Intellinet 561334-UK User Manual
Displayed below is the user manual for 561334-UK by Intellinet which is a product in the Network Switches category. This manual has pages.
Related Manuals

48-Port Gigabit Ethernet Web-
Managed Switch with 4 SFP
Ports
UserManual
Model561334
INT‐561334‐UM‐0616‐1
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
2
1 TABLEOFCONTENTS
2ProductIntroduction.........................................................................................................................4
2.1ProductOverview..............................................................................................................................4
2.2Features.............................................................................................................................................4
2.3Specifications.....................................................................................................................................5
2.4ExternalComponentDescription.....................................................................................................6
2.4.1FrontPanel............................................................................................................................................6
2.4.2RearPanel..............................................................................................................................................8
2.5PackageContents..............................................................................................................................8
3InstallingandConnectingtheSwitch...............................................................................................9
3.1DesktopInstallation...........................................................................................................................9
3.2Rack‐mountableInstallationin19‐inchCabinet..............................................................................9
3.3PowerontheSwitch.......................................................................................................................10
4ConnectiontotheSwitch................................................................................................................11
4.1ConnectingComputer.....................................................................................................................11
4.2HowtoLogintotheSwitch............................................................................................................11
5SavingtheConfiguration.................................................................................................................13
6SwitchConfiguration.......................................................................................................................14
6.1Home................................................................................................................................................14
6.1.1CPUandMemoryStatusInformation.................................................................................................14
6.1.2PortInformation..................................................................................................................................14
6.2QuickSetup......................................................................................................................................16
6.3PortSettings....................................................................................................................................17
6.3.1BasicConfig..........................................................................................................................................17
6.3.2PortAggregation..................................................................................................................................19
6.3.3PortMirroring......................................................................................................................................20
6.3.4Portspeedlimit...................................................................................................................................21
6.3.5Broadcaststorm..................................................................................................................................22
6.3.6Portisolation.......................................................................................................................................23
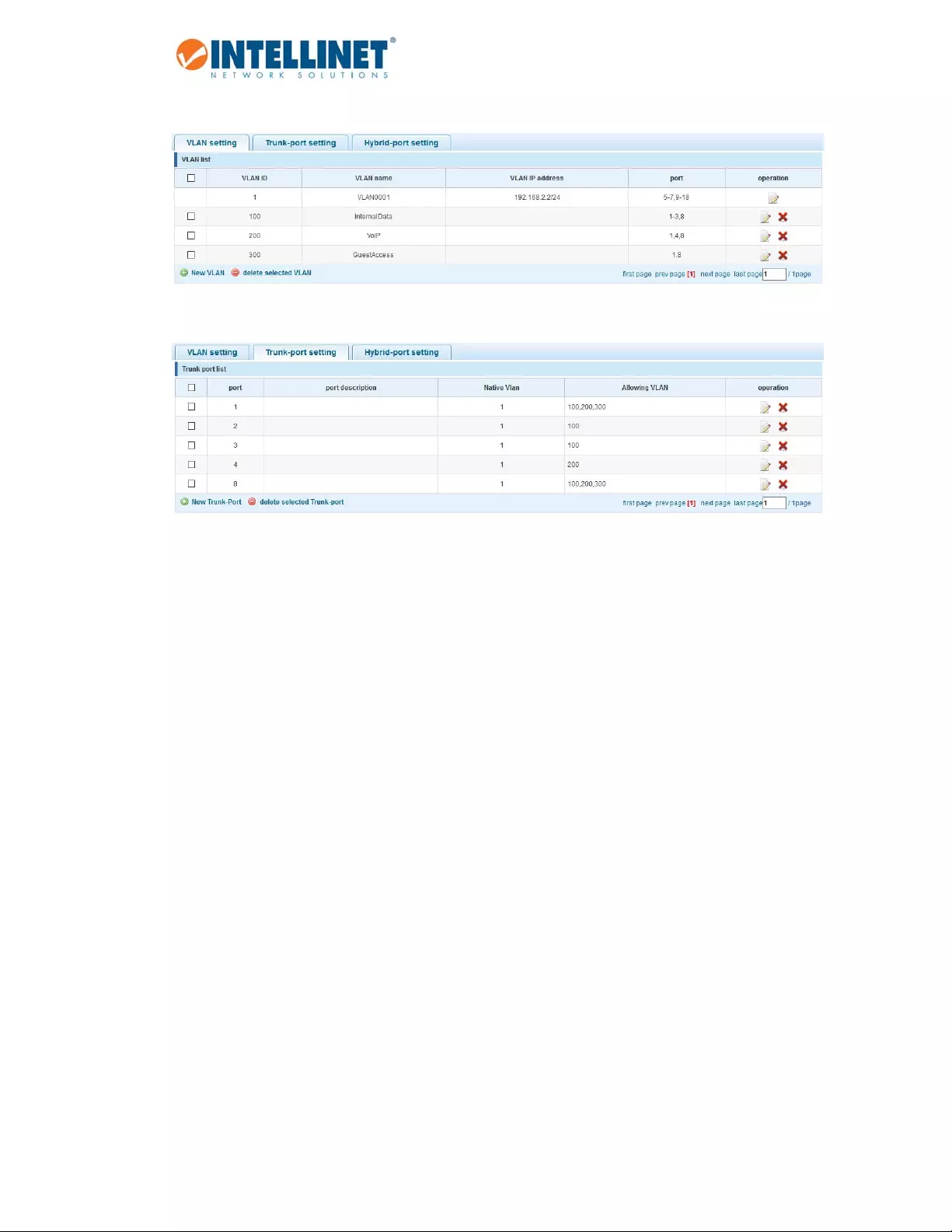
6.4VLAN.................................................................................................................................................26
6.4.1TrunkPortSettings..............................................................................................................................28
6.4.2HybridPortSettings.............................................................................................................................29
6.4.3SetupExample.....................................................................................................................................30
6.5Fault/Safety......................................................................................................................................33
6.5.1AntiAttack...........................................................................................................................................33
6.5.2ChannelDetection...............................................................................................................................40
6.5.3ACLAccessControlList........................................................................................................................42
6.6SpanningTreeProtocol(STP).........................................................................................................45
6.6.1MSTPRegion........................................................................................................................................48
6.6.2MSTPBridge........................................................................................................................................49
6.7DHCPRelayAgent............................................................................................................................51

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
3
6.7.1DHCPRelay..........................................................................................................................................51
6.7.2Option82..............................................................................................................................................51
6.8DHCPServer.....................................................................................................................................53
6.8.1DHCPConfig.........................................................................................................................................53
6.9TerminalAccessControllerAccess‐ControlSystem(TACACS+)....................................................56
6.10Radius...............................................................................................................................................58
6.10.1RadiusGeneralConfig.........................................................................................................................58
6.10.2RadiusServerConfig............................................................................................................................59
6.11AAA...................................................................................................................................................60
6.11.1EnableConfig.......................................................................................................................................60
6.11.2RegionConfig.......................................................................................................................................60
6.11.3ServerConfig.......................................................................................................................................61
6.11.4AAAAuthentication.............................................................................................................................62
6.12QoS–QualityofService..................................................................................................................64
6.12.1QoSRules.............................................................................................................................................64
6.12.2QueueConfig.......................................................................................................................................65
6.12.3QueueMapping...................................................................................................................................66
6.13AddressTable..................................................................................................................................67
6.13.1AddressTableConfig...........................................................................................................................67
6.14SNMP................................................................................................................................................69
6.14.1SNMPConfig........................................................................................................................................69
6.14.2RMONConfig.......................................................................................................................................74
6.15System..............................................................................................................................................78
6.15.1SystemConfig......................................................................................................................................78
6.15.2SystemUpdate....................................................................................................................................82
6.15.3ConfigurationManagement................................................................................................................83
6.15.4ConfigSave..........................................................................................................................................84
6.15.5UserAccounts......................................................................................................................................84
6.15.6InformationCollect..............................................................................................................................85
7Warranty.........................................................................................................................................86
8Copyright.........................................................................................................................................87
9FederalCommunicationCommissionInterferenceStatement.....................................................88

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
4
2 PRODUCTINTRODUCTION
CongratulationsonyourpurchaseoftheIntellinet48‐PortWeb‐ManagedGigabitEthernetSwitch.Beforeyou
installandusethisproduct,readthismanualcarefullyforafullunderstandingofitsfunctions.
2.1 PRODUCTOVERVIEW
TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPortsprovidesseamlessnetwork
connections.Itintegrates1000MbpsGigabitEthernet,100MbpsFastEthernetand10MbpsEthernetnetwork
capabilitiesinahighlyflexiblepackage.Eachofthe4810/100/1000MbpsAuto‐NegotiationRJ45ports
supportAutoMDI/MDIXfunction.Theswitchisahigh‐performanceupgradefromyouroldnetworktoa1000
MbpsGigabitnetwork.Itisessentialinsolvingnetworkbottlenecksthatfrequentlydevelopasmoreadvanced
computerusersandnewerapplicationsdemandgreaternetworkresources.Forefficientmanagement,the
switchisequippedwitharemoteWebinterface.Theswitchcanbeprogrammedforadvancedmanagement
functionssuchasPortManagement,LinkAggregation,VLAN,SpanningTree,Multicast,QoS,Security,Access
Control,MACAddressTable,Diagnostics,RMONandmore.
2.2 FEATURES
•
Forty‐eight10/100/1000Mbpsauto‐sensingportsautomaticallydetectoptimalnetworkspeeds
•
Foursmallform‐factorpluggableGBICmoduleslots(SFP)
•
ComplieswiththeIEEE802.3az(EnergyEfficientEthernetEEE)specification
•
SupportsSNMPmanagement
•
SupportsVLAN(tag‐basedandport‐based)
•
ProvidesIEEE802.1xport‐basedsecurity
•
Supportslinkaggregation(trunking
)
•
Supportsportmirroring
•
Supportsjumboframesupto9kBytes
•
SupportsRapidSpanningTree/SpanningTreeprotocol
•
Broadcaststormcontrolwithmulticastpacketratesettings
•
SupportstwotypesofQoS:port‐basedandDSCP
•
LEDsforpower,link/activity,connectionspeed
•
Fanlessdesignidealforsilentoperation
•
Includes19"rackmountbrackets

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
5
2.3 SPECIFICATIONS
Standards
•IEEE802.1d(SpanningTreeProtocol)
•IEEE802.1p(TrafficPrioritization)
•IEEE802.1q(VLANTagging)
•IEEE802.1w(RapidSpanningTreeProtocol)
•IEEE802.3ad(LinkAggregation)
•IEEE802.3(10Base‐TEthernet)
•IEEE802.3ab(TwistedPairGigabitEthernet)
•IEEE802.3ad(LinkAggregationControlProtocolLACP)
•IEEE802.3az(EnergyEfficientEthernetEEE)
•IEEE802.3u(100Base‐TXFastEthernet)
•IEEE802.3x(flowcontrol,forfullduplexmode)
Power
•Input:100–240VAC,50–60Hz
Environmental
•Metalhousing
•Dimensions:335(L)x440(W)x44(H)[mm](13.19(L)x17.32(W)x1.73(H)[in])
•Weight:4.2kg(9.26lbs.)
•Operatingtemperature:0–40°C(32–104°F)
•Operatinghumidity:10–90%RH,non‐condensing
•Storagetemperature:‐20–70°C(‐4–158°F)
PackageContents
•48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwithFourSFPPorts
•Powercable
•Usermanual
•19"rackmountbrackets

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
6
2.4 E
XTERNAL
C
OMPONENT
D
ESCRIPTION
2.4.1 FrontPanel
Thefrontpaneloftheswitchconsistsof4810/100/1000MbpsRJ‐45ports,fourSFPports,oneConsole
port,oneResetbuttonandaseriesofLEDindicatorsasshownbelow.
10/100/1000MbpsRJ‐45ports(1~48):
Designedtoconnecttothedevicewithabandwidthof10Mbps,100Mbpsor1000Mbps.Eachhasa
corresponding10/100/1000MbpsLED.
SFPports(SFP1,SFP2,SFP3,SFP4):
DesignedtoinstalltheSFPmoduleandconnecttothedevicewithabandwidthof1000Mbps.Allportshavea
corresponding1000MbpsLED.
Consoleport(Console):
Designedtoconnectwiththeserialportofacomputerorterminalformonitoringandconfiguringtheswitch.
Resetbutton(Reset):
Torestorethesystemfactorydefaultsettings,presstheresetbuttonforfivesecondswhilethedeviceis
poweredon.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
7
LEDindicators:
TheLEDindicatorswillallowyoutomonitor,diagnoseandtroubleshootanypotentialproblemwiththe
switch,itsconnectionorattacheddevices.
ThefollowingchartshowstheLEDindicatorsoftheswitchalongwithexplanationofeachindicator.
LED COLOR STATUS STATUSDESCRIPTION
Power Red On PowerOn
Off PowerOff
LINK/ACT/
Speed
(1~48)
10/100Mbps:
Amber
On Adeviceisconnectedtotheport
Off Nodeviceisconnectedtotheport
1000Mbps:
Green
Flashing Sendingorreceivingdata
SFP1
SFP2
SFP3
SFP4
Green On Adeviceisconnectedtotheport
Off Nodeviceisconnectedtotheport
Flashing Sendingorreceivingdata
Reset
Pressfor15seconds–20secondsinorderto
resetallsettingstofactorydefaultvalues.
Releasethebutton,oncetheLEDsstartflashing.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
8
2.4.2 RearPanel
ACPowerConnector:
PowerissuppliedthroughanexternalACpoweradapter.ItsupportsAC100‐240V,50/60Hz.
GroundingTerminal:
GroundtheswitchthroughthePEcableontheACcordorwithaseparategroundwire.
2.5 PACKAGECONTENTS
Beforeinstallingtheswitch,makesurethatthefollowingitemsareenclosed.Ifanypartismissingor
damaged,contactyourIntellinetagentimmediately.
• 48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
• Powercable
• QuickInstallationGuide
• Usermanual(onCD)
• Fourrubberfeet,twomountingearsandeightsscrews

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
9
3 INSTALLINGANDCONNECTINGTHESWITCH
ThischapterdescribeshowtoinstallyourWeb‐ManagedGigabitEthernetSwitchandmakeconnectionstoit.
Thefollowingstepswillhelppreventdamagetothedeviceandmaintainpropersecurity:
Placetheswitchonastablesurfaceordesktoptominimizethechancesofitfalling.
MakesuretheswitchworksintheproperACinputrangeandmatchesthevoltagelabeledonthe
switch.
Topreventelectrocution,donotopentheswitch’schassis,evenifitfailstoreceivepower.
Makesurethatthereisproperheatdissipationfromandadequateventilationaroundtheswitch.
Makesurethesurfaceonwhichtheswitchisplacedcansupporttheweightoftheswitchandits
accessories.
3.1 DESKTOPINSTALLATION
Wheninstallingtheswitchonadesktop(ifnotinarack),attachtheenclosedrubberfeettothebottom
cornersofittominimizevibration.Allowadequatespaceforventilationbetweenthedeviceandtheobjects
aroundit.
Figure4‐DesktopInstallation
3.2 RACK‐MOUNTABLEINSTALLATIONIN19‐INCHCABINET
TheswitchcanbemountedinanEIAstandard‐sized,19‐inchrack,whichcanbeplacedinawiringclosetwith
otherequipment.Toinstalltheswitch,followthesesteps:
Attachthemountingbracketsontheswitch’ssidepanels(oneoneachside)andsecurethemwiththescrews
provided.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
10
Figure5‐BracketInstallation
Usethescrewsprovidedwiththeequipmentracktomounttheswitchontherackandtightenit.
Figure6‐RackInstallation
3.3 POWERONTHESWITCH
TheswitchispoweredonbyconnectingittoanoutletusingtheAC100‐240V50/60Hzinternalhigh‐
performancepowersupply.
ACElectricalOutlet:
Itisrecommendedtouseasingle‐phase,three‐wirereceptaclewithaneutraloutletormultifunctional
professionalreceptacle.Besuretoconnectthemetalgroundconnectortothegroundingsourceontheoutlet.
ACPowerCordConnection:
ConnecttheACpowerconnectoronthebackpaneloftheswitchtoanexternalreceptaclewiththeincluded
powercord,thencheckthatthepowerindicatorisON.WhenitisON,thecorrespondingLEDisilluminated.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
11
4 CONNECTIONTOTHESWITCH
4.1 CONNECTINGCOMPUTER
UsestandardCat5/5eEthernetcables(UTP/STP)toconnecttheswitchtoendnodesasdescribedbelow.
Switchportswillautomaticallyadjusttothecharacteristics(MDI/MDI‐X,speed,duplex)ofthedevicetowhich
theyareconnected.
Figure7‐PCConnect
TheLNK/ACT/SpeedLEDsforeachportareilluminatedwhenthelinkisavailable.
4.2 HOWTOLOGINTOTHESWITCH
AstheswitchprovidesWeb‐basedmanagementlogin,configureyourcomputer’sIPaddressmanuallytolog
ontotheswitch.Thedefaultsettingsoftheswitchareshownbelow.
Parameter DefaultValue
DefaultIPaddress 192.168.2.1
DefaultUsername admin
DefaultPassword 1234
Logontotheconfigurationwindowoftheswitchthroughfollowingsteps:
1. ConnecttheswitchwiththecomputerNICinterface.
2. Powerontheswitch.
3. CheckwhethertheIPaddressofthecomputeriswithinthisnetworksegment:192.168.2.xxx(“xxx”
rangeis2‐254);forexample,192.168.2.100.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
12
Openthebrowser,andgototheURLhttp://192.168.2.1.Theswitchloginwindowappears,asshownbelow.
EntertheUsernameandPassword(thefactorydefaultUsernameisadminandthePasswordis1234),and
thenclick“LOGIN”tologintotheswitchconfigurationwindowasbelow.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
13
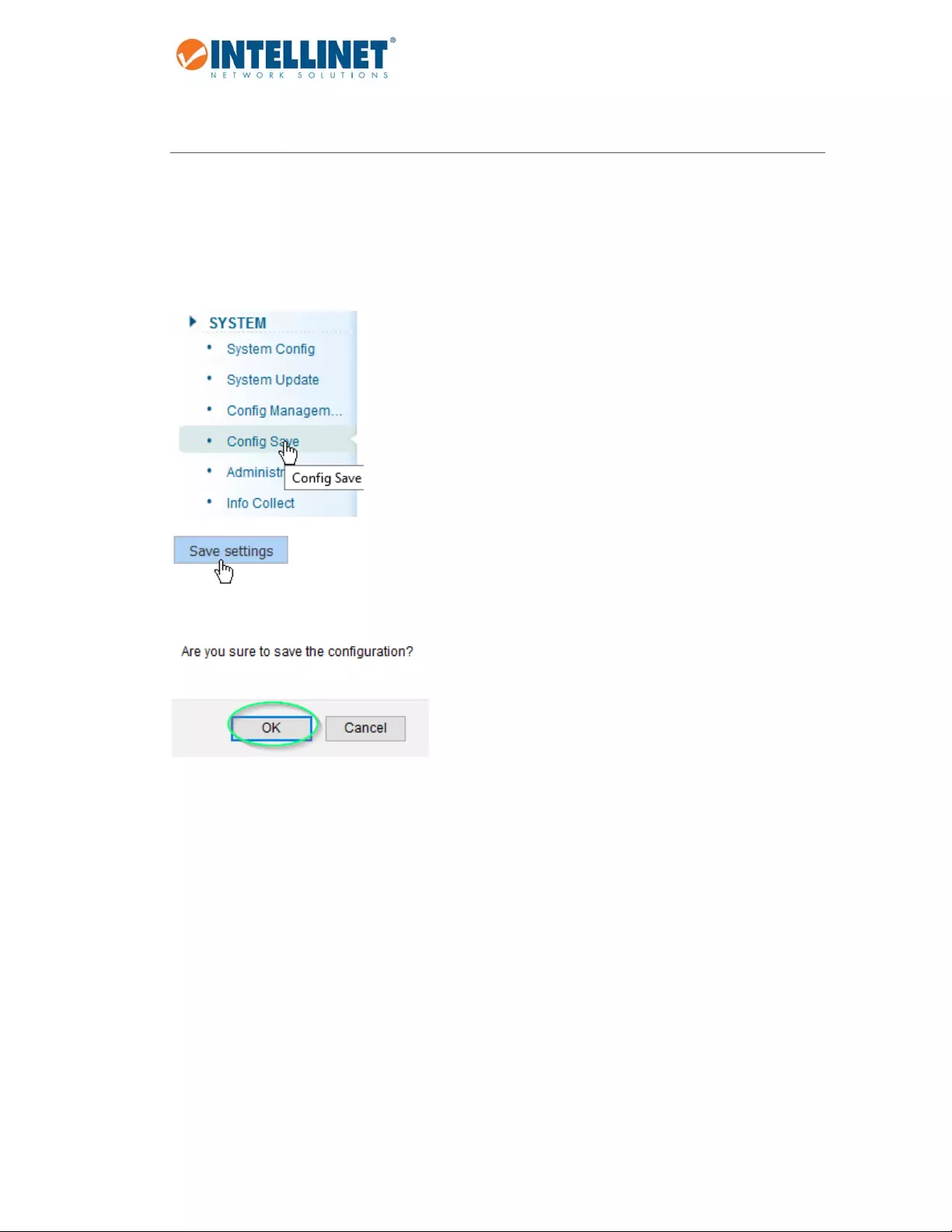
5 SAVINGTHECONFIGURATION
TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchprovidesamyriadofconfigurationoptions,many
ofwhicharedesignedforexperiencednetworkadministratorsandaren’teasytoconfigure.Itwouldbeareal
shameifalltheconfigurationdatawaslostafterapowerfailureoraftertheswitchwasrestarted.Inorderto
maketheconfigurationpermanent,itneedstobesaved.
Hereishow:
Ifyoudonotperformthisfunction,yourisklosingallthesettingsaftertheswitchrestarts.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
14
6 SWITCHCONFIGURATION
Thischapterdescribeshowtousetheweb‐basedmanagementinterface(WebUI)forthisswitch.
6.1 HOME
6.1.1 CPUandMemoryStatusInformation
Thissectionprovidesaquickoverviewoftheswitch’sbasicsystemresourcesintermsofmemoryutilization
andCPUload.Ifyoumouse‐overanyofthesesections,additionaldetailsarerevealed.
IftheCPUloadisunusuallyhigh,oriftheavailablememoryorFlashmemoryisgettinglow,youmayneedto
restarttheIntellinetswitchtofreeupsystemresources.InitiatetherebootviatheSYSTEM‐>SYSTEMCONFIG
‐>SYSTEMRESTARTmenu.
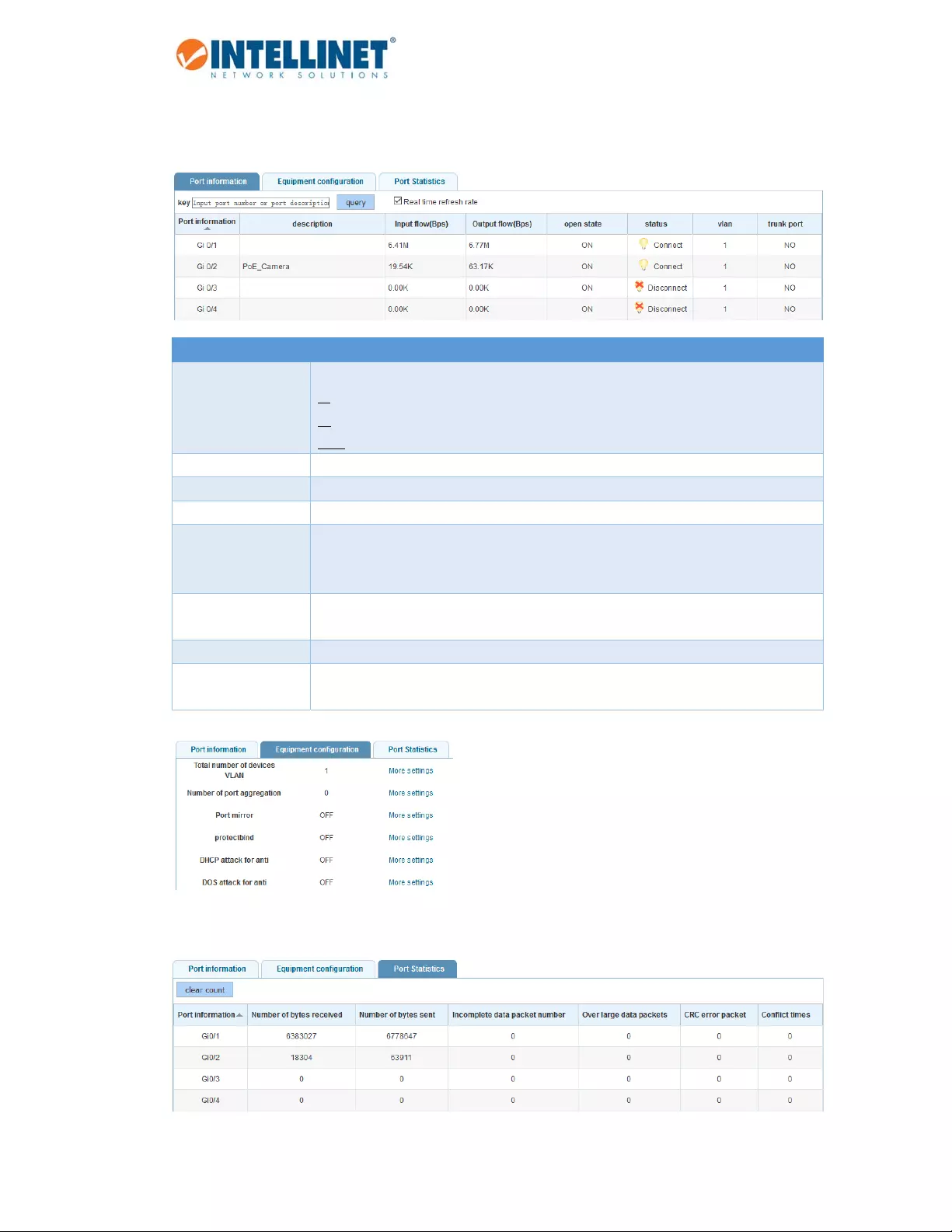
6.1.2 PortInformation
AgreensquaresindicatetheportlinkisupatGigabitspeeds.Anambersquareindicatesalinkspeedof100
Mbps.Agraysquaresindicatetheportlinkisdown.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
15
6.1.2.1 PortInformation,EquipmentConfigurationandPortStatistics
Thissectionprovidesreal‐timeinformationabouttheports,basicsettingsandtrafficstatistics.
Item Description
PortInformation Displaystheportnumber.Thenomenclatureisasfollows:
Gi=GigabitEthernet
0/=Switch0(whichmeansthisdevice)
1‐52=Portnumber.Ports49,50,51and52areSFPmoduleslots.
Description Optionaldescriptionfortheport,asenteredinthebasicportconfiguration.
InputFlow(bps) Inboundtrafficrate,measuredin"bitspersecond.”
OutputFlow(bps) Outboundtrafficrate,measuredin"bitspersecond.”
OpenState ON=Portisactivatedinthebasicportconfigurationandwillacceptconnections
fromnetworkingdevices.
OFF=Portisdeactivatedinbasicportconfiguration.
Status Connect:Anetworkingdeviceisconnectedtotheportandhasanactivelink.
Disconnect:Nodeviceisconnectedtotheport.
VLAN IftheportbelongstoaVLAN,itsIDisdisplayedhere.ID1=default.
TrunkPort Yes=TheportispartofanLACPtrunkinggroup.
No=TheportisnotpartofanLACPtrunkinggroup.
Thistabdisplaysinformationaboutvariousfunctionsandprovidesashort‐cutthatallowsdirectconfiguration
ofthatpartoftheswitchsettings.
Thistabdisplaysreal‐timeinformationaboutthedatapacketsforeachport.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
16
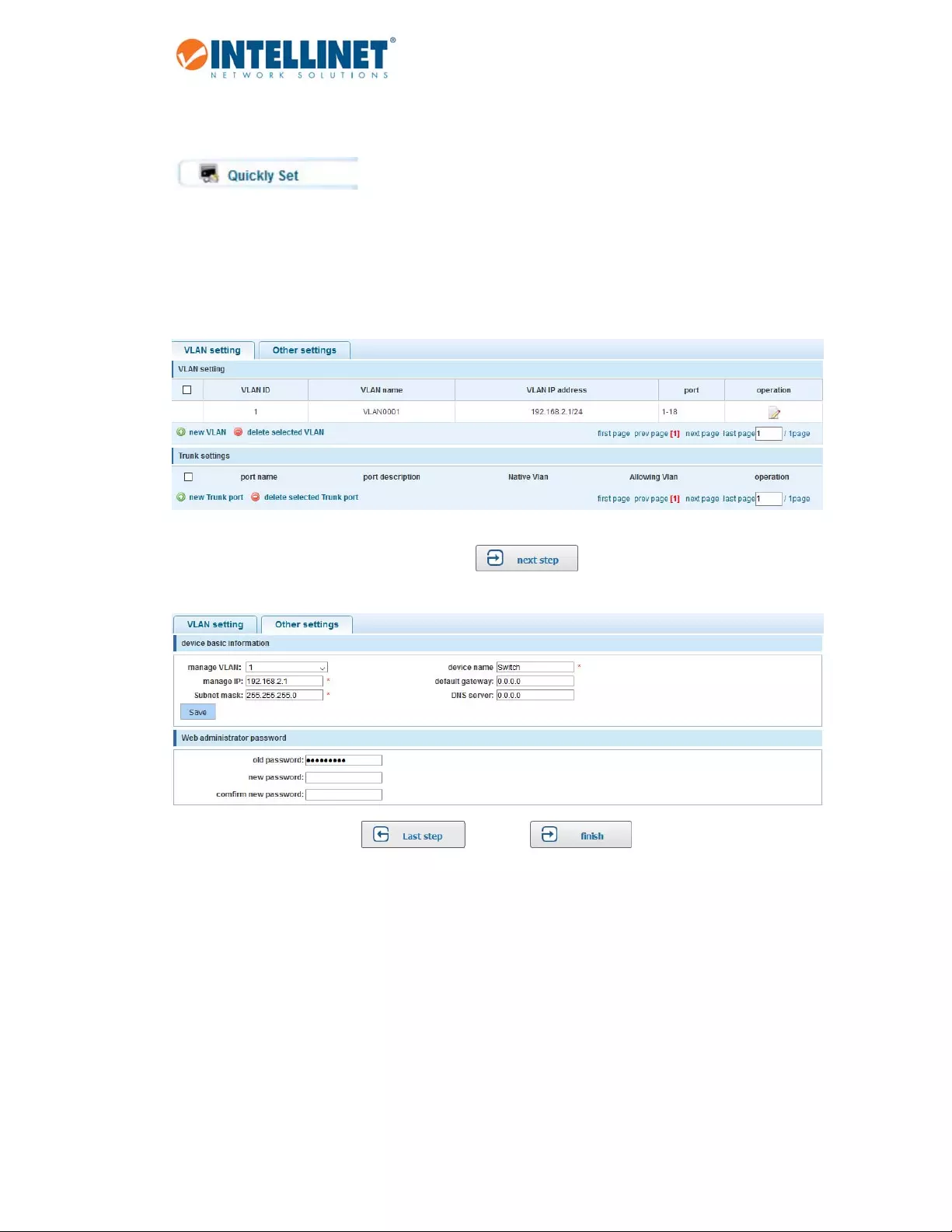
6.2 QUICKSETUP
TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchprovidesasettingthatoffersdirectaccessto
someofthecorefunctionsofthedevice,namelyVLAN,trunking,deviceIPaddressandadminpassword.Even
thoughthefunctioniscalled“QuicklySet,”thereisnoneedtorush.Takeasmuchtimeasyoulikewiththe
configuration.
Refertosubsequentsectionsinthisuserguideforadditionalinformationabouttheindividualfunctions.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
17
6.3 PORTSETTINGS
6.3.1 BasicConfig
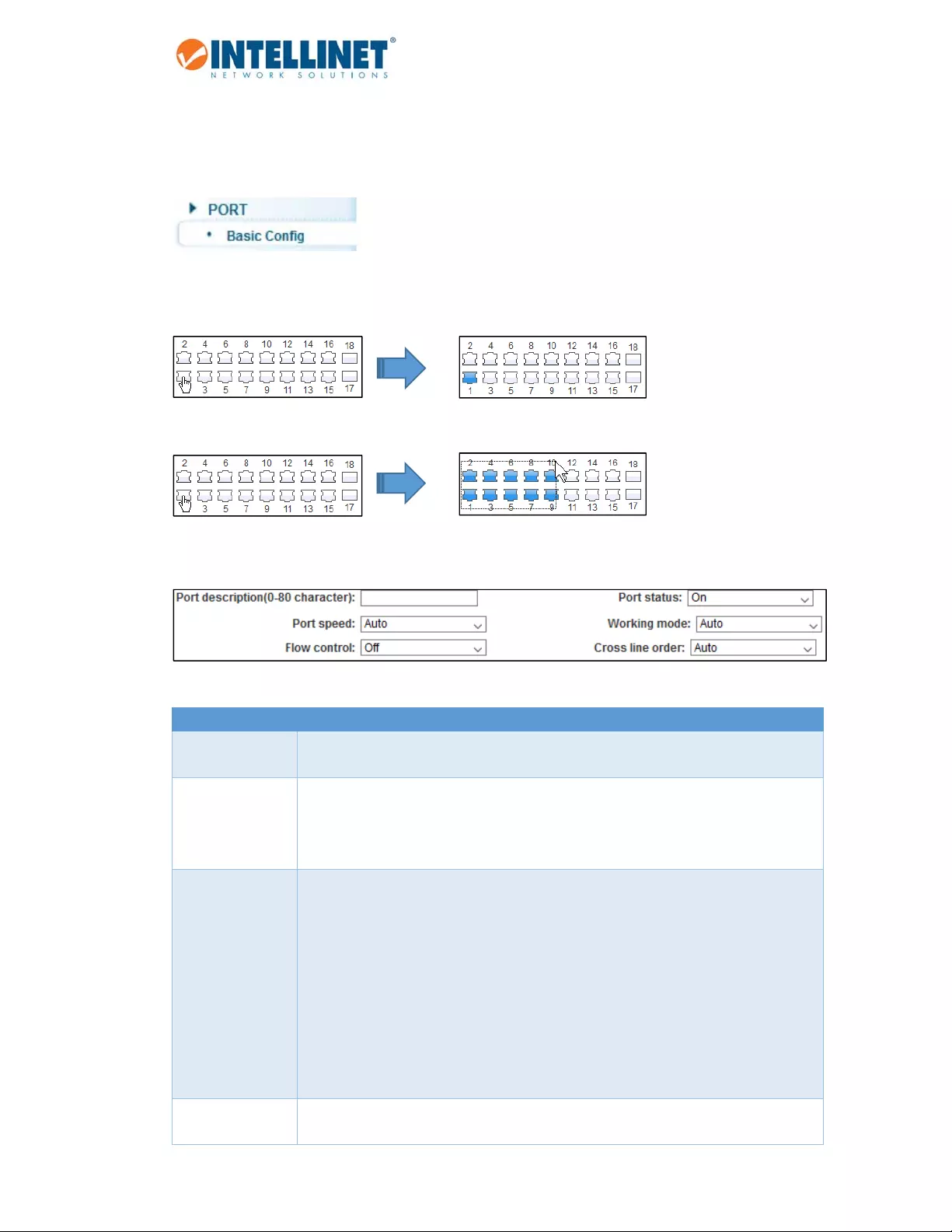
Accesstheparametersrelatedtoeachofthe18ports.Thescreenisdividedintotwosections.Theupper
sectiondisplaysanimageofthe18portsoftheIntellinetswitch.Inordertomakechangestoaport,simply
clicktoselectit.
Createaselectionofmultipleportsatonce:
Onceoneportormultipleportsareselected,makechangestotheportsettings.
Item Description
Portdescription Optionaldescriptionfortheport.Amaximumof80characterscanbeprovided.No
specialcharactersorspacesareallowed.
Portspeed 10M:Forceaconnectiontobemadeat10Mbps.
100M:Forceaconnectiontobemadeat100Mbps.
1000M:Forceaconnectiontobemadeat1000Mbps.
Auto:Theswitchandconnecteddevicenegotiatethebestpossibleconnectionspeed.
Flowcontrol IEEE802.3xflowcontrolistheprocessofmanagingtherateofdatatransmission
betweentwonodes(i.e.,theswitchandaconnectednetworkclient)topreventafast
senderfromoverwhelmingaslowreceiver.Itprovidesamechanismforthereceiver
tocontrolthetransmissionspeed,sothatthereceivingnodeisnotoverwhelmedwith
datafromthetransmittingnode.Thatsoundslikeitisagoodthing,anditis.Sowhyis
theoptionbydefaultsetto“disabled"?Theshortanswerisbecauseyounormally
don’tneeditandbecauseitcan,inveryrareinstances,haveanegativeimpactonthe
overallperformanceinyournetwork.TheTCPprotocolalreadyprovidesitsownflow
controlmechanism,allowingasendertothrottlebackthespeedifthereceiveris
havingproblemskeepingup.
Portstatus ON:Activatetheport.
OFF:Disablestheport.Noconnectionstoitcanbemade.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
18
Item Description
Workingmode Thisparametercontrolstheduplexmode.Inafull‐duplexsystem,bothpartiescan
communicatetotheothersimultaneously.Anexampleofafull‐duplexdeviceisa
telephone;thepartiesatbothendsofacallcanspeakandbeheardbytheotherparty
simultaneously.Innetworkingterms,fullduplexallowsreceivingandtransmittingof
dataatthesametime,whereashalfduplexdoesnot.Ifthetelephoneisanexample
forfullduplex,thenapush‐to‐talkCBradioor"walkie‐talkie"representshalfduplex.
Theswitchcaneitherreceiveorsenddata,butitcanneverhappensimultaneously.
Unlessyouhaveaspecificreasonnottodoso,thisshouldbeleftin“Auto”mode.
Crosslineorder AutoMDI‐Xautomaticallydetectstherequiredcable‐connectiontypeandconfigures
theconnectionappropriately,removingtheneedforcrossovercablestointerconnect
switchesorforconnectingPCspeer‐to‐peer.Aslongasitisenabledoneitherendofa
link,eithertypeofcablecanbeused.ForautoMDI‐Xtooperatecorrectly,thedata
rateontheinterfaceandduplexsettingmustbesetto"auto."WhentwoautoMDI‐X
portsareconnectedtogether,whichisnormalformodernproducts,thealgorithm
resolutiontimeistypically<500ms.However,a~1.4secondasynchronoustimeris
usedtoresolvetheextremelyrarecase(withaprobabilityoflessthan1in5×1021)ofa
loopwhereeachendkeepsswitching.Ifyoudon’tunderstandanyofthis,simplyleave
thisvalueon“Auto.”
Thescreenalsoshowsatablethatlistsall18portsalongwiththeirparameters.The“megaframe”valuerefers
tojumboframes,whichareEthernetframeswithmorethan1500bytesofpayload.Definethesizeofthe
jumboframesinthesectionSYSTEM‐>SYSTEMCONFIG.
Clickingthepencilallowseditingtheportsettings,exactlythesamewayasdirectlyselectingthe
port(s)asshownonthepreviouspage.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
19
6.3.2 PortAggregation
PortaggregationisamethodofusingmultipleEthernetportsinparalleltoincreasethroughputbeyondwhata
singleconnectioncouldsustainandtoprovideredundancyincaseoneofthelinksshouldfail.Asthisis
essentiallyagroupingofportsintoonelogicalunit,wecallthemLinkAggregationGroups,or“LAG”forshort.
ThispageisusedtosetupLAGs.CreateuptoeightdifferentLAGs;eachcanhaveuptoeightmemberports.
EachLAGcanbegivenacustomname,andyoumustselecttheportsfortheLAG.Theexamplebelowshows
anLAGgroupsetupwithfourmemberports.
Item Description
Aggregateportnumber Thisisthelinkaggregationgroup(LAG)number
Pleaseselecttheporttojointheaggregateport SelectthememberportsthatbelongtothisLAG
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
20
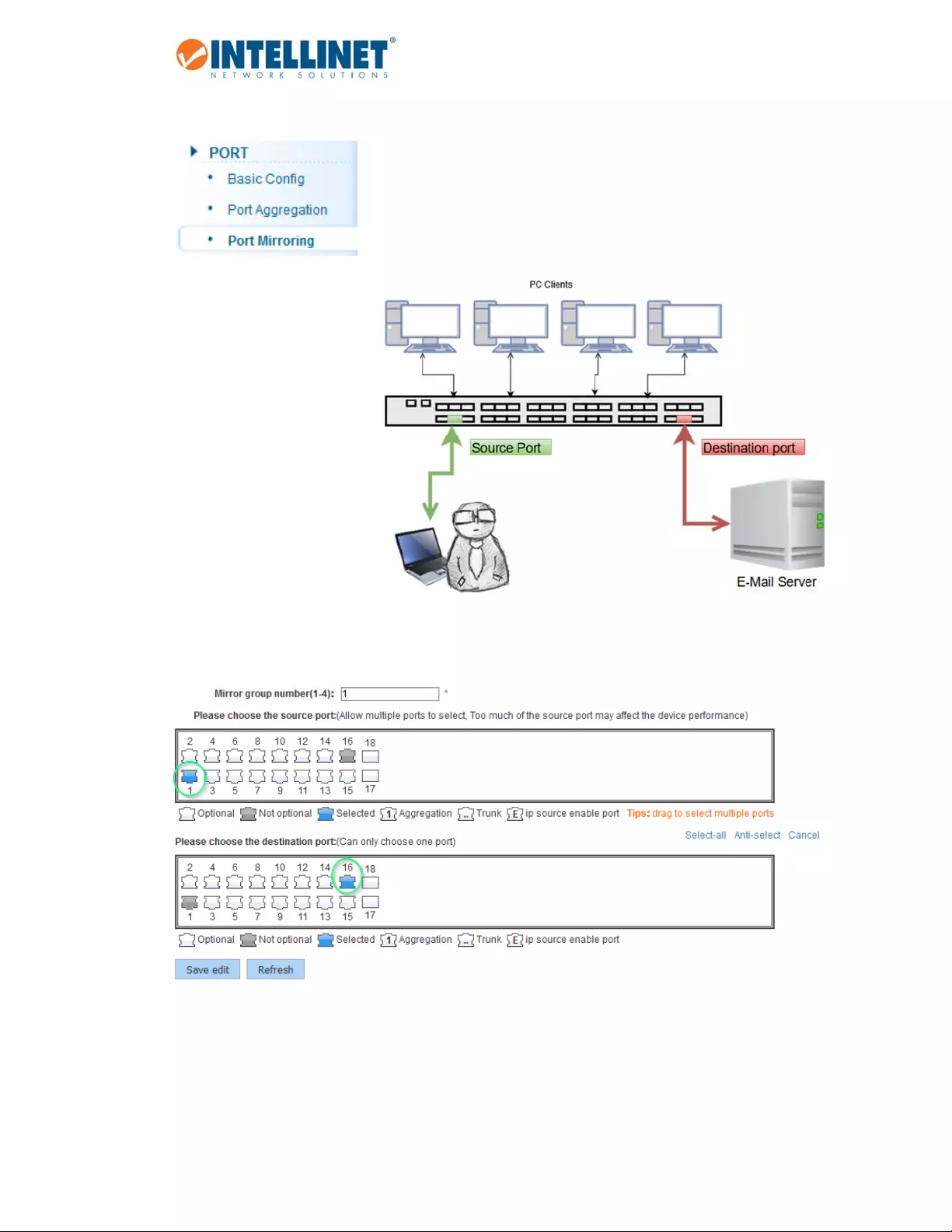
6.3.3 PortMirroring
Portmirroringistheabilityofa
networkswitchtosendacopyof
networkpacketsseenonaswitch
portorportstoanetwork‐
monitoringdeviceconnectedto
anotherswitchport(i.e.,a
computerequippedwithapacket
snifferutility).TheIntellinet48‐
PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐
ManagedSwitchprovidesupto
fourgroupsforport‐mirroring
settings.
Theexamplebelowshowssettinguponemirrorgroupwherealltrafficoccurringonport1isbeingmirrored
toport16.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
21
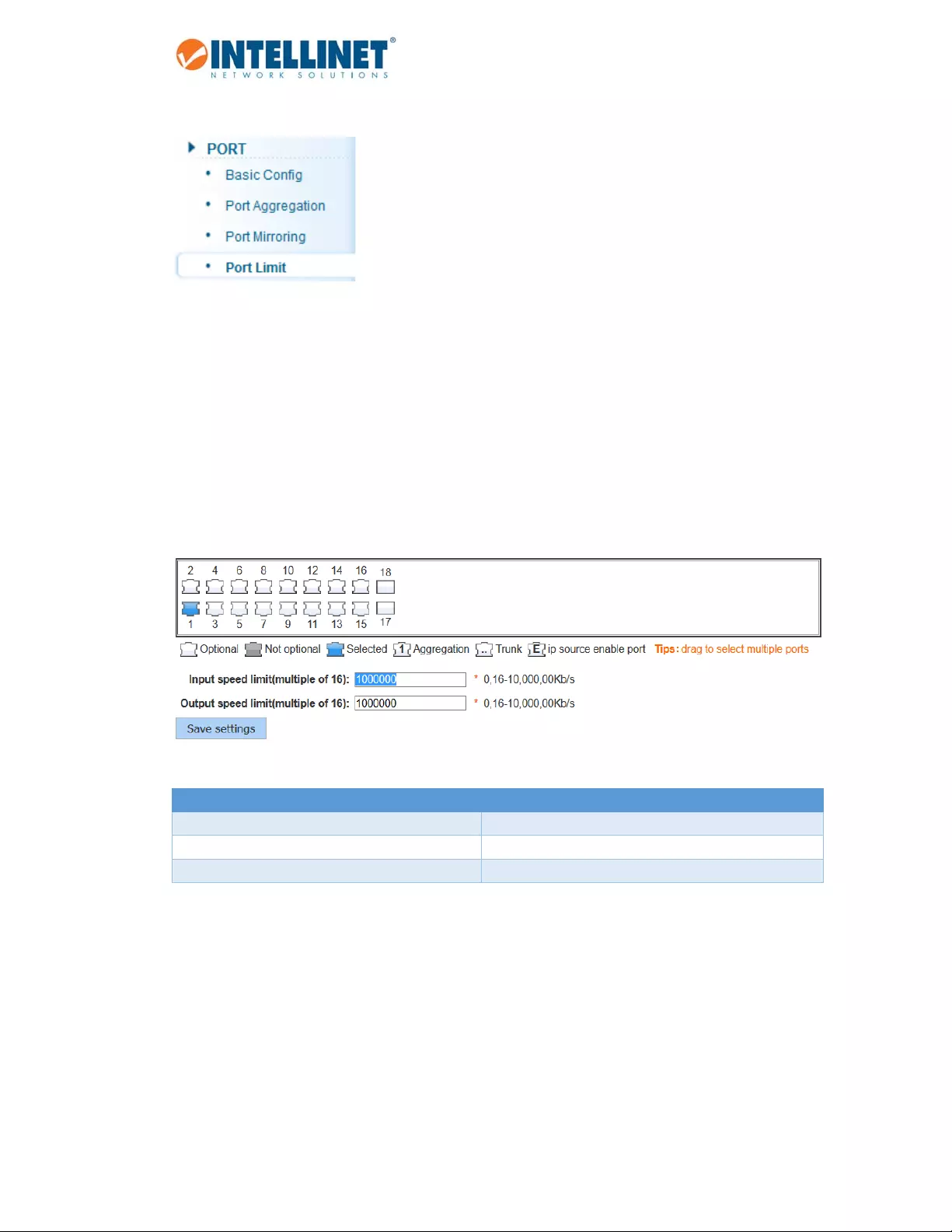
6.3.4 Portspeedlimit
ThisfeatureallowsyoutolimitthedataratesforaparticularportontheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernet
Web‐ManagedSwitch.Whenthedatarateexceedsuser‐configuredvalues,theIntellinetswitchdropspackets
immediately.Ratelimitingisconfiguredfortwotypesoftransmissions,whichareingressandegress.Ingress
trafficisreceivedonanygivenport(incoming,inbound,downloadorinputspeed),whereasegresstrafficis
trafficsentout(outgoing,outbound,uploadoroutputspeed)toanothernetworkclient.
TheIntellinetswitchallowscontrollingtheavailablebandwidthforeachportindividually.Thespeedis
measuredinkbps,whichstandsforkilobitspersecond.Thedefaultis1million,whichistheequivalentof1
Gigabitpersecond.Valuesenteredmustbemultiplesof“16”(e.g.,16,32,48,…,512,….,1024,etc.).
Item Description
Portnumber1‐18 Selectindividualportsorarangeofports.
Inputspeedlimit(multipleof16) Providetheingressrateinkbps.
Outputspeedlimit(multipleof16) Providetheegressrateinkbps.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
22
6.3.5 Broadcaststorm
StormcontrolpreventsLANinterfacesfrombeingdisruptedbyabroadcaststorm.Abroadcaststormoccurs
whenbroadcastpacketsfloodthesubnet,creatingexcessivetrafficanddegradingnetworkperformance.
Errorsintheprotocol‐stackimplementationorinthenetworkconfigurationcancauseabroadcaststorm.The
Intellinetswitchallowsconfiguringmaximumallowedppsratesforthreedifferenttypesofpackets.It's
possibletosetall18portstothesamevalueorprovideindividualvalues.
Item Description
Portnumber1‐52 Selectindividualportsorarangeofports.
Broadcastlimit Enterthemaximumpps(packetspersecond)forbroadcastpackets.
Multicastlimit Enterthemaximumpps(packetspersecond)formulticastpackets.
Unicastlimit Enterthemaximumpps(packetspersecond)forunicastpackets.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
23
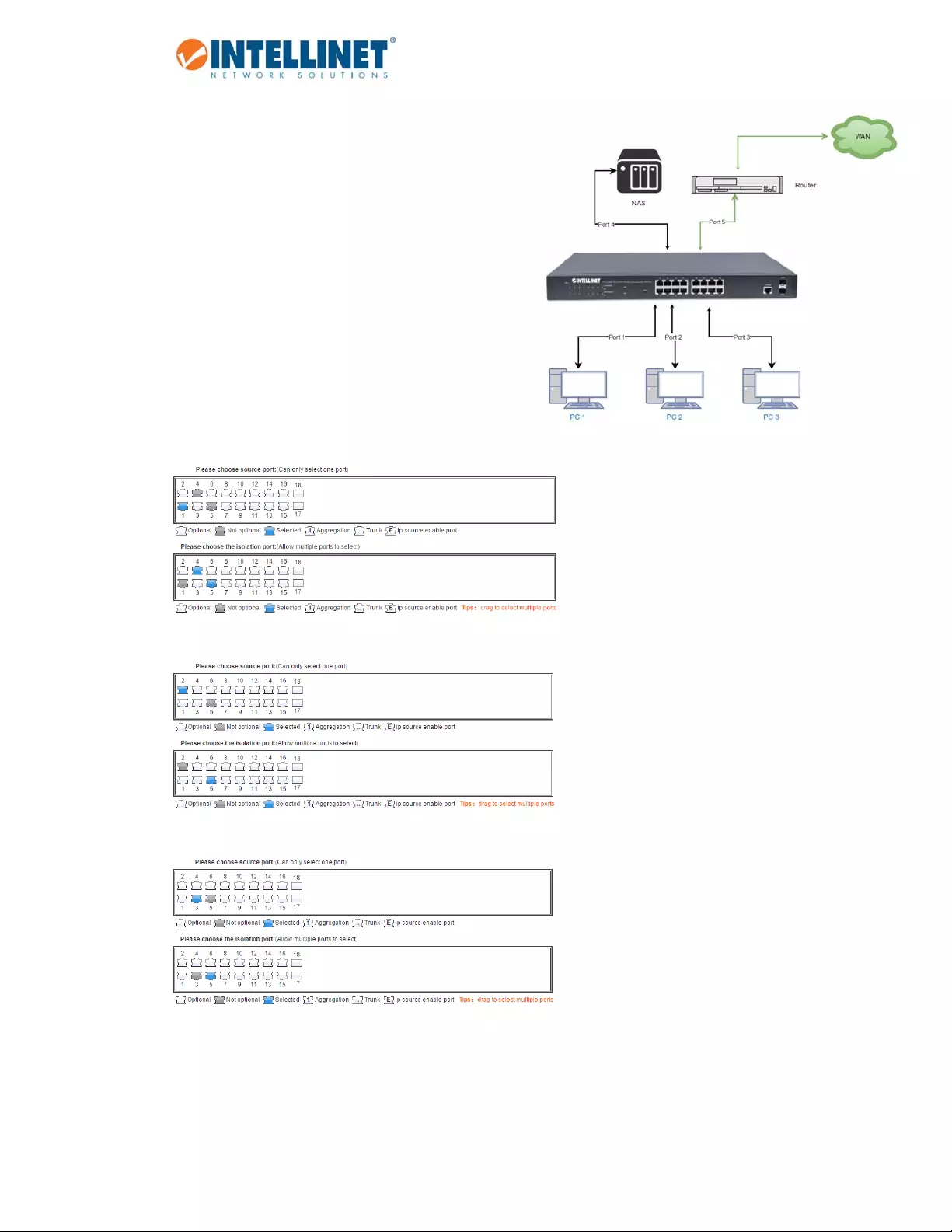
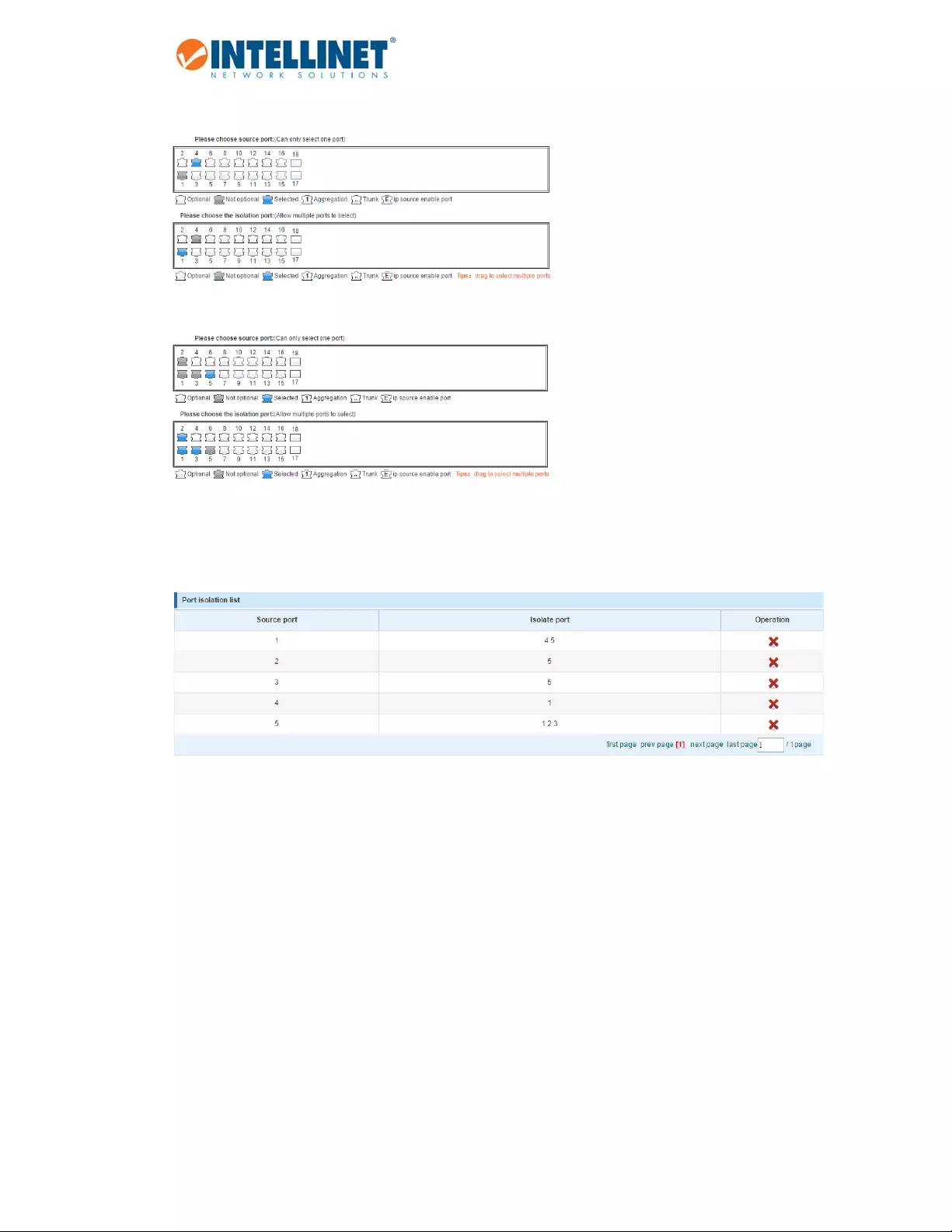
6.3.6 Portisolation
TheportisolationfunctionallowsyoutoconfiguretheIntellinetswitchinaway,thatpreventsPCsondifferent
portsfromcommunicatingwitheachother,andallthatwithoutconfiguringaVLAN.
Item Description
SourcePort Selecttheportyouwishtoisolate.
IsolationPort Selecttheport(s)towhichpacketsfromthesourceportcanbe
forwarded.Morethanoneportcanbeselectedhere.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
24
6.3.6.1 ConfigurationExample:
1. ThreePCs,oneNAS,andonerouterareconnected
totheIntellinetswitch
2. PC1isconnectedtoPort1
3. PC2isconnectedtoPort2
4. PC3isconnectedtoPort3
5. TheNASisconnectedtoPort4
6. TherouterisconnectedtoPort5
7. PC1canaccesstheNASandtherouter
8. PC2andPC3canonlyaccesstherouter
PC1onport1:
PC2onport2:
PC3onport3:
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
25
NASonPort4:
RouteronPort5:
Whencompleted,theconfigurationwilllooklikethis.Tobetterunderstandwhatishappening,ithelpsto
considertheisolatedportsastheportswithwhichthesourceportscancommunicate.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
26
6.4 VLAN
AvirtualLAN(VLAN)isanybroadcastdomainthatispartitionedandisolatedinacomputernetworkatthe
datalinklayer(OSIlayer2).VLANsaredatalinklayer(OSIlayer2)constructs,analogoustoIPsubnets,which
arenetwork‐layer(OSIlayer3)constructs.VLANscanbeusedtopartitionalocalnetworkintoseveral
distinctivesegments.
VLANtechnologyprovidesthefollowingadvantages:
1. BroadcasttrafficdoesnotcrossintodifferentVLANs,whichreducesbandwidthutilizationand
improvesnetworkperformance.
2. SecurityinyourLANcanbeimproved,sincepacketsindifferentVLANscannotcommunicatewith
eachotherdirectly.
3. WithVLAN,clientscanbeallocatedtodifferentworkinggroups,andusersfromthesamegroupdo
nothavetobewithinthesamephysicalarea,whichmakesnetworkmaintenancemucheasierand
moreflexible.
VLANtechnologyknowsthreetypesofports—access,trunkandhybridports.
1. AccessPorts(untagged)
a. AccessportsaredesignedtotaganyincomingpacketwiththeVLANIDtheporthasbeen
assignedto.
b. TaggedVLANpacketsarrivingattheaccessportaredroppedbytheswitch.
c. AsfarastheIntellinetswitchisconcerned,anyportthatisn’tdefinedasatrunkorhybrid
portisconsideredanaccessport.
2. TrunkPorts(tagged)
a. TrunkportsaredesignedtofilteroutpacketsthathaveeithernoVLANtagorVLANtagsthat
arenotontheallowedVLANIDlist.
b. TrunkportsdonotremoveanyexistingVLANtagsfromincomingpackets.
c. TrunkportsdonotaddaVLANtagtoanyincominguntaggedpacket.
d. Trunkportsareidealforswitch‐to‐switchconnectionsorfordevicesthathavetheabilityto
tagpacketsbythemselvessuchasVoIPphones.
3. HybridPorts
a. Theseareacombinationofaccessandtrunkports.
b. HybridportswilltaganyincomingpacketthathasnoVLANIDwiththeVLANIDtheporthas
beenassignedto.
c. HybridportswillalsoactastrunkportsforpacketsthathaveaVLANtag.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
27
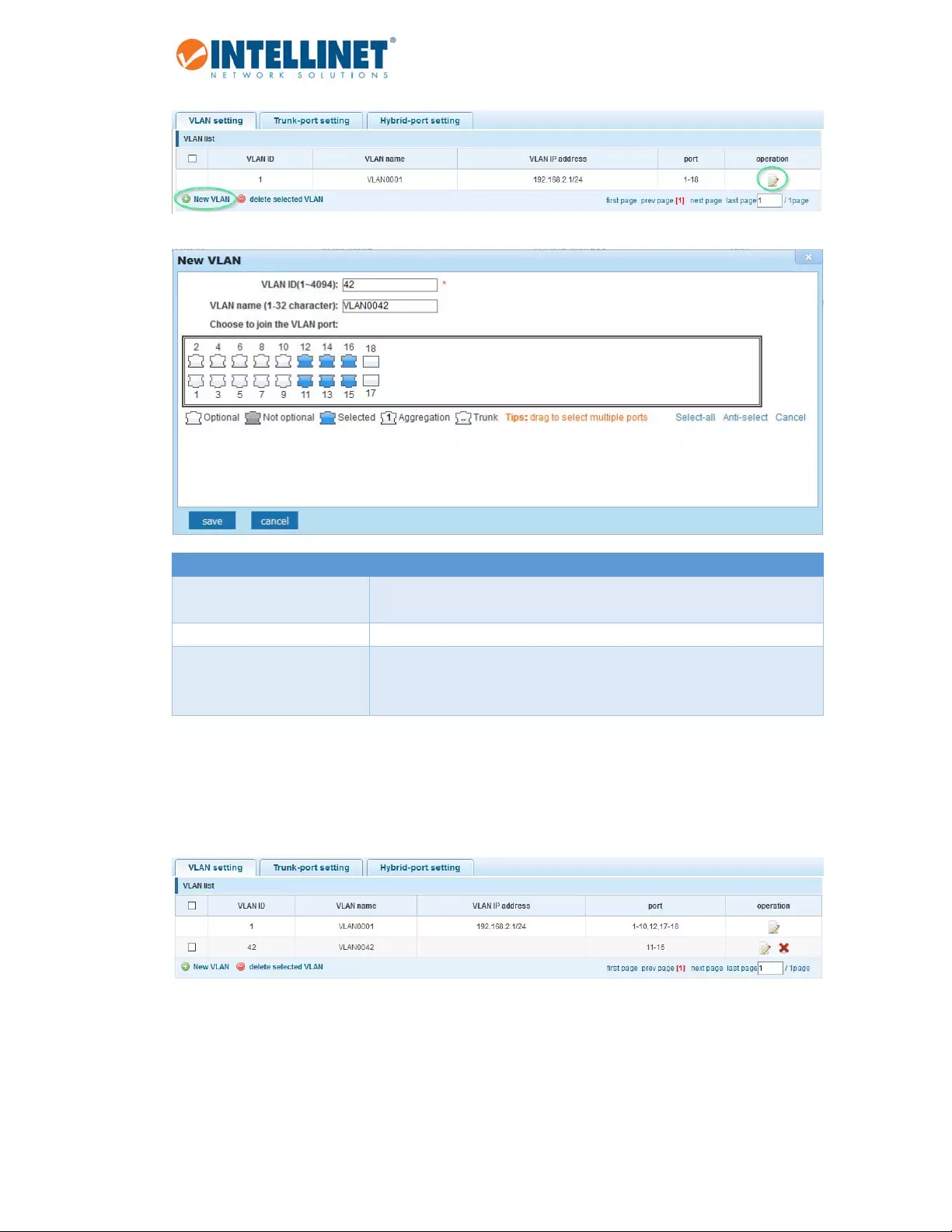
NewVLAN:
Item Description
VLANID TypeintheIDforthenewVLAN.Thisvaluecannotbe“1”noranyID
alreadysetupontheswitch.
VLANName ProvideadescriptivenamefortheVLAN(e.g.,“VOICE”).
ChoosetojointheVLANport SelectalltheportsyouwishtobeapartofthisVLAN.Notethatthese
portswillactasaccessports.TheywilladdtheVLANIDtoanyuntagged
packetandrejectanyincomingpacketsthathaveaVLANtag.
Note:VLANID1isthedefaultVLAN,whichcannotberemoved.However,accessportsthatareassignedto
anotherVLANwillbeautomaticallyremovedfromVLAN1.Thescreenshotbelowshowswhatthesetuplooks
likeaftertheaboveVLANhasbeenadded:

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
28
6.4.1 TrunkPortSettings
Atrunkporttransmitstaggedpacketsandisusedtoconnectdifferentswitcheswithoneanother.
NewTrunk‐Port:
Item Description
NativeVLANID ThenativeVLANIDistheuntaggedVLANonanIEEE802.1qtrunkedport.
ThenativeVLANandmanagementVLAN(seeSYSTEM‐>SYSTEMCONFIG)
canbethesame,butintermsofsecurity,itisbetterthattheyaren't.Ifa
switchreceivesanuntaggedframeonatrunkport,itisassumedtobe
partoftheNativeVLANthatisdesignatedontheswitchtrunkport.
AllowingVLAN EntertheIDsofallVLANs,whichyouwishthetrunkporttoforward.All
othertaggedpacketswillbedropped.
NotethatanyvalueyouenterheremustfirstbedefinedasaVLANinthe
previousVLANsettingspage.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
29
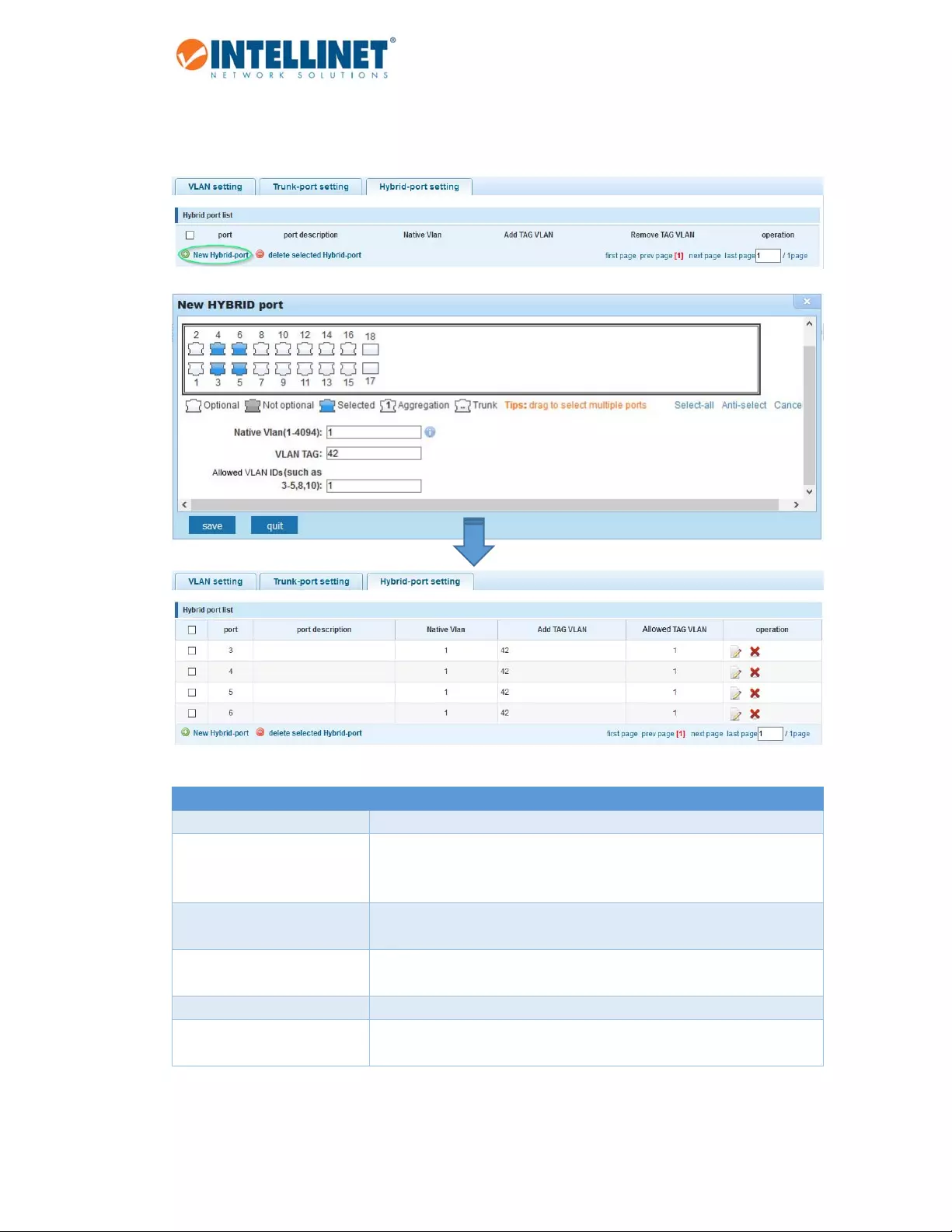
6.4.2 HybridPortSettings
AHybridportisacombinationofatrunkandanaccessport.
Item Description
NativeVLANID Seeprevioustrunkportsection.
VLANTAG VLANIDthatisaddedtoanyuntaggedpacketarrivingattheport.Note:
YoucannotentermultipleIDsorrangesofIDs.Whilethewebinterface
mayshowthis,itisincorrect.
AllowedVLANIDS EntertheIDsofallVLANs,whichyouwishthehybridporttoforward.All
othertaggedpacketswillbedropped.
PortDescription Thenameoftheportasdefinedinsection6.3.1.
AddTAGVLAN VLANIDthatisaddedtountaggedVLANpackets.
AllowedTAGVLAN TaggedVLANpacketsthatareallowedtopassthrough,allothertagged
packetswillbedropped.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
30
6.4.3 SetupExample
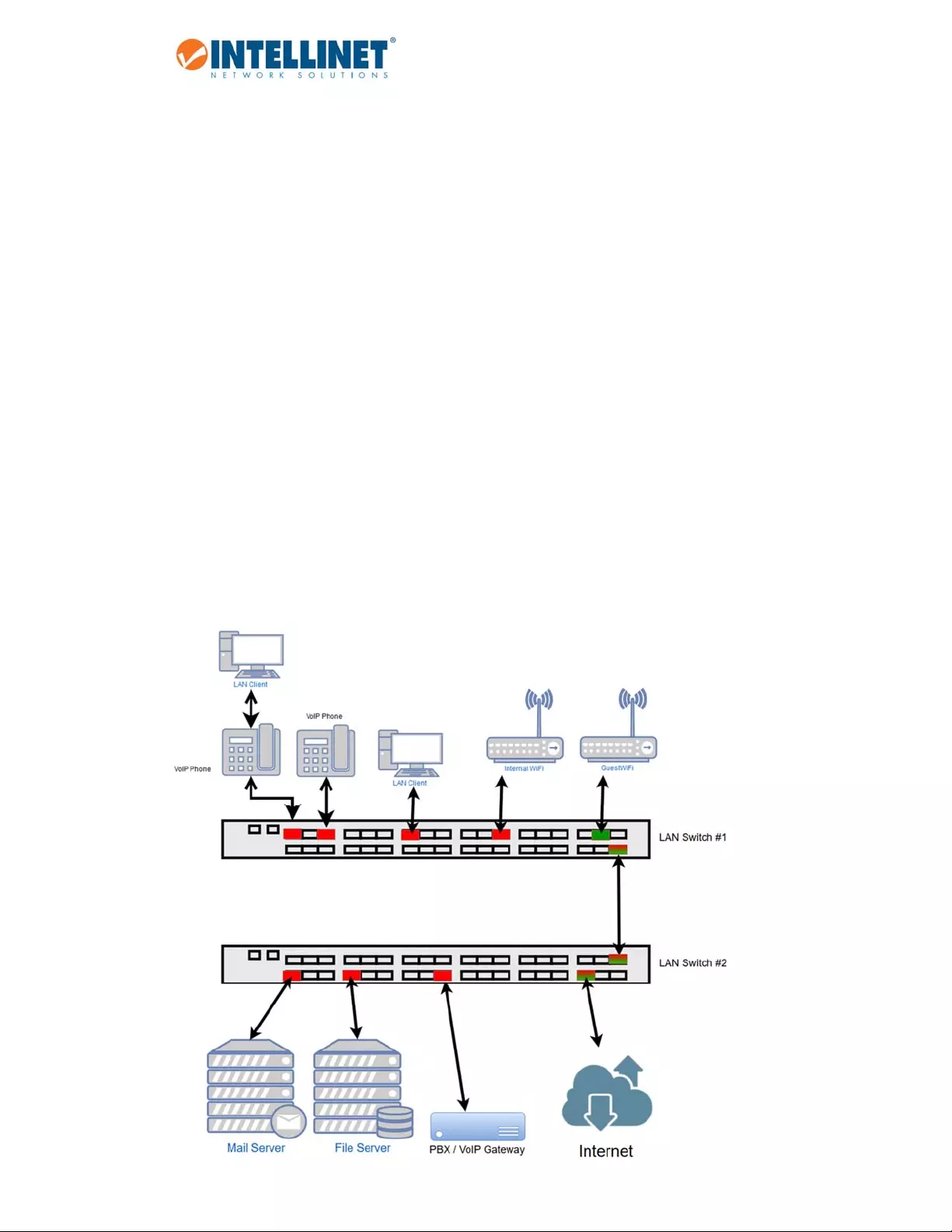
Thissectionprovidesareal‐lifeexampleandthecorrespondingsetupoftheIntellinetswitch,orinthiscase,
switches.
TherearethreeVLANsinthenetwork
o VLANID100–InternaldatanetworkwithaccesstoInternet
o VLANID200–VoIPnetwork
o VLANID300–GuestnetworkprovidesInternetaccess,butnothingelse
LANSwitch#1:
o Port2:VoIPphoneusingVLANID200,PCconnectedtobackofphone
o Port6:VoIPphoneusingVLANID200
o Port8:PC
o Port10:WirelessaccesspointforinternalnetworkandaccesstoInternet
o Port12:GuestwirelessaccesspointprovidesInternetaccessonly
o Port16:ConnectiontoLANswitch#2
LANSwitch#2:
o Port1:ConnectiontoLANswitch#1
o Port2:MailServer
o Port3:FileServer
o Port4:VoIPGateway/PBX
o Port8:Internetgateway,firewall,modem

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
31
6.4.3.1 SetupLANSwitch#1:
Trunkportsettings:
Port6:VoIPphone.Thisphonetagsallpacketsbyitself.Theswitchdoesnotneedtotagthepackets.
Port16:ConnectiontoLANswitch#2.ThisportpassesonalltrafficforVLANIDs100,200and300.Allother
trafficwillbedropped.
Hybridportsettings:
Port2isaspecialcasebecausetwonetworkingdevicesareconnected‐‐theVoIPphoneandaPC,whichis
connectedtothebackofthephone.TheVoIPphonetagsthepacketsitself,andtheswitchmustletthemgo
through,justlikeanormaltrunkportwould.However,thePCconnectedtoitcannottagthepacketsbyitself
andthereforemustrelyontheIntellinetswitchtodoso.
TheIntellinetswitchaddstheVLANID100toallpacketsthatarenottaggedasVLANID200.Portnumbertwo
actsasanuntaggedport(VLANID100)andtaggedport(VLANID200)atthesametime,hencethename
hybrid.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
32
6.4.3.2 SetupLANSwitch#2:
VLANID1(defaultVLAN)onlycontainsportsthatarenototherwiseassigned.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
33
6.5 F
AULT
/S
AFETY
6.5.1 AntiAttack
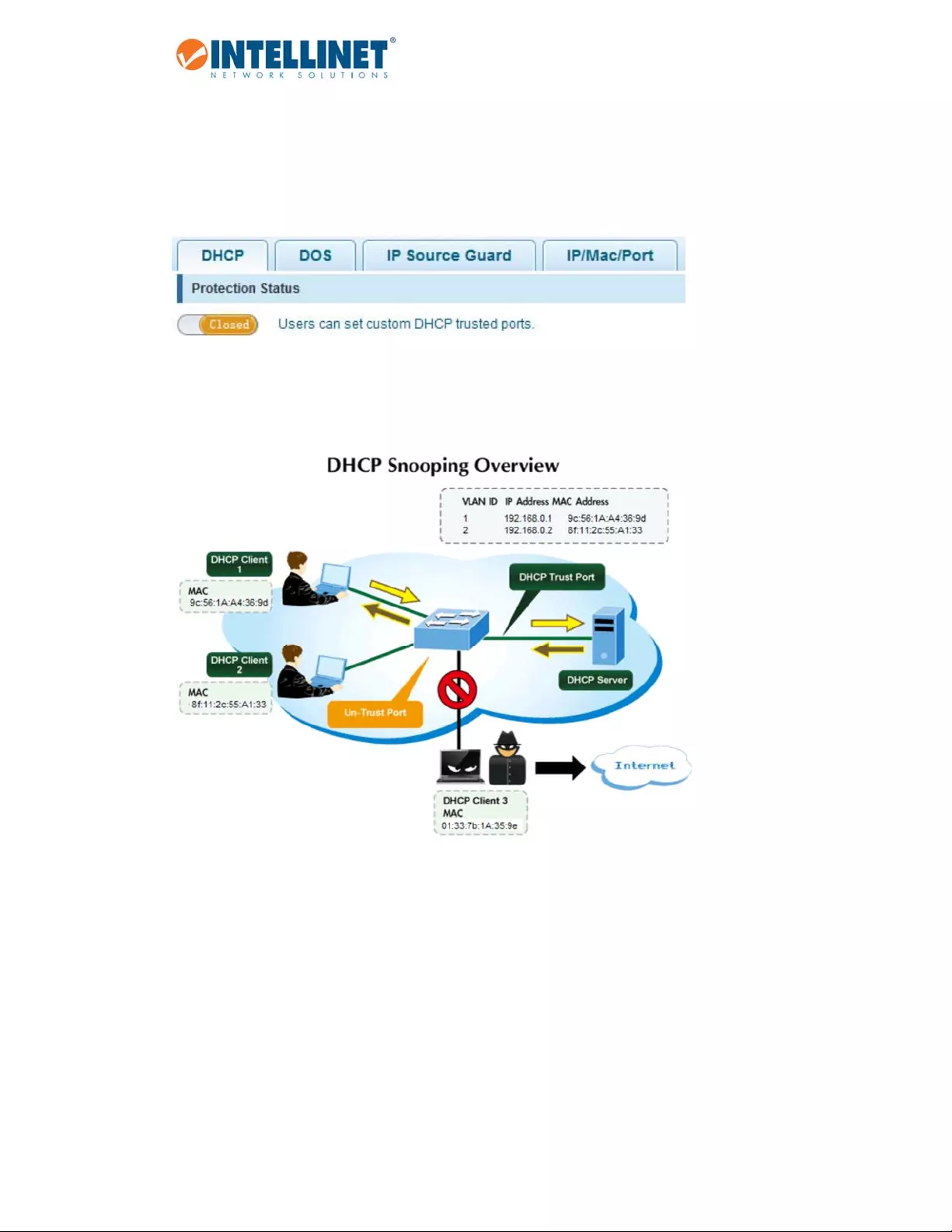
6.5.1.1 DHCPSnooping
DHCPsnoopingisasecuritytechnologybuiltintotheoperatingsystemofacapablenetworkswitchthatdrops
DHCPtrafficdeterminedtobeunacceptable.ThefundamentaluseforDHCPsnoopingistoprevent
unauthorized(rogue)DHCPserversofferingIPaddressestoDHCPclients.
CommandUsage
NetworktrafficmaybedisruptedwhenmaliciousDHCPmessagesarereceivedfromanoutsidesource.DHCP
snoopingisusedtofilterDHCPmessagesreceivedonanon‐secureinterfacefromoutsidethenetworkor
firewall.WhenDHCPsnoopingisenabledgloballyandenabledonaVLANinterface,DHCPmessagesreceived
onanuntrustedinterfacefromadevicenotlistedintheDHCPsnoopingtablewillbedropped.
Tableentriesareonlylearnedfortrustedinterfaces.AnentryisaddedorremoveddynamicallytotheDHCP
snoopingtablewhenaclientreceivesorreleasesanIPaddressfromaDHCPserver.EachentryincludesaMAC
address,IPaddress,leasetime,VLANidentifierandportidentifier.
WhenDHCPsnoopingisenabled,DHCPmessagesenteringanuntrustedinterfacearefilteredbasedupon
dynamicentrieslearnedviaDHCPsnooping.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
34
Item Description
NativeProtectionStatus Closed:AllDHCPrelatedtrafficwillpassthroughtheIntellinetswitch
withoutanyinterference.
Open:ActivatesDHCPsnooping.DHCPtrafficisnowsubjecttocertain
rules.
DHCPTrustedPort Thesearetrustedportsonyournetwork,whichareunderyourdirect
administratorcontrol.Connectedtotheseportsaretypicallyswitches,
routers,andserversinthenetwork.DHCPtrafficfromtrustedportsis
consideredsafe.
ProhibitDHCPForAddress Anyportbeyondthefirewalloroutsidethenetworkisuntrusted.DHCP
trafficfromtrustedportsisconsideredunsafe.DHCPresponsepacketson
theseportswillbedropped,thuspreventingapossibleman‐in‐the‐middle
attack.
Item Description
SourceMACVerify DHCPsnoopingMACaddressVerifyensuresthattheIntellinetswitch
verifiesthatthesourceMACaddressandtheclienthardwareaddress
matchinDHCPpacketsthatarereceivedonuntrustedports.
SourceMACVerifyEnable ChecktoactivateMACaddressverification.
MACAddress TypeintheMACaddress(formatxx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx).
Verify/NoVerify Verify:AddsMACaddresstotheconfiguration.
NoVerify:RemovespreviouslyenteredMACaddressfromconfiguration.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
35
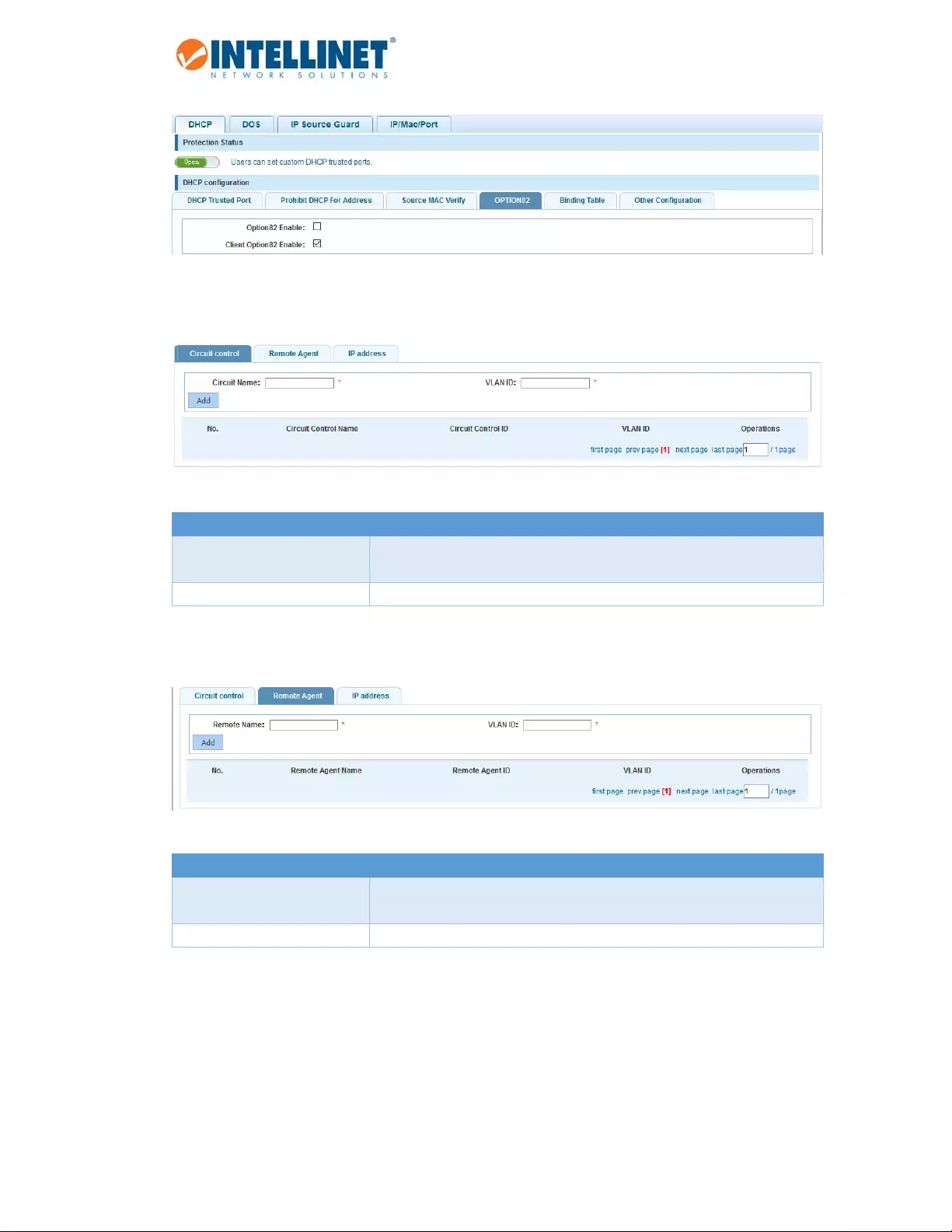
EnableOption82support.
ClientOption82enabledtrustmode.
Option82AgentCircuitID(suboption1)
Item Description
CircuitName CircuitID,anASCIIstringthatidentifiestheinterfaceonwhichtheclient
DHCPpacketisreceived.
VLANID SpecifytheOption82foraspecificVLANID(use1fordefaultVLAN).
Option82AgentRemoteID(suboption2)
Item Description
RemoteName RemoteID,anASCIIstringassignedbytheDHCPrelayagentthatsecurely
identifiestheclient.
VLANID SpecifytheOption82foraspecificVLANID(use1fordefaultVLAN).
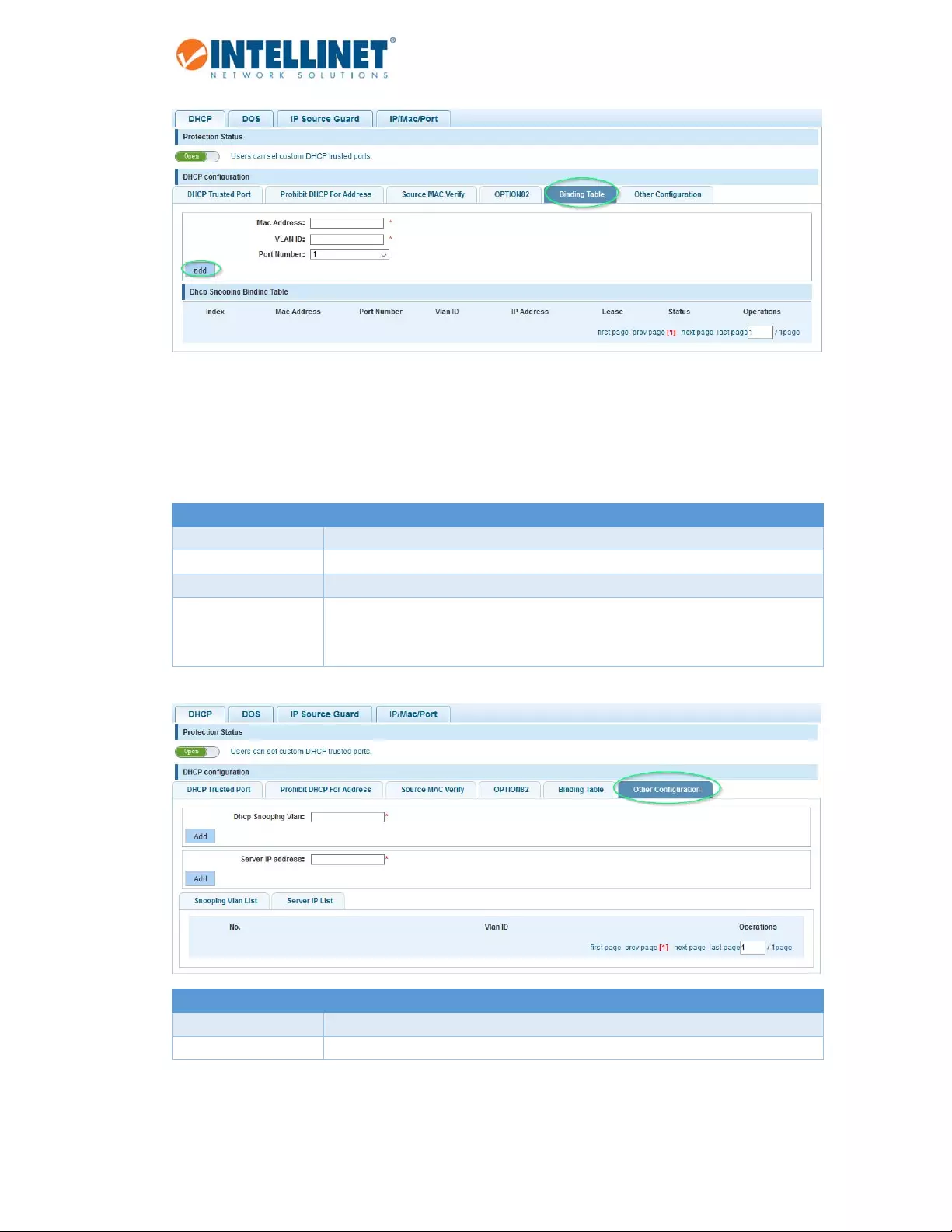
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
36
WhenDHCPsnoopingisenabled,theleaseinformationfromtheswitchingdeviceisusedtocreatetheDHCP
snoopingdatabase,alsoknownastheDHCPsnoopingbindingtable.ThetableshowstheIP‐MACbinding,as
wellastheleasetimefortheIPaddress,typeofbinding,VLANnameandinterfaceforeachhost.The
informationinthistableisgatheredduringrun‐timeasclientsjointhenetworkandrequestIPaddressesvia
DHCP.Whentheswitchreboots,theinformationislost,exceptforstaticbindings.
Item Description
MACAddress MACaddressforstaticentry.
VLANID SpecifytheVLANIDforthestaticentry.
PortNumber Selecttheport(1–52)forthestaticentry.
DHCPSnooping
BindingTable
Containsrun‐timeinformationofconnectedDHCPclients,includingtheirMAC
address,theportnumbertowhichtheyareconnected,theIPaddresstheyhave
beengiven,etc.
Item Description
DHCPSnoopingVLAN VLANtowhichyouwanttoapplyDHCPsnooping.
ServerIPAddress DHCPserverIPaddress.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
37
6.5.1.2 DoS
Adenial‐of‐service(DoS)attackisanattempttomakeamachineornetworkresourceunavailabletoits
intendedusers,suchastotemporarilyorindefinitelyinterruptorsuspendservicesofahostconnectedtothe
Internet.TheIntellinetswitchhasintegratedmechanismstocounterpossibleDoSattacks,suchaslandattacks
orillegalTCP/IPpackets.Thereareconfigurationoptions.Yousimplyactivateordeactivatethisfeature.
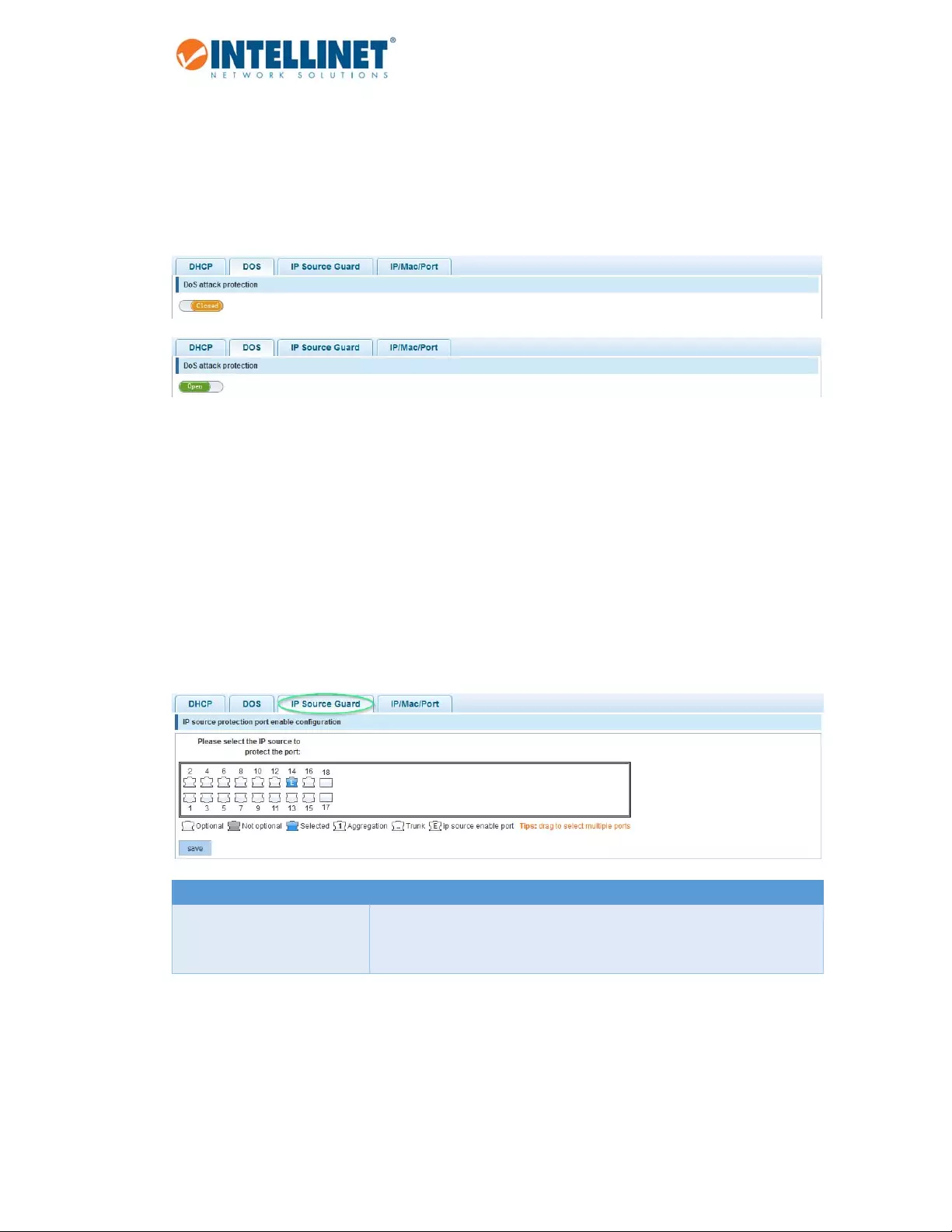
6.5.1.3 IPSourceGuard
IPSourceGuardisasecurityfeaturethatrestrictsIPtrafficonuntrustedLayer2portsbyfilteringtrafficbased
ontheDHCPsnoopingbindingtable(seesection6.5.1.1)ormanuallyconfiguredIPsourcebindings.Equipped
withthisfeature,theIntellinetswitchhelpspreventIPspoofingattacks.AnIPspoofingattackiswhenahost
triestospoof(fake)andusetheIPaddressofanotherhostinordertointercepttrafficboundforthathost.
IfyouenableIPSourceGuardforaportinitially,allIPtrafficontheprotectedportisblockedexceptforDHCP
packets.AfteraclientreceivesanIPaddressfromtheDHCPserveralltrafficwiththatIPsourceaddressis
permittedfromthatclient.InsteadofaDHCPserver,it'spossibletoprovidestaticIPsourcebinding,whichis
called“newsecurityport”ontheIntellinetswitchwebadminUI.
Item Description
PleaseselecttheIPsourceto
protecttheport:
Selecttheport(orports)thatyouwishtoprotectbyIPSourceGuard.The
exampleaboveshowsthatIPSourceGuardisenabledforport14.Note
thatIPSourceGuardisn’tsupportedonTrunkoraggregatedports.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
38
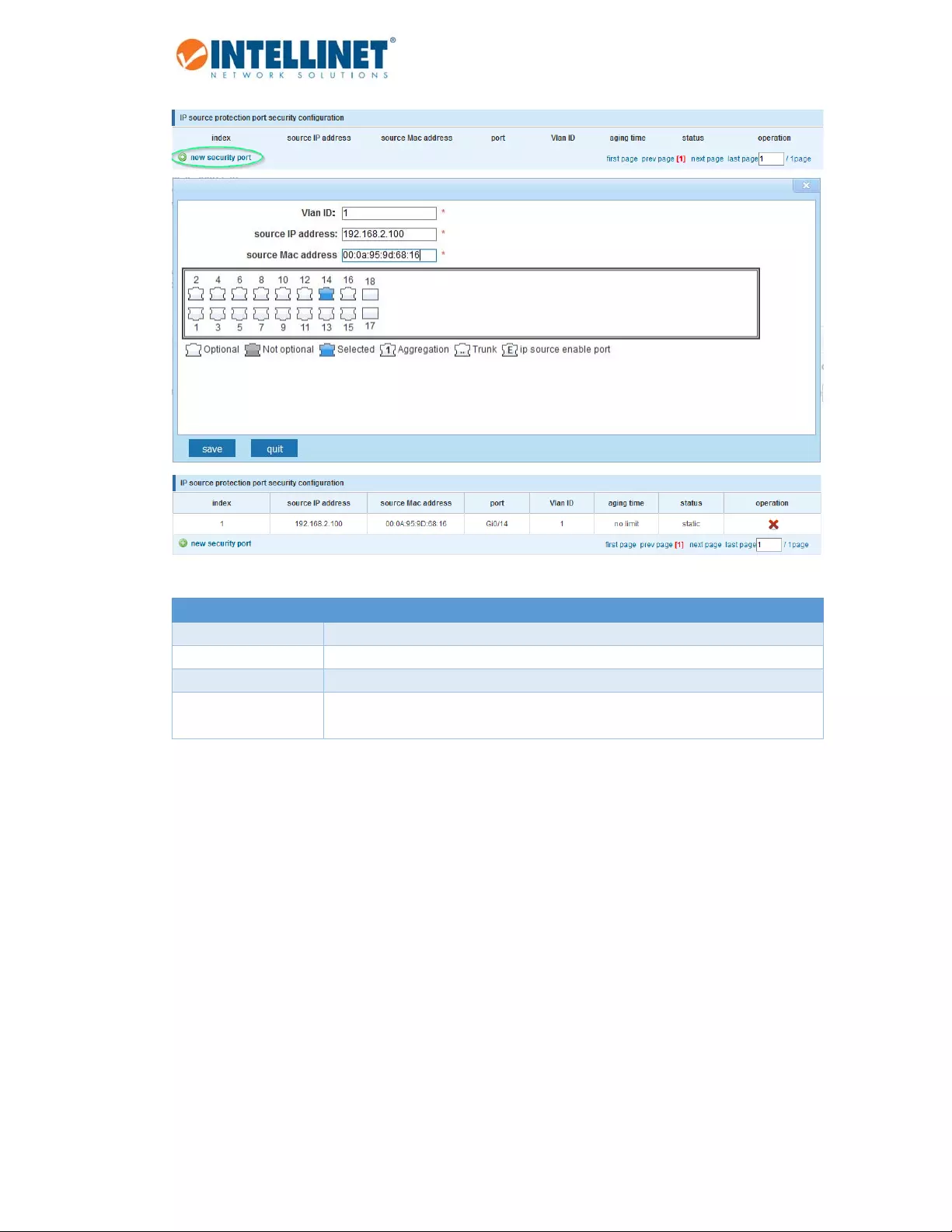
Item Description
VLANID SpecifytheVLANIDforthestaticentry.Leave1forthedefaultVLAN.
SourceIPAddress SpecifytheIPaddressoftheclientforthestaticentry.
SourceMACAddress SpecifytheMACaddressoftheclientforthestaticentry.
Ports Selecttheporttowhichtheclientisconnected(port14intheexampleabove).
Youcanonlyselectoneport.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
39
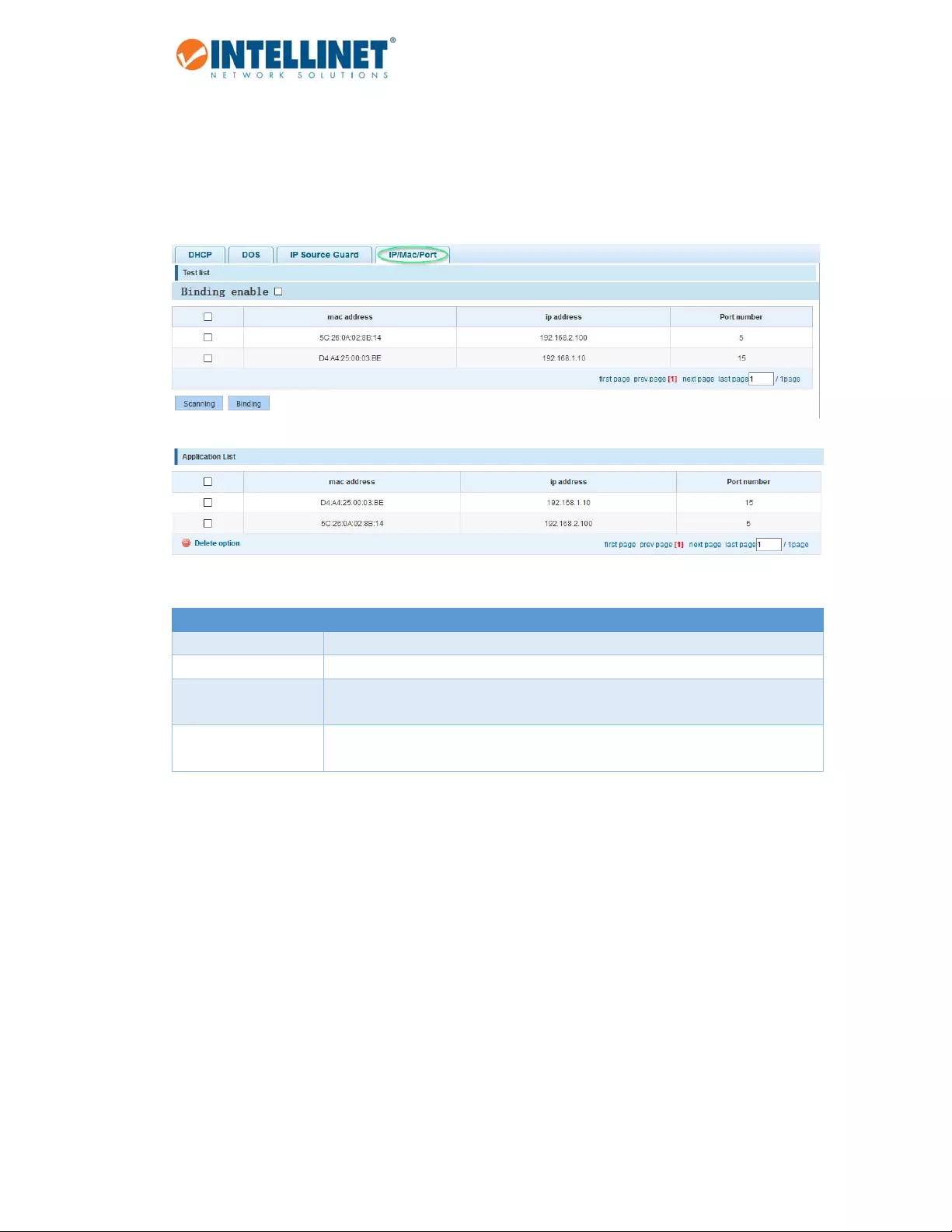
6.5.1.4 IPMACPortBinding
TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchfeaturesIP‐MAC‐PortBinding.Thisisapowerful
authenticationfunctionthatensuresthecorrectnessofhardware(MACaddress),software/user(IPaddress),
andlocation(Connectedport)fordevicesconnectedtothenetwork.Thisfeatureensurestheyareallfrom
legalsourcestopreventthedataleakagefromhackersfakingthelegalnetworkdevices.
Item Description
BindingEnable ChecktoactivateIPMacportbinding.
Scanning Clicktoscanforconnectednetworkclients.
Binding SelecttheclientsyouwishtoaddtotheIPMacportbindingtable,thenclickon
“Binding”.
ApplicationList Allcurrent,staticIP‐MAC‐portbindingentriesarelistedhere.Notethatthis
informationwillbelostaftertheswitchisrestarted.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
40
6.5.2 ChannelDetection
TheIntellinetswitchisequippedwithasetofnetworktoolsthatcanaidthenetworkadministratorin
troubleshootingproblems.
6.5.2.1 Ping
Item Description
DestinationIPaddress IPaddressyouwishtoping.
TimeoutPeriod Definethemaximumallowedresponsetime(s)beforetheresponseisconsidered
tohavetimed‐out.
Repeatnumber DefinehowmanypingrequestsyouwanttheIntellinetswitchtosendtothe
destinationIPaddress.
6.5.2.2 Tracert
Item Description
DestinationIPaddress IPaddressyouwishtorunatracertfor.
TimeoutPeriod Definethemaximumallowedresponsetime(s)beforetheresponseisconsidered
tohavetimed‐out.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
41
6.5.2.3 CableTest
Thecabletestutilityallowsaquickcheckoftheconnectedcables.
Item Description
SelectPort Selectoneofthe18ports,thenclickon“Starttest.”
TestResults Displaystheresultsofthecabletest.Notethatifyoutestaporttowhichnocable
isconnected,thetestreturnsthevalue“circuitbreaker.”

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
42
6.5.3 ACLAccessControlList
ACEisanacronymforAccessControlEntry.ItdescribesaccesspermissionassociatedwithaparticularACEID.
TherearethreeACEframetypes(EthernetType,ARPandIPv4)andtwoACEactions(permitanddeny).The
ACEalsocontainsmanydetailed,differentparameteroptionsthatareavailableforindividualapplication.
ACLisanacronymforAccessControlList.ItisthelisttableofACEs,containingaccesscontrolentriesthat
specifyindividualusersorgroupspermittedordeniedtospecifictrafficobjects,suchasaprocessora
program.EachaccessibletrafficobjectcontainsanidentifiertoitsACL.Theprivilegesdeterminewhether
therearespecifictrafficobjectaccessrights.
ACLimplementationscanbequitecomplex;forexample,whentheACEsareprioritizedforvarioussituations.
Innetworking,theACLreferstoalistofserviceportsornetworkservicesthatareavailableonahostorserver,
eachwithalistofhostsorserverspermittedordeniedtousetheservice.ACLcangenerallybeconfiguredto
controlinboundtraffic,andinthiscontext,theyaresimilartofirewalls.
6.5.3.1 Timetables
Thissectionallowsyoutosetupatimeframe.ThistimeframecanbeappliedtoACLrulestoeitherallowor
denyaccess.Thetimetabledoesnotdirectlyspecifywhetheraccessisdeniedorallowed.Rather,itissimplya
waytocreateaneasilyaccessibletimeframethatcanbeappliedtoACLrules.Theexamplebelowshowsthe
setupofatimetablecalled“WorkingHours.”NotethattheIntellinetswitchmustbesetupwithaproper
systemtime(seesectionSystemConfig).
Item Description
NewTimetableName Provideadescriptivenameforthetimetable.
TimeInterval Specifythedaysoftheweekandstartandendtime.Clickonthe toadd
additionaltimeframes.Click“Save”tosavethetimetable.
Timetableslist Drop‐downlistcontainsalltimetablespreviouslysetup.
Timeweek Selectedweekdaysfortheselectedtimetable.
TimeInterval Timeintervalforselectedtimetable.
Operation
Editselectedtimetable
Deledselectedtimetable

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
43
6.5.3.2 ACL
Inthissection,setuptheactualaccesscontrollist(ACL).TheACLconnectsIPaddressandportinformation
withatimetable(seesection6.5.3.1)andanactiontoeitherallowordenyaccesstothenetworkthroughthe
switch.TheexamplebelowcreatesanACL,whichallowsaccesstothenetworkforanycomputer
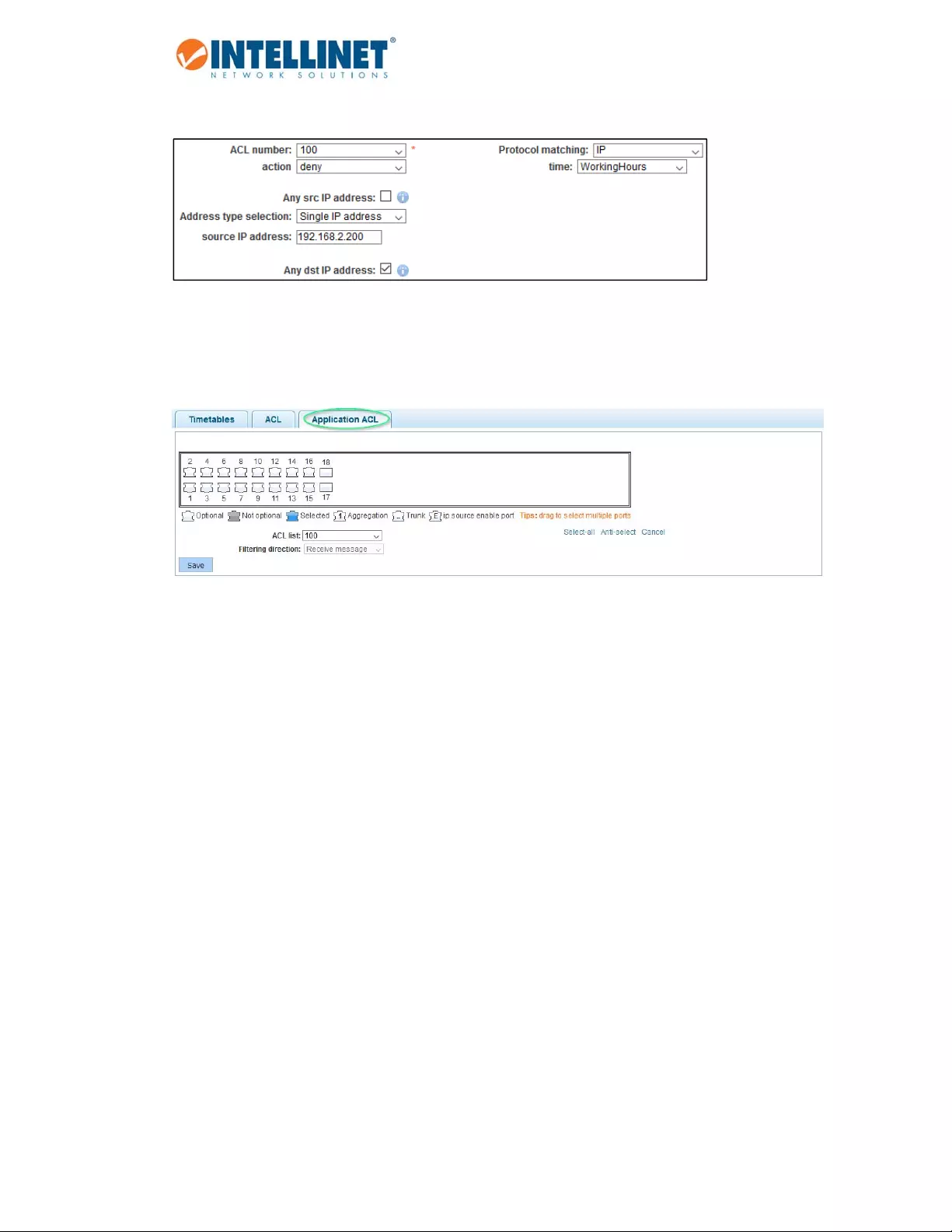
Item Description
ACLNumber EachACLrulegetsanumber.Selecttheonefromthedrop‐downlistforwhich
youwanttocreatethisACE(AccessControlEntry).
Action Definewhetherthisrulegrantsaccess(“allow”)tothenetwork,orprohibitsit
(“deny”).
SRC/DESTIPAddress SpecifythesourceanddestinationIPaddressforthisACE.Youcanprovidea
singleIPaddress(e.g.,192.168.2.100)oraspecificnetwork(e.g.,255.255.255.0).
SRC/DESTPort ThisoptionisonlyvisibleiftheACEiscreatedforTCPorUDP.Itwillnotshowfor
IPACLs(seenextparameter).Youcanprovideasingleportorarangeofports.
ProtocolMatching IP:TheACEisappliedtopacketsbasedontheirsourceand/ordestinationIP
address.
TCP/UDP:TheACEisappliedtopacketsbasedontheirsourceand/ordestination
IPaddressandtheportnumberfortheselectedprotocol.
Time IfyouwanttolimittheACEtoaspecifictimetable(seesection6.5.3.1),youcan
selectitfromthedrop‐downlist.
Example1–Disallowaccesstothenetworkforanycomputeroutsideoftheworkinghours.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
44
Example2–DisallowaccesstothenetworkforanindividualIPaddressduringtheworkinghours.
6.5.3.3 ApplicationACL
WiththisfunctionyoucanlinkanACLtooneormoreofthe18availableswitchports.
SelecttheportsandACLlist,andclick“Save”inordertoactivate.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
45
6.6 SPANNINGTREEPROTOCOL(STP)
TheSpanningTreeProtocolcanbeusedtodetectanddisablenetworkloopsandtoprovidebackuplinks
betweenswitches,bridgesorrouters.Thisallowstheswitchtointeractwithotherbridgingdevicesinyour
networktoensurethatonlyonerouteexistsbetweenanytwostationsonthenetwork.Italsoprovidesbackup
links,whichautomaticallytakeoverwhenaprimarylinkgoesdown.Thespanningtreealgorithmssupported
bythisswitchincludetheseversions:
STP–SpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1D)
RSTP–RapidSpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1w)
MSTP–MultipleSpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1s)
TheIEEE802.1DSpanningTreeProtocolandIEEE802.1wRapidSpanningTreeProtocolallowfortheblocking
oflinksbetweenswitchesthatformloopswithinthenetwork.Whenmultiplelinksbetweenswitchesare
detected,aprimarylinkisestablished.Duplicatedlinksareblockedfromuseandbecomestandbylinks.The
protocolallowsfortheduplicatelinkstobeusedintheeventofafailureoftheprimarylink.Oncethe
SpanningTreeProtocolisconfiguredandenabled,primarylinksareestablishedandduplicatedlinksare
blockedautomatically.Thereactivationoftheblockedlinks(atthetimeofaprimarylinkfailure)isalso
accomplishedautomaticallywithoutoperatorintervention.Thisautomaticnetworkreconfigurationprovides
maximumuptimetonetworkusers.However,theconceptsoftheSpanningTreeAlgorithmandprotocolarea
complicatedandcomplexsubjectandmustbefullyresearchedandunderstood.Itispossibletocauseserious
degradationtonetworkperformanceiftheSpanningTreeisincorrectlyconfigured.Pleasereadthefollowing
beforemakinganychangesfromthedefaultvalues.
TheSwitchSTPperformsthefollowingfunctions:
Createsasinglespanningtreefromanycombinationofswitchingorbridgingelements.
Createsmultiplespanningtrees–fromanycombinationofportscontainedwithinasingleswitch,in
userspecifiedgroups.
Automaticallyreconfiguresthespanningtreetocompensateforthefailure,additionorremovalof
anyelementinthetree.
Reconfiguresthespanningtreewithoutoperatorintervention.
BridgeProtocolDataUnits
ForSTPtoarriveatastablenetworktopology,thefollowinginformationisused:
Theuniqueswitchidentifier
Thepathcosttotherootassociatedwitheachswitchport
Theportidentifier

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
46
STPcommunicatesbetweenswitchesonthenetworkusingBridgeProtocolDataUnits(BPDUs).EachBPDU
containsthefollowinginformation:
Theuniqueidentifieroftheswitchthatthetransmittingswitchcurrentlybelievesistherootswitch
Thepathcosttotherootfromthetransmittingport
Theportidentifierofthetransmittingport
TheswitchsendsBPDUstocommunicateandconstructthespanning‐treetopology.Allswitchesconnectedto
theLANonwhichthepacketistransmittedwillreceivetheBPDU.BPDUsarenotdirectlyforwardedbythe
switch,butthereceivingswitchusestheinformationintheframetocalculateaBPDU,and,ifthetopology
changes,initiatesaBPDUtransmission.
ThecommunicationbetweenswitchesviaBPDUsresultsinthefollowing:
Oneswitchiselectedastherootswitch
Theshortestdistancetotherootswitchiscalculatedforeachswitch
Adesignatedswitchisselected.Thisistheswitchclosesttotherootswitchthroughwhichpackets
willbeforwardedtotheroot.
Aportforeachswitchisselected.Thisistheportprovidingthebestpathfromtheswitchtotheroot
switch.
PortsincludedintheSTPareselected.
CreatingaStableSTPTopology
IfallswitcheshaveSTPenabledwithdefaultsettings,theswitchwiththelowestMACaddressinthenetwork
willbecometherootswitch.Byincreasingthepriority(loweringtheprioritynumber)ofthebestswitch,STP
canbeforcedtoselectthebestswitchastherootswitch.WhenSTPisenabledusingthedefaultparameters,
thepathbetweensourceanddestinationstationsinaswitchednetworkmightnotbeideal.Forinstance,
connectinghigher‐speedlinkstoaportthathasahighernumberthanthecurrentrootportcancausearoot‐
portchange.
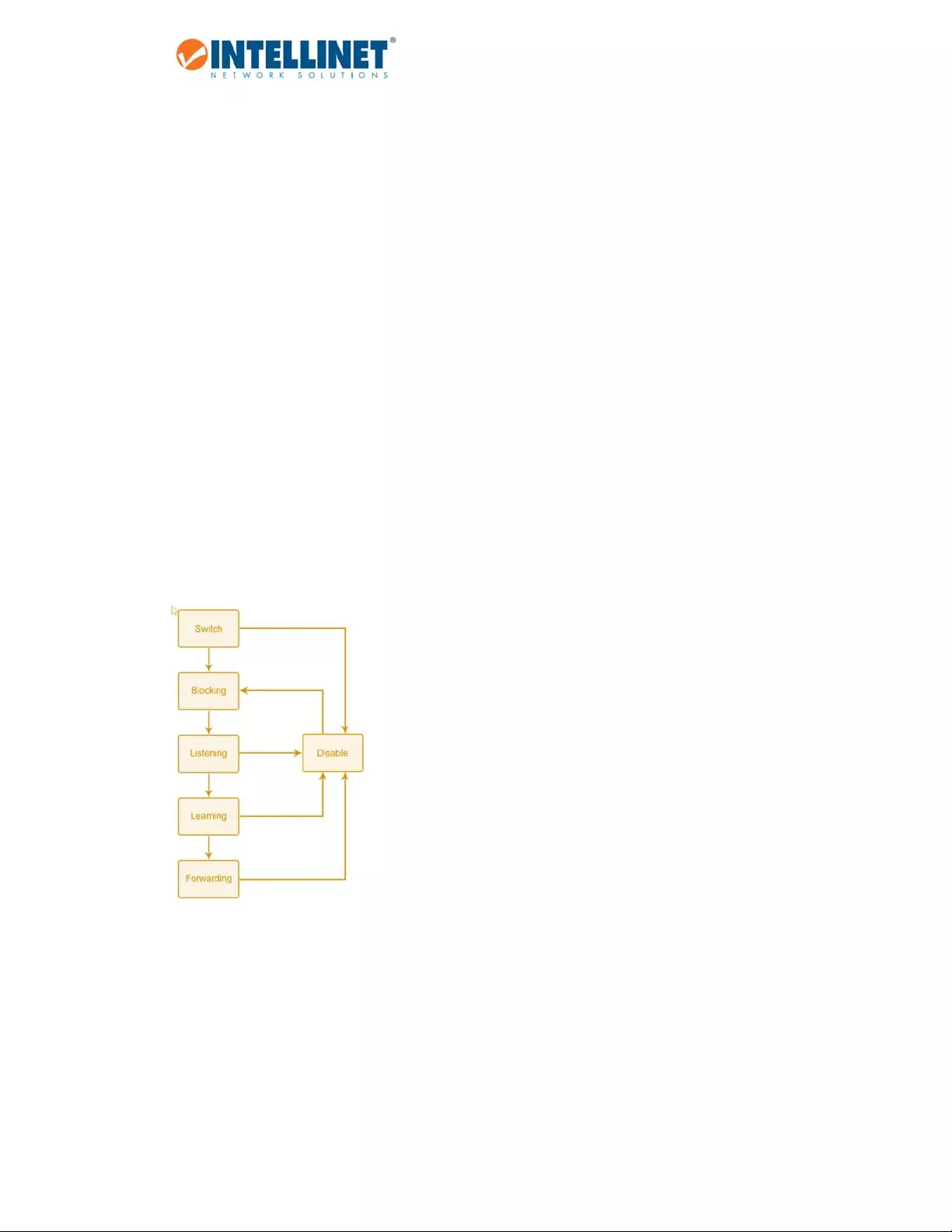
STPPortStates
BPDUstakesometimetopassthroughanetwork.Thispropagationdelaycanresultintopologychanges
whereaportthattransitioneddirectlyfromaBlockingstatetoaForwardingstatecouldcreatetemporary
dataloops.Portsmustwaitfornewnetworktopologyinformationtopropagatethroughoutthenetwork
beforestartingtoforwardpackets.TheymustalsowaitforthepacketlifetimetoexpireforBPDUpacketsthat
wereforwardedbasedontheoldtopology.Theforwarddelaytimerisusedtoallowthenetworktopologyto
stabilizeafteratopologychange.Inaddition,STPspecifiesaseriesofstatesaportmusttransitionthroughto
furtherensurethatastablenetworktopologyiscreatedafteratopologychange.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
47
EachportonaswitchusingSTPexistsisinoneofthefollowingfivestates:
Blocking–theportisblockedfromforwardingorreceivingpackets
Listening–theportiswaitingtoreceiveBPDUpacketsthatmaytelltheporttogobacktothe
blockingstate
Learning–theportisaddingaddressestoitsforwardingdatabase,butnotyetforwardingpackets
Forwarding–theportisforwardingpackets
Disabled–theportonlyrespondstonetworkmanagementmessagesandmustreturntotheblocking
statefirst
Aporttransitionsfromonestatetoanotherasfollows:
Frominitialization(switchboot)toblocking
Fromblockingtolisteningortodisabled
Fromlisteningtolearningortodisabled
Fromlearningtoforwardingortodisabled
Fromforwardingtodisabled
Fromdisabledtoblocking
It'spossibletomodifyeachportstatebyusingmanagementsoftware.WhenyouenableSTP,everyporton
everyswitchinthenetworkgoesthroughtheblockingstateandthentransitionsthroughthestatesof
listeningandlearningatpowerup.Ifproperlyconfigured,eachportstabilizestotheforwardingorblocking
state.Nopackets(exceptBPDUs)areforwardedfromorreceivedbySTPenabledports,untiltheforwarding
stateisenabledforthatport.
TheSwitchallowsfortwolevelsofoperation:theswitchlevelandtheportlevel.Theswitchlevelformsa
spanningtreeconsistingoflinksbetweenoneormoreswitches.Theportlevelconstructsaspanningtree
consistingofgroupsofoneormoreports.TheSTPoperatesinmuchthesamewayforbothlevels.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
48
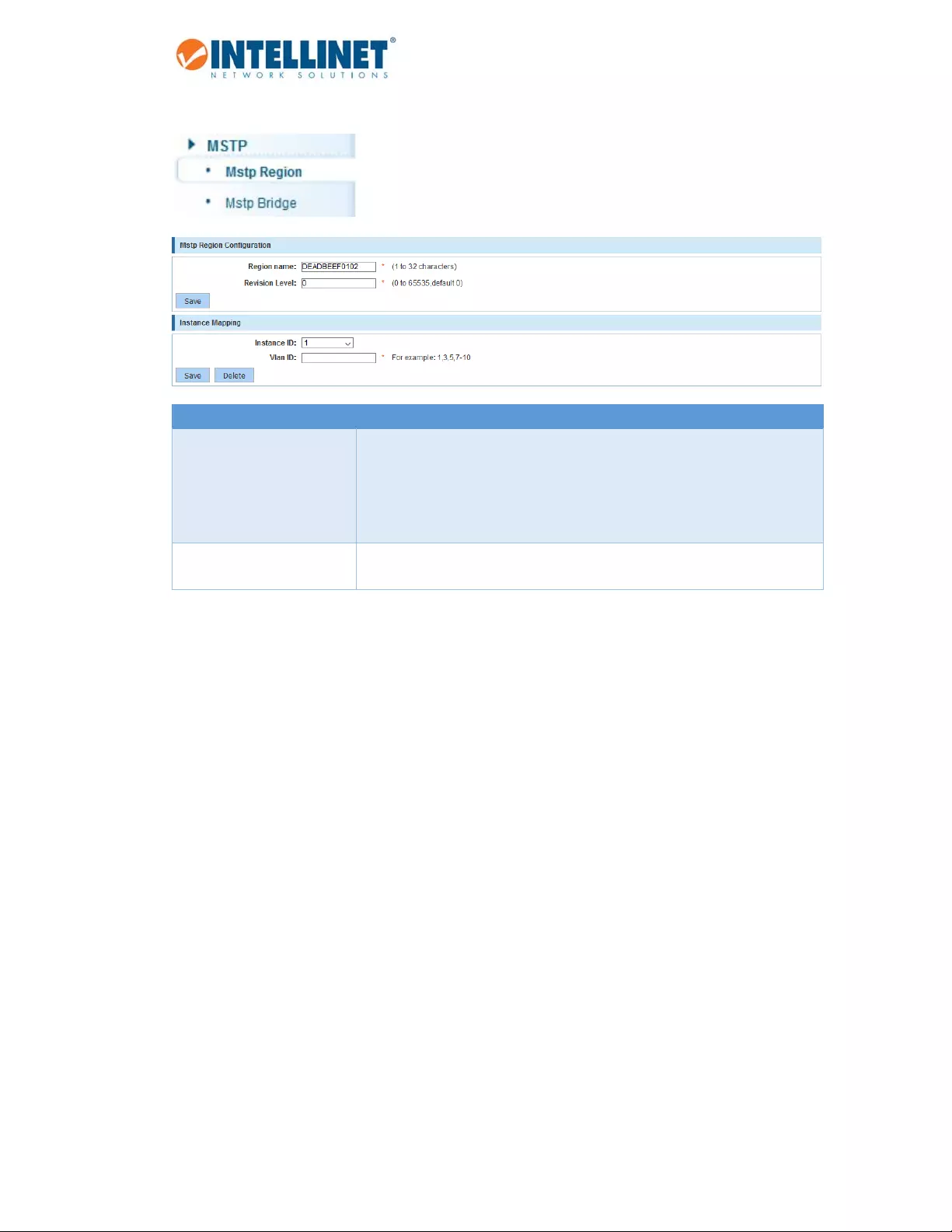
6.6.1 MSTPRegion
Item Description
MSTPRegionConfiguration EachswitchrunningMSTinthenetworkhasasingleMSTconfigurationthat
consistsofthesetwoattributes:
1. Regionname
a. Analphanumericconfigurationname
2. RevisionLevel
InstanceMapping Atablethatassociateseachofthepotential4096VLANIDstoagiven
instance.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
49
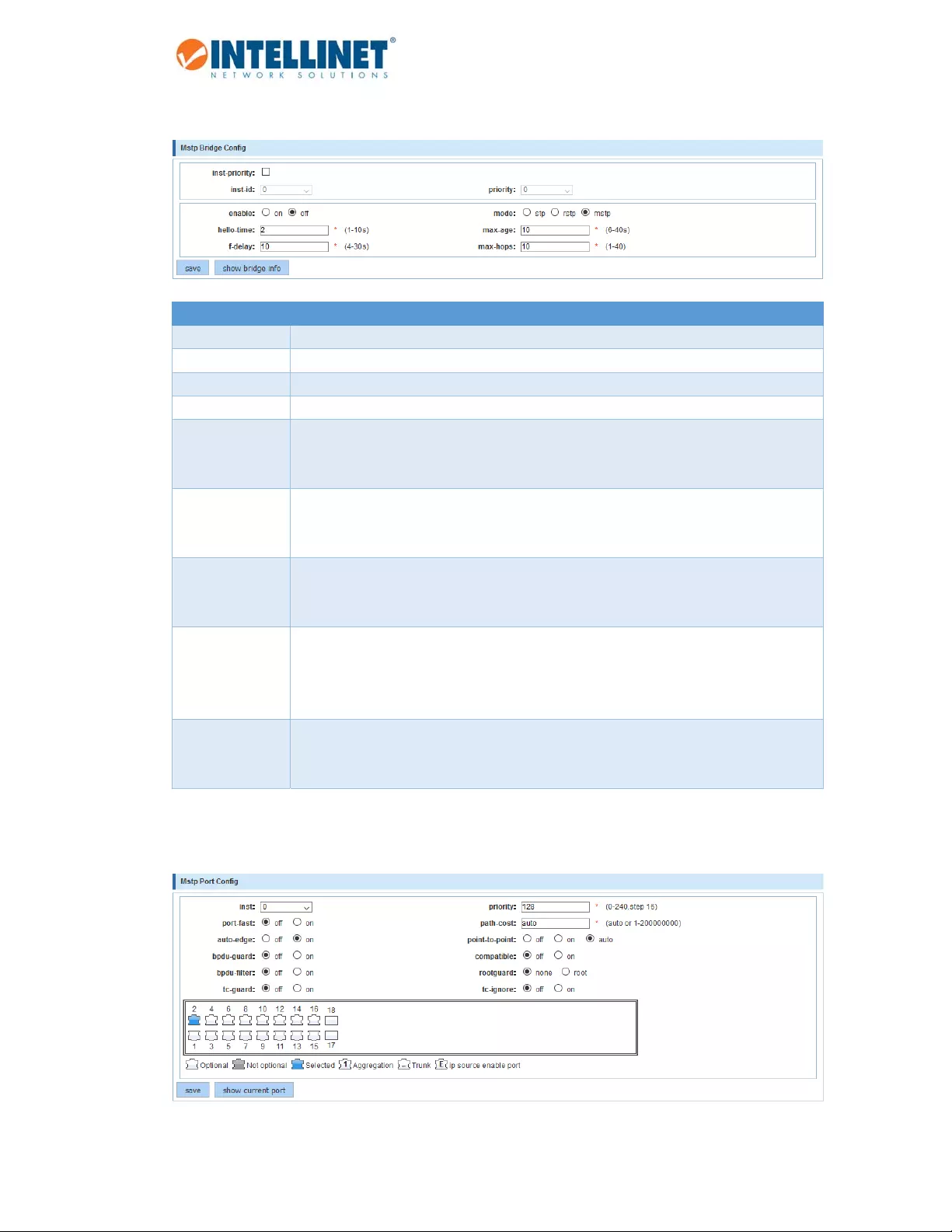
6.6.2 MSTPBridge
Item Description
inst‐priority Prioritycanbeconfiguredforaspecifiedinstance.
inst‐id SelecttheinstanceIDforwhichyouwanttodefineapriority.
Priority SelecttheprioritylevelfortheinstanceID.
Enable Enable/disableSTP.
Mode STP–SpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1D)
RSTP–RapidSpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1w)
MSTP–MultipleSpanningTreeProtocol(IEEE802.1s)
Hello‐time ThehellotimeristhetimeintervalbetweeneachBridgeProtocolDataUnit(BPDU)that
issentonaport.Thedefaulthellotimeris2seconds.AdjusttheSpanningTreeProtocol
(STP)hellotimertoanyvaluebetween1and10seconds.
f‐delay Theforwarddelaytimeristhetimeintervalthatisspentinthelisteningandlearning
state.Thedefaultforwarddelaytimeris10seconds.SettheSpanningTreeProtocol
(STP)forwarddelaytimertoanyvaluebetween4and30seconds.
Max‐age ThemaxagetimercontrolsthemaximumlengthoftimeintervalthatanSTPswitch
portsavesitsconfigurationBridgeProtocolDataUnit(BPDU)information.Thedefault
maxagetimeris10seconds.Adjustthemaxagetimertoanyvaluebetween6and40
seconds.
Max‐hops ForMultipleSpanningTreeProtocol(MSTP),configurethemaximumnumberofhopsa
BPDUcanbeforwardedintheMSTPregion.Thedefaultvalueis10.Possiblevalues
rangefrom1to40.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
50
Item Description
inst SelecttheinstanceID.
port‐fast ThetimeSpanningTreeProtocol(STP)takestotransitionportsovertotheforwarding
statecancauseproblems.Port‐fastisafunctiontoresolvethisproblem.Port‐fastsolves
theproblemofdelayswhenclientcomputersareconnectingtoswitches.Withport‐fast
enabledonaport,youeffectivelypreventtheimplementationofSTPonthatport.
auto‐edge Bydefault,“auto‐edge”isenabledonallports.ThiswilllookforBPDUsfor3secondsand,
ifnonearefound,willbeginforwardingpackets,andtheportissetas“edge.”Ifthereare
BPDUs,theportissetas“non‐edge.”
bdpu‐guard BPDUguarddisablestheportuponBPDUreceptionifport‐fastisenabledontheport.This
effectivelydeniesdevicesconnectedtotheseportsfromparticipatinginthedesignedSTP,
thusprotectingyourdata‐centercore.
bdpu‐filter EnablingBPDUfilteringforaportstopssendingorreceivingBPDUonthisinterface;thisis
thesameasdisablingspanningtreeontheinterface.Itisariskychoice,unlessyouaresure
thatnoswitchcaneverbeconnectedtothisport.
tc‐guard Incertainsituationsitcanbedesirabletopreventtopologychangesoriginatingator
receivedatagivenportfrombeingpropagatedtotherestofthenetwork.Thismaybethe
casewhenthenetworkisnotunderasingleadministrativecontrolanditisbeneficialto
preventdevicesexternaltothecoreofthenetworkfromcausingMAC‐addressflushingin
thecore.ThisbehaviorcanbeenabledbyconfiguringTopologyChangeGuard(TCGuard)
ontheport.
priority Ifaloopoccursinthenetwork,MSTPusestheportpriorityparameterwhenselectingan
interfacetoputintotheforwardingstate.Assignhigherpriorityvalues(lowernumbers)to
interfacesthatyouwantselectedfirstandlowerpriorityvalues(highernumbers)thatyou
wantselectedlast.Ifallinterfaceshavethesamepriorityvalue,MSTPputstheportwith
thelowestinterfacenumberintheforwardingstateandblockstheotherports.
path‐cost TheMSTPpathcostdefaultvalueisderivedfromthemediaspeedofaninterface.Ifaloop
occurs,MSTPusescostwhenselectinganinterfacetoputintheforwardingstate.Assign
lowercostvaluestointerfacesthatyouwantselectedfirstandhighercostvaluesthatyou
wantselectedlast.Ifallinterfaceshavethesamecostvalue,MSTPputstheinterfacewith
thelowestinterfacenumberintheforwardingstateandblockstheotherinterfaces.
point‐to‐point AdminPoint‐to‐PointLink‐‐SpecifywhetherthisportisconnectedtoasharedLANsegment
(value“off”)orapoint‐to‐pointLANsegment(value“on”).Apoint‐to‐pointLANsegmentis
connectedtoexactlyoneotherbridge(normallywithadirectcablebetweenthem).Only
point‐to‐pointlinksandedgeportscanrapidlytransitiontoforwardingstate.
Ifyousetthisvalueto“auto,”theswitchautomaticallydetectswhethertheportis
connectedtoasharedlinkorapoint‐to‐pointlink.
Rootguard Root‐guardensuresthatanunintendedswitchdoesnotbecomeanewrootbridge.Root
guardallowsthedevicetoparticipateinSTPaslongasthedevicedoesnottrytobecome
theroot.Ifrootguardblockstheport,subsequentrecoveryisautomatic.Recoveryoccurs
assoonastheoffendingdeviceceasestosendsuperiorBPDUs.
tc‐ignore Ignoretechnologychange(TC)onoroff.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
51
6.7 DHCPRELAYAGENT
ADHCPclientisanInternethostusingDHCPtoobtainconfigurationparameterssuchasanIPaddress.ADHCP
relayagentisanyhostthatforwardsDHCPpacketsbetweenclientsandservers.Relayagentsareusedto
forwardrequestsandrepliesbetweenclientsandserverswhentheyarenotonthesamephysicalsubnet.The
Intellinetswitchcanfulfilltheroleofsucharelayagent.
6.7.1 DHCPRelay
Item Description
DHCPrelayenable EnableordisableDHCPrelay.
DHCPOPTIONtrustfieldenable: Whenenabled,theclientthatreceivestheDHCPmessagewith
option82informationwillforwardit;otherwise,itwillbediscarded.
DHCPServerIP ProvidetheIPaddressoftheDHCPserver,andclick“add.”
6.7.2 Option82
6.7.2.1 CircuitControl
Item Description
CircuitControl ProvidethecircuitIDnumber.Possiblevaluesrangefrom3to63.
VLANID TypeintheVLANID.Usevalue1forthedefaultVLAN..
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
52
6.7.2.2 ProxyRemote
Item Description
ProxyRemote ASCIIRemoteIDstring,upto63characters.
VLANID TypeintheVLANID.Usevalue1forthedefaultVLAN.
6.7.2.3 IPAddress
Item Description
IPAddress IPaddressofDHCPserver.
VLANID TypeintheVLANID.Usevalue1forthedefaultVLAN.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
53
6.8 DHCPSERVER
TheDynamicHostConfigurationProtocol(DHCP)isa
standardizednetworkprotocolusedonInternetProtocol
(IP)networksfordynamicallydistributingnetwork
configurationparameterssuchasIPaddressesfor
interfacesandservices.AtypicalDHCPserverisarouter
oraWindowsserver.TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabit
EthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchcanalsofulfilltheroleof
aDHCPserver.
6.8.1 DHCPConfig
6.8.1.1 EnableConfig
Setthisoptionto“Open”inordertoactivatetheDHCPserverfunction.Notethatwhen
youwanttousetheDHCPServerfunction,youcannotusetheDHCPrelayfeature(see
section6.7DHCPRelayAgent)atthesametime.
6.8.1.2 PoolConfig
Item Description
PoolID IdentifiesthedynamicaddresspoolfromwhichtheDHCPrequestsareserved.
Domain Ifyouareonadomainnetwork,thedomainnameshouldgohere.
NetworkIP ThisisthefirstIPaddressofthesubnetendingin“.0”.Itcan’tbeassignedtoanactual
networkclient.
NetworkMask Providethenetworkmaskofchoiceforyournetwork.
StartIP DefinethelowestIPaddressoftheIPaddresspool.
EndIP DefinethehighestIPaddressoftheIPaddresspool.
LeaseTime DefineshowlongtheclientisallowedtokeeptheIPaddress.Whenthetimehaselapsed,
theswitchwillissueanewIPaddresstotheclient.
Note:TheDHCPIPaddressrangemustbeinthesamerangeastheIntellinetswitch'sLANIPrange(e.g.,
192.168.2.xxx).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
54
6.8.1.3 OptionConfig
ThispageallowsmodificationoftheDHCPoptions,asstatedinRFC2132.Theexamplebelowshowshowto
specifyaspecificNTPserver.
Item Description
PoolID IdentifiesthedynamicaddresspoolfromwhichtheDHCPrequestsareserved.
Code Possiblevaluesare–to255.ThesearethecodesortagsperRFC2132.
CodeValueType
Selecttheappropriatevalue(i.e.,selectIPifyouenteranIPaddressinthecodevalue
fieldbelow).
CodeValue Providethevaluefortthetag(code)youselected.
6.8.1.4 BindConfig
ThispagedisplaysallclientsthathaveobtainedanIPaddressfromtheIntellinetswitch.Clickon tosetthe
leasetimetoexpired,forcingtheconnectclienttoobtainanewIPaddressinstantly.
6.8.1.5 GatewayConfig
Onthispage,providetheGatewayIPaddressthatyouwishtoprovidetotheDHCPclients.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
55
6.8.1.6 DNSConfig
Onthispage,providetheDNSIPaddress(es)thatyouwishtoprovidetotheDHCPclients.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
56
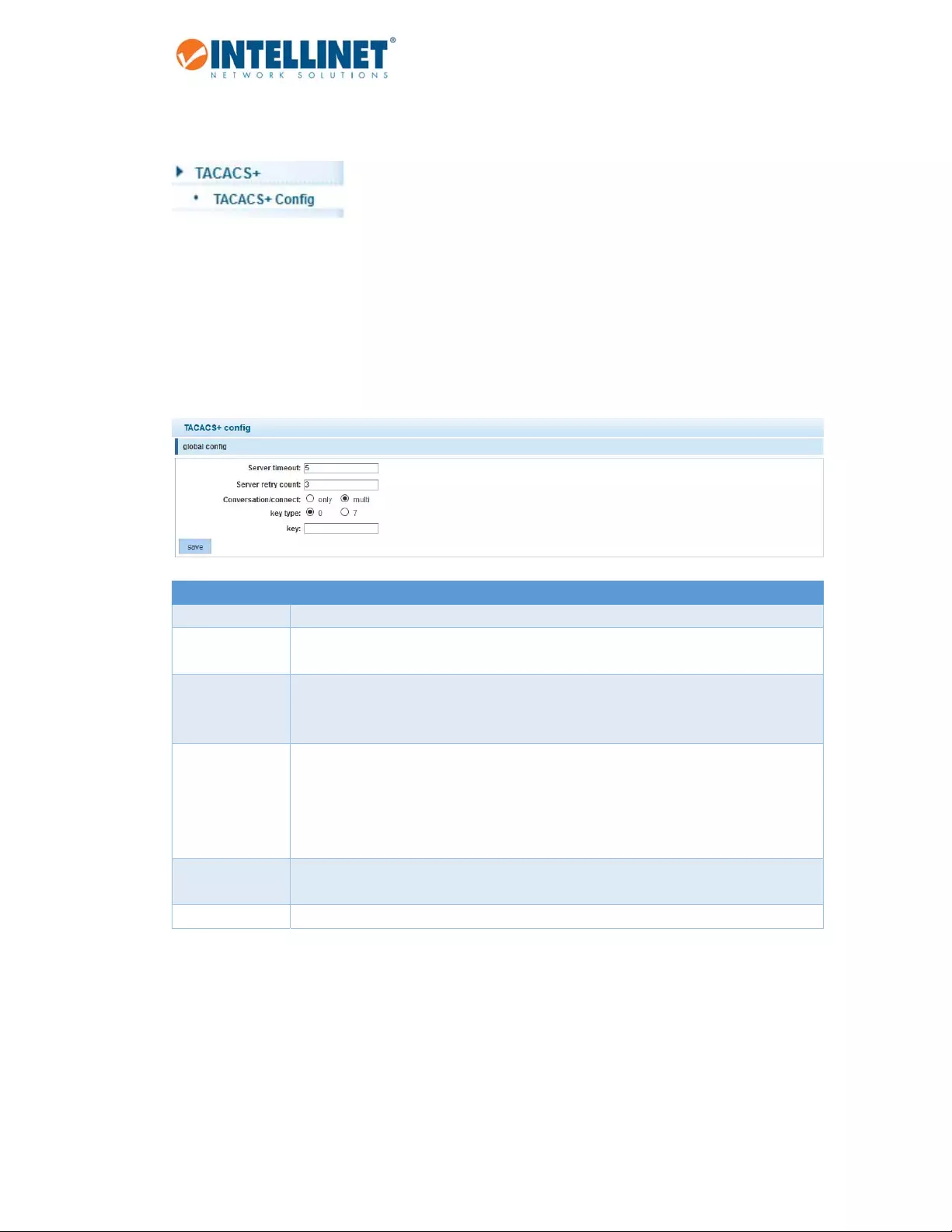
6.9 TERMINALACCESSCONTROLLERACCESS‐CONTROLSYSTEM(TACACS+)
TerminalAccessControllerAccess‐ControlSystem(TACACS,usually
pronouncedlike"tack‐axe")referstoafamilyofrelatedprotocolshandling
remoteauthenticationandrelatedservicesfornetworkedaccesscontrol
throughacentralizedserver.TheoriginalTACACSprotocol,whichdatesbackto1984,wasusedfor
communicatingwithanauthenticationserver,commoninolderUNIXnetworks;itspawnedrelatedprotocols.
TerminalAccessControllerAccess‐ControlSystemPlus(TACACS+)isaprotocolreleasedasanopenstandard
beginningin1993.AlthoughderivedfromTACACS,TACACS+isaseparateprotocolthathandles
authentication,authorizationandaccounting(AAA)services.ComparedtotheopenstandardRADIUS
authentication(section6.10Radius),TACACS+encryptstheentirepayloadwhereasRADIUSonlyencrypts
passwords.
Item Description
GlobalConfig Globalparametersthatcanbeoverwrittenbyport‐specificconfiguration.
Servertimeout TheglobaltimeoutintervaldetermineshowlongtheIntellinetswitchwaitsfor
responsesfromTACACS+serversbeforedeclaringatimeoutfailure.
Serverretry
count
SpecifiesthenumberofretryattemptsthatwillbemadetoestablishaTransmission
ControlProtocol(TCP)connectionbetweenaTACACS+clientandtheTACACS+server.
Thedefaultvalueis3.
Conversation/
Connect
Thisparameterdefineshowmanyconnectionstherewillbebetweenrouterdaemon.
Only:“single‐connection"
Thedaemonmustsupportsingle‐connectionmodeforthistobeeffective;otherwise,
theconnectionbetweenthenetworkaccessserverandthedaemonwilllockuporyou
willreceivespuriouserrors.
Keytype 0:Keyvalueincleartextformat
7:Keyvalueistype‐7encrypted.
Key Typeinthekeyvalue.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
57
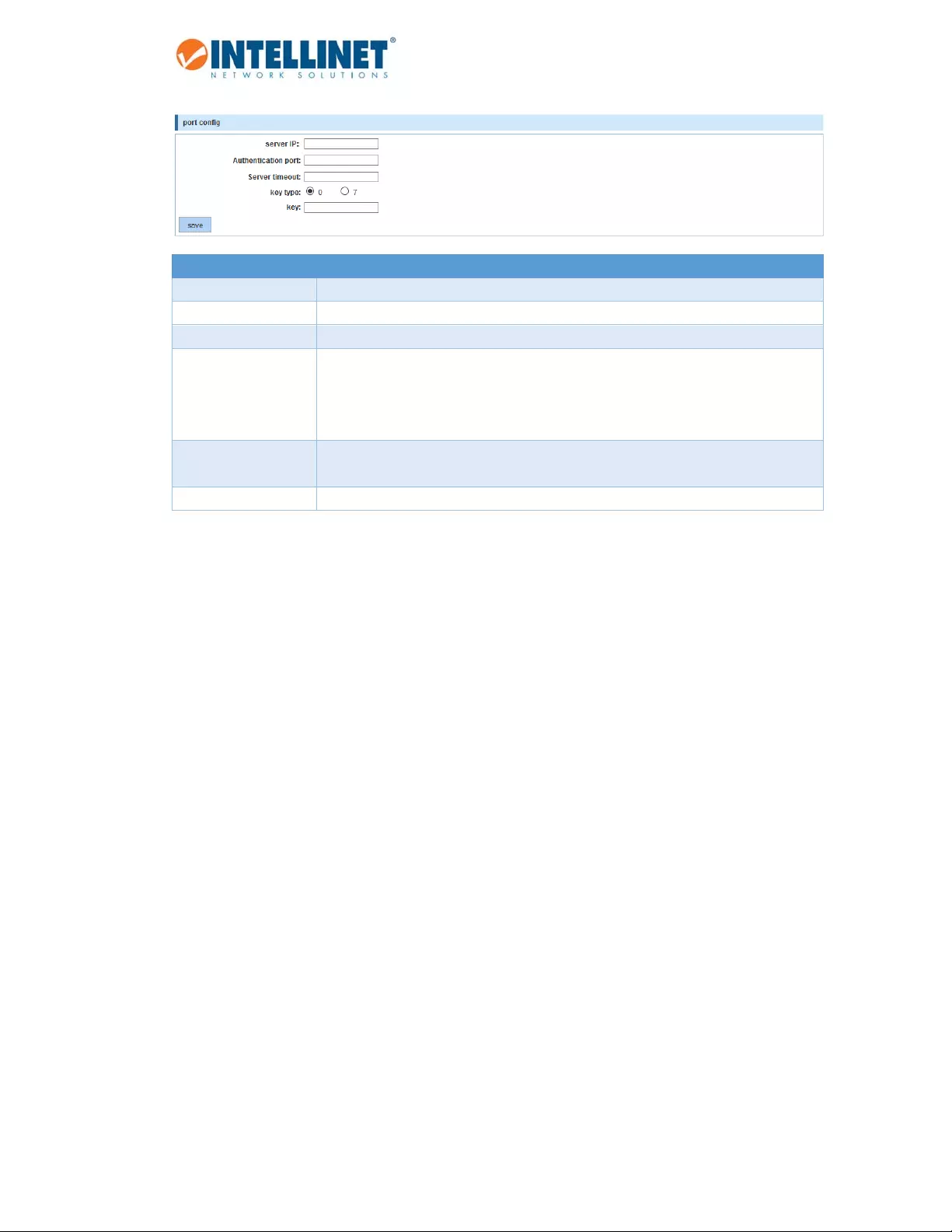
Item Description
PortConfig Globalparametersthatcanbeoverwrittenbyport‐specificconfiguration.
ServerIP IPAddressfortheTACSACS+server.
Authenticationport DefinetheTCPportnumberoftheTACSACS+serverconnection.
Servertimeout ThetimeoutintervaldetermineshowlongtheIntellinetswitchwaitsforresponses
fromaspecificTACACS+serverbeforedeclaringatimeoutfailure.Ifleftempty,the
globalservertimeoutvaluewillbeused;otherwise,theservertimeouttakes
precedence.
Keytype 0:Keyvalueincleartextformat
7:Keyvalueistype‐7encrypted.
Key Keyvalue.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
58
6.10 RADIUS
RemoteAuthenticationDial‐InUserService(RADIUS)isanetworkingprotocol
thatprovidescentralizedAuthentication,AuthorizationandAccounting(AAA
orTripleA)managementforuserswhoconnectanduseanetworkservice.
RADIUSisaclient/serverprotocolthatrunsintheapplicationlayerandcanuseeitherTCPorUDPastransport.
Networkaccessservers,thegatewaysthatcontrolaccesstoanetwork,usuallycontainaRADIUSclient
componentthatcommunicateswiththeRADIUSserver.RADIUSisoftentheback‐endofchoicefor802.1X
authenticationaswell.TheRADIUSserverisusuallyabackgroundprocessrunningonaUNIXorMicrosoft
Windowsserver.
6.10.1 RadiusGeneralConfig
Item Description
Serverrepeatnumber Specifiesthenumberofretryattemptsthatwillbemadetoestablisha
connectionbetweenaRADIUSclientandtheRADIUSserver.Thedefaultvalue
is3.
Servertimeout ThetimeoutintervaldetermineshowlongtheIntellinetswitchwaitsfor
responsesfromRADIUSserverbeforedeclaringatimeoutfailure.
Serverquiettime IftheIntellinetswitchisunabletoauthenticatetheclient,it’llwaitaspecified
amountoftimebeforetryingagain.Theamountoftimeisspecifiedwiththe
quiet‐periodparameter.Enteredinminutes;max.1440minutes(24hours).
Dead‐criteriaretrycount SetthenumberoftimesthattheIntellinetswitchdoesnotgetavalid
responsefromtheRADIUSserverbeforetheserverisconsideredunavailable.
Dead‐criteriatimeout SetthetimeinsecondsduringwhichtheIntellinetswitchdoesnotneedtoget
avalidresponsefromtheRADIUSserver.Therangeisfrom1to120seconds.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
59
6.10.2 RadiusServerConfig
Item Description
Serveraddress TypeintheaddressoftheRADIUSserver.
Chargingport TypetheaccountingportnumberontheRADIUSserver’shostcomputer.
Thedefaultportnumberis1813.
Authenticationport TypetheaccountingportnumberontheRADIUSserver’shostcomputer.
Thedefaultportnumberis1812.
Key Thekeyparameterintheradius‐servercommandisusedtoencryptRADIUS
packetsbeforetheyaresentoverthenetwork.Thevalueforthekey
parameterontheIntellinetswitchdeviceshouldmatchtheoneconfigured
ontheRADIUSserver.Thedefaultvalueis“radius”.
Activedetection EnablesordisablesactivedetectionofRADIUSserver.
Testname Theusernameforactivedetection.
Idletime TheintervaltimeforRADIUSsecurityserversendmessageonaccessible
state.Thedefaultvalueis60minutes.Possiblevaluesrangefrom0to1440
minutes(24hours).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
60
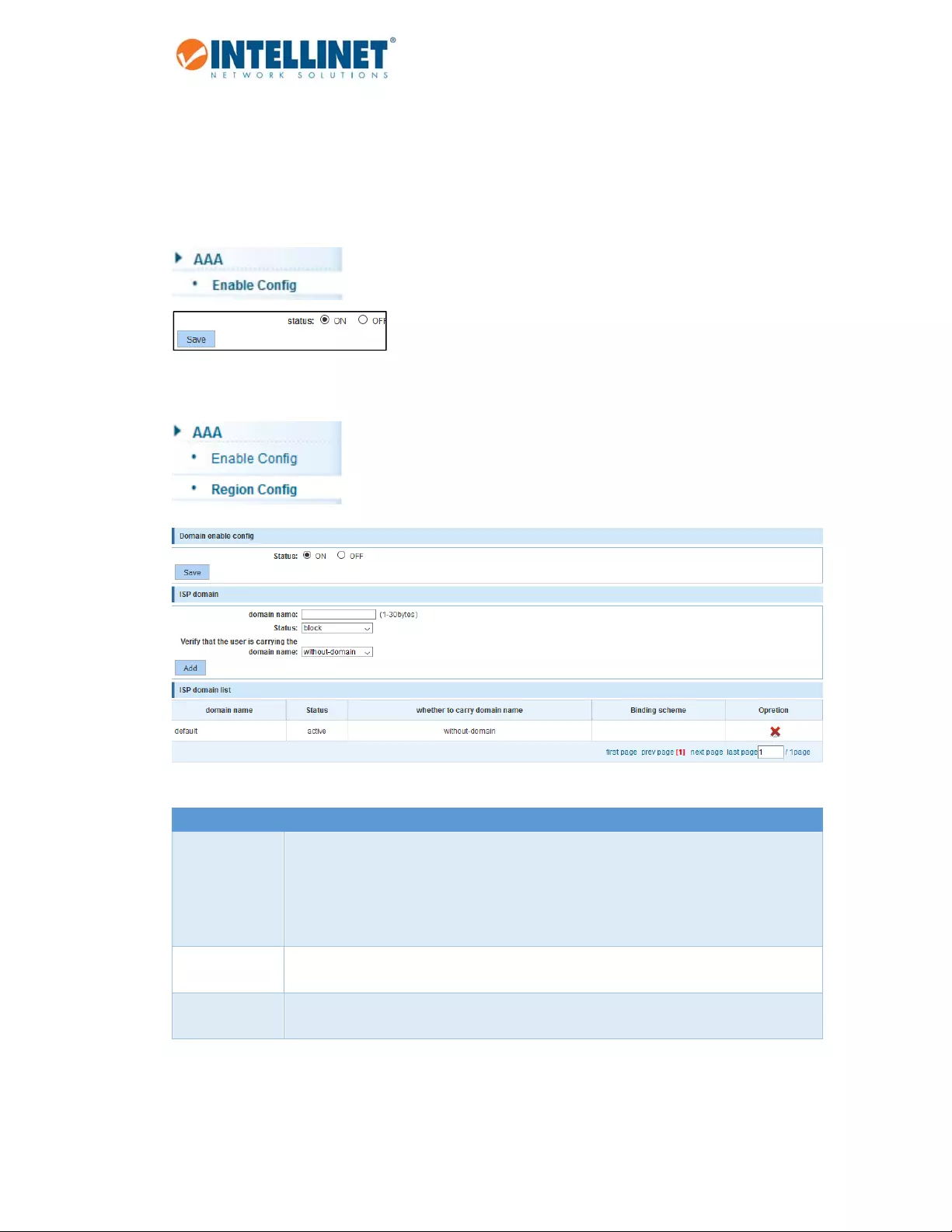
6.11 AAA
Authentication,authorizationandaccounting(AAA)isasystemfortrackinguseractivitiesonanIP‐based
networkandcontrollingtheiraccesstonetworkresources.AAAisoftenisimplementedasadedicatedserver.
6.11.1 EnableConfig
EnableordisableAAA.
6.11.2 RegionConfig
Item Description
DomainnameTypeinthenameoftheISPdomain.AnInternetserviceprovider(ISP)domainisagroup
ofuserswhobelongtothesameISP.Forausernameintheformatofuserid@isp‐name
oruserid.isp‐name,theisp‐namefollowingthe"@"or“.”characteristheISPdomain
name.Theaccessdeviceusesuseridastheusernameforauthentication,andisp‐name
asthedomainname.
StatusSettoeither“block”or“active.”Bydefault,anISPdomainisintheactivestate,which
meansthatalltheusersinthedomainareallowedtorequestnetworkservice.
Verifythatthe
user…
Verifythattheuseriscarryingthedomainname.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
61
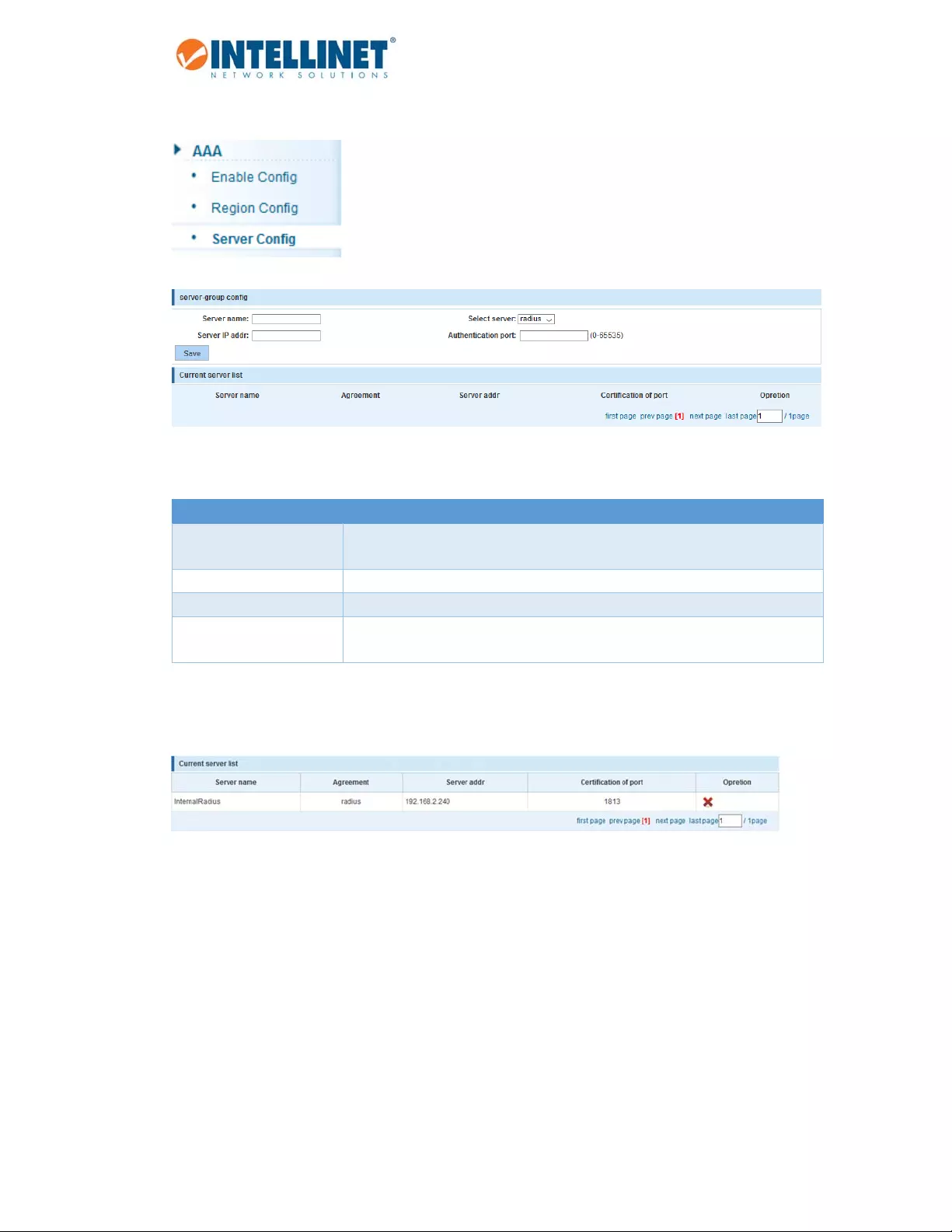
6.11.3 ServerConfig
Item Description
Servername Typeinthenamefortheserver.Thiscanbeadescriptivenameforeasier
identification.
ServerIPaddr ProvidetheIPaddressoftheRADIUSorTACACS+server.
Selectserver SettoeitherRADIUSorTACACS+.
Authenticationport ThisisanoptionalparameterforRADIUSservers.IfTACACS+isselected,the
portisfixedtoTCPport49.
ThescreenshotbelowshowsaRADIUSserverthathasbeenaddedtotheconfigurationusingthestandard
authenticationport1813(UDP).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
62
6.11.4 AAAAuthentication
6.11.4.1 LoginAuthentication
Item Description
Chooseadomain SelecttheISPdomain.
LoginAuthentication Checktoactivateit.
First–FourthMethod None:Eliminatestherequirementforanyauthenticationmethod.
Local:Usesthelocalpasswordconfiguredonthedevicetograntaccess.
GroupRADIUS:UsesthelistofallRADIUSserversforauthentication.
GroupTACACS+:UsesthelistofallTACACS+serversforauthentication.
CustomServerGroup:Usesauthenticationofacustomservergroup.
6.11.4.2 EnableAuthentication
Thispageallowstheusertoadd,editordeleteenableauthenticationlistsettings(the“default”listcannotbe
deleted).Thelinecombinedtothislistwillauthenticateauserwhoisissuingthe‘enable’commandbyoneof
thefourmethodsinthislist.Ifthefirstmethodfails,thenextprioritymethodwillbetriedtoauthenticate,and
soon.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
63
6.11.4.3 Dot1xAuthentication
The802.1xstandarddefinesaclient‐server‐basedaccesscontrolandauthenticationprotocolthatprevents
unauthorizedclientsfromconnectingtoaLANthroughpubliclyaccessibleports,unlesstheyareproperly
authenticated.Theauthenticationserverauthenticateseachclientconnectedtoaswitchportbeforemaking
availableanyservicesofferedbytheswitchortheLAN.
Note:Ifyouactivatethisbuthavenotconfiguredanyoftheauthenticationmethods(i.e.,RADIUS)correctly,
youwillloseaccesstotheIntellinetswitch,andyoumayneedtoperformahardwareresetinordertore‐gain
accesstothewebadmininterface.Seesection2.4.1FrontPanel.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
64
6.12 QOS–QUALITYOFSERVICE
QualityofService(QoS)isanadvancedtrafficprioritizationfeaturethatallowsyoutoestablishcontrolover
networktraffic.QoSenablesyoutoassignvariousgradesofnetworkservicetodifferenttypesoftraffic,such
asmulti‐media,video,protocol‐specific,timecritical,andfile‐backuptraffic.QoSreducesbandwidth
limitations,delay,loss,andjitter.Italsoprovidesincreasedreliabilityfordeliveryofyourdataandallowsyou
toprioritizecertainapplicationsacrossyournetwork.Youcandefineexactlyhowyouwanttheswitchtotreat
selectedapplicationsandtypesoftraffic.
YoucanuseQoSonyoursystemtocontrolawidevarietyofnetworktrafficby:
• Classifyingtrafficbasedonpacketattributes.
• Assigningprioritiestotraffic(forexample,tosethigherprioritiestotime‐criticalorbusiness‐critical
applications).
• Applyingsecuritypolicythroughtrafficfiltering.
• ProvidepredictablethroughputformultimediaapplicationssuchasvideoconferencingorVoiceoverIP
byminimizingdelayandjitter.
• Improveperformanceforspecifictypesoftrafficandpreserveperformanceastheamountoftraffic
grows.
• Reducetheneedtoconstantlyaddbandwidthtothenetwork.
• Managenetworkcongestion.
6.12.1 QoSRules
Despitethename“Remark”or“QoSMulti‐Label,thissectionactuallyallowsyoutocreateyourQualityof
Servicerules.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
65
Item Description
RuleIndex Keyintherulenumber.
Operationtype Setto“Equal”or“Alwaysmatch”.
Valuetype Thisvaluedefinesthekindofvalueyouintendtousefor
theQoSrule.
Value Keyinthevaluethatcorrespondstothevaluetypeyouselectedabove.
CoSmapping CoSstandsforClassofService.Thereareeightvaluestochoosefrom.
Priorityremark AsanalternativetoCoS
mapping,youcandefinethe
priorityvaluehere,values0–
7.
Chooseporttoconfig SelecttheportorportsfortheQoSrule.Selectallportsifyouwanttheruketo
applytowhicheverportthedevicesareconnectedto.
6.12.2 QueueConfig
InthissectionyoudefinewhichpriorityalgorithmyouwishtheIntellinetswitchtoutilize.
Item Description
Queuemode SP=StrictPriority,RR=RoundRobin,WRR=WeightedRoundRobinandWFQ=
WeightedFairQueuing.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
66
6.12.3 QueueMapping
6.12.3.1 CoS‐Queue‐Map
ThispageallowsthenetworkadministratortoclassifyCoSsettingstotrafficqueues.TheserverIDrepresents
theCoS(ClassofServer)ID.
6.12.3.2 DSCP‐CoS‐Map
ThisallowsnetworkmanagerstodeterminetheoutputqueuethatisassignedperaspecificDSCPfield.The
DSCPfieldIDisrepresentedbytheserverID,andtheQUEUEIDislistedastheserverlistonthescreen.
6.12.3.3 Port‐CoS‐Map
ThispageallowsthenetworkadministratortoclassifyCoSsettingstothe18physicalportsontheIntellinet
switch.TheserverIDrepresentstheCoS(ClassofServer)ID.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
67
6.13 ADDRESSTABLE
ToswitchdatapacketsbetweenLANportsefficiently,theIntellinetswitchmaintainsanaddresstable.When
theswitchreceivesaframe,itassociatesthemediaaccesscontrol(MAC)addressofthesendingnetwork
devicewiththeLANportonwhichitwasreceived.Indoingso,theswitchdrasticallycutsdownon
unnecessarynetworktraffic,becauseinsteadoffloodingallLANportsofthesameVLANwiththeinformation,
itonlysendsittotheportwheretherecipientisconnectedto.
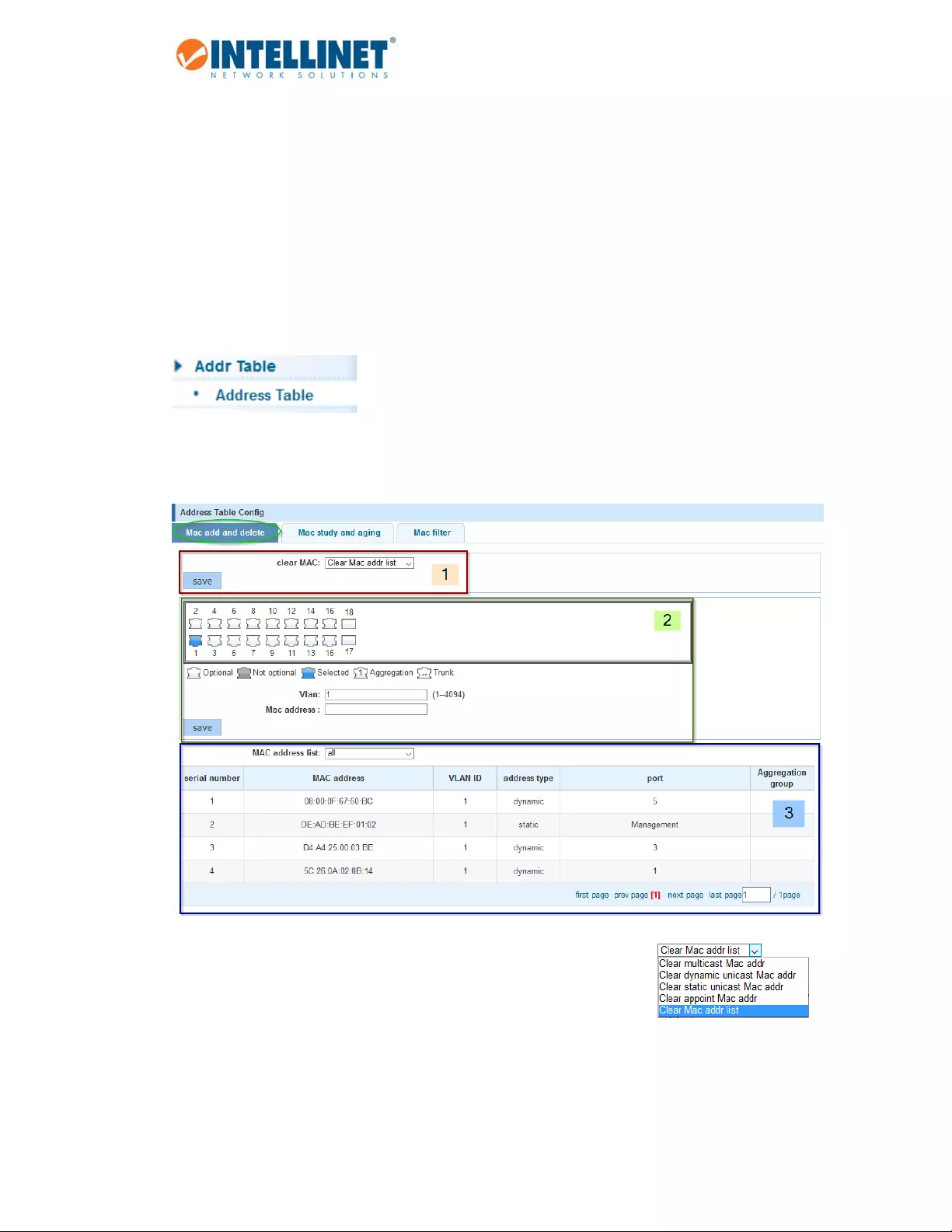
6.13.1 AddressTableConfig
6.13.1.1 MACAdd&Delete
Thescreenisdividedintothreesections.
Section1(“clearMacaddrlist”)allowsyoutocleartheMACaddresstable.
Section2canbeusedtomanuallyenteraVLAN–MACAddress–Portpairing.
Section3displaysallMACaddressesthatarecurrentlyintheMACaddresstable.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
68
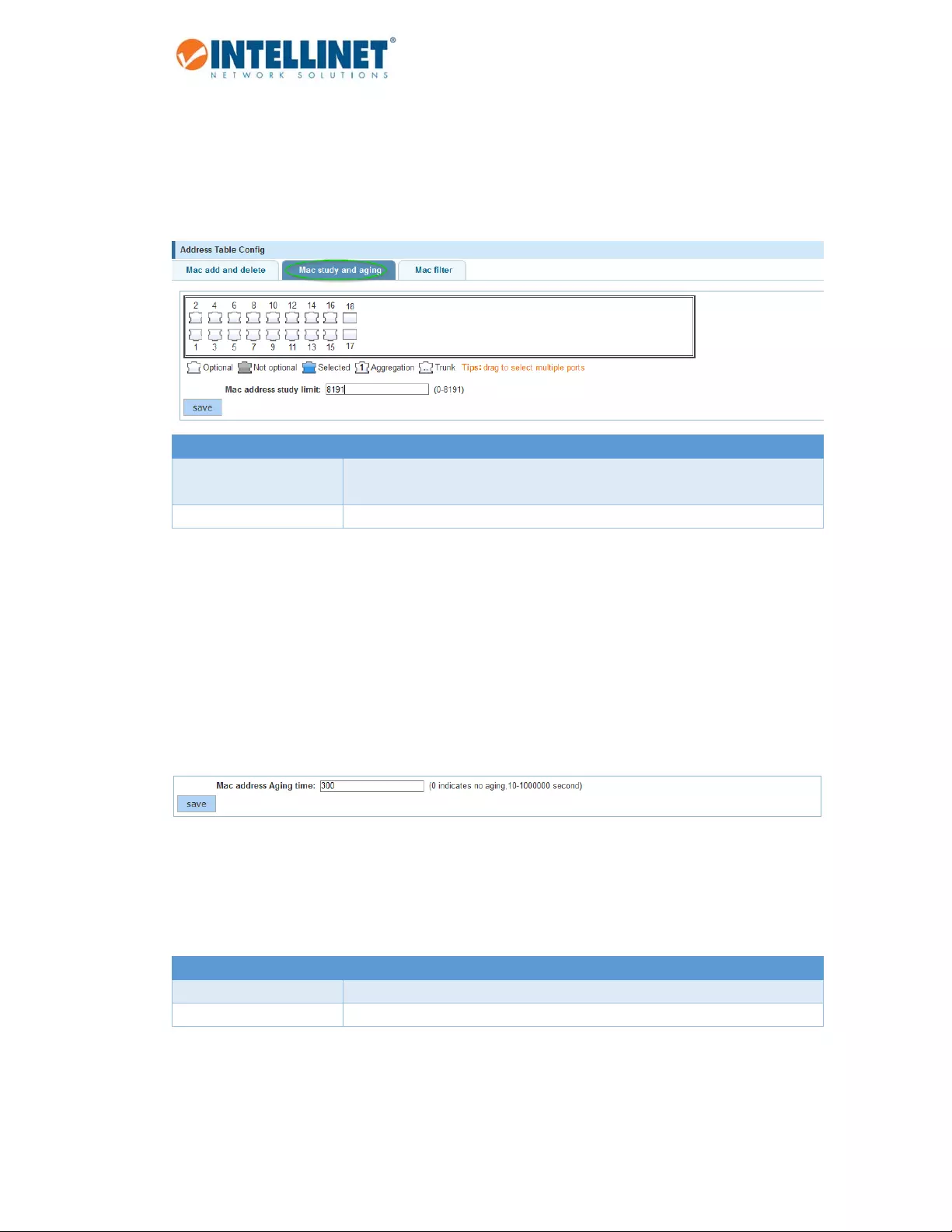
6.13.1.2 MACstudy&aging
ThissectionallowsthenetworkadministratortospecifythemaximumamountofMACaddressesthatcanbe
learntperport.YoucanconfigureamaximumnumberofsecureMACaddressesforeachport.Thedefault
interfacemaximumis8191addresses.Interfacemaximumscannotexceedthedevicemaximum,whichisalso
8191.
Item Description
Ports Selectoneormultipleports,forwhichyouwanttodefinetheMACaddres
studylimit
MACaddressstudylimit KeyinthemaximumMACaddresslimitfortheselectedport(s).
TheIntellinetswitchalsoprovidesamechanismtoadjusttheagingtimeforstoredMACaddresses.Theaging
timecontrolshowlongtheswitchkeepsstoringtheMACaddressintheMACaddresstable.Everytimeaclient
sendsorreceivestraffic,theagingtimefortheclient’sMACaddressisreset.IfthereisnotrafficforaMAC
addressinatimeframethatexceedsthetimedefinedintheagingtime,theMACaddressisremovedfromthe
MACaddresstable.Thedefaultagingtimeis300seconds.Settingthevalueto“0”disablestheagingtime
mechanism,whichmeansthataMACaddressthathasbeenlearntonce,willbekeptintheMACaddresstable
untiltheswitchisreset.ButthesincetheIntellinetswitchhasonlyfinitespacetoholdMACaddresses,itis
recommendedtokeeptheagingtimeat,oraroundthedefaultvalue.
6.13.1.3 MACFilter
WiththisfeaturethenetworkadministratorcanpreventaccesstothenetworkforselectedMACaddresses
andVLANIDs(1=defaultVLAN).
Item Description
MACAddress TypeintheMACaddressthatyouwanttoblock.
MACaddressstudylimit TypeintheVLANIDifapplicable.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
69
6.14 SNMP
SimpleNetworkManagementProtocol(SNMP)isanOSILayer7(ApplicationLayer)designedspecificallyfor
managingandmonitoringnetworkdevices.SNMPenablesnetworkmanagementstationstoreadandmodify
thesettingsofgateways,routers,switches,andothernetworkdevices.UseSNMPtoconfiguresystem
featuresforproperoperation,monitorperformanceanddetectpotentialproblemsintheSwitch,switchgroup
ornetwork.
6.14.1 SNMPConfig
ActivateordeactivateSNMP.
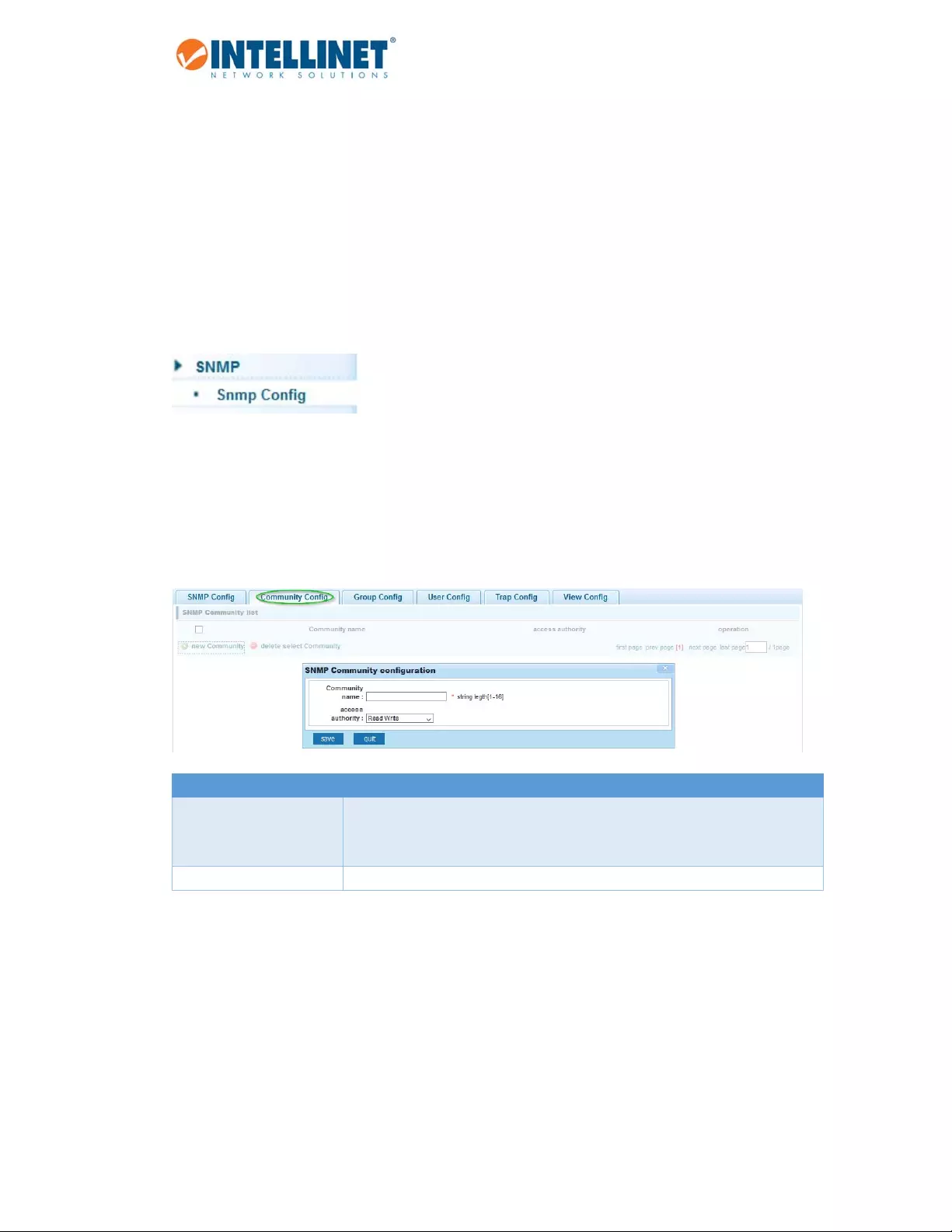
6.14.1.1 CommunityConfig
Item Description
Communityname SNMPCommunitystring.TheSNMPread‐onlycommunitystringislikea
password.ItissentalongwitheachSNMPGet‐Requestandallows(ordenies)
accesstodevice.
Accessauthority Settoread‐onlyorread‐write.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
70
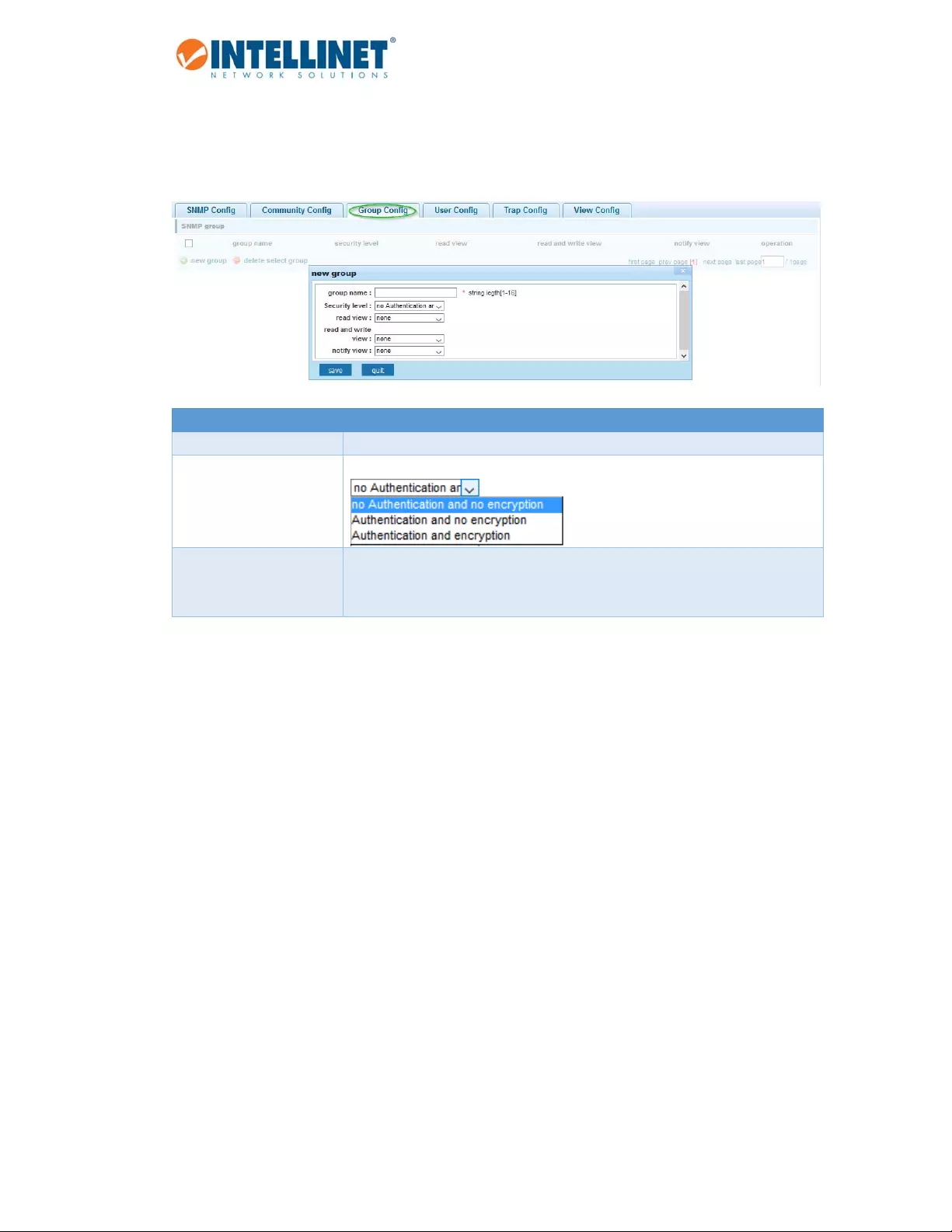
6.14.1.2 GroupConfig
TheIntellinetswitchusesaview‐basedaccesscontrolmodelthatallowsthenetworkadministratorto
configuretheaccessprivilegesgrantedtoagroup.
Item Description
Groupname Provideagroupname.
Securitylevel Selectthedesiredsecuritylevel.
Readview
Readandwriteview
Notifyview
Assignthedesiredview(aviewmustbecreatedfirst‐seeSNMPViewConfig).
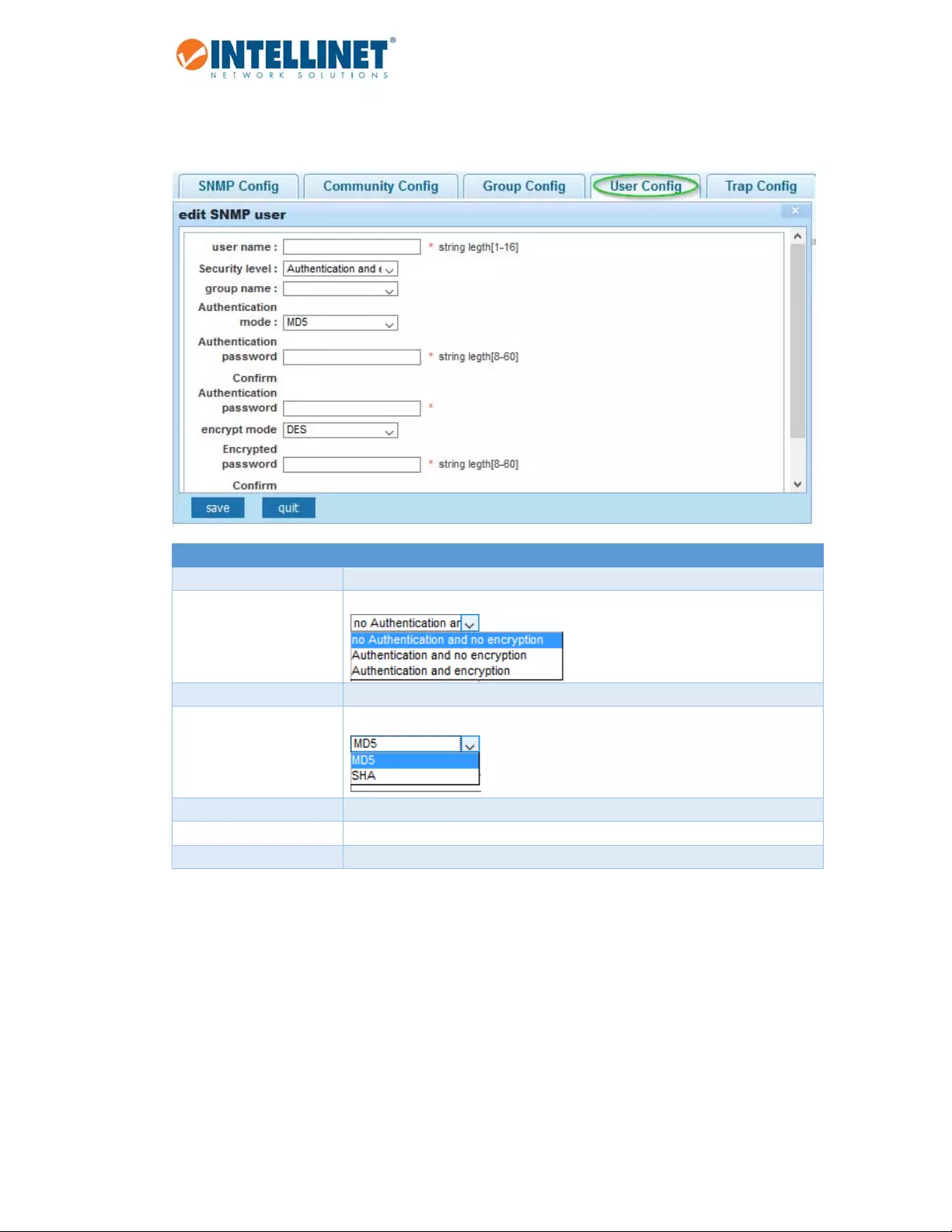
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
71
6.14.1.3 UserConfig
ThissectionallowssettingupSNMPusersandassignthemtoanSNMPgroup.
Item Description
Username Provideagroupname.
Securitylevel Selectthedesiredsecuritylevel.
Groupname Provideagroupname.
Authenticationmode Selectthehashfunctionofchoice.
Authenticationpassword Keyinthepassword.
Encryptionmode SelecteitherAESorDEStoencryptthepassword.
Encryptedpassword Keyintheencryptedpassword.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
72
6.14.1.4 TrapConfig
Item Description
DestinationIPAddress TheIPaddressoftheSNMPmanager(TRAPviewer).
Addresstype IPv4(andperhapslaterIPv6willbesupported)
Securityname Whenusingsecuritymodev3,youcanselectauserfromadropdown
list.ThatuserwascreatedintheSNMPuserconfig.
UDPportnumber PortforSimpleNetworkManagementProtocolTrap(SNMPTRAP).
Securitymode Selectthesecuritymode(V1,V2orV3).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
73
6.14.1.5 ViewConfig
SNMPv3definestheconceptofMIBviewsinRFC3415,View‐basedAccessControlModel(VACM)forSNMP.
MIBviewsprovideanagentbettercontroloverwhocanaccessspecificbranchesandobjectswithinitsMIB
tree.AviewconsistsofanameandacollectionofSNMPobjectidentifiers,whichareeitherexplicitlyincluded
orexcluded.Oncedefined,aviewisthenassignedtoanSNMPgroup‐seeSNMPGroupConfig.
Onceaviewhasbeencreated,youcancreatearulefortheview.
Item Description
Rule Alsoreferredtoasthe'"Type".Specifieswhethertoincludeorexcludetheview
subtreeorfamilyofsubtreesfromtheMIBview.
MIBsubtreeOID EnteranOIDstringforthesubtreetoincludeorexcludefromtheview.OIDstring
is256charactersinlength.Forexample,thesystemsubtreeisspecifiedbytheOID
string.1.3.6.1.2.1.1.
Subtreemask ProvidetheOIDmaskhere.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
74
6.14.2 RMONConfig
RemoteMonitoring(RMON)isastandardmonitoringspecificationthatenablesvariousnetworkmonitorsand
consolesystemstoexchangenetwork‐monitoringdata.RMONisthemostimportantexpansionofthe
standardSNMP.RMONisasetofMIBdefinitions,usedtodefinestandardnetworkmonitorfunctionsand
interfaces,enablingthecommunicationbetweenSNMPmanagementterminalsandremotemonitors.RMON
providesahighlyefficientmethodtomonitoractionsinsidethesubnets.
MIDofRMONconsistsof10groups.TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchsupports
themostfrequentlyusedgroup1,2,3and9:
Statistics:CollectsEthernet,FastEthernet,andGigabitEthernetstatisticsonaninterface.
History:CollectsahistorygroupofstatisticsonEthernet,FastEthernet,andGigabitEthernet
interfacesforaspecifiedpollinginterval.
Alarm:Monitorsaspecificmanagementinformationbase(MIB)objectforaspecifiedinterval,
triggersanalarmataspecifiedvalue(risingthreshold),andresetsthealarmatanothervalue(falling
threshold).Alarmscanbeusedwithevents;thealarmtriggersanevent,whichcangeneratealog
entryoranSNMPtrap.
Event:Determinestheactiontotakewhenaneventistriggeredbyanalarm.Theactioncanbeto
generatealogentryoranSNMPtrap.
RMONisspecifiedaspartoftheManagementInformationBase(MIB)inRFC1757asanextensionofthe
SimpleNetworkManagementProtocol(SNMP).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
75
6.14.2.1 StatisticsGroup
Item Description
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Interfacename SelectoneoftheeighteenGigabitportfromthedrop‐downlist.
Owner Optionalfieldthatallowsthenetworkadministratortoenterthenameofthe
owneroftheStatisticsRMONgroup.
6.14.2.2 HistoryGroup
Item Description
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Interfacename SelectoneoftheeighteenGigabitportfromthedrop‐downlist.
Maximumnumberof
samples
Thisisthenumberofsamples("buckets")tokeepbeforetheygetoverwritten.
Sampleperiod Thenumberofsecondsineachpollingcycle.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
76
6.14.2.3 AlarmGroup
Item Description
Index Specifythealarmtableindexnumber.
Statictable SpecifytheMIBvariablethatismonitoredbythealarmentry.
Statisticalgroupindex Thisisthenumberofsamples("buckets")tokeepbeforetheygetoverwritten.
Samplingtime
interval
Thenumberofsecondsineachpollingcycle.
Sampletype Thisisthemethodofsamplingtheselectedvariableandcalculatingthevaluetobe
comparedagainstthethresholds.
Owner Optionalfieldthatallowsthenetworkadministratortoenterthenameofthe
owneroftheAlarmRMONgroup.
Thealarmthreshold
limit
Thisistherisingthreshold,anumberatwhichthealarmistriggered.Thisvalue
rangesbetween0and2147483647.
Eventsexceeding
threshold
Theeventnumbertotriggerwhentherisingthresholdexceedsitslimit.
Alarmthresholdlimit Thisisthefallingthreshold,anumberatwhichthealarmisreset.Thisvalueranges
between0and2147483647.
Eventsbelow
thresholdlimit
Theeventnumbertotriggerwhenthefallingthresholdexceedsitslimit.
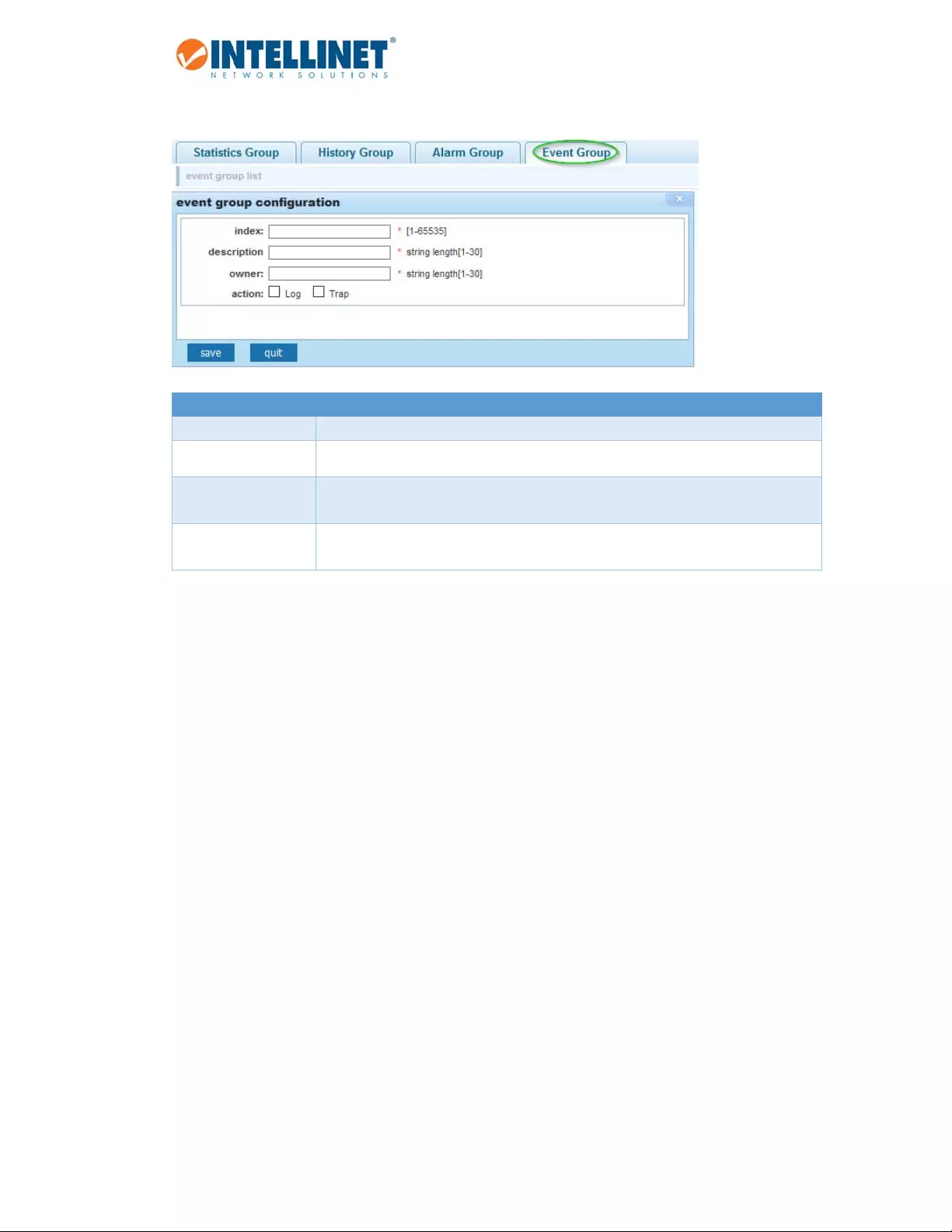
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
77
6.14.2.4 EventGroup
Item Description
Index Specifytheeventtableindexnumber.
Description Adescriptivenameoftheevent.
Owner Optionalfieldthatallowsthenetworkadministratortoenterthenameofthe
owneroftheEventRMONgroup.
Action Settoeither"Log"ifyouwanttogeneratealogentry,or"Trap"inordergenerate
atrapmessage.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
78
6.15 SYSTEM
6.15.1 SystemConfig
6.15.1.1 SystemSettings
Item Description
VLAN ThedefaultVLANIDoftheswitch("1:bydefault).
IP TheLANIPaddressoftheswitch.ThedefaultIPaddressis"192.168.2.1".
Mask Thedefaultnetworkmaskis255.255.255.0.
DefaultGateway TheoptionaldefaultgatewayonlyisneededwhenyourequireInternetaccessfor
theIntellinetswitch,forexampleinordertoobtaintimeinformationfromanNTP
server.
Jumboframe HereyoucanspecifythemaximumframesizesupportedbytheIntellinetswitch.
Themaximumis9216(kB).
DNSServer TheoptionalDNSserverisonlyneededwhenyourequireInternetaccessforthe
Intellinetswitch,forexampleinordertoobtaintimeinformationfromanNTP
server.
Logintimeout ThisparameterappliestothewebadministratorUI.Bydefault,userswillbe
automaticallyloggedoutafter30minutesofinactivity.
IPv6address OptionalIPv6addressfortheIntellinetswitch.
Devicename DevicenamefortheIntellinetswitch.
Deviceposition,
contactsandcontact
information
OptionaladditionalinformationyoucanprovidefortheIntellinetswitch.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
79
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Settime ClickinordertosetthetimefortheIntellinetswitchmanually.
[]NTPServer ActivatethisoptionifyouwanttheIntellinetswitchtoobtainthesystemtimefrom
aNTPserver.Forthattowork,besuretoprovideapropergatewayandDNS
serveraddress.
6.15.1.2 SystemRestart
Click"Restart"inordertohavetheIntellinetswitchperformasystemrestart.
6.15.1.3 Password
Onthisscreenyoucanchangetheadministratorpassword.Thedefaultpasswordis"1234".
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
80
6.15.1.4 EEEEnable
Energy‐EfficientEthernet(EEE)isasetofenhancementstothetwisted‐pairandbackplaneEthernetfamilyof
computernetworkingstandardsthatallowforlesspowerconsumptionduringperiodsoflowdataactivity.
Theintentionwastoreducepowerconsumptionby50%ormore,whileretainingfullcompatibilitywith
existingequipment.TheInstituteofElectricalandElectronicsEngineers(IEEE),throughtheIEEE802.3aztask
forcedevelopedthestandard.EEEisapowersavingoptionthatreducesthepowerusagewhenthereislow
ornotrafficutilization.EEEworksbypoweringdowncircuitswhenthereisnotraffic.
Whenaportispowereddownforsavingpower,theoutgoingtrafficisstoredinabufferuntiltheportis
poweredupagain.Usingthistechnique,morepowercanbesavedifthetrafficcanbebufferedupuntila
largeburstoftrafficcanbetransmitted.Keepinmindthatbufferingtrafficwillgivesomelatencyinthe
traffic.
ShouldyouencounterproblemsrelatedtoEEE,e.g.,relatedtoautonegotiation,youcandisableEEEsupport
andtheIntellinetswitchwillnolongeruseit.
6.15.1.5 SSHLogin
ActivateSSHsupportbysettingtheSSHCONFIGto"OPEN".
6.15.1.6 TelnetLogin
ActivateTelnetsupportbysettingtheTELNETCONFIGto"OPEN".

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
81
6.15.1.7 SystemLog
TheIntellinetswitchhastheabilitytocreateahistorylogofimportantevents.Theselogscanbestored
eitherintheswitchesownmemory,oronaremoteSyslogserver.Inordertoutilizetheloggingservice,you
mustfirstenableit.
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Logswitch SelectoneoftheeighteenGigabitportfromthedrop‐downlist.
ServerIP ProvidetheIPaddressoftheSyslogserver.NotethattheSyslogservermustbeset
toUDPport514.
Sendloglevel DefinetheamountofdetailyouwishtheIntellinetswitchtolog.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
82
6.15.2 SystemUpdate
Intellinetmayreleaseanewfirmwareforthisswitchprovingnewfunctions,andperhapsbugfixes.Youcan
installthenewfirmwareonthisscreen.Shouldanewfirmwarebemadeavailable,itwillbeavailableat
http://intellinet‐network.com/search?q=561334.
Howtoinstallthenewfirmware:
1. Downloadthefirmwarefromthewebsite
2. IfthefirmwareisacompressedfilesuchasRAR,7ZorZIP,youneedtouncompressthefilefirst,
beforeitcanbeinstalledontheintellinetswitch.
3. Thecorrectfileextensionforthefirmwareis".bix".
4. Click"Browse"andselectthe".bix"filefromyourcomputer'sHDD
5. Click"StartUpgrade".
6. ConfirmyourdecisionbyclickingOK.Theupgradewillnowbegin.
7. Hopethattherewon'tbeapoweroutageduringthenext3minutes.
Notethatifyoustillseethemessageaboveafter5minutes,openanewbrowserwindowandre‐connectto
theIPaddressoftheIntellinetswitch(default=http://192.168.2.1).
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
83
6.15.3 ConfigurationManagement
6.15.3.1 ConfigExportandImport
ThisfunctionallowstobackupandrestoretheconfigurationdataoftheIntellinetswitch.
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Showcurrentconfig Showsthecurrentswitchconfigurationinapop‐upwindow.
ExportConfig Letsyousavethecurrentconfigurationdatatoafileonyourcomputer'sHDD.
Backup Whenafilenameisprovided(seebelow),clickthisbuttontocreateabackupof
theconfiguration,whichtheIntellinetswitchisgoingtokeepinitsmemory.The
configrestorefunctionprovidesaccesstothesebackupsandletsyourestore
them,deletethem,renamethemorsavethemtoyourcomputer'sHDD.
Filename Filenameforbacklup,e.g.,backup.
Importconfiguration Inordertouploadapreviouslysavedconfiguration,activatetyhisoption,thenclick
on"Browse"andselectthecorrect".conf"fromyourcomputer'sHDD.Clickthe
"ImportConfiguration"buttontobegin.
6.15.3.2 ConfigRestore
Theconfigrestorefunctionprovidesaccesstobackupsthatwerecreatedpreviously,andletsyourestore
them,deletethem,renamethemorsavethemtoyourcomputer'sHDD.
6.15.3.3 FactoryReset
Thisfeatureallowstorestoreallsettingstothefactorydefaultvalues.Ifyoumanagedtolockyououtfrom
configuringtheswitchandhavelostaccesstothewebadmininterface,youcanreinstatethefactorydefault
settingsbypressingtheresetbuttononthefrontpftheswitchfor20seconds.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
84
6.15.4 ConfigSave
TheIntellinet48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchprovidesamyriadofconfigurationoptions,many
ofwhicharedesignedforexperiencednetworkadministratorsandaren’teasytoconfigure.Itwouldbeareal
shameifalltheconfigurationdatawaslostafterapowerfailureoraftertheswitchwasrestarted.Inorderto
maketheconfigurationpermanent,itneedstobesaved.
6.15.5 UserAccounts
Youcancreatenewuseraccountsandmodifyexistingonesonthispage.Auseraccountthatdoesnothave
administratorrightcanonlymonitorthemainstatusinformationoftheIntellinetswitch,butcannotmakeany
changestotheconfiguration.
Index Specifythehistorytableindexnumber.
Username Whencreatinganewaccount,typeinthenewusername.Ifeditingyouare
editinganexistingaccount,thefieldwillberead‐only.
Newpassword Typeinthenewpassword.
Confirmnewpassword Repeatthenewpassword.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
85
6.15.6 InformationCollect
Clickonthe buttoncreateafilethatcontainstheconfigurationdataoftheIntellinetswitch.Afew
secondslateryouwillbeaskedtoopenorsavethefile(orwhateverwebbrowserdefaultactionforunknown
filesisinplaceonyoursystem).Thisinformationcanbeusefulwhenitcomestotroubleshootingtechnical
problems.
48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
86
7 WARRANTY
Deutsch‐ GarantieinformationenfindenSiehierunterintellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
English‐Forwarrantyinformation,gotointellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
Español‐Sideseaobtenerinformaciónsobrelagarantía,visiteintellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
Français‐Pourconsulterlesinformationssurlagarantie,rendezvousàl’adresse
intellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
Italiano‐Perinformazionisullagaranzia,accedereaintellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
Polski‐Informacjedotyczącegwarancjiznajdująsięnastronieintellinetnetwork.com/warranty.
México‐PólizadeGarantíaIntellinet—DatosdelimportadoryresponsableanteelconsumidorICIntracom
México,S.A.P.I.deC.V.•Av.InterceptorPoniente#73,Col.ParqueIndustrialLaJoya,CuautitlanIzcalli,Estado
deMéxico,C.P.54730,México.•Tel.(55)1500‐4500
Lapresentegarantíacubrelossiguientesproductoscontracualquierdefectodefabricaciónensusmateriales
ymanodeobra.
A.GarantizamoscámarasIPyproductosconpartesmóvilespor3años.
B.Garantizamoslosdemásproductospor5años(productossinpartesmóviles),bajolassiguientes
condiciones:
1.Todoslosproductosaqueserefiereestagarantía,amparasucambiofísico,sinningúncargoparael
consumidor.
2.Elcomercializadornotienetalleresdeservicio,debidoaquelosproductosquesegarantizannocuentan
conreparaciones,nirefacciones,yaquesugarantíaesdecambiofísico.
3.Lagarantíacubreexclusivamenteaquellaspartes,equipososub‐ensamblesquehayansidoinstaladasde
fábricaynoincluyeenningúncasoelequipoadicionalocualesquieraquehayansidoadicionadosalmismo
porelusuarioodistribuidor.
Parahacerefectivaestagarantíabastaráconpresentarelproductoaldistribuidoreneldomiciliodondeue
adquiridooeneldomiciliodeICIntracomMéxico,S.A.P.I.deC.V.,juntoconlosaccesorioscontenidosnsu
empaque,acompañadodesupólizadebidamentellenadayselladaporlacasavendedoraindispensableel
selloyfechadecompra)dondeloadquirió,obien,lafacturaoticketdecompraoriginaldondesemencione
claramenteelmodelo,numerodeserie(cuandoaplique)yfechadeadquisición.Estagarantíanoesválidaen
lossiguientescasos:Sielproductosehubiesetilizadoencondicionesdistintasalasnormales;sielproductono
hasidooperadoconformealosinstructivosdeuso;osielproductohasidoalteradootratadodeserreparado
porelconsumidoroterceraspersonas.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
87
8 COPYRIGHT
Copyright©2016ICIntracom.Allrightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproduced,transmitted,
transcribed,storedinaretrievalsystem,ortranslatedintoanylanguageorcomputerlanguage,inanyformor
byanymeans,electronic,mechanical,magnetic,optical,chemical,manualorotherwise,withouttheprior
writtenpermissionofthiscompany
Thiscompanymakesnorepresentationsorwarranties,eitherexpressedorimplied,withrespecttothe
contentshereofandspecificallydisclaimsanywarranties,merchantabilityorfitnessforanyparticularpurpose.
Anysoftwaredescribedinthismanualissoldorlicensed"asis".Shouldtheprogramsprovedefective
followingtheirpurchase,thebuyer(andnotthiscompany,itsdistributor,oritsdealer)assumestheentirecost
ofallnecessaryservicing,repair,andanyincidentalorconsequentialdamagesresultingfromanydefectinthe
software.Further,thiscompanyreservestherighttorevisethispublicationandtomakechangesfromtimeto
timeinthecontentsthereofwithoutobligationtonotifyanypersonofsuchrevisionorchanges.

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
88
9 FEDERALCOMMUNICATIONCOMMISSIONINTERFERENCE
STATEMENT
ThisequipmenthasbeentestedandfoundtocomplywiththelimitsforaClassBdigitaldevice,pursuanttoPart15ofFCC
Rules.Theselimitsaredesignedtoprovidereasonableprotectionagainstharmfulinterferenceinaresidentialinstallation.
Thisequipmentgenerates,uses,andcanradiateradiofrequencyenergyand,ifnotinstalledandusedinaccordancewith
theinstructions,maycauseharmfulinterferencetoradiocommunications.However,thereisnoguaranteethat
interferencewillnotoccurinaparticularinstallation.Ifthisequipmentdoescauseharmfulinterferencetoradioor
televisionreception,whichcanbedeterminedbyturningtheequipmentoffandon,theuserisencouragedtotryto
correcttheinterferencebyoneormoreofthefollowingmeasures:
1.Reorientorrelocatethereceivingantenna.
2.Increasetheseparationbetweentheequipmentandreceiver.
3.Connecttheequipmentintoanoutletonacircuitdifferentfromthattowhichthereceiverisconnected.
4.Consultthedealeroranexperiencedradiotechnicianforhelp.
FCCCaution
Thisdeviceanditsantennamustnotbeco‐locatedoroperatinginconjunctionwithanyotherantennaortransmitter.This
devicecomplieswithPart15oftheFCCRules.Operationissubjecttothefollowingtwoconditions:(1)thisdevicemaynot
causeharmfulinterference,and(2)thisdevicemustacceptanyinterferencereceived,includinginterferencethatmay
causeundesiredoperation.Anychangesormodificationsnotexpresslyapprovedbythepartyresponsibleforcompliance
couldvoidtheauthoritytooperateequipment.
FCCRadiationExposureStatement:
ThisequipmentcomplieswithFCCradiationexposurelimitssetforthforanuncontrolledenvironment.Thisequipment
shouldbeinstalledandoperatedwithminimumdistance20cmbetweentheradiator&yourbody.
Safety
Thisequipmentisdesignedwiththeutmostcareforthesafetyofthosewhoinstallanduseit.However,specialattention
mustbepaidtothedangersofelectricshockandstaticelectricitywhenworkingwithelectricalequipment.Allguidelines
ofthisandofthecomputermanufacturemustthereforebeallowedatalltimestoensurethesafeuseoftheequipment.
EUCountriesIntendedforUse
TheETSIversionofthisdeviceisintendedforhomeandofficeuseinAustria,Belgium,Bulgaria,Cyprus,Czech,Denmark,
Estonia,Finland,France,Germany,Greece,Hungary,Ireland,Italy,Latvia,Lithuania,Luxembourg,Malta,Netherlands,
Poland,Portugal,Romania,Slovakia,Slovenia,Spain,Sweden,Turkey,andUnitedKingdom.TheETSIversionofthisdevice
isalsoauthorizedforuseinEFTAmemberstates:Iceland,Liechtenstein,Norway,andSwitzerland.
EUCountriesNotIntendedforUse
None

48‐PortGigabitEthernetWeb‐ManagedSwitchwith4SFPPorts
89
intellinetnetworkcom
©ICIntracom.Allrightsreserved.
IntellinetisatrademarkofICIntracom,registeredintheU.S.andothercountries.