Table of Contents
- Safety information
- Chapter 1: Product Introduction
- Chapter 2: Hardware Information
- 2.1 Chassis cover
- 2.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- 2.3 System memory
- 2.4 Storage devices
- 2.4.1 Installing a 3.5-inch storage device (for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
- 2.4.2 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device (for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
- 2.4.3 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to a front storage bay (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
- 2.4.4 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to an internal storage bay (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
- 2.5 Expansion slot
- 2.6 Cable connections
- 2.7 SATA/SAS backplane cabling
- 2.8 Storage device configuration and cabling
- 2.8.1 4 x NVMe and 4 x SATA storage device configuration and cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
- 2.8.2 12 x NVMe, 12 x SATA (front bay), and 4 x SATA (internal bay) storage device configuration and cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
- 2.8.3 12 x NVMe (front bay), and 4 x NVMe (internal bay) storage device configuration and cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
- 2.9 Optional components
- Chapter 3: Installation Options
- Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
- Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
- 5.1 Managing and updating your BIOS
- 5.2 BIOS setup program
- 5.3 Main menu
- 5.4 Performance Tuning menu
- 5.5 Advanced menu
- 5.5.1 Trusted Computing
- 5.5.2 PSP Firmware Versions
- 5.5.3 Redfish Host Interface Settings
- 5.5.4 AMD CBS
- 5.5.5 APM Configuration
- 5.5.6 Onboard LAN Configuration
- 5.5.7 Serial Port Console Redirection
- 5.5.8 CPU Configuration
- 5.5.9 PCI Subsystem Settings
- 5.5.10 USB Configuration
- 5.5.11 Network Stack Configuration
- 5.5.12 CSM Configuration
- 5.5.13 NVMe Configuration
- 5.5.14 SATA Configuration
- 5.5.15 AMD Mem Configuration Status
- 5.6 Chipset menu
- 5.7 Security menu
- 5.8 Boot menu
- 5.9 Tool menu
- 5.10 Event Logs menu
- 5.11 Server Mgmt menu
- 5.12 Exit menu
- Chapter 6: Driver Installation
- Appendix
ASUS RS500A-E11-RS4U/4NVME(800W) User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for RS500A-E11-RS4U/4NVME(800W) by ASUS which is a product in the Server Barebones category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

1U Rackmount Server
User Guide
RS500A-E11 Series
RS500A-E11-RS4U
RS500A-E11-RS12U

ii
Copyright © 2021 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form or by any means,
except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission
of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS provides this manual “as is” without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including but not
limited to the implied warranties or conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. In no
event shall ASUS, its directors, officers, employees, or agents be liable for any indirect, special, incidental,
or consequential damages (including damages for loss of profits, loss of business, loss of use or data,
interruption of business and the like), even if ASUS has been advised of the possibility of such damages
arising from any defect or error in this manual or product.
Specifications and information contained in this manual are furnished for informational use only, and are
subject to change at any time without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by ASUS.
ASUS assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this manual,
including the products and software described in it.
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modified or altered, unless
such repair, modification of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2) the serial number of the
product is defaced or missing.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or
copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or explanation and to the
owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
E18559
First Edition
July 2021

iii
Contents
Safety information ..................................................................................................... vii
About this guide ......................................................................................................... ix
Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1.1 System package contents ......................................................................... 1-2
1.2 Serial number label .................................................................................... 1-3
1.3 System specifications ...............................................................................1-4
1.4 Front panel features ...................................................................................1-6
1.5 Rear panel features ....................................................................................1-7
1.6 Internal features .........................................................................................1-8
1.7 LED information .......................................................................................1-10
1.7.1 Front panel LEDs ...................................................................... 1-10
1.7.2 LAN (RJ-45) LEDs .................................................................... 1-11
1.7.3 Storage device status LED........................................................ 1-12
1.7.4 Rear panel LEDs ....................................................................... 1-12
1.7.5 Q-Code table ............................................................................. 1-13
Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2.1 Chassis cover .............................................................................................2-2
2.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU) .................................................................2-3
2.2.1 Installing the CPU and heatsink .................................................. 2-3
2.3 System memory .........................................................................................2-7
2.3.1 Overview ..................................................................................... 2-7
2.3.2 Memory Configurations ............................................................... 2-7
2.3.3 Installing a DIMM ........................................................................ 2-8
2.3.4 Removing a DIMM ...................................................................... 2-8
2.4 Storage devices..........................................................................................2-9
2.4.1 Installing a 3.5-inch storage device
(for RS500A-E11-RS4U) ........................................................... 2-10
2.4.2 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device
(for RS500A-E11-RS4U) ........................................................... 2-11
2.4.3 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to a front storage bay
(for RS500A-E11-RS12U) ......................................................... 2-12
2.4.4 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to an internal storage bay
(for RS500A-E11-RS12U) ......................................................... 2-13
2.5 Expansion slot ..........................................................................................2-16
2.5.1 Installing an expansion card to the riser card bracket ............... 2-16
2.5.2 Installing an expansion card to the butterfly riser card
bracket ...................................................................................... 2-18

iv
Contents
2.5.3 Installing an ASUS PIKE II card ................................................ 2-20
2.5.4 Installing M.2 (NGFF) cards ...................................................... 2-22
2.5.5 Installing an OCP 3.0 card ........................................................ 2-24
2.5.6 Configuring an expansion card ................................................. 2-25
2.6 Cable connections ...................................................................................2-26
2.7 SATA/SAS backplane cabling .................................................................2-27
2.8 Storage device configuration and cabling ............................................2-29
2.8.1 4 x NVMe and 4 x SATA storage device configuration and
cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS4U) .............................................. 2-30
2.8.2 12 x NVMe, 12 x SATA (front bay), and 4 x SATA (internal bay)
storage device configuration and cabling
(for RS500A-E11-RS12U) ......................................................... 2-32
2.8.3 12 x NVMe (front bay), and 4 x NVMe (internal bay) storage
device configuration and cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS12U) .... 2-35
2.9 Optional components ..............................................................................2-38
2.9.1 Redundant power supply module.............................................. 2-38
Chapter 3: Installation Options
3.1 Tool-less Friction Rail Kit ..........................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Installing the tool-less rack rail .................................................... 3-2
3.1.2 Rail kit dimensions ...................................................................... 3-4
3.2 Ball bearing Rail Kit ...................................................................................3-5
3.2.1 Attaching the rack rails ............................................................... 3-6
3.3 Cable management arm (optional for 1200 mm rack rails) ..................3-11
3.3.1 Attaching the cable management arm ...................................... 3-11
Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4.1 Motherboard layout ....................................................................................4-2
4.2 Jumpers ......................................................................................................4-4
4.3 Internal LEDs .............................................................................................. 4-9
4.4 Internal connectors ..................................................................................4-11
Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.1 Managing and updating your BIOS ..........................................................5-2
5.1.1 ASUS CrashFree BIOS 3 utility................................................... 5-2
5.1.2 ASUS EZ Flash Utility ................................................................. 5-3
5.1.3 BUPDATER utility ....................................................................... 5-4
5.2 BIOS setup program ..................................................................................5-6
5.2.1 BIOS menu screen ...................................................................... 5-7

v
Contents
5.2.2 Menu bar ..................................................................................... 5-7
5.2.3 Menu items..................................................................................5-8
5.2.4 Submenu items ........................................................................... 5-8
5.2.5 Navigation keys ........................................................................... 5-8
5.2.6 General help................................................................................5-8
5.2.7 Configuration fields ..................................................................... 5-8
5.2.8 Pop-up window............................................................................5-8
5.2.9 Scroll bar ..................................................................................... 5-8
5.3 Main menu ..................................................................................................5-9
5.3.1 System Language [English] ........................................................ 5-9
5.3.2 System Date [Day xx/xx/xxxx] ..................................................... 5-9
5.3.3 System Time [xx:xx:xx] ............................................................... 5-9
5.4 Performance Tuning menu ......................................................................5-10
5.5 Advanced menu .......................................................................................5-12
5.5.1 Trusted Computing.................................................................... 5-13
5.5.2 PSP Firmware Versions ............................................................ 5-13
5.5.3 Redfish Host Interface Settings................................................. 5-13
5.5.4 AMD CBS .................................................................................. 5-14
5.5.5 APM Configuration .................................................................... 5-46
5.5.6 Onboard LAN Configuration ...................................................... 5-47
5.5.7 Serial Port Console Redirection ................................................ 5-48
5.5.8 CPU Configuration .................................................................... 5-50
5.5.9 PCI Subsystem Settings ........................................................... 5-51
5.5.10 USB Configuration .................................................................... 5-52
5.5.11 Network Stack Configuration..................................................... 5-53
5.5.12 CSM Configuration .................................................................... 5-54
5.5.13 NVMe Configuration .................................................................. 5-55
5.5.14 SATA Configuration .................................................................. 5-56
5.5.15 AMD Mem Configuration Status................................................ 5-56
5.6 Chipset menu ...........................................................................................5-57
5.7 Security menu ..........................................................................................5-60
5.8 Boot menu ................................................................................................5-64
5.9 Tool menu ................................................................................................. 5-65
5.10 Event Logs menu .....................................................................................5-66
5.10.1 Change Smbios Event Log Settings ......................................... 5-66
5.10.2 View Smbios Event Log ............................................................ 5-67
5.11 Server Mgmt menu ...................................................................................5-68
5.11.1 System Event Log ..................................................................... 5-69

vi
5.11.2 BMC network configuration ....................................................... 5-70
5.11.3 View System Event Log ............................................................ 5-73
5.12 Exit menu .................................................................................................. 5-74
Chapter 6: Driver Installation
6.1 Running the Support DVD .........................................................................6-2
Appendix
KMPA-U16 block diagram ...................................................................................... A-2
Notices .................................................................................................................... A-3
Service and Support ............................................................................................... A-5

vii
Safety information
Electrical Safety
• Before installing or removing signal cables, ensure that the power cables for the system
unit and all attached devices are unplugged.
• To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect the power cable from the electrical outlet
before relocating the system.
• When adding or removing any additional devices to or from the system, ensure that the
power cables for the devices are unplugged before the signal cables are connected. If
possible, disconnect all power cables from the existing system before you add a device.
• If the power supply is broken, do not try to fix it by yourself. Contact a qualified service
technician or your dealer.
Operation Safety
• Any mechanical operation on this server must be conducted by certified or experienced
engineers.
• Before operating the server, carefully read all the manuals included with the server
package.
• Before using the server, ensure all cables are correctly connected and the power cables
are not damaged. If any damage is detected, contact your dealer as soon as possible.
• To avoid short circuits, keep paper clips, screws, and staples away from connectors,
slots, sockets and circuitry.
• Avoid dust, humidity, and temperature extremes. Place the server on a stable surface.
This product is equipped with a three-wire power cable and plug for the user’s safety. Use
the power cable with a properly grounded electrical outlet to avoid electrical shock.
Restricted Access Location
This product is intended for installation only in a Computer Room where:
• Access can only be gained by SERVICE PERSONS or by USERS who have been
instructed about the reasons for the restrictions applied to the location and about any
precautions that shall be taken.
• Access is through the use of a TOOL, or other means of security, and is controlled by
the authority responsible for the location.
Heavy System
CAUTION! This server system is heavy. Ask for assistance when moving or carrying
the system.

viii
CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
Lithium-Ion Battery Warning
CAUTION! Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with
the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used
batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.

ix
About this guide
Audience
This user guide is intended for system integrators, and experienced users with at least basic
knowledge of configuring a server.
Contents
This guide contains the following parts:
1. Chapter 1: Product Introduction
This chapter describes the general features of the server, including sections on front
panel and rear panel specifications.
2. Chapter 2: Hardware Information
This chapter lists the hardware setup procedures that you have to perform when
installing or removing system components.
3. Chapter 3: Installation Options
This chapter describes how to install optional components into the barebone server.
4. Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
This chapter gives information about the motherboard that comes with the server. This
chapter includes the motherboard layout, jumper settings, and connector locations.
5. Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
This chapter tells how to change system settings through the BIOS Setup menus and
describes the BIOS parameters.
6. Chapter 6: Driver Installation
This chapter provides instructions for installing the necessary drivers for different
system components.

x
Conventions
To ensure that you perform certain tasks properly, take note of the following symbols used
throughout this manual.
Typography
Bold text Indicates a menu or an item to select.
Italics
Used to emphasize a word or a phrase.
<Key> Keys enclosed in the less-than and greater-than
sign means that you must press the enclosed key.
Example: <Enter> means that you must press
the Enter or Return key.
<Key1>+<Key2>+<Key3> If you must press two or more keys simultaneously,
the key names are linked with a plus sign (+).
Example: <Ctrl>+<Alt>+<Del>
Command Means that you must type the command
exactly as shown, then supply the required
item or value enclosed in brackets.
Example: At the DOS prompt, type the
command line: format A:/S
DANGER/WARNING: Information to prevent injury to yourself when
trying to complete a task.
CAUTION: Information to prevent damage to the components when
trying to complete a task.
NOTE: Tips and additional information to help you complete a task.
IMPORTANT: Instructions that you MUST follow to complete a task.
References
Refer to the following sources for additional information, and for product and software
updates.
1. ASUS Control Center (ACC) user guide
This manual tells how to set up and use the proprietary ASUS server management
utility.
2. ASUS websites
The ASUS websites provide updated information for all ASUS hardware and software
products. Visit https://www.asus.com for more information.

This chapter describes the general features of the chassis kit. It
includes sections on front panel and rear panel specifications.
1
Product Introduction
Chapter 1: Product Introduction

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-2
1.1 System package contents
Check your system package for the following items.
Model Name RS500A-E11-RS4U, RS500A-E11-RS12U
Chassis ASUS R12F 1U Rackmount Chassis
Motherboard ASUS KMPA-U16 Server Board
Component
2 x 800W Redundant Power Supply or
2 x 850W Redundant Power Supply
4 x Hot-swap 3.5-inch or 2.5-inch Storage Device Trays (RS500A-E11-RS4U)
12 x Hot-swap 2.5-inch Storage Device Trays (RS500A-E11-RS12U)
1 x SAS/SATA/NVMe Backplane
2 x PCI-E Riser Card
1 x Front I/O Board
7 x System Fans
1 x Redundant Power Supply Power Distribution Board
1 x Optional Mid-4bay Cage (RS500A-E11-RS12U)
Accessories
1 x Support DVD
1 x Bag of Screws
2 x AC Power Cable
Optional
Items
1 x CPU Heatsink
1 x Tool-less Friction Rail Kit or
1 x Ball-bearing Rail Kit (optional)
If any of the above items is damaged or missing, contact your retailer.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-3
1.2 Serial number label
Before requesting support from the ASUS Technical Support team, you must take note of the
product’s serial number containing 12 characters such as xxSxxxxxxxxx shown as the figure
below. With the correct serial number of the product, ASUS Technical Support team members
can then offer a quicker and satisfying solution to your problems.
xxSxxxxxxxxx
RS500A-E11-RS4U
xxSxxxxxxxxx
RS500A-E11-RS12U
1234

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-4
1.3 System specifications
The ASUS RS500A-E11 Series is a 1U barebone server system featuring the ASUS
KMPA-U16 Server Board. The server supports AMD EPYC™ 7002 & 7003 Series processors
plus other latest technologies through the chipsets onboard.
Model Name RS500A-E11-RS4U RS500A-E11-RS12U
Motherboard KMPA-U16
Processor Support 1 x Socket SP3 (LGA-4094)
AMD EPYC™ 7002 & 7003 series processors (up to 280W)
Core Logic System on Chip (SoC)
Memory
Total Slots 16 (8 channel, 2 DIMM per channel)
Capacity Maximum up to 2048GB
Memory Type DDR4 3200/2933 RDIMM/LR-DIMM/LR-DIMM 3DS
Memory Size 16GB, 32GB, 64GB, 128GB
* Refer to www.asus.com for the latest memory AVL update.
Expansion
Slots
Total PCI/
PCI-X/PCI-E
Slots
3+1
Slot Type
1 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16 link, FH, HL)
1 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16 link, LP, HL)
1 x PCIe x8 slot (Gen4 x8 link, LP, HL)
1 x OCP3.0 socket (Gen4 x16 link)
Disk
Controller
SATA
Controller CPU Integrated
SAS Controller
Optional kits:
- ASUS PIKE II 3008 8-port SAS HBA Card
- ASUS PIKE II 3108 8-port SAS HW RAID Card
Support SAS 12Gbps
NVMe
Controller CPU Integrated
Storage
Bays
I = internal
A or S = hot-
swappable
4 x 3.5”/2.5” Hot-swap Storage
Bays (backplane supports 4 x
SATA/SAS/NVMe)
12 x 2.5” Hot-swap Storage Bays
(backplane supports 12 x SATA/
SAS/NVMe)
Optional 4 x 2.5” Internal Storage
Bays (backplane supports 4 x
SATA/NVME)
2 x M.2 sockets (Gen4 x4 link
or SATA mode, up to 22110
module)
2 x M.2 sockets (Gen4 x4 link
or SATA mode, up to 22110
module)
Networking LAN 1 x Dual Port Intel® I350 Gigabit LAN Controller
Graphic VGA BMC Integrated (Aspeed AST2600)
Auxiliary Storage Device
Bay (Optical Drive) - -
Front I/O Ports 2 x USB 3.2 Gen1 ports
1 x VGA port -
(continued on the next page)

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-5
Model Name RS500A-E11-RS4U RS500A-E11-RS12U
Rear I/O Ports
2 x USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports
2 x Gigabit LAN ports (RJ45)
1 x Management port (RJ45)
1 x VGA port
Switch/LED
Rear:
1 x Power Button/LED
1 x Location Button/LED
1 x Message LED
Front:
1 x Power Button/LED
1 x Location Button/LED
1 x Message LED
1 x HDD LED
4 x LAN LED (1-2 for on-board
LAN, 3-4 for OCP LAN)
Rear:
1 x Power Button/LED
1 x Location Button/LED
1 x Message LED
Front:
1 x Power Button/LED
1 x Location Button/LED
1 x Message LED
2 x LAN LED
OS Support
Windows® Server 2019
RedHat®
SuSE®
Ubuntu
Vmware
Please find the latest OS support from http://www.asus.com/
Management
Solution
Software ASUS Control Center
Out of Band
Remote
Management
ASMB10-iKVM (on-board)
Regulatory Compliance CE, FCC, BSMI, RCM
Dimension (HH x WW x
DD)
842mm x 449mm x 44mm (1U)
33.15” x 17.68” x 1.73”
Net Weight Kg (CPU,
DRAM & Storage device
not included)
12 Kg 11 Kg
Gross Weight Kg (CPU,
DRAM & Storage device
not included, Packing
included)
18 Kg 17 Kg
Power Supply
(following different
configuration by region)
1+1 Redundant 800W 80 PLUS Platinum Power Supply or
1+1 Redundant 850W 80 PLUS Titanium Power Supply
Environment
Operation temperature: 10°C ~ 35°C
Non operation temperature: -40°C ~ 70°C
Non operation humidity: 20% ~ 90% ( Non condensing)
*Specifications are subject to change without notice.

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-6
1.4 Front panel features
The barebone server displays a simple yet stylish front panel with easily accessible features.
The power and reset buttons, LED indicators, slim type optical drive, and other ports and
buttons are located on the front panel, this may vary between models.
Refer to the Front panel LEDs section for the LED descriptions.
RS500A-E11-RS4U
RS500A-E11-RS12U
Asset tag
Rack screw
Rack screw
Power LED
LAN1 and LAN3 LED
LAN2 and LAN4 LED
Location LED
Message LED
Power button Reset button
Location button
Bay 1 Bay 3 Bay 5 Bay 7 Bay 9
Bay 10
Bay 11
Bay 12
Bay 2 Bay 4 Bay 6 Bay 8
1234
Rack screw Bay 1 Bay 2 Bay 3 Bay 4 Rack screw
VGA port
USB 3.2 Gen 1 port
Reset button
Location button (with LED)
Power button (with LED)
Storage device access LED
Message LED
LAN 1-4 LED
Asset tag
• Bay 1 to bay 4 supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires optional HBA/RAID
card. (supports tri-mode card)
• All bays support 3.5”/2.5” drives with trays.
• Bay 1 to bay 12 supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires optional HBA/RAID
card.
• All bays support 2.5” drives with trays.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-7
1.5 Rear panel features
The rear panel includes the expansion slots and system power socket. The middle part
includes the I/O shield with openings for the rear panel connectors on the motherboard.
Q-Code LED
Expansion slot Expansion slot Expansion slot
OCP 3.0 slot
Power button w/LED
VGA port
Location button w/LED
Redundant Power supply and
Power cord connector
USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports
Management LAN port*
LAN port 1
LAN port 2
*This port is for ASUS ASMB10-iKVM only.

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-8
1.6 Internal features
The barebone server includes the basic components as shown.
1. Redundant power supply
2. Butterfly riser card
(Gen4 x16 link and x8 link)
3. Riser card (Gen4 x16 link)
4. OCP 3.0 card slot
5. ASUS KMPA-U16 Server Board
6. System fans
7. SATA/SAS/NVMe backplane
(hidden)
8. Front I/O boards
9. 4 x 3.5” hot-swap storage bays
10. Asset tag (hidden)
The barebone server does not include a floppy disk drive. Connect a USB floppy disk drive
to any of the USB ports on the front or rear panel if you need to use a floppy disk.
WARNING
HAZARDOUS MOVING PARTS
KEEP FINGERS AND OTHER BODY PARTS AWAY
Turn off the system power and detach the power supply before removing or replacing any
system component.
RS500A-E11-RS4U

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-9
1. Redundant power supply
2. Butterfly riser card
(Gen4 x16 link and x8 link)
3. Riser card (Gen4 x16 link)
4. OCP 3.0 card slot
5. ASUS KMPA-U16 Server Board
6. System fans
7. 4 x 2.5“ internal easy-swap
storage bays (optional)
8. SATA/SAS/NVMe backplane
(hidden)
9. 12 x 2.5” storage device bays
10. Asset tag (hidden)
The barebone server does not include a floppy disk drive. Connect a USB floppy disk drive
to any of the USB ports on the front or rear panel if you need to use a floppy disk.
Turn off the system power and detach the power supply before removing or replacing any
system component.
WARNING
HAZARDOUS MOVING PARTS
KEEP FINGERS AND OTHER BODY PARTS AWAY
RS500A-E11-RS12U

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-10
1.7 LED information
1.7.1 Front panel LEDs
RS500A-E11-RS4U
LED Display status Description
Power LED ON System power ON
Message LED OFF
ON
System is normal; no incoming event
A hardware monitor event is indicated
Location LED
OFF
ON
Normal status
Location switch is pressed
(Press the location switch again to turn off)
Storage device
access LED
OFF
ON
No activity
Data activity
LAN LEDs
OFF
Blinking
ON
No LAN connection
LAN is transmitting or receiving data
LAN connection is present
1234
Storage device access LED
LAN4 LED
LAN3 LED
LAN2 LED
LAN1 LED
Power button with LED
Location button with LED
Message LED

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-11
1.7.2 LAN (RJ-45) LEDs
LAN port LED indications
Activity/Link LED Speed LED
Status Description Status Description
OFF No link OFF 10 Mbps connection
GREEN Linked ORANGE 100 Mbps connection
BLINKING Data activity GREEN 1 Gbps connection
Dedicated Management LAN port (for ASMB10 and DM_LAN1) LED
indications
Activity/Link LED Speed LED
Status Description Status Description
OFF No link OFF 10 Mbps connection
YELLOW Linked ORANGE 100 Mbps connection
BLINKING Data activity GREEN 1 Gbps connection DM LAN port
SPEED
LED
ACT/LINK
LED
LAN port
SPEED
LED
ACT/LINK
LED
RS500A-E11-RS12U
LED Display status Description
Power LED ON System power ON
Message LED OFF
ON
System is normal; no incoming event
A hardware monitor event is indicated
Location LED
OFF
ON
Normal status
Location switch is pressed
(Press the location switch again to turn off)
LAN LEDs
OFF
Blinking
ON
No LAN connection
LAN is transmitting or receiving data
LAN connection is present
Power LED
LAN1 and LAN3 LED
LAN2 and LAN4 LED Location LED
Power button
Location button
Message LED
Reset button

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-12
1.7.3 Storage device status LED
RS500A-E10-RS12URS500A-E11-RS4U
SATA/SAS Storage Device LED Description
GREEN ON SATA/SAS storage device power ON
RED ON Storage device has failed and should be swapped immediately
(For RAID card)
GREEN/
RED Blinking RAID rebuilding (For RAID card)
GREEN/
RED Blinking Locate (For RAID card)
GREEN/
RED OFF Storage device not found
GREEN Blinking Read/write data from/into the SATA/SAS/NVMe storage device
Red LED Green LED
1.7.4 Rear panel LEDs
Q-Code LED Power button w/LED
Location button w/LED
LED Display status Description
Power LED ON System power ON
Location LED
OFF
ON
Normal status
Location switch is pressed
(Press the location switch again to turn off)
Red LED
Green LED

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-13
1.7.5 Q-Code table
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
SEC Start up Security Phase
0x01 Progress First post code
0x02 Progress Load BSP microcode
0x03 Progress Perform early platform Initialization
0x04 Progress Set cache as ram for PEI phase
0x05 Progress Establish Stack
0x06 Progress CPU Early Initialization
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Error Post
Codes)
0x00 Error General - Success
0x01 Error Generic Error Code
0x02 Error Generic Memory Error
0x03 Error Buffer Overflow
0x04 Error Invalid Parameter(s)
0x05 Error Invalid Data Length
0x06 Error Data Alignment Error
0x07 Error Null Pointer Error
0x08 Error Unsupported Function
0x09 Error Invalid Service ID
0x0A Error Invalid Address
0x0B Error Out of Resource Error
0x0C Error Timeout
0x0D Error data abort exception
0x0E Error prefetch abort exception
0x0F Error Out of Boundary Condition Reached
0x10 Error Data corruption
0x11 Error Invalid command
0x12 Error The package type provided by BR is incorrect
0x13 Error Failed to retrieve FW header during FW validation
0x14 Error Key size not supported
0x15 Error Agesa0 verification error
0x16 Error SMU FW verification error
0x17 Error OEM SINGING KEY verification error
0x18 Error Generic FW Validation error
0x19 Error RSA operation fail - bootloader
0x1A Error CCP Passthrough operation failed - internal status
0x1B Error AES operation fail
0x1C Error CCP state save failed
0x1D Error CCP state restore failed
0x1E Error SHA256 operation fail - internal status
0x1F Error ZLib Decompression operation fail
0x20 Error HMAC-SHA256 operation fail - internal status
0x21 Error Booted from boot source not recognized by PSP
0x22 Error PSP directory entry not found
0x23 Error PSP failed to set the write enable latch
0x24 Error PSP timed out because spirom took too long
0x25 Error Cannot find BIOS directory
0x26 Error SpiRom is not valid
0x27 Error slave die has different security state from master
0x28 Error SMI interface init failure
0x29 Error SMI interface generic error
0x2A Error invalid die ID executes MCM related function
0x2B Error invalid MCM configuration table read from bootrom
0x2C Error Valid boot mode wasn't detected
0x2D Error NVStorage init failure
0x2E Error NVStorage generic error
0x2F Error MCM 'error' to indicate slave has more data to send
0x30 Error MCM error if data size exceeds 32B
0x31 Error Invalid client id for SVC MCM call
0x32 Error MCM slave status register contains bad bits
0x33 Error MCM call was made in a single die environment
0x34 Error PSP secure mapped to invalid segment (should be 0x400_0000)
0x35 Error No physical x86 cores were found on die
0x36 Error Insufficient space for secure OS (range of free SRAM to SVC stack base)
0x37 Error SYSHUB mapping memory target type is not supported
0x38 Error Attempt to unmap permanently mapped TLB to PSP secure region
AMD EPYC™ 7002 Series processors

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-14
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Error Post
Codes)
0x39 Error Unable to map an SMN address to AXI space
0x3A Error Unable to map a SYSHUB address to AXI space
0x3B Error The count of CCXs or cores provided by bootrom is not consistent
0x3C Error Uncompressed image size doesn't match value in compressed header
0x3D Error Compressed option used in case where not supported
0x3E Error Fuse info on all dies don't match
0x3F Error PSP sent message to SMU; SMU reported an error
0x40 Error Function RunPostX86ReleaseUnitTests failed in memcmp()
0x41 Error Interface between PSP to SMU not available.
0x42 Error Timer wait parameter too large
0x43 Error Test harness module reported an error
0x44 Error x86 wrote C2PMSG_0 interrupting PSP
0x45 Error A write to an L3 register failed
0x46 Error Mini-BL
0x47 Error Mini-BL CCP HMAC Unit-test failed
0x48 Error Potential stack corruption in jump to Mini BL
0x49 Error Error in Validate and Loading AGESA APOB SVC call
0x4A Error Correct fuse bits for DIAG_BL loading not set
0x4B Error The UmcProgramKeys() function was not called by AGESA
0x4C Error Secure unlock error
0x4D Error Syshub register programming mismatch during readback
0x4E Error Family ID in MP0_SFUSE_SEC[7:3] not correct
0x4F Error An operation was invoked that can only be performed by the GM
0x50 Error Failed to acquire host controller semaphore to claim ownership of SMB
0x51 Error Timed out waiting for host to complete pending transactions
0x52 Error Timed out waiting for slave to complete pending transactions
0x53 Error Unable to kill current transaction on host
0x54 Error One of: Illegal command
0x55 Error An SMBus transaction collision detected
0x56 Error Transaction failed to be started or processed by host
0x57 Error An unsolicited SMBus interrupt was received
0x58 Error An attempt to send an unsupported PSP-SMU message was made
0x59 Error An error/data corruption detected on response from SMU for sent msg
0x5A Error MCM Steady-state unit test failed
0x5B Error S3 Enter failed
0x5C Error AGESA BL did not set PSP SMU reserved addresses via SVC call
0x5E Error CcxSecBisiEn not set in fuse RAM
0x5F Error Received an unexpected result
0x60 Error VMG Storage Init failed
0x61 Error Failure in mbedTLS user app
0x62 Error An error occured whilst attempting to SMN map a fuse register
0x63 Error Fuse burn sequence/operation failed due to internal SOC error
0x64 Error Fuse sense operation timed out
0x65 Error Fuse burn sequence/operation timed out waiting for burn done
0x66 Error Failure status indicating that the given SecureOS has been
0x67 Error This PSP FW was revoked
0x68 Error The platform model/vendor id fuse is not matching the BIOS public key
token
0x69 Error The BIOS OEM public key of the BIOS was revoked for this platform
0x6A Error PSP level 2 directory not match expected value.
0x6B Error BIOS level 2 directory not match expected value.
0x6C Error HVB validation failure for BIOS RTM volume (OEM public/signature failed
to validate).
0x6D Error Generic error indicating the CCP HAL initialization failed
0x94 Error Knoll failed to idle correctly after being reset
0x95 Error Bad status returned by I2CKnollCheck
0x96 Error NACK to general call (no device on Knoll I2C bus)
0x97 Error Null pointer passed to I2CKnollCheck
0x98 Error Invalid device-ID found during Knoll authentication
0x99 Error Error during Knoll/Prom key derivation
0x9A Error Null pointer passed to Crypto function
0x9B Error Error in checksum from wrapped Knoll/Prom keys
0x9C Error Knoll returned an invalid response to a command
0x9D Error Bootloader failed in Knoll Send Command function
0x9E Error No Knoll device found by verifying MAC
(continued on the next page)

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-15
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Status Post
Codes)
0xA0 Progress Bootloader successfully entered C Main
0xA1 Progress Master initialized C2P / slave waited for master to init C2P
0xA2 Progress HMAC key successfully derived
0xA3 Progress Master got Boot Mode and sent boot mode to all slaves
0xA4 Progress SpiRom successfully initialized
0xA5 Progress BIOS Directory successfully read from SPI to SRAM
0xA6 Progress Early unlock check
0xA7 Progress Inline Aes key successfully derived
0xA8 Progress Inline-AES key programming is done
0xA9 Progress Inline-AES key wrapper derivation is done
0xAA Progress Bootloader successfully loaded HW IP configuration values
0xAB Progress Bootloader successfully programmed MBAT table
0xAC Progress Bootloader successfully loaded SMU FW
0xAD Progress PSP and SMU configured WAFL
0xAE Progress User mode test harness completed successfully
0xAF Progress Bootloader loaded Agesa0 from SpiRom
0xB0 Progress AGESA phase has completed
0xB1 Progress RunPostDramTrainingTests() completed successfully
0xB2 Progress SMU FW Successfully loaded to SMU Secure DRAM
0xB3 Progress Sent all required boot time messages to SMU
0xB4 Progress Validated and ran Security Gasket binary
0xB5 Progress UMC Keys generated and programmed
0xB6 Progress Inline AES key wrapper stored in DRAM
0xB7 Progress Completed FW Validation step
0xB8 Progress Completed FW Validation step
0xB9 Progress BIOS copy from SPI to DRAM complete
0xBA Progress Completed FW Validation step
0xBB Progress BIOS load process fully complete
0xBC Progress Bootloader successfully release x86
0xBD Progress Early Secure Debug completed
0xBE Progress GetFWVersion command received from BIOS is completed
0xBF Progress SMIInfo command received from BIOS is completed
0xC0 Progress Successfully entered WarmBootResume()
0xC1 Progress Successfully copied SecureOS image to SRAM
0xC2 Progress Successfully copied trustlets to PSP Secure Memory
0xC3 Progress About to jump to Secure OS (SBL about to copy and jump)
0xC4 Progress Successfully restored CCP and UMC state on S3 resume
0xC5 Progress PSP SRAM HMAC validated by Mini BL
0xC6 Progress About to jump to <t-base in Mini BL
0xC7 Progress VMG ECDH unit test started
0xC8 Progress VMG ECDH unit test passed
0xC9 Progress VMG ECC CDH primitive unit test started
0xCA Progress VMG ECC CDH primitive unit test passed
0xCB Progress VMG SP800-108 KDF-CTR HMAC unit test started
0xCC Progress VMG SP800-108 KDF-CTR HMAC unit test passed
0xCD Progress VMG LAUNCH_* test started
0xCE Progress VMG LAUNCH_* test passed
0xCF Progress MP1 has been taken out of reset
0xD0 Progress PSP and SMU Reserved Addresses correct
0xD1 Progress Reached Naples steady-state WFI loop
0xD2 Progress Knoll device successfully initialized
0xD3 Progress 32-byte RandOut successfully returned from Knoll
0xD4 Progress 32-byte MAC successfully received from Knoll.
0xD5 Progress Knoll device verified successfully
0xD6 Progress Done enabling power for Knoll
0xD7 Progress Enter recovery mode due to trustlet validation fail.
0xD8 Progress Enter recovery mode due to OS validation fail.
0xD9 Progress Enter recovery mode due to OEM public key not found.
(continued on the next page)

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-16
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
Quick VGA
PEI(Pre-EFI
Initialization) phase
0x10 Progress PEI Core Entry
0x11 Progress PEI cache as ram CPU initial
0x15 Progress NB Initialization before installed memory
0x19 Progress SB Initialization before installed memory
DXE(Driver
Execution
Environment)
phase
0x32 Progress CPU POST-Memory Initialization
0x33 Progress CPU Cache Initialization
0x34 Progress Application Processor(s) (AP) Initialization
0x35 Progress BSP Selection
0x36 Progress CPU Initialization
0x37 Progress Pre-memory NB Initialization
0x3B Progress Pre-memory SB Initialization
0x4F Progress DXE Initial Program Load(IPL)
0x60 Progress DXE Core Started
0x61 Progress DXE NVRAM Initialization
0x62 Progress SB run-time Initialization
0x63 Progress CPU DXE Initialization
0x68 Progress PCI HB Initialization
0x69 Progress NB DXE Initialization
0x6A Progress NB DXE SMM Initialization
0x70 Progress SB DXE Initialization
0x71 Progress SB DXE SMM Initialization
0x72 Progress SB DEVICES Initialization
0x78 Progress ACPI Module Initialization
0x79 Progress CSM Initialization
0xD0 Progress CPU PM Structure Initialization
Normal boot
BDS(Boot Device
Selection) phase
0x90 Progress BDS started
0x91 Progress Connect device event
0x92 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x93 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x94 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x95 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x96 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x97 Progress Console outout connect event
0x98 Progress Console input connect event
0x99 Progress AMI Super IO start
0x9A Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9B Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9C Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9D Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0xb2 Progress Legacy Option ROM Initialization
0xb3 Progress Reset system
0xb4 Progress USB hotplug
0xb6 Progress NVRAM clean up
0xb7 Progress NVRAM configuration reset
0xA0 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA1 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA2 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA3 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0x00~0xFF Progress Wait BMC ready
0xA8 Progress BIOS Setup Utility password verify
0xA9 Progress BIOS Setup Utility start
0xAB Progress BIOS Setup Utility input wait
0xAD Progress Ready to boot event
0xAE Progress Legacy boot event
Operating system
phase
0xAA Progress APIC mode
0xAC Progress PIC mode

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-17
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
SEC Start up Security Phase
0x01 Progress First post code
0x02 Progress Load BSP microcode
0x03 Progress Perform early platform Initialization
0x04 Progress Set cache as ram for PEI phase
0x05 Progress Establish Stack
0x06 Progress CPU Early Initialization
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Error Post
Codes)
0x00 error General - Success
0x01 error Generic Error Code
0x02 error Generic Memory Error
0x03 error Buffer Overflow
0x04 error Invalid Parameter(s)
0x05 error Invalid Data Length
0x06 error Data Alignment Error
0x07 error Null Pointer Error
0x08 error Unsupported Function
0x09 error Invalid Service ID
0x0A error Invalid Address
0x0B error Out of Resource Error
0x0C error Timeout
0x0D error data abort exception
0x0E error prefetch abort exception
0x0F error Out of Boundary Condition Reached
0x10 error Data corruption
0x11 error Invalid command
0x12 error The package type provided by BR is incorrect
0x13 error Failed to retrieve FW header during FW validation
0x14 error Key size not supported
0x15 error Agesa0 verification error
0x16 error SMU FW verification error
0x17 error OEM SINGING KEY verification error
0x18 error Generic FW Validation error
0x19 error RSA operation fail - bootloader
0x1A error CCP Passthrough operation failed - internal status
0x1B error AES operation fail
0x1C error CCP state save failed
0x1D error CCP state restore failed
0x1E error SHA256/384 operation fail - internal status
0x1F error ZLib Decompression operation fail
0x20 error HMAC-SHA256/384 operation fail - internal status
0x21 error Booted from boot source not recognized by PSP
0x22 error PSP directory entry not found
0x23 error PSP failed to set the write enable latch
0x24 error PSP timed out because spirom took too long
0x25 error Cannot find BIOS directory
0x26 error SpiRom is not valid
0x27 error slave die has different security state from master
0x28 error SMI interface init failure
0x29 error SMI interface generic error
0x2A error invalid die ID executes MCM related function
0x2B error invalid MCM configuration table read from bootrom
0x2C error Valid boot mode wasn't detected
0x2D error NVStorage init failure
0x2E error NVStorage generic error
0x2F error MCM 'error' to indicate slave has more data to send
0x30 error MCM error if data size exceeds 32B
0x31 error Invalid client id for SVC MCM call
0x32 error MCM slave status register contains bad bits
0x33 error MCM call was made in a single die environment
0x34 error PSP secure mapped to invalid segment (should be 0x400_0000)
0x35 error No physical x86 cores were found on die
0x36 error Insufficient space for secure OS (range of free SRAM to SVC stack base)
0x37 error SYSHUB mapping memory target type is not supported
0x38 error Attempt to unmap permanently mapped TLB to PSP secure region
0x39 error Unable to map an SMN address to AXI space
(continued on the next page)
AMD EPYC™ 7003 Series processors

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-18
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Error Post
Codes)
0x3A error Unable to map a SYSHUB address to AXI space
0x3B error The count of CCXs or cores provided by bootrom is not consistent
0x3C error Uncompressed image size doesn't match value in compressed header
0x3D error Compressed option used in case where not supported
0x3E error Fuse info on all dies don't match
0x3F error PSP sent message to SMU; SMU reported an error
0x40 error Function RunPostX86ReleaseUnitTests failed in memcmp()
0x41 error Interface between PSP to SMU not available.
0x42 error Timer wait parameter too large
0x43 error Test harness module reported an error
0x44 error x86 wrote C2PMSG_0 interrupting PSP, but the command has an invalid
format
0x45 error Failed to read from SPI the Bios Directory or Bios Combo Directory
0x46 error Mini-BL, validation of the PSP SRAM image failed on HMAC compare
0x47 error Failed to read the combo bios header
0x48 error Potential stack corruption in jump to Mini BL
0x49 error Error in Validate and Loading AGESA APOB SVC call
0x4A error Correct fuse bits for DIAG_BL loading not set
0x4B error The UmcProgramKeys() function was not called by AGESA
0x4C error Unconditional Unlock based on serial numbers failure
0x4D error Syshub register programming mismatch during readback
0x4E error Family ID in MP0_SFUSE_SEC[7:3] not correct
0x4F error An operation was invoked that can only be performed by the GM
0x50 error Failed to acquire host controller semaphore to claim ownership of SMB
0x51 error Timed out waiting for host to complete pending transactions
0x52 error Timed out waiting for slave to complete pending transactions
0x53 error Unable to kill current transaction on host, to force idle
0x54 error One of: Illegal command, Unclaimed cycle, or Host time out
0x55 error An smbus transaction collision detected, operation restarted
0x56 error Transaction failed to be started or processed by host, or not completed
0x57 error An unsolicited smbus interrupt was received
0x58 error An attempt to send an unsupported PSP-SMU message was made
0x59 error An error/data corruption detected on response from SMU for sent msg
0x5A error MCM Steady-state unit test failed
0x5B error S3 Enter failed
0x5C error AGESA BL did not set PSP SMU reserved addresses via SVC call
0x5E error CcxSecBisiEn not set in fuse RAM
0x5F error Received an unexpected result
0x60 error VMG Storage Init failed
0x61 error failure in mbedTLS user app
0x62 error An error occured whilst attempting to SMN map a fuse register
0x63 error Fuse burn sequence/operation failed due to internal SOC error
0x64 error Fuse sense operation timed out
0x65 error Fuse burn sequence/operation timed out waiting for burn done
0x66 error The PMU FW Public key certificate loading or authentication fails
0x67 error This PSP FW was revoked
0x68 error The platform model/vendor id fuse is not matching the BIOS public key
token
0x69 error The BIOS OEM public key of the BIOS was revoked for this platform
0x6A error PSP level 2 directory not match expected value.
0x6B error BIOS level 2 directory not match expected value.
0x6C error Reset image not found
0x6D error Generic error indicating the CCP HAL initialization failed
0x6E error failure to copy NVRAM to DRAM.
0x6F error Invalid key usage flag
0x71 error RSMU signaled a security violation
0x72 error Error programming the WAFL PCS registers
0x73 error Error setting wafl PCS threshold value
0x74 error Error loading OEM trustlets
0x75 error Recovery mode accross all dies is not sync'd
0x76 error Uncorrectable WAFL error detected
0x77 error Fatal MP1 error detected
0x78 error Bootloader failed to find OEM signature
0x79 error Error copying BIOS to DRAM
0x7A error Error validating BIOS image signature
(continued on the next page)

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 1-19
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
PSP Boot
PSP Boot Loader
phase (Status Post
Codes)
0x7B error
0x7C error Platform Vendor ID and/or Model ID binding violation
0x7D error Bootloader detects BIOS request boot from SPI-ROM, which is unsupported
for PSB.
0x7E error Requested fuse is already blown, reblow will cause ASIC malfunction
0x7F error Error with actual fusing operation
0x80 error (Local Master PSP on P1 socket) Error reading fuse info
0x81 error (Local Master PSP on P1 socket) Platform Vendor ID and/or Model ID
binding violation
0x82 error (Local Master PSP on P1 socket) Requested fuse is already blown, reblow
will cause ASIC malfunction
0x83 error (Local Master PSP on P1 socket) Error with actual fusing operation
0x84 error SEV FW Rollback attempt is detected
0x85 error / SEV download FW command fail to broadcase and clear the IsInSRAM
field on slave dies
0x86 error Agesa error injection failure
0x87 error Uncorrectable TWIX error detected
0x88 error Error programming the TWIX PCS registers
0x89 error Error setting TWIX PCS threshold value
0x8A error SW CCP queue is full, cannot add more entries
0x8B error CCP command description syntax error detected from input
0x8C error Return value stating that the command has not yet be scheduled
0x8D error The command is scheduled and being worked on
0x8E error The DXIO PHY SRAM Public key certificate loading or authentication fails
0x8F error fTPM binary size exceeds limit allocated in Private DRAM, need to increase
the limit
0x90 error The TWIX link for a particular CCD is not trained Fatal error
0x91 error Security check failed (not all dies are in same security state)
0x92 error FW type mismatch between the requested FW type and the FW type
embedded in the FW binary header
0x93 error SVC call input parameter address violation
0x94 error Knoll failed to idle correctly after being reset
0x95 error Bad status returned by I2CKnollCheck
0x96 error NACK to general call (no device on Knoll I2C bus)
0x97 error Null pointer passed to I2CKnollCheck
0x98 error Invalid device-ID found during Knoll authentication
0x99 error Error during Knoll/Prom key derivation
0x9A error Null pointer passed to Crypto function
0x9B error Error in checksum from wrapped Knoll/Prom keys
0x9C error Knoll returned an invalid response to a command
0x9D error Bootloader failed in Knoll Send Command function
0x9E error No Knoll device found by verifying MAC
0x9F error The maximum allowable error post code
Quick VGA
PEI(Pre-EFI
Initialization) phase
0x10 Progress PEI Core Entry
0x11 Progress PEI cache as ram CPU initial
0x15 Progress NB Initialization before installed memory
0x19 Progress SB Initialization before installed memory
DXE(Driver
Execution
Environment)
phase
0x32 Progress CPU POST-Memory Initialization
0x33 Progress CPU Cache Initialization
0x34 Progress Application Processor(s) (AP) Initialization
0x35 Progress BSP Selection
0x36 Progress CPU Initialization
0x37 Progress Pre-memory NB Initialization
0x3B Progress Pre-memory SB Initialization
0x4F Progress DXE Initial Program Load(IPL)
0x60 Progress DXE Core Started
0x61 Progress DXE NVRAM Initialization
0x62 Progress SB run-time Initialization
0x63 Progress CPU DXE Initialization
0x68 Progress PCI HB Initialization
0x69 Progress NB DXE Initialization
0x6A Progress NB DXE SMM Initialization
0x70 Progress SB DXE Initialization
0x71 Progress SB DXE SMM Initialization
0x72 Progress SB DEVICES Initialization
0x78 Progress ACPI Module Initialization
0x79 Progress CSM Initialization
0xD0 Progress CPU PM Structure Initialization
(continued on the next page)

Chapter 1: Product Introduction
1-20
Action PHASE POST CODE TYPE DESCRIPTION
Normal boot
BDS(Boot Device
Selection) phase
0x90 Progress BDS started
0x91 Progress Connect device event
0x92 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x93 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x94 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x95 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x96 Progress PCI Bus Enumeration
0x97 Progress Console outout connect event
0x98 Progress Console input connect event
0x99 Progress AMI Super IO start
0x9A Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9B Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9C Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0x9D Progress AMI USB Driver Initialization
0xb2 Progress Legacy Option ROM Initialization
0xb3 Progress Reset system
0xb4 Progress USB hotplug
0xb6 Progress NVRAM clean up
0xb7 Progress NVRAM configuration reset
0xA0 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA1 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA2 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0xA3 Progress IDE, AHCI Initialization
0x00~0xFF Progress Wait BMC ready
0xA8 Progress BIOS Setup Utility password verify
0xA9 Progress BIOS Setup Utility start
0xAB Progress BIOS Setup Utility input wait
0xAD Progress Ready to boot event
0xAE Progress Legacy boot event
Operating system
phase
0xAA Progress APIC mode
0xAC Progress PIC mode

This chapter lists the hardware setup procedures that you have
to perform when installing or removing system components.
2
Hardware Information
Chapter 2: Hardware Information

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-2
2.1 Chassis cover
2.1.1 Removing the rear cover
1. Remove the two (2) screws on both sides of the cover with a Phillips screwdriver.
2. Loosen the thumbscrew on the rear panel to release the cover from the chassis.
3. Firmly hold the cover and slide it towards the rear panel for about half an inch until it is
disengaged from the chassis.
4. Lift the cover from the chassis.

2-3
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.2 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The motherboard comes with a surface mount Socket SP3 designed for the AMD EPYC™
7002/7003 Series.
• Upon purchase of the motherboard, ensure that the PnP cap is on the socket and
the socket contacts are not bent. Contact your retailer immediately if the PnP cap
is missing, or if you see any damage to the PnP cap/socket contacts/motherboard
components. ASUS will shoulder the cost of repair only if the damage is shipment/
transit-related.
• Keep the cap after installing the motherboard. ASUS will process Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) requests only if the motherboard comes with the cap on the
Socket SP3.
• The product warranty does not cover damage to the socket contacts resulting from
incorrect CPU installation/removal, or misplacement/loss/incorrect removal of the PnP
cap.
2.2.1 Installing the CPU and heatsink
To install the CPU and heatsink:
1. Remove the rear cover. For more information, refer to Chassis cover.
2. Locate the CPU socket on your motherboard..

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-4
3. Loosen each screw one by one in the
sequence shown on the socket to open
the load plate.
4. Slightly lift open the rail frame.
External cap
Load plate
Rail frame
5. Slide the external cap out of the rail
frame.
Rail frame
External cap
PnP cap

2-5
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
6. Slide the carrier frame with CPU into the
rail frame, then remove the PnP cap.
The carrier frame with CPU fits in only
one correct orientation. DO NOT force
the carrier frame with CPU into the
rail frame.
Rail frame
Carrier frame
with CPU
PnP cap
7. Gently push the rail frame just enough
to let it sit on top of the CPU socket.
Carrier frame
with CPU
8. Close the load plate just enough to let
it sit on top of the CPU, then secure
each screw one by one in the sequence
shown on the socket to completely
secure the load plate.
The load plate screws are
T20 models. A torque value of
16.1±1.2 kgf-cm (14.0±1.0 lbf-in) is
recommended.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-6
9. Twist each of the four screws with a
screwdriver just enough to attach the
heatsink to the motherboard. When the
four screws are attached, tighten them
one by one in the sequence shown in
the illustration to completely secure the
heatsink.
The heatsink screws are T20 models.
A torque value of 16.1±1.2 kgf-cm
(14.0±1.0 lbf-in) is recommended.

2-7
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.3 System memory
2.3.1 Overview
The motherboard comes with 16 Double Data Rate 4 (DDR4) Dual Inline Memory Modules
(DIMM) sockets.
The figure illustrates the location of the DDR4 DIMM sockets:
2.3.2 Memory Configurations
You may install 16GB, 32GB, or 64GB RDIMM into the DIMM sockets. If you are not sure on
which slots to install the DIMMS, you can use the recommended memory configuration in this
section for reference.
• 6 DIMM configuration is recommended for AMD EPYC™ 7003 Series processors under
the condition that only 6 channels are to be populated.
• 6 DIMM configuration is not recommended for AMD EPYC™ 7002 Series processors.
• When mixing 2DPC and 1DPC, ensure that each channel’s total DIMM size should be
equal. The DIMM size of 2DPC should equal to that of 1DPC, for example, if 2DPC is
using a 32GB memory module (32GB * 2), then a 64GB memory module should be
installed for 1DPC.
• All memory modules for 2DPC should be the same.
• Always install DIMMs with the same CAS latency. For optimum compatibility, it is
recommended that you obtain memory modules from the same vendor.
Memory configurations
DIMM
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 E2 F1 F2 G1 G2 H1 H2
1 DIMM P
2 DIMMs P P
4 DIMMs P P P P
8 DIMMs P P P P P P P P
10 DIMMs P P PPPPP P P P
12 DIMMs PPP PPPPP PPP P
14 DIMMs PPPPPPPPPPPPP P
16 DIMMs PPPPPPPPPPPPPPPP

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-8
2.3.3 Installing a DIMM
3. Hold the DIMM by both of its ends
then insert the DIMM vertically into
the socket. Apply force to both ends
of the DIMM simultaneously until the
retaining clips snaps back into place.
Ensure that the DIMM is sitting firmly
on the DIMM slot.
Ensure to unplug the power supply before adding or removing DIMMs or other system
components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to both the motherboard and the
components.
1. Unlock a DIMM socket by pressing
the retaining clips outward.
2. Align a DIMM on the socket such that
the notch on the DIMM matches the
DIMM slot key on the socket.
A DIMM is keyed with a notch so that it fits in only one direction. DO NOT force a DIMM into
a socket in the wrong direction to avoid damaging the DIMM.
Always insert the DIMM into the socket VERTICALLY to prevent DIMM notch damage.
Locked Retaining Clip
Unlocked retaining clip
DIMM notch
DIMM slot key
2.3.4 Removing a DIMM
2. Simultaneously press the retaining
clips outward to unlock the DIMM.
3. Remove the DIMM from the socket.
Support the DIMM lightly with your fingers when pressing the retaining clips. The DIMM
might get damaged when it flips out with extra force.
1. Remove the chassis cover. For more information, see the section Chassis cover.

2-9
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.4 Storage devices
RS500A-E11-RS4U
The system supports four (4) 3.5” hot-swap SATA/SAS storage devices or four (4) 2.5”
hot-swap NVMe. The storage device installed on the storage device tray connects to the
motherboard SATA/SAS/NVMe ports via the SATA/SAS/NVMe backplane.
• Bay 1 to bay 4 supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires optional HBA/RAID
card. (supports tri-mode card)
• All bays support 3.5”/2.5” drives with trays.
1234
Bay 1 Bay 2 Bay 3 Bay 4
RS500A-E11-RS12U
The system supports twelve (12) 2.5” hot-swap SATA/SAS/NVMe storage devices. The
storage device installed on the storage device tray connects to the motherboard SATA/SAS/
NVMe ports via the SATA/SAS/NVMe backplane.
• Bay 1 to bay 12 supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires optional HBA/RAID
card.
• • All bays support 2.5” drives with trays.
Bay 1 Bay 3 Bay 5 Bay 7 Bay 9 Bay 11
Bay 2 Bay 4 Bay 6 Bay 10Bay 8 Bay 12

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-10
1. Press the spring lock.
3. Prepare the 3.5” storage device then place
the 3.5” storage device into the tray until it
clicks into place.
2.4.1 Installing a 3.5-inch storage device
(for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
2. Pull the tray lever outwards to remove the
drive tray.
4. Push the drive tray and HDD assembly all
the way into the depth of the bay until the
tray lever and spring lock clicks and secures
the drive tray in place.
• When installed, the SATA/SAS connector on the drive connects to the SATA/SAS/
NVMe interface on the backplane.
• The drive tray is correctly placed when its front edge aligns with the bay edge.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 to install the other 3.5” storage devices.

2-11
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.4.2 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device
(for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
1. Please follow steps 1 and 2 of the Installing a 3.5-inch storage device (for RS500A-
E11-RS4U) section to remove the drive tray from the chassis.
4. Please follow step 4 of the Installing a 3.5-inch storage device (for RS500A-E11-
RS4U) section to replace the drive tray.
• When installed, the SATA/SAS/NVMe connector on the drive connects to the SATA/
SAS/NVMe interface on the backplane.
• The drive tray is correctly placed when its front edge aligns with the bay edge.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 to install the other 2.5” storage devices.
2. Prepare the 2.5” storage device and align
it to the screw holes on the bottom of the
drive tray.
3. Secure the 2.5” storage device to the drive
tray using the bundled screws.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-12
4. Push the storage device tray and HDD
assembly all the way into the depth of the
bay until the tray lever and spring lock
clicks and secures the storage device tray
in place.
• When installed, the SATA/SAS/NVMe connector on the storage device connects to the
SATA/SAS/NVMe interface on the backplane.
• The storage device tray is correctly placed when its front edge aligns with the bay
edge.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 to install the other 2.5” storage devices.
2.4.3 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to a front storage
bay (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
1. Press the spring lock.
3. Place the 2.5” storage device into the
storage device tray then secure it with four
screws.
2. Pull the tray lever outwards to remove the
drive tray.

2-13
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.4.4 Installing a 2.5-inch storage device to an internal
storage bay (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
1. Remove the rear cover. For more information, refer to Chassis cover.
2. Remove the cushioning on the front side of the internal storage cage.
3. Pull the internal storage cage lock latch outwards (A) then lift the front of the internal
storage cage upwards (B) and release the storage cage lock latch (C). The storage
cage lock latch should secure the front of the internal storage cage so that the storage
device bays are easily accessed (D).
4. Push the spring lock to the right (A) then pull the tray lever outward (B) to release the
storage device tray. The storage device tray ejects slightly after you pull out the lever.
Spring lockTray lever
Internal storage cage
lock

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-14
5. Place the 2.5” storage device into the tray until it clicks into place.
6. Align and insert the 2.5” storage device and drive tray assembly into the drive bay.
7. Repeat steps 1-5 to install the other 2.5” storage devices.

2-15
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
8. Pull the internal storage cage lock outwards (A), then push the front of the internal
storage cage down (B) and release the internal storage cage lock (C). The internal
storage cage lock should secure the internal storage cage inside the system.
Internal storage cage lock

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-16
2.5 Expansion slot
2.5.1 Installing an expansion card to the riser card bracket
The barebone server comes with a riser card bracket. You need to remove the bracket if you
want to install PCIe x8 or x16 expansion cards.
2. Place the riser card bracket on a flat and stable surface.
3. Push the metal bracket lock counter clockwise (A) until the metal bracket can be
removed, then remove the metal bracket (B).
1. Firmly hold the handle on the butterfly riser card bracket, then pull it up to detach it from
the PCI Express slot on the motherboard.

2-17
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
4. Insert the expansion card into the PCIe slot. Ensure that the golden fingers are totally
inserted into the slot.
5. Push the metal bracket lock clockwise until it locks back and secures the expansion
card to the riser card bracket.
6. Install the riser card bracket and expansion card assembly back into the PCIe slot on
the motherboard. Ensure that the golden connectors of the riser card bracket is firmly
seated in place.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-18
2.5.2 Installing an expansion card to the butterfly riser card
bracket
The barebone server comes with a butterfly riser card bracket. You need to remove the
bracket if you want to install PCIe x8 or x16 expansion cards.
2. Place the butterfly riser card bracket on a flat and stable surface.
3. Push the metal bracket lock clockwise (A) until the metal bracket can be removed, then
remove the metal bracket (B).
1. Firmly hold the handle on the butterfly riser card bracket, then pull it up to detach it from
the PCI Express slot on the motherboard.

2-19
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
6. To install an expansion card to the other PCIe slot on this butterfly riser card bracket,
please refer to the Installing an ASUS PIKE II card section.
7. Install the butterfly riser card bracket and expansion card assembly back into the PCIe
slot on the motherboard. Ensure that the golden connectors of the butterfly riser card
bracket is firmly seated in place.
4. Insert the expansion card into the PCIe slot. Ensure that the golden fingers are totally
inserted into the slot.
5. Push the metal bracket lock counter clockwise until it locks back and secures the
expansion card to the butterfly riser card bracket.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-20
2.5.3 Installing an ASUS PIKE II card
You can install an ASUS PIKE II card to any of the PCIe slots on both riser card brackets, but
for this section we will be using the butterfly riser card bracket.
2. Place the butterfly riser card bracket on a flat and stable surface.
3. Push the metal bracket lock clockwise (A) until the metal bracket can be removed, then
remove the metal bracket (B).
1. Firmly hold the handle on the butterfly riser card bracket, then pull it up to detach it from
the PCI Express slot on the motherboard.

2-21
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
6. Connect the mini-SAS HD cable to the connectors of the ASUS PIKE II card.
4. Insert the ASUS PIKE II card into the PCIe slot. Ensure that the golden fingers are
totally inserted into the slot.
5. Push the metal bracket lock counter clockwise until it locks back and secures the ASUS
PIKE II card to the butterfly riser card bracket.
7. Install the butterfly riser card bracket and ASUS PIKE II card assembly back into the
PCIe slot on the motherboard. Ensure that the golden connectors of the butterfly riser
card bracket is firmly seated in place.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-22
2.5.4 Installing M.2 (NGFF) cards
2. Locate the M.2 (NGFF) connector on your motherboard.
1. Firmly hold the handle on the butterfly riser card bracket, then pull it up to detach it from
the PCI Express slot on the motherboard.

2-23
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
3. Select an appropriate screw hole on the motherboard for your M.2 card, then secure
the bundled stand to the motherboard.
4. Insert the M.2 into the M.2 (NGFF) slot, then secure it using the bundled screw.
5. Install the riser card bracket back into the PCIe slot on the motherboard. Ensure that
the golden connectors of the riser card bracket is firmly seated in place.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-24
2.5.5 Installing an OCP 3.0 card
1. Remove the screw securing the metal bracket of the OCP 3.0 slot (A), then remove the
metal bracket (B).
2. Insert and push the OCP 3.0 card all the way into the OCP 3.0 slot (A), then secure the
OCP 3.0 card using the thumbscrew (B).

2-25
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.5.6 Configuring an expansion card
After installing the expansion card, configure the it by adjusting the software settings.
1. Turn on the system and change the necessary BIOS settings, if any. See Chapter 5 for
information on BIOS setup.
2. Assign an IRQ to the card. Refer to the following tables.
3. Install the software drivers for the expansion card.
Standard Interrupt assignments
* These IRQs are usually available for ISA or PCI devices.
IRQ Priority Standard function
0 1 System Timer
1 2 Keyboard Controller
2 - Programmable Interrupt
3* 11 Communications Port (COM2)
4* 12 Communications Port (COM1)
5* 13 --
6 14 Floppy Disk Controller
7* 15 --
8 3 System CMOS/Real Time Clock
9* 4 ACPI Mode when used
10* 5 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
11* 6 IRQ Holder for PCI Steering
12* 7 PS/2 Compatible Mouse Port
13 8 Numeric Data Processor
14* 9 Primary IDE Channel
15* 10 Secondary IDE Channel

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-26
2.6 Cable connections
• The bundled system cables are pre-connected before shipment. You do not need to
disconnect these cables unless you will remove pre-installed components to install
additional devices.
• Refer to Chapter 4 for detailed information on the connectors.
RS500A-E11 Series
Pre-connected system cables
1. 24-pin EATXPWR1 power connector (connected to power board)
2. 8-pin EATX12V1 power connector (connected to power board)
3. 4-pin EATX12V2 power connector (connected to power board)
4. Panel connector (connected to front I/O board)
5. FRNT_FAN1-7 System fan connectors (from motherboard to system fans)
6. FRNT_FAN8 System fan connector (optional, from motherboard to system fans)
7. Slim PCIe connectors (connected to backplane)

2-27
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2.7 SATA/SAS backplane cabling
RS500A-E11-RS4U
Connects to NVMe/SAS/SATA storage
devices (SAS support requires an
optional HBA/RAID card)
Connects to SLMPCIE1
connector on motherboard
for NVMe support on Bay 1
and 2
Connects to SLMPCIE2
connector on motherboard
for NVMe support on Bay
3 and 4
Connects to HBA/RAID card for SAS support
on Bay 1 to Bay 4 or to the SLMSATA_PCIE7
connector on the motherboard for SATA
support on Bay 1 to Bay 4

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-28
RS500A-E10-RS12U
Connects to NVMe/SAS/SATA storage devices
(SAS support requires an optional HBA/RAID card)
Connects to SLMPCIE4
connector on motherboard for
NVMe support on Bay 7 and 8
Connects to SLMPCIE6
connector on motherboard for
NVMe support on Bay 11 and 12
Connects to HBA/RAID card for
SAS support on Bay 1 to Bay
4 or to the SLMSATA_PCIE8
connector on the motherboard for
SATA support on Bay 1 to Bay 4
Connects to HBA/RAID card for
SAS support on Bay 5 to Bay
8 or to the SLMSATA_PCIE8
connector on the motherboard for
SATA support on Bay 5 to Bay 8
Connects to HBA/RAID card for
SAS support on Bay 9 to Bay
12 or to the SLMSATA_PCIE7
connector on the motherboard for
SATA support on Bay 9 to Bay 12
Connects to SLMPCIE3
connector on motherboard for
NVMe support on Bay 5 and 6
Connects to SLMPCIE5
connector on motherboard for
NVMe support on Bay 9 and 10
Connects to SLMPCIE2
connector on motherboard for
NVMe support on Bay 3 and 4
Connects to SLMPCIE1 connector
on motherboard for NVMe support
on Bay 1 and 2
NVME3 ALED3
SLED3
NVME4 ALED4
SLED4
NVME1
ALED1
SLED1
NVME2 ALED2
SLED2
Connects to NVMe/SATA storage devices
HDD12 HDD34
MSAS_HD1
PWR0501
SLIMSATA_PCIE1 SLIMSATA_PCIE2
Connects to SLMSATA_PCIE8 connector
on motherboard for NVMe support on bay
1 and 2 of the internal storage bays
Connects to SLMSATA_PCIE7 connector
on motherboard for NVMe support on bay
3 and 4 of the internal storage bays
Connects to SLMSATA_PCIE7
connector on the motherboard for
SATA support on Bay 1 to 4 of the
internal storage bays
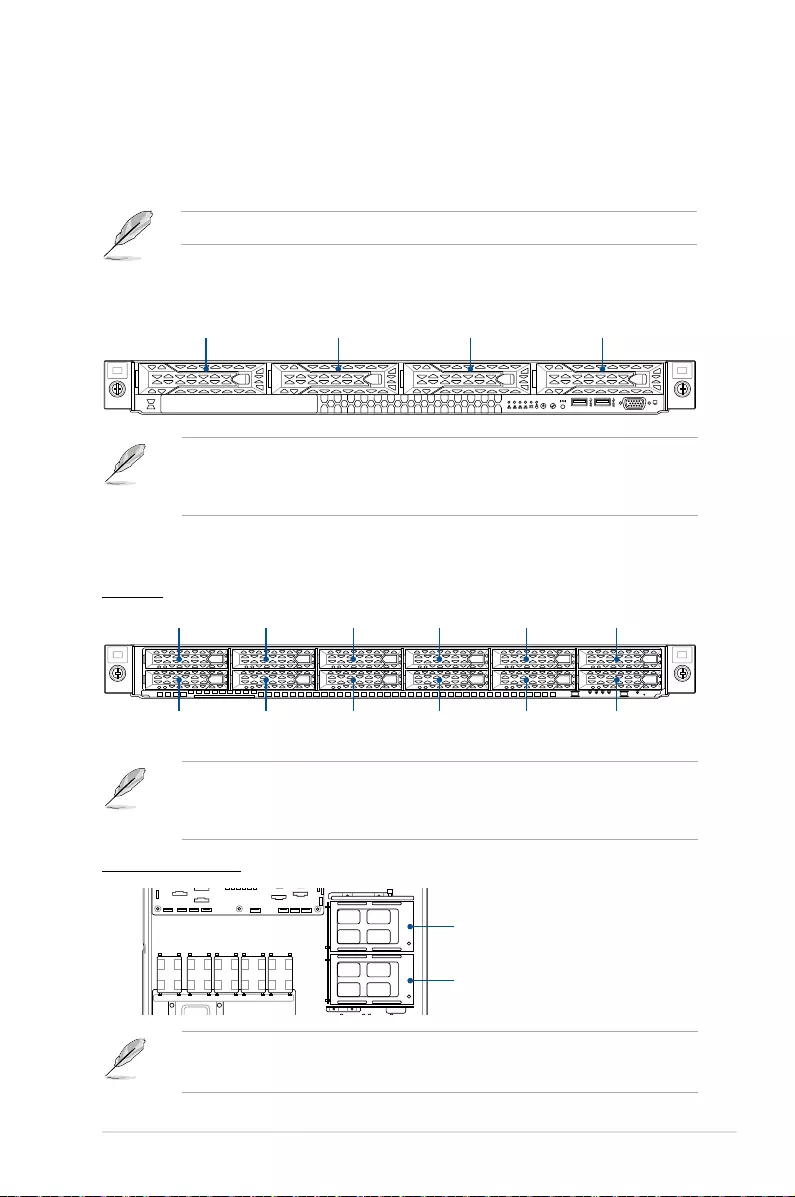
2-29
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
RS500A-E10-RS12U
Front bay
Internal bay (optional)
RS500A-E10-RS4U
2.8 Storage device configuration and cabling
This section illustrates some storage configurations that is recommended with your server
system. Before you start installing or removing the storage device cables, ensure that you
have installed the correct storage devices into the supported bays.
Refer to section Storage Devices for details on how to install storage devices.
• Bay 1 to bay 4 supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires optional HBA/RAID
card. (supports tri-mode card)
• All bays support 3.5”/2.5” drives with trays.
1234
Bay 1 Bay 2 Bay 3 Bay 4
• Bay 1 to bay 12 on the front bay supports NVMe/SATA/SAS. SAS support requires
optional HBA/RAID card.
• All bays support 2.5” drives with trays.
• Bay 1 to bay 4 on the internal bay supports NVMe/SATA.
• All bays support 2.5” drives with trays.
Bay 1 Bay 3 Bay 5 Bay 7 Bay 9 Bay 11
Bay 2 Bay 4 Bay 6 Bay 10Bay 8 Bay 12
Top: Bay 1
Bottom: Bay 2
Top: Bay 3
Bottom: Bay 4

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-30
1. Install the storage devices into the supported bays.
Refer to section Storage Devices for details on how to install storage devices.
Backplane
connector Cable Connect to
SLIMPCIE1 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE1 on motherboard
SLIMPCIE2 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE2 on motherboard
MSAS_HD1 Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-SAS HD SLMSATA_PCIE7 on motherboard
2.8.1 4 x NVMe and 4 x SATA storage device configuration
and cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS4U)
The illustrations in this section are for reference only and may vary between models.
1234
SATA/NVMe SATA/NVMe SATA/NVMe SATA/NVMe

2-31
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2. Connect the Slimline SAS cables and Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini SAS HD cable to the
motherboard and the front backplane.
SLIMPCIE1: Connect Slimline SAS
cable from the SLMPCIE1 connector
on the motherboard
SLIMPCIE2: Connect Slimline SAS
cable from the SLMPCIE2 connector
on the motherboard
MSAS_HD1: Connect Slimline SAS
to 2 x Mini-SAS HD cable from the
SLMSATA_PCIE7 connector on the
motherboard

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-32
Backplane
connector Cable Connect to
SLMPCIE1 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE1 on motherboard
SLMPCIE2 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE2 on motherboard
SLMPCIE3 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE3 on motherboard
SLMPCIE4 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE4 on motherboard
SLMPCIE5 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE5 on motherboard
SLMPCIE6 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE6 on motherboard
MSAS_HD1 Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-SAS HD SLMSATA_PCIE8 on motherboard
MSAS_HD2 Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-SAS HD SLMSATA_PCIE8 on motherboard
MSAS_HD3 Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-SAS HD SLMSATA_PCIE7 on motherboard
2.8.2 12 x NVMe, 12 x SATA (front bay), and 4 x SATA
(internal bay) storage device configuration and
cabling (for RS500A-E11-RS12U)
The illustrations in this section are for reference only and may vary between models.
Rear backplane
connector Cable Connect to
MSAS_HD1 Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-SAS HD SLMSATA_PCIE7 on motherboard

2-33
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
1. Install the storage devices into the supported bays.
Refer to section Storage Devices for details on how to install storage devices.
2. Remove the two (2) screws of the middle cover on both sides of the chassis with a
Phillips screwdriver (A), then remove the middle cover.
Front bay
Internal bay (optional)
NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA
NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA NVMe/SATANVMe/SATA NVMe/SATA
Top: SATA
Bottom: SATA
Top: SATA
Bottom: SATA

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-34
2. Connect the Slimline SAS cables and Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini SAS HD cables to the
motherboard and the front backplane.
3. Connect the Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini SAS HD cable to the motherboard and the
internal storage bay backplane.
SLMPCIE4: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE4
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE6: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE6
connector on the motherboard
MSAS_HD1: Connect Slimline SAS
to 2 x Mini-SAS HD cable from the
SLMSATA_PCIE8 connector on the
motherboard
MSAS_HD2: Connect Slimline SAS
to 2 x Mini-SAS HD cable from the
SLMSATA_PCIE8 connector on the
motherboard
MSAS_HD3: Connect
Slimline SAS to 2 x Mini-
SAS HD cable from the
SLMSATA_PCIE7 connector
on the motherboard
SLMPCIE3: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE3
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE5: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE5
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE2: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE2
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE1: Connect Slimline SAS
cable from the SLMPCIE1 connector
on the motherboard
Front backplane
Internal storage bay backplane
HDD12 HDD34
MSAS_HD1
PWR0501
SLIMSATA_PCIE1 SLIMSATA_PCIE2
MSAS_HD1: Connect Slimline SAS to 2 x
Mini-SAS HD cable from the SLMSATA_
PCIE7 connector on the motherboard

2-35
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Backplane
connector Cable Connect to
SLMPCIE1 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE1 on motherboard
SLMPCIE2 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE2 on motherboard
SLMPCIE3 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE3 on motherboard
SLMPCIE4 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE4 on motherboard
SLMPCIE5 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE5 on motherboard
SLMPCIE6 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMPCIE6 on motherboard
2.8.3 12 x NVMe (front bay), and 4 x NVMe (internal bay)
storage device configuration and cabling (for RS500A-
E11-RS12U)
The illustrations in this section are for reference only and may vary between models.
Rear backplane
connector Cable Connect to
SLIMSATA_PCIE1 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMSATA_PCIE7 on motherboard
SLIMSATA_PCIE2 Slimline SAS to Slimline SAS SLMSATA_PCIE8 on motherboard

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-36
1. Install the storage devices into the supported bays.
Refer to section Storage Devices for details on how to install storage devices.
2. Remove the two (2) screws of the middle cover on both sides of the chassis with a
Phillips screwdriver (A), then remove the middle cover.
Front bay
Internal bay (optional)
NVMe NVMe NVMe /SATA NVMe NVMe
NVMe NVMe NVMe NVMeNVMe NVMe
Top: NVMe
Bottom: NVMe
Top: NVMe
Bottom: NVMe

2-37
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2. Connect the Slimline SAS cables to the motherboard and the front backplane.
3. Connect the Slimline SAS cables to the motherboard and the internal storage bay
backplane.
SLMPCIE4: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE4
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE6: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE6
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE3: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE3
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE5: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE5
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE2: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMPCIE2
connector on the motherboard
SLMPCIE1: Connect Slimline SAS
cable from the SLMPCIE1 connector
on the motherboard
Front backplane
Internal storage bay backplane
SLIMSATA_PCIE1: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMSATA_PCIE7
connector on the motherboard
SLIMSATA_PCIE2: Connect Slimline
SAS cable from the SLMSATA_PCIE8
connector on the motherboard
HDD12 HDD34
MSAS_HD1
PWR0501
SLIMSATA_PCIE1 SLIMSATA_PCIE2

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-38
2.9 Optional components
This section describes on how to replace previously installed system components or install
optional components into the system.
Ensure that the system is turned off before removing any components.
You may need to remove previously installed component or factory shipped components
when installing optional components.
2.9.1 Redundant power supply module
To replace a failed redundant power supply module:
1. Lift up the power supply module lever (A), then hold the power supply module lever and
press the PSU latch (B) to pull the power supply module out of the system chassis (C).
2. Prepare the replacement power supply module.
3. Insert the replacement power supply module into the chassis then push it inwards until
the latch locks into place.
Module lever
PSU latch

2-39
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
• The system automatically combines the two power supply modules as a single one.
The combined output power varies with input voltages. Refer to the table below for
details.
800W
Input Voltage Max. Output Power (Watt) per PSU
100V-127Vac, 10.0A, 50-60Hz 800W
200V-240Vac, 5.0A, 50-60Hz 800W
850W
Input Voltage Max. Output Power (Watt) per PSU
100V-127Vac, 11.0A, 47-63Hz 850W
200V-240Vac, 5.0A, 47-63Hz 850W
• To enable the hot-swap feature (redundant mode), keep the total power consumption
of the system under the maximum output power of an individual power supply module.
• Always use PSUs with the same watt and power rating. Combining PSUs with different
wattage (e.g. 1 x 1620 W + 1 x 2000 W) may yield unstable results and potential
damage to your system.
• For a steady power input, use only the power cables that come with the server system
package.

Chapter 2: Hardware Information
2-40

This chapter describes how to install the optional components
and devices into the barebone server.
3
Installation Options
Chapter 3: Installation Options

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-2
3.1 Tool-less Friction Rail Kit
The tool less design of the rail kit allows you to easily install the rack rails into the server rack
without the need for additional tools. The kit also comes with a metal stopping bracket that
can be installed to provide additional support and stability to the server.
The tool-less rail kit package includes:
Tool-less rack rails
3.1.1 Installing the tool-less rack rail
To install the tool-less rack rails into the rack:
1. Secure the two fixing latches to the two sides of the server using the set of latch
screws.
The locations of the screw holes vary with different server models. Refer to your server user
manual for details.
Fixing latches Set of screws Latch screws Rail Washers Rail screws

3-3
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
2. Select a desired space and place the appropriate rack rail (left and right) on opposite
positions on the rack.
A 1U space is consists of three square mounting holes with two thin lips on the top and the
bottom.
3. Press the spring lock, then insert the studs into the selected square mounting holes on
the rack post.
4. Press the spring lock on the other end of rail then insert the stud into the mounting hole
on the rack post. Extend the rack rail, if necessary.
5. Perform steps 3 to 4 for the other rack rail.
Ensure that the installed rack rails (left and right) are aligned, secured, and stable in place.
Thin lips

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-4
6. Lift the server chassis and insert it into the rack rail.
• Ensure that the rack rail cabinet and the rack posts are stable and standing firmly on a
level surface.
• We strongly recommend that at least two able-bodied persons perform the steps
described in this guide.
• We recommend the use of an appropriate lifting tool or device, if necessary.
Ensure to include the side knots on the two sides of the server in the rack rail holders.
The illustrations shown above are for reference only.
RS500A-E11-RS4U
RS500A-E11-RS12U
3.1.2 Rail kit dimensions
589mm
43.6mm
900mm
43.6mm

3-5
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
3.2 Ball bearing Rail Kit
The rail kit package includes:
2 x 1200 mm rack rails (or 2 x 1000 mm rack rails)
4 x M4X4L screws
8 x ø17.1 screws 8 x #10-32 screws
(or 10 x #10-32 screws for 1000 mm rack rails)
2 x M5X20L screws
Rear end
Front end Rack rails
• The bundled screw package includes different types of screws for you to choose from,
not all screws are required for the installation.
• Package content and specifications are subject to change without notice.
4 x #6-32X4L screws

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-6
3.2.1 Attaching the rack rails
Installing the rack rail
To install the rack rails into the rack:
1. Select a desired space on the rack.
A 1U space consists of three
square mounting holes with two
thin lips on the top and the bottom. 1U
• The installation steps in this section uses a 1200 mm rack rail as an example, the
installation steps for a 1000 mm rack rail is exactly the same.
• The illustrations in this section are for reference only.
• Ensure that the rack rail cabinet and the rack posts are stable and standing firmly on a
level surface.
• We strongly recommend that at least two able-bodied persons perform the steps
described in this guide.
• We recommend the use of an appropriate lifting tool or device, if necessary.
2. Align and insert the front end of the
appropriate rack rail (left and right) into
the front rack post.
Front end of rack rail
Front rack post

3-7
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Outer rail
Intermediate rail
Intermediate rail
Inner rail
Blue release tab White release tab
Spring lock
Rear end of rack rail
Rear rack post
3. Press the spring lock on the rear end
of the rack rail and insert the studs into
the selected mounting holes on the rear
rack post.
4. Slide the intermediate rail out of the outer rail until it clicks to a stop.
5. Slide the inner rail out of the intermediate rail until it clicks to a stop. Slide the white
release tab outwards and remove the inner rail completely from the intermediate rail.
6. Repeat steps 2 to 5 for the other rack rail.
Ensure that the installed rack rails (left and right) are aligned, secured, and stable in place.
The blue release tab is available on 1200 mm rack rails. This blue release tab is used to
further extend or retract the inner rail.

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-8
8. Align the inner rails with the studs on both sides of the server system, install the inner
rails to the server system, then slide the inner rails toward the rear of the server system
until it locks in place.
7. Remove the three (3) screws from both left and right sides of the server system
chassis, then remove the metal plate.
The illustration below only shows one side of the server system chassis, but the screws on
the other side should be at the same place.
9. Secure the inner rails on both sides of the server system using the #6-32X4L screws.
Metal plate

3-9
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
10. Align the server system and gently
insert it into the rack rails.
11. (optional) Use the M5X20L screws to
secure the rack rails to the rack post. Front end of rack rail
Front rack post
Intermediate railInner rail
12. Gently push the server system until it is completely installed into the rack rail.
(optional) For 1200 mm rack rails, if the inner rail clicks to a stop while you are installing
the server system into the rack rails, slide the blue release tab outwards and gently
push the server system until it is completely installed into the rack rail.
Blue release tab White release tab
The blue release tab is available on 1200 mm rack rails. This blue release tab is used to
further extend or retract the inner rail.

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-10
RS500A-E11-RS4U
RS500A-E11-RS12U

3-11
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
3.3 Cable management arm
(optional for 1200 mm rack rails)
You can install an additional cable management arm (CMA) to the rack rails to help you
manage the cables from your server system. The CMA is designed with movable parts that
allow you to move the server system along the rack rail without the need to remove the CMA.
3.3.1 Attaching the cable management arm
Installing the cable management arm
To install the cable management arm:
1. Install the rack rails into the rack.
Refer to section Rail Kit for the steps on installing the rack rails into the rack.
2. Press the round button on the pivot receptor, then rotate the pivot receptor to the left or
right for a left pivot configuration or right pivot configuration.
Outer receptor
Inner receptor
Pivot receptor
Right pivot configurationLeft pivot configuration
Cable fasteners
Hook and loop fasteners

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-12
3. Align the three receptors on the CMA with the connectors on the rack rails.
4. Align and connect the inner
receptor on the CMA with the
connector on the inner rail.
5. Align and connect the outer
receptor on the CMA with the
connector on the intermediate
rail.
Intermediate rail connector
Pivot receptor
Inner receptor
Inner rail connector (hidden)
Intermediate rail
connector
Outer receptor
The installation steps in this section uses a Left pivot configuration as an example, the
installation steps for a Right pivot configuration is similar.

3-13
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
6. Align and connect the pivot receptor on the CMA with the connector on the other
intermediate rail.
7. Pass the cables from the server system through the hook and loop fasteners and the
cable fasteners on the CMA to complete.
Hook and loop fasteners
Cable fasteners

Chapter 3: Installation Options
3-14

This chapter includes the motherboard layout and brief
descriptions of the jumpers and internal connectors.
4
Motherboard Information
Chapter 4: Motherboard Information

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-2
4.1 Motherboard layout

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-3
Layout contents
Jumpers Page
1. Clear RTC RAM (3-pin CLRTC1) 4-4
2. VGA controller setting (3-pin VGA_SW1) 4-5
3. LANNCSI setting (3-pin LANNCSI_SEL1) 4-5
4. Baseboard Management Controller setting (3-pin BMC_EN1) 4-6
5. DMLAN setting (3-pin DM_IP_SEL1) 4-6
6. IPMI SW setting (3-pin IPMI_SW1) 4-7
7. Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) setting (3-pin SMART_PSU1) 4-7
8. LAN controller settings (3-pin LAN_SW1-2) 4-8
Onboard LEDs Page
1. Standby Power LED (SBPWR1) 4-9
2. Baseboard Management Controller LED (BMCLED1) 4-9
3. Message LED (MESLED1) 4-10
4. Hard disk activity LED (HDDLED1) 4-10
Internal connectors Page
1. Slim PCIe connector (SLIMPCIE1-10) 4-11
2. Slim SATA PCIe connector (SLMSATA_PCIE7-8) 4-11
3. USB 2.0 connector (10-1 pin USB2) 4-12
4. USB 3.2 Gen 1 connector (USB3_34) 4-12
5. Chassis Intrusion (2-pin INTRUSION1) 4-13
6. Serial port connector (10-1 pin COM1) 4-13
7. System fan connectors (6-pin FRNT_FAN1-8) 4-14
8. TPM connector (14-1 pin TPM1) 4-15
9. M.2 (NGFF) card connector (NGFF1-2) 4-15
10. Power connectors (24-pin EATXPWR; 8-pin EATX12V1; 4-pin EATX12V2) 4-16
11. VGA connector (16-pin VGA_HDR1) 4-16
12. Micro SD card slot (MSD1) 4-17
13. Hard disk activity LED connector (4-pin HDLED1) 4-17
14. System panel connector (10-1 pin SYS_PANEL1; 14-1 pin SYS_PANEL2) 4-18
15. VPP_I2C1 connector (10-1 pin VPP_I2C1) 4-19
16. BMC Debug UART connector (3-pin BMC_DEBUGUART1) 4-19
17. Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) setting (3-pin SMART_PSU1) 4-20
18. SLMPCIE SGPIO connector (6-1 pin SLM7_SGPIO1, SLM8_SGPIO1) 4-20

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-4
1. Clear RTC RAM (3-pin CLRTC1)
This jumper allows you to clear the Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM in CMOS. You can
clear the CMOS memory of date, time, and system setup parameters by erasing the
CMOS RTC RAM data. The onboard button cell battery powers the RAM data in
CMOS, which include system setup information such as system passwords.
To erase the RTC RAM:
1. Turn OFF the computer and unplug the power cord.
2. Move the jumper cap from pins 1–2 (default) to pins 2–3. Keep the cap on pins
2–3 for about 5–10 seconds, then move the cap back to pins 1–2.
3. Plug the power cord and turn ON the computer.
4. Hold down the <Del> key during the boot process and enter BIOS setup to re-
enter data.
Except when clearing the RTC RAM, never remove the cap on CLRTC jumper default
position. Removing the cap will cause system boot failure!
If the steps above do not help, remove the onboard battery and move the jumper again to
clear the CMOS RTC RAM data. After the CMOS clearance, reinstall the battery.
4.2 Jumpers

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-5
2. VGA controller setting (3-pin VGA_SW1)
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the onboard VGA controller. Set to pins
1–2 to activate the VGA feature.
3. LANNCSI setting (3-pin LANNCSI_SEL1)
This jumper allows you to select which LAN NCSI function to use.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-6
4. Baseboard Management Controller setting (3-pin BMC_EN1)
This jumper allows you to enable (default) or disable on-board BMC. Ensure to set this
BMC jumper to enabled to avoid system fan control and hardware monitor error.
5. DMLAN setting (3-pin DM_IP_SEL1)
This jumper allows you to select the DMLAN setting. Set to pins 2-3 to force the
DMLAN IP to static mode (IP=10.10.10.10, submask=255.255.255.0).
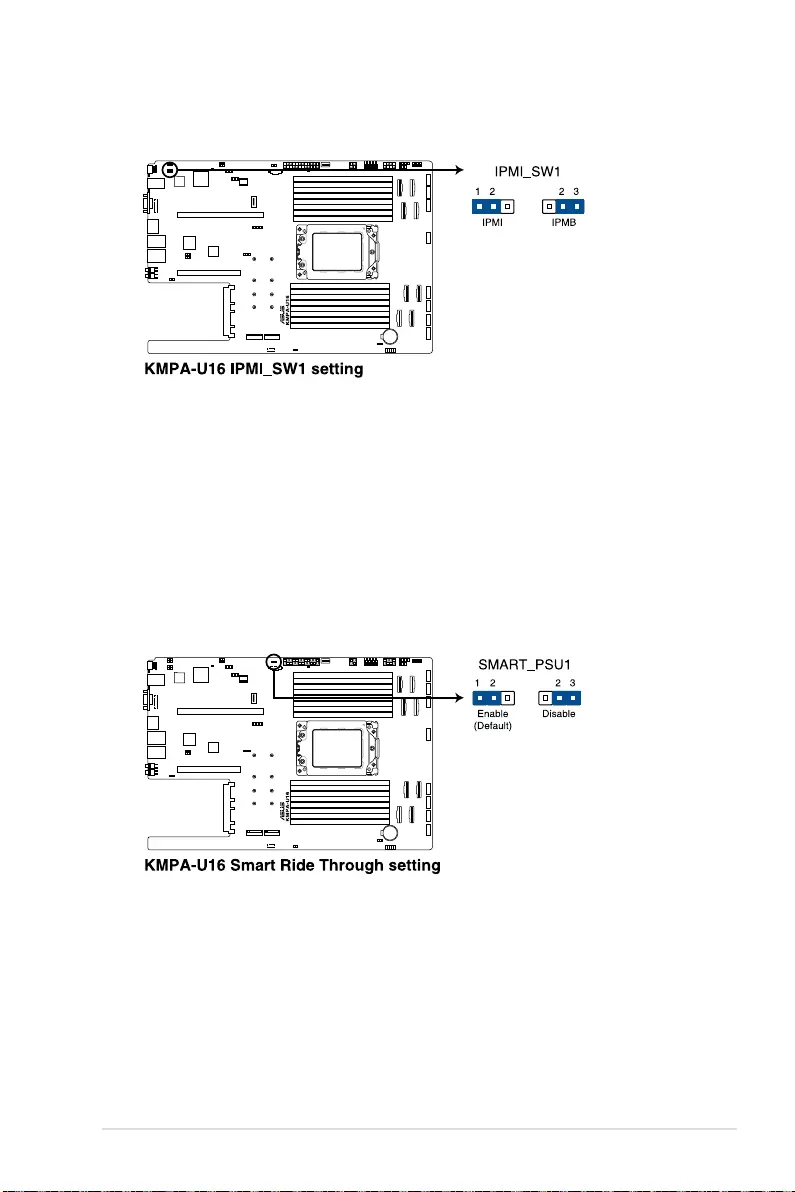
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-7
7. Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) setting (3-pin SMART_PSU1)
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) function.
This feature is enabled by default. Set to pins 2-3 to disable it. When enabled, SmaRT
allows uninterrupted operation of the system during an AC loss event.
6. IPMI SW setting (3-pin IPMI_SW1)
This jumper allows you to select which protocol in the GPU sensor to function.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-8
8. LAN controller settings (3-pin LAN_SW1-2)
These jumpers allow you to enable or disable the onboard LAN_SW1 or LAN_SW2.
Set to pins 1-2 to activate the Gigabit LAN feature.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-9
4.3 Internal LEDs
1. Standby Power LED (SBPWR1)
The motherboard comes with a standby power LED. The green LED lights up to
indicate that the system is ON, in sleep mode, or in soft-off mode. This is a reminder
that you should shut down the system and unplug the power cable before removing or
plugging in any motherboard component. The illustration below shows the location of
the onboard LED.
2. Baseboard Management Controller LED (BMCLED1)
The BMC LED lights up to indicate that the on-board BMC is functional.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-10
3. Message LED (MESLED1)
This onboard LED lights up to red when there is a BMC event log is generated.
4. Hard disk activity LED (HDDLED1)
This LED is for the storage devices connected to the onboard SATA, or SATA/SAS
add-on card. The read or write activities of any device connected to the onboard SATA,
or SATA/SAS add-on card causes the rear panel LED to light up.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-11
4.4 Internal connectors
1. Slim PCIe connector (SLMPCIE1-6)
Connects the PCIe signal to the front riser card or NVMe port on the backplane.
2. Slim SATA PCIe connector (SLMSATA_PCIE7-8)
Connects PCIe or SATA signal to backplane to support NVMe or SATA drives.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-12
3. USB 2.0 connector (10-1 pin USB2)
This connector is for USB 2.0 ports. Connect the USB module cable to the connector,
and then install the module to a slot opening at the back of the system chassis. The
USB connectors comply with USB 2.0 specification that supports up to 480 Mbps
connection speed.
4. USB 3.2 Gen 1 connector (USB3_34)
The USB 3.2 Gen 1 connector provides data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gb/s. The
Type-A connector allows you to directly connect a USB flash drive.
The USB port module is purchased separately.
KMPA-U16
KMPA-U16 USB 2.0 connector
USB2
PIN 1
USB+5V
USB_P6-
USB_P6+
GND
NC
USB+5V
USB_P7-
USB_P7+
GND
B
KMPA-U16
AUSB3_34
KMPA-U16 USB 3.2 Gen 1 connector

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-13
5. Chassis Intrusion (2-pin INTRUSION1)
These leads are for the intrusion detection feature for chassis with intrusion sensor or
microswitch. When you remove any chassis component, the sensor triggers and sends
a high level signal to these leads to record a chassis intrusion event. The default setting
is to short the CHASSIS# and the GND pin by a jumper cap to disable the function.
6. Serial port connector (10-1 pin COM1)
This connector is for a serial (COM) port. Connect the serial port module cable to this
connector, then install the module to a slot opening at the back of the system chassis.
The COM module is purchased separately.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-14
7. System fan connectors (6-pin FRNT_FAN1-8)
The fan connectors support cooling fans of 0.8A–1.0A (12 W max.) or a total of 6.4
A–8.0 A (96 W max.) at +12V. Connect the fan cables to the fan connectors on the
motherboard, making sure that the black wire of each cable matches the ground pin of
the connector.
DO NOT forget to connect the fan cables to the fan connectors. Insufficient air flow inside
the system may damage the motherboard components. These are not jumpers! DO NOT
place jumper caps on the fan connectors!

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-15
8. TPM connector (14-1 pin TPM1)
This connector supports a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) system, which can securely
store keys, digital certificates, passwords, and data. A TPM system also helps enhance
network security, protects digital identities, and ensures platform integrity.
9. M.2 (NGFF) card connector (NGFF1-2)
These connectors allow you to install M.2 devices.
This connector supports type 2242 / 2260 / 2280 / 22110 devices on both PCI-E and SATA
interface.
The M.2 (NGFF) device is purchased separately

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-16
10. Power connectors (24-pin EATXPWR; 8-pin EATX12V1; 4-pin EATX12V2)
These connectors are for the power supply plugs that connects to the power board.
The power supply plugs are designed to fit these connectors in only one orientation.
Find the proper orientation and push down firmly until the connectors completely fit.
DO NOT connect VGA cards to these connectors. Doing so may cause system boot errors
and permanent damage to your motherboard or device.
11. VGA connector (16-pin VGA_HDR1)
This connector supports the VGA High Dynamic-Range interface.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-17
12. Micro SD card slot (MSD1)
Your motherboard supports SD Memory Card v2.00 (SDHC) / v3.00 (SDXC).
Some memory cards may not be compatible with your motherboard. Ensure that you use
only compatible memory cards to prevent loss of data, damage to your device, or memory
card, or both.
Disconnect all power (including redundant PSUs) from the existing system before you add
or remove a Memory Card, then reboot the system to access the Memory Card.
13. Storage device activity LED connector (4-pin HDLED1)
This LED connector is for the storage add-on card cable connected to the SATA or
SAS add-on card. The read or write activities of any device connected to the SATA or
SAS add-on card causes the front panel LED to light up.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-18
14. System panel connector (10-1 pin SYS_PANEL1; 14-1 pin SYS_PANEL2)
This connector supports several chassis-mounted functions.
• System power LED (POWERLED)
This 2-pin connector is for the system power LED. Connect the chassis power LED
cable to this connector. The system power LED lights up when you turn on the system
power, and blinks when the system is in sleep mode.
• Message LED (2-pin MLED)
This 2-pin connector is for the message LED cable that connects to the front message
LED. The message LED is controlled by the BMC to indicate an abnormal event
occurrence.
• Locator LED connector (BMCLOCLED, LOCLED)
This connector allows you to connect the Locator LED. The Location LED helps visually
locate and identify the server in error on a server rack.
• Power Button/Soft-off Button connector (PWRBTN)
The 3-1 pin connector allows you to connect the system power button. Press the power
button to power up the system, or put the system into sleep or soft-off mode (depending
on the operating system settings).
• LAN activity LED connector (LAN1_LED, LAN2_LED, LAN3_LED, LAN4_LED)
This 2-pin connector allows you to connect the Gigabit LAN Activity LED.
• Reset button connector (RESET)
This connector allows you to connect the chassis-mounted reset button. Press the
reset button to reboot the system.
• TR1 Sensor connector (TR1 SENSOR)
This connector allows detection of the environmental temperature of the front panel. •
Locator button connector (BMCLOCBTN#)
This connector allows you to connect the Locator button. Press the button to light up
the Locator LED.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series 4-19
• Storage Device Activity LED connector (HDLED)
This connector allows you to connect the Storage Device Activity LED. The Storage
Device Activity LED lights up or blinks when data is read from or written to the storage
device or storage device add-on card.
15. VPP_I2C1 connector (10-1 pin VPP_I2C1)
This connector is used for the sensor readings.
16. BMC Debug UART connector (3-pin BMC_DEBUGUART1)
This connector is used for reading the BMC UART Debug log.

Chapter 4: Motherboard Information
4-20
17. Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) setting (3-pin SMART_PSU1)
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the Smart Ride Through (SmaRT) function.
This feature is enabled by default. Set to pins 2-3 to disable it. When enabled, SmaRT
allows uninterrupted operation of the system during an AC loss event.
18. SLMPCIE SGPIO connector (6-1 pin SLM7_SGPIO1, SLM8_SGPIO1)
This connector is the SGPIO header for controlling the HDD LED function.

5
BIOS Setup
This chapter tells how to change the system settings through
the BIOS Setup menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS
parameters are also provided.
Chapter 5: BIOS Setup

5-2 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.1 Managing and updating your BIOS
The following utilities allow you to manage and update the motherboard Basic Input/Output
System (BIOS) setup:
1. ASUS CrashFree BIOS 3
To recover the BIOS using a bootable USB flash disk drive when the BIOS file fails or
gets corrupted.
2. ASUS EzFlash
Updates the BIOS using a USB flash disk.
3. BUPDATER
Updates the BIOS in DOS mode using a bootable USB flash disk drive.
Refer to the corresponding sections for details on these utilities.
Recovering the BIOS from a USB flash drive
To recover the BIOS from a USB flash drive:
1. Insert the USB flash drive with the original or updated BIOS file to one USB port on the
system.
2. The utility will automatically recover the BIOS. It resets the system when the BIOS
recovery finished.
DO NOT shut down or reset the system while recovering the BIOS! Doing so would cause
system boot failure!
The recovered BIOS may not be the latest BIOS version for this motherboard. Visit the
ASUS website at www.asus.com to download the latest BIOS file.
Save a copy of the original motherboard BIOS file to a bootable USB flash disk drive in
case you need to restore the BIOS in the future. Copy the original motherboard BIOS using
the BUPDATER utility.
5.1.1 ASUS CrashFree BIOS 3 utility
The ASUS CrashFree BIOS 3 is an auto recovery tool that allows you to restore the BIOS file
when it fails or gets corrupted during the updating process. You can update a corrupted BIOS
file using a USB flash drive that contains the updated BIOS file.
Prepare a USB flash drive containing the updated motherboard BIOS before using this
utility.

5-3
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
3. Press Left arrow key to switch to the Drive field.
4. Press the Up/Down arrow keys to find the USB flash disk that contains the latest BIOS,
then press <Enter>.
5. Press Right arrow key to switch to the Folder Info field.
6. Press the Up/Down arrow keys to find the BIOS file, and then press <Enter> to perform
the BIOS update process. Reboot the system when the update process is done.
• This function can support devices such as a USB flash disk with FAT 32/16 format and
single partition only.
• DO NOT shut down or reset the system while updating the BIOS to prevent system
boot failure!
Ensure to load the BIOS default settings to ensure system compatibility and stability. Press
<F5> and select Yes to load the BIOS default settings.
5.1.2 ASUS EZ Flash Utility
The ASUS EZ Flash Utility feature allows you to update the BIOS without having to use a
DOS-based utility.
Before you start using this utility, download the latest BIOS from the ASUS website at
www.asus.com.
To update the BIOS using EZ Flash Utility:
1. Insert the USB flash disk that contains the latest BIOS file into the USB port.
2. Enter the BIOS setup program. Go to the Tool menu then select Start ASUS EzFlash.
Press <Enter>.
Current Platform
Platform : KMPA-U16
Version : 0215
Build date: 01/13/2021
New Platform
Platform : KMPA-U16
Version : 0401
Build date: 04/12/2021
ASUSTek. EzFlash Utility
FS0
FS1
FS2
FS3
[Up/Down/Left/Right]:Switch [Enter]:Choose [q]:Exit

5-4 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.1.3 BUPDATER utility
The succeeding BIOS screens are for reference only. The actual BIOS screen displays
may not be the same as shown.
The BUPDATER utility allows you to update the BIOS file in the DOS environment using a
bootable USB flash disk drive with the updated BIOS file.
Updating the BIOS file
To update the BIOS file using the BUPDATER utility:
1. Visit the ASUS website at www.asus.com and download the latest BIOS file for the
motherboard. Save the BIOS file to a bootable USB flash disk drive.
2. Copy the BUPDATER utility (BUPDATER.exe) from the ASUS support website at
www.asus.com/support to the bootable USB flash disk drive you created earlier.
3. Boot the system in DOS mode, then at the prompt, type:
BUPDATER /i[filename].CAP
where [filename] is the latest or the original BIOS file on the bootable USB flash disk
drive, then press <Enter>.
A:\>BUPDATER /i[file name].CAP

5-5
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
4. The utility verifies the file, then starts updating the BIOS file.
DO NOT shut down or reset the system while updating the BIOS to prevent system boot
failure!
5. The utility returns to the DOS prompt after the BIOS update process is completed.
Reboot the system from the hard disk drive.
The BIOS update is finished! Please restart your system.
C:\>
Current Platform
Platform : KMPA-U16
Version : 0215
Build date: 01/13/2021
New Platform
Platform : KMPA-U16
Version : 0401
Build date: 04/14/2021
ASUSTek. EzFlash Utility
Start Programming Flash. DO NOT SHUTDOWN THE SYSTEM!!!
Write
75%

5-6 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.2 BIOS setup program
This motherboard supports a programmable firmware chip that you can update using the
provided utility described in section 5.1 Managing and updating your BIOS.
Use the BIOS Setup program when you are installing a motherboard, reconfiguring your
system, or prompted to “Run Setup.” This section explains how to configure your system
using this utility.
Even if you are not prompted to use the Setup program, you can change the configuration of
your computer in the future. For example, you can enable the security password feature or
change the power management settings. This requires you to reconfigure your system using
the BIOS Setup program so that the computer can recognize these changes and record them
in the CMOS RAM of the firmware chip.
The firmware chip on the motherboard stores the Setup utility. When you start up the
computer, the system provides you with the opportunity to run this program. Press <Del>
during the Power-On Self-Test (POST) to enter the Setup utility; otherwise, POST continues
with its test routines.
If you wish to enter Setup after POST, restart the system by pressing <Ctrl>+<Alt>+<Delete>,
or by pressing the reset button on the system chassis. You can also restart by turning the
system off and then back on. Do this last option only if the first two failed.
The Setup program is designed to make it as easy to use as possible. Being a menu-driven
program, it lets you scroll through the various sub-menus and make your selections from the
available options using the navigation keys.
• The default BIOS settings for this motherboard apply for most conditions to ensure
optimum performance. If the system becomes unstable after changing any BIOS
settings, load the default settings to ensure system compatibility and stability. Press
<F5> and select Yes to load the BIOS default settings.
• The BIOS setup screens shown in this section are for reference purposes only, and
may not exactly match what you see on your screen.
• Visit the ASUS website (www.asus.com) to download the latest BIOS file for this
motherboard.

5-7
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.2.2 Menu bar
The menu bar on top of the screen has the following main items:
Main For changing the basic system configuration
Performance Tuning For changing the performance settings
Advanced For changing the advanced system settings
Chipset For changing the chipset settings
Security For changing the security settings
Boot For changing the system boot configuration
Tool For configuring options for special functions
Event Logs For changing the event log settings
Server Mgmt For changing the Server Mgmt settings
Exit For selecting the exit options
To select an item on the menu bar, press the right or left arrow key on the keyboard until the
desired item is highlighted.
5.2.1 BIOS menu screen
Navigation keys
General help
Menu bar Configuration fieldsMenu items

5-8 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.2.3 Menu items
The highlighted item on the menu bar displays the specific items for that menu. For example,
selecting Main shows the Main menu items.
The other items (such as Advanced) on the menu bar have their respective menu items.
5.2.4 Submenu items
A solid triangle before each item on any menu screen means that the item has a submenu.
To display the submenu, select the item then press <Enter>.
5.2.5 Navigation keys
At the bottom right corner of a menu screen are the navigation keys for the BIOS setup
program. Use the navigation keys to select items in the menu and change the settings.
5.2.6 General help
At the top right corner of the menu screen is a brief description of the selected item.
5.2.7 Configuration fields
These fields show the values for the menu items. If an item is user-configurable, you can
change the value of the field opposite the item. You cannot select an item that is not user-
configurable.
A configurable field is enclosed in brackets, and is highlighted when selected. To change the
value of a field, select it and press <Enter> to display a list of options.
5.2.8 Pop-up window
Select a menu item and press <Enter> to display a pop-up window with the configuration
options for that item.
5.2.9 Scroll bar
A scroll bar appears on the right side of a menu screen when there are items that do not fit on
the screen. Press the Up / Down arrow keys or <Page Up> / <Page Down> keys to display
the other items on the screen.

5-9
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.3 Main menu
When you enter the BIOS Setup program, the Main menu screen appears. The Main menu
provides you an overview of the basic system information, and allows you to set the system
date, time, and language settings.
5.3.1 System Language [English]
Allows you to select the system default language.
5.3.2 System Date [Day xx/xx/xxxx]
Allows you to set the system date.
5.3.3 System Time [xx:xx:xx]
Allows you to set the system time.

5-10 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.4 Performance Tuning menu
The Performance Tuning menu items allow you to change performance related settings for
different scenarios.
Optimized Performance Setting [Default]
Allows you to select performance settings for different scenarios.
[Default] Default settings.
[By Benchmark] Optimize for different kinds of benchmarks. Select this option, then select a
benchmark type from the >> list.
[By Workload] Optimize for different kinds of workloads. Select this option, then select a
workload type from the >> list.
The following item appears only when you set Power Balancer to [Disabled].
Core Optimizer [Disabled]
Allows you to keep the processor operating at the turbo highest frequency for the maximum
performance. For Windows Server 2019, please set Powercfg /setacvalueindex
scheme_current sub_processor perfautonomous 1 & Powercfg /setactive
scheme_current to enable this feature. For Linux, please set cpupower frequency-set
-g performance.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Linux support may vary by version of the OS.
The following item appears only when you set Optimized Performance Setting to
[Default].
Engine Boost [Disabled]
Enable this item to boost the CPU's frequency.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Operate with an ambient temperature of 25oC or lower for optimized performance.

5-11
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Overclocking [Disabled]
Enable this item to increase the CPU’s clock. Please use an external PCIe storage controller
for your hard drives when enabling this feature.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Please note that overclocking might cause component damage or system crashes, which
may reduce the lifespan of the system and the CPU. Use this tool at your own risk.

5-12 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.5 Advanced menu
The Advanced menu items allow you to change the settings for the CPU and other system
devices.
Take caution when changing the settings of the Advanced menu items. Incorrect field
values can cause the system to malfunction.

5-13
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.5.1 Trusted Computing
5.5.2 PSP Firmware Versions
This page displays the PSP firmware versions.
Configuration
Security Device Support [Enable]
Allows you to enable or disable the BIOS support for security device. O.S. will not show
Security Device. TCG EFI protocol and INT1A interface will not be available.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable]
5.5.3 Redfish Host Interface Settings
Allows you to configure the Advance Power Management (APM) settings.
Redfish [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable Redfish.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-14 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.5.4 AMD CBS
The items in this menu shows the AMD Common BIOS Specifications.
The AMD CBS menu will appear in the top menu for AMD EPIC™ 7002 Series processors.
CPU Common Options
Performance
OC Mode [Normal Operation]
Configuration options: [Normal Operation] [Customized]
The following items appear only when OC Mode is set to [Customized].
Custom Core Pstates
This option allows you to enable Core Pstates. Read the disclaimer and select
I Accept to continue.
Damage caused by use of your AMD processor outside of specification or in excess of
factory settings are not covered by your system manufacturers warranty.
The following items appear only when [Accept] is selected for Custom Core Pstates.
Custom Pstate0 [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Custom]

5-15
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following items appear only when Custom Pstate0 is set to [Custom].
Pstate0 Freq (MHz) [0]
Allows you to specify core frequency (MHz).
CCD/Core/Thread Enablement
This option allows you to enable CCD/Core/Thread Enablement.
S3 is not supported on systems where cores/threads have been removed/disabled.
CCD Control [Auto]
Sets the number of CCDs to be used. Once this option has been used
to remove any CCDs, a POWER CYCLE is required in order for future
selections to take effect.
Configuration options: [Auto] [2 CCDs] [3 CCDs] [4 CCDs] [6 CCDs]
Core Control [Auto]
Sets the number of cores to be used. Once this option has been used
to remove any cores, a POWER CYCLE is required in order for future
selections to take effect.
Configuration options: [Auto] [ONE (1 + 0)] [TWO (2 + 0)] [THREE (3 +
0)] [FOUR (4 + 0)] [FIVE (5 + 0)] [SIX (6 + 0)] [SEVEN (7 + 0)]
SMT Control [Auto]
Can be used to disable symmetric multithreading. To re-enable SMT, a
POWER CYCLE is needed after selecting the [Enable] option. Select [Auto]
based on BIOS PCD (PcdAmdSmtMode) defatul setting.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
S3 is not supported on systems where cores/threads have been removed/disabled.
Prefetcher settings
L1 Stream HW Prefetcher [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable L1 Stream HW Prefetcher.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
L1 Stride Prefetcher [Auto]
Uses memory access history of individual instructions to fetch additional lines
when each access is a constant distance from the previous.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
L1 Region Prefetcher [Auto]
Uses memory access history to fetch additional lines when the data access for
a given instruction tends to be followed by other data accesses.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
L2 Stream HW Prefetcher [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable L2 Stream HW Prefetcher.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
L2 Up/Down Prefetcher [Auto]
Uses memory access history to determine whether to fetch the next or previous
line for all memory access.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]

5-16 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Core Watchdog
Core Watchdog Timer Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable CPU Watchdog Timer.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
The following items are only available when Core Watchdog Timer Enable is set to
[Enabled].
Core Watchdog Timer Interval [Auto]
Configuration options: [21.461s] [10.730s] [5.364s] [2.681s] [1.340s]
[669.41ms] [334.05ms] [166.37ms] [82.53ms] [40.61ms] [20.970ms]
[10.484ms] [5.241ms] [2.620ms] [1.309ms] [654.08us] [326.4us] [162.56us]
[80.64us] [39.68us] [Auto]
Core Watchdog Timer Severity [Auto]
Allows you to specify the CPU watch dog timer severity.
Configuration options: [No Error] [Transparent] [Corrected] [Deferred]
[Uncorrected] [Fatal] [Auto]
RedirectForReturnDis [Auto]
This option is from a workaround for GCC/C000005 issue for XV Core on
CZ A0, setting MSRC001_1029 Decode Configuration (DE_CFG) bit 14
[DecfgNoRdrctForReturns] to 1.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1] [0]
Platform First Error Handling [Auto]
This option is from a workaround for GCC/C000005 issue for XV Core on
CZ A0, setting MSRC001_1029 Decode Configuration (DE_CFG) bit 14
[DecfgNoRdrctForReturns] to 1.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1] [0]
Core Performance Boost [Auto]
This option allows you to enable or disable CPB.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Auto]
Global C-state Control [Auto]
This option allows you to control IO based C-state generation and DF C-states.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Power Supply Idle Control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Low Current Idle] [Typical Current Idle] [Auto]
SEV ASID Count [Auto]
This field specifies the maximum valid ASID, which affects the maximum system
physical address space. 16TB of physical address space is available for systems that
support 253 ASIDs, while 8TB of physical address space is available for systems that
support 509 ASIDs.
Configuration options: [253 ASIDs] [509 ASIDs] [Auto]
SEV-ES ASID Space Limit Control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]

5-17
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following item appears only when SEV-ES ASID Space Limit Control is set to
[Manual].
SEV-ES ASID Space Limit [Auto]
SEV Vms using ASIDs below the SEV-ES ASID Space Limit must enable the SEV-ES
feature. ASIDs from SEV-ES ASID Space Limit to (SEV ASID Count + 1) can only be
used with SEV VMs. If this field is set to (SEV ASID Count + 1), all ASIDs are forced to
be SEV-ES ASIDs. Hence, the valid values for this field is 1 - (SEV ASID Count + 1).
Configuration options: [1] - [520]
Streaming Stores Control [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable the streaming stores functionality.
Configuration options: [1] – [520]
Local APIC Mode [Auto]
Configuration options: [Compatibility] [XAPIC] [X2APIC] [Auto]
ACPI _CST C1 Operation [Auto]
Determines whether or not to declare the C1 state to the OS.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
MCA error thresh enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable MCA error thresholding.
Configuration options: [False] [True] [Auto]
The following item appears only when MCA error thresh enable is set to [True].
MCA error thresh count [FF5]
Allows you to set the effective error threshold count = 4095(0xFFF) - <this value> (e.g.
the default value of 0xFF5 results in a threshold of 10).
SMU and PSP Debug Mode [Auto]
When this option is set to [Enabled], specific uncorrected errors detected by the PSP
FW or SMU FW will hang and not reset the system.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Xtrig7 Workaround [Auto]
This workaround is only applicable for Rev A.
[Auto] The bronze workaround is applied.
[No Workaround] Applied for Rev B, and changing the selection for this option
will not result in any changes.
[Bronze Workaround] DbReq and PDM function as expected, breakpoint redirect
capability compromised.
[Silver Workaround] DbReq, PDM, and breakpoint redirect function as expected,
SCAN capability compromised.
PPIN Opt-in [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable the PPIN feature.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-18 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
SNP Memory (RMP Table) Coverage [Auto]
Setting this option to [Enabled] will cover the entire system’s memory.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Custom] [Auto]
The following item appears only when SNP Memory (RMP Table) Coverage is set to
[Custom].
Amount of Memory to Cover [0]
Allows you to specify MB of System Memory to be covered in Hex.
SMEE [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable secure memory encryption control.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Action on BIST Failure [Auto]
Allows you to set action to take when a CCD BIST failure is detected.
Configuration options: [Do Nothing] [Down-CCD] [Auto]
Fast Short REP MOVSB [Enabled]
Default set to 1, can be set to zero for analysis purposes as long as OS supports it.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Enhanced REP MOVSB/STOSB [Enabled]
Default set to 1, can be set to zero for analysis purposes as long as OS supports it.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
REP-MOV/STOS Streaming [Enabled]
Allows REP-MOVS/STOS to use non-caching streaming stores for large sizes.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
X3D [Auto]
Allows you to set the override of X3D technology.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Disable] [1 stack] [2 stacks] [4 stacks]
IBS hardware workaround [Auto]
Set this option if using IBS execution sampling without software workaround for
erratum 1,285. May impact performance.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enabled]
DF Common Options
Scrubber
DRAM scrub time [Auto]
Allows you to set a number of hours to scrub memory.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [1 hour] [4 hours] [8 hours] [16 hours] [24
hours] [48 hours] [Auto]
Poison scrubber control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Redirect scrubber control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-19
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Redirect scrubber limit [Auto]
Configuration options: [2] [4] [8] [Infinite] [Auto]
Periodic Directory Rinse [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Memory Addressing
NUMA nodes per socket [Auto]
Specifies the number of desired NUMA nodes per socket. Zero will attempt to
interleave the two sockets together.
Configuration options: [NPS1] [NPS2] [NPS4] [Auto]
Memory interleaving [Auto]
This items allows for disabling memory interleaving. Note that NUMA nodes
per socket will be honored regardless of this setting.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Auto]
Memory interleaving size [Auto]
This item controls the memory interleaving size. The valid values are AUTO,
256 bytes, 512 bytes, 1 Kbytes, or 2 Kbytes. This also determines the starting
address of the interleave (bit 8, 9, 10, or 11).
Configuration options: [256 Bytes] [512 Bytes] [1 KB] [2 KB] [Auto]
1TB remap [Auto]
Attempt to remap DRAM out of the space just below the 1TB boundary. The
ability to remap depends on DRAM configuration, NPS, and interleaving
selection, and may not always be possible.
Configuration options: [Do not remap] [Attempt to remap] [Auto]
DRAM map inversion [Auto]
Inverting the map will cause the highest memory channels to get assigned the
lowest addresses in the system.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Location of private memory regions [Auto]
Controls whether or not the private memory regions (PSP, SMU, and CC6) are
at the top of DRAM or distributed. Note that distributed requires memory on
all dies. Note that it will always be at the top of DRAM id some dies don’t have
memory regardless of this option’s setting.
Configuration options: [Distributed] [Consolidated] [Consolidated to 1st DRAM
pair] [Auto]
ACPI
ACPI SRAT L3 Cache As NUMA Domain [Auto]
[Disabled] Memory Addressing \ NUMA nodes per socket will be
declared.
[Enabled] Each CCX in the system will be declared as a separate NUMA
Domain.
[Auto] Auto.
ACPI SLIT Distance Control [Auto]
This option determines how the SLIT distances are declared.
Configuration options: [Manual] [Auto]

5-20 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
The following item appears only when ACPI SLIT Distance Control is set to [Auto].
ACPI SLIT remote relative distance [Auto]
Allows you to set the remote socket distance for 2P systems as near (2.8) or
far (3.2).
Configuration options: [Near] [Far] [Auto]
The following items appear only when ACPI SLIT Distance Control is set to [Manual].
ACPI SLIT same socket distance [C]
Specify the distance to other physical domains within the same socket.
ACPI SLIT remote socket distance [20]
Specify the distance to domains the remote socket.
ACPI SLIT local SLink distance [32]
Specify the distance to an SLink domain on the same socket.
ACPI SLIT remote SLink distance [3C]
Specify the distance to an SLink domain on the other socket.
ACPI SLIT local inter-SLink distance [FF]
Specify the distance between two SLink domains on the same socket.
ACPI SLIT remote inter-SLink distance [FF]
Specify the distance between two SLink domains, each on a different socket.
Link
GMI encryption control [Auto]
Allows you to control the GMI link encryption.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
xGMI encryption control [Auto]
Allows you to control the xGMI link encryption.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
CAKE CRC perf bounds control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when CAKE CRC perf bounds control is set to [Manual].
CAKE CRC perf bounds [64]
This item specifies the amount of performance loss that is acceptable to enable
CRC protection. Units are in 0.00001%, RangeL disabled (0) - 10% (1000000).
xGMI Link Configuration [Auto]
Allows you to configure the number of xGMI2 links used on a multi-socket
system.
Configuration options: [Auto] [2 xGMI Links] [3 xGMI Links] [4 xGMI Links]

5-21
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
4-link xGMI max speed [Auto]
Configuration options: [6.4Gbps] [7.467Gbps] [8.533Gbps] [9.6Gbps]
[10.667Gbps] [11Gbps] [12Gbps] [13Gbps] [14Gbps] [15Gbps] [16Gbps]
[17Gbps] [18Gbps] [19Gbps] [20Gbps] [21Gbps] [22Gbps] [23Gbps] [24Gbps]
[25Gbps] [Auto]
3-link xGMI max speed [Auto]
Configuration options: [6.4Gbps] [7.467Gbps] [8.533Gbps] [9.6Gbps]
[10.667Gbps] [11Gbps] [12Gbps] [13Gbps] [14Gbps] [15Gbps] [16Gbps]
[17Gbps] [18Gbps] [19Gbps] [20Gbps] [21Gbps] [22Gbps] [23Gbps] [24Gbps]
[25Gbps] [Auto]
xGMI TXEQ Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the XGMI TXEQ/RX vetting mode.
Configuration options: [TXEQ_Disabled] [TXEQ_Lane] [TXEQ_Link] [TXEQ_
RX_Vet] [Auto]
xGMI 18GACOFC [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable the 18GACOFC control.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enable] [Disable]
Disable DF to external downstream IP SyncFloodPropagation [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Error propagation to UMC or any downstream slaves
e.g. FCH. Use this to avoid reset in failure scenario.
Configuration options: [Sync Flood disabled] [Sync Flood enabled] [Auto]
Disable DF sync flood propagation [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable propagation from PIE to other DF components and
eventually to SDP ports.
Configuration options: [Sync Flood disabled] [Sync Flood enabled] [Auto]
Freeze DF module queues on error [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable freezing of all DF queues on error and also forces a
sync flood on HWA even if MCAs are disabled.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
CC6 memory region encryption [Auto]
Allows you to control whether or not the CC6 save/restore memory is encrypted.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
System probe filter [Auto]
Allows you to control whether or not the probe filter is enabled. Has no effect on parts
where the probe filter is fuse disabled.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Memory Clear [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable memory clear. When this item is set to [Disabled],
BIOS does not implement MemClear after memory training (only if non-ECC DIMMs
are used).
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
PSP error injection support [False]
Configuration options: [False] [True]

5-22 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
UMC Common Option
DDR4 Common Options
DRAM Timing Configuration
Allows you to enable DRAM timing configuration.
Damage caused by use of your AMD processor outside of specification or in excess of
factory settings are not covered by your system manufacturers warranty.
The following items appear only when [Accept] is selected for DRAM Timing
Configuration.
Overclock [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enabled]
The following items appear only when Overclock is set to [Enabled].
Memory Clock Speed [Auto]
Specifies the memory clock frequency.
Configuration options: [Auto] [667MHz] [800MHz] [933MHz] [1067MHz]
[1200MHz] [1333MHz] [1467MHz] [1600MHz] [1633MHz] [1667MHz]
[1700MHz] [1733MHz] [1767MHz] [1800MHz] [400MHz]
Tcl [Auto]
Specifies the CAS latency.
Configuration options: [Auto] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
[0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk] [0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h
Clk] [15h Clk] [16h Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk]
[1Ch Clk] [1Dh Clk] [1Eh Clk] [1Fh Clk] [20h Clk] [21h Clk]
Trcdrd [Auto]
Specifies the RAS# Active to CAS# Read Delay Time.
Configuration options: [Auto] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
[0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk] [0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h
Clk] [15h Clk] [16h Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk]
Trcdwr [Auto]
Specifies the RAS# Active to CAS# Write Delay Time.
Configuration options: [Auto] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
[0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk] [0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h
Clk] [15h Clk] [16h Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk]
Trp [Auto]
Specifies the Row Precharge Delay Time.
Configuration options: [Auto] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
[0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk] [0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h
Clk] [15h Clk] [16h Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk]
Tras [Auto]
Specifies the Active to Precharge Delay Time.
Configuration options: [Auto] [15h Clk] [16h Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h
Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk] [1Ch Clk] [1Dh Clk] [1Eh Clk] [1Fh Clk] [20h
Clk] [21h Clk] [22h Clk] [23h Clk] [24h Clk] [25h Clk] [26h Clk] [27h Clk]
[28h Clk] [29h Clk] [2Ah Clk] [2Bh Clk] [2Ch Clk] [2Dh Clk] [2Eh Clk]
[2Fh Clk] [30h Clk] [31h Clk] [32h Clk] [33h Clk] [34h Clk] [35h Clk] [36h
Clk] [37h Clk] [38h Clk] [39h Clk] [3Ah Clk]

5-23
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Trc Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Trc.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Trc Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Trc [39]
Specifies Active to Active/Refresh Delay Time. Valid values 87h-1Dh.
TrrdS [Auto]
Specifies the Activate to Activate Delay Time, different back group
(tRRD_S).
Configuration options: [Auto] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk] [7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk]
[0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
TrrdL [Auto]
Specifies the Activate to Activate Delay Time, same back group
(tRRD_L).
Configuration options: [Auto] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk] [7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk]
[0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk]
Tfaw Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Tfaw.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Tfaw Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Tfaw [1]
Specifies the Four Activate Window Time. Valid values 36h-6h.
TwtrS [Auto]
Specifies the Minimum Write to Read Time, different bank group.
Configuration options: [Auto] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk] [7 Clk]
[8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
TwtrL [Auto]
Specifies the Minimum Write to Read Time, same bank group.
Configuration options: [Auto] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk] [7 Clk]
[8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
Twr Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Twr.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Twr Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Twr [12]
Specifies the Minimum Write Recovery Time. Valid values 51h-Ah.
Trcpage Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Trcpage.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Trcpage Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Trcpage [0]
SDRAM Optional Features (tMAW MAC). Valid values 3FFh-0h.

5-24 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
TrdrdScL Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies TrdrdScL.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when TrdrdScL Ctrl is set to [Manual].
TrdrdScL [3]
Specifies the CAS to CAS Delay Time, same bank group. Valid values
Fh-1h.
TwrwrScL Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies TwrwrScL.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when TwrwrScL Ctrl is set to [Manual].
TwrwrScL [3]
Specifies the CAS to CAS Delay Time, same bank group. Valid values
3Fh-1h.
Trfc Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Trfc.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Trfc Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Trfc [138]
Specifies the Refresh Recovery Delay Time (tRFC1). Valid values
3DEh-3Ch.
Trfc2 Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Trfc2.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Trfc2 Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Trfc2 [C0]
Specifies the Refresh Recovery Delay Time (tRFC2). Valid values
3DEh-3Ch.
Trfc4 Ctrl [Auto]
Specifies Trfc4.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following item appears only when Trfc4 Ctrl is set to [Manual].
Trfc4 [84]
Specifies the Refresh Recovery Delay Time (tRFC4). Valid values
3DEh-3Ch.
Tcwl [Auto]
Specifies the CAS Write Latency.
Configuration options: [Auto] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Eh
Clk] [10h Clk] [12h Clk] [14h Clk]

5-25
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Trtp [Auto]
Specifies theRead CAS# to Precharge Delay Time.
Configuration options: [Auto] [5 Clk] [6 Clk] [7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah
Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
Tcke [Auto]
Specifies the CKE minimum high and low pulse width in memory clock
cycles.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h Clk] [15h Clk] [16h
Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk] [1Ch Clk] [1Dh Clk]
[1Eh Clk] [1Fh Clk]
Trdwr [Auto]
Specifies the Read to Write turnaround timing.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk] [10h Clk] [11h Clk] [12h Clk] [13h Clk] [14h Clk] [15h Clk] [16h
Clk] [17h Clk] [18h Clk] [19h Clk] [1Ah Clk] [1Bh Clk] [1Ch Clk] [1Dh Clk]
[1Eh Clk] [1Fh Clk]
Twrrd [Auto]
Specifies the Write to Read turnaround timing.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
TwrwrSc [Auto]
Specifies the Write to Write turnaround timing in the same chipselect.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
TwrwrSd [Auto]
Specifies the Write to Write turnaround timing in the same DIMM.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
TwrwrDd [Auto]
Specifies the Write to Write turnaround timing in a different DIMM.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
TrdrdSc [Auto]
Specifies the Read to Read turnaround timing in the same chipselect.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
TrdrdSd [Auto]
Specifies the Read to Read turnaround timing in the same DIMM.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]

5-26 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
TrdrdDd [Auto]
Specifies the Read to Read turnaround timing in a different DIMM.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1 Clk] [2 Clk] [3 Clk] [4 Clk] [5 Clk] [6 Clk]
[7 Clk] [8 Clk] [9 Clk] [0Ah Clk] [0Bh Clk] [0Ch Clk] [0Dh Clk] [0Eh Clk]
[0Fh Clk]
ProcODT [Auto]
Specifies the Processor ODT.
Configuration options: [Auto] [High Impedance] [480 ohm] [240 ohm]
[160 ohm] [120 ohm] [96 ohm] [80 ohm] [68.6 ohm] [60 ohm] [53.3 ohm]
[48 ohm] [43.6 ohm] [40 ohm] [36.9 ohm] [34.3 ohm] [32 ohm] [30 ohm]
[28.2 ohm]
DRAM Controller Configuration
DRAM Power Options
Power Down Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable power down mode.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Power Down Entry Delay [BB8]
Allows you to specify value at UMC::CH::DramTiming17 [19:8]
PwrDownDly.
SubUrgRefLowerBound [4]
Specifies the stored refresh limit required to enter sub-urgent refresh
mode. Constraint: SubUrgRefLowerBound <= UrgRefLimit. Valid value:
6-1
UrgRefLimit [6]
Specifies the stored refresh limit required to enter urgent refresh mode.
Constraint: SubUrgRefLowerBound <= UrgRefLimit. Valid value: 6-1
DRAM Maximum Activate Count [Auto]
Override DIMM SPD Byte 7 [3:0]. Maximum Activate Count (MAC).
When set to [Auto] it will be based on SPD setting.
Configuration options: [Untested MAC] [700 K] [600 K] [500 K] [400 K]
[300 K] [200 K] [Unlimited MAC] [Auto]
DRAM Refresh Rate [7.8 usec]
Configuration options: [7.8 usec] [3.9 usec]
Self-Refresh Exit Staggering [Disabled]
Tcksrx += (Trfc/n * (UMC_Number % 4)), here n = 3 or 4.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Trfc / 3] [Trfc / 4]
Does not apply the extra addition if set to [Disabled].
Cmd2T
Select between 1T and 2T mode on ADDR/CMD.
Configuration options: [Auto] [1T] [2T]
Gear Down Mode
Configuration options: [Auto] [Disabled] [Enabled]
CAD Bus Configuration
CAD Bus Timing User Controls [Auto]
Allows you to set the CAD bus signals to Auto or Manual.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]

5-27
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following items appear only when you set CAD Bus Timing User Controls to
[Manual].
AddrCmdSetup [0]
Allows you to setup time on CAD bus signals.
Configuration options: [0] – [39]
CsOdtSetup [0]
Allows you to setup time on CAD bus signals.
Configuration options: [0] – [39]
CkeSetup [0]
Allows you to setup time on CAD bus signals.
Configuration options: [0] – [39]
CAD Bus Drive Strength User Controls [Auto]
Allows you to set the CAD bus signals to Auto or Manual.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following items appear only when you set CAD Bus Drive Strength User Controls to
[Manual].
ClkDrvStren [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [120.0 Ohm] [60.0 Ohm] [40.0 Ohm] [30.0
Ohm] [24.0 Ohm] [20.0 Ohm]
AddrCmdDrvStren [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [120.0 Ohm] [60.0 Ohm] [40.0 Ohm] [30.0
Ohm] [24.0 Ohm] [20.0 Ohm]
Cs0dtDrvStren [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [120.0 Ohm] [60.0 Ohm] [40.0 Ohm] [30.0
Ohm] [24.0 Ohm] [20.0 Ohm]
CkeDrvStren [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [120.0 Ohm] [60.0 Ohm] [40.0 Ohm] [30.0
Ohm] [24.0 Ohm] [20.0 Ohm]
Data Bus Configuration
Data Bus Configuration User Controls [Auto]
Allows you to specify the mode for drive strength.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
The following items appear only when you set Data Bus Configuration User Controls to
[Manual].
RttNom [Auto]
Configuration options: [Rtt_Nom Disable] [RZQ/4] [RZQ/2] [RZQ/6]
[RZQ/1] [RZQ/5] [RZQ/3] [RZQ/7] [Auto]
RttWr [Auto]
Configuration options: [Dynamic ODT Off] [RZQ/2] [RZQ/1] [Hi-Z]
[RZQ/3] [Auto]
RttPark [Auto]
Configuration options: [Rtt_PARK Disable] [RZQ/4] [RZQ/2] [RZQ/6]
[RZQ/1] [RZQ/5] [RZQ/3] [RZQ/7] [Auto]

5-28 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Common RAS
Data Poisoning [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
DRAM Post Package Repair [Disable]
Allows you to enable or disable DRAM POST Package Repair.
Configuration options: [Enable] [Disable]
RCD Parity [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
DRAM Address Command Parity Retry [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when you set DRAM Address Command Parity Retry to
[Enabled].
Max Parity Error Replay [8]
The values in hex, 1, 2, or 3 is invalid.
Configuration options: [0] – [39]
Write CRC Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
DRAM Write CRC Enable and Retry Limit [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when you set DRAM Write CRC Enable and Retry Limit
to [Enabled].
Max Write CRC Error Replay [8]
The values in hex, 1, 2, or 3 is invalid.
Configuration options: [0] – [39]
Disable Memory Error Injection [True]
Configuration options: [False] [True]
ECC Configuration
DRAM ECC Symbol Size [Auto]
Configuration options: [x4] [x8] [x16] [Auto]
DRAM ECC Enable [Auto]
This option allows you to enable or disable DRAM ECC. Auto will set
ECC to enable.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
DRAM UECC Retry [Auto]
This option allows you to enable or disable DRAM UECC Retry.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Security
TSME [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Data Scramble [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-29
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Phy Configuration
PMU Training
DFE Read Training [Auto]
Perform 2D Read Training with DFE on.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
FFE Write Training [Auto]
Perform 2D Read WriteTraining with FFE on.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
PMU Pattern Bits Control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Manual]
PMU Pattern Bits [0]
Configuration options: [0] - [9]
DRAM Memory Mapping
Chipselect Interleaving [Auto]
Allows you to set interleave memory blocks across the DRAM chip selects for
node 0.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Auto]
BankGroupSwap [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
BankGroupSwapAlt [Auto]
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
Address Hash Bank [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable bank address hashing.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
Address Hash CS [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable CS address hashing.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
Address Hash Rm [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable RM address hashing.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
SPD Read Optimization [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SPD Read Optimization, if set to [Enabled],
SPD reads are skipped for Reserved fields and most of upper 256 Bytes. If set
to [Disabled], read all 512 SPD Bytes.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
NVDIMM
Disable NVDIMM-N Feature [No]
Allows you to disable NVDIMM-N feature for memroy margin tool.
Configuration options: [No] [Yes]
Memory MBIST
MBIST Enable [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable Memory MBIST.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled]

5-30 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
The following items appear only when MBIST Enable is set to [Enabled].
MBIST Test Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the MBIST Test Mode - Interface Mode (Tests Single and
Multiple CS transactions and Basic Connectivity) or Data Eye Mode (Measures
Voltage vs. Timing).
Configuration options: [Interface Mode] [Data Eye Mode] [Both] [Auto]
MBIST Aggressors [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Memory Aggressor test.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
MBIST Per Bit Slave Die Reporting [Auto]
Reports 2D Data Eye Results in ABL Log for each DQ, Chipselect, and
Channel.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
Data Eye
Pattern Select [PRBS]
Configuration options: [PRBS] [SS0] [Both]
Pattern Length [3]
This token helps to determine the pattern length. The possible options
are N=3...12.
Configuration options: [3] – [9]
Aggressor Channel [1 Aggressor Channel]
This helps read the aggressors channels. If set to [Enabled], you can
read from one or more than one aggressor channel. The default is set
to [Disabled].
Configuration options: [Disabled] [1 Aggressor Channel] [3 Aggressor
Channels] [7 Aggressor Channels]
Aggressor Static Lane Control [Disabled]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items appear only when Aggressor Static Lane Control is set to [Enabled].
Aggressor Static Lane Select Upper 32 bits [0]
Static Lane Select for Upper 32 bits. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [99999999]
Aggressor Static Lane Select Lower 32 bits [0]
Static Lane Select for Lower 32 bits. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [99999999]
Aggressor Static Lane Select ECC [0]
Static Lane Select for ECC Lanes. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [9]
Aggressor Static Lane Value [0]
Configuration options: [0] - [9]
Target Static Lane Control [Disabled]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-31
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following items appear only when Target Static Lane Control is set to [Enabled].
Target Static Lane Select Upper 32 bits [0]
Static Lane Select for Upper 32 bits. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [99999999]
Target Static Lane Select Lower 32 bits [0]
Static Lane Select for Lower 32 bits. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [99999999]
Target Static Lane Select ECC [0]
Static Lane Select for ECC Lanes. The bit mask represents the bits to
be read.
Configuration options: [0] - [9]
Target Static Lane Value [0]
Configuration options: [0] - [9]
Worst Case Margin Granularity [Per Chip Select]
Configuration options: [Per Chip Select] [Per Nibble]
Read Voltage Sweep Step Size [1]
This option determines the step size for Read Data Eye voltage sweep.
Configuration options: [1] [2] [4]
Read Timing Sweep Step Size [1]
This option supports step size for Read Data Eye.
Configuration options: [1] [2] [4]
Write Voltage Sweep Step Size [1]
This option determines the step size for write Data Eye voltage sweep.
Configuration options: [1] [2] [4]
Write Timing Sweep Step Size [1]
This option supports step size for write Data Eye.
Configuration options: [1] [2] [4]
Memory Healing BIST [Disabled]
Allows you to enable a full memory test. The testing will increase the boot time.
BIOS mem BIST tests the full memory after training. Failing memory will be
repaired using soft or hard PPR depending on the PPC configuration. The test
will take 3 minutes per 16GN of installed memory. Self-Healing BIST runs the
JEDEC DRAM self healing if the device supports the feature. The DRAM will
do a hard repair for failing memory. The test will take 10 seconds per memory
rank per channel.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [BIOS Mem BIST] [Self-Healing Mem BIST]
[BIOS and Self-Healing Mem BIST]
The following items appear only when Memory Healing BIST is set to [BIOS Mem BIST].
Mem BIST Test Select [Vendor Tests Enabled]
Select the vendor specific tests to use with BIOS memory healing BIST.
Configuration options: [Vendor Tests Enabled] [Vendor Tests Disabled] [All
Tests - All Vendors]

5-32 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Mem BIST Post Package Repair Type [Soft Repair]
For DRAM errors found in the BIOS memory BIST select the repair type, soft,
hard, or test only and do not attempt to repair.
Configuration options: [Soft Repair] [Hard Repair] [No Repairs - Test only]
NBIO Common Options
IOMMU [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable IOMMU.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
DMAr Support [Auto]
Allows you to enable DMAr system protection during POST.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Enable AER Cap is set to [Auto] or [Enable].
ACS Enable [Auto]
AER must be enabled for ACS enable to work.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
PCIe ARI Support [Auto]
This item enables Alternative Routing-ID Interpretation.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
PCIe ARI Enumeration [Auto]
Allows ARI Forwarding for each downstream port.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
PCIe Ten Bit Tag Support [Auto]
This item enables PCIe ten bit tags for supported devices. [Auto] = [Disabled].
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable] [Auto]
HD Audio Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enable] [Auto]
SMU Common Options
Determinism Control [Manual]
[Auto] Use the fused Determinism.
[Manual] User can set customized Determinism.
The following item appears only when Determinism Control is set to [Manual].
Determinism Slider [Power]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Power] [Performance]
Fan Control
Fan Table Control [Auto]
[Auto] Use the default fan table.
[Manual] User can set customized fan table.

5-33
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following item appears only when Fan Table Control is set to [Manual].
Low Temperature [0]
Allows you to set the low temperature in °C.
Medium Temperature [0]
Allows you to set the medium temperature in °C.
High Temperature [0]
Allows you to set the high temperature in °C.
Critical Temperature [0]
Allows you to set the critical temperature in °C.
Low Pwm [0]
Allows you to set the low Pwm from 0-100.
Medium Pwm [0]
Allows you to set the medium Pwm from 0-100.
High Pwm [0]
Allows you to set the high Pwm from 0-100.
Temperature Hysteresis [0]
Allows you to set the temperature hysteresis in °C.
Pwm Frequency [25kHz]
Configuration options: [100Hz] [25kHz]
Fan Polarity [Negative]
Configuration options: [Negative] [Positive]
cTDP Control [Manual]
[Auto] Use the fused TDP.
[Manual] User can set customized TDP.
The following item appears only when cTDP Control is set to [Manual].
cTDP [280]
Allows you to customize cTDP.
EfficiencyModeEn [Auto]
[Auto] Use performance optimized CCLK DPM settings.
[Enabled] Use power efficiency optimized CCLK DPM settings.
Power Package Limit Control [Manual]
[Auto] Use the fused PPT.
[Manual] User can set customized PPT.
The following item appears only when Power Package Limit Control is set to [Manual].
Power Package Limit [280]
Allows you to customize PPT.
xGMI Link Width Control [Auto]
[Auto] Use default xGMI link width controller settings.
[Manual] User can set custom xGMI link width controller settings.

5-34 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
The following items appear only when xGMI Link Width Control is set to [Manual].
xGMI Force Link Width Control [Unforce]
[Unforce] Do not force the xGMI to a fixed width.
[Force] Force the xGMI to the user specified width.
The following item appears only when xGMI Force Link Width Control is set to [Force].
xGMI Force Link Width [2]
[0] Force xGMI link width to x2.
[1] Force xGMI link width to x8.
[2] Force xGMI link width to x16.
xGMI Max Link Width Control [Auto]
[Auto] Use default xGMI max supported link width.
[Manual] User can set custom xGMI max link width.
The following item appears only when xGMI Max Link Width Control is set to [Manual].
xGMI Max Link Width [1]
[0] Set max xGMI link width to x8.
[1] Set max xGMI link width to x16.
APBDIS [Auto]
[0] Not APBDIS (mission mode)
[1] APBDIS
[Auto] Auto
DF Cstates [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable DF C-states.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
CPPC [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
HSMP Support [Auto]
This option allows you to enable or disable HSMP support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
DLWM Support [Auto]
This option allows you to enable or disable DLWM support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
BoostFmaxEn [Auto]
[Auto] Use the default Fmax.
[Manual] User can set the boost Fmax.

5-35
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following item appears only when Boost FmaxEn is set to [Manual].
BoostFmax [0]
Allows you to specify the boost Fmax frequency limit to apply to all cores
(MHz).
EDC Current Tracking [Disable]
The generation of a correctable MCE when the telemetry current value is over
the set threshold defined by EDC Current Tracking Current Threshold.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable]
The following items appears only when EDC Current Tracking is set to [Enable].
EDC Tracking Current Threshold [0]
The current threshold in AMPs for EDC Current Tracking feature.
EDC Tracking Report Interval [1]
Reporting interval. Every nth observed excursion results in SMU logging a
correctable MCE.
LCLK Frequency Control
Root Complex 0x00 LCLK Frequency [Auto]
Set Root Complex LCLK Frequency (Bus range 0x00-0x3F).
[Auto] Dynamic Frequency Control (Enhanced PIO setting will be
in effect).
[593MHz] Set LCLK Frequency at 593MHz (Overrides Enhanced PIO
setting).
Root Complex 0x40 LCLK Frequency [Auto]
Set Root Complex LCLK Frequency (Bus range 0x40-0x7F).
[Auto] Dynamic Frequency Control (Enhanced PIO setting will be
in effect).
[593MHz] Set LCLK Frequency at 593MHz (Overrides Enhanced PIO
setting).
Root Complex 0x80 LCLK Frequency [Auto]
Set Root Complex LCLK Frequency (Bus range 0x80-0xBF).
[Auto] Dynamic Frequency Control (Enhanced PIO setting will be
in effect).
[593MHz] Set LCLK Frequency at 593MHz (Overrides Enhanced PIO
setting).
Root Complex 0xC0 LCLK Frequency [Auto]
Set Root Complex LCLK Frequency (Bus range 0xC0-0xFF).
[Auto] Dynamic Frequency Control (Enhanced PIO setting will be
in effect).
[593MHz] Set LCLK Frequency at 593MHz (Overrides Enhanced PIO
setting).

5-36 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
DF PState Mode Select [Auto]
[Normal] Normal
[Limit Highest] FCLK is limited to DF Pstate FCLK Limit, only the highest DF
Pstate is used.
[Limit All] FCLK is limited to DF Pstate FCLK limit, all DF Pstates are
used.
[Auto] Auto
EDC Control [Auto]
[Auto] Use the fused VDDCR_CPU EDC limit.
[Manual] User can set customized VDDCR_CPU EDC limit.
The following items appears only when EDC Control is set to [Manual].
EDC [0]
Allows you to set the VDDCR_CPU EDC Limit [A].
EDC Platform Limit [0]
Allows you to set the EDC Platform Limit [W].
NBIO RAS Common Options
NBIO RAS Control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [MCA] [Legacy] [Auto]
Egress Poison Severity High [30011]
Each bit set to 1 enables HIGH severity on the associated IOHC egress port. A
bit of 0 indicates LOW severity.
Egress Poison Severity Low [4]
Each bit set to 1 enables HIGH severity on the associated IOHC egress port. A
bit of 0 indicates LOW severity.
NBIO SyncFlood Generation [Auto]
This value may be used to mask SyncFlood caused by NBIO RAS options.
When set to TRUE, SyncFlood from NBIO is masked. When set to FALSE,
NBIO is capable of generating SyncFlood.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
NBIO SyncFlood Reporting [Auto]
This value may be used to enable SyncFlood reporting to APML. When set to
TRUE, SyncFlood will be reported to APML. When set to FALSE, the reporting
will be disabled.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Egress Poison Mask High [FFFCFFFF]
These set the enable mask for masking of errors logged in EGRESS_
POISON_STATUS. For each bit set to 1, errors are masked. For each bit set to
0, errors trigger response actions.
Egress Poison Mask Low [FFFFFFFB]
These set the enable mask for masking of errors logged in EGRESS_
POISON_STATUS. For each bit set to 1, errors are masked. For each bit set to
0, errors trigger response actions.

5-37
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Uncorrected Converted to Poison Enable Mask High [30000]
These set the enable mask for masking of uncorrectable parity errors on
internal arrays. For each bit set to 1, a system fatal error event is triggered for
UCP errors on arrays associated with that egress port. For each bit set to 0,
errors are masked.
Uncorrected Converted to Poison Enable Mask Low [4]
These set the enable mask for masking of uncorrectable parity errors on
internal arrays. For each bit set to 1, a system fatal error event is triggered for
UCP errors on arrays associated with that egress port. For each bit set to 0,
errors are masked.
System Hub Watchdog Timer [A28]
This value specifies the timer interval of the SYSHUB Watchdog Timer in
milliseconds.
SLink Read Response OK [Disabled]
This value specifies whether SLINK read response errors are converted to
an Okay response. When this value is set to TRUE, read response errors are
converted to Okay responses with data of all FFs. When set to FALSE, read
response errors are not converted.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SLink Read Response Error Handling [Log Errors in MCA]
This value specifies whether SLINK write response errors are converted
to an Okay response. When this value is set to 0, write response errors
will be logged in the MCA. When set to 1, write response errors will trigger
an MCOMMIT error. When this value is set to 2, write response errors are
converted.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Trigger MCOMMIT Error] [Log Errors in MCA]
Log Poison Data from SLINK [Disabled]
This value specifies whether poison data propagated from SLINK will generate
a deferred error. When this value is set to TRUE, deferred errors are enabled.
When set to FALSE, errors are not generated.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PCIe Aer Reporting Mechanism [Auto]
This value selects the method of reporting AER errors from PCI Express.
A value of 0 indicates that the hardware will report the error through MCA.
A value of 1 allows OS First handling of the errors through generation of a
system control interrupt (SCI). A value of 2 allows Firmware First handling of
the errors through generation of a system control interrupt (SCI).
Configuration options: [Firmware First] [OS First] [Auto]
Edpc Control [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
NBIO Poison Consumption [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sync Flood on PCIe Fatal Error [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [True] [False]
Enable AER Cap [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Advanced Error Reporting Capability.
Configuration options: [Enable] [Disabled] [Auto]

5-38 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Early Link Speed [Auto]
Allows you to set Early Link Speed.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Gen1] [Gen2]
Hot Plug Handling mode [Auto]
Allows you to control the Hot Plug Handling mode.
Configuration options: [OS First] [Firmware First] [Auto]
Presence Detect Select mode [Auto]
Allows you to control the Presence Detect Select mode.
Configuration options: [OR] [AND] [Auto]
Preferred IO [Auto]
Allows you to select the preferred IO select type.
Configuration options: [Bus] [Auto]
Data Link Feature Cap [Auto]
Allows you to set Data Link Feature Capability.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]]
CV test [Auto]
Set this to [Enabled] to support running PCIECV tool. Selecting [Auto] will preserve h/w
defaults.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Disabled] [Enabled]
SEV-SNP Support [Disable]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SRIS [Auto]
Configuration options: [Auto] [Disable] [Enable]
FCH Common Options
SATA Configuration Optoins
SATA Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable OnChip SATA controller.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when SATA Enable is set to [Enabled].
SATA Mode [AHCI]
Allows you to select the OnChip SATA Type.
Configuration options: [AHCI] [AHCI as ID 0x7904] [Auto]
Sata RAS Support [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata RAS Support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata Disabled AHCI Prefetch Function [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata Disabled AHCI Prefetch Function.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-39
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 0 [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 0 is set to
[Enabled].
DevSleep0 Port Number [0]
Allows you to set the DEVSLP port 0.
Configuration options: [0] - [7]
Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 1 [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 1 is set to
[Enabled].
DevSleep1 Port Number [0]
Allows you to set the DEVSLP port 1.
Configuration options: [0] - [7]
SATA Controller options
SATA Controller Enable
Sata0 Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata0. Each IOD has 4 Sata
Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata1 Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata1. Each IOD has 4 Sata
Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata2 Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata2. Each IOD has 4 Sata
Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata3 Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata3. Each IOD has 4 Sata
Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata4 (Socket1) Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata4 on Socket 1 (IOD1). Each IOD
has 4 Sata Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata5 (Socket1) Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata5 on Socket 1 (IOD1). Each IOD
has 4 Sata Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata6 (Socket1) Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata6 on Socket 1 (IOD1). Each IOD
has 4 Sata Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-40 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Sata7 (Socket1) Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable Sata7 on Socket 1 (IOD1). Each IOD
has 4 Sata Controllers.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
SATA Controller eSATA
SATA Controller DevSlp
Socket1 DevSlp
Socket1 DevSlp0 Enable [Auto]
Only Sata0 on each IOD/socket supports DevSlp.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Socket1 DevSlp0 Enable is set to [Enabled].
DevSleep0 Port Number [0]
Allows you to set DEVSLP port 0.
Configuration options: [0] - [7]
Socket1 DevSlp1 Enable [Auto]
Only Sata0 on each IOD/socket supports DevSlp.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Socket1 DevSlp1 Enable is set to [Enabled].
DevSleep0 Port Number [1]
Allows you to set DEVSLP port 1.
Configuration options: [0] - [7]
SATA Controller SGPIO
Sata0 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata0.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata1 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata1.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata2 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata2.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata3 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata3.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata4 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata4.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata5 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata5.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Sata6 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata6.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-41
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Sata7 SGPIO [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable SataSgpio on Sata7.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
USB Configuration Options
XHCI Controller0 enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable USB3 controller.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
XHCI Controller1 enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable USB3 controller.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
USB ecc SMI Enable [Auto]
MCM USB enable
XHCI2 enable (Socket1) [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable USB3 controller.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
XHCI3 enable (Socket1) [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable USB3 controller.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
SD Dump Options
SD Configuration Mode [SD Dump disabled]
Configuration options: [SD Dump disabled] [SD Dump enabled]
Ac Power Loss Options
AC Loss Control [Always On]
Allows you to select Ac Loss Control Method.
Configuration options: [Always Off] [Always On] [Reserved] [Previous] [Auto]
I2C Configuration Options
I2C 0 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
I2C 1 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
I2C 2 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
I2C 3 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
I2C 4 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
I2C 5 Enable [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]

5-42 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Uart Configuration Options
Uart 0 Enable [Auto]
Uart 0 has no HW FC is Uart 2 is enabled.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Uart 0 Enable is set to [Enabled].
Uart 0 Legacy Options [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [0x2E8] [0x2F8] [0x3E8] [0x3F8] [Auto]
Uart 1 Enable [Auto]
Uart 1 has no HW FC is Uart 3 is enabled.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Uart 1 Enable is set to [Enabled].
Uart 1 Legacy Options [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [0x2E8] [0x2F8] [0x3E8] [0x3F8] [Auto]
Uart 2 Enable (no HW FC) [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Uart 2 Enable (no HW FC) is set to [Enabled].
Uart 2 Legacy Options [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [0x2E8] [0x2F8] [0x3E8] [0x3F8] [Auto]
Uart 3 Enable (no HW FC) [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
The following item appears only when Uart 3 Enable (no HW FC) is set to [Enabled].
Uart 3 Legacy Options [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [0x2E8] [0x2F8] [0x3E8] [0x3F8] [Auto]
FCH RAS Options
ALink RAS Support [Auto]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Reset after sync flood [Auto]
Enable AB to forward downstream sync-flood message to system controller.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Miscellaneous Options
Boot Timer Enable [Auto]
[Disabled] Force PMx44 bit 27 = 1.
[Enabled] Force PMx44 bit 27 = 0.
[Auto] PMx44 bit 27 = PcdBootTimerEnable.

5-43
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
NTB Common Options
Socket-0 P0 NTB Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable NTB on Socket-0 P0 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enable]
The following items appear only when Socket-0 P0 NTB Enable is set to [Enabled].
Socket-0 P0 Start Lane [0]
Allows you to set the NTB Start Lane on Socket-0 P0 Link.
Configuration options: [0] - [15]
Socket-0 P0 End Lane [15]
Allows you to set the NTB End Lane on Socket-0 P0 Link.
Configuration options: [0] - [15]
Socket-0 P0 Link Speed [Auto]
Allows you to select the Link Speed for Socket-0 P0.
Configuration options: [Max Speed] [Gen 1] [Gen 2] [Gen 3] [Auto] [Gen 4]
Socket-0 P0 NTB Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the NTB Mode for Socket-0 P0 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [NTB Disabled] [NTB Primary] [NTB Secondary]
Socket-0 P1 NTB Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable NTB on Socket-0 P1 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enable]
The following items appear only when Socket-0 P1 NTB Enable is set to [Enabled].
Socket-0 P1 Start Lane [32]
Allows you to set the NTB Start Lane on Socket-0 P1 Link.
Configuration options: [32] - [47]
Socket-0 P1 End Lane [47]
Allows you to set the NTB End Lane on Socket-0 P1 Link.
Configuration options: [32] - [47]
Socket-0 P1 Link Speed [Auto]
Allows you to select the Link Speed for Socket-0 P1.
Configuration options: [Max Speed] [Gen 1] [Gen 2] [Gen 3] [Auto] [Gen 4]
Socket-0 P1 NTB Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the NTB Mode for Socket-0 P1 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [NTB Disabled] [NTB Primary] [NTB Secondary]
Socket-0 P2 NTB Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable NTB on Socket-0 P2 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enable]

5-44 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
The following items appear only when Socket-0 P2 NTB Enable is set to [Enabled].
Socket-0 P2 Start Lane [80]
Allows you to set the NTB Start Lane on Socket-0 P2 Link.
Configuration options: [80] - [95]
Socket-0 P2 End Lane [95]
Allows you to set the NTB End Lane on Socket-0 P2 Link.
Configuration options: [80] - [95]
Socket-0 P2 Link Speed [Auto]
Allows you to select the Link Speed for Socket-0 P2.
Configuration options: [Max Speed] [Gen 1] [Gen 2] [Gen 3] [Auto] [Gen 4]
Socket-0 P2 NTB Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the NTB Mode for Socket-0 P2 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [NTB Disabled] [NTB Primary] [NTB Secondary]
Socket-0 P3 NTB Enable [Auto]
Allows you to enable NTB on Socket-0 P3 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Enable]
The following items appear only when Socket-0 P3 NTB Enable is set to [Enabled].
Socket-0 P3 Start Lane [112]
Allows you to set the NTB Start Lane on Socket-0 P3 Link.
Configuration options: [112] - [127]
Socket-0 P3 End Lane [127]
Allows you to set the NTB End Lane on Socket-0 P3 Link.
Configuration options: [112] - [127]
Socket-0 P3 Link Speed [Auto]
Allows you to select the Link Speed for Socket-0 P3.
Configuration options: [Max Speed] [Gen 1] [Gen 2] [Gen 3] [Auto] [Gen 4]
Socket-0 P3 NTB Mode [Auto]
Allows you to select the NTB Mode for Socket-0 P3 Link.
Configuration options: [Auto] [NTB Disabled] [NTB Primary] [NTB Secondary]
Soc Miscellaneous Control
ABL Console Out Control [Auto]
[Disable] Disable ConsoleOut Function for ABL.
[Enable] Enable ConsoleOut Function for ABL.
[Auto] Keep default behavior.

5-45
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
The following items appear only when ABL Console Out Control is set to [Enable].
ABL Basic Console Out Control [Auto]
[Disable] Disable Basic ConsoleOut Function for ABL.
[Enable] Enable Basic ConsoleOut Function for ABL.
[Auto] Keep default behavior.
ABL PMU message Control [Auto]
Allows you to control the total number of PMU debug messages. Several major
controls are listed below:
1. Detailed debug messages (e.g. Eye delays)
2. Coarse debug messages (e.g. rank information)
3. Stage completion
4. Firmware completion message only
Configuration options: [Detailed debug message] [Coarse debug messages] [Stage
completion] [Firmware completion message only] [Auto]
Workload Tuning
Workload Profile [Auto]
Allows you to select the profile for different workloads.
[Disabled] Don’t use any workload profile.
[CPU Intensive] Tuned for CPU intensive workloads, providing optimal
integer and floating point performance.
[Java Throughput] Tuned for the highest level of throughput with java workloads.
[Java Latency] Tuned for the latency sensitive java workloads, to meet
critical SLA’s.
[Power Efficiency] Tuned for optimal power efficiency.
[Memory Throughput Intensive] Tuned for the highest memory throughput available.
[Storage IO Intensive] Tuned for the highest storage IO bandwidth.
[NIC Throughput Intensive] Tuned for maximum TCP/IP and RDMA network
throughput.
[NIC Latency Intensive] Tuned for network performance where the kernel performs
L3 packet forwarding.
[Accelerator Throughput] Tuned to maximum peer-to-peer PCIe throughput with
accelerators such as GPU’s.
[VMware vSphere Optimized] Tuned for general virt+P3+Q4.
[Linux KVM Optimized] Tuned for general virtualization performance when using
Linux KVM.
[Container Optimized] Optimized for container performance.
[RDBMS Optimized] Tuned for relational databases.
[Big Data Analytics Optimized] Tuned for big data analytics.

5-46 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
[IOT Gateway] Tuned for throughput analytics as observed by IOT
gateways.
[HPC Optimized] Tuned for general HPC performance.
[OpenStack NFV] Tuned for Openstack based NFV workloads.
[OpenStack for RealTime Kernel] Tuned for Openstack with RealTime kernal
enabled.
[Auto] Use BIOS default workload profile.
Performance Tracing [Auto]
Allows you to enable or disable allow capturing performance traces.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
5.5.5 APM Configuration
Allows you to configure the Advance Power Management (APM) settings.
Restore AC Power Loss [Last State]
[Power Off] The system goes into off state after an AC power loss.
[Power On] The system will reboot after an AC power loss.
[Last State] The system goes into either off or on state, whatever the system state was
before the AC power loss.
Power On By PCI-E [Disabled]
[Disabled] Disables the PCIE devices to generate a wake event.
[Enabled] Enables the PCIE devices to generate a wake event.
Power On By RTC [Disabled]
[Disabled] Disables RTC to generate a wake event.
[Enabled] When set to [Enabled], the items RTC Alarm Date (Days) and
Hour/Minute/Second will become user-configurable with set values.

5-47
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Onboard I350 LAN Configuration
Intel I350 LAN1
LAN Enable [JumperState]
Allows you to enable or disable the Intel LAN.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [JumperState]
The following item appears only when LAN Enable is set to [JumperState].
ROM Type [PXE]
Allows you to select the Intel LAN ROM type.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [PXE]
Intel I350 LAN2
LAN Enable [JumperState]
Allows you to enable or disable the Intel LAN.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following item appears only when LAN Enable is set to [JumperState].
ROM Type [Disabled]
Allows you to select the Intel LAN ROM type.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [PXE]
5.5.6 Onboard LAN Configuration

5-48 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
COM1/COM2
Console Redirection [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the console redirection feature.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following item appears only when Console Redirection is set to [Enabled].
Console Redirection Settings
These items become configurable only when you enable the Console Redirection
item. The settings specify how the host computer and the remote computer (which the
user is using) will exchange data. Both computers should have the same or compatible
settings.
Terminal Type [ANSI]
Allows you to set the terminal type.
[VT100] ASCII char set.
[VT100+] Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc.
[VT-UTF8] Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode chars onto 1 or more bytes.
[ANSI] Extended ASCII char set.
Bits per second [115200]
Selects serial port transmission speed. The speed must be matched on the other side.
Long or noisy lines may require lower speeds.
Configuration options: [9600] [19200] [38400] [57600] [115200]
Data Bits [8]
Configuration options: [7] [8]
5.5.7 Serial Port Console Redirection

5-49
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Parity [None]
A parity bit can be sent with the data bits to detect some transmission errors. [Mark]
and [Space] parity do not allow for error detection.
[None] None
[Even] parity bit is 0 if the num of 1’s in the data bits is even
[Odd] parity bit is 0 if num of 1’s in the data bits is odd
[Mark] parity bit is always 1
[Space] parity bit is always 0
Stop Bits [1]
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit indicates the beginning.)
The standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices may require more
than 1 stop bit.
Configuration options: [1] [2]
Flow Control [None]
Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow. When sending data, if the
receiving buffers are full, a “stop” signal can be sent to stop the data flow. Once the
buffers are empty, a “start” signal can be sent to re-start the flow. Hardware flow
control uses two wires to send start/stop signals.
Configuration options: [None] [Hardware RTS/CTS]
VT -UTF8 Combo Key Support [Enabled]
This allows you to enable the VT -UTF8 Combination Key Support for ANSI/VT100
terminals.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Recorder Mode [Disabled]
With this mode enabled only text will be sent. This is to capture Terminal data.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Resolution 100x31 [Enabled]
This allows you enable or disable extended terminal resolution.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Putty Keypad [VT100]
This allows you to select the FunctionKey and Keypad on Putty.
Configuration options: [VT100] [LINUX] [XTERMR6] [SCO] [ESCN] [VT400]
Legacy Console Redirection Settings
Legacy Console Redirection Port [COM1]
Allows you to select a COM port to display redirection of Legacy OS and Legacy
OPROM Messages.
Configuration options: [COM1] [COM2]
Resolution [80x24]
This allows you to set the number of rows and columns supported on the Legacy OS.
Configuration options: [80x24] [80x25]

5-50 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Redirection After POST [Always Enable]
This setting allows you to specify if Bootloader is selected than Legacy console
redirection.
Configuration options: [Always Enable] [Bootloader]
Serial Port for Out-of-Band Management/
Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS)
Console Redirection EMS [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the console redirection feature.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following item appears only when Console Redirection EMS is set to [Enabled].
Console Redirection Settings
Out-of-Band Mgmt Port [COM1]
Microsoft Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) allow for remote
management of a Windows Server OS through a serial port.
Configuration options: [COM1] [COM2]
Terminal Type [VT-UTF8]
Microsoft Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) allow for remote
management of a Windows Server OS through a serial port.
Configuration options: [VT100] [VT100+] [VT-UTF8] [ANSI]
Bits per second [115200]
Microsoft Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) allow for remote
management of a Windows Server OS through a serial port.
Configuration options: [9600] [19200] [57600] [115200]
Flow Control [None]
Microsoft Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) allow for remote
management of a Windows Server OS through a serial port.
Configuration options: [None] [Hardware RTS/CTS] [Software Xon/Xoff]
5.5.8 CPU Configuration
This page displays the CPU node information.
SVM Mode [Enable]
Allows you enable or disable CPU Virtualization.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enable]

5-51
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Node 0 Information
Allows you to view memory information related to Node 0.
5.5.9 PCI Subsystem Settings
Allows you to configure PCI, PCI-X, and PCI Express Settings.
Above 4G Decoding [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable 64-bit capable devices to be decoded in above 4G address
space. It only works if the system supports 64-bit PCI decoding.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items appear only when Above 4G Decoding is set to [Enabled].
LAN Device 4G Decode [Auto]
LAN Device 4G Decode.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Above_4G]
Re-Size BAR Support [Disabled]
If system has Resizable BAR capable PCIe Devices, this option enables or disables
Resizable BAR Support. (Only if system supports 64-bit PCI Decoding).
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Auto]
To enable Re-Size BAR Support for harnessing full GPU memory, please set CSM
(Compatibility Support Module) to [Disabled].
SR-IOV Support [Disabled]
This option enables or disables Single Root IO Virtualization Support if the system has SR-
IOV capable PCIe devices.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-52 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.5.10 USB Configuration
Legacy USB Support [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable Legacy USB device support.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] [Auto]
XHCI Hand-off [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable workaround for OSes without XHCI hand-off support. The
XHCI ownership change should be claimed by XHCI driver.
Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled]
USB Mass Storage Driver Support [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the USB Mass Storage driver support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Port 60/64 Emulation [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable I/O port 60h/64h emulation support. This should be enabled
for the complete keyboard legacy support for non-USB aware OSes.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Mass Storage Devices
Allows you to select the mass storage device emulation type for devices connected.
Configuration options: [Auto] [Floppy] [Forced FDD] [Hard Disk] [CD-ROM]
5-53
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Network stack [Disabled]
Enables or disables the network stack feature.
Configuration options: [Disable] [Enable]
The following item appears only when Network stack is set to [Enabled].
Ipv4 PXE Support [Disabled]
Enables or disables the Ipv4 PXE Boot Support. If disabled, Ipv4 PXE boot option will not be
created.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Ipv4 HTTP Support [Disabled]
Enables or disables the Ipv4 HTTP Boot Support. If disabled, Ipv4 HTTP boot option will not
be created.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Ipv6 PXE Support [Disabled]
Enables or disables the Ipv6 PXE Boot Support. If disabled, Ipv6 PXE boot option will not be
created.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Ipv6 HTTP Support [Disabled]
Enables or disables the Ipv6 HTTP Boot Support. If disabled, Ipv6 HTTP boot option will not
be created.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PXE boot wait time [0]
Set the wait time to press ESC key to abort the PXE boot. Use the <+> or <-> to adjust the
value. The values range from 0 to 5.
Media detect count [1]
Set the number of times presence of media will be checked. Use the <+> or <-> to adjust the
value. The values range from 1 to 50.
5.5.11 Network Stack Configuration

5-54 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.5.12 CSM Configuration
CSM Support [Disabled]
This option allows you to enable or disable CSM Support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items appear only when CSM Support is set to [Enabled].
GateA20 Active [Upon Request]
This allows you to set the GA20 option.
Configuration options: [Upon Request] [Always]
Option ROM Messages [Force BIOS]
This allows you to set the display mode for option ROM.
Configuration options: [Force BIOS] [Keep Current]
INT19 Trap Response [Immediate]
The BIOS reaction on INT19 trapping by Option ROM.
[Immediate] Execute the trap right away.
[Postponed] Execute the trap during legacy boot.
HDD Connection Order [Adjust]
This option allows you to select the HDD Connection Order. Some OS require HDD
handles to be adjusted, i.e. OS is installed on drive 80h.
Configuration options: [Adjust] [Keep]
Boot Option filter [UEFI and Legacy]
This option allows you to control the Legacy/UEFI ROMs priority.
Configuration options: [UEFI and Legacy] [Legacy only] [UEFI only]
Network [UEFI]
This option allows you to control the execution of UEFI and Legacy Network OpROM.
Configuration options: [Do Not Launch] [UEFI] [Legacy]
Storage [UEFI]
This option allows you to control the execution of UEFI and Legacy Storage OpROM.
Configuration options: [Do Not Launch] [UEFI] [Legacy]
Video [Legacy]
This option allows you to control the execution of UEFI and Legacy Video OpROM.
Configuration options: [Do Not Launch] [UEFI] [Legacy]
Other PCI devices [UEFI]
This item determines the OpROM execution policy for devices other than Network,
Storage, or Video.
Configuration options: [Do Not Launch] [UEFI] [Legacy]

5-55
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Device
The devices and names shown in the NVMe configuration list depends on the connected
devices. If no devices are connected, No NVMe Device Found will be displayed.
Self Test Option [Short]
This option allows you to select either Short or Extended Self Test. Short option will
take couple of minutes, and the extended option will take several minutes to complete.
Configuration options: [Short] [Extended]
Self Test Action [Controller Only Test]
Allows you to select either to test Controller alone or Controller and NameSpace.
Selecting Controller and Namespace option will take a lot longer to complete the test.
Configuration options: [Controller Only Test] [Controller and NameSpace Test]
Run Device Self Test
Press <Enter> to perform device self test for the corresponding Option and Action
selected by the user. Pressing the <ESC> key will abort the test. The results shown
below is the most recent result logged in the device.
5.5.13 NVMe Configuration
This page will display the NVMe controller and drive information.

5-56 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.5.14 SATA Configuration
This page will display the SATA controller and drive information.
5.5.15 AMD Mem Configuration Status
The items in this menu display the memory configuration (initialized by ABL) status.

5-57
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.6 Chipset menu
The Chipset menu items allow you to change the Chipset settings.
PCIe Link Training Type [1 Step]
Allows you to select PCIe Link Training in 1 or 2 steps.
Configuration options: [1 Step] [2 Step]
PCIe Compliance Mode [Off]
Allows you to turn the PCIe Compliance Mode on or off.
South Bridge
SB Debug Configuration
SB SATA DEBUG Configuration
The items in this submenu contains options for SATA DEBUG Configuration.
Aggressive Link PM Capability [Enabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support Auto-generating
Link Requests to the partial or slumber states when there are no
commands to process.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Port Multiplier Capability [Enabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support a port multiplier.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA Ports Auto Clock Control [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable SATA Ports Auto Clock Control.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-58 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
SATA Partial State Capability [Enabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support transitions to
the partial state.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA FIS Based Switching [Enabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support port multiplier
FIS-based switching.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA Command Completion Coalescing Support [Disabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support command
completion coalescing.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA Slumber State Capability [Enabled]
Indicates whether Host Bus Adapter (HBA) can support transitions to
the slumber state.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA Target Support 8 Devices [Disabled]
Indicates whether SATA target support 8 devices function.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Generic Mode [Disabled]
Allows you to SATA disable Generic Mode.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA AHCI Enclosure [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable SATA AHCI Enclosure Management.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA SGPIO 0 [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable SATA Serial General Purpose Input/
Output (SGPIO) 0.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SB FUSION DEBUG Configuration
The items in this submenu contains options for SB FUSION DEBUG
Configuration.
TimerTick Tracking [Disabled]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Clock Interrupt Tag [Disabled]
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SB MISC DEBUG Configuration
The items in this submenu contains options for SB DEBUG Configuration.
SB Clock Spread Spectrum [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable CG1_PLL Spread Spectrum.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
HPET In SB [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the HPET Function Switch.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
MsiDis in HPET [Enabled]
Expose MSI capability in HPET Capability register.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-59
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
North Bridge
Socket 0 Information
This item displays the memory information on Socket 0.

5-60 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.7 Security menu
This menu allows a new password to be created or a current password to be changed. The
menu also enables or disables the Secure Boot state and lets the user configure the System
Mode state.
Administrator Password
To set an administrator password:
1. Select the Administrator Password item and press <Enter>.
2. From the Create New Password box, key in a password, then press <Enter>.
3. Confirm the password when prompted.
To change an administrator password:
1. Select the Administrator Password item and press <Enter>.
2. From the Enter Current Password box, key in the current password, then press
<Enter>.
3. From the Create New Password box, key in a new password, then press <Enter>.
4. Confirm the password when prompted.
To clear the administrator password, follow the same steps as in changing an administrator
password, but press <Enter> when prompted to create/confirm the password.

5-61
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
User Password
To set a user password:
1. Select the User Password item and press <Enter>.
2. From the Create New Password box, key in a password, then press <Enter>.
3. Confirm the password when prompted.
To change a user password:
1. Select the User Password item and press <Enter>.
2. From the Enter Current Password box, key in the current password, then press
<Enter>.
3. From the Create New Password box, key in a new password, then press <Enter>.
4. Confirm the password when prompted.
To clear a user password:
1. Select the Clear User Password item and press <Enter>.
2. Select Yes from the Warning message window then press <Enter>.
Secure Boot
Allows you to customize the Secure Boot settings.
Secure Boot [Disabled]
Secure Boot feature is Active if Secure Boot is set to [Enabled], Platform Key(PK) is
enrolled, and the system is in User mode. A mode change requires a platform reset.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Secure Boot Mode [Custom]
Allows you to set the Secure Boot selector. In Custom mode, Secure Boot Policy variables
can be configured by a physically present user without fill authentication.
Configuration options: [Custom] [Standard]
The following items are only available when Secure Boot Mode is set to [Custom].
Restore Factory Keys
This option will force the system to User Mode, and install factory default Secure Boot key
databases.

5-62 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Key Management
This item only appears when the item Secure Boot Mode is set to [Custom]. The Key
Management item allows you to modify Secure Boot variables and set Key Management
page.
Factory Key Provision [Enabled]
Allows you to provision factory default Secure Boot keys when the system is in Setup
Mode.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Restore Factory Keys
This item will install all Factory Default keys.
Reset to Setup Mode
This item appears only when you load the default Secure Boot keys. Allows you to
clear all default Secure Boot keys.
Export Secure Boot Variables
This item will ask you if you want to save all secure boot variables. Select Yes if you
want to save all secure boot variables, otherwise select No.
Enroll Efi Image
This item will allow the image to run in Secure Boot mode.
Configuration options: [Set New] [Append]
Device Guard Ready
Remove ‘UEFI CA’ from DB
Remove Microsoft UEFI CA from Secure Boot DB.
Reset to Setup Mode
This option will delete all Secure Boot key databases from NVRAM.

5-63
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Restore DB defaults
Restore DB variable to factory defaults.
Platform Key (PK)
Configuration options: [Details] [Export] [Update] [Delete]
Key Exchange Keys (KEK) / Authorized Signatures (DB) / Forbidden Signatures
(DBX)
Configuration options: [Details] [Export] [Update] [Append] [Delete]
Authorized TimeStamps (DBT) / OsRecovery Signatures
Configuration options: [Update] [Append]

5-64 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Setup Prompt Timeout [1]
Allows you to set the number of seconds that the firmware waits before initiating the original
default boot selection. 65535(OxFFFF) means indefinite waiting. Use the <+> or <-> to adjust
the value.
Bootup NumLock State [On]
Allows you to select the power-on state for the NumLock.
Configuration options: [Off] [On]
Boot Logo Display [Disabled]
[Disabled] Hide the logo during POST.
[Enabled] Display the logo during POST.
Boot Option Priorities
These items specify the boot device priority sequence from the available devices. The
number of device items that appears on the screen depends on the number of devices
installed in the system.
• To select the boot device during system startup, press <F8> when ASUS Logo
appears.
• To access Windows OS in Safe Mode, please press <F8> after POST.
5.8 Boot menu
The Boot menu items allow you to change the system boot options.

5-65
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.9 Tool menu
The Tool menu items allow you to configure options for special functions. Select an item then
press <Enter> to display the submenu.
Start ASUS EzFlash
Allows you to run ASUS EzFlash BIOS ROM Utility when you press <Enter>. Refer to the
ASUS EzFlash Utility section for details.
IPMI Hardware Monitor
Allows you to run the IPMI hardware monitor.
ASUS SMBIOS Viewer
Allows you to run the ASUS SMBIOS Viewer
POST Report [5 sec]
Allows you to set the desired POST Report waiting time from 1 to 10 seconds.
Configuration options: [1 sec] - [10 sec] [Until Press ESC]

5-66 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.10 Event Logs menu
The Event Logs menu items allow you to change the event log settings and view the system
event logs.
5.10.1 Change Smbios Event Log Settings
Press <Enter> to change the Smbios Event Log configuration.
All values changed here do not take effect until computer is restarted.

5-67
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.10.2 View Smbios Event Log
Press <Enter> to view all smbios event logs.
Enabling/Disabling Options
Smbios Event Log [Enabled]
Change this to enable or disable all features of Smbios Event Logging during boot.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items appear only when Smbios Event Log is set to [Enabled].
Erasing Settings
Erase Event Log [No]
Choose options for erasing Smbios Event Log. Erasing is done prior to any logging activation
during reset.
Configuration options: [No] [Yes, Next reset] [Yes, Every reset]
When Log is Full [Do Nothing]
Choose options for reactions to a full Smbios Event Log.
Configuration options: [Do Nothing] [Erase Immediately]
Custom Options
Log EFI Status Code [Enabled]
This option allows you to enable or disable logging of the EFI Status Codes.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following item appears only when Log EFI Status Code is set to [Enabled].
Convert EFI Status Codes to Standard Smbios Type [Disabled]
This option allows you to enable or disable converting of EFI Status Codes to Standard
Smbios Type (Not all may be translated).
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-68 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.11 Server Mgmt menu
The Server Management menu displays the server management status and allows you to
change the settings.
OS Watchdog Timer [Disabled]
Allows you to start a BIOS timer which can only be shut off by Intel Management Software
after the OS loads.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items are configurable only when the OS Watchdog Timer is set to
[Enabled].
OS Wtd Timer Timeout [10]
Allows you to set the time in minutes for the OS Boot Watchdog Timer Expiration. Not
available if OS Boot Watchdog Timer is disabled.
Configuration options: [1] - [30]
OS Wtd Timer Policy [Reset]
Allows you to configure the how the system should respond if the OS Boot Watch Timer
expires. Not available if OS Boot Watchdog Timer is disabled.
Configuration options: [Do Nothing] [Reset] [Power Down]

5-69
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.11.1 System Event Log
Allows you to change the SEL event log configuration.
Erase SEL [No]
Allows you to choose options for erasing SEL.
Configuration options: [No] [Yes, On next reset] [Yes, On every reset]
All values changed here do not take effect until computer is restarted.

5-70 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
Configure IPV4 support
DM_LAN1 / Shared LAN
Configuration Address source [Previous State]
Allows you to configure LAN channel parameters statistically or dynamically (by BIOS or
BMC). [Previous State] option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS
phase.
Configuration options: [Previous State] [Static] [DynamicBmcDhcp]
The following items are available only when Configuration Address source is set to
[Static].
Station IP address
Allows you to set the station IP address.
Subnet mask
Allows you to set the subnet mask. We recommend that you use the same Subnet Mask you
have specified on the operating system network for the used network card.
Router IP address
Allows you to set the router IP address.
5.11.2 BMC network configuration
The sub-items in this configuration allow you to configure the BMC network parameters.
Scroll using <Page Up> / <Page Down> keys to see more items.

5-71
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Router MAC address
Allows you to set the router MAC address.
Configure IPV6 support
DM_LAN1
IPV6 Support [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable LAN1 IPV6 Support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following item appears only when IPV6 Support is set to [Enabled].
Configuration Address source [Previous State]
Allows you to configure LAN channel parameters statistically or dynamically (by BIOS or
BMC). [Previous State] option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS
phase.
Configuration options: [Previous State] [Static] [DynamicBmcDhcp]
The following items are available only when Configuration Address source is set to
[Static].
Station IPV6 address
Allows you to set the station IPV6 address.
Prefix Length
Allows you to set the prefix length (maximum of Prefix Length is 128).
Configuration Router Lan1 Address source [Previous State]
Select to configure LAN channel parameters statically or dynamically (by BIOS or by BMC).
Unspecified option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS phase.
The following items are available only when Configuration Router Lan1 Address source
is set to [Static].
IPv6 Router1 IP address
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router1 IP Address.
IPv6 Router1 Prefix Length Lan1
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router Prefix Length.
IPv6 Router1 Prefix Value Lan1
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router Prefix Value.
Shared LAN
IPV6 Support [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable LAN1 IPV6 Support.
Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]

5-72 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
The following item appears only when IPV6 Support is set to [Enabled].
Configuration Address source [Previous State]
Allows you to configure LAN channel parameters statistically or dynamically (by BIOS or
BMC). [Previous State] option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS
phase.
Configuration options: [Previous State] [Static] [DynamicBmcDhcp]
Station IPV6 address
Allows you to set the station IPV6 address.
Prefix Length
Allows you to set the prefix length (maximum of Prefix Length is 128).
Configuration Router Lan2 Address source [Previous State]
Select to configure LAN channel parameters statically or dynamically (by BIOS or by BMC).
Unspecified option will not modify any BMC network parameters during BIOS phase.
The following items are available only when Configuration Router Lan2 Address source
is set to [Static].
IPv6 Router1 IP address
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router1 IP Address.
IPv6 Router1 Prefix Length Lan2
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router Prefix Length.
IPv6 Router1 Prefix Value Lan2
Allows you to change the IPv6 Router Prefix Value.

5-73
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
5.11.3 View System Event Log
This item allows you to view the system event log records. Scroll using <Page Up> / <Page
Down> keys to see more items.

5-74 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup
5.12 Exit menu
The Exit menu items allow you to save or discard your changes to the BIOS items.
Pressing <Esc> does not immediately exit this menu. Select one of the options from this
menu or <F10> from the legend bar to exit.
Discard Changes and Exit
Exit system setup without saving any changes.
Save Changes and Reset
Reset system after saving the changes.
Discard Changes and Reset
Reset system setup without saving any changes.
Save Changes
Save changes done so far to any of the setup options.
Discard Changes
Discard changes done so far to any of the setup options.
Restore Defaults
Restore/load default values for all the setup options.

5-75
ASUS RS500A-E11 Series
Boot Override
These items displays the available devices. The device items that appears on the screen
depends on the number of devices installed in the system. Click an item to start booting from
the selected device.

5-76 Chapter 5: BIOS Setup

6
Driver Installation
This chapter provides the instructions for installing the
necessary drivers for different system components in the
Windows® Operating System.
Chapter 6: Driver Installation

6-2 Chapter 6: Driver Installation
The main screen of the Support DVD contains the following tabs:
1. Drivers - Shows the available device drivers that the system detects.
2. Utilities - Displays the software applications and utilities that the motherboard supports.
3. Manual - Provides the link to the user guide(s).
You need an internet browser installed in your OS to view the User Guide.
4. Contact - Displays the ASUS contact information, e-mail addresses, and useful links if
you need more information or technical support for your motherboard.
6.1 Running the Support DVD
The support DVD that is bundled with your motherboard contains drivers, management
applications, and utilities that you can install to maximize the features of your motherboard.
1. The contents of the support DVD are subject to change at any time without notice.
Visit the ASUS website (www.asus.com) for the latest updates on software and
utilities.
2. The support DVD is supported on Windows® Server 2012 R2 and Windows® Server
2016.

Appendix
Appendix

A-2 Appendix
KMPA-U16 block diagram

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series A-3
Notices
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his own expense.
The use of shielded cables for connection of the monitor to the graphics card is required
to assure compliance with FCC regulations. Changes or modifications to this unit not
expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority
to operate this equipment.
Compliance Statement of Innovation, Science and Economic
Development Canada (ISED)
This device complies with Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada licence
exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device
may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference, including
interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
CAN ICES-003(A)/NMB-003(A)
Déclaration de conformité de Innovation, Sciences et
Développement économique Canada (ISED)
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Innovation, Sciences et Développement
économique Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence. L’exploitation est
autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage,
et (2) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le fonctionnement.
CAN ICES-003(A)/NMB-003(A)
Japan JATE
本製品は電気通信事業者(移動通信会社、固定通信会社、インターネットプロバイダ等)の通信回
線(公衆無線LANを含む)に直接接続することができません。本製品をインターネットに接続する
場合は、必ずルータ等を経由し接続してください。

A-4 Appendix
Declaration of compliance for product environmental
regulation
ASUS follows the green design concept to design and manufacture our products, and
makes sure that each stage of the product life cycle of ASUS product is in line with global
environmental regulations. In addition, ASUS disclose the relevant information based on
regulation requirements.
Please refer to http://csr.asus.com/Compliance.htm for information disclosure based on
regulation requirements ASUS is complied with:
EU REACH and Article 33
Complying with the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of
Chemicals) regulatory framework, we published the chemical substances in our products at
ASUS REACH website at http://csr.asus.com/english/REACH.htm.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
DO NOT throw the motherboard in municipal waste. This product has been designed to
enable proper reuse of parts and recycling. This symbol of the crossed out wheeled bin
indicates that the product (electrical and electronic equipment) should not be placed in
municipal waste. Check local regulations for disposal of electronic products.
DO NOT throw the mercury-containing button cell battery in municipal waste. This symbol
of the crossed out wheeled bin indicates that the battery should not be placed in municipal
waste.
Australia statement notice
From 1 January 2012 updated warranties apply to all ASUS products, consistent with the
Australian Consumer Law. For the latest product warranty details please visit
https://www.asus.com/support/. Our goods come with guarantees that cannot be excluded
under the Australian Consumer Law. You are entitled to a replacement or refund for a major
failure and compensation for any other reasonably foreseeable loss or damage. You are also
entitled to have the goods repaired or replaced if the goods fail to be of acceptable quality
and the failure does not amount to a major failure.
If you require assistance please call ASUS Customer Service 1300 2787 88 or visit us at
https://www.asus.com/support/.
Japan statement notice
This product cannot be directly connected to the Internet (including public wireless LAN) of a
telecom carrier (mobile network companies, landline network companies, Internet providers,
etc.). When connecting this product to the Internet, be sure to connect it through a router or
switch.

ASUS RS500A-E11 Series A-5
EU RoHS
This product complies with the EU RoHS Directive. For more details, see
http://csr.asus.com/english/article.aspx?id=35
Japan JIS-C-0950 Material Declarations
Information on Japan RoHS (JIS-C-0950) chemical disclosures is available on
http://csr.asus.com/english/article.aspx?id=19
India RoHS
This product complies with the “India E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016” and prohibits
use of lead, mercury, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) and
polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in concentrations exceeding 0.1% by weight in
homogenous materials and 0.01% by weight in homogenous materials for cadmium, except
for the exemptions listed in Schedule II of the Rule.
Vietnam RoHS
ASUS products sold in Vietnam, on or after September 23, 2011,meet the requirements of
the Vietnam Circular 30/2011/TT-BCT.
Các sản phẩm ASUS bán tại Việt Nam, vào ngày 23 tháng 9 năm2011 trở về sau, đều phải đáp ứng các
yêu cầu của Thông tư 30/2011/TT-BCT của Việt Nam.
Turkey RoHS
AEEE Yönetmeliğine Uygundur
ASUS Recycling/Takeback Services
ASUS recycling and takeback programs come from our commitment to the highest standards
for protecting our environment. We believe in providing solutions for you to be able to
responsibly recycle our products, batteries, other components as well as the packaging
materials. Please go to http://csr.asus.com/english/Takeback.htm for detailed recycling
information in different regions.
Ecodesign Directive
European Union announced a framework for the setting of ecodesign requirements for
energy-related products (2009/125/EC). Specific Implementing Measures are aimed at
improving environmental performance of specific products or across multiple product types.
ASUS provides product information on the CSR website. The further information could be
found at https://csr.asus.com/english/article.aspx?id=1555.
Service and Support
Visit our multi-language website at https://www.asus.com/support.

A-6 Appendix