands in User Exec mode, but not any configuration commands in
Privileged Exec mode.
Parameter Description
<plain>Specifies the unencrypted password.
8Specifies a hidden password will follow.
<hidden>Specifies the hidden encrypted password. Use an encrypted
password for better security where a password crosses the network
or is stored on a TFTP server.
level Privilege level <1-15>. Level for which the password applies. You can
specify up to 16 privilege levels, using numbers 1 through 15. Level 1
is normal EXEC-mode user privileges for User Exec mode. If this
argument is not specified in the command or the no variant of the
command, the privilege level defaults to 15 (enable mode privileges)
for Privileged Exec mode. A privilege level of 7 can be set for
intermediate CLI security.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 148
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE SECRET
Note that the enable secret command is an alias for the enable password
command and one password per privilege level is allowed using these commands.
Do not assign one password to a privilege level with enable password and another
password to a privilege level with enable secret. Use enable password or enable
secret commands. Do not use both on the same level.
Using plain
passwords
The plain password is a clear text string that appears in the configuration file as
configured.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable secret mypasswd
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Using encrypted
passwords
Configure an encrypted password using the service password-encryption
command. First, use the enable password command to specify the string that you
want to use as a password (mypasswd). Then, use the service
password-encryption command to encrypt the specified string (mypasswd). The
advantage of using an encrypted password is that the configuration file does not
show mypasswd, it will only show the encrypted string fU7zHzuutY2SA.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable secret mypasswd
awplus(config)# service password-encryption
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Using hidden
passwords
Configure an encrypted password using the HIDDEN parameter (8) with the
enable password command. Use this method if you already know the encrypted
string corresponding to the plain text string that you want to use as a password. It
is not required to use the service password-encryption command for this method.
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password mypasswd
!
interface lo
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
service password-encryption
!
interface lo
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 149
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
ENABLE SECRET
The output in the configuration file will show only the encrypted string, and not
the text string:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# enable secret 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
awplus(config)# end
This results in the following show output:
Related
Commands
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable secret
service password-encryption
privilege level
show privilege
username
show running-config
awplus#show run
Current configuration:
hostname awplus
enable password 8 fU7zHzuutY2SA
!
interface lo

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 150
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
EXEC-TIMEOUT
exec-timeout
Overview This command sets the interval your device waits for user input from either a
console or VTY connection. Once the timeout interval is reached, the connection is
dropped. This command sets the time limit when the console or VTY connection
automatically logs off after no activity.
The no variant of this command removes a specified timeout and resets to the
default timeout (10 minutes).
Syntax exec-timeout {<minutes>} [<seconds>]
no exec-timeout
Default The default for the exec-timeout command is 10 minutes and 0 seconds
(exec-timeout 10 0).
Mode Line Configuration
Usage This command is used set the time the telnet session waits for an idle VTY session,
before it times out. An exec-timeout 0 0 setting will cause the telnet session to
wait indefinitely. The command exec-timeout 0 0 is useful while configuring a
device, but reduces device security.
If no input is detected during the interval then the current connection resumes. If
no connections exist then the terminal returns to an idle state and disconnects
incoming sessions.
Examples To set VTY connections to timeout after 2 minutes, 30 seconds if there is no
response from the user, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 32
awplus(config-line)# exec-timeout 2 30
To reset the console connection to the default timeout of 10 minutes 0 seconds if
there is no response from the user, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# no exec-timeout
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Parameter Description
<minutes> <0-35791> Required integer timeout value in minutes
<seconds> <0-2147483> Optional integer timeout value in seconds
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 152
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
FLOWCONTROL HARDWARE (ASYN/CONSOLE)
flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console)
Overview Use this command to enable RTS/CTS (Ready To Send/Clear To Send) hardware
flow control on a terminal console line (asyn port) between the DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment) and the DCE (Data Communications Equipment).
Syntax flowcontrol hardware
no flowcontrol hardware
Mode Line Configuration
Default Hardware flow control is disabled by default.
Usage Hardware flow control makes use of the RTS and CTS control signals between the
DTE and DCE where the rate of transmitted data is faster than the rate of received
data. Flow control is a technique for ensuring that a transmitting entity does not
overwhelm a receiving entity with data. When the buffers on the receiving device
are full, a message is sent to the sending device to suspend the transmission until
the data in the buffers has been processed.
Hardware flow control can be configured on terminal console lines (e.g. asyn0). For
Reverse Telnet connections, hardware flow control must be configured to match
on both the Access Server and the Remote Device. For terminal console sessions,
hardware flow control must be configured to match on both the DTE and the DCE.
Settings are saved in the running configuration. Changes are applied after reboot,
clear line console, or after closing the session.
Use show running-config and show startup-config commands to view hardware
flow control settings that take effect after reboot for a terminal console line. See
the show running-config command output:
Note that line configuration commands do not take effect immediately. Line
configuration commands take effect after one of the following commands or
events:
•issuing a clear line console command
•issuing a reboot command
• logging out of the current session
awplus#show running-config
!
line con 1
speed 9600
mode out 2001
flowcontrol hardware
!

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 153
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
FLOWCONTROL HARDWARE (ASYN/CONSOLE)
Examples To enable hardware flow control on terminal console line asyn0, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# flowcontrol hardware
To disable hardware flow control on terminal console line asyn0, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# no flowcontrol hardware
Related
Commands
clear line console
show running-config
speed (asyn)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 154
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
LENGTH (ASYN)
length (asyn)
Overview Use this command to specify the number of rows of output that the device will
display before pausing, for the console or VTY line that you are configuring.
The no variant of this command restores the length of a line (terminal session)
attached to a console port or to a VTY to its default length of 22 rows.
Syntax length <0-512>
no length
Mode Line Configuration
Default The length of a terminal session is 22 rows. The no length command restores the
default.
Usage If the output from a command is longer than the length of the line the output will
be paused and the ‘–More–’ prompt allows you to move to the next screen full of
data.
A length of 0 will turn off pausing and data will be displayed to the console as long
as there is data to display.
Examples To set the terminal session length on the console to 10 rows, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# length 10
To reset the terminal session length on the console to the default (22 rows), use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# no length
To display output to the console continuously, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# length 0
Related
Commands
terminal resize
terminal length
Parameter Description
<0-512> Number of lines on screen. Specify 0 for no pausing.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 155
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
LINE
line
Overview Use this command to enter line configuration mode for the specified VTYs or the
console. The command prompt changes to show that the device is in Line
Configuration mode.
Syntax line vty <first-line> [<last-line>]
line console 0
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command puts you into Line Configuration mode. Once in Line Configuration
mode, you can configure console and virtual terminal settings, including setting
speed (asyn), length (asyn), privilege level, and authentication (login
authentication) or accounting (accounting login) method lists.
To change the console (asyn) port speed, use this line command to enter Line
Configuration mode before using the speed (asyn)command. Set the console
speed (Baud rate) to match the transmission rate of the device connected to the
console (asyn) port on your device.
Note that line configuration commands do not take effect immediately. Line
configuration commands take effect after one of the following commands or
events:
•issuing a clear line console command
•issuing a reboot command
• logging out of the current session
Examples To enter Line Configuration mode in order to configure all VTYs, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 32
awplus(config-line)#
Parameter Description
<first-line> <0-32> Specify the first line number.
<last-line> <0-32> Specify the last line number.
console The console terminal line(s) for local access.
vty Virtual terminal for remote console access.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 156
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
LINE
To enter Line Configuration mode to configure the console (asyn 0) port terminal
line, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)#
Related
Commands
accounting login
clear line console
clear line vty
flowcontrol hardware (asyn/console)
length (asyn)
login authentication
privilege level
speed (asyn)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 157
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
PRIVILEGE LEVEL
privilege level
Overview This command sets a privilege level for VTY or console connections. The
configured privilege level from this command overrides a specific user’s initial
privilege level at the console login.
Syntax privilege level <1-15>
Mode Line Configuration
Usage You can set an intermediate CLI security level for a console user with this command
by applying privilege level 7 to access all show commands in Privileged Exec and
all User Exec commands. However, intermediate CLI security will not show
configuration commands in Privileged Exec.
Examples To set the console connection to have the maximum privilege level, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# privilege level 15
To set all VTY connections to have the minimum privilege level, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# privilege level 1
To set all VTY connections to have an intermediate CLI security level, to access all
show commands, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# privilege level 7
Related
Commands
enable password
line
show privilege
username
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 158
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD HISTORY
security-password history
Overview This command specifies the number of previous passwords that are unable to be
reused. A new password is invalid if it matches a password retained in the
password history.
The no variant of the command disables this feature.
Syntax security-password history <0-15>
no security-password history
Default The default history value is 0, which will disable the history functionality.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To restrict reuse of the three most recent passwords, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password history 3
To allow the reuse of recent passwords, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no security-password history
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Parameter Description
<0-15> The allowable range of previous passwords to match against. A
value of 0 will disable the history functionality and is equivalent to
the no security-password history command. If the history
functionality is disabled, all users’ password history is reset and all
password history is lost.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 159
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD FORCED-CHANGE
security-password forced-change
Overview This command specifies whether or not a user is forced to change an expired
password at the next login. If this feature is enabled, users whose passwords have
expired are forced to change to a password that must comply with the current
password security rules at the next login.
Note that to use this command, the lifetime feature must be enabled with the
security-password lifetime command and the reject-expired-pwd feature must be
disabled with the security-password reject-expired-pwd command.
The no variant of the command disables this feature.
Syntax security-password forced-change
no security-password forced-change
Default The forced-change feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To force a user to change their expired password at the next login, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password forced-change
Related
Commands
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 160
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD LIFETIME
security-password lifetime
Overview This command enables password expiry by specifying a password lifetime in days.
Note that when the password lifetime feature is disabled, it also disables the
security-password forced-change command and the security-password warning
command.
The no variant of the command disables this feature.
Syntax security-password lifetime <0-1000>
no security-password lifetime
Default The default password lifetime is 0, which will disable the lifetime functionality.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure the password lifetime to 10 days, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password lifetime 10
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Parameter Description
<0-1000> Password lifetime specified in days. A value of 0 will disable lifetime
functionality and the password will never expire. This is equivalent
to the no security-password lifetime command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 161
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD MIN-LIFETIME-ENFORCE
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
Overview Use this command to configure a minimum number of days before a password can
be changed by a user. With this feature enabled, once a user sets the password, the
user cannot change it again until the minimum lifetime has passed.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the minimum lifetime.
Syntax security-password min-lifetime-enforce <0-1000>
no security-password min-lifetime-enforce
Default By default, no minimum lifetime is enforced.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The minimum lifetime is helpful in conjunction with a security policy that prevents
people from re-using old passwords. For example, if you do not allow people to
re-use any of their last 5 passwords, a person can bypass that restriction by
changing their password 5 times in quick succession and then re-setting it to their
previous password. The minimum lifetime prevents that by preventing people
from changing their password in quick succession.
Example To force users to wait at least 2 days between changing passwords, use the
command:
awplus(config)# security-password min-lifetime-enforce 2
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.2: command added
Parameter Description
<0-1000> The minimum number of days before a password can be changed
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 162
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD MINIMUM-CATEGORIES
security-password minimum-categories
Overview This command specifies the minimum number of categories that the password
must contain in order to be considered valid. The password categories are:
• uppercase letters: A to Z
• lowercase letters: a to z
• digits: 0 to 9
• special symbols: all printable ASCII characters not included in the previous
three categories. The question mark (?) cannot be used as it is reserved for
help functionality.
Note that to ensure password security, the minimum number of categories should
align with the lifetime selected, i.e. the fewer categories specified the shorter the
lifetime specified.
Syntax security-password minimum-categories <1-4>
Default The default number of categories that the password must satisfy is 1.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure the required minimum number of character categories to be 3, use
the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password minimum-categories 3
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Parameter Description
<1-4> Number of categories the password must satisfy, in the range 1 to 4.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 163
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD MINIMUM-LENGTH
security-password minimum-length
Overview This command specifies the minimum allowable password length. This value is
checked against when there is a password change or a user account is created.
Syntax security-password minimum-length <1-23>
Default The default minimum password length is 1.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure the required minimum password length as 8, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password minimum-length 8
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Parameter Description
<1-23> Minimum password length in the range from 1 to 23.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 164
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD REJECT-EXPIRED-PWD
security-password reject-expired-pwd
Overview This command specifies whether or not a user is allowed to login with an expired
password. Users with expired passwords are rejected at login if this functionality is
enabled. Users then have to contact the Network Administrator to change their
password.
CAUTION: Once all users’ passwords are expired you are unable to login to the device
again if the security-password reject-expired-pwd command has been executed. You
will have to reboot the device with a default configuration file, or load an earlier
software version that does not have the security password feature.
We recommend you never have the command line “security-password
reject-expired-pwd” in a default config file.
Note that when the reject-expired-pwd functionality is disabled and a user logs on
with an expired password, if the forced-change feature is enabled with
security-password forced-change command, a user may have to change the
password during login depending on the password lifetime specified by the
security-password lifetime command.
The no variant of the command disables this feature.
Syntax security-password reject-expired-pwd
no security-password reject-expired-pwd
Default The reject-expired-pwd feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure the system to reject users with an expired password, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password reject-expired-pwd
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password warning
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 165
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SECURITY-PASSWORD WARNING
security-password warning
Overview This command specifies the number of days before the password expires that the
user will receive a warning message specifying the remaining lifetime of the
password.
Note that the warning period cannot be set unless the lifetime feature is enabled
with the security-password lifetime command.
The no variant of the command disables this feature.
Syntax security-password warning <0-1000>
no security-password warning
Default The default warning period is 0, which disables warning functionality.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure a warning period of three days, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# security-password warning 3
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
show running-config security-password
show security-password configuration
show security-password user
Parameter Description
<0-1000> Warning period in the range from 0 to 1000 days. A value 0 disables
the warning functionality and no warning message is displayed for
expiring passwords. This is equivalent to the no security-password
warning command. The warning period must be less than, or equal
to, the password lifetime set with the security-password lifetime
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 166
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SERVICE ADVANCED-VTY
service advanced-vty
Overview This command enables the advanced-vty help feature. This allows you to use TAB
completion for commands. Where multiple options are possible, the help feature
displays the possible options.
The no service advanced-vty command disables the advanced-vty help feature.
Syntax service advanced-vty
no service advanced-vty
Default The advanced-vty help feature is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To disable the advanced-vty help feature, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service advanced-vty
To re-enable the advanced-vty help feature after it has been disabled, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service advanced-vty

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 167
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SERVICE PASSWORD-ENCRYPTION
service password-encryption
Overview Use this command to enable password encryption. This is enabled by default.
When password encryption is enabled, the device displays passwords in the
running config in encrypted form instead of in plain text.
Use the no service password-encryption command to stop the device from
displaying newly-entered passwords in encrypted form. This does not change the
display of existing passwords.
Syntax service password-encryption
no service password-encryption
Mode Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service password-encryption
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Related
Commands
enable password

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 168
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SERVICE TELNET
service telnet
Overview Use this command to enable the telnet server. The server is enabled by default.
Enabling the telnet server starts the device listening for incoming telnet sessions
on the configured port.
The server listens on port 23, unless you have changed the port by using the
privilege level command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the telnet server. Disabling the
telnet server will stop the device listening for new incoming telnet sessions.
However, existing telnet sessions will still be active.
Syntax service telnet [ip|ipv6]
no service telnet [ip|ipv6]
Default The IPv4 and IPv6 telnet servers are enabled by default.
The configured telnet port is TCP port 23 by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable both the IPv4 and IPv6 telnet servers, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service telnet
To enable the IPv6 telnet server only, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service telnet ipv6
To disable both the IPv4 and IPv6 telnet servers, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service telnet
To disable the IPv6 telnet server only, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service telnet ipv6
Related
Commands
clear line vty
show telnet
telnet server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 169
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SERVICE TERMINAL-LENGTH (DELETED)
service terminal-length (deleted)
Overview This command has been deleted in Software Version 5.4.5-0.1 and later.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 170
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW AAA LOCAL USER LOCKED
show aaa local user locked
Overview This command displays the current number of failed attempts, last failure time and
location against each user account attempting to log into the device.
Note that once the lockout count has been manually cleared by another privileged
account using the clear aaa local user lockout command or a locked account
successfully logs into the system after waiting for the lockout time, this command
will display nothing for that particular account.
Syntax show aaa local user locked
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current failed attempts for local users, use the command:
awplus# show aaa local user locked
Output Figure 3-1: Example output from the show aaa local user locked command
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
clear aaa local user lockout
awplus# show aaa local user locked
Login Failures Latest failure From
bob 3 05/23/14 16:21:37 ttyS0
manager 5 05/23/14 16:31:44 192.168.1.200
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 171
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW PRIVILEGE
show privilege
Overview This command displays the current user privilege level, which can be any privilege
level in the range <1-15>. Privilege levels <1-6> allow limited user access (all User
Exec commands), privilege levels <7-14> allow restricted user access (all User Exec
commands plus Privileged Exec show commands). Privilege level 15 gives full user
access to all Privileged Exec commands.
Syntax show privilege
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage A user can have an intermediate CLI security level set with this command for
privilege levels <7-14> to access all show commands in Privileged Exec mode and
all commands in User Exec mode, but no configuration commands in Privileged
Exec mode.
Example To show the current privilege level of the user, use the command:
awplus# show privilege
Output Figure 3-2: Example output from the show privilege command
Related
Commands
privilege level
awplus#show privilege
Current privilege level is 15
awplus#disable
awplus>show privilege
Current privilege level is 1
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 172
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW SECURITY-PASSWORD CONFIGURATION
show security-password configuration
Overview This command displays the configuration settings for the various security
password rules.
Syntax show security-password configuration
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the current security-password rule configuration settings, use the
command:
awplus# show security-password configuration
Output Figure 3-3: Example output from the show security-password configuration
command
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show security-password user
Security Password Configuration
Minimum password length ............................ 8
Minimum password character categories to match ..... 3
Number of previously used passwords to restrict..... 4
Password lifetime .................................. 30 day(s)
Warning period before password expires ........... 3 day(s)
Reject expired password at login ................... Disabled
Force changing expired password at login ......... Enabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 173
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW SECURITY-PASSWORD USER
show security-password user
Overview This command displays user account and password information for all users.
Syntax show security-password user
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the system users’ remaining lifetime or last password change, use the
command:
awplus# show security-password user
Output Figure 3-4: Example output from the show security-password user command
Related
Commands
security-password forced-change
security-password history
security-password lifetime
security-password min-lifetime-enforce
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length
security-password reject-expired-pwd
security-password warning
show security-password configuration
User account and password information
UserName Privilege Last-PWD-Change Remaining-lifetime
----------------------------------------------------------------
manager 15 4625 day(s) ago No Expiry
bob15 15 0 day(s) ago 30 days
ted7 7 0 day(s) ago No Expiry
mike1 1 0 day(s) ago No Expiry
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 174
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW TELNET
show telnet
Overview This command shows the Telnet server settings.
Syntax show telnet
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the Telnet server settings, use the command:
awplus# show telnet
Output Figure 3-5: Example output from the show telnet command
Related
Commands
clear line vty
service telnet
show users
telnet server
Telnet Server Configuration
------------------------------------------------------------
Telnet server : Enabled
Protocol : IPv4,IPv6
Port : 23

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 175
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
SHOW USERS
show users
Overview This command shows information about the users who are currently logged into
the device.
Syntax show users
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the users currently connected to the device, use the command:
awplus# show users
Output Figure 3-6: Example output from the show users command
Line User Host(s) Idle Location Priv Idletime Timeout
con 0 manager idle 00:00:00 ttyS0 15 10 N/A
vty 0 bob idle 00:00:03 172.16.11.3 1 0 5
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show users command
Parameter Description
Line Console port user is connected to.
User Login name of user.
Host(s) Status of the host the user is connected to.
Idle How long the host has been idle.
Location URL location of user.
Priv The privilege level in the range 1 to 15, with 15 being the highest.
Idletime The time interval the device waits for user input from either a
console or VTY connection.
Timeout The time interval before a server is considered unreachable.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 176
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
TELNET
telnet
Overview Use this command to open a telnet session to a remote device.
Syntax telnet {<hostname>|[ip] <ipv4-addr>|[ipv6] <ipv6-addr>}
[<port>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To connect to TCP port 2602 on the device at 10.2.2.2, use the command:
awplus# telnet 10.2.2.2 2602
To connect to the telnet server host.example, use the command:
awplus# telnet host.example
To connect to the telnet server host.example on TCP port 100, use the
command:
awplus# telnet host.example 100
Parameter Description
<hostname>The host name of the remote system.
ip Keyword used to specify the IPv4 address or host name of a remote
system.
<ipv4-addr> An IPv4 address of the remote system.
ipv6 Keyword used to specify the IPv6 address of a remote system
<ipv6-addr> Placeholder for an IPv6 address in the format x:x::x:x, for
example, 2001:db8::8a2e:7334
<port>Specify a TCP port number (well known ports are in the range 1-
1023, registered ports are 1024-49151, and private ports are 49152-
65535).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 177
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
TELNET SERVER
telnet server
Overview This command enables the telnet server on the specified TCP port. If the server is
already enabled then it will be restarted on the new port. Changing the port
number does not affect the port used by existing sessions.
Syntax telnet server {<1-65535>|default}
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the telnet server on TCP port 2323, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# telnet server 2323
Related
Commands
show telnet
Parameter Description
<1-65535> The TCP port to listen on.
default Use the default TCP port number 23.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 178
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
TERMINAL LENGTH
terminal length
Overview Use the terminal length command to specify the number of rows of output that
the device will display before pausing, for the currently-active terminal only.
Use the terminal no length command to remove the length specified by this
command. The default length will apply unless you have changed the length for
some or all lines by using the length (asyn) command.
Syntax terminal length <length>
terminal no length [<length>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples The following example sets the number of lines to 15:
awplus# terminal length 15
The following example removes terminal length set previously:
awplus# terminal no length
Related
Commands
terminal resize
length (asyn)
Parameter Description
<length><0-512> Number of rows that the device will display on the
currently-active terminal before pausing.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 179
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
TERMINAL RESIZE
terminal resize
Overview Use this command to automatically adjust the number of rows of output on the
console, which the device will display before pausing, to the number of rows
configured on the user’s terminal.
Syntax terminal resize
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage When the user’s terminal size is changed, then a remote session via SSH or TELNET
adjusts the terminal size automatically. However, this cannot normally be done
automatically for a serial or console port. This command automatically adjusts the
terminal size for a serial or console port.
Examples The following example automatically adjusts the number of rows shown on the
console:
awplus# terminal resize
Related
Commands
length (asyn)
terminal length

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 180
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
USERNAME
username
Overview This command creates or modifies a user to assign a privilege level and a password.
NOTE: The default username privilege level of 1 is not shown in running-config output.
Any username privilege level that has been modified from the default is shown.
Syntax username <name> privilege <1-15> [password [8] <password>]
username <name> password [8] <password>
no username <name>
Mode Global Configuration
Default The privilege level is 1 by default. Note the default is not shown in running-config
output.
Parameter Description
<name>The login name for the user. Do not use punctuation marks such as single quotes (‘ ‘),
double quotes (“ “), or colons ( : ) with the user login name.
privilege The user’s privilege level. Use the privilege levels to set the access rights for each user.
<1-15> A privilege level: either 1-14 (limited access) or 15 (full access). A user
with privilege level 1-14 can only access higher privilege levels if an
enable password has been configured for the level the user tries to
access and the user enters that password.
A user at privilege level 1 can access the majority of show
commands. A user at privilege level 7 can access the majority of
show commands including platform show commands. Privilege
Level 15 (to access the Privileged Exec command mode) is required
to access configuration commands as well as show commands in
Privileged Exec.
password A password that the user must enter when logging in.
8Specifies that you are entering a password as a string that has
already been encrypted, instead of entering a plain-text password.
The running-config displays the new password as an encrypted
string even if password encryption is turned off.
Note that the user enters the plain-text version of the password
when logging in.
<password>The user’s password. The password can be up to 23 characters in
length and include characters from up to four categories. The
password categories are:
• uppercase letters: A to Z
• lowercase letters: a to z
• digits: 0 to 9
• special symbols: all printable ASCII characters not included in the
previous three categories. The question mark ? cannot be used as
it is reserved for help functionality.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 181
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
USER ACCESS COMMANDS
USERNAME
Usage An intermediate CLI security level (privilege level 7 to privilege level 14) allows a
CLI user access to the majority of show commands, including the platform show
commands that are available at privilege level 1 to privilege level 6. Note that some
show commands, such as show running-configuration and show
startup-configuration, are only available at privilege level 15.
Examples To create the user “bob” with a privilege level of 15, for all show commands
including show running-configuration and show startup-configuration and to
access configuration commands in Privileged Exec command mode, and the
password “bobs_secret”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# username bob privilege 15 password bobs_secret
To create a user “junior_admin” with a privilege level of 7, which will have
intermediate CLI security level access for most show commands, and the password
“show_only”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# username junior_admin privilege 7 password
show_only
Related
Commands
enable password
security-password minimum-categories
security-password minimum-length

4
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 182
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Feature Licensing
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for each of the Feature Licensing
commands. Feature Licensing enables you to use advanced features such as Layer
3 routing.
To see which Feature Licenses are available for your device, see the AlliedWare Plus
Datasheet.
With Software Version 5.4.6-1.x and later, new installations of Allied Telesis
Management Framework (AMF) require a Subscription License instead of a Feature
License. For information about Subscription Licensing commands, see the
Subscription Licensing Commands chapter.
Note that AMF Feature Licenses purchased prior to 5.4.6-1.x will still operate with
5.4.6-x.x and later software versions.
For step-by-step instructions about how to license AlliedWare Plus devices, see the
Licensing Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
Command List •“license” on page 183
•“show license” on page 185
•“show license brief” on page 187

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 183
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FEATURE LICENSING COMMANDS
LICENSE
license
Overview This command activates the licensed software feature set on a device.
Use the no variant of this command to deactivate the licensed software feature set
on a device.
For feature licenses, contact your authorized distributor or reseller. If a license key
expires or is incorrect so the license key is invalid, then some software features will
be unavailable.
NOTE: See the AlliedWare Plus™ datasheet for a list of current feature licenses available
by product. Purchase licenses from your authorized dealer or reseller.
In a live network, only install feature licenses during scheduled maintenance.
Syntax license <label> <key>
no license <label>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You can change the license label using this command to make it specific to you
when you initially add a license. Once a license is added, any change to the license
label first requires removal of the license before adding a license again with a new
license label.
The default feature license labels are issued along with encrypted license keys by
e-mail for you to apply using this command to activate features. You can change
default feature license labels, but they must be 15 characters or less.
For example, you may want to change the label of the premium license to
“premium-license”. You can check your new license label by using the show license
command.
If you add a feature license you will be prompted at the console that the feature
needs to restart. Restarting of individual protocols in this manner could result in
the loss of network traffic. Only install licenses in scheduled maintenance periods
for devices in a live environment.
Examples To activate the license called “Premium” that has the key
12345678ABCDE123456789ABCDE, use the command:
awplus# license Premium 12345678ABCDE123456789ABCDE
Parameter Description
<label> A name for the feature license. To determine names already in
use, use the show license command. This can be the default
name supplied for the feature, or a renamed feature name.
<key> The encrypted license key to enable a set of software features.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 185
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FEATURE LICENSING COMMANDS
SHOW LICENSE
show license
Overview This command displays information about a specific software feature license, or all
enabled software feature licenses on the device.
Syntax show license [feature] [<label>|index <index-number>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display full information about all enabled licenses, use the command:
awplus# show license
To display full information about the licenses with index number 1, use the
command:
awplus# show license index 1
Output Figure 4-1: Example output from show license
Parameter Description
feature Only display license information for any applied feature licenses.
<label>The license name to show information about. This can be used
instead of the index number to identify a specific license.
index
<index-number>The index number of the license to show information about. This
can be used instead of the license name to identify a specific
license.
awplus#show license
Board region: Global
Software Licenses
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index : 1
License name : Base License
Customer name : Base License
Quantity of licenses : 1
Type of license : Full
License issue date : 20-Mar-2019
License expiry date : N/A
Features included : IPv6Basic, LAG-FULL, MLDSnoop, RADIUS-100, ...
Table 4-1: Parameters in the output of show license
Parameter Description
Board region Name of the region for the Base License features.
Index Index identifying entry. The index is assigned
automatically by the software. It is not configured.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 186
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FEATURE LICENSING COMMANDS
SHOW LICENSE
Related
Commands
license
show license brief
License name Name of the license key bundle (case-sensitive).
Customer name Customer name.
Quantity of licenses Quantity of licensed installations.
Type of license Full or Trial.
License issue date Date the license was generated.
License expiry date Expiry date for trial license.
Features included List of features included in the feature license.
Table 4-1: Parameters in the output of show license (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 187
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FEATURE LICENSING COMMANDS
SHOW LICENSE BRIEF
show license brief
Overview This command displays information about a specific software feature license, or all
enabled software feature licenses on the device.
Syntax show license brief
show license [feature] [<label>|index <index-number>] brief
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display a brief summary of information about all licenses, use the command:
awplus# show license brief
Output Figure 4-2: Example output from show license brief
Parameter Description
feature Only display license information for any applied feature licenses.
<label>The license name to show information about. This can be used
instead of the index number to identify a specific license.
index
<index-number>The index number of the license to show information about. This
can be used instead of the license name to identify a specific
license.
brief Displays a brief summary of license information.
awplus#show license brief
Board region: Global
Software Licenses
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index License name Quantity Customer name
Type Version Period
------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Base License 1 Base License
Full N/A
Current enabled features for displayed licenses:
IPv6Basic, LAG-FULL, MLDSnoop ...
Table 4-2: Parameters in the output of show license brief
Parameter Description
Board region Name of the region for the Base License features.
Index Index identifying entry. The index is assigned
automatically by the software. It is not configured.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 188
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
FEATURE LICENSING COMMANDS
SHOW LICENSE BRIEF
Related
Commands
license
show license
License name Name of the license key bundle (case-sensitive).
Quantity Quantity of licensed installations.
Customer name Customer name.
Type Full or Trial.
Period Expiry date for trial license.
Current enabled features for
displayed licenses
List of features included in the license.
Table 4-2: Parameters in the output of show license brief (cont.)
Parameter Description

5
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 189
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Subscription
Licensing
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for each of the Subscription
Licensing commands.
Subscription Licensing enables you to use OpenFlow. To see the OpenFlow
subscriptions for your device, see the AlliedWare Plus Datasheet.
For step-by-step instructions about how to license AlliedWare Plus devices, see the
Licensing Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“license update (filename)” on page 190
•“license update online” on page 191
•“show license external” on page 192

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 190
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SUBSCRIPTION LICENSING COMMANDS
LICENSE UPDATE (FILENAME)
license update (filename)
Overview Use this command to load a license, after you have manually copied the license file
onto the device.
Only use this command if you cannot directly access the Allied Telesis Download
Center from this device. Otherwise, use the command license update online
instead.
Syntax license update <filename>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You can download subscription licenses from the Allied Telesis Download Center,
in order to copy them onto the device.
Examples To load a license onto a device from a file called “license_file.bin” that is stored at
the top level of Flash memory, use the following command:
awplus#license update license_file.bin
Related
Commands
license update online
show license external
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: usage changed by introduction of license update online
Parameter Description
<filename>Name and path of the license file on the device.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 191
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SUBSCRIPTION LICENSING COMMANDS
LICENSE UPDATE ONLINE
license update online
Overview Use this command to add or update subscription licenses from the Allied Telesis
Download Center, to subscribe to features such as OpenFlow.
When you enter this command, the device will:
1) Connect to the Download Center
2) Check if new or changed licenses are available for the device, keyed to the
device’s serial number
3) For each such license it finds, download and install the license.
Syntax license update online
Default AlliedWare Plus devices do not automatically connect to the Download Center and
check whether licenses are available. They only check when you run the license
update online command.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage Verifying the update
The update process normally takes approximately 5 seconds.
If the console does not respond for 10 or more seconds after typing the command,
a network, routing or firewall configuration error is probably preventing the
connection from establishing. If this happens, you can abort the command by
pressing Ctrl-C, or wait for the command to time out after 30 seconds.
If the connection to the Download Centers fails and times out, an error message
will be generated on the CLI to indicate the problem. If you abort the command,
no error message is displayed.
If the update is successful, the device will produce log messages to say which
features have had their licensing state updated (activated, deactivated, number of
items changed, or expiry date changed). If the command completes successfully
but there are no licenses available for the device, or no change in the licenses
already on the device, no log messages will be produced.
You should also use the show license external command to confirm which licenses
are active on the device after the update has been applied.
Example To add a subscription license, use the command:
awplus# license update online
Related
Commands
show license external
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 192
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SUBSCRIPTION LICENSING COMMANDS
SHOW LICENSE EXTERNAL
show license external
Overview Use this command to show information about subscription (external) licenses.
Syntax show license external
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To show information about what subscription features the device is licensed for,
use the following command:
awplus#show license external
Output Figure 5-1: Example output from show license external
Related
Commands
license update online
awplus#show license external
Features with installed entitlements:
OpenFlow
Currently licensed: Yes
Start date: 19 Sep 2016 00:00
Expiry date: 19 Sep 2017 23:59

6
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 193
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
the GUI.
For more information, see Getting Started with the Device GUI on Switches.
Command List •“atmf topology-gui enable” on page 194
•“gui-timeout” on page 195
•“http port” on page 196
•“http secure-port” on page 197
•“log event-host” on page 198
•“service http” on page 199
•“show http” on page 200

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 194
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
ATMF TOPOLOGY-GUI ENABLE
atmf topology-gui enable
Overview Use this command to enable the operation of Vista Manager EX on the Master
device.
Vista Manager EX delivers state-of-the-art monitoring and management for your
Autonomous Management Framework™ (AMF) network, by automatically creating
a complete topology map of switches, firewalls and wireless access points (APs).
An expanded view includes third-party devices such as security cameras.
Use the no variant of this command to disable operation of Vista Manager EX.
Syntax atmf topology-gui enable
no atmf topology-gui enable
Default Disabled by default on AMF Master and member nodes. Enabled by default on
Controllers.
Mode Global Configuration mode
Usage To use Vista Manager EX, you must also enable the HTTP service on all AMF nodes,
including all AMF masters and controllers. The HTTP service is enabled by default
on AlliedWare Plus switches and disabled by default on AR-Series firewalls. To
enable it, use the commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# service http
On one master in each AMF area in your network, you also need to configure the
master to send event notifications to Vista Manager EX. To do this, use the
commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# log event-host <ip-address> atmf-topology-event
Example To enable Vista Manager EX on Node1, use the following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# atmf topology-gui enable
To disable Vista Manager EX on Node1, use the following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# no atmf topology-gui enable
Related
Commands
atmf enable
gui-timeout
log event-host
service http
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 195
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
GUI-TIMEOUT
gui-timeout
Overview Use this command to configure an idle timeout period for a GUI session. The time
can be set in minutes and/or seconds.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the GUI session idle timeout.
Syntax gui-timeout <minutes> [<seconds>]
no gui-timeout
Default Disabled
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The GUI uses the configured timeout period (set in either minutes and/or seconds)
to determine when a GUI session should be closed. Once the GUI timeout has
expired, you will need to login to reactivate your session.
To enter seconds only, enter 0 for minutes, followed by a space, and then enter the
seconds.
If the GUI timeout is disabled, a GUI session will remain active until you terminate
it. No idle time will be configured.
The same timeout period will apply to all GUI sessions logged into a specific device.
Examples Use this command to configure the GUI timeout period for 3 minutes and 30
seconds for a GUI session.
awplus# gui-timeout 3 30
Use this command to configure the GUI timeout period for 0 minutes and 61
seconds for a GUI session.
awplus# gui-timeout 0 61
Use this command to disable the GUI timeout period.
awplus# no gui-timeout
Output Figure 6-1: Example output from gui-timeout
Related
Commands
show running-config
Parameter Description
<minutes> Specifies the idle time in minutes from 0 through 35791
<seconds> Specifies the idle time in seconds from 0 through 2147483
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#gui-timeout 3 30
The new gui-timeout settings [3 min 30 sec] will apply to new sessions only
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 196
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
HTTP PORT
http port
Overview Use this command to change the HTTP port used to access the web-based device
GUI, or to disable HTTP management.
Use the no variant of this command to return to using the default port, which is 80.
Syntax http port {<1-65535>|none}
no http port
Default The default port for accessing the GUI is port 80.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Do not configure the HTTP port to be the same as the HTTPS port.
Note that the device will redirect from HTTP to HTTPS unless you have disabled
HTTPS access, which we do not recommend doing.
Example To set the port to 8080, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# http port 8080
To return to using the default port of 80, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no http port
To stop users from accessing the GUI via HTTP, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# http port none
Related
Commands
http secure-port
service http
show http
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.4: command added on AR-Series devices
Version 5.4.8-0.2: command added on AlliedWare Plus switches
Parameter Description
<1-65535> The HTTP port number
none Disable HTTP management. You may want to do this if you need
to use port 80 for a different service or you do not need to use
HTTP at all.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 197
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
HTTP SECURE-PORT
http secure-port
Overview Use this command to change the HTTPS port used to access the web-based device
GUI, or to disable HTTPS management.
Use the no variant of this command to return to using the default port, which is
443.
Syntax http secure-port {<1-65535>|none}
no http secure-port
Default The default port for accessing the GUI is port 443.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Do not configure the HTTPS port to be the same as the HTTP port.
Note that if you are using Vista Manager EX and need to change the HTTPS port,
you must use certificate-based authorization in Vista Manager EX. See the Vista
Manager EX Installation and User Guide for instructions.
Example To set the port to 8443, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# http secure-port 8443
To return to using the default port of 443, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no http secure-port
To stop users from accessing the GUI via HTTPS, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# http secure-port none
Related
Commands
http port
service http
show http
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added on AR-Series devices
Version 5.4.7-2.4: none parameter added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: command added on AlliedWare Plus switches
Parameter Description
<1-65535> The HTTPS port number
none Disable HTTPS management. Do not do this if you want to use
Vista Manager EX or the GUI.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 198
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
LOG EVENT-HOST
log event-host
Overview Use this command to set up an external host to log AMF topology events through
Vista Manager. This command is run on the Master device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable log events through Vista Manager.
Syntax log event-host [<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>] atmf-topology-event
no log event-host [<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>] atmf-topology-event
Default Log events are disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Event hosts are set so syslog sends the messages out as they come.
Note that there is a difference between log event and log host messages:
• Log event messages are sent out as they come by syslog
• Log host messages are set to wait for a number of messages (20) to send
them out together for traffic optimization.
Example To enable Node 1 to log event messages from host IP address 192.0.2.31, use the
following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# log event-host 192.0.2.31 atmf-topology-event
To disable Node 1 to log event messages from host IP address 192.0.2.31, use the
following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# no log event-host 192.0.2.31 atmf-topology-event
Related
Commands
atmf topology-gui enable
Parameter Description
<ipv4-addr> ipv4 address of the event host
<ipv6-addr> ipv6 address of the event host

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 199
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
SERVICE HTTP
service http
Overview Use this command to enable the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) service.
This service is required to support Vista Manager EX™ and the device GUI.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the HTTP feature.
Syntax service http
no service http
Default Enabled
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the HTTP service, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service http
To disable the HTTP service, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service http
Related
Commands
http port
http secure-port
show http
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 200
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GUI COMMANDS
SHOW HTTP
show http
Overview This command shows the HTTP server settings.
Syntax show http
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the HTTP server settings, use the command:
awplus# show http
Output Figure 6-2: Example output from the show http command
Related
Commands
clear line vty
service http
awplus#show http
HTTP Server Configuration
------------------------------------------------------------
HTTP server : Enabled
Port : 80

7
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 201
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
System
Configuration and
Monitoring
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands for configuring and
monitoring the system.
Command List •“banner exec” on page 203
•“banner login (system)” on page 205
•“banner motd” on page 207
•“clock set” on page 209
•“clock summer-time date” on page 210
•“clock summer-time recurring” on page 212
•“clock timezone” on page 214
•“ecofriendly led” on page 215
•“findme” on page 216
•“findme trigger” on page 218
•“hostname” on page 219
•“no debug all” on page 221
•“reboot” on page 223
•“reload” on page 224
•“show clock” on page 225
•“show cpu” on page 227
•“show cpu history” on page 230
•“show debugging” on page 232
•“show ecofriendly” on page 233
•“show interface memory” on page 234

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 202
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
•“show memory” on page 236
•“show memory allocations” on page 238
•“show memory history” on page 240
•“show memory pools” on page 241
•“show memory shared” on page 242
•“show process” on page 243
•“show reboot history” on page 245
•“show router-id” on page 246
•“show system” on page 247
•“show system environment” on page 248
•“show system interrupts” on page 249
•“show system mac” on page 250
•“show system serialnumber” on page 251
•“show tech-support” on page 252
•“speed (asyn)” on page 254
•“system territory (deprecated)” on page 256
•“terminal monitor” on page 257
•“undebug all” on page 258

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 203
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
BANNER EXEC
banner exec
Overview This command configures the User Exec mode banner that is displayed on the
console after you login. The banner exec default command restores the User Exec
banner to the default banner. Use the no banner exec command to disable the
User Exec banner and remove the default User Exec banner.
Syntax banner exec <banner-text>
banner exec default
no banner exec
Default By default, the AlliedWare Plus™ version and build date is displayed at console
login, such as:
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure a User Exec mode banner after login (in this example, to tell people to
use the enable command to move to Privileged Exec mode), enter the following
commands:
To restore the default User Exec mode banner after login, enter the following
commands:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#banner exec Use enable to move to Priv Exec mode
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
awplus login: manager
Password:
Use enable to move to Priv Exec mode
awplus>
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#banner exec default
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
awplus login: manager
Password:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 204
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
BANNER EXEC
To remove the User Exec mode banner after login, enter the following commands:
Related
Commands
banner login (system)
banner motd
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#no banner exec
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
awplus login: manager
Password:
awplus>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 205
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
BANNER LOGIN (SYSTEM)
banner login (system)
Overview This command configures the login banner that is displayed on the console when
you login. The login banner is displayed on all connected terminals. The login
banner is displayed after the MOTD (Message-of-the-Day) banner and before the
login username and password prompts.
Use the no banner login command to disable the login banner.
Syntax banner login
no banner login
Default By default, no login banner is displayed at console login.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure a login banner of “Authorised users only” to be displayed when you
login, enter the following commands:
To remove the login banner, enter the following commands:
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#banner login
Type CNTL/D to finish.
Authorised users only
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
Authorised users only
awplus login: manager
Password:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus>
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#no banner login
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
awplus login: manager
Password:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus>
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 207
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
BANNER MOTD
banner motd
Overview Use this command to create or edit the text MotD (Message-of-the-Day) banner
displayed before login. The MotD banner is displayed on all connected terminals.
The MotD banner is useful for sending messages that affect all network users, for
example, any imminent system shutdowns.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the MotD banner.
Syntax banner motd <motd-text>
no banner motd
Default By default, the device displays the AlliedWare Plus™ OS version and build date
when you login.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure a MotD banner of “System shutdown at 6pm today” to be displayed
when you log in, enter the following commands:
To delete the login banner, enter the following commands:
Parameter Description
<motd-text> The text to appear in the Message of the Day banner.
awplus>enable
awplus#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
awplus(config)#banner motd System shutdown at 6pm today
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
System shutdown at 6pm today
awplus login: manager
Password:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 208
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
BANNER MOTD
Related
Commands
banner exec
banner login (system)
awplus>enable
awplus#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
awplus(config)#no banner motd
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#exit
awplus login: manager
Password:
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.9 01/02/19 12:00:00
awplus>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 209
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
CLOCK SET
clock set
Overview This command sets the time and date for the system clock.
Syntax clock set <hh:mm:ss> <day> <month> <year>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Configure the timezone before setting the local time. Otherwise, when you change
the timezone, the device applies the new offset to the local time.
NOTE: If Network Time Protocol (NTP) is enabled, then you cannot change the time or
date using this command. NTP maintains the clock automatically using an external
time source. If you wish to manually alter the time or date, you must first disable NTP.
Example To set the time and date on your system to 2pm on the 2nd of October 2016, use
the command:
awplus# clock set 14:00:00 2 oct 2016
Related
Commands
clock timezone
Parameter Description
<hh:mm:ss> Local time in 24-hour format
<day> Day of the current month, from 1 to 31
<month> The first three letters of the current month
<year> Current year, from 2000 to 2035

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 210
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
CLOCK SUMMER-TIME DATE
clock summer-time date
Overview This command defines the start and end of summertime for a specific year only,
and specifies summertime’s offset value to Standard Time for that year.
The no variant of this command removes the device’s summertime setting. This
clears both specific summertime dates and recurring dates (set with the clock
summer-time recurring command).
By default, the device has no summertime definitions set.
Syntax clock summer-time <timezone-name> date <start-day>
<start-month> <start-year> <start-time> <end-day> <end-month>
<end-year> <end-time> <1-180>
no clock summer-time
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set a summertime definition for New Zealand using NZST (UTC+12:00) as the
standard time, and NZDT (UTC+13:00) as summertime, with the summertime set to
begin on the 25th of September 2016 and end on the 2nd of April 2017:
awplus(config)# clock summer-time NZDT date 25 sep 2:00 2016 2
apr 2:00 2017 60
To remove any summertime settings on the system, use the command:
awplus(config)# no clock summer-time
Parameter Description
<timezone-name> A description of the summertime zone, up to 6 characters long.
date Specifies that this is a date-based summertime setting for just
the specified year.
<start-day> Day that the summertime starts, from 1 to 31.
<start-month> First three letters of the name of the month that the
summertime starts.
<start-year> Year that summertime starts, from 2000 to 2035.
<start-time> Time of the day that summertime starts, in the 24-hour time
format HH:MM.
<end-day> Day that summertime ends, from 1 to 31.
<end-month> First three letters of the name of the month that the
summertime ends.
<end-year> Year that summertime ends, from 2000 to 2035.
<end-time> Time of the day that summertime ends, in the 24-hour time
format HH:MM.
<1-180> The offset in minutes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 212
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
CLOCK SUMMER-TIME RECURRING
clock summer-time recurring
Overview This command defines the start and end of summertime for every year, and
specifies summertime’s offset value to Standard Time.
The no variant of this command removes the device’s summertime setting. This
clears both specific summertime dates (set with the clock summer-time date
command) and recurring dates.
By default, the device has no summertime definitions set.
Syntax clock summer-time <timezone-name> recurring <start-week>
<start-day> <start-month> <start-time> <end-week> <end-day>
<end-month> <end-time> <1-180>
no clock summer-time
Parameter Description
<timezone-
name> A description of the summertime zone, up to 6 characters long.
recurring Specifies that this summertime setting applies every year from
now on.
<start-week> Week of the month when summertime starts, in the range 1-5. The
value 5 indicates the last week that has the specified day in it for
the specified month. For example, to start summertime on the last
Sunday of the month, enter 5 for <start-week> and sun for
<start-day>.
<start-day> Day of the week when summertime starts. Valid values are mon,
tue, wed, thu, fri, sat or sun.
<start-month> First three letters of the name of the month that summertime
starts.
<start-time> Time of the day that summertime starts, in the 24-hour time
format HH:MM.
<end-week> Week of the month when summertime ends, in the range 1-5. The
value 5 indicates the last week that has the specified day in it for
the specified month. For example, to end summertime on the last
Sunday of the month, enter 5 for <end-week> and sun for <end-
day>.
<end-day> Day of the week when summertime ends. Valid values are mon,
tue, wed, thu, fri, sat or sun.
<end-month> First three letters of the name of the month that summertime
ends.
<end-time> Time of the day that summertime ends, in the 24-hour time format
HH:MM.
<1-180> The offset in minutes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 213
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
CLOCK SUMMER-TIME RECURRING
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set a summertime definition for New Zealand using NZST (UTC+12:00) as the
standard time, and NZDT (UTC+13:00) as summertime, with summertime set to
start on the last Sunday in September, and end on the 1st Sunday in April, use the
command:
awplus(config)# clock summer-time NZDT recurring 5 sun sep 2:00
1 sun apr 2:00 60
To remove any summertime settings on the system, use the command:
awplus(config)# no clock summer-time
Related
Commands
clock summer-time date
clock timezone

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 214
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
CLOCK TIMEZONE
clock timezone
Overview This command defines the device’s clock timezone. The timezone is set as a offset
to the UTC.
The no variant of this command resets the system time to UTC.
By default, the system time is set to UTC.
Syntax clock timezone <timezone-name> {minus|plus}
[<0-13>|<0-12>:<00-59>]
no clock timezone
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Configure the timezone before setting the local time. Otherwise, when you change
the timezone, the device applies the new offset to the local time.
Examples To set the timezone to New Zealand Standard Time with an offset from UTC of +12
hours, use the command:
awplus(config)# clock timezone NZST plus 12
To set the timezone to Indian Standard Time with an offset from UTC of +5:30
hours, use the command:
awplus(config)# clock timezone IST plus 5:30
To set the timezone back to UTC with no offsets, use the command:
awplus(config)# no clock timezone
Related
Commands
clock set
clock summer-time date
clock summer-time recurring
Parameter Description
<timezone-name> A description of the timezone, up to 6 characters long.
minusorplus The direction of offset from UTC. The minus option
indicates that the timezone is behind UTC. The plus option
indicates that the timezone is ahead of UTC.
<0-13> The offset in hours or from UTC.
<0-12>:<00-59> The offset in hours or from UTC.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 215
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
ECOFRIENDLY LED
ecofriendly led
Overview Use this command to enable the eco-friendly LED (Light Emitting Diode) feature,
which turns off power to the port LEDs.
You can also use the front-panel eco-switch button to enable or disable the
eco-friendly feature. Using this button overrides the configuration set with the
ecofriendly led command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the eco-friendly LED feature.
Syntax ecofriendly led
no ecofriendly led
Default The eco-friendly LED feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When the eco-friendly LED feature is enabled, a change in port status will not affect
the display of the associated LED. When the eco-friendly LED feature is disabled
and power is returned to port LEDs, the LEDs will correctly show the current state
of the ports.
For an example of how to configure a trigger to turn off power to port LEDs, see the
Triggers Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Examples To enable the eco-friendly LED feature which turns off power to all port LEDs, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ecofriendly led
To disable the eco-friendly LED feature, use the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ecofriendly led
Related
Commands
show ecofriendly

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 216
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
FINDME
findme
Overview Use this command to physically locate a specific device from a group of similar
devices. Activating the command causes a selected number of port LEDs to
alternately flash green then amber (if that device has amber LEDs) at a rate of 1 Hz.
Use the no variant of this command to deactivate the Find Me feature prior to the
timeout expiring.
Syntax findme [interface <port-list>] [timeout <duration>]
no findme
Default By default all port LEDs flash for 60 seconds.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Running the findme command causes the device’s port LEDs to flash. An optional
timeout parameter specifies the flash behavior duration. Normal LED behavior is
restored automatically after either the default time, or a specified time has elapsed,
or a no findme command is used. You can specify which interface or interfaces are
flashed with the optional interface parameter.
Example To activate the Find Me feature for the default duration (60 seconds) on all ports,
use the following command:
awplus# findme
To activate the Find Me feature for 120 seconds on all ports, use the following
command:
awplus# findme timeout 120
To activate the Find Me feature for the default duration (60 seconds) on switch port
interfaces port1.0.2 through port1.0.4, use the following command:
awplus# findme interface port1.0.2-1.0.4
In the example above, ports 2 to 4 will flash 4 times and then all ports will flash
twice. Each alternate flash will be amber (if that device has amber LEDs). This
pattern will repeat until timeout (default or set) or no findme commands are used.
Parameter Description
interface <port-list> The ports to flash. The port list can be:
• a switch port, e.g. port1.0.4
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen,
e.g. port1.0.1-1.0.4
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges,
e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.5-1.0.6.
timeout <duration>How long the LEDs flash, in seconds, in the range 5 to
3600 seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 217
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
FINDME
To deactivate the Find Me feature, use the following command:
awplus# no findme

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 218
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
FINDME TRIGGER
findme trigger
Overview When this command is enabled, the LED flashing functionality of the find-me
command is applied whenever any or all of the selected parameter conditions is
detected.
Use the no variant to remove the findme trigger function for the selected
parameter.
Syntax findme trigger {all|loopprot|thrash-limit|qsp}
no findme trigger {all|loopprot|thrash-limit|qsp}
Default The findme trigger function is disabled.
Mode Global config
Usage Note that findme trigger is not available if you have set the switch to take the
following actions in response to an event:
• For loop detection, the actions log-only and none
• For MAC address thrash-limiting, the actions learn-disable and none.
Example To enable action LED flashing for the loop protection function:
awplus# findme trigger loopprot
Related
Commands
findme
loop-protection loop-detect
Parameter Description
all Enable the find-me function whenever any of the listed parameter
conditions are detected
loopprot Enable the findme function whenever a loop protection condition
is detected.
thrash-limit Enable the findme function whenever a MAC address
thrash-limiting condition is detected.
qsp Enable the findme function whenever a QoS Storm Protection
condition is detected.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 219
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
HOSTNAME
hostname
Overview This command sets the name applied to the device as shown at the prompt. The
hostname is:
• displayed in the output of the show system command
• displayed in the CLI prompt so you know which device you are configuring
• stored in the MIB object sysName
Use the no variant of this command to revert the hostname setting to its default.
For devices that are not part of an AMF network, the default is “awplus”.
Syntax hostname <hostname>
no hostname [<hostname>]
Default awplus
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Within an AMF network, any device without a user-defined hostname will
automatically be assigned a name based on its MAC address.
To efficiently manage your network using AMF, we strongly advise that you devise
a naming convention for your network devices and apply an appropriate
hostname to each device.
The name must also follow the rules for ARPANET host names. The name must start
with a letter, end with a letter or digit, and use only letters, digits, and hyphens.
Refer to RFC 1035.
Example To set the system name to HQ-Sales, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# hostname HQ-Sales
This changes the prompt to:
HQ-Sales(config)#
To revert to the default hostname awplus, use the command:
HQ-Sales(config)# no hostname
This changes the prompt to:
awplus(config)#
Parameter Description
<hostname> Specifies the name given to a specific device. This is also referred to as
the Node name in AMF output screens.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 220
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
HOSTNAME
NOTE: When AMF is configured, running the no hostname command will apply a
hostname that is based on the MAC address of the device node, for example,
node_0000_5e00_5301.
Related
Commands
show system

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 221
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
NO DEBUG ALL
no debug all
Overview This command disables the debugging facility for all features on your device. This
stops the device from generating any diagnostic debugging messages.
You can optionally disable the debugging facility for only the given protocol or
feature. The features available depend on your device and will be a subset of the
features listed in the Syntax section below.
Syntax no debug all [bgp|ipv6|dot1x|nsm|ospf|pim dense-mode|pim
sparse-mode|rip|vrrp]
Default The debugging facility is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration and Privileged Exec
Example To disable debugging for all features, use the command:
awplus# no debug all
To disable all 802.1X debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug all dot1x
To disable all IPv6 debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug all ipv6
To disable all NSM debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug all nsm
Parameter Description
bgp Turns off all debugging for BGP (Border Gateway Protocol).
dot1x Turns off all debugging for IEEE 802.1X port-based network
access- control.
ipv6 Turns off all debugging for IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6).
nsm Turns off all debugging for the NSM (Network Services
Module).
ospf Turns off all debugging for OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
pim dense-mode Turns off all debugging for PIM (Protocol Independent
Multicast) Dense Mode.
pim sparse-mode Turns off all debugging for PIM (Protocol Independent
Multicast) Sparse Mode.
rip Turns off all debugging for RIP (Routing Information Protocol).
vrrp Turns off all debugging for VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy
Protocol).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 222
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
NO DEBUG ALL
To disable all RIP debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug all rip
Related
Commands
undebug all
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: RIP parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 223
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
REBOOT
reboot
Overview This command halts the device and performs a cold restart (also known as reload).
It displays a confirmation request before restarting.
Syntax reboot
reload
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The reboot and reload commands perform the same action.
Examples To restart the device, use the command:
awplus# reboot
reboot system? (y/n): y
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 225
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CLOCK
show clock
Overview This command displays the system’s current configured local time and date. It also
displays other clock related information such as timezone and summertime
configuration.
Syntax show clock
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the system’s current local time, use the command:
awplus# show clock
Output Figure 7-1: Example output from the show clock command for a device using
New Zealand time
Local Time: Mon, 17 Oct 2016 13:56:06 +1200
UTC Time: Mon, 17 Oct 2016 01:56:06 +0000
Timezone: NZST
Timezone Offset: +12:00
Summer time zone: NZDT
Summer time starts: Last Sunday in September at 02:00:00
Summer time ends: First Sunday in April at 02:00:00
Summer time offset: 60 mins
Summer time recurring: Yes
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show clock command
Parameter Description
Local Time Current local time.
UTC Time Current UTC time.
Timezone The current configured timezone name.
Timezone Offset Number of hours offset to UTC.
Summer time zone The current configured summertime zone name.
Summer time starts Date and time set as the start of summer time.
Summer time ends Date and time set as the end of summer time.
Summer time offset Number of minutes that summer time is offset from the
system’s timezone.
Summer time
recurring Whether the device will apply the summer time settings
every year or only once.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 227
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CPU
show cpu
Overview This command displays a list of running processes with their CPU utilization.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show cpu [sort {thrds|pri|sleep|runtime}]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To show the CPU utilization of current processes, sorting them by the number of
threads the processes are using, use the command:
awplus# show cpu sort thrds
Parameter Description
sort Changes the sorting order using the following fields. If you do not
specify a field, then the list is sorted by percentage CPU
utilization.
thrds Sort by the number of threads.
pri Sort by the process priority.
sleep Sort by the average time sleeping.
runtime Sort by the runtime of the process.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 228
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CPU
Output Figure 7-2: Example output from show cpu
CPU averages:
1 second: 12%, 20 seconds: 2%, 60 seconds: 2%
System load averages:
1 minute: 0.03, 5 minutes: 0.02, 15 minutes: 0.00
Current CPU load:
userspace: 6%, kernel: 4%, interrupts: 1% iowaits: 0%
user processes
==============
pid name thrds cpu% pri state sleep% runtime
1544 hostd 1 2.8 20 run 0 120
1166 exfx 17 1.8 20 sleep 0 3846
1284 aisexec 44 0.9 -2 sleep 0 2606
1 init 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 120
9772 sh 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 0
9773 corerotate 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 0
853 syslog-ng 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 356
859 klogd 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 1
910 inetd 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 3
920 portmap 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 0
931 crond 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 1
1090 openhpid 11 0.0 20 sleep 0 233
1111 hpilogd 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 0
1240 hsl 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 79
1453 authd 1 0.0 20 sleep 0 85
...
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show cpu command
Parameter Description
CPU averages Average CPU utilization for the periods stated.
System load
averages The average number of processes waiting for CPU time for the
periods stated.
Current CPU
load Current CPU utilization specified by load types.
pid Identifier number of the process.
name A shortened name for the process
thrds Number of threads in the process.
cpu% Percentage of CPU utilization that this process is consuming.
pri Process priority state.
state Process state; one of “run”, “sleep”, “zombie”, and “dead”.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 229
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CPU
Related
Commands
show memory
show memory allocations
show memory history
show memory pools
show process
sleep% Percentage of time that the process is in the sleep state.
runtime The time that the process has been running for, measured in
jiffies. A jiffy is the duration of one tick of the system timer
interrupt.
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show cpu command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 230
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CPU HISTORY
show cpu history
Overview This command prints a graph showing the historical CPU utilization.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show cpu history
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This command’s output displays three graphs of the percentage CPU utilization:
• per second for the last minute, then
• per minute for the last hour, then
• per 30 minutes for the last 30 hours.
Examples To display a graph showing the historical CPU utilization of the device, use the
command:
awplus# show cpu history
Output Figure 7-3: Example output from the show cpu history command
Per second CPU load history
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20 *
10 ******************************************* ****************
|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....
Oldest Newest
CPU load% per second (last 60 seconds)
* = average CPU load%
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 231
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW CPU HISTORY
Related
Commands
show memory
show memory allocations
show memory pools
show process
Per minute CPU load history
100
90
80
70
60 +
50
40
30
20 ++ +++++++++ +++++++ ++++ + ++++++ ++++ +++ +++++ +++++++++
10 ************************************************************
|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....
Oldest Newest
CPU load% per minute (last 60 minutes)
* = average CPU load%, + = maximum
Per (30) minute CPU load history
100
90
80
70 +
60
50
40
30
20
10 ***
|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....
Oldest Newest
CPU load% per 30 minutes (last 60 values / 30 hours)
* = average, - = minimum, + = maximum

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 232
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING
show debugging
Overview This command displays all debugging options in alphabetical order, indicating
whether debugging is enabled or disabled for each feature.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To find out what debugging is enabled, use the command:
awplus# show debugging
Output Figure 7-4: Example output from the show debugging command
awplus#show debugging
AAA debugging status:
Authentication debugging is off
Accounting debugging is off
% DHCP Snooping service is disabled
802.1X debugging status:
EPSR debugging status:
EPSR Info debugging is off
EPSR Message debugging is off
EPSR Packet debugging is off
EPSR State debugging is off
IGMP Debugging status:
IGMP Decoder debugging is off
IGMP Encoder debugging is off
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 233
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW ECOFRIENDLY
show ecofriendly
Overview This command displays the switch’s eco-friendly configuration status. The
ecofriendly led configuration status are shown in the show ecofriendly output.
Syntax show ecofriendly
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the switch’s eco-friendly configuration status, use the following
command:
awplus# show ecofriendly
Output Figure 7-5: Example output from the show ecofriendly command
awplus#show ecofriendly
Front panel port LEDs normal
Energy efficient ethernet
Port Name Configured Status
port1.0.1 Port 1 off -
port1.0.2 off off
port1.0.3 off -
port1.0.4 Port 4 off -
port1.0.5 off -
...
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show ecofriendly command
Parameter Description
normal The eco-friendly LED feature is disabled and port LEDs
show the current state of the ports. This is the default
setting.
off The eco-friendly LED feature is enabled and power to
the port LEDs is disabled.
Port Displays the port number as assigned by the switch.
Name Displays the port name if a name is configured for a
port number.
Configured Because LPI is not supported, this entry always shows
“off” or a dash (-).
Status Because LPI is not supported, this entry always shows
“off” or a dash (-).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 234
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE MEMORY
show interface memory
Overview This command displays the shared memory used by either all interfaces, or the
specified interface or interfaces. The output is useful for diagnostic purposes by
Allied Telesis authorized service personnel.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show interface memory
show interface <port-list> memory
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the shared memory used by all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show interface memory
To display the shared memory used by port1.0.1 and port1.0.3 to port1.0.4, use the
command:
awplus# show interface port1.0.1,port1.0.3-port1.0.4 memory
Output Figure 7-6: Example output from the show interface memory command
Parameter Description
<port-list> Display information about only the specified port or ports. The port
list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do not mix
port types in the same list.
awplus#show interface memory
Vlan blocking state shared memory usage
---------------------------------------------
Interface shmid Bytes Used nattch Status
port1.0.1 491535 512 1
port1.0.2 393228 512 1
port1.0.3 557073 512 1
...
lo 425997 512 1
po1 1179684 512 1
po2 1212453 512 1
sa3 1245222 512 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 235
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE MEMORY
Figure 7-7: Example output from show interface <port-list> memory for a list
of interfaces
Related
Commands
show interface brief
show interface status
show interface switchport
awplus#show interface port1.0.1,port1.0.3-port1.0.4 memory
Vlan blocking state shared memory usage
---------------------------------------------
Interface shmid Bytes Used nattch Status
port1.0.1 589842 512 1
port1.0.3 688149 512 1
port1.0.4 327690 512 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 236
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY
show memory
Overview This command displays the memory used by each process that is currently running
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show memory [sort {size|peak|stk}]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the memory used by the current running processes, use the command:
awplus# show memory
Output Figure 7-8: Example output from show memory
Parameter Description
sort Changes the sorting order for the list of processes. If you do not
specify this, then the list is sorted by percentage memory
utilization.
size Sort by the amount of memory the process is
currently using.
peak Sort by the amount of memory the process is
currently using.
stk Sort by the stack size of the process.
awplus#show memory sort stk
RAM total: 124384 kB; free: 64236 kB; buffers: 15888 kB
user processes
==============
pid name mem% size(kB) peak(kB) data(kB) stk(kB) virt(kB)
490 openhpid 1.5 1988 7480 1308 528 6704
578 hsl 7.1 8940 29312 5148 312 21052
18986 imish 1.3 1660 13668 3876 172 13668
18931 imish 3.6 4548 13668 3876 172 13668
576 imi 4.6 5772 14532 4428 144 14532
572 nsm 4.9 6128 15092 4480 140 15092
574 hostd 1.6 2048 8116 1876 140 8116
586 cntrd 2.5 3168 12140 3288 140 12136
606 sflowd 2.8 3564 12336 3408 140 12336
610 authd 3.0 3808 12604 3472 140 12604
616 mstpd 3.1 3856 12652 3480 140 12652
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 237
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY
Related
Commands
show memory allocations
show memory history
show memory pools
show memory shared
Table 4: Parameters in the output of the show memory command
Parameter Description
RAM total Total amount of RAM memory free.
free Available memory size.
buffers Memory allocated kernel buffers.
pid Identifier number for the process.
name Short name used to describe the process.
mem% Percentage of memory utilization the process is currently using.
size Amount of memory currently used by the process.
peak Greatest amount of memory ever used by the process.
data Amount of memory used for data.
stk The stack size.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 238
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY ALLOCATIONS
show memory allocations
Overview This command displays the memory allocations used by processes.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show memory allocations [<process>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the memory allocations used by all processes on your device, use the
command:
awplus# show memory allocations
Output Figure 7-9: Example output from the show memory allocations command
Parameter Description
<process> Displays the memory allocation used by the specified process.
awplus#show memory allocations
Memory allocations for imi
-----------------------------
Current 15093760 (peak 15093760)
Statically allocated memory:
- binary/exe : 1675264
- libraries : 8916992
- bss/global data : 2985984
- stack : 139264
Dynamically allocated memory (heap):
- total allocated : 1351680
- in use : 1282440
- non-mmapped : 1351680
- maximum total allocated : 1351680
- total free space : 69240
- releasable : 68968
- space in freed fastbins : 16
Context
filename:line allocated freed
+ lib.c:749 484
.
.
.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 240
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY HISTORY
show memory history
Overview This command prints a graph showing the historical memory usage.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show memory history
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This command’s output displays three graphs of the percentage memory
utilization:
• per second for the last minute, then
• per minute for the last hour, then
• per 30 minutes for the last 30 hours.
Examples To show a graph displaying the historical memory usage, use the command:
awplus# show memory history
Output Figure 7-10: Example output from the show memory history command
Related
Commands
show memory allocations
show memory pools
show memory shared
show tech-support
Per minute memory utilization history
100
90
80
70
60
50
40*************************************************************
30
20
10
|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....|....
Oldest Newest
Memory utilization% per minute (last 60 minutes)
* = average memory utilisation%.
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 241
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY POOLS
show memory pools
Overview This command shows the memory pools used by processes.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show memory pools [<process>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To shows the memory pools used by processes, use the command:
awplus# show memory pools
Output Figure 7-11: Example output from the show memory pools command
Related
Commands
show memory allocations
show memory history
show tech-support
Parameter Description
<process> Displays the memory pools used by the specified process.
awplus#show memory pools
Memory pools for imi
----------------------
Current 15290368 (peak 15290368)
Statically allocated memory:
- binary/exe : 1675264
- libraries : 8916992
- bss/global data : 2985984
- stack : 139264
Dynamically allocated memory (heap):
- total allocated : 1548288
- in use : 1479816
- non-mmapped : 1548288
- maximum total allocated : 1548288
- total free space : 68472
- releasable : 68200
- space in freed fastbins : 16
.
.
.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 242
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW MEMORY SHARED
show memory shared
Overview This command displays shared memory allocation information. The output is
useful for diagnostic purposes by Allied Telesis authorized service personnel.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show memory shared
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display information about the shared memory allocation used on the device,
use the command:
awplus# show memory shared
Output Figure 7-12: Example output from the show memory shared command
Related
Commands
show memory allocations
show memory history
show memory
awplus#show memory shared
Shared Memory Status
--------------------------
Segment allocated = 39
Pages allocated = 39
Pages resident = 11
Shared Memory Limits
--------------------------
Maximum number of segments = 4096
Maximum segment size (kbytes) = 32768
Maximum total shared memory (pages) = 2097152
Minimum segment size (bytes) = 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 243
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW PROCESS
show process
Overview This command lists a summary of the current running processes.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show process [sort {cpu|mem}]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This command displays a snapshot of currently-running processes. If you want to
see CPU or memory utilization history instead, use the commands show cpu
history or show memory history.
Example To display a summary of the current running processes, use the command:
awplus# show process
Output Figure 7-13: Example output from the show process command
Parameter Description
sort Changes the sorting order for the list of processes.
cpu Sorts the list by the percentage of CPU utilization.
mem Sorts the list by the percentage of memory
utilization.
CPU averages:
1 second: 8%, 20 seconds: 5%, 60 seconds: 5%
System load averages:
1 minute: 0.04, 5 minutes: 0.08, 15 minutes: 0.12
Current CPU load:
userspace: 9%, kernel: 9%, interrupts: 0% iowaits: 0%
RAM total: 514920 kB; free: 382600 kB; buffers: 16368 kB
user processes
==============
pid name thrds cpu% mem% pri state sleep%
962 pss 12 0 6 25 sleep 5
1 init 1 0 0 25 sleep 0
797 syslog-ng 1 0 0 16 sleep 88
...
kernel threads
==============
pid name cpu% pri state sleep%
71 aio/0 0 20 sleep 0
3 events/0 0 10 sleep 98
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 244
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW PROCESS
Related
Commands
show cpu
show cpu history
Table 5: Parameters in the output from the show process command
Parameter Description
CPU averages Average CPU utilization for the periods stated.
System load
averages The average number of processes waiting for CPU time for the
periods stated.
Current CPU
load Current CPU utilization specified by load types
RAM total Total memory size.
free Available memory.
buffers Memory allocated to kernel buffers.
pid Identifier for the process.
name Short name to describe the process.
thrds Number of threads in the process.
cpu% Percentage of CPU utilization that this process is consuming.
mem% Percentage of memory utilization that this process is consuming.
pri Process priority.
state Process state; one of “run”, “sleep”, “stop”, “zombie”, or “dead”.
sleep% Percentage of time the process is in the sleep state.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 245
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW REBOOT HISTORY
show reboot history
Overview Use this command to display the device’s reboot history.
Syntax show reboot history
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the reboot history, use the command:
awplus# show reboot history
Output Figure 7-14: Example output from the show reboot history command
Related
Commands
show tech-support
awplus#show reboot history
<date> <time> <type> <description>
-----------------------------------------------
2016-10-10 01:42:04 Expected User Request
2016-10-10 01:35:31 Expected User Request
2016-10-10 01:16:25 Unexpected Rebooting due to critical process (network/nsm)
failure!
2016-10-10 01:11:04 Unexpected Rebooting due to critical process (network/nsm)
failure!
2016-10-09 19:56:16 Expected User Request
2016-10-09 19:51:20 Expected User Request
Table 6: Parameters in the output from the show reboot history command
Parameter Description
Unexpected A non-intended reboot.
Expected A planned or user-triggered reboot.
User request User initiated reboot via the CLI.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 246
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW ROUTER-ID
show router-id
Overview Use this command to show the Router ID of the current system.
Syntax show router-id
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the Router ID of the current system, use the command:
awplus# show router-id
Output Figure 7-15: Example output from the show router-id command
awplus>show router-id
Router ID: 10.55.0.2 (automatic)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 247
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM
show system
Overview This command displays general system information about the device, including
the hardware, memory usage, and software version. It also displays location and
contact details when these have been set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display configuration information, use the command:
awplus# show system
Output Figure 7-16: Example output from show system
Related
Commands
show system environment
System Status Fri May 25 13:29:10 2018
Board ID Bay Board Name Rev Serial number
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Base 544 Base IE210L-18GP A-0 A10099G180500022
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RAM: Total: 511160 kB Free: 401264 kB
Flash: 125.9MB Used: 7.9MB Available: 117.9MB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Environment Status : Normal
Uptime : 0 days 03:46:46
Bootloader version : 3.2.6
Current software : IE210-5.4.8-0.2.rel
Software version : main-20180524-3
Build date : Thu May 24 06:19:19 UTC 2018
Current boot config: flash:/stk_a_1331_1001_40292.cfg (file exists)
System Name
awplus
System Contact
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 248
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT
show system environment
Overview This command displays the current environmental status of your device and any
attached PSU, XEM, or other expansion option. The environmental status covers
information about temperatures, fans, and voltage.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system environment
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the system’s environmental status, use the command:
awplus# show system environment
Output Figure 7-17: Example output from show system environment
Related
Commands
show system
awplus#show system environment
Environment Monitoring Status
Overall Status: Normal
Resource ID: 1 Name: IE210L-18GP
ID Sensor (Units) Reading Low Limit High Limit Status
1 Fan: Fan 1 (Rpm) 4418 2025 - Ok
2 Fan: Fan 2 (Rpm) 4440 2025 - Ok
3 Voltage: 2.5V (Volts) 2.508 2.339 2.859 Ok
4 Voltage: 1.0V (Volts) 1.014 0.891 1.090 Ok
5 Voltage: 3.3V (Volts) 3.355 3.028 3.545 Ok
6 Voltage: 1.5V (Volts) 1.545 1.335 1.649 Ok
7 Voltage: 12.0V (Volts) 11.874 10.767 13.166 Ok
8 Temp: System (Degrees C) 37 -11 81 Ok
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 249
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM INTERRUPTS
show system interrupts
Overview Use this command to display the number of interrupts for each IRQ (Interrupt
Request) used to interrupt input lines on a PIC (Programmable Interrupt Controller)
on your device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system interrupts
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display information about the number of interrupts for each IRQ in your device,
use the command:
awplus# show system interrupts
Output Figure 7-18: Example output from the show system interrupts command
Related
Commands
show system environment
awplus#show system interrupts
CPU0
27:1387835593 GIC Disabled 1 iproc_gtimer
29: 0 GIC Disabled 1 twd
62: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
63: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
64: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
65: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
66: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
67: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
68: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
69: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
70: 0 GIC Enabled 0 IDM
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 250
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM MAC
show system mac
Overview This command displays the physical MAC address of the device.
Syntax show system mac
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the physical MAC address enter the following command:
awplus# show system mac
Output Figure 7-19: Example output from the show system mac command
awplus#show system mac
eccd.6d9d.4eed (system)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 251
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM SERIALNUMBER
show system serialnumber
Overview This command shows the serial number information for the device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system serialnumber
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the serial number information for the device, use the command:
awplus# show system serialnumber
Output Figure 7-20: Example output from the show system serial number command
awplus#show system serialnumber
45AX5300X

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 252
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW TECH-SUPPORT
show tech-support
Overview This command generates system and debugging information for the device and
saves it to a file.
This command is useful for collecting a large amount of information so that it can
then be analyzed for troubleshooting purposes. The output of this command can
be provided to technical support staff when reporting a problem.
You can optionally limit the command output to display only information for a
given protocol or feature. The features available depend on your device and will be
a subset of the features listed in the table below.
Syntax show tech-support
{[all|atmf|auth|bgp|card|dhcpsn|epsr|firewall|igmp|ip|ipv6|mld
|openflow|ospf|ospf6|pim|rip|ripng|stack|stp|system|tacacs+|
update]} [outfile <filename>]
Parameter Description
all Display full information
atmf Display ATMF-specific information
auth Display authentication-related information
bgp Display BGP-related information
card Display Chassis Card specific information
dhcpsn Display DHCP Snooping specific information
epsr Display EPSR specific information
firewall Display firewall specific information
igmp Display IGMP specific information
ip Display IP specific information
ipv6 Display IPv6 specific information
mld Display MLD specific information
openflow Display information related to OpenFlow
ospf Display OSPF related information
ospf6 Display OSPF6 specific information
pim Display PIM related information
rip RIP related information
ripng Display RIPNG specific information
stack Display stacking device information
stp Display STP specific information
system Display general system information

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 253
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW TECH-SUPPORT
Default Captures all information for the device.
By default the output is saved to the file ‘tech-support.txt.gz’ in the current
directory. If this file already exists in the current directory then a new file is
generated with the time stamp appended to the file name, for example
‘tech-support20161009.txt.gz’, so the previous file is retained.
Usage The command generates a large amount of output, which is saved to a file in
compressed format. The output file name can be specified by outfile option. If the
output file already exists, a new file name is generated with the current time stamp.
If the output filename does not end with “.gz”, then “.gz” is appended to the
filename. Since output files may be too large for Flash on the device we
recommend saving files to external memory or a TFTP server whenever possible to
avoid device lockup. This method is not likely to be appropriate when running the
working set option of AMF across a range of physically separated devices.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To produce the output needed by technical support staff, use the command:
awplus# show tech-support
tacacs+ Display TACACS+ information
update Display resource update specific information
|Output modifier
>Output redirection
>> Output redirection (append)
outfile Output file name
<filename>Specifies a name for the output file. If no name is specified, this file
will be saved as: tech-support.txt.gz.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 254
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SPEED (ASYN)
speed (asyn)
Overview This command changes the console speed from the device. Note that a change in
console speed is applied for subsequent console sessions. Exit the current session
to enable the console speed change using the clear line console command.
Syntax speed <console-speed-in-bps>
Default The default console speed baud rate is 9600 bps.
Mode Line Configuration
Usage This command is used to change the console (asyn) port speed. Set the console
speed to match the transmission rate of the device connected to the console (asyn)
port on your device.
Example To set the terminal console (asyn0) port speed from the device to 57600 bps, then
exit the session, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# speed 57600
awplus(config-line)# exit
awplus(config)# exit
awplus# exit
Then log in again to enable the change:
awplus login:
Password:
awplus>
Parameter Description
<console-speed-in-bps>Console speed Baud rate in bps (bits per second).
1200 1200 Baud
2400 2400 Baud
9600 9600 Baud
19200 19200 Baud
38400 38400 Baud
57600 57600 Baud
115200 115200 Baud

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 256
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
SYSTEM TERRITORY (DEPRECATED)
system territory (deprecated)
Overview This command has been deprecated in Software Version 5.4.4-0.1 and later. It now
has no effect.
It is no longer useful to specify a system territory, so there is no alternative
command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 257
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION AND MONITORING COMMANDS
TERMINAL MONITOR
terminal monitor
Overview Use this command to display debugging output on a terminal.
To display the cursor after a line of debugging output, press the Enter key.
Use the command terminal no monitor or no terminal monitor to stop
displaying debugging output on the terminal. Alternatively, you can use the
timeout option to stop displaying debugging output on the terminal after a set
time.
Syntax terminal monitor [<1-60>]
terminal no monitor
no terminal monitor
Default Disabled
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display debugging output on a terminal, enter the command:
awplus# terminal monitor
To display debugging on the terminal for 60 seconds, enter the command:
awplus# terminal monitor 60
To stop displaying debugging output on the terminal, use the command:
awplus# no terminal monitor
Related
Commands
All debug commands
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: no terminal monitor added as an alias for terminal no monitor
Parameter Description
<1-60>Set a timeout between 1 and 60 seconds for terminal output.

8
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 259
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Pluggables and
Cabling Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
and monitor Pluggables and Cabling, including:
• Cable Fault Locator for finding faults in copper cabling
• Optical Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) to help find fiber issues when
links go down
• Active Fiber Monitoring for detecting changes in optical power received over
fiber cables.
For more information, see the Pluggables and Cabling Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Command List •“clear fiber-monitoring interface” on page 260
•“clear test cable-diagnostics tdr” on page 261
•“debug fiber-monitoring” on page 262
•“fiber-monitoring action” on page 264
•“fiber-monitoring baseline” on page 266
•“fiber-monitoring enable” on page 268
•“fiber-monitoring interval” on page 269
•“fiber-monitoring sensitivity” on page 270
•“show system fiber-monitoring” on page 272
•“show system pluggable” on page 275
•“show system pluggable detail” on page 277
•“show system pluggable diagnostics” on page 280
•“show test cable-diagnostics tdr” on page 282
•“test cable-diagnostics tdr interface” on page 283

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 260
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
CLEAR FIBER-MONITORING INTERFACE
clear fiber-monitoring interface
Overview Use this command to clear the Active Fiber Monitoring state of a port. It clears the
alarm, baseline and history and starts monitoring from the beginning. It does not
change the configuration.
Syntax clear fiber-monitoring interface <port>
Default n/a
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Normally, you do not need to clear the Active Fiber Monitoring state of a port. If the
issue resolves itself and the monitored optical power returns to the baseline, the
alarm clears automatically.
However, you may need to clear the Active Fiber Monitoring state if the optical
power level reduces for a known reason, causing the port to be stuck in the alarm
state. In this situation, the alarm will not clear automatically, because Active Fiber
Monitoring does not update the baseline when the port is in the alarm state, for
security reasons.
Example To clear the Active Fiber Monitoring state for interface port1.0.17, use the
command:
awplus# clear fiber-monitoring interface port1.0.17
Related
Commands
show system fiber-monitoring
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: command added
Parameter Description
<port> The name of the port to reset Active Fiber Monitoring on.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 261
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
CLEAR TEST CABLE-DIAGNOSTICS TDR
clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
Overview Use this command to clear the results of the last cable test that was run.
Syntax clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To clear the results of a previous cable-diagnostics test use the following
commands:
awplus# clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
Related
Commands
show test cable-diagnostics tdr
test cable-diagnostics tdr interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 262
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
DEBUG FIBER-MONITORING
debug fiber-monitoring
Overview Use this command to enable debugging of active fiber monitoring on the specified
ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable debugging on all ports or the
specified ports.
Syntax debug fiber-monitoring interface <port-list>
no debug fiber-monitoring [interface <port-list>]
Default Debugging of active fiber monitoring is disabled by default.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage While debugging is enabled by this command for a port, all the optical power
readings for the port are sent to the console.
Example To enable debugging messages for active fiber monitoring of port1.0.17 to be sent
to the console, use the commands:
awplus# debug fiber-monitoring interface port1.0.17
awplus# terminal monitor
To disable debugging messages for active fiber monitoring on port1.0.17, use the
command:
awplus# no debug fiber-monitoring interface port1.0.17
To disable all debugging messages for active fiber monitoring, use the command:
awplus# no debug fiber-monitoring
Parameter Description
<port-list> The list of fiber ports to enable or disable debugging for, as a
single port, a comma separated list or a hyphenated range.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 263
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
DEBUG FIBER-MONITORING
Output Figure 8-1: Example output from debug fiber-monitoring
Related
Commands
show system fiber-monitoring
awplus#debug fiber-monitoring interface port1.0.17
awplus#terminal monitor
% Warning: Console logging enabled
awplus#01:42:50 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1
Reading:1748 Baseline:1708 Threshold:1356
01:42:52 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1 Reading:1717
Baseline:1709 Threshold:1357
01:42:54 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1 Reading:1780
Baseline:1709 Threshold:1357
01:42:56 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1 Reading:1685
Baseline:1710 Threshold:1358
01:42:58 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1 Reading:1701
Baseline:1710 Threshold:1358
01:43:01 awplus Pluggable[522]: Fiber-monitor port2.0.1: Channel:1 Reading:1733
Baseline:1709 Threshold:1357
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 264
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING ACTION
fiber-monitoring action
Overview Use this command to specify an action to be taken if the optical power received on
the port changes from the baseline by the amount specified in the
fiber-monitoring sensitivity command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified action or all actions
from the port.
Syntax fiber-monitoring action [trap] [shutdown] [continuous]
no fiber-monitoring action [trap|shutdown]
Default By default a log message is generated, but no additional action is performed.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a fiber port.
Usage If fiber monitoring is enabled and this command is not used to set an action, a
change in received power on a fiber port only generates a log message.
Example To set the device to send an SNMP trap when port1.0.17 or port1.0.18 receive
reduced power and when that reduced-power alarm is cleared, use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring action trap
To set the device to send an SNMP trap when port1.0.17 or port1.0.18 receive
reduced power, and every polling interval after that until the alarm is cleared, use
the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring action trap continuous
To set the device to send an SNMP trap and to shut down the port when port1.0.17
or port1.0.18 receive reduced power, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring action trap shutdown
Parameter Description
trap Send an SNMP notification.
shutdown Shutdown the port.
continuous Make the action or actions happen continuously (every polling
interval) while the sensor is in the alarm state. Otherwise, the
action only happens when the alarm is triggered or cleared.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 265
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING ACTION
To set the device to stop shutting down the port if port1.0.17 or port1.0.18 receive
reduced power, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring action shutdown
If the device is set to send an SNMP trap for those ports, it will continue to do so.
To set the device not to perform any action when it receives reduced power on
port1.0.17 or port1.0.18, except sending a log message, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring action
Related
Commands
fiber-monitoring sensitivity
show system fiber-monitoring
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: continuous parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 266
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING BASELINE
fiber-monitoring baseline
Overview Use this command to configure how the baseline value for comparison is
calculated for active fiber monitoring on the port.
Note that alarm generation will not commence until the link has been up for a full
averaging period.
Use the no variant of this command to set the fiber-monitoring baseline to its
default value.
Syntax fiber-monitoring baseline average <12-150> [interval <2-86400>]
fiber-monitoring baseline fixed <1-65535>
no fiber-monitoring baseline
Default The default is a moving average of the last 12 values, taken at the same interval as
the monitoring interval. The monitoring interval is set using the fiber-monitoring
interval command. If the monitoring interval is set to its default of 5 seconds, the
fiber-monitoring baseline default will be the average over the last minute.
Mode Interface Configuration for a fiber port
Usage There are two ways to configure the baseline. The first is to choose a number of
readings to average. This is the default and recommended method. The second is
to set a fixed value in units of x0.0001mW.
If a fixed value is required, the easiest way to choose a value is to enable fiber
monitoring on the port and use the show system fiber-monitoring command to
see what readings you can expect.
Parameter Description
average
<12-150> Set the baseline optical power received to be based on the
moving average of the specified number of most recent
(non-zero) values. Default is to use this setting and 12 values.
interval
<2-86400> Optionally, specify the optical power polling interval for
determining the baseline, in seconds. By default, the baseline
polling interval is the same as the monitoring polling interval,
which is 5 seconds by default.
If specified, this baseline interval should be larger than the
monitoring interval.
Even if you specify a baseline interval, Active Fiber Monitoring will
use the monitoring interval to calculate the initial baseline
average. This means the first x baseline readings will be taken at
the monitoring interval, where x is the number of readings
specified in the average parameter.
See Usage below for more information.
fixed
<1-65535> Set the baseline to a fixed level of received optical power in
0.0001mW. Not recommended—see Usage below.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 267
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING BASELINE
CAUTION: We do not recommend setting a fixed value because gradual change over
time caused by temperature fluctuations, etc. could lead to unnecessary alarms.
If you use the averaging method, you can optionally specify how often Active Fiber
Monitoring polls the cable to determine the baseline. This allows Active Fiber
Monitoring to update the baseline less often than it polls the device for
monitoring.
In order to prevent the theoretical possibility of slow clamping, you can set the
baseline interval to a large value, so that the baseline average is only updated with
the current reading (for example) once per day or once per hour.
As fiber attenuation can be affected by ambient temperature, take care if changing
the baseline interval in environments with large daily temperature fluctuations.
Example To set the baseline optical power to a moving average of the last 30 monitoring
readings on port1.0.17 and port1.0.18, use the command:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring baseline average 30
To calculate the baseline based on 12 values taken 24 hours (86400 seconds) apart,
instead of using the monitoring interval, use the command:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring baseline average 12
interval 86400
To set the baseline to its default, averaging the last 12 readings, use the command:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring baseline
Related
Commands
fiber-monitoring interval
fiber-monitoring sensitivity
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: interval parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 268
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING ENABLE
fiber-monitoring enable
Overview Use this command to enable active fiber monitoring on a fiber port. If the port can
support fiber monitoring but does not have the correct SFP or fiber type installed,
the configuration will be saved, and monitoring will commence when a supported
SFP is inserted. Disabling and re-enabling fiber monitoring on a port resets the
baseline calculation.
Use the no variants of this command to disable active fiber monitoring on the
interface, or to remove all the configuration and state for the ports, respectively.
Syntax fiber-monitoring enable
no fiber-monitoring enable
no fiber-monitoring
Default Active fiber monitoring is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a fiber port
Examples To enable active fiber monitoring on port1.0.17 and port1.0.18, use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring enable
To disable fiber monitoring on the ports, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring enable
To remove all fiber-monitoring configuration and state for the ports, use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17-port1.0.18
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring
Related
Commands
fiber-monitoring action
fiber-monitoring sensitivity
show system fiber-monitoring
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 269
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING INTERVAL
fiber-monitoring interval
Overview Use this command to configure the fiber monitoring polling interval in seconds for
the port. The optical power will be read every <interval> seconds and compared
against the calculated threshold values to see if a log message or other action is
required.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the polling interval to the default (5
seconds).
Syntax fiber-monitoring interval <2-60>
no fiber-monitoring interval
Default The interval is set to 5 seconds by default.
Mode Interface configuration mode for a fiber port.
Example To set the fiber monitoring polling interval for port1.0.17 to 30 seconds, use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring interval 30
To reset the fiber monitoring polling interval back to the default (5s), use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring interval
Related
Commands
fiber-monitoring baseline
show system fiber-monitoring
Parameter Description
<2-60> Optical power polling interval in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 270
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
FIBER-MONITORING SENSITIVITY
fiber-monitoring sensitivity
Overview Use this command to configure the sensitivity of the alarm thresholds on the port
for active fiber monitoring.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the sensitivity to the default.
Syntax fiber-monitoring sensitivity (low|medium|high|highest|fixed
<25-65535>)|relative <0.01-10.0>
no fiber-monitoring sensitivity
Default The default is medium sensitivity.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage A log message is generated and configured actions are taken if the received optical
power drops below the baseline value by the sensitivity configured with this
command.
The sensitivity can be configured to one of four pre-defined levels in decibels or to
a fixed absolute delta in units of 0.0001mW. The alarm thresholds can be seen in
the show system fiber-monitoring output. The maximum absolute sensitivity
configurable is 0.0025 mW. Note that 0.0025 mW equates to a reduction of
approximately 1dB at the maximum attenuation of an AT-SPLX10/1.
Example To set the fiber monitoring sensitivity for port1.0.17 to a relative sensitivity of 0.1
dB, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring sensitivity relative 0.1
To reset the fiber monitoring sensitivity to the default (medium), use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.17
awplus(config-if)# no fiber-monitoring sensitivity
Related
Commands
fiber-monitoring action
fiber-monitoring baseline
Parameter Description
low Low sensitivity (+/-2 dB)
medium Medium sensitivity (1 dB) (default)
high High sensitivity (the greater of 0.5 dB and 0.0025 mW)
highest The highest sensitivity available: 0.0025mW
fixed<25-65535>Fixed sensitivity at the specified level in 0.0001 mW.
relative <0.01-10.0>Relative sensitivity at the specified level in dB.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 272
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM FIBER-MONITORING
show system fiber-monitoring
Overview Use this command to display settings and current status for Active Fiber
Monitoring.
Syntax show system fiber-monitoring
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display configuration and status for active fiber monitoring on ports, use the
command:
awplus# show system fiber-monitoring
Output Figure 8-2: Example output from show system fiber-monitoring
awplus#show sys fiber-monitoring
Fiber Monitoring Status
Reading units 0.0001mW
Interface port1.0.17
Status: enabled
Supported: Supported pluggable
Debugging: disabled
Interval: 2 seconds
Sensitivity: 1.00dB
Baseline type: average of last 35 values greater than 50
Status:
Baseline value: 496
Alarm threshold: 393
Alarm: no
Last 12 Readings: 498 498 498 498 498 498 498 498 498 498 498 498
Minimum reading: 486
Maximum reading: 498
Interface port1.0.18
Status: enabled
Supported: Supported pluggable
Debugging: disabled
Interval: 2 seconds
Sensitivity: 1.00dB
Baseline type: average of last 30 values greater than 50
Status:
Baseline value: 0
Alarm threshold: 0
Alarm: no
Last 12 Readings: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Minimum reading: 0
Maximum reading: 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 273
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM FIBER-MONITORING
Related
Commands
debug fiber-monitoring
fiber-monitoring action
fiber-monitoring baseline
fiber-monitoring enable
Table 8-1: Parameters in the output from show system fiber-monitoring
Parameter Description
Reading units The units for optical power readings in the rest of the
display, e.g. 0.0001mW.
Status Whether active fiber monitoring is enabled or disabled for
this port.
Supported Whether the pluggable inserted in this port supports
active fiber monitoring.
Debugging Whether debugging of active fiber monitoring is enabled
or disabled for this port.
Interval The configured interval between readings of optical
power on this port.
Sensitivity The configured sensitivity threshold for optical power
changes on this port.
Baseline type How the baseline optical power level is calculated: either
the average of the specified number of previous readings
or a specified fixed value in 0.0001mW.
Status Current values for the following parameters.
Baseline value The baseline value, calculated according to the configured
baseline method, in 0.0001mW.
Alarm threshold The current threshold for a change in optical power,
calculated according to the configured sensitivity method,
that will result in action.
Alarm Whether the optical power at the most recent reading
fallen below the threshold.
Last 12 readings The last 12 optical power values measured, in 0.0001mW,
with oldest value first.
Minimum reading The lowest optical power reading since the fiber
pluggable was last inserted, or since active fiber
monitoring was last enabled on the port.
Maximum reading The highest optical power reading since the fiber
pluggable was last inserted, or since active fiber
monitoring was last enabled on the port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 275
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE
show system pluggable
Overview This command displays brief pluggable transceiver information showing the
pluggable type, the pluggable serial number, and the pluggable port on the
device. Different types of pluggable transceivers are supported in different models
of device. See your Allied Telesis dealer for more information about the models of
pluggables that your device supports.
Syntax show system pluggable [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display brief information about all installed pluggable transceivers, use the
command:
awplus# show system pluggable
Output Figure 8-3: Example output from show system pluggable
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports to display information about. The port list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.17)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
portport1.0.17-port1.0.18)
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges (e.g.
port1.0.17,port1.0.18)
awplus#show system pluggable
System Pluggable Information
Port Vendor Device Serial Number Datecode Type
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.17 ATI AT-SPSX A03240R151300867 15032801 1000BASE-SX
port1.0.18 ATI AT-SPSX A03240R111800076 15032801 1000BASE-SX
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 9: Parameters in the output from the show system pluggable command
Parameter Description
Port Specifies the port number for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Vendor Specifies the vendor’s name for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Device Specifies the device name for the installed pluggable
transceiver.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 276
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE
Related
Commands
show system environment
show system pluggable detail
show system pluggable diagnostics
Serial Number Specifies the serial number for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Datecode Specifies the manufacturing datecode for the installed
pluggable transceiver. Checking the manufacturing
datecode with the vendor may be useful when
determining Laser Diode aging issues. For more
information, see ”Troubleshooting Fiber and Pluggable
Issues” in the "Pluggables and Cabling" Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide.
Type Specifies the device type for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Table 9: Parameters in the output from the show system pluggable command
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 277
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE DETAIL
show system pluggable detail
Overview This command displays detailed pluggable transceiver information showing the
pluggable type, the pluggable serial number, and the pluggable port on the
device. Different types of pluggable transceivers are supported in different models
of device. See your Allied Telesis dealer for more information about the models of
pluggables that your device supports.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system pluggable [<port-list>] detail
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage In addition to the information about pluggable transceivers displayed using the
show system pluggable command (port, manufacturer, serial number,
manufacturing datecode, and type information), the show system pluggable
detail command displays the following information:
•SFP Laser Wavelength: Specifies the laser wavelength of the installed
pluggable transceiver
•Single mode Fiber: Specifies the link length supported by the pluggable
transceiver using single mode fiber
•OM1 (62.5μ m) Fiber: Specifies the link length, in meters (m) or kilometers
(km) supported by the pluggable transceiver using 62.5 micron multi-mode
fiber.
•OM2 (50μ m) Fiber: Specifies the link length (in meters or kilometers)
supported by the pluggable transceiver using 50 micron multi-mode fiber.
•Diagnostic Calibration: Specifies whether the pluggable transceiver
supports DDM or DOM Internal or External Calibration.
–Internal is displayed if the pluggable transceiver supports DDM or
DOM Internal Calibration.
–External is displayed if the pluggable transceiver supports DDM or
DOM External Calibration.
– a dash (-) is displayed if neither Internal Calibration or External
Calibration is supported.
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports to display information about. The port list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.17)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
portport1.0.17-port1.0.18)
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges (e.g.
port1.0.17,port1.0.18)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 278
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE DETAIL
•Power Monitoring: Displays the received power measurement type, which
can be either OMA(Optical Module Amplitude) or Avg(Average Power)
measured in μW.
NOTE: For parameters that are not supported or not specified, a hyphen is displayed
instead.
Example To display detailed information about the pluggable transceivers installed in a
particular port on the device, use a command like:
awplus# show system pluggable port1.0.17 detail
To display detailed information about all the pluggable transceivers installed on
the device, use the command:
awplus# show system pluggable detail
Output Figure 8-4: Example output from show system pluggable detail for a port
awplus#show system pluggable port1.0.17 detail
System Pluggable Information Detail
port1.0.17
==========
Vendor Name: ATI
Device Name: AT-SPSX
Device Revision: A
Device Type: 1000BASE-SX
Serial Number: A02420N0607J0023
Manufacturing Datecode: 060704
SFP Laser Wavelength: 850nm
Link Length Supported
Single Mode Fiber : -
OM1 (62.5um) Fiber: 150m
OM2 (50um) Fiber : 300m
OM3 (50um) Fiber : -
Diagnostic Calibration: External
Power Monitoring: Average
Table 8-1: Parameters in the output from show system pluggable detail
Parameter Description
Port Specifies the port the pluggable transceiver is installed in.
Vendor Name Specifies the vendor’s name for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Device Name Specifies the device name for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Device Revision Specifies the hardware revision code for the pluggable
transceiver. This may be useful for troubleshooting because
different devices may support different pluggable
transceiver revisions.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 279
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE DETAIL
Related
Commands
show system environment
show system pluggable
show system pluggable diagnostics
Device Type Specifies the device type for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Serial Number Specifies the serial number for the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Manufacturing
Datecode Specifies the manufacturing datecode for the installed
pluggable transceiver. Checking the manufacturing
datecode with the vendor may be useful when
determining Laser Diode aging issues. For more
information, see “Troubleshooting Fiber and Pluggable
Issues” in the "Pluggables and Cabling" Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide.
SFP Laser
Wavelength Specifies the laser wavelength of the installed pluggable
transceiver.
Single Mode Fiber Specifies the link length supported by the pluggable
transceiver using single mode fiber.
OM1 (62.5um)
Fiber Specifies the link length (in μm - micron) supported by the
pluggable transceiver using 62.5 micron multi-mode fiber.
OM2 (50um) Fiber Specifies the link length (in μm - micron) supported by the
pluggable transceiver using 50 micron multi-mode fiber.
Diagnostic
Calibration Specifies whether the pluggable transceiver supports DDM
or DOM Internal or External Calibration:
Internal is displayed if the pluggable transceiver supports
DDM or DOM Internal Calibration.
External is displayed if the pluggable transceiver supports
DDM or DOM External Calibration.
- is displayed if neither Internal Calibration or External
Calibration is supported.
Power Monitoring Displays the received power measurement type, which can
be either OMA (Optical Module Amplitude) or Avg
(Average Power) measured in μW.
Table 8-1: Parameters in the output from show system pluggable detail (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 280
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE DIAGNOSTICS
show system pluggable diagnostics
Overview This command displays diagnostic information about pluggable transceivers that
support Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM).
Different types of pluggable transceivers are supported in different models of
device. See your device’s Datasheet for more information about the models of
pluggables that your device supports.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show system pluggable [<port-list>] diagnostics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Diagnostic monitoring features allow you to monitor real-time parameters of the
pluggable transceiver, such as optical output power, optical input power,
temperature, laser bias current, and transceiver supply voltage. Additionally, RX
LOS (Loss of Signal) is shown when the received optical level is below a preset
threshold. Monitor these parameters to check on the health of all transceivers,
selected transceivers or a specific transceiver installed in a device.
Examples To display detailed information about all pluggable transceivers installed on a
standalone device, use the command:
awplus# show system pluggable diagnostics
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports to display information about. The port list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.17)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
portport1.0.17-port1.0.18)
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges (e.g.
port1.0.17,port1.0.18)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 281
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW SYSTEM PLUGGABLE DIAGNOSTICS
Output Figure 8-5: Example output from the show system pluggable diagnostics
command on a device
Related
Commands
show system environment
show system pluggable
show system pluggable detail
awplus#show system pluggable diagnostics
System Pluggable Information Diagnostics
port1.0.17 Status Alarms Warnings
Reading Alarm Max Min Warning Max Min
Temp: (Degrees C) 44.871 - 100.00 -40.00 - 95.000 -30.00
Vcc: (Volts) 3.3043 - 3.4650 3.1350 - 3.4000 3.2000
Tx Bias: (mA) 3.468 - 13.264 0.000 - 10.264 0.264
Tx Power: (mW) 0.2376 - 0.7943 0.0562 - 0.6310 0.0708
Rx Power: (mW) 0.2104 - 1.0000 0.0126 - 0.7943 0.0200
Rx LOS: Rx Up
...
Table 9: Parameters in the output from the show system pluggables
diagnostics command
Parameter Description
Temp (Degrees C) Shows the temperature inside the transceiver.
Vcc (Volts) Shows voltage supplied to the transceiver.
Tx Bias (mA) Shows current to the Laser Diode in the transceiver.
Tx Power (mW) Shows the amount of light transmitted from the transceiver.
Rx Power (mW) Shows the amount of light received in the transceiver.
Rx LOS Rx Loss of Signal. This indicates whether:
• light is being received (Rx Up) and therefore the link is up,
or
• light is not being received (Rx Down) and therefore the
link is down
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 282
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
SHOW TEST CABLE-DIAGNOSTICS TDR
show test cable-diagnostics tdr
Overview Use this command to display the results of the last cable-diagnostics test that was
run using the TDR (Time Domain Reflectometer) on a fixed copper cable port.
The displayed status of the cable can be either:
•OK
•Open
• Short (within-pair)
• Short (across-pair)
• Error
Syntax show test cable-diagnostics tdr
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To show the results of a cable-diagnostics test use the following command:
awplus# show test cable-diagnostics tdr
Output Figure 8-6: Example output from the show test cable-diagnostics tdr
command
Related
Commands
clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
test cable-diagnostics tdr interface
Port Pair Length Status
-------------------------------------------------
1.0.1 A - OK
B - OK
C - OK
D - OK

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 283
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PLUGGABLES AND CABLING COMMANDS
TEST CABLE-DIAGNOSTICS TDR INTERFACE
test cable-diagnostics tdr interface
Overview Use this command to apply the Cable Fault Locator’s cable-diagnostics tests to
twisted pair data cables for a selected port. The tests will detect either correct,
short circuit, or open, circuit terminations. For more information on running the
CFL, see the Pluggables and Cabling Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
The test can take several seconds to complete. See the related show command to
display the test results.
A new test can only be started if no other test is in progress. CFL cannot run on a
port that is currently supplying power via PoE.
The displayed status of the cable can be either, OK, Short (within-pair), or Open.
The “Open” or “Short” status is accompanied with the distance from the source
port to the incorrect termination.
Syntax test cable-diagnostics tdr interface <interface>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To run a cable test on the cable inserted into port1.0.1 use the following command:
awplus# test cable-diagnostics tdr interface port1.0.1
You will receive the following message:
Link will go down while test is in progress. Continue? (y/n): y
Select y to continue.
awplus# y
You will then receive the following message:
Test started. This will take several seconds to complete. Use
"show test cable-diagnostics tdr" to print results.
Related
Commands
clear test cable-diagnostics tdr
show test cable-diagnostics tdr
Parameter Description
cable-diagnostics The cable diagnostic tests.
tdr Time Domain Reflectometry.
interface Selects the interface to test.
<interface> Interface number of the port to be tested, e.g. port1.0.2.

9
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 284
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Connectivity Fault
Management
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
Connectivity Fault Management.
For more information, see the Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“cc interval” on page 286
•“cc multicast” on page 288
•“cc unicast” on page 289
•“clear (MEP Attribute)” on page 290
•“clear ethernet cfm errorlog” on page 291
•“clear mep counter” on page 292
•“ethernet cfm domain-name” on page 293
•“ethernet cfm mep” on page 296
•“mep (FNG attributes)” on page 298
•“mep active” on page 300
•“mep ccm-ltm-priority” on page 302
•“mep crosscheck” on page 304
•“service ma-name” on page 306
•“show ethernet cfm details” on page 309
•“show ethernet cfm domain” on page 314
•“show ethernet cfm errorlog” on page 317
•“show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep” on page 319
•“show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep” on page 325
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 286
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CC INTERVAL
cc interval
Overview Use this command to set the CCM Interval.
Syntax cc ma-name <ma-name> interval <interval>
Default The default interval is 4 (1 second).
Mode Ethernet CFM Configuration
Usage Continuity Checks is another term for connectivity fault detection. This makes use
of Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) that are periodically sent by an MEP
(multicast or unicast) and received by other MEP(s). CCMs can be used to detect
connectivity faults across a link (using Link Level MEPs) or across a segment of a
VLAN using VLAN aware MEPs, both of which are used within an MD/MA. CCMs are
sent periodically at a given rate (or frame interval) that is agreed upon by all the
MEPs in the MA. The faster the rate, the more quickly faults can be detected.
If an MEP does not receive a CCM within 3.5 times the expected interval from a peer
MEP(s), that MEP declares a connectivity fault. This is known as a “defect”. Upon
detecting a defect, the detecting MEP will also set the Remote Defect Indicator
(RDI) bit for its outgoing CCM messages to its peer MEP(s) so as to notify the peer
MEPs that a defect has been detected. If the defect persists long enough (generally
2.5 seconds), then an “alarm” is declared. If an alarm is declared, then the defect has
to abate long enough (generally 10 seconds) for the alarm to clear.
Example To set the CCM interval of a Maintenance Association named “MA-INST2-1” to the
value of “4”, use the commands:
awplus(config)# ethernet cfm domain-name MD-INST2
awplus(config-ether-cfm)# cc ma-name MA-INST2-1 interval 4
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
Parameter Description
ma-name Specify the Maintenance Association for which the Interval is
used.
<ma-name> Specify the Maintenance Association's CLI instance name.
interval Specify the CCM Interval.
<interval> Specify the CCM Interval (CCI), using one of the following:
1 - CCI of 3 milliseconds (currently not supported)
2 - CCI of 10 milliseconds (currently not supported)
3 - CCI of 100 milliseconds
4 - CCI of 1 second
5 - CCI of 10 seconds
6 - CCI of 1 minute
7 - CCI of 10 minutes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 287
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CC INTERVAL
service ma-name
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 288
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CC MULTICAST
cc multicast
Overview Use this command to enable a Local MEP to send CCMs using multicast, or to
disable sending CCMs altogether.
Syntax cc multicast state {enable|disable}
Default Multicast is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Usage Continuity Checks is another term for connectivity fault detection. This makes use
of Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) that are periodically sent by an MEP
(multicast or unicast) and received by other MEP(s). CCMs can be used to detect
connectivity faults across a link (using Link Level MEPs) or across a segment of a
VLAN using VLAN aware MEPs, both of which are used within an MD/MA. CCMs are
sent using multicast or unicast (but not both).
In order to enable a Local MEP to send, the Local MEP's “active” administrative state
must be set to true, using the command mep active.
Example To configure a Local MEP to send CCMs using multicast, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# cc multicast state enable
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
service ma-name
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
state Specify to either enable or disable CFM multicast CCMs.
enable Start sending periodic multicast frames.
disable Stop sending multicast frames.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 289
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CC UNICAST
cc unicast
Overview Use this command to enable a Local MEP to send CCMs using unicast, or to disable
sending CCMs altogether.
Syntax cc unicast rmpid <rmep-id> state {enable|disable}
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Usage Continuity Checks is another term for connectivity fault detection. This makes use
of Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) that are periodically sent by an MEP
(multicast or unicast) and received by other MEP(s). CCMs can be used to detect
connectivity faults across a link (using Link Level MEPs) or across a segment of a
VLAN using VLAN aware MEPs, both of which are used within an MD/MA. CCMs are
sent using multicast or unicast (but not both).
In order to enable a Local MEP to send, the Local MEP's “active” administrative state
must be set to true, using the command mep active.
In order to send unicast CCMs, the Remote MEP has to be configured along with its
MAC address.
Example To configure a Local MEP to send CCMs using unicast, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# cc unicast rmpid 21 state enable
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
rmpid The remote MEP that the Local MEP is to unicast to.
<rmep-id> The remote MEP ID in the range 1-8191.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 290
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CLEAR (MEP ATTRIBUTE)
clear (MEP Attribute)
Overview Use this command to clear a Local MEP attribute.
Syntax clear {ccm-ltm-priority|lowest-priority-defect|fng-alarm-time
|reset-fng-time|active|all}
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Example To set the active state of the Local MEP to False, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# clear active
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
mep (FNG attributes)
service ma-name
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
ccm-ltm-priority Set the queuing and p-bit priority for CCM messages to their
default value of 7.
lowest-priority-
defect Set the Fault Notification Generation (FNG) lowest alarm
priority defect to the default value of 2.
fng-alarm-time Set the Fault Notification Generation (FNG) time for a defect to
be present before an alarm is raised to the default value of 2.5
seconds.
reset-fng-time Set the Fault Notification Generation (FNG) time for a defect to
abate before an alarm is cleared to the default value of 10
seconds.
active Set the Local MEP's Active state to the default value of False,
which sets the Local MEP's Administrative State to Down.
all Set all of the above attributes to their default values.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 291
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CLEAR ETHERNET CFM ERRORLOG
clear ethernet cfm errorlog
Overview Use this command to clear the Event List for all Maintenance Associations (MAs)
associated with the specified Maintenance Domain (MD).
Syntax clear ethernet cfm errorlog domain <domain-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage When a new error is detected for an MA that is associated with an MD, and the error
is due to an error from a received or missing CCM from a Remote MEP, an event is
logged to the CFM Errors Event List.
Example To clear the event list for all MA’s associated with an MD named “MD-INST2”, use
the command:
awplus# clear ethernet cfm errorlog domain MD-INST2
Related
Commands
show ethernet cfm errorlog
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<domain-name> Specify the domain name

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 292
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
CLEAR MEP COUNTER
clear mep counter
Overview Use this command to clear statistics counters for all Local MEPs within a given
Maintenance Association (MA) and its associated Maintenance Domain (MD), or to
optionally clear counters for one specific Local MEP.
Syntax clear mep counter domain <domain-name> service <ma-name>
[mep <mep-id>]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To clear the statistic counter for an MEP with the MEP ID “12”, use the command:
awplus# clear mep counter domain MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mep
12
Related
Commands
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
domain Specify the Maintenance Domain that Local MEP(s) are to have
their counters cleared for. Both domain and service must be
specified.
<domain-name> Specify the Maintenance Domain's CLI instance name.
service Specify the Maintenance Association that the Local MEP(s) are to
have their counters cleared for. Both domain and service must be
specified.
<ma-name> Specify the CLI name that identifies the service (Maintenance
Association (MA)) instance.
mep Specify one specific Local MEP.
<mep-id> Specify the Local MEP instance by MEP-id.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 293
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN-NAME
ethernet cfm domain-name
Overview Use this command to create and configure a CFM Maintenance Domain, or to enter
Ethernet CFM Configuration mode for an existing Maintenance Domain instance.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the Maintenance Domain's instance
that was previously created.
Syntax ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name>
ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name> md-type character-string
md-type-name <md-type-name> level <level> [mip-creation none]
ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name> md-type dns-based
md-type-name <md-type-name> level <level> [mip-creation none]
ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name> md-type mac md-type-name
<md-type-name> level <level> [mip-creation none]
ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name> md-type no-name level
<level> [mip-creation none]
no ethernet cfm domain-name <domain-name>
Parameter Description
<domain-name> The name that identifies this Maintenance Domain instance. If
creating this instance, specify the remaining parameters. If
re-entering configuration mode for this instance, use this
parameter to identify this instance, and do not enter the
remaining parameters.
md-type Specify the name type. The MD name part of the MAID field
may or may not appear in the CCM message. There are
different formats and conventions for the name depending on
type.
character-string Specify the md-type as Character String-based MD name
format. The <md-type-name> is a character string of 1 to 43
characters. This character string plus the Short MA name that
is configured for an MA make up the MAID field in a CCM
message.
md-type-name The Maintenance Domain type.
<md-type-name> The value of the MD type name, which depends on the
md-type selected.
dns-based Specify the md-type as DNS-based MD name format. The
<md-type-name> is a Domain Name like string of 1 to 43
characters. This is a globally unique text string derived from a
DNS name. This DNS based string plus the Short MA name
that is configured for an MA make up the MAID field in a CCM
message.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 294
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN-NAME
Mode Global Configuration
Usage A Maintenance Domain is a Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) term that
represents the administrative area of a network from which an operator can
manage VLANs that traverse their area. An MD can also be scoped to a simple
Ethernet link. To differentiate different administrative areas, an MD is made up of a
name and a level. As part of CFM, a Connectivity Check Message (CCM) is used to
detect Ethernet connectivity faults amongst nodes that participate in CFM. CCM
messages carry the MD name within the MAID field as well as carries the level of
the MD.
This command is used to configure the MD name, which can be chosen from a
variety of name format types, as well as the level.
Example To create a Maintenance Domain instance named “MD-INST2” with a character
string-based name of “MD-12L3” and a level of 3, use the command:
awplus(config)# ethernet cfm domain-name MD-INST2 md-type
character-string md-type-name MD-12L3 level 3
To enter Ethernet CFM Configuration mode for an existing MD instance named
“MD-INST2”, use the command:
awplus(config)# ethernet cfm domain-name MD-INST2
awplus(config-ether-cfm)#
To destroy a Maintenance Domain instance named “MD-INST2”, use the
command:
awplus(config)# no ethernet cfm domain-name MD-INST2
Related
Commands
cc interval
cc multicast
cc unicast
mac Specify the md-type as MAC-based MD name format. The
<md-type-name> consists of a MAC address + 2-octet
(unsigned) integer in the form of HHHH.HHHH.HHHH:<2-octet
integer>. This MAC based string plus the Short MA name that
is configured for an MA make up the MAID field in a CCM
message.
no-name Specify the md-type whereby no MD name is to appear in the
CCM message.
level Specify the Level the Domain operates in.
<level> 0 to 7.
mip-creation Optional parameter that specifies the MIP creation permission
value.
none Specifies that no MIPs are to be created (default and only
choice).
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 295
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN-NAME
cfm-sf-notify
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm mep
mep (FNG attributes)
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm domain
show ethernet cfm errorlog
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
show ethernet cfm service
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 296
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ETHERNET CFM MEP
ethernet cfm mep
Overview Use this command to create a Local MEP instance, or to enter Interface Ethernet
CFM MEP Configuration mode for an existing Local MEP's instance, so you can
configure it.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the Local MEP instance.
Syntax ethernet cfm mep down mpid <mep-id> domain-name <domain-name>
ma-name <ma-name>
no ethernet cfm mep down mpid <mep-id> domain-name <domain-name>
ma-name <ma-name>
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Maintenance Points are entities that exist within an MD/MA and can perform the
CFM/802.1ag functions such as Continuity Checks for fault management. The main
type of MP is a Maintenance End Point (MEP). This type of maintenance point sits
at the edges of a Maintenance Domain but is a member of only one MA within the
Maintenance Domain. Thus an MEP is used at the end of a VLAN segment, or it is
used at the end of a link. MPs live on bridge ports and station ports. On a bridge
port, there are two types.
• An Up Maintenance Entity is considered an inward MP. It communicates
across the inside of the bridge to the other side, and this allows it to reach the
outside world. It lives on a bridge port for a given VLAN, but it does not use
this port to send or receive to get to the outside world. Instead, it sends and
receives through the inside of the bridge and communicates to the outside
world through the other VLAN port members. An Up MP cannot be used for
Link Level CFM.
• A Down Maintenance Entity is considered an outward MP. It sends and
receives only through its bridge port outwardly to the outside world, and
does not communicate inside the bridge. A Down MP is not subject to
blocking due to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) or any other protocol trying to
Parameter Description
down Specify the Local MEP as a Down MEP.
mpid Specify the Local MEP ID.
<mep-id> 1-8191. This must be unique ID for all MEPs in the MA (both local
and remote).
domain-name Specify the Maintenance Domain that the Local MEP is to be
associated with.
<domain-name> Specify the Maintenance Domain's CLI instance name.
ma-name Specify the Maintenance Association that the Local MEP is to be
associated with.
<ma-name> Specify the Maintenance Association's CLI instance name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 297
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
ETHERNET CFM MEP
prevent loops in the network. As such, it is important that Down MPs be used
in an MD/MA that is not subject to topology loops. A Down MP can be VLAN
aware or link-local.
An MEP can be either Up or Down for a given MD/MA, but within a bridge for the
same MD/MA, there can only be one Up or Down MEP (not both). An Up MEP must
be VLAN aware. A Down MEP may be VLAN aware. Otherwise, a Down MEP is
allowed to be link local (VLAN unaware), and its scope is that of the entire link.
AlliedWare Plus supports Down Maintenance Entities only.
Example To create a local MEP instance context with a domain name of “MD-INST2” and an
MA name of “MA-INST2-1”, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
To re-enter a local MEP instance context with the domain name “MD-INST2” and
the MA name “MA-INST2-1”, use the commands:
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)#
To destroy a local MEP instance context with the domain name “MD-INST2” and
the MA name “MA-INST2-1”, use the commands:
awplus(config-if)# no ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
Related
Commands
cc multicast
cc unicast
cfm-sf-notify
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm domain-name
mep (FNG attributes)
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm errorlog
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
show ethernet cfm service
show mep-alarm status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 298
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP (FNG ATTRIBUTES)
mep (FNG attributes)
Overview Use this command to configure the Fault Notification Generation (FNG) attributes
of a Local MEP.
Syntax mep {lowest-priority-defect <defect-priority>|
fng-alarm-time <soak-time>|reset-fng-time <abate-time>}
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Usage Maintenance Points are entities that exist within an MD/MA and can perform the
CFM/802.1ag functions such as Continuity Checks for fault management. The main
type of MP is a Maintenance End Point (MEP). This type of maintenance point sits
at the edges of a Maintenance Domain but is a member of only one MA within the
Maintenance Domain. Thus an MEP is used at the end of a VLAN segment, or it is
used at the end of a link.
A Local MEP can detect defects in connectivity of a VLAN or a local link using
Continuity Check Messages (CCM) by sending and receiving CCMs with Remote
MEP peers. Any defects detected locally can also be conveyed to Remote MEP
peers by sending a Remote Defect Indicator (RDI) to the peers within a Continuity
Check Message (CCM). If defects persist long enough, an alarm can be generated.
Use this command to configure the following attributes of a Local MEP:
• Fault Notification Generation Lowest Alarm Priority Defect — the lowest
defect priority that can cause an alarm to be raised. This configuration
parameter specifies the lowest defect that has to occur before an alarm can
be generated. Any priority less than this will not result in an alarm
notification. Note that if a local defect is detected and its priority is not high
enough to generate an alarm, then the Local MEP will not send an RDI to its
Remote MEP peers, which is used to notify the peers of a connectivity fault.
We recommend you keep the lowest alarm priority defect set to 2.
• Fault Notification Generation Alarm timers — the timers that determine
whether a defect has been present long enough to result in an alarm being
generated, or whether a defect has been abated for long enough to clear an
alarm.
Parameter Description
lowest-priority-defect
<defect-priority> The lowest level defect allowed to generate alarms.
An integer in the range 1 to 6. T he default is 2.
fng-alarm-time
<soak-time> The time that the defects must be present before an
alarm is generated. An integer in the range of 250 to
1000 in increments of 10 ms. The default is 250 (2.5
seconds).
reset-fng-time
<abate-time> The time that the defect must be absent before the
alarm is cleared. An integer in the range of 250 to
1000 in increments of 10 ms. The default is 1000 (10
seconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 299
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP (FNG ATTRIBUTES)
Example To clear an alarm after the defect has been abated for 6 seconds, use the
commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# mep reset-fng-time 600
Related
Commands
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
service ma-name
show mep-alarm status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 300
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP ACTIVE
mep active
Overview Use this command to specify the administrative state of the Local MEP.
Syntax mep active {true|false}
Default false
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Usage Maintenance Points are entities that exist within an MD/MA and can perform the
CFM/802.1ag functions such as Continuity Checks for fault management. The main
type of MP is a Maintenance End Point (MEP). This type of maintenance point sits
at the edges of a Maintenance Domain but is a member of only one MA within the
Maintenance Domain. Thus an MEP is used at the end of a VLAN segment, or it is
used at the end of a link.
A Local MEP can detect defects in connectivity of a VLAN or a local link using
Continuity Check Messages (CCM) by sending and receiving CCMs with Remote
MEP peers. Any defects detected locally can also be conveyed to Remote MEP
peers by sending a Remote Defect Indicator (RDI) to the peers within a Continuity
Check Message (CCM). If defects persist long enough, an alarm can be generated.
Setting the Local MEP's Administrative State to true enables it to perform various
functions such as processing CCM messages. Setting the state to false deactivates
the Local MEP.
Example To set the administrative state of the local MEP to “active”, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# mep active true
Related
Commands
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
service ma-name
show mep-alarm status
Parameter Description
true Put the Local MEP into a state of active, which enables it to
perform various functions such as processing CCM messages.
false Specify the state of the Local MEP to cease functioning.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 301
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP ACTIVE
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 302
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP CCM-LTM-PRIORITY
mep ccm-ltm-priority
Overview Use this command to specify the queuing and p-bit priority for CCM messages.
Syntax mep ccm-ltm-priority <0-7>
Default 7
Mode Interface Ethernet CFM MEP Configuration
Usage Maintenance Points are entities that exist within an MD/MA and can perform the
CFM/802.1ag functions such as Continuity Checks for fault management. The main
type of MP is a Maintenance End Point (MEP). This type of maintenance point sits
at the edges of a Maintenance Domain but is a member of only one MA within the
Maintenance Domain. Thus an MEP is used at the end of a VLAN segment, or it is
used at the end of a link.
A Local MEP can detect defects in connectivity of a VLAN or a local link using
Continuity Check Messages (CCM) by sending and receiving CCMs with Remote
MEP peers. CCMs are high priority messages by default, but the priority is
configurable, although we do not recommend changing it. Any defects detected
locally can also be conveyed to Remote MEP peers by sending a Remote Defect
Indicator (RDI) to the peers within a Continuity Check Message (CCM). If defects
persist long enough, an alarm can be generated.
Example To set the queuing and p-bit priority for CCM messages to 6, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep down mpid 12 domain-name
MD-INST2 ma-name MA-INST2-1
awplus(config-if-eth-cfm-mep)# mep ccm-ltm-priority 6
CCMs should be the highest priority message so we recommend leaving their
priority as 7.
Related
Commands
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
service ma-name
show mep-alarm status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Parameter Description
<0-7> The queuing and p-bit priority for CCM messages.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 303
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP CCM-LTM-PRIORITY
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 304
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP CROSSCHECK
mep crosscheck
Overview Use this command within the MD instance context to create a Remote MEP
instance and configure its parameters.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the Remote MEP instance.
Syntax mep crosscheck mpid <rmep-id> ma-name <ma-name> [mac
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>]
no mep crosscheck mpid <rmep-id> ma-name <ma-name>
Mode Ethernet CFM Configuration
Usage Maintenance Points are entities that exist within an MD/MA and can perform the
CFM/802.1ag functions such as Continuity Checks for fault management. The main
type of MP is a Maintenance End Point (MEP). This type of maintenance point sits
at the edges of a Maintenance Domain but is a member of only one MA within the
Maintenance Domain. Thus an MEP is used at the end of a VLAN segment, or it is
used at the end of a link. MPs live on bridge ports and station ports. On a bridge
port, there are two types.
• An Up Maintenance Entity is considered an inward MP. It communicates
across the inside of the bridge to the other side, and this allows it to reach the
outside world. It lives on a bridge port for a given VLAN, but it does not use
this port to send or receive to get to the outside world. Instead, it sends and
receives through the inside of the bridge and communicates to the outside
world through the other VLAN port members. An Up MP cannot be used for
Link Level CFM.
• A Down Maintenance Entity is considered an outward MP. It sends and
receives only through its bridge port outwardly to the outside world, and
does not communicate inside the bridge. A Down MP is not subject to
blocking due to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) or any other protocol trying to
prevent loops in the network. As such, it is important that Down MPs be used
Parameter Description
mpid Specify the Remote MEP id.
<rmep-id> 1-8191. This must be unique ID for all MEPs in the MA (both
local and remote).
ma-name Specify the Maintenance Association that the Remote MEP is
to be associated with.
<ma-name> Specify the Maintenance Association's CLI instance name.
mac Optionally, when using unicast for communication between a
Local MEP and a Remote MEP, specify the remote MEP's MAC
address.
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH> Specify the Remote MEP's MAC address using the
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format where H is a hexadecimal value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 305
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
MEP CROSSCHECK
in an MD/MA that is not subject to topology loops. A Down MP can be VLAN
aware or link-local.
An MEP can be either Up or Down for a given MD/MA, but within a bridge for the
same MD/MA, there can only be one Up or Down MEP (not both). An Up MEP must
be VLAN aware. A Down MEP may be VLAN aware. Otherwise, a Down MEP is
allowed to be link local (VLAN unaware), and its scope is that of the entire link.
Example To create a remote MEP instance named “MA-INST2-1” with an MEP ID of 21, use
the command:
awplus(config-ether-cfm)# mep crosscheck mpid 21 ma-name
MA-INST2-1
To destroy the remote MEP instance named “MA-INST2-1” with the MEP ID of 21,
use the command:
awplus(config-ether-cfm)# no mep crosscheck mpid 21 ma-name
MA-INST2-1
Related
Commands
cc unicast
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm errorlog
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
show ethernet cfm service
show mep-alarm status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 306
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SERVICE MA-NAME
service ma-name
Overview Use this command to create a Maintenance Association instance within the MD
instance context and configure its parameters.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the Maintenance Association
instance.
Syntax service ma-name <ma-name> ma-type
{icc|integer|primary-vid|string|vpn-id} ma-type-name
<ma-type-name> [vlan <primary-vid> [mip-creation {none}]]
no service <ma-name>
Parameter Description
<ma-name> The CLI name that identifies this Maintenance Association (MA)
instance.
ma-type Specify the MA name type. The MA name part of the MAID field
appears in the CCM message. There are different formats and
conventions for the name depending on the type.
icc Specify the ma-type as ICC based MA name format. The
<ma-type-name> is a 13 byte character string consisting of a 1 to
6 character ITU Carrier Code (ICC) plus a 1 to 6 character Unique
MEGID (UMC) code for the name. Any remaining characters are
padding out with NULLs by the system to fill out the 13 bytes.
This can only be used with Maintenance Domain whose name
md-type is set to “No name”.
integer Specify the ma-type as Integer based MA name format. The
<ma-type-name> Is a number up to 2 Bytes (0..65535).
primary-vid Specify the ma-type as Primary VLAN-id based MA name format.
The <ma-type-name> Is the VLAN id number that has been
assigned to the MA as the primary VLAN.
string Specify the ma-type as Character String based MA name format.
The <ma-type-name> is a string of 1 to 45 characters.
vpn-id Specify the ma-type as an RFC2685 VPN ID based MA name
format. The <ma-type-name> is a 7 Byte value divided into two
parts. The first part makes up the VPN's OUI which is three octets
and the remaining four octets make up the VPN Index. The
format is HHHHHH.HHHHHHHH where H is a hexadecimal digit.
ma-type-name The Maintenance Association (MA) name type.
<ma-type-name> The value of the MA type name, which depends on the ma-type
selected (icc, integer, primary-vid, string, vpn-id).
vlan An optional parameter that specifies the VLAN.
<primvary-vid> Specify the ID of the primary VLAN in the MA.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 307
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SERVICE MA-NAME
Mode Ethernet CFM Configuration
Usage A Maintenance Association is a Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) term that
represents a particular segment of a network within a Maintenance Domain. An
MA can represent a segment of a VLAN that is managed for connectivity within
that segment. As a VLAN is often the granularity that a Network Service Provider
sells to their customer, an MA is often referred to as a “Service”. An MA can also be
used to represent a link and in this case the MA is VLAN unaware.
As part of CFM, a Connectivity Check Message (CCM) is used to detect Ethernet
connectivity faults amongst nodes that participate in CFM. CCM messages carry
the MA name within the MAID field. Within an MD instance context, this command
is used to configure the MA name, which can be chosen from a variety of format
types.
Example To create a Maintenance Association instance named “MA-INST2-1” with an MA
name type of “string” and value of “MA-12V100”, use the command:
awplus(config-ether-cfm)# service ma-name MA-INST2-1 ma-type
string ma-type-name MA-12V100
To destroy a Maintenance Association instance named “MA-INST2-1”, use the
command:
awplus(config-ether-cfm)# no service MA-INST2-1
Related
Commands
cc interval
cc multicast
cc unicast
cfm-sf-notify
clear (MEP Attribute)
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
mep (FNG attributes)
mep crosscheck
show ethernet cfm domain
show ethernet cfm errorlog
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
show ethernet cfm service
mip-creation Optional parameter that specifies the MIP creation permission
value.
none Specifies that no MIPs are to be created (the default and only
choice).
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 308
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SERVICE MA-NAME
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 309
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DETAILS
show ethernet cfm details
Overview Use this command to show CFM configuration, status, and statistics in detail for all
CFM entities that the system knows about.
Syntax show ethernet cfm details
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show CFM configuration, status, and statistics in detail for all CFM entities, use
the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm details
The output loops through the hierarchy of MDs, then MAs within each MD, then
local MEPs within that MA, and finally remote MEPs within that MA.
Output Figure 9-1: Example output from show ethernet cfm details
awplus#show ethernet cfm details
==========================================================
Maintenance Domain
==========================================================
Maintenance Domain Name........... MD-INST1
Maintenance Domain Name Format.... character-string
Maintenance Domain Name Value..... MD-12L3
Level............................. 3
Associated CFM Services........... (VLAN 400 ): MA-INST1-1
(VLAN 300 ): MA-INST1-2
MIP Creation...................... None
Service
-------
CFM Service Name.................. MA-INST1-1
CFM Domain Name................... MD-INST1
CFM Domain Level.................. 3
Primary VLAN...................... 400
Maintenance Assoc Name Format..... string
Maintenance Assoc Name Value...... MA-12V400
CCM Transmission Interval......... 1 second
Local MEPs........................ MEP DOWN
2 (interface port1.0.3)
Configured Remote MEPs............ 102
Missing Remote MEPs............... None
Current MEP Defects............... -
MIP Creation...................... None
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 310
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DETAILS
Local Maintenance End Point
---------------------------
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-1
MA Primary VLAN................... 400
MEP ID............................ 2
Direction......................... Down
Interface......................... port1.0. 3
MEP Active State.............. True
CC State...................... Enabled
CC Type....................... Multicast
PDU VLAN Priority............. 7
MAC-address................... eccd.6dc9.bef6
Tx-RDI........................ False
Current Defects............... -
Current Highest Defect Alarm.. -
Alarm Minimum Defect.......... 2 (someMACstatusDefect)
Alarm Trip Time............... AUTO (2.5 seconds)
Alarm Reset Time.............. AUTO (10 seconds)
Configured Remote MEPs........ 102
Missing Remote MEPs........... None
Error CCM Reason.............. N/A
Last Error CCM................ N/A
Cross-connect Defect Reason... N/A
Last Cross Connect CCM........ N/A
Counters
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-1
MA Service VLAN................... 400
MEP ID............................ 2
Direction......................... DOWN
Interface......................... port1.0. 3
Tx CCM Count................... 0
Rx Out-of-Sequence CCM......... 0
Remote Maintenance End Point
----------------------------
CFM Service Name.................. MA-INST1-1
CFM Domain Name................... MD-INST1
Remote MEPID...................... 102
Receiving CCMs.................... Wait
Rx RDI............................ -
MAC Address....................... -
Port Status....................... -
Interface Status.................. -
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 311
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DETAILS
Service
-------
CFM Service Name.................. MA-INST1-2
CFM Domain Name................... MD-INST1
CFM Domain Level.................. 3
Primary VLAN...................... 300
Maintenance Assoc Name Format..... string
Maintenance Assoc Name Value...... MA-12V300
CCM Transmission Interval......... 1 second
Local MEPs........................ MEP DOWN
1 (interface port1.0.1)
MEP DOWN
200 (interface port1.0.2)
Configured Remote MEPs............ 101,1001
Missing Remote MEPs............... 101,1001
Current MEP Defects............... 3 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
MIP Creation...................... None
Local Maintenance End Point
---------------------------
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-2
MA Primary VLAN................... 300
MEP ID............................ 1
Direction......................... Down
Interface......................... port1.0. 1
MEP Active State.............. True
CC State...................... Enabled
CC Type....................... Multicast
PDU VLAN Priority............. 7
MAC-address................... eccd.6dc9.bef6
Tx-RDI........................ True
Current Defects............... 3 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Current Highest Defect Alarm.. 4 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Alarm Minimum Defect.......... 2 (someMACstatusDefect)
Alarm Trip Time............... AUTO (2.5 seconds)
Alarm Reset Time.............. AUTO (10 seconds)
Configured Remote MEPs........ 101,1001
Missing Remote MEPs........... 101,1001
Error CCM Reason.............. N/A
Last Error CCM................ N/A
Cross-connect Defect Reason... N/A
Last Cross Connect CCM........ N/A
Counters
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-2
MA Service VLAN................... 300
MEP ID............................ 1
Direction......................... DOWN
Interface......................... port1.0. 1
Tx CCM Count................... 121
Rx Out-of-Sequence CCM......... 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 312
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DETAILS
Local Maintenance End Point
---------------------------
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-2
MA Primary VLAN................... 300
MEP ID............................ 200
Direction......................... Down
Interface......................... port1.0. 2
MEP Active State.............. True
CC State...................... Enabled
CC Type....................... Multicast
PDU VLAN Priority............. 7
MAC-address................... eccd.6dc9.bef6
Tx-RDI........................ True
Current Defects............... 3 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Current Highest Defect Alarm.. 4 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Alarm Minimum Defect.......... 2 (someMACstatusDefect)
Alarm Trip Time............... AUTO (2.5 seconds)
Alarm Reset Time.............. AUTO (10 seconds)
Configured Remote MEPs........ 101,1001
Missing Remote MEPs........... 101,1001
Error CCM Reason.............. N/A
Last Error CCM................ N/A
Cross-connect Defect Reason... N/A
Last Cross Connect CCM........ N/A
Counters
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-2
MA Service VLAN................... 300
MEP ID............................ 200
Direction......................... DOWN
Interface......................... port1.0. 2
Tx CCM Count................... 0
Rx Out-of-Sequence CCM......... 0
Remote Maintenance End Point
----------------------------
CFM Service Name.................. MA-INST1-2
CFM Domain Name................... MD-INST1
Remote MEPID...................... 101
Receiving CCMs.................... Fail
Rx RDI............................ -
MAC Address....................... -
Port Status....................... -
Interface Status.................. -
Remote Maintenance End Point
----------------------------
CFM Service Name.................. MA-INST1-2
CFM Domain Name................... MD-INST1
Remote MEPID...................... 1001
Receiving CCMs.................... Fail
Rx RDI............................ -
MAC Address....................... -
Port Status....................... -
Interface Status.................. -

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 313
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DETAILS
Related
Commands
show ethernet cfm domain
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep
show ethernet cfm service
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 314
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN
show ethernet cfm domain
Overview Use this command to show the Ethernet CFM Domain(s) that have been
configured in summary format. Options include the ability to show all domains
with detailed information, or to show a specified domain with detailed
information.
Syntax show ethernet cfm domain
show ethernet cfm domain details
show ethernet cfm domain <domain-name> details
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show all domain configurations in summary format, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm domain
To show all domains in detail, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm domain details
To show a specific domain named “MD-INST1” in detail, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm domain MD-INST1 details
Output Figure 9-2: Example output from show ethernet cfm domain
Parameter Description
<domain-name> The CLI name that identifies this Maintenance Domain instance.
details Provide detailed information in the output.
awplus#show ethernet cfm domain
CFM Domain Name Level
---------------------------------------
MD-INST1 0
MD-INST2 3
Table 9-1: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm domain
Parameter Description
CFM Domain Name The Maintenance Domain name for the managed object.
Level The level for the domain.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 315
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN
Figure 9-3: Example output from show ethernet cfm domain details
Figure 9-4: Example output from show ethernet cfm domain MD-INST1
details
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
awplus#show ethernet cfm domain details
Maintenance Domain Name.......... MD-INST1
Maintenance Domain Name Format... character-string
Maintenance Domain Name Value.... MD-12L0
Level............................ 0
Associated CFM Services.......... (Link Level ): MA-INST1-1
MIP Creation..................... None
------------------------------------------------------------------
Maintenance Domain Name.......... MD-INST2
Maintenance Domain Name Format... character-string
Maintenance Domain Name Value.... MD-12L3
Level............................ 3
Associated CFM Services.......... (Link Level ): MA-INST2-1
MIP Creation..................... None
------------------------------------------------------------------
awplus#show ethernet cfm domain MD-INST1 details
Maintenance Domain Name.......... MD-INST1
Maintenance Domain Name Format... character-string
Maintenance Domain Name Value.... MD-12L0
Level............................ 0
Associated CFM Services.......... (Link Level ): MA-INST1-1
MIP Creation..................... None
------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 9-2: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm domain details
Parameter Description
Domain Name The Maintenance Domain name for the managed object.
Domain Name Format
and Value The Maintenance Domain Name Format and Value. The
format is one of the following:
character-string
DNS
MAC
No name
Level The level for the domain.
Associated CFM
Services The Maintenance Associations (MA) instance names.
MIP Creation The MIP creation value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 316
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM DOMAIN
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm details
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 317
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM ERRORLOG
show ethernet cfm errorlog
Overview Use this command to list the CFM Errors that are in the CFM Errors Event List,
starting from the oldest at the top to the latest at the end.
Syntax show ethernet cfm errorlog domain <domain-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage When a new error is detected for a Maintenance Association (MA) that is associated
with a Maintenance Domain (MD), and such is due to an error from a received or
missing CCM from a Remote MEP, an event is logged to the CFM Errors Event List.
Example To show the list of errors for an MD named “MD-INST2”, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm errorlog domain MD-INST2
Output Figure 9-5: Example output from show ethernet cfm errorlog domain
MD-INST2
Parameter Description
<domain-name> Specify the domain name value.
awplus#show ethernet cfm errorlog domain MD-INST2
CFM Service Name Level VLAN MEPID Remote MAC Error Reason
------------------------------------------------------------------
MA-INST2-1 0 0 12 0000.0000.0000 Remote MEP Down
Table 9-3: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm errorlog domain
MD-INST2
Parameter Description
Level The level configured for the MD.
VLAN The VLAN ID used by the MA if any, otherwise is "0".
MEPID The MEP ID of the local MEP that detected the error.
Remote MAC The source MAC address of the received CCM causing the
error if known, 0000.0000.0000 otherwise.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 318
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM ERRORLOG
Related
Commands
clear ethernet cfm errorlog
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Error Reason One of the following:
“Remote MEP Down” - an RMEPCCMDefect has been
declared for this remote MEP. CCMs have not been
received from this remote MEP within the CCM interval.
“MEP Configuration” - the CCM received from the remote
MEP has the same MEP ID as the local MEP that received
the CCM. For unicast remote MEPs this error can also
indicate that even though the CCM received from the
remote MEP has an MEP ID that matches a configured
remote MEP ID in the MA, the source MAC address differs
from the configured MAC address for that remote MEP.
“Forwarding Loop” - the CCM received from the remote
MEP has an MEP ID that matches a configured local MEP ID
in the MA, and also has the same source MAC address as
the local MEP's MAC address that received the CCM.
“Cross Connected” - a xconCCMdefect was detected.
CFM Service Name The name of the MA associated with the MD for this
error(s).
Table 9-3: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm errorlog domain
MD-INST2 (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 319
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
local mep
Overview Use this command to show one or more Local MEPs, and their configuration and
status in summary format. Options include the ability to show Local MEP(s) for a
given interface with further option to show statistics counters. Another option is to
show Local MEPs for a given Maintenance Association (MA) and Maintenance
Domain (MD) either for statistics counters, or for one specific Local MEP with either
detailed information or statistics counters.
Syntax show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep interface <port>
[counters]
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep domain
<domain-name> service <ma-name> [counters]
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep domain
<domain-name> service <ma-name> mep <mep-id> {details|counters}
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Examples To show the configuration and status of all the Local MEP(s) on an interface, use the
command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep
interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
interface Specify the interface for which Local MEP(s) are to be shown.
<interface-
name> Specify the interface by name.
counters Specify that counter statistics are to be shown.
domain Specify the Maintenance Domain that Local MEP(s) are to be
shown for. Both this and service must be specified.
<domain-name> Specify the Maintenance Domain's CLI instance name.
service Specify the Maintenance Association that the Local MEP(s) are to
be shown for. Both this and domain must be specified.
<ma-name> Specify CLI name that identifies the service (Maintenance
Association (MA)) instance of interest.
mep Specify one particular Local MEP of interest.
<mep-id> Specify the Local MEP instance by MEP-id.
details Specify that details are to be included in the output.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 320
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
To show details of a specific Local MEP on an MA and its associated MD, use the
command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mep 12 details
Output Figure 9-6: Example output from show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
local mep interface port1.0.2
awplus#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep interface
port1.0.2
Service Name MEPID Dir Interface State Defect
------------------------------------------------------------------
MA-INST1-1 12 D port1.0.2 En ..3..
Table 9-4: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points local mep interface <interface-name>
Parameter Description
Service Name The MA service name.
MEPID The MEP ID of the local MEP of interest within the MA.
Dir The direction of this local MEP:
D - Down MEP.
U - Up MEP.
Note: Only Down is currently supported.
Interface The interface on which the local MEP resides.
State Whether the local MEP's CCM processing is enabled “En”
or disabled “Dis”.
Defect Defect bit list <dbl> indicating which of 5 possible defects
are currently being detected with each bit showing the
detected <defect-number> or . if there is no defect.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 321
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
Figure 9-7: Example output from show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
local mep domain MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mep 12
details
awplus#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mep 12 details
Domain Name....................... MD-INST1
MA Service Name................... MA-INST1-1
MA Primary VLAN................... 0
MEP ID............................ 12
Direction......................... Down
Interface......................... port1.0. 2
MEP Active State.............. True
CC State...................... Enabled
CC Type....................... Multicast
PDU VLAN Priority............. 7
MAC-address................... 000c.2526.95a1
Tx-RDI........................ True
Current Defects............... 3 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Current Highest Defect Alarm.. 4 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
Alarm Minimum Defect.......... 2 (someMACstatusDefect)
Alarm Trip Time............... AUTO (2.5 seconds)
Alarm Reset Time.............. AUTO (10 seconds)
Configured Remote MEPs........ 21
Missing Remote MEPs........... 21
Error CCM Reason.............. N/A
Last Error CCM................ N/A
Cross-connect Defect Reason... N/A
Last Cross Connect CCM........ N/A
Table 9-5: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points local mep domain <domain-name> service
<ma-name> mep <mep-id> details
Parameter Description
Domain Name and
MA Service Name Uniquely identify the MD and MA this local MEP is
associated with.
MA Primary VLAN The VLAN used by this MEP. A link-local MEP VLAN is
indicated by “-”.
MEP ID The local MEP's ID.
Direction The direction of the local MEP, either Down or Up.
Interface The Interface port or Interface lag that the local MEP is
configured against.
MEP Active State The MEP’s configured administrative state:
Up: True
Down: False.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 322
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
CC State The MEP's CCM configured administrative state:
Up: Enable
Down: Disable.
CC Type The configured CCM sending and receiving type, either
multicast or unicast. If not yet configured, it shows as
None.
Tx-RDI Whether this local MEP is sending RDI or not. An RDI is
sent when one or more of the following defects have been
declared by the local MEP:
someRMEPCCMdefect
someMACstatusDefect
errorCCMdefect
xconCCMdefect
Current Defects A list of defects the local MEP is currently detecting. It
shows the defect(s), as both a defect priority and name.
Current Highest
Defect Alarm The highest defect priority that has been encountered
while the local MEP has been in an alarm state.
Alarm Minimum
Defect The minimum defect the local MEP has to see before
declaring an alarm.
Alarm Trip Time The amount of time the defect has to exist before an alarm
is declared.
Configured Remote
MEP IDs A comma separated list of configured remote MEPs (by
MEP IDs) known by this local MEP. If the remote MEP also
has a configured unicast MAC address, the MEP ID will also
include -HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
Missing Remote
MEPs The remote MEPs (by MEP ID) that have been configured
against this local MEP but have not been heard from.
Table 9-5: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points local mep domain <domain-name> service
<ma-name> mep <mep-id> details (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 323
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
Related
Commands
clear mep counter
ethernet cfm mep
show ethernet cfm details
Error CCM Reason The reason that the local MEP is detecting the
errorCCMdefect condition (if any):
Wrong MEP ID Received - CCM received with correct level
and MAID, but MEP ID has not been configured in this MA.
My MEP ID Received - CCM received with correct level and
MAID, but an MEP ID that is the same as a local MEP in this
MA.
My MEP ID Received (loop) - as above, but the CCM
received also has the same MAC address as the local MEP
in the MA.
CCM Interval Mismatch - CCM received with correct level
and MAID, but CCM interval does not match that
configured for this MA.
MAC address mismatch - for a configured unicast RMEP
(via crosscheck) the MAC address did not match the
provisioned value in the associated MA.
N/A - indicates there is no error CCM defect being
detected.
Last Error CCM If an errorCCMdefect condition is detected, portions of the
CCM that caused this condition are displayed.
Cross Connect
Defect Reason The reason that the local MEP is detecting the
xconCCMdefect condition (if any):
Wrong MAID - CCM received with correct level but
incorrect MAID (mismatch in the domain name and/or
short MA name versus configured).
Wrong Level - CCM received with a level that is lower than
the level configured for this local MEP's domain.
N/A - indicates there is no error CCM defect being
detected.
Last Cross Connect
CCM If a xconCCMdefect condition is detected, portions of the
CCM that caused this condition are displayed.
Table 9-5: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points local mep domain <domain-name> service
<ma-name> mep <mep-id> details (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 324
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS LOCAL MEP
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 325
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS REMOTE MEP
show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
remote mep
Overview Use this command to show one or more Ethernet CFM maintenance points,
namely Remote Maintenance End Points (MEPs) within a given Maintenance
Association (MA) and its associated Maintenance Domain (MD), and their
configuration and status in summary format. Options include the ability to show
an individual Remote MEP in detail.
Syntax show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
<domain-name> service <ma-name> [{mac <rmep-mac-address>|rmep
<mep-id>} details]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show all the remote MEP(s)'s status for this MA and MD in summary form, use
the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1
To show a specific remote MEP by its ID in detail, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 rmep 21 details
To show a specific remote MEP by its MAC address in detail, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mac 000c.2526.95bf details
Parameter Description
domain Specify the Maintenance Domain that Remote MEP(s) are to
be shown for.
<domain-name> Specify the Maintenance Domain's CLI instance name.
service Specify the Maintenance Association that the Remote
MEP(s) are to be shown for.
<ma-name> Specify the service's (Maintenance Association (MA)) CLI
instance name.
mac Specify the remote MEP of interest by its MAC address.
<rmep-mac-address> Specify the value of the remote MEP's MAC address using
the format HHHH.HHHH.HHHH where H is a hexadecimal
digit.
rmep Specify the remote MEP of interest by its ID.
<mep-id> Specify the value of the remote MEP's ID in the range 1 to
8191.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 326
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS REMOTE MEP
Output Figure 9-8: Example output from show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
remote mep domain MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1
Figure 9-9: Example output from show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
remote mep domain MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 rmep 21
details
Figure 9-10: Example output from show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
remote mep domain MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mac
000c.2526.95bf details
awplus#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1
CFM Domain Name: MD-INST1
CFM Service Name: MA-INST1-1
RX RX Port Intf
MEPID CCM RDI Stat Stat
----------------------------
21 Yes No Up Up
awplus#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 rmep 21 details
CFM Service Name..... MA-INST1-1
CFM Domain Name...... MD-INST1
Remote MEPID......... 21
Receiving CCMs....... Yes
Rx RDI............... No
MAC Address.......... 000c.2526.95bf
Port Status.......... Up
Interface Status..... Up
awplus#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote mep domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1 mac 000c.2526.95bf details
CFM Service Name..... MA-INST1-1
CFM Domain Name...... MD-INST1
Remote MEPID......... 21
Receiving CCMs....... Yes
Rx RDI............... No
MAC Address.......... 000c.2526.95bf
Port Status.......... Up
Interface Status..... Up
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 327
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM MAINTENANCE-POINTS REMOTE MEP
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm details
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Table 9-6: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points remote mep
Parameter Description
CFM Domain Name
and CFM Service
Name
The instance identifiers that uniquely identify the MA and
MD for the remote MEP(s) of interest.
Remote MEPID The remote MEP ID that is configured for this MA.
Receiving CCMs The current state of the 802.1ag remote MEP state
machine:
Yes - RMEP_OK. CCMs are being received without any
error.
Wait - RMEP_START. Still preparing to receive remote MEP
CCMs without a timeout occurring.
Failed - RMEP_FAILED. While waiting to receive CCMs from
a remote MEP, a timeout occurred.
- - the state machine is not running.
RX RDI The current RDI being received from this remote MEP:
True - the last CCM received from the remote MEP has the
RDI set. This means the remote MEP itself is seeing one of
the following defects: someRMEPCCMDefect,
someMACstatusDefect, errorCCMdefect, xconCCMdefect.
False - the last CCM received from the remote MEP does
not have its RDI set.
MAC Address The configured or discovered MAC address of the remote
MEP.
Port Status If the CCM was received with a port status TLV, this
indicates the last value received, or "-" if none received.
Interface Status If the CCM was received with an interface status TLV, this
indicates the last value received, or "-" if none received.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 328
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM SERVICE
show ethernet cfm service
Overview Use this command to show the Ethernet CFM Services (Maintenance Associations
(MA)) configuration in summary format, or show a specified MA with detailed
information.
Syntax show ethernet cfm service [<ma-name> domain <domain-name>
details]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show details for all MAs in summary form, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm service
To show a specified MA in detailed form, use the command:
awplus# show ethernet cfm service MA-INST2-1 domain MD-INST2
details
Output Figure 9-11: Example output from show ethernet cfm service
Parameter Description
<ma-name> The CLI name that identifies the service (Maintenance Association
(MA)) instance of interest.
domain Specify the domain name by name.
<domain-name> The CLI name that identifies this Maintenance Domain instance.
awplus#show ethernet cfm service
CFM Domain Name CFM Service Name VLAN Defect
------------------------------------------------------------------
MD-INST1 MA-INST1-1 NONE .....
MD-INST2 MA-INST2-1 NONE ..3..
Table 9-7: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm service
Parameter Description
CFM Domain Name The Maintenance Domain name for the managed object.
CFM Service Name The Maintenance Associations (MA) instance name.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 329
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM SERVICE
Figure 9-12: Example output from show ethernet cfm service MA-INST2-1
domain MD-INST2 details
VLAN The Primary VLAN.
Defect A list of defects detected by the MA’s Local MEPs. The
defects shown can be:
1 - someRDIdefect is declared
2 - someMACstatusDefect is declared
3 - someRMEPCCMdefect is declared
4 - errorCCMdefect is declared
5 - xconCCMdefect is declared
awplus#show ethernet cfm service MA-INST2-1 domain MD-INST2
details
CFM Service Name................ MA-INST2-1
CFM Domain Name................. MD-INST2
CFM Domain Level................ 3
Primary VLAN.................... -
Maintenance Assoc Name Format... string
Maintenance Assoc Name Value.... MA-12V100
CCM Transmission Interval....... 1 second
Local MEPs...................... MEP DOWN 12 (interface
port1.0.2)
Configured Remote MEPs.......... 21
Missing Remote MEPs............. 21
Current MEP Defects............. 3 (someRMEPCCMdefect)
MIP Creation.................... None
Table 9-8: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm service
<ma-name> domain <domain-name> details
Parameter Description
CFM Service Name The Maintenance Associations (MA) instance name.
CFM Domain Name The Maintenance Domain name for the managed object.
CFM Domain Level The level of the domain.
Primary VLAN The Primary VLAN that was configured (if any).
Table 9-7: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm service (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 330
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERNET CFM SERVICE
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
mep crosscheck
service ma-name
show ethernet cfm details
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Maintenance Assoc
Name Format and
Value
The name and name format of the MA. The name format is
one of the following:
ICC - ICC string based name format
Integer - Integer based name format
Primary-vid - Primary VLAN based name format
String - Character string based name format
VPN-ID - VPN-ID based name format
CCM Transmission
Interval The CCI that was configured for this MA. It can be one of
the following:
3 - CCI of 100 milliseconds
4 - CCI of 1 second (default)
5 - CCI of 10 seconds
6 - CCI of 1 minute
7 - CCI of 10 minutes
Local MEPs A list of the Local MEPs configured for this MA. For each
MEP, it displays the MEP direction Up or Down, its MEP-id,
and the interface it was configured on.
Configured Remote
MEPs A list of Remote MEPs by MEP-id.
Missing Remote
MEPs A list of the configured Remote MEPs that this MA has not
received any CCM messages from within 3.5 times the
configured CCI.
Defect A list of defects detected by the MA’s Local MEPs. The
defects shown can be:
1 - someRDIdefect is declared
2 - someMACstatusDefect is declared
3 - someRMEPCCMdefect is declared
4 - errorCCMdefect is declared
5 - xconCCMdefect is declared
Table 9-8: Parameters in the output from show ethernet cfm service
<ma-name> domain <domain-name> details (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 331
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
CONNECTIVITY FAULT MANAGEMENT COMMANDS
SHOW MEP-ALARM STATUS
show mep-alarm status
Overview Use this command to show any alarms that have been declared by Local MEPs, and
the defect(s) that caused the alarm.
Syntax show mep-alarm status
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage A Local MEP is used to detect connectivity faults with other remote MEPs that are
in the same Maintenance Association (MA) and Maintenance Domain (MD) as the
Local MEP. A Local MEP looks first for connectivity defects, and if these defects
persist for a long enough period of time (typically 2.5 seconds), then an alarm is
declared.
Example To show the alarms on local MEPs, use the command:
awplus# show mep-alarm status
Output Figure 9-13: Example output from show mep-alarm status
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm mep
mep (FNG attributes)
mep crosscheck
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
awplus#show mep-alarm status
CFM Domain Name CFM Service Name MEP Active Alarm
------------------------------------------------------------------
MD-INST1 MA-INST1-1 12 someRMEPCCM
Table 9-9: Parameters in the output from show mep-alarm status
Parameter Description
CFM Domain Name The domain name.
CFM Service Name The MA name.
Active Alarms The highest priority defect causing the alarm, one of the
following: someRDI, someMACstatus, someRMEPCCM,
errorCCM, or xconCCM.
MEP The local MEP's ID.

10
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 332
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Logging Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
logging. See the Logging Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more
information about the different types of log and how to filter log messages.
Command List •“clear exception log” on page 334
•“clear log” on page 335
•“clear log buffered” on page 336
•“clear log external” on page 337
•“clear log permanent” on page 338
•“copy buffered-log” on page 339
•“copy permanent-log” on page 340
•“default log buffered” on page 341
•“default log console” on page 342
•“default log email” on page 343
•“default log external” on page 344
•“default log host” on page 345
•“default log monitor” on page 346
•“default log permanent” on page 347
•“log buffered” on page 348
•“log buffered (filter)” on page 349
•“log buffered exclude” on page 352
•“log buffered size” on page 355
•“log console” on page 356

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 333
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
•“log console (filter)” on page 357
•“log console exclude” on page 360
•“log email” on page 363
•“log email (filter)” on page 364
•“log email exclude” on page 367
•“log email time” on page 370
•“log external” on page 372
•“log external (filter)” on page 374
•“log external exclude” on page 377
•“log external rotate” on page 380
•“log external size” on page 382
•“log facility” on page 383
•“log host” on page 385
•“log host (filter)” on page 387
•“log host exclude” on page 390
•“log host source” on page 393
•“log host startup-delay” on page 394
•“log host time” on page 396
•“log monitor (filter)” on page 398
•“log monitor exclude” on page 401
•“log permanent” on page 404
•“log permanent (filter)” on page 405
•“log permanent exclude” on page 408
•“log permanent size” on page 411
•“log-rate-limit nsm” on page 412
•“log trustpoint” on page 413
•“show counter log” on page 414
•“show exception log” on page 415
•“show log” on page 416
•“show log config” on page 418
•“show log external” on page 420
•“show log permanent” on page 421
•“show running-config log” on page 422
•“unmount” on page 423

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 334
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
CLEAR EXCEPTION LOG
clear exception log
Overview This command resets the contents of the exception log, but does not remove the
associated core files.
Syntax clear exception log
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear exception log

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 335
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
CLEAR LOG
clear log
Overview This command removes the contents of the buffered and permanent logs.
Syntax clear log
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the contents of the buffered and permanent log use the command:
awplus# clear log
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
clear log permanent
show log

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 336
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
CLEAR LOG BUFFERED
clear log buffered
Overview This command removes the contents of the buffered log.
Syntax clear log buffered
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the contents of the buffered log use the following commands:
awplus# clear log buffered
Related
Commands
default log buffered
log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered size
log buffered exclude
show log
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 337
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
CLEAR LOG EXTERNAL
clear log external
Overview Use this command to delete the external log file from the SD card it is stored on.
If the external log is rotating between multiple files, this command deletes all
those files, not just the most recent one.
Syntax clear log external
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the external log file, use the command:
awplus# clear log external
Related
Commands
default log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 338
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
CLEAR LOG PERMANENT
clear log permanent
Overview This command removes the contents of the permanent log.
Syntax clear log permanent
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the contents of the permanent log use the following commands:
awplus# clear log permanent
Related
Commands
default log permanent
log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent exclude
log permanent size
show log config
show log permanent

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 339
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
COPY BUFFERED-LOG
copy buffered-log
Overview Use this command to copy the buffered log to an internal or external destination.
Syntax copy buffered-log <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To copy the buffered log file into a folder in Flash named “buffered-log” and name
the file “buffered-log.log”, use the command:
awplus# copy buffered-log flash:/buffered-log/buffered-log.log
To copy the buffered log file onto an SD card and name the file “buffered-log.log”,
use the command:
awplus# copy buffered-log card:/buffered-log.log
Related
Commands
log buffered
show file systems
show log
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
<destination-name> The filename and path for the destination file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 340
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
COPY PERMANENT-LOG
copy permanent-log
Overview Use this command to copy the permanent log to an internal or external
destination.
Syntax copy permanent-log <destination-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To copy the permanent log file into a folder in Flash named “perm-log” and name
the file “permanent-log.log”, use the command:
awplus# copy permanent-log flash:/perm-log/permanent-log.log
To copy the permanent log file onto an SD card and name the file
“permanent-log.log”, use the command:
awplus# copy permanent-log card:/permanent-log.log
Related
Commands
log permanent
show file systems
show log permanent
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
<destination-name> The filename and path for the destination file. See
Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 341
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG BUFFERED
default log buffered
Overview This command restores the default settings for the buffered log stored in RAM. By
default the size of the buffered log is 50 kB and it accepts messages with the
severity level of “warnings” and above.
Syntax default log buffered
Default The buffered log is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the buffered log to its default settings use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log buffered
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered size
log buffered exclude
show log
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 342
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG CONSOLE
default log console
Overview This command restores the default settings for log messages sent to the terminal
when a log console command is issued. By default all messages are sent to the
console when a log console command is issued.
Syntax default log console
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the log console to its default settings use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log console
Related
Commands
log console
log console (filter)
log console exclude
show log config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 343
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG EMAIL
default log email
Overview This command restores the default settings for log messages sent to an email
address. By default no filters are defined for email addresses. Filters must be
defined before messages will be sent. This command also restores the remote
syslog server time offset value to local (no offset).
Syntax default log email <email-address>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the default settings for log messages sent to the email address
admin@alliedtelesis.com use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log email admin@alliedtelesis.com
Related
Commands
log email
log email (filter)
log email exclude
log email time
show log config
Parameter Description
<email-address> The email address to send log messages to

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 344
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG EXTERNAL
default log external
Overview Use this command to restore the default settings for the external log. By default,
the size of the external log is 50 kB, it rotates through 1 additional file, and it
accepts messages with a severity level of notices and above.
Note that this command does not clear the configured filename for the external
log.
Syntax default log external
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the default settings for the external log, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log external
Related
Commands
clear log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 345
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG HOST
default log host
Overview This command restores the default settings for log sent to a remote syslog server.
By default no filters are defined for remote syslog servers. Filters must be defined
before messages will be sent. This command also restores the remote syslog server
time offset value to local (no offset).
Syntax default log host <ip-addr>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the default settings for messages sent to the remote syslog server with
IP address 10.32.16.21 use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log host 10.32.16.21
Related
Commands
log host
log host (filter)
log host exclude
log host source
log host time
show log config
Parameter Description
<ip-addr>The IP address of a remote syslog server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 346
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG MONITOR
default log monitor
Overview This command restores the default settings for log messages sent to the terminal
when a terminal monitor command is used.
Syntax default log monitor
Default All messages are sent to the terminal when a terminal monitor command is used.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the log monitor to its default settings use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log monitor
Related
Commands
log monitor (filter)
log monitor exclude
show log config
terminal monitor

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 347
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
DEFAULT LOG PERMANENT
default log permanent
Overview This command restores the default settings for the permanent log stored in Flash.
By default, the size of the permanent log is 50 kB and it accepts messages with the
severity level of warnings and above.
Syntax default log permanent
Default The permanent log is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To restore the permanent log to its default settings use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# default log permanent
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent exclude
log permanent size
show log config
show log permanent

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 348
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED
log buffered
Overview This command configures the device to store log messages in RAM. Messages
stored in RAM are not retained on the device over a restart. Once the buffered log
reaches its configured maximum allowable size old messages will be deleted to
make way for new ones.
Syntax log buffered
no log buffered
Default The buffered log is configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configured the device to store log messages in RAM use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered
To configure the device to not store log messages in a RAM buffer use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log buffered
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
copy buffered-log
default log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered size
log buffered exclude
show log
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 349
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED (FILTER)
log buffered (filter)
Overview Use this command to create a filter to select messages to be sent to the buffered
log. Selection can be based on the priority/ severity of the message, the program
that generated the message, the logging facility used, a sub-string within the
message or a combination of some or all of these.
The no variant of this command removes the corresponding filter, so that the
specified messages are no longer sent to the buffered log.
Syntax log buffered [level <level>] [program <program-name>] [facility
<facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log buffered [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Filter messages to the buffered log by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send to the buffered log. The level can be specified as
one of the following numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the
lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages to the buffered log by program. Include messages from a specified program in
the buffered log.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 350
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED (FILTER)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages to the buffered log by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from in the buffered log:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 351
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED (FILTER)
Default By default the buffered log has a filter to select messages whose severity level is
“notices (5)” or higher. This filter may be removed using the no variant of this
command.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To add a filter to send all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity of
notices or higher to the buffered log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered level notices program epsr
To add a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging initialization” to
the buffered log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered msgtext Bridging initialization
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to the buffered log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log buffered level notices program epsr
To remove a filter that sends all messages containing the text “Bridging
initialization” to the buffered log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log buffered msgtext Bridging initialization
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
default log buffered
log buffered
log buffered size
log buffered exclude
show log
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 352
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED EXCLUDE
log buffered exclude
Overview Use this command to exclude specified log messages from the buffered log. You
can exclude messages on the basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log buffered exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log buffered exclude [level <level>] [program
<program-name>] [facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 353
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED EXCLUDE
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 354
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered exclude msgtext example of
irrelevant message
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
default log buffered
log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered size
show log
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 355
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG BUFFERED SIZE
log buffered size
Overview This command configures the amount of memory that the buffered log is
permitted to use. Once this memory allocation has been filled old messages will be
deleted to make room for new messages.
Syntax log buffered size <50-250>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To allow the buffered log to use up to 100 kB of RAM use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered size 100
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
copy buffered-log
default log buffered
log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered exclude
show log
show log config
Parameter Description
<50-250>Size of the RAM log in kilobytes

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 356
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE
log console
Overview This command configures the device to send log messages to consoles. The
console log is configured by default to send messages to the device’s main console
port.
Use the no variant of this command to configure the device not to send log
messages to consoles.
Syntax log console
no log console
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure the device to send log messages use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log console
To configure the device not to send log messages in all consoles use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log console
Related
Commands
default log console
log console (filter)
log console exclude
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 357
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE (FILTER)
log console (filter)
Overview This command creates a filter to select messages to be sent to all consoles when
the log console command is given. Selection can be based on the priority/severity
of the message, the program that generated the message, the logging facility
used, a sub-string within the message or a combination of some or all of these.
Syntax log console [level <level>] [program <program-name>] [facility
<facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log console [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Filter messages by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send. The level can be specified as one of the following
numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages by program. Include messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 358
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE (FILTER)
Default By default the console log has a filter to select messages whose severity level is
critical or higher. This filter may be removed using the no variant of this
command. This filter may be removed and replaced by filters that are more
selective.
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 359
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE (FILTER)
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To create a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging initialization”
to console instances where the log console command has been entered, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log console msgtext "Bridging initialization"
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to consoles, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log console level notices program epsr
To remove a default filter that includes sending critical, alert and emergency
level messages to the console, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log console level critical
Related
Commands
default log console
log console
log console exclude
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 360
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE EXCLUDE
log console exclude
Overview Use this command to prevent specified log messages from being sent to the
console, when console logging is turned on. You can exclude messages on the
basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log console exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log console exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 361
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE EXCLUDE
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 362
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG CONSOLE EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log console exclude msgtext example of
irrelevant message
Related
Commands
default log console
log console
log console (filter)
show log config
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 363
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL
log email
Overview This command configures the device to send log messages to an email address.
The email address is specified in this command.
Syntax log email <email-address>
Default By default no filters are defined for email log targets. Filters must be defined before
messages will be sent.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To have log messages emailed to the email address
admin@alliedtelesis.com use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@alliedtelesis.com
Related
Commands
default log email
log email (filter)
log email exclude
log email time
show log config
Parameter Description
<email-address> The email address to send log messages to

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 364
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL (FILTER)
log email (filter)
Overview This command creates a filter to select messages to be sent to an email address.
Selection can be based on the priority/ severity of the message, the program that
generated the message, the logging facility used, a sub-string within the message
or a combination of some or all of these.
The no variant of this command configures the device to no longer send log
messages to a specified email address. All configuration relating to this log target
will be removed.
Syntax log email <email-address> [level <level>] [program
<program-name>] [facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log email <email-address> [level <level>] [program
<program-name>] [facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
<email-
address> The email address to send logging messages to
level Filter messages by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send. The level can be specified as one of the following
numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages by program. Include messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 365
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL (FILTER)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 366
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL (FILTER)
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To create a filter to send all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity of
notices or higher to the email address admin@homebase.com, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@homebase.com level notices
program epsr
To create a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging initialization”,
to the email address admin@homebase.com, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@homebase.com msgtext "Bridging
initialization"
To create a filter to send messages with a severity level of informational and
above to the email address admin@alliedtelesis.com, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@alliedtelesis.com level
informational
To stop the device emailing log messages emailed to the email address
admin@alliedtelesis.com, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log email admin@homebase.com
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to the email address admin@homebase.com, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log email admin@homebase.com level notices
program epsr
To remove a filter that sends messages with a severity level of informational and
above to the email address admin@alliedtelesis.com, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log email admin@alliedtelesis.com level
informational
Related
Commands
default log email
log email
log email exclude
log email time
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 367
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL EXCLUDE
log email exclude
Overview Use this command to prevent specified log messages from being emailed, when
the device is configured to send log messages to an email address. You can
exclude messages on the basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log email exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log email exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 368
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL EXCLUDE
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 369
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email exclude msgtext example of irrelevant
message
Related
Commands
default log email
log email
log email (filter)
log email time
show log config
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 370
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL TIME
log email time
Overview This command configures the time used in messages sent to an email address. If
the syslog server is in a different time zone to your device then the time offset can
be configured using either the utc-offset parameter option keyword or the
local-offset parameter option keyword, where utc-offset is the time difference
from UTC (Universal Time, Coordinated) and local-offset is the difference from
local time.
Syntax log email <email-address> time {local|local-offset|utc-offset
{plus|minus}<0-24>}
Default The default is local time.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use the local option if the email recipient is in the same time zone as this device.
Messages will display the time as on the local device when the message was
generated.
Use the offset option if the email recipient is in a different time zone to this device.
Specify the time offset of the email recipient in hours. Messages will display the
time they were generated on this device but converted to the time zone of the
email recipient.
Parameter Description
<email-address> The email address to send log messages to
time Specify the time difference between the email recipient and the
device you are configuring.
local The device is in the same time zone as the email recipient
local-offset The device is in a different time zone to the email recipient. Use
the plus or minus keywords and specify the difference (offset)
from local time of the device to the email recipient in hours.
utc-offset The device is in a different time zone to the email recipient. Use
the plus or minus keywords and specify the difference (offset)
from UTC time of the device to the email recipient in hours.
plus Negative offset (difference) from the device to the email
recipient.
minus Positive offset (difference) from the device to the email
recipient.
<0-24> World Time zone offset in hours

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 371
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EMAIL TIME
Examples To send messages to the email address test@home.com in the same time zone
as the device’s local time zone, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@base.com time local 0
To send messages to the email address admin@base.com with the time
information converted to the time zone of the email recipient, which is 3 hours
ahead of the device’s local time zone, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email admin@base.com time local-offset plus
3
To send messages to the email address user@remote.com with the time
information converted to the time zone of the email recipient, which is 3 hours
behind the device’s UTC time zone, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log email user@remote.com time utc-offset minus
3
Related
Commands
default log email
log email
log email (filter)
log email exclude
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 372
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL
log external
Overview Use this command to enable external logging. External logging sends syslog
messages to a file on an SD card.
If the file does not already exist on the storage device, it (and any specified
subdirectory) will be automatically created. If the file already exists, messages are
appended to it.
Use the no variant of this command to disable external logging.
Syntax log external <filename>
no log external
Default External logging is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage We strongly recommend using ext3 or ext4 as the file system on the external
storage device. These file systems have a lower risk of file corruption occurring if
the switch or firewall loses power.
You should also unmount the storage device before removing it from the switch
or firewall, to avoid corrupting the log file. To unmount the device, use the
unmount command.
Example To save messages to a file called “messages.log” in a directory called “log” on an SD
card, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external card:/log/messages.log
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Parameter Description
<filename> The file and optionally directory path to store the log messages in.
See Introduction on page 84 for valid syntax.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 373
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 374
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL (FILTER)
log external (filter)
Overview Use this command to create a filter to select messages to be sent to the external
log. You can include messages based on:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
The no variant of this command removes the corresponding filter, so that the
specified messages are no longer sent to the external log.
Syntax log external [level <level>] [program <program-name>] [facility
<facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log external [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Filter messages to the external log by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send to the external log. The level can be specified as
one of the following numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the
lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages to the external log by program. Include messages from a specified program in
the external log.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 375
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL (FILTER)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages to the external log by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from in the log:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 376
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL (FILTER)
Default By default the external log has a filter to select messages whose severity level is
“notices (5)” or higher. This filter may be removed using the no variant of this
command.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To add a filter to send all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity of
notices or higher to the external log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external level notices program epsr
To add a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging initialization” to
the external log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external msgtext Bridging initialization
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to the external log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log external level notices program epsr
To remove a filter that sends all messages containing the text “Bridging
initialization” to the external log, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log external msgtext Bridging initialization
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 377
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL EXCLUDE
log external exclude
Overview Use this command to exclude specified log messages from the external log. You
can exclude messages on the basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log external exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log external exclude [level <level>] [program
<program-name>] [facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 378
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL EXCLUDE
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 379
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global Configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external exclude msgtext example of
irrelevant message
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 380
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL ROTATE
log external rotate
Overview Use this command to configure the number of files that the external log can rotate
through.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default.
Syntax log external rotate <0-255>
no log external rotate
Default The default is 1, which rotates between the initial file and 1 additional file (for
example, rotates between messages.log and messages.log.1)
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The device rotates between the initial file and the number of additional files
specified by this command. For example, the diagram below shows how setting
rotate to 2 makes the device rotate through 3 files.
Note that if you set rotate to 0, and the external log file becomes full, then the
device deletes the full log file and creates a new (empty) file of the same name to
save messages into. For this reason, we recommend setting rotate to at least 1.
Example To set the rotation value to 2, and therefore rotate between 3 files, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external rotate 2
Parameter Description
<0-255> The number of additional files to rotate through. Note that the
device rotates between the initial file and the number of
additional files specified by this value - see the Usage section
below.
3UBSEQUENTROTATION3ECONDROTATION&IRSTROTATION3TARTOFLOGGING
MESSAGESLOG MESSAGESLOG MESSAGESLOGMESSAGESLOG
MESSAGESLOG MESSAGESLOG MESSAGESLOG
MESSAGESLOG MESSAGESLOG
LOG
EXTERNAL
SIZE
RENAMEDTO
DELETED
RENAMEDTO
8

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 381
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL ROTATE
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 382
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG EXTERNAL SIZE
log external size
Overview Use this command to configure the total amount of size that the external log is
permitted to use, in kilobytes. The maximum possible depends on the storage
device’s file system.
Note that if you are rotating between multiple files, this is the maximum size of all
files, not of each individual file. For example, if you are rotating between 2 files (log
external rotate 1), each file will have a maximum size of 25 kBytes by default.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default size.
Syntax log external size [<50-4194304>]
no log external size
Default 50 kBytes
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure a total log size of 100 kBytes, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log external size 100
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
show log external
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
<50-4194304> The total amount of size that the external log is permitted to use,
in kilobytes.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 383
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG FACILITY
log facility
Overview Use this command to assign a facility to all log messages generated on this device.
This facility overrides any facility that is automatically generated as part of the log
message.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured facility.
Syntax log facility {kern|user|mail|daemon|auth|syslog|lpr|news|uucp|
cron|authpriv|ftp|local0|local1|local2|local3|local4|local5|
local6|local7}
no log facility
Default None. The outgoing syslog facility depends on the log message.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Specifying different facilities for log messages generated on different devices can
allow messages from multiple devices sent to a common server to be
distinguished from each other.
Ordinarily, the facility values generated in log messages have meanings as shown
in the following table. Using this command will override these meanings, and the
new meanings will depend on the use you put them to.
Table 10-1: Ordinary meanings of the facility parameter in log messages
Facility Description
kern Kernel messages
user User-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by the syslog daemon
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UNIX-to-UNIX Copy Program subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization (private) messages

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 384
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG FACILITY
Example To specify a facility of local6, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log facility local6
Related
Commands
show log config
ftp FTP daemon
local<0..7>The facility labels above have specific meanings, while the
local facility labels are intended to be put to local use. In
AlliedWare Plus, some of these local facility labels are used
in log messages. In particular, local5 is assigned to log
messages generated by UTM Firewall security features.
Table 10-1: Ordinary meanings of the facility parameter in log messages (cont.)
Facility Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 385
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST
log host
Overview This command configures the device to send log messages to a remote syslog
server via UDP port 514. The IP address of the remote server must be specified. By
default no filters are defined for remote syslog servers. Filters must be defined
before messages will be sent.
Use the no variant of this command to stop sending log messages to the remote
syslog server.
Syntax log host <ipv4-addr> [secure]
log host <ipv6-addr>
no log host <ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use the optional secure parameter to configure a secure IPv4 syslog host. For
secure hosts, syslog over TLS is used to encrypt the logs. The certificate received
from the remote log server must have an issuer chain that terminates with the root
CA certificate for any of the trustpoints that are associated with the application.
The remote server may also request that a certificate is transmitted from the local
device. In this situation the first trustpoint added to the syslog application will be
transmitted to the remote server.
For detailed information about securing syslog, see the PKI Feature Overview_and
Configuration_Guide.
Examples To configure the device to send log messages to a remote secure syslog server with
IP address 10.32.16.99, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.99 secure
To stop the device from sending log messages to the remote syslog server with IP
address 10.32.16.99, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log host 10.32.16.99
Related
Commands
default log host
log host (filter)
Parameter Description
<ipv4-addr>Specify the source IPv4 address, in dotted decimal notation (A.B.C.D).
<ipv6-addr> Specify the source IPv6 address, in X:X::X:X notation.
secure Optional value to create a secure log destination. This option is only
valid for IPv4 hosts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 387
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST (FILTER)
log host (filter)
Overview This command creates a filter to select messages to be sent to a remote syslog
server. Selection can be based on the priority/severity of the message, the program
that generated the message, the logging facility used, a substring within the
message or a combination of some or all of these.
The no variant of this command configures the device to no longer send log
messages to a remote syslog server. The IP address of the syslog server must be
specified. All configuration relating to this log target will be removed.
Syntax log host <ip-addr> [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log host <ip-addr> [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
<ip-addr> The IP address of a remote syslog server.
level Filter messages by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send. The level can be specified as one of the following
numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages by program. Include messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 388
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST (FILTER)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 389
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST (FILTER)
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To create a filter to send all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity of
notices or higher to a remote syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.21 level notices program epsr
To create a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging initialization”,
to a remote syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.21 msgtext "Bridging
initialization"
To create a filter to send messages with a severity level of informational and
above to the syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.21 level informational
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to a remote syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log host 10.32.16.21 level notices program
epsr
To remove a filter that sends all messages containing the text “Bridging
initialization”, to a remote syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log host 10.32.16.21 msgtext "Bridging
initialization"
To remove a filter that sends messages with a severity level of informational and
above to the syslog server with IP address 10.32.16.21, use the following
commands:
awplusawpluls# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log host 10.32.16.21 level informational
Related
Commands
default log host
log host
log host exclude
log host source
log host time
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 390
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST EXCLUDE
log host exclude
Overview Use this command to prevent specified log messages from being sent to the
remote syslog server, when log host is enabled. You can exclude messages on the
basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log host exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log host exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 391
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST EXCLUDE
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 392
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host exclude msgtext example of irrelevant
message
Related
Commands
default log host
log host
log host (filter)
log host source
log host time
show log config
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 393
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST SOURCE
log host source
Overview Use this command to specify a source interface or IP address for the device to send
syslog messages from. You can specify any one of an interface name, an IPv4
address or an IPv6 address.
This is useful if the device can reach the syslog server via multiple interfaces or
addresses and you want to control which interface/address the device uses.
Note that AlliedWare Plus does not support source interface settings on secure log
hosts (which are hosts configured using “log host <ip-address> secure”).
Use the no variant of this command to stop specifying a source interface or
address.
Syntax log host source {<interface-name>|<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>}
no log host source
Default None (no source is configured)
Mode Global Configuration
Example To send syslog messages from 192.168.1.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host source 192.168.1.1
Related
Commands
default log host
log host
log host (filter)
log host exclude
log host time
show log config
Parameter Description
<interface-name> Specify the source interface name. You can enter a VLAN, eth
interface or loopback interface.
<ipv4-addr> Specify the source IPv4 address, in dotted decimal notation
(A.B.C.D).
<ipv6-addr> Specify the source IPv6 address, in X:X::X:X notation.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 394
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST STARTUP-DELAY
log host startup-delay
Overview Use this command to set the delay between the device booting up and it
attempting to connect to remote log hosts. This is to allow time for network
connectivity to the remote host to be established. During this period, the device
buffers log messages and sends them once it has connected to the remote host.
The startup delay begins when the message "syslog-ng starting up" appears in the
log.
If the default startup delay is not long enough for the boot and configuration
process to complete and the links to come up, you may see logging failure
messages on startup. In these cases, you can use the command to increase the
startup delay.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default delay values.
Syntax log host startup-delay [delay <1-600>] [messages <1-5000>]
no log host startup-delay
Default By default the system will buffer up to 2000 messages and wait 120 seconds from
when syslog starts before attempting to filter and transmit the buffered messages
to remote hosts.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To increase the delay to 180 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host startup-delay delay 180
Related
Commands
default log host
log host (filter)
log host exclude
log host source
log host time
log trustpoint
show log config
Parameter Description
delay <1-600> The time, in seconds, from when syslog starts before the
device attempts to filter and transmit the buffered
messages to remote hosts.
messages <1-5000>The maximum number of messages that the device will
buffer during the delay period.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 395
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST STARTUP-DELAY
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: defaults changed

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 396
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST TIME
log host time
Overview This command configures the time used in messages sent to a remote syslog
server. If the syslog server is in a different time zone to your device then the time
offset can be configured using either the utc-offset parameter option keyword or
the local-offset parameter option keyword, where utc-offset is the time
difference from UTC (Universal Time, Coordinated) and local-offset is the
difference from local time.
Syntax log host <email-address> time {local|local-offset|utc-offset
{plus|minus} <0-24>}
Default The default is local time.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use the local option if the remote syslog server is in the same time zone as the
device. Messages will display the time as on the local device when the message
was generated.
Use the offset option if the email recipient is in a different time zone to this device.
Specify the time offset of the remote syslog server in hours. Messages will display
the time they were generated on this device but converted to the time zone of the
remote syslog server.
Examples To send messages to the remote syslog server with the IP address 10.32.16.21
in the same time zone as the device’s local time zone, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.21 time local 0
Parameter Description
<email-address> The email address to send log messages to
time Specify the time difference between the email recipient and the
device you are configuring.
local The device is in the same time zone as the email recipient
local-offset The device is in a different time zone to the email recipient. Use
the plus or minus keywords and specify the difference (offset)
from local time of the device to the email recipient in hours.
utc-offset The device is in a different time zone to the email recipient. Use
the plus or minus keywords and specify the difference (offset)
from UTC time of the device to the email recipient in hours.
plus Negative offset (difference) from the device to the syslog server.
minus Positive offset (difference) from the device to the syslog server.
<0-24> World Time zone offset in hours

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 397
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG HOST TIME
To send messages to the remote syslog server with the IP address 10.32.16.12
with the time information converted to the time zone of the remote syslog server,
which is 3 hours ahead of the device’s local time zone, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.12 time local-offset plus 3
To send messages to the remote syslog server with the IP address 10.32.16.02
with the time information converted to the time zone of the email recipient, which
is 3 hours behind the device’s UTC time zone, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log host 10.32.16.02 time utc-offset minus 3
Related
Commands
default log host
log host
log host (filter)
log host exclude
log host source
show log config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 398
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR (FILTER)
log monitor (filter)
Overview This command creates a filter to select messages to be sent to the terminal when
the terminal monitor command is given. Selection can be based on the
priority/severity of the message, the program that generated the message, the
logging facility used, a sub-string within the message or a combination of some or
all of these.
Syntax log monitor [level <level>] [program <program-name>] [facility
<facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log monitor [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Filter messages by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send. The level can be specified as one of the following
numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages by program. Include messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 399
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR (FILTER)
Default By default there is a filter to select all messages. This filter may be removed and
replaced by filters that are more selective.
Mode Global Configuration
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 400
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR (FILTER)
Examples To create a filter to send all messages that are generated by authentication and
have a severity of info or higher to terminal instances where the terminal monitor
command has been given, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log monitor level info program auth
To remove a filter that sends all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity
of notices or higher to the terminal, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log monitor level notices program epsr
To remove a default filter that includes sending everything to the terminal, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log monitor level debugging
Related
Commands
default log monitor
log monitor exclude
show log config
terminal monitor

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 401
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR EXCLUDE
log monitor exclude
Overview Use this command to prevent specified log messages from being displayed on a
terminal, when terminal monitor is enabled. You can exclude messages on the
basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log console exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log console exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 402
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR EXCLUDE
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 403
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG MONITOR EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log monitor exclude msgtext example of
irrelevant message
Related
Commands
default log monitor
log monitor (filter)
show log config
terminal monitor
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 404
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT
log permanent
Overview This command configures the device to send permanent log messages to Flash
memory on the device. The content of the permanent log is retained over a reboot.
Once the permanent log reaches its configured maximum allowable size old
messages will be deleted to make way for new messages.
The no variant of this command configures the device not to send any messages
to the permanent log. Log messages will not be retained over a restart.
Syntax log permanent
no log permanent
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable permanent logging use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log permanent
To disable permanent logging use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log permanent
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
copy permanent-log
default log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent exclude
log permanent size
show log config
show log permanent

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 405
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT (FILTER)
log permanent (filter)
Overview This command creates a filter to select messages to be sent to the permanent log.
Selection can be based on the priority/ severity of the message, the program that
generated the message, the logging facility used, a sub-string within the message
or a combination of some or all of these.
The no variant of this command removes the corresponding filter, so that the
specified messages are no longer sent to the permanent log.
Syntax log permanent [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log permanent [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Filter messages sent to the permanent log by severity level.
<level>The minimum severity of message to send. The level can be specified as one of the following
numbers or level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Filter messages by program. Include messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program to log messages from. You can enter either one of the following
predefined program names (depending on your device model), or another program name
that you find in the log output. The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other
program names from the log output are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 406
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT (FILTER)
Default By default the buffered log has a filter to select messages whose severity level is
notices (5) or higher. This filter may be removed using the no variant of this
command.
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Filter messages by syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to include messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Select messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 407
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT (FILTER)
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To create a filter to send all messages generated by EPSR that have a severity of
notices or higher to the permanent log use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log permanent level notices program epsr
To create a filter to send all messages containing the text “Bridging
initialization”, to the permanent log use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log permanent msgtext Bridging initialization
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
default log permanent
log permanent
log permanent exclude
log permanent size
show log config
show log permanent

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 408
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT EXCLUDE
log permanent exclude
Overview Use this command to prevent specified log messages from being sent to the
permanent log. You can exclude messages on the basis of:
• the priority/severity of the message
• the program that generated the message
• the logging facility used
• a sub-string within the message, or
• a combination of some or all of these.
Use the no variant of this command to stop excluding the specified messages.
Syntax log permanent exclude [level <level>] [program <program-name>]
[facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
no log permanent exclude [level <level>] [program
<program-name>] [facility <facility>] [msgtext <text-string>]
Parameter Description
level Exclude messages of the specified severity level.
<level>The severity level to exclude. The level can be specified as one of the following numbers or
level names, where 0 is the highest severity and 7 is the lowest severity:
0|emergencies System is unusable
1|alerts Action must be taken immediately
2|critical Critical conditions
3|errors Error conditions
4|warnings Warning conditions
5|notices Normal, but significant, conditions
6|informational Informational messages
7|debugging Debug-level messages
program Exclude messages from a specified program.
<program-
name>The name of a program. You can enter either one of the following predefined program names
(depending on your device model), or another program name that you find in the log output.
The pre-defined names are not case sensitive but other program names from the log output
are.
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
ripng Routing Information Protocol - next generation (RIPng)
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
ospfv3 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) version 3 (OSPFv3)
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 409
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT EXCLUDE
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
pim-dm Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
pim-sm Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
pim-smv6 PIM-SM version 6 (PIM-SMv6)
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control
lacp Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
stp Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
rstp Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
mstp Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
imi Integrated Management Interface (IMI)
imish Integrated Management Interface Shell (IMISH)
epsr Ethernet Protection Switched Rings (EPSR)
irdp ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP)
rmon Remote Monitoring
loopprot Loop Protection
poe Power-inline (Power over Ethernet)
dhcpsn DHCP snooping (DHCPSN)
facility Exclude messages from a syslog facility.
<facility>Specify one of the following syslog facilities to exclude messages from:
kern Kernel messages
user Random user-level messages
mail Mail system
daemon System daemons
auth Security/authorization messages
syslog Messages generated internally by syslogd
lpr Line printer subsystem
news Network news subsystem
uucp UUCP subsystem
cron Clock daemon
authpriv Security/authorization messages (private)
ftp FTP daemon
msgtext Exclude messages containing a certain text string.
<text-
string>A text string to match (maximum 128 characters). This is case sensitive, and must be the last
text on the command line.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 410
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT EXCLUDE
Default No log messages are excluded
Mode Global configuration
Example To remove messages that contain the string “example of irrelevant message”, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log permanent exclude msgtext example of
irrelevant message
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
default log permanent
log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent size
show log config
show log permanent

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 411
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG PERMANENT SIZE
log permanent size
Overview This command configures the amount of memory that the permanent log is
permitted to use. Once this memory allocation has been filled old messages will be
deleted to make room for new messages.
Syntax log permanent size <50-250>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To allow the permanent log to use up to 100 kB of Flash use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log permanent size 100
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
copy permanent-log
default log permanent
log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent exclude
show log config
show log permanent
Parameter Description
<50-250>Size of the permanent log in kilobytes
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 412
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG-RATE-LIMIT NSM
log-rate-limit nsm
Overview This command limits the number of log messages generated by the device for a
given interval.
Use the no variant of this command to revert to the default number of log
messages generated by the device of up to 200 log messages per second.
Syntax log-rate-limit nsm messages <message-limit> interval
<time-interval>
no log-rate-limit nsm
Default By default, the device will allow 200 log messages to be generated per second.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This log rate limiting feature constrains the rate that log messages are generated
by the device. This makes sure that the device does not run out of memory from
generating a lot of log messages in extreme circumstances, such as if a packet
storm occurs.
Note that if within the given time interval, the number of log messages exceeds the
limit, then any excess log messages are discarded. At the end of the time interval,
a single log message is generated indicating that log messages were discarded
due to the log rate limit being exceeded.
If you expect that there will be a lot of discarded log messages due to log rate
limiting, then we recommend setting the time interval to no less than 100, which
means that there would only be one log message, indicating excessive log
messages have been discarded.
Examples To limit the device to generate up to 300 log messages per second, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log-rate-limit nsm messages 300 interval 100
To return the device the default setting, to generate up to 200 log messages per
second, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no log-rate-limit nsm
Parameter Description
<message-limit><1-65535>
The number of log messages generated by the device.
<time-interval><0-65535>
The time period for log message generation in 1/100 seconds.
If an interval of 0 is specified then no log message rate limiting
is applied.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 413
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
LOG TRUSTPOINT
log trustpoint
Overview This command adds one or more trustpoints to be used with the syslog
application. Multiple trustpoints may be specified, or the command may be
executed multiple times, to add multiple trustpoints to the application.
The no version of this command removes one or more trustpoints from the list of
trustpoints associated with the application.
Syntax log trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
no log trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
Default No trustpoints are created by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The device certificate associated with first trustpoint added to the application will
be transmitted to remote servers. The certificate received from the remote server
must have an issuer chain that terminates with the root CA certificate for any of the
trustpoints that are associated with the application.
If no trustpoints are specified in the command, the trustpoint list will be
unchanged.
If no log trustpoint is issued without specifying any trustpoints, then all
trustpoints will be disassociated from the application.
Example You can add multiple trustpoints by executing the command multiple times:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log trustpoint trustpoint_1
awplus(config)# log trustpoint trustpoint_2
Alternatively, add multiple trustpoints with a single command:
awplus(config)# log trustpoint trustpoint_2 trustpoint_3
Disassociate all trustpoints from the syslog application using the command:
awplus(config)# log trustpoint trustpoint_2 trustpoint_3
Related
Commands
log host
show log config
Parameter Description
<trustpoint-list> Specify one or more trustpoints to be added or deleted.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 414
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER LOG
show counter log
Overview This command displays log counter information.
Syntax show counter log
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the log counter information, use the command:
awplus# show counter log
Output Figure 10-1: Example output from the show counter log command
Related
Commands
show log config
Log counters
Total Received ......... 2328
Total Received P0 ......... 0
Total Received P1 ......... 0
Total Received P2 ......... 1
Total Received P3 ......... 9
Total Received P4 ......... 32
Total Received P5 ......... 312
Total Received P6 ......... 1602
Total Received P7 ......... 372
Table 11: Parameters in output of the show counter log command
Parameter Description
Total Received Total number of messages received by the log
Total Received P0 Total number of Priority 0 (Emergency) messages
received
Total Received P1 Total number of Priority 1 (Alert) messages received
Total Received P2 Total number of Priority 2 (Critical) messages received
Total Received P3 Total number of Priority 3 (Error) messages received
Total Received P4 Total number of Priority 4 (Warning) messages received
Total Received P5 Total number of Priority 5 (Notice) messages received
Total Received P6 Total number of Priority 6 (Info) messages received
Total Received P7 Total number of Priority 7 (Debug) messages received
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 415
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW EXCEPTION LOG
show exception log
Overview This command displays the contents of the exception log.
Syntax show exception log
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the exception log, use the command:
awplus# show exception log
Output Figure 10-2: Example output from the show exception log command on a
device
Output Figure 10-3: Example output from the show exception log command on a
device that has never had an exception occur
awplus#show exception log
Stack member 1:
<date> <time> <facility>.<severity> <program[<pid>]>: <message>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
2019 Apr 08 07:56:19 local7.debug awplus c orehandler : Proce ss imi (PID:1041) s ignal
11, core dumped to /flash/imi-test-1-1554663379-1041.tgz
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
awplus#show exception log
<date> <time> <facility>.<severity> <program[<pid>]>: <message>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
None
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
awplus#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 416
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG
show log
Overview This command displays the contents of the buffered log.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show log [tail [<10-250>]]
Default By default the entire contents of the buffered log is displayed.
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Usage If the optional tail parameter is specified, only the latest 10 messages in the
buffered log are displayed. A numerical value can be specified after the tail
parameter to select how many of the latest messages should be displayed.
The show log command is only available to users at privilege level 7 and above. To
set a user’s privilege level, use the command:
awplus(config)# username <name> privilege <1-15>
Examples To display the contents of the buffered log use the command:
awplus# show log
To display the 10 latest entries in the buffered log use the command:
awplus# show log tail 10
Parameter Description
tail Display only the latest log entries.
<10-250>Specify the number of log entries to display.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 417
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG
Output Figure 10-4: Example output from show log
Related
Commands
clear log buffered
copy buffered-log
default log buffered
log buffered
log buffered (filter)
log buffered size
log buffered exclude
show log config
awplus#show log
<date> <time> <facility>.<severity> <program[<pid>]>: <message>
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: Linux version 4.4.6-at1
(maker@maker03-build) (gcc version 4.9.3 (crosstool-NG crossto ol-ng-1.22.0) ) #1 SMP
Thu May 24 06:19:06 UTC 2018
2019 May 25 09:42:51 syslog.notice awplus syslog-ng[274]: syslog-ng starting up;
version='3.10.1'
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: Kernel command line:
console=ttyS0,115200 root=/dev/ram0 releasefile=IE210-tb200.rel bootversion=3.2.6
loglevel=1 extraflash=04000000 mtdoops.mtdd
ev=errlog securitylevel=1 ramdisk=19064 relhdr=1644167168,1647057220
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: Virtual kernel memory layout:
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: vector : 0xffff0000 - 0xffff1000
( 4 kB)
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: fixmap : 0xffc00000 - 0xfff00000
(3072 kB)
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: vmalloc : 0xe0800000 - 0xff800000
( 496 MB)
2019 May 25 09:42:51 kern.notice awplus kernel: lowmem : 0xc0000000 - 0xe0000000
( 512 MB)
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 418
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG CONFIG
show log config
Overview This command displays information about the logging system. This includes the
configuration of the various log destinations, such as buffered, permanent, syslog
servers (hosts) and email addresses. This also displays the latest status information
for each log destination.
Syntax show log config
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the logging configuration use the command:
awplus# show log config
Output Figure 10-5: Example output from show log config
Facility: default
PKI trustpoints: example_trustpoint
Buffered log:
Status ......... enabled
Maximum size ... 100kb
Filters:
*1 Level ........ notices
Program ...... any
Facility ..... any
Message text . any
2 Level ........ informational
Program ...... auth
Facility ..... daemon
Message text . any
Statistics ..... 1327 messages received, 821 accepted by filter (2016 Oct 11
10:36:16)
Permanent log:
Status ......... enabled
Maximum size ... 60kb
Filters:
1 Level ........ error
Program ...... any
Facility ..... any
Message text . any
*2 Level ........ warnings
Program ...... dhcp
Facility ..... any
Message text . "pool exhausted"
Statistics ..... 1327 messages received, 12 accepted by filter (2016 Oct 11
10:36:16)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 419
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG CONFIG
In the above example the ’*’ next to filter 1 in the buffered log configuration
indicates that this is the default filter. The permanent log has had its default filter
removed, so none of the filters are marked with ‘*’.
NOTE: Terminal log and console log cannot be set at the same time. If console logging
is enabled then the terminal logging is turned off.
Related
Commands
show counter log
show log
show log permanent
Host 10.32.16.21:
Time offset .... +2:00
Offset type .... UTC
Source ......... -
Secured ........ enabled
Filters:
1 Level ........ critical
Program ...... any
Facility ..... any
Message text . any
Statistics ..... 1327 messages received, 1 accepted by filter (2016 Oct 11
10:36:16)
Email admin@alliedtelesis.com:
Time offset .... +0:00
Offset type .... Local
Filters:
1 Level ........ emergencies
Program ...... any
Facility ..... any
Message text . any
Statistics ..... 1327 messages received, 0 accepted by filter (2016 Oct 11
10:36:16)
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 420
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG EXTERNAL
show log external
Overview Use this command to display the contents of the external log, which is stored on
an SD card.
Syntax show log external [tail [<10-250>]]
Mode Global Configuration
Privileged Exec
User Exec
Usage If the optional tail parameter is specified, only the latest 10 messages in the
permanent log are displayed. A numerical value can be specified after the tail
parameter to change how many of the latest messages should be displayed.
Example To display the last 5 entries in the external log, use the command:
awplus# show log external tail 5
Related
Commands
clear log external
default log external
log external
log external (filter)
log external exclude
log external rotate
log external size
show log config
unmount
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
tail Display only the latest log entries.
<10-250>Specify the number of log entries to display.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 421
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW LOG PERMANENT
show log permanent
Overview This command displays the contents of the permanent log.
Syntax show log permanent [tail [<10-250>]]
Usage If the optional tail parameter is specified only, the latest 10 messages in the
permanent log are displayed. A numerical value can be specified after the tail
parameter to change how many of the latest messages should be displayed.
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the permanent log, use the command:
awplus# show log permanent
Output Figure 10-6: Example output from show log permanent
Related
Commands
clear log permanent
copy permanent-log
default log permanent
log permanent
log permanent (filter)
log permanent exclude
log permanent size
show log config
Parameter Description
tail Display only the latest log entries.
<10-250>Specify the number of log entries to display.
awplus#show log permanent
<date> <time> <facility>.<severity> <program[<pid>]>: <message>
------------------------------------------------------------------------
2014 Jun 10 09:30:09 syslog.notice syslog-ng[67]: syslog-ng starting up;
version=\’2.0rc3\’
2014 Jun 10 09:30:09 auth.warning portmap[106]: user rpc not found, reverting to
user bin
2014 Jun 10 09:30:09 cron.notice crond[116]: crond 2.3.2 dillon, started, log
level 8
2014 Jun 10 09:30:14 daemon.err snmpd[181]: /flash/.configs/snmpd.conf: line 20:
Error: bad SUBTREE object
2014 Jun 10 09:30:14 user.info HSL[192]: HSL: INFO: Registering port port1.0.1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 422
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG LOG
show running-config log
Overview This command displays the current running configuration of the Log utility.
Syntax show running-config log
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration of the log utility, use the command:
awplus# show running-config log
Related
Commands
show log
show log config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 423
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOGGING COMMANDS
UNMOUNT
unmount
Overview Use this command to unmount an external storage device. We recommend you
unmount storage devices before removing them, to avoid file corruption. This is
especially important if files may be automatically written to the storage device,
such as external log files or AMF backup files.
Syntax unmount card
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To unmount an SD card and safely remove it from the device, use the command:
awplus# unmount card
Related
Commands
clear log external
log external
show file systems
show log config
show log external
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
card Unmount the SD card.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 425
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SCRIPTING COMMANDS
ACTIVATE
activate
Overview This command activates a script file.
Syntax activate [background] <script>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage When a script is activated, the privilege level is set to 1 enabling User Exec
commands to run in the script. If you need to run Privileged Exec commands in
your script you need to add an enable (Privileged Exec mode) command to the
start of your script. If you need to run Global Configuration commands in your
script you need to add a configure terminal command after the enable command
at the start of your script.
The activate command executes the script in a new shell. A terminal length shell
command, such as terminal length 0 may also be required to disable a delay that
would pause the display.
A script must be a text file with a filename extension of either . sh or . scp only for
the AlliedWare Plus™ CLI to activate the script file. The . sh filename extension
indicates the file is an ASH script, and the . scp filename extension indicates the file
is an AlliedWare Plus™ script.
Examples To activate a command script to run as a background process, use the command:
awplus# activate background test.scp
Related
Commands
configure terminal
echo
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
wait
Parameter Description
background Activate a script to run in the background. A process that is running in
the background will operate as a separate task, and will not interrupt
foreground processing. Generally, we recommend running short,
interactive scripts in the foreground and longer scripts in the
background. The default is to run the script in the foreground.
<script>The file name of the script to activate. The script is a command script
consisting of commands documented in this software reference.
Note that you must use either a . scp or a . sh filename extension for a
valid script text file, as described below in the usage section for this
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 426
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SCRIPTING COMMANDS
ECHO
echo
Overview This command echoes a string to the terminal, followed by a blank line.
Syntax echo <line>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This command may be useful in CLI scripts, to make the script print user-visible
comments.
Example To echo the string Hello World to the console, use the command:
awplus# echo Hello World
Output
Related
Commands
activate
wait
Parameter Description
<line>The string to echo
Hello World

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 427
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SCRIPTING COMMANDS
WAIT
wait
Overview This command pauses execution of the active script for the specified period of
time.
Syntax wait <delay>
Default No wait delay is specified by default.
Mode Privileged Exec (when executed from a script not directly from the command line)
Usage Use this command to pause script execution in an .scp (AlliedWare Plus™ script) or
an .sh (ASH script) file executed by the activate command. The script must contain
an enable command, because the wait command is only executed in the
Privileged Exec mode.
Example See an .scp script file extract below that will show port counters for interface
port1.0.2 over a 10 second interval:
Related
Commands
activate
echo
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
Parameter Description
<delay><1-65335> Specify the time delay in seconds
enable
show interface port1.0.2
wait 10
show interface port1.0.2

12
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 428
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Interface
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
and display interfaces.
Command List •“description (interface)” on page 429
•“interface (to configure)” on page 430
•“mru” on page 432
•“mtu” on page 433
•“service statistics interfaces counter” on page 434
•“show interface” on page 435
•“show interface brief” on page 438
•“show interface memory” on page 439
•“show interface status” on page 441
•“shutdown” on page 443

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 429
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (INTERFACE)
description (interface)
Overview Use this command to add a description to a specific port or interface.
Syntax description <description>
Mode Interface Configuration
Example The following example uses this command to describe the device that a switch
port is connected to.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# description Boardroom PC
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: valid character set changed to printable ASCII characters
Parameter Description
<description>Text describing the specific interface. Descriptions can contain any
printable ASCII characters (ASCII 32-126).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 430
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
INTERFACE (TO CONFIGURE)
interface (to configure)
Overview Use this command to select one or more interfaces to configure.
Syntax interface <interface-list>
Usage A local loopback interface is one that is always available for higher layer protocols
to use and advertise to the network. Although a local loopback interface is
assigned an IP address, it does not have the usual requirement of connecting to a
lower layer physical entity. This lack of physical attachment creates the perception
of a local loopback interface always being accessible via the network.
Local loopback interfaces can be utilized by a number of protocols for various
purposes. They can be used to improve access to the device and also increase its
reliability, security, scalability and protection. In addition, local loopback interfaces
can add flexibility and simplify management, information gathering and filtering.
Mode Global Configuration
Example The following example shows how to enter Interface mode to configure vlan1.
Note how the prompt changes.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)#
The following example shows how to enter Interface mode to configure the local
loopback interface.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface lo
awplus(config-if)#
Parameter Description
<interface-list>The interfaces to configure. An interface-list can be:
•a VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• the loopback interface (lo)
• a continuous range of interfaces separated by a hyphen
(e.g. vlan10-20)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. vlan1,vlan10-20). Do not mix
interface types in a list.
The specified interfaces must exist.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 432
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
MRU
mru
Overview Use this command to set the Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) size for switch ports,
where MRU is the maximum frame size (excluding headers) that switch ports can
receive. For more information, see the Switching Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a previously specified Maximum
Receive Unit (MRU) size for switch ports, and restore the default MRU size (1500
bytes) for switch ports.
NOTE: The MRU sizes specify the payload only. For an IEEE 802.1q frame, provision is
made (internally) for the following additional components:
• Source and Destination addresses
• EtherType field
• Priority and VLAN tag fields
•FCS
These additional components increase the frame size internally by 22 bytes. For
example, the default frame size is 1522 bytes, including headers.
Syntax mru <mru-size>
no mru
Default The default MRU size is 1500 bytes for switch ports.
Mode Interface Configuration for switch ports.
Examples To configure an MRU of 9194 bytes on port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# mru 9194
To restore the MRU default size of 1500 bytes on port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no mru
Related
Commands
show interface
Parameter Description
<mru-size>68-9194. This value specifies the Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) size in
bytes, where 1500 bytes is the default Ethernet MRU size for an
interface.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 433
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
MTU
mtu
Overview Use this command to set the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size for interfaces,
where MTU is the maximum packet size that interfaces can transmit. The MTU size
setting is applied to both IPv4 and IPv6 packet transmission.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a previously specified Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) size, and restore the default MTU size. For example the
VLAN interface default is 1500 bytes.
Syntax mtu <68-1582>
no mtu
Default The default MTU size, for example 1500 bytes for VLAN interfaces.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage If a device receives an IPv4 packet for Layer 3 switching to another interface with
an MTU size smaller than the packet size, and if the packet has the ‘don’t
fragment’ bit set, then the device will send an ICMP ‘destination unreachable’ (3)
packet type and a ‘fragmentation needed and DF set’ (4) code back to the source.
For IPv6 packets bigger than the MTU size of the transmitting interface, an ICMP
‘packet too big’ (ICMP type 2 code 0) message is sent to the source.
Note that show interface output will only show MTU size for VLAN interfaces.
Examples To configure an MTU size of 1500 bytes on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# mtu 1500
To restore the MTU size to the default MTU size of 1500 bytes on vlan2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no mtu
Related
Commands
show interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 434
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SERVICE STATISTICS INTERFACES COUNTER
service statistics interfaces counter
Overview Use this command to enable the interface statistics counter.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the interface statistics counter.
Syntax service statistics interfaces counter
no service statistics interfaces counter
Default The interface statistics counter is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the interface statistics counter, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service statistics interfaces counter
To disable the interface statistics counter, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service statistics interfaces counter
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 435
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE
show interface
Overview Use this command to display interface configuration and status.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show interface [<interface-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Note that the output displayed with this command will show MTU (Maximum
Transmission Unit) size for VLAN interfaces, and MRU (Maximum Received Unit)
size for switch ports.
Example To display configuration and status information for all interfaces, use the
command:
awplus# show interface
Parameter Description
<interface-list>The interfaces or ports to display. An interface-list can be:
•a VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
•a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• the loopback interface (lo)
• a continuous range of interfaces separated by a hyphen
(e.g. vlan10-20)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. vlan1,vlan10-20). Do not mix
interface types in a list.
The specified interfaces must exist.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 436
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE
Figure 12-1: Example output from the show interface command
To display configuration and status information for the loopback interface lo, use
the command:
awplus# show interface lo
Figure 12-2: Example output from the show interface lo command
To display configuration and status information for interface vlan1, use the
command:
awplus# show interface vlan1
awplus#show interface
Interface port1.0.1
Scope: both
Link is UP, administrative state is UP
Thrash-limiting
Status Not Detected, Action learn-disable, Timeout 1(s)
Hardware is Ethernet, address is 00c0.ffee.0401
index 5001 metric 1 mru 1500
current duplex full, current speed 1000, current polarity mdix
configured duplex auto, configured speed auto, configured polarity auto
<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST>
SNMP link-status traps: Disabled
input packets 2901115, bytes 212107158, dropped 0, multicast packets 1250912
output packets 317532, bytes 29171173, multicast packets 3, broadcast packets 3
input average rate : 30 seconds 5.09 Kbps, 5 minutes 3.72 Kbps
output average rate: 30 seconds 1.36 Kbps, 5 minutes 477 bps
input peak rate 152.06 Kbps at 2018/04/10 15:56:53
output peak rate 6.78 Mbps at 2018/04/10 15:56:53
Time since last state change: 7 days 03:06:10
...
awplus#show interface lo
Interface lo
Scope: both
Link is UP, administrative state is UP
Hardware is Loopback
index 1 metric 1
<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING>
SNMP link-status traps: Disabled
Router Advertisement is disabled
Router Advertisement default routes are accepted
Router Advertisement prefix info is accepted
Time since last state change: 8 days 00:01:09

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 437
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE
Figure 12-3: Example output from the show interface vlan1 command
Related
Commands
mru
mtu
show interface brief
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: average rate and peak rate added to output
awplus#show interface vlan1
Interface vlan1
Link is UP, administrative state is UP
Hardware is VLAN, address is 0000.cd38.026c
IPv4 address 192.168.1.1/24 broadcast 192.168.1.255
index 301 metric 1 mtu 1500
arp ageing timeout 300
<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST>
VRF Binding: Not bound
SNMP link-status traps: Disabled
Router Advertisement is disabled
Router Advertisement default routes are accepted
Router Advertisement prefix info is accepted
input packets 0, bytes 0, dropped 0, multicast packets 0
output packets 9, bytes 612, multicast packets 0, broadcast packets 0
input average rate : 30 seconds 0 bps, 5 minutes 0 bps
output average rate: 30 seconds 0 bps, 5 minutes 0 bps
output peak rate 140 bps at 2018/04/10 16:40:56
Time since last state change: 8 days 19:09:19

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 438
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE BRIEF
show interface brief
Overview Use this command to display brief interface, configuration, and status information,
including provisioning information.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show interface brief
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output Figure 12-4: Example output from show interface brief
Related
Commands
show interface
show interface memory
awplus#show int brief
Interface Status Protocol
port1.0.1 admin up down
port1.0.2 admin up down
port1.0.3 admin up down
port1.0.4 admin up down
port1.0.5 admin up down
port1.0.6 admin up running
lo admin up running
vlan1 admin up down
vlan2 admin up down
Table 12-1: Parameters in the output of show interface brief
Parameter Description
Interface The name or type of interface.
Status The administrative state. This can be either admin up or admin
down.
Protocol The link state. This can be either down, running, or provisioned.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 439
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE MEMORY
show interface memory
Overview This command displays the shared memory used by either all interfaces, or the
specified interface or interfaces. The output is useful for diagnostic purposes by
Allied Telesis authorized service personnel.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show interface memory
show interface <port-list> memory
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the shared memory used by all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show interface memory
To display the shared memory used by port1.0.1 and port1.0.3 to port1.0.4, use the
command:
awplus# show interface port1.0.1,port1.0.3-port1.0.4 memory
Output Figure 12-5: Example output from the show interface memory command
Parameter Description
<port-list> Display information about only the specified port or ports. The port
list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do not mix
port types in the same list.
awplus#show interface memory
Vlan blocking state shared memory usage
---------------------------------------------
Interface shmid Bytes Used nattch Status
port1.0.1 491535 512 1
port1.0.2 393228 512 1
port1.0.3 557073 512 1
...
lo 425997 512 1
po1 1179684 512 1
po2 1212453 512 1
sa3 1245222 512 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 440
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE MEMORY
Figure 12-6: Example output from show interface <port-list> memory for a list
of interfaces
Related
Commands
show interface brief
show interface status
show interface switchport
awplus#show interface port1.0.1,port1.0.3-port1.0.4 memory
Vlan blocking state shared memory usage
---------------------------------------------
Interface shmid Bytes Used nattch Status
port1.0.1 589842 512 1
port1.0.3 688149 512 1
port1.0.4 327690 512 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 441
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE STATUS
show interface status
Overview Use this command to display the status of the specified interface or interfaces.
Note that when no interface or interfaces are specified then the status of all
interfaces on the device are shown.
Syntax show interface [<port-list>] status
Examples To display the status of port1.0.1 to port1.0.3, use the commands:
awplus# show interface port1.0.1-port1.0.3 status
To display the status of all ports, use the commands:
awplus# show interface status
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports to display information about. The port list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do not mix
port types in the same list.
Table 13: Example output from the show interface <port-list> status command
awplus#show interface port1.0.1-port1.0.3 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
port1.0.1 notconnect 1 auto auto 1000BASE-T
port1.0.2 notconnect 1 auto auto 1000BASE-T
port1.0.3 notconnect 1 auto auto 1000BASE-T
Table 14: Example output from the show interface status command
awplus#show interface status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
port1.0.1 Trunk_Net connected trunk a-full a-1000 1000BaseTX
port1.0.2 Access_Net1 connected 1 full 1000 1000BaseTX
port1.0.3 Access_Net1 disabled 1 auto auto 1000BaseTX
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 442
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE STATUS
Related
Commands
show interface
show interface memory
Table 15: Parameters in the output from the show interface status command
Parameter Description
Port Name/Type of the interface.
Name Description of the interface.
Status The administrative and operational status of the interface; one of:
• disabled: the interface is administratively down.
• connect: the interface is operationally up.
• notconnect: the interface is operationally down.
Vlan VLAN type or VLAN IDs associated with the port:
• When the VLAN mode is trunk, it displays trunk (it does not
display the VLAN IDs).
• When the VLAN mode is access, it displays the VLAN ID.
• When the VLAN mode is private promiscuous, it displays the
primary VLAN ID if it has one, and promiscuous if it does not
have a VLAN ID.
• When the VLAN mode is private host, it displays the primary
and secondary VLAN IDs.
• When the port is an Eth port, it displays none: there is no VLAN
associated with it.
• When the VLAN is dynamically assigned, it displays the current
dynamically assigned VLAN ID (not the access VLAN ID), or
dynamic if it has multiple VLANs dynamically assigned.
Duplex The actual duplex mode of the interface, preceded by a- if it has
autonegotiated this duplex mode. If the port is disabled or not
connected, it displays the configured duplex setting.
Speed The actual link speed of the interface, preceded by a- if it has
autonegotiated this speed. If the port is disabled or not
connected, it displays the configured speed setting.
Type The type of interface, e.g. 1000BaseTX. For SFP bays, it displays
Unknown if it does not recognize the type of SFP installed, or Not
present if an SFP is not installed or is faulty.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 443
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
INTERFACE COMMANDS
SHUTDOWN
shutdown
Overview This command shuts down the selected interface. This administratively disables
the link and takes the link down at the physical (electrical) layer.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this function and therefore to bring
the link back up again.
Syntax shutdown
no shutdown
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage If you shutdown an aggregator, the device shows the admin status of the
aggregator and its component ports as “admin down”. While the aggregator is
down, the device accepts shutdown and no shutdown commands on
component ports, but these have no effect on port status. Ports will not come up
again while the aggregator is down.
Example To shut down port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# shutdown
To bring up port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no shutdown
To shut down vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# shutdown
To bring up vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no shutdown

13
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 444
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Port Mirroring and
Remote Mirroring
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
Port Mirroring and Remote Mirroring (also known as RSPAN).
For more information, see the Mirroring Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
Command List •“mirror interface” on page 445
•“remote-mirror interface” on page 447
•“show mirror” on page 449
•“show mirror interface” on page 450
•“show remote-mirror” on page 451
•“switchport remote-mirror-egress” on page 453
•“vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan” on page 454

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 445
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
MIRROR INTERFACE
mirror interface
Overview Use this command to define a mirror port and mirrored (monitored) ports and
direction of traffic to be mirrored. The port for which you enter interface mode will
be the mirror port.
The destination port is removed from all VLANs, and no longer participates in other
switching.
Use the no variant of this command to disable port mirroring by the destination
port on the specified source port.
Use the none variant of this command when using copy-to-mirror ACL and QoS
commands.
Syntax mirror interface <source-port-list> direction
{both|receive|transmit}
mirror interface none
no mirror interface <source-port-list>
no mirror interface none
Mode Interface Configuration
Parameter Description
<source-port-list> The source switch ports to mirror. A port-list can be:
• a port (e.g. port1.0.2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-port1.0.3
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.2-port1.0.4
The source port list cannot include dynamic or static
channel groups (link aggregators).
direction Specifies whether to mirror traffic that the source port
receives, transmits, or both.
both Mirroring traffic both received and transmitted by the
source port.
receive Mirroring traffic received by the source port.
transmit Mirroring traffic transmitted by the source port.
none Specify this parameter for use with the copy-to-mirror
parameter of:
- the ACL (Access Control List) access-list and ipv6
access-list commands or
- the QoS (Quality of Service) default action command.
The none parameter lets you specify the destination port
(the analyzer port) for the traffic without specifying a
source mirror port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 446
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
MIRROR INTERFACE
Usage Use this command to send traffic to another device connected to the mirror port
for monitoring.
For more information, see the Mirroring Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
A mirror port cannot be associated with a VLAN. If a switch port is configured to be
a mirror port, it is automatically removed from any VLAN it was associated with.
This command can only be applied to a single mirror (destination) port, not to a
range of ports, nor to a static or dynamic channel group. Do not apply multiple
interfaces with an interface command before issuing the mirror interface
command. One interface may have multiple mirror interfaces.
Access control lists can be used to mirror a subset of traffic from the mirrored port
by using the copy-to-mirror parameter in hardware ACL commands.
Example To mirror traffic received and transmitted on port1.0.1 to destination port1.0.2, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# mirror interface port1.0.1 direction both
To enable use with the access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets) ACL and
default-action QoS commands to destination port1.0.1 without specifying a source
port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# mirror interface none
To mirror all received or transmitted TCP traffic to analyzer port1.0.1, use the
sample configuration snippet below:
Related
Commands
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)
default-action
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
awplus#show running-config
mls qos enable
access-list 3000 copy-to-mirror tcp any any
access-group 3000
!
interface port1.0.1
mirror interface none

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 447
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
REMOTE-MIRROR INTERFACE
remote-mirror interface
Overview Use this command on the source device to specify the source port whose traffic is
to be remote-mirrored (monitored), and the remote mirroring VLAN ID these
mirrored frames will be tagged with when they egress from the source device. The
port for which Interface Configuration mode is entered is the port via which the
mirrored traffic egresses the source device towards the remote destination device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable remote mirroring of the specified
mirrored port by the egress (destination) port on the source device.
Syntax remote-mirror interface <port-list> direction
{both|receive|transmit} vlan <2-4090> [priority <0-7>]
remote-mirror interface none vlan <2-4090> [priority <0-7>]
no remote-mirror interface <port-list> [direction
{receive|transmit}]
no remote-mirror interface none
Default No ports are set to be remote mirrored by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage To prevent unwanted processing of mirrored traffic, we recommend configuring
remote monitoring on the receiving device before configuring it on the source
device.
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports from which to mirror traffic. A port-list can be:
• a port (e.g. port1.0.1)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-port1.0.4
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.3-port1.0.4
direction Specifies whether to mirror traffic that the source port
receives, transmits, or both.
both Mirroring traffic both received and transmitted by the source
port.
receive Mirroring traffic received by the source port.
transmit Mirroring traffic transmitted by the source port.
2-4090 The VLAN ID of the remote mirroring VLAN that this mirrored
traffic is to be tagged with at the egress port on the source
device.
priority The 802.1p priority tag to apply to mirrored packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 448
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
REMOTE-MIRROR INTERFACE
This command can only be used to configure a single egress port on the source
device, not a range of egress ports. Do not use the interface command with
multiple interfaces before using this remote-mirror interface command. One
egress (destination) port on the source device can transmit mirrored frames from
up to four remote mirrored (source) ports.
The egress port on the source device can be associated with other VLANs in
addition to the remote mirror VLAN, so it can function as an uplink for traffic from
multiple VLANs. This command does not change the VLAN associations of the
mirrored ports.
Only one port on the device can be configured as either a mirror port for port
mirroring (mirror interface command) or as an egress port on the source device
for remote mirroring (remote-mirror interface command).
All mirrored ports on a single device must use the same remote mirror VLAN and
priority.
Access control lists can be used to mirror a subset of traffic from the mirrored port
by using the copy-to-mirror parameter in hardware ACL commands.
Example To configure the source device to send all the traffic that it receives on
remote-mirrored port port1.0.2 out egress port port1.0.1 tagged with remote
mirroring VLAN ID 2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# remote-mirror interface port1.0.2 direction
receive vlan 2
To stop port1.0.1 remote-mirroring traffic received on mirrored port port1.0.2, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no remote-mirror interface port1.0.2
direction receive
Related
Commands
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)
default-action
mirror interface
remote-mirror interface
show remote-mirror
switchport remote-mirror-egress
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 449
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
SHOW MIRROR
show mirror
Overview Use this command to display the status of all mirrored ports.
Syntax show mirror
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the status of all mirrored ports, use the following command:
awplus# show mirror
Output Figure 13-1: Example output from the show mirror command
Mirror Test Port Name: port1.0.1
Mirror option: Enabled
Mirror direction: both
Monitored Port Name: port1.0.2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 450
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
SHOW MIRROR INTERFACE
show mirror interface
Overview Use this command to display port mirroring configuration for a mirrored
(monitored) switch port.
Syntax show mirror interface <port>
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Interface Configuration
Example To display port mirroring configuration for port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# show mirror interface port1.0.2
Output Figure 13-2: Example output from the show mirror interface command
Parameter Description
<port>The monitored switch port to display information about.
Mirror Test Port Name: port1.0.1
Mirror option: Enabled
Mirror direction: both
Monitored Port Name: port1.0.2
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 451
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
SHOW REMOTE-MIRROR
show remote-mirror
Overview Use this command to display information for remote-mirroring.
Syntax show remote-mirror
Mode User Exec
Example To display information about remote mirroring, use the command:
awplus# show remote-mirror
Output Figure 13-3: Example output from show remote-mirror
awplus#show remote-mirror
Remote mirror information:
Remote mirror destination:
Port: port1.0.3
VLAN: 259
User priority: 0
Monitored ports:
port1.0.1
direction: both
Remote mirror egress ports:
Remote mirror VLANs:
VLAN 259
Table 13-1: Parameters in the output from show remote-mirror
Parameter Description
Remote mirror
destination On the source device, this displays information about:
• the egress port for the mirrored traffic on the source
device
• the remote mirroring VLAN ID this traffic is tagged with
on egress
• the user priority this traffic is tagged with on egress
Monitored ports On the source device, this displays:
• the ports being mirrored (monitored)
• the direction—whether both received traffic,
transmitted traffic or both are mirrored
• ‘none (via ACL)’ if it is configured with the command
remote-mirror interface none to allow ACLs to select
the traffic to be mirrored

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 452
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
SHOW REMOTE-MIRROR
Related
Commands
remote-mirror interface
switchport remote-mirror-egress
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan
Remote mirror
egress ports On the destination device, this displays :
• the remote mirror egress ports
• the remote mirror VLANs they are associated with
Remote mirror
VLANs On source, destination and intermediate devices, this
displays a list of any VLANs configured in remote mirror
VLAN mode. To see a list of the ports associated with these
VLANs, use the command show vlan brief.
Table 13-1: Parameters in the output from show remote-mirror (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 453
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT REMOTE-MIRROR-EGRESS
switchport remote-mirror-egress
Overview Use this command on the device receiving remote mirrored traffic to set the
remote mirroring egress port for the specified remote mirroring VLAN. This port
removes the remote mirror VLAN tagging before transmitting the mirrored traffic.
Ingress traffic on this port is disabled.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the port to no longer function as a
remote mirror egress port.
Syntax switchport remote-mirror-egress vlan <vlan-id>
no switchport remote-mirror-egress
Default There is no remote mirror egress port by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a switch port
Usage To prevent unwanted processing of mirrored traffic, we recommend configuring
remote monitoring on the receiving device before configuring it on the source
device.
This command would typically be used for the port that transmits the
remote-mirrored traffic to a device that will analyze it. The port effectively
functions as an access port in the remote mirror VLAN, with the added feature of
not allowing ingress traffic on the port.
Example To set port1.0.2 on the destination device as the remote mirror egress port for
mirrored traffic that is tagged with VLAN ID 2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport remote-mirror-egress vlan 2
To unset port1.0.2 as a remote mirror egress port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport remote-mirror-egress
Related
Commands
remote-mirror interface
show remote-mirror
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan
Parameter Description
<vlan-id> The port will transmit the mirrored traffic it receives from this
remote mirror VLAN.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 454
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PORT MIRRORING AND REMOTE MIRRORING COMMANDS
VLAN MODE REMOTE-MIRROR-VLAN
vlan mode remote-mirror-vlan
Overview Use this command to create a single VLAN or a range of VLANs in remote mirror
mode to be used for remote mirroring.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the remote mirror VLAN from the
VLAN database and its configurations.
Syntax vlan [<vid>|<vid-range>] mode remote-mirror-vlan
no vlan [<vid>|<vid-range>]
Default There is no remote mirror VLAN by default.
Mode VLAN Configuration
Usage This remote mirror VLAN needs to be configured on the remote mirroring source
device, the destination (receiving) device, and any devices in between that are to
forward the mirrored traffic. We recommend configuring this on the receiving
device and intermediate devices before configuring the source device.
The remote mirror VLAN operates in a special mode— all traffic on the remote
mirror VLAN is flooded, and no learning or CPU processing is done for packets in
the VLAN. BPDU packets (link-local packets used to control features like spanning
tree or AMF) are dropped on remote mirror VLANs.
Disabling the remote-mirroring VLAN on the source switch does not prevent the
mirrored packets from being sent with the remote-mirror VLAN tag. To stop the
mirroring, the command no remote-mirror interface must be used.
Example To create a VLAN with VLAN ID 3 in remote mirror VLAN mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 3 mode remote-mirror-vlan
To remove the remote mirror VLAN with ID 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# no vlan 3
Related
Commands
remote-mirror interface
show remote-mirror
Parameter Description
<vid> The VLAN ID of the remote mirroring VLAN to be created.
<vid-range> The range of VLAN IDs for the remote mirroring VLANs to be
created.

14
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 456
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Alarm Monitoring
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
alarm monitoring. For more information, see the Alarm Monitoring Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“alarm facility” on page 457
•“debug alarm” on page 460
•“show alarm settings” on page 461
•“show debugging alarm” on page 462
•“show facility-alarm status” on page 463

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 457
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
ALARM FACILITY
alarm facility
Overview Use this command to enable alarm monitoring. Enabling alarms allows you to
monitor the switch environment and respond to problems as they occur.
Alarm monitoring is user-configured, including which alarms are enabled, and the
LED and relay settings for each alarm.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the alarm facility for a particular
alarm.
The command syntax varies depending on the type of alarm you are configuring.
The section below includes the syntax for each alarm type.
Syntax alarm facility epsr
alarm facility input-alarm <input-alarm-number>
alarm facility link-down <port-list>
alarm facility loopprot
alarm facility main-pse
alarm facility power-supply <power-supply-number>
alarm facility pse-port <port-list>
alarm facility temperature
no alarm facility {epsr|input-alarm <number>|link-aggregation
{partial-failure|total-failure}|link-down
<port-list>|loopprot|main-pse|power-supply <id>|pse-port
<port-list>|temperature}
alarm facility ufo
Parameter Description
epsr EPSR alarm
input-alarm External contact input alarm.
<input-alarm-number> The external contact input number. The current
models have only a single pair of input contacts, so
this number must be 1.
link-down Link failure alarm. This triggers if a link goes down on
a particular switch port or ports.
Note that you must also enable link-status traps on
the monitored ports. To do this, use the command
snmp trap link-status.
Note that if a port is part of a link aggregation group,
you cannot configure a link-down alarm on that port.
For example, if port 1.0.1 is in a link aggregation
group, you cannot enter commands like alarm
facility link-down port1.0.1 led.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 458
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
ALARM FACILITY
Default All alarms are disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To turn on the LED in case a loop occurs, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# alarm facility loopprot led
<port-list> The switch ports on which the alarm will be activated
or disabled. The port list can be any of the following:
•An individual port. Example: 1.0.3
• A continuous range of ports. Example: 1.0.1-1.0.3
• A combination of individual ports and port ranges,
separated by commas. Example: 1.0.1, 1.0.3-1.0.4
loopprot Loop protection alarm.
main-pse Main power source equipment failure alarm. This
triggers if the sum of the power consumed by all of
the PoE devices plugged into the switch exceeds the
maximum permitted.
Note: This alarm pertains to PoE models only.
power-supply Power supply failure alarm. This triggers if the
designated power supply is down.
<power-supply-number> The power supply unit number. The switch has two
power supplies, so the number must be 1 or 2.
pse-port PoE failure on a switch port alarm. This triggers if a PoE
device plugged into a port is consuming more than
the maximum power output for the port.
Note that if a port is part of a link aggregation group,
you cannot configure a pse-port alarm on that port.
For example, if port 1.0.1 is in a link aggregation
group, you cannot enter commands like alarm
facility pse-port port1.0.1 led.
temperature High temperature alarm. This triggers if the
temperature of the device exceeds 95 degrees Celsius.
led Enable or disable the LED for the alarm.
relay Enable or disable the relay output for the alarm.
alarm-position The position (open or closed) of the input contact
corresponding to the alarm that has occurred.
open The electrical circuit for the contact input is open.
close The electrical circuit for the contact input is closed.
ufo One or more UFO VLANs are isolated and can not
forward traffic.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 459
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
ALARM FACILITY
To have an alarm when the contact input is open, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# alarm facility input-alarm 1 alarm-position
open
To turn off the LED from flashing when the device temperature is too high, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no alarm facility temperature led
Related
Commands
show alarm settings
show facility-alarm status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: ufo parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 460
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
DEBUG ALARM
debug alarm
Overview Use this command to enable debugging of the Alarm Monitoring feature. When
debugging is enabled, the switch displays debugging messages on the terminal
monitor and in the log.
Use the no variant of this command to disable debugging of the Alarm Monitoring
feature.
Syntax debug alarm
no debug alarm
Default Disabled
Mode Global Configuration
Example To turn on Alarm debugging, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug alarm
Related
Commands
show debugging alarm
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 461
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW ALARM SETTINGS
show alarm settings
Overview Use this command to view all alarms configured on the switch. The output also
includes the alarm position for each contact input.
Syntax show alarm settings
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display all of the alarm settings enabled on the switch, use the command:
awplus# show alarm settings
Output Figure 14-1: Example output from the show alarm settings command
Related
Commands
alarm facility
show facility-alarm status
Alarm ID LED Relay
---------------------- --------- -------- --------
External PSU 1 Enabled Disabled
External PSU 2 Enabled Disabled
EPSR - Disabled Disabled
External contact input 1 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.1 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.2 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.3 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.4 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.5 Disabled Disabled
Link down port1.0.6 Disabled Disabled
Loop detect - Disabled Enabled
Main PSE failure - Disabled Disabled
PoE failure port1.0.1 Disabled Disabled
PoE failure port1.0.2 Disabled Disabled
PoE failure port1.0.3 Disabled Disabled
PoE failure port1.0.4 Disabled Disabled
Temperature - Enabled Enabled
Alarm ID Alarm position
---------------------- --------- --------------
External contact input 1 Open
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 462
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING ALARM
show debugging alarm
Overview Use this command to show whether Alarm Monitoring debugging is enabled or
disabled.
Syntax show debugging alarm
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show the status of Alarm Monitoring debugging, use the command:
awplus# show debugging alarm
Output Figure 14-2: Example output from show debugging alarm
Related
Commands
debug alarm
awplus#show debugging alarm
% Alarm debugging is disabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 463
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALARM MONITORING COMMANDS
SHOW FACILITY-ALARM STATUS
show facility-alarm status
Overview Use this command to view all of the alarms that are currently active on the switch.
Syntax show facility-alarm status
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display all of the currently active alarms on the switch, use the command:
awplus# show facility-alarm status
Output Figure 14-3: Example output from the show facility-alarm status command
Related
Commands
alarm facility
show alarm settings
Active alarms ID
---------------------- ---------
External PSU 2
EPSR -
G8032 -
UFO -
Link down port1.0.1
PoE failure port1.0.1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 464
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 2: Interfaces and Layer 2

15
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 465
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Switching
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
switching.
For more information, see the Switching Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
Command List •“backpressure” on page 467
•“clear loop-protection counters” on page 469
•“clear mac address-table dynamic” on page 470
•“clear mac address-table static” on page 472
•“clear port counter” on page 473
•“clear port-security intrusion” on page 474
•“debug loopprot” on page 477
•“debug platform packet” on page 478
•“duplex” on page 480
•“flowcontrol (switch port)” on page 481
•“linkflap action” on page 483
•“loop-protection loop-detect” on page 484
•“loop-protection action” on page 485
•“loop-protection action-delay-time” on page 486
•“loop-protection timeout” on page 487
•“mac address-table acquire” on page 488
•“mac address-table ageing-time” on page 489
•“mac address-table logging” on page 490

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 466
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
•“mac address-table static” on page 491
•“mac address-table thrash-limit” on page 492
•“platform hwfilter-size” on page 493
•“platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm” on page 494
•“platform load-balancing” on page 495
•“platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm” on page 496
•“platform multicast-ratelimit” on page 497
•“platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding” on page 498
•“platform vlan-stacking-tpid” on page 500
•“polarity” on page 501
•“show debugging loopprot” on page 502
•“show debugging platform packet” on page 503
•“show flowcontrol interface” on page 504
•“show interface err-disabled” on page 505
•“show interface switchport” on page 506
•“show loop-protection” on page 507
•“show mac address-table” on page 509
•“show mac address-table thrash-limit” on page 511
•“show platform” on page 512
•“show platform classifier statistics utilization brief” on page 515
•“show platform port” on page 518
•“show port-security interface” on page 520
•“show port-security intrusion” on page 521
•“show storm-control” on page 522
•“speed” on page 523
•“storm-control level” on page 525
•“switchport port-security” on page 526
•“switchport port-security aging” on page 527
•“switchport port-security maximum” on page 528
•“switchport port-security violation” on page 529
•“thrash-limiting” on page 530
•“undebug loopprot” on page 532
•“undebug platform packet” on page 533

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 467
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
BACKPRESSURE
backpressure
Overview This command provides a method of applying flow control to ports running in half
duplex mode. The setting will only apply when the link is in the half-duplex state.
You can disable backpressure on an interface using the off parameter or the no
variant of this command.
Syntax backpressure {on|off}
no backpressure
Default Backpressure is turned off by default. You can determine whether an interface has
backpressure enabled by viewing the running-config output; backpressure on is
shown for interfaces if this feature is enabled.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The backpressure feature enables half duplex Ethernet ports to control traffic flow
during congestion by preventing further packets arriving. Back pressure utilizes a
pre-802.3x mechanism in order to apply Ethernet flow control to switch ports that
are configured in the half duplex mode.
The flow control applied by the flowcontrol (switch port) command operates only
on full-duplex links, whereas back pressure operates only on half-duplex links.
If a port has insufficient capacity to receive further frames, the device will simulate
a collision by transmitting a CSMACD jamming signal from this port until the buffer
empties. The jamming signal causes the sending device to stop transmitting and
wait a random period of time, before retransmitting its data, thus providing time
for the buffer to clear. Although this command is only valid for switch ports
operating in half-duplex mode the remote device (the one sending the data) can
be operating in the full duplex mode.
To see the currently-negotiated duplex mode for ports whose links are up, use the
command show interface. To see the configured duplex mode (when different
from the default), use the command show running-config.
Examples To enable back pressure flow control on interfaces port1.0.1-port1.0.2
enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# backpressure on
Parameters Description
on Enables half-duplex flow control.
off Disables half-duplex flow control.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 468
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
BACKPRESSURE
To disable back pressure flow control on interface port1.0.2 enter the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# backpressure off
Validation
Commands
show running-config
show interface
Related
Commands
duplex

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 469
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR LOOP-PROTECTION COUNTERS
clear loop-protection counters
Overview Use this command to clear the counters for the Loop Protection counters.
Syntax clear loop-protection [interface <port-list>] counters
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To clear the counter information for all interfaces:
awplus# clear loop-protection counters
To clear the counter information for a single port:
awplus# clear loop-protection interface port1.0.1 counters
Parameters Description
interface The interface whose counters are to be cleared.
<port-list>A port, a port range, or an aggregated link.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 470
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR MAC ADDRESS-TABLE DYNAMIC
clear mac address-table dynamic
Overview Use this command to clear the filtering database of all entries learned for a selected
MAC address, an MSTP instance, a switch port interface or a VLAN interface.
Syntax clear mac address-table dynamic
[address <mac-address>|interface <port> [instance <inst>]|
vlan <vid>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command with options to clear the filtering database of all entries learned
for a given MAC address, interface or VLAN. Use this command without options to
clear any learned entries.
Use the optional instance parameter to clear the filtering database entries
associated with a specified MSTP instance Note that you must first specify a switch
port interface before you can specify an MSTP instance.
Compare this usage and operation with the clear mac address-table static
command. Note that an MSTP instance cannot be specified with the command
clear mac address-table static.
Examples This example shows how to clear all dynamically learned filtering database entries.
awplus# clear mac address-table dynamic
This example shows how to clear all dynamically learned filtering database entries
when learned through device operation for the MAC address 0000.5E00.5302.
awplus# clear mac address-table dynamic address 0000.5E00.5302
Parameter Description
address
<mac-address> Specify a MAC (Media Access Control) address to be cleared
from the filtering database, in the format
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
interface <port> Specify a switch port to be cleared from the filtering
database. The port can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
instance <inst> Specify an MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree) instance in the
range 1 to 63 to be cleared from the filtering database.
vlan <vid> Specify a VID (VLAN ID) in the range 1 to 4094 to be cleared
from the filtering database.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 471
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR MAC ADDRESS-TABLE DYNAMIC
This example shows how to clear all dynamically learned filtering database entries
when learned through device operation for a given MSTP instance 1 on switch port
interface port1.0.3.
awplus# clear mac address-table dynamic interface port1.0.3
instance 1
Related
Commands
clear mac address-table static
show mac address-table
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 472
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR MAC ADDRESS-TABLE STATIC
clear mac address-table static
Overview Use this command to clear the filtering database of all statically configured entries
for a selected MAC address, interface, or VLAN.
Syntax clear mac address-table static [address <mac-address>|interface
<port>|vlan <vid>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command with options to clear the filtering database of all entries made
from the CLI for a given MAC address, interface or VLAN. Use this command
without options to clear any entries made from the CLI.
Compare this usage with clear mac address-table dynamic command.
Examples This example shows how to clear all filtering database entries configured through
the CLI.
awplus# clear mac address-table static
This example shows how to clear all filtering database entries for a specific
interface configured through the CLI.
awplus# clear mac address-table static interface port1.0.3
This example shows how to clear filtering database entries configured through the
CLI for the MAC address 0000.5E00.5302.
awplus# clear mac address-table static address 0000.5E00.5302
Related
Commands
clear mac address-table dynamic
mac address-table static
show mac address-table
Parameter Description
address
<mac-address> Specify a MAC (Media Access Control) address to be cleared
from the filtering database, in the format
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
interface <port> Specify the port from which statically configured entries are
to be cleared. The port can be
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
vlan <vid> Specify a VID (VLAN ID) in the range 1 to 4094 to be cleared
from the filtering database.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 473
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR PORT COUNTER
clear port counter
Overview Use this command to clear the packet counters of the port.
Syntax clear port counter [<port>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear the packet counter for port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# clear port counter port1.0.1
Related
Commands
show platform port
Parameter Description
<port> The port number or range

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 474
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR PORT-SECURITY INTRUSION
clear port-security intrusion
Overview Use this command to clear the history of the port-security intrusion list on all ports,
or an individual port. If a port is not specified, the intrusion lists of all ports are
cleared. This command does not clear any MAC addresses the device has already
learned on the ports. If you want to clear MAC addresses on a switch port from the
filtering database, you can use the clear mac address-table dynamic command or
the clear mac address-table static command.
Syntax clear port-security intrusion [interface <port>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To see the port-security status on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security interface port1.0.2
To see the intrusion list on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
<port> Specify the switch port from which the history of violated address
entries will be cleared. The port can be a single switch port, (e.g.
port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2).
Table 15-1: Example output from show port-security interface
awplus#show port-security interface port1.0.2
Port Security configuration
------------------------------------------------------------
Security Enabled : YES
Port Status : ENABLED
Violation Mode : TRAP
Aging : OFF
Maximum MAC Addresses : 1
Total MAC Addresses : 1
Lock Status : LOCKED
Security Violation Count : 1
Last Violation Source Address : 801f.0200.19da
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 475
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR PORT-SECURITY INTRUSION
To clear the history of port-security intrusion list on port1.0.2, use the following
command:
awplus# clear port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
To see the port-security status on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security interface port1.0.2
NOTE: Note that the port status is still locked while the history of port violation is
cleared from the database.
To see the intrusion list on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
Table 15-2: Example output from show port-security intrusion
awplus#show port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
Port Security Intrusion List
------------------------------------------------------------
Interface: port1.0.2 - 1 intrusion(s) detected
801f.0200.19da
Table 15-3: Example output from show port-security interface
awplus#show port-security interface port1.0.2
Port Security configuration
------------------------------------------------------------
Security Enabled : YES
Port Status : ENABLED
Violation Mode : TRAP
Aging : OFF
Maximum MAC Addresses : 1
Total MAC Addresses : 1
Lock Status : LOCKED
Security Violation Count : 0
Last Violation Source Address : None
Table 15-4: Example output from show port-security intrusion
awplus#show port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
Port Security Intrusion List
------------------------------------------------------------
Interface: port1.0.2 - no intrusions detected

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 476
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR PORT-SECURITY INTRUSION
Related
Commands
show port-security interface
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security maximum
switchport port-security violation

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 477
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
DEBUG LOOPPROT
debug loopprot
Overview This command enables Loop Protection debugging.
The no variant of this command disables Loop Protection debugging.
Syntax debug loopprot {info|msg|pkt|state|nsm|all}
no debug loopprot {info|msg|pkt|state|nsm|all}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To enable debug for all state transitions, use the command:
awplus# debug loopprot state
Related
Commands
show debugging loopprot
undebug loopprot
Parameter Description
info General Loop Protection information.
msg Received and transmitted Loop Detection Frames (LDFs).
pkt Echo raw ASCII display of received and transmitted LDF packets to
the console.
state Loop Protection states transitions.
nsm Network Service Module information.
all All debugging information.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 478
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
DEBUG PLATFORM PACKET
debug platform packet
Overview This command enables platform to CPU level packet debug functionality on the
device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable platform to CPU level packet debug.
If the result means both send and receive packet debug are disabled, then any
active timeout will be canceled.
Syntax debug platform packet [recv] [send] [sflow] [timeout <timeout>]
[vlan <vid>|all]
no debug platform packet [recv] [send]
Default A 5 minute timeout is configured by default if no other timeout duration is
specified.
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to trace packets sent and received by the CPU. If a
timeout is not specified, then a default 5 minute timeout will be applied.
If a timeout of 0 is specified, packet debug will be generated until the no variant of
this command is used or another timeout value is specified. The timeout value
applies to both send and receive debug and is updated whenever the debug
platform packet command is used.
Examples To enable both receive and send packet debug for the default timeout of 5
minutes, enter:
awplus# debug platform packet
To enable receive packet debug for 10 seconds, enter:
awplus# debug platform packet recv timeout 10
To enable packet debug for sFlow packets only for the default timeout of 5
minutes, enter:
awplus# debug platform packet sflow
Parameter Description
recv Debug packets received.
send Debug packets sent.
sflow Debug sFlow packets.
timeout <timeout>Stop debug after a specified time. Specify the time in
seconds.
vlan <vid> Specify a VID (VLAN ID) in the range 1 to 4094 to limit
debug to that VLAN.
all Debug all VLANs (default setting).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 479
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
DEBUG PLATFORM PACKET
To enable send packet debug with no timeout, enter:
awplus# debug platform packet send timeout 0
To enable VLAN packet debug for VLAN 1 with a timeout duration of 3 minutes,
enter:
awplus# debug platform packet vlan 1 timeout 150
To disable receive packet debug, enter:
awplus# no debug platform packet recv
Related
Commands
show debugging platform packet
undebug platform packet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 480
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
DUPLEX
duplex
Overview This command changes the duplex mode for the specified port.
To see the currently-negotiated duplex mode for ports whose links are up, use the
command show interface. To see the configured duplex mode (when different
from the default), use the command show running-config.
Syntax duplex {auto|full|half}
Default By default, ports auto-negotiate duplex mode (except for 100Base-FX ports which
do not support auto-negotiation, so default to full duplex mode).
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Switch ports in a static or dynamic (LACP) channel group must have the same port
speed and be in full duplex mode. Once switch ports have been aggregated into a
channel group, you can set the duplex mode of all the switch ports in the channel
group by applying this command to the channel group.
Examples To specify full duplex for port1.0.4, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# duplex full
To specify half duplex for port1.0.4, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# duplex half
To auto-negotiate duplex mode for port1.0.4, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# duplex auto
Related
Commands
polarity
speed
show interface
Parameter Description
auto Auto-negotiate duplex mode.
full Operate in full duplex mode only.
half Operate in half duplex mode only.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 481
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
FLOWCONTROL (SWITCH PORT)
flowcontrol (switch port)
Overview Use this command to enable flow control, and configure the flow control mode for
the switch port.
Use the no variant of this command to disable flow control for the specified switch
port.
Syntax flowcontrol {send|receive} {off|on}
no flowcontrol
Default By default, flow control is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The flow control mechanism specified by 802.3x is only for full duplex links. It
operates by sending PAUSE frames to the link partner to temporarily suspend
transmission on the link.
Flow control enables connected Ethernet ports to control traffic rates during
congestion by allowing congested nodes to pause link operation at the other end.
If one port experiences congestion, and cannot receive any more traffic, it notifies
the other port to stop sending until the condition clears. When the local device
detects congestion at its end, it notifies the remote device by sending a pause
frame. On receiving a pause frame, the remote device stops sending data packets,
which prevents loss of data packets during the congestion period.
Flow control is not recommended when running QoS or ACLs, because the
complex queuing, scheduling, and filtering configured by QoS or ACLs may be
slowed by applying flow control.
For half-duplex links, an older form of flow control known as backpressure is
supported. See the related backpressure command.
For flow control on async serial (console) ports, see the flowcontrol hardware
(asyn/console) command.
Parameter Description
receive When the port receives pause frames, it temporarily stops (pauses)
sending traffic.
on Enable the specified flow control.
off Disable the specified flow control.
send When the port is congested (receiving too much traffic), it sends
pause frames to request the other end to temporarily stop (pause)
sending traffic.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 482
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
FLOWCONTROL (SWITCH PORT)
Examples To enable flow control on port1.0.2 (receive only), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# flowcontrol receive on
To enable flow control on port1.0.2 (send only), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# flowcontrol send on
To disable flow control on port1.0.2 (receive only), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# flowcontrol receive off
To disable flow control on port1.0.2 (send only), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# flowcontrol send off
Related
Commands
backpressure
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 483
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
LINKFLAP ACTION
linkflap action
Overview Use this command to detect flapping on all ports. If more than 15 flaps occur in less
than 15 seconds the flapping port will shut down.
Use the no variant of this command to disable flapping detection at this rate.
Syntax linkflap action [shutdown]
no linkflap action
Default Linkflap action is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the linkflap action command on the device, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# linkflap action shutdown
Parameter Description
linkflap Global setting for link flapping.
action Specify the action for port.
shutdown Shutdown the port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 484
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
LOOP-PROTECTION LOOP-DETECT
loop-protection loop-detect
Overview Use this command to enable the loop-protection loop-detect feature and
configure its parameters.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the loop-protection loop-detect
feature.
Syntax loop-protection loop-detect [ldf-interval <period>]
[ldf-rx-window <frames>] [fast-block]
no loop-protection loop-detect
Default The loop-protection loop-detect feature is disabled by default. The default interval
is 10 seconds, and the default window size is 3 frames.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage See the “Loop Protection” section in the Switching Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide for relevant conceptual, configuration, and overview
information prior to applying this command.
Example To enable the loop-detect mechanism on the switch, and generate loop-detect
frames once every 5 seconds, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# loop-protection loop-detect ldf-interval 5
Related
Commands
loop-protection action
loop-protection timeout
show loop-protection
Parameter Description
ldf-interval The time (in seconds) between successive loop-detect frames
being sent.
<period> Specify a period between 1 and 600 seconds. The default is 10
seconds.
ldf-rx-window The number of transmitted loop detect frames whose details
are held for comparing with frames arriving at the same port.
<frames> Specify a value for the window size between 1 and 5 frames.
The default is 3 frames.
[fast-block] The fast-block blocks transmitting port to keep partial
connectivity.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 485
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
LOOP-PROTECTION ACTION
loop-protection action
Overview Use this command to specify the protective action to apply when a network loop
is detected on an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the loop protection actions to the
default action, vlan-disable, on an interface.
Syntax loop-protection action
{link-down|log-only|port-disable|vlan-disable|none}
no loop-protection action
Default loop-protection action vlan-disable
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage See the “Loop Protection” section in the Switching Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide for relevant conceptual, configuration, and overview
information prior to applying this command.
Example To disable the interface port1.0.2 and bring the link down when a network
loop is detected, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# loop-protection action link-down
Related
Commands
loop-protection loop-detect
loop-protection timeout
show loop-protection
Parameter Description
link-down Block all traffic on a port (or aggregated link) that detected the
loop, and take down the link.
log-only Details of loop conditions are logged. No action is applied to the
port (or aggregated link).
port-disable Block all traffic on interface for which the loop occurred, but keep
the link in the up state.
vlan-disable Block all traffic for the VLAN on which the loop traffic was
detected. Note that setting this parameter will also enable ingress
filtering. This is the default action.
none Applies no protective action.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 486
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
LOOP-PROTECTION ACTION-DELAY-TIME
loop-protection action-delay-time
Overview Use this command to sets the loop protection action delay time for an interface to
specified values in seconds. The action delay time specifies the waiting period for
the action.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the loop protection action delay time
for an interface to default.
Syntax loop-protection action-delay-time <0-86400>
no loop-protection action
Default Action delay timer is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To configure a loop protection action delay time of 10 seconds on port1.0.4, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# loop-protection action-delay-time 10
Related
Commands
loop-protection loop-detect
loop-protection timeout
show loop-protection
Parameter Description
<0-86400> Time in seconds; 0 means action delay timer is disabled.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 487
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
LOOP-PROTECTION TIMEOUT
loop-protection timeout
Overview Use this command to specify the Loop Protection recovery action duration on an
interface.
Use the no variant of this command to set the loop protection timeout to the
default.
Syntax loop-protection timeout <duration>
no loop-protection timeout
Default The default is 7 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage See the “Loop Protection” section in the Switching_Feature Overview_and
Configuration_Guide for relevant conceptual, configuration, and overview
information prior to applying this command.
Example To configure a loop protection action timeout of 10 seconds for port1.0.4, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# loop-protection timeout 10
Related
Commands
loop-protection loop-detect
loop-protection action
show loop-protection
Parameter Description
<duration> The time (in seconds) for which the configured action will apply
before being disabled. This duration can be set between 0 and 86400
seconds (24 hours). The set of 0 means infinity so timeout does not
expire.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 488
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
MAC ADDRESS-TABLE ACQUIRE
mac address-table acquire
Overview Use this command to enable MAC address learning on the device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable learning.
Syntax mac address-table acquire
no mac address-table acquire
Default Learning is enabled by default for all instances.
Mode Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mac address-table acquire

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 489
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
MAC ADDRESS-TABLE AGEING-TIME
mac address-table ageing-time
Overview Use this command to specify an ageing-out time for a learned MAC address. The
learned MAC address will persist for at least the specified time.
The no variant of this command will reset the ageing-out time back to the default
of 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Syntax mac address-table ageing-time <ageing-timer> none
no mac address-table ageing-time
Default The default ageing time is 300 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples The following commands specify various ageing timeouts on the device:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mac address-table ageing-time 1000
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mac address-table ageing-time none
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no mac address-table ageing-time
Parameter Description
<ageing-timer> <10-1000000> The number of seconds of persistence.
none Disable learned MAC address timeout.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 490
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
MAC ADDRESS-TABLE LOGGING
mac address-table logging
Overview Use this command to create log entries when the content of the FDB (forwarding
database) changes. Log messages are produced when a MAC address is added to
or removed from the FDB.
CAUTION: MAC address table logging may impact the performance of the switch. Only
enable it when necessary as a debug tool.
Use the no variant of this command to stop creating log entries when the content
of the FDB changes.
Syntax mac address-table logging
no mac address-table logging
Default MAC address table logging is disabled by default.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage When MAC address table logging is enabled, the switch produces the following
messages:
Note that rapid changes may not be logged. For example, if an entry is added and
then removed within a few seconds, those actions may not be logged.
To see whether MAC address table logging is enabled, use the command show
running-config.
Example To create log messages when the content of the FDB changes, use the command:
awplus# mac address-table logging
Related
Commands
show running-config
Change Message format Example
MAC added MAC add <mac> <port> <vlan>MAC add eccd.6db5.68a7 port1.0.1 vlan2
MAC removed MAC remove <mac> <port> <vlan>MAC remove eccd.6db5.68a7 port1.0.1 vlan2
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 491
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
MAC ADDRESS-TABLE STATIC
mac address-table static
Overview Use this command to statically configure the MAC address-table to forward or
discard frames with a matching destination MAC address.
Syntax mac address-table static <mac-addr> {forward|discard} interface
<port> [vlan <vid>]
no mac address-table static <mac-addr> {forward|discard}
interface <port> [vlan <vid>]
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The mac address-table static command is only applicable to Layer 2 switched
traffic within a single VLAN. Do not apply the mac address-table static command
to Layer 3 switched traffic passing from one VLAN to another VLAN. Frames will not
be discarded across VLANs because packets are routed across VLANs. This
command only works on Layer 2 traffic.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mac address-table static 2222.2222.2222 forward
interface port1.0.4 vlan 3
Related
Commands
clear mac address-table static
show mac address-table
Parameter Description
<mac-addr> The destination MAC address in HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
interface
<port> Specify a switch port to be cleared from the filtering database. The
port can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
vlan <vid> The ID of a VLAN to apply the command to, in the range 1 to 4094. If
you do not specify a VLAN, the command applies to VLAN1.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 492
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
MAC ADDRESS-TABLE THRASH-LIMIT
mac address-table thrash-limit
Overview Use this command to set the thrash limit on the device.
Thrashing occurs when a MAC address table rapidly “flips” its mapping of a single
MAC address between two switchports on the same VLAN. This is usually because
of a network loop.
Use the no variant of this command to return the thrash limit to its default setting.
Syntax mac address-table thrash-limit <rate>
no mac address-table thrash-limit
Default 10 MAC thrashing flips per second
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to limit thrashing on the selected port range.
Example To apply a thrash limit of 20 MAC address flips per second:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mac address-table thrash-limit 20
Related
Commands
show interface
show mac address-table thrash-limit
thrash-limiting
Parameter Description
<rate> The maximum thrash rate at which limiting is applied. This rate can be set
to between 5 and 255 MAC thrashing flips per second. Once the thrash
limit rate is reached, the port is considered to be thrashing.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 493
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM HWFILTER-SIZE
platform hwfilter-size
Overview You can use this command to control the configuration of hardware Access
Control Lists (ACLs), which determines the total available number and
functionality of hardware ACLs.
For this command to take effect, you need to reboot the affected service.
You cannot attach an IPv6 ACL to a port if the ACL contains a specified source or
destination IPv6 address or both and the hw-filter size setting is
ipv4-limited-ipv6. If you do so, a diagnostic message will be generated.
Syntax platform hwfilter-size {ipv4-limited-ipv6|ipv4-full-ipv6}
Default The default mode is ipv4-limited-ipv6.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure hardware ACLs to filter IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform hwfilter-size ipv4-full-ipv6
Related
Commands
show platform
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
Parameter Description
hwfilter-size Configure hardware ACLs command.
ipv4-full-ipv6 Configure hardware ACLs to filter IPv4 traffic, MAC
addresses and IPv6 traffic, including filtering on source or
destination IPv6 addresses, or both; however, this will
reduce the total number of filters available in the hardware
table.
ipv4-limited-ipv6 Configure hardware ACLs to filter IPv4 traffic, MAC
addresses and IPv6 traffic. Source or destination IPv6
addresses or both are not filtered.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 494
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM L3-VLAN-HASHING-ALGORITHM
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Overview This command enables you to change the L3 VLAN hash-key-generating
algorithm.
The no variant of this command returns the hash-key algorithm to the default of
crc32l.
Syntax platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
{crc16l|crc16u|crc32l|crc32u}
no platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Default The hash-key algorithm is crc32l by default.
Mode Global configuration
Usage Occasionally, when using the Multiple Dynamic VLAN feature, a supplicant cannot
be authenticated because a collision occurs within the VLAN L3 table. This can
happen when more than four different IP addresses produce the same hash-key.
When this situation occurs, collisions can sometimes be avoided by changing the
hashing algorithm from its default of crc32l. Several different algorithms may need
to be tried to rectify the problem.
You must restart the switch for this command to take effect.
Note that this command is intended for technical support staff, or advanced end
users.
Example To change the hash-key generating algorithm applying to the lower bits of CRC-16,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm crc16l
Related
Commands
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
show platform
Parameter Description
crc16l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-16
crc16u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-16
crc32l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-32
crc32u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-32
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 495
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM LOAD-BALANCING
platform load-balancing
Overview This command selects which address fields are used as inputs into the load
balancing algorithm for aggregated links. The output from this algorithm is used
to select which individual path a given packet will traverse within an aggregated
link.
The no variant of this command applies its default setting.
Syntax platform load-balancing {src-dst-mac|src-dst-ip}
no platform load-balancing
Default The default is src-dst-ip.
Mode Global configuration
Examples To set the load balancing algorithm to include only Layer 2 MAC addresses, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform load-balancing src-dst-mac
To set the load balancing algorithm to include only Layer 3 IP addresses and Layer
4 ports, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform load-balancing src-dst-ip
Related
Commands
show platform
Parameter Description
src-dst-mac Include the source and destination MAC addresses (Layer 2)
src-dst-ip Include the source and destination IP addresses (Layer 3) and
UDP/TCP source and destination ports.
If you choose this option, the algorithm will use MAC addresses
to calculate load balancing for Layer 2 and non-IP packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 496
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM MAC-VLAN-HASHING-ALGORITHM
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Overview This command enables you to change the MAC VLAN hash-key-generating
algorithm.
The no variant of this command returns the hash-key algorithm to the default of
crc32l
Syntax platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
{crc16l|crc16u|crc32l|crc32u}
no platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Default The hash-key algorithm is crc32l by default.
Mode Global configuration
Usage Occasionally, when using the Multiple Dynamic VLAN feature, a supplicant cannot
be authenticated because a collision occurs within the VLAN MAC table. This can
happen when more than four different MAC addresses produce the same
hash-key.
When this situation occurs, collisions can sometimes be avoided by changing the
hashing algorithm from its default of crc32l. Several different algorithms may need
to be tried to rectify the problem.
You must restart the switch for this command to take effect.
Note that this command is intended for technical support staff, or advanced end
users.
Example To change the hash-key generating algorithm applying to the lower bits of CRC-16,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm crc16l
Related
Commands
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
show platform
Parameter Description
crc16l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-16
crc16u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-16
crc32l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-32
crc32u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-32

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 497
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM MULTICAST-RATELIMIT
platform multicast-ratelimit
Overview Use this command to set the maximum number of multicast packets to be
forwarded to the CPU (in packets per second). Setting the value to zero disables
rate limiting.
This command should be used with care. Increasing or removing the limit could
make the device less responsive under heavy multicast load.
Use the no variant of this command to return the limit to its default.
Syntax platform multicast-ratelimit <0-100>
no platform multicast-ratelimit
Default 10 packets per second (pps)
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If you find that the CPU load on your device from multicast traffic is higher than
desired, reducing this rate may reduce the CPU load.
If you need the device to process a large amount of multicast traffic, increasing this
rate may improve performance.
Example To set the rate to 30pps, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform multicast-ratelimit 30
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: default changed to 100pps on SBx908 GEN2, SBx8100, and x930
Series switches.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 498
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM STOP-UNREG-MC-FLOODING
platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
Overview If a multicast stream is arriving at a network device, and that network device has
received no IGMP reports that request the receipt of the stream, then that stream
is referred to as "unregistered". IGMP snooping actively prevents the flooding of
unregistered streams to all ports in the VLAN on which the stream is received.
However, there are brief moments at which this prevention is not in operation, and
an unregistered stream may be briefly flooded. This command stops this flooding
during even those brief periods when IGMP snooping is not explicitly preventing
the flooding.
Use the no variant of this command to revert to default behavior and disable this
feature.
NOTE: This command should not be used within any IPv6 networks. IPv6 neighbor
discovery operation is inhibited by this feature.
This command does not affect the flooding of Local Network Control Block IPv4
multicast packets in the address range 224.0.0.1 to 224.0.0.255 (224.0.0/24). Such
packets will continue to be uninterruptedly flooded, as they need to be.
Syntax platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
no platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
Default This feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command stops the periodic flooding of unknown or unregistered multicast
packets when the Group Membership interval timer expires and there are no
subscribers to a multicast group. If there is multicast traffic in a VLAN without
subscribers, multicast traffic temporarily floods out of the VLAN when the Group
Membership interval timer expires, which happens when the switch does not get
replies from Group Membership queries.
This command also stops the initial flood of multicast packets that happens when
a new multicast source starts to send traffic. This flooding lasts until snooping
realises that this the multicast group is arriving at the switch, and puts an entry into
hardware to prevent it from being flooded.
This command is useful in networks where low-performance devices are attached.
The operation of such devices can be impaired by them receiving unnecessary
streams of traffic. For example, in sites where IP cameras are in use, the flooding of
video streams to a whole VLAN can send enough traffic to the cameras to cause
interruption of their video streaming.
Output Do not use this command in IPv6 networks. The following console message is
displayed after entering this command to warn you of this:
% WARNING: IPv6 will not work with this setting enabled
% Please consult the documentation for more information

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 499
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM STOP-UNREG-MC-FLOODING
Examples To enable this feature and stop multicast packet flooding, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
To disable this feature and allow multicast packet flooding, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no platform stop-unreg-mc-flooding
Related
Commands
show platform
show running-config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 500
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
PLATFORM VLAN-STACKING-TPID
platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Overview This command specifies the Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID) value that applies to all
frames that are carrying double tagged VLANs. All nested VLANs must use the
same TPID value. (This feature is sometimes referred to as VLAN stacking or VLAN
double-tagging.)
Use the no variant of this command to revert to the default TPID value (0x8100).
NOTE: Because the additional tag increases the frame size beyond 1522 bytes, you
must increase the MRU size to activate VLAN-stacking. Go into interface mode for the
appropriate ports and use the mru command.
Syntax platform vlan-stacking-tpid <tpid>
no platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Default The default TPID value is 0x8100.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the VLAN stacking TPID value to 0x9100, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform vlan-stacking-tpid 9100
To reset the VLAN stacking TPID value to the default (0x8100), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Related
Commands
switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging)
show platform
show running-config
Parameter Description
<tpid> The Ethernet type of the tagged packet, as a two byte hexadecimal
number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 501
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
POLARITY
polarity
Overview This command sets the MDI/MDIX polarity on a copper-based switch port.
Syntax polarity {auto|mdi|mdix}
Default By default, switch ports set the polarity automatically (auto).
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage We recommend the default auto setting for MDI/MDIX polarity. Polarity applies to
copper 10BASE-T, 100BASE-T, and 1000BASE-T switch ports; it does not apply to
fiber ports. See the “MDI/MDIX Connection Modes” section in the Switching
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information.
Example To set the polarity for port1.0.4 to fixed MDI mode, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# polarity mdi
Parameter Description
mdi Sets the polarity to MDI (medium dependent interface).
mdix Sets the polarity to MDI-X (medium dependent interface crossover).
auto The switch port sets the polarity automatically. This is the default option.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 502
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING LOOPPROT
show debugging loopprot
Overview This command shows Loop Protection debugging information.
Syntax show debugging loopprot
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the enabled Loop Protection debugging modes, use the command:
awplus# show debugging loopprot
Related
Commands
debug loopprot

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 503
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING PLATFORM PACKET
show debugging platform packet
Overview This command shows platform to CPU level packet debugging information.
Syntax show debugging platform packet
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the platform packet debugging information, use the command:
awplus# show debugging platform packet
Related
Commands
debug platform packet
undebug platform packet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 504
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW FLOWCONTROL INTERFACE
show flowcontrol interface
Overview Use this command to display flow control information.
Syntax show flowcontrol interface <port>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the flow control for port1.0.3, use the command:
awplus# show flowcontrol interface port1.0.3
Output Figure 15-1: Example output from the show flowcontrol interface command
for a specific interface
Parameter Description
<port> Specifies the name of the port to be displayed.
Port Send FlowControl Receive FlowControl RxPause TxPause
admin oper admin oper
----- ------- -------- ------- -------- ------- -------
port1.0.3 on on on on 0 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 505
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE ERR-DISABLED
show interface err-disabled
Overview Use this command to show the ports which have been dynamically shut down by
protocols running on the device and the protocols responsible for the shutdown.
Syntax show interface [<interface-range> err-disabled]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show which protocols have shut down ports, use the commands:
awplus# show interface err-disabled
Output Figure 15-2: Example output from show interface err-disabled
Parameter Description
<interface-range> Interface range
err-disabled Brief summary of interfaces shut down by protocols
awplus#show interface err-disabled
Interface Reason
port1.0.1 loop protection
port1.0.2 loop protection

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 506
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE SWITCHPORT
show interface switchport
Overview Use this command to show VLAN information about each switch port.
Syntax show interface switchport
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display VLAN information about each switch port, enter the command:
awplus# show interface switchport
Output Figure 15-3: Example output from the show interface switchport command
Related
Commands
show interface memory
Interface name : port1.0.1
Switchport mode : access
Ingress filter : enable
Acceptable frame types : all
Default Vlan : 1
Configured Vlans : 2
Dynamic Vlans :
Interface name : port1.0.2
Switchport mode : trunk
Ingress filter : enable
Acceptable frame types : all
Default Vlan : 1
Configured Vlans : 1 4 5 6 7 8
Dynamic Vlans :
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 507
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW LOOP-PROTECTION
show loop-protection
Overview Use this command to display the current loop protection setup for the device.
Syntax show loop-protection [interface <port-list>] [counters]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This command is used to display the current configuration and operation of the
Loop Protection feature
Examples To display the current configuration status, use the command:
awplus# show loop-protection
Figure 15-4: Example output from the show loop-protection command
To display the counter information, use the command:
awplus# show loop-protection counters
Figure 15-5: Example output from the show loop-protection counters
command
Parameter Description
interface The interface selected for display.
<port-list>A port, a port range, or an aggregated link.
counters Displays counter information for loop protection.
awplus#show loop-protection
LDF Interval: 10
LDF Rx Window: 3
Fast Block: Disabled
Timeout
Int Enabled Action Status Timeout Remain Rx port
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.1 Yes vlan-dis Normal 7 - -
port1.0.2 Yes vlan-dis Normal 7 - -
port1.0.3 Yes vlan-dis Normal 7 - -
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 508
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW LOOP-PROTECTION
awplus#show loop-protection counters
Switch Loop Detection Counter
Interface Tx Rx Rx Invalid Last LDF Rx
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.1
vlan1 60 0 0 -
port1.0.2
vlan1 0 0 0 -
port1.0.3
vlan1 0 0 0 -
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 509
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW MAC ADDRESS-TABLE
show mac address-table
Overview Use this command to display the MAC address-table for all
configured VLANs.
Syntax show mac address-table
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage The show mac address-table command is only applicable to view a MAC
address-table for Layer 2 switched traffic within VLANs.
Example To display the mac address-table, use the following command:
awplus# show mac address-table
Output See the following sample output captured when there was no traffic being
switched:
See the sample output captured when packets were switched and MAC addresses
were learned:
Note the new MAC addresses learned for port1.0.2 and port1.0.3 added as dynamic
entries.
Note the first column of the output below shows VLAN IDs if multiple VLANs are
configured:
awplus#show mac address-table
VLAN port mac type
1 unknown 0000.cd28.0752 forward static
ARP - 0000.cd00.0000 forward static
awplus#show mac address-table
VLAN port mac type
1 unknown 0000.cd28.0752 forward static
1 port1.0.2 0030.846e.9bf4 forward dynamic
1 port1.0.3 0030.846e.bac7 forward dynamic
ARP - 0000.cd00.0000 forward static
awplus#show mac address-table
VLAN port mac type
1 unknown 0000.cd28.0752 forward static
1 port1.0.2 0030.846e.bac7 forward dynamic
2 unknown 0000.cd28.0752 forward static
2 port1.0.3 0030.846e.9bf4 forward dynamic
ARP - 0000.cd00.0000 forward static

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 510
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW MAC ADDRESS-TABLE
Also note if manually configured static MAC addresses exist, this is shown to the
right of the type column:
Related
Commands
clear mac address-table dynamic
clear mac address-table static
mac address-table static
awplus(config)#mac address-table static 0000.1111.2222 for int
port1.0.3 vlan 1
awplus(config)#end
awplus#
awplus#show mac address-table
VLAN port mac type
1 unknown 0000.cd28.0752 forward static
1 port1.0.2 0030.846e.bac7 forward dynamic
1 port1.0.3 0000.1111.2222 forward static
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 511
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW MAC ADDRESS-TABLE THRASH-LIMIT
show mac address-table thrash-limit
Overview Use this command to display the current thrash limit set for all interfaces on the
device.
Syntax show mac address-table thrash-limit
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current, use the following command:
awplus# show mac address-table thrash-limit
Output Figure 15-6: Example output from the show mac address-table thrash-limit
command
Related
Commands
mac address-table thrash-limit
% Thrash-limit 7 movements per second

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 512
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM
show platform
Overview This command displays the settings configured by using the platform commands.
Syntax show platform
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command displays the settings in the running config. For changes in some of
these settings to take effect, the device must be rebooted with the new settings in
the startup config.
Example To check the settings configured with platform commands on the device, use the
following command:
awplus# show platform
Output Figure 15-7: Example output from the show platform command
awplus# show platform
MAC vlan hashing algorithm crc32l
L3 hashing algorithm crc32l
Load Balancing src-dst-ip
stop-unreg-mc-flooding off
Vlan-stacking TPID 0x8100
Hardware Filter Size ipv4-limited-ipv6
Table 16: Parameters in the output of the show platform command. Note that the parameters
displayed depend on your device, and that not all displayed parameters can be modified on
all devices.
Parameter Description
Routing Ratio Whether all memory is allocated to IPv4 address table entries only, or whether it is
allocated evenly to both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses (set with the platform
routingratio command).
Route Weighting The split between multicast and unicast route entries (set with the platform
routingratio command).
MAC vlan hashing
algorithm
The MAC VLAN hash-key-generating algorithm (set with the platform
mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm command). The default algorithm is crc32l. The
algorithm may need to be changed in rare circumstances in which hash collisions
occur.
L3 hashing algorithm The L3 VLAN hash-key-generating algorithm (set with the platform
l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm command). The default algorithm is crc32l. The
algorithm may need to be changed in rare circumstances in which hash collisions
occur.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 513
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM
Load Balancing Which packet fields are used in the channel load balancing algorithm (set with the
platform load-balancing command).
Control-plane-
prioritization
Maximum traffic rate on the CPU port (set with the platform
control-plane-prioritization rate command).
Fdb-chain-length The length of the FDB hash chain (set with the platform fdb-chain-length
command). FDB entries are hashed and indexed using a hash. In rare
circumstances it may be useful to reduce the chain length.
L2MC overlapped group
check
Whether Layer 2 multicast entries are checked before deletion (set with the
platform l2mc-overlap command).
silicon-profile The silicon profile setting (set with the platform silicon-profile command) for the
switch hardware; one of:
•profile 1
•profile 2
•profile 3
• None (default)
fdb-l3-hosts mode Whether Host Mode is turned on or not. Host Mode increases the number of host
entries and is available for systems containing SBx81CFC960 controller cards and
SBx81XLEM line cards. See platform silicon-profile and platform fdb-l3-hosts
for details.
Jumboframe support Whether the jumbo frames setting is enabled or disabled (set with the platform
jumboframe command).
Traffic Manager A test setting that is disabled by default.
stop-unreg-mc-flooding Whether the stop-unreg-mc-flooding feature is on or off (set with the platform
stop-unreg-mc-flooding command). This feature prevents flooding of
unregistered multicast packets in the occasional situations in which IGMP
snooping does not prevent it.
Port Mode Whether each port on the AT-StackQS is configured as one 40Gbps port or four
10Gbps ports, if they are operating as network ports (set with the platform
portmode interface command).
Vlan-stacking TPID The value of the TPID set in the Ethernet type field when a frame has a double
VLAN tag (set with the platform vlan-stacking-tpid command).
PBR enabled Whether policy-based routing is globally enabled or not (set with the platform
pbr-enable command).
Table 16: Parameters in the output of the show platform command. Note that the parameters
displayed depend on your device, and that not all displayed parameters can be modified on
all devices. (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 514
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM
Hardware Filter Size Whether hardware ACLs can filter on IPv6 addresses (ipv4-full-ipv6) or not
(ipv4-limited-ipv6). This is set with the platform hwfilter-size command.
Vlan Ingress Filter Hard
Drop
The Bridge Vlan Ingress Filtering drops traffic if the VID assigned to the packet
does not match with the port’s VLAN membership.
There are two ways the traffic is dropped by the Ingress Filtering mechanism:
• HARD DROP - Traffic is dropped by the Bridge Engine and not forwarded or
trapped.
• SOFT DROP - Traffic may be mirrored or trapped by the Bridge Engine.
Table 16: Parameters in the output of the show platform command. Note that the parameters
displayed depend on your device, and that not all displayed parameters can be modified on
all devices. (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 515
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
show platform classifier statistics utilization
brief
Overview This command displays the number of used entries available for various platform
functions, and the percentage that number of entries represents of the total
available.
Syntax show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the platform classifier utilization statistics, use the following command:
awplus# show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Output Figure 15-8: Output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Output Figure 15-9: Output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
In this example, there is one UFO VLAN and one upstream port consuming 3 FP
entries.
#show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
[Instance 0]
Capacity: 503
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Allocated
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 119 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
Flooding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
QoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Rule Limit Reached (clear on read): 0
Total Rule Limit Reached from startup: 0
Space will be allocated to QOS as required.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 516
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
Output
parameters
Depending on your switch, you will see some of the following parameters in the
output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
#show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
[Instance 4]
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Total
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 117 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
DoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%
VLAN Counter
Group-Octet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Group-Packet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Floding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO 1476395012 3 / 128 ( 2%)
QoS 0 / 256 ( 0%)
[Instance 5]
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Total
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 117 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
DoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
VLAN Counter
Group-Octet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Group-Packet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Floding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO 1476395012 3 / 128 ( 2%)
QoS 0 / 256 ( 0%)
Parameter Description
IPv6 Multicast Reserved hardware space for use by IPv6 multicast.
System Fixed system entries. For example, resiliency links make use of system ACLs.
MLD Snooping Entries to send various packets that MLD Snooping is interested in to the CPU.
DHCP Snooping Entries used to send DHCP and ARP packets to the CPU. User-added DHCP
Snooping filters under ACLs are counted under the ACL or QoS categories.
Loop Detection Entries uses to send the special loop detection frame to the CPU.
EPSR Entries used to send EPSR control traffic to the CPU.
CFM Entries used by Connectivity Fault Management.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 517
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
Related
Commands
show platform
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
G8032 Entries used to send G.8032 control traffic to the CPU.
Global ACLs Entries for ACLs appear here if the ACLs are applied globally instead of per
switchport.
ACL Entries for ACL filters that have been applied directly to ports using the
access-group command.
VACL Entries for VLAN-based ACLs (ACLs that are applied to VLANs instead of ports).
DOS Entries used for Denial of Service protection.
UFO Entries used by Upward Forwarding Only (UFO).
QoS Entries for ACL filters and other class-map configurations, such as policers, applied
through policy maps using the service input command.
RA Guard Entries used to block IPv6 router advertisements, configured with the ipv6 nd
raguard command.
AMFAPPS Entries used by AMF Application Proxy. These entries enable the SES Controller to
block infected ports.
Pre-Ingress Entries used for VLAN ID Translation (and also for subnet-based and MAC-based
VLAN entries on SBx81XLEM cards).
Egress Entries used for VLAN ID Translation.
UDB User Defined Bytes (UDB), which are a limited resource of bytes that can be used to
implement additional arbitrary matching on packet bytes on some switches. The
software manages the use and allocation of these bytes automatically. The output
of this table is intended for use by Allied Telesis Customer Support only.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 518
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM PORT
show platform port
Overview This command displays the various port registers or platform counters for
specified switchports.
Syntax show platform port [<port-list>] [counters]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To display port registers for port1.0.1 to port1.0.4 use the following command:
awplus# show platform port port1.0.1-port1.0.4
To display platform counters for port1.0.1 to port1.0.4 use the following command:
awplus# show platform port port1.0.1-port1.0.4 counters
Output Figure 15-10: Example output from the show platform port command
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports to display information about. A port-list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do not mix
port types in the same list.
counters Show the platform counters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 519
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM PORT
awplus#show platform port port1.0.1
Phy register value for port1.0.1 (ifindex: 5001)
00:1140 01:79ed 02:600d 03:85b0 04:01e1 05:cde1 06:006d 07:2001
08:4006 09:0600 0a:7800 0b:0000 0c:0000 0d:4007 0e:0000 0f:3000
10:0021 11:2f00 12:0000 13:0000 14:0000 15:0236 16:0000 17:0000
18:4c00 19:871c 1a:0000 1b:ffff 1c:0000 1d:0405 1e:0000 1f:0000
Port configuration for lport 0x08002002:
Phy Driver: 542XX Gigabit PHY Driver
enabled: 1
loopback: 0
link: 1
speed: 1000 max speed: 1000
duplex: 1
linkscan: 2
autonegotiate: 1
master: 2
tx pause: 0 rx pause: 0
untagged vlan: 1
vlan filter: 3
stp state: 4
learn: 5
discard: 0
jam: 0
max frame size: 1482
MC Disable SA: no
MC Disable TTL: no
MC egress untag: 0
MC egress vid: 1
MC TTL threshold: -1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 520
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PORT-SECURITY INTERFACE
show port-security interface
Overview Use this command to show the current port-security configuration and the switch
port status.
Syntax show port-security interface <port>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To see the port-security status on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security interface port1.0.2
Output Figure 15-11: Example output from the show port-security interface command
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security maximum
switchport port-security violation
Parameter Description
<port> The port to display information about. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.2), a static channel group (e.g. sa3), or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po4).
Port Security configuration
Security Enabled : YES
Port Status : ENABLED
Violation Mode : TRAP
Aging : OFF
Maximum MAC Addresses : 3
Total MAC ddresses : 1
Lock Status : UNLOCKED
Security Violation Count : 0
Last Violation Source Address : None

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 521
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW PORT-SECURITY INTRUSION
show port-security intrusion
Overview Use this command to show the intrusion list. If the port is not specified, the entire
intrusion table is shown.
Syntax show port-security intrusion [interface <port>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To see the intrusion list on port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show port-security intrusion interface port1.0.2
Output Figure 15-12: Example output from the show port-security intrusion command
for port1.0.2
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security interface
switchport port-security
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security maximum
switchport port-security violation
Parameter Description
interface Specify a port
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.2), a static channel group (e.g. sa3), or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po4).
Port Security Intrusion List
Interface: port1.0.2 -3 intrusion(s) detected
11-22-33-44-55-04 11-22-33-44-55-06 11-22-33-44-55- 08
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 522
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW STORM-CONTROL
show storm-control
Overview Use this command to display storm-control information for all interfaces or a
particular interface.
Syntax show storm-control [<port>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display storm-control information for port1.0.2, use the following command:
awplus# show storm-control port1.0.2
Output Figure 15-13: Example output from the show storm-control command for
port1.0.2
Related
Commands
storm-control level
Parameter Description
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
Port BcastLevel McastLevel DlfLevel
port1.0.2 40. 0% 100. 0% 100. 0%

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 523
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SPEED
speed
Overview This command changes the speed of the specified port. You can optionally specify
the speed or speeds that get autonegotiated, so autonegotiation is only
attempted at the specified speeds.
To see the currently-negotiated speed for ports whose links are up, use the show
interface command. To see the configured speed (when different from the
default), use the show running-config command.
Syntax speed {10|100|1000}
speed auto [10] [100] [1000]
The following table shows the speed options for each type of port.
Mode Interface Configuration
Default By default, ports autonegotiate speed (except for 100Base-FX ports which do not
support auto-negotiation, so default to 100 Mbps).
Usage We recommend having autonegotiation enabled for link speeds of 1000 Mbps and
above. For example, to apply a fixed speed of 1000 Mbps use the command speed
auto 1000.
If multiple speeds are specified after the auto option to autonegotiate speeds, then
the device only attempts autonegotiation at those specified speeds.
Switch ports in a static or dynamic (LACP) channel group must have the same port
speed and be in full duplex mode. Once switch ports have been aggregated into a
channel group, you can set the speed of all the switch ports in the channel group
by applying this command to the channel group.
Port type Speed Options (units are Mbps)
RJ-45 copper ports auto (default)
10
100
1000
tri-speed copper SFPs auto (default)
10
100
1000
100 Mbps fiber SFPs 100
1000 Mbps fiber SFPs auto (default)
1000
1000 Mbps copper SFPs auto (default)
1000

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 524
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SPEED
Examples To set the speed of a tri-speed port to 100 Mbps, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# speed 100
To return the port to auto-negotiating its speed, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# speed auto
To set the port to auto-negotiate its speed at 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps, enter the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# speed auto 100 1000
To set the port to auto-negotiate its speed at 1000 Mbps only, which will fix this
port speed to 1000 Mbps, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# speed auto 1000
Related
Commands
duplex
polarity
show interface
speed (asyn)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 525
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
STORM-CONTROL LEVEL
storm-control level
Overview Use this command to specify the speed limiting level for broadcasting, multicast,
or destination lookup failure (DLF) traffic for the port. Storm-control limits the
selected traffic type to the specified percentage of the maximum port speed.
Use the no variant of this command to disable storm-control for broadcast,
multicast or DLF traffic.
Syntax storm-control {broadcast|multicast|dlf} level <level>
no storm-control {broadcast|multicast|dlf} level
Default By default, storm-control is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Flooding techniques are used to block the forwarding of unnecessary flooded
traffic. A packet storm occurs when a large number of broadcast packets are
received on a port. Forwarding these packets can cause the network to slow down
or time out.
Example To limit broadcast traffic on port1.0.2 to 30% of the maximum port speed, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# storm-control broadcast level 30
Related
Commands
show storm-control
Parameter Description
<level> <0-100> Specifies the percentage of the maximum port speed
allowed for broadcast, multicast or destination lookup failure traffic.
broadcast Applies the storm-control to broadcast frames.
multicast Applies the storm-control to multicast frames.
dlf Applies the storm-control to destination lookup failure traffic.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 526
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PORT-SECURITY
switchport port-security
Overview Use this command to enable the port-security feature. This feature is also known
as the port-based learn limit. It allows the user to set the maximum number of MAC
addresses that each port can learn.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the port-security feature.
Syntax switchport port-security
no switchport port-security
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To enable the port-security feature on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport port-security
To disable the port-security feature on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport port-security
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security interface
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security maximum
switchport port-security violation

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 527
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PORT-SECURITY AGING
switchport port-security aging
Overview Use this command to set MAC addresses that have been learned by port security
to age out.
Use the no variant of this command to set the MAC addresses to not age out.
Syntax switchport port-security aging
no switchport port-security aging
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To set port1.0.2 so that the MAC addresses that have been learned by port security
age out, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport port-security aging
To stop the MAC addresses that have been learned by port security from aging out
on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport port-security aging
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security interface
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security
switchport port-security maximum
switchport port-security violation

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 528
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PORT-SECURITY MAXIMUM
switchport port-security maximum
Overview Use this command to set the maximum number of MAC addresses that each port
can learn.
Use the no variant of this command to unset the maximum number of MAC
addresses that each port can learn. This is same as setting the maximum number
to 0. This command also resets the intrusion list table.
If a new MAC is seen on a port with port security enabled and the MAC is statically
configured for another port, a violation is triggered. The maximum learn limit will
be ignored and the specified intrusion action for the port will be carried out.
Syntax switchport port-security maximum <0-256>
no switchport port-security maximum
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To learn 3 MAC addresses on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 3
To remove the MAC learning limit on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport port-security maximum
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security interface
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security violation
Parameter Description
maximum <0-256> Specify the maximum number of addresses to learn.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 529
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PORT-SECURITY VIOLATION
switchport port-security violation
Overview Use this command to set the action taken on a switch port when the port exceeds
the learning limits. The port action can be either shutdown, restrict or protect. If
shutdown is set, the physical link will be disabled and “shutdown” will be shown
in the config. If restrict is set, the packet from the un-authorized MAC will be
discarded and SNMP TRAP will be generated to alert management. If protect is set,
the packet will simply be discarded by the packet processor silently.
Use the no variant of this command to set the violation action to default. The
default violation action is protect.
Syntax switchport port-security violation {shutdown|restrict|protect}
no switchport port-security violation
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To set the action to be shutdown on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport port-security violation shutdown
To set the port-security action to the default (protect) on port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport port-security violation
Related
Commands
clear port-security intrusion
show port-security interface
show port-security intrusion
switchport port-security
switchport port-security aging
switchport port-security maximum
Parameter Description
shutdown Disable the port.
restrict Alert the network administrator.
protect Discard the packet.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 530
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
THRASH-LIMITING
thrash-limiting
Overview Use this command to configure the thrash limit action that will be applied to a port
on the device when a thrashing condition is detected. The thrash-limiting timeout
specifies the time, in seconds, for which the action is employed.
Use the no variant of this command to return the action or timeout to its default
setting.
Syntax thrash-limiting {[action
{learn-disable|link-down|port-disable|vlan-disable|none}]
[timeout <0-86400>]}
no thrash-limiting {action|timeout}
Default The default action is learn-disable and the default timeout is 1 second.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Thrash-limiting actions are initiated when MAC addresses are added and removed
from a port’s MAC table faster than a given rate. The rate is 10 MAC address
changes per second by default. You can change it with the mac address-table
thrash-limit command.
See the “Thrash Limiting” section in the Switching Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide for more information.
Examples To set the action to learn disable for port1.0.1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# thrash-limiting action learn-disable
Parameter Description
action The action taken when MAC thrashing is detected.
learn-disable Disable MAC address learning
link-down Block all traffic on an interface - link down
port-disable Block all traffic on an interface - link remains up
vlan-disable Block all traffic on a VLAN if the switch detects thrashing for
that VLAN on the selected port. Note that setting this
parameter will also enable ingress filtering.
none No thrash action
timeout Set the duration for the thrash action
<0-86400> The duration of the applied thrash action in seconds. The
default is 1 seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 531
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SWITCHING COMMANDS
THRASH-LIMITING
To block all traffic on a VLAN on port1.0.1 if the switch detects thrashing for that
VLAN on that port, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# thrash-limiting action vlan-disable
To set the thrash limiting action to its default on port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no thrash-limiting action
To set the thrash limiting timeout to 5 seconds on port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# thrash-limiting timeout 5
To set the thrash limiting timeout value to its default on port1.0.1, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no thrash-limiting timeout
Related
Commands
mac address-table thrash-limit
show interface

16
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 534
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
VLANs. For more information see the VLAN Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
Command List •“debug private-vlan ufo” on page 536
•“port-vlan-forwarding-priority” on page 537
•“private-vlan” on page 540
•“private-vlan association” on page 542
•“platform vlan-stacking-tpid” on page 543
•“private-vlan ufo trap” on page 544
•“show debugging private-vlan” on page 545
•“show port-vlan-forwarding-priority” on page 546
•“show vlan” on page 547
•“show vlan access-map” on page 548
•“show vlan filter” on page 549
•“show vlan private-vlan” on page 550
•“show vlan private-vlan ufo” on page 551
•“switchport access vlan” on page 552
•“switchport mode access” on page 553
•“switchport mode private-vlan” on page 554
•“switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous” on page 555
•“switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary” on page 557
•“switchport mode private-vlan ufo” on page 559

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 535
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
•“switchport mode trunk” on page 561
•“switchport private-vlan host-association” on page 562
•“switchport private-vlan mapping” on page 563
•“switchport trunk allowed vlan” on page 564
•“switchport trunk native vlan” on page 567
•“switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging)” on page 568
•“switchport voice dscp” on page 569
•“switchport voice vlan” on page 570
•“switchport voice vlan priority” on page 572
•“vlan” on page 573
•“vlan access-map” on page 574
•“vlan database” on page 575
•“vlan filter” on page 576

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 536
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
DEBUG PRIVATE-VLAN UFO
debug private-vlan ufo
Overview Use this command to enable private-vlan Upward Forwarding Only (UFO)
debugging.
Use the no variant of this command to disable private-vlan UFO debugging.
Syntax debug private-vlan ufo
no debug private-vlan ufo
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command to enable or disable private-vlan ufo debugging.
Example To enable private-vlan UFO debugging, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug private-vlan ufo
Related
Commands
show debugging private-vlan
private-vlan ufo trap
switchport mode private-vlan ufo
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: added to x530 Series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 537
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PORT-VLAN-FORWARDING-PRIORITY
port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Overview Use this command to specify which protocol has the highest priority for controlling
transitions from blocking to forwarding traffic, when more than one of EPSR, Loop
Protection, and MAC thrashing protection are used on the switch.
These protocols use the same mechanism to block or forward traffic. This
command specifies either EPSR or Loop Protection as the highest priority protocol.
Setting the priority stops contention between protocols.
For more information, see the Usage section below.
CAUTION: The loop-protection and none parameter options must not be set on an
EPSR master node. Use the epsr parameter option on an EPSR master node instead.
Setting this command incorrectly on an EPSR master node could cause unexpected
broadcast storms.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default highest priority protocol
back to the default of EPSR.
For more information about EPSR, see the EPSR Feature Overview and
Configuration_Guide.
Syntax port-vlan-forwarding-priority {epsr|loop-protection|none}
no port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Default By default, the highest priority protocol is EPSR
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Usually, you only need to configure one of EPSR, Loop Protection and MAC
Thrashing protection on a switch, because they perform similar functions—each
prevents network loops by blocking a selected port for each (loop-containing)
VLAN.
However, if more than one of these three features is configured on a switch, you
can use this command to prioritize either EPSR or Loop Protection when their
Parameter Description
epsr Sets EPSR as the highest priority protocol. Use this parameter on
an EPSR master node to avoid unexpected broadcast storms.
loop-protection Sets Loop Protection as the highest priority protocol.
Note that this option must not be set on an EPSR master node.
Use the epsr parameter option on an EPSR master node to avoid
unexpected broadcast storms.
none Sets the protocols to have equal priority. This allows protocols to
override each other to set a port to forwarding for a VLAN.
Note that this option must not be set on a EPSR master node.
Use the epsr parameter option on an EPSR master node to avoid
unexpected broadcast storms.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 538
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PORT-VLAN-FORWARDING-PRIORITY
effects on a port would conflict and override each other. Without this command,
each protocol could set a port to forwarding for a VLAN, sometimes overriding the
previous setting by another protocol to block the port. This could sometimes lead
to unexpected broadcast storms.
This command means that, when a protocol is set to have the highest priority over
a data VLAN on a port, it will not allow other protocols to put that port-vlan into a
forwarding state if the highest priority protocol blocked it.
The priority mechanism is only used for blocking-to-forwarding transitions;
protocols remain independent on the forwarding-to-blocking transitions.
For example, consider an EPSR master node in a two-node ESPR ring with the
following settings:
• The EPSR master node primary port is configured to switchport interface
port1.0.1
• The EPSR master node secondary port is configured to switchport interface
port1.0.2
• The EPSR master node control VLAN is configured to VLAN interface vlan10
• The EPSR master node has a first data VLAN configured to VLAN interface
vlan20
• The EPSR master node has a second data VLAN configured to VLAN interface
vlan30.
Initially, the EPSR ring is complete, with port1.0.2 blocking data VLANs vlan20 and
vlan30 and some broadcast traffic flowing through. If the user removes vlan30
from EPSR, a storm is created on vlan30. MAC thrashing protection detects it and
blocks vlan30.
Then after the storm has stopped, MAC thrashing protection sets it to forwarding
again and it keeps oscillating between forwarding and blocking. In the meantime,
the user adds back vlan30 to EPSR as a data VLAN and EPSR blocks it on port1.0.2.
If the priority is set to none (port-vlan-forwarding-priority none), MAC thrashing
protection notices that the storm has stopped again and decides to put vlan30 on
port1.0.2 into forwarding state. This overrides what EPSR requires for this
port-VLAN and creates a storm.
If the priority is set to EPSR or default (port-vlan-forwarding-priority epsr), MAC
thrashing protection notices that the storm has stopped again and attempts to put
vlan30 on port1.0.2 into forwarding state. The higher priority protocol (EPSR) is
blocking the VLAN on this port, so it stays blocking and no storm occurs.
Example To prioritize EPSR over Loop Protection or MAC Thrashing protection settings, so
that Loop Protection or MAC Thrashing protection cannot set a port to the
forwarding state for a VLAN if EPSR has set it to the blocking state, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# port-vlan-forwarding-priority epsr

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 539
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PORT-VLAN-FORWARDING-PRIORITY
To prioritize Loop Protection over EPSR or MAC Thrashing protection settings, so
that EPSR or MAC Thrashing protection cannot set a port to the forwarding state
for a VLAN if Loop Protection has set it to the blocking state, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# port-vlan-forwarding-priority loop-protection
To set EPSR, Loop Protection, and MAC Thrashing protection protocols to have
equal priority for port forwarding and blocking, which allows the protocols to
override each other to set a port to the forwarding or blocking states, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# port-vlan-forwarding-priority none
To restore the default highest priority protocol back to the default of EPSR, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Related
Commands
show port-vlan-forwarding-priority

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 540
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PRIVATE-VLAN
private-vlan
Overview Use this command to a create a private VLAN. Private VLANs can be either primary
or secondary. Secondary VLANs can be either community or isolated.
Alternatively, private VLANs can be UFO (Upstream Forwarding Only). Private
VLAN port members are either ‘downstream’ or ‘upstream’. Once a private VLAN is
configured as UFO, its port members by default are downstream.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified private VLAN.
For more information, see the VLAN Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax private-vlan <vlan-id> {community|isolated|primary|ufo}
no private-vlan <vlan-id> {community|isolated|primary|ufo}
Mode VLAN Configuration
Examples To configure a set of private VLANs, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 2 name vlan2 state enable
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 3 name vlan3 state enable
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 4 name vlan4 state enable
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 2 primary
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 3 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 4 community
To remove a set of private VLANs, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# no private-vlan 2 primary
awplus(config-vlan)# no private-vlan 3 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# no private-vlan 4 community
Parameter Description
<vlan-id> VLAN ID in the range <2-4094> for the VLAN which is to be made a
private VLAN.
community Community VLAN.
isolated Isolated VLAN.
primary Primary VLAN.
ufo Upstream Forwarding Only (UFO) VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 541
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PRIVATE-VLAN
To configure a private VLAN for Upward Forwarding Only (UFO), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 512 name vlan512 state enable
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 512 ufo
Related
Commands
show vlan private-vlan
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: ufo parameter added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: ufo parameter added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: ufo parameter added to x530 Series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 542
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PRIVATE-VLAN ASSOCIATION
private-vlan association
Overview Use this command to associate a secondary VLAN to a primary VLAN. Only one
isolated VLAN can be associated to a primary VLAN. Multiple community VLANs
can be associated to a primary VLAN.
Use the no variant of this command to remove association of all the secondary
VLANs to a primary VLAN.
For more information, see the VLAN_Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax private-vlan <primary-vlan-id> association {add
<secondary-vlan-id>|remove <secondary-vlan-id>}
no private-vlan <primary-vlan-id> association
Mode VLAN Configuration
Examples The following commands associate primary VLAN 2 with secondary VLAN 3:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 2 association add 3
The following commands remove the association of primary VLAN 2 with
secondary VLAN 3:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 2 association remove 3
The following commands remove all secondary VLAN associations of primary
VLAN 2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# no private-vlan 2 association
Parameter Description
<primary-vlan-id>VLAN ID of the primary VLAN.
<secondary-vlan-id>VLAN ID of the secondary VLAN
(either isolated or community).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 543
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PLATFORM VLAN-STACKING-TPID
platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Overview This command specifies the Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID) value that applies to all
frames that are carrying double tagged VLANs. All nested VLANs must use the
same TPID value. (This feature is sometimes referred to as VLAN stacking or VLAN
double-tagging.)
Use the no variant of this command to revert to the default TPID value (0x8100).
NOTE: Because the additional tag increases the frame size beyond 1522 bytes, you
must increase the MRU size to activate VLAN-stacking. Go into interface mode for the
appropriate ports and use the mru command.
Syntax platform vlan-stacking-tpid <tpid>
no platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Default The default TPID value is 0x8100.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the VLAN stacking TPID value to 0x9100, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform vlan-stacking-tpid 9100
To reset the VLAN stacking TPID value to the default (0x8100), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no platform vlan-stacking-tpid
Related
Commands
switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging)
show platform
show running-config
Parameter Description
<tpid> The Ethernet type of the tagged packet, as a two byte hexadecimal
number.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 544
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
PRIVATE-VLAN UFO TRAP
private-vlan ufo trap
Overview Use this command to enable the sending of SNMP traps for private VLAN UFO.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the sending of SNMP traps for
private VLAN UFO.
Syntax private-vlan ufo trap
no private-vlan ufo trap
Default Enabled.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables SNMP traps for private-vlan UFO. If enabled, traps will be
sent when any UFO VLAN becomes "isolated", which occurs when traffic can not be
forwarded at Layer 2 because there is no upstream port for the UFO VLAN, and
Layer3 forwarding has not been configured for the VLAN.
Example To configure a private-vlan UFO trap use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# private-vlan ufo trap
Related
Commands
private-vlan
snmp-server enable trap
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: added to x530 Series products
Parameter Description
ufo Specifies private-vlan for those VLANs in UFO mode.
trap Enables or disables SNMP trap sending for private-vlan UFO.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 545
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING PRIVATE-VLAN
show debugging private-vlan
Overview Use this command to show whether debugging for a private-vlan, namely UFO, is
enabled.
Syntax show debugging private-vlan
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show if debugging is enabled for private-vlan UFO, use the command:
awplus# show debugging private-vlan
Output Figure 16-1: Example output from show debugging private-vlan
Related
Commands
debug private-vlan ufo
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added.
Version 5.4.8-2.1: added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: added to x530 Series products
awplus#show debugging private-vlan
Private-VLAN debugging status:
UFO debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 546
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW PORT-VLAN-FORWARDING-PRIORITY
show port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Overview Use this command to display the highest priority protocol that controls port-vlan
forwarding or blocking traffic. This command displays whether EPSR or Loop
Protection is set as the highest priority for determining whether a port forwards a
VLAN, as set by the port-vlan-forwarding-priority command.
For more information about EPSR, see the EPSR Feature Overview and
Configuration_Guide.
Syntax show port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the highest priority protocol, use the command:
awplus# show port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Output Figure 16-2: Example output from the show port-vlan-forwarding-priority
command
Related
Commands
port-vlan-forwarding-priority
Port-vlan Forwarding Priority: EPSR

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 547
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW VLAN
show vlan
Overview Use this command to display information about a particular VLAN by specifying its
VLAN ID. Selecting all will display information for all the VLANs configured.
Syntax show vlan
{all|brief|dynamic|static|auto|static-ports|<1-4094>}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display information about VLAN 2, use the command:
awplus# show vlan 2
Output Figure 16-3: Example output from the show vlan command
Related
Commands
vlan
Parameter Description
<1-4094> Display information about the VLAN specified by the VLAN ID.
all Display information about all VLANs on the device.
brief Display information about all VLANs on the device.
dynamic Display information about all VLANs learned dynamically.
static Display information about all statically configured VLANs.
auto Display information about all auto-configured VLANs.
static-ports Display static egress/forbidden ports.
VLAN ID Name Type State Member ports
(u)-Untagged, (t)-Tagged
======= ================ ======= ======= ====================================
2 VLAN0002 STATIC ACTIVE port1.0.3(u) port1.0.4(u) port1.0.5(u)
port1.0.6(u)
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 548
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW VLAN ACCESS-MAP
show vlan access-map
Overview Use this command to display information about the configured VLAN
access-maps. VLAN access-maps contain a series of ACLs and enable you to filter
traffic ingressing specified VLANs.
Syntax show vlan access-map [<name>]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To display the ACLs in all access-maps, use the command:
awplus# show vlan access-map
Output Figure 16-4: Example output from show vlan access-map
Related
Commands
vlan access-map
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<name> The name of the access-map to display.
awplus#show vlan access-map
Vlan access map : deny_all
Hardware MAC access list 4000
10 deny any any
Vlan access map : ip_range
Hardware IP access list 3000
10 deny ip 192.168.1.1/24 any

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 549
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW VLAN FILTER
show vlan filter
Overview Use this command to display information about the configured VLAN filters. VLAN
filters apply access-maps (and therefore ACLs) to VLANs. This enables you to filter
traffic ingressing specified VLANs.
Syntax show vlan filter [<access-map-name>]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To display information about the filter that uses the access-map named “deny_all”,
use the command:
awplus# show vlan filter deny_all
Output Figure 16-5: Example output from show vlan filter
Related
Commands
vlan access-map
vlan filter
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<access-map-name> The name of an access-map. The command output displays
only the filters that use that access-map.
awplus#show vlan filter deny_all
Vlan filter : deny_all
direction : ingress
vlan list : 48-49
access map : deny_all
Hardware MAC access list 4000
10 deny any any
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 550
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW VLAN PRIVATE-VLAN
show vlan private-vlan
Overview Use this command to display the private VLAN configuration and associations.
Syntax show vlan private-vlan
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the private VLAN configuration and associations, enter the command:
awplus# show vlan private-vlan
Output Figure 16-6: Example output from the show vlan private-vlan command
Related
Commands
private-vlan
private-vlan association
awplus#show vlan private-vlan
PRIMARY SECONDARY TYPE INTERFACES
------- --------- ---------- ----------
2 3 isolated
2 4 community
8 isolated

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 551
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SHOW VLAN PRIVATE-VLAN UFO
show vlan private-vlan ufo
Overview Use this command to show the configuration status of a private VLAN UFO-based
VLAN(s) and member interfaces.
Syntax show vlan private-vlan ufo {all|<vlan-id>}
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec.
Usage Private VLANs can be UFO (Upstream Forwarding Only). Private VLAN port
members are either "downstream" or "upstream" which are controlled by a
protocol or by static configuration.
Example To show all the private-vlan UFO interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show vlan private-vlan ufo all
Output Figure 16-7: Example output from show vlan private-vlan ufo all
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: added to x530 Series products
Parameter Description
<vlan-id> A specific VLAN. This must have been configured previously as a
private-vlan UFO.
all All VLANs that have been configured previously as private-vlan
UFO.
awplus#show vlan private-vlan ufo all
VLAN INTERFACES CONFIGURED TYPE PROTOCOL MISC
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
100 port1.0.1 primary-upstream upstream UFO -
100 port1.0.2 secondary-upstream downstream UFO -
100 port1.0.3 - downstream Static -
200 port1.0.4 epsr downstream EPSR -
200 sa1 epsr upstream EPSR 0030.846e.bac7
200 port1.0.5 - downstream Static -
300 port1.0.6 - downstream-fault Static -
300 port1.0.7 - downstream-fault Static -
300 port1.0.8 - downstream-fault Static -
400 Port1.0.9 stp upstream STP 0030.846e.9bf4
400 Port1.0.10 stp downstream STP -
400 Port1.0.11 downstream Static -

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 552
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ACCESS VLAN
switchport access vlan
Overview Use this command to change the port-based VLAN of the current port.
Use the no variant of this command to change the port-based VLAN of this port to
the default VLAN, vlan1.
Syntax switchport access vlan <vlan-id>
no switchport access vlan
Default Reset the default VLAN 1 to specified switchports using the negated form of this
command.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Any untagged frame received on this port will be associated with the specified
VLAN.
Examples To change the port-based VLAN to VLAN 3 for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport access vlan 3
To reset the port-based VLAN to the default VLAN 1 for port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport access vlan
Related
Commands
show interface switchport
show vlan
Parameter Description
<vlan-id><1-4094> The port-based VLAN ID for the port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 553
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE ACCESS
switchport mode access
Overview Use this command to set the switching characteristics of the port to access mode.
Received frames are classified based on the VLAN characteristics, then accepted or
discarded based on the specified filtering criteria.
Syntax switchport mode access [ingress-filter {enable|disable}]
Default By default, ports are in access mode with ingress filtering on.
Usage Use access mode to send untagged frames only.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access ingress-filter enable
Validation
Command
show interface switchport
Parameter Description
ingress-filter Set the ingress filtering for the received frames.
enable Turn on ingress filtering for received frames. This is the default.
disable Turn off ingress filtering to accept frames that do not meet the
classification criteria.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 554
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN
switchport mode private-vlan
Overview Use this command to make a Layer 2 port a private VLAN host port or a
promiscuous port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configuration.
Syntax switchport mode private-vlan {host|promiscuous}
no switchport mode private-vlan {host|promiscuous}
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To configure host mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan host
To configure promiscuous mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan promiscuous
To remove promiscuous mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# no switchport mode private-vlan promiscuous
Related
Commands
switchport private-vlan mapping
Parameter Description
host This port type can communicate with all other host ports assigned to
the same community VLAN, but it cannot communicate with the
ports in the same isolated VLAN. All communications outside of this
VLAN must pass through a promiscuous port in the associated
primary VLAN.
promiscuous A promiscuous port can communicate with all interfaces, including
the community and isolated ports within a private VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 555
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN TRUNK PROMISCUOUS
switchport mode private-vlan trunk
promiscuous
Overview Use this command to enable a port in trunk mode to be promiscuous port for
isolated VLANs.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a port in trunk mode as a
promiscuous port for isolated VLANs. You must first remove the secondary port, or
ports, in trunk mode associated with the promiscuous port with the no switchport
mode private-vlan trunk secondary command.
Syntax switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous group <group-id>
no switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous
Default By default, a port in trunk mode is disabled as a promiscuous port.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage A port must be put in trunk mode with switchport mode trunk command before it
can be enabled as a promiscuous port.
To add VLANs to be trunked over the promiscuous port, use the switchport trunk
allowed vlan command. These VLANs can be isolated VLANs, or non-private VLANs.
To configure the native VLAN for the promiscuous port, use the switchport trunk
native vlan command. The native VLAN can be an isolated VLAN, or a non-private
VLAN.
When you enable a promiscuous port, all of the secondary port VLANs associated
with the promiscuous port via the group ID number must be added to the
promiscuous port. In other words, the set of VLANs on the promiscuous port must
be a superset of all the VLANs on the secondary ports within the group.
Parameter Description
<group-id>The group ID is a numeric value in the range 1 to 32 that is
used to associate the promiscuous port with secondary ports.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 556
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN TRUNK PROMISCUOUS
Examples To create the isolated VLANs 2, 3 and 4 and then enable port1.0.2 in trunk mode as
a promiscuous port for these VLANs with the group ID of 3, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 2-4
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 2 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 3 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 4 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# exit
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2-4
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan trunk
promiscuous group 3
To remove port1.0.2 in trunk mode as a promiscuous port for a private VLAN, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport mode private-vlan trunk
promiscuous
Note that you must remove the secondary port or ports enabled as trunk ports that
are associated with the promiscuous port before removing the promiscuous port.
Related
Commands
switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan
switchport trunk native vlan
show vlan private-vlan

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 557
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN TRUNK SECONDARY
switchport mode private-vlan trunk
secondary
Overview Use this command to enable a port in trunk mode to be a secondary port for
isolated VLANs.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a port in trunk mode as a secondary
port for isolated VLANs.
Syntax switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary group <group-id>
no switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary
Default By default, a port in trunk mode is disabled as a secondary port.
When a port in trunk mode is enabled to be a secondary port for isolated VLANs,
by default it will have a native VLAN of none (no native VLAN specified).
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage A port must be put in trunk mode with switchport mode trunk command before
the port is enabled as a secondary port in trunk mode.
To add VLANs to be trunked over the secondary port use the switchport trunk
allowed vlan command. These must be isolated VLANs and must exist on the
associated promiscuous port.
To configure the native VLAN for the secondary port, use the switchport trunk
native vlan command. The native VLAN must be an isolated VLAN and must exist
on the associated promiscuous port.
Parameter Description
<group-id>The group ID is a numeric value in the range 1 to 32 that is
used to associate a secondary port with its promiscuous port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 558
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN TRUNK SECONDARY
Examples To create isolated private VLAN 2 and then enable port1.0.3 in trunk mode as a
secondary port for the this VLAN with the group ID of 3, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 2
awplus(config-vlan)# private-vlan 2 isolated
awplus(config-vlan)# exit
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan trunk secondary
group 3
To remove port1.0.3 in trunk mode as a secondary port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# no switchport mode private-vlan trunk
secondary
Related
Commands
switchport mode private-vlan trunk promiscuous
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan
switchport trunk native vlan
show vlan private-vlan

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 559
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN UFO
switchport mode private-vlan ufo
Overview Use this command to allow private VLAN UFO 802.1q member ports to be
configured as upstream or downstream.
Use the no variant of this command to change the role of the private VLAN UFO
802.1q member port to downstream.
Syntax switchport mode private-vlan ufo <vid-list>
{primary-upstream|secondary-upstream|stp|epsr}
no switchport mode private-vlan ufo <vid-list>
Default Downstream.
Note: The default setting for a private VLAN UFO member interface is downstream,
but it is not explicitly configured. Use the no variant of this command to make the
member interface downstream.
Mode Interface Configuration
Parameter Description
<vid-list> A hyphen-separated range or a comma-separated list of
VLAN IDs, all of which must have previously been configured
with the private-vlan setting of "ufo".
primary-upstream The primary interface port/LAG that this UFO VLAN will
attempt to use as the Upstream interface. More than one
primary-upstream interface can be configured.
secondary-upstream The interface that this UFO VLAN will revert to use as the
Upstream port if all the primary-upstream ports are
unavailable due to being either operationally down (i.e. Link
Down) or blocked from forwarding (e.g. STP). More than one
secondary-upstream interface can be configured.
stp Let STP determine whether this interface is upstream or
downstream. STP will determine if this interface plays the
role of an STP Root Port for the CIST, or for the MSTI that this
UFO VLAN belongs to. If it is, then UFO will designate this
interface as an Upstream interface member for this UFO
VLAN. Otherwise it is Downstream.
epsr Let EPSR determine whether this interface is upstream or
downstream. If this UFO VLAN is a protected data VLAN in an
EPSR instance, and this interface is one of the transit node's
interfaces, then this interface will determine if an EPSR
Master is reachable from this interface. If it is, then UFO will
designate this interface as an Upstream interface member
for this UFO VLAN. Otherwise it is Downstream.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 560
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE PRIVATE-VLAN UFO
Example To configure a private VLAN UFO trunk port as primary-upstream, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 100
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode private-vlan ufo 100
primary-upstream
To change the role of the private VLAN UFO 802.1q member port back to the
default of downstream, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport mode private-vlan ufo 100
Related
Commands
private-vlan
show vlan private-vlan ufo
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: added to SBx8100 Series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: added to x530 Series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 561
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT MODE TRUNK
switchport mode trunk
Overview Use this command to set the switching characteristics of the port to trunk.
Received frames are classified based on the VLAN characteristics, then accepted or
discarded based on the specified filtering criteria.
Syntax switchport mode trunk [ingress-filter {enable|disable}]
Default By default, ports are in access mode, are untagged members of the default VLAN
(vlan1), and have ingress filtering on.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage A port in trunk mode can be a tagged member of multiple VLANs, and an untagged
member of one native VLAN.
To configure which VLANs this port will trunk for, use the switchport trunk allowed
vlan command.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode trunk ingress-filter enable
Validation
Command
show interface switchport
Parameter Description
ingress-filter Set the ingress filtering for the frames received.
enable Turn on ingress filtering for received frames. This is the default.
disable Turn off ingress filtering to accept frames that do not meet the
classification criteria.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 562
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PRIVATE-VLAN HOST-ASSOCIATION
switchport private-vlan host-association
Overview Use this command to associate a primary VLAN and a secondary VLAN to a host
port. Only one primary and secondary VLAN can be associated to a host port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the association.
Syntax switchport private-vlan host-association <primary-vlan-id> add
<secondary-vlan-id>
no switchport private-vlan host-association
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport private-vlan host-association 2
add 3
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport private-vlan host-association
Parameter Description
<primary-vlan-id>VLAN ID of the primary VLAN.
<secondary-vlan-id>VLAN ID of the secondary VLAN (either isolated or com
munity).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 563
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT PRIVATE-VLAN MAPPING
switchport private-vlan mapping
Overview Use this command to associate a primary VLAN and a set of secondary VLANs to a
promiscuous port.
Use the no variant of this to remove all the association of secondary VLANs to
primary VLANs for a promiscuous port.
Syntax switchport private-vlan mapping <primary-vlan-id> add
<secondary-vid-list>
switchport private-vlan mapping <primary-vlan-id> remove
<secondary-vid-list>
no switchport private-vlan mapping
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage This command can be applied to a switch port or a static channel group, but not a
dynamic (LACP) channel group. LACP channel groups (dynamic/LACP
aggregators) cannot be promiscuous ports in private VLANs.
Examples awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport private-vlan mapping 2 add 3-4
awplus(config-if)# switchport private-vlan mapping 2 remove 3-4
awplus(config-if)# no switchport private-vlan mapping
Related
Commands
switchport mode private-vlan
Parameter Description
<primary-vlan-id>VLAN ID of the primary VLAN.
<secondary-vid-list>VLAN ID of the secondary VLAN (either isolated or
community), or a range of VLANs, or a comma-separated
list of VLANs and ranges.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 564
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT TRUNK ALLOWED VLAN
switchport trunk allowed vlan
Overview Use this command to add VLANs to be trunked over this switch port. Traffic for
these VLANs can be sent and received on the port.
Use the no variant of this command to reset switching characteristics of a specified
interface to negate a trunked configuration specified with switchport trunk
allowed vlan command.
Syntax switchport trunk allowed vlan all
switchport trunk allowed vlan none
switchport trunk allowed vlan add <vid-list>
switchport trunk allowed vlan remove <vid-list>
switchport trunk allowed vlan except <vid-list>
no switchport trunk
Default By default, ports are untagged members of the default VLAN (vlan1).
Mode Interface Configuration
Parameter Description
all Allow all VLANs to transmit and receive through the port.
none Allow no VLANs to transmit and receive through the port.
add Add a VLAN to the list of VLANs that are allowed to transmit and
receive through the port. Only use this parameter if a list of VLANs is
already configured on a port.
remove Remove a VLAN from the list of VLANs that are allowed to transmit
and receive through the port. Only use this parameter if a list of
VLANs is already configured on a port.
If you are removing VLAN port membership for a large number of
switchports and VLANs, note that this command may take a number
of minutes to run.
except All VLANs, except the VLAN for which the VID is specified, are part of
its port member set. Only use this parameter to remove VLANs after
either this parameter or the all parameter have added VLANs to a
port.
<vid-list><2-4094> The ID of the VLAN or VLANs that will be added to, or
removed from, the port. A single VLAN, VLAN range, or comma-
separated VLAN list can be set.
For a VLAN range, specify two VLAN numbers: lowest, then highest
number in the range, separated by a hyphen.
For a VLAN list, specify the VLAN numbers separated by commas.
Do not enter spaces between hyphens or commas when setting
parameters for VLAN ranges or lists.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 565
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT TRUNK ALLOWED VLAN
Usage The all parameter sets the port to be a tagged member of all the VLANs configured
on the device. The none parameter removes all VLANs from the port’s tagged
member set. The add and remove parameters will add and remove VLANs to and
from the port’s member set. The except parameter creates an exception to the list.
If you use the all parameter, and then you want to remove VLANs from the port’s
member list, you must use the except parameter to remove the unwanted VLANs.
Similarly, if you use the except parameter to remove a list of VLANs, and you want
to change that list, you must use the except parameter to make that change (not
the add and remove parameters).
For example, if you want to remove VLAN3-5 from a port and the port’s
configuration is currently switchport trunk allowed vlan all, then you should
remove VLAN3-5 by entering the except parameter, instead of using the remove
parameter. This means using the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan except 3-5
If you do this, then the configuration changes to:
For example, if you want to add VLAN4 back in again, and the port configuration is
currently switchport trunk allowed vlan except 3-5, then you should add VLAN4
by re-entering the except parameter with the list of VLANs to remove, instead of
using the add parameter. This means using the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.5
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan except 3,5
If you do this, then the configuration changes to:
awplus#show running-config
interface port1.0.6
switchport
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan except 3-5
awplus#show running-config
interface port1.0.5
switchport
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan except 3,5

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 566
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT TRUNK ALLOWED VLAN
Examples The following shows adding a single VLAN to the port’s member set.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2
The following shows adding a range of VLANs to the port’s member set.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2-4
The following shows adding a list of VLANs to the port’s member set.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2,3,4
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 567
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT TRUNK NATIVE VLAN
switchport trunk native vlan
Overview Use this command to configure the native VLAN for this port. The native VLAN is
used for classifying the incoming untagged packets. Use the none parameter with
this command to remove the native VLAN from the port and set the acceptable
frame types to vlan-tagged only.
Use the no variant of this command to revert the native VLAN to the default VLAN
ID 1. Command negation removes tagged VLANs, and sets the native VLAN to the
default VLAN.
Syntax switchport trunk native vlan {<vid>|none}
no switchport trunk native vlan
Default VLAN 1 (the default VLAN), which is reverted to using the no form of this
command.
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples The following commands show configuration of VLAN 2 as the native VLAN for
port1.0.2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 2
The following commands show the removal of the native VLAN for interface
port1.0.2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan none
The following commands revert the native VLAN to the default VLAN 1 for interface
port1.0.2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no switchport trunk native vlan
Parameter Description
<vid>The ID of the VLAN that will be used to classify the incoming
untagged packets, in the range 2-2094. The VLAN ID must be a part of
the VLAN member set of the port.
none No native VLAN specified. This option removes the native VLAN from
the port and sets the acceptable frame types to vlan-tagged only.
Note: Use the no variant of this command to revert to the default
VLAN 1 as the native VLAN for the specified interface switchport - not
none.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 568
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT VLAN-STACKING (DOUBLE TAGGING)
switchport vlan-stacking (double tagging)
Overview Use this command to enable VLAN stacking on a port and set it to be a
customer-edge-port or provider-port. This is sometimes referred to as VLAN
double-tagging, nested VLANs, or Q in Q.
Use no parameter with this command to disable VLAN stacking on an interface.
Syntax switchport vlan-stacking {customer-edge-port|provider-port}
no switchport vlan-stacking
Default By default, ports are not VLAN stacking ports.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Use VLAN stacking to separate traffic from different customers to that they can be
managed over a provider network.
Note that you must also set an MRU of 1504 or higher on the customer edge port,
using the mru command.
Traffic with an extra VLAN header added by VLAN stacking cannot be routed.
Example To apply vlan-stacking to the selected port, configure it to be a customer edge
port, and increase the MRU, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport vlan-stacking customer-edge-port
awplus(config-if)# mru 10240
Parameter Description
customer-edge-port Set the port to be a customer edge port. This port must
already be in access mode.
provider-port Set the port to be a provider port. This port must already
be in trunk mode.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 569
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT VOICE DSCP
switchport voice dscp
Overview Use this command for a specific port to configure the Layer 3 DSCP value
advertised when the transmission of LLDP-MED Network Policy TLVs for voice
devices is enabled. When LLDP-MED capable IP phones receive this network policy
information, they transmit voice data with the specified DSCP value.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the DSCP value to the default, 0.
Syntax switchport voice dscp <0-63>
no switchport voice dscp
Default A DSCP value of 0 will be advertised.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage LLDP-MED advertisements including Network Policy TLVs are transmitted via a
port if:
•LLDP is enabled (lldp run command)
• Voice VLAN is configured for the port (switchport voice vlan command)
• The port is configured to transmit LLDP advertisements—enabled by default
(lldp transmit receive command)
• The port is configured to transmit Network Policy TLVs—enabled by default
(lldp med-tlv-select command)
• There is an LLDP-MED device connected to the port
Example To tell IP phones connected to port1.0.2 to send voice data with DSCP value 27, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport voice dscp 27
Related
Commands
lldp med-tlv-select
show lldp
switchport voice vlan
Parameter Description
dscp Specify a DSCP value for voice data.
<0-63>DSCP value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 570
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT VOICE VLAN
switchport voice vlan
Overview Use this command to configure the Voice VLAN tagging advertised when the
transmission of LLDP-MED Network Policy TLVs for voice endpoint devices is
enabled. When LLDP-MED capable IP phones receive this network policy
information, they transmit voice data with the specified tagging. This command
also sets the ports to be spanning tree edge ports, that is, it enables spanning tree
portfast on the ports.
Use the no variant of this command to remove LLDP-MED network policy
configuration for voice devices connected to these ports. This does not change the
spanning tree edge port status.
Syntax switchport voice vlan [<vid>|dot1p|dynamic|untagged]
no switchport voice vlan
Default By default, no Voice VLAN is configured, and therefore no network policy is
advertised for voice devices.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage LLDP-MED advertisements including Network Policy TLVs are transmitted via a
port if:
•LLDP is enabled (lldp run command)
• Voice VLAN is configured for the port using this command (switchport voice
vlan)
• The port is configured to transmit LLDP advertisements—enabled by default
(lldp transmit receive command)
• The port is configured to transmit Network Policy TLVs—enabled by default
(lldp med-tlv-select command)
• There is an LLDP-MED device connected to the port.
To set the priority value to be advertised for tagged frames, use the switchport
voice vlan priority command.
If the Voice VLAN details are to be assigned by RADIUS, then the RADIUS server
must be configured to send the attribute “Egress-VLANID (56)” or
Parameter Description
dot1p The IP phone should send User Priority tagged packets, that is, packets in
which the tag contains a User Priority value, and a VID of 0. (The User
Priority tag is also known as the 802.1p priority tag, or the Class of Service
(CoS) tag.)
dynamic The VLAN ID with which the IP phone should send tagged packets will be
assigned by RADIUS authentication.
untagged The IP phone should send untagged packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 571
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT VOICE VLAN
“Egress-VLAN-Name (58)” in the RADIUS Accept message when authenticating a
phone attached to this port.
To set these attributes on the local RADIUS server, use the egress-vlan-id command
or the egress-vlan-name command.
Examples To tell IP phones connected to port1.0.5 to send voice data tagged for VLAN 10, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.5
awplus(config-if)# switchport voice vlan 10
To tell IP phones connected to ports 1.0.2-1.0.6 to send priority tagged packets
(802.1p priority tagged with VID 0, so that they will be assigned to the port VLAN)
use the following commands. The priority value is 5 by default, but can be
configured with the switchport voice vlan priority command.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2-port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# switchport voice vlan dot1p
To dynamically configure the VLAN ID advertised to IP phones connected to
port1.0.1 based on the VLAN assigned by RADIUS authentication (with RADIUS
attribute “Egress- VLANID” or “Egress-VLAN-Name” in the RADIUS accept packet),
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# switchport voice vlan dynamic
To remove the Voice VLAN, and therefore disable the transmission of LLDP-MED
network policy information for voice devices on port1.0.6, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no switchport voice vlan

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 572
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT VOICE VLAN PRIORITY
switchport voice vlan priority
Overview Use this command to configure the Layer 2 user priority advertised when the
transmission of LLDP-MED Network Policy TLVs for voice devices is enabled. This is
the priority in the User Priority field of the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tag, also known as the
Class of Service (CoS), or 802.1p priority. When LLDP-MED capable IP phones
receive this network policy information, they transmit voice data with the specified
priority.
Syntax switchport voice vlan priority <0-7>
no switchport voice vlan priority
To remove the Voice VLAN, and therefore disable the transmission of LLDP-MED
network policy information for voice devices on port1.0.6, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no switchport voice vlan
Parameter Description
priority Specify a user priority value for voice data.
<0-7>Priority value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 573
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
VLAN
vlan
Overview This command creates VLANs, assigns names to them, and enables or disables
them. Disabling the VLAN causes all forwarding over the specified VLAN ID to
cease. Enabling the VLAN allows forwarding of frames on the specified VLAN.
The no variant of this command destroys the specified VLANs or returns their MTU
to the default.
Syntax vlan <vid> [name <vlan-name>] [state {enable|disable}]
vlan <vid-range> [state {enable|disable}]
vlan {<vid>|<vlan-name>} [mtu <mtu-value>]
no vlan {<vid>|<vid-range>} [mtu]
Default By default, VLANs are enabled when they are created.
Mode VLAN Configuration
Examples To enable vlan 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 45 name accounts state enable
To destroy vlan 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# no vlan 45
Related
Commands
mtu
vlan database
show vlan
Parameter Description
<vid>The VID of the VLAN to enable or disable, in the range 1-4094.
<vlan-name>The ASCII name of the VLAN. Maximum length: 32 characters.
<vid-range>Specifies a range of VLAN identifiers.
<mtu-value>Specifies the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size in bytes, in the
range 68 to 1500 bytes, for the VLAN.
enable Puts the VLAN into an enabled state.
disable Puts the VLAN into a disabled state.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 574
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
VLAN ACCESS-MAP
vlan access-map
Overview Use this command to create a VLAN access-map and enter into VLAN access-map
mode, so you can add ACLs to the map. You can use any IPv4 or IPv6 hardware
ACLs. VLAN access-maps are used to attach ACLs to VLANs, and therefore to filter
traffic as it ingresses VLANs.
See the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information,
including information about the number of rules consumed by per-VLAN ACLs,
and ACL processing order.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a VLAN access-map.
Syntax vlan access-map <name>
no vlan access-map <name>
Default By default, no VLAN access-maps exist.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To apply ACL 3001 to VLAN 48, where the ACL drops IP traffic from any source to
any destination, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3001 deny ip any any
awplus(config)# vlan access-map deny_all
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# match access-group 3001
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# exit
awplus(config)# vlan filter deny_all vlan-list 48 input
Related
Commands
match access-group
show vlan access-map
vlan filter
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<name> A name for the access-map.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 575
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
VLAN DATABASE
vlan database
Overview Use this command to enter the VLAN Configuration mode.
Syntax vlan database
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to enter the VLAN configuration mode. You can then add or
delete a VLAN, or modify its values.
Example In the following example, note the change to VLAN configuration mode from
Configure mode:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)#
Related
Commands
vlan

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 576
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
VLAN COMMANDS
VLAN FILTER
vlan filter
Overview Use this command to apply a VLAN access-map to a list of VLANs. The switch uses
the ACLs in the access-map to filter traffic ingressing those VLANs.
See the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information,
including information about the number of rules consumed by per-VLAN ACLs,
and ACL processing order.
Use the no variant of this command to to remove the access-map filter from the
listed VLANs.
Syntax vlan filter <access-map-name> vlan-list <vid> input
no vlan filter <access-map-name> vlan-list <vid> input
Default By default, no VLAN filters exist.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To apply ACL 3001 to VLAN 48, where the ACL drops IP traffic from any source to
any destination, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3001 deny ip any any
awplus(config)# vlan access-map deny_all
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# match access-group 3001
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# exit
awplus(config)# vlan filter deny_all vlan-list 48 input
Related
Commands
match access-group
show vlan filter
vlan access-map
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<access-map-name> The name of the VLAN access-map to apply to the
specified list of VLANs
vlan-list <vid>The list of VLANs to filter. You can specify a single VLAN
(e.g. 49), a comma-separated list of VLANs (e.g. 49, 51), a
hyphenated range of VLANs (e.g. 49-51), or a combination
(e.g. 49,51-53)
input Apply the filter to ingress traffic

17
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 577
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Spanning Tree
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
RSTP, STP or MSTP. For information about spanning trees, including configuration
procedures, see the STP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“clear spanning-tree statistics” on page 579
•“clear spanning-tree detected protocols (RSTP and MSTP)” on page 580
•“debug mstp (RSTP and STP)” on page 581
•“instance priority (MSTP)” on page 585
•“instance vlan (MSTP)” on page 587
•“region (MSTP)” on page 589
•“revision (MSTP)” on page 590
•“show debugging mstp” on page 591
•“show spanning-tree” on page 592
•“show spanning-tree brief” on page 595
•“show spanning-tree mst” on page 596
•“show spanning-tree mst config” on page 597
•“show spanning-tree mst detail” on page 598
•“show spanning-tree mst detail interface” on page 600
•“show spanning-tree mst instance” on page 602
•“show spanning-tree mst instance interface” on page 603
•“show spanning-tree mst interface” on page 604
•“show spanning-tree statistics” on page 605
•“show spanning-tree statistics instance” on page 607

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 578
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
•“show spanning-tree statistics instance interface” on page 608
•“show spanning-tree statistics interface” on page 610
•“show spanning-tree vlan range-index” on page 612
•“spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP)” on page 613
•“spanning-tree bpdu” on page 614
•“spanning-tree cisco-interoperability (MSTP)” on page 616
•“spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)” on page 617
•“spanning-tree enable” on page 618
•“spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable” on page 620
•“spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval” on page 621
•“spanning-tree force-version” on page 622
•“spanning-tree forward-time” on page 623
•“spanning-tree guard root” on page 624
•“spanning-tree hello-time” on page 625
•“spanning-tree link-type” on page 626
•“spanning-tree max-age” on page 627
•“spanning-tree max-hops (MSTP)” on page 628
•“spanning-tree mode” on page 629
•“spanning-tree mst configuration” on page 630
•“spanning-tree mst instance” on page 631
•“spanning-tree mst instance path-cost” on page 632
•“spanning-tree mst instance priority” on page 634
•“spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role” on page 635
•“spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn” on page 637
•“spanning-tree path-cost” on page 638
•“spanning-tree portfast (STP)” on page 639
•“spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter” on page 641
•“spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard” on page 643
•“spanning-tree priority (bridge priority)” on page 645
•“spanning-tree priority (port priority)” on page 646
•“spanning-tree restricted-role” on page 647
•“spanning-tree restricted-tcn” on page 648
•“spanning-tree transmit-holdcount” on page 649
•“
undebug mstp” on page 650
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 579
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
CLEAR SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS
clear spanning-tree statistics
Overview Use this command to clear all the STP BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) statistics.
Syntax clear spanning-tree statistics
clear spanning-tree statistics [instance <mstp-instance>]
clear spanning-tree statistics [interface <port> [instance
<mstp-instance>]]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command with the instance parameter in MSTP mode. Specifying this
command with the interface parameter only not the instance parameter will work
in STP and RSTP mode.
Examples awplus# clear spanning-tree statistics
awplus# clear spanning-tree statistics instance 1
awplus# clear spanning-tree statistics interface port1.0.2
awplus# clear spanning-tree statistics interface port1.0.2
instance 1
Parameter Description
<port>The port to clear STP BPDU statistics for. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).
<mstp-
instance>The MSTP instance (MSTI - Multiple Spanning Tree Instance) to clear
MSTP BPDU statistics.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 580
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
CLEAR SPANNING-TREE DETECTED PROTOCOLS (RSTP AND MSTP)
clear spanning-tree detected protocols
(RSTP and MSTP)
Overview Use this command to clear the detected protocols for a specific port, or all ports.
Use this command in RSTP or MSTP mode only.
Syntax clear spanning-tree detected protocols [interface <port>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear spanning-tree detected protocols
Parameter Description
<port>The port to clear detected protocols for. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 581
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
DEBUG MSTP (RSTP AND STP)
debug mstp (RSTP and STP)
Overview Use this command to enable debugging for the configured spanning tree mode,
and echo data to the console, at various levels. Note that although this command
uses the keyword mstp it displays debugging output for RSTP and STP protocols
as well the MSTP protocol.
Use the no variant of this command to disable spanning tree debugging.
Syntax debug mstp {all|cli|protocol [detail]|timer [detail]}
debug mstp {packet {rx|tx} [decode] [interface <interface>]}
debug mstp {topology-change [interface <interface>]}
no debug mstp {all|cli|protocol [detail]|timer [detail]}
no debug mstp {packet {rx|tx} [decode] [interface <interface>]}
no debug mstp {topology-change [interface <interface>]}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration mode
Usage 1 Use the debug mstp topology-change interface command to generate
debugging messages when the device receives an indication of a topology change
in a BPDU from another device. The debugging can be activated on a per-port
basis. Although this command uses the keyword mstp, it displays debugging
output for RSTP and STP protocols as well as the MSTP protocol.
Due to the likely volume of output, these debug messages are best viewed using
the terminal monitor command before issuing the relevant debug mstp
Parameter Description
all Echoes all spanning tree debugging levels to the console.
cli Echoes spanning tree commands to the console.
packet Echoes spanning tree packets to the console.
rx Received packets.
tx Transmitted packets.
protocol Echoes protocol changes to the console.
timer Echoes timer information to the console.
detail Detailed output.
decode Interprets packet contents
topology-change Interprets topology change messages
interface Keyword before <interface> placeholder to specify an
interface to debug
<interface>Placeholder used to specify the name of the interface to
debug.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 582
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
DEBUG MSTP (RSTP AND STP)
command. The default terminal monitor filter will select and display these
messages. Alternatively, the messages can be directed to any of the other log
outputs by adding a filter for the MSTP application using log buffered (filter)
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# log buffered program mstp
Output 1
Usage 2 Use the debug mstp packet rx|tx decode interface command to generate
debugging messages containing the entire contents of a BPDU displayed in
readable text for transmitted and received xSTP BPDUs. The debugging can be
activated on a per-port basis and transmit and receive debugging is controlled
independently. Although this command uses the keyword mstp, it displays
debugging output for RSTP and STP protocols as well as the MSTP protocol.
Due to the likely volume of output, these debug messages are best viewed using
the terminal monitor command before issuing the relevant debug mstp
command. The default terminal monitor filter will select and display these
messages. Alternatively, the messages can be directed to any of the other log
outputs by adding a filter for the MSTP application using the log buffered (filter)
command:
awplus(config)# log buffered program mstp
Output 2 In MSTP mode - an MSTP BPDU with 1 MSTI:
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#debug mstp topology-change interface port1.0.4
10:09:09 awplus MSTP[1409]: Topology change rcvd on port1.0.4 (internal)
10:09:09 awplus MSTP[1409]: Topology change rcvd on MSTI 1 port1.0.4
awplus#debug mstp topology-change interface port1.0.6
10:09:29 awplus MSTP[1409]: Topology change rcvd on port1.0.6 (external)
10:09:29 awplus MSTP[1409]: Topology change rcvd on MSTI 1 port1.0.6
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 583
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
DEBUG MSTP (RSTP AND STP)
In STP mode transmitting a TCN BPDU:
In STP mode receiving an STP BPDU:
In RSTP mode receiving an RSTP BPDU:
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#debug mstp packet rx decode interface port1.0.4
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - start
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Protocol version: MSTP, BPDU type: RST
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST Flags: Agree Forward Learn role=Desig
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST root id : 0000:0000cd1000fe
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST ext pathcost : 0
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST reg root id : 0000:0000cd1000fe
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST port id : 8001 (128:1)
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: msg age: 0 max age: 20 hellotime: 2 fwd delay: 15
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Version 3 length : 80
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Format id : 0
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Config name : test
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Revision level : 0
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: Config digest : 3ab68794d602fdf43b21c0b37ac3bca8
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST int pathcost : 0
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST bridge id : 0000:0000cd1000fe
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST hops remaining : 20
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: MSTI flags : Agree Forward Learn role=Desig
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: MSTI reg root id : 8001:0000cd1000fe
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: MSTI pathcost : 0
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: MSTI bridge priority : 32768 port priority : 128
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: MSTI hops remaining : 20
17:23:42 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - finish
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#debug mstp packet tx decode interface port1.0.4
17:28:09 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU tx - start
17:28:09 awplus MSTP[1417]: Protocol version: STP, BPDU type: TCN
17:28:09 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU tx - finish
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#debug mstp packet rx decode interface port1.0.4
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - start
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Protocol version: STP, BPDU type: Config
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Flags: role=none
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Root id : 8000:0000cd1000fe
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Root pathcost : 0
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Bridge id : 8000:0000cd1000fe
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: Port id : 8001 (128:1)
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: msg age: 0 max age: 20 hellotime: 2 fwd delay: 15
17:31:36 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - finish

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 584
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
DEBUG MSTP (RSTP AND STP)
Examples awplus# debug mstp all
awplus# debug mstp cli
awplus# debug mstp packet rx
awplus# debug mstp protocol detail
awplus# debug mstp timer
awplus# debug mstp packet rx decode interface port1.0.2
awplus# debug mstp packet tx decode interface port1.0.6
Related
Commands
log buffered (filter)
show debugging mstp
terminal monitor
undebug mstp
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#debug mstp packet rx decode interface port1.0.4
awplus#17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - start
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: Protocol version: RSTP, BPDU type: RST
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST Flags: Forward Learn role=Desig
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST root id : 8000:0000cd1000fe
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST ext pathcost : 0
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST reg root id : 8000:0000cd1000fe
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: CIST port id : 8001 (128:1)
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: msg age: 0 max age: 20 hellotime: 2 fwd delay: 15
17:30:17 awplus MSTP[1417]: port1.0.4 xSTP BPDU rx - finish
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 585
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
INSTANCE PRIORITY (MSTP)
instance priority (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to set the priority for this device to become the root bridge for
the specified MSTI (Multiple Spanning Tree Instance).
Use this command for MSTP only.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the root bridge priority of the device
for the instance to the default.
Syntax instance <instance-id> priority <priority>
no instance <instance-id> priority
Default The default priority value for all instances is 32768.
Mode MST Configuration
Usage MSTP lets you distribute traffic more efficiently across a network by blocking
different links for different VLANs. You do this by making different devices into the
root bridge for each MSTP instance, so that each instance blocks a different link.
If all devices have the same root bridge priority for the instance, MSTP selects the
device with the lowest MAC address to be the root bridge. Give the device a higher
priority for becoming the root bridge for a particular instance by assigning it a
lower priority number, or vice versa.
Examples To set the root bridge priority for MSTP instance 2 to be the highest (0), so that it
will be the root bridge for this instance when available, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)# instance 2 priority 0
To reset the root bridge priority for instance 2 to the default (32768), use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)# no instance 2 priority
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<priority> Specify the root bridge priority for the device for the MSTI in the
range <0-61440>. Note that a lower priority number indicates a
greater likelihood of the device becoming the root bridge. The
priority values can be set only in increments of 4096. If you
specify a number that is not a multiple of 4096, it will be rounded
down. The default priority is 32768.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 587
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
INSTANCE VLAN (MSTP)
instance vlan (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to create an MST Instance (MSTI), and associate the specified
VLANs with it. An MSTI is a spanning tree instance that exists within an MST region
(MSTR).
When a VLAN is associated with an MSTI the member ports of the VLAN are
automatically configured to send and receive spanning-tree information for the
associated MSTI. You can disable this automatic configuration of member ports of
the VLAN to the associated MSTI by using a no spanning-tree mst instance
command to remove the member port from the MSTI.
Use the instance vlan command for MSTP only.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified VLANs from the MSTI.
Syntax instance <instance-id> vlan <vid-list>
no instance <instance-id> vlan <vid-list>
Mode MST Configuration
Usage The VLANs must be created before being associated with an MST instance (MSTI).
If the VLAN range is not specified, the MSTI will not be created.
This command removes the specified VLANs from the CIST and adds them to the
specified MSTI. If you use the no variant of this command to remove the VLAN from
the MSTI, it returns it to the CIST. To move a VLAN from one MSTI to another, you
must first use the no variant of this command to return it to the CIST.
Ports in these VLANs will remain in the control of the CIST until you associate the
ports with the MSTI using the spanning-tree mst instance command.
Example To associate VLAN 30 with MSTI 2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mode mstp
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)# instance 2 vlan 30
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<vid-list> Specify one or more VLAN identifiers (VID) to be associated with
the MSTI specified. This can be a single VID in the range 1-4094,
or a hyphen-separated range or a comma-separated list of VLAN
IDs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 589
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
REGION (MSTP)
region (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to assign a name to the device’s MST Region. MST Instances
(MSTI) of a region form different spanning trees for different VLANs.
Use this command for MSTP only.
Use the no variant of this command to remove this region name and reset it to the
default.
Syntax region <region-name>
no region
Default By default, the region name is My Name.
Mode MST Configuration
Usage The region name, the revision number, and the digest of the VLAN to MSTI
configuration table must be the same on all devices that are intended to be in the
same MST region.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)# region ATL
Related
Commands
revision (MSTP)
show spanning-tree mst config
Parameter Description
<region-name>Specify the name of the region, up to 32 characters. Valid
characters are upper-case, lower-case, digits, underscore.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 590
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
REVISION (MSTP)
revision (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to specify the MST revision number to be used in the
configuration identifier.
Use this command for MSTP only.
Syntax revision <revision-number>
Default The default of revision number is 0.
Mode MST Configuration
Usage The region name, the revision number, and the digest of the VLAN to MSTI
configuration table must be the same on all devices that are intended to be in the
same MST region.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)# revision 25
Related
Commands
region (MSTP)
show spanning-tree mst config
instance vlan (MSTP)
Parameter Description
<revision-number><0-65535> Revision number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 591
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING MSTP
show debugging mstp
Overview Use this command to show the MSTP debugging options set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging mstp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec mode
Example To display the MSTP debugging options set, enter the command:
awplus# show debugging mstp
Output Figure 17-1: Example output from show debugging mstp
Related
Commands
debug mstp (RSTP and STP)
MSTP debugging status:
MSTP receiving packet debugging is on
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 592
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE
show spanning-tree
Overview Use this command to display detailed spanning tree information on the specified
port or on all ports. Use this command for RSTP, MSTP or STP.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree [interface <port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Note that any list of interfaces specified must not span any interfaces that are not
installed.
A topology change counter has been included for RSTP and MSTP. You can see the
topology change counter for RSTP by using the show spanning-tree command.
You can see the topology change counter for MSTP by using the show
spanning-tree mst instance command.
Example To display spanning tree information about port1.0.3, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree interface port1.0.3
Parameter Description
interface Display information about the following port only.
<port-list>The ports to display information about. A port-list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6) a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4, or sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix switch ports, static channel
groups, and dynamic (LACP) channel groups in the same list
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 593
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE
Output Figure 17-2: Example output from show spanning-tree in RSTP mode
Output Figure 17-3: Example output from show spanning-tree
awplus#show spanning-tree
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: Root Path Cost 0 - Root Port 0 - Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20
% 1: Root Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: Bridge Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: last topology change Mon Oct 3 02:06:26 2016
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 300 sec
% port1.0.1: Port 5001 - Id 8389 - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.1: Designated Path Cost 0
% port1.0.1: Configured Path Cost 20000000 - Add type Explicit ref count 1
% port1.0.1: Designated Port Id 8389 - Priority 128 -
% port1.0.1: Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.1: Designated Bridge 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.1: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.1: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.1: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0 - topo change
timer 0
% port1.0.1: forward-transitions 0
% port1.0.1: Version Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send STP
% port1.0.1: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.1: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.1: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.1: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.1: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current shared
%
% port1.0.2: Port 5002 - Id 838a - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.2: Designated Path Cost 0
% port1.0.2: Configured Path Cost 20000000 - Add type Explicit ref count 1
% port1.0.2: Designated Port Id 838a - Priority 128 -
% port1.0.2: Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Designated Bridge 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.2: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.2: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0 - topo change
timer 0
% port1.0.2: forward-transitions 0
% port1.0.2: Version Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send STP
% port1.0.2: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.2: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.2: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current shared
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 594
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: Root Path Cost 0 - Root Port 0 - Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20
% 1: Root Id 80000000cd20f093
% 1: Bridge Id 80000000cd20f093
% 1: last topology change Mon Oct 3 02:06:26 2016
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 300 sec
% port1.0.3: Port 5023 - Id 839f - Role Designated - State Forwarding
% port1.0.3: Designated Path Cost 0
% port1.0.3: Configured Path Cost 200000 - Add type Explicit ref count 1
% port1.0.3: Designated Port Id 839f - Priority 128 -
% port1.0.3: Root 80000000cd20f093
% port1.0.3: Designated Bridge 80000000cd20f093
% port1.0.3: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.3: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.3: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 1 - topo change
timer 0
% port1.0.3: forward-transitions 32
% port1.0.3: Version Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send RSTP
% port1.0.3: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.3: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.3: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.3: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.3: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current point-to-point
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 595
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE BRIEF
show spanning-tree brief
Overview Use this command to display a summary of spanning tree status information on all
ports. Use this command for RSTP, MSTP or STP.
Syntax show spanning-tree brief
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Note that any list of interfaces specified must not span any interfaces that are not
installed.
A topology change counter has been included for RSTP and MSTP. You can see the
topology change counter for RSTP by using the show spanning-tree command.
You can see the topology change counter for MSTP by using the show
spanning-tree mst instance command.
Example To display a summary of spanning tree status information, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree brief
Output Figure 17-4: Example output from show spanning-tree brief
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
Parameter Description
brief A brief summary of spanning tree information.
Default: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
Default: Root Path Cost 40000 - Root Port 4501 - Bridge Priority 32768
Default: Root Id 8000:0000cd250001
Default: Bridge Id 8000:0000cd296eb1
Port Designated Bridge Port Id Role State
sa1 8000:001577c9744b 8195 Rootport Forwarding
po1 8000:0000cd296eb1 81f9 Designated Forwarding
port1.0.1 8000:0000cd296eb1 8389 Disabled Discarding
port1.0.2 8000:0000cd296eb1 838a Disabled Discarding
port1.0.3 8000:0000cd296eb1 838b Disabled Discarding
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 596
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST
show spanning-tree mst
Overview This command displays bridge-level information about the CIST and VLAN to MSTI
mappings.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Interface Configuration
Example To display bridge-level information about the CIST and VLAN to MSTI mappings,
enter the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst
Output Figure 17-5: Example output from show spanning-tree mst
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree mst interface
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: CIST Root Path Cost 0 - CIST Root Port 0 - CIST Bridge
Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20 - Max-hops 20
% 1: CIST Root Id 8000000475e93ffe
% 1: CIST Reg Root Id 8000000475e93ffe
% 1: CST Bridge Id 8000000475e93ffe
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 300 sec
%
% Instance VLAN
% 0: 1
% 2: 4
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 597
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST CONFIG
show spanning-tree mst config
Overview Use this command to display MSTP configuration identifier for the device.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst config
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Interface Configuration
Usage The region name, the revision number, and the digest of the VLAN to MSTI
configuration table must be the same on all devices that are intended to be in the
same MST region.
Example To display MSTP configuration identifier information, enter the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst config
Output Figure 17-6: Example output from show spanning-tree mst config
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
region (MSTP)
revision (MSTP)
awplus#show spanning-tree mst config
%
% MSTP Configuration Information:
%------------------------------------------------------
% Format Id : 0
% Name : My Name
% Revision Level : 0
% Digest : 0x80DEE46DA92A98CF21C603291B22880A
%------------------------------------------------------

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 598
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST DETAIL
show spanning-tree mst detail
Overview This command displays detailed information about each instance, and all
interfaces associated with that particular instance.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst detail
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Interface Configuration
Example To display detailed information about each instance, and all interfaces associated
with them, enter the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst detail
Output Figure 17-7: Example output from show spanning-tree mst detail
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: CIST Root Path Cost 0 - CIST Root Port 0 - CIST Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20 - Max-hops 20
% 1: CIST Root Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: CIST Reg Root Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: CIST Bridge Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 300 sec
% port1.0.1: Port 5001 - Id 8389 - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.1: Designated External Path Cost 0 -Internal Path Cost 0
% port1.0.1: Configured Path Cost 20000000 - Add type Explicit ref count 1
% port1.0.1: Designated Port Id 8389 - CIST Priority 128 -
% port1.0.1: CIST Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.1: Regional Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.1: Designated Bridge 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.1: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.1: CIST Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.1: CIST Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0 - topo
change timer 0
...
% port1.0.2: forward-transitions 0
% port1.0.2: Version Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send STP
% port1.0.2: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.2: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.2: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current shared
%
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 599
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST DETAIL
% port1.0.3: Port 5003 - Id 838b - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.3: Designated External Path Cost 0 -Internal Path Cost 0
% port1.0.3: Configured Path Cost 20000000 - Add type Explicit ref count 1
% port1.0.3: Designated Port Id 838b - CIST Priority 128 -
% port1.0.3: CIST Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.3: Regional Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.3: Designated Bridge 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.3: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.3: CIST Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.3: CIST Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0 - topo
change timer 0
% port1.0.3: forward-transitions 0
% port1.0.3: Version Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send STP
% port1.0.3: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.3: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.3: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.3: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.3: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current shared

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 600
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST DETAIL INTERFACE
show spanning-tree mst detail interface
Overview This command displays detailed information about the specified switch port, and
the MST instances associated with it.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst detail interface <port>
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Interface Configuration
Example To display detailed information about port1.0.3 and the instances associated with
it, enter the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst detail interface port1.0.3
Output Figure 17-8: Example output from show spanning-tree mst detail interface
Parameter Description
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch port
(e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic
(LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: CIST Root Path Cost 0 - CIST Root Port 0 - CIST Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20 - Max-hops 20
% 1: CIST Root Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: CIST Reg Root Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: CIST Bridge Id 80000000cd24ff2d
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 300 sec
% port1.0.2: Port 5002 - Id 838a - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.2: Designated External Path Cost 0 -Internal Path Cost 0
% port1.0.2: Configured Path Cost 20000000 - Add type Explicit ref count 2
% port1.0.2: Designated Port Id 838a - CIST Priority 128 -
% port1.0.2: CIST Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Regional Root 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Designated Bridge 80000000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Message Age 0 - Max Age 20
% port1.0.2: CIST Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.2: CIST Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0 - topo
change timer 0
% port1.0.2: forward-transitions 0
% port1.0.2: Version Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol - Received None - Send STP

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 601
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST DETAIL INTERFACE
% port1.0.2: No portfast configured - Current portfast off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-guard default - Current portfast bpdu-guard off
% port1.0.2: portfast bpdu-filter default - Current portfast bpdu-filter off
% port1.0.2: no root guard configured - Current root guard off
% port1.0.2: Configured Link Type point-to-point - Current shared
%
% Instance 2: Vlans: 2
% 1: MSTI Root Path Cost 0 -MSTI Root Port 0 - MSTI Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: MSTI Root Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% 1: MSTI Bridge Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Port 5002 - Id 838a - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.2: Designated Internal Path Cost 0 - Designated Port Id 838a
% port1.0.2: Configured Internal Path Cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: Configured CST External Path cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: CST Priority 128 - MSTI Priority 128
% port1.0.2: Designated Root 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Designated Bridge 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Message Age 0 - Max Age 0
% port1.0.2: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.2: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 602
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE
show spanning-tree mst instance
Overview This command displays detailed information for the specified instance, and all
switch ports associated with that instance.
A topology change counter has been included for RSTP and MSTP. You can see the
topology change counter for RSTP by using the show spanning-tree command.
You can see the topology change counter for MSTP by using the show
spanning-tree mst instance command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id>
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec, and Interface Configuration
Example To display detailed information for instance 2, and all switch ports associated with
that instance, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst instance 2
Output Figure 17-9: Example output from show spanning-tree mst instance
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
% 1: MSTI Root Path Cost 0 - MSTI Root Port 0 - MSTI Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: MSTI Root Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% 1: MSTI Bridge Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Port 5002 - Id 838a - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.2: Designated Internal Path Cost 0 - Designated Port Id 838a
% port1.0.2: Configured Internal Path Cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: Configured CST External Path cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: CST Priority 128 - MSTI Priority 128
% port1.0.2: Designated Root 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Designated Bridge 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Message Age 0 - Max Age 0
% port1.0.2: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.2: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0
%

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 603
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE INTERFACE
show spanning-tree mst instance interface
Overview This command displays detailed information for the specified MST (Multiple
Spanning Tree) instance, and the specified switch port associated with that MST
instance.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> interface <port>
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec, and Interface Configuration
Example To display detailed information for instance 2, interface port1.0.2, use the
command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst instance 2 interface port1.0.2
Output Figure 17-10: Example output from show spanning-tree mst instance
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic
(LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).
% 1: MSTI Root Path Cost 0 - MSTI Root Port 0 - MSTI Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: MSTI Root Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% 1: MSTI Bridge Id 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Port 5002 - Id 838a - Role Disabled - State Discarding
% port1.0.2: Designated Internal Path Cost 0 - Designated Port Id 838a
% port1.0.2: Configured Internal Path Cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: Configured CST External Path cost 20000000
% port1.0.2: CST Priority 128 - MSTI Priority 128
% port1.0.2: Designated Root 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Designated Bridge 80020000cd24ff2d
% port1.0.2: Message Age 0 - Max Age 0
% port1.0.2: Hello Time 2 - Forward Delay 15
% port1.0.2: Forward Timer 0 - Msg Age Timer 0 - Hello Timer 0
%

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 604
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE MST INTERFACE
show spanning-tree mst interface
Overview This command displays the number of instances created, and VLANs associated
with it for the specified switch port.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree mst interface <port>
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec, and Interface Configuration
Example To display detailed information about each instance, and all interfaces associated
with them, for port1.0.4, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree mst interface port1.0.4
Output Figure 17-11: Example output from show spanning-tree mst interface
Parameter Description
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch port
(e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic
(LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).
% 1: Bridge up - Spanning Tree Enabled
% 1: CIST Root Path Cost 0 - CIST Root Port 0 - CIST Bridge Priority 32768
% 1: Forward Delay 15 - Hello Time 2 - Max Age 20 - Max-hops 20
% 1: CIST Root Id 80000008c73a2b22
% 1: CIST Reg Root Id 80000008c73a2b22
% 1: CST Bridge Id 80000008c73a2b22
% 1: portfast bpdu-filter disabled
% 1: portfast bpdu-guard disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout disabled
% 1: portfast errdisable timeout interval 1 sec
%
% Instance VLAN
% 0: 1
% 1: 2-3
% 2: 4-5
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 605
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS
show spanning-tree statistics
Overview This command displays BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) statistics for all
spanning-tree instances, and all switch ports associated with all spanning-tree
instances.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree statistics
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage To display BPDU statistics for all spanning-tree instances, and all switch ports
associated with all spanning-tree instances, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree statistics
Output Figure 17-12: Example output from show spanning-tree statistics
Port number = 915 Interface = port1.0.6
================================
% BPDU Related Parameters
% -----------------------
% Port Spanning Tree : Disable
% Spanning Tree Type : Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
% Current Port State : Discarding
% Port ID : 8393
% Port Number : 393
% Path Cost : 20000000
% Message Age : 0
% Designated Root : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Designated Cost : 0
% Designated Bridge : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Designated Port Id : 8393
% Top Change Ack : FALSE
% Config Pending : FALSE
% PORT Based Information & Statistics
% -----------------------------------
% Config Bpdu's xmitted : 0
% Config Bpdu's received : 0
% TCN Bpdu's xmitted : 0
% TCN Bpdu's received : 0
% Forward Trans Count : 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 606
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS
% STATUS of Port Timers
% ---------------------
% Hello Time Configured : 2
% Hello timer : INACTIVE
% Hello Time Value : 0
% Forward Delay Timer : INACTIVE
% Forward Delay Timer Value : 0
% Message Age Timer : INACTIVE
% Message Age Timer Value : 0
% Topology Change Timer : INACTIVE
% Topology Change Timer Value : 0
% Hold Timer : INACTIVE
% Hold Timer Value : 0
% Other Port-Specific Info
------------------------
% Max Age Transitions : 1
% Msg Age Expiry : 0
% Similar BPDUS Rcvd : 0
% Src Mac Count : 0
% Total Src Mac Rcvd : 0
% Next State : Learning
% Topology Change Time : 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 607
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS INSTANCE
show spanning-tree statistics instance
Overview This command displays BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) statistics for the specified
MST (Multiple Spanning Tree) instance, and all switch ports associated with that
MST instance.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree statistics instance <instance-id>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display BPDU statistics information for MST instance 2, and all switch ports
associated with that MST instance, use the command:
awplus# show spanning-tree statistics instance 2
Output Figure 17-13: Example output from show spanning-tree statistics instance
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree statistics
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
% % INST_PORT port1.0.3 Information & Statistics
% ----------------------------------------
% Config Bpdu's xmitted (port/inst) : (0/0)
% Config Bpdu's received (port/inst) : (0/0)
% TCN Bpdu's xmitted (port/inst) : (0/0)
% TCN Bpdu's received (port/inst) : (0/0)
% Message Age(port/Inst) : (0/0)
% port1.0.3: Forward Transitions : 0
% Next State : Learning
% Topology Change Time : 0
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 608
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS INSTANCE INTERFACE
show spanning-tree statistics instance
interface
Overview This command displays BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) statistics for the specified
MST (Multiple Spanning Tree) instance and the specified switch port associated
with that MST instance.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree statistics instance <instance-id> interface
<port>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display BPDU statistics for MST instance 2, interface port1.0.2, use the
command:
awplus# show spanning-tree statistics instance 2 interface
port1.0.2
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch
port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 609
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS INSTANCE INTERFACE
Output Figure 17-14: Example output from show spanning-tree statistics instance
interface
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree statistics
awplus#sh spanning-tree statistics interface port1.0.2 instance 1
Spanning Tree Enabled for Instance : 1
==================================
% INST_PORT port1.0.2 Information & Statistics
% ----------------------------------------
% Config Bpdu's xmitted (port/inst) : (0/0)
% Config Bpdu's received (port/inst) : (0/0)
% TCN Bpdu's xmitted (port/inst) : (0/0)
% TCN Bpdu's received (port/inst) : (0/0)
% Message Age(port/Inst) : (0/0)
% port1.0.2: Forward Transitions : 0
% Next State : Learning
% Topology Change Time : 0
% Other Inst/Vlan Information & Statistics
% ----------------------------------------
% Bridge Priority : 0
% Bridge Mac Address : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Topology Change Initiator : 5023
% Last Topology Change Occured : Mon Oct 3 05:42:06 2016
% Topology Change : FALSE
% Topology Change Detected : FALSE
% Topology Change Count : 1
% Topology Change Last Recvd from : 00:00:00:00:00:00

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 610
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS INTERFACE
show spanning-tree statistics interface
Overview This command displays BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) statistics for the specified
switch port, and all MST instances associated with that switch port.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show spanning-tree statistics interface <port>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display BPDU statistics about each MST instance for port1.0.2, use the
command:
awplus# show spanning-tree statistics interface port1.0.2
Output Figure 17-15: Example output from show spanning-tree statistics interface
Parameter Description
<port>The port to display information about. The port may be a switch port
(e.g. port1.0.2), a static channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2).
awplus#show spanning-tree statistics interface port1.0.2
Port number = 906 Interface = port1.0.2
================================
% BPDU Related Parameters
% -----------------------
% Port Spanning Tree : Disable
% Spanning Tree Type : Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
% Current Port State : Discarding
% Port ID : 838a
% Port Number : 38a
% Path Cost : 20000000
% Message Age : 0
% Designated Root : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Designated Cost : 0
% Designated Bridge : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Designated Port Id : 838a
% Top Change Ack : FALSE
% Config Pending : FALSE

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 611
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE STATISTICS INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree statistics
% PORT Based Information & Statistics
% -----------------------------------
% Config Bpdu's xmitted : 0
% Config Bpdu's received : 0
% TCN Bpdu's xmitted : 0
% TCN Bpdu's received : 0
% Forward Trans Count : 0
% STATUS of Port Timers
% ---------------------
% Hello Time Configured : 2
% Hello timer : INACTIVE
% Hello Time Value : 0
% Forward Delay Timer : INACTIVE
% Forward Delay Timer Value : 0
% Message Age Timer : INACTIVE
% Message Age Timer Value : 0
% Topology Change Timer : INACTIVE
% Topology Change Timer Value : 0
% Hold Timer : INACTIVE
% Hold Timer Value : 0
% Other Port-Specific Info
------------------------
% Max Age Transitions : 1
% Msg Age Expiry : 0
% Similar BPDUS Rcvd : 0
% Src Mac Count : 0
% Total Src Mac Rcvd : 0
% Next State : Learning
% Topology Change Time : 0
% Other Bridge information & Statistics
--------------------------------------
% STP Multicast Address : 01:80:c2:00:00:00
% Bridge Priority : 32768
% Bridge Mac Address : ec:cd:6d:20:c0:ed
% Bridge Hello Time : 2
% Bridge Forward Delay : 15
% Topology Change Initiator : 5023
% Last Topology Change Occured : Mon Oct 3 05:41:20 2016
% Topology Change : FALSE
% Topology Change Detected : TRUE
% Topology Change Count : 1
% Topology Change Last Recvd from : 00:00:00:00:00:00
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 612
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SHOW SPANNING-TREE VLAN RANGE-INDEX
show spanning-tree vlan range-index
Overview Use this command to display information about MST (Multiple Spanning Tree)
instances and the VLANs associated with them including the VLAN range-index
value for the device.
Syntax show spanning-tree vlan range-index
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display information about MST instances and the VLANs associated with them
for the device, including the VLAN range-index value, use the following command:
awplus# show spanning-tree vlan range-index
Output Figure 17-16: Example output from show spanning-tree vlan range-index
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree statistics
awplus#show spanning-tree vlan range-index
% MST Instance VLAN RangeIdx
% 1 1 1%

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 613
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE AUTOEDGE (RSTP AND MSTP)
spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP)
Overview Use this command to enable the autoedge feature on the port.
The autoedge feature allows the port to automatically detect that it is an edge
port. If it does not receive any BPDUs in the first three seconds after linkup,
enabling, or entering RSTP or MSTP mode, it sets itself to be an edgeport and
enters the forwarding state.
Use this command for RSTP or MSTP.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this feature.
Syntax spanning-tree autoedge
no spanning-tree autoedge
Default Disabled
Mode Interface Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree autoedge
Related
Commands
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 614
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE BPDU
spanning-tree bpdu
Overview Use this command to configure BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) discarding or
forwarding, when STP is disabled on the switch. This may be needed for correct STP
operation in complex networks.
There is no no variant for this command. Instead, apply the discard parameter to
reset it back to the default then re-enable STP with the command spanning-tree
enable.
Syntax spanning-tree bpdu
{discard|forward|forward-untagged-vlan|forward-vlan}
Default The discard parameter is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables the switch to forward unsupported BPDUs with an
unsupported Spanning Tree Protocol, such as proprietary STP protocols with
unsupported BPDUs, by forwarding BDPU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) frames
unchanged through the switch.
You must disable RSTP with the no spanning-tree rstp enable command before
you can use this command.
When you want to revert to default behavior on the switch, issue a spanning-tree
bdpu discard command and re-enable Spanning Tree with a spanning-tree rstp
enable command.
Parameter Description
bpdu A port that has BPDU filtering enabled will not transmit any BPDUs
and will ignore any BPDUs received. This port type has one of the
following parameters (in Global Configuration mode):
discard Discards all ingress STP BPDU frames.
forward Forwards any ingress STP BPDU packets to all ports,
regardless of any VLAN membership.
forward-
untagged-
vlan
Forwards any ingress STP BPDU frames to all ports
that are untagged members of the ingress port’s
native VLAN.
forward-
vlan Forwards any ingress STP BPDU frames to all ports
that are tagged members of the ingress port’s native
VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 615
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE BPDU
Examples To enable STP BPDU discard in Global Configuration mode with STP disabled,
which discards all ingress STP BPDU frames, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree rstp enable
awplus(config)# spanning-tree bpdu discard
To enable STP BPDU forward in Global Configuration mode with STP disabled,
which forwards any ingress STP BPDU frames to all ports regardless of any VLAN
membership, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree rstp enable
awplus(config)# spanning-tree bpdu forward
To enable STP BPDU forwarding for untagged frames in Global Configuration
mode with STP disabled, which forwards any ingress STP BPDU frames to all ports
that are untagged members of the ingress port’s native VLAN, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree rstp enable
awplus(config)# spanning-tree bpdu forward-untagged-vlan
To enable STP BPDU forwarding for tagged frames in Global Configuration mode
with STP disabled, which forwards any ingress STP BPDU frames to all ports that are
tagged members of the ingress port’s native VLAN, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree rstp enable
awplus(config)# spanning-tree bpdu forward-vlan
To reset STP BPDU back to the default discard parameter and re-enable RSTP on
the switch, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree bpdu discard
awplus(config)# spanning-tree rstp enable
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 616
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE CISCO-INTEROPERABILITY (MSTP)
spanning-tree cisco-interoperability (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to enable/disable Cisco-interoperability for MSTP.
Use this command for MSTP only.
Syntax spanning-tree cisco-interoperability {enable|disable}
Default If this command is not used, Cisco interoperability is disabled.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage For compatibility with certain Cisco devices, all devices in the switched LAN
running the AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System must have Cisco-interoperability
enabled. When the AlliedWare Plus Operating System is interoperating with Cisco,
the only criteria used to classify a region are the region name and revision level.
VLAN to instance mapping is not used to classify regions when interoperating with
Cisco.
Examples To enable Cisco interoperability on a Layer 2 device:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree cisco-interoperability enable
To disable Cisco interoperability on a Layer 2 device:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree cisco-interoperability disable
Parameter Description
enable Enable Cisco interoperability for MSTP.
disable Disable Cisco interoperability for MSTP.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 617
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE EDGEPORT (RSTP AND MSTP)
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)
Overview Use this command to set a port as an edge-port.
Use this command for RSTP or MSTP.
This command has the same effect as the spanning-tree portfast (STP) command,
but the configuration displays differently in the output of some show commands.
Use the no variant of this command to set a port to its default state (not an
edge-port).
Syntax spanning-tree edgeport
no spanning-tree edgeport
Default Not an edge port.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Use this command on a switch port connected to a LAN that has no other bridges
attached. If a BPDU is received on the port that indicates that another bridge is
connected to the LAN, then the port is no longer treated as an edge port.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree edgeport
Related
Commands
spanning-tree autoedge (RSTP and MSTP)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 618
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE ENABLE
spanning-tree enable
Overview Use this command in Global Configuration mode to enable the specified spanning
tree protocol for all switch ports. Note that this must be the spanning tree protocol
that is configured on the device by the spanning-tree mode command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the configured spanning tree
protocol. This places all switch ports in the forwarding state.
Syntax spanning-tree {mstp|rstp|stp} enable
no spanning-tree {mstp|rstp|stp} enable
Default RSTP is enabled by default for all switch ports.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage With no configuration, spanning tree is enabled, and the spanning tree mode is set
to RSTP. To change the mode, see spanning-tree mode command.
Examples To enable STP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree stp enable
To disable STP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree stp enable
To enable MSTP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mstp enable
To disable MSTP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree mstp enable
To enable RSTP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree rstp enable
Parameter Description
mstp Enables or disables MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol).
rstp Enables or disables RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol).
stp Enables or disables STP (Spanning Tree Protocol).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 619
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE ENABLE
To disable RSTP in Global Configuration mode, enter the below commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree rstp enable
Related
Commands
spanning-tree bpdu
spanning-tree mode

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 620
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE ERRDISABLE-TIMEOUT ENABLE
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
Overview Use this command to enable the errdisable-timeout facility, which sets a timeout
for ports that are disabled due to the BPDU guard feature.
Use this command for RSTP or MSTP.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the errdisable-timeout facility.
Syntax spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
no spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
Default By default, the errdisable-timeout is disabled.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The BPDU guard feature shuts down the port on receiving a BPDU on a
BPDU-guard enabled port. This command associates a timer with the feature such
that the port is re- enabled without manual intervention after a set interval. This
interval can be configured by the user using the spanning-tree errdisable-timeout
interval command.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 621
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE ERRDISABLE-TIMEOUT INTERVAL
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval
Overview Use this command to specify the time interval after which a port is brought back
up when it has been disabled by the BPDU guard feature.
Use this command for RSTP or MSTP.
Syntax spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval <10-1000000>
no spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval
Default By default, the port is re-enabled after 300 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree errdisable-timeout interval 34
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree errdisable-timeout enable
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
Parameter Description
<10-1000000> Specify the errdisable-timeout interval in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 622
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE FORCE-VERSION
spanning-tree force-version
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to force the protocol version for the switch port. Use this command for RSTP or
MSTP only.
Syntax spanning-tree force-version <version>
no spanning-tree force-version
Default By default, no version is forced for the port. The port is in the spanning tree mode
configured for the device, or a lower version if it automatically detects one.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Examples Set the value to enforce the spanning tree protocol (STP):
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree force-version 0
Set the default protocol version:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree force-version
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
Parameter Description
<version> <0-3> Version identifier.
0Forces the port to operate in STP mode.
1Not supported.
2Forces the port to operate in RSTP mode. If it receives STP
BPDUs, it can automatically revert to STP mode.
3Forces the port to operate in MSTP mode (this option is only
available if MSTP mode is configured). If it receives RSTP or
STP BPDUs, it can automatically revert to RSTP or STP mode.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 623
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE FORWARD-TIME
spanning-tree forward-time
Overview Use this command to set the forward delay value. Use the no variant of this
command to reset the forward delay value to the default setting of 15 seconds.
The forward delay sets the time (in seconds) to control how fast a port changes its
spanning tree state when moving towards the forwarding state. If the mode is set
to STP, the value determines how long the port stays in each of the listening and
learning states which precede the forwarding state. If the mode is set to RSTP or
MSTP, this value determines the maximum time taken to transition from
discarding to learning and from learning to forwarding.
This value is used only when the device is acting as the root bridge. Devices not
acting as the Root Bridge use a dynamic value for the forward delay set by the root
bridge. The forward delay, max-age, and hello time parameters are interrelated.
Syntax spanning-tree forward-time <forward-delay>
no spanning-tree forward-time
Default The default is 15 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The allowable range for forward-time is 4-30 seconds.
The forward delay, max-age, and hello time parameters should be set according
to the following formula, as specified in IEEE Standard 802.1d:
2 x (forward delay - 1.0 seconds) >= max-age
max-age >= 2 x (hello time + 1.0 seconds)
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree forward-time 6
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree forward-time
spanning-tree hello-time
spanning-tree mode
Parameter Description
<forward-delay> <4-30> The forwarding time delay in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 624
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE GUARD ROOT
spanning-tree guard root
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port only to enable
the Root Guard feature for the switch port. The root guard feature disables
reception of superior BPDUs. You can use this command for RSTP, STP or MSTP.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the root guard feature for the port.
Syntax spanning-tree guard root
no spanning-tree guard root
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage The Root Guard feature makes sure that the port on which it is enabled is a
designated port. If the Root Guard enabled port receives a superior BPDU, it goes
to a Listening state (for STP) or discarding state (for RSTP and MSTP).
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 625
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE HELLO-TIME
spanning-tree hello-time
Overview Use this command to set the hello-time. This sets the time in seconds between the
transmission of device spanning tree configuration information when the device is
the Root Bridge of the spanning tree or is trying to become the Root Bridge.
Use this command for RSTP, STP or MSTP.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default of the hello time.
Syntax spanning-tree hello-time <hello-time>
no spanning-tree hello-time
Default Default is 2 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration for switch ports.
Usage The allowable range of values is 1-10 seconds.
The forward delay, max-age, and hello time parameters should be set according to
the following formula, as specified in IEEE Standard 802.1d:
2 x (forward delay - 1.0 seconds) >= max-age
max-age>= 2 x (hello time + 1.0 seconds)
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree hello-time 3
Related
Commands
spanning-tree forward-time
spanning-tree max-age
show spanning-tree
Parameter Description
<hello-time><1-10> The hello BPDU interval in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 626
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE LINK-TYPE
spanning-tree link-type
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to enable or disable point-to-point or shared link types on the switch port.
Use this command for RSTP or MSTP only.
Use the no variant of this command to return the port to the default link type.
Syntax spanning-tree link-type {point-to-point|shared}
no spanning-tree link-type
Default The default link type is point-to-point.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage You may want to set link type to shared if the port is connected to a hub with
multiple devices connected to it.
Examples awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree link-type point-to-point
Parameter Description
shared Disable rapid transition.
point-to-point Enable rapid transition.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 627
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MAX-AGE
spanning-tree max-age
Overview Use this command to set the max-age. This sets the maximum age, in seconds, that
dynamic spanning tree configuration information is stored in the device before it
is discarded.
Use this command for RSTP, STP or MSTP.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default of max-age.
Syntax spanning-tree max-age <max-age>
no spanning-tree max-age
Default The default of spanning-tree max-age is 20 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Max-age is the maximum time in seconds for which a message is considered valid.
Configure this value sufficiently high, so that a frame generated by the root bridge
can be propagated to the leaf nodes without exceeding the max-age.
The forward delay, max-age, and hello time parameters should be set according
to the following formula, as specified in IEEE Standard 802.1d:
2 x (forward delay - 1.0 seconds) >= max-age
max-age >= 2 x (hello time + 1.0 seconds)
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree max-age 12
Related
Commands
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree forward-time
spanning-tree hello-time
Parameter Description
<max-age><6-40> The maximum time, in seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 628
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MAX-HOPS (MSTP)
spanning-tree max-hops (MSTP)
Overview Use this command to specify the maximum allowed hops for a BPDU in an MST
region. This parameter is used by all the instances of the MST region.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default.
Use this command for MSTP only.
Syntax spanning-tree max-hops <hop-count>
no spanning-tree max-hops <hop-count>
Default The default max-hops in a MST region is 20.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Specifying the max hops for a BPDU prevents the messages from looping
indefinitely in the network. The hop count is decremented by each receiving port.
When a device receives an MST BPDU that has a hop count of zero, it discards the
BPDU.
Examples awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree max-hops 25
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no spanning-tree max-hops
Parameter Description
<hop-count> Specify the maximum hops the BPDU will be valid for in the range
<1-40>.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 629
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MODE
spanning-tree mode
Overview Use this command to change the spanning tree protocol mode on the device. The
spanning tree protocol mode on the device can be configured to either STP, RSTP
or MSTP.
Syntax spanning-tree mode {stp|rstp|mstp}
Default The default spanning tree protocol mode on the device is RSTP.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage With no configuration, the device will have spanning tree enabled, and the
spanning tree mode will be set to RSTP. Use this command to change the spanning
tree protocol mode on the device. MSTP is VLAN aware, but RSTP and STP are not
VLAN aware. To enable or disable spanning tree operation, see the spanning-tree
enable command.
Examples To change the spanning tree mode from the default of RSTP to MSTP, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mode mstp
Related
Commands
spanning-tree enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 630
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST CONFIGURATION
spanning-tree mst configuration
Overview Use this command to enter the MST Configuration mode to configure the Multiple
Spanning-Tree Protocol.
Syntax spanning-tree mst configuration
Mode Global Configuration
Examples The following example uses this command to enter MST Configuration mode. Note
the change in the command prompt.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree mst configuration
awplus(config-mst)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 631
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE
spanning-tree mst instance
Overview Use this command to assign a Multiple Spanning Tree instance (MSTI) to a switch
port or channel group.
Note that ports are automatically configured to send and receive spanning-tree
information for the associated MSTI when VLANs are assigned to MSTIs using the
instance vlan (MSTP) command.
Use the no variant of this command in Interface Configuration mode to remove the
MSTI from the specified switch port or channel group.
Syntax spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id>
no spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id>
Default A port automatically becomes a member of an MSTI when it is assigned to a VLAN.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port or channel group.
Usage You can disable automatic configuration of member ports of a VLAN to an
associated MSTI by using a no spanning-tree mst instance command to remove
the member port from the MSTI. Use the spanning-tree mst instance command
to add a VLAN member port back to the MSTI.
Examples To assign instance 3 to a switch port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree mst instance 3
To remove instance 3 from a switch port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree mst instance 3
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
spanning-tree mst instance priority
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15. The MST instance must
have already been created using the instance vlan (MSTP)
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 632
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE PATH-COST
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
Overview Use this command to set the cost of a path associated with a switch port, for the
specified MSTI.
This specifies the switch port’s contribution to the cost of a path to the MSTI
regional root via that port. This applies when the port is the root port for the MSTI.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default cost value of the path.
Syntax spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> path-cost <path-cost>
no spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> path-cost
Default The default path cost values and the range of recommended path cost values
depend on the port speed, as shown in the following table from the IEEE
802.1q-2003 standard.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage Before you can use this command to set a path-cost in a VLAN configuration, you
must explicitly add an MST instance to a port using the spanning-tree mst instance
command.
Examples To set a path cost of 1000 on instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree mst instance 3 path-cost 1000
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<path-cost> Specify the cost of path in the range of <1-200000000>, where
a lower path-cost indicates a greater likelihood of the specific
interface becoming a root.
Port speed Default path cost Recommended path cost range
Less than 100 Kb/s
1Mbps
10Mbps
100 Mbps
1 Gbps
10 Gbps
100 Gbps
1Tbps
10 Tbps
200,000,000
20,000,000
2,000,000
200,000
20,000
2,000
200
20
2
20,000,000-200,000,000
2,000,000-20,000,000
200,000-2,000,000
20,000-200,000
2,000-20,000
200-2,000
20-200
2-200
2-20

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 633
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE PATH-COST
To return the path cost to its default value on instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree mst instance 3 path-cost
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
spanning-tree mst instance
spanning-tree mst instance priority
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 634
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE PRIORITY
spanning-tree mst instance priority
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to set the port priority for an MST instance (MSTI).
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default priority value (128).
Syntax spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> priority <priority>
no spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> [priority]
Default The default is 128.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface.
Usage This command sets the value of the priority field contained in the port identifier.
The MST algorithm uses the port priority when determining the root port for the
switch in the MSTI. The port with the lowest value has the highest priority, so it will
be chosen as root port over a port that is equivalent in all other aspects but with a
higher priority value.
Examples To set the priority to 112 on instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree mst instance 3 priority 112
To return the priority to its default value of 128 on instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree mst instance 3 priority
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
spanning-tree priority (port priority)
spanning-tree mst instance
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15.
<priority>This must be a multiple of 16 and within the range <0-240>. A
lower priority indicates greater likelihood of the port becoming
the root port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 635
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE RESTRICTED-ROLE
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to enable the restricted role for an MSTI (Multiple Spanning Tree Instance) on a
switch port. Configuring the restricted role for an MSTI on a switch port prevents
the switch port from becoming the root port in a spanning tree topology.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the restricted role for an MSTI on a
switch port. Removing the restricted role for an MSTI on a switch port allows the
switch port to become the root port in a spanning tree topology.
Syntax spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> restricted-role
no spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> restricted-role
Default The restricted role for an MSTI instance on a switch port is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage The root port is the port providing the best path from the bridge to the root bridge.
Use this command to disable a port from becoming a root port. Use the no variant
of this command to enable a port to become a root port. See the STP Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide for root port information.
Examples To prevent a switch port from becoming the root port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree mst instance 3 restricted-role
To stop preventing the switch port from becoming the root port, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree mst instance 3
restricted-role
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15. The MST instance must
have already been created using the instance vlan (MSTP)
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 636
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE RESTRICTED-ROLE
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
spanning-tree priority (port priority)
spanning-tree mst instance
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 637
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE MST INSTANCE RESTRICTED-TCN
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-tcn
Overview Use this command to prevent a switch port from propagating received topology
change notifications and topology changes to other switch ports. This is named
restricted TCN (Topology Change Notification). A TCN is a simple Bridge Protocol
Data Unit (BPDU) that a bridge sends out to its root port to signal a topology
change.
Use the no variant of this command to stop preventing the switch port from
propagating received topology change notifications and topology changes to
other switch ports for the specified MSTI (Multiple Spanning Tree Instance).
The restricted TCN setting applies only to the specified MSTI (Multiple Spanning
Tree Instance).
Syntax spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> restricted-tcn
no spanning-tree mst instance <instance-id> restricted-tcn
Default Disabled. By default, switch ports propagate TCNs.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Examples To prevent a switch port from propagating received topology change notifications
and topology changes to other switch ports, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree mst instance 3 restricted-tcn
To stop preventing a switch port from propagating received topology change
notifications and topology changes to other switch ports, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no spanning-tree mst instance 3
restricted-tcn
Related
Commands
instance vlan (MSTP)
spanning-tree priority (port priority)
spanning-tree mst instance
spanning-tree mst instance path-cost
spanning-tree mst instance restricted-role
Parameter Description
<instance-id>Specify an MSTP instance in the range 1-15. The MST instance must
have already been created using the instance vlan (MSTP)
command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 638
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PATH-COST
spanning-tree path-cost
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to set the cost of a path for the specified port. This value then combines with others
along the path to the root bridge in order to determine the total cost path value
from the particular port, to the root bridge. The lower the numeric value, the
higher the priority of the path. This applies when the port is the root port.
Use this command for RSTP, STP or MSTP. When MSTP mode is configured, this will
apply to the port’s path cost for the CIST.
Syntax spanning-tree path-cost <pathcost>
no spanning-tree path-cost
Default The default path cost values and the range of recommended path cost values
depend on the port speed, as shown in the following table from the IEEE
802.1q-2003 and IEEE 802.1d-2004 standards.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for switch port interface only.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree path-cost 123
Parameter Description
<pathcost><1-200000000> The cost to be assigned to the port.
Port speed Default path cost Recommended path cost range
Less than 100 Kb/s
1Mbps
10Mbps
100 Mbps
1 Gbps
10 Gbps
100 Gbps
1Tbps
10 Tbps
200,000,000
20,000,000
2,000,000
200,000
20,000
2,000
200
20
2
20,000,000-200,000,000
2,000,000-20,000,000
200,000-2,000,000
20,000-200,000
2,000-20,000
200-2, 000
20-200
2-200
2-20

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 639
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST (STP)
spanning-tree portfast (STP)
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to set a port as an edge-port. The portfast feature enables a port to rapidly move
to the forwarding state, without having first to pass through the intermediate
spanning tree states. This command has the same effect as the spanning-tree
edgeport (RSTP and MSTP) command, but the configuration displays differently in
the output of some show commands.
NOTE: You can run either of two additional parameters with this command. To simplify
the syntax these are documented as separate commands. See the following additional
portfast commands:
•spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter command
•spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard command.
You can obtain the same effect by running the spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and
MSTP) command. However, the configuration output may display differently in
some show commands.
Use the no variant of this command to set a port to its default state (not an
edge-port).
Syntax spanning-tree portfast
no spanning-tree portfast
Default Not an edge port.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage Portfast makes a port move from a blocking state to a forwarding state, bypassing
both listening and learning states. The portfast feature is meant to be used for
ports connected to end-user devices. Enabling portfast on ports that are
connected to a workstation or server allows devices to connect to the network
without waiting for spanning-tree to converge.
For example, you may need hosts to receive a DHCP address quickly and waiting
for STP to converge would cause the DHCP request to time out. Ensure you do not
use portfast on any ports connected to another device to avoid creating a
spanning-tree loop on the network.
Use this command on a switch port that connects to a LAN with no other bridges
attached. An edge port should never receive BPDUs. Therefore if an edge port
receives a BPDU, the portfast feature takes one of three actions.
• Cease to act as an edge port and pass BPDUs as a member of a spanning tree
network (spanning-tree portfast (STP) command disabled).
• Filter out the BPDUs and pass only the data and continue to act as a edge
port (spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter command enabled).
• Block the port to all BPDUs and data (spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
command enabled).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 640
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST (STP)
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Related
Commands
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 641
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST BPDU-FILTER
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
Overview This command sets the bpdu-filter feature and applies a filter to any BPDUs (Bridge
Protocol Data Units) received. Enabling this feature ensures that configured ports
will not transmit any BPDUs and will ignore (filter out) any BPDUs received. BPDU
Filter is not enabled on a port by default.
Using the no variant of this command to turn off the bpdu-filter, but retain the
port’s status as an enabled port. If the port then receives a BPDU it will change its
role from an edge-port to a non edge-port.
Syntax (Global
Configuration) spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
no spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
Syntax (Interface
Configuration) spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
{default|disable|enable}
no spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
Default BPDU Filter is not enabled on any ports by default.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration
Usage This command filters the BPDUs and passes only data to continue to act as an edge
port. Using this command in Global Configuration mode applies the portfast
bpdu-filter feature to all ports on the device. Using it in Interface mode applies the
feature to a specific port, or range of ports.The command will operate in both RSTP
and MSTP networks.
Use the show spanning-tree command to display status of the bpdu-filter
parameter for the switch ports.
Example To enable STP BPDU filtering in Global Configuration mode, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter
Parameter Description
bpdu-filter A port that has bpdu-filter enabled will not transmit any BPDUs and
will ignore any BPDUs received. This port type has one of the
following parameters (in Interface Configuration mode):
default Takes the setting that has been configured for the whole
device, i.e. the setting made from the Global
configuration mode.
disable Turns off BPDU filter.
enable Turns on BPDU filter.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 642
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST BPDU-FILTER
To enable STP BPDU filtering in Interface Configuration mode, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter enable
Related
Commands
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree portfast (STP)
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 643
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST BPDU-GUARD
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
Overview This command applies a BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) guard to the port. A port
with the bpdu-guard feature enabled will block all traffic (BPDUs and user data), if
it starts receiving BPDUs.
Use this command in Global Configuration mode to apply BPDU guard to all ports
on the device. Use this command in Interface mode for an individual interface or a
range of interfaces specified. BPDU Guard is not enabled on a port by default.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the BPDU Guard feature on a device
in Global Configuration mode or to disable the BPDU Guard feature on a port in
Interface mode.
Syntax (Global
Configuration) spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
no spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
Syntax (Interface
Configuration) spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
{default|disable|enable}
no spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
Default BPDU Guard is not enabled on any ports by default.
Mode Global Configuration or Interface Configuration
Usage This command blocks the port(s) to all devices and data when enabled. BPDU
Guard is a port-security feature that changes how a portfast-enabled port behaves
if it receives a BPDU. When bpdu-guard is set, then the port shuts down if it
receives a BPDU. It does not process the BPDU as it is considered suspicious. When
bpdu-guard is not set, then the port will negotiate spanning-tree with the device
sending the BPDUs. By default, bpdu- guard is not enabled on a port.
You can configure a port disabled by the bpdu-guard to re-enable itself after a
specific time interval. This interval is set with the spanning-tree errdisable-timeout
interval command. If you do not use the errdisable-timeout feature, then you will
need to manually re-enable the port by using the no shutdown command.
Parameter Description
bpdu-guard A port that has bpdu-guard turned on will enter the STP blocking state
if it receives a BPDU. This port type has one of the following
parameters (in Interface Configuration mode):
default Takes the setting that has been configured for the whole
device, i.e. the setting made from the Global configuration
mode.
disable Turns off BPDU guard.
enable Turns on BPDU guard and will also set the port as an edge
port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 644
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PORTFAST BPDU-GUARD
Use the show spanning-tree command to display the device and port
configurations for the BPDU Guard feature. It shows both the administratively
configured and currently running values of bpdu-guard.
Example To enable STP BPDU guard in Global Configuration mode, enter the below
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard
To enable STP BPDU guard in Interface Configuration mode, enter the below
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpdu-guard enable
Related
Commands
spanning-tree edgeport (RSTP and MSTP)
show spanning-tree
spanning-tree portfast (STP)
spanning-tree portfast bpdu-filter

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 645
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PRIORITY (BRIDGE PRIORITY)
spanning-tree priority (bridge priority)
Overview Use this command to set the bridge priority for the device. A lower priority value
indicates a greater likelihood of the device becoming the root bridge.
Use this command for RSTP, STP or MSTP. When MSTP mode is configured, this will
apply to the CIST.
Use the no variant of this command to reset it to the default.
Syntax spanning-tree priority <priority>
no spanning-tree priority
Default The default priority is 32678.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage To force a particular device to become the root bridge use a lower value than other
devices in the spanning tree.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree priority 4096
Related
Commands
spanning-tree mst instance priority
show spanning-tree
Parameter Description
<priority><0-61440> The bridge priority, which will be rounded to a multiple of
4096.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 646
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE PRIORITY (PORT PRIORITY)
spanning-tree priority (port priority)
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to set the port priority for port. A lower priority value indicates a greater likelihood
of the port becoming part of the active topology.
Use this command for RSTP, STP, or MSTP. When the device is in MSTP mode, this
will apply to the CIST.
Use the no variant of this command to reset it to the default.
Syntax spanning-tree priority <priority>
no spanning-tree priority
Default The default priority is 128.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Usage To force a port to be part of the active topology (for instance, become the root port
or a designated port) use a lower value than other ports on the device. (This
behavior is subject to network topology, and more significant factors, such as
bridge ID.)
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree priority 16
Related
Commands
spanning-tree mst instance priority
spanning-tree priority (bridge priority)
show spanning-tree
Parameter Description
<priority><0-240>, in increments of 16. The port priority, which will be rounded
down to a multiple of 16.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 647
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE RESTRICTED-ROLE
spanning-tree restricted-role
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to restrict the port from becoming a root port.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the restricted role functionality.
Syntax spanning-tree restricted-role
no spanning-tree restricted-role
Default The restricted role is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree restricted-role

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 648
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE RESTRICTED-TCN
spanning-tree restricted-tcn
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only
to prevent TCN (Topology Change Notification) BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data
Units) from being sent on a port. If this command is enabled, after a topology
change a bridge is prevented from sending a TCN to its designated bridge.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the restricted TCN functionality.
Syntax spanning-tree restricted-tcn
no spanning-tree restricted-tcn
Default The restricted TCN is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a switch port interface only.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree restricted-tcn

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 649
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SPANNING TREE COMMANDS
SPANNING-TREE TRANSMIT-HOLDCOUNT
spanning-tree transmit-holdcount
Overview Use this command to set the maximum number of BPDU transmissions that are
held back.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default transmit hold-count
value.
Syntax spanning-tree transmit-holdcount
no spanning-tree transmit-holdcount
Default Transmit hold-count default is 3.
Mode Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# spanning-tree transmit-holdcount

18
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 651
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Unidirectional Link
Detection (UDLD)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
the Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) protocol.
UDLD is a data link protocol which monitors network cables and detects broken
bidirectional links. It complements the spanning tree protocol (STP), which is used
to eliminate Layer 2 loops.
A license is required to use this feature. Please contact your authorized Allied
Telesis representative for more information.
Command List •“debug udld” on page 652
•“show debugging udld” on page 653
•“show udld” on page 654
•“show udld neighbors” on page 655
•“show udld port” on page 656
•“udld aggressive-mode” on page 657
•“udld enable” on page 658
•“udld port” on page 659
•“udld port aggressive-mode” on page 660
•“udld port disable” on page 661
•“udld reset” on page 662
•“udld time disable-period” on page 663
•“udld time message-interval” on page 664
•“undebug udld” on page 665

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 652
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
DEBUG UDLD
debug udld
Overview Use this command to enable UDLD debugging.
Use the no variant of this command to disable UDLD debugging.
Syntax debug udld [info|pkt|state|nsm|all]
no debug udld [info|pkt|state|nsm|all]
Default Debugging is disabled for all by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Privileged Exec
Example To enable UDLD packet debugging, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug udld pkt
Related
Commands
show debugging udld
undebug udld
Parameter Description
info Enable or disable general UDLD debugging information.
pkt Enable or disable debugging of UDLD packets.
state Enable or disable UDLD state transition debugging.
nsm Enable or disable UDLD Network Service Module (NSM)
debugging information.
all Enable or disable the all UDLD debugging.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 653
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING UDLD
show debugging udld
Overview Use this command to show which UDLD debugging options are set.
Syntax show debugging udld
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show which UDLD debugging options are set, use the command:
awplus# show debugging udld
Output Figure 18-1: Example output from show debugging udld
Related
Commands
debug udld
awplus# show debugging udld
UDLD debugging status:
Info debugging : off
Packet debugging: off
State debugging : on
NSM debugging : off

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 654
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
SHOW UDLD
show udld
Overview Use this command to display global UDLD status and configuration settings.
Syntax show udld
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show global UDLD information, use the command:
awplus# show udld
Output Figure 18-2: Example output from show udld
Related
Commands
udld port
udld port disable
udld enable
awplus#show udld
Status : Enabled
Mode : Normal
Message-Interval: 7 seconds
Timeout-Interval: 5 seconds
Disable-Period : 15 seconds
[Fiber-Ports]
Port Status Mode Directional-State
------------ -------- ---------- -----------------
port1.0.1 Enabled Aggressive Bidirectional
port1.0.2 Disabled Normal -

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 655
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
SHOW UDLD NEIGHBORS
show udld neighbors
Overview Use this command to display UDLD neighbor status.
Syntax show udld neighbors [<interface-name>] [detail]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show UDLD information for all neighbors, use the command:
awplus# show udld neighbors
To show detailed UDLD neighbor information for port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show udld neighbours port1.0.1 detail
Output Figure 18-3: Example output from show udld neighbors
Figure 18-4: Example output from show udld neighbor port1.0.1 detail
Related
Commands
udld port
udld port disable
udld enable
Parameter Description
<interface-name>Show UDLD neighbor information for a specified interface.
detail This option provides a greater level of detail.
awplus#show udld neighbors
Port Device-ID Port-ID Device-Name Neighbor-State
----------- ------------ ------------ ------------- --------------
port1.0.1 0000F4272DA2 port2.0.1 X930 Bidirectional
port1.0.2 0000F5572632 port1.0.15 X610 Bidirectional
awplus# show udld neighbor port1.0.1 detail
[port1.0.1]
Device-ID : 0000F4272DA2
Port-ID : port2.0.1
Device-Name : X930
Operational-State: Bidirectional
Expiration-time : 35 seconds
Message-Interval : 15 seconds
Timeout-Interval : 5 seconds
Neighbors in Echo:
Device-ID Port-ID
------------ ------------
0000F4272DA2 port2.0.1
0000F5572632 port1.0.15

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 656
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
SHOW UDLD PORT
show udld port
Overview Use this command to display UDLD port status and configuration settings.
Syntax show udld port [<interface-name>] [detail]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show UDLD information for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show udld port
To show detailed UDLD information for port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show udld port port1.0.1 detail
Output Figure 18-5: Example output from show udld port
Figure 18-6: Example output from show udld port port1.0.1 detail
Related
Commands
udld port
udld port disable
udld enable
Parameter Description
<interface-name>Show UDLD information for a specified interface.
detail This option provides a greater level of detail.
awplus#show udld port
Port Status Mode Directional-State
------------ -------- ---------- -----------------
port1.0.1 Enabled Aggressive Bidirectional
port1.0.2 Disabled Normal -
awplus#show udld port port1.0.1 detail
[port1.0.1]
Status : Enabled
Mode : Aggressive
Directional-State: Bidirectional
Operational-State: Advertisement - single neighbor detected
Neighbors:
Device-ID Port-ID Device-Name Directional-State
------------ ------------ ---------------- -----------------
0000F4272DA2 port2.0.1 awplus Bidirectional

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 657
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD AGGRESSIVE-MODE
udld aggressive-mode
Overview Use this command to set UDLD to aggressive mode on all interfaces.
In normal mode, when the UDLD information times out:
• No action is taken by UDLD.
• The UDLD port state is set to undetermined.
• The port behaves according to its STP state.
In aggressive mode, when the UDLD information times out:
• UDLD tries to re-establish the state of the port.
• If not successful, after 8 retries, the port is disabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable aggressive mode on all interfaces.
Syntax udld aggressive-mode
no udld aggressive-mode
Default Aggressive mode is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable aggressive mode on interfaces, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# udld aggressive-mode
To disable aggressive mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no udld aggressive-mode
Related
Commands
udld port aggressive-mode
show udld

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 658
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD ENABLE
udld enable
Overview Use this command to enable UDLD on all of a device’s fiber-optic ports. It has no
effect on copper ports. Use the udld port command to enable UDLD on copper
ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the UDLD feature on all of a device’s
fiber interfaces.
Syntax udld enable
no udld enable
Default UDLD is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the UDLD feature on all fiber interfaces, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# udld enable
Related
Commands
show udld
show udld neighbors
udld aggressive-mode
udld port
udld port disable
udld reset
udld time disable-period
udld time message-interval

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 659
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD PORT
udld port
Overview Use this command to enable UDLD on an interface.This command enables UDLD
on both copper and fiber ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable UDLD on an interface.
Syntax udld port
no udld port
Default UDLD is disabled on an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage • This command always enables the UDLD feature on a port.
•The udld port disable command overwrites this command and disables
UDLD on an interface.
• If UDLD has been set globally, using the udld enable command, then
AlliedWare Plus ignores the no udld port command on a fiber interface.
Example To enable UDLD on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# udld port
To disable UDLD on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no udld port
Related
Commands
show udld port
show udld neighbors
udld enable
udld port disable
udld reset
udld time disable-period
udld time message-interval

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 660
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD PORT AGGRESSIVE-MODE
udld port aggressive-mode
Overview Use this command to enable UDLD aggressive mode on an interface.
In normal mode, when the UDLD information times out:
• No action is taken by UDLD.
• The UDLD port state is set to undetermined.
• The port behaves according to its STP state.
In aggressive mode, when the UDLD information times out:
• UDLD tries to re-establish the state of the port.
• If not successful, after 8 retries, the port is disabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable aggressive mode on an interface.
Syntax udld port aggressive-mode
no udld port aggressive-mode
Default Aggressive mode is disabled on an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To change the UDLD mode to aggressive on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# udld port aggressive-mode
To disable aggressive mode on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no port aggressive-mode
Related
Commands
udld aggressive-mode
show udld port

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 661
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD PORT DISABLE
udld port disable
Overview Use this command to disable UDLD on an interface. This command disables UDLD
on both copper and fiber ports
Use the no variant of this command to allow UDLD on a fiber port.
Syntax udld port disable
no udld port disable
Default UDLD disable is not set by default.
Usage • This command always disables the UDLD feature on a port.
•The udld port command overwrites this command and enables UDLD on an
interface.
• If UDLD has been set globally, using the udld enable command, then
AlliedWare Plus ignores the no udld port command on a fiber interface.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To disable UDLD on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# udld port disable
To enable UDLD on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no udld port disable
Related
Commands
udld enable
udld port
show udld port

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 662
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD RESET
udld reset
Overview Use this command to reset the status of any interface disabled by UDLD.
Syntax udld reset
Mode Global Configuration
Example To reset an interface that has been disabled by UDLD, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# udld reset
Output Figure 18-7: Example output from udld reset, when 2 ports are disabled
Figure 18-8: Example output from udld reset, when no ports are disabled
Related
Commands
show udld
udld enable
awplus#udld reset
2 ports disabled by udld reset
awplus#udld reset
No ports are disabled by udld reset

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 663
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD TIME DISABLE-PERIOD
udld time disable-period
Overview Use this command to set the UDLD disable period on all interfaces. The disable
period is the time (in seconds) that a port is marked disabled before UDLD
attempts to recheck it.
Manually reset the UDLD status of a port using the udld reset command.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the disable period to infinite.
Syntax udld time disable-period <seconds>
no udld time disable-period
Default The default time disable period is infinite.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To change the UDLD disable period to 60 sec on all interfaces, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# udld time disable-period 60
To reset the disable period to infinite, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no udld time disable-period
Related
Commands
udld enable
udld port
show udld
Parameter Description
<seconds>30-86400
Specify the disable period in seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 664
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
UNIDIRECTIONAL LINK DETECTION (UDLD) COMMANDS
UDLD TIME MESSAGE-INTERVAL
udld time message-interval
Overview Use this command to set the UDLD message send interval on all interfaces.
This is the time, in seconds, between UDLD probe messages.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the message send interval to 15
seconds.
Syntax udld time message-interval <seconds>
no udld time message-interval
Default The default message send interval is 15 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To change UDLD message sending interval to 30 sec on all interfaces, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# udld time message-interval 30
To reset the message sending interval to 15 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no udld time message-interval
Related
Commands
udld enable
udld port
show udld
Parameter Description
<seconds>7-90
Specify the message send interval in seconds.

19
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 666
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Link Aggregation
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure a
static channel group (static aggregator) and dynamic channel group (LACP
channel group, etherchannel or LACP aggregator). Link aggregation is also
sometimes referred to as channeling.
NOTE: AlliedWare Plus™ supports IEEE 802.3ad link aggregation and uses the Link
Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). LACP does not interoperate with devices that use
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP).
Link aggregation does not necessarily achieve exact load balancing across the links.
The load sharing algorithm is designed to ensure that any given data flow always goes
down the same link. It also aims to spread data flows across the links as evenly as
possible.
For example, for a 2 Gbps LAG that is a combination of two 1 Gbps ports, any one flow
of traffic can only ever reach a maximum throughput of 1 Gbps. However, the hashing
algorithm should spread the flows across the links so that when many flows are
operating, the full 2 Gbps can be utilized.
For information about load balancing see the platform load-balancing command.
For a description of static and dynamic link aggregation (LACP), and configuration
examples, see the Link Aggregation Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“channel-group” on page 668
•“clear lacp counters” on page 670
•“debug lacp” on page 671
•“lacp global-passive-mode enable” on page 672
•“lacp port-priority” on page 673
•“lacp system-priority” on page 674
•“lacp timeout” on page 675
•“platform load-balancing” on page 677

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 667
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
•“show debugging lacp” on page 678
•“show diagnostic channel-group” on page 679
•“show etherchannel” on page 681
•“show etherchannel detail” on page 682
•“show etherchannel summary” on page 683
•“show lacp sys-id” on page 684
•“show lacp-counter” on page 685
•“show port etherchannel” on page 686
•“show static-channel-group” on page 687
•“static-channel-group” on page 688
•“undebug lacp” on page 690

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 668
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
CHANNEL-GROUP
channel-group
Overview Use this command to create a dynamic channel group, or to add a port to an
existing dynamic channel group.
You can create up to 128 channel groups, in any combination of static and
dynamic (LACP) groups. This means you can create up to 128 dynamic channel
groups, if you have no static channel groups.
Use the no variant of this command to turn off link aggregation on the device port.
You will be returned to Global Configuration mode from Interface Configuration
mode.
Syntax channel-group <dynamic-channel-group-number> mode
{active|passive}
no channel-group
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage All the device ports in a channel-group must belong to the same VLANs, have the
same tagging status, and can only be operated on as a group. All device ports
within a channel group must have the same port speed and be in full duplex mode.
Once the LACP channel group has been created, it is treated as a device port. You
can specify it in other commands. If you are specifying it in:
• an LACP command, then use the channel-group number on its own. For
example, use the command show etherchannel 2 to show details about
channel group 2.
• a non-LACP command, then use po followed by the channel-group number.
For example, use the command show interface po2 to show details about
channel group 2's interface.
For more information about LACP, see the Link Aggregation Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide which is available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Parameter Description
<dynamic-channel-
group-number><1-248> Dynamic channel group number for an LACP link.
You can create up to 128 dynamic channel groups,
numbered in the range 1-248.
active Enables initiation of LACP negotiation on a port. The port
will transmit LACP dialogue messages whether or not it
receives them from the partner device.
passive Disables initiation of LACP negotiation on a port. The port
will only transmit LACP dialogue messages if the partner
device is transmitting them, i.e., the partner is in the active
mode.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 669
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
CHANNEL-GROUP
Examples To add device port1.0.2 to a newly created LACP channel group 2, in active mode,
use the commands below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# channel-group 2 mode active
To remove device port1.0.2 from any created LACP channel groups, use the
command below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no channel-group
To reference channel group 2 as an interface, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface po2
awplus(config-if)#
Related
Commands
show etherchannel
show etherchannel detail
show etherchannel summary
show port etherchannel
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: Ability added to create up to 128 groups as any combination of
static and dynamic channel groups. Also, numbering changed to 1-248.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 670
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
CLEAR LACP COUNTERS
clear lacp counters
Overview Use this command to clear all counters of all present LACP aggregators (channel
groups) or a given LACP aggregator.
Syntax clear lacp [<1-248>] counters
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear lacp 2 counters
Parameter Description
<1-248>Channel-group number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 671
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
DEBUG LACP
debug lacp
Overview Use this command to enable all LACP troubleshooting functions.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this function.
Syntax debug lacp {all|cli|event|ha|packet|sync|timer[detail]}
no debug lacp {all|cli|event|ha|packet|sync|timer[detail]}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples awplus# debug lacp timer detail
awplus# debug lacp all
Related
Commands
show debugging lacp
undebug lacp
Parameter Description
all Turn on all debugging for LACP.
cli Specifies debugging for CLI messages.
Echoes commands to the console.
event Specifies debugging for LACP events.
Echoes events to the console.
ha Specifies debugging for HA (High Availability) events.
Echoes High Availability events to the console.
packet Specifies debugging for LACP packets.
Echoes packet contents to the console.
sync Specified debugging for LACP synchronization.
Echoes synchronization to the console.
timer Specifies debugging for LACP timer.
Echoes timer expiry to the console.
detail Optional parameter for LACP timer-detail.
Echoes timer start/stop details to the console.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 672
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
LACP GLOBAL-PASSIVE-MODE ENABLE
lacp global-passive-mode enable
Overview Use this command to enable LACP channel-groups to dynamically self-configure
when they are connected to another device that has LACP channel-groups
configured with Active Mode.
Syntax lacp global-passive-mode enable
no lacp global-passive-mode enable
Default Enabled
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Do not mix LACP configurations (manual and dynamic). When LACP global passive
mode is turned on (by using the lacp global-passive-mode enable command),
we do not recommend using a mixed configuration in a LACP channel-group; i.e.
some links are manually configured (by the channel-group command) and others
are dynamically learned in the same channel-group.
Example To enable global passive mode for LACP channel groups, use the command:
awplus(config)# lacp global-passive-mode enable
To disable global passive mode for LACP channel groups, use the command:
awplus(config)# no lacp global-passive-mode enable
Related
Commands
show etherchannel
show etherchannel detail

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 673
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
LACP PORT-PRIORITY
lacp port-priority
Overview Use this command to set the priority of a device port. Ports are selected for
aggregation based on their priority, with the higher priority (numerically lower)
ports selected first.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the priority of port to the default.
Syntax lacp port-priority <1-65535>
no lacp port-priority
Default The default is 32768.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lacp port-priority 34
Parameter Description
<1-65535> Specify the LACP port priority.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 674
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
LACP SYSTEM-PRIORITY
lacp system-priority
Overview Use this command to set the system priority of a local system. This is used in
determining the system responsible for resolving conflicts in the choice of
aggregation groups.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the system priority of the local system
to the default.
Syntax lacp system-priority <1-65535>
no lacp system-priority
Default The default is 32768.
Mode Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lacp system-priority 6700
Parameter Description
<1-65535> LACP system priority. Lower numerical values have higher priorities.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 675
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
LACP TIMEOUT
lacp timeout
Overview Use this command to set the short or long timeout on a port. Ports will time out of
the aggregation if three consecutive updates are lost.
Syntax lacp timeout {short|long}
Default The default is long timeout (30 seconds).
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage This command enables the device to indicate the rate at which it expects to receive
LACPDUs from its neighbor.
If the timeout is set to long, then the device expects to receive an update every 30
seconds, and this will time a port out of the aggregation if no updates are seen for
90 seconds (i.e. 3 consecutive updates are lost).
If the timeout is set to short, then the device expects to receive an update every
second, and this will time a port a port out of the aggregation if no updates are
seen for 3 seconds (i.e. 3 consecutive updates are lost).
The device indicates its preference by means of the Timeout field in the Actor
section of its LACPDUs. If the Timeout field is set to 1, then the device has set the
short timeout. If the Timeout field is set to 0, then the device has set the long
timeout.
Setting the short timeout enables the device to be more responsive to
communication failure on a link, and does not add too much processing overhead
to the device (1 packet per second).
NOTE: It is not possible to configure the rate that the device sends LACPDUs; the device
must send at the rate which the neighbor indicates it expects to receive LACPDUs.
Examples The following commands set the LACP long timeout period for 30 seconds on
port1.0.2.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lacp timeout long
Parameter Description
timeout Number of seconds before invalidating a received LACP data unit
(DU).
short LACP short timeout. The short timeout value is 1 second.
long LACP long timeout. The long timeout value is 30 seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 676
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
LACP TIMEOUT
The following commands set the LACP short timeout for 1 second on port1.0.2.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lacp timeout short
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 677
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
PLATFORM LOAD-BALANCING
platform load-balancing
Overview This command selects which address fields are used as inputs into the load
balancing algorithm for aggregated links. The output from this algorithm is used
to select which individual path a given packet will traverse within an aggregated
link.
The no variant of this command applies its default setting.
Syntax platform load-balancing {src-dst-mac|src-dst-ip}
no platform load-balancing
Default The default is src-dst-ip.
Mode Global configuration
Examples To set the load balancing algorithm to include only Layer 2 MAC addresses, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform load-balancing src-dst-mac
To set the load balancing algorithm to include only Layer 3 IP addresses and Layer
4 ports, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform load-balancing src-dst-ip
Related
Commands
show platform
Parameter Description
src-dst-mac Include the source and destination MAC addresses (Layer 2)
src-dst-ip Include the source and destination IP addresses (Layer 3) and
UDP/TCP source and destination ports.
If you choose this option, the algorithm will use MAC addresses
to calculate load balancing for Layer 2 and non-IP packets.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 678
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING LACP
show debugging lacp
Overview Use this command to display the LACP debugging option set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging lacp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show debugging lacp
Output Figure 19-1: Example output from the show debugging lacp command
Related
Commands
debug lacp
LACP debugging status:
LACP timer debugging is on
LACP timer-detail debugging is on
LACP cli debugging is on
LACP packet debugging is on
LACP event debugging is on
LACP sync debugging is on
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 679
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW DIAGNOSTIC CHANNEL-GROUP
show diagnostic channel-group
Overview This command displays dynamic and static channel group interface status
information. The output of this command is useful for Allied Telesis authorized
service personnel for diagnostic purposes.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show diagnostic channel-group
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show diagnostic channel-group
Output Figure 19-2: Example output from the show diagnostic channel-group
command
awplus#show diagnostic channel-group
Channel Group Info based on NSM:
Note: Pos - position in hardware table
-------------------------------------------------------------
Dev Interface IfIndex Member port IfIndex Active Pos
-------------------------------------------------------------
sa3 4503 port1.0.15 5015 No
sa3 4503 port1.0.18 5018 No
po1 4601 port1.0.7 5007 No
po1 4601 port1.0.8 5008 No
po1 4601 port1.0.9 5009 No
Channel Group Info based on HSL:
Note: Pos - position in hardware table
-------------------------------------------------------------
Dev Interface IfIndex Member port IfIndex Active Pos
-------------------------------------------------------------
sa3 4503 N/a
po1 4601 N/a
Channel Group Info based on IPIFWD:
Note: Pos - position in hardware table
-------------------------------------------------------------
Dev Interface IfIndex Member port IfIndex Active Pos
-------------------------------------------------------------
sa3 4503 N/a
po1 4601 N/a

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 680
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW DIAGNOSTIC CHANNEL-GROUP
Related
Commands
show tech-support
Channel Group Info based on HW:
Note: Pos - position in hardware table
Only entries from first device are displayed.
-------------------------------------------------------------
Dev Interface IfIndex Member port IfIndex Active Pos
-------------------------------------------------------------
sa3 4503 N/a
po1 4601 N/a
No error found

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 681
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERCHANNEL
show etherchannel
Overview Use this command to display information about an LACP channel specified by the
channel group number.
The command output also shows the thrash limiting status. If thrash limiting is
detected and the action parameter of the thrash-limiting command is set to
vlan-disable, the output will also show the VLANs on which thrashing is detected.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show etherchannel [<1-248>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show etherchannel
Output Figure 19-3: Example output from show etherchannel
Example awplus# show etherchannel 1
Output Figure 19-4: Example output from show etherchannel for a particular channel
Parameter Description
<1-248>Channel-group number.
awplus#show etherchannel
LAG Maximum : 128
LAG Static Count : 0
LAG Dynamic Count : 1
LAG Total Count : 1
Lacp Aggregator: po1
Member:
port1.0.1
port1.0.2
awplus#show etherchannel 1
Aggregator po1 (4601)
Mac address: 00:00:00:00:00:00
Admin Key: 0001 - Oper Key 0000
Receive link count: 0 - Transmit link count: 0
Individual: 0 - Ready: 0
Partner LAG: 0x0000,00-00-00-00-00-00
Link: port1.0.1 (5001) disabled
Link: port1.0.2 (5002) disabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 682
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERCHANNEL DETAIL
show etherchannel detail
Overview Use this command to display detailed information about all LACP channels.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show etherchannel detail
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show etherchannel detail
Output Example output from show etherchannel detail
awplus#show etherchannel detail
Aggregator po1 (IfIndex: 4601)
Mac address: 00:00:cd:37:05:17
Admin Key: 0001 - Oper Key 0001
Receive link count: 2 - Transmit link count: 2
Individual: 0 - Ready: 1
Partner LAG: 0x8000,00-00-cd-37-02-9a,0x0001
Link: port1.0.1 (IfIndex: 8002) synchronized
Link: port1.0.2 (IfIndex: 20002) synchronized
Aggregator po2 (IfIndex: 4602)
Mac address: 00:00:cd:37:05:17
Admin Key: 0002 - Oper Key 0002
Receive link count: 2 - Transmit link count: 2
Individual: 0 - Ready: 1
Partner LAG: 0x8000,ec-cd-6d-aa-c8-56,0x0002
Link: port1.0.3 (IfIndex: 8001) synchronized
Link: port1.0.4 (IfIndex: 20001) synchronized
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 683
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW ETHERCHANNEL SUMMARY
show etherchannel summary
Overview Use this command to display a summary of all LACP channels.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show etherchannel summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show etherchannel summary
Output Example output from show etherchannel summary
awplus#show etherchannel summary
Aggregator po10 (IfIndex: 4610)
Admin Key: 0010 - Oper Key 0010
Link: port1.0.1 (IfIndex: 7007) synchronized
Link: port1.0.2 (IfIndex: 8007) synchronized
Link: port1.0.3 (IfIndex: 11007) synchronized

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 684
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW LACP SYS-ID
show lacp sys-id
Overview Use this command to display the LACP system ID and priority.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show lacp sys-id
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show lacp sys-id
Output Example output from show lacp sys-id
System Priority: 0x8000 (32768)
MAC Address: 0200.0034.5684

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 685
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW LACP-COUNTER
show lacp-counter
Overview Use this command to display the packet traffic on all ports of all present LACP
aggregators, or a given LACP aggregator.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show lacp-counter [<1-248>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show lacp-counter 2
Output Example output from show lacp-counter
Parameter Description
<1-248>Channel-group number.
% Traffic statistics
Port LACPDUs Marker Pckt err
Sent Recv Sent Recv Sent Recv
% Aggregator po2 (IfIndex: 4604)
port1.0.2 0 0 0 0 0 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 686
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW PORT ETHERCHANNEL
show port etherchannel
Overview Use this command to show LACP details of the device port specified.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show port etherchannel <port>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show port etherchannel port1.0.2
Output Example output from show port etherchannel
Parameter Description
<port> Name of the device port to display LACP information about.
awplus#show port etherchannel port1.0.2
LACP link info: port1.0.2 - 7007
Link: port1.0.2 (IfIndex: 7007)
Aggregator: po10 (IfIndex: 4610)
Receive machine state: Current
Periodic Transmission machine state: Slow periodic
Mux machine state: Collecting/Distributing
Actor Information: Partner Information:
Selected ................. Selected Partner Sys Priority ....... 0x8000
Physical Admin Key .............. 2 Partner System .. ec-cd-6d-d1-64-d0
Port Key ....................... 10 Port Key ....................... 10
Port Priority ............... 32768 Port Priority ............... 32768
Port Number .................. 7007 Port Number .................. 5001
Mode ....................... Active Mode ....................... Active
Timeout ...................... Long Timeout ...................... Long
Individual .................... Yes Individual .................... Yes
Synchronised .................. Yes Synchronised .................. Yes
Collecting .................... Yes Collecting .................... Yes
Distributing .................. Yes Distributing .................. Yes
Defaulted ...................... No Defaulted ...................... No
Expired ........................ No Expired ........................ No

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 687
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
SHOW STATIC-CHANNEL-GROUP
show static-channel-group
Overview Use this command to display all configured static channel groups and their
corresponding member ports. Note that a static channel group is the same as a
static aggregator.
The command output also shows the thrash limiting status. If thrash limiting is
detected and the action parameter of the thrash-limiting command is set to
vlan-disable, the output will also show the VLANs on which thrashing is detected.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide, which is
available on our website at alliedtelesis.com.
Syntax show static-channel-group
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show static-channel-group
Output Example output from show static-channel-group
Related
Commands
static-channel-group
% LAG Maximum : 128
% LAG Static Count : 2
% LAG Dynamic Count : 0
% LAG Total Count : 2
% Static Aggregator: sa2
% Member:
port1.0.1
port1.0.2
% Static Aggregator: sa3
% Member:
port1.0.3
port1.0.4
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 688
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
STATIC-CHANNEL-GROUP
static-channel-group
Overview Use this command to create a static channel group, or to add a port to an existing
static channel group. Static channel groups are also known as static aggregators.
You can create up to 128 channel groups, in any combination of static and
dynamic (LACP) groups. This means you can create up to 128 static channel
groups, if you have no dynamic channel groups.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the device port from the static
channel group.
Syntax static-channel-group <static-channel-group-number>
no static-channel-group
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage This command adds the device port to the static channel group with the specified
channel group number. If the channel group does not exist, it is created, and the
port is added to it. The no prefix detaches the port from the static channel group.
If the port is the last member to be removed, the static channel group is deleted.
All the ports in a channel group must have the same VLAN configuration: they
must belong to the same VLANs and have the same tagging status, and can only
be operated on as a group.
Once the static channel group has been created, it is treated as a device port. You
can specify it in other commands by using sa followed by the channel-group
number. For example, use the command show interface sa2 to show details
about channel group 2's interface:
Examples To define static channel group 2 on port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# static-channel-group 2
To reference static channel group 2 as an interface, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface sa2
awplus(config-if)#
Related
Commands
show static-channel-group
Parameter Description
<static-channel-
group-number> <1-248> Static channel group number.
You can create up to 128 static channel groups, numbered in
the range 1-248.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 689
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LINK AGGREGATION COMMANDS
STATIC-CHANNEL-GROUP
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: Ability added to create up to 128 groups as any combination of
static and dynamic channel groups. Also, numbering changed to 1-248.

20
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 691
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Power over
Ethernet
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter contains an alphabetical list of commands used to configure Power
over Ethernet (PoE). Each command contains a functional description and shows
examples of configuration and output screens for show commands. These
commands are only supported on PoE capable ports. An error message will display
on the console if you enter a PoE command on a port that does not support PoE.
The following documents offer further information for configuring PoE on
AlliedWare Plus switches.
•the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
•the Support for Allied Telesis Enterprise_MIBs_in AlliedWare Plus, for
information about which PoE MIB objects are supported.
•the SNMP Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide, for information about
SNMP traps.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology allowing devices such as security
cameras to receive power over LAN cabling.
The Powered Device (PD) referred to throughout this chapter is a PoE or PoE+
powered device, such as an IP phone or a Wireless Access Point (WAP).
Command List •“clear power-inline counters interface” on page 693
•“debug power-inline” on page 694
•“power-inline allow-legacy” on page 696
•“power-inline description” on page 697
•“power-inline enable” on page 698
•“power-inline max” on page 699
•“power-inline priority” on page 701
•“power-inline usage-threshold” on page 703
•“service power-inline” on page 704

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 692
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
•“show debugging power-inline” on page 705
•“show power-inline” on page 706
•“show power-inline counters” on page 709
•“show power-inline interface” on page 711
•“show power-inline interface detail” on page 714
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 693
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
CLEAR POWER-INLINE COUNTERS INTERFACE
clear power-inline counters interface
Overview This command will clear the counters from a specified port, a range of ports, or all
ports on the switch. If no ports are entered then PoE counters for all ports are
cleared. It will also clear all Power over Ethernet (PoE) counters supported by the
Power Ethernet MIB (RFC 3621).
Syntax clear power-inline counters interface [<port-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The PoE counters are displayed with the show power-inline counters command.
Examples To clear the PoE counters for port1.0.2 only, use the following command:
awplus# clear power-inline counters interface port1.0.2
To clear the PoE counters for port1.0.5 through port1.0.8, use the following
command:
awplus# clear power-inline counters interface
port1.0.5-port1.0.8
To clear the PoE counters for all ports, use the following command:
awplus# clear power-inline counters interface
Related
Commands
show power-inline counters
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Parameter Description
<port-list>Selects the port or ports whose counters are to be cleared.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 694
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
DEBUG POWER-INLINE
debug power-inline
Overview This command enables debugging display for messages that are specific to Power
over Ethernet (PoE).
Use the no variant of this command to disable the specified PoE debugging
messages.
Syntax debug power-inline [all|event|info|power]
no debug power-inline [all|event|info|power]
Default No debug messages are enabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use the terminal monitor command to display PoE debug messages on the
console.
Use the show debugging power-inline command to show the PoE debug
configuration.
Examples To enable PoE debugging and start the display of PoE event and info debug
messages on the console, use the following commands:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# debug power-inline event info
To enable PoE debugging and start the display of all PoE debugging messages on
the console, use the following commands:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# debug power-inline all
To stop the display of PoE info debug messages on the console, use the following
command:
awplus# no debug power-inline info
To disable all PoE debugging and stop the display of any PoE debugging messages
on the console, use the following command:
awplus# no debug power-inline all
Parameter Description
all Displays all (event, info, nsm, power) debug messages.
event Displays event debug information, showing any error conditions
that may occur during PoE operation.
info Displays informational level debug information, showing high-level
essential debugging, such as information about message types.
power Displays power management debug information.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 696
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE ALLOW-LEGACY
power-inline allow-legacy
Overview This command enables detection of pre-IEEE 802.3af Power Ethernet standard
legacy Powered Devices (PDs).
The no variant of this command disables detection of pre-IEEE 802.3af Power
Ethernet standard legacy Powered Devices (PDs).
Syntax power-inline allow-legacy
no power-inline allow-legacy
Default Detection of legacy PDs is disabled on all ports
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable detection of legacy PDs, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# power-inline allow-legacy
To disable detection of legacy PDs, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no power-inline allow-legacy
Validation
Commands
show power-inline
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.9-0.1: default changed to “disabled”
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 697
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE DESCRIPTION
power-inline description
Overview This command adds a description for a Powered Device (PD) connected to a PoE
port.
The no variant of this command clears a previously entered description for a
connected PD, resetting the PD description to the default (null).
Syntax power-inline description <pd-description>
no power-inline description
Default No description for a connected PD is set by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Select a PoE port, a list of PoE ports, or a range of PoE ports with the preceding
interface (to configure) command. If you specify a range or list of ports they must
all be PoE capable ports.
Examples To add the description “Desk Phone” for a connected PD on port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# power-inline description Desk Phone
To clear the description for the connected PD on port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no power-inline description
Related
Commands
show power-inline interface
show running-config <power-inline>
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Parameter Description
<pd-description>Description of the PD connected to the PoE capable port
(with a maximum 256 character string limit per PD
description).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 698
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE ENABLE
power-inline enable
Overview This command enables Power over Ethernet (PoE) to detect a connected Powered
Device (PD) and supply power.
The no variant of this command disables PoE functionality on the selected PoE
port(s). No power is supplied to a connected PD after PoE is disabled on the
selected PoE port(s).
Ports still provide Ethernet connectivity after PoE is disabled.
Syntax power-inline enable
no power-inline enable
Default PoE is enabled by default on all ports
Mode Interface Configuration for one or more ports.
Usage No PoE log messages are generated for ports on which PoE is disabled.
Examples To disable PoE on port1.0.1 to port1.0.4, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# no power-inline enable
To enable PoE on port1.0.1 to port1.0.4, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# power-inline enable
Related
Commands
show power-inline
show power-inline interface
show power-inline interface detail
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 699
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE MAX
power-inline max
Overview This command sets the maximum power allocated to a Power over an Ethernet
(PoE and PoE+) port. The amount of power actually supplied to the port depends
on the power requirements of the connected PD. It is also a function of the total
PoE power loading on the switch and the PoE priority set for the port by the
power-inline priority command. However this command (power-inline max) does
apply a maximum value to the power that the port is able to supply.
Note that the value set by this command will be the figure the switch will use when
apportioning the power budget for its ports. For example, if 15.4 W is assigned to
a port whose PD only consumes 5 W, the switch will reserve the full 15.4 W for this
port when determining its total power PoE power requirement.
The no variant of this command sets the maximum power supplied to a PoE port
to the default, which is set to the maximum power limit for the class of the
connected Powered Device (PD).
Syntax power-inline max <4000-30000>
no power-inline max
Default The switch supplies the maximum power limit for the class of the PD connected to
the port by default.
NOTE: See the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for further information
about power classes.
Mode Interface Configuration for one or more ports. If you specify a range or list of ports,
they must all be PoE capable ports.
Usage If you select a range of PoE ports in Interface Configuration mode before issuing
this command, then each port in the range selected will have the same maximum
power value configured. If the PoE port attempts to draw more than the maximum
power, this is logged and all power is removed.
Note that the value entered is rounded up to the next value supported by the
hardware. The actual value used is displayed after you enter the command, such as
in the following sample console output:
Parameter Description
<4000-30000>The maximum power supplied to a PoE port in milliwatts
(mW).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 700
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE MAX
See the LLDP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for information about
power monitoring at the PD.
Note the difference in power supplied from the PSE to the power available at the
PD due to line loss.
See the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for further information
about the difference between the power supplied from the PSE and the power
available at the PD.
Examples To set the maximum power supplied to ports in the range port1.0.1 to port1.0.4 to
6450mW per port, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# power-inline max 6450
To clear the user-configured maximum power supplied to port1.0.1, and revert to
using the default maximum power, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no power-inline max
Related
Commands
show power-inline interface
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)#power-line max 5300
% The maximum power has been rounded to 5450mW in hardware.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 701
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE PRIORITY
power-inline priority
Overview This command sets the Power over Ethernet (PoE) priority level of a PoE port to one
of three available priority levels:
•low
•high
•critical
The no variant of this command restores the PoE port priority to the default (low).
Syntax power-inline priority {low|high|critical}
no power-inline priority
Default The default priority is low for all PoE ports
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage Select a PoE port, a list of PoE ports, or a range of PoE ports with the preceding
interface (to configure) command. If you specify a range or list of ports they must
all be PoE capable ports.
PoE ports with higher priorities are given power before PoE ports with lower
priorities. If the priorities for two PoE ports are the same then the lower numbered
PoE port is given power before the higher numbered PoE port.
See the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for further information
about PoE priority.
Examples To set the priority level to high on port1.0.1 to port1.0.4, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# power-inline priority high
Parameter Description
low The lowest priority for a PoE enabled port (default). PoE ports
set to low only receive power if all the PoE ports assigned to
the other two levels are already receiving power.
high The second highest priority for a PoE enabled port. PoE ports
set to high receive power only if all the ports set to critical
are already receiving power.
critical The highest priority for a PoE enabled port. PoE ports set to
critical are guaranteed power before any ports assigned to
the other two priority levels. Ports assigned to the other
priority levels receive power only if all critical ports are
receiving power.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 702
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE PRIORITY
To reset the priority level to the default of low on port1.0.1 to port1.0.4, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# no power-inline priority
Related
Commands
power-inline usage-threshold
show power-inline
show power-inline interface
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 703
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
POWER-INLINE USAGE-THRESHOLD
power-inline usage-threshold
Overview This command sets the level at which the switch will issue a message that the
power supplied to all Powered Devices (PDs) has reached a critical level of the
nominal power rating for the switch. The level is set as a percentage of total
available power.
The no variant of this command resets the notification usage-threshold to the
default (80% of the nominal power rating).
Syntax power-inline usage-threshold <1-99>
no power-inline usage-threshold
Default The default power usage threshold is 80% of the nominal power rating
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use the snmp-server enable trap command to configure SNMP notification. An
SNMP notification is sent when the usage-threshold, as configured in the example,
is exceeded.
Examples To generate SNMP notifications when power supplied exceeds 70% of the nominal
power rating, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server enable trap power-inline
awplus(config)# power-inline usage-threshold 70
To reset the notification threshold to the default (80% of the nominal power
rating), use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no power-inline usage-threshold
Related
Commands
snmp-server enable trap
show power-inline interface
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Parameter Description
<1-99>The usage-threshold percentage configured with this
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 704
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SERVICE POWER-INLINE
service power-inline
Overview This command enables Power over Ethernet (PoE) globally on the switch, for all
PoE ports.
Syntax service power-inline
no service power-inline
Default PoE functionality is enabled by default
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To disable PoE, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service power-inline
To re-enable PoE, if PoE has been disabled, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service power-inline
Related
Commands
show power-inline
show running-config power-inline
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 705
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING POWER-INLINE
show debugging power-inline
Overview This command displays Power over Ethernet (PoE) debug settings.
Syntax show debugging power-inline
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display PoE debug settings, use the following command:
awplus# show debugging power-inline
Output Figure 20-1: Example output from the show debugging power-inline
command
Related
Commands
debug power-inline
terminal monitor
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
awplus#show debugging power-inline
PoE Debugging status:
PoE Informational debugging is disabled
PoE Event debugging is disabled
PoE Power Management debugging is disabled
PoE NSM debugging is enabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 706
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE
show power-inline
Overview This command displays the Power over Ethernet (PoE) status for all ports.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show power-inline
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the PoE status for all ports, use the following command:
awplus# show power-inline
Output Figure 20-2: Example output from show power-inline.
awplus#show power-inline
PoE Status:
Nominal Power: 247W
Power Allocated: 15W
Actual Power Consumption: 2W
Operational Status: On
Power Usage Threshold: 80% (198W)
Detection of legacy devices is enabled
RPS Boost Mode: Disabled
Power management mode: Static
PoE Interface:
Interface Admin Pri Oper Power Device Class Max
(mW) (mW)
port1.0.1 Enabled Low Off 0 n/a n/a n/a
port1.0.2 Enabled Low Off 0 n/a n/a n/a
port1.0.3 Enabled Low Off 0 n/a n/a n/a
port1.0.4 Enabled Low Powered 2427 n/a 0 15400 [C]
....
Table 1: Parameters in the show power-inline command output
Parameter Description
Nominal Power The nominal power available on the switch in watts (W).
Power Allocated The current power allocated in watts (W) that is available to
be drawn by any connected Powered Devices (PDs). This is
updated every 5 seconds.
Actual Power
Consumption
The current power consumption in watts (W) drawn by all
connected Powered Devices (PDs). This is updated every 5
seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 707
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE
Operational Status The operational status of the PSU hardware when this
command was issued:
•On if the PSU is installed and switched on.
•Off when the PSU is switched off (an RPS may be
connected to the switch to power PoE instead of the
PSU).
•Fault when there is an issue with the PSU hardware.
Power Usage Threshold
(%)
The configured SNMP trap / log threshold, as configured
from a power-inline usage-threshold command.
Power management
mode: Static
Indicates that PoE power is allocated statically. By default,
each port is allocated the maximum amount of power that
is required for the power class of the PD that is attached to
that port. Alternatively, you can use the power-inline max
command to specify the maximum for a port.
Interface The PoE port(s) in the format portx.y.z, where x is the device
number, y is the module number within the device, and z is
the PoE port number within the module.
Admin The administrative state of PoE on a PoE port, either
Enabled or Disabled.
Pri The current PoE priorities for PoE ports, as configured using
the power-inline priority command:
•Low is the lowest priority (this is the default).
•High is the second highest priority.
•Crit (critical) is the highest priority.
If the switch cannot supply all ports, it will supply critical
ports, then high-priority ports, then low-priority ports.
Oper The current PoE port state when this command was issued:
•Powered displays if there is a PD connected and power
is being supplied.
•Denied displays if supplying power would make the
switch go over the power budget.
•Off displays if the port is not supplying power but has
not been denied power by the switch. This is the default
state for ports that are not connected to a PD.
•Disabled displays if the PoE port is administratively
disabled.
•Syncing displays if PoE is still initializing the port when
you issue the command.
•Fault displays if there is a problem with PoE on the port.
•Unknown displays if PoE cannot determine the state of
the port.
Table 1: Parameters in the show power-inline command output (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 708
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE
Related
Commands
show power-inline counters
show power-inline interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Power The power consumption in milliwatts (mW) for the PoE
port when this command was entered.
Device The description of the connected PD device if a description
has been added with the power-inline description
command. No description is shown for PDs not configured
with the power-inline description command.
Class The class of the connected PD, if power is being supplied to
the PD.
Max (mW) The power in milliwatts (mW) allocated for the PoE port.
Additionally, note the following as displayed per PoE port:
•[U] if the power limit for a port was user configured (with
the power-inline max command).
•[L] if the power limit for a port was supplied by LLDP.
•[C] if the power limit for a port was supplied by the PD
class.
Table 1: Parameters in the show power-inline command output (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 709
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE COUNTERS
show power-inline counters
Overview This command displays Power over Ethernet (PoE) event counters for ports on the
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE). The PoE event counters displayed can also be
accessed by objects in the PoE MIB (RFC 3621). See the MIB Objects Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide for information about which PoE MIB objects
are supported.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show power-inline counters [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display all PoE event counters for all PoE ports, use the command:
awplus# show power-inline counters
To display the PoE event counters for the port range 1.0.1 to 1.0.3, use the
command:
awplus# show power-inline counters interface port1.0.1-1.0.3
Output Figure 20-3: Example output from the show power-inline counters command
Parameter Description
<port-list>Enter the PoE port(s) to display PoE event counters for them.
awplus#show power-inline counters interface port1.0.4-port1.0.12
PoE Counters:
Interface MPSAbsent Overload Short Invalid Denied
port1.0.4 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.5 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.6 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.7 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.8 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.9 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.10 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.11 0 0 0 0 0
port1.0.12 0 0 0 0 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 710
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE COUNTERS
Related
Commands
clear power-inline counters interface
show power-inline
show power-inline interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
Table 2: Parameters in the show power-inline counters command output
Parameter Description
Interface The PoE port(s) in the format portx.y.z, where x is the device
number, y is the module number within the device, and z is the
PoE port number within the module.
MPSAbsent The number of instances when the PoE MPS (Maintain Power
Signature) signal has been lost. The PoE MPS signal is lost when a
PD is disconnected from the PSE. Also increments
pethPsePortMPSAbsentCounter in the PoE MIB.
Overload The number of instances when a PD exceeds its configured power
limit (as configured by the power-inline max command). Also
increments pethPsePortOverLoadCounter in the PoE MIB.
Short The number of short circuits that have happened with a PD. Also
increments pethPsePortShortCounter in the PoE MIB.
Invalid The number of times a PD with an Invalid Signature (where the PD
has an open or short circuit, or is a legacy PD) is detected. Also
increments pethPseInvalidSignatureCounter in the PoE
MIB.
Denied The number of times a PD has been refused power due to power
budget limitations for the PSE. Also increments
pethPsePortPowerDeniedCounter in the PoE MIB.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 711
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE INTERFACE
show power-inline interface
Overview This command displays a summary of Power over Ethernet (PoE) information for
specified ports. If no ports are specified then PoE information is displayed for all
ports.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show power-inline interface [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the PoE port-specific information for all PoE ports on the switch, use the
following command:
awplus# show power-inline interface
To display the PoE port specific information for the port range1.0.1 to 1.0.4, use the
following command:
awplus# show power-inline interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
Output Figure 20-4: Example output from show power-inline interface
Parameter Description
<port-list>Enter the PoE port(s) to display PoE specific information in the show
output.
awplus#show power-inline interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
Interface Admin Pri Oper Power Device Class Max(mW)
port1.0.1 Disabled Low Disabled 0 n/a n/a n/a
port1.0.2 Enabled High Powered 3840 Desk Phone 1 5000 [U]
port1.0.3 Enabled Crit Powered 6720 AccessPoint 2 7000 [C]
port1.0.4 Disabled Low Disabled 0 n/a n/a n/a
Table 3: Parameters in show power-inline interface output
Parameter Description
Interface The PoE port(s) in the format portx.y.z, where x is the device
number, y is the module number within the device, and z is the
PoE port number within the module.
Admin The administrative state of PoE on a PoE port, either Enabled or
Disabled.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 712
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show power-inline
show power-inline interface detail
Pri The current PoE priorities for PoE ports on the PSE, as configured
from a power-inline priority command:
•Low displays when the low parameter is issued. The lowest
priority for a PoE enabled port (default).
•High displays when the high parameter is issued. The
second highest priority for a PoE enabled port.
•Crit displays when the critical parameter is issued. The
highest priority for a PoE enabled port.
Oper The current PoE port state when this command was issued:
•Powered displays if there is a PD connected and power is
being supplied.
•Denied displays if supplying power would make the switch
go over the power budget.
•Off displays if the port is not supplying power but has not
been denied power by the switch. This is the default state for
ports that are not connected to a PD.
•Disabled displays if the PoE port is administratively disabled.
•Syncing displays if PoE is still initializing the port when you
issue the command.
•Fault displays if there is a problem with PoE on the port.
•Unknown displays if PoE cannot determine the state of the
port.
Power The power consumption in milliwatts (mW) for the PoE port
when this command was entered.
Device The description of the connected PD device if a description has
been added with the power-inline description command. No
description is shown for PDs not configured with the
power-inline description command.
Class The class of the connected PD, if power is being supplied to the
PD from the PSE.
See the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for
further information about power classes.
Max (mW) The power in milliwatts (mW) allocated for the PoE port.
Additionally, note the following is displayed per PoE port:
•[U] if the power limit for a port was user configured (with the
power-inline max command).
•[L] if the power limit for a port was supplied by LLDP.
•[C] if the power limit for a port was supplied by the PD class.
Table 3: Parameters in show power-inline interface output (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 713
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE INTERFACE
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x550 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 714
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE INTERFACE DETAIL
show power-inline interface detail
Overview This command displays detailed information for one or more Power over Ethernet
(PoE) ports.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show power-inline interface [<port-list>] detail
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage The power allocated to each port is listed in the Power allocated row, and is
limited by the maximum power per Powered Device (PD) class, or a user
configured power limit.
Examples To display detailed PoE port specific information for the port range 1.0.1 to 1.0.3,
use the command:
awplus# show power-inline interface port1.0.1-1.0.3 detail
Output Figure 20-5: Example output from show power-inline interface detail
Parameter Description
<port-list>Enter the PoE port(s) to display information about only the specified
port or ports.
awplus#show power-inline interface port1.0.2 detail
Interface port1.0.2
Powered device type: Access Point #3
PoE admin: on
Configured Priority: Low
Actual Priority: Low
Detection status: Powered
Current power consumption: 6720 mW
Powered device class: 2
Power allocated: 7000 mW (from powered device class)
Detection of legacy devices is enabled
Powered pairs: Data
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 715
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
POWER OVER ETHERNET COMMANDS
SHOW POWER-INLINE INTERFACE DETAIL
Table 4: Parameters in show power-inline interface detail output
Parameter Description
Interface The PoE port(s) in the format portx.y.z, where x is the device
number, y is the module number within the device, and z is the
PoE port number within the module.
Powered
device type: The name of the PD, if connected and if power is being supplied
to the PD from the PSE, configured with the power-inline
description command. n/a displays if a description has not been
configured for the PD.
PoE admin The administrative state of PoE on a PoE capable port, either
Enabled or Disabled as configured from the power-inline enable
command or the no power-inline enable command
respectively.
Priority The PoE priority of a port, which is either Low, or High, or
Critical, as configured by the power-inline priority command.
Detection
status: The current PSE PoE port state when this command was issued:
•Powered displays when there is a PD connected and power is
being supplied from the PSE.
•Denied displays when supplying power would make the PSE
go over the power budget.
•Disabled displays when the PoE port is administratively
disabled.
•Off displays when PoE has been disabled for the port.
•Fault displays when a PSE goes over its power allocation.
Current power
consumption: The power consumption for the PoE port when this command
was entered. Note that the power consumption may have
changed since the command was entered and the power is
displayed.
Powered
device class: The class of the connected PD if connected, and if power is being
supplied to the PD from the PSE.
See the PoE Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for
further information about power classes.
Power
allocated: The power in milliwatts (mW) allocated for the PoE port.
Additionally, note the following as displayed per PoE port:
•[U] if the power limit for a port was user configured (with the
power-inline max command).
•[L] if the power limit for a port was supplied by LLDP.
•[C] if the power limit for a port was supplied by the PD class.
Detection of
legacy
devices is
The status of legacy PoE detection on the PoE port (enabled or
disabled), as configured for the PoE port with the power-inline
allow-legacy command. Legacy detection involves measuring for
a large capacitance value to confirm the presence of a legacy PD.
Powered
pairs: The IEEE 802.3af and IEEE 802.3at standards allow for either data
or spare twisted pairs to be used to transfer power to a PD.

21
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 717
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP Commands
Introduction
Overview With GVRP enabled the switch can exchange VLAN configuration information with
other GVRP enabled switches. VLANs can be dynamically created and managed
through trunk ports.
• There is a limit of 400 VLANs supported by the AlliedWare Plus GVRP
implementation. VLANs may be numbered 1-4094, but a limit of 400 of these
VLANs are supported.
• MSTP is not supported by the AlliedWare Plus GVRP implementation. GVRP
and MSTP are mutually exclusive. STP and RSTP are supported by GVRP.
This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
GVRP. For information about GVRP, including configuration, see the GVRP Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“clear gvrp statistics” on page 718
•“debug gvrp” on page 719
•“gvrp (interface)” on page 721
•“gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation” on page 722
•“gvrp enable (global)” on page 723
•“gvrp registration” on page 724
•“gvrp timer” on page 725
•“show debugging gvrp” on page 726
•“show gvrp configuration” on page 727
•“show gvrp machine” on page 728
•“show gvrp statistics” on page 729
•“show gvrp timer” on page 730

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 718
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
CLEAR GVRP STATISTICS
clear gvrp statistics
Overview Use this command to clear the GVRP statistics for all switchports, or for a specific
switchport.
Syntax clear gvrp statistics {all|<interface>}
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command together with the show gvrp statistics command to
troubleshoot GVRP.
Examples To clear all GVRP statistics for all switchport on the switch, enter the command:
awplus# clear gvrp statistics all
Related
Commands
show gvrp statistics
Parameter Description
all Specify all switchports to clear GVRP statistics.
<interface>Specify the switchport to clear GVRP statistics.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 719
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
DEBUG GVRP
debug gvrp
Overview Use this command to debug GVRP packets and commands, sending output to the
console.
Use the no variant of this command to turn off debugging for GVRP packets and
commands.
Syntax debug gvrp {all|cli|event|packet}
no debug gvrp {all|cli|event|packet}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To send debug output to the console for GVRP packets and GVRP commands, and
to enable the display of debug output on the console first, enter the commands:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug gvrp all
To send debug output for GVRP packets to the console, enter the commands:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug gvrp packets
To send debug output for GVRP commands to the console, enter the commands:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug gvrp cli
To stop sending debug output for GVRP packets and GVRP commands to the
console, and to stop the display of any debug output on the console, enter the
commands:
awplus# terminal no monitor
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no debug gvrp all
Parameter Description
all Specifies debugging for all levels.
cli Specifies debugging for commands.
event Specified debugging for events.
packet Specifies debugging for packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 721
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
GVRP (INTERFACE)
gvrp (interface)
Overview Use this command to enable GVRP for switchport interfaces.
Use the no variant of this command to disable GVRP for switchport interfaces.
Syntax gvrp
no gvrp
Mode Interface Configuration (for switchport interfaces).
Default Disabled by default.
Usage Use this command to enable GVRP on switchport interfaces. Note this command
does not enable GVRP for the switch. To enable GVRP on switchports use this
command in Interface Configuration mode. You must issue a gvrp enable (global)
command before issuing a gvrp (interface) command.
You must enable GVRP on both ends of a link for GVRP to propagate VLANs
between links.
NOTE: MSTP is not supported by the current AlliedWare Plus GVRP implementation.
GVRP and MSTP are mutually exclusive. STP and RSTP are supported by GVRP.
Private VLAN trunk ports are not supported by the current AlliedWare Plus GVRP
implementation. GVRP and private VLAN trunk ports are mutually exclusive.
Validation
Commands
show gvrp configuration
Related
Commands
gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
gvrp enable (global)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 722
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
GVRP DYNAMIC-VLAN-CREATION
gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
Overview Use this command to enable dynamic VLAN creation globally for the switch.
Use the no variant of this command to disable dynamic VLAN creation globally for
the switch.
Syntax gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
no gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
Mode Global Configuration
Default Disabled by default.
Usage You must enable GVRP on both ends of a link for GVRP to propagate VLANs
between links.
You must also enable GVRP globally in Global Configuration mode before enabling
GVRP on an interface in Interface Configuration mode. Both of these tasks must
occur to create VLANs.
NOTE: There is limit of 400 VLANs supported by the AlliedWare Plus GVRP
implementation. VLANs may be numbered 1-4094, but a limit of 400 of these VLANs are
supported.
Examples Enter the following commands for switches with hostnames switch1 and
switch2 respectively, so switch1 propagates VLANs to switch2 and
switch2 propagates VLANs to switch1:
Switch1:
switch1# configure terminal
switch1(config)# gvrp enable
switch1(config)# gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
Switch2:
switch2# configure terminal
switch2(config)# gvrp enable
switch2(config)# gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
To disable GVRP dynamic VLAN creation on the switch, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation
Validation
Commands
show gvrp configuration
Related
Commands
gvrp enable (global)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 723
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
GVRP ENABLE (GLOBAL)
gvrp enable (global)
Overview Use this command to enable GVRP globally for the switch.
Use the no variant of this command to disable GVRP globally for the switch.
Syntax gvrp enable
no gvrp enable
Mode Global Configuration
Default Disabled by default.
Usage Use this command to enable GVRP on the switch. Note that this command does
not enable GVRP on switchports. To enable GVRP on switchports use the gvrp
(interface) command in Interface Configuration mode. You must issue a gvrp
enable (global) command before issuing a gvrp (interface) command.
You must enable GVRP on both ends of a link for GVRP to propagate VLANs
between links.
NOTE: MSTP is not supported by the current AlliedWare Plus GVRP implementation.
GVRP and MSTP are mutually exclusive. STP and RSTP are supported by GVRP.
Private VLAN trunk ports are not supported by the current AlliedWare Plus GVRP
implementation. GVRP and private VLAN trunk ports are mutually exclusive.
Examples To enable GVRP for the switch, before enabling GVRP on switchports, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# gvrp enable
To disable GVRP on the switch, which will also disable GVRP enabled on
switchports, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no gvrp enable
Validation
Commands
show gvrp configuration
Related
Commands
gvrp (interface)
gvrp dynamic-vlan-creation

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 724
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
GVRP REGISTRATION
gvrp registration
Overview Use this command to set GVRP registration to normal, fixed, and forbidden
registration modes.
Use the no variant of this command to disable GVRP registration.
Syntax gvrp registration {normal|fixed|forbidden}
no gvrp registration {normal|fixed|forbidden}
Mode Interface Configuration
Default Normal registration is the default.
Usage Configuring a trunk port in normal registration mode allows dynamic creation of
VLANs. Normal mode is the default mode. Validate using the show gvrp
configuration command.
Configuring a trunk port in fixed registration mode allows manual creation of
VLANs.
Configuring a trunk port in forbidden registration mode prevents VLAN creation
on the port.
Validation
Commands
show gvrp configuration
Parameter Description
normal Specify dynamic GVRP registration and deregistration of VLANs.
fixed Specify fixed GVRP registration and deregistration of VLANs.
forbidden Specify no GVRP registration of VLANs. VLANs are deregistered.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 725
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
GVRP TIMER
gvrp timer
Overview Use this command to set GVRP timers in Interface Configuration mode for a given
interface.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the GVRP timers to the defaults
specified in the table below.
Syntax gvrp timer {join <timer-value>|leave <timer-value>|leaveall
<timer-value>}
no gvrp timer {join|leave|leaveall}
Mode Interface Configuration
Defaults The default join time value is 20 centiseconds (200 milliseconds), the default leave
timer value is 60 centiseconds (600 milliseconds), and the default leaveall timer
value is 1000 centiseconds (10,000 milliseconds).
Usage When configuring the leave timer, set it to more than or equal to three times the
join timer value. The settings for the leave and join timers must be the same
for all GVRP enabled switches. See also the section “Setting the GVRP Timers” in the
GVRP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Use the show gvrp timer command to confirm GVRP timers set with this command.
Related
Commands
show gvrp timer
Parameter Description
join Specifies the timer for joining the group (default is 20
centiseconds / hundredths of a second, or 200 milliseconds).
leave Specifies the timer for leaving a group (default is 60 centiseconds /
hundredths of a second, or 600 milliseconds).
leaveall Specifies the timer for leaving all groups (default is 1000
centiseconds / hundredths of a second, or 10,000 milliseconds).
<timer-value><1-65535> The timer value in hundredths of a second
(centiseconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 726
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING GVRP
show debugging gvrp
Overview Use this command to display the GVRP debugging option set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging gvrp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example Enter the following commands to display GVRP debugging output on the console:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug gvrp all
awplus(config)# exit
awplus# show debugging gvrp
Output See sample output from the show debugging gvrp command after entering
debug gvrp all:
Related
Commands
debug gvrp
GVRP debugging status:
GVRP Event debugging is on
GVRP CLI debugging is on
GVRP Timer debugging is on
GVRP Packet debugging is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 727
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
SHOW GVRP CONFIGURATION
show gvrp configuration
Overview Use this command to display GVRP configuration data for a switch.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show gvrp configuration
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show GVRP configuration for the switch, enter the command:
awplus# show gvrp configuration
Output The following is an output of this command displaying the GVRP configuration for
a switch:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 728
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
SHOW GVRP MACHINE
show gvrp machine
Overview Use this command to display the state machine for GVRP.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show gvrp machine
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the GVRP state machine for the switch, enter the command:
awplus# show gvrp machine
Output See the following output of this command displaying the GVRP state machine.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 729
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
SHOW GVRP STATISTICS
show gvrp statistics
Overview Use this command to display a statistical summary of GVRP information for the
switch.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show gvrp statistics [<interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command together with the clear gvrp statistics command to
troubleshoot GVRP.
Examples To show the GVRP statistics for all switchport interfaces, enter the command:
awplus# show gvrp statistics
Related
Commands
clear gvrp statistics
Parameter Description
<interface> The name of the switchport interface.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 730
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
GVRP COMMANDS
SHOW GVRP TIMER
show gvrp timer
Overview Use this command to display data for the GVRP timers set with the gvrp timer
command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show gvrp timer <interface>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To show the GVRP timers for all switchport interfaces, enter the command:
awplus# show gvrp timer
Related
Commands
gvrp timer
Parameter Description
<interface> The name of the switchport interface.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 731
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 3: Layer 3 Switching

22
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 732
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP Addressing and
Protocol Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
various IP features, including the following protocols:
• Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
For more information, see the IP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“arp-aging-timeout” on page 734
•“arp” on page 735
•“arp log” on page 736
•“arp opportunistic-nd” on page 739
•“arp-reply-bc-dmac” on page 740
•“clear arp-cache” on page 741
•“debug ip packet interface” on page 742
•“ip address (IP Addressing and Protocol)” on page 744
•“ip gratuitous-arp-link” on page 746
•“ip redirects” on page 748
•“ip tcp synack-retries” on page 749
•“ip unreachables” on page 750
•“ping” on page 752
•“show arp” on page 753
•“show debugging ip packet” on page 754
•“show ip flooding-nexthops” on page 756
•“show ip interface” on page 757
•“show ip sockets” on page 758

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 734
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP-AGING-TIMEOUT
arp-aging-timeout
Overview This command sets a timeout period on dynamic ARP entries associated with a
specific interface. If your device stops receiving traffic for the host specified in a
dynamic ARP entry, it deletes the ARP entry from the ARP cache after this timeout
is reached.
Your device times out dynamic ARP entries to ensure that the cache does not fill
with entries for hosts that are no longer active. Static ARP entries are not aged or
automatically deleted.
By default the time limit for dynamic ARP entries is 300 seconds on all interfaces.
The no variant of this command sets the time limit to the default of 300 seconds.
Syntax arp-aging-timeout <0-432000>
no arp-aging timeout
Default 300 seconds (5 minutes)
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To set the ARP entries on interface vlan2 to time out after two minutes, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# arp-aging-timeout 120
Related
Commands
clear arp-cache
show arp
Parameter Description
<0-432000> The timeout period in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 735
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP
arp
Overview This command adds a static ARP entry to the ARP cache. This is typically used to
add entries for hosts that do not support ARP or to speed up the address resolution
function for a host. The ARP entry must not already exist. Use the alias parameter
to allow your device to respond to ARP requests for this IP address.
The no variant of this command removes the static ARP entry. Use the clear
arp-cache command to remove the dynamic ARP entries in the ARP cache.
Syntax arp <ip-addr> <mac-address> [<port-number>] [alias]
no arp <ip-addr>
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To add the IP address 10.10.10.9 with the MAC address 0010.2533.4655 into the
ARP cache, and have your device respond to ARP requests for this address, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# arp 10.10.10.9 0010.2355.4566 alias
Related
Commands
clear arp-cache
show arp
Parameter Description
<ip-addr> The IPv4 address of the device you are adding as a static ARP
entry.
<mac-address> The MAC address of the device you are adding as a static ARP
entry, in hexadecimal notation with the format
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
<port-number> The port number associated with the IP address. Specify this
when the IP address is part of a VLAN.
alias Allows your device to respond to ARP requests for the IP
address. Proxy ARP must be enabled on the interface before
using this parameter.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 736
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP LOG
arp log
Overview This command enables the logging of dynamic and static ARP entries in the ARP
cache. The ARP cache contains mappings of device ports, VLAN IDs, and IP
addresses to physical MAC addresses for hosts.
This command can display the MAC addresses in the ARP log either using the
notation HHHH.HHHH.HHHH, or using the IEEE standard hexadecimal notation
(HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH).
Use the no variant of this command to disable the logging of ARP entries.
Syntax arp log [mac-address-format ieee]
no arp log [mac-address-format ieee]
Default The ARP logging feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You have the option to change how the MAC address is displayed in the ARP log
message. The output can either use the notation HHHH.HHHH.HHHH or
HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH.
Enter arp log to use HHHH.HHHH.HHHH notation.
Enter arp log mac-address-format ieee to use HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH notation.
Enter no arp log mac-address-format ieee to revert from HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH
to HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
Enter no arp log to disable ARP logging.
To display ARP log messages use the command show log | include ARP_LOG.
Examples To enable ARP logging and specify that the MAC address in the log message is
displayed in HHHH.HHHH.HHHH notation, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# arp log
To disable ARP logging on the device, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no arp log
Parameter Description
mac-address-format ieee Display the MAC address in the standard IEEE
format (HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH), instead of
displaying the MAC address with the format
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 737
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP LOG
To enable ARP logging and specify that the MAC address in the log message is
displayed in the standard IEEE format hexadecimal notation
(HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH), use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# arp log mac-address-format ieee
To leave ARP logging enabled, but stop using HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH format and
use HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format instead, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no arp log mac-address-format ieee
To display ARP log messages, use the following command:
awplus# show log | include ARP_LOG
Output Figure 22-1: Output from show log | include ARP_LOG after enabling ARP
logging using arp log. Note that this output uses
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
Figure 22-2: Output from show log | include ARP_LOG after enabling ARP
logging using arp log mac-address format ieee. Note that this
output uses HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH format.
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#arp log
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#show log | include ARP_LOG
2018 Oct 6 06:21:01 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 add
0013.4078.3b98 (192.168.2.4)
2018 Oct 6 06:22:30 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 del
0013.4078.3b98 (192.168.2.4)
2018 Oct 6 06:23:26 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 add
0030.940e.136b (192.168.2.20)
2018 Oct 6 06:23:30 user.notice awplus IMISH[1830]: show log | include ARP_LOG
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#arp log mac-address-format ieee
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#show log | include ARP_LOG
2018 Oct 6 06:25:28 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 add
00-17-9a-b6-03-69 (192.168.2.12)
2018 Oct 6 06:25:30 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 add
00-03-37-6b-a6-a5 (192.168.2.10)
2018 Oct 6 06:26:53 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 del
00-30-94-0e-13-6b (192.168.2.20)
2018 Oct 6 06:27:31 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 del
00-17-9a-b6-03-69 (192.168.2.12)
2018 Oct 6 06:28:09 user.notice awplus HSL[1007]: ARP_LOG port1.0.1 vlan1 del
00-03-37-6b-a6-a5 (192.168.2.10)
2018 Oct 6 06:28:14 user.notice awplus IMISH[1830]: show log | include ARP_LOG

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 738
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP LOG
The following table lists the parameters in output of the show log | include
ARP_LOG command. The ARP log message format is:
<date> <time> <severity> <hostname> <program-name>
ARP_LOG <port-number> <vid> <operation> <MAC> <IP>
Related
Commands
show log
show running-config
Table 22-1: Parameters in the output from show log | include ARP_LOG
Parameter Description
ARP_LOG Indicates that ARP log entry information follows.
<port-number>Indicates device port number for the ARP log entry.
<vid>Indicates the VLAN ID for the ARP log entry.
<operation>Indicates “add” if the ARP log entry displays an ARP addition.
Indicates “del” if the ARP log entry displays an ARP deletion.
<MAC>Indicates the MAC address for the ARP log entry, either in the
default hexadecimal notation (HHHH.HHHH.HHHH) or in the
IEEE standard format hexadecimal notation
(HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH) as specified with the arp log or the arp
log mac-address-format ieee command.
<IP>Indicates the IP address for the ARP log entry.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 739
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP OPPORTUNISTIC-ND
arp opportunistic-nd
Overview Use this command to enable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the global ARP
cache. This command changes the behavior for unsolicited ARP packet forwarding
on the device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable opportunistic neighbor discovery
for the global ARP cache.
Syntax arp opportunistic-nd
no arp opportunistic-nd
Default Opportunistic neighbor discovery is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When opportunistic neighbor discovery is enabled, the device will reply to any
received unsolicited ARP packets (but not gratuitous ARP packets). The source
MAC address for the unsolicited ARP packet is added to the ARP cache, so the
device forwards the ARP packet. When opportunistic neighbor discovery is
disabled, the source MAC address for the ARP packet is not added to the ARP
cache, so the ARP packet is not forwarded by the device.
Examples To enable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the global ARP cache, enter:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# arp opportunistic-nd
To disable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the global ARP cache, enter:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no arp opportunistic-nd
Related
Commands
ipv6 opportunistic-nd
show arp
show running-config interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 740
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
ARP-REPLY-BC-DMAC
arp-reply-bc-dmac
Overview Use this command to allow processing of ARP replies that arrive with a broadcast
destination MAC (ffff.ffff.ffff). This makes neighbors reachable if they send ARP
responses that contain a broadcast destination MAC.
Use the no variant of this command to turn off processing of ARP replies that arrive
with a broadcast destination MAC.
Syntax arp-reply-bc-dmac
no arp-reply-bc-dmac
Default By default, this functionality is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for VLAN interfaces
Example To allow processing of ARP replies that arrive on vlan2 with a broadcast destination
MAC, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# arp-reply-bc-dmac
Related
Commands
clear arp-cache
show arp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 741
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
CLEAR ARP-CACHE
clear arp-cache
Overview This command deletes dynamic ARP entries from the ARP cache. You can
optionally specify the IPv4 address of an ARP entry to be cleared from the ARP
cache.
Syntax clear arp-cache [<ip-address>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage To display the entries in the ARP cache, use the show arp command. To remove
static ARP entries, use the no variant of the arp command.
Example To clear all dynamic ARP entries, use the command:
awplus# clear arp-cache
To clear all dynamic ARP entries associated with the IPv4 address 192.168.1.1, use
the command:
awplus# clear arp-cache 192.168.1.1
Related
Commands
arp
show arp
Parameter Description
<ip-address> The IPv4 address of an ARP entry that is to be cleared from the
ARP cache.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 742
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
DEBUG IP PACKET INTERFACE
debug ip packet interface
Overview The debug ip packet interface command enables IP packet debug and is
controlled by the terminal monitor command.
If the optional icmp keyword is specified then ICMP packets are shown in the
output.
The no variant of this command disables the debug ip interface command.
Syntax debug ip packet interface {<interface-name>|all} [address
<ip-address>|verbose|hex|arp|udp|tcp|icmp]
no debug ip packet interface [<interface-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Parameter Description
<interface> Specify a single Layer 3 interface name (not a range of interfaces)
This keyword can be specified as either all or as a single Layer 3
interface to show debugging for either all interfaces or a single
interface.
all Specify all Layer 3 interfaces on the device.
<ip-address> Specify an IPv4 address.
If this keyword is specified, then only packets with the specified IP
address as specified in the ip-address placeholder are shown in the
output.
verbose Specify verbose to output more of the IP packet.
If this keyword is specified then more of the packet is shown in the
output.
hex Specify hex to output the IP packet in hexadecimal.
If this keyword is specified, then the output for the packet is shown
in hex.
arp Specify arp to output ARP protocol packets.
If this keyword is specified, then ARP packets are shown in the
output.
udp Specify udp to output UDP protocol packets.
If this keyword is specified then UDP packets are shown in the
output.
tcp Specify tcp to output TCP protocol packets.
If this keyword is specified, then TCP packets are shown in the
output.
icmp Specify icmp to output ICMP protocol packets.
If this keyword is specified, then ICMP packets are shown in the
output.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 743
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
DEBUG IP PACKET INTERFACE
Examples To turn on ARP packet debugging on vlan2, use the command:
awplus# debug ip packet interface vlan2 arp
To turn off IP packet interface debugging on interface vlan2, use the command:
awplus# no debug ip packet interface vlan2
To turn on all packet debugging on all interfaces on the device, use the command:
awplus# debug ip packet interface all
To turn off IP packet interface debugging on all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# no debug ip packet interface
To turn on TCP packet debugging on vlan2 and IP address 192.168.2.4, use the
command:
awplus# debug ip packet interface vlan2 address 192.168.2.4 tcp
Related
Commands
no debug all
tcpdump
terminal monitor
undebug ip packet interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 744
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP ADDRESS (IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL)
ip address (IP Addressing and Protocol)
Overview This command sets a static IP address on an interface.
The no variant of this command removes the IP address from the interface.
You cannot remove the primary address when a secondary address is present.
Syntax ip address <ip-addr/prefix-length> [secondary] [label <label>]
no ip address [<ip-addr/prefix-length>] [secondary]
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface or a local loopback interface.
Usage To set the primary IP address on the interface, specify only ip address
<ip-address/m>. This overwrites any configured primary IP address. To add
additional IP addresses on this interface, use the secondary parameter. You must
configure a primary address on the interface before configuring a secondary
address.
NOTE: Use show running-config interface not show ip interface brief when you
need to view a secondary address configured on an interface. show ip interface brief
will only show the primary address, not a secondary address for an interface.
Examples To add the IP address 10.10.10.50/24 to the interface vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.50/24
To add the secondary IP address 10.10.11.50/24 to the same interface, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip address 10.10.11.50/24 secondary
Parameter Description
<ip-addr/prefix-
length> The IPv4 address and prefix length you are assigning to the
interface.
secondary Secondary IP address.
label Adds a user-defined description of the secondary IP address.
<label> A user-defined description of the secondary IP address. Valid
characters are any printable character and spaces.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 745
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP ADDRESS (IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL)
To add the IP address 10.10.11.50/24 to the local loopback interface lo, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface lo
awplus(config-if)# ip address 10.10.11.50/24
Related
Commands
interface (to configure)
show ip interface
show running-config interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 746
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP GRATUITOUS-ARP-LINK
ip gratuitous-arp-link
Overview This command sets the Gratuitous ARP time limit for all switchports. The time limit
restricts the sending of Gratuitous ARP packets to one Gratuitous ARP packet
within the time in seconds.
NOTE: This command specifies time between sequences of Gratuitous ARP packets,
and time between individual Gratuitous ARP packets occurring in a sequence, to allow
legacy support for older devices and interoperation between other devices that are not
ready to receive and forward data until several seconds after linkup.
Additionally, jitter has been applied to the delay following linkup, so Gratuitous ARP
packets applicable to a given port are spread over a period of 1 second so are not all
sent at once. Remaining Gratuitous ARP packets in the sequence occur after a fixed
delay from the first one.
Syntax ip gratuitous-arp-link <0-300>
no ip gratuitous-arp-link
Default The default Gratuitous ARP time limit for all switchports is 8 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Every switchport will send a sequence of 3 Gratuitous ARP packets to each VLAN
that the switchport is a member of, whenever the switchport moves to the
forwarding state. The first Gratuitous ARP packet is sent 1 second after the
switchport becomes a forwarding switchport. The second and third Gratuitous
ARP packets are each sent after the time period specified by the Gratuitous ARP
time limit.
Additionally, the Gratuitous ARP time limit specifies the minimum time between
the end of one Gratuitous ARP sequence and the start of another Gratuitous ARP
sequence. When a link is flapping, the switchport’s state is set to forwarding several
times. The Gratuitous ARP time limit is imposed to prevent Gratuitous ARP packets
from being sent undesirably often.
Examples To disable the sending of Gratuitous ARP packets, use the commands :
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip gratuitous-arp-link 0
Parameter Description
<0-300>Specify the minimum time between sequences of Gratuitous ARPs and
the fixed time between Gratuitous ARPs occurring in a sequence, in
seconds.
0 disables the sending of Gratuitous ARP packets.
The default is 8 seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 747
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP GRATUITOUS-ARP-LINK
To restrict the sending of Gratuitous ARP packets to one every 20 seconds, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip gratuitous-arp-link 20
Validation
Commands
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 748
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP REDIRECTS
ip redirects
Overview This command enables the device to send ICMP redirects on one or more
interfaces.
Use the no variant of this command to stop the device from sending ICMP redirects
on one or more interfaces.
Syntax ip redirects
no ip redirects
Default ICMP redirects are disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage ICMP redirect messages are used to notify hosts that a better route is available to a
destination.
ICMP redirects are used when a packet is routed into the device on the same
interface that the packet is routed out of the device. ICMP redirects are only sent to
packet sources that are directly connected to the device.
Examples To enable the device to send ICMP redirects on interface vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip redirects
To stop the device from sending ICMP redirects on interface vlan2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ip redirects

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 749
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP TCP SYNACK-RETRIES
ip tcp synack-retries
Overview Use this command to specify how many times the switch will retry sending a SYN
ACK for a TCP connection for which it has received a SYN but not an ACK. Such
connections are called half-open TCP connections. This command allows you to
influence how long half-open TCP connections take to time out.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default setting of 5 retries.
Syntax ip tcp synack-retries <0-255>
no ip tcp synack-retries
Default 5 retries
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The following table shows the approximate correlation between the number of
retries and the time half-open TCP connections take to time out.
Example To retry twice, which leads to a timeout of approximately 7 seconds, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip tcp synack-retries 2
Related
Commands
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.2: command added
Parameter Description
<0-255> Number of times to retry sending the SYN ACK
Number of retries Approximate lower bound for the timeout
0 retries 1 second
1 retry 3 seconds
2 retries 7 seconds
3 retries 15 seconds
4 retries 31 seconds
5 retries 63 seconds

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 750
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP UNREACHABLES
ip unreachables
Overview Use this command to enable ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) type 3,
destination unreachable, messages.
Use the no variant of this command to disable destination unreachable messages.
This prevents an attacker from using these messages to discover the topology of a
network.
Syntax ip unreachables
no ip unreachables
Default Destination unreachable messages are enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When a device receives a packet for a destination that is unreachable it returns an
ICMP type 3 message, this message includes a reason code, as per the table below.
An attacker can use these messages to obtain information regarding the topology
of a network. Disabling destination unreachable messages, using the no ip
unreachables command, secures your network against this type of probing.
NOTE: Disabling ICMP destination unreachable messages breaks applications such as
traceroute and Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD), which depend on these messages to
operate correctly.
Table 22-2: ICMP type 3 reason codes and description
Code Description [RFC]
0Network unreachable [RFC792]
1Host unreachable [RFC792]
2Protocol unreachable [RFC792]
3Port unreachable [RFC792]
4Fragmentation required, and DF flag set [RFC792]
5Source route failed [RFC792]
6Destination network unknown [RFC1122]
7Destination host unknown [RFC1122]
8Source host isolated [RFC1122]
9Network administratively prohibited [RFC768]
10 Host administratively prohibited [RFC869]
11 Network unreachable for Type of Service [RFC908]
12 Host unreachable for Type of Service [RFC938]
13 Communication administratively prohibited [RFC905]
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 751
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
IP UNREACHABLES
Example To disable destination unreachable messages, use the commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip unreachables
To enable destination unreachable messages, use the commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip unreachables
14 Host Precedence Violation [RFC1812]
15 Precedence cutoff in effect [RFC1812]
Table 22-2: ICMP type 3 reason codes and description (cont.)
Code Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 752
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
PING
ping
Overview This command sends a query to another IPv4 host (send Echo Request messages).
Syntax ping [ip] <host> [broadcast] [df-bit {yes|no}] [interval
<0-128>] [pattern <hex-data-pattern>] [repeat
{<1-2147483647>|continuous}] [size <36-18024>] [source
<ip-addr>] [timeout <1-65535>] [tos <0-255>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To ping the IP address 10.10.0.5 use the following command:
awplus# ping 10.10.0.5
Parameter Description
<host>The destination IP address or hostname.
broadcast Allow pinging of a broadcast address.
df-bit Enable or disable the do-not-fragment bit in the IP header.
interval <0-128> Specify the time interval in seconds between sending ping
packets. The default is 1. You can use decimal places to
specify fractions of a second. For example, to ping every
millisecond, set the interval to 0.001.
pattern <hex-
data-pattern> Specify the hex data pattern.
repeat Specify the number of ping packets to send.
<1-2147483647> Specify repeat count. The default is 5.
continuous Continuous ping
size <36-18024> The number of data bytes to send, excluding the 8 byte ICMP
header. The default is 56 (64 ICMP data bytes).
source <ip-addr> The IP address of a configured IP interface to use as the
source in the IP header of the ping packet.
timeout
<1-65535> The time in seconds to wait for echo replies if the ARP entry is
present, before reporting that no reply was received. If no
ARP entry is present, it does not wait.
tos <0-255> The value of the type of service in the IP header.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 753
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW ARP
show arp
Overview Use this command to display entries in the ARP routing and forwarding table—the
ARP cache contains mappings of IP addresses to physical addresses for hosts. To
have a dynamic entry in the ARP cache, a host must have used the ARP protocol to
access another host.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show arp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Running this command with no additional parameters will display all entries in the
ARP routing and forwarding table.
Example To display all ARP entries in the ARP cache, use the following command:
awplus# show arp
Output Figure 22-3: Example output from the show arp command
Related
Commands
arp
clear arp-cache
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: Link layer addresses now shown as the hardware address (MAC
Address output parameter has been renamed to LL Address).
awplus#show arp
IP Address LL Address Interface Port Type
192.168.27.10 192.168.4.1 vlan1 port1.0.1 dynamic
192.168.27.100 0000.daaf.cd24 vlan1 port1.0.2 dynamic
192.168.1.100 192.168.20.1 vlan2 port1.0.3 static
Table 23: Parameters in the output of the show arp command
Parameter Meaning
IP Address IP address of the network device this entry maps to.
LL Address Hardware address of the network device.
Interface Interface over which the network device is accessed.
Port Physical port that the network device is attached to.
Type Whether the entry is a static or dynamic entry. Static
entries are added using the arp command. Dynamic entries
are learned from ARP request/reply message exchanges.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 754
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING IP PACKET
show debugging ip packet
Overview Use this command to show the IP interface debugging status. IP interface
debugging is set using the debug ip packet interface command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging ip packet
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the IP interface debugging status when the terminal monitor off, use the
command:
awplus# terminal no monitor
awplus# show debug ip packet
Output Figure 22-4: Example output from the show debugging ip packet command
with terminal monitor off
Example To display the IP interface debugging status when the terminal monitor is on, use
the command:
awplus# terminal monitor
awplus# show debug ip packet
Output Figure 22-5: Example output from the show debugging ip packet command
with terminal monitor on
awplus#terminal no monitor
awplus#show debug ip packet
IP debugging status:
interface all tcp (stopped)
interface vlan1 arp verbose (stopped)
awplus#terminal monitor
awplus#show debug ip packet
IP debugging status:
interface all tcp (running)
interface vlan1 arp verbose (running)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 756
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP FLOODING-NEXTHOPS
show ip flooding-nexthops
Overview Use this command to display the static and dynamic ARP entries in the ARP cache
that flood packets to multiple ports.
Syntax show ip flooding-nexthops
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display all of the flooding nexthop entries in the ARP cache, use the command:
awplus# show ip flooding-nexthops
Output Figure 22-6: Example output from show ip flooding-nexthops
Related
Commands
show arp
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
awplus#show ip flooding-nexthops
IP Address MAC Address Interface Flooding Mode Type
11.11.11.10 0300.0000.0011 vlan1 port-group static

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 757
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP INTERFACE
show ip interface
Overview Use this command to display information about interfaces and the IP addresses
assigned to them. To display information about a specific interface, specify the
interface name with the command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip interface [<interface-list>] [brief]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To show brief information for the assigned IP address for interface port1.0.2 use
the command:
awplus# show ip interface port1.0.2 brief
To show the IP addresses assigned to vlan2, use the command:
awplus# show ip interface vlan2 brief
Output Figure 22-7: Example output from the show ip interface brief command
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces to display information about. An interface-list
can be:
•a VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• the loopback interface (lo)
• a continuous range of interfaces separated by a hyphen
(e.g. vlan10-20)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. vlan1,vlan10-20). Do not mix
interface types in a list.
The specified interfaces must exist.
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
port1.0.1 unassigned admin up down
...
vlan1 192.168.1.1 admin up running
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 758
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP SOCKETS
show ip sockets
Overview Use this command to display information about the IP or TCP sockets that are
present on the device. It includes TCP and UDP listen sockets, and displays the
associated IP address and port.
The information displayed for established TCP sessions includes the remote IP
address, port, and session state. Raw IP protocol listen socket information is also
displayed for protocols such as ICMP6, which are configured to receive IP packets
with the associated protocol number.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip sockets
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command to verify that the socket being used is opening correctly. If there
is a local and remote endpoint, a connection is established with the ports
indicated.
Note that this command does not display sockets that are used internally for
exchanging data between the various processes that exist on the device and are
involved in its operation and management. It only displays sockets that are present
for the purposes of communicating with other external devices.
Example To display IP sockets currently present on the device, use the command:
awplus# show ip sockets
Output Figure 22-8: Example output from show ip sockets
Socket information
Not showing 40 local connections
Not showing 7 local listening ports
Typ Local Address Remote Address State
tcp 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0.0.0.0:23 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0.0.0.0:4743 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp :::23 :::* LISTEN
udp 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
udp 226.94.1.1:5405 0.0.0.0:*
udp 0.0.0.0:161 0.0.0.0:*
udp :::161 :::*
raw 0.0.0.0:112 0.0.0.0:* 112
raw :::58 :::* 58
raw :::112 :::* 112
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 759
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP SOCKETS
Table 22-1: Parameters in the output from show ip sockets
Parameter Description
Not showing
<number>
local
connections
This field refers to established sessions between processes internal
to the device, that are used in its operation and management.
These sessions are not displayed as they are not useful to the user.
<number> is some positive integer.
Not showing
<number>
local
listening
ports
This field refers to listening sockets belonging to processes internal
to the device, that are used in its operation and management. They
are not available to receive data from other devices. These sessions
are not displayed as they are not useful to the user. <number> is
some positive integer.
Typ This column displays the type of the socket. Possible values for this
column are:
tcp : IP Protocol 6
udp : IP Protocol 17
raw : Indicates that socket is for a non port-orientated protocol (i.e.
a protocol other than TCP or UDP) where all packets of a specified IP
protocol type are accepted. For raw socket entries the protocol type
is indicated in subsequent columns.
Local
Address For TCP and UDP listening sockets this shows the destination IP
address and destination TCP or UDP port number for which the
socket will receive packets. The address and port are separated by ’:’.
If the socket will accept packets addressed to any of the device’s IP
addresses, the IP address will be 0.0.0.0 for IPv4 or :: for IPv6. For
active TCP sessions the IP address will display which of the devices
addresses the session was established with. For raw sockets this
displays the IP address and IP protocol for which the socket will
accept IP packets. The address and protocol are separated by ’:’. If
the socket will accept packets addressed to any of the device’s IP
addresses, the IP address will be 0.0.0.0 for IPv4 and :: for IPv6. IP
Protocol assignments are described
at:www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 760
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP SOCKETS
Remote
Address For TCP and UDP listening sockets this shows the source IP address
(either IPv4 or IPv6) and source TCP or UDP port number for which
the socket will accept packets. The address and port are separated
by ’:’. If the socket will accept packets addressed from any IP
address, the IP address will be 0.0.0.0 for IPv4 . This is the usual case
for a listening socket. Normally for a listen socket any source port
will be accepted. This is indicated by “. For active TCP sessions the IP
address will display the remote address and port the session was
established with. For raw sockets the entry in this column will be
0.0.0.0: for IPv4 .
State This column shows the state of the socket. For TCP sockets this
shows the state of the TCP state machine. For UDP sockets this
column is blank. For raw sockets it contains the IP protocol number.
The possible TCP states are:
LISTEN
SYN-SENT
SYN-RECEIVED
ESTABLISHED
FIN-WAIT-1
FIN-WAIT-2
CLOSE-WAIT
CLOSING
LAST-ACK
TIME-WAIT
CLOSED
RFC793 contains the TCP state machine diagram with Section 3.2
describing each of the states.
Table 22-1: Parameters in the output from show ip sockets (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 761
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP TRAFFIC
show ip traffic
Overview Use this command to display statistics regarding IP traffic sent and received by all
interfaces on the device, showing totals for IP and IPv6 and then broken down into
sub-categories such as TCP, UDP, ICMP and their IPv6 equivalents when
appropriate.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip traffic
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display IP traffic statistics, use the command:
awplus# show ip traffic
Output Figure 22-9: Example output from the show ip traffic command
awplus#show ip traffic
IP:
168475 packets received
168475 delivered
208099 sent
35 dropped due to missing route
22646409 bytes received
126783216 bytes sent
InCsumErrors 0
InNoECTPkts 168475
InECT1Pkts 0
InECT0Pkts 0
InCEPkts 0
In107 Destination Unreachable
Out11 Destination Unreachable
IPv6:
14 packets received
14 received packets delivered
18 packets transmitted
...
ICMP6:
4 messages sent
...
UDP6:
Udp6RcvbufErrors 0
...
UDPLite6:
UdpLite6RcvbufErrors 0
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 762
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
SHOW IP TRAFFIC
TCP:
8 remote connections established
...
UDP:
79797 datagrams received
...
UDPLite:
InCsumErrors 0
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 763
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
TCPDUMP
tcpdump
Overview Use this command to start a tcpdump, which gives the same output as the
Unix-like tcpdump command to display TCP/IP traffic. Press <ctrl> + c to stop
a running tcpdump.
Syntax tcpdump <line>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To start a tcpdump running to capture IP packets, enter the command:
awplus# tcpdump ip
Output Figure 22-10: Example output from the tcpdump command
Related
Commands
debug ip packet interface
Parameter Description
<line>Specify the dump options. For more information on the
options for this placeholder see
http://www.tcpdump.org/tcpdump_man.html
03:40:33.221337 IP 192.168.1.1 > 224.0.0.13: PIMv2, Hello,
length: 34
1 packets captured
2 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 764
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IP ADDRESSING AND PROTOCOL COMMANDS
TRACEROUTE
traceroute
Overview Use this command to trace the route to the specified IPv4 host.
Syntax traceroute {<ip-addr>|<hostname>}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# traceroute 10.10.0.5
Parameter Description
<ip-addr> The destination IPv4 address. The IPv4 address uses the
format A.B.C.D.
<hostname>The destination hostname.

23
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 766
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Domain Name
Service (DNS)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
the Domain Name Service (DNS) client.
For more information about DNS for Switches, see the Domain Name System (DNS)
for AlliedWare Plus Switches Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
Command List •“ip domain-list” on page 767
•“ip domain-lookup” on page 768
•“ip domain-name” on page 769
•“ip name-server” on page 770
•“ip name-server preferred-order” on page 772
•“show hosts” on page 773
•“show ip domain-list” on page 774
•“show ip domain-name” on page 775
•“show ip name-server” on page 776
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 767
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
IP DOMAIN-LIST
ip domain-list
Overview This command adds a domain to the DNS list. Domains are appended to
incomplete host names in DNS requests. Each domain in this list is tried in turn in
DNS lookups. This list is ordered so that the first entry you create is checked first.
The no variant of this command deletes a domain from the list.
Syntax ip domain-list <domain-name>
no ip domain-list <domain-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If there are no domains in the DNS list, then your device uses the domain specified
with the ip domain-name command. If any domain exists in the DNS list, then the
device does not use the domain set using the ip domain-name command.
Example To add the domain example.net to the DNS list, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip domain-list example.net
Related
Commands
ip domain-lookup
ip domain-name
show ip domain-list
Parameter Description
<domain-name> Domain string, for example “company.com”.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 768
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
IP DOMAIN-LOOKUP
ip domain-lookup
Overview This command enables the DNS client on your device. This allows you to use
domain names instead of IP addresses in commands. The DNS client resolves the
domain name into an IP address by sending a DNS inquiry to a DNS server,
specified with the ip name-server command.
The no variant of this command disables the DNS client. The client will not attempt
to resolve domain names. You must use IP addresses to specify hosts in
commands.
Syntax ip domain-lookup
no ip domain-lookup
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The client is enabled by default. However, it does not attempt DNS inquiries unless
there is a DNS server configured.
Examples To enable the DNS client on your device, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip domain-lookup
To disable the DNS client on your device, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip domain-lookup
Related
Commands
ip domain-list
ip domain-name
ip name-server
show hosts
show ip name-server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 769
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
IP DOMAIN-NAME
ip domain-name
Overview This command sets a default domain for the DNS. The DNS client appends this
domain to incomplete host-names in DNS requests.
The no variant of this command removes the domain-name previously set by this
command.
Syntax ip domain-name <domain-name>
no ip domain-name <domain-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If there are no domains in the DNS list (created using the ip domain-list command)
then your device uses the domain specified with this command. If any domain
exists in the DNS list, then the device does not use the domain configured with this
command.
When your device is using its DHCP client for an interface, it can receive Option 15
from the DHCP server. This option replaces the domain name set with this
command.
Example To configure the domain name, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip domain-name company.com
Related
Commands
ip domain-list
show ip domain-list
show ip domain-name

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 770
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
IP NAME-SERVER
ip name-server
Overview This command adds IPv4 or IPv6 DNS server addresses. The DNS client on your
device sends DNS queries to IP addresses in this list when trying to resolve a host
name. Host names cannot be resolved until you have added at least one server to
this list. A maximum of three name servers can be added to this list.
The no variant of this command removes the specified DNS name-server address.
Syntax ip name-server <ip-addr>
no ip name-server <ip-addr>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage To allow the device to operate as a DNS proxy, your device must have learned
about a DNS name-server to forward requests to. Name-servers can be learned
through the following means:
• Manual configuration, using the ip name-server command
• Learned from DHCP server with Option 6
This command is used to statically configure a DNS name-server for the device to
use.
The order that you enter the servers in, is the order in which they will be used.
Examples To allow a device to send DNS queries to a DNS server with the IPv4 address
10.10.10.5, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip name-server 10.10.10.5
To enable your device to send DNS queries to a DNS server with the IPv6 address
2001:0db8:010d::1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip name-server 2001:0db8:010d::1
Related
Commands
ip domain-list
ip domain-lookup
ip domain-name
Parameter Description
<ip-addr> The IP address of the DNS server that is being added to the name
server list. The address is entered in the form A.B.C.D for an IPv4
address, or in the form X:X::X:X for an IPv6 address.
The order that you enter the servers in, is the order in which they
will be used.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 772
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
IP NAME-SERVER PREFERRED-ORDER
ip name-server preferred-order
Overview Use this command to choose between using statically-configured DNS servers or
dynamically-learned DNS servers.
Use the no variant of this command to set the DNS servers back to the default
setting of dynamic.
Syntax ip name-server preferred-order {dynamic|static}
no ip name-server preferred-order
Default dynamic
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command is used to choose which DNS server set to use first. Select either the
dynamic or static parameter.
Examples To configure the preference to use static servers first, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip name-server preferred-order static
To configure the preference to use dynamically-learned servers first, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip name-server preferred-order dynamic
or
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip name-server preferred-order
Related
Commands
ip address dhcp
ip name-server
ipv6 address dhcp
show ip name-server
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
dynamic Use dynamically learned DNS servers first.
static Use statically configured DNS servers first.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 773
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
SHOW HOSTS
show hosts
Overview This command shows the default domain, domain list, and name servers
configured on your device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show hosts
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the default domain, use the command:
awplus# show hosts
Output Figure 23-1: Example output from the show hosts command when no ip
domain-lookup is configured
Figure 23-2: Example output from the show hosts command when ip
domain-lookup is configured
Related
Commands
ip domain-list
ip domain-lookup
ip domain-name
ip name-server
awplus#show hosts
Default domain is not set
Name/address lookup is disabled
awplus#show hosts
Default domain is mycompany.com
Domain list: company.com
Name/address lookup uses domain service
Name servers are 10.10.0.2 10.10.0.88
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 774
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DOMAIN-LIST
show ip domain-list
Overview This command shows the domains configured in the domain list. The DNS client
uses the domains in this list to append incomplete hostnames when sending a
DNS inquiry to a DNS server.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip domain-list
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the list of domains in the domain list, use the command:
awplus# show ip domain-list
Output Figure 23-3: Example output from the show ip domain-list command
Related
Commands
ip domain-list
ip domain-lookup
awplus#show ip domain-list
alliedtelesis.com
mycompany.com
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 775
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DOMAIN-NAME
show ip domain-name
Overview This command shows the default domain configured on your device. When there
are no entries in the DNS list, the DNS client appends this domain to incomplete
hostnames when sending a DNS inquiry to a DNS server.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip domain-name
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the default domain configured on your device, use the command:
awplus# show ip domain-name
Output Figure 23-4: Example output from the show ip domain-name command
Related
Commands
ip domain-name
ip domain-lookup
awplus#show ip domain-name
alliedtelesis.com
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 776
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DNS) COMMANDS
SHOW IP NAME-SERVER
show ip name-server
Overview This command displays a list of IPv4 and IPv6 DNS server addresses that your
device will send DNS requests to. This is a static list configured using the ip
name-server command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip name-server
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the list of DNS servers that your device sends DNS requests to, use the
command:
awplus# show ip name-server
Output Figure 23-5: Example output from the show ip name-server command
Related
Commands
ip domain-lookup
ip name-server
awplus# show ip name-server
10.10.0.123
10.10.0.124
2001:0db8:010d::1

24
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 777
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPv6 Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
IPv6. For more information, see the IPv6 Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
Command List •“clear ipv6 neighbors” on page 779
•“ipv6 address” on page 780
•“ipv6 address autoconfig” on page 782
•“ipv6 address suffix” on page 784
•“ipv6 enable” on page 785
•“ipv6 eui64-linklocal” on page 787
•“ipv6 forwarding” on page 788
•“ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet” on page 789
•“ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo” on page 790
•“ipv6 nd current-hoplimit” on page 791
•“ipv6 nd managed-config-flag” on page 792
•“ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval” on page 793
•“ipv6 nd other-config-flag” on page 794
•“ipv6 nd prefix” on page 795
•“ipv6 nd ra-interval” on page 797
•“ipv6 nd ra-lifetime” on page 798
•“ipv6 nd raguard” on page 799
•“ipv6 nd reachable-time” on page 801
•“ipv6 nd retransmission-time” on page 802

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 778
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
•“ipv6 nd suppress-ra” on page 803
•“ipv6 neighbor” on page 804
•“ipv6 opportunistic-nd” on page 805
•“ipv6 unreachables” on page 806
•“optimistic-nd” on page 807
•“ping ipv6” on page 808
•“show ipv6 forwarding” on page 810
•“show ipv6 interface brief” on page 811
•“show ipv6 neighbors” on page 812
•“show ipv6 route” on page 813
•“show ipv6 route summary” on page 815
•“traceroute ipv6” on page 816

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 779
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
CLEAR IPV6 NEIGHBORS
clear ipv6 neighbors
Overview Use this command to clear all dynamic IPv6 neighbor entries.
Syntax clear ipv6 neighbors
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear ipv6 neighbors

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 780
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ADDRESS
ipv6 address
Overview Use this command to set the IPv6 address of an interface. The command also
enables IPv6 on the interface, which creates an EUI-64 link-local address as well as
enabling RA processing and SLAAC.
To stop the device from processing prefix information (routes and addresses from
the received Router Advertisements) use the command no ipv6 nd
accept-ra-pinfo.
To remove the EUI-64 link-local address, use the command no ipv6
eui64-linklocal.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the IPv6 address assigned and
disable IPv6. Note that if no global addresses are left after removing the IPv6
address then IPv6 is disabled.
Syntax ipv6 address <ipv6-addr/prefix-length>
no ipv6 address <ipv6-addr/prefix-length>
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Note that link-local addresses are retained in the system until they are negated by
using the no variant of the command that established them. See the ipv6 enable
command for more information.
Also note that the link-local address is retained in the system if the global address
is removed using another command, which was not used to establish the link-local
address. For example, if a link local address is established with the ipv6 enable
command then it will not be removed using a no ipv6 address command.
Examples To assign the IPv6 address 2001:0db8::a2/64 to the VLAN interface vlan2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:0db8::a2/64
To remove the IPv6 address 2001:0db8::a2/64 from the VLAN interface vlan2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 address 2001:0db8::a2/64
Parameter Description
<ipv6-addr/prefix-
length>Specifies the IPv6 address to be set. The IPv6
address uses the format X:X::X:X/Prefix-Length. The
prefix-length is usually set between 0 and 64.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 782
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ADDRESS AUTOCONFIG
ipv6 address autoconfig
Overview Use this command to enable IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for
an interface. This configures an IPv6 address on an interface derived from the MAC
address on the interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disable IPv6 SLAAC on an interface. Note
that if no global addresses are left after removing all IPv6 autoconfigured
addresses then IPv6 is disabled.
Syntax ipv6 address autoconfig
no ipv6 address autoconfig
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command enables automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses using stateless
autoconfiguration on an interface and enables IPv6.
IPv6 hosts can configure themselves when connected to an IPv6 network using
ICMPv6 (Internet Control Message Protocol version 6) router discovery messages.
Configured routers respond with a Router Advertisement (RA) containing
configuration parameters for IPv6 hosts.
The SLAAC process derives the interface identifier of the IPv6 address from the
MAC address of the interface. When applying SLAAC to an interface, note that the
MAC address of the default VLAN is applied to the interface if the interface does not
have its own MAC address.
Note that link-local addresses are retained in the system until they are negated by
using the no variant of the command that established them. See the ipv6 enable
command for more information.
Also note that the link-local address is retained in the system if the global address
is removed using another command that was not used to establish the link-local
address. For example, if a link local address is established with the ipv6 enable
command then it will not be removed using a no ipv6 address command.
Examples To enable SLAAC on vlan2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 address autoconfig
To disable SLAAC on vlan2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 address autoconfig

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 784
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ADDRESS SUFFIX
ipv6 address suffix
Overview Use this command to configure the suffix to use when generating an address from
prefix information. Any addresses that were created with the EUI-64 suffix will be
removed, and new addresses will be added after the next Router Advertisement.
Use the no variant of this command to set it back to the default of disabled or set
to :: for the same result as the no variant.
Syntax ipv6 address suffix <ipv6-addr-suffix>
no ipv6 address suffix
Default Disabled
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To configure the suffix to use when generating an address from prefix information
on vlan2, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 address suffix ::a2d8:0fd8
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
show running-config interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<ipv6-addr-suffix> In the format of ::X:X:X:X, for example ::a2d8:0fd8

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 785
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ENABLE
ipv6 enable
Overview Use this command to enable automatic configuration of a link-local IPv6 address
on an interface using Stateless Automatic Address Configuration (SLAAC). By
default, the EUI-64 method is used to generate the link-local address.
Use the no variant of this command to disable IPv6 on an interface without a global
address. Note, to stop EUI-64 from generating the automatic link-local address, use
the command no ipv6 eui64-linklocal.
Syntax ipv6 enable
no ipv6 enable
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage The ipv6 enable command automatically configures an IPv6 link-local address on
the interface and enables the interface for IPv6 processing.
A link-local address is an IP (Internet Protocol) address that is only used for
communications in the local network, or for a point-to-point connection. Routing
does not forward packets with link-local addresses. IPv6 requires that a link-local
address is assigned to each interface that has the IPv6 protocol enabled, and when
addresses are assigned to interfaces for routing IPv6 packets.
Note that link-local addresses are retained in the system until they are negated by
using the no variant of the command that established them.
Also note that the link-local address is retained in the system if the global address
is removed using another command that was not used to establish the link-local
address. For example, if a link local address is established with the ipv6 enable
command then it will not be removed using a no ipv6 address command.
Default All interfaces default to IPv6-down with no address.
Examples To enable IPv6 with only a link-local IPv6 address on the VLAN interface vlan2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
To disable IPv6 with only a link-local IPv6 address on the VLAN interface vlan2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 787
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 EUI64-LINKLOCAL
ipv6 eui64-linklocal
Overview When IPv6 is enabled on an interface, an EUI link-local address is generated and
installed on the interface. In other words, ipv6 eui64-linklocal is enabled by
default on any IPv6 enabled interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disallow the automatic generation of the
EUI-64 link-local address on an IPv6 enabled interface.
Syntax ipv6 eui64-linklocal
no ipv6 eui64-linklocal
Default The command ipv6 eui64-linklocal is enabled by default on any IPv6 enabled
interface.
Mode Interface
Example To enable IPv6 on the interface vlan1, and use the link-local address of fe80 : :1/10
instead of the EUI-64 link-local that is automatically generated, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 eui64-linklocal
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1/10
Related
Commands
ipv6 address
ipv6 address autoconfig
ipv6 enable
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 788
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 FORWARDING
ipv6 forwarding
Overview Use this command to turn on IPv6 unicast routing for IPv6 packet forwarding.
Execute this command globally on your device prior to issuing ipv6 enable on
individual interfaces.
Use this no variant of this command to turn off IPv6 unicast routing. Note IPv6
unicast routing is disabled by default.
Syntax ipv6 forwarding
no ipv6 forwarding
Mode Global Configuration
Default IPv6 unicast forwarding is disabled by default.
Usage Enable IPv6 unicast forwarding globally for all interface on your device with this
command. Use the no variant of this command to disable IPv6 unicast forwarding
globally for all interfaces on your device.
IPv6 unicast forwarding allows devices to communicate with devices that are more
than one hop away, providing that there is a route to the destination address. If
IPv6 forwarding is not enabled then pings to addresses on devices that are more
than one hop away will fail, even if there is a route to the destination address.
Examples To enable IPv6 unicast routing, use this command as shown below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 forwarding
To disable IPv6 unicast routing, use the no variant of this command as shown
below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ipv6 forwarding
Related
Commands
ipv6 enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 789
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 MULTICAST FORWARD-SLOW-PATH-PACKET
ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet
Overview Use this command to enable multicast packets to be forwarded to the CPU.
Enabling this command will ensure that the layer L3 MTU is set correctly for each
IP multicast group and will apply the value of the smallest MTU among the
outgoing interfaces for the multicast group.
It will also ensure that a received packet that is larger than the MTU value will result
in the generation of an ICMP Too Big message.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the above functionality.
Syntax ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet
no ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet
Default Disabled.
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enable the ipv6 multicast forward-slow-path-packet function, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip multicast forward-slow-path-packet
Related
Commands
show ipv6 forwarding

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 790
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND ACCEPT-RA-PINFO
ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
Overview Use this command to allow the processing of the prefix information included in a
received RA (Router Advertisement) on an IPv6 enabled interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disable an IPv6 interface from using the
prefix information within a received RA.
Syntax ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
no ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
Default The command ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo is enabled by default on any IPv6
interface.
Mode Interface
Usage By default, when IPv6 is enabled on an interface, SLAAC is also enabled. SLAAC
addressing along with the EUI-64 process, uses the prefix information included in
a received RA to generate an automatic link-local address on the IPv6 interface.
Note: an AlliedWare Plus device will, by default, add a prefix for the connected
interface IPv6 address(es) to the RA it transmits. However, this behavior can be
changed by using the command no ipv6 nd prefix auto-advertise, so there is no
guarantee that an RA will contain a prefix.
Example To enable IPv6 on vlan1 without installing a SLAAC address on the interface, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd accept-ra-pinfo
Related
Commands
ipv6 address
ipv6 address autoconfig
ipv6 enable
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 791
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND CURRENT-HOPLIMIT
ipv6 nd current-hoplimit
Overview Use this command to specify the advertised current hop limit used between IPv6
Routers.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the current advertised hop limit to its
default “0”.
Syntax ipv6 nd current-hoplimit <hoplimit>
no ipv6 nd current-hoplimit
Default 0 (No advertised current hop limit specified)
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Examples To set the advertised current hop limit to 2 between IPv6 Routers on vlan2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd current-hoplimit 2
To reset the advertised current hop limit to the default 0 on vlan2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd current-hoplimit
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
ipv6 nd prefix
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Parameter Description
<hoplimit>Specifies the advertised current hop limit value.
Valid values are from 0 to 255 hops.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 792
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND MANAGED-CONFIG-FLAG
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
Overview Use this command to set the managed address configuration flag, contained
within the router advertisement field.
Setting this flag indicates the operation of a stateful autoconfiguration protocol
such as DHCPv6 for address autoconfiguration, and that address information (i.e.
the network prefix) and other (non-address) information can be requested from
the device.
An unset flag enables hosts receiving the advertisements to use a stateless
autoconfiguration mechanism to establish their IPv6 addresses. The default is flag
unset.
Use the no variant of this command to reset this command to its default of having
the flag unset.
Syntax ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
no ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
Default Unset
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Advertisement flags will not be transmitted unless you have applied the ipv6 nd
suppress-ra command. This step is included in the example below.
Example To set the managed address configuration flag on the VLAN interface vlan2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 793
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND MINIMUM-RA-INTERVAL
ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode to set a minimum Router
Advertisement (RA) interval for a VLAN interface.
Use the no variant of this command in Interface Configuration mode to remove the
minimum RA interval for a VLAN interface.
Syntax ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval <seconds>
no ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval
Default The RA interval for a VLAN interface is unset by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Examples To set the minimum RA interval for the VLAN interface vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval 60
To remove the minimum RA interval for the VLAN interface vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd ra-interval
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
Parameter Description
<seconds>Specifies the number of seconds between IPv6 Router
Advertisements (RAs). Valid values are from 3 to 1350
seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 794
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND OTHER-CONFIG-FLAG
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
Overview Use this command to set the other stateful configuration flag (contained within
the router advertisement field) to be used for IPv6 address auto-configuration. This
flag is used to request the router to provide information in addition to providing
addresses.
Setting the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag command implies that the ipv6 nd
other-config-flag will also be set.
Use no variant of this command to reset the value to the default.
Syntax ipv6 nd other-config-flag
no ipv6 nd other-config-flag
Default Unset
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Advertisement flags will not be transmitted unless you have applied the ipv6 nd
suppress-ra command. This step is included in the example below.
Example To set the IPv6 other-config-flag on the VLAN interface vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd other-config-flag
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
ipv6 nd managed-config-flag

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 795
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND PREFIX
ipv6 nd prefix
Overview Use this command in Interface Configuration mode for a VLAN interface to specify
the IPv6 prefix information that is advertised by the router advertisement for IPv6
address auto-configuration.
Use the no parameter with this command to reset the IPv6 prefix for a VLAN
interface in Interface Configuration mode.
Syntax ipv6 nd prefix <ipv6-prefix/length>
ipv6 nd prefix <ipv6-prefix/length> [<valid-lifetime>]
ipv6 nd prefix <ipv6-prefix/length>
<valid-lifetime><preferred-lifetime> [no-autoconfig]
ipv6 nd prefix <ipv6-prefix/length>
<valid-lifetime><preferred-lifetime> off-link [no-autoconfig]
no ipv6 nd prefix [<ipv6-addr/prefix-length>|all]
Default Valid-lifetime default is 2592000 seconds (30 days). Preferred-lifetime default is
604800 seconds (7 days).
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Parameter Description
<ipv6-prefix/
length> The prefix to be advertised by the router advertisement
message.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the format X:X::/prefix-length.
The prefix-length is usually set between 0 and 64. The
default is X:X::/64.
<valid-lifetime> The the period during which the specified IPv6 address
prefix is valid. This can be set to a value between 0 and
4294967295 seconds. The default is 2592000 (30 days).
Note that this period should be set to a value greater than
that set for the prefix preferred-lifetime.
<preferred-
lifetime> Specifies theIPv6 prefix preferred lifetime. This is the period
during which the IPv6 address prefix is considered a current
(undeprecated) value. After this period, the command is still
valid but should not be used in new communications. Set to
a value between 0 and 4294967295 seconds. The default is
604800 seconds (7 days).
Note that this period should be set to a value less than that
set for the prefix valid-lifetime.
off-link Specify the IPv6 prefix off-link flag. The default is flag set.
no-autoconfig Specify the IPv6 prefix no autoconfiguration flag. Setting
this flag indicates that the prefix is not to be used for
autoconfiguration. The default is flag set.
all Specify all IPv6 prefixes associated with the VLAN interface.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 796
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND PREFIX
Usage This command specifies the IPv6 prefix flags that are advertised by the router
advertisement message.
Examples To configure the device to issue router advertisements on vlan2, and advertise the
address prefix of 2001:0db8::/64, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd prefix 2001:0db8::/64
To configure the device to issue router advertisements on vlan2, and advertise the
address prefix of 2001:0db8::/64 with a valid lifetime of 10 days and a preferred
lifetime of 5 days, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd prefix 2001:0db8::/64 864000 432000
To configure the device to issue router advertisements on vlan2 and advertise the
address prefix of 2001:0db8::/64 with a valid lifetime of 10 days, a preferred lifetime
of 5 days, and no prefix used for autoconfiguration, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd prefix 2001:0db8::/64 864000 432000
no-autoconfig
To reset router advertisements on vlan2, so the address prefix of 2001:0db8::/64 is
not advertised from the device, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd prefix 2001:0db8::/64
To reset all router advertisements on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd prefix all
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 797
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND RA-INTERVAL
ipv6 nd ra-interval
Overview Use this command to specify the interval between IPv6 Router Advertisements
(RA) transmissions.
Use no parameter with this command to reset the value to the default value (600
seconds).
Syntax ipv6 nd ra-interval <seconds>
no ipv6 nd ra-interval
Default 600 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Advertisement flags will not be transmitted unless you have applied the ipv6 nd
suppress-ra command as shown in the example below.
Example To set the advertisements interval on vlan2 to be 60 seconds, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd ra-interval 60
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd minimum-ra-interval
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
Parameter Description
<seconds>Specifies the number of seconds between IPv6 Router
Advertisements (RAs). Valid values are from 4 to 1800 seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 798
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND RA-LIFETIME
ipv6 nd ra-lifetime
Overview Use this command to specify the time period that this router can usefully act as a
default gateway for the network. Each router advertisement resets this time
period.
Use no parameter with this command to reset the value to default.
Syntax ipv6 nd ra-lifetime <seconds>
no ipv6 nd ra-lifetime
Default 1800 seconds
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command specifies the lifetime of the current router to be announced in IPv6
Router Advertisements.
Advertisement flags will not be transmitted unless you have applied the ipv6 nd
suppress-ra command. This instruction is included in the example shown below.
Examples To set the advertisement lifetime of 8000 seconds on the VLAN interface vlan2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd ra-lifetime 8000
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
Parameter Description
<seconds>Time period in seconds. Valid values are from 0 to 9000.
Note that you should set this time period to a value greater than the
value you have set using the ipv6 nd ra-interval command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 799
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND RAGUARD
ipv6 nd raguard
Overview Use this command to apply the Router Advertisements (RA) Guard feature from the
Interface Configuration mode for a device port. This blocks all RA messages
received on a device port.
For more information about RA Guard, see the IPv6 Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Use the no parameter with this command to disable RA Guard for a specified
device port.
Syntax ipv6 nd raguard
no ipv6 nd raguard
Default RA Guard is not disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a port.
Usage Router Advertisements (RAs) are used by Routers to announce themselves on the
link. Applying RA Guard to a device port disallows Router Advertisements and
redirect messages. RA Guard blocks RAs from untrusted hosts. Blocking RAs stops
untrusted hosts from flooding malicious RAs and stops any misconfigured hosts
from disrupting traffic on the local network.
Enabling RA Guard on a port blocks RAs from a connected host and indicates the
port and host are untrusted. Disabling RA Guard on a port allows RAs from a
connected host and indicates the port and host are trusted. Ports and hosts are
trusted by default to allow RAs.
Example To enable RA Guard on port1.0.1-port1.0.4, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd raguard
To verify RA Guard is enabled on port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show running-config interface port1.0.1
To disable RA Guard on port1.0.1-port1.0.4, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd raguard
When RA Guard is disabled on a port it is not displayed in show running-config
output.
Output Example output from using show running-config interface port1.0.1 to verify RA
Guard:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 801
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND REACHABLE-TIME
ipv6 nd reachable-time
Overview Use this command to specify the reachable time in the router advertisement to be
used for detecting reachability of the IPv6 neighbor.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the value to default.
Syntax ipv6 nd reachable-time <milliseconds>
no ipv6 nd reachable-time
Default 0 milliseconds
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command specifies the reachable time of the current router to be announced
in IPv6 Router Advertisements.
Advertisement flags will not be transmitted unless you have applied the ipv6 nd
suppress-ra command. This instruction is included in the example shown below.
Example To set the reachable-time in router advertisements on the VLAN interface vlan2 to
be 1800000 milliseconds, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd reachable-time 1800000
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
To reset the reachable-time in router advertisements on the VLAN interface vlan2
to an unspecified reachable-time (0 milliseconds), enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd reachable-time
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
Parameter Description
<milliseconds>Time period in milliseconds. Valid values are from 1000 to
3600000.
Setting this value to 0 indicates an unspecified reachable-time.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 802
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND RETRANSMISSION-TIME
ipv6 nd retransmission-time
Overview Use this command to specify the advertised retransmission interval for Neighbor
Solicitation in milliseconds between IPv6 Routers.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the retransmission time to the default
(1 second).
Syntax ipv6 nd retransmission-time <milliseconds>
no ipv6 nd retransmission-time
Default 1000 milliseconds (1 second)
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Examples To set the retransmission-time of Neighbor Solicitation on the VLAN interface
vlan2 to be 800000 milliseconds, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 nd retransmission-time 800000
To reset the retransmission-time of Neighbor Solicitation on the VLAN interface
vlan2 to the default 1000 milliseconds (1 second), enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd retransmission-time
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
ipv6 nd prefix
Parameter Description
<milliseconds>Time period in milliseconds. Valid values are from 1000 to
3600000.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 803
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 ND SUPPRESS-RA
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Overview Use this command to inhibit IPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) transmission for the
current interface. Router advertisements are used when applying IPv6 stateless
auto-configuration.
Use no parameter with this command to enable Router Advertisement
transmission.
Syntax ipv6 nd suppress-ra
no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Default Router Advertisement (RA) transmission is suppressed by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To enable the transmission of router advertisements from vlan2 on the device, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 nd suppress-ra
Related
Commands
ipv6 nd ra-interval
ipv6 nd prefix

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 804
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 NEIGHBOR
ipv6 neighbor
Overview Use this command to add a static IPv6 neighbor entry.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a specific IPv6 neighbor entry.
Syntax ipv6 neighbor <ipv6-address> <vlan-name> <mac-address>
<port-list>
no ipv6 neighbor <ipv6-address> <vlan-name> <port-list>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to clear a specific IPv6 neighbor entry. To clear all dynamic
address entries, use the clear ipv6 neighbors command.
Example To create a static neighbor entry for IPv6 address 2001:0db8::a2, on vlan2, with
MAC address 0000.cd28.0880, on port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 neighbor 2001:0db8::a2 vlan2
0000.cd28.0880 port1.0.1
Related
Commands
clear ipv6 neighbors
Parameter Description
<ipv6-address>Specify the neighbor’s IPv6 address in the format X:X::X:X.
<vlan-name>Specify the neighbor’s VLAN name.
<mac-address>Specify the MAC hardware address in hexadecimal notation in
the format HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
<port-list> Specify the port number, or port range.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 805
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 OPPORTUNISTIC-ND
ipv6 opportunistic-nd
Overview Use this command to enable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the global IPv6
ND cache. Opportunistic neighbor discovery changes the behavior for unsolicited
ICMPv6 ND packet forwarding on the device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable opportunistic neighbor discovery
for the global IPv6 ND cache.
Syntax ipv6 opportunistic-nd
no ipv6 opportunistic-nd
Default Opportunistic neighbor discovery is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When opportunistic neighbor discovery is enabled, the device will reply to any
received unsolicited ICMPv6 ND packets. The source MAC address for the
unsolicited ICMPv6 ND packet is added to the IPv6 ND cache, so the device
forwards the ICMPv6 ND packet. When opportunistic neighbor discovery is
disabled, the source MAC address for the ICMPv6 packet is not added to the IPv6
ND cache, so the ICMPv6 ND packet is not forwarded by the device.
Examples To enable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the IPv6 ND cache, enter:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 opportunistic-nd
To disable opportunistic neighbor discovery for the IPv6 ND cache, enter:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ipv6 opportunistic-nd
Related
Commands
arp opportunistic-nd
show ipv6 neighbors
show running-config interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 806
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
IPV6 UNREACHABLES
ipv6 unreachables
Overview Use this command to enable ICMPv6 (Internet Control Message Protocol version 6)
type 1, destination unreachable, messages.
Use the no variant of this command to disable destination unreachable messages.
This prevents an attacker from using these messages to discover the topology of a
network.
Syntax ipv6 unreachables
no ipv6 unreachables
Default Destination unreachable messages are enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When a device receives a packet for a destination that is unreachable it returns an
ICMPv6 type 1 message. This message includes a reason code, as per the table
below. An attacker can use these messages to obtain information regarding the
topology of a network. Disabling destination unreachable messages, using the no
ipv6 unreachables command, secures your network against this type of probing.
NOTE: Disabling ICMPv6 destination unreachable messages breaks applications such
as traceroute, which depend on these messages to operate correctly.
Example To disable destination unreachable messages, use the commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ipv6 unreachables
To enable destination unreachable messages, use the commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 unreachables
Table 24-1: ICMPv6 type 1 reason codes and description
Code Description [RFC]
0No route to destination [RFC4443]
1Communication with destination administratively prohibited [RFC4443]
2Beyond scope of source address [RFC4443]
3Address unreachable [RF4443]
4Port unreachable [RFC4443]
5Source address failed ingress/egress policy [RFC4443]
6Reject route to destination [RFC4443
7Error in Source Routing Header [RFC6554]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 807
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
OPTIMISTIC-ND
optimistic-nd
Overview Use this command to enable the optimistic neighbor discovery feature for both
IPv4 and IPv6.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the optimistic neighbor discovery
feature.
Syntax optimistic-nd
no optimistic-nd
Default The optimistic neighbor discovery feature is enabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage The optimistic neighbor discovery feature allows the device, after learning an IPv4
or IPv6 neighbor, to refresh the neighbor before the neighbor is deleted from the
hardware L3 switching table. The device puts the neighbour entry into the "stale"
state in the software switching table if is it not refreshed, then the 'stale' neighbors
are deleted from the hardware L3 switching table.
The optimistic neighbor discovery feature enables the device to sustain L3 traffic
switching to a neighbor without interruption. Without the optimistic neighbor
discovery feature enabled L3 traffic is interrupted when a neighbor is “stale” and is
then deleted from the L3 switching table.
If a neighbor receiving optimistic neighbor solicitations does not answer
optimistic neighbor solicitations with neighbor advertisements, then the neighbor
will be put into the “stale” state, and subsequently deleted from both the software
and the hardware L3 switching tables.
Examples To enable the optimistic neighbor discovery feature on vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# optimistic-nd
To disable the optimistic neighbor discovery feature on vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no optimistic-nd
Related
Commands
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 808
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
PING IPV6
ping ipv6
Overview This command sends a query to another IPv6 host (send Echo Request messages).
Syntax ping ipv6 {<host>|<ipv6-address>} [repeat
{<1-2147483647>|continuous}] [size <10-1452>] [interface
<interface-list>] [timeout <1-65535>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# ping ipv6 2001:0db8::a2
Parameter Description
<ipv6-addr> The destination IPv6 address. The IPv6 address uses the
format X:X::X:X.
<hostname>The destination hostname.
repeat Specify the number of ping packets to send.
<1-2147483647> Specify repeat count. The default is 5.
size <10-1452> The number of data bytes to send, excluding the 8 byte ICMP
header. The default is 56 (64 ICMP data bytes).
interface
<interface-list> The interface or range of configured IP interfaces to use as the
source in the IP header of the ping packet. The interface can
be one of:
•a VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• the loopback interface (lo)
• a continuous range of interfaces separated by a hyphen
(e.g. vlan10-20)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. vlan1,vlan10-20). Do not mix
interface types in a list.
You can only specify the interface when pinging a link local
address.
timeout
<1-65535> The time in seconds to wait for echo replies if the ARP entry is
present, before reporting that no reply was received. If no ARP
entry is present, it does not wait.
repeat Specify the number of ping packets to send.
<1-2147483647> Specify repeat count. The default is 5.
continuous Continuous ping.
size <10-1452> The number of data bytes to send, excluding the 8 byte ICMP
header. The default is 56 (64 ICMP data bytes).
timeout
<1-65535> The time in seconds to wait for echo replies if the ARP entry is
present, before reporting that no reply was received. If no ARP
entry is present, it does not wait.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 810
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 FORWARDING
show ipv6 forwarding
Overview Use this command to display IPv6 forwarding status.
Syntax show ipv6 forwarding
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show ipv6 forwarding
Output Figure 24-1: Example output from the show ipv6 forwarding command
ipv6 forwarding is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 811
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 INTERFACE BRIEF
show ipv6 interface brief
Overview Use this command to display brief information about interfaces and the IPv6
address assigned to them.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting_Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 interface [brief]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples awplus# show ipv6 interface brief
Output Figure 24-2: Example output from the show ipv6 interface brief command
Related
Commands
show interface brief
Parameter Description
brief Specify this optional parameter to display brief IPv6 interface
information.
awplus#show ipv6 interface brief
Interface IPv6-Address Status Protocol
lo unassigned admin up running
vlan1 2001:db8::1/48 admin up down
fe80::215:77ff:fee9:5c50/64

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 812
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 NEIGHBORS
show ipv6 neighbors
Overview Use this command to display all IPv6 neighbors.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting_Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 neighbors
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 813
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE
show ipv6 route
Overview Use this command to display the IPv6 routing table for a protocol or from a
particular table.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 route
[connected|database|static|summary|<ipv6-address>|
<ipv6-addr/prefix-length>)]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display an IP route with all parameters turned on, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route
To display all database entries for an IP route, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route database
Parameter Description
connected Displays only the routes learned from connected
interfaces.
database Displays only the IPv6 routing information extracted
from the database.
static Displays only the IPv6 static routes you have configured.
summary Displays summary information from the IPv6 routing
table.
<ipv6-address> Displays the routes for the specified address in the IP
routing table. The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X/Prefix-Length. The prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-prefix/length> Displays only the routes for the specified IP prefix.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 814
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE
Output Figure 24-3: Example output of the show ipv6 route command
Output Figure 24-4: Example output of the show ipv6 route database command
IPv6 Routing Table
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, B - BGP
S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001::a:0:0:c0a8:a6, vlan10
C 2001:db8::a:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan10
C 2001:db8::14:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan20
C 2001:db8::0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan30
C 2001:db8::28:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan40
C 2001:db8::fa:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan250
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan250
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan40
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan20
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan10
IPv6 Routing Table
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, B - BGP
> - selected route, * - FIB route, p - stale info
Timers: Uptime
S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001::a:0:0:c0a8:a01 inactive, 6d22h12m
[1/0] via 2001::fa:0:0:c0a8:fa01 inactive, 6d22h12m
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 815
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE SUMMARY
show ipv6 route summary
Overview Use this command to display the summary of the current NSM RIB entries.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 route summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display IP route summary, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route summary
Output Figure 24-5: Example output from the show ipv6 route summary command
Related
Commands
show ip route database
IPv6 routing table name is Default-IPv6-Routing-Table(0)
IPv6 routing table maximum-paths is 4
RouteSource Networks
connected 4
rip 5
Total 9
FIB 5

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 816
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 COMMANDS
TRACEROUTE IPV6
traceroute ipv6
Overview Use this command to trace the route to the specified IPv6 host.
Syntax traceroute ipv6 {<ipv6-addr>|<hostname>}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To run a traceroute for the IPv6 address 2001:0db8::a2, use the following
command:
awplus# traceroute ipv6 2001:0db8::a2
Related
Commands
ping ipv6
Parameter Description
<ipv6-addr> The destination IPv6 address. The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
<hostname>The destination hostname.

25
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 817
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Routing Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of routing commands that are
common across the routing IP protocols. For more information, see the Route
Selection Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“ip route” on page 818
•“ipv6 route” on page 820
•“maximum-paths” on page 821
•“show ip route” on page 822
•“show ip route database” on page 824
•“show ip route summary” on page 825
•“show ipv6 route” on page 826
•“show ipv6 route summary” on page 828

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 818
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
IP ROUTE
ip route
Overview This command adds a static route to the Routing Information Base (RIB). If this
route is the best route for the destination, then your device adds it to the
Forwarding Information Base (FIB). Your device uses the FIB to advertise routes to
neighbors and forward packets.
The no variant of this command removes the static route from the RIB and FIB.
Syntax ip route <subnet&mask> {<gateway-ip>|<interface>} [<distance>]
no ip route <subnet&mask> {<gateway-ip>|<interface>}
[<distance>]
Mode Global Configuration
Default The default administrative distance for a static route is 1.
Usage You can use administrative distance to determine which routes take priority over
other routes.
Examples To add the destination 192.168.3.0 with the mask 255.255.255.0 as a static route
available through the device at “10.10.0.2” with the default administrative
distance, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.0.2
Parameter Description
<subnet&mask>The IPv4 address of the destination subnet defined using either a
prefix length or a separate mask specified in one of the following
formats:
• The IPv4 subnet address in dotted decimal notation followed by
the subnet mask, also in dotted decimal notation.
• The IPv4 subnet address in dotted decimal notation, followed
by a forward slash, then the prefix length
<gateway-ip>The IPv4 address of the gateway device.
<interface>The interface that connects your device to the network. Enter the
name of the VLAN or its VID.
The gateway IP address or the interface is required.
<distance>The administrative distance for the static route in the range
<1-255>. Static routes by default have an administrative distance
of 1, which gives them the highest priority possible.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 819
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
IP ROUTE
To remove the destination 192.168.3.0 with the mask 255.255.255.0 as a static
route available through the device at “10.10.0.2” with the default administrative
distance, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.0.2
To add the destination 192.168.3.0 with the mask 255.255.255.0 as a static route
available through the device at “10.10.0.2” with an administrative distance of 128,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.0.2
128
Related
Commands
show ip route
show ip route database

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 820
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
IPV6 ROUTE
ipv6 route
Overview This command adds a static IPv6 route to the Routing Information Base (RIB). If this
route is the best route for the destination, then your device adds it to the
Forwarding Information Base (FIB). Your device uses the FIB to advertise routes to
neighbors and forward packets.
The no variant of this command removes the static route.
Syntax ipv6 route <dest-prefix> <dest-prefix/length>
{<gateway-ip>|<gateway-name>} [<distvalue>]
no ipv6 route <dest-prefix> <dest-prefix/length>
{<gateway-ip>|<gateway-name>} [<distvalue>]
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You can use administrative distance to determine which routes take priority over
other routes.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 route 2001:0db8::1/128 vlan2 32
Validation
Commands
show running-config
show ipv6 route
Parameter Description
<dest-prefix/
length>Specifies the IP destination prefix.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the format X:X::/prefix-length.
The prefix-length is usually set between 0 and 64.
<gateway-ip>Specifies the IP gateway (or next hop) address. The IPv6
address uses the format X:X::X:X/Prefix-Length. The
prefix-length is usually set between 0 and 64.
<gateway-name>Specifies the name of the gateway (or next hop) interface.
<distvalue>Specifies the administrative distance for the route. Valid
values are from 1 to 255.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 821
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
MAXIMUM-PATHS
maximum-paths
Overview This command enables ECMP on your device, and sets the maximum number of
paths that each route has in the Forwarding Information Base (FIB). ECMP is
enabled by default.
The no variant of this command sets the maximum paths to the default of 4.
Syntax maximum-paths <1-8>
no maximum-paths
Default By default the maximum number of paths is 4.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the maximum number of paths for each route in the FIB to 5, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# maximum-paths 5
To set the maximum paths for a route to the default of 4, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no maximum-paths
Parameter Description
<1-8> The maximum number of paths that a route can have in the FIB.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 822
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IP ROUTE
show ip route
Overview Use this command to display routing entries in the FIB (Forwarding Information
Base). The FIB contains the best routes to a destination, and your device uses these
routes when forwarding traffic. You can display a subset of the entries in the FIB
based on protocol.
To modify the lines displayed, use the | (output modifier token); to save the output
to a file, use the > output redirection token.
Syntax show ip route [connected|static|<ip-addr>|
<ip-addr/prefix-length>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the static routes in the FIB, use the command:
awplus# show ip route static
Output Each entry in the output from this command has a code preceding it, indicating the
source of the routing entry. The first few lines of the output list the possible codes
that may be seen with the route entries.
Typically, route entries are composed of the following elements:
•code
• a second label indicating the sub-type of the route
• network or host IP address
• administrative distance and metric
• next hop IP address
• outgoing interface name
• time since route entry was added
Parameter Description
connected Displays only the routes learned from connected
interfaces.
static Displays only the static routes you have configured.
<ip-addr> Displays the routes for the specified address. Enter
an IPv4 address.
<ip-addr/prefix-length> Displays the routes for the specified network. Enter
an IPv4 address and prefix length.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 823
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IP ROUTE
Figure 25-1: Example output from the show ip route command
Connected Route The connected route entry consists of:
This route entry denotes:
• Route entries for network 10.10.31.0/24 are derived from the IP address of
local interface vlan2.
• These routes are marked as Connected routes (C) and always preferred over
routes for the same network learned from other routing protocols.
Related
Commands
ip route
maximum-paths
show ip route database
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default
C 3.3.3.0/24 is directly connected, vlan1
C 10.10.31.0/24 is directly connected, vlan2
C 10.70.0.0/24 is directly connected, vlan4
C 33.33.33.33/32 is directly connected, lo
C 10.10.31.0/24 is directly connected, vlan2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 824
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IP ROUTE DATABASE
show ip route database
Overview This command displays the routing entries in the RIB (Routing Information Base).
When multiple entries are available for the same prefix, RIB uses the routes’
administrative distances to choose the best route. All best routes are entered into
the FIB (Forwarding Information Base). To view the routes in the FIB, use the show
ip route command.
To modify the lines displayed, use the | (output modifier token); to save the output
to a file, use the > output redirection token.
Syntax show ip route database [connected|static]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the static routes in the RIB, use the command:
awplus# show ip route database static
Output Figure 25-2: Example output from the show ip route database command
Related
Commands
maximum-paths
show ip route
Parameter Description
connected Displays only the routes learned from connected interfaces.
static Displays only the static routes you have configured.
awplus#show ip route database
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP
O - OSPF, D - DHCP, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
> - selected route, * - FIB route, p - stale info
S *> 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 10.34.1.1, vlan1
C *> 10.34.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan1
S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] is directly connected, vlan2 inactive
Gateway of last resort is not set
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 825
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IP ROUTE SUMMARY
show ip route summary
Overview This command displays a summary of the current RIB (Routing Information Base)
entries.
To modify the lines displayed, use the | (output modifier token); to save the output
to a file, use the > output redirection token.
Syntax show ip route summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display a summary of the current RIB entries, use the command:
awplus# show ip route summary
Output Figure 25-3: Example output from the show ip route summary command
Related
Commands
show ip route
show ip route database
IP routing table name is Default-IP-Routing-Table(0)
IP routing table maximum-paths is 4
Route Source Networks
connected 5
Total 8

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 826
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE
show ipv6 route
Overview Use this command to display the IPv6 routing table for a protocol or from a
particular table.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 route
[connected|database|static|summary|<ipv6-address>|
<ipv6-addr/prefix-length>)]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display an IP route with all parameters turned on, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route
To display all database entries for an IP route, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route database
Parameter Description
connected Displays only the routes learned from connected
interfaces.
database Displays only the IPv6 routing information extracted
from the database.
static Displays only the IPv6 static routes you have configured.
summary Displays summary information from the IPv6 routing
table.
<ipv6-address> Displays the routes for the specified address in the IP
routing table. The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X/Prefix-Length. The prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-prefix/length> Displays only the routes for the specified IP prefix.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 827
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE
Output Figure 25-4: Example output of the show ipv6 route command
Output Figure 25-5: Example output of the show ipv6 route database command
IPv6 Routing Table
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, B - BGP
S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001::a:0:0:c0a8:a6, vlan10
C 2001:db8::a:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan10
C 2001:db8::14:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan20
C 2001:db8::0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan30
C 2001:db8::28:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan40
C 2001:db8::fa:0:0:0:0/64 via ::, vlan250
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan250
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan40
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan20
C 2001:db8::/64 via ::, vlan10
IPv6 Routing Table
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, B - BGP
> - selected route, * - FIB route, p - stale info
Timers: Uptime
S ::/0 [1/0] via 2001::a:0:0:c0a8:a01 inactive, 6d22h12m
[1/0] via 2001::fa:0:0:c0a8:fa01 inactive, 6d22h12m
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 828
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ROUTING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ROUTE SUMMARY
show ipv6 route summary
Overview Use this command to display the summary of the current NSM RIB entries.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 route summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display IP route summary, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 route summary
Output Figure 25-6: Example output from the show ipv6 route summary command
Related
Commands
show ip route database
IPv6 routing table name is Default-IPv6-Routing-Table(0)
IPv6 routing table maximum-paths is 4
RouteSource Networks
connected 4
rip 5
Total 9
FIB 5

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 829
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 4: Multicast Applications

26
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 830
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP and IGMP
Snooping
Commands
Introduction
Overview Devices running AlliedWare Plus use IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
and MLD (Multicast Listener Discovery) to track which multicast groups their clients
belong to. This enables them to send the correct multimedia streams to the correct
destinations. IGMP is used for IPv4 multicasting, and MLD is used for IPv6
multicasting.
This chapter describes the commands to configure IGMP Querier behaviour and
selection and IGMP Snooping.
Command List •“clear ip igmp” on page 832
•“clear ip igmp group” on page 833
•“clear ip igmp interface” on page 834
•“debug igmp” on page 835
•“ip igmp” on page 836
•“ip igmp access-group” on page 837
•“ip igmp flood specific-query” on page 838
•“ip igmp immediate-leave” on page 839
•“ip igmp last-member-query-count” on page 840
•“ip igmp last-member-query-interval” on page 841
•“ip igmp limit” on page 842
•“ip igmp maximum-groups” on page 843
•“ip igmp querier-timeout” on page 845
•“ip igmp query-holdtime” on page 846
•“ip igmp query-interval” on page 848
•“ip igmp query-max-response-time” on page 850

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 831
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
•“ip igmp ra-option” on page 852
•“ip igmp robustness-variable” on page 853
•“ip igmp snooping” on page 854
•“ip igmp snooping fast-leave” on page 855
•“ip igmp snooping mrouter” on page 856
•“ip igmp snooping querier” on page 857
•“ip igmp snooping report-suppression” on page 858
•“ip igmp snooping routermode” on page 859
•“ip igmp snooping source-timeout” on page 861
•“ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit” on page 862
•“ip igmp source-address-check” on page 864
•“ip igmp static-group” on page 865
•“ip igmp startup-query-count” on page 867
•“ip igmp startup-query-interval” on page 868
•“ip igmp trusted” on page 869
•“ip igmp version” on page 870
•“show debugging igmp” on page 871
•“show ip igmp groups” on page 872
•“show ip igmp interface” on page 874
•“show ip igmp snooping mrouter” on page 876
•“show ip igmp snooping routermode” on page 877
•“show ip igmp snooping source-timeout” on page 878
•“show ip igmp snooping statistics” on page 879
•“undebug igmp” on page 881

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 832
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IP IGMP
clear ip igmp
Overview Use this command to clear all IGMP group membership records on all VLAN
interfaces.
Syntax clear ip igmp
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear ip igmp
Related
Commands
clear ip igmp group
clear ip igmp interface
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 833
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IP IGMP GROUP
clear ip igmp group
Overview Use this command to clear IGMP group membership records for a specific group
on either all interfaces, a single interface, or for a range of interfaces.
Syntax clear ip igmp group *
clear ip igmp group <ip-address> <interface>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command applies to groups learned by IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
In addition to the group, an interface can be specified. Specifying this will mean
that only entries with the group learned on the interface will be deleted.
Examples To delete all group records, use the command:
awplus# clear ip igmp group *
To delete records for 224.1.1.1 on vlan1, use the command:
awplus# clear ip igmp group 224.1.1.1 vlan1
Related
Commands
clear ip igmp
clear ip igmp interface
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Parameter Description
*Clears all groups on all interfaces. This has the same effect as the
clear ip igmp command.
<ip-address> Specifies the group whose membership records will be cleared
from all interfaces, entered in the form A.B.C.D.
<interface>Specifies the name of the interface; all groups learned on this
interface are deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 834
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IP IGMP INTERFACE
clear ip igmp interface
Overview Use this command to clear IGMP group membership records on a particular
interface.
Syntax clear ip igmp interface <interface>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example To delete records for vlan1, use the command:
awplus# clear ip igmp interface vlan1
Related
Commands
clear ip igmp
clear ip igmp group
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Parameter Description
<interface>Specifies the name of the interface. All groups learned on this
interface are deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 835
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
DEBUG IGMP
debug igmp
Overview Use this command to enable debugging of either all IGMP or a specific component
of IGMP.
Use the no variant of this command to disable all IGMP debugging, or debugging
of a specific component of IGMP.
Syntax debug igmp {all|decode|encode|events|fsm|tib}
no debug igmp {all|decode|encode|events|fsm|tib}
Modes Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug igmp all
Related
Commands
show debugging igmp
undebug igmp
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Parameter Description
all Enable or disable all debug options for IGMP
decode Debug of IGMP packets that have been received
encode Debug of IGMP packets that have been sent
events Debug IGMP events
fsm Debug IGMP Finite State Machine (FSM)
tib Debug IGMP Tree Information Base (TIB)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 836
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP
ip igmp
Overview Use this command to enable IGMP on an interface. The command configures the
device as an IGMP querier.
Use the no variant of this command to return all IGMP related configuration to the
default on this interface.
Syntax ip igmp
no ip igmp
Default Disabled
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage An IP address must be assigned to the interface first, before this command will
work.
Example To specify an interface as an IGMP querier, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp
Validation
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 837
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP ACCESS-GROUP
ip igmp access-group
Overview This command adds an access control list to a VLAN interface configured for IGMP
or IGMP Snooping. The access control list is used to control and filter the multicast
groups learned on the VLAN interface.
The no variant of this command disables the access control filtering on the
interface.
Syntax ip igmp access-group {<access-list-number>|<access-list-name>}
no ip igmp access-group
Default By default there are no access lists configured on any interface.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example In the following example, hosts serviced by VLAN interface vlan2 can only join the
group 225.2.2.2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 1 permit 225.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp access-group 1
Parameter Description
<access-list-number>Standard IP access-list number, in the range <1-99>.
<access-list-name>Standard IP access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 838
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP FLOOD SPECIFIC-QUERY
ip igmp flood specific-query
Overview Use this command if you want IGMP to flood specific queries to all VLAN member
ports, instead of only sending the queries to multicast group member ports.
Use the no variant of this command if you want IGMP to only send the queries to
multicast group member ports.
Syntax ip igmp flood specific-query
no ip igmp flood specific-query
Default By default, specific queries are flooded to all VLAN member ports.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage In an L2 switched network running IGMP, it is considered more robust to flood all
specific queries. In most cases, the benefit of flooding specific queries to all VLAN
member ports outweighs the disadvantages.
However, sometimes this is not the case. For example, if hosts with very low CPU
capability receive specific queries for multicast groups they are not members of,
their performance may degrade unacceptably. In this situation, it is desirable for
IGMP to send specific queries to known member ports only. This minimizes the
performance degradation of such hosts. In those circumstances, use this
command to turn off flooding of specific queries.
Example To cause IGMP to flood specific queries only to multicast group member ports, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip igmp flood specific-query
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 839
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP IMMEDIATE-LEAVE
ip igmp immediate-leave
Overview In IGMP version 2, use this command to minimize the leave latency of IGMP
memberships for specified multicast groups. The specified access list number or
name defines the multicast groups in which the immediate leave feature is
enabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this feature.
Syntax ip igmp immediate-leave group-list
{<access-list-number>|<access-list-number-expanded>|
<access-list-name>}
no ip igmp immediate-leave
Default Disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example The following example shows how to enable the immediate-leave feature on the
VLAN interface vlan2 for a specific range of multicast groups:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp immediate-leave group-list 34
awplus(config-if)# exit
awplus(config)# access-list 34 permit 225.192.20.0 0.0.0.255
Related
Commands
ip igmp last-member-query-interval
Parameter Description
<access-list-number>Access-list number, in the range <1-99>.
<access-list-number-expanded>Access-list number (expanded range), in
the range <1300-1999>.
<access-list-name>Standard IP access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 840
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP LAST-MEMBER-QUERY-COUNT
ip igmp last-member-query-count
Overview Use this command to set the last-member query-count value for an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default on an interface.
Syntax ip igmp last-member-query-count <2-7>
no ip igmp last-member-query-count
Default The default last member query count value is 2.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example To set the last-member query-count to 3 on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp last-member-query-count 3
Related
Commands
ip igmp last-member-query-interval
ip igmp startup-query-count
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Parameter Description
<2-7>Last member query count value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 841
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP LAST-MEMBER-QUERY-INTERVAL
ip igmp last-member-query-interval
Overview Use this command to configure the frequency at which the router sends IGMP
group specific host query messages.
Use the no variant of this command to set this frequency to the default.
Syntax ip igmp last-member-query-interval <interval>
no ip igmp last-member-query-interval
Default 1000 milliseconds
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example To change the IGMP group-specific host query message interval to 2 seconds
(2000 milliseconds) on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp last-member-query-interval 2000
Related
Commands
ip igmp last-member-query-count
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Parameter Description
<interval>The frequency in milliseconds at which IGMP group-specific host
query messages are sent, in the range 1000-25500.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 842
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP LIMIT
ip igmp limit
Overview Use this command to configure the limit on the maximum number of group
membership entries for the device as a whole or for the specified interface (if in
interface mode). Once the specified number of group memberships is reached, all
further membership reports will be ignored.
Optionally, you can configure an access-list to stop certain addresses from being
subject to the limit.
Use the no variant of this command to unset the limit and any specified exception
access-list.
Syntax ip igmp limit <limit-value> [except
{<access-list-number>|<access-list-number-extended>|
<access-list-name>}]
no ip igmp limit
Default The default limit, which is reset by the no variant of this command, is 512.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP or IGMP Snooping.
Example To configure an IGMP limit of 100 group membership entries on vlan2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp limit 100
To configure an IGMP limit of 100 group membership entries across all interfaces
on which IGMP is enabled, and exclude group 224.1.1.1 from this limitation, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 1 permit 224.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
awplus(config)# ip igmp limit 100 except 1
Parameter Description
<limit-value> Maximum number of group membership
entries, from 2 to 512.
<access-list-number>Access-list number, in the range 1 to 99.
<access-list-number-extended>Access-list number (expanded range), in
the range 1300 to 1999.
<access-list-name>IP access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 843
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP MAXIMUM-GROUPS
ip igmp maximum-groups
Overview Use this command to set a limit, per switch port, on the number of IGMP groups
clients can join. This stops a single client from using all the switch’s available
group-entry resources, and ensures that clients on all ports have a chance to join
IGMP groups.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the limit.
Syntax ip igmp maximum-groups <0-65535>
no ip igmp maximum-groups
Default The default is 0, which means no limit
Mode Interface mode for a switch port
Usage We recommend using this command with IGMP snooping fast leave on the
relevant VLANs. To enable fast leave, use the command:
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping fast-leave
The device keeps count of the number of groups learned by each port. This counter
is incremented when group joins are received via IGMP reports. It is decremented
when:
• Group memberships time out
• Group leaves are received via leave messages or reports
Also, the port's group counter is cleared when:
• The port goes down
• You run the command clear ip igmp group *
• The port is removed from a VLAN
You can see the current value of the group counter by using either of the
commands:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping statistics interface <port-list>
awplus# show ip igmp interface <port>
Parameter Description
<0-65535> The maximum number of IGMP groups clients can join on this
switch port. 0 means no limit.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 844
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP MAXIMUM-GROUPS
Example To limit clients to 10 groups on port 1.0.1, which is in vlan1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp maximum-groups 10
awplus(config-if)# exit
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping fast-leave
Related
Commands
clear ip igmp group
ip igmp snooping fast-leave
show ip igmp interface
show ip igmp snooping statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 845
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP QUERIER-TIMEOUT
ip igmp querier-timeout
Overview Use this command to configure the timeout period before the device takes over as
the querier for the interface after the previous querier has stopped querying.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default.
Syntax ip igmp querier-timeout <timeout>
no ip igmp querier-timeout
Default The default timeout interval is 255 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to VLAN interfaces configured for IGMP.
The timeout value should not be less than the current active querier’s general
query interval.
Example To configure the device to wait 130 seconds from the time it received the last query
before it takes over as the querier for vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp querier-timeout 130
Related
Commands
ip igmp query-interval
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Parameter Description
<timeout>IGMP querier timeout interval value in seconds, in the range 1-
65535.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 846
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP QUERY-HOLDTIME
ip igmp query-holdtime
Overview This command sets the time that an IGMP Querier waits after receiving a query
solicitation before it sends an IGMP Query. IGMP General Query messages will not
be sent during the hold time interval.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default query hold time
period.
Syntax ip igmp query-holdtime <interval>
no ip igmp query-holdtime
Default By default the delay before sending IGMP General Query messages is 500
milliseconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Use this command to configure a value for the IGMP query hold time in the current
network. IGMP Queries can be generated after receiving Query Solicitation (QS)
packets and there is a possibility of a DoS (Denial of Service) attack if a stream of
Query Solicitation (QS) packets are sent to the IGMP Querier, eliciting a rapid
stream of IGMP Queries. This command applies to interfaces on which the device
is acting as an IGMP Querier.
Use the ip igmp query-interval command when a delay for IGMP general query
messages is required and IGMP general query messages are required. The ip igmp
query-holdtime command stops IGMP query messages during the configured
holdtime interval, so the rate of IGMP Queries that can be sent out of an interface
can be restricted.
See the IGMP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for introductory
information about the Query Solicitation feature.
Examples To set the IGMP query holdtime to 900 ms for vlan20, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp query-holdtime 900
To reset the IGMP query holdtime to the default (500 ms) for vlan10, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp query-holdtime
Parameter Description
<interval>Query interval value in milliseconds, in the range <100-5000>.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 848
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP QUERY-INTERVAL
ip igmp query-interval
Overview Use this command to configure the period for sending IGMP General Query
messages.
The IGMP query interval specifies the time between IGMP General Query messages
being sent.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default query interval period.
NOTE: The IGMP query interval must be greater than IGMP query maximum response
time.
Syntax ip igmp query-interval <interval>
no ip igmp query-interval
Default The default IGMP query interval is 125 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP. Note that the IGMP query
interval is automatically set to a greater value than the IGMP query max response
time.
For example, if you set the IGMP query max response time to 2 seconds using the
ip igmp query-max-response-time command, and the IGMP query interval is
currently less than 3 seconds, then the IGMP query interval period will be
automatically reconfigured to be 3 seconds, so it is greater than the IGMP query
maximum response time.
Use the ip igmp query-interval command when a non-default interval for IGMP
General Query messages is required.
The ip igmp query-holdtime command can occasionally delay the sending of IGMP
Queries.
Examples To set the period between IGMP host-query messages to 3 minutes (180 seconds)
for vlan20, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp query-interval 180
Parameter Description
<interval>Query interval value in seconds, in the range <2-18000>.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 849
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP QUERY-INTERVAL
To reset the period between sending IGMP host-query messages to the default
(125 seconds) for vlan10, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp query-interval
Related
Commands
ip igmp query-holdtime
ip igmp query-max-response-time
ip igmp startup-query-interval
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 850
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP QUERY-MAX-RESPONSE-TIME
ip igmp query-max-response-time
Overview Use this command to configure the maximum response time advertised in IGMP
Queries.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default.
NOTE: The IGMP query maximum response time must be less than the IGMP query
interval.
Syntax ip igmp query-max-response-time <response-time>
no ip igmp query-max-response-time
Default The default IGMP query maximum response time is 10 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP.
Note that the IGMP query interval is automatically set to a greater value than the
IGMP query maximum response time.
For example, if you set the IGMP query interval to 3 seconds using the ip igmp
query-interval command, and the current IGMP query interval is less than 3
seconds, then the IGMP query maximum response time will be automatically
reconfigured to be 2 seconds, so it is less than the IGMP query interval time.
To get the network to converge faster, use the ip igmp
query-max-response-time command and set a low response time value, such as
one or two seconds, so that the clients will respond immediately with a report as a
response to the IGMP Queries.
Examples To set a maximum response time of 8 seconds for vlan20, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp query-max-response-time 8
To reset the default maximum response time to the default (10 seconds) for vlan10,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp query-max-response-time
Parameter Description
<response-time>Response time value in seconds, in the range 1-3180.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 852
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP RA-OPTION
ip igmp ra-option
Overview Use this command to enable strict Router Alert (RA) option validation. With strict
RA option enabled, IGMP packets without RA options are ignored.
Use the no variant of this command to disable strict RA option validation.
Syntax ip igmp ra-option
no ip igmp ra-option
Default The default state of RA validation is unset.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP and IGMP Snooping.
Examples To enable strict Router Alert (RA) option validation on vlan20, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp ra-option

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 853
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP ROBUSTNESS-VARIABLE
ip igmp robustness-variable
Overview Use this command to change the robustness variable value on an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default on an interface.
Syntax ip igmp robustness-variable <1-7>
no ip igmp robustness-variable
Default The default robustness variable value is 2.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP and IGMP Snooping.
Examples To set the robustness variable to 3 on vlan20, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp robustness-variable 3
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Parameter Description
<1-7>The robustness variable value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 854
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING
ip igmp snooping
Overview Use this command to enable IGMP Snooping. When this command is used in the
Global Configuration mode, IGMP Snooping is enabled at the device level. When
this command is used in Interface Configuration mode, IGMP Snooping is enabled
for the specified VLANs.
Use the no variant of this command to either globally disable IGMP Snooping, or
disable IGMP Snooping on a specified interface.
NOTE: IGMP snooping cannot be disabled on an interface if IGMP snooping has
already been disabled globally. IGMP snooping can be disabled on both an interface
and globally if disabled on the interface first and then disabled globally.
Syntax ip igmp snooping
no ip igmp snooping
Default By default, IGMP Snooping is enabled both globally and on all VLANs.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage For IGMP snooping to operate on particular VLAN interfaces, it must be enabled
both globally by using this command in Global Configuration mode, and on
individual VLAN interfaces by using this command in Interface Configuration
mode (both are enabled by default.)
Both IGMP snooping and MLD snooping must be enabled globally on the device
for IGMP snooping to operate. MLD snooping is also enabled by default. To enable
it if it has been disabled, use the ipv6 mld snooping command in Global
Configuration mode.
Examples To enable IGMP Snooping on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip igmp snooping
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping
Related
Commands
ipv6 mld snooping
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 855
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING FAST-LEAVE
ip igmp snooping fast-leave
Overview Use this command to enable IGMP Snooping fast-leave processing. Fast-leave
processing is analogous to immediate-leave processing. The IGMP
group-membership entry is removed as soon as an IGMP leave group message is
received, without sending out a group-specific query.
Use the no variant of this command to disable fast-leave processing.
Syntax ip igmp snooping fast-leave
no ip igmp snooping fast-leave
Default IGMP Snooping fast-leave processing is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This IGMP Snooping command can only be configured on VLAN interfaces.
Example To enable fast-leave processing on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping fast-leave
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 856
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING MROUTER
ip igmp snooping mrouter
Overview Use this command to statically configure the specified port as a multicast router
port for IGMP Snooping for an interface. This command applies to interfaces
configured for IGMP Snooping.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the static configuration of the port
as a multicast router port.
Syntax ip igmp snooping mrouter interface <port>
no ip igmp snooping mrouter interface <port>
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To configure port1.0.2 statically as a multicast router interface for vlan2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping mrouter interface port1.0.2
Related
Commands
show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Parameter Description
<port>The port may be a device port (e.g. port1.0.2), a static channel group
(e.g. sa3), or a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po4).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 857
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING QUERIER
ip igmp snooping querier
Overview Use this command to enable IGMP querier operation when no multicast routing
protocol is configured. When enabled, the IGMP Snooping querier sends out
periodic IGMP queries for all interfaces. This command applies to interfaces
configured for IGMP Snooping.
Use the no variant of this command to disable IGMP querier configuration.
Syntax ip igmp snooping querier
no ip igmp snooping querier
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage The IGMP Snooping querier uses the 0.0.0.0 Source IP address because it only
masquerades as a proxy IGMP querier for faster network convergence.
It does not start, or automatically cease, the IGMP Querier operation if it detects
query message(s) from a multicast router.
If an IP address is assigned to a VLAN, which has IGMP querier enabled on it, then
the IGMP Snooping querier uses the VLAN’s IP address as the Source IP Address in
IGMP queries.
The IGMP Snooping Querier will not stop sending IGMP Queries if there is another
IGMP Snooping Querier in the network with a lower Source IP Address.
NOTE: Do not enable the IGMP Snooping Querier feature on a Layer 2 device when
there is an operational IGMP Querier in the network.
Example To configure vlan2 as a Snooping querier, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping querier
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 858
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING REPORT-SUPPRESSION
ip igmp snooping report-suppression
Overview Use this command to enable report suppression for IGMP versions 1 and 2. This
command applies to interfaces configured for IGMP Snooping.
Report suppression stops reports being sent to an upstream multicast router port
when there are already downstream ports for this group on this interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disable report suppression.
Syntax ip igmp snooping report-suppression
no ip igmp snooping report-suppression
Default Report suppression does not apply to IGMPv3, and is turned on by default for
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 reports.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To enable report suppression for IGMPv2 reports for vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp version 2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping report-suppression
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 859
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING ROUTERMODE
ip igmp snooping routermode
Overview Use this command to set the destination IP addresses as router multicast
addresses.
Use the no variant of this command to set it to the default. You can also remove a
specified IP address from a custom list of multicast addresses.
Syntax ip igmp snooping routermode
{all|default|ip|multicastrouter|address <ip-address>}
no ip igmp snooping routermode [address <ip-address>]
Default The default routermode is default (not all) and shows the following reserved
multicast addresses:
Mode Global Configuration
Parameter Description
all All reserved multicast addresses (224.0.0.x).
Packets from all possible addresses in range 224.0.0.x are
treated as coming from routers.
default Default set of reserved multicast addresses.
Packets from 224.0.0.1, 224.0.0.2, 224.0.0.4, 224.0.0.5,
224.0.0.6, 224.0.0.9, 224.0.0.13, 224.0.0.15 and 224.0.0.24
are treated as coming from routers.
ip Custom reserved multicast addresses.
Packets from custom IP address in the 224.0.0.x range are
treated as coming from routers.
multicastrouter Packets from DVMRP (224.0.0.4) and PIM (224.0.0.13)
multicast addresses are treated as coming from routers.
address
<ip-address> Packets from the specified multicast address are treated as
coming from routers. The address must be in the 224.0.0.x
range.
Router mode.............Def
Reserved multicast address
224.0.0.1
224.0.0.2
224.0.0.4
224.0.0.5
224.0.0.6
224.0.0.9
224.0.0.13
224.0.0.15
224.0.0.24

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 860
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING ROUTERMODE
Examples To set ip igmp snooping routermode for all default reserved addresses enter:
awplus(config)# ip igmp snooping routermode default
To remove the multicast address 224.0.0.5 from the custom list of multicast
addresses enter:
awplus(config)# no ip igmp snooping routermode address
224.0.0.5
Related
commands
ip igmp trusted
show ip igmp snooping routermode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 861
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING SOURCE-TIMEOUT
ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Overview Use this command to set the global IGMP Snooping source time-out value (in
seconds) on the switch.
Use the no variant of this command to set the source time-out value to be the
same as the group membership timeout.
Syntax ip igmp snooping source-timeout <timeout>
no ip igmp snooping source-timeout <timeout>
Default Global IGMP Snooping source-timeout is disabled by default, and unregistered
multicast will be timed-out like normal entries.
Interface IGMP Snooping source timeout is disabled by default, and unregistered
multicast will be timed-out like normal entries.
Mode Interface/Global Configuration
Usage The timeout determines how long unregistered multicast entries will be kept for.
If the value ‘0’ is specified, then effectively all unregistered multicast entries will
never be timed out, and can only be cleared by using the command clear ip igmp
group. The interface settings will always take precedence over the global setting.
Example To configure IGMP Snooping source timeout on ‘vlan1’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping source-timeout 200
Related
Commands
show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Parameter Description
<timeout> Time-out value in seconds <0-86400>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 862
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING TCN QUERY SOLICIT
ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
Overview Use this command to enable IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
Snooping TCN (Topology Change Notification) Query Solicitation feature. When
this command is used in the Global Configuration mode, Query Solicitation is
enabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable IGMP Snooping TCN Query
Solicitation. When the no variant of this command is used in Interface
Configuration mode, this overrides the Global Configuration mode setting and
Query Solicitation is disabled.
Syntax ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
no ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
Default IGMP Snooping TCN Query Solicitation is disabled by default on the device, unless
the device is the Master Node in an EPSR ring, or is the Root Bridge in a Spanning
Tree.
When the device is the Master Node in an EPSR ring, or the device is the Root
Bridge in a Spanning Tree, then IGMP Snooping TCN Query Solicitation is enabled
by default and cannot be disabled using the Global Configuration mode
command. However, Query Solicitation can be disabled for specified interfaces
using the no variant of this command from the Interface Configuration mode.
Mode Global Configuration, and Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage Once enabled, if the device is not an IGMP Querier, on detecting a topology
change, the device generates IGMP Query Solicit messages that are sent to all the
ports of the vlan configured for IGMP Snooping on the device.
On a device that is not the Master Node in an EPSR ring or the Root Bridge in a
Spanning Tree, Query Solicitation can be disabled using the no variant of this
command after being enabled.
If the device that detects a topology change is an IGMP Querier then the device will
generate an IGMP Query message.
Note that the no variant of this command when issued in Global Configuration
mode has no effect on a device that is the Master Node in an EPSR ring or on a
device that is a Root Bridge in a Spanning Tree. Query Solicitation is not disabled
for the device these instances. However, Query Solicitation can be disabled on a
per-vlan basis from the Interface Configuration mode.
See the following state table that shows when Query Solicit messages are sent in
these instances:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 863
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SNOOPING TCN QUERY SOLICIT
See the IGMP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for introductory
information about the Query Solicitation feature.
Examples To enable Query Solicitation on a device, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
To disable Query Solicitation on a device, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
To enable Query Solicitation for vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
To disable Query Solicitation for vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp snooping tcn query solicit
Related
Commands
ip igmp query-holdtime
show ip igmp interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Command
issued from
Global
Configuration
Command issued
from Interface
Configuration
Device is STP Root
Bridge or the
EPSR Master Node
IGMP Query Solicit
message sent on VLAN
No Yes Yes Yes
Yes No Yes No
Yes Yes Yes Yes

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 864
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP SOURCE-ADDRESS-CHECK
ip igmp source-address-check
Overview This command enables the checking of the Source Address for an IGMP Report,
rejecting any IGMP Reports originating on devices outside of the local subnet.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the checking of the Source Address
for an IGMP Report, which allows IGMP Reports from devices outside of the local
subnet.
Syntax ip igmp source-address-check
no ip igmp source-address-check
Default Source address checking for IGMP Reports is enabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This is a security feature, and should be enabled unless IGMP Reports from outside
the local subnet are expected, for example, if Multicast VLAN Registration is active
in the network.
The no variant of this command is required to disable the IGMP Report source
address checking feature in networks that use Multicast VLAN Registration to allow
IGMP Reports from devices outside of the local subnet.
Examples To deny IGMP Reports from outside the current subnet for vlan20, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan20
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp source-address-check
To allow IGMP Reports from outside the current subnet for vlan10, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp source-address-check
Validation
Commands
show ip igmp interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 865
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP STATIC-GROUP
ip igmp static-group
Overview Use this command to statically configure multicast group membership entries on
a VLAN interface, or to statically forward a multicast channel out a particular port
or port range.
To statically add only a group membership, do not specify any parameters.
To statically add a (*,g) entry to forward a channel out of a port, specify only the
multicast group address and the switch port range.
To statically add an (s,g) entry to forward a channel out of a port, specify the
multicast group address, the source IP address, and the switch port range.
Use the no variant of this command to delete static group membership entries.
Syntax ip igmp static-group <ip-address> [source {<ip-source-addr>}]
[interface <port>]
no ip igmp static-group <ip-address> [source
{<ip-source-addr>}] [interface <port>]
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to IGMP operation, or to IGMP Snooping on a VLAN
interface.
Parameter Description
<ip-address> Standard IP Multicast group address, entered in the form
A.B.C.D, to be configured as a static group member.
source Optional.
<ip-source-addr> Standard IP source address, entered in the form A.B.C.D, to be
configured as a static source from where multicast packets
originate.
interface Use this parameter to specify a specific switch port or switch
port range to statically forward the multicast group out of. If
not used, static configuration is applied on all ports in the
VLAN.
<port>The port or port range to statically forward the group out of.
The port may be a switch port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static
channel group (e.g. sa2), or a dynamic (LACP) channel group
(e.g. po2).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 866
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP STATIC-GROUP
Example The following example show how to statically add group and source records for
IGMP on vlan3:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan3
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp static-group 226.1.2.4 source
10.2.3.4

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 867
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP STARTUP-QUERY-COUNT
ip igmp startup-query-count
Overview Use this command to configure the IGMP startup query count for an interface. The
IGMP startup query count is the number of IGMP General Query messages sent by
a querier at startup. The default IGMP startup query count is 2.
Syntax ip igmp startup-query-count <startup-query-count>
no ip igmp startup-query-count
Default The default IGMP startup query count is 2.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To set the IGMP startup query count to 4 on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp startup-query-count 4
Related
Commands
ip igmp last-member-query-count
ip igmp startup-query-interval
Parameter Description
<startup-query-count> Specify the IGMP startup query count, in the range
2-10.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 868
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP STARTUP-QUERY-INTERVAL
ip igmp startup-query-interval
Overview Use this command to configure the IGMP startup query interval for an interface.
The IGMP startup query interval is the amount of time in seconds between
successive IGMP General Query messages sent by a querier during startup. The
default IGMP startup query interval is one quarter of the IGMP query interval value.
Syntax ip igmp startup-query-interval <startup-query-interval>
no ip igmp startup-query-interval
Default The default IGMP startup query interval is one quarter of the IGMP query interval
value.
NOTE: The IGMP startup query interval must be one quarter of the IGMP query interval.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To set the IGMP startup query interval to 15 seconds for vlan2, which is one quarter
of the IGMP query interval of 60 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp query-interval 60
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp startup-query-interval 15
Related
Commands
ip igmp last-member-query-interval
ip igmp query-interval
ip igmp startup-query-count
Parameter Description
<startup-query-interval> Specify the IGMP startup query interval, in the
range of 2-1800 seconds. The value must be one
quarter of the IGMP query interval value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 869
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP TRUSTED
ip igmp trusted
Overview Use this command to allow IGMP to process packets received on certain trusted
ports only.
Use the no variant of this command to stop IGMP from processing specified
packets if the packets are received on the specified ports or aggregator.
Syntax ip igmp trusted {all|query|report|routermode}
no ip igmp trusted {all|query|report|routermode}
Default By default, all ports and aggregators are trusted interfaces, so IGMP is allowed to
process all IGMP query, report, and router mode packets arriving on all interfaces.
Mode Interface mode for one or more switch ports or aggregators
Usage Because all ports are trusted by default, use this command in its no variant to stop
IGMP processing packets on ports you do not trust.
For example, you can use this command to make sure that only ports attached to
approved IGMP routers are treated as router ports.
Example To stop ports port1.0.3-port1.0.6 from being treated as router ports by IGMP, use
the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3-port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no ip igmp trusted routermode
Parameter Description
all Specifies whether or not the interface is allowed to receive all
IGMP and other routermode packets
query Specifies whether or not the interface is allowed to receive IGMP
queries
report Specifies whether or not the interface is allowed to receive IGMP
membership reports
routermode Specifies whether or not the interface is allowed to receive
routermode packets

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 870
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP IGMP VERSION
ip igmp version
Overview Use this command to set the current IGMP version (IGMP version 1, 2 or 3) on an
interface.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default version.
Syntax ip igmp version <1-3>
no ip igmp version
Default The default IGMP version is 3.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Example To set the IGMP version to 2 for vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip igmp version 2
Related
Commands
show ip igmp interface
Parameter Description
version <1-3>IGMP protocol version number
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 871
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING IGMP
show debugging igmp
Overview Use this command to display the IGMP debugging options set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging igmp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the IGMP debugging options set, enter the command:
awplus# show debugging igmp
Output Figure 26-1: Example output from the show debugging igmp command
Related
Commands
debug igmp
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
IGMP Debugging status:
IGMP Decoder debugging is on
IGMP Encoder debugging is on
IGMP Events debugging is on
IGMP FSM debugging is on
IGMP Tree-Info-Base (TIB) debugging is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 872
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP GROUPS
show ip igmp groups
Overview Use this command to display the multicast groups with receivers directly
connected to the router, and learned through IGMP.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip igmp groups [<ip-address>|<interface> detail | brief]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example The following command displays local-membership information for all ports in all
interfaces:
awplus# show ip igmp groups
Output Figure 26-2: Example output from show ip igmp groups
Parameter Description
<ip-address> Address of the multicast group, entered in the form A.B.C.D.
<interface> Interface name for which to display local information.
brief Brief display of all interfaces
IGMP Connected Group Membership
Group Address Interface U ptime Expires Last Reporter
224.0.1.1 port1.0.1 00:00:09 00:04:17 10.10.0.82
224.0.1.24 port1.0.2 00:00:06 00:04:14 10.10.0.84
...
Table 26-1: Parameters in the output of show ip igmp groups
Parameter Description
Group
Address Address of the multicast group.
Interface Port through which the group is reachable.
Uptime The time in weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds that this
multicast group has been known to the device.
Expires Time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) until the entry expires.
Last
Reporter Last host to report being a member of the multicast group.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 873
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP GROUPS
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Version 5.4.8-2.3: brief parameter added.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 874
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP INTERFACE
show ip igmp interface
Overview Use this command to display the state of IGMP Snooping for a specified VLAN, or
all VLANs. IGMP is shown as Active or Disabled in the show output. You can also
display the number of groups a switch port belongs to.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip igmp interface [<interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output The following output shows IGMP interface status for vlan2 with IGMP Snooping
enabled:
The following output shows IGMP interface status for vlan2 with IGMP Snooping
disabled:
Parameter Description
<interface>The name of the interface.
If you specify a switch port number, the output displays the number
of groups the port belongs to, and the port’s group membership
limit, if a limit has been set (with the command ip igmp
maximum-groups).
awplus#show ip igmp interface vlan2
Interface vlan2 (Index 202)
IGMP Disabled, Inactive, Version 3 (default)
IGMP interface has 0 group-record states
IGMP activity: 0 joins, 0 leaves
IGMP robustness variable is 2
IGMP last member query count is 2
IGMP query interval is 125 seconds
IGMP query holdtime is 500 milliseconds
IGMP querier timeout is 255 seconds
IGMP max query response time is 10 seconds
Last member query response interval is 1000 milliseconds
Group Membership interval is 260 seconds
Strict IGMPv3 ToS checking is disabled on this interface
Source Address checking is enabled
IGMP Snooping is globally enabled
IGMP Snooping query solicitation is globally disabled
Num. query-solicit packets: 57 sent, 0 recvd
IGMP Snooping is enabled on this interface
IGMP Snooping fast-leave is not enabled
IGMP Snooping querier is not enabled
IGMP Snooping report suppression is enabled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 875
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP INTERFACE
The following output displays membership information for port1.0.1:
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
awplus#show ip igmp interface vlan2
Interface vlan2 (Index 202)
IGMP Disabled, Inactive, Version 3 (default)
IGMP interface has 0 group-record states
IGMP activity: 0 joins, 0 leaves
IGMP robustness variable is 2
IGMP last member query count is 2
IGMP query interval is 125 seconds
IGMP query holdtime is 500 milliseconds
IGMP querier timeout is 255 seconds
IGMP max query response time is 10 seconds
Last member query response interval is 1000 milliseconds
Group Membership interval is 260 seconds
Strict IGMPv3 ToS checking is disabled on this interface
Source Address checking is enabled
IGMP Snooping is globally enabled
IGMP Snooping query solicitation is globally disabled
Num. query-solicit packets: 57 sent, 0 recvd
IGMP Snooping is not enabled on this interface
IGMP Snooping fast-leave is not enabled
IGMP Snooping querier is not enabled
IGMP Snooping report suppression is enabled
awplus#show ip igmp interface port1.0.1
IGMP information for port1.0.1
Maximum groups limit set: 10
Number of groups port belongs to: 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 876
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP SNOOPING MROUTER
show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Overview Use this command to display the multicast router ports, both static and dynamic,
in a VLAN.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip igmp snooping mrouter [interface <interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show all multicast router interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping mrouter
To show the multicast router interfaces in vlan1, use the command:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping mrouter interface vlan1
Output Figure 26-3: Example output from show ip igmp snooping mrouter
Figure 26-4: Example output from show ip igmp snooping mrouter interface
vlan1
Related
Commands
ip igmp snooping mrouter
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Parameter Description
interface A specific interface.
<interface>The name of the VLAN interface.
VLAN Interface Static/Dynamic
1 port1.0.1 Statically configured
200 port1.0.2 Statically configured
VLAN Interface Static/Dynamic
1 port1.0.1 Statically configured
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 877
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP SNOOPING ROUTERMODE
show ip igmp snooping routermode
Overview Use this command to display the current router mode and the list of IP addresses
set as router multicast addresses from the ip igmp snooping routermode
command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip igmp snooping routermode
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the router mode and the list of router multicast addresses, use the
command:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping routermode
Output Figure 26-5: Example output from show ip igmp snooping routermode
Related
Commands
ip igmp snooping routermode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
awplus#show ip igmp snooping routermode
Router mode.............Def
Reserved multicast address
224.0.0.1
224.0.0.2
224.0.0.4
224.0.0.5
224.0.0.6
224.0.0.9
224.0.0.13
224.0.0.15
224.0.0.24

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 878
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP SNOOPING SOURCE-TIMEOUT
show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Overview Use this command to display the configured IGMP snooping source timeouts for a
specified VLAN or VLAN range.
Syntax show ip igmp snooping source-timeout [interface|
<interface-range>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the configured IGMP snooping source timeouts for all VLANs, use the
command:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Output Figure 26-6: Example output from show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Related
Commands
ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
Parameter Description
<interface-range>The name of the VLAN interface or VLAN range
awplus#show ip igmp snooping source-timeout
Global IGMP snooping source-timeout is enabled (60 secs)
vlan1 enabled (300 secs)
vlan2 inherits global setting
vlan1000 inherits global settingawplus#show ip igmp
snooping source-timeout int vlan1
Global IGMP snooping source-timeout is enabled (60 secs)vlan1
enabled (300 secs)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 879
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP SNOOPING STATISTICS
show ip igmp snooping statistics
Overview Use this command to display IGMP Snooping statistics data.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip igmp snooping statistics interface <interface-range>
[group [<ip-address>]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display IGMP statistical information for vlan1 and vlan2, use the command:
awplus# show ip igmp snooping statistics interface vlan1-vlan2
Output Figure 26-7: Example output from the show ip igmp snooping statistics
command for VLANs
Parameter Description
<ip-address> Optionally specify the address of the multicast group, entered in
the form A.B.C.D.
<interface> Specify the name of the interface or interface range. If you
specify a port number, the output displays the number of
groups the port belongs to, and the port’s group membership
limit, if a limit has been set (with the command ip igmp
maximum-groups)
awplus#show ip igmp interface vlan1-vlan2
IGMP Snooping statistics for vlan1
Interface: port1.0.1
Group: 224.1.1.1
Uptime: 00:00:09
Group mode: Exclude (Expires: 00:04:10)
Last reporter: 10.4.4.5
Source list is empty
IGMP Snooping statistics for vlan2
Interface: port1.0.2
Group: 224.1.1.2
Uptime: 00:00:19
Group mode: Exclude (Expires: 00:05:10)
Last reporter: 10.4.4.6
Source list is empty

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 880
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IGMP AND IGMP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP IGMP SNOOPING STATISTICS
Figure 26-8: Example output from the show ip igmp snooping statistics
command for a switch port
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: VRF-lite support added SBx8100.
Version 5.4.8-1.1: VRF-lite support added x930, SBx908 GEN2.
awplus#show ip igmp interface port1.0.1
IGMP information for port1.0.1
Maximum groups limit set: 10
Number of groups port belongs to: 0

27
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 882
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD Snooping
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of configuration, clear, and show
commands related to MLD Snooping.
Command List •“clear ipv6 mld” on page 883
•“clear ipv6 mld group” on page 884
•“clear ipv6 mld interface” on page 885
•“debug mld” on page 886
•“ipv6 mld immediate-leave” on page 887
•“ipv6 mld limit” on page 888
•“ipv6 mld snooping” on page 890
•“ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave” on page 892
•“ipv6 mld snooping mrouter” on page 893
•“ipv6 mld snooping querier” on page 895
•“ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression” on page 896
•“ipv6 mld static-group” on page 898
•“show debugging mld” on page 900
•“show ipv6 mld groups” on page 901
•“show ipv6 mld interface” on page 902
•“show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter” on page 903
•“show ipv6 mld snooping statistics” on page 904

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 883
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IPV6 MLD
clear ipv6 mld
Overview Use this command to clear all MLD local memberships on all interfaces.
Syntax clear ipv6 mld
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear ipv6 mld
Related
Commands
clear ipv6 mld group
clear ipv6 mld interface
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 884
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IPV6 MLD GROUP
clear ipv6 mld group
Overview Use this command to clear MLD specific local-membership(s) on all interfaces, for
a particular group.
Syntax clear ipv6 mld group {*|<ipv6-address>}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear ipv6 mld group *
Related
Commands
clear ipv6 mld
clear ipv6 mld interface
Parameter Description
*Clears all groups on all interfaces. This is an alias to the clear
ipv6 mld command.
<ipv6-address>Specify the group address for which MLD local-memberships
are to be cleared from all interfaces.
Specify the IPv6 multicast group address in the format in the
format X:X::X:X.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 885
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IPV6 MLD INTERFACE
clear ipv6 mld interface
Overview Use this command to clear MLD interface entries.
Syntax clear ipv6 mld interface <interface>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# clear ipv6 mld interface vlan2
Related
Commands
clear ipv6 mld
clear ipv6 mld group
Parameter Description
<interface> Specifies name of the interface; all groups learned from this interface
are deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 886
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
DEBUG MLD
debug mld
Overview Use this command to enable all MLD debugging modes, or a specific MLD
debugging mode.
Use the no variant of this command to disable all MLD debugging modes, or a
specific MLD debugging mode.
Syntax debug mld {all|decode|encode|events|fsm|tib}
no debug mld {all|decode|encode|events|fsm|tib}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug mld all
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug mld decode
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug mld encode
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# debug mld events
Related
Commands
show debugging mld
Parameter Description
all Debug all MLD.
decode Debug MLD decoding.
encode Debug MLD encoding.
events Debug MLD events.
fsm Debug MLD Finite State Machine (FSM).
tib Debug MLD Tree Information Base (TIB).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 887
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD IMMEDIATE-LEAVE
ipv6 mld immediate-leave
Overview Use this command to minimize the leave latency of MLD memberships.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this feature.
Syntax ipv6 mld immediate-leave group-list <IPv6-access-list-name>
no ipv6 mld immediate-leave
Default Disabled
Mode Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or a range of VLAN
interfaces.
Example The following example shows how to enable the immediate-leave feature on an
interface for a specific range of multicast groups. In this example, the router
assumes that the group access-list consists of groups that have only one node
membership at a time per interface:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 forwarding
awplus(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld immediate-leave v6grp
awplus(config-if)# exit
Parameter Description
<IPv6-access-
list-name> Specify a Standard or an Extended software IPv6 access-list
name that defines multicast groups in which the
immediate leave feature is enabled.
See IPv6 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands for
supported IPv6 ACLs.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 888
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD LIMIT
ipv6 mld limit
Overview Use this command to configure a limit on the maximum number of group
memberships that may be learned. The limit may be set for the device as a whole,
or for a specific interface.
Once the specified group membership limit is reached, all further
local-memberships will be ignored.
Optionally, an exception access-list can be configured to specify the
group-address(es) that are exempted from being subject to the limit.
Use the no variant of this command to unset the limit and any specified exception
access-list.
Syntax ipv6 mld limit <limitvalue> [except <IPv6-access-list-name>]
no ipv6 mld limit
Default The default limit, which is reset by the no variant of this command, is the same as
maximum number of group membership entries that can be learned with the ipv6
mld limit command.
The default limit of group membership entries that can be learned is 512 entries.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or
a range of VLAN interfaces.
Usage This command applies to interfaces configured for MLD Layer-3 multicast
protocols and learned by MLD Snooping.
Examples The following example configures an MLD limit of 100 group-memberships across
all VLAN interfaces on which MLD is enabled, and excludes groups in the range
ff1e:0db8:0001::/64 from this limitation:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 forwarding
awplus(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list standard v6grp permit
ff1e:0db8:0001::/64
awplus(config)# ipv6 mld limit 100 except v6grp
Parameter Description
<limitvalue><2-512> Maximum number of group membership states.
<IPv6-access-list-
name>Specify a Standard or an Extended software IPv6 access-list
name that defines multicast groups, which are exempted
from being subject to the configured limit.
See IPv6 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands for
supported IPv6 ACLs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 889
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD LIMIT
The following example configures an MLD limit of 100 group-membership states
on the VLAN interface vlan2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 forwarding
awplus(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld limit 100
The following example configures an MLD limit of 100 group-membership states
on the VLAN interfaces vlan2-vlan4:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 forwarding
awplus(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld limit 100
Related
Commands
ipv6 mld immediate-leave
show ipv6 mld groups

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 890
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING
ipv6 mld snooping
Overview Use this command to enable MLD Snooping. When this command is issued in the
Global Configuration mode, MLD Snooping is enabled globally for the device.
When this command is issued in Interface mode for a VLAN then MLD Snooping is
enabled for the specified VLAN. Note that MLD Snooping is enabled on the VLAN
only if it is enabled globally and on the VLAN.
Use the no variant of this command to globally disable MLD Snooping in Global
Configuration mode, or for the specified VLAN interface in Interface mode.
Syntax ipv6 mld snooping
no ipv6 mld snooping
Default By default, MLD Snooping is enabled both globally and on all VLANs.
Mode Global Configuration and Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or
a range of VLAN interfaces.
Usage For MLD Snooping to operate on particular VLAN interfaces, it must be enabled
both globally by using this command in Global Configuration mode, and on
individual VLAN interfaces by using this command in Interface Configuration
mode (both are enabled by default).
MLD requires memory for storing data structures, as well as the hardware tables to
implement hardware routing. As the number of ports, VLANs, static and dynamic
groups increases then more memory is consumed. You can track the memory used
for MLD with the command:
awplus# show memory pools nsm | grep MLD
Static and dynamic groups (LACP), ports and VLANs are not limited for MLD. For
VLANs, this allows you to configure MLD across more VLANs with fewer ports per
VLAN, or fewer VLANs with more ports per VLAN. For LACPs, you can configure
MLD across more LACP groups with fewer ports per LACP, or fewer LACP groups
with more ports per LACP.
Examples To configure MLD Snooping on the VLAN interfaces vlan2-vlan4, enter the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping
To disable MLD Snooping for the VLAN interfaces vlan2-vlan4, enter the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config)# no ipv6 mld snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 891
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING
To configure MLD Snooping globally for the device, enter the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 mld snooping
To disable MLD Snooping globally for the device, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ipv6 mld snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 892
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING FAST-LEAVE
ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave
Overview Use this command to enable MLD Snooping fast-leave processing. Fast-leave
processing is analogous to immediate-leave processing; the MLD
group-membership is removed as soon as an MLD leave group message is
received, without sending out a group-specific query.
Use the no variant of this command to disable fast-leave processing.
Syntax ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave
no ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave
Default MLD Snooping fast-leave processing is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or a range of VLAN
interfaces.
Usage This MLD Snooping command can only be configured on VLAN interfaces.
Examples This example shows how to enable fast-leave processing on the VLAN interface
vlan2.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave
This example shows how to enable fast-leave processing on the VLAN interface
vlan2- vlan4.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping fast-leave

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 893
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING MROUTER
ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
Overview Use this command to statically configure the specified port as a Multicast Router
interface for MLD Snooping within the specified VLAN.
See detailed usage notes below to configure static multicast router ports when
using static IPv6 multicast routes with EPSR, and the destination VLAN is an EPSR
data VLAN.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the static configuration of the
interface as a Multicast Router interface.
Syntax ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface <port>
no ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface <port>
Mode Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or a range of VLAN
interfaces.
Usage This MLD Snooping command statically configures a switch port as a Multicast
Router interface.
Note that if static IPv6 multicast routing is being used with EPSR and the
destination VLAN is an EPSR data VLAN, then multicast router (mrouter) ports must
be statically configured. This minimizes disruption for multicast traffic in the event
of ring failure or restoration.
When configuring the EPSR data VLAN, statically configure mrouter ports so that
the multicast router can be reached in either direction around the EPSR ring.
For example, if port1.0.1 and port1.0.6 are ports on an EPSR data VLAN vlan101,
which is the destination for a static IPv6 multicast route, then configure both ports
as multicast router (mrouter) ports as shown in the example commands listed
below:
Figure 27-1: Example ipv6 mld snooping mrouter commands when static IPv6
multicast routing is being used and the destination VLAN is an EPSR
data VLAN:
Parameter Description
<port>Specify the name of the port.
awplus>enable
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#interface vlan101
awplus(config-if)#ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)#ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface port1.0.6

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 894
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING MROUTER
Examples This example shows how to specify the next-hop interface to the multicast router
for VLAN interface vlan2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface
port1.0.5
This example shows how to specify the next-hop interface to the multicast router
for VLAN interfaces vlan2-vlan4:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping mrouter interface
port1.0.5

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 895
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING QUERIER
ipv6 mld snooping querier
Overview Use this command to enable MLD querier operation on a subnet (VLAN) when no
multicast routing protocol is configured in the subnet (VLAN). When enabled, the
MLD Snooping querier sends out periodic MLD queries for all interfaces on that
VLAN.
Use the no variant of this command to disable MLD querier configuration.
Syntax ipv6 mld snooping querier
no ipv6 mld snooping querier
Mode Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface.
Usage This command can only be configured on a single VLAN interface - not on multiple
VLANs.
The MLD Snooping querier uses the 0.0.0.0 Source IP address because it only
masquerades as an MLD querier for faster network convergence.
The MLD Snooping querier does not start, or automatically cease, the MLD Querier
operation if it detects query message(s) from a multicast router. It restarts as an
MLD Snooping querier if no queries are seen within the other querier interval.
Example awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping querier

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 896
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING REPORT-SUPPRESSION
ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
Overview Use this command to enable report suppression from hosts for Multicast Listener
Discovery version 1 (MLDv1) on a VLAN in Interface Configuration mode.
Use the no variant of this command to disable report suppression on a VLAN in
Interface Configuration mode.
Syntax ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
no ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
Default Report suppression does not apply to MLDv2, and is turned on by default for
MLDv1 reports.
Mode Interface Configuration for a specified VLAN interface or a range of VLAN
interfaces.
Usage This MLD Snooping command can only be configured on VLAN interfaces.
MLDv1 Snooping maybe configured to suppress reports from hosts. When a
querier sends a query, only the first report for particular set of group(s) from a host
will be forwarded to the querier by the MLD Snooping device. Similar reports (to
the same set of groups) from other hosts, which would not change group
memberships in the querier, will be suppressed by the MLD Snooping device to
prevent 'flooding' of query responses.
Examples This example shows how to enable report suppression for MLD reports on VLAN
interface vlan2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
This example shows how to disable report suppression for MLD reports on VLAN
interface vlan2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression
This example shows how to enable report suppression for MLD reports on VLAN
interfaces vlan2-vlan4:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 897
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD SNOOPING REPORT-SUPPRESSION
This example shows how to disable report suppression for MLD reports on VLAN
interfaces vlan2-vlan4:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 mld snooping report-suppression

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 898
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD STATIC-GROUP
ipv6 mld static-group
Overview Use this command to statically configure IPv6 group membership entries on an
interface. To statically add only a group membership, do not specify any
parameters.
Use the no variant of this command to delete static group membership entries.
Syntax ipv6 mld static-group <ipv6-group-address> [source
<ipv6-source-address>] [interface <port>]
no ipv6 mld static-group <ipv6-group-address> [source
<ipv6-source-address>] [interface <port>]
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage This command applies to MLD Snooping on a VLAN interface to statically add
groups and/or source records.
Examples To add a static group record, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld static-group ff1e::10
To add a static group and source record, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld static-group ff1e::10 source
fe80::2fd:6cff:fe1c:b
Parameter Description
<ipv6-group-
address>Specify a standard IPv6 Multicast group address to be
configured as a static group member.
The IPv6 address uses the format X:X::X:X.
<ipv6-source-
address>Optional. Specify a standard IPv6 source address to be
configured as a static source from where multicast
packets originate.
The IPv6 address uses the format X:X::X:X.
<port>Optional. Physical interface. This parameter specifies a
physical port. If this parameter is used, the static
configuration is applied to just to that physical interface.
If this parameter is not used, the static configuration is
applied on all ports in the VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 899
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
IPV6 MLD STATIC-GROUP
To add a static group record on a specific port on vlan2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 mld static-group ff1e::10 interface
port1.0.4
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 900
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING MLD
show debugging mld
Overview Use this command to display the MLD debugging modes enabled with the debug
mld command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting_Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
Syntax show debugging mld
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show debugging mld
Output
Related
Commands
debug mld
show debugging mld
MLD Debugging status:
MLD Decoder debugging is on
MLD Encoder debugging is on
MLD Events debugging is on
MLD FSM debugging is on
MLD Tree-Info-Base (TIB) debugging is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 901
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 MLD GROUPS
show ipv6 mld groups
Overview Use this command to display the multicast groups that have receivers directly
connected to the router and learned through MLD.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 mld groups [<ipv6-address>|<interface>] [detail]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples The following command displays local-membership information for all interfaces:
awplus# show ipv6 mld groups
Output Figure 27-2: Example output for show ipv6 mld groups
The following command displays local-membership information for all interfaces:
awplus# show ipv6 mld groups detail
Parameter Description
<ipv6-address>Optional. Specify Address of the multicast group in format
X:X::X:X.
<interface>Optional. Specify the Interface name for which to display local
information.
awplus#show ipv6 mld groups
MLD Connected Group Membership
Group Address Interface Uptime Expires
Last Reporter
ff08::1 vlan10 (port1.0.1) 00:07:27 00:03:10
fe80::200:1ff:fe20:b5ac
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 902
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 MLD INTERFACE
show ipv6 mld interface
Overview Use this command to display the state of MLD and MLD Snooping for a specified
interface, or all interfaces.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 mld interface [<interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example The following command displays MLD interface status on all interfaces enabled for
MLD:
awplus# show ipv6 mld interface
Output
Parameter Description
<interface>Interface name.
awplus#show ipv6 mld interface
Interface vlan1 (Index 301)
MLD Enabled, Active, Querier, Version 2 (default)
Internet address is fe80::215:77ff:fec9:7468
MLD interface has 0 group-record states
MLD activity: 0 joins, 0 leaves
MLD robustness variable is 2
MLD last member query count is 2
MLD query interval is 125 seconds
MLD querier timeout is 255 seconds
MLD max query response time is 10 seconds
Last member query response interval is 1000 milliseconds
Group Membership interval is 260 seconds
MLD Snooping is globally enabled
MLD Snooping is enabled on this interface
MLD Snooping fast-leave is not enabled
MLD Snooping querier is enabled
MLD Snooping report suppression is enabled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 903
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 MLD SNOOPING MROUTER
show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
Overview Use this command to display the multicast router interfaces, both configured and
learned, in a VLAN. If you do not specify a VLAN interface then all the VLAN
interfaces are displayed.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting_Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter [<interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples The following command displays the multicast router interfaces in vlan2:
awplus# show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter vlan2
Output
The following command displays the multicast router interfaces for all VLAN
interfaces:
awplus# show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
Output
Parameter Description
<interface>Optional. Specify the name of the VLAN interface. Note: If you do not
specify a single VLAN interface, then all VLAN interfaces are shown.
awplus#show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter vlan2
VLAN Interface Static/Dynamic
2 port1.0.2 Dynamically Learned
2 port1.0.3 Dynamically Learned
awplus#show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter
VLAN Interface Static/Dynamic
2 port1.0.2 Dynamically Learned
2 port1.0.3 Dynamically Learned
3 port1.0.4 Statically Assigned
3 port1.0.5 Statically Assigned

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 904
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MLD SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 MLD SNOOPING STATISTICS
show ipv6 mld snooping statistics
Overview Use this command to display MLD Snooping statistics data.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus”_Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 mld snooping statistics interface <interface>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example The following command displays MLDv2 statistical information for vlan1:
awplus# show ipv6 mld snooping statistics interface vlan1
Output
Parameter Description
<interface>The name of the VLAN interface.
awplus#show ipv6 mld snooping statistics interface vlan1
MLD Snooping statistics for vlan1
Interface: port1.0.1
Group: ff08::1
Uptime: 00:02:18
Group mode: Include ()
Last reporter: fe80::eecd:6dff:fe6b:4783
Group source list: (R - Remote, M - SSM Mapping, S - Static )
Source Address Uptime v2 Exp Fwd Flags
2001:db8::1 00:02:18 00:02:02 Yes R
2001:db8::3 00:02:18 00:02:02 Yes R

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 905
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 5: Access and Security

28
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 906
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPv4 Hardware
Access Control List
(ACL) Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of IPv4 Hardware Access Control
List (ACL) commands. It contains detailed command information and command
examples about IPv4 hardware ACLs, which you can apply directly to interfaces
using the access-group command.
To apply ACLs to an LACP channel group, apply it to all the individual switch ports
in the channel group. To apply ACLs to a static channel group, apply it to the static
channel group itself.
Most ACL command titles include information in parentheses:
• When the command title ends with words in parentheses, these words
indicate usage instead of keywords to enter into the CLI. For example, the
title access-list (numbered hardware ACL for ICMP) indicates that the
command is used to create an ACL with the syntax:
access-list <3000-3699> <action> icmp <source-ip> <dest-ip>
[icmp-type <number>] [vlan <1-4094>]
• When the command title is completely surrounded by parentheses, the title
indicates the type of ACL filter instead of keywords to enter into the CLI. For
example, the title (named hardware ACL: ICMP entry) represents a
command with the syntax:
[<sequence-number>] <action> icmp <source-ip> <dest-ip>
[icmp-type <number>] [vlan <1-4094>]
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
Sub-modes Many of the ACL commands operate from sub-modes that are specific to particular
ACL types. The following table shows the CLI prompts at which ACL commands are
entered.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 907
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
References For descriptions of ACLs, and further information about rules when applying them,
see the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
For more information on link aggregation see the following references:
•the Link Aggregation Feature Overview_and_Configuration_Guide.
•Link Aggregation Commands
Command List •“access-group” on page 909
•“access-list (numbered hardware ACL for ICMP)” on page 911
Table 28-1: IPv4 Hardware Access List Commands and Prompts
Command Name Command Mode Prompt
show interface access-group Privileged Exec awplus#
show access-group Privileged Exec awplus#
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs) Privileged Exec awplus#
show interface access-group Privileged Exec awplus#
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP
packets)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for
ICMP)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP
protocols)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for
TCP or UDP)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for
MAC addresses)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list hardware (named hardware
ACL)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
(named hardware ACL entry for IP packets) IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP) IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
(named hardware ACL entry for IP
protocols)
IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or
UDP)
IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
(named hardware ACL entry for MAC
addresses)
IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
commit (IPv4) IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
access-group Interface Configuration awplus(config-if)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 908
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
•“access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets)” on page 915
•“access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP protocols)” on page 918
•“access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)” on page 923
•“access-list (numbered hardware ACL for TCP or UDP)” on page 926
•“access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)” on page 930
•“(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP)” on page 932
•“(named hardware ACL entry for IP packets)” on page 936
•“(named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols)” on page 940
•“(named hardware ACL entry for MAC addresses)” on page 945
•“(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP)” on page 948
•“commit (IPv4)” on page 952
•“show access-group” on page 953
•“show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)” on page 954
•“show interface access-group” on page 956

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 909
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-GROUP
access-group
Overview This command adds or removes a hardware-based access-list to or from a switch
port interface or interfaces. The number of hardware numbered and named
access-lists that can be added to a switch port interface is determined by the
available memory in hardware-based packet classification tables.
This command works in Interface Configuration mode to apply hardware
access-lists to selected switch port interfaces.
The no variant of this command removes the selected access-list from an interface.
Syntax access-group
[<3000-3699>|<4000-4699>|<hardware-access-list-name>]
no access-group
[<3000-3699>|<4000-4699>|<hardware-access-list-name>]
Mode Interface Configuration for a switch port interface or interfaces
Default Any traffic on an interface controlled by a hardware ACL that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage First create an IP access-list that applies the appropriate permit/deny requirements
with the access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets) command, the
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses) command or the
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL) command. Then use this command to
apply this hardware access- list to a specific port or port range. Note that this
command will apply the access-list only to incoming data packets.
To apply ACLs to an LACP aggregated link, apply it to all the individual switch ports
in the aggregated group. To apply ACLs to a static channel group, apply it to the
static channel group itself. An ACL can even be applied to a static aggregated link
that spans more than one switch instance (Link Aggregation Commands).
Note that you cannot apply software numbered ACLs to switch port interfaces with
the access-group command. This command will only apply hardware ACLs.
NOTE: Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
Parameter Description
<3000-3699> Hardware IP access-list.
<4000-4699>Hardware MAC access-list.
<hardware-access-list-name>The hardware access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 910
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-GROUP
Examples To add the numbered hardware access-list 3005 to switch port interface port1.0.1,
enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# access-group 3005
To add the named hardware access-list “hw-acl” to switch port interface port1.0.2,
enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# access-group hw-acl
To apply an ACL to static channel group 2 containing switch port1.0.3 and
port1.0.4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.3-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# static-channel-group 2
awplus(config)# interface sa2
awplus(config-if)# access-group 3000
Related
Commands
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP packets)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)
show interface access-group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 911
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR ICMP)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for
ICMP)
Overview This command creates an access-list for use with hardware classification. The
access-list will match on ICMP packets that have the specified source and
destination IP addresses and, optionally, ICMP type. You can use the value any
instead of source or destination address if an address does not matter.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
The optional vlan parameter can be used to match tagged (802.1q) packets.
The no variant of this command removes the previously specified access-list.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax access-list <3000-3699> <action> icmp <source-ip> <dest-ip>
[icmp-type <number>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no access-list <3000-3699>
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 912
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR ICMP)
Parameter Description
<3000-3699>An ID number for this hardware IP access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
icmp Match against ICMP packets
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask in
dotted decimal format. For example,
entering “192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255” is the
same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
icmp-type
<number>The type of ICMP message to match against, as defined in RFC792
and RFC950. Values include:
0Echo replies.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 913
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR ICMP)
Mode Global Configuration
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage This command creates an ACL for use with hardware classification. Once you have
configured the ACL, use the access-group or the match access-group command to
apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
ACLs numbered in the range 3000-3699 match on packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses.
ICMP ACLs will match any ICMP packet that has the specified source and
destination IP addresses and ICMP type. The ICMP type is an optional parameter.
Examples To create an access-list that will permit ICMP packets with a source address of
192.168.1.0/24 with any destination address and an ICMP type of 5 enter the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3000 permit icmp 192.168.1.0/24 any
icmp-type 5
To destroy the access-list with an access-list identity of 3000 enter the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no access-list 3000
Related
Commands
access-group
3Destination unreachable messages.
4Source quench messages.
5Redirect (change route) messages.
8Echo requests.
11 Time exceeded messages.
12 Parameter problem messages.
13 Timestamp requests.
14 Timestamp replies.
15 Information requests.
16 Information replies.
17 Address mask requests.
18 Address mask replies.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 914
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR ICMP)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 915
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PACKETS)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP
packets)
Overview This command creates an access-list for use with hardware classification. The
access-list will match on packets that have the specified source and destination IP
addresses. You can use the value any instead of source or destination address if an
address does not matter.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
The optional vlan parameter can be used to match tagged (802.1q) packets.
The no variant of this command removes the previously specified IP hardware
access-list.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax access-list <3000-3699> <action> ip <source-ip> <dest-ip> [vlan
<1-4094>]
no access-list <3000-3699>
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 916
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PACKETS)
Table 28-2: IP and ICMP parameters in access-list (hardware IP numbered)
Parameter Description
<3000-3699>An ID number for this hardware IP access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
ip Match against IP packets
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask in
dotted decimal format. For example,
entering “192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255” is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 917
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PACKETS)
Mode Global Configuration
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage This command creates an ACL for use with hardware classification. Once you have
configured the ACL, use the access-group or the match access-group command to
apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
ACLs numbered in the range 3000-3699 match on packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses.
Examples To create an access-list that will permit IP packets with a source address of
192.168.1.1 and any destination address, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3000 permit ip 192.168.1.1/32 any
To destroy the access-list with an access-list identity of 3000 enter the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no access-list 3000
Related
Commands
access-group
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 918
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for IP
protocols)
Overview This command creates an access-list for use with hardware classification. The
access-list will match on packets that have the specified source and destination IP
addresses and IP protocol number. You can use the value any instead of source or
destination address if an address does not matter.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
The optional vlan parameter can be used to match tagged (802.1q) packets.
The no variant of this command removes the previously specified IP hardware
access-list.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax access-list <3000-3699> <action> proto <1-255> <source-ip>
<dest-ip> [vlan <1-4094>]
no access-list <3000-3699>
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 919
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
Table 28-3: Parameters in access-list (hardware IP numbered)
Parameter Description
<3000-3699>An ID number for this hardware IP access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
proto <1-255>The IP protocol number to match against, as defined by IANA
(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers)
See below for a list of IP protocol numbers and their descriptions.
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask in
dotted decimal format. For example,
entering “192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255” is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 920
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Table 28-4: IP protocol number and description
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]
1Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
3Gateway-to-Gateway [RFC823]
4IP in IP [RFC2003]
5Stream [RFC1190] [RFC1819]
6TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) [RFC793]
8EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) [RFC888]
9IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) [IANA]
11 Network Voice Protocol [RFC741]
17 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) [RFC768]
20 Host monitoring [RFC869]
27 RDP (Reliable Data Protocol) [RFC908]
28 IRTP (Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol) [RFC938]
29 ISO-TP4 (ISO Transport Protocol Class 4) [RFC905]
30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol [RFC969]
33 DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol) [RFC4340]
48 DSR (Dynamic Source Routing Protocol) [RFC4728]
50 ESP (Encap Security Payload) [RFC2406]
51 AH (Authentication Header) [RFC2402]
54 NARP (NBMA Address Resolution Protocol) [RFC1735]
58 ICMP for IPv6 [RFC1883]
59 No Next Header for IPv6 [RFC1883]
60 Destination Options for IPv6 [RFC1883]
Table 28-3: Parameters in access-list (hardware IP numbered) (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 921
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
Mode Global Configuration
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage This command creates an ACL for use with hardware classification. Once you have
configured the ACL, use the access-group or the match access-group command to
apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
ACLs numbered in the range 3000-3699 match on packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses.
Examples To create an access-list that will deny all IGMP packets (IP protocol 2) from the
192.168.0.0 network, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3000 deny proto 2 192.168.0.0/16
any
To destroy the access-list with an access-list identity of 3000 enter the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no access-list 3000
Related
Commands
access-group
88 EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
89 OSPFIGP [RFC1583]
97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation / RFC3378
98 Encapsulation Header / RFC1241
108 IP Payload Compression Protocol / RFC2393
112 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol / RFC3768
134 RSVP-E2E-IGNORE / RFC3175
135 Mobility Header / RFC3775
136 UDPLite / RFC3828
137 MPLS-in-IP / RFC4023
138 MANET Protocols / RFC-ietf-manet-iana-07.txt
139-252 Unassigned / IANA
253 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
254 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
255 Reserved / IANA
Table 28-4: IP protocol number and description (cont.)
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 922
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 923
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for
MAC addresses)
Overview This command creates an access-list for use with hardware classification. The
access-list will match on packets that have the specified source and destination
MAC addresses. You can use the value any instead of source or destination address
if an address does not matter.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
The no variant of this command removes the specified MAC hardware filter
access-list.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax access-list <4000-4699> <action> {<source-mac>|any}
{<dest-mac>|any} [vlan <1-4094>] [inner-vlan
<1-4094>]
no access-list <4000-4699>
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 924
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
Mode Global Configuration
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage This command creates an ACL for use with hardware classification. Once you have
configured the ACL, use the access-group or the match access-group command to
apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
ACLs numbered in the range 4000-4699 match on packets that have the specified
source and destination MAC addresses.
Examples To create an access-list that will permit packets with a source MAC address of
0000.00ab.1234 and any destination address, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 4000 permit 0000.00ab.1234
0000.0000.0000 any
Parameter Description
<4000-4699>Hardware MAC access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match against, followed by the mask.
Enter the address in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each H
is a hexadecimal number. For a mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
any Match against any source MAC address.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to match against, followed by the
mask.
Enter the address in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each H
is a hexadecimal number. For a mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
any Match against any destination MAC address.
vlan <1-4094>Match against the specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
inner-vlan
<1-4094>Match against the inner VLAN tag (VID). This parameter is used
within double-tagged VLANs. It is sometimes referred to as the
C-TAG (Customer VLAN TAG), where the vlan VID tag is referred to as
the S-TAG (Service VLAN TAG).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 925
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
To create an access-list that will permit packets if their source MAC address starts
with 0000.00ab, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 4001 permit 0000.00ab.1234
0000.0000.FFFF any
To create an access-list that will send a copy of packets to the mirror port if their
source MAC address starts with 0000.00ab, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 4001 copy-to-mirror 0000.00ab.1234
0000.0000.FFFF any
You also need to configure the mirror port with the mirror interface command.
To destroy the access-list with an access-list identity of 4000 enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no access-list 4000
Related
Commands
access-group
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 926
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR TCP OR UDP)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for TCP
or UDP)
Overview This command creates an access-list for use with hardware classification. The
access-list will match on TCP or UDP packets that have the specified source and
destination IP addresses and optionally, port values. You can use the value any
instead of source or destination IP address if an address does not matter.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
You can use the optional vlan parameter to match tagged (802.1q) packets.
The no variant of this command removes the specified IP hardware access-list.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax access-list <3000-3699> <action> {tcp|udp} <source-ip>
[<source-ports>] <dest-ip> [<dest-ports>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no access-list <3000-3699>
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 927
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR TCP OR UDP)
Parameter Description
<3000-3699>An ID number for this hardware IP access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
tcp Match against TCP packets.
udp Match against UDP packets.
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask in
dotted decimal format. For example,
entering “192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255” is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
<source-ports
>Match source TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 928
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR TCP OR UDP)
Mode Global Configuration
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage This command creates an ACL for use with hardware classification. Once you have
configured the ACL, use the access-group or the match access-group command to
apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
ACLs numbered in the range 3000-3699 match on packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses.
Examples To create an access-list that will permit TCP packets with a destination address of
192.168.1.1, a destination port of 80, and any source address and source port, enter
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3000 permit tcp any 192.168.1.1/32
eq 80
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ports>Match destination TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 929
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (NUMBERED HARDWARE ACL FOR TCP OR UDP)
To create an access-list that will copy TCP packets to the mirror port, if they have a
destination address of 192.168.1.1, a destination port of 80, and any source address
and source port, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3000 copy-to-mirror tcp any
192.168.1.1/32 eq 80
You also need to configure the mirror port with the mirror interface command.
Related
Commands
access-group
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 930
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST HARDWARE (NAMED HARDWARE ACL)
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
Overview This command creates a named hardware access-list and puts you into IPv4
Hardware ACL Configuration mode, where you can add filter entries to the ACL.
Once you have configured the ACL, you can use the access-group or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map.
The no variant of this command removes the specified named hardware ACL.
Syntax access-list hardware <name>
no access-list hardware <name>
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic on an interface controlled by a hardware ACL that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage Use this command to name a hardware ACL and enter the IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration mode. If the named hardware ACL does not exist, it will be created
after entry. If the named hardware ACL already exists, then this command puts you
into IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration mode for that existing ACL.
Entering this command moves you to the IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration mode
(config-ip-hw-acl prompt), so you can enter ACL filters with sequence numbers.
From this prompt, configure the filters for the ACL. See the ACL Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide for complete examples of configured sequenced
numbered ACLs.
NOTE: Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
Examples To create the hardware access-list named “ACL-1” and enter the IPv4 Hardware
ACL Configuration mode to specify the ACL filter entry, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware ACL-1
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#
To remove the hardware access-list named “ACL-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no access-list hardware ACL-1
Parameter Description
<name>Specify a name for the hardware ACL.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 931
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST HARDWARE (NAMED HARDWARE ACL)
Related
Commands
access-group
(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP)
(named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols)
(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP)
(access-list standard named filter)
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 932
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR ICMP)
(named hardware ACL entry for ICMP)
Overview Use this command to add a new ICMP filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The filter will match on any ICMP packet that has the specified source
and destination IP addresses and (optionally) ICMP type. You can specify the value
any if source or destination address does not matter.
If you specify a sequence number, the switch inserts the new filter at the specified
location. Otherwise, the switch adds the new filter to the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes an ICMP filter entry from the current
hardware access-list. You can specify the ICMP filter entry for removal by entering
either its sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its ICMP filter profile
without specifying its sequence number (e.g. no permit icmp 192.168.1.0/24 any
icmp-type 11).
You can find the sequence number by running the show access-list (IPv4 Hardware
ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> icmp <source-ip> <dest-ip>
[icmp-type <number>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> icmp <source-ip> <dest-ip> [icmp-type <number>]
[vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 933
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR ICMP)
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535. If you do not specify a
sequence number, the switch puts the entry at the end of the
ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number. .
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See
the table above for valid values.
icmp Match against ICMP packets
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the
valid formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host
with the IP address given by
<ip-addr> in dotted decimal
notation.
Values for the <action> parameter

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 934
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR ICMP)
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command access-list
hardware (named hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command access-list hardware (named
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named hardware ACL: entry” commands)
to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL. You can insert a
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet.
Specify the subnet by entering the
IPv4 address, then a forward slash,
then the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet.
Specify the subnet by entering a
reverse mask in dotted decimal
format. For example, entering
“192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255” is the same
as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
icmp-type
<number>The type of ICMP message to match against, as defined in
RFC792 and RFC950. Values include:
0Echo replies.
3Destination unreachable
messages.
4Source quench messages.
5Redirect (change route) messages.
8Echo requests.
11 Time exceeded messages.
12 Parameter problem messages.
13 Timestamp requests.
14 Timestamp replies.
15 Information requests.
16 Information replies.
17 Address mask requests.
18 Address mask replies.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 935
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR ICMP)
new filter entry into the middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate
sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the
entry at the end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number.
Then use the access-group or the match access-group command to apply this ACL
to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note that the ACL will only apply to incoming
data packets.
Examples To add an access-list filter entry with a sequence number of 100 to the access-list
named “my-list” that will permit ICMP packets with a source address of
192.168.1.0/24, any destination address and an ICMP type of 5, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# 100 permit icmp 192.168.1.0/24 any
icmp-type 5
To remove an access-list filter entry with a sequence number of 100 from the
access-list named “my-list”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# no 100
Related
Commands
access-group
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 936
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PACKETS)
(named hardware ACL entry for IP packets)
Overview Use this command to add an IP packet filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The filter will match on IP packets that have the specified IP and/or MAC
addresses. You can use the value any instead of source or destination IP or MAC
address if an address does not matter.
If you specify a sequence number, the switch inserts the new filter at the specified
location. Otherwise, the switch adds the new filter to the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no deny ip 192.168.0.0/16 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show access-list (IPv4 Hardware
ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> ip <source-ip> <dest-ip>
[<source-mac> <dest-mac>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> ip <source-ip> <dest-ip> [<source-mac> <dest-mac>]
[vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 937
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PACKETS)
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535. If you do not specify a sequence
number, the switch puts the entry at the end of the ACL and
assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number. .
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
ip Match against IP packets
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
dhcpsnooping Match the source address learned
from the DHCP Snooping binding
database.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 938
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PACKETS)
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command access-list
hardware (named hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match against. You can specify a
single MAC address, a range (through a mask), the address
learned from DHCP snooping, or any:
any Match against any source MAC
address.
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match
against, followed by the mask.
Enter the address in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number. For a
mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
dhcpsnooping Match the source address learned
from the DHCP Snooping binding
database.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to match against. You can specify a
single MAC address, a range (through a mask), or any:
any Match against any destination MAC
address.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to
match against, followed by the
mask.
Enter the address in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number. For a
mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 939
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PACKETS)
Usage To use this command, first run the command access-list hardware (named
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named hardware ACL: entry” commands)
to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL. You can insert a
new filter entry into the middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate
sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the
entry at the end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number.
Then use the access-group or the match access-group command to apply this ACL
to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note that the ACL will only apply to incoming
data packets.
Examples To add a filter entry to the access-list named “my-list” that will permit any IP packet
with a source address of 192.168.1.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# permit ip 192.168.1.1/32 any
To add a filter entry to the access-list named “my-list” that will permit any IP packet
with a source address of 192.168.1.1and a MAC source address of ffee.ddcc.bbaa,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# permit ip 192.168.1.1/32 any mac
ffee.ddcc.bbaa 0000.0000.0000 any
To add a filter entry to the access-list named “my-list” that will deny all IP packets
on vlan 2, use the commands:
awplus# enable
awplus(config)# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# deny ip any any vlan 2
Related
Commands
access-group
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 940
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
(named hardware ACL entry for IP protocols)
Overview Use this command to add an IP protocol type filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The filter will match on IP packets that have the specified IP protocol
number, and the specified IP and/or MAC addresses. You can use the value any
instead of source or destination IP or MAC address if an address does not matter.
If you specify a sequence number, the switch inserts the new filter at the specified
location. Otherwise, the switch adds the new filter to the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no deny proto 2 192.168.0.0/16 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show access-list (IPv4 Hardware
ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> proto <1-255> <source-ip>
<dest-ip> [<source-mac> <dest-mac>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> proto <1-255> <source-ip> <dest-ip> [<source-mac>
<dest-mac>] [vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 941
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
Table 28-5: Parameters in IP protocol ACL entries
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535. If you do not specify a sequence
number, the switch puts the entry at the end of the ACL and
assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number. .
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
proto <1-255>The IP protocol number to match against, as defined by IANA
(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers)
See below for a list of IP protocol numbers and their descriptions.
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
dhcpsnooping Match the source address learned
from the DHCP Snooping binding
database.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 942
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match against. You can specify a
single MAC address, a range (through a mask), the address
learned from DHCP snooping, or any:
any Match against any source MAC
address.
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match
against, followed by the mask.
Enter the address in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number. For a
mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
dhcpsnooping Match the source address learned
from the DHCP Snooping binding
database.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to match against. You can specify a
single MAC address, a range (through a mask), or any:
any Match against any destination MAC
address.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to
match against, followed by the
mask.
Enter the address in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format
<HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number. For a
mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Table 28-5: Parameters in IP protocol ACL entries (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 943
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
Table 28-6: IP protocol number and description
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]
1Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
3Gateway-to-Gateway [RFC823]
4IP in IP [RFC2003]
5Stream [RFC1190] [RFC1819]
6TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) [RFC793]
8EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) [RFC888]
9IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) [IANA]
11 Network Voice Protocol [RFC741]
17 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) [RFC768]
20 Host monitoring [RFC869]
27 RDP (Reliable Data Protocol) [RFC908]
28 IRTP (Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol) [RFC938]
29 ISO-TP4 (ISO Transport Protocol Class 4) [RFC905]
30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol [RFC969]
33 DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol)
[RFC4340]
48 DSR (Dynamic Source Routing Protocol) [RFC4728]
50 ESP (Encap Security Payload) [RFC2406]
51 AH (Authentication Header) [RFC2402]
54 NARP (NBMA Address Resolution Protocol) [RFC1735]
58 ICMP for IPv6 [RFC1883]
59 No Next Header for IPv6 [RFC1883]
60 Destination Options for IPv6 [RFC1883]
88 EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
89 OSPFIGP [RFC1583]
97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation / RFC3378
98 Encapsulation Header / RFC1241
108 IP Payload Compression Protocol / RFC2393
112 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol / RFC3768
134 RSVP-E2E-IGNORE / RFC3175
135 Mobility Header / RFC3775
136 UDPLite / RFC3828

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 944
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR IP PROTOCOLS)
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command access-list
hardware (named hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, run the command access-list hardware (named hardware
ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named hardware ACL: entry” commands)
to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL. You can insert a
new filter entry into the middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate
sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the
entry at the end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number.
Then use the access-group or the match access-group command to apply this ACL
to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note that the ACL will only apply to incoming
data packets.
Examples To add a filter entry to the access-list named “my-list” that will deny all IGMP
packets (protocol 2) from the 192.168.0.0 subnet, and give it a sequence number
of 50, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# 50 deny proto 2 192.168.0.0/16 any
Related
Commands
access-group
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added
137 MPLS-in-IP / RFC4023
138 MANET Protocols / RFC-ietf-manet-iana-07.txt
139-252 Unassigned / IANA
253 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
254 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
255 Reserved / IANA
Table 28-6: IP protocol number and description (cont.)
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 945
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
(named hardware ACL entry for MAC
addresses)
Overview Use this command to add a MAC address filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The access-list will match on packets that have the specified source and
destination MAC addresses. You can use the value any instead of source or
destination MAC address if an address does not matter.
If you specify a sequence number, the switch inserts the new filter at the specified
location. Otherwise, the switch adds the new filter to the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no permit mac aaaa.bbbb.cccc 0000.0000.0000 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show access-list (IPv4 Hardware
ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> mac {<source-mac>|any}
{<dest-mac>|any} [vlan <1-4094>] [inner-vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> mac {<source-mac>|any} {<dest-mac>|any} [vlan
<1-4094>] [inner-vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 946
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command access-list
hardware (named hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command access-list hardware (named
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named hardware ACL: entry” commands)
to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL. You can insert a
new filter entry into the middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.
Parameter Description
<4000-4699>Hardware MAC access-list.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
mac Match against MAC address
<source-mac> The source MAC address to match against, followed by the mask.
Enter the address in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each H
is a hexadecimal number. For a mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
any Match against any source MAC address.
<dest-mac> The destination MAC address to match against, followed by the
mask.
Enter the address in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each
H is a hexadecimal number.
Enter the mask in the format <HHHH.HHHH.HHHH>, where each H
is a hexadecimal number. For a mask, each value is either 0 or F,
where FF = Ignore, and 00 = Match.
any Match against any destination MAC address.
vlan <1-4094>Match against the specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
inner-vlan
<1-4094>Match against the inner VLAN tag (VID). This parameter is used
within double-tagged VLANs. It is sometimes referred to as the
C-TAG (Customer VLAN TAG), and the vlan VID tag is referred to as
the S-TAG (Service VLAN TAG).
Values for the <action> parameter

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 947
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR MAC ADDRESSES)
sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the
entry at the end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number.
Then use the access-group or the match access-group command to apply this ACL
to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note that the ACL will only apply to incoming
data packets.
Examples To add a filter entry to the access-list named “my-list” that will permit packets with
a source MAC address of 0000.00ab.1234 and any destination MAC address, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# permit mac 0000.00ab.1234
0000.0000.0000 any
To remove a filter entry that permit packets with a source MAC address of
0000.00ab.1234 and any destination MAC address, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# no permit mac 0000.00ab.1234
0000.0000.0000 any
Related
Commands
access-group
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 948
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR TCP OR UDP)
(named hardware ACL entry for TCP or UDP)
Overview Use this command to add a TCP or UDP filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The access-list will match on TCP or UDP packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses and optionally, port values. You can use the
value any instead of source or destination IP address if an address does not matter.
If you specify a sequence number, the switch inserts the new filter at the specified
location. Otherwise, the switch adds the new filter to the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no permit udp 192.168.0.0/16 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show access-list (IPv4 Hardware
ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> {tcp|udp} <source-ip>
[<source-ports>] <dest-ip> [<dest-ports>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> {tcp|udp} <source-ip> [<source-ports>] <dest-ip>
[<dest-ports>] [vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 949
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR TCP OR UDP)
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535. If you do not specify a sequence
number, the switch puts the entry at the end of the ACL and
assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number. .
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
tcp Match against TCP packets.
udp Match against UDP packets.
<source-ip> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<source-
ports> Match source TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
<dest-ip>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 950
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR TCP OR UDP)
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command access-list
hardware (named hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command access-list hardware (named
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named hardware ACL: entry” commands)
to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL. You can insert a
new filter entry into the middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate
sequence number. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ports>Match destination TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 951
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED HARDWARE ACL ENTRY FOR TCP OR UDP)
entry at the end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its
sequence number.
Then use the access-group or the match access-group command to apply this ACL
to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note that the ACL will only apply to incoming
data packets.
Example To add a filter entry to access-list named “my-list” that will permit TCP packets with
a destination address of 192.168.1.1, a destination port of 80, from any source, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# permit tcp any 192.168.1.1/32 eq 80
Related
Commands
access-group
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
match access-group
show running-config
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: send-to-vlan-port action parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 952
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
COMMIT (IPV4)
commit (IPv4)
Overview Use this command to commit the IPv4 ACL filter configuration entered at the
console to the hardware immediately without exiting the IPv4 Hardware ACL
Configuration mode.
This command forces the associated hardware and software IPv4 ACLs to
synchronize.
Syntax commit
Mode IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration
Usage Normally, when an IPv4 hardware ACL is edited, the new configuration state of the
IPv4 ACL is not written to hardware until you exit IPv4 Hardware ACL Configuration
mode. By entering this command you can ensure that the current state of a
hardware access-list that is being edited is written to hardware immediately.
Scripts typically do not include the exit command to exit configuration modes,
potentially leading to IPv4 ACL filters in hardware not being correctly updated.
Using this commit command in a configuration script after specifying an IPv4
hardware ACL filter ensures that it is updated in the hardware immediately.
Example To update the hardware with the IPv4 ACL filter configuration, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware my-hw-list
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# commit
Related
Commands
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 953
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW ACCESS-GROUP
show access-group
Overview Use this command to show the access-lists attached globally. If an access-list is
specified, only that access-list will be displayed.
Syntax show access-group
[{<3000-3699>|<4000-4699>|<access-list-name>}]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show all access-lists attached globally:
awplus# show access-group
Output Figure 28-1: Example output from the show access-group command
Related
Commands
access-group
show interface access-group
Parameter Description
<3000-3699>Specify a Hardware IP access-list.
<4000-4699>Specify a Hardware MAC access-list.
<access-list-name>Specify a Hardware IPv4 access-list name.
Global access control list
access-group 3000
access-group 4000

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 954
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW ACCESS-LIST (IPV4 HARDWARE ACLS)
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Overview Use this command to display the specified access-list, or all access-lists if none have
been specified. Note that only defined access-lists are displayed. An error message
is displayed for an undefined access-list.
Syntax show access-list
[<1-99>|<100-199>|<1300-1999>|<2000-2699>|<3000-3699>|<4000-44
99>|<access-list-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To show all access-lists configured on the switch:
awplus# show access-list
To show the access-list with an ID of 20:
awplus# show access-list 20
The following error message is displayed if you try to show an undefined
access-list.
awplus# show access-list 2
Parameter Description
<1-99>IP standard access-list.
<1300-1999>IP standard access-list (standard - expanded range).
<3000-3699>Hardware IP access-list.
<4000-4499>Hardware MAC access-list.
<access-list-name>IP named access-list.
Standard IP access list 1
deny 172.16.2.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
Standard IP access list 20
deny 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
deny 192.168.12.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
Hardware IP access list 3001
permit ip 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 any
Hardware IP access list 3020
permit tcp any 192.0.2.0/24
awplus#show access-list 20
Standard IP access-list 20
deny 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
deny 192.168.12.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 955
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW ACCESS-LIST (IPV4 HARDWARE ACLS)
Related
Commands
access-list extended (named)
access-list (numbered hardware ACL for MAC addresses)
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
% Can't find access-list 2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 956
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW INTERFACE ACCESS-GROUP
show interface access-group
Overview Use this command to display the access groups attached to a port. If an access
group is specified, then the output only includes the ports that the specified access
group is attached to. If no access group is specified then this command displays all
access groups that are attached to the ports that are specified with <port-list>.
Note that access group is the term given for an access-list when it is applied to an
interface.
Syntax show interface <port-list> access-group
[<3000-3699>|<4000-4699>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show all access-lists attached to port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show interface port1.0.1 access-group
Output Figure 28-2: Example output from the show interface access-group command
Related
Commands
access-group
Parameter Description
<port-list> Specify the ports to display information. A port-list can be
either:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6) a static channel group (e.g.
sa2) or a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.6 or port1.0.1-port1.0.6 or po1-po2
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.6. Do not mix switch ports, static
channel groups, and LACP channel groups in the same
list.
access group Select the access group whose details you want to show.
<3000-3699> Specifies the Hardware IP access-list.
<4000-4699> Specifies the Hardware MAC access-list.
Interface port1.0.1
access-group 3000
access-group 3002
access-group 3001

29
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 957
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPv4 Software
Access Control List
(ACL) Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for the IPv4 Software Access
Control List (ACL) commands, and contains detailed command information and
command examples about IPv4 software ACLs as applied to Routing and
Multicasting, which are not applied to interfaces.
For information about ACLs, see the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
To apply ACLs to an LACP channel group, apply it to all the individual switch ports
in the channel group. To apply ACLs to a static channel group, apply it to the static
channel group itself. For more information on link aggregation see the following
references:
•the Link Aggregation Feature Overview_and Configuration Guide.
•Link Aggregation Commands
NOTE: Text in parenthesis in command names indicates usage not keyword entry. For
example, access-list hardware (named) indicates named IPv4 hardware ACLs
entered as access-list hardware <name> where <name> is a placeholder not
a keyword.
Parenthesis surrounding ACL filters indicates the type of ACL filter not the keyword
entry in the CLI, such as (access-list standard numbered filter) represents command
entry in the format shown in the syntax:
[<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} {<source-address>|host
<host-address>|any}
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Sub-modes Many of the ACL commands operate from sub-modes that are specific to particular
ACL types. The following table shows the CLI prompts at which ACL commands are
entered.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 958
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
Command List •“access-list extended (named)” on page 959
•“access-list (extended numbered)” on page 967
•“(access-list extended ICMP filter)” on page 970
•“(access-list extended IP filter)” on page 972
•“(access-list extended IP protocol filter)” on page 975
•“(access-list extended TCP UDP filter)” on page 979
•“access-list standard (named)” on page 981
•“access-list (standard numbered)” on page 983
•“(access-list standard named filter)” on page 985
•“(access-list standard numbered filter)” on page 987
•“maximum-access-list” on page 989
•“show access-list (IPv4 Software ACLs)” on page 990
•“show ip access-list” on page 992
•“vty access-class (numbered)” on page 993
Table 29-1: IPv4 Software Access List Commands and Prompts
Command Name Command Mode Prompt
show ip access-list Privileged Exec awplus#
access-group Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (extended named) Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (extended numbered) Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (standard named) Global Configuration awplus(config)#
access-list (standard numbered) Global Configuration awplus(config)#
maximum-access-list Global Configuration awplus(config)#
(access-list extended ICMP filter) IPv4 Extended ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
(access-list extended IPfilter) IPv4 Extended ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
(access-list extended IP protocol filter) IPv4 Extended ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter) IPv4 Extended ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
(access-list standard named filter) IPv4 Standard ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-std-acl)#
(access-list standard numbered filter) IPv4 Standard ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ip-std-acl)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 959
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
access-list extended (named)
Overview This command configures an extended named access-list that permits or denies
packets from specific source and destination IP addresses. You can either create an
extended named ACL together with an ACL filter entry in the Global Configuration
mode, or you can use the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration mode for sequenced
ACL filter entry after entering a list name.
The no variant of this command removes a specified extended named access-list.
Syntax
[list-name] access-list extended <list-name>
no access-list extended <list-name>
Syntax [icmp] access-list extended <list-name>{deny|permit} icmp <source>
<destination> [icmp-type <type-number>] [log]
no access-list extended <list-name>{deny|permit} icmp <source>
<destination> [icmp-type <type-number>] [log]
Parameter Description
<list-name>A user-defined name for the access-list
Table 29-2: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - icmp
Parameter Description
<list-name>A user-defined name for the access-list.
deny The access-list rejects packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
permit The access-list permits packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
icmp The access-list matches only ICMP packets.
icmp-type Matches only a specified type of ICMP messages. This is valid only
when the filtering is set to match ICMP packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 960
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
<source> The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
any Matches any source IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This
matches any source IP address within
the specified subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
any Matches any destination IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This
matches any destination IP address
within the specified subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
Table 29-2: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - icmp
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 961
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
Syntax [tcp|udp] access-list extended <list-name> {deny|permit} {tcp|udp}
<source> [eq <sourceport>|lt <sourceport>|gt <sourceport>|ne
<sourceport>] <destination> [eq <destport>|lt <destport>|gt
<destport>|ne <destport>] [log]
no access-list extended <list-name> {deny|permit} {tcp|udp}
<source> [eq <sourceport>|lt <sourceport>|gt <sourceport>|ne
<sourceport>] <destination> [eq <destport> |lt <destport>|gt
<destport>|ne <destport>][log]
<type-number>The ICMP type, as defined in RFC792 and RFC950. Specify one of
the following integers to create a filter for the ICMP message type:
0Echo replies.
3Destination unreachable messages.
4Source quench messages.
5Redirect (change route) messages.
8Echo requests.
11 Time exceeded messages.
12 Parameter problem messages.
13 Timestamp requests.
14 Timestamp replies.
15 Information requests.
16 Information replies.
17 Address mask requests.
18 Address mask replies.
log Logs the results.
Table 29-2: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - icmp
Parameter Description
Table 29-3: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - tcp|udp
Parameter Description
<list-name>A user-defined name for the access-list.
deny The access-list rejects packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
permit The access-list permits packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
tcp The access-list matches only TCP packets.
udp The access-list matches only UDP packets.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 962
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
<source> The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
any Matches any source IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This
matches any source IP address within
the specified subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
any Matches any destination IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This
matches any destination IP address
within the specified subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<sourceport>The source port number, specified as an integer between 0 and
65535.
<destport>The destination port number, specified as an integer between 0
and 65535.
eq Matches port numbers equal to the port number specified
immediately after this parameter.
lt Matches port numbers less than the port number specified
immediately after this parameter.
gt Matches port numbers greater than the port number specified
immediately after this parameter.
Table 29-3: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - tcp|udp
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 963
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
Syntax
[proto|any| ip] access-list extended <list-name> {deny|permit} {proto
<ip-protocol>|any|ip} {<source>} {<destination>} [log]
no access-list extended <list-name>{deny|permit} {proto
<ip-protocol>|any|ip}{<source>}{<destination>}[log]
ne Matches port numbers not equal to the port number specified
immediately after this parameter.
log Log the results.
Table 29-3: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command - tcp|udp
Parameter Description
Table 29-4: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command -
proto|ip|any
Parameter Description
<list-name>A user-defined name for the access-list.
deny The access-list rejects packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
permit The access-list permits packets that match the type, source, and
destination filtering specified with this command.
proto Matches only a specified type of IP Protocol.
any The access-list matches any type of IP packet.
ip The access-list matches only IP packets.
<source> The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
any Matches any source IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single source host with the IP
address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This matches
any source IP address within the specified
subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For example,
entering 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255 is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 964
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
any Matches any destination IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single destination host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This matches
any destination IP address within the
specified subnet.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, you can enter a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For example,
entering 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255 is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
log Logs the results.
<ip-protocol> The IP protocol number, as defined by IANA (Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority
www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers)
See below for a list of IP protocol numbers and their descriptions.
Table 29-5: IP protocol number and description
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]
1Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
3Gateway-to-Gateway [RFC823]
4IP in IP [RFC2003]
5Stream [RFC1190] [RFC1819]
6TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) [RFC793]
8EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) [RFC888]
9IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) [IANA]
11 Network Voice Protocol [RFC741]
17 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) [RFC768]
20 Host monitoring [RFC869]
27 RDP (Reliable Data Protocol) [RFC908]
28 IRTP (Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol) [RFC938]
Table 29-4: Parameters in the access-list extended (named) command -
proto|ip|any (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 965
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage Use this command when configuring access-lists for filtering IP software packets.
You can either create access-lists from within this command, or you can enter
access-list extended followed by only the name. Entering only the name moves
you to the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration mode for the selected access-list.
29 ISO-TP4 (ISO Transport Protocol Class 4) [RFC905]
30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol [RFC969]
33 DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol)
[RFC4340]
48 DSR (Dynamic Source Routing Protocol) [RFC4728]
50 ESP (Encap Security Payload) [RFC2406]
51 AH (Authentication Header) [RFC2402]
54 NARP (NBMA Address Resolution Protocol) [RFC1735]
58 ICMP for IPv6 [RFC1883]
59 No Next Header for IPv6 [RFC1883]
60 Destination Options for IPv6 [RFC1883]
88 EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
89 OSPFIGP [RFC1583]
97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation / RFC3378
98 Encapsulation Header / RFC1241
108 IP Payload Compression Protocol / RFC2393
112 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol / RFC3768
134 RSVP-E2E-IGNORE / RFC3175
135 Mobility Header / RFC3775
136 UDPLite / RFC3828
137 MPLS-in-IP / RFC4023
138 MANET Protocols / RFC-ietf-manet-iana-07.txt
139-252 Unassigned / IANA
253 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
254 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
255 Reserved / IANA
Table 29-5: IP protocol number and description (cont.)
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 966
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED (NAMED)
From there you can configure your access-lists by using the commands (access-list
extended ICMP filter), (access-list extended IP filter), and (access-list extended IP
protocol filter).
Note that packets must match both the source and the destination details.
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples You can enter the extended named ACL in the Global Configuration mode
together with the ACL filter entry on the same line, as shown below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended TK deny tcp 2.2.2.3/24 eq
14 3.3.3.4/24 eq 12 log
Alternatively, you can enter the extended named ACL in Global Configuration
mode before specifying the ACL filter entry in the IPv4 Extended ACL
Configuration mode, as shown below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended TK
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny tcp 2.2.2.3/24 eq 14 3.3.3.4/24
eq 12 log
Related
Commands
(access-list extended ICMP filter)
(access-list extended IP filter)
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 967
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (EXTENDED NUMBERED)
access-list (extended numbered)
Overview This command configures an extended numbered access-list that permits or
denies packets from specific source and destination IP addresses. You can either
create an extended numbered ACL together with an ACL filter entry in the Global
Configuration mode, or you can use the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration mode
for sequenced ACL filter entry after entering a list number.
The no variant of this command removes a specified extended named access-list.
Syntax
[list-number] access-list {<100-199>|<2000-2699>}
no access-list {<100-199>|<2000-2699>}
Syntax [deny|
permit] access-list {<100-199>|<2000-2699>} {deny|permit} ip <source>
<destination>
no access-list {<100-199>|<2000-2699>}{deny|permit} ip <source>
<destination>
Parameter Description
<100-199>IP extended access-list.
<2000-2699>IP extended access-list (expanded range).
Parameter Description
<100-199>IP extended access-list.
<2000-2699>IP extended access-list (expanded range).
deny Access-list rejects packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Access-list permits packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
any Matches any source IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single source host with the IP
address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>An IPv4 address, followed by a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24. This matches any
source IP address within the specified
subnet.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 968
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (EXTENDED NUMBERED)
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage Use this command when configuring access-list for filtering IP software packets.
You can either create access-lists from within this command, or you can enter
access-list followed by only the number. Entering only the number moves you to
the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration mode for the selected access-list. From there
you can configure your access-lists by using the commands (access-list extended
ICMP filter), (access-list extended IP filter), and (access-list extended IP protocol
filter).
Note that packets must match both the source and the destination details.
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples You can enter the extended ACL in the Global Configuration mode together with
the ACL filter entry on the same line, as shown below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 101 deny ip 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255
any
Alternatively, you can enter the extended ACL in Global Configuration mode
before specifying the ACL filter entry in the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
mode, as shown below:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 101
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny ip 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255 any
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
any Matches any destination IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single destination host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>An IPv4 address, followed by a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24. This matches any
destination IP address within the specified
subnet.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 969
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (EXTENDED NUMBERED)
Related
Commands
(access-list extended ICMP filter)
(access-list extended IP filter)
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 970
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED ICMP FILTER)
(access-list extended ICMP filter)
Overview Use this ACL filter to add a new ICMP filter entry to the current extended access-list.
If the sequence number is specified, the new filter is inserted at the specified
location. Otherwise, the new filter is added at the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes an ICMP filter entry from the current
extended access-list. You can specify the ICMP filter entry for removal by entering
either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by entering its ICMP filter profile
without specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [icmp] [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} icmp <source> <destination>
[icmp-type <icmp-value>] [log]
no {deny|permit} icmp <source> <destination>[icmp-type
<icmp-value>] [log]
no <sequence-number>
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list.
deny Access-list rejects packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Access-list permits packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
icmp ICMP packet type.
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a
forward slash, then the prefix length.
This matches any source IP address
within the specified subnet.
any Matches any source IP address.
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a
forward slash, then the prefix length.
This matches any destination IP
address within the specified subnet.
any Matches any destination IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 971
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED ICMP FILTER)
Mode IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
(extended numbered) command or the access-list extended (named) command, with
the required access control list number, or name - but with no further parameters
selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples To add a new entry in access-list called my-list that will reject ICMP packets from
10.0.0.1 to 192.168.1.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny icmp 10.0.0.1/32 192.168.1.1/32
Use the following commands to add a new filter at sequence number 5 position of
the access-list called my-list. The filter will accept the ICMP type 8 packets from
10.1.1.0/24 network, to 192.168.1.0 network:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# 5 permit icmp 10.1.1.0/24
192.168.1.0/24 icmp-type 8
Related
Commands
access-group
show running-config
show ip access-list
icmp-type The ICMP type.
<icmp-value>The value of the ICMP
type.
log Log the results.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 972
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP FILTER)
(access-list extended IP filter)
Overview Use this ACL filter to add a new IP filter entry to the current extended access-list. If
the sequence number is specified, the new filter is inserted at the specified
location. Otherwise, the new filter is added at the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes an IP filter entry from the current
extended access-list. You can specify the IP filter entry for removal by entering
either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by entering its IP filter profile without
specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [ip] [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} ip <source> <destination>
no {deny|permit} ip <source> <destination>
no <sequence-number>
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list.
deny Access-list rejects packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Access-list permits packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
<source> The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
any Matches any source IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single source host with the IP
address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, enter an IPv4 address
followed by a reverse mask in dotted
decimal format. For example, enter
192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 973
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP FILTER)
Mode Extended ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
(extended numbered) command or the access-list extended (named) command, with
the required access control list number, or name - but with no further parameters
selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Example 1
[list-number]
First use the following commands to enter the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
mode and define a numbered extended access-list 101:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 101
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
Then use the following commands to add a new entry to the numbered extended
access- list 101 that will reject packets from 10.0.0.1 to 192.168.1.1:
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny ip host 10.0.0.1 host
192.168.1.1
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# 20 permit ip any any
Example 2
[list-name]
First use the following commands to enter the IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
mode and define a named access-list called my-acl:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-acl
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)#
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
any Matches any destination IP address.
host<ip-addr> Matches a single destination host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in dotted
decimal notation.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Alternatively, enter an IPv4 address
followed by a reverse mask in dotted
decimal format. For example, enter
192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 974
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP FILTER)
Then use the following commands to add a new entry to the named access-list
my-acl that will reject packets from 10.0.0.1 to 192.168.1.1:
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny ip host 10.0.0.1 host
192.168.1.1
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# 20 permit ip any any
Example 3
[list-number]
Use the following commands to remove the access-list filter entry with sequence
number 20 from extended numbered access-list 101.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 101
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# no 20
Example 4
[list-name]
Use the following commands to remove the access-list filter entry with sequence
number 20 from extended named access-list my-acl:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-acl
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# no 20
Related
Commands
access-list extended (named)
access-list (extended numbered)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 975
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP PROTOCOL FILTER)
(access-list extended IP protocol filter)
Overview Use this ACL filter to add a new IP protocol type filter entry to the current extended
access-list. If the sequence number is specified, the new filter is inserted at the
specified location. Otherwise, the new filter is added at the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes an IP protocol filter entry from the
current extended access-list. You can specify the IP filter entry for removal by
entering either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by entering its IP filter profile
without specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [proto] [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} proto <ip-protocol> <source>
<destination> [log]
no {deny|permit} proto <ip-protocol> <source> <destination>
[log]
no <sequence-number>
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list.
deny Access-list rejects packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Access-list permits packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
proto
<ip-protocol><1-255>
Specify IP protocol number, as defined by IANA (Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority
www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers)
See below for a list of IP protocol numbers and their descriptions.
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This matches
any source IP address within the specified
subnet.
any Matches any source IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 976
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP PROTOCOL FILTER)
<destination>The destination address of the packets. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all destinations. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the destination:
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a forward
slash, then the prefix length. This matches
any destination IP address within the
specified subnet.
any Matches any destination IP address.
log Log the results.
Table 29-6: IP protocol number and description
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]
1Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
3Gateway-to-Gateway [RFC823]
4IP in IP [RFC2003]
5Stream [RFC1190] [RFC1819]
6TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) [RFC793]
8EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) [RFC888]
9IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) [IANA]
11 Network Voice Protocol [RFC741]
17 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) [RFC768]
20 Host monitoring [RFC869]
27 RDP (Reliable Data Protocol) [RFC908]
28 IRTP (Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol) [RFC938]
29 ISO-TP4 (ISO Transport Protocol Class 4) [RFC905]
30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol [RFC969]
33 DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol)
[RFC4340]
48 DSR (Dynamic Source Routing Protocol) [RFC4728]
50 ESP (Encap Security Payload) [RFC2406]
51 AH (Authentication Header) [RFC2402]
54 NARP (NBMA Address Resolution Protocol) [RFC1735]
58 ICMP for IPv6 [RFC1883]
59 No Next Header for IPv6 [RFC1883]
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 977
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP PROTOCOL FILTER)
Mode IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
(extended numbered) command or the access-list extended (named) command, with
the required access control list number, or name - but with no further parameters
selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Example 1
[creating a list]
Use the following commands to add a new access-list filter entry to the access-list
named my-list that will reject IP packets from source address 10.10.1.1/32
to destination address 192.68.1.1/32:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny ip 10.10.1.1/32 192.168.1.1/32
60 Destination Options for IPv6 [RFC1883]
88 EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
89 OSPFIGP [RFC1583]
97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation / RFC3378
98 Encapsulation Header / RFC1241
108 IP Payload Compression Protocol / RFC2393
112 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol / RFC3768
134 RSVP-E2E-IGNORE / RFC3175
135 Mobility Header / RFC3775
136 UDPLite / RFC3828
137 MPLS-in-IP / RFC4023
138 MANET Protocols / RFC-ietf-manet-iana-07.txt
139-252 Unassigned / IANA
253 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
254 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
255 Reserved / IANA
Table 29-6: IP protocol number and description (cont.)
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 978
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED IP PROTOCOL FILTER)
Example 2
[adding to a list]
Use the following commands to add a new access-list filter entry at sequence
position 5 in the access-list named my-list that will accept packets from source
address 10.10.1.1/24 to destination address 192.68.1.1/24:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# 5 permit ip 10.10.1.1/24
192.168.1.1/ 24
Related
Commands
access-list extended (named)
access-list (extended numbered)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 979
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED TCP UDP FILTER)
(access-list extended TCP UDP filter)
Overview Use this ACL filter to add a new TCP or UDP filter entry to the current extended
access-list. If the sequence number is specified, the new filter is inserted at the
specified location. Otherwise, the new filter is added at the end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a TCP or UDP filter entry from the current
extended access-list. You can specify the TCP or UDP filter entry for removal by
entering either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by entering its TCP or UDP
filter profile without specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [tcp|udp] [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} {tcp|udp} <source> {eq
<sourceport> |lt <sourceport>|gt <sourceport>|ne <sourceport>}
<destination> [eq <destport>|lt <destport>|gt <destport>|ne
<destport>] [log]
no [<sequence-number>]{deny|permit} {tcp|udp} <source> {eq
<sourceport> |lt <sourceport>|gt <sourceport>|ne <sourceport>}
<destination> [eq <destport>|lt <destport>|gt <destport>|ne
<destport>] [log]
no <sequence-number>
Mode IPv4 Extended ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
(extended numbered) command or the access-list extended (named) command, with
the required access control list number, or name - but with no further parameters
selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Example 1
[creating a list]
To add a new entry to the access-list named my-list that will reject TCP packets
from 10.0.0.1on TCP port 10 to 192.168.1.1 on TCP port 20, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# deny tcp 10.0.0.1/32 eq 10
192.168.1.1/32 eq 20

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 980
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST EXTENDED TCP UDP FILTER)
Example 2
[adding to a list]
To insert a new entry with sequence number 5 of the access-list named my-list
that will accept UDP packets from 10.1.1.0/24 network to 192.168.1.0/24
network on UDP port 80, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list extended my-list
awplus(config-ip-ext-acl)# 5 permit udp 10.1.1.0/24
192.168.1.0/24 eq 80
Related
Commands
access-list extended (named)
access-list (extended numbered)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 981
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST STANDARD (NAMED)
access-list standard (named)
Overview This command configures a standard named access-list that permits or denies
packets from a specific source IP address. You can either create a standard named
ACL together with an ACL filter entry in the Global Configuration mode, or you can
use the IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration mode for sequenced ACL filter entry after
first entering an access-list name.
The no variant of this command removes a specified standard named access-list.
Syntax
[list-name] access-list standard <standard-access-list-name>
no access-list standard <standard-access-list-name>
Syntax
[deny|permit] access-list standard <standard-access-list-name> {deny|permit}
<source>
no access-list standard <standard-access-list-name>
{deny|permit} <source>
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Parameter Description
<standard-access-list-name
>Specify a name for the standard access-list.
Parameter Description
<standard-
access-list-
name>
Specify a name for the standard access-list.
deny The access-list rejects packets that match the source filtering
specified with this command.
permit The access-list permits packets that match the source filtering
specified with this command.
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
<ip-addr>/<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a
forward slash, then the prefix
length. This matches any source
IP address within the specified
subnet.
any Matches any source IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 982
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST STANDARD (NAMED)
Usage Use this command when configuring a standard named access-list for filtering IP
software packets.
You can either create access-lists from within this command, or you can enter
access-list standard followed by only the name. Entering only the name moves
you to the IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration mode for the selected access-list. From
there you can configure your access-lists by using the command (access-list
standard named filter).
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples To define a standard access-list named my-list and deny any packets from any
source, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list standard my-list deny any
Alternatively, to define a standard access-list named my-list and enter the IPv4
Standard ACL Configuration mode to deny any packets from any source, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ip-std-acl)# 5 deny any
Related
Commands
(access-list standard named filter)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 983
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (STANDARD NUMBERED)
access-list (standard numbered)
Overview This command configures a standard numbered access-list that permits or denies
packets from a specific source IP address. You can either create a standard
numbered ACL together with an ACL filter entry in the Global Configuration mode,
or you can use the IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration mode for sequenced ACL filter
entry after first entering an access-list number.
The no variant of this command removes a specified standard numbered
access-list.
Syntax
[list-number] access-list {<1-99>|<1300-1999>}
no access-list {<1-99>|<1300-1999>}
Syntax [deny|
permit] access-list {<1-99>|<1300-1999>} {deny|permit} <source>
no access-list {<1-99>|<1300-1999>} {deny|permit} <source>
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage Use this command when configuring a standard numbered access-list for filtering
IP software packets.
Parameter Description
<1-99>IP standard access-list.
<1300-1999>IP standard access-list (expanded range).
Parameter Description
<1-99>IP standard access-list.
<1300-1999>IP standard access-list (expanded range).
deny Access-list rejects packets from the specified source.
permit Access-list accepts packets from the specified source.
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify a single host, a
subnet, or all sources. The following are the valid formats for
specifying the source:
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Enter an IPv4 address followed by a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For example,
entering 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255 is
the same as entering 192.168.1.1/24.
any Matches any source IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 984
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
ACCESS-LIST (STANDARD NUMBERED)
You can either create access-lists from within this command, or you can enter
access-list followed by only the number. Entering only the number moves you to
the IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration mode for the selected access-list. From there
you can configure your access-lists by using the command (access-list standard
numbered filter).
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples To create ACL number 67 that will deny packets from subnet 172.16.10, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 67 deny 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255
Alternatively, to enter the IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration mode to create the
ACL filter and deny packets from subnet 172.16.10.0 for the standard
numbered access-list 67, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 67
awplus(config-ip-std-acl)# deny 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255
Related
Commands
(access-list standard named filter)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 985
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST STANDARD NAMED FILTER)
(access-list standard named filter)
Overview This ACL filter adds a source IP address filter entry to a current named standard
access-list. If the sequence number is specified, the new filter entry is inserted at
the specified location. Otherwise, the new entry is added at the end of the
access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a source IP address filter entry from the
current named standard access-list. You can specify the source IP address filter
entry for removal by entering either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by
entering its source IP address filter profile without specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} {<source> [exact-match]|any}
no {deny|permit} {<source> [exact-match]|any}
no <sequence-number>
Mode IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Parameter Description
<sequence-number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the
selected access control list.
deny Access-list rejects packets of the source filtering
specified.
permit Access-list allows packets of the source filtering
specified
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify
either a subnet or all sources. The following are the
valid formats for specifying the source:
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>An IPv4 address, followed by a
forward slash, then the prefix
length. This matches any
destination IP address within
the specified subnet.
<ip-addr> An IPv4 address in a.b.c.d
format.
exact-match Specify an exact IP prefix to match on.
any Matches any source IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 986
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST STANDARD NAMED FILTER)
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
standard (named) command with the required access control list name, but with no
further parameters selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples Use the following commands to add a new filter entry to access-list my-list that
will reject IP address 10.1.1.1:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ip-std-acl)# deny 10.1.1.1/32
Use the following commands to insert a new filter entry into access-list my-list
at sequence position number 15 that will accept IP network 10.1.2.0:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ip-std-acl)# 15 permit 10.1.2.0/24
Related
Commands
access-list standard (named)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 987
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST STANDARD NUMBERED FILTER)
(access-list standard numbered filter)
Overview This ACL filter adds a source IP address filter entry to a current standard numbered
access-list. If a sequence number is specified, the new filter entry is inserted at the
specified location. Otherwise, the new filter entry is added at the end of the
access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a source IP address filter entry from the
current standard numbered access-list. You can specify the source IP address filter
entry for removal by entering either its sequence number (e.g. no 10), or by
entering its source IP address filter profile without specifying its sequence number.
Note that the sequence number can be found by running the show access-list (IPv4
Software ACLs) command.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit} {<source>|host
<host-address>|any}
no {deny|permit} {<source>|host <host-address>|any}
no <sequence-number>
Mode IPv4 Standard ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Parameter Description
<sequence-number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the
selected access control list.
deny Access-list rejects packets of the type specified.
permit Access-list allows packets of the type specified
<source>The source address of the packets. You can specify
either a subnet or all sources. The following are the
valid formats for specifying the source:
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Enter a reverse mask for the
source address in dotted
decimal format. For example,
entering 192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255 is the same as
entering 192.168.1.1/24.
<ip-addr> An IPv4 address in a.b.c.d
format.
host A single source host.
<host-address>Single source host address.
any Matches any source IP address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 988
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(ACCESS-LIST STANDARD NUMBERED FILTER)
Usage An ACL can be configured with multiple ACL filters using sequence numbers. If the
sequence number is omitted, the next available multiple of 10 will be used as the
sequence number for the new filter. A new ACL filter can be inserted into the
middle of an existing list by specifying the appropriate sequence number.
NOTE: The access control list being configured is selected by running the access-list
(standard numbered) command with the required access control list number but with
no further parameters selected.
Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Example To add a new entry accepting the IP network 10.1.1.0/24 at the sequence
number 15 position, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 99
awplus(config-ip-std-acl)# 15 permit 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255
Related
Commands
access-list (standard numbered)
show running-config
show ip access-list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 989
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
MAXIMUM-ACCESS-LIST
maximum-access-list
Overview Use this command to set the maximum number of filters that can be added to any
access-list. These are access-lists within the ranges 1-199, 1300-1999 and
2000-2699, and named standard and extended access-lists.
The no variant of this command removes the limit on the number of filters that can
be added to a software access-list.
Syntax maximum-access-list <1-4294967294>
no maximum-access-list
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set the maximum number of software filters to 200, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# maximum-access-list 200
Parameter Description
<1-4294967294>Filter range.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 990
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW ACCESS-LIST (IPV4 SOFTWARE ACLS)
show access-list (IPv4 Software ACLs)
Overview Use this command to display the specified access-list, or all access-lists if none have
been specified. Note that only defined access-lists are displayed. An error message
is displayed for an undefined access-list
Syntax show access-list
[<1-99>|<100-199>|<1300-1999>|<2000-2699>|<3000-3699>|
<4000-4499>|<access-list-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To show all access-lists configured on the switch:
awplus# show access-list
To show the access-list with an ID of 20:
awplus# show access-list 20
Parameter Description
<1-99>IP standard access-list.
<100-199>IP extended access-list.
<1300-1999>IP standard access-list (standard - expanded range).
<2000-2699>IP extended access-list (extended - expanded range).
<3000-3699>Hardware IP access-list.
<4000-4499>Hardware MAC access-list.
<access-list-name>IP named access-list.
Standard IP access list 1
deny 172.16.2.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
Standard IP access list 20
deny 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
deny 192.168.12.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
Hardware IP access list 3001
permit ip 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0 any
Hardware IP access list 3020
permit tcp any 192.0.2.0/24
awplus#show access-list 20

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 991
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW ACCESS-LIST (IPV4 SOFTWARE ACLS)
Note the following error message is displayed if you attempt to show an undefined
access-list:
awplus# show access-list 2
Related
Commands
access-list standard (named)
access-list (standard numbered)
Standard IP access-list 20
deny 192.168.10.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
deny 192.168.12.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
% Can't find access-list 2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 992
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW IP ACCESS-LIST
show ip access-list
Overview Use this command to display IP access-lists.
Syntax show ip access-list
[<1-99>|<100-199>|<1300-1999>|<2000-2699>|<access-list-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show ip access-list
Output Figure 29-1: Example output from the show ip access-list command
Parameter Description
<1-99>IP standard access-list.
<100-199>IP extended access-list.
<1300-1999>IP standard access-list (expanded range).
<2000-2699>IP extended access-list (expanded range).
<access-list-name>IP named access-list.
Standard IP access-list 1
permit 172.168.6.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255
permit 192.168.6.0, wildcard bits 0.0.0.255

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 993
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV4 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
VTY ACCESS-CLASS (NUMBERED)
vty access-class (numbered)
Overview For IPv4, use this command to set a standard numbered software access list to be
the management ACL. This is then applied to all available VTY lines for controlling
remote access by Telnet and SSH. This command allows or denies packets
containing the IP addresses included in the ACL to create a connection to your
device.
ACLs that are attached using this command have an implicit deny-all filter as the
final entry in the ACL. So a typical configuration would be to permit a specific
address, or range of addresses, and rely on the deny-all filter to block all other
access.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the access list.
Syntax vty access-class {<1-99>|<1300-1999>}
no vty access-class [<1-99>|<1300-1999>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set access-list 4 to be the management ACL, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vty access-class 4
To remove access-list 4 from the management ACL, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no vty access-class 4
Output Figure 29-2: Example output from the show running-config command
Related
Commands
show running-config
vty ipv6 access-class (named)
Parameter Description
<1-99> IPv4 standard access-list number
<1300-1999> IPv4 standard access-list number (expanded range)
awplus#show running-config|grep access-class
vty access-class 4

30
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 994
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPv6 Hardware
Access Control List
(ACL) Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for the IPv6 Hardware Access
Control List (ACL) commands, and contains detailed command information and
command examples about IPv6 hardware ACLs, which are applied directly to
interfaces using the ipv6 traffic-filter command.
For information about ACLs, see the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
To apply ACLs to an LACP channel group, apply it to all the individual switch ports
in the channel group. To apply ACLs to a static channel group, apply it to the static
channel group itself. For more information on link aggregation see the following
references:
•Link Aggregation Feature Overview_and_Configuration_Guide.
•Link Aggregation Commands
Most ACL command titles include usage information in parentheses. When the
command title is completely surrounded by parentheses, the title indicates the
type of ACL filter instead of keywords to enter into the CLI. For example, the title
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry) represents a command with the
syntax:
[<sequence-number>] <action> proto <1-255> <source-addr>
<dest-addr> [vlan <1-4094>]
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
Sub-modes Many of the ACL commands operate from sub-modes that are specific to particular
ACL types. The following table shows the CLI prompts at which ACL commands are
entered.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 995
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
Command List •“commit (IPv6)” on page 996
•“ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)” on page 997
•“(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry)” on page 999
•“(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry)” on page 1003
•“(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry)” on page 1006
•“(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry)” on page 1011
•“ipv6 traffic-filter” on page 1015
•“show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)” on page 1016
Table 30-1: IPv6 Hardware Access List Commands and Prompts
Command Name Command Mode Prompt
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware
ACLs)
Privileged Exec awplus#
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6
hardware ACL)
Global Configuration awplus(config)#
ipv6 traffic-filter Interface Configuration awplus(config-if)#
commit (IPv6) IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6
packet entry)
IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP
entry)
IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP
protocol entry)
IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or
UDP entry)
IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 996
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
COMMIT (IPV6)
commit (IPv6)
Overview Use this command to commit the IPv6 ACL filter configuration entered at the
console to the hardware immediately without exiting the IPv6 Hardware ACL
Configuration mode.
This command forces the associated hardware and software IPv6 ACLs to
synchronize.
Syntax commit
Mode IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration
Usage Normally, when an IPv6 hardware ACL is edited, the new configuration state of the
IPv6 ACL is not written to hardware until you exit IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration
mode. By entering this command you can ensure that the current state of a
hardware access-list that is being edited is written to hardware immediately.
Scripts typically do not include the exit command to exit configuration modes,
potentially leading to IPv6 ACL filters in hardware not being correctly updated.
Using this commit command in a configuration script after specifying an IPv6
hardware ACL filter ensures that it is updated in the hardware.
Example To update the hardware with the IPv6 ACL filter configuration, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-ipv6-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# commit
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 997
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
IPV6 ACCESS-LIST (NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL)
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
Overview Use this command to either create a new IPv6 hardware access-list, or to select an
existing IPv6 hardware access-list in order to apply a filter entry to it.
Use the no variant of this command to delete an existing IPv6 hardware access-list.
NOTE: Before you can delete an access-list, you must first remove it from any interface
it is assigned to.
Syntax ipv6 access-list <ipv6-access-list-name>
no ipv6 access-list <ipv6-access-list-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic on an interface controlled by a hardware ACL that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage Use IPv6 hardware named access-lists to control the transmission of IPv6 packets
on an interface, and restrict the content of routing updates. The switch stops
checking the IPv6 hardware named access-list when a match is encountered.
This command moves you to the (config-ipv6-hw-acl) prompt for the selected IPv6
hardware named access-list number. From there you can configure the filters for
this selected IPv6 hardware named access-list.
Once you have configured the ACL, use the ipv6 traffic-filter or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note
that the ACL will only apply to incoming data packets.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
Examples To create an IPv6 access-list named “my-ipv6-acl”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-ipv6-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#
To delete the IPv6 access-list named “my-ipv6-acl”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ipv6 access-list my-ipv6-acl
Related
Commands
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry)
Parameter Description
<ipv6-access-list-name> Specify an IPv6 access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 998
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
IPV6 ACCESS-LIST (NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry)
ipv6 traffic-filter
match access-group
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 999
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: ICMP ENTRY)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry)
Overview Use this command to add a new ICMP filter entry to the current IPv6 hardware
access-list. The filter will match on any ICMP packet that has the specified IPv6
source and destination IP addresses and (optionally) ICMP type. You can specify
the value any if source or destination address does not matter.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current IPv6
hardware access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either
its sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without
specifying its sequence number (e.g. no deny icmp 2001:0db8::0/64 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show ipv6 access-list (IPv6
Hardware ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> icmp <source-addr> <dest-addr>
[icmp-type <number>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> icmp <source-addr> <dest-addr> [icmp-type <number>]
[vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1000
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: ICMP ENTRY)
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
icmp Match against ICMP packets
<source-addr> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a range, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source host.
<ipv6-src-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified source
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-src-address>
<ipv6-src-wildcard>Match the specified IPv6 source
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match
host
<ipv6-source-host>Match a single source host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
<dest-addr> The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a range, or all destination addresses. The following are
the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination host.
<ipv6-dest-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified destination
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-dest-address>
<ipv6-dest-wildcard>Match the specified destination
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1001
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: ICMP ENTRY)
Mode IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command ipv6
access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command ipv6 access-list (named IPv6
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named IPv6 hardware ACL: entry”
commands) to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL.
If you specify a sequence number, the new entry is inserted at the specified
location. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the entry at the
end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number.
Once you have configured the ACL, use the ipv6 traffic-filter or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note
that the ACL will only apply to incoming data packets.
host
<ipv6-dest-host>Match a single destination host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
icmp-type
<number>The type of ICMP message to match against, as defined in RFC792
and RFC950. Values include:
0Echo replies.
3Destination unreachable
messages.
4Source quench messages.
5Redirect (change route) messages.
8Echo requests.
11 Time exceeded messages.
12 Parameter problem messages.
13 Timestamp requests.
14 Timestamp replies.
15 Information requests.
16 Information replies.
17 Address mask requests.
18 Address mask replies.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1002
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: ICMP ENTRY)
Examples To add a filter entry to the ACL named “my-acl”, to block ICMP packets sent from
network 2001:0db8::0/64 , use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny icmp 2001:0db8::0/64 any
To remove a filter entry from the ACL named “my-acl” that blocks all ICMP packets
sent from network 2001:0db8::0/ 64 , use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# no deny icmp 2001:0db8::0/64 any
To specify an ACL named “my-acl1” and add a filter entry that blocks all ICMP6 echo
requests, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl1
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny icmp any any icmp-type 128
To specify an ACL named “my-acl2” and add a filter entry that blocks all ICMP6 echo
requests on the default VLAN (vlan1), enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl2
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny icmp any any icmp-type 128
vlan 1
To remove a filter entry that blocks all ICMP6 echo requests from the ACL named
“my-acl1”, enter the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl1
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# no deny icmp any any icmp-type 128
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
ipv6 traffic-filter
match access-group
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1003
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IPV6 PACKET ENTRY)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet
entry)
Overview Use this command to add an IPv6 packet filter entry to the current hardware
access-list. The filter will match on IPv6 packets that have the specified source and
destination IPv6 address and (optionally) prefix. You can use the value any instead
of source or destination IPv6 address if an address does not matter.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no deny ipv6 2001:0db8::0/64 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show ipv6 access-list (IPv6
Hardware ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> ipv6 <source-addr> <dest-addr>
[vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> ipv6 <source-addr> <dest-addr> [vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1004
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IPV6 PACKET ENTRY)
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
ipv6 Match against IPv6 packets
<source-addr> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a range, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source host.
<ipv6-src-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified source
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-src-address>
<ipv6-src-wildcard>Match the specified IPv6 source
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match
host
<ipv6-source-host>Match a single source host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
<dest-addr> The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a range, or all destination addresses. The following are
the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination host.
<ipv6-dest-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified destination
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-dest-address>
<ipv6-dest-wildcard>Match the specified destination
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1005
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IPV6 PACKET ENTRY)
Mode IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command ipv6
access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command ipv6 access-list (named IPv6
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named IPv6 hardware ACL: entry”
commands) to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL.
If you specify a sequence number, the new entry is inserted at the specified
location. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the entry at the
end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number.
Once you have configured the ACL, use the ipv6 traffic-filter or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note
that the ACL will only apply to incoming data packets.
Examples To add a filter entry to the ACL named “my-acl” to block IPv6 traffic sent from
network 2001:0db8::0/64, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny ipv6 2001:0db8::0/64 any
To remove a filter entry from the ACL named “my-acl” that blocks all IPv6 traffic
sent from network 2001:0db8::0/ 64, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# no deny ipv6 2001:0db8::0/64 any
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
ipv6 traffic-filter
match access-group
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
host
<ipv6-dest-host>Match a single destination host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1006
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IP PROTOCOL ENTRY)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol
entry)
Overview Use this command to add an IP protocol type filter entry to the current IPv6
hardware access-list. The filter will match on IPv6 packets that have the specified
IP protocol number, and the specified IPv6 addresses. You can use the value any
instead of source or destination IPv6 address if an address does not matter.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no deny proto 2 2001:0db8::0/64 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show ipv6 access-list (IPv6
Hardware ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> proto <1-255> <source-addr>
<dest-addr> [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> proto <1-255> <source-addr> <dest-addr> [vlan
<1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1007
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IP PROTOCOL ENTRY)
Table 30-2: Parameters in IP protocol ACL entries
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535.
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
proto <1-255>The IP protocol number to match against, as defined by IANA
(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers)
See below for a list of IP protocol numbers and their descriptions.
<source-addr> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a range, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source host.
<ipv6-src-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified source
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
<ipv6-src-address>
<ipv6-src-wildcard>Match the specified IPv6 source
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match
host
<ipv6-source-host>Match a single source host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
<dest-addr> The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a range, or all destination addresses. The following are
the valid formats for specifying the destination:
any Match any destination host.
<ipv6-dest-address/
prefix-length>Match the specified destination
address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the
format X:X::/prefix-length. The
prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1008
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IP PROTOCOL ENTRY)
<ipv6-dest-address>
<ipv6-dest-wildcard>Match the specified destination
address, masked using wildcard
bits.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
In the wildcard bits, 1 represents
bits to ignore, and 0 represents
bits to match
host
<ipv6-dest-host>Match a single destination host
address.
The IPv6 address uses the format
X:X::X:X.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Table 30-3: IP protocol number and description
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]
1Internet Control Message [RFC792]
2Internet Group Management [RFC1112]
3Gateway-to-Gateway [RFC823]
4IP in IP [RFC2003]
5Stream [RFC1190] [RFC1819]
6TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) [RFC793]
8EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol) [RFC888]
9IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) [IANA]
11 Network Voice Protocol [RFC741]
17 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) [RFC768]
20 Host monitoring [RFC869]
27 RDP (Reliable Data Protocol) [RFC908]
28 IRTP (Internet Reliable Transaction Protocol) [RFC938]
29 ISO-TP4 (ISO Transport Protocol Class 4) [RFC905]
30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol [RFC969]
33 DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol) [RFC4340]
48 DSR (Dynamic Source Routing Protocol) [RFC4728]
50 ESP (Encap Security Payload) [RFC2406]
51 AH (Authentication Header) [RFC2402]
Table 30-2: Parameters in IP protocol ACL entries (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1009
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IP PROTOCOL ENTRY)
Mode IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command ipv6
access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command ipv6 access-list (named IPv6
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named IPv6 hardware ACL: entry”
commands) to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL.
If you specify a sequence number, the new entry is inserted at the specified
location. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the entry at the
end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number.
Once you have configured the ACL, use the ipv6 traffic-filter or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note
that the ACL will only apply to incoming data packets.
54 NARP (NBMA Address Resolution Protocol) [RFC1735]
58 ICMP for IPv6 [RFC1883]
59 No Next Header for IPv6 [RFC1883]
60 Destination Options for IPv6 [RFC1883]
88 EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
89 OSPFIGP [RFC1583]
97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation / RFC3378
98 Encapsulation Header / RFC1241
108 IP Payload Compression Protocol / RFC2393
112 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol / RFC3768
134 RSVP-E2E-IGNORE / RFC3175
135 Mobility Header / RFC3775
136 UDPLite / RFC3828
137 MPLS-in-IP / RFC4023
138 MANET Protocols / RFC-ietf-manet-iana-07.txt
139-252 Unassigned / IANA
253 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
254 Use for experimentation and testing / RFC3692
255 Reserved / IANA
Table 30-3: IP protocol number and description (cont.)
Protocol Number Protocol Description [RFC]

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1010
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: IP PROTOCOL ENTRY)
Examples To add a filter entry to the ACL named “my-acl” to deny IGMP packets from
2001:0db8::0/64 , use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny proto 2 2001:0db8::0/64 any
To remove a filter entry that blocks IGMP packets from network 2001:0db8::0/64
from the ACL named “my-acl”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# no deny proto 2 2001:0db8::0/64 any
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
ipv6 traffic-filter
match access-group
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1011
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: TCP OR UDP ENTRY)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP
entry)
Overview Use this command to add a TCP or UDP filter entry to the current IPv6 hardware
access-list. The access-list will match on TCP or UDP packets that have the specified
source and destination IP addresses and optionally, port values. You can use the
value any instead of source or destination IP address if an address does not matter.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry from the current hardware
access-list. You can specify the filter entry for removal by entering either its
sequence number (e.g. no 100), or by entering its filter profile without specifying
its sequence number (e.g. no deny tcp 2001:0db8::0/64 any).
You can find the sequence number by running the show ipv6 access-list (IPv6
Hardware ACLs) command.
Hardware ACLs will permit access unless explicitly denied by an ACL action.
CAUTION: Specifying a “send” action enables you to use ACLs to redirect packets from
their original destination. Use such ACLs with caution. They could prevent control
packets from reaching the correct destination, such as EPSR healthcheck messages
and AMF messages.
Syntax [<sequence-number>] <action> {tcp|udp} <source-addr>
[<source-ports>] <dest-addr> [<dest-ports>] [vlan <1-4094>]
no <sequence-number>
no <action> {tcp|udp} <source-addr> [<source-ports>]
<dest-addr> [<dest-ports>] [vlan <1-4094>]
The following actions are available for hardware ACLs:
Values for the <action> parameter
deny Reject packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit Permit packets that match the source and destination
filtering specified with this command.
copy-to-cpu Send a copy of matching packets to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Send a copy of matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-mirror Send matching packets to the mirror port.
Use the mirror interface command to configure the mirror
port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified port, tagged with
the specified VLAN. The specified port must belong to the
specified VLAN.
send-to-cpu Send matching packets to the CPU.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1012
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: TCP OR UDP ENTRY)
Parameter Description
<sequence-
number>The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected access
control list, in the range 1-65535. If you do not specify a sequence
number, the switch puts the entry at the end of the ACL and
assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number. .
<action> The action that the switch will take on matching packets. See the
table above for valid values.
tcp Match against TCP packets.
udp Match against UDP packets.
<source-addr> The source addresses to match against. You can specify a single
host, a subnet, or all source addresses. The following are the valid
formats for specifying the source:
any Match any source IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single source host with the
IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering the IPv4 address,
then a forward slash, then the prefix
length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any source IP address within
the specified subnet. Specify the
subnet by entering a reverse mask
in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<source-ports>Match source TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
<dest-addr>The destination addresses to match against. You can specify a
single host, a subnet, or all destination addresses. The following
are the valid formats for specifying the destination:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1013
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: TCP OR UDP ENTRY)
Mode IPv6 Hardware ACL Configuration (accessed by running the command ipv6
access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL))
Default On an interface controlled by a hardware ACL, any traffic that does not explicitly
match a filter is permitted.
Usage To use this command, first run the command ipv6 access-list (named IPv6
hardware ACL) and enter the desired access-list name. This changes the prompt to
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)#.
Then use this command (and the other “named IPv6 hardware ACL: entry”
commands) to add filter entries. You can add multiple filter entries to an ACL.
If you specify a sequence number, the new entry is inserted at the specified
location. If you do not specify a sequence number, the switch puts the entry at the
any Match any destination IP address.
host <ip-addr> Match a single destination host with
the IP address given by <ip-addr> in
dotted decimal notation.
<ip-addr>/
<prefix>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering the IPv4
address, then a forward slash, then
the prefix length.
<ip-addr>
<reverse-mask>Match any destination IP address
within the specified subnet. Specify
the subnet by entering a reverse
mask in dotted decimal format. For
example, entering “192.168.1.1
0.0.0.255” is the same as entering
192.168.1.1/24.
<dest-ports>Match destination TCP or UDP port numbers. Port numbers are
specified as integers between 0 and 65535. You can specify one or
more port numbers as follows:
eq <0-65535> Match a single port number.
lt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are less
than the specified port number.
gt <0-65535> Match all port numbers that are
greater than the specified port
number.
ne <0-65535> Match all port numbers except the
specified port number.
range <start-port>
<end-port>Match a range of port numbers.
vlan <1-4094> The VLAN to match against. The ACL will match against the
specified ID in the packet’s VLAN tag.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1014
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(NAMED IPV6 HARDWARE ACL: TCP OR UDP ENTRY)
end of the ACL and assigns it the next available multiple of 10 as its sequence
number.
Once you have configured the ACL, use the ipv6 traffic-filter or the match
access-group command to apply this ACL to a port, VLAN or QoS class-map. Note
that the ACL will only apply to incoming data packets.
Examples To add a filter entry that blocks all SSH traffic from network 2001:0db8::0/64 to the
hardware IPv6 access-list named “my-acl”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny tcp 2001:0db8::0/64 any eq 22
To add a filter entry that blocks all SSH traffic from network 2001:0db8::0/64 on the
default VLAN (vlan1) to the hardware IPv6 access-list named “my-acl”, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# deny tcp 2001:0db8::0/64 any eq 22
vlan 1
To remove an ACL filter entry that blocks all SSH traffic from network 2001:0db8::0/
64 from the hardware IPv6 access-list named “my-acl”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list my-acl
awplus(config-ipv6-hw-acl)# no deny tcp 2001:0db8::0/64 any eq
22
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
ipv6 traffic-filter
match access-group
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1015
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
IPV6 TRAFFIC-FILTER
ipv6 traffic-filter
Overview This command adds an IPv6 hardware-based access-list to an interface. The
number of access-lists that can be added is determined by the amount of available
space in the hardware-based packet classification tables.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an IPv6 hardware-based access-list
from an interface.
Syntax ipv6 traffic-filter <ipv6-access-list-name>
no ipv6 traffic-filter <ipv6-access-list-name>
Mode Interface Configuration (to apply an IPv6 hardware ACL to a specific switch port).
Usage This command adds an IPv6 hardware-based access-list to an interface. The
number of access-lists that can be added is determined by the amount of available
space in the hardware-based packet classification tables.
Examples To add access-list “acl1” as a traffic-filter to interface port1.0.1, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 traffic-filter acl1
To remove access-list “acl1” as a traffic-filter from interface port1.0.1, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 traffic-filter acl1
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry)
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Parameter Description
<ipv6-access-list-name> Hardware IPv6 access-list name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1016
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 HARDWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ACCESS-LIST (IPV6 HARDWARE ACLS)
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Hardware ACLs)
Overview Use this command to display all configured hardware IPv6 access-lists or the IPv6
access-list specified by name. Omitting the optional name parameter will display
all IPv6 ACLs.
Syntax show ipv6 access-list [<name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show all configured IPv6 access-lists use the command:
awplus# show ipv6 access-list
Output Figure 30-1: Example output from the show ipv6 access-list command
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: ICMP entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IPv6 packet entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: IP protocol entry)
(named IPv6 hardware ACL: TCP or UDP entry)
ipv6 traffic-filter
Parameter Description
<name> Hardware IPv6 access-list name.
IPv6 access-list deny_ssh
deny tcp abcd::0/64 any eq 22

31
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1017
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPv6 Software
Access Control List
(ACL) Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for the IPv6 Software Access
Control List (ACL) commands, and contains detailed command information and
command examples about IPv6 software ACLs as applied to Routing and
Multicasting, which are not applied to interfaces.
For information about ACLs, see the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
To apply ACLs to an LACP channel group, apply it to all the individual switch ports
in the channel group. To apply ACLs to a static channel group, apply it to the static
channel group itself. For more information on link aggregation see the following
references:
•the Link Aggregation Feature Overview_and_Configuration Guide.
•Link Aggregation Commands
Note that text in parenthesis in command names indicates usage not keyword
entry. For example, ipv6-access-list (named) indicates named IPv6 ACLs entered
as ipv6-access-list <name> where <name> is a placeholder not a keyword.
Note also that parenthesis surrounding ACL filters indicates the type of ACL filter
not the keyword entry in the CLI. For example, (ipv6 access-list standard IPv6
filter) represents command entry in the format shown in the syntax:
[<sequence-number>] {deny|permit}
{<source-ipv6-address/prefix-length>|any}
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Sub-modes Many of the ACL commands operate from sub-modes that are specific to particular
ACL types. The following table shows the CLI prompts at which ACL commands are
entered.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1018
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
Command List •“ipv6 access-list standard (named)” on page 1019
•“(ipv6 access-list standard filter)” on page 1021
•“show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs)” on page 1023
•“vty ipv6 access-class (named)” on page 1024
Table 31-1: IPv6 Software Access List Commands and Prompts
Command Name Command Mode Prompt
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software
ACLs)
Privileged Exec awplus#
ipv6 access-list standard (named) Global Configuration awplus(config)#
(ipv6 access-list standard filter) IPv6 Standard ACL
Configuration awplus(config-ipv6-std-acl)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1019
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
IPV6 ACCESS-LIST STANDARD (NAMED)
ipv6 access-list standard (named)
Overview This command configures an IPv6 standard access-list for filtering frames that
permit or deny IPv6 packets from a specific source IPv6 address.
The no variant of this command removes a specified IPv6 standard access-list.
Syntax
[list-name] ipv6 access-list standard <ipv6-acl-list-name>
no ipv6 access-list standard <ipv6-acl-list-name>
Syntax [deny|
permit] ipv6 access-list standard <ipv6-acl-list-name> [{deny|permit}
{<ipv6-source-address/prefix-length>|any} [exact-match]]
no ipv6 access-list standard <ipv6-acl-list-name>
[{deny|permit} {<ipv6-source-address/prefix-length>|any}
[exact-match]]
Mode Global Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage Use IPv6 standard access-lists to control the transmission of IPv6 packets on an
interface, and restrict the content of routing updates. The switch stops checking
the IPv6 standard access-list when a match is encountered.
Parameter Description
<ipv6-acl-list-name> A user-defined name for the IPv6 software standard
access-list.
Parameter Description
<ipv6-acl-list-name> A user-defined name for the IPv6 software standard
access-list.
deny The IPv6 software standard access-list rejects
packets that match the type, source, and destination
filtering specified with this command.
permit The IPv6 software standard access-list permits
packets that match the type, source, and destination
filtering specified with this command.
<ipv6-source-address/
prefix-length> Specifies a source address and prefix length.
The IPv6 address prefix uses the format
X:X::/prefix-length. The prefix-length is usually set
between 0 and 64.
any Matches any source IPv6 address.
exact-match Exact match of the prefixes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1020
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
IPV6 ACCESS-LIST STANDARD (NAMED)
For backwards compatibility you can either create IPv6 standard access-lists from
within this command, or you can enter ipv6 access-list standard
followed by only the IPv6 standard access-list name. This latter (and preferred)
method moves you to the (config-ipv6-std-acl) prompt for the selected
IPv6 standard access-list, and from here you can configure the filters for this
selected IPv6 standard access-list.
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Example To enter the IPv6 Standard ACL Configuration mode for the access-list named
my-list, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ipv6-std-acl)#
Related
Commands
(ipv6 access-list standard filter)
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs)
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1021
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(IPV6 ACCESS-LIST STANDARD FILTER)
(ipv6 access-list standard filter)
Overview Use this ACL filter to add a filter entry for an IPv6 source address and prefix length
to the current standard IPv6 access-list. If a sequence number is specified, the new
entry is inserted at the specified location. Otherwise, the new entry is added at the
end of the access-list.
The no variant of this command removes a filter entry for an IPv6 source address
and prefix from the current standard IPv6 access-list. You can specify the filter
entry for removal by entering either its sequence number, or its filter entry profile.
Syntax [icmp] [<sequence-number>] {deny|permit}
{<ipv6-source-address/prefix-length>|any}
no {deny|permit} {<ipv6-source-address/prefix-length>|any}
no <sequence-number>
Mode IPv6 Standard ACL Configuration
Default Any traffic controlled by a software ACL that does not explicitly match a filter is
denied.
Usage The filter entry will match on any IPv6 packet that has the specified IPv6 source
address and prefix length. The parameter any may be specified if an address does
not matter.
NOTE: Software ACLs will deny access unless explicitly permitted by an ACL action.
Examples To add an ACL filter entry with sequence number 5 that will deny any IPv6 packets
to the standard IPv6 access-list named my-list, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ipv6-std-acl)# 5 deny any
Parameter Description
<sequence-number><1-65535>
The sequence number for the filter entry of the selected
access control list.
deny Specifies the packets to reject.
permit Specifies the packets to accept.
<ipv6-source-
address/prefix-
length>
IPv6 source address and prefix-length in the form X:X::X:X/P.
any Any IPv6 source host address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1022
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
(IPV6 ACCESS-LIST STANDARD FILTER)
To remove the ACL filter entry that will deny any IPv6 packets from the standard
IPv6 access-list named my-list, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ipv6-std-acl)# no deny any
Alternately, to remove the ACL filter entry with sequence number 5 to the
standard IPv6 access-list named my-list, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ipv6 access-list standard my-list
awplus(config-ipv6-std-acl)# no 5
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list standard (named)
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs)
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1023
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 ACCESS-LIST (IPV6 SOFTWARE ACLS)
show ipv6 access-list (IPv6 Software ACLs)
Overview Use this command to display all configured IPv6 access-lists or the IPv6 access-list
specified by name.
Syntax show ipv6 access-list [<access-list-name>]
show ipv6 access-list standard [<access-list-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show all configured IPv6 access-lists, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 access-list
Output Figure 31-1: Example output from show ipv6 access-list
Example To show the IPv6 access-list named deny_icmp, use the following command:
awplus# show ipv6 access-list deny_icmp
Output Figure 31-2: Example output from show ipv6 access-list for a named ACL
Related
Commands
ipv6 access-list standard (named)
(ipv6 access-list standard filter)
Parameter Description
<access-list-name>Only display information about an IPv6 access-list with
the specified name.
standard Only display information about standard access-lists.
IPv6 access-list deny_icmp
deny icmp any any vlan 1
IPv6 access-list deny_ssh
deny tcp abcd::0/64 any eq 22
IPv6 access-list deny_icmp
deny icmp any any vlan 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1024
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
IPV6 SOFTWARE ACCESS CONTROL LIST (ACL) COMMANDS
VTY IPV6 ACCESS-CLASS (NAMED)
vty ipv6 access-class (named)
Overview For IPv6, use this command to set a standard named software access list to be the
management ACL. This is then applied to all available VTY lines for controlling
remote access by Telnet and SSH. This command allows or denies packets
containing the IPv6 addresses included in the ACL to create a connection to your
device.
ACLs that are attached using this command have an implicit ‘deny-all’ filter as the
final entry in the ACL. A typical configuration is to permit a specific address, or
range of addresses, and rely on the ‘deny-all’ filter to block all other access.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the access list.
Syntax vty ipv6 access-class <access-name>
no vty ipv6 access-class [<access-name>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the named standard access-list named access-ctrl to be the IPv6
management ACL, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vty ipv6 access-class access-ctrl
To remove access-ctrl from the management ACL, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no vty ipv6 access-class access-ctrl
Output Figure 31-3: Example output from the show running-config command
Related
Commands
show running-config
vty access-class (numbered)
Parameter Description
<access-name> Specify an IPv6 standard software access-list name
awplus#showrunning-config|grep access-class
vty ipv6 access-class access-ctrl

32
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1025
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QoS Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for Quality of Service commands.
QoS uses ACLs. For more information about ACLs, see the ACL Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“class” on page 1027
•“class-map” on page 1028
•“clear mls qos interface policer-counters” on page 1029
•“default-action” on page 1030
•“description (QoS policy-map)” on page 1031
•“egress-rate-limit” on page 1032
•“match access-group” on page 1033
•“match cos” on page 1035
•“match dscp” on page 1036
•“match eth-format protocol” on page 1037
•“match inner-cos” on page 1040
•“match inner-vlan” on page 1041
•“match ip-precedence” on page 1042
•“match mac-type” on page 1043
•“match tcp-flags” on page 1044
•“match vlan” on page 1045
•“mls qos cos” on page 1046
•“mls qos enable” on page 1047
•“mls qos map cos-queue” on page 1048

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1026
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
•“mls qos map premark-dscp” on page 1049
•“no police” on page 1051
•“police single-rate action” on page 1052
•“police twin-rate action” on page 1054
•“policy-map” on page 1056
•“priority-queue” on page 1057
•“remark-map” on page 1058
•“remark new-cos” on page 1060
•“service-policy input” on page 1062
•“show class-map” on page 1063
•“show mls qos” on page 1064
•“show mls qos interface” on page 1065
•“show mls qos interface policer-counters” on page 1068
•“show mls qos interface queue-counters” on page 1069
•“show mls qos interface storm-status” on page 1070
•“show mls qos maps cos-queue” on page 1071
•“show mls qos maps premark-dscp” on page 1072
•“show platform classifier statistics utilization brief” on page 1073
•“show policy-map” on page 1076
•“storm-action” on page 1077
•“storm-downtime” on page 1078
•“storm-protection” on page 1079
•“storm-rate” on page 1080
•“storm-window” on page 1081
•“trust dscp” on page 1082
•“wrr-queue disable queues” on page 1083
•“wrr-queue egress-rate-limit queues” on page 1084
•“wrr-queue weight queues” on page 1085

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1027
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
CLASS
class
Overview Use this command to associate an existing class-map to a policy or policy-map
(traffic classification), and to enter Policy Map Class Configuration mode to
configure the class- map.
Use the no variant of this command to delete an existing class-map.
If your class-map does not exist, you can create it by using the class-map
command.
Syntax class {<name>|default}
no class <name>
Mode Policy Map Configuration
Example The following example creates the policy-map pmap1(using the policy-map
command), then associates this to an already existing class-map named cmap1,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)#
Related
Commands
class-map
policy-map
Parameter Description
<name>Name of the (already existing) class-map.
default Specify the default class-map.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1028
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
CLASS-MAP
class-map
Overview Use this command to create a class-map.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the named class-map.
Syntax class-map <name>
no class-map <name>
Mode Global Configuration
Example This example creates a class-map called cmap1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)#
Parameter Description
<name>Name of the class-map to be created.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1029
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
CLEAR MLS QOS INTERFACE POLICER-COUNTERS
clear mls qos interface policer-counters
Overview Resets an interface’s policer counters to zero. You can either clear a specific
class-map, or you can clear all class-maps by not specifying a class map.
Syntax clear mls qos interface <port> policer-counters [class-map
<class-map>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To reset the policy counters to zero for all class-maps for port1.0.4, use the
command:
awplus# clear mls qos interface port1.0.4 policer-counters
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface policer-counters
Parameter Description
<port>The port may be a switch port (e.g. port1.0.4), a static channel
group (e.g. sa3), or a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po4).
class-map Select a class-map.
<class-map>Class-map name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1030
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
DEFAULT-ACTION
default-action
Overview Sets the action for the default class-map belonging to a particular policy-map. The
action for a non-default class-map depends on the action of any ACL that is applied
to the policy-map.
The default action can therefore be thought of as specifying the action that will be
applied to any data that does not meet the criteria specified by the applied
matching commands.
Use the no variant of this command to reset to the default action of ‘permit’.
Syntax default-action <action>
no default-action
Default The default is permit.
Mode Policy Map Configuration
Examples To set the action for the default class-map to deny, use the command:
awplus(config-pmap)# default-action deny
To set the action for the default class-map to copy-to-mirror for use with the mirror
interface command, use the command:
awplus(config-pmap)# default-action copy-to-mirror
Related
Commands
mirror interface
Parameter Description
<action>permit Packets to permit.
deny Packets to deny.
send-to-cpu Specify packets to send to the CPU.
copy-to-cpu Specify packets to copy to the CPU.
copy-to-mirror Specify packets to copy to the mirror port.
send-to-mirror Specify packets to send to the mirror port.
send-to-vlan-port
vlan <vid> port
<port-number>
Send matching packets to the specified
port, tagged with the specified VLAN. The
specified port must belong to the specified
VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1031
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (QOS POLICY-MAP)
description (QoS policy-map)
Overview Adds a textual description of the policy-map. This can be up to 80 characters long.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the current description from the
policy-map.
Syntax description <line>
no description
Mode Policy Map Configuration
Example To add the description, VOIP traffic, use the command:
awplus(config-pmap)# description VOIP traffic
Parameter Description
<line>Up to 80 character long line description.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1032
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
EGRESS-RATE-LIMIT
egress-rate-limit
Overview Use this command to limit the amount of traffic that can be transmitted per second
from this port.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the limiting of traffic egressing on
the interface.
Syntax egress-rate-limit <rate-limit>
no egress-rate-limit
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To enable egress rate limiting on a port, with a limit of approximately 500Mbps, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# egress-rate-limit 500m
To disable egress rate limiting on a port, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no egress-rate-limit
Parameter Description
<rate-limit>Bandwidth <1-10000000 units per second> (usable units: k, m, g).
The egress rate limit can be configured in multiples of 64kbps. If
you configure a value that is not an exact multiple of 64kbps, then
the value will be rounded up to the nearest higher exact multiple
of 64kbps. The minimum is 64 Kb.
The default unit is Kb (k), but Mb (m) or Gb (g) can also be
specified. The command syntax is not case sensitive, so a value
such as 20m or 20M will be interpreted as 20 megabits.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1033
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH ACCESS-GROUP
match access-group
Overview Use this command to apply an ACL to a class-map or VLAN.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the match.
Syntax match access-group {<hw-IP-ACL>|<hw-MAC-ACL>|<hw-named-ACL>}
no match access-group
{<hw-IP-ACL>|<hw-MAC-ACL>|<hw-named-ACL>}
Mode Class Map or VLAN Access-Map
Usage First create an access-list that applies the appropriate action to matching packets.
Then use the match access-group command to apply this access-list as desired.
Note that this command will apply the access-list matching only to incoming data
packets.
Examples To configure a class-map named “cmap1”, which matches traffic against access-list
3001, which allows IP traffic from any source to any destination, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3001 permit ip any any
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match access-group 3001
To configure a class-map named “cmap2”, which matches traffic against access-list
4001, which allows MAC traffic from any source to any destination, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 4001 permit any any
awplus(config)# class-map cmap2
awplus(config-cmap)# match access-group 4001
Parameter Description
<hw-IP-ACL>Specify a hardware IP ACL number in the range <3000-3699>.
<hw-MAC-ACL>Specify a hardware MAC ACL number in the range <4000-4699>.
<hw-named-ACL>Specify a hardware named ACL (IP, IPv6 or MAC address entries).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1034
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH ACCESS-GROUP
To configure a class-map named “cmap3”, which matches traffic against access-list
“hw_acl”, which allows IP traffic from any source to any destination, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list hardware hw_acl
awplus(config-ip-hw-acl)# permit ip any any
awplus(config)# class-map cmap3
awplus(config-cmap)# match access-group hw_acl
To apply ACL 3001 to VLAN 48, where the ACL drops IP traffic from any source to
any destination, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# access-list 3001 deny ip any any
awplus(config)# vlan access-map deny_all
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# match access-group 3001
awplus(config-vlan-access-map)# exit
awplus(config)# vlan filter deny_all vlan-list 48 input
Related
Commands
class-map
vlan access-map
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: support for VLAN access-maps added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1035
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH COS
match cos
Overview Use this command to define a COS to match against incoming packets.
Use the no variant of this command to remove CoS.
Syntax match cos <0-7>
no match cos
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To set the class-map’s CoS to 4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match cos 4
To remove CoS from a class-map, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match cos
Parameter Description
<0-7>Specify the CoS value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1036
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH DSCP
match dscp
Overview Use this command to define the DSCP to match against incoming packets.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a previously defined DSCP.
Syntax match dscp <0-63>
no match dscp
Mode Class Map Configuration
Usage Use the match dscp command to define the match criterion after creating a
class-map.
Examples To configure a class-map named cmap1 with criterion that matches DSCP 56, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match dscp 56
To remove a previously defined DSCP from a class-map named cmap1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match dscp
Related
Commands
class-map
Parameter Description
<0-63>Specify DSCP value (only one value can be specified).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1037
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH ETH-FORMAT PROTOCOL
match eth-format protocol
Overview This command sets the Ethernet format and the protocol for a class-map to match
on.
Select one Layer 2 format and one Layer 3 protocol when you issue this command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured Ethernet format and
protocol from a class-map.
Syntax match eth-format <layer-two-format> protocol
<layer-three-protocol>
no match eth-format protocol
The following eth-formats and protocols are available (note that not all options are
available on all AlliedWare Plus switch models):
Parameter Description
<layer-two-formats>
802dot2-tagged 802.2 Tagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
802dot2-untagged 802.2 Untagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
ethii-tagged EthII Tagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
ethii-untagged EthII Untagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
ethii-any EthII Tagged or Untagged Packets (enter the parameter
name).
netwareraw-
tagged Netware Raw Tagged Packets (enter the parameter
name).
netwareraw-
untagged Netware Raw Untagged Packets (enter the parameter
name).
snap-tagged SNAP Tagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
snap-untagged SNAP Untagged Packets (enter the parameter name).
<layer-three-protocols>
<word> A Valid Protocol Number in hexidecimal.
any Note that the parameter “any” is only valid when used
with the netwarerawtagged and netwarerawuntagged
protocol options.
sna-path-control Protocol Number 04 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
proway-lan Protocol Number 0E (enter the parameter name or its
number).
eia-rs Protocol Number 4E (enter the parameter name or its number).
proway Protocol Number 8E (enter the parameter name or its number).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1038
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH ETH-FORMAT PROTOCOL
ipx-802dot2 Protocol Number E0 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
netbeui Protocol Number F0 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
iso-clns-is Protocol Number FE (enter the parameter name or its
number).
xdot75-internet Protocol Number 0801(enter the parameter name or its
number).
nbs-internet Protocol Number 0802 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ecma-internet Protocol Number 0803 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
chaosnet Protocol Number 0804 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
xdot25-level-3 Protocol Number 0805 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
arp Protocol Number 0806 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
xns-compat Protocol Number 0807 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
banyan-systems Protocol Number 0BAD (enter the parameter name or
its number).
bbn-simnet Protocol Number 5208 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-mop-dump-ld Protocol Number 6001 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-mop-rem-
cdons Protocol Number 6002 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-decnet Protocol Number 6003 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-lat Protocol Number 6004 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-diagnostic Protocol Number 6005 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-customer Protocol Number 6006 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-lavc Protocol Number 6007 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
rarp Protocol Number 8035 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
dec-lanbridge Protocol Number 8038 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1039
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH ETH-FORMAT PROTOCOL
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To set the eth-format to ethii-tagged and the protocol to 0800 (IP) for class-map
cmap1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match eth-format ethii-tagged protocol
0800
awplus#
awplus(config-cmap)# match eth-format ethii-tagged protocol ip
To remove the eth-format and the protocol from the class-map cmap1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match eth-format protocol
dec-encryption Protocol Number 803D (enter the parameter name or
its number).
appletalk Protocol Number 809B (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ibm-sna Protocol Number 80D5 (enter the parameter name or
its number).
appletalk-aarp Protocol Number 80F3 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
snmp Protocol Number 814CV.
ethertalk-2 Protocol Number 809B (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ethertalk-2-aarp Protocol Number 80F3 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ipx-snap Protocol Number 8137 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ipx-802dot3 Protocol Number FFFF (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ip Protocol Number 0800 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ipx Protocol Number 8137 (enter the parameter name or its
number).
ipv6 Protocol Number 86DD (enter the parameter name or
its number).
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1040
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH INNER-COS
match inner-cos
Overview Sets the Inner CoS for a class-map to match on.
Use the no variant of this command to remove CoS.
Syntax match inner-cos <0-7>
no match inner-cos
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To set the class-map’s inner-cos to 4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match inner-cos 4
To remove CoS from the class-map, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match inner-cos
Parameter Description
<0-7>Specify the Inner CoS value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1041
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH INNER-VLAN
match inner-vlan
Overview Use this command to define the inner VLAN ID as match criteria.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the VLAN ID used as match criteria.
Syntax match inner-vlan <1-4094>
no match inner-vlan
Mode Class Map Configuration
Usage This command is used in double-tagged networks to match on a VLAN ID
belonging to the client network. For more information on VLAN double-tagged
networks, see the VLAN_Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Examples To configure a class-map named cmap1 to match traffic from inner VLAN 3, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match inner-vlan 3
To disable the configured VLAN ID as a match criteria for the class-map named
cmap1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match inner-vlan
Parameter Description
<1-4094>The VLAN number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1042
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH IP-PRECEDENCE
match ip-precedence
Overview Use this command to identify IP precedence values as match criteria.
Use the no variant of this command to remove IP precedence values from a
class-map.
Syntax match ip-precedence <0-7>
no match ip-precedence
Mode Class Map Configuration
Example To configure a class-map named cmap1 to match all IPv4 packets with a
precedence value of 5, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match ip-precedence 5
Parameter Description
<0-7>The precedence value to be matched.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1043
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH MAC-TYPE
match mac-type
Overview Use this command to set the MAC type for a class-map to match on.
Use no variant of this command to remove the MAC type match entry.
Syntax match mac-type {l2bcast|l2mcast|l2ucast}
no match mac-type
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To set the class-map’s MAC type to Layer 2 multicast, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match mac-type l2mcast
To remove the class-map’s MAC type entry, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match mac-type
Parameter Description
l2bcast Layer 2 Broadcast traffic.
l2mcast Layer 2 Multicast traffic.
l2ucast Layer 2 Unicast traffic.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1044
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH TCP-FLAGS
match tcp-flags
Overview Sets one or more TCP flags (control bits) for a class-map to match on.
Use the no variant of this command to remove one or more TCP flags for a
class-map to match on.
Syntax match tcp-flags [ack] [fin] [psh] [rst] [syn] [urg]
no match tcp-flags [ack] [fin] [psh] [rst] [syn] [urg]
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To set the class-map’s TCP flags to ack and syn, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map
awplus(config-cmap)# match tcp-flags ack syn
To remove the TCP flags ack and rst, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map
awplus(config-cmap)# no match tcp-flags ack rst
Parameter Description
ack Acknowledge.
fin Finish.
psh Push.
rst Reset.
syn Synchronize.
urg Urgent.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1045
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MATCH VLAN
match vlan
Overview Use this command to define the VLAN ID as match criteria.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the VLAN ID used as match criteria.
Syntax match vlan <1-4094>
no match vlan
Mode Class Map Configuration
Examples To configure a class-map named cmap1 to include traffic from VLAN 3, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# match vlan 3
To disable the configured VLAN ID as a match criteria for the class-map named
cmap1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# class-map cmap1
awplus(config-cmap)# no match vlan
Parameter Description
<1-4094>The VLAN number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1046
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MLS QOS COS
mls qos cos
Overview This command assigns a CoS (Class of Service) user-priority value to untagged
frames entering a specified interface. By default, all untagged frames are assigned
a CoS value of 0.
Use the no variant of this command to return the interface to the default CoS
setting for untagged frames entering the interface.
Syntax mls qos cos <0-7>
no mls qos cos
Default By default, all untagged frames are assigned a CoS value of 0. Note that for tagged
frames, the default behavior is not to alter the CoS value.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To assign a CoS user priority value of 2 to all untagged packets entering port1.0.1
to port1.0.4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# mls qos cos 2
Parameter Description
<0-7>The Class of Service, user-priority value.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1047
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MLS QOS ENABLE
mls qos enable
Overview Use this command to enable QoS.
Use the no variant of this command to globally disable QoS and remove all QoS
configuration. The no variant of this command removes all class-maps,
policy-maps, and policers that have been created. Running the no mls qos
command will therefore remove all pre-existing QoS configurations on the switch.
Mode Global Configuration
Syntax mls qos enable
no mls qos
Example To enable QoS on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mls qos enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1048
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MLS QOS MAP COS-QUEUE
mls qos map cos-queue
Overview Use this command to set the default CoS to egress queue mapping. This is the
default queue mapping for packets that do not get assigned an egress queue via
any other QoS functionality.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the cos-queue map back to its default
setting. The default mappings for this command are:
Syntax mls qos map cos-queue <cos-priority> to <queue-number>
no mls qos map cos-queue
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To map CoS 2 to queue 0, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mls qos map cos-queue 2 to 0
To set the cos-queue map back to its defaults, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no mls qos map cos-queue
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface
CoS Priority : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
-----------------------------------
CoS QUEUE: 2 0 1 3 4 5 6 7
Parameter Description
<cos-priority>CoS priority value. Can take a value between 0 and 7.
<queue-number>Queue number. Can take a value between 0 and 7.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1049
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MLS QOS MAP PREMARK-DSCP
mls qos map premark-dscp
Overview This command configures the premark-dscp map. It is used when traffic is
classified by a class-map that has trust dscp configured. Based on a lookup DSCP,
the map determines new QoS settings for the traffic.
The no variant of this command resets the premark-dscp map to its defaults. If no
DSCP is specified then all DSCP entries will be reset to their defaults.
Syntax mls qos map premark-dscp <0-63> to
{[new-dscp <0-63>][new-cos <0-7>]
[new-bandwidth-class {green|yellow|red}]}
no mls qos map premark-dscp [<0-63>]
Mode Global Configuration
Usage With the trust dscp command set, this command (mls qos map premark-dscp)
enables you to remap the DSCP, CoS, output queue, or bandwidth class values.
However, note that you cannot simultaneously change the DSCP and CoS, because
they use the same byte in the IP header.
Example To set the entry for DSCP 1 to use a new DSCP of 2, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mls qos map premark-dscp 1 to new-dscp 2
Parameter Description
premark-dscp <0-63>The DSCP value on ingress.
new-dscp <0-63>The DSCP value that the packet will have on egress.
If unspecified, this value will remain the DSCP ingress
value.
new-cos <0-7>The CoS value that the packet will have on egress.
If unspecified, this value will retain its value on ingress.
new-bandwidth-class Modify Egress Bandwidth-class.
If unspecified, this value will be set to green.
green Egress Bandwidth-class green (marked down
Bandwidth-class).
yellow Egress Bandwidth-class yellow (marked down
Bandwidth-class).
red Egress Bandwidth-class red (marked down Bandwidth-
class).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1050
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
MLS QOS MAP PREMARK-DSCP
Example To set the entry for DSCP 1 to use a new CoS of 3, and a new bandwidth class of
yellow, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mls qos map premark-dscp 1 to new-cos 3
new-bandwidth-class yellow
Example To reset the entry for DSCP 1 use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no mls qos map premark-dscp 1
Related
Commands
show mls qos maps premark-dscp
trust dscp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1051
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
NO POLICE
no police
Overview Use this command to disable any policer previously configured on the class-map.
Syntax no police
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage This command disables any policer previously configured on the class-map.
Example To disable policing on a class-map, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map name
awplus(config-pmap)# class classname
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no police
Related
Commands
police single-rate action
police twin-rate action

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1052
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
POLICE SINGLE-RATE ACTION
police single-rate action
Overview Configures a single-rate policer for a class-map.
Syntax police single-rate <cir> <cbs> <ebs> action
{drop-red|remark-transmit}
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage You can use a policer to meter the traffic classified by the class-map and assign it
to one of three bandwidth classes.
The bandwidth classes are green (conforming), yellow (partially-conforming), and
red (non-conforming). A single-rate policer is based on three values. These are the
average rate, minimum burst and maximum burst.
Using an action of drop-red means that any packets classed as red are discarded.
NOTE: This command will not take effect when applied to a class-map that attaches to
a channel group whose ports span processor instances.
Note that the remark-map does not only apply to red traffic. If a remark-map is
configured on the same class-map as the policer, then the remark-map will apply
to green- colored and yellow-colored traffic irrespective of the value configured on
the action parameter of the policer. So, even if action is configured to drop-red,
the remark-map will be applied to green and yellow traffic. So, the action
parameter only applies to red- colored traffic. If action is set to drop-red, then red
Parameter Description
<cir>Specify the Committed Information Rate (CIR) (1-100000000 kbps).
<cbs>Specify the Committed Burst Size (CBS) (0-16777216 bytes).
<ebs>Specify a Excess Burst Size (EBS) (0-16777216 bytes).
action Specify the action if the rate is exceeded.
drop-red Drop the red packets.
remark-transmit Modify the packets using the remark map,
then transmit. You can configure the remark
map using the remark-map command.
Color Definition
green The traffic rate is less than the average rate and minimum burst.
yellow The traffic rate is between the minimum burst and the maximum
burst.
red The traffic rate exceeds the average rate and the maximum burst.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1053
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
POLICE SINGLE-RATE ACTION
traffic is dropped; if action is set to remark-transmit, then the red traffic has the
action of the remark map applied to it, and is then transmitted.
Example To configure a single rate meter measuring traffic of 100 Mbps that drops a
sustained burst of traffic over this rate, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map name
awplus(config-pmap)# class classname
awplus(config-pmap-c)# police single-rate 100000 1875000
1875000 action drop-red
Related
Commands
no police
police twin-rate action
remark-map

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1054
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
POLICE TWIN-RATE ACTION
police twin-rate action
Overview Configures a twin-rate policer for a class-map.
Syntax police twin-rate <cir> <pir> <cbs> <pbs> action
{drop-red|remark-transmit}
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage A policer can be used to meter the traffic classified by the class-map and as a result
will be given one of three bandwidth classes. These are green (conforming), yellow
(partially- conforming), and red (non-conforming).
A twin-rate policer is based on four values. These are the minimum rate (CIR),
minimum burst size (CBS), maximum rate (PIR), and maximum burst size (PBS). The
following table shows how these values define the bandwidth classes.
Using an action of drop-red means that any packets classed as red will be
discarded.
Parameter Description
<cir>Specify the Committed Information Rate (CIR) (1-100000000 kbps).
<pir>Specify the Peak Information Rate (PIR) (1-100000000 kbps).
<cbs>Specify the Committed Burst Size (CBS) (0-16777216 bytes).
<pbs>Specify the Peak Burst Size (PBS) (0-16777216 bytes).
action Specify the action if rate is exceeded.
drop-red Drop the red packets.
remark-transmit Modify the packets using the remark map, then
transmit. You can configure the remark map
using the remark-map command.
Bandwidth
Class Definition
green The sum of the number of existing (buffered) bytes plus those arriving
at the port per unit time results in a value that is less than that set for
the CBS.
yellow The sum of the number of existing (buffered) bytes plus those arriving
at the port per unit time results in a value that is between those set for
the CBS and the PBS.
red The sum of the number of existing (buffered) bytes plus those arriving
at the port per unit time results in a value that exceeds that set for the
PBS.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1055
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
POLICE TWIN-RATE ACTION
Using an action of remark-transmit means that the packet will be remarked with
the values configured in the policed-dscp map. The index into this map is
determined by the DSCP in the packet.
Note that the remark-map does not only apply to red traffic. If a remark-map is
configured on the same class-map as the policer, then the remark-map will apply
to green- colored and yellow-colored traffic irrespective of the value configured on
the action parameter of the policer. So, even if action is configured to drop-red,
the remark-map will be applied to green and yellow traffic. So, the action
parameter only applies to red-colored traffic. If action is set to drop-red, then red
traffic is dropped; if action is set to remark-transmit, then the red traffic has the
action of the remark map applied to it, and is then transmitted.
Example To configure a twin rate meter measuring a minimum rate of 10 Mbps and a
maximum rate of 20 Mbps, and drop red packets, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map name
awplus(config-pmap)# class classname
awplus(config-pmap-c)# police twin-rate 10000 20000 1875000
3750000 action drop-red
To configure a twin rate meter measuring a minimum rate of 10 Mbps and a
maximum rate of 20 Mbps that uses the premark map to remark any
non-conforming traffic, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map name
awplus(config-pmap)# class classname
awplus(config-pmap-c)# police twin-rate 10000 20000 1875000
3750000 action remark-transmit
Related
Commands
no police
police single-rate action

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1056
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
POLICY-MAP
policy-map
Overview Use this command to create a policy-map and to enter Policy Map Configuration
mode to configure the specified policy-map.
Use the no variant of this command to delete an existing policy-map.
Syntax policy-map <name>
no policy-map <name>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To create a policy-map called pmap1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)#
Related
Commands
class-map
Parameter Description
<name>Name of the policy-map.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1057
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
PRIORITY-QUEUE
priority-queue
Overview This command configures strict priority-based scheduling on the specified egress
queues. You must specify at least one queue.
Syntax priority-queue [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
Mode Interface Configuration.
Usage By default, the queues on all ports are set for priority queuing. You can change the
queue emptying sequence to weighted round robin, by using the wrr-queue
weight queues command. You can then use the priority-queue command to reset
the selected queues to priority queuing.
Note that the emptying sequence for priority queuing is always highest queue
number to lowest queue number.
Example To apply priority-based scheduling to egress queues 1 and 2, use the commands:
awplus#configure terminal
awplus(config)#interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)#priority-queue 1 2
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface
show mls qos interface queue-counters
wrr-queue weight queues
Parameter Description
[0][1]...[7] Specify the queues that will use strict priority scheduling. With
strict priority scheduling, the switch will completely empty the
highest numbered queue first, then start processing the next
lowest numbered queue.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1058
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
REMARK-MAP
remark-map
Overview Use this command to configure the remark map. If a re-mark map is applied to a
class, and a policer is also applied to the same class, then:
• green and yellow traffic will all be acted upon by the remark-map, and
• red traffic will be either dropped or acted upon by the remark-map,
depending on whether the policer action is set to drop-red or
remark-transmit.
The no variant of this command resets the remark map to its defaults. Specifying
the bandwidth class is optional. If no bandwidth class is specified, then all
bandwidth classes are reset to their defaults.
Syntax remark-map [bandwidth-class {green|yellow|red}] to {[new-dscp
<0-63>] [new-bandwidth-class {green|yellow|red}]}
no remark-map [bandwidth-class {green|yellow|red}] to
{[new-dscp <0-63>] [new-bandwidth-class {green|yellow|red}]}
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Examples To remark the policed green traffic to a new DSCP of 2 and a new bandwidth class
of yellow, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# remark-map bandwidth-class green to
new-dscp 2 new-bandwidth-class yellow
Parameter Description
bandwidth-class Specify the bandwidth class of packets to remark.
green Remark green packets.
yellow Remark yellow packets.
red Remark red packets.
new-dscp Specify the new DSCP value.
<0-63>The DSCP value.
new-bandwidth-class Specify the new bandwidth class.
green Remark the packet green.
yellow Remark the packet yellow.
red Remark the packet red.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1059
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
REMARK-MAP
To remark the policed green traffic to a new DSCP of 2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# remark-map bandwidth-class green to
new-dscp 2
To reset the DSCP for all bandwidth classes, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no remark-map to new-dscp
Related
Commands
police single-rate action
police twin-rate action

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1060
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
REMARK NEW-COS
remark new-cos
Overview This command enables you to configure and remark either or both of:
• the CoS flag in the data packet
• the input into the CoS to queue map, thus changing the destination egress
queue.
Syntax remark new-cos <0-7> [internal|external|both]
no remark new-cos [internal|external|both]
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage The default CoS to Queue mappings are shown in the following table:
The relationship between this command and the CoS to queue map is shown in
the following figure.
Parameter Description
<0-7>The new value for the CoS flag and/or the input into the CoS to queue
map.
external Remarks the CoS flag in the packet.
internal Remarks the new-CoS input into the CoS to queue map.
both Remarks (with the same value) both the CoS flag in the packet and the
input to the CoS to queue map.
CoS Value 01234567
Egress Queue No 20134567
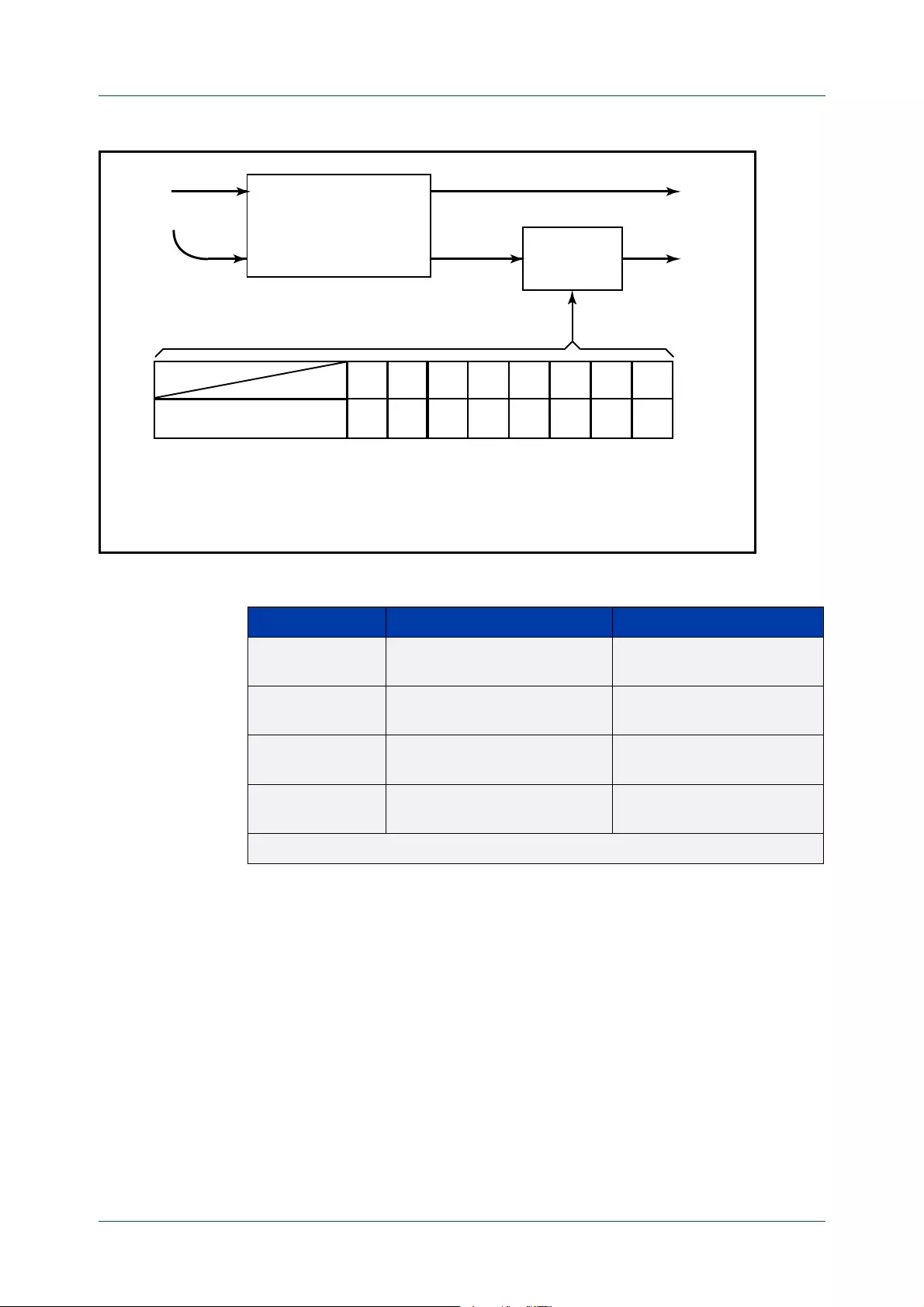
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1061
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
REMARK NEW-COS
Figure 32-1: Remarking and the CoS to Q map
Example For policy-map “pmap3” and class-map “cmap1”, set the CoS value to 2 and also set
the input to the CoS to queue map so that the traffic is assigned to egress queue 1:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap3
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# remark new-cos 2 both
Related
Commands
mls qos map cos-queue
show mls qos maps cos-queue
4HEABOVEMAPPINGISSETBYTHECOMMAND MLSQOSMAPCOSQUEUETOANDDISPLAYEDBYTHECOMMAND
SHOWMLSQOSMAPSCOSQUEUE7ITHTHE REMARKNEWCOSCOMMANDUNSETORSETTOEXTERNALTHEQUEUEMAPPING
TAKESITSINPUTFROMTHE%XISTING#O3VALUE7ITHTHE REMARKNEWCOSCOMMANDSETTOINTERNALORBOTHTHE
QUEUEMAPPINGTAKESITSINPUTFROMTHEVALUESETBYTHECOMMAND REMARKNEWCOS.OTETHATALTHOUGHTHE
#O3TO1UEUEMAPAPPLIESTOTHEWHOLESWITCHTHEREMARKNEWCOSCOMMANDAPPLIESPERINDIVIDUALCLASSMAP
%XISTING#O3VALUE
.EW#O3INTERNAL
%GRESSQUEUE
VALUE
#O36ALUE
%GRESS1UEUE
1O3??1?-AP?"
#OSTO1UEUE
-APPING
2EMARKNEWCOSEXTERNAL
#O3&LAGIN0ACKET
2EMARKNEWCOSBOTH
2EMARKNEWCOSINTERNAL
Table 32-1: CoS to egress queue remarking function
Input Command Output
CoS field = 1 Remark new-cos (not
configured)
CoS value = 1
Packet sent to egress queue 0
CoS field = 1 Remark new-cos 2 external CoS value = 2
Packet sent to egress queue 0
CoS set to 1 Remark new-cos 2 internal CoS value = 1
Packet sent to egress queue 1
CoS set to 1 Remark new-cos 2 both CoS value = 2
Packet sent to egress queue 1
Note: This table assumes that the CoS to Queue map is set to its default values.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1062
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SERVICE-POLICY INPUT
service-policy input
Overview Use this command to apply a policy-map to the input of an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a policy-map and interface
association.
Syntax service-policy input <policy-map>
no service-policy input <policy-map>
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage This command can be applied to switch ports or static channel groups, but not to
dynamic (LACP) channel groups.
Example To apply a policy-map named pmap1 to interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
wplus(config-if)# service-policy input pmap1
Parameter Description
<policy-map>Policy map name that will be applied to the input.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1063
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW CLASS-MAP
show class-map
Overview Use this command to display the QoS class-maps’ criteria for classifying traffic.
Syntax show class-map [<class-map-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display a QoS class-map’s match criteria for classifying traffic, use the command:
awplus# show class-map cmap1
Output Figure 32-2: Example output from the show class-map command
Related
Commands
class-map
Parameter Description
<class-map-name> Name of the class-map.
awplus#show class-map
CLASS-MAP-NAME: myClass
Match Mac Type: 2 l2mcast
CLASS-MAP-NAME: default
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1064
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS
show mls qos
Overview Use this command to display whether QoS is enabled or disabled on the switch.
Syntax show mls qos
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display whether QoS is enabled or disabled, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos
Output Figure 32-3: Example output from the show mls qos command
Related
Commands
mls qos enable
awplus#show mls qos
Enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1065
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE
show mls qos interface
Overview Displays the current settings for the interface. This includes its default CoS and
queue, scheduling used for each queue, and any policies/maps that are attached.
Syntax show mls qos interface [<port>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display current CoS and queue settings for interface port1.0.1, use the
command:
awplus# show mls qos interface port1.0.1
Output Figure 32-4: Example output from the show mls qos interfacecommand for
port1.0.1
Parameter Description
<port>Switch port.
awplus#show mls qos interface port1.0.1
Interface: port1.0.1
Number of egress queues: 8
Egress Queue: 0
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 1
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1066
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE
Egress Queue: 2
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 3
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Wrr Group 2
Weight: 10
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 4
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Wrr Group 1
Weight: 10
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 5
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 6
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Egress Queue: 7
Status: Enabled
Scheduler: Strict Priority
Queue Limit: 12%
Egress Rate Limit: 0 Kb
Trust Mode: Ports default priority
Port Default Priority: 0
VLAN Priority Overide: Not Configured
Egress Traffic Shaping: Not Configured
The number of COS Values mapped: 8
Cos (Queue): 0(0), 1(0), 2(0), 3(0), 4(0), 5(0), 6(0), 7(0)
Dscp (Queue): 0(0), 1(0), 2(0), 3(0), 4(0), 5(0), 6(0), 7(0)
Dscp (Queue): 8(0), 9(0), 10(0), 11(0), 12(0), 13(0), 14(0), 15(0)
Dscp (Queue): 16(0), 17(0), 18(0), 19(0), 20(0), 21(0), 22(0), 23(0)
Dscp (Queue): 24(0), 25(0), 26(0), 27(0), 28(0), 29(0), 30(0), 31(0)
Dscp (Queue): 32(0), 33(0), 34(0), 35(0), 36(0), 37(0), 38(0), 39(0)
Dscp (Queue): 40(0), 41(0), 42(0), 43(0), 44(0), 45(0), 46(0), 47(0)
Dscp (Queue): 48(0), 49(0), 50(0), 51(0), 52(0), 53(0), 54(0), 55(0)
Dscp (Queue): 56(0), 57(0), 58(0), 59(0), 60(0), 61(0), 62(0), 63(0)
Table 32-2: Parameters in the output of the show mls qos interface command
Parameter Description
Number of egress
queues The total number of egress queues available on this
interface.
Egress Queue Number of this egress queue.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1067
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE
Status Queue can either be enabled or disabled.
Scheduler The scheduling mode being used for servicing the
transmission of packets on this port.
Queue Limit The percentage of the port’s buffers that have been
allocated to this queue.
Egress Rate Limit The amount of traffic that can be transmitted via this
queue per second. 0 Kb means there is currently no
rate-limiting enabled.
Table 32-2: Parameters in the output of the show mls qos interface command
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1068
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE POLICER-COUNTERS
show mls qos interface policer-counters
Overview This command displays an interface’s policer counters. This can either be for a
specific class-map or for all class-maps attached to the interface. If no class-map is
specified then all class-map policer counters attached to the interface are
displayed.
Syntax show mls qos interface <port> policer-counters [class-map
<class-map>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Note that:
• The hardware does not record distinct counters for the number of Green or
Yellow bytes, so the field marked Green/Yellow is the summation of bytes
that have been marked Green or Yellow by the meter.
• The counters are based on metering performed on the specified class-map.
Therefore, the ‘Dropped Bytes’ counter is the number of bytes dropped due
to metering. This is different from packets dropped via a ‘deny’ action in the
ACL. If a policer is configured to perform re-marking, bytes can be marked
Red but are not dropped, and is shown with a value of 0 for the Dropped field
and a non-0 value for the ‘Red Bytes’ field.
Example To show the counters for all class-maps attached to port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos interface port1.0.1 policer-counters
Output Figure 32-5: Example output from show mls qos interface policer-counters on
a port
Parameter Description
<port>Switch port.
class-map Select a class-map.
<class-map>Class-map name.
awplus#show mls qos interface port1.0.1 policer-counters
Interface: port1.0.1
Class-map: default
Green/Yellow Bytes: 0
Red Bytes: 0
Dropped Bytes: 0
Non-dropped Bytes: 0
Class-map: cmap1
Green/Yellow Bytes: 1290
Red Bytes: 0
Dropped Bytes: 0
Non-dropped Bytes: 1290

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1069
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE QUEUE-COUNTERS
show mls qos interface queue-counters
Overview This command displays an interface’s egress queue counters. This can either be for
a specific queue or for all queues on the interface. If no queue is specified all queue
counters on the interface will be displayed.
The counters show the number of frames currently in the queue and the maximum
number of frames allowed in the queue, for individual egress queues and the port’s
queue (which will be a sum of all egress queues).
Syntax show mls qos interface <port> queue-counters [queue <number>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the counters for all queues on port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos interface port1.0.1 queue-counters
Output Figure 32-6: Example output from show mls qos interface queue-counters
Parameter Description
<port>Switch port.
queue <number>Queue number, from 0 to 7.
Interface port1.0.1 Queue Counters:
Port queue length 1169
Egress Queue length:
Queue 0 0
Queue 1 0
Queue 2 1169
Queue 3 0
Queue 4 0
Queue 5 0
Queue 6 0
Queue 7 0
Table 32-3: Parameters in the output from show mls qos interface
queue-counters
Parameter Description
Interface Port we are showing the counters for.
Port queue length Number of frames in the port’s queue. This will be the
sum of all egress queues on the port.
Egress Queue length Number of frames in a specific egress queue.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1070
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS INTERFACE STORM-STATUS
show mls qos interface storm-status
Overview Show the current configuration and status of the QoS Storm Protection (QSP) on
the given port.
Syntax show mls qos interface <port> storm-status
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To see the QSP status on port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos interface port1.0.1 storm-status
Output Figure 32-7: Example output from show mls qos interface storm-status
Related
Commands
storm-action
storm-downtime
storm-protection
storm-rate
storm-window
Parameter Description
<port>Switch port.
Interface: port1.0.1
Storm-Protection: Enabled
Port-status: Enabled
Storm Action: vlandisable
Storm Window: 5000 ms
Storm Downtime: 0 s
Timeout Remaining: 0 s
Last read data-rate: 0 kbps
Storm Rate: 1000 kbps
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1071
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS MAPS COS-QUEUE
show mls qos maps cos-queue
Overview Show the current configuration of the cos-queue map.
Syntax show mls qos maps cos-queue
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of the cos-queue map, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos maps cos-queue
Output Figure 32-8: Example output from show mls qos maps cos-queue
Related
Commands
mls qos map cos-queue
COS-TO-QUEUE-MAP:
COS : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
-----------------------------------
QUEUE: 2 0 1 3 4 5 6 7

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1072
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW MLS QOS MAPS PREMARK-DSCP
show mls qos maps premark-dscp
Overview This command displays the premark-dscp map. This map is used to replace the
DSCP, CoS and/or bandwidth class of a packet matching the class-map, based on a
lookup DSCP value.
Syntax show mls qos maps premark-dscp [<0-63>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the premark-dscp map for DSCP 1, use the command:
awplus# show mls qos maps premark-dscp 1
Output Figure 32-9: Example output from the show mls qos maps premark-dscp
command
Related
Commands
mls qos map premark-dscp
trust dscp
Parameter Description
<0-63>DSCP table entry.
PREMARK-DSCP-MAP:
DSCP 1
Bandwidth Class
-------------------------
New DSCP 2
New CoS 0
New Bandwidth Class green

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1073
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
show platform classifier statistics utilization
brief
Overview This command displays the number of used entries available for various platform
functions, and the percentage that number of entries represents of the total
available.
Syntax show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the platform classifier utilization statistics, use the following command:
awplus# show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Output Figure 32-10: Output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
Output Figure 32-11: Output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
In this example, there is one UFO VLAN and one upstream port consuming 3 FP
entries.
#show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
[Instance 0]
Capacity: 503
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Allocated
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 119 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
Flooding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
QoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Rule Limit Reached (clear on read): 0
Total Rule Limit Reached from startup: 0
Space will be allocated to QOS as required.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1074
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
Output
parameters
Depending on your switch, you will see some of the following parameters in the
output from show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
#show platform classifier statistics utilization brief
[Instance 4]
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Total
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 117 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
DoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%
VLAN Counter
Group-Octet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Group-Packet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Floding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO 1476395012 3 / 128 ( 2%)
QoS 0 / 256 ( 0%)
[Instance 5]
Number of Entries:
Policy Type Group ID Used / Total
----------------------------------------------
ACL 1476395010 0 / 117 ( 0%)
Interface 0
VACL 0
DoS Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
VLAN Counter
Group-Octet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Group-Packet Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Floding Nexthop Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
Remote-Mirror Inactive 0 / 0 ( 0%)
UFO 1476395012 3 / 128 ( 2%)
QoS 0 / 256 ( 0%)
Parameter Description
IPv6 Multicast Reserved hardware space for use by IPv6 multicast.
System Fixed system entries. For example, resiliency links make use of system ACLs.
MLD Snooping Entries to send various packets that MLD Snooping is interested in to the CPU.
DHCP Snooping Entries used to send DHCP and ARP packets to the CPU. User-added DHCP
Snooping filters under ACLs are counted under the ACL or QoS categories.
Loop Detection Entries uses to send the special loop detection frame to the CPU.
EPSR Entries used to send EPSR control traffic to the CPU.
CFM Entries used by Connectivity Fault Management.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1075
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW PLATFORM CLASSIFIER STATISTICS UTILIZATION BRIEF
Related
Commands
show platform
ipv6 access-list (named IPv6 hardware ACL)
G8032 Entries used to send G.8032 control traffic to the CPU.
Global ACLs Entries for ACLs appear here if the ACLs are applied globally instead of per
switchport.
ACL Entries for ACL filters that have been applied directly to ports using the
access-group command.
VACL Entries for VLAN-based ACLs (ACLs that are applied to VLANs instead of ports).
DOS Entries used for Denial of Service protection.
UFO Entries used by Upward Forwarding Only (UFO).
QoS Entries for ACL filters and other class-map configurations, such as policers, applied
through policy maps using the service input command.
RA Guard Entries used to block IPv6 router advertisements, configured with the ipv6 nd
raguard command.
AMFAPPS Entries used by AMF Application Proxy. These entries enable the SES Controller to
block infected ports.
Pre-Ingress Entries used for VLAN ID Translation (and also for subnet-based and MAC-based
VLAN entries on SBx81XLEM cards).
Egress Entries used for VLAN ID Translation.
UDB User Defined Bytes (UDB), which are a limited resource of bytes that can be used to
implement additional arbitrary matching on packet bytes on some switches. The
software manages the use and allocation of these bytes automatically. The output
of this table is intended for use by Allied Telesis Customer Support only.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1076
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
SHOW POLICY-MAP
show policy-map
Overview Displays the policy-maps configured on the switch. The output also shows
whether or not they are connected to a port (attached / detached) and shows their
associated class-maps.
Syntax show policy-map [<name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display a listing of the policy-maps configured on the switch, use the command:
awplus# show policy-map
Output Figure 32-12: Example output from the show policy-map command
Related
Commands
no police
service-policy input
Parameter Description
<name>The name of a specific policy-map.
POLICY-MAP-NAME: example
Interfaces:
Default class-map action: permit
CLASS-MAP-NAME: default
Policer counters enabled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1077
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
STORM-ACTION
storm-action
Overview Sets the action to be taken when triggered by QoS Storm Protection (QSP). There
are three available options:
•portdisable will disable the port in software.
•vlandisable will disable the port from the VLAN matched by the class-map
in class-map. This option requires the match vlan class-map to be present in
the class-map
•linkdown will physically bring the port down. .
The no variant of this command will negate the action set by the storm-action
command.
Syntax storm-action {portdisable|vlandisable|linkdown}
no storm-action
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Examples To apply the storm protection of vlandisable to the policy-map named “pmap2”
and the class-map named “cmap1”, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c# storm-action vlandisable
To negate the storm protection set on the policy-map named “pmap2” and the
class-map named “cmap1”, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c# no storm-action
Related
Commands
storm-downtime
storm-protection
storm-rate
storm-window
Parameter Description
portdisable Disable the port in software.
vlandisable Disable the VLAN.
linkdown Shutdown the port physically.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1078
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
STORM-DOWNTIME
storm-downtime
Overview Sets the time to re-enable a port that has been disabled by QoS Storm Protection
(QSP). The time is given in seconds, from a minimum of one second to maximum
of 86400 seconds (i.e. one day).
The no variant of this command resets the time to the default value of 10 seconds.
Syntax storm-downtime <1-86400>
no storm-downtime
Default 10 seconds
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Examples To re-enable the port in 1 minute, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# storm-downtime 60
To re-set the port to the default (10 seconds), use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap1
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no storm-downtime
Related
Commands
storm-action
storm-protection
storm-rate
storm-window
Parameter Description
<1-86400>Seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1079
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
STORM-PROTECTION
storm-protection
Overview Use this command to enable policy-based Storm Protection (such as QSP - QoS
Storm Protection). Storm protection is activated as soon as a port is enabled.
However, it will only be functional after storm-rate and storm-window have been
set.
The no variant of this command disables policy-based Storm Protection.
Syntax storm-protection
no storm-protection
Default By default, storm protection is disabled.
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Examples To enable QSP on cmap2 in pmap2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# storm-protection
To disable QSP on cmap2 in pmap2, use the following commands:
awplus# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no storm-protection
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface storm-status
storm-action
storm-downtime
storm-rate
storm-window

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1080
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
STORM-RATE
storm-rate
Overview Sets the data rate that triggers the storm-action. The rate is in kbps and the range
is from 1kbps to 40Gbps.
Note that this setting is made in conjunction with the storm-window command.
Use the no variant of this command to negate the storm-rate command.
Syntax storm-rate <1-40000000>
no storm-rate
Default No default
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage This setting is made in conjunction with the storm-window command.
Examples To limit the data rate to 100Mbps, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# storm-rate 100000
To negate the limit set previously, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no storm-rate
Related
Commands
storm-action
storm-downtime
storm-protection
storm-window
Parameter Description
<1-40000000>The range of the storm-rate.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1081
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
STORM-WINDOW
storm-window
Overview Sets the window size of QoS Storm Protection (QSP). This sets the time to poll the
data-rate every given milliseconds. Minimum window size is 100 ms and the
maximum size is 60 sec.
Use the no variant of this command to negate the storm-window command.
Syntax storm-window <100-60000>
no storm-window
Default No default
Mode Policy Map Class Configuration
Usage This command should be set in conjunction with the storm-rate command.
Examples To set the QSP window size to 5000 ms, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# storm-window 5000
To negate the QSP window size set previously, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap2
awplus(config-pmap)# class cmap2
awplus(config-pmap-c)# no storm-window
Related
Commands
storm-action
storm-downtime
storm-protection
storm-rate
Parameter Description
<100-60000>The window size, measured in milliseconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1082
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
TRUST DSCP
trust dscp
Overview This command enables the premark-dscp map to replace the DSCP,
bandwidth-class and/or CoS of classified traffic based on a lookup DSCP value.
With the no variant of this command, no premark-dscp mapping function will be
applied for the selected class-map. QoS components of the packet existing either
at ingress, or applied by the class-map, will pass unchanged.
Syntax trust dscp
no trust
Mode Policy-Map Configuration
Examples To enable the premark-dscp map lookup for policy-map pmap1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# trust dscp
To disable the premark-dscp map lookup for policy-map pmap1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# policy-map pmap1
awplus(config-pmap)# no trust
Related
Commands
mls qos map premark-dscp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1083
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
WRR-QUEUE DISABLE QUEUES
wrr-queue disable queues
Overview Use this command to disable an egress queue from transmitting traffic.
The no variant of this command enables an egress queue to transmit traffic.
Syntax wrr-queue disable queues [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
no wrr-queue disable queues [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To disable queue 1 on port1.0.1 from transmitting traffic, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# wrr-queue disable queues 1
To enable queue 1 on port1.0.1 to transmit traffic, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no wrr-queue disable queues 1
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface
Parameter Description
[0][2]...[7] Selects one or more queues numbered 0 to 7.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1084
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
WRR-QUEUE EGRESS-RATE-LIMIT QUEUES
wrr-queue egress-rate-limit queues
Overview Sets a limit on the amount of traffic that can be transmitted per second from these
queues. The default unit is in Kb, but Mb or Gb can also be specified. The minimum
is 651 Kb.
Syntax wrr-queue egress-rate-limit <bandwidth> queues
[0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
no wrr-queue egress-rate-limit <bandwidth> queues
[0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To limit the egress rate of queues 0, 1 and 2 on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# wrr-queue egress-rate-limit 500M queues 0 1
2
Related
Commands
show mls qos interface
Parameter Description
<bandwidth>Bandwidth <1-100000000 kbits> (usable units: k, m, g).
[0][2]...[7] Selects one or more queues numbered 0 to 7.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1085
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
QOS COMMANDS
WRR-QUEUE WEIGHT QUEUES
wrr-queue weight queues
Overview This command configures weighted round-robin based scheduling on the
specified egress queues on switch port interfaces only. The weights are specified
as ratios relative to each other.
Use the no wrr-queue command to remove weighted round-robin based
scheduling from the specified egress queue. The queue then reverts to its normal
priority-based scheduling.
Syntax wrr-queue weight <1-15> queues [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
no wrr-queue <queue-number>
Mode Interface Configuration for switch port interfaces only (not for static aggregated
interfaces).
Usage You cannot apply weighted round-robin based scheduling to static aggregated
interfaces (for example, sa2).
Example To apply a WRR weight of 6 to queues 0 and 1 on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# wrr-queue weight 6 queues 0 1
To remove weighted round-robin scheduling from egress queue 2 on port1.0.1,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no wrr-queue 2
Related
Commands
priority-queue
show mls qos interface
Parameter Description
<1-15>Weight (the higher the number the greater will be the queue
servicing).
[0][2]...[7] Selects one or more queues numbered 0 to 7.
<queue-number>Egress queue to revert to priority-based scheduling.

33
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1086
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
802.1X port access control. For more information, see the AAA and Port
Authentication_Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“dot1x accounting” on page 1088
•“dot1x authentication” on page 1089
•“debug dot1x” on page 1090
•“dot1x control-direction” on page 1091
•“dot1x eap” on page 1093
•“dot1x eapol-version” on page 1094
•“dot1x initialize interface” on page 1096
•“dot1x initialize supplicant” on page 1097
•“dot1x keytransmit” on page 1098
•“dot1x max-auth-fail” on page 1099
•“dot1x max-reauth-req” on page 1101
•“dot1x port-control” on page 1103
•“dot1x timeout tx-period” on page 1105
•“show debugging dot1x” on page 1107
•“show dot1x” on page 1108
•“show dot1x diagnostics” on page 1111
•“show dot1x interface” on page 1113
•“show dot1x sessionstatistics” on page 1118
•“show dot1x statistics interface” on page 1119

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1088
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X ACCOUNTING
dot1x accounting
Overview This command overrides the default RADIUS accounting method for IEEE
802.1X-based authentication on an interface by allowing you to apply a
user-defined named method list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method list.
Syntax dot1x accounting {default|<list-name>}
no dot1x accounting
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Mode
Example To apply the named list 'vlan10_acct' on the vlan10 interface, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# dot1x accounting vlan10_acct
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the authentication
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x accounting
Related
Commands
aaa accounting dot1x
Parameter Description
default Apply the default accounting method list
<list-name>Apply the user-defined named list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1089
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X AUTHENTICATION
dot1x authentication
Overview This command overrides the default 802.1X-based authentication method on an
interface by allowing you to apply a user-defined named list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method.
Syntax dot1x authentication {default|<list-name>}
no dot1x authentication
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Mode
Example To apply the named list 'vlan10_auth' on the vlan10 interface, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# dot1x authentication vlan10_auth
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the authentication
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x authentication
Related
Commands
aaa authentication dot1x
Parameter Description
default Apply the default authentication method list
<list-name>Apply the user-defined named list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1090
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DEBUG DOT1X
debug dot1x
Overview Use this command to enable 802.1X IEEE Port-Based Network Access Control
troubleshooting functions.
Use the no variant of this command to disable this function.
Syntax debug dot1x [all|auth-web|event|nsm|packet|timer]
no debug all dot1x
no debug dot1x [all|auth-web|event|nsm|packet|timer]
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Usage This command turns on a mode where trace-level information is output during?
authentication conversations. Be aware that this is a very verbose output.? It is
mostly useful to capture this as part of escalating an issue to ATI support.
Examples Use this command without any parameters to turn on normal 802.1X debug
information.
awplus# debug dot1x
awplus# show debugging dot1x
Related
Commands
show debugging dot1x
undebug dot1x
Parameter Description
all Used with the no variant of this command exclusively; turns off all
debugging for 802.1X.
auth-web Specifies debugging for 802.1X auth-web information.
events Specifies debugging for 802.1X events.
nsm Specifies debugging for NSM messages.
packet Specifies debugging for 802.1X packets.
timer Specifies debugging for 802.1X timers.
802.1X debugging status:
802.1X events debugging is
802.1X timer debugging is on
802.1X packets debugging is on
802.1X NSM debugging is on
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1091
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X CONTROL-DIRECTION
dot1x control-direction
Overview This command sets the direction of the filter for the unauthorized interface.
If the optional in parameter is specified with this command then packets entering
the specified port are discarded. The in parameter discards the ingress packets
received from the supplicant.
If the optional both parameter is specified with this command then packets
entering (ingress) and leaving (egress) the specified port are discarded. The both
parameter discards the packets received from the supplicant and sent to the
supplicant.
The no variant of this command sets the direction of the filter to both. The port will
then discard both ingress and egress traffic.
Syntax dot1x control-direction {in|both}
no dot1x control-direction
Default The authentication port direction is set to both by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the port direction to the default (both) for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x control-direction
To set the port direction to in for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x control-direction in
To set the port direction to in for authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x control-direction in
Parameter Description
in Discard received packets from the supplicant (ingress
packets).
both Discard received packets from the supplicant (ingress
packets) and transmitted packets to the supplicant (egress
packets).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1092
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X CONTROL-DIRECTION
To set the port direction to the default (both) for authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x control-direction
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show auth interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1093
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X EAP
dot1x eap
Overview This command selects the transmit mode for the EAP packet. If the authentication
feature is not enabled then EAP transmit mode is not enabled. The default setting
discards EAP packets.
Syntax dot1x eap {discard|forward|forward-untagged-vlan|forward-vlan}
Default The transmit mode is set to discard EAP packets by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the transmit mode of EAP packet to forward to forward EAP packets to all
ports on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# dot1x eap forward
To set the transmit mode of EAP packet to discard to discard EAP packets, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# dot1x eap discard
To set the transmit mode of EAP packet to forward-untagged-vlan to
forward EAP packets to ports with the same untagged vlan, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# dot1x eap forward-untagged-vlan
To set the transmit mode of EAP packet to forward-vlan to forward EAP
packets to ports with the same vlan, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# dot1x eap forward-vlan
Parameter Description
discard Discard.
forward Forward to all ports on the switch.
forward-untagged-vlan Forward to ports with the same untagged VLAN.
forward-vlan Forward to ports with the same VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1094
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X EAPOL-VERSION
dot1x eapol-version
Overview This command sets the EAPOL protocol version for EAP packets when 802.1X port
authentication is applied.
Use the no variant of this command to set the EAPOL protocol version to 1.
The default EAPOL protocol version is version 1.
Syntax dot1x eapol-version {1|2}
no dot1x eapol-version
Default The EAP version for 802.1X authentication is set to 1 by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the EAPOL protocol version to 2 for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x eapol-version 2
To set the EAPOL protocol version to the default version (1) for interface port1.0.2,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x eapol-version
To set the EAPOL protocol version to 2 for authentication profile 'student', use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x eapol-version 2
To set the EAPOL protocol version to the default version (1) for authentication
profile 'student', use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x eapol-version
Parameter Description
1EAPOL version.
2EAPOL version.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1096
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X INITIALIZE INTERFACE
dot1x initialize interface
Overview This command removes authorization for a specified connected interface. The
connection will attempt to re-authorize when the specified port attempts to make
use of the network connection.
NOTE: Reauthentication could be a long time after the use of this command because
the reauthorization attempt is not triggered by this command. The attempt is triggered
by the first packet from the interface trying to access the network resources.
Syntax dot1x initialize interface <interface-list>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To initialize 802.1X port authentication on the interface port1.0.2, use the
command:
awplus# dot1x initialize interface port1.0.2
To unauthorize switch port1.0.1 and attempt reauthentication on switch port1.0.1,
use the command:
awplus# dot1x initialize interface port1.0.1
To unauthorize all switch ports for a 24-port device and attempt reauthentication,
use the command:
awplus# dot1x initialize interface port1.0.1-port1.0.24
Validation
Commands
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
Related
Commands
dot1x initialize supplicant
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
• an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.6, or sa1-2,
or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.2-1.0.4. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1097
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X INITIALIZE SUPPLICANT
dot1x initialize supplicant
Overview This command removes authorization for a connected supplicant with the
specified MAC address or username. The connection will attempt to re-authorize
when the specified supplicant attempts to make use of the network connection.
NOTE: Reauthentication could be a long time after the use of this command because
the reauthorization attempt is not triggered by this command. The attempt is triggered
by the first packet from the supplicant trying to access the network resources.
Syntax dot1x initialize supplicant {<macadd>|username}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To initialize the supplicant authentication, use the commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# dot1x initialize supplicant 0090.99ab.a020
awplus(config)# dot1x initialize supplicant guest
Validation
Commands
show dot1x
show dot1x supplicant
Related
Commands
dot1x initialize interface
Parameter Description
dot1x IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Access Control.
initialize Initialize the port to attempt reauthentication.
supplicant Specify the supplicant to initialize.
<macadd>MAC (hardware address of the supplicant.
username The name of the supplicant entry.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1098
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X KEYTRANSMIT
dot1x keytransmit
Overview This command enables key transmission on the interface specified previously in
Interface mode.
The no variant of this command disables key transmission on the interface
specified.
Syntax dot1x keytransmit
no dot1x keytransmit
Default Key transmission for port authentication is enabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port.
Usage Use this command to enable key transmission over an Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP) packet between the authenticator and supplicant. Use the no
variant of this command to disable key transmission.
Examples To enable the key transmit feature on interface port1.0.2, after it has been disabled
by negation, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x keytransmit
To disable the key transmit feature from the default startup configuration on
interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x keytransmit
Validation
Commands
show dot1x
show dot1x interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1099
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X MAX-AUTH-FAIL
dot1x max-auth-fail
Overview Use this command to configure the maximum number of login attempts for a
supplicant (client device) using the auth-fail vlan feature, when using 802.1X port
authentication on an interface.
The no variant of this command resets the maximum login attempts for a
supplicant (client device) using the auth-fail vlan feature, to the default
configuration of 3 login attempts.
Syntax dot1x max-auth-fail <0-10>
no dot1x max-auth-fail
Default The default maximum number of login attempts for a supplicant on an interface
using 802.1X port authentication is three (3) login attempts.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage This command sets the maximum number of login attempts for supplicants on an
interface. The supplicant is moved to the auth-fail VLAN from the Guest VLAN after
the number of failed login attempts using 802.1X authentication is equal to the
number set with this command.
See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for information about:
• the auth-fail VLAN feature, and
• restrictions regarding combinations of authentication enhancements
working together
Examples To configure the maximum number of login attempts for a supplicant on interface
port1.0.2 to a single (1) login attempt, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x max-auth-fail 1
To configure the maximum number of login attempts for a supplicant on interface
port1.0.2 to the default number of three (3) login attempts, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x max-auth-fail
Parameter Description
<0-10>Specify the maximum number of login attempts for supplicants
on an interface using 802.1X port authentication.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1100
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X MAX-AUTH-FAIL
To configure the maximum number of login attempts for a supplicant on
authentication profile 'student' to a single (1) login attempt, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x max-auth-fail 1
To configure the maximum number of login attempts for a supplicant on
authentication profile 'student' to the default number of three (3) login attempts,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x max-auth-fail
Validation
Commands
show running-config
show dot1x interface
Related
Commands
auth auth-fail vlan
auth profile (Global Configuration)
dot1x max-reauth-req

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1101
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X MAX-REAUTH-REQ
dot1x max-reauth-req
Overview This command sets the number of reauthentication attempts before an interface
is unauthorized.
The no variant of this command resets the reauthentication delay to the default.
Syntax dot1x max-reauth-req <1-10>
no dot1x max-reauth-req
Default The default maximum reauthentication attempts for interfaces using 802.1X port
authentication is two (2) reauthentication attempts, before an interface is
unauthorized.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Use this command to set the maximum reauthentication attempts after failure.
Examples To configure the maximum number of reauthentication attempts for interface
port1.0.2 to a single (1) reauthentication request, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x max-reauth-req 1
To configure the maximum number of reauthentication attempts for interface
port1.0.2 to the default maximum number of two (2) reauthentication attempts,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x max-reauth-req
To configure the maximum number of reauthentication attempts for
authentication profile 'student' to a single (1) reauthentication request, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x max-reauth-req 1
Parameter Description
<1-10>Specify the maximum number of reauthentication attempts for
supplicants on an interface using 802.1X port authentication.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1102
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X MAX-REAUTH-REQ
To configure the maximum number of reauthentication attempts for
authentication profile 'student' to the default maximum number of two (2)
reauthentication attempts, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x max-reauth-req
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
dot1x max-auth-fail
show dot1x interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1103
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X PORT-CONTROL
dot1x port-control
Overview This command enables 802.1X port authentication on the interface specified, and
sets the control of the authentication port.
The no variant of this command disables the port authentication on the interface
specified.
Syntax dot1x port-control {force-unauthorized|force-authorized|auto}
no dot1x port-control
Default 802.1X port control is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Use this command to force a port state.
When port-control is set to auto, the 802.1X authentication feature is executed on
the interface, but only if the aaa authentication dot1x command has been issued.
Examples To enable port authentication on the interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control auto
To enable port authentication force authorized on the interface port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control force-authorized
Parameter Description
force-unauthorized Force the port state to unauthorized.
Specify this to force a port to always be in an unauthorized
state.
force-authorized Force the port state to authorized.
Specify this to force a port to always be in an authorized
state.
auto Allow the port client to negotiate authentication.
Specify this to enable authentication on the port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1104
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X PORT-CONTROL
To disable port authentication on the interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x port-control
To enable port authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x port-control auto
To enable port authentication force authorized on authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x port-control
force-authorized
To disable port authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x port-control
Validation
Commands
show dot1x interface
Related
Commands
aaa authentication dot1x
auth profile (Global Configuration)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1105
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
DOT1X TIMEOUT TX-PERIOD
dot1x timeout tx-period
Overview This command sets the transmit timeout for the authentication request on the
specified interface.
The no variant of this command resets the transmit timeout period to the default
(30 seconds).
Syntax dot1x timeout tx-period <1-65535>
no dot1x timeout tx-period
Default The default transmit period for port authentication is 30 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Use this command to set the interval between successive attempts to request an
ID.
Examples To set the transmit timeout period to 5 seconds on interface port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x timeout tx-period 5
To reset transmit timeout period to the default (30 seconds) on interface port1.0.2,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no dot1x timeout tx-period
To set the transmit timeout period to 5 seconds on authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# dot1x timeout tx-period 5
To reset transmit timeout period to the default (30 seconds) on authentication
profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no dot1x timeout tx-period
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1107
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING DOT1X
show debugging dot1x
Overview Use this command to display the 802.1X debugging option set.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show debugging dot1x
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage This is a sample output from the show debugging dot1x command.
awplus# debug dot1x
awplus# show debugging dot1x
Related
Commands
debug dot1x
802.1X debugging status:
802.1X events debugging is on
802.1X timer debugging is on
802.1X packets debugging is on
802.1X NSM debugging is on
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1108
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X
show dot1x
Overview This command shows authentication information for dot1x (802.1X) port
authentication.
If you specify the optional all parameter then this command also displays all
authentication information for each port available on the switch.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x [all]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show dot1x all
Parameter Description
all Displays all authentication information for each port available on the
switch.
Table 1: Example output from the show dot1x all command
awplus# show dot1x all
802.1X Port-Based Authentication Enabled
RADIUS server address: 150.87.18.89:1812
Next radius message id: 5
RADIUS client address: not configured
Authentication info for interface port1.0.2
portEnabled: true - portControl: Auto
portStatus: Authorized
reAuthenticate: disabled
reAuthPeriod: 3600
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
PAE: connectTimeout: 30
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in
KT: keyTxEnabled: false
critical: disabled
guestVlan: disabled
dynamicVlanCreation: single-dynamic-vlan
multiVlanSession: disabled
assignFailActionRule: deny
hostMode: multi-supplicant
maxSupplicant:
1024
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1109
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X
dot1x: enabled
protocolVersion: 1
authMac: enabled
method: PAP
reauthRelearning: disabled
authWeb: enabled
method: PAP
lockCount: 3
packetForwarding: disabled
twoStepAuthentication:
configured: enabled
actual: enabled
SupplicantMac: none
supplicantMac: none
Supplicant name: manager
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authenticationMethod: 802.1X Authentication
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 1
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 0
CD: adminControlledDirections: in - operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
criticalState: off
dynamicVlanId: 2
802.1X statistics for interface port1.0.2
EAPOL Frames Rx: 5 - EAPOL Frames Tx: 16
EAPOL Start Frames Rx: 0 - EAPOL Logoff Frames Rx: 0
EAP Rsp/Id Frames Rx: 3 - EAP Response Frames Rx: 2
EAP Req/Id Frames Tx: 8 - EAP Request Frames Tx: 2
Invalid EAPOL Frames Rx: 0 - EAP Length Error Frames Rx: 0
EAPOL Last Frame Version Rx: 1 - EAPOL Last Frame Src: 00d0.59ab.7037
Authentication session statistics for interface port1.0.2
session user name: manager
session authentication method: Remote server
session time: 19440 secs
session terminate cause: Not terminated yet
Authentication Diagnostics for interface port1.0.2
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authEnterConnecting: 2
authEaplogoffWhileConnecting: 1
authEnterAuthenticating: 2
authSuccessWhileAuthenticating: 1
authTimeoutWhileAuthenticating: 1
authFailWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticating: 0
Table 1: Example output from the show dot1x all command (cont.)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1110
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X
authEaplogoggWhileAuthenticating: 0
authReauthsWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEaplogoffWhileAuthenticated: 0
BackendResponses: 2
BackendAccessChallenges: 1
BackendOtherrequestToSupplicant: 3
BackendAuthSuccess: 1
BackendAuthFails: 0
Table 1: Example output from the show dot1x all command (cont.)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1111
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X DIAGNOSTICS
show dot1x diagnostics
Overview This command shows 802.1X authentication diagnostics for the specified interface
(optional), which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or
LACP) channel group or a switch port.
If no interface is specified then authentication diagnostics are shown for all
interfaces.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x diagnostics [interface <interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example See the sample output below showing 802.1X authentication diagnostics for
port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x diagnostics interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
interface Specify a port to show.
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
• an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.2-1.0.4. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1112
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X DIAGNOSTICS
Output Figure 33-1: Example output from the show dot1x diagnostics command
Authentication Diagnostics for interface port1.0.2
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authEnterConnecting: 2
authEaplogoffWhileConnecting: 1
authEnterAuthenticating: 2
authSuccessWhileAuthenticating: 1
authTimeoutWhileAuthenticating: 1
authFailWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEaplogoggWhileAuthenticating: 0
authReauthsWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEaplogoffWhileAuthenticated: 0
BackendResponses: 2
BackendAccessChallenges: 1
BackendOtherrequestToSupplicant: 3
BackendAuthSuccess: 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1113
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X INTERFACE
show dot1x interface
Overview This command shows the status of 802.1X port-based authentication on the
specified interface, which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a
dynamic (or LACP) channel group or a switch port.
Use the optional diagnostics parameter to show authentication diagnostics for
the specified interfaces. Use the optional sessionstatistics parameter to show
authentication session statistics for the specified interfaces. Use the optional
statistics parameter to show authentication diagnostics for the specified
interfaces. Use the optional supplicant parameter to show the supplicant state for
the specified interfaces.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x interface <interface-list>
[diagnostics|sessionstatistics|statistics|supplicant [brief]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples See the sample output below showing 802.1X authentication status for port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
• an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g.
port1.0.6), a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.5. Do not mix
interface types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
diagnostics Diagnostics.
sessionstatistics Session statistics.
statistics Statistics.
supplicant Supplicant.
brief Brief summary of supplicant state.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1114
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X INTERFACE
See the sample output below showing 802.1X authentication session statistics for
port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x interface port1.0.2 sessionstatistics
See sample output below showing 802.1X authentication diagnostics for port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x interface port1.0.2 diagnostics
Table 2: Example output from the show dot1x interface command for a port
awplus#show dot1x interface port1.0.2
Authentication info for interface port1.0.2
portEnabled: true - portControl: Auto
portStatus: Authorized
reAuthenticate: disabled
reAuthPeriod: 3600
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
PAE: connectTimeout: 30
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in
KT: keyTxEnabled: false
critical: disabled
guestVlan: disabled
dynamicVlanCreation: single-dynamic-vlan
assignFailActionRule: deny
multiVlanSession: disabled
hostMode: multi-supplicant
maxSupplicant:
1024
dot1x: enabled
protocolVersion: 1
authMac: enabled
method: PAP
reauthRelearning: disabled
authWeb: enabled
method: PAP
lockCount: 3
packetForwarding: disabled
twoStepAuthentication:
configured: enabled
actual: enabled
supplicantMac: none
awplus#show dot1x interface port1.0.2 sessionstatistics
Authentication session statistics for interface port1.0.2
session user name: manager
session authentication method: Remote server
session time: 19440 secs
session terminat cause: Not terminated yet
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1115
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X INTERFACE
See sample output below showing the supplicant on the interface port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x interface port1.0.2 supplicant
See sample output below showing 802.1X (dot1x) authentication statistics for
port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x statistics interface port1.0.2
awplus#show dot1x interface port1.0.2 diagnostics
Authentication Diagnostics for interface port1.0.2
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authEnterConnecting: 2
authEaplogoffWhileConnecting: 1
authEnterAuthenticating: 2
authSuccessWhileAuthenticating: 1
authTimeoutWhileAuthenticating: 1
authFailWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEaplogoggWhileAuthenticating: 0
authReauthsWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEaplogoffWhileAuthenticated: 0
BackendResponses: 2
BackendAccessChallenges: 1
BackendOtherrequestToSupplicant: 3
BackendAuthSuccess: 1
awplus#show dot1x interface port1.0.2 supplicant
authenticationMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Supplicant name: manager
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authenticationMethod: dot1x
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 4
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 3
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in -
operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1116
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X INTERFACE
awplus#show dot1x statistics interface port1.0.2
802.1X statistics for interface port1.0.2
EAPOL Frames Rx: 5 - EAPOL Frames Tx: 16
EAPOL Start Frames Rx: 0 - EAPOL Logoff Frames Rx: 0
EAP Rsp/Id Frames Rx: 3 - EAP Response Frames Rx: 2
EAP Req/Id Frames Tx: 8 - EAP Request Frames Tx: 2
Invalid EAPOL Frames Rx: 0 - EAP Length Error Frames Rx: 0
EAPOL Last Frame Version Rx: 1 - EAPOL Last Frame
Src:00d0.59ab.7037
Table 33-1: Parameters in the output of show dot1x interface
Parameter Description
portEnabled Interface operational status
(Up-true/down-false).
portControl Current control status of the port for 802.1X
control.
portStatus 802.1X status of the port
(authorized/unauthorized).
reAuthenticate Reauthentication enabled/disabled status on
port.
reAuthPeriod Value holds meaning only if reauthentication
is enabled.
abort Indicates that authentication should be
aborted when set to true.
fail Indicates failed authentication attempt when
set to false.
start Indicates authentication should be started
when set to true.
timeout Indicates authentication attempt timed out
when set to true.
success Indicates authentication successful when set
to true.
state Current 802.1X operational state of interface.
mode Configured 802.1X mode.
reAuthCount Reauthentication count.
quietperiod Time between reauthentication attempts.
reAuthMax Maximum reauthentication attempts.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1117
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show auth diagnostics
show dot1x sessionstatistics
show dot1x statistics interface
show dot1x supplicant interface
BE Backend authentication state machine
variables and constants.
state State of the state machine.
reqCount Count of requests sent to server.
suppTimeout Supplicant timeout.
serverTimeout Server timeout.
maxReq Maximum requests to be sent.
CD Controlled Directions State machine.
adminControlledDirections Administrative value (Both/In).
operControlledDirections Operational Value (Both/In).
KR Key receive state machine.
rxKey True when EAPOL-Key message is received by
supplicant or authenticator. false when key is
transmitted.
KT Key Transmit State machine.
keyAvailable False when key has been transmitted by
authenticator, true when new key is available
for key exchange.
keyTxEnabled Key transmission enabled/disabled status.
Table 33-1: Parameters in the output of show dot1x interface (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1118
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SESSIONSTATISTICS
show dot1x sessionstatistics
Overview This command shows authentication session statistics for the specified interface,
which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or LACP)
channel group or a switch port.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x sessionstatistics [interface <interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example See sample output below showing 802.1X (dot1x) authentication session statistics
for port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x sessionstatistics interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
interface Specify a port to show.
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
Authentication session statistics for interface port1.0.2
session user name: manager
session authentication method: Remote server
session time: 19440 secs
session terminat cause: Not terminated yet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1119
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X STATISTICS INTERFACE
show dot1x statistics interface
Overview This command shows the authentication statistics for the specified interface,
which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or LACP)
channel group or a switch port.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x statistics interface <interface-list>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example See sample output below showing 802.1X authentication statistics for port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x statistics interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or sa1-2,
or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
802.1X statistics for interface port1.0.2
EAPOL Frames Rx: 5 - EAPOL Frames Tx: 16
EAPOL Start Frames Rx: 0 - EAPOL Logoff Frames Rx: 0
EAP Rsp/Id Frames Rx: 3 - EAP Response Frames Rx: 2
EAP Req/Id Frames Tx: 8 - EAP Request Frames Tx: 2
Invalid EAPOL Frames Rx: 0 - EAP Length Error Frames Rx: 0
EAPOL Last Frame Version Rx: 1 - EAPOL Last Frame
Src:00d0.59ab.7037

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1120
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SUPPLICANT
show dot1x supplicant
Overview This command shows the supplicant state of the authentication mode set for the
switch.
This command shows a summary when the optional brief parameter is used.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x supplicant [<macadd>] [brief]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example See sample output below showing the 802.1X authenticated supplicant on the
switch:
awplus# show dot1x supplicant
Parameter Description
<macadd>MAC (hardware) address of the Supplicant.
brief Brief summary of the Supplicant state.
authenticationMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Supplicant name: manager
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authenticationMethod: dot1x
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: mac
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: dot1x
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 4
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 3
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in - operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
RADIUS server group (auth): radius
RADIUS server (auth): 192.168.1.40
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1121
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SUPPLICANT
See sample output below showing the supplicant on the switch using the brief
parameter:
awplus# show dot1x supplicant 00d0.59ab.7037 brief
See sample output below showing the supplicant on the switch using the brief
parameter:
awplus# show dot1x supplicant brief
For example, if two-step authentication is configured with 802.1X authentication
as the first method and web authentication as the second method then the output
is as follows:
Related
Commands
show dot1x supplicant interface
Interface port1.0.2
authenticationMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status IP Address Username
========== === ==== =============== ============= ============== ========
port1.0.2 2 D 00d0.59ab.7037 Authenticated 192.168.2.201 manager
Interface port1.0.2 authenticationMethod: dot1x/web
Two-Step Authentication
firstMethod: dot1x
secondMethod: web
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status IP Address Username
=========== ==== ==== ============== ================= =============== ========
port1.0.2 5 W 0008.0d5e.c216 Authenticated 192.168.1.200 web

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1122
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SUPPLICANT INTERFACE
show dot1x supplicant interface
Overview This command shows the supplicant state of the authentication mode set for the
interface, which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or
LACP) channel group or a switch port.
This command shows a summary when the optional brief parameter is used.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dot1x supplicant interface <interface-list> [brief]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples See sample output below showing the supplicant on the interface port1.0.2:
awplus# show dot1x supplicant interface port1.0.2
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
brief Brief summary of the Supplicant state.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1123
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SUPPLICANT INTERFACE
See sample output below showing the supplicant on the switch using the brief
parameter:
awplus# show dot1x supplicant interface brief
See the sample output below for static channel group (static aggregator) interface
sa1:
awplus# show dot1x interface sa1 supplicant brief
Interface port1.0.2
authenticationMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Supplicant name: VCSPCVLAN10
Supplicant address: 0000.cd07.7b60
authenticationMethod: 802.1X
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: mac
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: dot1x
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 3
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 2
CD: adminControlledDirections:in -
operControlledDirections:in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
Interface port1.0.2
authenticationMethod: dot1x
Two-Step Authentication:
firstMethod: mac
secondMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status IP Address Username
========= === ==== =========== ====== ========== ========
port1.0.2 2 D 00d0.59ab.7037 Authenticated 192.168.2.201 manager
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1124
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
802.1X COMMANDS
SHOW DOT1X SUPPLICANT INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show dot1x supplicant
awplus#show dot1x interface sa1 supplicant brief
Interface sa1
authenticationMethod: dot1x
Two-Step Authentication:
firstMethod: mac
secondMethod: dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status IP Address Username
========= ==== ==== ============== ================= =============== ========
sa1 1 D 00d0.59ab.7037 Authenticated -- test1

34
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1126
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Authentication
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for authentication commands. For
more information, see the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Command List •“auth auth-fail vlan” on page 1129
•“auth critical” on page 1131
•“auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease” on page 1132
•“auth dynamic-vlan-creation” on page 1134
•“auth guest-vlan” on page 1137
•“auth guest-vlan forward” on page 1139
•“auth host-mode” on page 1141
•“auth log” on page 1143
•“auth max-supplicant” on page 1145
•“auth multi-vlan-session” on page 1147
•“auth profile (Global Configuration)” on page 1148
•“auth profile (Interface Configuration)” on page 1149
•“auth reauthentication” on page 1150
•“auth roaming disconnected” on page 1151
•“auth roaming enable” on page 1153
•“auth supplicant-ip” on page 1155
•“auth supplicant-mac” on page 1157
•“auth timeout connect-timeout” on page 1160

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1127
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
•“auth timeout quiet-period” on page 1162
•“auth timeout reauth-period” on page 1163
•“auth timeout server-timeout” on page 1165
•“auth timeout supp-timeout” on page 1167
•“auth two-step enable” on page 1169
•“auth-mac accounting” on page 1172
•“auth-mac authentication” on page 1173
•“auth-mac enable” on page 1174
•“auth-mac method” on page 1176
•“auth-mac password” on page 1178
•“auth-mac reauth-relearning” on page 1179
•“auth-mac static” on page 1181
•“auth-mac username” on page 1182
•“auth-web accounting” on page 1183
•“auth-web authentication” on page 1184
•“auth-web enable” on page 1185
•“auth-web forward” on page 1187
•“auth-web max-auth-fail” on page 1190
•“auth-web method” on page 1192
•“auth-web-server blocking-mode” on page 1193
•“auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress” on page 1194
•“auth-web-server dhcp lease” on page 1195
•“auth-web-server dhcp-wpad-option” on page 1196
•“auth-web-server host-name” on page 1197
•“auth-web-server intercept-port” on page 1198
•“auth-web-server ipaddress” on page 1199
•“auth-web-server page language” on page 1200
•“auth-web-server login-url” on page 1201
•“auth-web-server page logo” on page 1202
•“auth-web-server page sub-title” on page 1203
•“auth-web-server page success-message” on page 1204
•“auth-web-server page title” on page 1205
•“auth-web-server page welcome-message” on page 1206
•“auth-web-server ping-poll enable” on page 1207
•“auth-web-server ping-poll failcount” on page 1208

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1128
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
•“auth-web-server ping-poll interval” on page 1209
•“auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh” on page 1210
•“auth-web-server ping-poll timeout” on page 1211
•“auth-web-server port” on page 1212
•“auth-web-server redirect-delay-time” on page 1213
•“auth-web-server redirect-url” on page 1214
•“auth-web-server session-keep” on page 1215
•“auth-web-server ssl” on page 1216
•“auth-web-server ssl intercept-port” on page 1217
•“copy proxy-autoconfig-file” on page 1218
•“copy web-auth-https-file” on page 1219
•“description (Authentication Profile)” on page 1220
•“erase proxy-autoconfig-file” on page 1221
•“erase web-auth-https-file” on page 1222
•“platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm” on page 1223
•“platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm” on page 1224
•“show auth” on page 1225
•“show auth diagnostics” on page 1227
•“show auth interface” on page 1229
•“show auth sessionstatistics” on page 1232
•“show auth statistics interface” on page 1233
•“show auth supplicant” on page 1234
•“show auth supplicant interface” on page 1237
•“show auth two-step supplicant brief” on page 1238
•“show auth-web-server” on page 1239
•“show auth-web-server page” on page 1240
•“show proxy-autoconfig-file” on page 1241

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1129
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH AUTH-FAIL VLAN
auth auth-fail vlan
Overview Use this command to enable the auth-fail vlan feature on the specified vlan
interface. This feature assigns supplicants (client devices) to the specified VLAN if
they fail port authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the auth-fail vlan feature for a
specified VLAN interface.
Syntax auth auth-fail vlan <1-4094>
no auth auth-fail vlan
Default The auth-fail vlan feature is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Use the auth-fail vlan feature when using Web-Authentication instead of the Guest
VLAN feature, when you need to separate networks where one supplicant (client
device) requires authentication and another supplicant does not require
authentication from the same interface.
This is because the DHCP lease time using the Web-Authentication feature is
shorter, and the auth-fail vlan feature enables assignment to a different VLAN if a
supplicant fails authentication.
To enable the auth-fail vlan feature with Web Authentication, you need to set the
Web Authentication Server virtual IP address by using the auth-web-server
ipaddress command or the auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress command.
When using 802.1X port authentication, use a dot1x max-auth-fail command to set
the maximum number of login attempts. Three login attempts are allowed by
default for 802.1X port authentication before supplicants trying to authenticate
are moved from the Guest VLAN to the auth-fail VLAN. See the dot1x max-auth-fail
on page 1099 for command information.
See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for information about:
• the auth-fail VLAN feature, which allows the Network Administrator to
separate the supplicants who attempted authentication, but failed, from the
supplicants who did not attempt authentication, and
• restrictions regarding combinations of authentication enhancements
working together
Use appropriate ACLs (Access Control Lists) on interfaces for extra security if a
supplicant allocated to the designated auth-fail vlan can access the same network
Parameter Description
<1-4094>Assigns the VLAN ID to any supplicants that have failed port
authentication.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1130
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH AUTH-FAIL VLAN
as a supplicant on the Guest VLAN. For more information about ACL concepts, and
configuring ACLs see the ACL Feature Overview and Configuration Guide. For
more information about ACL commands see:
•IPv4 Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands
•IPv4 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands
•IPv6 Software Access Control List (ACL) Commands
Examples To enable the auth-fail vlan feature for port1.0.2 and assign VLAN 100, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth auth-fail vlan 100
To disable the auth-fail vlan feature for port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth auth-fail vlan
To enable the auth-fail vlan feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth auth-fail vlan 100
To disable the auth-fail vlan feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth auth-fail vlan
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
dot1x max-auth-fail
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1131
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH CRITICAL
auth critical
Overview This command enables the critical port feature on the interface. When the critical
port feature is enabled on an interface, and all the RADIUS servers are unavailable,
then the interface becomes authorized.
The no variant of this command disables the critical port feature on the interface.
Syntax auth critical
no auth critical
Default The critical port of port authentication is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To enable the critical port feature on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth critical
To disable the critical port feature on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth critical
To enable the critical port feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth critical
To disable the critical port feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth critical
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth-web-server
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1132
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH DHCP-FRAMED-IP-LEASE
auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
Overview Use this command to enable DHCP Framed IP Lease on an interface.
When the DHCP Framed IP Lease feature is enabled on an interface, supplicants
authenticated using 802.1x or MAC authentication will be assigned a specific IP
address, and other network settings, gathered from the RADIUS server during the
authentication process.
Use the no variant of this command to disable DHCP Framed IP Lease.
Syntax auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
no auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
Default DHCP Framed IP Lease is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage You need to complete the following steps to configure the DHCP Framed IP Lease
feature on your network.
On the RADIUS server:
• Configure the RADIUS server with the username and password for 802.1x or
MAC authentication
• Configure the following ‘framed’ RADIUS attributes on the RADIUS server for
the that user:
– Framed-IP-Address (8): the IPv4 address for the supplicant
– Framed-IP-Netmask (9): the netmask for the supplicant
– Framed-Route (22): the default gateway IPv4 address for the
supplicant
– Session-Timeout (27): IP address lease time for the supplicant
NOTE: The Frame-IP-Address (8) attribute must be configured for this feature to work.
All other attributes are optional.
On the DHCP server:
•Configure the RADIUS client
• Enable 802.1x or MAC authentication on the required interface/s
• Enable DHCP Framed IP Lease feature on the required interface/s
• Setup a DHCP pool with the network range for the IP address/es registered
on the RADIUS server
•Enable DHCP server
For more information, see the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1133
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH DHCP-FRAMED-IP-LEASE
Example To enable DHCP Framed IP Lease on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
To disable DHCP Framed IP Lease on port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no auth dhcp-framed-ip-lease
Related
Commands
show dot1x supplicant
show ip dhcp pool
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1134
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH DYNAMIC-VLAN-CREATION
auth dynamic-vlan-creation
Overview This command enables and disables the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature.
The Dynamic VLAN assignment feature allows a supplicant (client device) to be
placed into a specific VLAN based on information returned from the RADIUS server
during authentication, on a given interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the Dynamic VLAN assignment
feature.
Syntax auth dynamic-vlan-creation [rule {deny|permit}] [type
{multi|single}]
no auth dynamic-vlan-creation
Default By default, the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage If the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature is enabled, VLAN assignment is dynamic.
If the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature is disabled then RADIUS attributes are
ignored and configured VLANs are assigned to ports. Dynamic VLANs may be
associated with authenticated MAC addresses if the type parameter is applied
with the rule parameter.
The rule parameter deals with the case where there are multiple supplicants
attached to a port, and the type parameter has been set to single-vlan. The
parameter specifies how the switch should act if different VLAN IDs end up being
assigned to different supplicants. The keyword value deny means that once a
given VID has been assigned to the first supplicant, then if any subsequent
supplicant is assigned a different VID, that supplicant is rejected. The keyword
value permit means that once a given VID has been assigned to the first
supplicant, then if any subsequent supplicant is assigned a different VID, that
supplicant is accepted, but it is actually assigned the same VID as the first
supplicant.
Parameter Description
rule VLAN assignment rule.
deny Deny a differently assigned VLAN ID. This is the default rule.
permit Permit a differently assigned VLAN ID.
type Specifies whether multiple different VLANs can be assigned to
supplicants (client devices) attached to the port, or whether only a
single VLAN can be assigned to supplicants on the port.
multi Multiple Dynamic VLAN.
single Single Dynamic VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1135
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH DYNAMIC-VLAN-CREATION
If you issue an auth dynamic-vlan-creation command without a rule parameter
then a second supplicant with a different VLAN ID is rejected. It is not assigned to
the first supplicant’s VLAN. Issuing an auth dynamic-vlan-creation command
without a rule parameter has the same effect as issuing an auth
dynamic-vlan-creation rule deny command rejecting supplicants with differing
VIDs.
The type parameter specifies whether multiple different VLANs can be assigned to
supplicants attached to the port, or whether only a single VLAN can be assigned to
supplicants on the port. The type parameter can select the port base VLAN or the
MAC base VLAN from the RADIUS VLAN ID. This can be used when the host-mode
is set to multi-supplicant. For single-host ports, the VLAN ID will be assigned to the
port. It is not supported with the Guest VLAN feature. Display the ID assigned using
a show vlan command. For multi-host ports, the VLAN ID will be assigned to the
MAC address of the authenticated supplicant. The VLAN ID assigned for the MAC
Base VLAN is displayed using the show platform table vlan command.
To configure Dynamic Vlan with Web Authentication, you need to set Web
Authentication Server virtual IP address by using the auth-web-server ipaddress
command or the auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress command. You also need to
create a hardware access-list that can be applied to the switch port interface.
You need to configure an IPv4 address for the VLAN interface on which Web
Authentication is running.
Examples To enable the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature on interface port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1/24
To enable the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature with Web Authentication on
interface port1.0.2 when Web Authentication is needed, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ipaddress 1.2.3.4
awplus(config)# access-list hardware acl-web send-to-cpu ip any
1.2.3.4
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# access-group acl-web
awplus(config-if)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1/24

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1136
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH DYNAMIC-VLAN-CREATION
To disable the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature on interface port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth dynamic-vlan-creation
To enable the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
To disable the Dynamic VLAN assignment feature on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth dynamic-vlan-creation
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
auth host-mode
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1137
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH GUEST-VLAN
auth guest-vlan
Overview This command enables and configures the Guest VLAN feature on the interface
specified by associating a Guest VLAN with an interface. This command does not
start authentication. The supplicant's (client device’s) traffic is associated with the
native VLAN of the interface if its not already associated with another VLAN. The
routing option enables routing from the Guest VLAN to another VLAN, so the
switch can lease DHCP addresses and accept access to a limited network.
The no variant of this command disables the guest VLAN feature on the interface
specified.
Syntax auth guest-vlan <1-4094> [routing]
no auth guest-vlan [routing]
Default The Guest VLAN authentication feature is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage The Guest VLAN feature may be used by supplicants (client devices) that have not
attempted authentication, or have failed the authentication process. Note that if a
port is in multi-supplicant mode with per-port dynamic VLAN configuration, after
the first successful authentication, subsequent hosts cannot use the guest VLAN
due to the change in VLAN ID. This may be avoided by using per-user dynamic
VLAN assignment.
When using the Guest VLAN feature with the multi-host mode, a number of
supplicants can communicate via a guest VLAN before authentication. A
supplicant’s traffic is associated with the native VLAN of the specified switch port.
The supplicant must belong to a VLAN before traffic from the supplicant can be
associated.
Note that you must enable 802.1X on the port and define a VLAN using the vlan
command before you can configure it as a guest VLAN.
Roaming Authentication cannot be enabled if DHCP snooping is enabled (service
dhcp-snooping command), and vice versa.
Note that Guest VLAN can use only untagged ports.
See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for information about:
• Guest VLAN, and
Parameter Description
<1-4094>VLAN ID (VID).
routing Enables routing from the Guest VLAN to other VLANs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1138
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH GUEST-VLAN
• restrictions regarding combinations of authentication enhancements
working together
Examples To define vlan100 and assign the guest VLAN feature to vlan100 on interface
port1.0.2, and enable routing from the guest VLAN to other VLANs, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 100
awplus(config-vlan)# exit
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control auto
awplus(config-if)# auth guest-vlan 100 routing
To disable the guest VLAN feature on port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth guest-vlan
To define vlan100 and assign the guest VLAN feature to vlan100 on authentication
profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# vlan database
awplus(config-vlan)# vlan 100
awplus(config-vlan)# exit
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth guest-vlan 100
To disable the guest VLAN feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth guest-vlan
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
auth guest-vlan forward
dot1x port-control
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1139
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH GUEST-VLAN FORWARD
auth guest-vlan forward
Overview Use this command to enable packet forwarding from the Guest VLAN to a
destination IP address or subnet. If this command is configured, the device can
lease DHCP addresses and accept access to a limited part of your network. Also,
when using NAP authentication, the supplicant can log on to a domain controller
to gain certification.
Use the no variant of this command to disable packet forwarding from the Guest
VLAN to a destination IP address or subnet.
Syntax auth guest-vlan forward {<ip-address>|<ip-address/mask>}
[dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>]
no auth guest-vlan forward {<ip-address>|<ip-address/mask>}
[dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>]
Default Forwarding is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration mode for a specified switch port, or Authentication Profile
mode
Usage Before using this command, you must configure the guest VLAN with the auth
guest-vlan command.
Example To enable packet forwarding from the guest VLAN to the destination IP address on
interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth guest-vlan forward 10.0.0.1
To enable forwarding of DNS packets from the guest VLAN to the destination IP
address on interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth guest-vlan forward 10.0.0.1 dns
Parameter Description
<ip-address>
<ip-address/
mask>
The IP address or subnet to which the guest VLAN can forward
packets, in dotted decimal notation
dns Enable forwarding of DNS packets
tcp <1-65535>Enable forwarding of packets for the specified TCP port number
udp <1-65535>Enable forwarding of packets for the specified UDP port number

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1140
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH GUEST-VLAN FORWARD
To disable forwarding of DNS packets from the guest VLAN to the destination IP
address on port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth guest-vlan forward 10.0.0.1 dns
To enable the tcp forwarding port 137 on authentication profile 'student', use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth guest-vlan forward 10.0.0.1
tcp 137
To disable the tcp forwarding port 137 authentication profile 'student', use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth guest-vlan forward
10.0.0.1 tcp 137
Related
Commands
auth guest-vlan
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1141
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH HOST-MODE
auth host-mode
Overview This command selects the host mode on the specified interface.
Use the no variant of this command to set host mode to the default setting (single
host).
Syntax auth host-mode {single-host|multi-host|multi-supplicant}
no auth host-mode
Default The default host mode for port authentication is for a single host.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Ports residing in the unauthorized state for host(s) or supplicant(s), change to an
authorized state when the host or supplicant has successfully authenticated with
the Authentication Server.
When multi-host mode is used or auth critical feature is used, all hosts do not need
to be authenticated.
Examples To set the host mode to multi-supplicant on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth host-mode multi-supplicant
Parameter Description
single-host Single host mode. In this mode, only one host may be
authorized with the port. If other hosts out the interface
attempt to authenticate, the authenticator blocks the
attempt.
multi-host Multi host mode. In this mode, multiple hosts may be
authorized with the port; however only one host must be
successfully authenticated at the Authentication Server for
all hosts to be authorized with the port. Upon one host being
successfully authenticated (state Authenticated), the other
hosts will be automatically authorized at the port (state
ForceAuthorized). If no host is successfully authenticated,
then all hosts are not authorized with the port.
multi-supplicant Multi supplicant (client device) mode. In this mode, multiple
hosts may be authorized with the port, but each host must
be individually authenticated with the Authentication Server
to be authorized with the port. Supplicants which are not
authenticated are not authorized with the port, while
supplicants which are successfully authenticated are
authorized with the port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1142
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH HOST-MODE
To set the host mode to default (single host) on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth host-mode
To set the host mode to multi-supplicant on authentication profile ‘student’, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth host-mode multi-supplicant
To set the host mode to default (single host) on authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth host-mode
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1143
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH LOG
auth log
Overview Use this command to configure the types of authentication feature log messages
that are output to the log file.
Use the no variant of this command to remove either specified types or all types of
authentication feature log messages that are output to the log file.
Syntax auth log {dot1x|auth-mac|auth-web}
{success|failure|logoff|all}
no auth log {dot1x|auth-mac|auth-web}
{success|failure|logoff|all}
Default All types of authentication log messages are output to the log file by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To configure the logging of MAC authentication failures to the log file for
supplicants (client devices) connected to interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth log auth-mac failure
Parameter Description
dot1x Specify only 802.1X-Authentication log messages are output to the log
file.
auth-mac Specify only MAC-Authentication log messages are output to the log
file.
auth-web Specify only Web-Authentication log messages are output to the log
file.
success Specify only successful authentication log messages are output to the
log file.
failure Specify only authentication failure log messages are output to the log
file.
logoff Specify only authentication log-off messages are output to the log file.
Note that link down, age out and expired ping polling messages will be
included.
all Specify all types of authentication log messages are output to the log
file. Note that this is the default behavior for the authentication logging
feature.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1144
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH LOG
To disable the logging of all types of authentication log messages to the log file for
supplicants (client devices) connected to interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth log all
To configure the logging of web authentication failures to the log file for
supplicants (client devices) connected to authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth log auth-web failure
To disable the logging of all types of authentication log messages to the log file for
supplicants (client devices) connected to authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth log all
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1145
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH MAX-SUPPLICANT
auth max-supplicant
Overview This command sets the maximum number of supplicants (client devices) that can
be authenticated on the selected port. Once this value is exceeded, further
supplicants will not be authenticated.
The no variant of this command resets the maximum supplicant number to the
default.
Syntax auth max-supplicant <2-1024>
no auth max-supplicant
Default The max supplicant of port authentication is 1024.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the maximum number of supplicants to 10 on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth max-supplicant 10
To reset the maximum number of supplicants to the default value on interface
port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth max-supplicant
To set the maximum number of supplicants to 10 on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth max-supplicant 10
To reset the maximum number of supplicants to the default value on
authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth max-supplicant
Parameter Description
<2-1024>Limit number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1147
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH MULTI-VLAN-SESSION
auth multi-vlan-session
Overview Use this command to enable packet forwarding on multiple VLANs for an
authenticated supplicant attached to a trunked (tagged VLAN) port.
By default, AlliedWare Plus only allows packet forwarding on the VLAN that a
device was authenticated on. This command enables packet forwarding to the
attached device on any VLAN configured on the switchport. After the device
authenticates it will have access to all VLANs configured on the switchport.
Use the no variant of this command to disable packet forwarding on multiple
VLANs for an authenticated supplicant.
Syntax auth multi-vlan-session
no auth multi-vlan-session
Default By default, multi-vlan-session is disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To allow a client attached to port1.0.2 to access all VLANs configured on the
AlliedWare Plus device, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
awplus(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan all
awplus(config-if)# auth host-mode multi-supplicant
awplus(config-if)# auth multi-vlan-session
To disable multi-vlan-session on interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth multi-vlan-session
Related
Commands
auth-mac enable
auth-web enable
dot1x port-control
show auth interface
show dot1x interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1148
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH PROFILE (GLOBAL CONFIGURATION)
auth profile (Global Configuration)
Overview Use this command to enter port authentication profile mode and configure a port
authentication profile.
If the specified profile does not exist a new authentication profile is created with
the name provided.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the specified port authentication
profile.
Syntax auth profile <profile-name>
no auth profile <profile-name>
Default No port authentication profiles are created by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage A port authentication profile is a configuration object that aggregates multiple
port authentication commands. These profiles are attached or detached from an
interface using the auth profile (Interface Configuration) command.
Example To create a new authentication profile ‘student’, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)#
To delete an authentication profile ‘student’, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth profile student
Related
Commands
auth profile (Interface Configuration)
description (Authentication Profile)
Parameter Description
<varname>Name of the profile to create or configure.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1149
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH PROFILE (INTERFACE CONFIGURATION)
auth profile (Interface Configuration)
Overview Use this command to attach a port authentication profile to the current interface.
Use the no variant of this command to detach a port authentication profile from
the current interface.
Syntax auth profile <profile-name>
no auth profile <profile-name>
Default No profile is attached by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage This command attaches a authentication profile, created using the auth profile
(Global Configuration) command, to a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel
group, or a switch port.
You can only attach one profile to an interface at a time, use the no variant of the
command to detach a profile before attempting to attach another one.
Example To attach the authentication profile ‘student’ to port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth profile student
To detach the authentication profile ‘student’ from port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth profile student
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
Parameter Description
<profile-name>The name of the profile to attach to the current interface.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1150
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH REAUTHENTICATION
auth reauthentication
Overview This command enables re-authentication on the interface specified in the Interface
mode, which may be a static channel group (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or
LACP) channel group or a switch port.
Use the no variant of this command to disable reauthentication on the interface.
Syntax auth reauthentication
no auth reauthentication
Default Reauthentication of port authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To enable reauthentication on interface port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth reauthentication
To disable reauthentication on interface port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth reauthentication
To enable reauthentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth reauthentication
To disable reauthentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth reauthentication
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1151
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH ROAMING DISCONNECTED
auth roaming disconnected
Overview This command allows a supplicant to move to another authenticating interface
without reauthentication, even if the link is down for the interface that the
supplicant is currently connected to.
You must enter the auth roaming enable command on both interfaces before
using this command.
The no variant of this command disables roaming authentication on interfaces
that are link-down, and forces a supplicant to be reauthenticated when moving
between interfaces.
See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for further information about this feature.
Syntax auth roaming disconnected
no auth roaming disconnected
Default By default, the authentication status for a roaming supplicant is deleted when an
interface goes down, so supplicants must reauthenticate.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Note that 802.1X port authentication, MAC-authentication, or Web-authentication
must be configured before using this feature. The port that the supplicant is
moving to must have the same authentication configuration as the port the
supplicant is moving from.
Roaming Authentication cannot be enabled if DHCP snooping is enabled (service
dhcp-snooping command), and vice versa.
Examples To allow supplicants to move from port1.0.2 without reauthentication even when
the link is down, when using 802.1X authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control auto
awplus(config-if)# auth roaming enable
awplus(config-if)# auth roaming disconnected
To require supplicants to reauthenticate when moving from port1.0.2 if the link is
down, when using 802.1X authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth roaming disconnected

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1152
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH ROAMING DISCONNECTED
To allow supplicants using authentication profile ‘student’ to move between ports
without reauthentication even when the link is down, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth roaming disconnected
To require supplicants using authentication profile ‘student’ to reauthenticate
when moving between ports if the link is down, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth roaming disconnected
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
auth-mac enable
auth roaming enable
auth-web enable
dot1x port-control
show auth interface
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1153
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH ROAMING ENABLE
auth roaming enable
Overview This command allows a supplicant to move to another authenticating interface
without reauthentication, providing the link is up for the interface that the
supplicant is is currently connected to.
The no variant of this command disables roaming authentication on an interface,
and forces a supplicant to be reauthenticated when moving between interfaces.
See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for further information about this feature.
Syntax auth roaming enable
no auth roaming enable
Default Roaming authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Note that 802.1X port authentication, MAC-authentication, or Web-authentication
must be configured before using this feature. The port that the supplicant is
moving to must have the same authentication configuration as the port the
supplicant is moving from.
This command only enables roaming authentication for links that are up. If you
want roaming authentication on links that are down, you must also use the
command auth roaming disconnected.
Roaming Authentication cannot be enabled if DHCP snooping is enabled (service
dhcp-snooping command), and vice versa.
Examples To enable roaming authentication for port1.0.4, when using auth-mac
authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac enable
awplus(config-if)# auth roaming enable
To disable roaming authentication for port1.0.4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# no auth roaming enable
To enable roaming authentication for authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth roaming enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1154
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH ROAMING ENABLE
To disable roaming authentication for authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth roaming enable
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
auth-mac enable
auth roaming disconnected
auth-web enable
dot1x port-control
show auth interface
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1155
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH SUPPLICANT-IP
auth supplicant-ip
Overview This command adds a supplicant (client device) IP address on a given interface and
provides parameters for its configuration.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the supplicant IP address and reset
other parameters to their default values. The IP address can be determined before
authentication for only auth-web client.
Syntax auth supplicant-ip <ip-addr> [max-reauth-req <1-10>]
[port-control {auto|force-authorized|force-unauthorized}]
[quiet-period <1-65535>] [reauth-period <1-4294967295>]
[supp-timeout <1-65535>] [server-timeout <1-65535>]
[reauthentication]
no auth supplicant-ip <ip-addr> [reauthentication]
Parameter Description
<ip-addr>IP address of the supplicant entry in A.B.C.D/P format.
max-reauth-req The number of reauthentication attempts before
becoming unauthorized.
<1-10>Count of reauthentication attempts (default 2).
port-control Port control commands.
auto A port control parameter that allows port clients to
negotiate authentication.
force-authorized A port control parameter that forces the port state to
authorized.
force-unauthorized A port control parameter that forces the port state to
unauthorized.
quiet-period Quiet period during which the port remains in the HELD
state (default 60 seconds).
<1-65535>Seconds for quiet period.
reauth-period Seconds between reauthorization attempts (default 3600
seconds).
<1-4294967295>Seconds for reauthorization attempts (reauth-period).
supp-timeout Supplicant response timeout.
<1-65535>Seconds for supplicant response timeout (default 30
seconds).
server-timeout The period, in seconds, before the authentication server
response times out.
<1-65535>The server-timeout period, in seconds, default 3600
seconds.
reauthentication Enable reauthentication on a port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1156
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH SUPPLICANT-IP
Default No supplicant IP address for port authentication exists by default until first created
with the auth supplicant-ip command. The defaults for parameters applied are as
shown in the table above.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To add the supplicant IP address 192.168.10.0/24 to force authorized port control
for interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth supplicant-ip 192.168.10.0/24
port-control force-authorized
To delete the supplicant IP address 192.168.10.0/24 for interface port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth supplicant-ip 192.168.10.0/24
To disable reauthentication for the supplicant(s) IP address 192.168.10.0/24 for
interface port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth supplicant-ip 192.168.10.0/24
reauthentication
To add the supplicant IP address 192.168.10.0/24 to force authorized port control
for auth profile 'student', use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth supplicant-ip
192.168.10.0/24 port-control force-authorized
To disable reauthentication for the supplicant IP address 192.168.10.0/24, for auth
profile 'student', use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-if)# no auth supplicant-ip 192.168.10.0/24
reauthentication
Related
Commands
show auth
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1157
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH SUPPLICANT-MAC
auth supplicant-mac
Overview This command adds a supplicant (client device) MAC address or MAC mask on a
given interface with the parameters as specified in the table below.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the supplicant MAC address and
reset other parameters to their default values.
Syntax auth supplicant-mac <mac-addr> [mask <mac-addr-mask>]
[max-reauth-req <1-10>] [port-control
{auto|force-authorized|force-unauthorized|skip-second-auth}]
[quiet-period <1-65535>] [reauth-period <1-4294967295>]
[supp-timeout <1-65535>] [server-timeout <1-65535>]
[reauthentication]
no auth supplicant-mac <mac-addr> [reauthentication]
Parameter Description
<mac-addr>MAC (hardware) address of the supplicant entry in
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH MAC address hexadecimal format.
mask A mask applied to MAC addresses in order to select only
those addresses containing a specific string.
<mac-addr-mask> The mask comprises a string of three (period separated)
bytes, where each byte comprises four hexadecimal
characters that will generally be either 1or 0. When the
mask is applied to a specific MAC address, a match is only
required for characters that correspond to a 1 in the mask.
Characters that correspond to a 0 in the mask are
effectively ignored.
In the examples section below, the mask ffff.ff00.0000 is
applied for the MAC address 0000.5E00.0000. The applied
mask will then match only those MAC addresses that begin
with 0000.5E (in this case the OUI component). The
remaining portion of the addresses (in this case the NIC
component) will be ignored.
port-control Port control commands.
auto Allow port client to negotiate authentication.
force-authorized Force port state to authorized.
force-unauthorized Force port state to unauthorized.
skip-second-auth Skip the second authentication.
quiet-period Quiet period in the HELD state (default 60 seconds).
<1-65535>Seconds for quiet period.
reauth-period Seconds between reauthorization attempts (default 3600
seconds).
<1-4294967295>Seconds for reauthorization attempts (reauth-period).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1158
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH SUPPLICANT-MAC
Default No supplicant MAC address for port authentication exists by default until first
created with the auth supplicant-mac command. The defaults for parameters are
shown in the table above.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To add the supplicant MAC address 0000.5E00.5343 to force authorized port
control for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth supplicant-mac 0000.5E00.5343
port-control force-authorized
To apply the mask ffff.ff00.0000 in order to add any supplicant whose MAC address
begins with 000.5E, and then to force authorized port control for port 1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth supplicant-mac 0000.5E00.0000 mask
ffff.ff00.0000 port-control force-authorized
To delete the supplicant MAC address 0000.5E00.5343 for port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth supplicant-mac 0000.5E00.5343
To reset reauthentication to disabled for the supplicant MAC address
0000.5E00.5343 for port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth supplicant-mac 0000.5E00.5343
reauthentication
supp-timeout Supplicant response timeout (default 30 seconds).
<1-65535>Seconds for supplicant response timeout.
server-timeout Authentication server response timeout (default 30
seconds).
<1-65535>Seconds for authentication server response timeout.
reauthentication Enable reauthentication on a port.
max-reauth-req No of reauthentication attempts before becoming
unauthorized (default 2).
<1-10>Count of reauthentication attempts.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1159
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH SUPPLICANT-MAC
To add the supplicant MAC address 0000.5E00.5343 to force authorized port
control for authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth supplicant-mac
0000.5E00.5343 port-control force-authorized
To delete the supplicant MAC address 0000.5E00.5343 for authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth supplicant-mac
0000.5E00.5343
To disable reauthentication for the supplicant MAC address 0000.5E00.5343 for
authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth supplicant-mac
0000.5E00.5343 reauthentication
Related
Commands
show auth
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1160
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT CONNECT-TIMEOUT
auth timeout connect-timeout
Overview This command sets the connect-timeout period for the interface.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the connect-timeout period to the
default.
Syntax auth timeout connect-timeout <1-65535>
no auth timeout connect-timeout
Default The connect-timeout default is 30 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage This command is used for MAC- and Web-Authentication. If the connect-timeout
has lapsed and the supplicant has the state connecting, then the supplicant is
deleted. When auth-web-server session-keep or auth two-step enable is enabled,
we recommend you configure a longer connect-timeout period.
Examples To set the connect-timeout period to 3600 seconds for port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth timeout connect-timeout 3600
To reset the connect-timeout period to the default (30 seconds) for port1.0.2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth timeout connect-timeout
To set the connect-timeout period to 3600 seconds for authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth timeout connect-timeout 3600
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Specifies the connect-timeout period (in seconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1161
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT CONNECT-TIMEOUT
To reset the connect-timeout period to the default (30 seconds) for authentication
profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth timeout connect-timeout
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show dot1x
show dot1x interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1162
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT QUIET-PERIOD
auth timeout quiet-period
Overview This command sets a time period for which another authentication request is not
accepted on a given interface, after an authentication request has failed.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the quiet period to the default.
Syntax auth timeout quiet-period <1-65535>
no auth timeout quiet-period
Default The quiet period for port authentication is 60 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the quiet period to 10 seconds for interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth timeout quiet-period 10
To reset the quiet period to the default (60 seconds) for interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth timeout quiet-period
To set the quiet period to 10 seconds for authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth timeout quiet-period 10
To reset the quiet period to the default (60 seconds) for authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth timeout quiet-period
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Specifies the quiet period (in seconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1163
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT REAUTH-PERIOD
auth timeout reauth-period
Overview This command sets the timer for reauthentication on a given interface. The
re-authentication for the supplicant (client device) is executed at this timeout. The
timeout is only applied if the auth reauthentication command is applied.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the reauth-period parameter to the
default (3600 seconds).
Syntax auth timeout reauth-period <1-4294967295>
no auth timeout reauth-period
Default The default reauthentication period for port authentication is 3600 seconds, when
reauthentication is enabled on the port.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the reauthentication period to 1 day for interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth timeout reauth-period 86400
To reset the reauthentication period to the default (3600 seconds) for interface
port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth timeout reauth-period
To set the reauthentication period to 1 day for authentication profile ‘student’, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth timeout reauth-period 86400
To reset the reauthentication period to the default (3600 seconds) for
authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth timeout reauth-period
Parameter Description
<1-4294967295>The reauthentication timeout period (in seconds).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1165
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT SERVER-TIMEOUT
auth timeout server-timeout
Overview This command sets the timeout for the waiting response from the RADIUS server
on a given interface.
The no variant of this command resets the server-timeout to the default (30
seconds).
Syntax auth timeout server-timeout <1-65535>
no auth timeout server-timeout
Default The server timeout for port authentication is 30 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the server timeout to 120 seconds for interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth timeout server-timeout 120
To set the server timeout to the default (30 seconds) for interface port1.0.2 use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth timeout server-timeout
To set the server timeout to 120 seconds for authentication profile ‘student’, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth timeout server-timeout 120
To set the server timeout to the default (30 seconds) for authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth timeout server-timeout
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Server timeout period (in seconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1167
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TIMEOUT SUPP-TIMEOUT
auth timeout supp-timeout
Overview This command sets the timeout of the waiting response from the supplicant (client
device) on a given interface.
The no variant of this command resets the supplicant timeout to the default (30
seconds).
Syntax auth timeout supp-timeout <1-65535>
no auth timeout supp-timeout
Default The supplicant timeout for port authentication is 30 seconds.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the supplicant timeout to 2 seconds for interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth timeout supp-timeout 2
To reset the supplicant timeout to the default (30 seconds) for interface port1.0.2,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth timeout supp-timeout
To set the supplicant timeout to 2 seconds for authentication profile ‘student’, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth timeout supp-timeout 2
To reset the supplicant timeout to the default (30 seconds) for authentication
profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth timeout supp-timeout
Parameter Description
<1-65535>The supplicant timeout period (in seconds).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1169
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TWO-STEP ENABLE
auth two-step enable
Overview This command enables a two-step authentication feature on an interface. When
this feature is enabled, the supplicant is authorized in a two-step process. If
authentication succeeds, the supplicant becomes authenticated. This command
will apply the two-step authentication method based on 802.1X-, MAC- or
Web-Authentication.
The no variant of this command disables the two-step authentication feature.
Syntax auth two-step enable
no auth two-step enable
Default Two step authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage The single step authentication methods (either user or device authentication) have
a potential security risk:
• an unauthorized user can access the network with an authorized device, or
• an authorized user can access the network with an unauthorized device.
Two-step authentication solves this problem by authenticating both the user and
the device. The supplicant will only become authenticated if both these steps are
successful. If the first authentication step fails, then the second step is not started.
Examples To enable the two step authentication feature, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth two-step enable
To disable the two step authentication feature, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth two-step enable
To enable MAC-Authentication followed by 802.1X-Authentication, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac enable
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control auto
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# auth two-step enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1170
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TWO-STEP ENABLE
To enable MAC-Authentication followed by Web-Authentication, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac enable
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# auth two-step enable
To enable 802.1X-Authentication followed by Web-Authentication, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
awplus(config-if)# dot1x port-control auto
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# auth two-step enable
To enable the two step authentication feature for authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth two-step enable
To disable the two step authentication feature for authentication profile ‘student’,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth two-step enable
Validation
Commands
show startup-config
show auth supplicant
show dot1x supplicant

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1171
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH TWO-STEP ENABLE
Relat ed
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth two-step supplicant brief
show auth
show auth interface
show auth supplicant
show dot1x
show dot1x interface
show dot1x supplicant

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1172
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC ACCOUNTING
auth-mac accounting
Overview This command overrides the default RADIUS accounting method for MAC-based
authentication on an interface by allowing you to apply a user-defined named list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method.
Syntax auth-mac accounting {default|<list-name>}
no auth-mac accounting
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To apply the named list 'vlan10_acct' on the vlan10 interface, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac accounting vlan10_acct
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the accounting
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no auth-mac accounting
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
default Apply the default accounting method list
<list-name>Apply the user-defined named list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1173
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC AUTHENTICATION
auth-mac authentication
Overview This command overrides the default MAC-based authentication method on an
interface by allowing you to apply a user-defined named list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method.
Syntax auth-mac authentication {default|<list-name>}
no auth-mac authentication
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To apply the named list 'vlan10_auth' on the vlan10 interface, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac authentication vlan10_auth
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the authentication
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no auth-mac authentication
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-mac
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
default Apply the default authentication method list
<list-name>Apply a user-defined named list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1174
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC ENABLE
auth-mac enable
Overview This command enables MAC-based authentication on the interface specified in the
Interface command mode.
Use the no variant of this command to disable MAC-based authentication on an
interface.
Syntax auth-mac enable
no auth-mac enable
Default MAC-Authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Enabling spanning-tree edgeport on ports after enabling MAC-based
authentication avoids unnecessary re-authentication when the port state changes,
which does not happen when spanning tree edgeport is enabled. Note that
re-authentication is correct behavior without spanning-tree edgeport enabled.
Applying switchport mode access on ports is also good practice to set the ports
to access mode with ingress filtering turned on, whenever ports for
MAC-Authentication are in a VLAN.
Examples To enable MAC-Authentication on interface port1.0.2 and enable spanning tree
edgeport to avoid unnecessary re-authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac enable
awplus(config-if)# spanning-tree edgeport
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access
To disable MAC-Authentication on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-mac enable
To enable MAC authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-mac enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1175
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC ENABLE
To disable MAC authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-mac enable
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1176
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC METHOD
auth-mac method
Overview This command sets the type of authentication method for MAC-Authentication
that is used with RADIUS on the interface specified in the Interface command
mode.
The no variant of this command resets the authentication method used to the
default method (PAP) as the RADIUS authentication method used by the
MAC-Authentication.
Syntax auth-mac method [eap-md5|pap]
no auth-mac method
Default The MAC-Authentication method is PAP.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the MAC-Authentication method to PAP on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac method pap
To set the MAC-Authentication method to the default on interface port1.0.2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-mac method
To set the MAC-Authentication method to EAP-MD5 on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-mac method eap-md5
Parameter Description
eap-md5 Enable EAP-MD5 as the authentication method.
pap Enable PAP as the authentication method.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1177
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC METHOD
To set the MAC-Authentication method to the default on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-mac method
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1178
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC PASSWORD
auth-mac password
Overview This command changes the password for MAC-based authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to return the password to its default.
Syntax auth-mac [encrypted] password <password>
no auth-mac password
Default By default, the password is the MAC address of the supplicant.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Changing the password increases the security of MAC-based authentication,
because the default password is easy for an attacker to discover. This is particularly
important if:
• some MAC-based supplicants on the network are intelligent devices, such as
computers, and/or
• you are using two-step authentication (see the “Ensuring Authentication
Methods Require Different Usernames and Passwords” section of the AAA
and Port Authentication Feature_Overview_and_Configuration_Guide).
Examples To change the password to verySecurePassword, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-mac password verySecurePassword
Related
Commands
auth two-step enable
show auth
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
auth-mac MAC-based authentication
encrypted Specify an encrypted password
password Configure the password
<password>The new password. Passwords can be up to 64 characters in length
and can contain any printable characters except:
•?
• " (double quotes)
•space

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1179
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC REAUTH-RELEARNING
auth-mac reauth-relearning
Overview This command sets the MAC address learning of the supplicant (client device) to
re-learning for re-authentication on the interface specified in the Interface
command mode.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the auth-mac re-learning option.
Syntax auth-mac reauth-relearning
no auth-mac reauth-relearning
Default Re-learning for port authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To enable the re-authentication re-learning feature on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-mac reauth-relearning
To disable the re-authentication re-learning feature on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awpl us(config-if)# no auth-mac reauth-relearning
To enable the re-authentication re-learning feature on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-mac reauth-relearning
To disable the re-authentication re-learning feature on authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-mac reauth-relearning
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1180
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC REAUTH-RELEARNING
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1181
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC STATIC
auth-mac static
Overview This command configures MAC authentication to use static entries in the FDB.
Static entries persist in the FDB, even if there is no traffic flow from the supplicant.
When static FDB entries are configured, the auth roaming disconnected command
is supported for MAC authentication. This command allows a supplicant to move
to another authenticating interface without re-authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to revert to dynamic FDB entries.
Syntax auth-mac static
no auth-mac static
Default By default MAC authentication supplicants are added to the FDB dynamically.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure MAC authentication to use static FDB entries, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-mac static
To configure MAC authentication to use dynamic FDB entries, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-mac static
Related
Commands
auth roaming disconnected
show auth
show dot1x
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.4: Command added
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1182
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-MAC USERNAME
auth-mac username
Overview Use this command to specify the format of the MAC address in the username and
password field when a request for MAC-based authorization is sent to a RADIUS
server.
Syntax auth-mac username {ietf|unformatted} {lower-case|upper-case}
Default auth-mac username ietf lower-case
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command is provided to allow other vendors’, AlliedWare, and AlliedWare
Plus switches to share the same format on the RADIUS server.
Example To configure the format of the MAC address in the username and password field to
be changed to IETF and upper-case, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-mac username ietf upper-case
Related
Commands
auth-mac username
show running-config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
ietf The MAC address includes a hyphen between each 2 bytes.
(Example: xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx)
unformatted The MAC address does not include hyphens. (Example:
xxxxxxxxxxxx)
lower-case The MAC address uses lower-case characters (a-f)
upper-case The MAC address uses upper-case characters (A-F)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1183
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB ACCOUNTING
auth-web accounting
Overview This command overrides the default RADIUS accounting method for Web-based
authentication on an interface by allowing you to apply a user-defined named list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method.
Syntax auth-web accounting {default|<list-name>}
no auth-web accounting
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To apply the named list ‘vlan10_acct' on the vlan10 interface, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# auth-web accounting vlan10_acct
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the accounting
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web accounting
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-web
Parameter Description
default Apply the default accounting method list
<list-name>Apply a named accounting method list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1184
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB AUTHENTICATION
auth-web authentication
Overview This command overrides the default Web-based authentication method on an
interface by allowing you to apply a user-defined named list.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the named list from the interface
and apply the default method.
Syntax auth-web authentication {default|<list-name>}
no auth-web authentication
Default The default method list is applied to an interface by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To apply the named list 'vlan10_auth' on the vlan10 interface, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# auth-web authentication vlan10_auth
To remove the named list from the vlan10 interface and set the authentication
method back to default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web authentication
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-web
Parameter Description
default Apply the default authentication method list
<list-name>Apply the user-defined named list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1185
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB ENABLE
auth-web enable
Overview This command enables Web-based authentication in Interface mode on the
interface specified.
Use the no variant of this command to apply its default.
Syntax auth-web enable
no auth-web enable
Default Web-Authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage Web-based authentication cannot be enabled if DHCP snooping is enabled by
using the service dhcp-snooping command, and vice versa. You need to configure
an IPv4 address for the VLAN interface on which Web Authentication is running.
Examples To enable Web-Authentication on static-channel-group 2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# static-channel-group 2
awplus(config-if)# exit
awplus(config)# interface sa2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
To disable Web-Authentication on static-channel-group 2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# static-channel-group 2
awplus(config-if)# exit
awplus(config)# interface sa2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web enable
To enable Web authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-web enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1186
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB ENABLE
To disable Web authentication on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web enable
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1187
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB FORWARD
auth-web forward
Overview This command enables the Web-authentication packet forwarding feature on the
interface specified. This command also enables ARP forwarding, and adds
forwarded packets to the tcp or udp port number specified.
The no variant of this command disables the specified packet forwarding feature
on the interface.
Syntax auth-web forward [<ip-address>|<ip-address/prefix-length>]
{dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>}
or
auth-web forward {arp|dhcp|dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>}
The no variants of this command are:
no auth-web forward [<ip-address>|<ip-address/prefix-length>]
{dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>}
or
no auth-web forward {arp|dhcp|dns|tcp <1-65535>|udp <1-65535>}
Default Packet forwarding for port authentication is enabled by default for “arp”, “dhcp”
and “dns”.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Usage For more information about the <ip-address> parameter, and an example, see the
“auth-web forward” section in the Alliedware Plus Technical Tips and Tricks.
Parameter Description
<ip-address>
<ip-address/
prefix-length>
The IP address or subnet on which the Web-authentication is to
be enabled.
arp Enable forwarding of ARP.
dhcp Enable forwarding of DHCP (67/udp).
dns Enable forwarding of DNS (53/udp).
tcp Enable forwarding of TCP specified port number.
<1-65535> TCP Port number.
udp Enable forwarding of UDP specified port number.
<1-65535> UDP Port number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1188
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB FORWARD
Examples To enable the ARP forwarding feature on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web forward arp
To add TCP forwarding port 137 on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web forward tcp 137
To add the DNS Server IP address 192.168.1.10 on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# switchport mode access
awplus(config-if)# auth-web enable
awplus(config-if)# auth dynamic-vlan-creation
awplus(config-if)# auth-web forward 192.168.1.10 dns
To disable the ARP forwarding feature on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web forward arp
To delete TCP forwarding port 137 on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web forward tcp 137
To delete all TCP forwarding on interface port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web forward tcp
To enable the ARP forwarding feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-web forward arp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1189
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB FORWARD
To add TCP forwarding port 137 on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-web forward tcp 137
To disable the ARP forwarding feature on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web forward arp
To delete TCP forwarding port 137 on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web forward tcp 137
To delete all TCP forwarding on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web forward tcp
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1190
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB MAX-AUTH-FAIL
auth-web max-auth-fail
Overview This command sets the number of authentication failures allowed before rejecting
further authentication requests. When the supplicant (client device) fails more
than the specified number of times, then login requests are refused during the
quiet period.
The no variant of this command resets the maximum number of authentication
failures to the default.
Syntax auth-web max-auth-fail <0-10>
no auth-web max-auth-fail
Default The maximum number of authentication failures is set to 3.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Examples To set the lock count to 5 on interface port1.0.2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web max-auth-fail 5
To set the lock count to the default on interface port1.0.2, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no auth-web max-auth-fail
To set the lock count to 5 on authentication profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-web max-auth-fail 5
To set the lock count to the default on authentication profile ‘student’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web max-auth-fail
Parameter Description
<0-10>The maximum number of authentication failures allowed
before login requests are refused.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1192
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB METHOD
auth-web method
Overview This command sets the Web-authentication access method that is used with
RADIUS on the interface specified.
The no variant of this command sets the authentication method to PAP for the
interface specified when Web-Authentication is also used with the RADIUS
authentication method.
Syntax auth-web method {eap-md5|pap}
no auth-web method
Default The Web-Authentication method is set to PAP by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a static channel, a dynamic (LACP) channel group, or a
switch port; or Authentication Profile mode.
Example To set the Web-Authentication method to EAP-MD5 on interface port1.0.2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# auth-web method eap-md5
To set the web authentication method to EAP-MD5 for authentication profile
‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# auth-web method eap-md5
To reset the web authentication method to the default (PAP) for authentication
profile ‘student’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no auth-web method
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
show auth
show auth interface
show running-config
Parameter Description
eap-md5 Enable EAP-MD5 as the authentication method.
pap Enable PAP as the authentication method.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1193
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER BLOCKING-MODE
auth-web-server blocking-mode
Overview Use this command to enable blocking mode for the Web-Authentication server.
The blocking mode displays an authentication success or failure screen
immediately from the response result from a RADIUS server.
Use the no variant of this command to disable blocking mode for the
Web-Authentication server.
Syntax auth-web-server blocking-mode
no auth-web-server blocking-mode
Default By default, blocking mode is disabled for the Web-Authentication server.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable blocking mode for the Web-Authentication server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server blocking-mode
To disable blocking mode for the Web-Authentication server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server blocking-mode
Related
Commands
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
show auth-web-server
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1194
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER DHCP IPADDRESS
auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress
Overview Use this command to assign an IP address and enable the DHCP service on the
Web-Authentication server for supplicants (client devices).
Use the no variant of this command to remove an IP address and disable the DHCP
service on the Web-Authentication server for supplicants.
Syntax auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress <ip-address/prefix-length>
no auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress
Default No IP address for the Web-Authentication server is set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for information about:
• using DHCP with web authentication, and
• restrictions regarding combinations of authentication enhancements
working together
You cannot use the IPv4 address assigned to the device’s interface as the
Web-Authentication server address.
Examples To assign the IP address 10.0.0.1 to the Web-Authentication server, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress 10.0.0.1/8
To remove an IP address on the Web-Authentication server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Related
Commands
show auth-web-server
auth-web-server dhcp lease
Parameter Description
<ip-addr/
prefix-length>The IPv4 address and prefix length assigned for the DHCP
service on the Web-Authentication server for supplicants.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1195
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER DHCP LEASE
auth-web-server dhcp lease
Overview Use this command to set the DHCP lease time for supplicants (client devices) using
the DHCP service on the Web-Authentication server.
Use the no variant of this command to reset to the default DHCP lease time for
supplicants using the DHCP service on the Web-Authentication server.
Syntax auth-web-server dhcp lease <20-60>
no auth-web-server dhcp lease
Default The default DHCP lease time for supplicants using the DHCP service on the Web-
Authentication server is set to 30 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage See the AAA and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide
for information about:
• using DHCP with web authentication, and
• restrictions regarding combinations of authentication enhancements
working together
Examples To set the DHCP lease time to 1 minute for supplicants using the DHCP service on
the Web-Authentication server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server dhcp lease 60
To reset the DHCP lease time to the default setting (30 seconds) for supplicants
using the DHCP service on the Web-Authentication server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server dhcp lease
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Related
Commands
show auth-web-server
auth-web-server dhcp ipaddress
Parameter Description
<20-60>DHCP lease time for supplicants using the DHCP service on the Web-
Authentication server in seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1196
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER DHCP-WPAD-OPTION
auth-web-server dhcp-wpad-option
Overview This command sets the DHCP WPAD (Web Proxy Auto-Discovery) option for the
Web-Authentication temporary DHCP service.
For more information and examples, see the “Web Auth Proxy” section in the
Alliedware Plus Technical Tips and Tricks.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the DHCP WPAD function.
Syntax auth-web-server dhcp wpad-option <url>
no auth-web-server dhcp wpad-option
Default The Web-Authentication server DHCP WPAD option is not set.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the supplicant is configured to use WPAD, the supplicant’s web browser will use
TCP port 80 as usual. Therefore, the packet can be intercepted by
Web-Authentication as normal, and the Web-Authentication Login page can be
sent. However, after authentication, the browser does not know where to get the
WPAD file and so cannot access external web pages. The WPAD file is usually
named proxy.pac file and tells the browser what web proxy to use.
Use this command to tell the supplicant where it can get this file from. The switch
itself can be specified as the source for this file, and it can deliver it to the
supplicant on request.
Example To specify that the proxy.pac file is found on the server at 192.168.1.100, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server dhcp wpad-option
http://192.168.1.100/proxy/proxy.pac
Related
Commands
show auth-web-server
Parameter Description
<url>URL to the server which gets a .pac file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1197
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER HOST-NAME
auth-web-server host-name
Overview This command assigns a hostname to the web authentication server.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the hostname from the web
authentication server.
Syntax auth-web-server host-name <hostname>
no auth-web-server host-name
Default The web authentication server has no hostname.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When the web authentication server uses HTTPS protocol, the web browser will
validate the certificate. If the certificate is invalid, the web page gives a warning
message before displaying server content. However, the web page will not give
warning message if the server has a hostname same as the one stored in the
installed certificate.
Examples To set the auth.example.com as the hostname of the web authentication server,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server host-name auth.example.com
To remove hostname auth.example.com from the web authentication server, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server host-name
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-web
auth-web enable
Parameter Description
<hostname>URL string of the hostname
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1198
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER INTERCEPT-PORT
auth-web-server intercept-port
Overview This command specifies any additional TCP port numbers that the
Web-Authentication server is to intercept.
Use the no variant of this command to stop intercepting the TCP port numbers.
Syntax auth-web-server intercept-port {<1-65535>|any}
no auth-web-server intercept-port {<1-65535>|any}
Default No additional TCP port numbers are intercepted by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If this command is not specified, AlliedWare Plus Web-Authentication intercepts
the supplicant’s initial TCP port 80 connection to a web page and sends it the Web-
Authentication Login page. However, if the supplicant is configured to use a web
proxy, then it will usually be using TCP port 8080 (or another user configured port
number). In this case Web-Authentication cannot intercept the connection.
To overcome this limitation you can use this command to tell the switch which
additional port it should intercept, and then send the Web-Authentication Login
page to the supplicant.
When the web authentication switch is in a guest network, the switch does not
know the proxy server’s port number in the supplicant’s proxy setting. To
overcome this limitation, you can use the any option in this command to intercept
all TCP packets.
When you use this command in conjunction with a proxy server configured in the
web browser, you must add the proxy server’s network as a ‘No Proxy’ network.
You can specify ‘No Proxy’ networks in the proxy settings in your web browser. For
more information, see the “Web Auth Proxy” section in the Alliedware Plus
Technical Tips and Tricks.
Example To additionally intercept port number 3128, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server intercept-port 3128
Related
Commands
show auth-web-server
Parameter Description
<1-65535>TCP port number.
any Intercept all TCP packets

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1199
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER IPADDRESS
auth-web-server ipaddress
Overview This command sets the IP address for the Web-Authentication server.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the IP address for the
Web-Authentication server.
You cannot use the IPv4 address assigned to the device’s interface as the
Web-Authentication server address.
Syntax auth-web-server ipaddress <ip-address>
no auth-web-server ipaddress
Default The Web-Authentication server address on the system is not set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the IP address 10.0.0.1 to the Web-Authentication server, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ipaddress 10.0.0.1
To delete the IP address from the Web-Authentication server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ipaddress
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<ip-address>Web-Authentication server dotted decimal IP address in
A.B.C.D format.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1200
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE LANGUAGE
auth-web-server page language
Overview Use this command to set the presentation language of Web authentication pages.
Titles and subtitles of Web authentication pages will be set accordingly. Note that
presently only English or Japanese are offered.
Use the no variant of this command to set the presentation language of Web
authentication pages to its default (English).
Syntax auth-web-server page language {english|japanese}
no auth-web-server page language
Default Web authentication pages are presented in English by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set Japanese as the presentation language of Web authentication pages, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page language japanese
To set English as the presentation language of Web authentication pages, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page language english
To unset the presentation language of Web authentication pages and use English
as the default presentation language, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page language
Related
Commands
auth-web-server page title
auth-web-server page sub-title
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
english Web authentication pages are presented in English.
japanese Web authentication pages are presented in Japanese.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1201
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER LOGIN-URL
auth-web-server login-url
Overview This command sets the web-authentication login page URL. This lets you replace
the login page with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA
and Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for details.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the URL.
Syntax auth-web-server login-url <URL>
no auth-web-server login-url
Default The built-in login page is set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set http://example.com/login.html as the login page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server login-url
http://example.com/login.html
To unset the login page URL, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server login-url
Related
Commands
show running-config
Parameter Description
<URL>Set login page URL

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1202
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE LOGO
auth-web-server page logo
Overview This command sets the type of logo that will be displayed on the web
authentication page.
Use the no variant of this command to set the logo type to auto.
Note that if you need to customize the login page extensively, you can instead
replace it with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA and
Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax auth-web-server page logo {auto|default|hidden}
no auth-web-server page logo
Default Logo type is auto by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To display the default logo with ignoring installed custom logo, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page logo default
To set back to the default logo type auto, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page logo
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
auto Display the custom logo if installed; otherwise display the
default logo
default Display the default logo
hidden Hide the logo

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1203
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE SUB-TITLE
auth-web-server page sub-title
Overview This command sets the custom sub-title on the web authentication page.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the sub-title to its default.
Note that if you need to customize the login page extensively, you can instead
replace it with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA and
Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax auth-web-server page sub-title {hidden|text <sub-title>}
no auth-web-server page sub-title
Default “Allied-Telesis” is displayed by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the custom sub-title, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page sub-title text Web
Authentication
To hide the sub-title, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page sub-title hidden
To change back to the default title, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page sub-title
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
hidden Hide the sub-title
<sub-title> Text string of the sub-title
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1204
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE SUCCESS-MESSAGE
auth-web-server page success-message
Overview This command sets the success message on the web-authentication page.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the success message.
Note that if you need to customize the login page extensively, you can instead
replace it with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA and
Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax auth-web-server page success-message text <success-message>
no auth-web-server page success-message
Default No success message is set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the success message on the web-authentication page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page success-message text Your
success message
To unset the success message on the web-authentication page, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page success-message
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
<success-message> Text string of the success message

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1205
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE TITLE
auth-web-server page title
Overview This command sets the custom title on the web authentication page.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the custom title.
Note that if you need to customize the login page extensively, you can instead
replace it with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA and
Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax auth-web-server page title {hidden|text <title>}
no auth-web-server page title
Default “Web Access Authentication Gateway” is displayed by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the custom title on the web authentication page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page title text Login
To hide the title on the web authentication page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page title hidden
To unset the custom title on the web authentication page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page title
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
hidden Hide the title
<title> Text string of the title
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1206
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE WELCOME-MESSAGE
auth-web-server page welcome-message
Overview This command sets the welcome message on the web-authentication login page.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the welcome message.
Note that if you need to customize the login page extensively, you can instead
replace it with your own page. See “Customising the Login Page” in the AAA and
Port Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax auth-web-server page welcome-message text <welcome-message>
no auth-web-server page welcome-message
Default No welcome message is set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the welcome message on the web-authentication page, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server page welcome-message text Your
welcome message
To remove the welcome message on the web-authentication page, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server page welcome-message
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server page
Parameter Description
<welcome-message> Text string of the welcome message

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1207
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PING-POLL ENABLE
auth-web-server ping-poll enable
Overview This command enables the ping polling to the supplicant (client device) that is
authenticated by Web-Authentication.
The no variant of this command disables the ping polling to the supplicant that is
authenticated by Web-Authentication.
Syntax auth-web-server ping-poll enable
no auth-web-server ping-poll enable
Default The ping polling feature for Web-Authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable the ping polling feature for Web-Authentication, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ping-poll enable
To disable the ping polling feature for Web-Authentication, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ping-poll enable
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1208
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PING-POLL FAILCOUNT
auth-web-server ping-poll failcount
Overview This command sets a fail count for the ping polling feature when used with
Web-Authentication. The failcount parameter specifies the number of
unanswered pings. A supplicant (client device) is logged off when the number of
unanswered pings are greater than the failcount set with this command.
Use the no variant of this command to resets the fail count for the ping polling
feature to the default (5 pings).
Syntax auth-web-server ping-poll failcount <1-100>
no auth-web-server ping-poll failcount
Default The default failcount for ping polling is 5 pings.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the failcount of ping polling to 10 pings, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ping-poll failcount 10
To set the failcount of ping polling to default, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ping-poll failcount
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<1-100>Count.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1209
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PING-POLL INTERVAL
auth-web-server ping-poll interval
Overview This command is used to change the ping poll interval. The interval specifies the
time period between pings when the supplicant (client device) is reachable.
Use the no variant of this command to reset to the default period for ping polling
(30 seconds).
Syntax auth-web-server ping-poll interval <1-65535>
no auth-web-server ping-poll interval
Default The interval for ping polling is 30 seconds by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the interval of ping polling to 60 seconds, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ping-poll interval 60
To set the interval of ping polling to the default (30 seconds), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ping-poll interval
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1210
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PING-POLL REAUTH-TIMER-REFRESH
auth-web-server ping-poll
reauth-timer-refresh
Overview This command modifies the reauth-timer-refresh parameter for the
Web-Authentication feature. The reauth-timer-refresh parameter specifies
whether a re-authentication timer is reset and when the response from a
supplicant (a client device) is received.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the reauth-timer-refresh parameter
to the default setting (disabled).
Syntax auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh
no auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh
Default The reauth-timer-refresh parameter is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable the reauth-timer-refresh timer, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ping-poll reauth-timer-refresh
To disable the reauth-timer-refresh timer, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ping-poll
reauth-timer-refresh
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1211
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PING-POLL TIMEOUT
auth-web-server ping-poll timeout
Overview This command modifies the ping poll timeout parameter for the
Web-Authentication feature. The timeout parameter specifies the time in seconds
to wait for a response to a ping packet.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the timeout of ping polling to the
default (1 second).
Syntax auth-web-server ping-poll timeout <1-30>
no auth-web-server ping-poll timeout
Default The default timeout for ping polling is 1 second.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the timeout of ping polling to 2 seconds, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ping-poll timeout 2
To set the timeout of ping polling to the default (1 second), use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ping-poll timeout
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<1-30>Seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1212
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER PORT
auth-web-server port
Overview This command sets the HTTP port number for the Web-Authentication server.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the HTTP port number to the default
(80).
Syntax auth-web-server port <port-number>
no auth-web-server port
Default The Web-Authentication server HTTP port number is set to 80 by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the HTTP port number 8080 for the Web-Authentication server, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server port 8080
To reset to the default HTTP port number 80 for the Web-Authentication server,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server port
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<port-number>Set the local Web-Authentication server port within the TCP
port number range 1 to 65535.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1213
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER REDIRECT-DELAY-TIME
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
Overview Use this command to set the delay time in seconds before redirecting the
supplicant to a specified URL when the supplicant is authorized.
Use the variant no to reset the delay time set previously.
Syntax auth-web-server redirect-delay-time <5-60>
no auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
Default The default redirect delay time is 5 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the delay time to 60 seconds for the Web-Authentication server, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server redirect-delay-time 60
To reset the delay time, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
Related
Commands
auth-web-server blocking-mode
auth-web-server redirect-url
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
redirect-delay-time Set the delay time before jumping to a specified
URL after the supplicant is authorized.
<5-60>The time in seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1214
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER REDIRECT-URL
auth-web-server redirect-url
Overview This command sets a URL for supplicant (client device) authentication. When a
supplicant is authorized it will be automatically redirected to the specified URL.
Note that if the http redirect feature is used then this command is ignored.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the URL string set previously.
Syntax auth-web-server redirect-url <url>
no auth-web-server redirect-url
Default The redirect URL for the Web-Authentication server feature is not set by default
(null).
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable and set redirect a URL string www.alliedtelesis.com for the Web-
Authentication server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server redirect-url
http://www.alliedtelesis.com
To delete a redirect URL string, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server redirect-url
Related
Commands
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
Parameter Description
<url>URL (hostname or dotted IP notation).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1215
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER SESSION-KEEP
auth-web-server session-keep
Overview This command enables the session-keep feature to jump to the original URL after
being authorized by Web-Authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the session keep feature.
Syntax auth-web-server session-keep
no auth-web-server session-keep
Default The session-keep feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This function doesn't ensure to keep session information in all cases.
Authenticated supplicant may be redirected to unexpected page when
session-keep is enabled. This issue occurred by supplicant sending HTTP packets
automatically after authentication page is displayed and the URL is written.
Examples To enable the session-keep feature, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server session-keep
To disable the session-keep feature, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server session-keep
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1216
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER SSL
auth-web-server ssl
Overview This command enables HTTPS functionality for the Web-Authentication server
feature.
Use the no variant of this command to disable HTTPS functionality for the
Web-Authentication server.
Syntax auth-web-server ssl
no auth-web-server ssl
Default HTTPS functionality for the Web-Authentication server feature is disabled by
default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable HTTPS functionality for the Web-Authentication server feature, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ssl
To disable HTTPS functionality for the Web-Authentication server feature, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ssl
Validation
Commands
show auth
show auth-web-server
show running-config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1217
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
AUTH-WEB-SERVER SSL INTERCEPT-PORT
auth-web-server ssl intercept-port
Overview Use this command to register HTTPS intercept port numbers when the HTTPS
server uses custom port number (not TCP port number 443).
Note that you need to use the auth-web-server intercept-port command to
register HTTP intercept port numbers.
Use the no variant of this command to delete registered port number.
Syntax auth-web-server ssl intercept-port <1-65535>
no auth-web-server ssl intercept-port <1-65535>
Default 443/TCP is registered by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To register HTTPS port number 3128, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth-web-server ssl intercept-port 3128
To delete HTTPS port number 3128, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth-web-server ssl intercept-port 3128
Validation
Commands
show auth-web-server
Related
Commands
auth-web-server intercept-port
Parameter Description
<1-65535>TCP port number in the range from 1 through 65535

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1218
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
COPY PROXY-AUTOCONFIG-FILE
copy proxy-autoconfig-file
Overview Use this command to download the proxy auto configuration (PAC) file to your
switch. The Web-Authentication supplicant can get the downloaded file from the
system web server.
Syntax copy <filename> proxy-autoconfig-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To download the PAC file to this device, use the command:
awplus# copy tftp://server/proxy.pac proxy-autoconfig-file
Related
Commands
show proxy-autoconfig-file
erase proxy-autoconfig-file
Parameter Description
<filename>The URL of the PAC file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1219
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
COPY WEB-AUTH-HTTPS-FILE
copy web-auth-https-file
Overview Use this command to download the SSL server certificate for web-based
authentication. The file must be in PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) format, and
contain the private key and the server certificate.
Syntax copy <filename> web-auth-https-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To download the server certificate file veriSign_cert.pem from the TFTP
server directory server, use the command:
awplus# copy tftp://server/veriSign_cert.pem
web-auth-https-file
Related
Commands
auth-web-server ssl
erase web-auth-https-file
show auth-web-server
Parameter Description
<filename>The URL of the server certificate file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1220
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (AUTHENTICATION PROFILE)
description (Authentication Profile)
Overview Use this command to add a description to an authentication profile in
Authentication Profile mode.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the current description.
Syntax description <description>
Default No description configured by default.
Mode Authentication Profile
Example To add a description to the authentication profile ‘student’, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# description student room setting
To remove a description from the authentication profile ‘student’, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth profile student
awplus(config-auth-profile)# no description
Related
Commands
auth profile (Global Configuration)
Parameter Description
<description>Text describing the selected authentication profile.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1221
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
ERASE PROXY-AUTOCONFIG-FILE
erase proxy-autoconfig-file
Overview Use this command to remove the proxy auto configuration file.
Syntax erase proxy-autoconfig-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To remove the proxy auto configuration file, use the command:
awplus# erase proxy-autoconfig-file
Related
Commands
show proxy-autoconfig-file
copy proxy-autoconfig-file

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1222
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
ERASE WEB-AUTH-HTTPS-FILE
erase web-auth-https-file
Overview Use this command to remove the SSL server certificate for web-based
authentication.
Syntax erase web-auth-https-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To remove the SSL server certificate file for web-based authentication use the
command:
awplus# erase web-auth-https-file
Related
Commands
auth-web-server ssl
copy web-auth-https-file
show auth-web-server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1223
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
PLATFORM L3-VLAN-HASHING-ALGORITHM
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Overview This command enables you to change the L3 VLAN hash-key-generating
algorithm.
The no variant of this command returns the hash-key algorithm to the default of
crc32l.
Syntax platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
{crc16l|crc16u|crc32l|crc32u}
no platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Default The hash-key algorithm is crc32l by default.
Mode Global configuration
Usage Occasionally, when using the Multiple Dynamic VLAN feature, a supplicant cannot
be authenticated because a collision occurs within the VLAN L3 table. This can
happen when more than four different IP addresses produce the same hash-key.
When this situation occurs, collisions can sometimes be avoided by changing the
hashing algorithm from its default of crc32l. Several different algorithms may need
to be tried to rectify the problem.
You must restart the switch for this command to take effect.
Note that this command is intended for technical support staff, or advanced end
users.
Example To change the hash-key generating algorithm applying to the lower bits of CRC-16,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm crc16l
Related
Commands
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
show platform
Parameter Description
crc16l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-16
crc16u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-16
crc32l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-32
crc32u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-32

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1224
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
PLATFORM MAC-VLAN-HASHING-ALGORITHM
platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Overview This command enables you to change the MAC VLAN hash-key-generating
algorithm.
The no variant of this command returns the hash-key algorithm to the default of
crc32l
Syntax platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
{crc16l|crc16u|crc32l|crc32u}
no platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm
Default The hash-key algorithm is crc32l by default.
Mode Global configuration
Usage Occasionally, when using the Multiple Dynamic VLAN feature, a supplicant cannot
be authenticated because a collision occurs within the VLAN MAC table. This can
happen when more than four different MAC addresses produce the same
hash-key.
When this situation occurs, collisions can sometimes be avoided by changing the
hashing algorithm from its default of crc32l. Several different algorithms may need
to be tried to rectify the problem.
You must restart the switch for this command to take effect.
Note that this command is intended for technical support staff, or advanced end
users.
Example To change the hash-key generating algorithm applying to the lower bits of CRC-16,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# platform mac-vlan-hashing-algorithm crc16l
Related
Commands
platform l3-vlan-hashing-algorithm
show platform
Parameter Description
crc16l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-16
crc16u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-16
crc32l The algorithm that will apply to the lower bits of CRC-32
crc32u The algorithm that will apply to the upper bits of CRC-32

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1225
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH
show auth
Overview This command shows the configuration state of authentication.
Syntax show auth [all]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display all authentication information, enter the command:
awplus# show auth all
Output Figure 34-1: Example output from the show auth command
Parameter Description
all Display all authentication information for each authenticated
interface. This can be a static channel (or static aggregator), or a
dynamic (or LACP) channel group, or a switch port.
awplus# show auth all
802.1X Port-Based Authentication Enabled
MAC-based Port Authentication Disabled
WEB-based Port Authentication Enabled
RADIUS server address (auth): 150.87.17.192:1812
Last radius message id: 4
Authentication Info for interface port1.0.1
portEnabled: true - portControl: Auto
portStatus: Authorized
reAuthenticate: disabled
reAuthPeriod: 3600
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in
KT: keyTxEnabled: false
critical: disabled
guestVlan: disabled
authFailVlan: disabled
dynamicVlanCreation: disabled
multiVlanCreation: disabled
hostMode: single-host
dot1x: enabled
protocolVersion: 1
authMac: disabled
authWeb: enabled
method: PAP
maxAuthFail: 3
packetForwarding:
10.0.0.1 80/tcp
dns
dhcp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1226
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH
Related
Commands
show dot1x
twoStepAuthentication:
configured: enabled
actual: enabled
supplicantMac: none
Supplicant name: oha
Supplicant address: 000d.6013.5398
authenticationMethod: WEB-based Authentication
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: dot1x
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: web
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 3
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 2
CD: adminControlledDirections: in - operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1227
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH DIAGNOSTICS
show auth diagnostics
Overview This command shows authentication diagnostics, optionally for the specified
interface, which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or
LACP) channel group or a switch port.
If no interface is specified then authentication diagnostics are shown for all
interfaces.
Syntax show auth diagnostics [interface <interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display authentication diagnostics for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth diagnostics interface port1.0.6
Parameter Description
interface Specify ports to show.
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or sa1-2,
or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1228
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH DIAGNOSTICS
Output Figure 34-2: Example output from the show auth diagnostics command
Related
Commands
show dot1x interface
Authentication Diagnostics for interface port1.0.6
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authEnterConnecting: 2
authEaplogoffWhileConnecting: 1
authEnterAuthenticating: 2
authSuccessWhileAuthenticating: 1
authTimeoutWhileAuthenticating: 1
authFailWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEaplogoggWhileAuthenticating: 0
authReauthsWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEaplogoffWhileAuthenticated: 0
BackendResponses: 2
BackendAccessChallenges: 1
BackendOtherrequestToSupplicant: 3
BackendAuthSuccess: 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1229
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH INTERFACE
show auth interface
Overview This command shows the status of port authentication on the specified interface,
which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or LACP)
channel group or a switch port.
Use the optional diagnostics parameter to show authentication diagnostics for
the specified interface. Use the optional sessionstatistics parameter to show
authentication session statistics for the specified interface. Use the optional
statistics parameter to show authentication diagnostics for the specified
interface. Use the optional supplicant (client device) parameter to show the
supplicant state for the specified interface.
Syntax show auth interface <interface-list>
[diagnostics|sessionstatistics|statistics|supplicant [brief]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the Web based authentication status for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.6
If web-based authentication is not configured, the output will be
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
diagnostics Diagnostics.
sessionstatistics Session statistics.
statistics Statistics.
supplicant Supplicant (client device).
brief Brief summary of supplicant state.
% Port-Control not configured on port1.0.6
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1230
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH INTERFACE
To display the Web based authentication status for port1.0.1, enter the command:
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.1
To display Web-Authentication diagnostics for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.6 diagnostics
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.1
Authentication Info for interface port1.0.1
portEnabled: true - portControl: Auto
portStatus: Authorized
reAuthenticate: disabled
reAuthPeriod: 3600
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in
KT: keyTxEnabled: false
critical: disabled
guestVlan: disabled
guestVlanForwarding:none
authFailVlan: disabled
dynamicVlanCreation: disabled
multiVlanCreation: disabled
hostMode: single-host
dot1x: enabled
protocolVersion: 1
authMac: disabled
authWeb: enabled
method: PAP
maxAuthFail: 3
packetForwarding:
10.0.0.1 80/tcp
dns
dhcp
twoStepAuthentication:
configured: enabled
actual: enabled
supplicantMac: none

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1231
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH INTERFACE
To display Web-Authentication session statistics for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.6 sessionstatistics
To display Web-Authentication statistics for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth statistics interface port1.0.6
To display the Web-Authenticated supplicant on interface port1.0.6, enter the
command:
awplus# show auth interface port1.0.6 supplicant
Related
Commands
show auth diagnostics
show dot1x sessionstatistics
show dot1x statistics interface
show dot1x supplicant interface
Authentication Diagnostics for interface port1.0.6
Supplicant address: 00d0.59ab.7037
authEnterConnecting: 2
authEaplogoffWhileConnecting: 1
authEnterAuthenticating: 2
authSuccessWhileAuthenticating: 1
authTimeoutWhileAuthenticating: 1
authFailWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticating: 0
authEaplogoggWhileAuthenticating: 0
authReauthsWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEapstartWhileAuthenticated: 0
authEaplogoffWhileAuthenticated: 0
BackendResponses: 2
BackendAccessChallenges: 1
BackendOtherrequestToSupplicant: 3
BackendAuthSuccess: 1
Authentication session statistics for interface port1.0.6
session user name: manager
session authentication method: Remote server
session time: 19440 secs
session terminat cause: Not terminated yet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1232
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH SESSIONSTATISTICS
show auth sessionstatistics
Overview This command shows authentication session statistics for the specified interface,
which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or LACP)
channel group or a switch port.
Syntax show auth sessionstatistics [interface <interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display authentication statistics for port1.0.6, enter the command:
awplus# show auth sessionstatistics interface port1.0.6
Output Figure 34-3: Example output from the show auth sessionstatistics command
Parameter Description
interface Specify ports to show.
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g.
port1.0.6), a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a
dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by
a hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or
sa1-2, or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix
interface types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
Authentication session statistics for interface port1.0.6
session user name: manager
session authentication method: Remote server
session time: 19440 secs
session terminat cause: Not terminated yet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1233
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH STATISTICS INTERFACE
show auth statistics interface
Overview This command shows the authentication statistics for the specified interface,
which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or a dynamic (or LACP)
channel group or a switch port.
Syntax show auth statistics interface <interface-list>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display Web-Authentication statistics for port1.0.4, enter the command:
awplus# show auth statistics interface port1.0.4
Related
Commands
show dot1x interface
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
• an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or sa1-2,
or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1234
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH SUPPLICANT
show auth supplicant
Overview This command shows the supplicant (client device) state when authentication is
configured for the switch. Use the optional brief parameter to show a summary of
the supplicant state.
Syntax show auth supplicant [<macadd>] [brief]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To display a summary of authenticated supplicant information on the device, enter
the command:
awplus# show auth supplicant brief
To display authenticated supplicant information on the device, enter the
command:
awplus# show auth supplicant
To display authenticated supplicant information for device with MAC address
0000.5E00.5301, enter the command:
awplus# show auth supplicant 0000.5E00.5301
Output Figure 34-4: Example output from show auth supplicant brief
Parameter Description
<macadd>Mac (hardware) address of the supplicant.
Entry format is HHHH.HHHH.HHHH (hexadecimal).
brief Brief summary of the supplicant state.
awplus#show auth supplicant brief
Interface port2.0.3
authenticationMethod: dot1x/mac/web
Two-Step Authentication
firstMethod: mac
secondMethod: dot1x/web
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0RADIUS Group Configuration
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status IP Address Username
=========== ==== ==== ============== ================= =============== ========
port2.0.3 1 W 001c.233e.e15a Authenticated 192.168.1.181 test
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1235
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH SUPPLICANT
Figure 34-5: Example output from show auth supplicant
Figure 34-6: Example output from show auth supplicant 0000.5E00.5301
awplus#show auth supplicant
Interface port2.0.3
authenticationMethod: dot1x/mac/web
Two-Step Authentication
firstMethod: mac
secondMethod: dot1x/web
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Supplicant name: test
Supplicant address: 0000.5E00.5301
authenticationMethod: WEB-based Authentication
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: mac
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: web
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 1
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 0
CD: adminControlledDirections: in - operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
RADIUS server group (auth): radius
RADIUS server (auth): 192.168.1.40
awplus#show auth supplicant 0000.5E00.5301
Interface port2.0.3
Supplicant name: test
Supplicant address: 0000.5E00.5301
authenticationMethod: WEB-based Authentication
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: mac
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: web
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 1
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 0
CD: adminControlledDirections: in - operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
RADIUS server group (auth): radius
RADIUS server (auth): 192.168.1.40

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1236
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH SUPPLICANT
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa authentication auth-mac
aaa authentication auth-web
aaa authentication dot1x

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1237
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH SUPPLICANT INTERFACE
show auth supplicant interface
Overview This command shows the supplicant (client device) state for the authentication
mode set for the interface, which may be a static channel (or static aggregator) or
a dynamic (or LACP) channel group or a switch port. Use the optional brief
parameter to show a summary of the supplicant state.
Syntax show auth-web supplicant interface <interface-list> [brief]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To display the authenticated supplicant on the interface port1.0.2, enter the
command:
awplus# show auth supplicant interface port1.0.2
To display brief summary output for the authenticated supplicant on the interface
port1.0.2, enter the command:
awplus# show auth supplicant interface port1.0.2 brief
Parameter Description
<interface-list> The interfaces or ports to configure. An interface-list can be:
•an interface (e.g. vlan2), a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6),
a static channel group (e.g. sa2) or a dynamic (LACP)
channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of interfaces, ports, static channel
groups or dynamic (LACP) channel groups separated by a
hyphen; e.g. vlan2-8, or port1.0.1-1.0.4, or sa1-2,
or po1-2
• a comma-separated list of the above; e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.4-1.0.6. Do not mix interface
types in a list
The specified interfaces must exist.
brief Brief summary of the supplicant state.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1238
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH TWO-STEP SUPPLICANT BRIEF
show auth two-step supplicant brief
Overview This command displays the supplicant state of the two-step authentication feature
on the interface.
Syntax show auth two-step supplicant [interface <ifrange>] brief
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Do not mix interface types in a list. The specified interfaces must exist.
Example To display the supplicant state of the two-step authentication feature, enter the
command:
awplus# show two-step supplicant interface port1.0.6 brief
Output Figure 34-7: Example output from show auth two-step supplicant brief
Related
Commands
auth two-step enable
Parameter Description
interface The interface selected for display.
<ifrange>The interface types which can be specified as <ifrange>
• Switch port (e.g. port1.0.6)
• Static channel group (e.g. sa3)
• Dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po4)
interface port1.0.6
authenticationMethod: dot1x/mac
Two-Step Authentication:
firstMethod:mac
secondMethod:dot1x
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Interface VID Mode MAC Address Status FirstStep SecondStep
========== === ==== =========== ====== ========= ==========
port1.0.6 1 D 000b..db67.00f7 Authenticated Pass Pass

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1239
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH-WEB-SERVER
show auth-web-server
Overview This command shows the Web-Authentication server configuration and status on
the switch.
Syntax show auth-web-server
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display Web-Authentication server configuration and status, enter the
command:
awplus# show auth-web-server
Output Figure 34-8: Example output from the show auth-web-server command
Related
Commands
auth-web-server ipaddress
auth-web-server port
auth-web-server redirect-delay-time
auth-web-server redirect-url
auth-web-server session-keep
auth-web-server ssl
Web authentication server
Server status: enabled
Server mode: none
Server address: 192.168.1.1/24
DHCP server enabled
DHCP lease time: 20
DHCP WPAD Option URL: http://192.168.1.1/proxy.pac
HTTP Port No: 80
Security: disabled
Certification: default
SSL Port No: 443
Redirect URL: --
Redirect Delay Time: 5
HTTP Redirect: enabled
Session keep: disabled
PingPolling: disabled
PingInterval: 30
Timeout: 1
FailCount: 5
ReauthTimerReFresh: disabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1240
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW AUTH-WEB-SERVER PAGE
show auth-web-server page
Overview This command displays the web-authentication page configuration and status.
Syntax show auth-web-server page
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To show the web-authentication page information, use the command:
awplus# show auth-web-server page
Figure 34-9: Example output from the show auth-web-server page command
Related
Commands
auth-web forward
auth-web-server page logo
auth-web-server page sub-title
auth-web-server page success-message
auth-web-server page title
auth-web-server page welcome-message
awplus#show auth-web-server page
Web authentication page
Logo: auto
Title: default
Sub-Title: Web Authentication
Welcome message: Your welcome message
Success message: Your success message
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1241
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AUTHENTICATION COMMANDS
SHOW PROXY-AUTOCONFIG-FILE
show proxy-autoconfig-file
Overview This command displays the contents of the proxy auto configuration (PAC) file.
Syntax show proxy-autoconfig-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the contents of the proxy auto configuration (PAC) file, enter the
command:
awplus# show auth proxy-autoconfig-file
Output Figure 34-10: Example output from show proxy-autoconfig-file
Related
Commands
copy proxy-autoconfig-file
erase proxy-autoconfig-file
function FindProxyForURL(url,host)
{
if (isPlainHostName(host) ||
isInNet(host, “192.168.1.0”,”255.255.255.0”)) {
return “DIRECT”;
}
else {
return “PROXY 192.168.110.1:8080”;
}
}

35
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1242
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for AAA commands for
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting. For more information, see the AAA
and Port_Authentication Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“aaa accounting auth-mac” on page 1244
•“aaa accounting auth-web” on page 1246
•“aaa accounting commands” on page 1248
•“aaa accounting dot1x” on page 1250
•“aaa accounting login” on page 1252
•“aaa accounting update” on page 1255
•“aaa authentication auth-mac” on page 1257
•“aaa authentication auth-web” on page 1259
•“aaa authentication dot1x” on page 1261
•“aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+” on page 1263
•“aaa authentication enable default local” on page 1265
•“aaa authentication login” on page 1266
•“aaa authorization commands” on page 1268
•“aaa authorization config-commands” on page 1270
•“aaa group server” on page 1271
•“aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time” on page 1273
•“aaa local authentication attempts max-fail” on page 1274
•“aaa login fail-delay” on page 1275
•“accounting login” on page 1276

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1243
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
•“authorization commands” on page 1277
•“clear aaa local user lockout” on page 1279
•“debug aaa” on page 1280
•“login authentication” on page 1281
•“proxy-port” on page 1282
•“radius-secure-proxy aaa” on page 1283
•“server (radsecproxy-aaa)” on page 1284
•“server mutual-authentication” on page 1286
•“server name-check” on page 1287
•“server trustpoint” on page 1288
•“show aaa local user locked” on page 1290
•“show aaa server group” on page 1291
•“show debugging aaa” on page 1292
•“show radius server group” on page 1293
•“undebug aaa” on page 1295

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1244
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING AUTH-MAC
aaa accounting auth-mac
Overview This command configures an accounting method list for MAC-based
authentication. An accounting method list specifies what type of accounting
messages are sent and which RADIUS servers the accounting messages are sent to.
Use this command to configure either the default method list, which is
automatically applied to interfaces with MAC-based authentication enabled, or a
named method list, which can be applied to an interface with the auth-mac
accounting command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
accounting method list for MAC-based authentication. Once all method lists are
disabled, AAA accounting for MAC-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa accounting auth-mac {default|<list-name>}
{start-stop|stop-only|none} group {<group-name>|radius}
no aaa accounting auth-mac {default|<list-name>}
Default RADIUS accounting for MAC-based Authentication is disabled by default
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default accounting method list
or a named accounting method list:
•default: the default accounting method list which is automatically applied
to all interfaces with MAC-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
auth-mac accounting command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
Parameter Description
default Configure the default accounting method list
<list-name>Configure a named accounting method list
start-stop Sends a start accounting message at the beginning of the session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
stop-only Only sends a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
none No accounting record sent.
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1245
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING AUTH-MAC
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
The accounting event to send to the RADIUS server is configured with the
following options:
•start-stop: sends a start accounting message at the beginning of a session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
•stop-only: sends a stop accounting message at the end of a session.
•none: disables accounting.
Examples To enable the default RADIUS accounting for MAC-based authentication, and use
all available RADIUS servers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting auth-mac default start-stop
group radius
To disable RADIUS accounting for MAC-based Authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting auth-mac default
To enable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for MAC-based
authentication, with the RADIUS server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting auth-mac vlan10_acct start-stop
group rad_group_vlan10
To disable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for MAC-based
authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting auth-mac vlan10_acct
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-mac
aaa group server
auth-mac accounting
auth-mac enable
radius-server host
show aaa server group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1246
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING AUTH-WEB
aaa accounting auth-web
Overview This command configures an accounting method list for Web-based
authentication. An accounting method list specifies what type of accounting
messages are sent and which RADIUS servers the accounting messages are sent to.
Use this command to configure either the default method list, which is
automatically applied to interfaces with Web-based authentication enabled, or a
named method list, which can be applied to an interface with the auth-web
accounting command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
accounting method list for Web-based authentication. Once all method lists are
disabled, AAA accounting for Web-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa accounting auth-web {default|<list-name>}
{start-stop|stop-only|none} group {<group-name>|radius}
no aaa accounting auth-web {default|<list-name>}
Default RADIUS accounting for Web-based authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default accounting method list
or a named accounting method list:
•default: the default accounting method list which is automatically applied
to all interfaces with Web-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
auth-web accounting command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
Parameter Description
default Configure the default accounting method list
<list-name>Configure a named accounting method list
start-stop Sends a start accounting message at the beginning of the session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
stop-only Only sends a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
none No accounting record sent.
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1247
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING AUTH-WEB
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
Configure the accounting event to be sent to the RADIUS server with the following
options:
•start-stop: sends a start accounting message at the beginning of a session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
•stop-only: sends a stop accounting message at the end of a session.
•none: disables accounting.
Examples To enable the default RADIUS accounting method for Web-based authentication,
and use all available RADIUS servers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting auth-web default start-stop
group radius
To disable the default RADIUS accounting method for Web-based authentication,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting auth-web default
To enable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for Web-based
authentication, with the RADIUS server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting auth-web vlan10_acct start-stop
group rad_group_vlan10
To disable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for Web-based
authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting auth-web vlan10_acct
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-web
aaa group server
auth-web accounting
auth-web enable
radius-server host
show aaa server group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1248
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING COMMANDS
aaa accounting commands
Overview This command configures and enables TACACS+ accounting on commands
entered at a specified privilege level. Once enabled for a privilege level, accounting
messages for commands entered at that privilege level will be sent to a TACACS+
server.
In order to account for all commands entered on a device, configure command
accounting for each privilege level separately.
The command accounting message includes, the command as entered, the date
and time the command finished executing, and the user-name of the user who
executed the command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable command accounting for a
specified privilege level.
Syntax aaa accounting commands <1-15> default stop-only group tacacs+
no aaa accounting commands <1-15> default
Default TACACS+ command accounting is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command only supports a default method list, this means that it is applied to
every console and VTY line.
The stop-only parameter indicates that the command accounting messages are
sent to the TACACS+ server when the commands have stopped executing.
The group tacacs+ parameters signifies that the command accounting messages
are sent to the TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server host command.
Note that up to four TACACS+ servers can be configured for accounting. The
servers are checked for reachability in the order they are configured with only the
first reachable server being used. If no server is found, the accounting message is
dropped.
Parameter Description
<1-15>The privilege level being configured, in the range 1 to 15.
default Use the default method list, this means the command is applied
globally to all user exec sessions.
stop-only Send accounting message when the commands have stopped
executing.
group Specify the server group where accounting messages are sent.
Only the tacacs+ group is available for this command.
tacacs+ Use all TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server host
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1249
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING COMMANDS
Command accounting cannot coexist with triggers. An error message is displayed
if you attempt to enable command accounting while a trigger is configured.
Likewise, an error message is displayed if you attempt to configure a trigger while
command accounting is configured.
Examples To configure command accounting for privilege levels 1, 7, and 15, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting commands 1 default stop-only
group tacacs+
awplus(config)# aaa accounting commands 7 default stop-only
group tacacs+
awplus(config)# aaa accounting commands 15 default stop-only
group tacacs+
To disable command accounting for privilege levels 1, 7, and 15, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting commands 1 default
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting commands 7 default
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting commands 15 default
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
aaa accounting login
accounting login
tacacs-server host

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1250
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING DOT1X
aaa accounting dot1x
Overview This command configures an accounting method list for IEEE 802.1X-based
authentication. An accounting method list specifies what type of accounting
messages are sent and which RADIUS servers the accounting messages are sent to.
Use this command to configure either the default method list, which is
automatically applied to interfaces with IEEE 802.1X-based authentication
enabled, or a named method list, which can be applied to an interface with the
dot1x accounting command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
accounting method list for 802.1X-based authentication. Once all method lists are
disabled, AAA accounting for 802.1x-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa accounting dot1x {default|<list-name>}
{start-stop|stop-only|none} group {<group-name>|radius}
no aaa accounting dot1x {default|<list-name>}
Default RADIUS accounting for 802.1X-based authentication is disabled by default (there
is no default server set by default).
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default accounting method list
or a named accounting method list:
•default: the default accounting method list which is automatically applied
to all interfaces with 802.1X-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
dot1x accounting command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages will be
sent:
Parameter Description
default Configure the default accounting method list
<list-name>Configure a named accounting method list
start-stop Sends a start accounting message at the beginning of the session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
stop-only Only sends a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
none No accounting record sent.
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1251
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING DOT1X
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command.
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command.
The accounting event to send to the RADIUS server is configured by the following
options:
•start-stop: sends a start accounting message at the beginning of a session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
•stop-only: sends a stop accounting message at the end of a session.
•none: disables accounting.
Examples To enable RADIUS accounting for 802.1X-based authentication, and use all
available RADIUS Servers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group
radius
To disable RADIUS accounting for 802.1X-based authentication, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting dot1x default
To enable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for 802.1X-based
authentication, with the RADIUS server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting dot1x vlan10_acct start-stop
group rad_group_vlan10
To disable a named RADIUS accounting method list 'vlan10_acct' for 802.1X-based
authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting dot1x vlan10_acct
Related
Commands
aaa accounting update
aaa authentication dot1x
aaa group server
dot1x accounting
dot1x port-control
radius-server host
show aaa server group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1252
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING LOGIN
aaa accounting login
Overview This command configures RADIUS and TACACS+ accounting for login shell
sessions. The specified method list name can be used by the accounting login
command in the Line Configuration mode. If the default parameter is specified,
then this creates a default method list that is applied to every console and VTY line,
unless another accounting method list is applied on that line.
Note that unlimited RADIUS servers and up to four TACACS+ servers can be
configured and consulted for accounting. The first server configured is regarded as
the primary server and if the primary server fails then the backup servers are
consulted in turn. A backup server is consulted if the primary server fails, i.e. is
unreachable.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an accounting method list for login
shell sessions configured by an aaa accounting login command. If the method list
being deleted is already applied to a console or VTY line, accounting on that line
will be disabled. If the default method list name is removed by this command, it will
disable accounting on every line that has the default accounting configuration.
Syntax aaa accounting login
{default|<list-name>}{start-stop|stop-only|none} {group
{radius|tacacs+|<group-name>}}
no aaa accounting login {default|<list-name>}
Default Accounting for login shell sessions is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Parameter Description
default Default accounting method list.
<list-name>Named accounting method list.
start-stop Start and stop records to be sent.
stop-only Stop records to be sent.
none No accounting record to be sent.
group Specify the servers or server group where accounting packets are
sent.
radius Use all RADIUS servers configured by the radius-server host
command.
tacacs+ Use all TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server host
command.
<group-name> Use the specified RADIUS server group, as configured by the aaa
group server command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1253
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING LOGIN
Usage This command enables you to define a named accounting method list. The items
that you define in the accounting options are:
• the types of accounting packets that will be sent
• the set of servers to which the accounting packets will be sent
You can define a default method list with the name default and any number of
other named method lists. The name of any method list that you define can then
be used as the <list-name> parameter in the accounting login command.
If the method list name already exists, the command will replace the existing
configuration with the new one.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius : use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
•group <group-name> : use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
There is one way to define servers where TACACS+ accounting messages are sent:
•group tacacs+ : use all TACACS+ servers configured by tacacs-server host
command
The accounting event to send to the RADIUS or TACACS+ server is configured with
the following options:
•start-stop : sends a start accounting message at the beginning of a session
and a stop accounting message at the end of the session.
•stop-only : sends a stop accounting message at the end of a session.
•none : disables accounting.
Examples To configure RADIUS accounting for login shell sessions, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting login default start-stop group
radius
To configure TACACS+ accounting for login shell sessions, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting login default start-stop group
tacacs+
To reset the configuration of the default accounting list, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting login default

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1254
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING LOGIN
Related
Commands
aaa accounting commands
aaa authentication login
aaa accounting login
aaa accounting update
accounting login
radius-server host
tacacs-server host
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1255
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING UPDATE
aaa accounting update
Overview This command enables periodic accounting reporting to either the RADIUS or
TACACS+ accounting server(s) wherever login accounting has been configured.
Note that unlimited RADIUS servers and up to four TACACS+ servers can be
configured and consulted for accounting. The first server configured is regarded as
the primary server and if the primary server fails then the backup servers are
consulted in turn. A backup server is consulted if the primary server fails, i.e. is
unreachable.
Use the no variant of this command to disable periodic accounting reporting to
the accounting server(s).
Syntax aaa accounting update [periodic <1-65535>]
no aaa accounting update
Default Periodic accounting update is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to enable the device to send periodic AAA login accounting
reports to the accounting server. When periodic accounting report is enabled,
interim accounting records are sent according to the interval specified by the
periodic parameter. The accounting updates are start messages.
If the no variant of this command is used to disable periodic accounting reporting,
any interval specified by the periodic parameter is reset to the default of 30
minutes when accounting reporting is reenabled, unless this interval is specified.
Examples To configure the switch to send period accounting updates every 30 minutes, the
default period, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting update
To configure the switch to send period accounting updates every 10 minutes, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa accounting update periodic 10
Parameter Description
periodic Send accounting records periodically.
<1-65535>The interval to send accounting updates (in minutes). The default is
30 minutes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1256
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA ACCOUNTING UPDATE
To disable periodic accounting update wherever accounting has been configured,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa accounting update
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa accounting login

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1257
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION AUTH-MAC
aaa authentication auth-mac
Overview This command enables MAC-based authentication globally and allows you to
enable either the default authentication method list (in this case, a list of RADIUS
servers), which is automatically applied to every interface running MAC-based
authentication, or a user named authentication method list, which is applied to an
interface with the auth-mac authentication command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
method list for MAC-based authentication. Once all method lists are disabled
MAC-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa authentication auth-mac {default|<list-name>} group
{<group-name>|radius}
no aaa authentication auth-mac {default|<list-name>}
Default MAC-based Port Authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default authentication method
list or a named authentication method list:
•default: the default authentication method list which is automatically
applied to all interfaces with Web-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
auth-web authentication command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
All configured RADIUS Servers are automatically members of the server group
radius. If a server is added to a named group <group-name>, it also remains a
member of the group radius.
Parameter Description
default Configure the default authentication method list
<list-name>Configure a named authentication method list
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1258
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION AUTH-MAC
Examples To enable MAC-based authentication globally for all RADIUS servers, and use all
available RADIUS servers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication auth-mac default group
radius
To disable MAC-based authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication auth-mac default
To enable MAC-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth', with RADIUS
server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication auth-mac vlan10_auth group
rad_group_vlan10
To disable MAC-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth', use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication auth-mac vlan10_acct
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa group server
auth-mac authentication
auth-mac enable
radius-server host
show aaa server group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1259
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION AUTH-WEB
aaa authentication auth-web
Overview This command enables Web-based authentication globally and allows you to
enable either the default authentication method list (in this case, a list of RADIUS
servers), which is automatically applied to every interface running Web-based
authentication, or a user named authentication method list, which is applied to an
interface with the auth-web authentication command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
method list for Web-based authentication. Once all method lists are disabled
Web-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa authentication auth-web {default|<list-name>} group
{<group-name>|radius}
no aaa authentication auth-web {default|<list-name>}
Default Web-based authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default authentication method
list or a named authentication method list:
•default: the default authentication method list which is automatically
applied to all interfaces with Web-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
auth-web authentication command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
Note that you need to configure an IPv4 address for the VLAN interface on which
Web authentication is running.
Parameter Description
default Configure the default authentication method list
<list-name>Configure a named authentication method list
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1260
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION AUTH-WEB
Examples To enable Web-based authentication globally for all RADIUS servers, and use all
available RADIUS servers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication auth-web default group
radius
To disable Web-based authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication auth-web default
To enable Web-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth', with RADIUS
server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication auth-web vlan10_auth group
rad_group_vlan10
To disable Web-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth', use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication vlan10_auth
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa group server
auth-web authentication
auth-web enable
radius-server host

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1261
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION DOT1X
aaa authentication dot1x
Overview This command enables IEEE 802.1X-based authentication globally and allows you
to enable either the default authentication method list (in this case, a list of RADIUS
servers), which is automatically applied to every interface running IEEE
802.1X-based authentication, or a user named authentication method list, which is
applied to an interface with the dot1x authentication command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable either the default or a named
method list for 802.1X-based authentication. Once all method lists are disabled
802.1x-based authentication is disabled globally.
Syntax aaa authentication dot1x {default|<list-name>} group
{<group-name>|radius}
no aaa authentication dot1x {default|<list-name>}
Default 802.1X-based Port Authentication is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command can be used to configure either the default authentication method
list or a named authentication method list:
•default: the default authentication method list which is automatically
applied to all interfaces with 802.1X-based authentication enabled.
•<list-name>: a user named list which can be applied to an interface using the
aaa authentication dot1x command.
There are two ways to define servers where RADIUS accounting messages are sent:
•group radius: use all RADIUS servers configured by radius-server host
command
•group <group-name>: use the specified RADIUS server group configured
with the aaa group server command
Examples To enable 802.1X-based authentication globally with all RADIUS servers, and use
all available RADIUS servers, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
Parameter Description
default Configure the default authentication method list
<list-name>Configure a named authentication method list
group Use a server group
<group-name>Server group name.
radius Use all RADIUS servers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1262
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION DOT1X
To disable 802.1X-based authentication, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication dot1x default
To enable 802.1X-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth', with RADIUS
server group 'rad_group_vlan10, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication dot1x vlan10_auth group
rad_group_vlan10
To disable 802.1X-based authentication for named list 'vlan10_auth use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication dot1x vlan10_acct
Related
Commands
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa group server
dot1x authentication
dot1x port-control
radius-server host
show aaa server group
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1263
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION ENABLE DEFAULT GROUP TACACS+
aaa authentication enable default group
tacacs+
Overview This command enables privilege level authentication against a TACACS+ server.
Use the no variant of this command to disable privilege level authentication.
Syntax aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ [local] [none]
no aaa authentication enable default
Default Local privilege level authentication is enabled by default (aaa authentication
enable default local command).
Mode Global Configuration
Usage A user is configured on a TACACS+ server with a maximum privilege level. When
they enter the enable (Privileged Exec mode) command they are prompted for an
enable password which is authenticated against the TACACS+ server. If the
password is correct and the specified privilege level is equal to or less than the
users maximum privilege level, then they are granted access to that level. If the
user attempts to access a privilege level that is higher than their maximum
configured privilege level, then the authentication session will fail and they will
remain at their current privilege level.
NOTE: If both local and none are specified, you must always specify local first.
If the TACACS+ server goes offline, or is not reachable during enable password
authentication, and command level authentication is configured as:
•aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+
then the user is never granted access to Privileged Exec mode.
•aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ local
then the user is authenticated using the locally configured enable password,
which if entered correctly grants the user access to Privileged Exec mode. If
no enable password is locally configured (enable password command),
then the enable authentication will fail until the TACACS+ server becomes
available again.
Parameter Description
local Use the locally configured enable password (enable password
command) for authentication.
none No authentication.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1264
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION ENABLE DEFAULT GROUP TACACS+
•aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ none
then the user is granted access to Privileged Exec mode with no
authentication. This is true even if a locally configured enable password is
configured.
•aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+ local none
then the user is authenticated using the locally configured enable password.
If no enable password is locally configured, then the enable authentication
will grant access to Privileged Exec mode with no authentication.
If the password for the user is not successfully authenticated by the server, then the
user is again prompted for an enable password when they enter enable via the CLI.
Examples To enable a privilege level authentication method that will not allow the user to
access Privileged Exec mode if the TACACS+ server goes offline, or is not reachable
during enable password authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+
To enable a privilege level authentication method that will allow the user to access
Privileged Exec mode if the TACACS+ server goes offline, or is not reachable during
enable password authentication, and a locally configured enable password is
configured, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+
local
To disable privilege level authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication enable default
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
aaa authentication enable default local
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable password
enable secret
tacacs-server host

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1265
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION ENABLE DEFAULT LOCAL
aaa authentication enable default local
Overview This command enables local privilege level authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to disable local privilege level authentication.
Syntax aaa authentication enable default local
no aaa authentication enable default
Default Local privilege level authentication is enabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The privilege level configured for a particular user in the local user database is the
privilege threshold above which the user is prompted for an enable (Privileged
Exec mode) command.
Examples To enable local privilege level authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication enable default local
To disable local privilege level authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication enable default
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
enable (Privileged Exec mode)
enable password
enable secret

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1266
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION LOGIN
aaa authentication login
Overview Use this command to create an ordered list of methods to use to authenticate user
login, or to replace an existing method list with the same name. Specify one or
more of the options local or group, in the order you want them to be applied. If
the default method list name is specified, it is applied to every console and VTY
line immediately unless another method list is applied to that line by the login
authentication command. To apply a non-default method list, you must also use
the login authentication command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an authentication method list for
user login. The specified method list name is deleted from the configuration. If the
method list name has been applied to any console or VTY line, user login
authentication on that line will fail.
Note that the no aaa authentication login default command does not remove
the default method list. This will return the default method list to its default state
(local is the default).
Syntax aaa authentication login {default|<list-name>} {[local] [group
{radius|tacacs+|<group-name>}]}
no aaa authentication login {default|<list-name>}
Default If the default server is not configured using this command, user login
authentication uses the local user database only.
If the default method list name is specified, it is applied to every console and VTY
line immediately unless a named method list server is applied to that line by the
loginauthentication command.
local is the default state for the default method list unless a named method list is
applied to that line by the login authentication command. Reset to the default
method list using the no aaa authentication login default command.
Mode Global Configuration
Parameter Description
default Set the default authentication server for user login.
<list-name>Name of authentication server.
local Use the local username database.
group Use server group.
radius Use all RADIUS servers configured by the radius-server
host command.
tacacs+ Use all TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server
host command.
<group-name>Use the specified RADIUS server group, as configured by
the aaa group server command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1267
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHENTICATION LOGIN
Usage When a user attempts to log in, the switch sends an authentication request to the
first authentication server in the method list. If the first server in the list is reachable
and it contains a username and password matching the authentication request,
the user is authenticated and the login succeeds. If the authentication server
denies the authentication request because of an incorrect username or password,
the user login fails. If the first server in the method list is unreachable, the switch
sends the request to the next server in the list, and so on.
For example, if the method list specifies group tacacs+ local, and a user attempts
to log in with a password that does not match a user entry in the first TACACS+
server, if this TACACS+ server denies the authentication request, then the switch
does not try any other TACACS+ servers not the local user database; the user login
fails.
Examples To configure the default authentication method list for user login to first use all
available RADIUS servers for user login authentication, and then use the local user
database, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication login default group radius
local
To configure a user login authentication method list called USERS to first use the
RADIUS server group RAD_GROUP1 for user login authentication, and then use the
local user database, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication login USERS group RAD_GROUP1
local
To configure a user login authentication method list called USERS to first use the
TACACS+ servers for user login authentication, and then use the local user
database, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authentication login USERS group tacacs+
local
To return to the default method list (local is the default server), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication login default
To delete an existing authentication method list USERS created for user login
authentication, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authentication login USERS
Related
Commands
aaa accounting commands
aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+
login authentication

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1268
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
aaa authorization commands
Overview This command configures a method list for commands authorization that can be
applied to console or VTY lines. When command authorization is enabled for a
privilege level, only authorized users can executed commands in that privilege
level.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a named method list or disable the
default method list for a privilege level.
Syntax aaa authorization commands <privilege-level>
{default|<list-name>} group tacac+ [none]
no aaa authorization commands <privilege-level>
{default|<list-name>}
Mode Global Configuration
Usage TACACS+ command authorization provides centralized control of the commands
available to a user of an AlliedWare Plus device. Once enabled:
• The command string and username are encrypted and sent to the first
available configured TACACS+ server (the first server configured) for
authorization.
Parameter Description
<privilege-level> The privilege level of the set of commands the method list
will be applied to.
AlliedWare Plus defines three sets of commands, that are
indexed by a level value:
Level = 1: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level between 1 and 6 inclusive
Level = 7: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level between 7 and 14 inclusive
Level = 15: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level 15
group Specify the server group where authorization messages are
sent. Only the tacacs+ group is available for this
command.
tacac+ Use all TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server
host command.
default Configure the default authorization commands method list.
<list-name>Configure a named authorization commands method list
none If specified, this provides a local fallback to command
authorization so that if authorization servers become
unavailable then the device will accept all commands
normally allowed for the privilege level of the user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1269
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
• The TACACS+ server decides if the user is authorized to execute the
command and returns the decision to the AlliedWare Plus device.
• Depending on this decision the device will then either execute the
command or notify the user that authorization has failed.
If multiple TACACS+ servers are configured, and the first server is unreachable or
does not respond, the other servers will be queried, in turn, for an authorization
decision. If all servers are unreachable and a local fallback has been configured,
with the none parameter, then commands are authorized based on the user’s
privilege level; the same behavior as if command authorization had not been
configured. If, however, the local fallback is not configured and all servers become
unreachable then all commands except logout, exit, and quit will be denied.
The default method list is defined with a local fallback unless configured
differently using this command.
Example To configure a commands authorization method list, named TAC15, using all
TACACS+ servers to authorize commands for privilege level 15, with a local
fallback, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization commands 15 TAC15 group
tacacs+ none
To configure the default method list to authorize commands for privilege level 7,
with no local fallback, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization commands 7 default group
tacacs+
To remove the authorization method list TAC15, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authorization commands 15 TAC15
Related
Commands
aaa authorization config-commands
authorization commands
tacacs-server host
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1270
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION CONFIG-COMMANDS
aaa authorization config-commands
Overview Use this command to enable command authorization on configuration mode
commands. By default, command authorization applies to commands in exec
mode only.
Use the no variant of this command to disable command authorization on
configuration mode commands.
Syntax aaa authorization config-commands
no aaa authorization config-commands
Default By default, command authorization is disabled on configuration mode commands.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If authorization of configuration mode commands is not enabled then all
configuration commands are accepted by default, including command
authorization commands.
NOTE: Authorization of configuration commands is required for a secure TACACS+
command authorization configuration as it prevents the feature from being disabled
to gain access to unauthorized exec mode commands.
Example To enable command authorization for configuration mode commands, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization config-commands
To disable command authorization for configuration mode commands, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authorization config-commands
Related
Commands
aaa authorization commands
authorization commands
tacacs-server host
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1271
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA GROUP SERVER
aaa group server
Overview This command configures a RADIUS server group. A server group can be used to
specify a subset of RADIUS servers in aaa commands. The group name radius is
predefined, which includes all RADIUS servers configured by the radius-server
host command.
RADIUS servers are added to a server group using the server command. Each
RADIUS server should be configured using the radius-server host command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an existing RADIUS server group.
Syntax aaa group server radius <group-name>
no aaa group server radius <group-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to create an AAA group of RADIUS servers, and to enter Server
Group Configuration mode, in which you can add servers to the group. Use a server
group to specify a subset of RADIUS servers in AAA commands. Each RADIUS server
must be configured by the radius-server host command. To add RADIUS servers
to a server group, use the server command.
Examples To create a RADIUS server group named GROUP1 with hosts 192.168.1.1,
192.168.2.1 and 192.168.3.1, use the commands:
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius GROUP1
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.1.1 auth-port 1812 acct-port
1813
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.2.1 auth-port 1812 acct-port
1813
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.3.1 auth-port 1812 acct-port
1813
To remove a RADIUS server group named GROUP1 from the configuration, use the
command:
awplus(config)# no aaa group server radius GROUP1
Parameter Description
<group-name>Server group name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1272
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA GROUP SERVER
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa accounting login
aaa authentication auth-mac
aaa authentication auth-web
aaa authentication dot1x
aaa authentication login
radius-server host
server (server group)
show radius server group

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1273
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA LOCAL AUTHENTICATION ATTEMPTS LOCKOUT-TIME
aaa local authentication attempts
lockout-time
Overview This command configures the duration of the user lockout period.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the duration of the user lockout
period to its default of 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Syntax aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time <lockout-tiime>
no aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
Mode Global Configuration
Default The default for the lockout-time is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Usage While locked out all attempts to login with the locked account will fail. The lockout
can be manually cleared by another privileged account using the clear aaa local
user lockout command.
Examples To configure the lockout period to 10 minutes (600 seconds), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
600
To restore the default lockout period of 5 minutes (300 seconds), use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa local authentication attempts
lockout-time
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Parameter Description
<lockout-time><0-10000>. Time in seconds to lockout the user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1274
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA LOCAL AUTHENTICATION ATTEMPTS MAX-FAIL
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Overview This command configures the maximum number of failed login attempts before a
user account is locked out. Every time a login attempt fails the failed login counter
is incremented.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the maximum number of failed
login attempts to the default setting (five failed login attempts).
Syntax aaa local authentication attempts max-fail <failed-logins>
no aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Mode Global Configuration
Default The default for the maximum number of failed login attempts is five failed login
attempts.
Usage When the failed login counter reaches the limit configured by this command that
user account is locked out for a specified duration configured by the aaa local
authentication attempts lockout-time command.
When a successful login occurs the failed login counter is reset to 0. When a user
account is locked out all attempts to login using that user account will fail.
Examples To configure the number of login failures that will lock out a user account to two
login attempts, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa local authentication attempts max-fail 2
To restore the number of login failures that will lock out a user account to the
default number of login attempts (five login attempts), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
clear aaa local user lockout
Parameter Description
<failed-logins><1-32>. Number of login failures allowed before locking out a
user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1275
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AAA LOGIN FAIL-DELAY
aaa login fail-delay
Overview Use this command to configure the minimum time period between failed login
attempts. This setting applies to login attempts via the console, SSH and Telnet.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the minimum time period to its default
value.
Syntax aaa login fail-delay <1-10>
no aaa login fail-delay
Default 1 second
Mode Global configuration
Example To apply a delay of at least 5 seconds between login attempts, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa login fail-delay 5
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
clear aaa local user lockout
Parameter Description
<1-10> The minimum number of seconds required between login
attempts

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1276
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
ACCOUNTING LOGIN
accounting login
Overview This command applies a login accounting method list to console or VTY lines for
user login. When login accounting is enabled using this command, logging events
generate an accounting record to the accounting server.
The accounting method list must be configured first using this command. If an
accounting method list is specified that has not been created by this command
then accounting will be disabled on the specified lines.
The no variant of this command resets AAA Accounting applied to console or VTY
lines for local or remote login. default login accounting is applied after issuing the
no accounting login command. Accounting is disabled with default.
Syntax accounting login {default|<list-name>}
no accounting login
Default By default login accounting is disabled in the default accounting server. No
accounting will be performed until accounting is enabled using this command.
Mode Line Configuration
Examples To apply the accounting server USERS to all VTY lines, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 32
awplus(config-line)# accounting login USERS
To reset accounting for login sessions on the console, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# no accounting login
Related
Commands
aaa accounting commands
aaa accounting login
Parameter Description
default Default accounting method list.
<list-name>Named accounting method list.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1277
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
authorization commands
Overview This command applies a command authorization method list, defined using the
aaa authorization commands command, to console and VTY lines.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the command authorization
configuration on the console and VTY lines.
Syntax authorization commands <privilege-level> {default|<list-name>}
no authorization commands <privilege-level>
Default The default method list is applied to each console and VTY line by default.
Mode Line Configuration
Usage If the specified method list does not exist users will not be enable to execute any
commands in the specified method list on the specified VTY lines.
Example To apply the TAC15 command authorization method list with privilege level 15 to
VTY lines 0 to 5, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# authorization commands 15 TAC15
To reset the command authorization configuration with privilege level 15 on VTY
lines 0 to 5, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# no authorization commands 15
Related
Commands
aaa authorization commands
Parameter Description
<privilege-level> The privilege level of the set of commands the method list
will be applied to.
AlliedWare Plus defines three sets of commands, that are
indexed by a level value:
Level = 1: All commands that can be accessed by a user with
privilege level between 1 and 6 inclusive
Level = 7: All commands that can be accessed by a user with
privilege level between 7 and 14 inclusive
Level = 15: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level 15
default Configure the default authorization commands method list.
<list-name>Configure a named authorization commands method list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1279
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
CLEAR AAA LOCAL USER LOCKOUT
clear aaa local user lockout
Overview Use this command to clear the lockout on a specific user account or all user
accounts.
Syntax clear aaa local user lockout {username <username>|all}
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To unlock the user account ‘bob’ use the following command:
awplus# clear aaa local user lockout username bob
To unlock all user accounts use the following command:
awplus# clear aaa local user lockout all
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
Parameter Description
username Clear lockout for the specified user.
<username> Specifies the user account.
all Clear lockout for all user accounts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1280
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
DEBUG AAA
debug aaa
Overview This command enables AAA debugging.
Use the no variant of this command to disable AAA debugging.
Syntax debug aaa [accounting|all|authentication|authorization]
no debug aaa [accounting|all|authentication|authorization]
Default AAA debugging is disabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To enable authentication debugging for AAA, use the command:
awplus# debug aaa authentication
To disable authentication debugging for AAA, use the command:
awplus# no debug aaa authentication
Related
Commands
show debugging aaa
undebug aaa
Parameter Description
accounting Accounting debugging.
all All debugging options are enabled.
authentication Authentication debugging.
authorization Authorization debugging.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1281
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
LOGIN AUTHENTICATION
login authentication
Overview Use this command to apply an AAA server for authenticating user login attempts
from a console or remote logins on these console or VTY lines. The authentication
method list must be specified by the aaa authentication login command. If the
method list has not been configured by the aaa authentication login command,
login authentication will fail on these lines.
Use the no variant of this command to reset AAA Authentication configuration to
use the default method list for login authentication on these console or VTY lines.
Command
Syntax login authentication {default|<list-name>}
no login authentication
Default The default login authentication method list, as specified by the aaa
authentication login command, is used to authenticate user login. If this has not
been specified, the default is to use the local user database.
Mode Line Configuration
Examples To apply the authentication method list called CONSOLE to the console port
terminal line (asyn 0), use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line console 0
awplus(config-line)# login authentication CONSOLE
To reset user authentication configuration on all VTY lines, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 32
awplus(config-line)# no login authentication
Related
Commands
aaa authentication login
line
Parameter Description
default The default authentication method list. If the default method
list has not been configured by the aaa authentication login
command, the local user database is used for user login
authentication.
<list-name> Named authentication server.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1282
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
PROXY-PORT
proxy-port
Overview Use this command to change the local UDP port used for communication between
local RADIUS client applications and the RadSecProxy AAA application. Any
unused UDP port may be selected. The default port is 1645.
Use the no variant of this command to change the UDP port back to the default of
1645.
Syntax proxy-port <port>
no proxy-port
Default The default port is 1645.
Mode RadSecProxy AAA Configuration Mode
Usage It is not necessary to change the value from the default unless UDP port 1645 is
required for another purpose.RADIUS requests received on this port from external
devices will be ignored. The port is only used for local (intra-device)
communication.
Example To configure change the UDP port to 7001, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# proxy-port 7001
Related
Commands
radius-secure-proxy aaa
server (radsecproxy-aaa)
server name-check
server trustpoint
Parameter Description
<port> UDP Port Number, 1-65536.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1283
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
RADIUS-SECURE-PROXY AAA
radius-secure-proxy aaa
Overview Use this command to enter the RadSecProxy AAA (authentication, authorization,
and accounting) application configuration mode. This application allows local
RADIUS-based clients on system to communicate with remote RadSec servers via
a secure (TLS) proxy.
Syntax radius-secure-proxy aaa
Mode Global Configuration Mode
Example To change mode from User Exec mode to the RadSecProxy AAA configuration
mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)#
Related
Commands
proxy-port
server (radsecproxy-aaa)
server name-check
server trustpoint

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1284
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SERVER (RADSECPROXY-AAA)
server (radsecproxy-aaa)
Overview Use this command to add a server to the RadSecProxy AAA application. Local
RADIUS client applications will attempt, via the proxy, to communicate with any
RadSec servers that are operational (in addition to any non-TLS RADIUS servers
that are configured).
Use the no variant of this command to delete a previously-configured server from
the RadSecProxy AAA application.
Syntax server {<hostname>|<ip-addr>} [timeout <1-1000>] [name-check
{on|off}]
no server {<hostname>|<ip-addr>}
Mode RadSecProxy AAA Configuration Mode
Usage The server may be specified by its domain name or by its IPv4 address. If a domain
name is used, it must be resolvable using a configured DNS name server.
Each server may be configured with a timeout; if not specified, the global timeout
value for RADIUS servers will be used. The global timeout may be changed using
the radius-server timeout command. The default global timeout is 5 seconds.
Each server may be configured to use certificate name-checking; if not specified,
the global behavior defined by server name-check or no server name-check will
be used. If name checking is enabled, the Common Name portion of the subject
field of the server’s X.509 certificate must match the domain name or IP address
specified in this command.
Parameter Description
<hostname>Hostname of RadSec server
<ip-addr>Specify the client IPv4 address, in dotted decimal notation
(A.B.C.D).
timeout Specify the amount of time that the RadSecProxy AAA application
should wait for replies from this server. RADIUS server timeout
(which defaults to 5 seconds).
<1-1000> Time in seconds to wait for a server reply.
name-check Specify whether or not to enforce certificate name checking for
this client. If the parameter is not specified then the global
behavior, which defaults to on, is used.
on Enable name checking for this client.
off Disable name checking for this client.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1285
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SERVER (RADSECPROXY-AAA)
Example To add a server ‘mynas.local’ with a timeout of 3 seconds, and name checking off,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# server mynas.local name-check
off
Related
Commands
proxy-port
radius-secure-proxy aaa
server name-check
server trustpoint

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1286
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SERVER MUTUAL-AUTHENTICATION
server mutual-authentication
Overview This command enables or disables mutual certificate authentication for all
RadSecProxy servers. When enabled, the RadSecProxy AAA application will send a
local X.509 certificate to the server when establishing a TLS connection.
Use the no variant of this command to disable mutual certificate validation
causing the RadSecProxy AAA application to not transmit a certificate to the server.
NOTE: If mutual authentication is disabled on the client (AAA) application but enabled
on the server, a connection will not be established.
Syntax server mutual-authentication
no server mutual-authentication
Default Mutual authentication is enabled by default.
Mode RadSecProxy AAA Configuration Mode
Example Disable mutual certificate validation with the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# no server
mutual-authentication
Related
Commands
radius-secure-proxy aaa
server name-check
server (radsecproxy-aaa)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1287
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SERVER NAME-CHECK
server name-check
Overview This command sets the global behavior for certificate name-checking for the
RadSecProxy AAA application to on. This behavior will be used for all servers
associated with the application that do not specify a behavior on a per-server basis.
If name-checking is enabled, the Common Name portion of the subject field of the
client’s X.509 certificate must match the domain name or IP address specified in
the server (radsecproxy-aaa) command.
Use the no variant of this command to set the global behavior for certificate name
checking to off
Syntax server name-check
no server name-check
Default Certificate name checking is on by default.
Mode RadSecProxy AAA Configuration Mode
Example Disable certificate name checking globally with the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# no server name-check
Related
Commands
proxy-port
radius-secure-proxy aaa
server (radsecproxy-aaa)
server trustpoint
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1288
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SERVER TRUSTPOINT
server trustpoint
Overview This command adds one or more trustpoints to be used with the RadSecProxy AAA
application. Multiple trustpoints may be specified, or the command may be
executed more than once, to add multiple trustpoints to the application.
The no version of this command removes one or more trustpoints from the list of
trustpoints associated with the application.
Syntax server trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
no server trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
Default By default, no trustpoints are associated with the application.
Mode RadSecProxy AAA Configuration Mode
Usage The device certificate associated with first trustpoint added to the application will
be transmitted to remote servers. The certificate received from the remote server
must have an issuer chain that terminates with the root CA certificate for any of the
trustpoints that are associated with the application.
If no trustpoints are specified in the command, the trustpoint list will be
unchanged.
If no server trustpoint is issued without specifying any trustpoints, then all
trustpoints will be disassociated from the application.
Example You can add multiple trustpoints to the RadSecProxy AAA application by
executing the command multiple times:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy aaa
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# server trustpoint example_1
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# server trustpoint example_2
Alternatively, add multiple trustpoints with a single command:
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# server trustpoint example_3
example_4
Disassociate all trustpoints from the RadSecProxy AAA application using the
command:
awplus(config-radsecproxy-aaa)# no server trustpoint
Related
Commands
proxy-port
radius-secure-proxy aaa
Parameter Description
<trustpoint-list> Specify one or more trustpoints to be added or deleted.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1290
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SHOW AAA LOCAL USER LOCKED
show aaa local user locked
Overview This command displays the current number of failed attempts, last failure time and
location against each user account attempting to log into the device.
Note that once the lockout count has been manually cleared by another privileged
account using the clear aaa local user lockout command or a locked account
successfully logs into the system after waiting for the lockout time, this command
will display nothing for that particular account.
Syntax show aaa local user locked
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current failed attempts for local users, use the command:
awplus# show aaa local user locked
Output Figure 35-1: Example output from the show aaa local user locked command
Related
Commands
aaa local authentication attempts lockout-time
aaa local authentication attempts max-fail
clear aaa local user lockout
awplus# show aaa local user locked
Login Failures Latest failure From
bob 3 05/23/14 16:21:37 ttyS0
manager 5 05/23/14 16:31:44 192.168.1.200

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1291
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SHOW AAA SERVER GROUP
show aaa server group
Overview Use this command to list AAA users and any method lists applied to them.
Syntax show aaa server group
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show the AAA configuration on a device, use the command:
awplus# aaa server group
Output Figure 35-2: Example output from aaa server group
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa authentication auth-web
aaa authentication dot1x
awplus#show aaa server group
User List Name Method Acct-Event
======== ==== ============= ================ ======= ==========
login auth default - local -
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
login acct - - - -
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
dot1x auth default radius group -
dot1x auth vlan30_auth rad_group_1 group -
dot1x auth vlan40_auth rad_group_2 group -
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
dot1x acct vlan30_acct rad_group_4 group start-stop
dot1x acct vlan40_acct rad_group_5 group start-stop
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
auth-mac auth default radius group -
auth-mac auth vlan10_auth rad_group_vlan10 group -
auth-mac auth vlan20_auth rad_group_vlan20 group -
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
auth-mac acct vlan10_acct rad_group_vlan10 group start-stop
auth-mac acct vlan20_acct rad_group_vlan20 group start-stop
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
auth-web auth default radius group -
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
auth-web acct default rad_group_3 group start-stop
-------- ---- ------------- ---------------- ------- ----------
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1292
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING AAA
show debugging aaa
Overview This command displays the current debugging status for AAA (Authentication,
Authorization, Accounting).
Syntax show debugging aaa
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current debugging status of AAA, use the command:
awplus# show debug aaa
Output Figure 35-3: Example output from the show debug aaa command
AAA debugging status:
Authentication debugging is on
Accounting debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1293
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS SERVER GROUP
show radius server group
Overview Use this command to show the RADIUS server group configuration.
Syntax show radius server group [<group-name>]
Default Command name is set to something by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command with the <group-name> parameter to display information for a
specific RADIUS server group, or without the parameter to display information for
all RADIUS server groups.
Example To display information for all RADIUS server groups, use the command:
awplus# show radius server group
To display a information for a RADIUS server group named ‘rad_group_list1’, use
the command:
awplus# show radius server group rad_group_list1
Output Figure 35-4: Example output from show radius server group
Parameter Description
<group-name>RADIUS server group name.
awplus#show radius server group
RADIUS Group Configuration
Group Name : radius?
Server Host/ Auth Acct Auth Acct
IP Address Port Port Status Status
------------------------------------------
192.168.1.101 1812 1813 Active Active
192.168.1.102 1812 1813 Active Active
Group Name : rad_group_list1
Server Host/ Auth Acct Auth Acct
IP Address Port Port Status Status
------------------------------------------
192.168.1.101 1812 1813 Active Active
Group Name : rad_group_list2
Server Host/ Auth Acct Auth Acct
IP Address Port Port Status Status
------------------------------------------
192.168.1.102 1812 1813 Active Active

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1294
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
AAA COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS SERVER GROUP
Figure 35-5: Example output from show radius server group rad_group_list1
Related
Commands
aaa group server
awplus#show radius server group rad_group_list1
RADIUS Group Configuration
Group Name : rad_group_list1
Server Host/ Auth Acct Auth Acct
IP Address Port Port Status Status
------------------------------------------
192.168.1.101 1812 1813 Active Active

36
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1296
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
the device to use RADIUS servers. For more information, see the RADIUS Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“auth radius send nas-identifier” on page 1297
•“auth radius send service-type” on page 1298
•“deadtime (RADIUS server group)” on page 1299
•“debug radius” on page 1300
•“ip radius source-interface” on page 1301
•“radius-server deadtime” on page 1302
•“radius-server host” on page 1303
•“radius-server key” on page 1306
•“radius-server retransmit” on page 1307
•“radius-server timeout” on page 1309
•“server (server group)” on page 1311
•“show debugging radius” on page 1313
•“show radius” on page 1314
•“show radius statistics” on page 1317
•“undebug radius” on page 1318
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1297
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
AUTH RADIUS SEND NAS-IDENTIFIER
auth radius send nas-identifier
Overview Use this command to enable the device to include the NAS-Identifier(32) attribute
in RADIUS authentication requests.
Use the no variant of this command to stop including the NAS-Identifier attribute.
Syntax auth radius send nas-identifier [<name>|vlan-id]
no auth radius send nas-identifier
Mode Global Configuration
Example To use a user-defined identifier of NASID100 as the NAS-Identifier attribute, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth radius send nas-identifier NASID100
To use the VLAN ID as the NAS-Identifier attribute, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth radius send nas-identifier vlan-id
To stop sending the NAS-Identifier attribute, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no auth radius send nas-identifier
Related
Commands
auth radius send service-type
Parameter Description
<name> Send this user-defined text as the NAS-Identifier. You can specify
up to 253 characters.
vlan-id Send the VLAN ID of the authentication port as the NAS-Identifier.
This is the configured VLAN ID, not the dynamic VLAN ID or guest
VLAN ID.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1298
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
AUTH RADIUS SEND SERVICE-TYPE
auth radius send service-type
Overview Use this command to enable the device to include the Service-Type(6) attribute in
RADIUS authentication requests. The Service-Type attribute has a value of:
• Framed(2) for 802.1x
• Call-Check(10) for MAC authentication
• Unbound(5) for Web authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to stop including the Service-Type attribute.
Syntax auth radius send service-type
no auth radius send service-type
Mode Global Configuration
Example To send the Service-Type attribute, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# auth radius send service-type
Related
Commands
auth radius send nas-identifier

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1299
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
DEADTIME (RADIUS SERVER GROUP)
deadtime (RADIUS server group)
Overview Use this command to configure the deadtime parameter for the RADIUS server
group. This command overrides the global dead-time configured by the
radius-server deadtime command. The configured deadtime is the time period in
minutes to skip a RADIUS server for authentication or accounting requests if the
server is “dead”. Note that a RADIUS server is considered “dead” if there is no
response from the server within a defined time period.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the deadtime configured for the
RADIUS server group. If the global deadtime for RADIUS server is configured the
value will be used for the servers in the group. The global deadtime for the RADIUS
server is set to 0 minutes by default.
Syntax deadtime <0-1440>
no deadtime
Default The deadtime is set to 0 minutes by default.
Mode Server Group Configuration
Usage If the RADIUS server does not respond to a request packet, the packet is
retransmitted the number of times configured for the retransmit parameter (after
waiting for a timeout period to expire). The server is then marked “dead”, and the
time is recorded. The deadtime parameter configures the amount of time to skip
a dead server; if a server is dead, no request message is sent to the server for the
deadtime period.
Examples To configure the deadtime for 5 minutes for the RADIUS server group “GROUP1”,
use the command:
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius GROUP1
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.1.1
awplus(config-sg)# deadtime 5
To remove the deadtime configured for the RADIUS server group “GROUP1”, use
the command:
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius GROUP1
awplus(config-sg)# no deadtime
Related
Commands
aaa group server
radius-server deadtime
Parameter Description
<0-1440>Amount of time in minutes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1300
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
DEBUG RADIUS
debug radius
Overview This command enables RADIUS debugging. If no option is specified, all debugging
options are enabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable RADIUS debugging. If no option is
specified, all debugging options are disabled.
Syntax debug radius [packet|event|all]
no debug radius [packet|event|all]
Default RADIUS debugging is disabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To enable debugging for RADIUS packets, use the command:
awplus# debug radius packet
To enable debugging for RADIUS events, use the command:
awplus# debug radius event
To disable debugging for RADIUS packets, use the command:
awplus# no debug radius packet
To disable debugging for RADIUS events, use the command:
awplus# no debug radius event
Related
Commands
show debugging radius
undebug radius
Parameter Description
packet Debugging for RADIUS packets is enabled or disabled.
event Debugging for RADIUS events is enabled or disabled.
all Enable or disable all debugging options.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1301
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
IP RADIUS SOURCE-INTERFACE
ip radius source-interface
Overview This command configures the source IP address of every outgoing RADIUS packet
to use a specific IP address or the IP address of a specific interface. If the specified
interface is down or there is no IP address on the interface, then the source IP
address of outgoing RADIUS packets depends on the interface the packets leave.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the source interface configuration.
The source IP address in outgoing RADIUS packets will be the IP address of the
interface from which the packets are sent.
Syntax ip radius source-interface {<interface>|<ip-address>}
no ip radius source-interface
Default Source IP address of outgoing RADIUS packets depends on the interface the
packets leave.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure all outgoing RADIUS packets to use the IP address of the interface
“vlan1” for the source IP address, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip radius source-interface vlan1
To configure the source IP address of all outgoing RADIUS packets to use
192.168.1.10, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip radius source-interface 192.168.1.10
To reset the source interface configuration for all outgoing RADIUS packets, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip radius source-interface
Related
Commands
radius-server host
show radius statistics
Parameter Description
<interface> Interface name.
<ip-address> IP address in the dotted decimal format A.B.C.D.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1302
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER DEADTIME
radius-server deadtime
Overview Use this command to specify the global deadtime for all RADIUS servers. If a
RADIUS server is considered dead, it is skipped for the specified deadtime. This
command specifies for how many minutes a RADIUS server that is not responding
to authentication requests is passed over by requests for RADIUS authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the global deadtime to the default of
0 seconds, so that RADIUS servers are not skipped even if they are dead.
Syntax radius-server deadtime <minutes>
no radius-server deadtime
Default The default RADIUS deadtime configured on the system is 0 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The RADIUS client considers a RADIUS server to be dead if it fails to respond to a
request after it has been retransmitted as often as specified globally by the
radius-server retransmit command or for the server by the radius-server host
command. To improve RADIUS response times when some servers may be
unavailable, set a deadtime to skip dead servers.
Examples To set the dead time of the RADIUS server to 60 minutes, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server deadtime 60
To disable the dead time of the RADIUS server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server deadtime
Related
Commands
deadtime (RADIUS server group)
radius-server host
radius-server retransmit
show radius statistics
Parameter Description
<minutes> RADIUS server deadtime in minutes in the range 0 to 1440 (24 hours).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1303
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER HOST
radius-server host
Overview Use this command to specify a remote RADIUS server host for authentication or
accounting, and to set server-specific parameters. The parameters specified with
this command override the corresponding global parameters for RADIUS servers.
This command specifies the IP address or host name of the remote RADIUS server
host and assigns authentication and accounting destination UDP port numbers.
This command adds the RADIUS server address and sets parameters to the RADIUS
server. The RADIUS server is added to the running configuration after you issue this
command. If parameters are not set using this command then common system
settings are applied.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified server host as a
RADIUS authentication and/or accounting server and set the destination port to
the default RADIUS server port number (1812).
Syntax radius-server host {<host-name>|<ip-address>} [acct-port
<0-65535>] [auth-port <0-65535>] [key <key-string>] [retransmit
<0-100>] [timeout <1-1000>]
no radius-server host {<host-name>|<ip-address>} [acct-port
<0-65535>] [auth-port <0-65535>]
Parameter Description
<host-name> Server host name. The DNS name of the RADIUS server host.
<ip-address> The IP address of the RADIUS server host.
acct-port Accounting port. Specifies the UDP destination port for RADIUS
accounting requests. If 0 is specified, the server is not used for
accounting. The default UDP port for accounting is 1813.
<0-65535>UDP port number
(Accounting port number is set to 1813 by default)
Specifies the UDP destination port for RADIUS accounting
requests. If 0 is specified, the host is not used for accounting.
auth-port Authentication port. Specifies the UDP destination port for
RADIUS authentication requests. If 0 is specified, the server is not
used for authentication. The default UDP port for authentication
is 1812.
<0-65535>UDP port number
(Authentication port number is set to 1812 by default)
Specifies the UDP destination port for RADIUS authentication
requests. If 0 is specified, the host is not used for authentication.
timeout Specifies the amount of time to wait for a response from the
server. If this parameter is not specified the global value
configured by the radius-server timeout command is used.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1304
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER HOST
Default The RADIUS client address is not configured (null) by default. No RADIUS server is
configured.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Multiple radius -server host commands can be used to specify multiple hosts. The
software searches for hosts in the order they are specified. If no host-specific
timeout, retransmit, or key values are specified, the global values apply to that
host. If there are multiple RADIUS servers for this client, use this command multiple
times—once to specify each server.
If you specify a host without specifying the auth port or the acct port, it will by
default be configured for both authentication and accounting, using the default
UDP ports. To set a host to be a RADIUS server for authentication requests only, set
the acct-port parameter to 0; to set the host to be a RADIUS server for accounting
requests only, set the auth-port parameter to 0.
A RADIUS server is identified by IP address, authentication port and accounting
port. A single host can be configured multiple times with different authentication
or accounting ports. All the RADIUS servers configured with this command are
<1-1000>Time in seconds to wait for a server reply
(timeout is set to 5 seconds by default)
The time interval (in seconds) to wait for the RADIUS server to
reply before retransmitting a request or considering the server
dead. This setting overrides the global value set by the radius-
server timeout command.
If no timeout value is specified for this server, the global value is
used.
retransmit Specifies the number of retries before skip to the next server. If
this parameter is not specified the global value configured by the
radius-server retransmit command is used.
<0-100>Maximum number of retries
(maximum number of retries is set to 3 by default)
The maximum number of times to resend a RADIUS request to
the server, if it does not respond within the timeout interval,
before considering it dead and skipping to the next RADIUS
server. This setting overrides the global setting of the radius-
server retransmit command.
If no retransmit value is specified, the global value is used.
key Set shared secret key with RADIUS servers
<key-string> Shared key string applied
Specifies the shared secret authentication or encryption key for
all RADIUS communications between this device and the RADIUS
server. This key must match the encryption used on the RADIUS
daemon. All leading spaces are ignored, but spaces within and at
the end of the string are used. If spaces are used in the string, do
not enclose the string in quotation marks unless the quotation
marks themselves are part of the key. This setting overrides the
global setting of the radius-server key c ommand. If no key
value is specified, the global value is used.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1305
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER HOST
included in the predefined RADIUS server group radius, which may be used by AAA
authentication, authorization and accounting commands. The client transmits
(and retransmits, according to the retransmit and timeout parameters) RADIUS
authentication or accounting requests to the servers in the order you specify them,
until it gets a response.
Examples To add the RADIUS server 10.0.0.20, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server host 10.0.0.20
To set the secret key to allied on the RADIUS server 10.0.0.20, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server host 10.0.0.20 key allied
To delete the RADIUS server 10.0.0.20, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server host 10.0.0.20
To configure rad1.company.com for authentication only, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server host rad1.company.com acct-port 0
To remove the RADIUS server rad1.company.com configured for
authentication only, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server host rad1.company.com
acct-port 0
To configure rad2.company.com for accounting only, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server host rad2.company.com auth-port 0
To configure 192.168.1.1 with authentication port 1000, accounting port 1001 and
retransmit count 5, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server host 192.168.1.1 auth-port 1000
acct-port 1001 retransmit 5
Related
Commands
aaa group server
radius-server key
radius-server retransmit
radius-server timeout
show radius statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1306
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER KEY
radius-server key
Overview This command sets a global secret key for RADIUS authentication on the device.
The shared secret text string is used for RADIUS authentication between the device
and a RADIUS server.
Note that if no secret key is explicitly specified for a RADIUS server, the global
secret key will be used for the shared secret for the server.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the secret key to the default (null).
Syntax radius-server key <key>
no radius-server key
Default The RADIUS server secret key on the system is not set by default (null).
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to set the global secret key shared between this client and its
RADIUS servers. If no secret key is specified for a particular RADIUS server using the
radius-server host c ommand, this global key is used.
After enabling AAA authentication with the aaa authentication login command,
set the authentication and encryption key using the radius-server key command
so the key entered matches the key used on the RADIUS server.
Examples To set the global secret key to allied for RADIUS server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server key allied
To set the global secret key to secret for RADIUS server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server key secret
To delete the global secret key for RADIUS server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server key
Related
Commands
radius-server host
show radius statistics
Parameter Description
<key>Shared secret among radius server and 802.1X client.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1307
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER RETRANSMIT
radius-server retransmit
Overview This command sets the retransmit counter to use RADIUS authentication on the
device. This command specifies how many times the device transmits each
RADIUS request to the RADIUS server before giving up.
This command configures the retransmit parameter for RADIUS servers globally.
If the retransmit parameter is not specified for a RADIUS server by the
radius-server host command then the global configuration set by this command
is used for the server instead.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the re-transmit counter to the default
(3).
Syntax radius-server retransmit <retries>
no radius-server retransmit
Default The default RADIUS retransmit count on the device is 3.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the RADIUS retransmit count to 1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server retransmit 1
To set the RADIUS retransmit count to the default (3), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server retransmit
To configure the RADIUS retransmit count globally with 5, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server retransmit 5
To disable retransmission of requests to a RADIUS server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server retransmit 0
Parameter Description
<retries> RADIUS server retries in the range <0-100>.
The number of times a request is resent to a RADIUS server that
does not respond, before the server is considered dead and the
next server is tried. If no retransmit value is specified for a
particular RADIUS server using the radius-server host
command, this global value is used.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1309
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER TIMEOUT
radius-server timeout
Overview Use this command to specify the RADIUS global timeout value. This is how long the
device waits for a reply to a RADIUS request before retransmitting the request, or
considering the server to be dead. If no timeout is specified for the particular
RADIUS server by the radius-server host command, it uses this global timeout
value.
Note that this command configures the timeout parameter for RADIUS servers
globally.
The no variant of this command resets the transmit timeout to the default (5
seconds).
Syntax radius-server timeout <seconds>
no radius-server timeout
Default The default RADIUS transmit timeout on the system is 5 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To globally set the device to wait 20 seconds before retransmitting a RADIUS
request to unresponsive RADIUS servers, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server timeout 20
To set the RADIUS timeout parameter to 1 second, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server timeout 1
To set the RADIUS timeout parameter to the default (5 seconds), use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server timeout
To configure the RADIUS server timeout period globally with 3 seconds, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server timeout 3
Parameter Description
<seconds> RADIUS server timeout in seconds in the range 1 to 1000.
The global time in seconds to wait for a RADIUS server to reply to
a request before retransmitting the request, or considering the
server to be dead (depending on the radius-server retransmit
command).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1310
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER TIMEOUT
To reset the global timeout period for RADIUS servers to the default, use the
following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no radius-server timeout
Related
Commands
radius-server deadtime
radius-server host
radius-server retransmit
show radius statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1311
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SERVER (SERVER GROUP)
server (server group)
Overview This command adds a RADIUS server to a server group in Server-Group
Configuration mode. The RADIUS server should be configured by the radius-server
host command.
The server is appended to the server list of the group and the order of
configuration determines the precedence of servers. If the server exists in the
server group already, it will be removed before added as a new server.
The server is identified by IP address and authentication and accounting UDP port
numbers. So a RADIUS server can have multiple entries in a group with different
authentication and/or accounting UDP ports. The auth-port specifies the UDP
destination port for authentication requests to the server. To disable
authentication for the server, set auth-port to 0. If the authentication port is
missing, the default port number is 1812. The acct-port specifies the UDP
destination port for accounting requests to the server. To disable accounting for
the server, set acct-port to 0. If the accounting port is missing, the default port
number is 1812.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a RADIUS server from the server
group.
Syntax server {<hostname>|<ip-address>} [auth-port
<0-65535>][acct-port <0-65535>]
no server {<hostname>|<ip-address>} [auth-port
<0-65535>][acct-port <0-65535>]
Parameter Description
<hostname> Server host name
<ip-address> Server IP address
The server is identified by IP address, authentication and
accounting UDP port numbers. So a RADIUS server can have
multiple entries in a group with different authentication and/or
accounting UDP ports.
auth-port Authentication port
The auth-port specifies the UDP destination port for
authentication requests to the server. To disable authentication
for the server, set auth-port to 0. If the authentication port is
missing, the default port number is 1812.
<0-65535>UDP port number (default: 1812)
acct-port Accounting port
The acct-port specifies the UDP destination port for accounting
requests to the server. To disable accounting for the server, set
acct-port to 0. If the accounting port is missing, the default port
number is 1813.
<0-65535>UDP port number (default: 1813)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1312
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SERVER (SERVER GROUP)
Default The default Authentication port number is 1812 and the default Accounting port
number is 1813.
Mode Server Group Configuration
Usage The RADIUS server to be added must be configured by the radius-server host
command. In order to add or remove a server, the auth-port and acct-port
parameters in this command must be the same as the corresponding parameters
in the radius-server host command.
Examples To create a RADIUS server group RAD_AUTH1 for authentication, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius RAD_AUTH1
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.1.1 acct-port 0
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.2.1 auth-port 1000 acct-port
0
To create a RADIUS server group RAD_ACCT1 for accounting, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius RAD_ACCT1
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.2.1 auth-port 0 acct-port
1001
awplus(config-sg)# server 192.168.3.1 auth-port 0
To remove server 192.168.3.1 from the existing server group GROUP1, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa group server radius GROUP1
awplus(config-sg)# no server 192.168.3.1
Related
Commands
aaa accounting auth-mac
aaa accounting auth-web
aaa accounting dot1x
aaa accounting login
aaa authentication auth-mac
aaa authentication auth-web
aaa authentication login
aaa group server
radius-server host
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1313
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING RADIUS
show debugging radius
Overview This command displays the current debugging status for the RADIUS servers.
Syntax show debugging radius
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current debugging status of RADIUS servers, use the command:
awplus# show debugging radius
Output Figure 36-1: Example output from the show debugging radius command
RADIUS debugging status:
RADIUS event debugging is off
RADIUS packet debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1314
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS
show radius
Overview This command displays the current RADIUS server configuration and status.
Syntax show radius
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current status of RADIUS servers, use the command:
awplus# show radius
Output Figure 36-2: Example output from the show radius command showing RADIUS
servers
Example See the sample output below showing RADIUS client status and RADIUS
configuration:
awplus# show radius
RADIUS Global Configuration
Source Interface : not configured
Secret Key : secret
Timeout : 5 sec
Retransmit Count : 3
Deadtime : 20 min
Server Host : 192.168.1.10
Authentication Port : 1812
Accounting Port : 1813
Secret Key : secret
Timeout : 3 sec
Retransmit Count : 2
Server Host : 192.168.1.11
Authentication Port : 1812
Accounting Port : not configured
Server Name/ Auth Acct Auth Acct
IP Address Port Port Status Status
------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.1.10 1812 1813 Alive Alive
192.168.1.11 1812 N/A Alive N/A

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1315
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS
Output Figure 36-3: Example output from the show radius command showing RADIUS
client status
RADIUS global interface name: awplus
Secret key:
Timeout: 5
Retransmit count: 3
Deadtime: 0
Server Address: 150.87.18.89
Auth destination port: 1812
Accounting port: 1813
Secret key: swg
Timeout: 5
Retransmit count: 3
Deadtime: 0show radius local-server group
Output Parameter Meaning
Source
Interface The interface name or IP address to be used for the source
address of all outgoing RADIUS packets.
Secret Key A shared secret key to a radius server.
Timeout A time interval in seconds.
Retransmit
Count The number of retry count if a RADIUS server does not
response.
Deadtime A time interval in minutes to mark a RADIUS server as “dead”.
Interim-Update A time interval in minutes to send Interim-Update Accounting
report.
Group Deadtime The deadtime configured for RADIUS servers within a server
group.
Server Host The RADIUS server hostname or IP address.
Authentication
Port The destination UDP port for RADIUS authentication requests.
Accounting Port The destination UDP port for RADIUS accounting requests.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1316
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS
Auth Status The status of the authentication port.
The status (“dead”, “error”, or “alive”) of the RADIUS authentica
tion server and, if dead, how long it has been dead for.
Alive The server is alive.
Error The server is not responding.
Dead The server is detected as dead and it will not be
used for deadtime period. The time displayed in
the output shows the server is in dead status for
that amount of time.
Unknown The server is never used or the status is unknown.
Acct Status The status of the accounting port.
The status (“dead”, “error”, or “alive”) of the RADIUS accounting
server and, if dead, how long it has been dead for.
Output Parameter Meaning
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1317
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RADIUS COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS STATISTICS
show radius statistics
Overview This command shows the RADIUS client statistics for the device.
Syntax show radius statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example See the sample output below showing RADIUS client statistics and RADIUS
configuration:
awplus# show radius statistics
Output Figure 36-4: Example output from the show radius statistics command:
RADIUS statistics for Server: 150.87.18.89
Access-Request Tx : 5 - Retransmit : 0
Access-Accept Rx : 1 - Access-Reject Rx : 2
Access-Challenge Rx : 2
Unknown Type : 0 - Bad Authenticator : 0
Malformed Access-Resp : 0 - Wrong Identifier : 0
Bad Attribute : 0 - Packet Dropped : 0
TimeOut : 0 - Dead count : 0
Pending Request : 0

37
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1319
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Local RADIUS Server
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
the local RADIUS server on the device. For more information, see the Local RADIUS
Server Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“attribute” on page 1321
•“authentication” on page 1324
•“client (radsecproxy-srv)” on page 1325
•“client mutual-authentication” on page 1327
•“client name-check” on page 1328
•“client trustpoint” on page 1329
•“clear radius local-server statistics” on page 1330
•“copy fdb-radius-users (to file)” on page 1331
•“copy local-radius-user-db (from file)” on page 1333
•“copy local-radius-user-db (to file)” on page 1334
•“crypto pki enroll local (deleted)” on page 1335
•“crypto pki enroll local local-radius-all-users (deleted)” on page 1336
•“crypto pki enroll local user (deleted)” on page 1337
•“crypto pki export local pem (deleted)” on page 1338
•“crypto pki export local pkcs12 (deleted)” on page 1339
•“crypto pki trustpoint local (deleted)” on page 1340
•“debug crypto pki (deleted)” on page 1341
•“domain-style” on page 1342
•“egress-vlan-id” on page 1343

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1320
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
•“egress-vlan-name” on page 1345
•“group” on page 1347
•“nas” on page 1348
•“radius-secure-proxy local-server” on page 1349
•“radius-server local” on page 1350
•“server auth-port” on page 1351
•“server enable” on page 1352
•“show radius local-server group” on page 1353
•“show radius local-server nas” on page 1354
•“show radius local-server statistics” on page 1355
•“show radius local-server user” on page 1356
•“user (RADIUS server)” on page 1358
•“vlan (RADIUS server)” on page 1360

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1321
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
ATTRIBUTE
attribute
Overview Use this command to define a RADIUS attribute for the local RADIUS server user
group.
For a complete list of defined RADIUS attributes and values, see the Local RADIUS
Server Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
When used with the help parameter the attribute command displays a list of
standard and vendor specific valid RADIUS attributes that are supported by the
local RADIUS server.
If an attribute name is specified with the help parameter, then the attribute
command displays a list of predefined attribute names. Note that you can only use
the defined RADIUS attribute names and not define your own.
When used with the value parameter the attribute command configures RADIUS
attributes to the user group. If the specified attribute is already defined then it is
replaced with the new value.
Use the no variant of this command to delete an attribute from the local RADIUS
server user group.
Syntax attribute [<attribute-name>|<attribute-id>] help
attribute {<attribute-name>|<attribute-id>} <value>
no attribute {<attribute-name>|<attribute-id>}
Default By default, no attributes are configured.
Mode RADIUS Server Group Configuration
Usage For the Standard attributes, the attribute may be specified using either the
attribute name, or its numeric identifier. For example, the command:
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute acct-terminate-cause
help
will produce the same results as the command:
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute 49 help
Parameter Description
<attribute-name>RADIUS attribute name for standard attributes or Vendor-
Specific attributes (see the Local RADIUS Server Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide for tables of attributes).
<attribute-id>RADIUS attribute numeric identifier for standard attributes.
<value>RADIUS attribute value.
help Display a list of available attribute types.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1322
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
ATTRIBUTE
In the same way, where the specific attribute has a pre-defined value, the
parameter <value> may be substituted with the Value Name or with its numeric
value, for example the command:
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute acct-terminate-cause
user-request
will produce the same results as the command:
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute 49 1
or the command:
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute acct-terminate-cause 1
Examples To check a list of all available defined RADIUS attribute names, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group Admin
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute help
A list of Vendor-specific Attributes displays after the list of defined Standard
Attributes.
To get help for valid RADIUS attribute values for the attribute Service-Type,
use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group Admin
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute Service-Type help
This results in the following output:
Service-Type : integer (Integer number)
Pre-defined values :
Administrative-User (6)
Authenticate-Only (8)
Authorize-Only (17)
Callback-Administrative (11)
Callback-Framed-User (4)
Callback-Login-User (3)
Callback-NAS-Prompt (9)
Call-Check (10)
Framed-User (2)
Login-User (1)
NAS-Prompt-User (7)
Outbound-User (5)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1323
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
ATTRIBUTE
To define the attribute name ‘Service-Type’ with Administrative User (6) to the
RADIUS User Group ‘Admin’, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group Admin
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# attribute Service-Type 6
To delete the attribute ‘Service-Type’ from the RADIUS User Group ‘Admin’, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group Admin
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# no attribute Service-Type
Related
Commands
egress-vlan-id
egress-vlan-name

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1324
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
AUTHENTICATION
authentication
Overview Use this command to enable the specified authentication methods on the local
RADIUS server.
Use the no variant of this command to disable specified authentication methods
on the local RADIUS server.
Syntax authentication {mac|eapmd5|eaptls|peap}
no authentication {mac|eapmd5|eaptls|peap}
Default All authentication methods are enabled by default.
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Examples The following commands enable EAP-MD5 authentication methods on the local
RADIUS server.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# authentication eapmd5
The following commands disable EAP-MD5 authentication methods on Local
RADIUS server.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no authentication eapmd5
Related
Commands
server enable
show radius local-server statistics
Parameter Description
mac Enable MAC authentication method.
eapmd5 Enable EAP-MD5 authentication method.
eaptls Enable EAP-TLS authentication method.
peap Enable EAP-PEAP authentication method.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1325
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CLIENT (RADSECPROXY-SRV)
client (radsecproxy-srv)
Overview Use this command to add a RadSec client (for example, a NAS device) to the
RadSecProxy local-server application. The application will accept RADIUS requests
from all configured clients.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a previously-configured client from
the RadSecProxy local-server application.
Syntax client {<hostname>|<ip-addr>} [name-check {on|off}]
no client {<hostname>|<ip-addr>}
Mode RadSecProxy Local Server Configuration
Usage The client may be specified by its domain name or by its IPv4 address. If a domain
name is used, it must be resolvable using a configured DNS name server.
Each client may be configured to use certificate name-checking; if not specified,
the global behavior defined by client name-check or no client name-check will
be used. If name checking is enabled, the Common Name portion of the subject
field of the client’s X.509 certificate must match the domain name or IP address
specified in this command.
NOTE: If mutual authentication is disabled then this parameter has no effect, see the
client mutual-authentication command.
Example To add a client called ‘mynas.local’ with certificate name checking off, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy local-server
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# client mynas.local name-check
off
Related
Commands
client mutual-authentication
client name-check
Parameter Description
<hostname>Hostname of client.
<ip-addr>Specify the client IPv4 address, in dotted decimal notation
(A.B.C.D).
name-check Specify whether or not to enforce certificate name checking for
this client. If the parameter is not specified then the global
behavior, which defaults to on, is used.
on Enable name checking for this client.
off Disable name checking for this client.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1327
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CLIENT MUTUAL-AUTHENTICATION
client mutual-authentication
Overview This command enables or disables mutual certificate authentication for all
RadSecProxy clients. When enabled, the RadSecProxy local-server application will
request and validate an X.509 certificate from the client when establishing a
connection.
The no variant of this command disables mutual certificate validation. The
local-server application will still transmit the local server certificate to the client,
but will not expect or validate a certificate from the client.
Syntax client mutual-authentication
no client mutual-authentication
Default Mutual authentication is enabled by default.
Mode RadSecProxy Local Server Configuration
Example Disable mutual certificate validation with the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy local-server
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# no client
mutual-authentication
Related
Commands
client (radsecproxy-srv)
client name-check
radius-secure-proxy local-server
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1328
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CLIENT NAME-CHECK
client name-check
Overview This command sets the global behavior for certificate name-checking for the
RadSecProxy localserver application to on. This behavior will be used for all clients
associated with the application that do not specify a behavior on a per-client basis.
If name-checking is enabled, the Common Name portion of the subject field of the
client’s X.509 certificate must match the domain name or IP address specified in
the client (radsecproxy-aaa) command.
Use the no variant of this command to set the global behavior for certificate name
checking to off
Syntax client name-check
no client name-check
Default Certificate name checking is on by default.
Mode RadSecProxy Local Server Configuration
Example Disable certificate name checking globally with the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy local-server
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# no client name-check
Related
Commands
client (radsecproxy-srv)
client trustpoint
radius-secure-proxy local-server
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1329
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CLIENT TRUSTPOINT
client trustpoint
Overview This command adds one or more trustpoints to be used with the RadSecProxy
local-server application. Multiple trustpoints may be specified, or the command
may be executedmore than once, to add multiple trustpoints to the application.
The no version of this command removes one or more trustpoints from the list of
trustpoints associated with the application.
Syntax client trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
no client trustpoint [<trustpoint-list>]
Mode RadSecProxy Local Server Configuration
Usage The device certificate associated with first trustpoint added to the application will
be transmitted to remote servers. The certificate received from the remote server
must have an issuer chain that terminates with the root CA certificate for any of the
trustpoints that are associated with the application.
If no trustpoints are specified in the command, the trustpoint list will be
unchanged.
If no client trustpoint is issued without specifying any trustpoints, then all
trustpoints will be disassociated from the application.
Example You can add multiple trustpoints to the RadSecProxy local-server by executing the
command multiple times:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy local-server
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# client trustpoint example_1
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# client trustpoint example_2
Alternatively, add multiple trustpoints with a single command:
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# client trustpoint example_3
example_4
Disassociate all trustpoints from the RadSecProxy local-server application using
the command:
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)# no client trustpoint
Related
Commands
client (radsecproxy-srv)
client name-check
radius-secure-proxy local-server
Parameter Description
<trustpoint-list> Specify one or more trustpoints to be added or deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1330
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CLEAR RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER STATISTICS
clear radius local-server statistics
Overview Use this command to clear the statistics stored on the device for the local RADIUS
server.
Use this command without any parameters to clear all types of local RADIUS server
statistics.
Syntax clear radius local-server statistics [nas|server|user]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Refer to the sample output for the show radius local-server statistics for further
information about the type of statistics each parameter option for this command
clears. Both the nas and server parameters clear unknown username and invalid
passwords statistics, while the user parameter clears the number of successful
and failed logins for each local RADIUS server user.
Examples To clear the NAS (Network Access Server) statistics stored on the device, use the
command:
awplus# clear radius local-server statistics nas
To clear the local RADIUS server statistics stored on the device, use the command:
awplus# clear radius local-server statistics server
To clear the local RADIUS server user statistics stored on the device, use the
command:
awplus# clear radius local-server statistics user
Related
Commands
show radius local-server statistics
Parameter Description
nas Clear the NAS (Network Access Server) statistics on the device. For
example, clearing statistics stored for NAS server invalid
passwords.
server Clear the Local RADIUS Server statistics on the device. For example,
clearing Local RADIUS Servers statistics for all failed login attempts.
user Clear the Local RADIUS Server user statistics. For example, clearing
statistics stored for the number of successful user logins.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1331
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
COPY FDB-RADIUS-USERS (TO FILE)
copy fdb-radius-users (to file)
Overview Use this command to create a set of local RADIUS server users from MAC addresses
in the local FDB. A local RADIUS server user created using this command can be
used for MAC authentication.
Syntax copy fdb-radius-users
{local-radius-user-db|flash|card|debug|tftp|scp|
fserver|<url>} [interface <port>] [vlan <vid>] [group <name>]
[export-vlan [<radius-group-name>]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The local RADIUS server users created are written to a specified destination file in
local RADIUS user CSV (Comma Separated Values) format. The local RADIUS server
users can then be imported to a local RADIUS server using the copy
local-radius-user-db (from file) command.
The name and password of the local RADIUS server users created use a MAC
address, which can be used for MAC authentication.
Parameter Description
local-radius-
user-db Copy the local RADIUS server users created to the local
RADIUS server.
flash Copy the local RADIUS server users created to Flash memory.
card Copy the local RADIUS server users created to SD card.
debug Copy the local RADIUS server users created to debug.
tftp Copy the local RADIUS server users created to the TFTP
destination.
scp Copy the local RADIUS server users created to the SCP
destination.
fserver Copy the local RADIUS server users created to the remote file
server.
<url>Copy the local RADIUS server users created to the specified
URL.
interface <port>Copy only MAC addresses learned on a specified device port.
Wildcards may be used when specifying an interface name.
vlan <vid>Copy only MAC addresses learned on a specified VLAN.
group <name>Assign a group name to the local RADIUS server users created.
export-vlan Export VLAN ID assigned to exported FDB entry.
<radius-group-
name> Prefix for Radius group name storing VLAN ID

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1332
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
COPY FDB-RADIUS-USERS (TO FILE)
This command does not copy a MAC address learned by the CPU or the
management port.
This command can filter FDB entries by the interface name and the VLAN ID. When
the interface name and the VLAN ID are specified, this command generates local
RADIUS server users from only the MAC address learned on the specified interface
and on the specified VLAN.
Examples To register the local RADIUS server users from the local FDB directly to the local
RADIUS server, use the command:
awplus# copy fdb-radius-users local-radius-user-db
To register the local RADIUS server users from the interface port1.0.1 to the local
RADIUS server, use the command:
awplus# copy fdb-radius-users local-radius-user-db interface
port1.0.1
To copy output generated as local RADIUS server user data from MAC addresses
learned on vlan10 on interface port1.0.1 to the file radius-user.csv, use the
command:
awplus# copy fdb-radius-users radius-user.csv interface
port1.0.1 vlan10
To copy output generated as local RADIUS server user data from MAC addresses
learned on vlan10 on interface port1.0.1 to a file on the remote file server, use the
command:
awplus# copy fdb-radius-users fserver interface port1.0.1
vlan10
Related
Commands
copy local-radius-user-db (to file)
copy local-radius-user-db (from file)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1333
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
COPY LOCAL-RADIUS-USER-DB (FROM FILE)
copy local-radius-user-db (from file)
Overview Use this command to copy the Local RADIUS server user data from a file. The file,
including the RADIUS user data in the file, must be in the CSV (Comma Separated
Values) format.
You can select add or replace as the copy method. The add parameter option
copies the contents of specified file to the local RADIUS server user database. If the
same user exists then the old user is removed before adding a new user. The
replace parameter option deletes all contents of the local RADIUS server user
database before copying the contents of specified file.
Syntax copy <source-url> local-radius-user-db [add|replace]
Default When no copy method is specified with this command the replace option is
applied.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To replace the current local RADIUS server user data to the contents of
http://datahost/ user.csv, use the following command:
awplus# copy http://datahost/user.csv local-radius-user-db
To add the contents of http://datahost/user.csv to the current local RADIUS server
user database, use the following command:
awplus# copy http://datahost/user.csv local-radius-user-db add
Related
commands
copy fdb-radius-users (to file)
copy local-radius-user-db (to file)
Parameter Description
<source-url>URL of the source file.
add Add file contents to local RADIUS server user database.
replace Replace current local RADIUS server user database with
file contents.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1334
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
COPY LOCAL-RADIUS-USER-DB (TO FILE)
copy local-radius-user-db (to file)
Overview Use this command to copy the local RADIUS server user data to a file. The output
file produced is CSV (Comma Separated Values) format.
Syntax copy local-radius-user-db
{flash|card|tftp|scp|<destination-url>}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example Copy the current local RADIUS server user data to http://datahost/user.csv.
awplus# copy local-radius-user-db http://datahost/user.csv
Related
Commands
copy fdb-radius-users (to file)
copy local-radius-user-db (from file)
Parameter Description
flash Copy to Flash memory.
card Copy to SD card.
tftp Copy to TFTP destination.
scp Copy to SCP destination.
<destination-url>URL of the Destination file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1335
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL LOCAL (DELETED)
crypto pki enroll local (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the following command instead:
crypto pki enroll <trustpoint>
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1336
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL LOCAL LOCAL-RADIUS-ALL-USERS (DELETED)
crypto pki enroll local local-radius-all-users
(deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the following command instead:
crypto pki enroll <trustpoint> local-radius-all-users
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1337
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL LOCAL USER (DELETED)
crypto pki enroll local user (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the following command instead:
crypto pki enroll <trustpoint> user <username>
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1338
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI EXPORT LOCAL PEM (DELETED)
crypto pki export local pem (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the crypto pki export pem
command instead:
crypto pki export <trustpoint> pem [terminal|<url>]
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1339
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI EXPORT LOCAL PKCS12 (DELETED)
crypto pki export local pkcs12 (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the crypto pki export pkcs12
command instead:
crypto pki export <trustpoint> pkcs12 {ca|server|<username>}
<url>
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1340
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI TRUSTPOINT LOCAL (DELETED)
crypto pki trustpoint local (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available. Please use the following command instead:
crypto pki trustpoint <trustpoint>
Note that “local” is a valid name for a trustpoint, so you do not need to modify
existing configurations or scripts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1341
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
DEBUG CRYPTO PKI (DELETED)
debug crypto pki (deleted)
Overview This command is no longer available.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1342
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
DOMAIN-STYLE
domain-style
Overview Use this command to enable a specified domain style on the local RADIUS server.
The local RADIUS server decodes the domain portion of a username login string
when this command is enabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the specified domain style on the
local RADIUS server.
Syntax domain-style {suffix-atsign|ntdomain}
no domain-style {suffix-atsign|ntdomain}
Default This feature is disabled by default.
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Usage When both domain styles are enabled, the first domain style configured has the
highest priority. A username login string is matched against the first domain style
enabled. Then, if the username login string is not decoded, it is matched against
the second domain style enabled.
Examples To enable NT domain style on the local RADIUS server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# domain-style ntdomain
To disable NT domain style on the local RADIUS server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no domain-style ntdomain
Related
Commands
server enable
Parameter Description
suffix-atsign Enable at sign “@” delimited suffix style, i.e. “user@domain”.
ntdomain Enable NT domain style, i.e. “domain\user”.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1343
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
EGRESS-VLAN-ID
egress-vlan-id
Overview Use this command to configure the standard RADIUS attribute “Egress-VLANID
(56)” for the local RADIUS Server user group.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the Egress-VLANID attribute from
the local RADIUS server user group.
Syntax egress-vlan-id <vid> [tagged|untagged]
no egress-vlan-id
Default By default, no Egress-VLANID attributes are configured.
Mode RADIUS Server Group Configuration
Usage When a Voice VLAN is configured for dynamic VLAN allocation (switchport voice
vlan command), the RADIUS server must be configured to send the VLAN
information when an IP phone is successfully authenticated. Use either the
egress-vlan-id command or the egress-vlan-name command, and specify the
tagged parameter.
Examples To set the “Egress-VLANID” attribute for the NormalUsers local RADIUS server user
group to VLAN identifier 200, with tagged frames, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# egress-vlan-id 200 tagged
To remove the “Egress-VLANID” attribute for the NormalUsers local RADIUS server
user group, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# no egress-vlan-id
Parameter Description
<vid>The VLAN identifier to be used for the Egress VLANID attribute, in
the range 1 to 4094.
tagged Set frames on the VLAN as tagged. This sets the tag indication field
to indicate that all frames on this VLAN are tagged.
untagged Set all frames on the VLAN as untagged. This sets the tag indication
field to indicate that all frames on this VLAN are untagged.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1345
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
EGRESS-VLAN-NAME
egress-vlan-name
Overview Use this command to configure the standard RADIUS attribute
“Egress-VLAN-Name (58)” for the local RADIUS server user group.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the Egress-VLAN-Name attribute
from the local RADIUS server user group.
Syntax egress-vlan-name <vlan-name> [tagged|untagged]
no egress-vlan-name
Default By default, no Egress-VLAN-Name attributes are configured.
Mode RADIUS Server Group Configuration
Usage When a Voice VLAN is configured for dynamic VLAN allocation (switchport voice
vlan command), the RADIUS server must be configured to send the VLAN
information when an IP phone is successfully authenticated. Use either the
egress-vlan-id command or the egress-vlan-name command, and specify the
tagged parameter.
Examples To configure the “Egress-VLAN-Name” attribute for the RADIUS server user group
NormalUsers with the VLAN name vlan2 and all frames on this VLAN tagged, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# egress-vlan-name vlan2 tagged
To delete the “Egress-VLAN-Name” attribute for the NormalUsers group, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# no egress-vlan-name
Parameter Description
<vlan-name>The VLAN name to be configured as the Egress-VLAN-Name
attribute.
tagged Set frames on the VLAN as tagged. This sets the tag indication field
to indicate that all frames on this VLAN are tagged.
untagged Set all frames on the VLAN as untagged. This sets the tag indication
field to indicate that all frames on this VLAN are untagged.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1347
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
GROUP
group
Overview Use this command to create a local RADIUS server user group, and enter local
RADIUS Server User Group Configuration mode.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the local RADIUS server user group.
Syntax group <user-group-name>
no group <user-group-name>
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Examples The following command creates the user group NormalUsers.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
The following command deletes user group NormalUsers.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no group NormalUsers
Related
Commands
user (RADIUS server)
show radius local-server user
vlan (RADIUS server)
Parameter Description
<user-group-name>User group name string.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1348
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
NAS
nas
Overview This command adds a client device (the Network Access Server or the NAS) to the
list of devices that are able to send authentication requests to the local RADIUS
server. The NAS is identified by its IP address and a shared secret (also referred to
as a shared key) must be defined that the NAS will use to establish its identity.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a NAS client from the list of devices
that are allowed to send authentication requests to the local RADIUS server.
Syntax nas <ip-address> key <nas-keystring>
no nas <ip-address>
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Examples The following commands add the NAS with an IP address of 192.168.1.2 to the
list of clients that may send authentication requests to the local RADIUS server.
Note the shared key that this NAS will use to establish its identify is
NAS_PASSWORD.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# nas 192.168.1.2 key NAS_PASSWORD
The following commands remove the NAS with an IP address of 192.168.1.2
from the list of clients that are allowed to send authentication requests to the local
RADIUS server:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no nas 192.168.1.2
Related
Commands
show radius local-server nas
Parameter Description
<ip-address>RADIUS NAS IP address.
<nas-keystring>NAS shared keystring.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1349
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
RADIUS-SECURE-PROXY LOCAL-SERVER
radius-secure-proxy local-server
Overview Use this command to enter the RadSecProxy local-server application configuration
mode. This application allows remote RadSec clients to communicate with the
local RADIUS server process via a secure (TLS) proxy.
Syntax radius-secure-proxy local-server
Mode Global Configuration Mode
Example To change mode from User Exec mode to the RadSecProxy local-server
configuration mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-secure-proxy local-server
awplus(config-radsecproxy-srv)#
Related
Commands
client (radsecproxy-srv)
client name-check
client trustpoint
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1350
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
RADIUS-SERVER LOCAL
radius-server local
Overview Use this command to navigate to the Local RADIUS server configuration
mode(config-radsrv) from the Global Configuration mode (config).
Syntax radius-server local
Mode Global Configuration
Example Local RADIUS Server commands are available from config-radsrv
configuration mode. To change mode from User Exec mode to the Local RADIUS
Server mode (config- radsrv), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)#
Output
Related
Commands
server enable
show radius local-server group
show radius local-server nas
show radius local-server statistics
show radius local-server user
awplus(config)#radius-server local
Creating Local CA repository.....OK
Enrolling Local System to local trustpoint..OK
awplus(config-radsrv)#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1351
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SERVER AUTH-PORT
server auth-port
Overview Use this command to change the UDP port number for local RADIUS server
authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the RADIUS server authentication port
back to the default.
Syntax server auth-port <1-65535>
no server auth-port
Default The default local RADIUS server UDP authentication port number is 1812.
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Examples The following commands set the RADIUS server authentication port to 10000.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# server auth-port 10000
The following commands reset the RADIUS server authentication port back to the
default UDP port of 1812.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no server auth-port
Related
Commands
server enable
show radius local-server statistics
Parameter Description
<1-65535>UDP port number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1352
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SERVER ENABLE
server enable
Overview This command enables the local RADIUS server. The local RADIUS server feature is
started immediately when this command is issued.
The no variant of this command disables local RADIUS server. When this command
is issued, the local RADIUS server stops operating.
Syntax server enable
no server enable
Default The local RADIUS server is disabled by default and must be enabled for use with
this command.
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Examples To enable the local RADIUS server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# server enable
To disable the local RADIUS server, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no server enable
Related
Commands
server auth-port
show radius local-server statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1353
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER GROUP
show radius local-server group
Overview Use this command to display information about the local RADIUS server user
group.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show radius local-server group [<user-group-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example The following command displays Local RADIUS server user group information.
awplus# show radius local-server group
Output
Related
Commands
group
Parameter Description
<user-group-name>User group name string.
Table 1: Example output from the show radius local-server group command
Group-Name Vlan
----------------------------------------------------------------
NetworkOperators ManagementNet
NormalUsers CommonNet
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show radius local-server group
command
Parameter Description
Group-Name Group name.
Vlan VLAN name assigned to the group.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1354
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER NAS
show radius local-server nas
Overview Use this command to display information about NAS (Network Access Servers)
registered to the local RADIUS server.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show radius local-server nas [<ip-address>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example The following command displays NAS information.
awplus# show radius local-server nas
Output
Related
Commands
nas
Parameter Description
<ip-address> Specify NAS IP address for show output.
Table 3: Example output from the show radius local-server nas command
NAS-Address Shared-Key
----------------------------------------------------------
127.0.0.1 awplus-local-radius-server
Table 4: Parameters in the output of the show radius local-server nas
command
Parameter Description
NAS-Address IP address of NAS.
Shared-Key Shared key used for RADIUS connection.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1355
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER STATISTICS
show radius local-server statistics
Overview Use this command to display statistics about the local RADIUS server.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show radius local-server statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Both unknown usernames and invalid passwords will display as failed logins in the
show output.
Example The following command displays Local RADIUS server statistics.
awplus# show radius local-server statistics
Output
Related
Commands
clear radius local-server statistics
radius-server local
server enable
server auth-port
Table 5: Example output from the show radius local-server statistics command
Server status : Run (administrative status is enable)
Enabled methods: MAC EAP-MD5 EAP-TLS EAP-PEAP
Successes :1 Unknown NAS :0
Failed Logins :0 Invalid packet from NAS :0
Internal Error :0 Unknown Error :0
NAS : 127.0.0.1
Successes :0 Shared key mismatch :0
Failed Logins :0 Unknown RADIUS message :0
Unknown EAP message :0 Unknown EAP auth type :0
Corrupted packet :0
NAS : 192.168.1.61
Successes :0 Shared key mismatch :0
Failed Logins :0 Unknown RADIUS message :0
Unknown EAP message :0 Unknown EAP auth type :0
Corrupted packet :0
Username Successes Failures
a 1 0
admin 0 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1356
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER USER
show radius local-server user
Overview Use this command to display information about the local RADIUS server user.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show radius local-server user [<user-name>]
show radius local-server user [<user-name>] format csv
show radius local-server user [<user-name>] detail
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples The following command displays Local RADIUS server user information for user
Tom.
awplus# show radius local-server user Tom
The following command displays all Local RADIUS server information for all users.
awplus# show radius local-server user
The following command displays Local RADIUS server user information for Tom in
CSV format.
awplus# show radius local-server user Tom format csv
The following command displays detailed Local RADIUS server user information
for all users.
awplus# show radius local-server detail
Parameter Description
<user-name>RADIUS user name. If no user name is specified, information for all
users is displayed.
format csv Format output as CSV.
detail display detailed information about the user.
Table 6: Example output from the show radius local-server user command
User-Name Password Group Vlan
----------------------------------------------------------------
Tom abcd NetworkOperators ManagementNet
Table 7: Example output from the show radius local-server user Tom format
csv command
true,"NetworkOperators","Tom","abcd",0,2099/01/01,1,"","","Managem
entNet",false,3600,false,0,"",false,"

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1357
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
SHOW RADIUS LOCAL-SERVER USER
Related
Commands
group
user (RADIUS server)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: detail parameter added
Table 8: Example output from the show radius local-server detail command
awplus# show radius local-server user detail
------------------------------------------------------------------
Username : 00-00-cd-38-00-68
Password: mssv+c7URUgtfltKy46Rt0VgPefRdihWOXEUeCmS8Bw=
Group : GroupName
Vlan : VlanName
Username : Tom:port1.0.5:00-00-cd-38-00-68
Password: 0cVvLd4+oyQlO2eckFXtV9d9JO/lXbqlDiRvyTOd+Wk=
Group : GroupName
Vlan : VlanName
Table 9: Parameters in the output from the show radius local-server user
command
Parameter Description
User-Name User name.
Password User password.
Group Group name assigned to the user.
Vlan VLAN name assigned to the user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1358
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
USER (RADIUS SERVER)
user (RADIUS server)
Overview Use this command to register a user to the local RADIUS server.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a user from the local RADIUS server.
Syntax user <radius-user-name> [encrypted] password <user-password>
[group <user-group>]
no user <radius-user-name>
Mode RADIUS Server Configuration
Usage RADIUS user names cannot contain question mark (?), space ( ), or quote (“ “)
characters. RADIUS user names containing the below characters cannot use
certificate authentication:
/ \ ‘$ &()*;< > ‘|
Certificates cannot be created and exported for RADIUS user names that contain
the above characters. We advise you to avoid using these characters in RADIUS
user names if you need to use certificate authentication, because you will not be
able to create and export certificates.
You also can use the IEEE standard format hexadecimal notation
(HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH) to specify a supplicant MAC address to configure the
user name and user password parameters to use local RADIUS server for MAC
Authentication. See the AAA and Port_Authentication Feature Overview and
Configuration_Guide for a sample MAC configuration. See also the command user
Parameter Description
<radius-user-name>RADIUS user name. This can also be a MAC address in the
IEEE standard format of HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH if you are
configuring MAC authentication to use local RADIUS server.
encrypted Specifies that the password is being entered in its
encrypted form, so that it is not further encrypted.
When creating a new user, enter the password in plaintext,
and do not use the encrypted parameter.
Use the encrypted parameter only when referring to a user
that has previously been created. For instance, when
adding an existing user from another RADIUS server, use
the encrypted parameter, and enter the encrypted version
of the password that appears in the output of show
commands for the user.
<user-password>User password. This can also be a MAC address in the IEEE
standard format of HH-HH-HH-HH-HH-HH if you are
configuring MAC authentication to use local RADIUS server.
group Specify the group for the user.
<user-group>User group name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1359
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
USER (RADIUS SERVER)
00-db-59-ab-70-37 password 00-db-59-ab-70-37 as shown in the command
examples.
Examples The following commands add user “Tom” to the local RADIUS server and sets his
password to “QwerSD”.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# user Tom password QwerSD
The following commands add user “Tom” to the local RADIUS server user group
“NormalUsers” and sets his password “QwerSD”.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# user Tom password QwerSD group
NormalUsers
The following commands remove user “Tom” from the local RADIUS server:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no user Tom
The following commands add the supplicant MAC address 00-d0-59-ab-70-37 to
the local RADIUS server:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# user 00-db-59-ab-70-37 password
00-db-59-ab-70-37
The following commands remove the supplicant MAC address 00-d0-59-ab-70-37
from the local RADIUS server:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# no user 00-db-59-ab-70-37
Related
Commands
group
show radius local-server user

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1360
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LOCAL RADIUS SERVER COMMANDS
VLAN (RADIUS SERVER)
vlan (RADIUS server)
Overview Use this command to set the VLAN ID or name for the local RADIUS server user
group. The VLAN information is used for authentication with the dynamic VLAN
feature.
Use the no variant of this command to clear the VLAN ID or VLAN name for the local
RADIUS server user group.
Syntax vlan {<vid>|<vlan-name>}
no vlan
Default VLAN information is not set by default.
Mode RADIUS Server Group Configuration
Examples The following commands set VLAN ID 200 to the group named NormalUsers:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# vlan 200
The following commands remove VLAN ID 200 from the group named
NormalUsers:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# radius-server local
awplus(config-radsrv)# group NormalUsers
awplus(config-radsrv-group)# no vlan
Related
Commands
group
show radius local-server user
Parameter Description
<vid>VLAN ID.
<vlan-name>VLAN name.

38
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1361
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Public Key
Infrastructure
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) capabilities on an AlliedWare Plus device. For
more information about PKI, see the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“crypto key generate rsa” on page 1362
•“crypto key zeroize” on page 1363
•“crypto pki authenticate” on page 1364
•“crypto pki enroll” on page 1365
•“crypto pki enroll user” on page 1366
•“crypto pki export pem” on page 1368
•“crypto pki export pkcs12” on page 1369
•“crypto pki import pem” on page 1371
•“crypto pki import pkcs12” on page 1373
•“crypto pki trustpoint” on page 1374
•“enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode)” on page 1375
•“fingerprint (trustpoint configuration mode)” on page 1376
•“no crypto pki certificate” on page 1378
•“rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode)” on page 1379
•“show crypto key mypubkey rsa” on page 1380
•“show crypto pki certificates” on page 1381
•“show crypto pki enrollment user” on page 1383
•“show crypto pki trustpoint” on page 1384
•“subject-name (trustpoint configuration)” on page 1385
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1362
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY GENERATE RSA
crypto key generate rsa
Overview Use this command to generate a cryptographic public/private key pair for the
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption algorithm.
Syntax crypto key generate rsa [label <keylabel>] [<1024-4096>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The generated key may be used for multiple server certificates in the system. A key
is referenced by its label. A bit length between 1024 and 4096 bits may be
specified. Larger bit lengths are more secure, but require more computation time.
The specified key must not already exist.
Example To create a key with the label "example-server-key" and a bit length of 2048, use
the commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto key generate rsa label example-server-key 2048
Related
Commands
crypto key zeroize
rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode)
show crypto key mypubkey rsa
Parameter Description
<keylabel> The name of the key to be created. The name must start with an
alphanumeric character, and may only contain alphanumeric
characters, underscores, dashes, or periods. The maximum length
of the name is 63 characters. If no label is specified the default
value “server-default” is used.
<1024-4096> The bit length for the key. If no bit length is specified the default
of 2048 is used.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1363
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY ZEROIZE
crypto key zeroize
Overview Use this command to delete one or all cryptographic public/private key pairs.
Syntax crypto key zeroize rsa <keylabel>
crypto key zeroize all
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Note that this command has the same effect as using the delete command (it
deletes the file from Flash memory but does not overwrite it with zeros).
The specified key must exist but must not be in use for any existing server
certificates.
A key may not be deleted if it is associated with the server certificate or server
certificate signing request for an existing trustpoint. To remove a server certificate
so that the key may be deleted, use the no crypto pki enroll command to
de-enroll the server.
Example To delete an RSA key named "example-server-key", use the following command:
awplus# crypto key zeroize rsa example-server-key
Related
Commands
crypto key generate rsa
show crypto key mypubkey rsa
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: zeroize functionality added to x930 Series
Version 5.4.8-1.2: zeroize functionality added to x220, XS900MX, x550 Series
Version 5.4.8-2.1: zeroize functionality added to SBx908 GEN2, x950 Series
Parameter Description
rsa <keylabel> Delete a single key pair for the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
encryption algorithm.
all Delete all keys.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1364
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI AUTHENTICATE
crypto pki authenticate
Overview Use this command to authenticate a trustpoint by generating or importing the
root CA certificate. This must be done before the server can be enrolled to the
trustpoint.
Syntax crypto pki authenticate <trustpoint>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If the trustpoint’s enrollment setting is “selfsigned”, then this command causes a
private key to be generated for the root CA, and a self-signed certificate to be
generated based on that key.
If the trustpoint’s enrollment setting is “terminal”, then this command prompts
the user to paste a certificate Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) file at the CLI terminal.
If the certificate is a valid selfsigned CA certificate, then it will be stored as the
trustpoint’s root CA certificate.
The specified trustpoint must already exist, and its enrollment mode must have
been defined.
Example To show the enrollment setting of a trustpoint named “example” and then
generate a certificate from it, use the commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# enrollment selfsigned
awplus(config)# exit
awplus# exit
awplus# crypto pki authenticate example
Related
Commands
crypto pki import pem
crypto pki trustpoint
enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode)
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint to be authenticated.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1365
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL
crypto pki enroll
Overview Use this command to enroll the local server to the specified trustpoint.
Use the no variant of this command to de-enroll the server by removing its
certificate
Syntax crypto pki enroll <trustpoint>
no crypto pki enroll <trustpoint>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage For the local server, “enrollment” is the process of creating of a certificate for the
server that has been signed by a CA associated with the trustpoint. The public
portion of the RSA key pair specified using the rsakeypair parameter for the
trustpoint will be included in the server certificate.
If the trustpoint represents a locally self-signed certificate authority, then this
command results in the direct generation of the server certificate, signed by the
root CA for the trustpoint.
If the trustpoint represents an external certificate authority, then this command
results in the generation of a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) file, which is
displayed at the terminal in Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format, suitable for
copying and pasting into a file or message. The CSR must be sent to the external
CA for processing. When the CA replies with the signed certificate, that certificate
should be imported using the crypto pki import pem command, to complete the
enrollment process.
The specified trustpoint must already exist, and it must already be authenticated.
Example To enroll the local server with the trustpoint “example”, use the following
commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki enroll example
Related
Commands
crypto pki enroll user
crypto pki import pem
crypto pki trustpoint
enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode)
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint to be enrolled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1366
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL USER
crypto pki enroll user
Overview Use this command to enroll a single RADIUS user or all RADIUS users to the
specified trustpoint.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the PKCS#12 file from the system.
Note that the PKCS#12 files are generated in a temporary (volatile) file system, so a
system restart also results in removal of all of the files.
Syntax crypto pki enroll <trustpoint>
{user <username>|local-radius-all-users}
no crypto pki enroll <trustpoint>
{user <username>|local-radius-all-users}
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage For RADIUS users, “enrollment” is the process of generating a private key and a
corresponding client certificate for each user, with the certificate signed by the
root CA for the trustpoint. The resulting certificates may be exported to client
devices, for use with PEAP or EAP-TLS authentication with the local RADIUS server.
The specified trustpoint must represent a locally self-signed certificate authority.
The private key and certificate are packaged into a PKCS#12-formatted file,
suitable for export using the crypto pki export pkcs12 command. The private key
is encrypted for security, with a passphrase that is entered at the command line.
The passphrase is required when the PKCS#12 file is imported on the client system.
The passphrase is not stored anywhere on the device, so users are responsible for
remembering it until the export-import process is complete.
If local-radius-all-users is specified instead of an individual user, then keys and
certificates for all RADIUS users will be generated at once. All the keys will be
encrypted using the same passphrase.
The specified trustpoint must already exist, it must represent a locally self-signed
CA, and it must already have been authenticated.
Example To enroll the user “example-user” with the trustpoint “example”, use the following
commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki enroll example user example-user
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint to which users are to be enrolled.
<username> The name of the user to enroll to the trustpoint.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1367
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI ENROLL USER
To enroll all local RADIUS users with the trustpoint “example”, use the following
commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki enroll example local-radius-all-users
Related
Commands
crypto pki export pkcs12
crypto pki trustpoint
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1368
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI EXPORT PEM
crypto pki export pem
Overview Use this command to export the root CA certificate for the given trustpoint to a file
in Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format. The file may be transferred to the specified
destination URL, or displayed at the terminal.
Syntax crypto pki export <trustpoint> pem [terminal|<url>]
Default The PEM will be displayed to the terminal by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The specified trustpoint must already exist, and it must already be authenticated.
Example To display the PEM file for the trustpoint “example” to the terminal, use the
following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki export example pem terminal
To export the PEM file “example.pem” for the trustpoint “example” to the URL
“tftp://server_a/”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki export example pem
tftp://server_a/example.pem
Related
Commands
crypto pki authenticate
crypto pki import pem
crypto pki trustpoint
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint for which the root CA certificate is
tobe exported.
terminal Display the PEM file to the terminal.
<url> Transfer the PEM file to the specified URL.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1369
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI EXPORT PKCS12
crypto pki export pkcs12
Overview Use this command to export a certificate and private key for an entity in a
trustpoint to a file in PKCS#12 format at the specified URL. The private key is
encrypted with a passphrase for security.
Syntax crypto pki export <trustpoint> pkcs12 {ca|server|<username>}
<url>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If the ca option is specified, this command exports the root CA certificate and the
corresponding private key, if the trustpoint has been authenticated as a locally
selfsigned CA. (If the trustpoint represents an external CA, then there is no private
key on the system corresponding to the root CA certificate. Use the crypto pki
export pem file to export the certificate by itself.) The command prompts for a
passphrase to encrypt the private key.
If the server option is specified, this command exports the server certificate and
the corresponding private key, if the server has been enrolled to the trustpoint. The
command prompts for a passphrase to encrypt the private key.
If a RADIUS username is specified, this command exports the PKCS#12 file that was
generated using the crypto pki enroll user command. (The key within the file was
already encrypted as part of the user enrollment process.)
In the event that there is a RADIUS user named “ca” or “server”, enter “user:ca” or
“user:server” as the username.
The key and certificate must already exist.
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint for which the certificate and key are
tobe exported.
ca If this option is specified, the command exports the root CA
certificate and corresponding key.
server If this option is specified, the command exports the server
certificate and corresponding key.
<username> If a RADIUS username is specified, the command exports the
PKCS#12 file that was previously generated using the crypto pki
enroll user command. To avoid ambiguity with keywords, the
username may be prefixed by the string “user:”.
<url> The destination URL for the PKCS#12 file. The format of the URLis
the same as any valid destination for a file copy command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1370
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI EXPORT PKCS12
Example To export the PKCS#12 file “example.pk12” for the trustpoint “example” to the URL
“tftp://backup/”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki export example pkcs12 ca
tftp://backup/example.pk12
Related
Commands
crypto pki enroll user
crypto pki export pem
crypto pki import pkcs12

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1371
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI IMPORT PEM
crypto pki import pem
Overview This command imports a certificate for the given trustpoint from a file in
Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format. The file may be transferred from the specified
destination URL, or entered at the terminal.
Syntax crypto pki import <trustpoint> pem [terminal|<url>]
Default The PEM will be imported from the terminal by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The command is generally used for trustpoints representing external certificate
authorities. It accepts root CA certificates, intermediate CA certificates, and server
certificates. The system automatically detects the certificate type upon import.
Using this command to import root CA certificates at the terminal is identical to the
functionality provided by the crypto pki authenticate command, for external
certificate authorities. The imported certificate is validated to ensure it is a proper
CA certificate.
Intermediate CA certificates are validated to ensure they are proper CA certificates,
and that the issuer chain ends in a root CA certificate already installed for the
trustpoint. If there is no root CA certificate for the trustpoint (i.e., if the trustpoint is
unauthenticated) then intermediate CA certificates may not be imported.
Server certificates are validated to ensure that the issuer chain ends in a root CA
certificate already installed for the trustpoint. If there is no root CA certificate for
the trustpoint (i.e., if the trustpoint is unauthenticated) then server certificates may
not be imported.
The specified trustpoint must already exist. If the imported certificate is
self-signed, then no certificates may exist for the trustpoint. Otherwise, the issuer’s
certificate must already be present for the trustpoint.
Example To import the PEM file for the trustpoint “example” from the terminal, use the
following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki import example pem
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint for which the root CA certificate is to
be imported.
terminal Optional parameter, If specified, the command prompts the user
to enter (or paste) the PEM file at the terminal. If parameter is
specified terminal is assumed by default.
<url> Optional parameter, If specified, the PEM file is transferred from
the specified URL

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1372
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI IMPORT PEM
To import the PEM file for the trustpoint “example” from the URL “tftp://server_a/”,
use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki import example pem
tftp://server_a/example.pem
Related
Commands
crypto pki authenticate
crypto pki export pem
crypto pki trustpoint

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1373
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI IMPORT PKCS12
crypto pki import pkcs12
Overview This command imports a certificate and private key for an entity in a trustpoint
from a file in PKCS#12 format at the specified URL. The command prompts for a
passphrase to decrypt the private key within the file.
Syntax crypto pki import <trustpoint> pkcs12 {ca|server} <url>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If the ca option is specified, this command imports the root CA certificate and the
corresponding private key. This is only valid if the root CA certificate does not
already exist for the trustpoint (i.e., if the trustpoint is unauthenticated).
If the server option is specified, this command imports the server certificate and
the corresponding private key. The imported private key is given a new unique
label of the form “localN”, where N is a non-negative integer. This operation is only
valid if the server certificate does not already exist for the trustpoint (i.e., if the
server is not enrolled to the trustpoint).
PKCS#12 files for RADIUS users may not be imported with this command. (There is
no value in doing so, as the files are not needed on the local system.)
The specified trustpoint must already exist. The key and certificate must not
already exist.
Example To import the PKCS#12 file “example.pk12” for the trustpoint “example” to the URL
“tftp://backup/”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# crypto pki import example pkcs12 ca
tftp://backup/example.pk12
Related
Commands
crypto pki export pkcs12
crypto pki import pem
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint for which the certificate and key are to
be imported.
ca If this option is specified, the command imports the root CA
certificate and corresponding key.
server If this option is specified, the command imports the server
certificate and corresponding key.
<url> The source URL for the PKCS#12 file. The format of the URLis the
same as any valid destination for a file copy command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1374
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
CRYPTO PKI TRUSTPOINT
crypto pki trustpoint
Overview Use this command to declare the named trustpoint and enter trustpoint
configuration mode.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the trustpoint.
Syntax crypto pki trustpoint <trustpoint>
no crypto pki trustpoint <trustpoint>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the trustpoint did not previously exist, it is created as a new trustpoint. The
trustpoint will be empty (unauthenticated) unless the name “local” is selected, in
which case the system will automatically authenticate the trustpoint as a local
self-signed certificate authority.
The no variant of this command destroys the trustpoint by removing all CA and
server certificates associated with the trustpoint, as well as the private key
associated with the root certificate (if the root certificate was locally self-signed).
This is a destructive and irreversible operation, so this command should be used
with caution.
Example To configure a trustpoint named “example”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
Related
Commands
show crypto pki certificates
show crypto pki trustpoint
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added to x930 Series
Version 5.4.8-1: command added to x220, XS900MX, x550 Series
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added to SBx908 GEN2, x950 Series
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint. The name must start with an
alphanumeric character, and may only contain alphanumeric
characters, underscores, dashes, or periods. The maximum length
of the name is 63 characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1375
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
ENROLLMENT (TRUSTPOINT CONFIGURATION MODE)
enrollment (trustpoint configuration mode)
Overview Use this command to declare how certificates will be added to the system for the
current trustpoint.
Syntax enrollment {selfsigned|terminal}
Mode Trustpoint Configuration
Usage If the enrollment is set to selfsigned, then the system will generate a root CA
certificate and its associated key when the crypto pki authenticate command is
issued. It will generate a server certificate (signed by the root CA certificate) when
the crypto pki enroll command is issued.
If the enrollment is set to terminal, then the system will prompt the user to paste
the root CA certificate Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) file at the terminal, when the
crypto pki authenticate command is issued. It will create a Certificate Signing
Request (CSR) file for the local server when the crypto pki enroll command is
issued. The server certificate received from the external CA should be imported
using the crypto pki import pem command.
The trustpoint named “local” may only use the selfsigned enrollment setting.
If no enrollment mode is specified, the crypto pki authenticate command will fail
for the trustpoint.
Example To configure the trustpoint named "example" and set its enrollment to selfsigned,
use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# enrollment selfsigned
Related
Commands
crypto pki enroll
Parameter Description
selfsigned Sets the enrollment mode for the current trustpoint to selfsigned.
terminal Sets the enrollment mode for the current trustpoint to terminal.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1376
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
FINGERPRINT (TRUSTPOINT CONFIGURATION MODE)
fingerprint (trustpoint configuration mode)
Overview Use this command to declare that certificates with the specified fingerprint should
be automatically accepted, when importing certificates from an external certificate
authority. This can affect the behavior of the crypto pki authenticate and crypto
pki import pem commands.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified fingerprint from the
pre-accepted list.
Syntax fingerprint <word>
no fingerprint <word>
Default By default, no fingerprints are pre-accepted for the trustpoint.
Mode Trustpoint Configuration
Usage Specifying a fingerprint adds it to a list of pre-accepted fingerprints for the
trustpoint. When a certificate is imported, if it matches any of the pre-accepted
values, then it will be saved in the system automatically. If the imported
certificate’s fingerprint does not match any pre-accepted value, then the user will
be prompted to verify the certificate contents and fingerprint visually.
This command is useful when certificates from an external certificate authority are
being transmitted over an insecure channel. If the certificate fingerprint is
delivered via a separate messaging channel, then pre-entering the fingerprint
value via cut-and-paste may be less errorprone than attempting to verify the
fingerprint value visually.
The fingerprint is a series of 40 hexadecimal characters. It may be entered as a
continuous string, or as a series of up to multiple strings separated by spaces. The
input format is flexible because different certificate authorities may provide the
fingerprint string in different formats.
Example To configure a fingerprint “5A81D34C 759CC4DA CFCA9F65 0303AD83 410B03AF”
for the trustpoint named “example”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# fingerprint 5A81D34C 759CC4DA CFCA9F65
0303AD83 410B03AF
Related
Commands
crypto pki authenticate
Parameter Description
<word> The fingerprint as a series of 40 hexadecimal characters,
optionally separated into multiple character strings.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1378
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
NO CRYPTO PKI CERTIFICATE
no crypto pki certificate
Overview Use this command to delete a certificate with the specified fingerprint from the
specified trustpoint.
Syntax no crypto pki certificate <trustpoint> <word>
Default By default, no fingerprints are pre-accepted for the trustpoint.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The fingerprint can be found in the output of the show crypto pki certificates
command. If there are dependent certificates in the trustpoint (i.e., if other
certificates were signed by the specified certificate), the command will be rejected.
If the specified certificate is the root CA certificate and the trustpoint represents a
locally selfsigned CA, then the corresponding private key is also deleted from the
system. Deleting the root CA certificate effectively resets the trustpoint to an
unauthenticated state.
Example To delete a certificate with the fingerprint "594EDEF9 C7C4308C 36D408E0
77E784F0 A59E8792" from the trustpoint “example”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# no crypto pki certificate example
594EDEF9 C7C4308C 36D408E0 77E784F0 A59E8792
Related
Commands
no crypto pki trustpoint
show crypto pki certificates
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint.
<word> The fingerprint as a series of 40 hexadecimal characters,
optionally separated into multiple character strings.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1379
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
RSAKEYPAIR (TRUSTPOINT CONFIGURATION MODE)
rsakeypair (trustpoint configuration mode)
Overview Use this command to declare which RSA key pair should be used to enroll the local
server with the trustpoint. Note that this defines the key pair used with the server
certificate, not the key pair used with the root CA certificate.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default value, “server-default”.
Syntax rsakeypair <keylabel> [<1024-4096>]
no rsakeypair
Default The default value for keylabel is “server-default”.
The default value for the key bit length is 2048.
Mode Trustpoint Configuration
Usage If the label specified does not refer to an existing key created by the crypto key
generate rsa command, the key will be implicitly generated when the crypto pki
enroll command is issued to generate the server certificate or the server certificate
signing request. The optional numeric parameter defines the bit length for the key,
and is only applicable for keys that are implicitly created during enrollment.
This command does not affect server certificates or server certificate signing
requests that have already been generated. The trustpoint’s server certificate is set
to use whatever key pair was specified for the trustpoint at the time the crypto pki
enroll command is issued.
The default key pair is “server-default”. The default bit length is 2048 bits.
Example To configure trustpoint "example" to use the key pair "example-server-key" with a
bit length of 2048, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# rsakeypair example-server-key 2048
Related
Commands
crypto key generate rsa
Parameter Description
<keylabel> The key to be used with the server certificate for this trustpoint.
The name must start with an alphanumeric character, and may
only contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, dashes, or
periods. The maximum length of the name is 63 characters.
<1024-4096>The bit length for the key, to be used if the key is implicitly
generated during server enrollment.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1380
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY MYPUBKEY RSA
show crypto key mypubkey rsa
Overview Use this command to display information about the specified
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman encryption key.
Syntax show crypto key mypubkey rsa [<keylabel>]
Default By default, all keys will be shown.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If no key label is specified, information about all keys is shown. The command
displays the bit length of the key, a key fingerprint (a hash of the key contents to
help uniquely identify a key), and a list of trustpoints in which the server certificate
is using the key.
The specified keys must exist.
Example To show all keys, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# show crypto key mypubkey rsa
Output Figure 38-1: Example output from show crypto key mypubkey rsa
Related
Commands
crypto key generate rsa
Parameter Description
<keylabel> The name of the key to be shown, if specified.
awplus#show crypto key mypubkey rsa
--------------------
RSA Key Pair "example-server-key":
Key size : 2048 bits
Fingerprint : 1A605D73 C2274CB7 853886B3 1C802FC6 7CDE45FB
Trustpoints : example
--------------------
RSA Key Pair "server-default":
Key size : 2048 bits
Fingerprint : 34AC4D2D 5249A168 29D426A3 434FFC59 C4A19901
Trustpoints : local

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1381
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO PKI CERTIFICATES
show crypto pki certificates
Overview Use this command to display information about existing certificates for the
specified trustpoint.
Syntax show crypto pki certificates [<trustpoint>]
Default By default, the certificates for all trustpoints are shown.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If no trustpoint is specified, certificates for all trustpoints are shown. The command
displays the certificates organized into certificate chains. It starts with the server
certificate and then displays its issuer, and continues up the issuer chain until the
root CA certificate is reached.
For each certificate, the command displays the certificate type, the subject’s
distinguished name (the entity identified by the certificate), the issuer’s
distinguished name (the entity that signed the certificate), the validity dates for the
certificate, and the fingerprint of the certificate. The fingerprint is a cryptographic
hash of the certificate contents that uniquely identifies the certificate.
The specified trustpoints must already exist.
Example To show the certificates for the trustpoint “example”, use the following command:
awplus> enable
awplus# show crypto pki certificates example
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The trustpoint for which the certificates are to be shown.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1382
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO PKI CERTIFICATES
Output Figure 38-2: Example output from show crypto pki certificates
Related
Commands
crypto pki trustpoint
awplus>enable
awplus#show crypto pki certificates example
--------------------
Trustpoint "example" Certificate Chain
--------------------
Server certificate
Subject : /O=local/CN=local.loc.lc
Issuer : /C=NZ/CN=local_Signing_CA
Valid From : Nov 11 15:35:21 2015 GMT
Valid To : Aug 31 15:35:21 2018 GMT
Fingerprint : 5A81D34C 759CC4DA CFCA9F65 0303AD83 410B03AF
Intermediate CA certificate
Subject : /C=NZ/CN=example_Signing_CA
Issuer : /C=NZ/CN=example_Root_CA
Valid From : Sep 3 18:45:01 2015 GMT
Valid To : Oct 10 18:45:01 2020 GMT
Fingerprint : AE2D5850 9867D258 ABBEE95E 2E0E3D81 60714920
Imported root certificate
Subject : /C=NZ/CN=example_Root_CA
Issuer : /C=NZ/CN=example_Root_CA
Valid From : Jul 23 18:12:10 2015 GMT
Valid To : May 12 18:12:10 2025 GMT
Fingerprint : 594EDEF9 C7C4308C 36D408E0 77E784F0 A59E8792

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1383
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO PKI ENROLLMENT USER
show crypto pki enrollment user
Overview Use this command to display a list of trustpoints for which RADIUS user
enrollments have been performed, using the crypto pki enroll user command.
This indicates that PKCS#12 files for the user are available for export for the given
trustpoints, using the crypto pki export pkcs12 command.
Syntax crypto pki enrollment user <username>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show the list of trustpoints to which user “exampleuser1” is enrolled, use the
following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus(config)# show crypto pki enrollment user exampleuser1
Output Figure 38-3: Example output from show crypto pki enrollment user
Related
Commands
crypto pki enroll user
crypto pki export pkcs12
Parameter Description
<username> The user for which enrollments are to be shown.
awplus> enable
awplus# show crypto pki enrollment user exampleuser1
User "exampleuser1" is enrolled to the following trustpoints:
local,example

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1384
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO PKI TRUSTPOINT
show crypto pki trustpoint
Overview Use this command to display information about the specified trustpoint.
Syntax show crypto pki trustpoint [<trustpoint>]
Default By default, all trustpoints are shown.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If no trustpoint is specified, information about all trustpoints is shown. The
command displays the authentication status of the trustpoint, the fingerprint of
the root CA certificate (if it exists), the enrollment status of the local server with the
trustpoint, a list of any applications that are configured to use the trustpoint, and
the trustpoint parameters that were configured from trustpoint-configuration
mode.
The specified trustpoints must already exist.
Example To show the details of the trustpoint “example”, use the following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# show crypto pki trustpoint example
Output Figure 38-4: Example output from show crypto pki trustpoint
Related
Commands
crypto pki trustpoint
show crypto pki certificates
Parameter Description
<trustpoint> The name of the trustpoint to be shown
awplus> enable
awplus# show crypto pki trustpoint example
--------------------
Trustpoint "example"
Type : Self-signed certificate authority
Root Certificate: 50C1856B EEC7555A 0F3A61F6 690D9463 67DF74D1
Local Server : The server is enrolled to this trustpoint.
Server Key : example-server-key
Applications : RADIUS
Authentication and Enrollment Parameters:
Enrollment : selfsigned
RSA Key Pair : example-server-key (2048 bits)
--------------------

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1385
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE COMMANDS
SUBJECT-NAME (TRUSTPOINT CONFIGURATION)
subject-name (trustpoint configuration)
Overview Use this command to specify the distinguished name string that should be used for
the subject field in the server certificate, when enrolling the server (generating the
server certificate or server certificate signing request).
Syntax subject-name <word>
Default If no subject name is specified for the trustpoint, then the system automatically
builds a name of the form “/O=AlliedWare Plus/CN=xxxx.yyyy.zzz”, where “xxxx” is
the hostname of the system and “yyyy.zzz” is the default search domain for the
system.
Mode Trustpoint Configuration
Usage The subject name is specified as a variable number of fields, where each field
begins with a forward-slash character (“/”). Each field is of the form “XX=value”,
where “XX” is the abbreviation of the node type in the tree.
Common values include:
• “C” (country),
• “ST” (state),
•“L” (locality),
• “O” (organization),
• “OU” (organizational unit), and
• “CN” (common name).
Of these fields, “CN” is usually the most important.
NOTE: For a server certificate, many applications require that the network name of the
server matches the common name in the server’s certificate.
Example To configure the trustpoint named "example" and set its subject name, use the
following commands:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint example
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# subject-name "/O=My
Company/CN=192.168.1.1
Parameter Description
<word> Specify the subject name as a distinguished name string.
Complex strings (e.g., strings containing spaces) should be
surrounded with double-quote characters.

39
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1387
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
the device to use TACACS+ servers. For more information about TACACS+, see the
TACACS+ Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“authorization commands” on page 1388
•“aaa authorization commands” on page 1390
•“aaa authorization config-commands” on page 1392
•“ip tacacs source-interface” on page 1393
•“show tacacs+” on page 1394
•“tacacs-server host” on page 1396
•“tacacs-server key” on page 1398
•“tacacs-server timeout” on page 1399

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1388
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
authorization commands
Overview This command applies a command authorization method list, defined using the
aaa authorization commands command, to console and VTY lines.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the command authorization
configuration on the console and VTY lines.
Syntax authorization commands <privilege-level> {default|<list-name>}
no authorization commands <privilege-level>
Default The default method list is applied to each console and VTY line by default.
Mode Line Configuration
Usage If the specified method list does not exist users will not be enable to execute any
commands in the specified method list on the specified VTY lines.
Example To apply the TAC15 command authorization method list with privilege level 15 to
VTY lines 0 to 5, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# authorization commands 15 TAC15
To reset the command authorization configuration with privilege level 15 on VTY
lines 0 to 5, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# line vty 0 5
awplus(config-line)# no authorization commands 15
Related
Commands
aaa authorization commands
Parameter Description
<privilege-level> The privilege level of the set of commands the method list
will be applied to.
AlliedWare Plus defines three sets of commands, that are
indexed by a level value:
Level = 1: All commands that can be accessed by a user with
privilege level between 1 and 6 inclusive
Level = 7: All commands that can be accessed by a user with
privilege level between 7 and 14 inclusive
Level = 15: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level 15
default Configure the default authorization commands method list.
<list-name>Configure a named authorization commands method list

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1390
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
aaa authorization commands
Overview This command configures a method list for commands authorization that can be
applied to console or VTY lines. When command authorization is enabled for a
privilege level, only authorized users can executed commands in that privilege
level.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a named method list or disable the
default method list for a privilege level.
Syntax aaa authorization commands <privilege-level>
{default|<list-name>} group tacac+ [none]
no aaa authorization commands <privilege-level>
{default|<list-name>}
Mode Global Configuration
Usage TACACS+ command authorization provides centralized control of the commands
available to a user of an AlliedWare Plus device. Once enabled:
• The command string and username are encrypted and sent to the first
available configured TACACS+ server (the first server configured) for
authorization.
Parameter Description
<privilege-level> The privilege level of the set of commands the method list
will be applied to.
AlliedWare Plus defines three sets of commands, that are
indexed by a level value:
Level = 1: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level between 1 and 6 inclusive
Level = 7: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level between 7 and 14 inclusive
Level = 15: All commands that can be accessed by a user
with privilege level 15
group Specify the server group where authorization messages are
sent. Only the tacacs+ group is available for this
command.
tacac+ Use all TACACS+ servers configured by the tacacs-server
host command.
default Configure the default authorization commands method list.
<list-name>Configure a named authorization commands method list
none If specified, this provides a local fallback to command
authorization so that if authorization servers become
unavailable then the device will accept all commands
normally allowed for the privilege level of the user.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1391
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION COMMANDS
• The TACACS+ server decides if the user is authorized to execute the
command and returns the decision to the AlliedWare Plus device.
• Depending on this decision the device will then either execute the
command or notify the user that authorization has failed.
If multiple TACACS+ servers are configured, and the first server is unreachable or
does not respond, the other servers will be queried, in turn, for an authorization
decision. If all servers are unreachable and a local fallback has been configured,
with the none parameter, then commands are authorized based on the user’s
privilege level; the same behavior as if command authorization had not been
configured. If, however, the local fallback is not configured and all servers become
unreachable then all commands except logout, exit, and quit will be denied.
The default method list is defined with a local fallback unless configured
differently using this command.
Example To configure a commands authorization method list, named TAC15, using all
TACACS+ servers to authorize commands for privilege level 15, with a local
fallback, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization commands 15 TAC15 group
tacacs+ none
To configure the default method list to authorize commands for privilege level 7,
with no local fallback, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization commands 7 default group
tacacs+
To remove the authorization method list TAC15, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authorization commands 15 TAC15
Related
Commands
aaa authorization config-commands
authorization commands
tacacs-server host
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1392
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
AAA AUTHORIZATION CONFIG-COMMANDS
aaa authorization config-commands
Overview Use this command to enable command authorization on configuration mode
commands. By default, command authorization applies to commands in exec
mode only.
Use the no variant of this command to disable command authorization on
configuration mode commands.
Syntax aaa authorization config-commands
no aaa authorization config-commands
Default By default, command authorization is disabled on configuration mode commands.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If authorization of configuration mode commands is not enabled then all
configuration commands are accepted by default, including command
authorization commands.
NOTE: Authorization of configuration commands is required for a secure TACACS+
command authorization configuration as it prevents the feature from being disabled
to gain access to unauthorized exec mode commands.
Example To enable command authorization for configuration mode commands, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# aaa authorization config-commands
To disable command authorization for configuration mode commands, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no aaa authorization config-commands
Related
Commands
aaa authorization commands
authorization commands
tacacs-server host
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1393
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
IP TACACS SOURCE-INTERFACE
ip tacacs source-interface
Overview This command sets the source interface, or IP address, to use for all TACACS+
packets sent from the device. By default, TACACS+ packets use the source IP
address of the egress interface.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the source interface configuration
and use the source IP address of the egress interface.
Syntax ip tacacs source-interface {<interface>|<ip-address>}
no ip tacacs source-interface
Default The source IP address of outgoing TACACS+ packets default to the IP address of
the egress interface.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Setting the source interface ensures that all TACACS+ packets sent from the device
will have the same source IP address. Once configured this affects all TACACS+
packets, namely accounting, authentication, and authorization.
If the specified interface is down or there is no IP address on the interface, then the
source IP address of outgoing TACACS+ packets will default to the IP address of the
egress interface.
Example To configure all outgoing TACACS+ packets to use the IP address of the loop-back
“lo” interface as the source IP address, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip tacacs source-interface lo
To reset the source interface configuration for all TACACS+ packets, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip tacacs source-interface
Related
Commands
tacacs-server host
show tacacs+
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<interface> Interface name.
<ip-address> IP address in the dotted decimal format A.B.C.D.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1394
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
SHOW TACACS+
show tacacs+
Overview This command displays the current TACACS+ server configuration and status.
Syntax show tacacs+
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current status of TACACS+ servers, use the command:
awplus# show tacacs+
Output Figure 39-1: Example output from the show tacacs+ command
TACACS+ Global Configuration
Source Interface : not configured
Timeout : 5 sec
Server Host/ Server
IP Address Status
------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.1.10 Alive
192.168.1.11 Unknown
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show tacacs+ command
Output Parameter Meaning
Source Interface IP address of source interface if set with ip tacacs
source-interface.
Timeout A time interval in seconds.
Server Host/IP Address TACACS+ server hostname or IP address.
Server Status The status of the authentication port.
Alive The server is alive.
Dead The server has timed out.
Error The server is not responding or
there is an error in the key string
entered.
Unknown The server is never used or the
status is unkown.
Unreachable The server is unreachable.
Unresolved The server name can not be
resolved.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1395
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
SHOW TACACS+
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: Source Interface parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1396
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
TACACS-SERVER HOST
tacacs-server host
Overview Use this command to specify a remote TACACS+ server host for authentication,
authorization and accounting, and to set the shared secret key to use with the
TACACS+ server. The parameters specified with this command override the
corresponding global parameters for TACACS+ servers.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified server host as a
TACACS+ authentication and authorization server.
Syntax tacacs-server host {<host-name>|<ip-address>} [key
[8]<key-string>]
no tacacs-server host {<host-name>|<ip-address>}
Default No TACACS+ server is configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage A TACACS+ server host cannot be configured multiple times like a RADIUS server.
As many as four TACACS+ servers can be configured and consulted for login
authentication, enable password authentication and accounting. The first server
configured is regarded as the primary server and if the primary server fails then the
backup servers are consulted in turn. A backup server is consulted if the primary
server fails, not if a login authentication attempt is rejected. The reasons a server
would fail are:
• it is not network reachable
• it is not currently TACACS+ capable
Parameter Description
<host-name>Server host name. The DNS name of the TACACS+ server host.
<ip-address>The IP address of the TACACS+ server host, in dotted decimal
notation A.B.C.D.
key Set shared secret key with TACACS+ servers.
8Specifies that you are entering a password as a string that has
already been encrypted instead of entering a plain text password.
The running config displays the new password as an encrypted
string even if password encryption is turned off.
<key-string>Shared key string applied, a value in the range 1 to 64 characters.
Specifies the shared secret authentication or encryption key for all
TACACS+ communications between this device and the TACACS+
server. This key must match the encryption used on the TACACS+
server. This setting overrides the global setting of the
tacacs-server key command. If no key value is specified, the global
value is used.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1397
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
TACACS-SERVER HOST
• it cannot communicate with the switch properly due to the switch and the
server having different secret keys
Examples To add the server tac1.company.com as the TACACS+ server host, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# tacacs-server host tac1.company.com
To set the secret key to secret on the TACACS+ server 192.168.1.1, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.1 key secret
To remove the TACACS+ server tac1.company.com, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no tacacs-server host tac1.company.com
Related
Commands
aaa accounting commands
aaa authentication login
tacacs-server key
tacacs-server timeout
show tacacs+
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1398
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
TACACS-SERVER KEY
tacacs-server key
Overview This command sets a global secret key for TACACS+ authentication, authorization
and accounting. The shared secret text string is used for TACACS+
communications between the switch and all TACACS+ servers.
Note that if no secret key is explicitly specified for a TACACS+ server with the
tacacs-server host command, the global secret key will be used for the shared
secret for the server.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the global secret key.
Syntax tacacs-server key [8] <key-string>
no tacacs-server key
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to set the global secret key shared between this client and its
TACACS+ servers. If no secret key is specified for a particular TACACS+ server using
the tacacs-server host command, this global key is used.
Examples To set the global secret key to secret for TACACS+ server, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# tacacs-server key secret
To delete the global secret key for TACACS+ server, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no tacacs-server key
Related
Commands
tacacs-server host
show tacacs+
Parameter Description
8Specifies a string in an encrypted format instead of plain text.
The running config will display the new password as an
encrypted string even if password encryption is turned off.
<key-string>Shared key string applied, a value in the range 1 to 64 characters.
Specifies the shared secret authentication or encryption key for
all TACACS+ communications between this device and all
TACACS+ servers. This key must match the encryption used on
the TACACS+ server.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1399
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TACACS+ COMMANDS
TACACS-SERVER TIMEOUT
tacacs-server timeout
Overview Use this command to specify the TACACS+ global timeout value. The timeout
value is how long the device waits for a reply to a TACACS+ request before
considering the server to be dead.
Note that this command configures the timeout parameter for TACACS+ servers
globally.
The no variant of this command resets the transmit timeout to the default (5
seconds).
Syntax tacacs-server timeout <seconds>
no tacacs-server timeout
Default The default timeout value is 5 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the timeout value to 3 seconds, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# tacacs-server timeout 3
To reset the timeout period for TACACS+ servers to the default, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no tacacs-server timeout
Related
Commands
tacacs-server host
show tacacs+
Parameter Description
<seconds>TACACS+ server timeout in seconds, in the range 1 to 1000.

40
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1400
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP Snooping
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter gives detailed information about the commands used to configure
DHCP snooping. For detailed descriptions of related ACL commands, see IPv4
Hardware Access Control List (ACL) Commands. For more information about DHCP
snooping, see the DHCP Snooping Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
DHCP snooping can operate on static link aggregators (e.g. sa2) and dynamic link
aggregators (e.g. po2), as well as on switch ports (e.g. port1.0.2).
Command List •“arp security” on page 1402
•“arp security violation” on page 1403
•“clear arp security statistics” on page 1405
•“clear ip dhcp snooping binding” on page 1406
•“clear ip dhcp snooping statistics” on page 1407
•“debug arp security” on page 1408
•“debug ip dhcp snooping” on page 1409
•“ip dhcp snooping” on page 1410
•“ip dhcp snooping agent-option” on page 1411
•“ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted” on page 1412
•“ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet” on page 1413
•“ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id” on page 1414
•“ip dhcp snooping binding” on page 1415
•“ip dhcp snooping database” on page 1416
•“ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client” on page 1417
•“ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown” on page 1418
•“ip dhcp snooping max-bindings” on page 1419

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1401
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
•“ip dhcp snooping trust” on page 1420
•“ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address” on page 1421
•“ip dhcp snooping violation” on page 1422
•“ip source binding” on page 1423
•“service dhcp-snooping” on page 1425
•“show arp security” on page 1427
•“show arp security interface” on page 1428
•“show arp security statistics” on page 1430
•“show debugging arp security” on page 1432
•“show debugging ip dhcp snooping” on page 1433
•“show ip dhcp snooping” on page 1434
•“show ip dhcp snooping acl” on page 1435
•“show ip dhcp snooping agent-option” on page 1438
•“show ip dhcp snooping binding” on page 1440
•“show ip dhcp snooping interface” on page 1442
•“show ip dhcp snooping statistics” on page 1444
•“show ip source binding” on page 1447

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1402
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
ARP SECURITY
arp security
Overview Use this command to enable ARP security on untrusted ports in the VLANs, so that
the switch only responds to/forwards ARP packets if they have recognized IP and
MAC source addresses.
Use the no variant of this command to disable ARP security on the VLANs.
Syntax arp security
no arp security
Default Disabled
Mode Interface Configuration (VLANs)
Usage Enable ARP security to provide protection against ARP spoofing. DHCP snooping
must also be enabled on the switch (service dhcp-snooping command), and on the
VLANs (ip dhcp snooping command).
Example To enable ARP security on VLANs 2 to 4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# arp security
Related
Commands
arp security violation
show arp security
show arp security interface
show arp security statistics
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1403
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
ARP SECURITY VIOLATION
arp security violation
Overview Use this command to specify an additional action to perform if an ARP security
violation is detected on the ports. ARP security must also be enabled (arp security
command).
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified action, or all actions.
Traffic violating ARP security will be dropped, but no other action will be taken.
Syntax arp security violation {log|trap|link-down} ...
no arp security violation [log|trap|link-down] ...
Default When the switch detects an ARP security violation, it drops the packet. By default,
it does not perform any other violation actions.
Mode Interface Configuration (switch ports, static or dynamic aggregated links)
Usage When the switch detects an ARP security violation on an untrusted port in a VLAN
that has ARP security enabled, it drops the packet. This command sets the switch
to perform additional actions in response to ARP violations.
If a port has been shut down in response to a violation, to bring it back up again
after any issues have been resolved, use the shutdown command.
Example To send SNMP notifications for ARP security violations on ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.6, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server enable trap dhcpsnooping
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# arp security violation trap
Parameter Description
log Generate a log message. To display these messages, use the show log
command.
trap Generate an SNMP notification (trap). To send SNMP notifications,
SNMP must also be configured, and DHCP snooping notifications must
be enabled using the snmp-server enable trap command.
Notifications are limited to one per second and to one per source MAC
and violation reason. Additional violations within a second of a
notification being sent will not result in further notifications.
Default: disabled.
link-down Shut down the port that received the packet.
Default: disabled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1405
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR ARP SECURITY STATISTICS
clear arp security statistics
Overview Use this command to clear ARP security statistics for the specified ports, or for all
ports.
Syntax clear arp security statistics [interface <port-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear statistics for ARP security on interface port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# clear arp security statistics interface port1.0.1
Related
Commands
arp security violation
show arp security
show arp security statistics
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports to clear statistics for. If no ports are specified, statistics are
cleared for all ports. The ports may be switch ports, or static or
dynamic link aggregators.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1406
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IP DHCP SNOOPING BINDING
clear ip dhcp snooping binding
Overview Use this command to remove one or more DHCP Snooping dynamic entries from
the DHCP Snooping binding database. If no options are specified, all entries are
removed from the database.
CAUTION: If you remove entries from the database for current clients, they will
lose IP connectivity until they request and receive a new DHCP lease. If you clear
all entries, all clients connected to untrusted ports will lose connectivity.
Syntax clear ip dhcp snooping binding [<ipaddr>] [interface
<port-list>] [vlan <vid-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command removes dynamic entries from the database. Note that dynamic
entries can also be deleted by using the no variant of the ip dhcp snooping binding
command.
Dynamic entries can individually restored by using the ip dhcp snooping binding
command.
To remove static entries, use the no variant of the ip source binding command.
Example To remove a dynamic lease entry from the DHCP snooping database for a client
with the IP address 192.168.1.2, use the command:
awplus# clear ip dhcp snooping binding 192.168.1.2
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping binding
ip source binding
show ip dhcp snooping binding
Parameter Description
<ipaddr>Remove the entry for this client IP address.
<port-list> Remove all entries for these ports. The port list may contain
switch ports, and static or dynamic link aggregators (channel
groups).
<vid-list> Remove all entries associated with these VLANs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1407
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
CLEAR IP DHCP SNOOPING STATISTICS
clear ip dhcp snooping statistics
Overview Use this command to clear DHCP snooping statistics for the specified ports, or for
all ports.
Syntax clear ip dhcp snooping statistics [interface <port-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear statistics for the DHCP snooping on interface port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# clear ip dhcp snooping statistics interface port1.0.1
Related
Commands
clear arp security statistics
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping statistics
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports to clear statistics for. If no ports are specified, statistics are
cleared for all ports. The port list can contain switch ports, or static or
dynamic link aggregators.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1408
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
DEBUG ARP SECURITY
debug arp security
Overview Use this command to enable ARP security debugging.
Use the no variant of this command to disable debugging for ARP security.
Syntax debug arp security
no debug arp security
Default Disabled
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enable ARP security debugging, use the commands:
awplus# debug arp security
Related
Commands
show debugging arp security
show log
terminal monitor

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1409
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
DEBUG IP DHCP SNOOPING
debug ip dhcp snooping
Overview Use this command to enable the specified types of debugging for DHCP snooping.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the specified types of debugging.
Syntax debug ip dhcp snooping {all|acl|db|packet [detail]}
no debug ip dhcp snooping {all|acl|db|packet [detail]}
Default Disabled
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enable access list debugging for DHCP snooping, use the commands:
awplus# debug ip dhcp snooping acl
Related
Commands
debug arp security
show debugging ip dhcp snooping
show log
terminal monitor
Parameter Description
all All DHCP snooping debug.
acl DHCP snooping access list debug.
db DHCP snooping binding database debug.
packet DHCP snooping packet debug. For the no variant of this command,
this option also disables detailed packet debug, if it was enabled.
detail Detailed packet debug.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1410
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING
ip dhcp snooping
Overview Use this command to enable DHCP snooping on one or more VLANs.
Use the no variant of this command to disable DHCP snooping on the VLANs.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping
no ip dhcp snooping
Default DHCP snooping is disabled on VLANs by default.
Mode Interface Configuration (VLANs)
Usage For DHCP snooping to operate on a VLAN, it must:
• be enabled on the particular VLAN by using this command
• be enabled globally on the switch by using the service dhcp-snooping
command
• have at least one port connected to a DHCP server configured as a trusted
port by using the ip dhcp snooping trust command
Any ACLs on a port that permit traffic matching DHCP snooping entries and block
other traffic, will block all traffic if DHCP snooping is disabled on the port. If you
disable DHCP snooping on particular VLANs using this command, you must also
remove any DHCP snooping ACLs from the ports to maintain connectivity (no
access-group command).
Examples To enable DHCP snooping on VLANs 2 to 4, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping
To disable DHCP snooping on the switch, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2-vlan4
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp snooping
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping trust
service dhcp-snooping
show ip dhcp snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1411
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
Overview Use this command to enable DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information insertion on
the switch. When this is enabled, the switch:
• inserts DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information into DHCP packets that it
receives on untrusted ports
• removes DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information from DHCP packets that
it sends to untrusted ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable DHCP Relay Agent Option 82
insertion.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping agent-option
no ip dhcp snooping agent-option
Default DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 insertion is enabled by default when DHCP snooping
is enabled.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage DHCP snooping must also be enabled on the switch (service dhcp-snooping
command), and on the VLANs (ip dhcp snooping command).
Example To disable DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp snooping agent-option
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping
ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted
service dhcp-snooping
show ip dhcp snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1412
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION ALLOW-UNTRUSTED
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
allow-untrusted
Overview Use this command to enable DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information reception
on untrusted ports. When this is enabled, the switch accepts incoming DHCP
packets that contain DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information on untrusted ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable DHCP Relay Agent Option 82
information reception on untrusted ports.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted
no ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted
Default Disabled
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the switch is connected via untrusted ports to edge switches that insert DHCP
Relay Agent Option 82 information into DHCP packets, you may need to allow
these DHCP packets through the untrusted ports, by using this command.
When this is disabled (default), the switch treats incoming DHCP packets on
untrusted ports that contain DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 information as DHCP
snooping violations: it drops them and applies any violation action specified by the
ip dhcp snooping violation command. The switch stores statistics for packets
dropped; to display these statistics, use the show ip dhcp snooping statistics
command.
Example To enable DHCP snooping Option 82 information reception on untrusted ports,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp snooping agent-option allow-untrusted
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
ip dhcp snooping violation
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1413
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION CIRCUIT-ID VLANTRIPLET
ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id
vlantriplet
Overview Use this command to specify the Circuit ID sub-option of the DHCP Relay Agent
Option 82 field as the VLAN ID and port number. The Circuit ID specifies the switch
port and VLAN ID that the client-originated DHCP packet was received on.
Use the no variant of this command to set the Circuit ID to the default, the VLAN ID
and Ifindex (interface number).
Syntax ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet
no ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id
Default By default, the Circuit ID is the VLAN ID and Ifindex (interface number).
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage The Circuit ID sub-option is included in the DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 field of
forwarded client DHCP packets:
• DHCP snooping Option 82 information insertion is enabled (ip dhcp
snooping agent-option command; enabled by default), and
• DHCP snooping is enabled on the switch (service dhcp-snooping) and on the
VLAN to which the port belongs (ip dhcp snooping)
Examples To set the Circuit ID to vlantriplet for client DHCP packets received on vlan1,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id
vlantriplet
To return the Circuit ID format to the default for vlan1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping agent-option

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1414
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION REMOTE-ID
ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
Overview Use this command to specify the Remote ID sub-option of the DHCP Relay Agent
Option 82 field. The Remote ID identifies the device that inserted the Option 82
information. If a Remote ID is not specified, the Remote ID sub-option is set to the
switch’s MAC address.
Use the no variant of this command to set the Remote ID to the default, the
switch’s MAC address.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id <remote-id>
no ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
Default The Remote ID is set to the switch’s MAC address by default.
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Usage The Remote ID sub-option is included in the DHCP Relay Agent Option 82 field of
forwarded client DHCP packets:
• DHCP snooping Option 82 information insertion is enabled (ip dhcp
snooping agent-option command; enabled by default), and
• DHCP snooping is enabled on the switch (service dhcp-snooping) and on the
VLAN to which the port belongs (ip dhcp snooping)
Examples To set the Remote ID to myid for client DHCP packets received on vlan1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id myid
To return the Remote ID format to the default for vlan1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan1
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
Parameter Description
<remote-id>An alphanumeric (ASCII) string, 1 to 63 characters in length. If
the Remote ID contains spaces, it must be enclosed in double
quotes. Wildcards are not allowed.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1415
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING BINDING
ip dhcp snooping binding
Overview Use this command to manually add a dynamic-like entry (with an expiry time) to
the DHCP snooping database. Once added to the database, this entry is treated as
a dynamic entry, and is stored in the DHCP snooping database backup file. This
command is not stored in the switch’s running configuration.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a dynamic entry for an IP address
from the DHCP snooping database, or to delete all dynamic entries from the
database.
CAUTION: If you remove entries from the database for current clients, they will
lose IP connectivity until they request and receive a new DHCP lease. If you clear
all entries, all clients connected to untrusted ports will lose connectivity.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping binding <ipaddr> [<macaddr>] vlan <vid>
interface <port> expiry <expiry-time>
no ip dhcp snooping binding [<ipaddr>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Note that dynamic entries can also be deleted from the DHCP snooping database
by using the clear ip dhcp snooping binding command.
To add or remove static entries from the database, use the ip source binding
command.
Example To restore an entry in the DHCP snooping database for a DHCP client with the IP
address 192.168.1.2, MAC address 0001.0002.0003, on port1.0.6 of vlan6, and with
an expiry time of 1 hour, use the commands:
awplus# ip dhcp snooping binding 192.168.1.2 0001.0002.0003
vlan 6 interface port1.0.6 expiry 3600
Related
Commands
clear ip dhcp snooping binding
ip source binding
show ip dhcp snooping binding
Parameter Description
<ipaddr>Client’s IP address.
<macaddr>Client’s MAC address in HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
<vid>The VLAN ID for the entry, in the range 1 to 4094.
<port> The port the client is connected to. The port can be a switch port,
or a static or dynamic link aggregation (channel group).
<expiry-time>The expiry time for the entry, in the range 5 to 2147483647
seconds.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1416
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING DATABASE
ip dhcp snooping database
Overview Use this command to set the location of the file to which the dynamic entries in the
DHCP snooping database are written. This file provides a backup for the DHCP
snooping database.
Use the no variant of this command to set the database location back to the
default, a folder named nvs within Flash memory.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping database {nvs|flash|card}
no ip dhcp snooping database
Default nvs
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the location of the backup file is changed by using this command, a new file is
created in the new location, and the old version of the file remains in the old
location. This can be removed if necessary (hidden file: .dhcp.dsn.gz).
Example To set the location of the DHCP snooping database to Flash memory, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp snooping database flash
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping
Parameter Description
nvs The switch checks the database and writes the file to a folder named nvs
within Flash memory on the switch at 2 second intervals if it has
changed.
flash The switch checks the database and writes the file to Flash memory on
the switch at 60 second intervals if it has changed.
card The switch checks the database and writes the file to an SD card installed
in the switch at 2 second intervals if it has changed.
Note that a current DHCP snooping backup database file is essential to
maintain connectivity for DHCP clients after a switch reboot. If you
configure the switch to save this file to an SD card, we recommend that
you ensure the card is always present.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1417
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING DELETE-BY-CLIENT
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
Overview Use this command to set the switch to remove a dynamic entry from the DHCP
snooping database when it receives a valid DHCP release message with matching
IP address, VLAN ID, and client hardware address on an untrusted port, and to
discard release messages that do not match an entry in the database.
Use the no variant of this command to set the switch to forward DHCP release
messages received on untrusted ports without removing any entries from the
database.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
no ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
Default Enabled: by default, DHCP lease entries are deleted from the DHCP snooping
database when matching DHCP release messages are received.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage DHCP clients send a release message when they no longer wish to use the IP
address they have been allocated by a DHCP server. Use this command to enable
DHCP snooping to use the information in these messages to remove entries from
its database immediately. Use the no variant of this command to ignore these
release messages. Lease entries corresponding to ignored DHCP release messages
eventually time out when the lease expires.
Examples To set the switch to delete DHCP snooping lease entries from the DHCP snooping
database when a matching release message is received, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
To set the switch to forward and ignore the content of any DHCP release messages
it receives, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp snooping delete-by-client
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1418
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING DELETE-BY-LINKDOWN
ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
Overview Use this command to set the switch to remove a dynamic entry from the DHCP
snooping database when its port goes down. If the port is part of an aggregated
link, the entries in the database are only deleted if all the ports in the aggregated
link are down.
Use the no variant of this command to set the switch not to delete entries when
ports go down.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
no ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
Default Disabled: by default DHCP Snooping bindings are not deleted when an interface
goes down.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the switch to delete DHCP snooping lease entries from the DHCP snooping
database when links go down, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
To set the switch not to delete DHCP snooping lease entries from the DHCP
snooping database when links go down, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp snooping delete-by-linkdown
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1419
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING MAX-BINDINGS
ip dhcp snooping max-bindings
Overview Use this command to set the maximum number of DHCP lease entries that can be
stored in the DHCP snooping database for each of the ports. Once this limit has
been reached, no further DHCP lease allocations made to devices on the port are
stored in the database.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the maximum to the default, 1.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping max-bindings <0-520>
no ip dhcp snooping max-bindings
Default The default for maximum bindings is 1.
Mode Interface Configuration (port)
Usage The maximum number of leases cannot be changed for a port while there are
DHCP snooping Access Control Lists (ACL) associated with the port. Before using
this command, remove any DHCP snooping ACLs associated with the ports. To
display ACLs used for DHCP snooping, use the show ip dhcp snooping acl
command.
In general, the default (1) will work well on an edge port with a single directly
connected DHCP client. If the port is on an aggregation switch that is connected to
an edge switch with multiple DHCP clients connected through it, then use this
command to increase the number of lease entries for the port.
If there are multiple VLANs configured on the port, the limit is shared between all
the VLANs on this port. For example, the default only allows one lease to be stored
for one VLAN. To allow connectivity for the other VLANs, use this command to
increase the number of lease entries for the port.
Example To set the maximum number of bindings to be stored in the DHCP snooping
database to 10 per port for ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping max-bindings 10
Related
Commands
access-group
show ip dhcp snooping acl
show ip dhcp snooping interface
Parameter Description
<0-520>The maximum number of bindings that will be stored for the port in
the DHCP snooping binding database. If 0 is specified, no entries will
be stored in the database for the port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1420
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING TRUST
ip dhcp snooping trust
Overview Use this command to set the ports to be DHCP snooping trusted ports.
Use the no variant of this command to return the ports to their default as untrusted
ports.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping trust
no ip dhcp snooping trust
Default All ports are untrusted by default.
Mode Interface Configuration (port)
Usage Typically, ports connecting the switch to trusted elements in the network (towards
the core) are set as trusted ports, while ports connecting untrusted network
elements are set as untrusted. Configure ports connected to DHCP servers as
trusted ports.
Example To set switch ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.2 to be trusted ports, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1421
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING VERIFY MAC-ADDRESS
ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
Overview Use this command to verify that the source MAC address and client hardware
address match in DHCP packets received on untrusted ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable MAC address verification.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
no ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
Default Enabled—source MAC addresses are verified by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When MAC address verification is enabled, the switch treats DHCP packets with
source MAC address and client hardware address that do not match as DHCP
snooping violations: it drops them and applies any other violation action specified
by the ip dhcp snooping violation command. To bring the port back up again after
any issues have been resolved, use the shutdown command.
Example To disable MAC address verification on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping violation
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping statistics
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1422
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP DHCP SNOOPING VIOLATION
ip dhcp snooping violation
Overview Use this command to specify the action the switch will take when it detects a DHCP
snooping violation by a DHCP packet on the ports.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the specified violation actions, or all
violation actions.
Syntax ip dhcp snooping violation {log|trap|link-down} ...
no ip dhcp snooping violation [{log|trap|link-down} ...]
Default By default, DHCP packets that violate DHCP snooping are dropped, but no other
violation action is taken.
Mode Interface Configuration (port)
Usage If a port has been shut down in response to a violation, to bring it back up again
after any issues have been resolved, use the shutdown command.
IP packets dropped by DHCP snooping filters do not result in other DHCP snooping
violation actions.
Example To set the switch to send an SNMP notification and set the link status to link-down
if it detects a DHCP snooping violation on switch ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.4, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server enable trap dhcpsnooping
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping violation trap link-down
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping interface
show log
snmp-server enable trap
Parameter Description
log Generate a log message. To display these messages, use the show log
command.
Default: disabled.
trap Generate an SNMP notification (trap). To send SNMP notifications,
SNMP must also be configured, and DHCP snooping notifications
must be enabled using the snmp-server enable trap command.
Notifications are limited to one per second and to one per source
MAC and violation reason.
Default: disabled.
link-down Set the port status to link-down.
Default: disabled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1423
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP SOURCE BINDING
ip source binding
Overview Use this command to add or replace a static entry in the DHCP snooping database.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the specified static entry or all static
entries from the database.
Syntax ip source binding <ipaddr> [<macaddr>] vlan <vid> interface
<port>
no ip source binding [<ipaddr>]
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command removes static entries from the database.
To remove dynamic entries, use the clear ip dhcp snooping binding command or
the no variant of the ip dhcp snooping binding command.
Examples To add a static entry to the DHCP snooping database for a client with the IP address
192.168.1.2, MAC address 0001.0002.0003, on port1.0.6 of vlan6, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip source binding 192.168.1.2 0001.0002.0003
vlan 6 interface port1.0.6
To remove the static entry for IP address 192.168.1.2 from the database, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip source binding 192.168.1.2
To remove all static entries from the database, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip source binding
Parameter Description
<ipaddr>Client’s IP address. If there is already an entry in the DHCP
snooping database for this IP address, then this command
replaces it with the new entry.
<macaddr>Client’s MAC address in HHHH.HHHH.HHHH format.
<vid>The VLAN ID associated with the entry.
<port>The port the client is connected to.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1425
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SERVICE DHCP-SNOOPING
service dhcp-snooping
Overview Use this command to enable the DHCP snooping service globally on the switch.
This must be enabled before other DHCP snooping configuration commands can
be entered.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the DHCP snooping service on the
switch. This removes all DHCP snooping configuration from the running
configuration, except for any DHCP snooping maximum bindings settings (ip dhcp
snooping max-bindings command), and any DHCP snooping-based Access
Control Lists (ACLs), which are retained when the service is disabled.
Syntax service dhcp-snooping
no service dhcp-snooping
Default DHCP snooping is disabled on the switch by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage For DHCP snooping to operate on a VLAN, it must be enabled on the switch by
using this command, and also enabled on the particular VLAN by using the ip dhcp
snooping command.
For DHCP snooping to operate on a VLAN, it must:
• be enabled globally on the switch by using this command
• be enabled on the particular VLAN by using the ip dhcp snooping command
• have at least one port connected to a DHCP server configured as a trusted
port by using the ip dhcp snooping trust command
If you disable the DHCP snooping service by using the no variant of this command,
all DHCP snooping configuration (including ARP security, but excluding maximum
bindings and ACLs) is removed from the running configuration, and the DHCP
snooping database is deleted from active memory. If you re-enable the service, the
switch repopulates the DHCP snooping database from the dynamic lease entries
in the database backup file (see the ip dhcp snooping database command). The
lease expiry times are updated.
The DHCP snooping service cannot be enabled on a switch that is configured with
any of the following features, or vice versa:
• web authentication (auth-web enable command)
• roaming authentication (auth roaming enable command, auth roaming
disconnected command)
• guest VLAN authentication (auth guest-vlan command).
Any ACLs on a port that permit traffic matching DHCP snooping entries and block
other traffic, will block all traffic if DHCP snooping is disabled on the port. If you
disable DHCP snooping on the switch using this command, you must also remove
any DHCP snooping ACLs from the ports to maintain connectivity (no
access-group command).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1426
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SERVICE DHCP-SNOOPING
Examples To enable DHCP snooping on the switch, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service dhcp-snooping
To disable DHCP snooping on the switch, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service dhcp-snooping
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping
ip dhcp snooping database
ip dhcp snooping max-bindings
show ip dhcp snooping
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1427
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW ARP SECURITY
show arp security
Overview Use this command to display ARP security configuration.
Syntax show arp security
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display ARP security configuration on the switch use the command:
awplus# show arp security
Related
Commands
arp security
show arp security interface
show arp security statistics
Table 1: Example output from the show arp security command
awplus# show arp security
ARP Security Information:
Total VLANs enabled ............. 2
Total VLANs disabled ............ 11
vlan1 .............. Disabled
vlan2 .............. Disabled
vlan3 .............. Disabled
vlan4 .............. Disabled
vlan5 .............. Disabled
vlan100 ............ Disabled
vlan101 ............ Disabled
vlan102 ............ Disabled
vlan103 ............ Disabled
vlan104 ............ Disabled
vlan105 ............ Enabled
vlan1000 ........... Disabled
vlan1001 ........... Enabled
Table 2: Parameters in the output from the show arp security command
Parameter Description
Total VLANs enabled The number of VLANs that have ARP security enabled.
Total VLANs disabled The number of VLANs that have ARP security disabled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1428
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW ARP SECURITY INTERFACE
show arp security interface
Overview Use this command to display ARP security configuration for the specified ports or
all ports.
Syntax show arp security interface [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display ARP security configuration for ports, use the command:
awplus# show arp security interface
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports to display ARP security information about. The port list can
include switch ports, and static or dynamic aggregated links.
Table 3: Example output from the show arp security interface command
awplus#show arp security interface
Arp Security Port Status and Configuration:
Port: Provisioned ports marked with brackets, e.g. (portx.y.z)
KEY: LG = Log
TR = Trap
LD = Link down
Port Action
-------------------------------
port1.0.1 -- -- --
port1.0.2 -- -- --
port1.0.3 LG TR LD
port1.0.4 LG -- --
port1.0.5 LG -- --
port1.0.6 LG TR --
port1.0.7 LG -- LD
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1429
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW ARP SECURITY INTERFACE
Related
Commands
arp security violation
show arp security
show arp security statistics
show log
snmp-server enable trap
Table 4: Parameters in the output from the show arp security interface
command
Parameter Description
Action The action the switch takes when it detects an ARP security violation
on the port.
Port The port. Parentheses indicate that ports are configured for
provisioning.
LG, Log Generate a log message
TR, Trap Generate an SNMP notification (trap).
LD, Link
down Shut down the link.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1430
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW ARP SECURITY STATISTICS
show arp security statistics
Overview Use this command to display ARP security statistics for the specified ports or all
ports.
Syntax show arp security statistics [detail] [interface <port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the brief statistics for the ARP security, use the command:
awplus# show arp security statistics
Parameter Description
detail Display detailed statistics.
interface <port-list>Display statistics for the specified ports. The port list
can include switch ports, and static or dynamic
aggregated links
Table 5: Example output from the show arp security statistics command
awplus# show arp security statistics
DHCP Snooping ARP Security Statistics:
In In
Interface Packets Discards
---------------------------------
port1.0.3 20 20
port1.0.4 30 30
port1.0.12 120 0
Table 6: Parameters in the output from the show arp security statistics
command
Parameter Description
Interface A port name. Parentheses indicate that ports are configured for
provisioning.
In Packets The total number of incoming ARP packets that are processed by
DHCP Snooping ARP Security
In
Discards The total number of ARP packets that are dropped by DHCP Snooping
ARP Security.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1431
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW ARP SECURITY STATISTICS
Related
Commands
arp security
arp security violation
clear arp security statistics
show arp security
show arp security interface
show log
Table 7: Example output from the show arp security statistics detail command
awplus#show arp security statistics detail
DHCP Snooping ARP Security Statistics:
Interface ...................... port1.0.3
In Packets ................... 20
In Discards .................. 20
No Lease ................... 20
Bad Vlan ................... 0
Bad Port ................... 0
Source Ip Not Allocated .... 0
Interface ...................... port1.0.4
In Packets ................... 30
In Discards .................. 30
No Lease ................... 30
Bad Vlan ................... 0
Bad Port ................... 0
Source Ip Not Allocated .... 0
Interface ...................... port1.0.12
In Packets ................... 120
In Discards .................. 0
No Lease ................... 0
Bad Vlan ................... 0
Bad Port ................... 0
Source Ip Not Allocated .... 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1432
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING ARP SECURITY
show debugging arp security
Overview Use this command to display the ARP security debugging configuration.
Syntax show debugging arp security
Mode User and Privileged Exec
Example To display the debugging settings for ARP security on the switch, use the
command:
awplus# show debugging arp security
Related
Commands
arp security violation
debug arp security
Table 8: Example output from the show debugging arp security command
awplus# show debugging arp security
ARP Security debugging status:
ARP Security debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1433
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING IP DHCP SNOOPING
show debugging ip dhcp snooping
Overview Use this command to display the DHCP snooping debugging configuration.
Syntax show debugging ip dhcp snooping
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the DHCP snooping debugging configuration, use the command:
awplus# show debugging ip dhcp snooping
Related
Commands
debug ip dhcp snooping
show log
Table 9: Example output from the show debugging ip dhcp snooping
command
awplus# show debugging ip dhcp snooping
DHCP snooping debugging status:
DHCP snooping debugging is off
DHCP snooping all debugging is off
DHCP snooping acl debugging is off
DHCP snooping binding DB debugging is off
DHCP snooping packet debugging is off
DHCP snooping detailed packet debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1434
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING
show ip dhcp snooping
Overview Use this command to display DHCP snooping global configuration on the switch.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display global DHCP snooping configuration on the switch, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping
Related
Commands
service dhcp-snooping
show arp security
show ip dhcp snooping acl
show ip dhcp snooping binding
show ip dhcp snooping interface
Table 40-1: Example output from show ip dhcp snooping
DHCP Snooping Information:
DHCP Snooping service ............. Enabled
Binding delete by client .......... Disabled
Binding delete by link down ....... Disabled
Verify MAC address ................ Disabled
SNMP DHCP Snooping trap ........... Disabled
DHCP Snooping database:
Database location ................. nvs Number of entries in
database ..... 2
DHCP Snooping VLANs:
Total VLANs enabled ............... 1
Total VLANs disabled .............. 9
vlan1 .............. Enabled
vlan2 .............. Disabled
vlan3 .............. Disabled
vlan4 .............. Disabled
vlan5 .............. Disabled
vlan100 ............ Disabled
vlan101 ............ Disabled
vlan105 ............ Disabled
vlan1000 ........... Disabled
vlan1001 ........... Disabled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1435
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING ACL
show ip dhcp snooping acl
Overview Use this command to display information about the Access Control Lists (ACL) that
are using the DHCP snooping database.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping acl
show ip dhcp snooping acl [detail|hardware] [interface
[<interface-list>]]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display DHCP snooping ACL information, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping acl
To display DHCP snooping hardware ACL information, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping acl hardware
Parameter Description
detail Detailed DHCP Snooping ACL information.
hardware DHCP Snooping hardware ACL information.
interface ACL Interface information.
<interface-list>The interfaces to display information about.
Table 41: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping acl command
awplus#show ip dhcp snooping acl
DHCP Snooping Based Filters Summary:
Maximum Template Attached
Interface Bindings Bindings Filters Hardware Filters
----------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.1 1 520 0 0
port1.0.2 1 3 2 6
port1.0.3 1 2 4 8
port1.0.4 1 2 7 14
port1.0.5 0 2 6 12
port1.0.6 0 1 0 0
port1.0.7 0 1 0 0
port1.0.8 0 1 0 0
port1.0.9 0 1 0 0
port1.0.10 0 1 0 0
port1.0.11 0 1 0 0
port1.0.12 0 1 0 0
(port2.0.1 ) 0 520 0 0
(port2.0.2 ) 0 1 0 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1436
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING ACL
To display detailed DHCP snooping ACL information for port 1.0.4, use the
command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping acl detail interface port1.0.4
Table 42: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping acl hardware command
awplus#show ip dhcp snooping acl hardware
DHCP Snooping Based Filters in Hardware:
Interface Access-list(/ClassMap) Source IP Source MAC
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 10.10.10.10 aaaa.bbbb.cccc
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 20.20.20.20 0000.aaaa.bbbb
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.2 dhcpsn1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 30.30.30.30 aaaa.bbbb.dddd
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 40.40.40.40 0000.aaaa.cccc
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 50.50.50.50 0000.aaaa.dddd
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 60.60.60.60 0000.aaaa.eeee
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.3 dhcpsn2/cmap1 0.0.0.0 0000.0000.0000
port1.0.4 dhcpsn3/cmap2 70.70.70.70
port1.0.4 dhcpsn3/cmap2 80.80.80.80
port1.0.4 dhcpsn2/cmap1 70.70.70.70
port1.0.4 dhcpsn2/cmap1 80.80.80.80
port1.0.4 dhcpsn1 70.70.70.70
port1.0.4 dhcpsn1 80.80.80.80

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1437
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING ACL
Related
Commands
access-list hardware (named hardware ACL)
show access-list (IPv4 Hardware ACLs)
Table 43: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping acl detail interface command
awplus#show ip dhcp snooping acl detail interface port1.0.4
DHCP Snooping Based Filters Information:
port1.0.4 : Maximum Bindings ........... 2
port1.0.4 : Template filters ........... 7
port1.0.4 : Attached hardware filters .. 14
port1.0.4 : Current bindings ........... 1, 1 free
port1.0.4 Client 1 ................ 120.120.120.120
port1.0.4 : Templates: cheese (via class-map: cmap2)
port1.0.4 : 10 permit ip dhcpsnooping 100.0.0.0/8
port1.0.4 : Template: dhcpsn2 (via class-map: cmap1)
port1.0.4 : 10 permit ip dhcpsnooping any
port1.0.4 : 20 permit ip dhcpsnooping 10.0.0.0/8
port1.0.4 : 30 permit ip dhcpsnooping 20.0.0.0/8
port1.0.4 : 40 permit ip dhcpsnooping 30.0.0.0/8
port1.0.4 : Template: dhcpsn1 (via access-group)
port1.0.4 : 10 permit ip dhcpsnooping any mac dhcpsnooping abcd.0000.0000 00
00.ffff.ffff
port1.0.4 : 20 permit ip dhcpsnooping any

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1438
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION
show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
Overview Use this command to display DHCP snooping Option 82 information for all
interfaces, a specific interface or a range of interfaces.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping agent-option [interface <interface-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display DHCP snooping Option 82 information for all interfaces, use the
command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
To display DHCP snooping Option 82 information for vlan1, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping agent-option interface vlan1
To display DHCP snooping Option 82 information for port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping agent-option interface port1.0.1
Parameter Description
interface Specify the interface.
<interface-list>The name of the interface or interfaces.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1439
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING AGENT-OPTION
Output Figure 40-1: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
command
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping agent-option
ip dhcp snooping agent-option circuit-id vlantriplet
ip dhcp snooping agent-option remote-id
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping interface
awplus#show ip dhcp snooping agent-option
DHCP Snooping Option 82 Configuration:
Key: C Id = Circuit Id Format
R Id = Remote Id
S Id = Subscriber Id
Option 82 insertion ............... Enabled
Option 82 on untrusted ports ...... Not allowed
----------------------------------------------------------------
vlan1 C Id = vlanifindex
R Id = Access-Island-01-M1
vlan2 C Id = vlantriplet
R Id = Access-Island-01-M1
vlan3 C Id = vlantriplet
R Id = Access-Island-01-M3
vlan4 C Id = vlantriplet
R Id = 0000.cd28.074c
vlan5 C Id = vlantriplet
R Id = 0000.cd28.074c
vlan6 C Id = vlantriplet
R Id = 0000.cd28.074c
port1.0.1 S Id =
port1.0.2 S Id =
port1.0.3 S Id = phone_1
port1.0.4 S Id =
port1.0.5 S Id = PC_1
port1.0.6 S Id = phone_2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1440
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING BINDING
show ip dhcp snooping binding
Overview Use this command to display all dynamic and static entries in the DHCP snooping
binding database.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping binding
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display entries in the DHCP snooping database, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping binding
Table 44: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping binding command
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping binding
DHCP Snooping Bindings:
Client MAC Server Expires
IP Address Address IP Address VLAN Port (sec) Type
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.2.3.4 aaaa.bbbb.cccc -- 7 1.0.6 Infinite Stat
1.2.3.6 any -- 4077 1.0.6 Infinite Stat
1.3.4.5 any -- 1 sa1 Infinite Stat
111.111.100.101 0000.0000.0001 111.112.1.1 1 1.0.6 4076 Dyna
111.111.101.108 0000.0000.0108 111.112.1.1 1 1.0.6 4084 Dyna
111.111.101.109 0000.0000.0109 111.112.1.1 1 1.0.6 4085 Dyna
111.211.100.101 -- -- 1 1.0.2 2147483325 Dyna
111.211.100.109 00b0.0000.0009 111.112.111.111 1 1.0.2 21 Dyna
111.211.101.101 00b0.0000.0101 111.112.111.111 1 1.0.2 214 Dyna
Total number of bindings in database: 9
Table 45: Parameters in the output from the show ip dhcp snooping binding
command
Parameter Description
Client IP The IP address of the DHCP client.
MAC Address The MAC address of the DHCP client.
Server IP The IP address of the DHCP server.
VLAN The VLAN associated with this entry.
Port The port the client is connected to.
Expires (sec) The time in seconds until the lease expires.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1441
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING BINDING
Related
Commands
ip dhcp snooping binding
ip dhcp snooping max-bindings
show ip source binding
Type The source of the entry:
• Dyna: dynamically entered by snooping DHCP traffic,
configured by the ip dhcp snooping binding
command, or loaded from the database backup file.
• Stat: added statically by the ip source binding
command
Total number of
bindings in
database
The total number of dynamic and static lease entries in
the DHCP snooping database.
Table 45: Parameters in the output from the show ip dhcp snooping binding
command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1442
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING INTERFACE
show ip dhcp snooping interface
Overview Use this command to display information about DHCP snooping configuration and
leases for the specified ports, or all ports.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping interface [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display DHCP snooping information for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping interface
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports to display DHCP snooping configuration information
for. If no ports are specified, information for all ports is displayed.
Table 46: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping interface command
awplus#show ip dhcp snooping interface
DHCP Snooping Port Status and Configuration:
Port: Provisioned ports marked with brackets, e.g. (portx.y.z)
Action: LG = Log
TR = Trap
LD = Link down
Full Max
Port Status Leases Leases Action Subscriber-ID
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.1 Untrusted 1 1 LG -- --
port1.0.2 Untrusted 0 50 LG TR LD Building 1 Level 1
port1.0.3 Untrusted 0 50 LG -- --
port1.0.4 Untrusted 0 50 LG -- -- Building 1 Level 2
port1.0.5 Untrusted 0 50 LG -- LD Building 2 Level 1
port1.0.6 Untrusted 0 1 LG -- --
port1.0.7 Untrusted 0 1 LG -- --
port1.0.8 Untrusted 0 1 LG -- --
port1.0.9 Untrusted 0 1 -- TR --
port1.0.10 Untrusted 0 1 -- -- LD
port1.0.11 Trusted 0 1 -- -- --
port1.0.12 Trusted 0 1 -- -- --

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1443
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp snooping
show ip dhcp snooping statistics
show running-config dhcp
Table 47: Parameters in the output from the show ip dhcp snooping interface
command
Parameter Description
Port The port interface name.
Status The port status: untrusted (default) or trusted.
Full Leases The number of entries in the DHCP snooping database for the
port.
Max Leases The maximum number of entries that can be stored in the
database for the port.
Action The DHCP snooping violation actions for the port.
Subscriber
ID The subscriber ID for the port. If the subscriber ID is longer than 34
characters, only the first 34 characters are displayed. To display
the whole subscriber ID, use the command show running-config
dhcp.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1444
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING STATISTICS
show ip dhcp snooping statistics
Overview Use this command to display DHCP snooping statistics.
Syntax show ip dhcp snooping statistics [detail] [interface
<interface-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the current DHCP snooping statistics for all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping statistics
Parameter Description
detail Display detailed statistics.
interface
<interface-list>Display statistics for the specified interfaces. The interface list
can contain switch ports, static or dynamic link aggregators
(channel groups), or VLANs.
Table 48: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping statistics
command
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping statistics
DHCP Snooping Statistics:
In BOOTP In BOOTP In In
Interface Packets Requests Replies Discards
------------------------------------------------------------
vlan1 444 386 58 223
port1.0.1 386 386 0 223
port1.0.2 0 0 0 0
port1.0.3 0 0 0 0
port1.0.4 0 0 0 0
port1.0.5 0 0 0 0
port1.0.6 58 0 58 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1445
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING STATISTICS
Table 49: Example output from the show ip dhcp snooping statistics detail command
awplus# show ip dhcp snooping statistics detail
DHCP Snooping Statistics:
Interface ........................................ port1.0.1, All counters 0
Interface ........................................ port1.0.2, All counters 0
Interface ........................................ port1.0.3, All counters 0
Interface ........................................ port1.0.4
In Packets ..................................... 50
In BOOTP Requests ............................ 25
In BOOTP Replies ............................. 25
In Discards .................................... 1
Invalid BOOTP Information .................... 0
Invalid DHCP ACK ............................. 0
Invalid DHCP Release or Decline .............. 0
Invalid IP/UDP Header ........................ 0
Max Bindings Exceeded ........................ 1
Reply Received On Untrusted Port ............. 0
Source MAC/CHADDR Mismatch ................... 0
Static Entry Already Exists .................. 0
Interface ........................................ port1.0.5, All counters 0
Interface ........................................ port1.0.6, All counters 0
Table 50: Parameters in the output from the show ip dhcp snooping statistics
command
Parameter Description
Interface The interface name.
In Packets The total number of incoming packets that are processed
by DHCP Snooping.
In BOOTP Requests The total number of incoming BOOTP Requests.
In BOOTP Replies The total number of incoming BOOTP Replies.
In Discards The total number of incoming packets that have been
discarded.
Invalid BOOTP
Information Packet contained invalid BOOTP information, such as an
invalid BOOTP.OPCode.
Invalid DHCP ACK A DHCP ACK message was discarded, for reasons such as
missing Server Option or Lease Option.
Invalid DHCP
Release or Decline A DHCP Release or Decline message was discarded, for
reasons such as mismatch between received interface
and current binding information.
Invalid IP/UDP
Header A problem was detected in the IP or UDP header of the
packet.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1446
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SNOOPING STATISTICS
Related
Commands
clear ip dhcp snooping statistics
ip dhcp snooping
ip dhcp snooping violation
Max Bindings
Exceeded Accepting the packet would cause the maximum
number of bindings on a port to be exceeded.
Reply Received On
Untrusted Port A BOOTP reply was received on an untrusted port.
Source MAC/CHADDR
Mismatch The L2 Source MAC address of the packet did not match
the client hardware address field (BOOTP.CHADDR).
Static Entry
Already Exists An entry could not be added as a static entry already
exists.
Table 50: Parameters in the output from the show ip dhcp snooping statistics
command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1447
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP SOURCE BINDING
show ip source binding
Overview Use this command to display static entries in the DHCP snooping database. These
are the entries that have been added by using the ip source binding command.
Syntax show ip source binding
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display static entries in the DHCP snooping database information, use the
command:
awplus# show ip source binding
Related
Commands
ip source binding
show ip dhcp snooping binding
Table 51: Example output from the show ip source binding command
awplus# show ip source binding
IP Source Bindings:
Client MAC Expires
IP Address Address VLAN Port (sec) Type
----------------------------------------------------------------
1.1.1.1 0000.1111.2222 1 port1.0.1 Infinite Static
Table 52: Parameters in the output from the show ip source binding command
Parameter Description
Client IP
Address The IP address of the DHCP client.
MAC Address The MAC address of the DHCP client.
VLAN The VLAN ID the packet is received on.
Port The Layer 2 port name the packet is received on.
Expires (sec) Always infinite for static bindings, or when the leave time in
the DHCP message was 0xffffffff (infinite).
Type DHCP Snooping binding type: Static

41
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1448
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OpenFlow
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
the OpenFlow protocol.
Command List •“openflow” on page 1449
•“openflow controller” on page 1450
•“openflow datapath-id” on page 1452
•“openflow failmode” on page 1453
•“openflow failmode standalone” on page 1455
•“openflow inactivity” on page 1456
•“openflow native vlan” on page 1457
•“openflow ssl peer certificate” on page 1458
•“openflow ssl trustpoint” on page 1459
•“openflow version” on page 1460
•“show openflow config” on page 1461
•“show openflow coverage” on page 1463
•“show openflow flows” on page 1465
•“show openflow rules” on page 1468
•“show openflow ssl” on page 1470
•“show openflow status” on page 1471

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1449
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW
openflow
Overview Use this command to specify a port or static aggregator as a data plane port. The
ingress and egress traffic on the data plane port become controlled by the
OpenFlow Controller. A data plane port number is assigned to the port
automatically.
Use the no variant of this command to cancel the setting of a port as a data plane
port.
Syntax openflow
no openflow
Default All the ports are non-data plane ports by default.
Mode Interface mode for a switch port (e.g. port1.0.1) or static aggregator (e.g. sa1)
Example To specify port1.0.1 as a data plane port:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# openflow
Related
Commands
show openflow config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1450
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW CONTROLLER
openflow controller
Overview Use this command to specify the controller name, address, and port number of the
OpenFlow Controller. If you do not specify a controller name, a name will
automatically be created using the following format: ‘ocxx’, where ‘xx’ is the
sequential number starting from 1.
You can specify one or more OpenFlow Controllers to the switch.
Use the no variant of this command to delete one or more OpenFlow Controllers
specified to the switch.
You can delete a controller by specifying only the controller name. If you do not
know the controller name, you can identify it from the show openflow config
command output.
Syntax openflow controller <protocol> <address> <port>
openflow controller <controller-name> <protocol> <address>
<port>
no openflow controller <controller-name>
Default No OpenFlow Controller is configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The older version of this command is supported. If you enter the legacy CLI syntax
(without the controller name), it will automatically adapt and display in the
running configuration as the newer syntax.
Parameter Description
<controller-name>The user specified or auto-generated (in the case of
legacy syntax) controller name that can contain
alphanumeric and/or special characters other than the
fo l l owing se t o f c h a rac ters: ' : ', ' =', ',', '[', ']', ' {', '}', '!', ' < ', '>'
<protocol> The protocol type to communicate with the OpenFlow
Controller.
There are two options: TCP and SSL.
Use TCP for an insecure connection. Use SSL for a
connection protected by TLS. OpenFlow switches
support TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2. The TLS version
used between an OpenFlow switch and OpenFlow
Controller is determined by peer negotiation.
<address> The IPv4 address of the Controller.
<port> Port number used to communicate with the Controller.
The IANA has assigned the number 6653 for this
purpose, but a different number can be used for local
reasons.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1451
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW CONTROLLER
For example, entering the legacy command:
awplus(config)# openflow controller tcp 192.168.1.2 6653
Displays as following in the running-config:
awplus(config)# openflow controller oc1 tcp 192.168.1.2 6653
Examples To add an OpenFlow Controller with the address 10.1.1.1 using the TCP protocol
and the IANA assigned port number of 6653, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow controller tcp 10.1.1.1 6653
To add an OpenFlow Controller for the switch whose name is controller1, with the
address 10.1.2.1 using the TCP protocol on port number 6653, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow controller controller1 tcp 10.1.2.1
6653
To delete an OpenFlow Controller whose name is controller1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow controller controller1
Related
Commands
show openflow config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Version 5.4.8-2.1: <controller-name> parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1452
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW DATAPATH-ID
openflow datapath-id
Overview Use this command to change the Datapath Identifier (DPID) of the OpenFlow
switch.
Use the no variant of this command to revert back to the default DPID.
Syntax openflow datapath-id <dpid>
no openflow datapath-id
Default Each OpenFlow instance on a switch is identified by a Datapath Identifier. This is a
64 bit number. By default, the lower 48 bits are configured based on the switch
MAC address. The top 16 bits are padded with zeros.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command changes the DPID, which is used as the OpenFlow switch ID in
OpenFlow Controller(s).
Example To change the DPID to “0000000000000001”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow datapath-id 1
To revert back to the default DPID, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow datapath-id
Related
Commands
show openflow status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Parameter Description
<dpid>The DPID field consists of 16 Hex digits. If you specify a DPID less
than 16 Hex digits, then the upper bits are padded out with zeros.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1453
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW FAILMODE
openflow failmode
Overview Use this command to set the operation mode for the switch when the Controller
connection fails or no Controllers are defined.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default secure mode.
Syntax openflow failmode secure non-rule-expired
openflow failmode standalone
no openflow failmode
Default Secure.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If an OpenFlow switch loses contact with all Controllers as a result of echo request
timeouts, then the OpenFlow switch goes into fail mode. There are two fail modes
available:
•In standalone mode, if no message is received from the OpenFlow
Controller for three times the inactivity probe interval, then OpenFlow will
take over responsibility for setting up flows. OpenFlow will cause the switch
to act like an ordinary MAC-learning switch, but continue to retry connecting
to the Controller in the background. When the connection succeeds, it will
discontinue its standalone behavior.
NOTE: If the OpenFlow switch is in fail mode, and the user changes the
configured fail mode to or from standalone mode, OpenFlow will flush all
existing rules.
•In secure mode, OpenFlow will not set up new flows on its own when the
Controller connection fails or when no Controllers are defined, but all
existing flows are left in place. The switch will continue to retry connecting
to any defined Controllers forever. When the non-rule-expired option is
enabled, existing rules won’t be expired regardless of their timeouts while
under fail mode. In other words, the OpenFlow switch will ignore timeout
values of both idle timeout and hard timeout in existing rules.
Example To set the fail mode to standalone mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow failmode standalone
Parameter Description
non-rule-expired Disable rule expiration while under fail mode. This means the
OpenFlow switch will ignore timeout values of both idle
timeout and hard timeout in existing rules.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1454
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW FAILMODE
To revert the fail mode to the default mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow failmode
Related
Commands
openflow controller
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.1: non-rule-expired parameter added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1455
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW FAILMODE STANDALONE
openflow failmode standalone
Overview Use this command to set the operation mode to standalone if the Controller fails.
Use the no variant of this command to turn off standalone mode and return to the
default secure mode.
Syntax openflow failmode standalone
no openflow failmode standalone
Default Secure mode
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the Controller connection fails, there are two operation modes available:
•In standalone mode, if no message is received from the OpenFlow
Controller for three times the inactivity probe interval, then OpenFlow will
take over responsibility for setting up flows. OpenFlow will cause the switch
to act like an ordinary MAC-learning switch, but continue to retry connecting
to the Controller in the background. When the connection succeeds, it will
discontinue its standalone behavior.
•In secure mode, OpenFlow will not set up new flows on its own when the
Controller connection fails or when no Controllers are defined, but all
existing flows are left in place. The switch will continue to retry connecting
to any defined Controllers forever.
Example To set the Controller to standalone mode, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow failmode standalone
Related
Commands
openflow controller
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1456
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW INACTIVITY
openflow inactivity
Overview Use this command to set the value of the Controller inactivity timeout.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the inactivity timeout value to its
default.
Syntax openflow inactivity <5-2073600>
no openflow inactivity
Default 10 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage OpenFlow uses the inactivity probe timer to monitor its connection to
Controller(s). If no message is received from any Controller for three times the
inactivity probe interval, then OpenFlow will take over responsibility for setting up
flows, if in standalone mode.
Example To configure the inactivity probe timeout to 20 seconds, enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow inactivity 20
To reset the inactivity probe timeout to its default value of 10 seconds, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow inactivity
Related
Commands
openflow controller
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Parameter Description
<5-2073600> Specifies the timeout value in seconds
inactivity OpenFlow inactivity probe

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1457
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW NATIVE VLAN
openflow native vlan
Overview Use this command to specify a VLAN as a native VLAN for the data plane ports. You
must create a VLAN (using the vlan database command) before specifying the
VLAN as a native VLAN.
The OpenFlow native VLAN must be different from the native VLAN of the control
plane. This prevents the OpenFlow ports from receiving any broadcast or multicast
traffic flooded on the control plane native VLAN.
The VLAN used as the OpenFlow native VLAN should not be used on
non-OpenFlow ports.
Use the no variant of this command to change the native VLAN for the data plane
ports back to the default VLAN 1.
Syntax openflow native vlan <vlan-id>
no openflow native vlan
Default The native VLAN for the data plane ports is VLAN 1 by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To specify VLAN 100 as a native VLAN for the data plane ports:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow native vlan 100
To change the native VLAN for the data plane ports back to the VLAN 1:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow native vlan
Related
Commands
show openflow config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Parameter Description
<vlan-id> VLAN ID in the range <1-4090>
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1458
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW SSL PEER CERTIFICATE
openflow ssl peer certificate
Overview Use this command to enable a peer certificate to be sent from the machine that the
OpenFlow Controller is running.
Use the no variant of this command to disable a peer certificate from being sent
from the machine that the OpenFlow Controller is running.
Syntax openflow ssl peer certificate {<file>|bootstrap}
no openflow ssl peer certificate
Default Peer certificate validation is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables or disables peer certification on an OpenFlow Controller.
Example To validate a peer certificate using the bootstrap mode, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow ssl peer certificate bootstrap
To disable peer certificate validation, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no openflow ssl peer certificate
Related
Commands
show openflow ssl
openflow controller
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Parameter Description
<file> The CA certificate of an OpenFlow Controller must be in PEM
format and specified with an absolute path using the format
flash:cacert.pem.
You must copy the file from the machine on which the OpenFlow
Controller is running beforehand to the OpenFlow switch.
bootstrap In bootstrap mode, when the switch first connects to the
OpenFlow Controller, it accepts and saves to RAM a self-signed CA
certificate sent from the Controller. Thereafter, the OpenFlow
switch will only connect to OpenFlow Controllers signed by the
same CA certificate.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1459
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW SSL TRUSTPOINT
openflow ssl trustpoint
Overview Use this command to configure the local trustpoint to be used for authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the local trustpoint.
Syntax openflow ssl trustpoint local
no openflow ssl trustpoint local
Default There is no trustpoint configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration mode.
Usage Use this command to specify a local self-signed certificate authority trustpoint for
authentication. You must first create the trustpoint using the crypto pki
trustpoint command.
Example To configure a local trustpoint, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# openflow ssl trustpoint local
To delete the local trustpoint, use the command:
awplus(config)# no openflow ssl trustpoint
Related
Commands
openflow controller
openflow ssl trustpoint
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1460
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
OPENFLOW VERSION
openflow version
Overview Use this command to change the supported OpenFlow version numbers on the
switch. You can specify a list of version numbers.
Use the no variant of this command to change the version number of the
OpenFlow protocol back to the default version 1.3.
Syntax openflow version <version-list>
no openflow version
Default The OpenFlow version is set to 1.3 by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command overwrites any previously configured OpenFlow versions with the
default OpenFlow version 1.3.
Example To change the OpenFlow protocol version to 1.0 and 1.3:
awplus(config)# openflow version 1.0 1.3
To change the OpenFlow protocol version to the default 1.3:
awplus(config)# no openflow version
Related
Commands
show openflow config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
Parameter Description
<version-list> Specifies a list of version numbers separated by a space. The
version numbers are 1.0 and 1.3.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1461
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW CONFIG
show openflow config
Overview Use this command to display the OpenFlow configuration database on the switch.
Syntax show openflow config
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show the contents of the OpenFlow configuration database on the switch:
awplus# show openflow config
Output Figure 41-1: Example output from show openflow config
awplus# show openflow config
258a3d74-d349-4d18-9d75-09ab66e19d81
Bridge "of0"
Controller "tcp:192.168.1.2:6653"
is_connected: true
fail_mode: standalone
Port "of0"
Interface "of0"
type: internal
Port "port1.0.4"
Interface "port1.0.4"
type: system
options: {ifindex="5004", mtu="1500", native_vlan="4090"}
Port "port1.0.8"
Interface "port1.0.8"
type: system
options: {ifindex="5008", mtu="1500", native_vlan="4090"}
...
Table 41-1: Parameters in the output from show openflow config
Parameter Description
First line The switch ID
Bridge “of0” The configuration of Bridge “br0”
Controller The address of the OpenFlow Controller and SSL port
number
is_connected: true Indicates that the switch is connected to the OpenFlow
Controller. If the switch is not connected to the
Controller, “is_connected” is not displayed.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1462
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW CONFIG
Related
Commands
openflow controller
openflow native vlan
show openflow status
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
fail_mode The fail mode. When the fail mode is “secure,” OpenFlow
on the switch does not set up flows when the OpenFlow
Controller fails.
When the fail mode is “standalone”, OpenFlow on the
switch sets up flows to work as a Layer 2 switch when the
OpenFlow Controller fails.
Port The port information
Interface The interface of the port.
type: The type of the port
options: The options for the port
Table 41-1: Parameters in the output from show openflow config (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1463
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW COVERAGE
show openflow coverage
Overview Use this command to display the OpenFlow counters from the Open vSwitch.
Syntax show openflow coverage
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage The information displayed by this command is for troubleshooting. Contact Allied
Telesis Technical Support for assistance.
Example To show OpenFlow counters:
awplus# show openflow coverage
Output Figure 41-2: Example output from show openflow coverage
awplus# show openflow coverage
Event coverage, avg rate over last: 5 seconds, last minute, last hour,
hash=86bbd699:
netlink_sent 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 14
netlink_recv_jumbo 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 4
netlink_received 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 49
nln_changed 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 18
vconn_sent 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.4703/sec total: 1801
vconn_received 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.4594/sec total: 1768
vconn_open 0.4/sec 0.267/sec 0.2372/sec total: 876
util_xalloc 370.2/sec 354.183/sec 416.7711/sec total: 1590959
unixctl_replied 0.0/sec 0.017/sec 0.0028/sec total: 10
unixctl_received 0.0/sec 0.017/sec 0.0028/sec total: 10
stream_open 0.4/sec 0.267/sec 0.2372/sec total: 877
pstream_open 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 6
rconn_sent 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.4219/sec total: 1606
rconn_queued 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.4219/sec total: 1606
poll_zero_timeout 0.0/sec 0.033/sec 0.0875/sec total: 362
poll_create_node 60.6/sec 55.967/sec 68.2844/sec total: 256721
txn_success 0.2/sec 0.200/sec 0.1953/sec total: 734
txn_incomplete 0.2/sec 0.267/sec 0.2622/sec total: 994
txn_unchanged 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0019/sec total: 34
netdev_get_stats 1.2/sec 1.200/sec 1.1850/sec total: 4411
netdev_sent 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.1219/sec total: 475
netdev_received 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.2608/sec total: 1005
hmap_expand 10.0/sec 9.433/sec 11.0714/sec total: 42476
hmap_pathological 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 58
hindex_expand 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0006/sec total: 3
miniflow_malloc 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.2611/sec total: 1008
flow_extract 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0006/sec total: 5

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1464
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW COVERAGE
Related
Commands
show openflow status
show openflow flows
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
dpif_flow_del 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.1342/sec total: 516
dpif_flow_put 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0014/sec total: 5
dpif_flow_flush 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 2
dpif_port_add 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 25
cmap_shrink 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.2939/sec total: 1157
cmap_expand 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0006/sec total: 3
ttp_rev_flow_table 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.1050/sec total: 410
ttp_rev_port_toggled 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 2
ttp_rev_reconfigure 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0006/sec total: 20
xlate_actions 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.3969/sec total: 1530
revalidate_missed_dp_flow 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.1356/sec total: 521
handler_duplicate_upcall 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.1258/sec total: 483
ofproto_update_port 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 29
ofproto_recv_openflow 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.4111/sec total: 1573
ofproto_queue_req 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0003/sec total: 1
ofproto_packet_out 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0006/sec total: 4
ofproto_flush 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 1
bridge_reconfigure 0.0/sec 0.000/sec 0.0000/sec total: 19
72 events never hit
Table 41-2: Parameters in the output from
Parameter Description
Event coverage The name of a coverage event
avg rate over
last: 5 seconds The rate at which the event occurred for the last 5 seconds
last minute The rate at which the event occurred for the last one
minute
last hour The rate at which the event occurred for the last one hour
hash The name of the internal hash on the counter
total: The total number of occurrences of the event
events never hit The number of coverage events that have never occurred.
When the value is 0, this information is not displayed.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1465
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW FLOWS
show openflow flows
Overview Use this command to display all the entries in the switch’s flow tables that resulted
from receiving packets on OpenFlow ports.
Syntax show openflow flows
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The switch uses OpenFlow rules from the Controller to create a rule table that tells
the switch what to do with packets. From the rules, the switch creates a software
flow table to process packets. From the software flow table, the switch creates
entries in its silicon hardware flow tables, when possible. When silicon table entries
exist, the switch uses them to switch packets. When silicon table entries do not
exist, the switch uses the software flow table to process packets.
See the “Communication and Packet Processing” section of the OpenFlow Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide for a detailed explanation of how the switch
puts entries into the software and silicon flow tables.
This command displays flows in both the software and silicon flow tables. A symbol
at the start of each flow output indicates whether it is a silicon or software table
entry:
• # indicates silicon flow table entries, and
• ~ indicates software flow table entries
Example To show the entries of the flow tables on the switch:
awplus# show openflow flows
Output Where possible, the switch uses OpenFlow rules from the Controller to create
entries in its silicon hardware flow tables, and switches packets according to the
silicon flow tables.
In the following example output, the OpenFlow ports are port1.0.14, port1.0.15,
port1.0.16, port1.0.33 and sa3 (port1.0.27 and port1.0.38). As LOCAL and LAG ports
are now supported, the first OpenFlow port number is used as the local port.
OpenFlow port numbering becomes:
• port1.0.14 is OpenFlow port number 2
• port1.0.15 is OpenFlow port number 3
• port1.0.33 is OpenFlow port number 5
• sa3 is OpenFlow port number 6
The clients are connected to port1.0.15 and port1.0.33 in this scenario and sa3 is
used as OpenFlow ports for the uplink. The show openflow flows command
shows the following:

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1466
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW FLOWS
Figure 41-3: Example output from show openflow flows
NOTE: This output includes added line spacing for readability purposes
Related
Commands
show openflow coverage
show openflow rules
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
awplus# show openflow flows
~recirc_id(0),in_port(3),eth(src=08:00:27:9a:b6:7f,dst=08:00:27:4b:ef:3b),eth_type(0
x0800),ipv4(frag=no), packets:0, bytes:0, used:never,
actions:push_vlan(vid=79,pcp=0),6
~recirc_id(0),in_port(6),eth(dst=08:00:27:96:2d:48),eth_type(0x8100),vlan(vid=79,pcp
=0),encap(eth_type(0x0806)), packets:1, bytes:64, used:8.990s, actions:pop_vlan,5
~recirc_id(0),in_port(6),eth(dst=08:00:27:9a:b6:7f),eth_type(0x8100),vlan(vid=79,pcp
=0),encap(eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no)), packets:1, bytes:346, used:3.938s,
actions:pop_vlan,3
#recirc_id(0),in_port(6),eth(dst=ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff/01:00:00:00:00:00),eth_type(0x080
0),ipv4(frag=no), packets:28, bytes:2019, used:2.110s, actions:drop
~recirc_id(0),in_port(5),eth(src=08:00:27:96:2d:48,dst=08:00:27:4b:ef:3b),eth_type(0
x0806), packets:0, bytes:0, used:never, actions:push_vlan(vid=79,pcp =0),6
Table 41-3: Parameters in the output from show openflow flows
Parameter Description
recirc_id Used to select the next packet processing steps among
multiple instances of recirculation. Packets initially enter
the process with an ID of 0, which indicates no
recirculation.
in_port The OpenFlow port number
eth The source and destination MAC address of the packet
eth_type The Ethernet type
ipv4 The information in the IPv4 header
packets The number of matched packets
bytes The number of matched bytes
actions A set of actions for the packets that match the key

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1467
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW FLOWS
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1468
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW RULES
show openflow rules
Overview Use this command to display the software flow table and rules set by the
OpenFlow controller.
Syntax show openflow rules
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To show the contents of the flow table on the switch:
awplus# show openflow rules
Output Figure 41-4: Example output from show openflow rules
awplus# show openflow rules
duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=399,in_port=1,dl_src=ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd,actions=drop
duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=399,in_port=2,dl_src=ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd,actions=drop
duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=399,in_port=3,dl_src=ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd,actions=drop
duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=399,in_port=4,dl_src=ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd,actions=drop
duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=299,in_port=1,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00,
actions=goto_table:2duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=298,in_port=1,actions=goto_table:3duration=14s,
n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=99,arp,actions=CONTROLLER: 65535duration=14 s, n_packets=0,
n_bytes=0,
priority=99,udp,tp_dst=67,actions=CONTROLLER:65535duration=14s,
n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, priority=0,actions=drop
table_id=1, duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=99,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00,actions=got
o_table:2table_id=1, duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=0,actions=droptable_id=2, duration =14s, n_packets= 0,
n_bytes=0, priority=98,in_port=1,actions=drop

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1469
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW RULES
Related
Commands
show openflow flows
show openflow coverage
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
table_id=2, duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=97,actions=output:1table_i d=2, duration=14s, n_pack ets=0,
n_bytes=0, priority=0,actions=drop
table_id=3, duration=14s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=0,actions=drop
table_id=254, duration=85668s, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0,
priority=2,recirc_id=0,actions=drop
table_id=254, duration=85668s, n_packets=736, n_bytes=144050,
priority=0,reg0=0x1,actions=controller(reason=no_match)
table_id=254, duration=85668s, n_packets=19, n_bytes=5668,
priority=0,reg0=0x2,actions=drop
Table 41-4: Parameters in the output from show openflow rules
Parameter Description
duration The duration of the flow entry in seconds
n_packets The number of packets that match the flow entry
n_bytes The number of bytes that match the flow entry
priority The priority of the flow entry
in_port The OpenFlow port number on which the packets are
received
dl_src The source address
dl_dst The destination address
actions A set of actions applied to a packet. The actions are: “drop”,
“goto_table”, “pop_vlan”, or “push_vlan”
table_id The table ID of the flow entry
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1470
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW SSL
show openflow ssl
Overview Use this command to display the current SSL configuration for OpenFlow.
Syntax show openflow ssl
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command displays the current SSL configuration for OpenFlow.
Example To display the current SSL configuration for OpenFlow, use the command:
awplus# show openflow ssl
Output Figure 41-5: Example output from show openflow ssl
Related
Commands
openflow ssl trustpoint
openflow controller
openflow ssl peer certificate
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
awplus#show openflow ssl
Private key: /flash/.certs/pki/local/cakey.pem
Certificate: /flash/.certs/pki/local/cacert.pem
CA Certificate: /etc/openvswitch/cacert.pem
Bootstrap: true

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1471
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW STATUS
show openflow status
Overview Use this command to display the status of each data plane port and the OpenFlow
protocol messages queried by the OpenFlow Controller.
Syntax show openflow status
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show the status of a switch with four OpenFlow ports, enter the command:
awplus# show openflow status
Output Figure 41-6: Example output from show openflow status
awplus#show openflow status
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (OF1.3) (xid=0x2): dpid:0000eccd6dc421bd
n_tables:254, n_buffers:0
capabilities: FLOW_STATS TABLE_STATS PORT_STATS GROUP_STATS
QUEUE_STATS
OFPST_PORT_DESC reply (OF1.3) (xid=0x3):
1(port1.0.1): addr:ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd
config: 0
state: 0
current: 1GB-FD
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 1000 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
2(port1.0.2): addr:ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd
config: 0
state: LINK_DOWN
current: AUTO_NEG
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 0 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
3(port1.0.3): addr:ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd
config: 0
state: 0
current: 1GB-FD
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 1000 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
4(port1.0.4): addr:ec:cd:6d:c4:21:bd
config: 0
state: LINK_DOWN
current: AUTO_NEG
supported: 1GB-FD
speed: 0 Mbps now, 1000 Mbps max
LOCAL(of0): addr:1e:f3:f8:c7:13:df
config: 0
state: 0
current: 10MB-FD
speed: 10 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
OFPT_GET_CONFIG_REPLY (OF1.3) (xid=0x5): frags=normal
miss_send_len=0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1472
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW STATUS
Table 41-5: Parameters in the output from show openflow status
Parameter Description
OFPT_FEATURES_REP
LY (OF1.3)
(xid=0x2):
Indicates that the following information is from the
OpenFlow version 1.3 Feature reply.
dpid: The datapath ID
n_tables The number of tables supported by the switch
n_buffers The maximum number of packets that the switch can
buffer when sending packets to the OpenFlow controller
capabilities A list of the OpenFlow capabilities: FLOW_STATS (flow
statistics), TABLE_STATS (table statistics), PORT_STATS
(port statistics), IP_REASM (IP fragments reassemble),
QUEUE_STATS (queue statistics), and GROUP_STATS
(group statistics
OFPST_PORT_DESC
replay (OF1.3)
(xid=0x3):
Indicates that the following information is from the
OpenFlow version 1.3 Port Description Reply.
1(port1.0.1):
addr:ec:cd:6d:c4:
21:bd
The port number and MAC address.
config: The port status: 0 (the port is up) or PORT_DOWN (the
port is down.)
state: The link status: 0 (the link is up) or LINK_DOWN (the link is
down.)
current: The current feature status.
supported: A list of the supported features: 1GB-FD, 10GB-FD,
AUTO-NEG, etc.
Not displayed from software release 5.4.7 onwards for
interfaces that do not have this capability, i.e. static LAG
interfaces or the of0 bridge interface.
speed: The current port speed and maximum speed.
OFPT_GET_CONFIG_R
EPLY (OF1.3)
(xid=0x5):
Indicates that the switch responds to a configuration
request by an OFPT_GET_CONFIG_REPLY message with
the following information.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1473
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
OPENFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW OPENFLOW STATUS
Related
Commands
show openflow flows
show openflow rules
show openflow config
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-1.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added to GS900MX, XS900MX, x550 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added to IE300, IE500 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx908 GEN2
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to IE210L series products
frags: The action for the IP fragments: normal, dropped, or
reassembled. Normal means that an attempt should be
made to pass the fragments through the OpenFlow tables.
miss_send_len=0: The number of bytes of each packet that was sent to the
OpenFlow controller when a flow table fails or reaches the
controller
Table 41-5: Parameters in the output from show openflow status (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1474
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 6: Network Availability

42
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1475
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Ethernet Protection
Switched Ring
(EPSRing™)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
Ethernet Protection Switched Ring (EPSRing™). For more information, see the EPSR
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“debug epsr” on page 1477
•“epsr” on page 1478
•“epsr configuration” on page 1479
•“epsr datavlan” on page 1480
•“epsr enhancedrecovery enable” on page 1481
•“epsr mode master controlvlan primary port” on page 1482
•“epsr mode transit controlvlan” on page 1483
•“epsr priority” on page 1484
•“epsr state” on page 1485
•“epsr topology-change” on page 1486
•“epsr trap” on page 1487
•“show debugging epsr” on page 1488
•“show epsr” on page 1489
•“show epsr common segments” on page 1493
•“show epsr config-check” on page 1494
•“show epsr <epsr-instance>” on page 1495
•“show epsr <epsr-instance> counters” on page 1496
•“show epsr counters” on page 1497

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1477
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
DEBUG EPSR
debug epsr
Overview This command enables EPSR debugging.
The no variant of this command disables EPSR debugging.
Syntax debug epsr {info|msg|pkt|state|timer|all}
no debug epsr {info|msg|pkt|state|timer|all}
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To enable state transition debugging, use the command:
awplus# debug epsr state
To disable EPSR packet debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug epsr pkt
Related
Commands
undebug epsr
Parameter Description
info Send general EPSR information to the console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude the above information from being sent to the console.
msg Send the decoded received and transmitted EPSR packets to the console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude the above packets from being sent to the console.
pkt Send the received and transmitted EPSR packets as raw ASCII text to the
console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude the above packets from being sent to the console.
state Send EPSR state transitions to the console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude state transitions from being sent to the console.
timer Send EPSR timer information to the console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude timer information from being sent to the console.
all Send all EPSR debugging information to the console.
Using this parameter with the no debug epsr command will explicitly
exclude any debugging information from being sent to the console.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1478
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR
epsr
Overview This command sets the timer values for an EPSR instance. These are only valid for
master nodes.
NOTE: This command will only run on switches that are capable of running as an EPSR
master node. However, even if your switch cannot function as an EPSR master node,
you still may need to configure this command on whatever switch is the master within
your EPSR network.
CAUTION: Using the “no” variant of this command will remove the specified EPSR
instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1479
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR CONFIGURATION
epsr configuration
Overview Use this command to enter EPSR Configuration mode so that EPSR can be
configured.
Syntax epsr configuration
Mode Global Configuration
Example To change to EPSR mode, use the command:
awplus(config)# epsr configuration
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr
show epsr

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1480
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR DATAVLAN
epsr datavlan
Overview This command adds a data VLAN or a range of VLAN identifiers to a specified EPSR
instance.
The no variant of this command removes a data VLAN or data VLAN range from an
EPSR instance.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> datavlan {<vlanid>|<vlanid-range>}
no epsr <epsr-instance> datavlan {<vlanid>|<vlanid-range>}
Mode EPSR Configuration
Usage We recommend you
• set the EPSR control VLAN to vlan2, using the epsr mode master controlvlan
primary port and epsr mode transit controlvlan commands, then
• set the EPSR data VLAN between to be a value between 3 and 4094, using the
epsr datavlan command.
Examples To add vlan3 to the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue datavlan vlan3
To add vlan2 and vlan3 to the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue datavlan vlan2-vlan3
To remove vlan3 from the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr blue datavlan vlan3
To remove vlan2 and vlan3 from the EPSR instance called blue, use the
command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr blue datavlan vlan2-vlan3
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.
datavlan Adds a data VLAN to be protected by the EPSR instance.
<vlanid>The VLAN’s VID - a number between 1 and 4094 excluding
the number selected for the control VLAN.
<vlanid-range>Specify a range of VLAN identifiers using a hyphen to
separate identifiers.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1481
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR ENHANCEDRECOVERY ENABLE
epsr enhancedrecovery enable
Overview This command enables EPSR’s enhanced recovery mode. Enhanced recovery
mode enables a ring to apply additional recovery procedures when a ring with
more than one break partially mends. For more information, see the EPSR Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
The no variant of this command disables the enhanced recovery mode.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> enhancedrecovery enable
no epsr <epsr-instance> enhancedrecovery enable
Default Default is that enhanced recovery mode disabled.
Mode EPSR Configuration
Example To apply enhanced recovery on the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue enhancedrecovery enable
Related
Commands
show epsr
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1482
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR MODE MASTER CONTROLVLAN PRIMARY PORT
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
Overview NOTE: This command will only run on switches that are capable of running as an EPSR
master node. However, even if your switch cannot function as an EPSR master node,
you still need to configure this command on whatever switch is the master within your
EPSR network.
This command creates a master EPSR instance. Your switch is unable to run this
command because it cannot function as an EPSR master node. To include these
switches in an EPSR ring you will need to use an alternative Allied Telesis switch,
such as an x610 Series switch, as the master node. For more information on this
command, refer to the manual of your master EPSR node’s switch.
NOTE: The software allows you to configure more than two ports or static channel
groups to the control VLAN within a single switch. However, we advise against this
because in certain situations it can produce unpredictable results.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1483
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR MODE TRANSIT CONTROLVLAN
epsr mode transit controlvlan
Overview This command creates a transit EPSR instance.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> mode transit controlvlan <2-4094>
NOTE: The software allows you to configure more than two ports or static channel
groups to the control VLAN within a single switch. However, we advise against this
because in certain situations it can produce unpredictable results.
If the control VLAN contains more than two ports (or static channels) an algorithm
selects the two ports or channels with the lowest number to be the ring ports. However
if the switch has only one channel group is defined to the control vlan, EPSR will not
operate on the secondary port.
EPSR does not support Dynamic link aggregation (LACP).
Mode EPSR Configuration
Example To create a transit EPSR instance called blue with vlan2 as the control VLAN, use
the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue mode transit controlvlan vlan2
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.
mode Determines the node is acting as a transit node.
transit Sets switch to be the transit node for the named EPSR ring.
controlvlan The VLAN that will transmit EPSR control frames.
<2-4094>VLAN id.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1484
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR PRIORITY
epsr priority
Overview This command sets the priority of an EPSR instance on an EPSR node. Priority is
used to prevent “superloops” forming under fault conditions with particular ring
configurations. Setting a node to have a priority greater than one, also has the
effect of turning on superloop protection.
The no variant of this command returns the priority of the EPSR instance back to its
default value of 0, which also disables EPSR Superloop prevention.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> priority <0-127>
no <epsr-instance> priority
Default The default priority of an EPSR instance on an EPSR node is 0. The negated form of
this command resets the priority of an EPSR instance on an EPSR node to the
default value.
Mode EPSR Configuration
Example To set the priority of the EPSR instance called blue to the highest priority (127),
use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue priority 127
To reset the priority of the EPSR instance called blue to the default (0), use the
command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr blue priority
Related
Commands
epsr configuration
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.
priority The priority of the ring instance selected by the epsr-name
parameter.
<0-127>The priority to be applied (0 is the lowest priority and
represents no superloop protection).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1485
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR STATE
epsr state
Overview This command enables or disables an EPSR instance.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> state {enabled|disabled}
Mode EPSR Configuration
Example To enable the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue state enabled
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> The name of the EPSR instance.
state The operational state of the ring.
enabled EPSR instance is enabled.
disabled EPSR instance is disabled.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1486
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR TOPOLOGY-CHANGE
epsr topology-change
Overview Use this command to allow the given EPSR instance to accept notifications from
other topology protocols, namely G.8032, for Topology Change Notifications
(TCN).
Use the no variant of this command to return the EPSR instance to where it does
not accept TCNs from the other specified protocol, and as a result does not send
out a “flush FDB” message.
Syntax epsr <epsr-name> topology-change g8032
no epsr <epsr-name> topology-change g8032
Default The default value is no notifications are accepted and in turn no “flush FDB”
messages are sent.
Mode EPSR Configuration
Usage The purpose of this command is to allow EPSR to accept notifications from other
topology protocols, namely G.8032, about Topology Change Notifications (TCN).
Once EPSR accepts the TCN, it will in turn notify the other nodes on the EPSR ring
to perform an FDB flush.
Example To configure an EPSR instance named “red” to accept G.8032 TCNs, use the
following command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr red topology-change g8032
To configure an EPSR instance named “red” to no longer accept G.8032 TCNs, use
the following command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr red topology-change g8032
Related
Commands
show epsr
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
<epsr-name> The name of the EPSR instance for which the topology-change
applies to.
topology-change The topology-change value to be set for the instance.
g8032 Specify that G.8032 is the other protocol that the
topology-change notifications are allowed to be accepted from in
order to send "flush FDB" messages to other EPSR nodes in the
ring.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1487
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
EPSR TRAP
epsr trap
Overview This command enables SNMP traps for an EPSR instance. The traps will be sent
when the EPSR instance changes state.
The no variant of this command disables SNMP traps for an EPSR instance. The
traps will no longer be sent when the EPSR instance changes state.
Syntax epsr <epsr-instance> trap
no epsr <epsr-instance> trap
Mode EPSR Configuration
Example To enable traps for the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr blue trap
To disable traps for the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr blue trap
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.
trap SNMP trap for the EPSR instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1488
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING EPSR
show debugging epsr
Overview This command shows the debugging modes enabled for EPSR.
Syntax show debugging epsr
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the enabled debugging modes, use the command:
awplus# show debugging epsr
Related
Commands
debug epsr
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1489
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR
show epsr
Overview This command displays information about all EPSR instances.
Syntax show epsr
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the current settings of all EPSR instances, use the command:
awplus# show epsr
Output:
non-superloop
topology
The following examples show the output display for a non-superloop topology
network.
NOTE: The above output is only displayed on an EPSR master.
Output:
superloop
topology
The following examples show the output display for superloop topology network
NOTE: The above output is only displayed on an EPSR master.
Table 1: Example output from the show epsr command run on a transit node
EPSR Information
------------------------------------------------------------
Name .......................... test2
Mode .......................... Transit
Status ........................ Enabled
State ......................... Links-Up
Control Vlan .................. 2
Data VLAN(s) .................. 10
Interface Mode ................ Ports Only
First Port .................... port1.0.1
First Port Status ............. Down
First Port Direction .......... Unknown
Second Port ................... port1.0.2
Second Port Status ............ Down
Second Port Direction ......... Unknown
Trap .......................... Enabled
Master Node ................... Unknown
Enhanced Recovery ............. Disabled
------------------------------------------------------------
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1490
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR
Table 2: Example output from the show epsr command run on a Transit Node
EPSR Information
------------------------------------------------------------
Name .......................... test4
Mode .......................... Transit
Status ........................ Enabled
State ......................... Complete
Control Vlan .................. 4
Data VLAN(s) .................. 20
Interface Mode ................ Ports Only
Primary Port .................. port1.0.3
Status ...................... Forwarding (logically blocking)
Is On Common Segment ........ No
Blocking Control ............ Physical
Secondary Port ................ port1.0.4
Status ...................... Blocked
Is On Common Segment ........ No
Blocking Control ............ Physical
Hello Time .................... 1 s
Failover Time ................. 2 s
Ring Flap Time ................ 0 s
Trap .......................... Enabled
Enhanced Recovery ............. Disabled
SLP Priority .................. 12
------------------------------------------------------------
Table 3: Parameters displayed in the output of the show epsr command
Parameter on
Master Node
Parameter on
Transit Node Description
Name Name The name of the EPSR instance.
Mode Mode The mode in which the EPSR instance is configured - either Master or
Transit
Status Status Indicates whether the EPSR instance is enabled or disabled
State State Indicates state of the EPSR instance's state machine. Master states
are: Idle, Complete, and Failed. Transit states are Links-Up,
Links-Down, and Pre-Forwarding.
Control Vlan Control Vlan Displays the VID of the EPSR instance's control VLAN.
Data VLAN(s) Data VLAN(s) The VID(s) of the instance's data VLANs.
Interface
Mode Interface
Mode Whether the EPSR instance's ring ports are both physical ports (Ports
Only) or are both static aggregators (Channel Groups Only).
Primary Port First Port The EPSR instance's primary ring port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1491
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR
- Status - Status Whether the ring port is forwarding (Forwarding) or blocking
(Blocked), or has link down (Down), and if forwarding or blocking,
“(logical)” indicates the instance has only logically set the blocking
state of the port because it does not have physical control of it.
- Direction The ring port on which the last EPSR control packet was received is
indicated by “Upstream”. The other ring port is then “Downstream”
- Is On
Common
Segment
- Is On
Common
Segment
Whether the ring port is on a shared common segment link to
another node, and if so, “(highest rank)” indicates it is the highest
priority instance on that common segment.
- Blocking
Control - Blocking
Control Whether the instance has “physical” or “logical” control of the ring
port's blocking in the instance's data VLANs.
Secondary
Port Second Port The EPSR instance's secondary port.
- Status - Status Whether the ring port is forwarding (Forwarding) or blocking
(Blocked), or has link down (Down), and if forwarding or blocking,
“(logical)” indicates the instance has only logically set the blocking
state of the port, because it does not have physical control of it. Note
that on a master configured for SuperLoop Prevention (non-zero
priority) its secondary ring port can be physically forwarding, but
logically blocking. This situation arises when it is not the highest
priority node in the topology (and so does not receive LINKS-DOWN
messages upon common segment breaks) and a break on a common
segment in its ring is preventing reception of its own health
messages.
- Direction The ring port on which the last EPSR control packet was received is
indicated by “Upstream”. The other ring port is then “Downstream”
- Is On
Common
Segment
- Is On
Common
Segment
Whether the ring port is on a shared common segment link to
another node, and if so, “(highest rank)” indicates it is the highest
priority instance on that common segment
- Blocking
Control - Blocking
Control Whether the instance has “physical” or “logical” control of the ring
port's blocking in the instance's data VLANs
Hello Time The EPSR instance's setting for the interval between transmissions of
health check messages (in seconds)
Failover
Time The time (in seconds) the EPSR instance waits to receive a health
check message before it decides the ring is down
Ring Flap
Time The minimum time the EPSR instance must remain in the failed state
Trap Trap Whether the EPSR instance has EPSR SNMP traps enabled
Table 3: Parameters displayed in the output of the show epsr command (cont.)
Parameter on
Master Node
Parameter on
Transit Node Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1492
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr counters
Enhanced
Recovery Enhanced
Recovery Whether the EPSR instance has enhanced recovery mode enabled
SLP Priority SLP Priority The EPSR instance's priority (for SuperLoop Prevention)
Table 3: Parameters displayed in the output of the show epsr command (cont.)
Parameter on
Master Node
Parameter on
Transit Node Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1493
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR COMMON SEGMENTS
show epsr common segments
Overview This command displays information about all the superloop common segment
ports on the switch.
Syntax show epsr common segments
Example To display information about all the superloop common segment ports on the
switch, use the command:
awplus# show epsr common segments
Related
Commands
show epsr
show epsr summary
show epsr counters
Table 4: Example output from the show epsr common segments command
EPSR Common Segments
Common Seg EPSR Port Phys Ctrl Ring
Ring Port Instance Mode Prio Type of Port? Port Status
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
port1.0.4 test_inst_Red Transit 127 Second Yes Fwding
test_inst_Blue Transit 126 Second No Fwding (logical)
test_inst_Green Transit 125 First No Fwding (logical)
sa4 testA Master 15 Primary Yes Blocking
testB Transit 14 Second No Fwding (logical)
sa5 test_55 Transit 8 First Yes Down
test_77 Transit 7 First No Down
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1494
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR CONFIG-CHECK
show epsr config-check
Overview This command checks the configuration of a specified EPSR instance, or all EPSR
instances.
If an instance is enabled, this command will check for the following errors or
warnings:
• The control VLAN has the wrong number of ports.
• There are no data VLANs.
• Some of the data VLANs are not assigned to the ring ports.
• The instance is a master with its secondary port on a common segment.
Syntax show epsr [<instance>] config-check
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To check the configuration of all EPSR instances and display the results, use the
command:
awplus# show epsr config-check
Related
Commands
show epsr
Parameter Description
<instance>Name of the EPSR instance to check on.
Table 42-1: Example output from show epsr config-check
EPSR Status Description
Instance
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
red OK.
white OK.
blue Warning Primary port is not in data VLANs 29-99.
orange OK.
Don't forget to check that this node's configuration is consistant with all
other nodes in the ring.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1495
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR <EPSR-INSTANCE>
show epsr <epsr-instance>
Overview This command displays information about the specified EPSR instance.
Syntax show epsr <epsr-instance>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the current settings of the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus# show epsr blue
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr counters
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance> Name of the EPSR instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1496
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR <EPSR-INSTANCE> COUNTERS
show epsr <epsr-instance> counters
Overview This command displays counter information about the specified EPSR instance.
Syntax show epsr <epsr-instance> counters
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the counters of the EPSR instance called blue, use the command:
awplus# show epsr blue counters
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr
Parameter Description
<epsr-instance>Name of the EPSR instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1497
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR COUNTERS
show epsr counters
Overview This command displays counter information about all EPSR instances.
Syntax show epsr counters
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the counters of all EPSR instances, use the command:
awplus# show epsr counters
Related
Commands
epsr mode master controlvlan primary port
epsr mode transit controlvlan
show epsr
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1498
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ETHERNET PROTECTION SWITCHED RING (EPSRING™) COMMANDS
SHOW EPSR SUMMARY
show epsr summary
Overview This command displays summary information about all EPSR instances on the
switch
Syntax show epsr summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display EPSR summary information, use the command:
awplus# show epsr summary
Table 43: Example output from the show epsr summary command
EPSR Summary Information
Abbreviations:
M = Master node
T = Transit node
C = is on a common segment with other instances
P = instance on a common segment has physical control of the shared port's
data VLAN blocking
LB = ring port is Logically Blocking - applicable to master only
EPSR Ctrl Primary/1st Secondary/2nd
Instance Mode Status State VLAN Prio Port Status Port Status
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test-12345 T Enabled Links-Down 6 127 Blocking (C,P) Blocking (C,P)
test1 M Enabled Complete 5 12 Fwding Fwding (LB)
test2 T Enabled Pre-Fwding 4 126 Fwding (C) Blocking (C)
localB T Disabled Idle 40 0 Unknown Unknown
localC T Disabled Idle 41 0 Unknown Unknown
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------

43
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1500
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 Ethernet
Ring Protection
Switching
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching.
For more information, see the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“cfm-sf-notify” on page 1502
•“clear g8032 erp-instance” on page 1504
•“clear g8032 erp-instance statistics” on page 1506
•“data-traffic” on page 1507
•“debug g8032” on page 1509
•“enable (G.8032)” on page 1510
•“epsr topology-change” on page 1511
•“erp-instance” on page 1512
•“g8032 erp-instance” on page 1513
•“g8032 forced-switch erp-instance” on page 1515
•“g8032 manual-switch erp-instance” on page 1517
•“g8032 physical-ring” on page 1518
•“g8032 profile” on page 1520
•“level (G.8032)” on page 1521
•“physical-ring” on page 1522
•“profile name” on page 1523
•“raps-channel” on page 1524
•“rpl role” on page 1525

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1501
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
•“show debugging g8032” on page 1527
•“show g8032 erp-instance” on page 1528
•“show g8032 erp-instance statistics” on page 1533
•“show g8032 physical-ring” on page 1535
•“show g8032 profile” on page 1537
•“sub-ring” on page 1539
•“timer (G.8032)” on page 1540
•“topology-change” on page 1542
•“trap (G.8032)” on page 1544
•“undebug g8032” on page 1545

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1502
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
CFM-SF-NOTIFY
cfm-sf-notify
Overview Use this command to configure this ERP instance to receive signal fail notifications
from a Local MEP(s). This command can be used multiple times to allow multiple
Local MEPs to be specified.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a Local MEP from sending
notifications to this G.8032 ERP instance.
Syntax cfm-sf-notify mep mpid <mep-id> domain <domain-name> service
<ma-name>
no cfm-sf-notify mep mpid <mep-id> domain <domain-name> service
<ma-name>
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage CFM and Continuity Check Messaging (CCM) can be configured to detect link faults
on the East or West interface ports as a whole, or faults on the R-APS VLAN on the
East or West interface. In this situation CFM Local MEPs can notify G.8032 of defects
it detects. G.8032 will treat these notifications as a Signal Fail (SF) for that East or
West ring port. Similarly, CFM Local MEPs can notify G.8032 that the fault has
cleared. When this command is used, this G.8032 ERP instance will ensure that the
specified Local MEP is a Down MEP for the East or West interface used by this
instance or for the R-APS VLAN on the East or West interface used by this instance.
Example To configure an ERP instance to receive signal fail notifications from a local MEP
with an MEP ID of “12”, an MD named “MD-INST1”, and an MA named
“MA-INST1-1”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance ring2
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# cfm-sf-notify mep mpid 12 domain
MD-INST1 service MA-INST1-1
Parameter Description
mep Specify that a Local Maintenance End Point (MEP) is to provide the
Signal Fail notification to this G.8032 ERP instance.
mpid Specify that the Local MEP is to be identified by MEP-id.
<mep-id> 1-8191. Specify the Local MEP's ID.
domain Specify the Maintenance Domain that the Local MEP is associated
with.
<domain-name> Specify the Maintenance Domain's CLI instance name.
service Specify the Maintenance Association that the Local MEP is
associated with.
<ma-name> Specify the Maintenance Association's CLI instance name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1503
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
CFM-SF-NOTIFY
Related
Commands
ethernet cfm domain-name
ethernet cfm mep
g8032 erp-instance
service ma-name
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1504
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
clear g8032 erp-instance
Overview Use this command to:
• trigger a reversion immediately, without waiting for timers to expire, or
• clear a forced-switch or manual-switch command that was previously
successfully entered on a G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax clear g8032 erp-instance <erp-instance-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command can be used after a protection switch has occurred and the failure
has cleared. If reversion is enabled, this command will trigger a reversion
immediately, without having to wait for certain timers to expire (such as WTB or
WTR). If reversion has been disabled, this command will trigger a reversion.
Alternatively, this command can be used on an ERP instance where a forced-switch
or manual-switch command has been successfully entered to clear that action. The
command will be ignored if a force-switch or manual-switch command had not
been previously entered successfully, even if such node is in the FORCED_SWITCH
or MANUAL_SWITCH state.
Examples To trigger a reversion immediately without waiting for a timer to expire on an ERP
instance named “blue”, use the following command:
awplus# clear g8032 erp-instance blue
Alternatively, to clear a previously applied forced-switch from an ERP instance
named “blue”, use the following command:
awplus# clear g8032 erp-instance blue
The forced-switch would be created using a command like this one, which forces a
protection switch on the East interface of an ERP instance named “blue”:
awplus# g8032 forced-switch erp-instance blue east-interface
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
g8032 forced-switch erp-instance
g8032 manual-switch erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of the G.8032 ERP instance

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1505
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1506
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
CLEAR G8032 ERP-INSTANCE STATISTICS
clear g8032 erp-instance statistics
Overview Use this command to clear the statistics data being collected by a G.8032 Ethernet
Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax clear g8032 erp-instance <erp-instance-name> statistics
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage A G.8032 ERP instance keeps statistical data as counts on a variety of data such as
the number of certain types of Ring-Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS)
messages sent and received over its ring port(s) and error conditions detected. Use
this command to clear the statistics data.
Example To clear the statistics for an ERP instance named “blue”, use the following
command:
awplus# clear g8032 erp-instance blue statistics
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance statistics
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of a specific G.8032 ERP instance
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1507
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
DATA-TRAFFIC
data-traffic
Overview Use this command to add a data traffic VLAN or a range of VLANs to be protected
by this G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a data traffic VLAN or a range of
VLANs.
Syntax data-traffic <vid-list>
no data-traffic <vid-list>
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage • A G.8032 ERP instance can protect 0, 1 or more VLANs carrying data traffic.
• This ERP instance must be associated with a physical ring instance.
• Other ERP instances using the same physical ring instance are not allowed to
have the same data traffic VLAN(s) as this ERP instance.
• The data VLAN(s) must already exist.
• The data VLAN(s)’ port members should be members of the ring interface(s),
but it is not enforced.
• When a data traffic VLAN(s) is removed, any blocks that were in place on the
ring ports for this VLAN(s) are removed. The user should make sure when
removing the VLAN(s) from the ERP instance that a loop is not formed.
• Data traffic VLAN(s) can be added or removed while the ERP instance is
enabled or disabled.
Example To add a data traffic VLAN with a VLAN ID of “103” to an ERP instance named “blue”,
use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# data-traffic 103
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Parameter Description
<vid-list> The data traffic VLAN ID(s). This can be a single VLAN ID, or can be
a range of VLAN IDs separated by hyphen, or a comma separated
list of VLAN IDs and ranges. Each VLAN ID can take on the range of
1 to 4094

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1508
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
DATA-TRAFFIC
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1509
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
DEBUG G8032
debug g8032
Overview Use this command to enable G.8032 debugging.
Use the no variant of this command to disable G.8032 debugging.
Syntax debug g8032 {all|event|rx|tx}
no debug g8032 {all|event|rx|tx}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enable all G.8032 debugging, use the following command:
awplus# debug g8032 all
Related
Commands
show debugging
show debugging g8032
undebug g8032
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
all Turn on all G.8032 debugging
event Turn on G.8032 Event debugging
rx Turn on G.8032 Receive debugging
tx Turn on G.8032 Transmit debugging

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1510
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
ENABLE (G.8032)
enable (G.8032)
Overview Use this command to change the revertive or non-revertive operation of the
associated G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax enable {revertive|non-revertive}
Default By default, the mode of operation is revertive.
Mode G8032 Profile Configuration
Usage An ERP instance uses a profile which contains timer configurations and
configurations for revertive modes of operation. Once a ring failure has abated, a
G.8032 ring instance will check its mode of operation, and if the mode is revertive,
it will attempt to revert back to where the RPL-Owner controls the blocking of the
ring. Otherwise, it operates in non-revertive mode.
Example To enable revertive mode for a profile named “prof_1”, use the following
commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 profile prof_1
awplus(g8032-profile-config)# enable revertive
Related
Commands
g8032 profile
show g8032 profile
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
revertive This allows the ERP instance associated with this profile to operate
in revertive mode.
non-revertive This allows the ERP instance associated with this profile to operate
in non- revertive mode.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1511
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
EPSR TOPOLOGY-CHANGE
epsr topology-change
Overview Use this command to allow the given EPSR instance to accept notifications from
other topology protocols, namely G.8032, for Topology Change Notifications
(TCN).
Use the no variant of this command to return the EPSR instance to where it does
not accept TCNs from the other specified protocol, and as a result does not send
out a “flush FDB” message.
Syntax epsr <epsr-name> topology-change g8032
no epsr <epsr-name> topology-change g8032
Default The default value is no notifications are accepted and in turn no “flush FDB”
messages are sent.
Mode EPSR Configuration
Usage The purpose of this command is to allow EPSR to accept notifications from other
topology protocols, namely G.8032, about Topology Change Notifications (TCN).
Once EPSR accepts the TCN, it will in turn notify the other nodes on the EPSR ring
to perform an FDB flush.
Example To configure an EPSR instance named “red” to accept G.8032 TCNs, use the
following command:
awplus(config-epsr)# epsr red topology-change g8032
To configure an EPSR instance named “red” to no longer accept G.8032 TCNs, use
the following command:
awplus(config-epsr)# no epsr red topology-change g8032
Related
Commands
show epsr
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
<epsr-name> The name of the EPSR instance for which the topology-change
applies to.
topology-change The topology-change value to be set for the instance.
g8032 Specify that G.8032 is the other protocol that the
topology-change notifications are allowed to be accepted from in
order to send "flush FDB" messages to other EPSR nodes in the
ring.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1512
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
ERP-INSTANCE
erp-instance
Overview Use this command to enable or disable a G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP)
instance.
Syntax erp-instance {enabled|disabled}
Default The ERP instance is disabled.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage Once a G.8032 ERP instance has been configured with the correct parameter
settings or defaults, it can be enabled to run the G.8032 protocol. To change
certain ERP instance parameters, the instance may need to be disabled.
When enabled, the instance is restarted back to the G8032_ST_INIT state. In this
state, if the node has an RPL-Owner or RPL-Neighbor port, it will be blocked.
Otherwise the node will block one of its ring ports. All the nodes will send
Ring-Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages initially. The G.8032
protocol and state machines will transition the ring into another more appropriate
state.
When disabled, the ERP instance will no longer process incoming R-APS messages
for that instance, nor send any R-APS messages. The raps-channel VLAN and any
data-traffic VLANs used by this instance will be put in the forwarding state for its
physical ring ports. Caution should be taken to avoid loops when disabling an ERP
instance.
Example To enable an ERP instance named “blue”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# erp-instance enabled
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance
trap (G.8032)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
enabled The G.8032 ERP instance is enabled
disabled The G.8032 ERP instance is disabled

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1513
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
g8032 erp-instance
Overview Use this command to create a G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance, or to
enter an existing instance's context.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the specified instance.
Syntax g8032 erp-instance <erp-instance-name>
no g8032 erp-instance <erp-instance-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The ERP protocol in AlliedWare Plus™ can run one or more instances. A G.8032 ERP
instance is made up of:
•two ERP ring ports,
• a Control VLAN that carries Ring-Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS)
messages, and
• zero, one, or more Protected traffic data VLANs that the instance protects
when the ring fails.
An ERP instance must be associated with a G.8032 physical ring and a G.8032
profile.
Example To enter the context of an instance named “blue”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)#
Related
Commands
clear g8032 erp-instance
clear g8032 erp-instance statistics
data-traffic
erp-instance
g8032 forced-switch erp-instance
g8032 manual-switch erp-instance
level (G.8032)
physical-ring
profile name
raps-channel
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of the G.8032 ERP instance. This can be up to 32
characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1514
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
rpl role
show g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance statistics
sub-ring
topology-change
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1515
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 FORCED-SWITCH ERP-INSTANCE
g8032 forced-switch erp-instance
Overview Use this command to force a protection switch on a G.8032 Ethernet Ring
Protection (ERP) instance ring port.
Syntax g8032 forced-switch erp-instance <erp-instance-name>
{east-interface|west-interface|terminating-interface}
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage G.8032 supports a Forced Protection Switch action initiated by the operator. A
Forced Protection Switch command is to be issued at a given G.8032 node and
given port in the ring. This results in a block being applied at that ring port (and an
unblock on the opposite ring port), and a R-APS designated Forced Switch
message to flow around the ring causing the RPL to become unblocked.
Multiple Forced Switch actions can take place along a G.8032 ring. Care must be
taken when using the Force Switch command as it can only be undone by issuing
a Clear command and not by a failure nor the clearing of a failure. If a node that was
issued a Force Switch command later fails, then it becomes difficult to remove the
Force Switch condition from the ring. In this situation, the operator has to go to the
nodes that are adjacent to the failed node, and for each one, issue a Forced Switch
command on the ring link facing the failed node followed by a Clear command.
If the G.8032 Physical Ring instance associated with the specified ERP instance is
set to terminating-interface, then only one ring port is available and
terminating-interface must be used in this command, otherwise specify the
east-interface or the west-interface.
To clear this action command, use the clear g8032 erp-instance command.
Example To issue a Forced Protection Switch on the East interface of an ERP instance named
“blue”, use the following command:
awplus# g8032 forced-switch erp-instance blue east-interface
Related
Commands
clear g8032 erp-instance
g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of the G.8032 ERP instance
east-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's East ring port
west-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's West ring port
terminating-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's Terminating ring port

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1516
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 FORCED-SWITCH ERP-INSTANCE
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1517
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 MANUAL-SWITCH ERP-INSTANCE
g8032 manual-switch erp-instance
Overview Use this command to manually cause a protection switch on a G.8032 Ethernet
Ring Protection (ERP) instance ring port.
Syntax g8032 manual-switch erp-instance <erp-instance-name>
{east-interface|west-interface|terminating-interface}
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage G.8032 supports a Manual Protection Switch action initiated by the operator. A
Manual Protection Switch command is to be issued at a given G.8032 node and
given port in the ring. This results in a block being applied at that ring port (and an
unblock on the opposite ring port), and a R-APS designated Manual Switch
message to flow around the ring causing the RPL to become unblocked.
The difference between a Manual switch and a Forced switch is that the Manual
Switch will be ignored under various conditions. In particular, only one Manual
Switch is allowed on a G.8032 ring at a time.
If the G.8032 Physical Ring instance associated with the specified ERP instance is
set to terminating-interface, then only one ring port is available and
terminating-interface must be used in this command, otherwise specify the
east-interface or the west-interface.
To clear this action command, use the clear g8032 erp-instance command.
Example To issue a Manual Protection Switch on the East interface of an ERP instance named
“blue”, use the following command:
awplus# g8032 manual-switch erp-instance blue east-interface
Related
Commands
clear g8032 erp-instance
g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of the G.8032 ERP instance
east-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's East ring port
west-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's West ring port
terminating-interface The G.8032 ERP instance's Terminating ring port

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1518
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 PHYSICAL-RING
g8032 physical-ring
Overview Use this command to create a G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) physical ring
profile which specifies the Ethernet ports that will be used as G.8032 ring ports.
Syntax g8032 physical-ring <physical-ring-name> {east-interface
<interface-name1> west-interface <interface-name2>|
terminating-interface <interface-name>}
no g8032 physical-ring <physical-ring-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Each ERP instance will be associated with a physical ring profile. A physical ring
profile is made up of two physical Ethernet ports or aggregated interfaces, unless
it is the terminating point of a sub-ring in which case only one port is needed.
When two ports are used, they are referred to as East and West ports. When only a
single port is used, it is referred to as a Terminating port.
Example To create a physical ring profile named “red” where the East interface port is
“port1.0.5” and the West interface port is “port1.0.6”, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# g8032 physical-ring red east-interface
port1.0.5 west-interface port1.0.6
Related
Commands
physical-ring
rpl role
show g8032 physical-ring
Parameter Description
<physical
-ring-name> The name of the profile (up to 37 characters)
east-interface The East G.8032 ring port
<interface-name1> The name of the switch interface, either port or channel
group, for the East ring port. It must differ from the West ring
port.
west-interface The West G.8032 ring port
<interface-name2> The name of the switch interface, either port or channel
group, for the West ring port. It must differ from the East ring
port.
terminating
-interface The Terminating ring port. This should only be used for
G.8032 ERP instance that is at the end of a sub-ring.
<interface-name> The name of the switch interface, either port or channel
group, for the Terminating ring port.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1519
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 PHYSICAL-RING
sub-ring
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1520
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
G8032 PROFILE
g8032 profile
Overview Use this command to create a G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance
profile, or to enter that instance's profile context.
Use the no variant of this command to destroy the specified instance.
Syntax g8032 profile {<erp-profile-name>|default-profile}
no g8032 profile <erp-profile-name>
Default A profile with the name "default-profile" will exist in the system and is used by
default by an ERP instance. All the parameters in the default profile take on the
default values.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enter the context of a profile named “prof_1”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 profile prof_1
awplus(g8032-profile-config)#
Related
Commands
enable (G.8032)
profile name
show g8032 profile
timer (G.8032)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-profile-name> The name of the G.8032 profile. This can be up to 32
characters.
default-profile The name of the system's default profile for G.8032. This
profile is created by the system automatically and can not
be destroyed.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1521
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
LEVEL (G.8032)
level (G.8032)
Overview Use this command to configure the level for Ring-Automatic Protection Switching
(R-APS) messages.
Syntax level <0-7>
Default The default level is 0.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage Inside the R-APS messages is the Level field. The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection
(ERP) instance will use the configured level for sending R-APS messages, and is the
level that the instance expects to receive. If the node receives an R-APS message
with the improper level then the message will not be processed.
The ERP instance must be disabled to change the level, otherwise the setting is
denied.
Example To set the R-APS message level field for an ERP instance named “blue” to 3, use the
following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# level 3
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<0-7> The level used by the G.8032 ERP instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1522
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
PHYSICAL-RING
physical-ring
Overview Use this command to specify which G.8032 physical ring instance is to be used by
this G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax physical-ring <physical-ring-name>
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage A G.8032 ERP instance in general has two ring ports, unless it is at the end of a
sub-ring in which case it has only one ring port. Ring port(s) are specified using a
G.8032 physical ring instance.
This command can only be accepted when the ERP instance is disabled.
Example To configure an ERP instance named “blue” to use a physical ring instance named
“red”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# physical-ring red
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
g8032 physical-ring
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<physical-ring-name> The name of the physical ring instance.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1523
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
PROFILE NAME
profile name
Overview Use this command to associate a G.8032 profile instance with this G.8032 Ethernet
Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax profile name <erp-profile-name>
Default If this command is not used, a profile with the name “default-profile” will be used
for this G.8032 ERP instance.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch Mode
Usage A G.8032 ERP instance uses a profile which contains timer configurations and
configurations for revertive modes of operation. This configuration can be
accepted regardless of the ERP instance being disabled or enabled. Any
parameters from a changed profile will take effect the next time the G.8032 state
machine uses the parameters in the updated profile.
Example To associate a G.8032 profile named “prof_1” with a G.8032 ERP instance named
“blue”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# profile name prof_1
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
g8032 profile
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<erp-profile-name> The name of the G.8032 profile
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1524
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
RAPS-CHANNEL
raps-channel
Overview Use this command to specify which VLAN to use as a channel for G.8032
Ring-Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages sent and received by this
G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the VLAN from being used as the
R-APS channel VLAN.
Syntax raps-channel <vid>
no raps-channel
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage For a G.8032 ERP instance, a VLAN is used as a channel for carrying an R-APS
message. This VLAN is also used to identify the proper ring instance to all the other
nodes in the ring.
The VLAN must be tagged members of the G.8032 physical ring instance
associated with this ERP instance. A G.8032 physical ring instance must be
associated with this ERP instance. The ERP instance can not be enabled until this
raps-channel VLAN has been configured properly.
The ERP instance must be disabled when using the no variant.
Example To configure a VLAN with a VLAN-id of “103” as a R-APS channel for an ERP instance
named “blue”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# raps-channel 103
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
<vid> A single VLAN-id in the range 2 to 4094.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1525
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
RPL ROLE
rpl role
Overview Use this command to specify the role of each G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection
(ERP) ring port (also known as a link). The role can be specified as to whether it is a
Ring Protection Link (RPL) or not, and if it is an RPL, whether it is the Owner or
Neighbor end of an RPL.
Use the none variant of this command to set all the ERP instance's ring ports' RPL
role to none.
Syntax rpl role {owner|neighbor}{east-interface|west-interface|
terminating-interface}
rpl role none
Default A RPL role of “none” is the default.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage If a node has one of its ring ports set to Owner or Neighbor, then none is
automatically set on any other ring port as none is the only possible setting for the
other ring port.
When using this command to set the RPL role to none, an interface need not be
specified, as this command will set all the ring ports RPL role to none.
The command can only be accepted when the G.8032 ERP Instance is disabled, and
the ERP instance must also have an association to a ERP Physical Ring instance.
As in the case of a sub-ring with only one physical ring port, use
terminating-interface when specifying the RPL role as Owner or Neighbor.
Example To configure the east-interface of a ring port named “blue” to be an RPL Owner, use
the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# rpl role owner east-interface
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
Parameter Description
owner This sets the specified ring port to be an RPL Owner
neighbor This sets the specified ring port to be an RPL Neighbor
east-interface The ring port's east-interface.
west-interface The ring port's west-interface.
terminating-
interface The ring port's terminating-interface
none This sets all the ERP instance's ring ports' RPL role to none.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1526
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
RPL ROLE
g8032 physical-ring
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1527
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING G8032
show debugging g8032
Overview Use this command to show the debugging modes enabled for G.8032.
Syntax show debugging g8032
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the debugging modes enabled for G.8032, use the following command:
awplus# show debugging g8032
Output Figure 43-1: Example output from the show debugging g8032 command.
Related
Commands
debug g8032
undebug g8032
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
awplus#show debugging g8032
G.8032 event debugging is off
G.8032 receive debugging is off
G.8032 transmit debugging is off

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1528
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
show g8032 erp-instance
Overview Use this command to show one or all G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP)
instance(s) configuration and dynamic state data.
Syntax show g8032 erp-instance {<erp-instance-name>|all}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the configuration and dynamic state data for an ERP instance named
“blue”, use the following command:
awplus# show g8032 erp-instance blue
Output Figure 43-2: Example output from the show g8032 erp-instance command.
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of a specific G.8032 ERP instance.
all Use this to show all instances.
awplus#show g8032 erp-instance blue
------------------------------------------------------------------
Instance Name : blue
Admin State : enabled
G.8032 State : IDLE
Failure of Proto-TO : false
Phy Ring : R1 - East (port2.0.25) : West (sa1)
East Link : Link_Unblocked
West Link : Link_blocked
RPL Role East Link : NONE
RPL Role West Link : OWNER
CFM MEP East : -
CFM MEP West : -
ERP Profile : default-profile
Level : 0
Ring-ID : 1
RAPS-Channel VLAN : 900
Sub-ring : disabled
Virtual Channel : disabled
Data Traffic VLANs : 910,920,930,940
TCN To Inst : -
TCN Flush Event : G8032
Wait-To-Restore : -
Wait-To-Block : -
NodeID : 0000.cd37.0c25
SNMP Traps : enabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1529
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
------------------------------------------------------------------
East Receiving | West Receiving
------------------------------------------------------------------
Hold Off Timer - | Hold Off Timer -
Signal Fail - | Signal Fail -
Failure of Proto-PM false | Failure of Proto-PM false
Version - | Version -
Request - | Request -
RPL-Block - | RPL-Block -
DNF - | DNF -
Block Port Ref - | Block Port Ref -
NodeID - | NodeID -
------------------------------------------------------------------
East Sending | West Sending
------------------------------------------------------------------
Version 1 | Version 1
Request NR | Request NR
RPL-Block RB | RPL-Block RB
DNF 1 | DNF 1
Block Port Ref 1 | Block Port Ref 1
NodeID 0000.cd37.0c25 | NodeID 0000.cd37.0c25
------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 1: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 erp-instance
command.
Parameter Description
Instance name The configured <erp-instance-name> for this instance.
Admin State The configured administrative state of this instance, either
enabled or disabled. When the ERP instance is disabled, all
dynamic data for other parameters in this table will be
shown as "-", except for the East Link or West Link which
will show the last known block or unblocked state.
G.8032 State A dynamic parameter showing the current state of the
instance per the G.8032 state machine. If the ERP Instance
is disabled, it will be in the INIT state.
Phy Ring Shows the Physical Ring Instance name that this ERP
Instance is associated with along with the East/West or
Terminating Interface used by the Physical Ring Instance.
East Link or West
Link A dynamic variable showing whether the instance's ring
port and its VLANs are blocked or not. In the special case
of an interconnection node where a sub-ring terminates,
both the East Link and the West Link are the same.
RPL Role East Link
or West Link Shows the configuration of the link's role.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1530
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
CFM MEP East or
West Identifies the configured MEP, if any, that is being used to
provide a CFM based Signal Fail indication to this instance.
The MEP is identified by its direction (Up or Down), its
MEP-id, and the Maintenance Domain (MD) and
Maintenance Association (MA) it is associated with by
name.
ERP Profile Identifies the ERP Profile instance that was configured for
use by this ERP Ring instance.
Level The Level that was configured for R-APS messages that are
used by this ERP Ring instance.
Ring-ID The Ring-ID that is to be used by this ERP instance.
RAPS-Channel VLAN The VLAN-id that is configured used for sending and
receiving R-APS messages for this ERP instance.
Sub-ring Specifies whether the ring is operating as a Sub-ring or
otherwise as a Major ring.
Virtual Channel Specifies whether the sub-ring is operating with a virtual
channel or not.
Data Traffic VLANs A comma-separated list of configured VLAN-ids
(individually, or range) that are used for data-traffic and
protected by this ERP instance.
TCN To Inst A comma-separated list of protocols and their instances
that are to be notified when a Topology Change
Notification occurs for this ERP instance. This only applies
to a sub-ring with a Terminating interface and in which
case "-" will be displayed if no target instances have been
identified. Otherwise a "-" is displayed anyway.Identifies
the protocol to notify. Only "G8032" will be supported
initially.<instance-name> - Identifies the instance to notify
for the given protocol.
TCN Flush Event Specifies if this instance as a target instance is to send out
Flush FDB messages upon TCN notifications by a
detecting instance.Identifies the notifying protocol
allowed. Only "G8032" will be supported initially. If no
protocols have been configured then display "-".
SNMP Traps Indicates whether SNMP traps have been enabled or
disabled for this ERP instance.
Table 1: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 erp-instance
command. (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1531
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
Signal Fail Indicates whether a Signal Fail condition is being received
over the East or West ring interface. <signal-fail> consists
of:
"-" no Signal Fail is being indicated
"Link" - indicates the interface port or LAG has gone
operationally down.
"CFM MEP <mep-id>" - indicates that a local CFM MEP has
indicated a Signal Fail, and which MEP by mep-id.
Failure of
Protocol Indicates that there are defects in the receipt of an R-APS
message. There are the following types:
FOP-PM (Provisioning Mismatch) - "true" indicates per
G.8032,that the RPL-Owner is receiving R-APS(NR,RB)
messages with a node-id not of itself. In addition, since the
initial implementation does not support version 1, any
R-APS messages with version 1 will also indicate a FOP-PM
error. The FOP-PM error can occur on an East or a West
Port.
FOP-TO (Time Out) - "true" indicates that a node has not
received an R-APS message on any of its ring ports for 3.5
times the R-APS message interval even though one or
both ring ports are capable of receiving R-APS messages
(no SF, Admin Up).
Version The version of the R-APS message that is being received or
sent over the East or West ring interface. An R-APS
message version of "1" corresponds to G.8032 version 2.
Request Indicates the protection switch request being sent or
received in the R-APS message. Consists of one of: NR - No
Request for protection switching SF - Signal Fail MS -
Manual Switch request FS - Force Switch request Event -
Request a Flush to be performed. Note this is a transient
condition.
RPL Block Indicates whether the RPL is being blocked or not. consists
of one of the following: "RB" - RPL Block is being applied
by the RPL-Owner. "-" - No RPL Block is being applied by
the RPL-Owner, or the R-APS message originated from a
non-RPL-Owner.
DNF Indicates the value of the Do Not Flush bit in the R-APS
message. The value is either "0" or "1".
Block Port Ref Block Port Reference refers to the node's East or West port
that is being blocked and shows as "0" or "1" in accordance
to G.8032.
Node-ID The MAC address of this Node or the MAC address used in
sending/receiving R-APS messages.
Table 1: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 erp-instance
command. (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1532
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE
Related
Commands
data-traffic
erp-instance
g8032 erp-instance
level (G.8032)
physical-ring
profile name
rpl role
sub-ring
topology-change
trap (G.8032)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
East Sending or
West Sending If this local node is not sending R-APS, then all the fields
are shown as "-"
Timers Wait-to-Restore - "Running" indicates this timer is active,
otherwise is "-".Wait-to-Block - "Running" indicates this
timer is active, otherwise is "-".Hold Off Timer - "Running"
indicates this timer is active, otherwise is "-".
Table 1: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 erp-instance
command. (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1533
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE STATISTICS
show g8032 erp-instance statistics
Overview Use this command to show the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance
statistics.
Syntax show g8032 erp-instance <erp-instance-name> statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the statistics for an ERP instance named “blue”, use the following
command:
awplus# show g8032 erp-instance blue statistics
Output Figure 43-3: Example output from the show g8032 erp-instance statistics
command.
Parameter Description
<erp-instance-name> The name of a specific G.8032 ERP instance
awplus#show g8032 erp-instance blue statistics
----------------------------------
Instance Name : blue
Local Clear : 0
FOP-TO : 0
-----------------------------------
East Receiving | West Receiving
---------------- - ----------------
RAPS NR 15 | RAPS NR 11
RAPS NR-RB 2 | RAPS NR-RB 0
RAPS SF 0 | RAPS SF 0
RAPS FS 0 | RAPS FS 0
RAPS MS 0 | RAPS MS 0
RAPS Event 0 | RAPS Event 0
Drop Guard 0 | Drop Guard 0
Drop Error 0 | Drop Error 0
Local SF 1 | Local SF 1
FOP-PM 0 | FOP-PM 0
-----------------------------------
East Sending | West Sending
---------------- - ----------------
RAPS NR 17 | RAPS NR 17
RAPS NR-RB 20067 | RAPS NR-RB 20067
RAPS SF 10 | RAPS SF 10
RAPS FS 0 | RAPS FS 0
RAPS MS 0 | RAPS MS 0
RAPS Event 0 | RAPS Event 0
-----------------------------------
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1534
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 ERP-INSTANCE STATISTICS
Related
Commands
clear g8032 erp-instance statistics
g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Table 2: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 erp-instance statistics
command
Parameter Description
Instance Name The configured <erp-instance-name> for this instance.
Local clear The number of Clear commands invoked locally.
FOP-TO The number of Failure of Protocol Time Out events seen
locally.
RAPS NR The number of R-APS messages with a No Request (NR)
being received or sent.
RAPS NR-RB The number of R-APS messages with a No Request, RPL
Blocked (NR,RB) being received or sent.
RAPS SF The number of R-APS messages with Signal Fail (SF) being
received or sent.
RAPS FS The number of R-APS messages with Forced Switch (FS)
being received or sent.
RAPS MS The number of R-APS messages with Manual Switch (MS)
being received or sent.
RAPS Event The number of R-APS messages with Event (Flush) being
received or sent.
Drop Guard The number of R-APS messages discarded due to Guard
Timer.
Drop Error The number of R-APS messages discarded due to incorrect
MAC Address (unmatched Ring-ID), incorrect version,
unusable Request/State, or other invalid code point in one
of the message fields.
Local SF The number of Signal Fail events seen locally.
FOP-PM The number of Failure of Protocol events seen locally.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1535
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 PHYSICAL-RING
show g8032 physical-ring
Overview Use this command to show the G.8032 physical ring instance information.
Syntax show g8032 physical-ring {<physical-ring-name>|all}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the details of a physical ring instance named “red”, use the following
command:
awplus# show g8032 physical-ring red
Output Figure 43-4: Example output from the show g8032 physical-ring command.
Related
Commands
g8032 physical-ring
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
<physical-ring-name> The name of the physical ring
all This shows all physical ring instances that have been
configured
awplus#show g8032 physical-ring red
Ring : red
====================
East : port1.0.5
West : port1.0.6
ERP Inst : blue
Table 3: Parameters in the output from the show g8032 physical-ring
command.
Parameter Description
Ring The name of the physical ring that was configured for this
physical ring instance.
East, West,
Terminating The physical interface port or LAG of the East or West Ring
interface, or the Terminating interface that was configured
for this physical ring instance.
ERP Inst A comma-separated list of ERP instances by name that
have been configured to use this physical ring instance, or
"-" if none.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1536
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 PHYSICAL-RING
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1537
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 PROFILE
show g8032 profile
Overview Use this command to show one specific G.8032 profile or all G.8032 profiles, and
the configured information within each profile.
Syntax show g8032 profile {<erp-profile-name>|default-profile|all}
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the profile details for a profile named “prof1”, use the following
command:
awplus# show g8032 profile prof1
Output Figure 43-5: Example output from the show g8032 profile command.
Parameter Description
<erp-profile-name> The name of the G.8032 profile that was created by the
user.
default-profile The default name of the G.8032 profile that was created
automatically by the system.
all Using this will show all G.8032 profiles.
awplus#show g8032 profile prof1
Profile : prof1
===========================
Wait-To-Restore : 5 mins
Hold Off Timer : 0 ms
Guard Timer : 500 ms
Wait-To-Block : 5500 ms
Protection Type : Revertive
ERP Inst : blue
Table 4: Parameters in the output from show g8032 profile command.
Parameter Description
Wait-To-Restore The configured value in <1-12> minutes.
Hold Off Timer The configured value but shown instead in milliseconds
which ranges from 0 to 10,000 (10s) in 100 ms increments.
Guard Timer The configured value which ranges from 10 to 2000 in 10
ms increments.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1538
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SHOW G8032 PROFILE
Related
Commands
enable (G.8032)
g8032 profile
timer (G.8032)
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Wait-To-Block 5 seconds more than the configured Guard Time. The
range is 5010 to 5200.
ERP Inst Comma separated list of ERP instances using this profile,
or "-" if there are none.
Table 4: Parameters in the output from show g8032 profile command. (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1539
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
SUB-RING
sub-ring
Overview Use this command to configure the mode of operation for the G.8032 Ethernet
Ring Protection (ERP) instance as a sub-ring.
Use the no variant of this command to change the mode of operation to that of a
normal fully enclosed ring.
Syntax sub-ring
no sub-ring
Default By default the mode is no sub-ring.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage An ERP instance can operate normally as a fully enclosed ring, commonly called a
major ring, or as a partially enclosed ring, called a sub-ring. Sub-rings must be
attached to either a major ring (one that is fully closed) or to other sub-rings where
one of the other sub-rings itself is attached to a major ring.
Setting the mode to sub-ring should also be set for all nodes in the sub-ring, as the
G.8032 state machine is different from that of a major ring.
This configuration can only be accepted when the ERP instance is disabled.
When the physical ring instance used by this ERP instance is configured for
terminating interface, then this ERP instance will automatically be configured to be
in the sub-ring mode and can not be changed.
Example To configure an ERP instance named “blue” as a sub-ring, use the following
commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# sub-ring
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
g8032 physical-ring
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1540
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
TIMER (G.8032)
timer (G.8032)
Overview Use this command to configure a timer for a specified G.8032 Ethernet Ring
Protection (ERP) instance profile.
Syntax timer wait-to-restore {<1-12>|default}
timer hold-off {<0-100>|default}
timer guard-timer {<1-200>|default}
Mode G8032 Profile Configuration
Example To set the wait-to-restore timer of a profile named “prof_1” to a value of 1 minute,
use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 profile prof_1
awplus(g8032-profile-config)# timer wait-to-restore 1
Parameter Description
wait-to-restore This timer is used to soak signal failure abatement to ensure the
signal failure abatement is not intermittent. This timer is only
used by the RPL Owner when in the revertive operation, and
thus is attempting to restore the ring. It is configurable in steps
of 1 to 12 minutes (default is 5 minutes).
hold-off This timer allows any other underlying protection schemes to
recover before G.8032 reacts to its defect as this gives time for
the G.8032 defect to clear. A classic example is when the ERP
Physical ring port is carried over a SONET/SDH transmission
system that itself has 50ms recovery times. If G.8032 detects a
failure, then increasing this timer to some value greater than
50ms would allows the SONET/SDH system to recover and have
the defect that G.8032 detected disappear thus preventing the
need for G.8032 to try and recover. The Hold Off timer is
configurable in 0 to 10 seconds in steps of 100ms (default is 0
ms).
guard-timer This is the amount of time that an ERP instance discards most
R-APS messages before being allowed to process them. It is
used when a clearing condition occurs yet at the same time
older messages are still propagating around the ring with failure
indications. For example two nodes that just noticed a link
failure abatement condition could start clearing and almost
immediately one of them could receive an old Signal Fail
indication message from the other node (that was still in flight)
which in turn causes the receiving node to react to the Signal
Fail inadvertently. This timer is particularly useful where R-APS
propagation time through the ring is large. Refer to ITU-T G.8032
for more information. The Guard timer is configurable in 10ms
steps between 10ms and 2 seconds (default is 50 for 500ms).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1541
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
TIMER (G.8032)
Related
Commands
g8032 profile
show g8032 profile
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1542
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
TOPOLOGY-CHANGE
topology-change
Overview Use this command to enable this G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) instance to
send a Flush Event message after notification of a Topology Change Notification
(TCN) by a detecting instance.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the sending of the Flush Event.
Syntax topology-change {g8032}
no topology-change {g8032}
Default Topology change is enabled by default for G.8032.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage If this ERP instance is on an interconnecting node, then the ERP instance may need
to be notified of a topology change that occurred in another G.8032 sub-ring
attached to this node. The former will be termed the "target" ERP instance, and the
latter the "detecting" ERP instance.
The criteria for notification is:
• the detecting ERP instance is configured as a sub-ring with a Terminating
interface,
• it is protecting the same data VLANs as the target instance, and
• the target ERP instance must have two ring ports.
When the detecting ERP instance detects a topology change on its sub-ring,
AlliedWare Plus™ will automatically determine which target ERP instance(s) needs
to be notified. It does this by comparing the same data VLANs in the detecting ERP
instance with all the other instances.
If target ERP instances are identified and these instances also have both an East
and a West interface configured, then those target instances are notified. Upon
notification, the target ERP instance has a couple of actions that it has to perform:
• To flush the FDB on both its East and West interfaces for the protected
VLANs.
• To send out an R-APS flush event message over its East and West interfaces.
The flush event message is sent around the target ring and each node on the
target ring will perform an FDB flush of its protected VLANs. The sending of
a R-APS flush event may not be needed in some cases and as such it is
configurable.
Parameter Description
g8032 Specify that G.8032 is the protocol that is affected by this
command.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1543
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
TOPOLOGY-CHANGE
Example To enable sending of R-APS flush event messages on an ERP instance named
“blue”, use the following commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# topology-change g8032
Related
Commands
g8032 erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1544
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
TRAP (G.8032)
trap (G.8032)
Overview Use this command to enable or disable SNMP traps for a G.8032 Ethernet Ring
Protection (ERP) instance.
Syntax trap {enabled|disabled}
Default The SNMP traps for the ERP instance are enabled.
Mode G8032 Configure Switch
Usage Globally, ERP traps are disabled by default but can be enabled globally using the
snmp-server enable trap command.
Example To disable the SNMP traps for an ERP instance named “blue”, use the following
commands:
awplus(config)# g8032 erp-instance blue
awplus(g8032-config-switch)# trap disabled
Related
Commands
erp-instance
show g8032 erp-instance
snmp-server enable trap
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
enabled Enable this ERP instance to generate traps.
disabled Disable this ERP instance from generating traps.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1545
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
G.8032 ETHERNET RING PROTECTION SWITCHING COMMANDS
UNDEBUG G8032
undebug g8032
Overview Use this command to turn off debugging for various G.8032 debug attributes.
Syntax undebug g8032 {all|event|rx|tx}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To turn off all G.8032 debugging, use the following command:
awplus# undebug g8032 all
Related
Commands
debug g8032
show debugging g8032
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.7-1.1: added to x310 series products
Version 5.4.7-2.1: added to x550 series products
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to SBx8100 series products
Version 5.4.8-1.1: added to SBx908 GEN2 series products
Parameter Description
all All G.8032 debugging
event G.8032 debugging events
rx G.8032 debugging Receive activities
tx G.8032 debugging Transmit activities

44
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1546
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RRP Snooping
Commands
Introduction
Overview This section provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
the Router Redundancy Protocol (RRP).
Command List •“ip rrp snooping” on page 1547
•“show ip rrp snooping” on page 1548

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1547
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RRP SNOOPING COMMANDS
IP RRP SNOOPING
ip rrp snooping
Overview Use this command to enable RRP snooping.
Use the no variant of this command to disable RRP Snooping.
Syntax ip rrp snooping
no ip rrp snooping
Default The default is disabled.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Use this command to enable the RRP Snooping feature. You cannot use RRP
Snooping at the same time as the following features:
• STP, RSTP, or MSTP, except for edge ports. RSTP is enabled by default. To
disable it, use the command spanning-tree enable on page 618.
• Port security (the command switchport port-security)
• Port authentication
•EPSR
• Port mirroring
Examples The example below shows you how to enable RRP Snooping.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip rrp snooping
Related
Commands
show ip rrp snooping

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1548
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RRP SNOOPING COMMANDS
SHOW IP RRP SNOOPING
show ip rrp snooping
Overview Use this command to display Router Redundancy Protocol snooping global
settings and status.
Syntax show ip rrp snooping
Mode Privileged Exec
Output The following example show the output display for the show ip rrp snooping
command
The following table shows the output display for the show ip rrp snooping
command
Related
Commands
ip rrp snooping
awplus#show ip rrp snooping
Status : Enabled
Vlan Master Virtual MAC Address UpTime
------------ ---------- ----------------------- ----------------
vlan1 Port1.0.1 00e0.2b00.0085 00:00:39
----------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Description
Status Displays if RRP Snooping is enabled or disabled
Vlan Displays the VLAN ID
Master Displays the port ID connected to the master router or the network of
the master router
Virtual MAC
Address Displays the virtual MAC address of the router
UpTime Displays the time that the current master router has been the master
router

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1549
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Part 7: Network Management

45
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1550
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Allied Telesis
Management
Framework™ (AMF)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for Allied Telesis Management
Framework™ (AMF) commands.
AMF master
nodes
Every AMF network must have at least one master node, which acts as the core of
the AMF network. Not all AlliedWare Plus devices are capable of acting as an AMF
master. See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for information
about AMF master support.
AMF edge CentreCOM® FS980M, GS900MX, GS970M, and XS900MX Series switches can only
be used as edge switches in an AMF network. The full management power and
convenience of AMF is available on these switches, but they can only link to one
other AMF node. They cannot form cross-links or virtual links.
AMF naming
convention
When AMF is enabled on a device, it will automatically be assigned a host name. If
a host name has already been assigned, by using the command hostname on page
219, this will remain. If however, no host name has been assigned, then the name
applied will be the prefix, host_ followed (without a space) by the MAC address of
the device. For example, a device whose MAC address is 0016.76b1.7a5e will have
the name host_0016_76b1_7a5e assigned to it.
To efficiently manage your network using AMF, we strongly advise that you devise
a naming convention for your network devices, and apply an appropriate
hostname to each device in your AMF network.
AMF and STP On AR-Series firewalls, you cannot use STP at the same time as AMF.
Command List •“application-proxy whitelist enable” on page 1555
•“application-proxy whitelist server” on page 1556
•“area-link” on page 1558
•“atmf area” on page 1560
•“atmf area password” on page 1562

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1551
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
•“atmf authorize” on page 1564
•“atmf authorize provision” on page 1566
•“atmf backup” on page 1568
•“atmf backup area-masters delete” on page 1569
•“atmf backup area-masters enable” on page 1570
•“atmf backup area-masters now” on page 1571
•“atmf backup area-masters synchronize” on page 1572
•“atmf backup bandwidth” on page 1573
•“atmf backup delete” on page 1574
•“atmf backup enable” on page 1575
•“atmf backup guests delete” on page 1576
•“atmf backup guests enable” on page 1577
•“atmf backup guests now” on page 1578
•“atmf backup guests synchronize” on page 1579
•“atmf backup now” on page 1580
•“atmf backup redundancy enable” on page 1582
•“atmf backup server” on page 1583
•“atmf backup stop” on page 1585
•“atmf backup synchronize” on page 1586
•“atmf cleanup” on page 1587
•“atmf container” on page 1588
•“atmf container login” on page 1589
•“atmf controller” on page 1590
•“atmf distribute firmware” on page 1591
•“atmf domain vlan” on page 1593
•“atmf enable” on page 1596
•“atmf group (membership)” on page 1597
•“atmf guest-class” on page 1599
•“atmf log-verbose” on page 1601
•“atmf management subnet” on page 1602
•“atmf management vlan” on page 1605
•“atmf master” on page 1607
•“atmf mtu” on page 1608
•“
atmf network-name” on page 1609
•“atmf provision (interface)” on page 1610

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1552
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
•“atmf provision node” on page 1611
•“atmf reboot-rolling” on page 1613
•“atmf recover” on page 1617
•“atmf recover guest” on page 1619
•“atmf recover led-off” on page 1620
•“atmf recovery-server” on page 1621
•“atmf remote-login” on page 1623
•“atmf restricted-login” on page 1625
•“atmf secure-mode” on page 1627
•“atmf secure-mode certificate expire” on page 1629
•“atmf secure-mode certificate expiry” on page 1630
•“atmf secure-mode certificate renew” on page 1631
•“atmf secure-mode enable-all” on page 1632
•“atmf select-area” on page 1634
•“atmf topology-gui enable” on page 1635
•“atmf trustpoint” on page 1636
•“atmf virtual-crosslink” on page 1638
•“atmf virtual-link” on page 1640
•“atmf virtual-link protection” on page 1643
•“atmf working-set” on page 1645
•“bridge-group” on page 1647
•“clear atmf links” on page 1648
•“clear atmf links virtual” on page 1649
•“clear atmf links statistics” on page 1650
•“clear atmf recovery-file” on page 1651
•“clear atmf secure-mode certificates” on page 1652
•“clear atmf secure-mode statistics” on page 1653
•“clone (amf provisioning)” on page 1654
•“configure boot config (amf provisioning)” on page 1656
•“configure boot system (amf provisioning)” on page 1658
•“create (amf provisioning)” on page 1660
•“debug atmf” on page 1662
•“debug atmf packet” on page 1664
•“
delete (amf provisioning)” on page 1667
•“discovery” on page 1669

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1553
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
•“description (amf container)” on page 1671
•“erase factory-default” on page 1672
•“http-enable” on page 1673
•“identity (amf provisioning)” on page 1675
•“license-cert (amf provisioning)” on page 1677
•“locate (amf provisioning)” on page 1679
•“log event-host” on page 1680
•“modeltype” on page 1681
•“show application-proxy whitelist interface” on page 1682
•“show application-proxy whitelist server” on page 1684
•“show application-proxy whitelist supplicant” on page 1685
•“show atmf” on page 1687
•“show atmf area” on page 1691
•“show atmf area guests” on page 1694
•“show atmf area guests-detail” on page 1696
•“show atmf area nodes” on page 1698
•“show atmf area nodes-detail” on page 1700
•“show atmf area summary” on page 1702
•“show atmf authorization” on page 1703
•“show atmf backup” on page 1706
•“show atmf backup area” on page 1710
•“show atmf backup guest” on page 1712
•“show atmf container” on page 1714
•“show atmf detail” on page 1717
•“show atmf group” on page 1719
•“show atmf group members” on page 1721
•“show atmf guests” on page 1723
•“show atmf guests detail” on page 1725
•“show atmf links” on page 1728
•“show atmf links detail” on page 1730
•“show atmf links guest” on page 1739
•“show atmf links guest detail” on page 1741
•“show atmf links statistics” on page 1745
•“show atmf nodes” on page 1748
•“show atmf provision nodes” on page 1750

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1554
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
•“show atmf recovery-file” on page 1752
•“show atmf secure-mode” on page 1753
•“show atmf secure-mode audit” on page 1755
•“show atmf secure-mode audit link” on page 1756
•“show atmf secure-mode certificates” on page 1757
•“show atmf secure-mode sa” on page 1760
•“show atmf secure-mode statistics” on page 1763
•“show atmf tech” on page 1765
•“show atmf virtual-links” on page 1768
•“show atmf working-set” on page 1770
•“show debugging atmf” on page 1771
•“show debugging atmf packet” on page 1772
•“show running-config atmf” on page 1773
•“state” on page 1774
•“switchport atmf-agentlink” on page 1776
•“switchport atmf-arealink remote-area” on page 1777
•“switchport atmf-crosslink” on page 1779
•“switchport atmf-guestlink” on page 1781
•“switchport atmf-link” on page 1783
•“type atmf node” on page 1784
•“undebug atmf” on page 1787
•“username” on page 1788

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1555
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST ENABLE
application-proxy whitelist enable
Overview Use this command to enable application-proxy whitelist based authentication on
an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the whitelist authentication.
Syntax application-proxy whitelist enable
no application-proxy whitelist enable
Default Application-proxy whitelist is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To enable application-proxy whitelist authentication on the interface port1.0.4,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# application-proxy whitelist enable
To disable application-proxy whitelist authentication on the interface port1.0.4,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.4
awplus(config-if)# no application-proxy whitelist enable
Related
Commands
application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist interface
show application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1556
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST SERVER
application-proxy whitelist server
Overview Use this command to set an AMF master to act as a whitelist authentication proxy
between AMF members, acting as Network Access Servers, and an external
whitelist RADIUS server.
Use the no variant of this command disable the whitelist proxy functionality.
Syntax application-proxy whitelist server <ip-address> key <key>
[auth-port <1-65535>]
no application-proxy whitelist server
Default Application-proxy whitelist proxy is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To configure an AMF Master to work as a proxy to the external RADIUS server
192.168.1.10, with shared secret 'mysecurekey', on port 1822, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# application-proxy whitelist server 192.168.1.10
key mysecurekey auth-port 1822
To configure an AMF Master to work as a proxy to the external RADIUS server
192.168.1.10, with shared secret 'mysecurekey', on the default port (1812), use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# application-proxy whitelist server 192.168.1.10
key mysecurekey
To disable the application-proxy whitelist feature, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no application-proxy whitelist server
Related
Commands
application-proxy whitelist enable
show application-proxy whitelist interface
show application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Parameter Description
<ip-address>IPv4 address of the upstream RADIUS server in dotted
decimal format A.B.C.D.
key <key>Set the shared secret encryption key for communication
with the upstream RADIUS server.
auth-port <1-65535>Set the RADIUS server UDP port. This is only necessary if
you don’t want to use the default port 1812.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1557
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST SERVER
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1558
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
AREA-LINK
area-link
Overview Use this command to create an area-link between a Virtual AMF Appliance (VAA)
host controller and an AMF container.
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an area-link from a container.
Syntax area-link <area-name>
no area-link
Mode AMF Container Configuration
Usage The AMF area-link connects the AMF controller on a VAA host to the AMF
container. Once a container has been created with the atmf container command
and an area-link configured with the area-link command, it can be enabled using
the state command.
You can only configure a single area-link on a container. You will see the following
message if you try and configure a second one:
% AreaLink already configured for this container
Each container has two virtual interfaces:
• Interface eth0, used to connect to the AMF controller on the VAA host via an
AMF area-link, configured using this area-link command.
• Interface eth1, used to connect to the outside world using a bridged L2
network link, configured using the bridge-group command.
See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide for more information on
these virtual interfaces and links.
Example To create the area-link to “wlg” on container “vac-wlg-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# area-link wlg
Parameter Description
<area-name> AMF area name of the container’s area.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1559
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
AREA-LINK
To remove an area-link from container “vac-wlg-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# no area-link
Related
Commands
atmf container
show atmf container
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1560
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF AREA
atmf area
Overview This command creates an AMF area and gives it a name and ID number.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the AMF area.
This command is only valid on AMF controllers, master nodes and gateway nodes.
Syntax atmf area <area-name> id <1-126> [local]
no atmf area <area-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command enables you to divide your AMF network into areas. Each area is
managed by at least one AMF master node. Each area can have up to 120 nodes,
depending on the license installed on that area’s master node.
The whole AMF network is managed by up to 8 AMF controllers. Each AMF
controller can communicate with multiple areas. The number of areas supported
on a controller depends on the license installed on that controller.
You must give each area in an AMF network a unique name and ID number.
Only one local area can be configured on a device. You must specify a local area on
each controller, remote AMF master, and gateway node.
Example To create the AMF area named New-Zealand, with an ID of 1, and specify that it is
the local area, use the command:
controller-1(config)# atmf area New-Zealand id 1 local
To configure a remote area named Auckland, with an ID of 100, use the command:
controller-1(config)# atmf area Auckland id 100
Parameter Description
<area-name> The AMF area name. The area name can be up to 15
characters long. Valid characters are:
a..z
A..Z
0..9
-
_
Names are case sensitive and must be unique within an
AMF network. The name cannot be the word “local” or an
abbreviation of the word “local” (such as “l”, “lo” etc.).
<1-126>An ID number that uniquely identifies this area.
local Set the area to be the local area. The local area contains the
device you are configuring.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1562
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF AREA PASSWORD
atmf area password
Overview This command sets a password on an AMF area.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the password.
This command is only valid on AMF controllers, master nodes and gateway nodes.
The area name must have been configured first.
Syntax atmf area <area-name> password [8] <password>
no atmf area <area-name> password
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You must configure a password on each area that an AMF controller
communicates with, except for the controller’s local area. The areas must already
have been created using the atmf area command.
Enter the password identically on both of:
• the area that locally contains the controller, and
• the remote AMF area masters
The command show running-config atmf will display the encrypted version of
this password. The encryption keys will match between the controller and the
remote AMF master.
If multiple controller and masters exist in an area, they must all have the same area
configuration.
Example To give the AMF area named Auckland a password of “secure#1” use the following
command on the controller:
controller-1(config)# atmf area Auckland password secure#1
and also use the following command on the master node for the Auckland area:
auck-master(config)# atmf area Auckland password secure#1
Parameter Description
<area-name> The AMF area name.
8This parameter is displayed in show running-config
output to indicate that it is displaying the password in
encrypted form. You should not enter 8 on the CLI
yourself.
<password> The password is between 8 and 32 characters long. It
can include spaces.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1564
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF AUTHORIZE
atmf authorize
Overview On an AMF network, with secure mode enabled, use this command on an AMF
master to authorize an AMF node to join the network. AMF nodes waiting to be
authorized appear in the pending authorization queue, which can be examined
using the show atmf authorization command with the pending parameter.
Use the no variant of this command to revoke authorization for an AMF node on
an AMF master.
Syntax atmf authorize {<node-name> [area <area-name>]|all-pending}
no atmf authorize <node-name> [area <area-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage On an AMF controller, AMF remote-area masters must be authorized by the
controller, and the AMF remote-area masters will also need to authorized access
from the AMF controller.
Example To authorize all AMF nodes in the pending authorization queue on an AMF master,
use the command:
awplus# atmf authorize all-pending
To authorize a node called “node2” in remote AMF area “area3”, use the command:
awplus# atmf authorize node2 area “area3”
To authorize a node called “node4” on an AMF master, use the command:
awplus# atmf authorize node4
To revoke authorization for a node called “node4” on an AMF master, use the
command:
awplus# no atmf authorize node4
Related
Commands
atmf secure-mode
clear atmf secure-mode certificates
show atmf authorization
show atmf secure-mode
Parameter Description
<node-name> The name of the node to be authorized or have its authorization
revoked.
area Specify an AMF area.
<area-name>This is the name of the area the node belongs to.
all-pending Authorize all nodes in the pending queue.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1566
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF AUTHORIZE PROVISION
atmf authorize provision
Overview Use this command from an AMF controller or AMF master to pre-authorize a node
on an AMF network running in secure mode. This allows a node to join the AMF
network the moment the atmf secure-mode command is run on that node.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a provisional authorization from
and AMF controller or AMF master.
Syntax atmf authorize provision [timeout <minutes>] node <node-name>
interface <interface-name> [area <area-name>]
atmf authorize provision [timeout <minutes>] mac <mac-address>
atmf authorize provision [timeout <minutes>] all
no atmf authorize provision node <node-name> interface
<interface-name> [area <area-name>]
no atmf authorize provision mac <mac-address>
no atmf authorize provision all
Default The default timeout is 60 minutes.
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To provisionally authorize all non-secure AMF nodes, use the command:
awplus# atmf authorize provision all
Parameter Description
timeout Timeout for provisional authorization. Authorization for
provisioned nodes expires after the timeout period
specified.
<minutes>Timeout in minutes. A value between 1 and 6000 is
permissible with the default being 60 minutes.
node Specify a node to provision by node name.
<node-name> The name of the node to provisionally authorize.
interface Specify the interface the node will connect on.
<interface-name>The name of the interface, this can be a switchport, link
aggregator, LACP link, or virtual link.
area Specify the AMF area.
<area-name> This is the name of the area the node belongs to.
mac Specify a node to provision by MAC address.
<mac-address>Enter a MAC address to provisionally authorize in the format
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH.
all Provision authorization for all secure mode capable nodes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1567
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF AUTHORIZE PROVISION
To authorize a node with a MAC address of 0000.cd28.0880 for 2 hours, use the
command:
awplus# authorize provision timeout 120 mac 0000.cd28.0880
To remove all provisional authorization, on an AMF master, use the command:
awplus# no atmf authorize provision all
Related
Commands
show atmf authorization
show atmf secure-mode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1568
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP
atmf backup
Overview This command can only be applied to a master node. It manually schedules an AMF
backup to start at a specified time and to execute a specified number of times per
day.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the schedule.
Syntax atmf backup {default|<hh:mm> frequency <1-24>}
Default Backups run daily at 03:00 AM, by default
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Running this command only configures the schedule. To enable the schedule, you
should then apply the command atmf backup enable.
We recommend using the ext3 or ext4 filesystem on external media that are used
for AMF backups.
Example To schedule backup requests to begin at 11 am and execute twice per day (11 am
and 11 pm), use the following command:
node_1# configure terminal
node_1(config)# atmf backup 11:00 frequency 2
CAUTION: File names that comprise identical text, but with differing case, such as
Test.txt and test.txt, will not be recognized as being different on FAT32 based backup
media such as a USB storage device. However, these filenames will be recognized as
being different on your Linux based device. Therefore, for good practice, ensure that
you apply a consistent case structure for your back-up file names.
Related
Commands
atmf backup enable
atmf backup stop
show atmf backup
Parameter Description
default Restore the default backup schedule.
<hh:mm>Sets the time of day to apply the first backup, in hours and
minutes. Note that this parameter uses the 24 hour clock.
backup Enables AMF backup to external media.
frequency <1-24>Sets the number of times within a 24 hour period that
backups will be taken.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1569
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP AREA-MASTERS DELETE
atmf backup area-masters delete
Overview Use this command to delete from external media, a backup of a specified node in
a specified area.
Note that this command can only be run on an AMF controller.
Syntax atmf backup area-masters delete area <area-name> node
<node-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the backup of the remote area-master named “well-gate” in the AMF
area named Wellington, use the command:
controller-1# atmf backup area-masters delete area Wellington
node well-gate
Related
Commands
show atmf backup area
Parameter Description
<area-name>The area that contains the node whose backup will be deleted.
<node-name>The node whose backup will be deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1570
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP AREA-MASTERS ENABLE
atmf backup area-masters enable
Overview Use this command to enable backup of remote area-masters from the AMF
controller. This command is only valid on AMF controllers.
Use the no form of the command to stop backups of remote area-masters.
Syntax atmf backup area-masters enable
no atmf backup area-masters enable
Mode Global configuration
Default Remote area backups are disabled by default
Usage Use the following commands to configure the remote area-master backups:
•atmf backup to configure when the backups begin and how often they run
•atmf backup server to configure the backup server.
We recommend using the ext3 or ext4 filesystem on external media that are used
for AMF backups.
Example To enable scheduled backups of AMF remote area-masters, use the commands:
controller-1# configure terminal
controller-1(config)# atmf backup area-masters enable
To disable scheduled backups of AMF remote area-masters, use the commands:
controller-1# configure terminal
controller-1(config)# no atmf backup area-masters enable
Related
Commands
atmf backup server
atmf backup
show atmf backup area

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1571
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP AREA-MASTERS NOW
atmf backup area-masters now
Overview Use this command to run an AMF backup of one or more remote area-masters from
the AMF controller immediately.
This command is only valid on AMF controllers.
Syntax atmf backup area-masters now [area <area-name>|area <area-name>
node <node-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To back up all local master nodes in all areas controlled by controller-1, use the
command
controller-1# atmf backup area-masters now
To back up all local masters in the AMF area named Wellington, use the command
controller-1# atmf backup area-masters now area Wellington
To back up the local master “well-master” in the Wellington area, use the
command
controller-1# atmf backup area-masters now area Wellington node
well-master
Related
Commands
atmf backup area-masters enable
atmf backup area-masters synchronize
show atmf backup area
Parameter Description
<area-name>The area whose area-masters will be backed up.
<node-name>The node that will be backed up.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1572
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP AREA-MASTERS SYNCHRONIZE
atmf backup area-masters synchronize
Overview Use this command to synchronize backed-up area-master files between the active
remote file server and the backup remote file server. Files are copied from the
active server to the remote server.
Note that this command is only valid on AMF controllers.
Syntax atmf backup area-masters synchronize
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To synchronize backed-up files between the remote file servers for all
area-masters, use the command:
controller-1# atmf backup area-masters synchronize
Related
Commands
atmf backup area-masters enable
atmf backup area-masters now
show atmf backup area

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1573
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP BANDWIDTH
atmf backup bandwidth
Overview This command sets the maximum bandwidth in kilobytes per second (kBps)
available to the AMF backup process. This command enables you to restrict the
bandwidth that is utilized for downloading file contents during a backup.
NOTE: This command will only run on an AMF master. An error message will be
generated if the command is attempted on node that is not a master.
Also note that setting the bandwidth value to zero will allow the transmission of as
much bandwidth as is available, which can exceed the maximum configurable speed
of 1000 kBps. In effect, zero means unlimited.
Use the no variant of this command to reset (to its default value of zero) the
maximum bandwidth in kilobytes per second (kBps) available when initiating an
AMF backup. A value of zero tells the backup process to transfer files using
unlimited bandwidth.
Syntax atmf backup bandwidth <0-1000>
no atmf backup bandwidth
Default The default value is zero, allowing unlimited bandwidth when executing an AMF
backup.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set an atmf backup bandwidth of 750 kBps, use the commands:
node2# configure terminal
node2(config)# atmf backup bandwidth 750
To set the AMF backup bandwidth to the default value for unlimited bandwidth,
use the commands:
node2# configure terminal
node2(config)# no atmf backup bandwidth
Related
Commands
show atmf backup
Parameter Description
<0-1000>Sets the bandwidth in kilobytes per second (kBps)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1574
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP DELETE
atmf backup delete
Overview This command removes the backup file from the external media of a specified AMF
node.
Note that this command can only be run from an AMF master node.
Syntax atmf backup delete <node-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To delete the backup file from node2, use the following command:
Node_1# atmf backup delete node2
Related
Commands
show atmf backup
atmf backup now
atmf backup stop
Parameter Description
<node-name> The AMF node name of the backup file to be deleted.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1575
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP ENABLE
atmf backup enable
Overview This command enables automatic AMF backups on the AMF master node that you
are connected to. By default, automatic backup starts at 3:00 AM. However, this
schedule can be changed by the atmf backup command. Note that backups are
initiated and stored only on the master nodes.
Use the no variant of this command to disable any AMF backups that have been
scheduled and previously enabled.
Syntax atmf backup enable
no atmf backup enable
Default Automatic AMF backup functionality is enabled on the AMF master when it is
configured and external media, i.e. an SD card or a USB storage device or remote
server, is detected.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage A warning message will appear if you run the atmf backup enable command with
either insufficient or marginal memory availability on your external storage device.
You can use the command show atmf backup on page 1706 to check the amount
of space available on your external storage device.
We recommend using the ext3 or ext4 filesystem on external media that are used
for AMF backups.
Example To turn on automatic AMF backup, use the following command:
AMF_Master_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# atmf backup enable
Related
Commands
show atmf
show atmf backup
atmf backup
atmf backup now
atmf enable

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1576
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP GUESTS DELETE
atmf backup guests delete
Overview This command removes a guest node’s backup files from external media such as a
USB drive, SD card, or an external file server.
Syntax atmf backup guests delete <node-name> <guest-port>
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example On a parent node named “node1” (which, in this case, the user has a direct console
connection to) use the following command to remove the backup files of the guest
node that is directly connected to port1.0.3.
node1# atmf backup guests delete node1 port1.0.3
Related
Command
atmf backup delete
atmf backup area-masters delete
show atmf backup guest
Parameter Description
<node-name> The name of the guest’s parent node.
<guest-port> The port number on the parent node.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1577
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP GUESTS ENABLE
atmf backup guests enable
Overview Use this command to enable backups of remote guest nodes from an AMF master.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the ability of the guest nodes to be
backed up.
Syntax atmf backup guests enable
no atmf backup guests enable
Default Guest node backups are enabled by default.
Mode Global Config
Usage We recommend using the ext3 or ext4 filesystem on external media that are used
for AMF backups.
Example On the AMF master node, enable all scheduled guest node backups:
atmf-master# configure terminal
atmf-master(config)# atmf backup guests enable
Related
Commands
atmf backup area-masters enable
show atmf backup guest
atmf backup guests synchronize

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1578
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP GUESTS NOW
atmf backup guests now
Overview This command manually triggers an AMF backup of guest nodes on a AMF Master.
Syntax atmf backup guests now [<node-name>] [<guest-port>]
Default n/a
Mode Privileged Exec
Example Use the following command to manually trigger the backup of all guests in the
AMF network
awplus# atmf backup guests now
Example To manually trigger the backup of a guest node connected to port 1.0.23 of node1,
use the following command:
awplus# atmf backup guests now node1 port1.0.23
Related
Commands
show atmf backup guest
Parameter Description
<node-name> The name of the guest’s parent node.
<guest-port> The port number that connects to the guest node.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1579
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP GUESTS SYNCHRONIZE
atmf backup guests synchronize
Overview This command initiates a manual synchronization of all guest backup file-sets
across remote file servers and various redundancy backup media, such as USB
storage devices. This facility ensures that each device contains the same backup
image files. Note that this backup synchronization process will occur as part of the
regular backups scheduled by the atmf backup command.
Syntax atmf backup guests synchronize
Default n/a
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To synchronize backups across remote file servers and storage devices, use the
command:
Node1#atmf backup guests synchronize
Related
Commands
atmf backup redundancy enable
show atmf guests
atmf backup guests enable
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1580
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP NOW
atmf backup now
Overview This command initiates an immediate AMF backup of either all AMF members, or
a selected AMF member. Note that this backup information is stored in the
external media on the master node of the device on which this command is run,
even though the selected AMF member may not be a master node.
Note that this command can only be run on an AMF master node.
Syntax atmf backup now [<nodename>]
Default A backup is initiated for all nodes on the AMF (but stored on the master nodes).
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage Although this command will select the AMF node to be backed-up, it can only be
run from any AMF master node.
NOTE: The backup produced will be for the selected node but the backed-up config will
reside on the external media of the AMF master node on which the command was run.
However, this process will result in the information on one master being more
up-to-date. To maintain concurrent backups on both masters, you can apply the
backup now command to the master working-set. This is shown in Example 4 below.
Example 1 In this example, an AMF member has not been assigned a host name. The
following command is run on the AMF_Master_2 node to immediately backup the
device that is identified by its MAC address of 0016.76b1.7a5e:
AMF_Master_2# atmf backup now host_0016_76b1_7a5e
NOTE: When a host name is derived from its MAC address, the syntax format entered
changes from XXXX.XXXX.XXXX to XXXX_XXXX_XXXX.
Example 2 In this example, an AMF member has the host name, office_annex. The following
command will immediately backup this device:
AMF_Master_2# atmf backup now office_annex
This command is initiated on the device’s master node named AMF_Master_2
and initiates an immediate backup on the device named office_annex.
Parameter Description
<nodename>
or
<hostname>
The name of the AMF member to be backed up, as set by the
command hostname on page 219. Where no name has been assigned
to this device, then you must use the default name, which is the word
“host”, then an underscore, then (without a space) the MAC address of
the device to be backed up. For example host_0016_76b1_7a5e.
Note that the node-name appears as the command Prompt when in
Privileged Exec mode.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1581
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP NOW
Example 3 To initiate from AMF_master_1 an immediate backup of all AMF member nodes,
use the following command:
AMF_Master_1# amf backup now
Example 4 To initiate an immediate backup of the node with the host-name “office_annex”
and store the configuration on both masters, use the following process:
From the AMF_master_1, set the working-set to comprise only of the automatic
group, master nodes.
AMF_Master_1# atmf working-set group master
This command returns the following display:
Backup the AMF member with the host name, office_annex on both the master
nodes as defined by the working set.
AMF_Master[2]# atmf backup now office_annex
Note that the [2] shown in the command prompt indicates a 2 node working-set.
Related
Commands
atmf backup
atmf backup stop
hostname
show atmf backup
============================
AMF_Master_1, AMF_Master_2
===============================
Working set join

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1582
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP REDUNDANCY ENABLE
atmf backup redundancy enable
Overview This command is used to enable or disable AMF backup redundancy.
Syntax atmf backup redundancy enable
no atmf backup redundancy enable
Default Disabled
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If the AMF Master or Controller supports any removable media (SD card/USB), it
uses the removable media as the redundant backup for the AMF data backup.
This feature is valid only if remote file servers are configured on the AMF Master or
Controller.
We recommend using the ext3 or ext4 filesystem on external media that are used
for AMF backups.
Example To enable AMF backup redundancy, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf backup redundancy enable
To disable AMF backup redundancy, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf backup redundancy enable
Related
Commands
atmf backup synchronize
show atmf backup
show atmf backup area

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1583
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP SERVER
atmf backup server
Overview This command configures remote file servers as the destination for AMF backups.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the destination server(s). When all
servers are removed the system will revert to backup from external media.
Syntax atmf backup server id {1|2} <hostlocation> username <username>
[path <path>|port <1-65535>]
no atmf backup server id {1|2}
Defaults Remote backup servers are not configured. The default SSH TCP port is 22. The
path utilized on the remote file server is the home directory of the username.
Mode Global Exec
Usage The hostname and username parameters must both be configured.
Examples To configure server 1 with an IPv4 address and a username of backup1, use the
commands:
AMF_Master_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# atmf backup server id 1 192.168.1.1
username backup1
Parameter Description
id Remote server backup server identifier.
{1|2} The backup server identifier number (1 or 2). Note that there can
be up to two backup servers, numbered 1 and 2 respectively, and
you would need to run this command separately for each server.
<hostlocation>Either the name or the IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) of the selected
backup server (1 or 2).
username Configure the username to log in with on the selected remote file
server.
<username>The selected remote file server’s username.
path The location of the backup files on the selected remote file
server. By default this will be the home directory of the username
used to log in with.
<path>The directory path utilized to store the backup files on the
selected remote file server. No spaces are allowed in the path.
port The connection to the selected remote backup file server using
SSH. By default SSH connects to a device on TCP port 22 but this
can be changed with this command.
<1-65535> A TCP port within the specified range.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1584
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP SERVER
To configure server 1 with an IPv6 address and a username of backup1, use the
command:
AMF_backup1_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# atmf backup server id 1 FFEE::01 username
backup1
To configure server 2 with a hostname and username, use the command:
AMF_Master_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# atmf backup server id 2 www.example.com
username backup2
To configure server 2 with a hostname and username in addition to the optional
path and port parameters, use the command:
AMF_Master_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# atmf backup server id 2 www.example.com
username backup2 path tokyo port 1024
To unconfigure the AMF remote backup file server 1, use the command:
AMF_Master_1# configure terminal
AMF_Master_1(config)# no atmf backup server id 1
Related
Commands
show atmf backup

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1585
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP STOP
atmf backup stop
Overview Running this command stops a backup that is currently running on the master
node you are logged onto. Note that if you have two masters and want to stop
both, then you can either run this command separately on each master node, or
add both masters to a working set, and issue this command to the working set.
Note that this command can only be run on a master node.
Syntax atmf backup stop
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command is used to halt an AMF backup that is in progress. In this situation
the backup process will finish on its current node and then stop.
Example To stop a backup that is currently executing on master node node-1, use the
following command:
AMF_Master_1# amf backup stop
Related
Commands
atmf backup
atmf backup enable
atmf backup now
show atmf backup

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1586
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF BACKUP SYNCHRONIZE
atmf backup synchronize
Overview For the master node you are connected to, this command initiates a system
backup of files from the node’s active remote file server to its backup remote file
server. Note that this process happens automatically each time the network is
backed up.
Note that this command can only be run from a master node.
Syntax atmf backup synchronize
Mode Privileged Exec
Example When connected to the master node AMF_Master_1, the following command will
initiate a backup of all system related files from its active remote file server to its
backup remote file server.
AMF_Master_1# atmf backup synchronize
Related
Commands
atmf backup enable
atmf backup redundancy enable
show atmf
show atmf backup

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1587
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF CLEANUP
atmf cleanup
Overview This command erases all data from Flash excluding the following:
• the boot release file (a .rel file) and its release setting file
• all license files
• the latest GUI release file
It then reboots to put the device in a clean state ready to be used as a replacement
node on a provisioned port.
Syntax atmf cleanup
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command is an alias to the erase factory-default command.
Example To erase data, use the command:
Node_1# atmf cleanup
This command will erase all NVS, all flash contents except for
the boot release,a GUI resource file, and any license files, and
then reboot the switch. Continue? (y/n):y
Related
Commands
erase factory-default
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1588
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF CONTAINER
atmf container
Overview Use this command to create or update an AMF container on a Virtual AMF
Appliance (VAA) virtual machine.
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an AMF container.
Syntax atmf container <container-name>
no atmf container <container-name>
Mode AMF Container Configuration
Usage You cannot delete a container while it is still running. First use the state disable
command to stop the container.
Examples To create or update the AMF container “vac-wlg-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)#
To remove the AMF container “vac-wlg-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf container vac-wlg-1
Related
Commands
area-link
atmf container login
bridge-group
description (amf container)
show atmf container
state
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
<container-name> The name of the AMF container to create, update, or remove.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1589
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF CONTAINER LOGIN
atmf container login
Overview Use this command to login to an AMF container on a Virtual AMF Appliance (VAA).
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Syntax atmf container login <container-name>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If you try to login to a AMF container that has not been created, or is not running,
you will see the following message:
% Container does not exist or is not running.
To exit from a container and return to the host VAA press <Ctrl+a q>.
Example To login to container “vac-wlg-1”, use the command:
awplus# atmf container login vac-wlg-1
You will then be presented with a login screen for that container:
Related
Commands
atmf container
show atmf container
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
<container-name> The name of the AMF container you wish to login into.
Connected to tty 1
Type <Ctrl+a q> to exit the console, <Ctrl+a Ctrl+a> to enter Ctrl+a itself
vac-wlg-1 login: manager
Password: friend
AlliedWare Plus (TM) 5.4.7 02/03/17 08:46:12
vac-wlg-1>

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1590
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF CONTROLLER
atmf controller
Overview Use this command to configure the device as an AMF controller. This enables you
to split a large AMF network into multiple areas.
AMF controller is a licensed feature. The number of areas supported on a controller
depends on the license installed on that controller.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the AMF controller functionality.
Syntax atmf controller
no atmf controller
Mode Global configuration
Usage If a valid AMF controller license is not available on the device, the device will accept
this command but will not act as a controller until you install a valid license. The
following message will warn you of this:
“An AMF Controller license must be installed before this feature will become
active”
NOTE: If the AMF controller functionality is removed from a device using the no atmf
controller command then the device must be rebooted if it is to function properly as
an AMF master.
Example To configure the node named controller-1 as an AMF controller, use the
commands:
controller-1# configure terminal
controller-1(config)# atmf controller
To stop the node named controller-1 from being an AMF controller, use the
commands:
controller-1# configure terminal
controller-1(config)# no atmf controller
Related
Commands
atmf area
show atmf

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1591
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF DISTRIBUTE FIRMWARE
atmf distribute firmware
Overview This command can be used to upgrade software one AMF node at a time. A URL
can be selected from any media location. The latest compatible release for a node
will be selected from this location.
Several procedures are performed to ensure the upgrade will succeed. This
includes checking the current node release boots from flash. If there is enough
space on flash the software release is copied to flash on the new location.
The new release name is updated using the boot system command. The old release
will become the backup release file. If a release file exists in a remote device (such
as TFTP or HTTP, for example) then the URL should specify the exact release
filename without using a wild card character.
The command will continue to upgrade software until all nodes are upgraded. At
the end of the upgrade cycle the command should be used on the working-set.
Syntax atmf distribute firmware <filename>
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To upgrade nodes in a AMF network with a predefined AMF group called “teams”,
use the following commands:
Team1# atmf working-set group teams
ATMF_NETWORK[3]# atmf distribute firmware card:*.rel
Parameter Description
<filename>The filename and path of the file. See the File Management Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide for valid syntax.
=============================
Team1, Team2, Team3:
=============================
Working set join

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1592
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF DISTRIBUTE FIRMWARE
Related
Commands
atmf working-set
Retrieving data from Team1
Retrieving data from Team2
Retrieving data from Team3
ATMF Firmware Upgrade:
Node Name New Release File Status
----------------------------------------------------------------
Team1 x510-5.4.7-1.1.rel Release ready
Team2 x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel Release ready
Team3 x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel Release ready
Continue the rolling reboot ? (y/n):y
================================================================
Copying Release : x510-5.4.7-1.1.rel to Team1
Updating Release : x510-5.4.7-1.1.rel information on Team1
================================================================
Copying Release : x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel to Team2
Updating Release : x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel information on Team2
================================================================
Copying Release : x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel to Team3
Updating Release : x930-5.4.7-1.1.rel information on Team3
================================================================
New firmware will not take effect until nodes are rebooted.
================================================================
ATMF_NETWORK[3]#

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1593
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF DOMAIN VLAN
atmf domain vlan
Overview The AMF domain VLAN is created when the AMF network is first initiated and is
assigned a default VID of 4091. This command enables you to change the VID from
this default value on this device.
The AMF domain VLAN is one of AMF’s internal VLANs (the management VLAN is
the other internal VLAN). AMF uses these internal VLANs to communicate network
status information between nodes. These VLANs must be reserved for AMF and not
used for other purposes.
An important point conceptually is that although the domain VLAN exists globally
across the AMF network, it is assigned separately to each domain. The AMF
network therefore can be thought of as comprising a series of domain VLANs each
having the same VID and each being applied to a horizontal slice (domain) of the
AMF. It follows therefore that the domain VLANs are only applied to ports that form
cross-links and not to ports that form uplinks/downlinks.
CAUTION: Every member of your AMF network must have the same domain VLAN,
management VLAN, and management subnet.
CAUTION: If you change the domain VLAN, management VLAN, or management
subnet of a node, that change takes effect immediately and the node will immediately
leave the AMF network and try to rejoin it. The AMF network will not be complete until
you have given all devices the same setting, so they can all rejoin the AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the VLAN ID to its default value of
4091.
Syntax atmf domain vlan <2-4090>
no atmf domain vlan
Default VLAN 4091
Mode Global Configuration
Usage We recommend you only change the domain VLAN when first creating the AMF
network, and only if VLAN 4091 is already being used in your network.
Parameter Description
<2-4090>The VLAN number in the range 2 to 4090.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1594
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF DOMAIN VLAN
However, if you do need to change the VLAN on an existing AMF network, use the
following steps:
1) Create a working set of the whole of your AMF network, using the
commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
You must use working-set group all if changing the domain VLAN. If you
use a different working-set, nodes that are not in that working-set will lose
contact with the AMF network.
2) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Record
this number. In this example, the network is named “test” and has 10 nodes:
test[10]#
3) Enter the new VLAN ID, using the commands:
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf domain vlan <2-4090>
The nodes will execute the command in parallel, leave the AMF network, and
attempt to rejoin through the new VLAN.
4) Create the working set again, using the commands:
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
5) Save the configuration, using the command:
test[10]# write
6) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Check that
this is the same as the number in step 1. If it is not, you will need to change
the VLAN on missing devices by logging into their consoles directly.
NOTE: The domain VLAN will automatically be assigned an IP subnet address based on
the value configured by the command atmf management subnet.
The default VLAN ID lies outside the user-configurable range. If you need to reset
the VLAN to the default VLAN ID, use the no variant of this command to do so.
Examples To change the AMF domain VLAN to 4090 in an existing AMF network, use the
following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf domain vlan 4090
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1595
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF DOMAIN VLAN
To reset the AMF domain VLAN to its default of 4091in an existing AMF network,
use the following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# no atmf domain vlan
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write
Related
commands
atmf management subnet
atmf management vlan
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1596
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF ENABLE
atmf enable
Overview This command manually enables (turns on) the AMF feature for the device being
configured.
Use the no variant of this command to disable (turn off) the AMF feature on the
member node.
Syntax atmf enable
no atmf enable
Default Once AMF is configured, the AMF feature starts automatically when the device
starts up.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The device does not auto negotiate AMF domain specific settings such as the
Network Name. You should therefore, configure your device with any domain
specific (non default) settings before enabling AMF.
Examples To turn off AMF, use the command:
MyNode# config terminal
MyNode(config)# no atmf enable
To turn on AMF, use the command:
MyNode(config)# atmf enable
This command returns the following display:
% Warning: The ATMF network config has been set to enable
% Save the config and restart the system for this change to take
effect.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1597
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF GROUP (MEMBERSHIP)
atmf group (membership)
Overview This command configures a device to be a member of one or more AMF groups.
Groups exist in three forms: Implicit Groups, Automatic Groups, and User-defined
Groups.
•Implicit Groups
– all: All nodes in the AMF
– current: The current working-set
– local: The originating node.
Note that the Implicit Groups do not appear in show group output.
• Automatic Groups - These are defined by hardware architecture, e.g. x510,
x230, x8100, AR3050S, AR4050S.
• User-defined Groups - These enable you to define arbitrary groups of AMF
members based on your own criteria.
Each node in the AMF is automatically assigned membership to the implicit
groups, and the automatic groups that are appropriate to its node type, e.g. x230,
PoE. Similarly, nodes that are configured as masters are automatically assigned to
the master group.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the membership.
Syntax atmf group <group-list>
no atmf group <group-list>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You can use this command to define your own arbitrary groups of AMF members
based on your own network’s configuration requirements. Applying a node to a
non existing group will result in the group automatically being created.
Note that the master nodes are automatically assigned to be members of the
pre-existing master group.
The following example configures the device to be members of three groups; two
are company departments, and one comprises all devices located in building_2. To
avoid having to run this command separately on each device that is to be added to
these groups, you can remotely assign all of these devices to a working-set, then
use the capabilities of the working-set to apply the atmf group (membership)
command to all members of the working set.
Parameter Description
<group-list> A list of group names. These should be entered as a comma
delimited list without spaces.
Names can contain alphanumeric characters, hyphens and
underscores.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1598
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF GROUP (MEMBERSHIP)
Example 1 To specify the device to become a member of AMF groups named marketing, sales,
and building_2, use the following commands:
node-1# configure terminal
node-1(config)# atmf group marketing,sales,building_2
Example 2 To add the nodes member_node_1 and member_node_2 to groups building1 and
sales, first add the nodes to the working-set:
master_node# atmf working-set member_node_1,member_node_2
This command returns the following output confirming that the nodes
member_node_1 and member_node_2 are now part of the working-set:
Then add the members of the working set to the groups:
atmf-net[2]# configure terminal
atmf-net[2](config)# atmf group building1,sales
atmf-net[2](config)# exit
atmf-net[2]# show atmf group
This command returns the following output displaying the groups that are
members of the working-set.
Related
Commands
show atmf group
show atmf group members
============================
member_node_1, member_node_2
============================
Working set join
====================
member_node_1
====================
AMF group information
building1, sales
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1599
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF GUEST-CLASS
atmf guest-class
Overview This modal command creates a guest-class. Guest-classes are modal templates
that can be applied to selected guest types. Once you have created a guest-class,
you can select it by entering its mode. From here, you can then configure a further
set of operational settings specifically for the new guest-class. These settings can
then all be applied to a guest link by running the switchport atmf-guestlink
command. The following settings can be configured from each guest class mode:
•discovery method
•model type
• http-enable setting
• guest port, user name, and password
The no variant of this command removes the guest-class. Note that you cannot
remove a guest-class that is assigned to a port.
Syntax atmf guest-class <guest-class-name>
no atmf guest-class
Mode Interface
Example 1 To create a guest-class named camera use the following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# atmf guest-class camera
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Example 2 To remove the guest-class named phone use the following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# no atmf guest-class phone
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Related
Commands
show atmf area guests
discovery
http-enable
username
modeltype
switchport atmf-guestlink
Parameter Description
<guest-class-name>The name assigned to the guest-class type. This can be
chosen from an arbitrary string of up to 15 characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1601
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF LOG-VERBOSE
atmf log-verbose
Overview This command limits the number of log messages displayed on the console or
permanently logged.
Use the no variant of this command to reset to the default.
Syntax atmf log-verbose <1-3>
no atmf log-verbose
Default The default log display is 3.
Usage This command is intended for use in large networks where verbose output can
make the console unusable for periods of time while nodes are joining and leaving.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set the log-verbose to noise level 2, use the command:
node-1# configure terminal
node-1(config)# atmf log-verbose 2
Validation
Command
show atmf
Parameter Description
<1-3> The verbose limitation (3 = noisiest, 1 = quietest)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1602
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MANAGEMENT SUBNET
atmf management subnet
Overview This command is used to assign a subnet that will be allocated to the AMF
management and domain management VLANs. From the address space defined
by this command, two subnets are created, a management subnet component
and a domain component, as explained in the Usage section below.
AMF uses these internal IPv4 subnets to communicate network status information
between nodes. These subnet addresses must be reserved for AMF and not used
for other purposes.
CAUTION: Every member of your AMF network must have the same domain VLAN,
management VLAN, and management subnet.
CAUTION: If you change the domain VLAN, management VLAN, or management
subnet of a node, that change takes effect immediately and the node will immediately
leave the AMF network and try to rejoin it. The AMF network will not be complete until
you have given all devices the same setting, so they can all rejoin the AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the assigned subnet.
Syntax atmf management subnet <a.b.0.0>
no atmf management subnet
Default 172.31.0.0. A subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 will automatically be applied.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Running this command will result in the creation of a further two subnets (within
the class B address space assigned) and the mask will extend from /16 to /17.
For example, if the management subnet is assigned the address 172.31.0.0/16, this
will result in the automatic creation of the following two subnets:
• 172.31.0.0/17 assigned to the atmf management vlan
• 172.31.128.0/17 assigned to the atmf domain vlan.
We recommend you only change the management subnet when first creating the
AMF network, and only if 172.31.0.0 is already being used in your network.
Parameter Description
<a.b.0.0> The IP address selected for the management subnet. Because a
mask of 255.255.0.0 (i.e. /16) will be applied automatically, an IP
address in the format a.b.0.0 must be selected.
Usually this subnet address is selected from an appropriate
range from within the private address space of 172.16.0.0 to
172.31.255.255, or 192.168.0.0, as defined in RFC1918.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1603
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MANAGEMENT SUBNET
However, if you do need to change the subnet on an existing AMF network, use the
following steps:
1) Create a working set of the whole of your AMF network, using the
commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
You must use working-set group all if changing the domain VLAN,
management VLAN, or management subnet. If you use a different
working-set, nodes that are not in that working-set will lose contact with the
AMF network.
2) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Record
this number. In this example, the network is named “test” and has 10 nodes:
test[10]#
3) Enter the new subnet address, using the commands:
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf management subnet <a.b.0.0>
The nodes will execute the command in parallel, leave the AMF network, and
attempt to rejoin through the new subnet.
4) Create the working set again, using the commands:
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
5) Save the configuration, using the command:
test[10]# write
6) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Check that
this is the same as the number in step 1. If it is not, you will need to change
the subnet on missing devices by logging into their consoles directly.
Examples To change the AMF management subnet address to 172.25.0.0 in an existing AMF
network, use the following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf management subnet 172.25.0.0
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1604
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MANAGEMENT SUBNET
To reset the AMF management subnet address to its default of 172.31.0.0 in an
existing AMF network, use the following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# no atmf management subnet
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write
Related
commands
atmf domain vlan
atmf management vlan

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1605
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MANAGEMENT VLAN
atmf management vlan
Overview The AMF management VLAN is created when the AMF network is first initiated and
is assigned a default VID of 4092. This command enables you to change the VID
from this default value on this device.
The AMF management VLAN is one of AMF’s internal VLANs (the domain VLAN is
the other internal VLAN). AMF uses these internal VLANs to communicate network
status information between nodes. These VLANs must be reserved for AMF and not
used for other purposes.
CAUTION: Every member of your AMF network must have the same domain VLAN,
management VLAN, and management subnet.
CAUTION: If you change the domain VLAN, management VLAN, or management
subnet of a node, that change takes effect immediately and the node will immediately
leave the AMF network and try to rejoin it. The AMF network will not be complete until
you have given all devices the same setting, so they can all rejoin the AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the VID to the default of 4092.
Syntax atmf management vlan <2-4090>
no atmf management vlan
Default VLAN 4092
Mode Global Configuration
Usage We recommend you only change the management VLAN when first creating the
AMF network, and only if VLAN 4092 is already being used in your network.
However, if you do need to change the VLAN on an existing AMF network, use the
following steps to ensure you change it on all nodes simultaneously:
1) Create a working set of the whole of your AMF network, using the
commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
You must use working-set group all if changing the management VLAN. If
you use a different working-set, nodes that are not in that working-set will
lose contact with the AMF network.
2) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Record
this number. In this example, the network is named “test” and has 10 nodes:
test[10]#
Parameter Description
<2-4090>The VID assigned to the AMF management VLAN.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1606
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MANAGEMENT VLAN
3) Enter the new VLAN ID, using the commands:
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf management vlan <2-4090>
The nodes will execute the command in parallel, leave the AMF network, and
attempt to rejoin through the new VLAN.
4) Create the working set again, using the commands:
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
5) Save the configuration, using the command:
test[10]# write
6) The prompt will display the number of nodes in the AMF network. Check that
this is the same as the number in step 1. If it is not, you will need to change
the VLAN on missing devices by logging into their consoles directly.
NOTE: The management VLAN will automatically be assigned an IP subnet address
based on the value configured by the command atmf management subnet.
The default VLAN ID lies outside the user-configurable range. If you need to reset
the VLAN to the default VLAN ID, use the no variant of this command to do so.
Examples To change the AMF management VLAN to 4090 in an existing AMF network, use
the following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# atmf management vlan 4090
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write
To reset the AMF management VLAN to its default of 4092 in an existing AMF
network, use the following commands:
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# configure terminal
test(config)[10]# no atmf management vlan
master(config)# exit
master# atmf working-set group all
test[10]# write
Related
commands
atmf domain vlan
atmf management subnet

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1607
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MASTER
atmf master
Overview This command configures the device to be an AMF master node and automatically
creates an AMF master group. The master node is considered to be the core of the
AMF network, and must be present for the AMF to form. The AMF master has its
node depth set to 0. Note that the node depth vertical distance is determined by
the number of uplinks/downlinks that exist between the node and its master.
An AMF master node must be present for an AMF network to form. Up to two AMF
master nodes may exist in a network, and they must be connected by an AMF
crosslink.
NOTE: Master nodes are an essential component of an AMF network. In order to run
AMF, an AMF License is required for each master node.
If the crosslink between two AMF masters fails, then one of the masters will
become isolated from the rest of the AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the device as an AMF master node.
The node will retain its node depth of 0 until the network is rebooted.
NOTE: Node depth is the vertical distance (or level) from the master node (whose depth
value is 0).
Syntax atmf master
no atmf master
Default The device is not configured to be an AMF master node.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To specify that this node is an AMF master, use the following command:
node-1# configure terminal
node-1(config)# atmf master
Related
Commands
show atmf
show atmf group
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1608
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF MTU
atmf mtu
Overview This command configures the AMF network Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU).
The MTU value will be applied to the AMF Management VLAN, the AMF Domain
VLAN and AMF Area links.
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default MTU.
Syntax atmf mtu <1300-1442>
no atmf mtu
Default 1300
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The default value of 1300 will work for all AMF networks (including those that
involve virtual links over IPsec tunnels). If there are virtual links over IPsec tunnels
anywhere in the AMF network, we recommend not changing this default. If there
are no virtual links over IPsec tunnels, then this AMF MTU value may be increased
for network efficiency.
Example To change the ATMF network MTU to 1442, use the command:
awplus(config)# atmf mtu 1442
Related
Commands
show atmf detail
Parameter Description
<1300-1442>The value of the maximum transmission unit for the
AMF network, which sets the maximum size of all AMF
packets generated from the device.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1609
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF NETWORK-NAME
atmf network-name
Overview This command applies an AMF network name to a (prospective) AMF node. In
order for an AMF network to be valid, its network-name must be configured on at
least two nodes, one of which must be configured as a master and have an AMF
License applied. These nodes may be connected using either AMF downlinks or
crosslinks.
For more information on configuring an AMF master node, see the command atmf
master.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the AMF network name.
Syntax atmf network-name <name>
no atmf network-name
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This is one of the essential commands when configuring AMF and must be entered
on each node that is to be part of the AMF.
A switching node (master or member) may be a member of only one AMF network.
CAUTION: Ensure that you enter the correct network name. Entering an incorrect name
will cause the AMF network to fragment (at the next reboot).
Example To set the AMF network name to amf_net use the command:
Node_1(config)# atmf network-name amf_net
Parameter Description
<name> The AMF network name. Up to 15 printable characters
can be entered for the network-name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1610
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF PROVISION (INTERFACE)
atmf provision (interface)
Overview This command configures a specified port on an AMF node to accept a provisioned
node, via an AMF link, some time in the future.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the provisioning on the node.
Syntax atmf provision <nodename>
no atmf provision
Mode Interface Configuration for a switchport, a static aggregator or a dynamic channel
group.
Usage The port should be configured as an AMF link or cross link and should be “down”
to add or remove a provisioned node.
Example To provision an AMF node named node1 for port1.0.1, use the command:
host1(config)# interface port1.0.1
host1(config-if)# atmf provision node1
Related
Commands
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
show atmf links
switchport atmf-link
switchport atmf-crosslink
Parameter Description
<nodename> The name of the provisioned node that will appear on
the AMF network in the future.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1611
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF PROVISION NODE
atmf provision node
Overview Use this command to provision a replacement node for a specified interface. Node
provisioning is effectively the process of creating a backup file-set on a master
node that can be loaded onto a provisioned node some time in the future. This
file-set is created just as if the provisioned node really existed and was connected
to the network. Typically these comprise configuration, operating system, and
license files etc.
You can optionally provision a node with multiple device-type backups. When a
device is then attached to the network, AMF uses its device-type to find the correct
configuration to use. For example you can create an x510 and an x530 provisioning
configuration for a node called ‘node1’ and if either an x510 or an x530 is attached
to that node the appropriate configuration will be used.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a provisioned node.
Syntax atmf provision node <nodename> [device <device-type>]
no atmf provision node <nodename> [device <device-type>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command creates the directory structure for the provisioned node’s file-set. It
also switches to the AMF provision node prompt so that the nodes backup file-set
can be created or updated. This is typically done with the create (amf provisioning)
or clone (amf provisioning) commands.
For more information on AMF provisioning, see the AMF Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide..
Example To configure node named ‘node1’, use the command:
awplus# atmf provision node node1
awplus(atmf-provision)#
To configure a node named ‘node1’ for device type ‘x530’, use the command:
awplus# atmf provision node node1 device x530
awplus(atmf-provision)#
Parameter Description
<nodename>The name of the provisioned node that will appear on the AMF
network.
device Optionally specify a device type.
<device-type>Any valid device type e.g. AR3050s, ie200, x950. For a full list of
valid device types use the command atmf provision node
<nodename> device ?.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1612
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF PROVISION NODE
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1613
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REBOOT-ROLLING
atmf reboot-rolling
Overview This command enables you to reboot the nodes in an AMF working-set, one at a
time, as a rolling sequence in order to minimize downtime. Once a rebooted node
has finished running its configuration and its ports are up, it re-joins the AMF
network and the next node is rebooted.
By adding the url parameter, you can also upgrade your devices’ software one AMF
node at a time.
The force parameter forces the rolling reboot to continue even if a previous node
does not rejoin the AMF network. Without the force parameter, the unsuitable
node will time-out and the rolling reboot process will stop. However, with the
force parameter applied, the process will ignore the timeout and move on to
reboot the next node in the sequence.
This command can take a significant amount of time to complete.
Syntax atmf reboot-rolling [force] [<url>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You can load the software from a variety of locations. The latest compatible release
for a node will be selected from your selected location, based on the parameters
and URL you have entered.
For example card:/5.4.6/x*-5.4.6-*.rel will select from the folder card:/5.4.6 the
latest file that matches the selection x (wildcard) -5.4.6-(wildcard).rel. Because x* is
applied, each device type will be detected and its appropriate release file will be
installed.
Other allowable entries are:
Parameter Description
force Ignore a failed node and move on to the next node. Where a
node fails to reboot a timeout is applied based on the time
taken during the last reboot.
<url>The path to the software upgrade file.
Entry Used when loading software
card:*.rel: from an SD card
tftp:<ip-address>:from a TFTP server
usb: from a USB flash drive
flash: from flash memory, e.g. from one x930 switch to another
scp: using secure copy
http: from an HTTP file server
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1614
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REBOOT-ROLLING
Several checks are performed to ensure the upgrade will succeed. These include
checking the current node release boots from flash. If there is enough space on
flash, the software release is copied to flash to a new location on each node as it is
processed. The new release name will be updated using the boot
system<release-name> command, and the old release will become the backup
release file.
NOTE: If you are using TFTP or HTTP, for example, to access a file on a remote device
then the URL should specify the exact release filename without using wild card
characters.
On bootup the software release is verified. Should an upgrade fail, the upgrading
unit will revert back to its previous software version. At the completion of this
command, a report is run showing the release upgrade status of each node.
NOTE: Take care when removing external media or rebooting your devices. Removing
an external media while files are being written entails a significant risk of causing a file
corruption.
Example 1 To reboot all x510 nodes in an AMF network, use the following command:
Bld2_Floor_1# atmf working-set group x510
This command returns the following type of screen output:
ATMF_NETWORK[3]# atmf reboot-rolling
When the reboot has completed, a number of status screens appear. The selection
of these screens will depend on the parameters set.
====================
node1, node2, node3:
====================
Working set join
AMF_NETWORK[3]#
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1615
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REBOOT-ROLLING
Example 2 To update firmware releases, use the following command:
Node_1# atmf working-set group all
ATMF_NETWORK[9]# atmf reboot-rolling
card:/5.4.6/x*-5.4.6-*.rel
Bld2_Floor_1#atmf working-set group x510
=============================
SW_Team1, SW_Team2, SW_Team3:
=============================
Working set join
ATMF_NETWORK[3]#atmf reboot-rolling
ATMF Rolling Reboot Nodes:
Timeout
Node Name (Minutes)
-----------------------------
SW_Team1 14
SW_Team2 8
SW_Team3 8
Continue the rolling reboot ? (y/n):y
==================================================
ATMF Rolling Reboot: Rebooting SW_Team1
==================================================
% SW_Team1 has left the working-set
Reboot of SW_Team1 has completed
==================================================
ATMF Rolling Reboot: Rebooting SW_Team2
==================================================
% SW_Team2 has left the working-set
Reboot of SW_Team2 has completed
==================================================
ATMF Rolling Reboot: Rebooting SW_Team3
==================================================
% SW_Team3 has left the working-set
Reboot of SW_Team3 has completed
==================================================
ATMF Rolling Reboot Complete
Node Name Reboot Status
-----------------------------------
SW_Team1 Rebooted
SW_Team2 Rebooted
SW_Team3 Rebooted
==================================================

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1616
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REBOOT-ROLLING
ATMF Rolling Reboot Nodes:
Timeout
Node Name (Minutes) New Release File Status
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
SW_Team1 8 x510-5.4.6-0.1.rel Release Ready
SW_Team2 10 x510-5.4.6-0.1.rel Release Ready
SW_Team3 8 --- Not Supported
HW_Team1 6 --- Incompatible
Bld1_Floor_2 2 x930-5.4.6-0.1.rel Release Ready
Bld1_Floor_1 4 --- Incompatible
Building_1 2 --- Incompatible
Building_2 2 x908-5.4.6-0.1.rel Release Ready
Continue upgrading releases ? (y/n):
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1617
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVER
atmf recover
Overview This command is used to manually initiate the recovery (or replication) of an AMF
node, usually when a node is being replaced.
Syntax atmf recover [<node-name> master <node-name>]
atmf recover [<node-name> controller <node-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage The recovery/replication process involves loading the configuration file for a node
that is either about to be replaced or has experienced some problem. You can
specify the configuration file of the device being replaced by using the
<node-name> parameter, and you can specify the name of the master node or
controller holding the configuration file.
If the <node-name> parameter is not entered then the node will attempt to use
one that has been previously configured. If the replacement node has no previous
configuration (and has no previously used node-name), then the recovery will fail.
If the master or controller name is not specified then the device will poll all known
AMF masters and controllers and execute an election process (based on the last
successful backup and its timestamp) to determine which to use. If no valid backup
master or controller is found, then this command will fail.
No error checking occurs when this command is run. Regardless of the last backup
status, the recovering node will attempt to load its configuration from the
specified master node or controller.
If the node has previously been configured, we recommend that you suspend any
AMF backup before running this command. This is to prevent corruption of the
backup files on the AMF master as it attempts to both backup and recover the
node at the same time.
Parameter Description
<node-name>The name of the device whose configuration is to be
recovered or replicated.
master
<node-name> The name of the master device that holds the required
configuration information.
Note that although you can omit both the node name and
the master name; you cannot specify a master name unless
you also specify the node name.
controller <node-
name> The name of the controller that holds the required
configuration information.
Note that although you can omit both the node name and
the controller name; you cannot specify a controller name
unless you also specify the node name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1618
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVER
Example To recover the AMF node named Node_10 from the AMF master node named
Master_2, use the following command:
Master_2# atmf recover Node_10 master Master_2
Related
Commands
atmf backup stop
show atmf backup
show atmf

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1619
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVER GUEST
atmf recover guest
Overview Use this command to initiate a guest node recovery or replacement by reloading
its backup file-set that is located within the AMF backup system. Note that this
command must be run on the edge node device that connects to the guest node.
Syntax atmf recover guest [<guest-port>]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example To recover a guest on node1 port1.0.1, use the following command
node1# atmf recover guest port1.0.1
Related
Commands
show atmf backup guest
Parameter Description
<guest-port> The port number that connects to the guest node.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1620
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVER LED-OFF
atmf recover led-off
Overview This command turns off the recovery failure flashing port LEDs. It reverts the LED’s
function to their normal operational mode, and in doing so assists with resolving
the recovery problem. You can repeat this process until the recovery failure has
been resolved. For more information, see the AMF Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Syntax atmf recover led-off
Default Normal operational mode
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To revert the LEDs on Node1 from recovery mode display to their normal
operational mode, use the command:
Node1# atmf recover led-off
Related
Commands
atmf recover

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1621
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVERY-SERVER
atmf recovery-server
Overview Use this command on an AMF master to process recovery requests from isolated
AMF nodes. An isolated node is an AMF member that is only connected to the rest
of the AMF network via a virtual-link.
This option allows these nodes, which have no AMF neighbors, to be identified for
recovery or provisioning purposes. They are identified using an identity token
which is stored on the AMF master.
Use the no variant of this command to disable processing of recovery requests
from isolated AMF nodes.
Syntax atmf recovery-server
no atmf recovery-server
Default Recovery-server is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Once recovery-server is enabled on an AMF network, the next time an isolated
node is backed up its identity token will be stored in the AMF master’s database.
Should the device fail it can then be replaced and auto-recovery will occur as long
as:
• the AMF master is accessible to the isolated node, and
• either, a DHCP server is configured to send the Uniform Resource Identifier
(URI) of the AMF master to the recovering node, or
• a DNS server is configured to resolve the default recovery URI (
https://amfrecovery.alliedtelesis.com) to the IP address of the AMF master.
Provisioning of isolated nodes is achieved by creating an identity token for the new
node using the identity (amf provisioning) command.
See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for information on
preparing your network for recovering or provisioning isolated nodes.
Example To enable recovery-server on an AMF master, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf recovery-server
To disable recovery-server on an AMF master, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf recovery-server
Related
Commands
atmf backup
atmf cleanup
identity (amf provisioning)
atmf virtual-link

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1622
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RECOVERY-SERVER
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1623
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REMOTE-LOGIN
atmf remote-login
Overview Use this command to remotely login to other AMF nodes in order to run
commands as if you were a local user of that node.
Syntax atmf remote-login [user <name>] <nodename>
Mode Privileged Exec (This command will only run at privilege level 15)
Usage You do not need a valid login on the local device in order to run this command. The
session will take you to the enable prompt on the new device. If the remote login
session exits for any reason (e.g. device reboot) you will be returned to the
originating node.
You can create additional user accounts on nodes. AMF's goal is to provide a
uniform management plane across the whole network, so we recommend you use
the same user accounts on all the nodes in the network.
In reality, though, it is not essential to have the same accounts on all the nodes.
Users can remote login from one node to a second node even if they are logged
into the first node with a user account that does not exist on the second node
(provided that atmf restricted-login is disabled and the user account on the first
node has privilege level 15).
Moreover, it is possible to use a RADIUS or TACACS+ server to manage user
authentication, so users can log into AMF nodes using user accounts that are
present on the RADIUS or TACACS+ server, and not present in the local user
databases of the AMF nodes.
The software will not allow you to run multiple remote login sessions. You must
exit an existing session before starting a new one.
If you disconnect from the VTY session without first exiting from the AMF remote
session, the device will keep the AMF remote session open until the exec-timeout
time expires (10 minutes by default). If the exec-timeout time is set to infinity
(exec-timeout 0 0), then the device is unable to ever close the remote session. To
avoid this, we recommend you use the exit command to close AMF remote
sessions, instead of closing the associated VTY sessions. We also recommend you
avoid setting the exec-timeout to infinity.
Example To remotely login from node Node10 to Node20, use the following command:
Node10# atmf remote-login node20
Node20>
Parameter Description
<name> The name of a user on the remote node.
<nodename> The name of the remote AMF node you are connecting to.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1624
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF REMOTE-LOGIN
To close the session on Node20 and return to Node10’s command line, use the
following command:
Node20# exit
Node10#
In this example, user User1 is a valid user of node5. They can remotely login from
node5 to node3 by using the following commands:
node5# atmf remote-login user User1 node3
node3> enable
Related
Commands
atmf restricted-login
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: changes to AMF user account requirements

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1625
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RESTRICTED-LOGIN
atmf restricted-login
Overview By default, users who are logged into any node on an AMF network are able to
manage any other node by using either working-sets or an AMF remote login. If the
access provided by this feature is too wide, or contravenes network security
restrictions, it can be limited by running this command, which changes the access
so that:
• users who are logged into non-master nodes cannot execute any commands
that involve working-sets, and
• from non-master nodes, users can use remote-login, but only to login to a
user account that is valid on the remote device (via a statically configured
account or RADIUS/TACACS+). Users are also required to enter the password
for that user account.
Once entered on any AMF master node, this command will propagate across the
network.
Use the no variant of this command to disable restricted login on the AMF
network. This allows access to the atmf working-set command from any node in
the AMF network.
Syntax atmf restricted-login
no atmf restricted-login
Mode Privileged Exec
Default Master nodes operate with atmf restricted-login disabled.
Member nodes operate with atmf restricted-login enabled.
NOTE: The default conditions of this command vary from those applied by its “no”
variant. This is because the restricted-login action is only applied by master nodes, and
in the absence of a master node, the default is to apply the restricted action to all
member nodes with AMF configured.
Usage In the presence of a master node, its default of atmf restricted-login disabled
will propagate to all its member nodes. Similarly, any change in this command’s
status that is made on a master node, will also propagate to all its member nodes
Note that once you have run this command, certain other commands that utilize
the AMF working-set command, such as the include, atmf reboot-rolling and
show atmf group members commands, will operate only on master nodes.
Restricted-login must be enabled on AMF areas with more than 120 nodes.
Example To enable restricted login, use the command
Node_20(config)# atmf restricted-login node20
Related
Commands
atmf remote-login
show atmf

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1626
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF RESTRICTED-LOGIN
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: changes to AMF user account requirements

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1627
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE
atmf secure-mode
Overview Use this command to enable AMF secure mode on an AMF node. AMF secure mode
makes an AMF network more secure by:
• Adding an authorization mechanism before and AMF member is allowed to
join an AMF network.
• The encryption of all AMF packets sent between AMF nodes.
• Adding support for user login authentication by RADIUS or TACACS+, and
removing the requirement to have the same privileged user account in the
local user database on all devices in the AMF network.
• Adding additional logging which enables network administrators to monitor
attempts to gain unauthorized access to the AMF network.
Once the secure mode command is run on all nodes on an AMF network, the AMF
masters and AMF controllers manage the addition of AMF nodes and AMF areas to
the AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to disable AMF secure mode on an AMF node.
Syntax atmf secure-mode
no atmf secure-mode
Default Secure mode is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage When an AMF network is running in AMF secure mode the atmf restricted-login
feature is automatically enabled. This restricts the atmf working-set command to
users that are logged on to an AMF master. This feature cannot be disabled
independently of secure mode.
When AMF secure mode is enabled the AMF controllers and masters in the AMF
network form a group of certificate authorities. A node may only join a secure AMF
network once it has been authorized by a master or controller. When enabled, all
devices in the AMF network must be running in secure mode. Unsecured devices
will not be able to join a secure AMF network.
Example To enable AMF secure mode on an AMF node, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf secure-mode
To disable AMF secure mode on an AMF node, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf secure-mode
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf secure-mode certificate expiry

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1628
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE
clear atmf secure-mode certificates
clear atmf secure-mode statistics
show atmf
show atmf authorization
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode certificates
show atmf secure-mode sa
show atmf secure-mode statistics
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1629
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATE EXPIRE
atmf secure-mode certificate expire
Overview Use this command on an AMF master to expire a secure mode certificate. Running
this command will force the removal of the AMF node from the network.
Syntax atmf secure-mode certificate expire <node-name> [area
<area-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To remove an AMF node named “node3” from an AMF network, use the following
command on the AMF master:
awplus# atmf secure-mode certificate expire node3
To remove an AMF node named “node2” in an area named “area2”, use the
following command on the AMF master:
awplus# atmf secure-mode certificate expire node2 area area2
Related
Commands
atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Parameter Description
<node-name> Name of the AMF node you want to expire the certificate for.
area Specify an AMF area.
<area-name> Name of the AMF area you want to expire the AMF nodes
certificate for.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1630
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATE EXPIRY
atmf secure-mode certificate expiry
Overview Use this command to set the expiry time of AMF secure mode certificates. Once an
AMF node’s certificate expires it must re-authorize and obtain a new certificate
from the AMF master.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the expiry time to 180 days.
Syntax atmf secure-mode certificate expiry {<days>|infinite}
no atmf secure-mode certificate expiry
Default The default expiry time is 180 days.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set AMF secure mode certificate expiry to 7 days, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf secure-mode certificate expiry 7
To set AMF secure mode certificates to never expire, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf secure-mode certificate expiry infinite
To reset the certificate expiry to 180 days, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf secure-mode certificate expiry
Related
Commands
atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Parameter Description
<days>Length of time, in days, that an AMF secure mode certificate
remains valid. A value between 1 and 365.
infinite The authorization certificate does not expire, in other words AMF
nodes stay authorized indefinitely.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1631
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATE RENEW
atmf secure-mode certificate renew
Overview Use this command to force all local certificates to expire and be renewed on an
AMF secure mode network.
Secure mode certificates renew automatically but this command could be used to
renew a certificate in a situation where the automatic renewal may happen while
the device is not attached to the AMF network.
Syntax atmf secure-mode certificate renew
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To renew a local certificate on a AMF member or AMF master, use the command:
awplus# atmf secure-mode certificate renew
Related
Commands
show atmf secure-mode certificates
show atmf secure-mode statistics
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1632
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE ENABLE-ALL
atmf secure-mode enable-all
Overview Use this command to enable AMF secure mode on an entire network. AMF secure
mode makes an AMF network more secure by:
• Adding an authorization mechanism before an AMF member is allowed to
join an AMF network.
• The encryption of all AMF packets sent between AMF nodes.
• Adding support for user login authentication by RADIUS or TACACS+, and
removing the requirement to have the same privileged user account in the
local user database on all devices in the AMF network.
• Adding additional logging which enables network administrators to monitor
attempts to gain unauthorized access to the AMF network.
Once this command is run on an AMF network, the AMF masters and AMF
controllers manage the addition of AMF nodes and AMF areas to the AMF network.
This command can only be run on an AMF master.
Use the no variant of this command to disable AMF secure mode on an entire
network.
Syntax atmf secure-mode enable-all
no atmf secure-mode enable-all
Default Secure mode is disabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage When an AMF network is running in AMF secure mode the atmf restricted-login
feature is automatically enabled. This restricts the atmf working-set command to
users that are logged on to an AMF master. This feature cannot be disabled
independently of secure mode.
When AMF secure mode is enabled the AMF controllers and masters in the AMF
network form a group of certificate authorities. A node may only join a secure AMF
network once it has been authorized by a master or controller. When enabled, all
devices in the AMF network must be running in secure mode. Unsecured devices
will not be able to join a secure AMF network.
Running atmf secure-mode enable-all:
• Groups all AMF members in a working set.
•Executes clear atmf secure-mode certificates on the working set of members,
which removes existing secure mode certificates from all the nodes.
• Groups all the AMF masters in a working set.
•Executes atmf authorize provision all on the working set of masters, so all
masters provision all nodes.
• Groups all AMF nodes in a working set.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1633
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SECURE-MODE ENABLE-ALL
• Runs a script which executes atmf secure-mode and then writes the
configuration file on each node.
• Starts a timer that ticks every 10 seconds, for a maximum of 10 times, and
checks if all the secure mode capable nodes rejoin the AMF network.
Running no atmf secure-mode enable-all:
• Groups all AMF nodes in a working set.
• Runs a script which executes no atmf secure-mode and then writes the
configuration file on each node.
• Starts a timer that ticks every 10 seconds, for a maximum of 10 times, and
checks if all the secure mode capable nodes rejoin the AMF network.
NOTE: Enabling or disabling secure mode on the network saves the running-config on
every device.
Example To enable AMF secure mode on the entire network, use the command:
awplus# atmf secure-mode enable-all
You will be prompted to confirm the action:
To disable AMF secure mode on the entire network, use the command:
awplus# no atmf secure-mode enable-all
You will be prompted to confirm the action:
Related
Commands
aaa authentication auth-web
show atmf
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Total number of nodes 21
21 nodes support secure-mode
Enable secure-mode across the AMF network ? (y/n): y
% Warning: All security certificates will be deleted.
Disable secure-mode across the AMF network ? (y/n): y

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1634
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF SELECT-AREA
atmf select-area
Overview Use this command to access devices in an area outside the core area on the
controller network. This command will connect you to the remote area-master of
the specified area.
This command is only valid on AMF controllers.
The no variant of this command disconnects you from the remote area-master.
Syntax atmf select-area {<area-name>|local}
no atmf select-area
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage After running this command, use the atmf working-set command to select the set
of nodes you want to access in the remote area.
Example To access nodes in the area Canterbury, use the command
controller-1# atmf select-area Canterbury
This displays the following output:
To return to the local area for controller-1, use the command
controller-1# atmf select-area local
Alternatively, to return to the local area for controller-1, use the command
controller-1# no atmf select-area
Related
Commands
atmf working-set
Parameter Description
<area-name>Connect to the remote area-master of the area with this name.
local Return to managing the local controller area.
Test_network[3]#atmf select-area Canterbury
==============================================
Connected to area Canterbury via host Avensis:
==============================================

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1635
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF TOPOLOGY-GUI ENABLE
atmf topology-gui enable
Overview Use this command to enable the operation of Vista Manager EX on the Master
device.
Vista Manager EX delivers state-of-the-art monitoring and management for your
Autonomous Management Framework™ (AMF) network, by automatically creating
a complete topology map of switches, firewalls and wireless access points (APs).
An expanded view includes third-party devices such as security cameras.
Use the no variant of this command to disable operation of Vista Manager EX.
Syntax atmf topology-gui enable
no atmf topology-gui enable
Default Disabled by default on AMF Master and member nodes. Enabled by default on
Controllers.
Mode Global Configuration mode
Usage To use Vista Manager EX, you must also enable the HTTP service on all AMF nodes,
including all AMF masters and controllers. The HTTP service is enabled by default
on AlliedWare Plus switches and disabled by default on AR-Series firewalls. To
enable it, use the commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# service http
On one master in each AMF area in your network, you also need to configure the
master to send event notifications to Vista Manager EX. To do this, use the
commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# log event-host <ip-address> atmf-topology-event
Example To enable Vista Manager EX on Node1, use the following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# atmf topology-gui enable
To disable Vista Manager EX on Node1, use the following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# no atmf topology-gui enable
Related
Commands
atmf enable
gui-timeout
log event-host
service http
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1636
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF TRUSTPOINT
atmf trustpoint
Overview Use this command to set a PKI trustpoint for an AMF network. This command
needs to be run on an AMF master or controller.
The self-signed certificate authority (CA) certificate is distributed to every node on
the AMF network. It is used to verify client certificates signed by the trustpoint.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an AMF trustpoint.
Syntax atmf trustpoint <trustpoint-name>
no atmf trustpoint <trustpoint-name>
Default No trustpoint is configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Before using the atmf trustpoint command you will need to establish a trustpoint.
For example, you can create a local self-signed trustpoint using the procedure
outlined below.
Create a self-signed trustpoint called ‘our_trustpoint’ with keypair ‘our_key’:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto pki trustpoint our_trustpoint
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# enrollment selfsigned
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# rsakeypair our_key
awplus(ca-trustpoint)# exit
awplus(config)# exit
Create the root and server certificates for this trustpoint:
awplus# crypto pki authenticate our_trustpoint
awplus# crypto pki enroll our_trustpoint
For more information about the AlliedWare Plus implementation of Public Key
Infrastructure (PKI), see the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide
Example To configure an AMF trustpoint for the trustpoint ‘our_trustpoint’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf trustpoint our_trustpoint
Parameter Description
<trustpoint-name>Name of the trustpoint.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1637
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF TRUSTPOINT
To remove an AMF trustpoint for the trustpoint ‘our_trustpoint’, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no atmf trustpoint our_trustpoint
Related
Commands
crypto pki trustpoint
show atmf
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1638
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-CROSSLINK
atmf virtual-crosslink
Overview Use this command to create a virtual crosslink. A virtual crosslink connects an AMF
master or controller on a physical device to a Virtual AMF Appliance (VAA) master
or controller.
All AMF master nodes must reside in the same AMF domain and are required to be
directly connected using AMF crosslinks. In order to be able to meet this
requirement for AMF masters running on VAAs, a virtual crosslink connects the
AMF master or controller on the physical device to the master or controller on the
VAA.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a virtual crosslink.
Syntax atmf virtual-crosslink id <local-id> ip <local-ip> remote-id
<remote-id> remote-ip <remote-ip>
no atmf virtual-crosslink id <local-id>
Default No AMF virtual crosslinks are created by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command allows a virtual tunnel to be created between two remote sites over
a layer 3 link. The tunnel encapsulates AMF packets and allows them to be sent
transparently across a Wide Area Network (WAN) such as the Internet.
Configuration involves creating a local tunnel ID, a local IP address, a remote
tunnel ID and a remote IP address. Each side of the tunnel must be configured with
the same, but mirrored parameters.
NOTE: Virtual crosslinks are not supported on AMF container masters, therefore if
multiple tenants on a single VAA host are configured for secure mode, only a single
AMF master is supported per area.
Example To setup a virtual link from a local site, “siteA”, to a remote site, “siteB”, (assuming
there is already IP connectivity between the sites), run the following commands at
the local site:
siteA# configure terminal
siteA(config)# atmf virtual-crosslink id 5 ip 192.168.100.1
remote-id 10 remote-ip 192.168.200.1
Parameter Description
<local-id>ID of the local tunnel port, a value between 1 and 4094.
<local-ip>IPv4 address of the local tunnel port in a.b.c.d format.
<remote-id>ID of the remote tunnel port, a value between 1 and 4094.
<remote-ip>IPv4 address of the remote tunnel port in a.b.c.d format.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1639
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-CROSSLINK
At the remote site, run the commands:
siteB# configure terminal
siteB(config)# atmf virtual-crosslink id 10 ip 192.168.200.1
remote-id 5 remote-ip 192.168.100.1
To remove this virtual crosslink, run the following commands on the local site:
siteA# configure terminal
siteA(config)# no atmf virtual-crosslink id 5
On the remote site, run the commands:
siteB# configure terminal
siteB(config)# no atmf virtual-crosslink id 10
Related
Commands
atmf virtual-crosslink
show atmf links
switchport atmf-crosslink
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1640
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-LINK
atmf virtual-link
Overview This command creates one or more Layer 2 tunnels that enable AMF nodes to
transparently communicate across a wide area network using Layer 2 connectivity
protocols.
Once connected through the tunnel, the remote member will have the same AMF
capabilities as a directly connected AMF member.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified virtual link.
Syntax atmf virtual-link id <1-4094> ip <a.b.c.d> remote-id <1-4094>
remote-ip <a.b.c.d> [remote-area <area-name>]
atmf virtual-link id <1-4094> interface <interface-name>
remote-id <1-4094> remote-ip <a.b.c.d> [remote-area
<area-name>]
no atmf virtual-link id <1-4094>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The Layer 2 tunnel that this command creates enables a local AMF session to
appear to pass transparently across a Wide Area Network (WAN) such as the
Internet. The addresses configured as the local and remote tunnel IP addresses
must have IP connectivity to each other. If the tunnel is configured to connect a
head office and branch office over the Internet, typically this would involve using
some type of managed WAN service such as a site-to-site VPN. Tunnels are only
supported using IPv4.
Parameter Description
id <1-4094>ID of the local tunnel point, in the range 1 to 4094.
ip <a.b.c.d>Specify the local IP address of the local interface for the
virtual-link (alternatively you can specify the interface’s
name, see below).
interface
<interface-name>Specify the local interface name for the virtual-link. This
allows you to use a dynamic, rather than a static, local IP
address.
remote-id<1-4094> The ID of the (same) tunnel that will be applied by the
remote node. Note that this must match the local-id that is
defined on the remote node. This means that (for the same
tunnel) the local and remote tunnel IDs are reversed on the
local and remote nodes.
remote-ip
<a.b.c.d>The IP address of the remote node.
remote-area
<area-name>The name of the remote area connected to this virtual-link
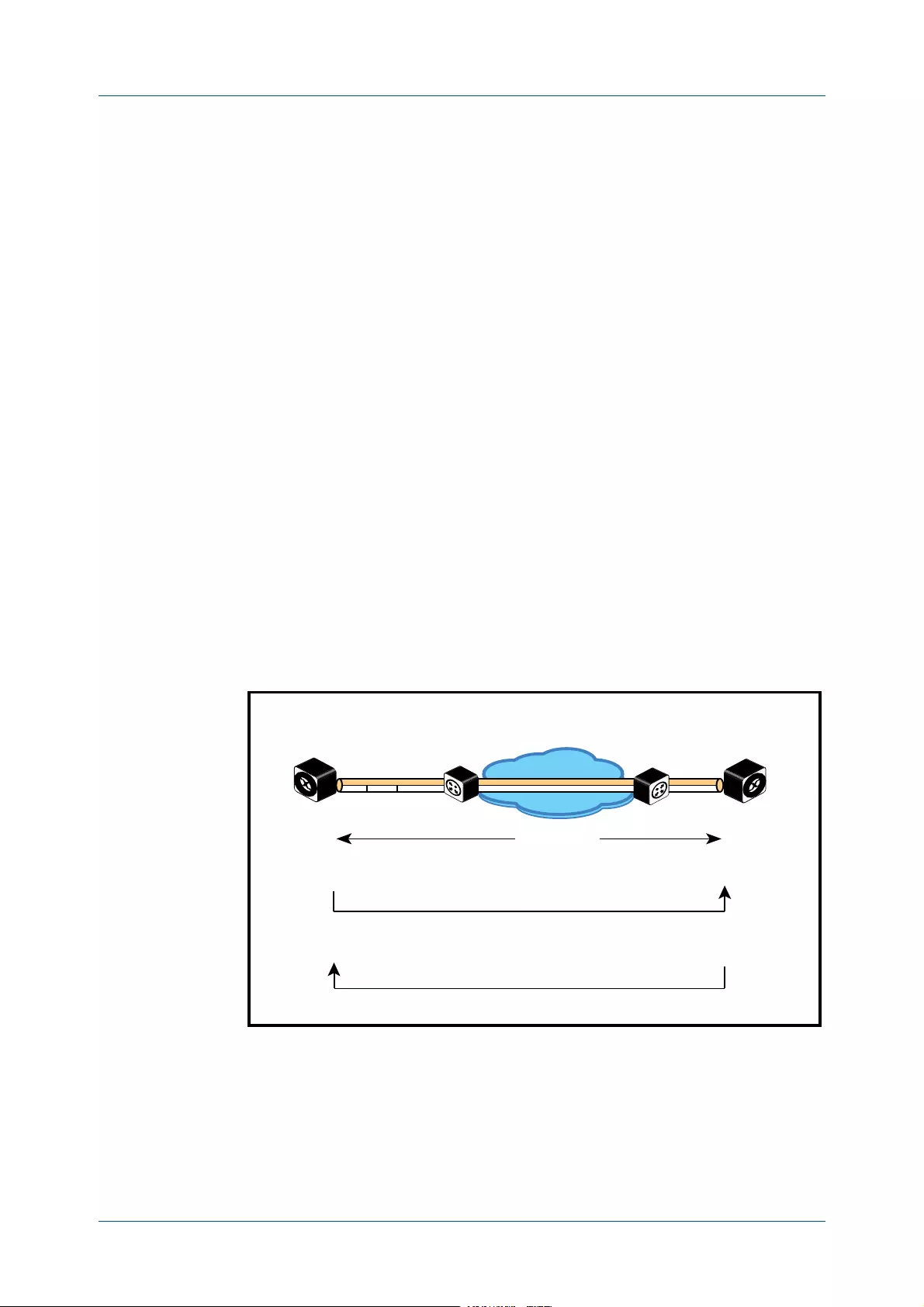
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1641
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-LINK
Configuration involves creating a local tunnel ID, a local IP address, a remote
tunnel ID and a remote IP address. A reciprocal configuration is also required on
the corresponding remote device. The local tunnel ID must be unique to the device
on which it is configured.
If an interface acquires its IP address dynamically then the local side of the tunnel
can be specified by using the interface’s name instead of using its IP address. When
using a dynamic local address the remote address of the other side of the
virtual-link must be configured with either:
• the IP address of the NAT device the dynamically configured interface is
behind, or
• 0.0.0.0, if the virtual-link is configured as a secure virtual-link.
For instructions on how to configure dynamic IP addresses on virtual-links, see the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
The tunneled link may operate via external (non AlliedWare Plus) routers in order
to provide wide area network connectivity. However in this configuration, the
routers perform a conventional router to router connection. The protocol
tunneling function is accomplished by the AMF nodes.
NOTE: AMF cannot achieve zero touch replacement of the remote device that
terminates the tunnel connection, because you must pre-configure the local IP address
and tunnel ID on that remote device.
Example 1 Use the following commands to create the tunnel shown in the figure below.
Figure 45-1: AMF virtual link example
Node_10(config)# atmf virtual-link id 1 ip 192.168.1.1
remote-id 2 remote-ip 192.168.2.1
Node_20(config)# atmf virtual-link id 2 ip 192.168.2.1
remote-id 1 remote-ip 192.168.1.1
)0.ETWORK
!-&
,OCAL3ITE
SUBNET
ATMFVIRTUALLINK)$AND)0%XAMPLEEPS
!-&VIRTUALLINKIDIPREMOTEIDREMOTEIP%XAMPLE
!-&
2EMOTE3ITE
SUBNET
3WITCH
!-&.ODE
2OUTER 2OUTER
4UNNEL)$
4UNNELREMOTE)$
4UNNEL)$
4UNNELREMOTE)$
4UNNELLED0ACKET
5$0(EADER
)0(EADER
3WITCH
!-&.ODE

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1642
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-LINK
Example 2 To set up an area virtual link to a remote site (assuming IP connectivity between
the sites already), one site must run the following commands:
SiteA# configure terminal
SiteA(config)# atmf virtual-link id 5 ip 192.168.100.1
remote-id 10 remote-ip 192.168.200.1 remote-area SiteB-AREA
The second site must run the following commands:
SiteB# configure terminal
SiteB(config)# atmf virtual-link id 10 ip 192.168.200.1
remote-id 5 remote-ip 192.168.100.1 remote-area SiteA-AREA
Before you can apply the above atmf virtual-link command, you must configure
the area names SiteB-AREA and SiteA-AREA.
Related
Commands
atmf virtual-link protection
show atmf
show atmf links
show atmf virtual-links
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: interface parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1643
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-LINK PROTECTION
atmf virtual-link protection
Overview Use this command to add protection to an existing AMF virtual-link. Secure AMF
virtual-links encapsulate the L2TPv3 frames of the virtual-link with IPsec.
Use the no variant of this command to remove protection from an AMF virtual-link.
Syntax atmf virtual-link id <1-4094> protection ipsec key [8]
<key-string>
no atmf virtual-link id <1-4094> protection
Default Protection is off by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The following limitations need to be considered when creating secure virtual-links.
• Switch devices support a maximum of 20 downstream AMF nodes when
using a secure virtual-link as an uplink.
• When there are two or more AMF members behind a shared NAT device,
only one of the members will be able to use secure virtual-links.
• An AMF Multi-tenant environment supports a maximum cumulative total of
1200 secure virtual-links across all AMF containers.
Secure virtual-links are only supported on the following device listed in the table
below. There is also a limit to the number of links these devices support.
Parameter Description
id Specify the link ID.
<1-4094> Link ID in the range 1 to 4094,
protection Protection is on for this link.
ipsec Security provided using IPsec.
key Set the shared key.
8Specifies a string in an encrypted format instead of plain text. The
running config will display the new password as an encrypted
string even if password encryption is turned off.
<key-string> Specify the shared key for the link.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1644
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF VIRTUAL-LINK PROTECTION
Example To create and configure a virtual link with protection first create the virtual-link:
Host-A# configure terminal
Host-A(config)# atmf virtual-link id 1 ip 192.168.1.1 remote-id
2 remote-ip 192.168.2.1
Enable protection on the virtual link:
Host-A(config)# atmf virtual-link id 1 protection ipsec key
securepassword
Repeat these steps on the other side of the link:
Host-B(config)# atmf virtual-link id 2 ip 192.168.2.1 remote-id
1 remote-ip 192.168.1.1
Host-B(config)# atmf virtual-link id 2 protection ipsec key
securepassword
Related
Commands
atmf virtual-link
show atmf
show atmf links
show atmf virtual-links
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
Device Virtual-link Limit
AMF Cloud/ VAA 300
AR4050S
AR3050S
AR2050V
AR2010V
60
x220
x230/x230L
x310
x510/x510L
IX5-28GPX
2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1645
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF WORKING-SET
atmf working-set
Overview Use this command to execute commands across an individually listed set of AMF
nodes or across a named group of nodes.
Note that this command can only be run on a master node.
Use the no variant of this command to remove members or groups from the
current working-set.
Syntax atmf working-set {[<node-list>]|[group
{<group-list>|all|local|current}]}
no atmf working-set {[<node-list>]|[group <group-list>]}
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You can put AMF nodes into groups by using the atmf group (membership)
command.
This command opens a session on multiple network devices. When you change the
working set to anything other than the local device, the prompt will change to the
AMF network name, followed by the size of the working set, shown in square
brackets. This command has to be run at privilege level 15.
In addition to the user defined groups, the following system assigned groups are
automatically created:
•Implicit Groups
– local: The originating node.
– current: All nodes that comprise the current working-set.
– all: All nodes in the AMF.
Parameter Description
<node-list> A comma delimited list (without spaces) of nodes to be included
in the working-set.
group The AMF group.
<group-list> A comma delimited list (without spaces) of groups to be included
in the working-set. Note that this can include either defined
groups, or any of the Automatic, or Implicit Groups shown earlier
in the bulleted list of groups.
all All nodes in the AMF.
local Local node
Running this command with the parameters group local will
return you to the local prompt and local node connectivity.
current Nodes in current list.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1646
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ATMF WORKING-SET
• Automatic Groups - These can be defined by hardware architecture, e.g.
x510, x610, x8100, AR3050S or AR4050S, or by certain AMF nodal
designations such as master.
Note that the Implicit Groups do not appear in show atmf group command output.
If a node is an AMF master it will be automatically added to the master group.
Example 1 To add all nodes in the AMF to the working-set, use the command:
node1# atmf working-set group all
NOTE: This command adds the implicit group “all” to the working set, where “all”
comprises all nodes in the AMF.
This command displays an output screen similar to the one shown below:
Example 2 To return to the local prompt, and connect to only the local node, use the
command:
ATMF_Network_Name[6]# atmf working-set group local
node1#
The following table describes the meaning of the prompts in this example.
=========================================
node1, node2, node3, node4, node5, node6:
==============================================
Working set join
ATMF_NETWORK_Name[6]#
Parameter Description
ATMF_Network_Name The name of the AMF network, as set by the atmf
network-name command.
[6] The number of nodes in the working-set.
node1 The name of the local node, as set by the hostname
command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1647
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
BRIDGE-GROUP
bridge-group
Overview Use this command to connect an AMF container to a bridge created on a Virtual
AMF Appliance (VAA) virtual machine. This allows the AMF container to connect to
a physical network.
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a bridge-group from an AMF
container.
Syntax bridge-group <bridge-id>
no bridge-group
Mode AMF Container Configuration
Usage Each container has two virtual interfaces:
1) Interface eth0, used to connect to the AMF controller on the VAA host via an
AMF area-link, and configured using this area-link command.
2) Interface eth1, used to connect to the outside world using a bridged L2
network link, and configured using the bridge-group command.
Before using this command, a bridge must be created with the same bridge-id on
the VAA host using the bridge <bridge-id> command.
See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on
configuring the bridge.
Example To create a bridge group for AMF container “vac-wlg-1” and , use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# bridge-group 1
Related
Commands
atmf container
show atmf container
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
<bridge-id> The ID of the bridge group to join, a number between 1 and 64.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1648
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF LINKS
clear atmf links
Overview Use this command with no parameters to manually reset all the AMF links on a
device. You can optionally specify an interface or range of interfaces to reset the
links on.
Certain events or topology changes can cause AMF links to be incorrect or
outdated. Clearing the links forces AMF to relearn the information from
neighboring nodes and create a fresh, correct, view of the network.
Syntax clear atmf links [<interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear all AMF links on a device, use the following command:
awplus# clear atmf links
To clear all AMF links on port1.0.1 to port1.0.4 and static aggregator sa1, use the
following command:
awplus# clear atmf links port1.0.1-port1.0.4,sa1
Related
Commands
clear atmf links virtual
show atmf links
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<interface-list>The interfaces or ports to perform the reset on. An
interface-list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.1)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a local port (e.g. of0)
• You can specify a continuous range of interfaces
separated by a hyphen, or a comma-separated list (e.g.
port1.0.1, port1.0.4-port1.0.18).
The specified interfaces must exist.
If this parameter is left out then all links of the specified type
will be reset on the device.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1649
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF LINKS VIRTUAL
clear atmf links virtual
Overview Use this command with no parameters to manually reset all the AMF virtual links
on a device. You can, optionally, specify a comma separated list of virtual links to
reset.
Certain events or topology changes can cause AMF links to be incorrect or
outdated. Clearing the links forces AMF to relearn the information from
neighboring nodes and create a fresh, correct view of the network.
Syntax clear atmf links virtual [<virtuallink-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear all AMF virtual links on a device, use the following command:
awplus# clear atmf links virtual
To clear AMF virtual links vlink11 and vlink21, use the following command:
awplus# clear atmf links virtual vlink11,vlink22
Related
Commands
clear atmf links
show atmf links
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<virtuallink-list>A single, or list, of AMF virtual link identifiers to reset. This
must be a comma separated list of links e.g. vlink1, vlink2,
vlink3. Specifying a link range e.g vlink1-vlink3 is not
supported.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1650
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF LINKS STATISTICS
clear atmf links statistics
Overview This command resets the values of all AMF link, port, and global statistics to zero.
Syntax clear atmf links statistics
Mode Privilege Exec
Example To reset the AMF link statistics values, use the command:
node_1# clear atmf links statistics
Related
Commands
show atmf links statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1651
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF RECOVERY-FILE
clear atmf recovery-file
Overview Use this command to delete all of a node’s recovery files. It deletes the recovery
files stored on:
•the local node,
•neighbor nodes, and
• external media (USB or SD card).
Syntax clear atmf recovery-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage AMF recovery files are created for nodes with special links. Special links include:
•virtual links,
• area links terminating on an AMF master, and
• area virtual links terminating on an AMF master.
An AMF node with one of these special links pushes its startup configuration to its
neighbors and to any attached external media. It then fetches and applies this
configuration at recovery time. This configuration enables it to contact the AMF
master and initiate a recovery.
Recovery files can become out of date if:
• a node’s neighbor is off line when changes are made to its configuration, or
• when a node no longer contains a special link.
Example To clear a node’s recovery files, use the command:
node1# clear atmf recovery-file
Output Figure 45-2: If AlliedWare Plus detects that a node contains a special link then
the following message is displayed
Related
Commands
show atmf recovery-file
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: command added
node1#clear atmf recovery-file
% Warning: ATMF recovery files have been removed.
ATMF recovery may fail. Please save running-configuration.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1652
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATES
clear atmf secure-mode certificates
Overview Use this command to remove all certificates from an AMF member or master. AMF
nodes will need to be re-authorized once this command has been run.
Syntax clear atmf secure-mode certificates
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear all certificates from an AMF node, use the command:
awplus# clear atmf secure-mode certificates
If this is the only master on the network you will see the following warning:
On an AMF member you will see the following message:
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf secure-mode
show atmf authorization
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
% Warning: This node is the only master in the network!
All the nodes will become isolated and refuse to join any ATMF
network. The certificates on all the isolated nodes must be
cleared before rejoining an ATMF network will be possible.
To clear certificates a reboot of the device is required.
Clear certificates and Reboot ? (y/n):
To clear certificates a reboot of the device is required.
Clear certificates and Reboot ? (y/n):

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1653
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLEAR ATMF SECURE-MODE STATISTICS
clear atmf secure-mode statistics
Overview Use this command to reset all secure mode statistics to 0.
Syntax clear atmf secure-mode statistics
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To reset the AMF secure mode statistics information, use the command:
awplus# clear atmf secure-mode statistic
Related
Commands
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode statistics
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1654
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLONE (AMF PROVISIONING)
clone (amf provisioning)
Overview This command sets up a space on the backup media for use with a provisioned
node and copies into it almost all files and directories from a chosen backup or
provisioned node.
Alternatively, you can set up a new, unique provisioned node by using the
command create (amf provisioning).
Syntax clone <source-nodename>
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage This command is only available on master nodes in the AMF network.
When using this command it is important to be aware of the following:
•A copy of <media>:atmf/<atmf_name>/nodes/<source_node>/flash will be
made for the provisioned node and stored in the backup media.
•The directory <node_backup_dir>/flash/.config/ssh is excluded from the
copy.
• All contents of <root_backup_dir>/nodes/<nodename> will be deleted or
overwritten.
• Settings for the expected location of other provisioned nodes are excluded
from the copy.
The active and backup configuration files are automatically modified in the
following ways:
•The hostname command is modified to match the name of the provisioned
node.
•The stack virtual-chassis-id command is removed, if present.
Example To copy from the backup of ‘device2’ to create backup files for the new provisioned
node ‘device3’ use the following command:
device1# atmf provision node device3
device1(atmf-provision)# clone device2
Figure 45-3: Sample output from the clone command
Parameter Description
<source-nodename> The name of the node whose configuration is to be
copied for loading to the clone.
device1# atmf provision node device3
device1(atmf-provision)#clone device2
Copying...
Successful operation
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1655
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CLONE (AMF PROVISIONING)
To confirm that a new provisioned node has been cloned, use the command:
device1# show atmf backup
The output from this command is shown in the following figure, and shows the
details of the new provisioned node ‘device3’.
Figure 45-4: Sample output from the show atmf backup command
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
device1#show atmf backup
Scheduled Backup ...... Enabled
Schedule ............ 1 per day starting at 03:00
Next Backup Time .... 01 Oct 2018 03:00
Backup Bandwidth ...... Unlimited
Backup Media .......... USB (Total 7446.0MB, Free 7297.0MB)
Server Config .........
Synchronization ..... Unsynchronized
Last Run .......... -
1 .................. Unconfigured
2 .................. Unconfigured
Current Action ........ Idle
Started ............. -
Current Node ........ -
---------------------------------------------------------------
Node Name Date Time In ATMF On Media Status
---------------------------------------------------------------
device3 - - No Yes Prov
device1 30 Sep 2018 00:05:49 No Yes Good
device2 30 Sep 2018 00:05:44 Yes Yes Good

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1656
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CONFIGURE BOOT CONFIG (AMF PROVISIONING)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
Overview This command sets the configuration file to use during the next boot cycle. This
command can also set a backup configuration file to use if the main configuration
file cannot be accessed for an AMF provisioned node. To unset the boot
configuration or the backup boot configuration use the no boot command.
Syntax configure boot config [backup] <file-path|URL>
configure no boot config [backup]
Default No boot configuration files or backup configuration files are specified for the
provisioned node.
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage When using this command to set a backup configuration file, the specified AMF
provisioned node must exist. The specified file must exist in the flash directory
created for the provisioned node in the AMF remote backup media.
Examples To set the configuration file ‘branch.cfg’ on the AMF provisioned node ‘node1’, use
the command:
MasterNodeName# atmf provision node node1
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure boot config
branch.cfg
To set the configuration file ‘backup.cfg’ as the backup to the main configuration
file on the AMF provisioned node ‘node1’, use the command:
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure boot config backup
usb:/atmf/amf_net/nodes/node1/config/backup.cfg
To unset the boot configuration, use the command:
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure no boot config
To unset the backup boot configuration, use the command:
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure no boot config backup
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
Parameter Description
backup Specify that this is the backup configuration file.
<file-path|URL> The path or URL and name of the configuration file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1657
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CONFIGURE BOOT CONFIG (AMF PROVISIONING)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1658
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CONFIGURE BOOT SYSTEM (AMF PROVISIONING)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
Overview This command sets the release file that will load onto a specified provisioned node
during the next boot cycle. This command can also set the backup release file to be
loaded for an AMF provisioned node. To unset the boot system release file or the
backup boot release file use the no boot command.
Use the no variant of this command to return to the default.
This command can only be run on AMF master nodes.
Syntax configure boot system [backup] <file-path|URL>
configure no boot system [backup]
Default No boot release file or backup release files are specified for the provisioned node.
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage When using this command to set a backup release file, the specified AMF
provisioned node must exist. The specified file must exist in the flash directory
created for the provisioned node in the AMF remote backup media.
Examples To set the release file x930-5.4.9-0.1.rel on the AMF provisioned node ‘node1’, use
the command:
MasterNodeName# atmf provision node node1
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure boot system
x930-5.4.9-0.1.rel
To set the backup release file x930-5.4.8-2.5.rel as the backup to the main release
file on the AMF provisioned node ‘node1’, use the command:
MasterNodeName# atmf provision node node1
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure boot system backup
card:/atmf/amf_net/nodes/node1/flash/x930-5.4.8-2.5.rel
To unset the boot release, use the command:
MasterNodeName# atmf provision node node1
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure no boot system
To unset the backup boot release, use the command:
MasterNodeName# atmf provision node node1
MasterNodeName(atmf-provision)# configure no boot system backup
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
Parameter Description
<file-path|URL> The path or URL and name of the release file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1659
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CONFIGURE BOOT SYSTEM (AMF PROVISIONING)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1660
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CREATE (AMF PROVISIONING)
create (amf provisioning)
Overview This command sets up an empty directory on the backup media for use with a
provisioned node. This directory can have configuration and release files copied to
it from existing devices. Alternatively, the configuration files can be created by the
user.
An alternative way to create a new provisioned node is with the command clone
(amf provisioning).
This command can only run on AMF master nodes.
Syntax create
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage This command is only available on master nodes in the AMF network.
A date and time is assigned to the new provisioning directory reflecting when this
command was executed. If there is a backup or provisioned node with the same
name on another AMF master then the most recent one will be used.
Example To create a new provisioned node named “device2” use the command:
device1# atmf provision node device2
device1(atmf-provision)# create
Running this command will create the following directories:
•<media>:atmf/<atmf_name>/nodes/<node>
•<media>:atmf/<atmf_name>/nodes/<node>/flash
To confirm the new node’s settings, use the command:
device1# show atmf backup
The output for the show atmf backup command is shown in the following figure,
and shows details for the new provisioned node ‘device2’.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1661
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
CREATE (AMF PROVISIONING)
Figure 45-5: Sample output from the show atmf backup command
For instructions on how to configure on a provisioned node, see the AMF Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
device1#show atmf backup
Scheduled Backup ...... Enabled
Schedule ............ 1 per day starting at 03:00
Next Backup Time .... 01 Oct 2018 03:00
Backup Bandwidth ...... Unlimited
Backup Media .......... USB (Total 7446.0MB, Free 7315.2MB)
Server Config .........
Synchronization ..... Unsynchronized
Last Run .......... -
1 .................. Unconfigured
2 .................. Unconfigured
Current Action ........ Idle
Started ............. -
Current Node ........ -
---------------------------------------------------------------
Node Name Date Time In ATMF On Media Status
---------------------------------------------------------------
device2 - - No Yes Prov
device1 30 Sep 2018 00:05:49 No Yes Good

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1662
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DEBUG ATMF
debug atmf
Overview This command enables the AMF debugging facilities, and displays information
that is relevant (only) to the current node. The detail of the debugging displayed
depends on the parameters specified.
If no additional parameters are specified, then the command output will display all
AMF debugging information, including link events, topology discovery messages
and all notable AMF events.
The no variant of this command disables either all AMF debugging information, or
only the particular information as selected by the command’s parameters.
Syntax debug atmf
[link|crosslink|arealink|database|neighbor|error|all]
no debug atmf
[link|crosslink|arealink|database|neighbor|error|all]
Default All debugging facilities are disabled.
Mode User Exec and Global Configuration
Usage If no additional parameters are specified, then the command output will display all
AMF debugging information, including link events, topology discovery messages
and all notable AMF events.
NOTE: An alias to the no variant of this command is undebug atmf on page 1787.
Examples To enable all AMF debugging, use the command:
node_1# debug atmf
To enable AMF uplink and downlink debugging, use the command:
node_1# debug atmf link
To enable AMF error debugging, use the command:
node_1# debug atmf error
Parameter Description
link Output displays debugging information relating to uplink or
downlink information.
crosslink Output displays all crosslink events.
arealink Output displays all arealink events.
database Output displays only notable database events.
neighbor Output displays only notable AMF neighbor events.
error Output displays AMF error events.
all Output displays all AMF events.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1664
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DEBUG ATMF PACKET
debug atmf packet
Overview This command configures AMF Packet debugging parameters. The debug only
displays information relevant to the current node. The command has following
parameters:
Syntax debug atmf packet [direction {rx|tx|both}] [level {1|2|3}]
[timeout <seconds>] [num-pkts <quantity>]
[filter {node <name>|interface <ifname>}
[pkt-type [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]]]
Simplified
Syntax
NOTE: You can combine the syntax components shown, but when doing so, you must
retain their original order.
Default Level 1, both Tx and Rx, a timeout of 60 seconds with no filters applied.
NOTE: An alias to the no variant of this command - undebug atmf - can be found
elsewhere in this chapter.
Mode User Exec and Global Configuration
Usage If no additional parameters are specified, then the command output will apply a
default selection of parameters shown below:
debug atmf packet [direction {rx|tx|both}]
[level {[1][2|3}]
[timeout <seconds>]
[num-pkts <quantity>]
debug atmf packet filter [node <name>]
[interface <ifname>]
[pkt-type
[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]]
Parameter Description
direction Sets debug to packet received, transmitted, or both
rx packets received by this node
tx Packets sent from this node
1AMF Packet Control header Information, Packet Sequence
Number. Enter 1 to select this level.
2AMF Detailed Packet Information. Enter 2 to select this level.
3AMF Packet HEX dump. Enter 3 to select this level.
timeout Sets the execution timeout for packet logging

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1665
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DEBUG ATMF PACKET
Examples To set a packet debug on node 1 with level 1 and no timeout, use the command:
node_1# debug atmf packet direction tx timeout 0
To set a packet debug with level 3 and filter packets received from AMF node 1:
node_1# debug atmf packet direction tx level 3 filter node_1
To enable send and receive 500 packets only on vlink1 for packet types 1, 7, and 11,
use the command:
node_1# debug atmf packet num-pkts 500 filter interface vlink1
pkt-type 1 7 11
<seconds> Seconds
num-pkts Sets the number of packets to be dumped
<quantity> The actual number of packets
filter Sets debug to filter packets
node Sets the filter on packets for a particular Node
<name> The name of the remote node
interface Sets the filter to dump packets from an interface (portx.x.x) on the
local node
<ifname>Interface port or virtual-link
pkt-type Sets the filter on packets with a particular AMF packet type
1Crosslink Hello BPDU packet with crosslink links information. Enter
1 to select this packet type.
2Crosslink Hello BPDU packet with downlink domain information.
Enter 2 to select this packet type.
3Crosslink Hello BPDU packet with uplink information. Enter 3 to
select this packet type.
4Downlink and uplink hello BPDU packets. Enter 4 to select this
packet type.
5Non broadcast hello unicast packets. Enter 5 to select this packet
type.
6Stack hello unicast packets. Enter 6 to select this packet type.
7Database description. Enter 7 to select this packet type.
8DBE request. Enter 8 to select this packet type.
9DBE update. Enter 9 to select this packet type.
10 DBE bitmap update. Enter 10 to select this packet type.
11 DBE acknowledgment. Enter 11 to select this packet type.
12 Area Hello Packets. Enter 12 to select this packet type.
13 Gateway Hello Packets. Enter 13 to select this packet type.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1666
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DEBUG ATMF PACKET
This example applies the debug atmf packet command and combines many of its
options:
node_1# debug atmf packet direction rx level 1 num-pkts 60
filter node x930 interface port1.0.1 pkt-type 4 7 10

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1667
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DELETE (AMF PROVISIONING)
delete (amf provisioning)
Overview This command deletes files that have been created for loading onto a provisioned
node. It can only be run on master nodes.
Syntax delete
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage This command is only available on master nodes in the AMF network. The
command will only work if the provisioned node specified in the command has
already been set up (although the device itself is still yet to be installed). Otherwise,
an error message is shown when the command is run.
You may want to use the delete command to delete a provisioned node that was
created in error or that is no longer needed.
This command cannot be used to delete backups created by the AMF backup
procedure. In this case, use the command atmf backup delete to delete the files.
NOTE: This command allows provisioned entries to be deleted even if they have been
referenced by the atmf provision (interface) command, so take care to only delete
unwanted entries.
Example To delete backup files for a provisioned node named device3 use the command:
device1# atmf provision node device3
device1(atmf-provision)# delete
To confirm that the backup files for provisioned node device3 have been deleted
use the command:
device1# show atmf backup
The output should show that the provisioned node device3 no longer exists in the
backup file, as shown in the figure below:
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1668
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DELETE (AMF PROVISIONING)
Figure 45-6: Sample output showing the show atmf backup command
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
device1#show atmf backup
Scheduled Backup ...... Enabled
Schedule ............ 1 per day starting at 03:00
Next Backup Time .... 01 Oct 2016 03:00
Backup Bandwidth ...... Unlimited
Backup Media .......... USB (Total 7446.0MB, Free 7297.0MB)
Server Config .........
Synchronization ..... Unsynchronized
Last Run .......... -
1 .................. Unconfigured
2 .................. Unconfigured
Current Action ........ Idle
Started ............. -
Current Node ........ -
---------------------------------------------------------------
Node Name Date Time In ATMF On Media Status
---------------------------------------------------------------
device1 30 Sep 2016 00:05:49 No Yes Good
device2 30 Sep 2016 00:05:44 Yes Yes Good

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1669
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DISCOVERY
discovery
Overview Use this command to specify how AMF learns about guest nodes.
AMF nodes gather information about guest nodes by using one of two internally
defined discovery methods: static or dynamic.
With dynamic learning (the default method), AMF learns IP address and MAC
addresses of guest nodes from LLDP or DHCP snooping. Dynamic learning is only
supported when using IPv4. For IPv6, use static learning.
With dynamic learning, ensure that the command ip dhcp snooping
delete-by-linkdown is set.
With static learning, you use the switchport atmf-guestlink command to specify
the guest class name and IP address of the guest node attached to each individual
switch port. AMF then learns the MAC addresses of each of the guests of that class
from ARP or Neighbor discovery tables.
If you are using the static method, ensure that you have configured the
appropriate class type for each of your statically discovered guest nodes.
The no variant of this command returns the discovery method to dynamic.
Syntax discovery [static|dynamic]
no discovery
Default Dynamic.
Mode ATMF Guest Configuration Mode.
Usage This command is one of several modal commands that are configured and applied
for a specific guest-class (mode). Its settings are automatically applied to a
guest-node link by the switchport atmf-guestlink command.
NOTE: AMF guest nodes are not supported on ports using the OpenFlow protocol.
Example 1 To configure the discovery of the guest-class camera to operate statically, use the
following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# atmf guest-class camera
Node1(config-guest)# discovery static
Parameter Description
static Statically assigned.
dynamic Learned from DCHCP Snooping or LLDP.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1670
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DISCOVERY
Example 2 To return the discovery method for the guest class TQ4600-1 to its default of
dynamic, use the following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# atmf guest-class TQ4600-1
Node1(config-guest)# no discovery
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
switchport atmf-guestlink
show atmf links guest
show atmf nodes
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1671
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (AMF CONTAINER)
description (amf container)
Overview Use this command to set the description on an AMF container on a Virtual AMF
Appliance (VAA).
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the description from an AMF
container.
Syntax description <description>
no description
Mode AMF Container Configuration
Example To set the description for AMF container “vac-wlg-1” to “Wellington area”, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# description Wellington area
To remove the description for AMF container “vac-wlg-1”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# no description
Related
Commands
atmf container
show atmf container
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Parameter Description
<description> Enter up to 128 characters of text describing the AMF container.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1672
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
ERASE FACTORY-DEFAULT
erase factory-default
Overview This command erases all data from Flash except the following:
• the boot release file (a .rel file) and its release setting file
• all license files
• the latest GUI release file
The device is then rebooted and returned to its factory default condition. The
device can then be used for AMF automatic node recovery.
Syntax erase factory-default
Mode Privileged Exec.
Usage This command is an alias to the atmf cleanup command.
Example To erase data, use the command:
Node_1# erase factory-default
This command will erase all NVS, all flash contents except for
the boot release, a GUI resource file, and any license files,
and then reboot the switch. Continue? (y/n):y
Related
Commands
atmf cleanup

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1673
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
HTTP-ENABLE
http-enable
Overview This command is used to enable GUI access to a guest node. When http-enable is
configured the port number is set to its default of 80. If the guest node is using a
different port for HTTP, you can configure this using the port <PORTNO> attribute.
This command is used to inform the GUI that this device has an HTTP interface at
the specified port number so that a suitable URL can be provided to the user.
Use the no variant of this command to disable HTTP.
Syntax http-enable [port <port-number>]
no http-enable
Default http-enable is off.
If http-enable is selected without a port parameter the port number will default to
80.
Mode ATMF Guest Configuration Mode
Example 1 To enable HTTP access to a guest node on port 80 (the default), use the following
commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)#atmf guest-class Camera
node1(config-atmf-guest)#http-enable
node1(config-atmf-guest)#
Example 2 To enable HTTP access to a guest node on port 400, use the following commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)#atmf guest-class Camera
node1(config-atmf-guest)#http-enable port 400
node1(config-atmf-guest)#
Example 3 To disable HTTP access to a guest node, use the following commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)#atmf guest-class Camera
node1(config-atmf-guest)#no http-enable
node1(config-atmf-guest)#
Parameter Description
port TCP port number.
<port-number>The port number to be configured.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1675
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
IDENTITY (AMF PROVISIONING)
identity (amf provisioning)
Overview Use this command to create an identity token for provisioning an isolated AMF
node. An isolated node is an AMF member that is only connected to the rest of the
AMF network via a virtual-link.
This command allows these nodes, which have no AMF neighbors, to be identified
for provisioning purposes. They are identified using an identity token which is
based on either the next-hop MAC address of the provisioned node, or the serial
number of the device being provisioned. This identity token is stored on the AMF
master.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the identity token for a node.
Syntax identity mac-address <mac-address> prefix
<ip-address/prefix-length>
identity serial-number <serial-number> prefix
<ip-address/prefix-length>
no identity
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage To provision an isolated node, first create a configuration for the node using the
create (amf provisioning) and/or the clone (amf provisioning) commands.
Then create an identity token for the provisioned node by either specifying its
next-hop MAC address or by specifying the serial number of the replacement
device. The advantage of using the next-hop MAC address is that any device,
regardless of its serial number, can be added to the network but using the serial
number maybe preferred in situations where the next-hop MAC address is not easy
to obtain.
The atmf recovery-server option must be enabled on the AMF master before
attempting to provision the device. This option allows the AMF master to process
recovery requests from isolated AMF nodes.
Parameter Description
mac-address Specify the next-hop MAC address of the device being
provisioned.
<mac-address>MAC address of the port the provisioned node is connected to,
in the format xxxx.xxxx.xxxx.
serial-number Specify the serial number of the device to be provisioned.
<serial-number>Serial number of the device that is being provisioned.
prefix IPv4 address, and prefix length, of the virtual-link interface on
the isolated node
<ip-address/
prefix-length>IPv4 address, and prefix length, in A.B.C.D/M format.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1676
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
IDENTITY (AMF PROVISIONING)
See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for information on
preparing your network for recovering or provisioning isolated nodes.
Example To create a identity token on your AMF master for a device named “my-x930” with
serial number “A10064A172100008”, use the command:
awplus# atmf provision node my-x930
awplus(atmf-provision)# identity serial-number
A10064A172100008 prefix 192.168.2.25/24
To create a identity token on your AMF master for a device named “my-x930” with
next-hop MAC address ”0000.cd28.0880”, use the command:
awplus# atmf provision node my-x930
awplus(atmf-provision)# identity mac-address 0000.cd28.0880
prefix 192.168.2.25/24
To delete the identity token from your AMF master for a device named “my-x930”,
use the command:
awplus# atmf provision node my-x930
awplus(atmf-provision)# no identity
Related
Commands
atmf cleanup
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
atmf recovery-server
atmf virtual-link
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1677
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
LICENSE-CERT (AMF PROVISIONING)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
Overview This command is used to set up the license certificate for a provisioned node.
The certificate file usually has all the license details for the network, and can be
stored anywhere in the network. This command makes a hidden copy of the
certificate file and stores it in the space set up for the provisioned node on AMF
backup media.
For node provisioning, the new device has not yet been part of the AMF network,
so the user is unlikely to know its product ID or its MAC address. When such a
device joins the network, assuming that this command has been applied
successfully, the copy of the certificate file will be applied automatically to the
provisioned node.
Once the new device has been resurrected on the network and the certificate file
has been downloaded to the provisioned node, the hidden copy of the certificate
file is deleted from AMF backup media.
Use the no variant of this command to set it back to the default.
This command can only be run on AMF master nodes.
Syntax license-cert <file-path|URL>
no license-cert
Default No license certificate file is specified for the provisioned node.
Mode AMF Provisioning
Usage This command is only available on master nodes in the AMF network. It will only
operate if the provisioned node specified in the command has already been set up,
and if the license certification is present in the backup file. Otherwise, an error
message is shown when the command is run.
Example 1 To apply the license certificate ‘cert1.txt’ stored on a TFTP server for AMF
provisioned node “device2”, use the command:
device1# atmf provision node device2
device1(atmf-provision)# license-cert
tftp://192.168.1.1/cert1.txt
Example 2 To apply the license certificate ‘cert2.txt’ stored in the AMF master's flash directory
for AMF provisioned node ‘host2’, use the command:
device1# atmf provision node host2
device1(atmf-provision)# license-cert /cert2.txt
Parameter Description
<file-path|URL> The name of the certificate file. This can include the
file-path of the file.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1678
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
LICENSE-CERT (AMF PROVISIONING)
To confirm that the license certificate has been applied to the provisioned node,
use the command show atmf provision nodes. The output from this command is
shown below, and displays license certification details in the last line.
Figure 45-7: Sample output from the show atmf provision nodes command
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
device1#show atmf provision nodes
ATMF Provisioned Node Information:
Backup Media .............: SD (Total 3827.0MB, Free 3481.1MB)
Node Name : device2
Date & Time : 06-Oct-2016 & 23:25:44
Provision Path : card:/atmf/nodes
Boot configuration :
Current boot image : x510-5.4.6-1.4.rel (file exists)
Backup boot image : x510-5.4.6-1.3.rel (file exists)
Default boot config : flash:/default.cfg (file exists)
Current boot config : flash:/abc.cfg (file exists)
Backup boot config : flash:/xyz.cfg (file exists)
Software Licenses :
Repository file : ./.configs/.sw_v2.lic
: ./.configs/.swfeature.lic
Certificate file : card:/atmf/lok/nodes/awplus1/flash/.atmf-lic-cert

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1679
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
LOCATE (AMF PROVISIONING)
locate (amf provisioning)
Overview This command changes the present working directory to the directory of a
provisioned node. This makes it easier to edit files and create a unique provisioned
node in the backup.
This command can only be run on AMF master nodes.
NOTE: We advise that after running this command, you return to a known working
directory, typically flash.
Syntax locate
Mode AMF Provisioning
Example To change the working directory that happens to be on device1 to the directory of
provisioned node device2, use the following command:
device1# atmf provision node device2
device1[atmf-provision]# locate
The directory of the node device2 should now be the working directory. You can
use the command pwd to check this, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 45-8: Sample output from the pwd command
The output above shows that the working directory is now the flash of device2.
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
delete (amf provisioning)
identity (amf provisioning)
license-cert (amf provisioning)
locate (amf provisioning)
pwd
show atmf provision nodes
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: syntax change due to new AMF provisioning mode
device2#pwd
card:/atmf/building_2/nodes/device2/flash
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1680
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
LOG EVENT-HOST
log event-host
Overview Use this command to set up an external host to log AMF topology events through
Vista Manager. This command is run on the Master device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable log events through Vista Manager.
Syntax log event-host [<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>] atmf-topology-event
no log event-host [<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>] atmf-topology-event
Default Log events are disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Event hosts are set so syslog sends the messages out as they come.
Note that there is a difference between log event and log host messages:
• Log event messages are sent out as they come by syslog
• Log host messages are set to wait for a number of messages (20) to send
them out together for traffic optimization.
Example To enable Node 1 to log event messages from host IP address 192.0.2.31, use the
following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# log event-host 192.0.2.31 atmf-topology-event
To disable Node 1 to log event messages from host IP address 192.0.2.31, use the
following commands:
Node1# configure terminal
Node1(config)# no log event-host 192.0.2.31 atmf-topology-event
Related
Commands
atmf topology-gui enable
Parameter Description
<ipv4-addr> ipv4 address of the event host
<ipv6-addr> ipv6 address of the event host

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1681
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
MODELTYPE
modeltype
Overview This command sets the expected model type of the guest node. Guest nodes can
be one of various types: alliedware, aw+, tq or other. The model type will default to
other if nothing is set.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the model type to other.
Syntax modeltype [alliedware|aw+|tq|other]
Default Will default to other
Mode ATMF Guest Configuration Mode
Example 1 To assign the model type tq to the guest-class called tq_device, use the following
commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)# atmf guest-class tq_device
node1(config-atmf-guest)# modeltype tq
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Example 2 To remove the model type tq from the guest-class called tq_device, and reset it to
the default of other, use the following commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)# atmf guest-class tq_device
node1(config-atmf-guest)# no modeltype
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
switchport atmf-guestlink
show atmf links guest
Parameter Description
alliedware A legacy Allied Telesis operating system.
aw+ The Allied Telesis AlliedWare Plus operating system.
tq An Allied Telesis TQ Series wireless access point.
other Used where the model type is outside the above definitions.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1682
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST INTERFACE
show application-proxy whitelist interface
Overview Use this command to display the status of port authentication on the specified
interface.
Syntax show application-proxy whitelist interface [<interface-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the port authentication information for all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show application-proxy whitelist interface
To display the port authentication information for port1.0.4, use the command
awplus# show application-proxy whitelist interface port1.0.4
Parameter Description
<interface-list>The interfaces or ports to display information about. An
interface-list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do
not mix port types in the same list.
The specified interface must exist.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1683
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST INTERFACE
Output Figure 45-9: Example output from show application-proxy whitelist interface
Related
Commands
application-proxy whitelist enable
application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
awplus#sh application-proxy whitelist interface
Authentication Info for interface port1.0.1
portEnabled: false - portControl: Auto
portStatus: Unknown
reAuthenticate: disabled
reAuthPeriod: 3600
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2 - txPeriod: 30
PAE: connectTimeout: 30
BE: suppTimeout: 30 - serverTimeout: 30
CD: adminControlledDirections: in
KT: keyTxEnabled: false
critical: disabled
guestVlan: disabled
guestVlanForwarding:
none
authFailVlan: disabled
dynamicVlanCreation: disabled
multiVlanSession: disabled
hostMode: single-host
dot1x: disabled
authMac: enabled
method: PAP
scheme: mac
reauthRelearning: disabled
authWeb: disabled
twoStepAuthentication:
configured: disabled
actual: disabled
supplicantMac: none
supplicantIpv4: none
Authentication Info for interface port1.0.2
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1684
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST SERVER
show application-proxy whitelist server
Overview Use this command to display the external RADIUS server details for the
application-proxy whitelist feature.
Syntax show application-proxy whitelist server
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the external RADIUS server details for the application-proxy whitelist
feature, use the command:
awplus# show application-proxy whitelist server
Output Figure 45-10: Example output from show application-proxy whitelist server
Related
Commands
application-proxy whitelist enable
application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist interface
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
awplus#show application-proxy whitelist server
Application Proxy Whitelist Details:
External Server Details:
IP: 192.168.1.10
Port: 1812
Proxy Details:
IP: 172.31.0.5
Status: Alive

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1685
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST SUPPLICANT
show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Overview Use this command to display the current configuration and status for each
supplicant attached to an application-proxy whitelist port.
Syntax show application-proxy whitelist supplicant [interface
<interface-list>|<mac-addr>|brief]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the supplicant information for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
To display the supplicant information for port1.0.4, use the command:
awplus# show application-proxy whitelist supplicant interface
port1.0.4
Parameter Description
interface
<interface-list>The interfaces or ports to display information about. An
interface-list can be:
• a switchport (e.g. port1.0.4)
• a static channel group (e.g. sa2)
• a dynamic (LACP) channel group (e.g. po2)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen (e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.4)
• a comma-separated list (e.g. port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.4). Do
not mix port types in the same list.
The specified interface must exist.
<mac-addr>MAC (hardware) address of the supplicant.Entry format is
HHHH.HHHH.HHHH (hexadecimal)
brief Brief summary of the supplicant state.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1686
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW APPLICATION-PROXY WHITELIST SUPPLICANT
Output Figure 45-11: Example output from show application-proxy whitelist
supplicant
Related
Commands
application-proxy whitelist enable
application-proxy whitelist server
show application-proxy whitelist interface
show application-proxy whitelist server
Command
changes
Version 5.4.9-0.1: command added
awplus#show application-proxy whitelist supplicant
Interface port1.0.4
authenticationMethod: dot1x/mac/web
Two-Step Authentication
firstMethod: mac
secondMethod: dot1x/web
totalSupplicantNum: 1
authorizedSupplicantNum: 1
macBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
dot1xAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
webBasedAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 1
otherAuthenticationSupplicantNum: 0
Supplicant name: test
Supplicant address: 001c.233e.e15a
authenticationMethod: WEB-based Authentication
Two-Step Authentication:
firstAuthentication: Pass - Method: mac
secondAuthentication: Pass - Method: web
portStatus: Authorized - currentId: 1
abort:F fail:F start:F timeout:F success:T
PAE: state: Authenticated - portMode: Auto
PAE: reAuthCount: 0 - rxRespId: 0
PAE: quietPeriod: 60 - maxReauthReq: 2
BE: state: Idle - reqCount: 0 - idFromServer: 0
CD: adminControlledDirections: in operControlledDirections: in
CD: bridgeDetected: false
KR: rxKey: false
KT: keyAvailable: false - keyTxEnabled: false
RADIUS server group (auth): radius
RADIUS server (auth): 192.168.1.40
...

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1687
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF
show atmf
Overview Displays information about the current AMF node.
Syntax show atmf [summary|tech|nodes|session]
Default Only summary information is displayed.
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage AMF uses internal VLANs to communicate between nodes about the state of the
AMF network. Two VLANs have been selected specifically for this purpose. Once
these have been assigned, they are reserved for AMF and cannot be used for other
purposes
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Example 1 To show summary information on AMF node_1 use the following command:
node_1# show atmf summary
Example 2 To show information specific to AMF nodes use the following command:
node_1# show atmf nodes
Example 3 The show amf session command displays all CLI (Command Line Interface)
sessions for users that are currently logged in and running a CLI session.
Parameter Description
summary Displays summary information about the current AMF node.
tech Displays global AMF information.
nodes Displays a list of AMF nodes together with brief details.
session Displays information on an AMF session.
Table 1: Output from the show atmf summary command
node_1#show atmf summary
ATMF Summary Information:
ATMF Status : Enabled
Network Name : Test_network
Node Name : node_1
Role : Master
Restricted login : Disabled
Current ATMF Nodes : 3
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1688
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF
To display AMF active sessions, use the following command:
node_1# show atmf session
For example, in the output below, node_1 and node_5 have active users logged in.
Example 4 The AMF tech command collects all the AMF commands, and displays them. You
can use this command when you want to see an overview of the AMF network.
To display AMF technical information, use the following command:
node_1# show atmf tech
Table 2: Output from the show atmf session command
node_1#show atmf session
CLI Session Neighbors
Session ID : 73518
Node Name : node_1
PID : 7982
Link type : Broadcast-cli
MAC Address : 0000.0000.0000
Options : 0
Our bits : 0
Link State : Full
Domain Controller : 0
Backup Domain Controller : 0
Database Description Sequence Number : 00000000
First Adjacency : 1
Number Events : 0
DBE Retransmit Queue Length : 0
DBE Request List Length : 0
Session ID : 410804
Node Name : node_5
PID : 17588
Link type : Broadcast-cli
MAC Address : 001a.eb56.9020
Options : 0
Our bits : 0
Link State : Full
Domain Controller : 0
Backup Domain Controller : 0
Database Description Sequence Number : 00000000
First Adjacency : 1
Number Events : 0
DBE Retransmit Queue Length : 0
DBE Request List Length : 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1689
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF
Table 3: Output from the show atmf tech command
node_1#show atmf tech
ATMF Summary Information:
ATMF Status : Enabled
Network Name : ATMF_NET
Node Name : node_1
Role : Master
Current ATMF Nodes : 8
ATMF Technical information:
Network Name : ATMF_NET
Domain : node_1's domain
Node Depth : 0
Domain Flags : 0
Authentication Type : 0
MAC Address : 0014.2299.137d
Board ID : 287
Domain State : DomainController
Domain Controller : node_1
Backup Domain Controller : node2
Domain controller MAC : 0014.2299.137d
Parent Domain : -
Parent Domain Controller : -
Parent Domain Controller MAC : 0000.0000.0000
Number of Domain Events : 0
Crosslink Ports Blocking : 0
Uplink Ports Waiting on Sync : 0
Crosslink Sequence Number : 7
Domains Sequence Number : 28
Uplink Sequence Number : 2
Number of Crosslink Ports : 1
Number of Domain Nodes : 2
Number of Neighbors : 5
Number of Non Broadcast Neighbors : 3
Number of Link State Entries : 1
Number of Up Uplinks : 0
Number of Up Uplinks on This Node : 0
DBE Checksum : 84fc6
Number of DBE Entries : 0
Management Domain Ifindex : 4391
Management Domain VLAN : 4091
Management ifindex : 4392
Management VLAN : 4092
Table 4: Parameter definitions from the show atmf tech command
Parameter Definition
ATMF Status The Node’s AMF status, either Enabled or Disabled.
Network Name The AMF network that a particular node belongs to.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1690
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF
Related
Commands
show atmf detail
Node Name The name assigned to a particular node.
Role The role configured for this AMF device, either Master or Member.
Current ATMF
Nodes The count of AMF nodes in an AMF Network.
Node Address An address used to access a remotely located node (.atmf).
Node ID A unique identifier assigned to a Node on an AMF network.
Node Depth The number of nodes in path from this node to level of the AMF root node. It can be
thought of as the vertical depth of the AMF network from a particular node to the
zero level of the AMF root node.
Domain State The state of Node in a Domain in AMF network as Controller/Backup.
Recovery State The AMF node recovery status. Indicates whether a node recovery is in progress on
this device - Auto, Manual, or None.
Management VLAN The VLAN created for traffic between Nodes of different domain (up/down links).
• VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4092 is configured as the Management VLAN.
• Management Subnet - Network prefix for the subnet.
• Management IP Address - The IP address allocated for this traffic.
• Management Mask - The subnet mask used to create a subnet for this traffic
(255.255.128.0).
Domain VLAN The VLAN assigned for traffic between Nodes of same domain (crosslink).
• VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4091 is configured as the domain VLAN.
• Domain Subnet. The subnet address used for this traffic.
• Domain IP Address. The IP address allocated for this traffic.
• Domain Mask. The subnet mask used to create a subnet for this traffic
(255.255.128.0).
Device Type The Product Series name.
ATMF Master Whether the node is an AMF master node for its area (‘Y‘ if it is and ‘N’ if it is not).
SC The device configuration, one of C - Chassis (SBx8100 Series), S - Stackable (VCS) or N
- Standalone.
Parent The node to which the current node has an active uplink.
Node Depth The number of nodes in the path from this node to the master node.
Table 4: Parameter definitions from the show atmf tech command (cont.)
Parameter Definition

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1691
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA
show atmf area
Overview Use this command to display information about an AMF area. On AMF controllers,
this command displays all areas that the controller is aware of. On remote AMF
masters, this command displays the controller area and the remote local area. On
gateways, this command displays the controller area and remote master area.
Syntax show atmf area [detail] [<area-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To show information about all areas, use the command:
controller-1# show atmf area
The following figure shows example output from running this command on a
controller.
The following figure shows example output from running this command on a
remote master.
Parameter Description
detail Displays detailed information
<area-name>Displays information about master and gateway nodes in the
specified area only.
Table 5: Example output from the show atmf area command on a Controller.
controller-1#show atmf area
ATMF Area Information:
* = Local area
Area Area Local Remote Remote Node
Name ID Gateway Gateway Master Count
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* NZ 1 Reachable N/A N/A 3
Wellington 2 Reachable Reachable Auth OK 120
Canterbury 3 Reachable Reachable Auth Error -
SiteA-AREA 14 Unreachable Unreachable Unreachable -
Auckland 100 Reachable Reachable Auth Start -
Southland 120 Reachable Reachable Auth OK 54
Area count: 6 Area node count: 177
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1692
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA
Table 6: Example output from the show atmf area command on a remote master.
Canterbury#show atmf area
ATMF Area Information:
* = Local area
Area Area Local Remote Remote Node
Name ID Gateway Gateway Master Count
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
NZ 1 Reachable N/A N/A -
* Canterbury 3 Reachable N/A N/A 40
Area count: 2 Local area node count: 40
Table 7: Parameter definitions from the show atmf area command
Parameter Definition
*Indicates the area of the device on which the command is being run.
Area Name The name of each area.
Area ID The ID of the area.
Local Gateway Whether the local gateway node is reachable or not.
Remote Gateway Whether the remote gateway node is reachable or not. This is one of the following:
• Reachable, if the link has been established.
• Unreachable, if a link to the remote area has not been established. This could
mean that a port or vlan is down, or that inconsistent VLANs have been configured
using the switchport atmf-arealink remote-area command.
• N/A for the area of the controller or remote master on which the command is
being run, because the gateway node on that device is local.
• Auth Start, which may indicate that the area names match on the controller and
remote master, but the IDs do not match.
• Auth Error, which indicates that the areas tried to authenticate but there is a
problem. For example, the passwords configured on the controller and remote
master may not match, or a password may be missing on the remote master.?
• Auth OK, which indicates that area authentication was successful and you can
now use the atmf select-area command.
Remote Master Whether the remote master node is reachable or not. This is N/A for the area of the
controller or remote master on which the command is being run, because the
master node on that device is local.
Node Count The number of nodes in the area.
Area Count The number of areas controlled by the controller.
Area Node Count The total number of nodes in the area.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1693
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA
Example 2 To show detailed information about the areas, use the command:
controller-1# show atmf area detail
The following figure shows example output from running this command.
Related
Commands
show atmf area summary
show atmf area nodes
show atmf area nodes-detail
Table 8: Output from the show atmf area detail command
controller-1#show atmf area detail
ATMF Area Detail Information:
Controller distance : 0
Controller Id : 21
Backup Available : FALSE
Area Id : 2
Gateway Node Name : controller-1
Gateway Node Id : 342
Gateway Ifindex : 6013
Masters Count : 1
Master Node Name : well-master (329)
Node Count : 2
Area Id : 3
Gateway Node Name : controller-1
Gateway Node Id : 342
Gateway Ifindex : 4511
Masters Count : 2
Master Node Name : cant1-master (15)
Master Node Name : cant2-master (454)
Node Count : 2
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1694
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA GUESTS
show atmf area guests
Overview This command will display details of all guests that the controller is aware of.
Syntax show atmf area guests [<area-name> [<node-name>]]
Default n/a
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example 1 To display atmf area guest nodes on a controller, use the command,
GuestNode[1]#show atmf area guests
Output Figure 45-12: Example output from the show atmf area guests command
Parameter Description
<area-name> The area name for guest information
<node-name> The name of the node that connects to the guests.
main-building Area Guest Node Information:
Device MAC IP/IPv6
Type Address Parent Port Address
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 0008.5d10.7635 x230 1.0.3 192.168.5.4
AT-TQ4600 eccd.6df2.da60 wireless-node1 1.0.4 192.168.5.3
- 0800.239e.f1fe x230 1.0.4 192.168.4.8
AT-TQ4600 001a.eb3b.dc80 wireless-node2 1.0.7 192.168.4.12
main-building guest node count 4
GuestNode[1]#
Table 9: Parameters in the output from show atmf area guests command
Parameter Description
Device Type The device type as read from the guest node.
MAC Address The MAC address of the guest-node
Parent The device that directly connects to the guest-node
Port The port number on the parent node that connects to the guest
node.
IP/IPv6 The IP or IPv6 address of the guest node.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1696
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA GUESTS-DETAIL
show atmf area guests-detail
Overview This command displays the local and remote guest information from an AMF
controller.
Syntax show atmf area guests-detail [<area-name> [<node-name>]]
Default n/a.
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display detailed information for all guest nodes attached to “node1”, which is
located within the area named “northern”, use the following command:
AMF_controller#show atmf area guests-detail northern node1
Output Figure 45-13: Example output from the show atmf guest detail command.
Parameter Description
<area-name>The name assigned to the AMF area. An area is an AMF network
that is under the control of an AMF Controller.
<node-name>The name assigned to the network node.
#show atmf guest detail
Node Name : Node1
Port Name : port1.0.5
Ifindex : 5005
Guest Description : tq4600
Device Type : AT-TQ4600
Configuration Mismatch : No
Backup Supported : Yes
MAC Address : eccd.6df2.da60
IP Address : 192.168.4.50
IPv6 Address : Not Set
HTTP Port : 80
Firmware Version :
Node Name : poe
Port Name : port1.0.6
Ifindex : 5006
Guest Description : tq3600
Device Type : AT-TQ2450
Configuration Mismatch : No
Backup Supported : Yes
MAC Address : 001a.eb3b.cb80
IP Address : 192.168.4.9
IPv6 Address : Not Set
HTTP Port : 80
Firmware Version :
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1697
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA GUESTS-DETAIL
Related
Commands
show atmf area nodes-detail
show atmf area guests
Table 10: Parameters shown in the output of the show atmf guest detail
command
Parameter Description
Node Name The name of the guest’s parent node.
Port Name The port on the parent node that connects to the guest.
IFindex An internal index number that maps to the port number
on the parent node.
Guest Description A brief description of the guest node as manually entered
into the description (interface) command for the guest
node port on the parent node.
Device Type The device type as supplied by the guest node itself.
Backup Supported Indicates whether AMF supports backup of this guest
node.
MAC Address The MAC address of the guest node.
IP Address The IP address of the guest node.
IPv6 Address The IPv6 address of the guest node.
HTTP Port The HTTP port enables you to specify a port when
enabling http to allow a URL for the http user interface of
a Guest Node. This is determined by the http-enable
command.
Firmware Version The firmware version that the guest node is currently
running.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1698
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA NODES
show atmf area nodes
Overview Use this command to display summarized information about an AMF controller’s
remote nodes.
Note that this command can only be run from a controller node.
Syntax show atmf area nodes [<area-name> [<node-name>]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If you do not limit the output to a single area or node, this command lists all remote
nodes that the controller is aware of. This can be a very large number of nodes.
Example To show summarized information about all the nodes the controller is aware of,
use the command:
controller-1# show atmf area nodes
The following figure shows partial example output from running this command.
Parameter Description
<area-name>Displays information about nodes in the specified area.
<node-name>Displays information about the specified node.
Table 11: Output from the show atmf area nodes command
controller-1#show atmf area nodes
Wellington Area Node Information:
Node Device ATMF Node
Name Type Master SC Parent Depth
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
well-gate x230-18GP N N well-master 1
well-master AT-x930-28GPX Y N none 0
Wellington node count 2
...
Table 12: Parameter definitions from the show atmf area nodes command
Parameter Definition
Node Name The name assigned to a particular node.
Device Type The Product series name.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1699
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA NODES
Related
Commands
show atmf area
show atmf area nodes-detail
ATMF Master Whether the node is an AMF master node for its area (‘Y‘ if it is and ‘N’ if it is not).
SC The device configuration, one of C - Chassis (SBx8100 series), S - Stackable (VCS) or N
- Standalone.
Parent The node to which the current node has an active uplink.
Node Depth The number of nodes in the path from this node to the master node.
Table 12: Parameter definitions from the show atmf area nodes command (cont.)
Parameter Definition
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1700
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA NODES-DETAIL
show atmf area nodes-detail
Overview Use this command to display detailed information about an AMF controller’s
remote nodes.
Note that this command can only be run from a controller node.
Syntax show atmf area nodes-detail [<area-name> [<node-name>]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage If you do not limit the output to a single area or node, this command displays
information about all remote nodes that the controller is aware of. This can be a
very large number of nodes.
Example To show information about all the nodes the controller is aware of, use the
command:
controller-1# show atmf area nodes-detail
The following figure shows partial example output from running this command.
Parameter Description
<area-name>Displays detailed information about nodes in the specified area.
<node-name>Displays detailed information about the specified node.
Table 13: Output from the show atmf area nodes-detail command
controller-1#show atmf area nodes-detail
Wellington Area Node Information:
Node name well-gate
Parent node name : well-master
Domain id : well-gate’s domain
Board type : 368
Distance to core : 1
Flags : 50
Extra flags : 0x00000006
MAC Address : 001a.eb56.9020
Node name well-master
Parent node name : none
Domain id : well-master’s domain
Board type : 333
Distance to core : 0
Flags : 51
Extra flags : 0x0000000c
MAC Address : eccd.6d3f.fef7
...
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1701
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA NODES-DETAIL
Related
Commands
show atmf area
show atmf area nodes
Table 14: Parameter definitions from the show atmf area nodes-detail command
Parameter Definition
Node name The name assigned to a particular node.
Parent node name The node to which the current node has an active uplink.
Domain id
Board type The Allied Telesis code number for the device.
Distance to core The number of nodes in the path from the current node to the master node in its
area.
Flags Internal AMF information
Extra flags Internal AMF information
MAC Address The MAC address of the current node

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1702
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AREA SUMMARY
show atmf area summary
Overview Use this command to display a summary of IPv6 addresses used by AMF, for one or
all of the areas controlled by an AMF controller.
Syntax show atmf area summary [<area-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To show a summary of IPv6 addresses used by AMF, for all of the areas controlled
by controller-1, use the command:
controller-1# show atmf area summary
The following figure shows example output from running this command.
Related
Commands
show atmf area
show atmf area nodes
show atmf area nodes-detail
Parameter Description
<area-name>Displays information for the specified area only.
Table 15: Output from the show atmf area summary command
controller-1#show atmf area summary
ATMF Area Summary Information:
Management Information
Local IPv6 Address : fd00:4154:4d46:1::15
Area Information
Area Name : NZ (Local)
Area ID : 1
Area Master IPv6 Address : -
Area Name : Wellington
Area ID : 2
Area Master IPv6 Address : fd00:4154:4d46:2::149
Area Name : Canterbury
Area ID : 3
Area Master IPv6 Address : fd00:4154:4d46:3::f
Area Name : Auckland
Area ID : 100
Area Master IPv6 Address : fd00:4154:4d46:64::17
Interface : vlink2000
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1703
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AUTHORIZATION
show atmf authorization
Overview Use this command on an AMF master to display the authorization status of other
AMF members and masters on the network.
On an AMF controller this command will show the authorization status of remote
area AMF masters.
Syntax show atmf authorization {current|pending|provisional}
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display all authorized AMF nodes on an AMF controller or AMF master, use the
command:
awplus# show atmf authorization current
To display AMF nodes which are requesting authorization on an AMF controller or
AMF master, use the command:
awplus# show atmf authorization pending
To display AMF nodes which have provisional authorization, use the command:
awplus# show atmf authorization provisional
Output Figure 45-14: Example output from show atmf authorization current
Parameter Description
current Show the status of all authorized nodes.
pending Show the status of unauthorized nodes in the pending queue.
These are nodes that enabled secure mode with atmf
secure-mode but have not yet been authorized with atmf
authorize.
provisional Show the status of provisionally authorized nodes. These are
nodes that have been provisioned with atmf authorize provision.
NZ Authorized Nodes:
Node Name Signer Expires
----------------------------------------------------------------
master_1 master_1 4 Mar 2017
area_1_node_1 master_1 4 Mar 2017
area_1_node_2 master_1 4 Mar 2017
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1704
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AUTHORIZATION
Output Figure 45-15: Example output from show atmf authorization pending
Output Figure 45-16: Example output from show atmf authorization provisional
Table 45-1: Parameters in the output from show atmf authorization current
Parameter Description
Node Name AMF node name of the authorized node.
Signer Name of the AMF master that authorized the node.
Expires Expiry date of the authorization. Authorization expiry time
is set using atmf secure-mode certificate expiry.
Pending Authorizations:
NZ Requests:
Node Name Product Parent Node Interface
------------------------------------------------------------------
area_1_node_3 x230-18GP master_1 port1.2.9
area_1_node_4 x510-52GTX master_1 sa1
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf authorization pending
Parameter Description
Node Name Name of the node that is requesting authorization.
Product Product name.
Parent Node Authorization authority of the requesting node.
Interface Interface that the authorization request came in on.
ATMF Provisional Authorization:
Area - Node Name Start Timeout
or MAC Address Interface Time Minutes
------------------------------------------------------------------
3333.4444.5555 5 Sep 2016 02:35:54 3
1111.2222.3333 5 Sep 2016 02:35:24 60
NZ - blue port1.0.3 5 Sep 2016 02:35:06 60
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1705
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF AUTHORIZATION
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf authorize provision
atmf secure-mode
clear atmf secure-mode certificates
show atmf
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Table 45-3: Parameters in the output from show atmf authorization provisional
Parameter Description
Area - Node Name
or MAC Address MAC address or node name of the node that has been
provisionally authorized.
Interface Interface that the node has been provisioned on.
Start Time Time the node was provisioned.
Timeout Minutes Length of time from Start Time until the provisional
authorization expires.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1706
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP
show atmf backup
Overview This command displays information about AMF backup status for all the nodes in
an AMF network. It can only be run on AMF master and controller nodes.
Syntax show atmf backup [logs|server-status|synchronize [logs]]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To display the AMF backup information, use the command:
node_1# show atmf backup
To display log messages to do with backups, use the command:
node_1# show atmf backup logs
Parameter Description
logs Displays detailed log information.
server-status Displays connectivity diagnostics information for each
configured remote file server.
synchronize Display the file server synchronization status
logs For each remote file server, display the logs for the last
synchronization
Table 45-4: Output from show atmf backup
Node_1# show atmf backup
ScheduledBackup ......Enabled
Schedule............1 per day starting at 03:00
Next Backup Time....01 Oct 2016 03:00
Backup Bandwidth .....Unlimited
Backup Media..........SD (Total 1974.0 MB, Free197.6MB)
Current Action........Starting manual backup
Started...............30 Sep 2016 10:08
CurrentNode...........atmf_testbox1
Backup Redundancy ....Enabled
Local media ........SD (Total 3788.0MB, Free 3679.5MB)
State ..............Active
Node Name Date Time In ATMF On Media Status
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
atmf_testbox1 30 Sep 2016 09:58:59 Yes Yes In Progress
atmf_testbox2 30 Sep 2016 10:01:23 Yes Yes Good
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1707
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP
Example 2 To display the AMF backup synchronization status, use the command:
node_1# show atmf backup synchronize
To display log messages to do with synchronization of backups, use the command:
node_1# show atmf backup synchronize logs
Example 3 To display the AMF backup information with the optional parameter
server-status, use the command:
Node_1# show atmf backup server-status
Table 45-5: Output from show atmf backup logs
Node_1#show atmf backup logs
Backup Redundancy ..... Enabled
Local media ......... SD (Total 3788.0MB, Free 1792.8MB)
State ............... Inactive (Remote file server is not available)
Log File Location: card:/atmf/ATMF/logs/rsync_<node name>.log
Node
Name Log Details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
atmf_testbox
2016/09/30 18:16:51 [9045] receiving file list
2016/09/30 18:16:51 [9047] .d..t.... flash/
2016/09/30 18:16:52 [9047] >f+++++++ flash/a.rel
Table 45-6: Output from show atmf backup synchronize
Node_1#show atmf backup synchronize
ATMF backup synchronization:
* = Active file server
Id Date Time Status
------------------------------------------------------------------
1 30 Sep 2016 22:25:57 Synchronized
* 2 - - Active
Table 45-7: Output from show atmf backup synchronize logs
Node_1#show atmf backup synchronize logs
Id Log Details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 2016/09/30 22:25:54 [8039] receiving file list
2016/09/30 22:25:54 [8039] >f..t.... backup_Box1.info
2016/09/30 22:25:54 [8039] sent 46 bytes received 39 bytes total size 40
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1708
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP
Node1#sh atmf backup server-status
Id Last Check State
-------------------------------------
1 186 s File server ready
2 1 s SSH no route to host
Table 46: Parameter definitions from the show atmf backup command
Parameter Definition
Scheduled
Backup Indicates whether AMF backup scheduling is enabled or disabled.
Schedule Displays the configured backup schedule.
Next Backup Time Displays the date and time of the next scheduled.
Backup Media The current backup medium in use.
This will be one of USB, SD, or NONE.
Utilized and available memory (MB) will be indicated if backup media memory is
present.
Current Action The task that the AMF backup mechanism is currently performing. This will be a
combination of either (Idle, Starting, Doing, Stopping), or (manual, scheduled).
Started The date and time that the currently executing task was initiated in the format DD
MMM YYYY HH:MM
Current Node The name of the node that is currently being backed up.
Backup
Redundancy Whether backup redundancy is enabled or disabled.
Local media The local media to be used for backup redundancy; SD or USB or NONE, and total
and free memory available on the media.
State Whether SD or USB media is installed and available for backup redundancy. May be
Active (if backup redundancy is functional—requires both the local redundant
backup media and a remote server to be configured and available) or Inactive.
Node Name The name of the node that is storing backup data - on its backup media.
Date The data of the last backup in the format DD MMM YYYY.
Time The time of the last backup in the format HH:MM:SS.
In ATMF Whether the node shown is active in the AMF network, (Yes or No).
On Media Whether the node shown has a backup on the backup media (Yes or No).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1709
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Related
Commands
show atmf
atmf network-name
Status The output can contain one of four values:
• “-” meaning that the status file cannot be found or cannot be read.
• “Errors” meaning that there are issues - note that the backup may still be deemed
successful depending on the errors.
• “Stopped” meaning that the backup attempt was manually aborted.
• “Good” meaning that the backup was completed successfully.
• “In Progress” meaning that the backup is currently running on that node.
Log File
Location All backup attempts will generate a result log file in the identified directory based on
the node name. In the above example this would be:
card:/amf/office/logs/rsync_amf_testbox1.log.
Log Details The contents of the backup log file.
server-status Displays connectivity diagnostics information for each configured remove file server.
Table 46: Parameter definitions from the show atmf backup command (cont.)
Parameter Definition
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1710
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP AREA
show atmf backup area
Overview Use this command to display backup status information for the master nodes in
one or more areas.
Note that this command is only available on AMF controllers.
Syntax show atmf backup area [<area-name> [<node-name>]] [logs]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show information about backups for an area, use the command:
controller-1# show atmf backup area
Parameter Description
logs Displays the logs for the last backup of each node.
<area-name>Displays information about nodes in the specified area.
<node-name>Displays information about the specified node.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1711
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP AREA
Related
Commands
atmf backup area-masters enable
show atmf area
show atmf area nodes-detail
switchport atmf-arealink remote-area
Table 47: Output from the show atmf backup area command
controller-1#show atmf backup area
Scheduled Backup ...... Enabled
Schedule ............ 12 per day starting at 14:30
Next Backup Time .... 15 Oct 2016 04:30
Backup Bandwidth ...... Unlimited
Backup Media .......... FILE SERVER 1 (Total 128886.5MB, Free 26234.2MB)
Server Config .........
* 1 .................. Configured (Mounted, Active)
Host .............. 10.37.74.1
Username .......... root
Path .............. /tftpboot/backups_from_controller-1
Port .............. -
2 .................. Configured (Unmounted)
Host .............. 10.37.142.1
Username .......... root
Path .............. -
Port .............. -
Current Action ........ Idle
Started ............. -
Current Node ........ -
Backup Redundancy ..... Enabled
Local media ......... USB (Total 7604.0MB, Free 7544.0MB)
State ............... Active
Area Name Node Name Id Date Time Status
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Wellington camry 1 14 Oct 2016 02:30:22 Good
Canterbury corona 1 14 Oct 2016 02:30:23 Good
Canterbury Avensis 1 14 Oct 2016 02:30:22 Good
Auckland RAV4 1 14 Oct 2016 02:30:23 Good
Southland MR2 1 14 Oct 2016 02:30:24 Good
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1712
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP GUEST
show atmf backup guest
Overview This command displays backup status information of guest nodes in an AMF
network.This command can only be run on a device configured as an AMF Master
and has an AMF guest license.
Syntax show atmf backup guest [<node-name> [<guest-port>]] [logs]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Example On the switch named x930-master, to display information about the AMF backup
guest status, use the command:
x930-master# show atmf backup guest
Output Figure 45-17: Example output from show atmf backup guest
Parameter Description
<node-name> The name of parent guest node
<guest-port> The port number on the parent node
x930-master#sh atmf backup guest
Guest Backup .......... Enabled
Scheduled Backup ...... Disabled
Schedule ............ 1 per day starting at 03:00
Next Backup Time .... 20 Jan 2016 03:00
Backup Bandwidth ...... Unlimited
Backup Media .......... FILE SERVER 2 (Total 655027.5MB,
Free 140191.5MB)
Server Config
1 .................. Configured (Mounted)
Host .............. 11.0.24.1
Username .......... bob
Path .............. guest-project
Port .............. -
* 2 .................. Configured (Mounted, Active)
Host .............. 11.0.24.1
Username .......... bob
Path .............. guest-project-second
Port.................-
Current Action .......Idle
Started ............. -
Current Node ........ -
Backup Redundancy ....Enabled
Local media ......... USB (Total 7376.0MB, Free 7264.1MB)
State ............... Active

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1713
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF BACKUP GUEST
Related
Commands
show atmf backup area
show atmf backup
show atmf links guest
show atmf nodes
show atmf backup guest
atmf backup guests delete
atmf backup guests enable
Parent Node Name Port Name Id Date Time Status
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
x230 port1.0.4 2 19 Jan 2016 22:21:46 Good
1 19 Jan 2016 22:21:46 Good
USB 19 Jan 2016 22:21:46 Good
Table 45-1: Parameters in the output from show atmf backup guest
Parameter Description
Guest Backup The status of the guest node backup process
Scheduled Backup The timing configured for guest backups.
Schedule Displays the configured backup schedule.
Next Backup Time The time the next backup process will be initiated.
Backup Bandwidth The bandwidth limit applied to the backup data flow
measured in kilo Bytes /second. Note that unlimited
means there is no limit set specifically for the backup data
flow.
Backup Media Detail of the memory media used to store the backup files
and the current memory capacity available.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1714
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF CONTAINER
show atmf container
Overview Use this command to display information about the AMF containers created on a
a Virtual AMF Appliance (VAA).
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and_Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Syntax show atmf container [detail] [<container-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Output Figure 45-18: Example output from show atmf container
Figure 45-19: Example output from show atmf container vac-wlg-1
Parameter Description
detail Show detailed information.
<container-name> The name of the AMF container you wish to display
information for.
awplus#show atmf container
ATMF Container Information:
Container Area Bridge State Memory CPU%
------------------------------------------------------------------
vac-wlg-1 wlg br1 running 70.3 MB 1.2
vac-akl-1 akl br2 stopped 0 bytes 0.0
vac-nsn-1 nsn br3 running 53.2 MB 0.7
Current ATMF Container count: 3
awplus#show atmf container vac-wlg-1
ATMF Container Information:
Container Area Bridge State Memory CPU%
------------------------------------------------------------------
vac-wlg-1 wlg br1 running 70.3 MB 1.2
Current ATMF Container count: 1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1715
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF CONTAINER
Figure 45-20: Example output from show atmf container detail vac-wlg-1
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf container
Parameter Description
Container Name of the AMF container.
Area Name of the area the container is in.
Bridge Name of the bridge connecting the container to the physical
network.
State Container state, running or stopped. This is set with the
state command.
Memory The amount of memory the container is using on the VAA
host.
CPU% The percentage of CPU time the container is using on the VAA,
at the time the show command is run.
awplus#show atmf container detail vac-wlg-1
ATMF Container Information:
Name: vac-wlg-1
State: RUNNING
PID: 980
IP: 172.31.0.1
IP: 192.168.0.2
IP: fd00:4154:4d46:3c::1
CPU use: 3.95 seconds
Memory use: 67.07 MiB
Memory use: 0 bytes
Link: vethP31UFA
TX bytes: 166.01 KiB
RX bytes: 141.44 KiB
Total bytes: 307.45 KiB
Link: vethYCT7BB
TX bytes: 674.27 KiB
RX bytes: 698.27 KiB
Total bytes: 1.34 MiB
Table 45-3: Parameters in the output from show atmf container detail
Parameter Description
Name Name of the AMF container.
State Container state, RUNNING or STOPPED. This is set with the
state command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1716
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF CONTAINER
Related
Commands
area-link
atmf area
atmf area password
atmf container
atmf container login
bridge-group
description (amf container)
state
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
PID Internal container id.
IP This lists the IP addresses used by the container. These include
the eth1 IP address and the AMF management IP address.
CPU use The CPU usage of the container since it was enabled.
Memory use Container memory usage.
Link Each container has two links:
1 An AMF area-link, this connects the container to the AMF
controller and uses virtual interface eth0 on the AMF
container.
2 A bridged L2 network link, this connects the container to
the outside world and uses the virtual interface eth1 on the
AMF container.
See the AMF Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide for
more information on these links.
TX/RX bytes Bytes sent and received on a link.
Total bytes Total bytes transferred on a link.
Table 45-3: Parameters in the output from show atmf container detail (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1717
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF DETAIL
show atmf detail
Overview This command displays details about an AMF node. It can only be run on AMF
master and controller nodes.
Syntax show atmf detail
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To display the AMF node1 information in detail, use the command:
controller-1# show atmf detail
A typical output screen from this command is shown below:
Parameter Description
detail Displays output in greater depth.
atmf-1#show atmf detail
ATMF Detail Information:
Network Name : Test_network
Network Mtu : 1300
Node Name : controller-1
Node Address : controller-1.atmf
Node ID : 342
Node Depth : 0
Domain State : BackupDomainController
Recovery State : None
Log Verbose Setting : Verbose
Management VLAN
VLAN ID : 4000
Management Subnet : 172.31.0.0
Management IP Address : 172.31.1.86
Management Mask : 255.255.128.0
Management IPv6 Address : fd00:4154:4d46:1::156
Management IPv6 Prefix Length : 64
Domain VLAN
VLAN ID : 4091
Domain Subnet : 172.31.128.0
Domain IP Address : 172.31.129.86
Domain Mask : 255.255.128.0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1718
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF DETAIL
Table 46: Parameter definitions from the show atmf detail command
Parameter Definition
Network MTU The network MTU for the ATMF network.
Network Name The AMF network that a particular node belongs to.
Node Name The name assigned to a particular node.
Node Address An Address used to access a remotely located node. This is simply the Node Name
plus the dotted suffix atmf (.atmf).
Node ID A Unique identifier assigned to a Node on an AMF network.
Node Depth The number of nodes in path from this node to level of the AMF root node. It can be
thought of as the vertical depth of the AMF network from a particular node to the
zero level of the AMF root node.
Domain State The state of Node in a Domain in AMF network as Controller/Backup.
Recovery State The AMF node recovery status. Indicates whether a node recovery is in progress on
this device - Auto, Manual, or None.
Management VLAN The VLAN created for traffic between Nodes of different domain (up/down links).
• VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4092 is configured as the Management VLAN.
• Management Subnet - Network prefix for the subnet.
• Management IP Address - The IP address allocated for this traffic.
• Management Mask - The subnet mask used to create a subnet for this traffic
(255.255.128.0).
Domain VLAN The VLAN assigned for traffic between Nodes of same domain (crosslink).
• VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4091 is configured as the domain VLAN.
• Domain Subnet. The subnet address used for this traffic.
• Domain IP Address. The IP address allocated for this traffic.
• Domain Mask. The subnet mask used to create a subnet for this traffic
(255.255.128.0).
Node Depth The number of nodes in the path from this node to the Core domain.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1719
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GROUP
show atmf group
Overview This command can be used to display the group membership within to a particular
AMF node. It can also be used with the working-set command to display group
membership within a working set.
Each node in the AMF is automatically added to the group that is appropriate to its
hardware architecture, e.g. x510, x230. Nodes that are configured as masters are
automatically assigned to the master group.
You can create arbitrary groups of AMF members based on your own selection
criteria. You can then assign commands collectively to any of these groups.
Syntax show atmf group [user-defined|automatic]
Default All groups are displayed
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To display group membership of node2, use the following command:
node2# show atmf group
A typical output screen from this command is shown below:
This screen shows that node2 contains the groups master and x510. Note that
although the node also contains the implicit groups, these do not appear in the
show output.
Example 2 The following commands (entered on node2) will display all the automatic groups
within the working set containing node1 and all nodes that have been pre-defined
to contain the sysadmin group:
First define the working-set:
node1# #atmf working-set node1 group sysadmin
A typical output screen from this command is shown below:
Parameter Description
user-defined User-defined-group information display.
automatic Automatic group information display.
ATMF group information
master, x510
node2#
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1720
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GROUP
This confirms that the six nodes (node1 to node6) are now members of the
working-set and that these nodes reside within the AMF-NETWORK.
Note that to run this command, you must have previously entered the command
atmf working-set on page 1645. This can be seen from the network level prompt,
which in this case is AMF_NETWORK[6]#.
ATMF group information
master, poe, x8100
===============================================
node1, node2, node3, node4, node5, node6:
===============================================
ATMF group information
sysadmin, x8100
AMF_NETWORK[6]#
Table 47: Sample output from the show atmf group command for a working
set.
AMF_NETWORK[6]#show atmf group
===============================
node3, node4, node5, node6:
===============================
ATMF group information
edge_switches, x510
Table 48: Parameter definitions from the show atmf group command for a
working set
Parameter Definition
ATMF group information Displays a list of nodes and the groups that they
belong to, for example:
• master - Shows a common group name for Nodes
configured as AMF masters.
• Hardware Arch - Shows a group for all Nodes
sharing a common Hardware architecture, e.g.
x8100, x230, for example.
• User-defined - Arbitrary groups created by the
user for AMF nodes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1721
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GROUP MEMBERS
show atmf group members
Overview This command will display all group memberships within an AMF working-set.
Each node in the AMF working set is automatically added to automatic groups
which are defined by hardware architecture, e.g. x510, x230. Nodes that are
configured as masters are automatically assigned to the master group. Users can
define arbitrary groupings of AMF members based on their own criteria, which can
be used to select groups of nodes.
Syntax show atmf group members [user-defined|automatic]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display group membership of all nodes in a working-set, use the command:
ATMF_NETWORK[9]# show atmf group members
Parameter Description
user-defined User defined group membership display.
automatic Automatic group membership display.
Table 49: Sample output from the show atmf group members command
ATMF Group membership
Automatic Total
Groups Members Members
----------------------------------------------------------------
master 1 Building_1
poe 1 HW_Team1
x510 3 SW_Team1 SW_Team2 SW_Team3
x930 1 HW_Team1
x8100 2 Building_1 Building_2
ATMF Group membership
User-defined Total
Groups Members Members
----------------------------------------------------------------
marketing 1 Bld1_Floor_1
software 3 SW_Team1 SW_Team2 SW_Team3
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1722
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GROUP MEMBERS
Related
Commands
show atmf group
show atmf
atmf group (membership)
Table 50: Parameter definitions from the show atmf group members command
Parameter Definition
Automatic Groups Lists the Automatic Groups and their nodal
composition. The sample output shows AMF nodes
based on the same Hardware type or belonging to
the same Master group.
User-defined Groups Shows the grouping of AMF nodes in user defined
groups.
Total Members Shows the total number of members in each group.
Members Shows the list of AMF nodes in each group.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1723
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GUESTS
show atmf guests
Overview This command is available on any AMF master or controller in the network. It
displays a summary of the AMF guest nodes that exist in the AMF network,
including device type, parent node, and IP address.
Syntax show atmf guests
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command to display all guest nodes in a network. If you want to see only
the guests attached to a single node, use the show atmf links guest command,
which shows information about the guest nodes and also about their link to their
parent node.
Example To display the AMF guest output, use the command:
awplus# show atmf guests
Output Figure 45-21: Example output from the show atmf guests command
master#show atmf guests
Guest Information:
Device Device Parent Guest IP/IPv6
Name Type Node Port Address
---------------------------------------------------------------------
node1-2.0.1 x600-24Ts node1 2.0.1 192.168.2.10
wireless-zone1 AT-TQ4600 node2 1.0.1 192.168.1.10
wireless-zone2 AT-TQ4600 node2 1.0.2 192.168.1.12
Current ATMF guest node count 3
Table 51: Parameters shown in the output of the show atmf guests command
Parameter Description
Device Name The name that is discovered from the device, or failing
that, a name that is auto-assigned by AMF. The
auto-assigned name consists of:
<parent node name>-<attached port number>
You can change this by configuring a description on the
port.
Device Type The product name of the guest node, which is discovered
from the device. If no device type can be discovered, this
shows the name of the AMF guest-class that has been
assigned to the guest node by the atmf guest-class
command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1724
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GUESTS
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
switchport atmf-guestlink
show atmf backup guest
show atmf links guest
Parent Node The name of the AMF node that directly connects to the
guest node.
Guest Port The port on the parent node that directly connects to the
guest node.
IP/IPv6 Address The address discovered from the node, or statically
configured on the parent node's attached port.
Table 51: Parameters shown in the output of the show atmf guests command
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1725
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GUESTS DETAIL
show atmf guests detail
Overview This command is available on any AMF master in the network. It displays details
about the AMF guest nodes that exist in the AMF network, such as device type, IP
address, MAC address etc.
Syntax show atmf guests detail [<node-name>] [<guest-port>]
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage If you want to see only the guests attached to a single node, you can use either:
• this command and specify the node name, or
•show atmf links guest detail, which shows information about the guest
nodes and also about their link to their parent node.
Note that the parameters that are displayed depend on the guest node’s model.
Example To display the AMF guest output, use the command:
awplus# show atmf guests detail
Output Figure 45-22: Example output from show atmf guests detail
Parameter Description
<node-name> The name of the guest node’s parent.
<guest-port>The port name on the parent node.
master#show atmf guests detail
ATMF Guest Node Information:
Node Name : master
Port Name : port1.0.9
Ifindex : 5009
Guest Description : red-1.0.9
Device Type : x600-24Ts
Backup Supported : No
MAC Address : 0000.cd38.0c4d
IP Address : 192.168.1.5
IPv6 Address : Not Set
HTTP Port : 0
Firmware Version : 5.4.2-0.1

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1726
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF GUESTS DETAIL
Node Name : node1
Port Name : port1.0.13
Ifindex : 5013
Guest Description : node1-1.0.13
Device Type : AT-TQ4600
Backup Supported : Yes
MAC Address : eccd.6df2.daa0
IP Address : 192.168.5.6
IPv6 Address : Not Set
HTTP Port : 80
Firmware Version : 3.1.0 B01
Table 52: Parameters in the output from show atmf guests detail.
Parameter Description
Node Name The name of the parent node, which is the AMF node that
directly connects to the guest node.
Port Name The port on the parent node that connects to the guest.
IfIndex An internal index number that maps to the port number
on the parent node.
Guest Description A description that is discovered from the device, or failing
that, auto-assigned by AMF. The auto-assigned name
consists of:
<parent node name>-<attached port number>.
You can change this by configuring a description on the
port.
Device Type The product name of the guest node, which is discovered
from the device. If no device type can be discovered, this
shows the name of the AMF guest-class that has been
assigned to the guest node by the atmf guest-class
command.
Username The user name configured on the guest node.
Backup Supported Whether the guest node supports AMF backup
functionality.
MAC Address The MAC address of the guest node.
IP Address The IP address of the guest node.
IPv6 Address The IPv6 address of the guest node.
Firmware Version The version of the firmware operating on the guest node.
HTTP port The HTTP port as specified with the http-enable
command when defining a guest class. You can set this if
the guest node provides an HTTP user interface on a
non-standard port (any port other than port 80).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1728
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS
show atmf links
Overview This command displays information about AMF links on a switch. The display
output contains link status state information.
Syntax show atmf links [brief]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage The show atmf links and show atmf links brief commands both produce a table
of summarized link information. For a more detailed view use the show atmf links
detail command.
This command does not show links that are configured on provisioned ports.
Example To display a brief summary of the AMF links, use the following command:
node-1# show atmf links brief
Figure 45-23: Example output from show atmf links brief
Parameter Description
brief A brief summary of AMF links, their configuration and status.
Example-core# show atmf links
ATMF Link Brief Information:
Local Link Link ATMF Adjacent Adjacent Link
Port Type Status State Node Ifindex State
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.0.10 Crosslink Down Init *crosslink1 - Blocking
1.0.14 Crosslink Down Init *crosslink2 - Blocking
1.0.1 Downlink Down Init - - Blocking
1.0.2 Downlink Up Full Node2 5001 Forwarding
1.0.8 Downlink Up Full downlink1 5001 Forwarding
* = Provisioned.
Table 45-1: Parameter in the output from show atmf links brief
Parameter Definition
Local Port Shows the local port on the selected node.
Link Type Shows link type as Uplink or Downlink (parent and child) or Cross-link (nodes in
same domain).
Link Status Shows the link status of the local port on the node as either Up or Down.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1729
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Related
Commands
no debug all
clear atmf links statistics
show atmf
show atmf links detail
show atmf links guest
show atmf links guest detail
show atmf links statistics
show atmf nodes
ATMF State Shows AMF state of the local port:
• Init - Link is down.
• Hold - Link transitioned to up state, but waiting for hold period to ensure link
is stable.
• Incompatible - Neighbor rejected the link because of inconsistency in AMF
configurations.
• OneWay - Link is up and has waited the hold down period and now
attempting to link to another unit in another domain.
• OneWaySim - Device is running in secure mode and link is up but waiting for
authorization from an AMF master.
• Full - Link hello packets are sent and received from its neighbor with its own
node id.
• Shutdown - Link has been shut down by user configuration.
Adjacent Node Shows the Adjacent AMF Node to the one being configured.
Adjacent IF Index Shows the IF index for the Adjacent AMF Node connected to the node being
configured.
Link State Shows the state of the AMF link. Valid states are either Forwarding or Blocking.
Table 45-1: Parameter in the output from show atmf links brief (cont.)
Parameter Definition

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1730
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
show atmf links detail
Overview This command displays detailed information on all the links configured in the AMF
network. It can only be run on AMF master and controller nodes.
Syntax show atmf links detail
Mode User Exec
Usage For summarized link information see the show atmf links command.
This command does not show links that are configured on provisioned ports.
Example To display the AMF link details use this command:
device1# show atmf links detail
The output from this command will display all the internal data held for AMF links.
The following example gives details of the links that are summarized in the
example in show atmf links.
Parameter Description
detail Detailed AMF links information.
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links detail command
device1# show atmf links detail
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Crosslink Ports Information
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port : sa1
Ifindex : 4501
Port Status : Down
Port State : Init
Last event :
Port BPDU Receive Count : 0
Port : po10
Ifindex : 4610
Port Status : Up
Port State : Full
Last event : AdjNodeLSEPresent
Port BPDU Receive Count : 140
Adjacent Node Name : Building-B
Adjacent Ifindex : 4610
Adjacent MAC : eccd.6dd1.64d0
Port Last Message Response : 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1731
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Port : po30
Ifindex : 4630
Port Status : Up
Port State : Full
Last event : AdjNodeLSEPresent
Port BPDU Receive Count : 132
Adjacent Node Name : Building-A
Adjacent Ifindex : 4630
Adjacent MAC : eccd.6daa.c861
Port Last Message Response : 0
Link State Entries:
Crosslink Ports Blocking : False
Node.Ifindex : Building-A.4630 - Example-core.4630
Transaction ID : 2 - 2
MAC Address : eccd.6daa.c861 - 0000.cd37.054b
Link State : Full - Full
Node.Ifindex : Building-B.4610 - Example-core.4610
Transaction ID : 2 - 2
MAC Address : eccd.6dd1.64d0 - 0000.cd37.054b
Link State : Full - Full
Domain Nodes Tree:
Node : Building-A
Links on Node : 1
Link 0 : Building-A.4630 - Example-core.4630
Forwarding State : Forwarding
Node : Building-B
Links on Node : 1
Link 0 : Building-B.4610 - Example-core.4610
Forwarding State : Forwarding
Node : Example-core
Links on Node : 2
Link 0 : Building-A.4630 - Example-core.4630
Forwarding State : Forwarding
Link 1 : Building-B.4610 - Example-core.4610
Forwarding State : Forwarding
Crosslink Transaction Entries:
Node : Building-B
Transaction ID : 2
Uplink Transaction ID : 6
Node : Building-A
Transaction ID : 2
Uplink Transaction ID : 6
Uplink Information:
Waiting for Sync : 0
Transaction ID : 6
Number of Links : 0
Number of Local Uplinks : 0
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links detail command (cont.)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1732
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Originating Node : Building-A
Domain : -'s domain
Node : Building-A
Ifindex : 0
Node Depth : 0
Transaction ID : 6
Flags : 32
Domain Controller : -
Domain Controller MAC : 0000.0000.0000
Originating Node : Building-B
Domain : -'s domain
Node : Building-B
Ifindex : 0
Node Depth : 0
Transaction ID : 6
Flags : 32
Domain Controller : -
Domain Controller MAC : 0000.0000.0000
Downlink Domain Information:
Domain : Dept-A's domain
Domain Controller : Dept-A
Domain Controller MAC : eccd.6d20.c1d9
Number of Links : 2
Number of Links Up : 2
Number of Links on This Node : 2
Links are Blocked : 0
Node Transaction List
Node : Building-B
Transaction ID : 8
Node : Building-A
Transaction ID : 8
Domain List
Domain : Dept-A's domain
Node : Example-core
Ifindex : 4621
Transaction ID : 8
Flags : 1
Domain : Dept-A's domain
Node : Example-core
Ifindex : 4622
Transaction ID : 8
Flags : 1
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links detail command (cont.)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1733
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Domain : Dorm-D's domain
Domain Controller : Dorm-D
Domain Controller MAC : 0000.cd37.082c
Number of Links : 2
Number of Links Up : 2
Number of Links on This Node : 2
Links are Blocked : 0
Node Transaction List
Node : Building-B
Transaction ID : 20
Node : Building-A
Transaction ID : 20
Domain List
Domain : Dorm-D's domain
Node : Building-A
Ifindex : 0
Transaction ID : 20
Flags : 32
Domain : Dorm-D's domain
Node : Building-B
Ifindex : 0
Transaction ID : 20
Flags : 32
Domain : Dorm-D's domain
Node : Example-core
Ifindex : 4510
Transaction ID : 20
Flags : 1
Domain : Dorm-D's domain
Node : Example-core
Ifindex : 4520
Transaction ID : 20
Flags : 1
Domain : Example-edge's domain
Domain Controller : Example-edge
Domain Controller MAC : 001a.eb93.7aa6
Number of Links : 1
Number of Links Up : 1
Number of Links on This Node : 0
Links are Blocked : 0
Node Transaction List
Node : Building-B
Transaction ID : 9
Node : Building-A
Transaction ID : 9
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links detail command (cont.)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1734
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Domain List
Domain : Example-edge's domain
Node : Building-A
Ifindex : 0
Transaction ID : 9
Flags : 32
Domain : Example-edge's domain
Node : Building-B
Ifindex : 5027
Transaction ID : 9
Flags : 1
----------------------------------------------------------------
Up/Downlink Ports Information
----------------------------------------------------------------
Port : sa10
Ifindex : 4510
Port Status : Up
Port State : Full
Last event : LinkComplete
Adjacent Node : Dorm-A
Adjacent Internal ID : 211
Adjacent Ifindex : 4510
Adjacent Board ID : 387
Adjacent MAC : eccd.6ddf.6cdf
Adjacent Domain Controller : Dorm-D
Adjacent Domain Controller MAC : 0000.cd37.082c
Port Forwarding State : Forwarding
Port BPDU Receive Count : 95
Port Sequence Number : 11
Port Adjacent Sequence Number : 7
Port Last Message Response : 0
Port : po21
Ifindex : 4621
Port Status : Up
Port State : Full
Last event : LinkComplete
Adjacent Node : Dept-A
Adjacent Internal ID : 29
Adjacent Ifindex : 4621
Adjacent Board ID : 340
Adjacent MAC : eccd.6d20.c1d9
Adjacent Domain Controller : Dept-A
Adjacent Domain Controller MAC : eccd.6d20.c1d9
Port Forwarding State : Forwarding
Port BPDU Receive Count : 96
Port Sequence Number : 8
Port Adjacent Sequence Number : 9
Port Last Message Response : 0
Special Link Present : FALSE
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links detail command (cont.)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1735
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Table 47: Parameter definitions from the show atmf links detail command output
Parameter Definition
Crosslink Ports
Information Show details of all Crosslink ports on this Node:
• Port - Name of the Port or static aggregation (sa<*>).
•Ifindex - Interface index for the crosslink port.
• VR ID - Virtual router id for the crosslink port.
• Port Status - Status of the local port on the Node as UP or DOWN.
• Port State - AMF State of the local port.
– Init - Link is down.
– Hold - Link transitioned to up state, but waiting for hold period to ensure
link is stable.
– Incompatible - Neighbor rejected the link because of inconsistency in
AMF configurations.
– OneWay - Link is up and has waited the hold down period and now
attempting to link to
– another unit in another domain
– Full - Link hello packets are sent and received from its neighbor with its
own node id.
– Shutdown - Link has been shut down by user configuration.
Port BPDU Receive Count - The number of AMF protocol PDU's received.
• Adjacent Node Name - The name of the adjacent node connected to this
node.
• Adjacent Ifindex - Adjacent AMF Node connected to this Node.
• Adjacent VR ID - Virtual router id of the adjacent node in the domain.
• Adjacent MAC - MAC address of the adjacent node in the domain.
• Port Last Message Response - Response from the remote neighbor to our
AMF last hello packet.
Link State Entries Shows all the link state database entries:
• Node.Ifindex - Shows adjacent Node names and Interface index.
• Transaction ID - Shows transaction id of the current crosslink transaction.
• MAC Address - Shows adjacent Node MAC addresses.
• Link State - Shows AMF states of adjacent nodes on the link.
Domain Nodes Tree Shows all the nodes in the domain:
• Node - Name of the node in the domain.
• Links on Node - Number of crosslinks on a vertex/node.
• Link no - Shows adjacent Node names and Interface index.
• Forwarding State - Shows state of AMF link Forwarding/Blocking.
Crosslink
Transaction Entries Shows all the transaction entries:
• Node - Name of the AMF node.
• Transaction ID - transaction id of the node.
• Uplink Transaction ID - transaction id of the remote node.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1736
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
Uplink Information Show all uplink entries.
• Waiting for Sync - Flag if uplinks are currently waiting for synchronization.
• Transaction ID - Shows transaction id of the local node.
• Number of Links - Number of up downlinks in the domain.
• Number of Local Uplinks - Number of uplinks on this node to the parent
domain.
• Originating Node - Node originating the uplink information.
• Domain - Name of the parent uplink domain.
• Node - Name of the node in the parent domain, that is connected to the
current domain.
• Ifindex - Interface index of the parent node's link to the current domain.
• VR ID - Virtual router id of the parent node’s link to the current domain.
• Transaction ID - Transaction identifier for the neighbor in crosslink.
• Flags - Used in domain messages to exchange the state:
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_DOWN = 0
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_UP = 1
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_BLOCK = 2
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_NOT_PRESENT = 4
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_NO_NODE = 8
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_NOT_ACTIVE_PARENT = 16
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_NOT_LINKS = 32
ATMF_DOMAIN_FLAG_NO_CONFIG = 64
• Domain Controller - Domain Controller in the uplink domain
• Domain Controller MAC - MAC address of Domain Controller in uplink
domain
Downlink Domain
Information Shows all the downlink entries:
• Domain - Name of the downlink domain.
• Domain Controller - Controller of the downlink domain.
• Domain Controller MAC - MAC address of the domain controller.
• Number of Links - Total number of links to this domain from the Node.
• Number of Links Up - Total number of links that are in UP state.
• Number of Links on This Node - Number of links terminating on this node.
• Links are Blocked - 0 links are not blocked to the domain. 1 All links are
blocked to the domain.
Table 47: Parameter definitions from the show atmf links detail command output (cont.)
Parameter Definition
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1737
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS DETAIL
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Node Transaction
List List of transactions from this downlink domain node.
• Node - 0 links are not blocked to the domain. 1 All links are blocked to the
domain.
• Transaction ID - Transaction id for this node.
• Domain List: Shows list of nodes in the current domain and their links to the
downlink domain.:
• Domain - Domain name of the downlink node.
• Node - Name of the node in the current domain.
• Ifindex - Interface index for the link from the node to the downlink domain.
• Transaction ID - Transaction id of the node in the current domain.
• Flags - As mentioned above.
Up/Downlink Ports
Information Shows all the configured up and down link ports on this node:
• Port - Name of the local port.
•Ifindex - Interface index of the local port.
• VR ID - Virtual router id for the local port.
• Port Status - Shows status of the local port on the Node as UP/DOWN.
• Port State - AMF state of the local port.
• Adjacent Node - nodename of the adjacent node.
• Adjacent Internal ID - Unique node identifier of the remote node.
• Adjacent Ifindex - Interface index for the port of adjacent AMF node.
• Adjacent Board ID - Product identifier for the adjacent node.
• Adjacent VR ID - Virtual router id for the port on adjacent AMF node.
• Adjacent MAC - MAC address for the port on adjacent AMF node.
• Adjacent Domain Controller - nodename of the Domain controller for
Adjacent AMF node.
• Adjacent Domain Controller MAC - MAC address of the Domain controller for
Adjacent AMF node.
• Port Forwarding State - Local port forwarding state Forwarding or Blocking.
• Port BPDU Receive Count - count of AMF protocol PDU's received.
• Port Sequence Number - hello sequence number, incremented every time
the data in the hello packet changes.
• Port Adjacent Sequence Number - remote ends sequence number used to
check if we need to process this packet or just note it arrived.
• Port Last Message Response - response from the remote neighbor to our last
hello packet.
Table 47: Parameter definitions from the show atmf links detail command output (cont.)
Parameter Definition

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1739
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST
show atmf links guest
Overview This command displays information about guest nodes visible to an AMF device.
Syntax show atmf links guest [interface <interface-range>]
Default With no parameters specified this command will display its standard output for all
ports with guest nodes connected.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command to display the guest nodes connected to a single parent node.
If you want to see a list of all the guests in the AMF network, use show atmf guests.
Example 1 To display information about AMF guests that are connectible from node1, use the
command:
node1# show atmf links guest
Output Figure 45-24: Example output from show atmf links guest
Parameter Description
interface
<interface-range>Select a specific range of ports to display information about
guest nodes.
node1#sh atmf links guest
Guest Link Information:
DC = Discovery configuration
S = static D = dynamic
Local Guest Model MAC IP / IPv6
Port Class Type DC Address Address
---------------------------------------------------------------
1.0.1 - other D 0013.1a1e.4589 192.168.1.2
1.0.2 aastra-phone other D 0008.5d10.7635 192.168.1.3
1.0.3 cisco-phone2 other S - 192.168.2.1
1.0.4 panasonic... other D 0800.239e.f1fe 192.168.1.5
Table 45-1: Parameters in the output from show atmf links guest
Parameter Description
Local Port The port on the parent node that connects to the guest.
Guest Class The name of the ATMF guest-class that has been assigned
to the guest node by the atmf guest-class command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1740
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
discovery
http-enable
username
modeltype
switchport atmf-guestlink
show atmf backup guest
Model Type The model type of the guest node, as entered by the
modeltype command. Can be one of the following:
• alliedware
•aw+
•tq
•other
DC The discovery method as applied by the discovery
command. This can be either dynamic (D) or static (S).
MAC Address The MAC address of the guest node.
IP / IPv6 Address The IP address of the guest node.
Table 45-1: Parameters in the output from show atmf links guest (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1741
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST DETAIL
show atmf links guest detail
Overview This command displays detailed information about guest nodes visible to an AMF
device.
Syntax show atmf links guest detail [interface <interface-range>]
Default Display details for all ports with guest nodes connected.
Mode User Exec/Privileged Exec
Usage Use this command to display the guest nodes connected to a single parent node.
If you want to see a list of all the guests in the AMF network, use show atmf guests
detail.
Note that the parameters that are displayed depend on the guest node’s model
and state.
Example To display detailed information about AMF guests, use the command:
node1# show atmf links guest detail
Parameter Description
interface
<interface-range>Select a specific range of ports to display information about
guest nodes.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1742
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST DETAIL
Output Figure 45-25: Example output from show atmf links guest detail
node1#show atmf links guest detail
Detailed Guest Link Information:
Interface : port1.0.13
Link State : Down
Class Name : test
Model Type : Other
Discovery Method : Static
IP Address : 192.168.1.13
Node State : Down
Interface : port1.0.17
Link State : Full
Class Name : access
Model Type : TQ
Discovery Method : Dynamic
IP Address : 192.168.5.8
Username : manager
Node State : Full
Backup Supported : Yes
MAC address : 001a.ebad.ce60
Device Type : AT-TQ3400
Description : node1-1.0.17
Firmware Version : 3.2.1 A02
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf links guest detail
Parameter Description
Interface The port on the parent node that connects to the guest.
Link State The state of the link to the guest node; one of:
• Down: The physical link is down.
• Up: The physical link has come up, but it is still during a
timeout period that is enforced to allow other links to
come up.
• Learn: The timeout period described above has
elapsed, and the link is now learning information from
the AMF guest node. You can see what information it is
learning from the “Node State” field below.
• Full: The node connected by this link has joined the
AMF network.
• Fail: The port is physically up but something has
prevented the guest node from joining the AMF
network.
Class Name The name of the ATMF guest-class that has been assigned
to the guest node by the atmf guest-class command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1743
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST DETAIL
Model Type The model type of the guest node, as entered by the
modeltype command. Can be one of the following:
• alliedware
•aw+
•tq
•other
Discovery Method The discovery method as applied by the discovery
command. This can be either dynamic or static.
IP Address The IP address of the guest node.
Username The user name configured on the guest node.
Node state The state of the guest node; one of:
• Down: The initial state when a link to a guest node is
first configured. This is also the state if the physical link
goes down.
• Getting IP: The AMF device is in the process of retrieving
the IP address of the guest node.
• Getting Mac: The AMF device is in the process of
retrieving the MAC address of the guest node.
• Getting Info: The AMF device is in the process of
retrieving any other available information from the
guest (firmware version etc). The information available
depends on what device the guest node is.
•Full: The AMF device has retrieved all necessary
information and the guest node has joined the AMF
network. Once this state is reached, the Link State also
changes to “Full”.
• Failure: The physical link is up but the AMF member has
failed to retrieve enough information to allow the guest
node to join the AMF network.
Backup Supported Whether the guest node supports AMF backup
functionality.
MAC Address The MAC address of the guest node.
Device Type Model information for the guest node. This field shows the
model information that AMF retrieved from the guest
node. In contrast, the Model Type shows what a user
entered as the type of device they intended this guest
node to be.
Description By default, this is a concatenation of the guest node’s
parent node and the port to which it is attached. You can
change it by configuring a description on the port.
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf links guest detail (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1744
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS GUEST DETAIL
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
discovery
http-enable
username
modeltype
switchport atmf-guestlink
show atmf backup guest
Serial Number The serial number of the guest node.
Firmware Name The name of the firmware operating on the guest node.
Firmware Version The version of the firmware operating on the guest node.
HTTP port The HTTP port as specified with the http-enable
command when defining a guest class. You can set this if
the guest node provides an HTTP user interface on a
non-standard port (any port other than port 80).
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf links guest detail (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1745
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS STATISTICS
show atmf links statistics
Overview This command displays details of the AMF links configured on the device and also
displays statistics about the AMF packet exchanges between the devices.
It is also possible to display the AMF link configuration and packet exchange
statistics for a specified interface.
This command can only be run on AMF master and controller nodes
Syntax show atmf links statistics [interface [<port_number>]]
Mode User Exec
Example 1 To display AMF link statistics for the whole device, use the command:
device1# show atmf links statistics
Parameter Description
interface Specifies that the command applies to a specific interface
(port) or range of ports. Where both the interface and port
number are unspecified, full statistics (not just those relating to
ports will be displayed.
<port_number> Enter the port number for which statistics are required. A port
range, a static channel or LACP link can also be specified.
Where no port number is specified, statistics will be displayed
for all ports on the device.
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links statistics command
ATMF Statistics:
Receive Transmit
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Arealink Hello 318 327
Crosslink Hello 164 167
Crosslink Hello Domain 89 92
Crosslink Hello Uplink 86 88
Hello Link 0 0
Hello Neighbor 628 630
Hello Stack 0 0
Hello Gateway 1257 1257
Database Description 28 28
Database Request 8 6
Database Update 66 162
Database Update Bitmap 0 29
Database Acknowledge 144 51

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1746
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS STATISTICS
Example 2 To display the AMF links statistics on interface port1.0.5, use the command:
device1# show atmf links statistics interface
port1.0.5
Transmit Fails 0 1
Discards 0 0
Total ATMF Packets 2788 2837
ATMF Database Statistics:
Database Entries 18
Database Full Ages 0
ATMF Virtual Link Statistics:
Virtual Receive Transmit
link Receive Dropped Transmit Dropped
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
vlink2000 393 0 417 0
ATMF Packet Discards:
Type0 0 : Gateway hello msg received from unexpected neighbor
Type1 0 : Stack hello msg received from unexpected neighbor
Type2 0 : Discard TX update bitmap packet - bad checksum
Type3 0 : Discard TX update packet - neighbor not in correct state
Type4 0 : Discard update packet - bad checksum or type
Type5 0 : Discard update packet - neighbor not in correct state
Type6 0 : Discard update bitmap packet - bad checksum or type
Type7 0 : Incarnation is not possible with the data received
Type8 0 : Discard crosslink hello received - not correct state
Type9 0 : Discard crosslink domain hello received on non crosslink
Type10 0 : Discard crosslink domain hello - not in correct state
Type11 0 : Crosslink uplink hello received on non crosslink port
Type12 0 : Discard crosslink uplink hello - not in correct state
Type13 0 : Wrong network-name for this ATMF
Type14 0 : Packet received on port is too long
Type15 0 : Bad protocol version, received on port
Type16 0 : Bad packet checksum calculation
Type17 0 : Bad authentication type
Type18 0 : Bad simple password
Type19 0 : Unsupported authentication type
Type20 0 : Discard packet - unknown neighbor
Type21 0 : Discard packet - port is shutdown
Type22 0 : Non broadcast hello msg received from unexpected neighbor
Type23 0 : Arealink hello msg received on non arealink port
Type24 0 : Discard arealink hello packet - not in correct state
Type25 0 : Discard arealink hello packet - failed basic processing
Type26 0 : Discard unicast packet - MAC address does not match node
Type27 0 : AMF Master license node limit exceeded
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf links statistics command (cont.)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1747
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF LINKS STATISTICS
Figure 45-26: Sample output from the show atmf links statistics command for
interface 1.0.5
Figure 45-27: Parameter definitions from the show atmf links statistics
command output
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Related
Commands
no debug all
clear atmf links statistics
show atmf
device1# show atmf links statistics interface port1.0.5
ATMF Port Statistics:
Transmit Receive
port1.0.5 Crosslink Hello 231 232
port1.0.5 Crosslink Hello Domain 116 116
port1.0.5 Crosslink Hello Uplink 116 115
port1.0.5 Hello Link 0 0
port1.0.5 Arealink Hello 0 0
Parameter Definition
Receive Shows a count of AMF protocol packets received per message type.
Transmit Shows the number of AMF protocol packets transmitted per message type.
Database Entries Shows the number of AMF elements existing in the distributed database.
Database Full Ages Shows the number of times the entries aged in the database.
ATMF Packet
Discards Shows the number of discarded packets of each type.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1748
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF NODES
show atmf nodes
Overview This command displays nodes currently configured within the AMF network.
Note that the output also tells you whether or not node map exchange is active.
Node map exchange improves the tracking of nodes joining and leaving an AMF
network. This improves the efficiency of AMF networks. Node map exchange is
only available if every node in your AMF network is running version 5.4.6-2.1 or
later. We recommend running the latest version on all nodes in your network, so
you receive the advantages of node map exchange and other improvements.
Syntax show atmf nodes [guest|all]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage You can use this command to display one of three sets of nodes:
• all nodes except guest nodes, by specifying show atmf nodes
• all nodes including guest nodes, by specifying show atmf nodes all
• only guest nodes, by specifying show atmf nodes guest
Examples To display AMF information for all nodes except guest nodes, use the command:
node1# show atmf nodes
Parameter Description
guest Display only guest nodes in the AMF network.
all Display all nodes in the AMF network, including guest nodes.
Table 45-1: Sample output from show atmf nodes
node1#show atmf nodes guest
Node Information:
* = Local device
SC = Switch Configuration:
C = Chassis S = Stackable N = Standalone
Node Device ATMF Parent Node
Name Type Master SC Domain Depth
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* M1 x510-28GTX Y S none 0
N3 x230-18GP N N M1 1
N1 AR4050S N N M1 1
Node map exchange is active
Current ATMF node count 3
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1749
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF NODES
To display AMF information for all nodes, including guest nodes, use the
command:
node1# show atmf nodes all
To display AMF information for guest nodes only, use the command:
node1# show atmf nodes guest
Related
Commands
show atmf
show atmf area nodes
discovery
http-enable
show atmf backup guest
Table 46: Sample output from show atmf nodes all. In this example, not all nodes support node map
exchange, as shown by the message at the end
node1#show atmf nodes all
Node and Guest Information:
* = Local device
SC = Switch Configuration:
C = Chassis S = Stackable N = Standalone G = Guest
Node/Guest Device ATMF Parent Node
Name Type Master SC Domain Depth
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* M1 x510-28GTX Y S none 0
N3 x230-18GP N N M1 1
N1 AR4050S N N M1 1
N3-1.0.24 AT-TQ4600 N G N3 -
Node map exchange is inactive
Firmware on some nodes does not support node map exchange, eg AR4050S
Current ATMF node count 4 (guests 1)
Table 45-1: Sample output from show atmf nodes guest
node1#show atmf nodes guest
Guest Information:
Device MAC IP/IPv6
Name Address Parent Port Address
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
aastra-... 0008.5d10.7635 Node-1 1.0.2 192.168.4.7
poe-1.0.1 0013.1a1e.4589 Node-1 1.0.1 192.168.4.6
ip-camera 0800.239e.f1fe Node-1 1.0.4 192.168.4.8
tq4600 eccd.6df2.da60 Node-1 1.0.5 192.168.4.50

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1750
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF PROVISION NODES
show atmf provision nodes
Overview This command displays information about each provisioned node with details
about date and time of creation, boot and configuration files available in the
backup, and license files present in the provisioned backup. This includes nodes
that have joined the network but are yet to run their first backup.
This command can only be run on AMF master and controller nodes.
Syntax show atmf provision nodes
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command will only work if provisioned nodes have already been set up.
Otherwise, an error message is shown when the command is run.
Example To show the details of all the provisioned nodes in the backup use the command:
NodeName# show atmf provision nodes
Figure 45-28: Sample output from the show atmf provision nodes command
Related
commands
atmf provision (interface)
atmf provision node
clone (amf provisioning)
configure boot config (amf provisioning)
configure boot system (amf provisioning)
create (amf provisioning)
device1#show atmf provision nodes
ATMF Provisioned Node Information:
Backup Media .............: SD (Total 3827.0MB, Free 3481.1MB)
Node Name : device2
Date& Time : 06-Oct-2016 & 23:25:44
Provision Path : card:/atmf/provision_nodes
Boot configuration :
Current boot image : x510-5.4.9-0.1.rel (file exists)
Backup boot image : x510-5.4.8-2.3.rel (file exists)
Default boot config : flash:/default.cfg (file exists)
Current boot config : flash:/abc.cfg (file exists)
Backup boot config : flash:/xyz.cfg (file exists)
Software Licenses :
Repository file : ./.configs/.sw_v2.lic
: ./.configs/.swfeature.lic
Certificate file : card:/atmf/nodes/awplus1/flash/.atmf-lic-cert

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1752
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF RECOVERY-FILE
show atmf recovery-file
Overview Use this command to display the recovery file information for an AMF node.
AMF recovery files are created for nodes with special links. Special links include:
•virtual links,
• area links terminating on an AMF master, and
• area virtual links terminating on an AMF master.
Syntax show atmf recovery-file
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display recovery file information for an AMF node, use the command:
node1# show atmf recovery-file
Output Figure 45-29: Example output from show atmf recovery-file
Related
Commands
clear atmf recovery-file
show atmf backup
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-0.2: command added
node1#show atmf recovery-file
ATMF Recovery File Info: Special Link Present
Location Date Time
USB storage device 30 Apr 2018 14:50:32
Master 30 Apr 2018 14:56:45
node1 30 Apr 2018 14:56:45
node3 30 Apr 2018 14:56:45
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1753
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE
show atmf secure-mode
Overview Use this command to display an overview of the secure mode status of an AMF
network.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display an overview of AMF secure mode on an AMF master or member node,
use the command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode
Output Figure 45-30: Example output from show atmf secure-mode on an AMF master
Figure 45-31: Example output from show atmf secure-mode on an AMF node
ATMF Secure Mode:
Secure Mode Status : Enabled
Certificate Expiry : 180 Days
Certificates Total : 8
Certificates Revoked : 0
Certificates Rejected : 0
Certificates Active : 8
Provisional Authorization : 0
Pending Requests : 0
Trusted Master : master_1
Trusted Master : master_2
Key Fingerprint:
48:37:d9:a0:37:32:22:9b:5c:22:da:a2:62:49:a7:e5:a9:bc:12:88
ATMF Secure Mode:
Secure Mode Status : Enabled
Trusted Master : master_1
Trusted Master : master_2
Key Fingerprint:
93:f0:52:a9:74:8f:ae:ea:5b:e2:ee:62:cb:6b:21:22:5a:08:db:98
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1754
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf secure-mode
atmf secure-mode certificate expiry
show atmf authorization
show atmf secure-mode audit link
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Table 45-2: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode
Parameter Description
Secure Mode Status Shows the status of secure mode, Enabled or
Disabled.
Certificate Expiry Certificate expiry time. Set with atmf secure-mode
certificate expiry
Certificates Total Total number of certificates.
Certificates
Revoked Certificates that have been revoked by the AMF master.
Certificates
Rejected Certificates that have been rejected by the AMF master.
Certificates Active Certificates that are currently active.
Provisional
Authorization Number of nodes with provisional authorization. For
more information use the show atmf authorization
provisional command.
Pending Requests Number of nodes waiting for authorization on the AMF
master. For more information use the show atmf
authorization pending command.
Trusted Master List of trusted masters in the AMF area.
Key Fingerprint The AMF node’s key fingerprint.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1755
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE AUDIT
show atmf secure-mode audit
Overview Use this command to detect security vulnerabilities on a node.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode audit
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display AMF secure mode link audits for a node, use the command
awplus# show atmf secure-mode audit
Output Figure 45-32: Example output from show atmf secure-mode audit
Related
Commands
show atmf secure-mode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
ATMF Secure Mode Audit:
Warning : The default username and password is enabled.
Good : SNMP V1 or V2 is disabled.
Warning : Telnet server is enabled.
Good : ATMF is enabled. Secure-Mode is on.
Good : ATMF Topology-GUI is disabled. No trustpoints configured.
ATMF Secure Mode Log Events:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
2017 Feb 2 00:59:25 user.notice node1 ATMF[848]: Sec_Audit - ATMF Secure
Mode is enabled.
2017 Feb 2 01:30:00 user.notice node1 ATMF[848]: Sec_Audit - Established
secure connection to area_1_node_1 on interface vlink1.
Table 45-3: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode audit link
Parameter Description
ATMF Secure Mode
Audit A list of security recommendations to secure the AMF
network. Items prefaced with Warning need to be fixed.
In the sample above the default username and password,
and telnet, should be disabled.
ATMF Secure Mode
Log Events A list of recorded secure mode log events.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1756
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE AUDIT LINK
show atmf secure-mode audit link
Overview Use this command to detect security vulnerabilities by identifying devices that are
connected to a secure mode node that are not in secure mode or are not
authorized.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode audit link
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display AMF secure mode link audits for a node, use the command
awplus# show atmf secure-mode audit link
Output Figure 45-33: Example output from show atmf secure-mode audit link
Related
Commands
show atmf
show atmf secure-mode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
ATMF Secure Mode Audit Link:
* ATMF links connected to devices which are not authorized
or are not in secure-mode.
Port Link Type Discovered Node/Area Name
---------------------------------------------------------
vlink1 Downlink 16/02/2017 09:28:22 Member3
Table 45-4: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode audit link
Parameter Description
Port Port name on local device.
Link Type Link type.
Discovered Date discovered
Node/Area Name Node or area name of remote device.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1757
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATES
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Overview Use this command to display the certificate status details when secure mode is
enabled on an AMF network.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode certificates [detail] [area <area-name>]
[node <node-name>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display AMF secure mode certificates on a master or member node, use the
command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode certificates
To display detailed information about AMF secure mode certificates for a node
named “area_2_node_1” in an area named “area-2”, use the command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode certificates detail area area-2
node area_2_node_1
Output Figure 45-34: Example output from show atmf secure-mode certificates
Parameter Description
detail Display detailed certificate information.
area Specify an AMF area.
<area-name>The AMF area you want to see the certificate information for.
node Specify an AMF node.
<node-name>The AMF node you want to see information for.
Area-1 Certificates:
Node Name Signer Expires Status
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
area_1_node_1 master_1 11 Mar 2017
master_2 4 Mar 2017 Active
area_1_node_2 master_1 11 Mar 2017
master_2 4 Mar 2017 Revoked
Area-2 Certificates:
Node Name Signer Expires Status
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
area_2_node_1 master_1 18 Mar 2017 Active
area_2_node_2 master_1 18 Mar 2017 Rejected
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1758
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATES
Output Figure 45-35: Example output from show atmf secure-mode certificates detail
area area-2 node area_2_node_1
Table 45-5: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode certificates
Parameter Description
Node Name Name of AMF node the certificate was issued to.
Signer Name of AMF master that issued the certificate.
Expires Certificate expiry date.
Status The status column will display Active before a member
node is trusted, and can be accessed using AMF
commands. Valid statuses are Active, Revoked, and
Rejected.
Certificates Detail:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
area_2_node_1 (area:area-2)
MAC Address : 0000.cd37.0003
Status : Active
Serial Number : A24SC8001
Product : x510-28GTX
Key Fingerprint : cd:b4:c9:cd:7b:87:6a:30:98:25:d7:3c:89:8e:cb:74:e8:91:56:9d
Flags : 00000011
Signer : master_1
Expiry Date : 18 Mar 2017 21:17:42
Table 45-6: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode certificates
detail
Parameter Description
MAC Address MAC address of AMF node.
Status The device status will show Active if a member node is
trusted, and can be accessed using AMF commands. Valid
statuses are Active, Revoked, and Rejected.
Serial Number Device serial number.
Product Device product type.
Key Fingerprint AMF node key fingerprint.
Flags Internal AMF information.
Signer Name of AMF master that issued the certificate.
Expiry Date Certificate expiry date.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1759
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE CERTIFICATES
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf secure-mode
atmf secure-mode certificate expire
atmf secure-mode certificate renew
clear atmf secure-mode certificates
show atmf secure-mode sa
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1760
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE SA
show atmf secure-mode sa
Overview Use this command to display the security associations on the network. This is the
list of links and neighbors that are trusted.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode sa [detail] [link|neighbor|broadcast]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display an overview of AMF secure mode security associations on a master or
member node, use the command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode sa
To display a detailed overview of AMF secure mode neighbor security associations
on a master or member node, use the command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode sa detail neighbor
Output Figure 45-36: Example output from show atmf secure-mode sa
Parameter Description
detail Display detailed security association information.
link Display security associations for type links.
neighbor Display security associations for type neighbors.
broadcast Display security associations for type broadcast.
ATMF Security Associations:
Type State ID Details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Neighbor Node Complete 175 master_1
Broadcast Complete 4095
CrossLink Complete 4501 sa1
AreaLink Cert Exchg 4511 sa11
Link Complete 6009 port1.2.9
AreaLink CA Exchg Init 6013 port1.2.13
AreaLink Cert Exchg 13001 port1.9.1
Link CA Exchg Init 16779521 vlink3
Neighbor Gateway Complete 83 master_2
Neighbor Gateway Complete 175 master_1
Neighbor Cntl-Master Complete 83 master_2
Neighbor Cntl-Master Complete 175 master_1
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1761
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE SA
Figure 45-37: Example output from show atmf secure-mode sa detail neighbor
Security Associations Detail:
--------------------------------------------------------------
Id : 175 (af)
Type : Neighbor Node
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : eccd.6d82.6c16
Flags : 000003c0
Id : 83 (40000053)
Type : Neighbor Gateway
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : 001a.eb54.e53b
Flags : 000003c0
Id : 175 (400000af)
Type : Neighbor Gateway
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : eccd.6d82.6c16
Flags : 000003c0
Id : 83 (80000053)
Type : Neighbor Cntl-Master
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : 001a.eb54.e53b
Flags : 000003c0
Id : 175 (800000af)
Type : Neighbor Cntl-Master
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : eccd.6d82.6c16
Flags : 000003c0
Id : 321 (80000141)
Type : Neighbor Cntl-Master
State : Complete
Remote MAC Address : 0000.f427.93da
Flags : 000003c0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1762
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE SA
Related
Commands
atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode
show atmf secure-mode certificates
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
Table 45-7: Parameters in the output from show atmf secure-mode sa
Parameter Description
Type Security Association (SA) types:
•Link - SA for link
• CrossLink - SA for crosslink
• AreaLink - SA for area link
• Neighbor Node - SA for node neighbor relationship
• Neighbor Gateway - SA for gateway neighbor
relationship
• Neighbor Cntl-Master - SA for controller/master
neighbor relationship
• Broadcast - SA for working-set broadcast requests
State Current state of the Security Association. The state must
be Complete before a member node is trusted, and can
be accessed using AMF commands.
• CA Exchg Init - SA is ready to begin the SA exchange
process
• CA Exchg - SA is currently exchanging CAs
• Cert Exchg - SA is currently exchanging certificates
• Key Exchg - SA is currently exchanging ephemeral keys
• Complete - SA exchange has completed
ID Security Association ID.
• For Neighbor types this is the remote node ID.
• For Link types this is the local ifindex.
• For Broadcast type this is always 4095.
Details Human readable translation of ID.
• For Neighbor types this is the node name
• For Link types this is the interface name
Remote MAC Address MAC address of the remote partner of the security
association.
Flags Internal AMF information.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1763
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE STATISTICS
show atmf secure-mode statistics
Overview Use this command to display AMF secure mode statistics. These statistics are from
when AMF secure mode was first enabled or the statistics were cleared with the
clear atmf secure-mode statistics command.
Syntax show atmf secure-mode statistics
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display AMF secure mode statistics on a master or member node, use the
command:
awplus# show atmf secure-mode statistics
Output Figure 45-38: Example output from show atmf secure-mode statistics on an
AMF master.
ATMF Secure Mode Statistics:
Certificates:
New ............. 7 Expired .......... 0
Updated ......... 7 Deleted .......... 0
Revoked ......... 1 Renewed .......... 2
Rejected ........ 1 Re-authorized .... 1
Authorized ...... 0
Local Certificates:
Valid ........... 4 Invalid ......... 0
Certificates Validation:
Request Valid ..................................... 2
Request Invalid ................................... 0
Common Valid ...................................... 13
Common Invalid .................................... 0
Issuer Valid ...................................... 14
Issuer Invalid .................................... 0
Signature Verified ................................ 29
Signature Invalid ................................. 0
Signature Purpose Invalid ......................... 0
Signatures Signed ................................. 12
Master Certificates:
Re-issued ......................................... 3
Downgraded to member .............................. 0
Public key change ................................. 2
Invalid SA public key ............................. 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1764
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF SECURE-MODE STATISTICS
Output Figure 45-39: Example output from show atmf secure-mode statistics on an
AMF node.
Related
Commands
atmf authorize
atmf secure-mode
atmf secure-mode certificate renew
clear atmf secure-mode statistics
show atmf secure-mode
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.3: command added
ATMF Secure Mode Statistics:
Local Certificates:
Valid ........... 3 Invalid ......... 0
Certificates Validation:
Request Valid ..................................... 0
Request Invalid ................................... 0
Common Valid ...................................... 0
Common Invalid .................................... 0
Issuer Valid ...................................... 12
Issuer Invalid .................................... 0
Signature Verified ................................ 12
Signature Invalid ................................. 3
Signature Purpose Invalid ......................... 0
Signatures Signed ................................. 0
Master Certificates:
Re-issued ......................................... 0
Downgraded to member .............................. 0
Public key change ................................. 2
Invalid SA public key ............................. 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1765
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF TECH
show atmf tech
Overview This command collects and displays all the AMF command output. The command
can thus be used to display a complete picture of an AMF network.
Syntax show atmf tech
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display output for all AMF commands, use the command:
NodeName# show atmf tech
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf tech command.
node1#show atmf tech
ATMF Summary Information:
ATMF Status : Enabled
Network Name : ATMF_NET
Node Name : node1
Role : Master
Current ATMF Nodes : 8
ATMF Technical information:
Network Name : ATMF_NET
Domain : node1's domain
Node Depth : 0
Domain Flags : 0
Authentication Type : 0
MAC Address : 0014.2299.137d
Board ID : 287
Domain State : DomainController
Domain Controller : node1
Backup Domain Controller : node2
Domain controller MAC : 0014.2299.137d
Parent Domain : -
Parent Domain Controller : -
Parent Domain Controller MAC : 0000.0000.0000
Number of Domain Events : 0
Crosslink Ports Blocking : 0
Uplink Ports Waiting on Sync : 0

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1766
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF TECH
Crosslink Sequence Number : 7
Domains Sequence Number : 28
Uplink Sequence Number : 2
Number of Crosslink Ports : 1
Number of Domain Nodes : 2
Number of Neighbors : 5
Number of Non Broadcast Neighbors : 3
Number of Link State Entries : 1
Number of Up Uplinks : 0
Number of Up Uplinks on This Node : 0
DBE Checksum : 84fc6
Number of DBE Entries : 0
...
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf tech command. (cont.)
Table 47: Parameter definitions from the show atmf tech command
Parameter Definition
ATMF Status Shows status of AMF feature on the Node as
Enabled/Disabled.
Network Name The name of the AMF network to which this node belongs.
Node Name The name assigned to the node within the AMF network.
Role The role configured on the device within the AMF - either master or member.
Current ATMF Nodes A count of the AMF nodes in the AMF network.
Node Address The identity of a node (in the format name.atmf) that enables its access it from a
remote location.
Node ID A unique identifier assigned to an AMF node.
Node Depth The number of nodes in the path from this node to the core domain.
Domain State A node’s state within an AMF Domain - either controller or backup.
Recovery State The AMF node recovery status. Indicates whether a node recovery is in progress
on this device - either Auto, Manual, or None.
Management VLAN The VLAN created for traffic between nodes of different domains (up/down
links).
VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4092 is configured as the Management VLAN.
Management Subnet - the Network prefix for the subnet.
Management IP Address - the IP address allocated for this traffic.
Management Mask - the Netmask used to create a subnet for this traffic
255.255.128.0 (= prefix /17)
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1767
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF TECH
NOTE: The show atmf tech command can produce very large output. For this reason
only the most significant terms are defined in this table.
Domain VLAN The VLAN assigned for traffic between Nodes of same domain (crosslink).
VLAN ID - In this example VLAN 4091 is configured as the domain VLAN.
Domain Subnet - the Subnet address used for this traffic.
Domain IP Address - the IP address allocated for this traffic.
Domain Mask - the Netmask used to create a subnet for this traffic 255.255.128.0
(= prefix /17)
Device Type Shows the Product Series Name.
ATMF Master Indicates the node’s membership of the core domain (membership is indicated
by Y)
SC Shows switch configuration:
• C - Chassis (such as SBx8100 series)
•S - Stackable (VCS)
•N - Standalone
Parent A node that is connected to the present node’s uplink, i.e. one layer higher in the
hierarchy.
Node Depth Shows the number of nodes in path from the current node to the Core domain.
Table 47: Parameter definitions from the show atmf tech command (cont.)
Parameter Definition

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1768
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF VIRTUAL-LINKS
show atmf virtual-links
Overview This command displays a summary of all virtual links (L2TP tunnels) currently in the
running configuration.
Syntax show atmf virtual-links [macaddr]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example 1 To display AMF virtual links, use the command:
node_1# show atmf virtual-links
In the above example, a centrally located switch has the IP address space
192.0.2.x/24. It has two VLANs assigned the subnets 192.0.2.33 and 192.0.2.65
using the prefix /27. Each subnet connects to a virtual link. The first link has the IP
address 192.168.1.1 and has a Local ID of 1. The second has the IP address
192.168.2.1 and has the Local ID of 2.
Example 2 To display AMF virtual links’ MAC address information, use the command:
node_1# show atmf virtual-links macaddr
Parameter Description
macaddr Display the virtual AMF links’ MAC addresses.
Table 45-1: Example output from show atmf virtual-links
ATMF Link Remote Information:
Local Local Remote Tunnel Tunnel
Port ID IP ID IP Protect State
------------------------------------------------------------------------
vlink1 1 172.16.24.2 2 1.0.0.2 - Complete
vlink2 2 172.16.24.2* 10 172.16.24.3* ipsec Complete
vlink3 3 (eth0)* 1 1.2.3.4 - AcquireLocal
* = Dynamic Address.
Virtual Links Configured: 3
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1769
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF VIRTUAL-LINKS
Related
Commands
atmf virtual-link
Table 45-2: Example output from show atmf virtual-links macaddr
ATMF Link Remote Information:
ATMF Management Bridge Information:
Bridge: br-atmfmgmt
port no mac addr is local? ageing timer
1 00:00:cd:27:c2:07 yes 0.00
2 8e:c7:ae:81:7e:68 yes 0.00
2 00:00:cd:28:bf:e7 no 0.01
Table 45-3: Parameters in the output from show atmf virtual-links
Parameter Definition
vlink1 The tunnel named vlink1, equivalent to an L2TP tunnel.
Local ID The local ID of the virtual link. This matches the vlink<number>
State The operational state of the vlink (either Up or Down). This state is
always displayed once a vlink has been created.
mac addr AMF virtual links terminate on an internal soft bridge. The “show
atmf virtual-links macaddress” command displays MAC Address
information.
is local? Indicates whether the MAC displayed is for a local or a remote
device.
ageing timer Indicates the current aging state for each MAC address.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1770
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW ATMF WORKING-SET
show atmf working-set
Overview This command displays the nodes that form the current AMF working-set.
Syntax show atmf working-set
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To show current members of the working-set, use the command:
ATMF_NETWORK[6]# show atmf working-set
Related
Commands
atmf working-set
show atmf
show atmf group
Table 46: Sample output from the show atmf working-set command.
ATMF Working Set Nodes:
node1, node2, node3, node4, node5, node6
Working set contains 6 nodes
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1771
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING ATMF
show debugging atmf
Overview This command shows the debugging modes status for AMF.
Syntax show debugging atmf
Mode User Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the AMF debugging status, use the command:
node_1# show debugging atmf
Figure 45-40: Sample output from the show debugging atmf command.
Related
Commands
debug atmf packet
Table 45-1:
node1# show debugging atmf
ATMF debugging status:
ATMF arealink debugging is on
ATMF link debugging is on
ATMF crosslink debugging is on
ATMF database debugging is on
ATMF neighbor debugging is on
ATMF packet debugging is on
ATMF error debugging is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1772
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING ATMF PACKET
show debugging atmf packet
Overview This command shows details of AMF Packet debug command settings.
Syntax show debugging atmf packet
Mode User Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the AMF packet debugging status, use the command:
node_1# show debug atmf packet
Figure 45-41: Sample output from the show debugging atmf packet command.
Related
Commands
debug atmf
debug atmf packet
Table 45-2:
ATMF packet debugging is on
=== ATMF Packet Debugging Parameters===
Node Name: x908
Port name: port1.1.1
Limit: 500 packets
Direction: TX
Info Level: Level 2
Packet Type Bitmap:
2. Crosslink Hello BPDU pkt with downlink domain info
3. Crosslink Hello BPDU pkt with uplink info
4. Down and up link Hello BPDU pkts
6. Stack hello unicast pkts
8. DBE request
9. DBE update
10. DBE bitmap update

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1773
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG ATMF
show running-config atmf
Overview This command displays the running system information that is specific to AMF.
Syntax show running-config atmf
Mode User Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration of AMF, use the following commands:
node_1# show running-config atmf
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Related
Commands
show running-config
no debug all

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1774
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
STATE
state
Overview This command sets the running state of an AMF container on a Virtual AMF
Appliance (VAA).
An AMF container is an isolated instance of AlliedWare Plus with its own network
interfaces, configuration, and file system. The features available inside an AMF
container are a sub-set of the features available on the host VAA. These features
enable the AMF container to function as a uniquely identifiable AMF master and
allows for multiple tenants (up to 60) to run on a single VAA host. See the
AMF Feature Overview and Configuration Guide for more information on running
multiple tenants on a single VAA host.
Syntax state {enable|disable}
Default By default, state is disabled.
Mode AMF Container Configuration
Usage The first time the state enable command is executed on a container it assigns the
container to an area and configures it as an AMF master. This is achieved by
automatically adding the following configuration to the AMF container:
For this reason the state enable command should be run after the container has
been created with the atmf container command and an area-link configured with
the area-link command.
Once the start-up configuration has been saved from within the AMF container, all
further configuration changes need to be made manually.
Parameter Description
disable Stop the AMF container. The container’s state changes to
stopped.
enable Start the AMF container. The container’s state changes to
running.
atmf network-name <AMF network-name>
atmf master
atmf area <container area-name> <co ntainer area-id> local
atmf area <container area-name> password <container area-password>
atmf area <host area-name> <host area-id>
interface eth0
atmf-arealink remote-area <host area-name> vlan 4094

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1775
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
STATE
Example To start the AMF container “vac-wlg-1” use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# state enable
To stop the AMF container “vac-wlg-1” use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# atmf container vac-wlg-1
awplus(config-atmf-container)# state disable
Related
Commands
atmf container
show atmf container
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1776
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-AGENTLINK
switchport atmf-agentlink
Overview Use this command to configure a link between this device and an x600 Series
switch, in order to integrate the x600 Series switch into your AMF network. The
x600 Series switch is called an “AMF agent”, and the link between the x600 and this
device is called an “agent link”.
The x600 Series switch must be running version 5.4.2-3.16 or later.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the agent link. If the x600 Series
switch is still connected to the switch port, it will no longer be part of the AMF
network.
Syntax switchport atmf-agentlink
no switchport atmf-agentlink
Default By default, no agent links exist and x600 Series switches are not visible to AMF
networks.
Mode Interface mode for a switch port. Note that the link between the x600 and the AMF
network must be a single link, not an aggregated link.
Usage The x600 Series switch provides the following information to the AMF node that it
is connected to:
•The MAC address
•The IPv4 address
•The IPv6 address
• The name/type of the device (Allied Telesis x600)
• The name of the current firmware
• The version of the current firmware
• The configuration name
AMF guestnode also makes most of this information available from x600 Series
switches, but requires configuration with DHCP and/or LLDP. AMF agent is simpler;
as soon the x600 is connected to an appropriately configured port of an AMF node,
it is immediately integrated into the AMF network.
To see information about the x600 Series switch, use the show atmf links guest
detail command.
Example To configure port1.0.1 as an agent link, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# switchport atmf-agentlink
Related
Commands
show atmf links guest

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1777
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-AREALINK REMOTE-AREA
switchport atmf-arealink remote-area
Overview This command enables you to configure a port or aggregator to be an AMF
arealink. AMF arealinks are designed to operate between two nodes in different
areas in an AMF network.
Use the no variant of this command to remove any AMF-arealink that may exist for
the selected port or aggregated link.
This command is only available on AMF controllers and master nodes.
Syntax switchport atmf-arealink remote-area <area-name> vlan <2-4094>
no switchport atmf-arealink
Default By default, no arealinks are configured
Mode Interface Configuration for a switchport, a static aggregator or a dynamic channel
group.
Usage Run this command on the port or aggregator at both ends of the link.
Each area must have the area-name configured, and the same area password must
exist on both ends of the link.
Running this command will automatically place the port or static aggregator into
trunk mode (i.e. switchport mode trunk) and will synchronize the area information
stored on the two nodes.
You can configure multiple arealinks between two area nodes, but only one
arealink at any time will be in use. All other arealinks will block information, to
prevent network storms.
Example To make switchport port1.0.2 an arealink to the Auckland area on VLAN 6, use the
following commands
controller-1# configure terminal
controller-1(config)# interface port1.0.2
controller-1(config-if)# switchport atmf-arealink remote-area
Auckland vlan 6
Parameter Description
<area-name>The name of the remote area that the port is connecting to.
<2-4094>The VLAN ID for the link. This VLAN cannot be used for any other
purpose, and the same VLAN ID must be used at each end of the link.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1779
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-CROSSLINK
switchport atmf-crosslink
Overview This command configures the selected port, statically aggregated link or dynamic
channel group (LACP) to be an AMF crosslink. Running this command will
automatically place the port or aggregator into trunk mode (i.e. switchport mode
trunk).
The connection between two AMF masters must utilize a crosslink. Crosslinks are
used to carry the AMF control information between master nodes. Multiple
crosslinks can be configured between two master nodes, but only one crosslink
can be active at any particular time. All other crosslinks between masters will be
placed in the blocking state, in order to prevent broadcast storms.
Use the no variant of this command to remove any crosslink that may exist for the
selected port or aggregated link.
Syntax switchport atmf-crosslink
no switchport atmf-crosslink
Mode Interface Configuration for a switchport, a static aggregator or a dynamic channel
group.
Usage Crosslinks can be used anywhere within an AMF network. They have the effect of
separating the AMF network into separate domains.
Where this command is used, it is also good practice to use the switchport trunk
native vlan command with the parameter none selected. This is to prevent a
network storm on a topology of ring connected devices.
Example 1 To make switchport port1.0.1 an AMF crosslink, use the following commands:
Node_1# configure terminal
Node_1(config)# interface port1.0.1
Node_1(config-if)# switchport atmf-crosslink
Example 2 This example is shown twice. Example 2A is the most basic command sequence.
Example 2B is a good practice equivalent that avoids problems such as broadcast
storms that can otherwise occur.
Example 2A To make static aggregator sa1 an AMF crosslink, use the following commands:
Node_1# configure terminal
Node_1(config)# interface sa1
Node_1(config-if)# switchport atmf-crosslink

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1780
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-CROSSLINK
Example 2B To make static aggregator sa1 an AMF crosslink, use the following commands for
good practice:
Node_1# configure terminal
Node_1(config)# interface sa1
Node_1(config-if)# switchport atmf-crosslink
Node_1(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2
Node_1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan none
In this example VLAN 2 is assigned to the static aggregator, and the native VLAN
(VLAN 1) is explicitly excluded from the aggregated ports and the crosslink
assigned to it.
NOTE: The AMF management and domain VLANs are automatically added to the
aggregator and the crosslink.
Related
Commands
show atmf links statistics

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1781
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-GUESTLINK
switchport atmf-guestlink
Overview Guest links are used to provide basic AMF functionality to non AMF capable
devices. Guest links can be configured for either a selected switch port or a range
of switch ports and use generic protocols to collect status and configuration
information that the guest devices make available.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the guest node functionality from
the selected port or ports.
NOTE: AMF guest nodes are not supported on ports using the OpenFlow protocol.
Syntax switchport atmf-guestlink [class <guest-class>] [ip <A.B.C.D>|
ipv6 <X:X::X:X>]
no switchport atmf-guestlink
Default No guest links are configured.
Mode Interface
Example 1 To configure switchport port1.0.1 to be a guest link, that will connect to a guest
node having a guest class of camera and an IPv4 address of 192.168.3.3, use the
following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# int port1.0.1
node1(config-if)# switchport atmf-guestlink class camera ip
192.168.3.3
Example 2 To configure switchport port1.0.1 to be a guest link, which will connect to a guest
node having a guest class of phone and an IPv6 address of 2001:db8:21e:10d::5,
use the following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# int port1.0.1
node1(config-if)# switchport atmf-guestlink class phone ipv6
2000:db8:21e:10d::5
Parameter Description
class Set a guest class
<guest-class>The name of the guest class.
ip Specifies that the address following will have an IPv4 format
<A.B.C.D>The guest node’s IP address in IPv4 format.
ipv6 Specifies that the address following will have an IPv6 format
<X:X::X:X>The guest node’s IP address in IPv6 format.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1782
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-GUESTLINK
Example 3 To configure switchport port1.0.1 to be a guest link, using the default model type
and learning method address, use the following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# int port1.0.1
node1(config-if)# switchport atmf-guestlink
Example 4 To configure switchports port1.0.1 to port1.0.3 to be guest links, for the guest class
camera, use the following commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# int port1.0.1-port1.0.3
node1(config-if)# switchport atmf-guestlink class camera
Example 5 To remove the guest-link functionality from switchport port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
node1# configure terminal
node1(config)# int port1.0.1
node1(config-if)# no switchport atmf-guestlink
Related
Commands
atmf guest-class
discovery
http-enable
username
modeltype
show atmf links guest
show atmf guests

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1783
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
SWITCHPORT ATMF-LINK
switchport atmf-link
Overview This command enables you to configure a port or aggregator to be an AMF
up/down link. Running this command will automatically place the port or
aggregator into trunk mode. If the port was previously configured in access mode,
the configured access VLAN will be removed.
Use the no variant of this command to remove any AMF-link that may exist for the
selected port or aggregated link.
Syntax switchport atmf-link
no switchport atmf-link
Mode Interface Configuration for a switchport, a static aggregator or a dynamic channel
group.
Usage Up/down links and virtual links interconnect domains in a vertical hierarchy, with
the highest domain being the core domain. In effect, they form a tree of
interconnected AMF domains. This tree must be loop-free. Therefore, you must
configure your links so that no rings are formed only from up/down links and/or
virtual links.
Within each domain, cross-links between AMF nodes define those nodes as
siblings within the same domain. You can form rings by combining cross-links with
up/down links and/or virtual links, as long as each AMF domain links upwards to
only a single parent domain. Each domain may link downwards to multiple child
domains.
Example To make switchport port1.0.1 an AMF up/down link, use the following commands:
Node_1# configure terminal
Node_1(config)# interface port1.0.1
Node_1(config-if)# switchport atmf-link

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1784
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
TYPE ATMF NODE
type atmf node
Overview This command configures a trigger to be activated at an AMF node join event or
leave event.
Syntax type atmf node {join|leave}
Mode Trigger Configuration
CAUTION: Only configure this trigger on one device because it is a network wide event.
Example 1 To configure trigger 5 to activate at an AMF node leave event, use the following
commands. In this example the command is entered on node-1:
node1(config)# trigger 5
node1(config-trigger) type atmf node leave
Example 2 The following commands will configure trigger 5 to activate if an AMF node join
event occurs on any node within the working set:
node1# atmf working-set group all
This command returns the following display:
Note that the running the above command changes the prompt from the name of
the local node, to the name of the AMF-Network followed, in square brackets, by
the number of member nodes in the working set.
AMF-Net[3]# conf t
AMF-Net[3](config)# trigger 5
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# type atmf node leave
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# description “E-mail on AMF Exit”
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# active
Enter the name of the script to run at the trigger event.
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# script 1 email_me.scp
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# end
Parameter Description
join AMF node join event.
leave AMF node leave event.
====================
node1, node2, node3:
====================
Working set join
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1785
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
TYPE ATMF NODE
Display the trigger configurations
AMF-Net[3]# show trigger
This command returns the following display:
Display the triggers configured on each of the nodes in the AMF Network.
AMF-Net[3]# show running-config trigger
This command returns the following display:
=======
node1:
========
TR# Type & Details Description Ac Te Tr Repeat #Scr Days/Date
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
001 Periodic (2 min) Periodic Status Chk Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
005 ATMF node (leave) E-mail on ATMF Exit Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
==============
Node2, Node3,
==============
TR# Type & Details Description Ac Te Tr Repeat #Scr Days/Date
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
005 ATMF node (leave) E-mail on ATMF Exit Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
========
Node1:
========
trigger 1
type periodic 2
script 1 atmf.scp
trigger 5
type atmf node leave
description “E-mail on ATMF Exit”
script 1 email_me.scp
!
============
Node2, Node3:
============
trigger 5
type atmf node leave
description “E-mail on ATMF Exit”
script 1 email_me.scp
!

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1788
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
ALLIED TELESIS MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK™ (AMF) COMMANDS
USERNAME
username
Overview This command enables you to assign a username to a guest class. Guests may
require a username and possibly also a password. In its non-encypted form the
password must be between 1 and 32 characters and will allow spaces. In its
encrypted form the password must be between 1 to 64 characters and will allow
any character
Syntax username <NAME> password [8] <USERPASS>
no username
Default No usernames configured
Mode AMF Guest Configuration Mode
Example 1 To assign the user name reception and the password of secret to an AMF guest
node that has the guest class of phone1 use the following commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)# amf guest-class phone1
node1(config-atmf-guest)# username reception password secret
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Example 2 To remove a guest node username and password for the user guest class phone1,
use the following commands:
node1# conf t
node1(config)# atmf guest-class phone1
node1(config-atmf-guest)# no username
node1(config-atmf-guest)# end
Related
Commands
show atmf links detail
atmf guest-class
switchport atmf-guestlink
Parameter Description
username Indicates that a user name is to follow
<NAME> User name of the guest node
password Indicates that a password (or specifier) is to follow.
8Specifier indicating that the following password is encrypted. It's
primary purpose is to differentiate between the configuration
input and the CLI input. You should not specify this for CLI input
<USERPASS>The password to be entered for the guest node.

46
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1790
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Dynamic Host
Configuration
Protocol (DHCP)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
DHCP.
For more information, see the DHCP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide,
which is available at the above link on alliedtelesis.com.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide. This guide is
available at the above link on alliedtelesis.com.
Command List •“bootfile” on page 1792
•“clear ip dhcp binding” on page 1793
•“default-router” on page 1794
•“dns-server” on page 1795
•“domain-name” on page 1796
•“host (DHCP)” on page 1797
•“ip address dhcp” on page 1798
•“ip dhcp bootp ignore” on page 1800
•“ip dhcp leasequery enable” on page 1801
•“ip dhcp option” on page 1802
•“ip dhcp pool” on page 1804
•“ip dhcp-client default-route distance” on page 1805
•“ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific” on page 1807
•“ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class” on page 1808
•“lease” on page 1809
•“network (DHCP)” on page 1811

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1791
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
•“next-server” on page 1812
•“option” on page 1813
•“probe enable” on page 1815
•“probe packets” on page 1816
•“probe timeout” on page 1817
•“probe type” on page 1818
•“range” on page 1819
•“route” on page 1820
•“service dhcp-server” on page 1821
•“short-lease-threshold” on page 1822
•“show counter dhcp-client” on page 1824
•“show counter dhcp-server” on page 1825
•“show dhcp lease” on page 1826
•“show ip dhcp binding” on page 1827
•“show ip dhcp pool” on page 1828
•“show ip dhcp server statistics” on page 1833
•“show ip dhcp server summary” on page 1835
•“subnet-mask” on page 1836
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1792
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
BOOTFILE
bootfile
Overview This command sets the boot filename for a DHCP server pool. This is the name of
the boot file that the client should use in its bootstrap process. It may need to
include a path.
The no variant of this command removes the boot filename from a DHCP server
pool.
Syntax bootfile <filename>
no bootfile
Mode DHCP Configuration
Example To configure the boot filename for a pool P2, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# bootfile boot/main_boot.bt
Parameter Description
<filename> The boot file name.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1793
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
CLEAR IP DHCP BINDING
clear ip dhcp binding
Overview
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1794
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
DEFAULT-ROUTER
default-router
Overview This command adds a default router to the DHCP address pool you are configuring.
You can use this command multiple times to create a list of default routers on the
client’s subnet. This sets the router details using the pre-defined option 3. Note
that if you add a user-defined option 3 using the option command, then you will
override any settings created with this command.
The no variant of this command removes either the specified default router, or all
default routers from the DHCP pool.
Syntax default-router <ip-address>
no default-router [<ip-address>]
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To add a router with an IP address 192.168.1.2 to the DHCP pool named P2, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.1.2
To remove a router with an IP address 192.168.1.2 to the DHCP pool named P2, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no default-router 192.168.1.2
To remove all routers from the DHCP pool named P2, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no default-router
Parameter Description
<ip-address>IPv4 address of the default router, in dotted decimal notation.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1795
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
DNS-SERVER
dns-server
Overview This command adds a Domain Name System (DNS) server to the DHCP address
pool you are configuring. You can use this command multiple times to create a list
of DNS name servers available to the client. This sets the DNS server details using
the pre-defined option 6.
The no variant of this command removes either the specified DNS server, or all DNS
servers from the DHCP pool.
Syntax dns-server <ip-address>
no dns-server [<ip-address>]
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To add the DNS server with the assigned IP address 192.168.1.1 to the DHCP pool
named P1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# dns-server 192.168.1.1
To remove the DNS server with the assigned IP address 192.168.1.1 from the DHCP
pool named P1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no dns-server 192.168.1.1
To remove all DNS servers from the DHCP pool named P1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no dns-server
Related
Commands
default-router
show ip dhcp pool
subnet-mask
Parameter Description
<ip-address>IPv4 address of the DNS server, in dotted decimal notation.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1796
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
DOMAIN-NAME
domain-name
Overview This command adds a domain name to the DHCP address pool you are
configuring. Use this command to specify the domain name that a client should
use when resolving host names using the Domain Name System. This sets the
domain name details using the pre-defined option 15.
The no variant of this command removes the domain name from the address pool.
Syntax domain-name <domain-name>
no domain-name
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To add the domain name Nerv_Office to DHCP pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# domain-name Nerv_Office
Parameter Description
<domain-name>The domain name you wish to assign the DHCP pool. Valid
characters are any printable character. If the name contains
spaces then you must enclose it in “quotation marks”.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1797
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
HOST (DHCP)
host (DHCP)
Overview
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1798
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP ADDRESS DHCP
ip address dhcp
Overview This command activates the DHCP client on the interface you are configuring. This
allows the interface to use the DHCP client to obtain its IP configuration details
from a DHCP server on its connected network.
The client-id and hostname parameters are identifiers that you may want to set in
order to interoperate with your existing DHCP infrastructure. If neither option is
needed, then the DHCP server uses the MAC address field of the request to identify
the host.
The DHCP client supports the following IP configuration options:
• Option 1 - the subnet mask for your device.
• Option 51 - lease expiration time.
The no variant of this command stops the interface from obtaining IP
configuration details from a DHCP server.
Syntax ip address dhcp [client-id <interface>] [hostname <hostname>]
no ip address dhcp
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface.
Examples To set the interface vlan2 to use DHCP to obtain an IP address, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip address dhcp
To stop the interface vlan2 from using DHCP to obtain its IP address, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ip address dhcp
Parameter Description
client-id
<interface> The name of the interface you are activating the DHCP client on. If
you specify this, then the MAC address associated with the
specified interface is sent to the DHCP server in the optional
identifier field.
Default: no default
hostname
<hostname> The hostname for the DHCP client on this interface. Typically this
name is provided by the ISP.
Default: no default

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1800
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP BOOTP IGNORE
ip dhcp bootp ignore
Overview This command configures the DHCP server to ignore any BOOTP requests it
receives. The DHCP server accepts BOOTP requests by default.
The no variant of this command configures the DHCP server to accept BOOTP
requests. This is the default setting.
Syntax ip dhcp bootp ignore
no ip dhcp bootp ignore
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure the DHCP server to ignore BOOTP requests, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp bootp ignore
To configure the DHCP server to respond to BOOTP requests, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp bootp ignore
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp server summary

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1801
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP LEASEQUERY ENABLE
ip dhcp leasequery enable
Overview Use this command to enable the DHCP server to respond to DHCPLEASEQUERY
packets. Enabling the DHCP leasequery feature allows a DHCP Relay Agent to
obtain IP address information directly from the DHCP server using
DHCPLEASEQUERY messages.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the support of DHCPLEASEQUERY
packets.
For more information, see the DHCP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax ip dhcp leasequery enable
no ip dhcp leasequery enable
Default DHCP leasequery support is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable DHCP leasequery support, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp leasequery enable
To disable DHCP leasequery support, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp leasequery enable
Related
Commands
show counter dhcp-server
show ip dhcp server statistics
show ip dhcp server summary

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1802
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP OPTION
ip dhcp option
Overview This command creates a user-defined DHCP option. Options with the same
number as one of the pre-defined options override the standard option definition.
The pre-defined options use the option numbers 1, 3, 6, 15, and 51.
The no variant of this command removes either the specified user-defined option,
or removes all user-defined options. This also automatically removes the
user-defined options from the associated DHCP address pools.
Syntax ip dhcp option <1-254> [name <option-name>] [<option-type>]
no ip dhcp option [<1-254>|<option-name>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To define a user-defined ASCII string option as option 66, without a name, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp option 66 ascii
Parameter Description
<1-254> The option number of the option. Options with the same number
as one of the standard options overrides the standard option
definition.
<option-name> Option name used to identify the option. You cannot use a
number as the option name. Valid characters are any printable
character. If the name contains spaces then you must enclose it
in “quotation marks”.
Default: no default
<option-type> The option value. You must specify a value that is appropriate to
the option type:
asci An ASCII text string
hex A hexadecimal string. Valid characters are the
numbers 0–9 and letters a–f. Embedded spaces are
not valid. The string must be an even number of
characters, from 2 and 256 characters long.
ip An IPv4 address or mask that has the dotted decimal
A.B.C.D notation. To create a list of IP addresses, you
must add each IP address individually by using the
option command multiple times.
integer A number from 0 to 4294967295.
flag A value that either sets (to 1) or unsets (to 0) a flag:
true, on, or enabled will set the flag.
f alse, off or disabled will unset the flag.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1803
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP OPTION
To define a user-defined hexadecimal string option as option 46, with the name
“tcpip-node-type”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp option 46 name tcpip-node-type hex
To define a user-defined IP address option as option 175, with the name
special-address, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp option 175 name special-address ip
To remove the specific user-defined option with the option number 12, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp option 12
To remove the specific user-defined option with the option name
perform-router-discovery, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp option perform-router-discovery
To remove all user-defined option definitions, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp option
Related
Commands
default-router
dns-server
domain-name
show ip dhcp server summary
subnet-mask
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1804
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP POOL
ip dhcp pool
Overview This command will enter the configuration mode for the pool name specified. If
the name specified is not associated with an existing pool, the device will create a
new pool with this name, then enter the configuration mode for the new pool.
Once you have entered the DHCP configuration mode, all commands executed
before the next exit command will apply to this pool.
You can create multiple DHCP pools on devices with multiple interfaces. This
allows the device to act as a DHCP server on multiple interfaces to distribute
different information to clients on the different networks.
The no variant of this command deletes the specific DHCP pool.
Syntax ip dhcp pool <pool-name>
no ip dhcp pool <pool-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Example To create the DHCP pool named P2 and enter DHCP Configuration mode, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)#
To delete the DHCP pool named P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ip dhcp pool P2
Parameter Description
<pool-name> Description used to identify this DHCP pool. Valid characters
are any printable character. If the name contains spaces then
you must enclose it in “quotation marks”.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1805
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP-CLIENT DEFAULT-ROUTE DISTANCE
ip dhcp-client default-route distance
Overview Use this command to specify an alternative Administrative Distance (AD) for the
current default route (from DHCP) for an interface.
Use the no variant of this command to set the AD back to the default of 1.
Syntax ip dhcp-client default-route distance [<1-255>]
no ip dhcp-client default-route distance
Default 1
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage DHCP client interfaces can automatically add a default route with an AD of 1 into
the IP Routing Information Base (RIB).
Any pre-existing default route(s) via alternative interfaces (configured with a
higher AD) will no longer be selected as the preferred forwarding path for traffic
when the DHCP based default route is added to the IP routing table.
This can be problematic if the DHCP client is operating via an interface that is only
intended to be used for back-up interface redundancy purposes, such as a VLAN
containing a single switchport, or a 4G cellular interface on an AR-Series Firewall.
Use this command to set the AD of the default route (via a specific DHCP client
interface) to a non-default (higher cost) value, ensuring any pre-existing default
route(s) via any other interface(s) continue to be selected as the preferred
forwarding path for network traffic.
When the command is used, the static default route is deleted from the RIB, the
distance value of the route is modified to the configured distance value, then it is
reinstalled into the RIB.
Examples To configure vlan10 as a DHCP client and to set the AD for the default route added
by DHCP to 150, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# ip address dhcp
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp-client default-route distance 150
Parameter Description
<1-255> Administrative Distance (AD) from the range 1 though 255.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1806
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP-CLIENT DEFAULT-ROUTE DISTANCE
To set the AD for the default route back to the default value of 1, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan10
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp-client default-route distance
Related
Commands
show ip route
show ip route database
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.2 Command added.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1807
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP-CLIENT REQUEST VENDOR-IDENTIFYING-SPECIFIC
ip dhcp-client request
vendor-identifying-specific
Overview Use this command to add vendor-identifying vendor-specific information (option
125) requests to the DHCP discovery packets sent by an interface. This option,
along with option 124, can be used to send vendor specific information back to a
DHCP client.
See RFC3925 for more information on Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options for
DHCPv4.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the vendor-identifying-specific
request from an interface.
Syntax ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific
no ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific
Default The vendor-identifying-specific request is not configured by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The DHCP client must be activated on the interface, using the ip address dhcp
command, so that DHCP discovery packets are sent.
Example To add the vendor-identifying-specific request on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ip dhcp-client request
vendor-identifying-specific
To remove the vendor-identifying-specific request on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp-client request
vendor-identifying-specific
Related
Commands
ip address dhcp
ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1808
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
IP DHCP-CLIENT VENDOR-IDENTIFYING-CLASS
ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
Overview Use this command to add a vendor-identifying vendor class (option 124) to the
DHCP discovery packets sent by an interface. This option places the Allied Telesis
Enterprise number (207) into the discovery packet. Option 124, along with option
125, can be used to send vendor specific information back to a DHCP client.
See RFC3925 for more information on Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options for
DHCPv4.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the vendor-identifying-class from
an interface.
Syntax ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
no ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
Default The vendor-identifying-class is not configured by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The DHCP client must be activated on the interface, using the ip address dhcp
command, so that DHCP discovery packets are sent.
Example To remove the vendor-identifying-specific request on vlan2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ip dhcp-client vendor-identifying-class
Related
Commands
ip address dhcp
ip dhcp-client request vendor-identifying-specific
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1809
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
LEASE
lease
Overview This command sets the expiration time for a leased address for the DHCP address
pool you are configuring. The time set by the days, hours, minutes and seconds is
cumulative. The minimum total lease time that can be configured is 20 seconds.
The maximum total lease time that can be configured is 120 days.
Note that if you add a user-defined option 51 using the option command, then you
will override any settings created with this command. Option 51 specifies a lease
time of 1 day.
Use the infinite parameter to set the lease expiry time to infinite (leases never
expire).
Use the no variant of this command to return the lease expiration time back to the
default of one day.
Syntax lease <days> <hours> <minutes> [<seconds>]
lease infinite
no lease
Default The default lease time is 1 day.
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To set the lease expiration time for address pool P2 to 35 minutes, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# lease 0 0 35
Parameter Description
<days>The number of days, from 0 to 120, that the lease expiry time is
configured for.
Default: 1
<hours>The number of hours, from 0 to 24, that the lease expiry time is
configured for.
Default: 0
<minutes>The number of minutes, from 0 to 60, the lease expiry time is configured
for.
Default: 0
<seconds>The number of seconds, from 0 to 60, the lease expiry time is configured
for.
infinite The lease never expires.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1810
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
LEASE
To set the lease expiration time for the address pool Nerv_Office to 1 day, 5
hours, and 30 minutes, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool Nerv_Office
awplus(dhcp-config)# lease 1 5 30
To set the lease expiration time for the address pool P3 to 20 seconds, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P3
awplus(dhcp-config)# lease 0 0 0 20
To set the lease expiration time for the pool to never expire, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# lease infinite
To return the lease expiration time to the default of one day, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# no lease
Related
Commands
option
service dhcp-server
short-lease-threshold
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1811
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
NETWORK (DHCP)
network (DHCP)
Overview This command sets the network (subnet) that the DHCP address pool applies to.
The no variant of this command removes the network (subnet) from the DHCP
address pool.
Syntax network
{<ip-subnet-address/prefix-length>|<ip-subnet-address/mask>}
no network
Mode DHCP Configuration
Usage This command will fail if it would make existing ranges invalid. For example, if they
do not lie within the new network you are configuring.
The no variant of this command will fail if ranges still exist in the pool. You must
remove all ranges in the pool before issuing a no network command to remove a
network from the pool.
Examples To configure a network for the address pool P2, where the subnet is 192.0.2.5
and the mask is 255.255.255.0, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# network 192.0.2.5/24
or you can use dotted decimal notation instead of slash notation for the
subnet-mask:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# network 192.0.2.5 255.255.255.0
Related
Commands
service dhcp-server
subnet-mask
Parameter Description
<ip-subnet-address/
prefix-length> The IPv4 subnet address in dotted decimal notation
followed by the prefix length in slash notation.
<ip-subnet-address/
mask> The IPv4 subnet address in dotted decimal notation
followed by the subnet mask in dotted decimal
notation.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1812
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
NEXT-SERVER
next-server
Overview This command sets the next server address for a DHCP server pool. It is the address
of the next server that the client should use in its bootstrap process.
The no variant of this command removes the next server address from the DHCP
address pool.
Syntax next-server <ip-address>
no next-server
Mode DHCP Configuration
Example To set the next-server address for the address pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# next-server 192.0.2.2
Parameter Description
<ip-address> The server IP address, entered in dotted decimal notation.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1813
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
OPTION
option
Overview This command adds a user-defined option to the DHCP address pool you are
configuring. For the hex, integer, and flag option types, if the option already
exists, the new option overwrites the existing option’s value. Options with an ip
type can hold a list of IP addresses or masks (i.e. entries that have the A.B.C.D
address format), so if the option already exists in the pool, then the new IP address
is added to the list of existing IP addresses.
Options with the same number as one of the pre-defined options override the
standard option definition. The pre-defined options use the option numbers 1, 3,
6, 15, and 51.
The no variant of this command removes the specified user-defined option from
the DHCP pool, or all user-defined options from the DHCP pool.
Syntax option [<1-254>|<option-name>] <option-value>
no option [<1-254>|<option-value>]
Mode DHCP Configuration
Parameter Description
<1-254> The option number of the option. Options with the same
number as one of the standard options overrides the standard
option definition.
<option-name> Option name associated with the option.
<option-value> The option value. You must specify a value that is appropriate
to the option type:
hex A hexadecimal string. Valid characters are the
numbers 0–9 and letters a–f. Embedded spaces
are not valid. The string must be an even
number of characters, from 2 and 256 characters
long.
ip An IPv4 address or mask that has the dotted
decimal A.B.C.D notation. To create a list of IP
addresses, you must add each IP address
individually using the option command multiple
times.
integer A number from 0 to 4294967295.
flag A value of either true, on, or enabled to set the
flag, or false, off or disabled to unset the flag.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1814
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
OPTION
Examples To add the ASCII-type option named tftp-server-name to the pool P2 and
give the option the value server1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# option tftp-server-name server1
To add the hex-type option named tcpip-node-type to the pool P2 and give
the option the value 08af, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# option tcpip-node-type 08af
To add multiple IP addresses for the ip-type option 175, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# option 175 192.0.2.6
awplus(dhcp-config)# option 175 192.0.2.12
awplus(dhcp-config)# option 175 192.0.2.33
To add the option 179 to a pool, and give the option the value 123456, use the
command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# option 179 123456
To add a user-defined flag option with the name
perform-router-discovery, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# option perform-router-discovery yes
To clear all user-defined options from a DHCP address pool, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# no option
To clear a user-defined option, named tftp-server-name, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# no option tftp-server-name
Related
Commands
dns-server
ip dhcp option
lease
service dhcp-server
show ip dhcp pool

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1815
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
PROBE ENABLE
probe enable
Overview Use this command to enable lease probing for a DHCP pool. Probing is used by the
DHCP server to check if an IP address it wants to lease to a client is already being
used by another host.
The no variant of this command disables probing for a DHCP pool.
Syntax probe enable
no probe enable
Default Probing is enabled by default.
Mode DHCP Pool Configuration
Examples To enable probing for pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# probe enable
To disable probing for pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no probe enable
Related
Commands
probe packets
probe timeout
probe type
show ip dhcp pool

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1816
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
PROBE PACKETS
probe packets
Overview Use this command to specify the number of packets sent for each lease probe.
Lease probing is configured on a per-DHCP pool basis. When set to 0 probing is
effectively disabled.
The no variant of this command sets the number of probe packets sent to the
default of 5.
Syntax probe packets <0-10>
no probe packets
Default The default is 5.
Mode DHCP Pool Configuration
Examples To set the number of probe packets to 2 for pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# probe packets 2
To set the number of probe packets to the default 5 for pool P2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no probe packets
Related
Commands
probe enable
probe timeout
probe type
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
<0-10>The number of probe packets sent.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1817
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
PROBE TIMEOUT
probe timeout
Overview Use this command to set the timeout value in milliseconds that the server waits for
a response after each probe packet is sent. Lease probing is configured on a
per-DHCP pool basis.
The no variant of this command sets the probe timeout value to the default
setting, 200 milliseconds.
Syntax probe timeout <50-5000>
no probe timeout
Default The default timeout interval is 200 milliseconds.
Mode DHCP Pool Configuration
Examples To set the probe timeout value to 500 milliseconds for pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# probe timeout 500
To set the probe timeout value for pool P2 to the default, 200 milliseconds, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no probe timeout
Related
Commands
probe enable
probe packets
probe type
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
<50-5000>Timeout interval in milliseconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1818
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
PROBE TYPE
probe type
Overview Use this command to set the probe type for a DHCP pool. The probe type specifies
how the DHCP server checks whether an IP address is being used by other hosts,
referred to as lease probing. If arp is specified, the server sends an ARP request to
determine if an address is in use. If ping is specified, the server will send an ICMP
Echo Request (ping).
The no variant of this command sets the probe type to the default setting, ping.
Syntax probe type {arp|ping}
no probe type
Default The default probe type is ping.
Mode DHCP Pool Configuration
Examples To set the probe type to arp for the pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# probe type arp
To set the probe type for the pool P2 to the default, ping, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no probe type
Related
Commands
probe enable
probe packets
probe timeout
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
arp Probe using ARP.
ping Probe using ping.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1819
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
RANGE
range
Overview This command adds an address range to the DHCP address pool you are
configuring. The DHCP server responds to client requests received from the pool’s
network. It assigns an IP addresses within the specified range. The IP address range
must lie within the network. You can add multiple address ranges and individual IP
addresses for a DHCP pool by using this command multiple times.
The no variant of this command removes an address range from the DHCP pool.
Use the no range all command to remove all address ranges from the DHCP pool.
Syntax range <ip-address> [<ip-address>]
no range <ip-address> [<ip-address>]
no range all
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To add an address range of 192.0.2.5 to 192.0.2.16 to the pool
Nerv_Office, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool Nerv_Office
awplus(dhcp-config)# range 192.0.2.5 192.0.2.16
To add the individual IP address 192.0.2.2 to a pool, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# range 192.0.2.2
To remove all address ranges from a pool, use the command:
awplus(dhcp-config)# no range all
Related
Commands
service dhcp-server
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
<ip-address> IPv4 address range for DHCP clients, in dotted decimal
notation. The first IP address is the low end of the range, the
second IP address is the high end. Specify only one IP address
to add an individual IP address to the address pool.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1820
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
ROUTE
route
Overview This command allows the DHCP server to provide static routes to clients.
Syntax route A.B.C.D/M A.B.C.D {both|opt249|rfc3442}
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To distribute static routes for route 0.0.0.0/0 whose next hop is 192.16.1.1
to clients using both opt249 and rfc3442, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool pubic
awplus(dhcp-config)# route 0.0.0.0/0 192.16.1.1 both
Parameter Description
A.B.C.D/M Subnet for the route
A.B.C.D Next hop for the route
both opt249 and rft3442
opt249 Classless static route option for DHCP
rfc3442 Classless static route option for DHCP

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1821
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SERVICE DHCP-SERVER
service dhcp-server
Overview This command enables the DHCP server on your device. The server then listens for
DHCP requests on all IP interfaces. It will not run if there are no IP interfaces
configured.
The no variant of this command disables the DHCP server.
Syntax service dhcp-server
no service dhcp-server
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable the DHCP server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service dhcp-server
Related
Commands
show ip dhcp server summary
subnet-mask
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1822
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHORT-LEASE-THRESHOLD
short-lease-threshold
Overview Use this command to configure a short lease threshold.
Use the no variant of this command to return the short lease threshold to the
default of one minute.
Syntax short-lease-threshold <hours> <minutes>
no short-lease-threshold
Default 1 minute.
Mode DHCP Configuration
Usage DHCP leases need to be backed up in NVS so that when the DHCP server reboots
or goes through a power cycle it won't lose all the knowledge of these leases.
Some networks have a high number of mobile devices repeatedly requesting
DHCP leases every few seconds before their existing lease expires. This can happen
for example, when mobile devices move in and out of a Wi-Fi zone or when Wi-Fi
signal strength changes. This means the same IP address can have multiple lease
entries which can take up unnecessary backup file space.
The short-lease-threshold command allows you to configure the threshold for a
short lease, from 1 minute to 24 hours. Any lease less than the threshold is deemed
to be a short lease and will NOT be backed up to NVS.
This is useful if you have:
• limited backup file space, and
• you don’t need to restore leases after a device reboot or power cycle
Example To set the short lease threshold for address pool P2 to 40 minutes, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# short-lease-threshold 0 40
To set the short lease threshold for address pool Nerv_Office to 5 hours and 35
minutes, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool Nerv_Office
awplus(dhcp-config)# short-lease-threshold 5 35
Parameter Description
<hours> The number of hours, from 0 to 24.
<minutes> The number of minutes, from 0 to 60.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1823
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHORT-LEASE-THRESHOLD
To return the short lease threshold to the default of one minute, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no short-lease-threshold
Related
Commands
lease
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1824
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER DHCP-CLIENT
show counter dhcp-client
Overview This command shows counters for the DHCP client on your device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show counter dhcp-client
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the message counters for the DHCP client on your device, use the
command:
awplus# show counter dhcp-client
Output Figure 46-1: Example output from the show counter dhcp-client command
Related
Commands
ip address dhcp
show counter dhcp-client
DHCPDISCOVER out ......... 10
DHCPREQUEST out ......... 34
DHCPDECLINE out ......... 4
DHCPRELEASE out ......... 0
DHCPOFFER in ......... 22
DHCPACK in ......... 18
DHCPNAK in ......... 0
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter dhcp-client command
Parameter Description
DHCPDISCOVER out The number of DHCP Discover messages sent by the client.
DHCPREQUEST out The number of DHCP Request messages sent by the client.
DHCPDECLINE out The number of DHCP Decline messages sent by the client.
DHCPRELEASE out The number of DHCP Release messages sent by the client.
DHCPOFFER in The number of DHCP Offer messages received by the client.
DHCPACK in The number of DHCP Acknowledgement messages received
by the client.
DHCPNAK in The number of DHCP Negative Acknowledgement
messages received by the client.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1825
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER DHCP-SERVER
show counter dhcp-server
Overview

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1826
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW DHCP LEASE
show dhcp lease
Overview This command shows details about the leases that the DHCP client has acquired
from a DHCP server for interfaces on the device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see “Controlling “show”
Command Output” in the “Getting Started with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show dhcp lease [<interface>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the current lease expiry times for all interfaces, use the command:
awplus# show dhcp lease
To show the current lease for vlan1, use the command:
awplus# show dhcp lease vlan1
Output Figure 46-2: Example output from the show dhcp lease vlan1 command
Related
Commands
ip address dhcp
Parameter Description
<interface> Interface name to display DHCP lease details for.
Interface vlan1
----------------------------------------------------------------
IP Address: 192.168.22.4
Expires: 13 Mar 2017 20:10:19
Renew: 13 Mar 2017 18:37:06
Rebind: 13 Mar 2017 19:49:29
Server:
Options:
subnet-mask 255.255.255.0
routers 19.18.2.100,12.16.2.17
dhcp-lease-time 3600
dhcp-message-type 5
domain-name-servers 192.168.100.50,19.88.200.33
dhcp-server-identifier 192.168.22.1
domain-name alliedtelesis.com

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1827
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP BINDING
show ip dhcp binding
Overview This command shows the lease bindings that the DHCP server has allocated
clients.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip dhcp binding [<ip-address>|<address-pool>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display all leases for every client in all address pools, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp binding
To display the details for the leased IP address 172.16.2.16, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp binding 172.16.2.16
To display the leases from the address pool MyPool, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp binding MyPool
Output Figure 46-3: Example output from the show ip dhcp binding command
Related
Commands
clear ip dhcp binding
ip dhcp pool
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
<ip-address> IPv4 address of a leased IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
This displays the lease information for the specified IP address.
<address-pool> Name of an address pool. This displays the lease information
for all clients within the address pool.
Pool 30_2_network Network 172.16.2.0/24
DHCP Client Entries
IP Address ClientId Type Expiry
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
172.16.2.100 0050.fc82.9ede Dynamic 21 Sep 2007 19:02:58
172.16.2.101 000e.a6ae.7c14 Static Infinite
172.16.2.102 000e.a6ae.7c4c Static Infinite
172.16.2.103 000e.a69a.ac91 Static Infinite
172.16.2.104 00e0.189d.5e41 Static Infinite
172.16.2.150 00e0.2b04.5800 Static Infinite
172.16.2.167 4444.4400.35c3 Dynamic 21 Sep 2007 14:58:41

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1828
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP POOL
show ip dhcp pool
Overview This command displays the configuration details and system usage of the DHCP
address pools configured on the device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip dhcp pool [<address-pool>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example awplus# show ip dhcp pool
Output Figure 46-4: Example output from the show ip dhcp pool command
Parameter Description
<address-pool>Name of a specific address pool. This displays the
configuration of the specified address pool only.
Pool p1 :
network: 192.168.1.0/24
address ranges:
addr: 192.168.1.10 to 192.168.1.18
static host addresses:
addr: 192.168.1.12 MAC addr: 1111.2222.3333
lease <days:hours:minutes:seconds> <1:0:0:0>
subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 (pool's network mask)
Probe: Default Values
Status: Enabled [Enabled]
Type: ARP [Ping]
Packets: 2 [5]
Timeout: 200 msecs [200]
Dynamic addresses:
Total: 8
Leased: 2
Utilization: 25.0 %
Static host addresses:
Total: 1
Leased: 1
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1829
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP POOL
Figure 46-5: Example output from the show ip dhcp pool command with IP
address 192.168.1.12 assigned to a VLAN interface on the device:
Pool p1 :
network: 192.168.1.0/24
address ranges:
addr: 192.168.1.10 to 192.168.1.18
(interface addr 192.168.1.12 excluded)
(static host addr 192.168.1.12 excluded)
static host addresses:
addr: 192.168.1.12 MAC addr: 1111.2222.3333
(= interface addr, so excluded)
lease <days:hours:minutes:seconds> <1:0:0:0>
subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 (pool's network mask)
Probe: Default Values
Status: Enabled [Enabled]
Type: ARP [Ping]
Packets: 2 [5]
Timeout: 200 msecs [200]
Dynamic addresses:
Total: 8
Leased: 2
Utilization: 25.0 %
Static host addresses:
Total: 1
Leased: 1
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1830
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP POOL
Figure 46-6: Example output from the show ip dhcp pool command with a host
with MAC 0000.cd38.05f9 is registered as a static host by DHCP
Framed IP Lease feature from AUTHD:
Pool p1 :
network: 10.1.1.0/24
address ranges:
addr: 10.1.1.101 to 10.1.1.199
(static host addr 10.1.1.122 excluded)
(static host addr 10.1.1.111 excluded)
static host addresses:
addr: 10.1.1.122 MAC addr: 0000.1111.2222
addr: 10.1.1.111 MAC addr: 0000.cd38.05f9
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
Gateway : 10.1.1.1
Lease : 60 seconds
Added by AUTHD
lease <1:0:0:0>
subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 (pool's network mask)
Probe: Default Values
Status: Enabled [Enabled]
Type: Ping [Ping]
Packets: 5 [5]
Timeout: 200 msecs [200]
Dynamic addresses:
Total: 97
Leased: 1
Utilization: 1.0 %
Static host addresses:
Total: 2
Leased: 2
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show ip dhcp pool command
Parameter Description
Pool Name of the pool.
network Subnet and mask length of the pool.
address ranges Individual IP addresses and address ranges
configured for the pool. The DHCP server can offer
clients an IP address from within the specified
ranges only.
Any of these addresses that match an interface
address on the device, or a static host address
configured in the pool, will be automatically
excluded from the range, and a message to this
effect will appear beneath the range entry.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1831
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP POOL
static host addresses The static host addresses configured on the pool.
Each IP address is permanently assigned to the
client with the matching MAC address.
Any of these addresses that match an interface
address on the device will be automatically
excluded, and a message to this effect will appear
beneath the static host entry.
lease <days:hours:minutes> The lease duration for address allocated by this
pool.
domain The domain name sent by the pool to clients. This is
the domain name that the client should use when
resolving host names using DNS.
subnet mask The subnet mask sent by the pool to clients.
Probe - Status Whether lease probing is enabled or disabled.
Probe - Type The lease probe type configured. Either ping or ARP.
Probe - Packets The number of packets sent for each lease probe in
the range 0 to 10.
Probe - Timeout The timeout value in milliseconds to wait for a
response after each probe packet is sent. In the
range 50 to 5000.
dns servers The DNS server addresses sent to by the pool to
clients.
default-router(s) The default router addresses sent by the pool to
clients.
user-defined options The list of user-defined options sent by the pool to
clients.
Dynamic addresses- Total The total number of IP addresses that have been
configured in the pool for dynamic allocation to
DHCP clients.
Dynamic addresses- Leased The number of IP addresses in the pool that have
been dynamically allocated (leased) to DHCP
clients.
Dynamic addresses - Utilization The percentage of IP addresses in the pool that are
currently dynamically allocated to clients.
Static host addresses- Total The number of static IP addresses configured in the
pool for specific DHCP client hosts.
Static host addresses - Leased The number of static IP addresses assigned to
specific DHCP client hosts.
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show ip dhcp pool command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1833
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SERVER STATISTICS
show ip dhcp server statistics
Overview This command shows statistics related to the DHCP server.
You can display the server counters using the show counter dhcp-server command
as well as with this command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip dhcp server statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the server statistics, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp server statistics
Output Figure 46-7: Example output from the show ip dhcp server statistics
command
DHCP server counters
DHCPDISCOVER in ......... 20
DHCPREQUEST in ......... 12
DHCPDECLINE in ......... 1
DHCPRELEASE in ......... 0
DHCPINFORM in ......... 0
DHCPOFFER out ......... 8
DHCPACK out ......... 4
DHCPNAK out ......... 0
BOOTREQUEST in ......... 0
BOOTREPLY out ......... 0
DHCPLEASEQUERY in ....... 0
DHCPLEASEUNKNOWN out ....... 0
DHCPLEASEACTIVE out ....... 0
DHCPLEASEUNASSIGNED out ....... 0
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show ip dhcp server statistics
command
Parameter Description
DHCPDISCOVER in The number of Discover messages received by the
DHCP server.
DHCPREQUEST in The number of Request messages received by the
DHCP server.
DHCPDECLINE in The number of Decline messages received by the
DHCP server.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1834
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SERVER STATISTICS
Related
Commands
show counter dhcp-server
show ip dhcp binding
show ip dhcp pool
DHCPRELEASE in The number of Release messages received by the
DHCP server.
DHCPINFORM in The number of Inform messages received by the
DHCP server.
DHCPOFFER out The number of Offer messages sent by the DHCP
server.
DHCPACK out The number of Acknowledgement messages sent
by the DHCP server.
DHCPNAK out The number of Negative Acknowledgement
messages sent by the DHCP server. The server
sends these after receiving a request that it cannot
fulfil because either there are no available IP
addresses in the related address pool, or the
request has come from a client that doesn’t fit the
network setting for an address pool.
BOOTREQUEST in The number of bootp messages received by the
DHCP server from bootp clients.
BOOTREPLY out The number of bootp messages sent by the DHCP
server to bootp clients.
DHCPLEASEQUERY in The number of Lease Query messages received by
the DHCP server from DHCP Relay Agents.
DHCPLEASEUNKNOWN out The number of Lease Unknown messages sent by
the DHCP server to DHCP Relay Agents.
DHCPLEASEACTIVE out The number of Lease Active messages sent by the
DHCP server to DHCP Relay Agents.
DHCPLEASEUNASSIGNED
out The number of Lease Unassigned messages sent by
the DHCP server to DHCP Relay Agents.
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show ip dhcp server statistics
command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1835
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SHOW IP DHCP SERVER SUMMARY
show ip dhcp server summary
Overview This command shows the current configuration of the DHCP server. This includes:
• whether the DHCP server is enabled
• whether the DHCP server is configured to ignore BOOTP requests
• whether the DHCP server is configured to support DHCP lease queries
• the details of any user-defined options
• a list of the names of all DHCP address pools currently configured
This show command does not include any configuration details of the address
pools. You can display these using the show ip dhcp pool command.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ip dhcp server summary
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of the DHCP server, use the command:
awplus# show ip dhcp server summary
Output Figure 46-8: Example output from the show ip dhcp server summary
command
Related
Commands
DHCP Server service is disabled
BOOTP ignore is disabled
DHCP leasequery support is disabled
Pool list: p2

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1836
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DYNAMIC HOST CONFIGURATION PROTOCOL (DHCP) COMMANDS
SUBNET-MASK
subnet-mask
Overview This command sets the subnet mask option for a DHCP address pool you are
configuring. Use this command to specify the client’s subnet mask as defined in
RFC 950. This sets the subnet details using the pre-defined option 1. Note that if
you create a user-defined option 1 using the option command, then you will
override any settings created with this command. If you do not specify a subnet
mask using this command, then the pool’s network mask (specified using the
next-server command) is applied.
The no variant of this command removes a subnet mask option from a DHCP pool.
The pool reverts to using the pool’s network mask.
Syntax subnet-mask <mask>
no subnet-mask
Mode DHCP Configuration
Examples To set the subnet mask option to 255.255.255.0 for DHCP pool P2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# subnet-mask 255.255.255.0
To remove the subnet mask option from DHCP pool P2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ip dhcp pool P2
awplus(dhcp-config)# no subnet-mask
Related
Commands
default-router
dns-server
domain-name
show ip dhcp pool
Parameter Description
<mask> Valid IPv4 subnet mask, in dotted decimal notation.

47
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1837
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP for IPv6
(DHCPv6)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
DHCPv6. For more information, see the DHCPv6 Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
DHCPv6 is a network protocol used to configure IPv6 hosts with IPv6 addresses and
IPv6 prefixes for an IPv6 network. DHCPv6 is used instead of SLAAC (Stateless
Address Autoconfiguration) at sites where centralized management of IPv6 hosts
is needed. IPv6 routers require automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses and IPv6
prefixes.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
NOTE: The IPv6 addresses shown use the address space 2001:0db8::/32, defined in RFC
3849 for documentation purposes. These addresses should not be used for practical
networks (other than for testing purposes) nor should they appear on any public
network.
Command List •“clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client” on page 1838
•“clear ipv6 dhcp client” on page 1839
•“ipv6 address dhcp” on page 1840
•“show counter ipv6 dhcp-client” on page 1841
•“show ipv6 dhcp” on page 1843
•“show ipv6 dhcp interface” on page 1844

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1838
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
CLEAR COUNTER IPV6 DHCP-CLIENT
clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Overview Use this command in Privileged Exec mode to clear DHCPv6 client counters.
Syntax clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To clear DHCPv6 client counters, use the following command:
awplus# clear counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Related
Commands
show counter ipv6 dhcp-client

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1839
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
CLEAR IPV6 DHCP CLIENT
clear ipv6 dhcp client
Overview Use this command in Privileged Exec mode to restart a DHCPv6 client on an
interface.
Syntax clear ipv6 dhcp client <interface>
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To restart a DHCPv6 client on interface vlan1, use the following command:
awplus# clear ipv6 dhcp client vlan1
Parameter Description
<interface>Specify the interface name to restart a DHCPv6 client on.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1840
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
IPV6 ADDRESS DHCP
ipv6 address dhcp
Overview Use this command to activate the DHCPv6 client on the interface that you are
configuring. This allows the interface to use the DHCPv6 client to obtain its IPv6
configuration details from a DHCPv6 server on its connected network.
The command also enables IPv6 on the interface, which creates an EUI-64 link-local
address as well as enabling RA processing and SLAAC.
Use the no variant of this command to stop the interface from obtaining IPv6
configuration details from a DHCPv6 server.
The DHCPv6 client supports the following IP configuration options:
• Option 1 - the subnet mask for your device.
• Option 3 - a list of default routers.
• Option 6 - a list of DNS servers.
• Option 15 - a domain name used to resolve host names.
• Option 51 - lease expiration time.
Syntax ipv6 address dhcp [default-route-to-server]
no ipv6 address dhcp
Mode Interface Configuration for a VLAN interface or a local loopback interface.
Usage Use the default-route-to-server option to allow the automatic configuration of a
default route to the DHCPv6 server. Note that this option is not enabled by default
when you enable the DHCP client on an interface.
Examples To set the interface vlan2 to use DHCPv6 to obtain an IPv6 address, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 enable
awplus(config-if)# ipv6 address dhcp
To stop the interface vlan2 from using DHCPv6 to obtain its IPv6 address, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface vlan2
awplus(config-if)# no ipv6 address dhcp
Related
Commands
clear ipv6 dhcp client
ipv6 address
show ipv6 dhcp interface
show running-config
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1841
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER IPV6 DHCP-CLIENT
show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Overview Use this command in User Exec or Privilege Exec mode to show DHCPv6 client
counter information.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the DHCPv6 client counter information, use the command:
awplus# show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
Output Figure 47-1: Example output from the show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
command
awplus#show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
SOLICIT out ......... 20
ADVERTISE in ......... 12
REQUEST out ......... 1
CONFIRM out ......... 0
RENEW out ......... 0
REBIND out ......... 0
REPLY in ......... 0
RELEASE out ......... 0
DECLINE out ......... 0
INFORMATION-REQUEST out ......... 0
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
command
Parameter Description
SOLICIT out Displays the count of SOLICIT messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
ADVERTISE in Displays the count of ADVERTISE messages received by the
DHCPv6 client.
REQUEST out Displays the count of REQUEST messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
CONFIRM out Displays the count of CONFIRM messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
RENEW out Displays the count of RENEW messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1842
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER IPV6 DHCP-CLIENT
REBIND out Displays the count of REBIND messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
REPLY in Displays the count of REPLY messages received by the DHCPv6
client.
RELEASE out Displays the count of RELEASE messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
DECLINE out Displays the count of DECLINE messages sent by the DHCPv6
client.
INFORMATION-
REQUEST out Displays the count of INFORMATION-REQUEST messages sent
by the DHCPv6 client.
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter ipv6 dhcp-client
command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1843
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 DHCP
show ipv6 dhcp
Overview Use this command in User Exec or Privileged Exec mode to show the DHCPv6
unique identifier (DUID) configured on your device.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 dhcp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage The DUID is based on the link-layer address for both DHCPv6 client and DHCPv6
server identifiers. The device uses the MAC address from the lowest interface
number for the DUID.
The DUID is used by a DHCPv6 client to obtain an IPv6 address from a DHCPv6
server. A DHCPv6 server compares the DUID with its database of DUIDs and sends
configuration data for an IPv6 address plus the preferred and valid lease time
values to a DHCPv6 client.
Example To display the DUID configured on your device, use the command:
awplus# show ipv6 dhcp
Output Figure 47-2: Example output from the show ipv6 dhcp command
Related
Commands
ipv6 address dhcp
awplus#show ipv6 dhcp
DHCPv6 Server DUID: 0001000117ab6876001577f7ba23

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1844
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
DHCP FOR IPV6 (DHCPV6) COMMANDS
SHOW IPV6 DHCP INTERFACE
show ipv6 dhcp interface
Overview Use this command in User Exec or Privileged Exec mode to display DHCPv6
information for a specified interface, or all interfaces when entered without the
interface parameter.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Syntax show ipv6 dhcp interface [<interface-name>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display DHCPv6 information for all interfaces DHCPv6 is configured on, use the
command:
awplus# show ipv6 dhcp interface
Output Figure 47-3: Example output from the show ipv6 dhcp interface command
Parameter Description
<interface-name> Optional. Specify the name of the interface to show DHCPv6
information about. Omit this optional parameter to display
DHCPv6 information for all interfaces DHCPv6 is configured on.
awplus# show ipv6 dhcp interface
vlan1 is in client mode
Address 1001::3c0:1
preferred lifetime 9000, valid lifetime 5000
starts at 20 Jan 2012 09:21:35
expires at 20 Jan 2012 10:25:32
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show counter dhcp-client command
Parameter Description
<interface> is in
client mode Displays that the specified interface is in client
mode.
Address Displays the address of the DHCPv6 server on the
interface.
Preference Displays the preference value for the DHCPv6
server.

48
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1845
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
the Network Time Protocol (NTP). For more information, see the NTP Feature
Overview and_Configuration Guide.
The device can act as an NTP client to receive time from one or more NTP servers,
and as an NTP server.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare_Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“ntp access-group (deprecated)” on page 1847
•“ntp authenticate” on page 1848
•“ntp authentication-key” on page 1849
•“ntp broadcastdelay” on page 1850
•“ntp discard” on page 1851
•“ntp master” on page 1852
•“ntp peer” on page 1853
•“ntp rate-limit” on page 1855
•“ntp restrict” on page 1856
•“ntp server” on page 1858
•“ntp source” on page 1860
•“ntp trusted-key (deprecated)” on page 1862
•“show counter ntp (deprecated)” on page 1863
•“show ntp associations” on page 1864
•“show ntp counters” on page 1866
•“show ntp counters associations” on page 1867

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1847
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP ACCESS-GROUP (DEPRECATED)
ntp access-group (deprecated)
Overview This command has been deprecated in Software Version 5.4.6-1.1. Please use the
command ntp restrict instead.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1848
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP AUTHENTICATE
ntp authenticate
Overview This command enables NTP authentication. This allows NTP to authenticate the
associations with other systems for security purposes.
The no variant of this command disables NTP authentication.
Syntax ntp authenticate
no ntp authenticate
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable NTP authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp authenticate
To disable NTP authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp authenticate

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1849
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP AUTHENTICATION-KEY
ntp authentication-key
Overview This command defines each of the authentication keys. Each key has a key number,
a type (MD5 or SHA1), and a value.
The no variant of this disables the authentication key.
Syntax ntp authentication-key <keynumber> {md5|sha1} <key> [trusted]
no ntp authentication-key <keynumber>
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To define an MD5 authentication key number 134343 and a key value “mystring”,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp authentication-key 134343 md5 mystring
To disable the authentication key number 134343 with the key value “mystring”,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp authentication-key 134343 md5 mystring
Parameter Description
<keynumber><1-4294967295> An identification number for the key.
md5 Define an MD5 key.
sha1 Define an SHA1 key.
<key>The authentication key. For SHA1, this is a 20 hexadecimal character
string. For MD5, this is a string of up to 31 ASCII characters.
trusted Add this key to the list of authentication keys that this server trusts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1850
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP BROADCASTDELAY
ntp broadcastdelay
Overview Use this command to set the estimated round-trip delay for broadcast packets.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the round-trip delay for broadcast
packets to the default offset of 0 microseconds.
Syntax ntp broadcastdelay <delay>
no ntp broadcastdelay
Default 0 microsecond offset, which can only be applied with the no variant of this
command.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the estimated round-trip delay to 23464 microseconds for broadcast
packets, use these commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp broadcastdelay 23464
To reset the estimated round-trip delay for broadcast packets to the default setting
(0 microseconds), use these commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp broadcastdelay
Parameter Description
<delay> <1-999999> The broadcast delay in microseconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1851
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP DISCARD
ntp discard
Overview Use this command to limit the time between NTP packets on the host or hosts
specified by the command ntp restrict. Packets that arrive at greater frequency
than the limits are dropped or sent a kiss-of-death response.
Use the no variant of this command to return the limits to their default values.
Syntax ntp discard minimum <1-60>
ntp discard average <1-16>
no ntp discard minimum
no ntp discard average
Default Minimum: 2
Average: 3 (8 seconds)
Mode Global Configuration
Example To drop NTP packets from the 192.168.1.0/16 subnet if they arrive more frequently
than every 5 seconds, and also send kiss-of-death messages, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp discard minimum 5
awplus(config)# ntp restrict 192.168.1.0/16 limited kod
To silently drop all NTP packets if they arrive more frequently than once every 4
seconds on average (2 to the power of 2), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp discard average 2
awplus(config)# ntp restrict default-v4 limited
awplus(config)# ntp restrict default-v6 limited
Related
Commands
ntp restrict
Parameter Description
minimum <1-60> The minimum time between NTP packets, in seconds.
average <1-16> A value that determines the minimum average time
between NTP packets. The number of seconds is 2 to the
power of the specified value (e.g. if you specify 4, the
minimum average time is 16 seconds).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1852
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP MASTER
ntp master
Overview Use this command to make the device to be an authoritative NTP server, even if the
system is not synchronized to an outside time source.
Use the no variant of this command to stop the device being the designated NTP
server.
Syntax ntp master [<stratum>]
no ntp master
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The stratum levels define the distance from the reference clock and exist to
prevent cycles in the hierarchy. Stratum 1 is used to indicate time servers, which
are more accurate than Stratum 2 servers. For more information on the Network
Time Protocol go to: www.ntp.org
Examples To stop the device from being the designated NTP server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp master
To make the device the designated NTP server with stratum number 2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp master 2
Parameter Description
<stratum><1-15> The stratum number defines the configured level that is set
for this master within the NTP hierarchy. The default stratum number
is 12.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1853
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP PEER
ntp peer
Overview Use this command to configure an NTP peer association. An NTP association is a
peer association if this system is willing to either synchronize to the other system,
or allow the other system to synchronize to it.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured NTP peer
association.
Syntax ntp peer {<peeraddress>|<peername>}
ntp peer {<peeraddress>|<peername>} [prefer] [key <key>]
[version <version>]
no ntp peer {<peeraddress>|<peername>}
Mode Global Configuration
Examples See the following commands for options to configure NTP peer association, key
and NTP version for the peer with an IPv4 address of 192.0.2.23:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 prefer
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 prefer version 4
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 prefer version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 version 4
awplus(config)# ntp peer 192.0.2.23 key 1234
To remove an NTP peer association for this peer with an IPv4 address of
192.0.2.23, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp peer 192.0.2.23
Parameter Description
<peeraddress>Specify the IP address of the peer, entered in the form
A.B.C.D for an IPv4 address, or in the form X:X::X:X for an IPv6
address.
<peername>Specify the peer hostname. The peer hostname can resolve
to an IPv4 and an IPv6 address.
prefer Prefer this peer when possible.
key <key><1-4294967295>
Configure the peer authentication key.
version <version><1-4>
Configure for this NTP version.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1854
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP PEER
See the following commands for options to configure NTP peer association, key
and NTP version for the peer with an IPv6 address of 2001:0db8:010d::1:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 prefer
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 prefer version 4
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 prefer version 4 key
1234
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 version 4
awplus(config)# ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1 key 1234
To remove an NTP peer association for this peer with an IPv6 address of
2001:0db8:010d::1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp peer 2001:0db8:010d::1
Related
Commands
ntp server
ntp source

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1855
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP RATE-LIMIT
ntp rate-limit
Overview Use this command to enable NTP server response rate-limiting. Limiting NTP
server responses can reduce network traffic when occurrences such as
misconfigured or broken NTP clients poll the NTP server too frequently. Excessive
polling can lead to network overload.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the rate-limit configuration.
Syntax ntp rate-limit {interval<1-4096>|burst <1-255>|leak <2-16>}
no ntp rate-limit
Mode Global Configuration
Default Interval - 8 seconds.
Burst - 8 responses.
Leak - 4.
Example To configure an NTP rate-limiting interval of 30 seconds, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp rate-limit interval 30
Related
Commands
ntp restrict
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: command added
Parameter Description
interval The minimum interval between responses configured in seconds.
The default interval is 8 seconds.
burst The maximum number of responses that can be sent in a burst,
temporarily exceeding the limit specified by the interval option.
The default burst is 8 responses.
leak The rate at which responses are randomly allowed even if the
limits specified by the interval and burst options are exceeded.
The default leak is 4, i.e. on average, every fourth request has a
response.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1856
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP RESTRICT
ntp restrict
Overview Use this command to configure a restriction (allow or deny) on NTP packets or NTP
functionality for a specific host/network or all hosts of a given IP family.
This means you can control host access to NTP service and NTP server status
queries.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a restriction from one or more
hosts.
Syntax ntp restrict
{default-v4|default-v6|<host-address>|<host-subnet>}
{allow|deny}
ntp restrict
{default-v4|default-v6|<host-address>|<host-subnet>} query
{allow|deny}
ntp restrict
{default-v4|default-v6|<host-address>|<host-subnet>} serve
{allow|deny}
no ntp restrict
{default-v4|default-v6|<host-address>|<host-subnet>}
Default By default, time service is allowed to all hosts, and NTP server status querying is
denied to all hosts.
Mode Global Configuration
Parameter Description
default-v4 Apply this restriction to all IPv4 hosts.
default-v6 Apply this restriction to all IPv6 hosts.
<host-address> Apply this restriction to the specified IPv4 or IPv6 host.
Enter an IPv4 address in the format A.B.C.D.
Enter an IPv6 address in the format X:X::X:X.
<host-subnet> Apply this restriction to the specified IPv4 subnet or IPv6 prefix.
Enter an IPv4 subnet in the format A.B.C.D/M.
Enter an IPv6 prefix in the format X:X::X:X/X.
query Control NTP server status queries to matching hosts.
serve Control NTP time service to matching hosts.
allow Allow the configured restriction.
deny Deny the configured restriction.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1857
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP RESTRICT
Example To prevent all IPv4 hosts from accessing a device for NTP service, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp restrict default-v4 deny
To prevent the host 192.168.1.1 from accessing a device for NTP service, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp restrict 198.168.1.1 deny
To allow all hosts in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet to access a device for NTP server
status, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp restrict 10.10.10.0/24 query allow
Related
Commands
ntp rate-limit
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1858
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP SERVER
ntp server
Overview Use this command to configure an NTP server. This means that this system will
synchronize to the other system, and not vice versa.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured NTP server.
Syntax ntp server {<serveraddress>|<servername>}
ntp server {<serveraddress>|<servername>} [prefer] [key <key>]
[version <version>]
no ntp server {<serveraddress>|<servername>}
Mode Global Configuration
Examples See the following commands for options to configure an NTP server association,
key and NTP version for the server with an IPv4 address of 192.0.1.23:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 prefer
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 prefer version 4
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 prefer version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 version 4
awplus(config)# ntp server 192.0.1.23 key 1234
To remove an NTP peer association for this peer with an IPv4 address of 192.0.1.23,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp server 192.0.1.23
Parameter Description
<serveraddress>Specify the IP address of the peer, entered in the form
A.B.C.D for an IPv4 address, or in the form X:X::X.X for
an IPv6 address.
<servername>Specify the server hostname. The server hostname can
resolve to an IPv4 and an IPv6 address.
prefer Prefer this server when possible.
key <key><1-4294967295>
Configure the server authentication key.
version <version><1-4>
Configure for this NTP version.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1859
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP SERVER
See the following commands for options to configure an NTP server association,
key and NTP version for the server with an IPv6 address of 2001:0db8:010e::2:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 prefer
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 prefer version 4
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 prefer version 4
key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 version 4 key 1234
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 version 4
awplus(config)# ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2 key 1234
To remove an NTP peer association for this peer with an IPv6 address of
2001:0db8:010e::2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp server 2001:0db8:010e::2
Related
Commands
ntp peer
ntp source

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1860
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP SOURCE
ntp source
Overview Use this command to configure an IPv4 or an IPv6 address for the NTP source
interface. This command defines the socket used for NTP messages, and only
applies to NTP client behavior.
Note that you cannot use this command when using AMF (Allied Telesis
Management Framework).
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured IPv4 or IPv6 address
from the NTP source interface.
Syntax ntp source <source-address>
no ntp source
Default An IP address is selected based on the most appropriate egress interface used to
reach the NTP peer if a configured NTP client source IP address is unavailable or
invalid.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Adding an IPv4 or an IPv6 address allows you to select which source interface NTP
uses for peering. The IPv4 or IPv6 address configured using this command is
matched to the interface.
When selecting a source IP address to use for NTP messages to the peer, if the
configured NTP client source IP address is unavailable then default behavior will
apply, and an alternative source IP address is automatically selected. This IP
address is based on the most appropriate egress interface used to reach the NTP
peer. The configured NTP client source IP may be unavailable if the interface is
down, or an invalid IP address is configured that does not reside on the device.
Note that this command only applies to NTP client behavior. The egress interface
that the NTP messages use to reach the NTP server is determined by the ntp peer
and ntp server commands.
Note that you cannot use this command when using AMF (Allied Telesis
Management Framework).
Examples To configure the NTP source interface with the IPv4 address 192.0.2.23, enter the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp source 192.0.2.23
Parameter Description
<source-address>Specify the IP address of the NTP source interface, entered
in the form A.B.C.D for an IPv4 address, or in the form
X:X::X.X for an IPv6 address.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1861
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP SOURCE
To configure the NTP source interface with the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:010e::2,
enter the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ntp source 2001:0db8:010e::2
To remove a configured address for the NTP source interface, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ntp source
Related
Commands
ntp peer
ntp server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1862
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
NTP TRUSTED-KEY (DEPRECATED)
ntp trusted-key (deprecated)
Overview This command has been deprecated in Software Version 5.4.6-1.1. Please use the
trusted parameter of the command ntp authentication-key instead.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1864
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
SHOW NTP ASSOCIATIONS
show ntp associations
Overview Use this command to display the status of NTP associations.
Syntax show ntp associations
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example See the sample output of the show ntp associations command displaying the
status of NTP associations.
Table 48-1: Example output from show ntp associations
awplus#show ntp associations
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset disp
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*server1.example.com
192.0.2.2 4 u 47 64 377 0.177 0.021 0.001
+192.168.1.10 10.32.16.80 5 u 46 64 377 0.241 -0.045 0.000
* system peer, # backup, + candidate, - outlier, x false ticker
Table 48-2: Parameters in the output from show ntp associations
Parameter Description
* system
peer The peer that NTP uses to calculate variables like the offset and root
dispersion of this AlliedWare Plus device. NTP passes these variables
to the clients using this AlliedWare Plus device.
# backup Peers that are usable, but are not among the first six peers sorted by
synchronization distance. These peers may not be used.
+
candidate Peers that the NTP algorithm has determined can be used, along
with the system peer, to discipline the clock (i.e. to set the time on
the AlliedWare Plus device).
- outlier Peers that are not used because their time is significantly different
from the other peers.
x false
ticker Peers that are not used because they are not consider trustworthy.
space Peers that are not used because they are, for example, unreachable.
remote The peer IP address
refid The IP address of the reference clock, or an abbreviation indicating
the type of clock (e.g. GPS indicates that the server uses GPS for the
reference clock). INIT indicates that the reference clock is initializing,
so it is not operational.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1865
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
SHOW NTP ASSOCIATIONS
st The stratum, which is the number of hops between the server and
the accurate time source such as an atomic clock.
tType, one of:
u: unicast or manycast client
b: broadcast or multicast clientl: local reference clock
s: symmetric peer
A: manycast server
B: broadcast server
M: multicast server
when When last polled (seconds ago, h hours ago, or d days ago).
poll Time between NTP requests from the device to the server.
reach An indication of whether or not the NTP server is responding to
requests. 0 indicates there has never been a successful poll; 1
indicates that the last poll was successful; 3 indicates that the last
two polls were successful; 377 indicates that the last 8 polls were
successful.
delay The round trip communication delay to the remote peer or server, in
milliseconds.
offset The mean offset (phase) in the times reported between this local
host and the remote peer or server (root mean square, milliseconds).
disp The amount of clock error (in milliseconds) of the server due to clock
resolution, network congestion, etc.
Table 48-2: Parameters in the output from show ntp associations (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1866
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
SHOW NTP COUNTERS
show ntp counters
Overview This command displays packet counters for NTP.
Syntax show ntp counters
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display counters for NTP use the command:
awplus# show ntp counters
Figure 48-1: Example output from show ntp counters
awplus#show ntp counters
Server Received 4
Server Dropped 0
Client Sent 90
Client Received 76
Client Valid Received 76
Table 48-3: Parameters in the output from show ntp counters
Parameter Description
Server
Received Number of NTP packets received from NTP clients.
Server Dropped Number of NTP packets received from NTP clients but dropped.
Client Sent Number of NTP packets sent to servers.
Client
Received Number of NTP packets received from servers
Client Valid
Received Number of valid NTP packets received from servers.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1867
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
SHOW NTP COUNTERS ASSOCIATIONS
show ntp counters associations
Overview Use this command to display NTP packet counters for individual servers and peers.
Syntax show ntp counters associations
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To display packet counters for each NTP server and peer that is associated with a
device, use the command:
awplus# show ntp counters associations
Output Figure 48-2: Example output from show ntp counters associations
Related
Commands
ntp discard
ntp restrict
awplus#show ntp counters associations
Peer 2001::1
sent: -
received: -
Peer 10.37.219.100
sent: 7
received: 7
Table 48-4: Parameters in the output from show ntp counters associations
Parameter Description
Peer An NTP peer or server that the device is associated with.
sent The number of NTP packets that this device sent to the
peer.
received The number of NTP packets that this device received from
the peer.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1868
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
NTP COMMANDS
SHOW NTP STATUS
show ntp status
Overview Use this command to display the status of the Network Time Protocol (NTP).
Syntax show ntp status
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To see information about NTP status, use the command:
awplus# show ntp status
For information about the output displayed by this command, see ntp.org.
Figure 48-3: Example output from show ntp status
awplus#show ntp status
Reference ID : C0A8010A (192.168.1.10)
Stratum : 4
Ref time (UTC) : Fri Jun 15 05:32:38 2018
System time : 0.000002004 seconds fast of NTP time
Last offset : -0.002578615 seconds
RMS offset : 0.000928071 seconds
Frequency : 5.099 ppm slow
Residual freq : -9.120 ppm
Skew : 17.486 ppm
Precision : -21 (0.000000477 seconds)
Root delay : 0.031749818 seconds
Root dispersion : 0.133974627 seconds
Update interval : 65.3 seconds
Leap status : Normal

49
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1869
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Precision Time
Protocol (PTP) and
Transparent Clock
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference of commands used to configure
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Transparent Clock.
For more information, see the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and Transparent Clock
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“clock-port” on page 1870
•“ptp-clk” on page 1871
•“ptp global” on page 1873
•“show ptp data transparent” on page 1874
•“show ptp port” on page 1875

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1870
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
CLOCK-PORT
clock-port
Overview Use this command to associate the port with the clock and enable the required PTP
functionality for 1588v2 packets entering and leaving this port. For the transparent
clock, this specifically means modification of the Correction Factor to reflect the
residence time in the bridge.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the port from the clock and disable
modification of the Correction Factor.
Syntax clock-port
no clock-port
Default Ports are unassociated and disabled with the clock by default.
Mode Interface Configuration (port)
Example To configure the clock-port on port1.0.1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# clock-port
To remove port1.0.1 from the clock and disable modification of the Correction
Factor, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no clock-port
Related
Commands
ptp global
ptp-clk
show ptp data transparent
show ptp port
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x230, x550 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1871
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
PTP-CLK
ptp-clk
Overview Use this command to configure the PTP clock instance on the switch. All values
must be specified.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the clock and disable timing
support on any other ports that were set as clock-ports.
Syntax ptp-clk {ordinary|boundary|transparent} transport-type {udp
{v4|v6}|ethernet} delay-mechanism {e2e|p2p} step-type
{onestep|twostep}
no ptp-clk
Default This command is disabled by default.
Mode Global configuration
Parameter Description
ordinary An ordinary clock, able to act as Master, Slave, or Grand Master
boundary A clock able to manage downstream fan-out for an upstream
Master
transparent A device that acts as a bridge between a Master and a Slave and
participates in the timing protocol by adding the bridge
residence time to the correction factor in the packets
udp v4 Timing protocol forwarded in IPv4 UDP Packets
udp v6 Timing protocol forwarded in IPv6 UDP Packets
ethernet Timing protocol forwarded in Ethernet frames
e2e Specifies that the clock supports end to end messaging
sequences between the Master and the Slave and that the
Correction Factor is updated based on the Bridge residence time.
A Delay_Request sequence is required to determine the link delay
p2p Specifies that the clock supports end to end messaging
sequences between the Master and the Slave as well as peer to
peer messaging sequences to determine the link delay between
this device and its peers.
The Correction Factor is updated based on the Bridge residence
time plus the peer to peer link delay - so there is no need for a
delay_request message sequence.
onestep Specifies that the clock supports modification of the correction
factor as the message is transiting the switch
twostep Specifies that the clock requires that a follow-up message be sent
that is used to carry the correction factor for the previous 1588v2
message (sync, delay_request or pdelay_req)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1872
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
PTP-CLK
Usage The clock is not active until the PTP timing service is enabled via the ptp global
command. It is not possible to make a port a clock port - if the clock has not been
configured.
Example To configure a PTP instance on the switch, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ptp-clk transparent transport-type ethernet
delay-mechanism e2e step-type onestep
Related
Commands
ptp global
show ptp data transparent
show ptp port
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7- 0.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x230, x550 series products

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1873
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
PTP GLOBAL
ptp global
Overview Use this command to enable 1588v2 based timing support on the device.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the timing support.
Syntax ptp global
no ptp global
Default Disabled
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable 1588v2 timing support on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ptp global
To disable 1588v2 timing support on the switch, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ptp global
Related
Commands
clock-port
ptp-clk
show ptp data transparent
show ptp port
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x230, x550 series products
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1874
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
SHOW PTP DATA TRANSPARENT
show ptp data transparent
Overview Use this command to display configuration information for the PTP transparent
clock.
Syntax show ptp data transparent
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display configuration for PTP transparent clock, use the following command:
awplus# show ptp data transparent
Output Figure 49-1: Example output from show ptp data transparent
Related
Commands
ptp-clk
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x230, x550 series products
IE300-1#show ptp data transparent
CLOCK(Transparent)
Global Enable : Enabled
Clock Identity : 00:0c:25:ff:fe:03:92:47
Number Of Ports : 2
Transport Type : Ethernet
Delay Mechanism : End To End
Primary Domain : 0
Step-type : One Step
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1875
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PRECISION TIME PROTOCOL (PTP) AND TRANSPARENT CLOCK COMMANDS
SHOW PTP PORT
show ptp port
Overview Use this command to display the configuration and status information of the
individual ports that have been associated with the clock.
Syntax show ptp port
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display configuration and status information of the individual ports associated
with the clock, use the command:
awplus# show ptp port
Output Figure 49-2: Example output from show ptp port
Related
Commands
ptp-clk
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-0.1: command added
Version 5.4.8-0.2: added to x230, x550 series products
IE300-1#show ptp port
==================================================================
% Transparent clock
Global Enable : Enabled
Clock Identity :
00:0c:25:ff:fe:03:92:47
Port Number : 1 (Interface
port1.0.1)
Peer Delay Request Interval (log base 2) : 1
Peer Mean Path Delay : 0
Faulty Flag : False
==================================================================
% Transparent clock
Global Enable : Enabled
Clock Identity :
00:0c:25:ff:fe:03:92:47
Port Number : 2 (Interface
port1.0.2)
Peer Delay Request Interval (log base 2) : 1
Peer Mean Path Delay : 0
Faulty Flag : False

50
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1876
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
SNMP. For more information, see:
•the Support for Allied Telesis Enterprise_MIBs in AlliedWare Plus, for
information about which MIB objects are supported.
•the SNMP Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“alias (interface)” on page 1878
•“debug snmp” on page 1879
•“show counter snmp-server” on page 1880
•“show debugging snmp” on page 1884
•“show running-config snmp” on page 1885
•“show snmp-server” on page 1886
•“show snmp-server community” on page 1887
•“show snmp-server group” on page 1888
•“show snmp-server user” on page 1889
•“show snmp-server view” on page 1890
•“snmp trap link-status” on page 1891
•“snmp trap link-status suppress” on page 1892
•“snmp-server” on page 1894
•“snmp-server community” on page 1896
•“snmp-server contact” on page 1897
•“snmp-server enable trap” on page 1898

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1877
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
•“snmp-server engineID local” on page 1901
•“snmp-server engineID local reset” on page 1903
•“snmp-server group” on page 1904
•“snmp-server host” on page 1906
•“snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus” on page 1908
•“snmp-server location” on page 1909
•“snmp-server source-interface” on page 1910
•“snmp-server startup-trap-delay” on page 1911
•“snmp-server user” on page 1912
•“snmp-server view” on page 1915
•“undebug snmp” on page 1916

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1878
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
ALIAS (INTERFACE)
alias (interface)
Overview Use this command to set an alias name for a port, as returned by the SNMP ifMIB in
OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.18.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an alias name from a port.
Syntax alias <ifAlias>
no alias
Default Not set.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The interface alias can also be set via SNMP.
Third-party management systems often use standard MIBs to access device
information. Network managers can specify an alias interface name to provide a
non-volatile way to access the interface.
Example To configure the alias interface name “uplink_a” for port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# alias uplink_a
To remove an alias interface name from port1.0.1, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no alias
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<ifAlias> 64 character name for an interface in a network management
system. All printable characters are valid.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1879
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
DEBUG SNMP
debug snmp
Overview This command enables SNMP debugging.
The no variant of this command disables SNMP debugging.
Syntax debug snmp
[all|detail|error-string|process|receive|send|xdump]
no debug snmp
[all|detail|error-string|process|receive|send|xdump]
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To start SNMP debugging, use the command:
awplus# debug snmp
To start SNMP debugging, showing detailed SNMP debugging information, use
the command:
awplus# debug snmp detail
To start SNMP debugging, showing all SNMP debugging information, use the
command:
awplus# debug snmp all
Related
Commands
show debugging snmp
terminal monitor
undebug snmp
Parameter Description
all Enable or disable the display of all SNMP debugging information.
detail Enable or disable the display of detailed SNMP debugging
information.
error-string Enable or disable the display of debugging information for SNMP
error strings.
process Enable or disable the display of debugging information for
processed SNMP packets.
receive Enable or disable the display of debugging information for
received SNMP packets.
send Enable or disable the display of debugging information for sent
SNMP packets.
xdump Enable or disable the display of hexadecimal dump debugging
information for SNMP packets.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1880
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER SNMP-SERVER
show counter snmp-server
Overview This command displays counters for SNMP messages received by the SNMP agent.
Syntax show counter snmp-server
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the counters for the SNMP agent, use the command:
awplus# show counter snmp-server
Output Figure 50-1: Example output from the show counter snmp-server command
SNMP-SERVER counters
inPkts ......... 11
inBadVersions ......... 0
inBadCommunityNames ......... 0
inBadCommunityUses ......... 0
inASNParseErrs ......... 0
inTooBigs ......... 0
inNoSuchNames ......... 0
inBadValues ......... 0
inReadOnlys ......... 0
inGenErrs ......... 0
inTotalReqVars ......... 9
inTotalSetVars ......... 0
inGetRequests ......... 2
inGetNexts ......... 9
inSetRequests ......... 0
inGetResponses ......... 0
inTraps ......... 0
outPkts ......... 11
outTooBigs ......... 0
outNoSuchNames ......... 2
outBadValues ......... 0
outGenErrs ......... 0
outGetRequests ......... 0
outGetNexts ......... 0
outSetRequests ......... 0
outGetResponses ......... 11
outTraps ......... 0
UnSupportedSecLevels ......... 0
NotInTimeWindows ......... 0
UnknownUserNames ......... 0
UnknownEngineIDs ......... 0
WrongDigest ......... 0
DecryptionErrors ......... 0
UnknownSecModels ......... 0
InvalidMsgs ......... 0
UnknownPDUHandlers ......... 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1881
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER SNMP-SERVER
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter snmp-server command
Parameter Meaning
inPkts The total number of SNMP messages received by the
SNMP agent.
inBadVersions The number of messages received by the SNMP agent
for an unsupported SNMP version. It drops these
messages.The SNMP agent on your device supports
versions 1, 2C, and 3.
inBadCommunityNames The number of messages received by the SNMP agent
with an unrecognized SNMP community name. It
drops these messages.
inBadCommunityUses The number of messages received by the SNMP agent
where the requested SNMP operation is not permitted
from SNMP managers using the SNMP community
named in the message.
inASNParseErrs The number of ASN.1 or BER errors that the SNMP
agent has encountered when decoding received SNMP
Messages.
inTooBigs The number of SNMP PDUs received by the SNMP
agent where the value of the error-status field is
‘tooBig'. This is sent by an SNMP manager to indicate
that an exception occurred when processing a request
from the agent.
inNoSuchNames The number of SNMP PDUs received by the SNMP
agent where the value of the error-status field is
‘noSuchName'. This is sent by an SNMP manager to
indicate that an exception occurred when processing a
request from the agent.
inBadValues The number of SNMP PDUs received by the SNMP
agent where the value of the error-status field is
‘badValue'. This is sent by an SNMP manager to indicate
that an exception occurred when processing a request
from the agent.
inReadOnlys The number of valid SNMP PDUs received by the SNMP
agent where the value of the error-status field is
‘readOnly'. The SNMP manager should not generate a
PDU which contains the value ‘readOnly' in the error-
status field. This indicates that there is an incorrect
implementations of the SNMP.
inGenErrs The number of SNMP PDUs received by the SNMP
agent where the value of the error-status field is
‘genErr'.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1882
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER SNMP-SERVER
inTotalReqVars The number of MIB objects that the SNMP agent has
successfully retrieved after receiving valid SNMP
Get-Request and Get-Next PDUs.
inTotalSetVars The number of MIB objects that the SNMP agent has
successfully altered after receiving valid SNMP Set-
Request PDUs.
inGetRequests The number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs that the SNMP
agent has accepted and processed.
inGetNexts The number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs that the SNMP
agent has accepted and processed.
inSetRequests The number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs that the SNMP
agent has accepted and processed.
inGetResponses The number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs that the
SNMP agent has accepted and processed.
inTraps The number of SNMP Trap PDUs that the SNMP agent
has accepted and processed.
outPkts The number of SNMP Messages that the SNMP agent
has sent.
outTooBigs The number of SNMP PDUs that the SNMP agent has
generated with the value ‘tooBig’ in the error-status
field. This is sent to the SNMP manager to indicate that
an exception occurred when processing a request from
the manager.
outNoSuchNames The number of SNMP PDUs that the SNMP agent has
generated with the value `noSuchName' in the
error-status field. This is sent to the SNMP manager to
indicate that an exception occurred when processing a
request from the manager.
outBadValues The number of SNMP PDUs that the SNMP agent has
generated with the value ‘badValue’ in the error-status
field. This is sent to the SNMP manager to indicate that
an exception occurred when processing a request from
the manager.
outGenErrs The number of SNMP PDUs that the SNMP agent has
generated with the value ‘genErr' in the error-status
field. This is sent to the SNMP manager to indicate that
an exception occurred when processing a request from
the manager.
outGetRequests The number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs that the SNMP
agent has generated.
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter snmp-server command
Parameter Meaning
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1883
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER SNMP-SERVER
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
outGetNexts The number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs that the SNMP
agent has generated.
outSetRequests The number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs that the SNMP
agent has generated.
outGetResponses The number of SNMP Get-Response PDUs that the
SNMP agent has generated.
outTraps The number of SNMP Trap PDUs that the SNMP agent
has generated.
UnSupportedSecLevel
sThe number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they requested a securityLevel
unknown or not available to the SNMP agent.
NotInTimeWindows The number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they appeared outside of the
authoritative SNMP agent’s window.
UnknownUserNames The number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they referenced an unknown
user.
UnknownEngineIDs The number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they referenced an unknown
snmpEngineID.
WrongDigest The number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they didn't contain the expected
digest value.
DecryptionErrors The number of received packets that the SNMP agent
has dropped because they could not be decrypted.
UnknownSecModels The number of messages received that contain a
security model that is not supported by the server.
Valid for SNMPv3 messages only.
InvalidMsgs The number of messages received where the security
model is supported but the authentication fails. Valid
for SNMPv3 messages only.
UnknownPDUHandlers The number of times the SNMP handler has failed to
process a PDU. This is a system debugging counter.
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter snmp-server command
Parameter Meaning
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1884
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING SNMP
show debugging snmp
Overview This command displays whether SNMP debugging is enabled or disabled.
Syntax show debugging snmp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the status of SNMP debugging, use the command:
awplus# show debugging snmp
Output Figure 50-2: Example output from the show debugging snmp command
Related
Commands
debug snmp
Snmp (SMUX) debugging status:
Snmp debugging is on

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1885
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG SNMP
show running-config snmp
Overview This command displays the current configuration of SNMP on your device.
Syntax show running-config snmp
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of SNMP on your device, use the command:
awplus# show running-config snmp
Output Figure 50-3: Example output from the show running-config snmp command
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server contact AlliedTelesis
snmp-server location Philippines
snmp-server group grou1 auth read view1 write view1 notify view1
snmp-server view view1 1 included
snmp-server community public
snmp-server user user1 group1 auth md5 password priv des
password
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1886
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW SNMP-SERVER
show snmp-server
Overview This command displays the status and current configuration of the SNMP server.
Syntax show snmp-server
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the status of the SNMP server, use the command:
awplus# show snmp-server
Output Figure 50-4: Example output from the show snmp-server command
Related
Commands
debug snmp
show counter snmp-server
snmp-server
snmp-server engineID local
snmp-server engineID local reset
SNMP Server .......................... Enabled
IP Protocol .......................... IPv4
SNMPv3 Engine ID (configured name) ... Not set
SNMPv3 Engine ID (actual) ............ 0x80001f888021338e4747b8e607
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1887
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW SNMP-SERVER COMMUNITY
show snmp-server community
Overview This command displays the SNMP server communities configured on the device.
SNMP communities are specific to v1 and v2c.
Syntax show snmp-server community
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the SNMP server communities, use the command:
awplus# show snmp-server community
Output Figure 50-5: Example output from the show snmp-server community
command
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server community
SNMP community information:
Community Name ........... public
Access ................. Read-only
View ................... none

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1888
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW SNMP-SERVER GROUP
show snmp-server group
Overview This command displays information about SNMP server groups. This command is
used with SNMP version 3 only.
Syntax show snmp-server group
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the SNMP groups configured on the device, use the command:
awplus# show snmp-server group
Output Figure 50-6: Example output from the show snmp-server group command
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server group
SNMP group information:
Group name .............. guireadgroup
Security Level ........ priv
Read View ............. guiview
Write View ............ none
Notify View ........... none
Group name .............. guiwritegroup
Security Level ........ priv
Read View ............. none
Write View ............ guiview
Notify View ........... none
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1889
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW SNMP-SERVER USER
show snmp-server user
Overview This command displays the SNMP server users and is used with SNMP version 3
only.
Syntax show snmp-server user
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the SNMP server users configured on the device, use the command:
awplus# show snmp-server user
Output Figure 50-7: Example output from the show snmp-server user command
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server user
Name Group name Auth Privacy
------- ------------- ------- ----------
freddy guireadgroup none none
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1890
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SHOW SNMP-SERVER VIEW
show snmp-server view
Overview This command displays the SNMP server views and is used with SNMP version 3
only.
Syntax show snmp-server view
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the SNMP server views configured on the device, use the command:
awplus# show snmp-server view
Output Figure 50-8: Example output from the show snmp-server view command
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server view
SNMP view information:
View Name ............... view1
OID .................... 1
Type ................... included
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1891
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP TRAP LINK-STATUS
snmp trap link-status
Overview Use this command to enable SNMP to send link status notifications (traps) for the
interfaces when an interface goes up (linkUp) or down (linkDown).
Use the no variant of this command to disable the sending of link status
notifications.
Syntax snmp trap link-status [enterprise]
no snmp trap link-status
Default By default, link status notifications are disabled.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The link status notifications can be enabled for the following interface types:
• switch port (e.g. port1.0.1)
• VLAN (e.g. vlan2)
• static and dynamic link aggregation (e.g. sa2, po2)
To specify where notifications are sent, use the snmp-server host command. To
configure the device globally to send other notifications, use the snmp-server
enable trap command.
Examples To enable SNMP to send link status notifications for port1.0.1 to port1.0.3 use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# snmp trap link-status
To disable the sending of link status notifications for port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no snmp trap link-status
Related
Commands
show interface
snmp trap link-status suppress
snmp-server enable trap
snmp-server host
Parameter Description
enterprise Send an Allied Telesis enterprise type of link trap.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1892
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP TRAP LINK-STATUS SUPPRESS
snmp trap link-status suppress
Overview Use this command to enable the suppression of link status notifications (traps) for
the interfaces beyond the specified threshold, in the specified interval.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the suppression of link status
notifications for the ports.
Syntax snmp trap link-status suppress {time {<1-60>|default}|threshold
{<1-20>|default}}
no snmp trap link-status suppress
Default By default, if link status notifications are enabled (they are enabled by default), the
suppression of link status notifications is enabled: notifications that exceed the
notification threshold (default 20) within the notification timer interval (default 60
seconds) are not sent.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage An unstable network can generate many link status notifications. When
notification suppression is enabled, a suppression timer is started when the first
link status notification of a particular type (linkUp or linkDown) is sent for an
interface. If the threshold number of notifications of this type is sent before the
timer reaches the suppress time, any further notifications of this type generated for
the interface during the interval are not sent. At the end of the interval, the sending
of link status notifications resumes, until the threshold is reached in the next
interval.
Examples To suppress link status notifications for port1.0.1 to port1.0.3 after 10 notifications
in 40 seconds, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1-port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# snmp trap link-status suppress time 40
threshold 10
Parameter Description
time Set the suppression timer for link status notifications.
<1-60>The suppress time in seconds.
default The default suppress time in seconds (60).
threshold Set the suppression threshold for link status notifications. This is the
number of link status notifications after which to suppress further
notifications within the suppression timer interval.
<1-20>The number of link status notifications.
default The default number of link status notifications (20).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1893
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP TRAP LINK-STATUS SUPPRESS
To stop suppressing link status notifications for port1.0.1, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no snmp trap link-status suppress
Related
Commands
show interface
snmp trap link-status

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1894
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER
snmp-server
Overview Use this command to enable the SNMP agent (server) on the device. The SNMP
agent receives and processes SNMP packets sent to the device, and generates
notifications (traps) that have been enabled by the snmp-server enable trap
command.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the SNMP agent on the device.
When SNMP is disabled, SNMP packets received by the device are discarded, and
no notifications are generated. This does not remove any existing SNMP
configuration.
Syntax snmp-server [ip|ipv6]
no snmp-server [ip|ipv6]
Default By default, the SNMP agent is enabled for both IPv4 and IPv6. If neither the ip
parameter nor the ipv6 parameter is specified for this command, then SNMP is
enabled or disabled for both IPv4 and IPv6.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable SNMP on the device for both IPv4 and IPv6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server
To enable the SNMP agent for IPv4 on the device, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server ip
To disable the SNMP agent for both IPv4 and IPv6 on the device, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server
To disable the SNMP agent for IPv4, use the commands:
awplus(config)# no snmp-server ipv4
Parameter Description
ip Enable or disable the SNMP agent for IPv4.
ipv6 Enable or disable the SNMP agent for IPv6.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1895
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
show snmp-server community
show snmp-server user
snmp-server community
snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable trap
snmp-server engineID local
snmp-server group
snmp-server host
snmp-server location
snmp-server view

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1896
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER COMMUNITY
snmp-server community
Overview This command creates an SNMP community, optionally setting the access mode
for the community. The default access mode is read only. If view is not specified,
the community allows access to all the MIB objects. The SNMP communities are
only valid for SNMPv1 and v2c and provide very limited security. Communities
should not be used when operating SNMPv3.
The no variant of this command removes an SNMP community. The specified
community must already exist on the device.
Syntax snmp-server community <community-name> {view
<view-name>|ro|rw|<access-list>}
no snmp-server community <community-name> [{view
<view-name>|<access-list>}]
Mode Global Configuration
Example The following command creates an SNMP community called “public” with read
only access to all MIB variables from any management station.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server community public ro
The following command removes an SNMP community called “public”
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server community public
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
show snmp-server community
snmp-server view
Parameter Description
<community-name> Community name. The community name is a case sensitive
string of up to 20 characters.
view Configure SNMP view. If view is not specified, the community
allows access to all the MIB objects.
<view-name> View name. The view name is a string up to 20 characters long
and is case sensitive.
ro Read-only community.
rw Read-write community.
<access-list> <1-99> Access list number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1897
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER CONTACT
snmp-server contact
Overview This command sets the contact information for the system. The contact name is:
• displayed in the output of the show system command
• stored in the MIB object sysContact
The no variant of this command removes the contact information from the system.
Syntax snmp-server contact <contact-info>
no snmp-server contact
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set the system contact information to “support@alliedtelesis.co.nz”, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server contact
support@alliedtelesis.co.nz
Related
Commands
show system
snmp-server location
snmp-server group
Parameter Description
<contact-info> The contact information for the system, from 0 to 255 characters
long. Valid characters are any printable character and spaces.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1898
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENABLE TRAP
snmp-server enable trap
Overview Use this command to enable the switch to transmit the specified notifications
(traps).
Note that the Environmental Monitoring traps defined in the AT-ENVMONv2-MIB
are enabled by default.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the transmission of the specified
notifications.
Syntax snmp-server enable trap <trap-list>
no snmp-server enable trap <trap-list>
Depending on your device model, you can enable some or all of the traps in the
following table:
Parameter Description
atmf AMF traps.
atmflink AMF link traps.
atmfnode AMF node traps.
atmfrr AMF reboot-rolling traps.
auth Authentication failure.
bgp BGP traps.
chassis Chassis traps.
dhcpsnooping DHCP snooping and ARP security traps. These notifications must
also be set using the ip dhcp snooping violation command,
and/or the arp security violation arp security violation
command.
epsr EPSR traps.
g8032 G.8032 ERP traps.
lldp Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) traps. These notifications
must also be enabled using the lldp notifications command,
and/or the lldp med-notifications command.
loopprot Loop Protection traps.
mstp MSTP traps.
nsm NSM traps.
ospf OSPF traps.
pim PIM traps.
power-inline Power-inline traps (Power Ethernet MIB RFC 3621).
qsp QoS Storm Protection

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1899
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENABLE TRAP
Default By default, no notifications are generated.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage This command cannot be used to enable link status notifications globally. To
enable link status notifications for particular interfaces, use the snmp trap
link-status command.
To specify where notifications are sent, use the snmp-server host command.
Note that you can enable (or disable) multiple traps with a single command, by
specifying a space-separated list of traps.
Examples To enable the device to send a notification if an AMF node changes its status, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server enable trap atmfnode
To enable the device to send MAC address Thrash Limiting traps, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server enable trap thrash-limit
To disable the device from sending MAC address Thrash Limiting traps, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server enable trap thrash-limit
To disable OSPF traps being sent out by the device, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server enable trap ospf
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
show ip dhcp snooping
snmp trap link-status
snmp-server host
trap (G.8032)
private-vlan ufo trap
rmon RMON traps.
thrash-limit MAC address Thrash Limiting traps.
vcs VCS traps.
vrrp Virtual Router Redundancy (VRRP) traps.
ufo Upstream Forwarding Only (UFO) traps.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1900
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENABLE TRAP
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: ufo parameter added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1901
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENGINEID LOCAL
snmp-server engineID local
Overview Use this command to configure the SNMPv3 engine ID. The SNMPv3 engine ID is
used to uniquely identify the SNMPv3 agent on a device when communicating
with SNMP management clients. Once an SNMPv3 engine ID is assigned, this
engine ID is permanently associated with the device until you change it.
Use the no variant of this command to set the user defined SNMPv3 engine ID to a
system generated pseudo-random value by resetting the SNMPv3 engine. The no
snmp-server engineID local command has the same effect as the snmp-server
engineID local default command.
Note that the snmp-server engineID local reset command is used to force the
system to generate a new engine ID when the current engine ID is also system
generated.
Syntax snmp-server engineID local {<engine-id>|default}
no snmp-server engineID local
Mode Global Configuration
Usage All devices must have a unique engine ID which is permanently set unless it is
configured by the user.
Example To set the SNMPv3 engine ID to 800000cf030000cd123456, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server engineID local
800000cf030000cd123456
To set a user defined SNMPv3 engine ID back to a system generated value, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server engineID local
Output The following example shows the engine ID values after configuration:
Parameter Description
<engine-id> Specify SNMPv3 Engine ID value, a string of up to 27 characters.
default Set SNMPv3 engine ID to a system generated value by resetting the
SNMPv3 engine, provided the current engine ID is user defined. If the
current engine ID is system generated, use the snmp-server engineID
local reset command to force the system to generate a new engine
ID.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1902
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENGINEID LOCAL
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
snmp-server engineID local reset
snmp-server group
awplus(config)#snmp-server engineid local asdgdfh231234d
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#show snmp-server
SNMP Server .......................... Enabled
IP Protocol .......................... IPv4
SNMPv3 Engine ID (configured name) ... asdgdfh231234d
SNMPv3 Engine ID (actual) ............ 0x80001f888029af52e149198483
awplus(config)#no snmp-server engineid local
awplus(config)#exit
awplus#show snmp-server
SNMP Server .......................... Enabled
IP Protocol .......................... IPv4
SNMPv3 Engine ID (configured name) ... Not set
SNMPv3 Engine ID (actual) ............ 0x80001f888029af52e149198483

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1903
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER ENGINEID LOCAL RESET
snmp-server engineID local reset
Overview Use this command to force the device to generate a new pseudo-random SNMPv3
engine ID by resetting the SNMPv3 engine. If the current engine ID is user defined,
use the snmp-server engineID local command to set SNMPv3 engine ID to a system
generated value.
Syntax snmp-server engineID local reset
Mode Global Configuration
Example To force the SNMPv3 engine ID to be reset to a system generated value, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server engineID local reset
Related
Commands
snmp-server engineID local
show snmp-server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1904
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER GROUP
snmp-server group
Overview This command is used with SNMP version 3 only, and adds an SNMP group,
optionally setting the security level and view access modes for the group. The
security and access views defined for the group represent the minimum required
of its users in order to gain access.
The no variant of this command deletes an SNMP group, and is used with SNMPv3
only. The group with the specified authentication/encryption parameters must
already exist.
Syntax snmp-server group <groupname> {auth|noauth|priv} [read
<readname>|write <writename>|notify <notifyname>]
no snmp-server group <groupname> {auth|noauth|priv}
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To add SNMP group, for ordinary users, user the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server group usergroup noauth read
useraccess write useraccess
To delete SNMP group usergroup, use the following commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server group usergroup noauth
Parameter Description
<groupname>Group name. The group name is a string up to 20 characters long
and is case sensitive.
auth Authentication.
noauth No authentication and no encryption.
priv Authentication and encryption.
read Configure read view.
<readname>Read view name.
write Configure write view.
<writename>Write view name. The view name is a string up to 20 characters long
and is case sensitive.
notify Configure notify view.
<notifyname>Notify view name. The view name is a string up to 20 characters
long and is case sensitive.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1906
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER HOST
snmp-server host
Overview This command specifies an SNMP trap host destination to which Trap or Inform
messages generated by the device are sent.
For SNMP version 1 and 2c you must specify the community name parameter. For
SNMP version 3, specify the authentication/encryption parameters and the user
name. If the version is not specified, the default is SNMP version 1. Inform
messages can be sent instead of traps for SNMP version 2c and 3.
Use the no variant of this command to remove an SNMP trap host. The trap host
must already exist.
The trap host is uniquely identified by:
• host IP address (IPv4 or IPv6),
• inform or trap messages,
• community name (SNMPv1 or SNMP v2c) or the authentication/encryption
parameters and user name (SNMP v3).
Syntax snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>} [traps]
[version 1] <community-name>]
snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>}
[informs|traps] version 2c <community-name>
snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>}
[informs|traps] version 3 {auth|noauth|priv} <user-name>
no snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>} [traps]
[version 1] <community-name>
no snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>}
[informs|traps] version 2c <community-name>
no snmp-server host {<ipv4-address>|<ipv6-address>}
[informs|traps] version 3 {auth|noauth|priv} <user-name>
Parameter Description
<ipv4-address> IPv4 trap host address in the format A.B.C.D, for example,
192.0.2.2.
<ipv6-address>IPv6 trap host address in the format x:x::x:x for example,
2001:db8::8a2e:7334.
informs Send Inform messages to this host.
traps Send Trap messages to this host (default).
version SNMP version to use for notification messages. Default:
version 1.
1Use SNMPv1(default).
2c Use SNMPv2c.
3Use SNMPv3.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1907
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER HOST
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure the device to send generated traps to the IPv4 host destination
192.0.2.5 with the SNMPv2c community name public, use the following
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server host version 2c public192.0.2.5
To configure the device to send generated traps to the IPv6 host destination
2001:db8::8a2e:7334 with the SNMPv2c community name private, use the
following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server host version 2c
private2001:db8::8a2e:7334
To remove a configured trap host of 192.0.2.5 with the SNMPv2c community name
public, use the following command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server host version 2c public192.0.2.5
Related
Commands
snmp trap link-status
snmp-server enable trap
snmp-server view
auth Authentication.
noauth No authentication.
priv Encryption.
<community-name>The SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c community name.
<user-name>SNMPv3 user name.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1908
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER LEGACY-IFADMINSTATUS
snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus
Overview Use this command to set the ifAdminStatus to reflect the operational state of the
interface, rather than the administrative state.
The no variant of this command sets the ifAdminStatus to reflect the
administrative state of the interface.
Syntax snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus
no snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus
Default Legacy ifAdminStatus is turned off by default, so by default the SNMP
ifAdminStatus reflects the administrative state of the interface.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Note that if you enable Legacy ifAdminStatus, the ifAdminStatus will report a link’s
status as Down when the link has been blocked by a process such as loop
protection.
Example To turn on Legacy ifAdminStatus, use the command:
awplus#snmp-server legacy-ifadminstatus
Related
Commands
show interface

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1909
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER LOCATION
snmp-server location
Overview This command sets the location of the system. The location is:
• displayed in the output of the show system command
• stored in the MIB object sysLocation
The no variant of this command removes the configured location from the system.
Syntax snmp-server location <location-name>
no snmp-server location
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set the location to “server room 523”, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server location server room 523
Related
Commands
show snmp-server
show system
snmp-server contact
Parameter Description
<location-name>The location of the system, from 0 to 255 characters long. Valid
characters are any printable character and spaces.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1910
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER SOURCE-INTERFACE
snmp-server source-interface
Overview Use this command to specify the originating interface for SNMP traps or informs.
An interface specified by this command must already have an IP address assigned
to it.
Use the no variant of this command to reset the interface to its default value (the
originating egress interface).
Syntax snmp-server source-interface {traps|informs} <interface-name>
no snmp-server source-interface {traps|informs}
Default By default, the source interface is the originating egress interface of the traps and
informs messages.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage An SNMP trap or inform message that is sent from an SNMP server carries the
notification IP address of its originating interface. Use this command to assign this
interface.
Example The following commands set vlan2 to be the interface whose IP address is used as
the originating address in SNMP informs packets.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server source-interface informs vlan2
The following commands reset the originating source interface for SNMP trap
messages to be the default interface (the originating egress interface):
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server source-interface traps
Validation
Commands
show running-config
Parameter Description
traps SNMP traps.
informs SNMP informs.
<interface-name>Interface name (must already have an IP address assigned).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1911
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER STARTUP-TRAP-DELAY
snmp-server startup-trap-delay
Overview Use this command to set the time in seconds after following completion of the
device startup sequence before the device sends any SNMP traps (or SNMP
notifications).
Use the no variant of this command to restore the default startup delay of 30
seconds.
Syntax snmp-server startup-trap-delay <delay-time>
no snmp-server startup-trap-delay
Default The SNMP server trap delay time is 30 seconds. The no variant restores the default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To delay the device sending SNMP traps until 60 seconds after device startup, use
the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server startup-trap-delay 60
To restore the sending of SNMP traps to the default of 30 seconds after device
startup, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server startup-trap-delay
Validation
Commands
show snmp-server
Parameter Description
<delay-time>Specify an SNMP trap delay time in seconds in the range of 30
to 600 seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1912
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER USER
snmp-server user
Overview Use this command to create or move users as members of specified groups. This
command is used with SNMPv3 only.
The no variant of this command removes an SNMPv3 user. The specified user must
already exist.
Syntax snmp-server user <username> <groupname> [encrypted] [auth
{md5|sha} <auth-password>] [priv {des|aes} <privacy-password>]
no snmp-server user <username>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Additionally this command provides the option of selecting an authentication
protocol and (where appropriate) an associated password. Similarly, options are
offered for selecting a privacy protocol and password.
• Note that each SNMP user must be configured on both the manager and
agent entities. Where passwords are used, these passwords must be the
same for both entities.
•Use the encrypted parameter when you want to enter already encrypted
passwords in encrypted form as displayed in the running and startup configs
stored on the device. For example, you may need to move a user from one
group to another group and keep the same passwords for the user instead
of removing the user to apply new passwords.
Parameter Description
<username>User name. The user name is a string up to 20 characters
long and is case sensitive.
<groupname>Group name. The group name is a string up to 20
characters long and is case sensitive.
encrypted Use the encrypted parameter when you want to enter
encrypted passwords.
auth Authentication protocol.
md5 MD5 Message Digest Algorithms.
sha SHA Secure Hash Algorithm.
<auth-password>Authentication password. The password is a string of 8 to
20 characters long and is case sensitive.
priv Privacy protocol.
des DES Data Encryption Standard.
aes AES Advanced Encryption Standards.
<privacy-password>Privacy password. The password is a string of 8 to 20
characters long and is case sensitive.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1913
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER USER
• User passwords are entered using plaintext without the encrypted
parameter and are encrypted according to the authentication and privacy
protocols selected.
• User passwords are viewed as encrypted passwords in running and startup
configs shown from show running-config and show startup-config
commands respectively. Copy and paste encrypted passwords from
running-configs or startup-configs to avoid entry errors.
Examples To add SNMP user authuser as a member of group usergroup, with
authentication protocol md5, authentication password Authpass, privacy
protocol des and privacy password Privpass, use the following commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server user authuser usergroup auth md5
Authpass priv des Privpass
Validate the user is assigned to the group using the show snmp-server user
command:
To enter existing SNMP user authuser with existing passwords as a member of
group newusergroup with authentication protocol md5 plus the encrypted
authentication password 0x1c74b9c22118291b0ce0cd883f8dab6b74, privacy
protocol des plus the encrypted privacy password
0x0e0133db5453ebd03822b004eeacb6608f, use the following commands
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# snmp-server user authuser newusergroup
encrypted auth md5 0x1c74b9c22118291b0ce0cd883f8dab6b74 priv
des 0x0e0133db5453ebd03822b004eeacb6608f
NOTE: Copy and paste the encrypted passwords from the running-config or the
startup-config displayed, using the show running-config and show startup- config
commands respectively, into the command line to avoid key stroke errors issuing this
command.
Validate the user has been moved from the first group using the show
snmp-server user command:
To delete SNMP user authuser, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no snmp-server user authuser
awplus#show snmp-server user
Name Group name Auth Privacy
------- ------------- ------- ----------
authuser usergroup md5 des
awplus#show snmp-server user
Name Group name Auth Privacy
------- ------------- ------- ----------
authuser newusergroup md5 des

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1915
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SNMP COMMANDS
SNMP-SERVER VIEW
snmp-server view
Overview Use this command to create an SNMP view that specifies a sub-tree of the MIB.
Further sub-trees can then be added by specifying a new OID to an existing view.
Views can be used in SNMP communities or groups to control the remote
manager’s access.
NOTE: The object identifier must be specified in a sequence of integers separated by
decimal points.
The no variant of this command removes the specified view on the device. The
view must already exist.
Syntax snmp-server view <view-name> <mib-name> {included|excluded}
no snmp-server view <view-name>
Mode Global Configuration
Examples The following command creates a view called “loc” that includes the system
location MIB sub-tree.
awplus(config)# snmp-server view loc 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 included
To remove the view “loc” use the following command
awplus(config)# no snmp-server view loc
Related
Commands
show snmp-server view
snmp-server community
Parameter Description
<view-name>SNMP server view name.
The view name is a string up to 20 characters long and is case
sensitive.
<mib-name>Object identifier of the MIB.
included Include this OID in the view.
excluded Exclude this OID in the view.

51
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1917
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP Commands
Introduction
Overview LLDP and LLDP-MED can be configured using the commands in this chapter, or by
using SNMP with the LLDP-MIB and LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB (see the Support for
Allied Telesis Enterprise MIBs in AlliedWare Plus).
The Voice VLAN feature can be configured using commands in VLAN Commands
chapter.
For more information about LLDP, see the LLDP Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
LLDP can transmit a lot of data about the network. Typically, the network
information gathered using LLDP is transferred to a Network Management System
by SNMP. For security reasons, we recommend using SNMPv3 for this purpose (see
the SNMP Feature Overview and Configuration Guide).
LLDP operates over physical ports only. For example, it can be configured on switch
ports that belong to static or dynamic channel groups, but not on the channel
groups themselves.
Command List •“clear lldp statistics” on page 1919
•“clear lldp table” on page 1920
•“debug lldp” on page 1921
•“lldp faststart-count” on page 1923
•“lldp holdtime-multiplier” on page 1924
•“lldp management-address” on page 1925
•“lldp med-notifications” on page 1926
•“lldp med-tlv-select” on page 1927
•“lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check” on page 1930
•“lldp notification-interval” on page 1931
•“lldp notifications” on page 1932

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1918
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
•“lldp port-number-type” on page 1933
•“lldp reinit” on page 1934
•“lldp run” on page 1935
•“lldp timer” on page 1936
•“lldp tlv-select” on page 1937
•“lldp transmit receive” on page 1939
•“lldp tx-delay” on page 1940
•“location civic-location configuration” on page 1941
•“location civic-location identifier” on page 1945
•“location civic-location-id” on page 1946
•“location coord-location configuration” on page 1947
•“location coord-location identifier” on page 1949
•“location coord-location-id” on page 1950
•“location elin-location” on page 1952
•“location elin-location-id” on page 1953
•“show debugging lldp” on page 1954
•“show lldp” on page 1956
•“show lldp interface” on page 1958
•“show lldp local-info” on page 1960
•“show lldp neighbors” on page 1965
•“show lldp neighbors detail” on page 1967
•“show lldp statistics” on page 1971
•“show lldp statistics interface” on page 1973
•“show location” on page 1975

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1919
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
CLEAR LLDP STATISTICS
clear lldp statistics
Overview This command clears all LLDP statistics (packet and event counters) associated
with specified ports. If no port list is supplied, LLDP statistics for all ports are
cleared.
Syntax clear lldp statistics [interface <port-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To clear the LLDP statistics on ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# clear lldp statistics interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
To clear all LLDP statistics for all ports, use the command:
awplus# clear lldp statistics
Related
Commands
show lldp statistics
show lldp statistics interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports for which the statistics are to be cleared.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1920
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
CLEAR LLDP TABLE
clear lldp table
Overview This command clears the table of LLDP information received from neighbors
through specified ports. If no port list is supplied, neighbor information is cleared
for all ports.
Syntax clear lldp table [interface <port-list>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To clear the table of neighbor information received on ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the
command:
awplus# clear lldp table interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
To clear the entire table of neighbor information received through all ports, use the
command:
awplus# clear lldp table
Related
Commands
show lldp neighbors
Parameter Description
<port-list> The ports for which the neighbor information table is to be cleared.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1921
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
DEBUG LLDP
debug lldp
Overview This command enables specific LLDP debug for specified ports. When LLDP
debugging is enabled, diagnostic messages are entered into the system log. If no
port list is supplied, the specified debugging is enabled for all ports.
The no variant of this command disables specific LLDP debug for specified ports. If
no port list is supplied, the specified debugging is disabled for all ports.
Syntax debug lldp {[rx][rxpkt][tx][txpkt]} [interface [<port-list>]]
debug lldp operation
no debug lldp {[rx][rxpkt][tx][txpkt]} [interface
[<port-list>]]
no debug lldp operation
no debug lldp all
Default By default no debug is enabled for any ports.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To enable debugging of LLDP receive on ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# debug lldp rx interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
To enable debugging of LLDP transmit with packet dump on all ports, use the
command:
awplus# debug lldp tx txpkt
To disable debugging of LLDP receive on ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# no debug lldp rx interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
To turn off all LLDP debugging on all ports, use the command:
awplus# no debug lldp all
Parameter Description
rx LLDP receive debug.
rxpkt Raw LLDPDUs received in hex format.
tx LLDP transmit debug.
txpkt Raw Tx LLDPDUs transmitted in hex format.
<port-list>The ports for which debug is to be configured.
operation Debug for LLDP internal operation on the switch.
all Disables all LLDP debugging for all ports.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1923
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP FASTSTART-COUNT
lldp faststart-count
Overview Use this command to set the fast start count for LLDP-MED. The fast start count
determines how many fast start advertisements LLDP sends from a port when it
starts sending LLDP-MED advertisements from the port, for instance, when it
detects a new LLDP-MED capable device.
The no variant of this command resets the LLDPD-MED fast start count to the
default (3).
Syntax lldp faststart-count <1-10>
no lldp faststart-count
Default The default fast start count is 3.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the fast start count to 5, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp faststart-count 5
To reset the fast start count to the default setting (3), use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp faststart-count
Related
Commands
show lldp
Parameter Description
<1-10>The number of fast start advertisements to send.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1924
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP HOLDTIME-MULTIPLIER
lldp holdtime-multiplier
Overview This command sets the holdtime multiplier value. The transmit interval is
multiplied by the holdtime multiplier to give the Time To Live (TTL) value that is
advertised to neighbors.
The no variant of this command sets the multiplier back to its default.
Syntax lldp holdtime-multiplier <2-10>
no lldp holdtime-multiplier
Default The default holdtime multiplier value is 4.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The Time-To-Live defines the period for which the information advertised to the
neighbor is valid. If the Time-To-Live expires before the neighbor receives another
update of the information, then the neighbor discards the information from its
database.
Examples To set the holdtime multiplier to 2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp holdtime-multiplier 2
To set the holdtime multiplier back to its default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp holdtime-multiplier 2
Related
Commands
show lldp
Parameter Description
<2-10>The multiplier factor.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1925
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP MANAGEMENT-ADDRESS
lldp management-address
Overview This command sets the IPv4 address to be advertised to neighbors (in the
Management Address TLV) via the specified ports. This address will override the
default address for these ports.
The no variant of this command clears the user-configured management IP
address advertised to neighbors via the specified ports. The advertised address
reverts to the default.
Syntax lldp management-address <ipaddr>
no lldp management-address
Default The local loopback interface primary IPv4 address if set, else the primary IPv4
interface address of the lowest numbered VLAN the port belongs to, else the MAC
address of the device’s baseboard if no VLAN IP addresses are configured for the
port.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage To see the management address that will be advertised, use the show lldp
interface command or show lldp local-info command.
Examples To set the management address advertised by port1.0.1 and port1.0.2, to be
192.168.1.6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lldp management-address 192.168.1.6
To clear the user-configured management address advertised by port1.0.1 and
port1.0.2, and revert to using the default address, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no lldp management-address
Related
Commands
show lldp interface
show lldp local-info
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
<ipaddr>The IPv4 address to be advertised to neighbors, in dotted
decimal format. This must be one of the IP addresses already
configured on the device.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1926
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP MED-NOTIFICATIONS
lldp med-notifications
Overview Use this command to enable LLDP to send LLDP-MED Topology Change Detected
SNMP notifications relating to the specified ports. The switch sends an SNMP event
notification when a new LLDP-MED compliant IP Telephony device is connected to
or disconnected from a port on the switch.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the sending of LLDP-MED Topology
Change Detected notifications relating to the specified ports.
Syntax lldp med-notifications
no lldp med-notifications
Default The sending of LLDP-MED notifications is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To enable the sending of LLDP-MED Topology Change Detected notifications
relating to ports port1.0.1 and port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lldp med-notifications
To disable the sending of LLDP-MED notifications relating to port1.0.1 and
port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no lldp med-notifications
Related
Commands
lldp notification-interval
lldp notifications
snmp-server enable trap
show lldp interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1927
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP MED-TLV-SELECT
lldp med-tlv-select
Overview Use this command to enable LLDP-MED Organizationally Specific TLVs for
transmission in LLDP advertisements via the specified ports. The LLDP-MED
Capabilities TLV must be enabled before any of the other LLDP-MED
Organizationally Specific TLVs are enabled.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the specified LLDP-MED
Organizationally Specific TLVs for transmission in LLDP advertisements via these
ports. In order to disable the LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV, you must also disable the
rest of these TLVs. Disabling all these TLVs disables LLDP-MED advertisements.
Syntax lldp med-tlv-select [capabilities] [network-policy] [location]
[inventory-management]
lldp med-tlv-select all
no lldp med-tlv-select [capabilities] [network-policy]
[location] [inventory-management]
no lldp med-tlv-select all
Parameter Description
capabilities LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV. When this is enabled, the
MAC/PHY Configuration/Status TLV from IEEE 802.3
Organizationally Specific TLVs is also automatically
included in LLDP-MED advertisements, whether or not it
has been explicitly enabled by the lldp tlv-select
command.
network-policy Network Policy TLV. This TLV is transmitted if Voice VLAN
parameters have been configured using the commands:
•switchport voice dscp
•switchport voice vlan
•switchport voice vlan priority
location Location Identification TLV. This TLV is transmitted if
location information has been configured using the
commands:
•location elin-location-id
•location civic-location identifier
•location civic-location configuration
•location coord-location identifier
•location coord-location configuration
•location elin-location

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1928
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP MED-TLV-SELECT
Default By default LLDP-MED Capabilities, Network Policy, Location Identification and
Extended Power-via-MDI TLVs are enabled. Therefore, if LLDP is enabled using the
lldp run command, by default LLDP-MED advertisements are transmitted on ports
that detect LLDP-MED neighbors connected to them.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage LLDP-MED TLVs are only sent in advertisements via a port if there is an
LLDP-MED-capable device connected to it. To see whether there are LLDP-MED
capable devices connected to the ports, use the show lldp neighbors command.
Examples To enable inclusion of the Inventory TLV Set in advertisements transmitted via
port1.0.1 and port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lldp med-tlv-select inventory-management
To exclude the Inventory TLV Set in advertisements transmitted via port1.0.1 and
port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no lldp med-tlv-select inventory-management
To disable LLDP-MED advertisements transmitted via port1.0.1 and port1.0.2,
disable all these TLVs using the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no lldp med-tlv-select all
inventory-management Inventory Management TLV Set, including the following
TLVs:
• Hardware Revision
• Firmware Revision
• Software Revision
• Serial Number
• Manufacturer Name
•Model Name
• Asset ID
all All LLDP-MED Organizationally Specific TLVs.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1929
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP MED-TLV-SELECT
Related
Commands
lldp tlv-select
location elin-location-id
location civic-location identifier
location civic-location configuration
location coord-location identifier
location coord-location configuration
location elin-location
show lldp interface
switchport voice dscp
switchport voice vlan
switchport voice vlan priority
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1930
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP NON-STRICT-MED-TLV-ORDER-CHECK
lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check
Overview Use this command to enable non-strict order checking for LLDP-MED
advertisements it receives. That is, use this command to enable LLDP to receive
and store TLVs from LLDP-MED advertisements even if they do not use standard
TLV order.
Use the no variant of this command to disable non-strict order checking for
LLDP-MED advertisements, that is, to set strict TLV order checking, so that LLDP
discards any LLDP-MED TLVs that occur before the LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV in
an advertisement.
Syntax lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check
no lldp non-strict-med-tlv-order-check
Default By default TLV non-strict order checking for LLDP-MED advertisements is disabled.
That is, strict order checking is applied to LLDP-MED advertisements, according to
ANSI/TIA-1057, and LLDP-MED TLVs in non-standard order are discarded.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage The ANSI/TIA-1057 specifies standard order for TLVs in LLDP-MED advertisements,
and specifies that if LLDP receives LLDP advertisements with non-standard
LLDP-MED TLV order, the TLVs in non-standard order should be discarded. This
implementation of LLDP-MED follows the standard: it transmits TLVs in the
standard order, and by default discards LLDP-MED TLVs that occur before the
LLDP-MED Capabilities TLV in an advertisement. However, some implementations
of LLDP transmit LLDP-MED advertisements with non-standard TLV order. To
receive and store the data from these non-standard advertisements, enable
non-strict order checking for LLDP-MED advertisements using this command.
Examples To enable strict TLV order checking, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp tlv-order-check
To disable strict TLV order checking, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp tlv-order-check
Related
Commands
show running-config lldp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1931
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP NOTIFICATION-INTERVAL
lldp notification-interval
Overview This command sets the notification interval. This is the minimum interval between
LLDP SNMP notifications (traps) of each kind (LLDP Remote Tables Change
Notification and LLDP-MED Topology Change Notification).
The no variant of this command sets the notification interval back to its default.
Syntax lldp notification-interval <5-3600>
no lldp notification-interval
Default The default notification interval is 5 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the notification interval to 20 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp notification-interval 20
To set the notification interval back to its default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp notification-interval
Related
Commands
lldp notifications
show lldp
Parameter Description
<5-3600>The interval in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1932
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP NOTIFICATIONS
lldp notifications
Overview This command enables the sending of LLDP SNMP notifications (traps) relating to
specified ports.
The no variant of this command disables the sending of LLDP SNMP notifications
for specified ports.
Syntax lldp notifications
no lldp notifications
Default The sending of LLDP SNMP notifications is disabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To enable sending of LLDP SNMP notifications for ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# lldp notifications
To disable sending of LLDP SNMP notifications for ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no lldp notifications
Related
Commands
lldp notification-interval
show lldp interface
snmp-server enable trap
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1933
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP PORT-NUMBER-TYPE
lldp port-number-type
Overview This command sets the type of port identifier used to enumerate, that is to count,
the LLDP MIB local port entries. The LLDP MIB (IEEE Standard 802.1AB-2005,
Section 12, LLDP MIB Definitions.) requires the port number value to count LLDP
local port entries.
This command also enables you to optionally set an interface index to enumerate
the LLDP MIB local port entries, if required by your management system.
The no variant of this command resets the type of port identifier back to the
default setting (number).
Syntax lldp port-number-type [number|ifindex]
no lldp port-number-type
Default The default port identifier type is number. The no variant of this command sets the
port identifier type to the default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the type of port identifier used to enumerate LLDP MIB local port entries to
port numbers, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp port-number-type number
To set the type of port identifier used to enumerate LLDP MIB local port entries to
interface indexes, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp port-number-type ifindex
To reset the type of port identifier used to enumerate LLDP MIB local port entries
the default (port numbers), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp port-number-type
Related
Commands
show lldp
Parameter Description
number Set the type of port identifier to a port number to enumerate the
LLDP MIB local port entries.
ifindex Set the type of port identifier to an interface index to enumerate the
LLDP MIB local port entries.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1934
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP REINIT
lldp reinit
Overview This command sets the value of the reinitialization delay. This is the minimum time
after disabling LLDP on a port before it can reinitialize.
The no variant of this command sets the reinitialization delay back to its default
setting.
Syntax lldp reinit <1-10>
no lldp reinit
Default The default reinitialization delay is 2 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the reinitialization delay to 3 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp reinit 3
To set the reinitialization delay back to its default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp reinit
Related
Commands
show lldp
Parameter Description
<1-10>The delay in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1935
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP RUN
lldp run
Overview This command enables the operation of LLDP on the device.
The no variant of this command disables the operation of LLDP on the device. The
LLDP configuration remains unchanged.
Syntax lldp run
no lldp run
Default LLDP is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable LLDP operation, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp run
To disable LLDP operation, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp run
Related
Commands
show lldp

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1936
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP TIMER
lldp timer
Overview This command sets the value of the transmit interval. This is the interval between
regular transmissions of LLDP advertisements.
The no variant of this command sets the transmit interval back to its default.
Syntax lldp timer <5-32768>
no lldp timer
Default The default transmit interval is 30 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the transmit interval to 90 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp timer 90
To set the transmit interval back to its default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp timer
Related
Commands
lldp tx-delay
show lldp
Parameter Description
<5-32768>The transmit interval in seconds. The transmit interval must be at
least four times the transmission delay timer (lldp tx-delay
command).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1937
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP TLV-SELECT
lldp tlv-select
Overview This command enables one or more optional TLVs, or all TLVs, for transmission in
LLDP advertisements via the specified ports. The TLVs can be specified in any
order; they are placed in LLDP frames in a fixed order (as described in IEEE
802.1AB). The mandatory TLVs (Chassis ID, Port ID, Time To Live, End of LLDPDU)
are always included in LLDP advertisements.
In LLDP-MED advertisements the MAC/PHY Configuration/Status TLV will be
always be included regardless of whether it is selected by this command.
The no variant of this command disables the specified optional TLVs, or all optional
TLVs, for transmission in LLDP advertisements via the specified ports.
Syntax lldp tlv-select {[<tlv>]...}
lldp tlv-select all
no lldp tlv-select {[<tlv>]...}
no lldp tlv-select all
Default By default no optional TLVs are included in LLDP advertisements. The MAC/PHY
Configuration/Status TLV ( mac-phy-config) is included in LLDP-MED
advertisements whether or not it is selected by this command.
Mode Interface Configuration
Parameter Description
<tlv>The TLV to transmit in LLDP advertisements. One of
these keywords:
• port-description (specified by the description
(interface) command)
• system-name (specified by the hostname command)
• system-description
• system-capabilities
• management-address
•port-vlan
• port-and-protocol-vlans
•vlan-names
•protocol-ids
• mac-phy-config
• power-management (Power Via MDI TLV)
• link-aggregation
• max-frame-size
all All TLVs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1938
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP TLV-SELECT
Examples To include the management-address and system-name TLVs in advertisements
transmitted via ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# lldp tlv-select management-address
system-name
To include all optional TLVs in advertisements transmitted via ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# lldp tlv-select all
To exclude the management-address and system-name TLVs from advertisements
transmitted via ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no lldp tlv-select management-address
system-name
To exclude all optional TLVs from advertisements transmitted via ports 1.0.1 and
1.0.6, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
awplus(config-if)# no lldp tlv-select all
Related
Commands
description (interface)
hostname
lldp med-tlv-select
show lldp interface
show lldp local-info
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1939
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP TRANSMIT RECEIVE
lldp transmit receive
Overview This command enables transmission and/or reception of LLDP advertisements to
or from neighbors through the specified ports.
The no variant of this command disables transmission and/or reception of LLDP
advertisements through specified ports.
Syntax lldp {[transmit] [receive]}
no lldp {[transmit] [receive]}
Default LLDP advertisement transmission and reception are enabled on all ports by
default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Examples To enable transmission of LLDP advertisements on port1.0.1 and port1.0.2, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lldp transmit
To enable LLDP advertisement transmission and reception on port1.0.1 and
port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# lldp transmit receive
To disable LLDP advertisement transmission and reception on port1.0.1 and
port1.0.2, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no lldp transmit receive
Related
Commands
show lldp interface
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
transmit Enable or disable transmission of LLDP advertisements via this port
or ports.
receive Enable or disable reception of LLDP advertisements via this port or
ports.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1940
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LLDP TX-DELAY
lldp tx-delay
Overview This command sets the value of the transmission delay timer. This is the minimum
time interval between transmitting LLDP advertisements due to a change in LLDP
local information.
The no variant of this command sets the transmission delay timer back to its
default setting.
Syntax lldp tx-delay <1-8192>
no lldp tx-delay
Default The default transmission delay timer is 2 seconds.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the transmission delay timer to 12 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# lldp tx-delay 12
To set the transmission delay timer back to its default, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no lldp tx-delay
Related
Commands
lldp timer
show lldp
Parameter Description
<1-8192>The transmission delay in seconds. The transmission delay cannot be
greater than a quarter of the transmit interval (lldp timer command).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1941
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
location civic-location configuration
Overview Use these commands to configure a civic address location. The country parameter
must be specified first, and at least one of the other parameters must be
configured before the location can be assigned to a port.
Use the no variants of this command to delete civic address parameters from the
location.
Syntax country <country>
state <state>
no state
county <county>
no county
city <city>
no city
division <division>
no division
neighborhood <neighborhood>
no neighborhood
street-group <street-group>
no street-group
leading-street-direction <leading-street-direction>
no leading-street-direction
trailing-street-suffix <trailing-street-suffix>
no trailing-street-suffix
street-suffix <street-suffix>
no street-suffix
house-number <house-number>
no house-number
house-number-suffix <house-number-suffix>
no house-number-suffix
landmark <landmark>
no landmark
additional-information <additional-information>
no additional-information

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1942
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
Syntax (cont.) name <name>
no name
postalcode <postalcode>
no postalcode
building <building>
no building
unit <unit>
no unit
floor <floor>
no floor
room <room>
no room
place-type <place-type>
no place-type
postal-community-name <postal-community-name>
no postal-community-name
post-office-box <post-office-box>
no post-office-box
additional-code <additional-code>
no additional-code
seat <seat>
no seat
primary-road-name <primary-road-name>
no primary-road-name
road-section <road-section>
no road-section
branch-road-name <branch-road-name>
no branch-road-name
sub-branch-road-name <sub-branch-road-name>
no sub-branch-road-name
street-name-pre-modifier <street-name-pre-modifier>
no street-name-pre-modifier
streetname-post-modifier <streetname-post-modifier>
no streetname-post-modifier

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1943
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
Parameter Description
<country>Upper-case two-letter country code, as
specified in ISO 3166.
<state>State (Civic Address (CA) Type 1): national
subdivisions (state, canton, region).
<county>County (CA Type 2): County, parish, gun (JP),
district (IN).
<city>City (CA Type 3): city, township, shi (JP).
<division>City division (CA Type 4): City division, borough,
city district, ward, chou (JP).
<neighborhood>Neighborhood (CA Type 5): neighborhood,
block.
<street-group>Street group (CA Type 6): group of streets below
the neighborhood level.
<leading-street-
direction>Leading street direction (CA Type 16).
<trailing-street-suffix>Trailing street suffix (CA Type 17).
<street-suffix>Street suffix (CA Type 18): street suffix or type.
<house-number>House number (CA Type 19).
<house-number-suffix>House number suffix (CA Type 20).
<landmark>Landmark or vanity address (CA Type 21).
<additional-information>Additional location information (CA Type 22).
<name>Name (CA Type 23): residence and office
occupant.
<postal-code>Postal/zip code (CA Type 24).
<building>Building (CA Type 25): structure.
<unit>Unit (CA Type 26): apartment, suite.
<floor>Floor (CA Type 27).
<room>Room (CA Type 28).
<place-type>Type of place (CA Type 29).
<postal-community-name>Postal community name (CA Type 30).
<post-office-box>Post office box (P.O. Box) (CA Type 31).
<additional-code>Additional code (CA Type 32).
<seat>Seat (CA Type 33): seat (desk, cubicle,
workstation).
<primary-road-name>Primary road name (CA Type 34).
<road-section>Road section (CA Type 35).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1944
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
Default By default no civic address location information is configured.
Mode Civic Address Location Configuration
Usage The country parameter must be configured before any other parameters can be
configured; this creates the location. The country parameter cannot be deleted.
One or more of the other parameters must be configured before the location can
be assigned to a port. The country parameter must be entered as an upper-case
two-letter country code, as specified in ISO 3166. All other parameters are entered
as alpha-numeric strings. Do not configure all the civic address parameters (this
would generate TLVs that are too long). Configure a subset of these parameters—
enough to consistently and precisely identify the location of the device. If the
location is to be used for Emergency Call Service (ECS), the particular ECS
application may have guidelines for configuring the civic address location. For
more information about civic address format, see the LLDP Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
To specify the civic address location, use the location civic-location identifier
command. To delete the civic address location, use the no variant of the location
civic-location identifier command. To assign the civic address location to
particular ports, so that it can be advertised in TLVs from those ports, use the
command location civic-location-id command.
Examples To configure civic address location 1 with location "27 Nazareth Avenue,
Christchurch, New Zealand" in civic-address format, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# location civic-location identifier 1
awplus(config-civic)# country NZ
awplus(config-civic)# city Christchurch
awplus(config-civic)# primary-road-name Nazareth
awplus(config-civic)# street-suffix Avenue
awplus(config-civic)# house-number 27
Related
Commands
location civic-location-id
location civic-location identifier
show lldp local-info
show location
<branch-road-name>Branch road name (CA Type 36).
<sub-branch-road-name>Sub-branch road name (CA Type 37).
<street-name-pre-
modifier>Street name pre-modifier (CA Type 38).
<street-name-post-
modifier>Street name post-modifier (CA Type 39).
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1945
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION IDENTIFIER
location civic-location identifier
Overview Use this command to enter the Civic Address Location Configuration mode to
configure the specified location.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a civic address location. This also
removes the location from any ports it has been assigned to.
Syntax location civic-location identifier <civic-loc-id>
no location civic-location identifier <civic-loc-id>
Default By default there are no civic address locations.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage To configure the location information for this civic address location identifier, use
the location civic-location configuration command. To associate this civic location
identifier with particular ports, use the location elin-location-id command.
Up to 400 locations can be configured on the switch for each type of location
information, up to a total of 1200 locations.
Examples To enter Civic Address Location Configuration mode for the civic address location
with ID 1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# location civic-location identifier 1
awplus(config-civic)#
To delete the civic address location with ID 1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no location civic-location identifier 1
Related
Commands
location civic-location-id
location civic-location configuration
show location
show running-config lldp
Parameter Description
<civic-loc-id>A unique civic address location ID, in the range 1 to 4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1946
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION CIVIC-LOCATION-ID
location civic-location-id
Overview Use this command to assign a civic address location to the ports. The civic address
location must already exist. This replaces any previous assignment of civic address
location for the ports. Up to one location of each type can be assigned to a port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a location identifier from the ports.
Syntax location civic-location-id <civic-loc-id>
no location civic-location-id [<civic-loc-id>]
Default By default no civic address location is assigned to ports.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The civic address location associated with a port can be transmitted in Location
Identification TLVs via the port.
Before using this command, create the location using the following commands:
•location civic-location identifier command
•location civic-location configuration command
If a civic-address location is deleted using the no variant of the location
civic-location identifier command, it is automatically removed from all ports.
Examples To assign the civic address location 1 to port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# location civic-location-id 1
To remove a civic address location from port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no location civic-location-id
Related
Commands
lldp med-tlv-select
location civic-location identifier
location civic-location configuration
show location
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
<civic-loc-id>Civic address location ID, in the range 1 to 4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1947
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION COORD-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
location coord-location configuration
Overview Use this command to configure a coordinate-based location. All parameters must
be configured before assigning this location identifier to a port.
Syntax latitude <latitude>
lat-resolution <lat-resolution>
longitude <longitude>
long-resolution <long-resolution>
altitude <altitude> {meters|floor}
alt-resolution <alt-resolution>
datum {wgs84|nad83-navd|nad83-mllw}
Default By default no coordinate location information is configured.
Mode Coordinate Configuration
Usage Latitude and longitude values are always stored internally, and advertised in the
Location Identification TLV, as 34-bit fixed-point binary numbers, with a 25-bit
fractional part, irrespective of the number of digits entered by the user. Likewise
Parameter Description
<lat-resolution>Latitude resolution, as a number of valid bits, in the range 0 to
34.
<latitude>Latitude value in degrees in the range -90.0 to 90.0
<long-
resolution>Longitude resolution, as a number of valid bits, in the range 0
to 34.
<longitude>Longitude value in degrees, in the range -180.0 to 180.0.
<alt-resolution>Altitude resolution, as a number of valid bits, in the range 0 to
30. A resolution of 0 can be used to indicate an unknown
value.
<altitude>Altitude value, in meters or floors.
meters The altitude value is in meters.
floors The altitude value is in floors.
datum The geodetic system (or datum) that the specified coordinate
values are based on.
wgs84 World Geodetic System 1984.
nad83-navd North American Datum 1983 - North American Vertical
Datum.
nad83-mllw North American Datum 1983 - Mean Lower Low Water vertical
datum.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1948
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION COORD-LOCATION CONFIGURATION
altitude is stored as a 30- bit fixed point binary number, with an 8-bit fractional
part. Because the user-entered decimal values are stored as fixed point binary
numbers, they cannot always be represented exactly—the stored binary number
is converted to a decimal number for display in the output of the show location
command. For example, a user-entered latitude value of “2.77” degrees is
displayed as “2.7699999809265136718750000”.
The lat-resolution, long-resolution, and alt-resolution parameters allow the
user to specify the resolution of each coordinate element as the number of valid
bits in the internally-stored binary representation of the value. These resolution
values can be used by emergency services to define a search area.
To specify the coordinate identifier, use the location coord-location identifier
command. To remove coordinate information, delete the coordinate location by
using the no variant of that command. To associate the coordinate location with
particular ports, so that it can be advertised in TLVs from those ports, use the
location elin-location-id command.
Example To configure the location for the White House in Washington DC, which has the
coordinates based on the WGS84 datum of 38.89868 degrees North (with 22 bit
resolution), 77.03723 degrees West (with 22 bit resolution), and 15 meters height
(with 9 bit resolution), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# location coord-location identifier 1
awplus(config-coord)# la-resolution 22
awplus(config-coord)# latitude 38.89868
awplus(config-coord)# lo-resolution 22
awplus(config-coord)# longitude -77.03723
awplus(config-coord)# alt-resolution 9
awplus(config-coord)# altitude 15 meters
awplus(config-coord)# datum wgs84
Related
Commands
location coord-location-id
location coord-location identifier
show lldp local-info
show location

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1949
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION COORD-LOCATION IDENTIFIER
location coord-location identifier
Overview Use this command to enter Coordinate Location Configuration mode for this
coordinate location.
Use the no variant of this command to delete a coordinate location. This also
removes the location from any ports it has been assigned to.
Syntax location coord-location identifier <coord-loc-id>
no location coord-location identifier <coord-loc-id>
Default By default there are no coordinate locations.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Up to 400 locations can be configured on the switch for each type of location
information, up to a total of 1200 locations.
To configure this coordinate location, use the location coord-location
configuration command. To associate this coordinate location with particular
ports, so that it can be advertised in TLVs from those ports, use the location
coord-location-id command.
Examples To enter Coordinate Location Configuration mode to configure the coordinate
location with ID 1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# location coord-location identifier 1
awplus(config-coord)#
To delete coordinate location 1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no location coord-location identifier 1
Related
Commands
location coord-location-id
location coord-location configuration
show lldp local-info
show location
Parameter Description
<coord-loc-id>A unique coordinate location identifier, in the range 1 to
4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1950
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION COORD-LOCATION-ID
location coord-location-id
Overview Use this command to assign a coordinate location to the ports. The coordinate
location must already exist. This replaces any previous assignment of coordinate
location for the ports. Up to one location of each type can be assigned to a port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a location from the ports.
Syntax location coord-location-id <coord-loc-id>
no location coord-location-id [<coord-loc-id>]
Default By default no coordinate location is assigned to ports.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The coordinate location associated with a port can be transmitted in Location
Identification TLVs via the port.
Before using this command, configure the location using the following
commands:
•location coord-location identifier command
•location coord-location configuration command
If a coordinate location is deleted using the no variant of the location
coord-location identifier command, it is automatically removed from all ports.
Examples To assign coordinate location 1 to port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# location coord-location-id 1
To remove a coordinate location from port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no location coord-location-id
Related
Commands
lldp med-tlv-select
location coord-location identifier
location coord-location configuration
show location
Parameter Description
<coord-loc-id>Coordinate location ID, in the range 1 to 4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1951
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION COORD-LOCATION-ID
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1952
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION ELIN-LOCATION
location elin-location
Overview Use this command to create or modify an ELIN location.
Use the no variant of this command to delete an ELIN location, and remove it from
any ports it has been assigned to.
Syntax location elin-location <elin> identifier <elin-loc-id>
no location elin-location identifier <elin-loc-id>
Default By default there are no ELIN location identifiers.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Up to 400 locations can be configured on the switch for each type of location
information, up to a total of 1200 locations.
To assign this ELIN location to particular ports, so that it can be advertised in TLVs
from those ports, use the location elin-location-id command.
Examples To create a new ELIN location with ID 1, and configure it with ELIN "1234567890",
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# location elin-location 1234567890 identifier 1
To delete existing ELIN location with ID 1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no location elin-location identifier 1
Related
Commands
location elin-location-id
show lldp local-info
show location
Parameter Description
<elin>Emergency Location Identification Number (ELIN) for
Emergency Call Service (ECS), in the range 10 to 25 digits long. In
North America, ELINs are typically 10 digits long.
<elin-loc-id>A unique ELIN location identifier, in the range 1 to 4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1953
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
LOCATION ELIN-LOCATION-ID
location elin-location-id
Overview Use this command to assign an ELIN location to the ports. The ELIN location must
already exist. This replaces any previous assignment of ELIN location for the ports.
Up to one location of each type can be assigned to a port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove a location identifier from the ports.
Syntax location elin-location-id <elin-loc-id>
no location elin-location-id [<elin-loc-id>]
Default By default no ELIN location is assigned to ports.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage An ELIN location associated with a port can be transmitted in Location
Identification TLVs via the port.
Before using this command, configure the location using the location elin-location
command.
If an ELIN location is deleted using the no variant of one of the location
elin-location command, it is automatically removed from all ports.
Examples To assign ELIN location 1 to port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# location elin-location-id 1
To remove ELIN location 1 from port1.0.1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# no location elin-location-id 1
Related
Commands
lldp med-tlv-select
location elin-location
show location
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Parameter Description
<elin-loc-id>ELIN location identifier, in the range 1 to 4095.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1954
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING LLDP
show debugging lldp
Overview This command displays LLDP debug settings for specified ports. If no port list is
supplied, LLDP debug settings for all ports are displayed.
Syntax show debugging lldp [interface <port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display LLDP debug settings for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show debugging lldp
To display LLDP debug settings for ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# show debugging lldp interface port1.0.1-1.0.6
Output Figure 51-1: Example output from the show debugging lldp command
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports for which the LLDP debug settings are shown.
LLDP Debug settings:
Debugging for LLDP internal operation is on
Port Rx RxPkt Tx TxPkt
------------------------------------
1.0.1 Yes Yes No No
1.0.2 Yes No No No
1.0.3 No No No No
1.0.4 Yes Yes Yes No
1.0.5 Yes No Yes No
1.0.6 Yes Yes Yes Yes
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show debugging lldp command
Parameter Description
Port Port name.
Rx Whether debugging of LLDP receive is enabled on the port.
RxPkt Whether debugging of LLDP receive packet dump is enabled on the
port.
Rx Whether debugging of LLDP transmit is enabled on the port.
RxPkt Whether debugging of LLDP transmit packet dump is enabled on the
port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1956
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP
show lldp
Overview This command displays LLDP status and global configuration settings.
Syntax show lldp
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display LLDP status and global configuration settings, use the command:
awplus# show lldp
Output
Table 2: Example output from the show lldp command
awplus# show lldp
LLDP Global Configuration: [Default Values]
LLDP Status ............... Enabled [Disabled]
Notification Interval ..... 5 secs [5]
Tx Timer Interval ......... 30 secs [30]
Hold-time Multiplier ...... 4 [4]
(Computed TTL value ....... 120 secs)
Reinitialization Delay .... 2 secs [2]
Tx Delay .................. 2 secs [2]
Port Number Type........... Ifindex [Port-Number]
Fast Start Count .......... 5 [3]
LLDP Global Status:
Total Neighbor Count ...... 47
Neighbors table last updated 0 hrs 0 mins 43 secs ago
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show lldp command
Parameter Description
LLDP Status Whether LLDP is enabled. Default is disabled.
Notification
Interval Minimum interval between LLDP notifications.
Tx Timer
Interval Transmit interval between regular transmissions of LLDP
advertisements.
Hold-time
Multiplier The holdtime multiplier. The transmit interval is multiplied
by the holdtime multiplier to give the Time To Live (TTL)
value that is advertised to neighbors.
Reinitialization
Delay The reinitialization delay. This is the minimum time after
disabling LLDP transmit on a port before it can reinitialize
again.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1957
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP
Related
Commands
show lldp interface
show running-config lldp
Tx Delay The transmission delay. This is the minimum time interval
between transmitting advertisements due to a change in
LLDP local information.
Port Number Type The type of port identifier used to enumerate LLDP MIB
local port entries, as set by the lldp port-number-type
command.
Fast Start Count The number of times fast start advertisements are sent for
LLDP-MED.
Total Neighbor
Count Number of LLDP neighbors discovered on all ports.
Neighbors table
last updated The time since the LLDP neighbor table was last updated.
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show lldp command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1958
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP INTERFACE
show lldp interface
Overview This command displays LLDP configuration settings for specified ports. If no port
list is specified, LLDP configuration for all ports is displayed.
Syntax show lldp interface [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display LLDP configuration settings for ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# show lldp interface port1.0.1-1.0.6
To display LLDP configuration settings for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show lldp interface
Output Figure 51-2: Example output from the show lldp interface command
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports for which the LLDP configuration settings are to be shown.
awplus# show lldp interface port1.0.1-1.0.8
LLDP Port Status and Configuration:
* = LLDP is inactive on this port because it is a mirror analyser port
Notification Abbreviations:
RC = LLDP Remote Tables Change TC = LLDP-MED Topology Change
TLV Abbreviations:
Base: Pd = Port Description Sn = System Name
Sd = System Description Sc = System Capabilities
Ma = Management Address
802.1: Pv = Port VLAN ID Pp = Port And Protocol VLAN ID
Vn = VLAN Name Pi = Protocol Identity
802.3: Mp = MAC/PHY Config/Status Po = Power Via MDI (PoE)
La = Link Aggregation Mf = Maximum Frame Size
MED: Mc = LLDP-MED Capabilities Np = Network Policy
Lo = Location Identification Pe = Extended PoE In = Inventory
Optional TLVs Enabled for Tx
Port Rx/Tx Notif Management Addr Base 802.1 802.3 MED
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.0.1 Rx Tx RC -- 192.168.100.123 PdSnSdScMa -------- -------- McNpLoPe--
*1.0.2 -- Tx RC -- 192.168.100.123 PdSnSdScMa -------- -------- McNpLoPe--
1.0.3 Rx Tx RC -- 192.168.100.123 Pd--SdScMa PvPpVnPi -------- McNpLoPe--
1.0.4 -- -- RC -- 192.168.100.123 PdSnSd--Ma -------- -------- McNpLoPe--
1.0.5 Rx Tx RC TC 192.168.100.123 PdSnSdScMa PvPpVnPi -------- McNpLoPe--
1.0.6 Rx Tx RC TC 192.168.100.123 Pd----ScMa -------- -------- McNpLoPe--
1.0.7 Rx Tx -- TC 192.168.100.123 PdSnSdScMa PvPpVnPi MpPoLaMf McNpLoPeIn
1.0.8 Rx Tx -- TC 192.168.1.1 PdSn--ScMa PvPpVnPi -------- McNp------
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1959
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP INTERFACE
Related
Commands
show lldp
show running-config lldp
Table 4: Parameters in the output of the show lldp interface command
Parameter Description
Port Port name.
Rx Whether reception of LLDP advertisements is enabled on
the port.
Tx Whether transmission of LLDP advertisements is enabled
on the port.
Notif Whether sending SNMP notification for LLDP is enabled on
the port:
• RM = Remote Tables Change Notification
•TP = LLDP-MED Topology Change Notification
Management Addr Management address advertised to neighbors.
Base TLVs Enabled
for Tx List of optional Base TLVs enabled for transmission:
• Pd = Port Description
• Sn =System Name
• Sd = System Description
• Sc =System Capabilities
• Ma = Management Address
802.1 TLVs
Enabled for Tx List of optional 802.1 TLVs enabled for transmission:
•Pv = Port VLAN ID
• Pp = Port And Protocol VLAN ID
•Vn = VLAN Name
• Pi =Protocol Identity
802.3 TLVs
Enabled for Tx List of optional 802.3 TLVs enabled for transmission:
• Mp = MAC/PHY Configuration/Status
• Po = Power Via MDI (PoE)
• La = Link Aggregation
• Mf = Maximum Frame Size
MED TLVs Enabled
for Tx List of optional LLDP-MED TLVs enabled for transmission:
• Mc = LLDP-MED Capabilities
•Np = Network Policy
• Lo = Location Information,
• Pe = Extended Power-Via-MDI
• In = Inventory

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1960
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP LOCAL-INFO
show lldp local-info
Overview This command displays local LLDP information that can be transmitted through
specified ports. If no port list is entered, local LLDP information for all ports is
displayed.
Syntax show lldp local-info [base] [dot1] [dot3] [med] [interface
<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Usage Whether and which local information is transmitted in advertisements via a port
depends on:
• whether the port is set to transmit LLDP advertisements (lldp transmit
receive command)
• which TLVs it is configured to send (lldp tlv-select command, lldp
med-tlv-select command)
Examples To display local information transmitted via port 1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show lldp local-info interface port1.0.1
To display local information transmitted via all ports, use the command:
awplus# show lldp local-info
Output Figure 51-3: Example output from show lldp local-info
Parameter Description
base Information for base TLVs.
dot1 Information for 802.1 TLVs.
dot3 Information for 802.3 TLVs.
med Information for LLDP-MED TLVs.
<port-list>The ports for which the local information is to be shown.
LLDP Local Information:
Local port1.0.1:
Chassis ID Type .................. MAC address
Chassis ID ....................... 0015.77c9.7453
Port ID Type ..................... Interface alias
Port ID .......................... port1.0.1
TTL .............................. 120
Port Description ................. [not configured]
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1961
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP LOCAL-INFO
System Name ...................... awplus
System Description ............... Allied Telesis router/switch, AW+
v5.4.6
System Capabilities - Supported .. Bridge, Router
- Enabled .... Bridge, Router
Management Address ............... 192.168.1.6
Port VLAN ID (PVID) .............. 1
Port & Protocol VLAN - Supported . Yes
- Enabled ... No
- VIDs ...... 0
VLAN Names ....................... default
Protocol IDs ..................... 9000, 0026424203000000, 888e01, aaaa03,
88090101, 00540000e302, 0800, 0806, 86dd
MAC/PHY Auto-negotiation ......... Supported, Enabled
Advertised Capability ....... 1000BaseTFD, 100BaseTXFD, 100BaseTX,
10BaseTFD, 10BaseT
Operational MAU Type ........ 1000BaseTFD (30)
Power Via MDI (PoE) .............. Supported, Enabled
Port Class .................. PSE
Pair Control Ability ........ Disabled
Power Class ................. Unknown
Link Aggregation ................. Supported, Disabled
Maximum Frame Size ............... 1522
LLDP-MED Device Type ............. Network Connectivity
LLDP-MED Capabilities ............ LLDP-MED Capabilities, Network Policy,
Location Identification,
Extended Power - PSE, Inventory
Network Policy ................... [not configured]
Location Identification .......... Civic Address
Country Code ................ NZ
City ........................ Christchurch
Street Suffix ............... Avenue
House Number ................ 27
Primary Road Name ........... Nazareth
Location Identification .......... ELIN
ELIN ........................ 123456789012
LLDP-MED Device Type ............. Network Connectivity
LLDP-MED Capabilities ............ LLDP-MED Capabilities, Network Policy,
Location Identification,
Extended Power - PSE, Inventory
Extended Power Via MDI (PoE) ..... PSE
Power Source ................ Primary Power
Power Priority .............. Low
Power Value ................. 4.4 Watts
Inventory Management:
Hardware Revision ........... A-0
Firmware Revision ........... 1.1.0
Software Revision ........... v5.4.6
Serial Number ............... G1Q78900B
Manufacturer Name ........... Allied Telesis Inc.
Model Name .................. AT-x930-52GPX
Asset ID .................... [zero length]
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1962
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP LOCAL-INFO
Table 51-1: Parameters in the output of show lldp local-info
Parameter Description
Chassis ID Type Type of the Chassis ID.
Chassis ID Chassis ID that uniquely identifies the local device.
Port ID Type Type of the Port ID.
Port ID Port ID of the local port through which advertisements
are sent.
TTL Number of seconds that the information advertised by
the local port remains valid.
Port Description Port description of the local port, as specified by the
description (interface) command.
System Name System name, as specified by the hostname command.
System Description System description.
System
Capabilities
(Supported)
Capabilities that the local port supports.
System
Capabilities
(Enabled)
Enabled capabilities on the local port.
Management
Addresses Management address associated with the local port. To
change this, use the lldp management-address
command.
Port VLAN ID (PVID) VLAN identifier associated with untagged or priority
tagged frames received via the local port.
Port & Protocol
VLAN (Supported) Whether Port & Protocol VLANs (PPV) is supported on
the local port.
Port & Protocol
VLAN (Enabled) Whether the port is in one or more Port & Protocol
VLANs.
Port & Protocol
VLAN (VIDs) List of identifiers for Port & Protocol VLANs that the port
is in.
VLAN Names List of VLAN names for VLANs that the local port is
assigned to.
Protocol IDs List of protocols that are accessible through the local
port.
MAC/PHY Auto-
negotiation Auto-negotiation support and current status of the 802.3
LAN on the local port.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1963
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP LOCAL-INFO
Power Via MDI (PoE) PoE-capability and current status on the local port.
Port Class Whether the device is a PSE (Power Sourcing Entity) or a
PD (Powered Device)
Pair Control
Ability Whether power pair selection can be controlled
Power Pairs Which power pairs are selected for power ("Signal Pairs"
or "Spare Pairs") if pair selection can be controlled
Power Class The power class of the PD device on the port (class 0, 1, 2,
3 or 4)
Link Aggregation Whether the link is capable of being aggregated and it is
currently in an aggregation.
Aggregated Port-ID Aggregated port identifier.
Maximum Frame Size The maximum frame size capability of the implemented
MAC and PHY.
LLDP-MED Device
Type LLDP-MED device type
LLDP-MED
Capabilities Capabilities LLDP-MED capabilities supported on the
local port.
Network Policy List of network policies configured on the local port.
VLAN ID VLAN identifier for the port for the specified application
type
Tagged Flag Whether the VLAN ID is to be used as tagged or
untagged
Layer-2 Priority: Layer 2 User Priority (in the range 0 to 7)
DSCP Value Diffserv codepoint (in the range 0 to 63)
Location
Identification Location configured on the local port.
Extended Power Via
MDI (PoE) PoE-capability and current status of the PoE parameters
for Extended Power-Via-MDI TLV on the local port.
Power Source The power source the switch currently uses; either
primary power or backup power.
Power Priority The power priority configured on the port; either critical,
high or low.
Table 51-1: Parameters in the output of show lldp local-info (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1964
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP LOCAL-INFO
Related
Commands
description (interface)
hostname
lldp transmit receive
Power Value The total power the switch can source over a maximum
length cable to a PD device on the port. The value shows
the power value in Watts from the PD side.
Inventory
Management Inventory information for the device.
Table 51-1: Parameters in the output of show lldp local-info (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1965
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS
show lldp neighbors
Overview This command displays a summary of information received from neighbors via
specified ports. If no port list is supplied, neighbor information for all ports is
displayed.
Syntax show lldp neighbors [interface <port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display neighbor information received via all ports, use the command:
awplus# show lldp neighbors
To display neighbor information received via ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6 with LLDP-MED
configuration, use the command:
awplus# show lldp neighbors interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
Output Figure 51-4: Example output from the show lldp neighbors command
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports for which the neighbor information is to be shown.
LLDP Neighbor Information:
Total number of neighbors on these ports .... 4
System Capability Codes:
O = Other P = Repeater B = Bridge W = WLAN Access Point
R = Router T = Telephone C = DOCSIS Cable Device S = Station Only
LLDP-MED Device Type and Power Source Codes:
1 = Class I 3 = Class III PSE = PoE Both = PoE&Local Prim = Primary
2 = Class II N = Network Con. Locl = Local Unkn = Unknown Back = Backup
Local Neighbor Neighbor Neighbor System MED
Port Chassis ID Port ID Sys Name Cap. Ty Pwr
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.0.1 002d.3044.7ba6 port1.0.2 awplus OPBWRTCS
1.0.1 0011.3109.e5c6 port1.0.3 AT-9924 switch/route... --B-R---
1.0.6 0000.10cf.8590 port3 AR-442S --B-R---
1.0.6 00ee.4352.df51 192.168.1.2 Jim’s desk phone --B--T-- 3 PSE
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1966
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS
Related
Commands
show lldp neighbors detail
Table 52: Parameters in the output of the show lldp neighbors command
Parameter Description
Local Port Local port on which the neighbor information was
received.
Neighbor Chassis ID Chassis ID that uniquely identifies the neighbor.
Neighbor Port Name Port ID of the neighbor.
Neighbor Sys Name System name of the LLDP neighbor.
Neighbor Capability Capabilities that are supported and enabled on the
neighbor.
System Capability System Capabilities of the LLDP neighbor.
MED Device Type LLDP-MED Device class (Class I, II, III or Network
Connectivity)
MED Power Source LLDP-MED Power Source

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1967
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS DETAIL
show lldp neighbors detail
Overview This command displays in detail the information received from neighbors via
specified ports. If no port list is supplied, detailed neighbor information for all ports
is displayed.
Syntax show lldp neighbors detail [base] [dot1] [dot3] [med] [interface
<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display detailed neighbor information received via all ports, use the command:
awplus# show lldp neighbors detail
To display detailed neighbor information received via ports 1.0.1, use the
command:
awplus# show lldp neighbors detail interface port1.0.1
Parameter Description
base Information for base TLVs.
dot1 Information for 802.1 TLVs.
dot3 Information for 803.1 TLVs.
med Information for LLDP-MED TLVs.
<port-list>The ports for which the neighbor information is to be shown.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1968
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS DETAIL
Output Figure 51-5: Example output from the show lldp neighbors detail command
awplus#show lldp neighbors detail interface port1.0.1
LLDP Detailed Neighbor Information:
Local port1.0.1:
Neighbors table last updated 0 hrs 0 mins 40 secs ago
Chassis ID Type .................. MAC address
Chassis ID ....................... 0004.cd28.8754
Port ID Type ..................... Interface alias
Port ID .......................... port1.0.6
TTL .............................. 120 (secs)
Port Description ................. [zero length]
System Name ...................... awplus
System Description ............... Allied Telesis router/switch, AW+ v5.4.6
System Capabilities - Supported .. Bridge, Router
- Enabled .... Bridge, Router
Management Addresses ............. 0004.cd28.8754
Port VLAN ID (PVID) .............. 1
Port & Protocol VLAN - Supported . Yes
- Enabled ... Yes
- VIDs ...... 5
VLAN Names ....................... default, vlan5
Protocol IDs ..................... 9000, 0026424203000000, 888e01, 8100,
88090101, 00540000e302, 0800, 0806, 86dd
MAC/PHY Auto-negotiation ......... Supported, Enabled
Advertised Capability ....... 1000BaseTFD, 100BaseTXFD, 100BaseTX,
10BaseTFD, 10BaseT
Operational MAU Type ........ 1000BaseTFD (30)
Power Via MDI (PoE) .............. [not advertised]
Link Aggregation ................. Supported, Disabled
Maximum Frame Size ............... 1522 (Octets)
LLDP-MED Device Type ............. Network Connectivity
LLDP-MED Capabilities ............ LLDP-MED Capabilities, Network Policy,
Location Identification,
Extended Power - PSE, Inventory
Network Policy ................... [not advertised]
Location Identification .......... [not advertised]
Extended Power Via MDI (PoE) ..... PD
Power Source ............ PSE
Power Priority .......... High
Power Value ............. 4.4 Watts
Inventory Management:
Hardware Revision ....... X1-0
Firmware Revision ....... 1.1.0
Software Revision ....... v5.4.6
Serial Number ........... M1NB73008
Manufacturer Name ....... Allied Telesis Inc.
Model Name .............. x230-28GP
Asset ID ................ [zero length]
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1969
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS DETAIL
Table 53: Parameters in the output of the show lldp neighbors detail command
Parameter Description
Chassis ID Type Type of the Chassis ID.
Chassis ID Chassis ID that uniquely identifies the
neighbor.
Port ID Type Type of the Port ID.
Port ID Port ID of the neighbor.
TTL Number of seconds that the information
advertised by the neighbor remains valid.
Port Description Port description of the neighbor’s port.
System Name Neighbor’s system name.
System Description Neighbor’s system description.
System Capabilities
(Supported) Capabilities that the neighbor supports.
System Capabilities
(Enabled) Capabilities that are enabled on the
neighbor.
Management Addresses List of neighbor’s management addresses.
Port VLAN ID (PVID) VLAN identifier associated with untagged or
priority tagged frames for the neighbor port.
Port & Protocol VLAN
(Supported) Whether Port & Protocol VLAN is supported
on the LLDP neighbor.
Port & Protocol VLAN
(Enabled) Whether Port & Protocol VLAN is enabled on
the LLDP neighbor.
Port & Protocol VLAN (VIDs) List of Port & Protocol VLAN identifiers.
VLAN Names List of names of VLANs that the neighbor’s
port belongs to.
Protocol IDs List of protocols that are accessible through
the neighbor’s port.
MAC/PHY Auto-negotiation Auto-negotiation configuration and status
Power Via MDI (PoE) PoE configuration and status of 802.3 Power-
Via-MDI TLV
Link Aggregation Link aggregation information
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1970
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP NEIGHBORS DETAIL
Related
Commands
show lldp neighbors
Maximum Frame Size The maximum frame size capability
LLDP-MED Device Type LLDP-MED Device type
LLDP-MED Capabilities LLDP-MED capabilities supported
Network Policy List of network policies
Location Identification Location information
Extended Power Via MDI
(PoE) PoE-capability and current status
Inventory Management Inventory information
Table 53: Parameters in the output of the show lldp neighbors detail command
(cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1971
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP STATISTICS
show lldp statistics
Overview This command displays the global LLDP statistics (packet and event counters).
Syntax show lldp statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display global LLDP statistics information, use the command:
awplus# show lldp statistics
Output
Table 54: Example output from the show lldp statistics command
awplus# show lldp statistics
Global LLDP Packet and Event counters:
Frames: Out ................... 345
In .................... 423
In Errored ............ 0
In Dropped ............ 0
TLVs: Unrecognized .......... 0
Discarded ............. 0
Neighbors: New Entries ........... 20
Deleted Entries ....... 20
Dropped Entries ....... 0
Entry Age-outs ........ 20
Table 55: Parameters in the output of the show lldp statistics command
Parameter Description
Frames Out Number of LLDPDU frames transmitted.
Frames In Number of LLDPDU frames received.
Frames In Errored Number of invalid LLDPDU frames received.
Frames In Dropped Number of LLDPDU frames received and discarded for any
reason.
TLVs
Unrecognized Number of LLDP TLVs received that are not recognized but
the TLV type is in the range of reserved TLV types.
TLVs Discarded Number of LLDP TLVs discarded for any reason.
Neighbors New
Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been inserted into the neighbor table.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1972
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP STATISTICS
Related
Commands
clear lldp statistics
show lldp statistics interface
Neighbors
Deleted Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been removed from the neighbor table.
Neighbors
Dropped Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
could not be entered into the neighbor table because of
insufficient resources.
Neighbors Entry
Age-outs Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been removed from the neighbor table because the
information TTL interval has expired.
Table 55: Parameters in the output of the show lldp statistics command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1973
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP STATISTICS INTERFACE
show lldp statistics interface
Overview This command displays the LLDP statistics (packet and event counters) for
specified ports. If no port list is supplied, LLDP statistics for all ports are displayed.
Syntax show lldp statistics interface [<port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display LLDP statistics information for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show lldp statistics interface
To display LLDP statistics information for ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.6, use the command:
awplus# show lldp statistics interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
Output
Parameter Description
<port-list>The ports for which the statistics are to be shown.
Table 56: Example output from the show lldp statistics interface command
awplus# show lldp statistics interface port1.0.1,port1.0.6
LLDP Packet and Event Counters:
port1.0.1
Frames: Out ................... 27
In .................... 22
In Errored ............ 0
In Dropped ............ 0
TLVs: Unrecognized .......... 0
Discarded ............. 0
Neighbors: New Entries ........... 3
Deleted Entries ....... 0
Dropped Entries ....... 0
Entry Age-outs ........ 0
port1.0.6
Frames: Out ................... 15
In .................... 18
In Errored ............ 0
In Dropped ............ 0
TLVs: Unrecognized .......... 0
Discarded ............. 0
Neighbors: New Entries ........... 1
Deleted Entries ....... 0
Dropped Entries ....... 0
Entry Age-outs ........ 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1974
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LLDP STATISTICS INTERFACE
Related
Commands
clear lldp statistics
show lldp statistics
Table 57: Parameters in the output of the show lldp statistics interface
command
Parameter Description
Frames Out Number of LLDPDU frames transmitted.
Frames In Number of LLDPDU frames received.
Frames In
Errored Number of invalid LLDPDU frames received.
Frames In
Dropped Number of LLDPDU frames received and discarded for any
reason.
TLVs
Unrecognized Number of LLDP TLVs received that are not recognized but
the TLV type is in the range of reserved TLV types.
TLVs Discarded Number of LLDP TLVs discarded for any reason.
Neighbors New
Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been inserted into the neighbor table.
Neighbors
Deleted Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been removed from the neighbor table.
Neighbors
Dropped Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
could not be entered into the neighbor table because of
insufficient resources.
Neighbors Entry
Age-outs Entries Number of times the information advertised by neighbors
has been removed from the neighbor table because the
information TTL interval has expired.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1975
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LOCATION
show location
Overview Use this command to display selected location information configured on the
switch.
Syntax show location {civic-location|coord-location|elin-location}
show location {civic-location|coord-location|elin-location}
identifier {<civic-loc-id>|<coord-loc-id>|<elin-loc-id>}
show location {civic-location|coord-location|elin-location}
interface <port-list>
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Examples To display a civic address location configured on port1.0.1, use the command:
awplus# show location civic-location interface port1.0.1
To display coordinate location information configured on the identifier 1, use the
command:
awplus# show location coord-location identifier 1
Parameter Description
civic-location Display civic location information.
coord-location Display coordinate location information.
elin-location Display ELIN (Emergency Location Identifier Number)
information.
<civic-loc-id>Civic address location identifier, in the range 1 to 4095.
<coord-loc-id>Coordinate location identifier, in the range 1 to 4095.
<elin-loc-id>ELIN location identifier, in the range 1 to 4095.
<port-list>Ports to display information about.
Table 58: Example output from the show location command
awplus# show location civic-location interface port1.0.1
Port ID Element Type Element Value
----------------------------------------------------------------
1.0.1 1 Country NZ
City Christchurch
Street-suffix Avenue
House-number 27
Primary-road-name Nazareth

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1976
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
LLDP COMMANDS
SHOW LOCATION
The coordinate location information displayed may differ from the information
entered because it is stored in binary format. For more information, see the
location coord-location configuration command.
To display all ELIN location information configured on the switch, use the
command:
awplus# show location elin-location
Related
Commands
location elin-location-id
location civic-location identifier
location civic-location configuration
location coord-location identifier
location coord-location configuration
location elin-location
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: Command added to AR2050V, AR3050S, AR4050S
Table 59: Example output from the show location command
awplus# show location coord-location identifier 1
ID Element Type Element Value
--------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Latitude Resolution 15 bits
Latitude 38.8986481130123138427734375 degrees
Longitude Resolution 15 bits
Longitude 130.2323232293128967285156250 degrees
Altitude Resolution 10 bits
Altitude 2.50000000 meters
Map Datum WGS 84
Table 60: Example output from the show location elin-location command
awplus# show location elin-location
ID ELIN
-----------------------------------
1 1234567890
2 5432154321

52
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1977
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Mail (SMTP)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
mail. The mail feature uses Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to transfer mail
from an internal email client operating within the AlliedWare Plus device. This
feature is typically used to email event notifications to an external email server
from the AlliedWare Plus device.
For information on using the mail feature, see the Mail (SMTP) Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“debug mail” on page 1978
•“delete mail” on page 1979
•“mail” on page 1980
•“mail from” on page 1982
•“mail smtpserver” on page 1983
•“mail smtpserver authentication” on page 1984
•“mail smtpserver port” on page 1986
•“show counter mail” on page 1988
•“show mail” on page 1989
•“undebug mail” on page 1990

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1978
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
DEBUG MAIL
debug mail
Overview This command turns on debugging for sending emails.
The no variant of this command turns off debugging for sending emails.
Syntax debug mail
no debug mail
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To turn on debugging for sending emails, use the command:
awplus# debug mail
To turn off debugging for sending emails, use the command:
awplus# no debug mail
Related
Commands
delete mail
mail
mail from
mail smtpserver
show counter mail
show mail
undebug mail
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1979
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
DELETE MAIL
delete mail
Overview This command deletes mail from the queue.
You need the mail-id from the show mail command output to delete specific
emails, or use the all parameter to clear all messages in the queue completely.
Syntax delete mail [mail-id <mail-id>|all]
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To delete the unique mail item “20060912142356.1234” from the queue, use the
command:
awplus# delete mail 20060912142356.1234
To delete all mail from the queue, use the command:
awplus# delete mail all
Related
Commands
debug mail
mail
mail from
mail smtpserver
show mail
Parameter Description
mail-id Deletes a single mail from the mail queue.
<mail-id> A unique mail ID number. Use the show mail
command to display this for an item of mail.
all Delete all the mail in the queue.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1980
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL
mail
Overview This command sends an email using the SMTP protocol. If you specify a file the text
inside the file is sent in the message body.
If you do not specify the to, file, or subject parameters, the CLI prompts you for the
missing information.
Before you can send mail using this command, you must specify the sending email
address using the mail from command and a mail server using the mail smtpserver
command.
Syntax mail [to <to>] [subject <subject>] [file <filename>]
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage When you use the mail command you can use parameter substitutions in the
subject field. The following table lists the parameters that can be substituted and
their descriptions:
NOTE: If no local time is configured, it will use UTC.
Parameter Description
to The email recipient.
<to>Email address.
subject Description of the subject of this email. Use quote marks when the
subject text contains spaces.
<subject>String.
file File to insert as text into the message body.
<filename>String.
Parameter Description
<%N>When this parameter is specified, the %N is replaced by the
host name of your device.
<%S>When this parameter is specified, the %S is replaced by the
serial number of your device.
<%D>
<%L>
<%T>
When any of these parameters is specified, they are replaced
by the current date and time (local time) on your device.
<%U>When this parameter is specified, the %U is replaced by the
current date and time (UTC time) on your device.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1981
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL
Examples To send an email to “admin@example.com” with the subject “test email” and with
the message body inserted from the file “test.conf”, use the command:
awplus# mail to admin@example.com subject "test email" filename
test.conf
To send an email using parameter substitutions for the host name, serial number
and date, use the commands:
awplus# mail to admin@example.com subject "Sending email from
Hostname:%N Serial Number:%S Date:%T"
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail from
mail smtpserver
mail smtpserver authentication
mail smtpserver port
show counter mail
show mail

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1982
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL FROM
mail from
Overview This command sets an email address as the sender. You must specify a sending
email address with this command before you can send email.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the “mail from” address.
Syntax mail from <from>
no mail from
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set up your email address as the sender “kaji@nerv.com”, use the command:
awplus(config)# mail from kaji@nerv.com
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail
mail smtpserver
show counter mail
show mail
undebug mail
Parameter Description
<from>The email address that the mail is sent from (also known as the
hostname).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1983
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL SMTPSERVER
mail smtpserver
Overview This command specifies the IP address or domain name of the SMTP server that
your device sends email to. You must specify a mail server with this command
before you can send email.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured mail server.
Syntax mail smtpserver {<ip-address>|<name>}
no mail smtpserver
Mode Global Configuration
Usage If you specify the server by specifying its domain name, you must also ensure that
the DNS client on your device is enabled. It is enabled by default but if it has been
disabled, you can re-enable it by using the ip domain-lookup command.
Examples To specify a mail server at “192.168.0.1”, use the command:
awplus(config)# mail smtpserver 192.168.0.1
To specify a mail server that has a host name of “smtp.example.com”, use the
command:
awplus(config)# mail smtpserver smtp.example.com
To remove the configured mail server, use the command:
awplus(config)# no mail smtpserver
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail
mail from
show counter mail
show mail
Parameter Description
<ip-address>Internet Protocol (IP) address for the mail server.
<name>Domain name (FQDN) for the mail server (also known as the host
name).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1984
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL SMTPSERVER AUTHENTICATION
mail smtpserver authentication
Overview Use this command to configure SMTP mail server authentication.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured SMTP mail server
authentication.
Syntax mail smtpserver authentication {crammd5|login|plain} username
<username> password [8] <password>
no mail smtpserver authentication
Default No authentication option is set by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You cannot change the IP address or Domain Name of the SMTP server if
authentication is configured. If you attempt to change it when authentication is
configured, the following error message is displayed:
% Error: authentication configuration still exists
Examples To configure the SMTP mail server authentication to crammd5, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mail smtpserver authentication crammd5 username
admin password unguessablePassword
To remove SMTP mail server authentication, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no mail smtpserver authentication
Parameter Description
crammd5 This is a Challenge Request Authentication Mechanism based on
the HMAC-MD5 mechanism and is the most secure option.
login A BASE64 encryption method
plain A BASE64 encryption method
<username> Registered user name
8The registered user password is presented in an already
encrypted format. This is how the running configuration stores
the plain text password and is not for general use.
<password> Registered user password
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1985
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL SMTPSERVER AUTHENTICATION
Output Figure 52-1: Example output from show mail:
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail
mail from
mail smtpserver
mail smtpserver port
show counter mail
show mail
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: command added
awplus#show mail
Mail Settings
------------------------------------------------------------
State : Alive
SMTP Server : 1.2.3.4
Host Name : admin@example.com
Authentication : crammd5
Username : admin
Debug : Disabled
awplus#show running-config
!
mail smtpserver authentication plain username admin password 8
aF0a9pkjbmXGfl6TlSk/GakeIK5tMYN6LqMYT8Ia2qw=
!

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1986
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
MAIL SMTPSERVER PORT
mail smtpserver port
Overview Use this command to configure the SMTP mail client/server communication port.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the configured port and set it back
to the default port 25.
Syntax mail smtpserver port <port>
no mail smtpserver port
Default Port 25 is the default port.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To configure the mail server communication over port 587, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# mail smtpserver port 587
To remove the configured port and set it back to the default port 25, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no mail smtpserver port
Output Figure 52-2: Example output from show mail:
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail
Parameter Description
<port> Port number from the range 1 to 65535
awplus#show mail
Mail Settings
------------------------------------------------------------
State : Alive
SMTP Server : 10.24.165.4
Host Name : admin@example.com
Authentication : plain
Username : admin
Port : 587
Debug : Disabled
awplus#show running-config
!
mail smtpserver port 587
!
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1988
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER MAIL
show counter mail
Overview This command displays the mail counters.
Syntax show counter mail
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To show the emails in the queue use the command:
awplus# show counter mail
Output Figure 52-3: Example output from the show counter mail command
Related
Commands
debug mail
delete mail
mail
mail from
show mail
Mail Client (SMTP) counters
Mails Sent ......... 2
Mails Sent Fails ......... 1
Table 1: Parameters in the output of the show counter mail command
Parameter Description
Mails Sent The number of emails sent successfully since the last device
restart.
Mails Sent Fails The number of emails the device failed to send since the last
device restart.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1989
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
MAIL (SMTP) COMMANDS
SHOW MAIL
show mail
Overview This command displays the emails in the queue.
Syntax show mail
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the emails in the queue use the command:
awplus# show mail
Output Figure 52-4: Example output from the show mail command:
Related
Commands
delete mail
mail
mail from
mail smtpserver
show counter mail
undebug mail
awplus#show mail
Mail Settings
------------------------------------------------------------
State : Alive
SMTP Server : example.net
Host Name : test@example.com
Debug : Enabled
Messages
------------------------------------------------------------
To : rei@nerv.com
Subject : The WAN is down
Message-ID : 20180615121150.8663
To : rei@nerv.com
Subject : WAN is not connecting in the lab
Message-ID : 20180614142502.19308
To : rei@nerv.com
Subject : The LAN is not functioning
Message-ID : 20180614141911.29709

53
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1991
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
Remote Monitoring (RMON).
For an introduction to RMON and an RMON configuration example, see the RMON
Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
RMON is disabled by default in AlliedWare Plus™. No RMON alarms or events are
configured.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“rmon alarm” on page 1992
•“rmon collection history” on page 1994
•“rmon collection stats” on page 1995
•“rmon event” on page 1996
•“show rmon alarm” on page 1997
•“show rmon event” on page 1998
•“show rmon history” on page 2000
•“show rmon statistics” on page 2002

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1992
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
RMON ALARM
rmon alarm
Overview Use this command to configure an RMON alarm to monitor the value of an SNMP
object, and to trigger specified events when the monitored object crosses
specified thresholds.
To specify the action taken when the alarm is triggered, use the event index of an
event defined by the rmon event command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the alarm configuration.
NOTE: Only alarms for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
configured.
Syntax rmon alarm <alarm-index> <oid> interval <1-2147483647>
{delta|absolute} rising-threshold <1-2147483647> event
<rising-event-index> falling-threshold <1-2147483647> event
<falling-event-index> alarmstartup [1|2|3] [owner <owner>]
no rmon alarm <alarm-index>
Parameter Description
<alarm-index><1-65535> Alarm entry index value.
<oid>The variable SNMP MIB Object Identifier (OID) name
to be monitored, in the format
etherStatsEntry.<field>.<stats-index>.
For example, etherStatsEntry.5.22 is the OID for the
etherStatsPkts field in the etherStatsEntry table for
the interface defined by the <stats-index> 22 in the
rmon collection stats command.
interval
<1-2147483647>Polling interval in seconds.
delta The RMON MIB alarmSampleType: the change in the
monitored MIB object value between the beginning
and end of the polling interval.
absolute The RMON MIB alarmSampleType: the value of the
monitored MIB object.
rising-threshold
<1-2147483647>Rising threshold value of the alarm entry in seconds.
<rising-event-index><1-65535> The event to be triggered when the
monitored object value reaches the rising threshold
value. This is an event index of an event specified by
the rmon event command.
falling-threshold
<1-2147483647>Falling threshold value of the alarm entry in seconds.
<falling-event-index><1-65535> The event to be triggered when the
monitored object value reaches the falling threshold
value. This is an event index of an event specified by
the rmon event command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1993
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
RMON ALARM
Default By default, there are no alarms.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage RMON alarms have a rising and falling threshold. Once the alarm monitoring is
operating, you cannot have a falling alarm unless there has been a rising alarm and
vice versa.
However, when you start RMON alarm monitoring, an alarm must be generated
without the other type of alarm having first been triggered. The alarmstartup
parameter allows this. It is used to say whether RMON can generate a rising alarm
(1), a falling alarm (2) or either alarm (3) as the first alarm.
Note that the SNMP MIB Object Identifier (OID) indicated in the command syntax
with <oid> must be specified as a dotted decimal value with the form
etherStatsEntry.<field>.<stats-index>, for example, etherStatsEntry.22.5.
Example To configure an alarm to monitor the change per minute in the etherStatsPkt value
for interface 22 (defined by stats-index 22 in the rmon collection stats command),
to trigger event 2 (defined by the rmon event command) when it reaches the rising
threshold 400, and to trigger event 3 when it reaches the falling threshold 200, and
identify this alarm as belonging to Maria, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# rmon alarm 229 etherStatsEntry.22.5 interval 60
delta rising-threshold 400 event 2 falling-threshold 200 event
3 alarmstartup 3 owner maria
Related
Commands
rmon collection stats
rmon event
alarmstartup {1|2|3} Whether RMON can trigger a falling alarm (1), a rising
alarm (2) or either (3) when you first start monitoring.
See the Usage section for more information.
The default is setting 3 (either).
owner <owner>Arbitrary owner name to identify the alarm entry.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1994
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
RMON COLLECTION HISTORY
rmon collection history
Overview Use this command to create a history statistics control group to store a specified
number of snapshots (buckets) of the standard RMON statistics for the switch port,
and to collect these statistics at specified intervals. If there is sufficient memory
available, then the device will allocate memory for storing the set of buckets that
comprise this history control.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the specified history control
configuration.
NOTE: Only a history for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
collected.
Syntax rmon collection history <history-index> [buckets <1-65535>]
[interval <1-3600>] [owner <owner>]
no rmon collection history <history-index>
Default The default interval is 1800 seconds and the default buckets is 50 buckets.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To create a history statistics control group with ID 200 to store 500 snapshots with
an interval of 600 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# rmon collection history 200 buckets 500
interval 600 owner herbert
To disable the history statistics control group, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no rmon collection history 200
Parameter Description
<history-index><1-65535> A unique RMON history control entry index
value.
buckets <1-65535>Number of requested buckets to store snapshots. Default
50 buckets.
interval <1-3600>Polling interval in seconds. Default 1800 second polling
interval.
owner <owner>Owner name to identify the entry.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1995
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
RMON COLLECTION STATS
rmon collection stats
Overview Use this command to enable the collection of RMON statistics on a switch port, and
assign an index number by which to access these collected statistics.
Use the no variant of this command to stop collecting RMON statistics on this
switch port.
NOTE: Only statistics for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
collected.
Syntax rmon collection stats <collection-index> [owner <owner>]
no rmon collection stats <collection-index>
Default RMON statistics are not enabled by default.
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To enable the collection of RMON statistics with a statistics index of 200, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# rmon collection stats 200 owner myrtle
To to stop collecting RMON statistics, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.2
awplus(config-if)# no rmon collection stats 200
Parameter Description
<collection-index> <1-65535> Give this collection of statistics an index
number to uniquely identify it. This is the index to use to
access the statistics collected for this switch port.
owner <owner>An arbitrary owner name to identify this statistics
collection entry.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1996
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
RMON EVENT
rmon event
Overview Use this command to create an event definition for a log or a trap or both. The
event index for this event can then be referred to by the rmon alarm command.
Use the no variant of this command to remove the event definition.
NOTE: Only the events for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
collected.
Syntax rmon event <event-index> [description <description>|owner
<owner>| trap <trap>]
rmon event <event-index> [log [description <description>|owner
<owner>|trap <trap>] ]
rmon event <event-index> [log trap [description
<description>|owner <owner] ]
no rmon event <event-index>
Default No event is configured by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To create an event definition for a log with an index of 299, use this command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# rmon event 299 log description cond3 owner
alfred
To to remove the event definition, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no rmon event 299
Related
Commands
rmon alarm
Parameter Description
<event-index> <1-65535> Unique event entry index value.
log Log event type.
trap Trap event type.
log trap Log and trap event type.
description<description>Event entry description.
owner <owner>Owner name to identify the entry.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1997
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
SHOW RMON ALARM
show rmon alarm
Overview Use this command to display the alarms and threshold configured for the RMON
probe.
NOTE: Only the alarms for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
shown.
Syntax show rmon alarm
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the alarms and threshold, use this command:
awplus# show rmon alarm
Related
Commands
rmon alarm
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 1998
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
SHOW RMON EVENT
show rmon event
Overview Use this command to display the events configured for the RMON probe.
NOTE: Only the events for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be shown.
Syntax show rmon event
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output Figure 53-1: Example output from the show rmon event command
NOTE: The following etherStats counters are not currently available for Layer 3
interfaces:
• etherStatsBroadcastPkts
• etherStatsCRCAlignErrors
• etherStatsUndersizePkts
•etherStatsOversizePkts
• etherStatsFragments
• etherStatsJabbers
• etherStatsCollisions
• etherStatsPkts64Octets
• etherStatsPkts65to127Octets
• etherStatsPkts128to255Octets
• etherStatsPkts256to511Octets
• etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets
• etherStatsPkts1024to1518Octets
awplus#sh rmon event
event Index = 787
Description TRAP
Event type log & trap
Event community name gopher
Last Time Sent = 0
Owner RMON_SNMP
event Index = 990
Description TRAP
Event type trap
Event community name teabo
Last Time Sent = 0
Owner RMON_SNMP

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2000
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
SHOW RMON HISTORY
show rmon history
Overview Use this command to display the parameters specified on all the currently defined
RMON history collections on the device.
NOTE: Only the history for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be
shown.
Syntax show rmon history
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output Figure 53-2: Example output from the show rmon history command
NOTE: The following etherStats counters are not currently available for Layer 3
interfaces:
• etherStatsBroadcastPkts
• etherStatsCRCAlignErrors
• etherStatsUndersizePkts
•etherStatsOversizePkts
• etherStatsFragments
• etherStatsJabbers
• etherStatsCollisions
• etherStatsPkts64Octets
• etherStatsPkts65to127Octets
• etherStatsPkts128to255Octets
• etherStatsPkts256to511Octets
• etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets
awplus#sh rmon history
history index = 56
data source ifindex = 4501
buckets requested = 34
buckets granted = 34
Interval = 2000
Owner Andrew
history index = 458
data source ifindex = 5004
buckets requested = 400
buckets granted = 400
Interval = 1500
Owner trev
========================================================

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2001
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
SHOW RMON HISTORY
• etherStatsPkts1024to1518Octets
Example To display the parameters specified on all the currently defined RMON history
collections, us the commands:
awplus# show rmon history
Related
Commands
rmon collection history
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2002
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
RMON COMMANDS
SHOW RMON STATISTICS
show rmon statistics
Overview Use this command to display the current values of the statistics for all the RMON
statistics collections currently defined on the device.
NOTE: Only statistics for switch port interfaces, not for VLAN interfaces, can be shown.
Syntax show rmon statistics
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current values of the statistics for all the RMON statistics collections,
us the commands:
awplus# show rmon statistics
Output Figure 53-3: Example output from the show rmon statistics command
NOTE: The following etherStats counters are not currently available for Layer 3
interfaces:
• etherStatsBroadcastPkts
• etherStatsCRCAlignErrors
• etherStatsUndersizePkts
•etherStatsOversizePkts
• etherStatsFragments
• etherStatsJabbers
• etherStatsCollisions
• etherStatsPkts64Octets
• etherStatsPkts65to127Octets
• etherStatsPkts128to255Octets
• etherStatsPkts256to511Octets
• etherStatsPkts512to1023Octets
awplus#show rmon statistics
rmon collection index 45
stats->ifindex = 4501
input packets 1279340, bytes 85858960, dropped 00, multicast packets 1272100
output packets 7306090, bytes 268724, multicast packets 7305660 broadcast
packets 290
rmon collection index 679
stats->ifindex = 5013
input packets 00, bytes 00, dropped 00, multicast packets 00
output packets 8554550, bytes 26777324, multicast packets 8546690 broadcast
packets 7720

54
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2004
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Secure Shell (SSH)
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
Secure Shell (SSH). For more information, see the SSH Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Command List •“banner login (SSH)” on page 2006
•“clear ssh” on page 2007
•“crypto key destroy hostkey” on page 2008
•“crypto key destroy userkey” on page 2009
•“crypto key generate hostkey” on page 2010
•“crypto key generate userkey” on page 2012
•“crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts” on page 2013
•“crypto key pubkey-chain userkey” on page 2015
•“debug ssh client” on page 2017
•“debug ssh server” on page 2018
•“service ssh” on page 2019
•“show banner login” on page 2021
•“show crypto key hostkey” on page 2022
•“show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts” on page 2024
•“show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey” on page 2025
•“show crypto key userkey” on page 2026
•“show running-config ssh” on page 2027
•“show ssh” on page 2029
•“show ssh client” on page 2031

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2005
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
•“show ssh server” on page 2032
•“show ssh server allow-users” on page 2034
•“show ssh server deny-users” on page 2035
•“ssh” on page 2036
•“ssh client” on page 2038
•“ssh server” on page 2040
•“ssh server allow-users” on page 2042
•“ssh server authentication” on page 2044
•“ssh server deny-users” on page 2046
•“ssh server max-auth-tries” on page 2048
•“ssh server resolve-host” on page 2049
•“ssh server scp” on page 2050
•“ssh server sftp” on page 2051
•“undebug ssh client” on page 2052
•“undebug ssh server” on page 2053

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2006
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
BANNER LOGIN (SSH)
banner login (SSH)
Overview This command configures a login banner on the SSH server. This displays a
message on the remote terminal of the SSH client before the login prompt. SSH
client version 1 does not support this banner.
To add a banner, first enter the command banner login, and hit [Enter]. Write your
message. You can use any character and spaces. Use Ctrl+D at the end of your
message to save the text and re-enter the normal command line mode.
The banner message is preserved if the device restarts.
The no variant of this command deletes the login banner from the device.
Syntax banner login
no banner login
Default No banner is defined by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set a login banner message, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# banner login
The screen will prompt you to enter the message:
Type CNTL/D to finish.
... banner message comes here ...
Enter the message. Use Ctrl+D to finish, like this:
^D
awplus(config)#
To remove the login banner message, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no banner login
Related
Commands
show banner login
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2007
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CLEAR SSH
clear ssh
Overview This command deletes Secure Shell sessions currently active on the device. This
includes both incoming and outgoing sessions. The deleted sessions are closed.
You can only delete an SSH session if you are a system manager or the user who
initiated the session. If all is specified then all active SSH sessions are deleted.
Syntax clear ssh {<1-65535>|all}
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To stop the current SSH session 123, use the command:
awplus# clear ssh 123
To stop all SSH sessions active on the device, use the command:
awplus# clear ssh all
Related
Commands
service ssh
ssh
Parameters Description
<1-65535>Specify a session ID in the range 1 to 65535 to delete a specific session.
all Delete all SSH sessions.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2008
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY DESTROY HOSTKEY
crypto key destroy hostkey
Overview This command deletes the existing public and private keys of the SSH server.
When you enable the SSH server, the server automatically generates an SSHv2 host
key pair (public and private keys), using RSA with 1024-bit key generation. If you
need a key with different parameters than this, you can use the crypto key
generate hostkey command to generate that key before you enable the SSH
server.
Syntax crypto key destroy hostkey {dsa|ecdsa|rsa|rsa1}
Mode Global Configuration
Example To destroy the RSA host key used for SSH version 2 connections, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key destroy hostkey rsa
Related
Commands
crypto key generate hostkey
service ssh
Parameters Description
dsa Deletes the existing DSA public and private keys.
ecdsa Deletes the existing ECDSA public and private keys.
rsa Deletes the existing RSA public and private keys configured for SSH
version 2 connections.
rsa1 Deletes the existing RSA public and private keys configured for SSH
version 1 connections.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2009
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY DESTROY USERKEY
crypto key destroy userkey
Overview This command destroys the existing public and private keys of an SSH user
configured on the device.
Syntax crypto key destroy userkey <username> {dsa|rsa|rsa1}
Mode Global Configuration
Example To destroy the RSA user key for the SSH user remoteuser, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key destroy userkey remoteuser rsa
Related
Commands
crypto key generate hostkey
show ssh
show crypto key hostkey
Parameters Description
<username>Name of the user whose userkey you are destroying. The username
must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all numbers, letters, and
the underscore, hyphen and full stop symbols.
dsa Deletes the existing DSA userkey.
rsa Deletes the existing RSA userkey configured for SSH version 2
connections.
rsa1 Deletes the existing RSA userkey for SSH version 1 connections.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2010
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY GENERATE HOSTKEY
crypto key generate hostkey
Overview This command generates public and private keys for the SSH server.
When you enable the SSH server, the server automatically generates an SSHv2 host
key pair (public and private keys), using RSA with 1024-bit key generation.
If you need a key with different parameters than this, you can use this command to
generate that key before you enable the SSH server. If a host key exists with the
same cryptography algorithm, this command replaces the old host key with the
new key.
This command is not saved in the device configuration. However, the device saves
the keys generated by this command in the non-volatile memory.
Syntax crypto key generate hostkey {dsa} [<768-1024>]
crypto key generate hostkey {rsa|rsa1} [<768-32768>]
crypto key generate hostkey {ecdsa} [<256|384>]
Default The default key length for RSA and DSA is 1024 bits.
The default key size for ECDSA is 256 bits.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To generate an RSA host key for SSH version 2 connections that is 2048 bits in
length, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate hostkey rsa 2048
To generate a DSA host key, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate dsa
Parameters Description
dsa Creates a DSA hostkey. Both SSH version 1 and 2 connections can
use the DSA hostkey.
rsa Creates an RSA hostkey for SSH version 2 connections.
rsa1 Creates an RSA hostkey for SSH version 1 connections.
ecdsa Creates an ECDSA hostkey. Both SSH version 1 and 2 connections
can use the ECDSA hostkey.
<768-32768>The length in bits of the generated key. The default is 1024 bits.
<256|384>The ECDSA key size in bits. The default is 256, but it can be set to
384.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2011
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY GENERATE HOSTKEY
To generate an ECDSA host key with an elliptic curve size of 384 bits, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate ecdsa 384
Related
Commands
crypto key destroy hostkey
service ssh
show crypto key hostkey

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2012
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY GENERATE USERKEY
crypto key generate userkey
Overview This command generates public and private keys for an SSH user using either an
RSA or DSA cryptography algorithm. To use public key authentication, copy the
public key of the user onto the remote SSH server.
This command is not saved in the device configuration. However, the device saves
the keys generated by this command in the non-volatile memory.
Syntax crypto key generate userkey <username> {dsa} [<768-1024>]
crypto key generate userkey <username> {rsa|rsa1} [<768-32768>]
crypto key generate userkey <username> {ecdsa} [<256|384>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To generate a 2048-bits RSA user key for SSH version 2 connections for the user
“bob”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate userkey bob rsa 2048
To generate a DSA user key for the user “lapo”, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate userkey lapo dsa
Related
Commands
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
show crypto key userkey
Parameters Description
<username>Name of the user that the user key is generated for. The username
must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all numbers, letters, and
the underscore, hyphen and full stop symbols.
dsa Creates a DSA userkey. Both SSH version 1 and 2 connections can use
a key created with this command.
rsa Creates an RSA userkey for SSH version 2 connections.
rsa1 Creates an RSA userkey for SSH version 1 connections.
ecdsa Creates an ECDSA hostkey. Both SSH version 1 and 2 connections can
use the ECDSA hostkey.
<768-32768>The length in bits of the generated key. The default is 1024 bits.
<256|384>The ECDSA key size in bits. The default is 256, but it can be set to 384.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2013
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN KNOWNHOSTS
crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
Overview This command adds a public key of the specified SSH server to the known host
database on your device. The SSH client on your device uses this public key to
verify the remote SSH server.
The key is retrieved from the server. Before adding a key to this database, check
that the key sent to you is correct.
If the server’s key changes, or if your SSH client does not have the public key of the
remote SSH server, then your SSH client will inform you that the public key of the
server is unknown or altered.
The no variant of this command deletes the public key of the specified SSH server
from the known host database on your device.
Syntax crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts [ip|ipv6] <hostname>
[rsa|dsa|rsa1]
no crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts <1-65535>
Default If no cryptography algorithm is specified, then rsa is used as the default
cryptography algorithm.
Mode Privilege Exec
Usage This command adds a public key of the specified SSH server to the known host
database on the device. The key is retrieved from the server. The remote SSH server
is verified by using this public key. The user is requested to check the key is correct
before adding it to the database.
Parameter Description
ip Keyword used prior to specifying an IPv4 address
ipv6 Keyword used prior to specifying an IPv6 address
<hostname> IPv4/IPv6 address or hostname of a remote server in the
format a.b.c.d for an IPv4 address, or in the format
x:x::x:x for an IPv6 address.
rsa Specify the RSA public key of the server to be added to the
known host database.
dsa Specify the DSA public key of the server to be added to the
known host database.
rsa1 Specify the SSHv1 public key of the server to be added to the
know host database.
<1-65535>Specify a key identifier when removing a key using the no
parameter.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2014
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN KNOWNHOSTS
If the remote server’s host key is changed, or if the device does not have the public
key of the remote server, then SSH clients will inform the user that the public key
of the server is altered or unknown.
Examples To add the RSA host key of the remote SSH host IPv4 address 192.0.2.11 to the
known host database, use the command:
awplus# crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts 192.0.2.11
To delete the second entry in the known host database, use the command:
awplus# no crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts 2
Validation
Commands
show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2015
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN USERKEY
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
Overview This command adds a public key for an SSH user on the SSH server. This allows the
SSH server to support public key authentication for the SSH user. When
configured, the SSH user can access the SSH server without providing a password
from the remote host.
The no variant of this command removes a public key for the specified SSH user
that has been added to the public key chain. When a SSH user’s public key is
removed, the SSH user can no longer login using public key authentication.
Syntax crypto key pubkey-chain userkey <username> [<filename>]
no crypto key pubkey-chain userkey <username> <1-65535>
Mode Global Configuration
Usage You should import the public key file from the client node. The device can read the
data from a file on the flash or user terminal.
Or you can add a key as text into the terminal. To add a key as text into the terminal,
first enter the command crypto key pubkey-chain userkey <username>, and hit
[Enter]. Enter the key as text. Note that the key you enter as text must be a valid SSH
RSA key, not random ASCII text. Use [Ctrl]+D after entering it to save the text and
re-enter the normal command line mode.
Note you can generate a valid SSH RSA key on the device first using the crypto key
generate host rsa command. View the SSH RSA key generated on the device using
the show crypto hostkey rsa command. Copy and paste the displayed SSH RSA
key after entering the crypto key pubkey-chain userkey <username> command.
Use [Ctrl]+D after entering it to save it.
Parameters Description
<username> Name of the user that the SSH server associates the key with. The
username must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all numbers,
letters, and the underscore, hyphen and full stop symbols.
Default: no default
<filename> Filename of a key saved in flash. Valid characters are any printable
character. You can add a key as a hexadecimal string directly into the
terminal if you do not specify a filename.
<1-65535>The key ID number of the user’s key. Specify the key ID to delete a key.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2016
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN USERKEY
Examples To generate a valid SSH RSA key on the device and add the key, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key generate host rsa
awplus(config)# exit
awplus# show crypto key hostkey
rsaAAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAIEAr1s7SokW5aW2fcOw1TStpb9J20bWluh
nUC768EoWhyPW6FZ2t5360O5M29EpKBmGqlkQaz5V0mU9IQe66+5YyD4UxOKSD
tTI+7jtjDcoGWHb2u4sFwRpXwJZcgYrXW16+6NvNbk+h+c/pqGDijj4SvfZZfe
ITzvvyZW4/I4pbN8=
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key pubkey-chain userkey joeType CNTL/D
to
finish:AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAIEAr1s7SokW5aW2fcOw1TStpb9J20b
WluhnUC768EoWhyPW6FZ2t5360O5M29EpKBmGqlkQaz5V0mU9IQe66+5YyD4Ux
OKSDtTI+7jtjDcoGWHb2u4sFwRpXwJZcgYrXW16+6NvNbk+h+c/pqGDijj4Svf
ZZfeITzvvyZW4/I4pbN8=control-D
awplus(config)#
To add a public key for the user graydon from the file key.pub, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key pubkey-chain userkey graydon key.pub
To add a public key for the user tamara from the terminal, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# crypto key pubkey-chain userkey tamara
and enter the key. Use Ctrl+D to finish.
To remove the first key entry from the public key chain of the user john, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no crypto key pubkey-chain userkey john 1
Related
Commands
show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2017
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
DEBUG SSH CLIENT
debug ssh client
Overview This command enables the SSH client debugging facility. When enabled, any SSH,
SCP and SFTP client sessions send diagnostic messages to the login terminal.
The no variant of this command disables the SSH client debugging facility. This
stops the SSH client from generating diagnostic debugging message.
Syntax debug ssh client [brief|full]
no debug ssh client
Default SSH client debugging is disabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To start SSH client debugging, use the command:
awplus# debug ssh client
To start SSH client debugging with extended output, use the command:
awplus# debug ssh client full
To disable SSH client debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug ssh client
Related
Commands
debug ssh server
show ssh client
undebug ssh client
Parameter Description
brief Enables brief debug mode.
full Enables full debug mode.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2018
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
DEBUG SSH SERVER
debug ssh server
Overview This command enables the SSH server debugging facility. When enabled, the SSH
server sends diagnostic messages to the system log. To display the debugging
messages on the terminal, use the terminal monitor command.
The no variant of this command disables the SSH server debugging facility. This
stops the SSH server from generating diagnostic debugging messages.
Syntax debug ssh server [brief|full]
no debug ssh server
Default SSH server debugging is disabled by default.
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To start SSH server debugging, use the command:
awplus# debug ssh server
To start SSH server debugging with extended output, use the command:
awplus# debug ssh server full
To disable SSH server debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug ssh server
Related
Commands
debug ssh client
show ssh server
undebug ssh server
Parameter Description
brief Enables brief debug mode.
full Enables full debug mode.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2019
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SERVICE SSH
service ssh
Overview This command enables the Secure Shell server on the device. Once enabled,
connections coming from SSH clients are accepted.
When you enable the SSH server, the server automatically generates an SSHv2 host
key pair (public and private keys), using RSA with 1024-bit key generation. If you
need a key with different parameters than this, you can use the crypto key
generate hostkey command to generate that key before you enable the SSH
server.
The no variant of this command disables the Secure Shell server. When the Secure
Shell server is disabled, connections from SSH, SCP, and SFTP clients are not
accepted. This command does not affect existing SSH sessions. To terminate
existing sessions, use the clear ssh command.
Syntax service ssh [ip|ipv6]
no service ssh [ip|ipv6]
Default The Secure Shell server is disabled by default. Both IPv4 and IPv6 Secure Shell
server are enabled when you issue service ssh without specifying the optional ip
or ipv6 parameters.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable both the IPv4 and the IPv6 Secure Shell server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service ssh
To enable the IPv4 Secure Shell server only, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service ssh ip
To enable the IPv6 Secure Shell server only, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# service ssh ipv6
To disable both the IPv4 and the IPv6 Secure Shell server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service ssh
To disable the IPv4 Secure Shell server only, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service ssh ip
To disable the IPv6 Secure Shell server only, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no service ssh ipv6

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2021
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW BANNER LOGIN
show banner login
Overview This command displays the banner message configured on the device. The banner
message is displayed to the remote user before user authentication starts.
Syntax show banner login
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec, Global Configuration, Interface Configuration, Line
Configuration
Example To display the current login banner message, use the command:
awplus# show banner login
Related
Commands
banner login (SSH)

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2022
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY HOSTKEY
show crypto key hostkey
Overview This command displays the public keys generated on the device for the SSH server.
When you enable the SSH server, the server automatically generates an SSHv2 host
key pair (public and private keys), using RSA with 1024-bit key generation. If you
need a key with different parameters than this, you can use the crypto key
generate hostkey command to generate that key before you enable the SSH
server.
The private key remains on the device secretly. The public key is copied to SSH
clients to identify the server. This command displays the public key.
Syntax show crypto key hostkey [dsa|ecdsa|rsa|rsa1]
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To show the public keys generated on the device for SSH server, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key hostkey
To display the RSA public key of the SSH server, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key hostkey rsa
Output Figure 54-1: Example output from the show crypto key hostkey command
Parameter Description
dsa Displays the DSA algorithm public key. Both SSH version 1 and 2
connections can use the DSA hostkey
ecdsa Displays the ECDSA algorithm public key. Both SSH version 1 and 2
connections can use the ECDSA hostkey.
rsa Displays the RSA algorithm public key for SSH version 2 connections.
rsa1 Displays the RSA algorithm public key for SSH version 1 connections.
Type Bits Fingerprint
-----------------------------------------------------------
rsa 2058 4e:7d:1d:00:75:79:c5:cb:c8:58:2e:f9:29:9c:1f:48
dsa 1024 fa:72:3d:78:35:14:cb:9a:1d:ca:1c:83:2c:7d:08:43
rsa1 1024 e2:1c:c8:8b:d8:6e:19:c8:f4:ec:00:a2:71:4e:85:8b

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2023
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY HOSTKEY
Related
Commands
crypto key destroy hostkey
crypto key generate hostkey
Table 1: Parameters in output of the show crypto key hostkey command
Parameter Description
Type Algorithm used to generate the key.
Bits Length in bits of the key.
Fingerprint Checksum value for the public key.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2024
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN KNOWNHOSTS
show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
Overview This command displays the list of public keys maintained in the known host
database on the device.
Syntax show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts [<1-65535>]
Default Display all keys.
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To display public keys of known SSH servers, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
To display the key data of the first entry in the known host data, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts 1
Output Figure 54-2: Example output from the show crypto key public-chain
knownhosts command
Related
Commands
crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
Parameter Description
<1-65535>Key identifier for a specific key. Displays the public key of the entry if
specified.
No Hostname Type Fingerprint
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 172.16.23.1 rsa c8:33:b1:fe:6f:d3:8c:81:4e:f7:2a:aa:a5:be:df:18
2 172.16.23.10 rsa c4:79:86:65:ee:a0:1d:a5:6a:e8:fd:1d:d3:4e:37:bd
3 5ffe:1053:ac21:ff00:0101:bcdf:ffff:0001
rsa1 af:4e:b4:a2:26:24:6d:65:20:32:d9:6f:32:06:ba:57
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show crypto key public-chain
knownhosts command
Parameter Description
No Number ID of the key.
Hostname Host name of the known SSH server.
Type The algorithm used to generate the key.
Fingerprint Checksum value for the public key.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2025
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY PUBKEY-CHAIN USERKEY
show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
Overview This command displays the public keys registered with the SSH server for SSH
users. These keys allow remote users to access the device using public key
authentication. By using public key authentication, users can access the SSH server
without providing password.
Syntax show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey <username> [<1-65535>]
Default Display all keys.
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the public keys for the user manager that are registered with the SSH
server, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key pubkey-chain userkey manager
Output Figure 54-3: Example output from the show crypto key public-chain userkey
command
Related
Commands
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
Parameter Description
<username> User name of the remote SSH user whose keys you wish to display.
The username must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all
numbers, letters, and the underscore, hyphen and full stop symbols.
<1-65535>Key identifier for a specific key.
No Type Bits Fingerprint
----------------------------------------------------------------
1 dsa 1024 2b:cc:df:a8:f8:2e:8f:a4:a5:4f:32:ea:67:29:78:fd
2 rsa 2048 6a:ba:22:84:c1:26:42:57:2c:d7:85:c8:06:32:49:0e
Table 3: Parameters in the output of the show crypto key userkey command
Parameter Description
No Number ID of the key.
Type The algorithm used to generate the key.
Bits Length in bits of the key.
Fingerprint Checksum value for the key.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2026
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW CRYPTO KEY USERKEY
show crypto key userkey
Overview This command displays the public keys created on this device for the specified SSH
user.
Syntax show crypto key userkey <username> [dsa|rsa|rsa1]
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Examples To show the public key generated for the user, use the command:
awplus# show crypto key userkey manager
To store the RSA public key generated for the user manager to the file “user.pub”,
use the command:
awplus# show crypto key userkey manager rsa > manager-rsa.pub
Output Figure 54-4: Example output from the show crypto key userkey command
Related
Commands
crypto key generate userkey
Parameter Description
<username>User name of the local SSH user whose keys you wish to display. The
username must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all numbers,
letters, and the underscore, hyphen and full stop symbols.
dsa Displays the DSA public key.
rsa Displays the RSA public key used for SSH version 2 connections.
rsa1 Displays the RSA key used for SSH version 1 connections.
Type Bits Fingerprint
-------------------------------------------------------------
rsa 2048 e8:d6:1b:c0:f4:b6:e6:7d:02:2e:a9:d4:a1:ca:3b:11
rsa1 1024 12:25:60:95:64:08:8e:a1:8c:3c:45:1b:44:b9:33:9b
Table 4: Parameters in the output of the show crypto key userkey command
Parameter Description
Type The algorithm used to generate the key.
Bits Length in bits of the key.
Fingerprint Checksum value for the key.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2027
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG SSH
show running-config ssh
Overview This command displays the current running configuration of Secure Shell (SSH).
Syntax show running-config ssh
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration of SSH, use the command:
awplus# show running-config ssh
Output Figure 54-5: Example output from the show running-config ssh command
!
ssh server session-timeout 600
ssh server login-timeout 30
ssh server allow-users manager 192.168.1.*
ssh server allow-users john
ssh server deny-user john*.a-company.com
ssh server
Table 5: Parameters in the output of the show running-config ssh command
Parameter Description
ssh server SSH server is enabled.
ssh server v2 SSH server is enabled and only support SSHv2.
ssh server<port> SSH server is enabled and listening on the
specified TCP port.
no ssh server scp SCP service is disabled.
no ssh server sftp SFTP service is disabled.
ssh server
session-timeout Configure the server session timeout.
ssh server login-timeout Configure the server login timeout.
ssh server max-startups Configure the maximum number of concurrent
sessions waiting authentication.
no ssh server
authentication password Password authentication is disabled.
no ssh server
authentication publickey Public key authentication is disabled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2028
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG SSH
Related
Commands
service ssh
show ssh server
ssh server allow-users Add the user (and hostname) to the allow list.
ssh server deny-users Add the user (and hostname) to the deny list.
Table 5: Parameters in the output of the show running-config ssh command
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2029
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH
show ssh
Overview This command displays the active SSH sessions on the device, both incoming and
outgoing.
Syntax show ssh
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current SSH sessions on the device, use the command:
awplus# show ssh
Output Figure 54-6: Example output from the show ssh command
Secure Shell Sessions:
ID Type Mode Peer Host Username State Filename
----------------------------------------------------------------
414 ssh server 172.16.23.1 root open
456 ssh client 172.16.23.10 manager user-auth
459 scp client 172.16.23.12 root download example.awd
463 ssh client 5ffe:33fe:5632:ffbb:bc35:ddee:0101:ac51
manager user-auth
Table 6: Parameters in the output of the show ssh command
Parameter Description
ID Unique identifier for each SSH session.
Type Session type; either SSH, SCP, or SFTP.
Mode Whether the device is acting as an SSH client (client) or SSH server
(server) for the specified session.
Peer Host The hostname or IP address of the remote server or client.
Username Login user name of the server.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2030
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH
Related
Commands
clear ssh
State The current state of the SSH session. One of:
connecting The device is looking for a remote server.
connected The device is connected to the remote server.
accepted The device has accepted a new session.
host-auth host-to-host authentication is in progress.
user-auth User authentication is in progress.
authenticated User authentication is complete.
open The session is in progress.
download The user is downloading a file from the
device.
upload The user is uploading a file from the device.
closing The user is terminating the session.
closed The session is closed.
Filename Local filename of the file that the user is downloading or uploading.
Table 6: Parameters in the output of the show ssh command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2031
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH CLIENT
show ssh client
Overview This command displays the current configuration of the Secure Shell client.
Syntax show ssh client
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration for SSH clients on the login shell, use the
command:
awplus# show ssh client
Output Figure 54-7: Example output from the show ssh client command
Related
Commands
show ssh server
Secure Shell Client Configuration
----------------------------------------------------------------
Port : 22
Version : 2,1
Connect Timeout : 30 seconds
Session Timeout : 0 (off)
Debug : NONE
Table 7: Parameters in the output of the show ssh client command
Parameter Description
Port SSH server TCP port where the SSH client connects to. The default
is port 22.
Version SSH server version; either “1”, “2” or “2,1”.
Connect
Timeout Time in seconds that the SSH client waits for an SSH session to
establish. If the value is 0, the connection is terminated when it
reaches the TCP timeout.
Debug Whether debugging is active on the client.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2032
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH SERVER
show ssh server
Overview This command displays the current configuration of the Secure Shell server.
Note that changes to the SSH configuration affects only new SSH sessions coming
from remote hosts, and does not affect existing sessions.
Syntax show ssh server
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the current configuration of the Secure Shell server, use the command:
awplus# show ssh server
Output Figure 54-8: Example output from the show ssh server command
Secure Shell Server Configuration
----------------------------------------------------------------
SSH Server : Enabled
Port : 22
Version : 2
Services : scp, sftp
User Authentication : publickey, password
Resolve Hosts : Disabled
Session Timeout : 0 (Off)
Login Timeout : 60 seconds
Maximum Authentication Tries : 6
Maximum Startups : 10
Debug : NONE
Table 8: Parameters in the output of the show ssh server command
Parameter Description
SSH Server Whether the Secure Shell server is enabled or disabled.
Port TCP port where the Secure Shell server listens for
connections. The default is port 22.
Version SSH server version; either “1”, “2” or “2,1”.
Services List of the available Secure Shell service; one or more of
SHELL, SCP or SFTP.
Authentication List of available authentication methods.
Login Timeout Time (in seconds) that the SSH server will wait the SSH
session to establish. If the value is 0, the client login will be
terminated when TCP timeout reaches.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2033
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH SERVER
Related
Commands
show ssh
show ssh client
Idle Timeout Time (in seconds) that the SSH server will wait to receive data
from the SSH client. The server disconnects if this timer limit
is reached. If set at 0, the idle timer remains off.
Maximum
Startups The maximum number of concurrent connections that are
waiting authentication. The default is 10.
Debug Whether debugging is active on the server.
Table 8: Parameters in the output of the show ssh server command (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2034
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH SERVER ALLOW-USERS
show ssh server allow-users
Overview This command displays the user entries in the allow list of the SSH server.
Syntax show ssh server allow-users
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the user entries in the allow list of the SSH server, use the command:
awplus# show ssh server allow-users
Output Figure 54-9: Example output from the show ssh server allow-users command
Related
Commands
ssh server allow-users
ssh server deny-users
Username Remote Hostname (pattern)
----------------- ------------------------- -------
awplus 192.168.*
john
manager *.alliedtelesis.com
Table 9: Parameters in the output of the show ssh server allow-users command
Parameter Description
Username User name that is allowed to access the SSH server.
Remote Hostname
(pattern) IP address or hostname pattern of the remote client. The user
is allowed requests from a host that matches this pattern. If no
hostname is specified, the user is allowed from all hosts.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2035
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SHOW SSH SERVER DENY-USERS
show ssh server deny-users
Overview This command displays the user entries in the deny list of the SSH server. The user
in the deny list is rejected to access the SSH server. If a user is not included in the
access list of the SSH server, the user is also rejected.
Syntax show ssh server deny-users
Mode User Exec, Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the user entries in the deny list of the SSH server, use the command:
awplus# show ssh server deny-users
Output Figure 54-10: Example output from the show ssh server deny-users command
Related
Commands
ssh server allow-users
ssh server deny-users
Username Remote Hostname (pattern)
----------------- ------------------------- -------
john *.b-company.com
manager 192.168.2.*
Table 10: Parameters in the output of the show ssh server deny-user command
Parameter Description
Username The user that this rule applies to.
Remote
Hostname
(pattern)
IP address or hostname pattern of the remote client. The user is
denied requests from a host that matches this pattern. If no
hostname is specified, the user is denied from all hosts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2036
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH
ssh
Overview This command initiates a Secure Shell connection to a remote SSH server.
If the server requests a password to login, you need to type in the correct password
at the “Password:” prompt.
An SSH client identifies the remote SSH server by its public key registered on the
client device. If the server identification is changed, server verification fails. If the
public key of the server has been changed, the public key of the server must be
explicitly added to the known host database.
NOTE: A hostname specified with SSH cannot begin with a hyphen (-) character.
Syntax ssh [ip|ipv6] [user <username>|port <1-65535>|version {1|2}]
<remote-device> [<command>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Parameter Description
ip Specify IPv4 SSH.
ipv6 Specify IPv6 SSH.
user Login user. If user is specified, the username is used for login
to the remote SSH server when user authentication is
required. Otherwise the current user name is used.
<username>User name to login on the remote server.
port SSH server port. If port is specified, the SSH client connects to
the remote SSH server with the specified TCP port. Other-
wise, the client port configured by “ssh client” command or
the default TCP port (22) is used.
<1-65535>TCP port.
version SSH client version. If version is specified, the SSH client
supports only the specified SSH version. By default, SSH client
uses SSHv2 first. If the server does not support SSHv2, it will
try SSHv1. The default version can be configured by “ssh
client” command.
1Use SSH version 1.
2Use SSH version 2.
<remote-device>IPv4/IPv6 address or hostname of a remote server. The
address is in the format A.B.C.D for an IPv4 address, or in the
format X:X::X:X for an IPv6 address. Note that a hostname
specified with SSH cannot begin with a hyphen (-) character.
<command> A command to execute on the remote server. If a command is
specified, the command is executed on the remote SSH server
and the session is disconnected when the remote command
finishes.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2037
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH
Examples To login to the remote SSH server at 192.0.2.5, use the command:
awplus# ssh ip 192.0.2.5
To login to the remote SSH server at 192.0.2.5 as user “manager”, use the
command:
awplus# ssh ip user manager 192.0.2.5
To login to the remote SSH server at 192.0.2.5 that is listening TCP port 2000, use
the command:
awplus# ssh port 2000 192.0.2.5
To login to the remote SSH server with example_host using IPv6 session, use the
command:
awplus# ssh ipv6 example_host
To run the cmd command on the remote SSH server at 192.0.2.5, use the
command:
awplus# ssh ip 192.0.2.5 cmd
Related
Commands
crypto key generate userkey
crypto key pubkey-chain knownhosts
debug ssh client
ssh client
Command
changes
Version 5.4.6-2.1: VRF-lite support added for AR-Series devices.
Version 5.4.8-1.2: secure mode syntax added for x220, x930, x550, XS900MX.
Version 5.4.8-2.1: secure mode syntax added for x950, SBx908 GEN2.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2038
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH CLIENT
ssh client
Overview This command modifies the default configuration parameters of the Secure Shell
(SSH) client. The configuration is used for any SSH client on the device to connect
to remote SSH servers. Any parameters specified on SSH client explicitly override
the default configuration parameters.
The change affects the current user shell only. When the user exits the login
session, the configuration does not persist. This command does not affect existing
SSH sessions.
The no variant of this command resets configuration parameters of the Secure
Shell (SSH) client changed by the ssh client command, and restores the defaults.
This command does not affect the existing SSH sessions.
Syntax ssh client {port <1-65535>|version {1|2}|session-timeout
<0-3600>|connect-timeout <1-600>}
no ssh client {port|version|session-timeout|connect-timeout}
Parameter Description
port The default TCP port of the remote SSH server. If an SSH client
specifies an explicit port of the server, it overrides the default TCP
port.
Default: 22
<1-65535>TCP port number.
version The SSH version used by the client for SSH sessions.
The SSH client supports both version 2 and version 1
Default: version 2
Note: SSH version 2 is the default SSH version. SSH client supports
SSH version 1 if SSH version 2 is not configured using a ssh version
command.
1SSH clients on the device supports SSH version 1
only.
2SSH clients on the device supports SSH version 2
only
session-
timeout The global session timeout for SSH sessions. If the session timer
lapses since the last time an SSH client received data from the
remote server, the session is terminated. If the value is 0, then the
client does not terminate the session. Instead, the connection is
terminated when it reaches the TCP timeout.
Default: 0 (session timer remains off)
<0-3600>Timeout in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2039
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH CLIENT
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To configure the default TCP port for SSH clients to 2200, and the session timer to
10 minutes, use the command:
awplus# ssh client port 2200 session-timeout 600
To configure the connect timeout of SSH client to 10 seconds, use the command:
awplus# ssh client connect-timeout 10
To restore the connect timeout to its default, use the command:
awplus# no ssh client connect-timeout
Related
Commands
show ssh client
ssh
connect-
timeout The maximum time period that an SSH session can take to become
established. The SSH client terminates the SSH session if this timeout
expires and the session is still not established.
Default: 30
<1-600>Timeout in seconds.
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2040
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER
ssh server
Overview This command modifies the configuration of the SSH server. Changing these
parameters affects new SSH sessions connecting to the device.
The no variant of this command restores the configuration of a specified
parameter to its default. The change affects the SSH server immediately if the
server is running. Otherwise, the configuration is used when the server starts.
To enable the SSH server, use the service ssh command.
Syntax ssh server {[v1v2|v2only]|<1-65535>}
ssh server {[session-timeout <0-3600>] [login-timeout <1-600>]
[max-startups <1-128>]}
no ssh server {[session-timeout] [login-timeout]
[max-startups]}
Mode Global Configuration
Parameter Description
v1v2 Supports both SSHv2 and SSHv1client connections.
Default: v1v2
v2only Supports SSHv2 client connections only.
<1-65535>The TCP port number that the server listens to for incoming SSH
sessions.
Default: 22
session-
timeout The maximum time period that the server waits before deciding that a
session is inactive and should be terminated. The server considers the
session inactive when it has not received any data from the client, and
when the client does not respond to keep alive messages.
Default: 0 (session timer remains off).
<0-3600>Timeout in seconds.
login-
timeout The maximum time period the server waits before disconnecting an
unauthenticated client.
Default: 60
<1-600>Timeout in seconds.
max-
startups The maximum number of concurrent unauthenticated connections
the server accepts. When the number of SSH connections awaiting
authentication reaches the limit, the server drops any additional
connections until authentication succeeds or the login timer expires
for a connection.
Default: 10
<1-128>Number of sessions.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2041
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER
Examples To configure the session timer of SSH server to 10 minutes (600 seconds), use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server login-timeout 600
To configure the login timeout of SSH server to 30 seconds, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server login-timeout 30
To limit the number of SSH client connections waiting authentication from SSH
server to 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server max-startups
To set max-startups parameters of SSH server to the default configuration, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server max-startups
To support the Secure Shell server with TCP port 2200, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server 2200
To force the Secure Shell server to support SSHv2 only, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server v2only
To support both SSHv2 and SSHv1, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server v1v2
Related
Commands
show ssh server
ssh client
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2042
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER ALLOW-USERS
ssh server allow-users
Overview This command adds a username pattern to the allow list of the SSH server. If the
user of an incoming SSH session matches the pattern, the session is accepted.
When there are no registered users in the server’s database of allowed users, the
SSH server does not accept SSH sessions even when enabled.
SSH server also maintains the deny list. The server checks the user in the deny list
first. If a user is listed in the deny list, then the user access is denied even if the user
is listed in the allow list.
The no variant of this command deletes a username pattern from the allow list of
the SSH server. To delete an entry from the allow list, the username and hostname
pattern should match exactly with the existing entry.
Syntax ssh server allow-users <username-pattern> [<hostname-pattern>]
no ssh server allow-users <username-pattern>
[<hostname-pattern>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To allow the user john to create an SSH session from any host, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server allow-users john
To allow the user john to create an SSH session from a range of IP address (from
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.255), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server allow-users john 192.168.1.*
To allow the user john to create a SSH session from a-company.com domain,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server allow-users john *.a-company.com
Parameter Description
<username-pattern> The username pattern that users can match to. An asterisk
acts as a wildcard character that matches any string of
characters.
<hostname-pattern>The host name pattern that hosts can match to. If specified,
the server allows the user to connect only from hosts
matching the pattern. An asterisk acts as a wildcard
character that matches any string of characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2043
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER ALLOW-USERS
To delete the existing user entry john 192.168.1.* in the allow list, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server allow-users john 192.168.1.*
Related
Commands
show running-config ssh
show ssh server allow-users
ssh server deny-users

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2044
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER AUTHENTICATION
ssh server authentication
Overview This command enables RSA public-key or password user authentication for SSH
Server. Apply the password keyword with the ssh server authentication
command to enable password authentication for users. Apply the publickey
keyword with the ssh server authentication command to enable RSA public-key
authentication for users.
Use the no variant of this command to disable RSA public-key or password user
authentication for SSH Server. Apply the password keyword with the no ssh
authentication command to disable password authentication for users. Apply the
required publickey keyword with the no ssh authentication command to disable
RSA public-key authentication for users.
Syntax ssh server authentication {password|publickey}
no ssh server authentication {password|publickey}
Default Both RSA public-key authentication and password authentication are enabled by
default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage For password authentication to authenticate a user, password authentication for a
user must be registered in the local user database or on an external RADIUS server,
before using the ssh server authentication password command.
For RSA public-key authentication to authenticate a user, a public key must be
added for the user, before using the ssh server authentication publickey
command.
Examples To enable password authentication for users connecting through SSH, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server authentication password
To enable publickey authentication for users connecting through SSH, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server authentication publickey
Parameter Description
password Specifies user password authentication for SSH server.
publickey Specifies user publickey authentication for SSH server.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2045
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER AUTHENTICATION
To disable password authentication for users connecting through SSH, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server authentication password
To disable publickey authentication for users connecting through SSH, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server authentication publickey
Related
Commands
crypto key pubkey-chain userkey
service ssh
show ssh server
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2046
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER DENY-USERS
ssh server deny-users
Overview This command adds a username pattern to the deny list of the SSH server. If the
user of an incoming SSH session matches the pattern, the session is rejected.
SSH server also maintains the allow list. The server checks the user in the deny list
first. If a user is listed in the deny list, then the user access is denied even if the user
is listed in the allow list.
If a hostname pattern is specified, the user is denied from the hosts matching the
pattern.
The no variant of this command deletes a username pattern from the deny list of
the SSH server. To delete an entry from the deny list, the username and hostname
pattern should match exactly with the existing entry.
Syntax ssh server deny-users <username-pattern> [<hostname-pattern>]
no ssh server deny-users <username-pattern>
[<hostname-pattern>]
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To deny the user john to access SSH login from any host, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server deny-users john
To deny the user john to access SSH login from a range of IP address (from
192.168.2.1 to 192.168.2.255), use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server deny-users john 192.168.2.*
To deny the user john to access SSH login from b-company.com domain, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server deny-users john*.b-company.com
Parameter Description
<username-pattern> The username pattern that users can match to. The
username must begin with a letter. Valid characters are all
numbers, letters, and the underscore, hyphen, full stop and
asterisk symbols. An asterisk acts as a wildcard character
that matches any string of characters.
<hostname-pattern> The host name pattern that hosts can match to. If specified,
the server denies the user only when they connect from
hosts matching the pattern. An asterisk acts as a wildcard
character that matches any string of characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2047
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER DENY-USERS
To delete the existing user entry john 192.168.2.* in the deny list, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server deny-users john 192.168.2.*
Related
Commands
show running-config ssh
show ssh server deny-users
ssh server allow-users

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2048
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER MAX-AUTH-TRIES
ssh server max-auth-tries
Overview Use this command to specify the maximum number of SSH authentication
attempts that the device will allow.
Use the no variant of this command to return the maximum number of attempts
to its default value of 6.
Syntax ssh server max-auth-tries <1-32>
no ssh server max-auth-tries
Default 6 attempts
Mode Global Configuration
Usage By default, users must wait one second after a failed login attempt before trying
again. You can increase this gap by using the command aaa login fail-delay.
Example To set the maximum number of SSH authentication attempts to 3, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server max-auth-tries 3
Related
Commands
show ssh server
Parameter Description
<1-32> Maximum number of SSH authentication attempts the device will
allow.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2049
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER RESOLVE-HOST
ssh server resolve-host
Overview This command enables resolving an IP address from a host name using a DNS
server for client host authentication.
The no variant of this command disables this feature.
Syntax ssh server resolve-hosts
no ssh server resolve-hosts
Default This feature is disabled by default.
Mode Global Configuration
Usage Your device has a DNS Client that is enabled automatically when you add a DNS
server to your device.
Example To resolve a host name using a DNS server, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server resolve-hosts
Related
Commands
ip name-server
show ssh server
ssh server allow-users
ssh server deny-users

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2050
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER SCP
ssh server scp
Overview This command enables the Secure Copy (SCP) service on the SSH server. Once
enabled, the server accepts SCP requests from remote clients.
You must enable the SSH server as well as this service before the device accepts
SCP connections. The SCP service is enabled by default as soon as the SSH server is
enabled.
The no variant of this command disables the SCP service on the SSH server. Once
disabled, SCP requests from remote clients are rejected.
Syntax ssh server scp
no ssh server scp
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable the SCP service, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server scp
To disable the SCP service, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server scp
Related
Commands
show running-config ssh
show ssh server

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2051
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SECURE SHELL (SSH) COMMANDS
SSH SERVER SFTP
ssh server sftp
Overview This command enables the Secure FTP (SFTP) service on the SSH server. Once
enabled, the server accepts SFTP requests from remote clients.
You must enable the SSH server as well as this service before the device accepts
SFTP connections. The SFTP service is enabled by default as soon as the SSH server
is enabled. If the SSH server is disabled, SFTP service is unavailable.
The no variant of this command disables SFTP service on the SSH server. Once
disabled, SFTP requests from remote clients are rejected.
Syntax ssh server sftp
no ssh server sftp
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enable the SFTP service, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ssh server sftp
To disable the SFTP service, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ssh server sftp
Related
Commands
show running-config ssh
show ssh server

55
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2054
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Trigger Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
Triggers. For more information, see the Triggers Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“active (trigger)” on page 2056
•“day” on page 2057
•“debug trigger” on page 2059
•“description (trigger)” on page 2060
•“repeat” on page 2061
•“script” on page 2062
•“show debugging trigger” on page 2064
•“show running-config trigger” on page 2065
•“show trigger” on page 2066
•“test” on page 2071
•“time (trigger)” on page 2072
•“trap” on page 2074
•“trigger” on page 2075
•“trigger activate” on page 2076
•“type atmf node” on page 2077
•“type card” on page 2080
•“type cpu” on page 2081
•“type interface” on page 2082

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2055
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
•“type linkmon-probe” on page 2083
•“type log” on page 2085
•“type memory” on page 2086
•“type periodic” on page 2087
•“type ping-poll” on page 2088
•“type reboot” on page 2089
•“type time” on page 2090
•“undebug trigger” on page 2091

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2056
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
ACTIVE (TRIGGER)
active (trigger)
Overview This command enables a trigger. This allows the trigger to activate when its trigger
conditions are met.
The no variant of this command disables a trigger. While in this state the trigger
cannot activate when its trigger conditions are met.
Syntax active
no active
Default Active, which means that triggers are enabled by default
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage Configure a trigger first before you use this command to activate it.
For information about configuring a trigger, see the Triggers_Feature Overview
and Configuration Guide.
Examples To enable trigger 172, so that it can activate when its trigger conditions are met,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 172
awplus(config-trigger)# active
To disable trigger 182, preventing it from activating when its trigger conditions are
met, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 182
awplus(config-trigger)# no active
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
trigger activate

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2057
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
DAY
day
Overview This command specifies the days or date that the trigger can activate on. You can
specify one of:
• A specific date
• A specific day of the week
• A list of days of the week
• A day of any month of any year
• A day of a specific month in any year
•Every day
By default, the trigger can activate on any day.
Syntax day every-day
day <1-31>
day <1-31> <month>
day <1-31> <month> <year>
day <weekday>
Default every-day, so by default, the trigger can activate on any day.
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage For example trigger configurations that use the day command, see “Restrict
Internet Access” and “Turn off Power to Port LEDs” in the Triggers Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Parameter Description
every-day Sets the trigger so that it can activate on any day.
<1-31>Day of the month the trigger is permitted to activate on.
<month>Sets the month that the trigger is permitted to activate on. Valid
keywords are: january, february, march, april, may, june, july,
august, september, october, november, and december.
<year>Sets the year that the trigger is permitted to activate in, between
2000 and 2035.
<weekday>Sets the days of the week that the trigger can activate on. You can
specify one or more week days in a space separated list. Valid
keywords are: monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday,
saturday, and sunday.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2058
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
DAY
Examples To permit trigger 55 to activate on the 1 June 2019, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 55
awplus(config-trigger)# day 1 jun 2019
To permit trigger 12 to activate on Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 12
awplus(config-trigger)# day monday wednesday friday
To permit trigger 17 to activate on the 5th day of any month, in any year, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 17
awplus(config-trigger)# day 5
To permit trigger 6 to activate on the 20th day of September, in any year, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 6
awplus(config-trigger)# day 20 september
To permit trigger 14 to activate on the 1st day of each month, in any year, at
11.00am, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 14
awplus(config-trigger)# day 1
awplus(config-trigger)# type time 11:00
Related
Commands
show trigger
type time
trigger
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-2.1: day of the month functionality added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2059
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
DEBUG TRIGGER
debug trigger
Overview This command enables trigger debugging. This generates detailed messages
about how your device is processing the trigger commands and activating the
triggers.
The no variant of this command disables trigger debugging.
Syntax debug trigger
no debug trigger
Mode Privilege Exec
Examples To start trigger debugging, use the command:
awplus# debug trigger
To stop trigger debugging, use the command:
awplus# no trigger
Related
Commands
show debugging trigger
show trigger
test
trigger
undebug trigger
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2060
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (TRIGGER)
description (trigger)
Overview This command adds an optional description to help you identify the trigger. This
description is displayed in show command outputs and log messages.
The no variant of this command removes a trigger’s description. The show
command outputs and log messages stop displaying a description for this trigger.
Syntax description <description>
no description
Mode Trigger Configuration
Examples To give trigger 240 the description daily status report, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 240
awplus(config-trigger)# description daily status report
To remove the description from trigger 36, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 36
awplus(config-trigger)# no description
Related
Commands
show trigger
test
trigger
Parameter Description
<description> A word or phrase that uniquely identifies this trigger or its purpose.
Valid characters are any printable character and spaces, up to a
maximum of 40 characters.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2061
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
REPEAT
repeat
Overview This command specifies the number of times that a trigger is permitted to activate.
This allows you to specify whether you want the trigger to activate:
• only the first time that the trigger conditions are met
• a limited number of times that the trigger conditions are met
• an unlimited number of times
Once the trigger has reached the limit set with this command, the trigger remains
in your configuration but cannot be activated. Use the repeat command again to
reset the trigger so that it is activated when its trigger conditions are met.
By default, triggers can activate an unlimited number of times. To reset a trigger to
this default, specify either yes or forever.
Syntax repeat {forever|no|once|yes|<1-4294967294>}
Mode Trigger Configuration
Examples To allow trigger 21 to activate only once, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 21
awplus(config-trigger)# repeat no
To allow trigger 22 to activate an unlimited number of times whenever its trigger
conditions are met, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 22
awplus(config-trigger)# repeat forever
To allow trigger 23 to activate only the first 10 times the conditions are met, use
the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 23
awplus(config-trigger)# repeat 10
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
yes|forever The trigger repeats indefinitely, or until disabled.
no|once The trigger activates only once.
<1-4292967294> The trigger repeats the specified number of times.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2062
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SCRIPT
script
Overview This command specifies one or more scripts that are to be run when the trigger
activates. You can add up to five scripts to a single trigger.
The sequence in which the trigger runs the scripts is specified by the number you
set before the name of the script file. One script is executed completely before the
next script begins.
Scripts may be either ASH shell scripts, indicated by a . sh filename extension suffix,
or AlliedWare Plus™ scripts, indicated by a . scp filename extension suffix.
AlliedWare Plus™ scripts only need to be readable.
The no variant of this command removes one or more scripts from the trigger’s
script list. The scripts are identified by either their name, or by specifying their
position in the script list. The all parameter removes all scripts from the trigger.
Syntax script <1-5> {<filename>}
no script {<1-5>|<filename>|all}
Mode Trigger Configuration
Examples To configure trigger 71 to run the script flash:/cpu_trig.sh in position 3 when the
trigger activates, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 71
awplus(config-trigger)# script 3 flash:/cpu_trig.sh
To configure trigger 99 to run the scripts flash:reconfig.scp, flash:cpu_trig.sh
and flash:email.scp in positions 2, 3 and 5 when the trigger activates, use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 99
awplus(config-trigger)# script 2 flash:/reconfig.scp 3
flash:/cpu_trig.sh 5 flash:/email.scp
To remove the scripts 1, 3 and 4 from trigger 71’s script list, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 71
awplus(config-trigger)# no script 1 3 4
Parameter Description
<1-5>The position of the script in execution sequence. The trigger runs the
lowest numbered script first.
<filename>The path to the script file.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2063
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SCRIPT
To remove the script flash:/cpu_trig.sh from trigger 71’s script list, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 71
awplus(config-trigger)# no script flash:/cpu_trig.sh
To remove all the scripts from trigger 71’s script list, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 71
awplus(config-trigger)# no script all
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2064
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING TRIGGER
show debugging trigger
Overview This command displays the current status for trigger utility debugging. Use this
command to show when trigger debugging has been turned on or off from the
debug trigger command.
Syntax show debugging trigger
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of trigger debugging, use the command:
awplus# show debugging trigger
Output Figure 55-1: Example output from the show debugging trigger command
Related
Commands
debug trigger
awplus#debug trigger
awplus#show debugging trigger
Trigger debugging status:
Trigger debugging is on
awplus#no debug trigger
awplus#show debugging trigger
Trigger debugging status:
Trigger debugging is off
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2065
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG TRIGGER
show running-config trigger
Overview This command displays the current running configuration of the trigger utility.
Syntax show running-config trigger
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display the current configuration of the trigger utility, use the command:
awplus# show running-config trigger
Output Figure 55-2: Example output from the show running-config trigger command
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger 1
type card in
trigger 2
type card out
!
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2066
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW TRIGGER
show trigger
Overview This command displays configuration and diagnostic information about the
triggers configured on the device. Specify the show trigger command without
any options to display a summary of the configuration of all triggers.
Syntax show trigger [<1-250>|counter|full]
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To get summary information about all triggers, use the following command:
awplus# show trigger
Parameter Description
<1-250>Displays detailed information about a specific trigger, identified by its
trigger ID.
counter Displays statistical information about all triggers.
full Displays detailed information about all triggers.
Table 55-1: Example output from show trigger
awplus#show trigger
TR# Type & Details Name Ac Te Repeat #Scr Days/Date
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
001 CPU (80% any) Busy CPU Y N 5 1 smtwtfs
005 Periodic (30 min) Regular status check Y N Continuous 1 -mtwtf-
007 Memory (85% up) High mem usage Y N 8 1 smtwtfs
011 Time (00:01) Weekend access Y N Continuous 1 ------s
013 Reboot Y N Continuous 2 smtwtfs
017 Interface (vlan1 .. Change config for... Y N Once 1 2-apr-2008
019 Ping-poll (5 up) Connection to svr1 Y N Continuous 1 smtwtfs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table 55-2: Parameters in the output of show trigger
Parameter Description
TR# Trigger identifier (ID).
Type &
Details The trigger type, followed by the trigger details in brackets.
Name Descriptive name of the trigger configured with the description
(trigger) command.
Ac Whether the trigger is active (Y), or inactive (N).
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2067
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW TRIGGER
To display detailed information about trigger 3, use the command:
awplus# show trigger 3
Figure 55-3: Example output from show trigger for a specific trigger
To display detailed information about all triggers, use the command:
awplus# show trigger full
Te Whether the trigger is in test mode (Y) or not (N).
Repeat Whether the trigger repeats continuously, and if not, the configured
repeat count for the trigger. To see the number of times a trigger has
activated, use the show trigger <1-250> command.
#Scr Number of scripts associated with the trigger.
Days/Date Days or date when the trigger may be activated. For the days options,
the days are shown as a seven character string representing Sunday to
Saturday. A hyphen indicates days when the trigger cannot be
activated.
awplus#show trigger 1
Trigger Configuration Details
------------------------------------------------------------
Trigger ..................... 1
Name ........................ display cpu usage when pass 80%
Type and details ............ CPU (80% up)
Days ........................ smtwtfs
Active ...................... Yes
Test ........................ No
Trap ........................ Yes
Repeat ...................... Continuous
Modified .................... Fri Feb 3 17:18:44 2017
Number of activations ....... 0
Last activation ............. not activated
Number of scripts ........... 1
1. shocpu.scp
2.
3.
4.
5.
------------------------------------------------------------
Table 55-2: Parameters in the output of show trigger (cont.)
Parameter Description
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2068
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW TRIGGER
Table 55-3: Example output from show trigger full
awplus#show trigger full
Trigger Configuration Details
------------------------------------------------------------
Trigger ..................... 1
Name ........................ Busy CPU
Type and details ............ CPU (80% up)
Days ........................ smtwtfs
Active ...................... Yes
Test ........................ No
Trap ........................ Yes
Repeat ...................... Continuous
Modified .................... Fri Feb 3 17:05:16 2017
Number of activations ....... 0
Last activation ............. not activated
Number of scripts ........... 2
1. flash:/cpu_alert.sh
2. flash:/reconfig.scp
3.
4.
5.
Trigger ..................... 5
Name ........................ Regular status check
Type and details ............ Periodic (30 min)
Days ........................ smtwtfs
Active ...................... Yes
Test ........................ No
Trap ........................ Yes
Repeat ...................... 5 (2)
Modified .................... Fri Feb 3 17:18:44 2017
Number of activations ....... 0
Last activation ............. Fri Feb 10 18:00:00 2017
Number of scripts ........... 1
1. flash:/stat_check.scp
2.
3.
4.
5.
------------------------------------------------------------
Table 56: Parameters in the output of show trigger full and show trigger for a
specific trigger
Parameter Description
Trigger The ID of the trigger.
Name Descriptive name of the trigger.
Type and
details The trigger type and its activation conditions.
Days The days on which the trigger is permitted to activate.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2069
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
SHOW TRIGGER
To display counter information about all triggers use the command:
awplus# show trigger counter
Figure 55-4: Example output from show trigger counter
Date The date on which the trigger is permitted to activate. Only
displayed if configured, in which case it replaces “Days”.
Active Whether or not the trigger is permitted to activate.
Test Whether or not the trigger is operating in diagnostic mode.
Trap Whether or not the trigger is enabled to send SNMP traps.
Repeat Whether the trigger repeats an unlimited number of times
(Continuous) or for a set number of times. When the trigger can
repeat only a set number of times, then the number of times
the trigger has been activated is displayed in brackets.
Modified The date and time of the last time that the trigger was modified.
Number of
activations Number of times the trigger has been activated since the last
restart of the device.
Last
activation The date and time of the last time that the trigger was
activated.
Number of
scripts How many scripts are associated with the trigger, followed by
the names of the script files in the order in which they run.
awplus# show trigger counter
Trigger Module Counters
-------------------------------------------------------
Trigger activations 4
Last trigger activated 55
Time triggers activated today 0
Periodic triggers activated today 0
Interface triggers activated today 1
CPU triggers activated today 2
Memory triggers activated today 1
Reboot triggers activated today 0
Ping-poll triggers activated today 0
USB event triggers activated today 0
Stack master fail triggers activated today 0
Stack member triggers activated today 0
Stack link triggers activated today 0
ATMF node triggers activated today 0
Log triggers activated today 0
-------------------------------------------------------
Table 56: Parameters in the output of show trigger full and show trigger for a
specific trigger (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2071
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TEST
test
Overview This command puts the trigger into a diagnostic mode. In this mode the trigger
may activate but when it does it will not run any of the trigger’s scripts. A log
message will be generated to indicate when the trigger has been activated.
The no variant of this command takes the trigger out of diagnostic mode, restoring
normal operation. When the trigger activates the scripts associated with the
trigger will be run, as normal.
Syntax test
no test
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage Configure a trigger first before you use this command to diagnose it. For
information about configuring a trigger, see the Triggers_Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Examples To put trigger 5 into diagnostic mode, where no scripts will be run when the trigger
activates, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 5
awplus(config-trigger)# test
To take trigger 205 out of diagnostic mode, restoring normal operation, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 205
awplus(config-trigger)# no test
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2072
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TIME (TRIGGER)
time (trigger)
Overview This command specifies the time of day when the trigger is permitted to activate.
The after parameter specifies the start of a time period that extends to midnight
during which trigger may activate. By default the value of this parameter is
00:00:00 (am); that is, the trigger may activate at any time. The before parameter
specifies the end of a time period beginning at midnight during which the trigger
may activate. By default the value of this parameter is 23:59:59; that is, the trigger
may activate at any time. If the value specified for before is later than the value
specified for after, a time period from “ after ” to “ before ” is defined, during which
the trigger may activate. This command is not applicable to time triggers ( type
time).
The following figure illustrates how the before and after parameters operate.
Syntax time {[after <hh:mm:ss>] [before <hh:mm:ss>]}
Mode Trigger Configuration
ää\ää äÈ\ää £Ó\ää £n\ää ää\ää
ää\ää äÈ\ää £Ó\ää £n\ää ää\ää
ää\ää äÈ\ää £Ó\ää £n\ää ää\ää
ää\ää äÈ\ää £Ó\ää £n\ää ää\ää
"%&/2%
!&4%2
!&4%2"%&/2%
!&4%2"%&/2%
*iÀ`ÊÜiÊÌÀ}}iÀÊ>ÞÊ>VÌÛ>Ìi°iÞ\
*iÀ`ÊÜiÊÌÀ}}iÀÊ>ÞÊÌÊ>VÌÛ>Ìi°
/,ÚäÓ
Parameter Description
after<hh:mm:ss>The earliest time of day when the trigger may be activated.
before<hh:mm:ss>The latest time of day when the trigger may be activated.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2073
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TIME (TRIGGER)
Usage For example trigger configurations that use the time (trigger) command, see
“Restrict Internet Access” and “Turn off Power to Port LEDs” in the Triggers Feature
Overview and Configuration Guide.
Examples To allow trigger 63 to activate between midnight and 10:30am, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 63
awplus(config-trigger)# time before 10:30:00
To allow trigger 64 to activate between 3:45pm and midnight, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 64
awplus(config-trigger)# time after 15:45:00
To allow trigger 65 to activate between 10:30am and 8:15pm, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 65
awplus(config-trigger)# time after 10:30:00 before 20:15:00
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2074
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TRAP
trap
Overview This command enables the specified trigger to send SNMP traps.
Use the no variant of this command to disable the sending of SNMP traps from the
specified trigger.
Syntax trap
no trap
Default SNMP traps are enabled by default for all defined triggers.
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage You must configure SNMP before using traps with triggers. For more information,
see:
•Support for Allied Telesis Enterprise_MIBs_in_AlliedWare Plus, for
information about which MIB objects are supported.
•the SNMP Feature Overview and Configuration_Guide.
•the SNMP Commands chapter.
Since SNMP traps are enabled by default for all defined triggers, a common usage
will be for the no variant of this command to disable SNMP traps from a specified
trap if the trap is only periodic. Refer in particular to AT-TRIGGER-MIB in the
Support for Allied Telesis Enterprise_MIBs_in AlliedWare Plus for further
information about the relevant SNMP MIB.
Examples To enable SNMP traps to be sent from trigger 5, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 5
awplus(config-trigger)# trap
To disable SNMP traps being sent from trigger 205, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 205
awplus(config-trigger)# no trap
Related
Commands
trigger
show trigger
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2075
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TRIGGER
trigger
Overview This command is used to access the Trigger Configuration mode for the specified
trigger. Once Trigger Configuration mode has been entered the trigger type
information can be configured and the trigger scripts and other operational
parameters can be specified. At a minimum the trigger type information must be
specified before the trigger can become active.
The no variant of this command removes a specified trigger and all configuration
associated with it.
Syntax trigger <1-250>
no trigger <1-250>
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To enter trigger configuration mode for trigger 12, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 12
To completely remove all configuration associated with trigger 12, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no trigger 12
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger activate
Parameter Description
<1-250>A trigger ID.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2076
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TRIGGER ACTIVATE
trigger activate
Overview This command is used to manually activate a specified trigger from the Privileged
Exec mode, which has been configured with the trigger command from the Global
Configuration mode.
Syntax trigger activate <1-250>
Mode Privileged Exec
Usage This command manually activates a trigger without the normal trigger conditions
being met.
The trigger is activated even if it has been configured as inactive by using the
command no active. The scripts associated with the trigger will be executed even
if the trigger is in the diagnostic test mode.
Triggers activated manually do not have their repeat counts decremented or their
'last triggered' time updated, and do not result in updates to the '[type] triggers
today' counters.
Example To manually activate trigger 12 use the command:
awplus# trigger activate 12
Related
Commands
active (trigger)
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<1-250>A trigger ID.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2077
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE ATMF NODE
type atmf node
Overview This command configures a trigger to be activated at an AMF node join event or
leave event.
Syntax type atmf node {join|leave}
Mode Trigger Configuration
CAUTION: Only configure this trigger on one device because it is a network wide
event.
Example 1 To configure trigger 5 to activate at an AMF node leave event, use the following
commands. In this example the command is entered on node-1:
node1(config)# trigger 5
node1(config-trigger) type atmf node leave
Example 2 The following commands will configure trigger 5 to activate if an AMF node join
event occurs on any node within the working set:
node1# atmf working-set group all
This command returns the following display:
Note that the running the above command changes the prompt from the name of
the local node, to the name of the AMF-Network followed, in square brackets, by
the number of member nodes in the working set.
AMF-Net[3]# conf t
AMF-Net[3](config)# trigger 5
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# type atmf node leave
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# description “E-mail on AMF Exit”
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# active
Parameter Description
join AMF node join event.
leave AMF node leave event.
====================
node1, node2, node3:
====================
Working set join

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2078
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE ATMF NODE
Enter the name of the script to run at the trigger event.
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# script 1 email_me.scp
AMF-Net[3](config-trigger)# end
Display the trigger configurations
AMF-Net[3]# show trigger
This command returns the following display:
Display the triggers configured on each of the nodes in the AMF Network.
AMF-Net[3]# show running-config trigger
This command returns the following display:
=======
node1:
=======
TR# Type & Details Description Ac Te Tr Repeat #Scr Days/Date
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
001 Periodic (2 min) Periodic Status Chk Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
005 ATMF node (leave) E-mail on ATMF Exit Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
==============
Node2, Node3,
==============
TR# Type & Details Description Ac Te Tr Repeat #Scr Days/Date
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
005 ATMF node (leave) E-mail on ATMF Exit Y N Y Continuous 1 smtwtfs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2079
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE ATMF NODE
Related
Commands
show trigger
========
Node1:
========
trigger 1
type periodic 2
script 1 atmf.scp
trigger 5
type atmf node leave
description “E-mail on ATMF Exit”
script 1 email_me.scp
!
============
Node2, Node3:
============
trigger 5
type atmf node leave
description “E-mail on ATMF Exit”
script 1 email_me.scp
!

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2080
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE CARD
type card
Overview Use this command to configure a trigger that activates on either the removal or the
insertion of a Secure Digital (SD) or Secure Digital High Capacity (SDHC) card.
Syntax type card {in|out}
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage Card triggers cannot execute script files from a card.
For example trigger configurations that use the type card command, see “Capture
Show Output and Save to an SD Card” in the Triggers Feature Overview and
Configuration_Guide.
Examples To configure trigger 1 to activate on the insertion of a card, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 1
awplus(config-trigger)# type card in
Related
Commands
trigger
show running-config trigger
show trigger
Parameter Description
in Trigger activates on insertion of a card.
out Trigger activates on removal of a card.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2081
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE CPU
type cpu
Overview This command configures a trigger to activate based on CPU usage level. Selecting
the up option causes the trigger to activate when the CPU usage exceeds the
specified usage level. Selecting the down option causes the trigger to activate
when CPU usage drops below the specified usage level. Selecting any causes the
trigger to activate in both situations. The default is any.
Syntax type cpu <1-100> [up|down|any]
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage For an example trigger configuration that uses the type cpu command, see
“Capture Unusual CPU and RAM Activity” in the Triggers Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
Examples To configure trigger 28 to be a CPU trigger that activates when CPU usage exceeds
80% use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 28
awplus(config-trigger)# type cpu 80 up
To configure trigger 5 to be a CPU trigger that activates when CPU usage either
rises above or drops below 65%, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 5
awplus(config-trigger)# type cpu 65
or
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 5
awplus(config-trigger)# type cpu 65 any
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<1-100> The percentage of CPU usage at which to trigger.
up Activate when CPU usage exceeds the specified level.
down Activate when CPU usage drops below the specified level
any Activate when CPU usage passes the specified level in either
direction

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2082
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE INTERFACE
type interface
Overview This command configures a trigger to activate based on the link status of an
interface. The trigger can be activated when the interface becomes operational by
using the up option, or when the interface closes by using the down option. The
trigger can also be configured to activate when either one of these events occurs
by using the any option.
Syntax type interface <interface> [up|down|any]
Mode Trigger Configuration
Example To configure trigger 19 to be an interface trigger that activates when port1.0.2
becomes operational, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 19
awplus(config-trigger)# type interface port1.0.2 up
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<interface>Interface name. This can be the name of a device port, an
eth-management port, or a VLAN.
up Activate when interface becomes operational.
down Activate when the interface closes.
any Activate when any interface link status event occurs.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2083
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE LINKMON-PROBE
type linkmon-probe
Overview Use this command to create a trigger that will run a script when a Link Health
Monitoring probe reports that a link becomes “good”, “bad”, or “unreachable”.
Syntax type linkmon-probe <probename> <profilename>
{good|bad|unreachable|any}
Mode Trigger Configuration
Example When the Link Health Monitoring probes sent to the “test-probe” destination no
longer meet the performance profile “test-profile” the link will be deemed “bad”.
To create a trigger that will run a script when a Link Health Monitoring probe is
deemed “bad”, use the following commands:
awplus# trigger 1
awplus(config)# script 1 link-bad.scp
awplus(config)# type linkmon-probe test-probe test-profile bad
To create a trigger that will run a script when the link is deemed “good” again, use
the following commands:
awplus# trigger 2
awplus(config)# script 1 link-good.scp
awplus(config)# type linkmon-probe test-probe test-profile good
Related
Commands
trigger
Parameter Description
<probename> The name of the Link Health Monitoring probe that will be used
for executing the trigger.
<profilename> The name of the Link Health Monitoring performance profile that
will be used for determine if the Link Health Monitoring probe is
good, bad, or unreachable.
good If the Link Health Monitoring probe becomes 'good' according to
the Link Health Monitoring performance profile then the trigger
will be executed.
bad If the Link Health Monitoring probe goes 'bad' according to the
Link Health Monitoring performance profile then the trigger will
be executed.
unreachable If the Link Health Monitoring probe becomes 'unreachable'
according to the Link Health Monitoring performance profile then
the trigger will be executed.
any If the Link Health Monitoring probe changes state according to
the Link Health Monitoring performance profile then the trigger
will be executed.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2084
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE LINKMON-PROBE
Command
changes
Version 5.4.8-1.1: command added

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2085
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE LOG
type log
Overview Use this command to configure a trigger to activate based on the content of log
messages matching a string or regular expression.
Syntax type log <log-message-string>
Default There is no type or log message string set by default.
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage Log type triggers fully support regular expressions using PCRE (Perl-Compatible
Regular Expression) syntax.
Only log messages of severity level notice or higher can activate a trigger.
Note that any command executed by the script will generate a log message with
level notice, and will include ‘[SCRIPT]’ before the command string. Therefore, if
something in the script matches the configured log message trigger string, it will
retrigger indefinitely.
Example To configure trigger 6 to activate when a log message of level notice or higher
indicates that any port has ‘failed’, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 6
awplus(config-trigger)# type log port.+ failed
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Command
changes
Version 5.4.7-2.1: command added
Parameter Description
<log-message-string> A string or a regular expression (PCRE) to match a log
message or part of a log message.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2086
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE MEMORY
type memory
Overview This command configures a trigger to activate based on RAM usage level. Selecting
the up option causes the trigger to activate when memory usage exceeds the
specified level. Selecting the down option causes the trigger to activate when
memory usage drops below the specified level. Selecting any causes the trigger to
activate in both situations. The default is any.
Syntax type memory <1-100> [up|down|any]
Mode Trigger Configuration
Examples To configure trigger 12 to be a memory trigger that activates when memory usage
exceeds 50% use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 12
awplus(config-trigger)# type memory 50 up
To configure trigger 40 to be a memory trigger that activates when memory usage
either rises above or drops below 65%, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 40
awplus(config-trigger)# type memory 65
or
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 40
awplus(config-trigger)# type memory 65 any
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<1-100>The percentage of memory usage at which to trigger.
up Activate when memory usage exceeds the specified level.
down Activate when memory usage drops below the specified level.
any Activate when memory usage passes the specified level in either
direction.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2087
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE PERIODIC
type periodic
Overview This command configures a trigger to be activated at regular intervals. The time
period between activations is specified in minutes.
Syntax type periodic <1-1440>
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage A combined limit of 10 triggers of the type periodic and time can be configured. If
you attempt to add more than 10 triggers the following error message is displayed:
For an example trigger configuration that uses the type periodic command, see
“See Daily Statistics” in the Triggers_Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Example To configure trigger 44 to activate periodically at 10 minute intervals use the
following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 44
awplus(config-trigger)# type periodic 10
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<1-1440>The number of minutes between activations.
% Cannot configure more than 10 triggers with the type time or
periodic
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2088
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE PING-POLL
type ping-poll
Overview This command configures a trigger that activates when Ping Polling identifies that
a target device’s status has changed. This allows you to run a configuration script
when a device becomes reachable or unreachable.
Syntax type ping-poll <1-100> {up|down}
Mode Trigger Configuration
Example To configure trigger 106 to activate when ping poll 12 detects that its target
device is now unreachable, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 106
awplus(config-trigger)# type ping-poll 12 down
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<1-100>The ping poll ID.
up The trigger activates when ping polling detects that the target is
reachable.
down The trigger activates when ping polling detects that the target is
unreachable.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2089
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE REBOOT
type reboot
Overview This command configures a trigger that activates when your device is rebooted.
Syntax type reboot
Mode Trigger Configuration
Example To configure trigger 32 to activate when your device reboots, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 32
awplus(config-trigger)# type reboot
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2090
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
TRIGGER COMMANDS
TYPE TIME
type time
Overview This command configures a trigger that activates at a specified time of day.
Syntax type time <hh:mm>
Mode Trigger Configuration
Usage A combined limit of 10 triggers of the type time and type periodic can be
configured. If you attempt to add more than 10 triggers the following error
message is displayed:
Example To configure trigger 86 to activate at 15:53, use the following commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# trigger 86
awplus(config-trigger)# type time 15:53
Related
Commands
show trigger
trigger
Parameter Description
<hh:mm>The time to activate the trigger.
% Cannot configure more than 10 triggers with the type time or
periodic

56
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2092
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
Ping-Polling
Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for commands used to configure
Ping Polling. For more information, see the Ping Polling Feature Overview and
Configuration Guide.
For information on filtering and saving command output, see the “Getting Started
with AlliedWare Plus” Feature Overview and Configuration Guide.
Command List •“active (ping-polling)” on page 2094
•“clear ping-poll” on page 2095
•“critical-interval” on page 2096
•“debug ping-poll” on page 2097
Table 56-1: The following table lists the default values when configuring a ping
poll
Default Value
Critical-interval 1 second
Description No description
Fail-count 5
Length 32 bytes
Normal-interval 30 seconds
Sample-size 5
Source-ip The IP address of the interface from which the ping packets are
transmitted
Time-out 1 second
Up-count 30

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2093
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
•“description (ping-polling)” on page 2098
•“fail-count” on page 2099
•“ip (ping-polling)” on page 2100
•“length (ping-poll data)” on page 2101
•“normal-interval” on page 2102
•“ping-poll” on page 2103
•“sample-size” on page 2104
•“show counter ping-poll” on page 2106
•“show ping-poll” on page 2108
•“source-ip” on page 2112
•“timeout (ping polling)” on page 2114
•“up-count” on page 2115
•“undebug ping-poll” on page 2116

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2094
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
ACTIVE (PING-POLLING)
active (ping-polling)
Overview This command enables a ping-poll instance. The polling instance sends ICMP echo
requests to the device with the IP address specified by the ip (ping-polling)
command.
By default, polling instances are disabled. When a polling instance is enabled, it
assumes that the device it is polling is unreachable.
The no variant of this command disables a ping-poll instance. The polling instance
no longer sends ICMP echo requests to the polled device. This also resets all
counters for this polling instance.
Syntax active
no active
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To activate the ping-poll instance 43, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# active
To disable the ping-poll instance 43 and reset its counters, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no active
Related
Commands
debug ping-poll
ip (ping-polling)
ping-poll
show ping-poll
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2095
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
CLEAR PING-POLL
clear ping-poll
Overview This command resets the specified ping poll, or all ping poll instances. This clears
the ping counters, and changes the status of polled devices to unreachable. The
polling instance changes to the polling frequency specified with the
critical-interval command. The device status changes to reachable once the device
responses have reached the up-count.
Syntax clear ping-poll {<1-100>|all}
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To reset the ping poll instance 12, use the command:
awplus# clear ping-poll 12
To reset all ping poll instances, use the command:
awplus# clear ping-poll all
Related
Commands
active (ping-polling)
ping-poll
show ping-poll
Parameter Description
<1-100>A ping poll ID number. The specified ping poll instance has its
counters cleared, and the status of the device it polls is
changed to unreachable.
all Clears the counters and changes the device status of all polling
instances.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2096
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
CRITICAL-INTERVAL
critical-interval
Overview This command specifies the time period in seconds between pings when the
polling instance has not received a reply to at least one ping, and when the device
is unreachable.
This command enables the device to quickly observe changes in state, and should
be set to a much lower value than the normal-interval command.
The no variant of this command sets the critical interval to the default of one
second.
Syntax critical-interval <1-65536>
no critical-interval
Default The default is 1 second.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To set the critical interval to 2 seconds for the ping-polling instance 99, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 99
awplus(config-ping-poll)# critical-interval 2
To reset the critical interval to the default of one second for the ping-polling
instance 99, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 99
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no critical-interval
Related
Commands
fail-count
normal-interval
sample-size
show ping-poll
timeout (ping polling)
up-count
Parameter Description
<1-65536>Time in seconds between pings, when the device has failed to
a ping, or the device is unreachable.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2097
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
DEBUG PING-POLL
debug ping-poll
Overview This command enables ping poll debugging for the specified ping-poll instance.
This generates detailed messages about ping execution.
The no variant of this command disables ping-poll debugging for the specified
ping-poll.
Syntax debug ping-poll <1-100>
no debug ping-poll {<1-100>|all}
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To enable debugging for ping-poll instance 88, use the command:
awplus# debug ping-poll 88
To disable all ping poll debugging, use the command:
awplus# no debug ping-poll all
To disable debugging for ping-poll instance 88, use the command:
awplus# no debug ping-poll 88
Related
Commands
active (ping-polling)
clear ping-poll
ping-poll
show ping-poll
undebug ping-poll
Parameter Description
<1-100>A unique ping poll ID number.
all Turn off all ping-poll debugging.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2098
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
DESCRIPTION (PING-POLLING)
description (ping-polling)
Overview This command specifies a string to describe the ping-polling instance. This allows
the ping-polling instance to be recognized easily in show commands. Setting this
command is optional.
By default ping-poll instances do not have a description.
Use the no variant of this command to delete the description set.
Syntax description <description>
no description
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To add the text “Primary Gateway” to describe the ping-poll instance 45, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# description Primary Gateway
To delete the description set for the ping-poll instance 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no description
Related
Commands
ping-poll
show ping-poll
Parameter Description
<description> The description of the target. Valid characters are any printable
character and spaces. There is no maximum character length.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2099
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
FAIL-COUNT
fail-count
Overview This command specifies the number of pings that must be unanswered, within the
total number of pings specified by the sample-size command, for the ping-polling
instance to consider the device unreachable.
If the number set by the sample-size command and the fail-count commands are
the same, then the unanswered pings must be consecutive. If the number set by
the sample-size command is greater than the number set by the fail-count
command, then a device that does not always reply to pings may be declared
unreachable.
The no variant of this command resets the fail count to the default.
Syntax fail-count <1-100>
no fail-count
Default The default is 5.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To specify the number of pings that must fail within the sample size to determine
that a device is unreachable for ping-polling instance 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# fail-count 5
To reset the fail-count to its default of 5 for ping-polling instance 45, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no fail-count
Related
Commands
critical-interval
normal-interval
ping-poll
sample-size
show ping-poll
timeout (ping polling)
up-count
Parameter Description
<1-100>The number of pings within the sample size that a reachable device
must fail to respond to before it is classified as unreachable.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2100
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
IP (PING-POLLING)
ip (ping-polling)
Overview This command specifies the IPv4 address of the device you are polling.
Syntax ip {<ip-address>|<ipv6-address>}
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To set ping-poll instance 5 to poll the device with the IP address 192.168.0.1,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 5
awplus(config-ping-poll)# ip 192.168.0.1
To set ping-poll instance 10 to poll the device with the IPv6 address 2001:db8::,
use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 10
awplus(config-ping-poll)# ip 2001:db8::
Related
Commands
ping-poll
source-ip
show ping-poll
Parameter Description
<ip-address>An IPv4 address in dotted decimal notation A.B.C.D
<ipv6-address> An IPv6 address in hexadecimal notation X:X::X:X
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2101
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
LENGTH (PING-POLL DATA)
length (ping-poll data)
Overview This command specifies the number of data bytes to include in the data portion of
the ping packet. This allows you to set the ping packets to a larger size if you find
that larger packet types in your network are not reaching the polled device, while
smaller packets are getting through. This encourages the polling instance to
change the device’s status to unreachable when the network is dropping packets
of the size you are interested in.
The no variant of this command resets the data bytes to the default of 32 bytes.
Syntax length <4-1500>
no length
Default The default is 32.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To specify that ping-poll instance 12 sends ping packet with a data portion of 56
bytes, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 12
awplus(config-ping-poll)# length 56
To reset the number of data bytes in the ping packet to the default of 32 bytes for
ping- poll instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 12
awplus(config-ping-poll)# length
Related
Commands
ping-poll
show ping-poll
Parameter Description
<4-1500>The number of data bytes to include in the data portion of the ping
packet.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2102
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
NORMAL-INTERVAL
normal-interval
Overview This command specifies the time period between pings when the device is
reachable.
The no variant of this command resets the time period to the default of 30 seconds.
Syntax normal-interval <1-65536>
no normal-interval
Default The default is 30 seconds.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To specify a time period of 60 seconds between pings when the device is reachable
for ping-poll instance 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# normal-interval 60
To reset the interval to the default of 30 seconds for ping-poll instance 45, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no normal-interval
Related
Commands
critical-interval
fail-count
ping-poll
sample-size
show ping-poll
timeout (ping polling)
up-count
Parameter Description
<1-65536>Time in seconds between pings when the target is reachable.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2103
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
PING-POLL
ping-poll
Overview This command enters the ping-poll configuration mode. If a ping-poll exists with
the specified number, then this command enters its configuration mode. If
no-ping poll exists with the specified number, then this command creates a new
ping poll with this ID number.
To configure a ping-poll, create a ping poll using this command, and use the ip
(ping-polling) command to specify the device you want the polling instance to
poll. It is not necessary to specify any further commands unless you want to
change a command’s default.
The no variant of this command deletes the specified ping poll.
Syntax ping-poll <1-100>
no ping-poll <1-100>
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To create ping-poll instance 3 and enter ping-poll configuration mode, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 3
awplus(config-ping-poll)#
To delete ping-poll instance 3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no ping-poll 3
Related
Commands
active (ping-polling)
clear ping-poll
debug ping-poll
description (ping-polling)
ip (ping-polling)
length (ping-poll data)
show ping-poll
source-ip
Parameter Description
<1-100>A unique ping poll ID number.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2104
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SAMPLE-SIZE
sample-size
Overview This command sets the total number of pings that the polling instance inspects
when determining whether a device is unreachable. If the number of pings
specified by the fail-count command go unanswered within the inspected
sample, then the device is declared unreachable.
If the numbers set in this command and fail-count command are the same, the
unanswered pings must be consecutive. If the number set by this command is
greater than that set with the fail-count command, a device that does not always
reply to pings may be declared unreachable.
You cannot set this command’s value lower than the fail-count value.
The polling instance uses the number of pings specified by the up-count
command to determine when a device is reachable.
The no variant of this command resets this command to the default.
Syntax sample-size <1-100>
no sample size
Default The default is 5.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To set the sample-size to 50 for ping-poll instance 43, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# sample-size 50
To reset sample-size to the default of 5 for ping-poll instance 43, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no sample-size
Parameter Description
<1-100>Number of pings that determines critical and up counts.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2106
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER PING-POLL
show counter ping-poll
Overview This command displays the counters for ping polling.
Syntax show counter ping-poll [<1-100>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output Figure 56-1: Example output from the show counter ping-poll command
Parameter Description
<1-100>A unique ping poll ID number. This displays the counters for the specified
ping poll only. If you do not specify a ping poll, then this command
displays counters for all ping polls.
Ping-polling counters
Ping-poll: 1
PingsSent ......... 15
PingsFailedUpState ......... 0
PingsFailedDownState ......... 0
ErrorSendingPing ......... 2
CurrentUpCount ......... 13
CurrentFailCount ......... 0
UpStateEntered ......... 0
DownStateEntered ......... 0
Ping-poll: 2
PingsSent ......... 15
PingsFailedUpState ......... 0
PingsFailedDownState ......... 0
ErrorSendingPing ......... 2
CurrentUpCount ......... 13
CurrentFailCount ......... 0
UpStateEntered ......... 0
DownStateEntered ......... 0
Ping-poll: 5
PingsSent ......... 13
PingsFailedUpState ......... 0
PingsFailedDownState ......... 2
ErrorSendingPing ......... 2
CurrentUpCount ......... 9
CurrentFailCount ......... 0
UpStateEntered ......... 0
DownStateEntered ......... 0
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2107
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW COUNTER PING-POLL
Example To display counters for the polling instances, use the command:
awplus# show counter ping-poll
Related
Commands
debug ping-poll
ping-poll
show ping-poll
Table 57: Parameters in output of the show counter ping-poll command
Parameter Description
Ping-poll The ID number of the polling instance.
PingsSent The total number of pings generated by the polling
instance.
PingsFailedUpState The number of unanswered pings while the target
device is in the Up state. This is a cumulative counter
for multiple occurrences of the Up state.
PingsFailedDownState Number of unanswered pings while the target device
is in the Down state. This is a cumulative counter for
multiple occurrences of the Down state.
ErrorSendingPing The number of pings that were not successfully sent to
the target device.
This error can occur when your device does not have a
route to the destination.
CurrentUpCount The current number of sequential ping replies.
CurrentFailCount The number of ping requests that have not received a
ping reply in the current sample-size window.
UpStateEntered Number of times the target device has entered the Up
state.
DownStateEntered Number of times the target device has entered the
Down state.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2108
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW PING-POLL
show ping-poll
Overview This command displays the settings and status of ping polls.
Syntax show ping-poll [<1-100>|state {up|down}] [brief]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Output Figure 56-2: Example output from the show ping-poll brief command
Parameter Description
<1-100>Displays settings and status for the specified polling instance.
state Displays polling instances based on whether the device they are
polling is currently reachable or unreachable.
up Displays polling instance where the device state is
reachable.
down Displays polling instances where the device state is
unreachable.
brief Displays a summary of the state of ping polls, and the devices they
are polling.
Ping Poll Configuration
----------------------------------------------------------
Id Enabled State Destination
----------------------------------------------------------
1 Yes Down 192.168.0.1
2 Yes Up 192.168.0.100
Table 58: Parameters in output of the show ping-poll brief command
Parameter Meaning
Id The ID number of the polling instance, set when creating the polling
instance with the ping-poll command.
Enabled Whether the polling instance is enabled or disabled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2109
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW PING-POLL
Figure 56-3: Example output from the show ping-poll command
State The current status of the device being polled:
Up The device is reachable.
Down The device is unreachable.
Critical
Up The device is reachable but recently the polling
instance has not received some ping replies, so the
polled device may be going down.
Critical
Down The device is unreachable but the polling instance
received a reply to the last ping packet, so the
polled device may be coming back up.
Destinatio
nThe IP address of the polled device, set with the ip (ping-polling)
command.
Ping Poll Configuration
----------------------------------------------------------
Poll 1:
Description : Primary Gateway
Destination IP address : 192.168.0.1
Status : Down
Enabled : Yes
Source IP address : 192.168.0.10
Critical interval : 1
Normal interval : 30
Fail count : 10
Up count : 5
Sample size : 50
Length : 32
Timeout : 1
Debugging : Enabled
Table 58: Parameters in output of the show ping-poll brief command (cont.)
Parameter Meaning

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2110
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW PING-POLL
Poll 2:
Description : Secondary Gateway
Destination IP address : 192.168.0.100
Status : Up
Enabled : Yes
Source IP address : Default
Critical interval : 5
Normal interval : 60
Fail count : 20
Up count : 30
Sample size : 100
Length : 56
Timeout : 2
Debugging : Enabled
Table 59: Parameters in output of the show ping-poll command
Parameter Description
Description Optional description set for the polling instance with the
description (ping-polling) command.
Destination
IP address The IP address of the polled device, set with the ip (ping-polling)
command.
Status The current status of the device being polled:
Up The device is reachable.
Down The device is unreachable.
Critic
a l Up The device is reachable but recently the polling
instance has not received some ping replies, so the
polled device may be going down.
Critic
a l
Down
The device is unreachable but the polling instance
received a reply to the last ping packet, so the
polled device may be coming back up.
Enabled Whether the polling instance is enabled or disabled. The active
(ping-polling) and active (ping-polling) commands enable and
disable a polling instance.
Source IP
address The source IP address sent in the ping packets. This is set using
the source-ip command.
Critical
interval The time period in seconds between pings when the polling
instance has not received a reply to at least one ping, and when
the device is unreachable. This is set with the critical-interval
command.
Normal
interval The time period between pings when the device is reachable.
This is set with the normal-interval command.
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2111
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SHOW PING-POLL
Examples To display the ping poll settings and the status of all the polls, use the command:
awplus# show ping-poll
To display a summary of the ping poll settings, use the command:
awplus# show ping-poll brief
To display the settings for ping poll 6, use the command:
awplus# show ping-poll 6
To display a summary of the state of ping poll 6, use the command:
awplus# show ping-poll 6 brief
To display the settings of ping polls that have reachable devices, use the
command:
awplus# show ping-poll state up
To display a summary of ping polls that have unreachable devices, use the
command:
awplus# show ping-poll 6 state down brief
Related
Commands
debug ping-poll
ping-poll
Fail count The number of pings that must be unanswered, within the total
number of pings specified by the sample-size command, for the
polling instance to consider the device unreachable. This is set
using the fail-count command.
Up count The number of consecutive pings that the polling instance must
receive a reply to before classifying the device reachable again.
This is set using the up-count command.
Sample size The total number of pings that the polling instance inspects
when determining whether a device is unreachable. This is set
using the sample-size command.
Length The number of data bytes to include in the data portion of the
ping packet. This is set using the length (ping-poll data)
command.
Timeout The time in seconds that the polling instance waits for a
response to a ping packet. This is set using the timeout (ping
polling) command.
Debugging Indicates whether ping polling debugging is Enabled or
Disabled.
This is set using the debug ping-poll command.
Table 59: Parameters in output of the show ping-poll command (cont.)
Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2112
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
SOURCE-IP
source-ip
Overview This command specifies the source IP address to use in ping packets.
By default, the polling instance uses the address of the interface through which it
transmits the ping packets. It uses the device’s local interface IP address when it is
set. Otherwise, the IP address of the interface through which it transmits the ping
packets is used.
The no variant of this command resets the source IP in the packets to the device’s
local interface IP address.
Syntax source-ip {<ip-address>|<ipv6-address>}
no source-ip
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To configure the ping-polling instance 43 to use the source IP address
192.168.0.1 in ping packets, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# source-ip 192.168.0.1
To configure the ping-polling instance 43 to use the source IPv6 address
2001:db8:: in ping packets, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# source-ip 2001:db8::
To reset the source IP address to the device’s local interface IP address for ping-poll
instance 43, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no source-ip
Parameter Description
<ip-address>An IPv4 address in dotted decimal notation A.B.C.D
<ipv6-address> An IPv6 address in hexadecimal notation X:X::X:X

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2114
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
TIMEOUT (PING POLLING)
timeout (ping polling)
Overview This command specifies the time in seconds that the polling instance waits for a
response to a ping packet. You may find a higher time-out useful in networks
where ping packets have a low priority.
The no variant of this command resets the set time out to the default of one
second.
Syntax timeout <1-30>
no timeout
Default The default is 1 second.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To specify the timeout as 5 seconds for ping-poll instance 43, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# timeout 5
To reset the timeout to its default of 1 second for ping-poll instance 43, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 43
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no timeout
Related
Commands
critical-interval
fail-count
normal-interval
ping-poll
sample-size
show ping-poll
up-count
Parameter Description
<1-30>Length of time, in seconds, that the polling instance waits for a
response from the polled device.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2115
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
PING-POLLING COMMANDS
UP-COUNT
up-count
Overview This command sets the number of consecutive pings that the polling instance
must receive a reply to before classifying the device reachable again.
The no variant of this command resets the up count to the default of 30.
Syntax up-count <1-100>
no up-count
Default The default is 30.
Mode Ping-Polling Configuration
Examples To set the upcount to 5 consecutive pings for ping-polling instance 45, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# up-count 5
To reset the upcount to the default value of 30 consecutive pings for ping-polling
instance 45, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# ping-poll 45
awplus(config-ping-poll)# no up-count
Related
Commands
critical-interval
fail-count
normal-interval
ping-poll
sample-size
show ping-poll
timeout (ping polling)
Parameter Description
<1-100>Number of replied pings before an unreachable device is classified as
reachable.

57
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2117
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
sFlow Commands
Introduction
Overview This chapter provides an alphabetical reference for sFlow commands.
Command List •“debug sflow” on page 2118
•“debug sflow agent” on page 2119
•“sflow agent (address)” on page 2120
•“sflow collector (address)” on page 2122
•“sflow collector max-datagram-size” on page 2124
•“sflow enable” on page 2125
•“sflow max-header-size” on page 2126
•“sflow polling-interval” on page 2128
•“sflow sampling-rate” on page 2129
•“show debugging sflow” on page 2130
•“show running-config sflow” on page 2132
•“show sflow” on page 2133
•“show sflow interface” on page 2135
•“undebug sflow” on page 2136

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2118
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
DEBUG SFLOW
debug sflow
Overview This command enables sFlow® debug message logging, for sFlow sampling and
polling activity on the specified ports. If no ports are specified, sampling and/or
polling debug messages are enabled for all ports.
The no variant of this command disables sFlow sampling and or polling debug
message logging on the ports selected. If no ports are specified, sampling and/or
polling debug messages are disabled on all ports.
Syntax debug sflow [interface <port-list>] [sampling][polling]
no debug sflow [interface <port-list>] [sampling][polling]
Default The sFlow sampling and or polling debug is disabled.
Mode Privileged Exec
Examples To enable sFlow debug message logging for polling and sampling on port1.0.1
and port1.0.7, use the commands:
awplus# debug sflow interface port1.0.1,port1.0.7 sampling
polling
To enable logging and polling of sFlow debug messages for polling and sampling
on all ports, use the command:
awplus# debug sflow sampling polling
Related
Commands
show debugging sflow
no debug all
Parameter Description
interface Interface information.
<port-list> The ports for which sFlow debug is to be enabled. The ports to
display information about. The port list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.12)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.24
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.1-1.0.24.
sampling Debug sFlow sampling for the specified port(s).
polling Debug sFlow polling for the specified port(s).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2119
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
DEBUG SFLOW AGENT
debug sflow agent
Overview This command enables sFlow® debug message logging that is not specific to
particular ports. For example, sending an sFlow datagram to the collector.
The no variant of this command applies the command default.
Syntax debug sflow agent
no debug sflow agent
Default The sFlow agent debug message logging (that is not port specific) is disabled.
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To enable logging of sFlow agent debug messages, use the following command:
awplus# debug sflow agent
Related
Commands
show debugging sflow
debug sflow
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2120
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW AGENT (ADDRESS)
sflow agent (address)
Overview This command sets the sFlow® agent IP address on the switch. This address is
inserted into every sFlow datagram sent from the sFlow agent switch to the sFlow
collector device. The sFlow collector can then uses this address to uniquely identify
and to access the switch, such as for SNMP. We therefore recommend that you
change this address as little as possible.
Although the agent address can be set to any valid IPv4 or IPv6 address; we
recommended that you set the sFlow® agent IP address to be the local address
that is configured on the switch. For information on local addresses and how to set
them up, see the interface (to configure) command. This ensures that the sFlow
collector can maintain connectivity to the switch irrespective of the addition or
deletion of VLAN interfaces (each of which will have its own specific IP address).
Note that sFlow is rendered inactive whenever the agent address is not set.
The no variant of this command applies its default setting to remove a configured
address.
Syntax sflow agent {ip <ip-address>|ipv6 <ipv6-address>}
no sflow agent {ip|ipv6}
Default The sFlow agent address is unset.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the sFlow agent (IPv4) address to 192.0.2.23, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow agent ip 192.0.2.23
To remove the sFlow agent (IPv4) address, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow agent ip
To set the sFlow agent (IPv6) address to 2001:0db8::1, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow agent ipv6 2001:0db8::1
To remove the sFlow agent (IPv6) address, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow agent ipv6
Parameter Description
<ip-address>The IPv4 address of the switch that is acting as the sFlow agent.
<ipv6-address>The IPv6 address of the switch that is acting as the sFlow agent.
The IPv6 address uses the format X:X::X:X.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2122
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW COLLECTOR (ADDRESS)
sflow collector (address)
Overview This command sets the sFlow® agent's collector IP address and/or UDP port. This is
the destination IP address and UDP port, for sFlow datagrams sent from the sFlow
agent. The IP address can be any valid IPv4 or IPv6 address. Note that sFlow is
rendered inactive whenever the collector address is set to 0.0.0.0 (for IPv4) or ::
(for IPv6).
The no variant of this command returns the IP address and UDP port values to their
defaults, which will result in sFlow being deactivated.
Syntax sflow collector {[ip <ip-address>|ipv6 <ipv6-address>]|[port
<1-65535>]}
no sflow collector {[ip|ipv6]|[port]}
Default The collector address is 0.0.0.0 (which renders sFlow inactive), and the UDP
port is 6343.
Mode Global Configuration
Examples To set the sFlow collector address to 1920.2.25 and UDP port to 9000, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow collector ip 192.0.2.25 port 9000
To remove the sFlow collector IPv4 address and leave the UDP port unchanged,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow collector ip
To remove the sFlow collector IPv4 address and to remove the UDP port, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow collector ip port
Parameter Description
<ip-address>IPv4 address of the remote sFlow collector.
<ipv6-address>IPv6 address of remote sFlow collector.
The IPv6 address uses the format X:X::X:X.
port Destination UDP port for sFlow datagrams sent to the
collector.
<1-65535>UDP port number (default: 6343).

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2123
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW COLLECTOR (ADDRESS)
To set the sFlow collector address to 2001:0db8::1 and leave the UDP port
unchanged, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow collector ipv6 2001:0db8::1
To remove the sFlow collector IPv6 address and leave the UDP port unchanged,
use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow collector ipv6
To remove the sFlow collector IPv6 address and to remove the UDP port, use the
command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# no sflow collector ipv6 port
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2124
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW COLLECTOR MAX-DATAGRAM-SIZE
sflow collector max-datagram-size
Overview This command sets the maximum size of the sFlow® datagrams sent to the
collector.
The no variant of this command resets the maximum-datagram-size to the default.
Syntax sflow collector max-datagram-size <200-1500>
no sflow collector max-datagram-size
Default 1400 bytes
Mode Global Configuration
Example To set the maximum datagram size to 1200, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow collector max-datagram-size 1200
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow
Parameter Description
<200-1500>The maximum number of bytes that can be sent in an sFlow
datagram sent from the agent to the collector.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2125
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW ENABLE
sflow enable
Overview This command enables sFlow® globally on the switch.
The no variant of this command disables sFlow globally on the switch.
Note that enabling sFlow does not automatically set its operational status to
active. To activate sFlow the following conditions need to be met:
•sFlow is enabled.
• The sFlow agent address is set.
• The sFlow collector address is set to a valid (non zero) IPv4 or IPv6 address.
• Polling or sampling is enabled on the ports to be sampled or polled.
Syntax sflow enable
no sflow enable
Default sFlow is disabled globally on the switch.
Mode Global Configuration
Example To enable sFlow operation, use the command:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# sflow enable
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2126
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW MAX-HEADER-SIZE
sflow max-header-size
Overview This command sets the maximum header size of the Ethernet frames sampled on
a specified port. The maximum header size is measured in bytes, referenced from
the first byte of the Ethernet destination address and excludes the Ethernet FCS
fields.
If a sampled Ethernet frame is longer than the maximum header size set by this
command, then the frame will be truncated to the first N bytes before being placed
in the sFlow datagram, where N is the maximum header size set by this command.
The no variant of this command resets the max-header-size to its default.
Syntax sflow max-header-size <14-200>
no sflow max-header-size
Default The max-header-size is 128 bytes.
Mode Interface Configuration
Usage The header size is measured from the first byte of the Ethernet frame MAC
Destination Address.
• For an environment using standard TCP IPv4 over Ethernet frames, consider
the following basic protocol structure:
Ethernet header (including the 4 byte 802.1Q header component) = 18 bytes
IPv4 header = 24 bytes
TCP header = 24 bytes
Total = 66 bytes
CAUTION: For IPv4, any data existing between 66 bytes and the value set by this
command will be included in the sFlow packet samples. For example, with the
default of 128 applied, up to 128-66=62 bytes of user data could be included in
the sFlow datagram samples sent between the Agent and the Collector.
For more information, see the sFlow Feature Overview and Configuration
Guide.
Parameter Description
<14-200>The maximum number of header bytes to be sampled.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2127
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW MAX-HEADER-SIZE
• A similar consideration can be made for an environment using TCP IPv6 over
Ethernet:
Ethernet header (including the 4 byte 802.1Q header component) = 18 bytes
IPv6 header = 40 bytes
TCP header = 24 bytes
Total = 82 bytes
CAUTION: For IPv6, any data existing between 82 bytes and the value set by this
command will be included in the sFlow packet samples. For example, with the
default of 128 applied, up to 128-82=46 bytes of user data could be included in
the sFlow datagram samples sent between the Agent and the Collector.
Note that the agent-to-collector datagrams contain their own UDP headers, which
are outside this calculation.
Example To set the maximum header size to 160 bytes for ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.7, use the
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.7
awplus(config-if)# sflow max-header-size 160
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow interface
sflow max-header-size

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2128
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW POLLING-INTERVAL
sflow polling-interval
Overview This command sets the sFlow® counter polling interval (in seconds) for the
specified ports. A value of 0 disables polling. A counter sample is taken every N
seconds where N is the value set by this command.
The no variant of this command applies the default.
Syntax sflow polling-interval {0|<1-16777215>}
no sflow polling-interval
Default The polling-interval is 0 (polling disabled).
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To set the polling interval to 60 seconds for ports 1.0.1 and 1.0.7, use the following
commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.7
awplus(config-if)# sflow polling-interval 60
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow interface
Parameter Description
0Disable polling (the default).
<1-16777215>The polling interval in seconds.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2129
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SFLOW SAMPLING-RATE
sflow sampling-rate
Overview This command sets the mean sFlow® sampling rate for the specified ports.
Sampling occurs every N frames (on average), where N is the rate value set via this
command. The sampling rate applies to ingress and egress frames independently.
For example, a value of 1000 will sample one frame in every 1000 frames received,
i.e. one in every 1000 frames sent from the specified port. A value of 0 disables
sampling on the specified port(s).
The no variant of this command applies the default.
Syntax sflow sampling-rate <256-16777215>
no sflow sampling-rate
Default The sampling-rate is 0 (sampling disabled).
Mode Interface Configuration
Example To set the sampling rate to 500 for port1.0.1 and port1.0.3, use the commands:
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1,port1.0.3
awplus(config-if)# sflow sampling-rate 500
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow interface
Parameter Description
<256-16777215>The sampling rate N, measured in Ethernet frames.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2130
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW DEBUGGING SFLOW
show debugging sflow
Overview This command displays sFlow® debug settings for agent operation, and for
sampling and polling on specific interface ports. If no interface ports are specified,
sampling and polling will be applied to all ports.
Syntax show debugging sflow [interface <port-list>]
Mode User Exec and Privileged Exec
Example To display sFlow debug settings on the agent, and for sampling and polling on
ports 1.0.1 to 1.0.9, use the command:
awplus# show debugging sflow interface port1.0.1-1.0.9
Output Figure 57-1: Sample obtained for an sFlow agent
To display sFlow debug settings for all ports, use the command:
awplus# show debugging sflow
Parameter Description
interface The interface information.
<port-list> The ports for which the sFlow debug settings are to be shown.
The ports to display information about. The port list can be:
• a switch port (e.g. port1.0.6)
• a continuous range of ports separated by a hyphen, e.g.
port1.0.1-1.0.6
• a comma-separated list of ports and port ranges, e.g.
port1.0.1,port1.0.3-1.0.6.
awplus# show debugging sflow interface port1.0.1-1.0.9
sFlow Agent Debug: Enabled
Sampling Polling
Port Debug Debug
-------------------------------
1.0.1 Enabled Enabled
1.0.2 Enabled -
1.0.3 - -
1.0.4 - -
1.0.5 - -
1.0.6 - Enabled
1.0.7 - -
1.0.8 - Enabled
1.0.9 - Enabled
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2132
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW RUNNING-CONFIG SFLOW
show running-config sflow
Overview This command displays the running system information specific to the sFlow
feature.
Syntax show running-config sflow
Mode Privileged Exec and Global Configuration
Example To display the sFlow running configuration information, use the command:
awplus# show running-config sflow
Output Figure 57-2: Example output from the show running-config sflow command
Related
Commands
show running-config
awplus#sh run sflow
!
sflow agent ip 192.0.2.33
sflow collector ip 192.0.2.65
sflow collector max-datagram-size 1200
sflow enable
!
interface port1.0.11-port1.0.22
sflow sampling-rate 512
C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2133
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW SFLOW
show sflow
Overview This command displays non-port-specific sFlow agent configuration and
operational status.
Syntax show sflow
Mode Privileged Exec
Example To display sFlow configuration and operational status, use the command:
awplus# show sflow
Output
Table 1: Example output from the show sflow command
sFlow Agent Configuration: Default Values
sFlow Admin Status ........ Disabled [Disabled]
sFlow Agent Address ....... [not set] [not set]
Collector Address ......... 0.0.0.0 [0.0.0.0]
Collector UDP Port ........ 6343 [6343]
Tx Max Datagram Size ...... 1200 [1400]
sFlow Agent Status:
Polling/sampling/Tx ....... Inactive because:
- sFlow is disabled
- Agent Addr is not set
- Collector Addr is 0.0.0.0
- Polling & sampling disabled
on all ports
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show sflow command
Output Parameter Description
sFlow Admin
Status Whether sFlow agent operation is administratively
enabled.
sFlow Agent
Address The sFlow agent IPv4 or IPv6 address for the device. sFlow
is rendered inactive whenever the agent address is not set.
Collector Address The IPv4 or IPv6 collector address to which sFlow
datagrams are sent. sFlow is rendered inactive whenever
the collector address is set to 0.0.0.0 or 0:0::0.0.
Collector UDP
Port The UDP port on the collector to which sFlow datagrams
are sent.

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2134
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW SFLOW
Related
Commands
show running-config sflow
show sflow interface
Tx Max Datagram
Size The maximum size of the sFlow datagrams sent to the
collector.
Polling/sampling/
Tx Whether sFlow sampling and/or polling (and hence sFlow
datagram transmission) are active. If inactive the reasons
are listed.
Table 2: Parameters in the output of the show sflow command (cont.)
Output Parameter Description

C613-50292-01 Rev A Command Reference for IE210L Series 2135
AlliedWare Plus™ Operating System - Version 5.4.9-0.x
SFLOW COMMANDS
SHOW SFLOW INTERFACE
show sflow interface
Overview This command displays sFlow agent sampling and polling configuration for
specified ports.
Syntax show sflow interface <ifrange>
Mode Privileged Exec
Parameter Description
<ifrange>The interface range.




































































































