Table of Contents
- Chapter 1
- Chapter 2
- Chapter 3
- Chapter 4
- Chapter 5
- Contents
- Preface
- Chapter 1
- Getting Started
- Chapter 2
- System
- Save All Applied Changes
- ARP Cache
- System Resources
- System Description
- Network Connectivity Configuration
- HTTP
- Telnet Session
- User Accounts Configuration
- Login Sessions
- Forwarding Database Configuration
- Forwarding Database Search
- Buffered Log Configuration
- Buffered Log
- Command Logger Configuration
- Console Log Configuration
- Event Log
- Hosts Log Configuration
- Persistent Log Configuration
- Persistent Log
- Syslog Configuration
- Diagnosis Log Configuration
- SNMP Community Configuration
- Trap Receiver Configuration
- Supported MIBs
- Controller Detailed Statistics
- Controller Statistics Summary
- System Reset
- Reset Configuration To Default
- Erase Startup Configuration File
- Reset Passwords to Defaults
- Download File to Controller
- Upload File from Controller
- HTTP File Download
- Software Upgrade
- Ping
- TraceRoute
- Trap Flags
- Trap Logs
- DNS Global Configuration
- DNS Server Configuration
- HostName IP Mapping Summary
- SNTP Global Configuration
- SNTP Global Status
- SNTP Server Configuration
- SNTP Server Status
- License
- System
- Chapter 3
- Chapter 4
- Security
- CP Global Configuration
- CP Configuration Summary
- CP Web Customization
- Local User Summary
- Interface Association
- CP Status
- Interface Status
- Client Connection Status
- RADIUS Configuration
- RADIUS Server Configuration
- RADIUS Named Server Status
- RADIUS Server Statistics
- Accounting Server Configuration
- Named Accounting Server Status
- Accounting Server Statistics
- RADIUS Clear Statistics
- Secure HTTP
- Security
- Chapter 5
- Wireless LAN
- WLAN Basic Setup > Global
- WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery
- WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP
- AP Management Reset
- RF Management > Configuration
- RF Management > Channel Plan History
- RF Management > Manual Channel Plan
- Access Point Software Download
- Managed AP Advanced Settings
- Status/Statistics > Global
- Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Status
- Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Statistics
- Status/Statistics > Associated Client
- Viewing Status Summary
- Viewing the Detailed Status
- Viewing the Status of Neighbor APs
- Viewing the Status of Distributed Tunneling
- Viewing the Status of SSID
- Viewing the Status of VAP
- Viewing the Status of Controller
- Viewing the Summary Statistics of Association
- Viewing the Detailed Statistics of Association
- Status/Statistics > Peer Controller
- Status/Statistics > WDS Managed APs
- Rogue/RF Scan
- Detected Clients
- Ad Hoc Clients
- AP Authentication Failure
- De-Auth Attack Status
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > SNMP Traps
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > Distributed Tunneling
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > Centralized L2 Tunneling
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known Client
- WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks
- Access Point Profile List
- Access Point Profile Global Configuration
- Access Point Profile Radio Configuration
- Access Point Profile VAP Configuration
- Access Point Profile QoS Configuration
- Peer Controller > Configuration Request Status
- Peer Controller > Configuration Enable/Disable
- WIDS AP Configuration
- WIDS Client Configuration
- Local OUI Database Summary
- WDS Group Configuration
- WDS AP Configuration
- WDS Link Configuration
- Wireless LAN
Allied Telesis UWC-60-APL User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for UWC-60-APL by Allied Telesis which is a product in the Gateways/Controllers category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals
613-001893 Rev. A
AT-UWC Series
Wireless LAN Controller for Enterprise
AT-UWC-60-APL
AT-UWC WLAN Controller on a Server
Web GUI User’s Guide

Copyright © 2014 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Microsoft and Internet Explorer are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Netscape Navigator is a registered
trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation. All other product names, company names, logos or other
designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document
without prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied
Telesis, Inc. be liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to
lost profits, arising out of or related to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been
advised of, known, or should have known, the possibility of such damages.

3
Contents
Preface ..................................................................................................................................................................................9
Safety Symbols Used in this Document................................................................................................................................10
Contacting Allied Telesis ......................................................................................................................................................11
Chapter 1: Getting Started ................................................................................................................................................13
AT-UWC Wireless LAN Controller........................................................................................................................................14
Web Graphic User Interface (GUI) ................................................................................................................................14
Management Workstation .............................................................................................................................................14
Preparing the Management Workstation ..............................................................................................................................15
Starting a Management Session ..........................................................................................................................................16
Registering the License Key.................................................................................................................................................17
License Key...................................................................................................................................................................17
30-day Free Trial License..............................................................................................................................................17
Registering the License Key..........................................................................................................................................17
Downloading the Free Trail License .....................................................................................................................................18
Changing the IP Address......................................................................................................................................................21
Enabling JavaScript..............................................................................................................................................................25
Configuring the AT-UWC WLAN Controller..........................................................................................................................28
Saving the Changes .............................................................................................................................................................29
Using Online Help.................................................................................................................................................................31
Ending a Management Session............................................................................................................................................35
Chapter 2: System .............................................................................................................................................................37
Save All Applied Changes ....................................................................................................................................................39
ARP Cache...........................................................................................................................................................................40
System Resources ...............................................................................................................................................................41
System Description...............................................................................................................................................................43
Network Connectivity Configuration......................................................................................................................................45
HTTP ....................................................................................................................................................................................47
Telnet Session......................................................................................................................................................................49
User Accounts Configuration................................................................................................................................................50
Login Sessions .....................................................................................................................................................................52
Forwarding Database Configuration.....................................................................................................................................54
Forwarding Database Search...............................................................................................................................................55
Viewing the Forwarding Database ................................................................................................................................55
Searching a MAC Address ............................................................................................................................................56
Buffered Log Configuration...................................................................................................................................................57
Buffered Log .........................................................................................................................................................................59
Command Logger Configuration...........................................................................................................................................60
Console Log Configuration ...................................................................................................................................................61
Event Log .............................................................................................................................................................................62
Hosts Log Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................63
Persistent Log Configuration ................................................................................................................................................65
Severity Levels ..............................................................................................................................................................67
Persistent Log.......................................................................................................................................................................68
Syslog Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................69
Diagnosis Log Configuration ................................................................................................................................................71
SNMP Community Configuration..........................................................................................................................................73
Adding or Modifying Community Strings .......................................................................................................................73
Deleting a Community String.........................................................................................................................................74

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
4
Trap Receiver Configuration.................................................................................................................................................75
Supported MIBs ....................................................................................................................................................................77
Controller Detailed Statistics.................................................................................................................................................78
Controller Statistics Summary...............................................................................................................................................81
System Reset .......................................................................................................................................................................82
Reset Configuration To Default.............................................................................................................................................83
Guidelines for Resetting the Configuration....................................................................................................................83
Resetting the Configuration ...........................................................................................................................................83
Erase Startup Configuration File...........................................................................................................................................85
Guidelines for Erasing the Startup Configuration File....................................................................................................85
Deleting the Startup Configuration File..........................................................................................................................85
Reset Passwords to Defaults................................................................................................................................................87
Download File to Controller...................................................................................................................................................88
Upload File from Controller...................................................................................................................................................90
HTTP File Download.............................................................................................................................................................92
Software Upgrade.................................................................................................................................................................94
Guideline for upgrading Management Software ............................................................................................................94
Upgrading Management Software.................................................................................................................................94
Ping.......................................................................................................................................................................................96
TraceRoute ...........................................................................................................................................................................98
Trap Flags...........................................................................................................................................................................100
Trap Logs............................................................................................................................................................................102
DNS Global Configuration...................................................................................................................................................104
Viewing the DNS Client ...............................................................................................................................................104
Enabling the DNS Client ..............................................................................................................................................105
Changing the Properties..............................................................................................................................................105
Adding a DNS Name ...................................................................................................................................................105
Deleting a DNS Name .................................................................................................................................................106
DNS Server Configuration ..................................................................................................................................................107
Viewing the DNS Server List .......................................................................................................................................107
Adding a DNS Server ..................................................................................................................................................107
Deleting a DNS Server ................................................................................................................................................108
HostName IP Mapping Summary .......................................................................................................................................109
Viewing DNS Static and Dynamic Entries ...................................................................................................................109
Adding a Static Entry ...................................................................................................................................................110
Deleting a DNS Static Entry.........................................................................................................................................111
Deleting All the DNS Dynamic Entries.........................................................................................................................111
SNTP Global Configuration.................................................................................................................................................112
SNTP Global Status............................................................................................................................................................114
SNTP Server Configuration ................................................................................................................................................117
SNTP Server Status............................................................................................................................................................119
License ...............................................................................................................................................................................121
Viewing License Information........................................................................................................................................121
Adding License Key.....................................................................................................................................................122
Deleting License Key...................................................................................................................................................123
Chapter 3: Switching .......................................................................................................................................................125
VLAN Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................126
Modifying the VLAN Properties....................................................................................................................................126
Creating a VLAN..........................................................................................................................................................127
Deleting VLAN’s ..........................................................................................................................................................128
VLAN Status .......................................................................................................................................................................130
VLAN Port Configuration.....................................................................................................................................................131
VLAN Port Summary...........................................................................................................................................................133
Reset VLAN Configuration..................................................................................................................................................135
Default VLAN Settings.................................................................................................................................................135
Resetting the VLAN Configuration...............................................................................................................................135
Chapter 4: Security ..........................................................................................................................................................137
CP Global Configuration .....................................................................................................................................................138
CP Configuration Summary ................................................................................................................................................140

Contents
5
Viewing a List of CP Profiles .......................................................................................................................................140
Adding or Modify a CP Profile .....................................................................................................................................141
Deleting a CP Profile ...................................................................................................................................................145
CP Web Customization.......................................................................................................................................................146
Global Parameters ......................................................................................................................................................147
Authentication Page ....................................................................................................................................................148
Welcome Page ............................................................................................................................................................151
Logout Page ................................................................................................................................................................152
Logout Success Page .................................................................................................................................................153
Local User Summary ..........................................................................................................................................................155
Viewing a List of Local Users ......................................................................................................................................155
Adding or Modify a Local User ....................................................................................................................................155
Deleting a Local User ..................................................................................................................................................157
Interface Association ..........................................................................................................................................................159
Guidelines for Associating a CP Profile.......................................................................................................................159
Adding and Deleting Wireless Networks from a CP Profile .........................................................................................159
CP Status ...........................................................................................................................................................................161
Viewing the CP Global Status .....................................................................................................................................161
Viewing the Activity Status per CP Profile...................................................................................................................162
Interface Status ..................................................................................................................................................................164
Viewing the Interface Activation Status .......................................................................................................................164
Viewing the Interface Capability Status .......................................................................................................................165
Client Connection Status ....................................................................................................................................................167
Client Summary ...........................................................................................................................................................167
Client Detail .................................................................................................................................................................168
Client Statistics............................................................................................................................................................169
Interface - Client Status...............................................................................................................................................169
CP - Client Status........................................................................................................................................................170
RADIUS Configuration........................................................................................................................................................172
RADIUS Server Configuration ............................................................................................................................................175
RADIUS Named Server Status...........................................................................................................................................176
RADIUS Server Statistics ...................................................................................................................................................178
Accounting Server Configuration........................................................................................................................................181
Named Accounting Server Status.......................................................................................................................................182
Accounting Server Statistics ...............................................................................................................................................184
RADIUS Clear Statistics .....................................................................................................................................................186
Secure HTTP......................................................................................................................................................................187
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN .................................................................................................................................................189
WLAN Basic Setup > Global...............................................................................................................................................191
WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery .........................................................................................................................................194
Discovery by L3 IP Discovery......................................................................................................................................194
Importing a List of IP Addresses .................................................................................................................................195
Guidelines for Importing a CVS file .............................................................................................................................196
Discovery by L2 VLAN Discovery................................................................................................................................196
WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP ...........................................................................................................................................198
Steps for Access Points to be Managed .....................................................................................................................198
Viewing Valid AP List ..................................................................................................................................................198
Adding an Access Point ..............................................................................................................................................199
Importing a List of Access Points ................................................................................................................................201
Guidelines for Importing a CVS file .............................................................................................................................202
Modifying the Access Point .........................................................................................................................................202
Deleting Access Points................................................................................................................................................202
AP Management Reset ......................................................................................................................................................204
RF Management > Configuration .......................................................................................................................................205
Guidelines for the Channel Plan Algorithm..................................................................................................................205
RF Management > Channel Plan History ...........................................................................................................................208
RF Management > Manual Channel Plan ..........................................................................................................................210
Access Point Software Download.......................................................................................................................................212
Managed AP Advanced Settings ........................................................................................................................................215
Viewing the AP Advanced Settings .............................................................................................................................215

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
6
Changing the Debug Status ........................................................................................................................................216
Changing the Channel or Power .................................................................................................................................217
Status/Statistics > Global....................................................................................................................................................220
Viewing Global Status and Statistics ...........................................................................................................................220
Viewing Controller Status and Statistics......................................................................................................................225
Viewing IP Discovery...................................................................................................................................................228
Viewing Configuration Received..................................................................................................................................229
Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Status ...........................................................................................................................232
Viewing a List of Managed AP’s and Deleting an AP ..................................................................................................232
Viewing the Detailed Status of a Managed AP............................................................................................................234
Viewing the Detailed Status of Radio ..........................................................................................................................236
Viewing the Status of Neighbor AP’s ...........................................................................................................................238
Viewing the Status of Neighbor Clients .......................................................................................................................240
Viewing the Status of Virtual Access Points ................................................................................................................241
Viewing the Status of Distributed Tunneling................................................................................................................242
Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Statistics.......................................................................................................................244
Viewing the Statistics of Managed Access Points .......................................................................................................244
Viewing The Statistics of Ethernet...............................................................................................................................245
Viewing the Detailed Statistics of Managed Access Point s........................................................................................246
Viewing the Statistics of Radio ....................................................................................................................................249
Viewing the Statistics of VAP ......................................................................................................................................252
Viewing the Statistics of Distributed Tunneling............................................................................................................253
Status/Statistics > Associated Client ..................................................................................................................................256
Viewing Status Summary.............................................................................................................................................256
Viewing the Detailed Status.........................................................................................................................................258
Viewing the Status of Neighbor APs............................................................................................................................260
Viewing the Status of Distributed Tunneling................................................................................................................261
Viewing the Status of SSID .........................................................................................................................................262
Viewing the Status of VAP...........................................................................................................................................263
Viewing the Status of Controller ..................................................................................................................................263
Viewing the Summary Statistics of Association...........................................................................................................264
Viewing the Detailed Statistics of Association .............................................................................................................265
Status/Statistics > Peer Controller ......................................................................................................................................266
Viewing the Status of Peer Controllers........................................................................................................................266
Viewing Peer Controller Configuration.........................................................................................................................267
Viewing Managed AP by Peer Controller ....................................................................................................................268
Status/Statistics > WDS Managed APs ..............................................................................................................................270
Viewing WDS Group Status.........................................................................................................................................270
Viewing WDS AP Status..............................................................................................................................................271
Viewing WDS Link Status............................................................................................................................................272
Viewing WDS Link Statistics........................................................................................................................................273
Rogue/RF Scan ..................................................................................................................................................................276
Viewing Access Points Detected by RF Scan .............................................................................................................276
Viewing an Access Point Detected by RF Scan ..........................................................................................................277
Viewing AP Triangulation Status .................................................................................................................................280
Viewing WIDS AP Rogue Classification ......................................................................................................................282
Detected Clients .................................................................................................................................................................284
Viewing a List of Detected Clients ...............................................................................................................................284
Viewing a Detected AP Client......................................................................................................................................285
Viewing Rogue Classification ......................................................................................................................................289
Viewing Pre-Auth History.............................................................................................................................................290
Viewing Triangulation Information ...............................................................................................................................291
Viewing Roam History .................................................................................................................................................293
Ad Hoc Clients ....................................................................................................................................................................295
AP Authentication Failure ...................................................................................................................................................297
Viewing Failed Access Points and Adding Them to Valid AP List...............................................................................297
Viewing Detailed Information about Failed Access Points...........................................................................................298
De-Auth Attack Status ........................................................................................................................................................301
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global............................................................................................................................302
WLAN Advanced Configuration > SNMP Traps .................................................................................................................305

Contents
7
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Distributed Tunneling....................................................................................................308
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Centralized L2 Tunneling..............................................................................................310
Adding VLAN’s to the List............................................................................................................................................310
Deleting VLAN’s to the List..........................................................................................................................................311
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known Client.................................................................................................................312
Viewing a List of Known Clients ..................................................................................................................................312
Adding an AP Client to the Known Client List..............................................................................................................313
Adding AP Clients Using CSV File ..............................................................................................................................314
Guidelines for Importing a CVS file .............................................................................................................................315
Deleting AP Clients from the Known Client List...........................................................................................................315
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks.......................................................................................................................316
Adding a Wireless Network .........................................................................................................................................316
Modifying a Wireless Network .....................................................................................................................................323
Deleting a Wireless Network from the List...................................................................................................................324
Access Point Profile List .....................................................................................................................................................325
Guidelines for Applying an AP Profile..........................................................................................................................325
Viewing and Adding Access Point Profiles..................................................................................................................325
Copying An Access Point Profile.................................................................................................................................326
Modifying An Access Point Profile...............................................................................................................................327
Deleting An Access Point Profile.................................................................................................................................327
Applying An Access Point Profile ................................................................................................................................327
Access Point Profile Global Configuration..........................................................................................................................328
Access Point Profile Radio Configuration...........................................................................................................................331
Modulation and Coding Scheme Table .......................................................................................................................338
Access Point Profile VAP Configuration .............................................................................................................................339
Access Point Profile QoS Configuration .............................................................................................................................342
Peer Controller > Configuration Request Status ................................................................................................................346
Peer Controller > Configuration Enable/Disable.................................................................................................................348
WIDS AP Configuration ......................................................................................................................................................351
WIDS Client Configuration..................................................................................................................................................354
Local OUI Database Summary ...........................................................................................................................................357
Viewing a List of OUI Entries and Deleting Them .......................................................................................................357
Adding an OUI Entry ...................................................................................................................................................358
WDS Group Configuration..................................................................................................................................................359
Guidelines for a WDS Group.......................................................................................................................................359
Configuring WDS.........................................................................................................................................................360
Viewing a List of WDS Groups and Adding a New Group...........................................................................................361
Deleting WDS Groups .................................................................................................................................................362
Pushing the WDS Information to Peer Controllers ......................................................................................................363
WDS AP Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................364
Viewing a List of AP Members and Adding an AP.......................................................................................................364
Deleting AP Members .................................................................................................................................................365
WDS Link Configuration .....................................................................................................................................................366
Viewing Link Combinations and Adding a New Link ...................................................................................................366
Deleting a Link Combination .......................................................................................................................................368

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
8

9
Preface
This manual is the Web Graphic User Interface (GUI) user’s guide for the
AT-UWC Wireless LAN Controller. The instructions in this guide explain
how to configure the management tool. The user’s guide applies to:
AT-UWC-60-APL
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Software
This preface contains the following sections:
“Safety Symbols Used in this Document” on page 10
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 11

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
10
Safety Symbols Used in this Document
This document uses the following conventions:
Note
Notes provide additional information.
Caution
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
Warning
Warnings inform you that an eye and skin hazard exists due to the
presence of a Class 1 laser device.

Preface
11
Contacting Allied Telesis
If you need assistance with this product, you may contact Allied Telesis
technical support by going to the Support & Services section of the Allied
Telesis web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. You can find links for
the following services on this page:
24/7 Online Support - Enter our interactive support center to
search for answers to your questions in our knowledge database,
check support tickets, learn about Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA), and contact Allied Telesis technical experts.
USA and EMEA phone support - Select the phone number that
best fits your location and customer type.
Hardware warranty information - Learn about Allied Telesis
warranties and register your product online.
Replacement Services - Submit an RMA request via our interactive
support center.
Documentation - View the most recent installation guides, user
guides, software release notes, white papers and data sheets for
your product.
Software Updates - Download the latest software releases for your
product.
For sales or corporate contact information, go to
www.alliedtelesis.com/purchase and select your region.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
12

13
Chapter 1
Getting Started
This chapter provides an overview of the AT-UWC Wireless LAN
Controller and how to perform basic operations.
It contains the following sections:
“AT-UWC Wireless LAN Controller” on page 14
“Preparing the Management Workstation” on page 15
“Starting a Management Session” on page 16
“Registering the License Key” on page 17
“Changing the IP Address” on page 21
“Enabling JavaScript” on page 25
“Configuring the AT-UWC WLAN Controller” on page 28
“Saving the Changes” on page 29
“Using Online Help” on page 31
“Ending a Management Session” on page 35

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
14
AT-UWC Wireless LAN Controller
The AT-UWC Wireless LAN (WLAN) Controller is a software-based
management tool that allows you to control Allied Telesis TQ series
wireless access points in an enterprise network.
You can deploy the AT-UWC WLAN Controller to your network as the
following forms:
AT-UWC WLAN Controller on a server
The AT-UWC WLAN Controller is installed to a server or virtual
machine in your network using the AT-UWC-Install program. To
install the AT-UWC WLAN Controller to a server and install the
server to your network, see “AT-UWC Wireless LAN Controller
Installation Guide.”
AT-UWC-60-APL device
The AT-UWC-60-APL is a device that deploys the AT-UWC WLAN
Controller. To install the AT-UWC-60-APL device to your network.
See “AT-UWC-60-APL Installation Guide.”
In this manual, the AT-UWC WLAN Controller on a server and
AT-UWC-60-APL device are referred as the AT-UWC WLAN Controller or
WLAN Controller.
Web Graphic
User Interface
(GUI)
The AT-UWC WLAN Controller is accessed via the Web Graphic User
Interface (GUI).
The following web browsers are supported:
Microsoft Windows Explorer 7
Microsoft Windows Explorer 8
Microsoft Windows Explorer 9 using the Compatibility View
Management
Workstation
You access the AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI using a management
workstation. The management workstation must have the following
applications:
Windows Internet Explorer 7, 8, or 9 with Java Plug-in
Oracle Java Runtime Environment Version 6
JavaScript
Note
To enable JavaScript, see “Enabling JavaScript” on page 25.

Chapter 1: Getting Started
15
Preparing the Management Workstation
To access the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, you must have a management
workstation.
The management workstation is a computer that you use to manage the
AT-UWC WLAN Controller. The management workstation must be
connected to the network that the AT-UWC WLAN Controller server
belongs to. See an example shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. AT-UWC WLAN Controller and Management Workstation
The AT-UWC WLAN Controller server has the following default IP address
and subnet mask assigned:
192.168.1.1/255.255.255.0
For the first time you access the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, your
management workstation must have an IP address in the following range:
192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254
Note
To change the IP address of the management workstation, see
“Changing the IP Address” on page 21.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
16
Starting a Management Session
The AT-UWC WLAN Controller is managed from the management
workstation through the Web GUI.
To start a management session of the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, do the
following:
1. Login to the management workstation.
If you do not have a management workstation, see “Preparing the
Management Workstation” on page 15.
2. Open Internet Explorer 7 or 8, and enter the IP address of the
AT-UWC WLAN Controller server.
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
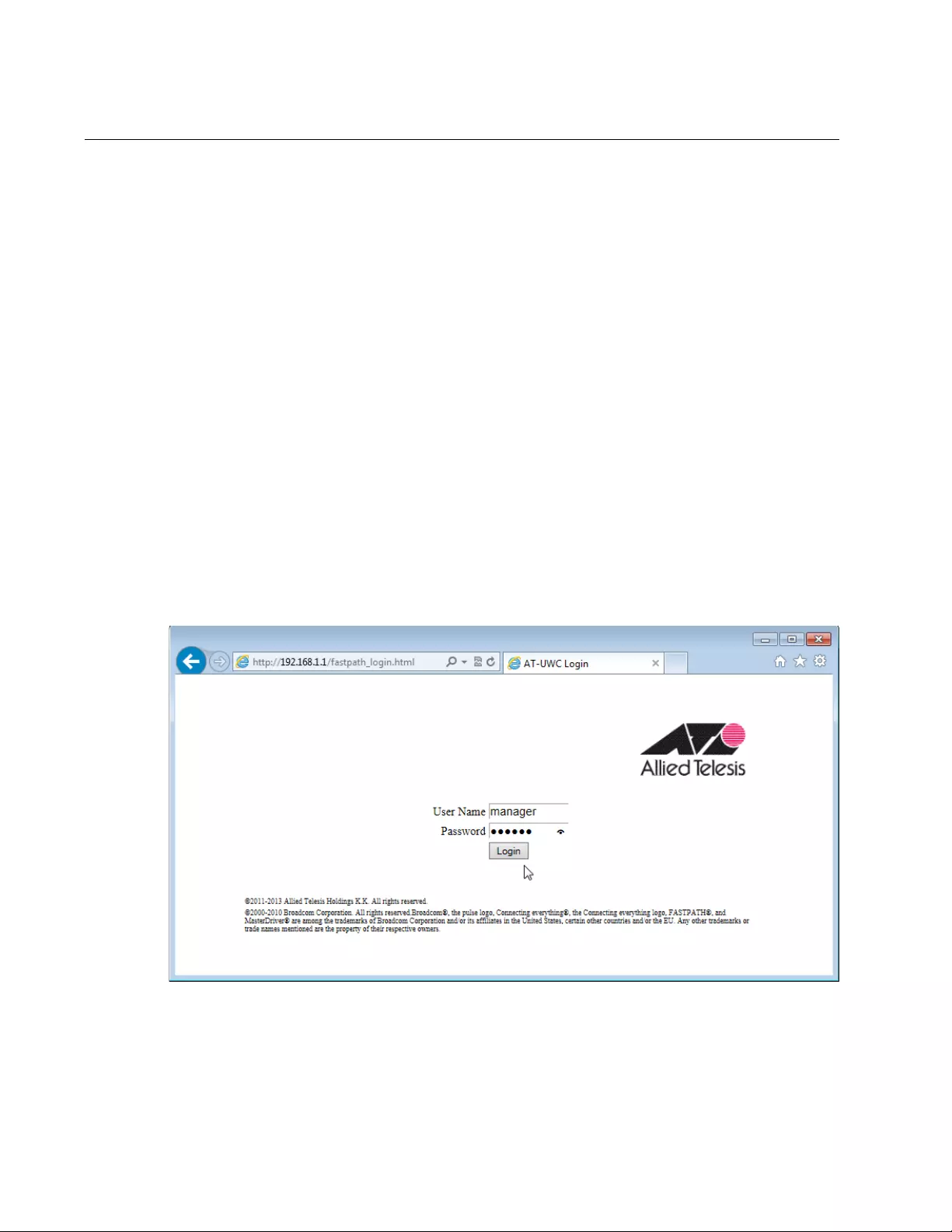
3. Enter the user name and password. See Figure 2.
The following are the default settings:
User name: manager
Password: friend
Figure 2. AT-UWC WLAN Controller Login Screen
4. Press Login.

Chapter 1: Getting Started
17
Registering the License Key
Registering the license key activates the AT-UWC WLAN Controller. For
the first time you login to the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, you must register
the license key.
License Key The license key is formed with the following two information:
A serial number
An authentication key
When you purchase the AT-UWC WLAN Controller software, you obtain a
license key that allows you to control 10 access point devices. To control
more access point devices, you can purchase an additional license key.
30-day Free Trial
License
Allied Telesis offers a 30-day free trial for new users. Two types of free trial
license keys are available:
AT-UWC-TrialST (NA): for users in North America
AT-UWC-TrialST (WW): for users worldwide except North America
You can download a free trial license from Allied Telesis Restricted
Software Downloads website. To obtain a free trial license, see
“Downloading the Free Trail License” on page 18 and follow the
instructions. On step 6, save AT-UWC-TrialST_(NA).pdf or
AT-UWC-TrialST_(WW).pdf.
Registering the
License Key
To register the license key, see “License” on page 121.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
18
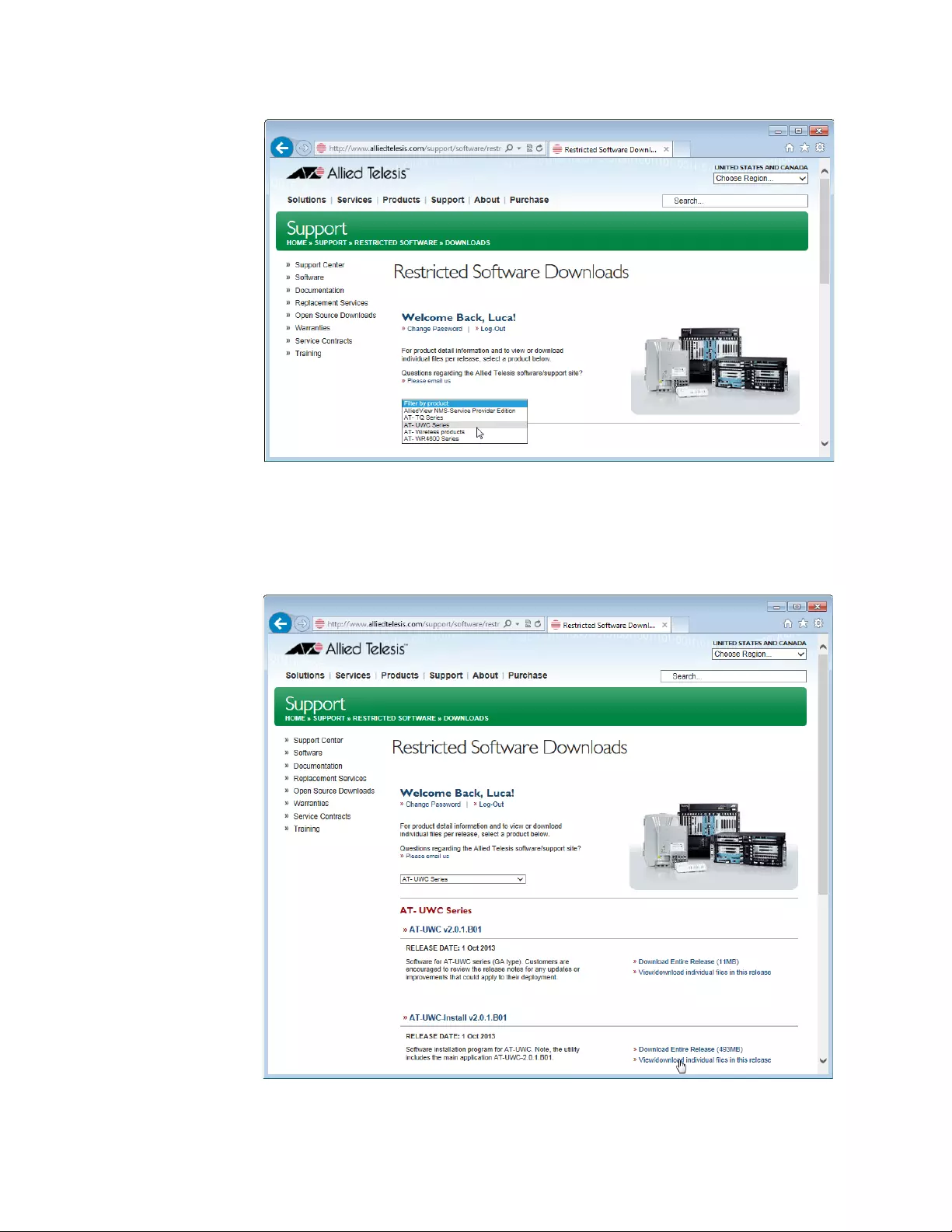
Downloading the Free Trail License
Allied Telesis provides the license key from the Restricted Software
Downloads website.
To download the license key, do the following:
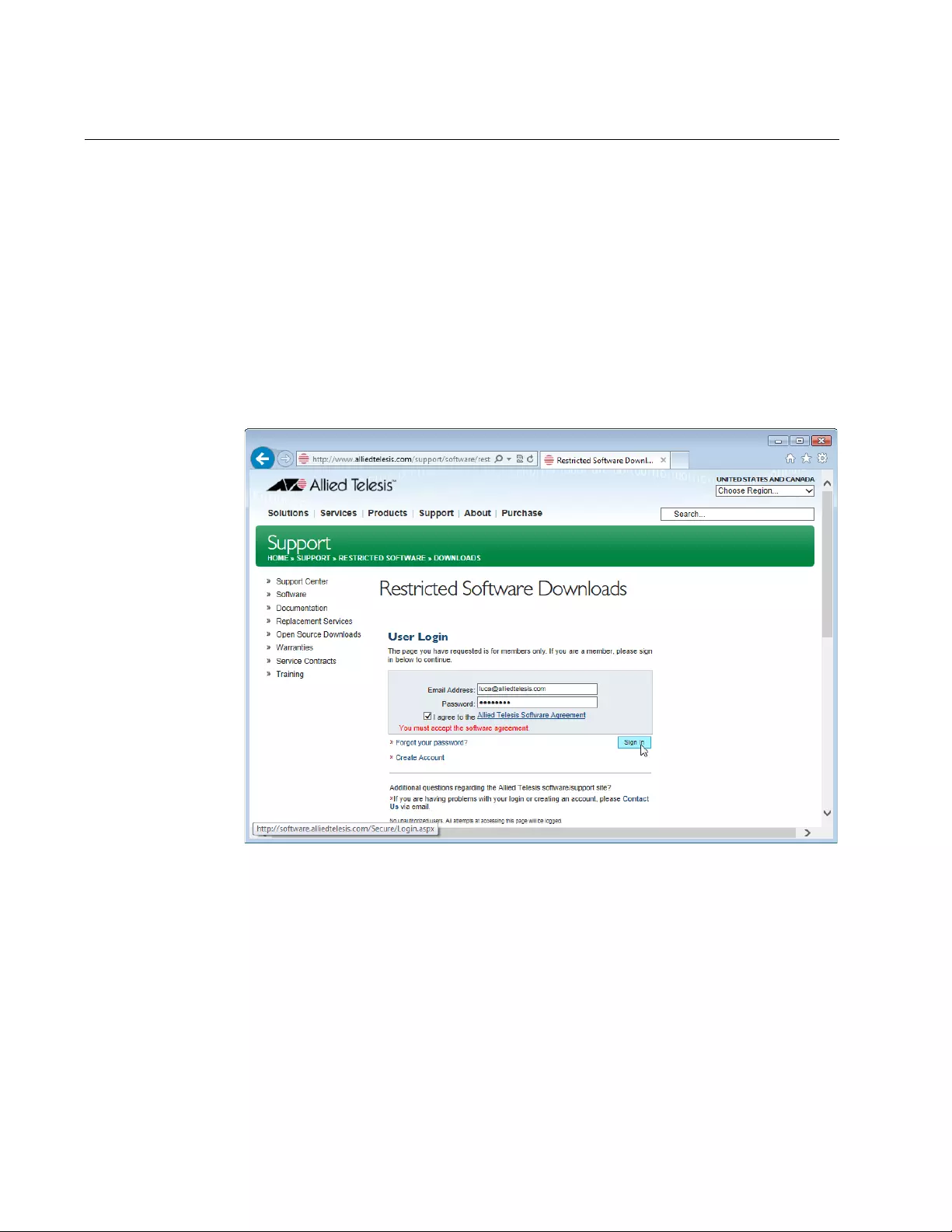
1. Open a web browser, such as Internet Explorer or FireFox, on your
system and enter the following:
http://www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software/restricted
The browser prompts you to enter a user name and password as
shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Restricted Software Downloads Login Page
2. Enter your email address and password.
If you do not have an account, create one. Click Create Account and
follow the instructions.
3. Read the Allied Telesis Software Agreement.
If you agree, check the checkbox and press Sign in.
An example of the Restricted Software Downloads Welcome page is
displayed as shown in Figure 4 on page 19.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
20
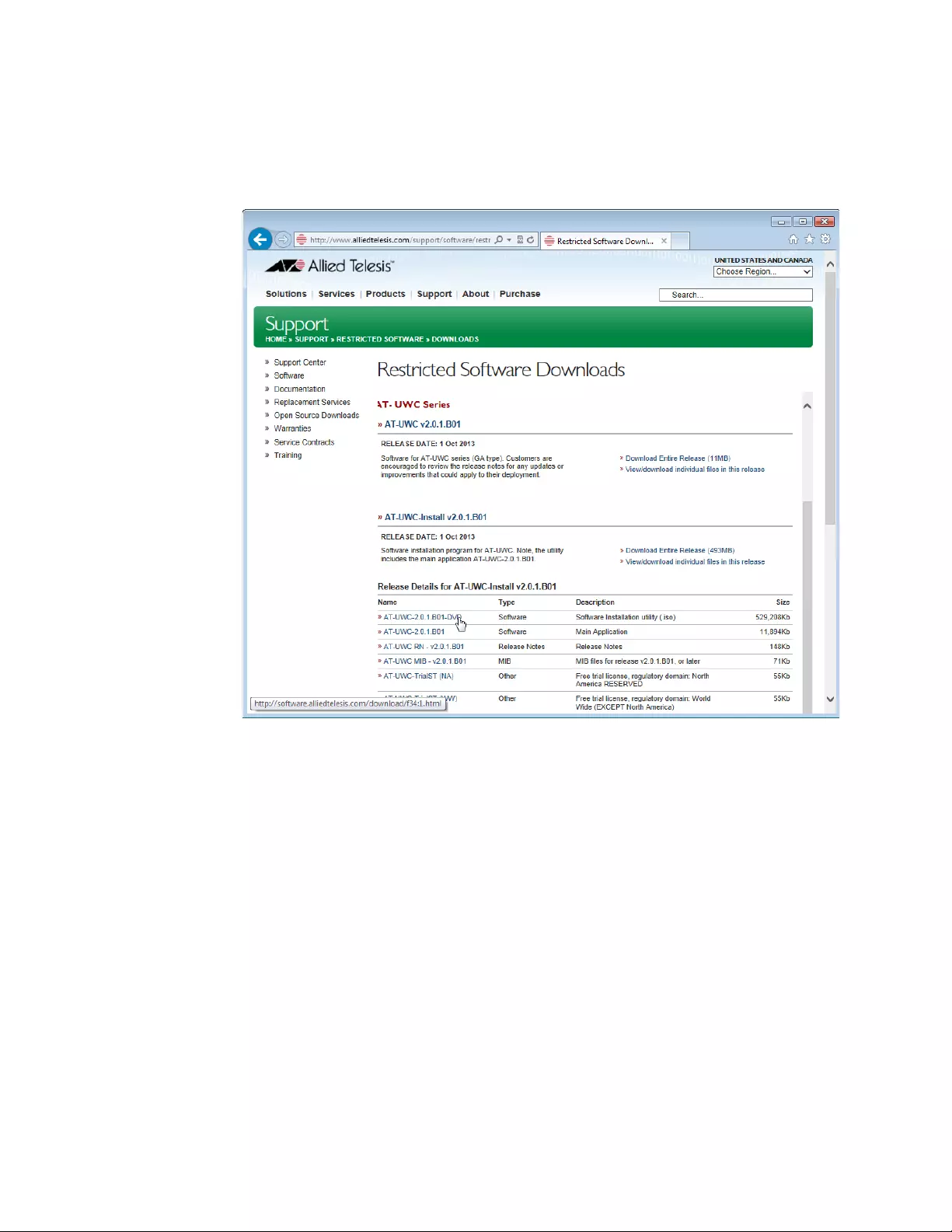
5. Click View/download individual files in this release under the
AT-UWC-Install v2.0.1.B01 section.
The available AT-UWC files are listed as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Restricted Software Downloads AT-UWC Page
6. Select AT-UWC-TrialST (NA) or AT-UWC-TrialST (WW) rom the list
and save it onto your system.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
21
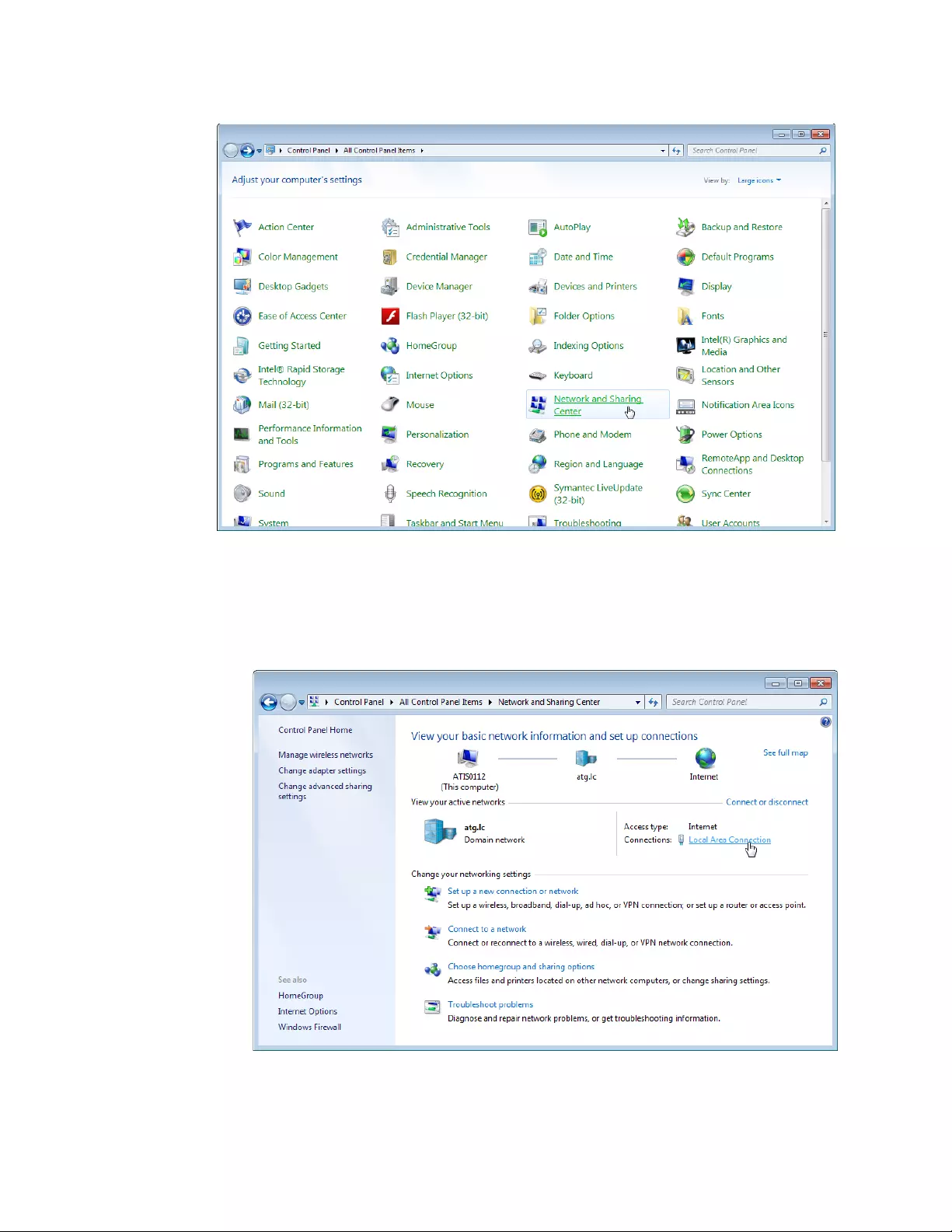
Changing the IP Address
When you access the AT-UWC WLAN Controller from the management
workstation, it must have an IP address form the same network as the
AT-UWC WLAN Controller server.
The procedures for changing the IP address is slightly different among
Windows Operating Systems. The following is the procedures using
Windows 7 as an example.
To change the IP address of a PC installed on Windows 7, do the
following:
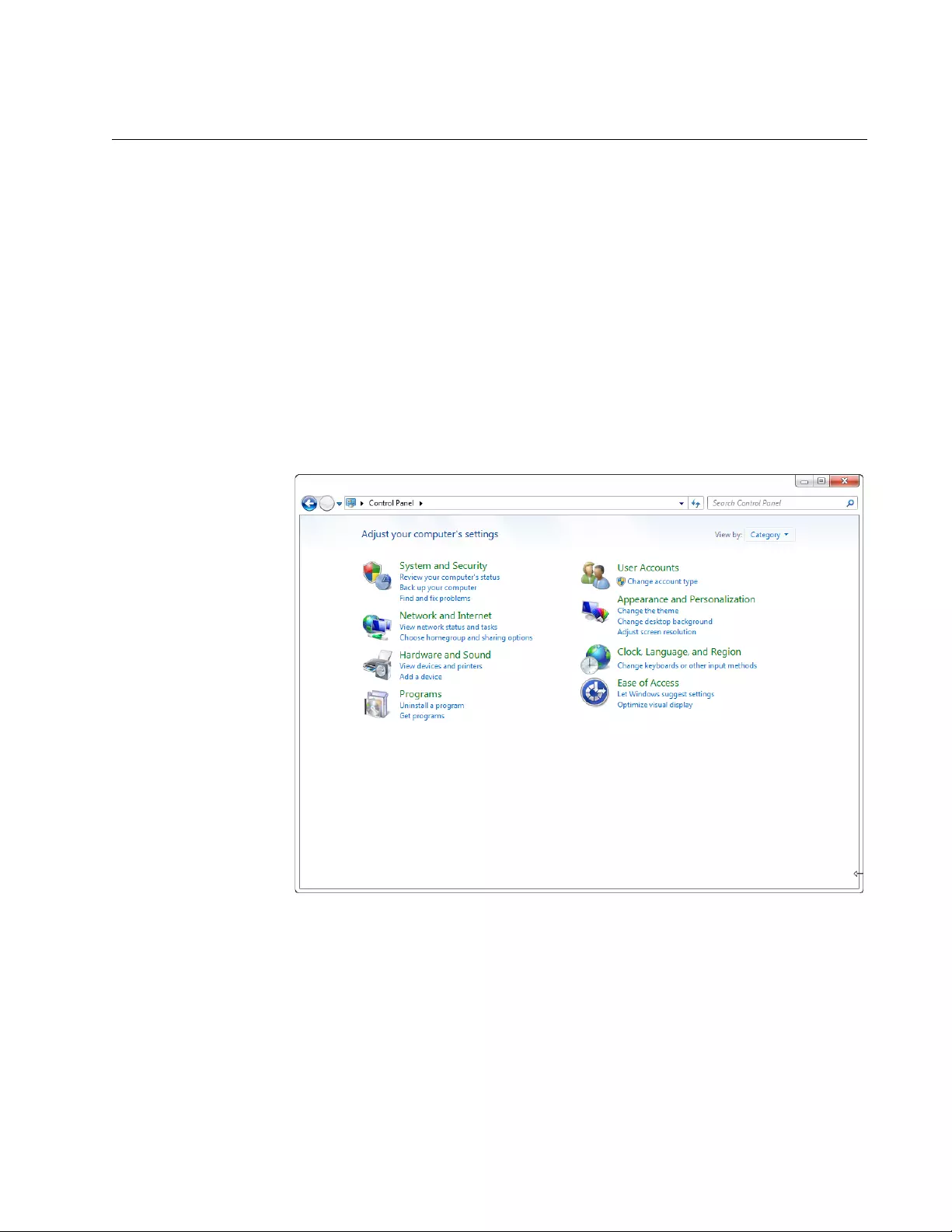
1. Click Control Panel from the Start button.
The control panel appears as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Control Panel
2. Click Category at the upper right corner of the window and select
Large icons.
Control Panel displays items with large icons as shown in Figure 8 on
page 22.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
23
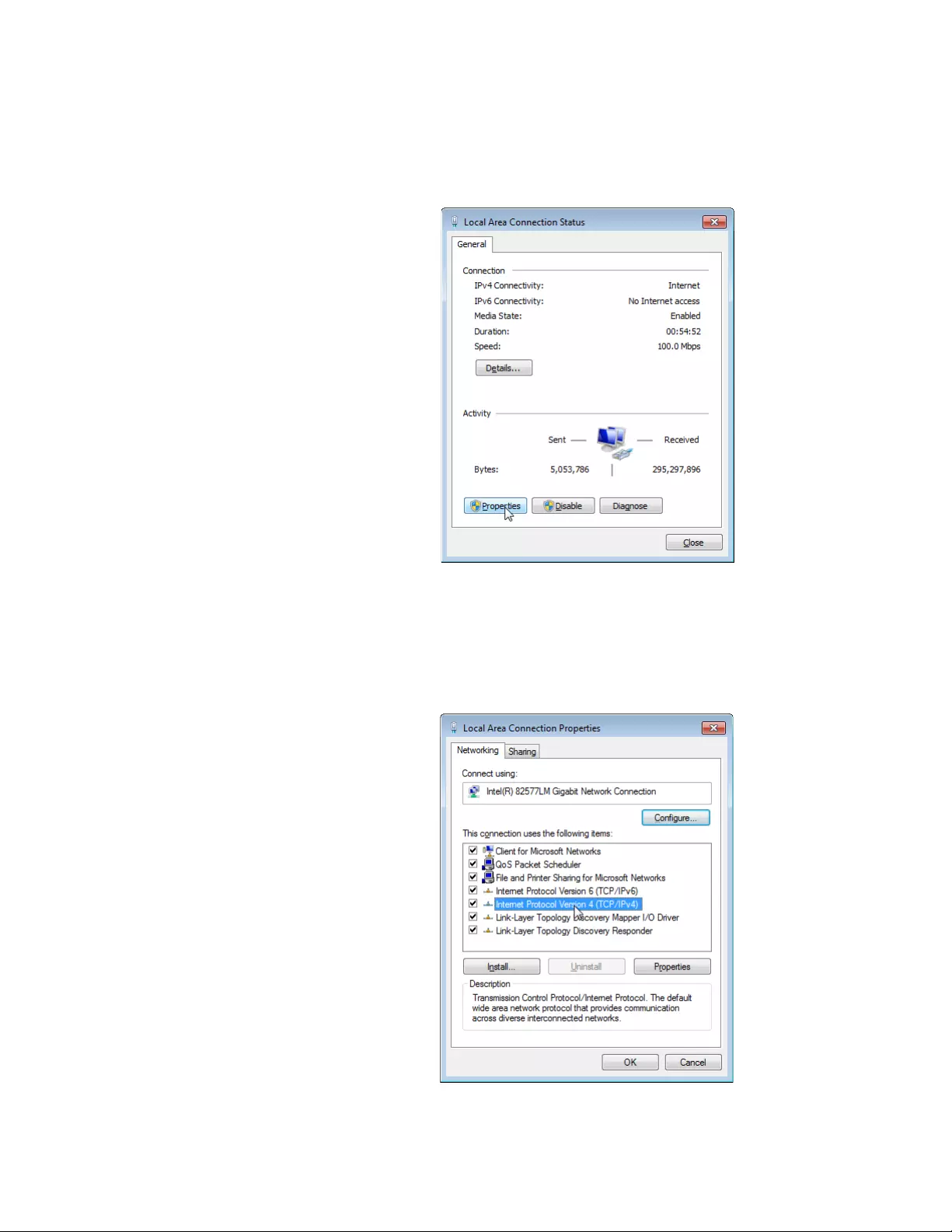
4. Click Local Area Connection.
The Local Area Connection Status window appears as shown in
Figure 10.
Figure 10. Local Area Connection Status Window
5. Click the Properties button at the bottom.
The Local Area Connection Properties window appears as shown in
Figure 11.
Figure 11. Local Area Connection Properties Window
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
24
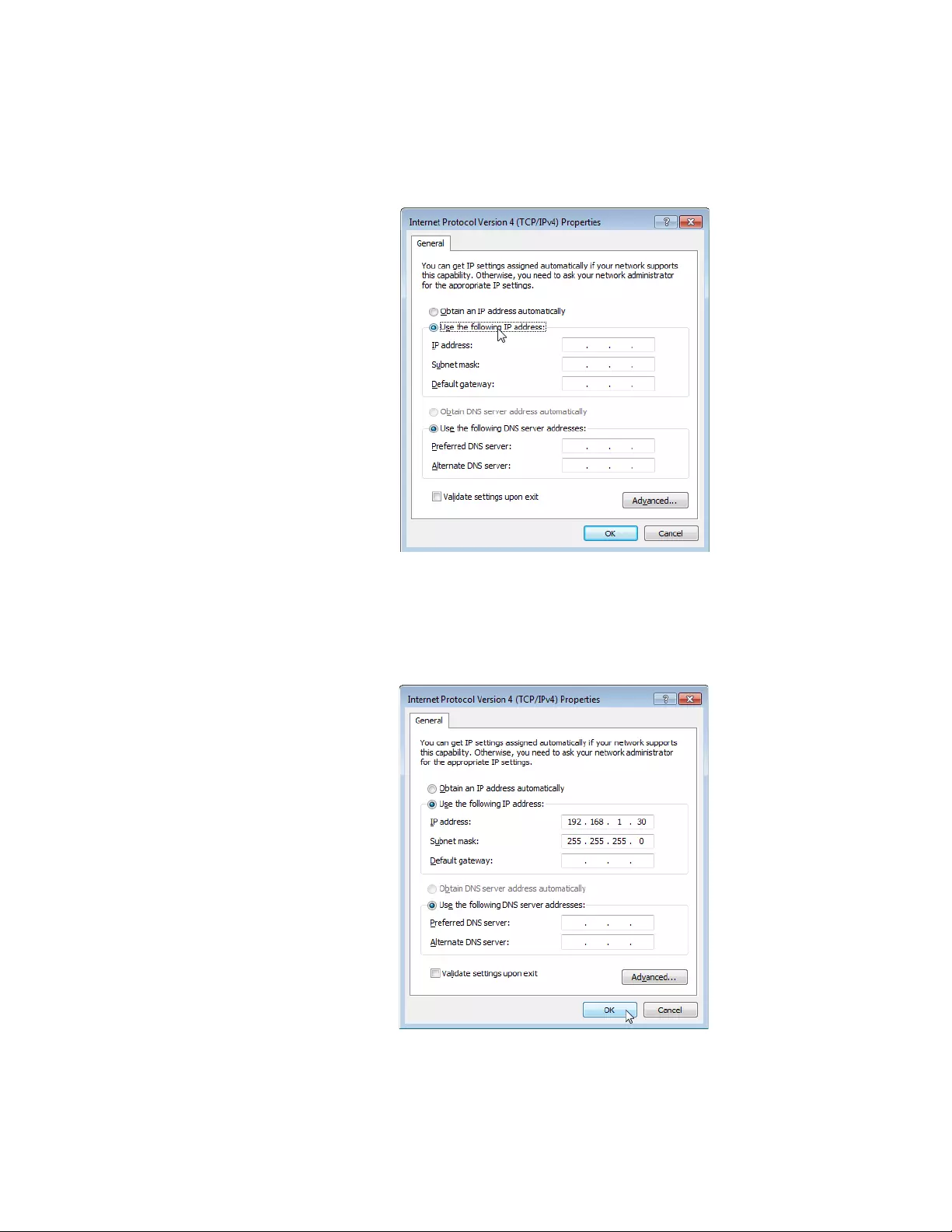
6. Double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
The Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) Properties window appears as
shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12. IPv4 Properties Window
7. Select the radio button labeled “Use the following IP address.”
8. Enter the IP address and Subnet mask. See Figure 13.
Figure 13. IPv4 Properties Window Example
9. Click OK.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
25
Enabling JavaScript
To access the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, you must enable JavaScript for
your Windows Internet Explorer. You can enable JavaScript only when
accessing the AT-UWC WLAN Controller.
Note
When JavaScript is already enabled, you do not have to change the
setting.
To enable JavaScript only for the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, do the
following:
1. Open the Windows Internet Explorer.
2. Click Tools from the menu bar.
3. Select Internet options from the drop-down menu.
The Internet Options window pops up.
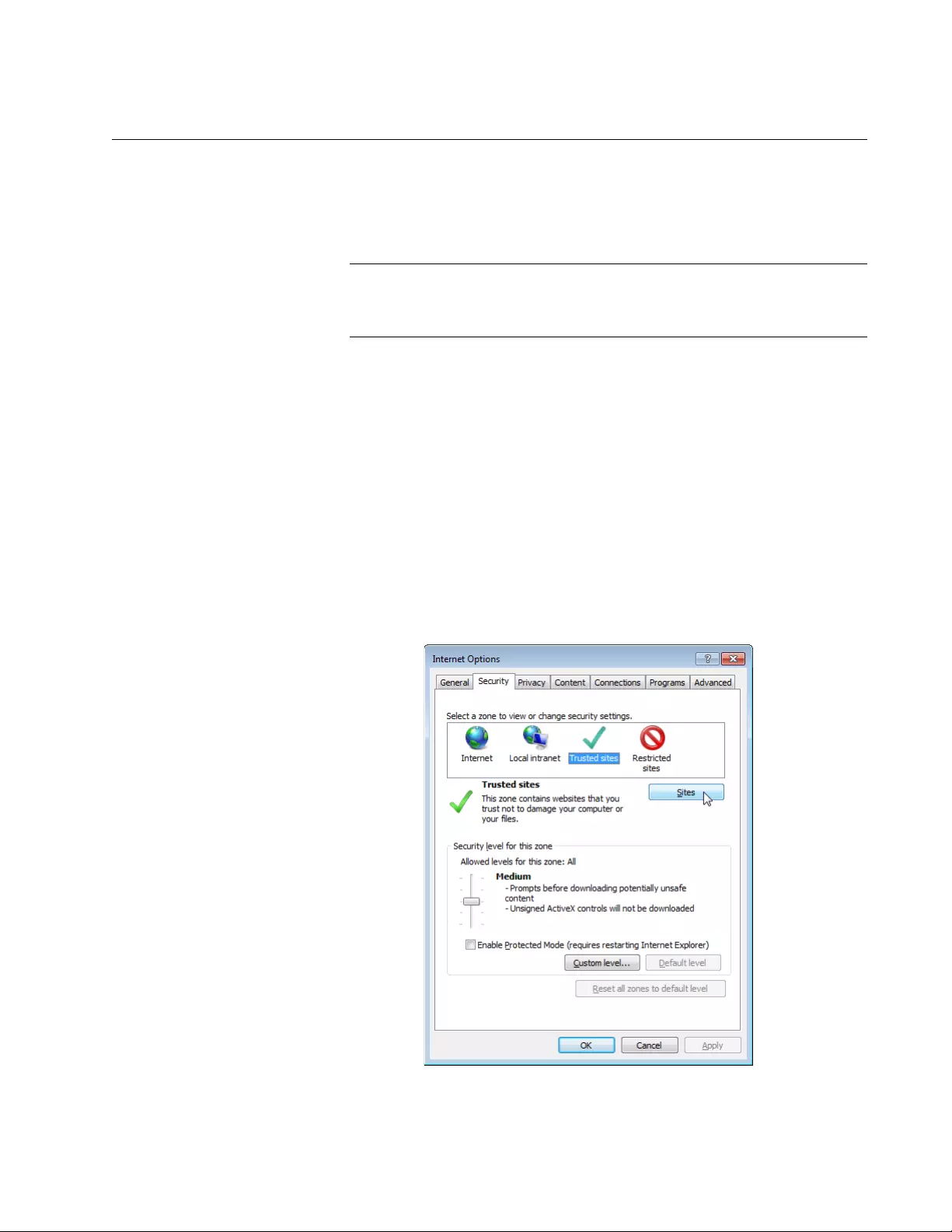
4. Click the Security tab on the Internet Options window.
The Internet Options window appears as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14. Internet Options Window Security Tab
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
26
5. Select the Trusted sites icon in the box and press the Sites button.
The Trusted sites window appears as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15. Trusted Sites Window
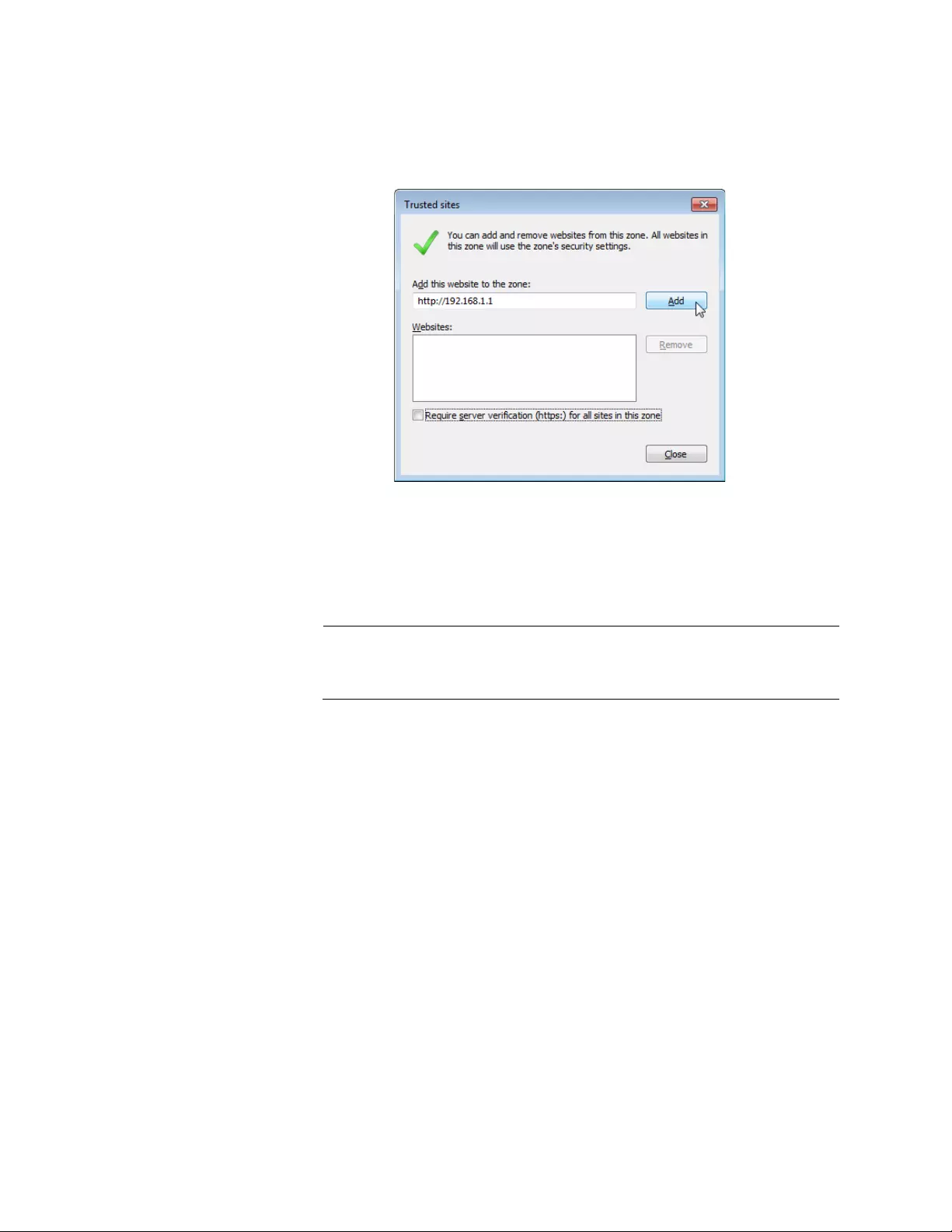
6. Enter the IP address of the AT-UWC WLAN Controller server and
check the checkbox of “Require server verification (https:) for all sites
in this zone.
Note
By the default, the IP address of the AT-UWC WLAN Controller
server 192.168.1.1.
7. Click Add.
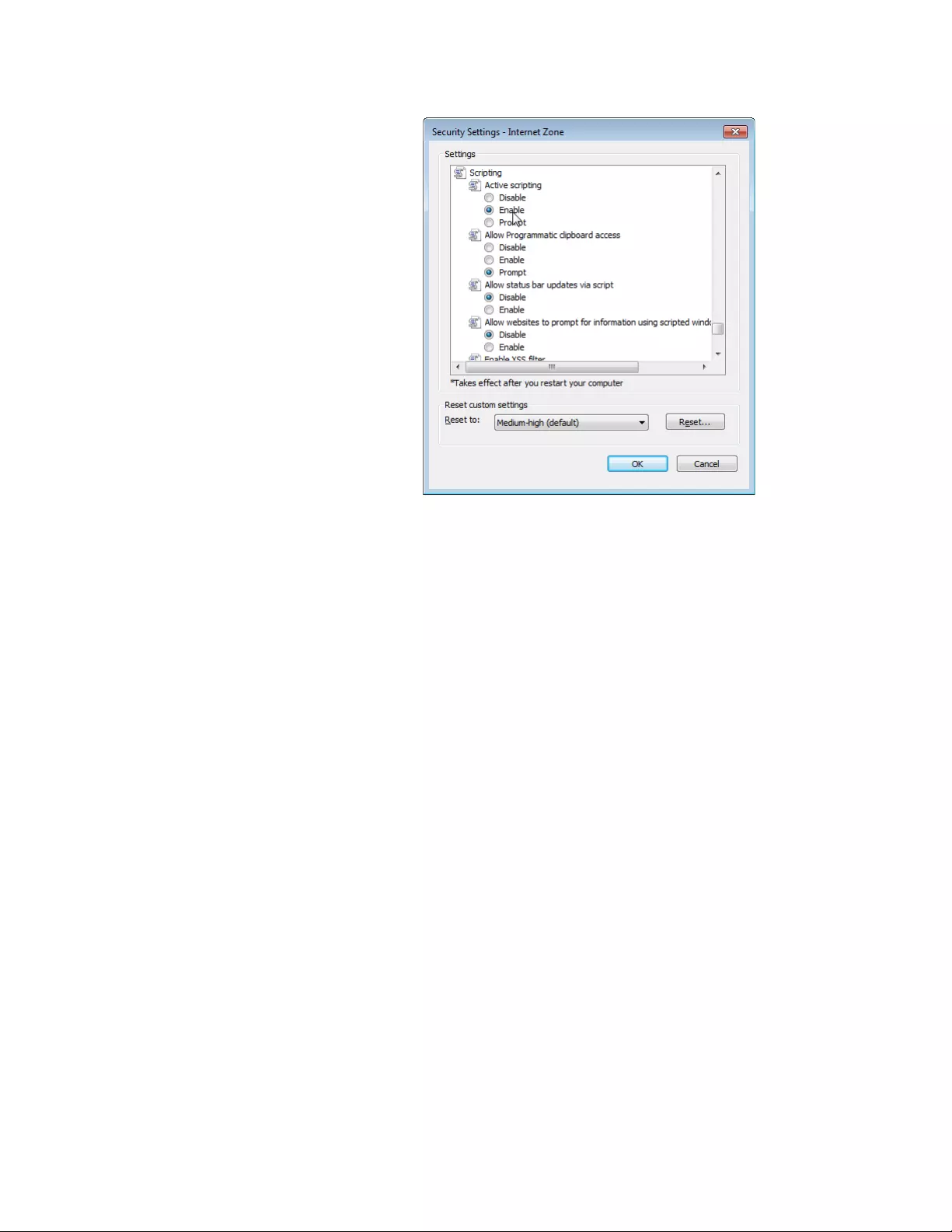
The Security Settings Internet Zone window appears as shown in
Figure 16 on page 27.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
27
Figure 16. Security Settings Window
8. Change the setting of Active scripting to Enable.
9. Click OK.
10. Restart the Internet Explorer.
JavaScript is enabled only when you access the AT-UWC WLAN
Controller.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
28
Configuring the AT-UWC WLAN Controller
To configure the features of the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, look at the
Navigation panel on the left of the web page. Go to the page that you want
to configure. For more information on each page, see the following
chapters:
Chapter 2, “System” on page 37
Chapter 3, “Switching” on page 125
Chapter 4, “Security” on page 137
Chapter 5, “Wireless LAN” on page 189
Chapter 1: Getting Started
29
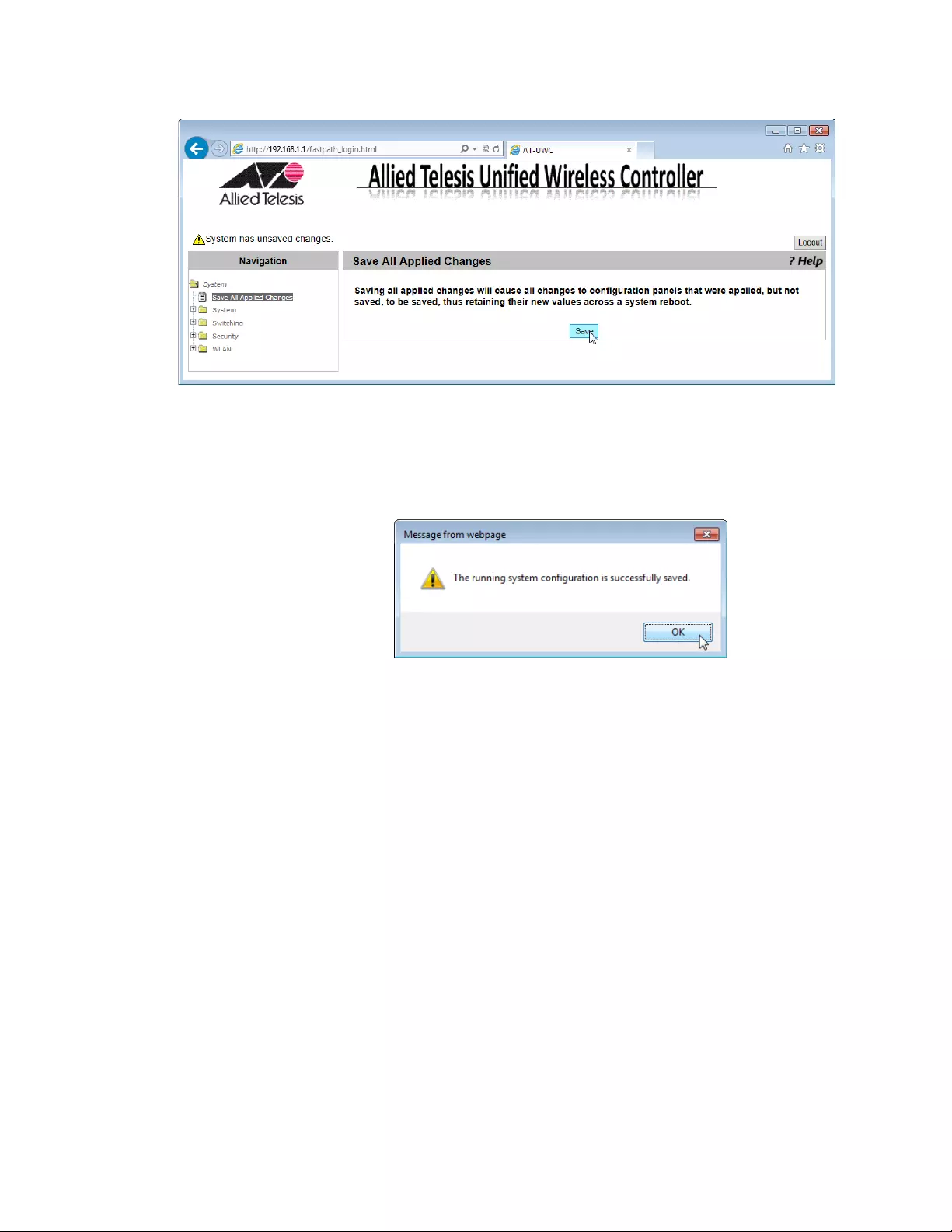
Saving the Changes
When you change settings of the AT-UWC WLAN Controller and click the
Submit button on each page, the changes are stored in the running
configuration. The settings in the running configuration are deleted when
the AT-UWC WLAN Controller reboots. You must save the changes to the
startup configuration if you want to keep the changes after the AT-UWC
WLAN Controller reboots.
To save the changes to the startup configuration, do the following:
1. Start a management session. See “Starting a Management Session”
on page 16.
The Allied Telesis Unified Wireless Controller starts as shown in
Figure 17.
Figure 17. AT-UWC WLAN Controller Screen
2. From the Navigation panel on the left, go to System > Save All
Applied Changes.
The Save All Applied Changes screen is displayed as shown in Figure
18 on page 30.
Chapter 1: Getting Started
31
Using Online Help
When you have a question about the AT-UWC WLAN Controller, the
Online Help can be a good place to look for your answer.
To access the Online Help, do the following:
1. Start a management session. See “Starting a Management Session”
on page 16.
The Allied Telesis Unified Wireless Controller screen is displayed as
shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20. AT-UWC WLAN Controller Screen
2. Click ?Help.
The Online Help is displayed shown in Figure 21 on page 32.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
34
Figure 23. AT-UWC WLAN Controller Online Help Example
Chapter 1: Getting Started
35
Ending a Management Session
You can end a management session at any time during a management
session.
To end a management session, do the following:
1. Save the changes to the startup configuration.
See “Saving the Changes” on page 29. If you do not want to save your
changes, skip this step.
2. Click the Logout button on the right side of the screen.
See Figure 24 as an example.
Figure 24. AT-UWC WLAN Controller Screen
The management session ends.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
36

37
Chapter 2
System
This chapter includes the following topics. Each topic corresponds to the
same title in the System folder in the Navigation Panel on the Web GUI.
“Save All Applied Changes” on page 39
“ARP Cache” on page 40
“System Resources” on page 41
Configuration
“System Description” on page 43
“Network Connectivity Configuration” on page 45
“HTTP” on page 47
“Telnet Session” on page 49
“User Accounts Configuration” on page 50
“Login Sessions” on page 52
Forwarding Database
“Forwarding Database Configuration” on page 54
“Forwarding Database Search” on page 55
Logs
“Buffered Log Configuration” on page 57
“Buffered Log” on page 59
“Command Logger Configuration” on page 60
“Console Log Configuration” on page 61
“Event Log” on page 62
“Hosts Log Configuration” on page 63
“Persistent Log Configuration” on page 65
“Persistent Log” on page 68
“Syslog Configuration” on page 69
“Diagnosis Log Configuration” on page 71
SNMP
“SNMP Community Configuration” on page 73

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
38
“Trap Receiver Configuration” on page 75
“Supported MIBs” on page 77
Statistics
“Controller Detailed Statistics” on page 78
“Controller Statistics Summary” on page 81
System Utility
“System Reset” on page 82
“Reset Configuration To Default” on page 83
“Erase Startup Configuration File” on page 85
“Reset Passwords to Defaults” on page 87
“Download File to Controller” on page 88
“Upload File from Controller” on page 90
“Buffered Log Configuration” on page 57
“Software Upgrade” on page 94“Ping” on page 96
“Ping” on page 96
“TraceRoute” on page 98
Trap Manager
“Trap Flags” on page 100
“Trap Logs” on page 102
DNS
“DNS Global Configuration” on page 104
“DNS Server Configuration” on page 107
“HostName IP Mapping Summary” on page 109
SNTP
“SNTP Global Configuration” on page 112
“SNTP Global Status” on page 114
“SNTP Server Configuration” on page 117
“SNTP Server Status” on page 119
License
“License” on page 121
Chapter 2: System
39
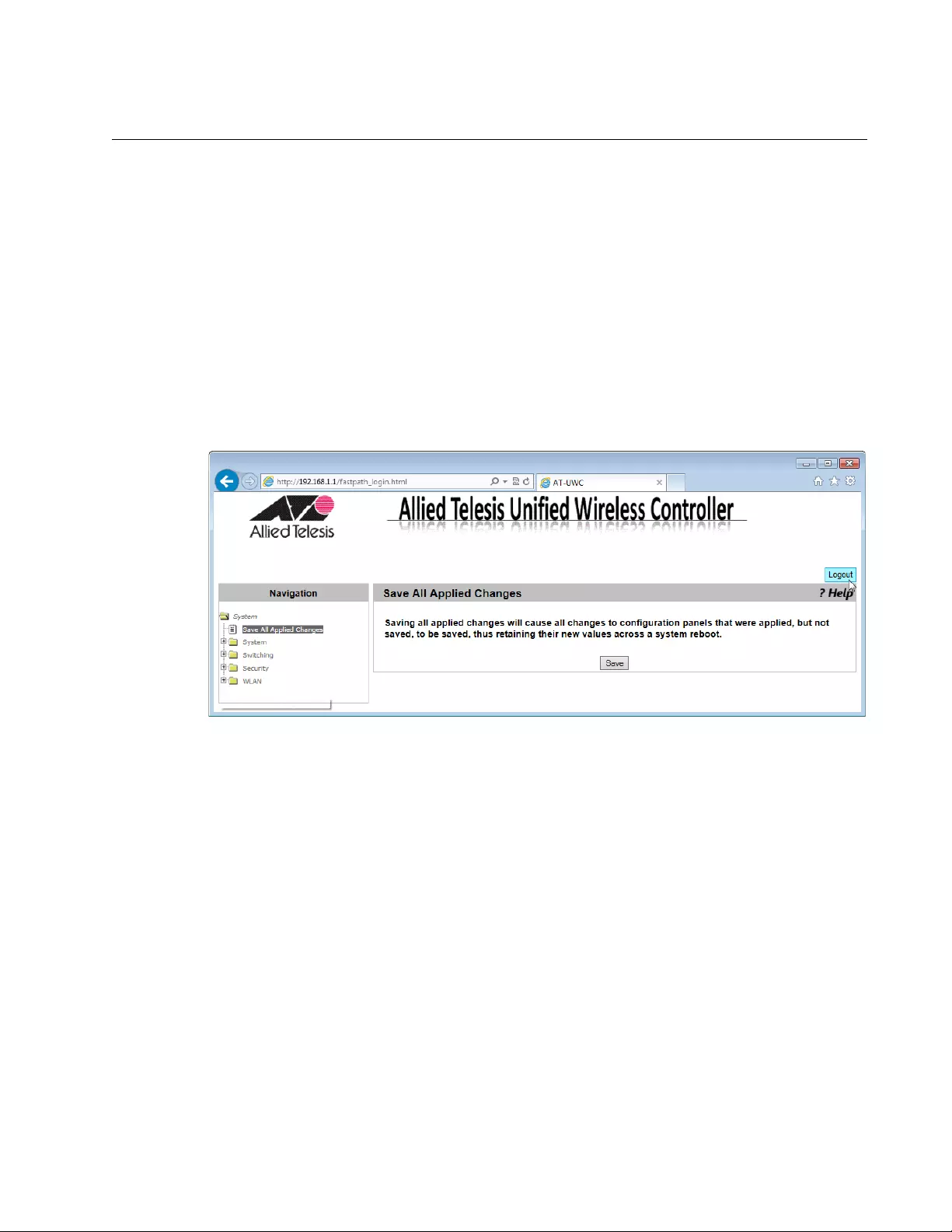
Save All Applied Changes
From the Save All Applied Changes page, you can save all the changes
you have made to the startup configuration file. When you save your
changes to the startup configuration file, the changes are effective after
the system reboots.
Note
When you click Submit on each page, you save your changes on
the page to the running configuration file. The changes are effective
immediately; however, when the system is reset, the changes are
lost.
To save all the changes to the startup configuration file, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Save All Applied Changes.
The Save All Applied Changes page is displayed as shown in
Figure 25.
Figure 25. Save All Applied Changes Page
2. Click Save.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
40
ARP Cache
From the ARP Cache page, you can view and clear the Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache. ARP stores map entries in the ARP
cache to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. Clear the ARP cache
when it may be corrupted or damaged.
To view and clear the ARP cache, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > ARP Cache.
The ARP Cache page is displayed as shown in Figure 26.
Figure 26. System ARP Cache Page
2. Observe the ARP cache.
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Clear — Delete all entries in the ARP Cache.
Chapter 2: System
41
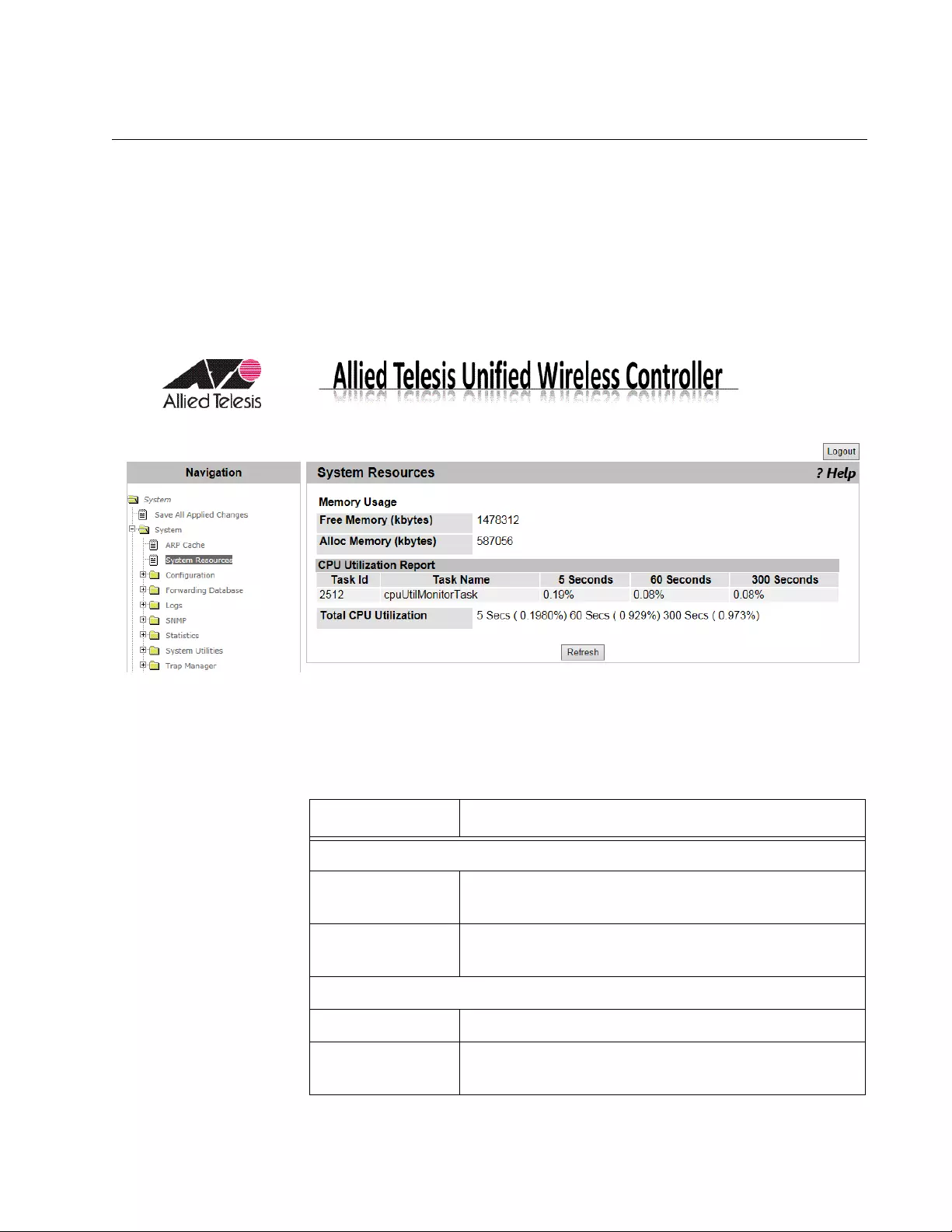
System Resources
From the System Resources page, you can view the information about the
system resources.
To view the system resources, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Resources.
The System Resources page is displayed as shown in Figure 27.
Figure 27. System Resources Page
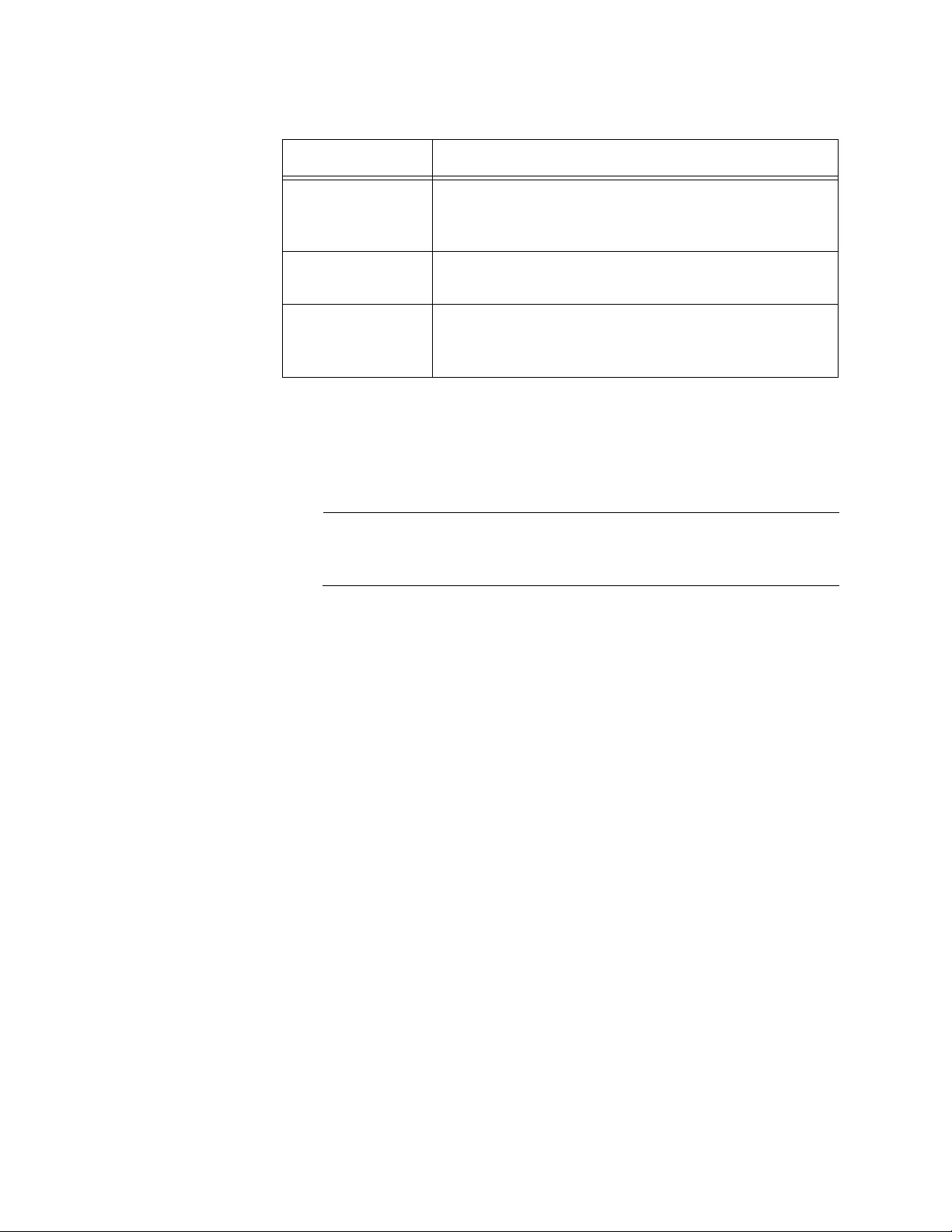
2. Observe the fields described in Table 1.
Table 1. System Resources
Field Description
Memory Usage
Free Memory
(kbytes)
Displays the available memory on the system in
kilo bytes.
Alloc Memory
(kbytes)
Displays the allocated memory on the system in
kilo bytes.
CPU Utilization Report
Task Id Displays the ID of the task that is currently running.
Task Name Displays the name of the task that is currently
running.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
42
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
5 Seconds Displays the CPU usage by the task in the last 5
seconds.
60 Seconds Displays the CPU usage by the task in the last 60
seconds.
300 Seconds Displays the CPU usage by the task in the last 300
seconds.
Total C P U
Utilization
Displays the total CPU usage by all the tasks.
Table 1. System Resources (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
43
System Description
From the System Description page, you can view and modify system
information.
To view and modify the system information, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, click System or go to System >
Configuration > System Description.
The System Description page is displayed as shown in Figure 28.
Figure 28. System Description Page
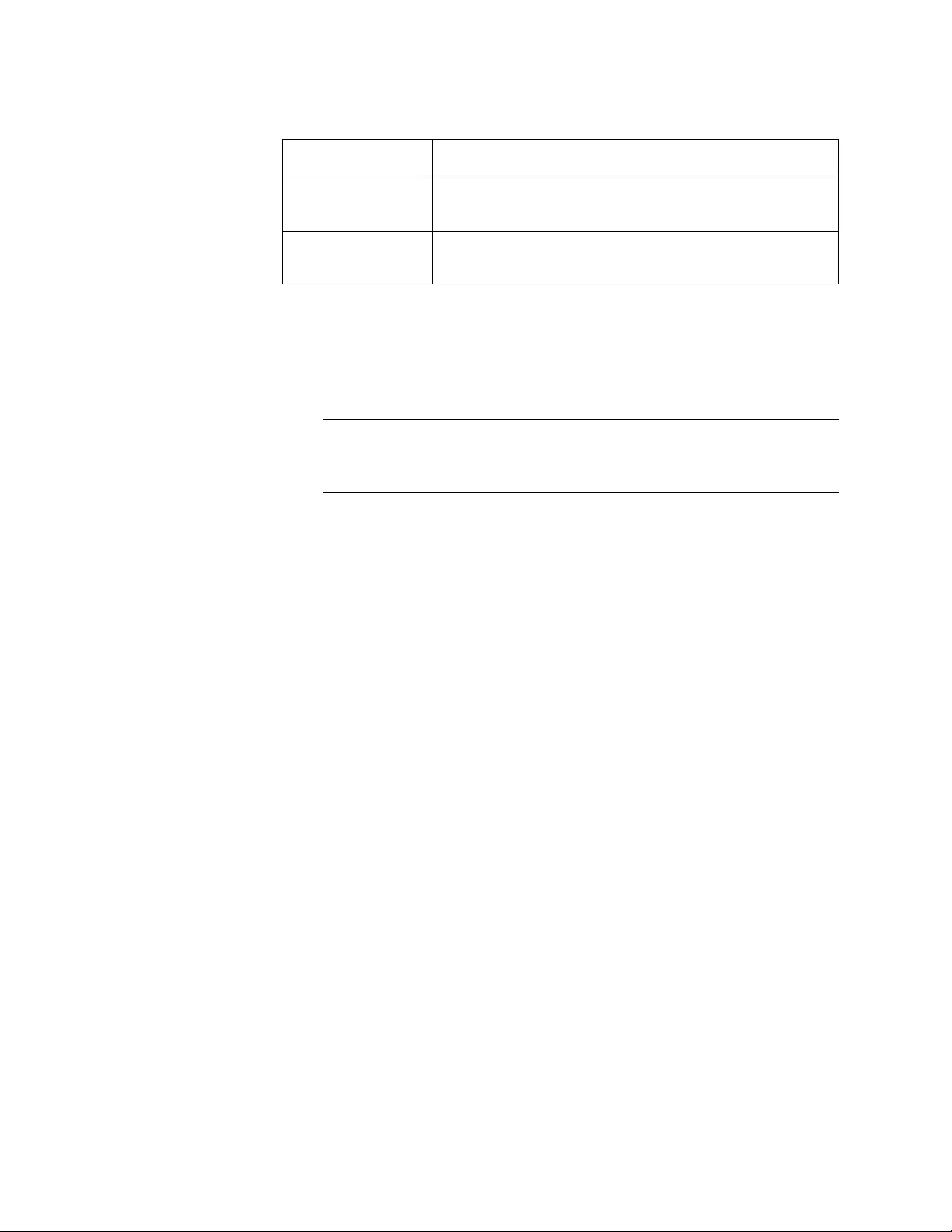
2. Observe and modify the values in the fields described in Table 2.
Table 2. System Description
Field Description
System
Description
Displays the product name, version, and time
stamp of the currently installed WLAN Controller
software.
System Name Displays the system name of the WLAN Controller.
By default, no system name is assigned.
System Location Displays the system location of the WLAN
Controller. By default, no system name is assigned.
System Contact Displays the contact information. By default, no
system contact is assigned.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
44
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller. To
change the IP address, see “Network Connectivity
Configuration” on page 45.
System Up Time Displays the length of time since the lWLAN
Controller last rebooted.
Current SNTP
Synchronized
Time
Displays the system time from the currently
synchronized SNTP. For information about SNTP,
see ““SNTP Global Status” on page 114”
Table 2. System Description (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
45
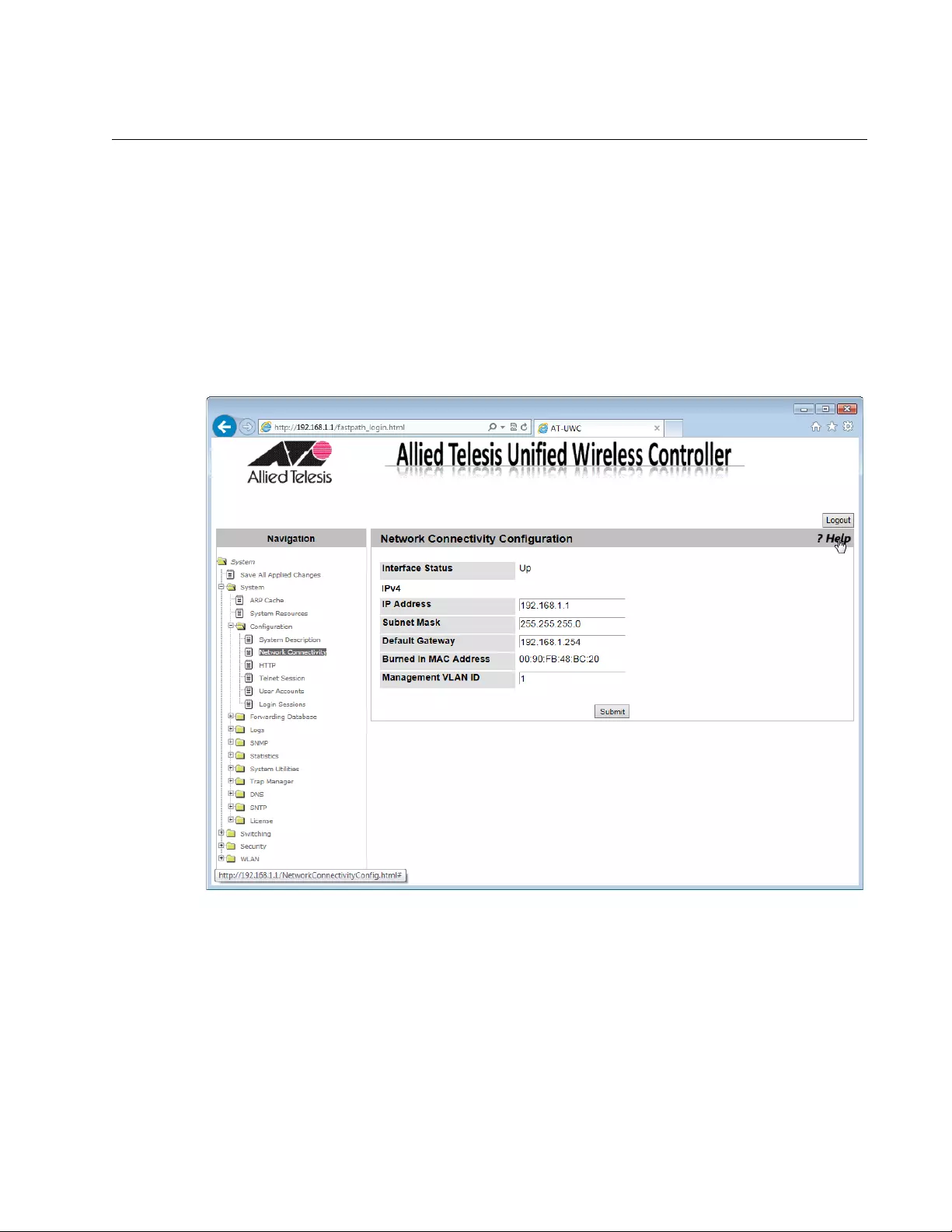
Network Connectivity Configuration
From the Network Connectivity Configuration page, you can view and
modify the network interface properties.
To view and modify the network interface properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Configuration > Network
Connectivity Configuration.
The Network Connectivity Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 29.
Figure 29. Network Connectivity Configuration Page
2. Observe or modify the values in the fields described in Table 3.
Table 3. Network Connectivity Configuration
Field Description
Interface Status Displays the status of the interface on the WLAN
Controller.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller.
The default value is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask Displays the subnet mask of the WLAN Controller.
The default value is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway Displays the default gateway to the WLAN
Controller. By default, no value is assigned.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
46
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Burned In MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the WLAN Controller.
Management
VLAN ID
Displays the management VLAN ID. The default
value is VLAN 1
Table 3. Network Connectivity Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
47
HTTP
On the HTTP Configuration page, you can view and modify the property
settings for HTTP connections.
To view and modify the HTTP settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Configuration > HTTP.
The HTTP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 30.
Figure 30. HTTP Configuration Page
2. Observe or modify the values in the fields described in Table 4.
Table 4. HTTP Configuration
Field Description
HTTP Admin
Mode
Displays Enable or Disable. By default, HTTP is
enabled. When you enable HTTPS, HTTP is
disabled. See “Secure HTTP” on page 187.
HTTP Session
Soft Timeout
(Minutes)
Displays the period of time in minutes. When this
specified time has passed since the last user-
interaction to the system, the system ends the
session. The default setting is 5 minutes.
HTTP Session
Hard Timeout
(Hours)
Displays the period of time in hours. When this
specified time has passed since the time you
logged in, the system ends the session. The default
setting is 24 hours.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
48
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Maximum
Number of HTTP
Session
Displays the maximum number of HTTP sessions
that you allows to the WLAN Controller. The default
setting is 16 sessions.
Table 4. HTTP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
49
Telnet Session
Note
The current AT-UWC WLAN Controller does not support the Telnet
Session.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
50
User Accounts Configuration
From the User Accounts Configuration page, you can modify the
password for the manager account.
Note
The create option in the User field and guest account are not
supported for the current version.
Note
Allied Telesis recommends not changing the access level of the
manager account. Change only the password of the manager
account.
To modify the password of the manager account, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Configuration > User
Accounts Configuration.
The User Accounts Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 31.
Figure 31. User Accounts Configuration Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 5 on page 51.

Chapter 2: System
51
3. Click Submit.
The changes are saved to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Table 5. User Accounts Configuration
Field Description
User Select the manager option. The following items are
visible from the select list:
manager: Modifies the manager account.
quest: Not supported.
create: Not supported.
User Name Displays the name of the user account. You cannot
modify the name.
Password Enter a password. The password is not displayed.
Confirm
Password
Re-enter the password.
Access Level Allied Telesis recommends not changing the
access level.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
52
Login Sessions
From the Login Sessions page, you can view information about your
current login session.
To view information about your login session, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Configuration > Login
Sessions.
The Login Sessions page is displayed as shown in Figure 32.
Figure 32. Login Sessions Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 6.
Table 6. Login Session
Field Description
ID Displays the ID number of your login session.
User Name Displays the name of login user.
Connection From Displays the IP address of your management
workstation.
Idle Time Displays the length of time since the WLAN
Controller received traffic last time.
Session Time Displays the length of time since you logged into
the WLAN Controller.

Chapter 2: System
53
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Session Type Displays the connection type, either HTTP or
HTTPS.
Table 6. Login Session (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
54
Forwarding Database Configuration
From the Forwarding Database Configuration page, you can change the
aging interval for the forwarding database. A forwarding database is also
called a MAC address table that Layer 2 devices keep to associate MAC
addresses to the ports.
To change the aging interval for the forwarding database, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Forwarding Database >
Configuration.
The Forwarding Database Configuration page is displayed as shown
in Figure 33.
Figure 33. Forwarding Database Configuration Page
2. Specify the aging interval in seconds.
The aging interval is the number of seconds the entry of a MAC
address is kept in the forwarding database. The default is 300
seconds.
3. Click Submit.
The change is saved to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.

Chapter 2: System
55
Forwarding Database Search
From the Forwarding Database Search page, you can view MAC address
entries and search a specific MAC address from the database.
Viewing the
Forwarding
Database
To view the forwarding database, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > Forwarding
Database > Search.
The Forwarding Database Search page is displayed as shown in
Figure 34.
Figure 34. Forwarding Database Search Page
2. Observe the fields as shown in Table 7.
Table 7. Forwarding Database
Field Description
MAC address The first two groups of hexadecimal digits
indicate the VLAN ID. The rest of the
hexadecimal digits indicates the MAC address.
Source Slot/Port(0) Indicates the port number.
Interface Index Indicates the interface index.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
56
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Searching a MAC
Address
To search a MAC address from the forwarding database, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > Forwarding
Database > Search.
The Forwarding Database Search page is displayed as shown in
Figure 34 on page 55.
2. Select one of the following filtering options from the select list:
All: Specifies the search in the entire forwarding database.
Learned: Specifies the search in the MAC addresses with the
Learned status.
3. Enter the combination of a VLAN ID and a MAC address in
hexadecimal in the following format:
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
4. Click Search.
The result is displayed.
Status Indicates the status of the MAC address entry.
The options are:
Learned: The MAC address was learned
from received frames.
Management: Indicates that MAC
address is of the WLAN Controller.
Table 7. Forwarding Database (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
57
Buffered Log Configuration
From the Buffered Log Configuration page, you can enable or disable the
Buffered Log function. The system stores up to 200 log messages in the
buffer and deletes them when the system shuts down.
Note
To download buffered log messages, see “Upload File from
Controller” on page 90.
To enable or disable the buffered log function, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Buffered Log
Configuration.
The Buffered Log Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 35.
Figure 35. Buffered Log Configuration Page
2. Select the options in the fields described in Table 8 on page 58.
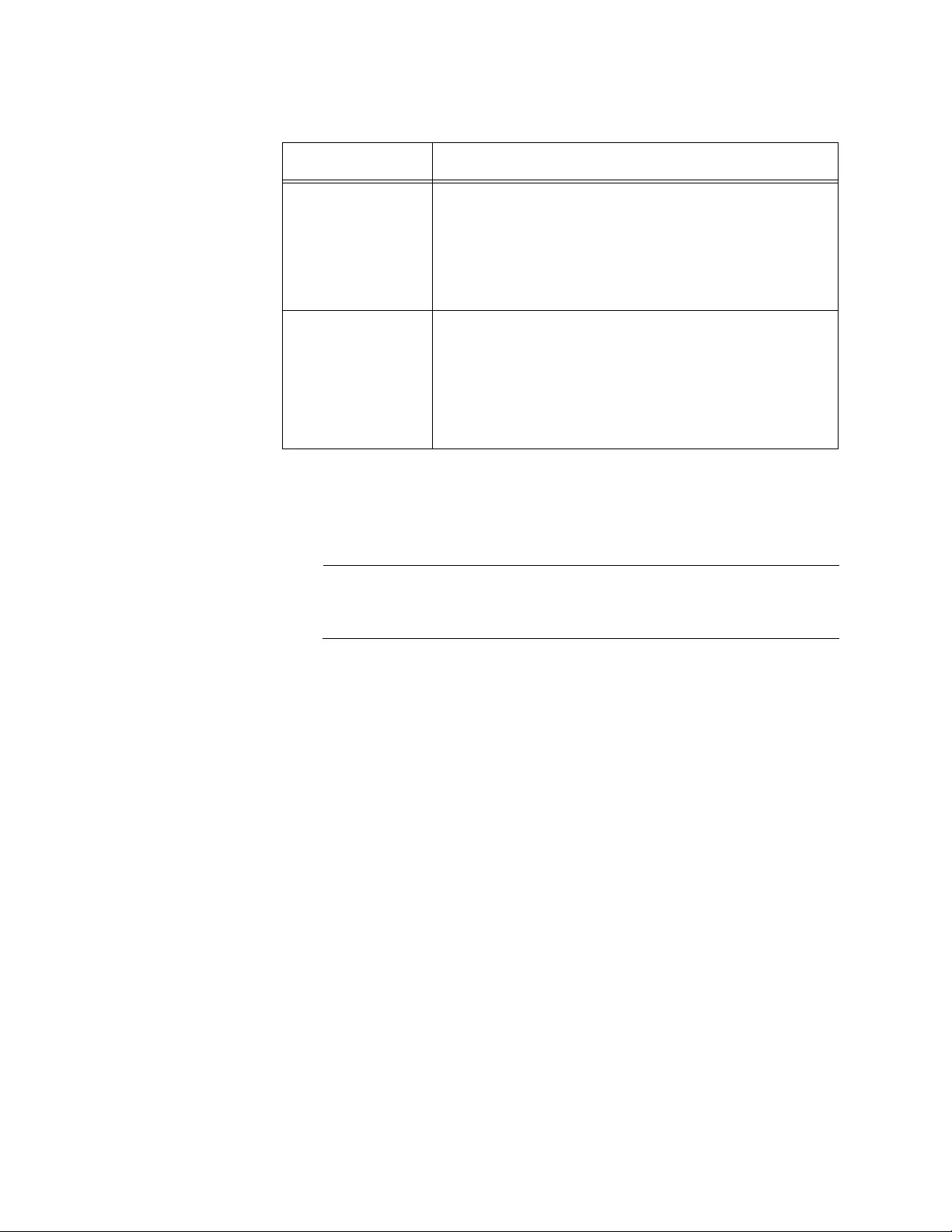
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
58
3. Click one of the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Saves the changes to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Table 8. Buffered Log Configuration
Field Description
Admin Status Starts or stops logging messages. The options are:
Enable: Starts logging messages into the
buffer.
Disable: Stops logging messages into the
buffer.
Behavior Specifies the logging behavior. The options are:
Wrap: Replaces the last saved messages
with new messages when the buffer is full.
Stop on Full: Stops logging when the buffer
is full.

Chapter 2: System
59
Buffered Log
From the Buffered Log page, you can view messages stored in the buffer
on the WLAN Controller.
To view messages in the buffered log, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Buffered Log.
The Buffered Log page is displayed as shown in Figure 36.
Figure 36. Buffered Log Page
2. Observe the messages.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
60
Command Logger Configuration
Note
The current AT-UWC WLAN Controller does not support the
Command Logger.

Chapter 2: System
61
Console Log Configuration
Note
The current AT-UWC WLAN Controller does not support the
Console Log.
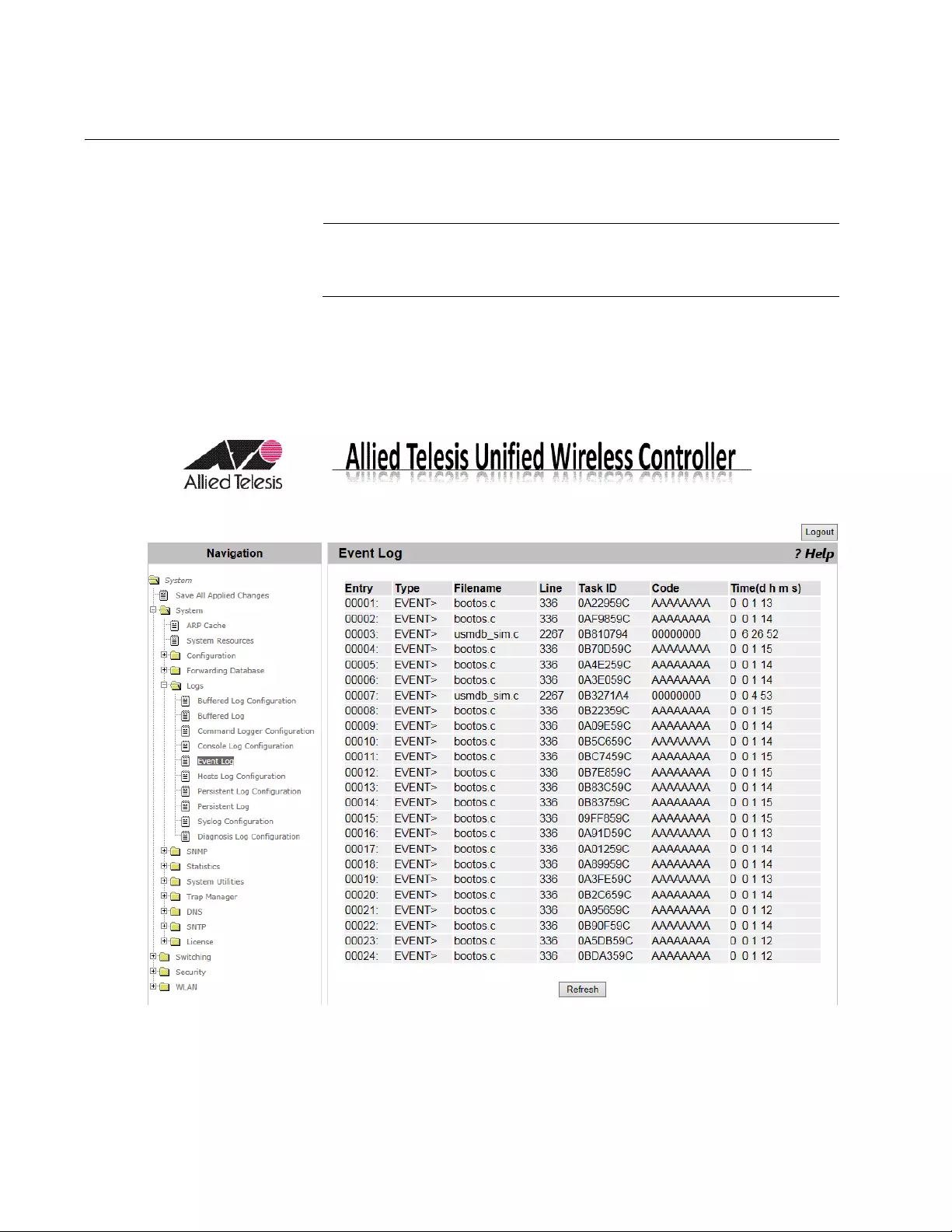
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
62
Event Log
From the Event Log page, you can view event log messages.
Note
To download event log messages, see “Upload File from Controller”
on page 90.
To view event log messages, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Event Log.
The Event Log page is displayed as shown in Figure 37.
Figure 37. Event Log Page
2. Observe the messages.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.

Chapter 2: System
63
Hosts Log Configuration
From the Hosts Log Configuration page, you can add Syslog servers.
Note
To start or stop sending log messages to Syslog servers, see
“Syslog Configuration” on page 69.
To add a Syslog server, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System >> Logs > Hosts Log
Configuration.
The Hosts Log Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 38.
Figure 38. Hosts Log Configuration Page
2. Select the options in the fields described in Table 9.
Table 9. Hosts Log Configuration
Field Description
Host Displays the action. Add is the only option.
IP Address
Hostname
Specifies an IPv4 address or host name of the
Syslog server where log messages are sent.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
64
3. Click one of the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Saves the changes to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
IP Address Type Specifies the IP address type. The options are:
IPv4: Specifies a Syslog server with its IPv4
address.
DNS: Specifies a Syslog server with its host
name.
Table 9. Hosts Log Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
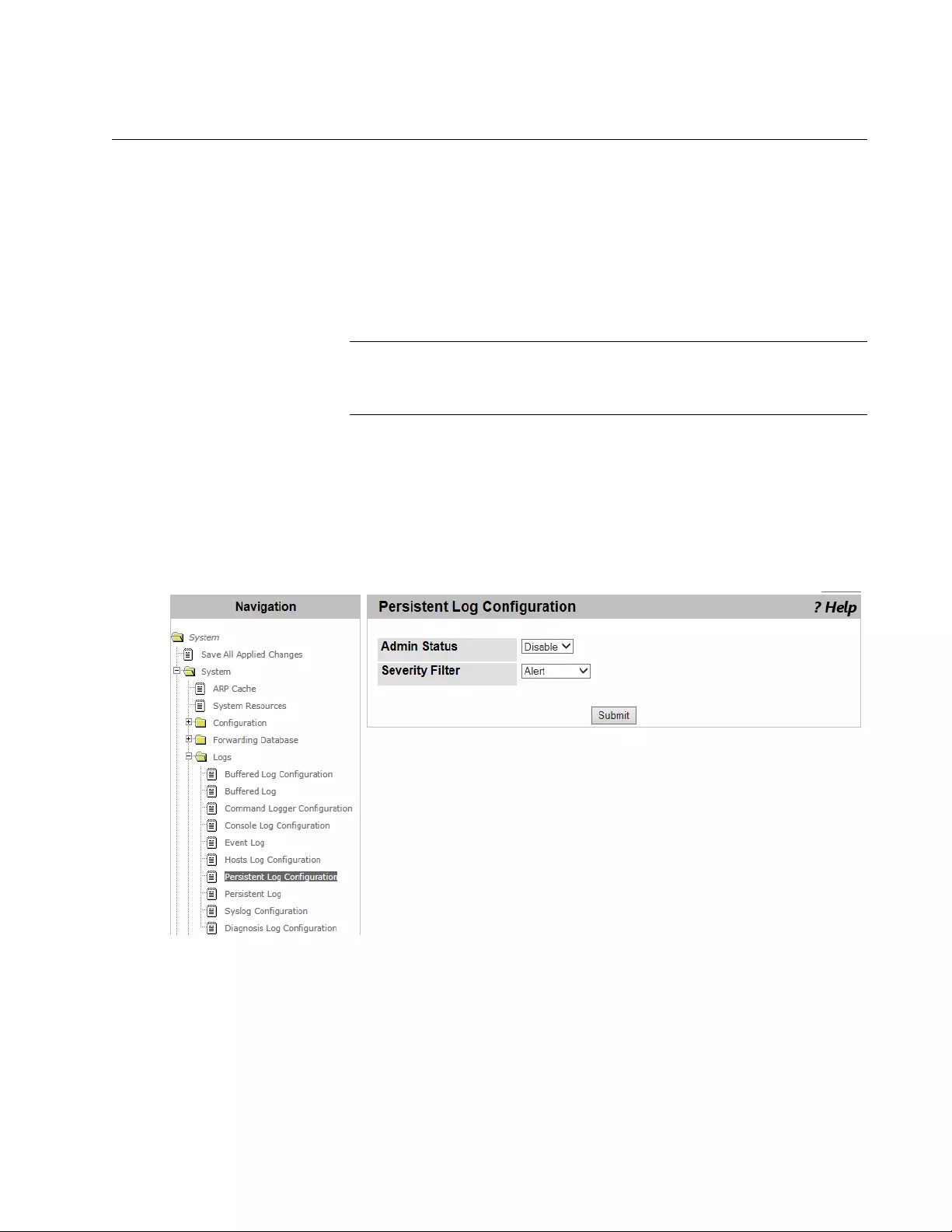
Chapter 2: System
65
Persistent Log Configuration
From the Persistent Log Configuration page, you can enable or disable the
Persistent Log feature.
When the Persistent Log feature is enabled, the system stores log
messages in a file on the hard disk. The system creates a new log file
when rebooting. When the system has three log files, it replaces the oldest
log file with a new.
Note
To download persistent log messages, see “Upload File from
Controller” on page 90.
To enable or disable the Persistent Log feature, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Persistent Log
Configuration.
The Persistent Log Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 39.
Figure 39. Persistent Log Configuration Page
2. Select the options in the fields described in Table 10 on page 66.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
66
3. Click Submit.
The change is saved to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Table 10. Persistent Log Configuration
Field Description
Admin Status Starts or stops logging messages in the hard disc.
The options are:
Enable: Starts logging messages on the
hard disc.
Disable: Stops logging messages on the
hard disc.
Severity Filter Specifies the Severity filter. The options are:
Emergency: Stores messages with the
emergency level. This is the highest level of
severity.
Alert: Stores messages with the alert and
the higher severity level.
Critical: Stores messages with the critical
and the higher severity levels.
Error: Stores messages with the error and
the higher severity levels.
Warning: Stores messages with the
warning and the higher severity levels.
Notice: Stores messages with the notice
and the higher severity levels.
Info: Stores messages with the info and the
higher severity levels.
Debug: Stores messages with the debug
and all the other levels.
For more information about the severity filter, see
“Log Message Levels” on page 67.

Chapter 2: System
67
Severity Levels Table 11 describes the severity levels in decreasing order of severity.
Table 11. Log Message Levels
Severity Level Description
0 Emergency The system is disabled. This is the highest
level of severity.
1 Alert The system requires an immediate action.
2 Critical The system is in the critical condition.
3 Error An error occurred.
4 Warning An event that leads to an error occurred.
5 Notice A noticeable event occurred.
6 Info Incudes information.
7 Debug Includes information to help debugging.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
68
Persistent Log
From the Persistent Log page, you can view persistent log messages
stored in the hard disk on the WLAN Controller.
Note
To configure the Persistent Log feature, see “Persistent Log
Configuration” on page 65.
To view messages in the Persistent log, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Persistent Log.
The Persistent Log page is displayed as shown in Figure 40.
Figure 40. Persistent Log Page
2. Observe the messages.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
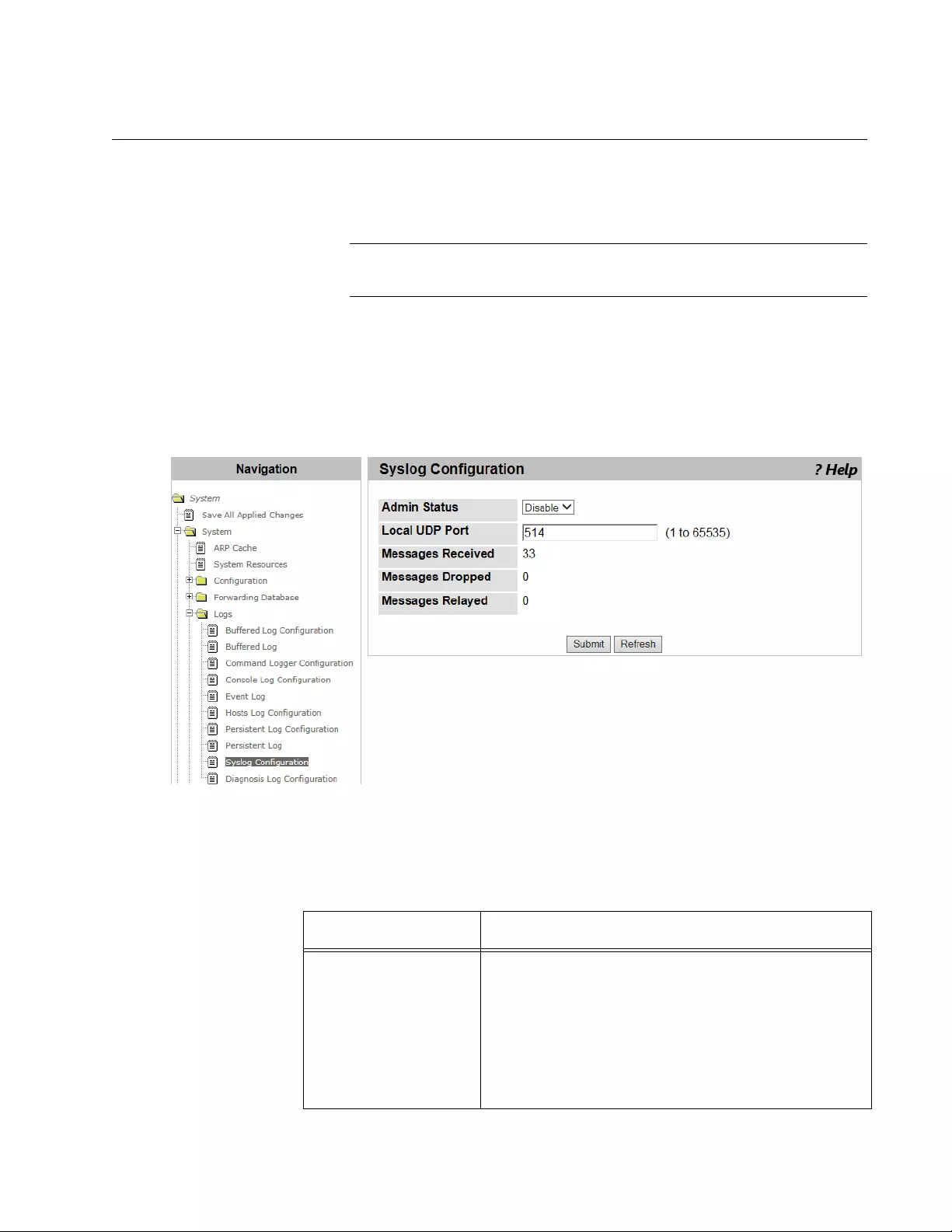
Chapter 2: System
69
Syslog Configuration
From the Syslog Configuration page, you can start or stop sending log
messages to Syslog servers.
Note
To set Syslog servers, see “Hosts Log Configuration” on page 63.
To start or stop sending log messages to Syslog servers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > Logs > Syslog
Configuration.
The Syslog Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 41.
Figure 41. Syslog Configuration Page
2. Select the options in the fields described in Table 12.
Table 12. Syslog Configuration
Field Description
Admin Status Starts or stops sending messages to syslog
servers. The options are:
Enable: Starts sending log messages to
Syslog servers.
Disable: Stops sending log messages to
Syslog servers.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
70
3. Click Submit.
The change is saved to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Local UDP Port Displays the UDP port number used to sent log
messages to syslog servers. The default port
number is 514.
Messages Received Displays the number of log messages that the
process received, including discarded messages.
Messages Dropped Displays the number of log messages that have
an error or were discarded due to lack of space.
Messages Relayed Displays the total number of log messages that
were sent to syslog servers. If a message is sent
to three syslog servers, the message is counted
three.
Table 12. Syslog Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
71
Diagnosis Log Configuration
From the Diagnosis Log Configuration page, you can start or stop storing
diagnosis messages that include more detailed information than debug
messages. When the system operates normally, disable this function.
Note
To view diagnosis log messages, you must download the file to a
TFTP server. See “Upload File from Controller” on page 90.
To start or stop storing diagnosis log messages, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Logs > Diagnosis Log
Configuration.
The Diagnosis Log Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 42.
Figure 42. Diagnosis Log Configuration Page
2. Select one of the following Admin Status options from the select list:
Enable: Starts storing diagnosis log messages.
Disable: Stops storing diagnosis log messages.
3. Click one of the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Saves the changes to the running configuration file.
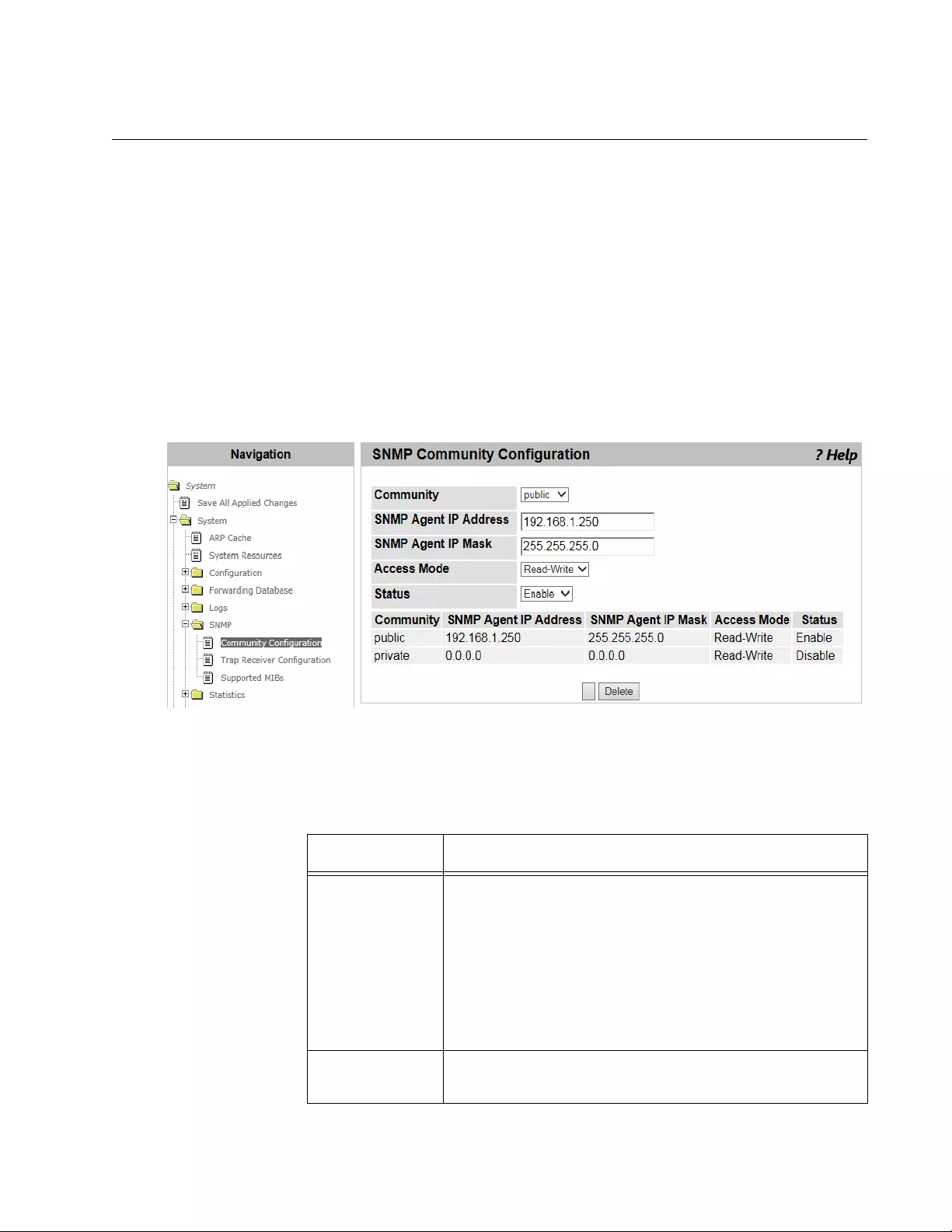
Chapter 2: System
73
SNMP Community Configuration
From the SNMP Community Configuration page, you can view a list of
community strings, modify the properties of a community string, add a
community string, and delete it. A community string acts as a password to
access the SNMP service.
Adding or
Modifying
Community
Strings
To add or modify community strings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNMP > Community
Configuration.
The SNMP Community Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 43.
Figure 43. SNMP Community Configuration Page
2. Select and specify the following fields in Table 13.
.Table 13. SNMP Community Configuration
Field Description
Community Specifies the name of a community string or the
action. The options are:
Create - Adds a new community string.
public - Modifies the properties of the
community public.
private - Modifies the properties of the
community private.
Community Specifies the name of new community. This field is
displayed only when Create is selected.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
74
3. Click Submit.
The change is saved to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Deleting a
Community
String
To delete a community string, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNMP > Community
Configuration.
The SNMP Community Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 43 on page 73.
2. Select a community string from the Community select list:
3. Click Delete.
The selected community is deleted.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
SNMP Agent
IP address
Specifies the IPv4 address of the SNMP agent.
SNMP Agent
IP Mask
Specifies the subnet mask of the SNMP agent.
Access Mode Specifies the access modes of the community string.
The options are:
Read-Only
Read-Write
Status Specifies the status of the community string. The
options are:
Enable
Disable
Table 13. SNMP Community Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
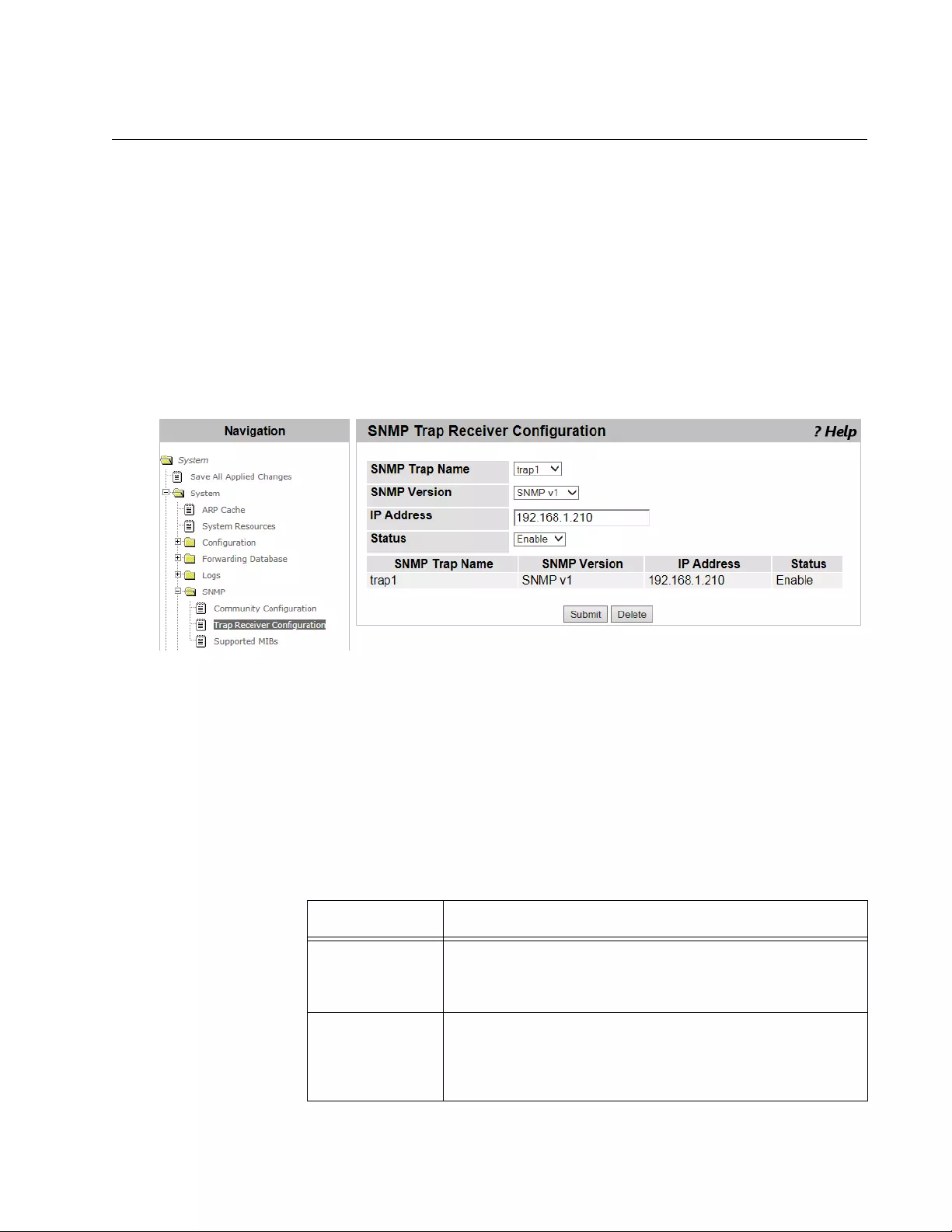
Chapter 2: System
75
Trap Receiver Configuration
From the SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration page, you can view a list of
SNMP trap receivers on the WLAN Controller. You can also add, delete, or
modify a trap receiver.
To add, delete, or modify a trap receiver, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNMP > Trap Receiver
Configuration.
The SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 44.
Figure 44. SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration Page
2. Select an item from the SNMP Trap Name select list:
Create - Adds a field to specify the SNMP Trap Name.
SNMP_Trap_name - Displays the settings of the SNMP trap
receiver.
3. Specify the following fields in Table 14.
.Table 14. SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration
Field Description
SNMP Trap
Name
Specifies the name of the SNMP trap receiver. You
can specify the name using up to 16 alphanumeric
characters.
SNMP Version Specifies the version of the SNMP. The options are:
SNMP v1
SNMP v2c

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
76
4. Click one of the following buttons:
Delete — Deletes the selected SNMP trap receiver.
Submit — Saves the changes to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
IP Address Specifies the IP address of the SNMP trap receiver.
Status Displays the status of the trap receiver. The options
are:
Enable
Disable
Table 14. SNMP Trap Receiver Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
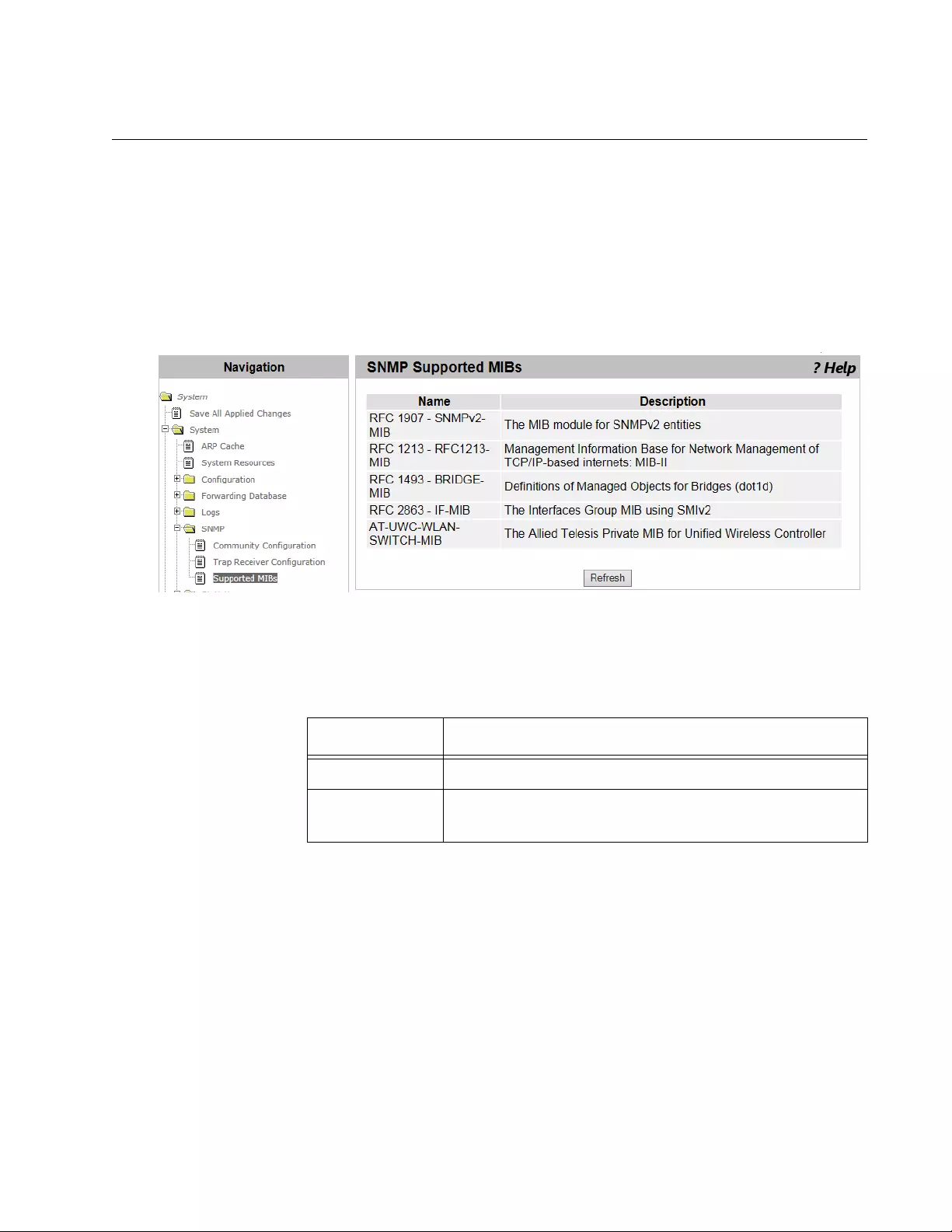
Chapter 2: System
77
Supported MIBs
From the Supported MIBs page, you can view a list of MIB’s that the
WLAN Controller supports.
To view a list of supported MIB’s, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNMP > Supported MIBs.
The Supported MIBs page is displayed as shown in Figure 45.
Figure 45. SNMP Supported MIBs Page
2. Observe the following fields in Table 15.
.
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Table 15. SNMP Supported MIBs
Field Description
Name Displays the RFC number and MIB module name.
Description Displays the RFC title or description of the MIB
module.
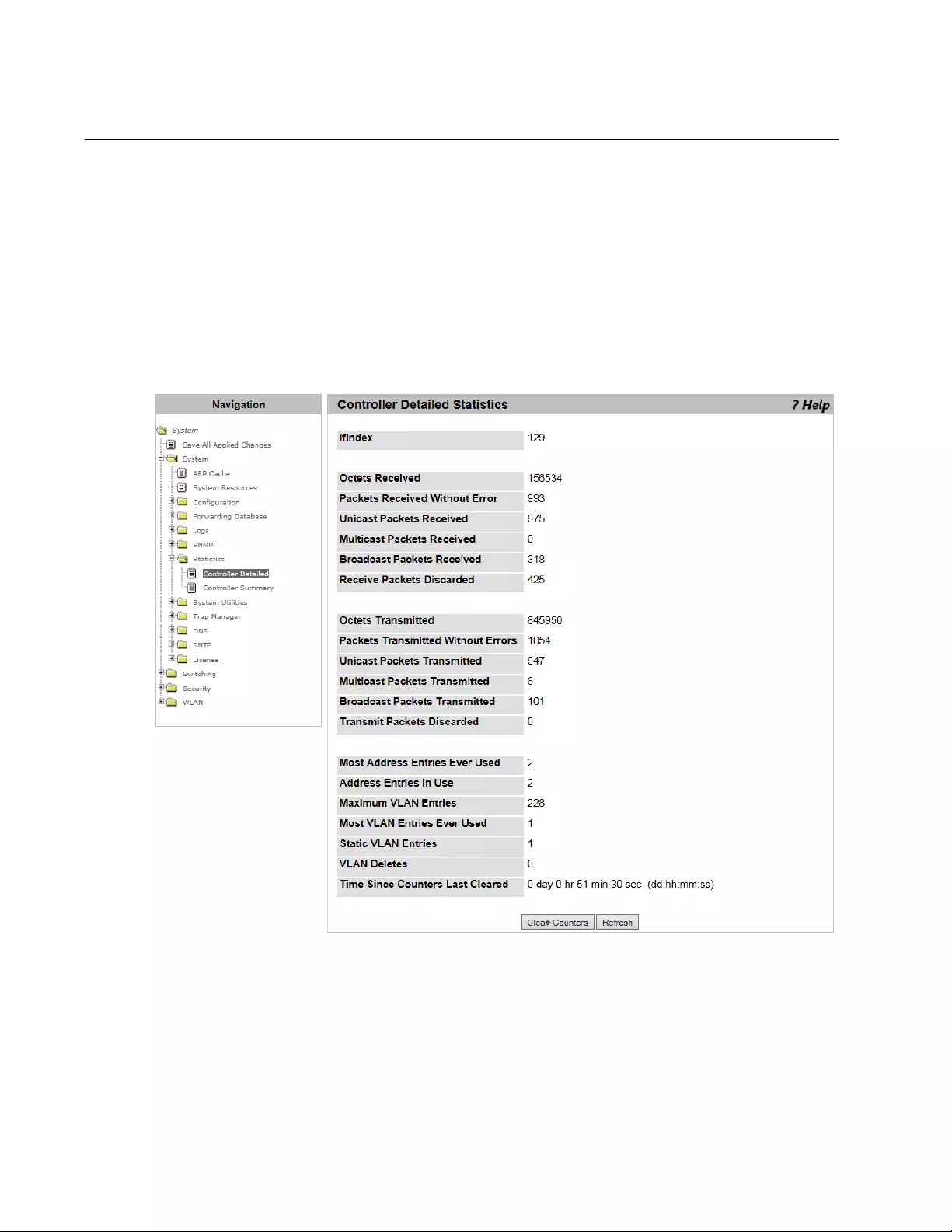
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
78
Controller Detailed Statistics
From the Controller Detailed Statistics page, you can view statistics data
about the activities of WLAN Controller.
To view statistics information, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Statistics > Controller
Detailed.
The Controller Detailed Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 46.
Figure 46. Controller Detailed Statistics Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 16 on page 79.
Chapter 2: System
79
.Table 16. Statistics Controller Detail
Field Description
ifIndex Displays the value of the interface index.
Octets Received Displays the number of received octets, including
FCS and excluding the frame bit.
Packets Received
Without Error
Displays the number of received broadcast and
multicast packets without errors.
Unicast Packets
Received
Displays the number of received unicast packets.
Multicast Packets
Received
Displays the number of received multicast packets.
Broadcast Packets
Received
Displays the number of received broadcast packets.
Receive Packets
Discarded
Displays the number of the received packets that
were discarded, excluding packets with an error. A
packet can be discarded due to a lack of buffer
space.
Octets Transmitted Displays the number of transmitted octets including
frame bits.
Packets
Transmitted Without
Errors
Displays the number of transmitted packets.
Unicast Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of requested unicast packets
including the packets that were not transmitted or
discarded in the lower layer.
Multicast Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of requested multicast packets
including the packets that were not transmitted or
discarded in the lower layer.
Broadcast Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of requested broadcast
packets including the packets that were not
transmitted or discarded in the lower layer.
Transmit Packets
Discarded
Displays the number of the transmitted packets that
were discarded, excluding packets with an error. A
packet can be discarded due to a lack of buffer
space.
Most Address
Entries Ever Used
Displays the maximum number of the forwarding
database entries that were learned since the last
time system was rebooted.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
80
3. Click one of the following buttons if necessary:
Clear Counters — Clears the counters.
Refresh — Displays the most recent statistics data.
Address Entries in
Use
Displays the number of entries in the forwarding
database at this moment.
Maximum VLAN
Entries
Displays the maximum number of VLAN’s that the
system is allowed to have.
Most VLAN Entries
Used
Displays the number of VLAN’s that are active since
the last time the system was rebooted.
Static VLAN Entries Displays the number of VLAN’s that were statically
created and are currently active.
VLAN Deletes Displays the number of VLAN’s that were statically
created, then deleted.
Time Since Counter
Last Cleared
Displays the time passed since the statistics data
was cleared.
Table 16. Statistics Controller Detail (Continued)
Field Description
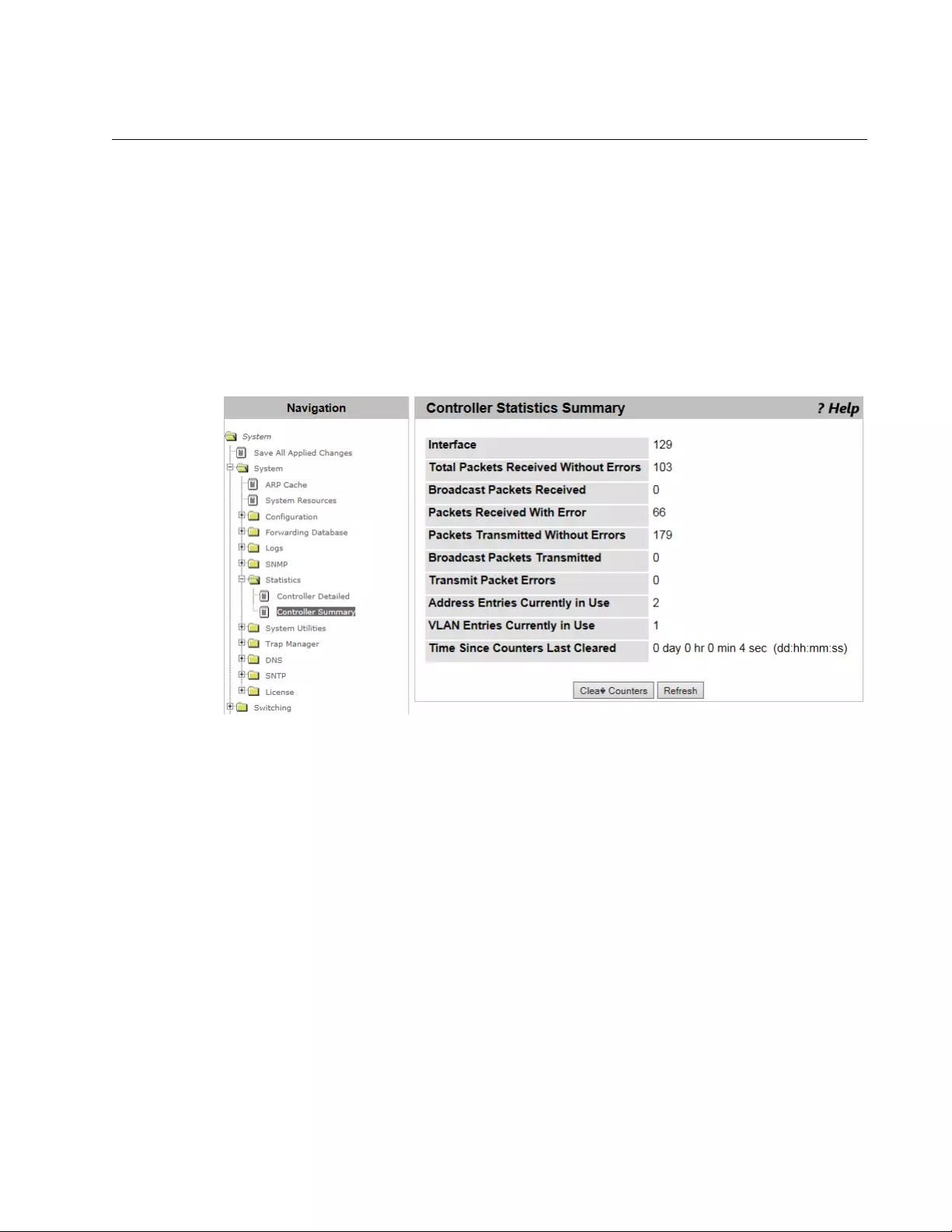
Chapter 2: System
81
Controller Statistics Summary
From the Controller Statistics Summary page, you can view statistics data
about the activities of WLAN Controller. This page displays the subset of
the items displayed on the Controller Detailed Statistics page.
To view statistics information, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Statistics > Controller
Summary.
The Controller Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 47.
Figure 47. Controller Statistics Summary Page
2. Observed the fields. The fields are explained in Table 16 on page 79.
3. Click one of the following buttons as needed:
Clear Counters — Clears the counters.
Refresh — Displays the most recent statistics data.
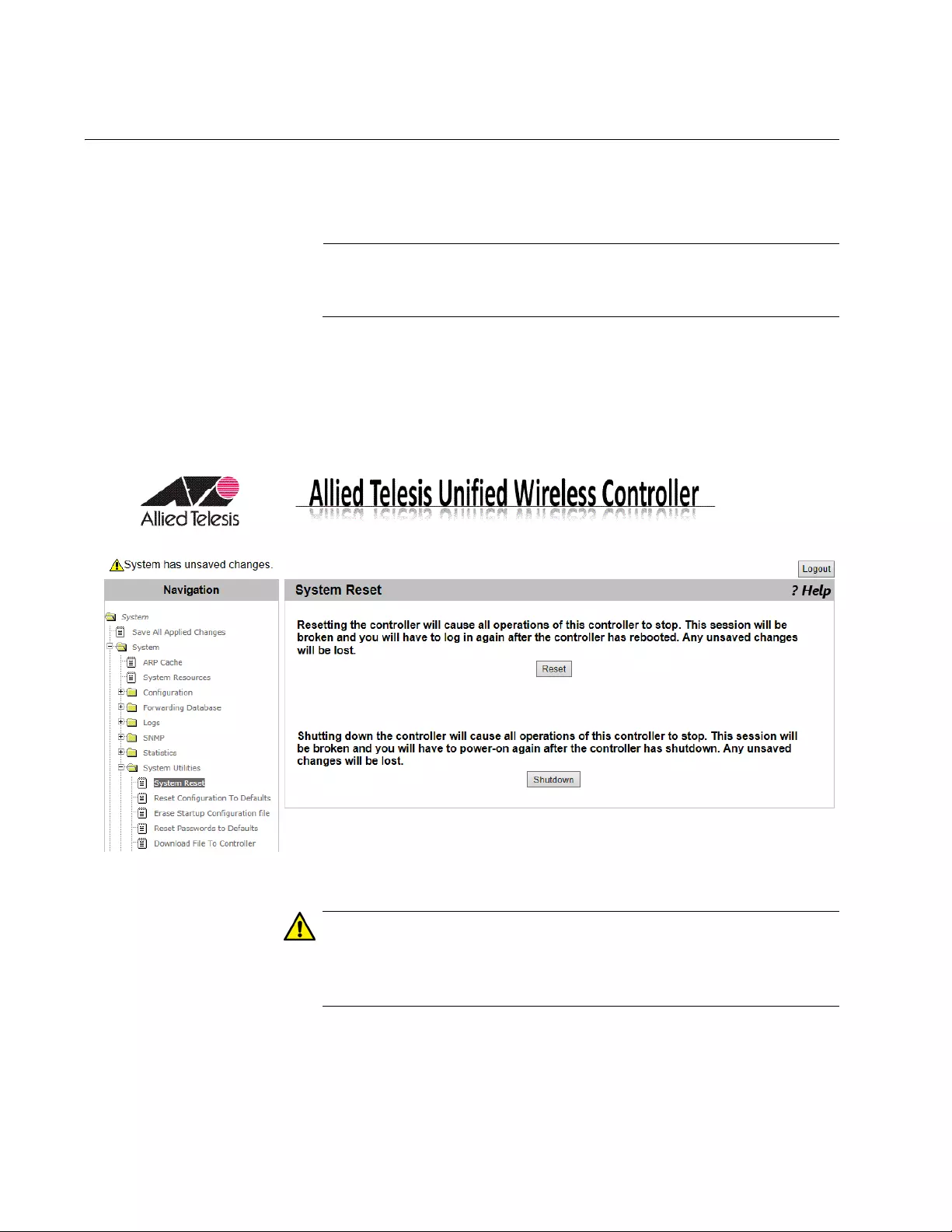
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
82
System Reset
From the System Reset page, you can reset or shut down the WLAN
Controller.
Note
To reboot the AT-UWC WLAN Controller from a PC-based server,
press Ctrl+Alt+Delete keys from the keyboard of the server.
To reset or shut down the system, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > System
Reset.
The System Reset page is displayed as shown in Figure 48.
Figure 48. System Reset Page
Caution
When resetting or shutting down the WLAN Controller, you lose your
unsaved changes. To save your changes to the startup
configuration file, see “Save All Applied Changes” on page 39.
2. Click one of the following buttons:
Reset — Power-cycles the WLAN Controller device.
Shutdown — Turns off the WLAN Controller device.
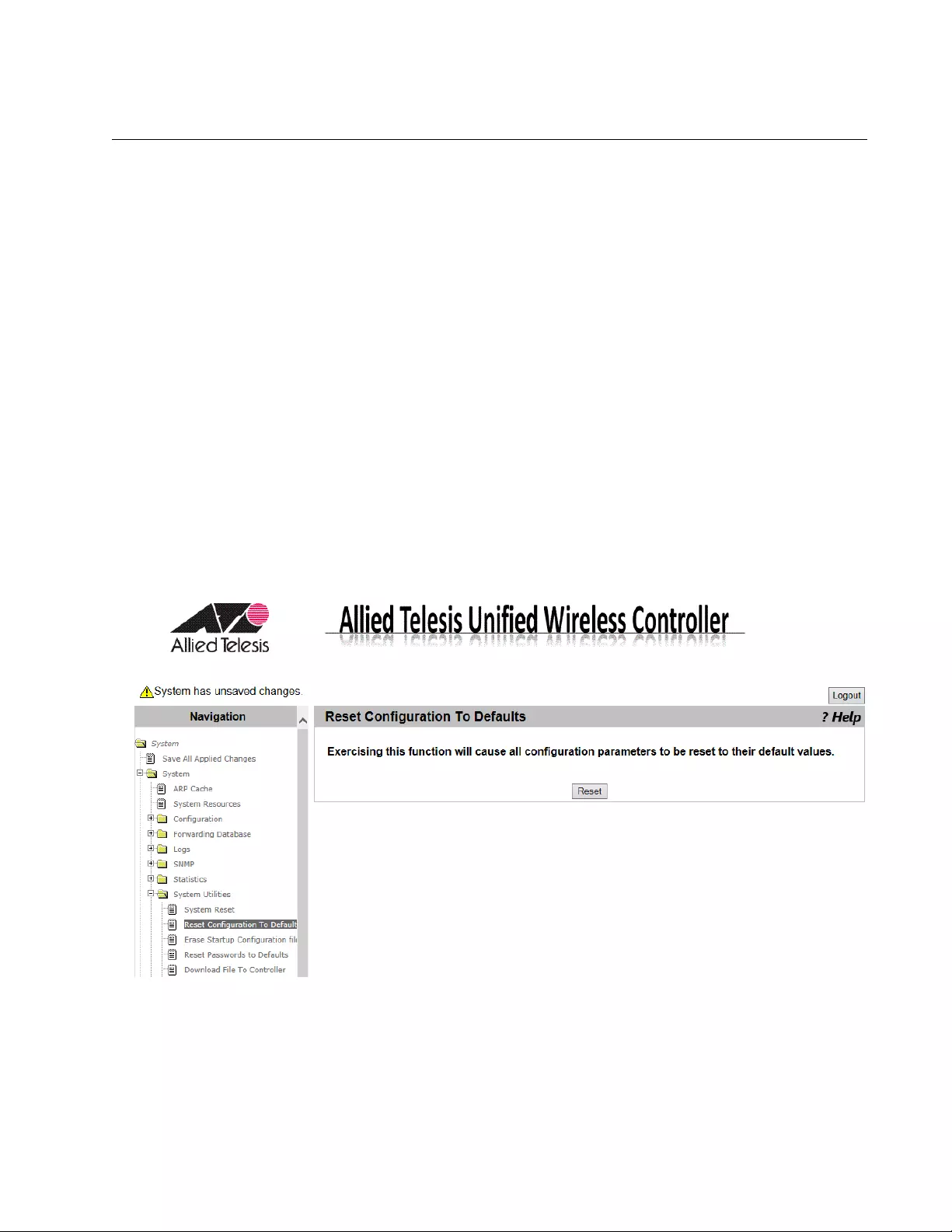
Chapter 2: System
83
Reset Configuration To Default
From the Reset Configuration To Default page, you can restore the default
settings to the WLAN Controller.
Guidelines for
Resetting the
Configuration
Here are the guidelines when you reset the configuration to the default
settings:
Since the IP address is reset to 192.168.1.1, you lose the
connection if the IP address was changed.
The password for the manager account is reset to “friend.”
Licenses are not deleted.
Resetting the
Configuration
To restore the default settings to the WLAN Controller system, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > Reset
Configuration To Default.
The Reset Configuration To Default page is displayed as shown in
Figure 49.
Figure 49. Reset Configuration To Default Page
2. Click Reset.
The Confirm Reset Configuration To Defaults page is displayed.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
84
3. Click one of the following options:
Yes - Resets the configuration to the default settings.
No - Cancels the operation.
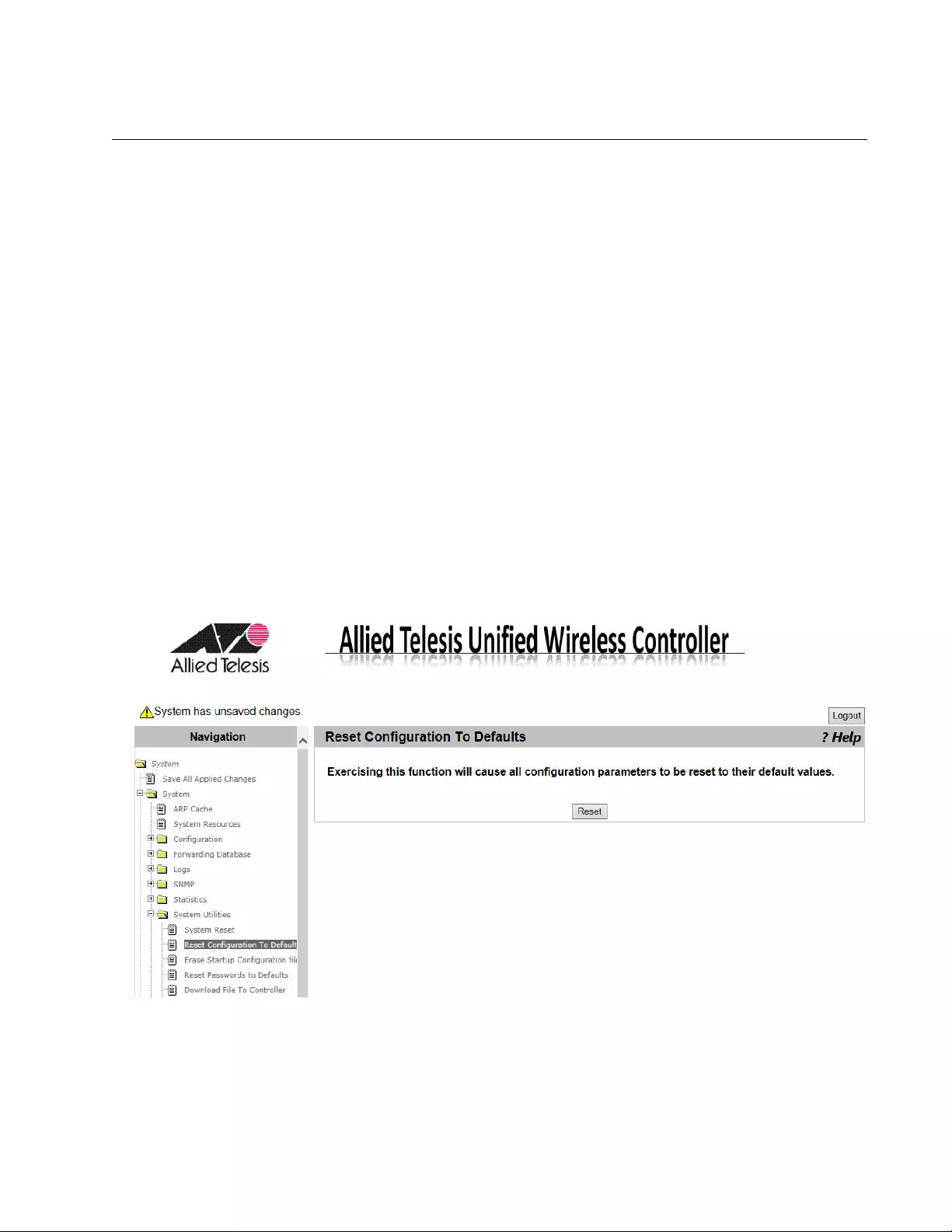
Chapter 2: System
85
Erase Startup Configuration File
From the Erase Startup Configuration File page, you can delete the startup
configuration file stored in the WLAN Controller. The startup configuration
file is a file that includes the current saved settings, which the WLAN
Controller loads when it reboots.
Guidelines for
Erasing the
Startup
Configuration
File
Here are the guidelines for erasing the startup configuration file:
The WLAN Controller keeps operating based on the settings on the
running configuration file unless the system resets.
Licenses are not deleted.
The image files downloaded from “Network Visualization
Downloaded Image,” are not deleted.
Deleting the
Startup
Configuration
File
To delete the startup configuration file, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > Erase
Startup Configuration File.
The Erase Startup Configuration File page is displayed as shown in
Figure 50.
Figure 50. Erase Startup Configuration File Page
2. Click Erase.
The Confirm Erase Startup Configuration File page is displayed.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
86
3. Click one of the following options:
Yes - Erases the startup configuration file.
No - Cancels the operation.
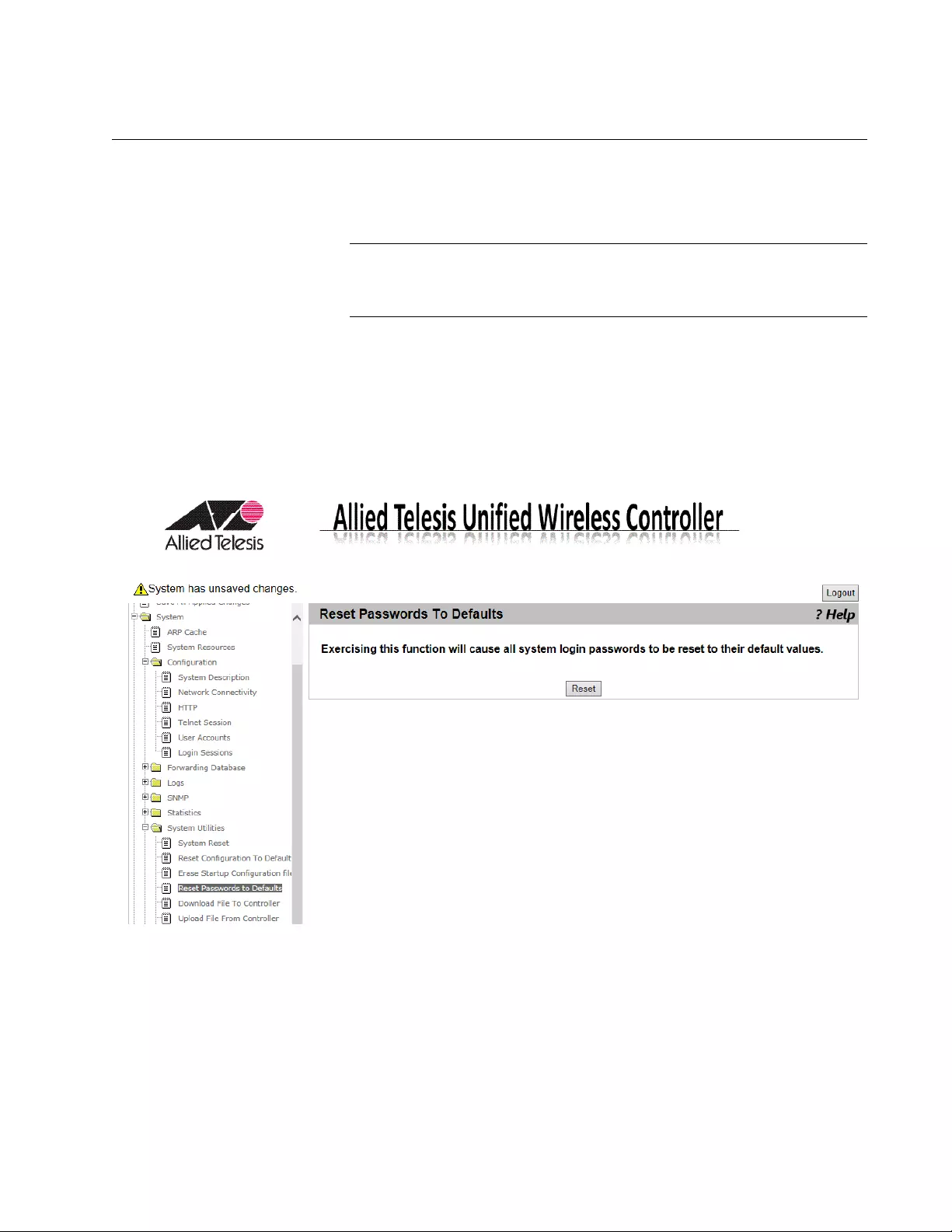
Chapter 2: System
87
Reset Passwords to Defaults
From the Reset Passwords to Defaults page, you can reset the password
of the manager account to the default password “friend.”
Note
The guest account is not supported for the current version. See
“User Accounts Configuration” on page 50.
To restore the default password of the manager account, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > Reset
Passwords to Defaults.
The Reset Passwords to Defaults page is displayed as shown in
Figure 51.
Figure 51. Reset Passwords to Defaults Page
2. Click Reset.
The password of the manager account is set to “friend.”
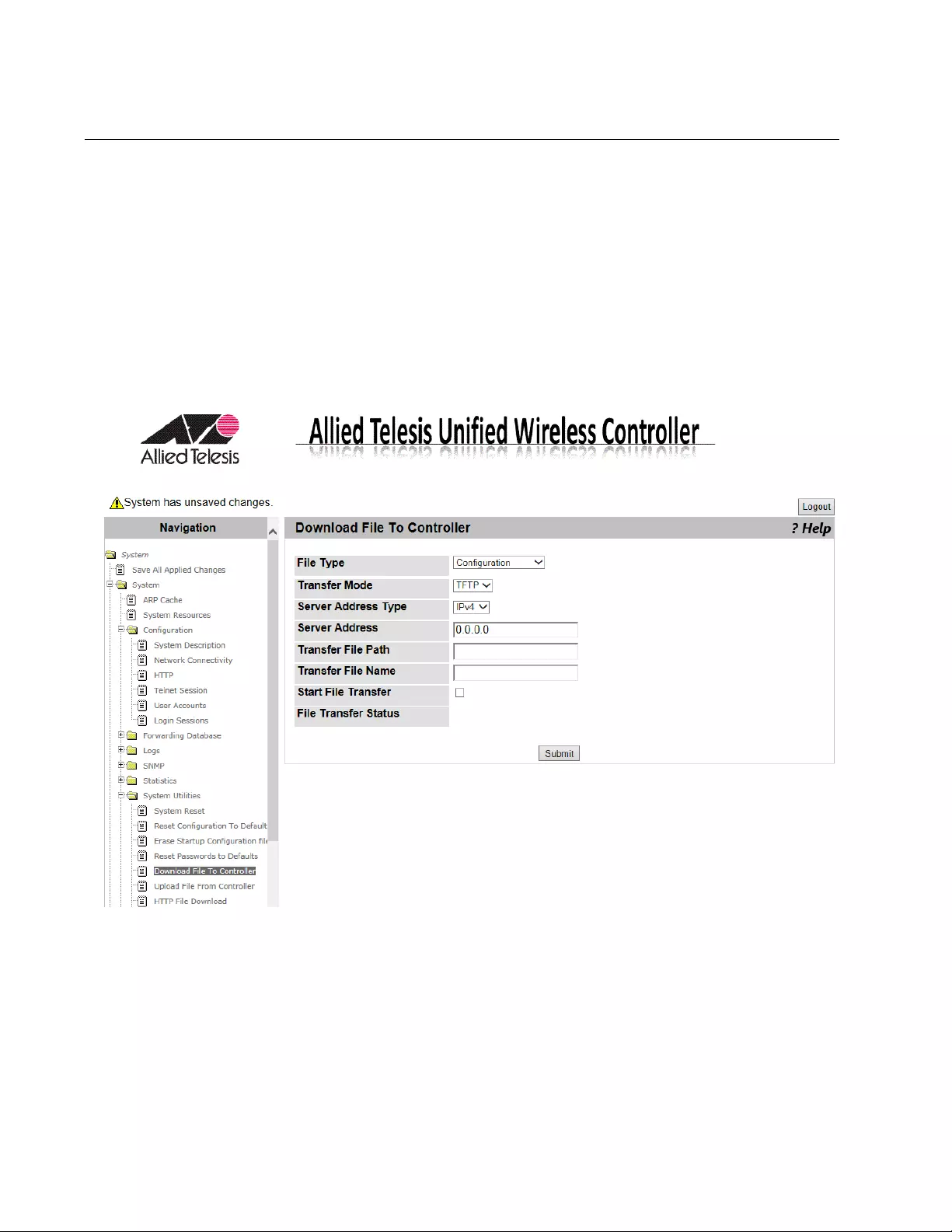
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
88
Download File to Controller
From the Download File to Controller page, you can transfer a file from the
TFTP server to the WLAN Controller.
To transfer a file from the TFTP server to the WLAN Controller, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities >
Download File to Controller.
The Download File to Controller page is displayed as shown in
Figure 52.
Figure 52. Download File to Controller Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 17 on page 89.

Chapter 2: System
89
.
3. Click Submit.
The status is displayed in the File Transfer Status field.
Table 17. Download File to Controller
Field Description
File Type Select one of the following file types:
Configuration: Specifies a binary file that
includes graphics used for the captive portal
and network visualization.
Text Configuration: Specifies a startup
configuration file.
Transfer Mode Displays the protocol TFTP, which is the only option.
Server
Address Type
Select one of the following types:
IPv4: Specifies a TFTP server with its IPv4
address.
DNS: Specifies a TFTP server with its host
name.
Server
Address
Enter the IPv4 address or host name of the TFTP
server.
Transfer File
Path
Enter the path of the file on the TFTP server. The path
must be up to 32 characters.
Transfer File
Name
Enter the name of the file you want to download from
the TFTP server to the WLAN Controller system.
Start File
Transfer
Check the checkbox to start the file transfer.
File Transfer
Status
Displays the progress of the file transfer.
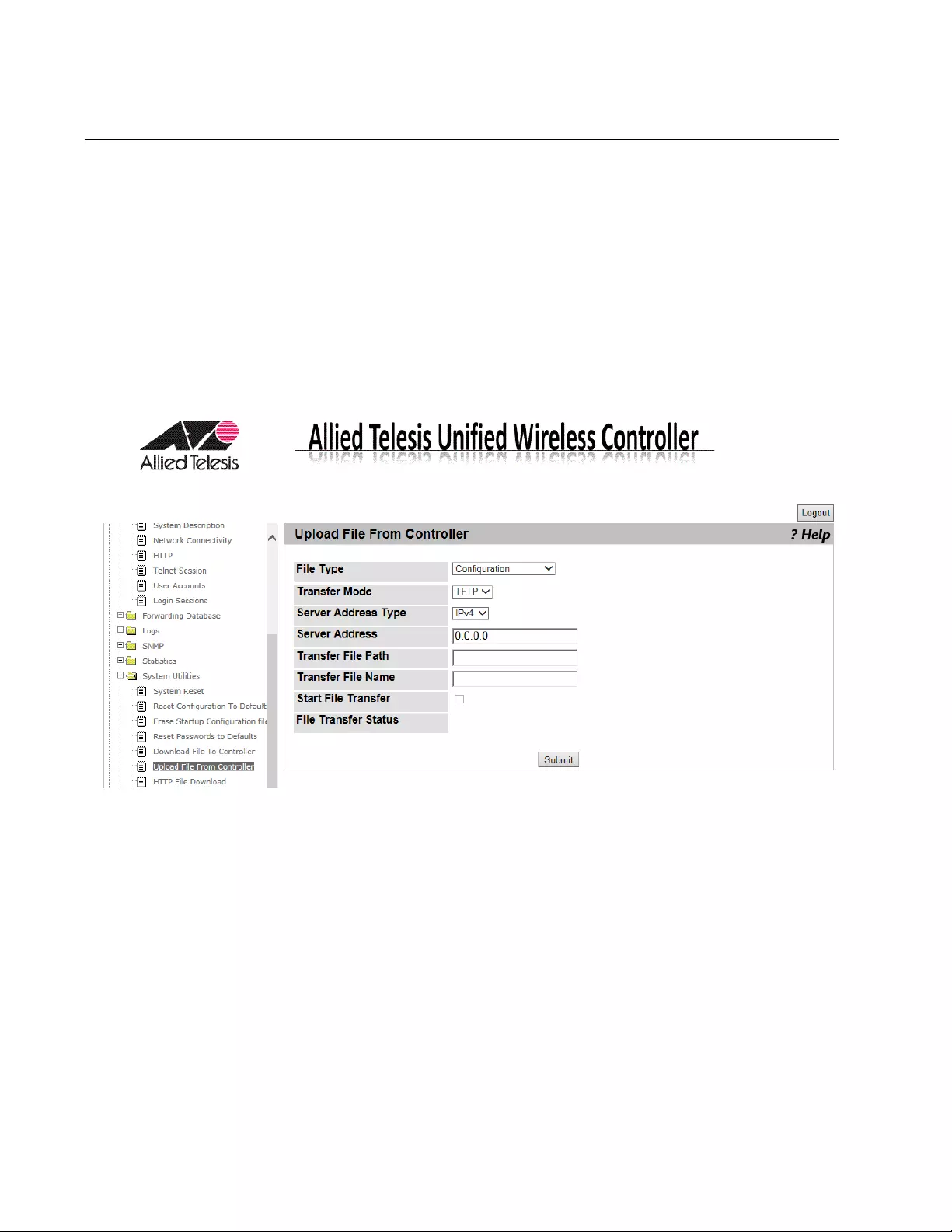
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
90
Upload File from Controller
From the Upload File from Controller page, you can transfer a file from the
WLAN Controller to a TFTP server.
To transfer a file from the WLAN Controller to a TFTP server, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > System Utilities >
Upload File from Controller.
The Upload File from Controller page is displayed as shown in
Figure 53.
Figure 53. Upload File from Controller Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 18 on page 91.

Chapter 2: System
91
.
3. Click Submit.
The status is displayed in the File Transfer Status field.
Table 18. Upload File from Controller
Field Description
File Type Select one of the following file types:
Configuration: Specifies a binary file that
includes graphics used for the captive portal
and network visualization.
Text Configuration: Specifies a startup
configuration file.
Error Log: Not supported.
Buffered Log: Specifies a buffered log file.
Persistent Log: Specifies a persistent log file
including all persistent log messages.
Diagnosis Log: Specifies a diagnosis log file.
ValidAccessPoint DB: Not supported.
Transfer Mode Displays the protocol TFTP, which is the only option.
Server
Address Type
Select one of the following types:
IPv4: Specifies a TFTP server with its IPv4
address.
DNS: Specifies a TFTP server with its host
name.
Server
Address
Enter the IPv4 address or host name of the TFTP
server.
Transfer File
Path
Enter the location where you place the file on the
TFTP server. The maximum length is 32 characters
Transfer File
Name
Enter the name of the file that you upload from the
WLAN Controller. Spaces and special characters are
not allowed.
Start File
Transfer
Check the checkbox to start the file transfer.
File Transfer
Status
Displays the progress of the file transfer.
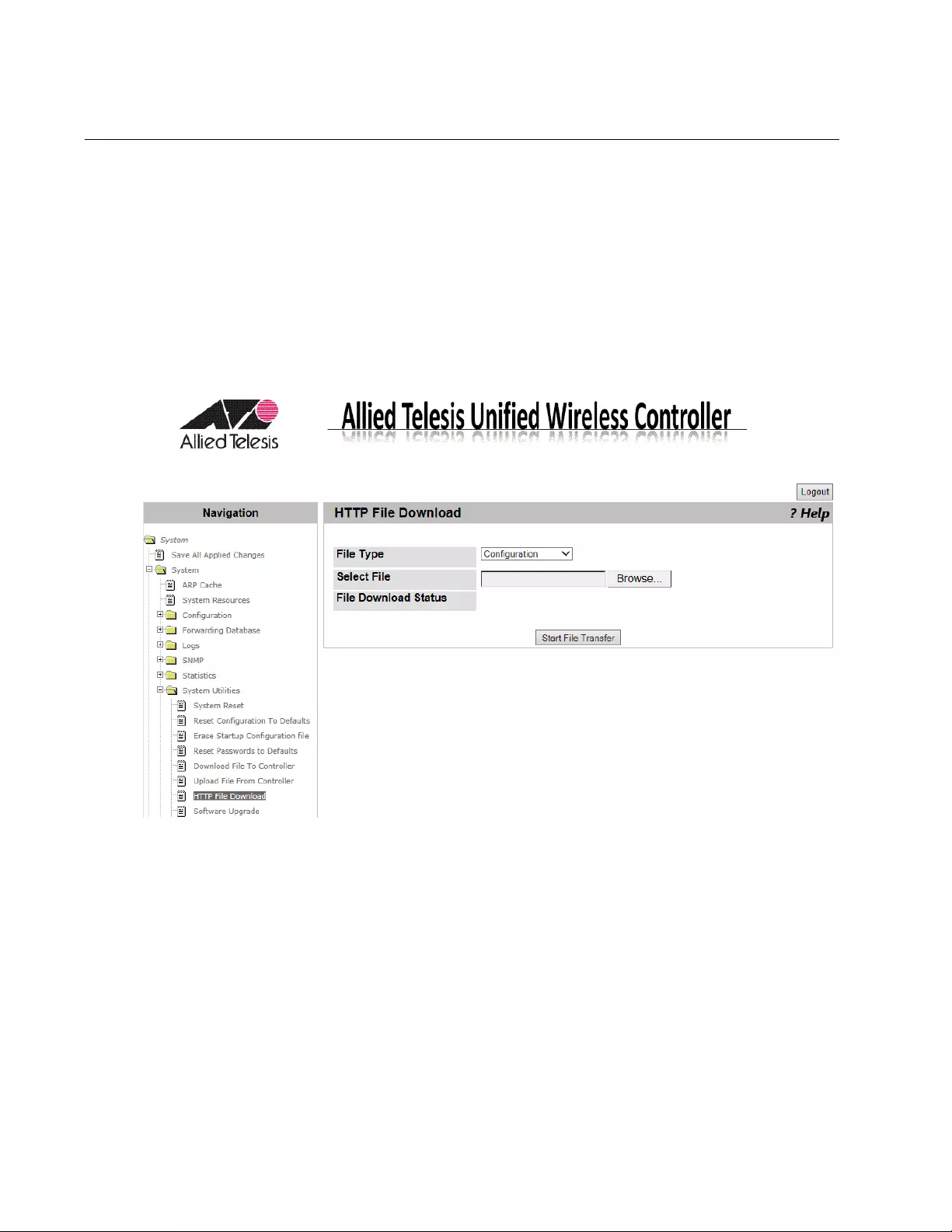
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
92
HTTP File Download
From the HTTP File Download page, you can transfer a file from your
management workstation to the WLAN Controller.
To transfer a file from your management workstation to the WLAN
Controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > HTTP
File Download.
The HTTP File Download page is displayed as shown in Figure 54.
Figure 54. HTTP File Download Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 19 on page 93.

Chapter 2: System
93
.
3. Click Start File Transfer.
The status is displayed in the File Download Status field.
Table 19. HTTP File Download
Field Description
File Type Select one of the following file types:
Configuration: Specifies a binary file
that includes graphics used for the
captive portal and network
visualization.
Text Configuration: Specifies a
startup configuration file.
Select File Click Browse and specify the file to download.
File Download Status Displays the progress of the file download.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
94
Software Upgrade
From the Software Upgrade page, you can upgrade management
software from your management workstation to the WLAN Controller.
Note
After downloading management software, you must reset the WLAN
Controller to load the software. See “System Reset” on page 82.
Guideline for
upgrading
Management
Software
Here are the guidelines for upgrading management software
After downloading management software, you must reboot the
WLAN Controller to load the software. See “System Reset” on
page 82.
The startup configuration stays the same after the system was
upgraded.
You cannot install older versions of software.
The file name of the management software is not allowed to
include space or symbols.
Upgrading
Management
Software
To download management software, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > Software
Upgrade.
The Software Upgrade page is displayed as shown in Figure 55 on
page 95.
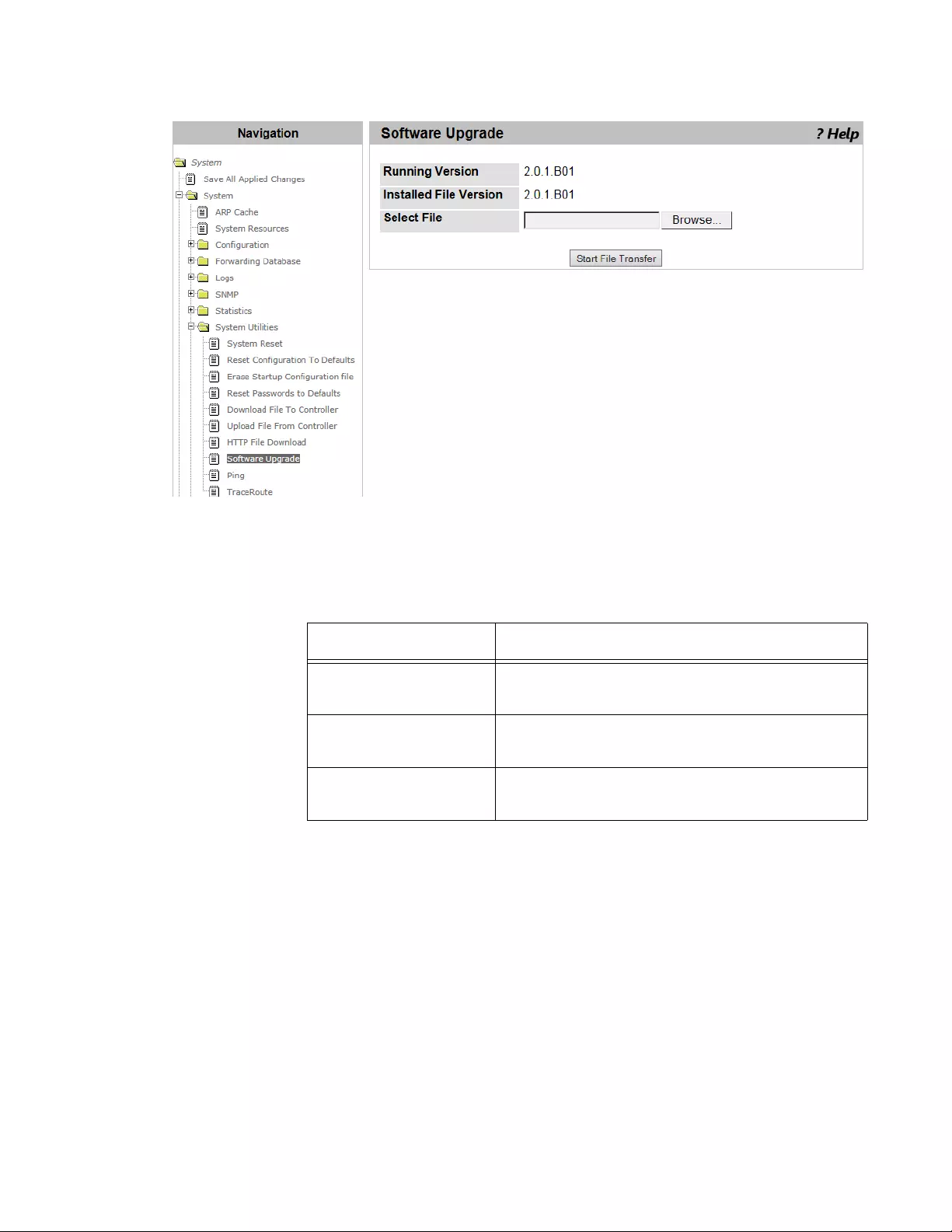
Chapter 2: System
95
Figure 55. Software Upgrade Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 20.
.
3. Click Start File Transfer.
The specified management software is downloaded.
Table 20. Software Upgrade
Field Description
Running Version Displays the version of the management
software currently running.
Installed File Version Displays the version of the management
software downloaded to the WLAN Controller.
Select File Click Browse and select a management
software file.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
96
Ping
From the Ping page, you can test network connections between the
WLAN Controller and the destination using the ping utility.
To test network connections using the ping utility, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities > Ping.
The Ping page is displayed as shown in Figure 56.
Figure 56. Ping Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 21.
.Table 21. Ping
Field Description
Host Name/IP
Address
Specifies the destination with the host name or
IPv4 address.
Count Specifies how many time to send request packets.
The default is 1 time.
Interval Specifies time in seconds to wait before sending
another request packet.

Chapter 2: System
97
3. Click Submit.
Size Specifies the size of a request packet in bytes.
Ping Displays the results of executing the ping utility.
Table 21. Ping (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
98
TraceRoute
From the TraceRoute page, you can trace the path that an IP packet takes
to reach the destination.
To trace the path to the destination using the traceroute utility, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System Utilities >
TraceRoute.
The TraceRoute page is displayed as shown in Figure 57.
Figure 57. TraceRoute Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 22.
.Table 22. TraceRoute
Field Description
Host Name/IP
Address
Specifies the destination with the host name or
IPv4 address.

Chapter 2: System
99
3. Click Submit.
Probes per Hop Specifies the number of probe packets per hop.
The default setting is 3 packets.
Max TTL Specifies the maximum number of hops to allow
probe packets to travel. Time to live (TTL) is
specified by hop counts. The default setting is 30
hops.
InitTTL Specifies the number set in the initial TTL. The
default setting is 1.
MaxFail Specifies the number of attempts to send a probe
packet. The default setting is 5 times.
Interval(secs) Specifies the time period in seconds to wait before
sending another packet. The default value is 3
seconds.
Port Specifies the UDP port number used for probe
packets. The default port number is 33434.
Size Specifies the size of a probe packet in bytes.
TraceRoute Displays the results of executing the TraceRoute
utility.
Table 22. TraceRoute (Continued)
Field Description
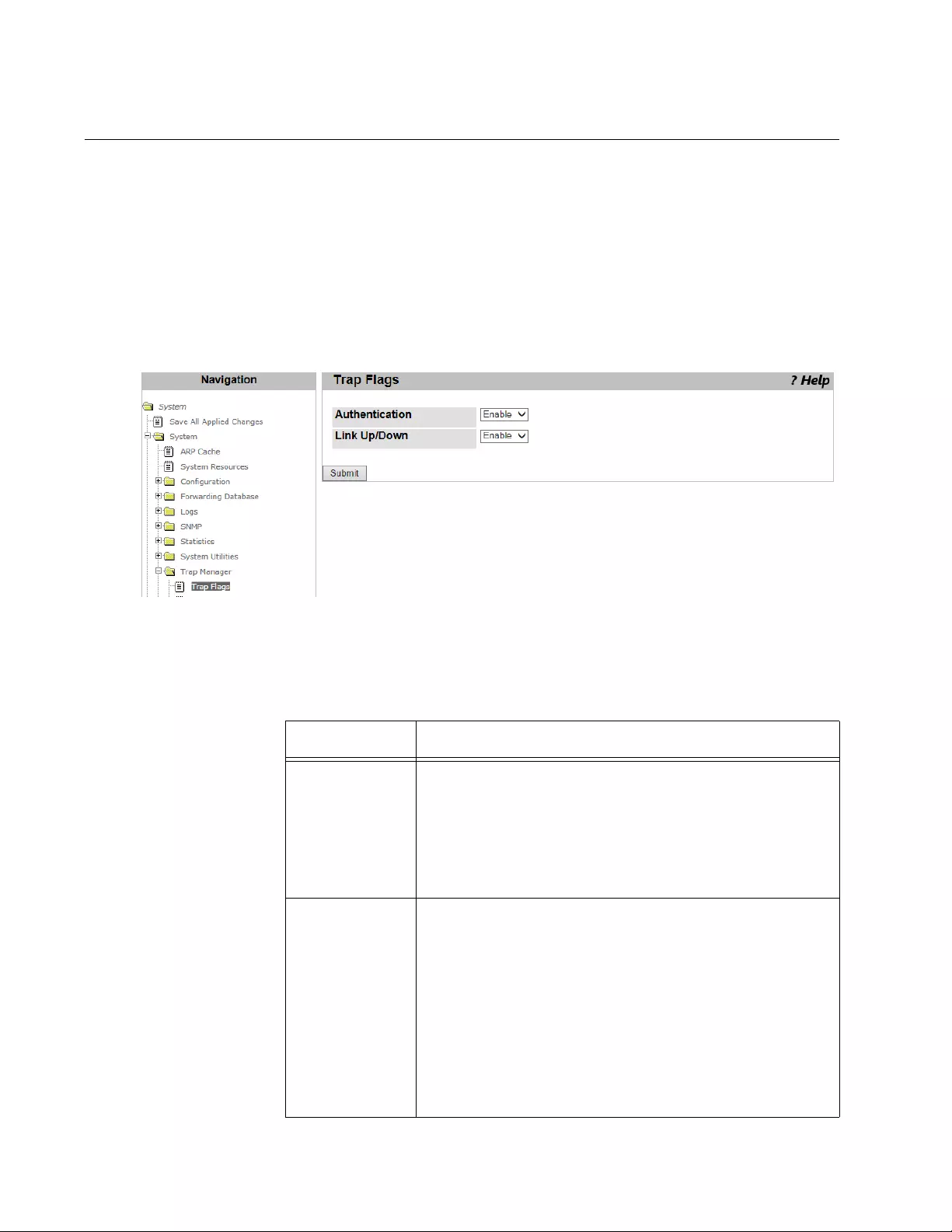
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
100
Trap Flags
From the Trap Flags page, you can enable or disable the system to send
traps when the SNMP authentication failed or the link status changed.
To enable or disable sending traps, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Trap Manager > Trap
Flags.
The Trap Flags page is displayed as shown in Figure 58.
Figure 58. Trap Flags Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 23.
.Table 23. Trap Flags
Field Description
Authentication Select one of the options:
Enable: The system sends traps when the
SNMP authentication failed.
Disable: The system does not send traps
when the SNMP authentication failed.
Link Up/Down Select one of the options;
Enable: The system sends traps when the link
status of the Ethernet port on the WLAN
Controller changed or when the status of a
managed AP changed.
Disable: The system does not send traps
when the link status of the Ethernet port on
the WLAN Controller changed or when the
status of managed AP changed.

Chapter 2: System
101
3. Click Submit.
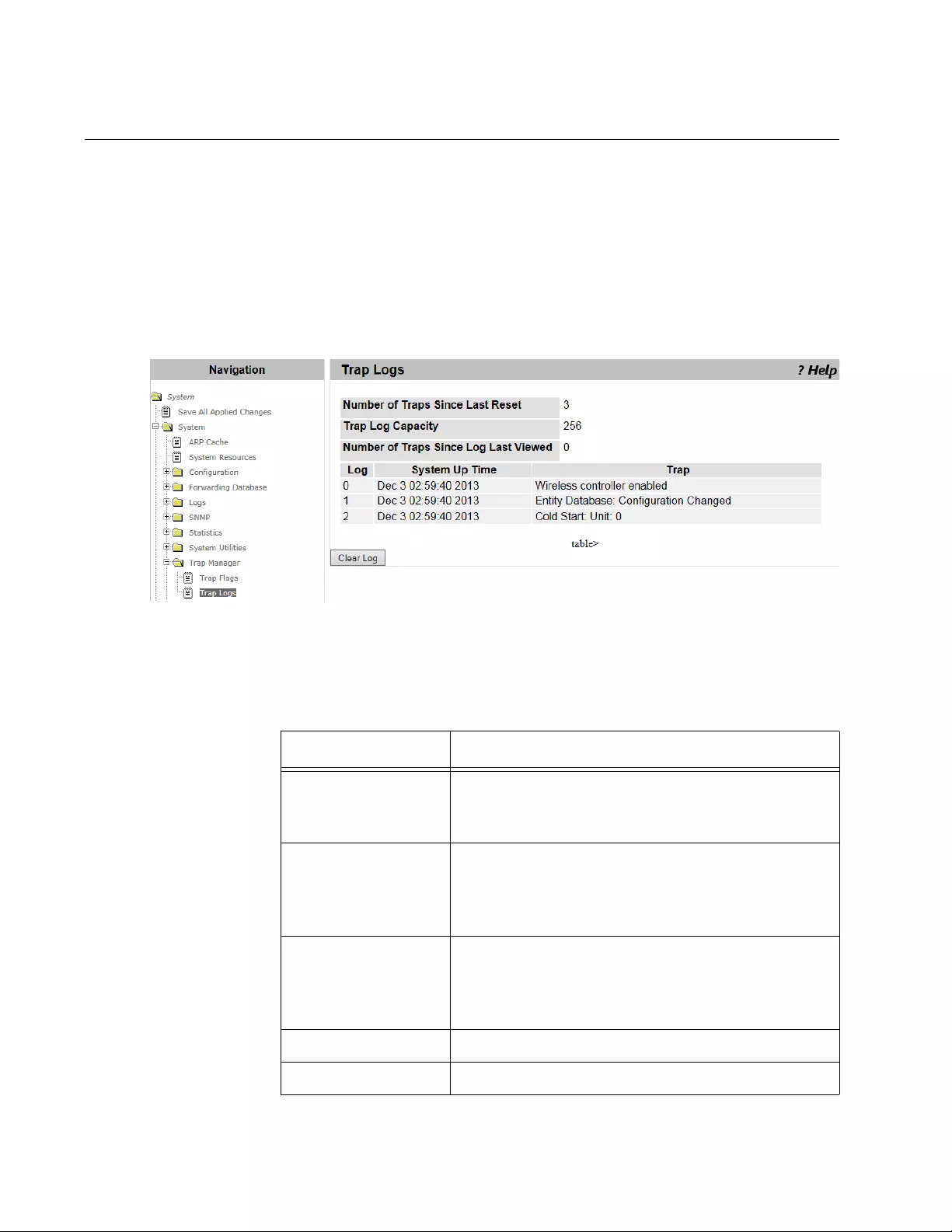
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
102
Trap Logs
From the Trap Logs page, you can view information about traps and a list
of traps that the WLAN Controller has generated.
To view trap logs, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Trap Manager > Trap Logs.
The Trap Logs page is displayed as shown in Figure 59.
Figure 59. Trap Logs Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 24.
.Table 24. Trap Logs
Field Description
Number of Traps
Since Last Reset
Displays the number of traps that the WLAN
Controller has generated since the log was
cleared.
Trap Log Capacity Displays the maximum number of traps that the
system can log. When reaching the Trap Log
Capacity, the system replaces a new trap entry
with the oldest trap entry.
Number of Traps
Since Log Last
Viewed
Displays the number of traps that have been
generated since the last time the Trap Logs page
was viewed. When the page is viewed using a
web browser, the number is reset.
Log Displays the sequence number of the trap log.
System Up Time Displays the time when the trap is generated.

Chapter 2: System
103
3. If you want to clear the log, click Clear Log.
Trap Displays the information about the trap.
Table 24. Trap Logs (Continued)
Field Description
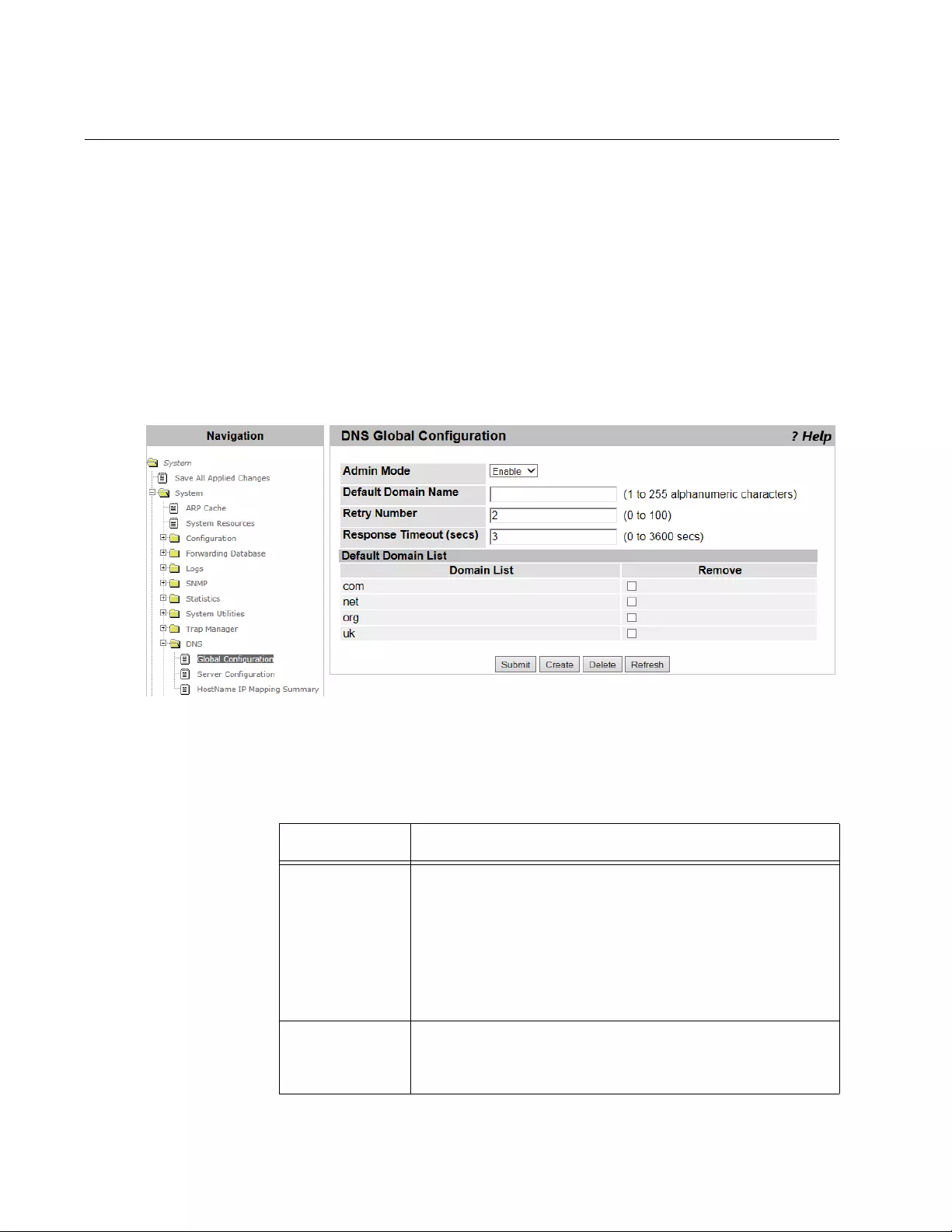
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
104
DNS Global Configuration
From the Domain Name Server (DNS) Global Configuration page, you can
view the domain list, enable or disable the DNS client, add a domain name
to the list, change the properties, and delete a domain name.
Viewing the DNS
Client
To view the domain list on the WLAN Controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > Global
Configuration.
The DNS Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 60.
Figure 60. DNS Global Configuration Page
2. Observe the following fields in Table 25.
.Table 25. DNS Global Configuration
Field Description
Admin Mode Select one of the options:
Enable: The DNS client on the WLAN
Controller is enabled. This is the default
setting.
Disable: The DNS client on the WLAN
Controller is disabled.
Default
Domain Name
Displays the default domain name. The DNS client
appends the default domain name to incomplete host
names in DNS requests.

Chapter 2: System
105
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Enabling the DNS
Client
To enable or disable the DNS client on the WLAN Controller, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > Global
Configuration.
The DNS Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
60 on page 104.
2. Select Enable or Disable from the Admin Mode select list:
3. Click Submit.
Changing the
Properties
To change the properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > Global
Configuration.
The DNS Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
60 on page 104.
2. Specify the following fields described in Table 25.
Default Domain Name
Retry Number
Response Timeout (secs)
3. Click Submit.
Adding a DNS
Name
To add a DNS name to the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > Global
Configuration.
Retry Number Displays the number of times that the DNS client tries
to resolve a host name. The default setting is 2 times.
Response
Timeout (secs)
Displays the time period in seconds the DNS client
waits for a response. The default setting is 3 seconds.
Domain List Displays a list of domain names added to the WLAN
Controller.
Remove Check the checkbox to delete the domain name.
Table 25. DNS Global Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
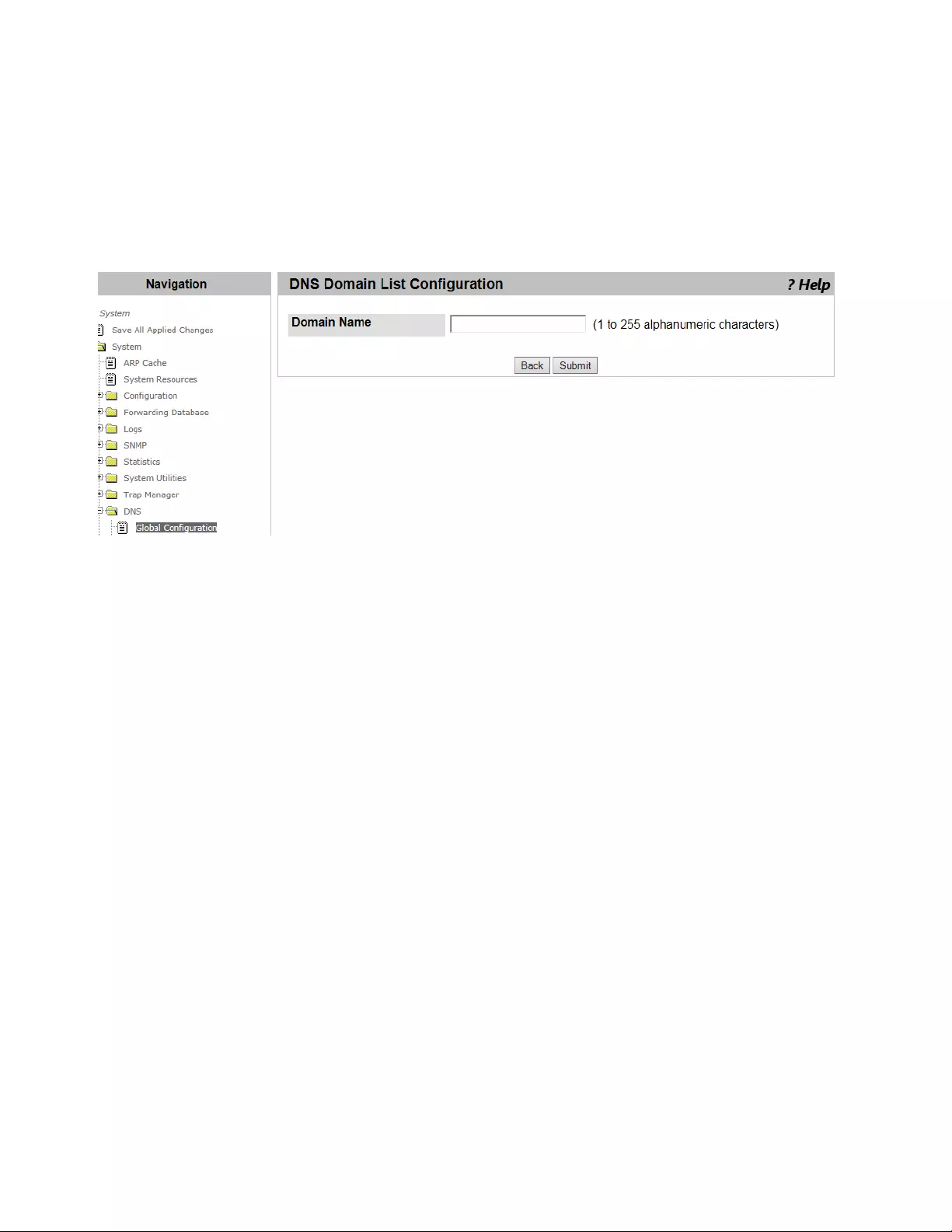
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
106
The DNS Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
60 on page 104.
2. Click Create.
The DNS Domain List Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 61.
Figure 61. DNS Domain List Configuration Page
3. Specify a domain name in the Domain Name box.
4. Click Submit.
5. If you want to add another domain name, repeat steps 3 and 4.
6. Click Back.
The domain names that you added are listed on the DNS Global
Configuration page. See Figure 60 on page 104.
Deleting a DNS
Name
To delete a DNS name from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS > Global
Configuration.
The DNS Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
60 on page 104.
2. Check the Remove checkbox of the domain name.
3. Click Delete.
The domain name is deleted from the list.
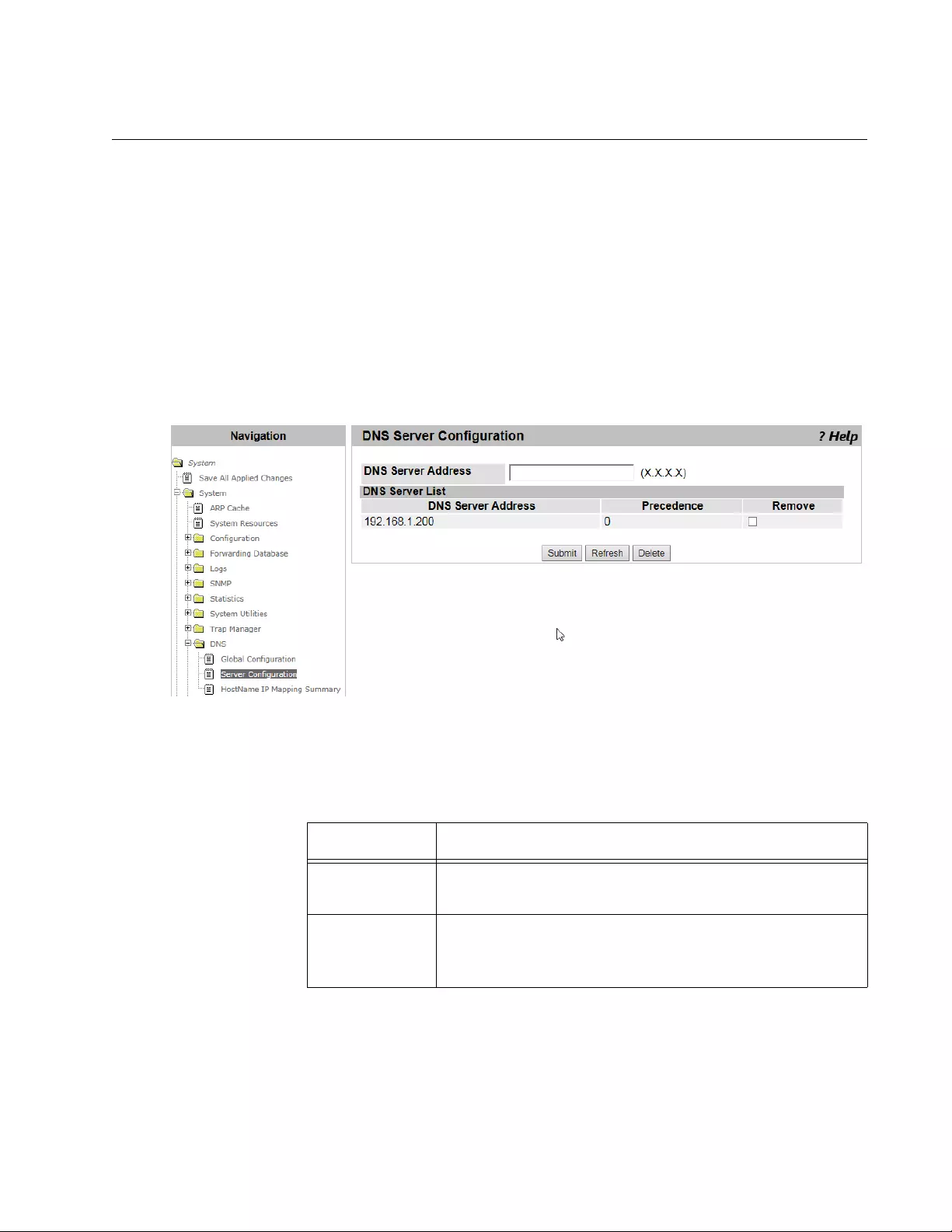
Chapter 2: System
107
DNS Server Configuration
From the DNS Server Configuration page, you can view the DNS server
list, add or delete a DNS server where the system sends queries in order
to resolve host names. You can add multiple DNS servers.
Viewing the DNS
Server List
To view the DNS server list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > DNS Server
Configuration.
The DNS Server Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 62.
Figure 62. DNS Server Configuration Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 26.
Adding a DNS
Server
To add a DNS server, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > DNS > DNS Server
Configuration.
Table 26. DNS Server List
Field Description
DNS Server
Address
Displays the IPv4 address of a DNS server.
Preference Displays the priority number of the DNS server. The
DNS client tries to access a DNS server with a smaller
preference number first.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
108
The DNS Server Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
62 on page 107.
2. Specify the IP address of a DNS server in the DNS Server Address
box.
3. Click Submit.
The DNS server is added to the DNS server List.
Deleting a DNS
Server
To delete a DNS server from the DNS server list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS > Server
Configuration.
The DNS Server Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
62 on page 107.
2. Check the Remove checkbox of the domain name.
3. Click Delete.
The domain name is deleted from the list.
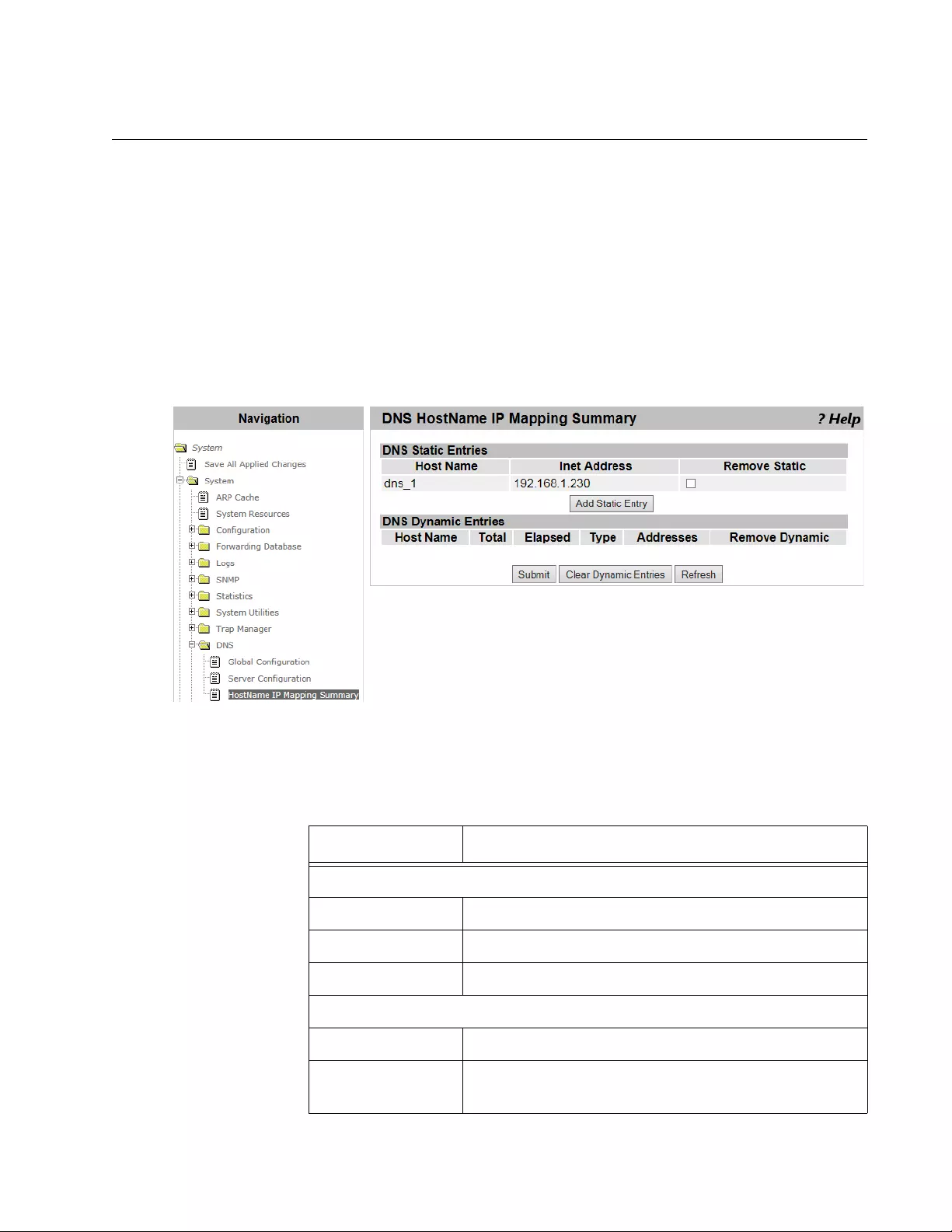
Chapter 2: System
109
HostName IP Mapping Summary
From the HostName IP Mapping Summary page, you can view the DNS
static and dynamic entries, add a static entry, and delete the entries.
Viewing DNS
Static and
Dynamic Entries
To view the DNS entries, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS >
HostName IP Mapping Summary.
The DNS HostName IP Mapping Summary page is displayed as
shown in Figure 63.
Figure 63. DNS HostName IP Mapping Summary Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 27.
Table 27. DNS HostName IP Mapping Summary
Field Description
DNS Static Entries
Host Name Displays the domain name entered manually.
Inet Address Displays the IP address of the host.
Remove Static Check the checkbox to remove the host.
DNS Dynamic Entries
Host Name Displays the domain name obtained dynamically.
Total Displays the time duration in seconds that the host
remains on the list.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
110
3. If you want to display the most current information, click Refresh.
Adding a Static
Entry
To add a static entry do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS >
HostName IP Mapping Summary.
The DNS HostName Mapping Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 63 on page 109.
2. Click Add Static Entry.
The DNS HostName IP Mapping Configuration page is displays as
shown in Figure 64.
Figure 64. DNS HostName IP Mapping Configuration Page
3. Specify the following fields described in Table 28.
Elapsed Displays the time duration in seconds that the entry
has stayed on the list.
Type Displays the type of the entry.
Address Displays the IP address of the host.
Remove Dynamic Check the checkbox to remove the host.
Table 27. DNS HostName IP Mapping Summary (Continued)
Field Description
Table 28. DNS HostName IP Mapping Configuration
Field Description
Host Name Specify the name of the host.

Chapter 2: System
111
4. Click Submit.
The domain and its IP address are entered in to the DNS HostName IP
Mapping.
Deleting a DNS
Static Entry
To delete a DNS static entry, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS >
HostName IP Mapping Summary.
The DNS HostName Mapping Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 63 on page 109.
2. Check the Remove Static checkbox of the entry that you want to
delete.
3. Click Submit.
The entry is deleted from the list.
Deleting All the
DNS Dynamic
Entries
To delete all the DNS dynamic entries, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > DNS >
HostName IP Mapping Summary.
The DNS HostName Mapping Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 63 on page 109.
2. Click Clear Dynamic Entries.
The dynamic entries are all deleted.
Inet Address Specify the IP address of the host.
Table 28. DNS HostName IP Mapping Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
112
SNTP Global Configuration
From the SNTP Global Configuration page, you can enable or disable the
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client on the WLAN Controller and
modify the settings. SNTP synchronizes the system time on the WLAN
Controller with an SNTP server.
To enable or disable the SNTP client on the WLAN Controller, or modify
the settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNTP > Global
Configuration.
The SNTP Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 65.
Figure 65. SNTP Global Configuration Page
2. Specify the following fields in Table 29 on page 113.
Chapter 2: System
113
.
3. Click Submit.
Table 29. SNTP Global Configuration
Field Description
Client Mode Select one of the options:
Disabled — Disables the SNTP client. This is
the default setting.
Unicast — The SNTP client sends time
requests to the specified SNTP server. To set
an SNTP server, see “SNTP Server
Configuration” on page 117.
Broadcast — The SNTP client listens for
broadcast messages and synchronizes the
system time to the clock of the SNTP server
that the SNTP client received the first
broadcast message from.
Port Specifies the UDP port number used to send time
requests in the unicast mode and receive broadcasts
in the broadcast mode. The default port number is
123.
Unicast Poll
Interval
Specify how frequently the SNTP client sends time
requests in the unicast mode. The range is 6 to 10.
The default value is 6. The interval is 2 to the power
the number specified. The options are:
6 — 64 (26) seconds
7 — 128 (27) seconds
8 — 256 (28) seconds
9 — 512 (29) seconds
10 — 1024 (210) seconds
Broadcast poll
Interval
Not Supported.
Unicast Poll
Timeout
Specify the time period in seconds for the SNTP client
to wait for a reply from an SNTP server. The range is
1 to 30 seconds. The default setting is 5 seconds.
Unicast Poll
Retry
Specify how many times the SNTP client tries to send
a request to an SNTP server before sending requests
to another SNTP server. The range is 0 to 10 times.
The default setting is 1 time.
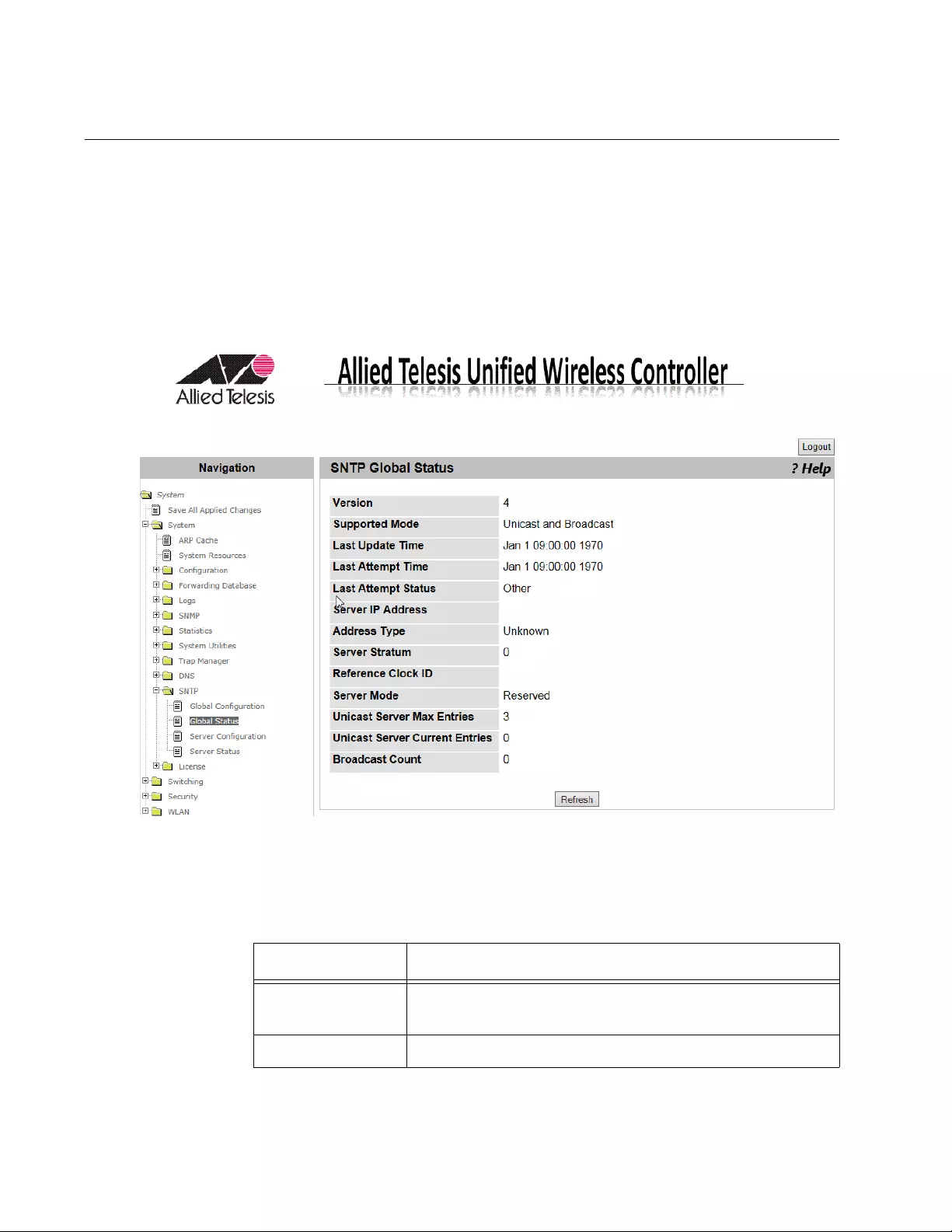
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
114
SNTP Global Status
From the SNTP Global Status page, you can view the SNTP status on the
WLAN Controller.
To view the SNTP client information, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNTP > Global Status.
The SNTP Global Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 66.
Figure 66. SNTP Global Status Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 30.
Table 30. SNTP Global Status
Field Description
Version Displays the version number of the SNTP client on the
WLAN Controller.
Supported Mode Displays the modes that the SNTP client supports.
Chapter 2: System
115
Last Update Time Displays the last time when the SNTP client updated
the system time on the WLAN Controller.
Last Attempt
Time
Displays the last time when the SNTP client sent a
time request or received a message.
Last Attempt
Status
Displays one of the following options as the status of
the last attempt:
Success — SNTP successfully synchronized
the system time.
Request Timed Out — The SNTP client did
not receive a reply to the last request.
Bad Data Encoded — The time from the
SNTP server was invalid.
Version Not Supported — The versions of the
SNTP client and server are not compatible.
Server Unsynchronized — The SNTP server
is not synchronized to the peers, such as other
NTP servers and the local clock. The SNTP
server notifies this status to the client using the
leap indicator (LI) field of the message.
Server Kiss of Death — The SNTP server
stops accepting requests from SNTP clients.
The SNTP server notifies this status to the
client using the stratum field of the message set
to zero.
Server IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the SNTP server where the
SNTP client received the last valid time message
Address Type Displays the address type of the SNTP server.
Server Stratum Displays the stratum value of the SNTP server where
the SNTP client received the last valid time message.
Reference Clock
ID
Displays the ID of the clock that the SNTP server
refers to. It is normally the name of the NTP server
connected to the SNTP server.
Server Mode Displays the server mode of the SNTP server.
Unicast Server
Max Entries
Displays the maximum number of SNTP servers that
the SNTP client is allowed to register.
Unicast Server
Current Entry
Displays the number of valid SNTP servers that the
SNTP client currently registered.
Table 30. SNTP Global Status (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
116
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Broadcast Count Displays the number of time messages that the SNTP
client received since the WLAN Controller last
rebooted.
Table 30. SNTP Global Status (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
117
SNTP Server Configuration
From the SNTP Server Configuration page, you can add an SNTP server.
SNTP synchronizes the system time on the WLAN Controller with the
SNTP server.
To add an SNTP server on the WLAN Controller, or modify the settings, do
the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > System > SNTP > Server
Configuration.
The SNTP Server Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 67.
Figure 67. SNTP Server Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 31.
Table 31. SNTP Server Configuration
Field Description
Server Select the action. The action Create is only the
option.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
118
3. Click Submit.
Address /
Hostname
Enter the IPv4 address or host name of the SNTP
server, depending on the address type selected
below.
Address Type Select one of the following types:
IPv4: Specifies the SNTP server with its IPv4
address.
DNS: Specifies the SNTP server with its host
name.
Port Specify the UDP port number used to send time
requests in the unicast mode and receive broadcasts
in the broadcast mode. The default port number is
123.
Priority Specify the priority of the SNTP server. When the
SNTP client has more than one SNTP server
registered, it sends requests to an SNTP server
based on the priority number.
An SNTP server with a smaller priority number has a
higher priority. When multiple SNTP servers have the
same priority, the first listed SNTP server list.
Version Specify the version of the SNTP server.
Table 31. SNTP Server Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
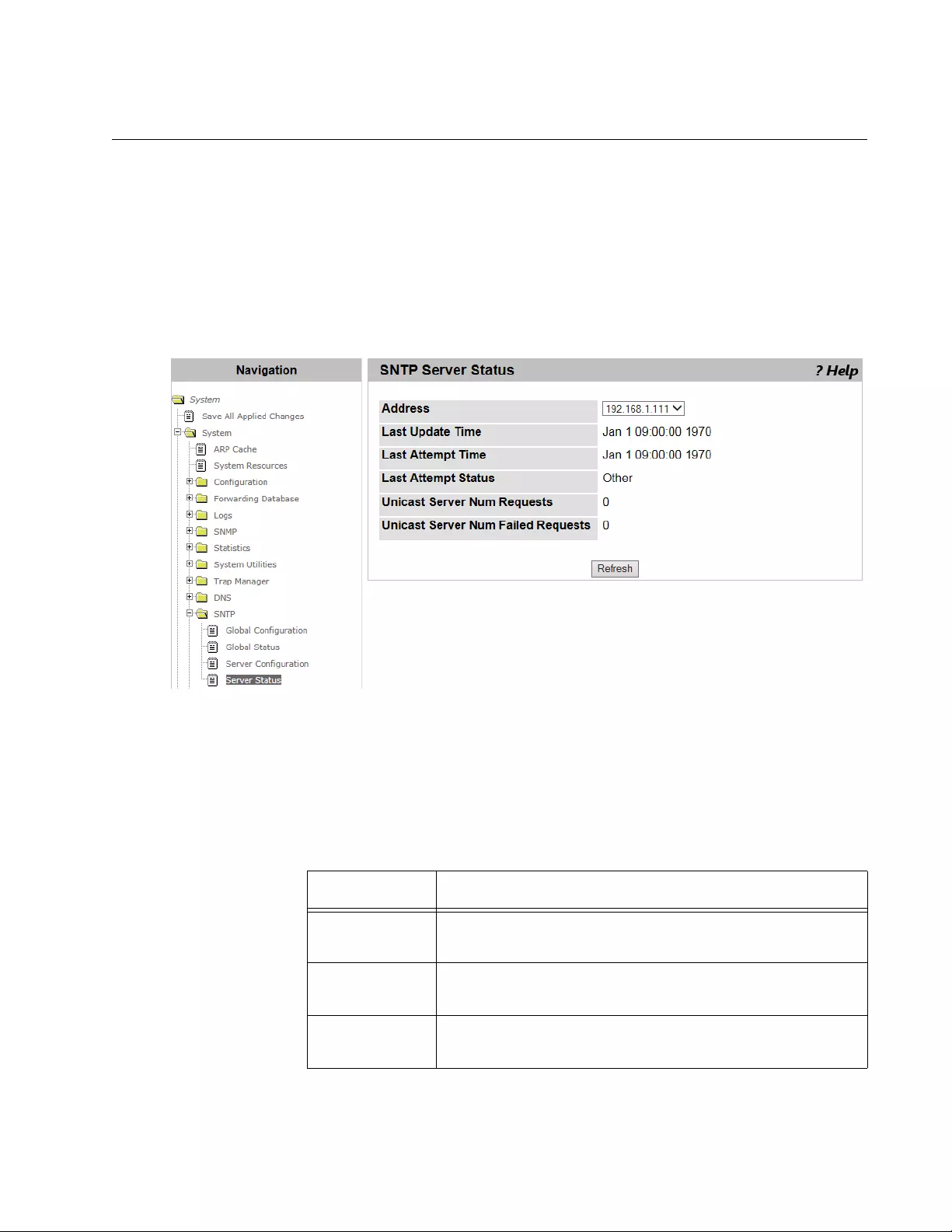
Chapter 2: System
119
SNTP Server Status
From the SNTP Server Status page, you can view the registered SNTP
servers on the WLAN Controller.
To view a list of the SNTP servers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > SNTP > Server Status.
The SNTP Server Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 68.
Figure 68. SNTP Server Status Page
2. Select the IP address of the SNTP server that you want to view from
the Address select list.
3. Observed the fields described in Table 32.
Table 32. SNTP Server Status
Field Description
Address Select an SNTP server address. The information about
the SNTP server is displayed.
Last Update
Time
Displays the last time when SNTP updated the system
time on the WLAN Controller.
Last Attempt
Time
Displays the last time when the SNTP client sent a
time request to the SNTP server.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
120
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Last Attempt
Status
Displays one of the following options as the status of
the last attempt:
Success — SNTP successfully synchronized
the system time.
Request Timed Out — The SNTP client did
not receive a reply to the last request from the
SNTP server.
Bad Data Encoded — The time from the
SNTP server was invalid.
Version Not Supported — The versions of the
SNTP client and server were not compatible.
Server Unsynchronized — The SNTP server
is not synchronized to the peers, such as other
NTP servers and the local clock. The SNTP
server notifies this status to the client using the
leap indicator (LI) field of the message.
Server Kiss of Death — The SNTP server
stops accepting requests from SNTP clients.
The SNTP server notifies this status to the
client using the stratum field of the message
set to zero.
Unicast
Server Num
Requests
Displays the number of SNTP requests that the SNTP
client sent.
Unicast
Server Num
Failed
Requests
Displays the number of SNTP requests with errors.
Table 32. SNTP Server Status (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
121
License
From the License page, you can view information about the currently
registered license, add a license key, or delete an existing license key.
Viewing License
Information
To view information about the currently registered license, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > License > License.
The License Management page is displayed as shown in Figure 69.
Figure 69. License Management Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 33.
Table 33. License Management
Field Description
Country Code Displays the country code of the registered license.
AP License Displays the total number of access point devices that
the WLAN Controller is allowed to manage with the
registered licenses.
Current
Managed AP
Displays the number of access point devices that the
WLAN Controller is currently managing.
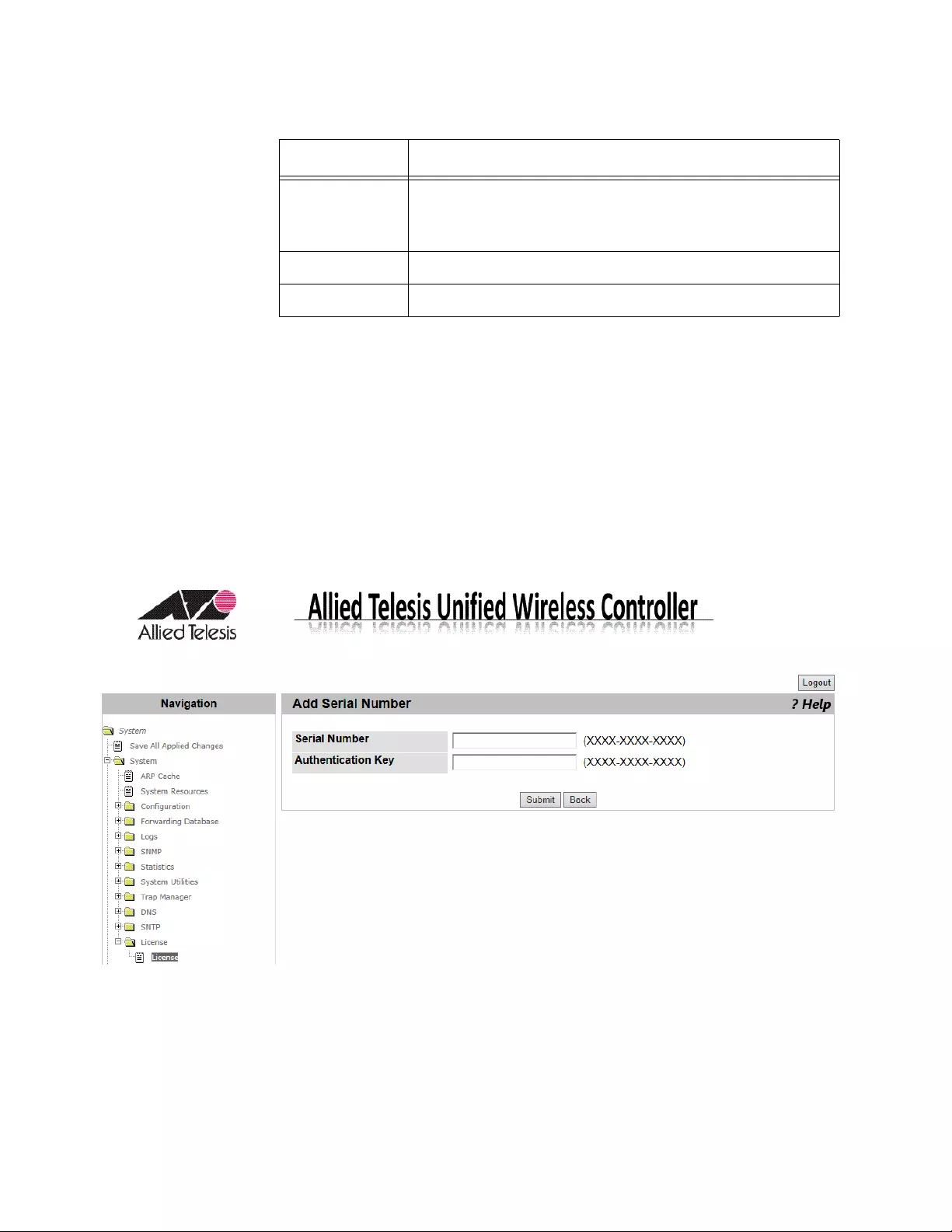
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
122
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Adding License
Key
To add a license key, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > License > License.
The License Management page is displayed as shown in Figure 69 on
page 121.
2. Click Add Serial Number.
The Add Serial Number page is displayed as shown in Figure 70.
Figure 70. Add Serial Number Page
3. Enter your serial number and an authentication key.
The license key consists of a serial number and authentication key.
4. Click Submit.
Serial Number Displays the serial number of the registered license.
The license key consists of a serial number and an
authentication key.
Description Displays the name of the license key.
Remove Check the checkbox to remove the license key.
Table 33. License Management (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 2: System
123
Note
After adding the first license key, you must reboot the AT-UWC
WLAN Controller server to make the license effective. See “System
Reset” on page 82.
Deleting License
Key
To delete a license key, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > License > License.
The License page is displayed as shown in Figure 69 on page 121.
2. Check the Remove checkbox of the license that you want to delete.
3. Click Submit.
The license key is deleted.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
124
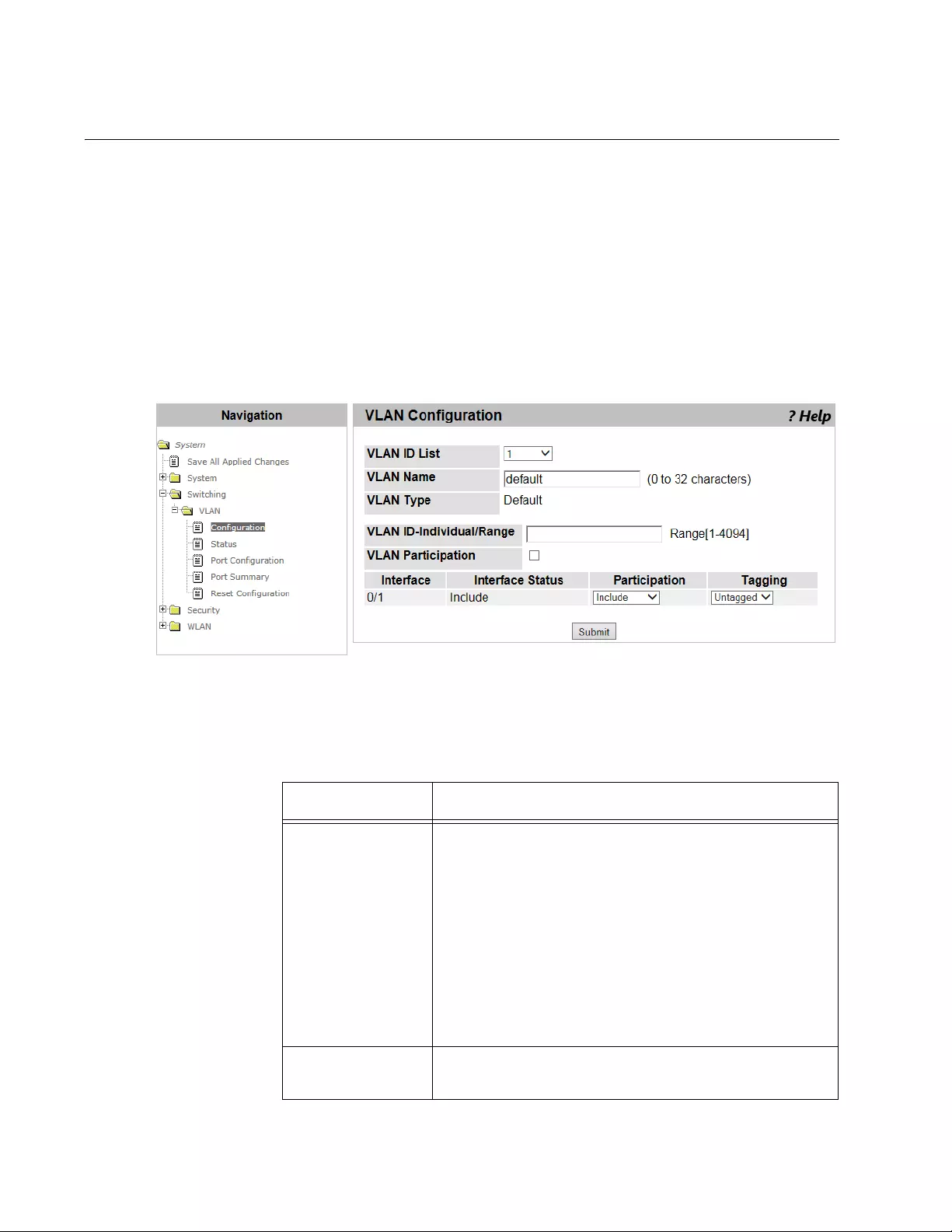
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
126
VLAN Configuration
From the VLAN Configuration page, you can modify the properties of
VLAN’s, add and delete VLAN’s. You can modify, add, and delete single
VLAN or multiple VLAN’s at a time.
Modifying the
VLAN Properties
To modify the properties of VLAN, such as a VLAN name and tagging
status, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching > VLAN > Configuration.
The VLAN Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 71.
Figure 71. VLAN Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 34.
Table 34. VLAN Configuration
Field Description
VLAN ID List Select one of the following options from the select
list:
1 - Modifies the properties of the default
VLAN.
VLAN_ID: Modifies the properties of the
selected VLAN.
Create - Moves to the page to add VLAN’s.
Delete - Moves to the page to delete
VLAN’s.
VLAN Name Specifies the VLAN name. You cannot modify the
VLAN name of the default VLAN, which is VLAN 1.
Chapter 3: Switching
127
3. Click Submit.
The properties of the VLAN(‘s) are updated.
Creating a VLAN To create a new VLAN, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching > VLAN > Configuration.
VLAN Type Displays the VLAN type. The options are:
Default - Default VLAN
Static - Manually added VLAN
Dynamic - Automatically added VLAN
VLAN ID-
Individual/Range
Enter a range of VLAN ID’s. For example,
10-20
When you modify the properties of multiple VLAN’s,
click the VLAN Participation checkbox before
enter the range.
VLAN
Participation
Check the checkbox if you want to modify the
properties of multiple VLAN’s with the same values.
Interface Displays the name of the port interface for the
VLAN.
Interface Status Displays the current setting of the participation
described below.
Participation Specify whether the VLAN is assigned to a port.
Select one of the following options:
Include - Adds the port interface to a
member of the VLAN(‘s).
Exclude - Removes the port interface from
the VLAN membership.
Autodetect - Not supported.
Tagging Displays whether the port with the VLAN
membership is untagged or tagged.
Untagged - Removes a tag from frames
that are sent to the VLAN(‘s). This is the
default setting.
Tagged - Adds a tag to frames that are sent
to the VLAN(‘s).
Table 34. VLAN Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
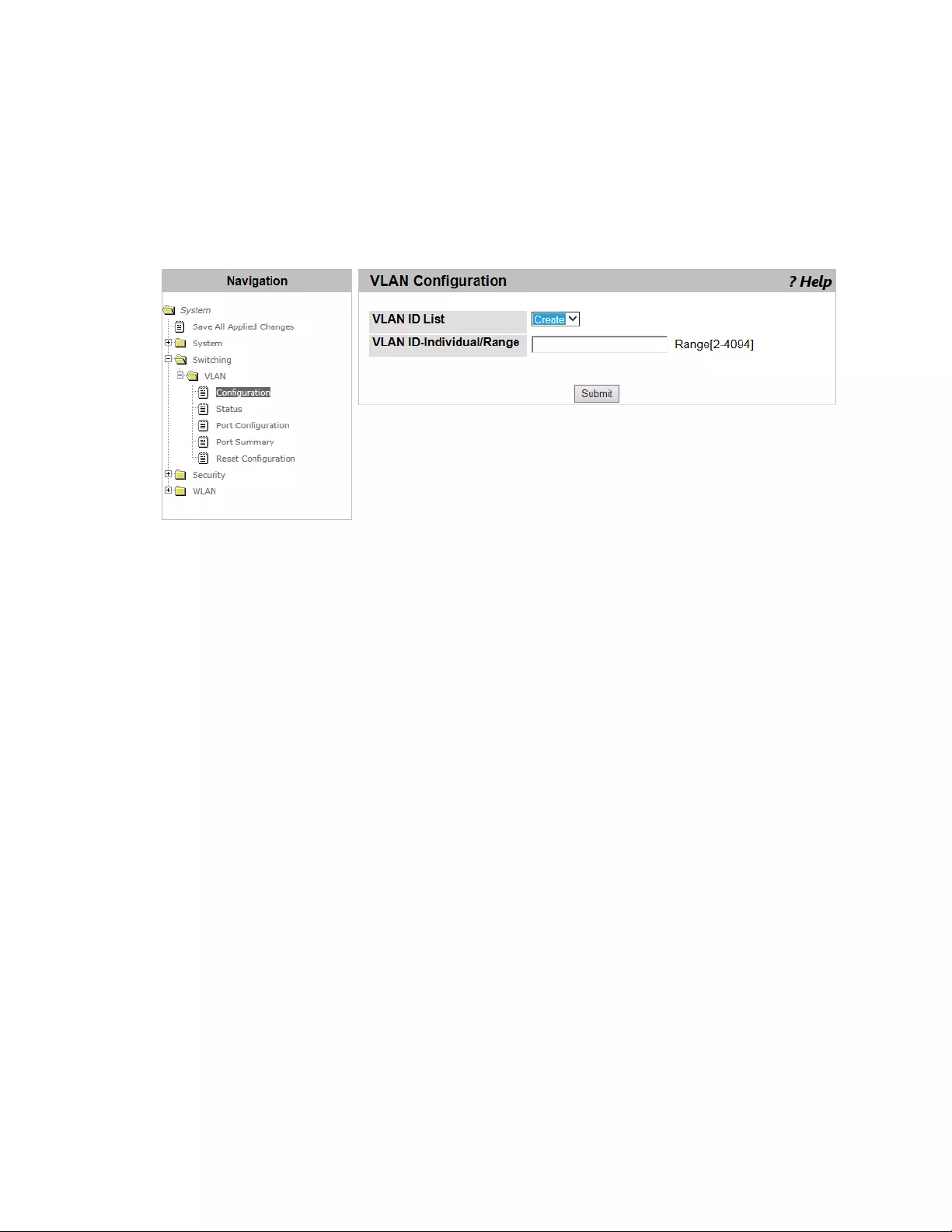
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
128
The VLAN Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 71 on
page 126.
2. Select Create from the VLAN ID select list.
The VLAN Configuration (Create) page is displayed as shown in
Figure 72.
Figure 72. VLAN Configuration (Create) Page
3. Enter the range of VLAN’s in the VLANID-Individual/Range box.
For example, enter “10-15.”
4. Click Submit.
The VLAN’s, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 are created.
5. If you want to change the properties of the VLAN’s that you just
created, see “Modifying the VLAN Properties” on page 126.
Deleting VLAN’s To delete VLAN’s, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching > VLAN > Configuration.
The VLAN Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 71 on
page 126.
2. Select Delete from the VLAN ID select list.
The VLAN Configuration (Delete) page is displayed as shown in Figure
73 on page 129.
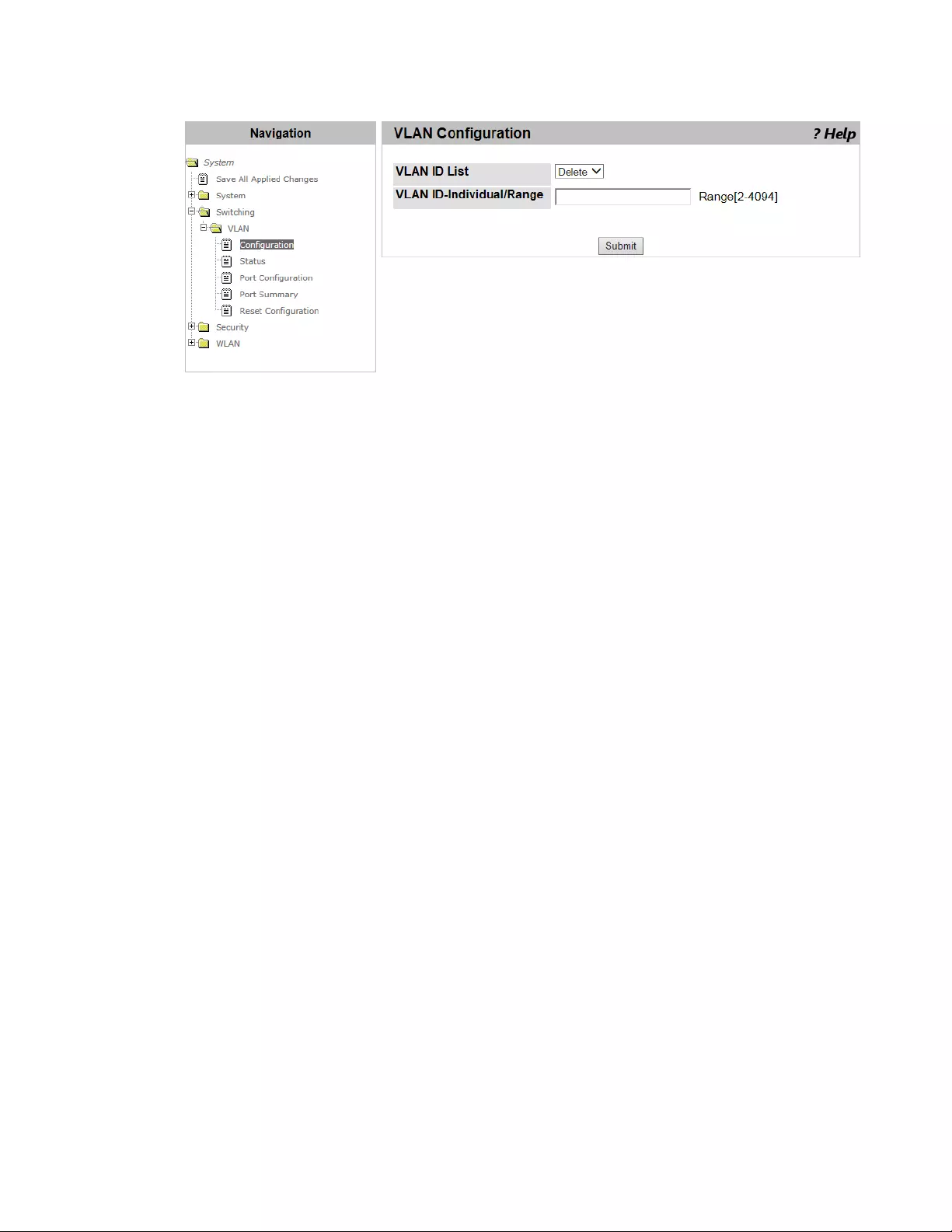
Chapter 3: Switching
129
Figure 73. VLAN Configuration (Delete) Page
3. Enter the range of VLAN’s in the VLANID-Individual/Range box.
For example, enter “10-15.”
4. Click Submit.
The VLAN’s, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 are deleted.
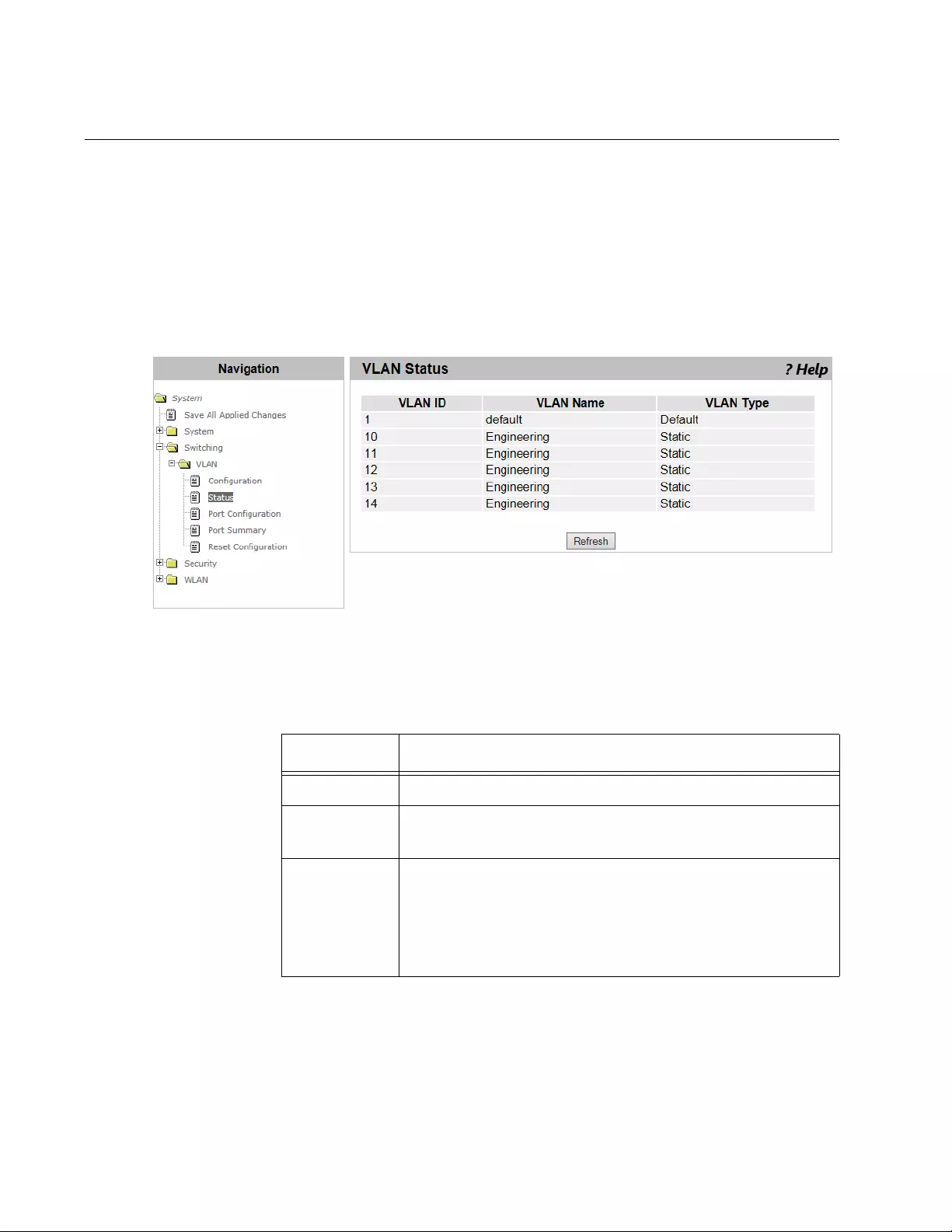
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
130
VLAN Status
From the VLAN Status page, you can view the information about VLAN’s
on the WLAN Controller.
To view the information about VLAN’s, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, click Switching > VLAN > Status.
The VLAN Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 74.
Figure 74. VLAN Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 35.
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Table 35. VLAN Status
Field Description
VLAN ID Displays the ID of the VLAN.
VLAN Name Displays the name of the VLAN. The VLAN ID 1 is
always “default.”
VLAN Type Displays the following VLAN types:
Default - Indicates that the VLAN is default
VLAN, which is the VLAN ID 1.
Static - Indicates the VLAN is manually created.
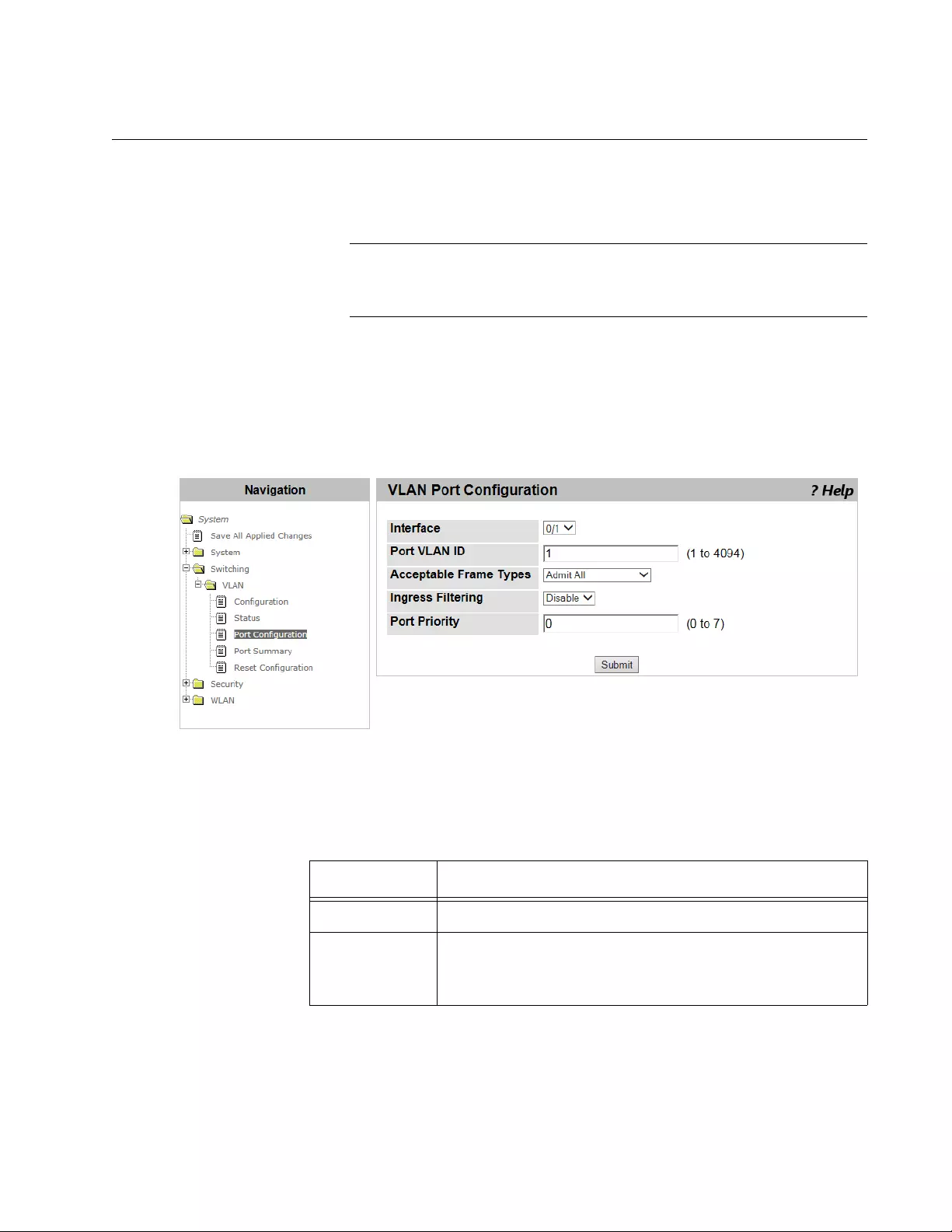
Chapter 3: Switching
131
VLAN Port Configuration
From the VLAN Port Configuration page, you can modify the properties of
the port interface.
Note
The WLAN Controller has only one port interface that you can
modify its properties.
To modify the port interface 0/1, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching > VLAN > Port
Configuration.
The VLAN Port Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 75.
Figure 75. VLAN Port Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 36.
Table 36. VLAN Port Configuration
Fields Description
Interface Select “0/1.” The other option is not supported.
Port VLAN ID Specify a VLAN ID. The port applies this VLAN ID to
untagged frames and frames with a priority tag. The
default setting is VLAN ID 1.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
132
3. Click Submit.
Acceptable
Frame Types
Specify one of the following options:
Admit ALL - The port accepts any frame
types. It forwards tagged frames as defined in
IEEE802.1Q. This is the default setting.
AdmitTaggedOnly - The port accepts only
tagged frames and forwards them as defined in
IEEE 802.1Q.
AdmitUntaggedOnly - The port accepts only
untagged frames.
Ingress
Filtering
Specify one of the following options for tagged frames:
Enable- The port discards the tagged frames
with other than the specified port VLAN ID.
Disable - The port accepts all tagged frames.
Port Priority Specify a priority to apply untagged frames. The
priority is from 0 to 7. The highest priority is 7.
Table 36. VLAN Port Configuration (Continued)
Fields Description
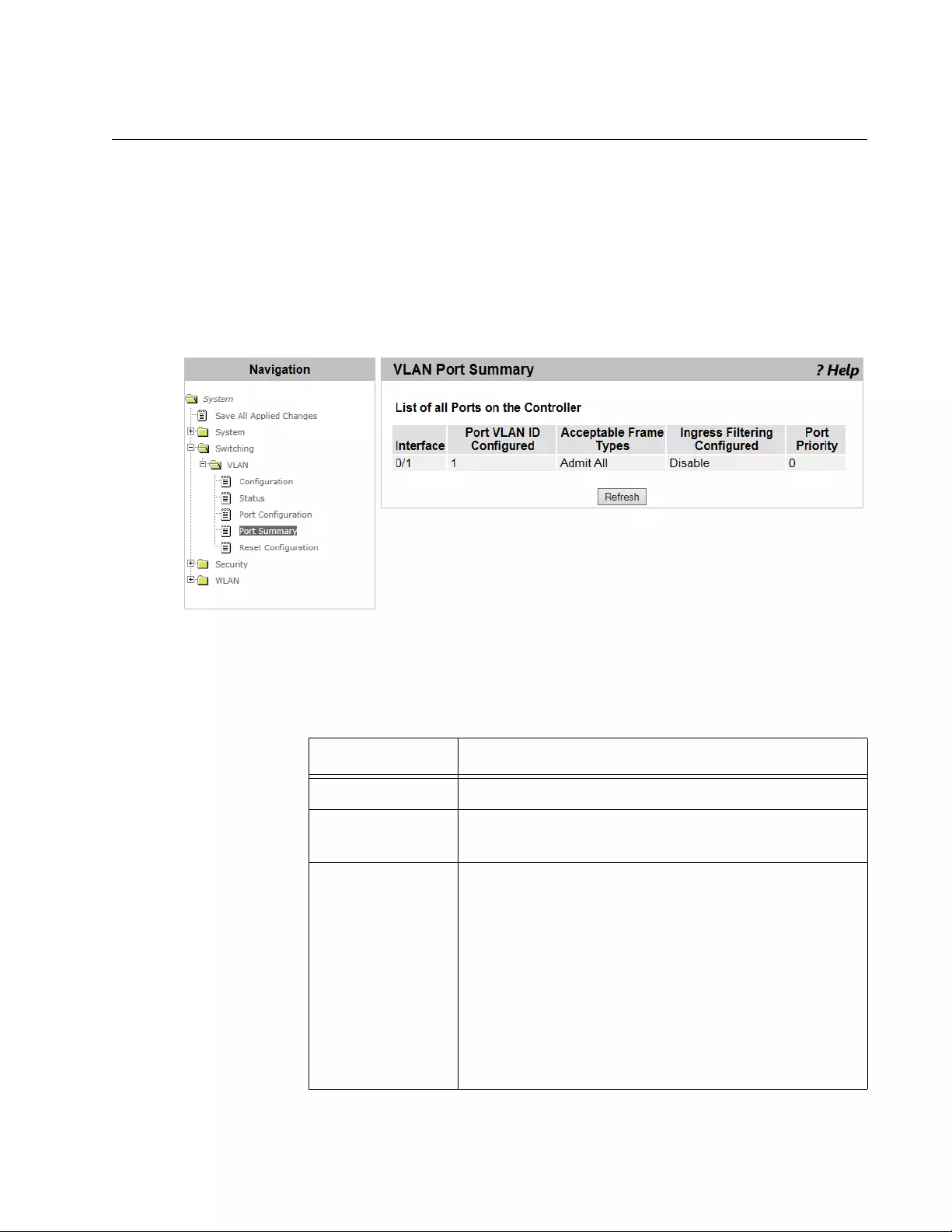
Chapter 3: Switching
133
VLAN Port Summary
From the VLAN Port Summary page, you can view the port setting.
To view the port setting, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching> VLAN > VLAN Port
Summary.
The VLAN Port Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 76.
Figure 76. VLAN Port Summary Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 37.
Table 37. VLAN Port Summary
Field Description
Interface Displays the port interface.
Port VLAN ID
Configured
Indicates the VLAN ID that the port applies to
untagged frames and frames with a priority tag.
Acceptable
Frame Types
Indicates one of the following options:
Admit ALL - The port accepts any frame
types. It forwards tagged frames as defined
in IEEE802.1Q. This is the default setting.
AddmitTaggedOnly - The port accepts only
tagged frames and forwards them as
defined in IEEE 802.1Q.
AddmitUntaggedOnly - The port discards
tagged frames.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
134
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Ingress Filtering
Configured
Indicates one of the following options for tagged
frames:
Enable- The port discards the tagged
frames with other than the specified port
VLAN ID. When receiving untagged frames,
the port applies the specified port VLAN ID
to the frames.
Disable - The port forwards frames as
defined in IEEE802.1Q.
Port Priority Indicates the priority that the port applied to
untagged frames.
Table 37. VLAN Port Summary (Continued)
Field Description
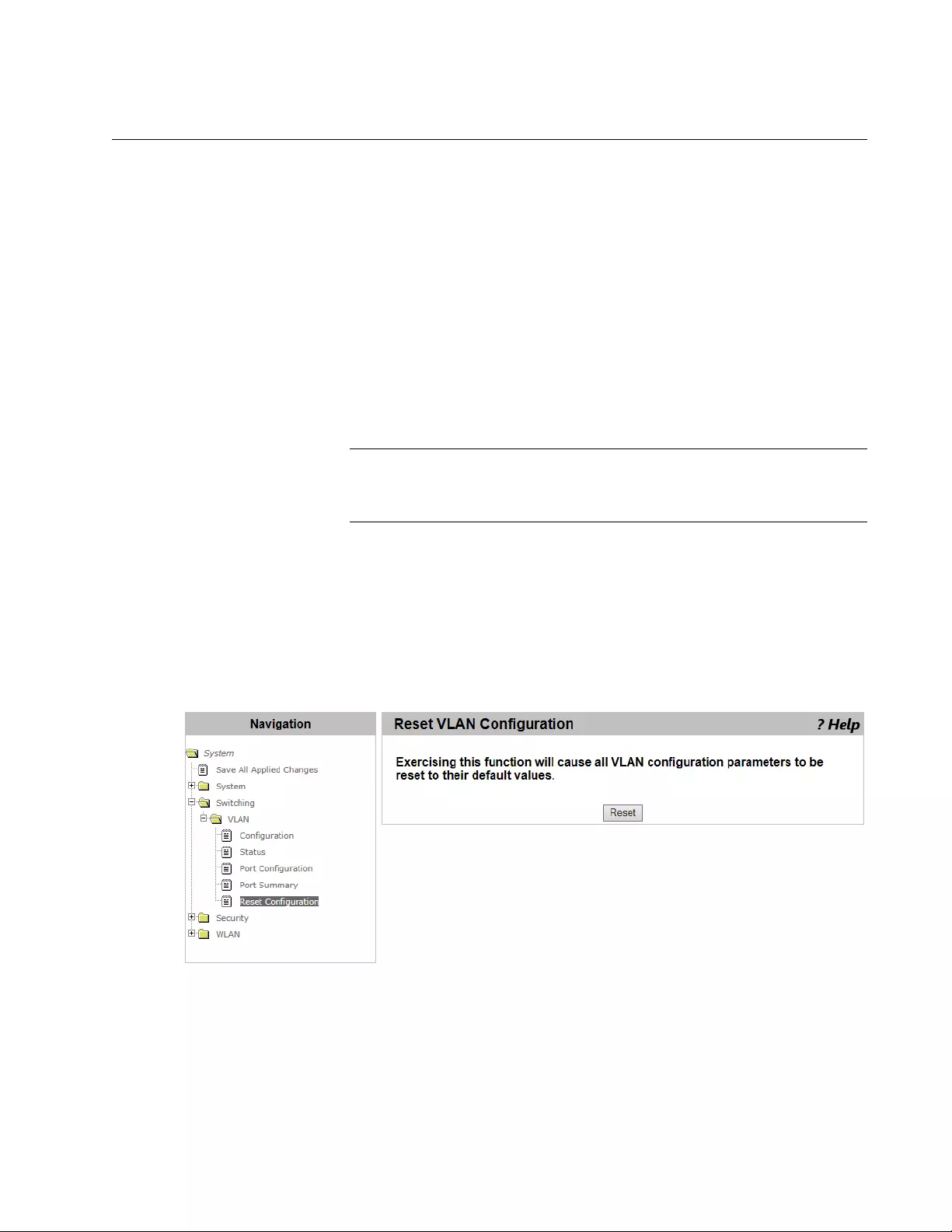
Chapter 3: Switching
135
Reset VLAN Configuration
From the Reset VLAN Configuration page, you can reset the VLAN
configuration to the default settings.
Default VLAN
Settings
Here are the default VLAN settings:
Only VLAN 1 is on the WLAN Controller, which is the default
VLAN.
The Port VLAN ID is set to VLAN 1.
The Acceptable Frame Type on the port is the “Admit All” option.
The Ingress Filtering on the port is set to “disable.”
The port sends only untagged frames.
Note
For the descriptions of VLAN port properties, see Table 37 on
page 133
Resetting the
VLAN
Configuration
To reset the VLAN configuration, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Switching > VLAN > Reset VLAN
Configuration.
The Reset VLAN Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 77.
Figure 77. Reset VLAN Configuration Page
2. Click Reset.
The Reset VLAN Configuration to Factory Defaults page is displayed.
3. Click Reset.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
136

137
Chapter 4
Security
This chapter includes the following topics:
Captive Portal
“CP Global Configuration” on page 138
“CP Configuration Summary” on page 140
“CP Web Customization” on page 146
“Local User Summary” on page 155
“Interface Association” on page 159
“CP Status” on page 161
“Interface Status” on page 164
“Client Connection Status” on page 167
RADIUS
“RADIUS Configuration” on page 172
“RADIUS Server Configuration” on page 175
“RADIUS Named Server Status” on page 176
“RADIUS Server Statistics” on page 178
“Accounting Server Configuration” on page 181
“Named Accounting Server Status” on page 182
“Accounting Server Statistics” on page 184
“RADIUS Clear Statistics” on page 186
Secure HTTP
“Secure HTTP” on page 187
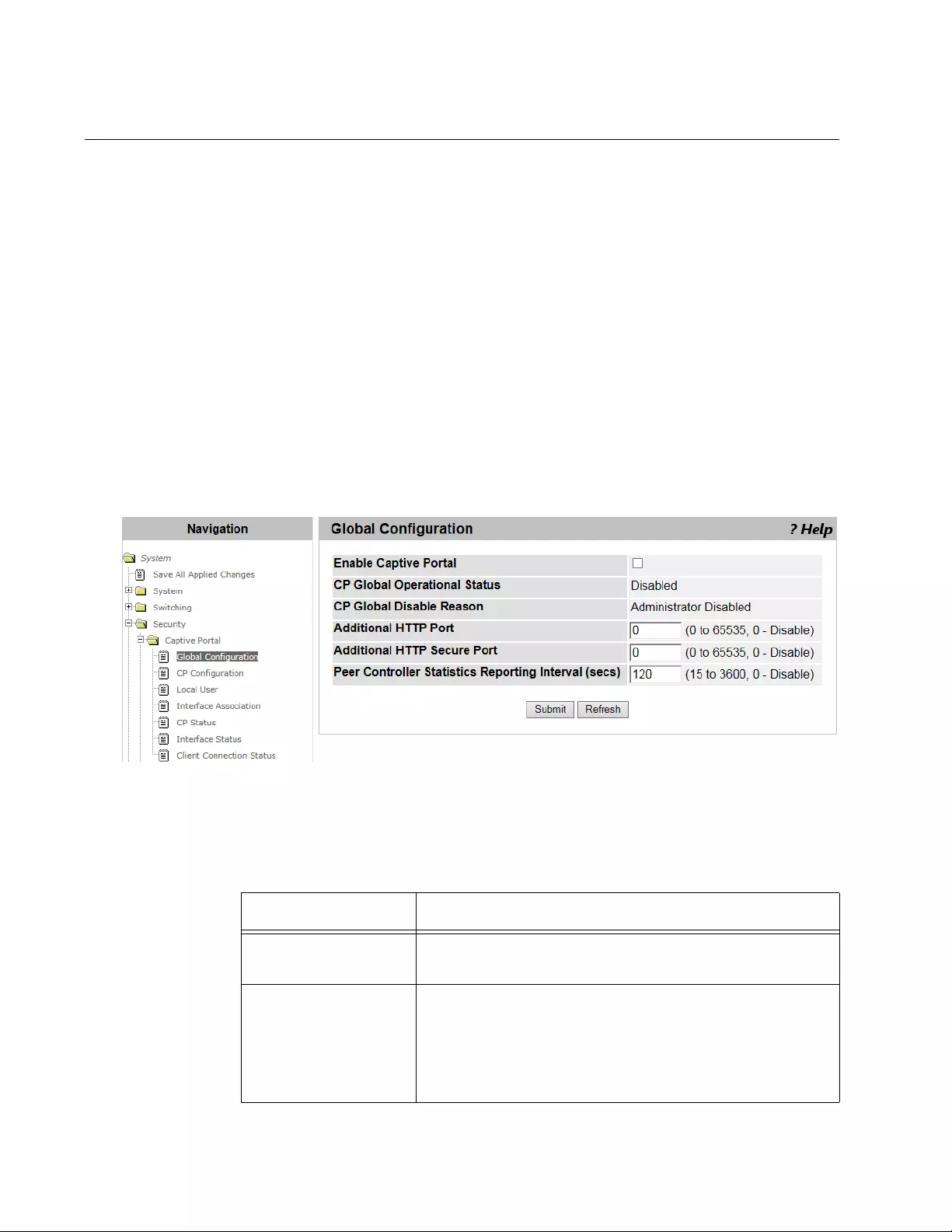
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
138
CP Global Configuration
From the Captive Portal (CP) Global Configuration page, you can enable
Captive Portal, view and modify the CP global configuration on the WLAN
Controller.
Captive Portal is the feature that blocks AP clients from accessing the
network until the AP clients are authenticated. Captive Portal also directs
the user of the AP clients to the authentication web page when the AP
clients send the first HTTP or HTTPS packets.
To enable Captive Portal, view, and modify the CP global configuration, do
the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Global
Configuration.
The CP Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 78.
Figure 78. CP Global Configuration Page
2. Observe or specify the fields described in Table 38.
Table 38. CP Global Configuration
Field Description
Enable Captive
Portal
Check the checkbox to enable Captive Portal.
CP Global
Operational Status
Displays the status of Captive Portal on the WLAN
Controller. The options are:
Enabled
Disabled
Chapter 4: Security
139
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
CP Global Disable
Reason
Displays the reason when Captive Portal is disabled
on the WLAN Controller. The options are:
Administrator Disabled
No IPv4 Address
Routing Enabled, but no IPv4 routing
interface
None - None of the above reasons is
applicable.
Additional HTTP
Port
Specifies the number of other HTTP ports that are
addition to port 80. The value 0 indicates that no
additional HTTP port is specified.
The authentication page can be displayed only using
TCP port 80.
Additional HTTP
Secure Port
Specifies the number of other HTTPS ports that are
addition to port 443. The value 0 indicates that no
additional HTTPS port is specified.
Authentication can be done only using TCP port 443.
Peer Controller
Statistics Reporting
Interval (secs)
Specifies the time interval in seconds that the WLAN
Controller sends statistics information about
authenticated AP clients to the cluster controllers
when clustering is enabled on the WLAN Controller.
Table 38. CP Global Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
140
CP Configuration Summary
From the Captive Portal (CP) Summary page, you can view a list of CP
profiles, add CP profiles, and delete them. You can apply a Captive portal
profile to wireless network interfaces.
Viewing a List of
CP Profiles
To view a list of CP profiles, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Captive Portal > CP
Configuration.
The CP Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 79.
Figure 79. CP Summary Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 39.
Table 39. CP Summary
Field Description
Configuration Displays the name of the CP profile.
Mode Displays the CP mode of the CP profile: Enable or
Disable.
Protocol Displays the protocol that the CP profile uses: HTTP
or HTTPS.

Chapter 4: Security
141
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Adding or Modify
a CP Profile
To add or modify a CP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > CP
Configuration.
The CP Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 79 on page
140.
2. Perform one of the following steps.
To add a new CP profile, click Add.
To modify an existing CP profile, click one of the name of the CP
profile that you wan to modify.
The CP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 80 on
page 142.
Verification Displays the verification type of the CP profile. The
options are:
Guest - No verification is implemented.
Local - Verification is implemented on the
specified local users.
RADIUS server - Verification is implemented
by the RADIUS server.
Languages Displays the number of languages for the welcome
page specified to the CP profile.
Table 39. CP Summary (Continued)
Field Description
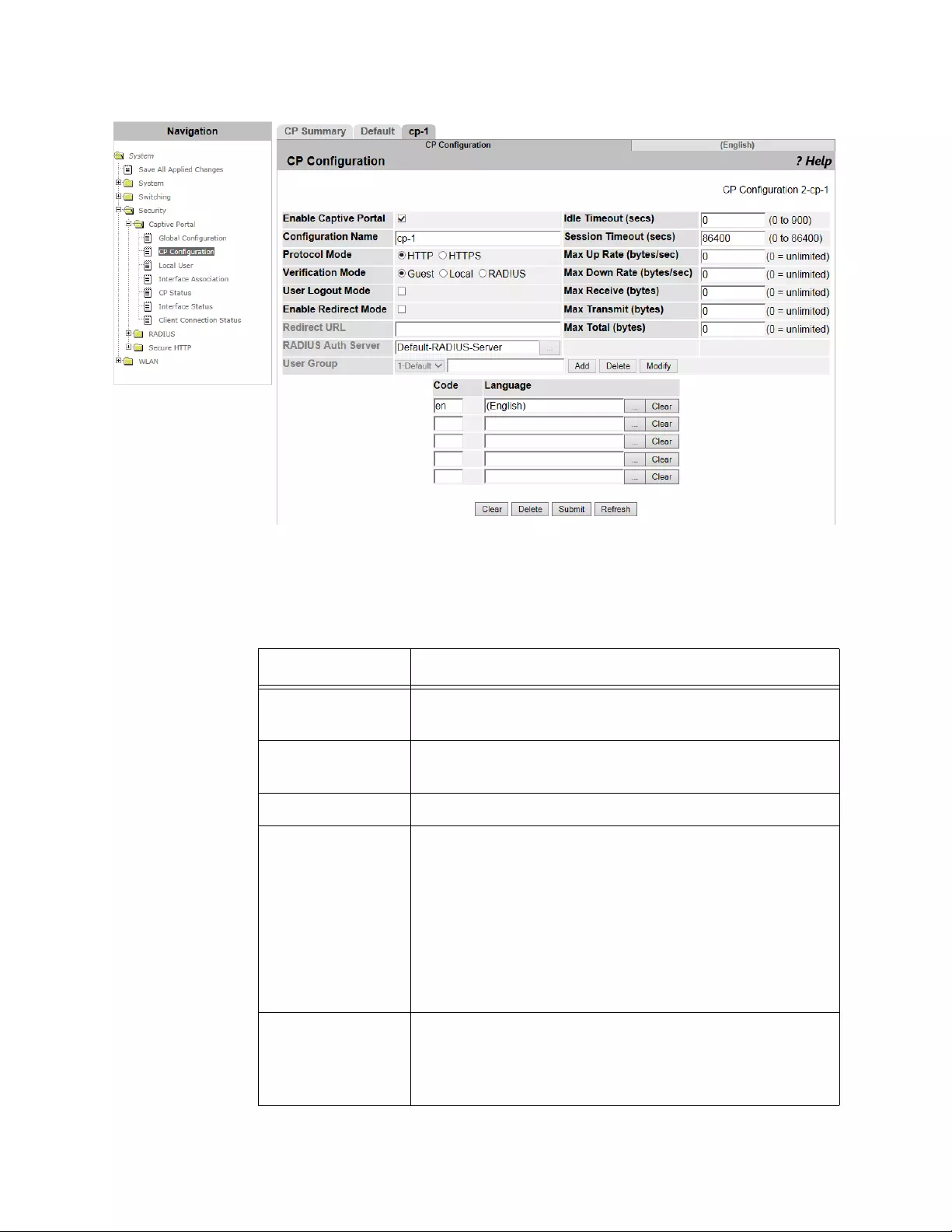
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
142
Figure 80. CP Configuration Page
3. Specify the fields described in Table 40.
Table 40. CP Configuration
Field Description
Enable Captive
Portal
Check the checkbox to enable the CP profile.
Configuration
Name
Specify the name of the CP profile.
Protocol Mode Select the protocol mode: HTTP or HTTPS.
Verification Mode Select the verification type of the CP profile. The
options are:
Guest - No verification is implemented.
Local - Verification is implemented on the
specified local users. See...
RADIUS server - Verification is implemented
by the RADIUS server.
Mode Check the checkbox to allow a user of the AP client to
cancel verification. When the checkbox is unchecked,
the AP client is required for authentication until
Captive Portal cancels the authentication.
Chapter 4: Security
143
Enable Redirect
Mode
Check the checkbox to direct the authenticated clients
to the specified URL. The welcome page in the
specified language is displayed.
Redirect URL Specify the URL that the verified users of the AP client
are directed. You must check the checkbox of Enable
Redirect Mode to specify this field.
RADIUS Auth
Server
Specify or select the name of the RADIUS server
when Verification Mode is set to RADIUS. The WLAN
Controller becomes a RADIUS client and implements
RADIUS transactions for AP clients.
User Group Assigns an existing user group to the CP profile. You
can also adds and delete a user group. Users in the
User Group can access the network through Captive
Portal.
Perform the one of the following tasks as needed:
To add a new user group, enter a group name
and click Add.
To modify the user group, select a user group
from the select list, enter a new group name,
and click Modify.
To delete a user group, select a user group
from the select list and click Delete.
Here are guidelines:
The user group can be assigned when
Verification Mode is Local or RADIUS.
The newly added user group is not
automatically assigned to the CP profile. You
must select the new user group from the select
list after creating one.
To add users to the user group, see “Adding or
Modify a Local User” on page 155.
Idle Timeout
(secs)
Specify the time period in seconds to allow a user of
the AP client to stay connected when no interaction is
made. When Idle Timeout has passed without
interaction from the user, the user is automatically
logged out.
Table 40. CP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
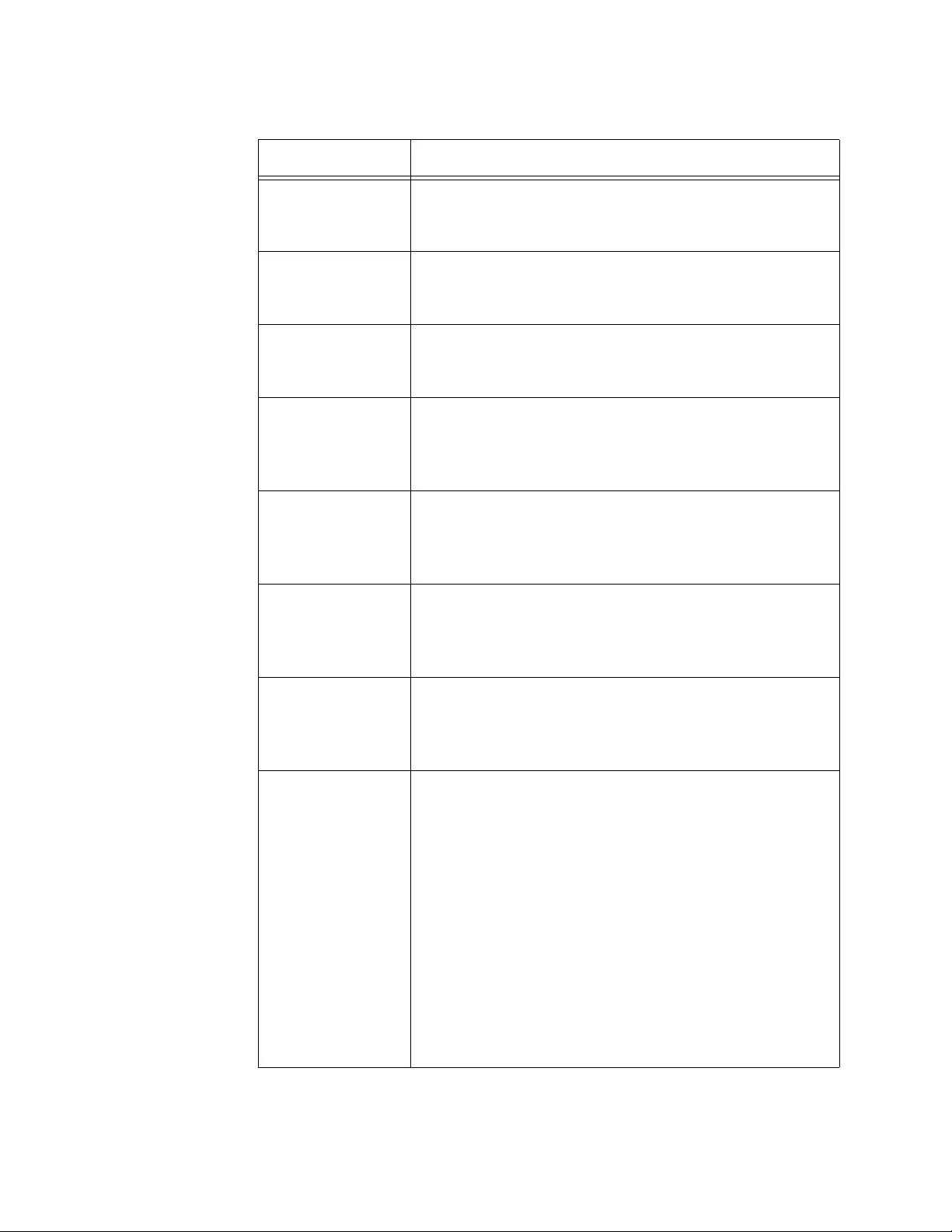
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
144
4. Click Submit.
Session Timeout
(secs)
Specify the time period in seconds to allow a user to
stay connected. When Session Timeout has passed,
the user is automatically logged out.
Max Up Rate
(bytes/sec)
Specify the maximum transmission rate that AP clients
send traffic to the network when Captive Portal is
activated.
Max Down Rate
(bytes/sec)
Specify the maximum receiving rate that AP clients
receive traffic from the network when Captive Portal is
activated.
Max Receive
(bytes)
Specify the maximum size in bytes to allow AP clients
to send to the access point when Captive Portal is
activated. When the maximum size is exceeded, the
AP client is disconnected.
Max Transmit
(bytes)
Specify the maximum size in bytes to allow AP clients
to receive from the access point when Captive Portal
is activated. When the maximum size is exceeded, the
AP client is disconnected.
Max Total (bytes) Specify the maximum total size in bytes to allow AP
clients to send and receive when Captive Portal is
activated. The maximum total size is exceeded, the
AP client is disconnected.
Code Specify the code of the language that you want to add.
Enter the value of a subtag, such as “ja” for Japanese
and “fr” for French from the IANA Language Subtag
Registry.
Language Specify the name of the language that you want to
add. You can add up to 5 languages. When the AP
client sends the first HTTP or HTTPS packet, Captive
Portal directs the AP client to the authentication page
in the specified language. If more than one language
is specified, the locale setting of the web browser of
the user determines the language in the authentication
page.
Perform the one of the following tasks as needed:
To select a language from the select list, click
the ... button.
To clear the language row, click Clear.
Table 40. CP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 4: Security
145
The changes are saved.
Deleting a CP
Profile
To delete a CP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > CP
Configuration.
The CP Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 79 on page
140.
2. Check the checkbox of the CP profile that you want to delete.
3. Click Delete.
The CP profile is deleted from the list.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
146
CP Web Customization
From the CP Web Customization page, you can customize the web pages
to be displayed to the browser of AP clients. When the AP client sends the
first HTTP or HTTPS packet, Captive Portal directs the AP client to the
authentication page in the specified language.
You can set the global parameters and four web pages:
Global Parameter
Authentication page
Welcome page
Logout page
Logout Success page
Note
Total size of images that are send to AP clients is up to10 Mbytes.
To customize the settings of the authentication page in the specific
language, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > CP
Configuration.
The CP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 79 on
page 140.
2. Perform one of the following steps.
To add a new CP profile, click Add.
To modify an existing CP profile, click the name of a CP profile that
you want to modify.
The CP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 80 on
page 142.
3. Click the language subtab.
4. The CP Web Customization (Global Parameter) page is displayed as
shown in Figure 81 on page 147.

Chapter 4: Security
147
Figure 81. CP Web Customization (Global Parameter) Page
Global
Parameters
5. Modify the fields described in Table 41.
Table 41. CP Web Customization (Global Parameter)
Field Description
Available Images View the available images, delete an image file, or
download a new image file for the web pages.
Perform one of the following tasks as needed:
To view the image that have already
downloaded, select the file name from the
select list, click the ... button.
To delete an image file, select a file name
from the select list and click Delete.
To download a new image file, click Browse to
select a file and click Download.
Background Image Select the image file for the background on the web
pages.
Branding Image Select the image file for the branding image on the
Web page. The specified image is displayed at the
upper left corner of the web pages.
Fonts Specify the font face to be used in the web pages.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
148
6. Click the following buttons as needed:
Clear — Reset to the default settings.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Authentication
Page
7. Select Authentication Page from the select list under the tab bar.
8. The CP Web Customization (Authentication Page) page is displayed
as shown in Figure 82 on page 149.
Script Text Specify the text to require the user to activate
JavaScript. To display the logout window for AP client
users, JavaScript must be activated.
Script Text is only available when Mode is enabled.
See Table 40 on page 142.
Popup Text Specify the text to require the user to allow popup
windows. To display the logout page for AP client
user, popup windows must be allowed in the web
browser.
Popup Text is only available when Mode is enabled.
See Table 40 on page 142.
Table 41. CP Web Customization (Global Parameter) (Continued)
Field Description
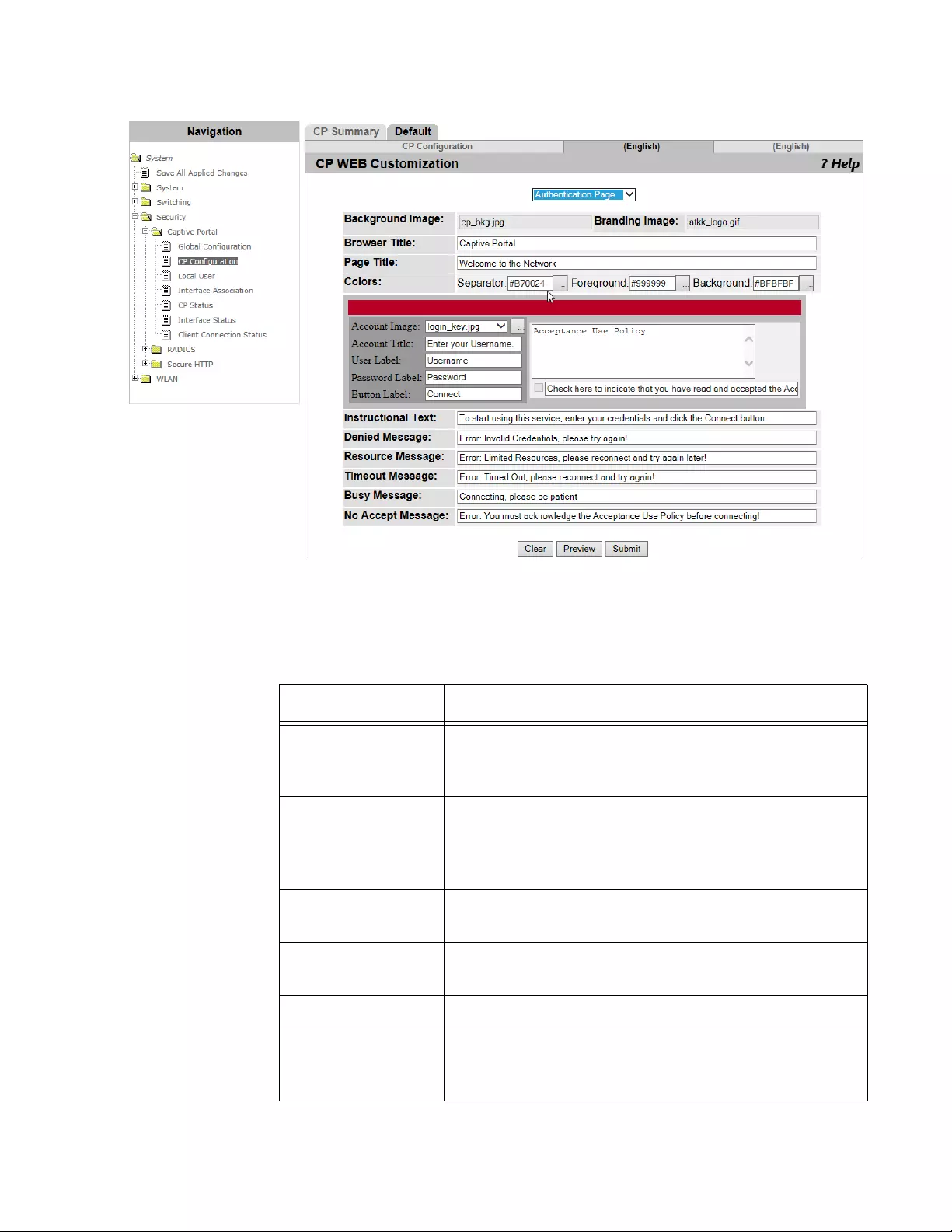
Chapter 4: Security
149
Figure 82. CP Web Customization (Authentication Page) Page
9. Modify the fields described in Table 42.
Table 42. CP Web Customization (Authentication Page)
Field Description
Background Image Displays the image file for the background on the
Authentication page. This image is specified in the
Global Parameters.
Branding Image Displays the image file for the branding image on the
Authentication page. The specified image is
displayed at the upper left corner of the Web page.
This image is specified in the Global Parameters.
Browser Title Specify the title to be displayed on the title bar or tab
of the Authentication page.
Page Title Specify the title to be displayed as the page title on
the Authentication page.
Colors Select the colors by clicking the ... button.
Account Image Specify the image file to be displayed above the login
section. The display area is 55 x 310 pixels. The
image is adjusted to be fit in the area.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
150
10. Click the following buttons as needed:
Preview — Displays the web page with the current settings.
Clear — Reset to the default settings.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Account Title Specify the text to prompt the user to authenticate.
User Label Specify the text to be displayed next to the user name
text box.
Password Label Specify the text to be displayed next to the password
text box.
Button Label Specify the text to be displayed on the button to
connect to the network.
Acceptance Use
Policy Text Box
Specify the text to be displayed for the Acceptance
Use Policy that shows the user the acceptance
conditions to connect to the network.
Acceptance
Checkbox Title
Specify the text to be displayed next to the checkbox
for the user to accept the Acceptance Use Policy.
Instructional Text Specify the text for authentication instructions.
Denied Message Specify the text to be displayed when the user does
not meet acceptance conditions.
Resource
Message
Specify the text to be displayed when the
authentication failed due to the lack of system
resource.
Timeout Message Specify the text to be displayed when the
authentication failed because the transaction
exceeded the time limit.
Busy Message Specify the text to be displayed when the
authentication is in process.
No Accept
Message
Specify the text to be displayed when the user did not
check the Acceptance checkbox.
Table 42. CP Web Customization (Authentication Page) (Continued)
Field Description
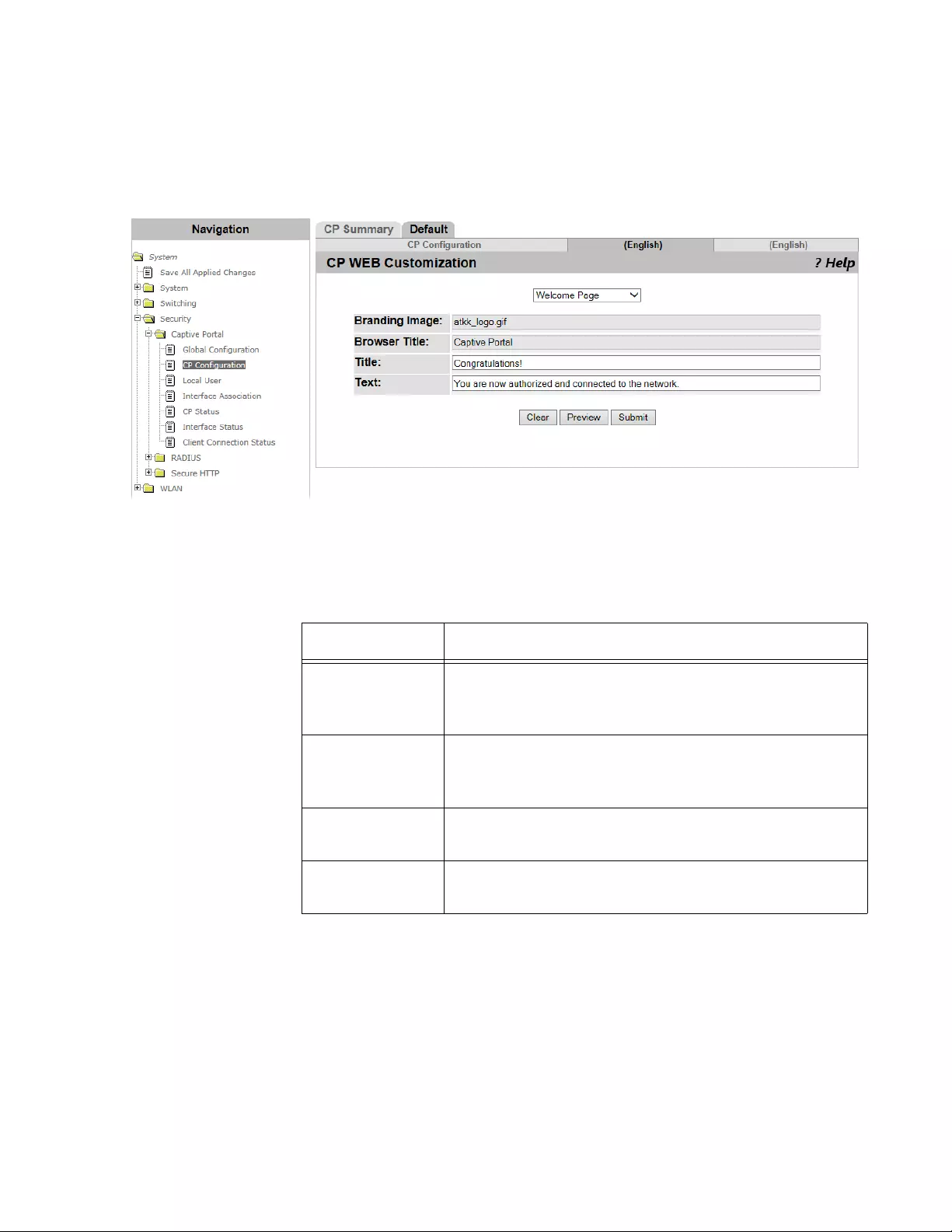
Chapter 4: Security
151
Welcome Page 11. Select Welcome Page from the select list.
12. The CP Web Customization (Welcome Page) page is displayed as
shown in Figure 83.
Figure 83. CP Web Customization (Welcome Page) Page
13. Modify the fields described in Table 43.
14. Click the following buttons as needed:
Preview — Displays the web page with the current settings.
Clear — Reset to the default settings.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Table 43. CP Web Customization (Welcome Page)
Field Description
Background
Image
Displays the image file for the background on the
Welcome page. The image is specified in the Global
Parameters.
Browser Title Displays the title to be displayed as the title bar or tab
of the Welcome page. This title is specified in the
Authentication page.
Title Specify the title to be displayed when the user is
connected to the network.
Text Specify the text to be displayed under the welcome
title.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
152
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Logout Page 15. Select Logout Page from the select list.
You can customize the Logout page settings only when Mode is
enabled. See Table 40 on page 142.
16. The CP Web Customization (Logout Page) page is displayed as
shown in Figure 84.
Figure 84. CP Web Customization (Logout Page) Page
17. Modify the fields described in Table 44.
18. Click the following buttons as needed:
Preview — Displays the web page with the current settings.
Table 44. CP Web Customization (Logout Page)
Field Description
Browser Title Specify the title to be displayed as the title bar of the
Logout page.
Page Title Specify the title to be displayed as the page title.
Instructional Text Specify the text for authentication instructions.
Button Label Specify the text to be displayed on the button to
cancel the authentication.
Confirmation Text Specify the text to confirm canceling the
authentication.
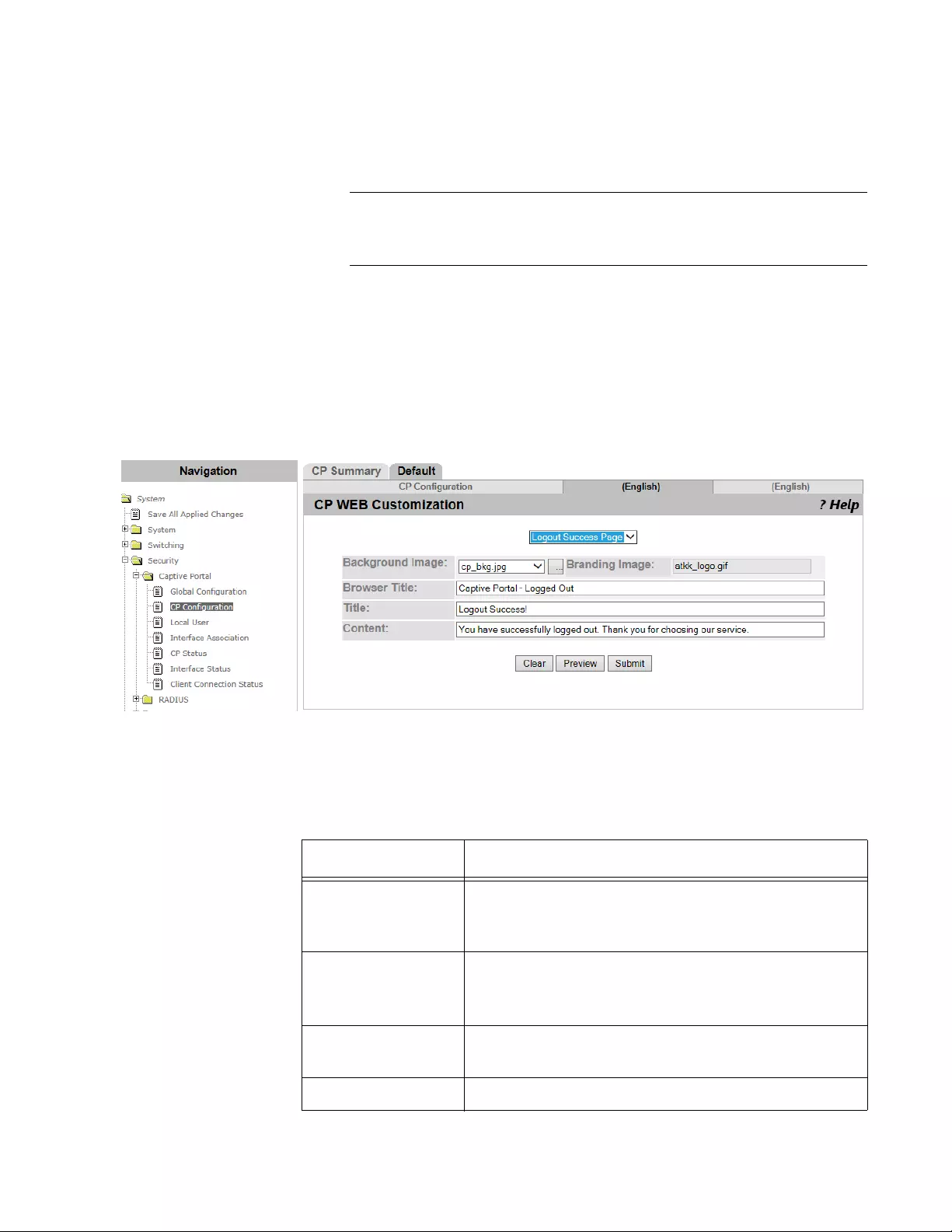
Chapter 4: Security
153
Clear — Reset to the default settings.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Logout Success
Page
19. Select Logout Success Page from the select list.
You can customize the Logout Success page settings only when Mode
is enabled. See Table 40 on page 142.
20. The CP Web Customization (Logout Success Page) page is displayed
as shown in Figure 85.
Figure 85. CP Web Customization (Logout Success Page) Page
21. Modify the fields described in Table 45.
Table 45. CP Web Customization (Logout Success Page)
Field Description
Background Image Displays the image file for the background on the
Logout Success page. The image is specified in
the Global Parameters.
Branding Image Displays the image file for the brand on the Logout
Success page. The image is specified in the Global
Parameters.
Browser Title Specify the title to be displayed as the title bar of
the Logout Success page.
Title Specify the title to be displayed as the page title.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
154
22. Click the following buttons as needed:
Preview — Displays the web page with the current settings.
Clear — Reset to the default settings.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Content Specify the text to be displayed when the
authentication is cancelled.
Table 45. CP Web Customization (Logout Success Page) (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 4: Security
155
Local User Summary
From the Local User Summary page, you can view a list of local users,
add or delete local users, and modify the properties. You can also assign
users to the user group specified for the CP profiles.
Viewing a List of
Local Users
To view a list of local users, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Captive Portal > Local
User.
The Local User Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 86.
Figure 86. Local User Summary Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 46.
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Adding or Modify
a Local User
To add or modify a local user, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Local
User.
Table 46. Local User Summary
Field Description
User Displays the name of the local user.
Session Time Displays the time period in seconds to allow the user
to stay connected to the network. When Session Time
is set to 0, no time limit is imposed to the user.
Idle Timeout Displays the time period in seconds. When the user is
not active for more than the specified time period, the
user is automatically logged out. When Idle Timeout is
set to 0, no time limit is imposed to the user.
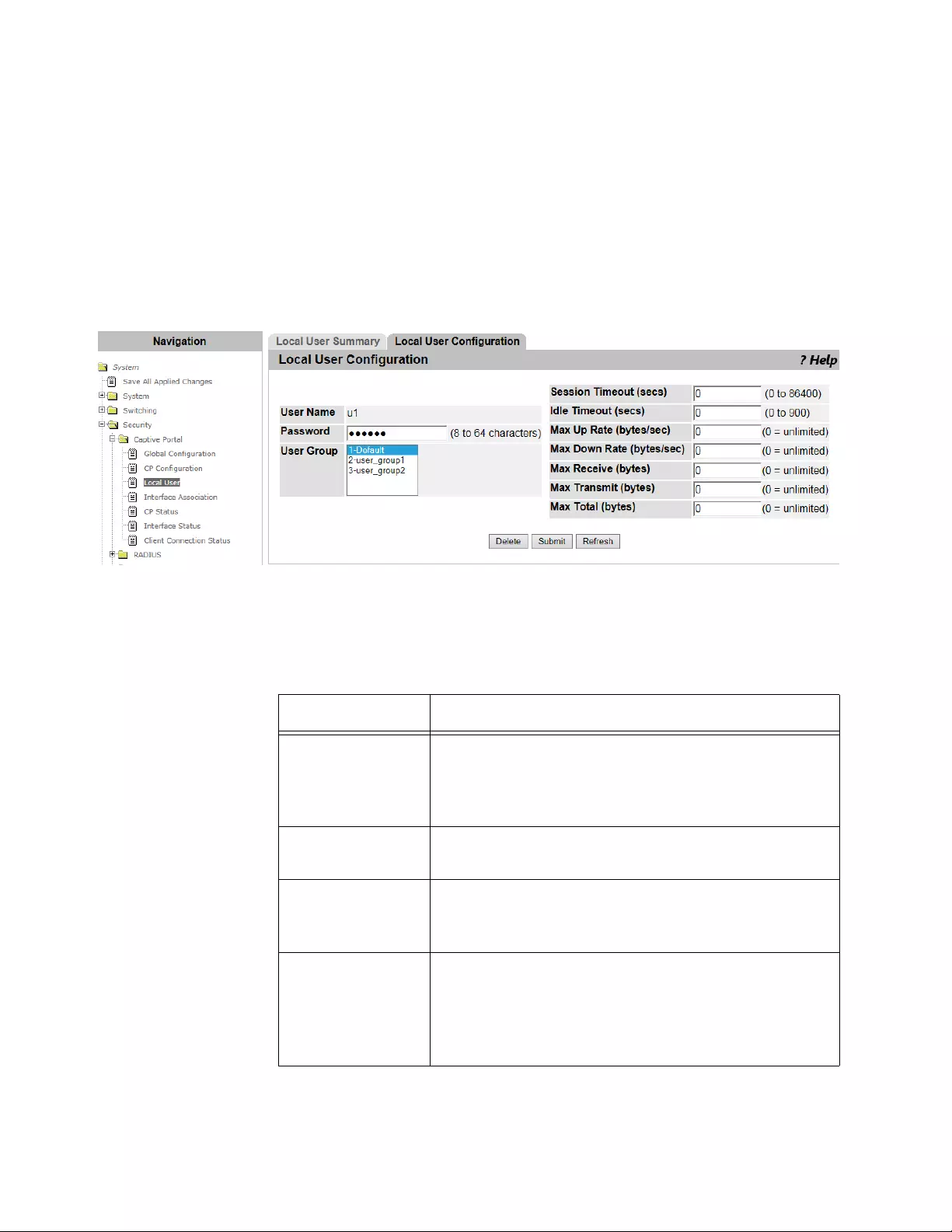
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
156
The Local User Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 86 on
page 155.
2. Perform one of the following steps.
To add a new local user, click Add.
To modify an existing local user, click the name of the local user
that you want to modify.
The Local User Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 87.
Figure 87. Local User Configuration Page
3. Specify the fields described in Table 47.
Table 47. Local User Configuration
Field Description
User Name Specify the name of a local user using up to 32
alphanumeric characters. When you are modifying
the local user, this field displays the name of the
local user.
Password Specify the user password from 8 to 64
alphanumeric characters.
User Group Assigns a user group from the list. You can add
more than one user group by holding the Ctrl key
and clicking the user names.
Idle Timeout
(secs)
Specify the time period in seconds to allow a user of
the AP client to stay connected when no interaction
is made. When Idle Timeout has passed without
interaction from the user, the user is automatically
logged out.

Chapter 4: Security
157
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Delete — Deletes the local user.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Deleting a Local
User
To delete a local user, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Local
User.
The Local User Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 86 on
page 155.
2. Check the checkbox of the user that you want to delete.
Session Timeout
(secs)
Specify the time period in seconds to allow a user to
stay connected. When Session Timeout has
passed, the user is automatically logged out.
Max Up Rate
(bytes/sec)
Specify the maximum transmission rate that AP
clients send traffic to the network when Captive
Portal is activated.
Max Down Rate
(bytes/sec)
Specify the maximum receiving rate that AP clients
receive traffic from the network when Captive Portal
is activated.
Max Receive
(bytes)
Specify the maximum size in bytes to allow AP
clients to send to the access point when Captive
Portal is activated. When the maximum size is
exceeded, the AP client is disconnected.
Max Transmit
(bytes)
Specify the maximum size in bytes to allow AP
clients to receive from the access point when
Captive Portal is activated. When the maximum
size is exceeded, the AP client is disconnected.
Max Total (bytes) Specify the maximum total size in bytes to allow AP
clients to send and receive when Captive Portal is
activated. The maximum total size is exceeded, the
AP client is disconnected.
Table 47. Local User Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
158
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete ALL — Deletes all the local users on the list.
Delete — Deletes the selected local user.
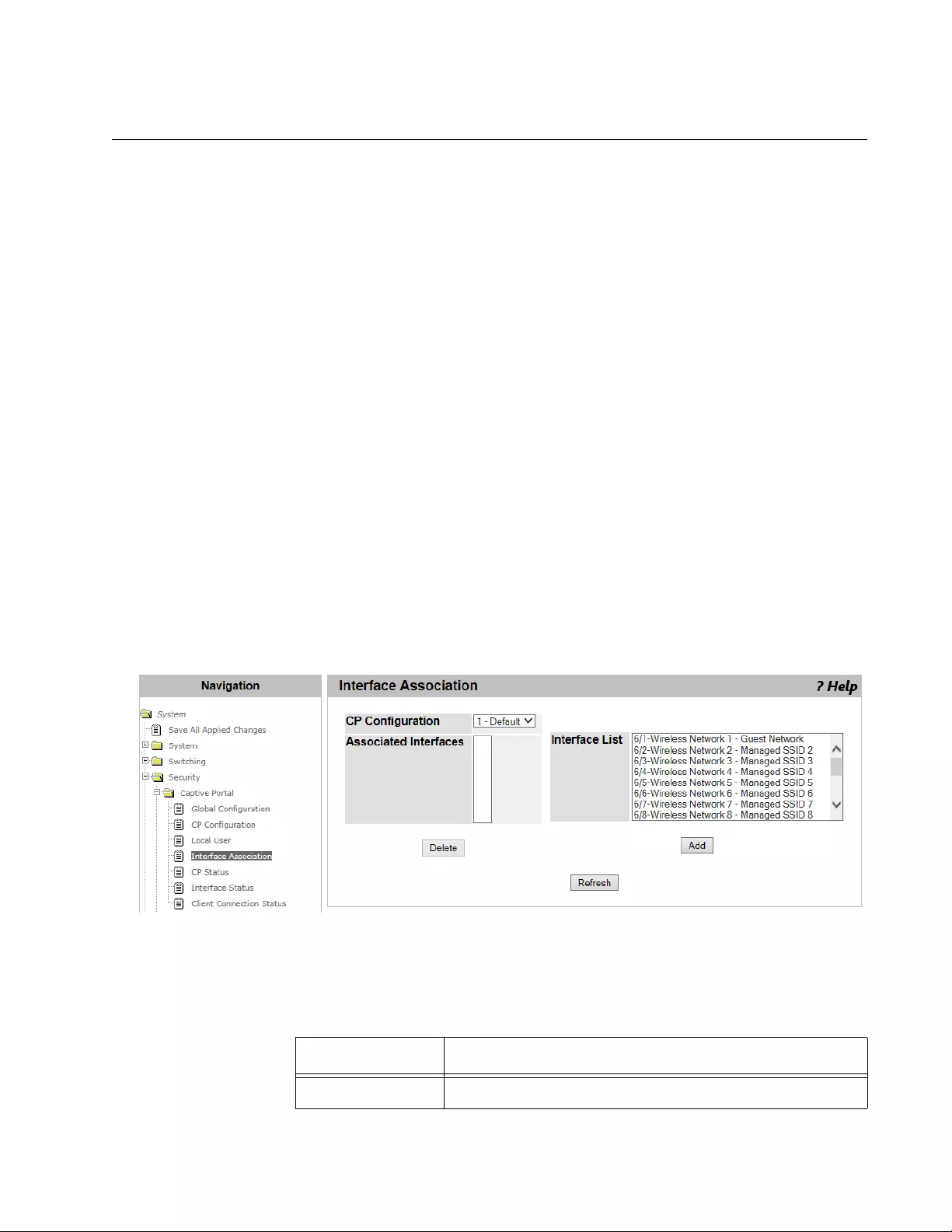
Chapter 4: Security
159
Interface Association
From the Interface Association page, you can view a list of wireless
network interfaces or Service Set Identifiers (SSID’s) that are associated
to a CP profile. You can also associate a CP profile to a wireless network
interface and delete an associated wireless network interface from a CP
profile.
Guidelines for
Associating a CP
Profile
Here are the guidelines for associating a CP profile to a wireless network
interface:
You can associate one CP profile with multiple wireless network
interfaces; however, one wireless network interface can be
associated with only one CP profile.
The wireless network interfaces that use Captive Portal must be
assigned to the same VLAN ID as the management VLAN of the
WLAN Controller.
Adding and
Deleting Wireless
Networks from a
CP Profile
To associate a CP profile to wireless network interfaces or delete an
associated wireless network interface form a CP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Interface
Association.
The Interface Association page is displayed as shown in Figure 88.
Figure 88. Interface Association Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 48.
Table 48. Interface Association
Field Description
CP Configuration Select one of the CP profiles from the select list.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
160
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Associated
Interfaces
Displays a list of wireless network interfaces that are
associated to the CP profile.
To delete an Associated Interface, select one or more
Associated Interfaces and click Delete.
To select more than one Associated Interface, hold
the Ctrl key and click another Associated Interface.
Delete (button) Click Delete to delete the selected Associated
Interfaces from the list.
Interface List Displays a list of available wireless network interfaces
that are not associated to the CP profile.
To add an Interface, select one or more Interfaces
and click Add.
To select more than one Interface, hold the Ctrl key
and click another Interface.
Add (button) Click Add to add the selected Interfaces to the
Associated Interfaces list.
Table 48. Interface Association (Continued)
Field Description
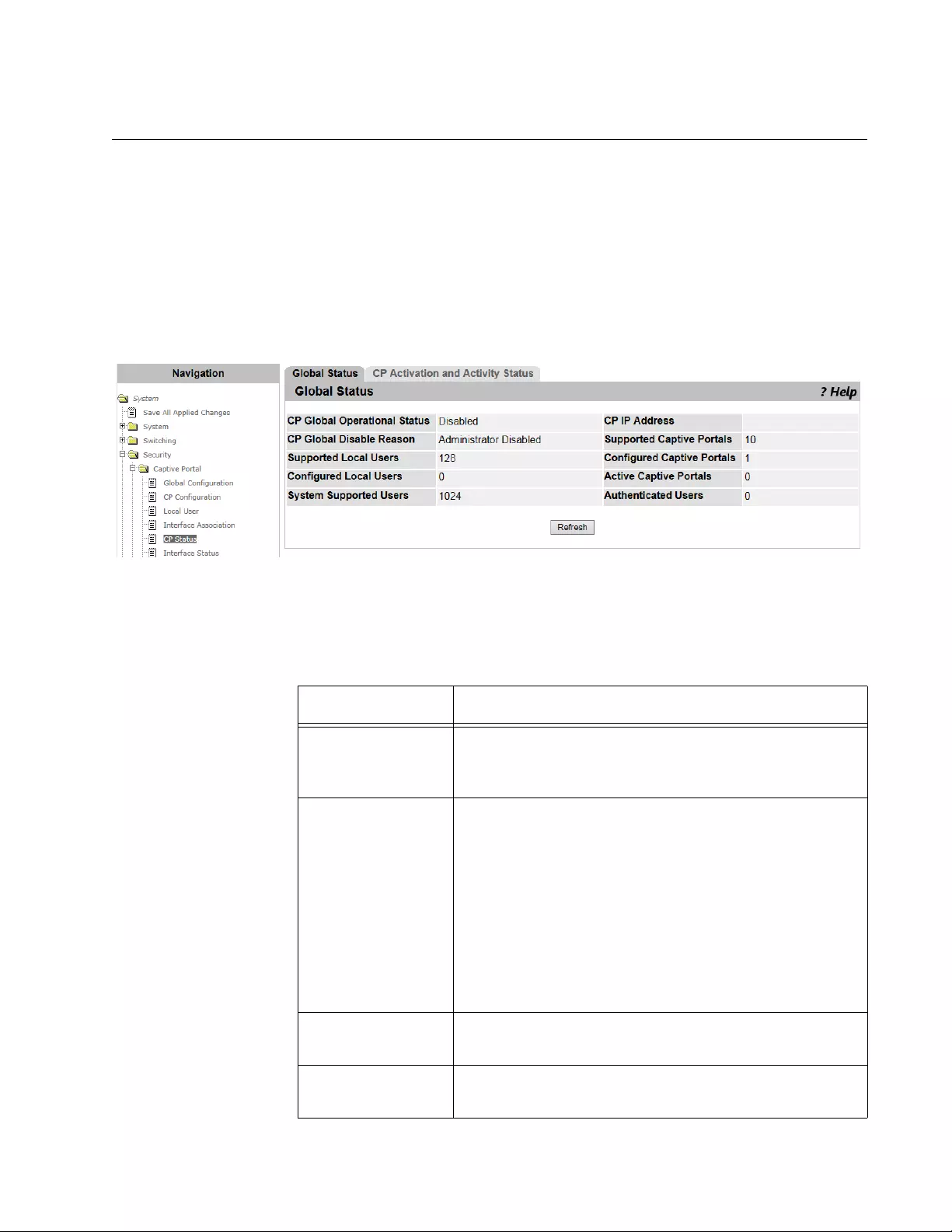
Chapter 4: Security
161
CP Status
From the CP Status page, you can view the information about Captive
Portal on the WLAN Controller.
Viewing the CP
Global Status
To view the information about Captive Portal, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Captive Portal > CP Status.
The CP Global Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 89.
Figure 89. CP Global Status Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 49.
Table 49. CP Global Status
Field Description
CP Global
Operational
Status
Displays the status whether Captive Portal is
enabled or disabled on the WLAN Controller.
CP Global
Disable Reason
Displays the reason when Captive Portal is disabled
on the WLAN Controller. The options are:
Administrator Disabled
No IPv4 Address
Routing Enabled, but no IPv4 routing
interface
None - None of the above reasons is
applicable.
Supported Local
Users
Displays the number of local users that are
supported in the local user database.
Configured Local
Users
Displays the number of local users that are defined
to the WLAN Controller.
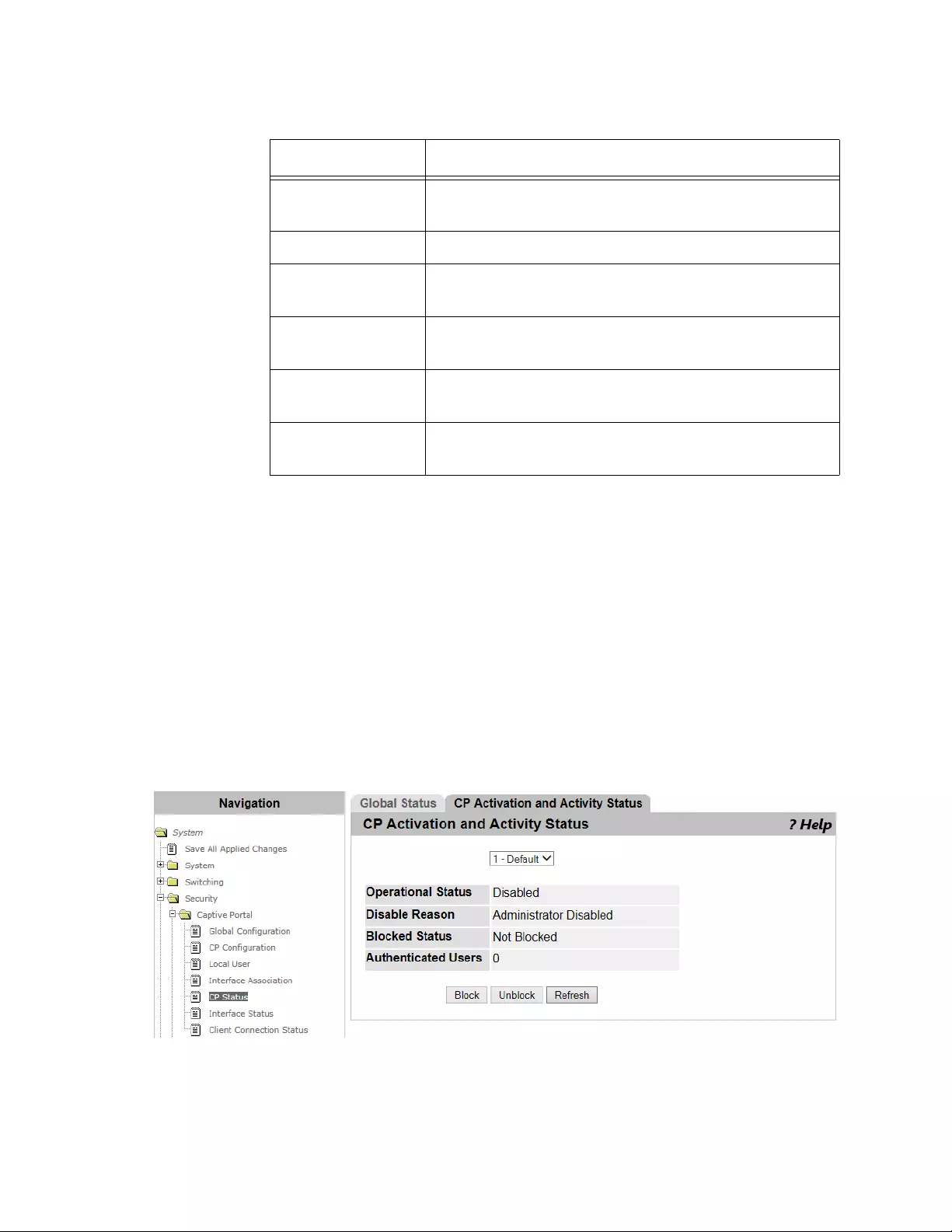
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
162
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Activity Status
per CP Profile
To view the information about each CP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > CP
Status.
The CP Global Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 89 on
page 161.
2. Click CP Activation and Activity Status tab.
The CP Activation and Activity Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 90.
Figure 90. CP Activation and Activity Status Page
3. Select a CP profile from the select list.
System
Supported Users
Displays the number of authenticated users that the
system supports.
CP IP Address Displays the IP address of Captive Portal.
Supported
Captive Portals
Displays the number of CP profiles that the system
supports.
Configured
Captive Portals
Displays the number of CP profiles that are defined
to the WLAN Controller.
Active Captive
Portals
Displays the number of active CP instances.
Authenticated
Users
Displays the number of users that are currently
authenticated in all the CP instances.
Table 49. CP Global Status (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 4: Security
163
The information about the CP profile displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 50.
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Block — Blocks the network access via Captive Portal.
Unblock — Cancels the blocking.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Table 50. CP Activation and Activity Status
Field Description
Operational
Status
Displays the status whether the CP profile is
enabled or disabled.
Disable Reason Displays the reason when the CP profile is disabled.
The options are:
No display - The CP profile is enabled.
Administrator Disabled
RADIUS Authentication mode enabled,
but RADIUS server is not defined.
Not associated with any interfaces
The associated interfaces do not exist or
do not support the CP capability.
Blocked Status Displays the CP authentication blocking status. The
options are:
Block - Users cannot access the network
via Captive Portal authentication. Click
Block to block the network access via
Captive portal.
Unblock - Users can access the network via
Captive Portal authentication. Click
Unblock to cancel blocking.
Authenticated
Users
Displays the number of authenticated users who
are currently using Captive Portal.
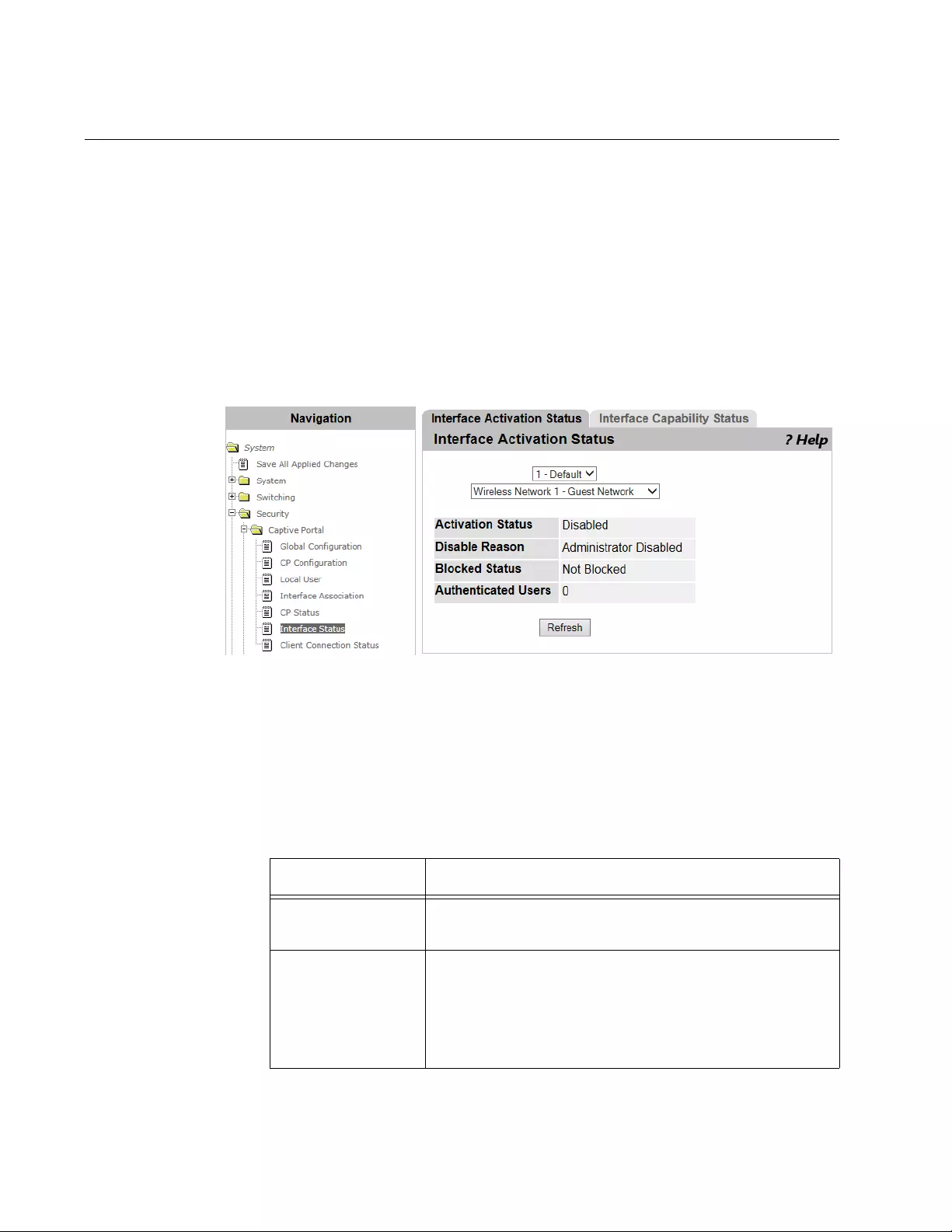
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
164
Interface Status
From the Interface Activation Status page, you can view the information
about the wireless network interface that is associated to a CP profile.
Viewing the
Interface
Activation Status
To view the information about Captive Portal, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to System > Captive Portal > Interface
Status.
The Interface Activation Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 91.
Figure 91. Interface Activation Status Page
2. Select a CP profile from the select list.
3. Select a wireless network interface from the select list.
4. Observed the fields described in Table 51.
Table 51. Interface Activation Status
Field Description
Activation Status Displays the status whether Captive Portal to the
wireless network interface is enabled or disabled.
Disable Reason Displays the reason when Captive Portal is disabled
to the wireless network interface. The options are:
Interface Not Attached
Disabled by Administrator
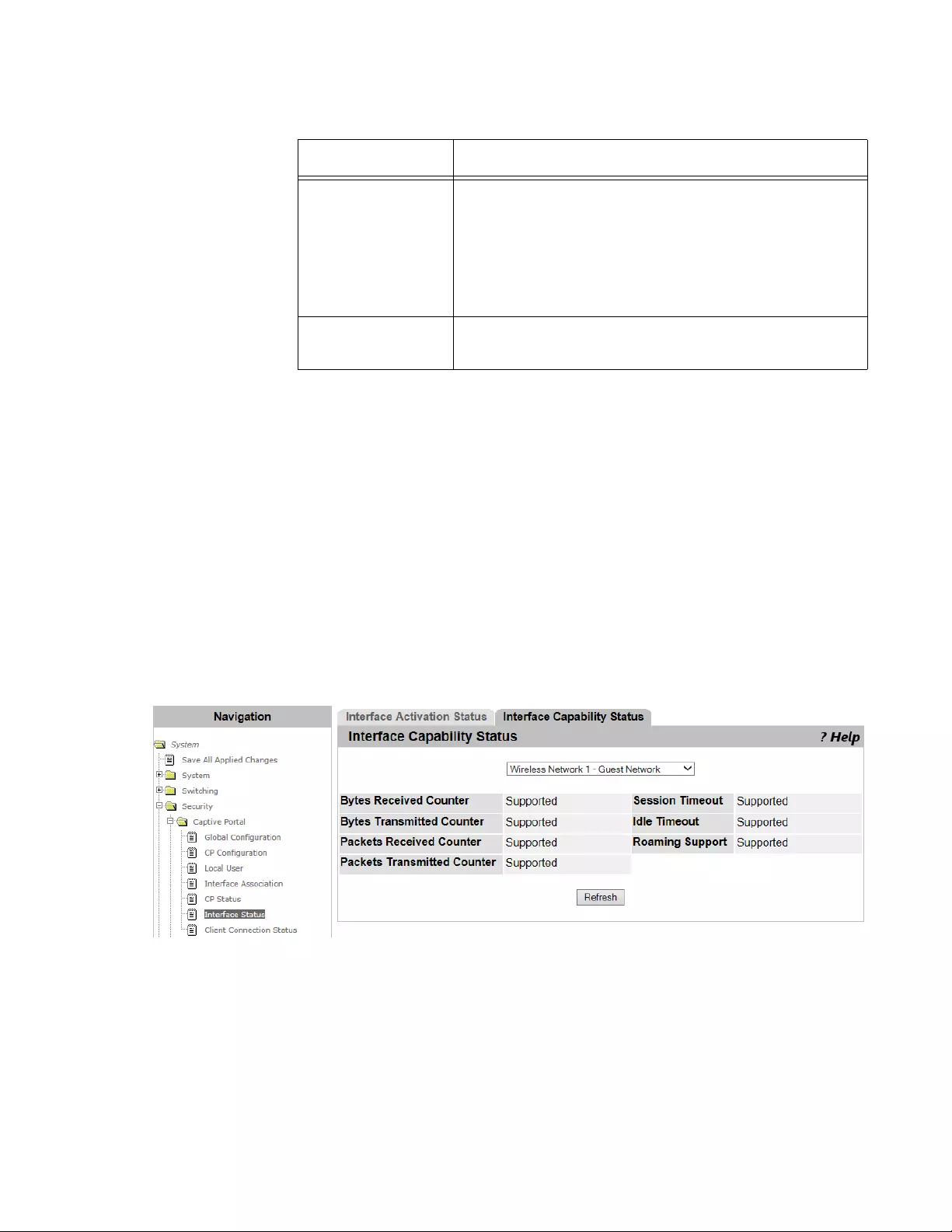
Chapter 4: Security
165
5. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Interface
Capability Status
To view the information about each wireless network interface, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Interface
Status.
The Interface Capability Status page is displayed as shown in Figure
91 on page 164.
2. Click the Interface Capability Status tab.
The Interface Capability Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 92.
Figure 92. Interface Capability Status Page
3. Observe the fields described in Table 52 on page 166.
Blocked Status Displays the CP blocking status. The options are:
Block - Users cannot access the network via
Captive Portal authentication.
Unblock - Users can access the network via
Captive Portal authentication.
Authenticated
Users
Displays the number of users that are currently
authenticated in all the CP instances.
Table 51. Interface Activation Status (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
166
4. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Table 52. Interface Capability Status
Field Description
Bytes Received
Counter
Displays whether the counter of the bytes received
from the AP clients is supported by the wireless
network interface or not.
Bytes
Transmitted
Counter
Displays whether the counter of the bytes
transmitted from the AP clients is supported by the
wireless network interface or not.
Packets
Received
Counter
Displays whether the counter of the packets
received from the AP clients is supported by the
wireless network interface or not.
Packets
Transmitted
Counter
Displays whether the counter of the packets
transmitted from the AP clients is supported by the
wireless network interface or not.
Session Timeout Displays whether Session Timeout for the user is
supported by the wireless network interface or not.
Idle Timeout Displays whether Idle Timeout for the user is
supported by the wireless network interface or not.
Roaming Support Displays whether Roaming for AP clients is
supported by the wireless network interface or not.

Chapter 4: Security
167
Client Connection Status
From the Client Connection Status page, you can view the information
about connected AP clients. You can also disconnect the AP clients from
the page.
You can visit 5 pages from the Client Connection Status page:
Client Summary page
Client Detail page
Client Statistics page
Interface - Client Status page
CP - Client Status page
Client Summary To view the information about connected AP clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Client
Connection Status.
The Client Summary page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 53.
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Table 53. Client Summary
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client. When the
* symbol is marked at the end of the MAC address,
the AP client was authenticated by the peer
controller.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the AP client.
User Displays the user name or guest ID of the connected
AP client.
Protocol Displays the protocol that is connected through:
HTTP or HTTPS.
Verification Displays the account type. The options are:
Guest
Local
RADIUS
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
168
Delete — Deletes the selected AP client.
Delete All — Deletes all the AP clients.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Client Detail To view the detailed information about connected AP clients, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Client
Connection Status.
The Client Summary page is displayed.
2. Click the Client Detail tab.
The Client Detail page is displayed.
3. Observed the fields described in Table 54.
Table 54. Client Detail
Field Description
Client IP Address Displays the IP Address of the AP client.
CP Configuration Displays the CP profile that the AP client is currently
using.
Protocol Displays the protocol that is connected through:
HTTP or HTTPS.
Session Time Displays the time period since the AP client was
authenticated.
Controller Type Displays the type of the WLAN Controller that
authenticates the AP client: Local or Peer.
User Name Displays the user name or guest ID of the connected
AP client.
Interface Displays the interface that the AP client is using.
Verification Displays the account type. The options are:
Guest
Local
RADIUS
Controller MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the WLAN Controller
that authenticated the AP client. When clustering is
supported, the MAC address of the peer controller
may be shown.
Chapter 4: Security
169
4. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Client Statistics To view the statistics of connected AP clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Client
Connection Status.
The Client Summary page is displayed.
2. Click the Client Statistics tab.
The Client Statistics page is displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 55.
4. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Interface - Client
Status
To view the information about the interface of AP clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Client
Connection Status.
The Client Summary page is displayed.
2. Click the Interface - Client Status tab.
The Interface - Client Status page is displayed.
Controller IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller that
authenticated the AP client. When clustering is
supported, the IP address of the peer controller may
be shown.
Table 54. Client Detail (Continued)
Field Description
Table 55. Client Statistics
Field Description
Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the total size of data in bytes that are sent to
the AP client.
Bytes Received Displays the total size of data in bytes that are
received from the AP client.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of the packets that are sent to
the AP client.
Packets
Received
Displays the number of the packets that are received
from the AP client.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
170
3. Select the wireless network interface from the select list.
The information about the selected wireless network interface is
displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 56.
5. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
CP - Client Status To view a list of AP clients that connected through a Capital Portal profile,
do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Captive Portal > Client
Connection Status.
The Client Summary page is displayed.
2. Click the CP - Client Status tab.
The CP - Client Status page is displayed.
3. Select the CP profile from the select list.
A list of AP clients that are connected through the selected CP profile
is displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 57 on page 171.
Table 56. Interface - Client Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client. When the
* symbol is marked at the end of the MAC address,
the AP client was authenticated by the peer
controller.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the AP client.
Interface Displays the interface that the AP client is using.
Protocol Displays the protocol that is connected through:
HTTP or HTTPS.
Verification Displays the account type. The options are:
Guest
Local
RADIUS

Chapter 4: Security
171
5. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Table 57. CP - Client Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client. When the
* symbol is marked at the end of the MAC address,
the AP client was authenticated by the peer
controller.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the AP client.
Interface Displays the interface that the AP client is using.
Protocol Displays the protocol that is connected through:
HTTP or HTTPS.
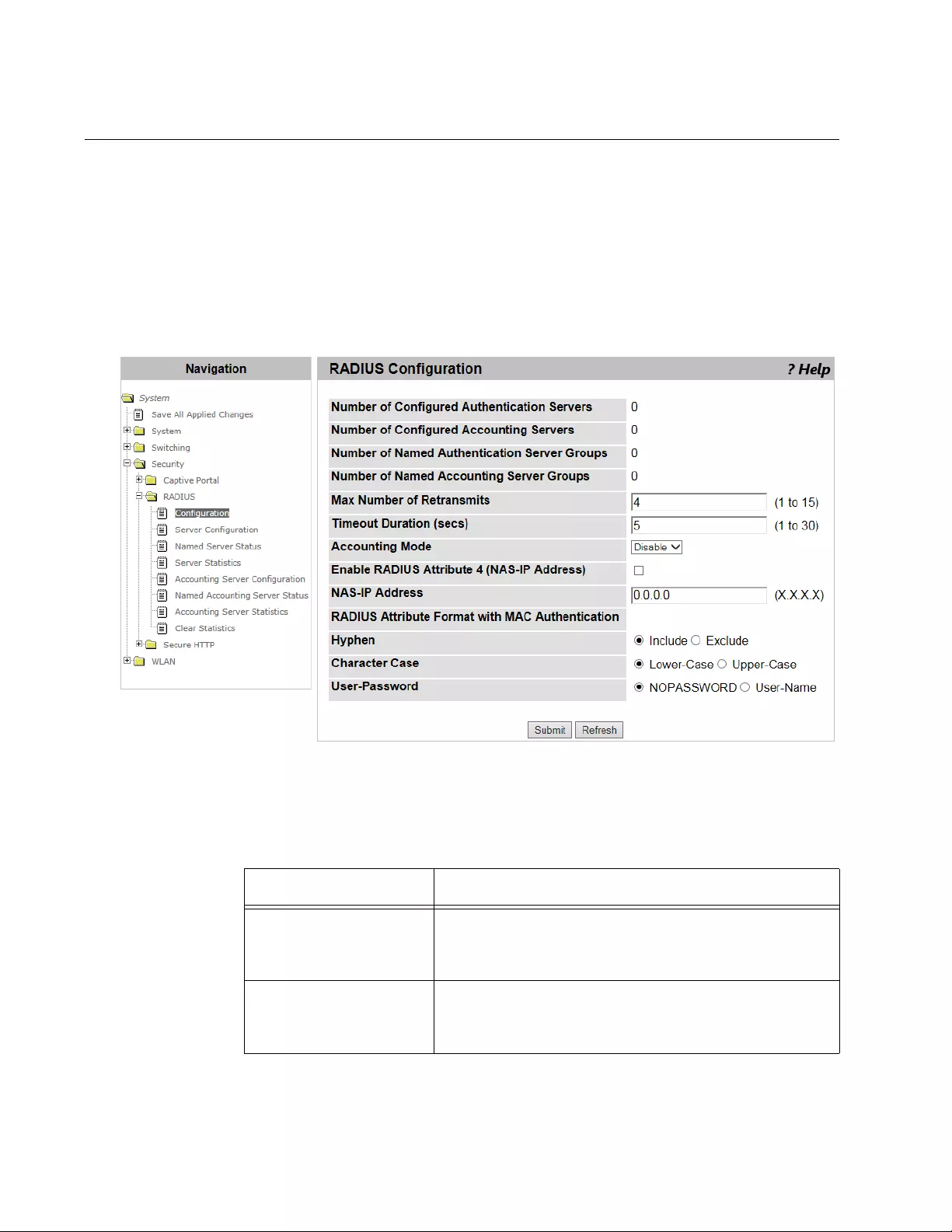
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
172
RADIUS Configuration
From the RADUUS Configuration page, you can view and modify the
RADIUS settings.
To view or modify the RADIUS settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Configuration.
The RADIUS Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 93.
Figure 93. RADIUS Configuration Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 58.
Table 58. RADIUS Configuration
Field Description
Number of Configured
Authentication
Servers
Displays the number of the RADIUS servers that
are configured on the WLAN Controller used for
authentication. The range is 0 to 32 servers.
Number of Configured
Accounting Servers
Displays the number of the RADIUS servers that
are configured on the WLAN Controller used for
accounting information. The range is 0 -32 servers.
Chapter 4: Security
173
Number of Named
Authentication Server
Groups
Displays the number of the RADIUS server groups
that are configured on the WLAN Controller used
for authentication.
Number of Named
Accounting Server
Groups
Displays the number of the RADIUS server groups
that are configured on the WLAN Controller used
for accounting information.
Max Number of
Retransmits
Specifies how many times that the WLAN
Controller re- tries to transmit the request packet to
a RADIUS server when the request is timeout. The
range is 1 to 15 times.
Timeout Duration
(secs)
Specifies how long the WLAN Controller waits for
responses to the request packets from RADIUS
servers.
Accounting Mode Specifies the account mode. The options are:
Enable - The RADIUS accounting mode is
enabled on the RADIUS server.
Disable - The RADIUS accounting mode is
disabled on the RADIUS server. This is the
default setting.
Enable RADIUS
Attribute 4 (NAS-IP
Address)
Check the checkbox before entering an address in
NAS-IP Address.
NAS-IP Address Specifies the IPv4 address of Network Access
Server. Check the Enable RADIUS Attribute 4
checkbox before specifying this field.
RADIUS Attribute Format with MAC Authentication
Hyphen Specifies an option for hyphens to present a MAC
address in the RADIUS attribute for authentication.
The options are:
Include - Hyphens are included to present
a MAC address, for example, ab-cd-ef-01-
23-45. This is the default setting.
Exclude - Hyphens are excluded to present
a MAC address, for example,
abcdef012345.
Table 58. RADIUS Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
174
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Character Case Specifies an option for the character case to
present a MAC address in the RADIUS attribute for
authentication. The options are:
Lower-Case - The MAC address are
presented in lower-case, for example: ab-
cd-ef-01-23-45. This is the default setting.
Upper-Case - The MAC address are
presented in upper-case, for example, AB-
CD-EF-01-23-45.
User-Password Specifies an option for the RADIUS user-password
attribute for MAC address authentication. The
options are:
NOPASSWORD - The MAC address are
presented in lower-case, for example, ab-
cd-ef-01-23-45. This is the default setting.
User-Name - The MAC address are
presented in upper-case, for example, AB-
CD-EF-01-23-45.
Table 58. RADIUS Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
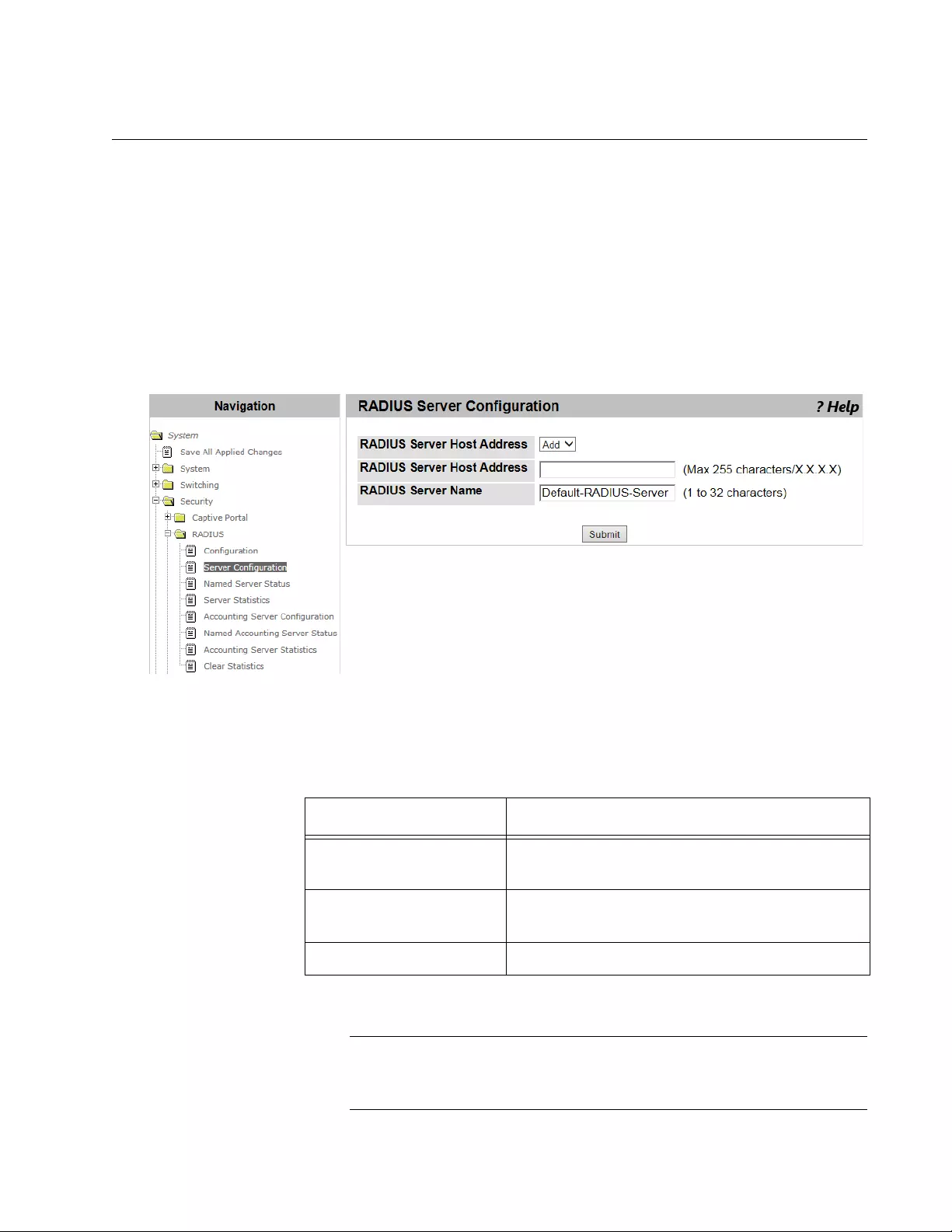
Chapter 4: Security
175
RADIUS Server Configuration
From the RADIUS Server Configuration page, you can add a RADIUS
server to the WLAN Controller.
To view and modify the network interface properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Server
Configuration.
The RADIUS Server Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 94.
Figure 94. RADIUS Server Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 59.
3. Click Submit.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Table 59. RADIUS Server Configuration
Field Description
RADIUS Server Host
Address
Displays the action. Add is the only option.
RADIUS Server Host
Address
Specify the IPv4 address of The RADIUS
server.
RADIUS Server Name Specify the name of the RADIUS server.
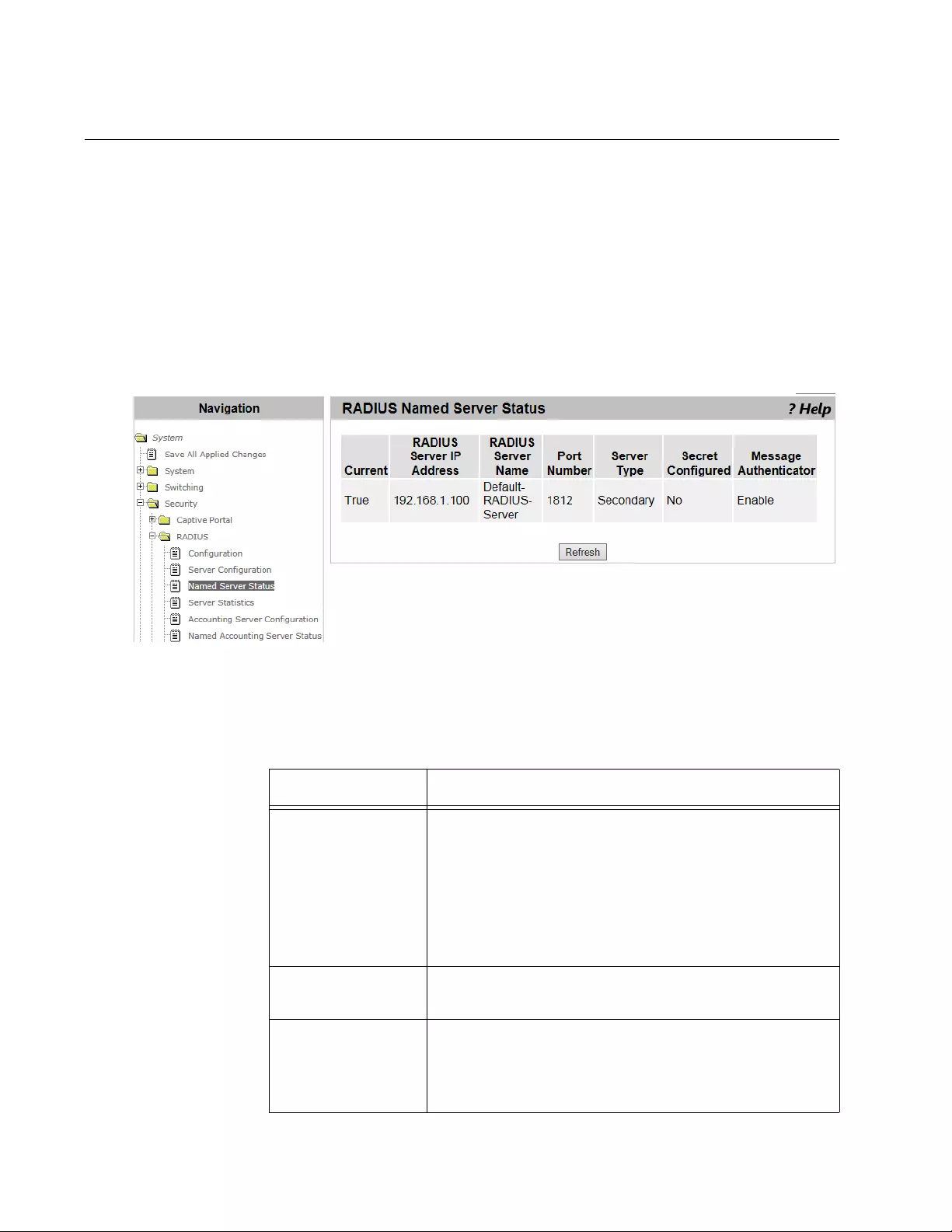
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
176
RADIUS Named Server Status
From the RADIUS Named Server Status page, you can view a list of
configured RADIUS servers on the WLAN Controller.
To view a list of configured RADIUS servers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Named Server
Status.
The RADIUS Named Server Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 95.
Figure 95. RADIUS Named Server Status Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 60.
Table 60. RADIUS Named Server Status
Field Description
Current Displays the current mode of the RADIUS server.
The options are:
True- indicates that the RADIUS server is
currently used.
False - indicates that the RADIUS server is a
backup server.
RADIUS Server
IP Address
Displays the IPv4 address of the current RADIUS
server.
RADIUS Server
Name
Displays the name of the RADIUS server. More than
one RADIUS server can have the same server
name. The RADIUS client can use a server with the
same name as a backup server.
Chapter 4: Security
177
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Port Number Displays the UDP port number of the RADIUS
server.
Server Type Displays the server type. The options are:
Primary- indicates that the RADIUS server
is the primary server.
Secondary - indicates that the RADIUS
server is a secondary server.
Secret Configured Displays if the password to access the RADIUS
server is assigned. The options are:
Yes - The password is assigned.
No - No password is assigned.
Message
Authenticator
Displays if the message authenticator to the
RADIUS server is enabled or disabled. The options
are:
Enable
Disable
Table 60. RADIUS Named Server Status (Continued)
Field Description
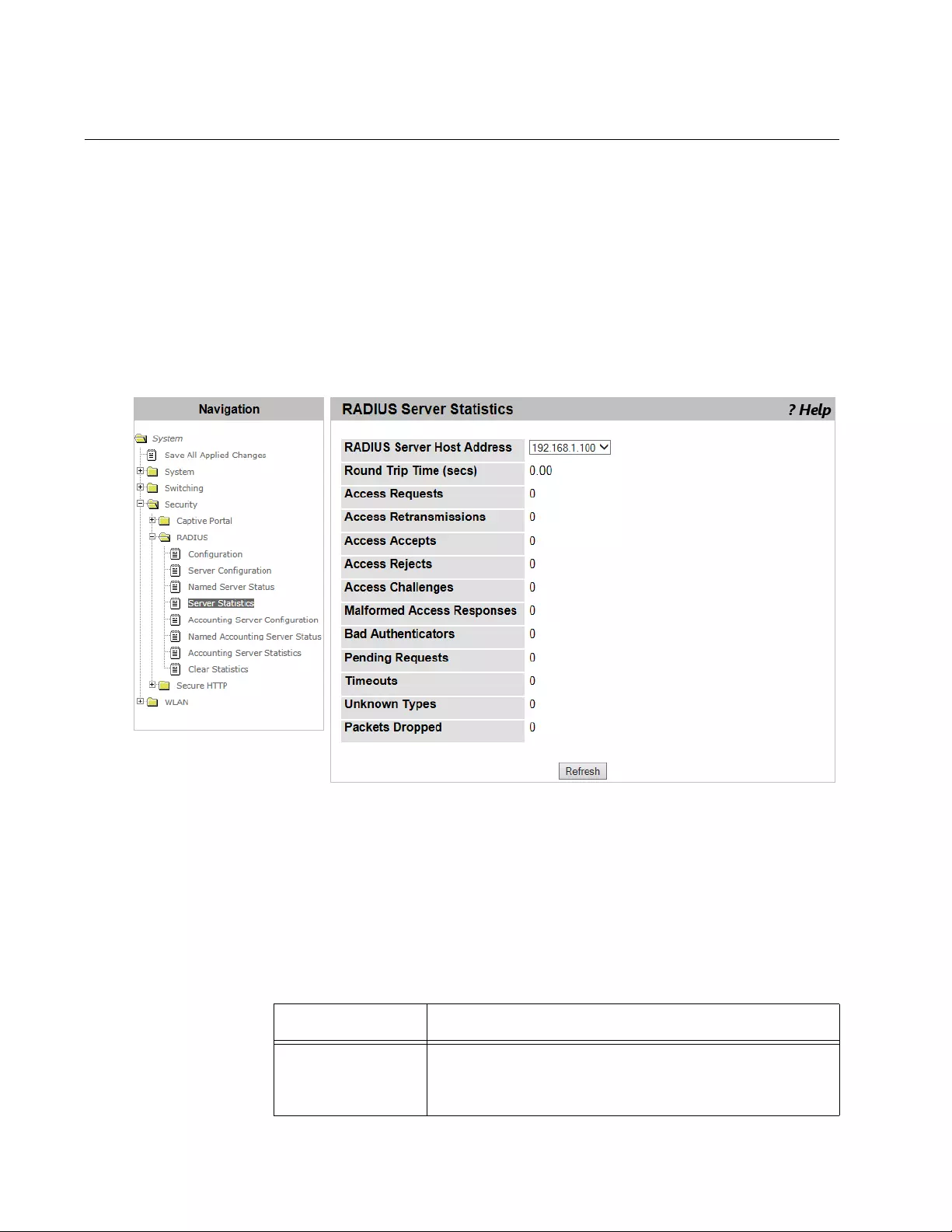
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
178
RADIUS Server Statistics
From the RADIUS Server Statistics page, you can view information about
a RADIUS server.
To view information about a RADIUS server, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Server
Statistics.
The RADIUS Server Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 96.
Figure 96. RADIUS Server Statistics Page
2. Select the IPv4 address of a RADIUS server from the RADIUS Server
Host Address select list.
The information about the selected RADIUS server is displayed.
3. Observed the fields described in Table 61.
Table 61. RADIUS Server Statistics
Field Description
Round Trip Time
(secs)
Displays the time in second that the RADIUS client
received the Access-Reply or Access-Challenge
packet after sending the Access-Request.
Chapter 4: Security
179
Access Requests Displays the number of RADIUS Access-Request
packets that the RADIUS client on the WLAN
Controller sent to the RADIUS server.
Access
Retransmissions
Displays the number of RADIUS Access-Request
packets that the RADIUS client on the WLAN
Controller re-sent to the RADIUS server.
Access Accepts Displays the number of RADIUS Access-Accept
packets, including both valid and invalid, that the
RADIUS client on the WLAN Controller received
from the RADIUS server.
Access Rejects Displays the number of RADIUS Access-Reject
packets, including both valid and invalid, that the
RADIUS client on the WLAN Controller
received.from the RADIUS server.
Access
Challenges
Displays the number of RADIUS Access-Challenge
packets, including both valid and invalid, that the
RADIUS client on the WLAN Controller received
from the RADIUS server.
Malformed
Access
Responses
Displays the number of malformed RADIUS Access
Response packets, including a packet with an
invalid length. Packets with a bad authenticator,
invalid authenticator attribute, or a unknown type are
not counted as malformed packets.
Bad
Authenticators
Displays the number of RADIUS Access Response
packets with a bad authenticator or invalid
authenticator attribute that the RADIUS client on the
WLAN Controller received from the RADIUS server.
Pending
Requests
Displays the number of pending RADIUS Access
request is a packet that has not received its
responses from the RADIUS server and has not
passed the timeout.
Timeouts Displays the number of timeout authentication from
the RADIUS server.
Unknown Types Displays the number of RADIUS packets with an
unknown type that the RADIUS client received from
the authentication port on the RADIUS server.
Packets Dropped Displays the number of the RADIUS packets from
the authentication port on the RADIUS server that
the RADIUS client discarded.
Table 61. RADIUS Server Statistics (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
180
4. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
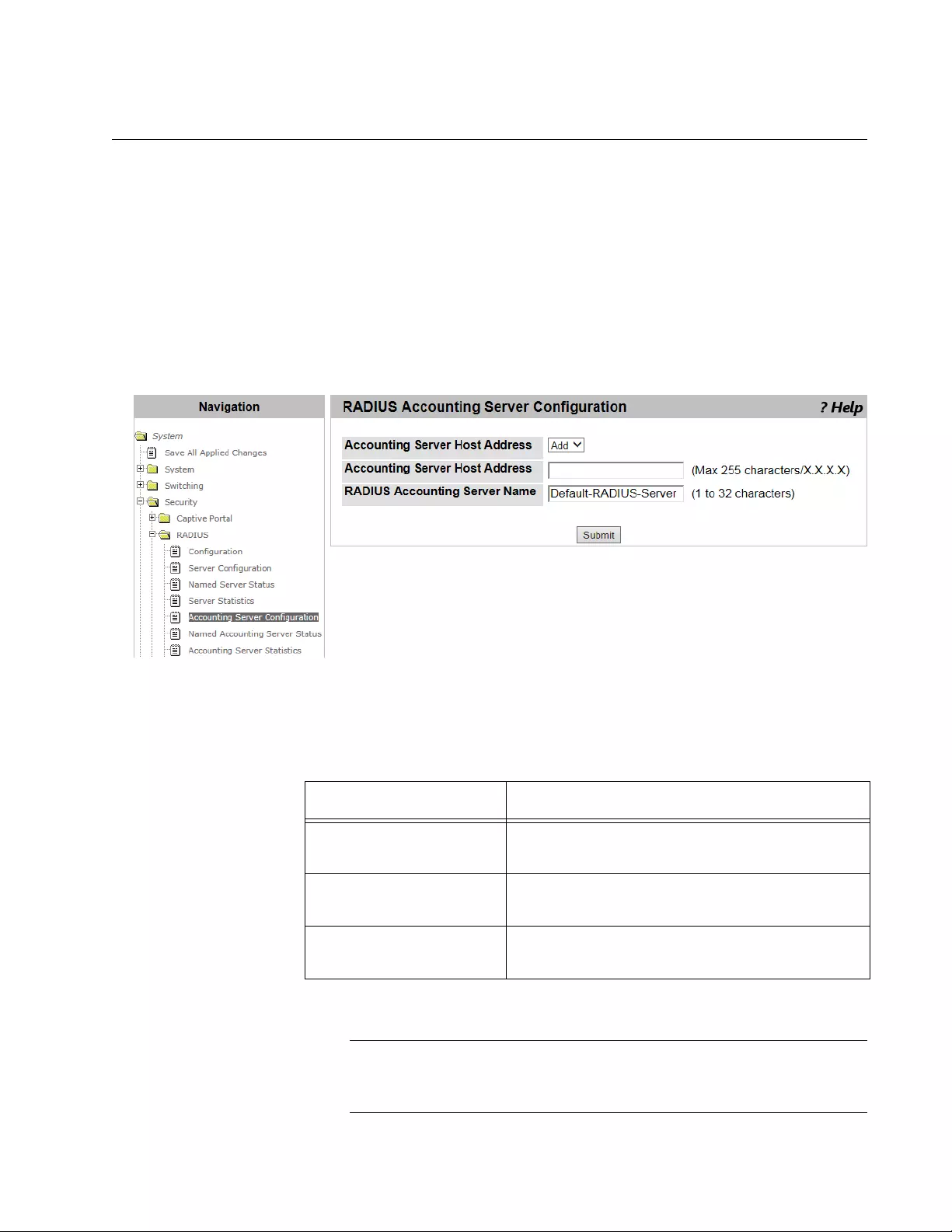
Chapter 4: Security
181
Accounting Server Configuration
From the Port Configuration page, you can modify the network interface
properties.
To modify the network interface properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Accounting
Server Configuration.
The RADIUS Accounting Server Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 97.
Figure 97. RADIUS Accounting Server Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 62.
3. Click Submit.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Table 62. RADIUS Accounting Server Configuration
Field Description
Accounting Server Host
Address
Displays the action. Add is the only option.
Accounting Server Host
Address
Specify the IPv4 address of The RADIUS
accounting server.
RADIUS Accounting
Server Name
Specify the name of the RADIUS accounting
server.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
182
Named Accounting Server Status
From the RADIUS Named Accounting Server Status page, you can view a
list of configured RADIUS accounting servers on the WLAN Controller.
To view a list of configured RADIUS accounting servers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Named
Accounting Server Status.
The RADIUS Named Accounting Server Status page is displayed as
shown in Figure 98.
Figure 98. RADIUS Named Accounting Server Status Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 63.
Table 63. RADIUS Named Accounting Server Status
Field Description
RADIUS
Accounting
Server Name
Displays the name of the RADIUS accounting
server. More than one RADIUS accounting server
can have the same name.
IP Address Displays the IPv4 address of the RADIUS
accounting server.
Port Number Displays the port number of the that the RADIUS
accounting server.

Chapter 4: Security
183
3. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Secret
Configured
Displays if the password to access the RADIUS
accounting server is assigned. The options are:
Yes - The password is assigned.
No - No password is assigned.
Table 63. RADIUS Named Accounting Server Status (Continued)
Field Description
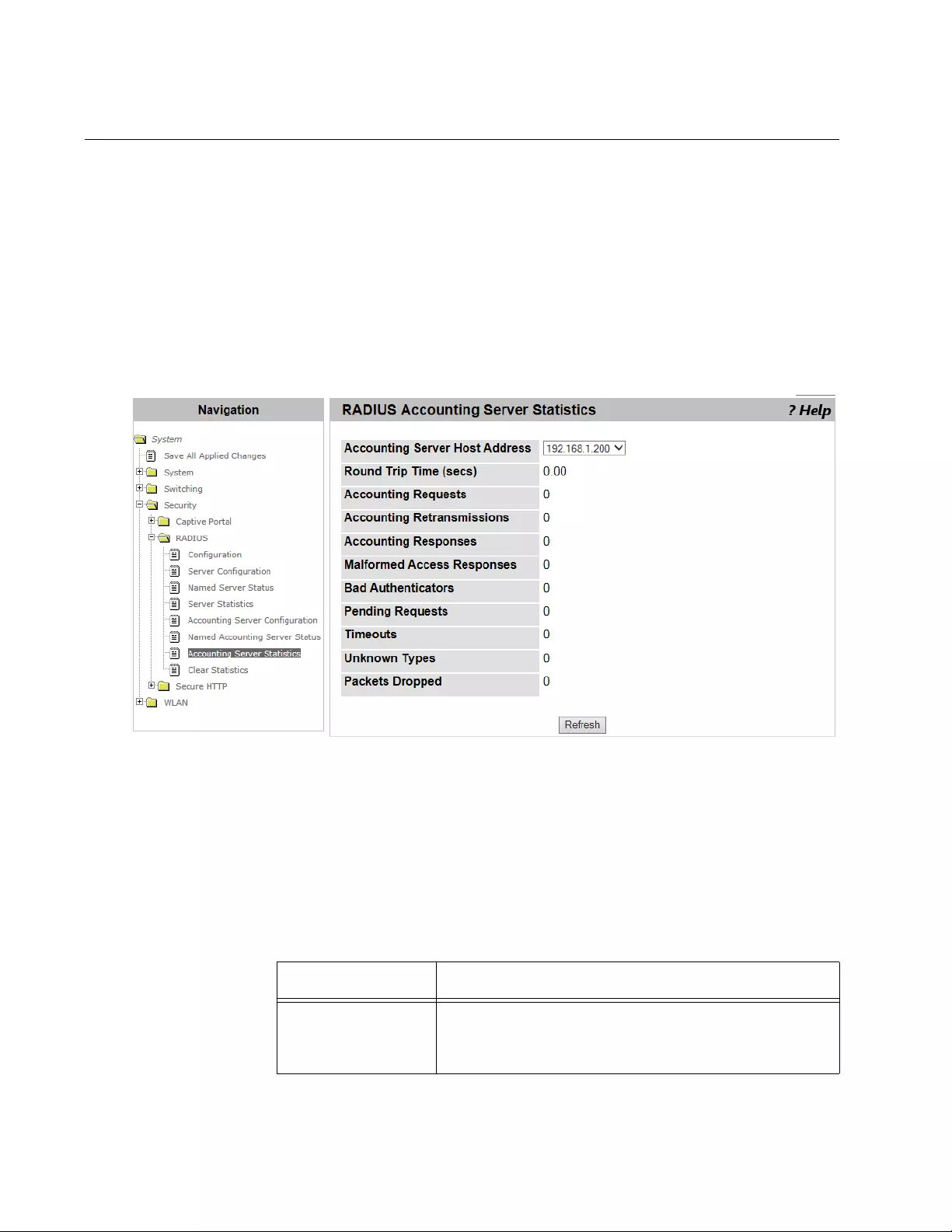
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
184
Accounting Server Statistics
From the Accounting Server Statistics page, you can view information
about a RADIUS accounting server.
To view information about an Accounting server, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Accounting
Server Statistics.
The Accounting Server Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 99.
Figure 99. Accounting Server Statistics Page
2. Select the IPv4 address of an accounting server from the Accounting
Server Host Address select list.
The information about the selected RADIUS Serve is displayed.
3. Observed the fields described in Table 64.
Table 64. Accounting Server Statistics
Field Description
Round Trip Time
(secs)
Displays the time in second that the RADIUS client
received the Access-Reply or Access-Challenge
packet after sending the Access-Request.
Chapter 4: Security
185
4. If you want to view the most current information, click Refresh.
Accounting
Requests
Displays the number of RADIUS Accounting
Request packets that the RADIUS client on the
WLAN Controller sent to the RADIUS server.
Accounting
Retransmissions
Displays the number of RADIUS Accounting
Request packets that the RADIUS client on the
WLAN Controller re-sent to the RADIUS server.
Accounting
Responses
Displays the number of RADIUS packets that were
sent from the accounting port on the RADIUS
accounting server.
Malformed
Accounting
Responses
Displays the number of malformed RADIUS
Accounting Response packets, including a packet
with an invalid length. Packets with a bad
authenticator, invalid authenticator attribute, or a
unknown type are not counted as malformed
packets.
Bad
Authenticators
Displays the number of RADIUS Accounting
Response packets with a bad authenticator or
invalid authenticator attribute that the RADIUS
client on the WLAN Controller received from the
RADIUS server.
Pending Requests Displays the number of pending RADIUS
Accounting request packets. A pending RADIUS
Accounting request is a packet that has not
received its responses from the RADIUS server
and has not passed the timeout.
Timeouts Displays the number of timeout authentication from
the RADIUS server.
Unknown Types Displays the number of RADIUS packets with an
unknown type that the RADIUS client received
from the accounting port on the RADIUS server.
Packets Dropped Displays the number of the RADIUS packets from
the accounting port on the RADIUS server that the
RADIUS client discarded.
Table 64. Accounting Server Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
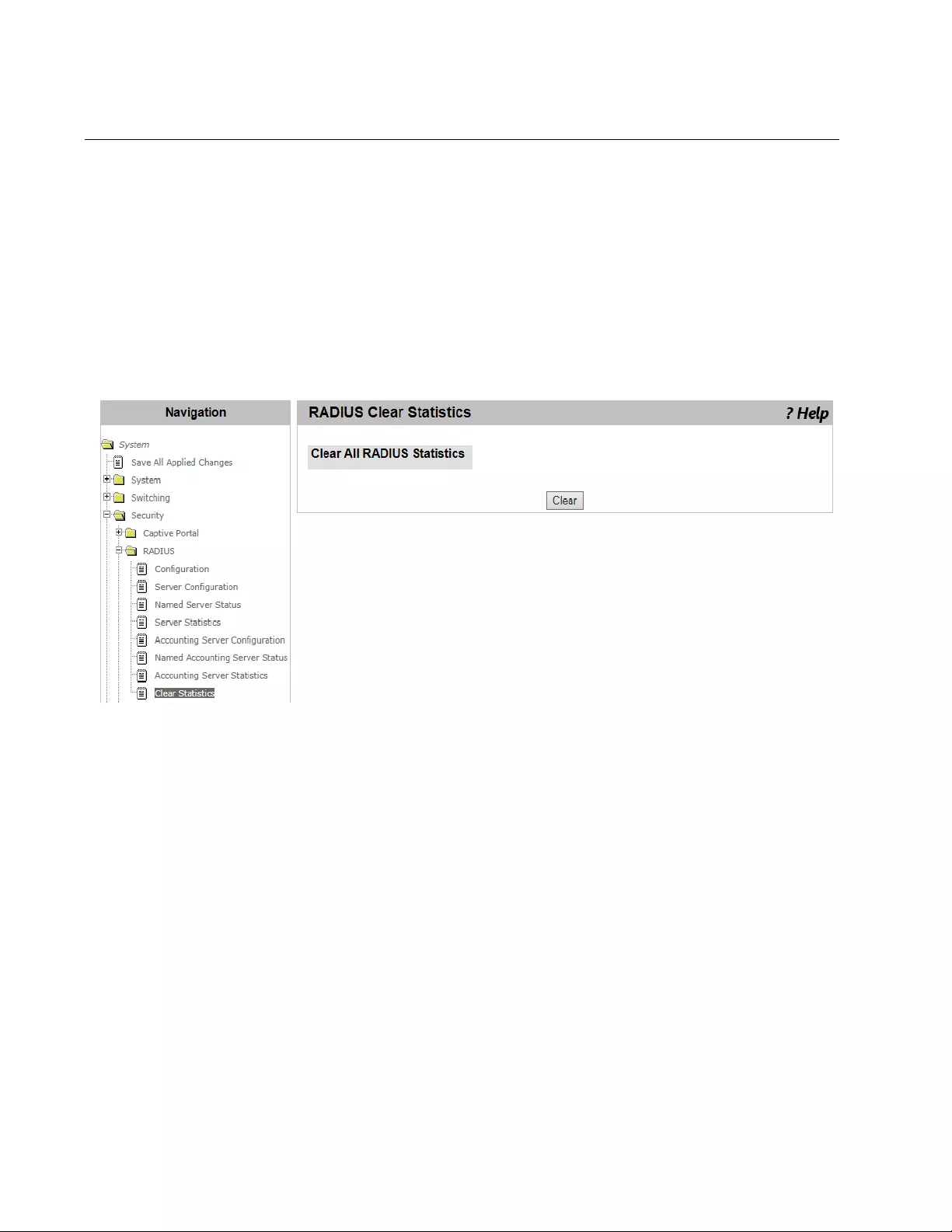
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
186
RADIUS Clear Statistics
From the RADIUS Clear Statistics page, you can clear all the RADIUS
counters.
To clear the RADIUS authentication and accounting counters, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > RADIUS > Clear Statistics.
The RADIUS CLEAR Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 100.
Figure 100. RADIUS Clear Statistics Page
2. Click Clear.
All the counters for RADIUS authentication and accounting servers.

Chapter 4: Security
187
Secure HTTP
On the Secure HTTP (HTTPS) Configuration page, you can enable or
disable HTTPS, modify the properties for HTTPS connections, generate a
certificate, and delete a certificate.
To modify HTTPS settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to Security > Secure HTTP >
Configuration.
The Secure HTTP Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 101.
Figure 101. Secure HTTP Configuration Page
2. Modify the property settings described in Table 65.
Table 65. HTTPS Configuration
Field Description
HTTPS Admin
Mode
Enables or disables HTTPS. By default, HTTPS is
disabled and HTTP is enabled. See “HTTP” on
page 47.
TLS Version 1 Enable or disable TLS Version 1. By default, the
TLS Version 1 is enabled.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
188
3. Click one of the following buttons as needed.
Delete Certificate — Deletes the certificate.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Generate Certificate — Generates a certificate.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
SSL Version 3 Enables or disables SSL Version 3. By default, the
SSL version 3 is disabled.
HTTPS Port Specifies the HTTPS port number. The default
number is 443.
HTTPS Session
Soft Timeout
(Minutes)
Specifies a period of time in minutes. When this
specified time has passed since the last user-
interaction to the system, the system ends the
session. The default setting is 5 minutes.
HTTPS Session
Hard Timeout
(Hours)
Specifies a period of time in hours. When this
specified time has passed since the time you
logged in, the system ends the session. The default
setting is 24 hours.
Maximum
Number of
HTTPS Session
Displays the maximum number of HTTPS sessions
that you allows to the WLAN Controller. The default
setting is 16 sessions.
Certificate
Present
Displays whether the system has a certificate. The
options are:
True - A certificate is present.
False - No certificate.
Certificate
Generation
Status
Displays the status of generating a certificate.
Table 65. HTTPS Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

189
Chapter 5
Wireless LAN
This chapter includes the following topics:
WLAN
“WLAN Basic Setup > Global” on page 191
“WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery” on page 194
“WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP” on page 198
WLAN > AP Management
“AP Management Reset” on page 204
“RF Management > Configuration” on page 205
“RF Management > Channel Plan History” on page 208
“RF Management > Manual Channel Plan” on page 210
“Access Point Software Download” on page 212
“Managed AP Advanced Settings” on page 215
WLAN > Status/Statistics
“Status/Statistics > Global” on page 220
“Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Status” on page 232
“Status/Statistics > Associated Client” on page 256
“Status/Statistics > Peer Controller” on page 266
“Status/Statistics > WDS Managed APs” on page 270
WLAN > Intrusion Detection
“Rogue/RF Scan” on page 276
“Detected Clients” on page 284
“Ad Hoc Clients” on page 295
“AP Authentication Failure” on page 297
“De-Auth Attack Status” on page 301
WLAN > Advanced Configuration
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global” on page 302
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > SNMP Traps” on page 305
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Distributed Tunneling” on page 308

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
190
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Centralized L2 Tunneling” on
page 310
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known Client” on page 312
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks” on page 316
“Access Point Profile List” on page 325
“Access Point Profile Global Configuration” on page 328
“Access Point Profile Radio Configuration” on page 331
“Access Point Profile VAP Configuration” on page 339
“Access Point Profile QoS Configuration” on page 342
“Peer Controller > Configuration Request Status” on page 346
“Peer Controller > Configuration Enable/Disable” on page 348
“WIDS AP Configuration” on page 351
“WIDS Client Configuration” on page 354
“Local OUI Database Summary” on page 357
WLAN > WDS Configuration
“WDS Group Configuration” on page 359
“WDS AP Configuration” on page 364
“WDS Link Configuration” on page 366
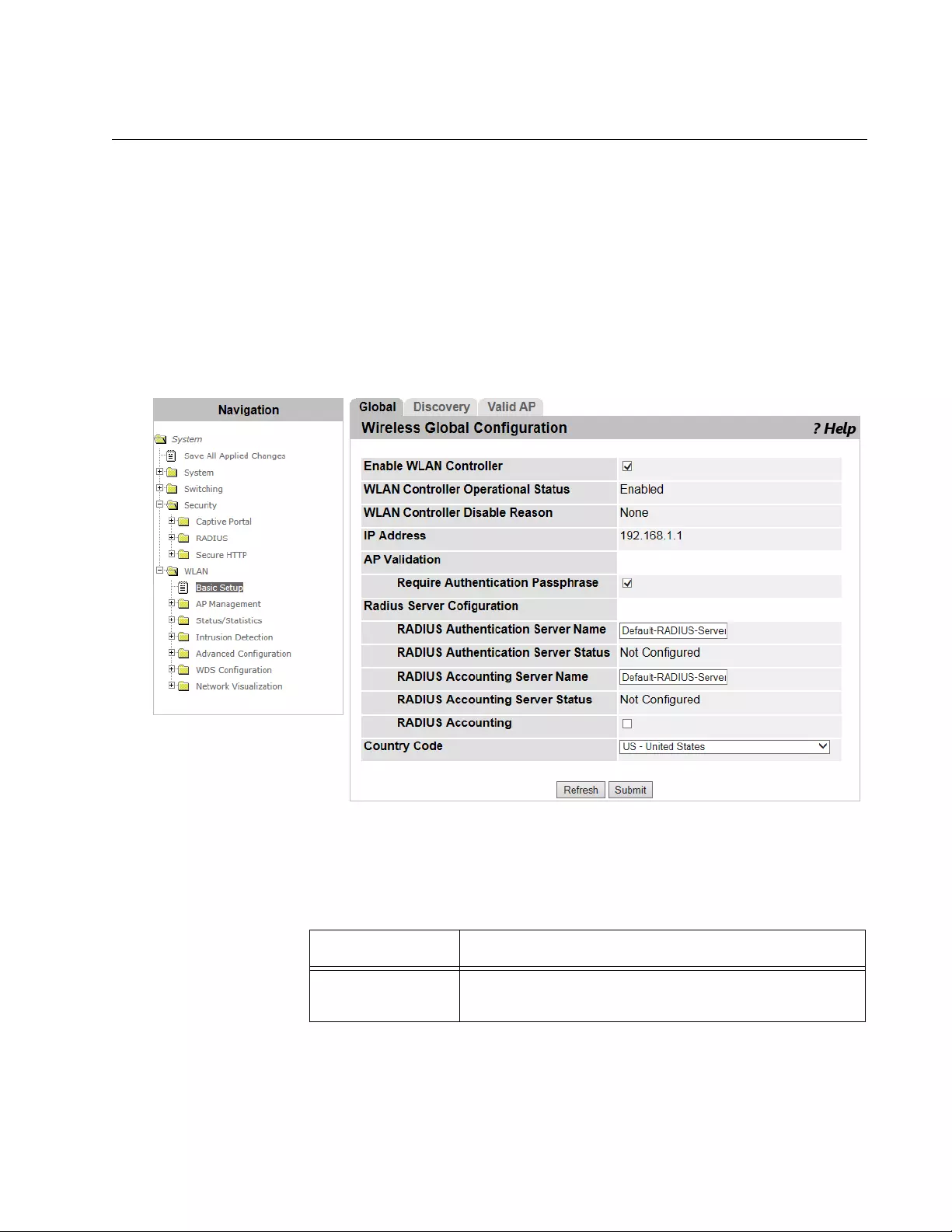
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
191
WLAN Basic Setup > Global
From the Wireless Global Configuration page, you can enable or disable
the WLAN Controller. You can also view and modify the basic settings.
To enable or disable the WLAN Controller, view, and modify the basic
settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup.
The Wireless Global Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 102.
Figure 102. Wireless Global Configuration Page
2. Observe and modify the settings described in Table 66.
Table 66. Wireless Global Configuration
Field Description
Enable WLAN
Controller
Check the checkbox to enable the WLAN
Controller.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
192
WLAN Controller
Operational
Status
Displays the status of the WLAN Controller. The
options are:
Enabled
Disabled
Enable Pending
Disable Pending
WLAN Controller
Disable Reason
Displays the reason why the WLAN Controller is
disabled. The options are:
None - The WLAN Controller is enabled or
the reason is unknown.
Admin - The WLAN Controller is disabled in
the Enable WLAN Controller field.
No SSL Files - A Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL) file does not exist.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller.
AP Validation
Require
Authentication
Passphrase
Check the checkbox to require the WLAN
Controller to authenticate access points with the
pass phrase.
If the access point is in the Managed mode, you
can specify the pass phrase in the Valid AP list.
See “WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP” on page 198.
If the access point is in the standalone mode, you
must specify the pass phrase on the access point.
RADIUS Server Configuration
RADIUS
Authentication
Server Name
Specifies the name of the RADIUS authentication
server. This server is used for authentication when
no RADIUS authentication server is configured on
the WLAN Controller. To see configured RADIUS
servers, see “RADIUS Named Server Status” on
page 176.
RADIUS
Authentication
Server Status
Displays whether the RADIUS authentication
server is configured on the WLAN Controller. To
add a RADIUS authentication server, see “RADIUS
Server Configuration” on page 175.
Table 66. Wireless Global Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
193
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
RADIUS
Accounting
Server Name
Specifies the name of the RADIUS accounting
server. This server is used for accounting when no
RADIUS accounting server is configured on the
WLAN Controller. To see configured RADIUS
accounting servers, see “Named Accounting
Server Status” on page 182.
RADIUS
Accounting
Server Status
Displays whether the RADIUS accounting server is
configured on the WLAN Controller. To add a
RADIUS accounting server, see “Accounting
Server Configuration” on page 181.
RADIUS
Accounting
Check the checkbox to enable RADIUS
accounting.
Country Code Specifies the country code that is applied to the
managed access points. For example, if the
country applied to the access points is the United
States, select “US - United States” from the select
list.
Before managing access points, you must specify
the country code.
Table 66. Wireless Global Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
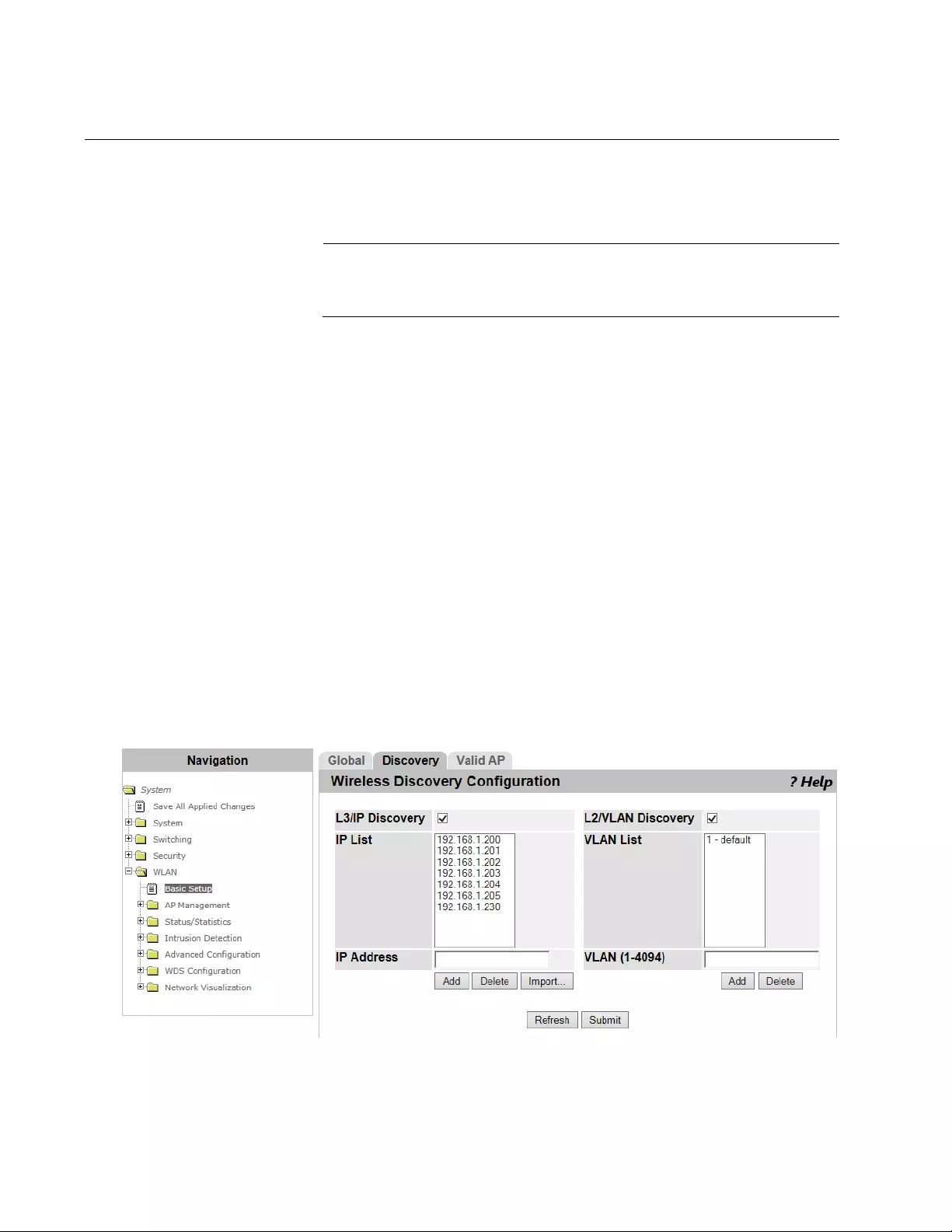
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
194
WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery
To manage access points, the WLAN Controller discovers access points
or access points discover the WLAN Controller.
Note
To configure access points to be discovered, see the documents for
the access points.
The WLAN Controller discovers access points by sending discovery
packets to a list of the IP addresses and/or sending broadcast discovery
frames to VLAN’s. In addition to access points, the WLAN Controller
discovers peer controllers with the same discovery messages.
From the Wireless Discovery Configuration page, you can configure two
methods for the WLAN Controller to discover access points:
Layer 3: IP address
Layer 2: VLAN
Discovery by L3
IP Discovery
To enable the L3/IP discovery, view a list of the IP addresses, add the IP
address of an access point, or delete it, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Discovery tab.
The Wireless Discovery Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 103.
Figure 103. Wireless Discovery Configuration Page
2. Specify the following fields described in Table 67 on page 195.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
195
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Importing a List
of IP Addresses
You can add a list of IP addresses for L3/IP Discovery by importing a CVS
file. To upload a list of IP addresses, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Discovery tab.
The Wireless Discovery Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 103 on page 194.
2. Click Import...
The L3/IP Discovery List Importing page is displayed.
3. Import a CVS file onto the system.
Table 67. Wireless Discovery Configuration (L3/IP)
Field Description
L3/IP Discovery Check the checkbox to enable L3/IP discovery.
IP List Displays a list of the IP addresses that the WLAN
Controller sends discovery packets to. You can
add up to 256 IP addresses.
To delete IP addresses from the list, select one or
more IP addresses.
IP Address Specify an IP address to add to the list.
(Buttons) Click one of the buttons as needed:
Add - The IP address specified in the IP
Address field is added to the IP List.
Delete - The selected IP address is deleted
from the IP List.
Import... - Moves to the L3/IP Discovery
List Importing page to upload a CVS file.
The IP addresses in the file are added to
the IP List.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
196
Guidelines for
Importing a CVS
file
Here are guidelines for importing a CVS file to upload IP addresses:
Spaces are not allowed in the name of the CVS file.
Commas are not allowed as delimiters in the CVS file.
Enter one access point in a row. Figure 104 shows an example of
the CVS file created with Microsoft Excel.
Figure 104. CVS File for a List of IP Addresses
Discovery by L2
VLAN Discovery
To enable the L2/VLAN discovery, view a list of the VLAN’s, add a VLAN,
or delete it, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Discovery tab.
The Wireless Discovery Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 103 on page 194.
2. Specify the following fields described in Table 68 on page 196.
Table 68. Wireless Discovery Configuration (L2/VLAN)
Field Description
L2/VLAN
Discovery
Check the checkbox to enable L2/VLAN discovery.
VLAN List Displays a list of the VLAN ID’s that the WLAN
Controller sends broadcast discovery frames to.
You can add up to 16 VLAN’s.
Delete VLAN’s from the list, select one or more
VLAN’s from the list.
VLAN (1-4094) Specify a VLAN to add to the list.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
197
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
(Buttons) Click one of the buttons as needed:
Add - The VLAN specified in VLAN is
added to the VLAN List.
Delete - The selected VLAN is deleted from
the VLAN List.
Table 68. Wireless Discovery Configuration (L2/VLAN) (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
198
WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP
From the Valid Access Point Summary page, you can view a list of valid
access points. The valid access point is an access point to be managed by
the WLAN Controller. You can also add access points to the valid AP list,
delete them, and modify the properties.
Note
You can add the MAC addresses of peer controllers to the valid AP
list. The WLAN Controller discovers peer controllers as well as
access points.
Steps for Access
Points to be
Managed
Here are steps for access points to be managed by the WLAN Controller:
1. Add the IP addresses of the access points to the IP List, or VLAN’s to
the VLAN list.
To specify IP addresses or VLAN’s, see “WLAN Basic Setup >
Discovery” on page 194.
Note
For an access point to discover the WLAN Controller, see the
documents for the access point.
2. The WLAN Controller sends discovery messages to the IP addresses
on the IP list or broadcast discovery messages to the VLAN’s on the
VLAN list.
After discovered, the access points on the valid AP list are managed
by the WLAN Controller. The access points not on the valid AP list are
listed on the Access Point Authentication Failure Status list. See.“AP
Authentication Failure” on page 297.
3. Perform one of the following actions:
Add the MAC address of the access point to be managed to the
Valid AP List.
Accept the access point to be managed from the Access Point
Authentication Failure Status page.
Accept the access point to be managed from the Rogue/RF Scan
page. See “Rogue/RF Scan” on page 276.
Viewing Valid AP
List
To view a list of valid access points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Valid AP tab.
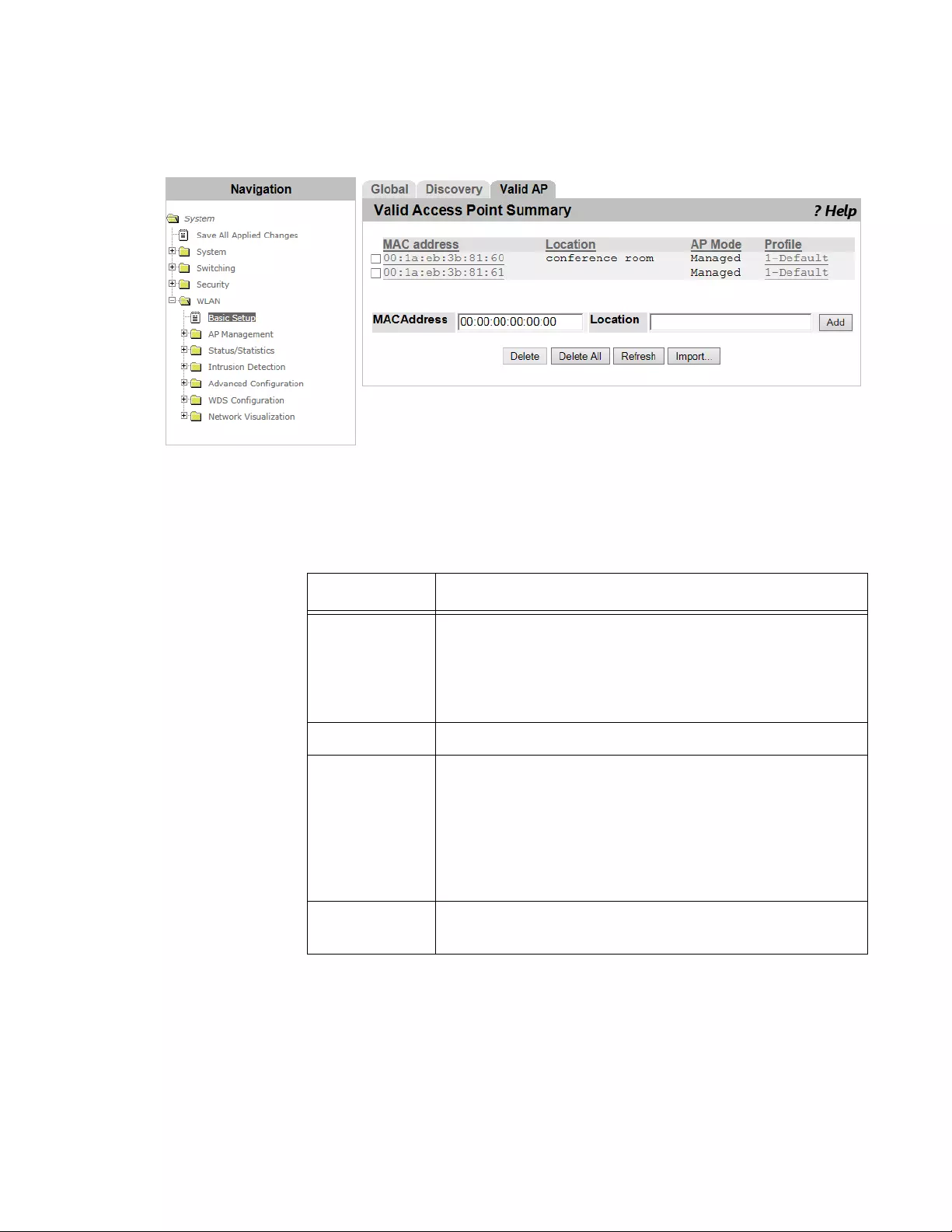
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
199
The Valid Access Point Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 105.
Figure 105. Valid Access Point Summary Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 69.
3. Click Refresh as needed.
Adding an Access
Point
To add an access point to the valid AP list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Valid AP tab.
Table 69. Valid Access Point Summary
Field Description
MAC address Displays the MAC address of an access point on the
valid AP list on the WLAN Controller.
Click the MAC address, Figure 106 on page 200 is
displayed.
Location Displays the location information of the access point.
AP Mode Displays the AP mode of the access point. The options
are:
Managed - Managed by the WLAN Controller
Standalone - Managed independently
Rogue - Classified as a threat by WIDS
Profile Displays the AP profile assigned to the access point.
Click the profile, Figure 162 on page 328 is displayed.
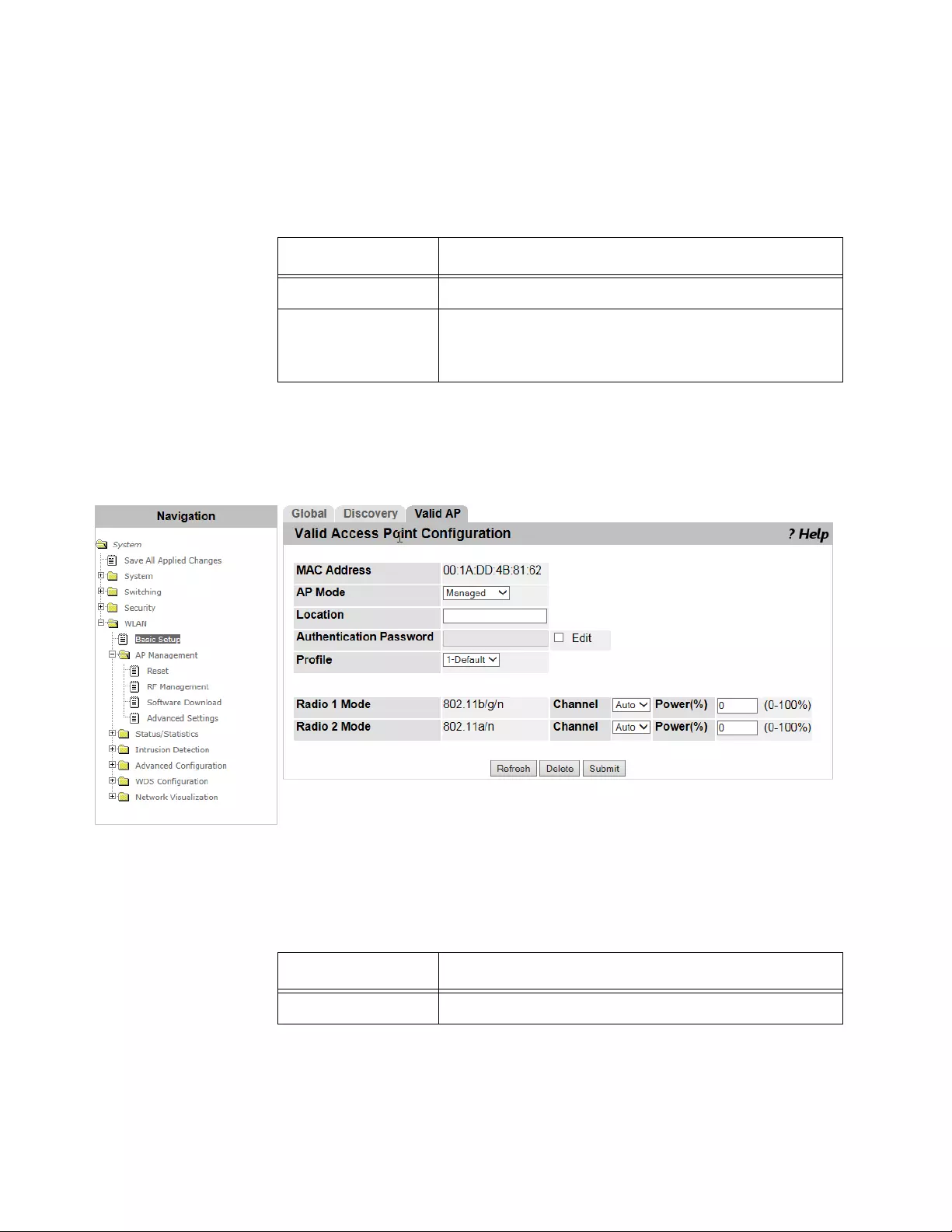
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
200
The Valid Access Point Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 105 on page 199.
2. Specify the fields described in Table 70.
3. Click Add.
The Valid Access Point Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 106.
Figure 106. Valid Access Point Configuration Page
4. Specify the fields described in Table 71.
Table 70. Valid Access Point Summary (Adding)
Field Description
MAC Address Specify the MAC address of the access point.
Location Specify the location information of the access
point. This is optional. The location can be up to 32
alphanumeric characters.
Table 71. Valid Access Point Configuration
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of an access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
201
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Delete — Cancels adding the access point.
Submit — Adds or modifies the access points with the settings and
saves them to the running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Importing a List
of Access Points
To import a list of access points with a CSV file, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Valid AP tab.
The Valid Access Point Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure
105 on page 199.
2. Click Import.
The Valid Access Point Database Importing page is displayed.
AP Mode Select the AP mode of the access point. The
options are:
Managed - Managed by the WLAN
Controller
Standalone - Managed independently
Rogue - Classified as a threat by WIDS
Location Specify the location information of the access
point. This is optional. The location can be up to 32
alphanumeric characters.
Authentication
Password
Specify the authentication password. Before
entering the value, you mush check the Edit
checkbox.
Edit Check the checkbox to enter the authentication
password.
Profile Select an AP profile.
Channel Select a channel from the select list.
Power Specify the power in percentage.
Table 71. Valid Access Point Configuration
Field Description
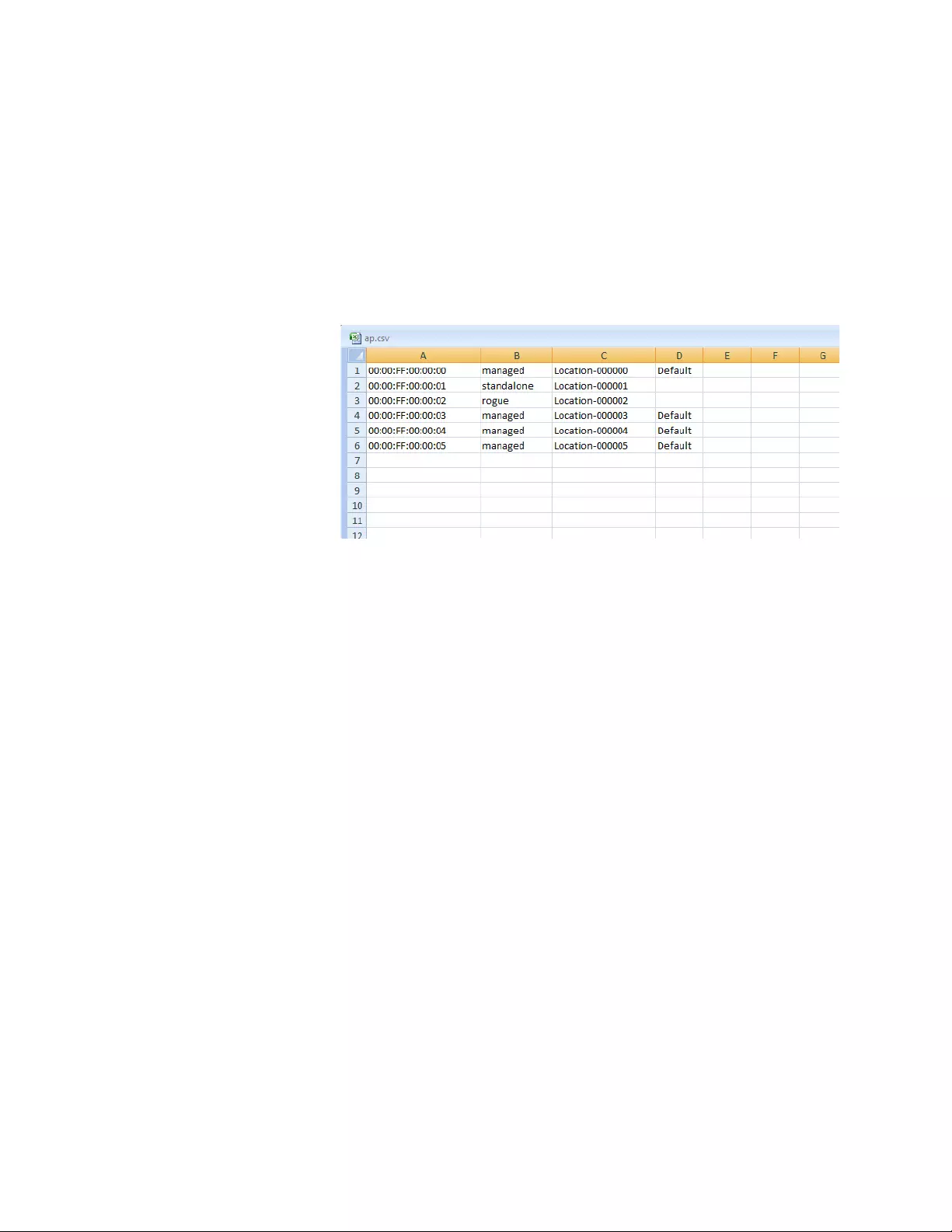
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
202
3. Import a CVS file onto the system.
Guidelines for
Importing a CVS
file
Here are guidelines for importing a CVS file to upload a list of access
points:
Spaces are not allowed in the name of the CVS file.
Commas are not allowed as delimiters in the CVS file.
Enter one access point in a row. Figure 107 shows an example of
the CVS file created with Microsoft Excel.
Figure 107. CVS File for a List of Access Points
Modifying the
Access Point
To modify the settings of the access point on the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Valid AP tab.
The Valid Access Point Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 105 on page 199.
2. Click the MAC address of the access point you want to modify its
settings.
The Valid Access Point Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 106 on page 200.
3. Go to step 4 in “Adding an Access Point” on page 199.
Deleting Access
Points
To delete the access point from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Basic Setup and click the
Valid AP tab.
The Valid Access Point Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 105 on page 199.
2. Check the checkbox at the left of the MAC address of the access point
that you want to delete.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
203
To delete all the access points on the list, skip this step.
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete — Deletes the selected access point.
Delete All — Deletes all the access points on the list.
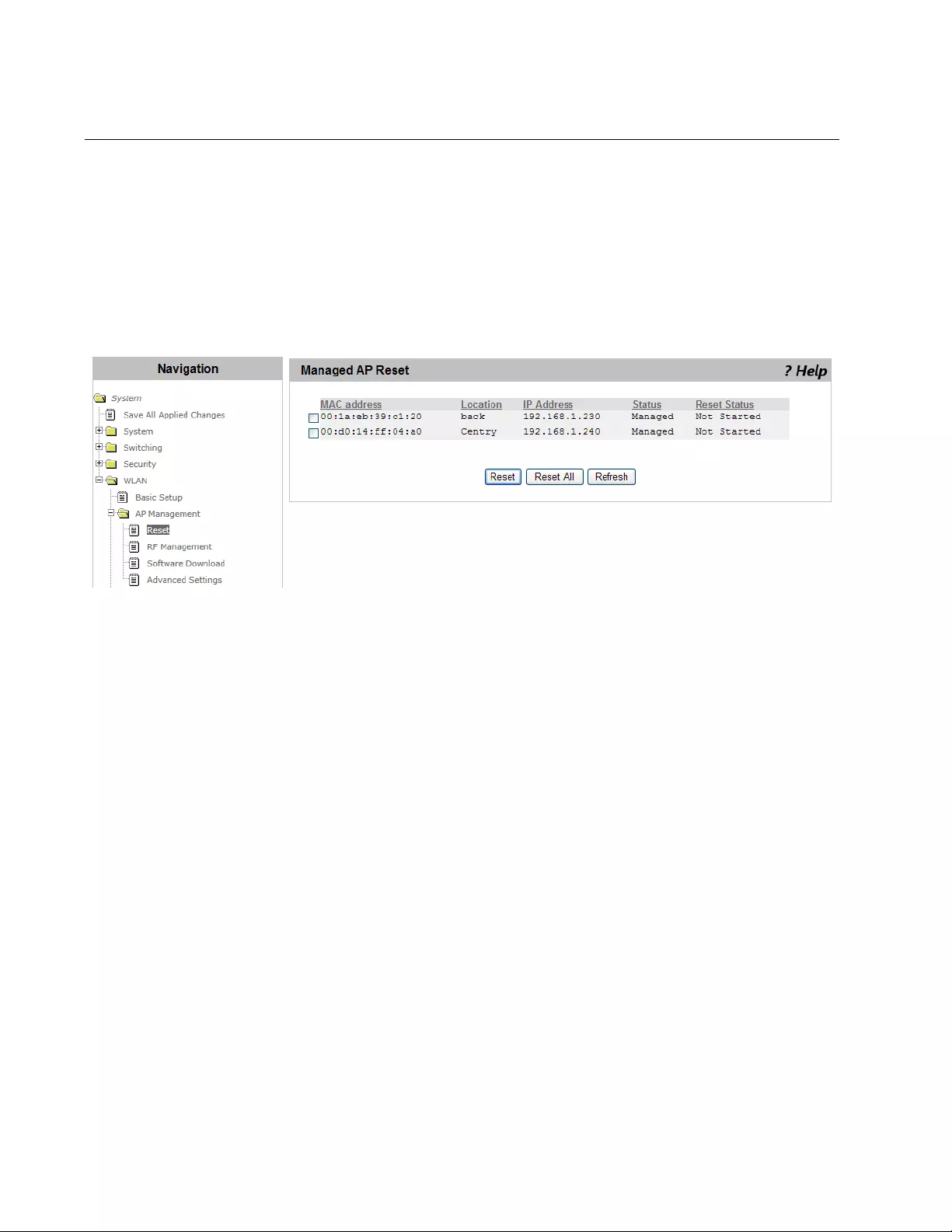
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
204
AP Management Reset
From the Managed AP (Access Point) Reset page, you can reboot the
selected access points.
To reboot access points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management > Reset.
The Managed AP Reset page is displayed as shown in Figure 108.
Figure 108. Managed AP Reset Page
2. Check the checkbox next to the MAC address of the access point that
you want to reboot.
3. Click the following buttons:
Reset — Reboots the selected access points.
Reset All — Reboots all the access points on the list.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
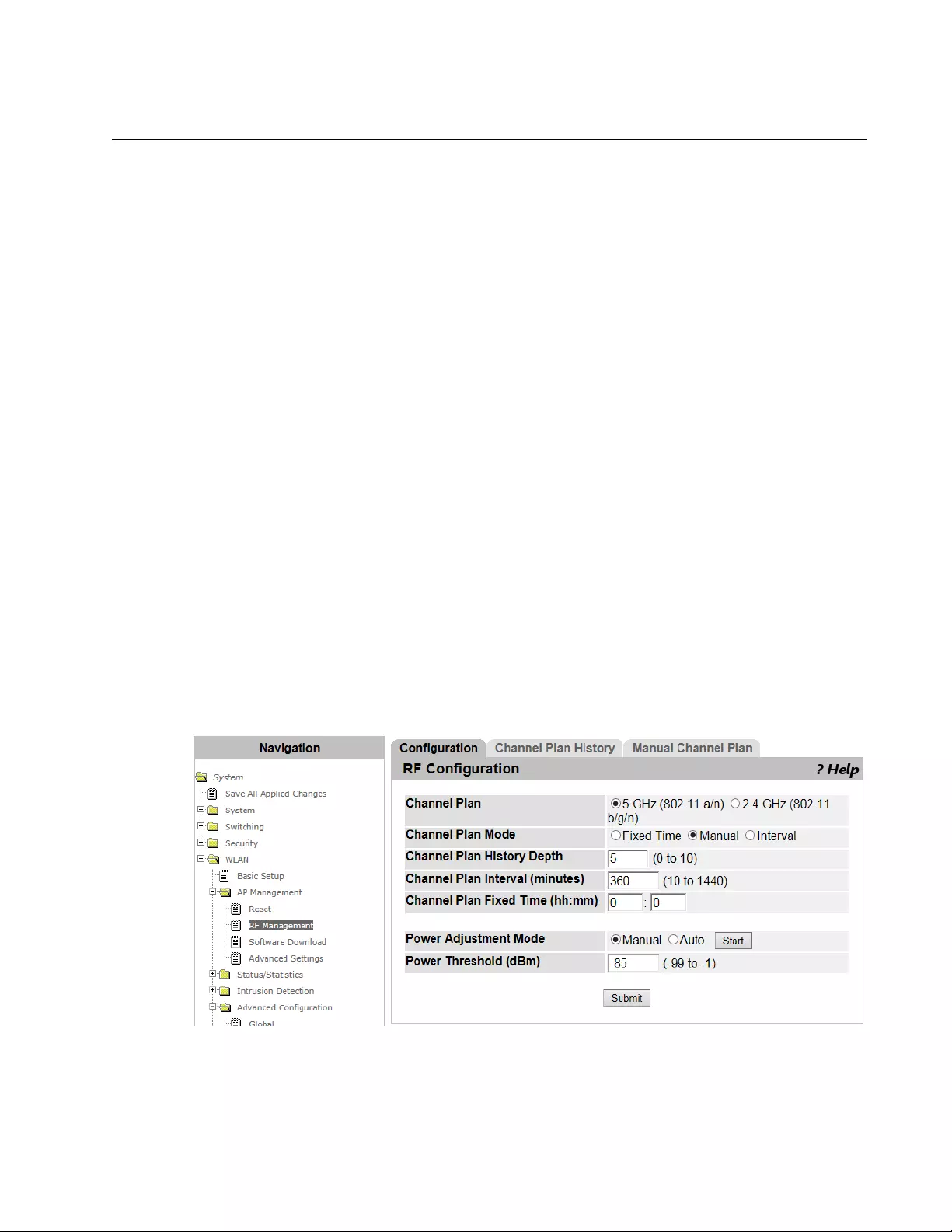
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
205
RF Management > Configuration
From the RF Configuration page, you can view and modify the RF settings
on managed access points.
Guidelines for the
Channel Plan
Algorithm
The WLAN Controller has the channel plan algorithm that evaluates
interference of the channels used by the access points and changes the
channels when interference is detected.
Here are guidelines for running the channel plan algorithm:
The WLAN Controller automatically runs the channel plan
algorithm on managed access points when Channel Plan Mode is
selected Fixed Time or Interval.
The WLAN Controller does not run the channel plan algorithm on
the access point if the channel is manually assigned to the access
point. See “Changing the Channel or Power” on page 217.
The WLAN Controller does not run the channel plan algorithm on
the access point when Automatic Channel is disabled in the AP
profile that the access point is applied to. See “Access Point Profile
Radio Configuration” on page 331.
To view and modify the RF settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management > RF
Management.
The RF Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 109.
Figure 109. RF Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 72 on page 206.
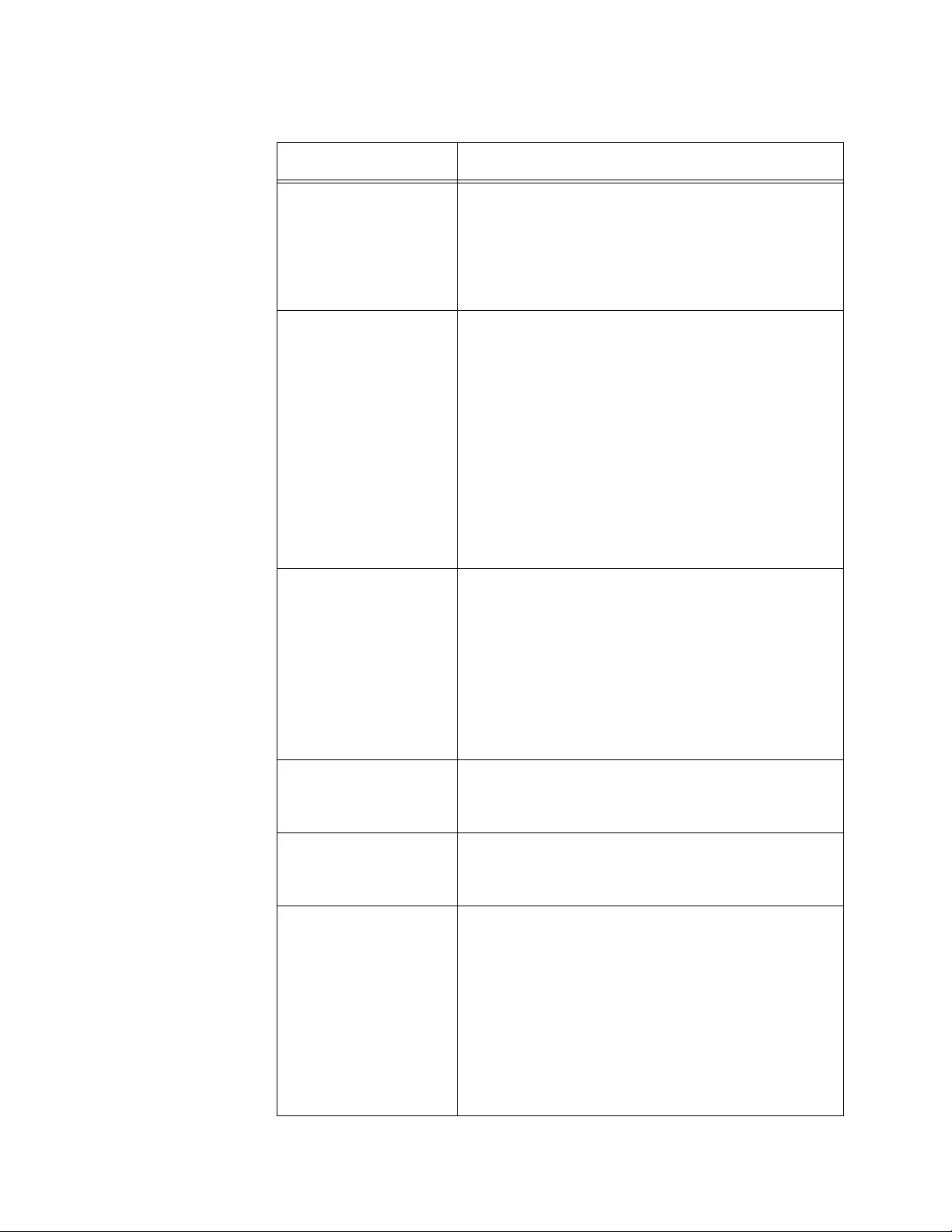
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
206
Table 72. RF Configuration
Field Description
Channel Plan Specifies the RF band that the access points use
to send and receive data. The options are:
5 GHz (802.11 a/n) - This is the default
setting.
2.4 GHz (802.11 b/g/n)
Channel Plan Mode Specifies the channel plan mode. The options
are:
Fixed Time - The channel plan algorithm
runs at the time specified in Channel
Plan Fixed Time (hh:mm) in the day.
Manual - The channel plan algorithm and
allocation are manually controlled and
started. This is the default setting.
Interval - The channel plan algorithm
runs at intervals that specified in Channel
Plan Interval.
Channel Plan History
Depth
Specifies how frequently the channel is
reassigned to the access point. The default
value is 5.
For example, when the depth is 5, after the
channel is assigned to the access point, the
channel plan algorithm does not change the
channel for the access point for next five times of
channel plan algorithm runs.
Channel Plan
Interval (minutes)
Specifies the interval that the channel plan
algorithm runs when Interval is selected as
Channel Plan Mode.
Channel Plan Fixed
Time (hh:mm)
Specifies the time that the channel plan
algorithm runs when Fixed Time is selected as
Channel Plan Mode.
Power Adjustment
Mode
Specifies the transmit RF power adjustment
mode. The options are:
Manual - Manually starts the transmit RF
power adjustment for the access points.
You must click Start after selecting this
option.
Auto - The WLAN Controller
automatically adjusts the transmit RF
power for the access points.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
207
3. Click Submit.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Power Threshold
(dBm)
Specifies the RF power threshold. The access
points managed by the WLAN Controller adjust
the RF power using the power threshold.
For example, access point 1 transmits the RF
and other access points detect the RF from
access point 1. Among the other access points,
access point 2 detects the highest level of RF
power from access point 1. When access points
1 and 2 are using the same channel and the RF
level that access point 2 detects is greater than
the power threshold, the power threshold of
access point 2 is lowered by 5%.
Table 72. RF Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
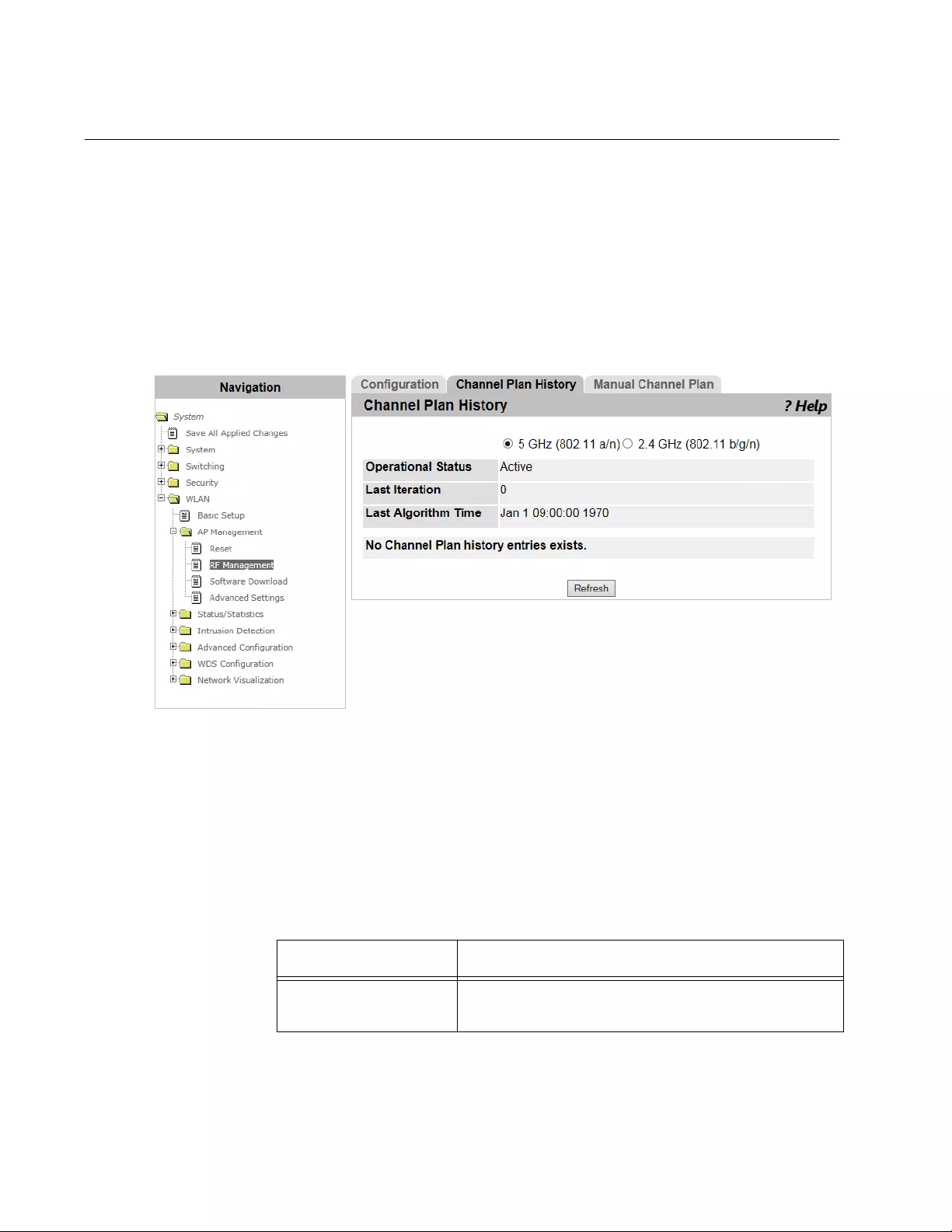
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
208
RF Management > Channel Plan History
From the Channel Plan History page, you can view the channel history for
managed access points.
To view the channel history, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management > RF
Management and click the Channel Plan History tab.
The Channel Plan History page is displayed as shown in Figure 110.
Figure 110. Channel Plan History Page
2. Select one of the following radio bands:
5 GHz (802.11 a/n)
2.4 GHz (802.11 b/g/n)
3. Observe the fields described in Table 73.
Table 73. Channel Plan History
Field Description
Operational Status Displays whether the channel plan algorithm is
set to run automatically or not.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
209
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Last Iteration Displays how many time the channel plan
algorithm runs since the current channel was
assigned. When this value reaches to the
channel plan history depth, the channel plan
algorithm reassigns a new channel to the access
point. See “Channel Plan History Depth” on
page 206.
Last Algorithm Time Displays the date and time when the channel
plan algorithm run last time.
Table 73. Channel Plan History (Continued)
Field Description
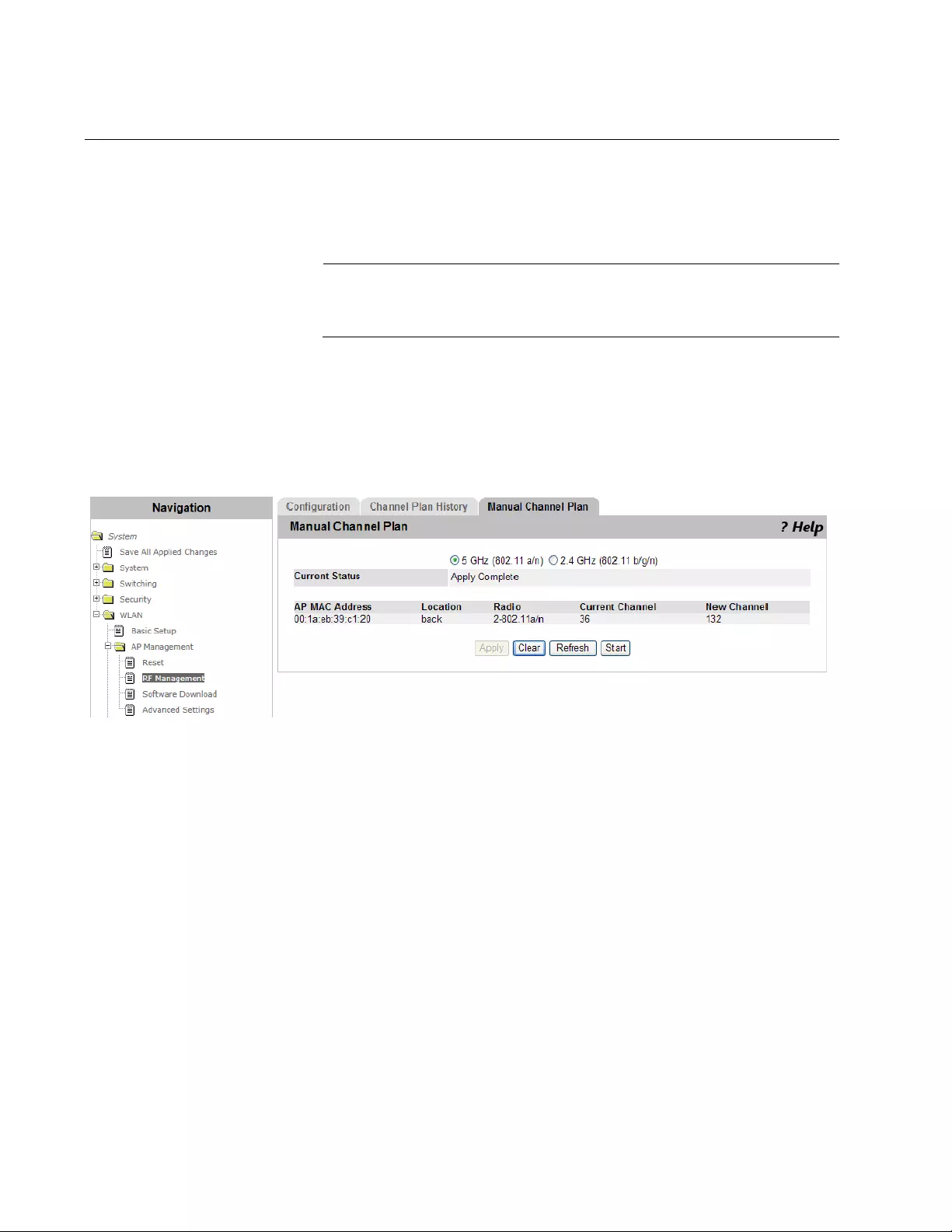
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
210
RF Management > Manual Channel Plan
From the RF Management > Manual Channel Plan page, you can start the
channel plan algorithm manually and apply the suggested new channel to
the access points.
Note
The channel plan algorithm only suggests a new channel. You must
click the Apply button to apply the new channel.
To start the channel plan algorithm and apply the change, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management > RF
Management and click the Manual Channel Plan tab.
The Manual Channel Plan page is displayed as shown in Figure 111.
Figure 111. Manual Channel Plan Page
2. Select one of the following channel plan to run the algorithm:
5 GHz (802.11 a/n)
2.4 GHz (802.11 b/g/n)
3. Click Start.
4. Observe the status and suggested channel plans described in
Table 74 on page 211.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
211
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Apply — Applies the suggested channel to the access points when
the algorithm is completed.
Clear — Clears the suggested plan.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Table 74. Manual Channel Plan
Field Description
Current Status Displays the status of executing the channel plan
algorithm. The options are:
Algorithm In Progress - The channel plan
algorithm is running.
Algorithm Complete - The channel plan
algorithm is completed and the result is
displayed.
Apply In Progress - The result of channel
plan algorithm is applying to the access point.
Apply Complete - The application of the
channel plan algorithm is completed.
None - The channel plan algorithm has not
been started manually.
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Location Displays the location information of the access point.
Radio Displays the radio band of the access point.
Current
Channel
Displays the current channel of the access point.
New Channel Displays the suggested new channel for the access
point.
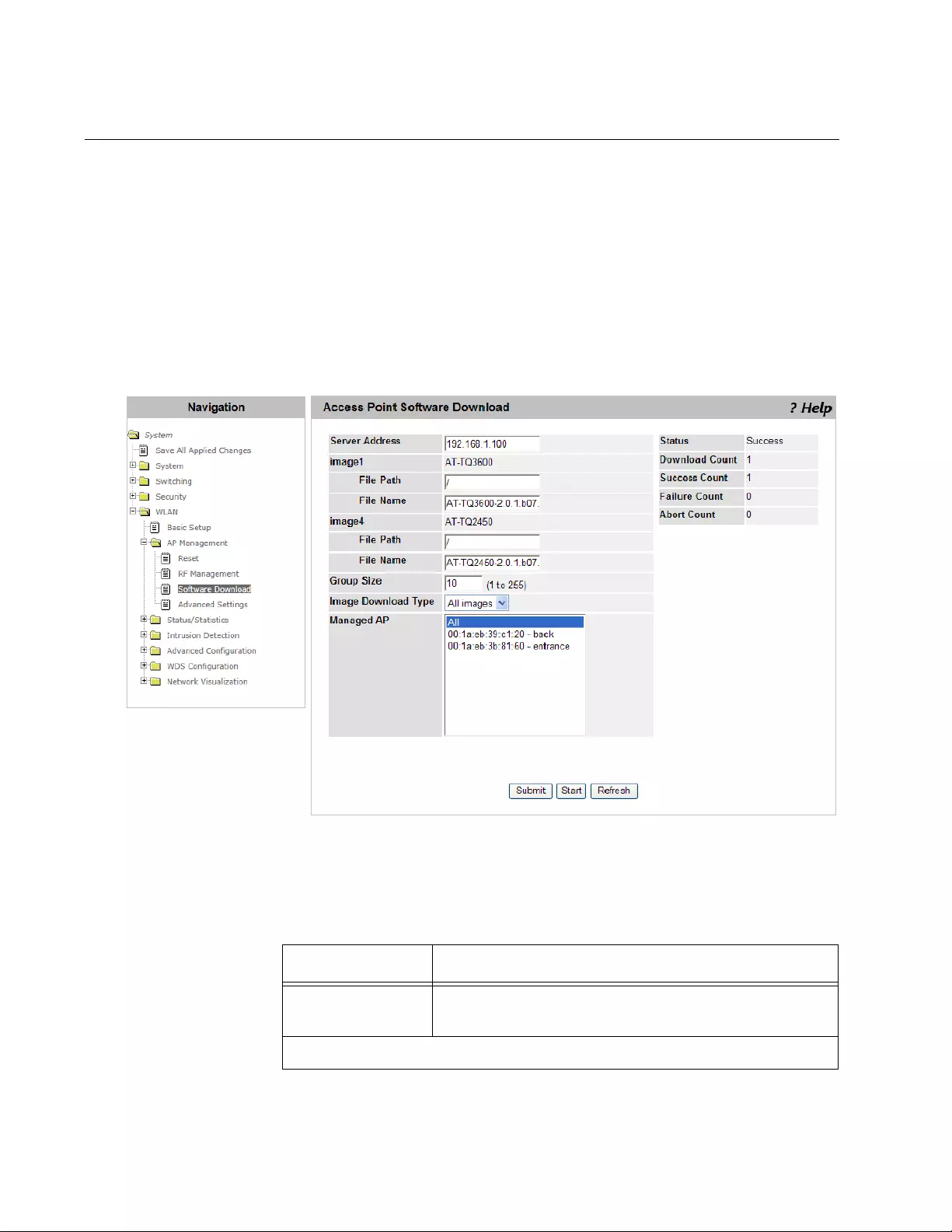
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
212
Access Point Software Download
From the Access Point Software Download page, you can upgrade
software on the access points that the WLAN Controller manages.
To upgrade software on the access points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, click System or go to WLAN > AP
Management > Software Download.
The Access Point Software Download page is displayed as shown in
Figure 112.
Figure 112. Access Point Software Download Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 75.
Table 75. Access Point Software Download
Field Description
Server Address Specify the IP address of the TFTP server where
the software resides.
image1: AT-TQ3600
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
213
3. Click Start.
The status is displayed.
4. Observe the status and counters described in Table 76 on page 214.
File Path Specify the path of the AT-TQ3600 software file on
the TFTP server.
File Name Specify the name of the AT-TQ3600 software file.
image4: AT-TQ2450
File Path Specify the path of the AT-TQ2450 software file on
the TFTP server.
File Name Specify the name of the AT-TQ2450 software file.
Group Size Specify the number of access points that you want
to upgrade software at a time in order to prevent
the TFTP server from being overloaded.
Image Download
Type
Specify the file image that you want to upgrade.
The options are:
All images- Both AT-TQ3600 and AT-
TQ2450 software files
image1 - AT-TQ3600 software file
image2 - Not supported
image3 - Not supported
image4 - AT-TQ2450 software file
Managed AP Select access points that you want to upgrade. You
can select multiple access points using the Ctrl key.
Allied Telesis recommends upgrading all the
access points that the WLAN Controller manages
at the same time.
Table 75. Access Point Software Download (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
214
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 76. Access Point Software Download after Start
Field Description
Status Displays the progress of upgrading the software to
access points. The options are:
Not Started - The WLAN Controller has not
started downloading the software.
Requested - The WLAN Controller
requested access points to download
software.
Code Transfer in Progress - Downloading
is in progress.
Failure - Downloading failed.
Aborted - Downloading was aborted before
the access point downloads software from
the TFTP server.
NVRAM-Update-In-Progress -
Downloading was successful. The WLAN
Controller sent the “reset” command.
Success - Downloading was successful. All
the access points are connected to the
WLAN Controller.
Download Count Displays the number of access points that
downloaded software.
Success Count Displays the number of access points that have the
success status.
Failure Count Displays the number of access points that have the
failure status.
Abort Count Displays the number of access points that have the
abort status.
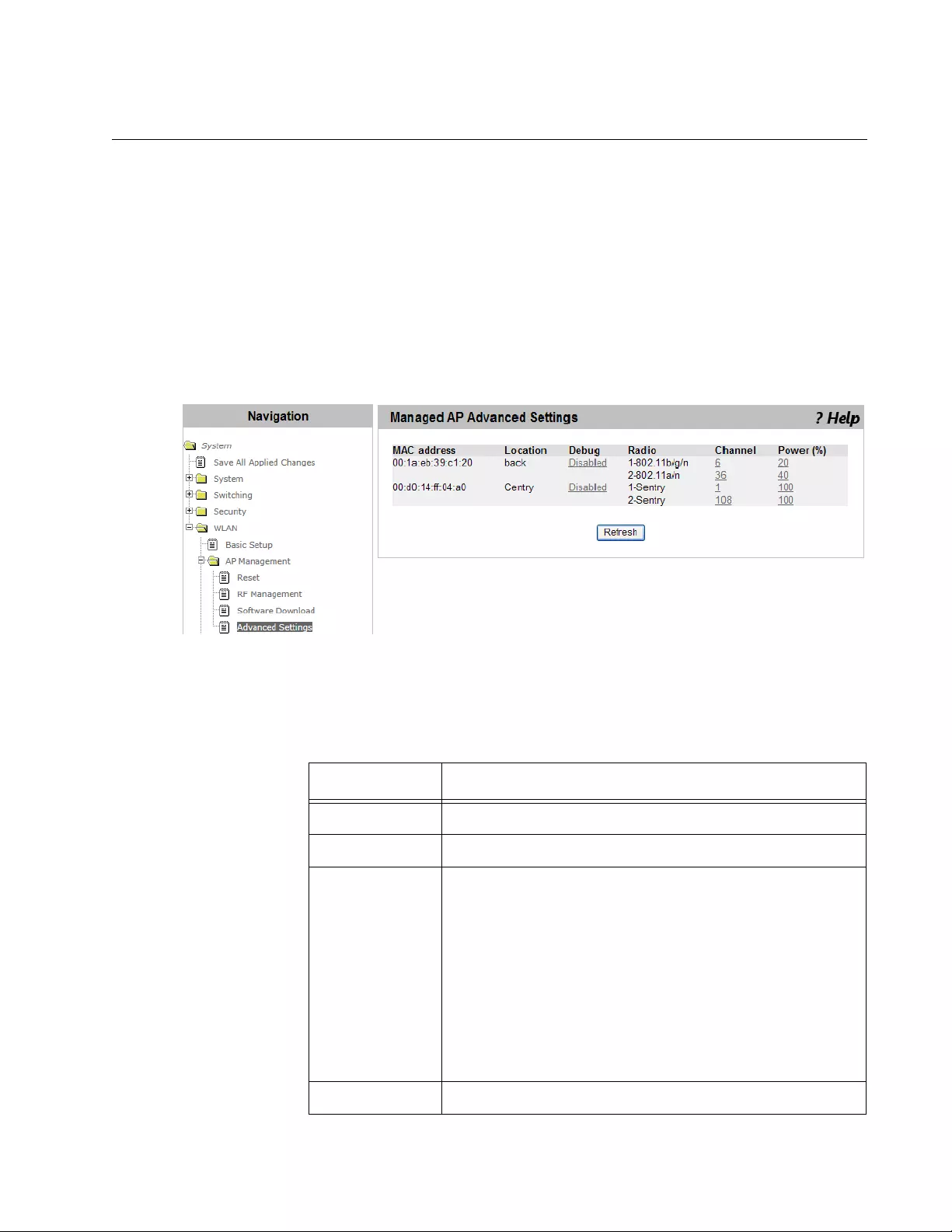
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
215
Managed AP Advanced Settings
From the Managed AP Advanced Settings page, you can view AP
advanced settings, change the debug status, channel, and power level.
Viewing the AP
Advanced
Settings
To view the AP advanced settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management >
Advanced Settings.
The Managed AP Advanced Settings page is displayed as shown in
Figure 113.
Figure 113. Managed AP Advanced Settings Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 77.
Table 77. Managed AP Advanced Settings
Field Description
MAC address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Location Displays the location information of the access point.
Debug Displays the status of accessing the access point
through the Web GUI. The options are:
Disabled - You cannot access the access
point through the Web GUI.
Set Requested - The request is made.
Set in Progress - The request is in progress.
Enabled - You can access the access point
through the Web GUI.
Radio Displays the RF band of the access point.
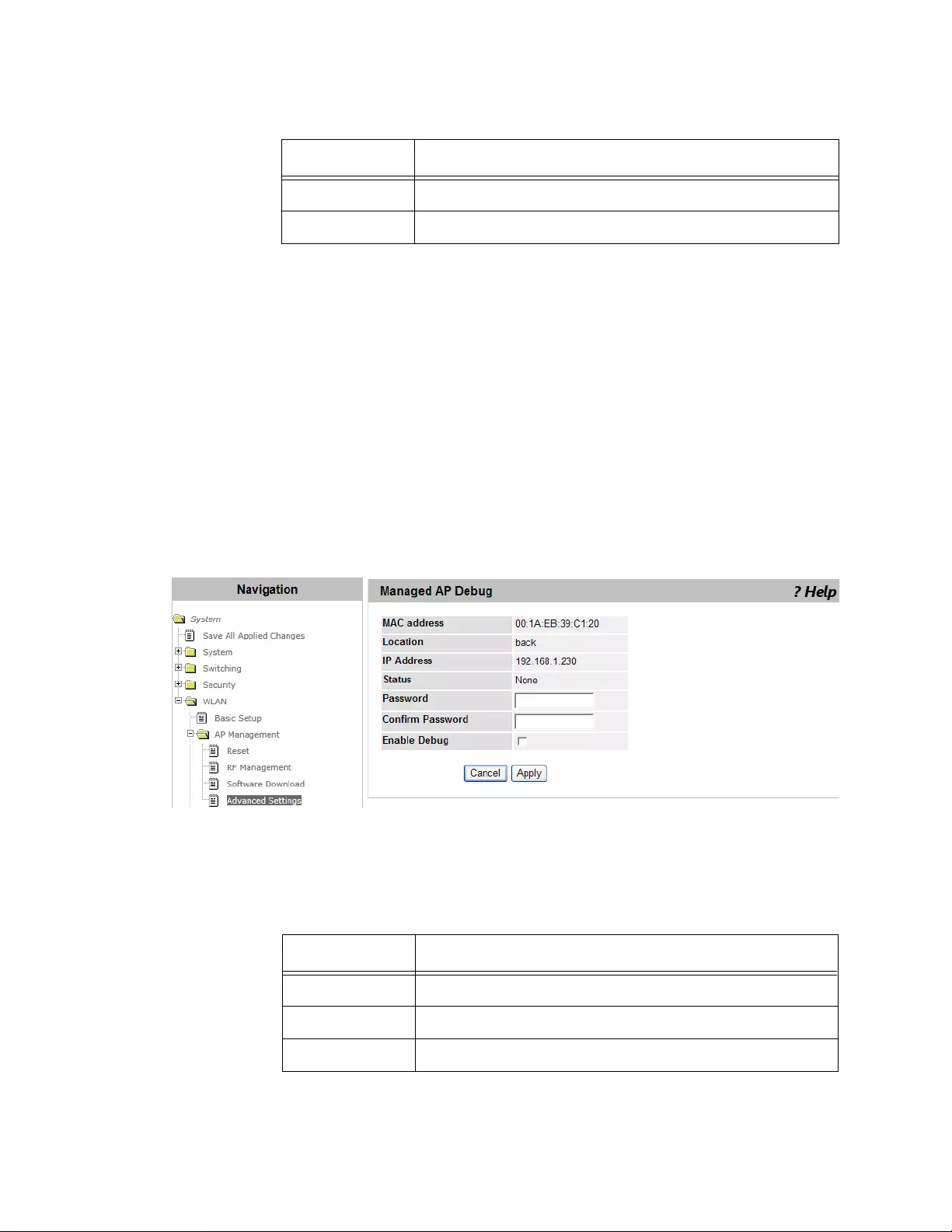
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
216
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Changing the
Debug Status
To change the debug status, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management >
Advanced Settings.
The Managed AP Advanced Settings page is displayed as shown in
Figure 113 on page 215.
2. Click the value in the Debug column for the access point that you want
to change the status.
The Managed AP Advanced Debug page is displayed as shown in
Figure 114.
Figure 114. Managed AP Debug Page
3. Specifies the fields described in Table 78 on page 216.
Channel Displays the channel assigned to the access point.
Power Displays the RF power level of the access point.
Table 77. Managed AP Advanced Settings (Continued)
Field Description
Table 78. Managed AP Debug
Field Description
MAC address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Location Displays the location information of the access point.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
217
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Cancel — Cancels the changes.
Apply — Applies the changes.
Changing the
Channel or
Power
To change the channel or power level of the access point, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > AP Management >
Advanced Settings.
The Managed AP Advanced Settings page is displayed as shown in
Figure 113 on page 215.
2. Click the value in the Channel or Power column for the access point
that you want to change its value.
The Managed AP Channel/Power Adjust page is displayed as shown
in Figure 115 on page 218.
Status Displays the debug status.
The options are:
None - No setting.
Set Requested - The request of changing the
debug status is made.
Set Complete - The process of enabling or
disabling the debug status is completed.
Password Enter the password for logging in to the Web console
of the access point. The default password is “friend.”
Confirm
Password
Re-enter the password.
Enable Debug Check the checkbox to enable the debugging.
Table 78. Managed AP Debug (Continued)
Field Description
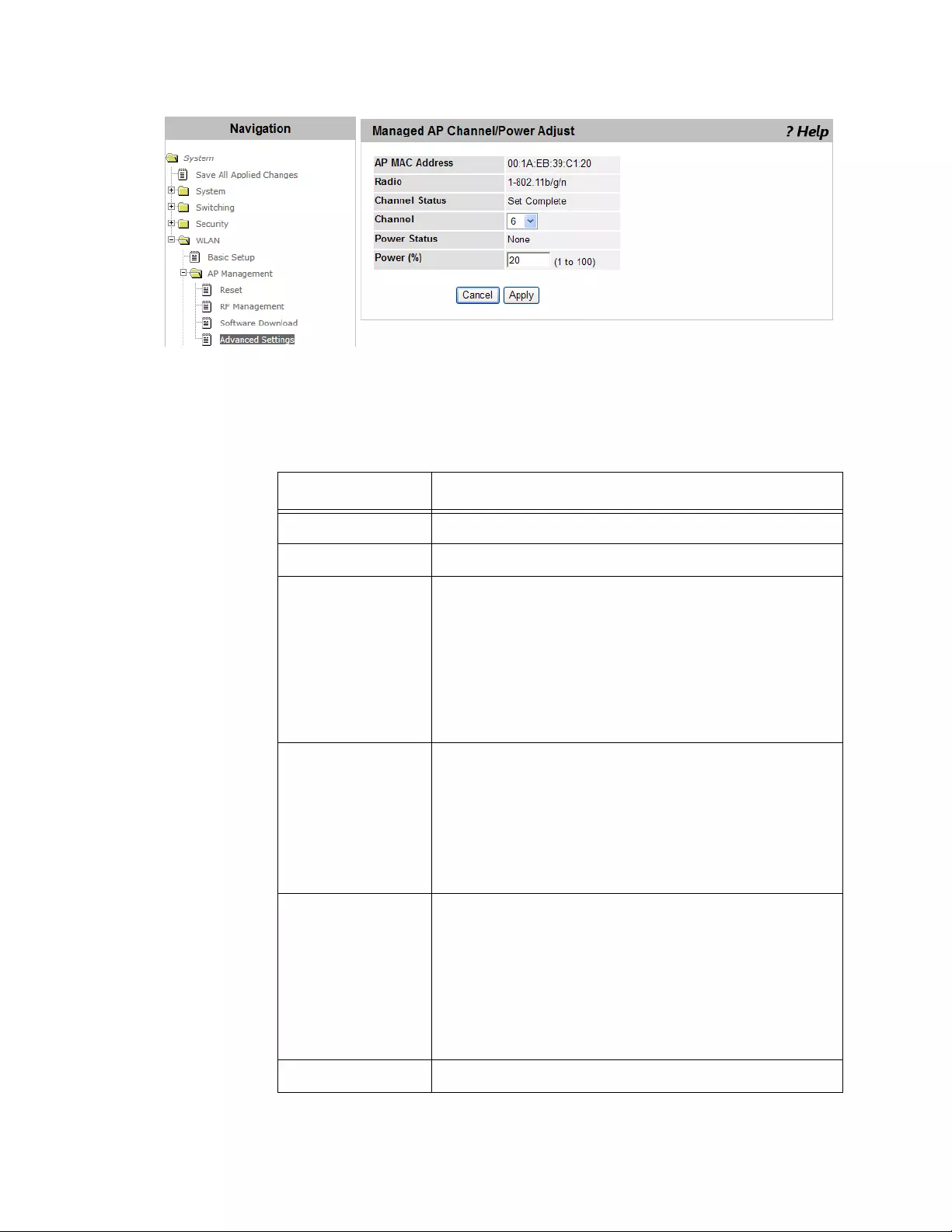
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
218
Figure 115. Managed AP Channel/Power Adjust Page
3. Specify the fields described in Table 79.
Table 79. Managed AP Channel/Power Adjust
Field Description
AP MAC address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Radio Displays the radio band of the access point.
Channel Status Displays the status of channel status of the access
point. The options are:
None - No setting.
Set Requested - The request is made.
Set Complete - The process of enabling or
disabling is complete.
Channel Select the channel from the select list. When Auto is
selected, the WLAN Controller adjust the channels
of the access points to reduce radio interference.
When the access point reboots or the AP profile is
applied to the access point, the manually specified
channel is overwritten.
Power Status Displays the power status of the access point. The
options are:
None - No setting.
Set Requested - The request is made.
Set Complete - The process of enabling or
disabling is complete.
Power (%) Change the power level. The range is 1 to 100%.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
219
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Cancel — Cancels the changes.
Apply — Applies the changes.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
220
Status/Statistics > Global
From the Wireless Global Status/Statistics page, you can view the status
and statistics:
Global Status and Statistics - Access points and AP clients
managed by the peer group
Controller Status - Status about each WLAN Controller in the peer
group
IP Discovery - Communications between the WLAN Controller and
peer controllers or access points
Configuration received - Configuration received from another peer
controller
Viewing Global
Status and
Statistics
To view the status and statistics about the access points and AP clients
that the WLAN Controllers manage including the information received
from peer controllers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics.
The Wireless Global Status/Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 116 on page 221.
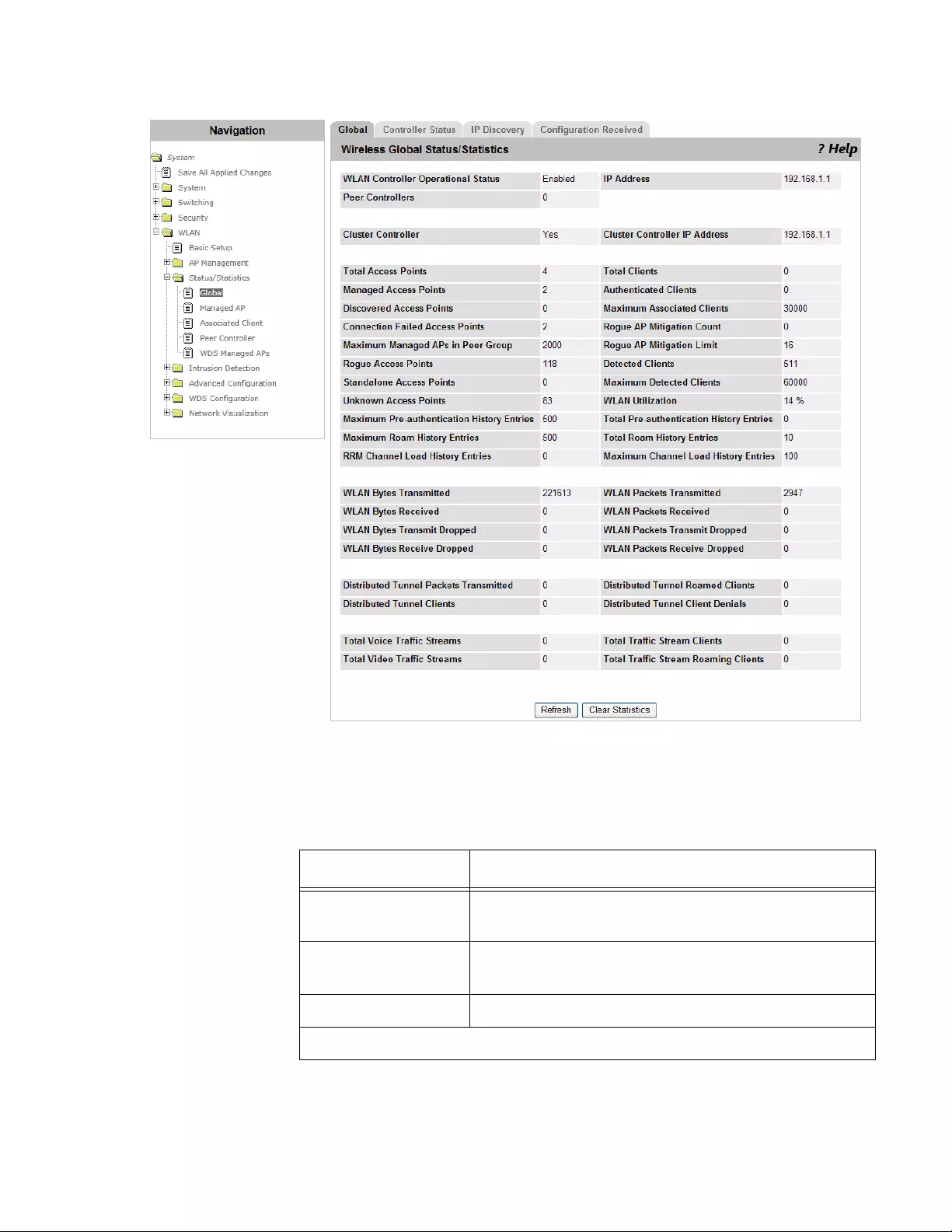
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
221
Figure 116. Wireless Global Status/Statistics Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 80 on page 221.
Table 80. Wireless Global Status/Statistics
Field Description
WLAN Controller
Operational Status
Displays whether the WLAN Controller is enabled
or disabled.
Peer Controllers Displays the number of the peer controllers in the
peer group.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
222
Cluster Controller Displays whether the WLAN Controller is the
cluster controller or not.
The cluster controller is a root controller in a peer
group setting. WLAN Controllers under the peer
group report information of all the managed access
points and their AP clients as well as the results of
RF scans to the cluster controller.
Cluster Controller
IP Address
Displays the IP address of the cluster controller in
the peer group.
Total Access Points Displays the total number of the following access
points:
Managed Access Points
Connection Failed Access Points
Discovered Access Points.
Managed Access
Points
Displays the number of access points that are
successfully authenticated and actively connected
to the WLAN Controller.
Discovered Access
Points
Displays the number of access points that are
discovered or authenticated, but not configured
completely.
Connection Failed
Access Points
Displays the number of access points that were
authenticated before, but are not currently
connected to the WLAN Controller.
Maximum Managed
APs in Peer Group
Displays the maximum number of access points
that the peer group manages.
Rogue Access
Points
Displays the number of rogue access points that
the WLAN Controller currently classifies as.
Standalone Access
Points
Displays the number of access points in the
standalone mode in the network. The WLAN
Controller does not manage standalone access
points.
Unknown Access
Points
Displays the number of access points, which are
detected as unknown.
Table 80. Wireless Global Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
223
Maximum Pre-
authentication
History Entires
Displays the maximum number of Client Pre-
Authentication entries that the WLAN Controller
can store.
Maximum Roam
History Entries
Displays the maximum number of roam history
entires. You can specify detected AP clients to
have roam history entries up to this number.
RRM Channel Load
History Entries
Displays the number of entries in the RRM Channel
Load History table. When the entries exceeds this
limit, the oldest entry is replaced with the newest
entry.
Total Clients Displays the total number of the following AP
clients:
Authenticated AP clients
Associated AP clients
Disassociated AP clients
Authenticated
Clients
Displays the number of authenticated AP clients.
Maximum
Associated Clients
Displays the maximum number of AP clients that
can be connected to the WLAN Controller. This
number is the same as the maximum entires of the
Associated Client database.
Rogue AP
Mitigation Count
Displays the number of access points that the
WLAN Controller sends de-authentication frames
to in order to reduce rogue access points.
Rogue AP
Mitigation Limit
Displays the maximum number of access points
that the WLAN Controller is allowed to send de-
authentication frames to.
Detected Clients Displays the number of the detected AP clients on
the wireless network.
Maximum Detected
Clients
Displays the maximum number of AP clients that
the WLAN Controller can detect.
WLAN Utilization Displays the utilization of the wireless network by
the managed access points.
Tota l P r e -
authentication
History
Displays the current number of pre-authentication
history entires in the WLAN Controller.
Table 80. Wireless Global Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
224
Total Roam History
Entires
Displays the current number of roam history entires
in the WLAN Controller.
Maximum Channel
Load History
Displays the maximum number of channel load
history entires that the WLAN Controller can store.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that all the managed
access points have transmitted.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that all the managed
access points have received.
WLAN Bytes
Transmit Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that all the managed
access points have transmitted but discarded.
WLAN Bytes
Receive Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that all the managed
access points have received but discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the total number of packets that all the
managed access points have transmitted.
WLAN Packets
Received
Displays the total number of packets that all the
managed access points have received.
WLAN Packets
Transmit Dropped
Displays the total number of packets that all the
managed access points have transmitted but
discarded.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the total number of packets that all the
managed access points have received but
discarded.
Distributed Tunnel
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the total number of packets that all the
access points managed by the WLAN Controller
have transmitted through the distributed tunnel.
Distributed Tunnel
Clients
Displays the number of AP clients that are
connected to the access points using the
distributed tunnel.
Distributed Tunnel
Roamed Clients
Displays the number of AP clients that successfully
roamed from the home AP.
Distributed Tunnel
Client Denials
Displays the number of AP clients that the
distributed tunnel was not established for the AP
clients when they roamed.
Table 80. Wireless Global Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
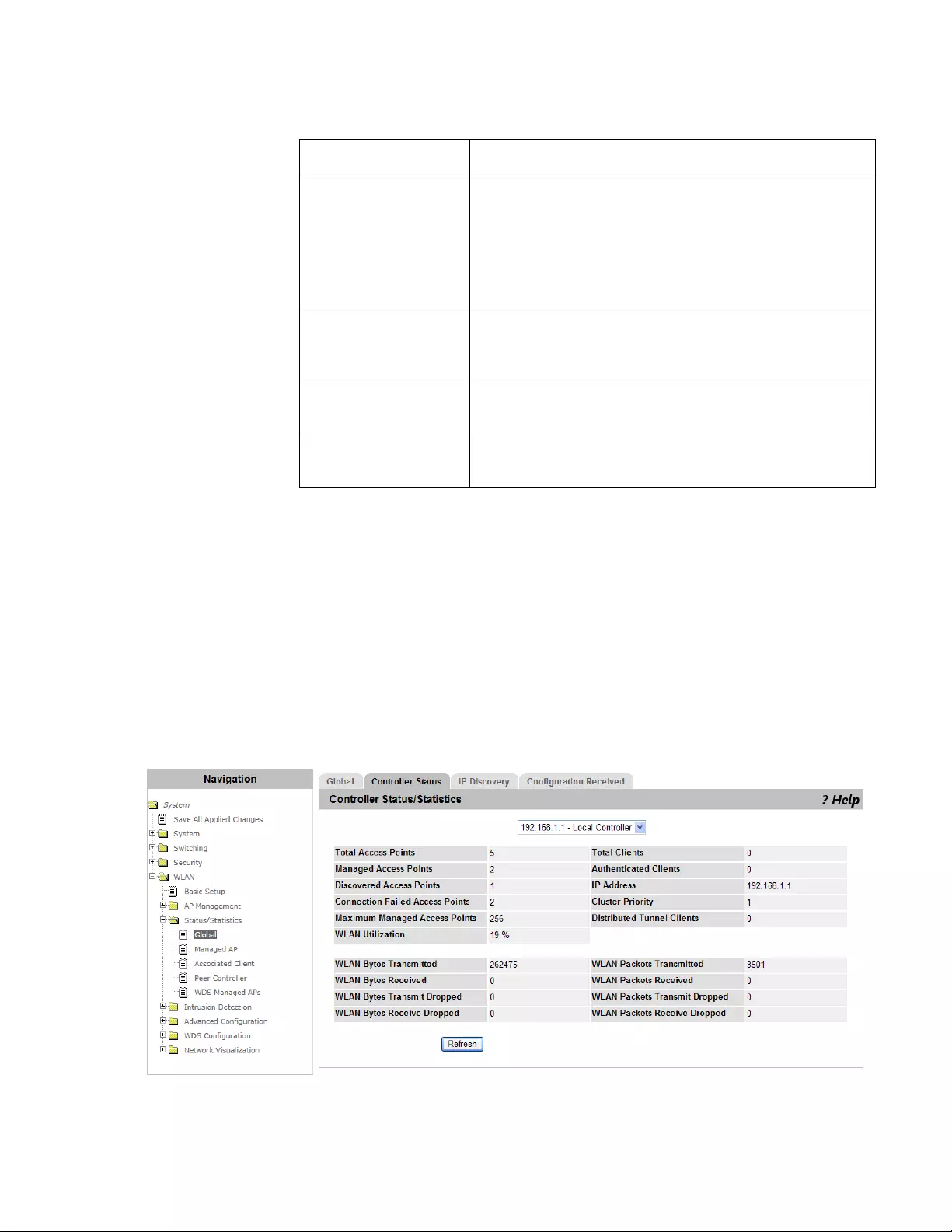
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
225
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Clear Statistics — Clears all the counters.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing
Controller Status
and Statistics
To view the status about a WLAN Controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics and click
the Controller Status tab.
The Controller Status/Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 117.
Figure 117. Controller Status/Statistics Page
Total Voice Traffic
Streams
Displays the total number of voice traffic that all AP
clients have transmitted through the access points
managed by the WLAN Controller.
The traffic stream is a group of packets with the
same priority that the access point assigned.
Total Video Traffic
Streams
Displays the total number of video traffic that all AP
clients have transmitted through the access points
managed by the WLAN Controller.
Tota l Traff i c Str e a m
Clients
Displays the number of AP clients are currently
transmitting traffic streams.
Tota l Traff i c Str e a m
Roaming Clients
Displays the number of AP clients are currently
roaming and transmitting traffic streams.
Table 80. Wireless Global Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
226
2. Select the IP address of the WLAN Controller that you want to view the
status and statistics.
The status and statistics about the selected WLAN Controller is
displayed.
Note
To view the status and statistics about other WLAN Controllers, your
local WLAN Controller must be the cluster controller.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 81.
Table 81. Controller Status/Statistics
Field Description
Total A c cess
Points
Displays the total number of the following access
points:
Managed Access Points
Connection Failed Access Points
Discovered Access Points.
Managed Access
Points
Displays the number of access points that are
successfully authenticated and actively connected
to the WLAN Controller.
Discovered
Access Points
Displays the number of access points that are
discovered or Authenticated, but not configurated
completely.
Connection
Failed Access
Points
Displays the number of access points that were
authenticated before, but are not currently
connected to the WLAN Controller.
Maximum
Managed Access
Points
Displays the maximum number of access points
that WLAN Controller manages.
WLAN Utilization Displays the utilization of the wireless network by
the access points managed by the WLAN
Controller.
Total Clients Displays the total number of the following AP
clients:
Associated AP clients
Authenticated AP clients
Disassociated AP clients
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
227
Authenticated
Clients
Displays the number of authenticated AP clients.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller.
Cluster Priority Displays the cluster priority of the WLAN Controller.
In the peer group, a WLAN Controller with the
highest cluster priority becomes the cluster
controller. If more than one WLAN Controller have
the same cluster priority, the WLAN Controller that
has the lowest number of the IP address becomes
the cluster controller.
Distributed
Tunnel Clients
Displays the number of AP clients that are
connected to the access points using the
distributed tunnel.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that all the access
points managed by WLAN Controller have
transmitted.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that all the access
points managed by WLAN Controller have
received.
WLAN Bytes
Transmit
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that all the access
points managed by WLAN Controller have
transmitted but discarded.
WLAN Bytes
Receive Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that all the access
points managed by WLAN Controller have received
but discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the total number of packets that all the
access points managed by WLAN Controller have
transmitted.
WLAN Packets
Received
Displays the total number of packets that all the
access points managed by WLAN Controller have
received.
WLAN Packets
Transmit
Dropped
Displays the total number of packets that all the
access points managed by WLAN Controller have
transmitted but discarded.
Table 81. Controller Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
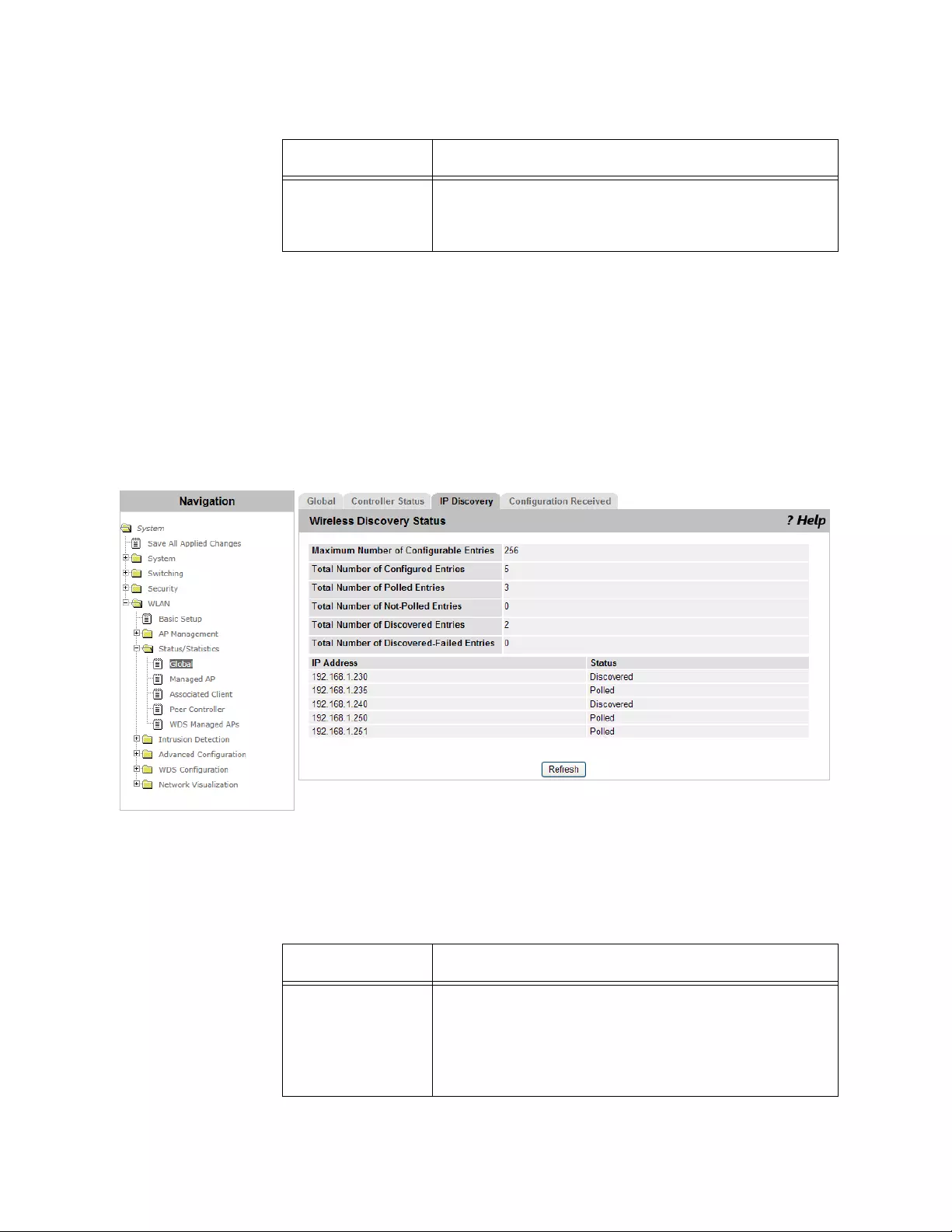
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
228
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing IP
Discovery
To view the information about communication between the WLAN
Controller and access points or peer controllers, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics and click
the IP Discovery tab.
The Wireless Discovery Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 118.
Figure 118. Wireless Discovery Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 82.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the total number of packets that all the
access points managed by WLAN Controller have
received but discarded.
Table 81. Controller Status/Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
Table 82. Wireless Discovery Status
Field Description
Maximum
Number of
Configurable
Entires
Displays the maximum number of IP addresses
that the WLAN Controller can register for IP
discovery. These IP addresses are in the IP List.
See “WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery” on
page 194.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
229
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing
Configuration
Received
To view information about the configuration that the WLAN Controller
received from another peer controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics and click
the Configuration Received tab.
The Peer Controller Configuration Received Status page is displayed
as shown in Figure 119 on page 230.
Total Numb e r of
Configured
Entries
Displays the number of IP addresses that are
currently registered in the IP List.
Total Numb e r of
Polled Entries
Displays the number of IP addresses in the IP List
that the WLAN Controller sent discovery packets
to.
Total Numb e r of
Non-Polled
Entries
Displays the number of IP addresses in the IP List
that the WLAN Controller has not sent discovery
packets to.
Total Numb e r of
Discovered
Entires
Displays the number of IP addresses in the IP List
that the WLAN Controller successfully discovered
and authenticated or validated by polling.
Total Numb e r of
Discovered-
Failed Entires
Displays the number of IP addresses in the IP List
that the WLAN Controller failed to discover,
authenticate, or validate by polling.
IP Address Displays the IP address in the IP List.
Status Displays the status of the IP address. The options
are:
Not Polled
Polled
Discovered
Discovered Failed
Table 82. Wireless Discovery Status (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
230
Figure 119. Peer Controller Configuration Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 83 on page 230.
Table 83. Peer Controller Configuration Received Status
Field Description
Current Receive
Status
Displays the status of receiving a configuration
from another peer controller. The options are:
Not Started
Receiving Configuration
Saving Configuration
Applying AP Profile Configuration
Success
Failure-Invalid Code Version
Failure-Invalid Hardware Version
Failure-Invalid Configuration
Last Configuration Received
Peer Controller
IP Address
Displays the IP addresses of the peer controller
that the WLAN Controller received the
configuration from.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
231
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Configuration Displays the type of configuration that the WLAN
Controller received. The options are:
Global
Discovery
Channel/Power
AP Database
AP Profiles
Known Client
Captive Portal
RADIUS Client
None
Timestamp Displays the time when the WLAN Controller
received the configuration.
Table 83. Peer Controller Configuration Received Status (Continued)
Field Description
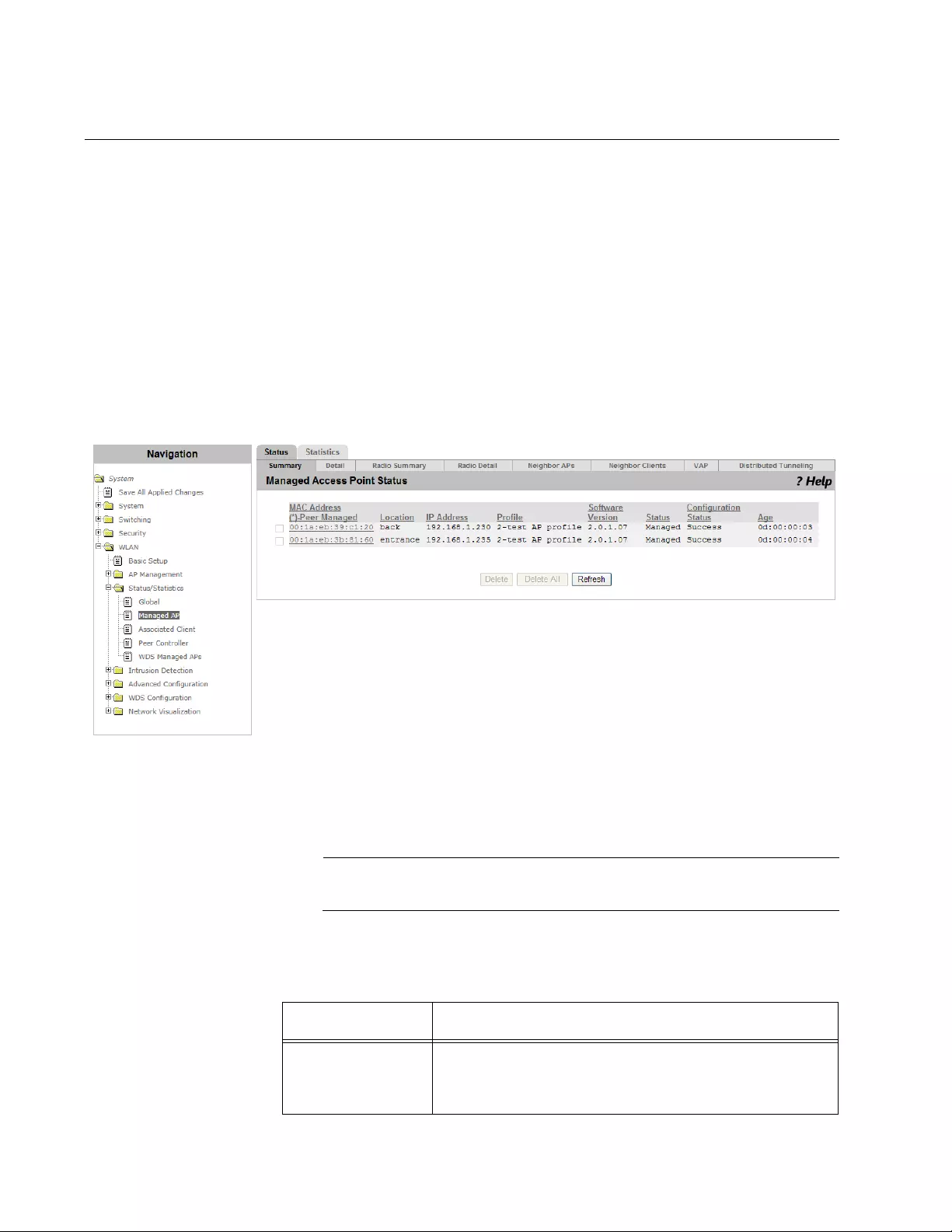
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
232
Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Status
From the Managed Access Point Status page, you can view the status of
access points, AP clients, and wireless network managed by the WLAN
Controllers.
Viewing a List of
Managed AP’s
and Deleting an
AP
To view the status of the managed access points and delete access pints
from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP.
The Managed Access Point Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 120.
Figure 120. Managed Access Point Status Page
2. If you want to delete an access point from the list, check the checkbox
of the access point.
Note
You can delete only the access points with the Failed status.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 84 on page 232.
Table 84. Managed Access Point Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point. The
asterisk following the MAC address indicates that
the peer controller manages the access point.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
233
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete — Deletes the selected access points from the list. You can
delete only the access points with the Failed status.
Delete All — Deletes all the access points with the Failed status.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Location Displays the location information of the access
point.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.
Profile Displays the AP profile that the WLAN Controller
applies to the access point.
Software Version Displays the software version of the access point.
Status Displays the status of the access point. The options
are:
Discovered - Discovered but not
authenticated.
Authenticated - Authenticated, but an AP
profile is not applied.
Managed - Managed by he WLAN
Controller and operating.
Failed - Failed to connect.
Configuration
Status
Displays the status of applying an AP profile to the
access point. The options are:
Not Configured
In Progress
Success
Partial Success - The access point has an
error with the AP profile, but is operating.
Failure - The access point has an error with
the AP profile and fails to operate.
Age Displays the time period since the access point
connected to the WLAN Controller.
Table 84. Managed Access Point Status (Continued)
Field Description
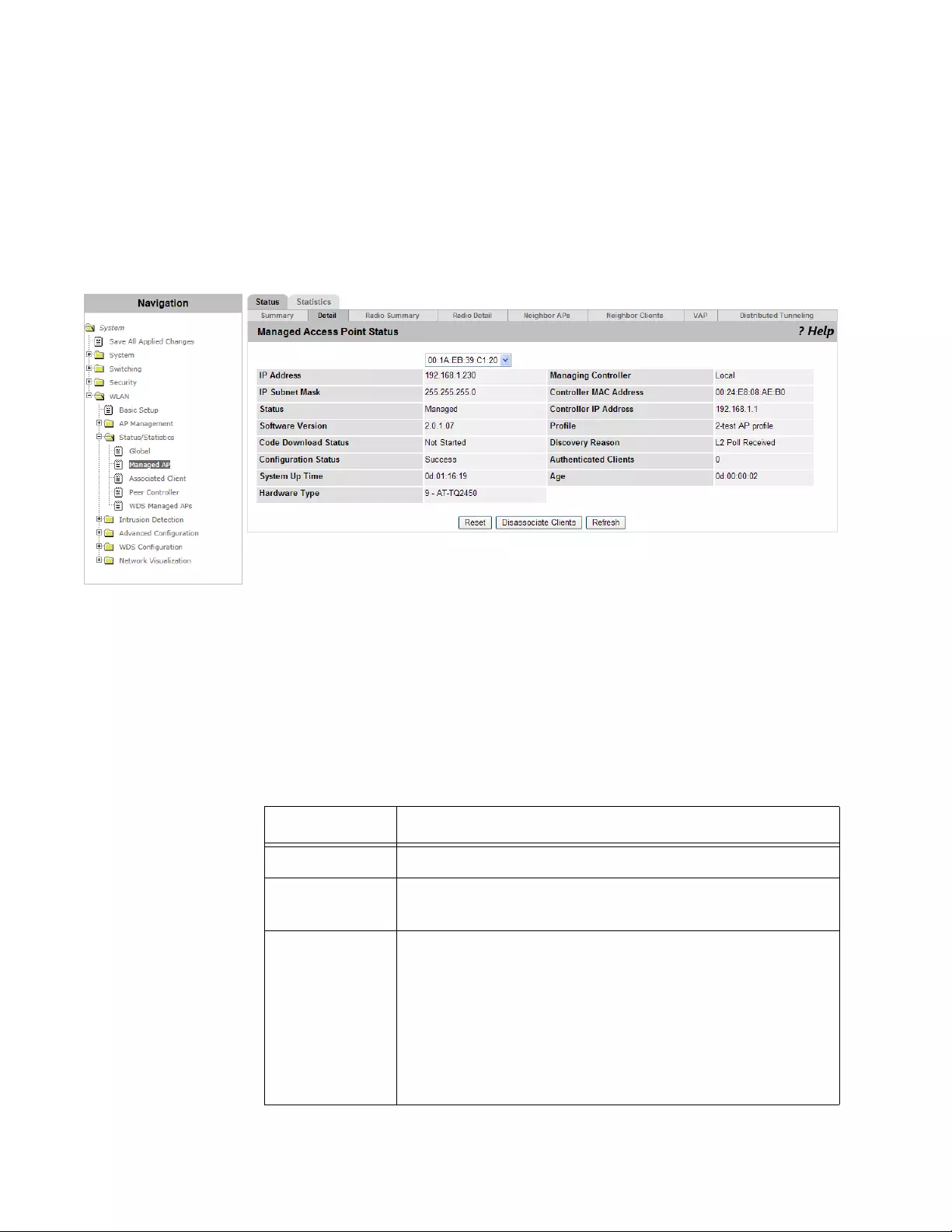
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
234
Viewing the
Detailed Status of
a Managed AP
To view the detailed status of the managed access points, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the Detail subtab.
The Managed Access Point Status (Detail) page is displayed as shown
in Figure 121.
Figure 121. Managed Access Point Status (Detail) Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
status.
The status about the selected access point is displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 85.
Table 85. Managed Access Point Status (Detail)
Field Description
IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.
IP Subnet
Mask
Displays the IP subnet mask of the access point.
Status Displays the status of the access point. The options are:
Discovered - Discovered but not authenticated.
Authenticated - Authenticated, but an AP profile
is not applied.
Managed - Managed by he WLAN Controller.
Failed - Failed to connect.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
235
Software
Version
Displays the software version of the access point.
Code
Download
Status
Displays information about downloading the software.
The options are:
Not Started
Requested
Code-Transfer-In-Progress
Failure
Aborted
Waiting-For-APs-To-Download
NVRAM-Update-In-Progress
Time-Out
Configuration
Status
Displays the status of applying an AP profile to the
access point. The options are:
Not Configured
In Progress
Success
Partial Success - The access point has an error
with the AP profile, but is operating.
Failure - The access point has an error with the
AP profile and fails to operate.
Configuration
Failure Error
Message
Displays the message of an error that occurred when
the AP profile was applied.
Configuration
Failure
Element
Displays the error code that was issued when the AP
profile was applied.
System Up
Time
Displays the time period since the access point started.
Hardware
Type
Displays the hardware ID that is assigned to the access
point hardware platform.
Managing
Controller
Displays the WLAN Controller type that manages the
access point: Local or Peer.
Controller
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the WLAN Controller that
manages the access point.
Table 85. Managed Access Point Status (Detail) (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
236
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Reset — Restarts the access point.
When the AP profile is modified, you must restart the access points
to apply the change.
Disassociate Clients — Disconnects the AP clients from the
access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Detailed Status of
Radio
To view the radio information about each access point, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the Radio Detail subtab.
The Managed Access Point Radio Status Detail page is displayed as
shown in Figure 122 on page 237.
Controller IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller that
manages the access point.
Profile Displays the AP profile that applied to the access point.
Discovery
Reason
Displays the reason why the access point was
discovered.
IP Poll Received - The WLAN Controller polled
and discovered the access point.
Controller IP Configured - The access point has
the IP address of the WLAN Controller.
Controller IP DHCP - The access point obtained
the IP address of he WLAN Controller through
DHCP option 43.
L2 Poll Received - The WLAN Controller
discovered the access point with the L2 VLAN
discover method.
Authenticated
Clients
Displays the number of AP clients that were
authenticated by the access point.
Age Displays the time period since the access point
connected to the WLAN Controller.
Table 85. Managed Access Point Status (Detail) (Continued)
Field Description
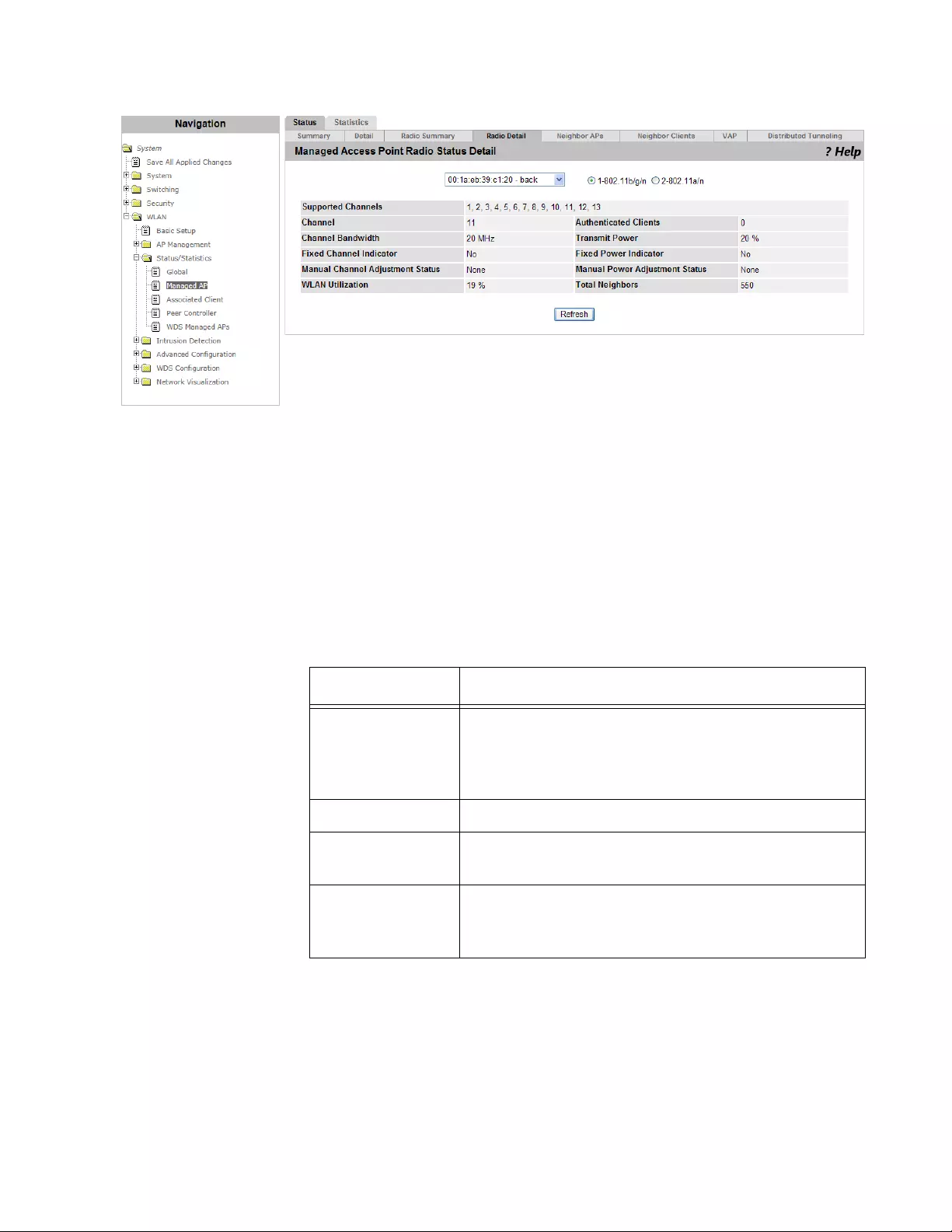
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
237
Figure 122. Managed Access Point Radio Status Detail Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
radio information.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
The radio information about the selected access point is displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 86.
Table 86. Managed Access Point Radio Status Detail
Field Description
Supported
Channels
Displays a list of supported channels. The
supported channels depend upon the country code,
access point hardware type, and selected channel
restriction.
Channel Displays the channel that is currently active.
Channel
bandwidth
Displays the channel bandwidth: 20MHz or 40MHz.
Fixed Channel
Indicator
Displays whether the channel is manually assigned
or not. To fix the channel, see “WLAN Basic Setup
> Valid AP” on page 198.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
238
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Status of
Neighbor AP’s
To view the information about neighbor access points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the Neighbor APs subtab.
The Managed Access Point Neighbor AP Status page is displayed as
shown in Figure 123 on page 239.
Manual Channel
Adjustment
Status
Displays information about manually applying the
channel plan. The options are:
Not Started
Requested
In Progress
Success
Failure
WLAN Utilization Displays the utilization of the wireless network by
the managed access points.
Authenticated
Clients
Displays the number of authenticated AP clients
per radio band.
Transmit Power Displays the current transmitting power.
Fixed Power
Indicator
Displays whether the power is manually assigned
or not. To fix the power, see “WLAN Basic Setup >
Valid AP” on page 198.
Manual Power
Adjustment
Status
Displays information about the power adjustment
that is manually requested. The options are:
None
Requested
In Progress
Success
Failure
Total Neighbors Displays the number of access points and AP
clients that are detected by the RF scan.
Table 86. Managed Access Point Radio Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
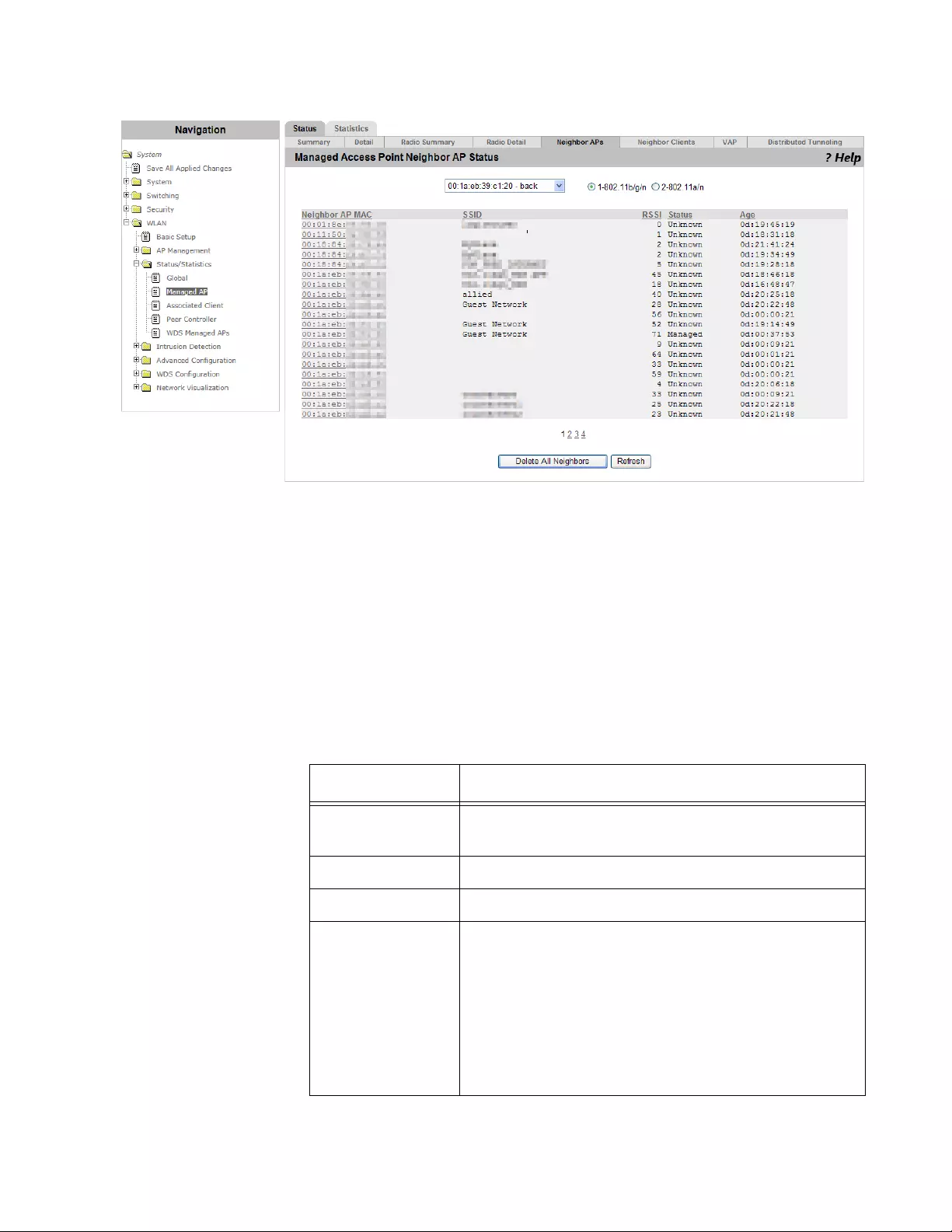
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
239
Figure 123. Managed Access Point Neighbor AP Status Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
neighbor access point information.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
The neighbor access point information on the selected access point is
displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 87.
Table 87. Managed Access Point Neighbor AP Status
Field Description
Neighbor AP
MAC
Displays the MAC address of a neighbor access
point.
SSID Displays the SSID of the neighbor access point.
RSSI Displays the RSSI of the neighbor access point.
Status Displays the management status of the neighbor
access point. The options are:
Managed
Standalone
Rogue
Unknown
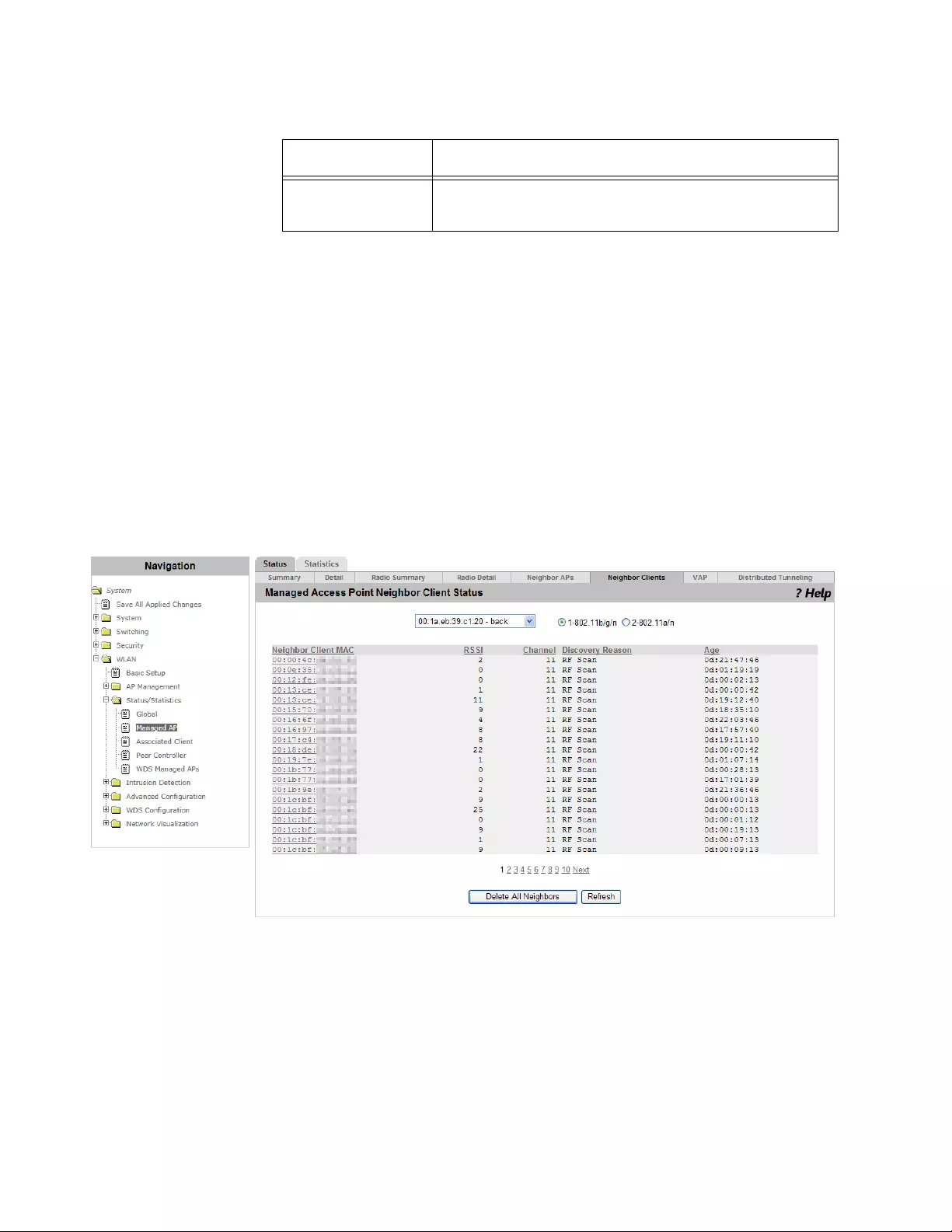
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
240
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete All Neighbors — Deletes all the entires on the Managed
Access Point Neighbor AP Status and Managed Access Point
Neighbor Client Status pages.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Status of
Neighbor Clients
To view the information about neighbor AP clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the Neighbor Clients subtab.
The Managed Access Point Neighbor Client Status page is displayed
as shown in Figure 124 on page 240.
Figure 124. Managed Access Point Neighbor Client Status Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
neighbor AP client information.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
The neighbor AP client information on the selected access point is
displayed.
Age Displays the time period since the neighbor access
point was detected through the RF scan.
Table 87. Managed Access Point Neighbor AP Status (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
241
4. Observe the fields described in Table 88.
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete All Neighbors — Deletes all the entires on the Managed
Access Point Neighbor AP Status and Managed Access Point
Neighbor Client Status pages.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Status of Virtual
Access Points
To view the information about Virtual Access Points (VAP), do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the VAP subtab.
The Managed Access Point VAP Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 125 on page 242.
Table 88. Managed Access Neighbor Client Status
Field Description
Neighbor Client
MAC
Displays the MAC address of a neighbor AP client.
RSSI Displays the RSSI of the neighbor AP client.
Channel Displays the channel of the access point that
received frames from the AP client.
Discovery
Reason
Displays how the AP client was discovered. The
options are:
RF Scan Discovered
Probe Request
Associated to Managed AP
Associated to this AP
Associated to Peer AP
Ad Hoc Rogue
Multiple reasons can be displayed at a time.
Age Displays the time period since the neighbor AP
client was detected through the RF scan.
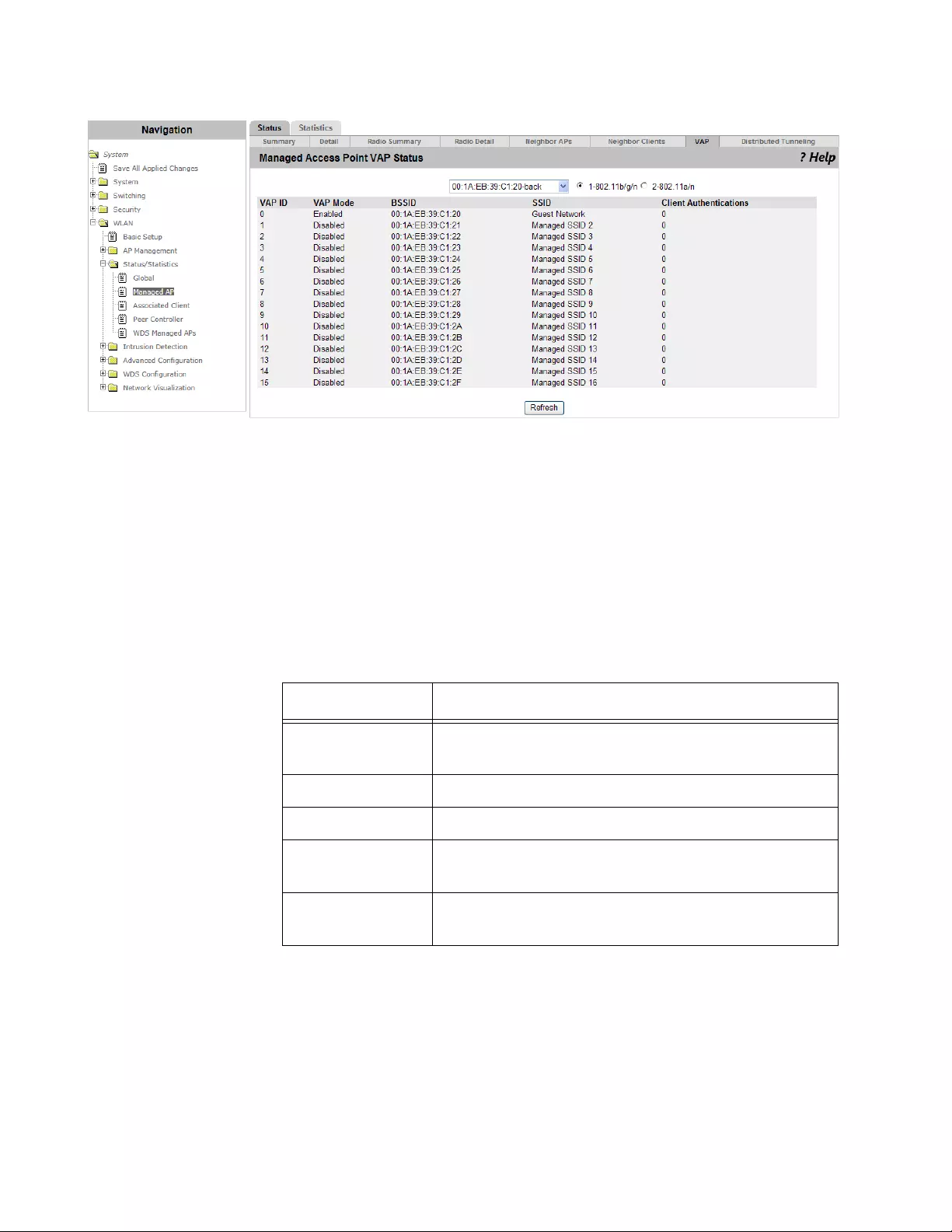
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
242
Figure 125. Managed Access Point VAP Status Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
Virtual Access Points.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
The VAP information on the selected access point is displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 89 on page 242.
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Status of
Distributed
Tunneling
To view the information about distributed tunneling, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and clicked the Distributed Tunneling subtab.
Table 89. Managed Access VAP Status
Field Description
VAP ID Displays the VAP identification number. The range
is 0 to 15.
VAP Mode Displays the VAP mode: enabled or disabled.
BSSID Displays the MAC address of the VAP.
SSID Displays the wireless network that is assigned to
the VAP.
Client
Authentication
Displays the number of the AP clients that are
currently authenticated by the VAP.
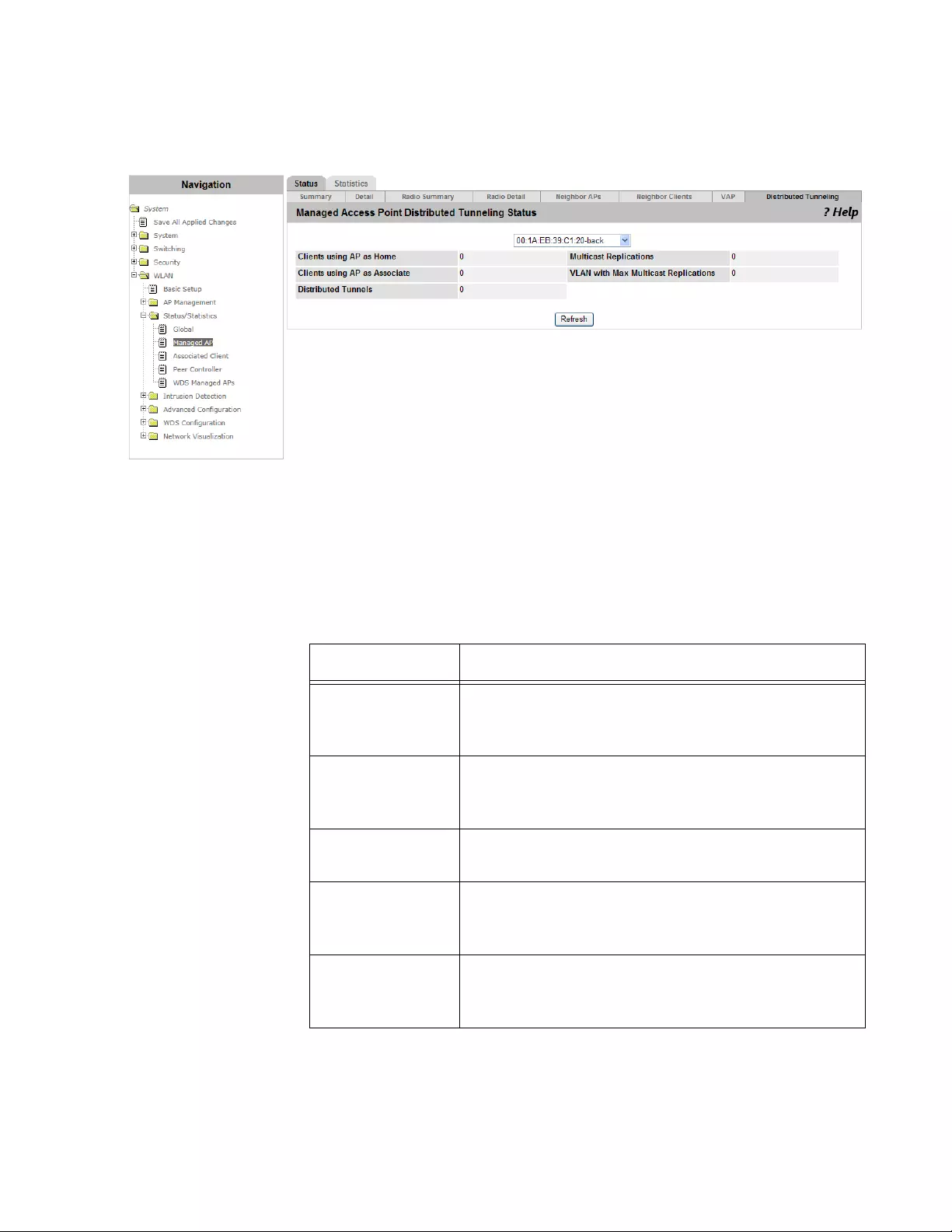
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
243
The Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Status page is
displayed as shown in Figure 126.
Figure 126. Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Status Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
distributed tunneling information.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 90.
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 90. Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Status
Field Description
Clients using AP
as Home
Displays the number of AP clients that roam and
send data to this home access point through the
distributed tunnel.
Clients using AP
as Associate
Displays the number of AP clients that roam to this
access point and send data to their home access
point through the distributed tunnel.
Distributed
Tunnels
Displays the number of other access points that
have the distributed tunnel with the access point.
Multicast
Replications
Displays the number of distribute tunnels that are
formed with other home access points in the same
VLAN.
VLAN Max
Multicast
Replications
Displays the maximum number of VLAN that the
access point created in order to send multicast
frames through distributed tunnels.
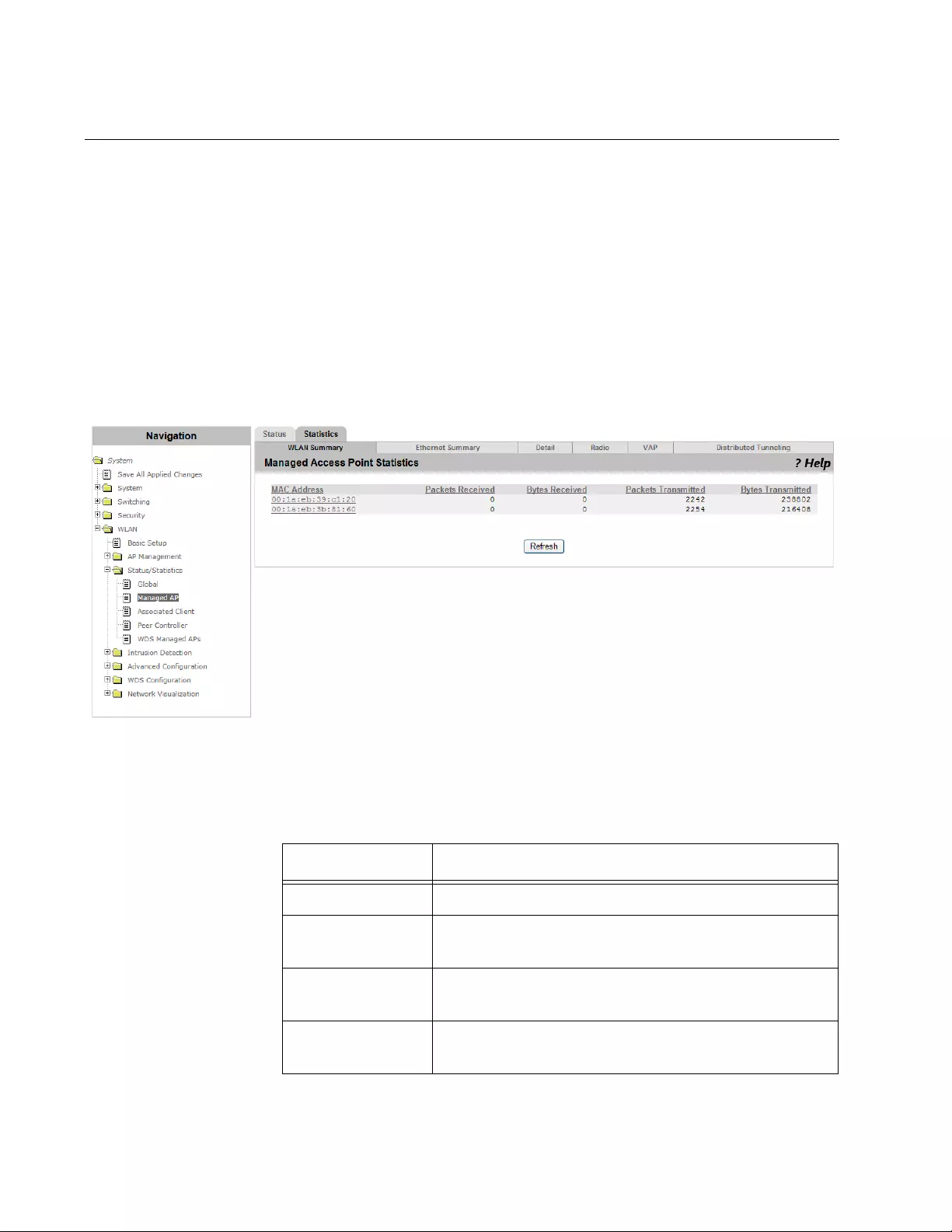
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
244
Status/Statistics > Managed AP > Statistics
From the Managed Access Point Statistics page, you can view the traffic
information on managed access points, Ethernet, radio, VAP, and
distributed tunneling.
Viewing the
Statistics of
Managed Access
Points
To view the statistics about the managed access points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP and click the Statistics tab.
The Managed Access Point Statistics page is displayed as shown in
Figure 127.
Figure 127. Managed Access Point Statistics Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 91.
Table 91. Managed Access Point Statistics
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
Bytes Received Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
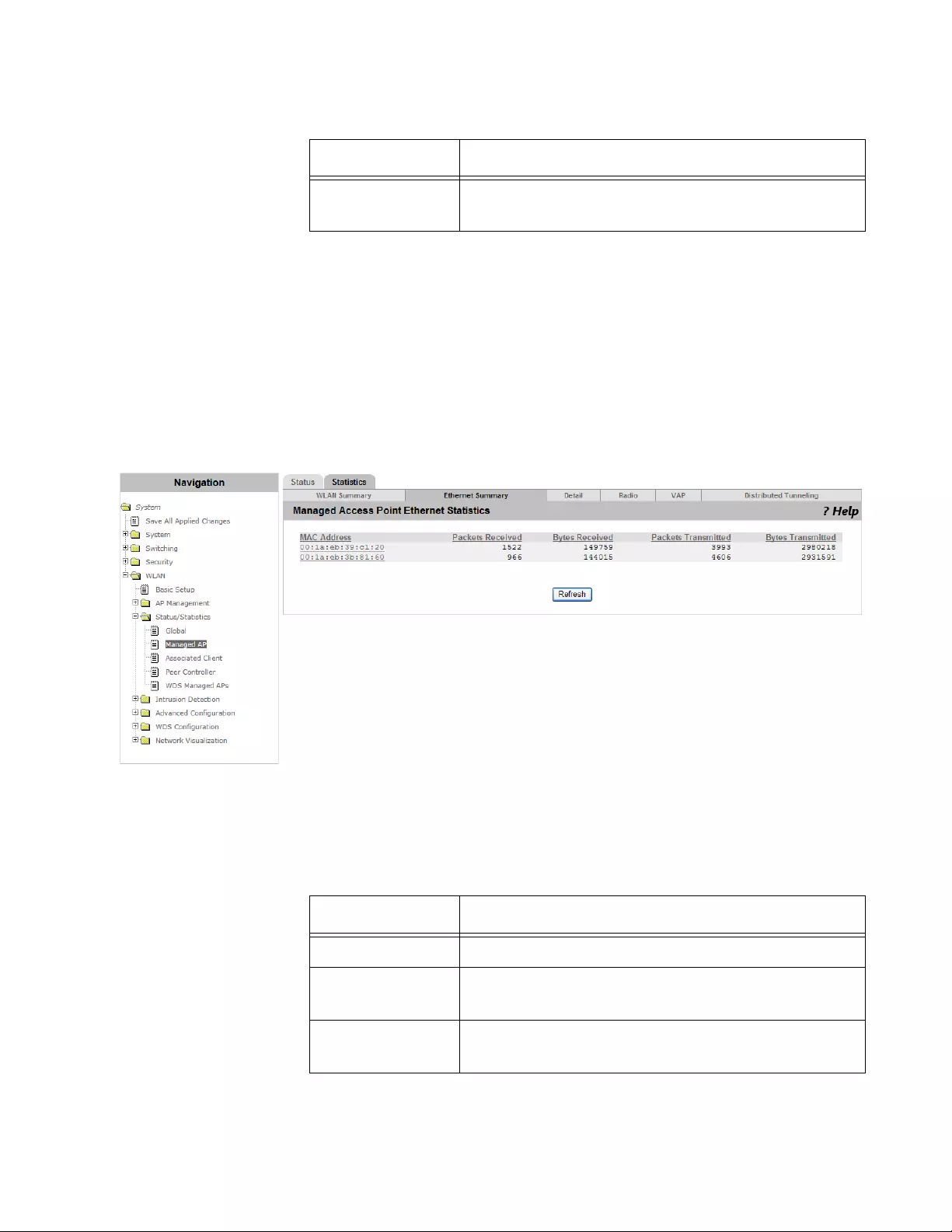
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
245
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing The
Statistics of
Ethernet
To view the Ethernet statistics about the managed access points, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP, click the Statistics tab, then click the Ethernet Summary subtab.
The Managed Access Point Ethernet Statistics page is displayed as
shown in Figure 128.
Figure 128. Managed Access Point Ethernet Statistics Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 92.
Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
Table 91. Managed Access Point Statistics
Field Description
Table 92. Managed Access Point Ethernet Statistics
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the Ethernet.
Bytes Received Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the Ethernet.
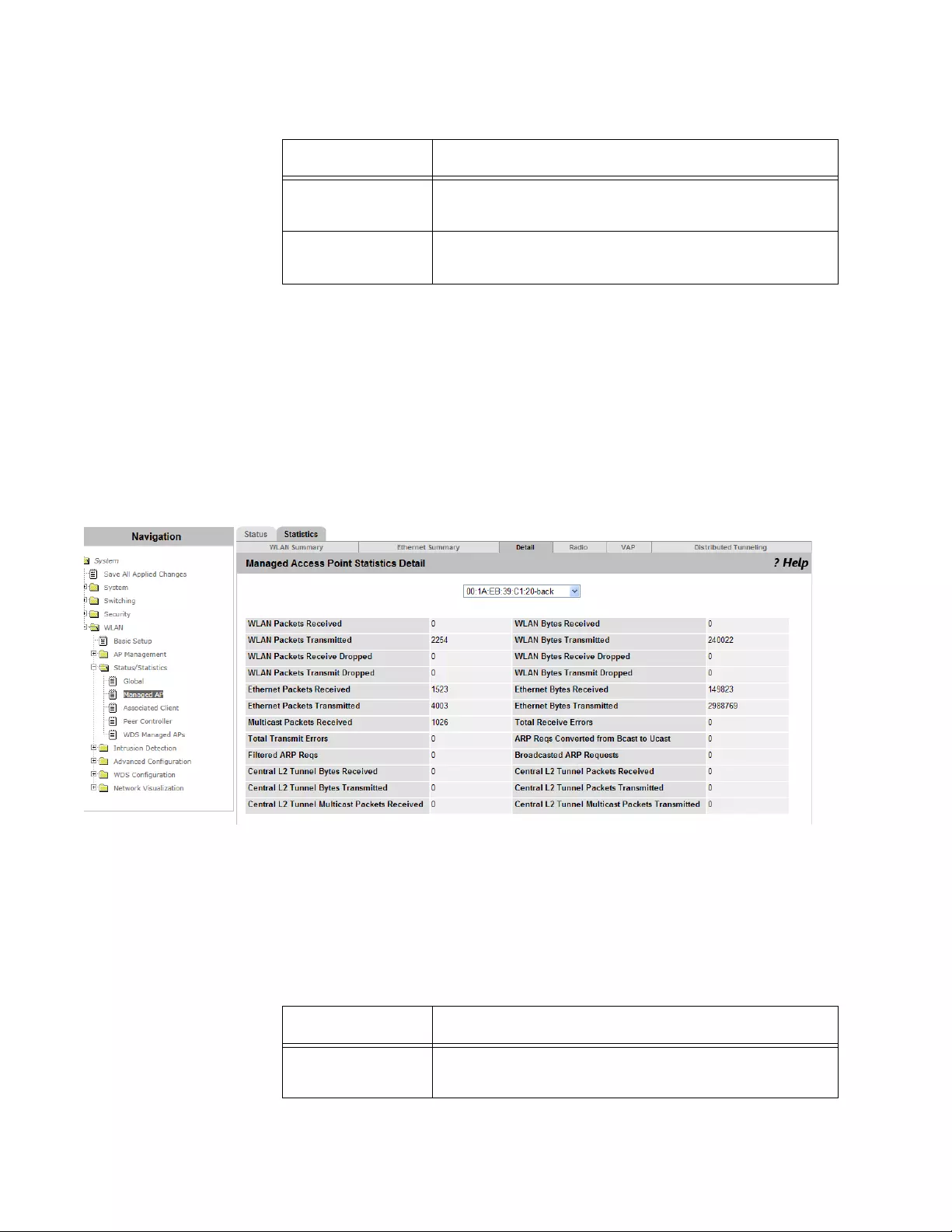
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
246
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Detailed Statistics
of Managed
Access Point s
To view the detailed statistics about the managed access points, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP, click the Statistics tab, then click the Detail subtab.
The Managed Access Point Detail Statistics page is displayed as
shown in Figure 129.
Figure 129. Managed Access Point Detail Statistics Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
detail information.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 93.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the Ethernet.
Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the Ethernet.
Table 92. Managed Access Point Ethernet Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
Table 93. Managed Access Point Detail Statistics
Field Description
WLAN Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
247
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network, but
discarded.
Ethernet Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the LAN.
Ethernet Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the LAN.
Multicast
Packets
Received
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point has received from the LAN.
Total Transmit
Errors
Displays the number of errors that the access point
causes when transmitting data to the LAN.
Filtered ARP
Reqs
Displays the number of the ARP requests that the
access point discarded.
Central L2
Tunnel Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point received from the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point transmitted to the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Multicast
Packets
Received
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point received from the centralized tunnel.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
Table 93. Managed Access Point Detail Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
248
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network, but
discarded.
Ethernet Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the LAN.
Ethernet Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the LAN.
Multicast
Packets
Received
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point has received from the LAN.
Total Transmit
Errors
Displays the number of errors that the access point
causes when transmitting data to the LAN.
Filtered ARP
Reqs
Displays the number of the ARP requests that the
access point discarded.
Central L2
Tunnel Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point received from the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point transmitted to the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Multicast
Packets
Received
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point received from the centralized tunnel.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
Table 93. Managed Access Point Detail Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
249
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Statistics of Radio
To view the radio statistics about the managed access points, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP, click the Statistics tab, then click the Radio subtab.
The Managed Access Point Radio Statistics page is displayed as
shown in Figure 130 on page 250.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network, but
discarded.
Ethernet Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the LAN.
Ethernet Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the LAN.
Total Receive
Errors
Displays the number of errors that the access point
caused when receiving data from the LAN.
ARP Reqs
Converted From
Bcast to Ucast
Displays the number of ARP requests that the
access point converted from broadcast to unicast.
Broadcast ARP
Requests
Displays the number of ARP requests that are sent
as broadcast messages to VAP’s. One ARP
request can be counted multiple times if multiple
VAP’s broadcast the ARP request.
Central L2
Tunnel Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point received from the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point transmitted to the centralized tunnel.
Central L2
Tunnel Multicast
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point transmitted to the centralized tunnel.
Table 93. Managed Access Point Detail Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
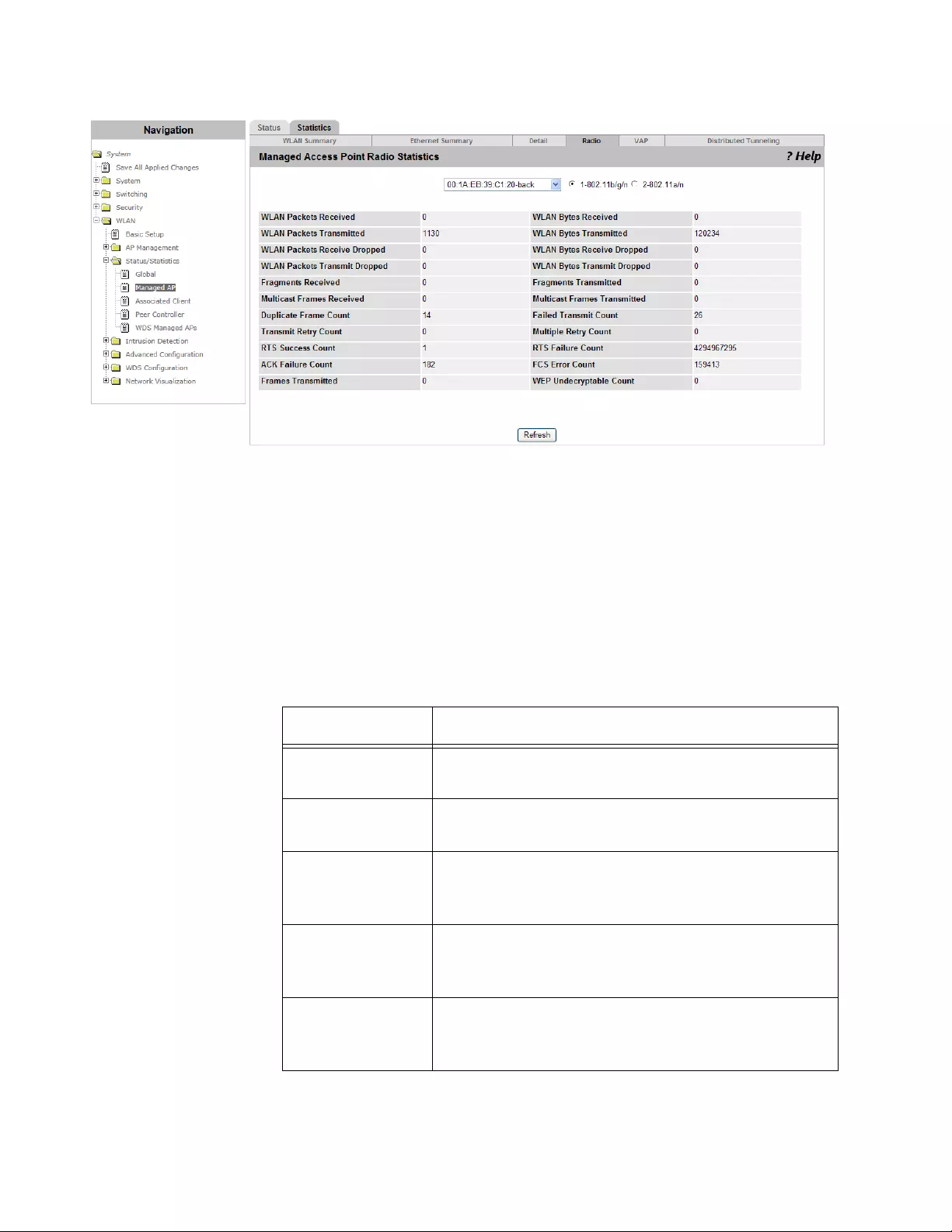
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
250
Figure 130. Managed Access Point Radio Statistics Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
radio information.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
The radio information about the selected access point is displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 94.
Table 94. Managed Access Point Radio Statistics
Field Description
WLAN Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network, but
discarded.
Fragments
Received
Displays the number of MPDU frames that the
access point received. The Type of MPDU frame
must be data or management.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
251
Multicast Frames
Received
Displays the number of multicast MSDU frames
that the access point received.
Duplicate Frame
Count
Displays the number of duplicate frames that the
access point received. The duplicate frame is
determined based on the sequence control field of
the MAC header.
Transmit Retry
Count
Displays the number of MSDU frames that were
transmitted successfully after one retry.
RTS Success
Count
Displays the number of CTS frames that the access
point received as a response to RTS frames.
ACK Failure
Count
Displays the number of ACK frames that the
access point failed to receive.
Frames
Transmitted
Displays the number of MSDU frames that were
successfully transmitted.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has received from the wireless network, but
discarded.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point has transmitted to the wireless network, but
discarded.
Fragments
Transmitted
Displays the number of MPDU frames that the
access point transmitted. The Type of MPDU frame
must be data or management.
Multicast Frames
Transmitted
Displays the number of multicast MSDU frames
that the access point transmitted.
Failed Transmit
Count
Displays the number of MSDU frames that the
access point failed to transmit due to the excess of
the short retry limit or long retry limit.
Multiple Retry
Count
Displays the number of MSDU frames that were
transmitted successfully after multiple retries.
Table 94. Managed Access Point Radio Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
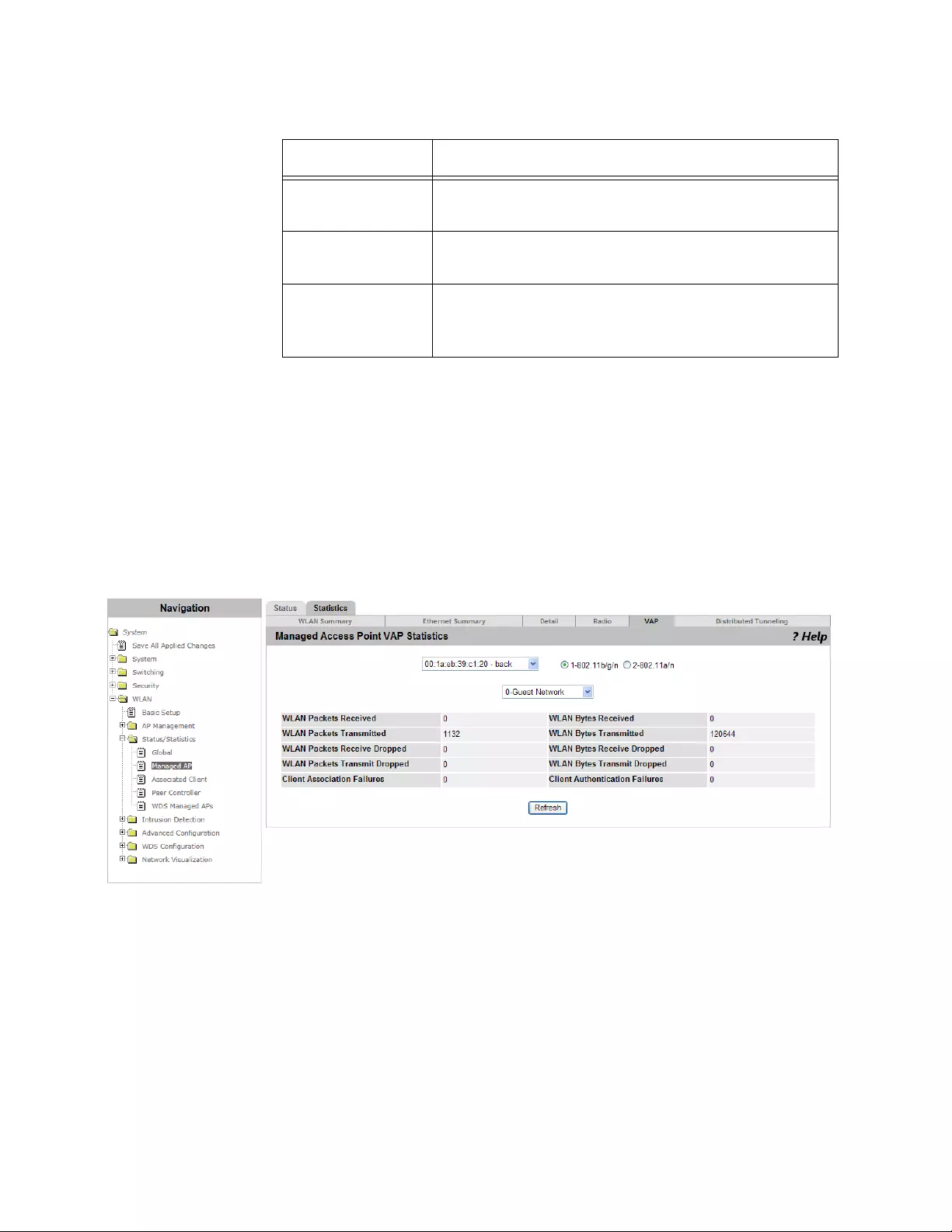
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
252
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Statistics of VAP
To view the VAP statistics about the managed access points, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP, click the Statistics tab, then click the VAP subtab.
The Managed Access Point VAP Statistics page is displayed as shown
in Figure 131.
Figure 131. Managed Access Point VAP Statistics Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point that have information
about the VAP.
3. Select the radio band: 802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n.
4. Select the VAP from the select list.
The VAP information is displayed.
RTS Failure
Count
Displays the number of CTS frames that the access
point did not receive as a response to RTS frames.
FCS Error Count Displays the number of FCS errors from the MPDU
frames that the access point received.
WEP
Undecryptable
Count
Displays the number of frames that are not required
to be encrypted or discarded because the receiving
device has no privacy option.
Table 94. Managed Access Point Radio Statistics (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
253
5. Observe the fields described in Table 95.
6. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Statistics of
Distributed
Tunneling
To view the statistics about the distributed tunnel on the managed access
points, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Managed
AP, click the Statistics tab, then click the Distributed Tunneling subtab.
The Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Statistics page is
displayed as shown in Figure 132 on page 254.
Table 95. Managed Access Point VAP Statistics
Field Description
WLAN Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the VAP has
received from the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the VAP has
transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Packets
Receive Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the VAP has
received from the wireless network, but discarded.
WLAN Packets
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that the VAP has
transmitted to the wireless network, but discarded.
Client
Association
Failure
Displays the number of AP clients that the VAP
rejected.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the VAP has
received from the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the VAP has
transmitted to the wireless network.
WLAN Bytes
Received
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the VAP has
received from the wireless network, but discarded.
WLAN Bytes
Transmitted
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that the VAP has
transmitted to the wireless network, but discarded.
Client
Authentication
Failure
Displays the number of AP clients that failed to be
authenticated.
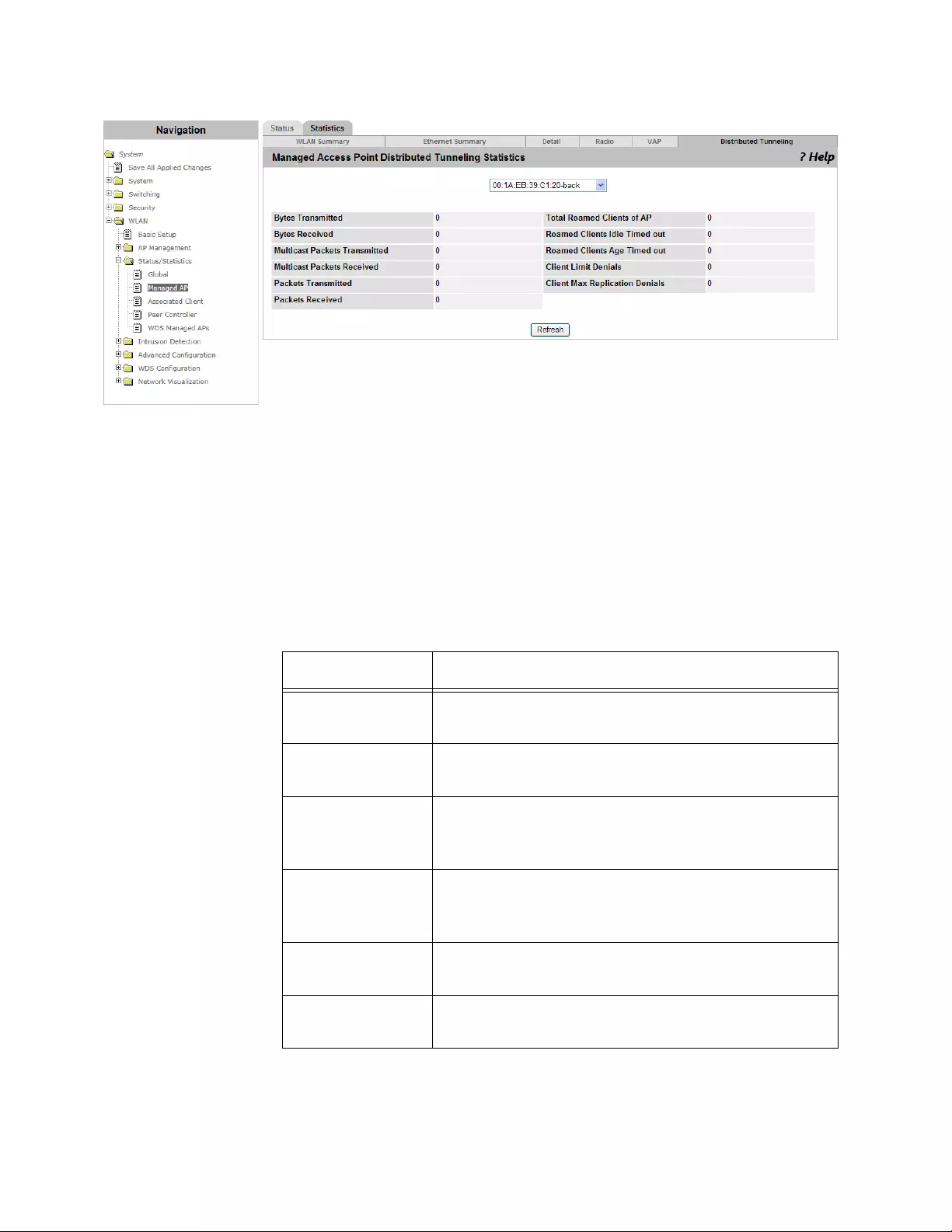
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
254
Figure 132. Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Statistics Page
2. Select the MAC address of the access point to display information
about the distributed tunneling.
The distributed tunneling information about the access point is
displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 96.
Table 96. Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Statistics
Field Description
Bytes
Transmitted
Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point transmitted through distributed tunnels.
Bytes Received Displays the data size in bytes that the access
point received through distributed tunnels.
Multicast
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point transmitted through distributed
tunnels.
Multicast
Packets
Received
Displays the number of multicast packets that the
access point received through distributed tunnels.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that the access
point transmitted through distributed tunnels.
Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the access
point received through distributed tunnels.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
255
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Total Roamed
Clients of AP
Displays the number of AP clients that used the
access point through distributed tunnels. This
number includes AP clients that roam to and from
this access point.
Roam Clients
Idle Timed Out
Displays the number of AP clients that exceeded
the timeout limit because they were away from the
access point.
Roam Clients
Age Timed Out
Displays the number of AP clients that exceeded
the distributed tunnel timeout limit because they
were away from the access point.
Client Limit
Denials
Displays the number of times that the access point
refused AP clients to form a distributed tunnel
because the access point reached the maximum
number of tunneling clients.
Client Max
Replication
Denials
Displays the number of times that the access point
refused AP clients to form a distributed tunnel
because the access point reached the maximum
number of VLAN replication.
Table 96. Managed Access Point Distributed Tunneling Statistics
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
256
Status/Statistics > Associated Client
From WLAN > Status/Statistics > Associated Client page, you can view
the status and statistics of AP clients. This page has several pages to go
to with tabs and subtabs as described in Table 97.
Viewing Status
Summary
To view the status summary of the access point and AP clients and
disassociate an AP client, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client.
The Associated Client Status Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 133 on page 257.
Table 97. Associated Client
Tab Subtab Description
Status Summary Displays the basic information of the access
point and AP clients. You can also
disconnect AP clients from this page.
Detail Displays the detailed information of each AP
client
Neighbor
AP’s
Displays the information about access points
that the AP client can roam.
Distributed
Tunneling
Displays the distributed tunneling
information on the AP client.
SSID
Status
Displays the SSID status of each AP client.
VAP
Status
Displays the status of the VAP that the AP
client is associated with.
Controller
Status
Displays a list of WLAN Controllers that each
AP client is associated with.
Statistics Association
Summary
Displays the basic statistics of the access
point and AP clients.
Session
Summary
Displays the session statistics when the AP
client roams.
Association
Detail
Displays the detailed statistics of the access
point and AP clients.
Session
Detail
Displays the detailed session statistics when
the AP client roams.
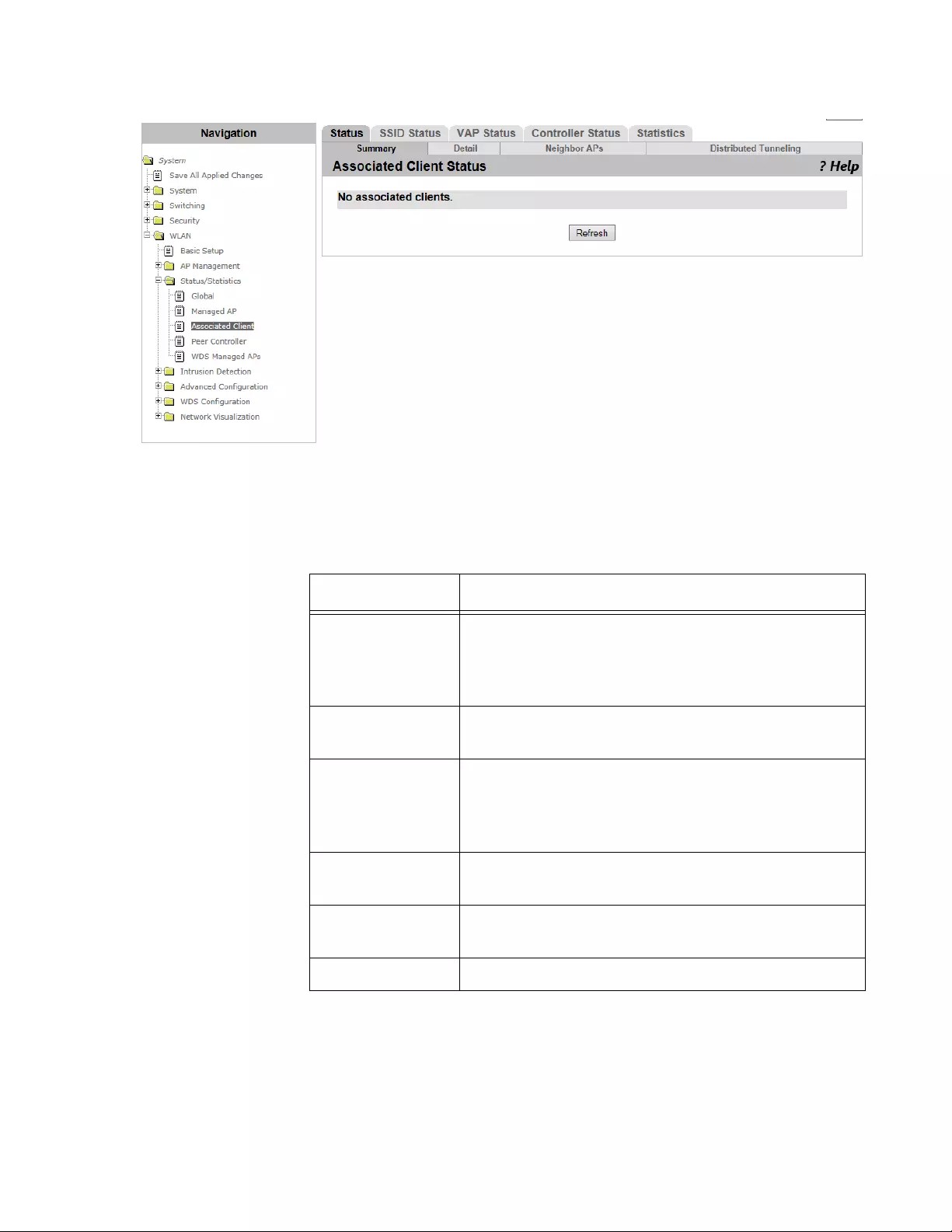
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
257
Figure 133. Associated Client Status Summary Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 98.
Table 98. Associated Client Status Summary
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client. The
asterisk following the MAC address indicates that
the AP client is connected to the access point
managed by the peer controller.
Detected IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the AP client if available.
NetBIOS Name Displays the NetBIOS name of the AP client. The
NetBIOS name in the Windows Operating system
is the host name of the AP client or based on the
host name.
SSID Displays the SSID that the AP client is connected
to.
BSSID Displays the MAC address of the VAP that the AP
client is associated with.
Channel Displays the channel that the AP client is using.
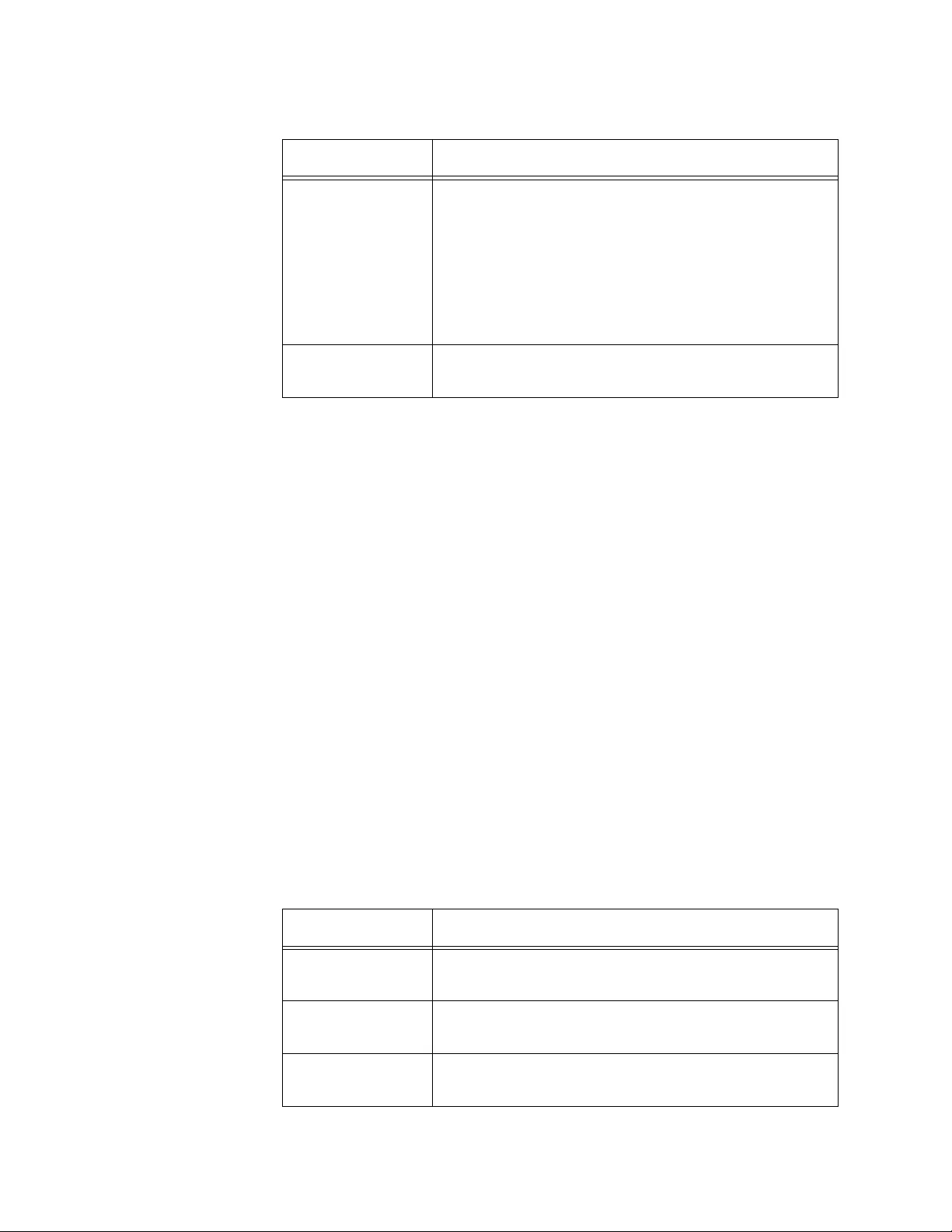
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
258
3. If you want to disconnect an AP client, check the checkbox next to the
MAC address of the AP client.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Disassociate — Disconnect the selected AP client from the
access point.
Disassociate All — Disconnected all the AP clients from the
access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Detailed Status
To view the detailed information about the access point and AP clients and
disassociate an AP client, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Detail subtab.
2. Select the MAC address of the AP client from the select list.
The Associated Client Status Detail page is displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 99.
Status Displays the status of the AP client. The options
are:
Associated
Authenticated
Disassociate - The AP client is not
associated with the access point.
Network Time Displays the time that has passed since the AP
client was authenticated.
Table 98. Associated Client Status Summary (Continued)
Field Description
Table 99. Associated Client Status Detail
Field Description
SSID Displays the SSID that the AP client is associated
with.
BSSID Displays the MAC address of the VAP that the AP
client is associated with.
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the home access
point of the AP client.
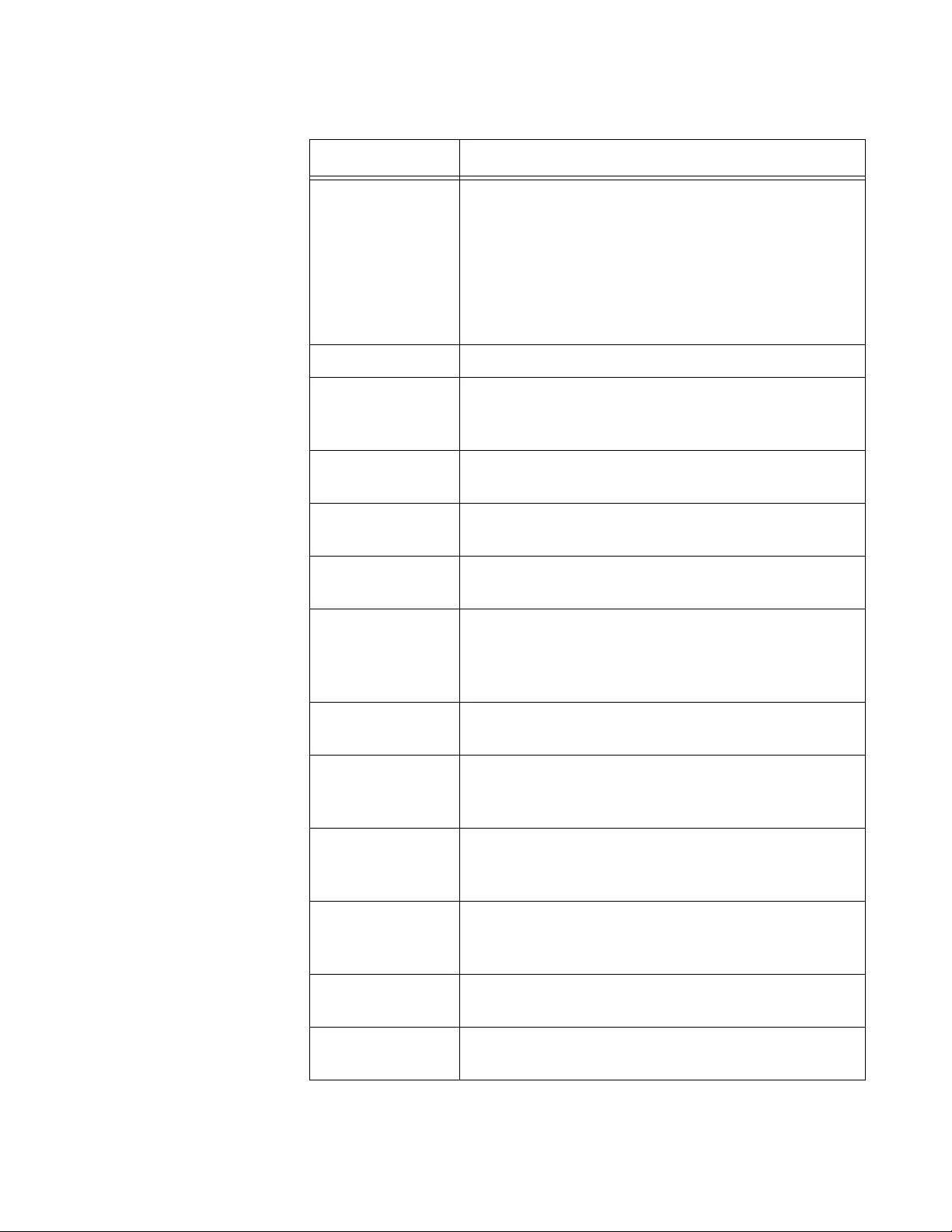
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
259
Status Displays the status of the AP client. The options
are:
Associated
Authenticated
Disassociate - The AP client is not
associated with the access point.
Channel Displays the channel that the AP client is using.
User Name Displays the user name of the AP client
authenticated by 802.1x. When AP client uses
other 802.1x, the user name is not shown.
Inactive Period Displays the time that has passed since the AP
client received a data packet last time.
Age Displays the time that has passed since this
statistics updated.
Dot11n Capable Displays whether the AP client supports the IEEE
802.11n standard.
NetBIOS Name Displays the NetBIOS name of the AP client. The
NetBIOS name in the Windows Operating system
is the host name of the AP client or based on the
host name.
Tunnel IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the distributed tunnel.
Associating
Controller
Displays the WLAN Controller that manges the
access point, which the AP client is associated
with: Local or Peer.
Controller MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the WLAN Controller
that manges the access point, which the AP client
is associated with.
Controller IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller
that manges the access point, which the AP client
is associated with.
Location Displays the location information of the access
point.
Radio Displays the wireless network that the access point
that the AP client is associated with.
Table 99. Associated Client Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
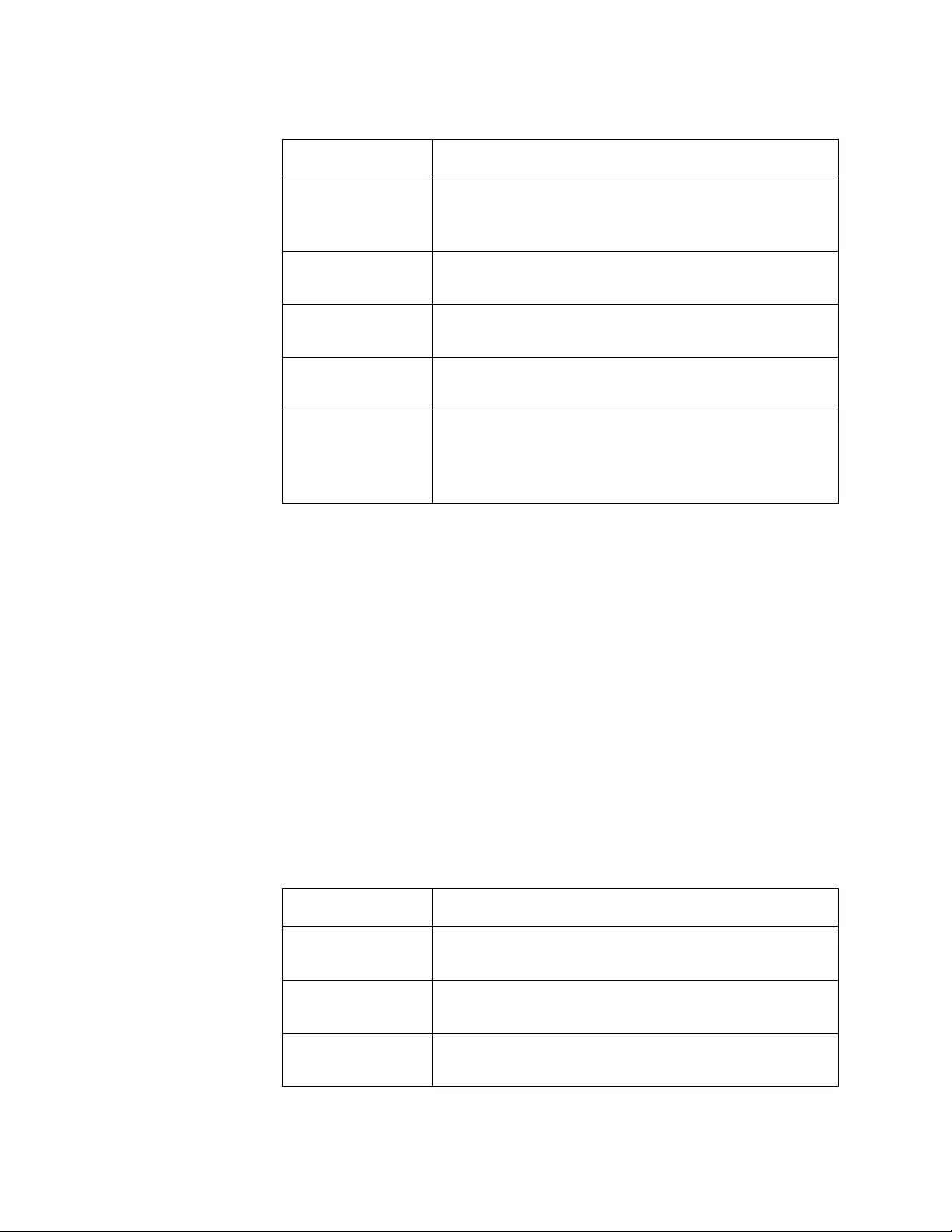
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
260
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Disassociate — Disconnect the AP client from the access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Status of
Neighbor APs
To view the information about neighbor access points that the AP client
can roam, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Neighbor APs subtab.
2. Select the MAC address of the AP client from the select list.
The Associated Client Status Neighbor APs page is displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 100.
VLAN Displays the VLAN ID that is assigned to the AP
client if the AP client is associated with the VAP in
the VLAN forwarding mode.
Transmit Data
Rate
Displays the transmit data rate of the AP client.
Network Time Displays the time that has passed since the AP
client was authenticated.
Detected IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the AP client if available.
Captive Portal Displays the link to the Captive Portal Client Status
page if the AP client is authenticated via Captive
Portal. See “Client Connection Status” on
page 167.
Table 99. Associated Client Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
Table 100. Associated Client Status Neighbor APs
Field Description
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the home access
point of the AP client.
Location Displays the location information of the access
point, which is set in the AP profile.
Radio Displays the radio band of the access point that the
AP client is associated with.
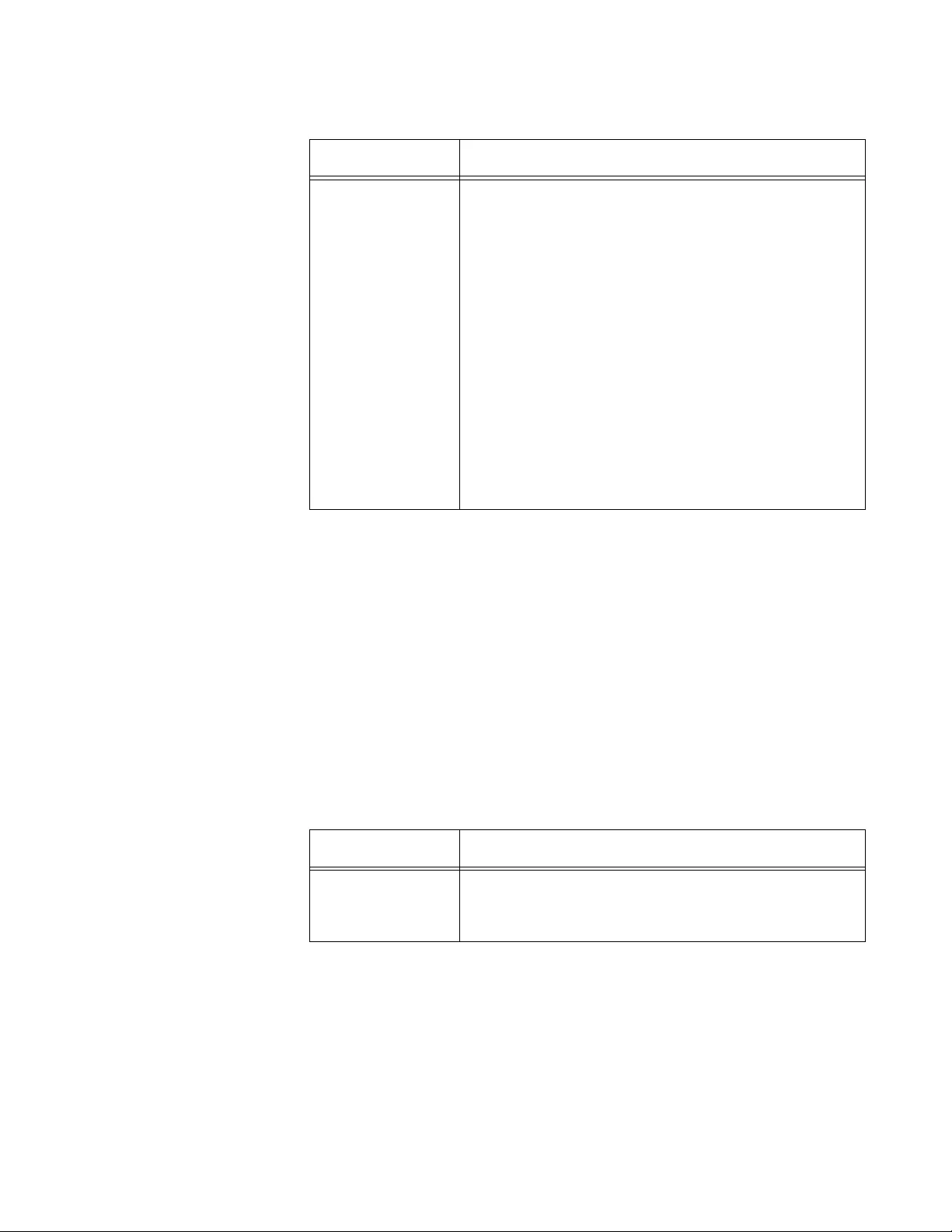
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
261
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Status of
Distributed
Tunneling
To view the information about the distributing tunnels on the AP client, do
the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Distributed Tunneling subtab.
2. Select the MAC address of the AP client from the select list.
The Associated Client Status Distributed Tunneling page is displayed.
3. Observe the fields described in Table 101.
Discovery
Reason
Displays how the access point was discovered. The
options are:
RF Scan
Probe Request - The access point
received probe requests from the AP client.
Associated to Managed AP - The AP client
is associated with the access point.
Associated to Peer AP - The AP client is
associated with the access point managed
by the peer controller.
Ad Hoc Rogue - The access point detected
the AP client on the ah hoc network.
Multiple reasons can be displayed at a time.
Table 100. Associated Client Status Neighbor APs (Continued)
Field Description
Table 101. Associated Client Status Distributed Tunneling
Field Description
Distributed
Tunneling Status
Displays whether or not the AP client is associated
with the wireless network that supports distributed
tunneling.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
262
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing the
Status of SSID
To view the SSID status of the AP clients and disassociate an AP client
form the wireless network, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the SSID Status tab.
The Associated Client SSID Status page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 102.
3. If you want to disconnect an AP client, check the checkbox next to the
MAC address of the AP client.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Disassociate — Disconnect the selected AP client from the
access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Client Roam
Status
Displays the roaming status of the AP client. The
options are:
Home - The AP client is not using the
distributed tunnel.
Roaming - The AP client is associated
through the distributed tunnel, or the
distributed tunneling is disabled.
Home AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the home access
point of the AP client.
Associated AP
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point that
the AP client roams to and is associated with.
Table 101. Associated Client Status Distributed Tunneling (Continued)
Field Description
Table 102. Associated Client SSID Status
Field Description
SSID Displays the SSID that the AP client is connected
to.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
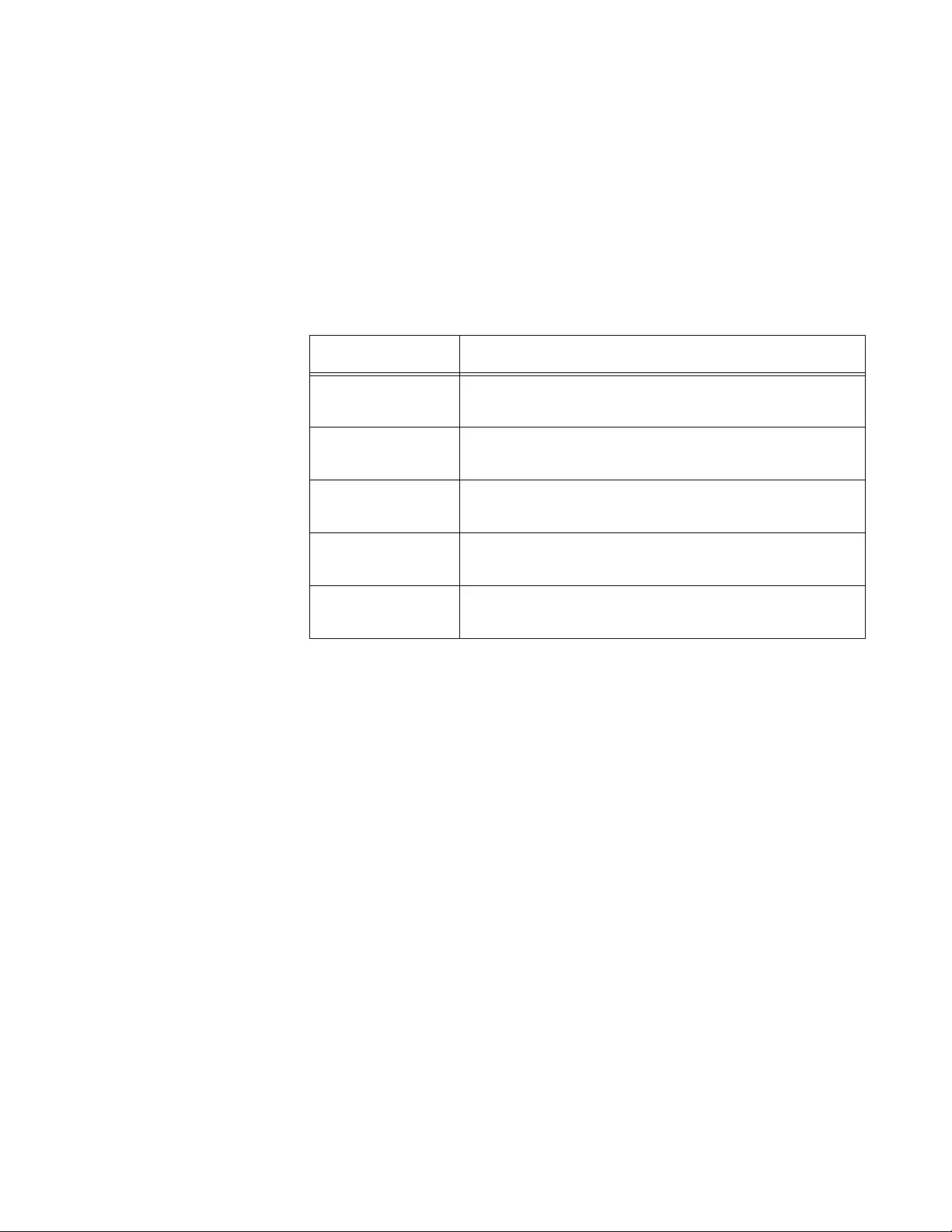
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
263
Viewing the
Status of VAP
To view the VAP status of the AP clients and disassociate an AP client
form the wireless network, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the VAP Status tab.
The Associated Client VAP Status page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 103.
3. If you want to disconnect an AP client, check the checkbox next to the
MAC address of the AP client.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Disassociate — Disconnect the selected AP client from the
access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Status of
Controller
To view the status of the WLAN Controller that manages the access point
which AP client is associated with and disassociate an AP client form the
wireless network, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Controller Status tab.
The Associated Client Controller Status page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 104 on page 264.
Table 103. Associated Client VAP Status
Field Description
BSSID Displays the MAC address of the VAP on the
access point that the AP client is associated with.
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point.
Location Displays the location information set to the AP
profile.
Radio Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface.
Client MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
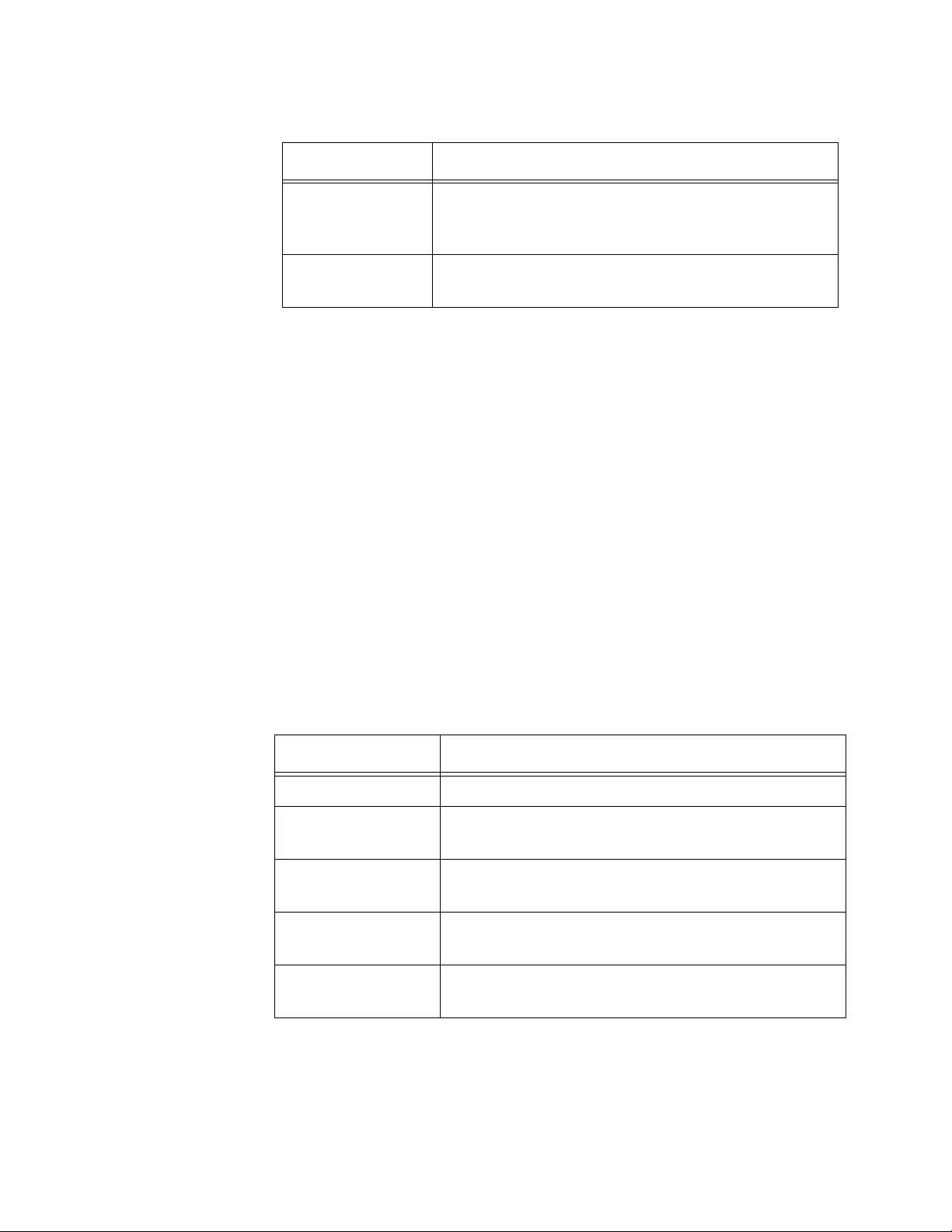
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
264
3. If you want to disconnect an AP client, check the checkbox next to the
MAC address of the AP client.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Disassociate — Disconnect the selected AP client from the
access point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing the
Summary
Statistics of
Association
To view the statistics of the traffic between the access point and AP
clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Association Summary Statistics tab.
The Association Summary Statistics page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 105.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 104. Associated Client Controller Status
Field Description
Controller IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller
that manges the access point, which the AP client
is associated with.
Client MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
Table 105. Association Summary Statistics
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the client station.
Packets Received Displays the number of packets that are received
from the client.
Bytes Received Displays the data size in bytes that are received
from the client.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that are
transmitted to the client.
Bytes Transmitted Displays the data size in bytes that are transmitted
to the client.
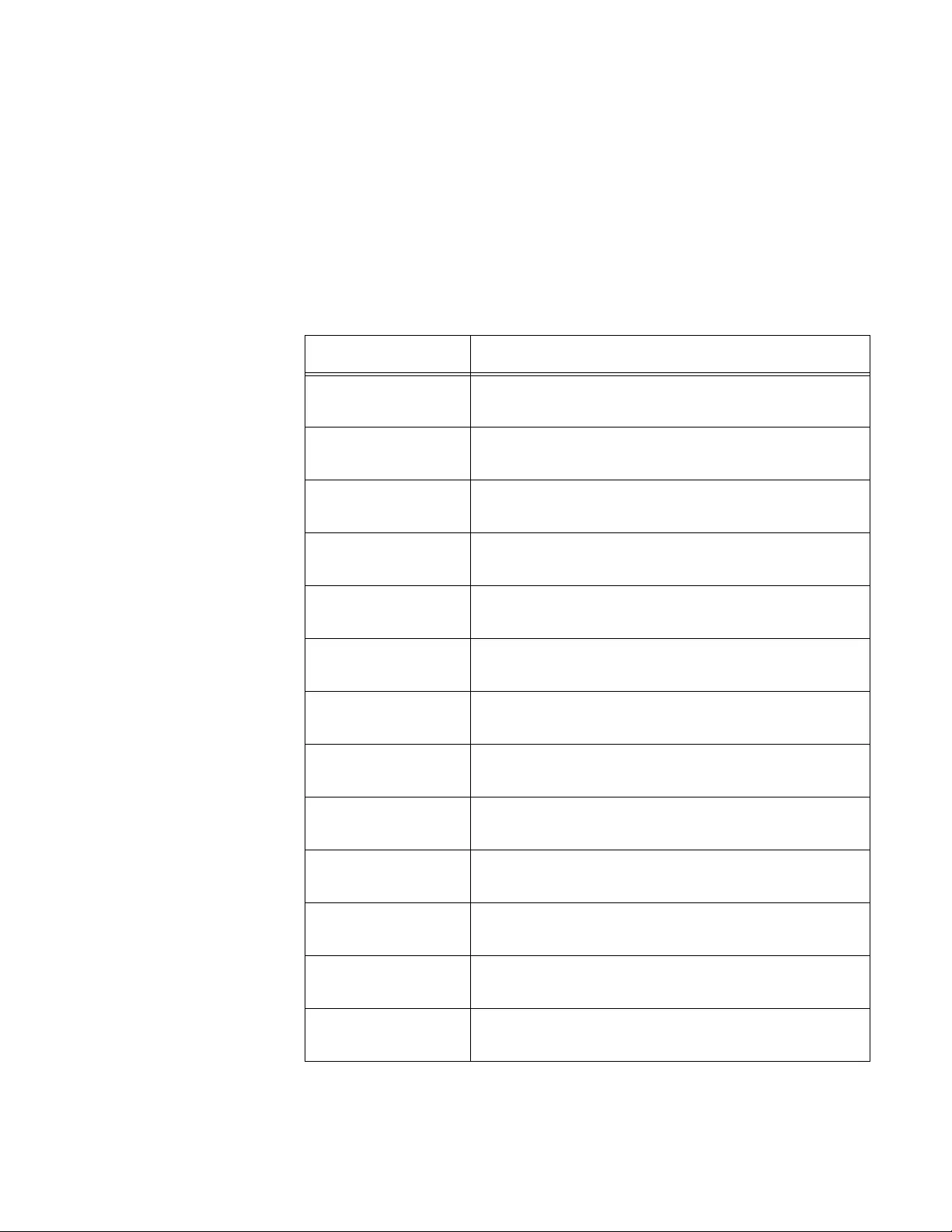
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
265
Viewing the
Detailed Statistics
of Association
To view the detailed statistics of the traffic between the access point and
AP clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics >
Associated Client and click the Association Detail Statistics tab.
The Association Detail Statistics page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 106.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 106. Association Detail Statistics
Field Description
Packets Received Displays the number of packets that are received
from the client.
Bytes Received Displays the data size in bytes that are received
from the client.
Packets
Transmitted
Displays the number of packets that are
transmitted to the client.
Bytes Transmitted Displays the data size in bytes that are transmitted
to the client.
Packets Receive
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that are received
from the client, but dropped.
Bytes Received
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that are received
from the client, but dropped.
Packets Transmit
Dropped
Displays the number of packets that are
transmitted to the client, but dropped.
Bytes Transmit
Dropped
Displays the data size in bytes that are transmitted
to the client, but dropped.
Fragments
Received
Displays the number of fragments of the packets
that are received from the client.
Fragments
Transmitted
Displays the number of fragments of the packets
that are transmitted to the client.
Transmit Retires Displays the number of times that traffic is
transmitted successfully to the client after the retry.
Transmit Retries
Failed
Displays the number of times that traffic failed to
be transmitted to the client after the retry.
Duplicate Received Displays the number of duplicated packets that are
received from the client.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
266
Status/Statistics > Peer Controller
From WLAN > Status/Statistics > Peer Controller page, you can view the
information about peer controllers.
Viewing the
Status of Peer
Controllers
To view a list of peer controllers in the same peer group as the WLAN
Controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Peer
Controller.
The Peer Controller Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 134.
Figure 134. Peer Controller Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 107.
Table 107. Peer Controller Status
Field Description
IP Address Displays the IP address of the peer controller.
Software Version Displays the version of the software that is currently
installed on the peer controller.
Protocol Version Displays the version of the Protocol that the
software on the peer controller supports.
Discovery
Reason
Displays the method that the peer controller was
discovered with: L2 Poll or IP Poll.
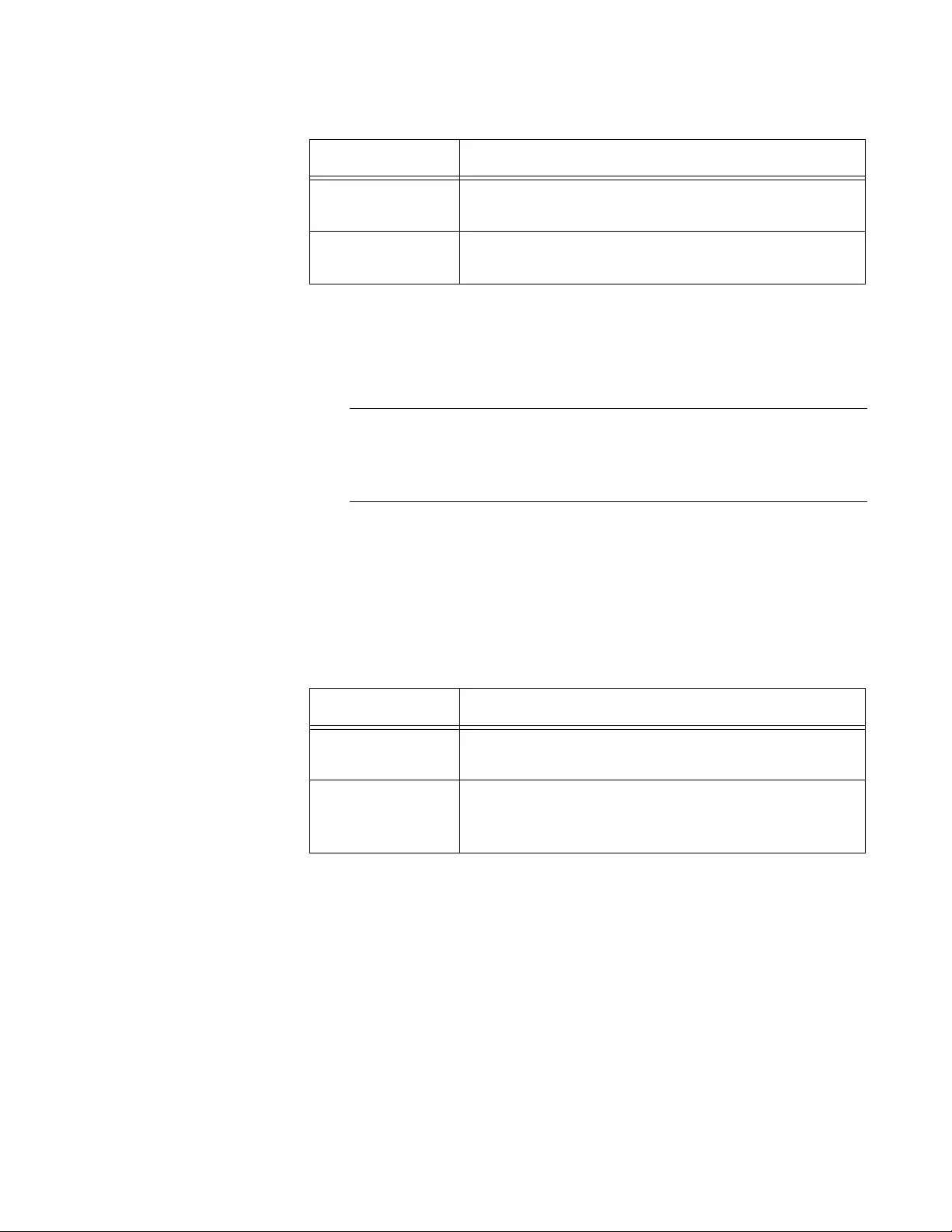
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
267
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing Peer
Controller
Configuration
To view information about the configuration that the peer controller
pushed, do the following:
Note
To view the information about the configuration that the WLAN
Controller received, see “Viewing Configuration Received” on
page 229.
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Peer
Controller and click the Configuration tab.
The Peer Controller Configuration page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 108.
Managed AP
Count
Displays the number of access points that the peer
controller currently manages.
Age Displays the time period since the WLAN Controller
communicated with the peer controller last time.
Table 107. Peer Controller Status (Continued)
Field Description
Table 108. Peer Controller Configuration
Field Description
Peer IP Address Displays the IP address of the peer controller that
received.
Configuration
Controller IP
Address
Displays the IP address of the peer controller that
pushed the configuration.
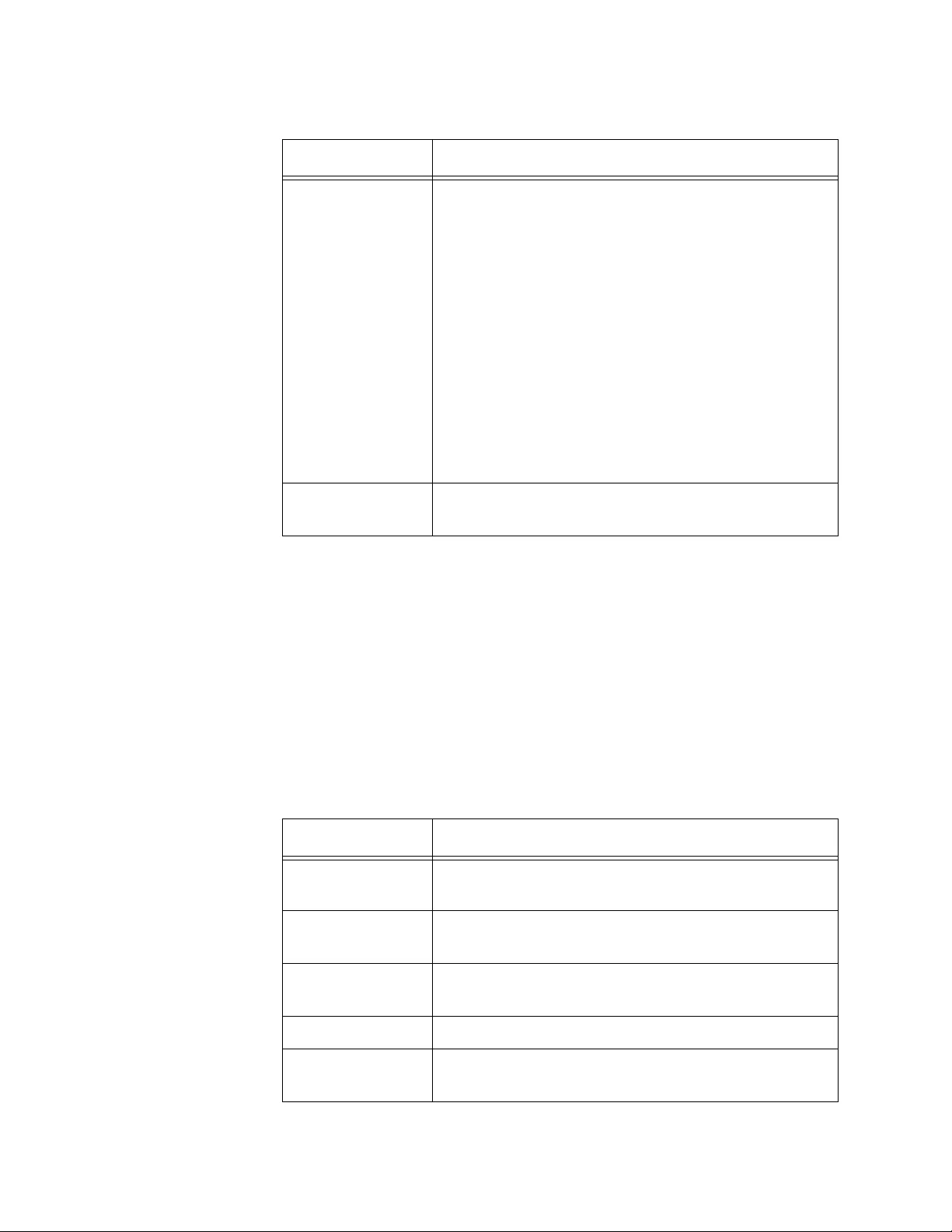
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
268
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing
Managed AP by
Peer Controller
To view information about the managed access points that the peer
controllers manage, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > Peer
Controller and click the Managed AP tab.
The Managed AP by Peer Controller page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 109.
Configuration Displays the type of the configuration that the peer
controller received. The options are:
Global
Discovery
Channel/Power
AP Database
AP Profiles
Known Client
Captive Portal
RADIUS Client
None
Timestamp Displays the UTC time when the peer controller
received the configuration.
Table 108. Peer Controller Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Table 109. Managed AP by Peer Controller
Field Description
Peer Managed
AP MAC
Displays the MAC address of the access point that
the peer controller manages.
Peer Controller
IP Address
Displays the IP address of the peer controller that
manages the access point.
Location Displays the location information of the AP profile
that is applied to the access point.
AP IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.
Profile Displays the AP profile that the peer controller
applied to the access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
269
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Hardware Type Displays the hardware ID of the access point.
Table 109. Managed AP by Peer Controller (Continued)
Field Description
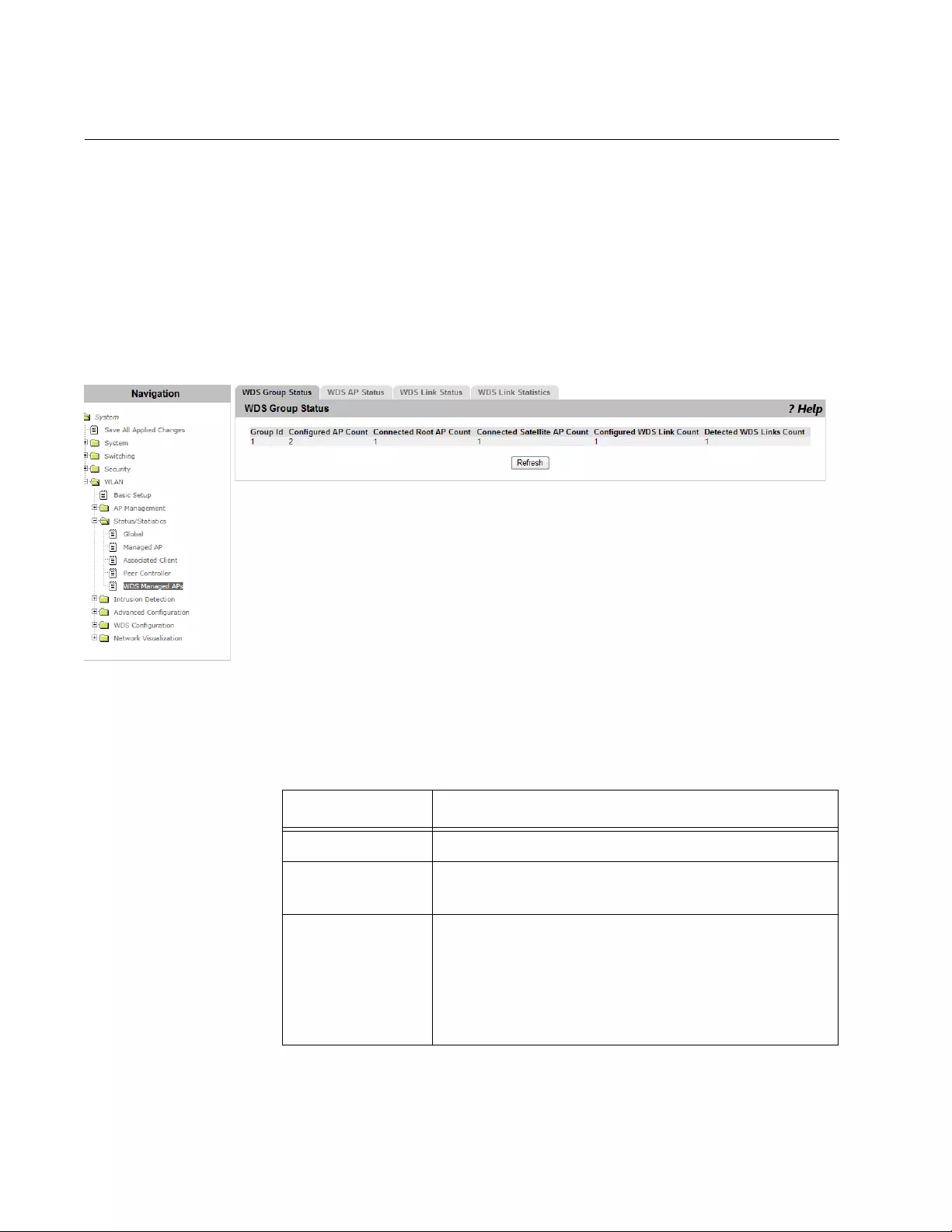
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
270
Status/Statistics > WDS Managed APs
From WLAN > Status/Statistics > WDS Managed APs, you can view the
information about Wireless Distribution System (WDS).
Viewing WDS
Group Status
To view the status of the WDS group, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > WDS
Managed APs.
The WDS Group Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 135.
Figure 135. WDS Group Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 110.
Table 110. WDS Group Status
Field Description
Group Id Displays the unique group ID of the WDS group.
Configured AP
Count
Displays the number of access points in the WDS
group that the WLAN Controller manages.
Connected Root
AP Count
Displays the number of root access points in the
WDS group that are managed by the WLAN
Controller.
The root access point is an access point connected
to the WLAN Controller through the Ethernet.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
271
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing WDS AP
Status
To view the status of the access point in the WDS group, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > WDS
Managed APs and click the WDS AP Status tab.
The WDS AP Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 136.
Figure 136. WDS AP Status Page
2. Select the group ID and group name from the select list.
To show all the access points in all the WDS groups, select All from
the select list.
Connected
Satellite AP
Count
Displays the number of satellite access points in
the WDS group that are managed by the WLAN
Controller.
The satellite access point is an access point
connected to the WLAN Controller through the
WDS connection.
Configured WDS
Link Count
Displays the number of WDS connections that are
configured in the WDS group.
Deleted WDS
Links Count
Displays the number of WDS connections that are
established in the WDS group.
Table 110. WDS Group Status (Continued)
Field Description
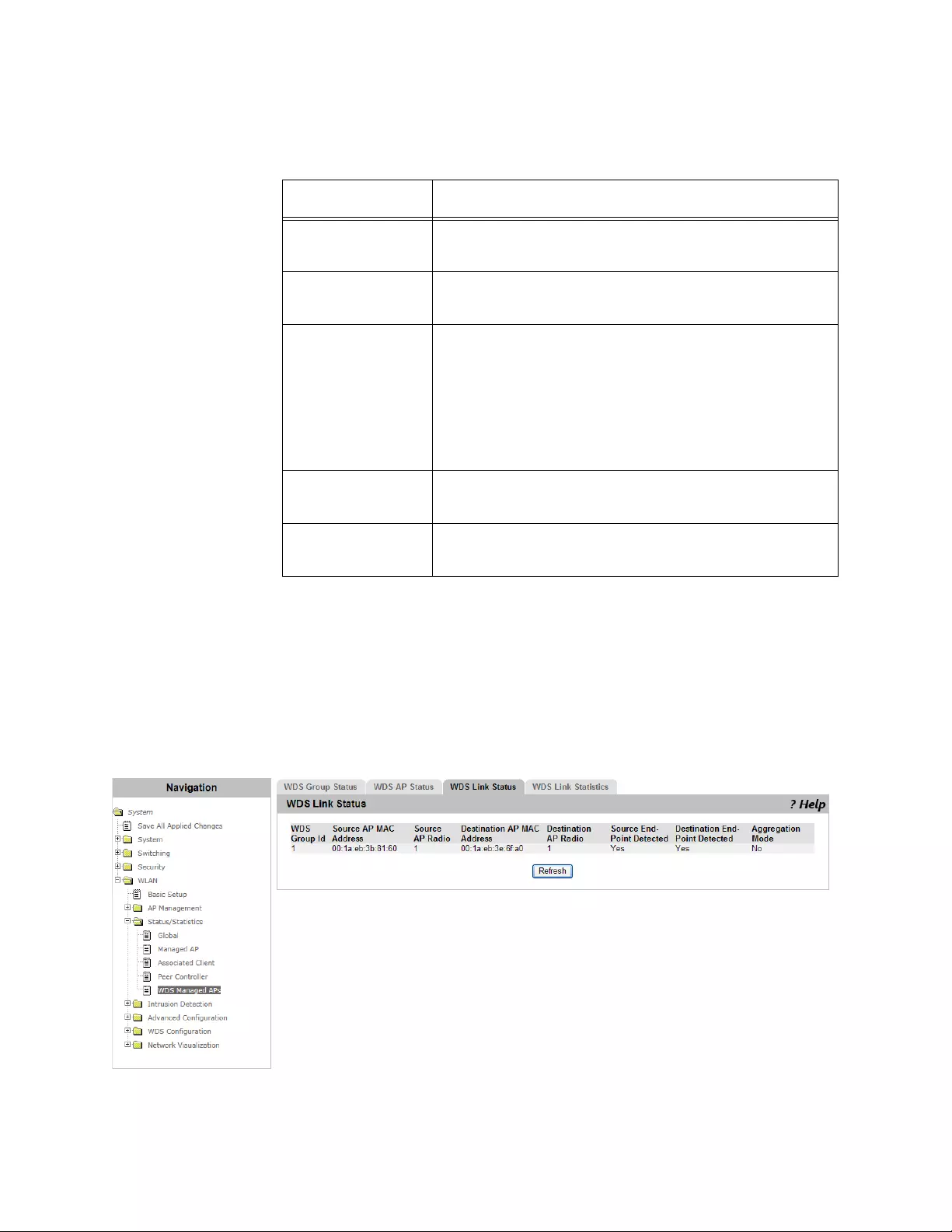
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
272
3. Observe the fields described in Table 111.
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing WDS
Link Status
To view the link status in the WDS group, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > WDS
Managed APs and click the WDS Link Status tab.
The WDS Link Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 137.
Figure 137. WDS Link Status Page
Table 111. WDS AP Status
Field Description
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point.
AP Connection
Status
Displays whether the access point is connected to
the WLAN Controller or not.
Satellite Mode Displays the mode of the access point. The options
are:
Satellite
Wired - Root access point
None - No WDS connection
Ethernet Port
Mode
Displays the Ethernet port mode. This field always
shows Enabled.
Ethernet Port
Link State
Displays the link state of the Ethernet port: Up or
Down.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
273
2. Observe the fields described in Table 112.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing WDS
Link Statistics
To view the link statistics in the WDS group, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Status/Statistics > WDS
Managed APs and click the WDS Link Statistics tab.
The WDS Link Statistics page is displayed as shown in Figure 138 on
page 274.
Table 112. WDS Link Status
Field Description
WDS Group Id Displays the unique WDS group ID.
Source AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the source access
point of the WDS group.
Source AP Radio Displays the radio band of the source access point.
The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz
Destination AP
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the destination
access point of the WDS group.
Destination AP
Radio
Displays the radio band of the destination access
point. The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz
Source End-
Point Detected
Displays whether the destination access point
detects the source access point or not.
Destination End-
Point Detested
Displays whether the source access point detects
the destination access point or not.
Aggregation
Mode
Not Supported.
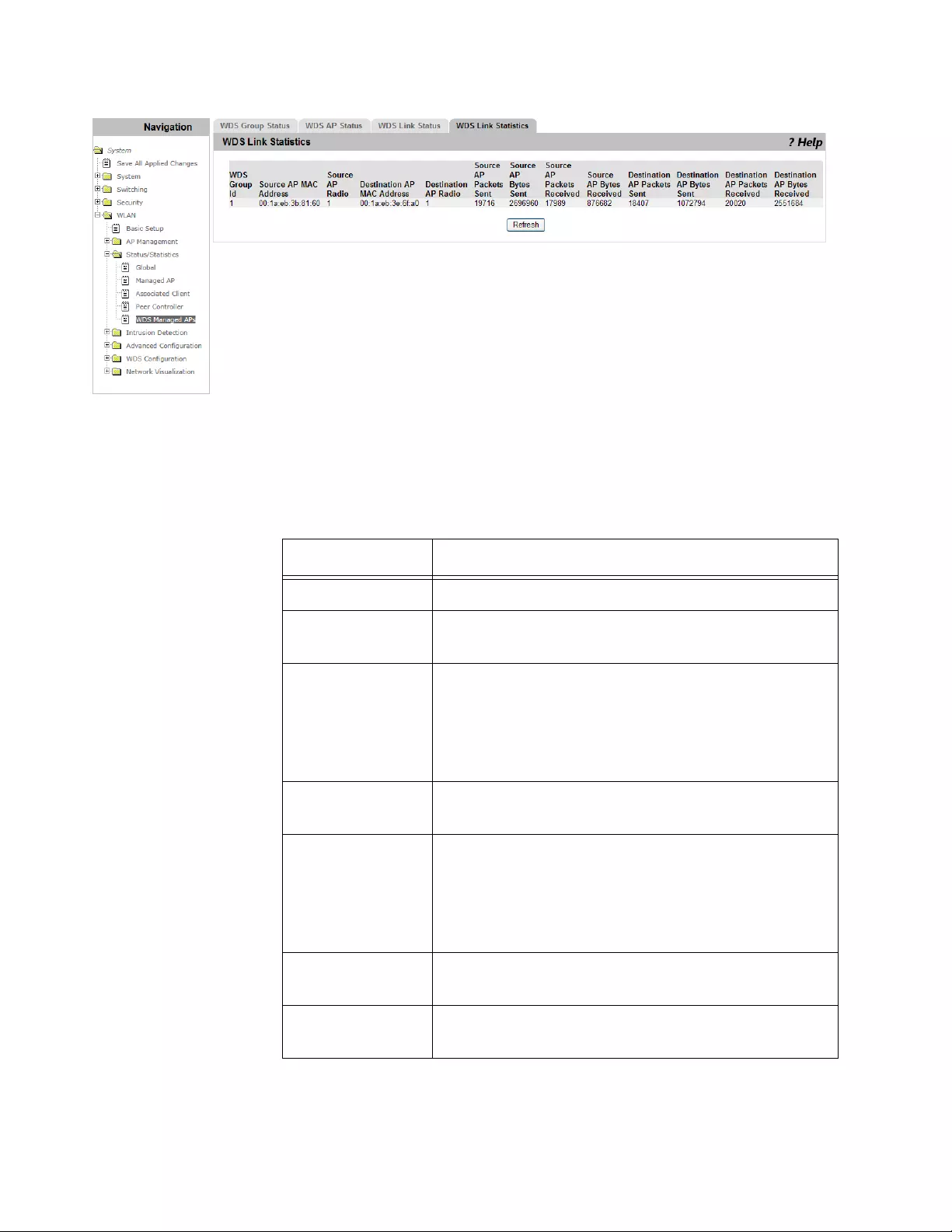
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
274
Figure 138. WDS Link Statistics Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 113.
Table 113. WDS Link Statistics
Field Description
WDS Group Id Displays the unique WDS group ID.
Source AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the source access
point of the WDS group.
Source AP Radio Displays the radio band of the source access point.
The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz
Destination AP
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the destination
access point of the WDS group.
Destination AP
Radio
Displays the radio band of the destination access
point. The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz
Source AP
Packets Sent
Displays the number of packets that the source
access point transmitted.
Source AP Bytes
Sent
Displays the data size in bytes that the source
access point transmitted.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
275
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Source AP
Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the source
access point received.
Source AP Bytes
Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the source
access point received.
Destination AP
Packets Sent
Displays the number of packets that the destination
access point transmitted.
Destination AP
Bytes Sent
Displays the data size in bytes that the destination
access point transmitted.
Destination AP
Packets
Received
Displays the number of packets that the destination
access point received.
Destination AP
Bytes Received
Displays the data size in bytes that the destination
access point received.
Table 113. WDS Link Statistics (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
276
Rogue/RF Scan
The access point scans the specified channels in the radio band, classifies
detected access points or AP clients as rogue if they fail to the tests, and
reports the results to the WLAN Controller.
From the Rogue/RF Scan page, you can view a list of access points that
the managed access points detected through RF scanning.
To view a list of AP clients that are detected, see “Detected Clients” on
page 284.
Viewing Access
Points Detected
by RF Scan
To view a list of access points detected by RF scan, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Rogue/RF Scan.
The Access Point RF Scan Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 139.
Figure 139. Access Point RF Scan Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 114.
Table 114. Access Point RF Scan Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point or
VAP.
OUI Displays the vendor, manufacturer, or organization
of the access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
277
3. Check the checkbox of the MAC address of access point to manage or
clear the rogue status.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete ALL — Deletes all the access point entires from the RF
scan list.
Manage — Makes the WLAN Controller manage the selected
rogue access points, add to the Valid AP list, and apply the default
AP profile next time the WLAN Controller detect them.
Acknowledge — Clears the classification of the selected rogue
access points.
Acknowledge All Rogues — Clears the classification of all the
rogue access points.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing an
Access Point
Detected by RF
Scan
To view the detailed information about the access point detected by RF
scan, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Rogue/RF Scan.
SSID Displays the SSID in the beacon frames from the
access point.
Physical Mode Displays the mode of IEEE 802.11 that the access
point uses.
Channel Displays the channel that the access point is using
to communicates.
Status Displays the status of the access point. The options
are:
Managed - An access point managed by
the WLAN Controller
Standalone - An access point on the Valid
AP list of the WLAN Controller
Rogue - An access point classified as an
threat by WIDS
Unknown - An access point classified not
as an intruder by WIDS
Age Displays the time period since the access point was
detected by RF Scan.
Table 114. Access Point RF Scan Status (Continued)
Field Description
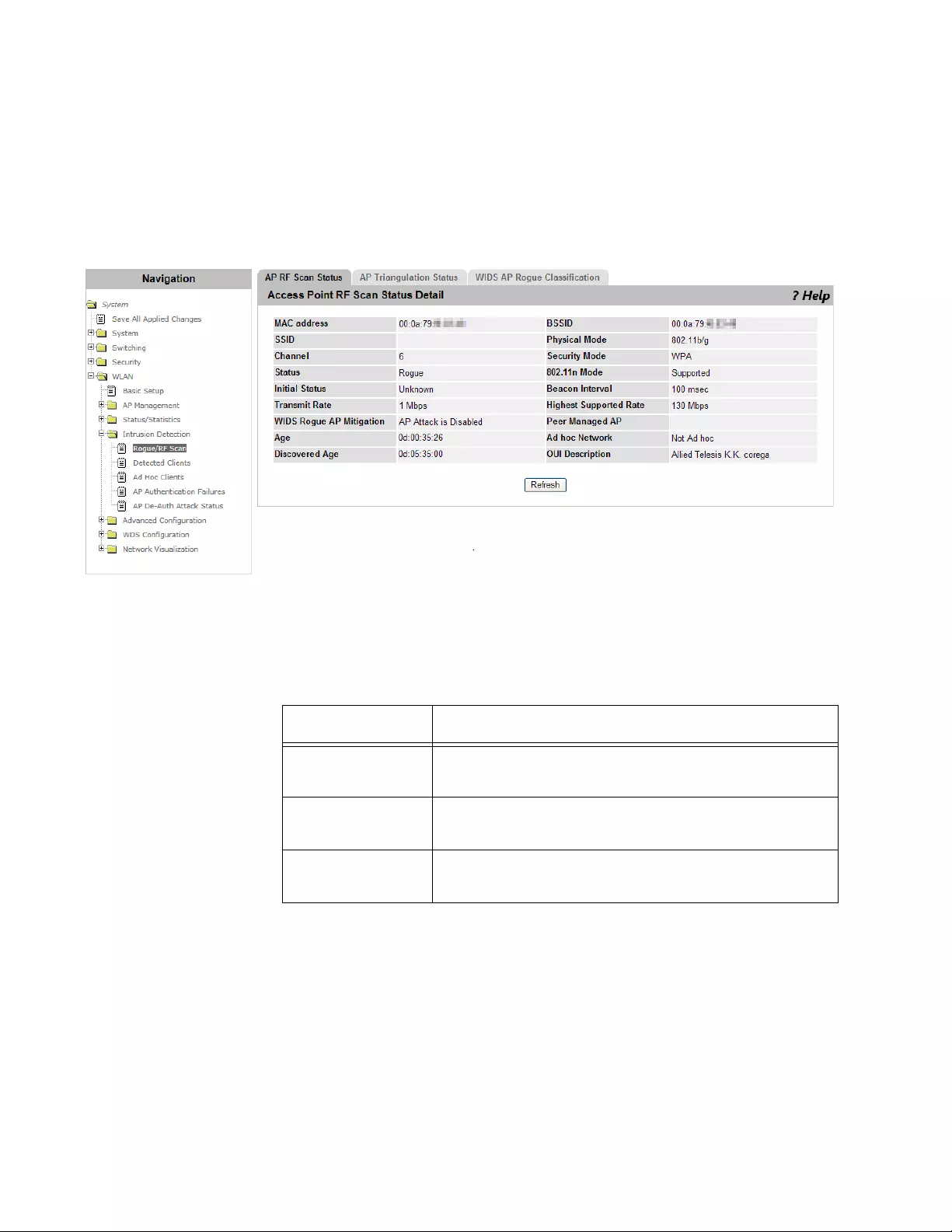
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
278
The Access Point RF Scan Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 139 on page 276.
2. Click a MAC address from the Access Point RF Scan Status.
The Access Point RF Scan Status Detail page is displayed as shown in
Figure 140.
Figure 140. Access Point RF Scan Status Detail Page
3. Observe the fields described in Table 115.
Table 115. Access Point RF Scan Status Detail
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point or
VAP.
SSID Displays the SSID in the beacon frames from the
access point.
Channel Displays the channel that the access point
communicates through
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
279
Status Displays the status of the access point. The options
are:
Managed - An access point managed by
the WLAN Controller
Standalone - An access point on the Valid
AP list of the WLAN Controller
Rogue - An access point classified as an
threat by WIDS
Unknown - An access point classified not
as rogue by WIDS
Initial Status Displays the initial status of the access point that is
later classified as rogue. The options are:
Managed
Standalone
Unknown
The initial status is the same as status for access
points that are not rogue.
Transmit Rate Displays the transmit rate of the access point.
WIDS Rogue AP
Mitigation
Displays the reason why the mitigation is not
applied. The mitigation is a feature to reduce the
risks.The options are:
Not Required
Already mitigating too many APs
AP is operating on an illegal channel
AP is spoofing valid managed AP MAC
address.
AP is ad hoc.
Age Displays the time period since last RF scan by
which the access point was detected.
Discovered Age Displays the time period since first RF scan by
which the access point was detected.
BSSID Displays the BSSID in the beacon frames from the
access point.
Physical Mode Displays the IEEE 802.11 mode that the access
point is using.
Table 115. Access Point RF Scan Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
280
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing AP
Triangulation
Status
You can view a list of access points that detected the rogue access point.
Based on the information, you can determine the approximate location of
the rogue access point. The AP Triangulation Status page is for rogue
access points only.
To view a list of access points that detected the rogue access point, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Rogue/RF Scan.
The Access Point RF Scan Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 139 on page 276.
2. Click a MAC address from the Access Point RF Scan Status.
The Access Point RF Scan Status Detail page is displayed as shown in
Figure 140 on page 278.
3. Click the AP Triangulation Status tab.
The AP Triangulation Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 141
on page 281.
Security Mode Displays the security mode that the access point is
using.
802.11n Mode Displays whether or not the access point supports
IEEE 802.11n mode.
Beacon Interval Displays the time interval between sending
beacons.
Highest
Supported Rate
Displays the highest supported rate in Mbps that
the access point informs of in the beacon frames.
Peer Managed
AP
Displays whether the access point is managed by a
WLAN Controller in the peer group.
Ad hoc Network Displays whether the beacon frames are sent from
the ad hoc network or not.
OUI Description Displays the vendor, manufacturer, or organization
of the access point.
Table 115. Access Point RF Scan Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
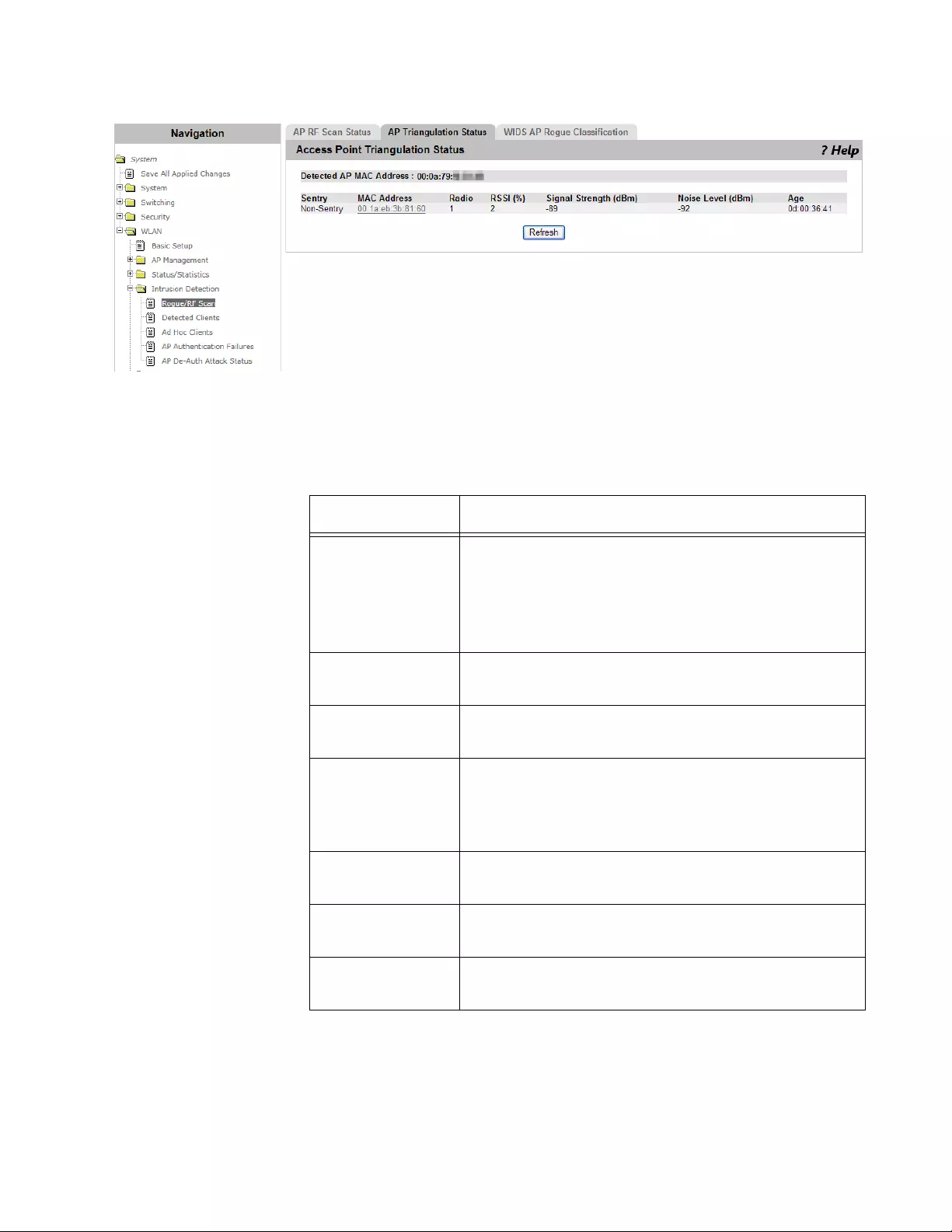
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
281
Figure 141. AP Triangulation Status Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 116 on page 281.
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 116. AP Triangulation Status
Field Description
Sentry Displays the sentry mode of the access point. The
options are:
Sentry
Not Sentry
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point or
VAP.
Radio Displays the radio band that the access point is
detected in.
RSSI (%) Displays Received Signal Strength Indication
(RSSI) of the non-sentry access point in
percentage. RSSI is a measurement of the power
represent in a received radio signal.
Signal Strength
(dBm)
Displays Received Signal Strength Indication
(RSSI) of the non-sentry AP in dBm.
Noise Level
(dBm)
Displays the noise level that the non-sentry access
point reported.
Age Displays the time period since the last RF scan that
the access point was detected.
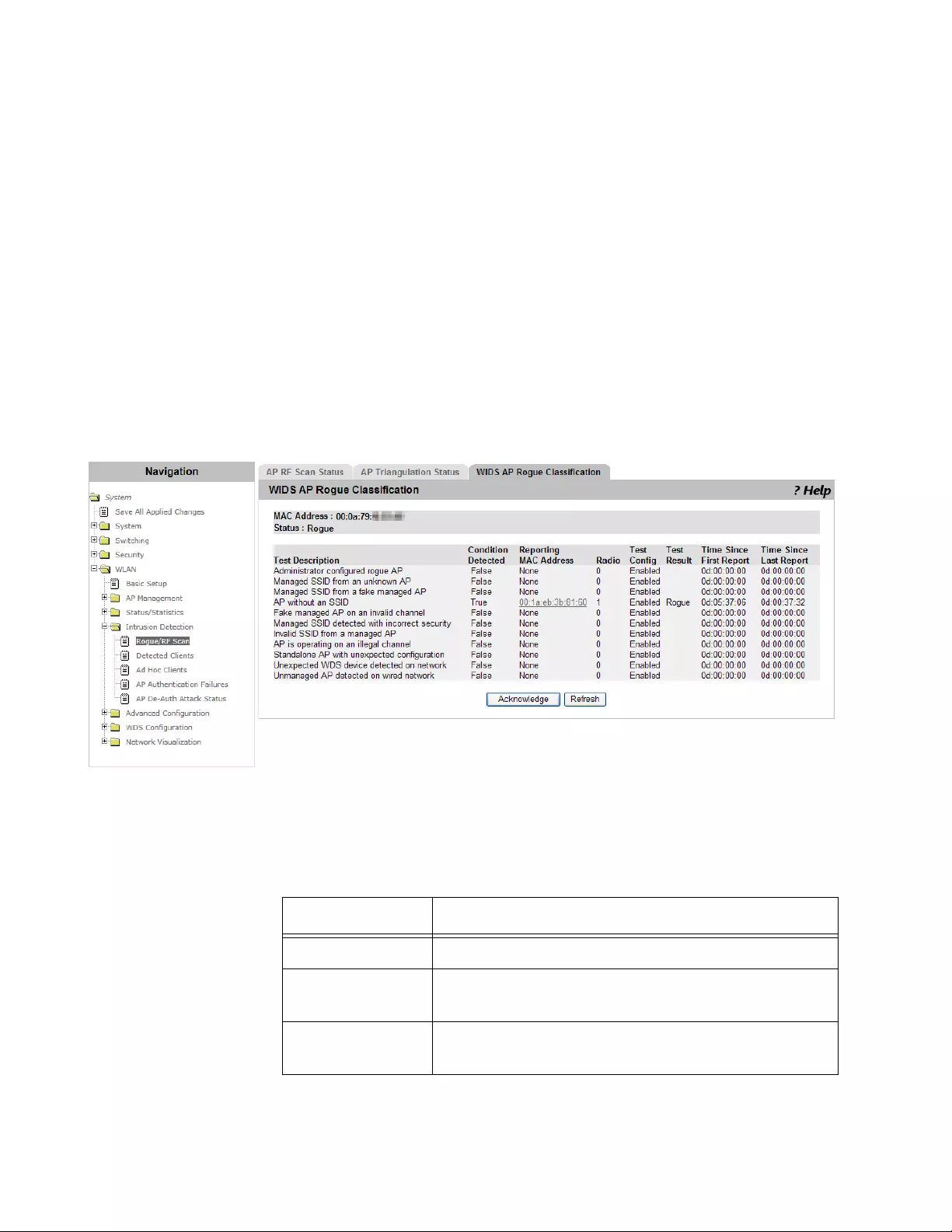
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
282
Viewing WIDS
AP Rogue
Classification
To view the WIDS AP Rogue Classification, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Rogue/RF Scan.
The Access Point RF Scan Status page is displayed as shown in
Figure 139 on page 276.
2. Click a MAC address from the Access Point RF Scan Status.
The Access Point RF Scan Status Detail page is displayed as shown in
Figure 140 on page 278.
3. Click the WIDS AP Rogue Classification tab.
The WIDS AP Rogue Classification page is displayed as shown in
Figure 142.
Figure 142. WIDS AP Rogue Classification Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 117.
Table 117. WIDS AP Rogue Classification
Field Description
Test Description Displays the test description.
Condition
Detected
Displays the result of the test: True or False.
Reporting MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the managed access
point.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
283
5. Click the following buttons as needed:
Acknowledge — Clears the rogue classification of the access
point.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Radio Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface.
Test Config Displays the test condition: Enabled or Disabled.
Test Result Displays whether the test reports that the access
point is rogue or not.
Time Since First
Report
Displays the time period since the current test
result was reported for the first time.
Time Since Last
Report
Displays the time period since the current test
result was reported.
Table 117. WIDS AP Rogue Classification (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
284
Detected Clients
The WLAN Controller detects the AP clients that are connected to access
points or send messages to access points.
From the Detected Clients page, you can view a list of detected AP clients.
Viewing a List of
Detected Clients
To view a list of deleted clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143.
Figure 143. Detected Client Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 118.
Table 118. Detected Client Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
OUI Displays the vendor, manufacturer, or organization
of the wireless LAN adapter of the AP client.
Client Name Displays the name of the AP client if it has a name
on the Known Client database.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
285
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete — Deletes all the AP client entires from the Detected Client
list.
Delete ALL — Deletes all the AP client entires from the Detected
Client list.
Acknowledge All Rogues — Clears the classification of all the
rogue AP clients.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing a
Detected AP
Client
To view the detailed information about the detected AP client, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143
on page 284.
2. Click a MAC address from the AP client on the list.
The Detected Client Status Detail page is displayed as shown in Figure
144 on page 286.
Client Status Displays the status of the AP client. The options
are:
Authenticated
Detected - Not authenticated, but not
classified as rogue.
Black-Listed - Access is denied because
the AP client is on the MAC Authentication
Black-List.
Rogue - The AP client is classified as a
threat by WIDS.
Age Displays the time period since the AP client was
updated on the Detected Client list last time.
Create Time Displays the time period since the AP client is
added to the Detected Client list for the first time.
Table 118. Detected Client Status (Continued)
Field Description
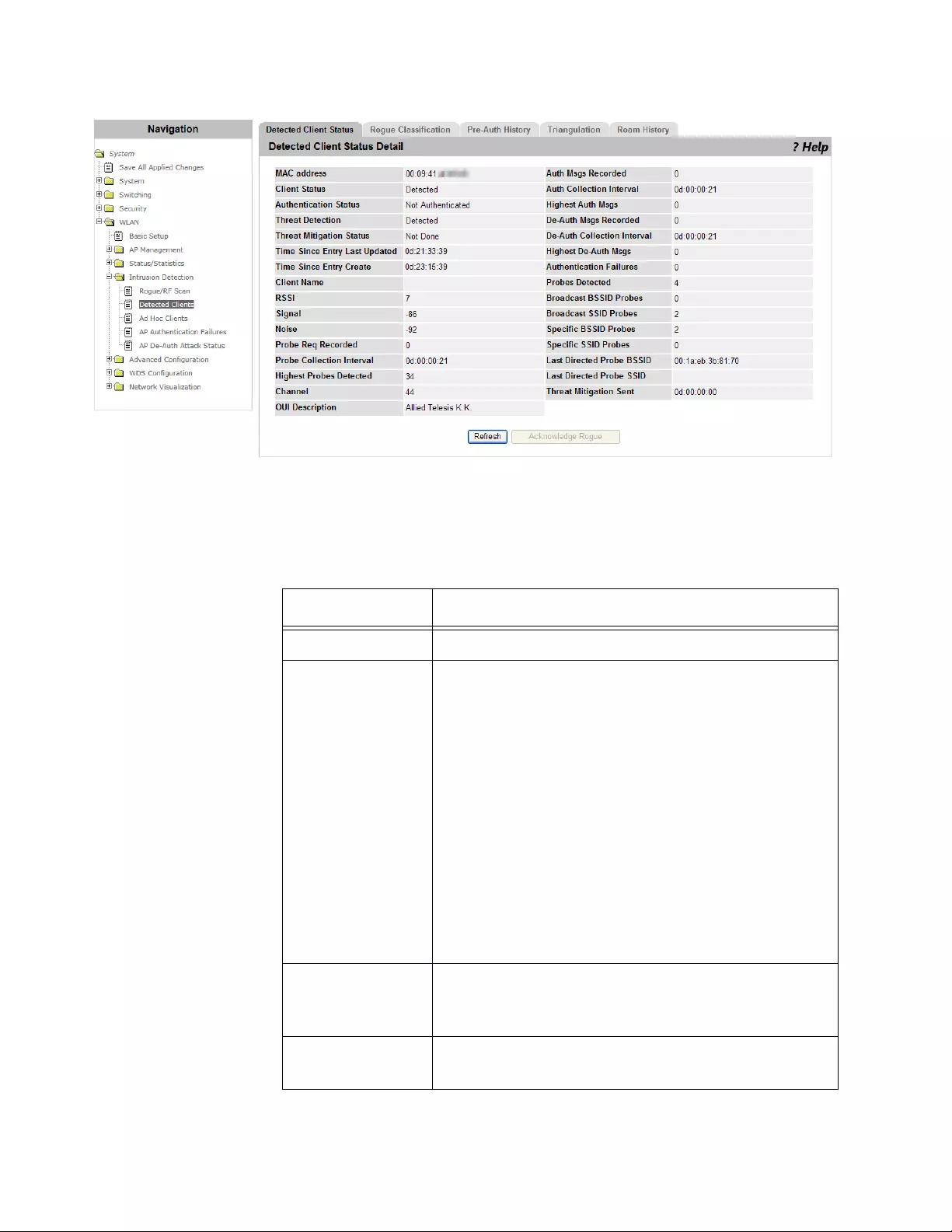
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
286
Figure 144. Detected Client Status Detail Page
3. Observe the fields described in Table 119.
Table 119. Detected Client Status Detail
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
Client Status Displays the status of the AP client. The options
are:
Authenticated
Detected - Not authenticated nor on the
Known Client list, but not classified as
rogue.
Known - The AP client is not authenticated,
but on the Known Client list.
Black-Listed - The AP client is denied
access based on the black list.
Rogue - The AP client is classified as a
threat by WIDS.
Authentication
Status
Displays whether the AP client is authenticated or
not. An AP client can be authenticated even when
classified as rogue.
Threat Detection Displays whether the threat is detected on AP client
or not.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
287
Threat Mitigation
Status
Displays whether the mitigation is implemented or
not.
Time Since Entry
Last Updated
Displays the time period since the AP client was
updated on the Detected Client list.
Time Since Entry
Create
Displays the time period since the AP client was
added to the Detected Client list for the first time.
Client Name Displays the name of the AP client if it has a name
on the Known Client database.
RSSI Displays Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
in percentage that the access point reported.
Signal Displays the signal strength level in dBm that the
access point reported. The range is from -127 to
128 dBm.
Noise Displays the noise strength level in dBm that the
access point reported. The range is from -127 to
128 dBm.
Probe Req
Recorded
Displays the number of probes that the AP client
received in the current interval. The interval is set in
Probe Requests Threshold Interval. See “WIDS
Client Configuration” on page 354.
Probe Collection
Interval
Displays the time period since the current interval
started. The interval is set in Probe Requests
Threshold Interval. See “WIDS Client
Configuration” on page 354.
Highest Probes
Detected
Displays the highest number of probes that the AP
client received in an interval.
Channel Displays the channel that the AP client is using.
OUI Description Displays the vendor, manufacturer, or organization
of the network adapter of the AP client.
Auth Msgs
Recorded
Displays the number of IEEE 802.11 authentication
messages that the AP client received in the current
interval. The interval is set in Authentication
Requests Threshold Interval. See “WIDS Client
Configuration” on page 354.
Table 119. Detected Client Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
288
Auth Collection
Interval
Displays the time period since the current interval
started. The interval is set in Authentication
Requests Threshold Interval. See “WIDS Client
Configuration” on page 354.
Highest Auth
Msgs
Displays the highest number of authentication
messages that the AP client received in an interval.
De-Auth Msgs
Recorded
Displays the number of IEEE 802.11 de-
authentication messages that the AP client
received in the current interval. The interval is set in
De-Authentication Requests Threshold Interval.
See “WIDS Client Configuration” on page 354.
De-Auth
Collection
Interval
Displays the time period since the current interval
started. The interval is set in De-Authentication
Requests Threshold Interval. See “WIDS Client
Configuration” on page 354.
Highest De-Auth
Msgs
Displays the highest number of de-authentication
messages that the AP client received in an interval.
Authentication
Failures
Displays the number of authentication that the AP
client failed.
Probes Detected Displays the number of probes that were detected
by the last RF scan.
Broadcast
BSSID Probes
Displays the number of probes against broadcast
BSSID’s that were detected by the last RF scan.
Broadcast SSID
Probes
Displays the number of probes against broadcast
SSID’s that were detected by the last RF scan.
Specific BSSID
Probes
Displays the number of probes against the specific
broadcast BSSID that were detected by the last RF
scan.
Specific SSID
Probes
Displays the number of probes against the specific
broadcast SSID that were detected by the last RF
scan.
Last Directed
Probe BSSID
Displays the MAC address of the last non-
broadcast BSSID that was detected by the RF
scan.
Last Directed
Probe SSID
Displays the MAC address of the last non-
broadcast SSID that was detected by the RF scan.
Table 119. Detected Client Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
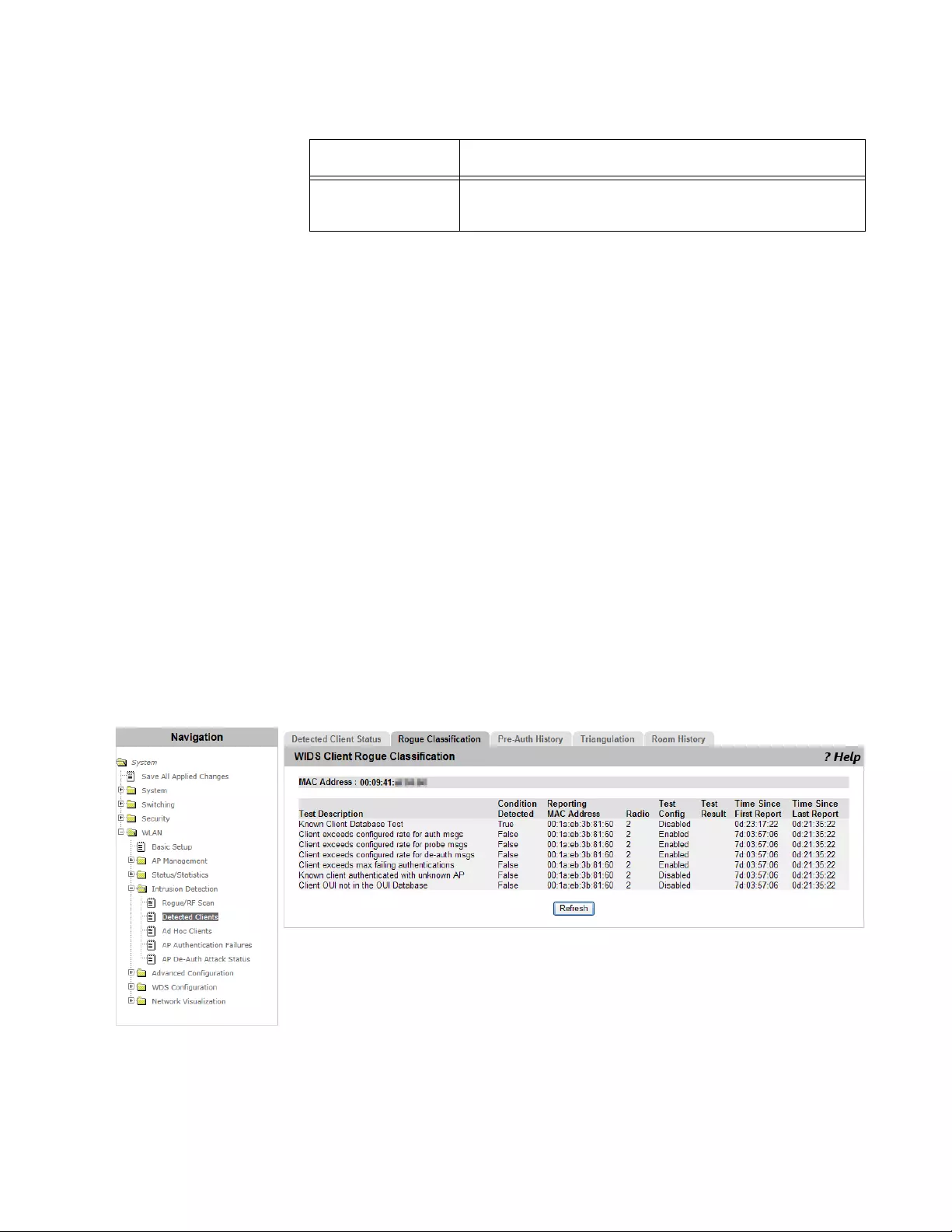
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
289
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Acknowledge All Rogues — Clears the classification of all the
rogue AP clients.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing Rogue
Classification
To view a list of tests that classified failed AP clients as rogue, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143
on page 284.
2. Click a MAC address from the AP client on the list.
The Detected Client Status Detail page is displayed as shown in Figure
144 on page 286.
3. Click the Rogue Classification tab.
The Rogue Classification page is displayed as shown in Figure 145.
Figure 145. Rogue Classification Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 120 on page 290.
Treat Mitigation
Sent
Displays whether the mitigation is implemented or
not.
Table 119. Detected Client Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
290
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing Pre-
Auth History
When WPA Pre-Authentication is enabled, the AP client can roam to other
access points without going through the re-authentication process and re-
reconnecting to the wireless network. The access points report pre-
authentication requests from AP clients to the WLAN Controller.
To view the pre-authentication request from the AP client, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143
on page 284.
2. Click a MAC address from the AP client on the list.
The Detected Client Status Detail page is displayed as shown in
Figure 144 on page 286.
Table 120. Rogue Classification
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
Test Description Displays the test description.
Condition
Detected
Displays the result of the test: True or False.
Reporting MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point that
reported the test result.
Radio Displays the radio band in that the test result is
observed.
Test Config Displays the test status. The options are:
Enabled - Failing the test classifies the AP
client as rogue.
Disabled - The test result does not classify
the AP client.
Test Result Displays whether or not the test reported the AP
client as rogue.
Time Since First
Report
Displays the time period since the current test
result was reported for the first time.
Time Since Last
Report
Displays the time period since the current test
result was reported.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
291
3. Click the Pre-Auth History tab.
The Pre-Auth History page is displayed.
4. Observe the fields described in Table 121.
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing
Triangulation
Information
You can view a list of access points that detected the rogue AP client.
Based on the information, you can determine the approximate location of
the rogue AP client. The Detected Client Triangulation page is only for
rogue AP clients.
To view a list of access points that detected the AP client, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143
on page 284.
2. Click a MAC address from the AP client on the list.
Table 121. Pre-Auth History
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point that
pre-authenticated the AP client.
Radio Interface
Number
Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface.
VAP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the VAP that the AP
client roamed.
SSID Displays the SSID that the VAP is serving.
Age Displays the time period since this Pre-Auth history
was recorded.
User Name Displays the user name of the AP client when the
client was 802.1x authenticated.
Pre-
Authentication
Status
Displays the status of the pre-authentication. The
options are:
Success
Failure
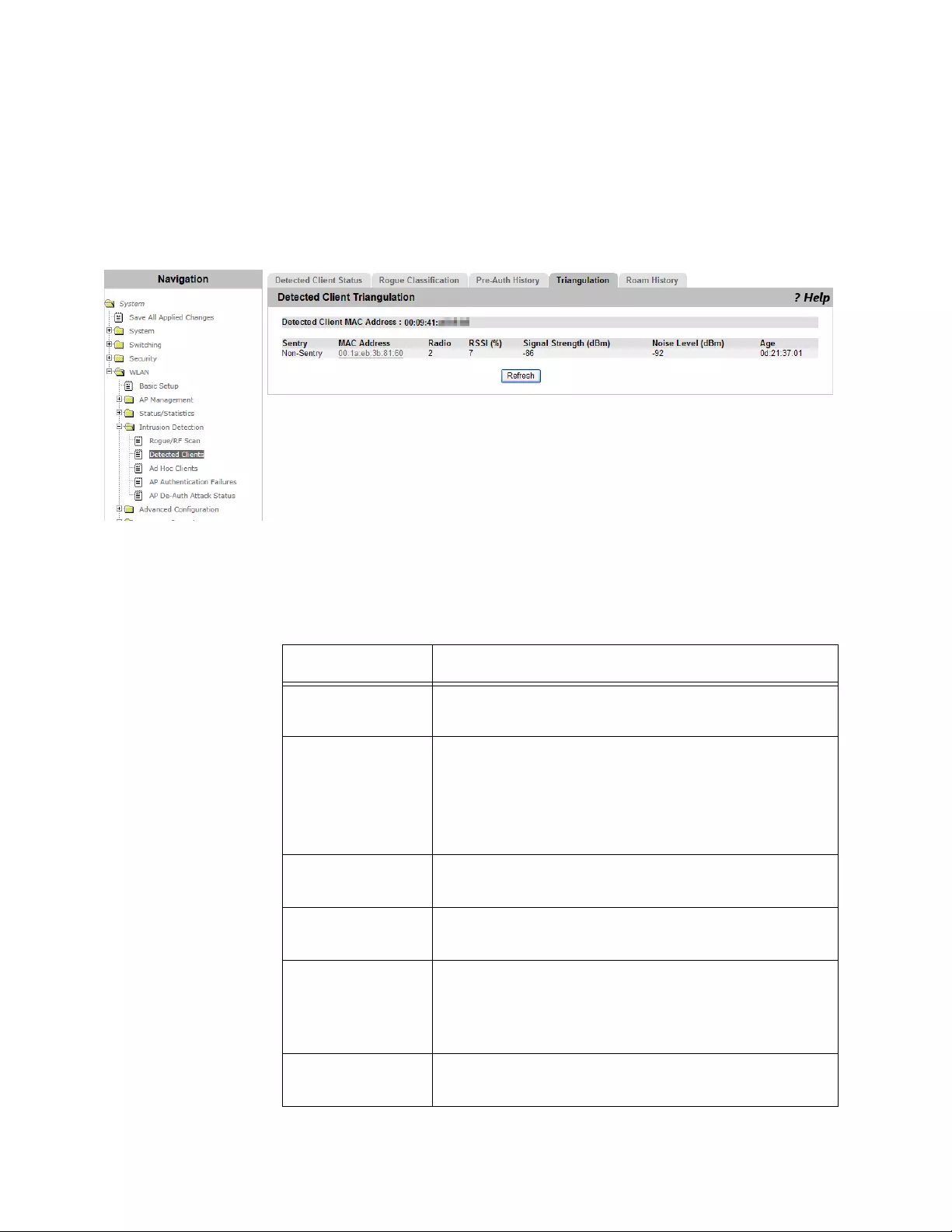
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
292
The Detected Client Status Detail page is displayed as shown in
Figure 144 on page 286.
3. Click the Triangulation tab.
The Detected Client Triangulation page is displayed as shown in
Figure 146.
Figure 146. Detected Client Triangulation Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 122.
Table 122. Detected Client Triangulation
Field Description
Detected Client
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
Sentry Displays the sentry mode of the access point that
detected the AP client. The options are:
Sentry
Not Sentry
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point that
detected the AP client.
Radio Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface.
RSSI (%) Displays Received Signal Strength Indication
(RSSI) of the non-sentry AP in percentage. RSSI is
a measurement of the power represent in a
received radio signal.
Signal Strength
(dBm)
Displays Received Signal Strength Indication
(RSSI) of the non-sentry access point in dBm.
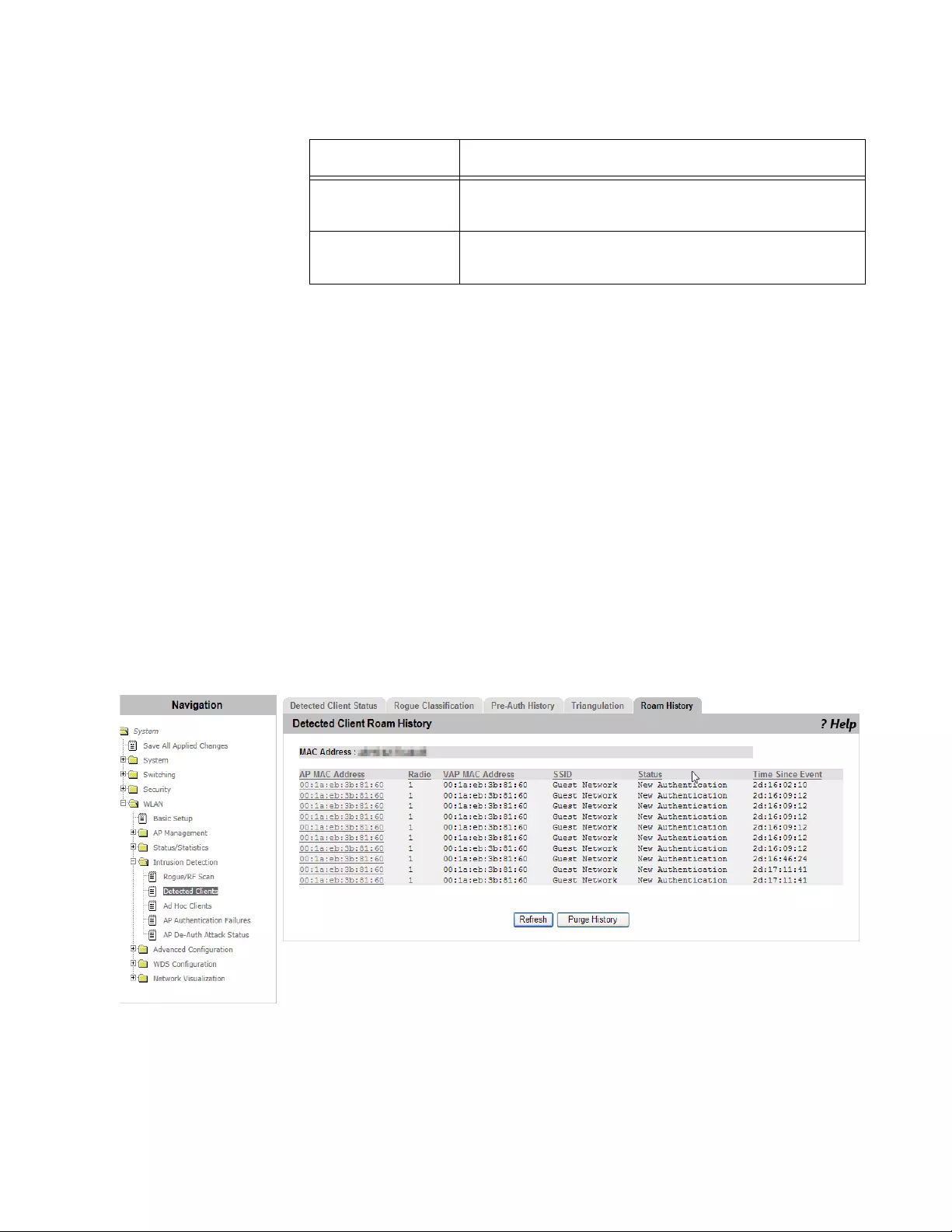
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
293
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Viewing Roam
History
To view the roaming history of the AP client, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
Detected Clients.
The Detected Client Status page is displayed as shown in Figure 143
on page 284.
2. Click a MAC address from the AP client on the list.
The Detected Client Status Detail page is displayed as shown in Figure
144 on page 286.
3. Click the Roam History tab.
The Detected Client Roam History page is displayed as shown in
Figure 147.
Figure 147. Detected Client Roam History Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 123 on page 294.
Noise Level
(dBm)
Displays the noise level that the non-sentry access
point reported.
Age Displays the time that passed since the access
point detected the AP client.
Table 122. Detected Client Triangulation (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
294
5. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 123. Detected Client Roam History
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
AP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point that
the AP client connected to.
Radio Interface
Number
Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface of the access point.
VAP MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of VAP that the AP
client roamed.
SSID Displays the SSID that the VAP is serving.
New
Authentication
Displays whether the AP client was newly
authenticated or roamed.
Age Displays the time period since the history recorded.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
295
Ad Hoc Clients
From the Ad Hoc Client page, you can view AP clients connected to
wireless LAN via another AP client.
To view ad hoc clients, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection > Ad Hoc
Clients.
The Ad Hoc Clients page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 124.
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete All — Clears all the entries from the list. Clicking this button
does not disconnect the ad-hoc clients.
Deny — Denies the ad-hoc client. When the client is on the Known
Table 124. Ad Hoc Clients
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
AP MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the base access
point that detected the AP client.
Location Displays the location information of the AP client.
Radio Displays the radio band of the wireless network
interface of the access point.
Detection Mode Displays how the AP client was found as ad hoc.
The options are:
Beacon
Data Frame
When it is Beacon, the AP client is listed as an
access point in Access Point RF Scan Status
and AP Triangulation Status pages. See “Rogue/
RF Scan” on page 276.
When it is Data Frame, the AP client is listed in
the Known Client list. See “WLAN Advanced
Configuration > Known Client” on page 312.
Age Displays the time period since the AP client was
detected.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
296
Client list and the Authentication Action is Grant, this button is not
effective.
Allow — Allows the ad-hoc client. When the client is on the Known
Client list and the Authentication Action is Deny, this button is not
effective.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
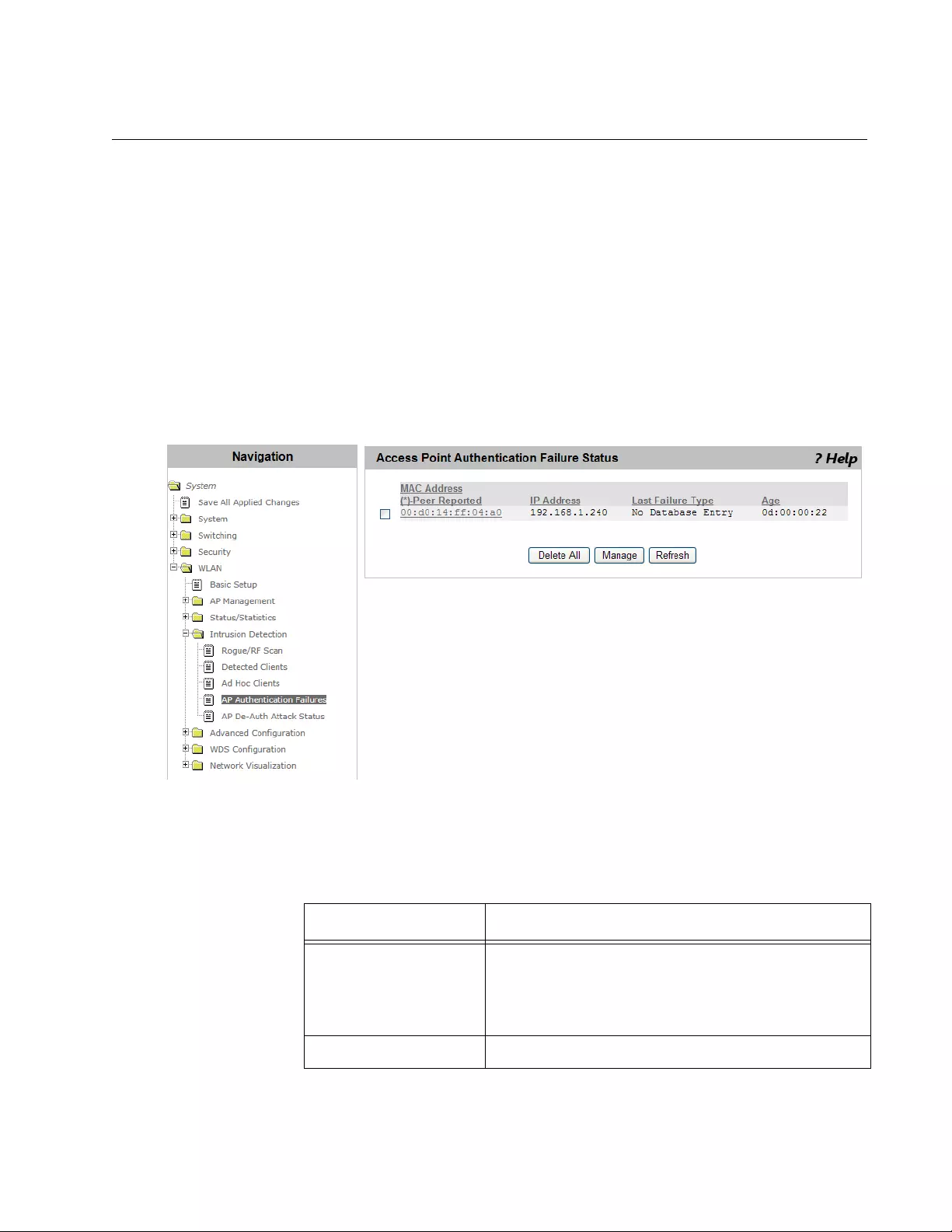
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
297
AP Authentication Failure
From the AP Authentication Failure page, you can view a list of access
points that failed to connect to the WLAN Controller. You can also add
failed access points to the Valid AP list.
Viewing Failed
Access Points and
Adding Them to
Valid AP List
To view failed access points and add them to the valid AP list, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection > AP
Authentication Failures.
The Access Point Authentication Failure Status page is displayed as
shown in Figure 148.
Figure 148. Access Point Authentication Failure Status Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 125.
Table 125. Access Point Authentication Failure Status
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
The asterisk following the MAC address
indicates that the peer controller reported the
failure.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
298
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Delete All — Clears all the entries from the list.
Manage — Adds the selected access points to the Valid AP
database.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Viewing Detailed
Information
about Failed
Access Points
To view the detailed information about an access point that failed to
connected to the WLAN Controller, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection > AP
Authentication Failures.
The Access Point Authentication Failure Status page is displayed as
shown in Figure 148 on page 297.
2. Click the MAC address of the access point that you want to view the
detail information.
The Access Point Authentication Failure Status Detail page is
displayed as shown in Figure 149 on page 299.
Last Failure type Displays the type of connection failure. The
options are:
Local Authentication
No Database Entry
Not Managed
Profile Mismatch-Hardware Type
Age Displays the time period since the access point
failed to connect.
Table 125. Access Point Authentication Failure Status (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
299
Figure 149. Access Point Authentication Failure Status Detail Page
3. Observe the fields described in Table 126.
Table 126. Access Point Authentication Failure Status Detail
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the access point.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the access point.
Last Failure type Displays the type of connection failure. The
options are:
Local Authentication
No Database Entry
Not Managed
Protocol Version Displays the protocol version that the access
point supports to connect to the WLAN
Controller.
Software Version Displays the software version of the access
point.
Reporting Controller Displays the controller that reports the
connection failure.
Controller MAC
Address
Displays the MAC address of the WLAN
Controller that reported the connection failure.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
300
4. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Controller IP Address Displays the IP address of the WLAN Controller
that reported the connection failure.
Validation Failure Displays how many times that the access point
failed to connect.
Authentication
Failure
Displays how many times that the access point
failed to be authenticated.
Age Displays the time period since the access point
failed to connect.
Table 126. Access Point Authentication Failure Status Detail (Continued)
Field Description

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
301
De-Auth Attack Status
From the AP De-Auth Attack Status page, you can view a list of access
points that the WLAN Controller is targeting for the de-authentication
attack.
When the de-authentication attack is enabled, the WLAN Controller calls
the managed access points to send IEEE802.11 de-authentication
management frames to rogue access points in order to disconnect them
from the wireless network. To enable the de-authentication attack, see
“WIDS AP Configuration” on page 351.
To view access points that WLAN Controller is targeting for the de-
authentication attack, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Intrusion Detection >
AP De-Auth Attack Status.
The WIDS AP De-Authentication Attack Status page is displayed.
2. Observe the fields described in Table 127.
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Table 127. WIDS AP De-Authentication Attack Status
Field Description
BSSID Displays the MAC address of the access point
targeted for the de-authentication attack.
Channel Displays the channel that the access point
communicates through.
Time Since Attack
Started
Displays the time period since the de-
authentication attack started.
RF Scan Report Age Displays the time period since the access point
was detected by the RF scan.
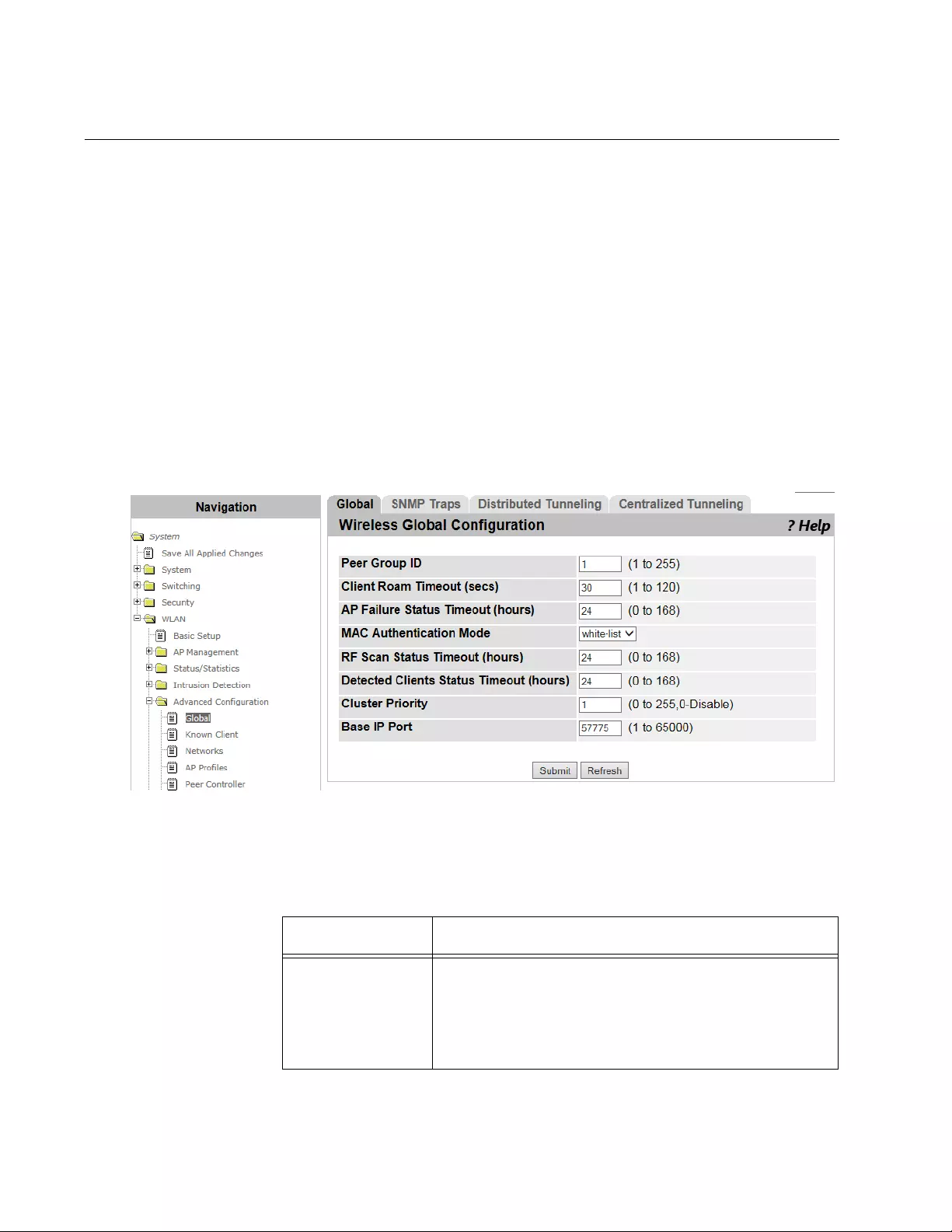
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
302
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global
From the WLAN Advanced Configuration page, you can modify the
advanced settings including the settings of a peer group.
One WLAN Controller can manage up to 210 access points; however, to
manage more than 210 access points in a large network, you must create
a peer group of WLAN Controllers. One peer group can consists of up to
64 WLAN Controllers.
To modify the advanced settings, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Global.
The Wireless Global Configuration (Advanced) page is displayed as
shown in Figure 150.
Figure 150. Wireless Global Configuration (Advanced) Page
2. Modify the settings described in Table 128.
Table 128. Wireless Global Configuration (Advanced)
Field Description
Peer Group ID Specify the ID of a peer group that the WLAN
Controller belongs to. The WLAN Controllers with
the same Peer Group ID are called a peer group or
cluster. One peer group can have up to 64 WLAN
Controllers.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
303
Client Roam
Timeout (secs)
Specify the time period in seconds used by the
WLAN Controller to remove the entry of an AP
client from the “Associated Client Status” list after
the AP client is disconnected from the access point.
AP Failure Status
Timeout (hours)
Specify the time period in hours used by the WLAN
Controller to remove the entry of an AP client from
the “Access Point Authentication Failure Status”
list. See “AP Authentication Failure” on page 297.
MAC
Authentication
Mode
Select the mode to authenticate AP clients with the
MAC address. The options are:
white-list - Allows to authenticate the AP
clients on the “Known Client” list.
black-list - Blocks authenticating the AP
clients on the “Known Client” list.
For the Known Client list, see “WLAN Advanced
Configuration > Known Client” on page 312. To
make a RADIUS server to authenticate AP clients
with the MAC address, see “WLAN Advanced
Configuration > Networks” on page 316.
RF Scan Status
Timeout (hours)
Specify the time period in hours used by the WLAN
Controller to remove the entry of a rogue AP client
from the “Access Point RF Scan Status.” See
“Rogue/RF Scan” on page 276.
Detected Clients
Status Timeout
(hours)
Specify the time period in hours used by the WLAN
Controller to remove the entry from the “Detected
Client Status.”
Cluster Priority Specify the priority of the WLAN Controller in the
peer group. The range is 1 to 255. The WLAN
Controller with the highest priority number in the
peer group is selected as the cluster controller. If
two WLAN Controllers have the highest priority
number, the WLAN Controller with the smaller IP
address is selected as the cluster controller.
Table 128. Wireless Global Configuration (Advanced) (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
304
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Base IP Port Specify the base port. The WLAN Controller sends
packets out of a port from the range between the
number of the base port and the number of the
base port plus 9. The default base port is 57775.
For example, by default, the WLAN Controller
sends packets out of a port between 57775 and
57784.
When you change the base IP port of the WLAN
Controller, you must change the base IP port of
access points and peer controllers.
Table 128. Wireless Global Configuration (Advanced) (Continued)
Field Description
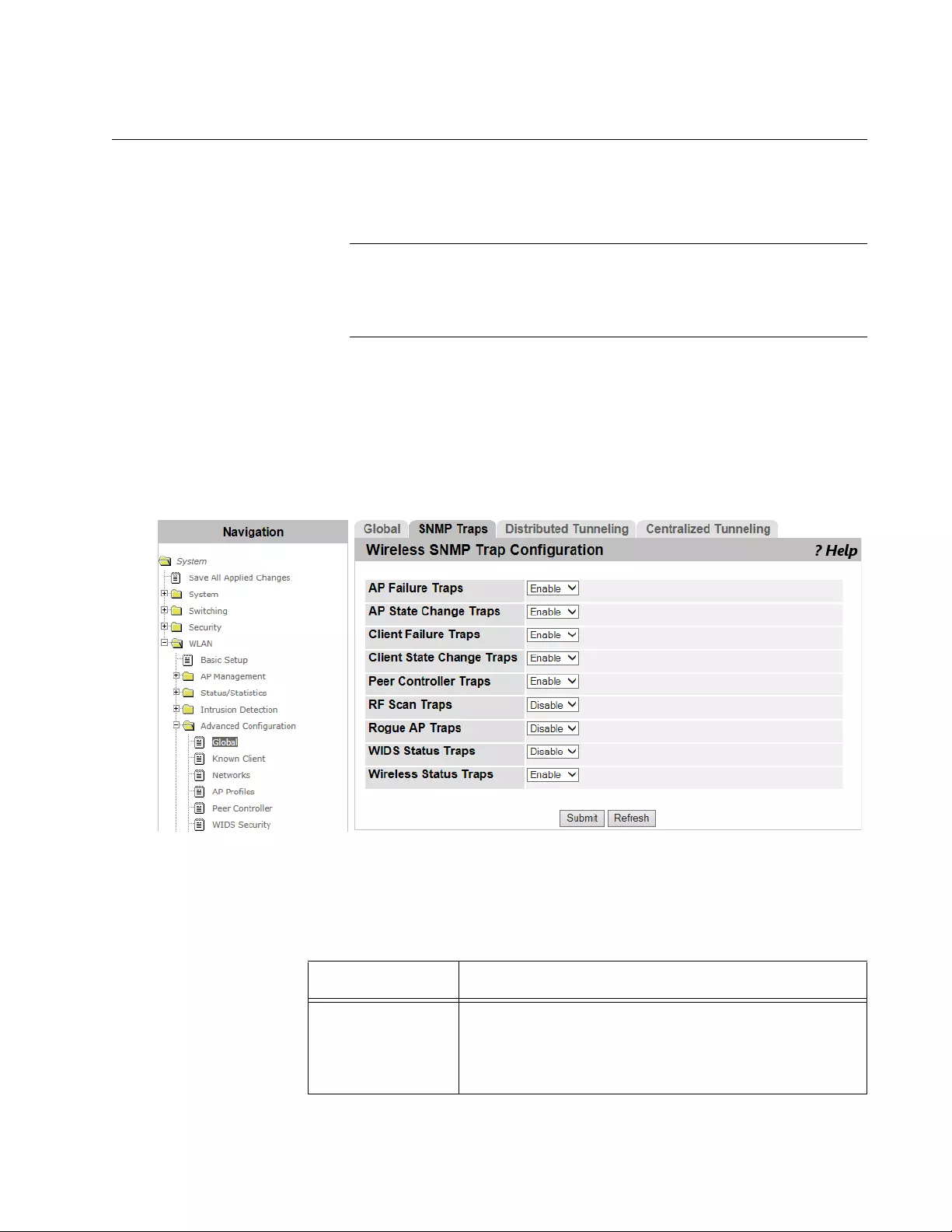
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
305
WLAN Advanced Configuration > SNMP Traps
From the Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration page, you can enable and
disable sending traps to SNMP servers.
Note
The WLAN Controller sends traps based on its own events and the
events learned from the access points that the WLAN Controller
manages. The access points do not send traps to SNMP servers.
To enable and disable SNMP traps, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Global and click the SNMP Traps tab.
The Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 151.
Figure 151. Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration Page
2. Enable or disable the SNMP traps described in Table 129.
Table 129. Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration
Field Description
AP Failure Traps Enable or disable sending AP Failure traps. When it
is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a trap in the
event of an error when the WLAN Controller
authenticates or connects to the access point.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
306
AP State Change
Traps
Enable or disable sending AP state Change traps.
When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a
trap in the following events:
Managed AP Discovered - The WLAN
Controller discovers the access point on the
valid AP list.
Managed AP Failed - The WLAN Controller
detects an error on the access point.
Managed AP Unknown Protocol
Discovered - The WLAN Controller detects
communication with the access point using
unknown protocol.
Client Failure
Traps
Enable or disable sending Client Failure traps.
When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a
trap in the event of an error when the access point
authenticates or connects to its client.
Client State
Change Traps
Enable or disable sending Client state Change
traps. When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller
sends a trap in the following events:
Client Association Detected - The access
point connects to a client.
Client Disassociation Detected - The
access points disconnects a client.
Client Roam Detected - The access point
detects a client roaming.
Peer Controller
Traps
Enable or disable sending Peer Controller traps.
When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a
trap in the following events:
Peer Controller Discovered - The WLAN
Controller discovers a peer controller.
Peer Controller Failed - The WLAN
Controller disconnects the peer controller.
Peer Controller Unknown Protocol
Discovered - The WLAN Controller detects
communication with the peer controller
using unknown protocol.
RF Scan Traps Enable or disable sending RF Scan traps. When it
is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a trap when
an access point, AP client, or ad-hoc client is
detected:
Table 129. Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
307
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Rogue AP Traps Enable or disable sending Rogue AP traps. When it
is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a trap when
a rogue access point is detected.
WIDS Status
Traps
Enable or disable sending WIDS Status traps.
When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a
trap when the Wireless Intrusion Detection System
(WIDS) generates a message.
Wireless Status
Traps
Enable or disable sending Wireless Status traps.
When it is enabled, the WLAN Controller sends a
trap when the WLAN Controller changes its
operational status.
In addition, the WLAN Controller sends a trap when
one of the following lists or database reaches the
maximum entry:
Managed AP database
AP Neighbor List
Client Neighbor List
AP Authentication Failure List
RF Scan SP List
Client Association Database
Client Authentication Failure List
Table 129. Wireless SNMP Trap Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
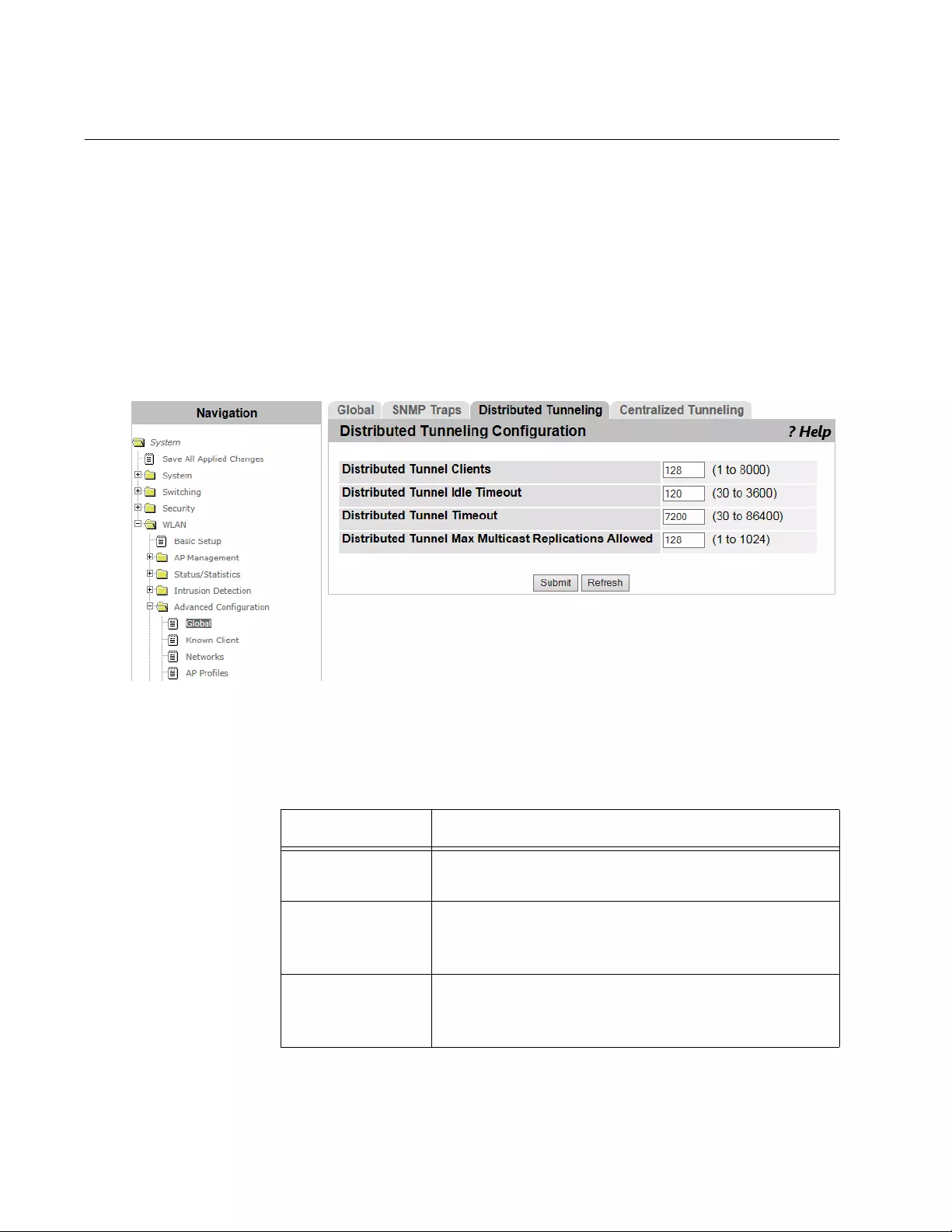
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
308
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Distributed Tunneling
From the Distributed Tunneling Configuration page, you can modify the
settings for Distributed Tunneling.
To modify the settings for Distributed Tunneling, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Global and click the Distributed Tunneling tab.
The Distributed Tunneling Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 152.
Figure 152. Distributed Tunneling Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 130.
Table 130. Distributed Tunneling Configuration
Field Description
Distributed
Tunnel Clients
Specifies the maximum number of AP clients that
are allowed to roam.
Distributed
Tunnel Idle
Timeout
Specifies the time period in seconds that the
roaming client is disconnected after the client
stopped communicating.
Distributed
Tunnel Timeout
Specifies the time period in seconds that the AP
client can roam before the client is forced to be
disconnected.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
309
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Distributed
Tunnel Max
Multicast
Replications
Allowed
Specifies the maximum number of distributed
tunnels that the access points is allowed to send
copies of a multicast frame to.
Table 130. Distributed Tunneling Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
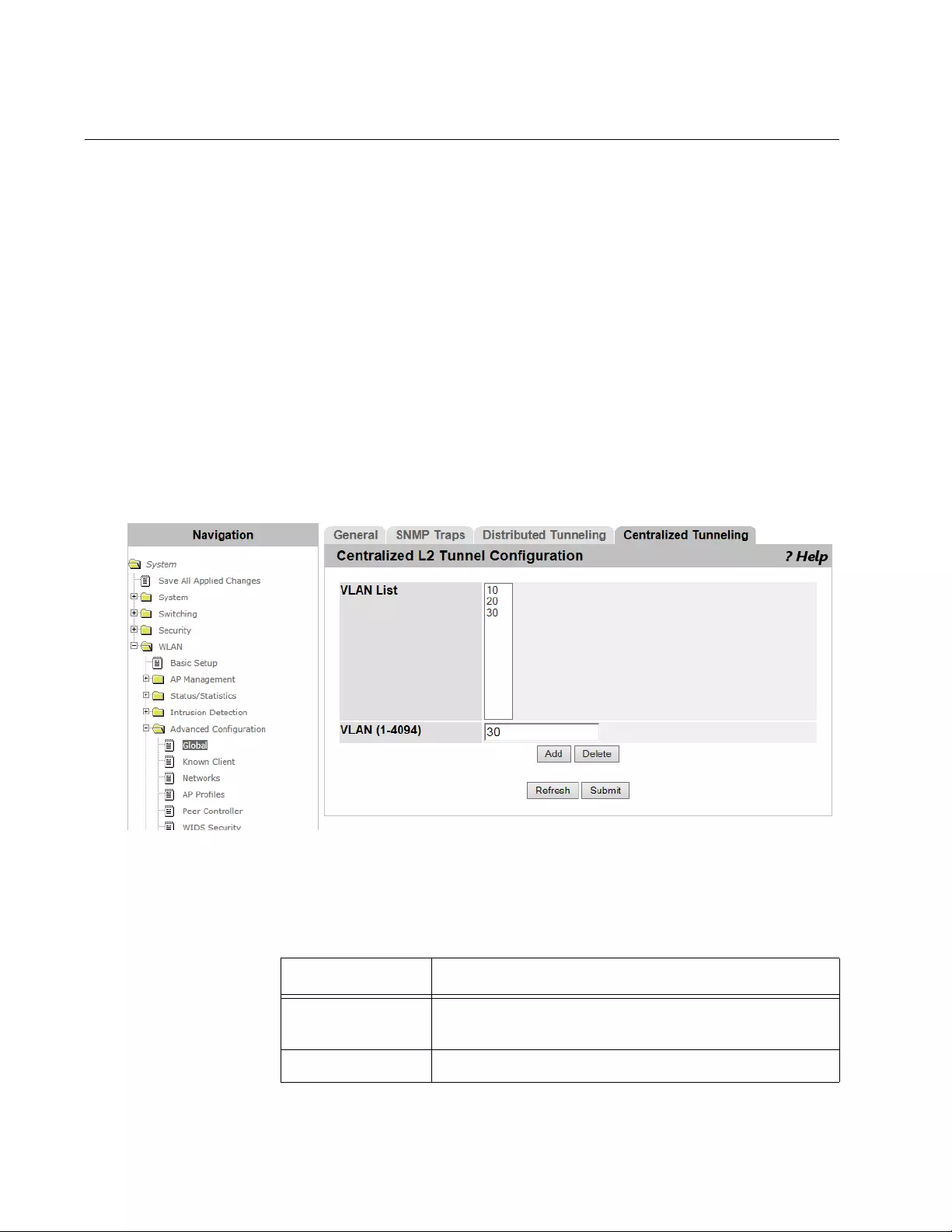
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
310
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Centralized L2 Tunneling
From the Centralized Tunneling Configuration page, you can add or delete
VLAN’s for Centralized Layer 2 Tunneling.
Centralized L2 Tunneling enables AP clients to roam among the access
points in different subnets. When you specify VLAN’s to participate in
Centralized L2 Tunneling on this page, the WLAN Controller establishes
the L2 tunnel among the peer controllers and managed access points
using the specified VLAN’s.
Adding VLAN’s
to the List
To add a VLAN for Centralized L2 Tunneling, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Global and click the Centralized Tunneling tab.
The Centralized L2 Tunneling Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 153.
Figure 153. Centralized L2 Tunneling Configuration Page
2. Specify the fields described in Table 131.
Table 131. Centralized Tunneling Configuration
Field Description
VLAN List Displays a list of VLAN’s by which the WLAN
Controller establishes the L2 tunnel.
VLAN (1-4094) Specify a VLAN ID to add the list.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
311
3. Click Add.
The VLAN is added to the VLAN List.
4. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Deleting VLAN’s
to the List
To delete a VLAN for Centralized L2 Tunneling from the list, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Global and click the Centralized Tunneling tab.
The Centralized L2 Tunneling Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 153 on page 310.
2. Select a VLAN that you want to delete in the VLAN List.
3. Click Delete.
The VLAN is deleted from the VLAN List.
4. Click the following buttons
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
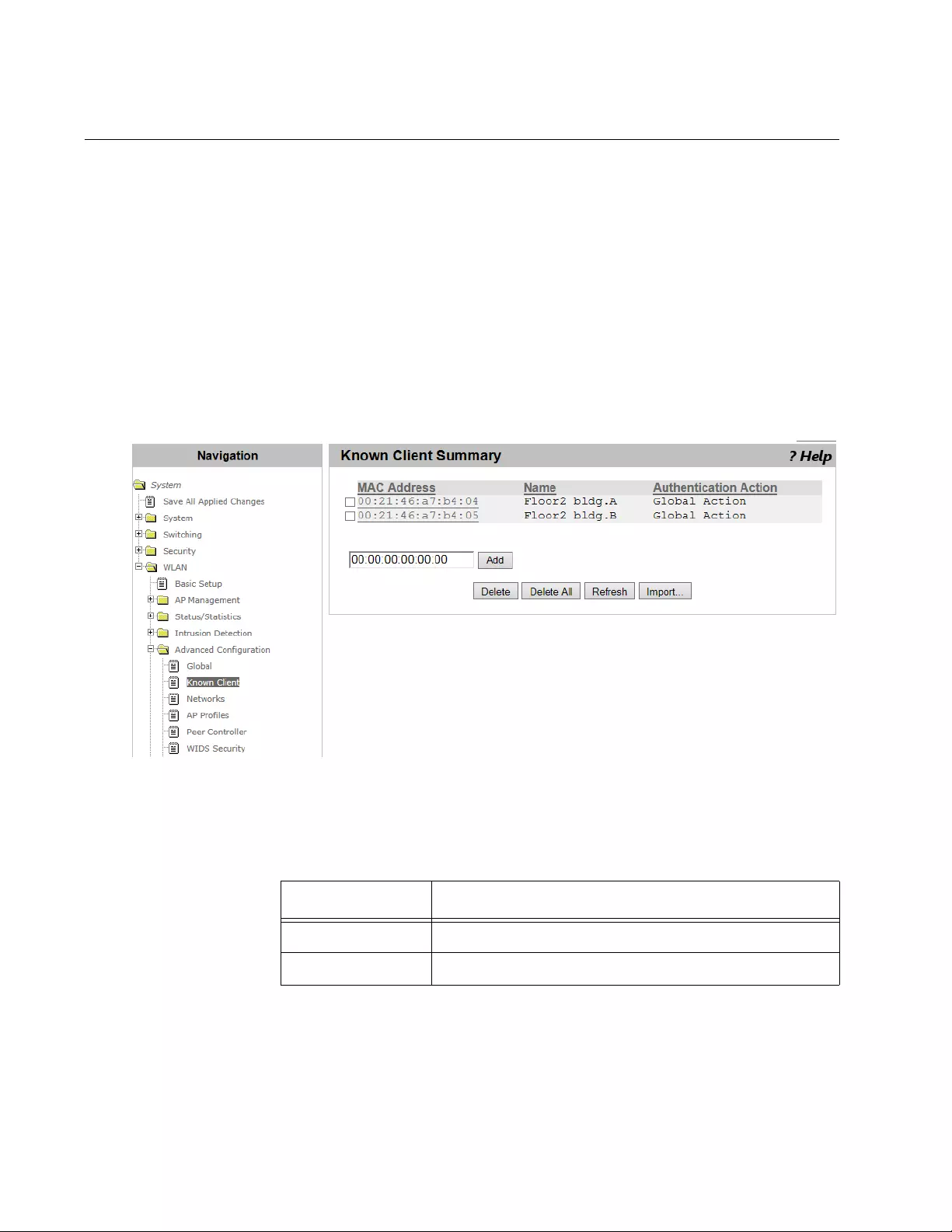
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
312
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known Client
From the Known Client Summary page, you can view a list of AP clients
that the WLAN Controller manages. You can also add or delete AP clients
from the lis. The Known Client list is used for local MAC authentication or
with a RADIUS server.
Viewing a List of
Known Clients
To view a list of access points that the WLAN Controller manages, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Known Client.
The Known Client Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 154.
Figure 154. Known Client Summary Page
2. Observe the fields described in Table 132.
Table 132. Known Client Summary
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the AP client.
Name Displays the name of the AP client.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
313
3. If you want to refresh the display, click Refresh.
Adding an AP
Client to the
Known Client
List
To add an AP client that the WLAN Controller manages, do the following:
Note
To add a list of AP clients using a CVS file, go to “Adding AP Clients
Using CSV File” on page 314.
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Known Client.
The Known Client Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 154
on page 312.
2. Specify the MAC address of an AP client in the text box.
3. Click Add.
The Known Client Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
155 on page 314.
Authentication
Action
Displays the authentication action that the WLAN
Controller takes.The options are:
Grant - Allows the network access.
Deny - Denies the network access.
Global Action - The action depends upon
the setting of The MAC Authentication Mode
in the Wireless Global Configuration. See
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global”
on page 302.
The WLAN Controller takes the action when MAC
authentication is enabled. See “WLAN Advanced
Configuration > Networks” on page 316.
Table 132. Known Client Summary (Continued)
Field Description
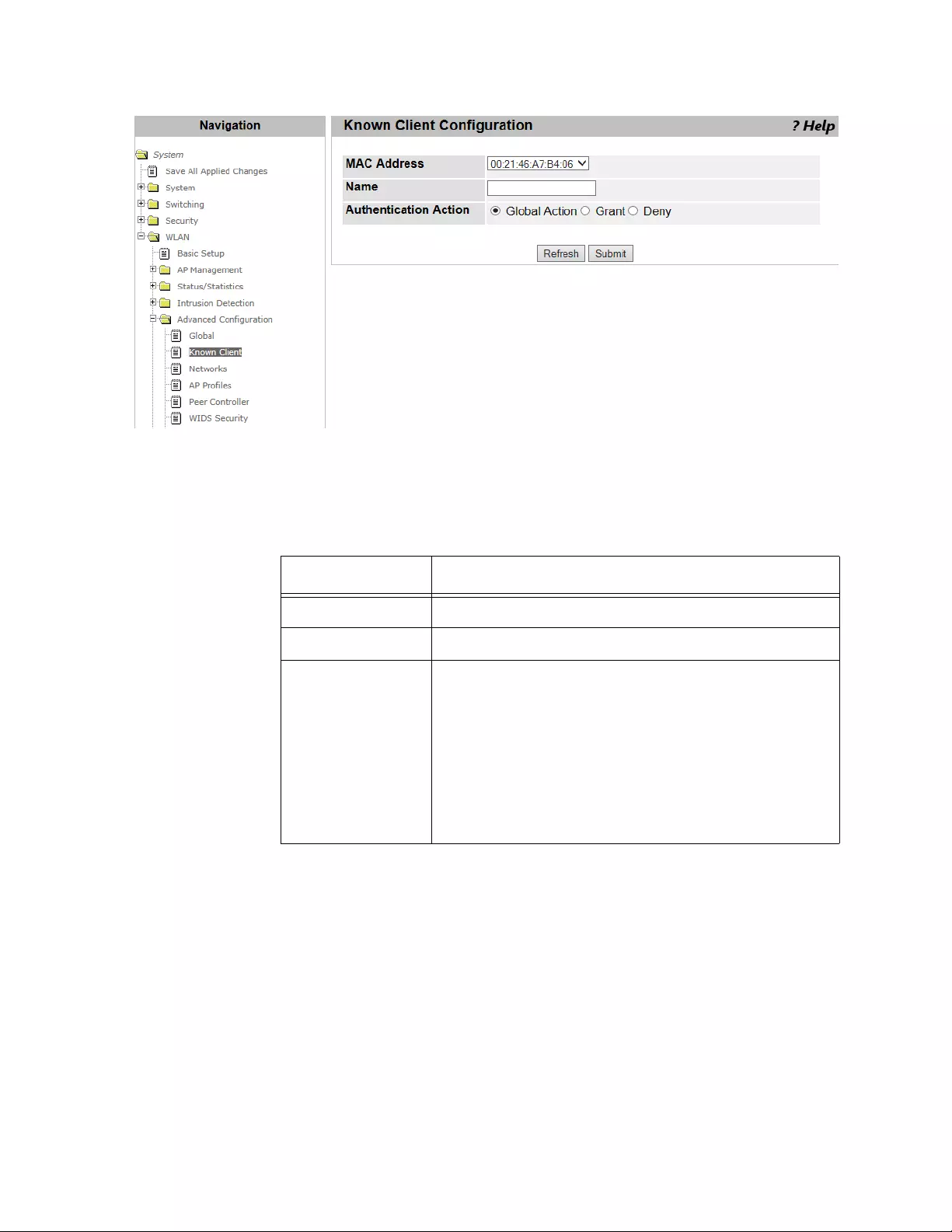
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
314
Figure 155. Known Client Configuration Page
4. Observe the fields described in Table 133.
5. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Adds the AP client to the Known Client list.
Adding AP
Clients Using
CSV File
To add AP clients using a CVS file. do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Known Client.
The Known Client Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 154
on page 312.
Table 133. Known Client Configuration
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of an AP client to add.
Name Specify the name of the AP client.
Authentication
Action
Select the authentication action. The options are:
Grant
Deny
Global Action
For more information, see Table 132, “Known Client
Summary” on page 312.
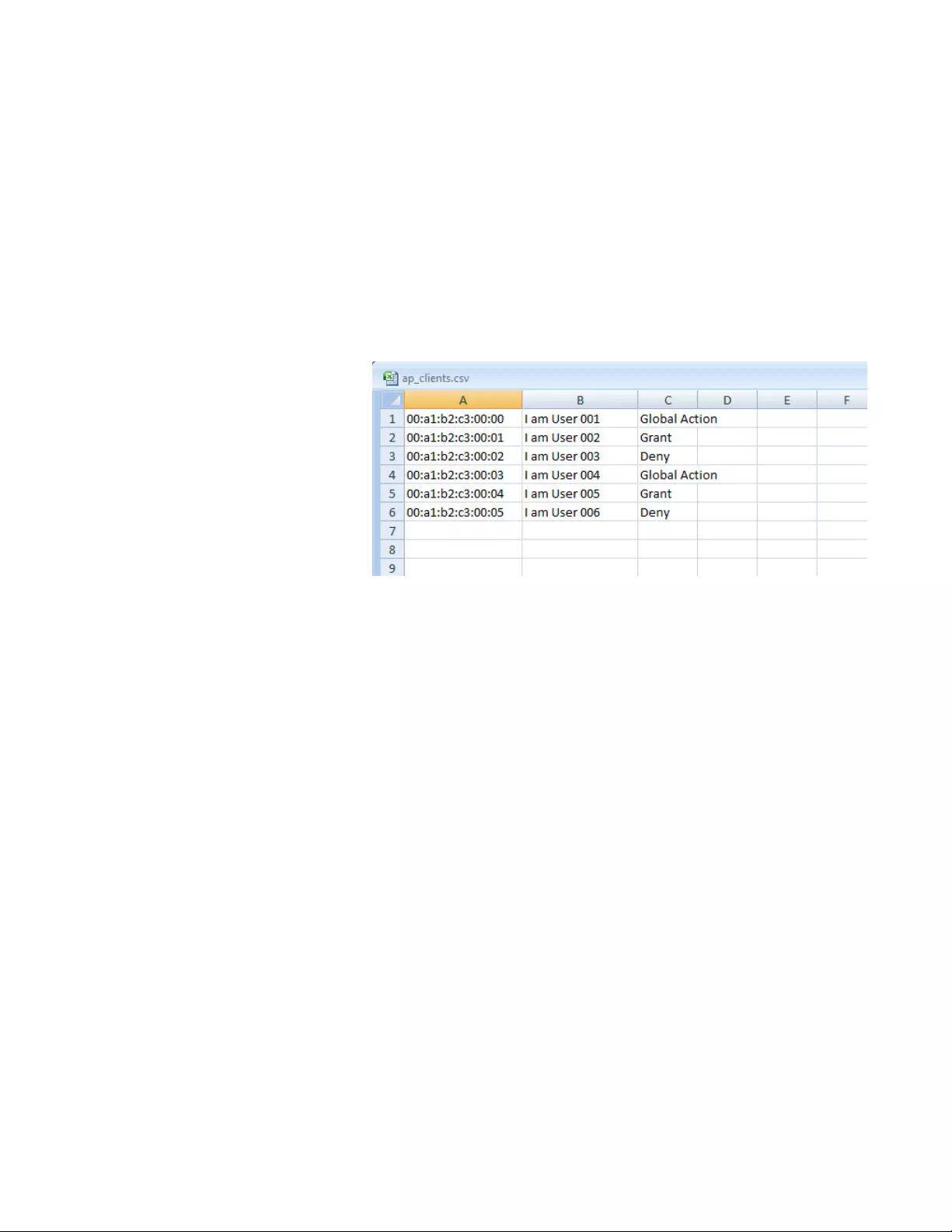
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
315
2. Click Import....
The page moves to the Known Client Database Importing page.
Upload a CVS file on the system.
Guidelines for
Importing a CVS
file
Here are guidelines for importing a CVS file to upload AP clients:
Spaces are not allowed in the name of the CVS file.
Commas are not allowed as delimiters in the CVS file.
Enter one AP client in a row. Figure 156 shows an example of the
CVS file created with Microsoft Excel.
Figure 156. CVS File for a List of AP Clients
Deleting AP
Clients from the
Known Client
List
To delete an AP client from the Known Client list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Known Client.
The Known Client Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure 154
on page 312.
2. Check the checkbox on the left of the MAC address.
3. Click the following buttons:
Delete — Deletes the selected AP client from the Known Client list.
Delete All — Deletes all the AP clients on the Known Client list.
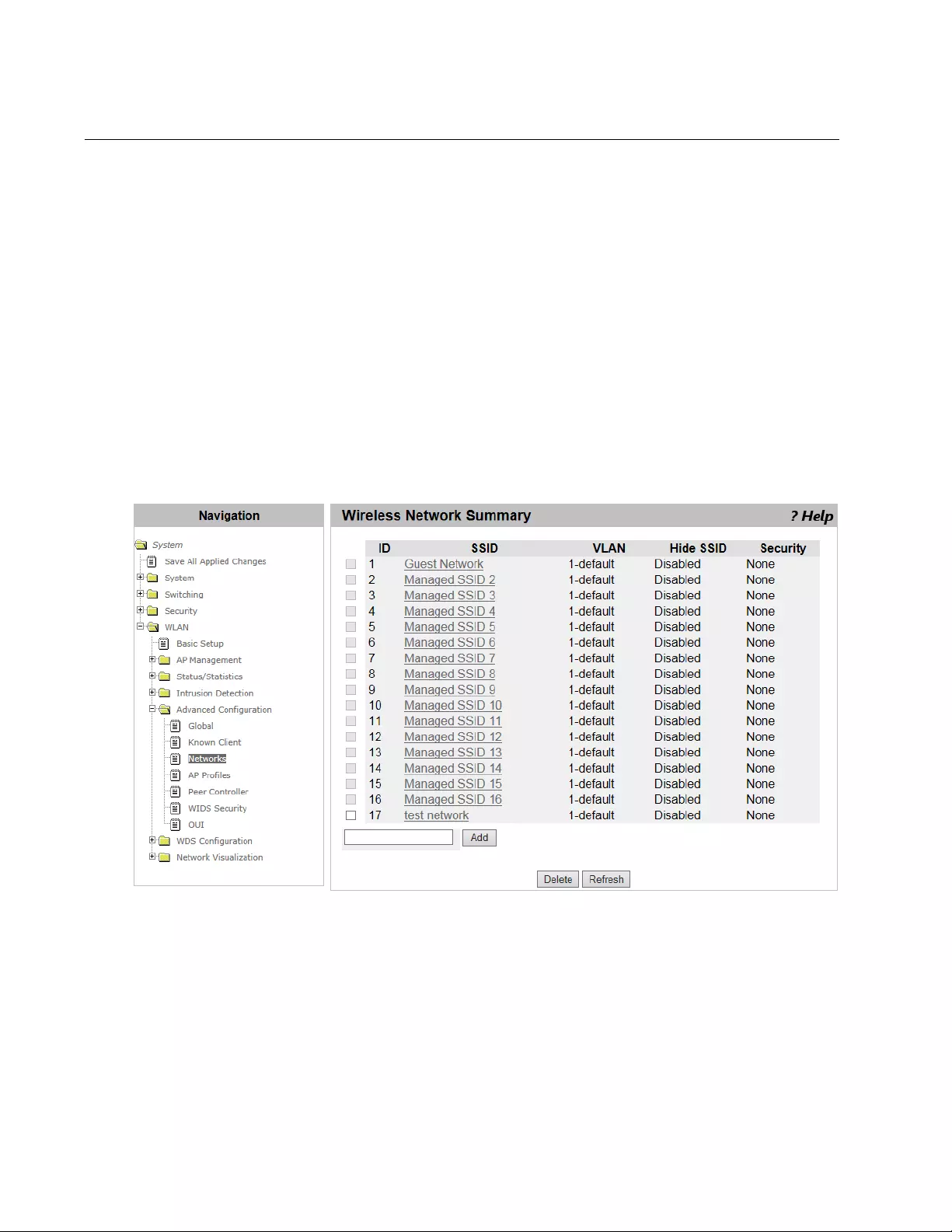
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
316
WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks
From the Networks page, you can add or delete wireless network that the
WLAN Controller manages.
The WLAN Controller has 16 wireless networks by default. You can
modify these properties, but cannot delete them. You can add up to 239
wireless networks. With the default wireless networks, the WLAN
Controller can have total 255 wireless networks.
Adding a
Wireless Network
To add a wireless network to the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Networks.
The Wireless Network Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 157.
Figure 157. Wireless Network Summary Page
2. Enter the SSID in the text box.
3. Click Add.
The Wireless Network Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 158 on page 317.
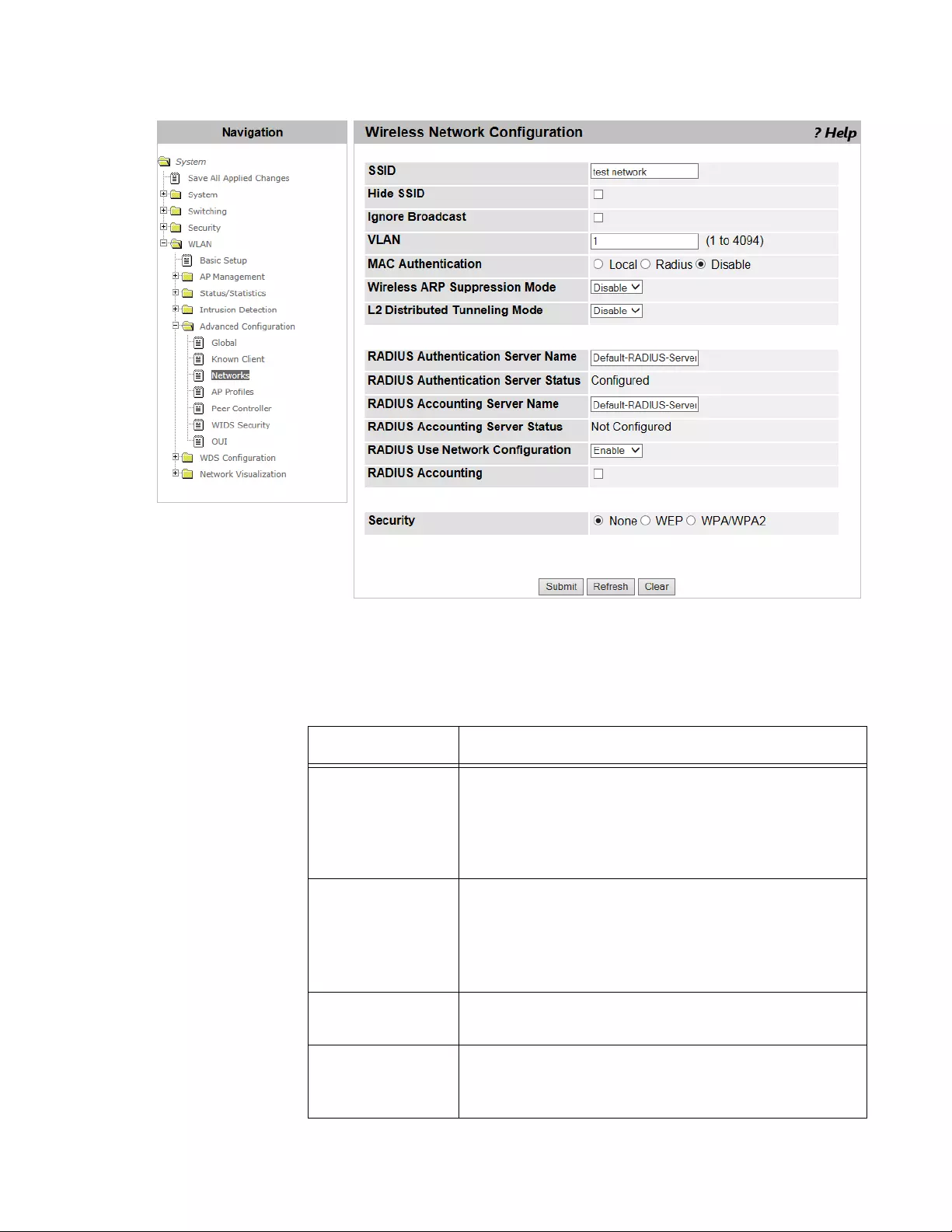
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
317
Figure 158. Wireless Network Configuration Page
4. Specify the fields described in Table 134.
Table 134. Wireless Network Configuration
Field Description
SSID Specify a Server Set Identifier (SSID) with up to 32
alphanumeric characters. SSID is the name of a
wireless LAN. All wireless devices on a WLAN must
have the same SSID to communicate with each
other.
Hide SSID Check the checkbox not to broadcast the SSID. If
Hide SSID is enabled, AP clients cannot
automatically detect an access point so that AP
clients must have the SSID of the access point to
connect to.
Ignore Broadcast Check the checkbox not to allow access points to
respond to probes from AP clients.
VLAN Specify a VLAN ID. The access point adds a VLAN
tag with the specified VLAN ID to frames from the
clients connected using the SSID.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
318
MAC
Authentication
Select the MAC authentication mode. To
authenticate clients with the MAC address, the
WLAN Controller or RADIUS server must have a
known client list. The options are:
Local - Authenticates using the known client
list on the WLAN Controller.
Radius - Authenticates using the known
client list on a RADIUS server.
Disable - Does not authenticate clients.
For more information about the know client list, see
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known Client” on
page 312.
Wireless ARP
Suppression
Mode
Select the Wireless ARP Suppression mode from
the select list. The options are:
Enable - Suppresses broadcast ARP
messages at the wireless interface.
Disable - Does not suppress broadcast
ARP messages at the wireless interface.
L2 Distributed
Tunneling Mode
Select the L2 Distributed Tunneling mode from the
select list. The options are:
Enable - Supports Distributed L2 Tunneling
for AP clients.
Disable - Does not support Distributed L2
Tunneling.
RADIUS
Authentication
Server Name
Specify the name of RADIUS server for
authentication. When the RADIUS Use Network
Configuration on the page is enabled, this RADIUS
server overrides the setting in the WLAN Basic
Setup page. See “WLAN Basic Setup > Global” on
page 191.
You must use the server name as it was added to
the RADIUS Named Server list. See “RADIUS
Server Configuration” on page 175.
The WLAN Controller performs RADIUS
transactions in behalf of access points and AP
clients.
Table 134. Wireless Network Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
319
RADIUS
Authentication
Server Status
Displays the configuration status of a RADIUS
authentication server.
RADIUS
Accounting
Server Name
Specify the name of RADIUS server for accounting.
When the RADIUS Use Network Configuration on
the page is enabled, this RADIUS server overrides
the setting in the WLAN Basic Setup page. See
“WLAN Basic Setup > Global” on page 191.
You must use the server name as it was added to
the RADIUS Named Server list. See “Accounting
Server Configuration” on page 181.
The WLAN Controller performs RADIUS
transactions in behalf of access points and AP
clients.
RADIUS
Accounting
Server Status
Displays the configuration status of a RADIUS
accounting server.
RADIUS Use
Network
Configuration
Select which RADIUS server the WLAN Controller
refers to. The options are:
Enable - The RADIUS servers that
configured on this page override the setting
on the WLAN Basic Setup page.
Disable - The RADIUS servers that
configured on the WLAN Basic Setup page
overrides the setting on this page.
RADIUS
Accounting
Check the checkbox to enable RADIUS accounting
for the WLAN Controller.
Security Select the security options on the wireless network.
The options are:
None - Any AP client can access to the
access points in the network. The messages
between the access points and AP clients
are not encrypted.
WEP - Expands the page to include the
WEP settings.
WPA/WPA2 - Expands the page to include
the WPA/WPA2.
Table 134. Wireless Network Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
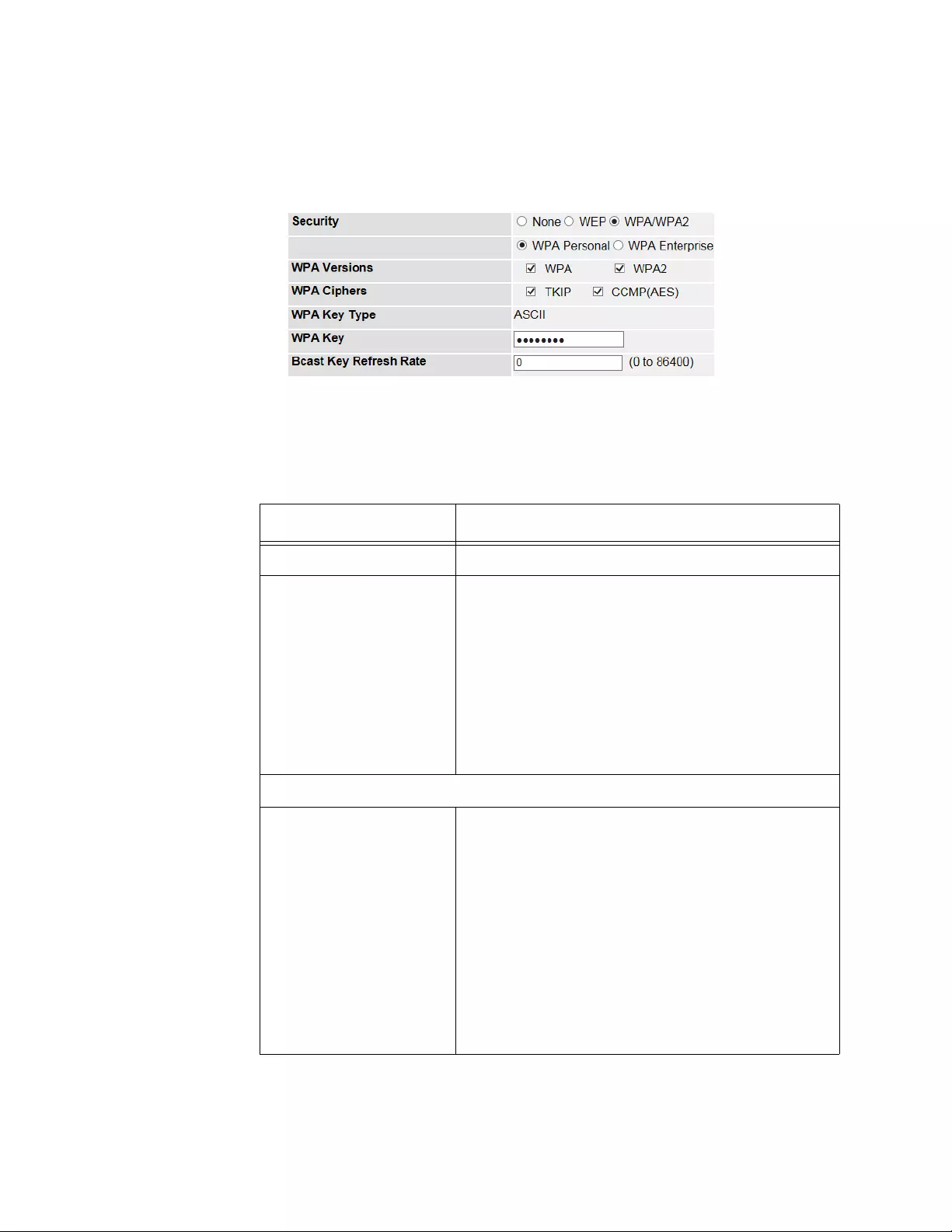
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
320
5. When you select WEP the Security field, the page adds the following
fields shown in Figure 159.
6. If you select WPA/WPA2, go to step 8.
Figure 159. Wireless Network Configuration - WEP Page
7. Specify the relevant fields described in Table 135.
Table 135. Wireless Network Configuration - WEP
Field Description
Security Displays the WEP selection.
Select one of the WEP types. The options are:
Static WEP - Uses the WEP key
specified manually to the access point
and AP clients.
WEP IEEE802.1x- Uses the WEP key
generated dynamically to the access
point and AP clients. It requires a
RADIUS server.
When Static WEP is Selected
Authentication Select either or both of the Authentication types.
The options are:
Open System - No authentication.
Shared Key- Authenticated with the
shared key. Security can be weaker than
Open System.
Both - The AP client with a valid WEP
key can connect to the access point. The
AP client specified using the open
system can connect to the access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
321
8. When you select WPA/WPA2 the Security field, the page adds the
following fields shown in Figure 160.
Figure 160. Wireless Network Configuration - WPA/WPA2 Page
9. Specify the relevant fields described in Table 136 on page 322.
WEP Key Type Select the one of the WEP key type. The options
are:
ASCII - A WEP key is generated from
ASCII characters.
HEX - A WEP key is generated from Hex
decimal numbers.
WEP Key Length (bits) Select the WEP key length in bits. The options
are:
64bits
128bits
WEP Keys Specify four keys and select one of the keys. To
communicate with an AP client, it must have the
same key specified in this field.
WEP IEEE802.1x is Selected
Bcast Key Refresh
Rate
Specify time period in seconds to update the
broadcast group key for the AP clients
connected to the valid access points. The range
is 0 to 86400 seconds.
Session Key Refresh
Rate
Specify time period in seconds to update the
unicast key for the AP clients connected to the
valid access points. The range is 30 to 86400
seconds.
Table 135. Wireless Network Configuration - WEP
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
322
Table 136. Wireless Network Configuration - WPA/WPA2
Field Description
Security Displays the WPA/WPA2 selection.
Select one of the WPA/WPA2 types. The
options are:
WPA Personal - Uses the WPA key
specified manually to the access point
and AP clients.
WPA Enterprise- Uses the WPA key
generated dynamically to the access
point and AP clients. It requires a
RADIUS server.
WPA Versions Select either or both of the WPA versions. The
options are:
WPA
WPA2
WPA Ciphers Select either or both of the WPA cipher types.
The options are:
TKIP
CCMP(AES)
Bcast Key Refresh
Rate
Specify time period in seconds to update the
broadcast group key for the AP clients
connected to the valid access points. The range
is 0 to 86400 seconds.
When WPA Personal is Selected
WPA Key Type Displays the ASCII type.
WPA Key Specify the pre-shared key between 8 and 63
alphanumeric characters. The key is case-
sensitive.
WPA Enterprise is Selected
Pre-Authentication Check the checkbox to speed up authentication
process. When the filed is checked, the home
access point passes the pre-authentication
information to the visited access point before the
AP client roams.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
323
10. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Clear — Clears the changes you made before clicking Submit.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Modifying a
Wireless Network
To modify the properties of a wireless network to the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Networks.
The Wireless Network Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure
157 on page 316.
2. Click the SSID that you want to modify its properties.
The Wireless Network Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 158 on page 317.
3. Modify the fields described in Table 134 on page 317.
Pre-Authentication
Limit
Specifies the maximum number of pre-
authentication that the access point can proceed
at a time. Limiting the number of pre-
authentication processes prevents a RADIUS
server from being overloaded.
Key Cashing Hold
Time
Specifies time in minutes that the access point
hold Pairwise Master Keys (PMK).
The value of the Session-Timeout attribute
responded by the RADIUS server overrides this
value.
If you do not specify any value, the access point
does not send PMK to other access points.
Session Key Refresh
Rate
Specify time period in seconds to update the
unicast key for the AP clients connected to the
valid access points. The range is 30 to 86400
seconds.
Table 136. Wireless Network Configuration - WPA/WPA2
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
324
4. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Clear — Clears the changes you made before clicking Submit.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Deleting a
Wireless Network
from the List
To delete a wireless network from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Networks.
The Wireless Network Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure
157 on page 316.
2. Check the checkbox on the left of the SSID that you want to delete
from the list.
Note
You cannot delete the default wireless networks.
3. Click Delete.
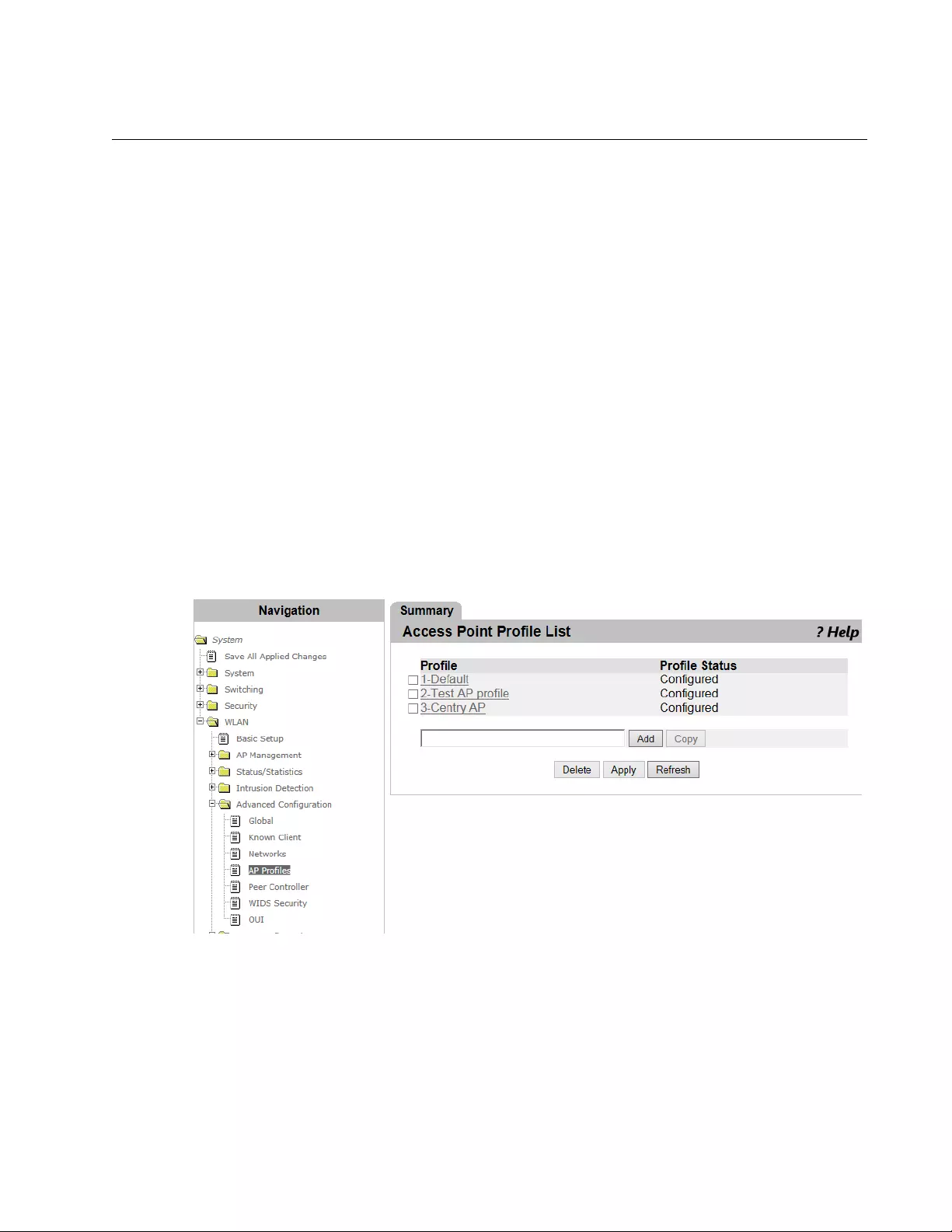
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
325
Access Point Profile List
From the Access Point (AP) Profile List page, you can view the access
point profile list, add, delete, or modify an access point profile, and apply
an access point profile to the access point.
Guidelines for
Applying an AP
Profile
Here are guidelines for applying an access point profile to access points.
After you modify the properties of an AP profile, you must re-apply
the AP profile to the associated access points.
When applying an AP profile to an access point, it reboots.
To associate an access point with an AP profile, see “WLAN Basic
Setup > Valid AP” on page 198.
Viewing and
Adding Access
Point Profiles
To view the access point profile list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in
Figure 161.
Figure 161. Access Point Profile List Page
2. View the fields described in Table 137 on page 326.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
326
3. Specify the name of the access point profile in the text box.
4. Click Add.
To configure the AP profile, go to “Access Point Profile Global
Configuration” on page 328.
5. If you want to refresh the displays on this page, click Refresh.
Copying An
Access Point
Profile
To copy an access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Check the checkbox of the profile that you want to make a copy.
3. Click Copy.
To configure the AP profile, go to “Access Point Profile Global
Configuration” on page 328.
Table 137. Access Point Profile List
Field Description
Profile Displays the name of the access point profile.
Profile Status Displays the status of the access point profile. The
options are:
Associated - One or more managed
access points are associated with the
profile.
Associated-Modified - The profile is
modified after one or more managed
access points are associated with the
profile. The profile must be re-applied to
these access points.
Apply Requested - Applying the profile is
requested.
Apply In Progress - Applying the profile to
the access points is in progress. During the
process, the access points reboot and the
WLAN Controller is disconnected.
Configured - The profile is configured, but
not applied to any access point.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
327
Modifying An
Access Point
Profile
To modify an access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Click the name of the profile that you want to modify the properties.
To configure the AP profile, go to “Access Point Profile Global
Configuration” on page 328.
Deleting An
Access Point
Profile
To delete an access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Check the checkbox of the profile that you want to delete.
3. Click Delete.
The AP profile is deleted.
Applying An
Access Point
Profile
To apply an access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Check the checkbox of the profile that you want to apply.
3. Click Apply.
The access points associated to the profile reboot.
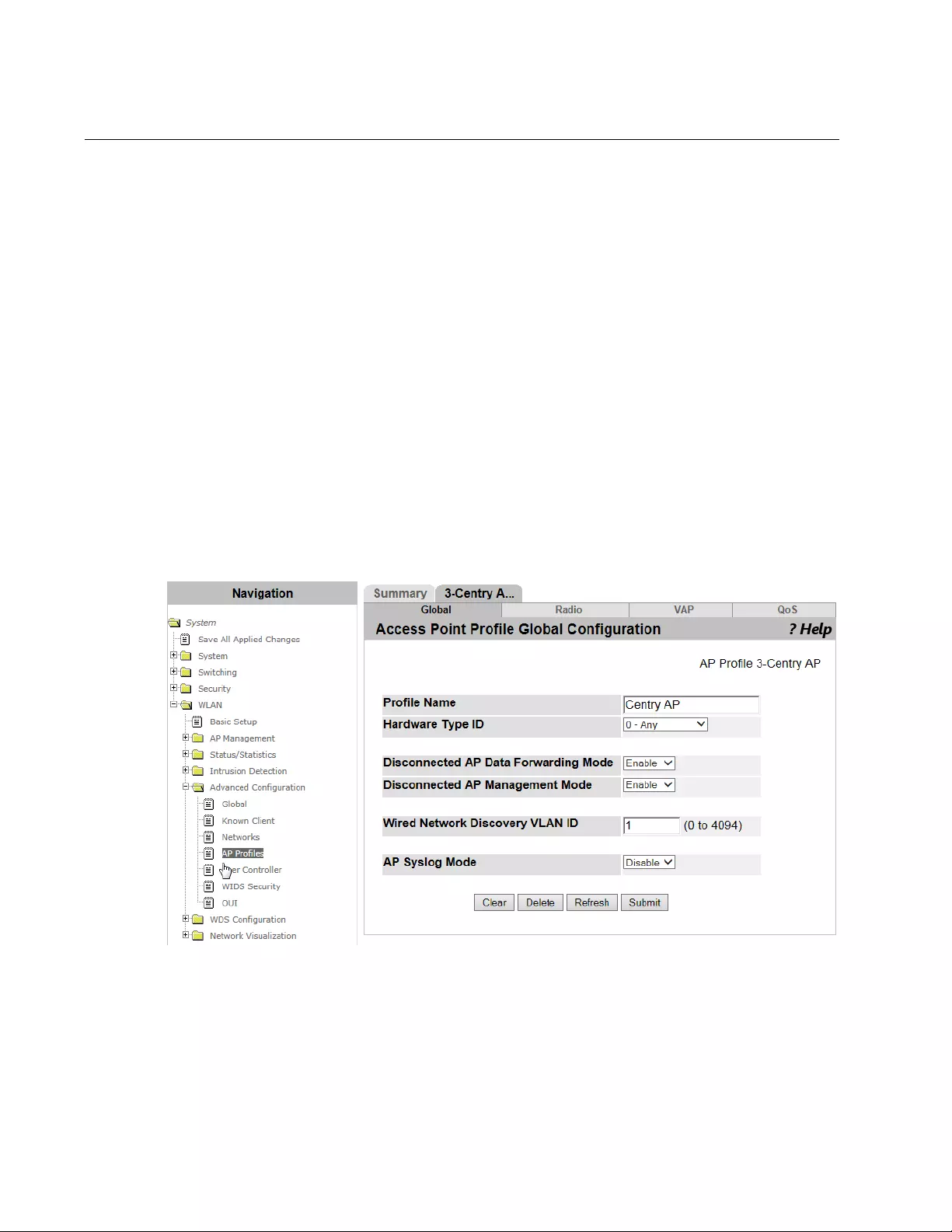
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
328
Access Point Profile Global Configuration
From the Access Point (AP) Profile Global Configuration page, you can
modify the properties of an access point profile.
To modify the properties of an AP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Take one of the following actions:
“Viewing and Adding Access Point Profiles” on page 325
“Copying An Access Point Profile” on page 326
“Modifying An Access Point Profile” on page 327
The Access Points Profile Global Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 162.
Figure 162. Access Point Profile Global Configuration Page
3. Modify the fields described in Table 138 on page 329.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
329
4. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Clear — Clears the changes you made before clicking Submit.
Table 138. Access Point Profile Global Configuration
Field Description
Profile Name Specifies the name of the AP profile.
Hardware Type ID Specifies the model of the access point that the
profile is applied to. The options are:
0 - Any - Either AT-TQ3600 or AT-TQ2450
5 - AT-TQ3600
9 - AT-TQ2450
Disconnected AP
Data Forwarding
Mode
Specifies how the access point behaves when
disconnected from the WLAN Controller. The
options are:
Enable - The access point operates as a
standalone based on the information
provided by the WLAN Controller.
Disable - The access point stops sending
receiving messages and changes to the
wait state.
Disconnected AP
Management
Mode
Specifies whether access from SNMP is enabled or
disabled when the access point is disconnected
and operates as a standalone. The options are:
Enable - Enables the management of the
access point by SNMP.
Disable - Disables the management of the
access point by SNMP.
Wired Network
Discovery VLAN
ID
Specifies the VLAN ID that the WLAN Controller
uses to send tracer packets. Tracer packets are
sent to detect the access points that are connected
to the Ethernet.
AP Syslog Mode Specifies whether Syslog is enabled or disabled on
the managed access points.The options are:
Enable - The access point sends log
messages to the remote host.
Disable - The access point does not send
log messages to the remote host.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
331
Access Point Profile Radio Configuration
From the Access Point Profile Global Configuration page, you can modify
the properties of an access point profile.
To modify the properties of an AP profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Take one of the following actions:
“Viewing and Adding Access Point Profiles” on page 325
“Copying An Access Point Profile” on page 326
“Modifying An Access Point Profile” on page 327
The Access Points Profile Global Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 162 on page 328.
3. Click the Radio tab.
The Access Points Profile Radio Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 163 on page 332.
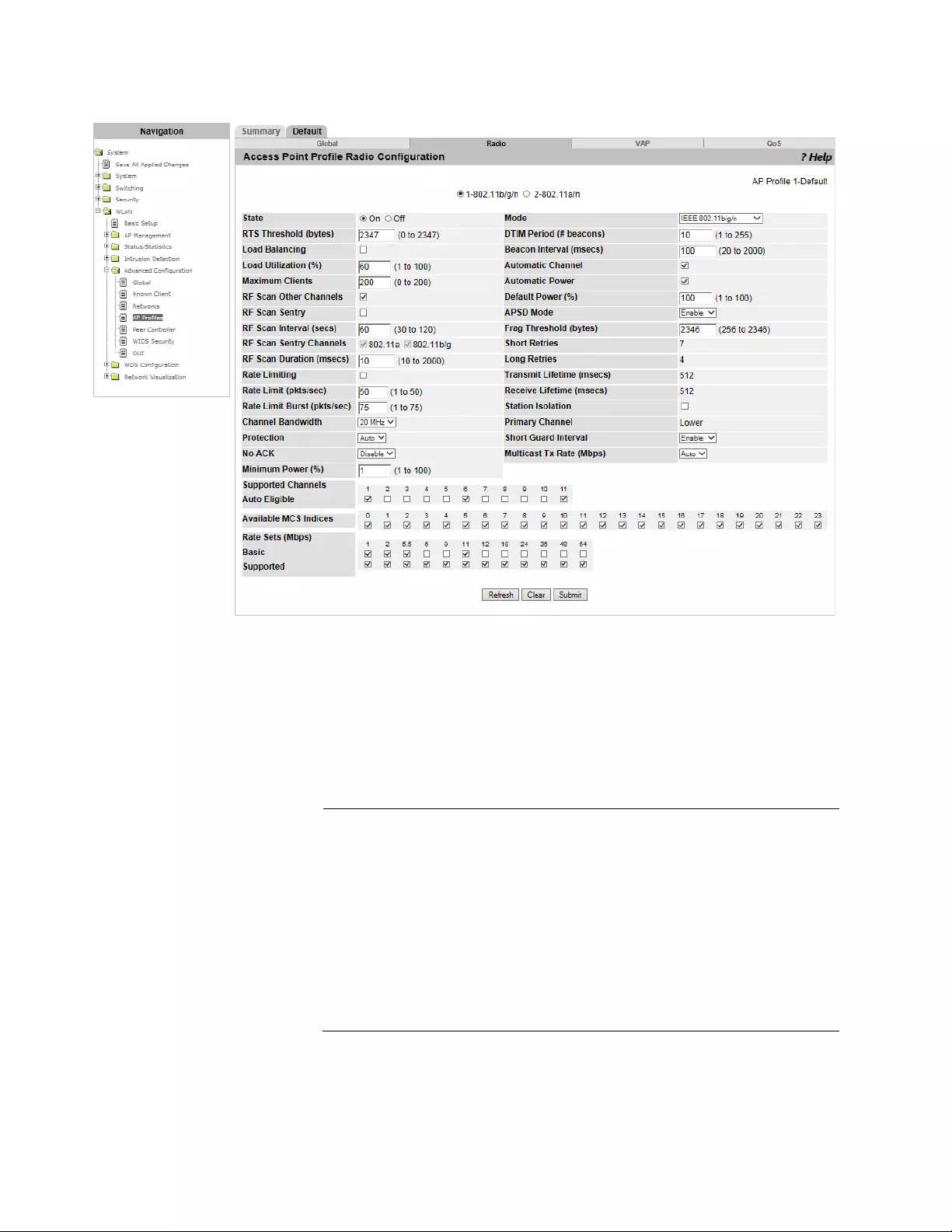
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
332
Figure 163. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration Page
4. Select the radio button, either 1 or 2 on the top of the table.
The values of 1 and 2 depends on the country code. For the
description of the country code, see Table 66 on page 191.
5. Modify the fields described in Table 139 on page 333.
Note
The following fields depend upon the Country Code:
State
Mode
Channel Bandwidth
Supported Channels Auto Eligible
Figure 163 displays a set of fields when “US - United States” is
selected as the country code.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
333
Table 139. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration
Field Description
State Turn on or off the radio signal from the access
point. The options are:
On - The access point emits the radio
signal.
Off - The access point sends a disconnect
frame to the AP clients before shutting
down.
RTS Threshold (bytes) Specifies the Request To Send (RTS) threshold in
bytes. Before sending a packet larger than the
RTS threshold, the access point sends an RTS
packet. The default value is 2347. When the RTS
threshold is 2348, the access point sends an RTS
packet.
Load Balancing Check the checkbox to enable Load Balancing.
When it is enabled, the access point controls
traffic based on the value of Load Utilization.
Load Utilization (%) Specifies the load utilization threshold in
percentage. When the network bandwidth
utilization reaches the Load Utilization, the access
point stops accepting new AP client. The default
is 60%.
Maximum Clients Specifies the maximum number of AP clients that
the access point is allowed to connect. When the
field is set to 0, the access point does not connect
to any AP client.
RF Scan Other
Channels
Check the checkbox for the access point to scan
other channels in the same radio band to collect
information about wireless devices and report the
information to the WLAN Controller.
When the access point scans other channels, the
access point stops using the channel in use.
RF Scan Sentry Check the checkbox to designate the access
point as an RF sentry, which intercepts beacon
frames and messages between other access
points. The designated RF scan sentry does not
send beacon frames or connect to AP clients.
RF Scan Interval (secs) Specifies an interval in seconds that the access
point moves to another channel for RF scanning.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
334
RF Scan Sentry
Channels
Displays which band is used when the access
point is a RF scan sentry. Always both of 802.11a
and 802.1b/g are selected.
RF Scan Duration
(msecs)
Specifies the time period in milliseconds that the
access point scan one channel.
Rate Limiting Check the checkbox to control transmission of
redundancy packets.
Rate Limit (pkts/sec) Specifies the Rate Limit, which is the number of
packets to be transmitted per second. When Rate
Limiting is enabled, the access point postpones
transmitting redundancy packets when the Rate
Limit is reached.
Rate Limit Burst (pkts/
sec)
Specifies the Rate Limit Burst threshold. The
range is the value of the Rate Limit to 75. When
the packets transmitted per second exceeds this
value, the traffic bursts intermittently. This value is
valid only when Rate Limiting is enabled.
Channel Bandwidth
(Only IEEE 802.11n)
Specifies the bandwidth to use. The access point
with the IEEE 802.11n mode is able to use two
neighboring 20MHz channels as one 40MHz
channel. The options are:
20MHz - This is the default value in the
2.4GHz radio band.
40MHz - This is the default value in the
5GHz radio band.
Protection Select the protection setting. The options are:
Auto - The access point with the IEEE
802.11n standard detects wireless devices
of the IEEE 802.11 a/b/g standard in the
channel. The access point emits
protection signal to avoid interference.
When wireless devices of both standards
are in the network, set to Auto.
Off - The access point does not emit
protection signals.
Table 139. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
335
No ACK Specifies whether sending ACK frames or not.
The options are:
Enable - Requests AP clients not to send
ACK frames. The access point also does
not send ACK frames.
Disable - No ACK frames to be sent.
Minimum Power (%) Specifies the minimum power in percentage for
the automatic power adjustment algorithm. See
“RF Management > Configuration” on page 205.
Mode Specifies the wireless standard that the access
point uses.
DTIM Period (#
beacons)
Specifies how often the access point sends a
beacon frame with the Delivery traffic Indication
Message (DTIM) element. The default value is 10.
When the DTIM Period is set to 10, the access
point sends a beacon frame after sending 9
beacon frames without DTIM.
Beacon Interval
(msecs)
Specifies the time interval in milliseconds
between beacon transmissions. The default value
is 100 milliseconds.
Automatic Channel Check the checkbox for the automatic channel
selection.
When Channel Plan Mode is selected to Fixed
Time or Interval, this filed must be checked. See
“RF Management > Configuration” on page 205.
Automatic Power Check the checkbox for the automatic RF power
adjustment.
Default Power (%) Specifies the default power level in percentage
against the maximum power.
APSD Mode Enables or disables Automatic Power Save
Delivery (APSD). APSD is the algorithm that
decrease the power consumption of VoIP phones
to extend the duration of call.
Frag Threshold (bytes) Specifies the packet size threshold for
fragmentation. The value must be an even
number between 256 and 2346. The access point
fragments a packet larger than this value before
transmitting.
Table 139. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
336
Short Retries Specifies the maximum number of re-tires for
short frames. The short frame is a frame whose
length is the specified RTS threshold or shorter.
Long Retries Specifies the maximum number of re-tires for long
frames. The long frame is a frame whose length is
longer than the specified RTS threshold.
Transmit Lifetime
(msecs)
Specifies the time period in seconds from starting
the first MAC Service Data Unit (MSDU)
transmission to completing the MSDU
transmission.
Receive Lifetime
(msecs)
Specifies the time period in seconds from
receiving the first fragmented MAC Service Data
Unit (MSDU) or MAC Management Protocol Data
Unit (MMPDU) transmission to reconstructing the
MSDU or MMPDU.
Station Isolation Indicates the permission for the AP client to
communicate with another AP that is connected
to the same VAP.
When the checkbox is checked, the VAP blocks
the communication between the AP clients.
Primary Channel
(Only IEEE 802.11n)
Specifies the channel for IEEE 802.11n AP clients
that support only 40 MHz bandwidth. The options
are:
Lower - The lower part of the 40MHz band
Upper - The upper part of the 40MHz
band
Short Guard Interval
(Only IEEE 802.11n)
Enables or disables the short guard interval to
reduce multi-pass transmission interference. The
options are:
Enable - Reduces the guard interval to
400ns when the AP client supports 400ns.
Disable - Uses 800ns for the guard
interval the same as IEEE 802.11a/g
devices.
Table 139. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
337
6. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Clear — Clears the changes you made before clicking Submit.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Multicast Tx Rate
(Mbps)
Specifies the rate of multicast transmission in
Mbps.The rate is also applied to broadcast and
beacon transmissions. When the rate is set to
Auto, the lowest basic rate is applied.
The options for 802.11b/g/n are:
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54.
The options for 802.11a/n are:
6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, or 54.
Supported
Channels
Auto
Eligible
Specifies the channels that are used for the
automatic channel assignment. When the
checkbox is checked, the channel is eligible for
the automatic channel assignment.
Available MCS Indices Specifies selected data rates. The index numbers
are associated with the IEEE 802.11n Modulation
and Coding Scheme (MCS) described in
Table 140 on page 338.
Rate Sets Basic Specifies the basic rate set that the access point
requires to the AP clients. The access point does
not allow to connect to an AP client that does not
support this basic rate set.
Supported Specifies the rates that the access point supports.
Table 139. Access Point Profile Radio Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
338
Modulation and
Coding Scheme
Table
Table 140 describes the IEEE 802.11n Modulation and Coding Scheme
(MCS).
Table 140. Modulation and Coding Scheme
Index Number of
Streams
Data Rate (Mbit/s)
800ns 400ns
20MHz 40MHz 20MHz 40MHz
0
1
6.5 13.5 7.2 15
1132714.430
2 1935 40.5 21.7 45
3265428.960
4398143.390
5 52 108 57.8 120
6 58.5 121.5 65 135
7 65 135 72.2 150
8
2
13 27 14.4 30
9265428.960
10 39 81 43.3 90
11 52 108 57.8 120
12 78 162 86.7 180
13 104 216 115.6 240
14 117 243 130 270
15 130 270 144.4 300
16
3
19.5 40.5 21.7 45
17 39 81 43.3 90
18 58.5 121.5 65 135
19 78 162 86.7 180
20 117 243 130 270
21 156 324 173.3 360
22 175.5 364.5 195 405
23 195 405 216.7 450

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
339
Access Point Profile VAP Configuration
From the Access Point Profile Virtual Access Point (VAP) Configuration
page, you can associate VAP’s with the access point profile. You can also
go to the Wireless Network Configuration page to edit each VAP.
To associate VAP’s to the access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Take one of the following actions:
“Viewing and Adding Access Point Profiles” on page 325
“Copying An Access Point Profile” on page 326
“Modifying An Access Point Profile” on page 327
The Access Points Profile Global Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 162 on page 328.
3. Click the VAP tab.
The Access Points Profile VAP Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 164 on page 340.
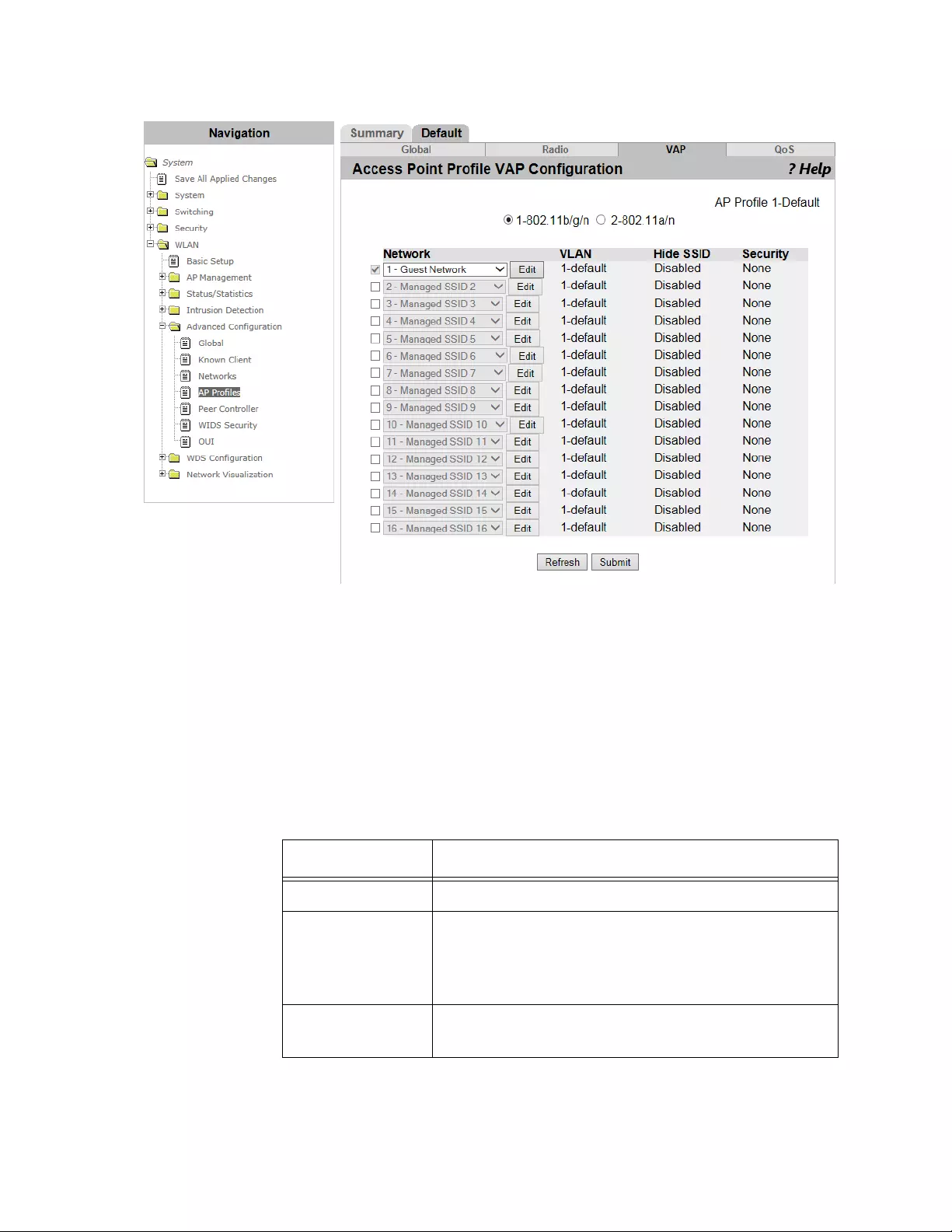
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
340
Figure 164. Access Point Profile VAP Configuration Page
4. Select 1-802.11b/g/n or 2-802.11a/n to configure.
5. Check the checkbox of a VAP.
The VAP is enabled on the access point profile. You can enable
multiple VAP’s on one access point profile.
6. Observe the fields described in Table 141.
Table 141. Access Point Profile VAP Configuration
Field Description
Network Displays the name of the wireless network.
Edit Button Brings the page to edit the wireless network. To
edit the properties of the wireless network, see
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks” on
page 316.
VLAN Displays the VLAN ID that the wireless network
uses.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
341
7. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Hide SSID Displays whether the SSID is included in the
broadcast AP beacon frames. The options are:
Enabled — The SSID is not included in the
broadcast AP beacon frames.
Disabled — The SSID is included in the
broadcast AP beacon frames.
Security Displays the security setting for the access point
profile.
Table 141. Access Point Profile VAP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
342
Access Point Profile QoS Configuration
From the Access Point Profile Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
page, you can configure QoS on the access point profile. The QoS
settings are applied to the access points, not to the AP clients.
To configure QoS on the access point profile, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
AP Profiles.
The Access Point Profile List page is displayed as shown in Figure 161
on page 325.
2. Take one of the following actions:
“Viewing and Adding Access Point Profiles” on page 325
“Copying An Access Point Profile” on page 326
“Modifying An Access Point Profile” on page 327
The Access Points Profile Global Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 162 on page 328.
3. Click the QoS tab.
The Access Points Profile QoS Configuration page is displayed as
shown in Figure 165 on page 343.
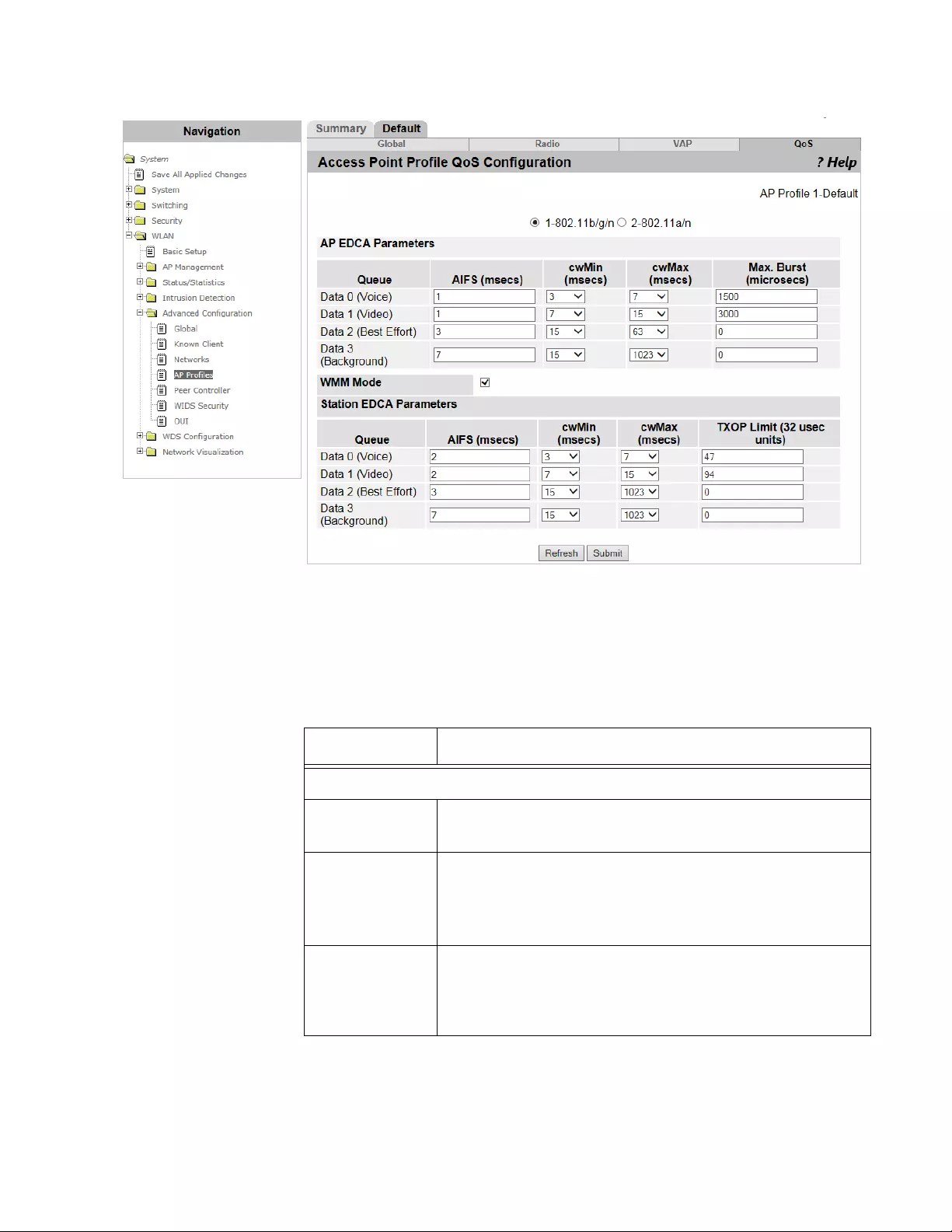
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
343
Figure 165. Access Point Profile QoS Configuration Page
4. Select 1-802.11b/g/n or 2-802.11a/n to configure.
5. Observe the fields described in Table 142.
Table 142. Access Point Profile QoS Configuration
Field Description
AP EDCA Parameters
Queue Displays four queues. You can specify AIFS, cwMin,
cwMax, and Max. Burst for each queue.
AIFS (msecs) Specifies the interval with a slot time between frames
being transmitted. The range is from 1 to 255 slot time.
Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFS) is a method of
prioritizing one access category over the other.
cwMin (msecs) Specifies the minimum Contention Window (cwMin).
The value must be 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or
1023 and equal to or smaller than cwMax.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
344
6. Click the following buttons:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
cwMax
(msecs)
Specifies the maximum Contention Window (cwMax).
The value must be 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or
1023 and equal to larger than cwMin.
Max. Burst
(microsecs)
Specifies the time period in microseconds to transmit
multiple packets continuously. The range is 0 to
999,900 microseconds.
General Parameter
WMM Mode Check the checkbox to enable Wi-Fi Multimedia
(WMM). When WMM is enabled, the Station EDCA
parameters are applied to the communication from AP
clients to the access point.
Station EDCA Parameters
Queue Displays four queues. You can specify AIFS, cwMin,
cwMax, and TXOP Limit for each queue.
AIFS (msecs) Specifies the interval with a slot time between frames
being transmitted. The range is from 1 to 255 slot time.
Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFS) is a method of
prioritizing one access category over the other.
cwMin (msecs) Specifies the minimum Contention Window (cwMin).
The value must be 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or
1023 and equal to or smaller than cwMax.
cwMax
(msecs)
Specifies the maximum Contention Window (cwMax).
The value must be 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, or
1023 and equal to larger than cwMin.
TXOP Limit Specifies the Transmit Opportunity (TXOP) Limit.
TXOP is a time period that an AP client can transmit as
many frames as possible. The specified number is
multiplied by 32 microseconds. For example, the
default TXOP limit of Data 0 is 1504 microseconds
because the default set number 47 is multiplied by 32
microseconds.
Table 142. Access Point Profile QoS Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
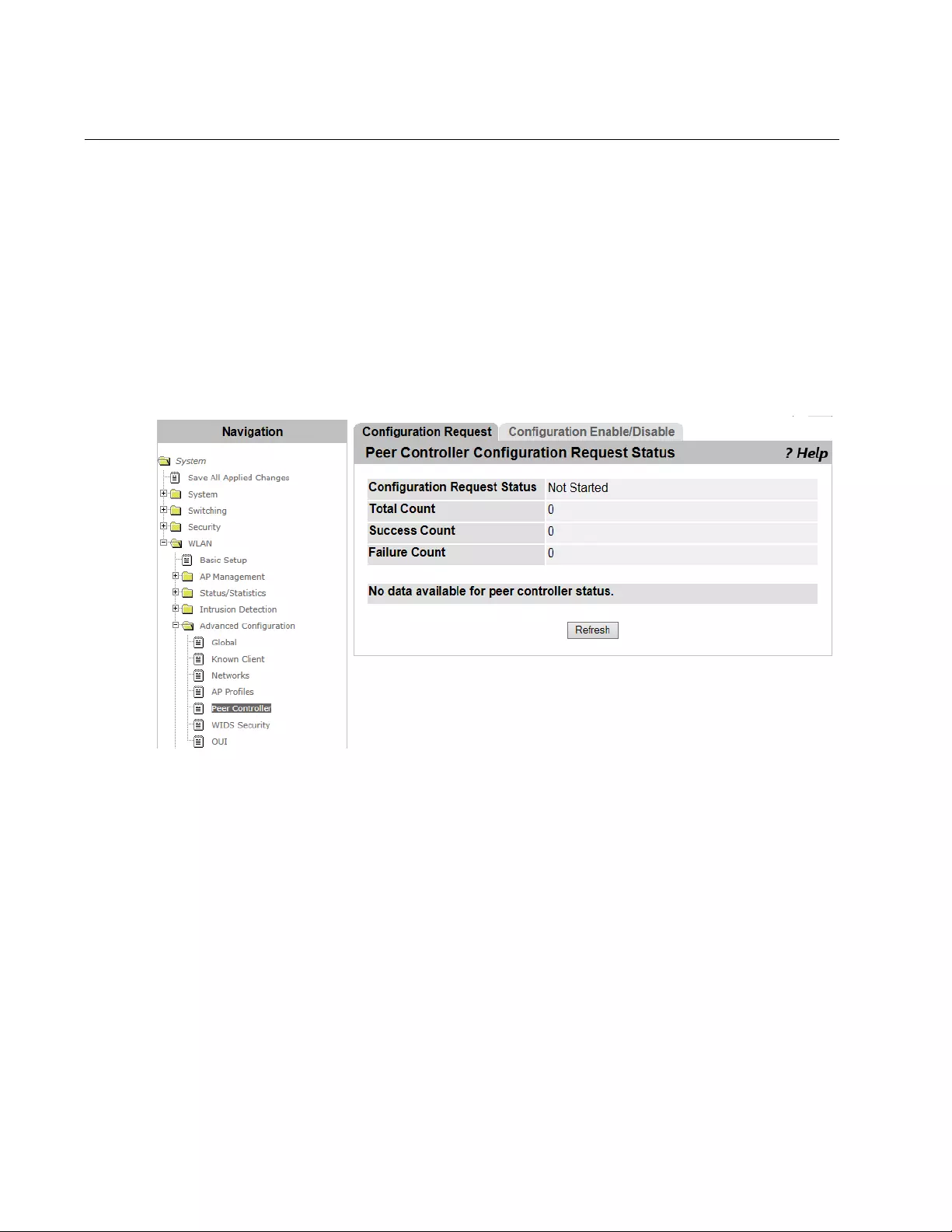
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
346
Peer Controller > Configuration Request Status
From the Peer Controller Configuration Request page, you can request
other peer controllers in the peer group to download the configuration of
the WLAN Controller and view the status of the request.
To view the status and make a configuration request, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Peer Controller.
The Peer Controller Configuration Request Status page is displayed
as shown in Figure 166.
Figure 166. Peer Controller Configuration Request Status Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 143 on page 347.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
347
3. Check the checkbox of the peer controller that you want to download
the configuration from the WLAN Controller.
You can select one ore more peer controllers.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Start — Starts the request to the selected peer controllers to
download the configuration of the WLAN Controller.
Start All — Starts the request to all the peer controllers on the list
to download the configuration of the WLAN Controller.
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Table 143. Peer Controller Configuration Request Status
Field Description
Configuration
Request Status
Displays the status of the configuration request
made to peer controllers. The options are:
Not Started
Receiving Configuration
Saving Configuration
Success
Failure-Invalid Code Version
Failure-Invalid Hardware Version
Failure-Invalid Configuration
Total Count Displays the number of peer controllers that the
configuration request is made to.
Success Count Displays the number of peer controllers that have
successfully downloaded the configuration.
Failure Count Displays the number of peer controllers that failed
to download the configuration.
Peer IP Address Displays a list of IP addresses of peer controller
and the status of the configuration request.
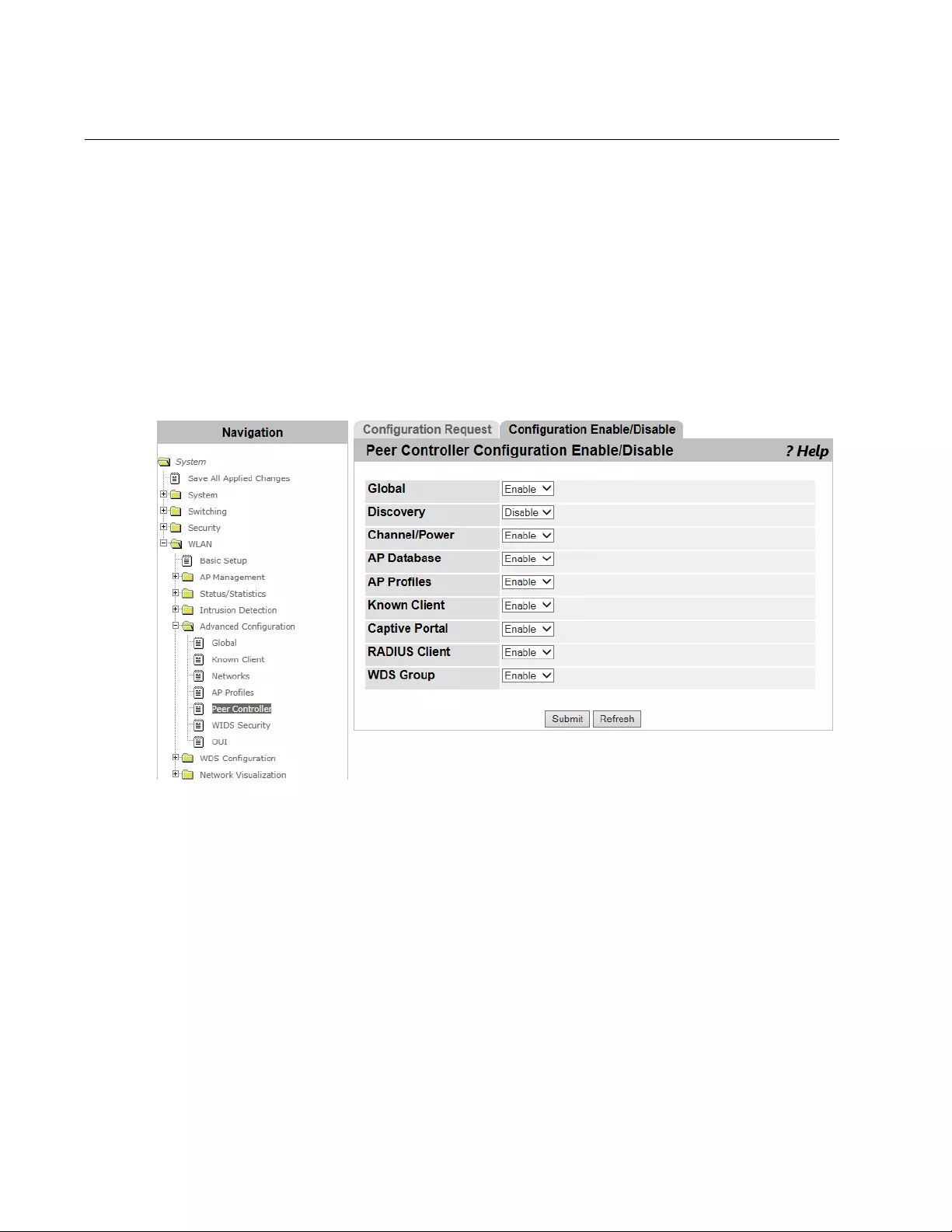
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
348
Peer Controller > Configuration Enable/Disable
From the Peer Controller Configuration Enable/Disable page, you can
specify which categories of the configuration for peer controllers to
download.
To enable or disable configuration categories, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
Peer Controller and click the Configuration Enable/Disable tab.
The Peer Controller Configuration Enable/Disable page is displayed as
shown in Figure 167.
Figure 167. Peer Controller Configuration Enable/Disable Page
2. Observed the fields described in Table 144.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
349
Table 144. Peer Controller Configuration Enable/Disable
Field Description
Global Check the checkbox to specify the Global
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers. The Global
configuration does not include the IP address of the
controller.
See “WLAN Basic Setup > Global” on page 191
and “WLAN Advanced Configuration > Global” on
page 302.
Discovery Check the checkbox to specify the Discovery
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers. The IP list of
the wireless discovery must include the IP
addresses of the WLAN Controller and the peer
controllers that receive the configuration request.
See “WLAN Basic Setup > Discovery” on
page 194.
Channel/Power Check the checkbox to specify the Channel /Power
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “RF Management > Configuration” on
page 205.
AP Database Check the checkbox to specify the valid AP
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “WLAN Basic Setup > Valid AP” on page 198.
AP Profiles Check the checkbox to specify the AP profile
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers. The AP profile
configuration includes the Global, Radio, VAP, and
QoS settings.
See “Access Point Profile List” on page 325.
Known Client Check the checkbox to specify the Known Client
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “WLAN Advanced Configuration > Known
Client” on page 312.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
350
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Captive Portal Check the checkbox to specify the Captive Portal
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “CP Global Configuration” on page 138.
RADIUS Client Check the checkbox to specify the RADIUS Client
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “RADIUS Configuration” on page 172.
WDS Group Check the checkbox to specify the WDS Group
configuration of the WLAN Controller to be
downloaded to the peer controllers.
See “WDS Group Configuration” on page 359.
Table 144. Peer Controller Configuration Enable/Disable (Continued)
Field Description
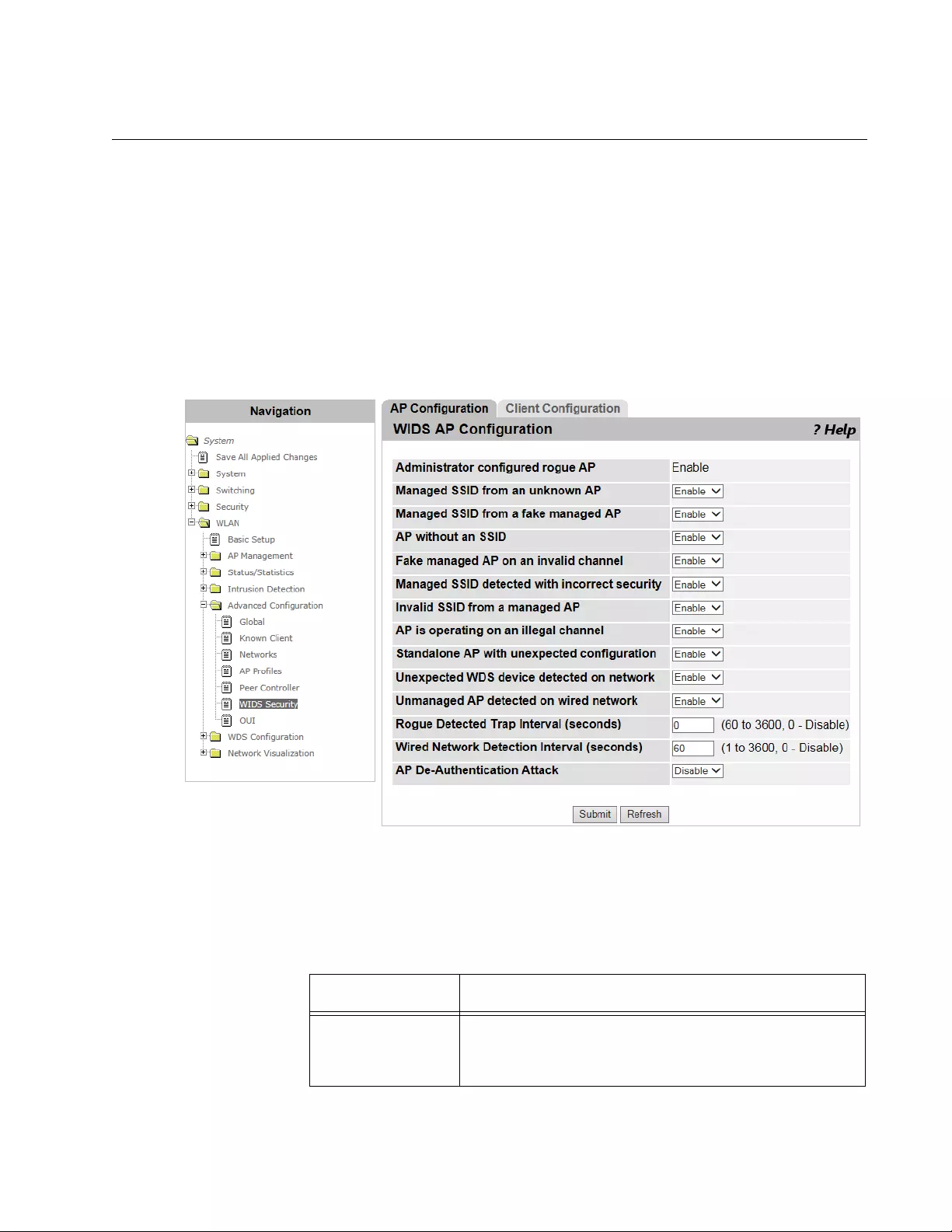
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
351
WIDS AP Configuration
From the Wireless Intrusion Detection System (WIDS) AP Configuration
page, you can enable or disable each WIDS feature on access points and
specify the properties.
To enable or disable WIDS and specify the properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
WIDS Security.
The WIDS AP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 168.
Figure 168. WIDS AP Configuration Page
2. Enable or disable each WIDS feature and specify the fields described
in Table 145.
Table 145. WIDS AP Configuration
Field Description
Administrator
configured rogue
AP
Displays whether the feature of detecting an
access point on the Valid AP list and marking the
access point as rogue is enabled or disabled.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
352
Managed SSID
from an unknown
AP
Enables or disables detecting the unknown AP that
sends the beacon frames including the SSID
managed by the WLAN Controller and marking the
access point as a rogue access point.
The unknown AP can be malicious; however, in a
large network with multiple peer groups, a unknown
AP sending the managed SSID can be legitimate.
Managed SSID
from a fake
managed AP
Enables or disables detecting a fake managed
access point that sends the beacon frames
including the SSID managed by the WLAN
Controller.
The fake managed access point is an access point
that sends beacon frames without the specific
value in the vendor field.
AP without an
SSID
Enables or disables detecting an access point that
sends beacon frames in which the SSID is hidden.
The SSID field is optional in beacon frames;
however, the field may be intentionally hidden for
malicious purposes.
Fake managed
AP on an invalid
channel
Enables or disables detecting a fake managed
access point using an invalid channel. Even if the
source MAC address of the beacon frame is
proper, the access point sending the beacon frame
is marked as a fake access point when using an
invalid channel.
Managed SSID
detected with
incorrect security
Enables or disables detecting an access point that
sends beacon frames with the incorrect security
method by RF scan and marking the access point
as a rogue access point.
Invalid SSID
from a managed
AP
Enables or disables detecting an access point that
sends beacon frames with an unknown SSID and
marking the access point as rogue.
AP is operating
on an illegal
channel
Enables or disables detecting an access point
operating through an illegal channel.
To enable this detection, you must have the
designated access point with the sentry mode.
Table 145. WIDS AP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
353
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
Standalone AP
with unexpected
configuration
Enables or disables detecting an access point with
the standalone mode that is not operating as its
settings. The standalone access point is tested in
the channel, SSID, security method, WDS mode,
and wired connection.
Unexpected
WDS device
detected on
network
Enables or disables detecting a managed or
unknown AP that is operating in the WDS mode
and marking the access point as rogue.
Unmanaged AP
detected on
wired network
Enables or disables detecting an unknown AP that
is connected to the wired network and marking the
access point as rogue.
To enable this detection, you must have the
designated access point with the sentry mode.
Rogue Detected
Trap Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval that SNMP traps with
Rogue AP information are sent. When 0 is set, no
SNMP traps are sent.
Wired Network
Detection
Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval that probe frames are
sent to the wired network. When 0 is set, no probe
frames are sent.
AP De-
Authentication
Attack
Enables or disables AP De-Authentication Attack.
AP De-Authentication Attack is a feature to
disconnect rogue access points by sending IEEE
802.11 de-authentication frames to the rogue
access points.
Table 145. WIDS AP Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
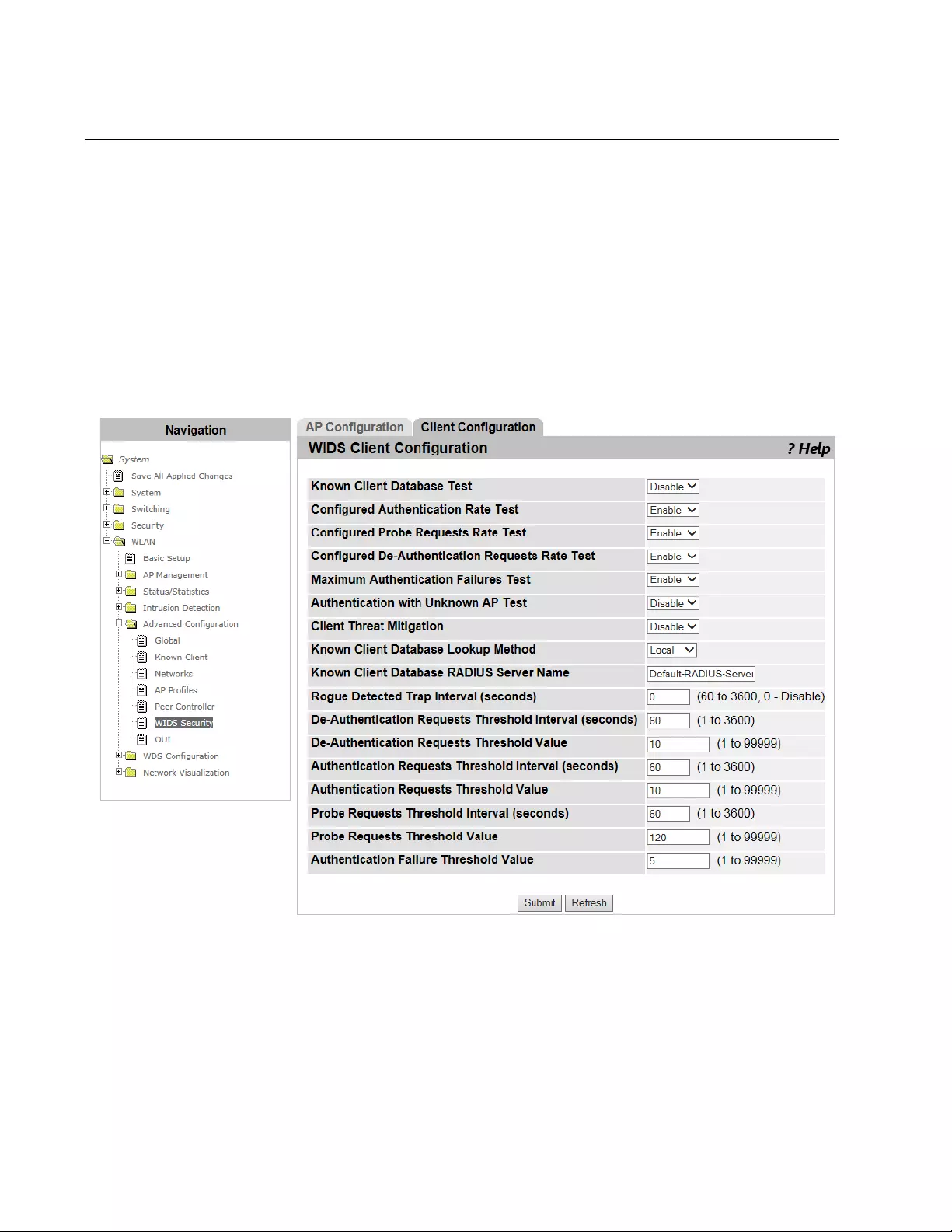
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
354
WIDS Client Configuration
From the Wireless Intrusion Detection System (WIDS) Client
Configuration page, you can enable or disable WIDS types on access
point clients and specify the properties.
To enable or disable WIDS and specify the properties, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
WIDS Security and click the Client Configuration tab.
The WIDS Client Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 169.
Figure 169. WIDS Client Configuration Page
2. Enable or disable WIDS types on AP clients and specify the fields
described in Table 146 on page 355.
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
355
Table 146. WIDS Client Configuration
Field Description
Known Client
Database Test
Displays whether or not detecting an AP client on
the Known Client list with the Deny setting or on
the blacklist.
Configured
Authentication
Rate Test
Enables or disables detecting an AP client that
exceeds the maximum transmission rate when
sending 802.11 Authentication messages.
Configured Probe
Requests Rate Test
Enables or disables detecting an AP client that
exceeds the maximum rate when sending probe
requests.
Configured De-
Authentication
Requests Rate Test
Enables or disables detecting an AP client that
exceeds the maximum rate when sending De-
Authentication requests.
Maximum
Authentication
Failure Test
Enables or disables detecting an AP client that
exceeds the limit of authentication failure.
Authentication with
Unknown AP Test
Enables or disables detecting an AP client on the
Known Client list that is connected to the unknown
AP.
Client Threat
Mitigation
Enables or disables sending De-Authentication
requests to an AP client when the AP client on the
Known Client connects to an unknown AP.
Authentication with Unknown AP Test must be
enabled.
Known Client
Database Lookup
Method
Specifies the type of the Known Client database:
Local or RADIUS.
Known Client
Database RADIUS
Server Name
Specifies the name of the RADIUS server to refer
to the Known Client database when the Known
Client Database Lookup Method is selected
RADIUS.
Rogue Detected
Trap Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval that SNMP traps with
Rogue information are sent. When 0 is set, no
SNMP traps are sent.
De-Authentication
Requests
Threshold Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval to count the number of
De-Authentication requests.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
356
3. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Submit — Makes the changes effective and saves them to the
running configuration file.
Note
To save your changes to the startup configuration file, see “Save All
Applied Changes” on page 39.
De-Authentication
Requests
Threshold Value
Specifies the maximum number of De-
Authentication requests during a De-
Authentication Requests Threshold Interval.
Authentication
Requests
Threshold Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval to count the number of
Authentication requests.
Authentication
Requests
Threshold Value
Specifies the maximum number of Authentication
requests during an Authentication Requests
Threshold Interval.
Probe Requests
Threshold Interval
(seconds)
Specifies the time interval to count the number of
probe requests.
Probe Requests
Threshold Value
Specifies the maximum number of probe requests
during a Probe Requests Threshold Interval.
Authentication
Failure Threshold
Value
Specifies the maximum number of 802.1x
authentication failure.
Table 146. WIDS Client Configuration (Continued)
Field Description
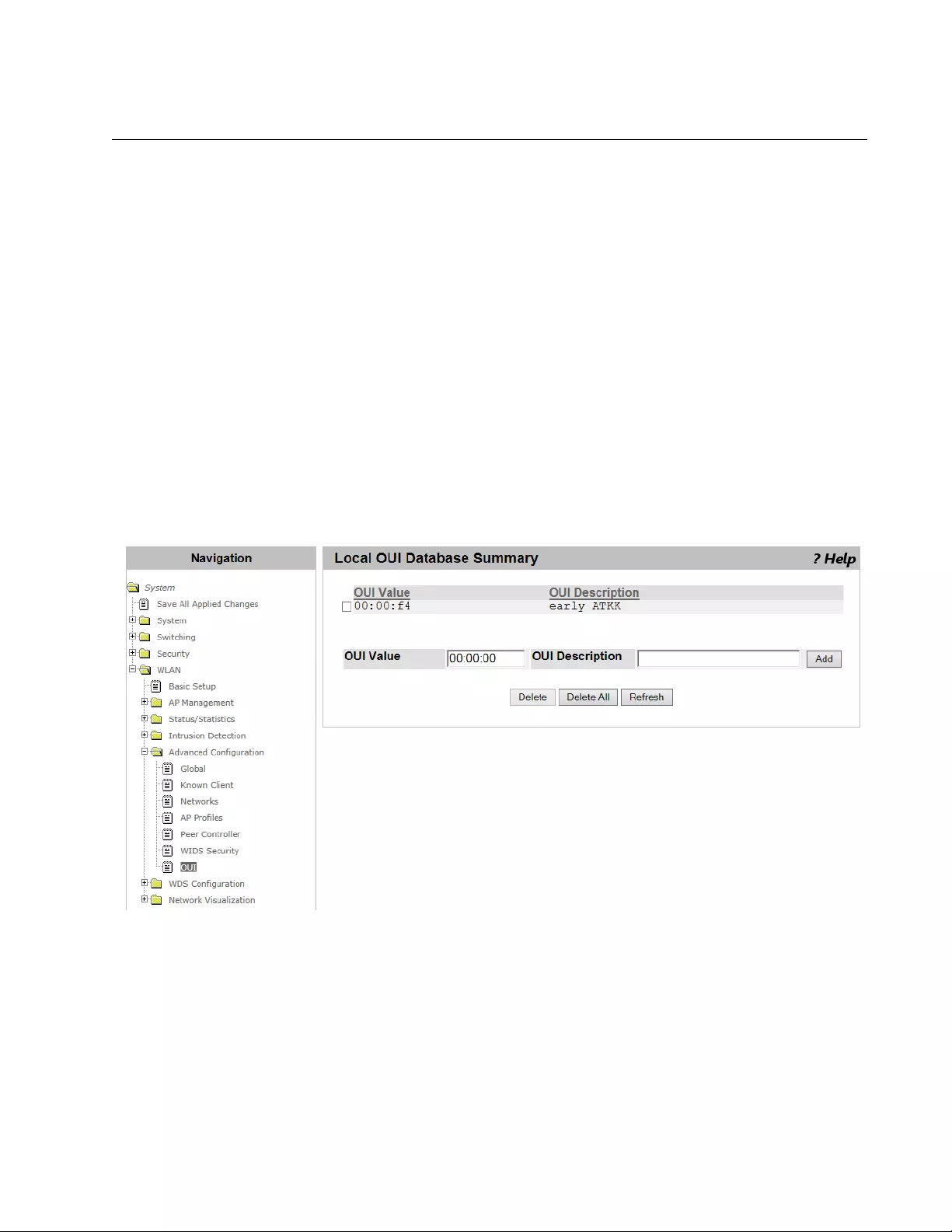
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
357
Local OUI Database Summary
The first three bytes of the MAC address is called an Organizationally
Unique Identifier (OUI), which identifies the vendor, manufacturer, or other
organization of a device. With a built-in OUI database, the WLAN
Controller displays the vendor, manufacturer, or organization of an access
point and peer controller on the Detected Client Status list. See “Detected
Clients” on page 284.
From the Local OUI Database Summary page, you can view a list of OUI
entries, add new OUI entries, and delete them.
Viewing a List of
OUI Entries and
Deleting Them
To view a list of added OUI entires and delete them, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
OUI.
The Local Database Summary page is displayed as shown in
Figure 170.
Figure 170. Local OUI Database Summary Page
2. Observe the following fields described in Table 147 on page 358.
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
358
3. Check the checkbox of the OUI entry that you want to delete.
4. Click the following buttons as needed:
Refresh — Refreshes the display on this page.
Delete — Deletes the checked OUI entries.
Delete All — Deletes all the OUI entries on the list.
Adding an OUI
Entry
To add an OUI entry, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > Advanced Configuration >
OUI.
The Local Database Summary page is displayed as shown in Figure
170 on page 357.
2. Enter the values in the following fields:
OUI Value
OUI Description
3. Click Add.
The OUI entry is added to the OUI list.
Table 147. Local OUI Database Summary
Field Description
OUI Value Displays an OUI. The OUI is the first 3 bytes of the
MAC address. The format is FF:FF:FF.
OUI Description Displays the name of vendor, manufacturer or
organization up to 32 alphanumeric characters.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
359
WDS Group Configuration
From the WDS Group Configuration page, you can view a list of WDS
groups and add a new WDS group. You can also delete existing WDS
groups.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) enables access points to connect
with one another and allows the WLAN Controller to manage these access
points. Figure 171 illustrates an example of a topology using WDS.
Figure 171. WDS Group Configuration Example
Guidelines for a
WDS Group
Here are the guidelines for using a WDS group.
The access point that is connected to a LAN is called a root access
point.
The access point that is connected to the root access point through
the wireless network is called a satellite access point.
The access points that belong to the same WDS group must be the
same model and have the same version of software installed.
The satellite access points that belong to the same WDS group
must have the same password.
When the WLAN Controller is using WDS, the Wireless ARP
Suppression feature is disabled. See “WLAN Advanced
Configuration > Networks” on page 316.
When the WLAN Controller is using WDS, the Distributed
Tunneling and Centralized Tunneling are disabled. See “WLAN
Advanced Configuration > Distributed Tunneling” on page 308 and
“WLAN Advanced Configuration > Centralized L2 Tunneling” on
page 310.

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
360
Configuring
WDS
To configure WDS, do the following:
1. Configure the root and satellite access points for a WDS bridge.
To include the root and satellite access points in the same WDS group,
these access points must be set to the same radio band, channel, and
security level. See the documentations for the access point.
2. Create a WDS network.
See “WLAN Advanced Configuration > Networks” on page 316. Allied
Telesis recommends that you select WPA/WPA2 in the Security field
and enter the password.
3. Create an AP profile for the WDS network.
See “Access Point Profile List” on page 325.
4. Associate the WDS network that you created in step 2 to the access
point profile.
See “Access Point Profile VAP Configuration” on page 339.
5. Add the root access point to the Valid AP database.
See “Viewing Failed Access Points and Adding Them to Valid AP List”
on page 297.
6. Apply the AP profile that you created in step 3 to the root access point.
See “Adding an Access Point” on page 199.
7. Add the satellite access points to the Valid AP database from “WLAN
Basic Setup > Valid AP” on page 198.
8. Create a WDS group.
See “Viewing a List of WDS Groups and Adding a New Group” on
page 361.
9. Add the root and satellite access points to the WDS group.
See “Viewing a List of AP Members and Adding an AP” on page 364.
10. Configure the link between the root access point and satellite access
points.
See “WDS Link Configuration” on page 366.
11. Push the WDS group information to the peer controllers.
See “Pushing the WDS Information to Peer Controllers” on page 363.
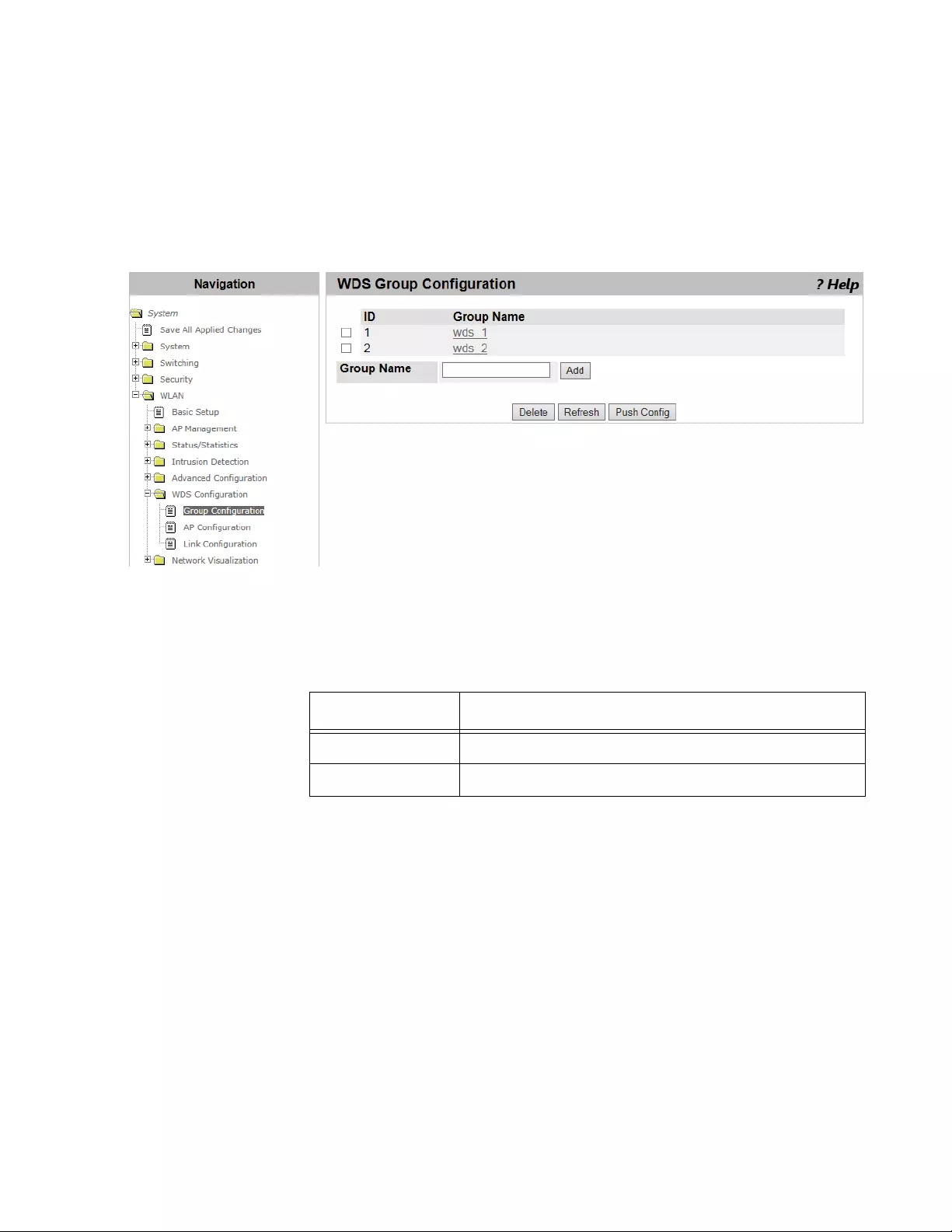
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
361
Viewing a List of
WDS Groups and
Adding a New
Group
To view a list of WDS groups and add a WDS group, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Group
Configuration.
The WDS Group Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 172.
Figure 172. WDS Group Configuration Page
2. Observe the following fields described in Table 148.
3. Enter a name of the WDS group to add.
4. Click Add.
Another WDS Group Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 173 on page 362.
Table 148. WDS Group Configuration
Field Description
ID Displays the ID of the WDS group.
Group Name Displays the name of the WDS group.
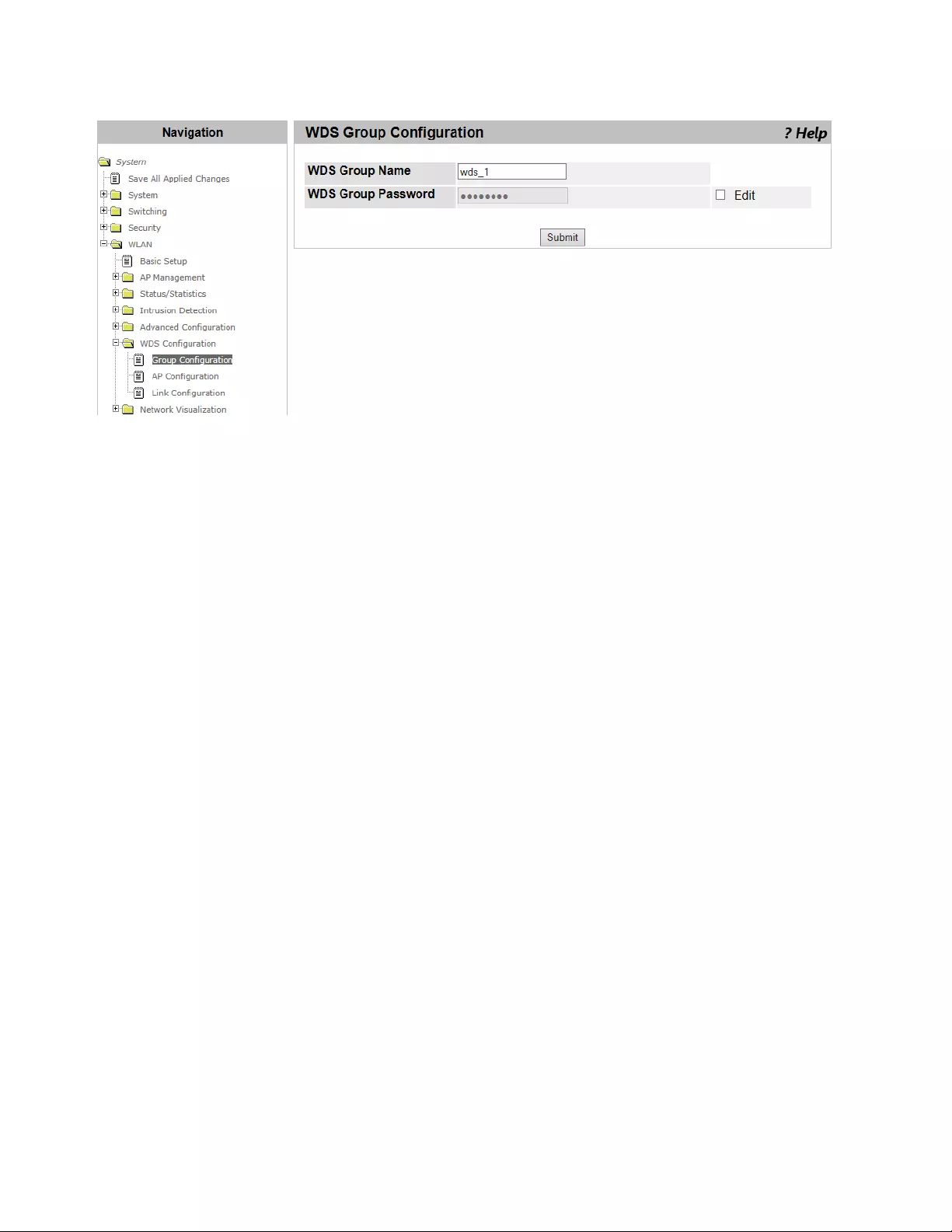
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
362
Figure 173. WDS Group Configuration Page 2
5. Check the Edit checkbox.
You can enter a password in the WDS Group Password field.
6. Enter the same password as the WDS group password for the satellite
AP.
7. Click Submit.
8. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Group
Configuration.
The WDS Group Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
172 on page 361.
9. Click Push Config.
The information about WDS on WLAN Controller is pushed to other
peer controllers.
Deleting WDS
Groups
To delete WDS groups from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Group
Configuration.
The WDS Group Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
172 on page 361.
2. Check the checkbox of the WDS group to delete.
3. Click Delete.
4. If you want to refresh the displays on this page, click Refresh.

Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
363
Pushing the WDS
Information to
Peer Controllers
To push the WDS group information to the peer controllers, do the
following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Group
Configuration.
The WDS Group Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
172 on page 361.
2. Check the checkbox of the WDS group to push the WDS group
information to the peer controllers.
3. Click Push Config.
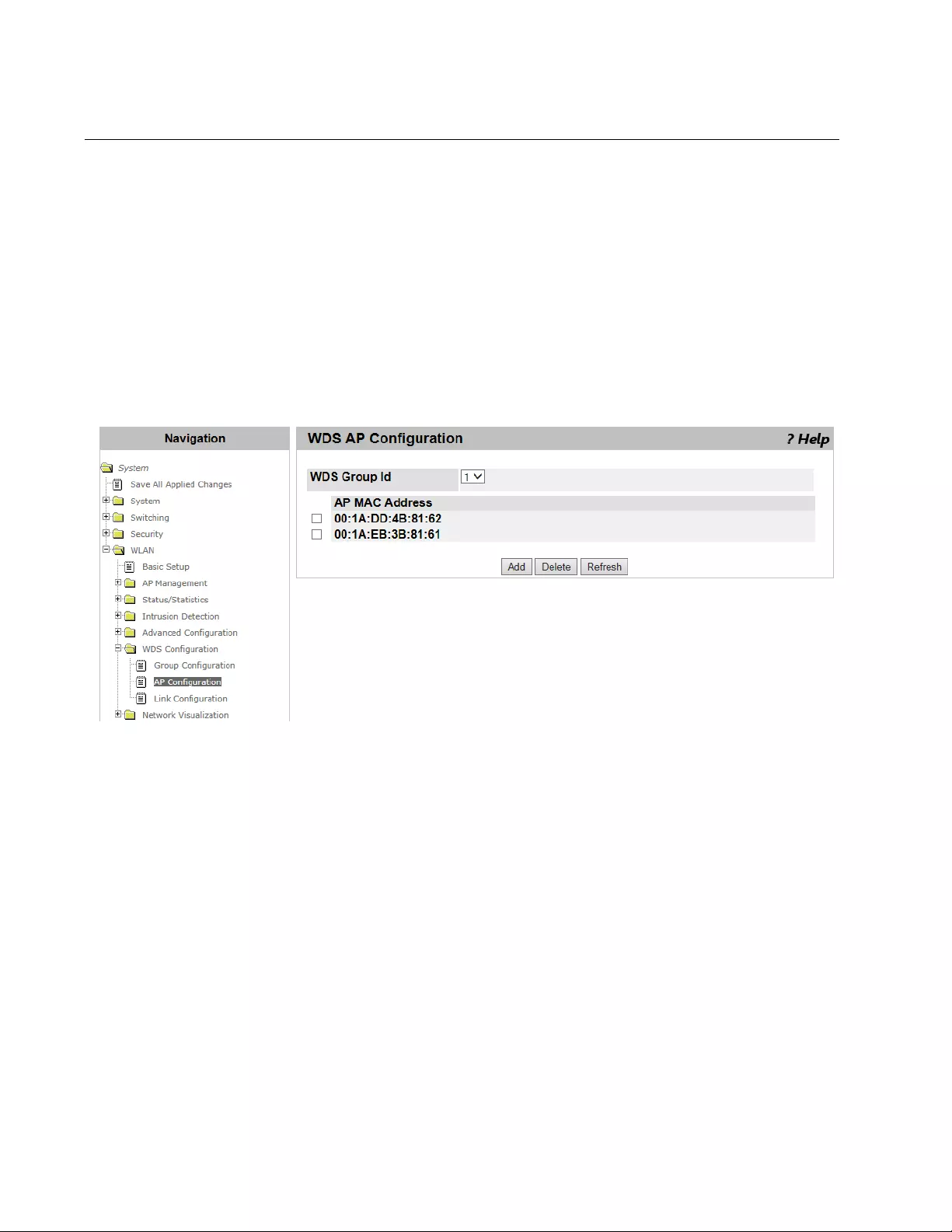
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
364
WDS AP Configuration
From the WDS AP Configuration page, you can view access point
members that belong to a WDS group and add a new access point
member.
Viewing a List of
AP Members and
Adding an AP
To view access point members that belong to a WDS group and add a
new access point member, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > AP
Configuration.
The WDS AP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 174.
Figure 174. WDS AP Configuration Page
2. Select a WDS group ID to view its access point members from the
select list.
A list of MAC addresses of the access points that belong to the
selected WDS group is displayed.
3. Click Add to add a new access point member.
Another WDS AP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
175 on page 365.
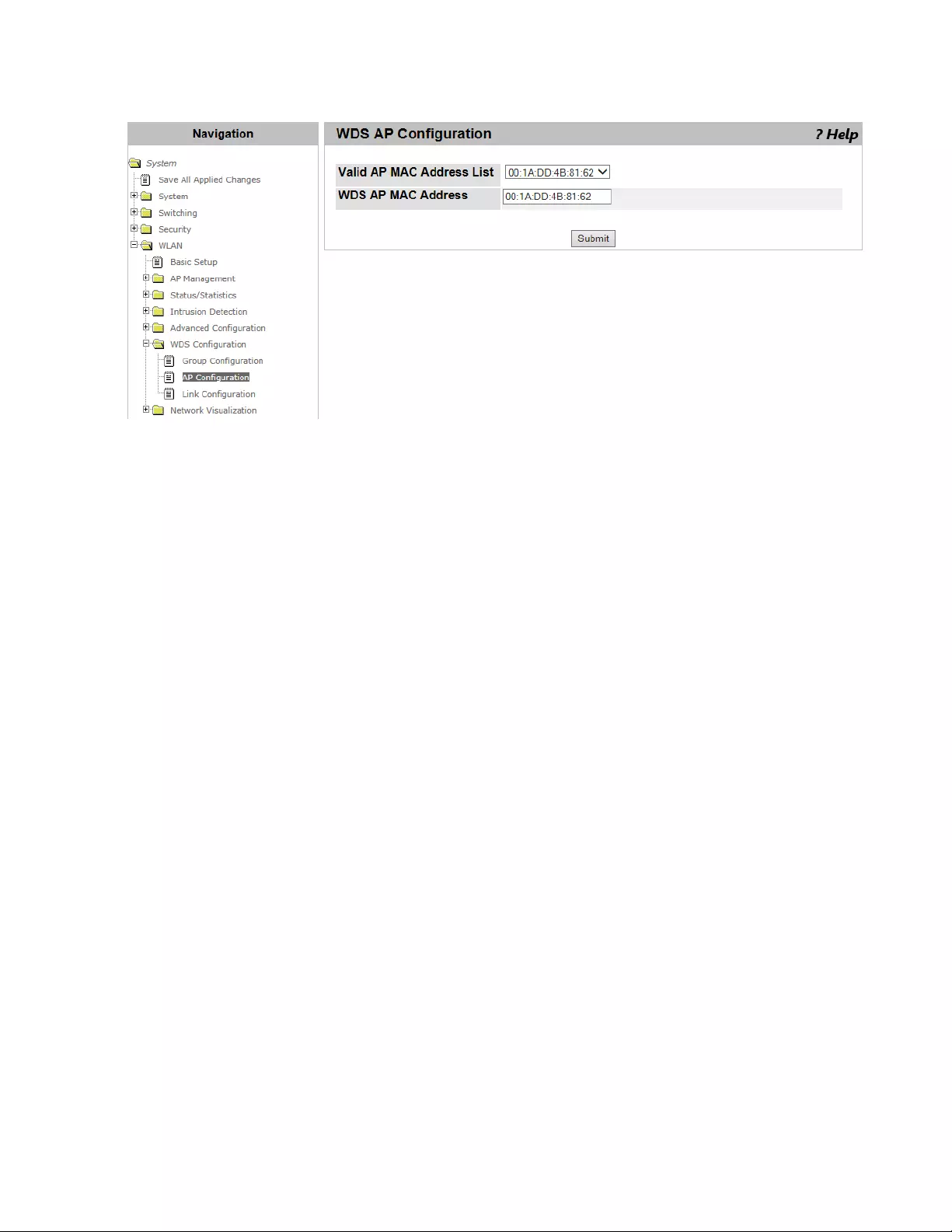
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
365
Figure 175. WDS AP Configuration Page 2
4. Select the MAC address of the AP to add from the Valid AP MAC
Address select list.
5. Click Submit.
Deleting AP
Members
To delete access point members from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > AP
Configuration.
The WDS AP Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 174
on page 364.
2. Select a WDS group ID to view its access point members from the
select list.
A list of MAC addresses of the access points that belong to the
selected WDS group is displayed.
3. Check the checkbox of the MAC address for the access point to delete.
4. Click Delete.
5. If you want to refresh the displays on this page, click Refresh.
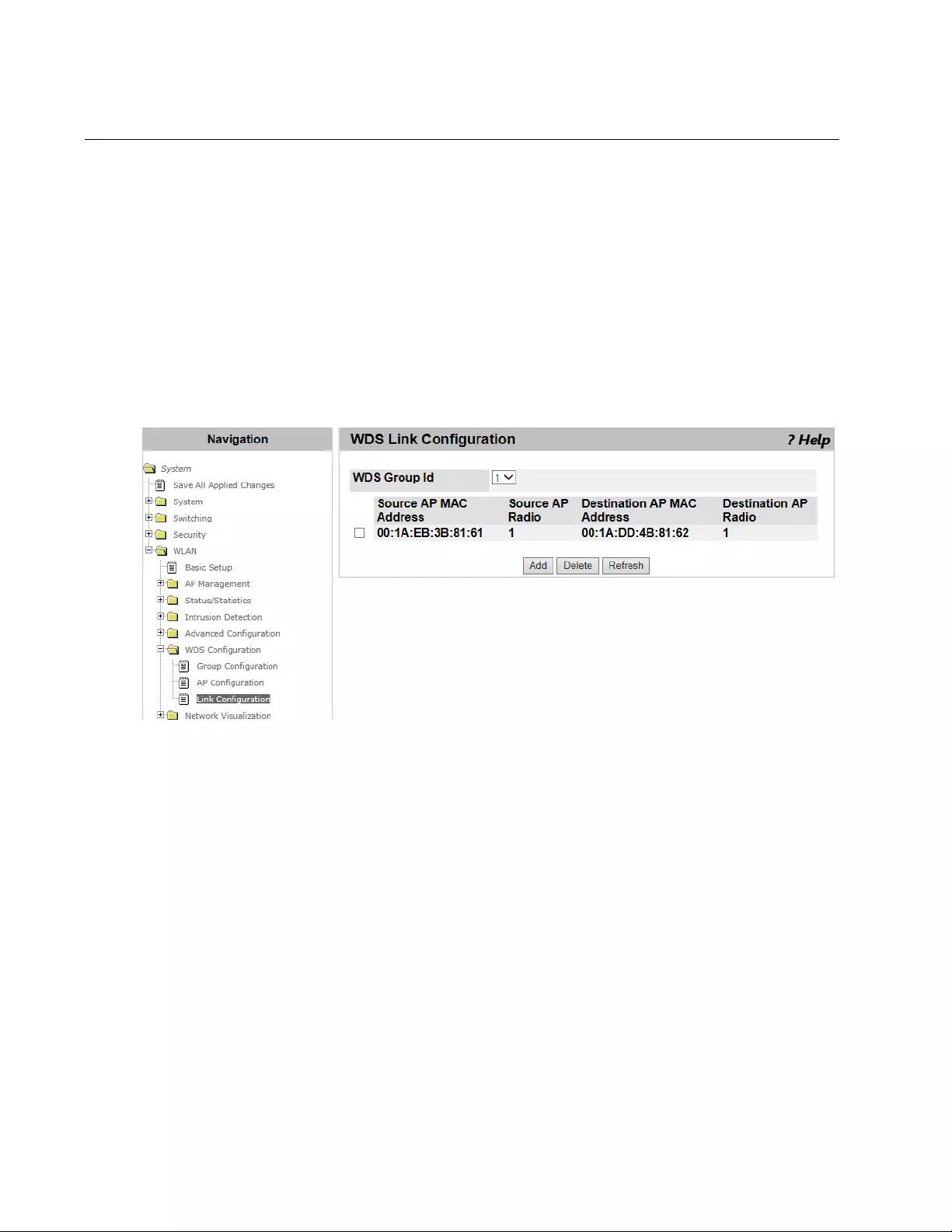
AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
366
WDS Link Configuration
From the WDS Link Configuration page, you can view a list of link
combinations of two access points and add a new link combination.
Viewing Link
Combinations
and Adding a
New Link
To view AP members that belong to a WDS group and add a new AP
member, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Link
Configuration.
The WDS Link Configuration page is displayed as shown in
Figure 176.
Figure 176. WDS Link Configuration Page
2. Select a WDS group ID to view the link combinations from the select
list.
A list of link combinations that belong to the selected WDS group is
displayed.
3. Click Add to add a new link.
Another WDS Link Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure
177 on page 367.
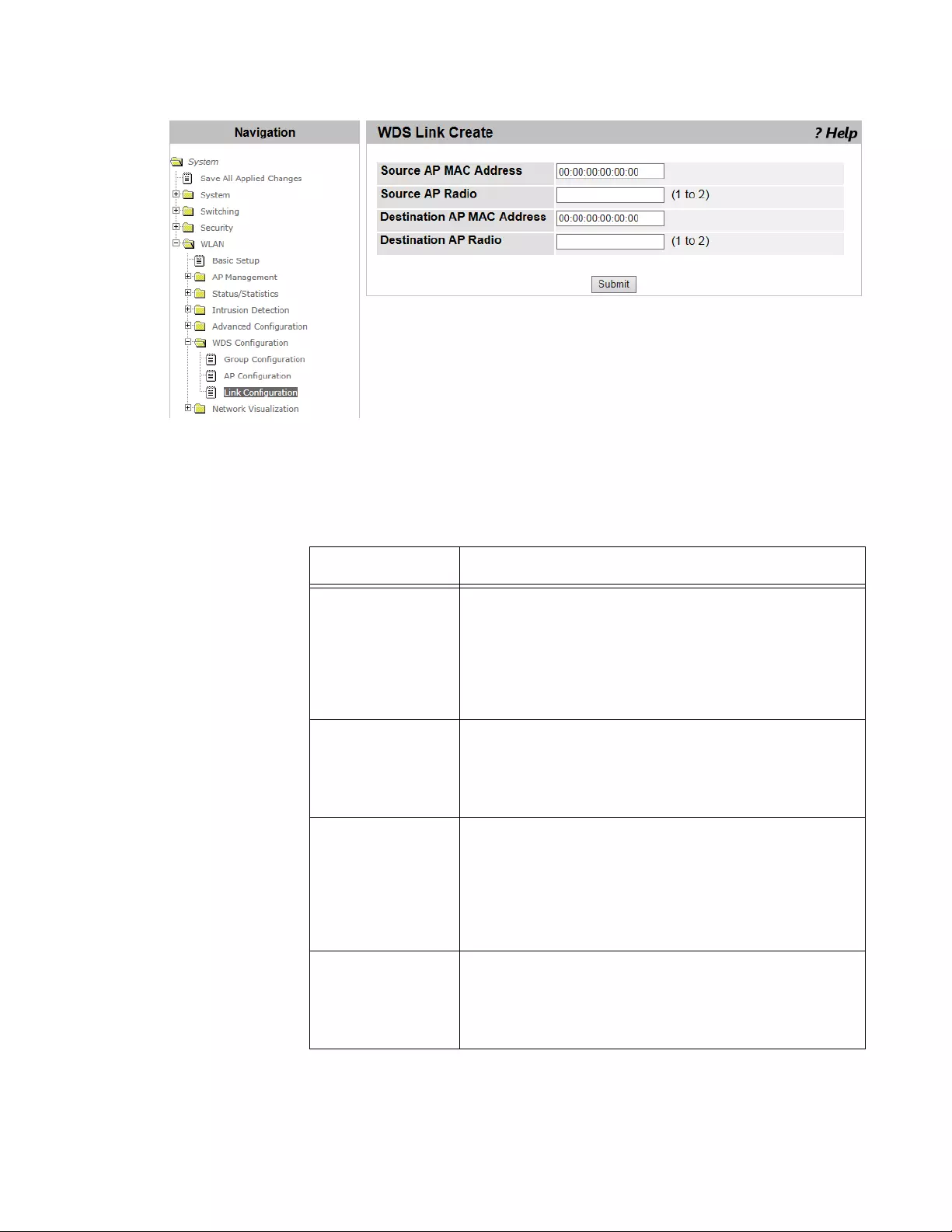
Chapter 5: Wireless LAN
367
Figure 177. WDS Link Configuration Page 2
4. Enter the following fields described in Table 149.
5. Click Submit.
Table 149. WDS Link Configuration
Field Description
Source AP MAC
Address
Specify the source AP MAC address. It can be
either the MAC address of the root access point or
the satellite access point. The MAC address must
be associated with the WDS group. See “Viewing a
List of AP Members and Adding an AP” on
page 364.
Source AP Radio Specify the radio band. The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz
Destination AP
MAC Address
Specify the destination AP MAC address. It can be
either the MAC address of the root access point or
the satellite access point. The MAC address must
be associated with the WDS group. See “Viewing a
List of AP Members and Adding an AP” on
page 364.
Source AP Radio Specify the radio band. The options are:
1 - 2.4GHz
2 - 5GHz

AT-UWC WLAN Controller Web GUI User’s Guide
368
Deleting a Link
Combination
To delete a link combination from the list, do the following:
1. From the Navigation pane, go to WLAN > WDS Configuration > Link
Configuration.
The WDS Link Configuration page is displayed as shown in Figure 176
on page 366.
2. Check the checkbox of the link combination that you want to delete.
3. Click Delete.
4. If you want to refresh the displays on this page, click Refresh.